Patents
Literature
54 results about "Aircraft vectoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aircraft vectoring is a navigation service provided to aircraft by air traffic control. The controller decides on a particular airfield traffic pattern for the aircraft to fly, composed of specific legs or vectors. The aircraft then follows this pattern when the controller instructs the pilot to fly specific headings at appropriate times.
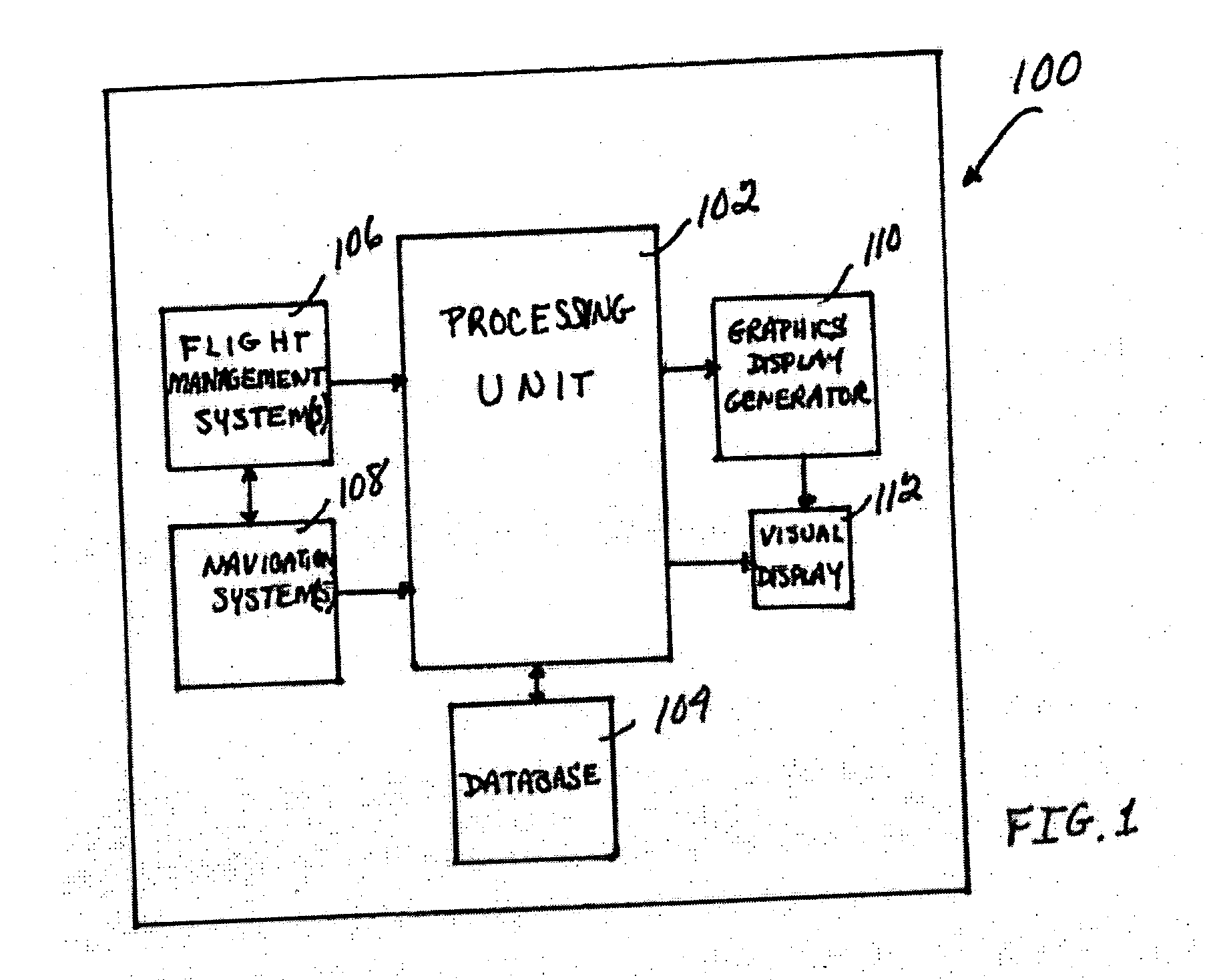
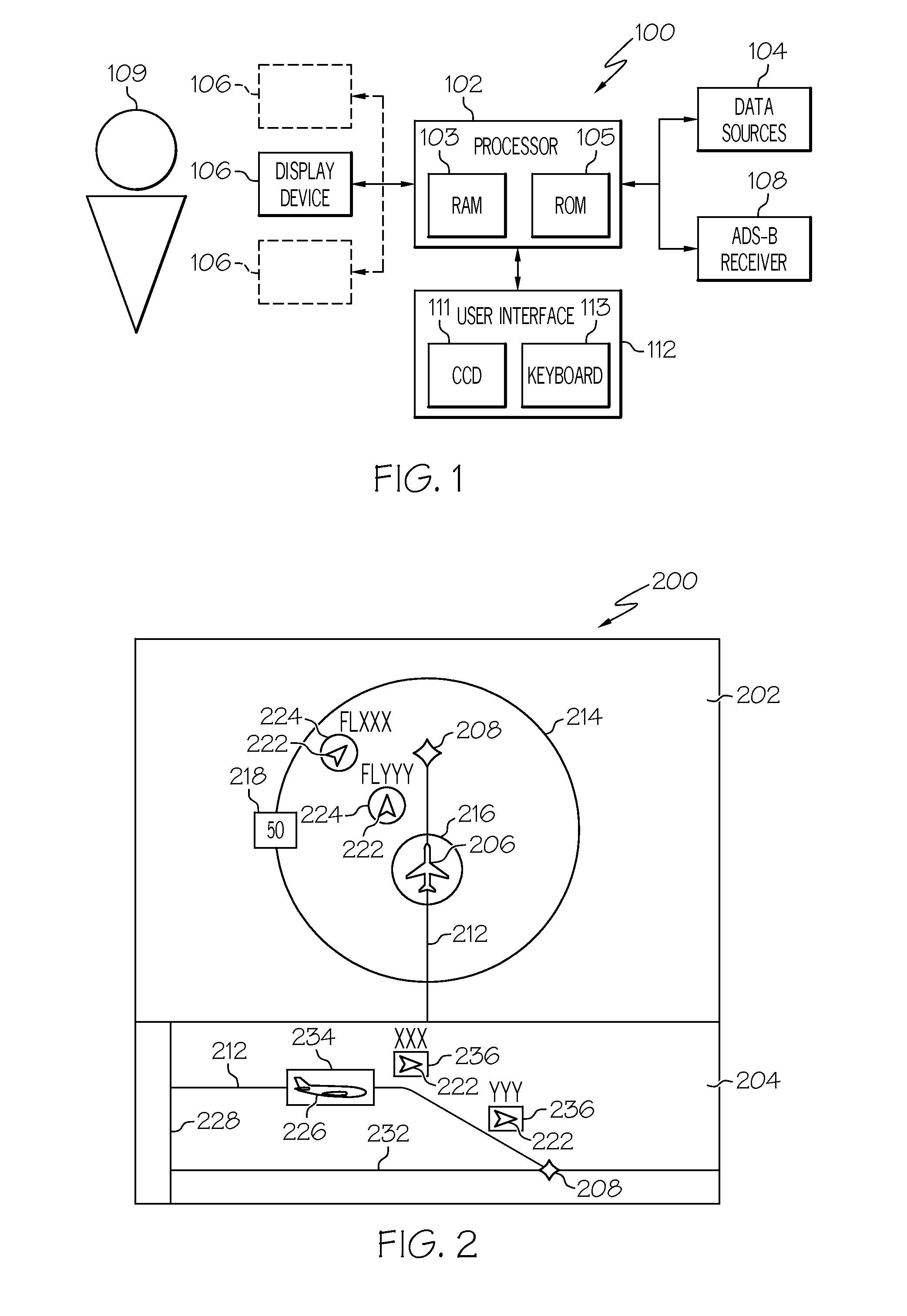
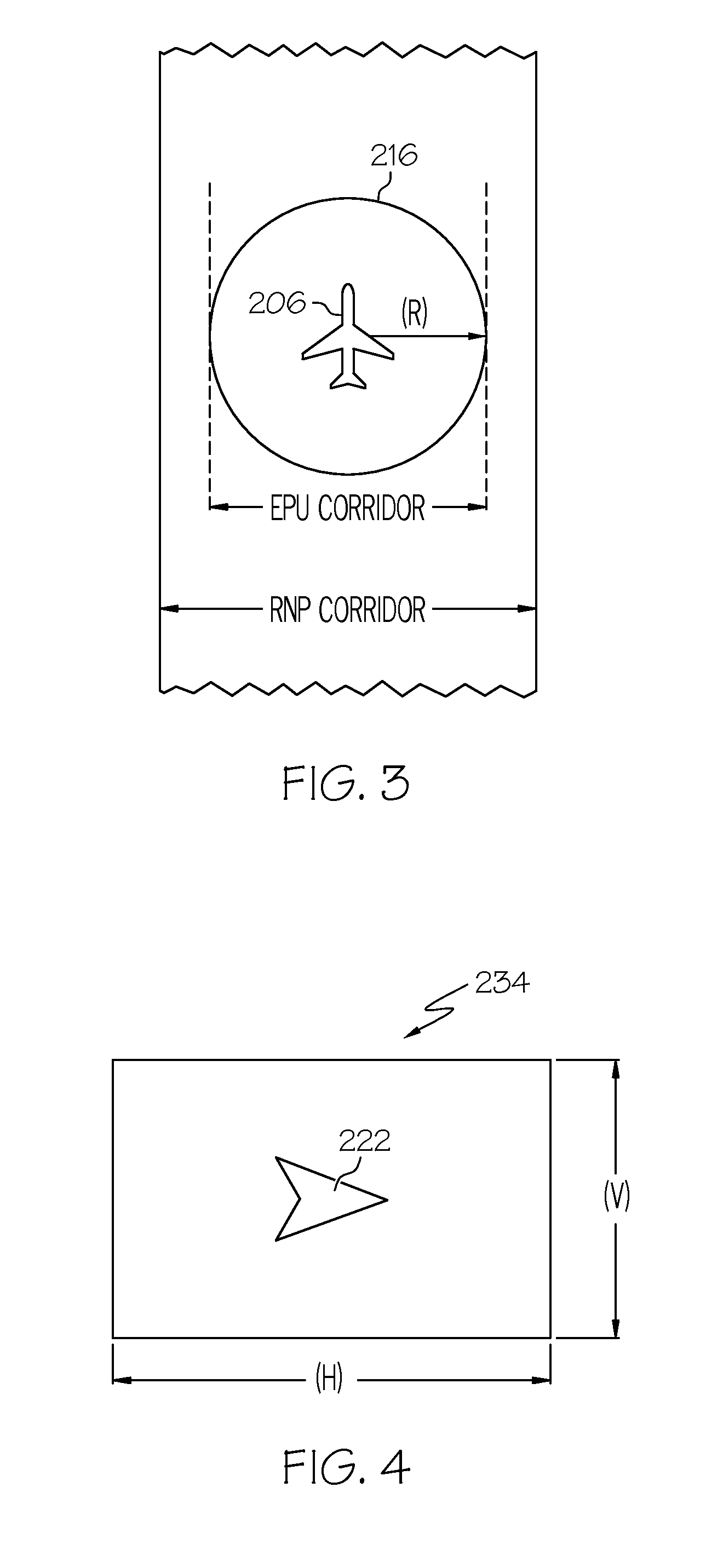
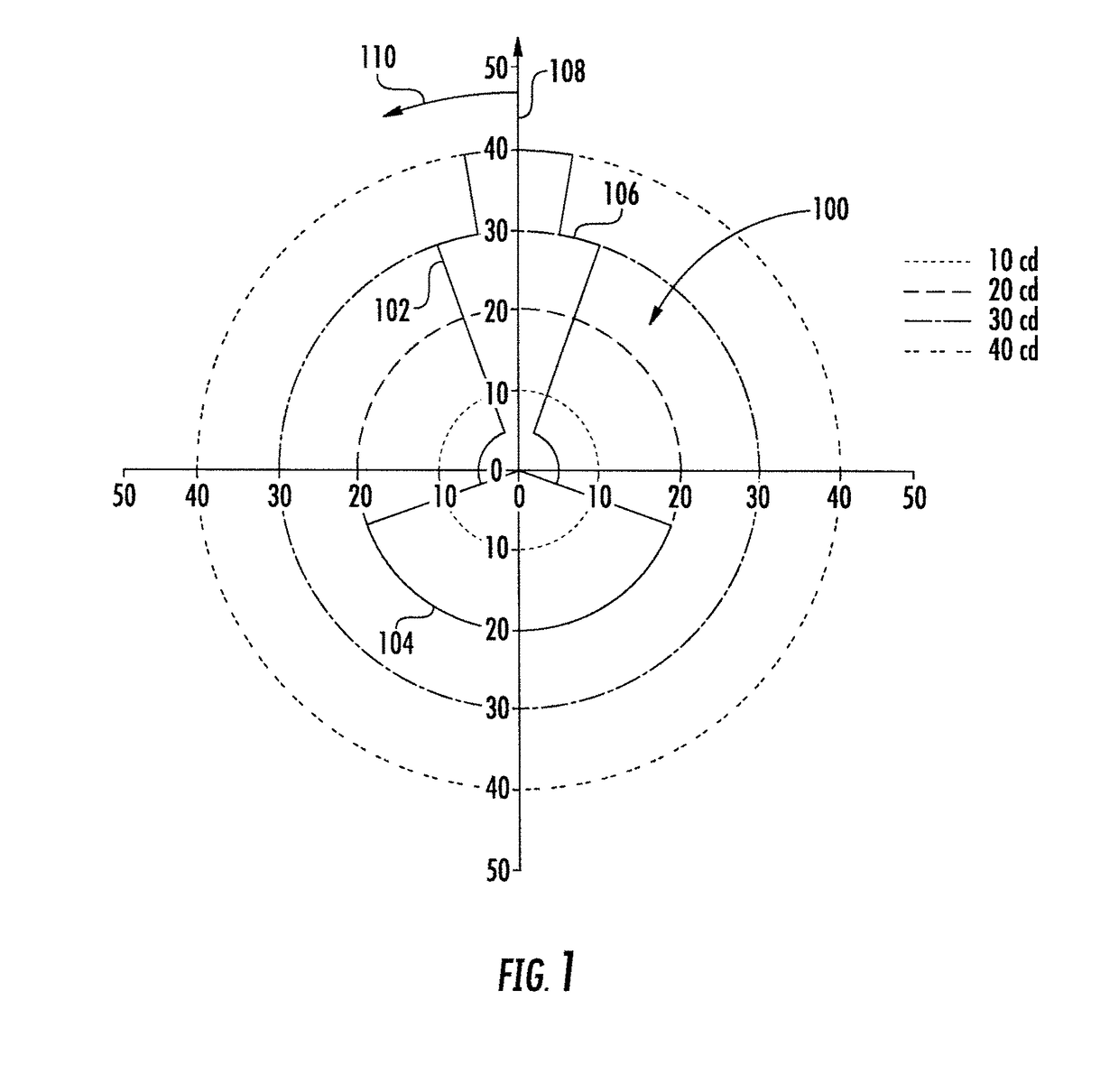
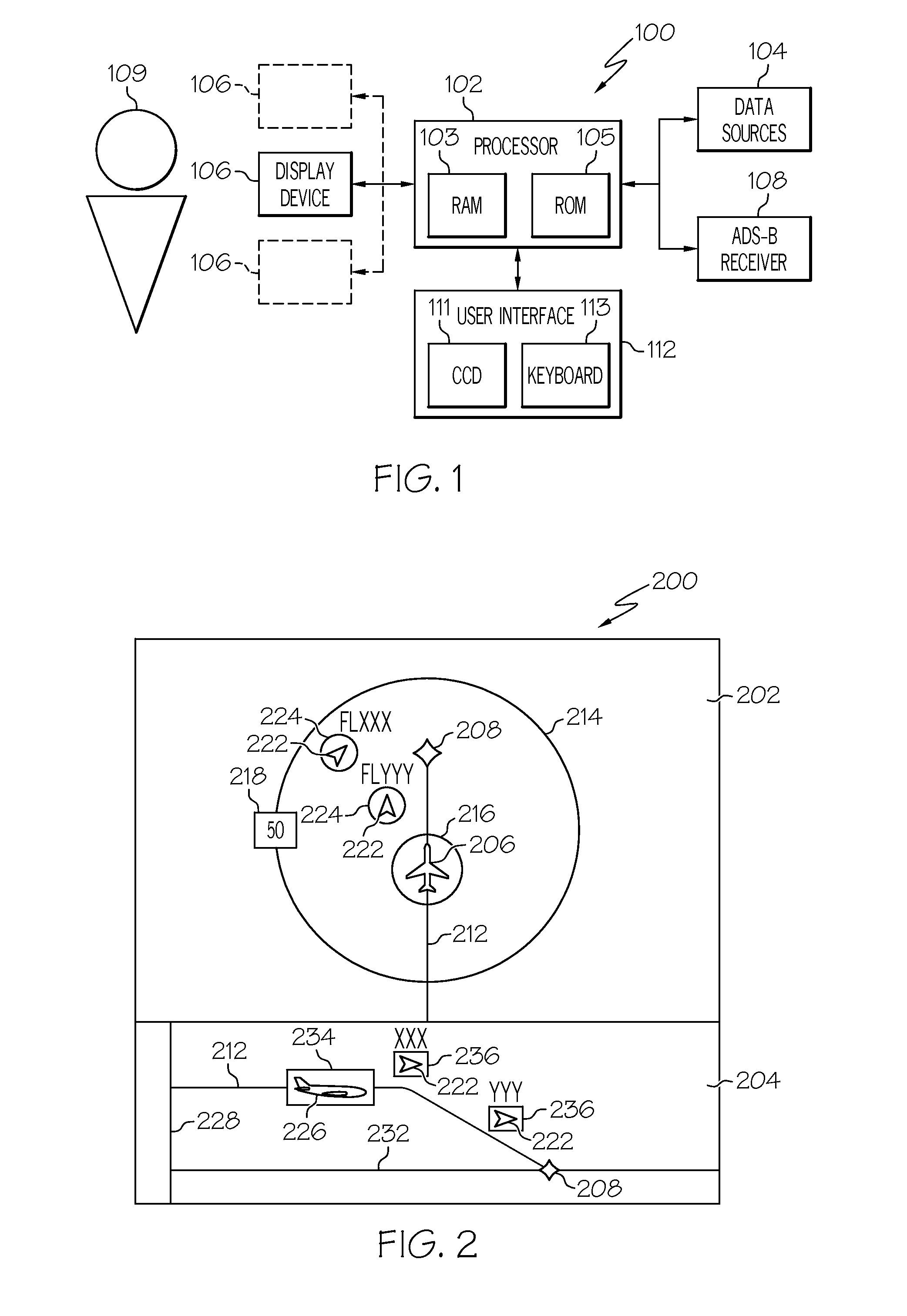
Graphical display for aircraft navigation
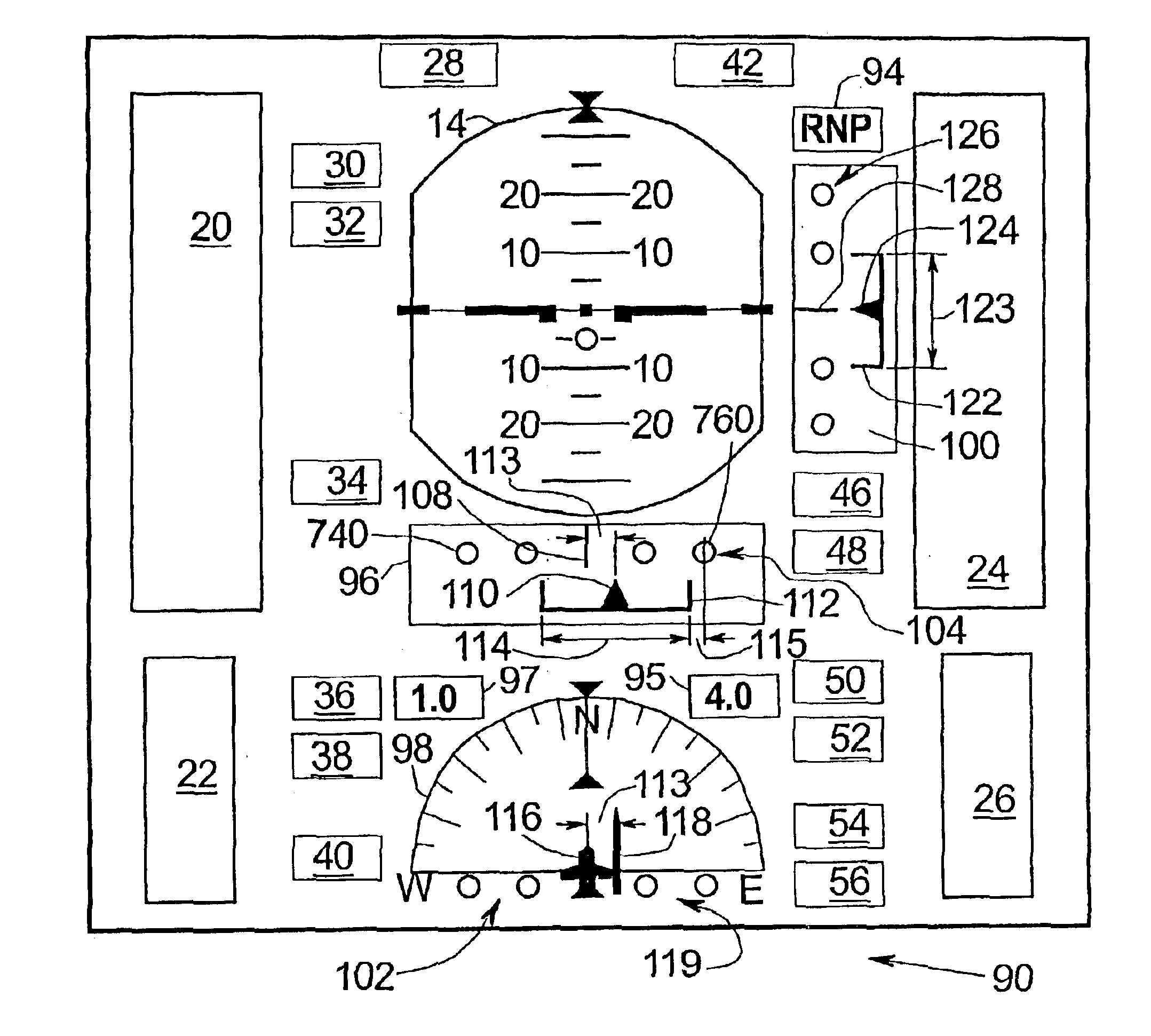
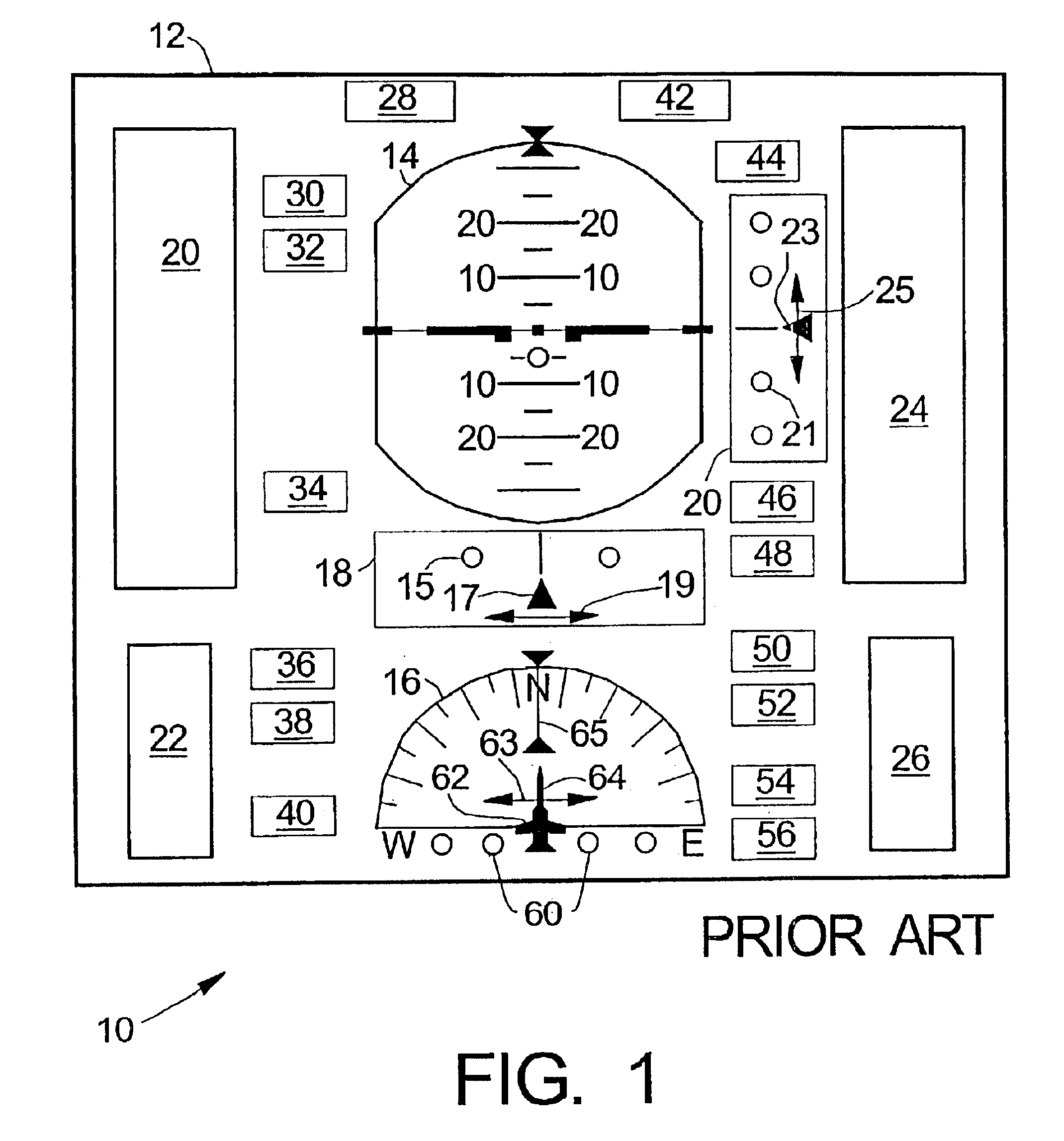
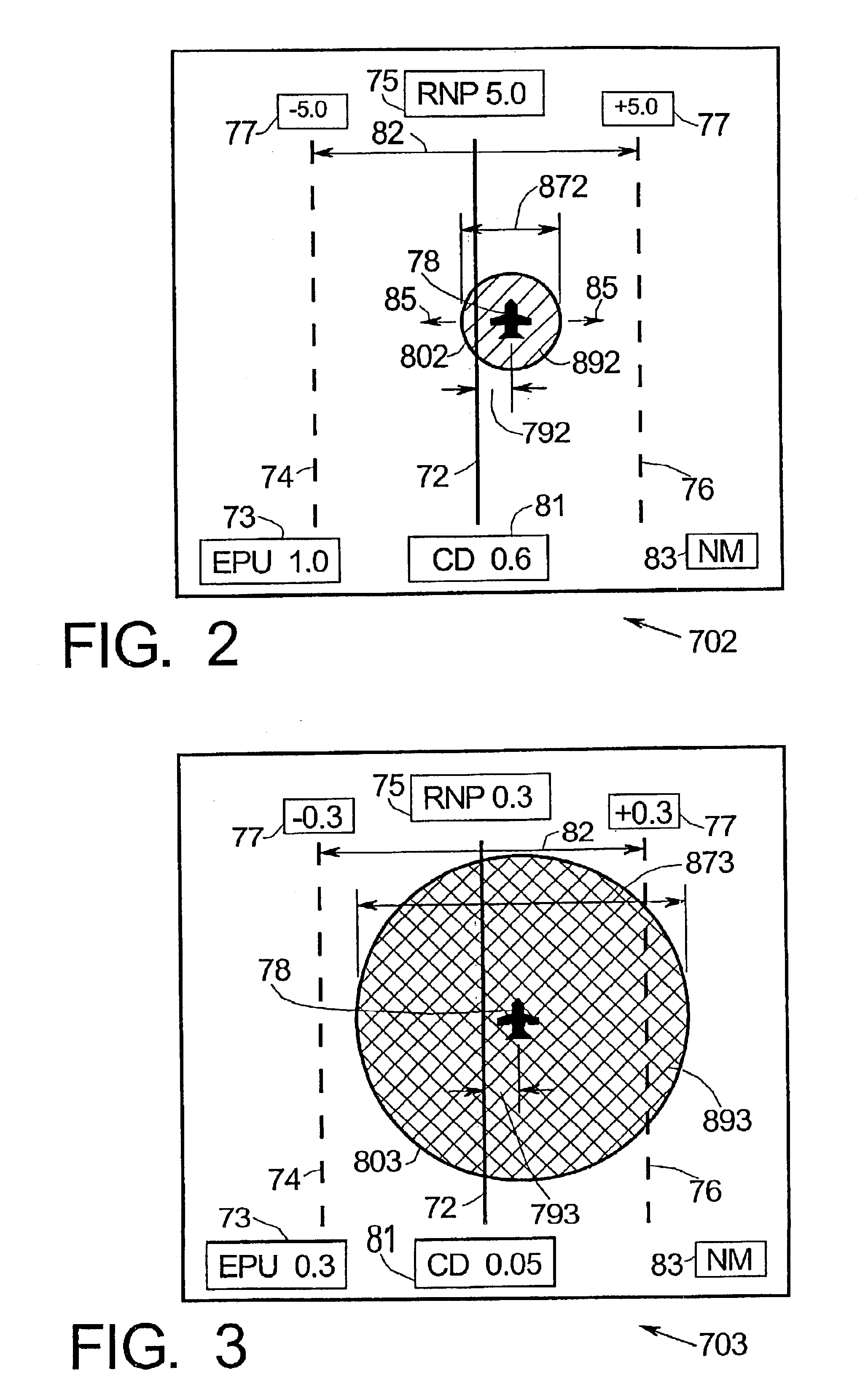
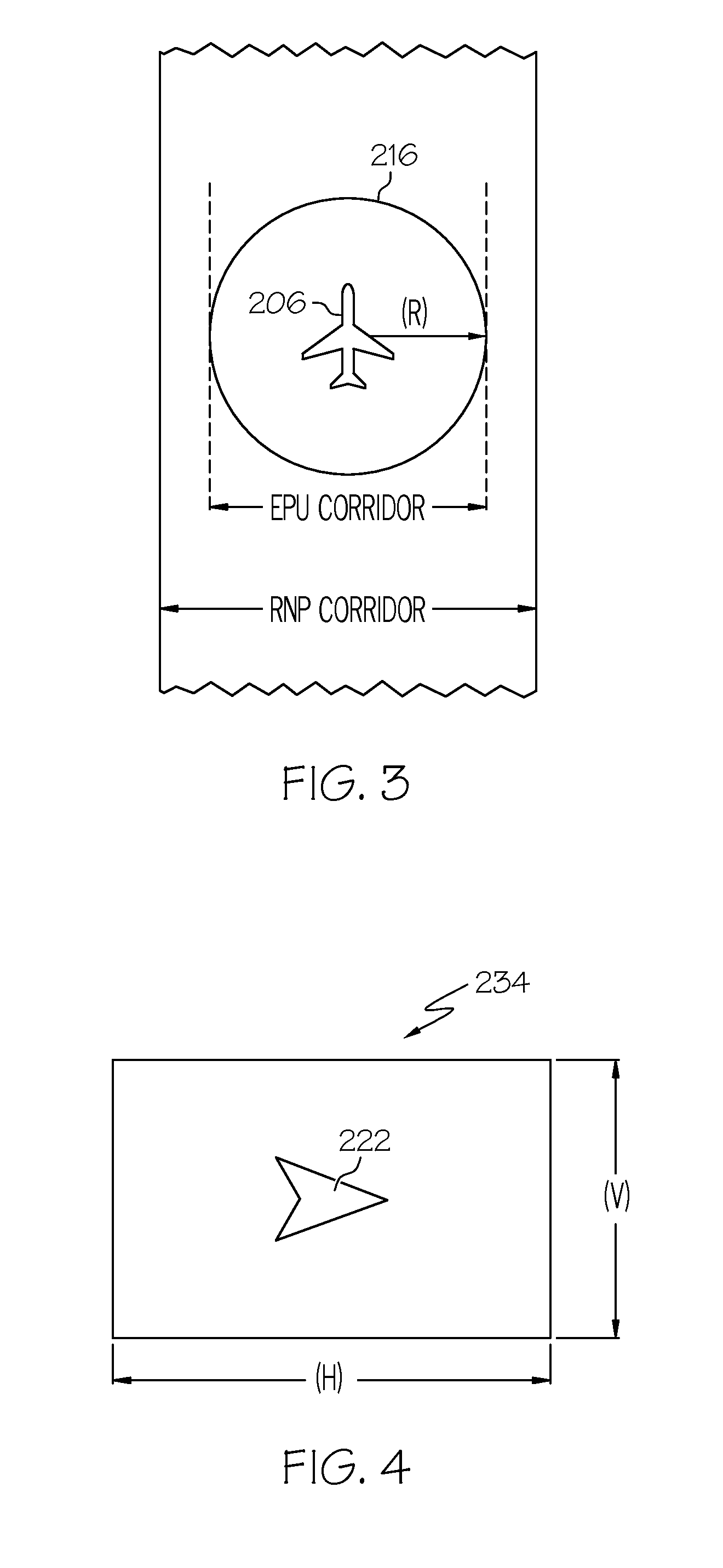
InactiveUS6885313B2Enhanced informationAnalogue computers for trafficNavigation instrumentsGraphicsRequired navigation performance
Methods and apparatus are provided for indicating safe or potentially hazardous operating conditions of an aircraft in a required navigational performance (RNP) environment. The apparatus comprises a course deviation display field with first and second markers defining outer boundaries of the RNP width and a central marker indicating the desired course within the RNP width, an aircraft estimated position uncertainty (EPU) marker in the display field whose size corresponds to the EPU relative to the RNP and a current aircraft position marker coupled to the EPU marker and moving therewith as the aircraft position changes with respect to the RNP width. The display desirably changes color and / or flashes to alert a pilot to a potentially hazardous condition when an outer boundary of the EPU marker approaches to within a predetermined guard-band distance of or overlaps either of the first or second markers. An audible warning can be included.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
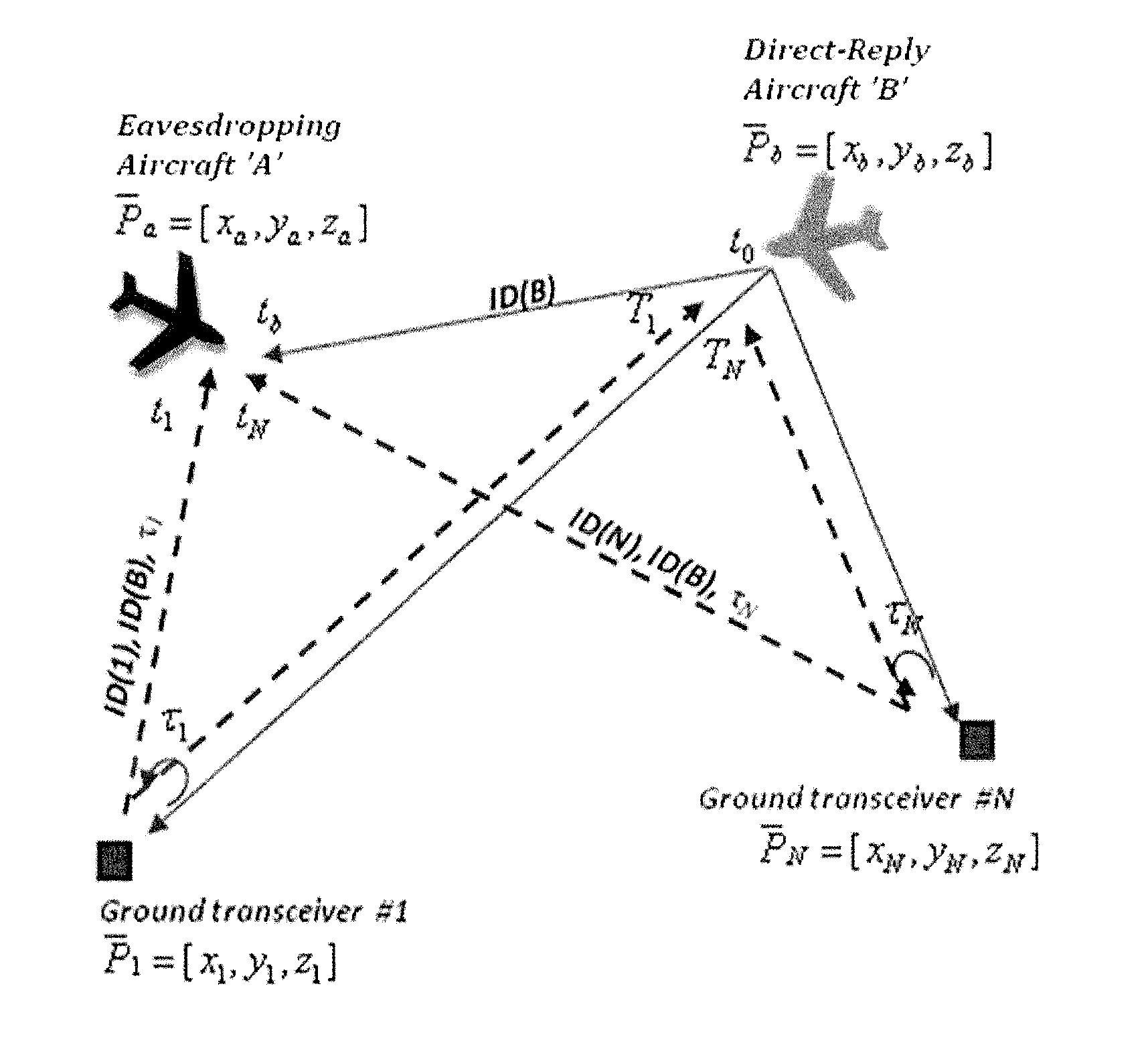
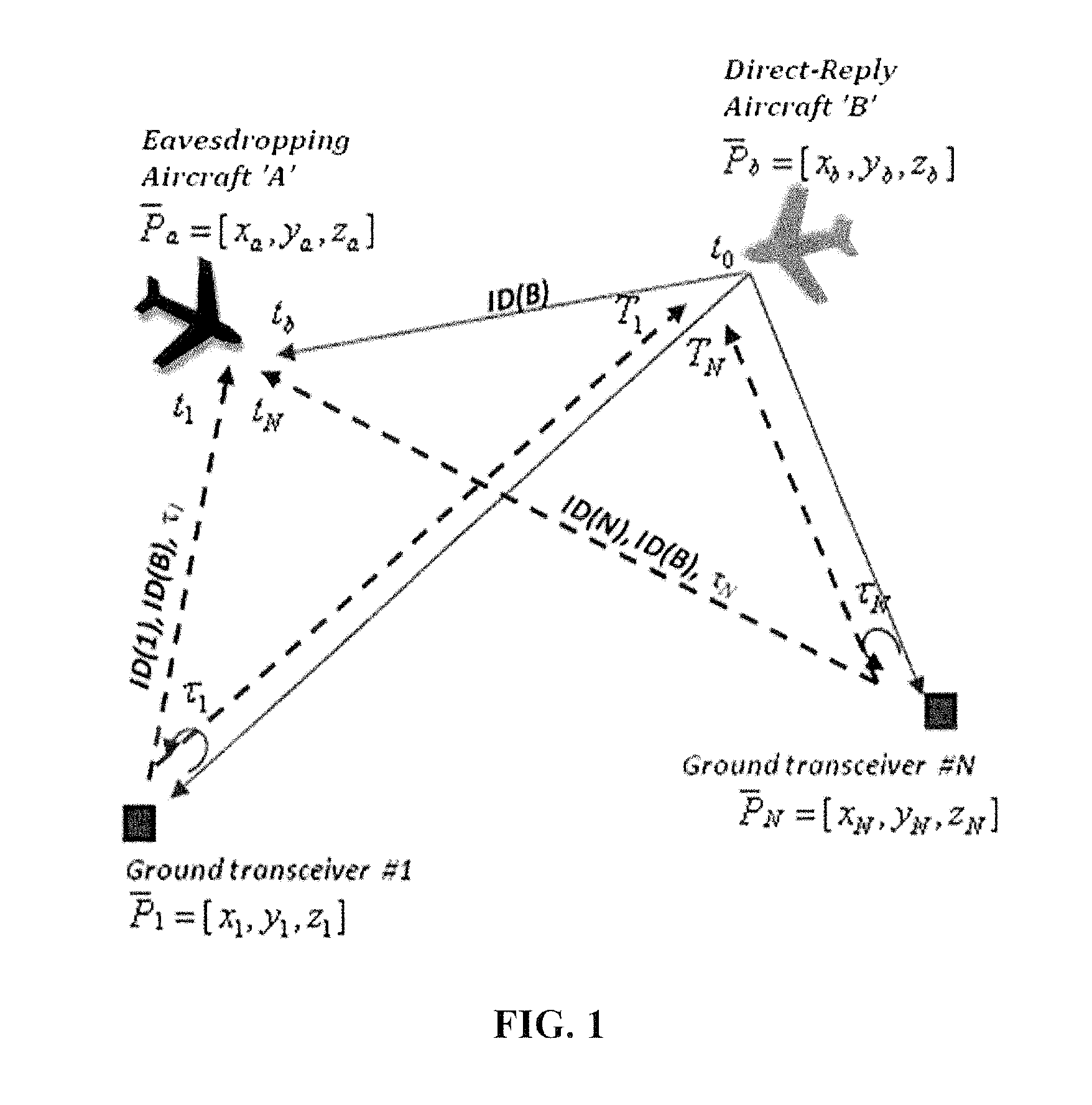
System and method for aircraft navigation based on diverse ranging algorithm using ads-b messages and ground transceiver responses
A method of aircraft navigation via receiving signals emitted by other aircraft and corresponding reply message transmitted by ground transceivers and the using a new diverse-ranging algorithm that solves for the positions of a eavesdropping aircraft and the positions of direct-reply aircraft emitting the signals received by the eavesdropping aircraft.
Owner:SAAB INC
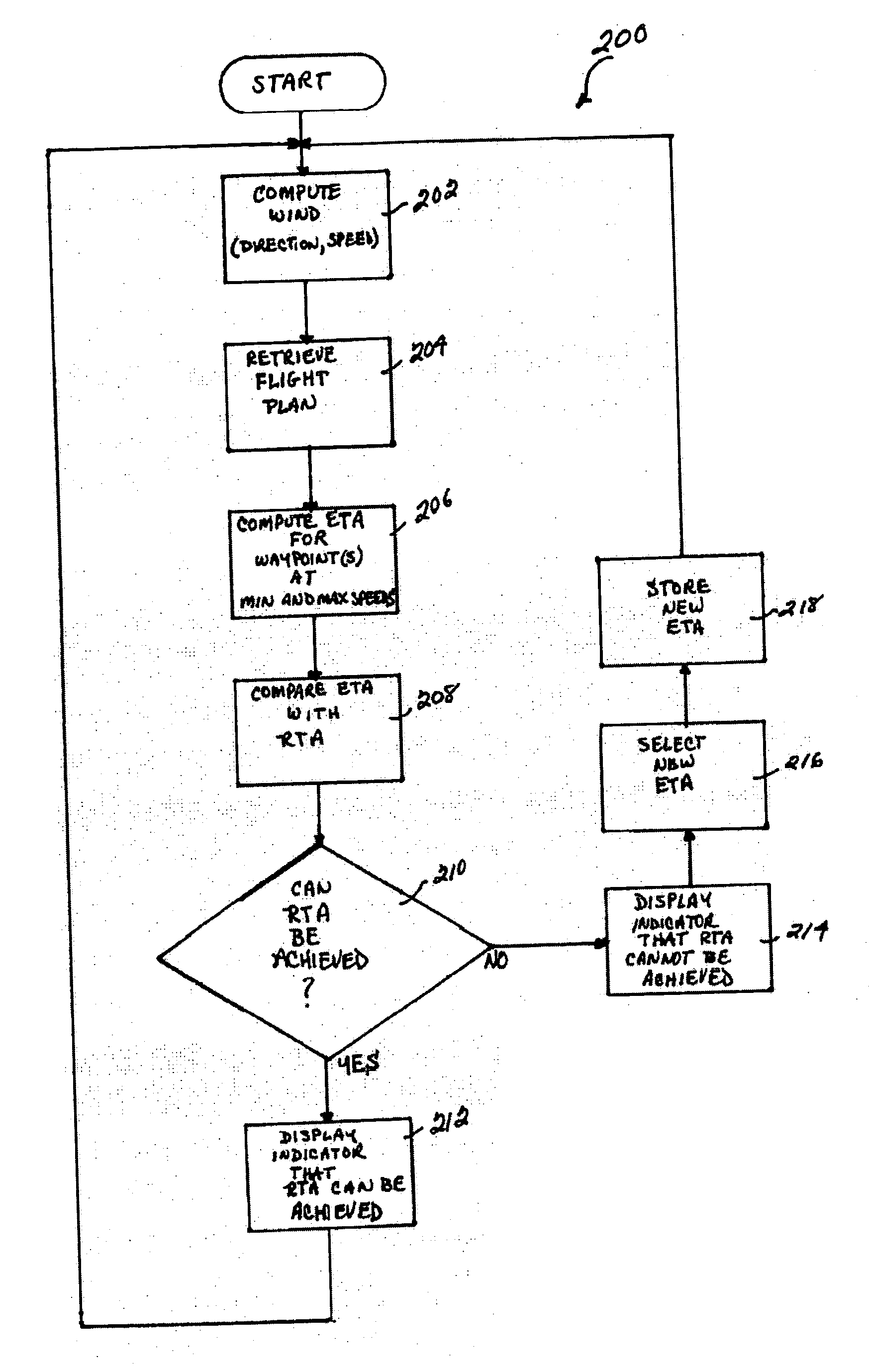
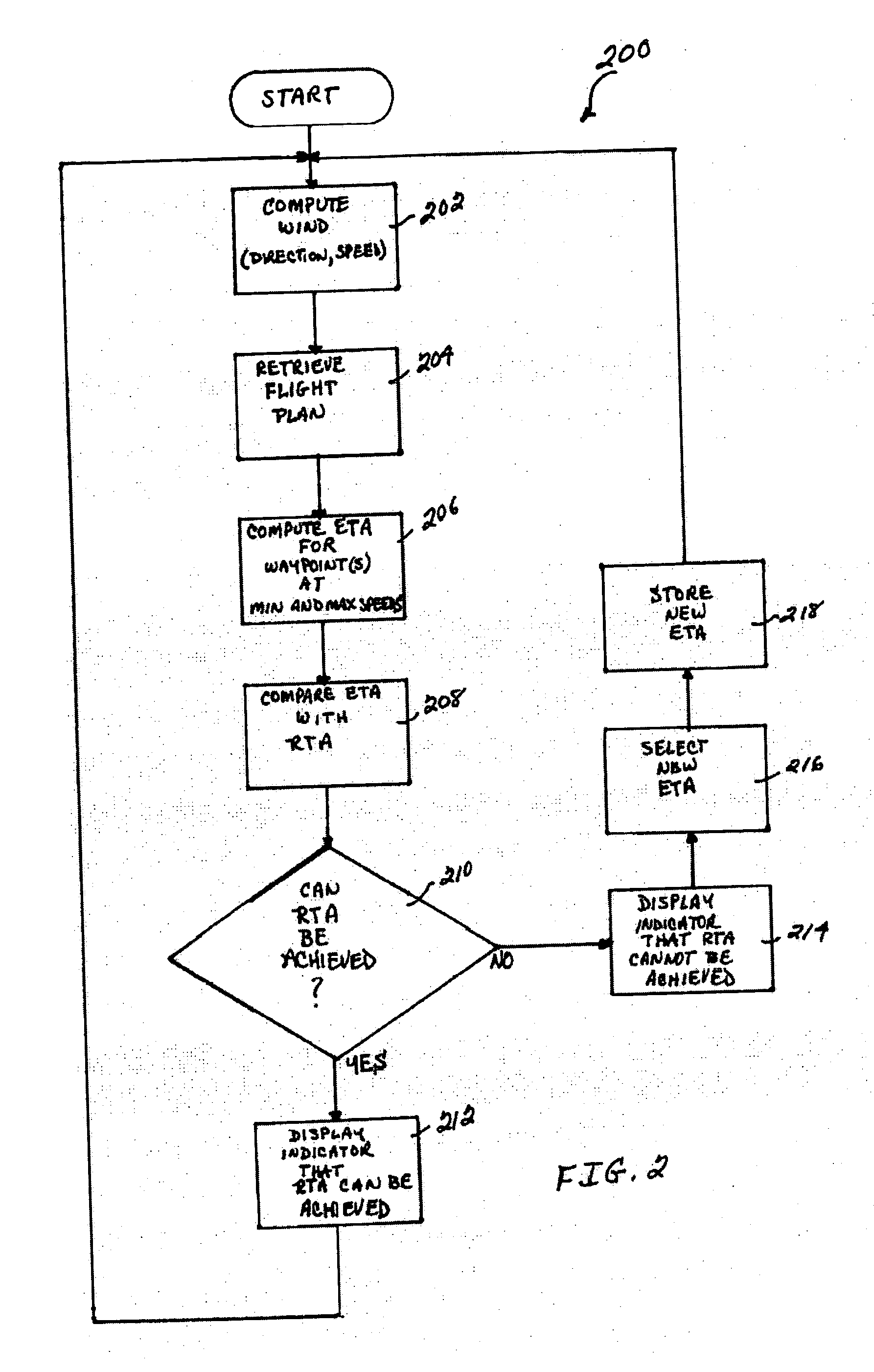
System and method for performing 4-dimensional navigation
InactiveUS20070100538A1Reliable predictionFuel is wastedInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlRoad traffic controlGraphics
A system and method are disclosed for computing a vehicle's motion in four dimensions (e.g., three spatial dimensions and time) and reliably predicting the vehicle's arrival time at a predetermined location, by providing a graphical display to an operator of the vehicle's progress that enables the operator to adjust the vehicle's movement and achieve the desired arrival time. Specifically, a system and method are disclosed for computing the movement of an aircraft in four dimensions, predicting its arrival time at a predetermined waypoint, and displaying (in a highly intuitive format) the aircraft's progress in achieving that desired arrival time. The pilot can then adjust the movement (e.g., speed) of the aircraft in accordance with the parameter(s) displayed, in order to achieve the desired arrival time. Thus, for example, numerous aircraft could be scheduled to arrive at a specific final approach waypoint at a predetermined rate (e.g., one aircraft per minute), which would enable the traffic controllers to optimize runway traffic without having to stack the aircraft in holding patterns and thereby waste fuel. Notably, although an example of an aircraft navigation and control system and method is disclosed, the system and method can be implemented for any type of vehicle (e.g., aircraft, spacecraft, ship, submarine, bus, train, automobile, etc.) whose operator desires to reach a particular location at a specified time.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
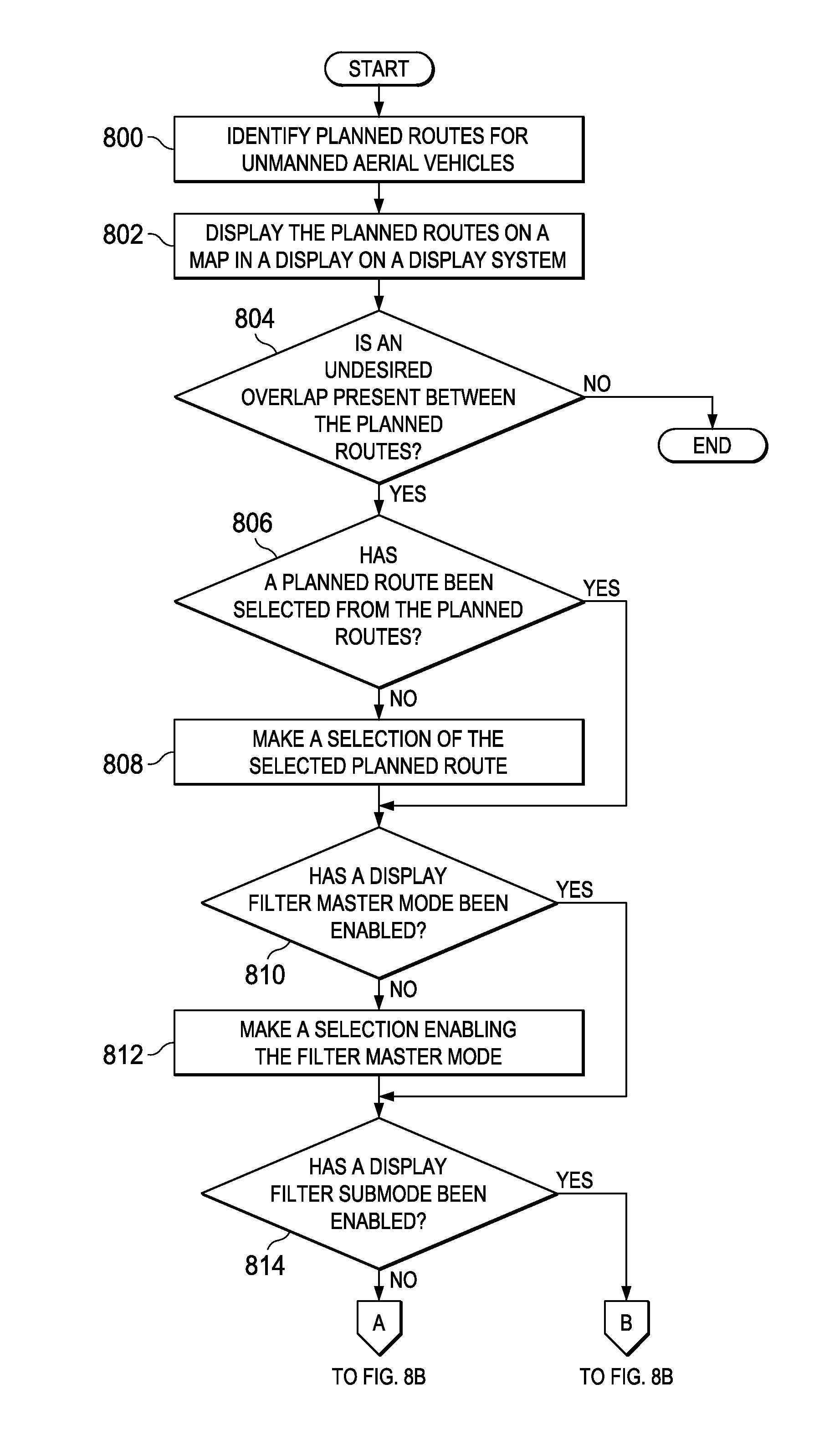
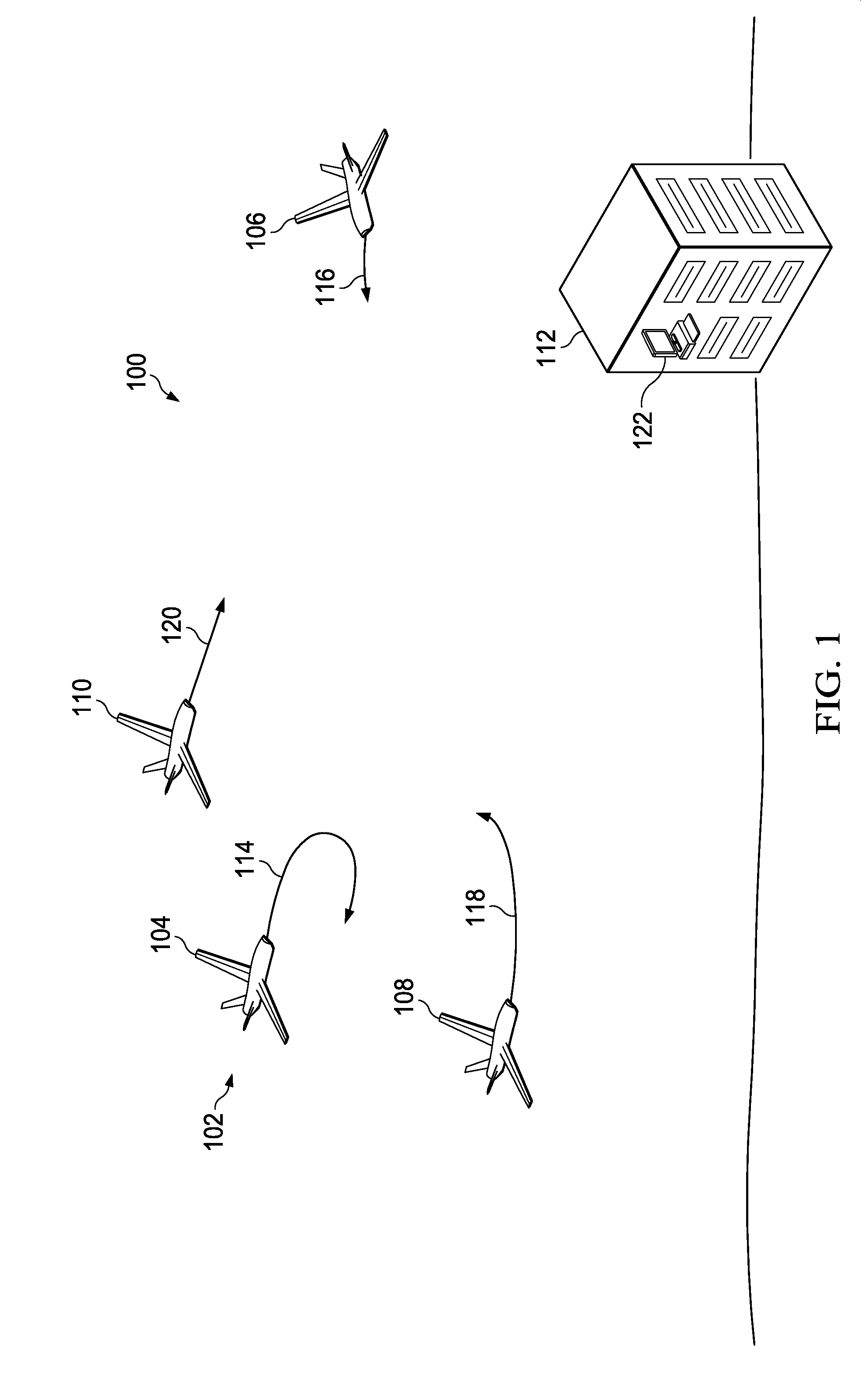
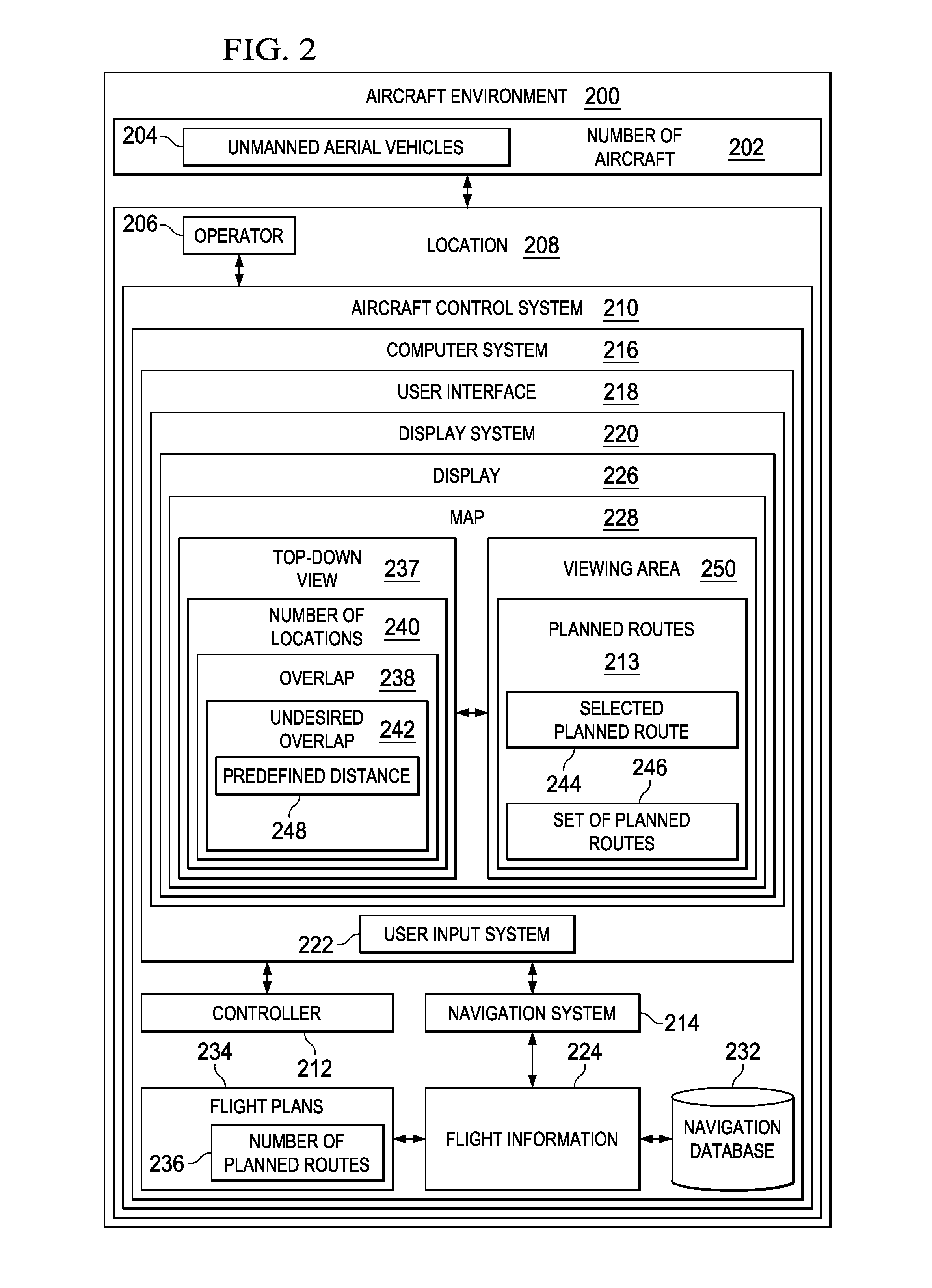
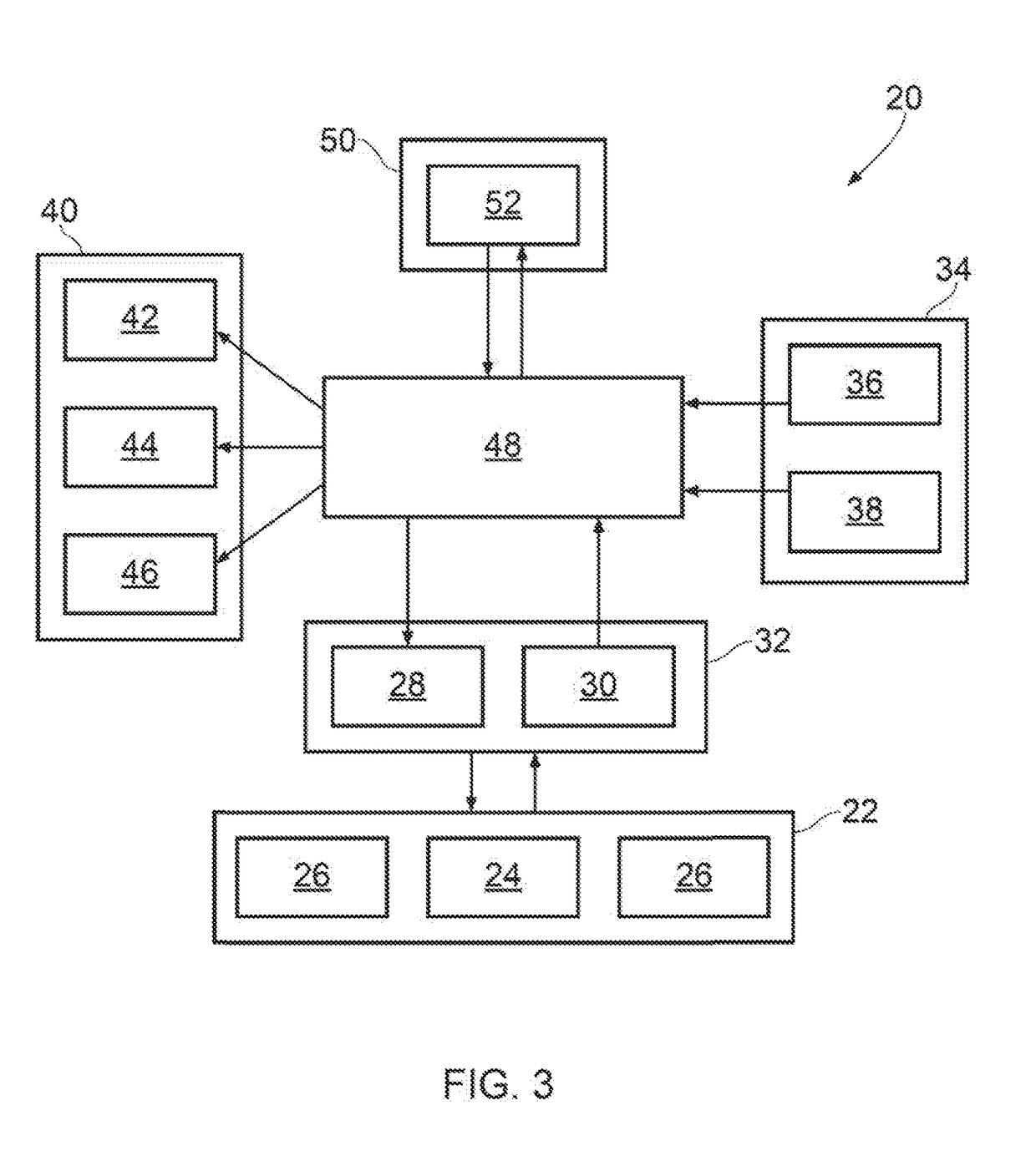
Aircraft navigation system
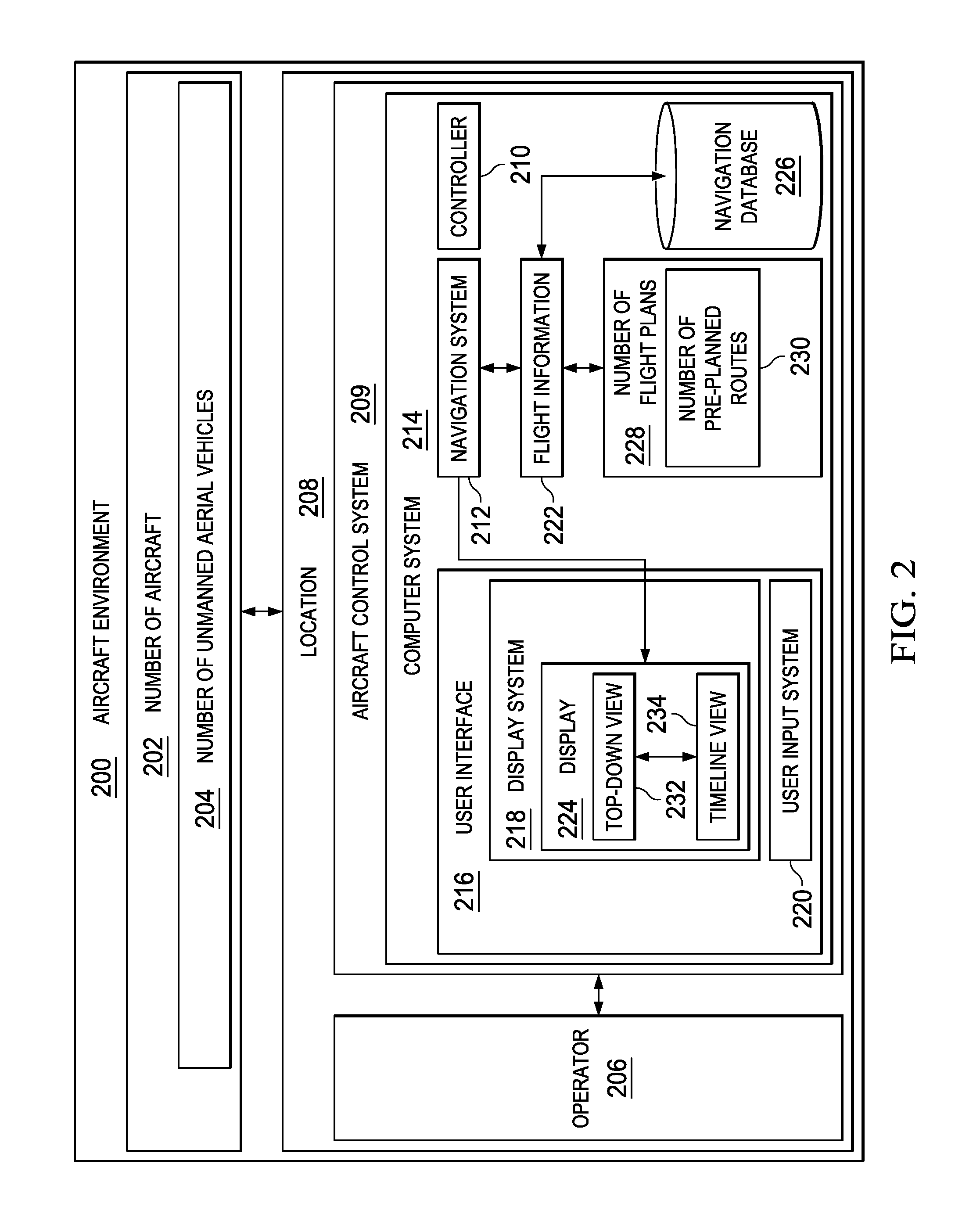
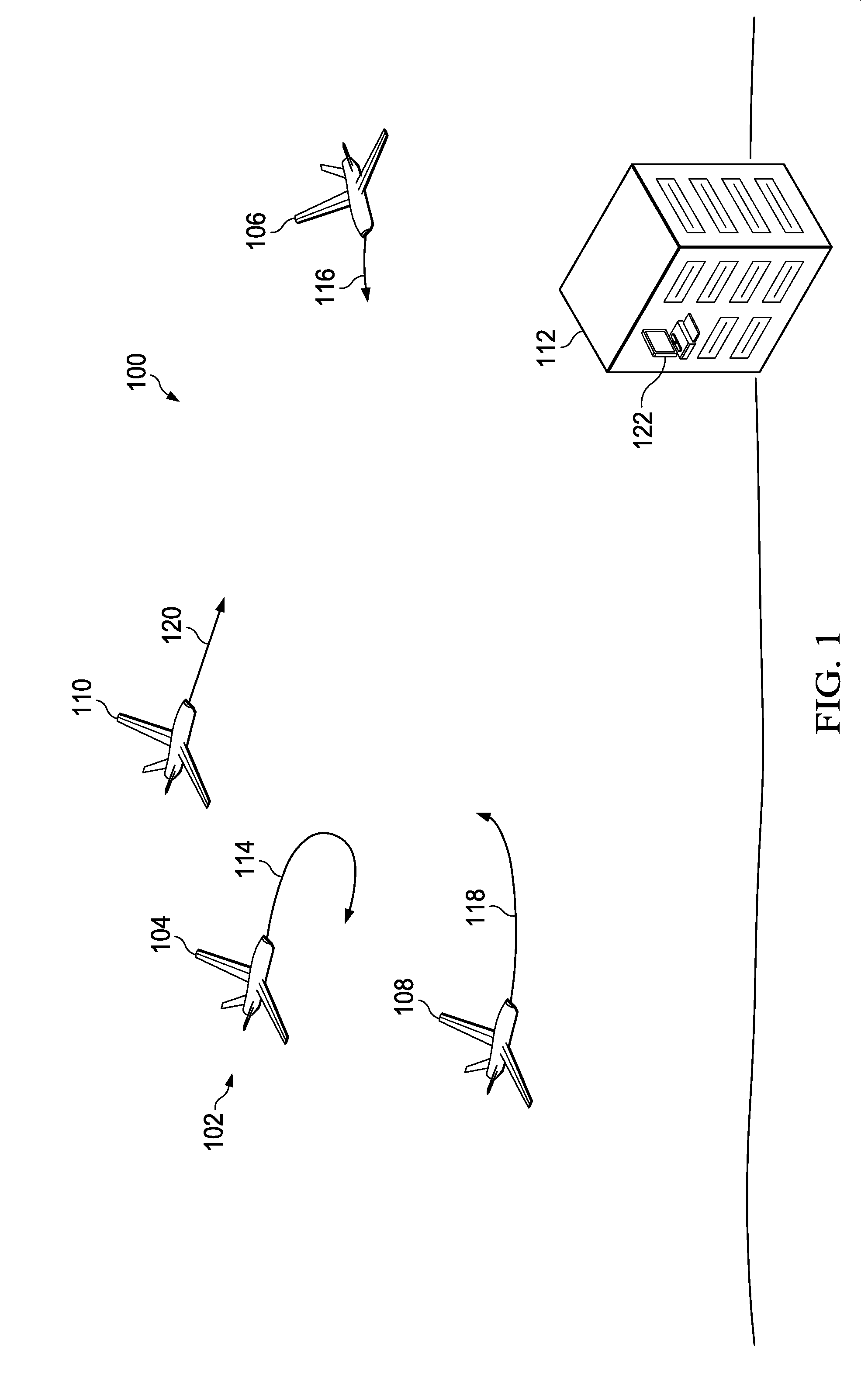
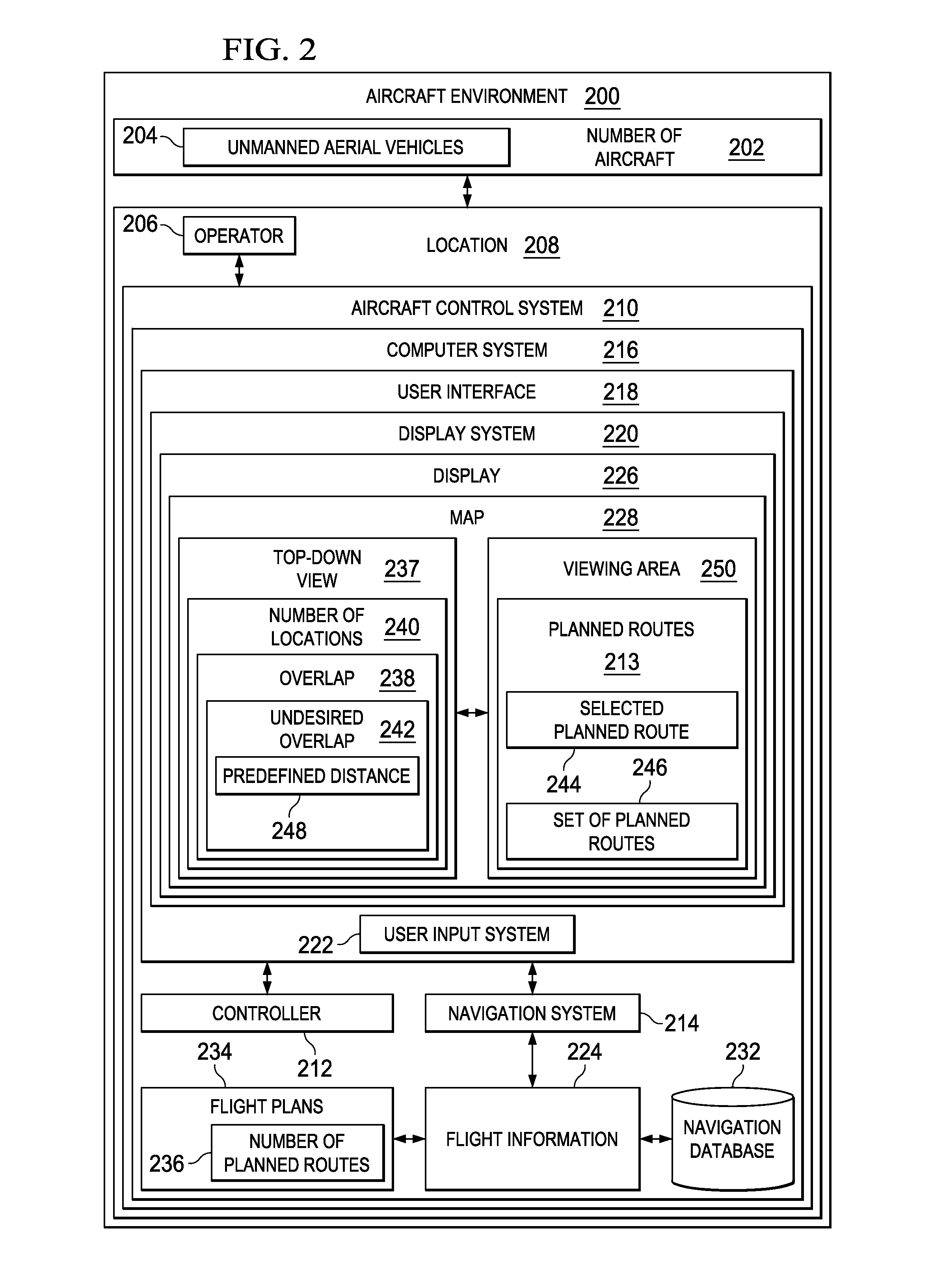
A method and apparatus for assisting in management of unmanned aerial vehicles. Planned routes are identified for the unmanned aerial vehicles. The planned routes are displayed on a map. A set of planned routes is identified that is within a predefined distance of a selected planned route during substantially a same point in time within a viewing area on the map.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
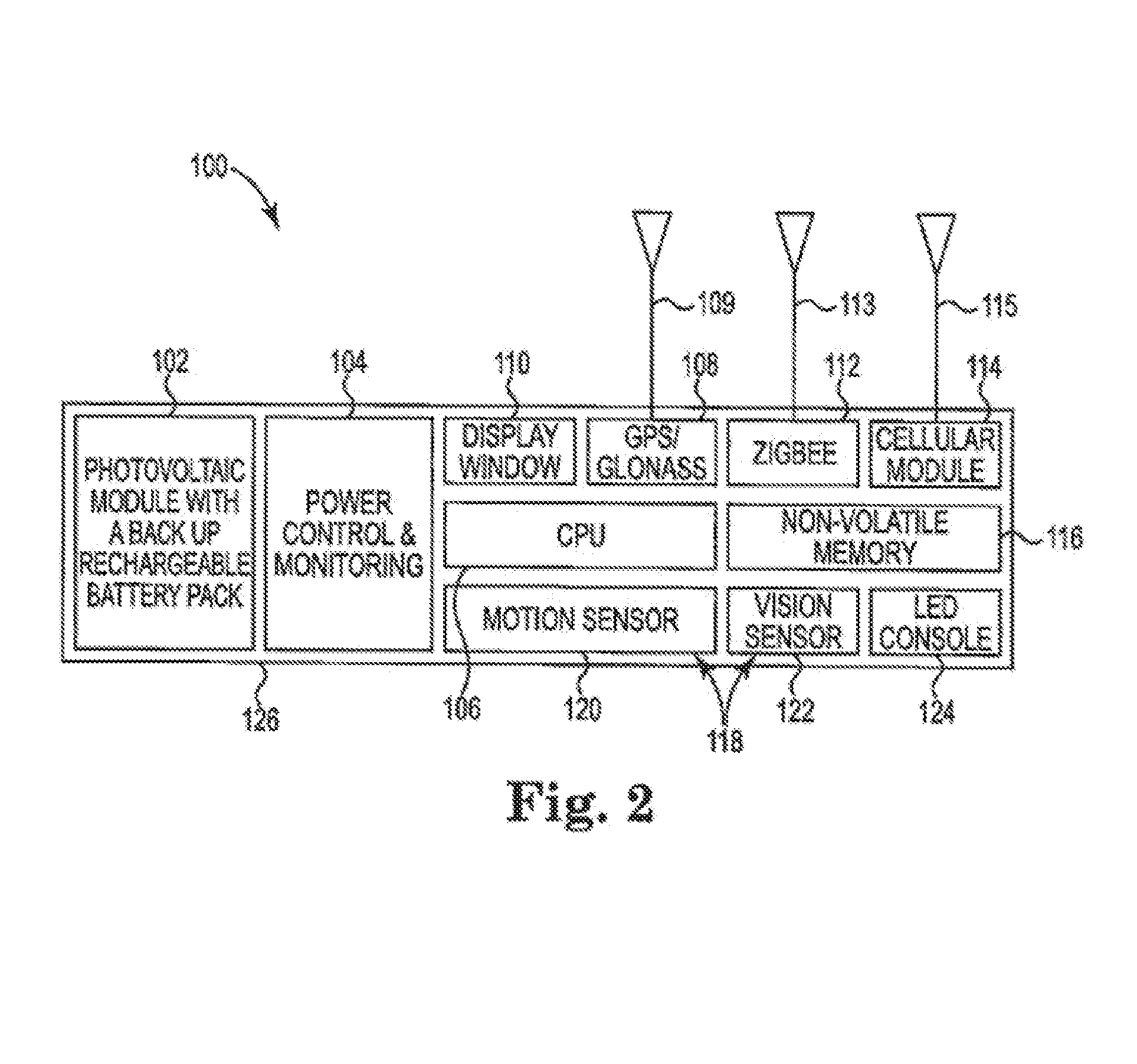
Aircraft container tracking device
ActiveUS20160205500A1Particular environment based servicesSatellite radio beaconingCommunications systemBiological activation
A wireless transmitter device that has a baseline ‘off’ status, turning its data transmission module ‘on’ only under certain specific circumstances, thus allowing the device to be used on aircraft without concern of the device activating and transmitting location data that might interfere with the aircraft navigation and / or communication systems. The data transmission module may be turned on manually (i.e., manual activation), may be activated based on time (i.e., time-based activation), or may be activated based on motion (i.e., motion-based activation). Activation of the data transmission module occurs only after it has been determined that it is safe to activate the module(s), for example, if no motion of the device has been sensed for a predetermined period of time. Only after the device has assuredly determined that the aircraft is in a mode where data transmission is allowed (e.g., not in flight) is the data transmission module activated.
Owner:ROAMBEE
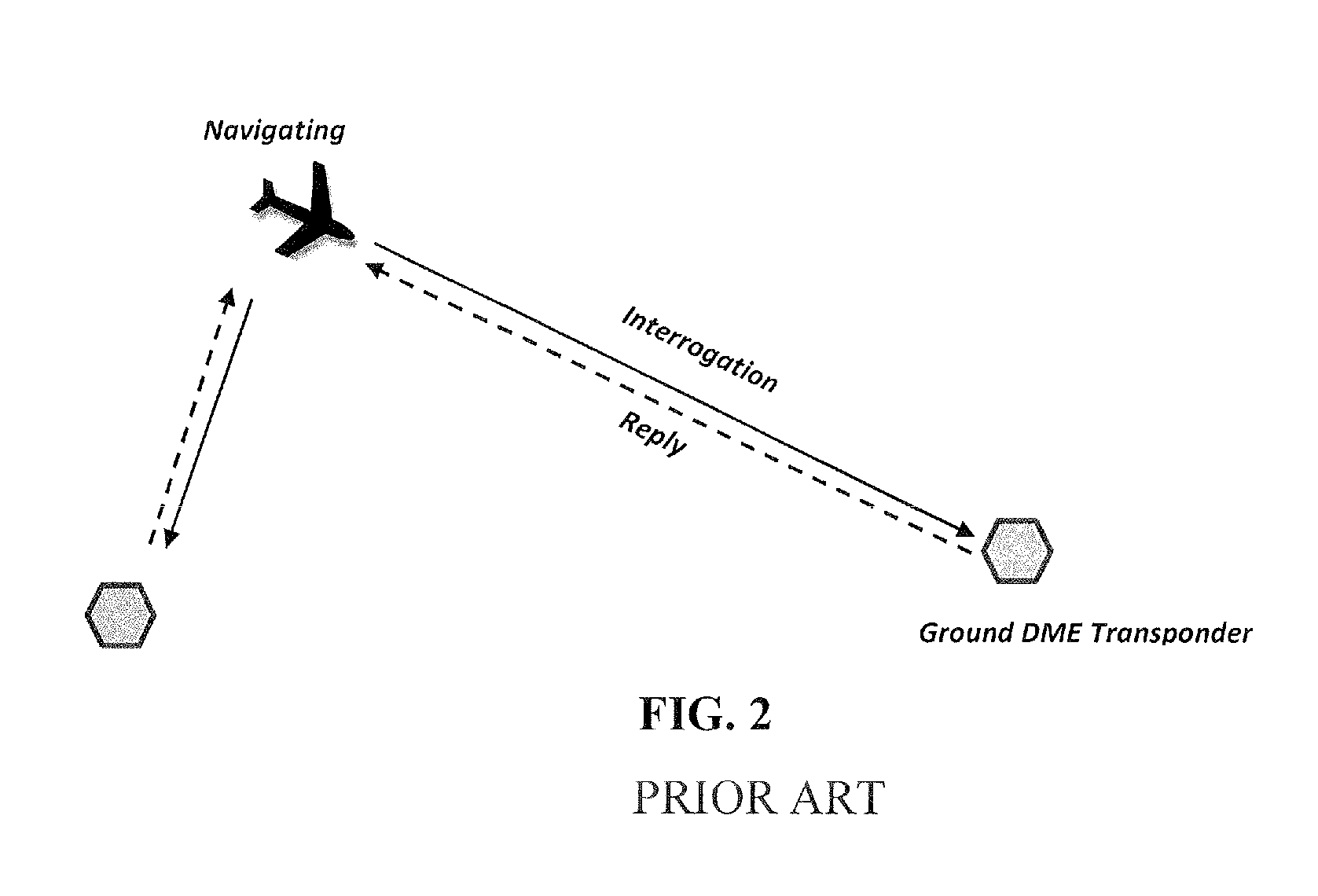
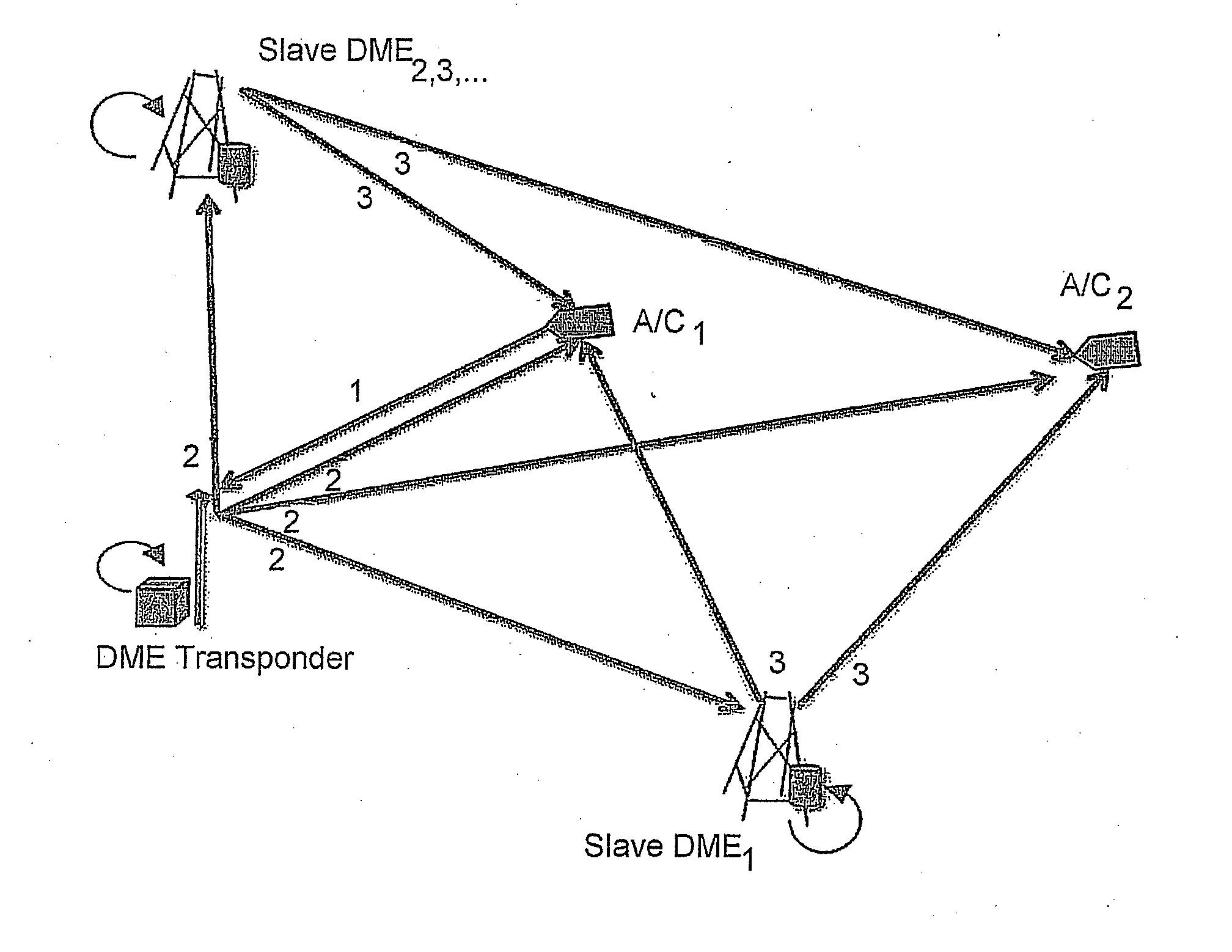
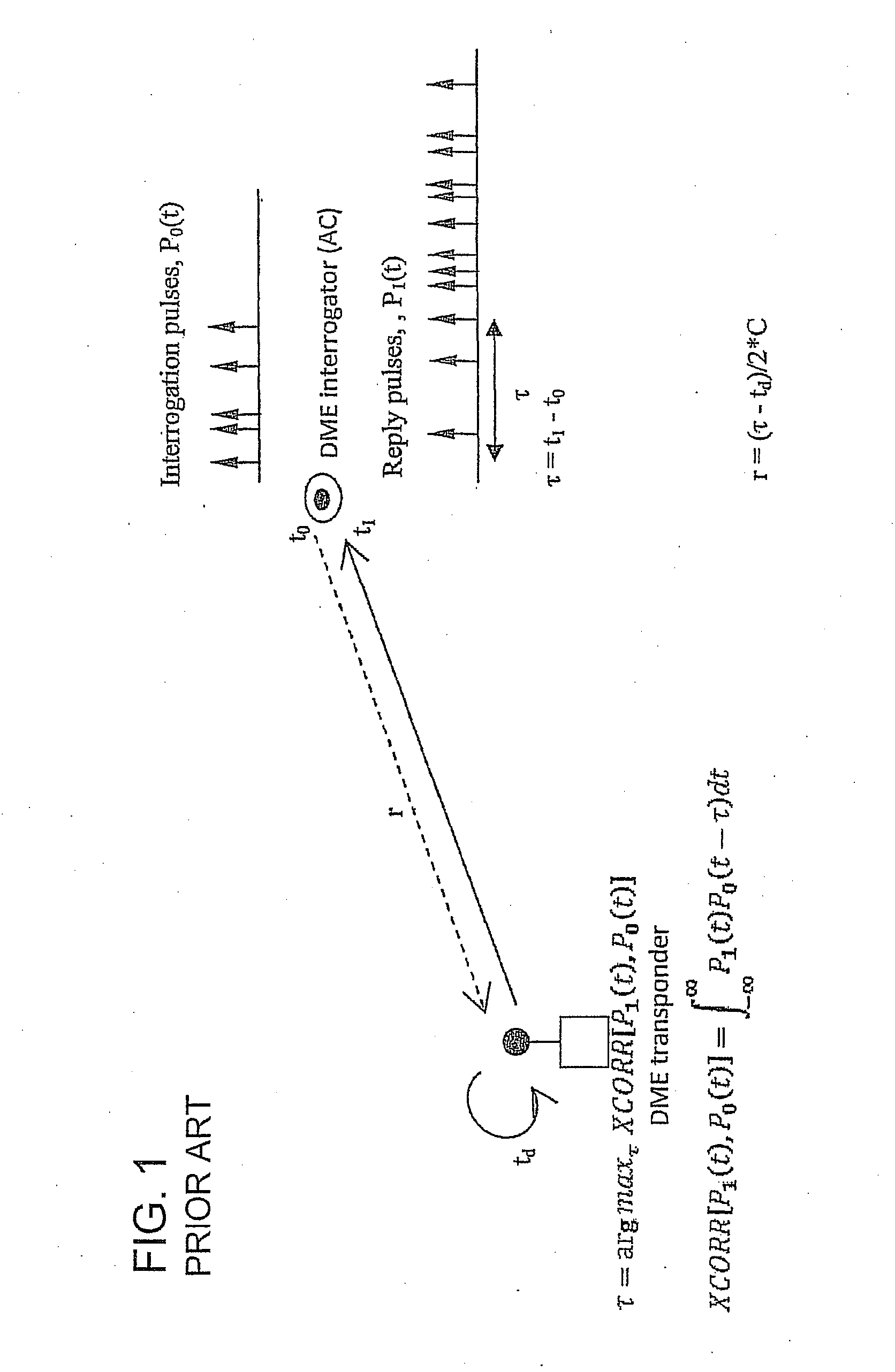
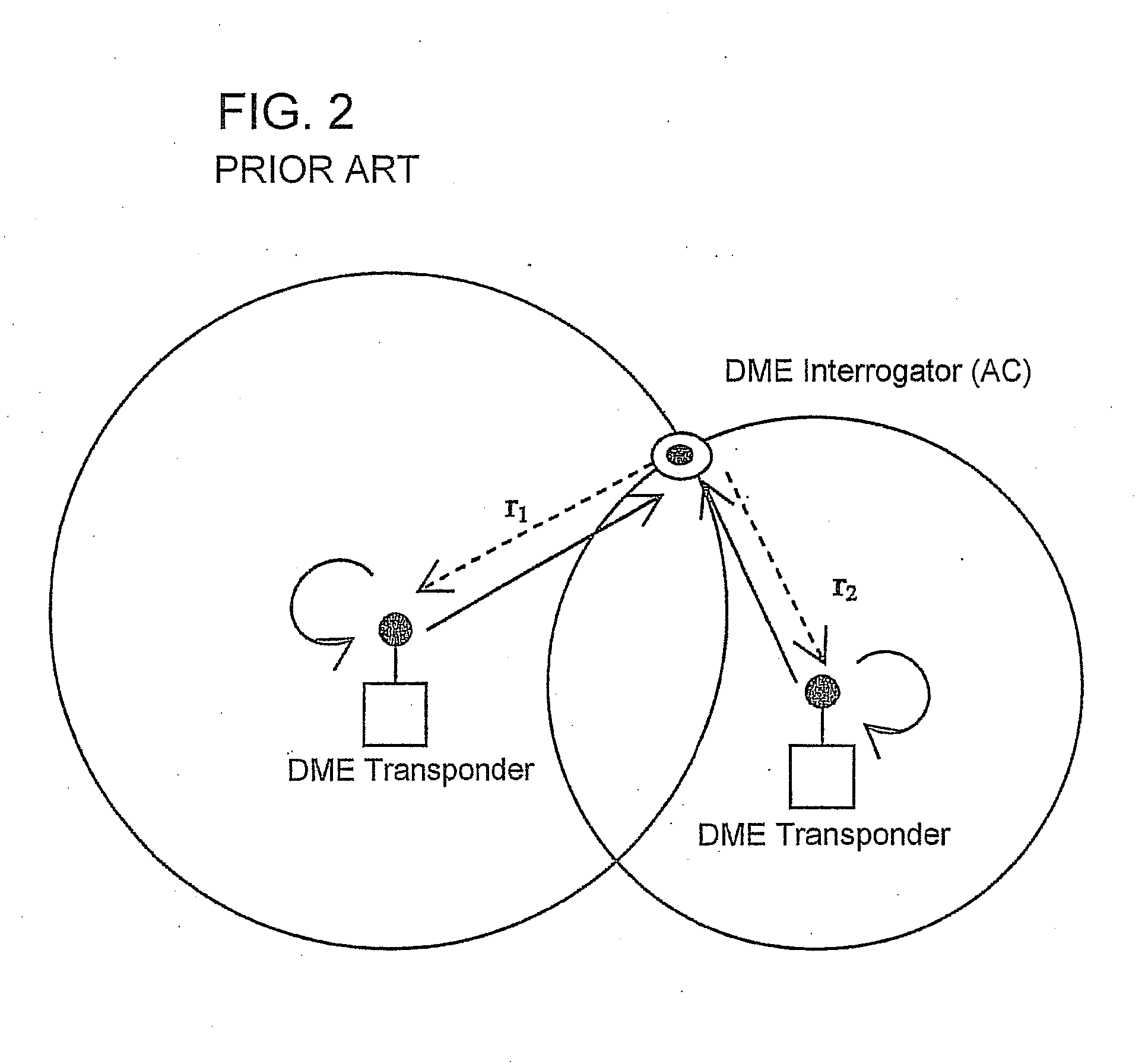
System and method for aircraft navigation using signals transmitted in the dme transponder frequency range
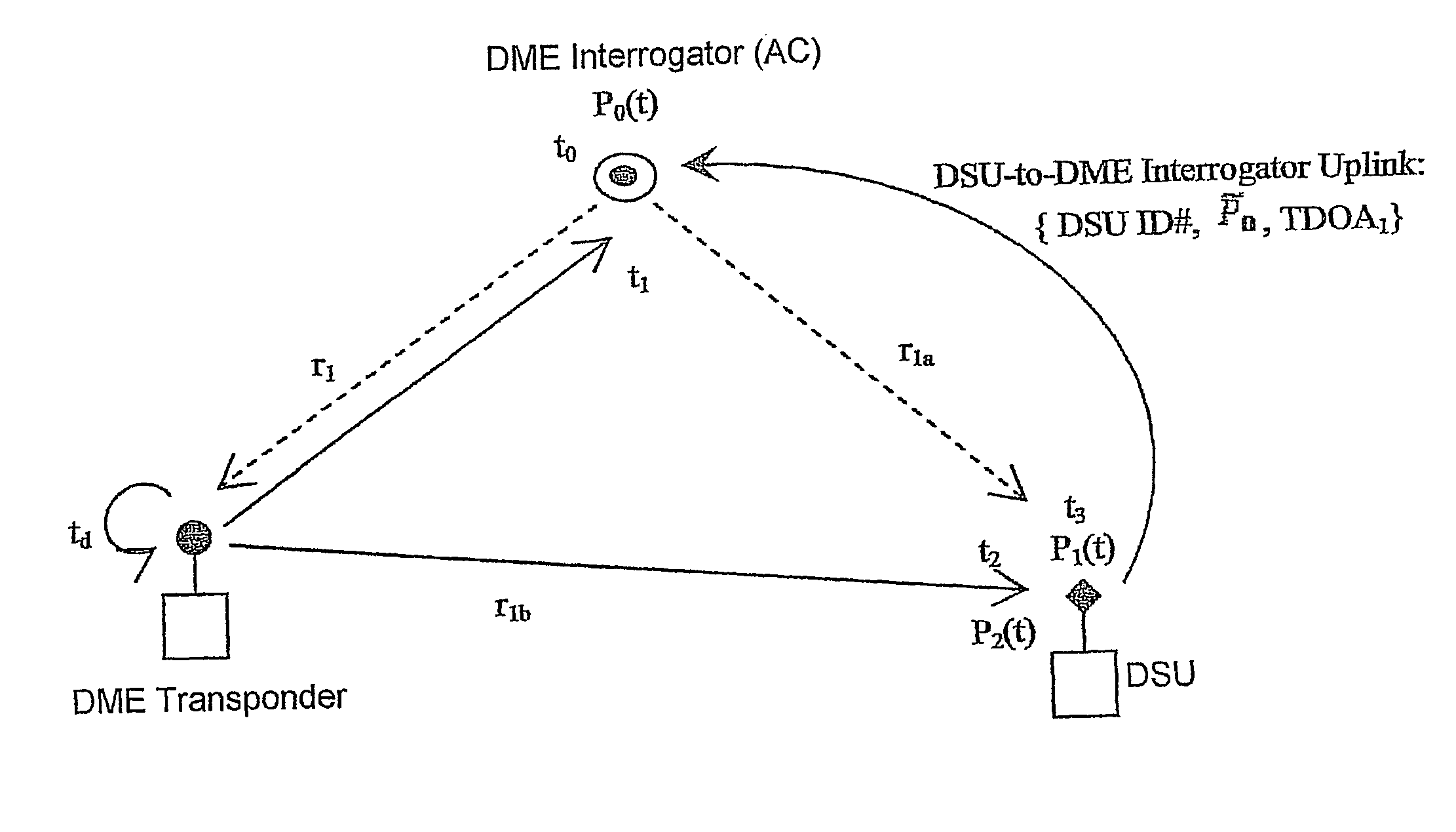
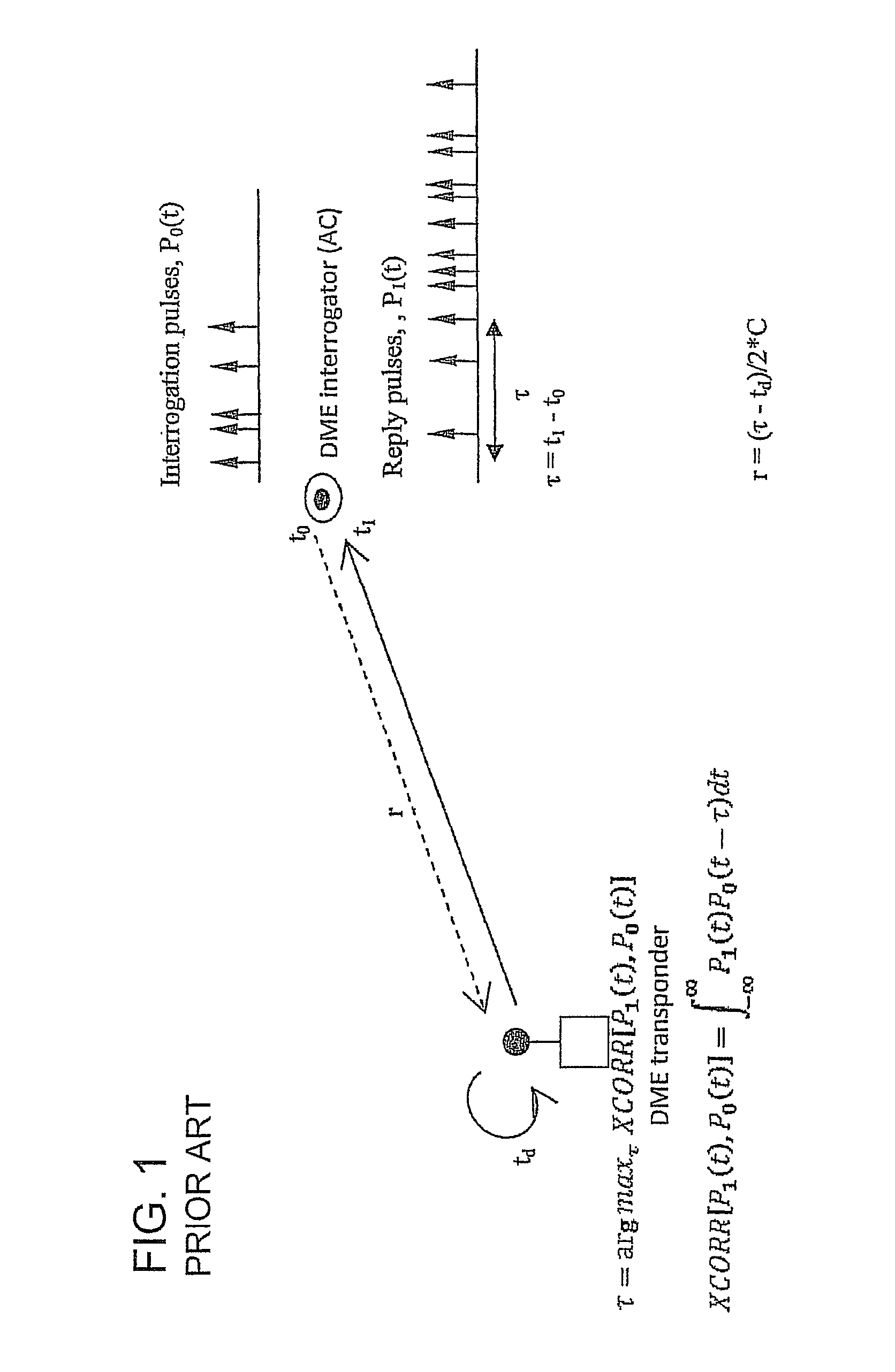
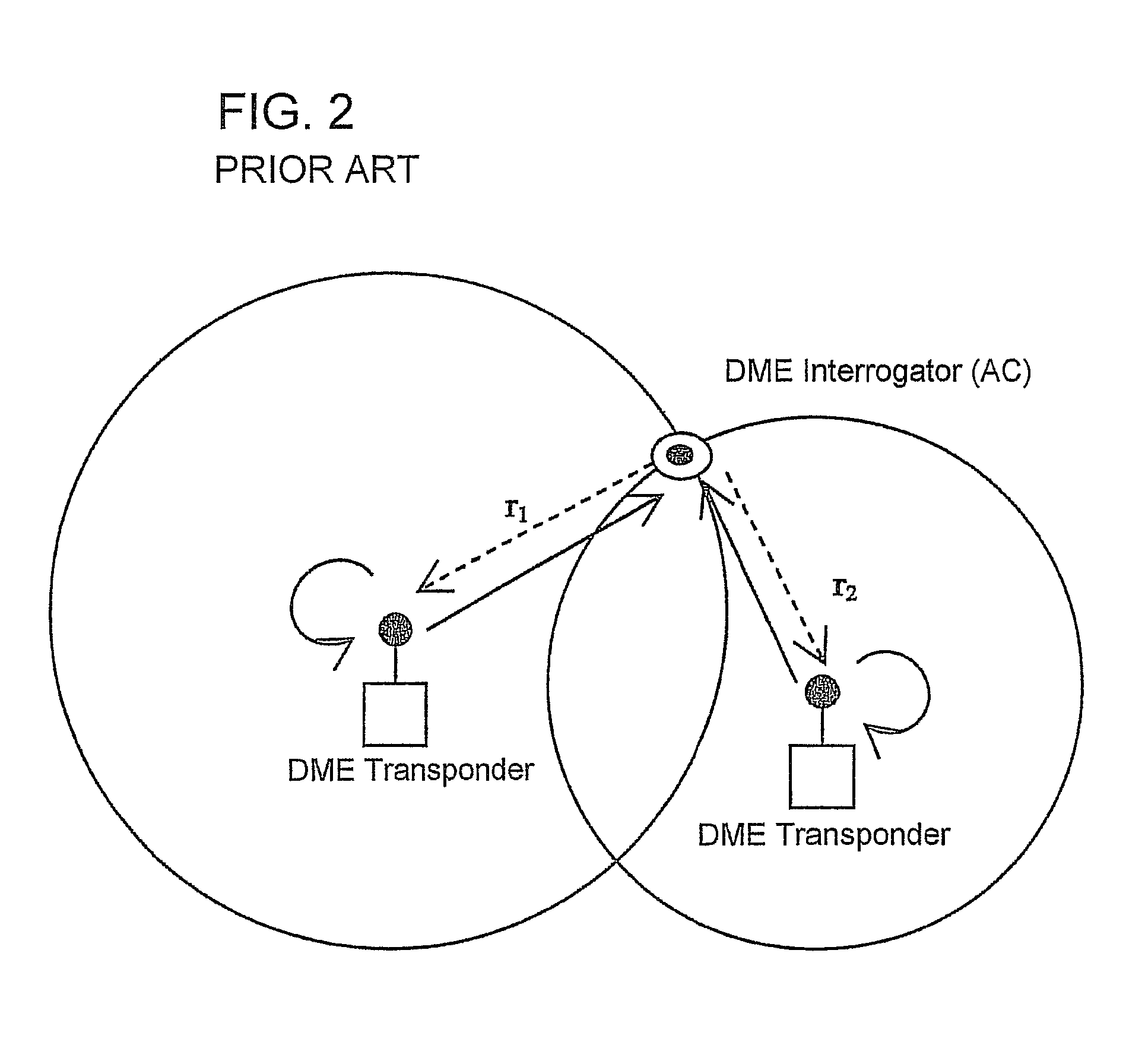
ActiveUS20120162014A1Low positioning accuracy requirementsPosition fixationBeacon systemsDeep integrationNavigation system
The present invention provides a system and method for aircraft to determine own position and navigate using a navigation heartbeat signal broadcast on a DME uplink and / or a Mode-S uplink frequency. The present invention enables deep integration between the existing navigation systems (DME interrogation-reply ranges and GPS / WAAS raw TDOA or pseudo range measurements) and the DME heartbeat TDOAs or Mode-S heartbeat TDOAs to provide a highly accurate navigation positioning capability and provide necessary backup capability in lieu of GPS to maintain the necessary RNP / RNAV capability and avoid degrading aircraft operational safety.
Owner:SAAB INC
Unmanned aircraft navigation system
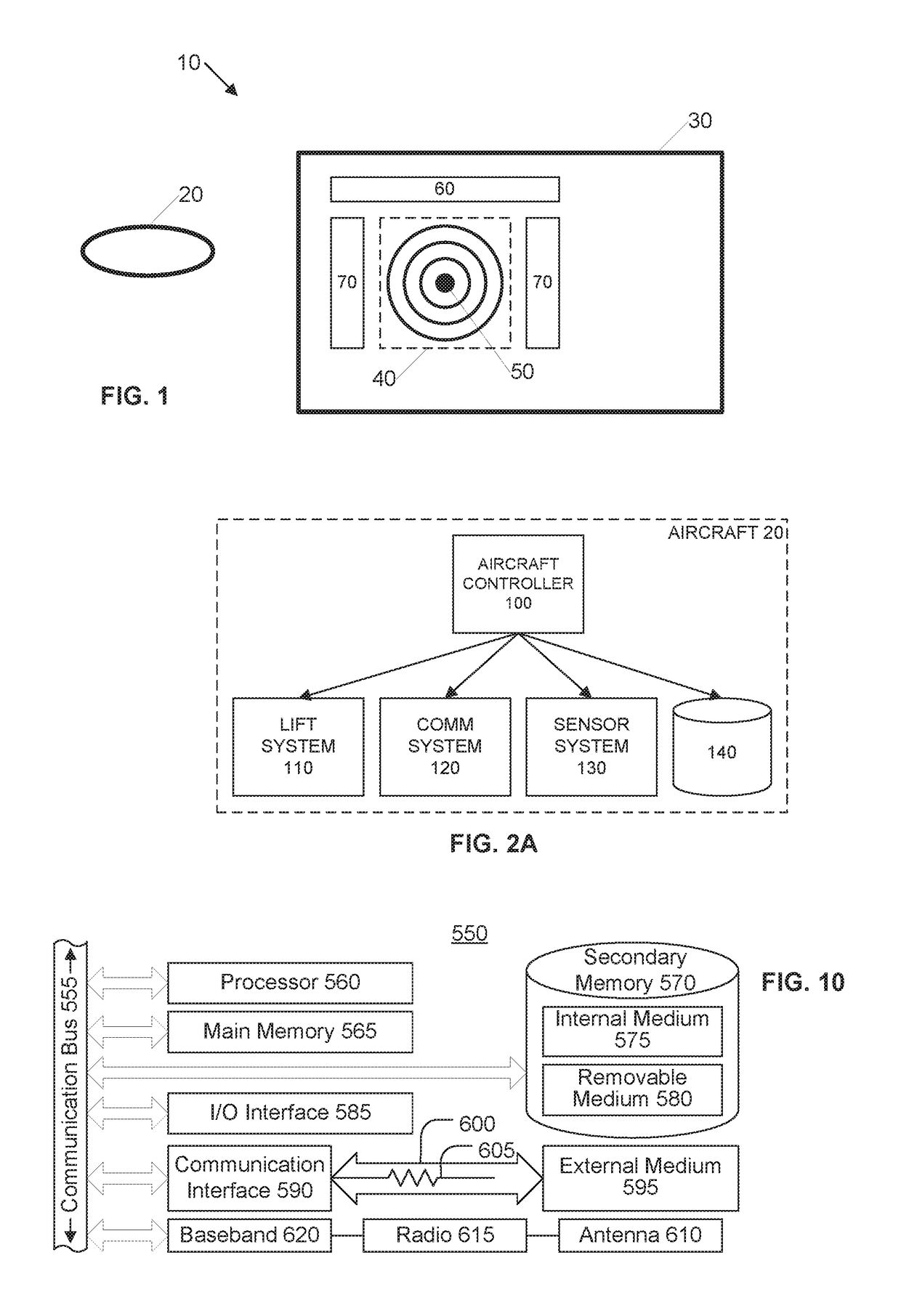
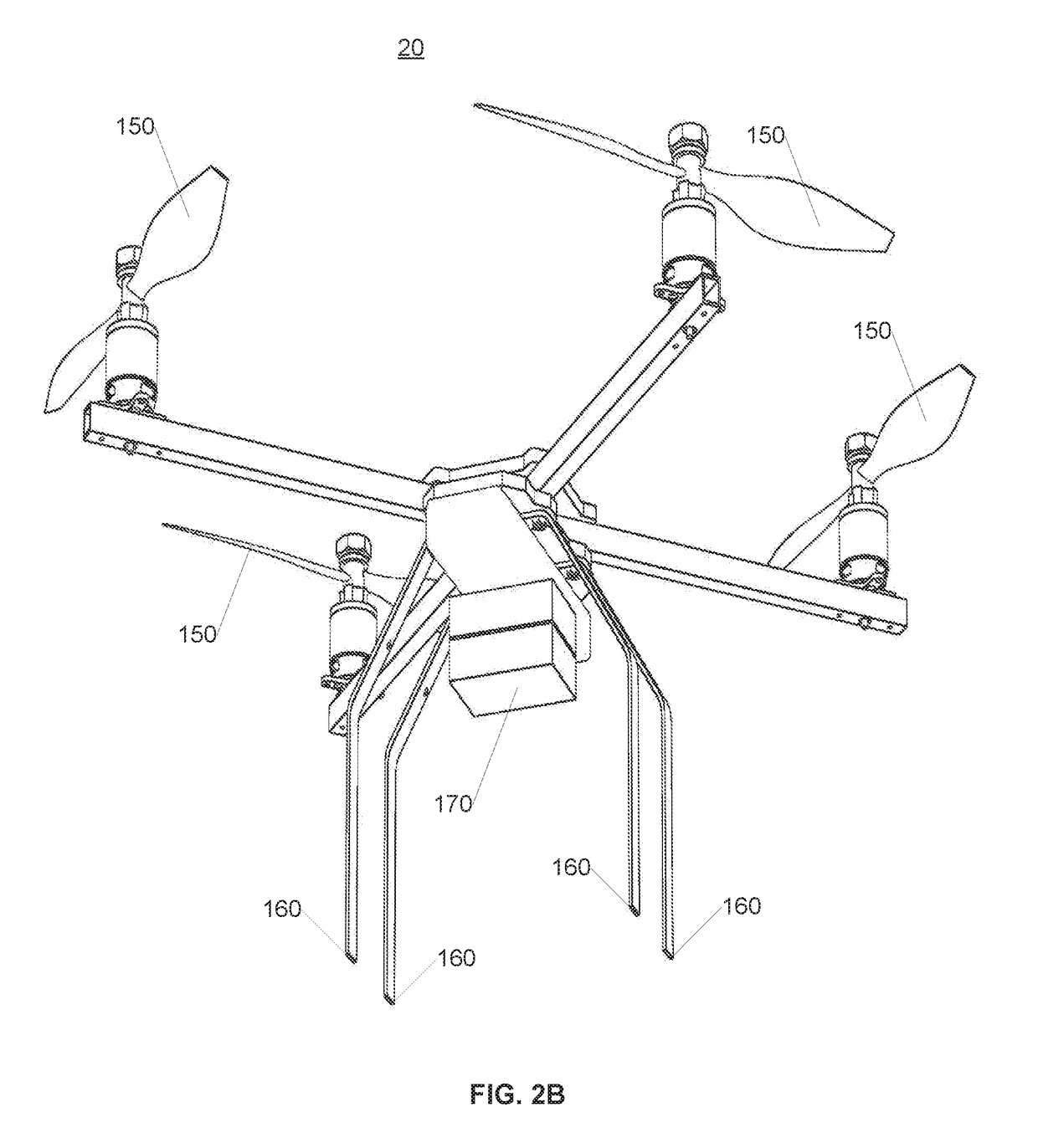
ActiveUS8977481B1Analogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficNavigation systemAircraft vectoring
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Device for assisting in the navigation of an aircraft in an airport zone
ActiveUS20080109160A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesOn boardNavigation system
The invention relates to a device for assisting in the navigation of an aircraft in an airport zone comprising a surface navigation system and means of acquiring in real time, while navigating on the ground or in flight, new information or temporary information relating to the navigation in the airport zone. The surface navigation system uses information relating to the navigation in the airport zone. The information is previously stored in a database on board the aircraft. The device includes means for decoding and analysing the new or temporary information relating to the navigation in the airport zone, means of filtering the information according to the airport concerned and the validity date of the information, means of correlating the information with the information previously stored, and means of displaying the information.
Owner:THALES SA
Air Navigation Aid Method and System Making it Possible to Maintain Vertical Margins
ActiveUS20100004801A1Improve flight safetySurprising effectDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsDisplay deviceNavigation system
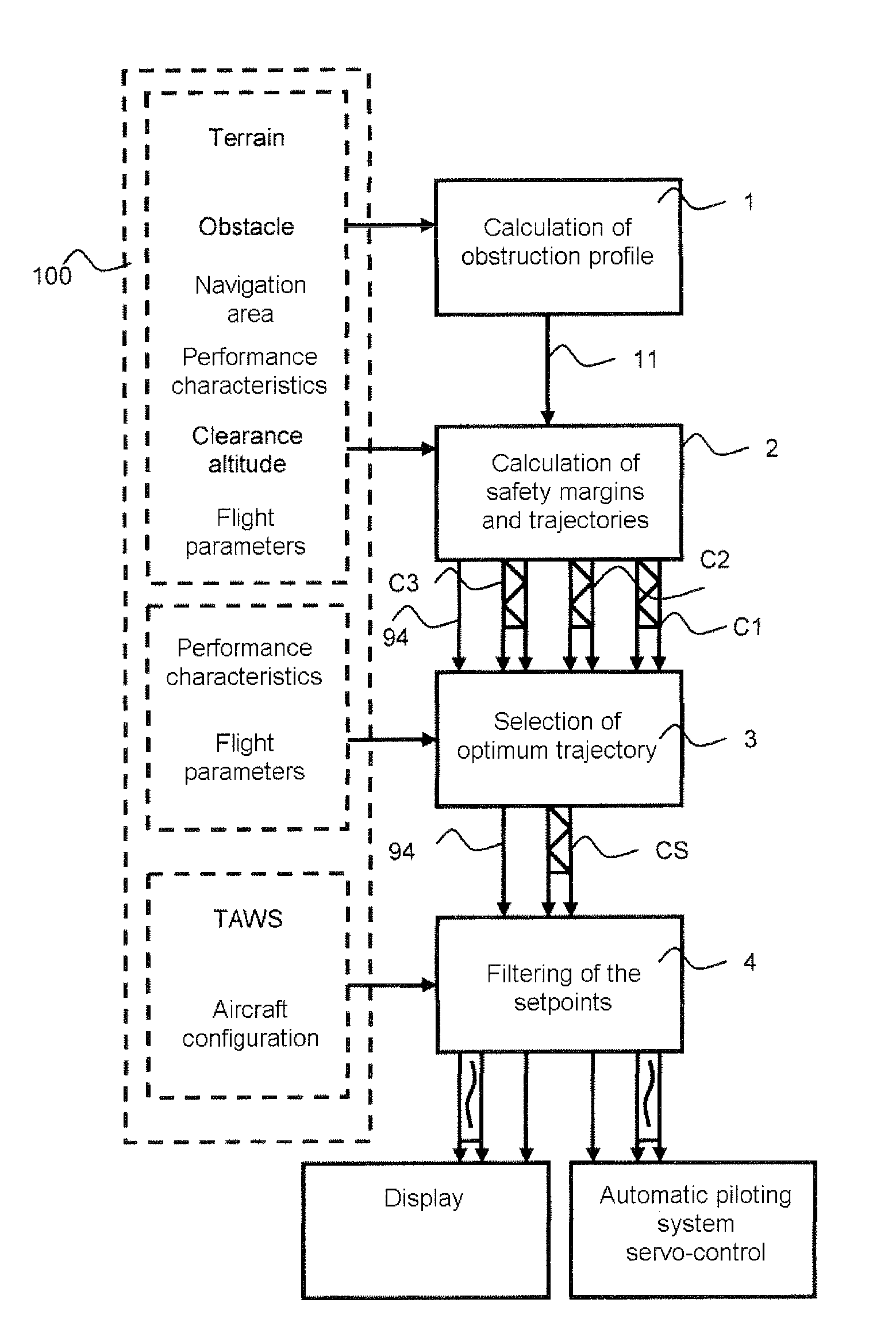
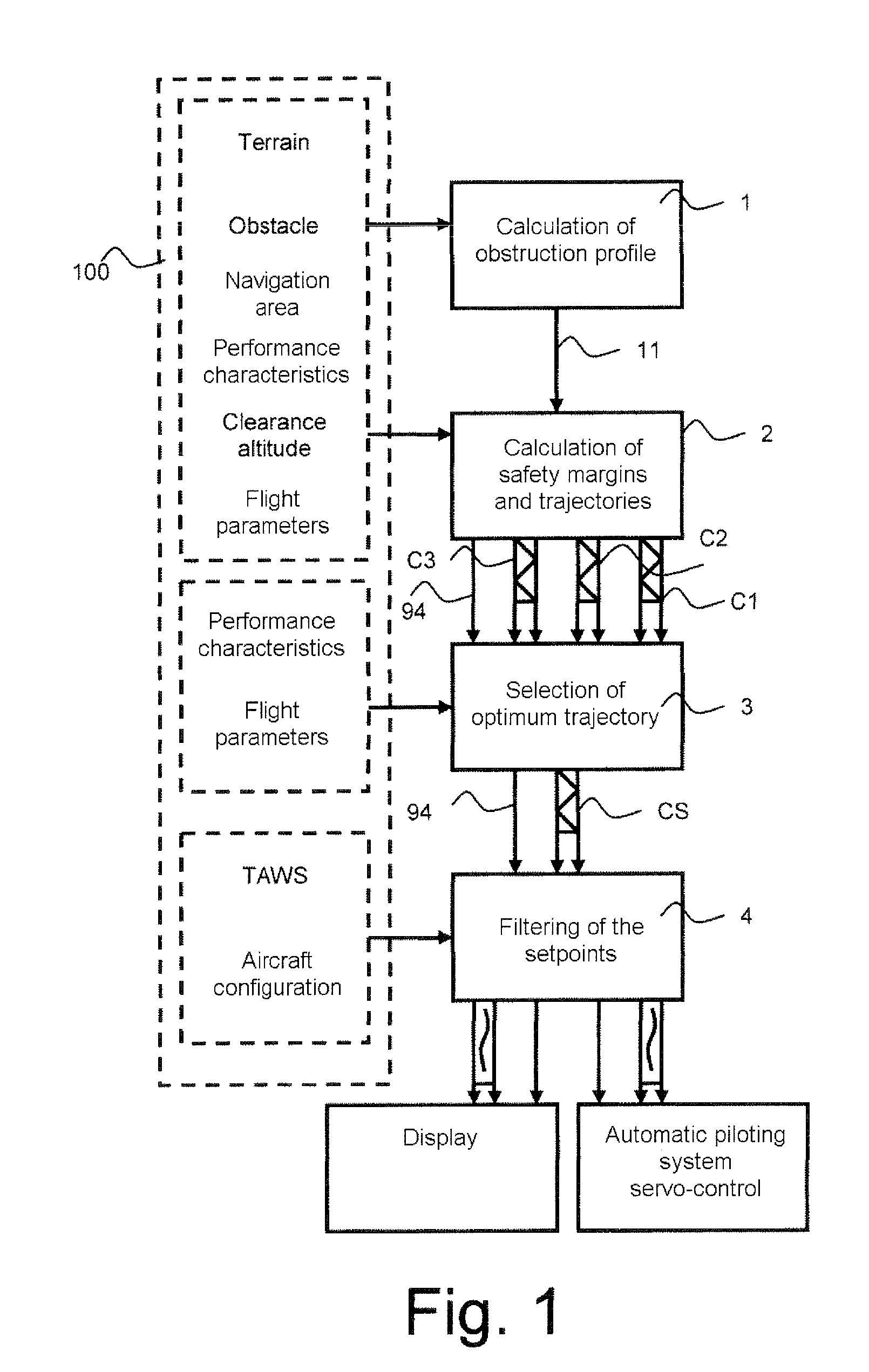
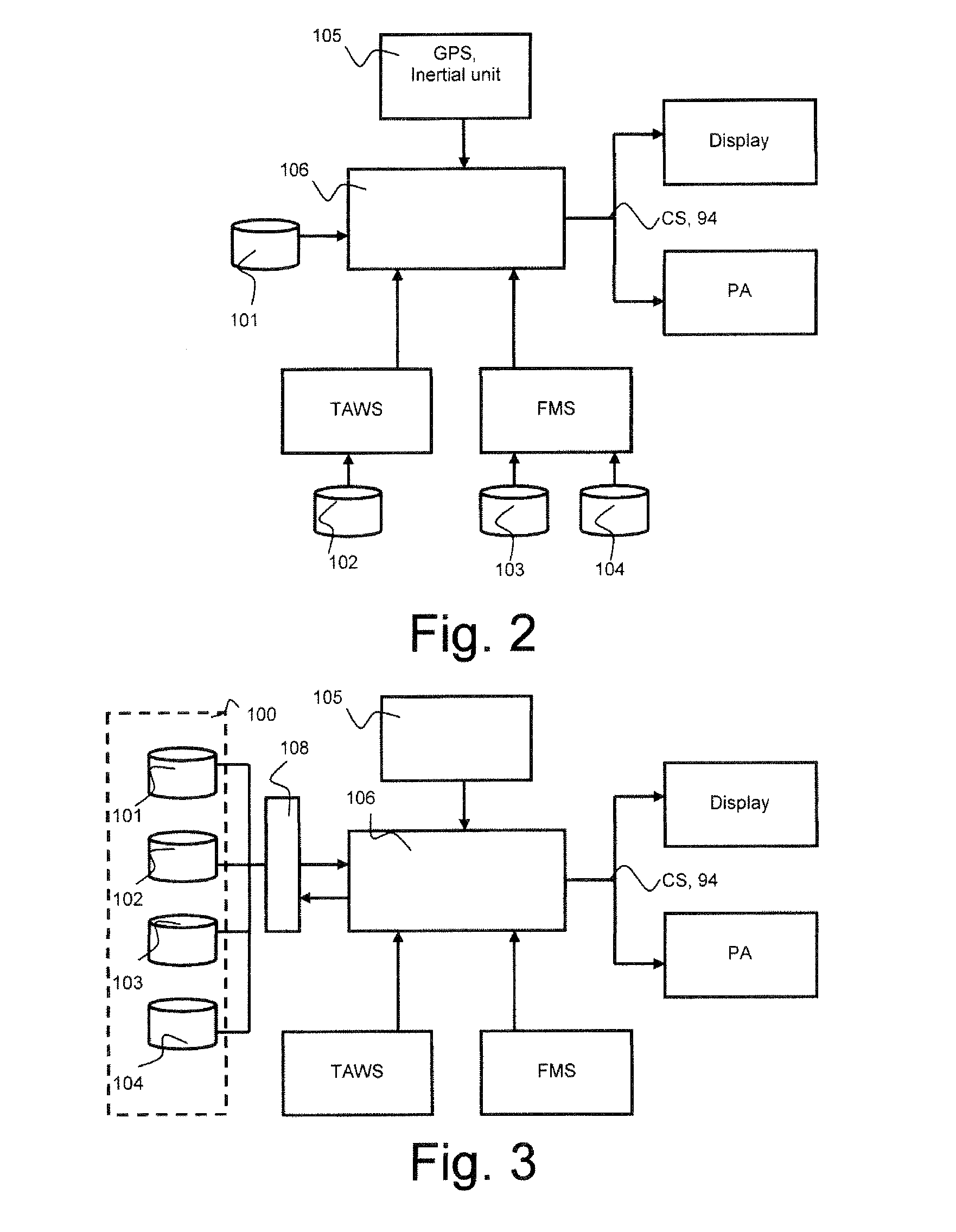
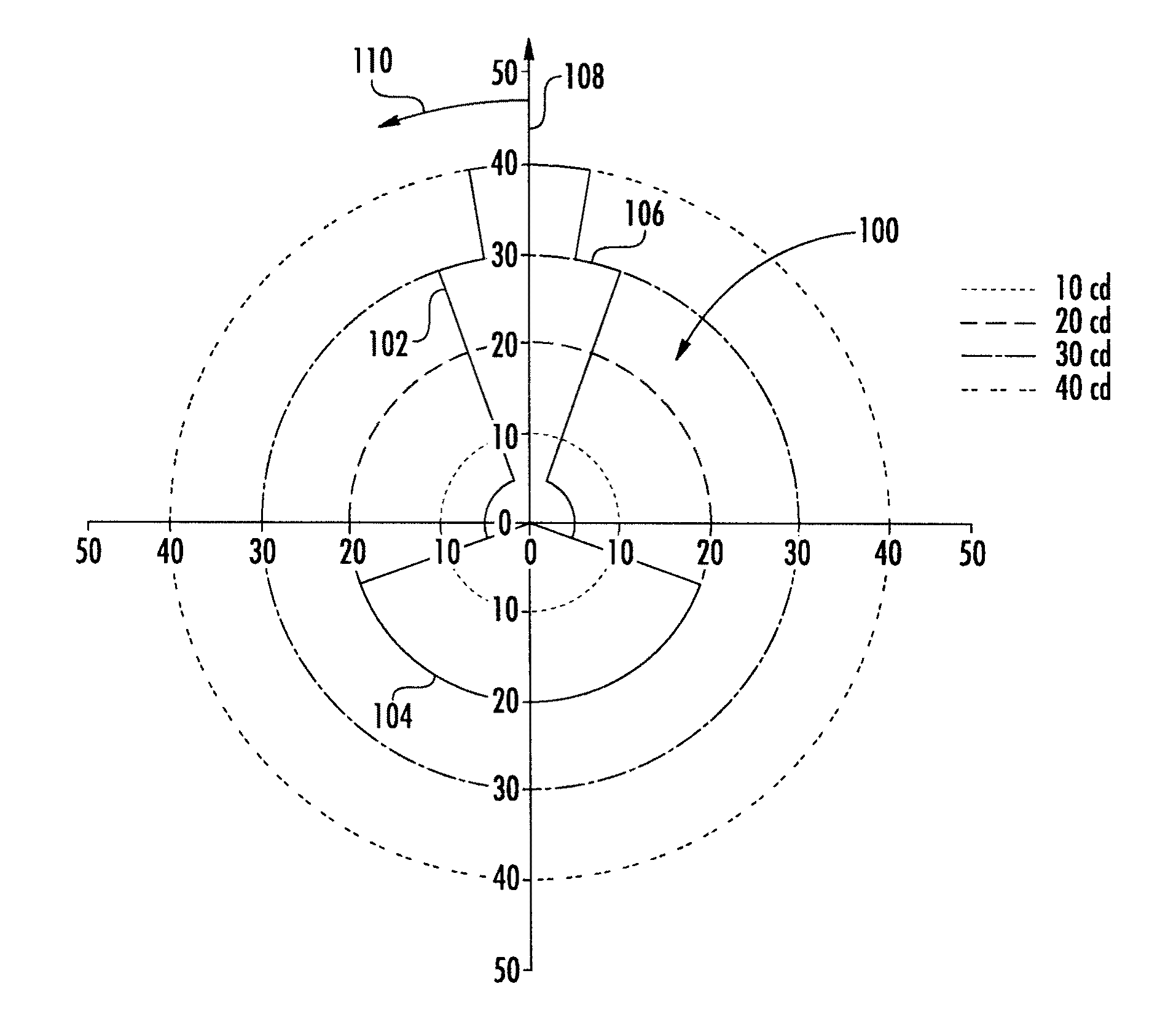
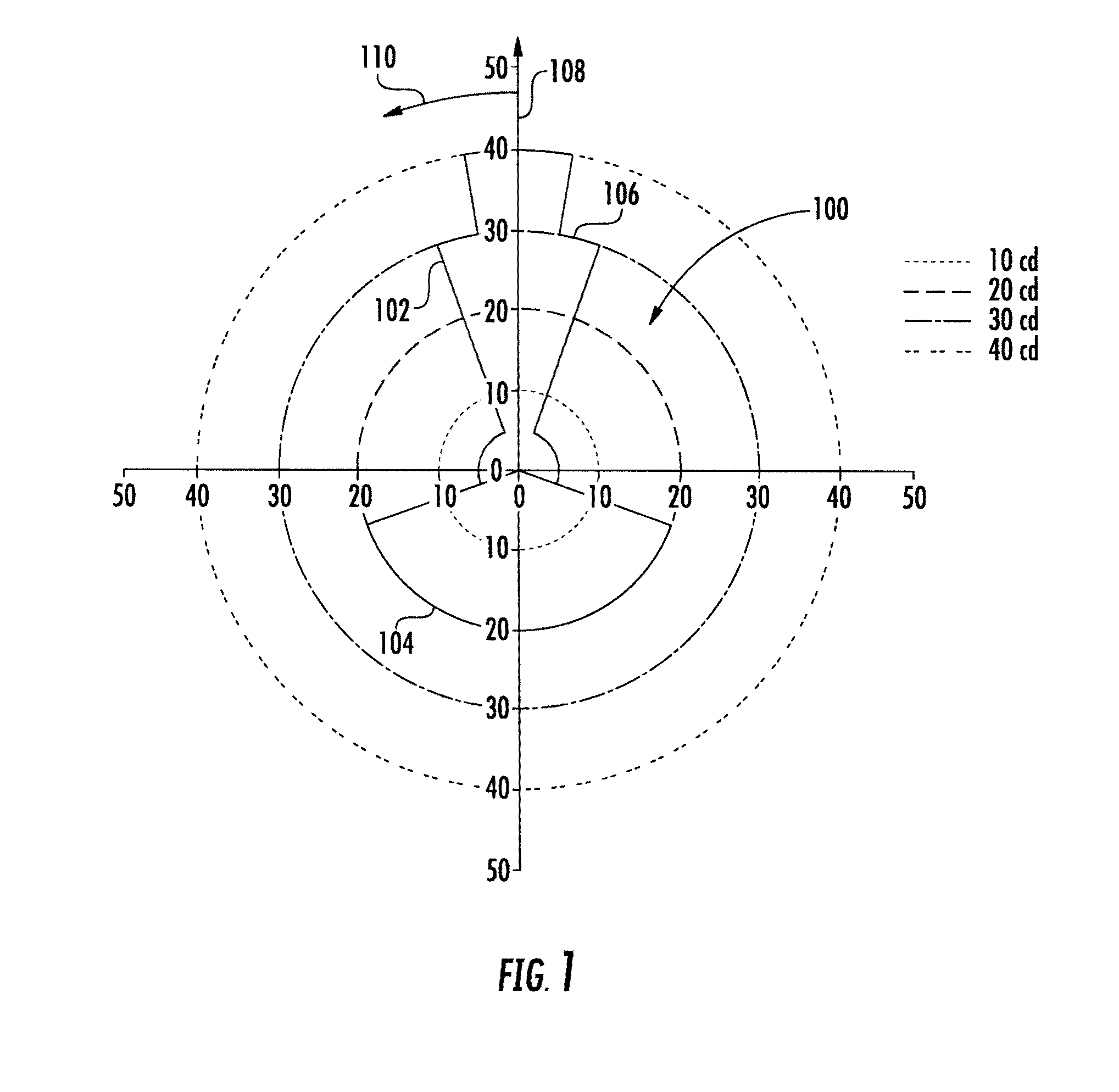
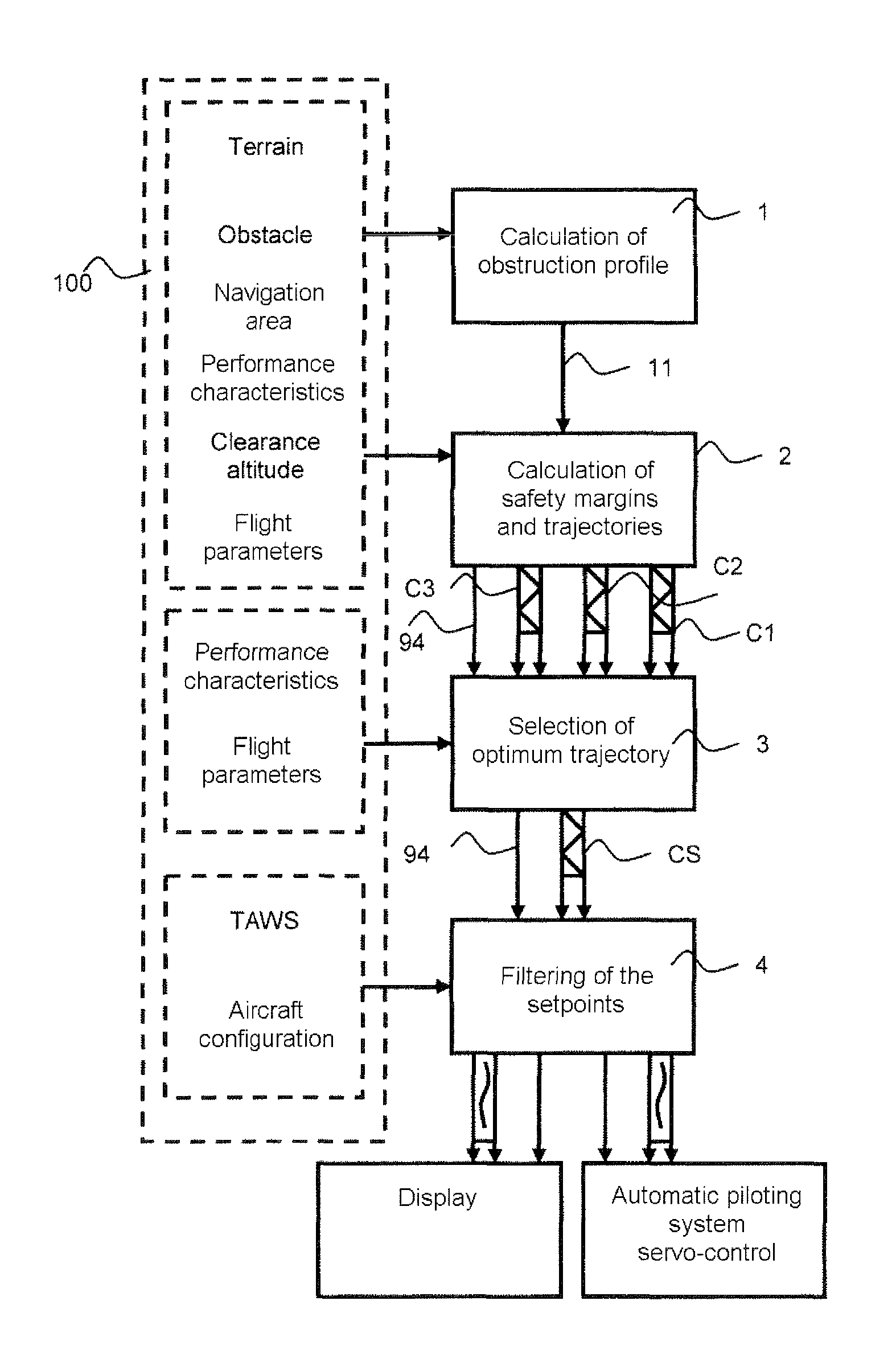
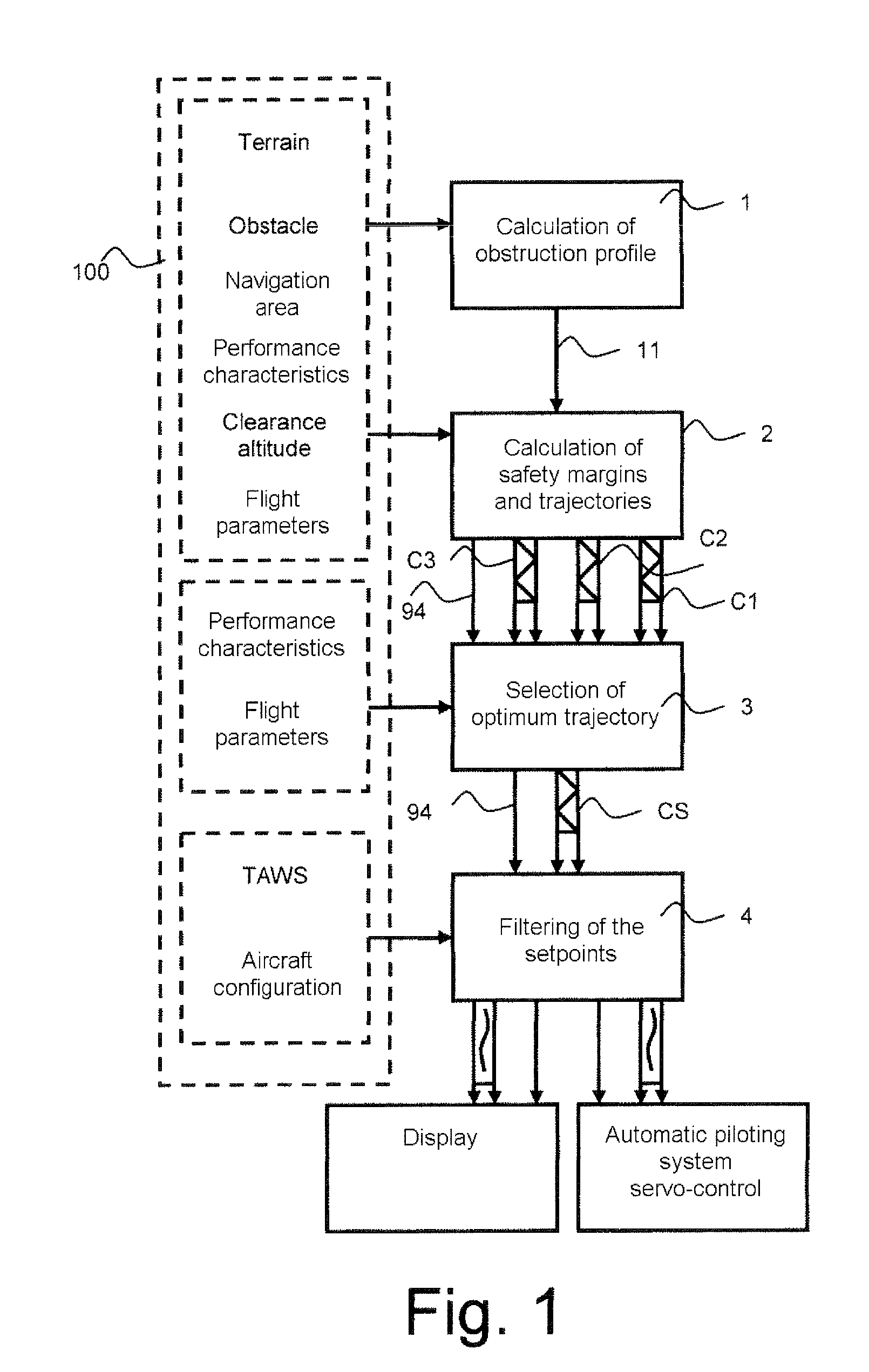
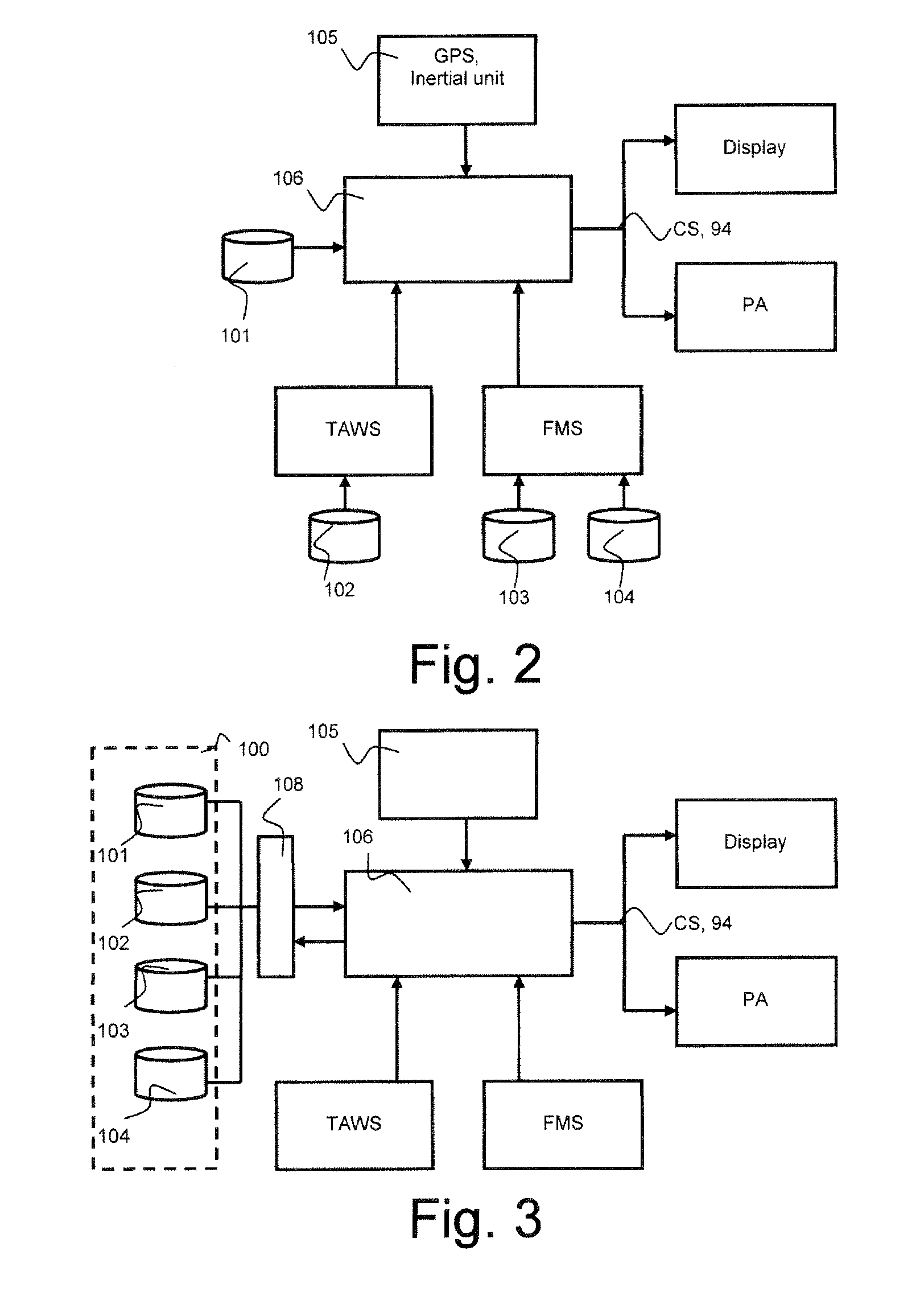
The invention relates to a calculation method for an aircraft navigation aid system making it possible to maintain a vertical safety margin with an obstruction profile, the aircraft comprising a navigation system, an automatic piloting system, a database system and a display device, characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: calculation of an obstruction altitude profile, calculation of a vertical safety margin with respect to the obstruction profile, of a plurality of vertical safety trajectories and of the respective flight setpoints for the aircraft to execute the trajectories, selection of the flight setpoints making it possible to maintain the aircraft as close as possible to the obstruction profile while maintaining between the aircraft and the obstruction profile at least the vertical safety margin, filtering of the flight set point values so that the variation of the values of the setpoints does not exceed a variation difference in a duration predefined in the system.
Owner:THALES SA
Unmanned aircraft navigation system and method
ActiveUS20180173245A1Readily apparentNavigational calculation instrumentsUnmanned aerial vehiclesAircraft landingNavigation system
Owner:AEROVIRONMENT INC
Method for determining conflicting paths between mobile airborne vehicles and associated system and computer software program product
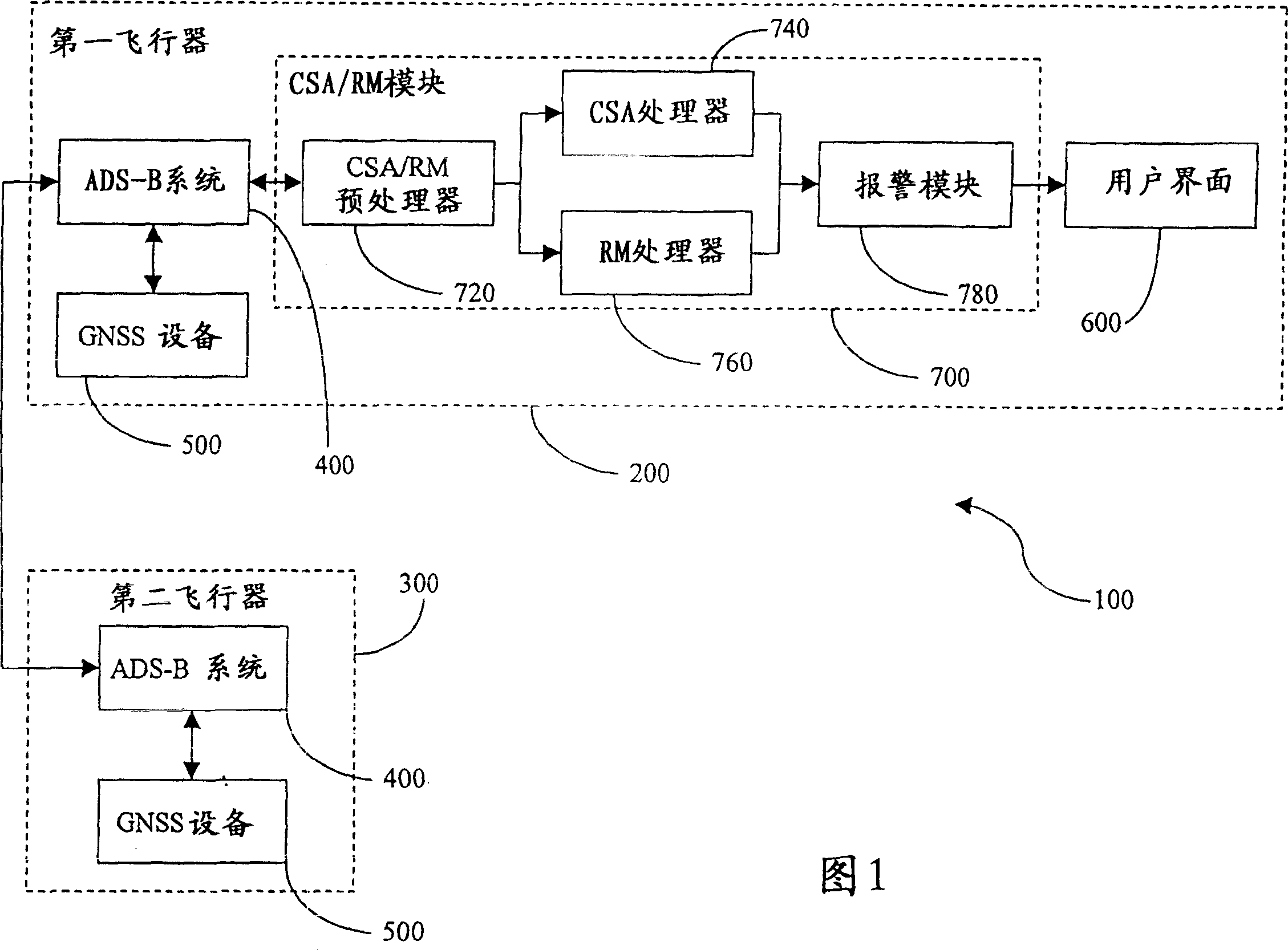
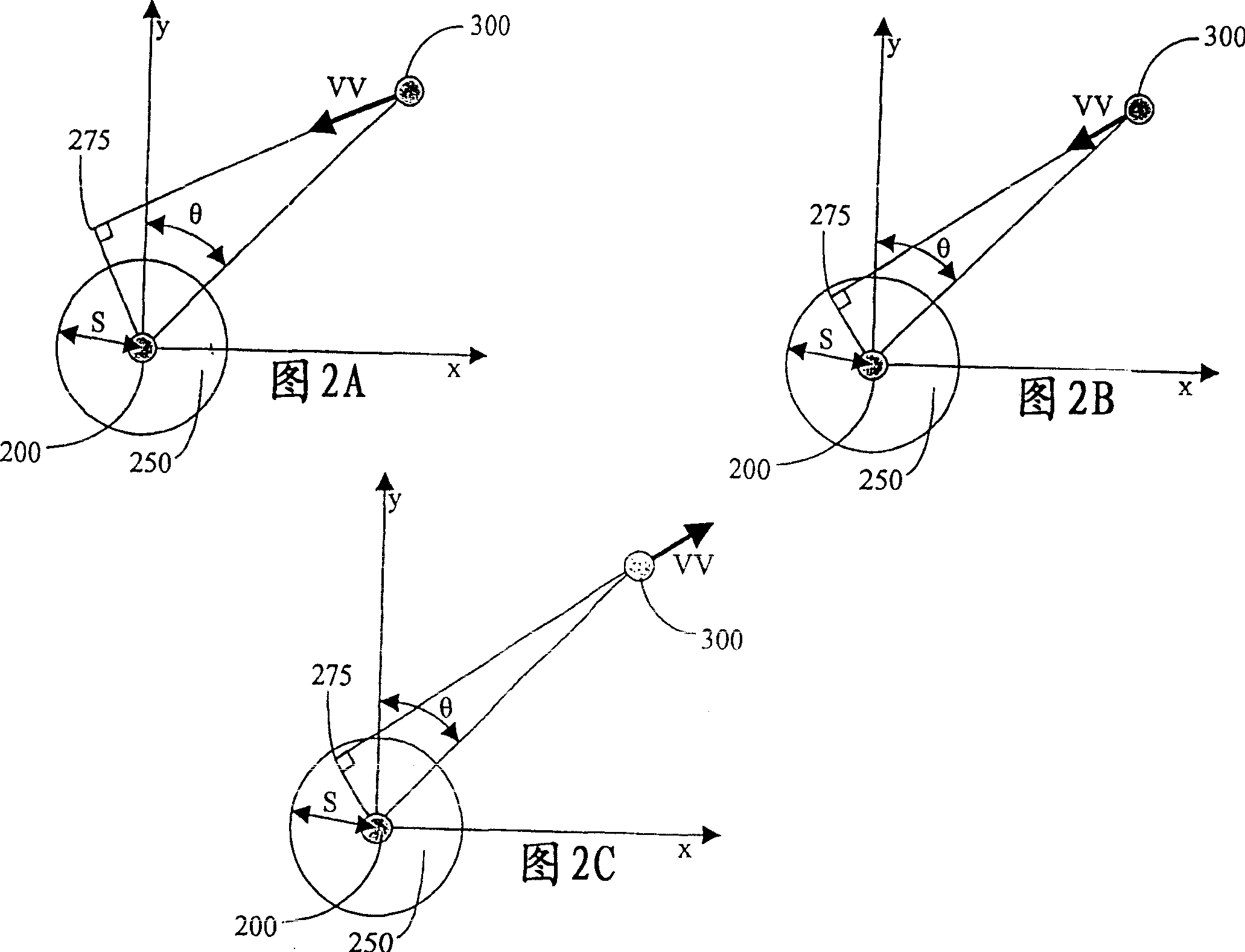
InactiveCN1592919AImprove friendlinessData processing applicationsPosition fixationTime rangeCommunications system
A method of determining conflicting flight paths between a first and a second airborne vehicle is provided, wherein each vehicle comprises an aircraft-to-aircraft navigational communication system having a navigational device. First, a position and a velocity vector are determined for each of the airborne vehicles. A cylindrical volume is then defined about the first airborne vehicle. A separation distance is then determined between the vehicles at a selected time and using a great circle earth model. An accuracy factor is thereafter determined for the position of each vehicle. The separation distance is then modified by the accuracy factor. A determination is then made as to whether the modified separation distance is within the cylindrical volume about the first airborne vehicle during a time range to thereby determine whether conflicting flight paths exist between the vehicles. An associated system and computer software program product are also provided.
Owner:UNITED PARCEL SERVICE OF AMERICAN INC
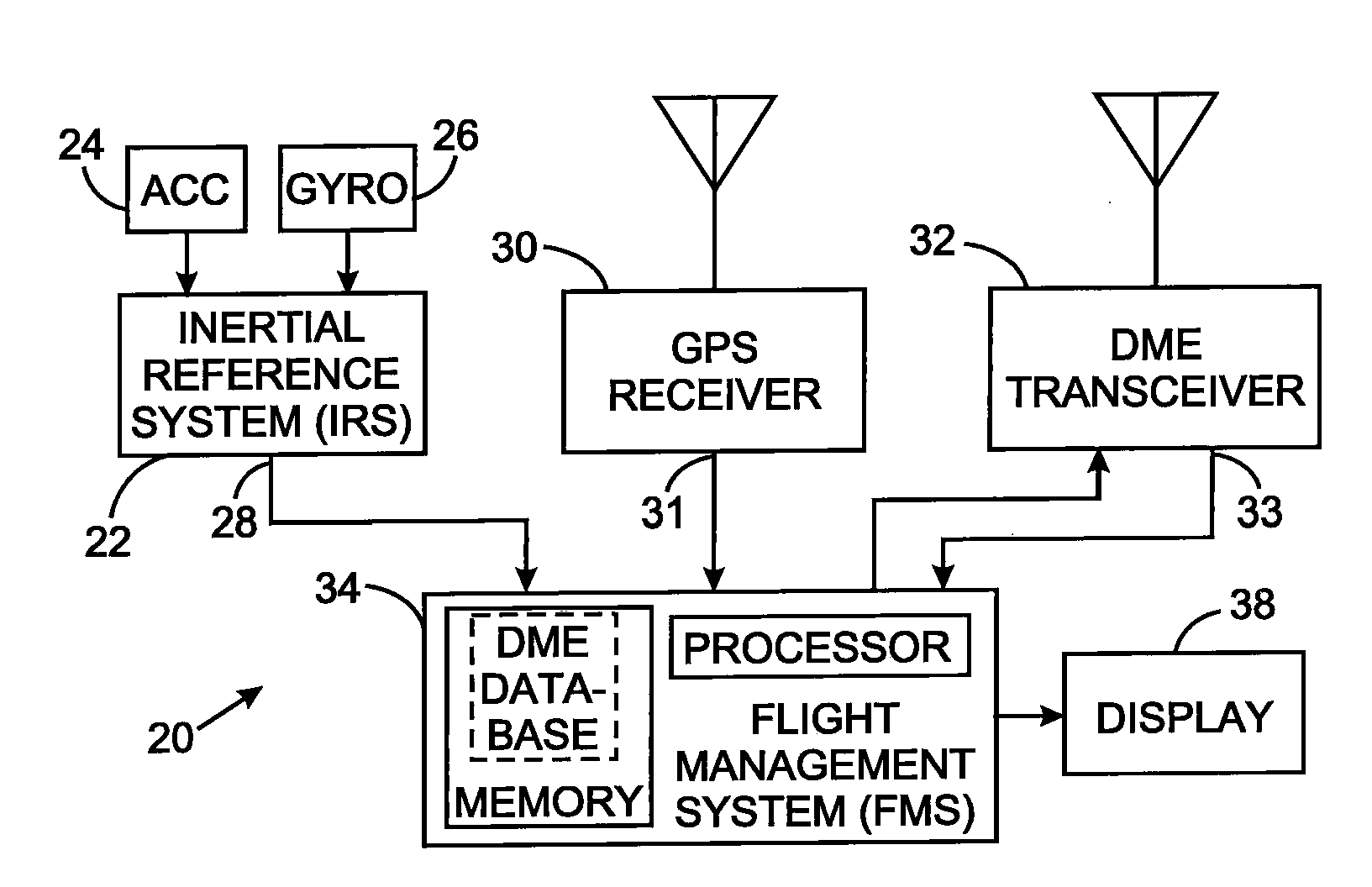
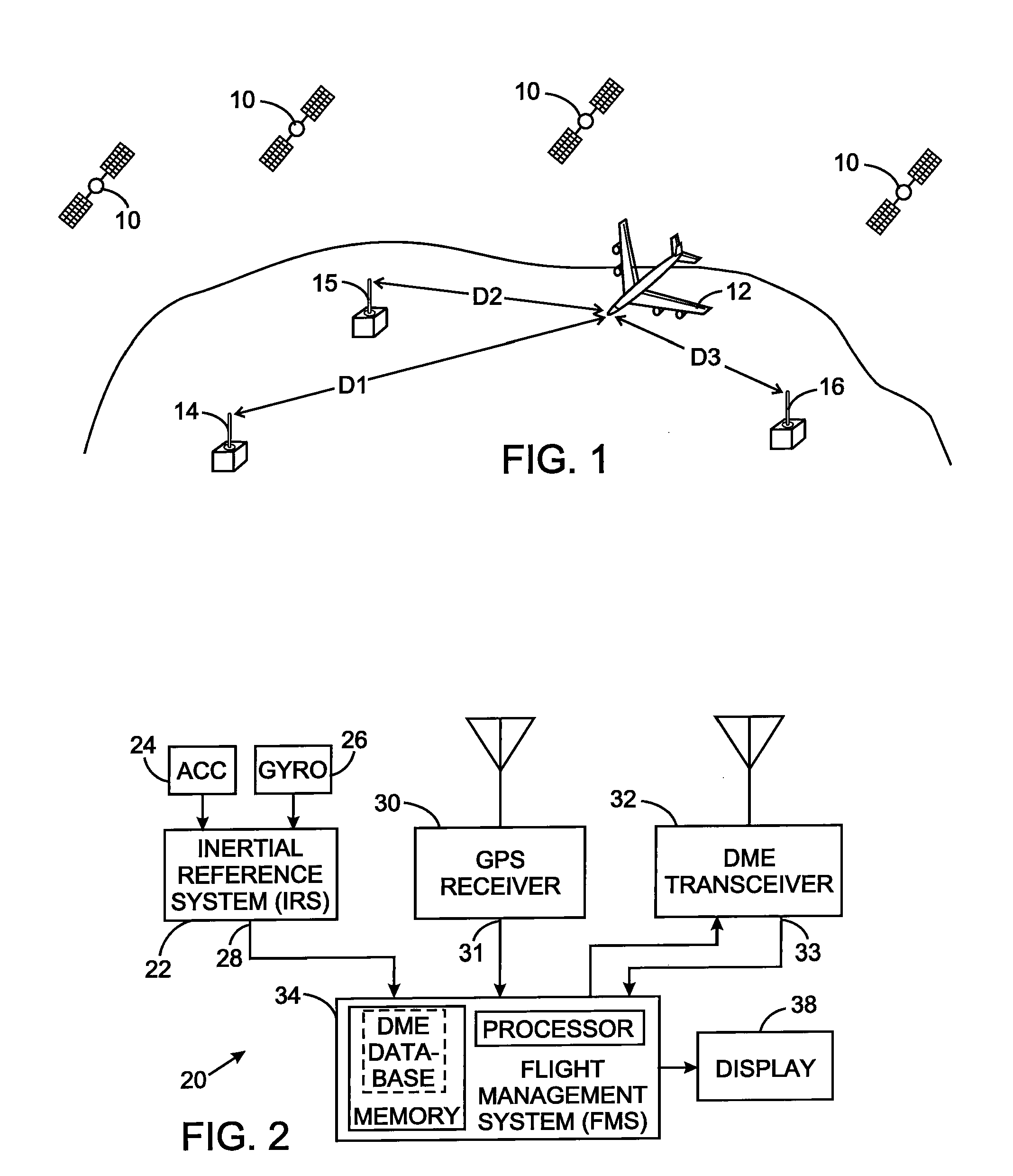
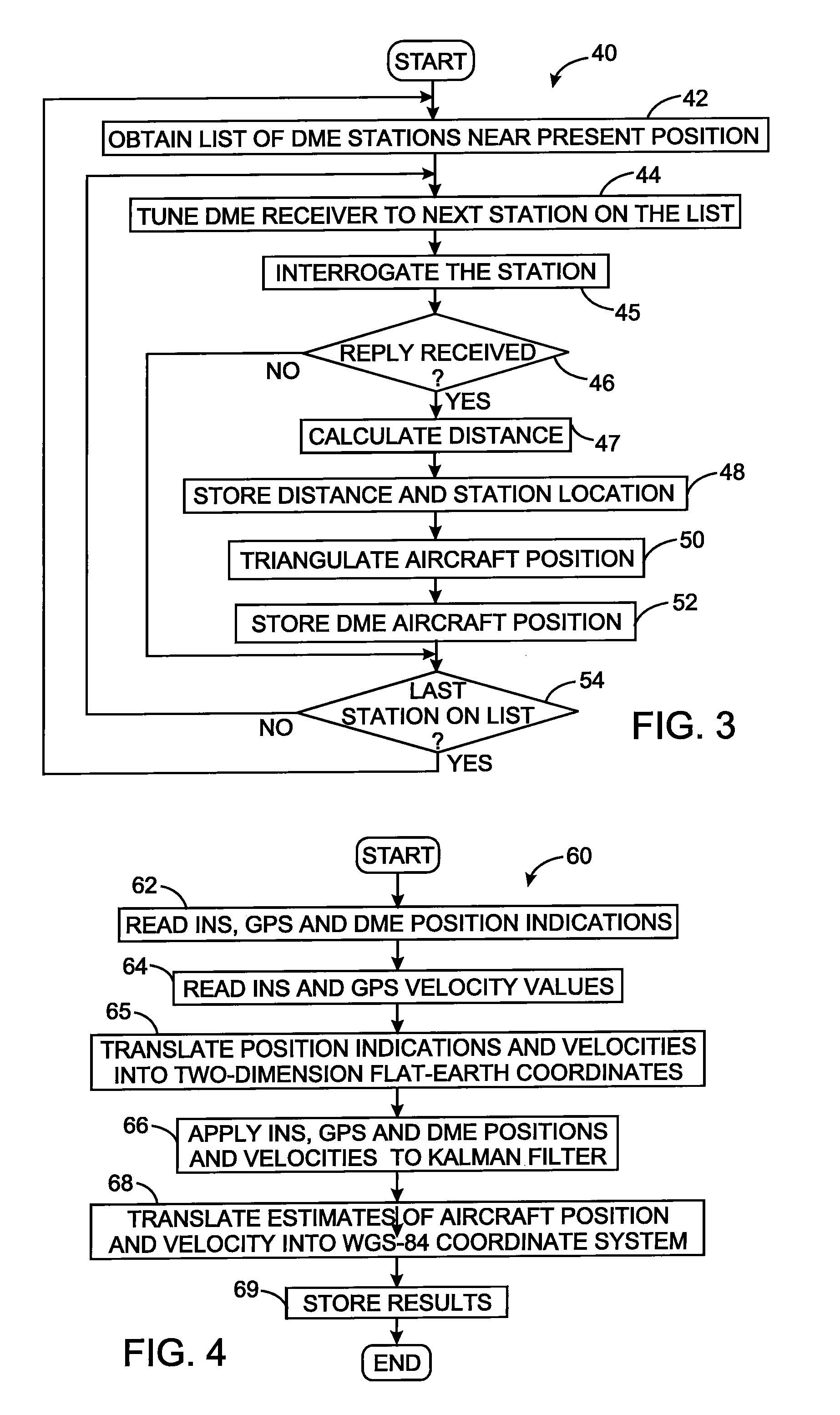
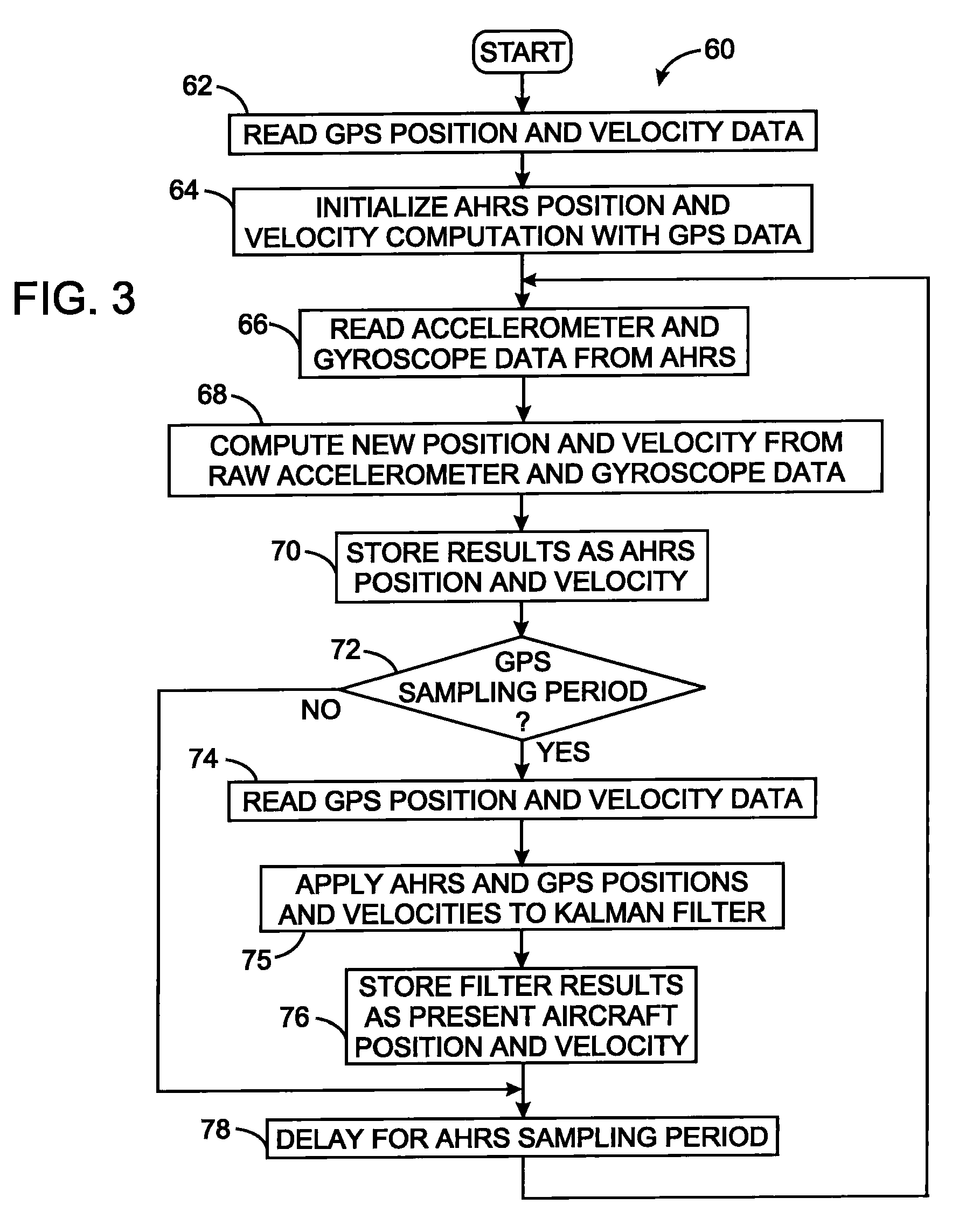
Aircraft navigation using the global positioning system, inertial reference system, and distance measurements
InactiveUS20100106416A1Position fixationNavigation instrumentsInertial frame of referenceGlobal Positioning System
A navigation technique for a vehicle employs an inertial reference system to derive a first position indication and a first velocity value. A first receiver processes signals of a global positioning system from which a second position indication and a second velocity value are derived. A second receiver processes signals from a plurality of distance measuring equipment stations at fixed positions on the earth and determines the distance between the vehicle and each of those stations. A third position indication is derived from those distances. A Kalman filter function is applied to the first, second and third position indications and to the first and second velocity values to compensate for uncertainty in the first position indication and in the first velocity value and thereby produce a vehicle position estimate and a vehicle velocity estimate.
Owner:UNIVERSAL AVIONICS SYST
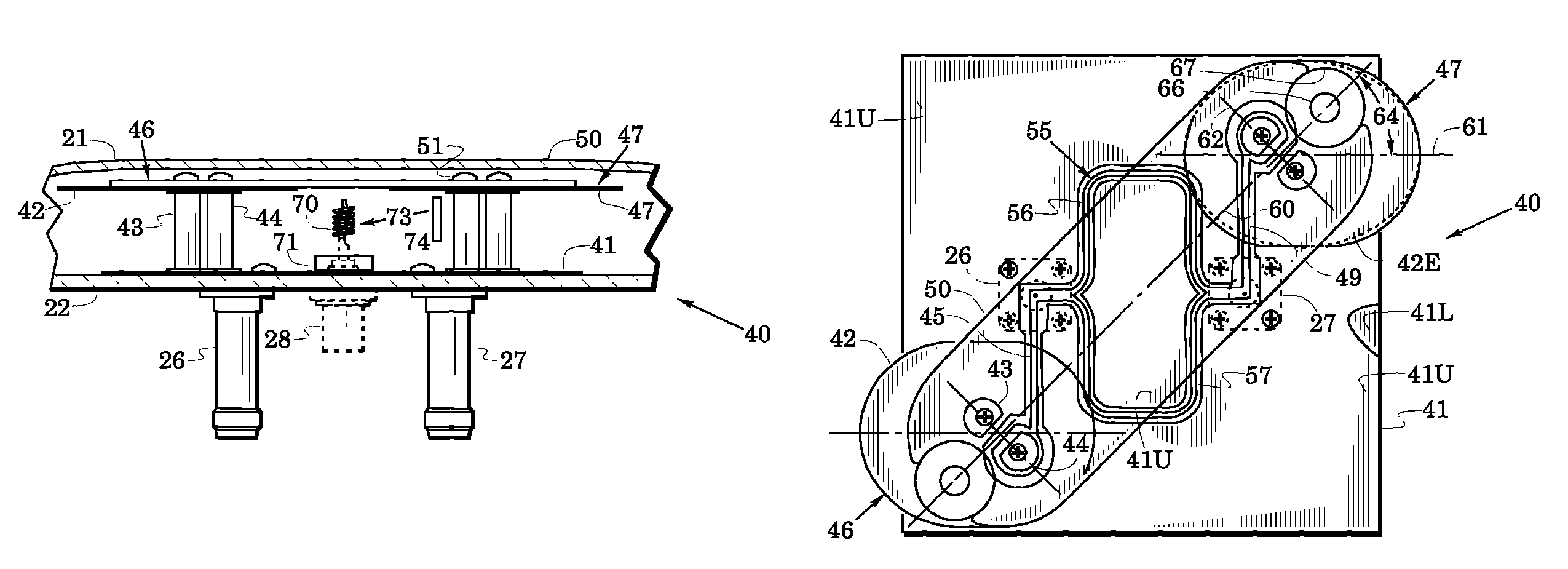
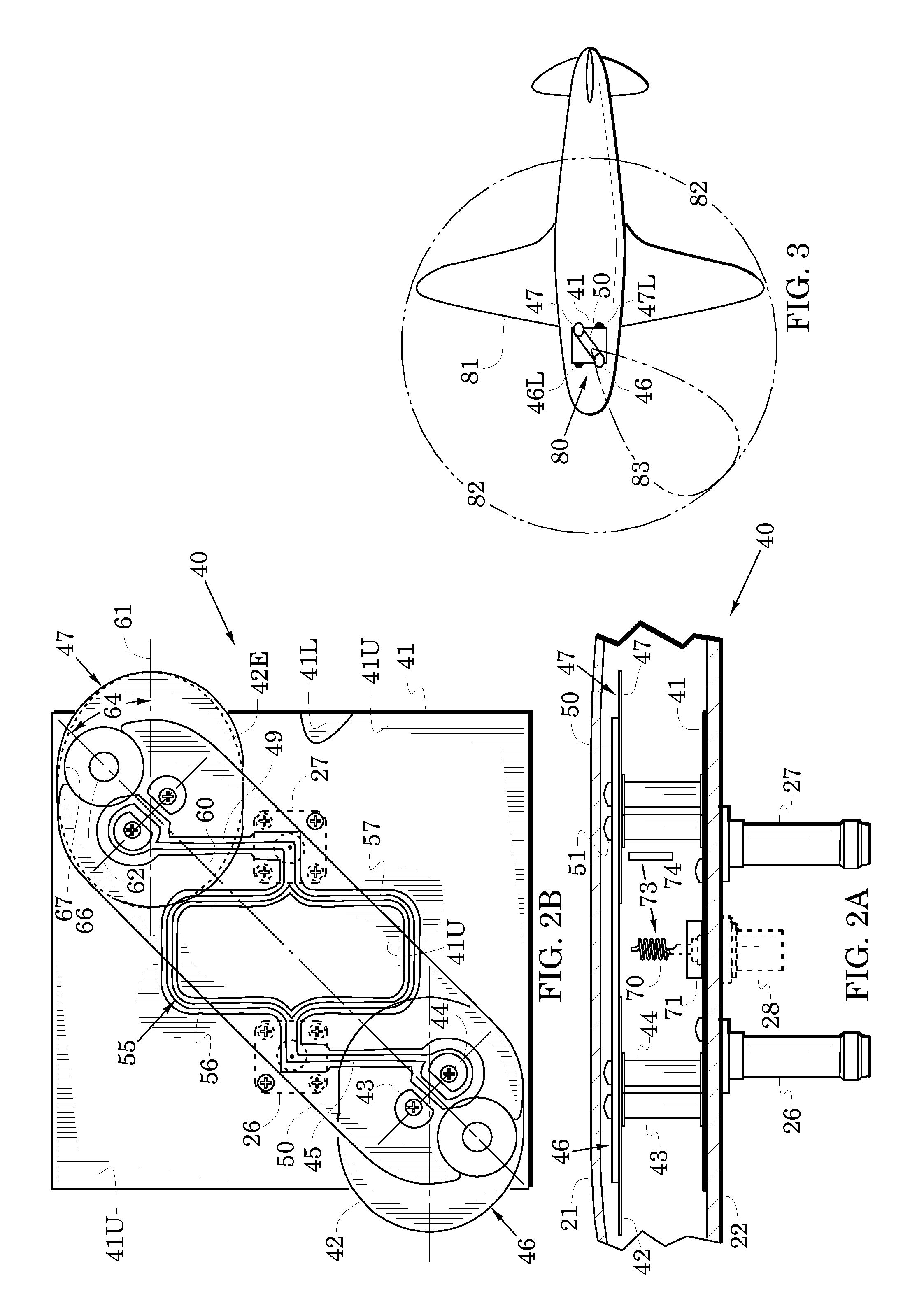
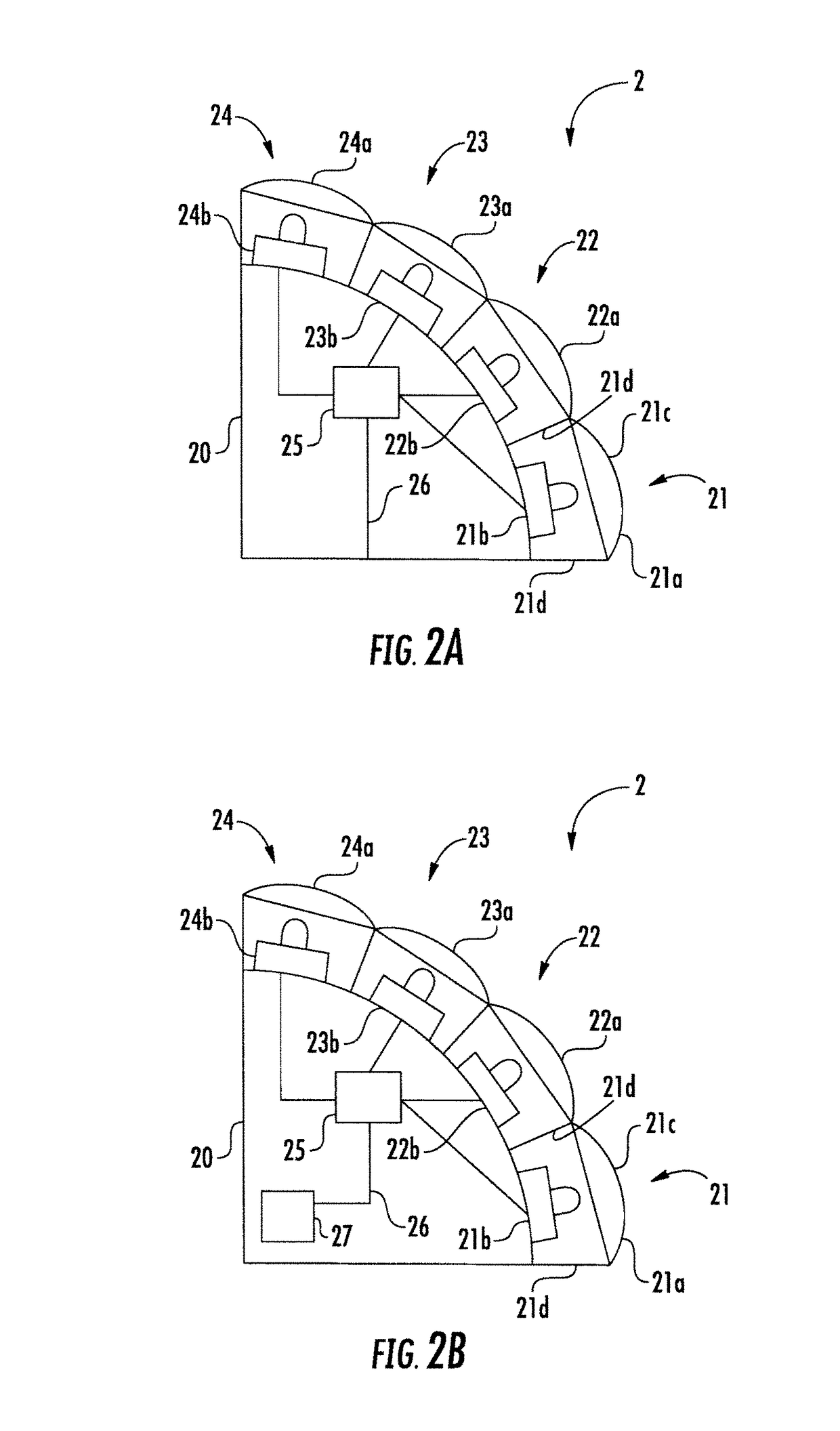
Exterior aircraft navigation light and method of controlling an exterior aircraft navigation light
An exterior aircraft navigation light for an aircraft having a nominal forward flight direction and being able to fly into the nominal forward flight direction as well as into a plurality of further flight directions, such as sideways or backwards, has at least one light emission unit and control circuitry coupled to the at least one light emission unit, wherein the exterior aircraft navigation light is configured such that each of the at least one light emission unit has a unit-specific light emission direction that has a pre-defined horizontal angle with respect to the nominal forward flight direction, and wherein each of the at least one light emission unit includes a multi-color light source configured to emit red light, white light and green light, and an optical system for conditioning the red light, the white light and the green light emitted by the multi-color light source.
Owner:GOODRICH LIGHTING SYST GMBH
Air navigation aid method and system making it possible to maintain vertical margins
ActiveUS8145365B2Improve flight safetySurprising effectAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficDisplay deviceNavigation system
The invention relates to a calculation method for an aircraft navigation aid system making it possible to maintain a vertical safety margin with an obstruction profile, the aircraft comprising a navigation system, an automatic piloting system, a database system and a display device, characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: calculation of an obstruction altitude profile, calculation of a vertical safety margin with respect to the obstruction profile, of a plurality of vertical safety trajectories and of the respective flight setpoints for the aircraft to execute the trajectories, selection of the flight setpoints making it possible to maintain the aircraft as close as possible to the obstruction profile while maintaining between the aircraft and the obstruction profile at least the vertical safety margin, filtering of the flight set point values so that the variation of the values of the setpoints does not exceed a variation difference in a duration predefined in the system.
Owner:THALES SA
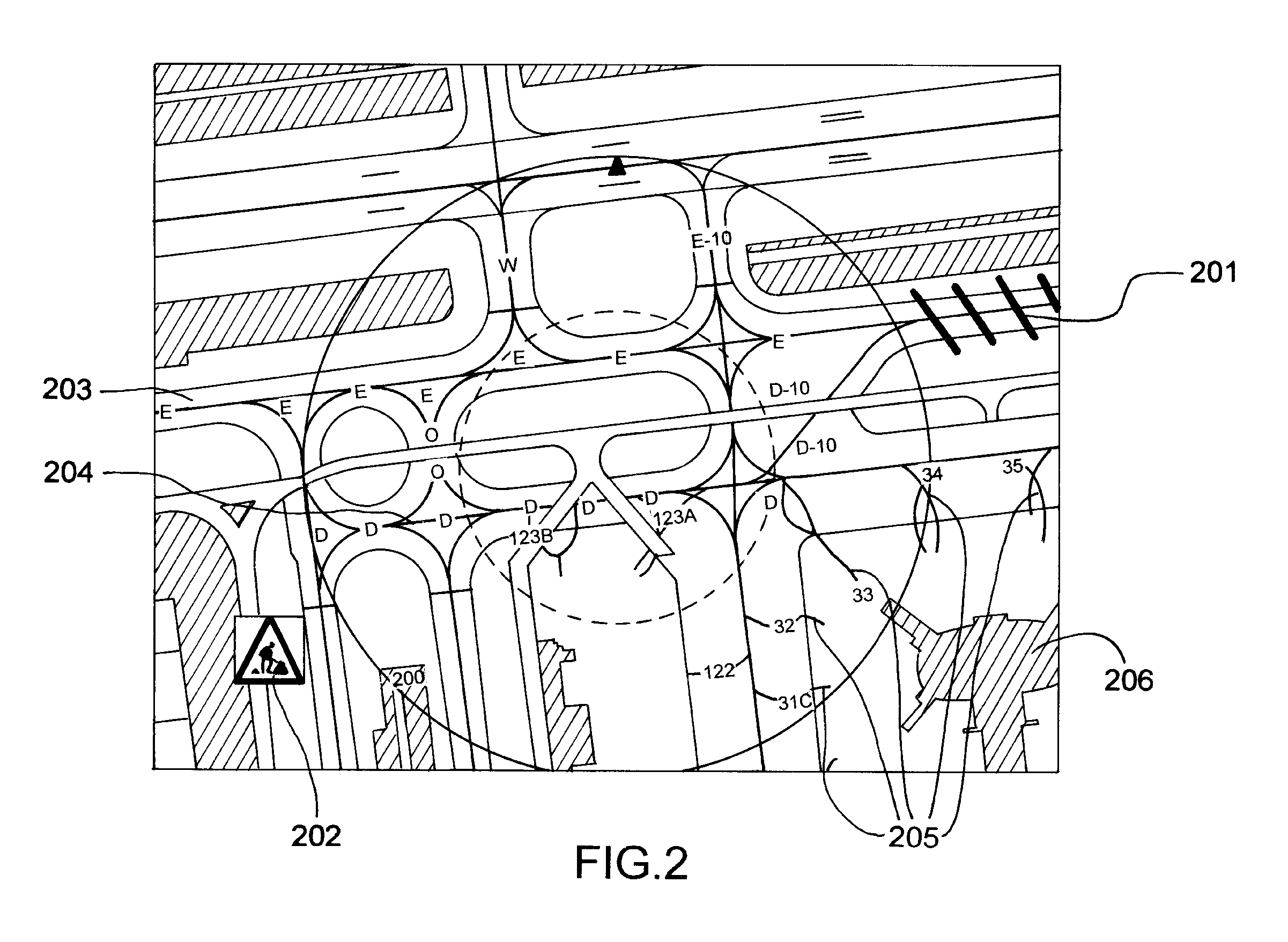
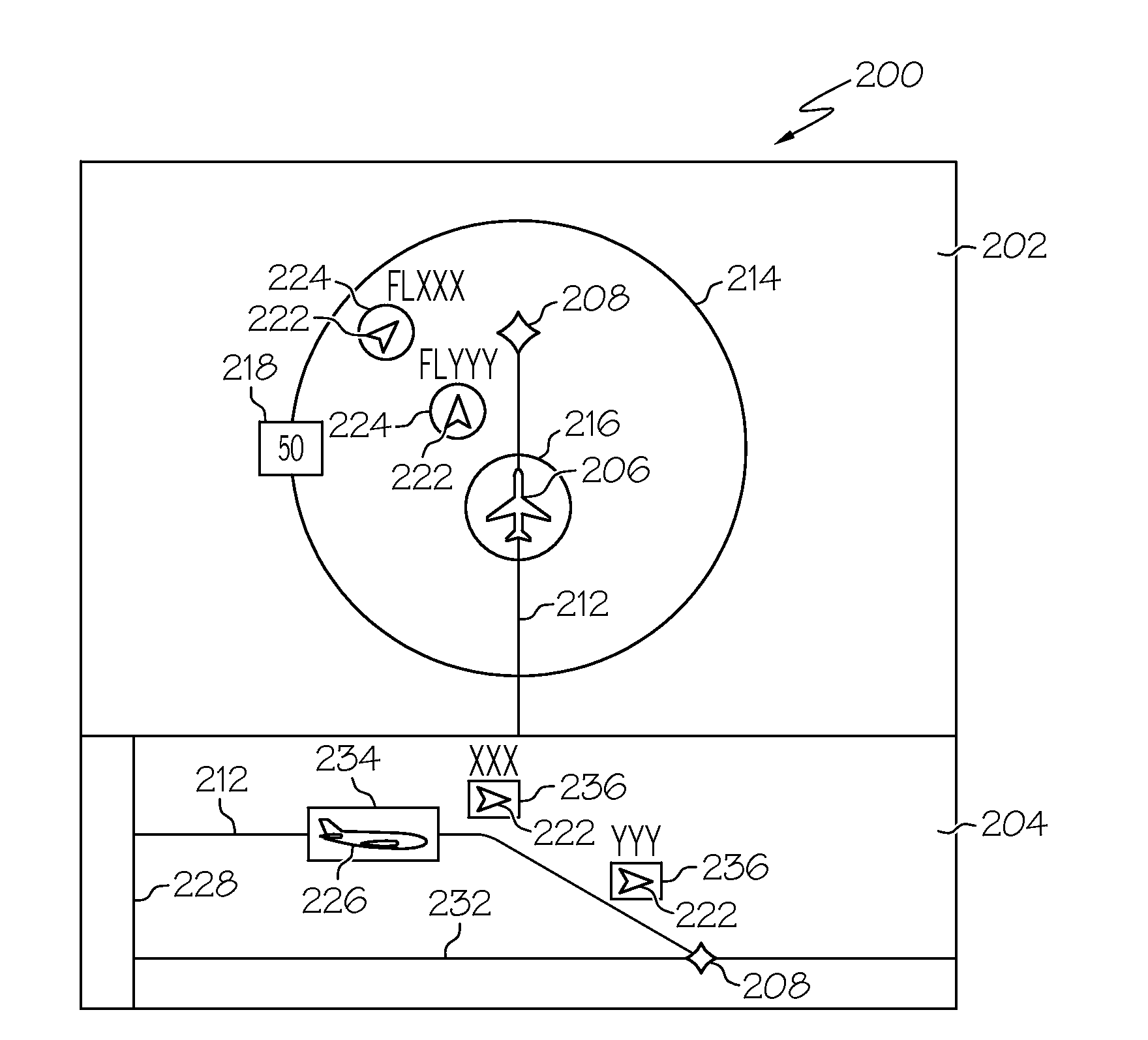
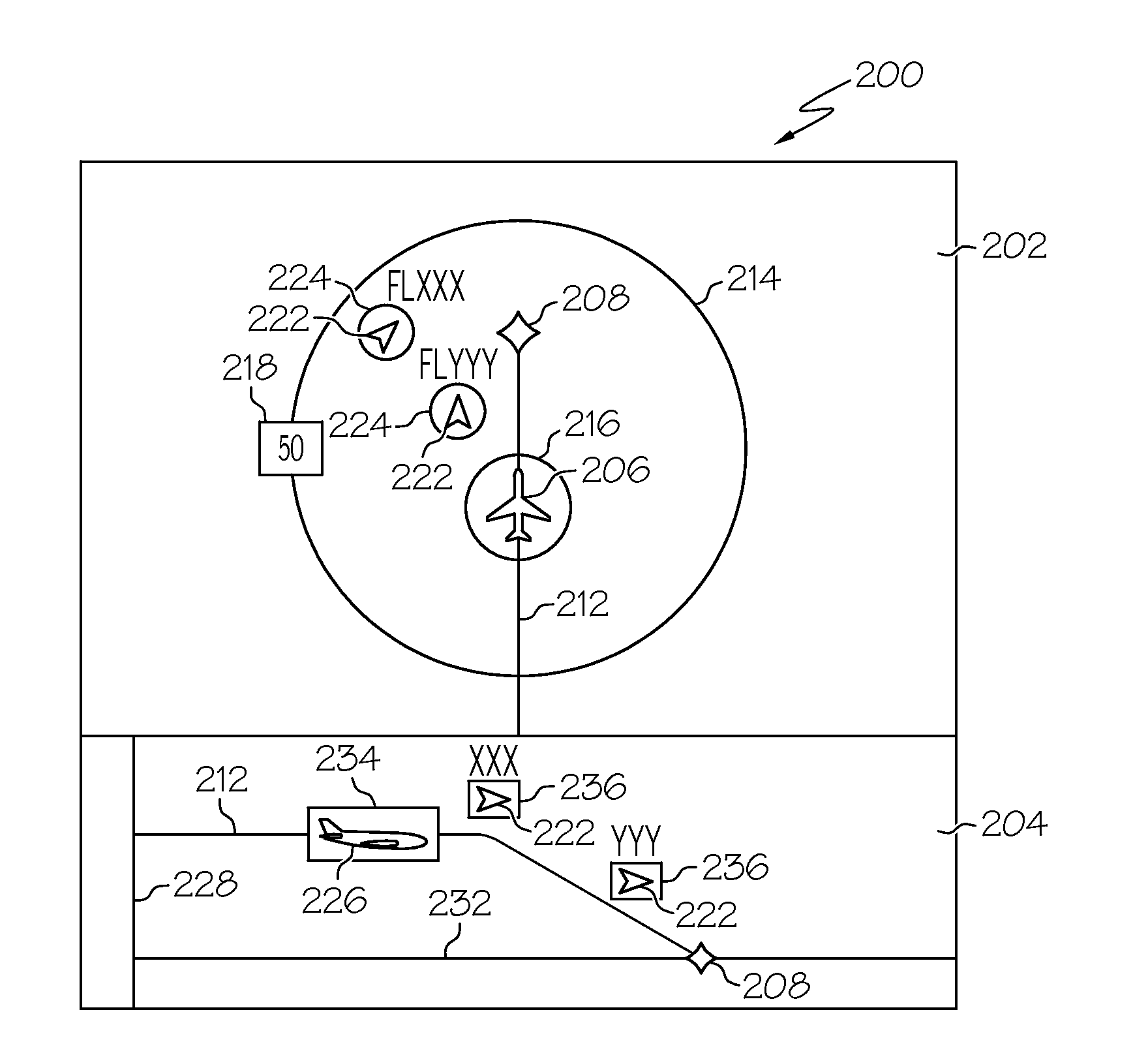
Aircraft navigation accuracy display system
An aircraft display system is provided for rendering at least aircraft estimated position uncertainty (EPU) and / or vertical estimated position uncertainty (VEPU) values non-numerically and in a fairly intuitive manner. The system may also render the EPU and VEPU values non-numerically for other traffic entities within range of the aircraft.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
System and method for aircraft navigation using signals transmitted in the DME transponder frequency range
The present invention provides a system and method for aircraft to determine own position and navigate using a navigation heartbeat signal broadcast on a DME uplink and / or a Mode-S uplink frequency. The present invention enables deep integration between the existing navigation systems (DME interrogation-reply ranges and GPS / WAAS raw TDOA or pseudo range measurements) and the DME heartbeat TDOAs or Mode-S heartbeat TDOAs to provide a highly accurate navigation positioning capability and provide necessary backup capability in lieu of GPS to maintain the necessary RNP / RNAV capability and avoid degrading aircraft operational safety.
Owner:SAAB INC
Aircraft navigation system
ActiveUS8781650B2Analogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficProgram planningNavigation system
Owner:THE BOEING CO
General airplane landing radial line navigation method
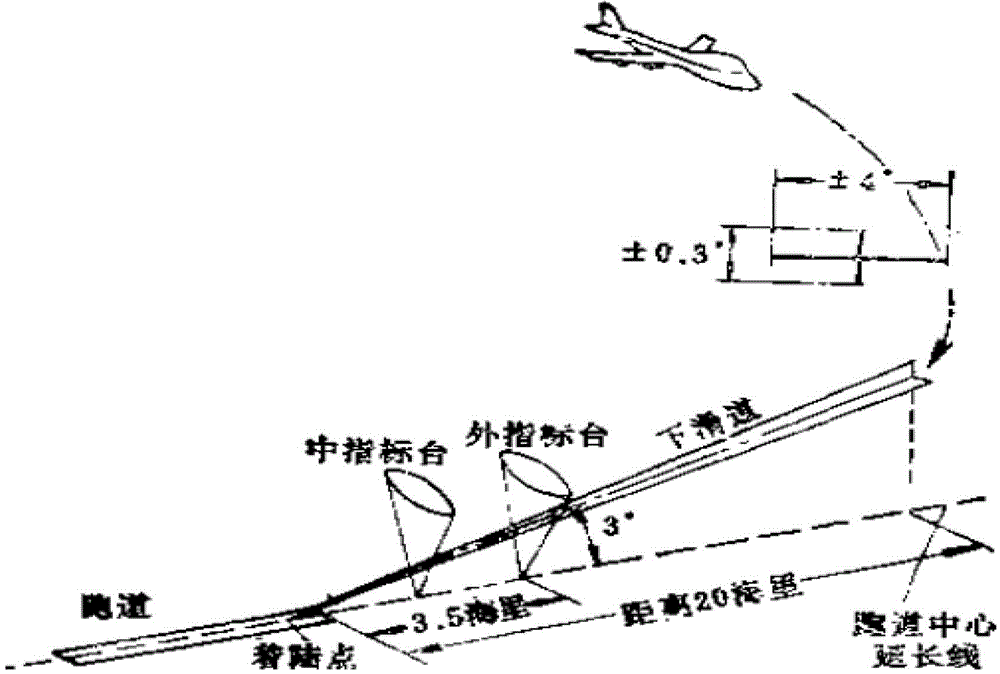
InactiveCN102980573ALanding safetyPrecision landingInstruments for road network navigationJet aeroplaneMarine navigation
The invention relates to a general airplane landing radial line navigation method. The general airplane landing radial line navigation method comprises the following steps of 1, building a landing radial line by airborne navigation equipment according to airplane real-time position information provided by an airplane instrument, navigation information provided by a ground navigation station, and a received landing radial line building instruction, carrying out calculation, and displaying the landing radial line and a reverse-direction extending line of the landing radial line by cockpit display equipment, and 2, carrying out landing according to the landing radial line and the navigation information provided by the ground navigation station, guiding an airplane to the reverse-direction extending line of the landing radial line, and adjusting the airplane to make it fly or land along a direction of the landing radial line. The general airplane landing radial line navigation method solves the problem that the existing landing navigation method has a large potential safety hazard in a zone without ground navigation facilities. The general airplane landing radial line navigation method is a real-time, visual, convenient and reliable airplane navigation calculation method, improves an implementation method of real-time flight guidance of a general airplane and pilot autonomous operation display, and provides a visual and accurate landing navigation method.
Owner:AVIC NO 631 RES INST
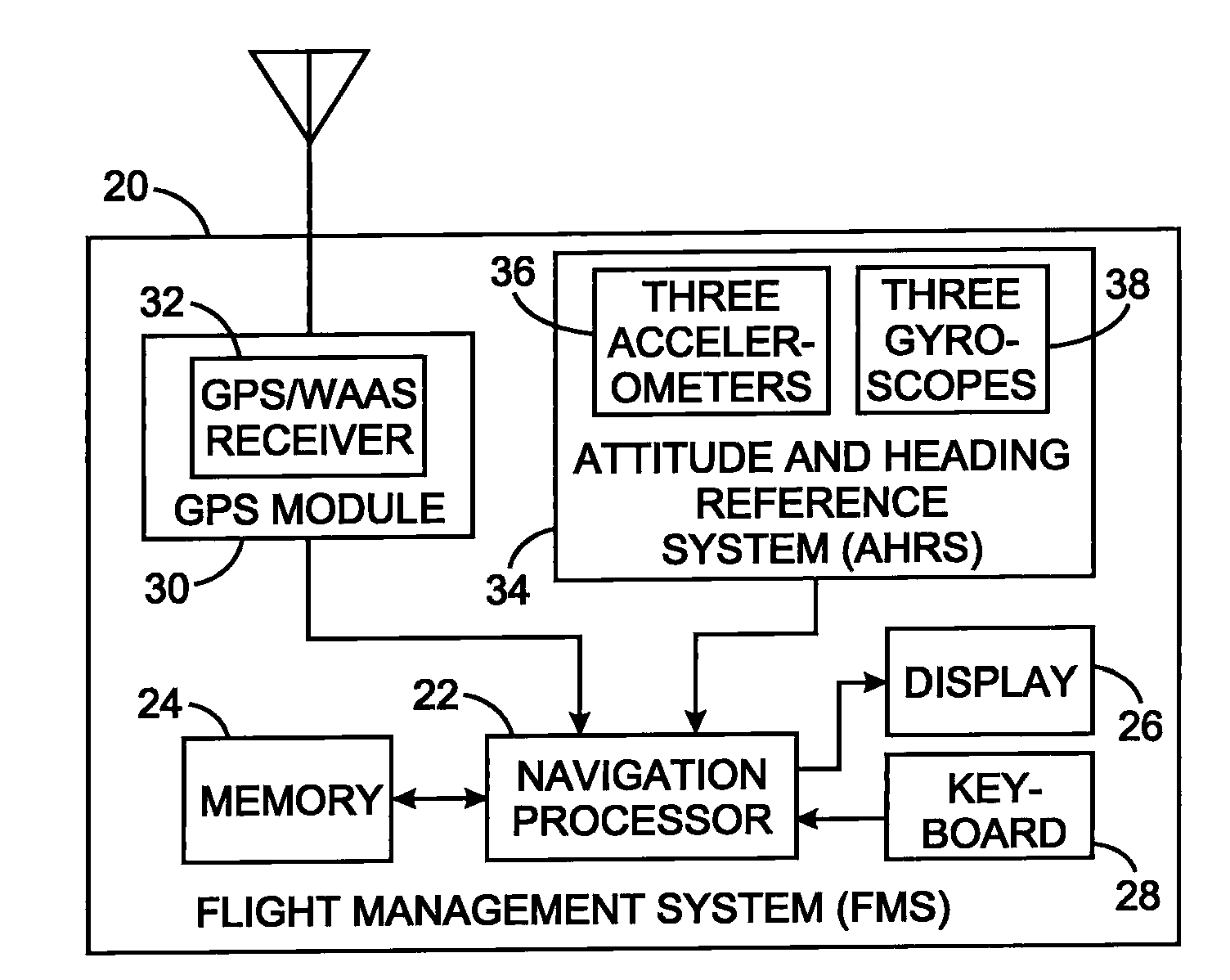
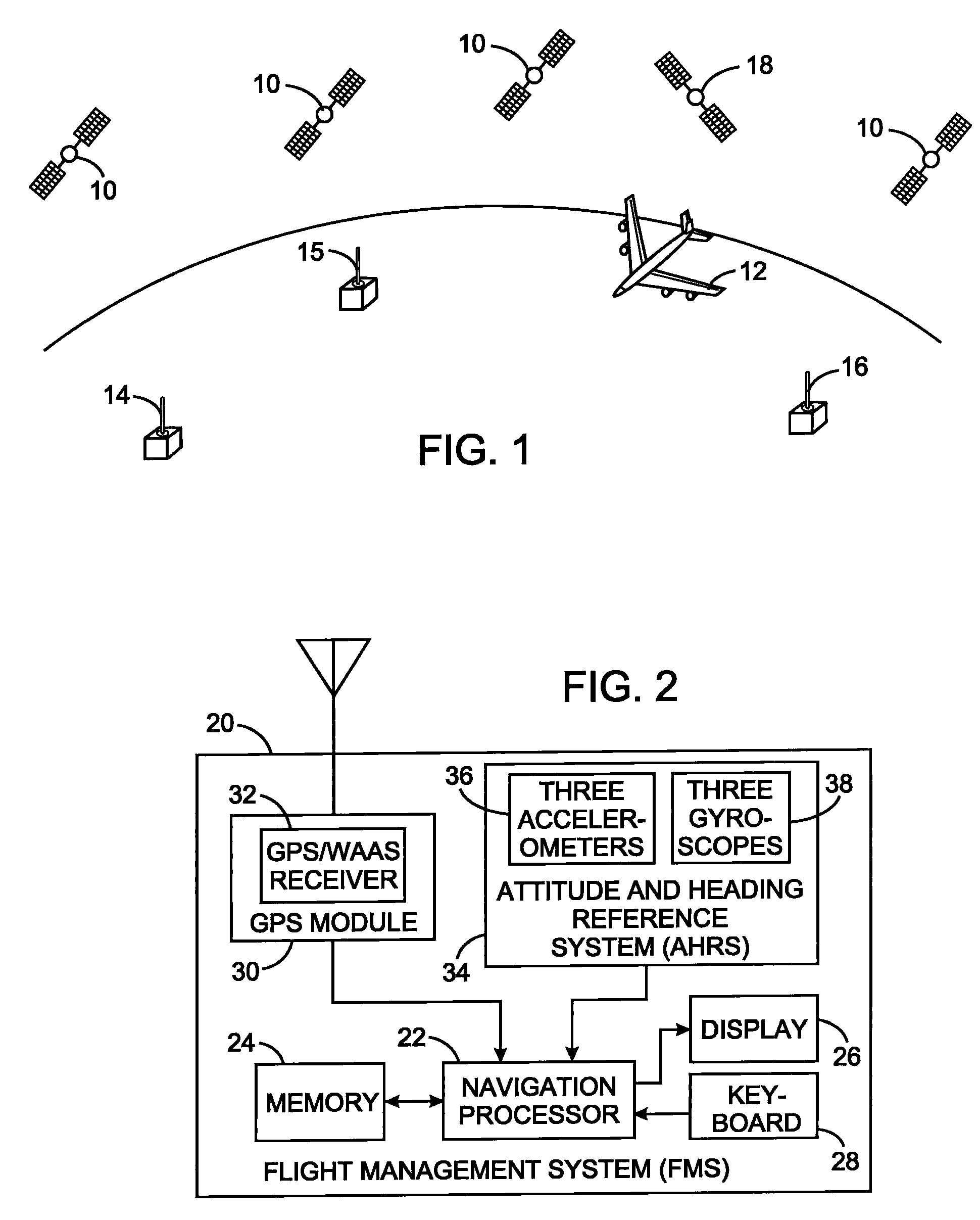
Aircraft navigation using the global positioning system and an attitude and heading reference system
ActiveUS8082099B2Navigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPosition fixationAttitude and heading reference systemKaiman filter
A vehicle navigation technique uses a receiver for signals of a global positioning system to produce a first position indication and a first velocity indication. An attitude and heading reference system employs accelerometers and gyroscopes oriented along three axes. The raw signals from the accelerometers and gyroscopes are used to derive a second position indication and a second velocity value. A Kalman filter function is applied to the first and second position indications and to the first and second velocity indications to thereby produce a present position indication and a present velocity indication. The Kalman filter function exploits GPS data to corrects periodic drift in the position and velocity indications derived form the accelerometers and gyroscopes by calculating accelerometer and gyroscope biases, thereby enabling relatively inexpensive devices to be utilized.
Owner:UNIVERSAL AVIONICS SYST
Aircraft navigation aid method and device
ActiveUS7173545B2Increased safety marginAnalogue computers for trafficAnti-collision systemsPoint of no returnComputer science
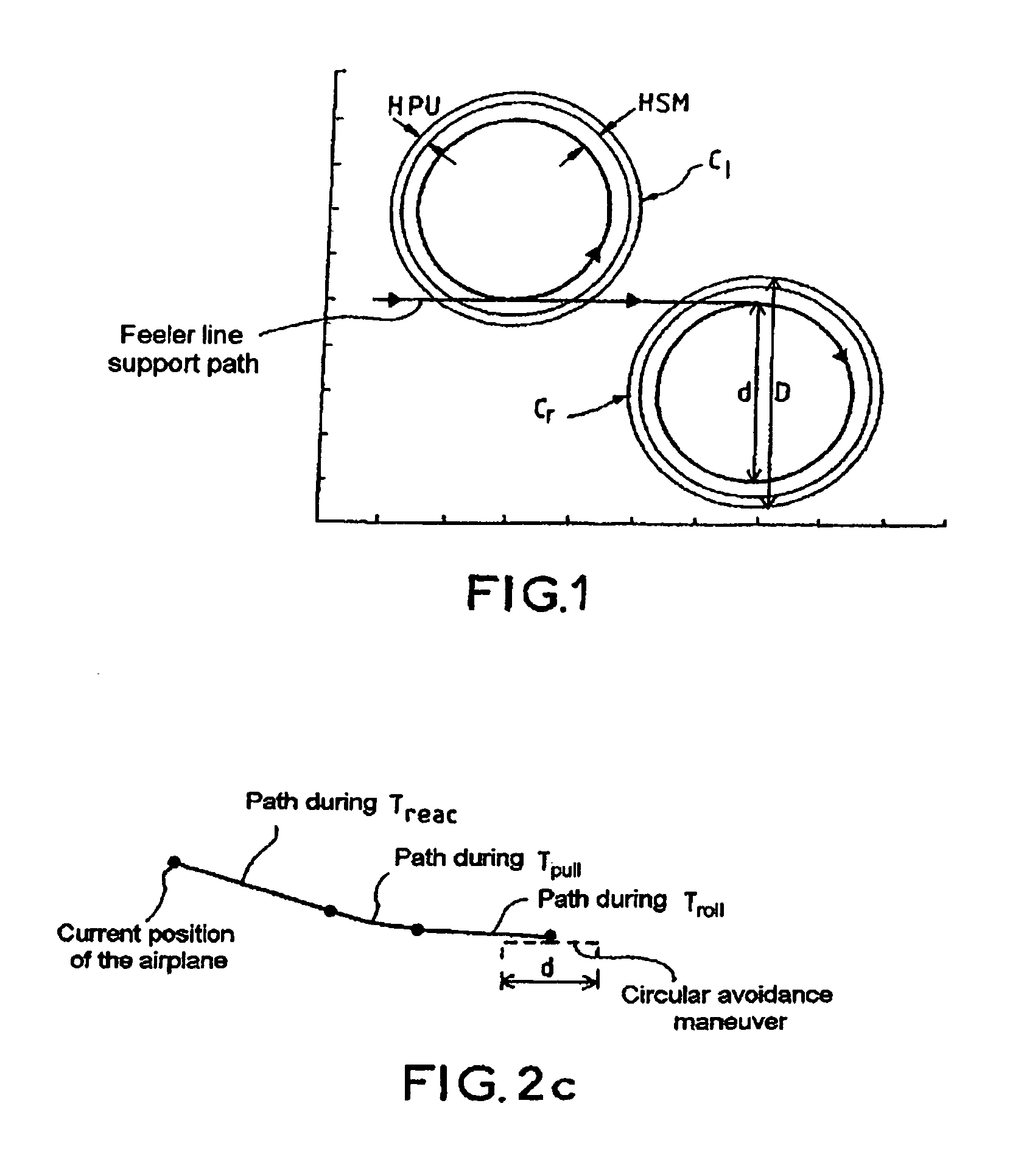
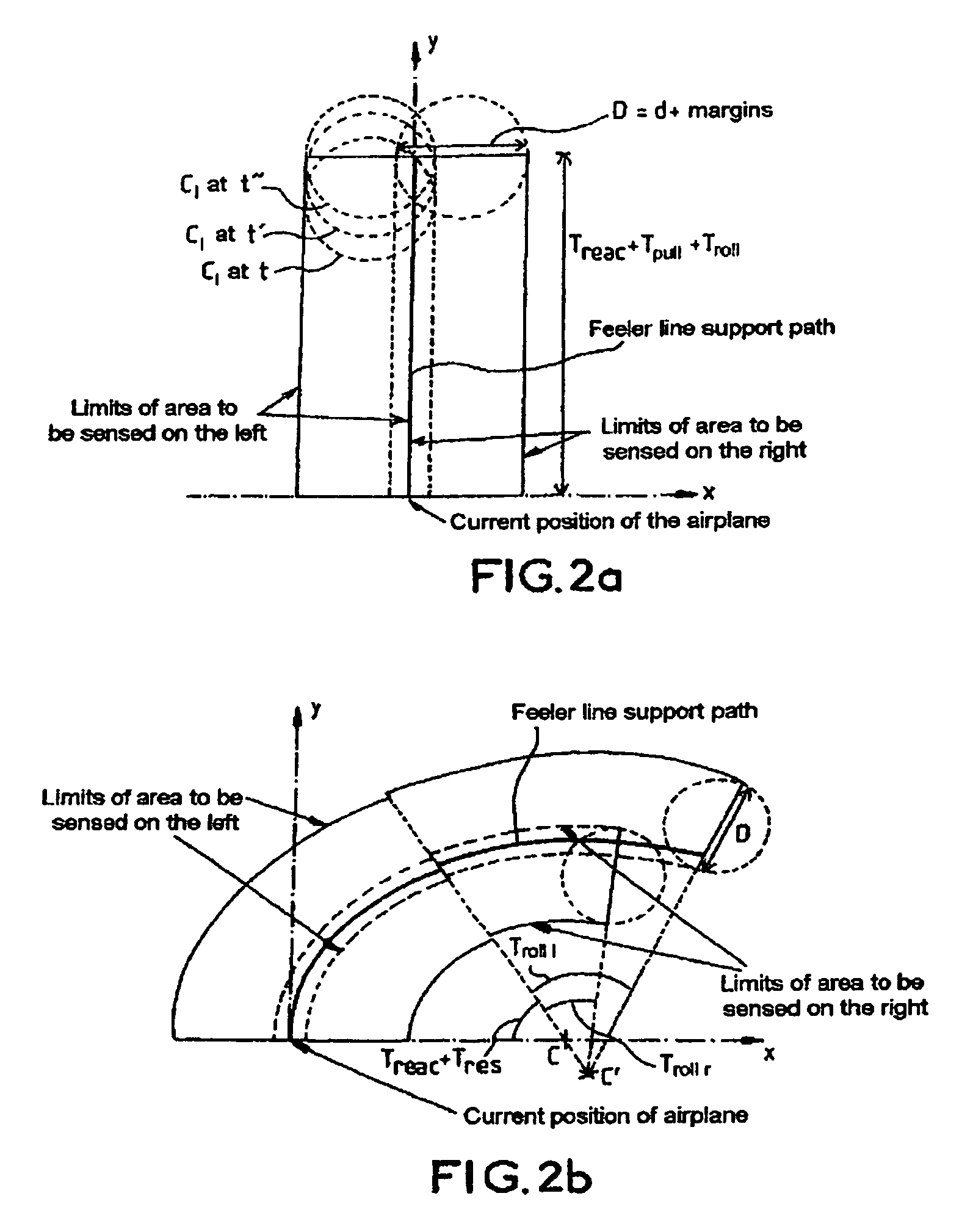
The invention relates to an aircraft navigation aid method. It comprises the following steps of defining an area to be sensed to the right and to the left of a first hypothetical path of the aircraft, sensing, for each of the two areas to be sensed to the right and to the left, a corresponding predefined underlying relief, in order to identify dangerous sub-zones to the right and / or to the left, computing, for each of the dangerous sub-zones to the right and / or to the left, a time ΔT remaining to begin an avoidance maneuver before a point of no return, and determining for the dangerous sub-zones to the right a minimum ΔT denoted ΔT right and / or for the dangerous sub-zones to the left a minimum ΔT denoted ΔT left, establishing a navigation aid from ΔT right and / or ΔT left.
Owner:THALES SA
Aircraft assembly and method
ActiveUS20180170529A1Reduce noiseClean airframeActuated automaticallyAircraft landing aidsNavigation systemAirplane
An aircraft assembly having landing gear with a known deployment value, apparatus for permitting landing gear deployment, down-lock sensing apparatus, a navigation system, a landing gear control system, a flight control system, and a deployment controller. The deployment controller is configured to: calculate a touch down value using the aircraft position and speed information provided by the aircraft navigation system; command the landing gear control system to provide the deploy signal when the touch down value reaches a deployment threshold value which is greater than the landing gear deployment value; and command the flight control system to execute a landing abort sequence if the controller does not receive the down-lock signal from the landing gear sensing apparatus within a deployment value window which is greater than or equal to the known deployment value for the landing gear but less than the touch down value.
Owner:MESSIER DOWTY
Navigation method of universal airplane aircraft route
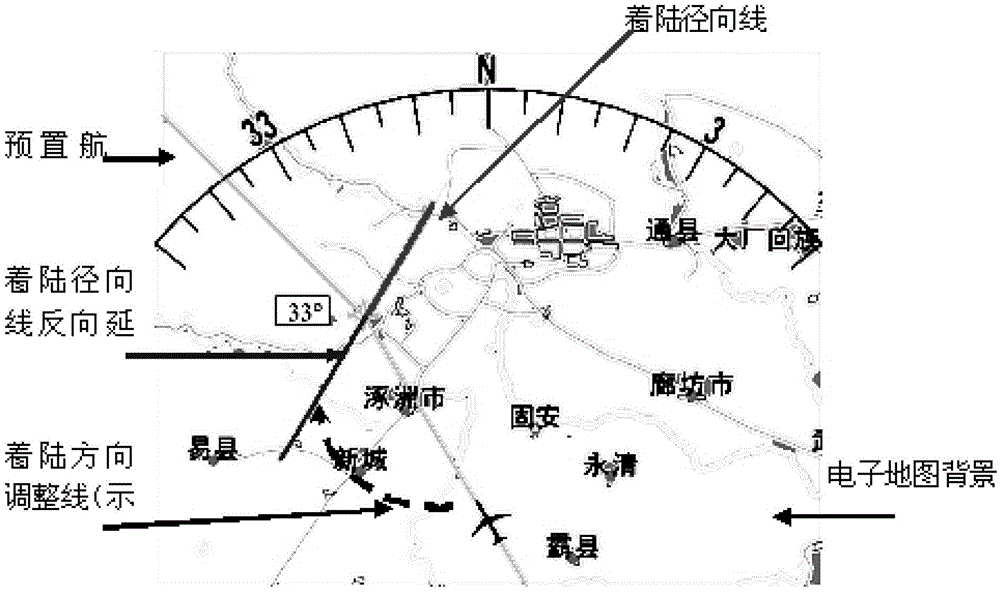
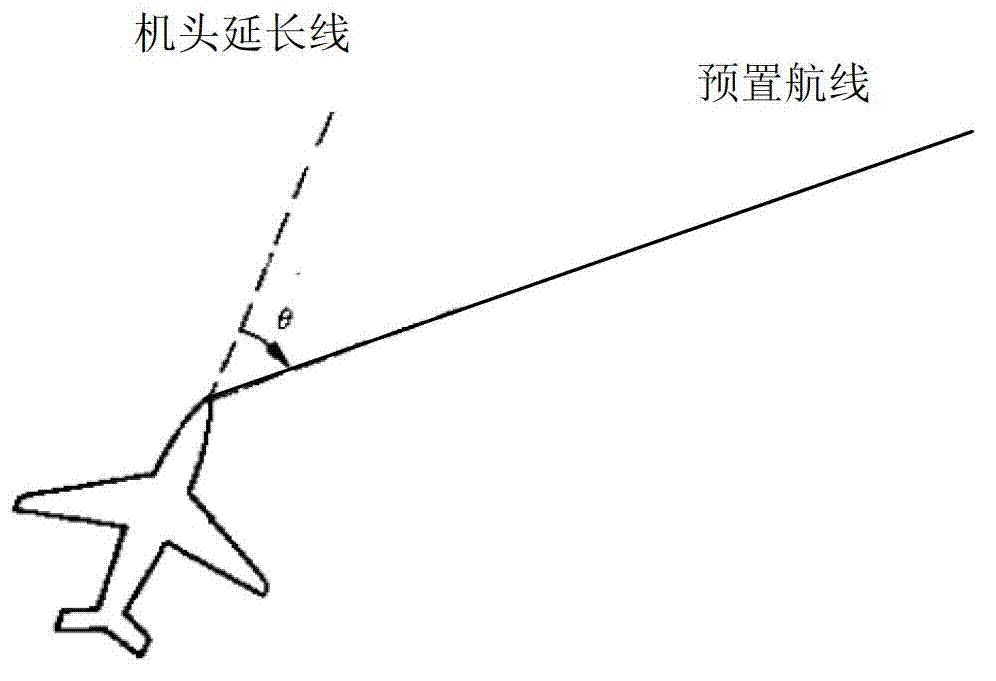
InactiveCN102829778AExpand flight areaEnhance autonomous controlNavigational calculation instrumentsJet aeroplaneFlight direction
The invention provides a navigation method of a universal airplane aircraft route to solve the technical problems that a pilot cannot autonomously and intuitively know and grasp deviation between a current flight direction and a preset flight direction or planned flight course and cannot accurately carry out flight guide and navigation in the prior art. The navigation method comprises the steps as follows: airborne navigation equipment sets a preset route as a reference route, takes position information of a territorial navigation station and present position information of the airplane as reference information, calculates current airplane position and flight direction in real time, and calculates out the angle difference of an extension line of a nose direction and the reference route; the reference route and the prolonging line of the handpiece direction are displayed on a navigation map interface for prompting the pilot to operate and guide the airplane to fly along the preset route accurately. The technical scheme is convenient to carry out, safe and reliable, visual and clear in display mode, not only can be applied to universal airplane navigation indication, but also can be applied to various airplanes. The flight navigation indication method is enriched and completed.
Owner:AVIC NO 631 RES INST
Computer-assisted aerial surveying and navigation
ActiveUS20190340938A1Navigational calculation instrumentsPicture taking arrangementsComputer-aidedSurveyor
Owner:ARKIDAN SYST INC
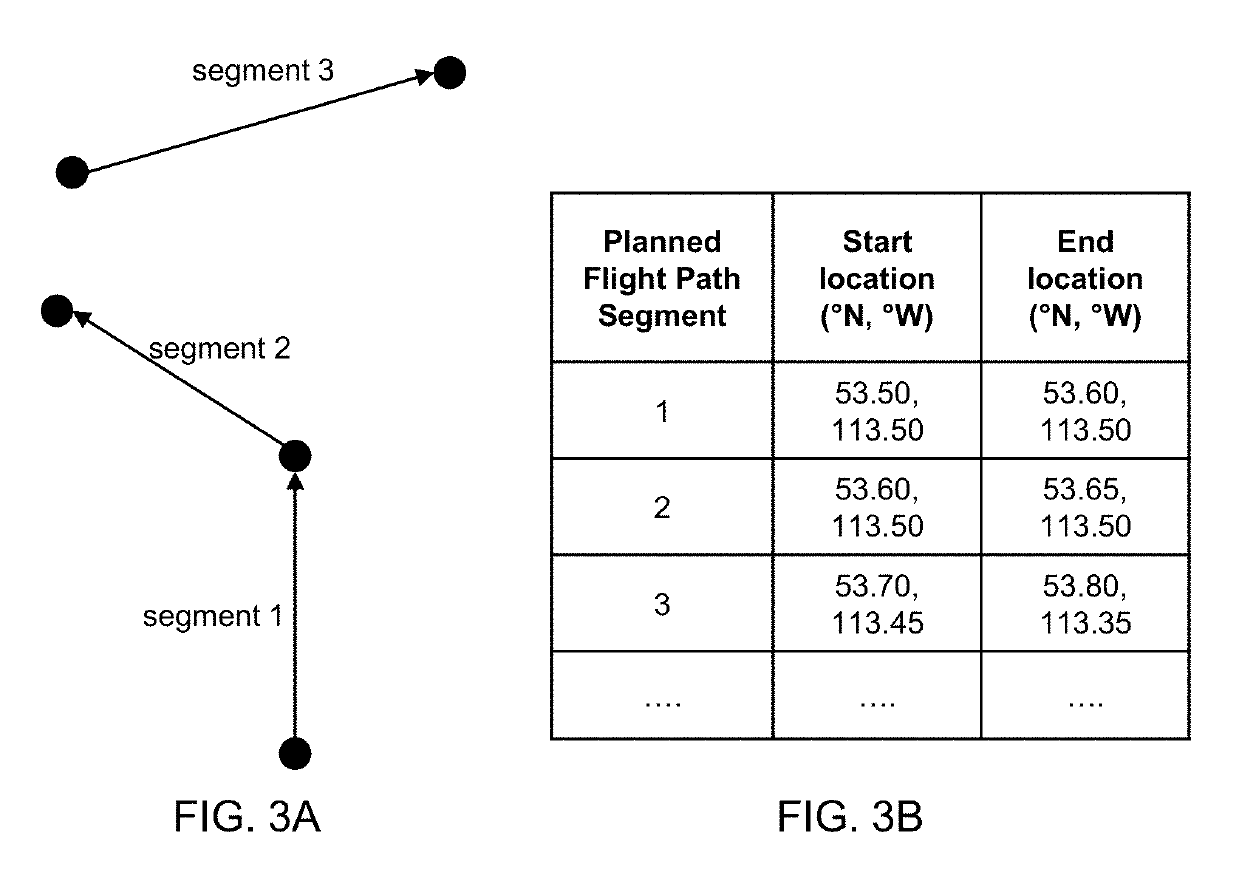
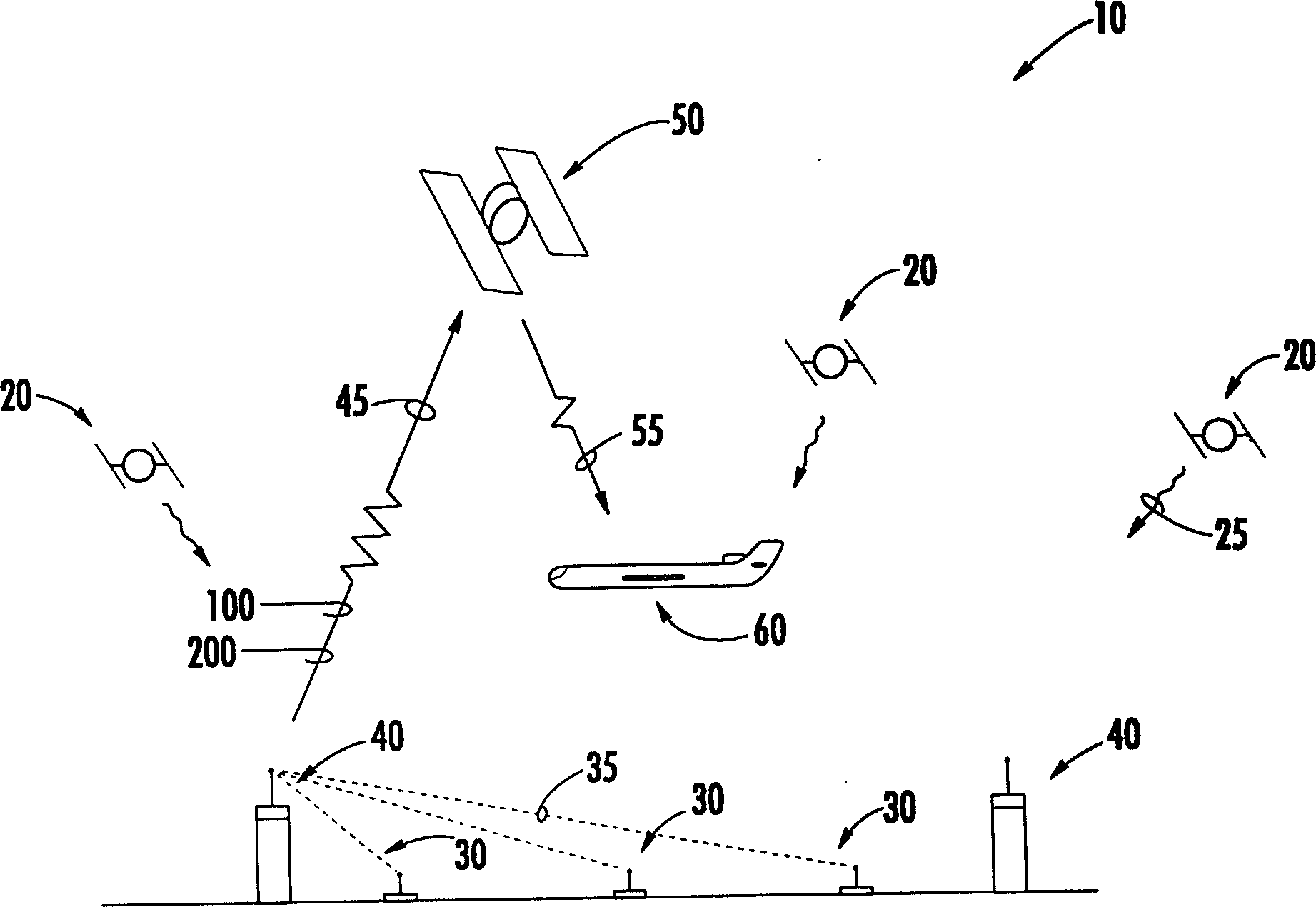
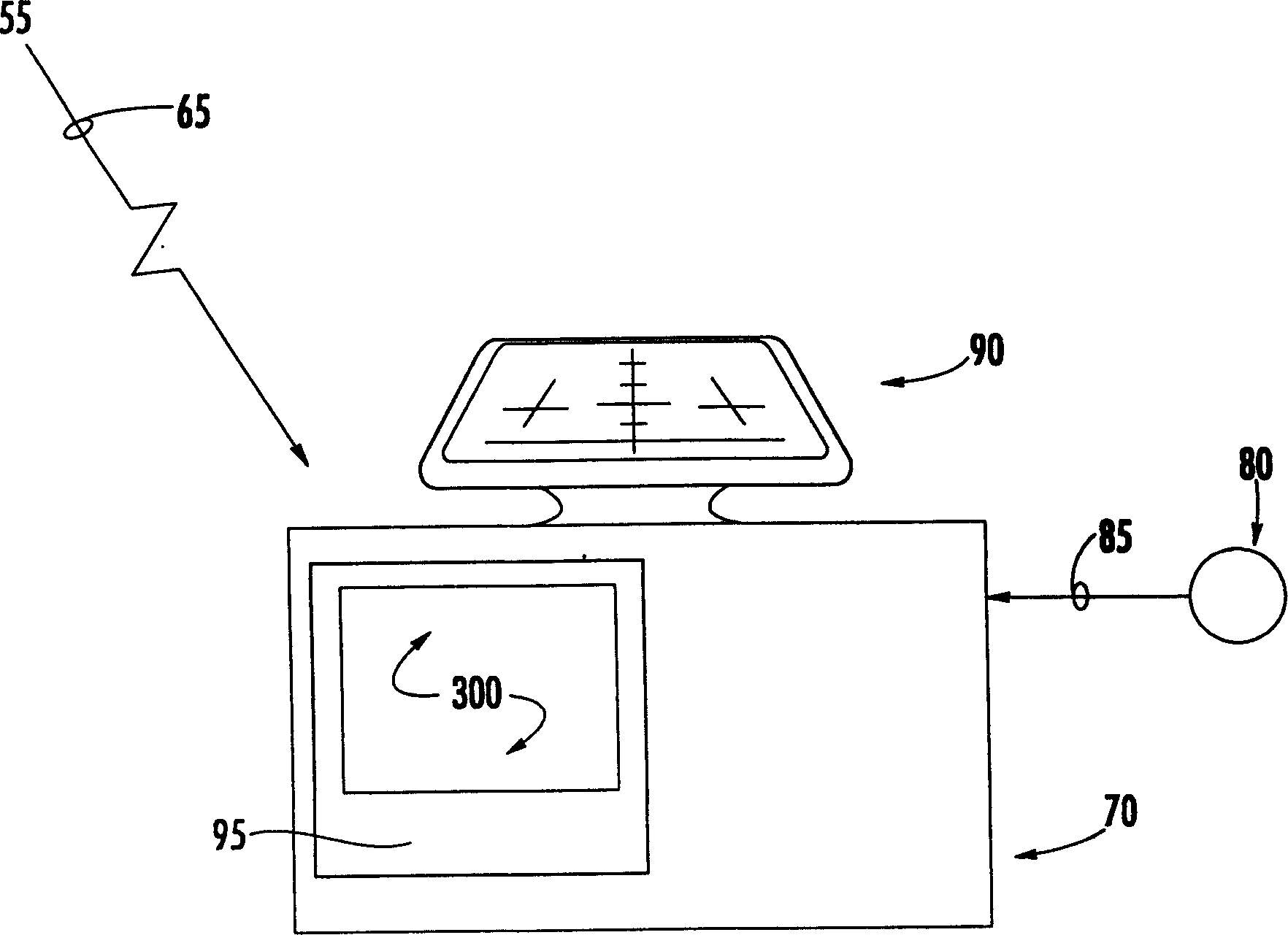
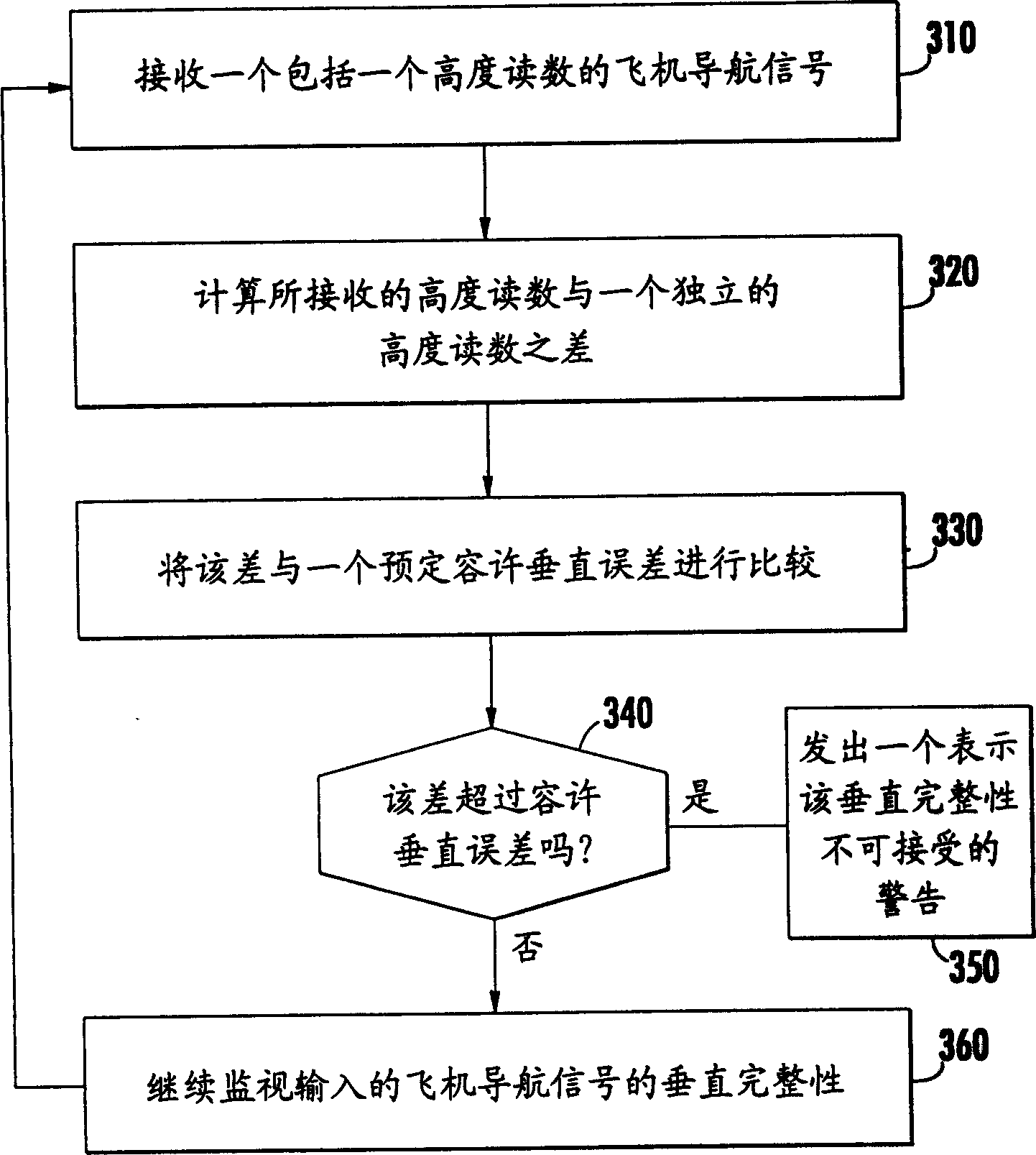
Receiver-autonomous vertical integrity monitoring
InactiveCN1481522AIntegrityBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationSignaling systemMultiple case
A system and method for determining the vertical integrity of an altitude component of an aircraft navigational signal through the use of a receiver-autonomous vertical integrity monitoring (RAVIM) algorithm. The system and methods also provide timely warning to vehicle operators if the integrity of the signal is unacceptable or unknown. The system and methods are capable of determining the vertical integrity of an incoming signal without relying upon data embedded within the incoming signal itself. In addition, the system and methods of the present invention provide vertical integrity to vehicle operators in instances, such as when the specific aircraft navigational signal is not operating, when the specific aircraft navigational signal is not available in a particular region, or when an aircraft is operating outside the geographic area covered by the specific aircraft navigational signal system.
Owner:UNITED PARCEL SERVICE OF AMERICAN INC
Navigation, identification, and collision avoidance antenna systems
InactiveUS8269684B2Antenna adaptation in movable bodiesElongated active element feedLong axisGround plane
Antenna embodiments are illustrated that are particularly suited for use in aircraft navigation, identification and collision avoidance systems. An exemplary antenna embodiment operates about a center wavelength and in association with a ground plane and comprises first and second grounded, shortened, and top loaded monopoles. These monopoles are spaced apart above a ground plane and each of them includes a feed post, a shorted post, and a top load wherein the shorted post is spaced from the feed post, is coupled to the ground plane, and has a length less than one fourth of the center wavelength. In addition, the top load is coupled to the feed post and the shorted post and is configured along orthogonal minor and major axes of the top load to have a width along the minor axis and a length along the major axis that exceeds the width.
Owner:SENSOR SYST
Exterior aircraft navigation light and method of controlling an exterior aircraft navigation light
ActiveUS9850003B2Improve passive safetyAccurately deducedAircraft lightsFlight directionFlight vehicle
An exterior aircraft navigation light for an aircraft having a nominal forward flight direction and being able to fly into the nominal forward flight direction as well as into a plurality of further flight directions, such as sideways or backwards, has at least one light emission unit and control circuitry coupled to the at least one light emission unit, wherein the exterior aircraft navigation light is configured such that each of the at least one light emission unit has a unit-specific light emission direction that has a predefined horizontal angle with respect to the nominal forward flight direction, and wherein each of the at least one light emission unit includes a multi-color light source configured to emit red light, white light and green light, and an optical system for conditioning the red light, the white light and the green light emitted by the multi-color light source.
Owner:GOODRICH LIGHTING SYST GMBH
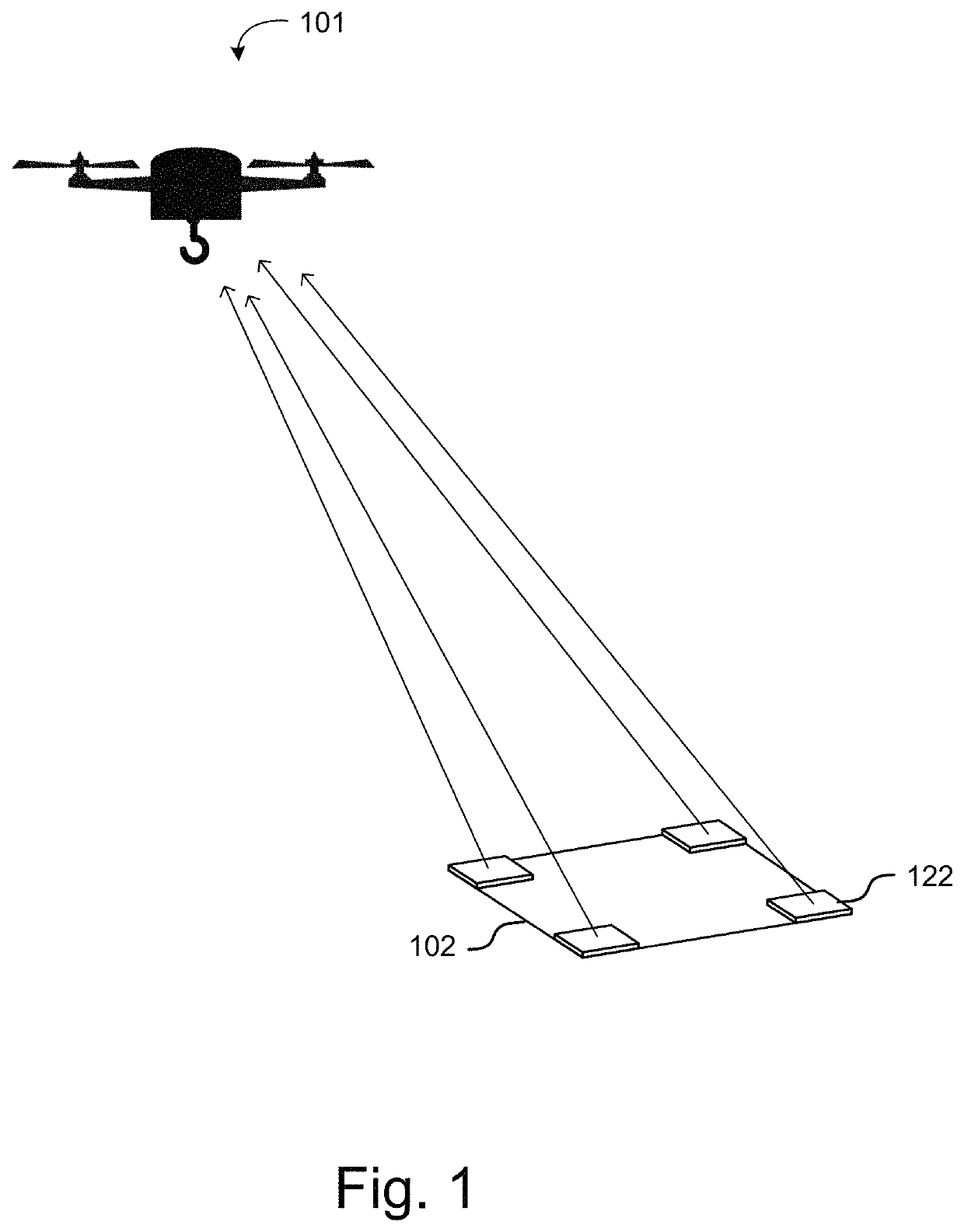
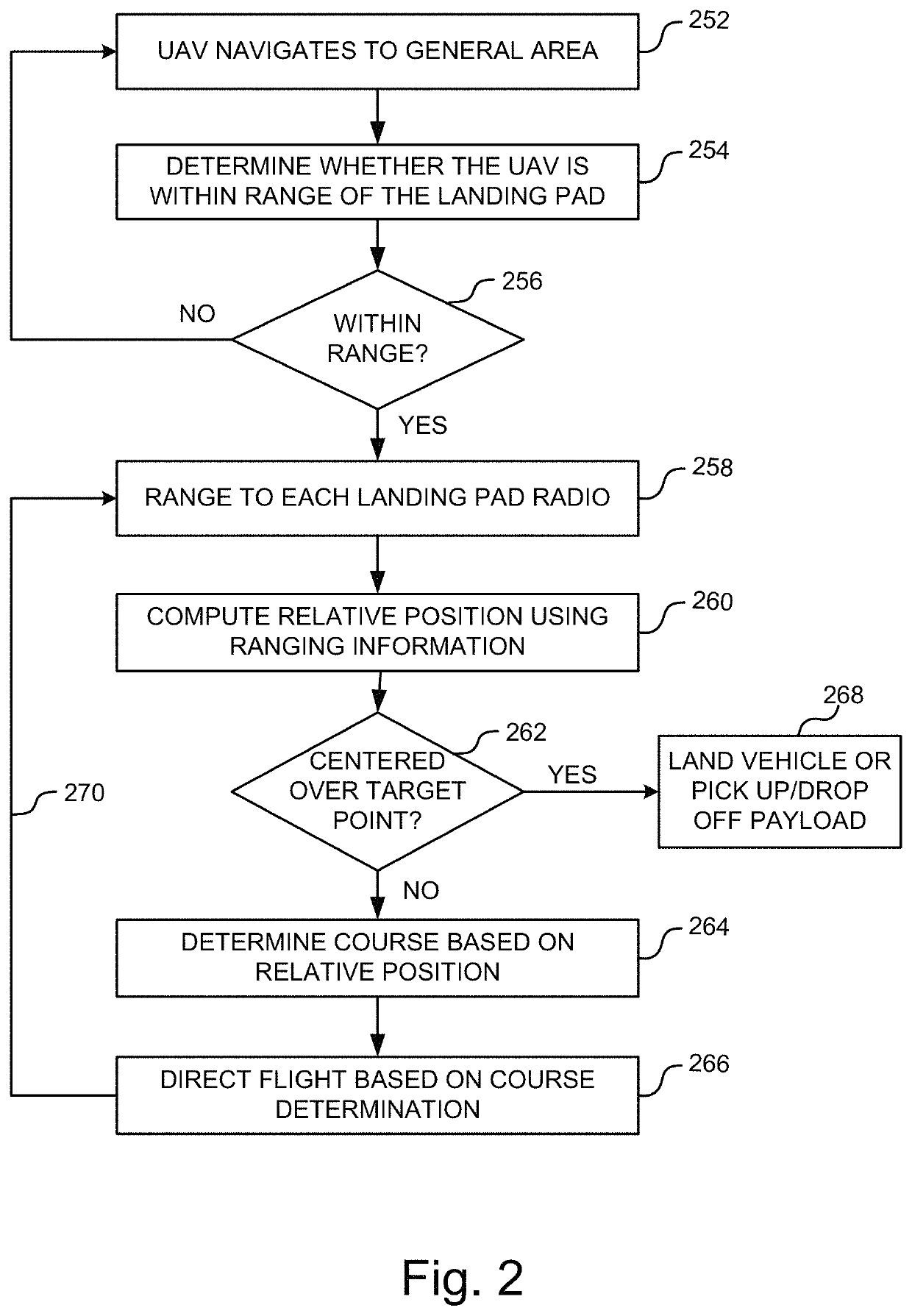
Automated landing solution systems and methods
ActiveUS10713958B2Beacon systems using radio wavesUnmanned aerial vehiclesFlight vehicleRadiotransmitter
A UAV landing system can include a landing pad defining a landing area including a target point; a plurality of positioning radio transmitters positioned in a spaced apart relation and equidistant from the target point, each radio transmitter transmitting a ranging signal; and a position determination and aircraft navigation system at the incoming UAV to receive the ranging signals; determine a range to each positioning radio using the received ranging signals; compute a position of the UAV relative to the target point; determine a course for the UAV to a point above the target point of the landing pad; fly the UAV to the point above the target point of the landing pad, and cause the aircraft to descend vertically toward the target point when the UAV reaches the point above the target point.
Owner:BENCHMARK ELECTRONICS INC
Aircraft navigation accuracy display system
An aircraft display system is provided for rendering at least aircraft estimated position uncertainty (EPU) and / or vertical estimated position uncertainty (VEPU) values non-numerically and in a fairly intuitive manner. The system may also render the EPU and VEPU values non-numerically for other traffic entities within range of the aircraft.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Aircraft navigation system and method of navigating an aircraft
ActiveUS9753143B2Operational safety is enhancedOperational securityBeacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingJet aeroplaneCommand and control
An aircraft navigation system and navigation method. The system comprises a civil-certified GPS-receiver for determining first position information based on C / A-GPS-signals, and a military-type GPS-receiver for determining a second position information based on P(Y)-GPS-signals. A monitoring unit detects a first abnormal condition during jamming conditions within the C / A-GPS-signals. The unit compares the first position information with the second position information and detects a second abnormal condition when a difference between these position information is larger than a threshold value for more than a threshold duration. Upon detecting an abnormal condition, an alert procedure is initiated. In remotely piloted aircraft, Command & Control link-loss is also monitored and during link-loss, a transponder code automatically indicates communication failure. When in such situation an abnormal condition is additionally detected, a transponder code indicates airborne emergency and, subsequently, the aircraft navigation system is switched to navigating based on position information from the military-type GPS-receiver.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com