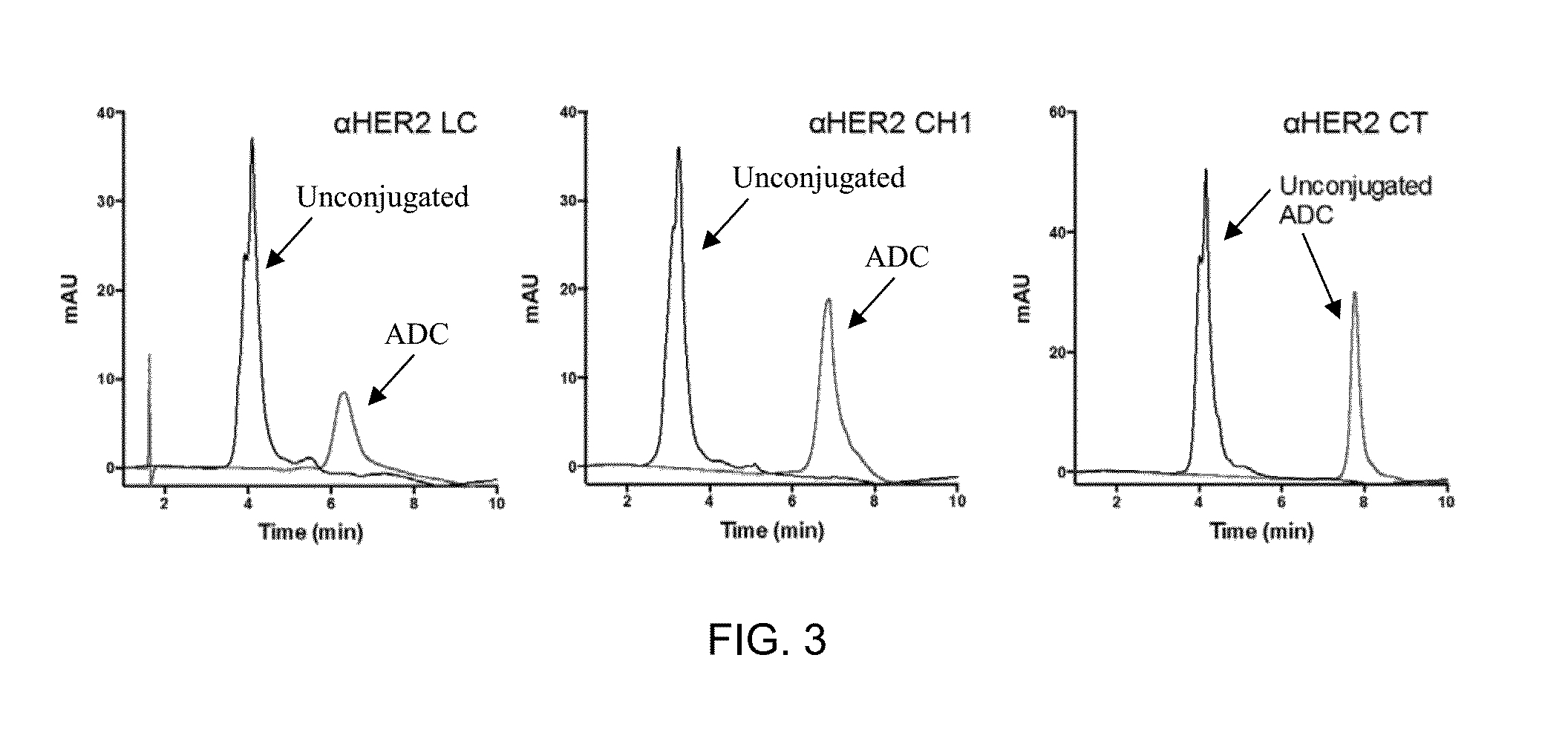
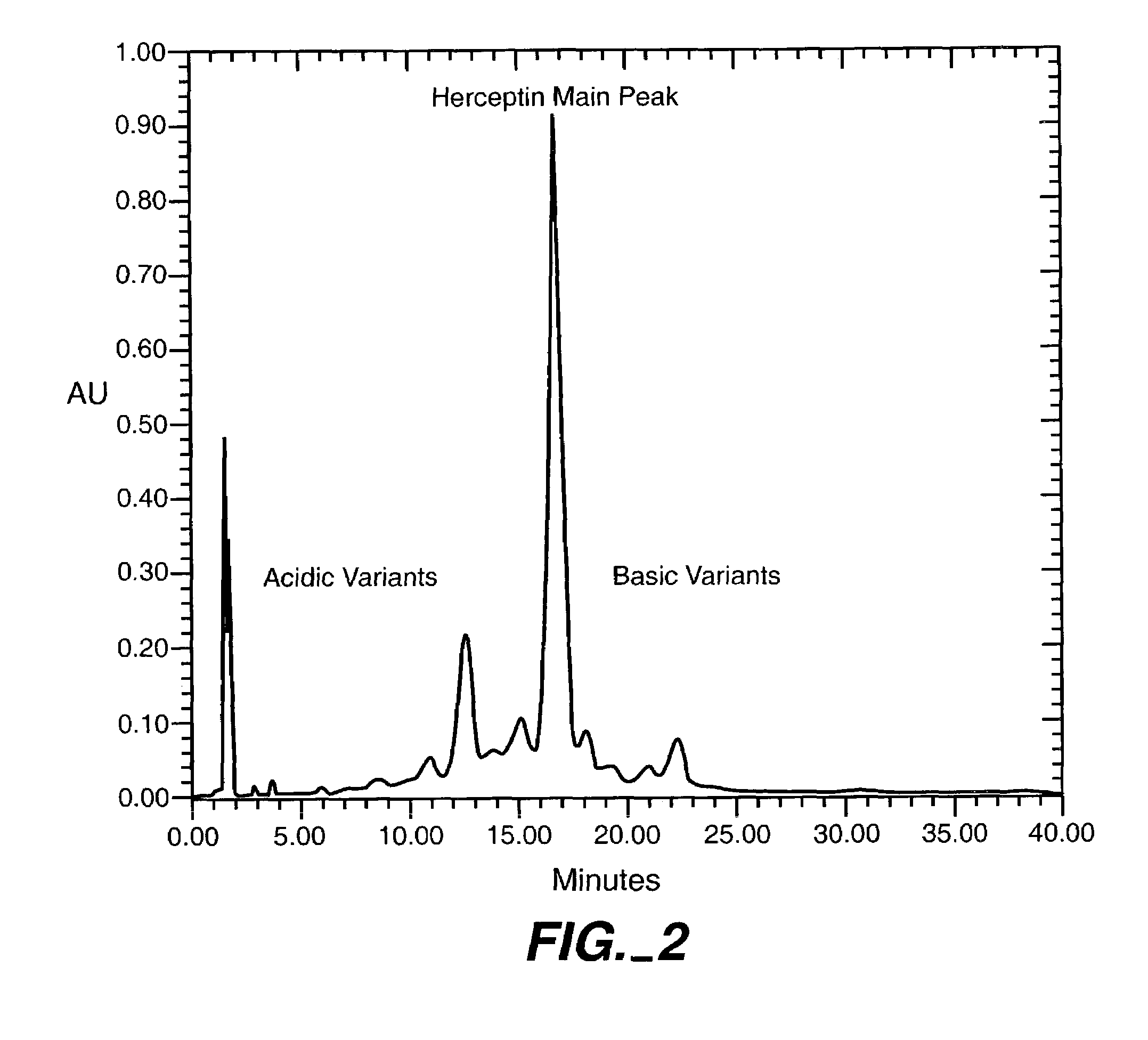
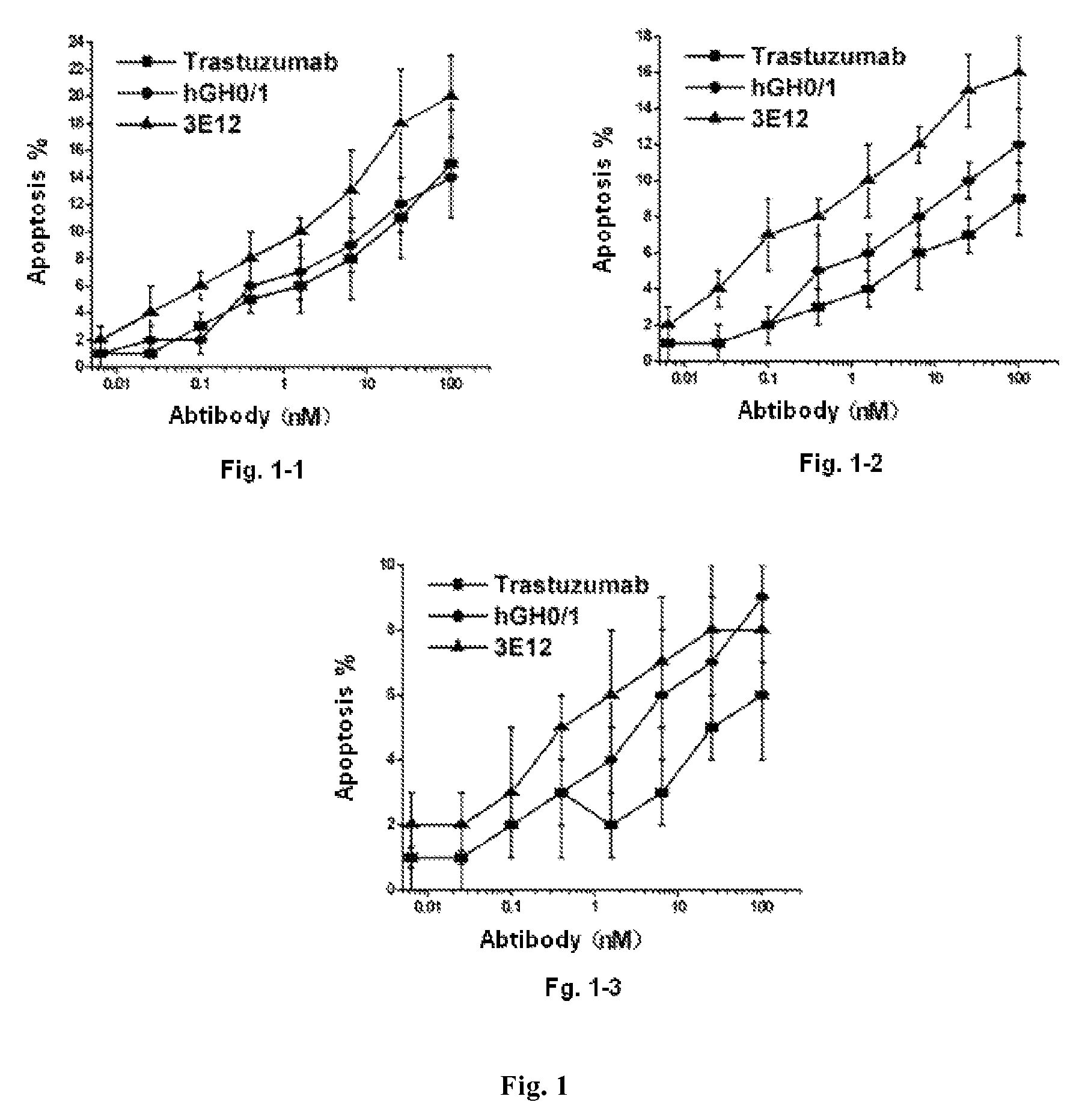
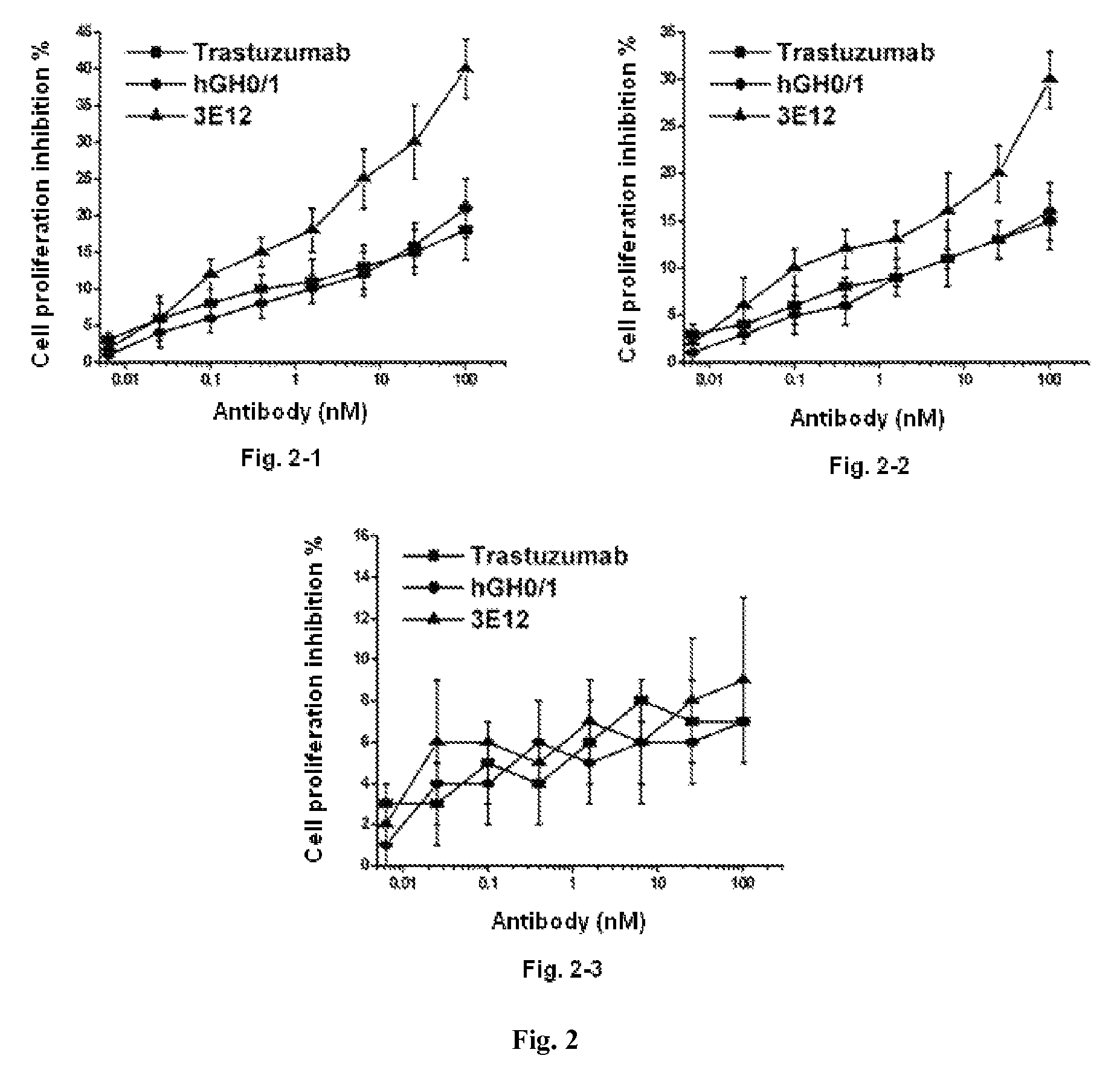
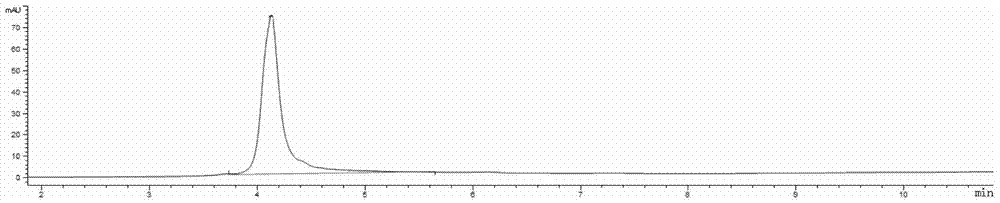
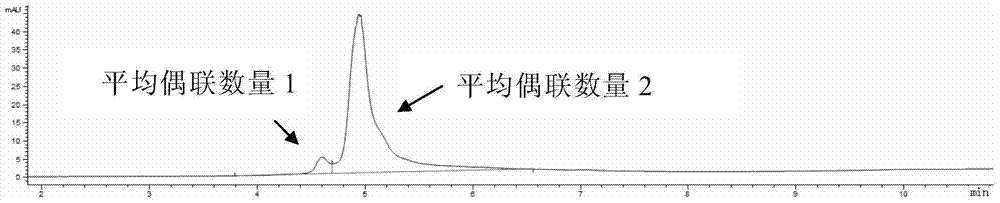
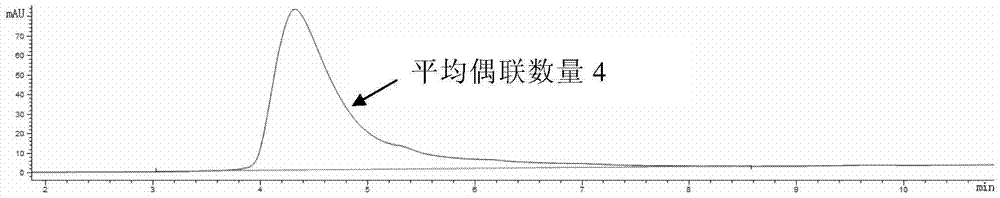
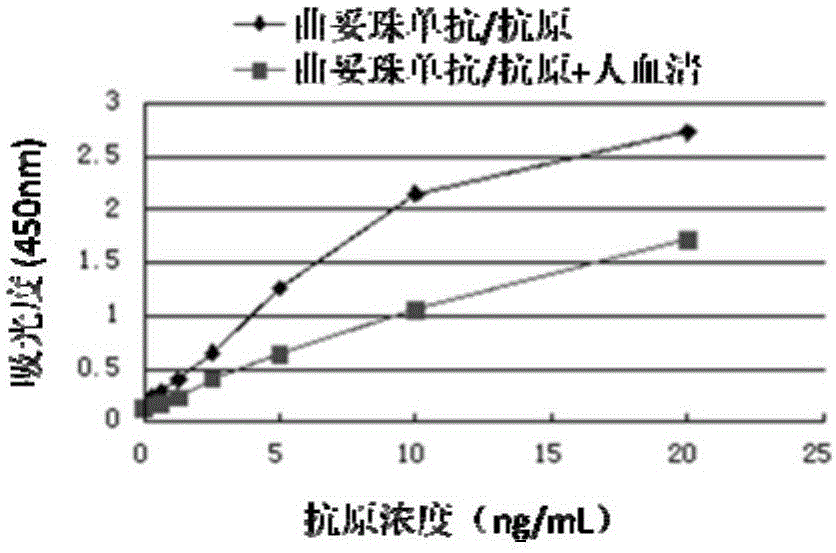
Patents
Literature
62 results about "Anti-HER2 Antibody" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
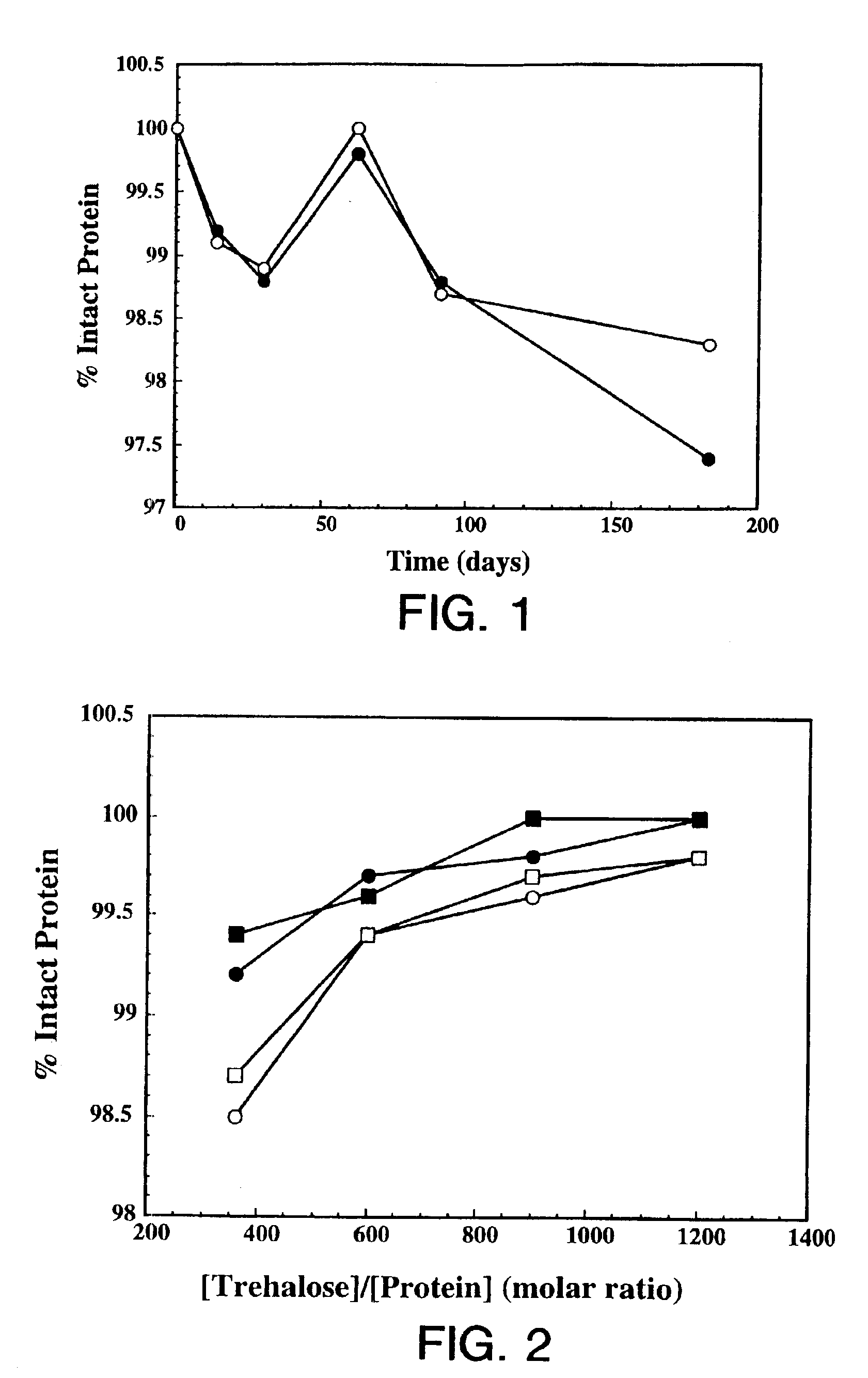
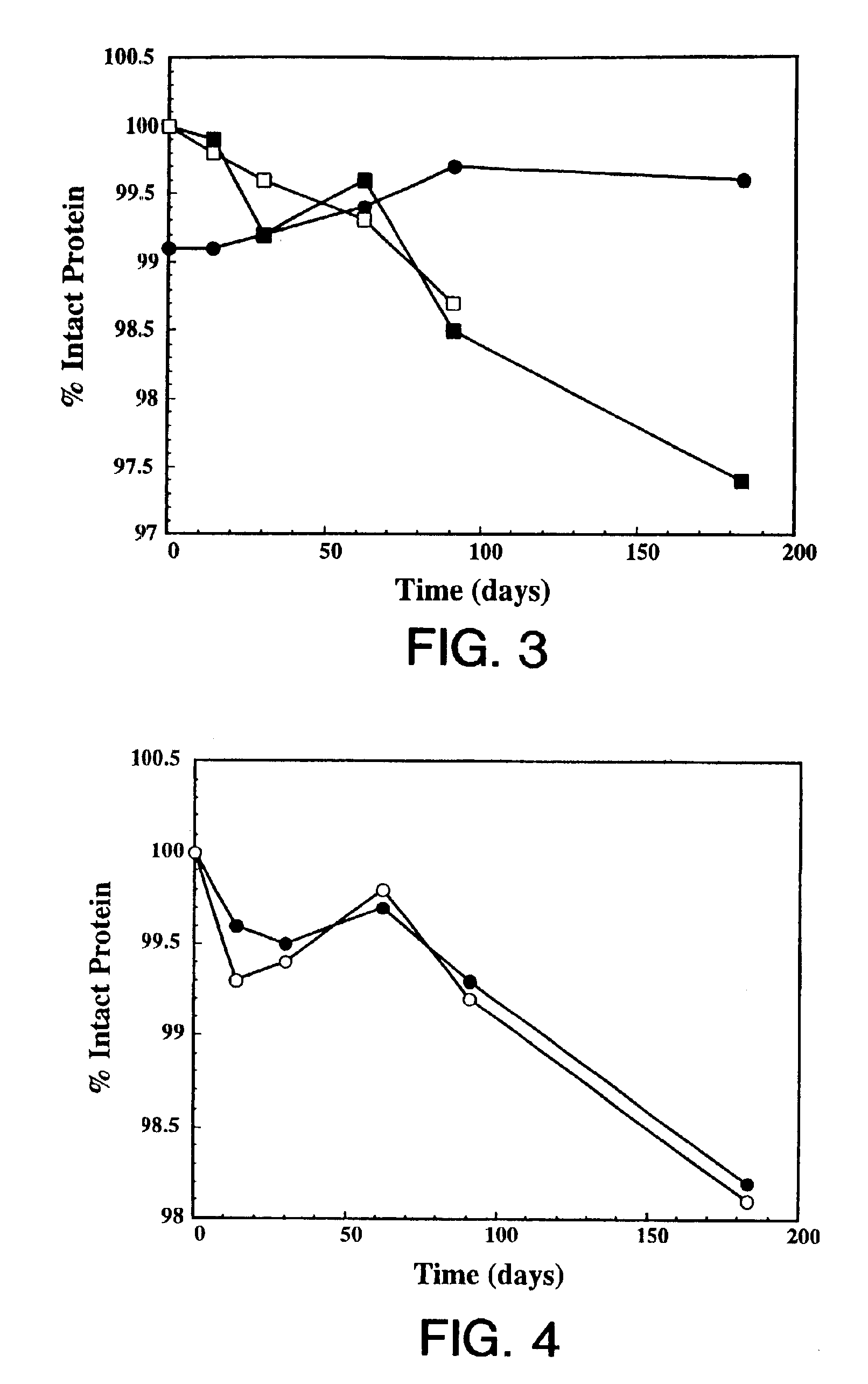
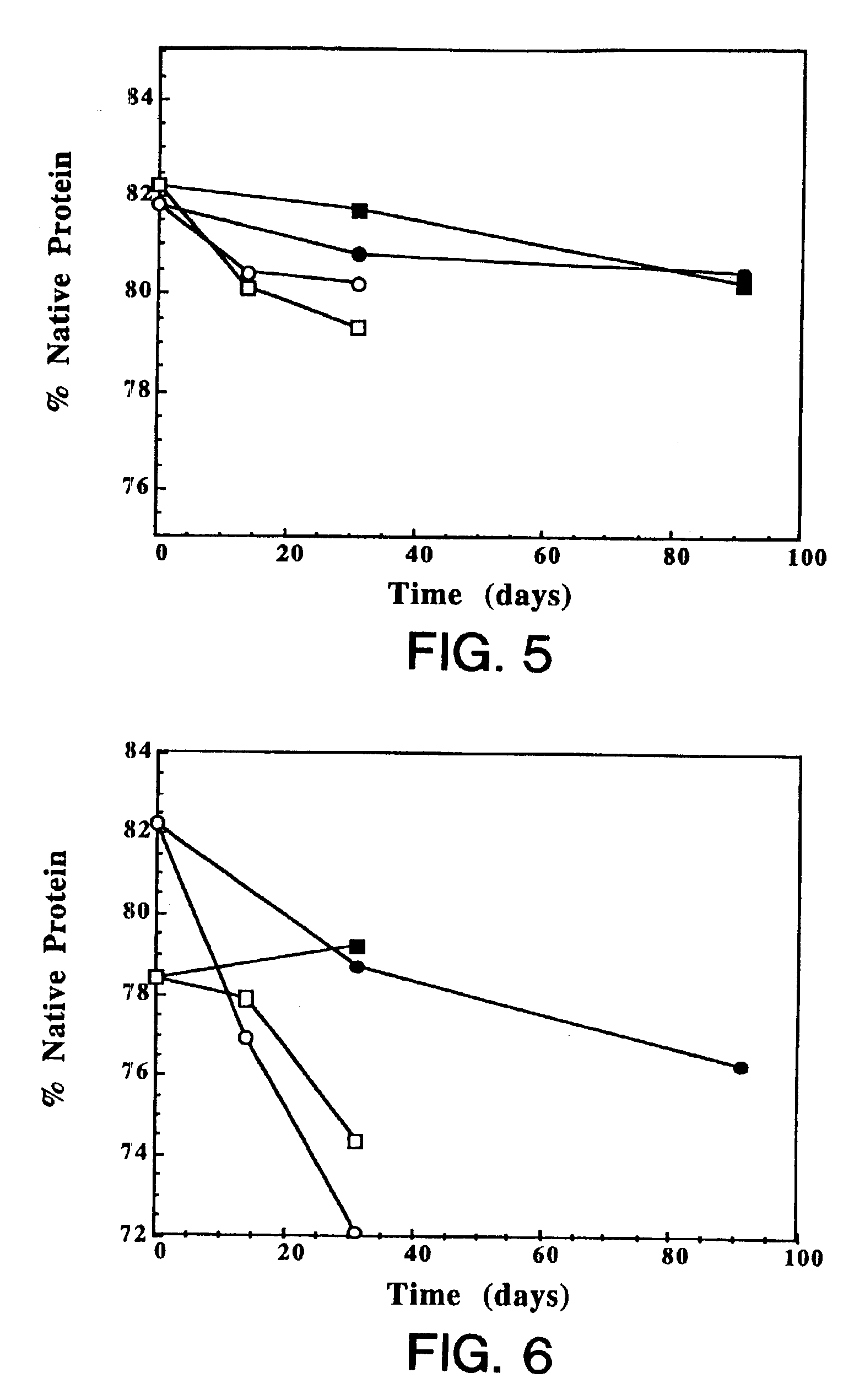
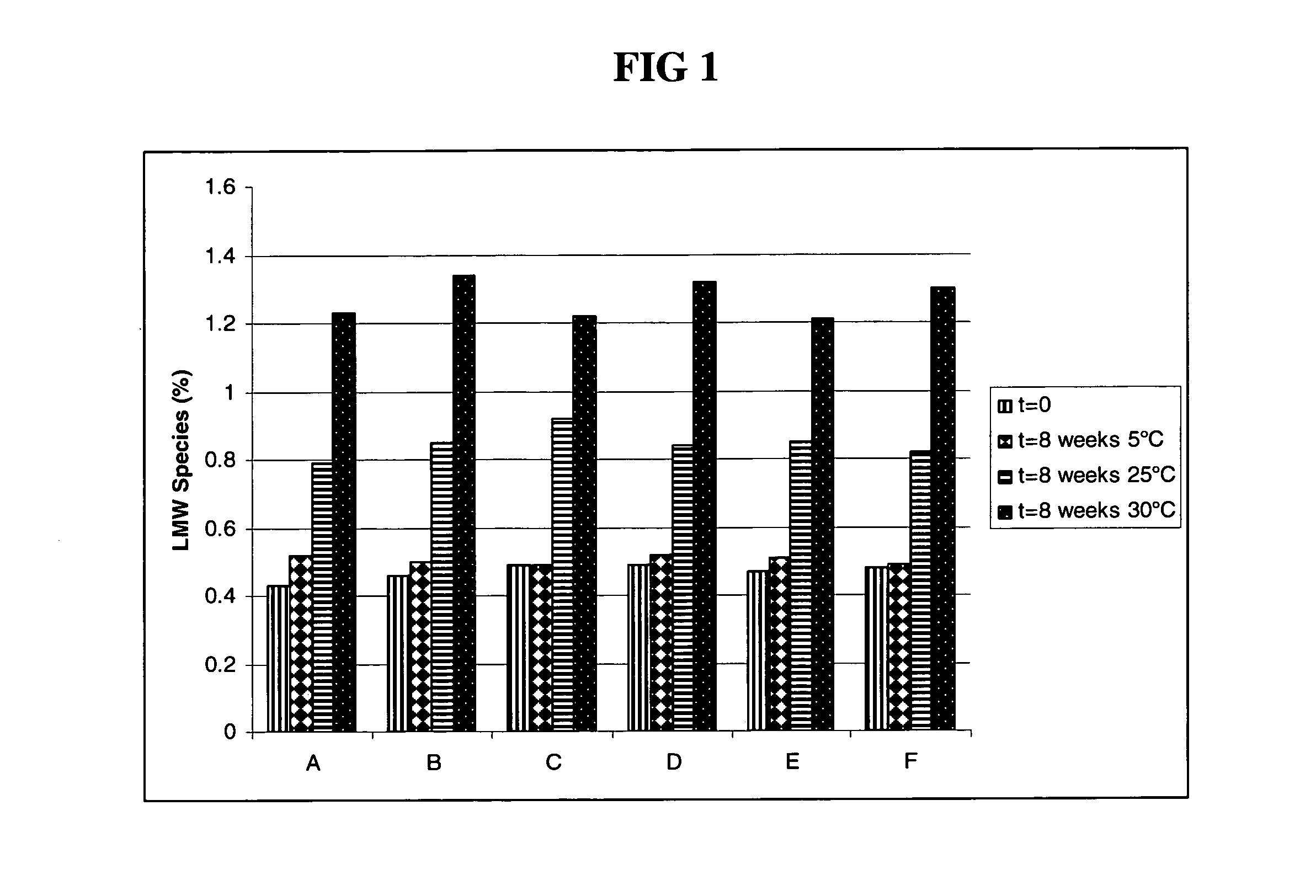
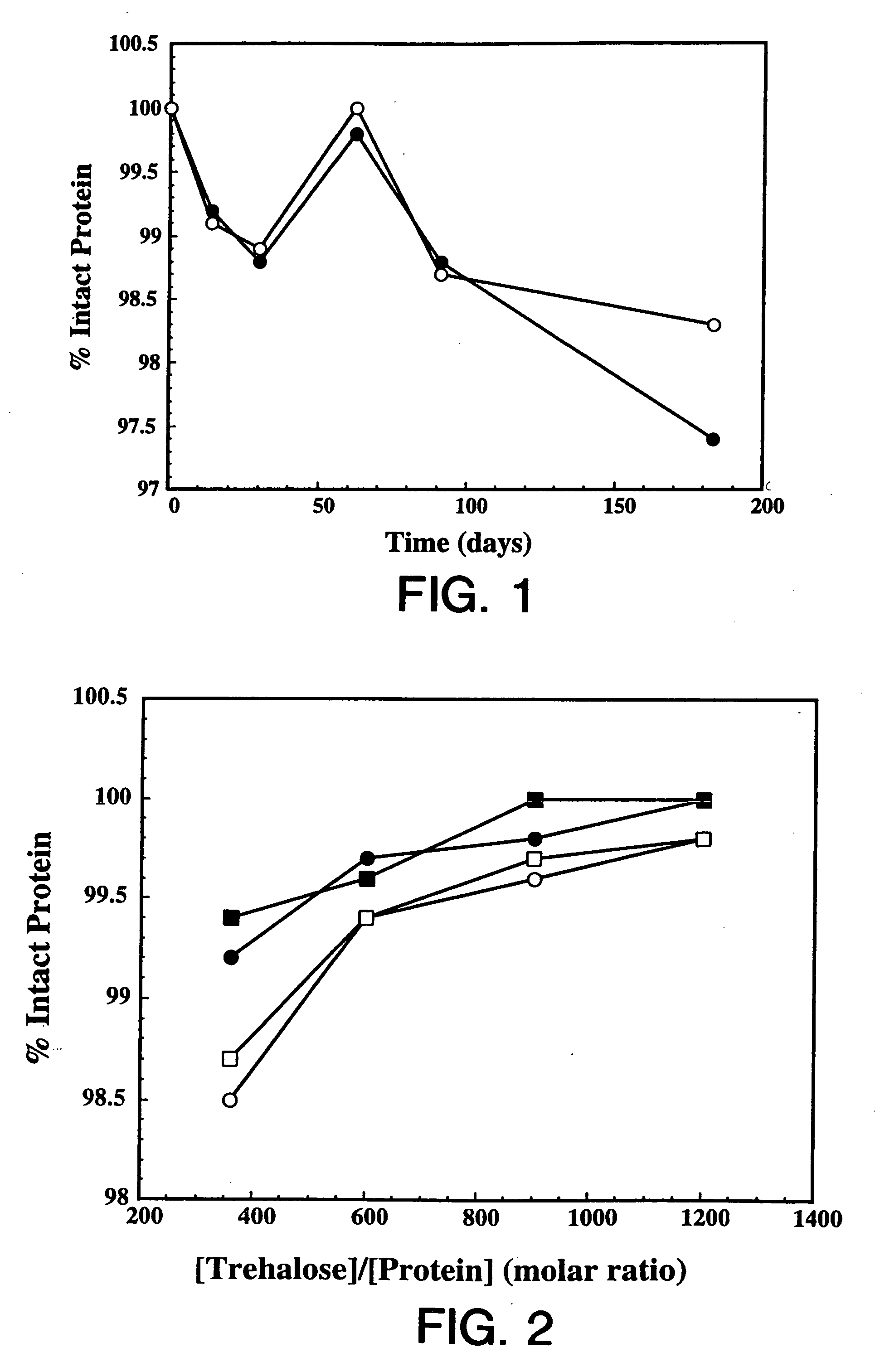
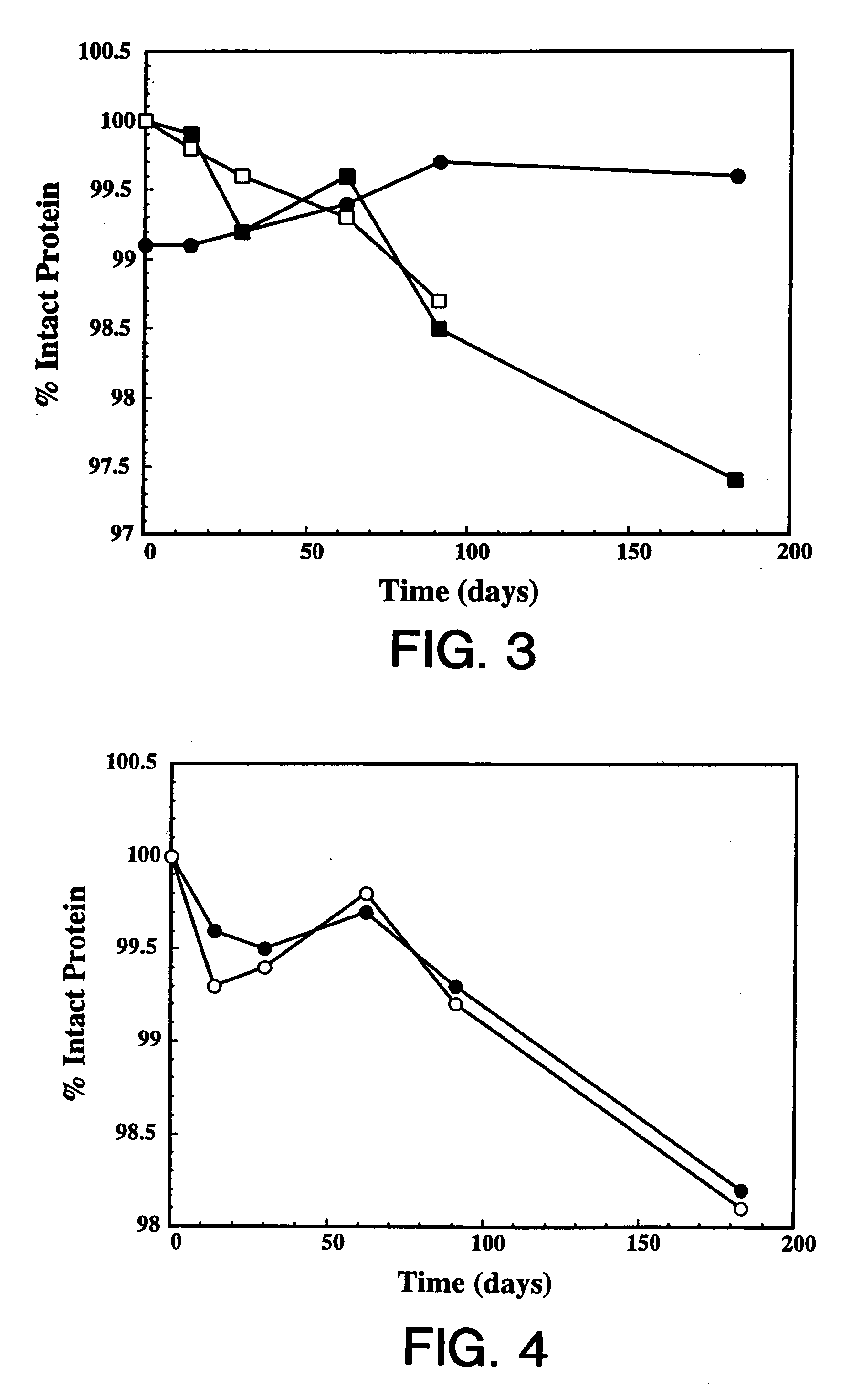
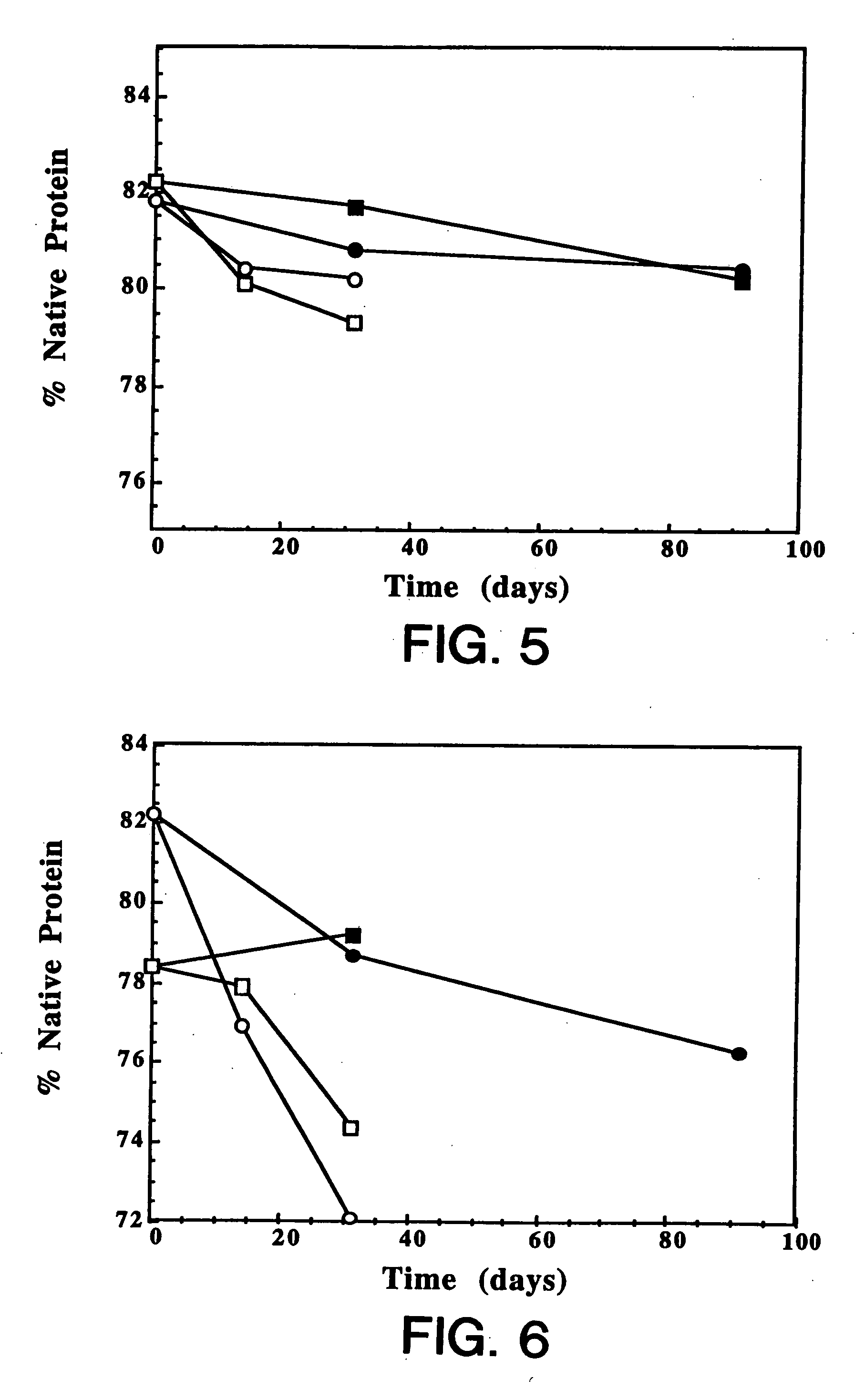
Protein formulation
InactiveUS7060268B2Reduce aggregationReduce formation of particulateBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiluentHigh protein
A stable lyophilized protein formulation is described which can be reconstituted with a suitable diluent to generate a high protein concentration reconstituted formulation which is suitable for subcutaneous administration. For example, anti-IgE and anti-HER2 antibody formulations have been prepared by lyophilizing these antibodies in the presence of a lyoprotectant. The lyophilized mixture thus formed is reconstituted to a high protein concentration without apparent loss of stability of the protein.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Subcutaneous anti-HER2 antibody formulations and uses thereof
The present invention relates to a highly concentrated, stable pharmaceutical formulation of a pharmaceutically active anti-HER2 antibody, such as e.g. Trastuzumab (HERCEPTIN™), Pertuzumab or T-DM1, or a mixture of such antibody molecules for subcutaneous injection. In particular, the present invention relates to formulations comprising, in addition to a suitable amount of the anti-HER2 antibody, an effective amount of at least one hyaluronidase enzyme as a combined formulation or for use in form of a co-formulation. The formulations comprise additionally at least one buffering agent, such as e.g. a histidine buffer, a stabilizer or a mixture of two or more stabilizers (e.g. a saccharide, such as e.g. α,α-trehalose dihydrate or sucrose, and optionally methionine as a second stabilizer), a nonionic surfactant and an effective amount of at least one hyaluronidase enzyme. Methods for preparing such formulations and their uses thereof are also provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
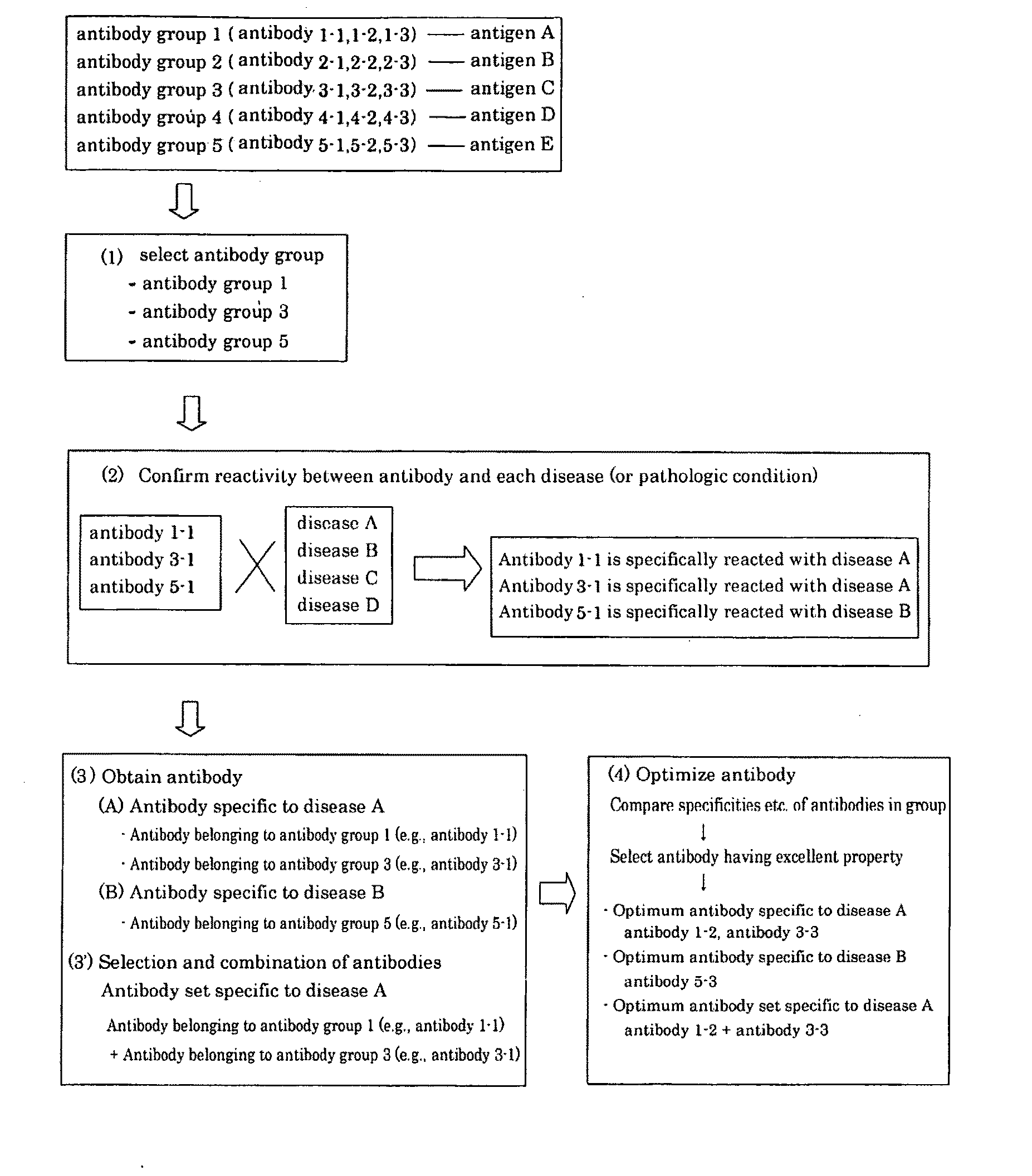
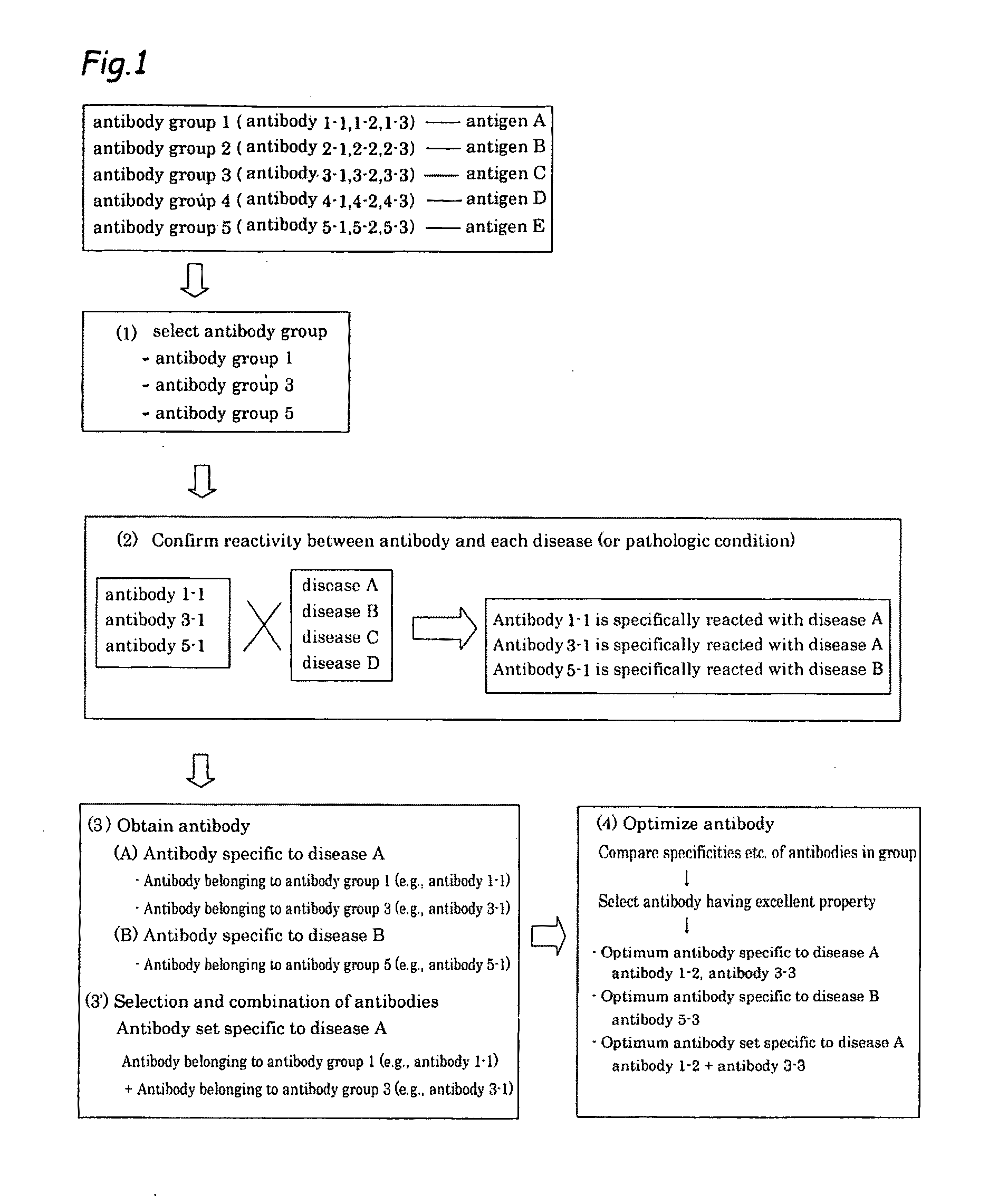
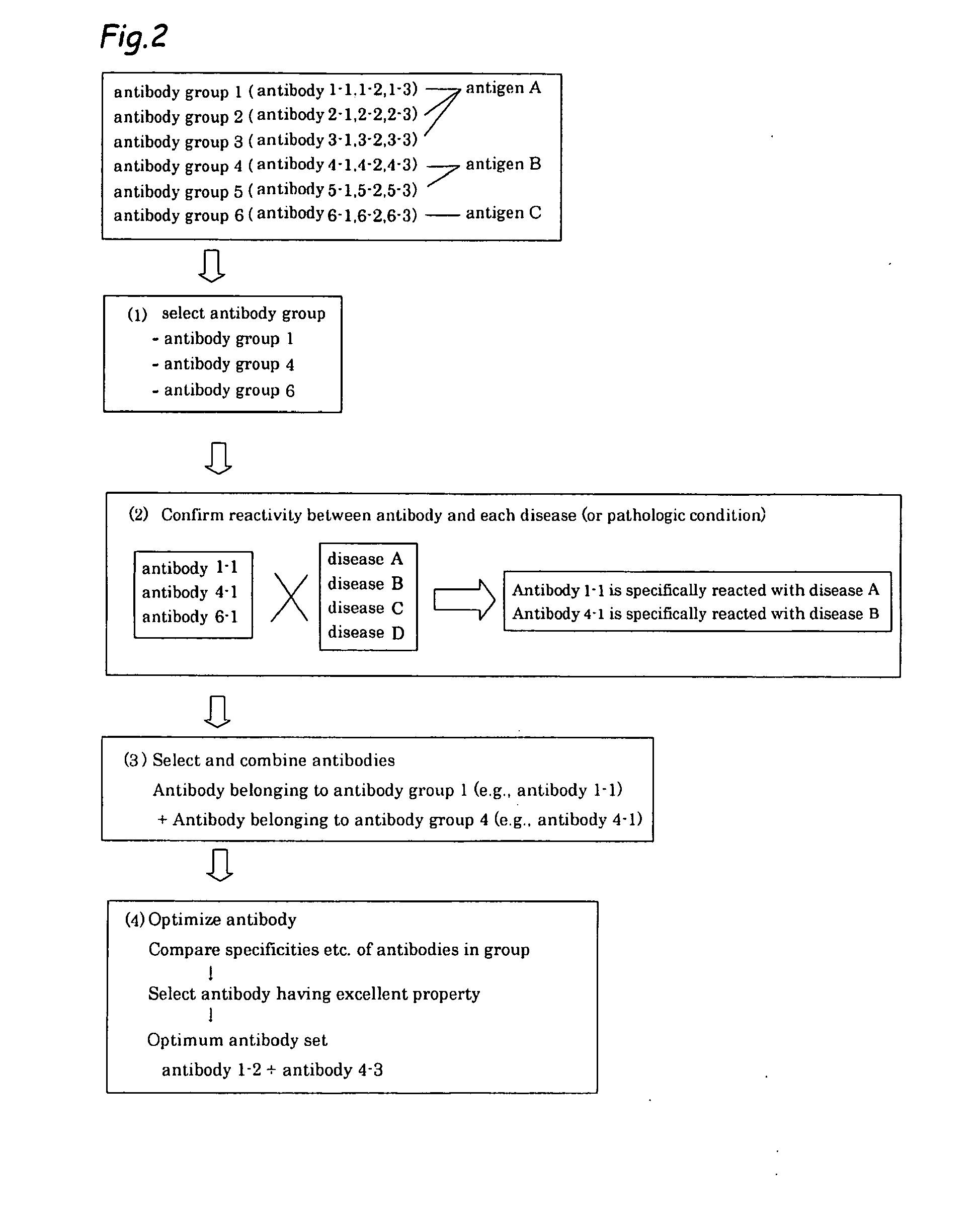
Method of classifying antibody, method of identifying antigen, method of obtaining antibody or antibody set, method of constructing antibody panel and antibody or antibody set and use of the same
InactiveUS20090203538A1Labor moreMany timesPeptide librariesLibrary screeningAntigenCell Surface Antigens
It is intended to provide a method whereby a plural number of antibodies against cell surface antigens are quickly classified and to provide a method whereby antigens of the thus classified antibodies are quickly identified. Further, it is intended to provide a method of promoting the utilization of the useful data obtained by the above methods. Furthermore, it is intended to provide an antibody which is effective in treating or diagnosing cancer. Namely, a method of classifying antibodies which comprises: (1) the step of preparing a plural number of antibodies respectively recognizing cell surface antigens; (2) the step of bringing each of these antibodies into contact with a cell of the same species; (3) the step of analyzing each of the cells having been treated in the step (2) by flow cytometry and thus obtaining data indicating the reactivity of each antibody with its cell surface antigen; and (4) the step of comparing the thus obtained data and classifying the individual antibodies depending on the similarity. A method of identifying antigens which further comprises: (5) the step of selecting one to several antibodies from each antibody group formed in the step (4) and identifying antigens thereof; and (6) on the assumption that antigens of the antibodies belonging to a single antibody group are the same or highly related to one another, making relations between the antigens having been identified in the step (5) and the antibody groups to thereby identify the antigens. An antibody against HER1, an antibody against HER2, an antibody against CD46, an antibody against ITGA3, an antibody against ICAM1, an antibody against ALCAM, an antibody against CD147, an antibody against C1qR, an antibody against CD44, an antibody against CD73, an antibody against EpCAM and an antibody against HGFR, each obtained by using the above methods.
Owner:FUJITA HEALTH UNIVERSITY
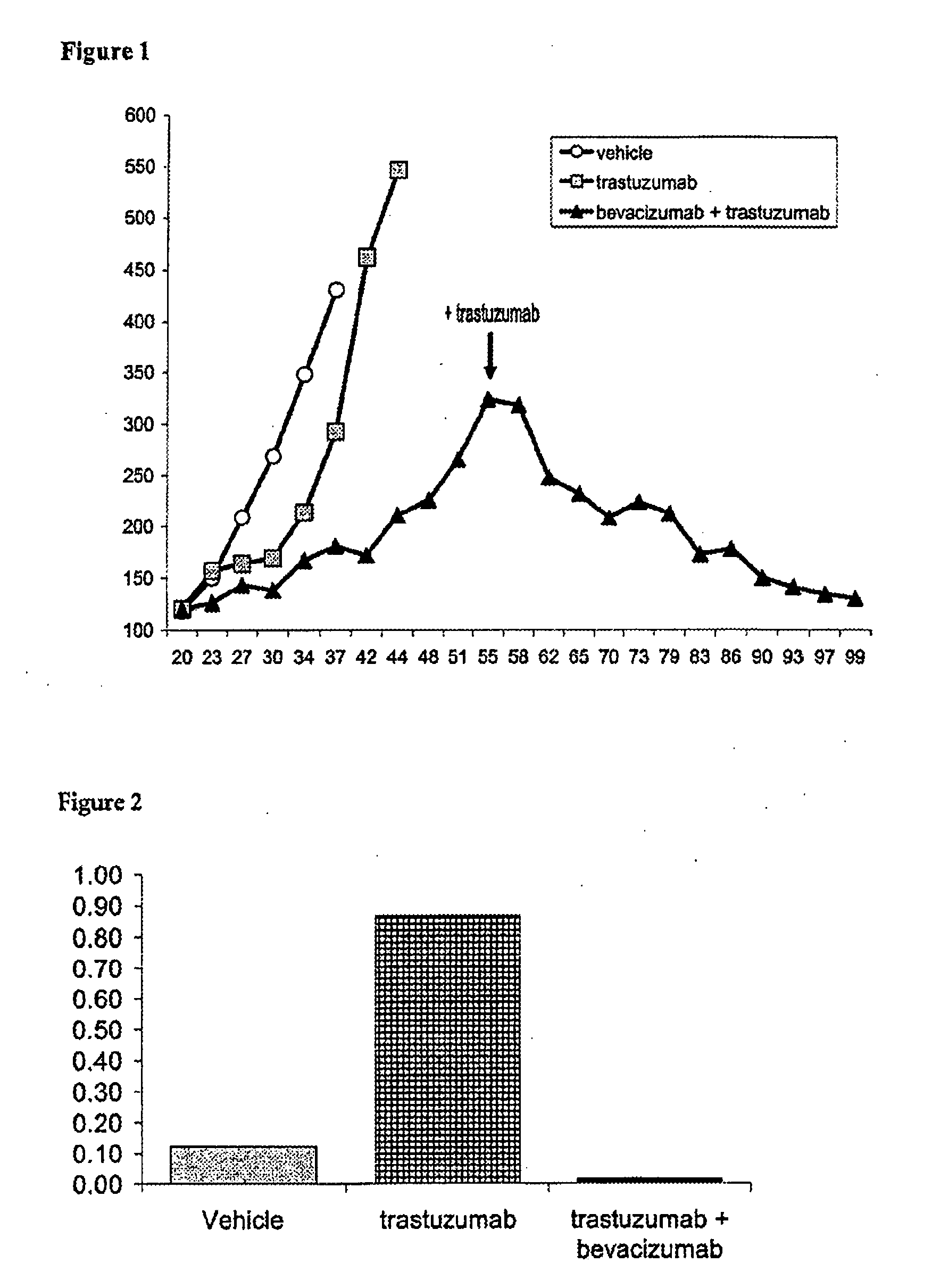
Tumor therapy with an antibody for vascular endothelial growth factor and an antibody for human epithelial growth factor receptor type 2
InactiveUS20070224203A1Prolong survival timeProlong progression-free survivalImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseTumor therapy
The present invention provides a method of treating a breast cancer disease in a patient who has failed prior treatment with an anti-VEGF antibody, comprising administering to the patient a therapeutically effective amount of an anti-HER2 antibody while continuing said anti-VEGF antibody therapy. The invention also provides corresponding pharmaceutical kits and pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
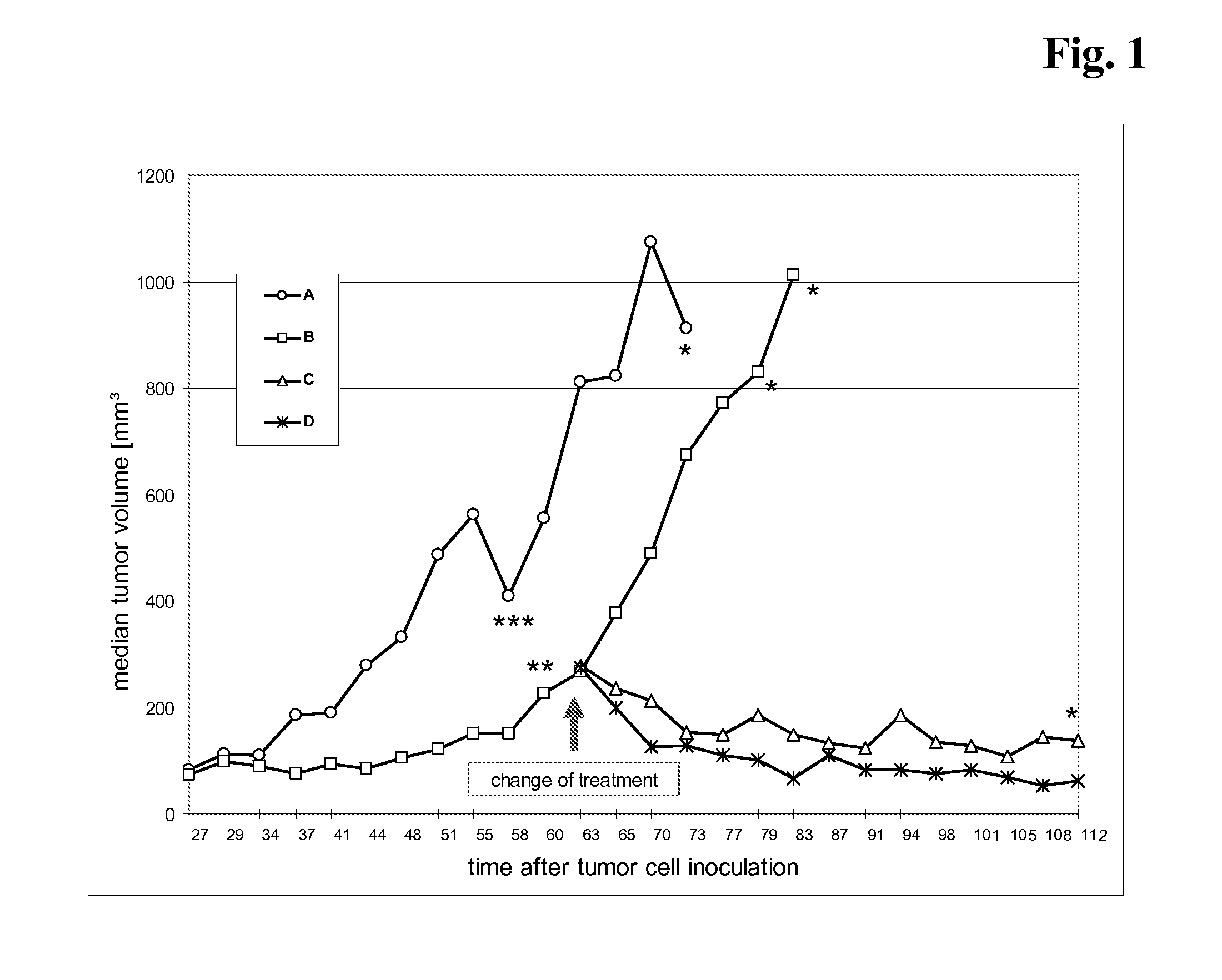
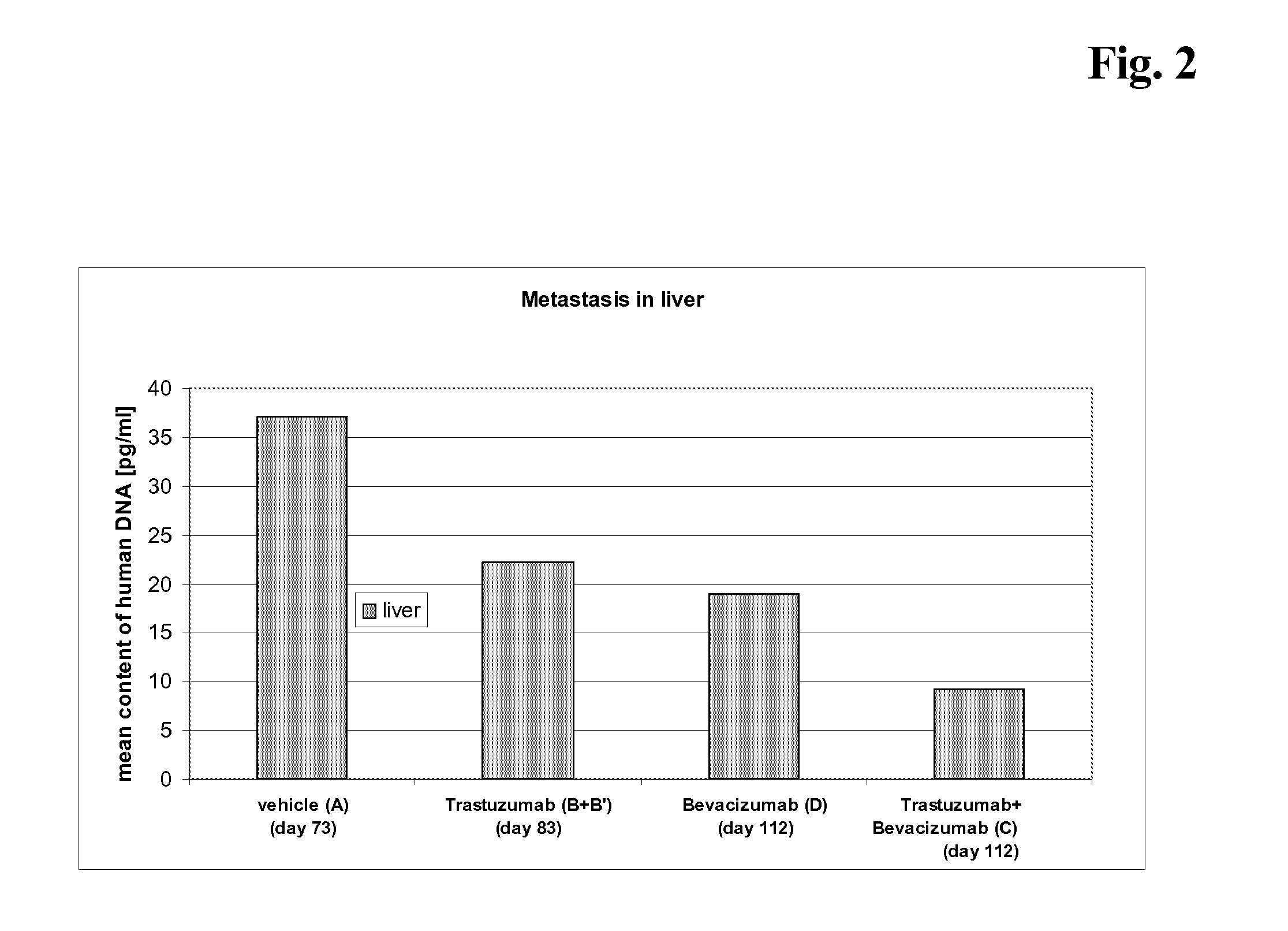
Tumor therapy with an Anti-vegf antibody
InactiveUS20100285010A1Prevents and reduces metastasisImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAntibody ingredientsAfter treatmentAnti vegf antibody
Owner:FRIESS THOMAS +2
Protein formulation
A stable lyophilized protein formulation is described which can be reconstituted with a suitable diluent to generate a high protein concentration reconstituted formulation which is suitable for subcutaneous administration. For example, anti-IgE and anti-HER2 antibody formulations have been prepared by lyophilizing these antibodies in the presence of a lyoprotectant. The lyophilized mixture thus formed is reconstituted to a high protein concentration without apparent loss of stability of the protein.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Methods of therapy for cancers characterized by overexpression of the HER2 receptor protein
InactiveUS7306801B2Promotes therapeutic responseImproved therapeutic responsePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDosing regimenAnti her2
Methods for treating a subject with a cancer that is characterized by overexpression of HER2 receptor protein using a combination of interleukin-2 (IL-2) or variant thereof and at least one anti-HER2 antibody or fragment thereof are provided. These anti-tumor agents are administered as two separate pharmaceutical compositions, one containing IL-2 (or variant thereof), the other containing at least one anti-HER2 antibody (or fragment thereof), according to a dosing regimen. Administering of these two agents together potentiates the effectiveness of the anti-HER2 antibody alone, resulting in a positive therapeutic response that is improved with respect to that observed with this anti-tumor agent.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC +1
Pyrrolobenzodiazepine-Anti-her2 antibody conjugates
InactiveUS20150273077A1Organic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsPyrrolobenzodiazepineHER2 Antibody
Owner:ADC THERAPEUTICS SA +1
Gene detection assay for improving the likelhood of an effective response to an ErbB antagonist cancer therapy
InactiveUS20060228745A1Great likelihoodChoose accuratelyOrganic active ingredientsBiocideFhit geneTumor cells
The invention provides a method for more effective treatment of patients susceptible to or diagnosed with tumors overexpressing ErbB, as determined by a gene amplification assay, with an ErbB antagonist. Such method comprises administering a cancer-treating dose of the ErbB antagonist, preferably in addition to chemotherapeutic agents, to a subject in whose tumor cells ErbB has been found to be amplified e.g., by fluorescent in situ hybridization. ErbB antagonists described include an anti-HER2 antibody. Pharmaceutical packaging for providing the components for such treatment is also provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Tumor therapy with an antibody for vascular endothelial growth factor and an antibody for human epithelial growth factor receptor type 2
InactiveUS20110064736A1Prolong survival timeProlong progression-free survivalImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseFactor ii
The present invention provides a method of treating a breast cancer disease in a patient who has failed prior treatment with an anti-VEGF antibody, comprising administering to the patient a therapeutically effective amount of an anti-HER2 antibody while continuing said anti-VEGF antibody therapy. The invention also provides corresponding pharmaceutical kits and pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Therapeutic Anti-her2 antibody fusion polypeptides
InactiveUS20090226466A1Enhanced cell killing of cellImprove efficiencySugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTherapeutic proteinAnti her2
Therapeutic protein fusions comprising anti-HER2 antibody and MicB sequences are described along with methods for their production and use
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Combination Therapy Using Anti-EGFR and Anti-HER2 Antibodies
InactiveUS20090214541A1Good curative effectPrevent dimerizationAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsEGFR AntibodyAnti her2
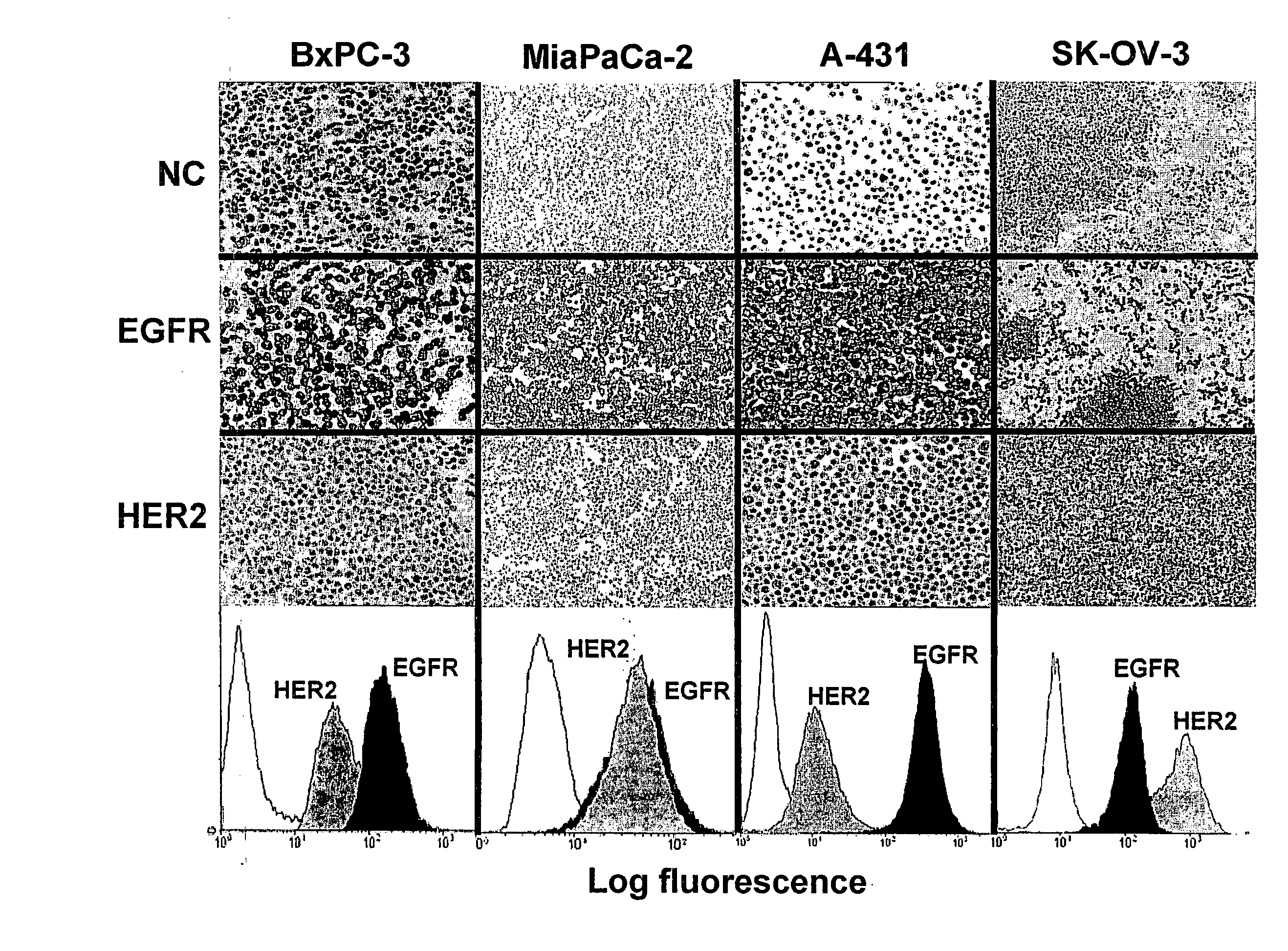
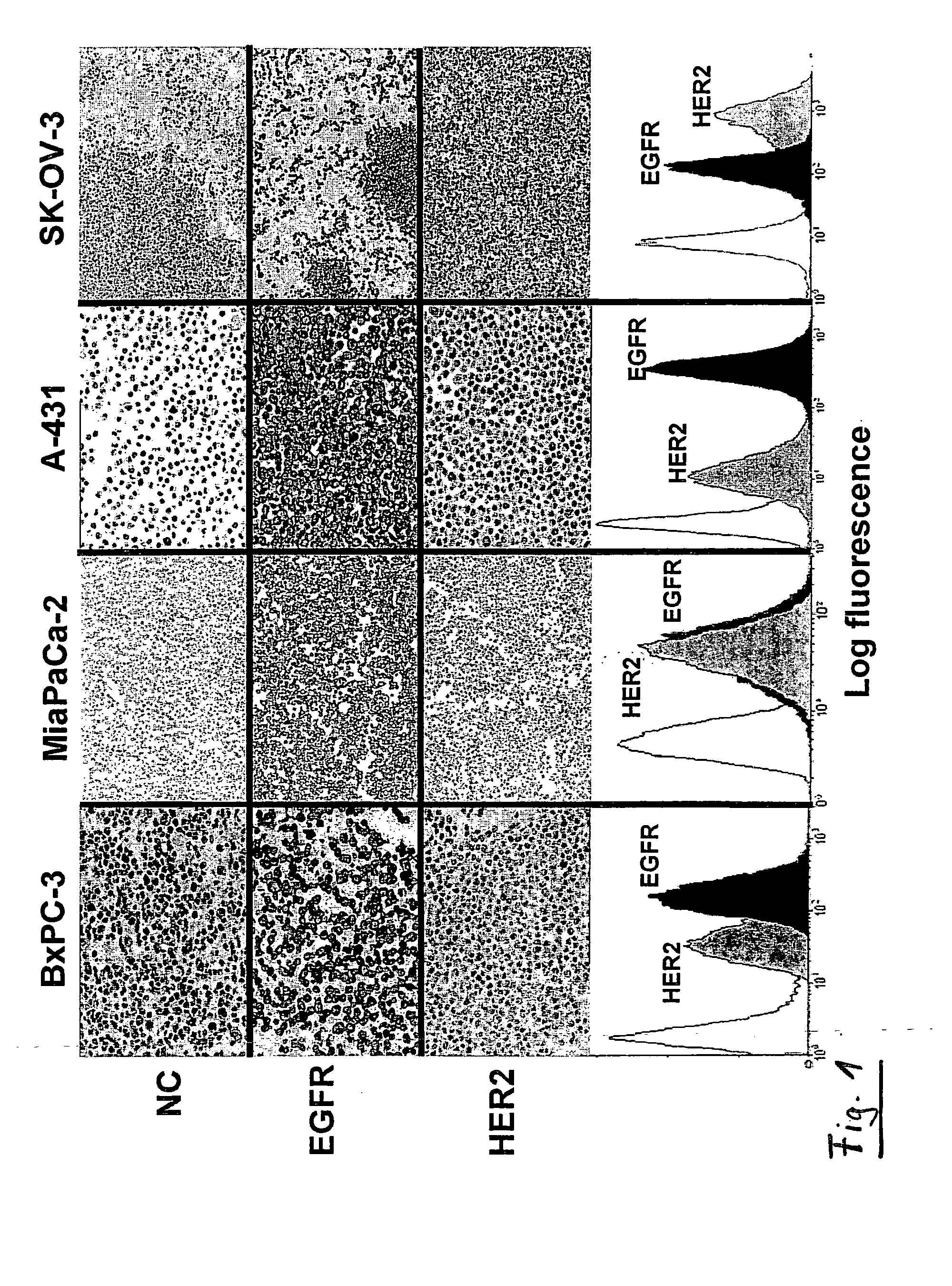
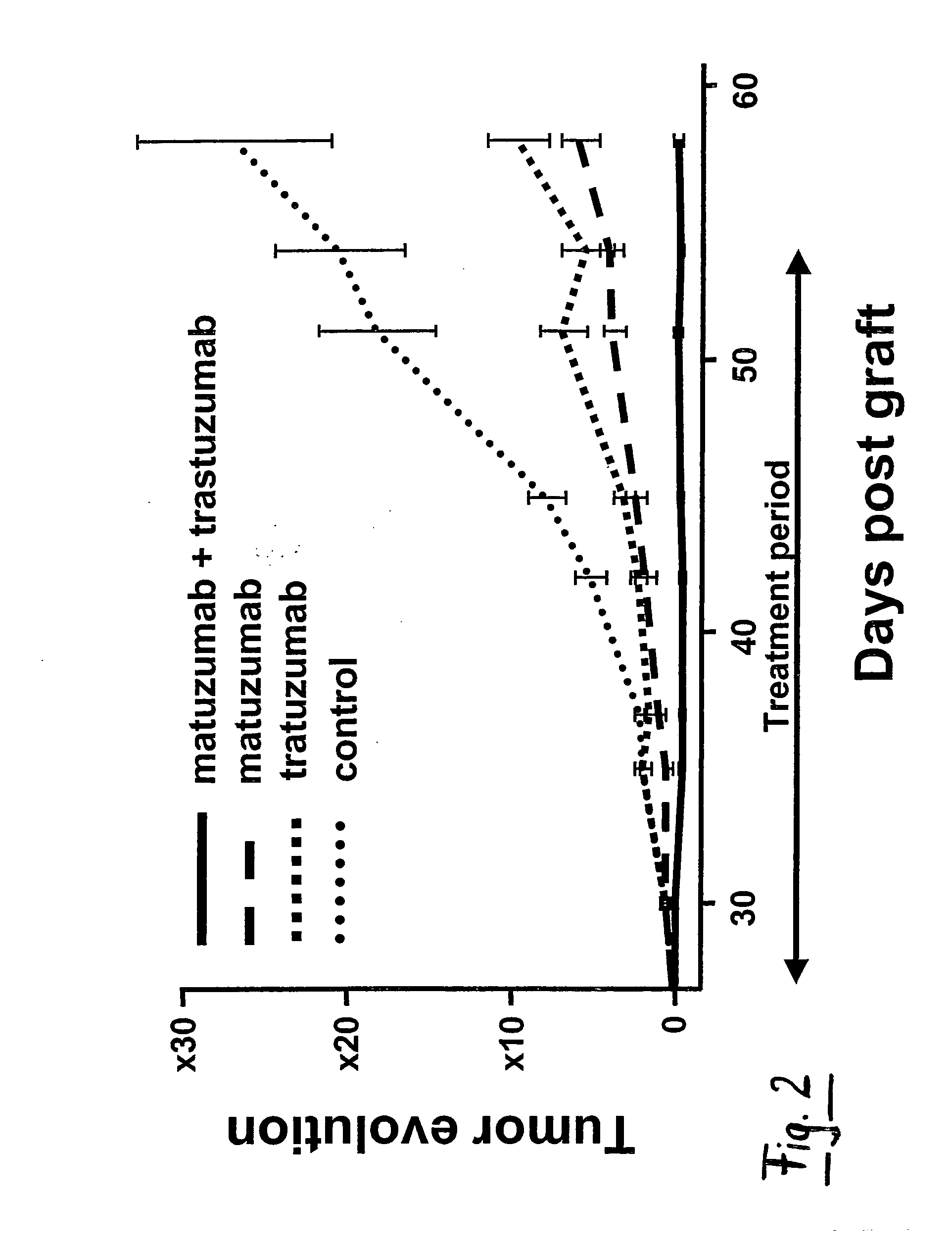
The invention relates to the combined use of anti-EGFR antibodies and anti-Her2 antibodies for the treatment of cancer, especially suitable for cancer expressing high levels of the EGFR type and low levels of HER2. The invention refers in particular monoclonal antibody “trastuzumab” (HERCEPTIN®) directed against the HER2 receptors the efficacy of which can be significantly increased in vivo when combined with monoclonal antibody “matuzumab” (hmAB 425, EMD 72000) directed against EGF receptors. The combination treatment is suitable for patients suffering from cancer having said receptor profile, preferably pancreatic cancer.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
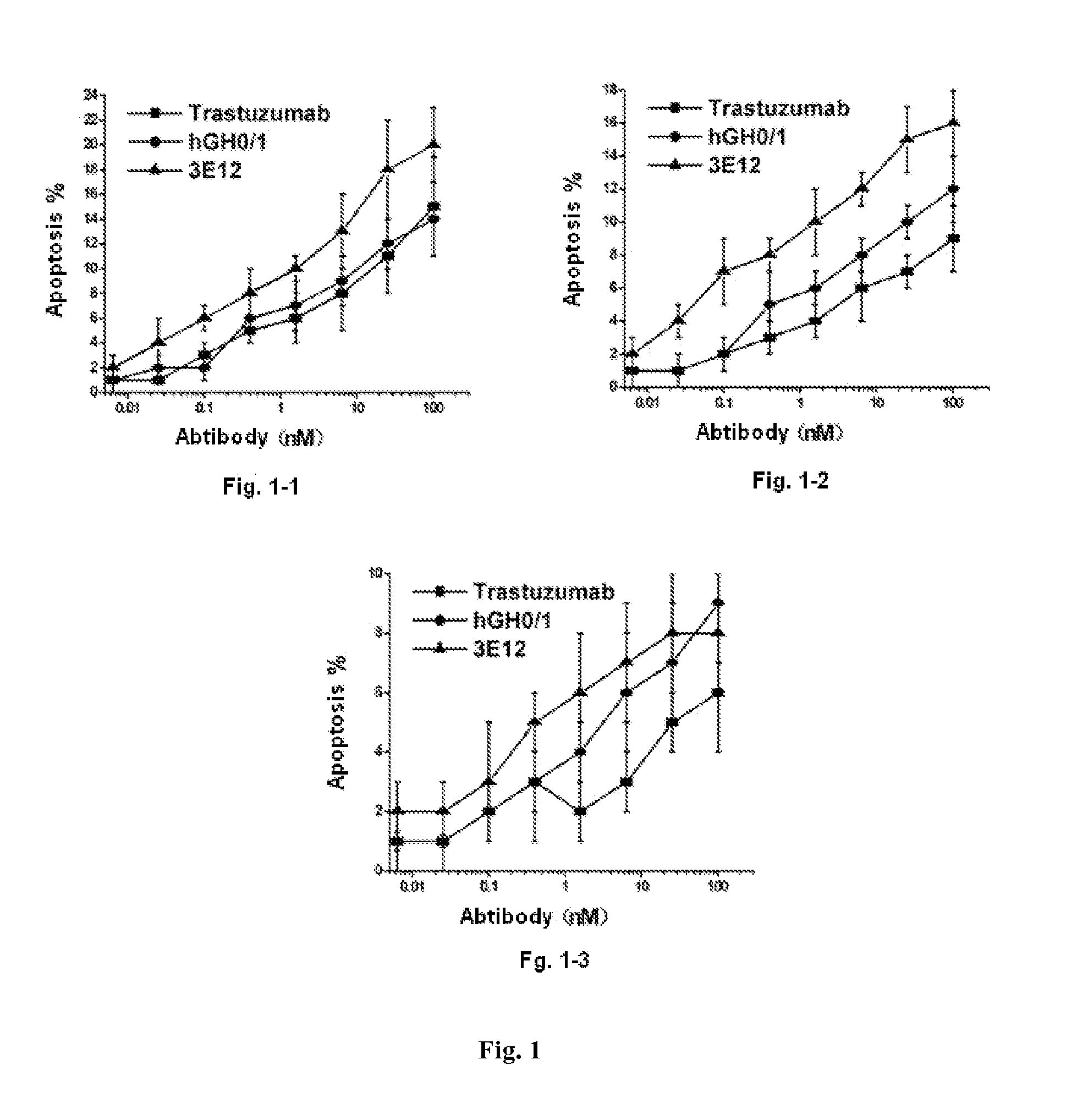
Anti-HER2 antibodies and compositions
The present invention relates to novel therapeutic antibodies directed against HER2 (ErbB2), as well as recombinant polyclonal anti-HER2 antibody compositions comprising at least two of said recombinant anti-HER2 antibodies, and use of the antibodies and antibody compositions for treatment of cancer.
Owner:SYMPHOGEN AS
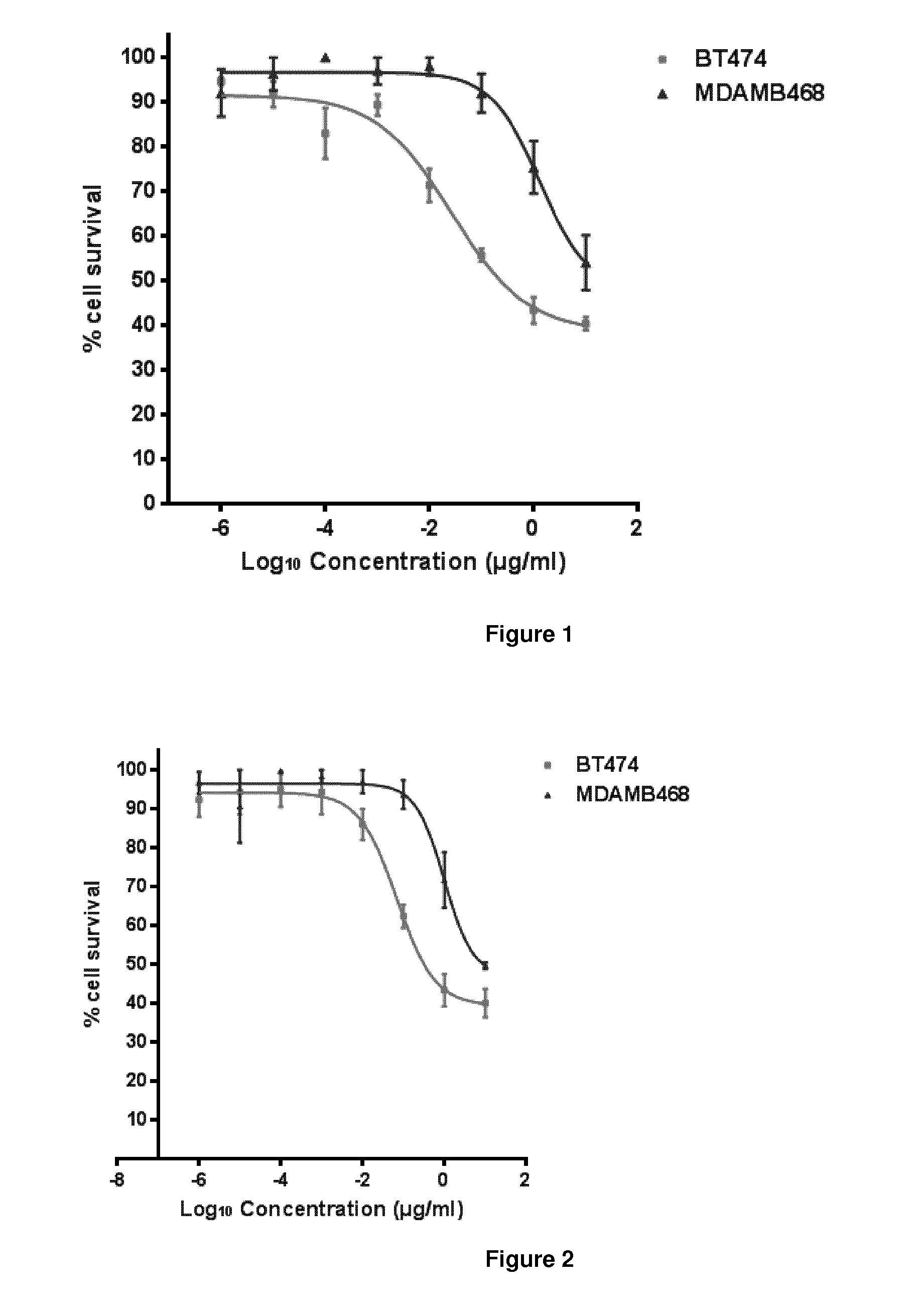
Antibody composition preparation and application thereof
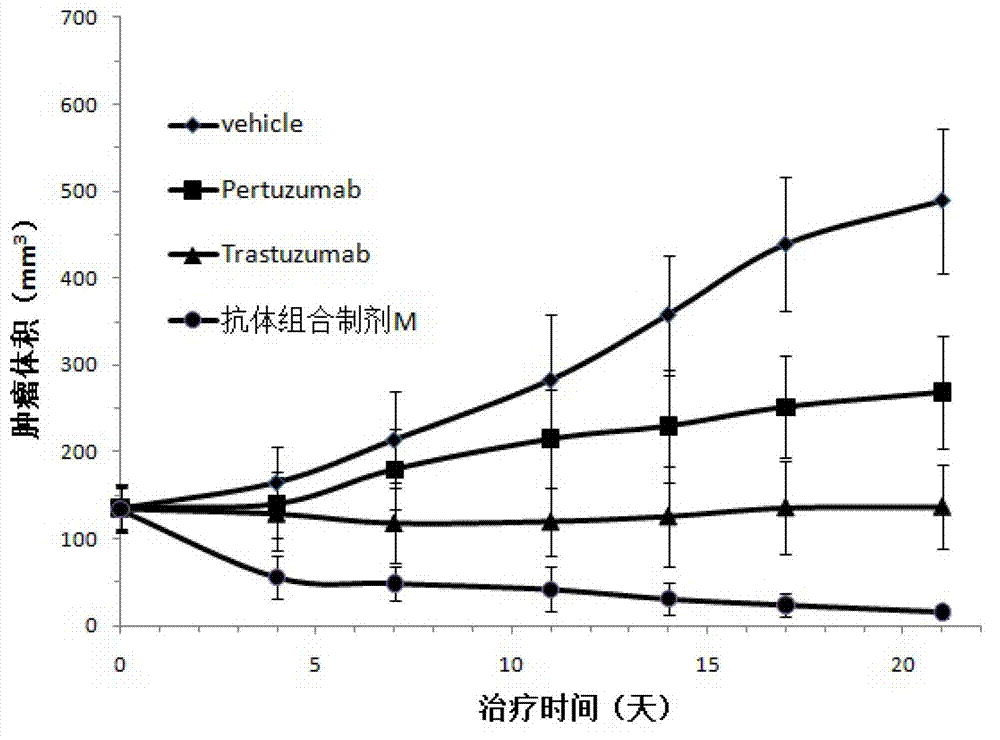
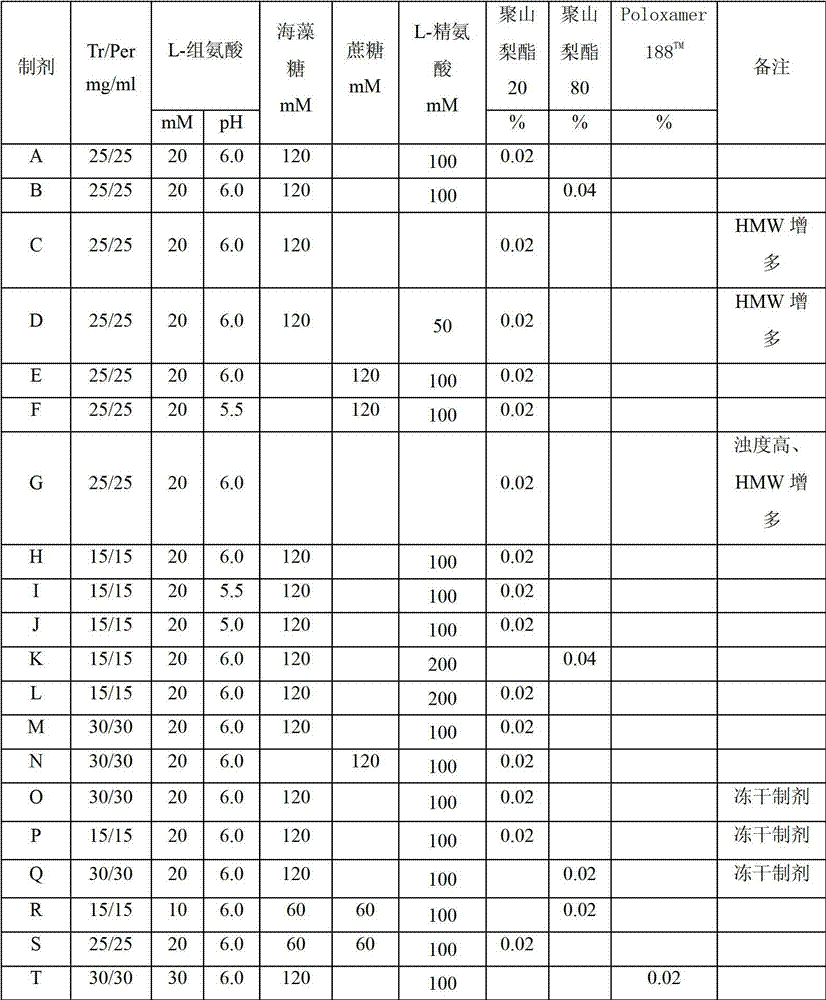
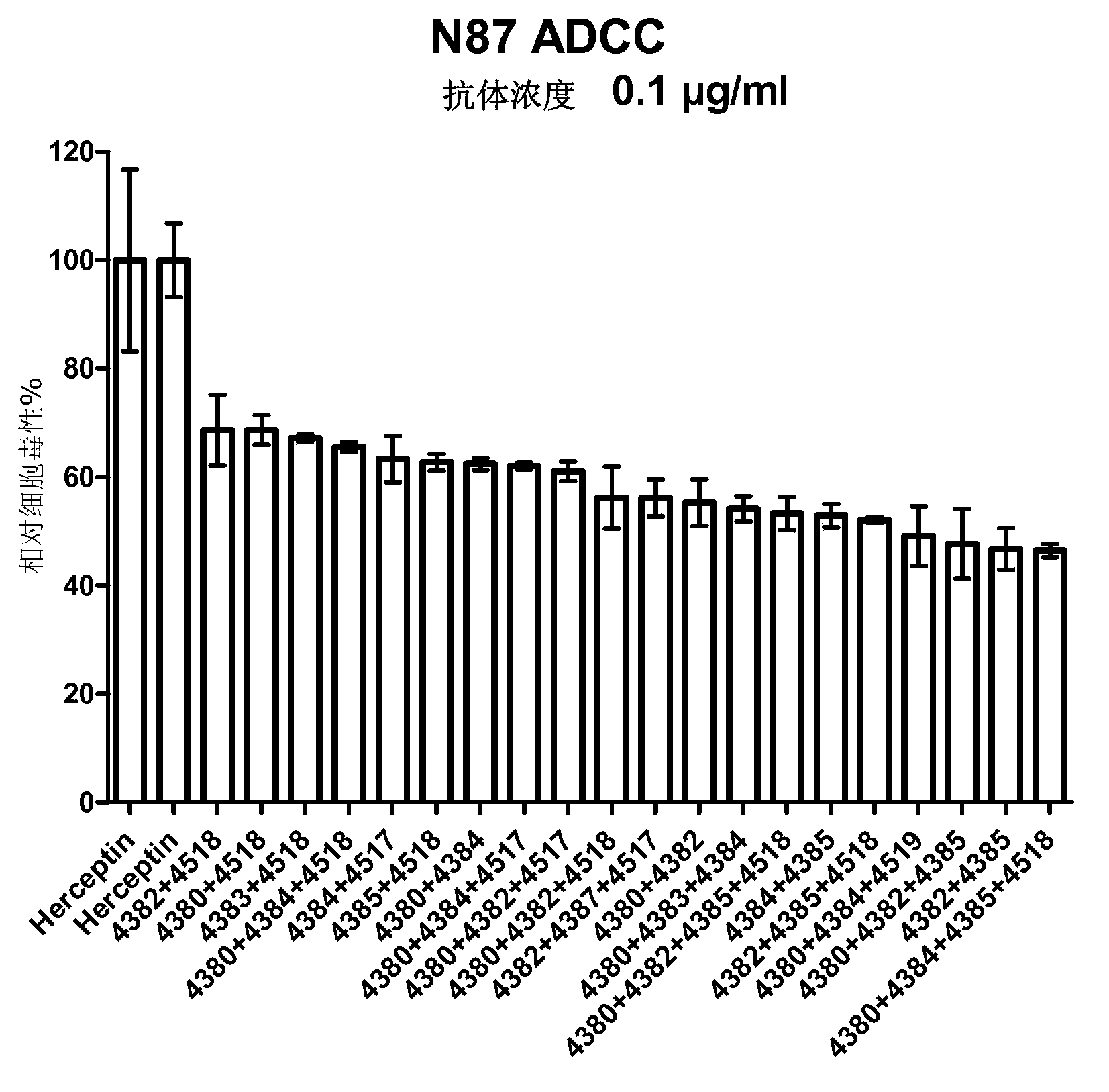
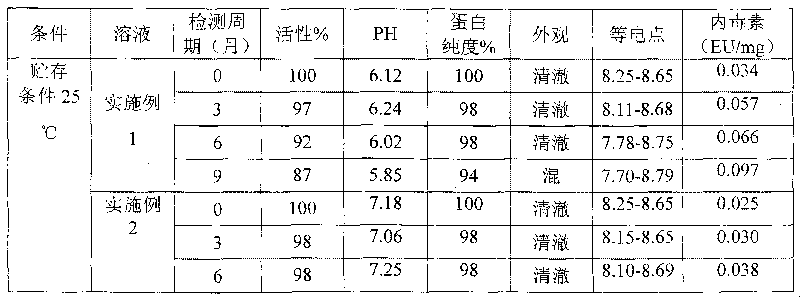
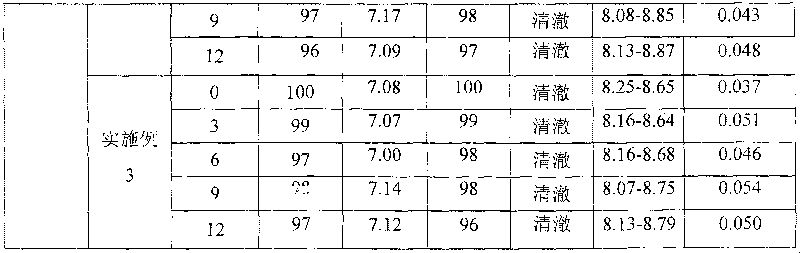
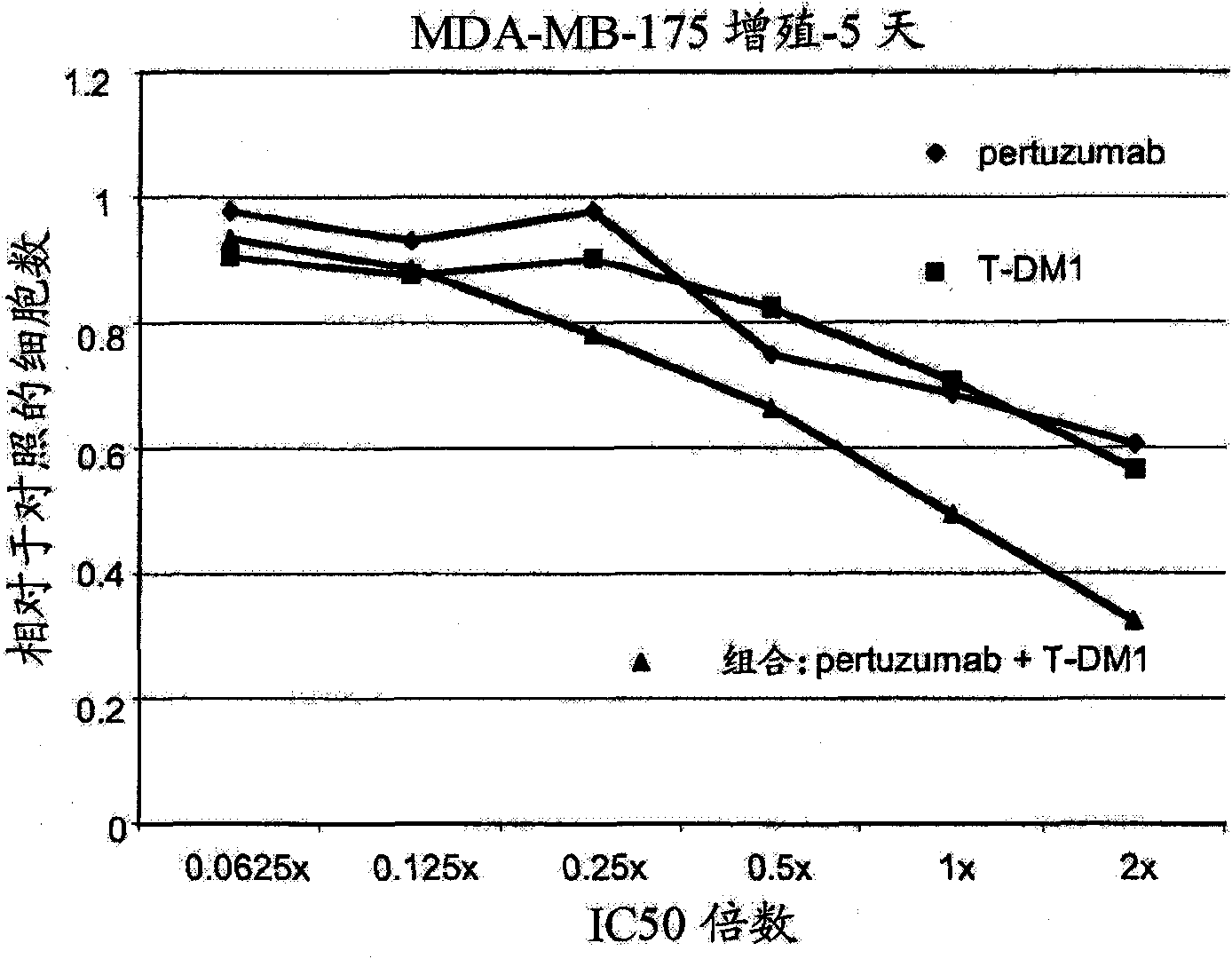
ActiveCN102961745AAvoid formingAvoid gatheringAntibody ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAnti her2Pertuzumab
Relating to the technical field of pharmaceutical preparations, the invention provides an antibody composition preparation composed of Trastuzumab and Pertuzumab. The antibody composition preparation has better tumor treatment activity. Compared with the independent treatment of Trastuzumab and Pertuzumab, the composition preparation shows a synergistic effect of the two antibodies, and can reach a tumor control rate of 92.43%. And the preparation provided in the invention has better stability, thus being in favor of long-term preservation of the antibody composition preparation. The antibody composition preparation provided in the invention is applicable to preparation of drugs treating diseases or symptoms suited to anti-HER2 antibody therapy. During application, the antibody composition preparation disclosed in the invention is used with a chemotherapeutic agent jointly or sequentially.
Owner:SUZHOU KANGJU BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Anti-HER2 antibodies and immunoconjugates
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Subcutaneous anti-HER2 Antibody Formulations and Uses Thereof
The present invention relates to a highly concentrated, stable pharmaceutical formulation of a pharmaceutically active anti-HER2 antibody, such as e.g. Trastuzumab (HERCEPTIN™), Pertuzumab or T-DM1, or a mixture of such antibody molecules for subcutaneous injection. In particular, the present invention relates to formulations comprising, in addition to a suitable amount of the anti-HER2 antibody, an effective amount of at least one hyaluronidase enzyme as a combined formulation or for use in form of a co-formulation. The formulations comprise additionally at least one buffering agent, such as e.g. a histidine buffer, a stabilizer or a mixture of two or more stabilizers (e.g. a saccharide, such as e.g. α,α-trehalose dihydrate or sucrose, and optionally methionine as a second stabilizer), a nonionic surfactant and an effective amount of at least one hyaluronidase enzyme. Methods for preparing such formulations and their uses thereof are also provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Anti-Her2 Antibody-Maytansine Conjugates and Methods of Use Thereof
ActiveUS20150352225A1Efficient managementEfficient releaseOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMethods of productionStereochemistry
The present disclosure provides anti-HER2 antibody-maytansine conjugate structures. The disclosure also encompasses methods of production of such conjugates, as well as methods of using the same.
Owner:REDWOOD BIOSCI
Stable anti-HER2 humanized antibody preparation
The invention discloses a humanized anti-HER2 antibody preparation, which contains humanized anti-HER2 antibody, protective agent, buffering agent, surfactant and isotonic regulator. The invention has the advantages of stability and low price.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT OF ANTIBODY MEDICINE
Stabilizing polypeptides which have been exposed to urea
Methods for stabilizing polypeptides, such as anti-HER2 antibodies, which have been exposed to urea.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Fully humanized anti-HER2 antibody, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveUS8974785B2High affinityEnhanced inhibitory effectAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHeavy chainNucleotide
The invention provides a fully human anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody, which has an amino acid sequence of heavy chain variable region as shown in SEQ ID NO: 6 and an amino acid sequence of light chain variable region as shown in SEQ ID NO: 8. The invention also discloses the nucleotide sequence encoding the antibody, the expression vector and the host cell comprising the nucleotide sequence, and the use of the antibody for manufacturing the medicament for the treatment of tumor.
Owner:YUEHAI BIOPHARM SHAOXING LTD
Bispecific Anti-her2 antibody
The present invention relates to humanized bispecific anti-HER2 antibodies that comprise one antigen binding site containing variable regions of heavy and light chain of trastuzumab, and another antigen binding site containing variable regions of heavy and light chain of pertuzumab. The bispecific anti-HER2 antibodies is effective for treating cancer, such as breast cancer, gastric cancer, or ovarian cancer. Preferred bispecific anti-HER antibodies of the present invention are afucosylated antibodies. The present invention also relates to Chinese Hamster ovary (CHO) mutant cell line that has a dysfunctional Slc35C1 gene, which is the only dysfunctional gene in the mutant that affects glycan regulation.
Owner:BEIJING MABWORKS BIOTECH
Anti-her2 antibody-drug conjugate
ActiveUS20160333112A1Good antitumor effectImprove securityOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDrug conjugationTherapeutic effect
As an antitumor drug which is excellent in terms of antitumor effect and safety and has an excellent therapeutic effect, there is provided an antibody-drug conjugate in which an antitumor compound represented by the following formula is conjugated to an anti-HER2 antibody via a linker having a structure represented by the following formula: -L1-L2-LP-NH—(CH2)n1-La-(CH2)n2—C(═O)— wherein the anti-HER2 antibody is connected to the terminal L1, and the antitumor compound is connected to the carbonyl group of the —(CH2)n2—C(═O)— moiety with the nitrogen atom of the amino group at position 1 as the connecting position.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Anti-HER2 antibodies and compositions
InactiveCN102884084AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCross-linkTherapeutic antibody
The present invention relates to novel therapeutic antibodies directed against HER2 (ErbB2), as well as recombinant polyclonal anti-HER2 antibody compositions, and use of the antibodies and antibody composition for treatment of cancers. The antibody composition comprises at least three recombinant antibodies that bind distinct epitopes of HER2. Two of the antibodies bind to HER2 on the surface of a cell such that they generate a cross-linked antibody-receptor lattice on the cell surface and thereby result in HER2 receptor internalization. The third antibody in the composition binds HER2 such that it blocks heterodimerization between HER2 and HER3.
Owner:SYMPHOGEN AS
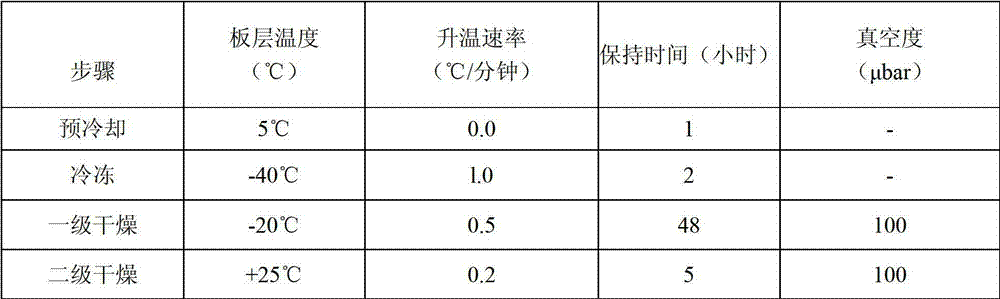
Lyophilized preparation of anti-human Her2 antibody
InactiveCN101721700AImprove stabilityEasy to storePowder deliveryAntibody ingredientsMedicineExcipient
The invention provides a preparation method of a lyophilized preparation of an anti-human Her2 antibody. The lyophilized preparation of the anti-Her2 antibody is prepared from the anti-Her2 antibody, a protective agent, excipient and buffer salts through lyophilization. The lyophilized preparation of the anti-Her2 antibody has the advantages of good stability, prolonged valid period, and easy storage and transportation.
Owner:HARBIN PHARMA GROUP BIOLOGICAL ENG
Fully humanized Anti-her2 antibody, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveUS20120309942A1Antibody affinity is highEnhanced inhibitory effectAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHeavy chainNucleotide
The invention provides a fully human anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody, which has an amino acid sequence of heavy chain variable region as shown in SEQ ID NO: 6 and an amino acid sequence of light chain variable region as shown in SEQ ID NO: 8. The invention also discloses the nucleotide sequence encoding the antibody, the expression vector and the host cell comprising the nucleotide sequence, and the use of the antibody for manufacturing the medicament for the treatment of tumor.
Owner:YUEHAI BIOPHARM SHAOXING LTD
Combinations of an anti-HER2 antibody-drug conjugate and chemotherapeutic agents, and methods of use
ActiveCN102036660AImprove anti-tumor activityCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsMetaboliteAnti her2
Combinations of the antibody-drug conjugate trastuzumab-MCC-DM1 and chemotherapeutic agents, including stereoisomers, geometric isomers, tautomers, solvates, metabolites and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, are useful for inhibiting tumor cell growth, and for treating disorders such as cancer mediated by HER2 and KDR (VEGFR receptor 1). Methods of using such combinations for in vitro, in situ, and in vivo diagnosis, prevention or treatment of such disorders in mammalian cells, or associated pathological conditions, are disclosed.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
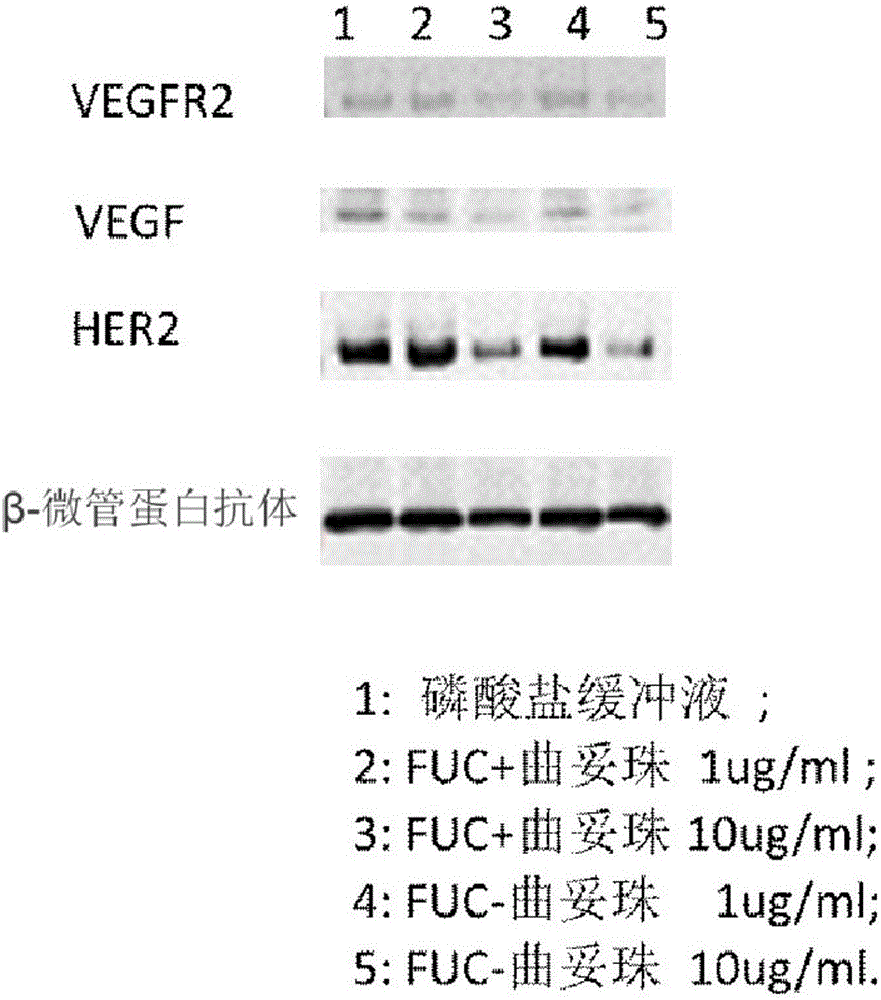
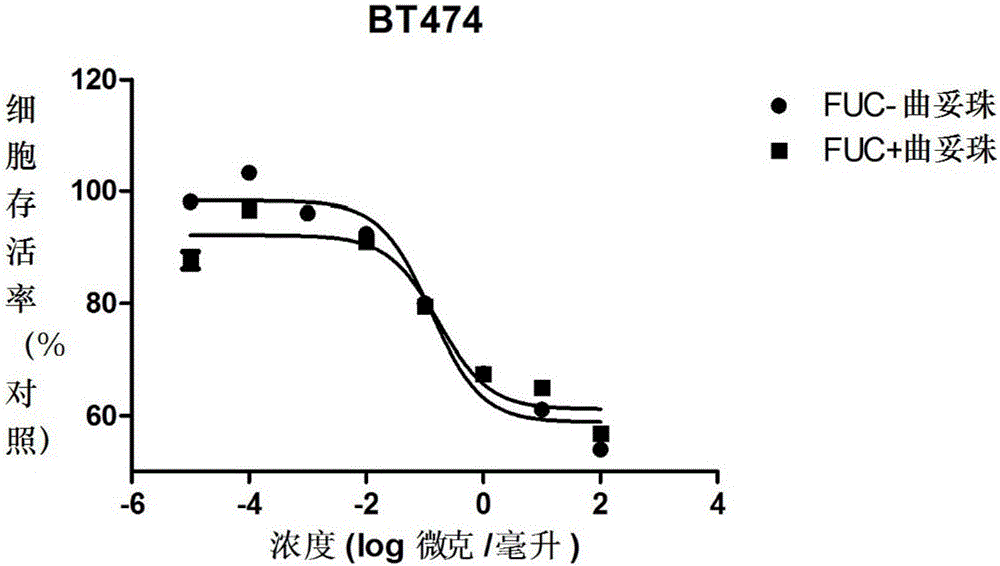
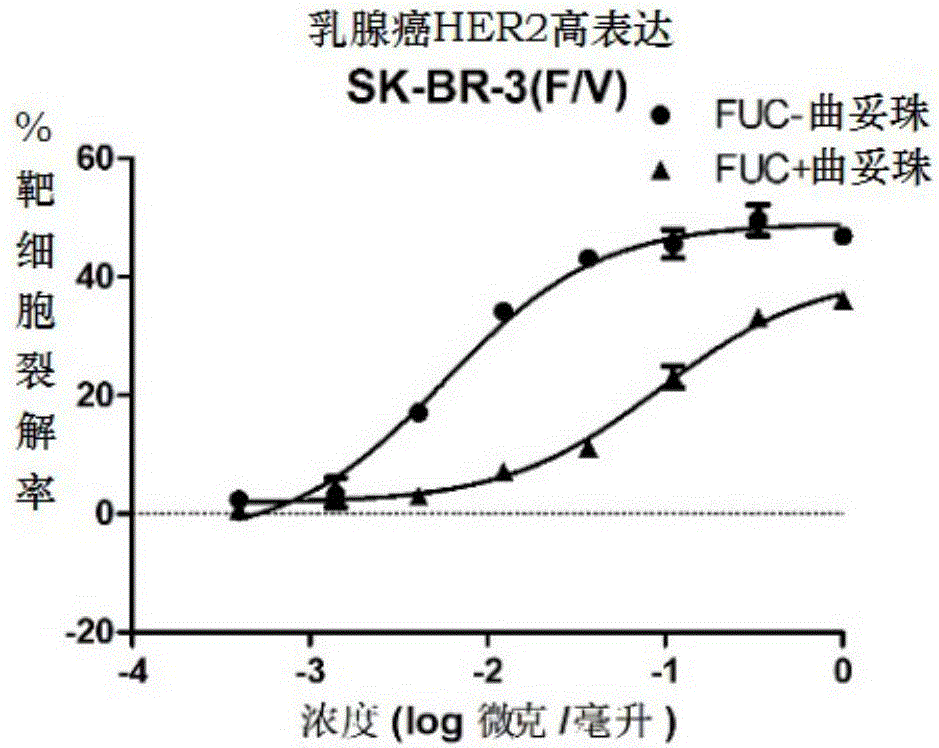
Fucose-removed anti-HER2 antibody and application thereof
InactiveCN106543286AGrowth inhibitionSuppress generationAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsAnti her2BULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention provides a fucose-removed anti-HER2 antibody which is produced by cells with the FUT8 gene knocked out. The amino acid sequence of the fucose-removed anti-HER2 antibody is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and the nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. Furthermore, the antibody comprises a CH2 structural domain; the amount of fucose in the CH2 structural domain is zero. The invention further provides a medicine with the fucose-removed anti-HER2 antibody serving as an active ingredient, and a reagent, a composition or a kit with the fucose-removed anti-HER2 antibody serving as an active ingredient. Compared with a fucose-containing anti-HER2 antibody, the antibody disclosed by the invention is higher in activity, and shows good tumor inhibition activity in both expression and low expression of herceptin-resistant HER2.
Owner:BIORAY LABORATORIES INC
HER2-resisting antibody-medicine conjugate and applications thereof
The invention provides an HER2-resisting antibody-medicine conjugate and applications of the HER2-resisting antibody-medicine conjugate. Specifically, the invention provides the HER2-resisting antibody-medicine conjugate. The experimental result proves that the antibody-medicine conjugate has the obvious anti-tumor effect. The invention further discloses the pharmacy applications of the HER2-resisting antibody-medicine conjugate, and the effects of the HER2-resisting antibody-medicine conjugate in inhibiting or preventing tumor.
Owner:HANGZHOU ADCORIS BIOPHARMA CO LTD
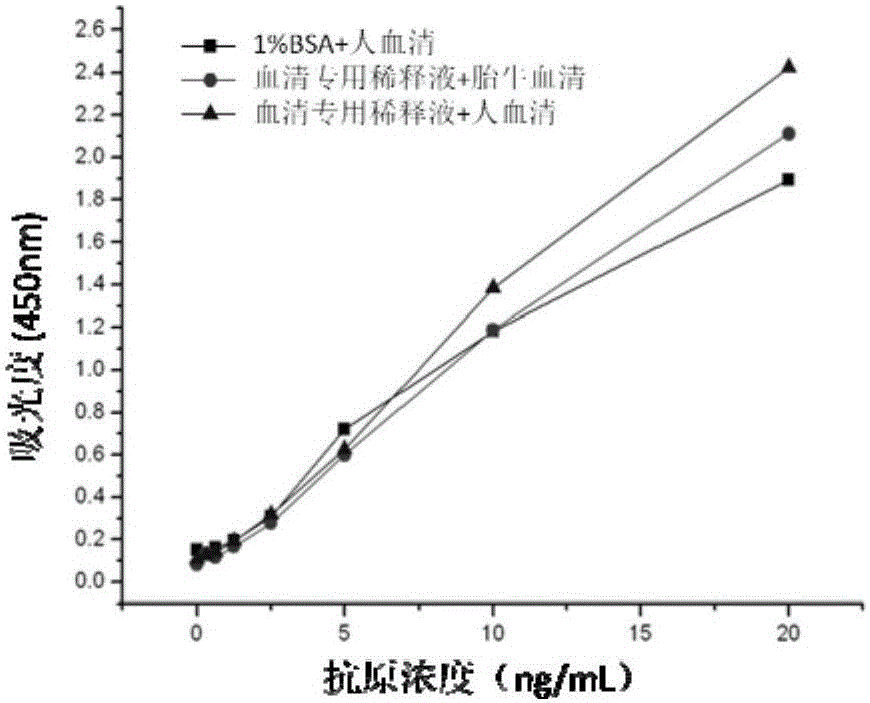
Reagent kit for detecting serum HER2 and application
InactiveCN105158474AAvoid or mitigate the phenomenon of interferenceImprove stabilityDisease diagnosisMonoclonal antibodyAnti her2
The invention provides a reagent kit for detecting serum HER2 and application. The reagent kit comprises HER2-resistant monoclonal antibody trastuzumab and biotinylated A18 which are paired. The invention further provides application of HER2-resistant antibodies and special sample diluent for serum to detect serum HER2 and application of manufacturing of the reagent kit for detecting serum HER2. The reagent kit for detecting serum HER2 and application can serve as a non-invasive, simple, convenient and fast method for diagnosing and detecting HER2 positive tumor disease course development.
Owner:ANHUI PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL
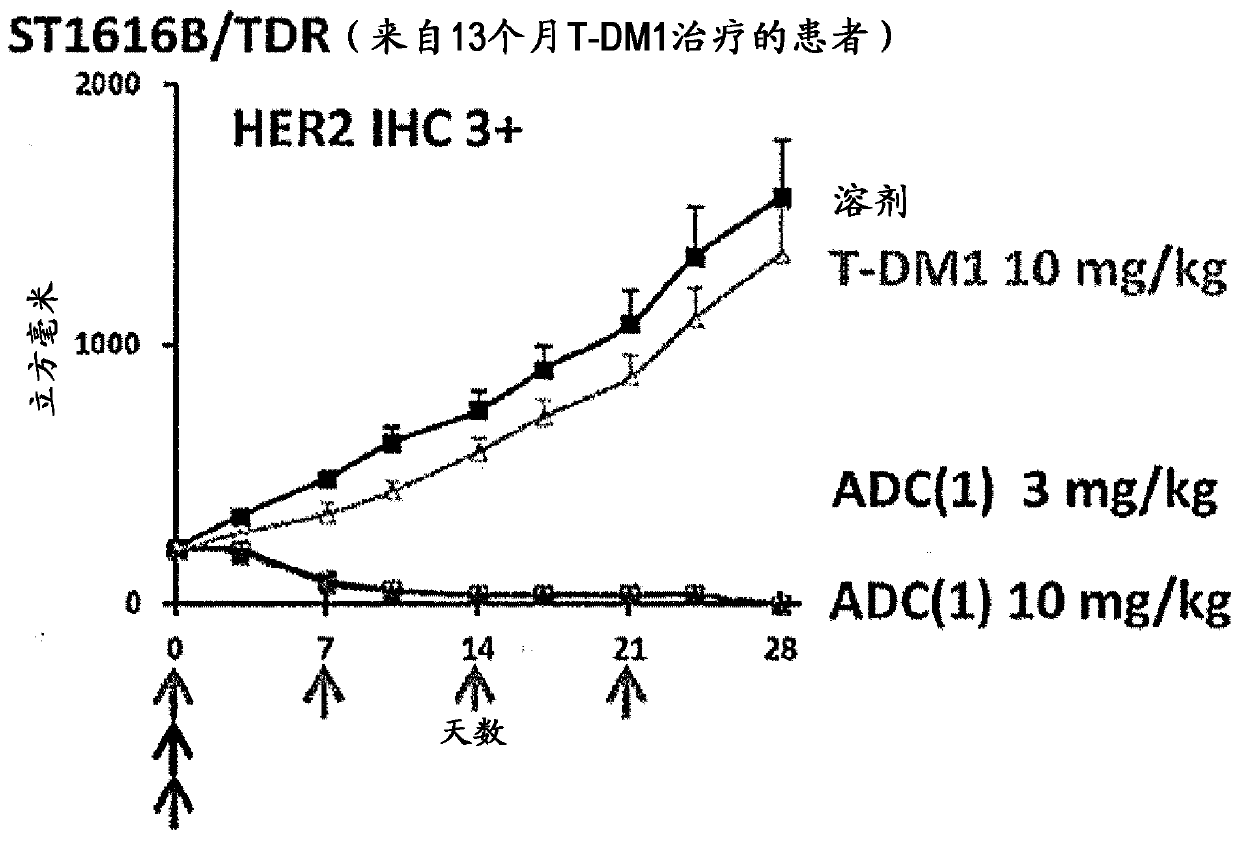
Therapy for drug-resistant cancer by administration of anti-HER2 antibody/drug conjugate
PendingCN109789211AImprove anti-tumor effectImprove securityOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsHer2 expressionAnti her2
A therapeutic agent and therapeutic method for HER2 expression cancers, which are resistant to or are not easily cured by conventional anti-HER2 drugs, are provided in which use is made of an antibody / drug conjugate comprising a linker and a drug, which are represented by the formula -(Succinimid-3-yl-N)-CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2-C(=O)-GGFG-NH-CH2-O-CH2-C(=O)-(NH-DX), and an anti-HER2 antibody bonded thereto. The therapeutic agent and method are effective against HER2 expression cancers, which are resistant to or are not easily cured by conventional anti-HER2 drugs.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com