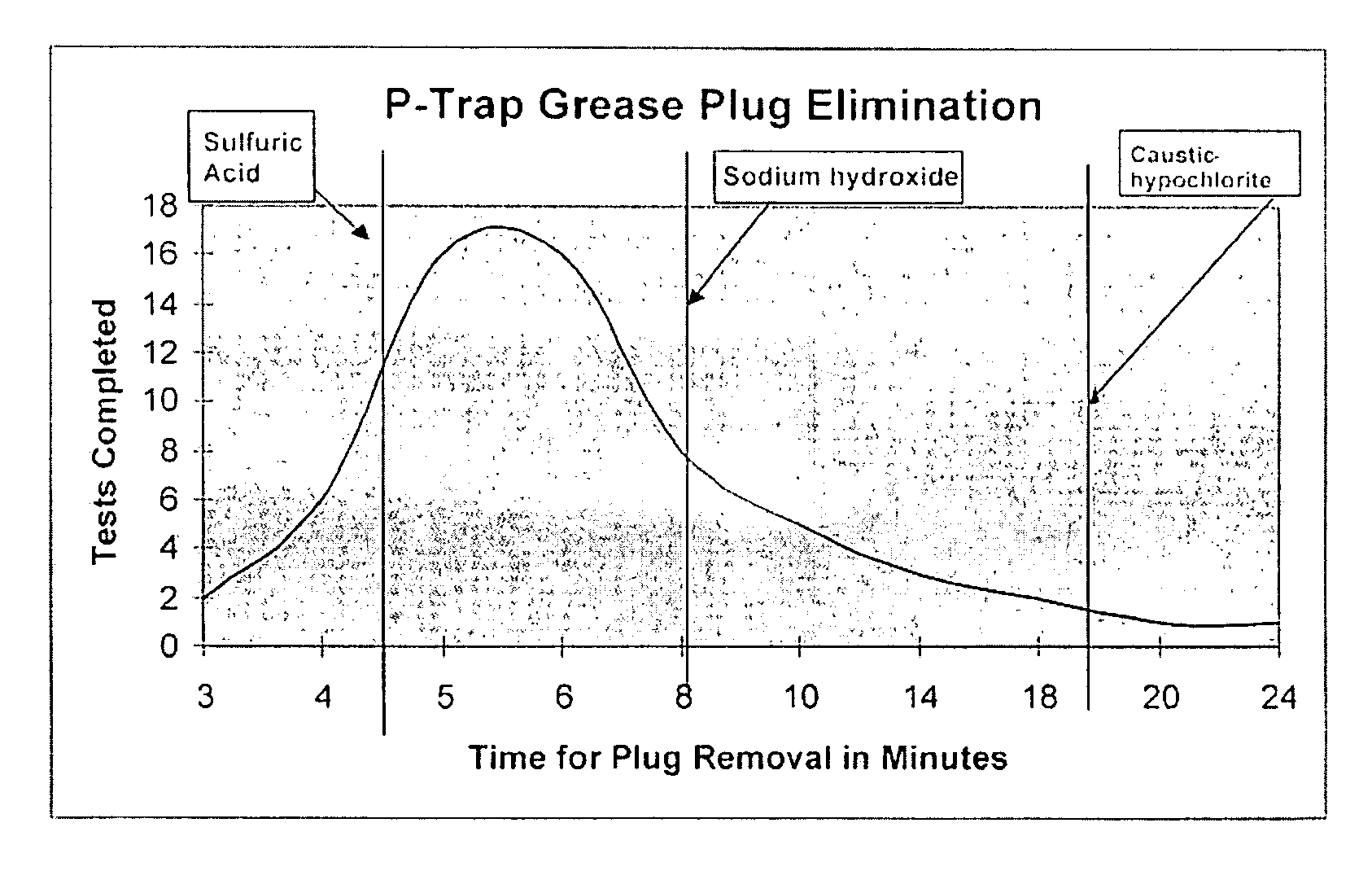
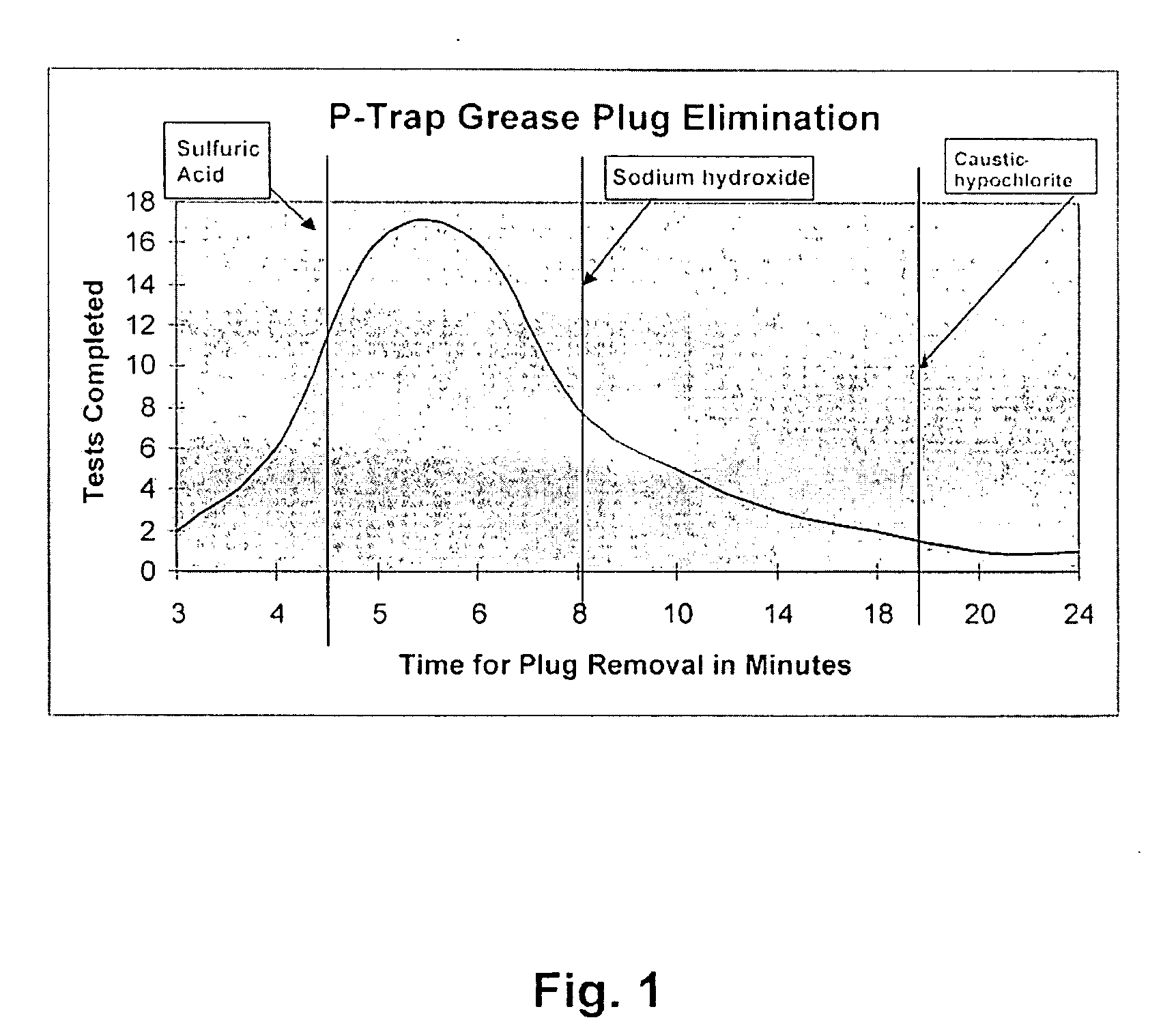
Patents
Literature
53 results about "Drain cleaner" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A drain cleaner is a chemical-based consumer product that unblocks sewer pipes or clogged wastewater drains. The term may also refer to a mechanical device such as a plumber's snake, drain auger, toilet plunger, or similar device. Occasionally, the term is applied to a plumber or other individual who performs the drain cleaning and hygiene.
Foaming drain cleaner
InactiveUS6479444B1Process stabilityIncrease contact timeInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsHigh foaming compositionsHalf-lifeEngineering
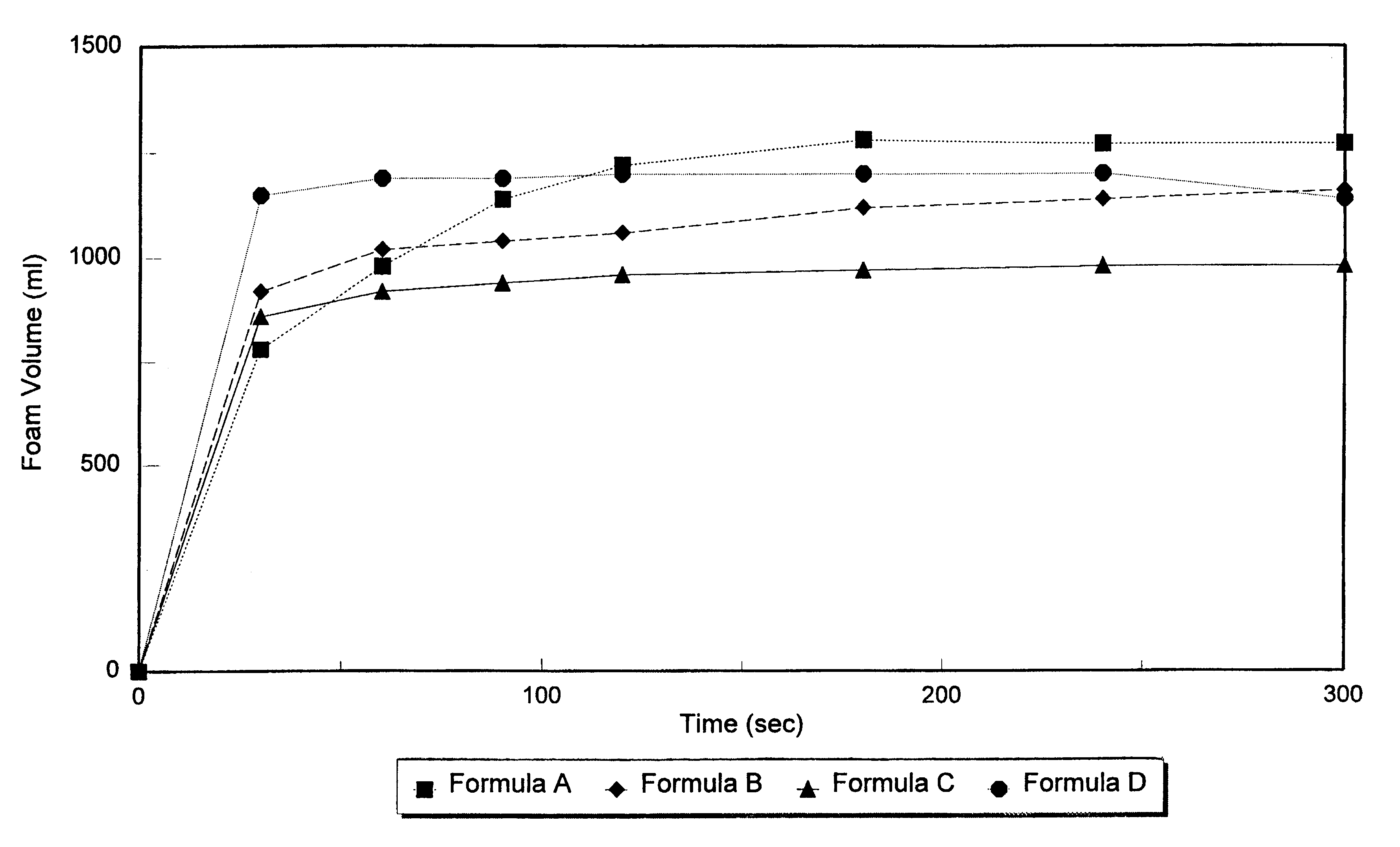
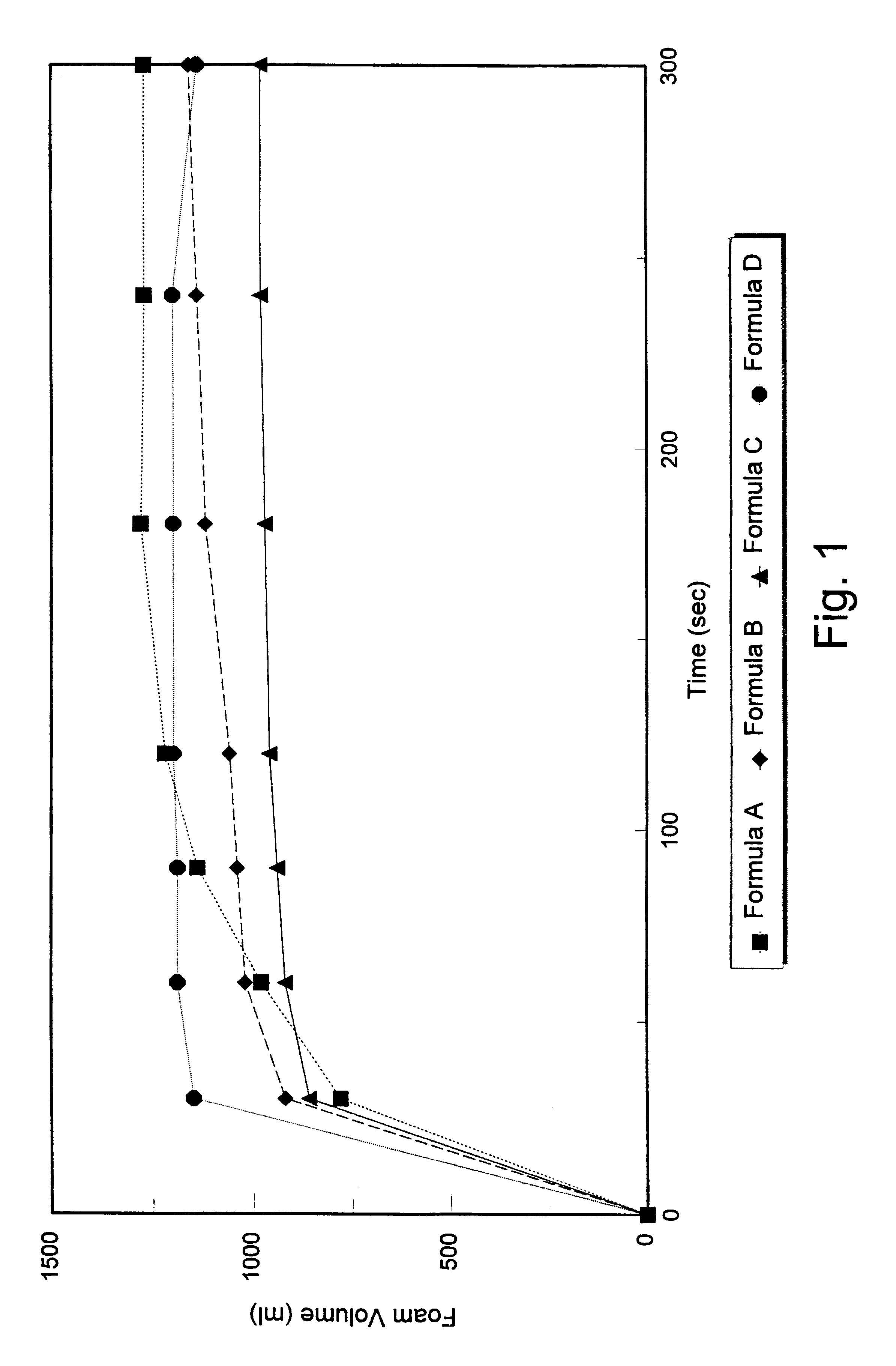
A composition is provided comprising two liquids which are separately maintained prior to forming an admixture during delivery to a surface to be treated, whereupon the admixture generates a foam sufficient for cleaning efficacy and stability. A first liquid preferably includes a hypohalite, or a hypohalite generating agent and a second liquid preferably includes a peroxygen agent. As the two liquids are initially separated, the hypohalite generating agent can be maintained in an environment free of peroxygen agent and otherwise conducive to their cleaning activity and stability up to the time of use. When the two liquids are allowed to mix, for example, by simultaneously pouring into a drain, the hypohalite and peroxygen react to liberate oxygen gas. As foam generation occurs, the escaping gas contacts surfactant in the solution, and creates foam which expands to completely fill the drain pipe. The expanded foam contains an excess of the hypohalite, which acts to clean the drain. A method of cleaning drains is provided which comprises the step of pouring into a drain at least one liquid which generates foam in situ, the foam characterized by a density of at least about 0.1 g / ml, a half life of greater than about thirty minutes, a volume of at least about 500 ml, and wherein the foam contains a cleaning-effective amount of a drain cleaning active.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
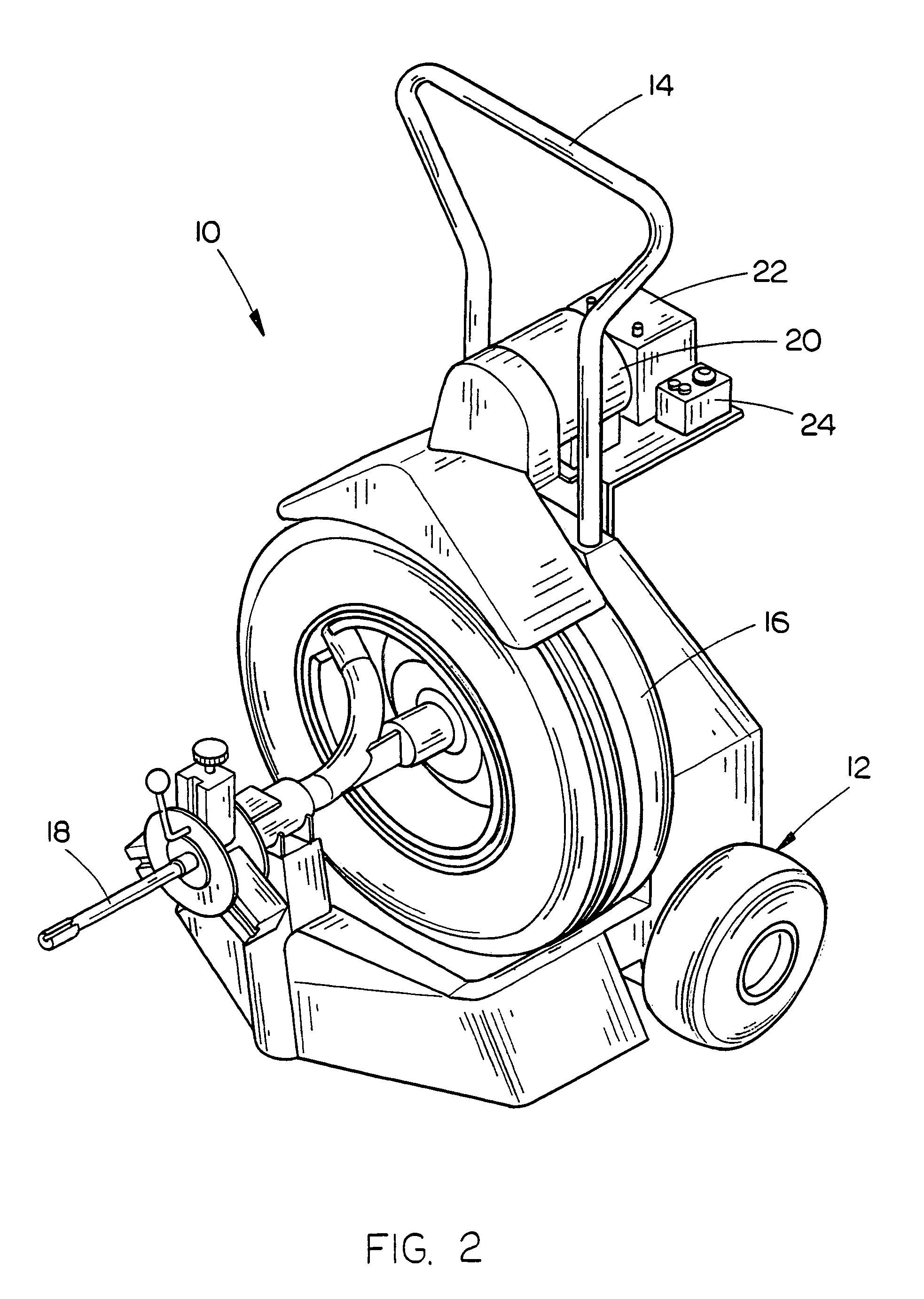
Battery-powered sewer and drain cleaner
InactiveUS7676879B1Eliminate the risk of electric shockProtection elementHollow article cleaningCleaning using toolsPower flowElectrical battery
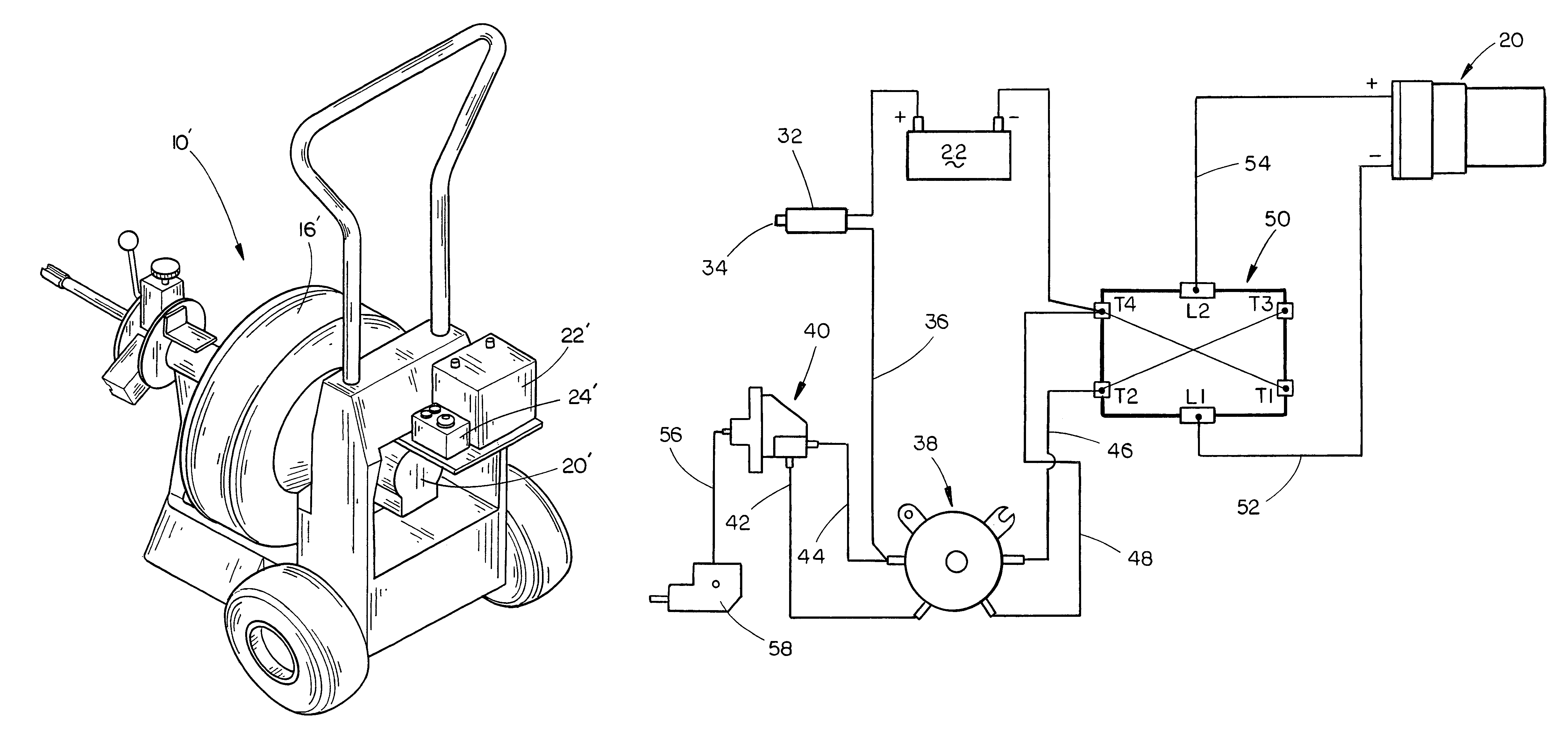
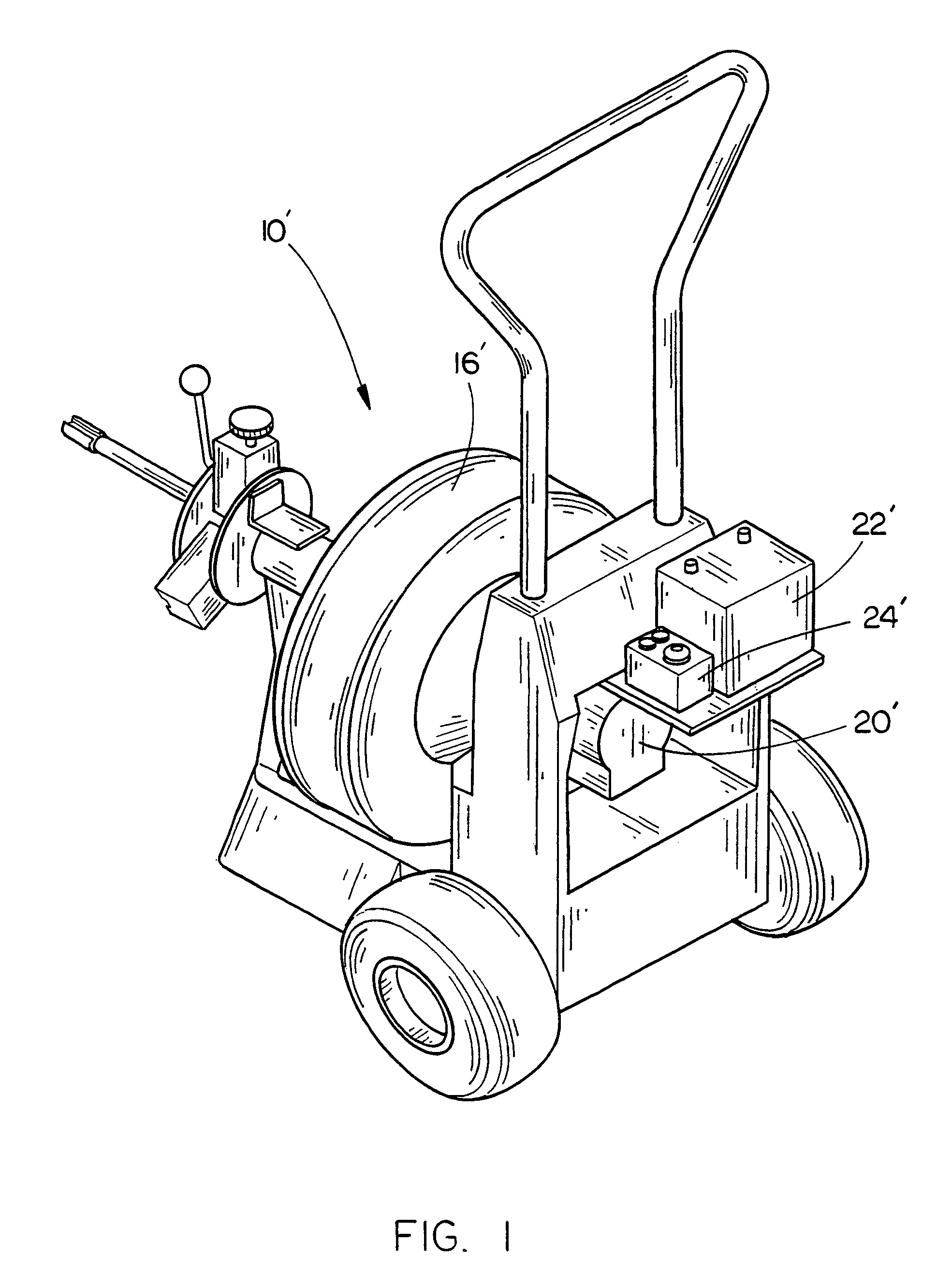
A battery-powered sewer and drain cleaner comprising a frame, a rotatable drum mounted on the frame which has a flexible plumber's snake associated therewith, a DC motor mounted on the frame for driving the drum and a rechargeable battery mounted on the frame for powering the DC motor. A control is connected to the DC motor for controlling the operation thereof. The use of DC power for the cleaner eliminates the electrocution hazard associated with AC-driven sewer and drain cleaners and eliminates the need for an extension cord. The sewer and drain cleaner of this invention includes new and unique circuitry to bypass the motor high current demand around the more delicate circuitry.
Owner:RUTENBERG KEITH H +1
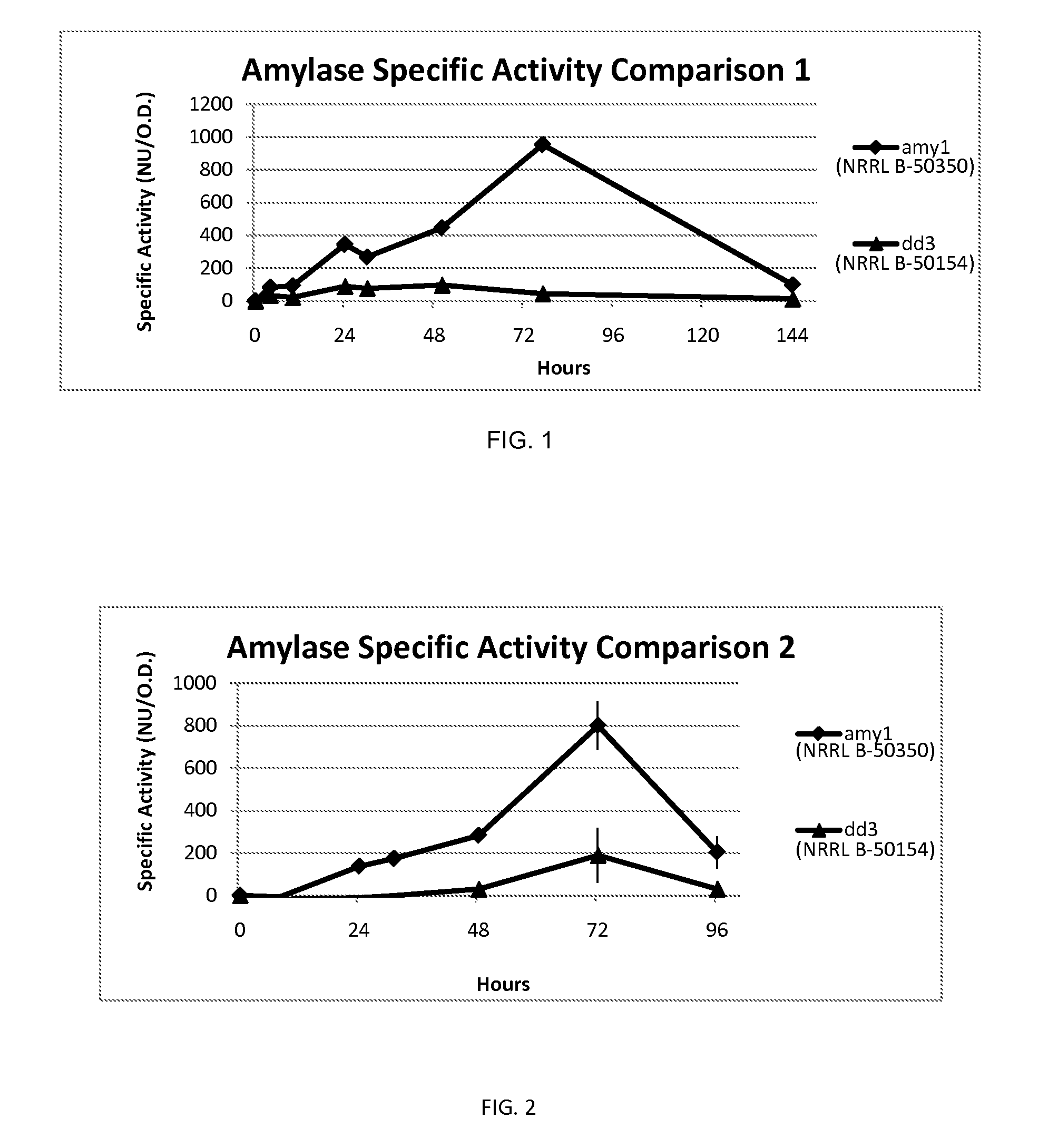
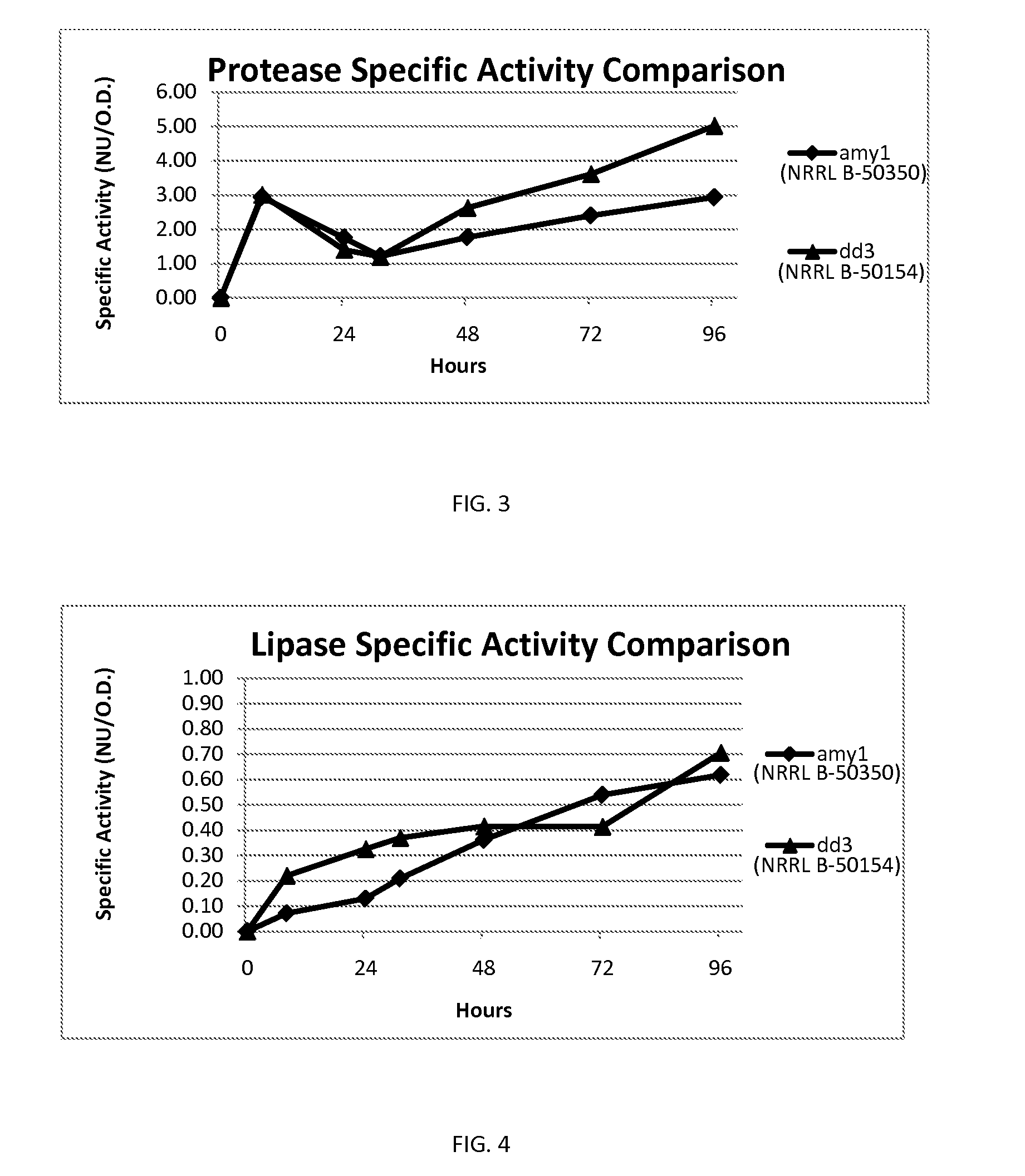
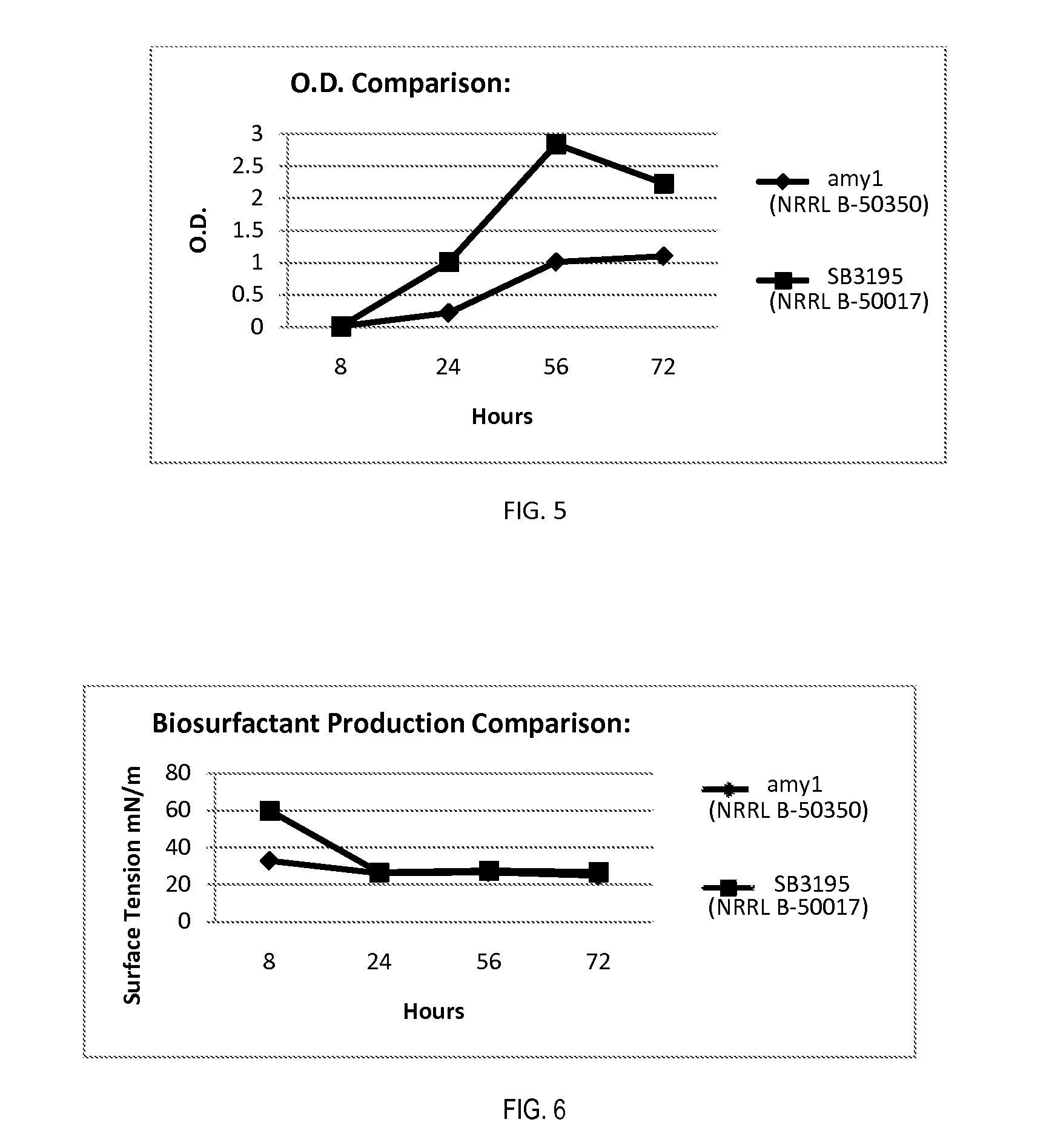
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Strain
ActiveUS20110274673A1Preventing and alleviating and undesirable conditionImprove seed qualityBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyBacteroides
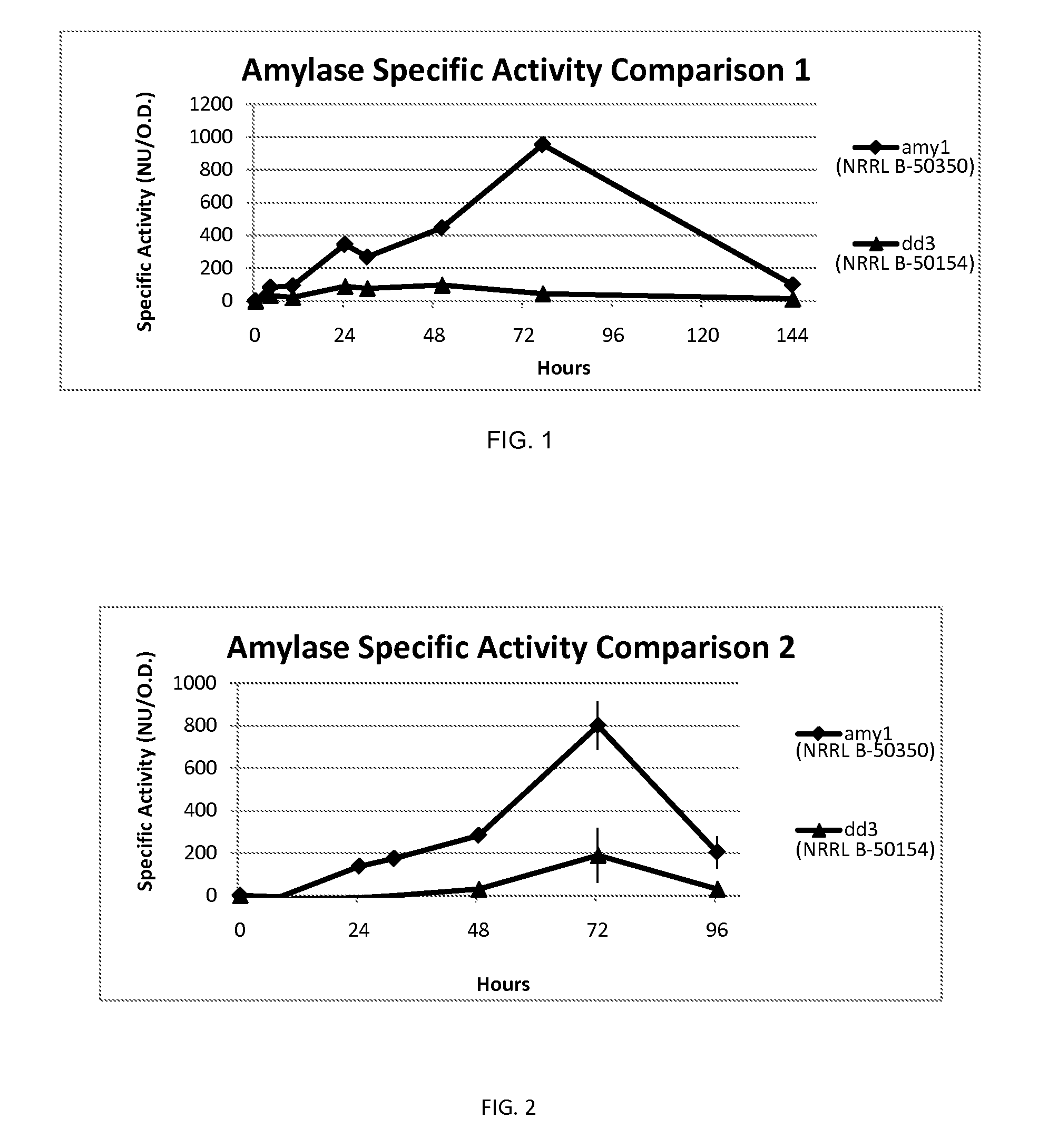
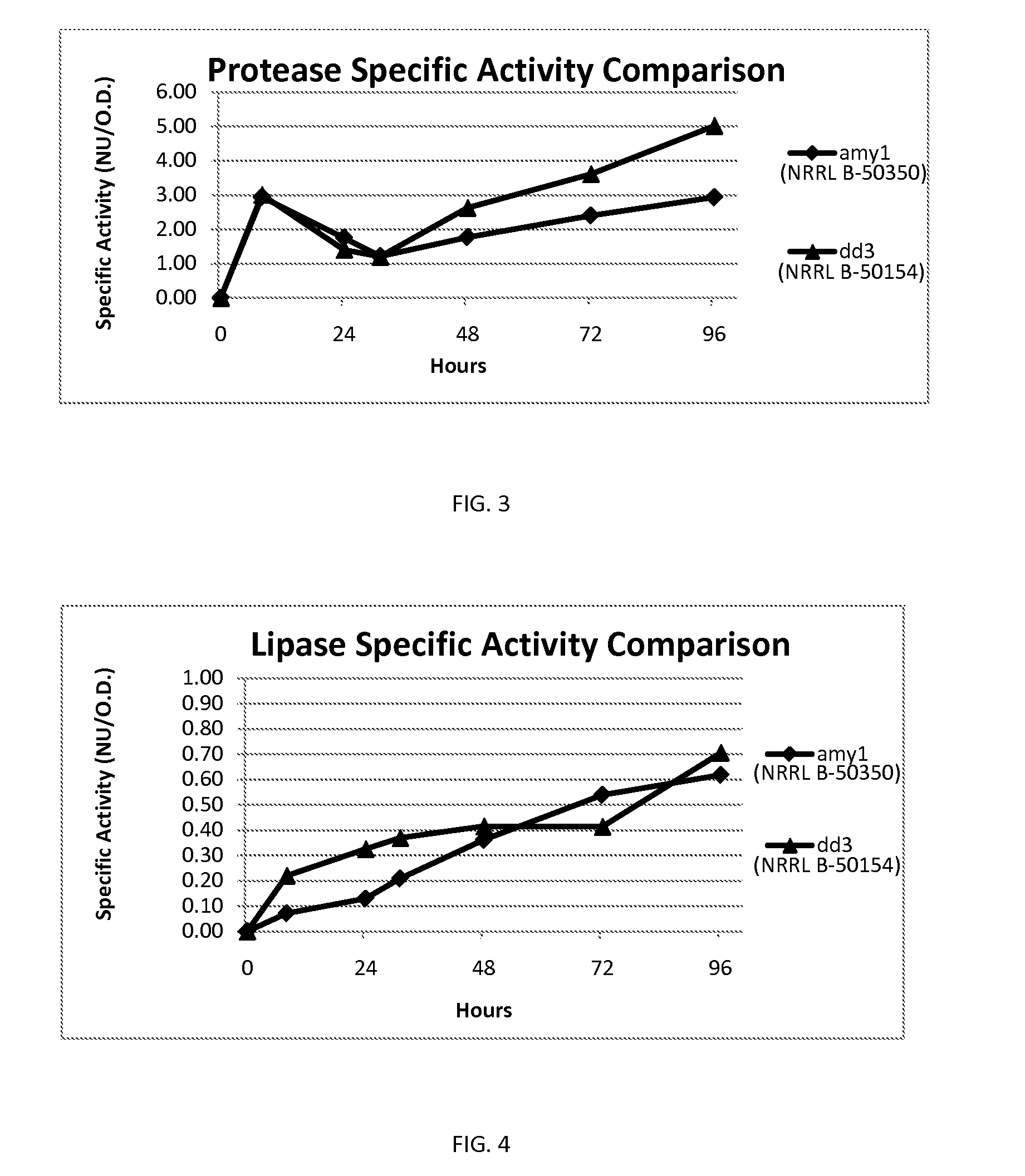
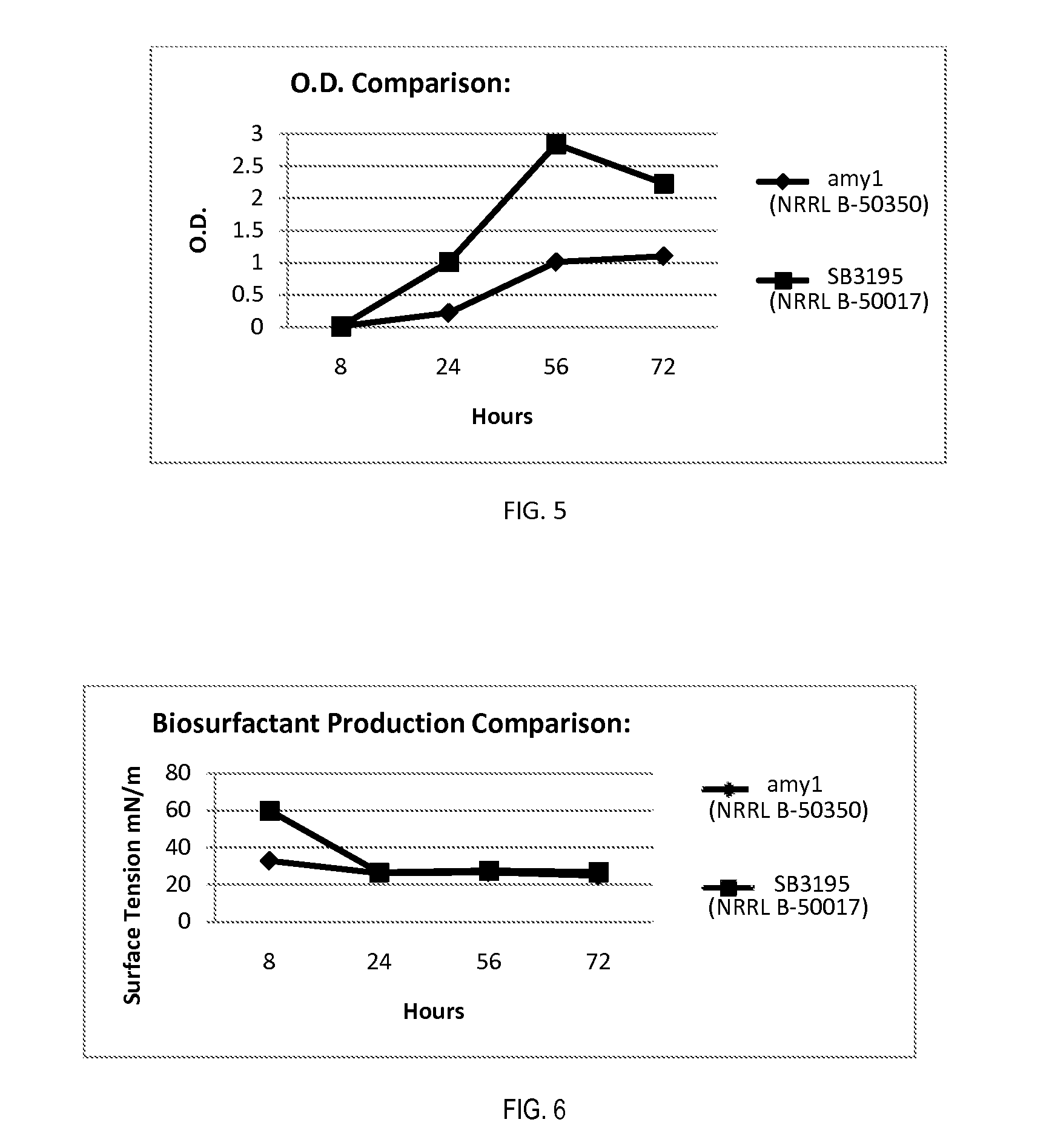
The present disclosure relates to a strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens bacteria that hyperproduces amylase enzyme and protease enzyme. The strain is also suitable for producing lipase for the degradation of oleaginous materials such as fats, greases and cooking oils. The strain also has excellent fungicidal and / or fungistatic qualities. The strain of the present disclosure and the enzymes produced thereby have a number of applications, including agricultural uses, laundry and dish detergents, drain cleaners and spot removers, and among other things, baking applications.
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOLOGICALS
Binary foaming drain cleaner
InactiveUS20030171234A1Improve efficacyKeep for a long timeOrganic detergent compounding agentsHigh foaming compositionsTime of useSURFACTANT BLEND
A composition is provided comprising two liquids which are separately maintained prior to forming an admixture during delivery to a surface to be treated, whereupon the admixture generates a foam sufficient for cleaning efficacy and stability. A first liquid preferably includes a hypohalite, or a hypohalite generating agent and a second liquid preferably includes a peroxygen agent. The first liquid is thickened to a specified rheology, resulting in the generation of a highly effective foam. As the two liquids are initially separated, the hypohalite generating agent can be maintained in an environment free of peroxygen agent and otherwise conducive to their cleaning activity and stability up to the time of use. When the two liquids are allowed to mix, for example, by simultaneously pouring into a drain, the hypohalite and peroxygen react to liberate oxygen gas. As foam generation occurs, the escaping gas contacts surfactant in the solution, and creates foam which expands to completely fill the drain pipe. The expanded foam contains an excess of the hypohalite, which acts to clean the drain.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
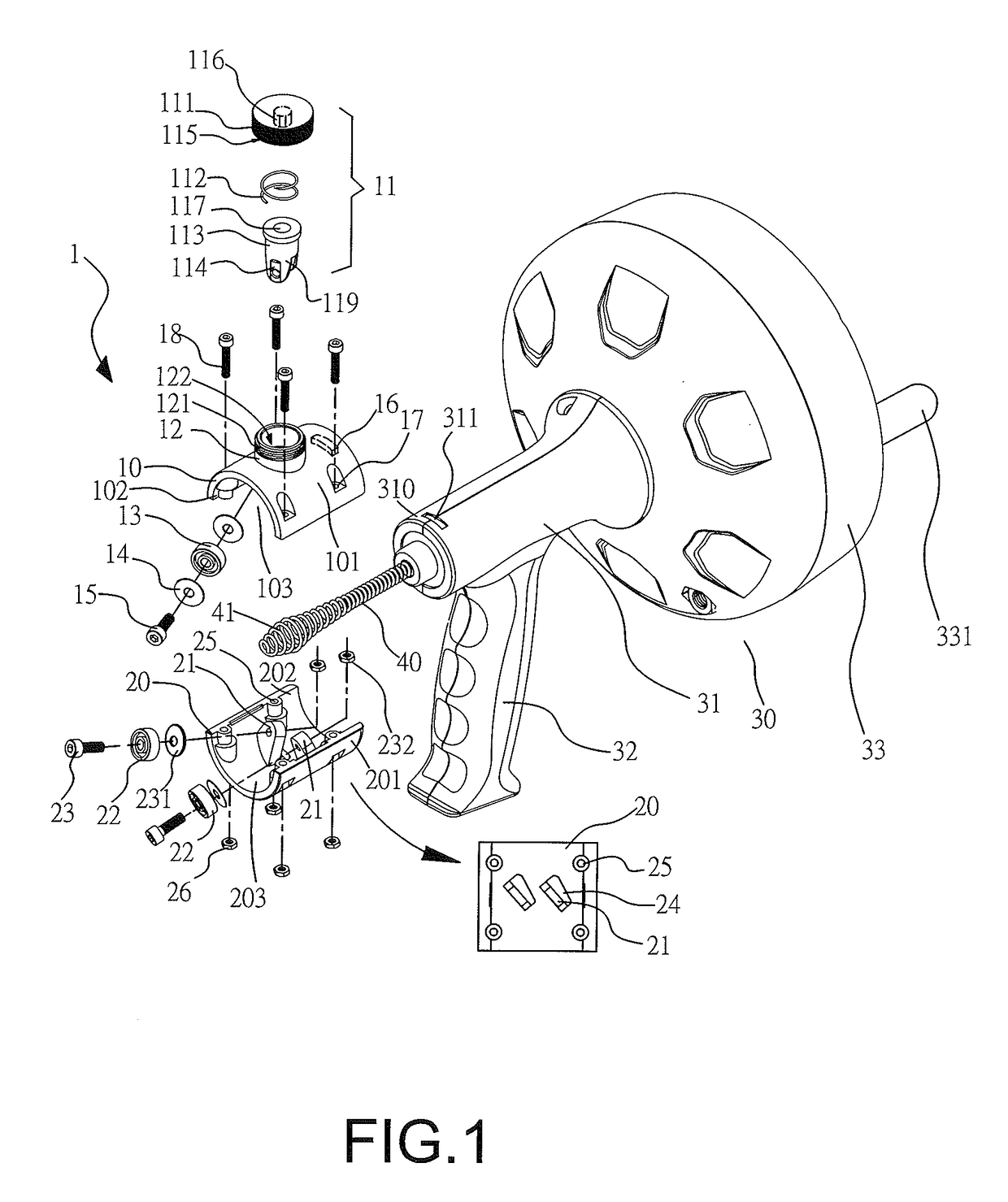
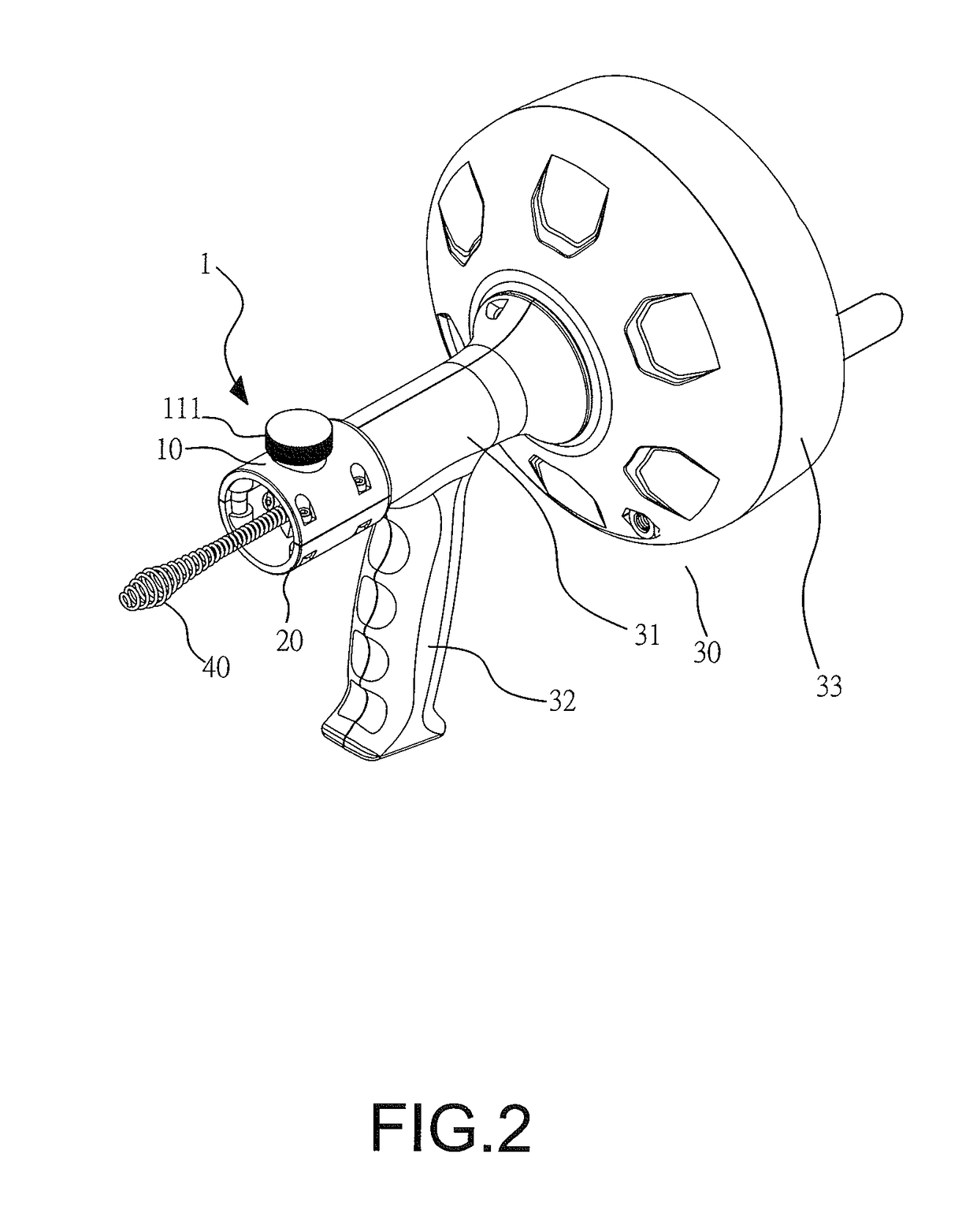
Feed control lock for hand operated drain cleaner
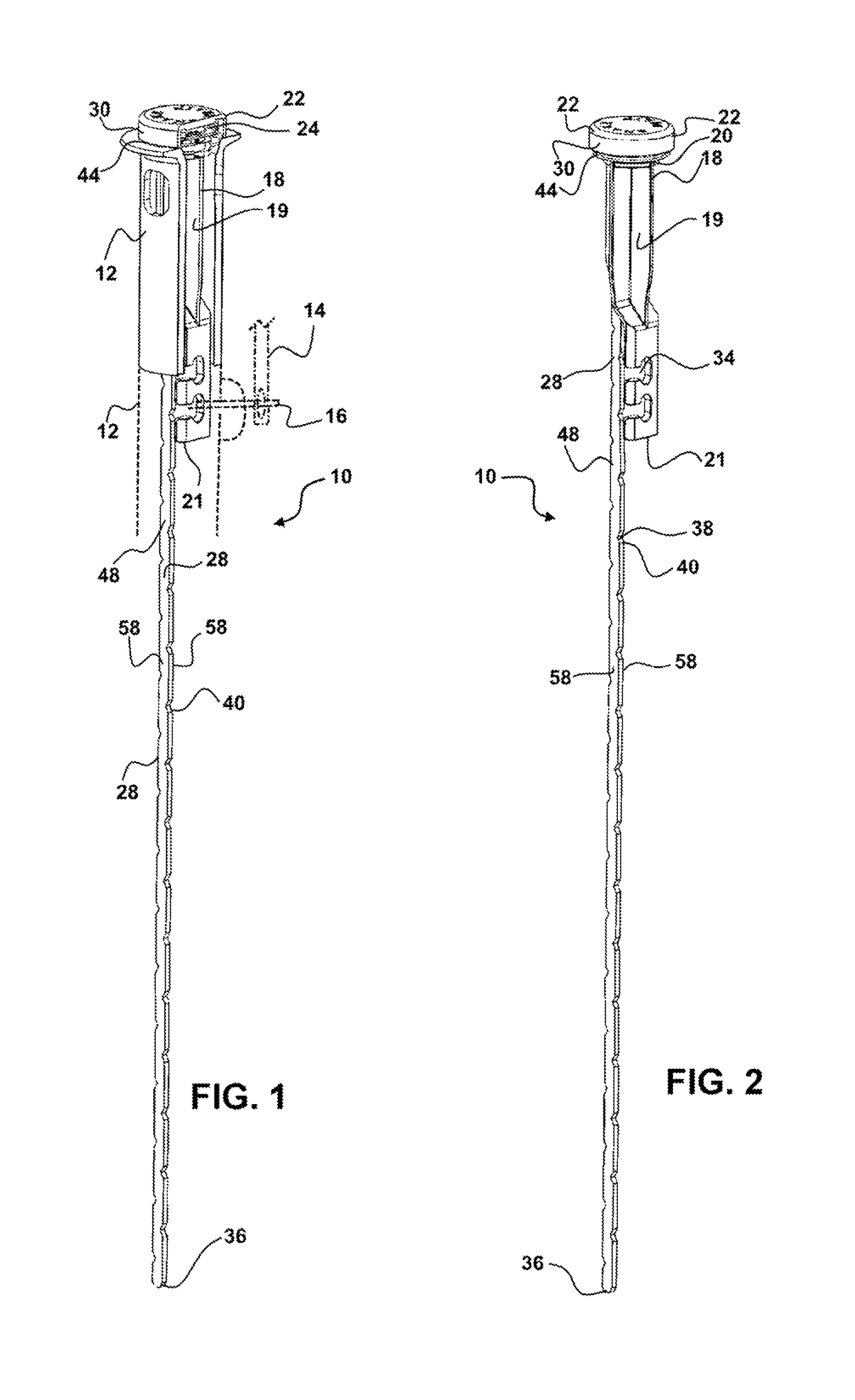
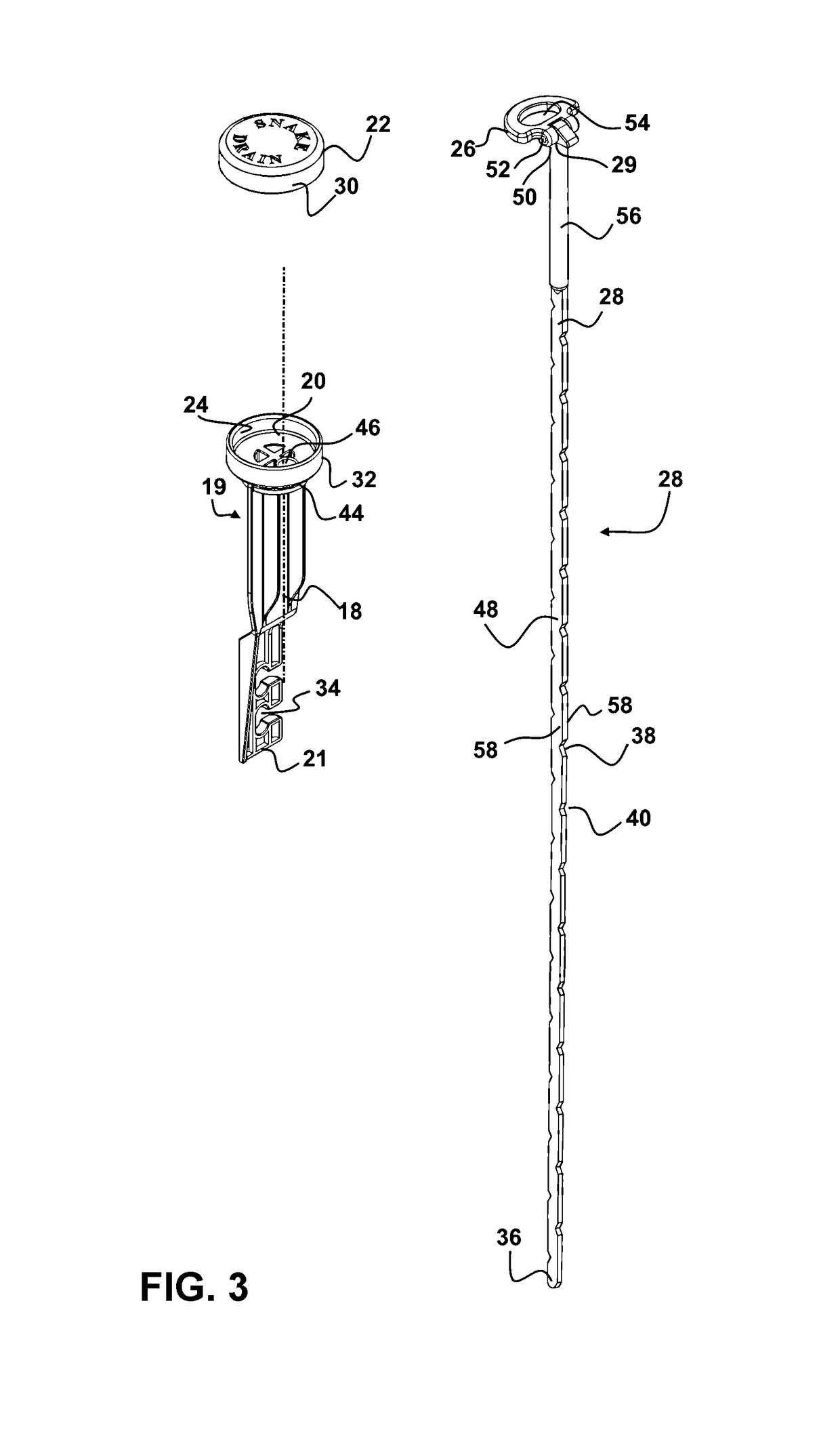
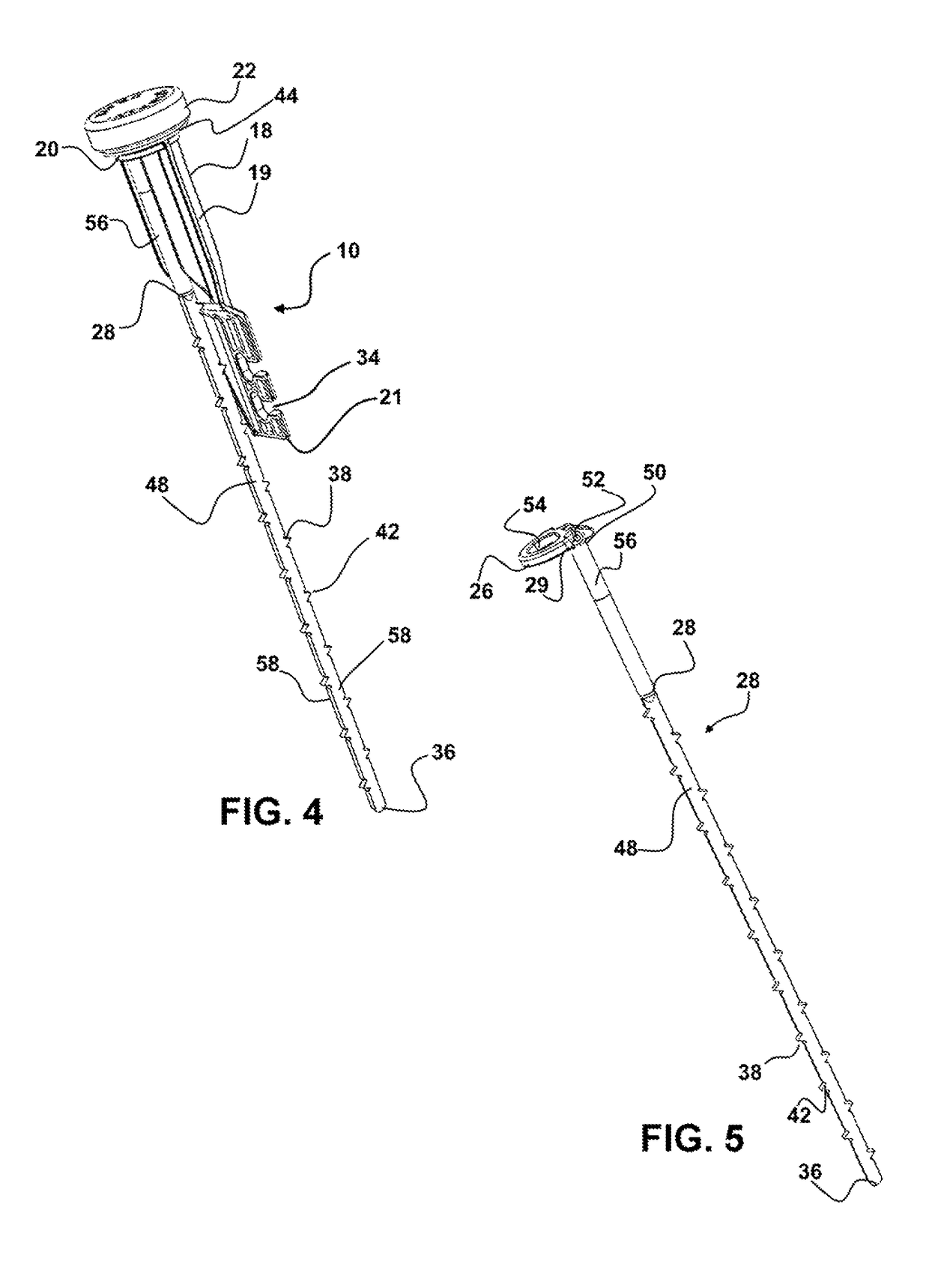
A hand operated drain cleaner includes a manually operated rotatable drum and an elongated flexible cable at least partially held in the drum. A portion of the cable extending from the drum has a cable axis, and rotation of the drum rotates the cable portion about the cable axis. A handle is adapted to rotatably support the drum. The handle includes a barrel portion and a handle portion. A feed control device includes a housing having a feed passage axially therethrough for receiving the cable and a trigger for moving the feed control device between a non-actuating position and an actuating position. In the actuating position, a feed control device is pivoted relative to the handle such that the driving mechanism engages the cable thereby inducing axial movement of the cable via rotation of the drum. A locking mechanism is opera operably associated with the feed control device.
Owner:EMERSON ELECTRIC CO
Feed control lock for hand operated drain cleaner
A hand operated drain cleaner includes a manually operated rotatable drum and an elongated flexible cable at least partially held in the drum. A portion of the cable extending from the drum has a cable axis, and rotation of the drum rotates the cable portion about the cable axis. A handle is adapted to rotatably support the drum. The handle includes a barrel portion and a handle portion. A feed control device includes a housing having a feed passage axially therethrough for receiving the cable and a trigger for moving the feed control device between a non-actuating position and an actuating position. In the actuating position, a feed control device is pivoted relative to the handle such that the driving mechanism engages the cable thereby inducing axial movement of the cable via rotation of the drum. A locking mechanism is opera operably associated with the feed control device.
Owner:EMERSON ELECTRIC CO
Enzymatic detergent composition and method for degrading and removing bacterial cellulose
InactiveUS6020293AReduce riskMinimize ecological harmInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsWater solubleCellulose breakdown
This invention relates to an enzymatic detergent drain cleaner composition containing: 0.015-20 wt % of an acid cellulase enzyme having hydrolytic activity specific to beta -glucosidic bonds; 1-70 wt % of a water soluble carbonate salt; 1-70 wt % of a water soluble acid that reacts in an aqueous medium with the carbonate salt to form carbon dioxide that dissolves in the aqueous medium; 0.1-10 wt % of a surfactant; and 0.05-5 wt % of a thickening agent. This detergent composition may be used as an enzymatic detergent drain cleaner or in a method for removing or preventing bacterial cellulose deposits in an aqueous system at a solution temperature of up to about 60 DEG C. and a pH of about 2 to about 7.
Owner:KAY CHEM
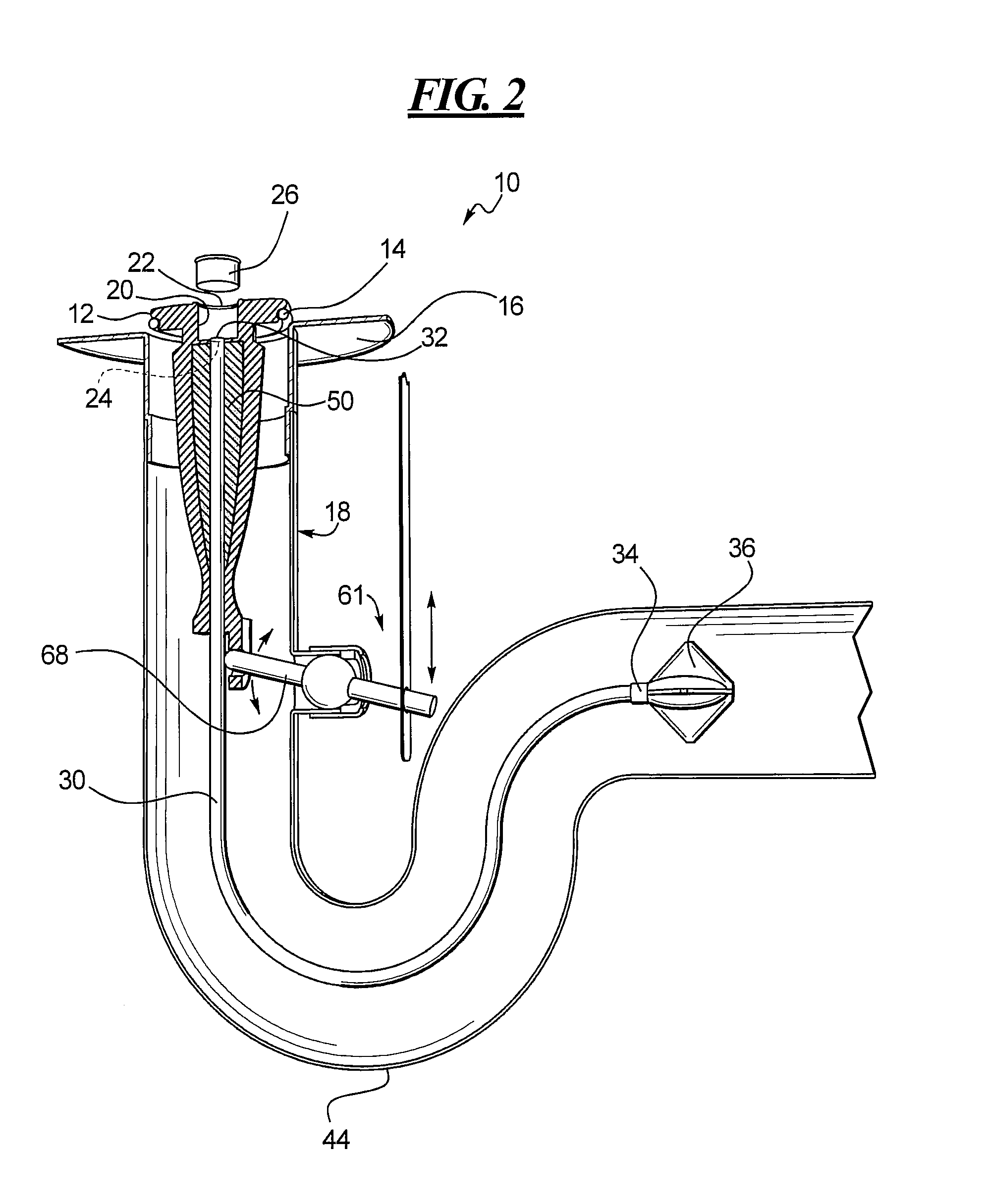
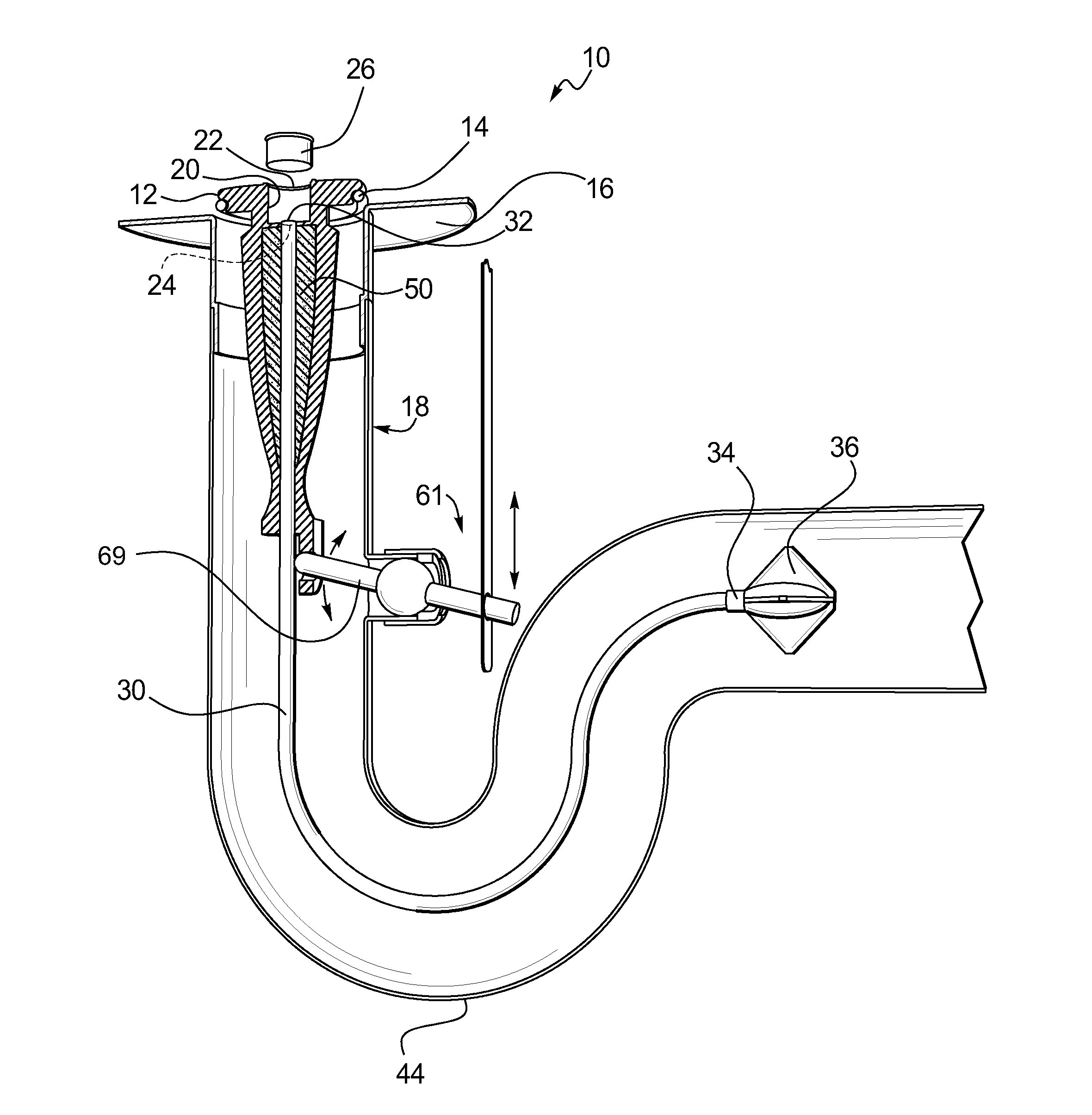
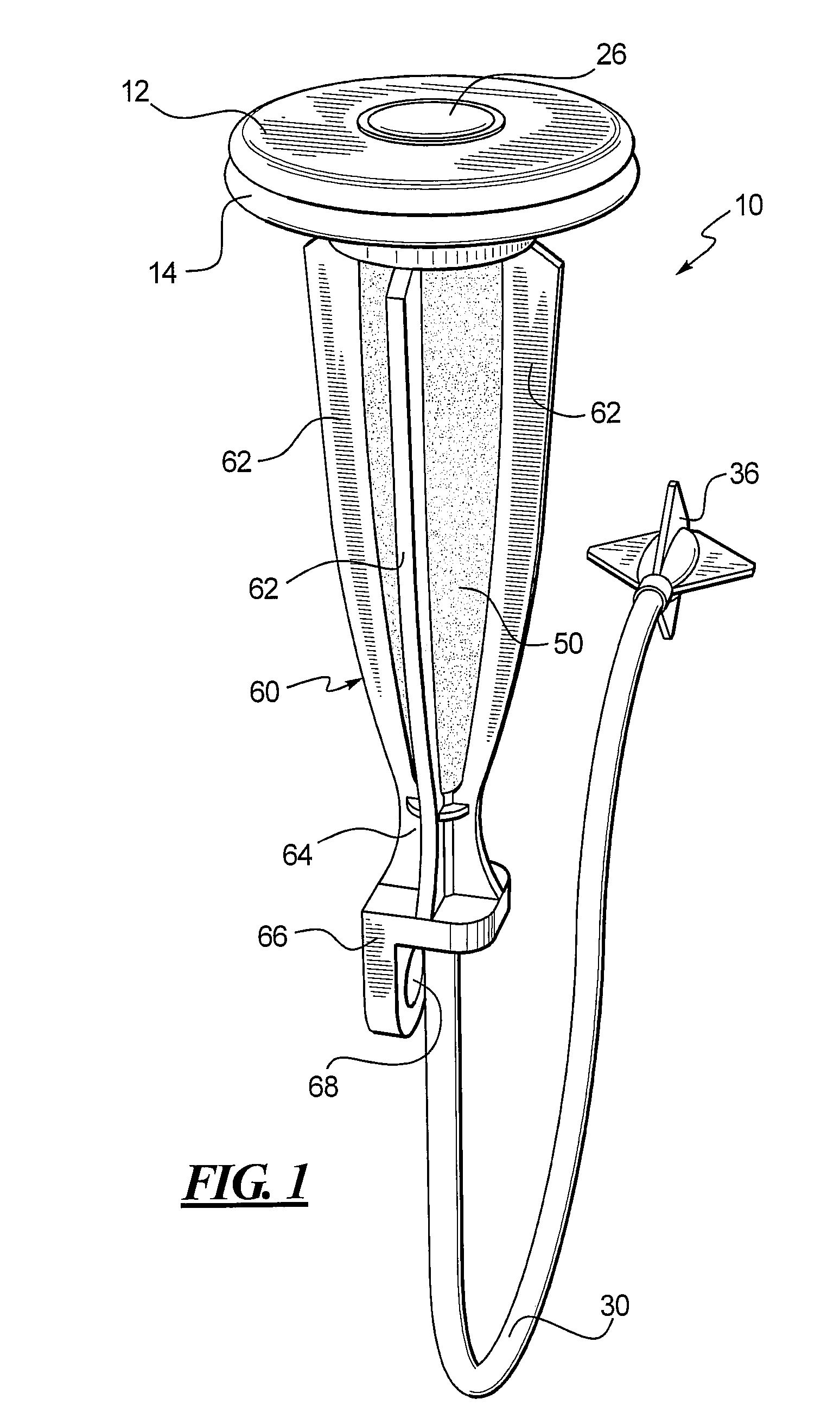
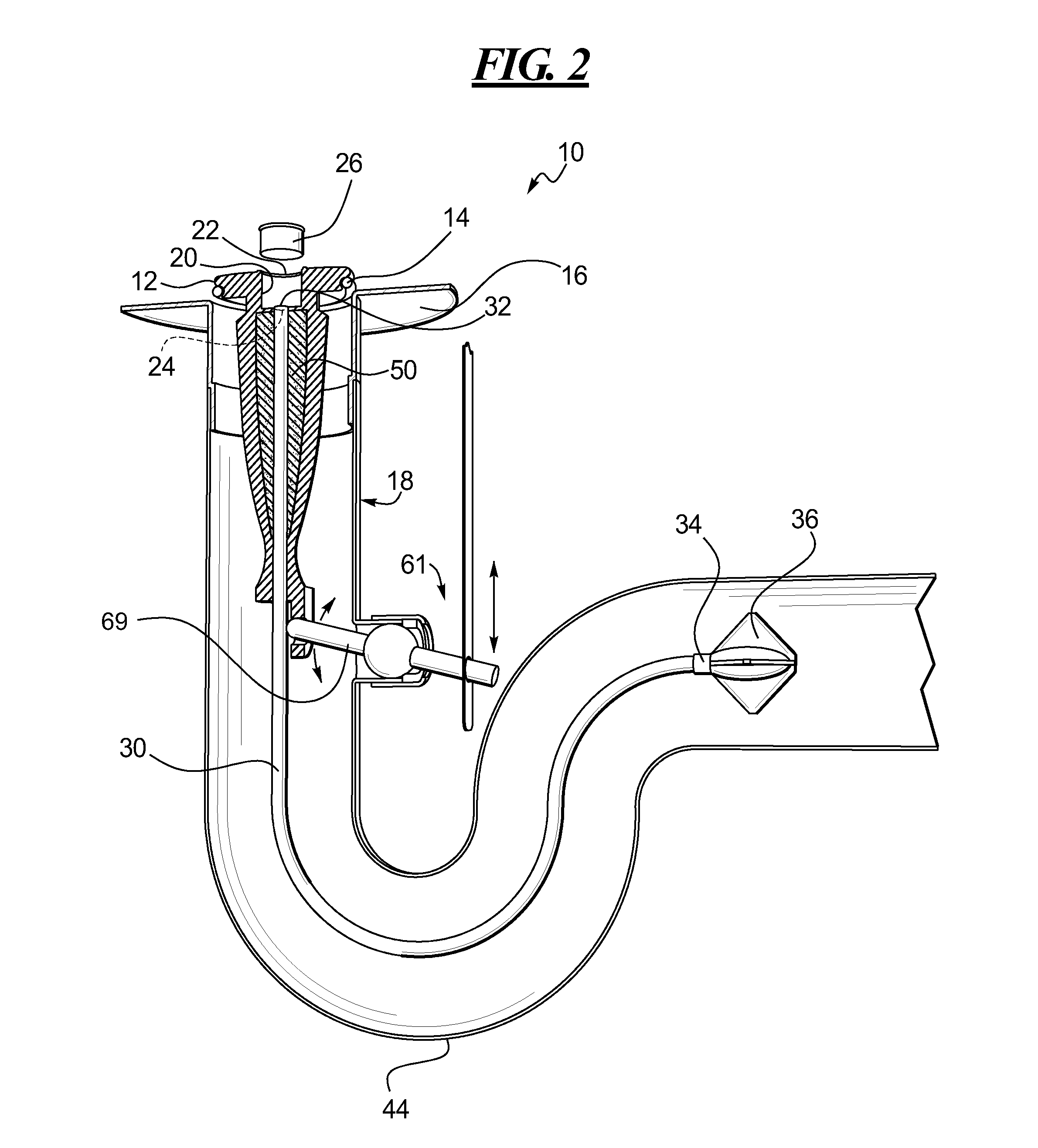
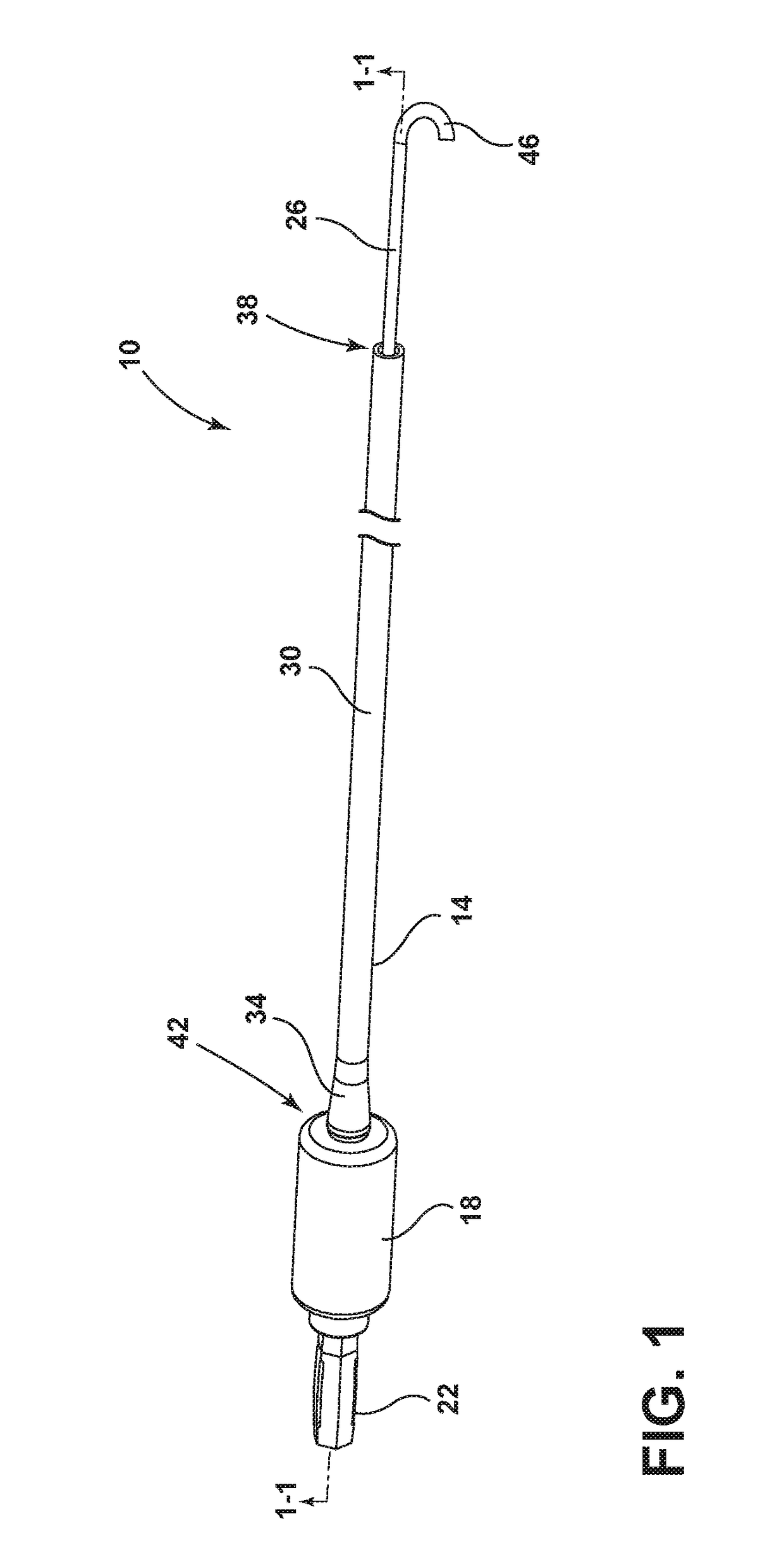
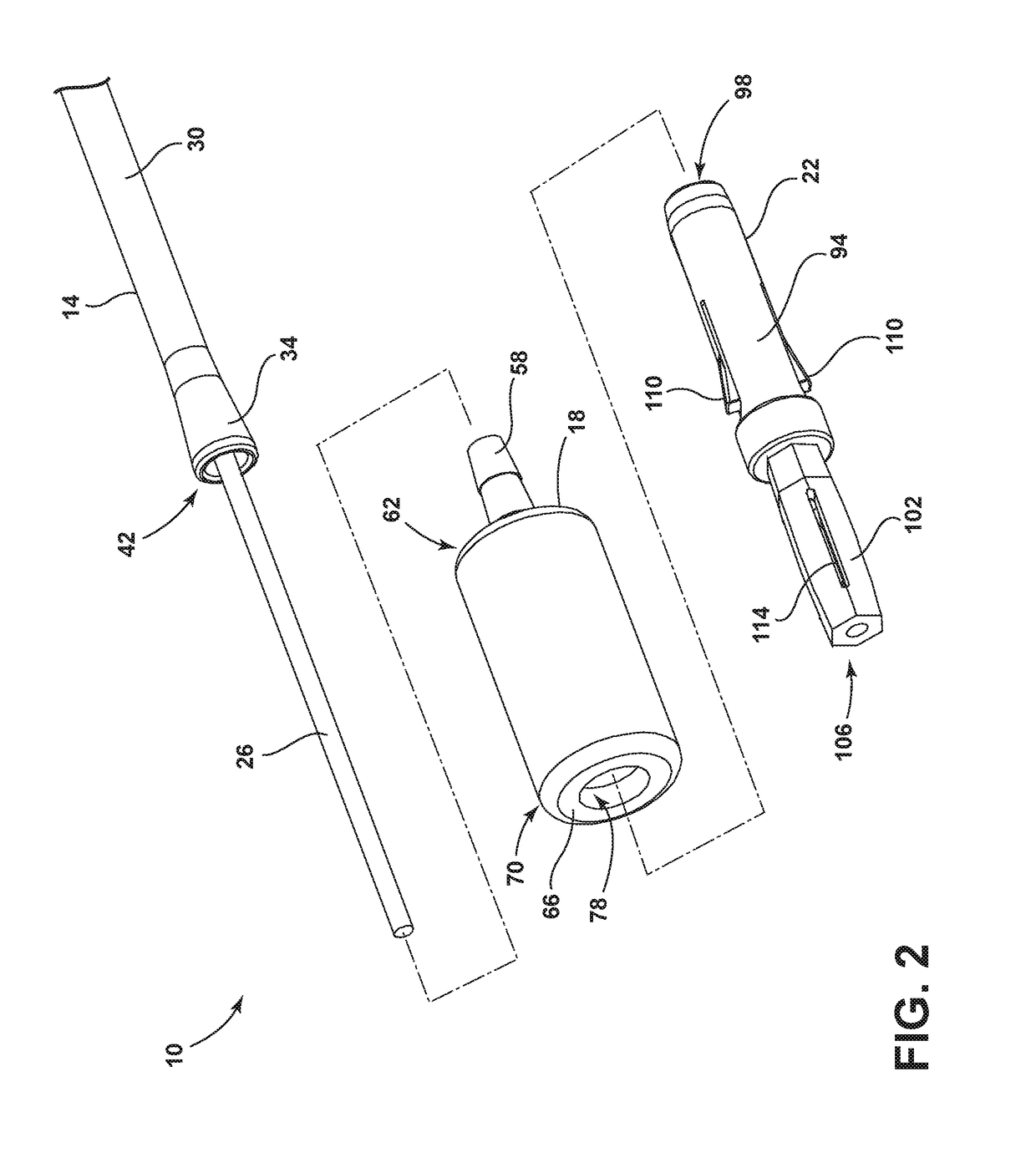
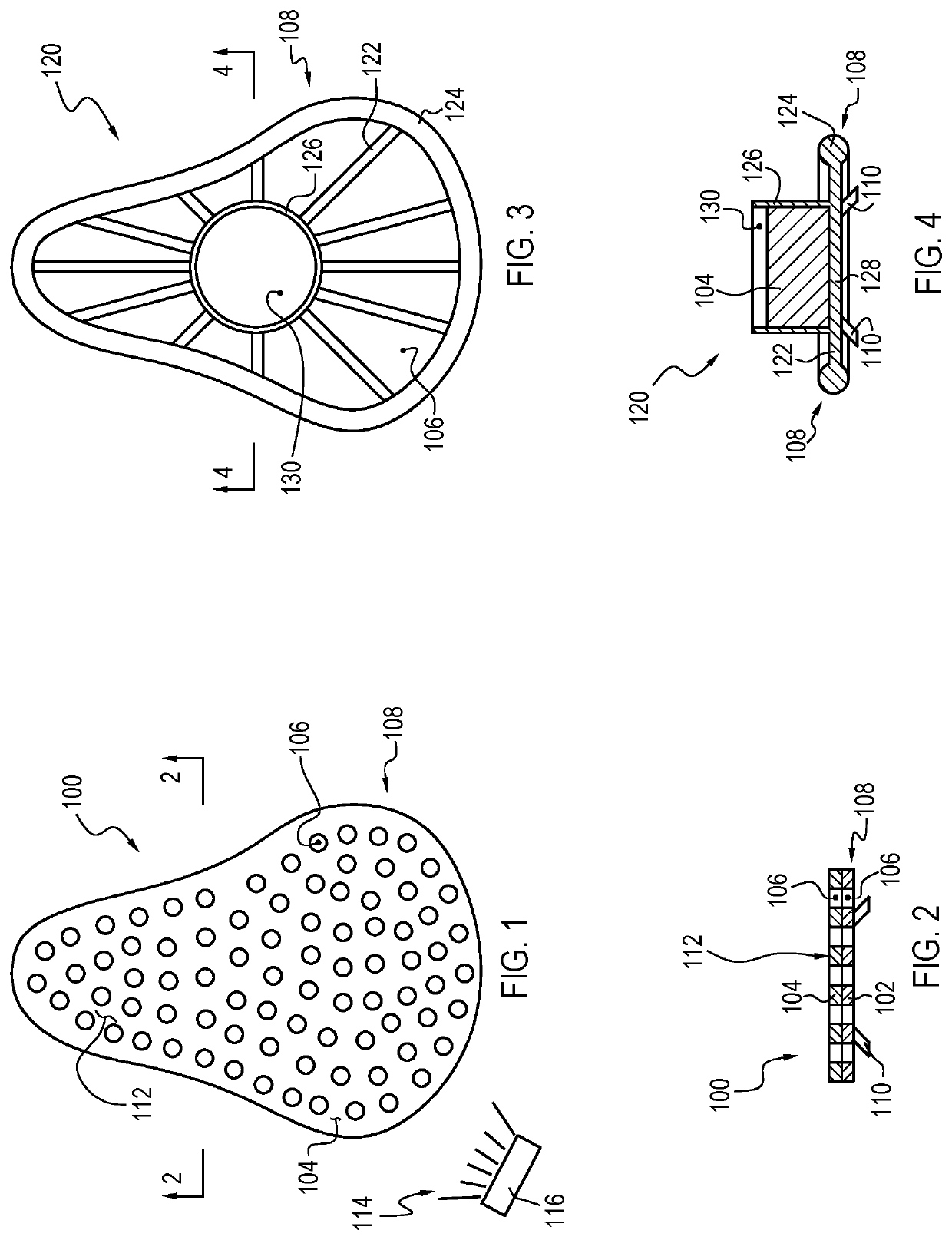
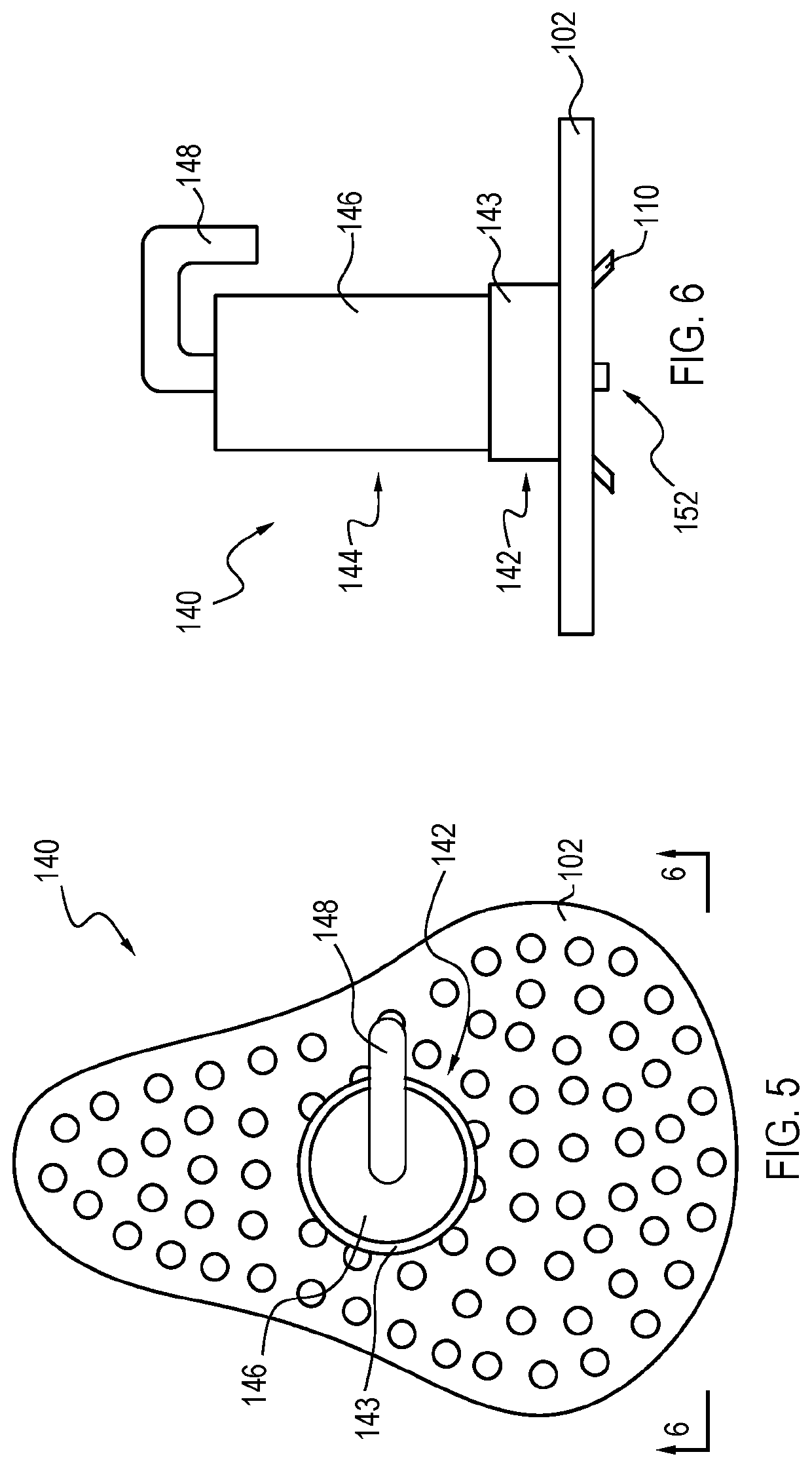
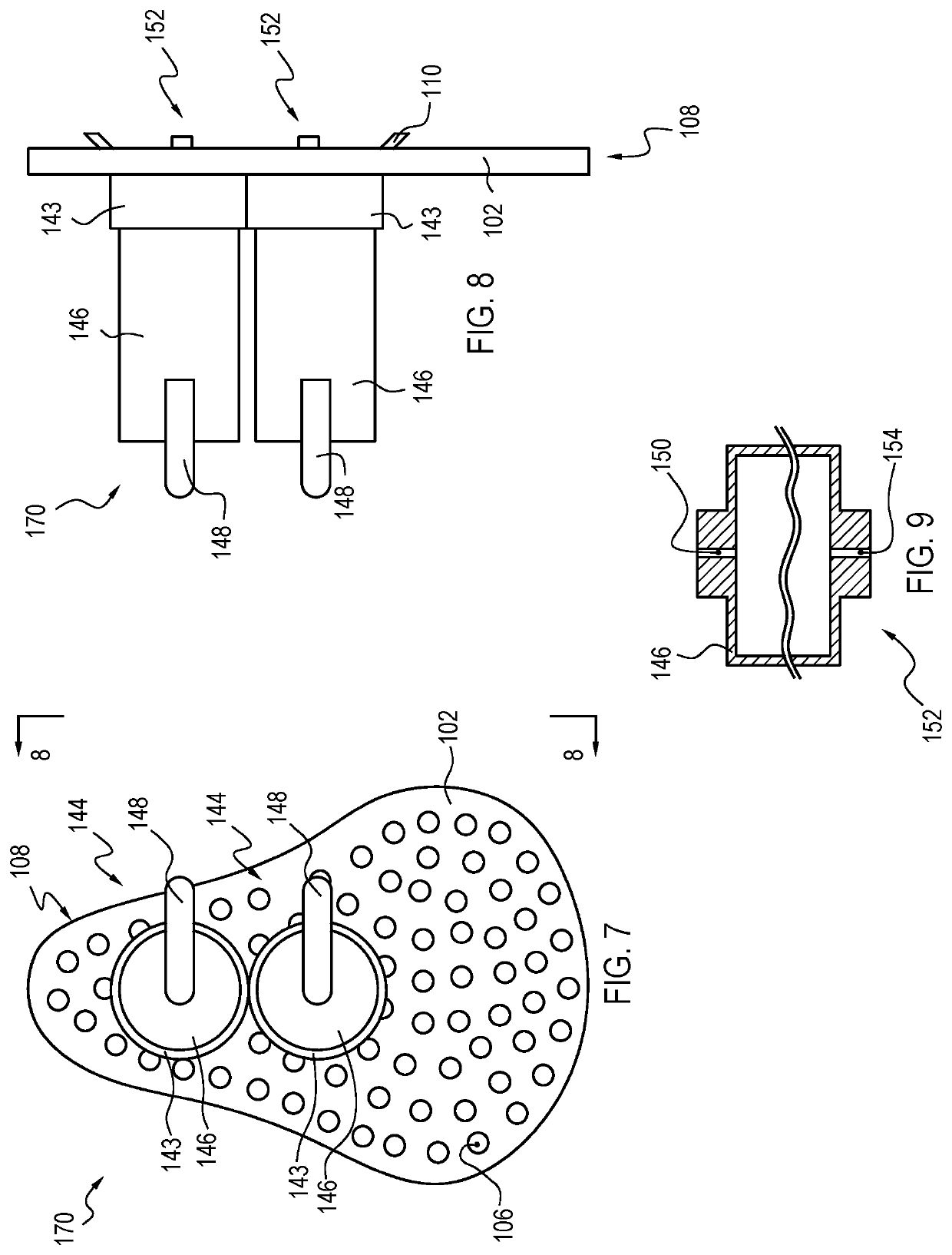
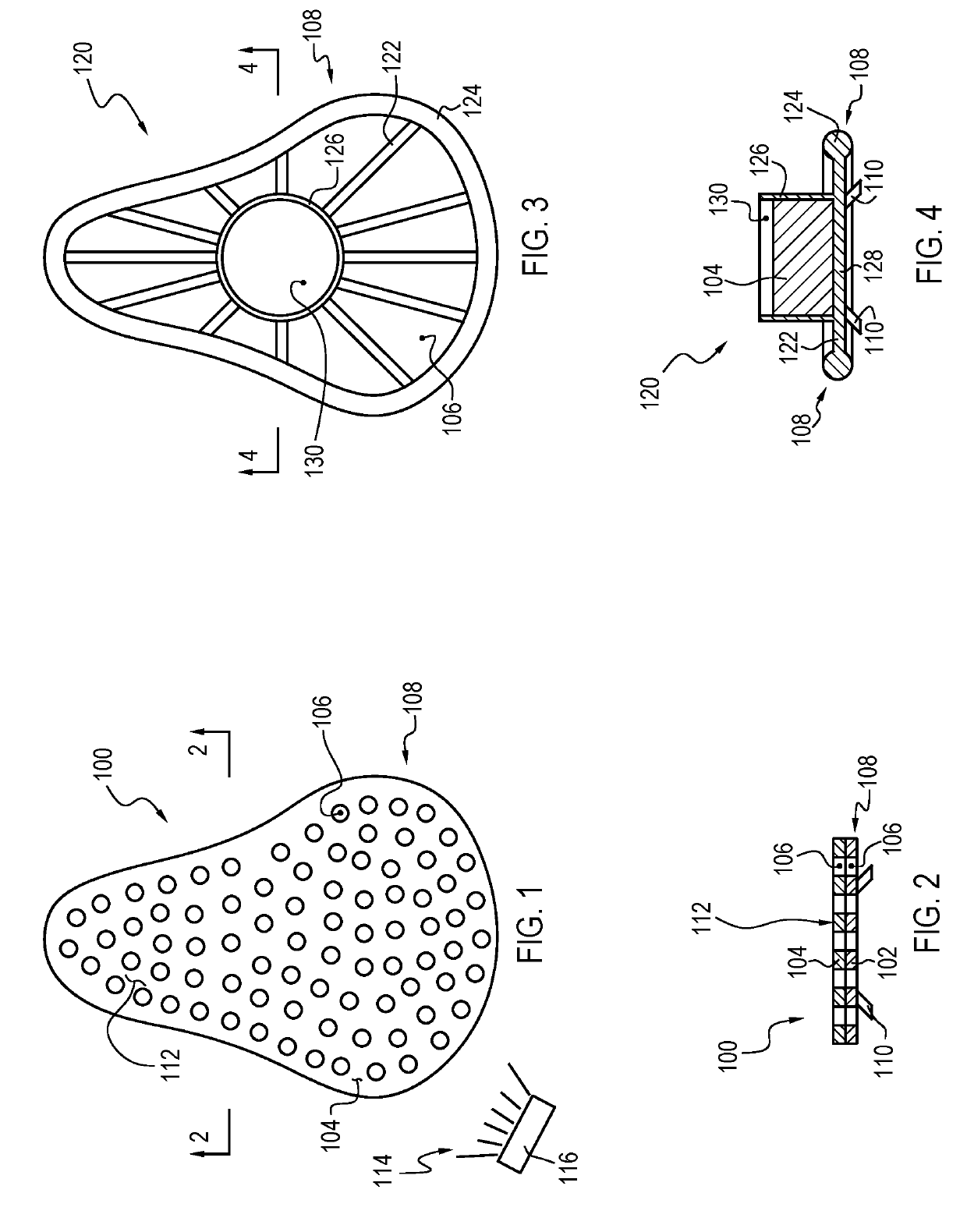
Drain cleaner
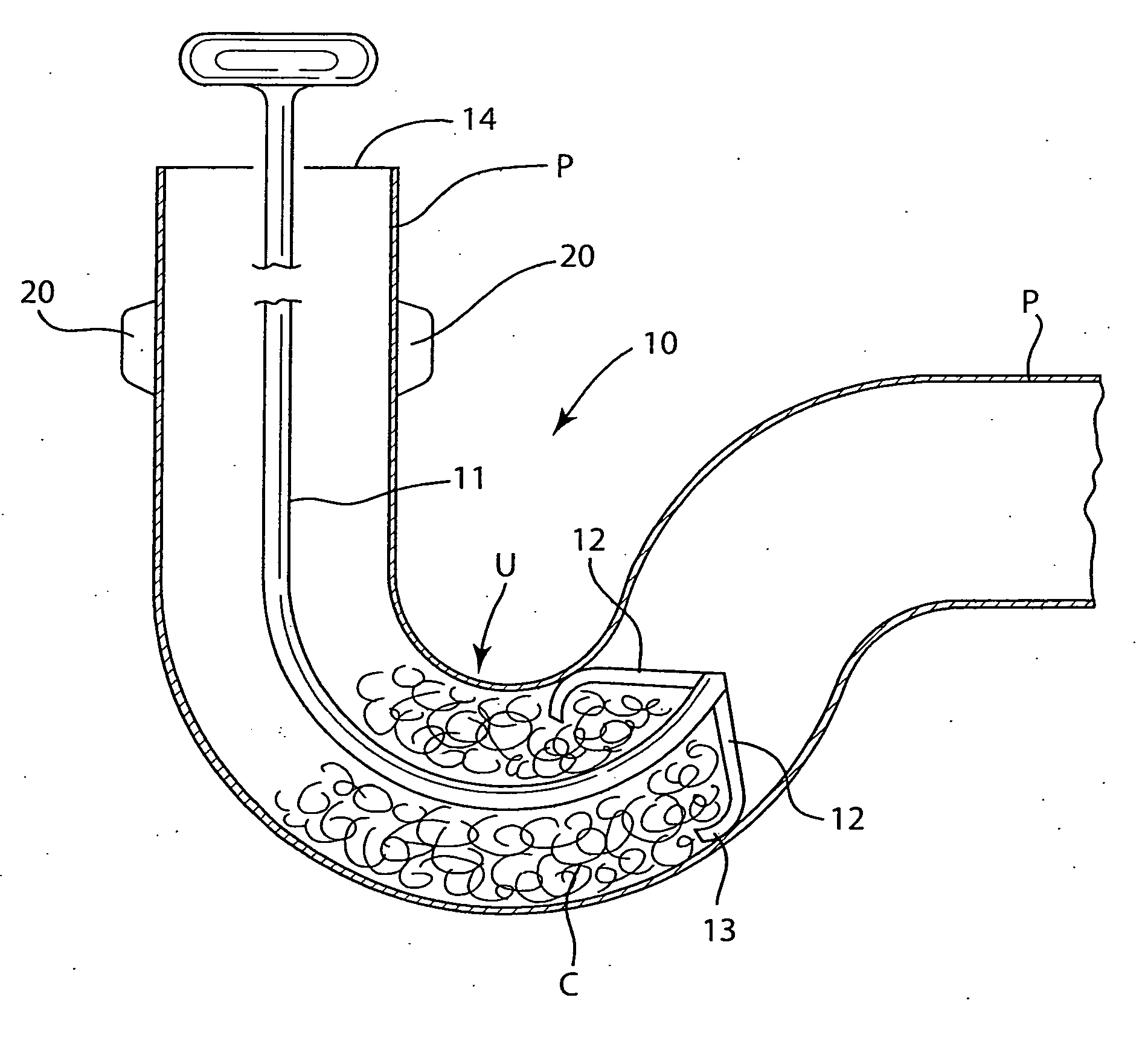
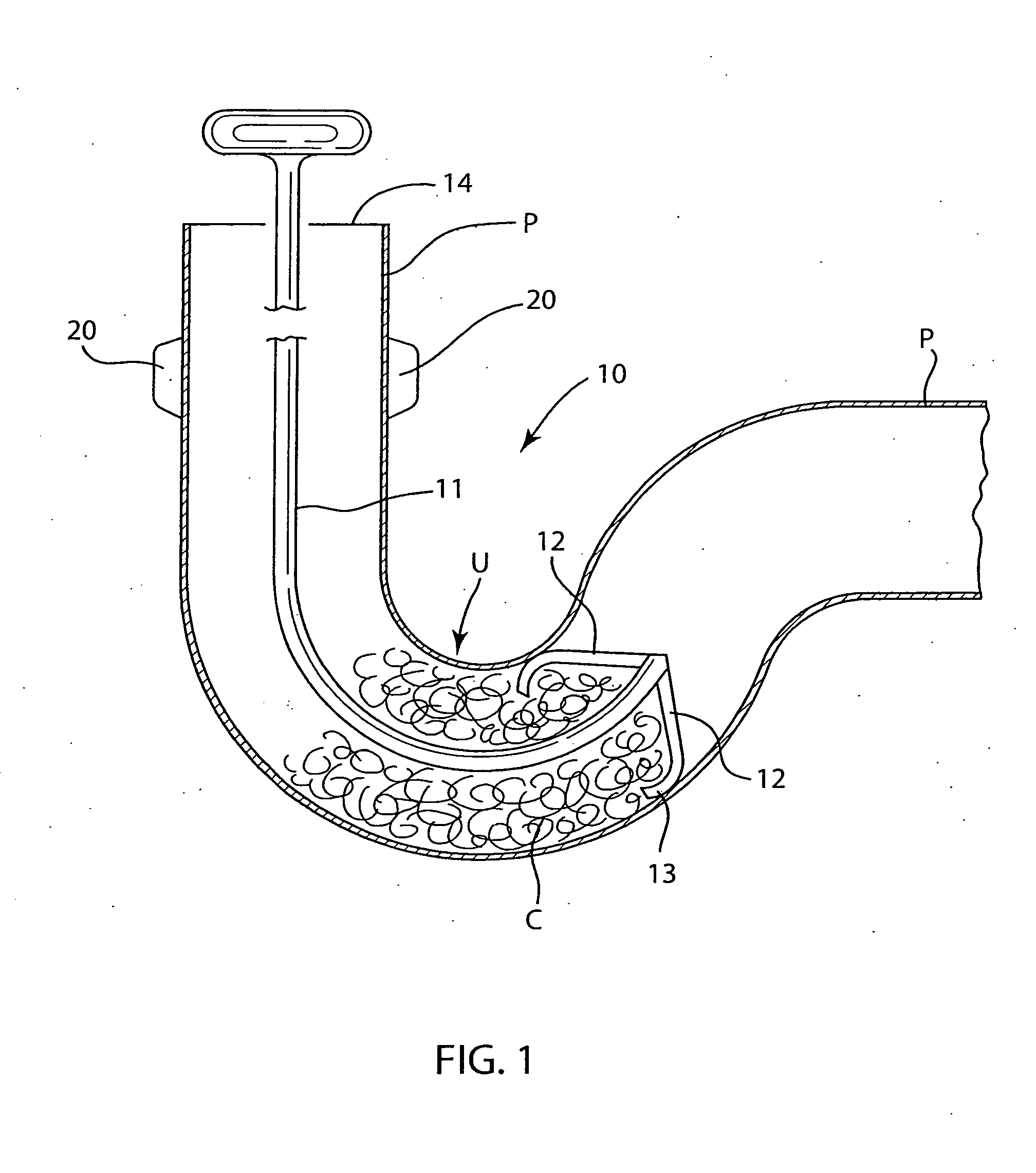
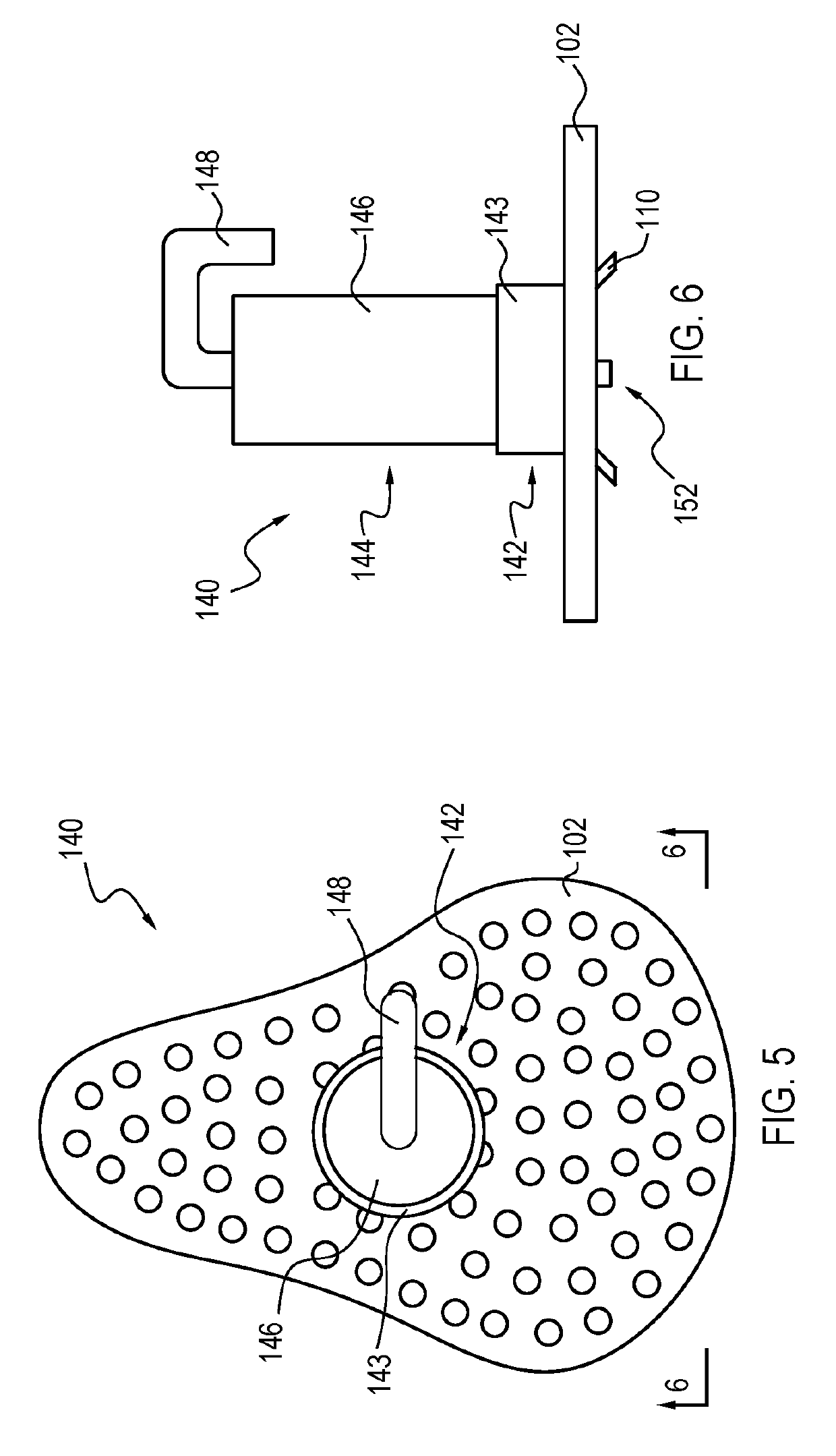
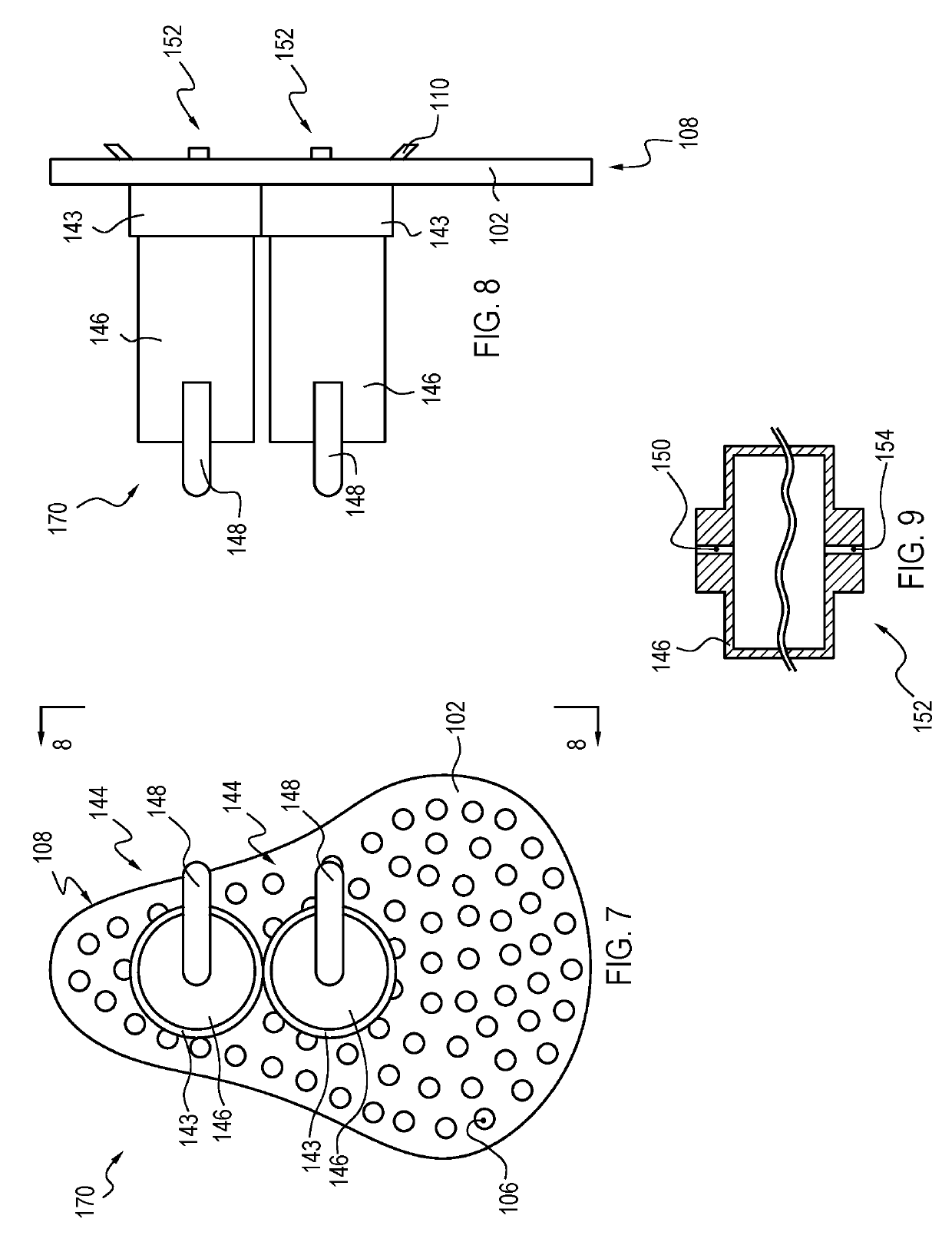
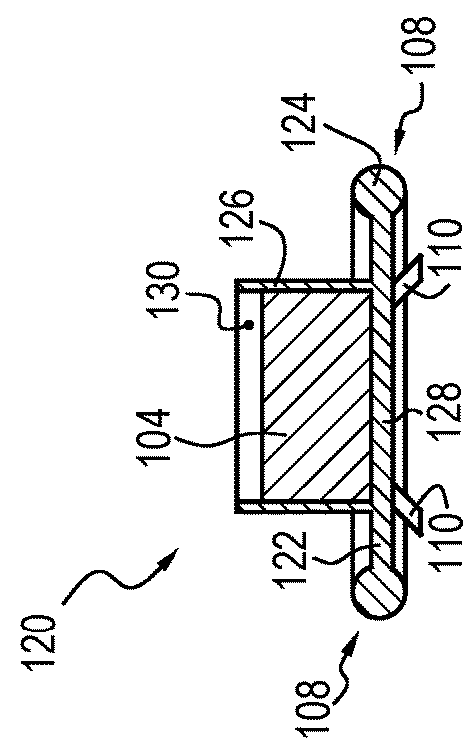
A drain cleaner is disclosed for use with a drain assembly having a drain pipe, a flange coupled to the drain pipe and defining a drain inlet, and a pop-up assembly having an actuating arm disposed in the drain pipe. The drain cleaner includes a stopper head having a seal sized to engage the drain inlet and an inlet passage extending from an inlet port formed in a top surface of the stopper head to an outlet port formed in a bottom surface of the stopper head. A stopper guide has a proximal end coupled to the stopper head bottom surface and a distal end, the stopper guide distal end including a tail piece adapted to operatively engage the actuating arm of the pop-up assembly. A drain cleaning composition is supported below the stopper head bottom surface.
Owner:BROOKS STEVENS DESIGN +1
Drain cleaner
A drain cleaner is disclosed for use with a drain assembly having a drain pipe, a flange coupled to the drain pipe and defining a drain inlet, and a pop-up assembly having an actuating arm disposed in the drain pipe. The drain cleaner includes a stopper head having a seal sized to engage the drain inlet and an inlet passage extending from an inlet port formed in a top surface of the stopper head to an outlet port formed in a bottom surface of the stopper head. A stopper guide has a proximal end coupled to the stopper head bottom surface and a distal end, the stopper guide distal end including a tail piece adapted to operatively engage the actuating arm of the pop-up assembly. A drain cleaning composition is supported below the stopper head bottom surface.
Owner:BROOKS STEVENS DESIGN +1
Drain pipe cleaning device and method
InactiveUS9194114B2Easy constructionEasy to operateHollow article cleaningDomestic plumbingEngineeringDrain cleaner
A drain cleaner for cleaning entangled obstructions such as a clog from a drain pipe such as a sink, tub or shower. A rod extending into the drain pipe is formed of a material which is either metal or plastic but stiff enough that it will not buckle but flexible enough to bend around curves. Arms connected to the distal end of the rod normally flex outwardly such that when the arms are inserted into the pipe they are resiliently flexed against the inside wall of the pipe, the arms being circumferentially spaced apart from each other to create spaces between them and each arm can each flex resiliently independent of the other arms. The device may push some of the clog through to be washed out of the pipe. Obstruction material which is not moved downstream will then be grasped by the arms as the arms move outwardly against the inside wall of the pipe. The rod is then pulled back rearwardly toward the drain opening and the arms catch the obstruction material which did not get flushed downstream, and pull the obstruction material rearwardly to and out of the drain opening. A method for cleaning a drain pipe using the device of the present invention.
Owner:PETRY MARVIN
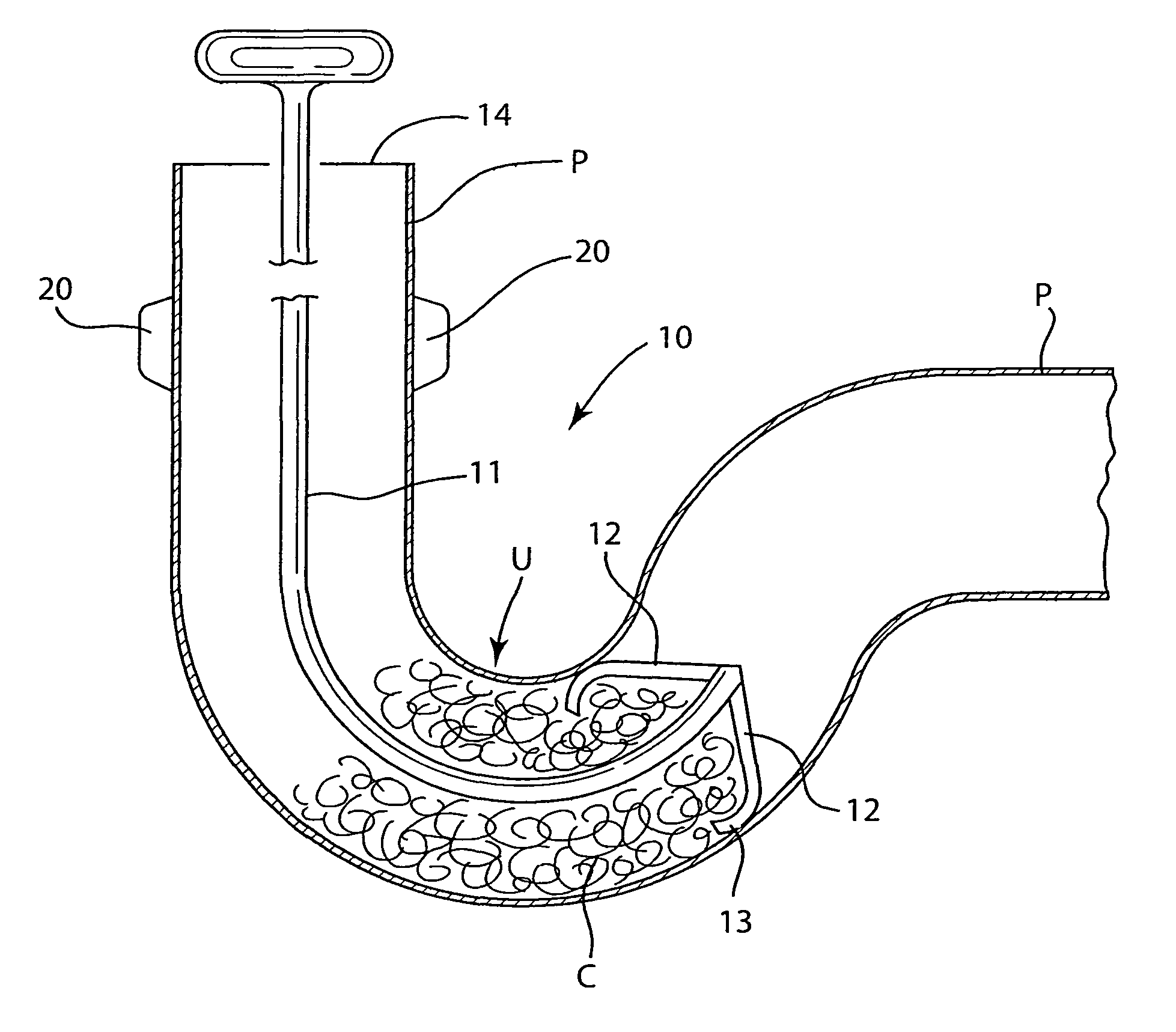
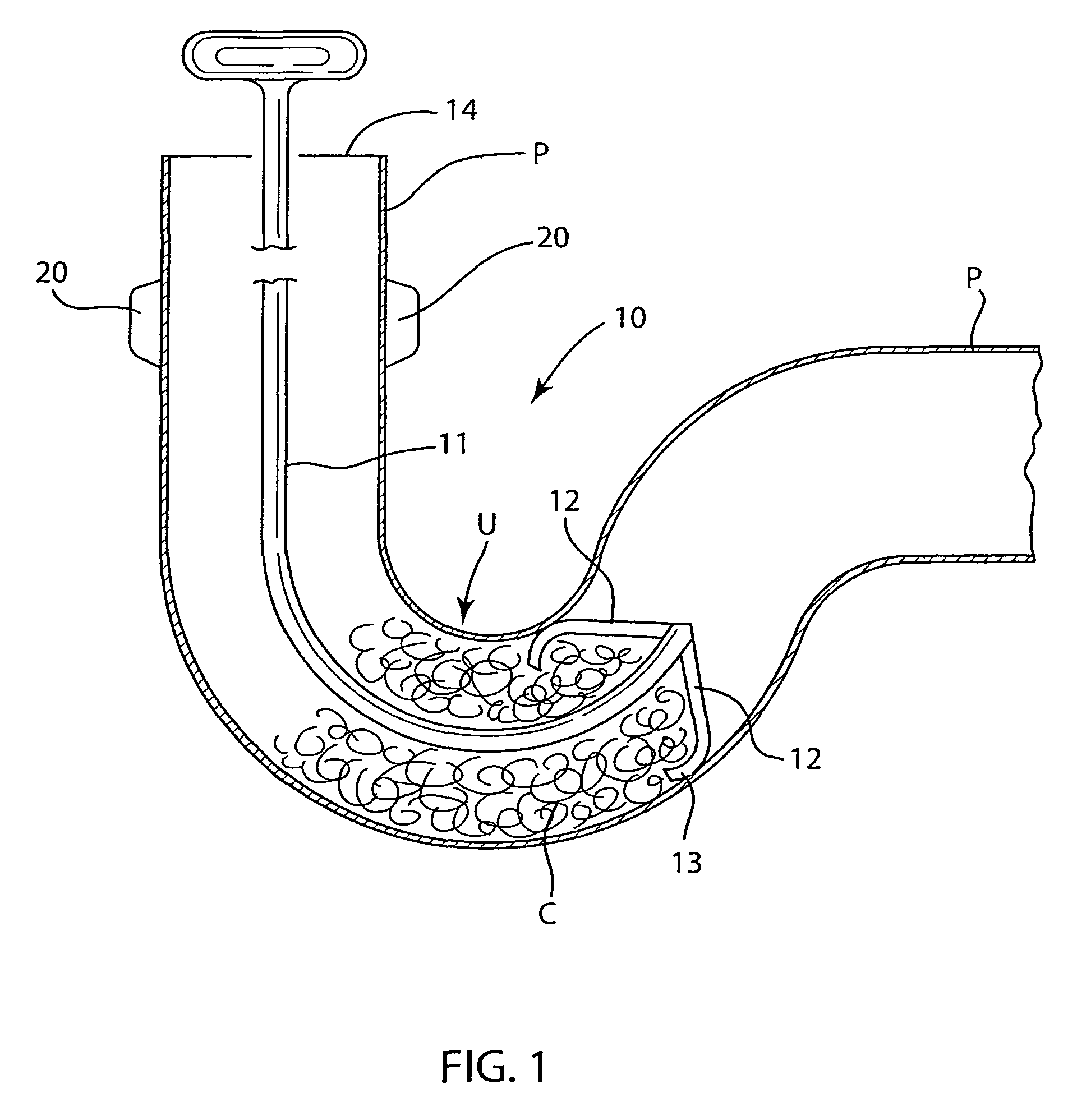
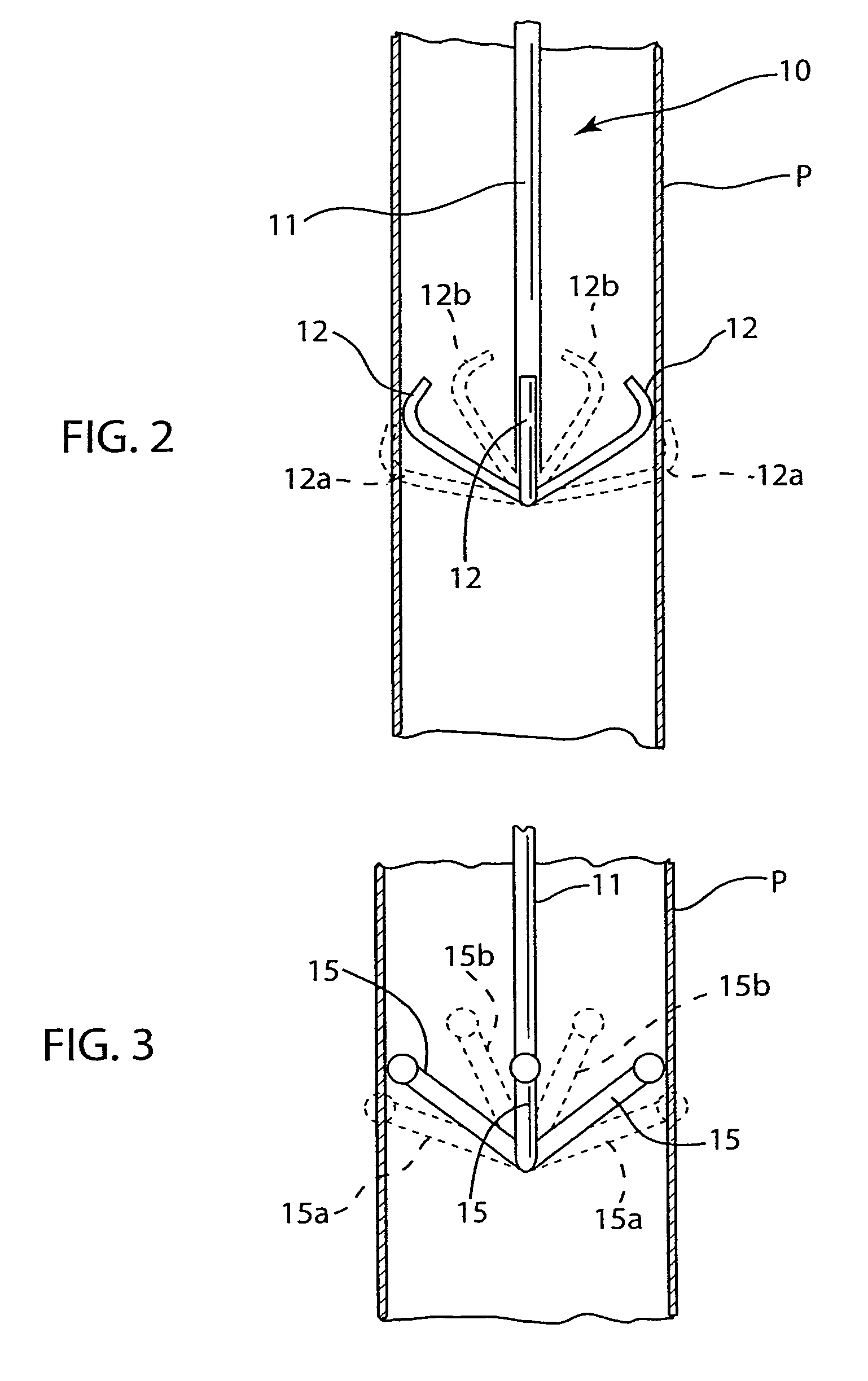
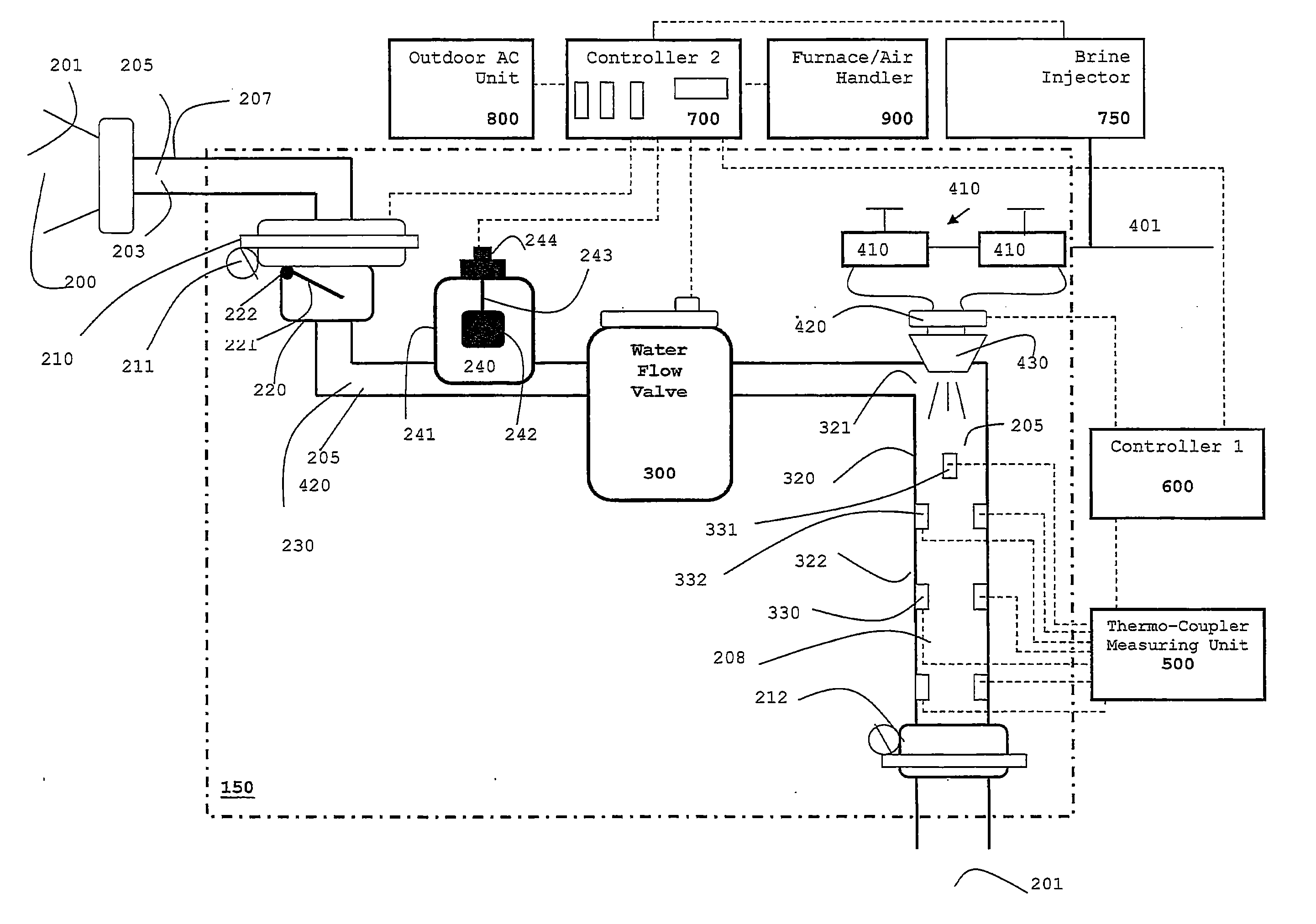
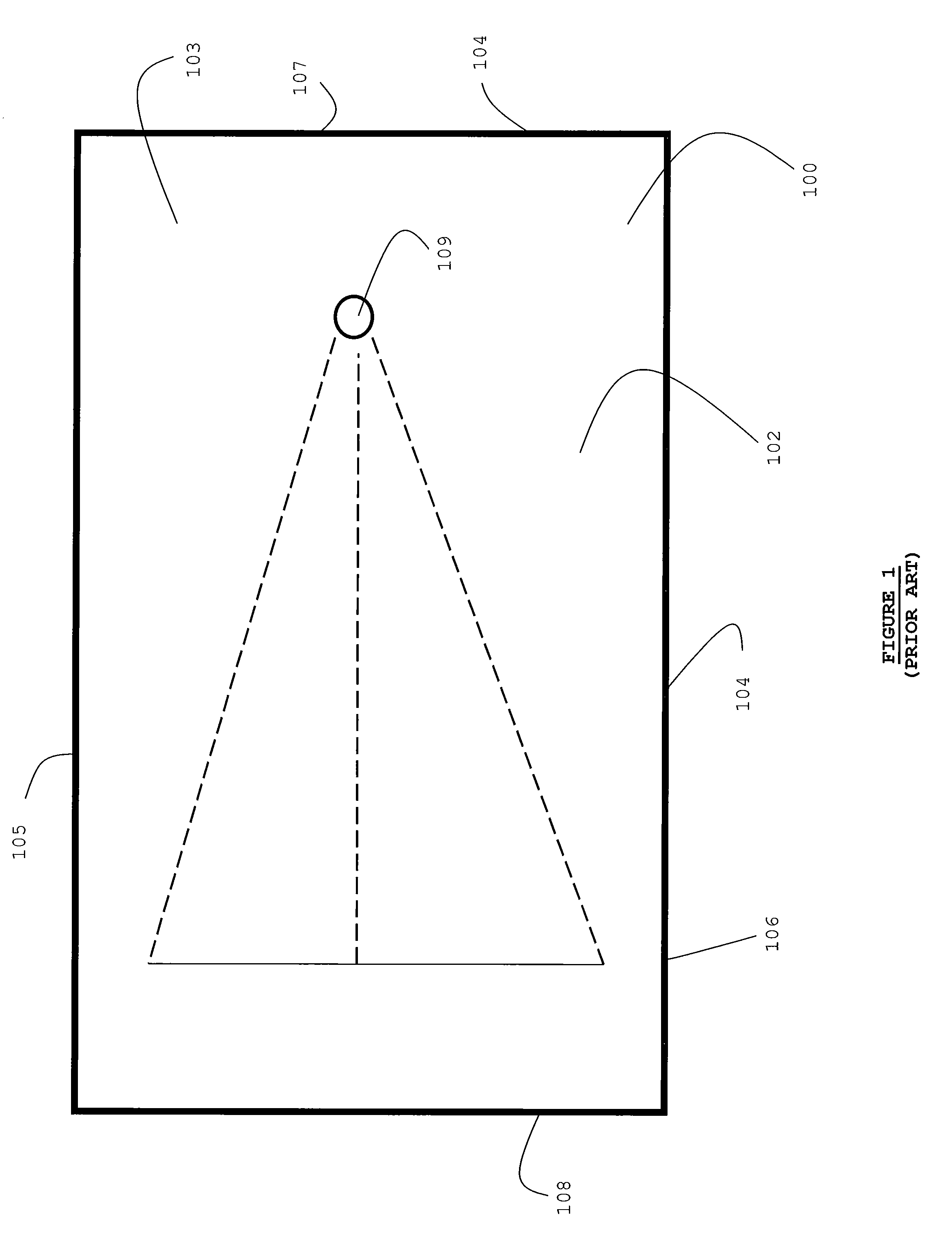
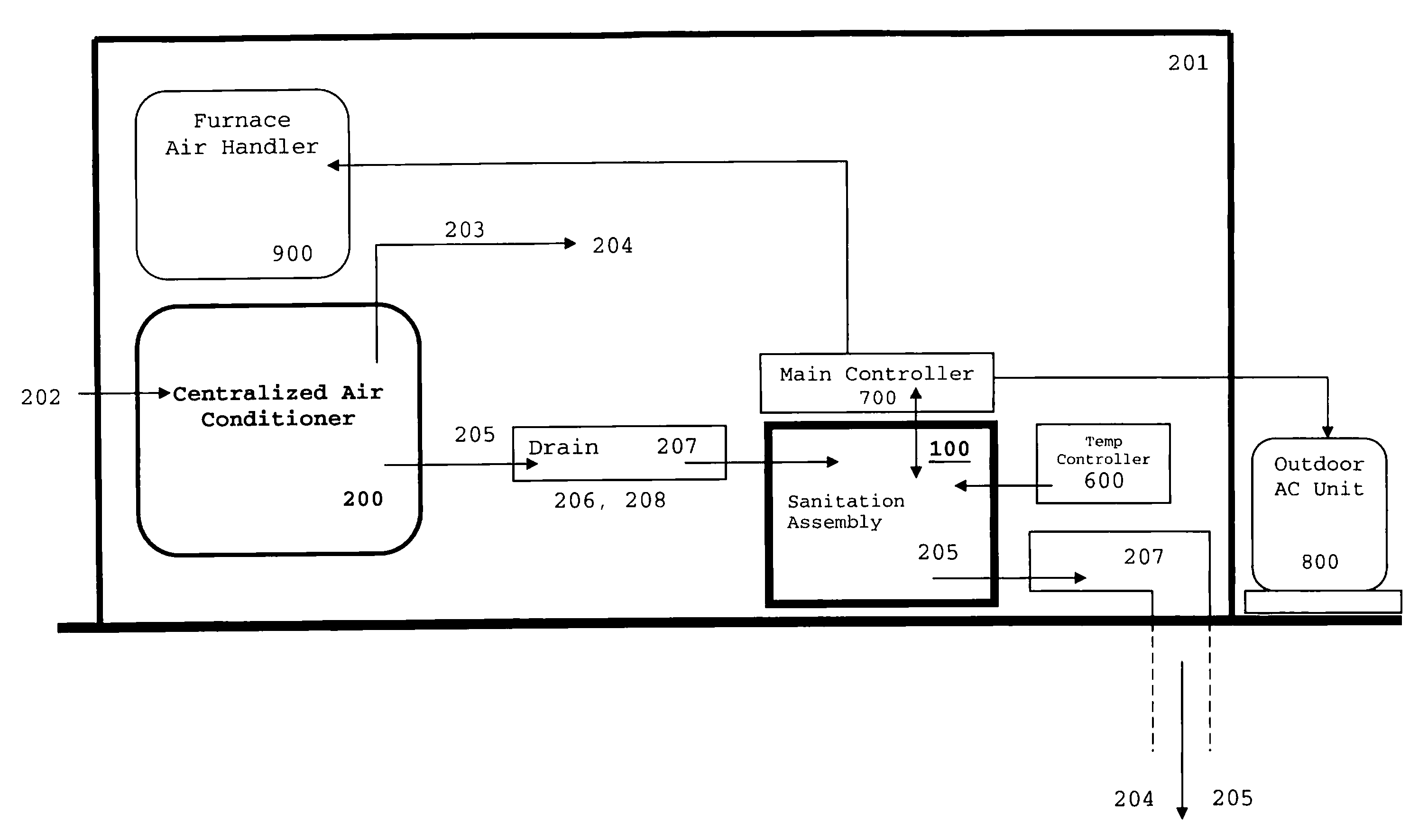
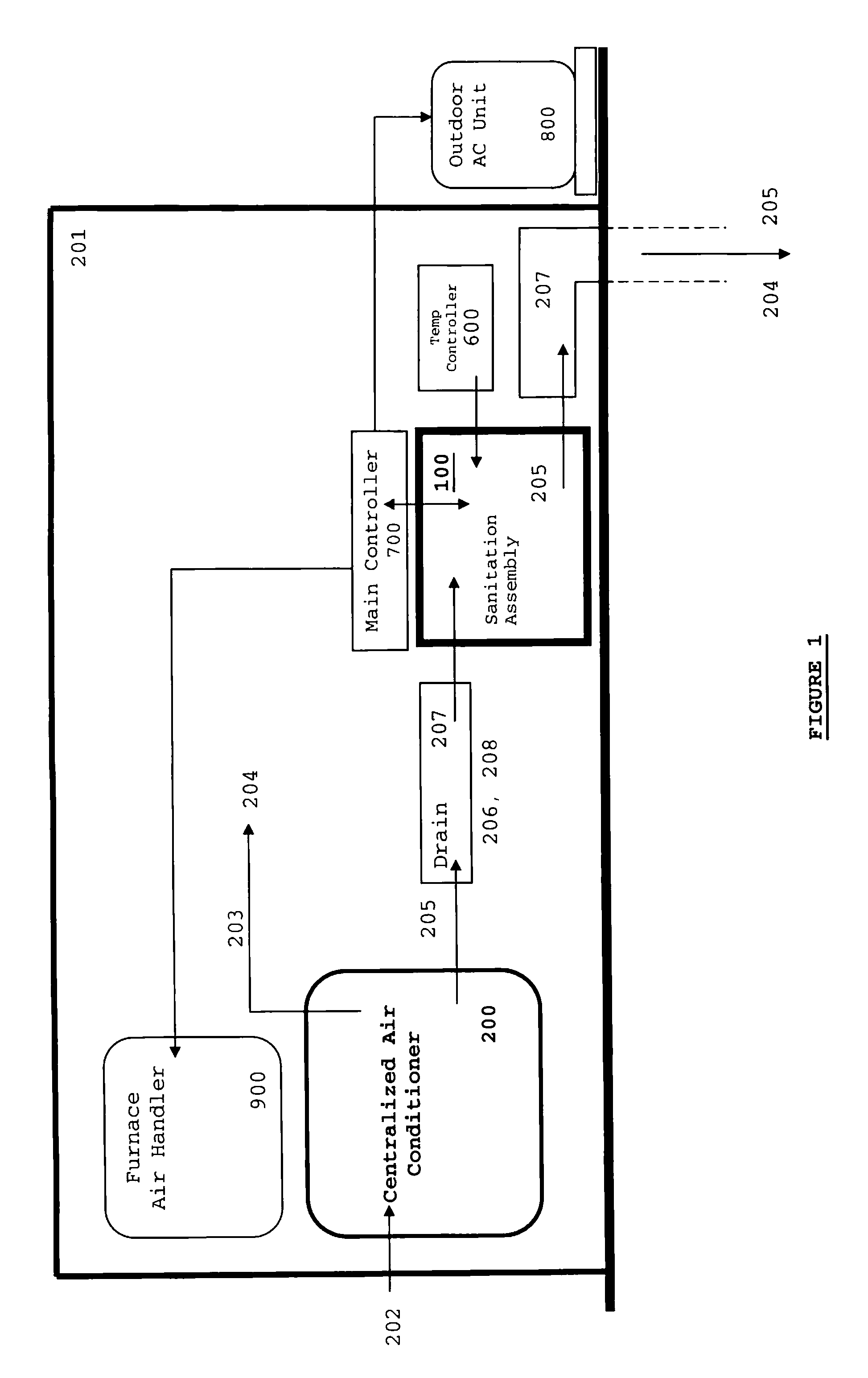
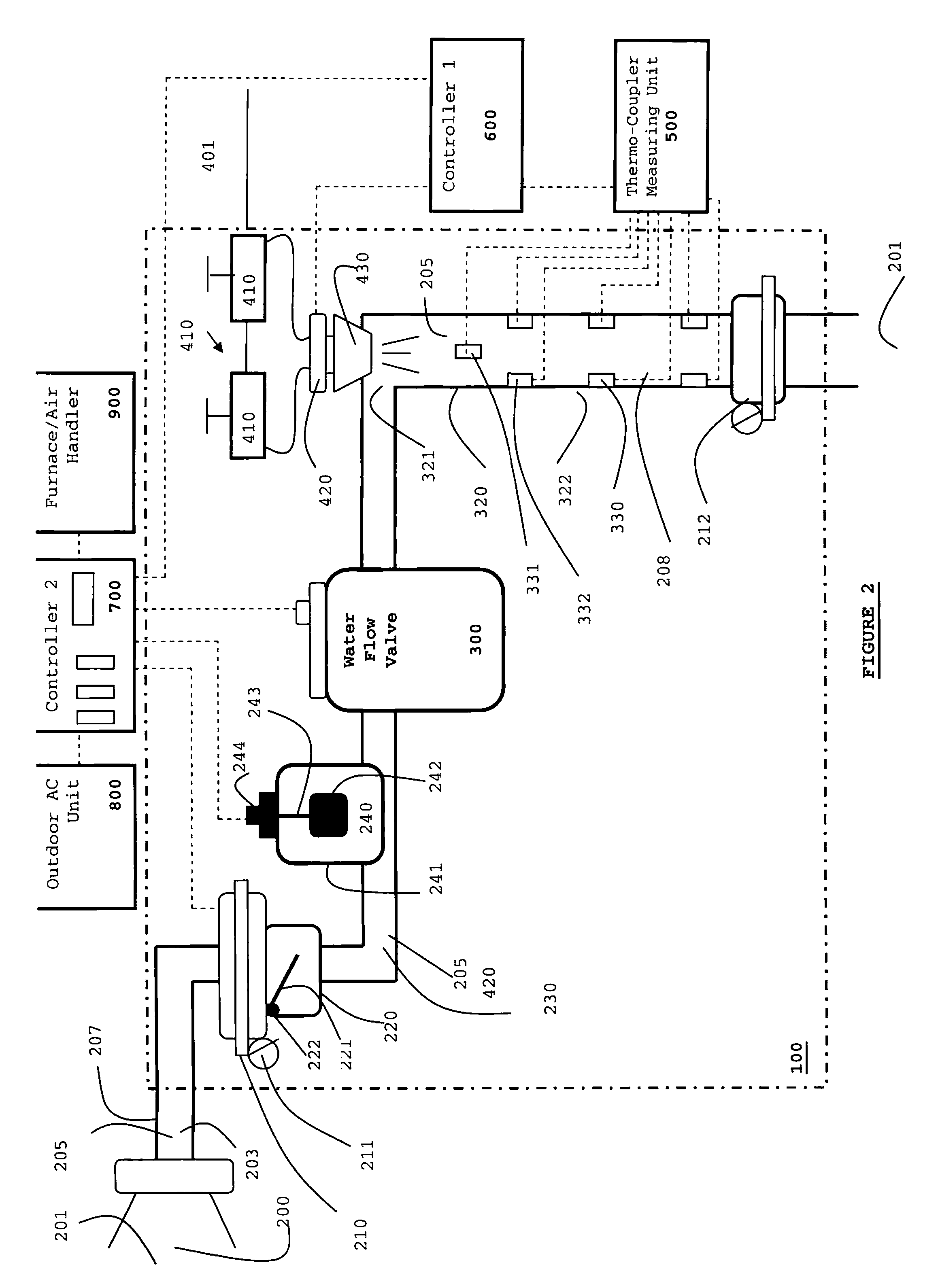
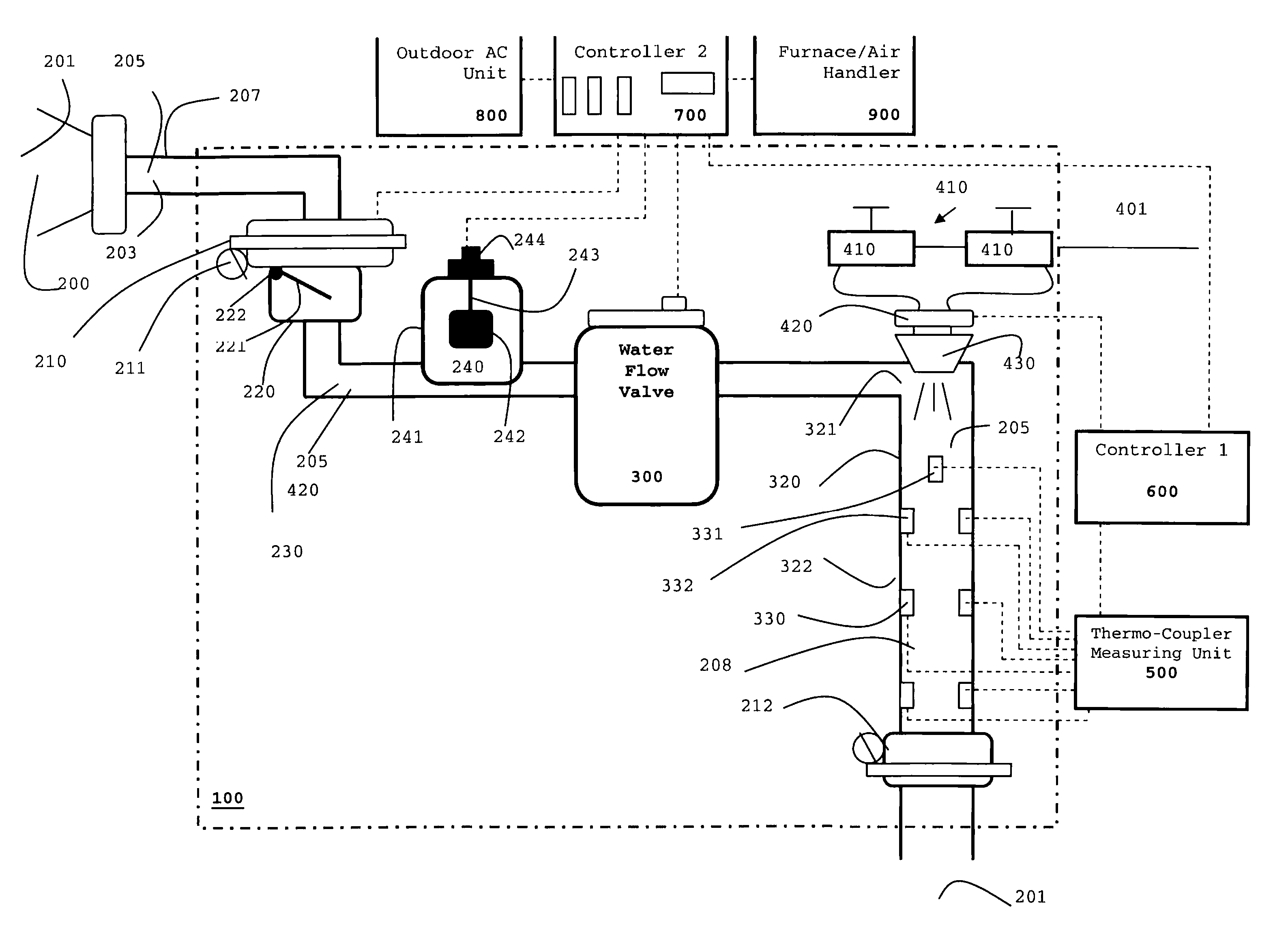
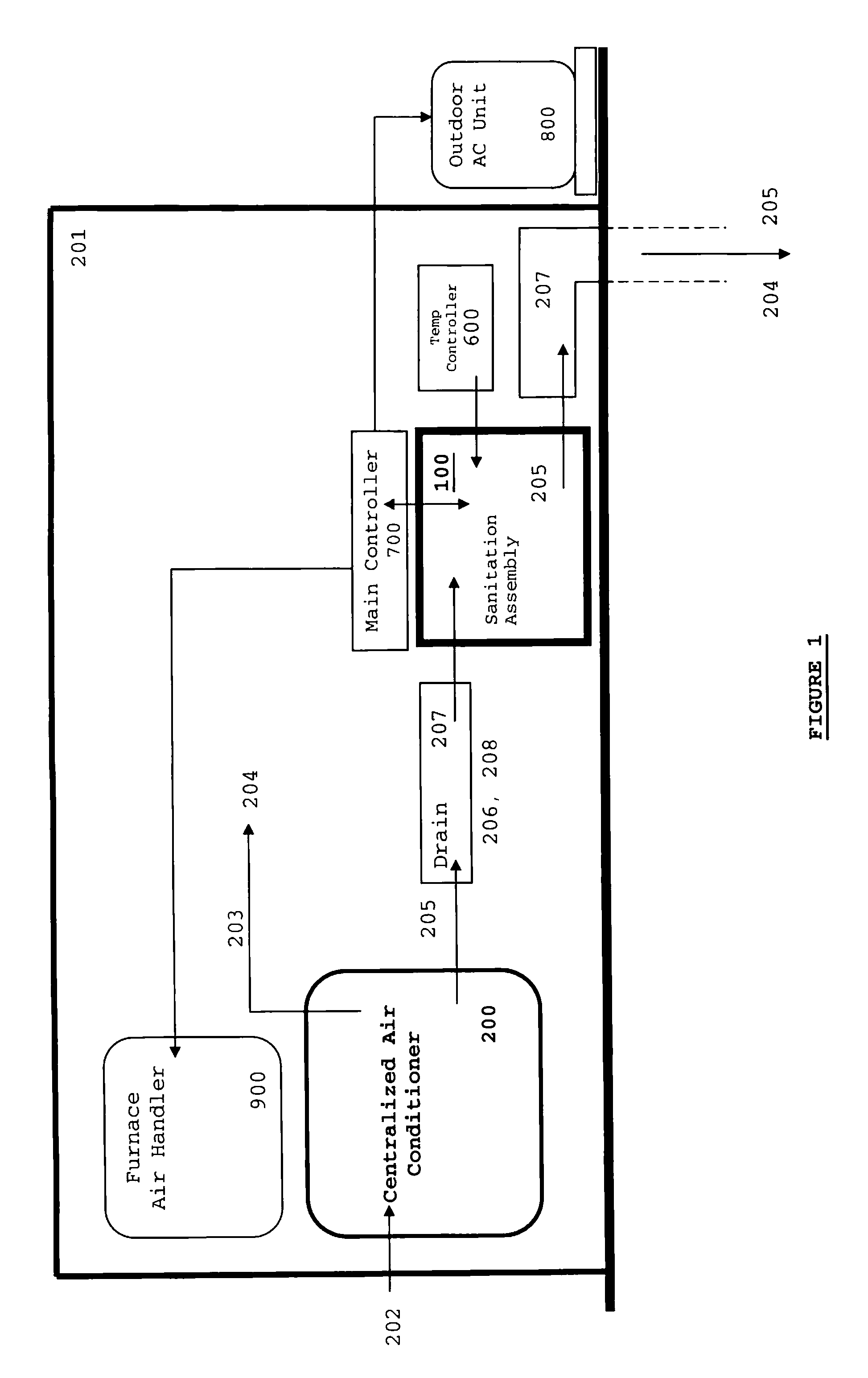
Combination Anti-Microbial Drain Pan Float and High Temperature Brine Injected Automated Drain Cleaner
InactiveUS20110308557A1Reduce and impede growthPrevent freezingLighting and heating apparatusHollow article cleaningSaline waterSludge
The invention is directed toward a brine injector for sanitizing a condensate drain to reduce sludge and pathogens. The bring injector, which attaches to a spray assembly within the condensate drain, supplies brine (23.3% sodium chloride and 76.7% hot water) into the a saddle valve of the spray assembly. The brine injector may include a brine reservoir having a polyethylene non-corrosive coating, a pump to draw brine out of the brine reservoir, and a filter casing. The filter casing is coated with a polyethylene interior lining. Filter casing further includes 15-micron nickel copper alloy weaved filter cloth. The brine reservoir may include an electric heater to heat the brine prior to injection. A main controller communicates with the treatment chamber and spray assembly. Such main controller is capable of engaging the spray assembly to disperse a sufficient quantity and pressure of hot water within the shaft to dislodge any sludge.
Owner:PLEXAIRE
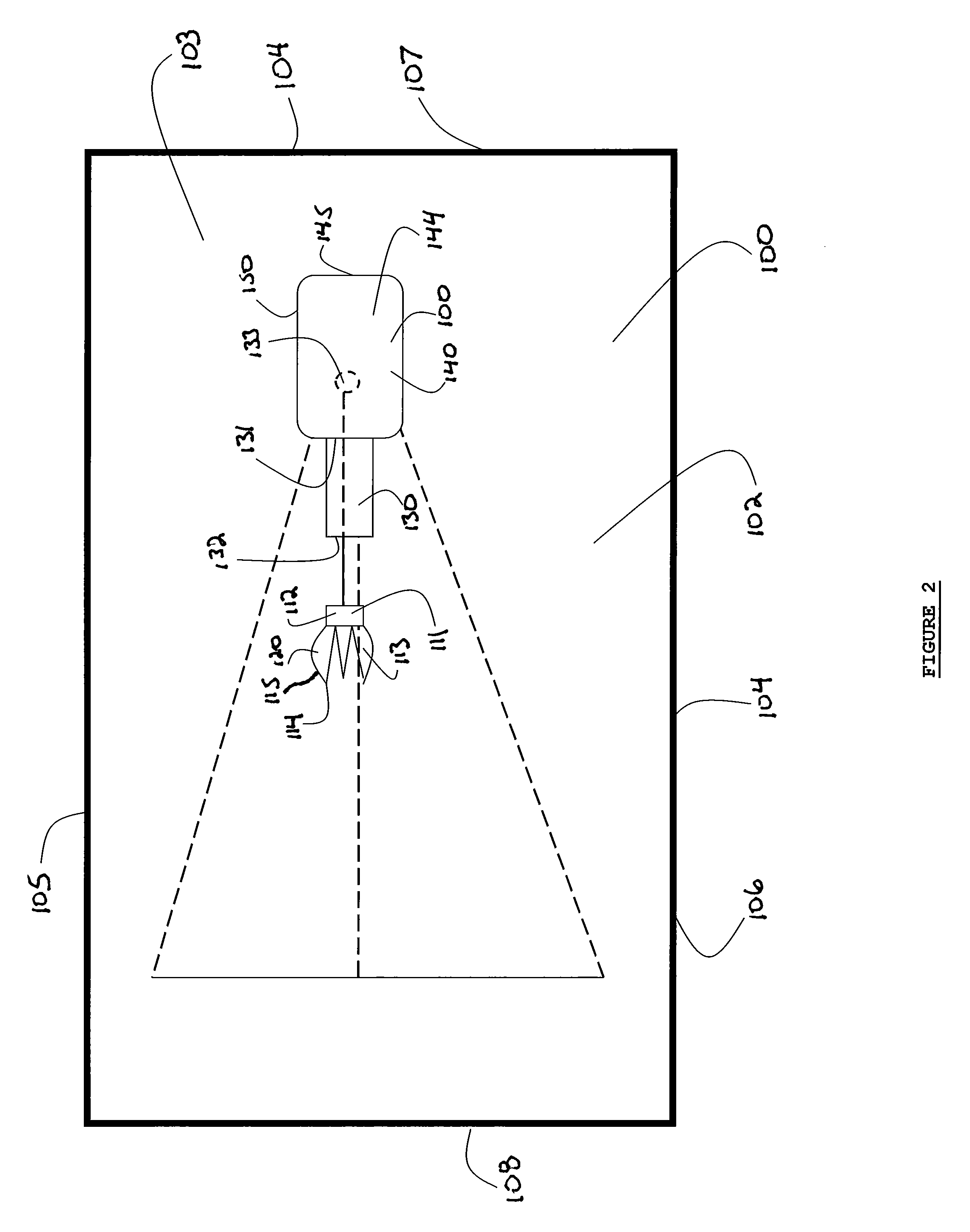
Self-sanitizing automated condensate drain cleaner and related method of use
ActiveUS20110308546A1Sludge reductionReducing other pathogenLighting and heating apparatusHollow article cleaningWater sourceSludge
The invention is directed toward a system and method for sanitizing a condensate drain to reduce sludge and related pathogens. The system is directed to a sanitizing assembly having a treatment chamber connected to the condensate drain, where the treatment chamber includes a top end and a shaft. A spray assembly is positioned proximate to the top end of the treatment chamber. This spray assembly has a nozzle spray connected to a hot water source. A spray controller within the spray assembly helps disperse a sufficient quantity and pressure of hot water within the shaft to dislodge sludge, when necessary.
Owner:PLEXAIRE
Snake tool adaptor
A snake tool adaptor capable of coupling commercially available heavy duty drain cleaning cables and attachments normally associated with heavy electric drain cleaners with a portable rotary driving tool such as a hand-held drill. Adaptors of the subject invention include a hand grip having a proximal end terminating in a shank for operable attachment to a the chuck of a power drill, and a distal end terminating in coupling means for removable mating engagement with various heavy duty drain cleaning cables and their attachments normally associated with heavy electric drain cleaners.
Owner:KHONSARY CYRUS
Multi-action drain cleaning composition and method
InactiveUS20090263884A1Reducing and preventing buildupImprove handling safetyBacteriaUnicellular algaeChemical compositionDecomposition
The present invention relates to aspects of drain cleaning compositions, methods, and systems involving multiple levels of attack to facilitate decomposition of clogs in pipe systems. Aspects of the invention relate to a multi-action drain cleaning composition including chemical and biological components capable of producing an exothermic reaction, an oxidation reaction, and an enzymatic reaction. Generally, the chemical components act immediately to clear a clog in a pipe system and the biological components act over a longer period of time to provide longer-term maintenance of the pipe system. Additional aspects of the invention relate to a composition for use as a component of a multi-action drain cleaner that includes bacteria selectively cultured to subsist in a peroxygen-rich environment, a high-heat environment, and / or a high-pH environment. A bio-film for reducing or preventing a buildup of organic material in a pipe system including a matrix and a selectively cultured bacteria is also provided.
Owner:PATHWAY HLDG
Binary foaming drain cleaner
InactiveUS20020115579A1Process stabilityImproving efficacy of cleanerHigh foaming compositionsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsTime of useSURFACTANT BLEND
A composition is provided comprising two liquids which are separately maintained prior to forming an admixture during delivery to a surface to be treated, whereupon the admixture generates a foam sufficient for cleaning efficacy and stability. A first liquid preferably includes a hypohalite, or a hypohalite generating agent and a second liquid preferably includes a peroxygen agent. The first liquid is thickened to a specified rheology, resulting in the generation of a highly effective foam. As the two liquids are initially separated, the hypohalite generating agent can be maintained in an environment free of peroxygen agent and otherwise conducive to their cleaning activity and stability up to the time of use. When the two liquids are allowed to mix, for example, by simultaneously pouring into a drain, the hypohalite and peroxygen react to liberate oxygen gas. As foam generation occurs, the escaping gas contacts surfactant in the solution, and creates foam which expands to completely fill the drain pipe. The expanded foam contains an excess of the hypohalite, which acts to clean the drain.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
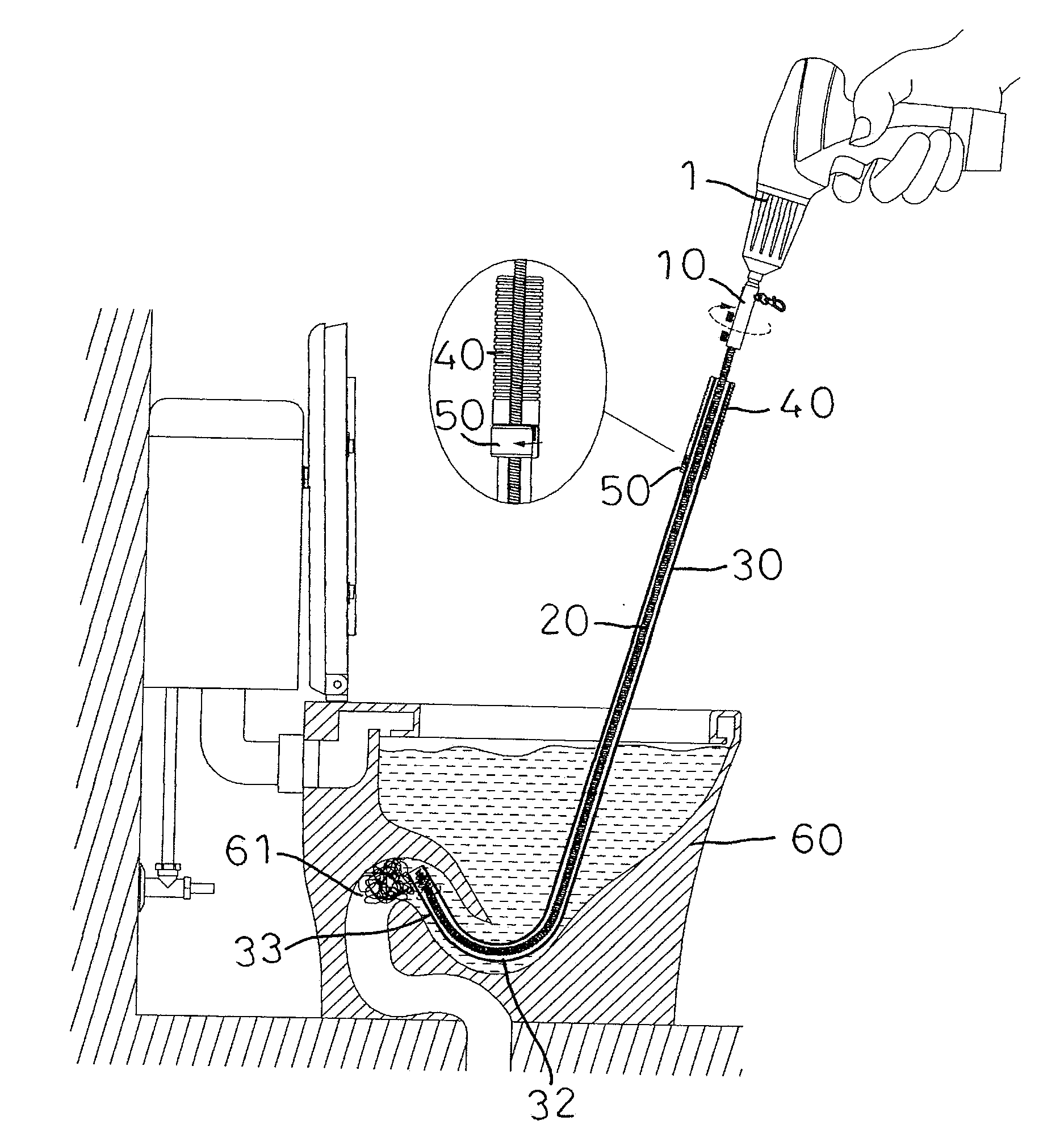
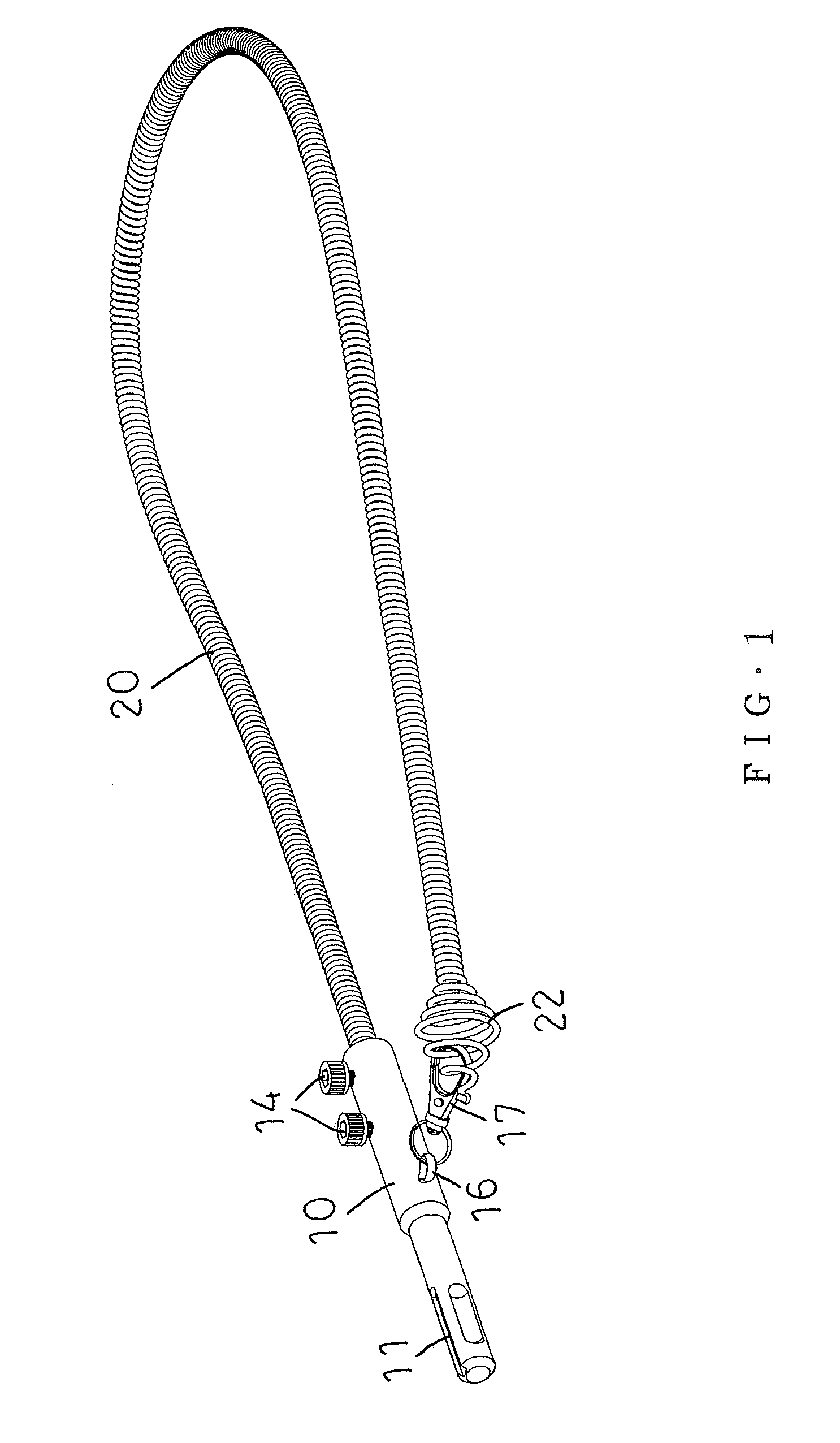
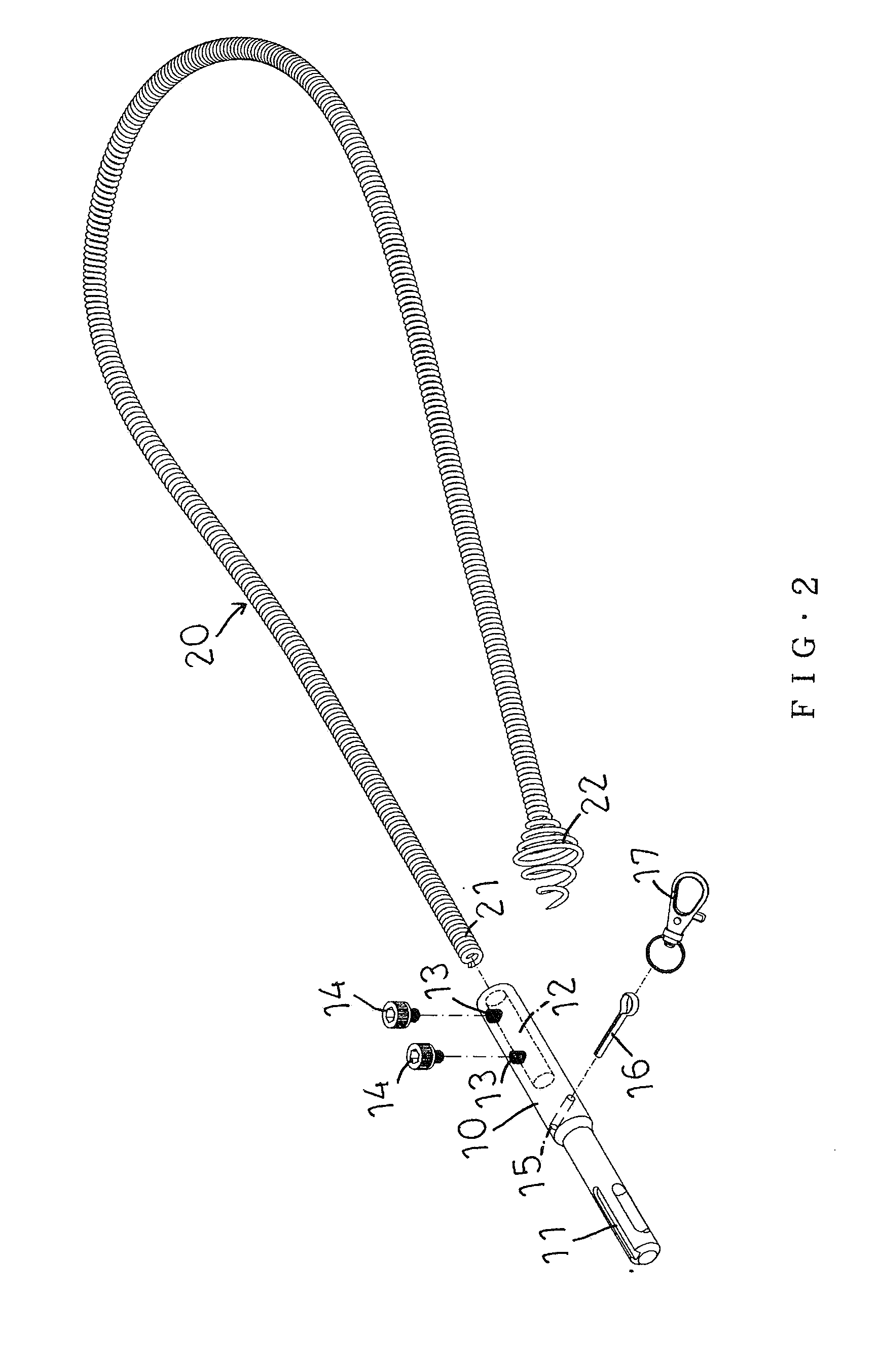
Cable Feeding Device for Drain Cleaner
InactiveUS20170304879A1Improve the problemEasy to useSewer cleaningHollow article cleaningPlastic injection moldingEngineering
A cable feeding device for a drain cleaner includes an upper body mounted on a support tube of the drain cleaner, a control subassembly, and a lower body. The upper body in which an upper feeding roller is held and the lower body in which two lower feeding rollers are held join each other. A cable inside a cable drum of the drain cleaner can extend through a region encircled with the upper and lower feeding rollers and can be resisted by the upper and lower feeding rollers for controllable forward or backward movements of the cable into a drain to be cleaned. The lower body has at least one separate mold-stripping hole for easy manufacturing of the upper and lower bodies in a plastic injection molding process. The upper and lower feeding rollers are not exposed to the outside for longer service life to clip the cable.
Owner:SDY INT
Self-sanitizing automated condensate drain cleaner and related method of use
The invention is directed toward a system and method for sanitizing a condensate drain to reduce sludge and related pathogens. The system is directed to a sanitizing assembly having a treatment chamber connected to the condensate drain, where the treatment chamber includes a top end and a shaft. A spray assembly is positioned proximate to the top end of the treatment chamber. This spray assembly has a nozzle spray connected to a hot water source. A spray controller within the spray assembly helps disperse a sufficient quantity and pressure of hot water within the shaft to dislodge sludge, when necessary.
Owner:PLEXAIRE
Cable feeding device for drain cleaner
A cable feeding device for a drain cleaner includes an upper body mounted on a support tube of the drain cleaner, a control subassembly, and a lower body. The upper body in which an upper feeding roller is held and the lower body in which two lower feeding rollers are held join each other, so that a cable inside a cable drum of the drain cleaner can extend through a region encircled with the upper and lower feeding rollers and can be resisted by the upper and lower feeding rollers for controllable forward or backward movements of the cable into a drain to be cleaned. The lower body has at least one separate mold-stripping hole for easy manufacturing of the upper and lower bodies in a plastic injection molding process. The upper and lower feeding rollers are not exposed to the outside for longer service life to hold the cable.
Owner:SDY INT
Impact type drain cleaner
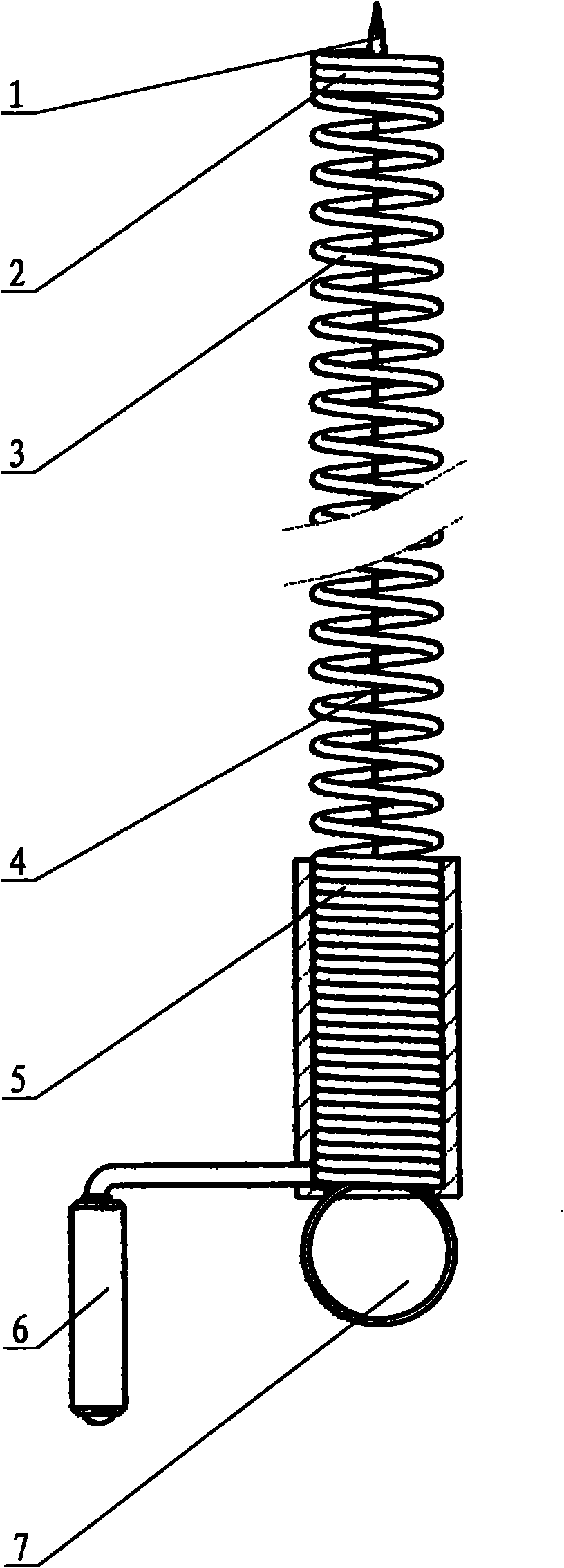
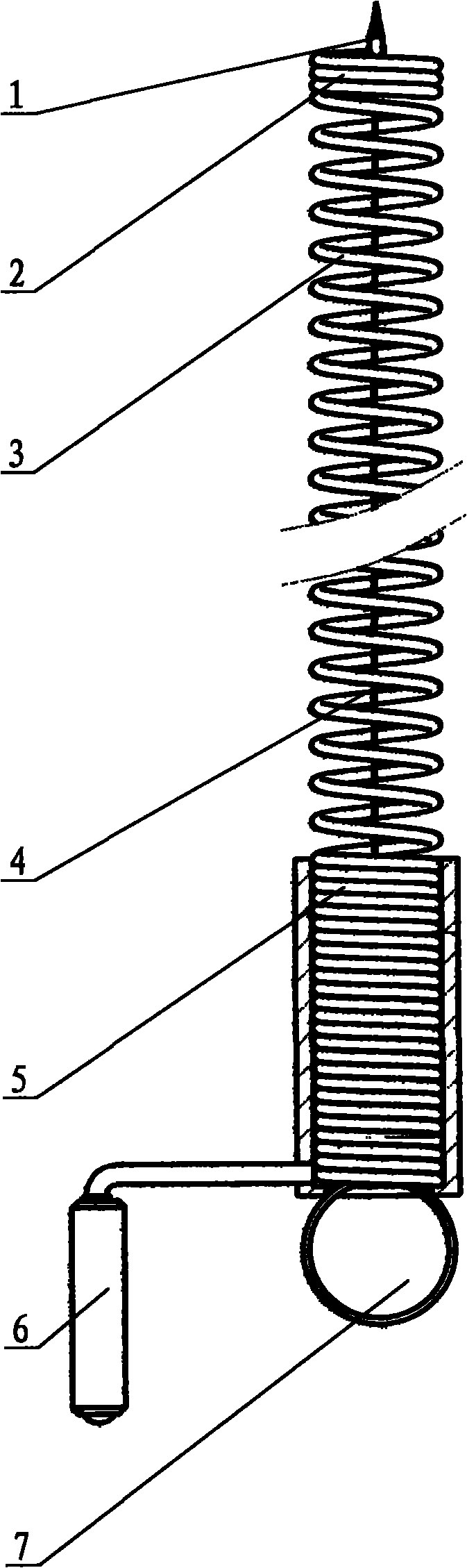
The invention provides a domestic impact type drain cleaner which can take tampers out of domestic sewer pipelines and make the sewer pipelines smooth; and in addition, the impact type drain cleaner is small and exquisite as well as cheap, is easy and convenient to operate and is easy to learn. The impact type drain cleaner comprises a spring soft shaft, a manual mechanism and impactor; a drill is arranged at the front end of a front straining ring in the spring soft shaft; the rear end of the front straining ring is connected with the front end of a desludging ring; the rear end of the desludging ring is connected with a rear straining ring; the manual mechanism is fixed to the tail end of the rear straining ring; an inhaul cable of the impactor is embedded in the spring soft shaft, the front end of the inhaul cable is fixed on the front straining ring and the rear end of the inhaul cable is connected with a handle; meanwhile, the front part of the drill is provided with threads; and in addition, the inhaul cable is made of steel wire rope with a sleeve preferentially.
Owner:张光裕
Drain pipe cleaning deivce and method
InactiveUS20140190516A1Easy constructionEasy to operateHollow article cleaningDomestic plumbingEngineeringDrain cleaner
A drain cleaner for cleaning entangled obstructions such as a clog from a drain pipe such as a sink, tub or shower. A rod extending into the drain pipe is formed of a material which is either metal or plastic but stiff enough that it will not buckle but flexible enough to bend around curves. Arms connected to the distal end of the rod normally flex outwardly such that when the arms are inserted into the pipe they are resiliently flexed against the inside wall of the pipe, the arms being circumferentially spaced apart from each other to create spaces between them and each arm can each flex resiliently independent of the other arms. The device may push some of the clog through to be washed out of the pipe. Obstruction material which is not moved downstream will then be grasped by the arms as the arms move outwardly against the inside wall of the pipe. The rod is then pulled back rearwardly toward the drain opening and the arms catch the obstruction material which did not get flushed downstream, and pull the obstruction material rearwardly to and out of the drain opening. A method for cleaning a drain pipe using the device of the present invention.
Owner:PETRY MARVIN
High surface area reservoir for volatile fluid dispenser
ActiveUS10307503B2Reduce the probability of dischargeImprove discharge rateGaseous substancesDeodrantsEvaporationEngineering
Owner:MICROLIN
Bacillus amylollquefaciens strain
The present disclosure relates to a strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens bacteria that hyperproduces amylase enzyme and protease enzyme. The strain is also suitable for producing lipase for the degradation of oleaginous materials such as fats, greases and cooking oils. The strain also has excellent fungicidal and / or fungistatic qualities. The strain of the present disclosure and the enzymes produced thereby have a number of applications, including agricultural uses, laundry and dish detergents, drain cleaners and spot removers, and among other things, baking applications.
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOLOGICALS
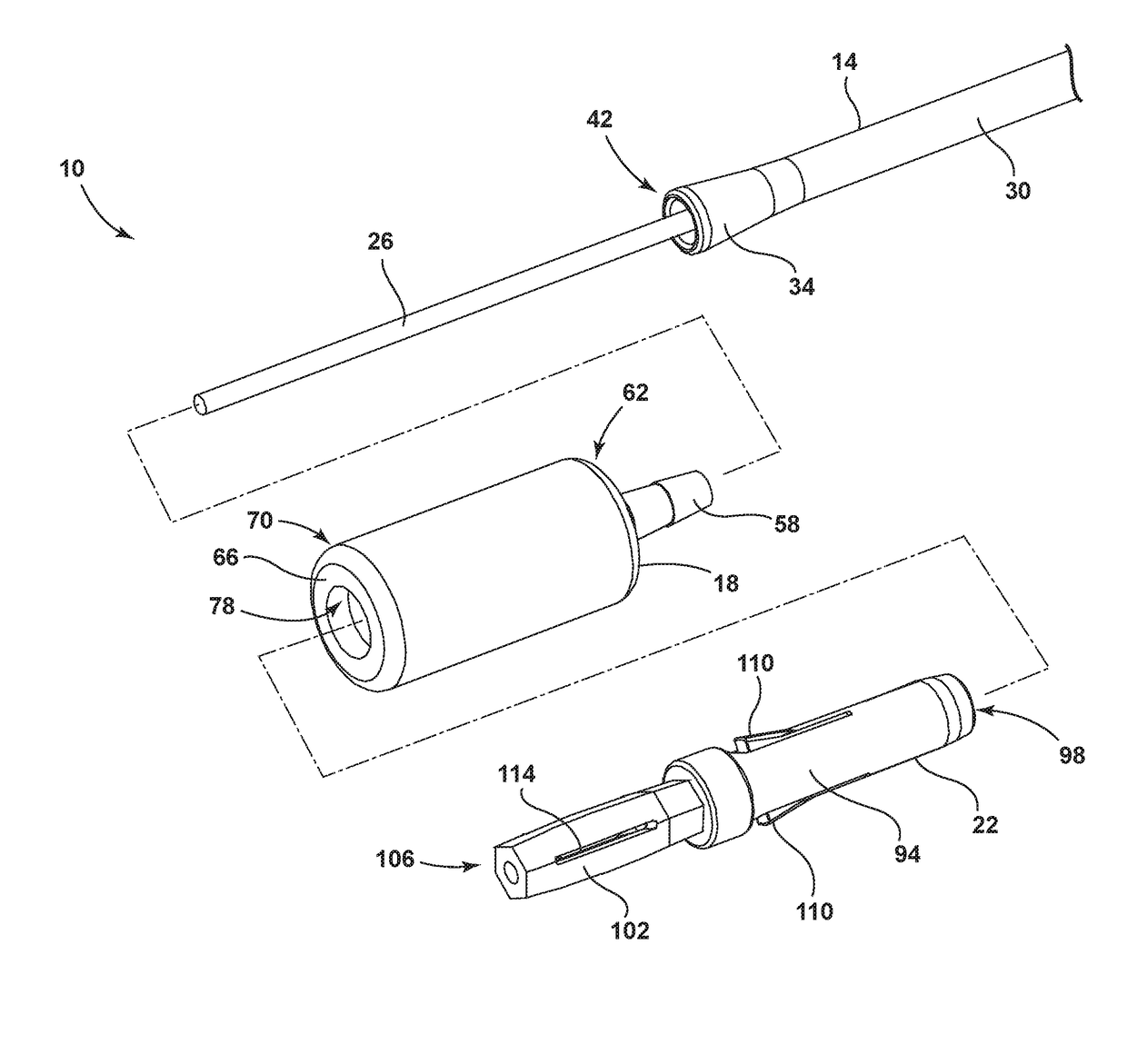
Drain cleaning device
A drain cleaner including a snake configured to be inserted into a drain, a conduit through which the snake extends, where the conduit includes an attachment member, and a linkage including a first engagement element on a first end and a second engagement element on a second end opposite the first end. The first engagement element is coupled to the attachment member of the conduit. The drain cleaner further includes an adapter having a first end coupled to the second engagement element of the linkage and a second end configured to be received by an operation portion of a power tool.
Owner:TTI MACAO COMML OFFSHORE LTD
Hair cleaner
Provided is a hair cleansing composition containing (A) an amphipathic amide lipid, (B) an anionic surfactant and (C) an organic or inorganic acid, or a salt thereof, and having a pH of from 1 to 4.5 when diluted with water to 20 times the weight. The hair cleansing composition of the present invention has advantages including protecting hair from physical or chemical stimulation and preventing split ends or breakage of hair without impairing the cleansing ability and feeling upon use, imparting hair with a pleasant feeling to the touch and moisture retention properties such as natural smoothness, moist feeling, and suppleness which healthy hair inherently possesses, and has excellent stability.
Owner:KAO CORP
Drain Cleaner
InactiveUS20160298325A1The process is simple and convenientEasy to reinforceSewer cleaningDomestic plumbingArchitectural engineeringDrain cleaner
A drain cleaner includes a shank, a clearing member connected with the shank, a support pipe allowing passage of the clearing member, a handgrip mounted on the support pipe, and a mounting sleeve mounted on the support pipe and connected with the handgrip. The support pipe has an upper end provided with a slit and a lower end provided with an arcuate portion and an extension. The handgrip is located outside of the support pipe and is provided with a slit. The mounting sleeve is located outside of the support pipe and is provided with a slit. The slit of the mounting sleeve is connected between the slit of the support pipe and the slit of the handgrip.
Owner:YU MU TSUN
Urinal air freshener
ActiveUS10973942B2Increase probabilityReduce fluid and moisture uptakeUrinalsGaseous substancesAir pumpEnvironmental engineering
Owner:MICROLIN
Urinal air freshener
ActiveUS10350322B2Increase probabilityReduce fluid and moisture uptakeUrinalsLavatory sanitoryEvaporationEngineering
Owner:MICROLIN
Urinal air freshener
ActiveUS20180272022A1Increase probabilityReduce fluid and moisture uptakeUrinalsLavatory sanitoryEvaporationEngineering
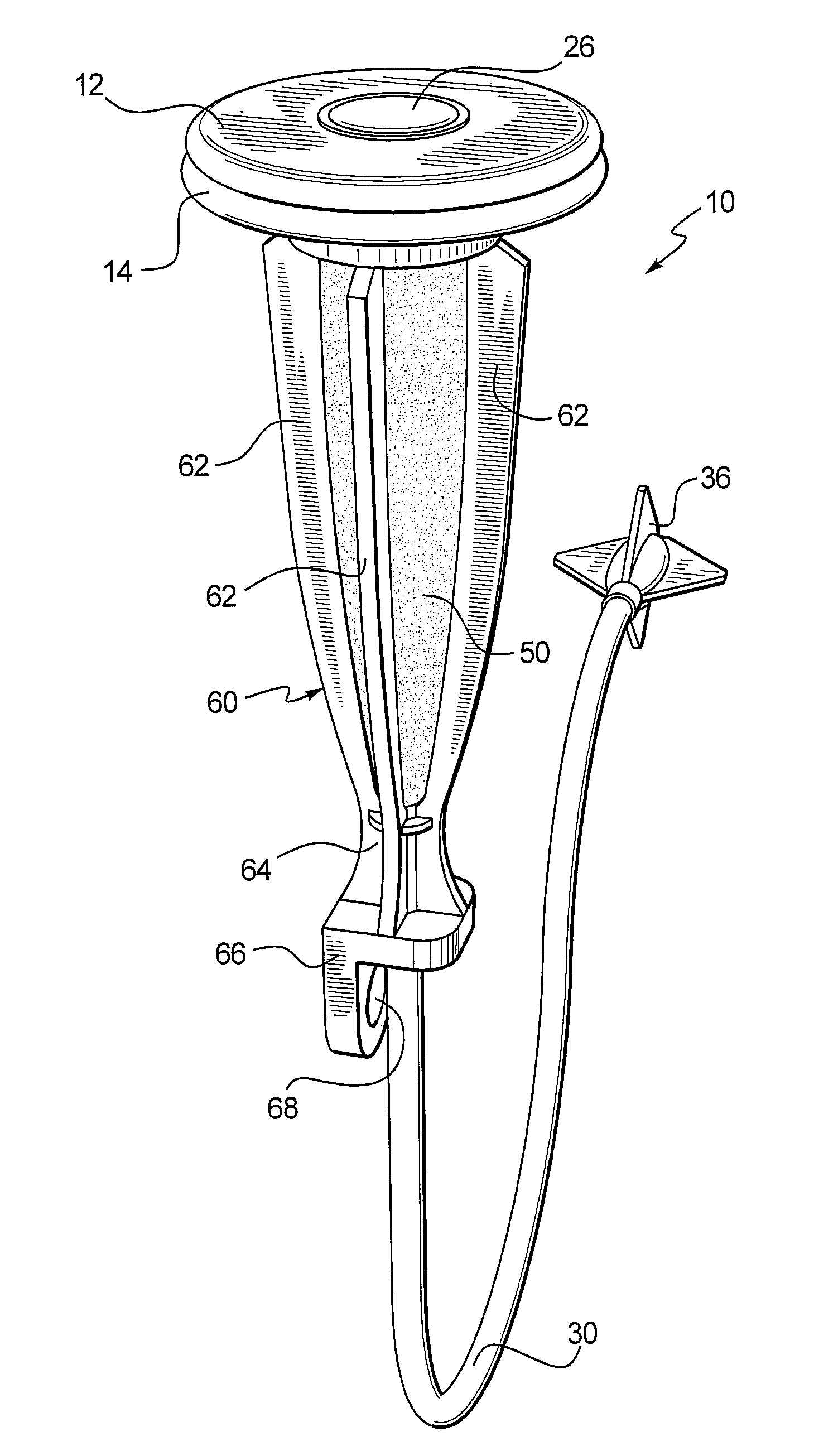
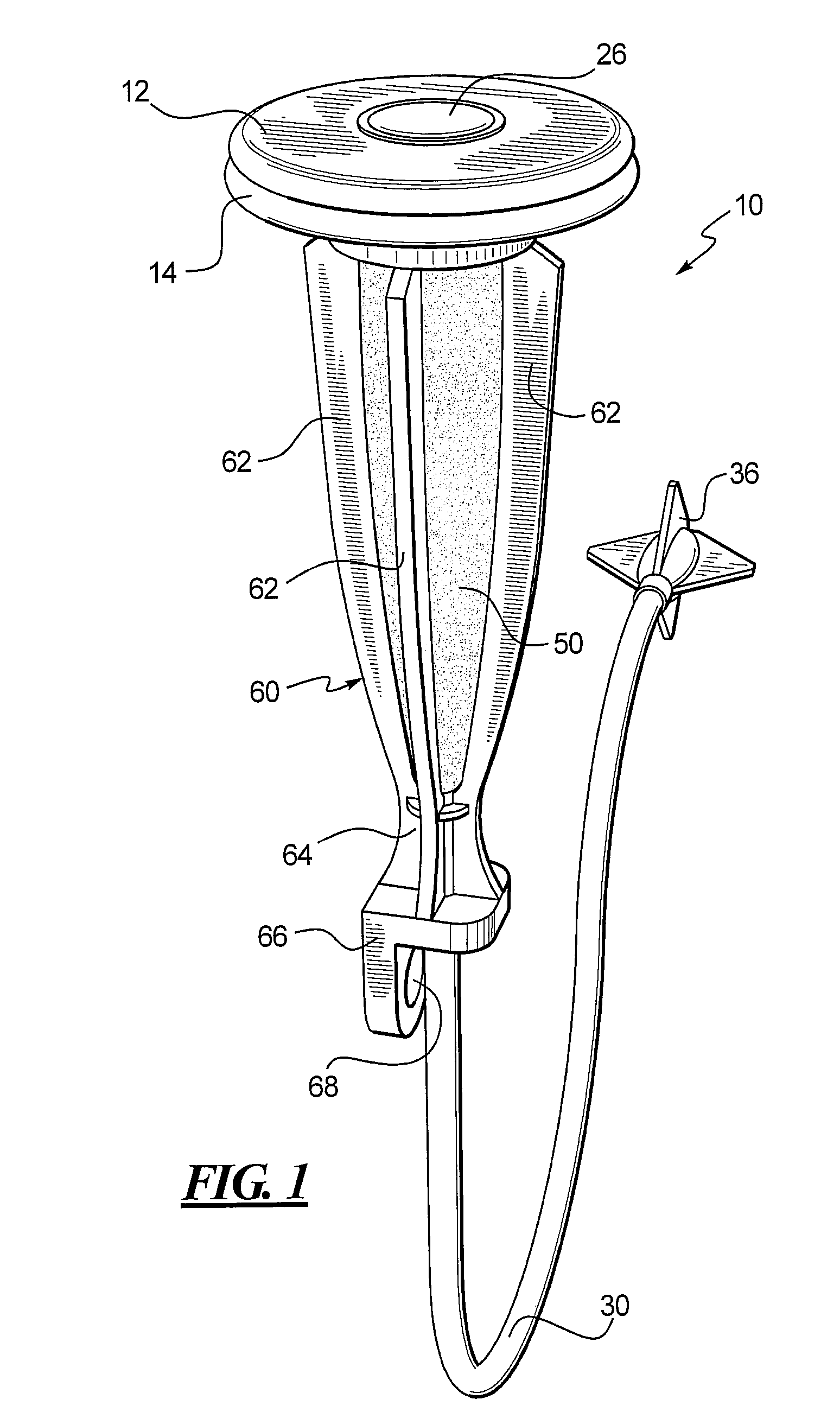
An automatic dispensing device for volatile fluid operable to apply one or more agent to a local environment for more than 14 days. Preferred devices dispense a first agent for air freshening, and may optionally dispense a second agent, such as a drain cleaner. A workable drain cleaner is structured to permit a slow release of drain cleaning agent. A dispensing device may nonexclusively operate by evaporation of volatile fluid from a polymer or rubber-like carrier material that is infused with the volatile fluid; gravity-induced drip from a bulk supply of volatile fluid through a small orifice onto an emanator; osmotic transfer of volatile fluid from a bulk supply; gas-pump drive of volatile fluid at controlled pressure; or diffusion of volatile fluid through a wall of a container of bulk volatile fluid; and combinations thereof.
Owner:MICROLIN
Drain closer with disengageable drain cleaner
A drain closer having a body forming a plug configured for engagement in a drain or sink. The drain closure includes a flexible member translatable through a passage in the body of the plug for snagging hair or fibrous matter within the drain. The flexible member is engageable and disengageable from the plug positioned in the drain by sliding it into and out of the passage running axially through the body of the plug.
Owner:VONG BINH GIA
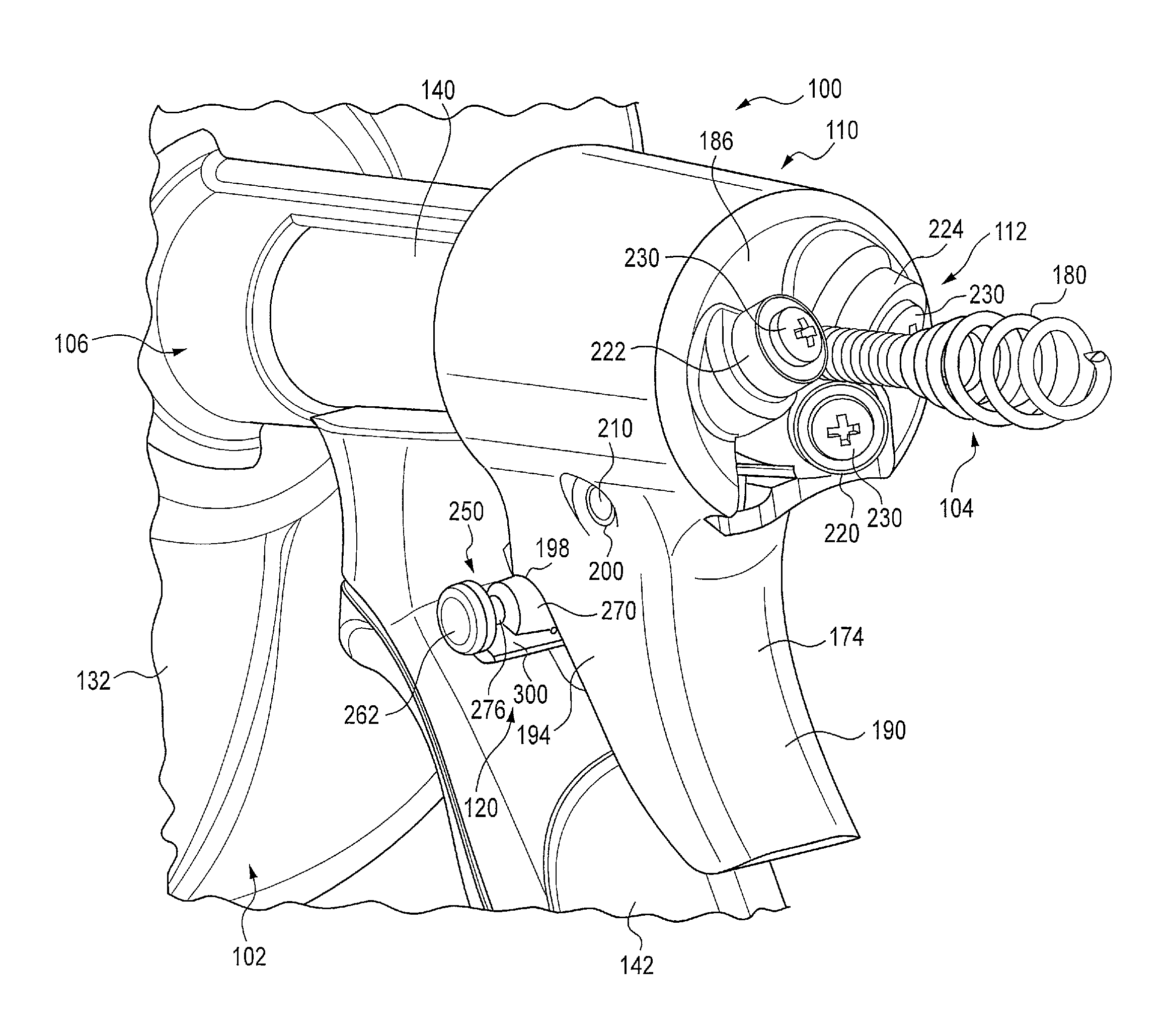
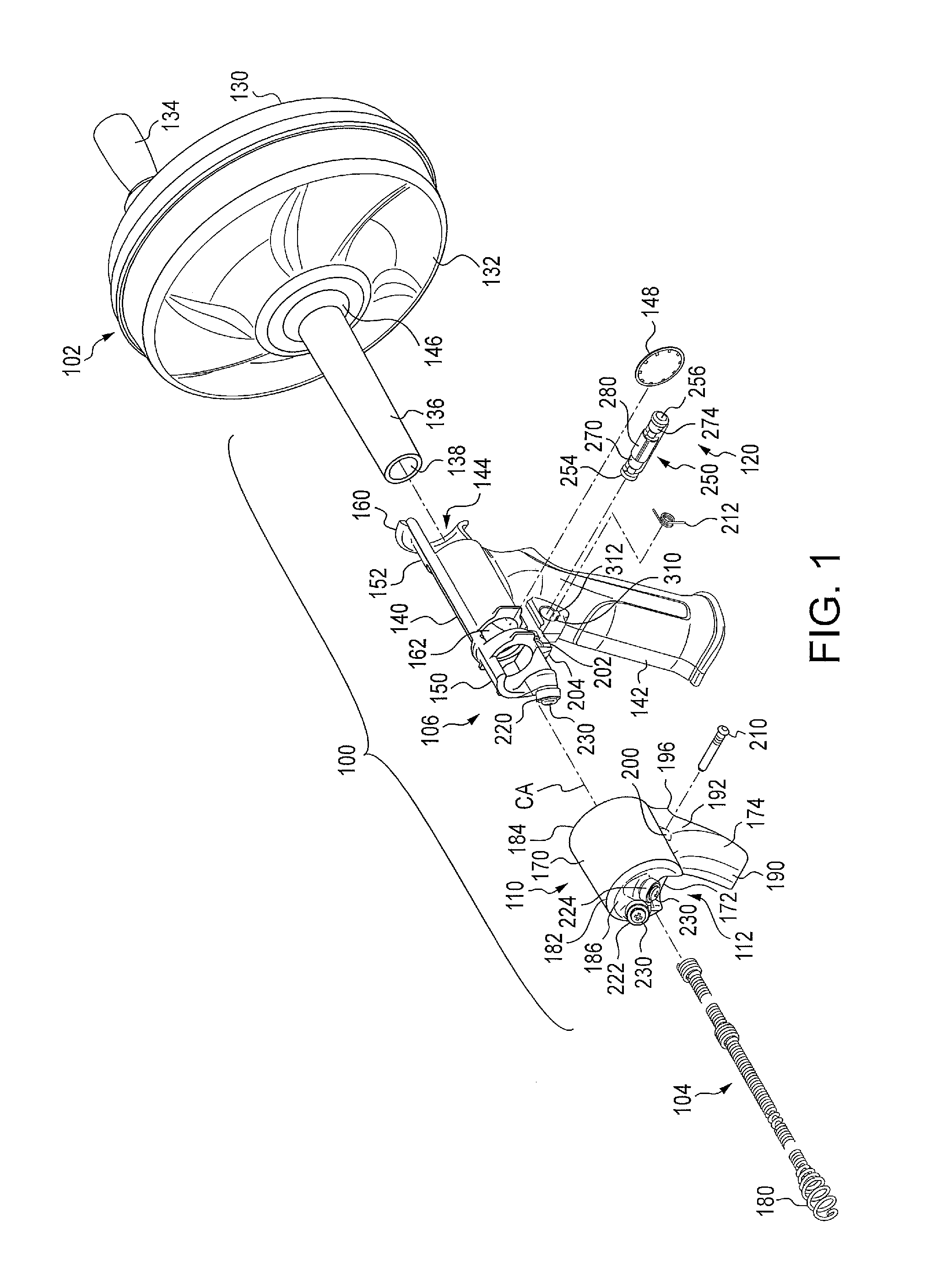
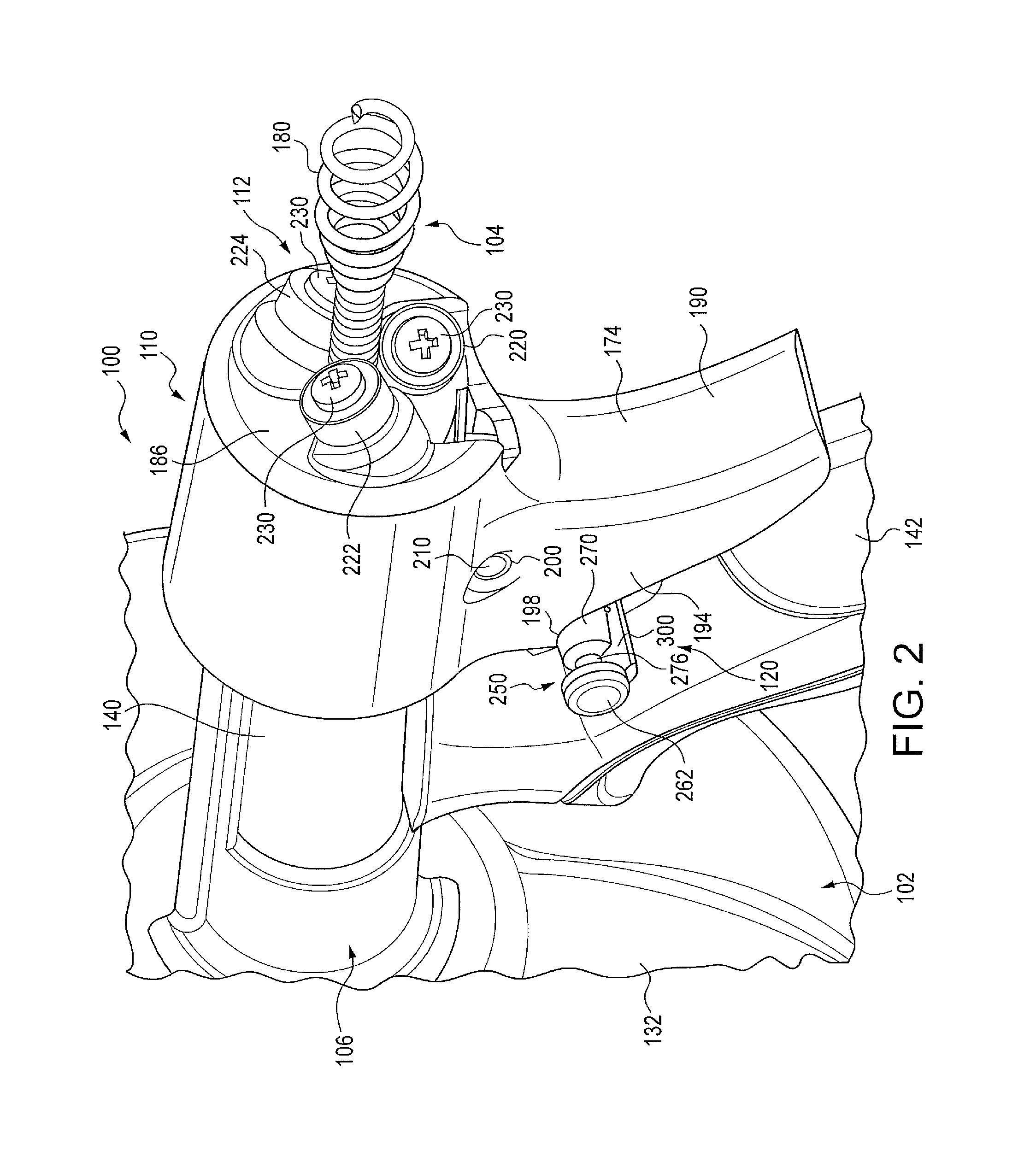
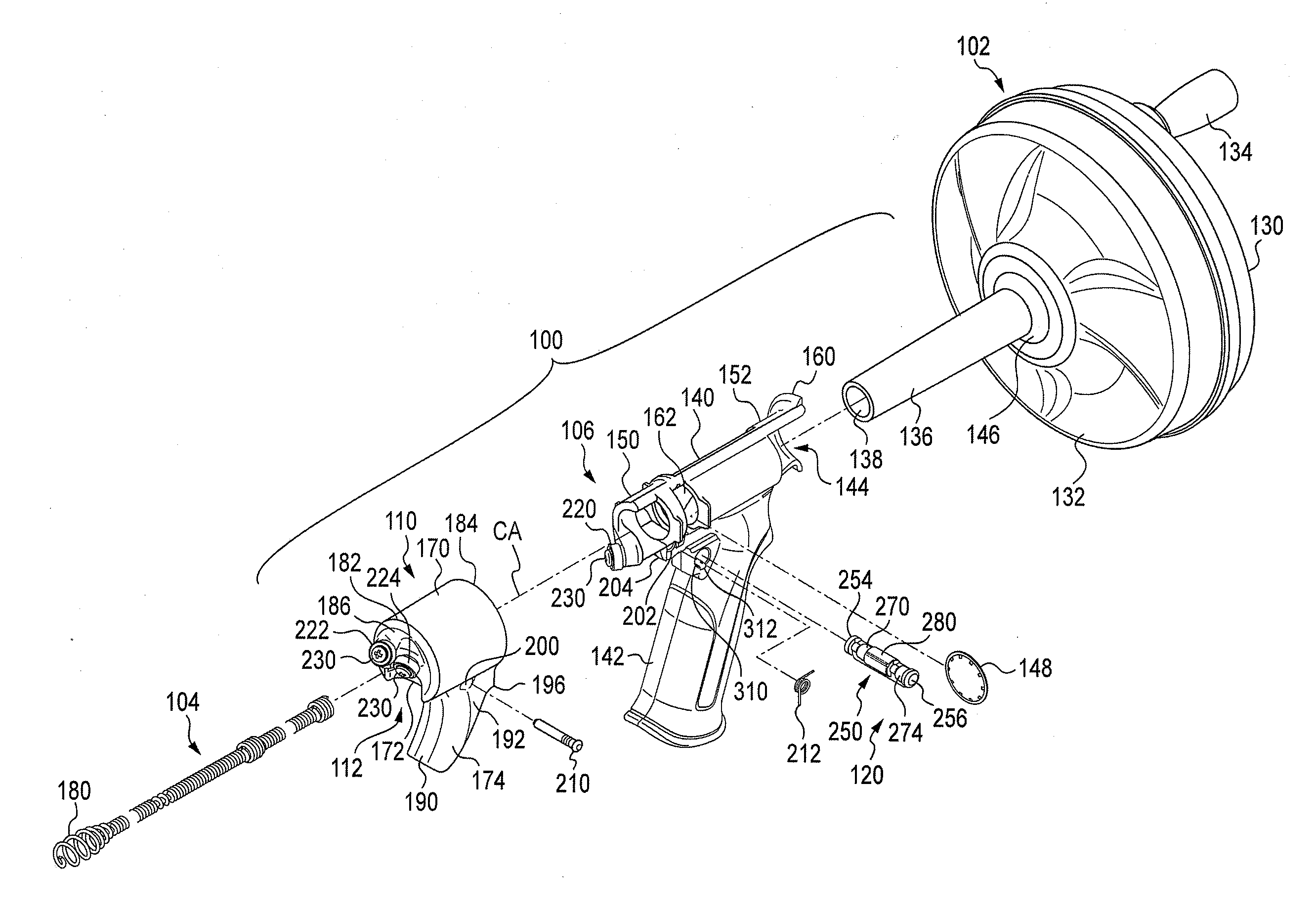
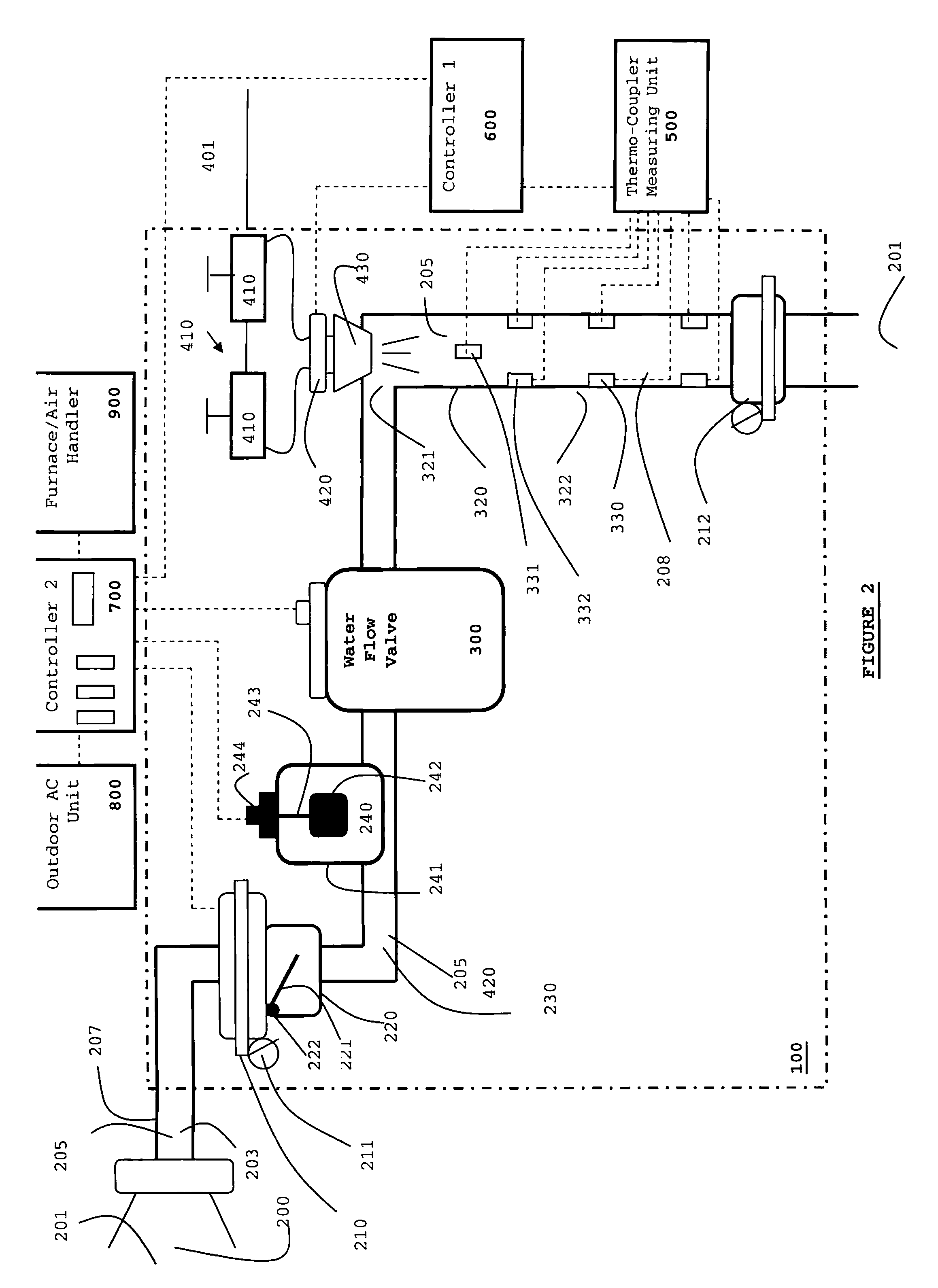
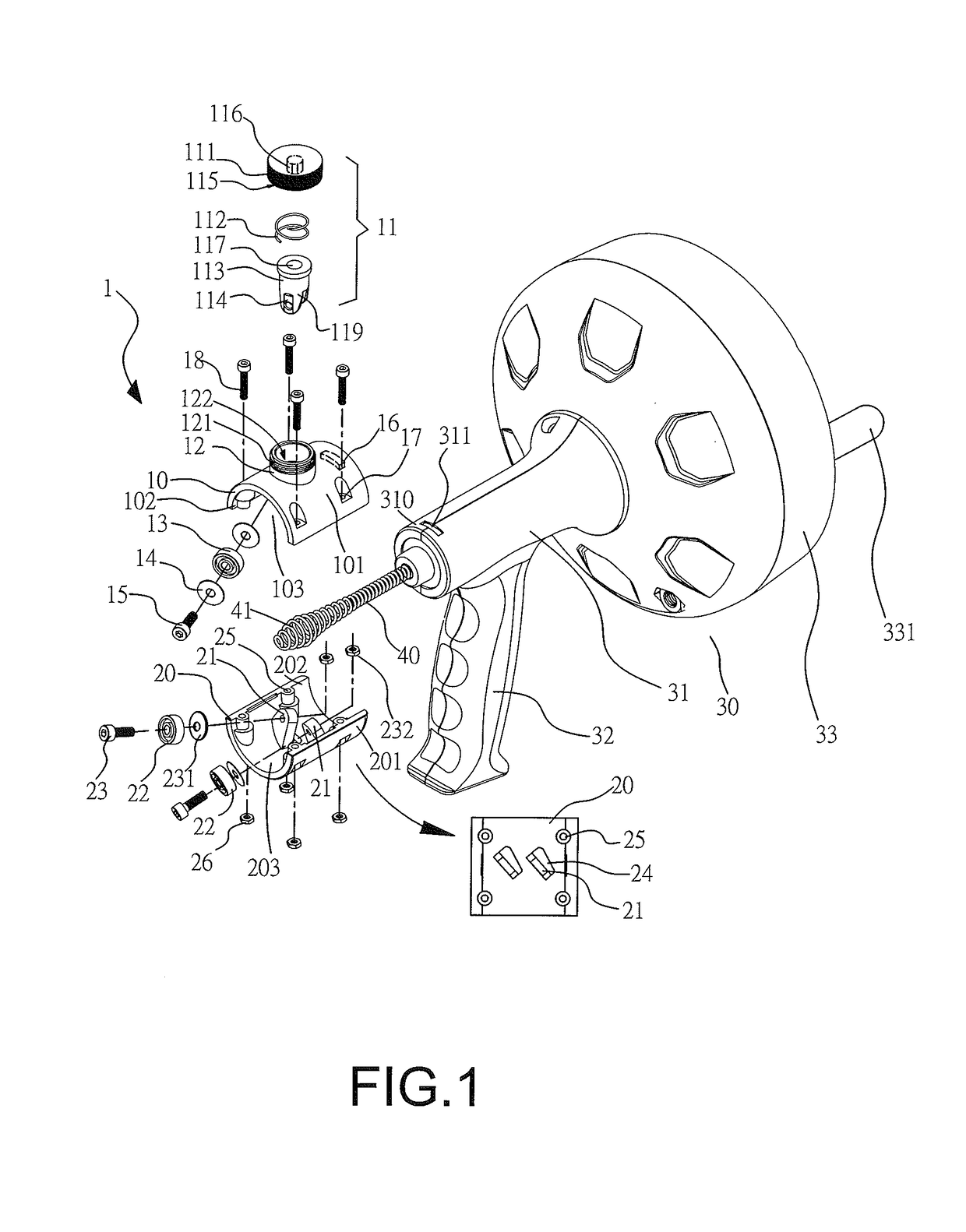
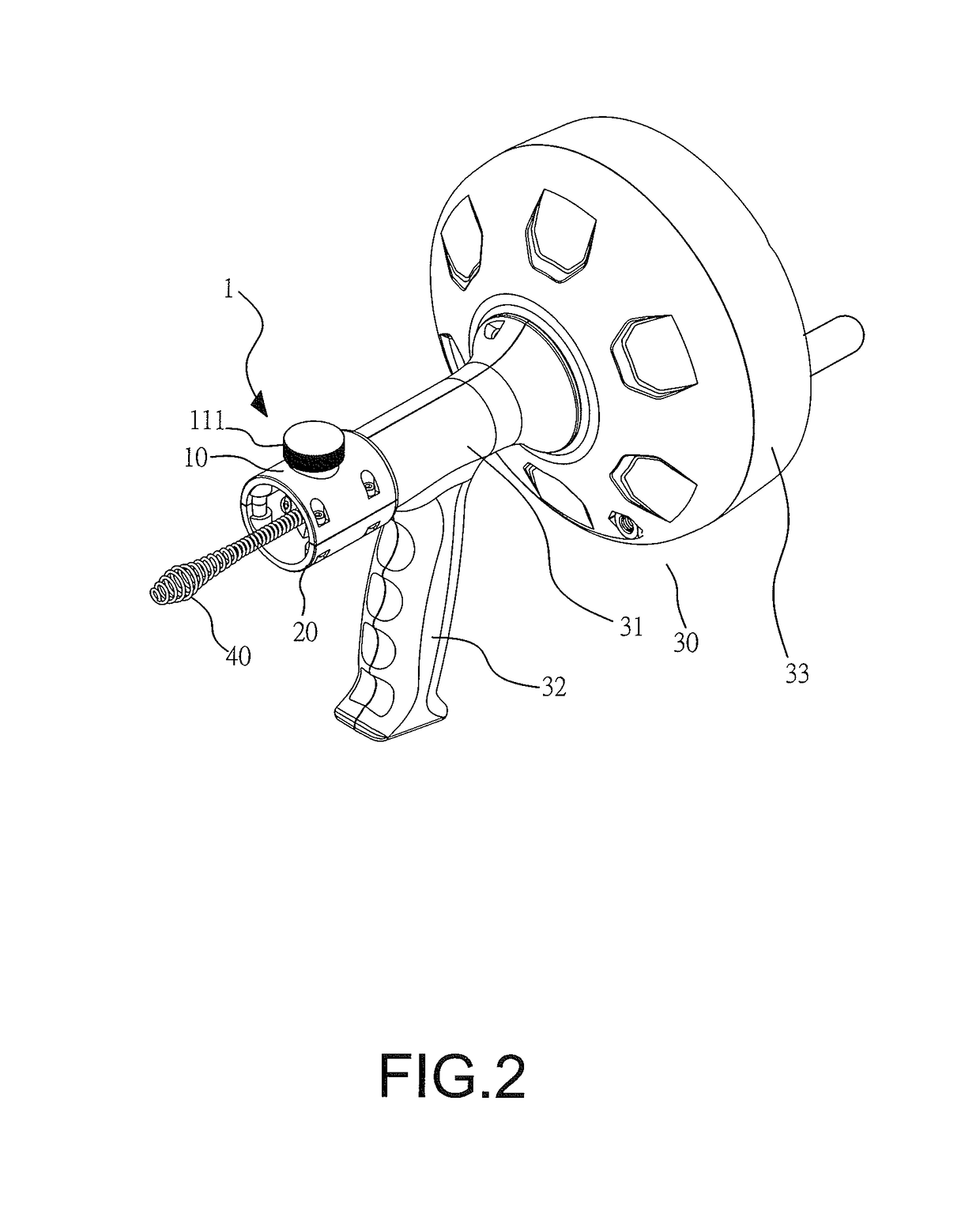
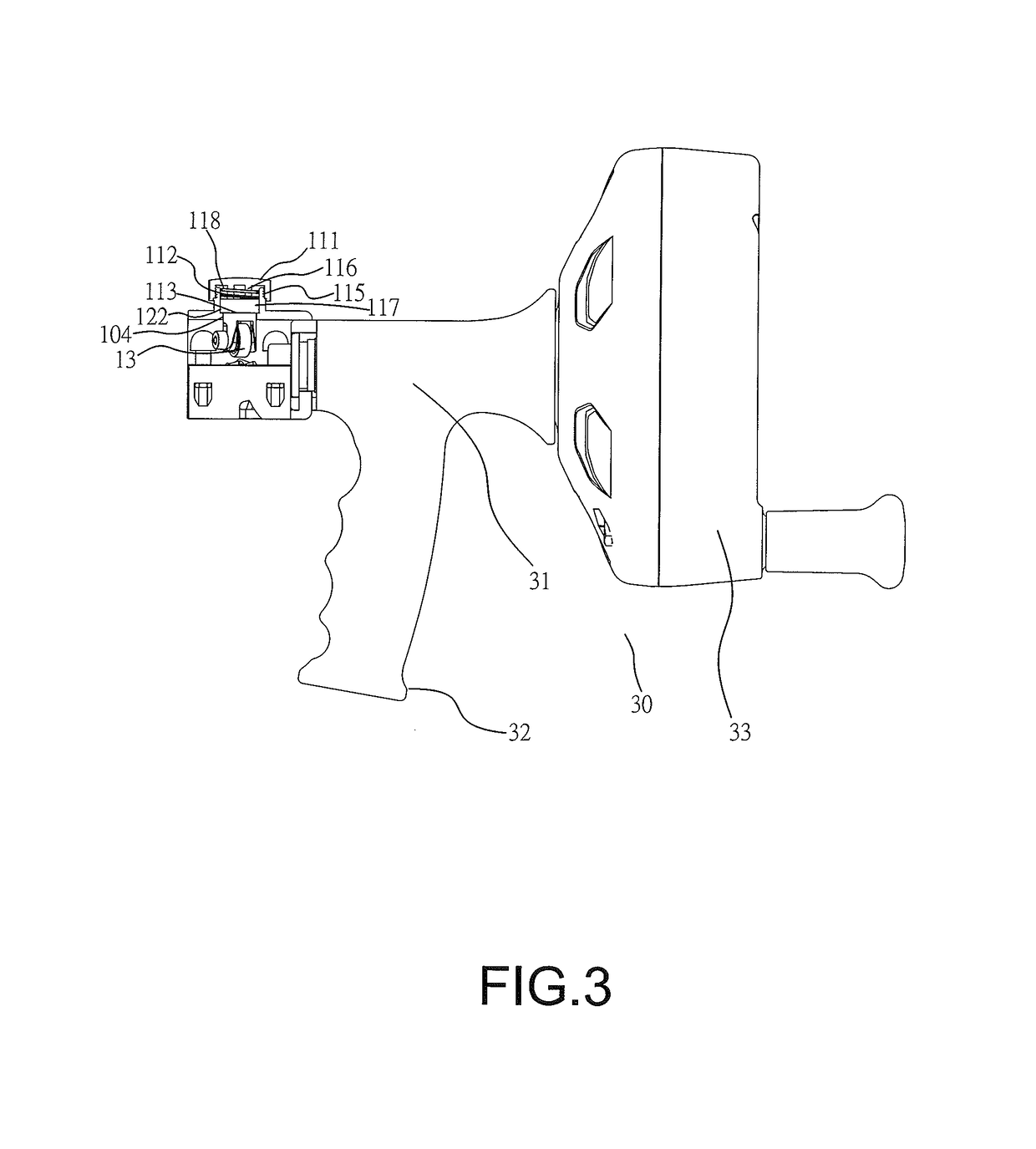
Drain cleaner
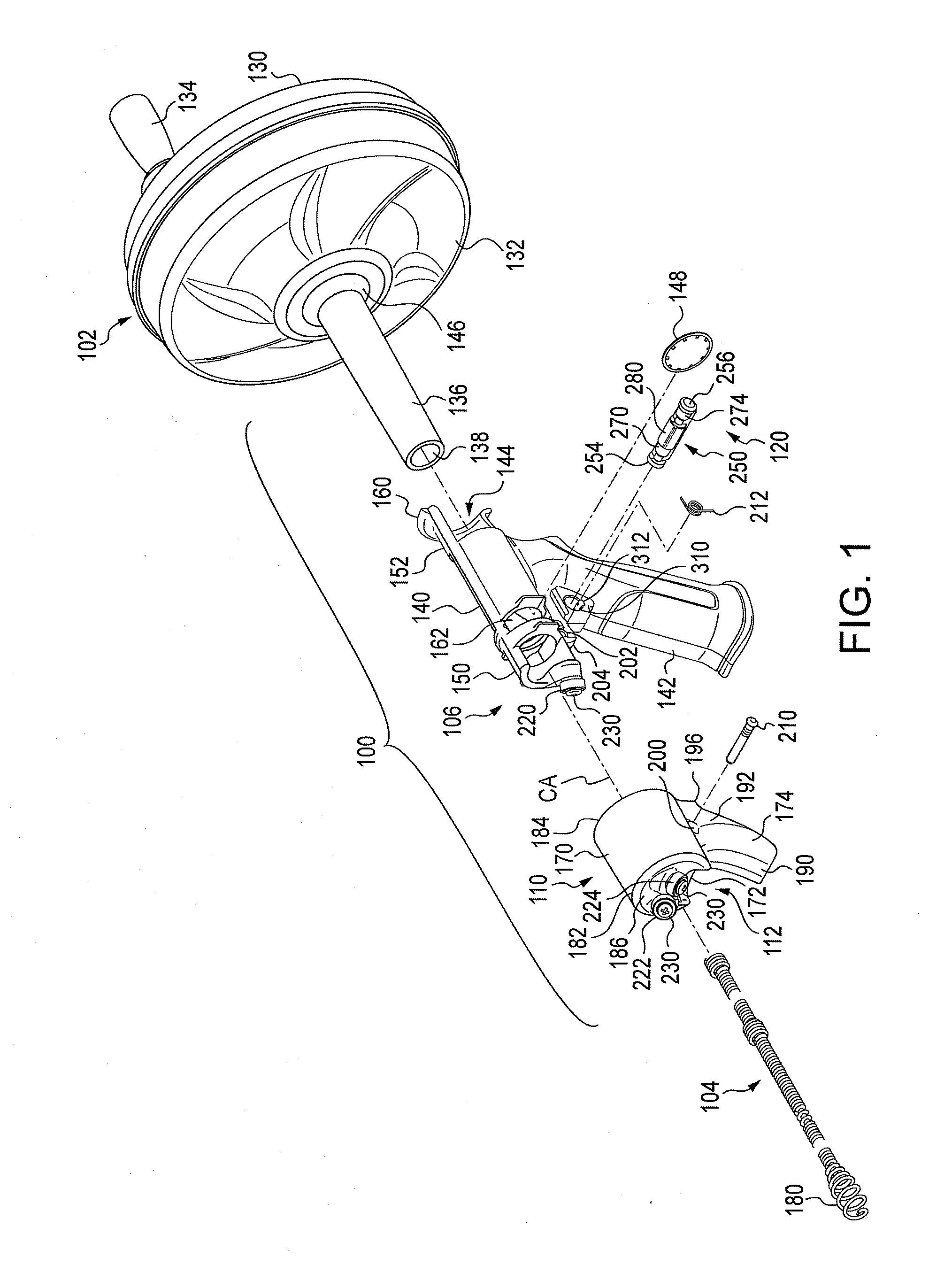
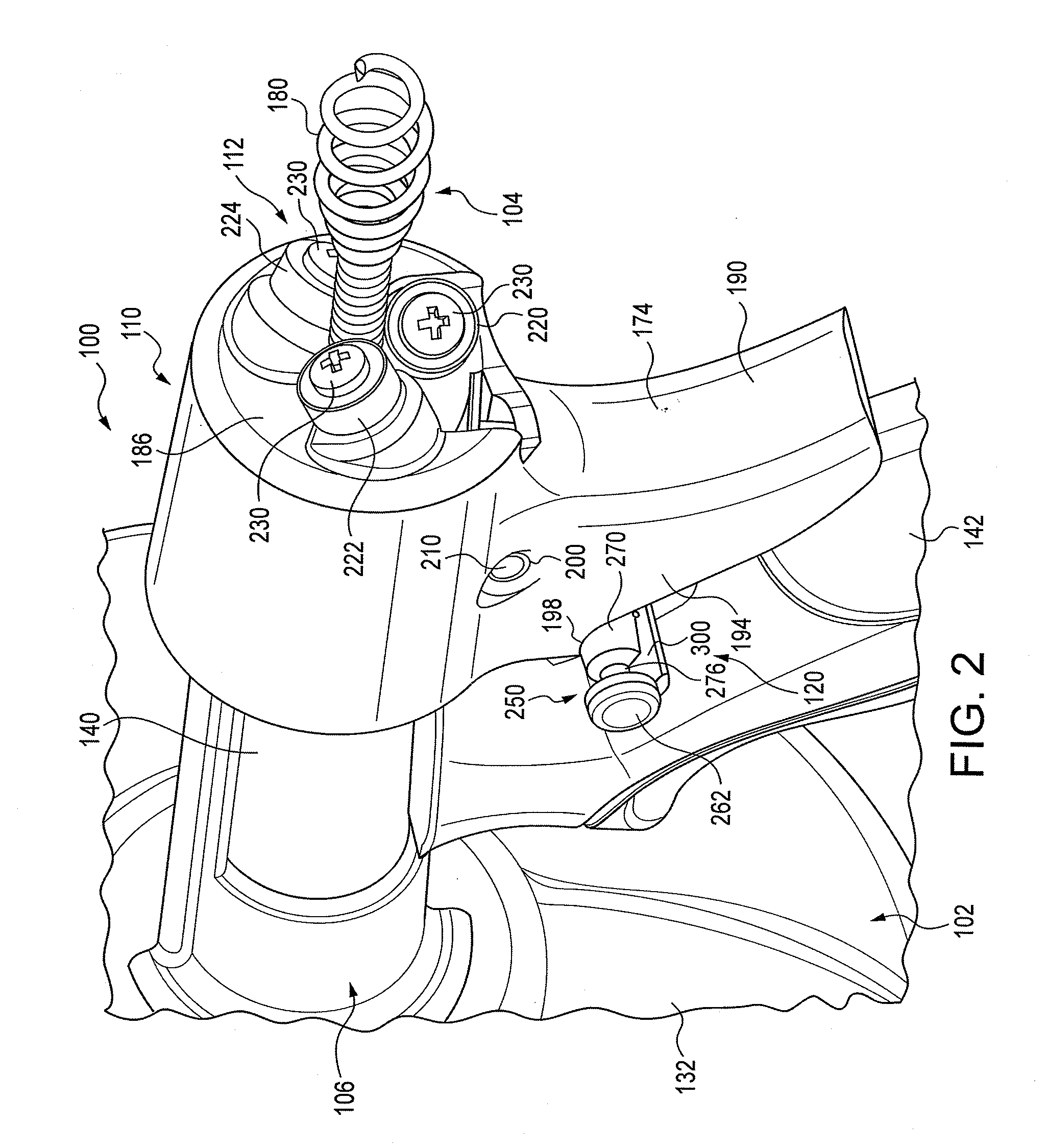
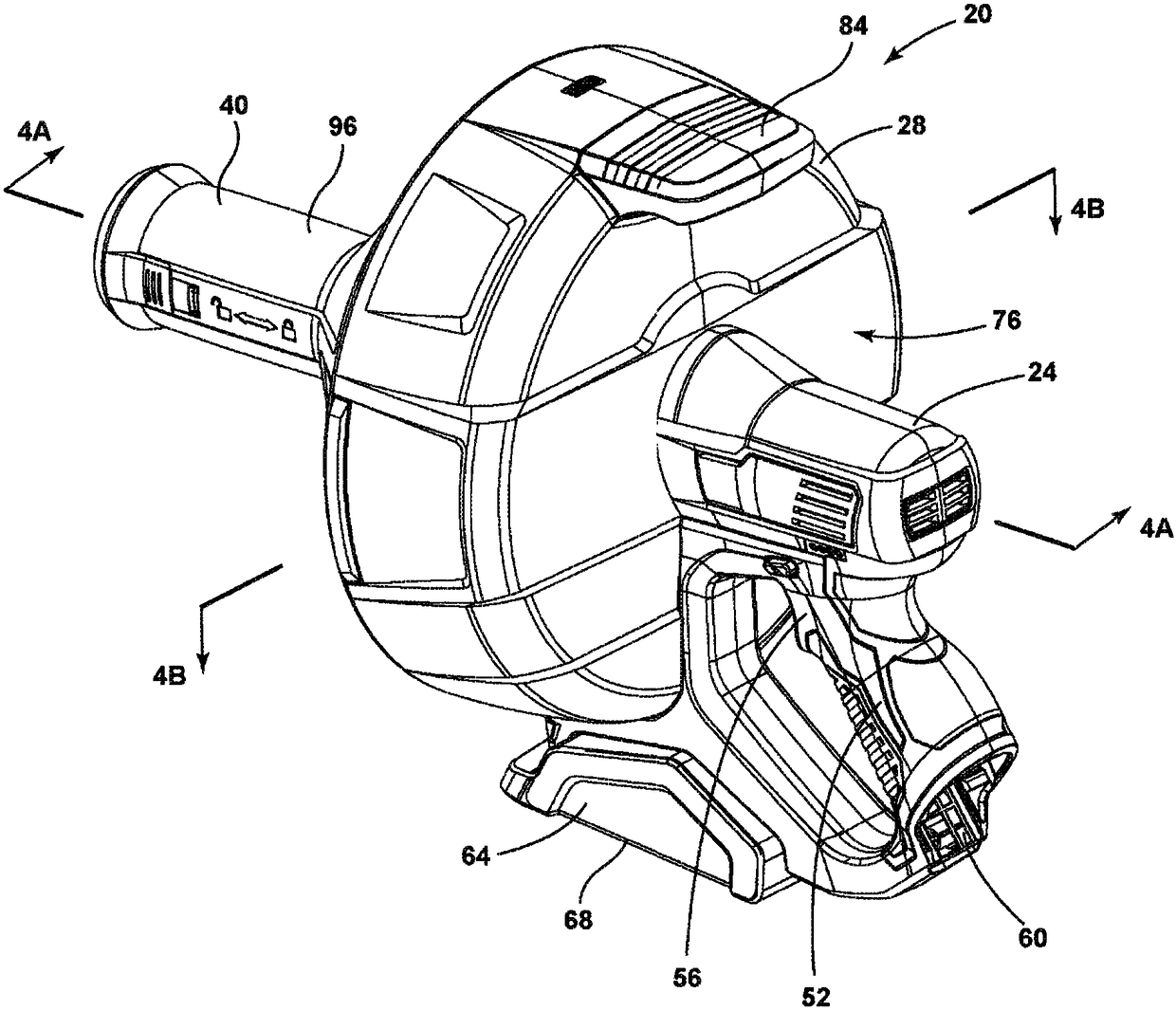
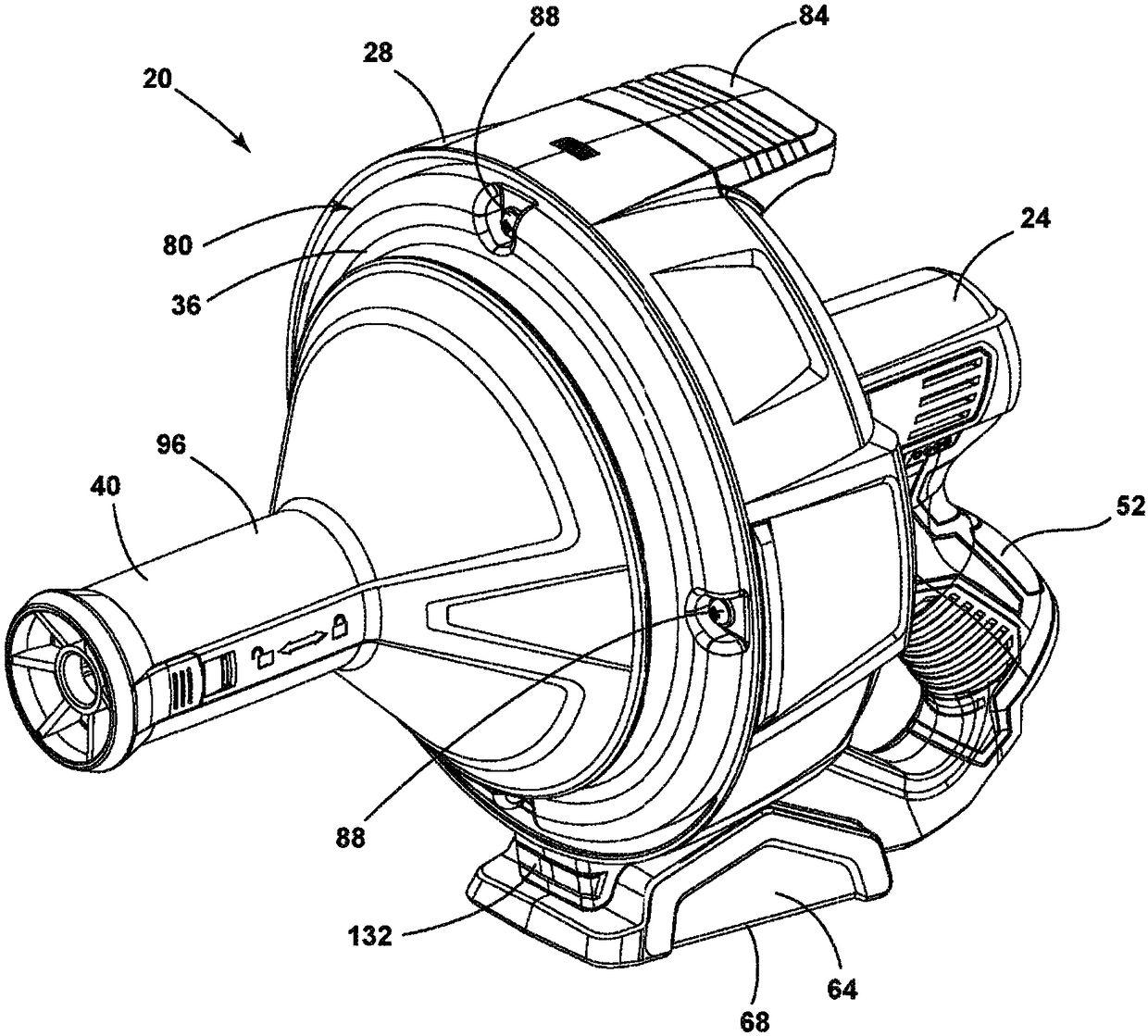
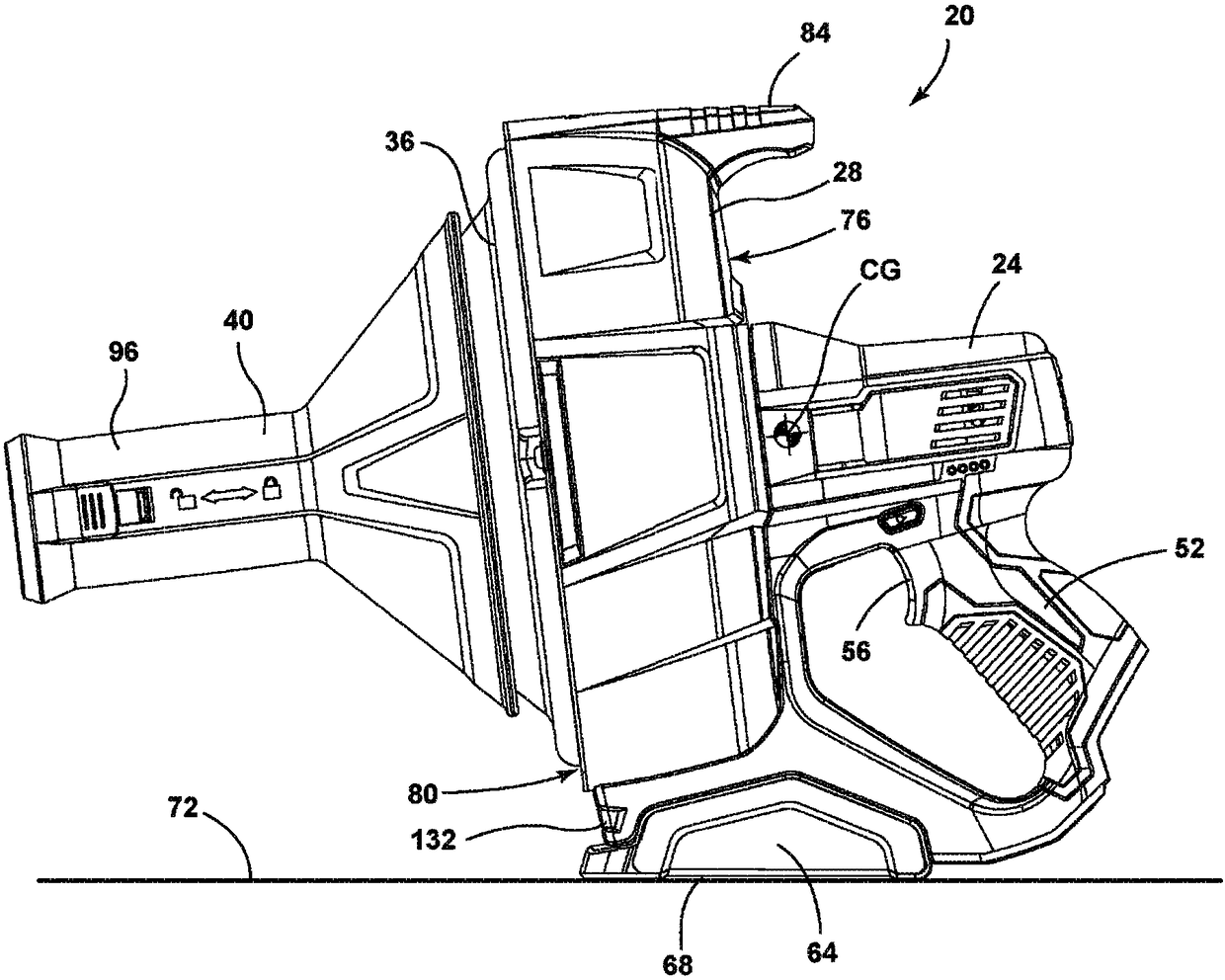
A drain cleaner includes a handle assembly having a grip, a motor positioned within the handle assembly, and an actuator supported by the handle assembly adjacent the grip. The actuator is electrically coupled to the motor and operable to selectively energize the motor. The drain cleaner also includes a shroud fixed to and extending forwardly from the handle assembly. The shroud includes a closedend adjacent the handle assembly. The drain cleaner further includes a drum assembly rotatably coupled to the handle assembly and positioned within the shroud. The drum assembly is operable to be rotated by the motor relative to the handle assembly and the shroud. The drain cleaner also includes a flexible cable stored within the drum assembly. The flexible cable is configured to be extended out of the drum assembly and into a drain.
Owner:MILWAUKEE ELECTRIC TOOL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com