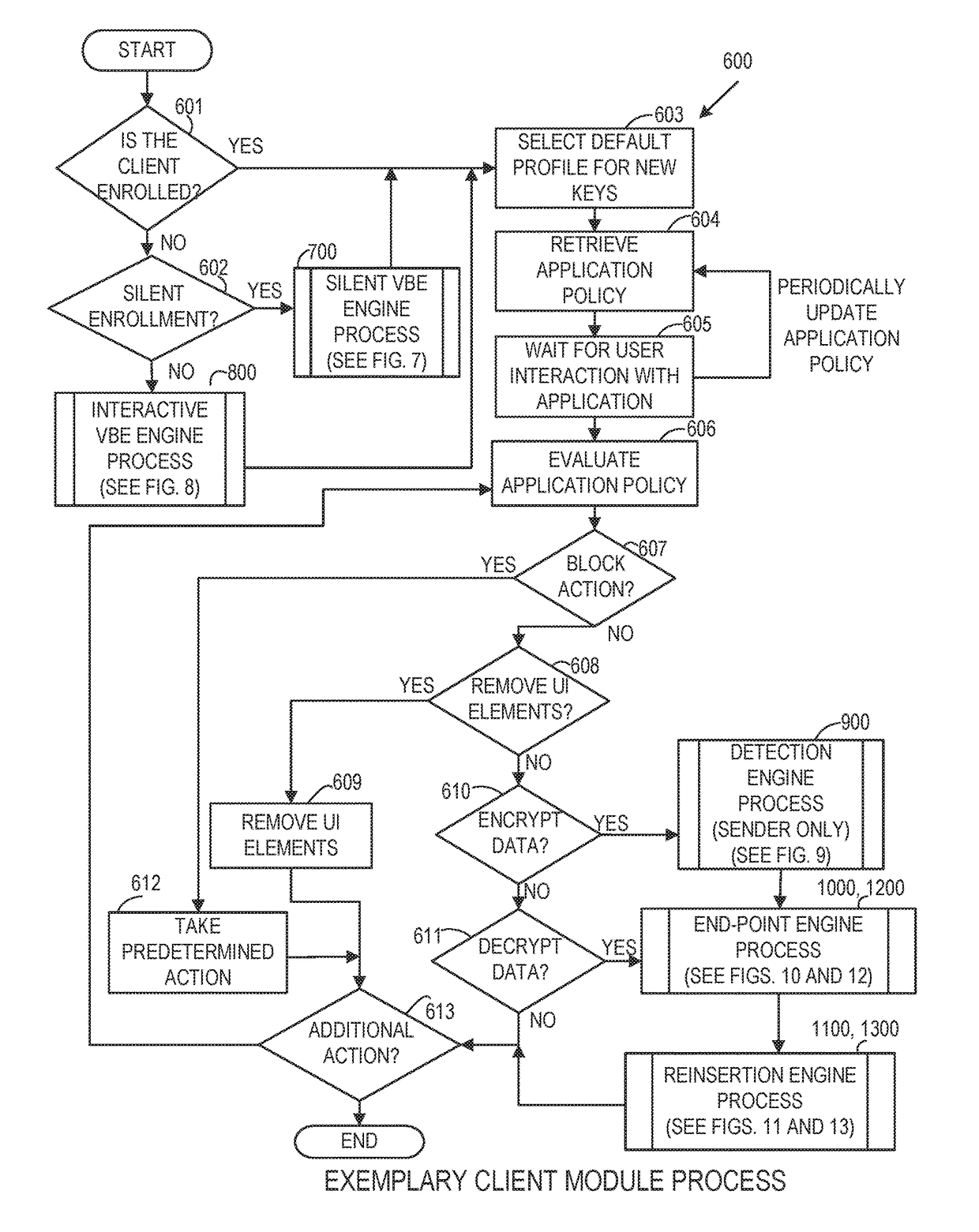
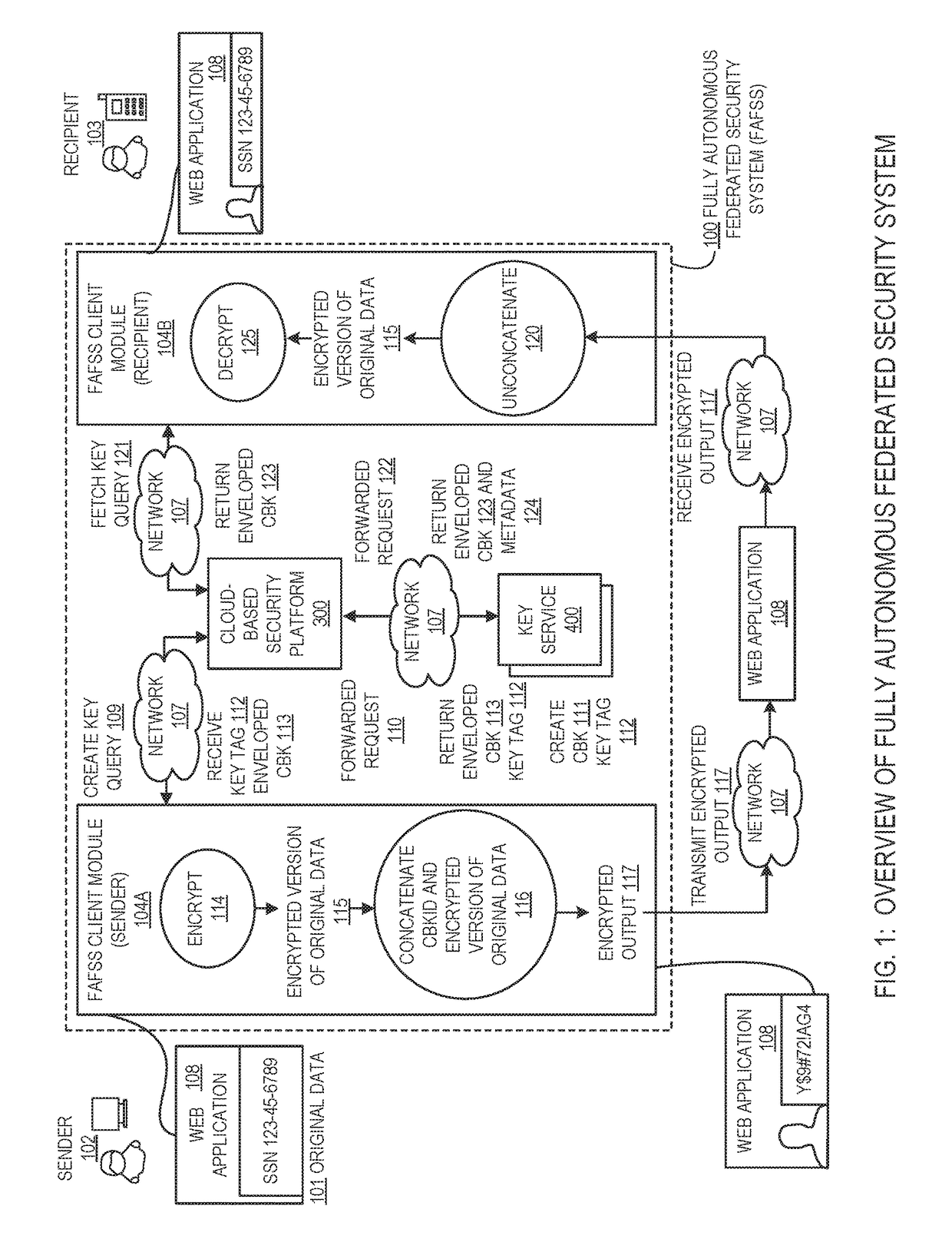
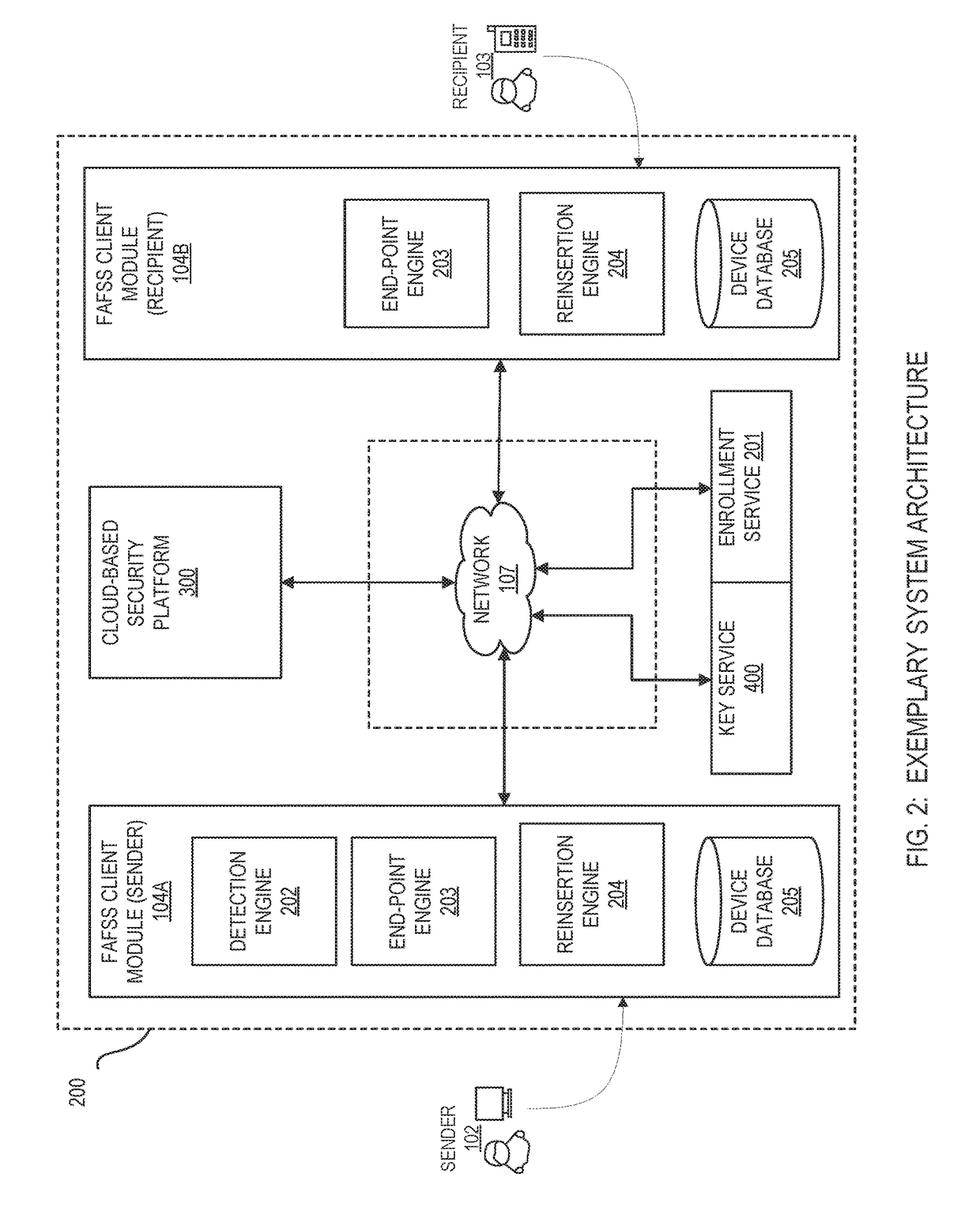
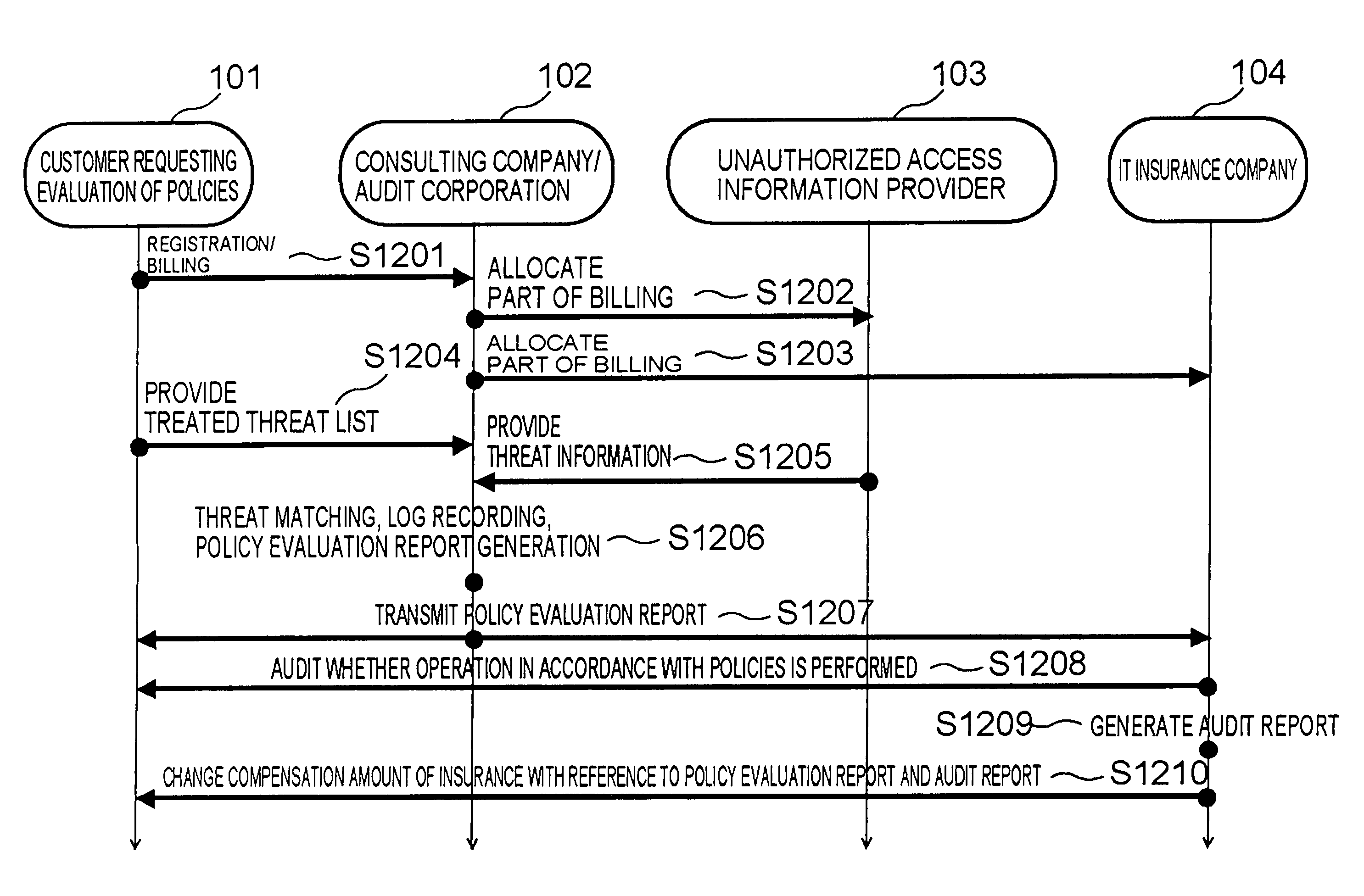
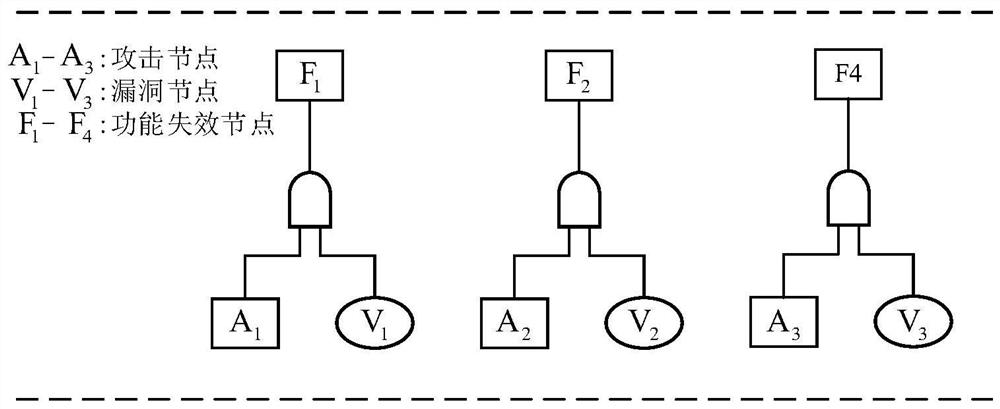
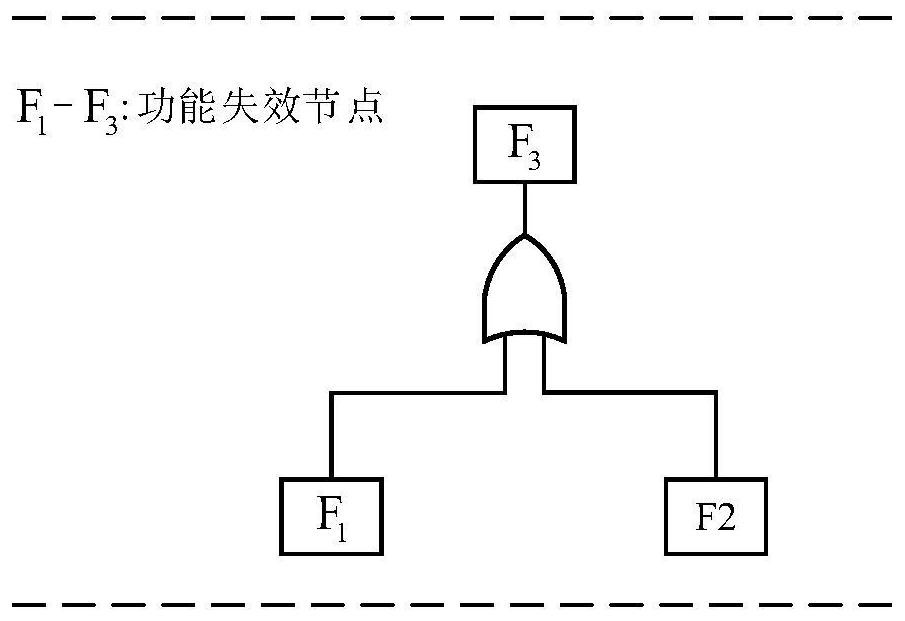
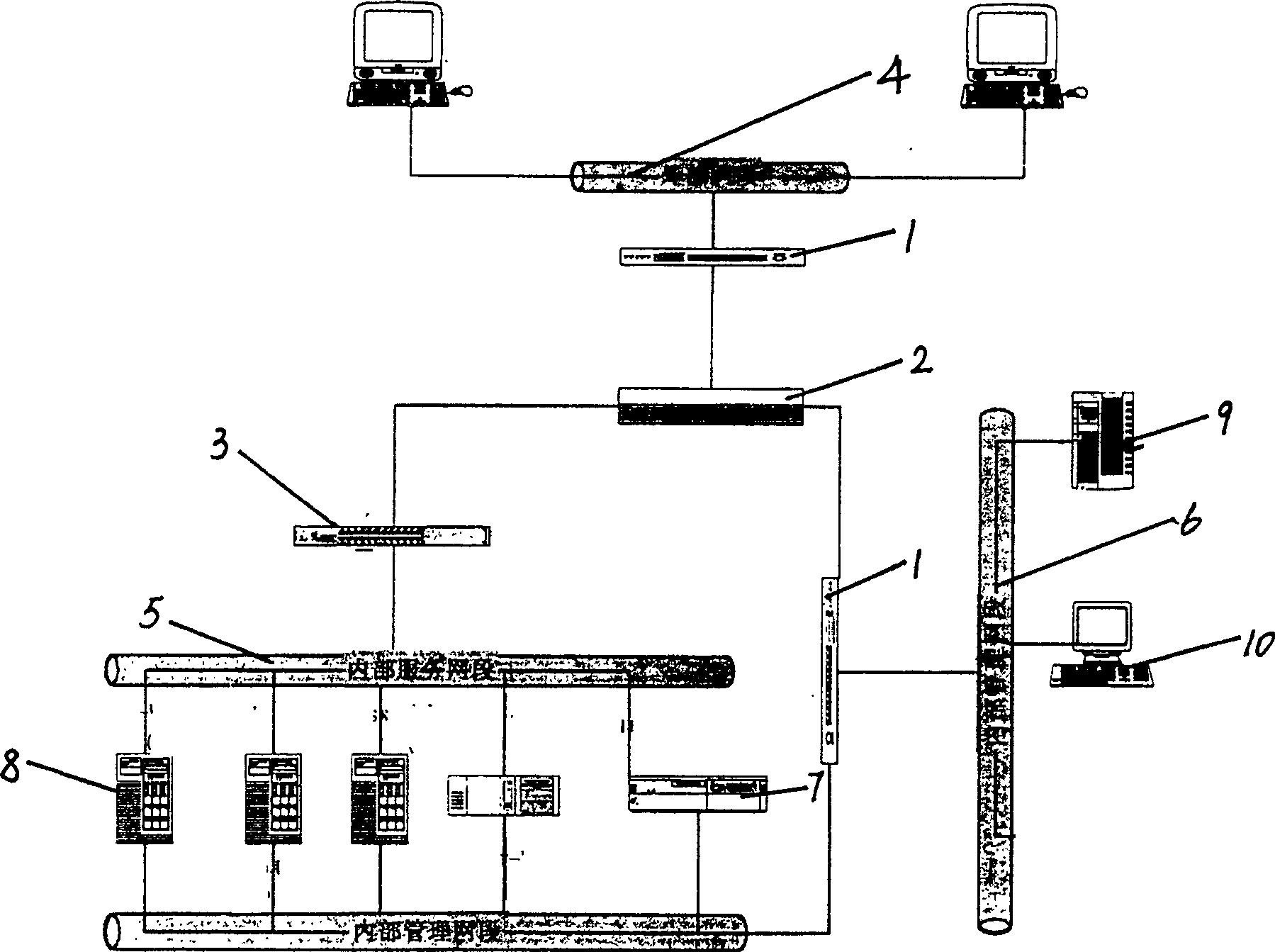
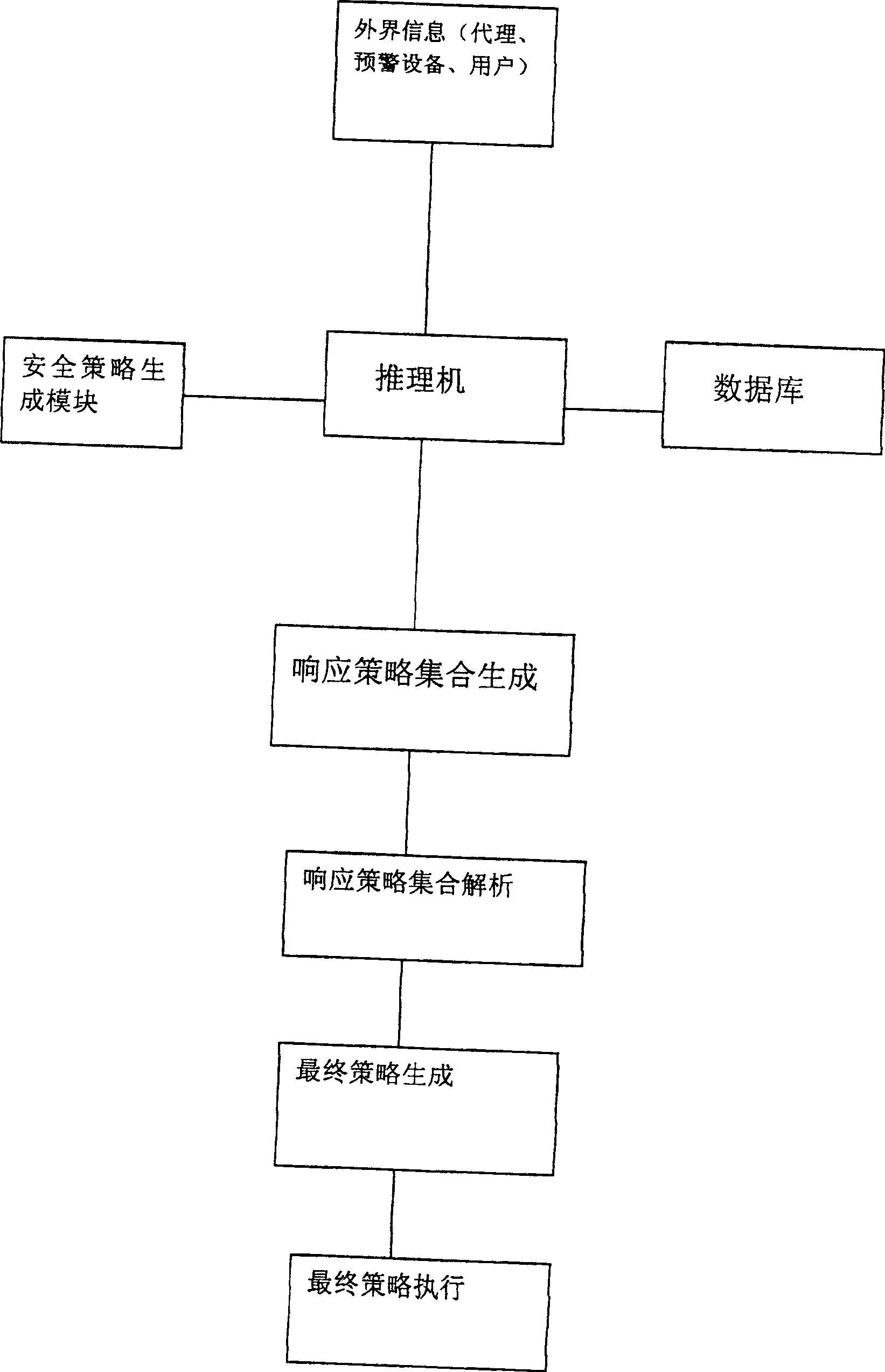
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Information security policy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Information Security Policy (ISP) is a set of rules enacted by an organization to ensure that all users or networks of the IT structure within the organization’s domain abide by the prescriptions regarding the security of data stored digitally within the boundaries the organization stretches its authority. An ISP is governing the protection of information, which is one of the many assets a corporation needs to protect.
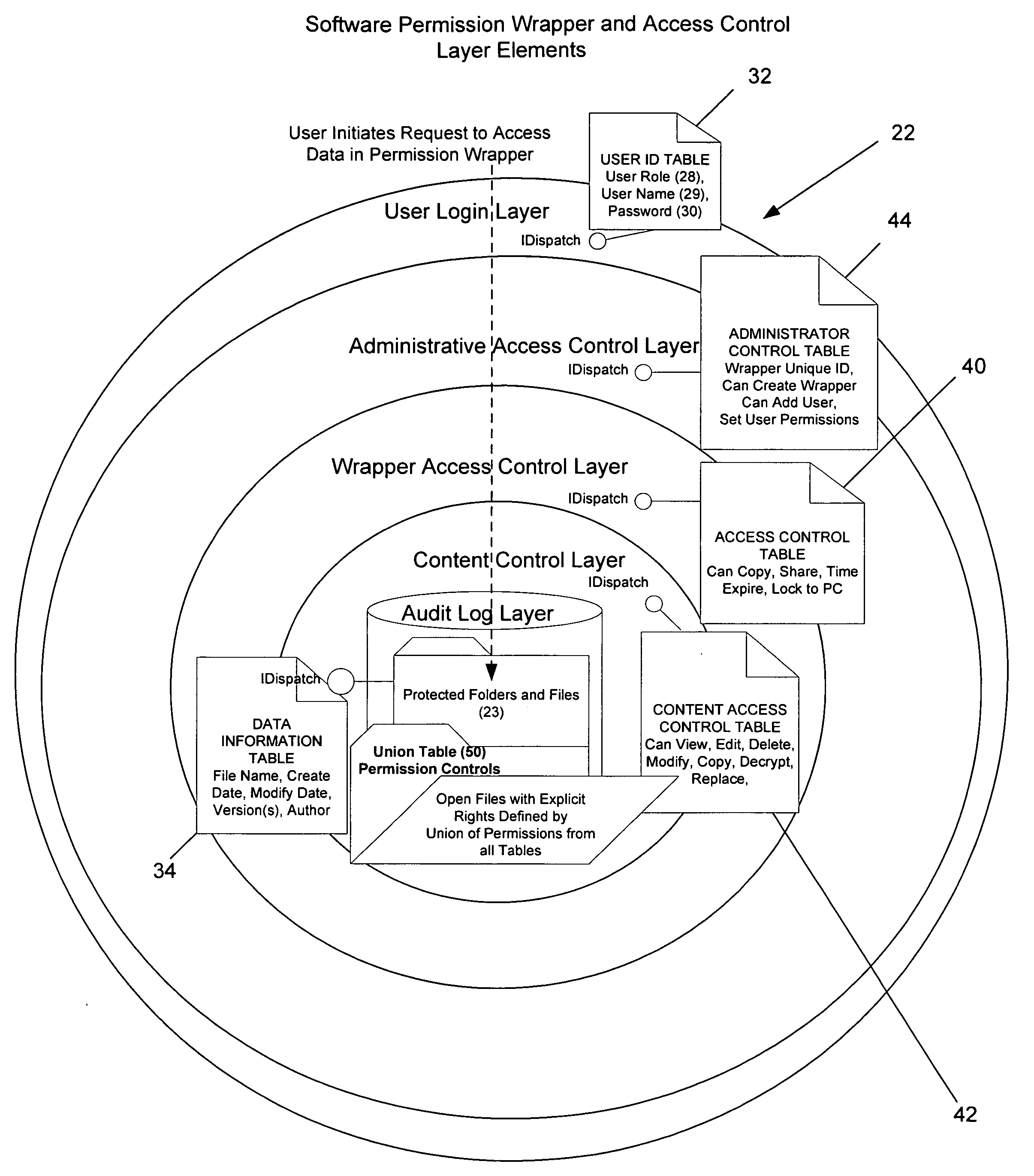
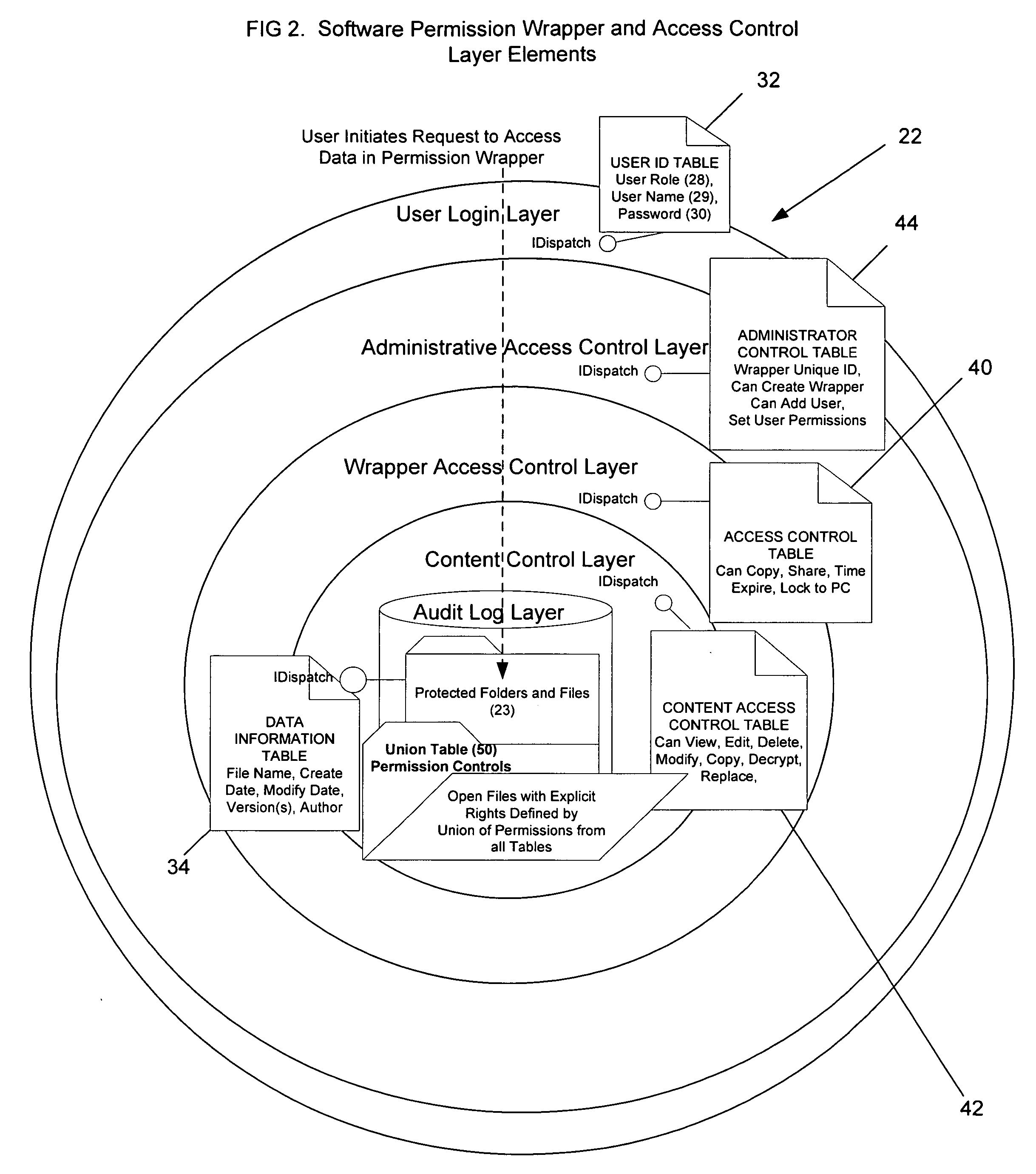
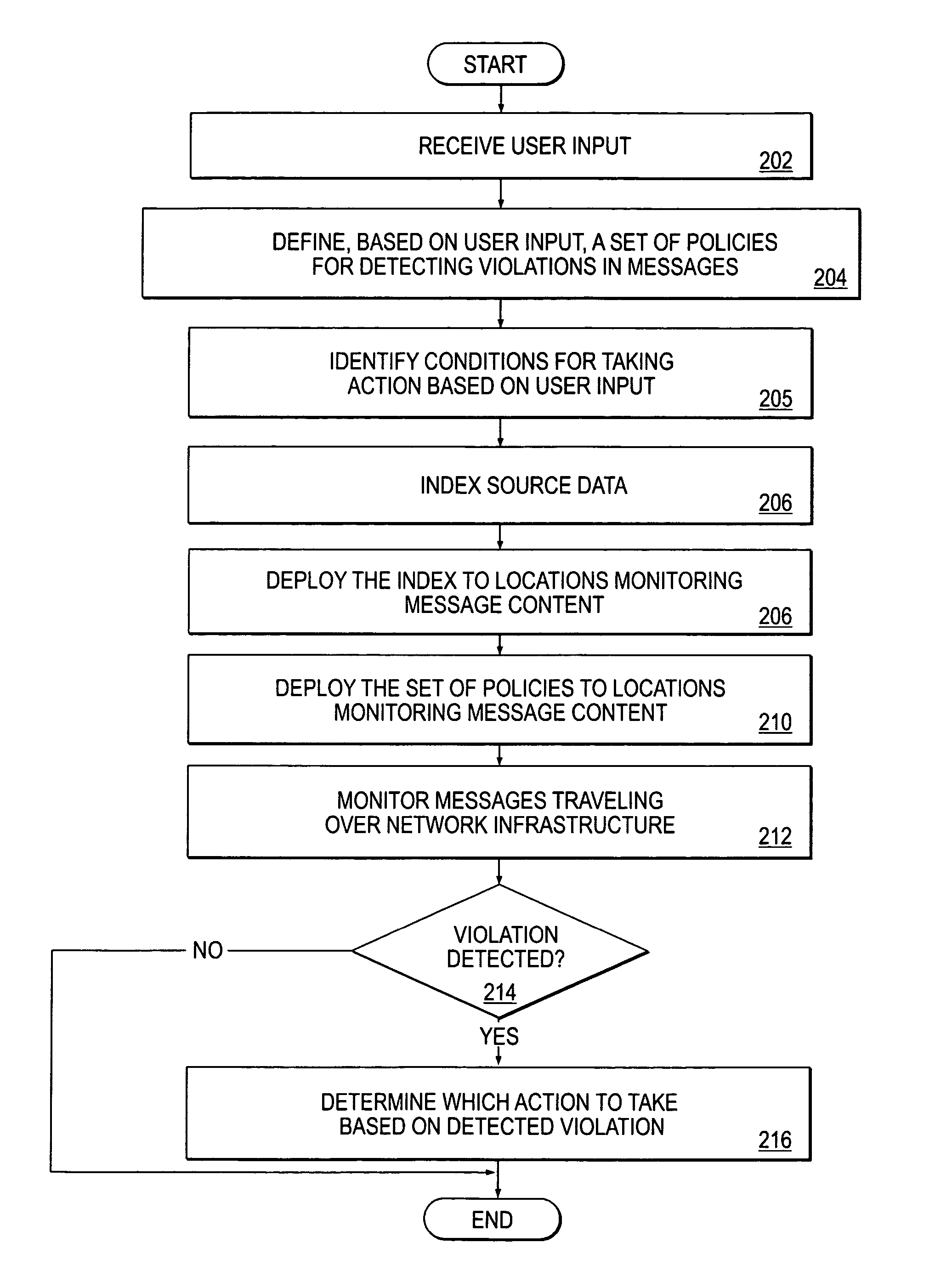
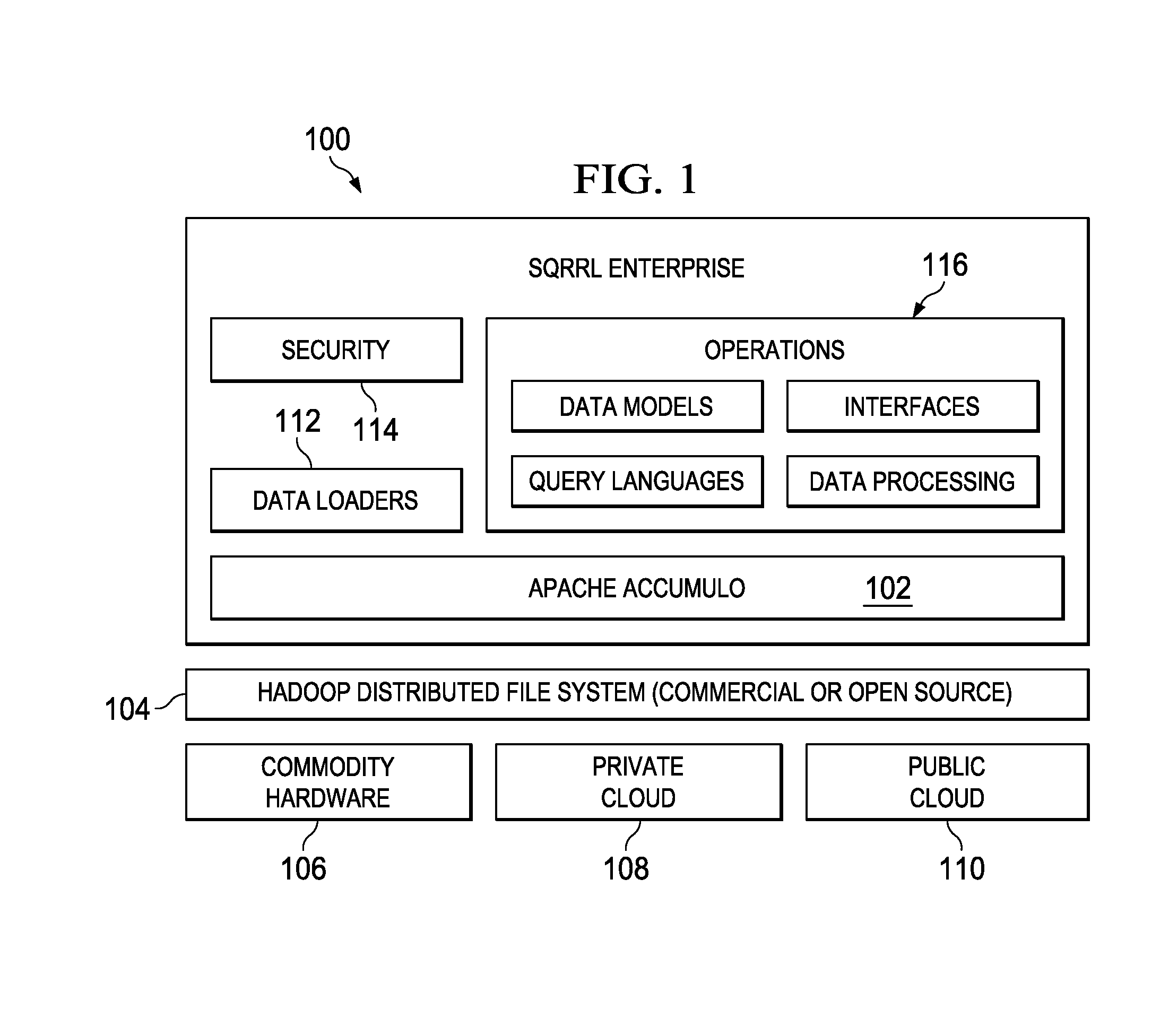
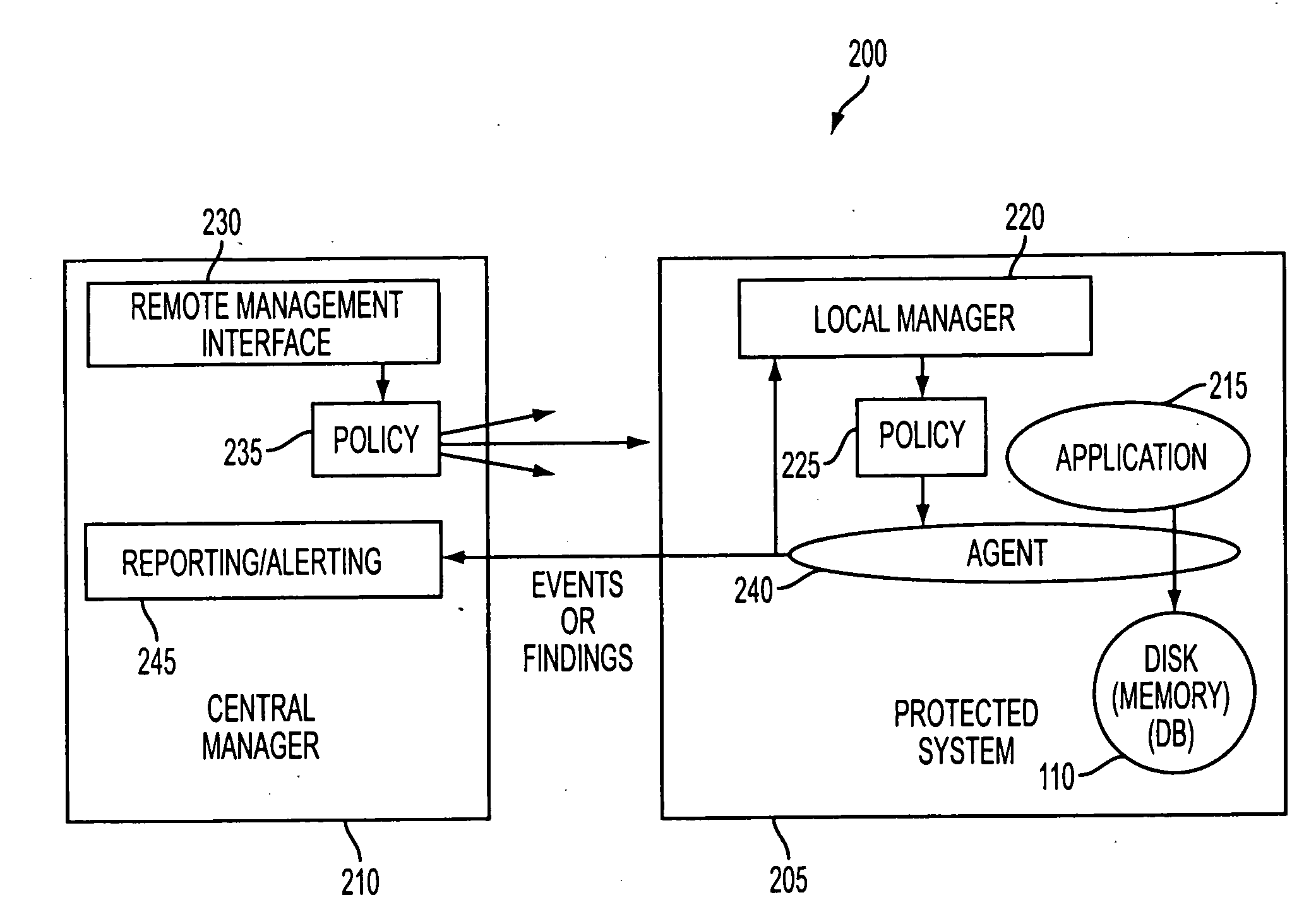
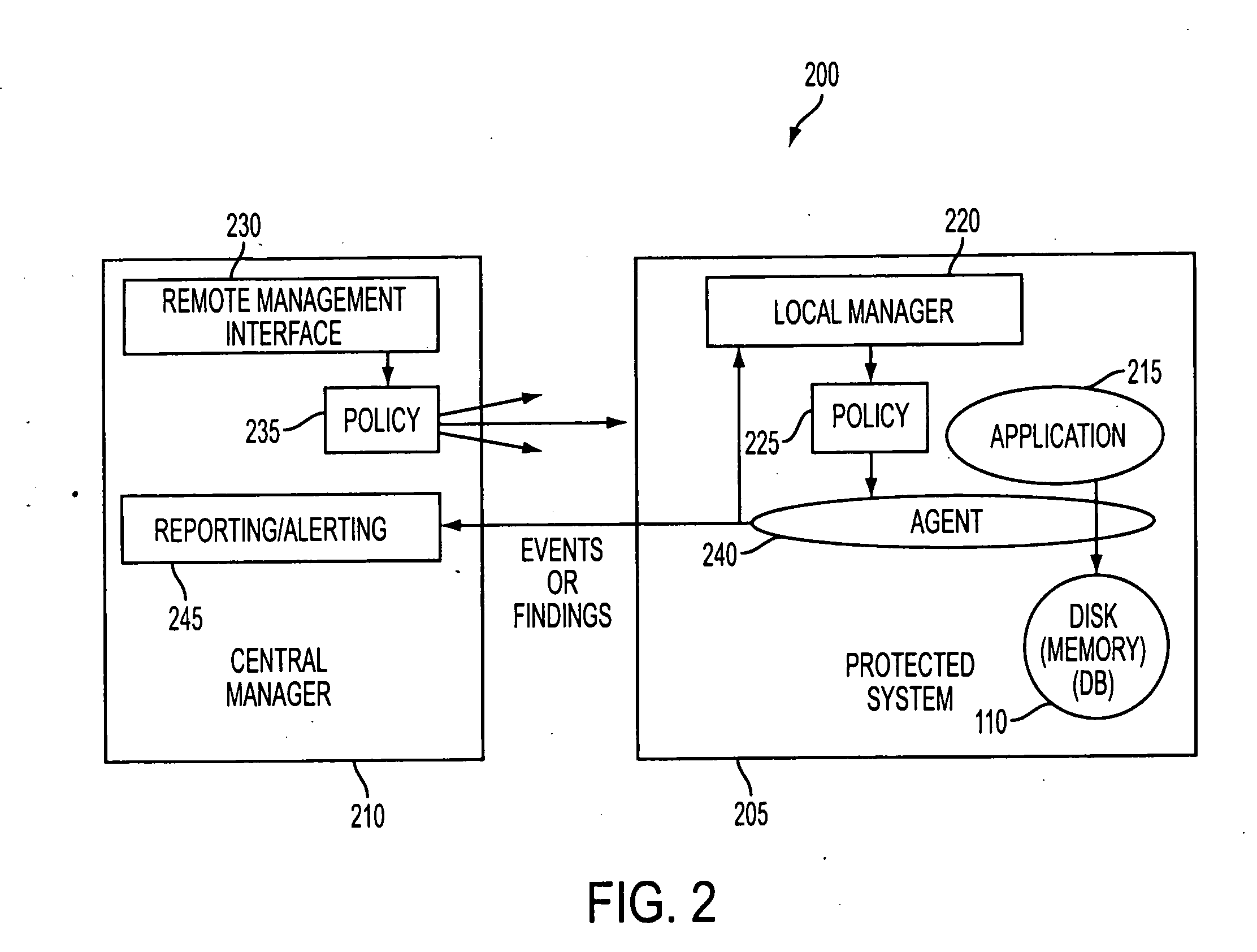
Method and apparatus for automatically detecting sensitive information, applying policies based on a structured taxonomy and dynamically enforcing and reporting on the protection of sensitive data through a software permission wrapper
InactiveUS20060048224A1Reduce spreadMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionInformation controlAutomatic control
The present invention relates to the automatic detection of sensitive digital information, and the identification methods, application and enforcement of information security policies for digital information controlled through a software permission wrapper throughout the useful life of the information. This invention includes a unique taxonomy that defines the policies and rules regarding how the information is controlled automatically throughout its useful lifecycle based on the type of information, the stage of the information lifecycle, the user / group role accessing the information, the locality of the information, and the expected threats to the information. The taxonomy is maintained in a database that associates information security control policies and actions to sensitive data. These policies are enforced through a software permission wrapper that is used to encapsulate sensitive digital information. The software permission wrapper is used to control access and enforce digital rights to the information based on the taxonomy based policies for that information. The permission wrapper can automatically change the protection of the information based on pre-defined protection states that can automatically enforce discretionary access control rights to the sensitive information controlled in the permission wrapper. The changes to the level of protection occur dynamically based on changes in user locality, stage of information lifecycle, and user / group role and the detection of threats. In addition, there is provided an internal audit capability describing what actions the user has performed, where the data is located, with whom and how the data has been shared.
Owner:ENCRYPTX CORP
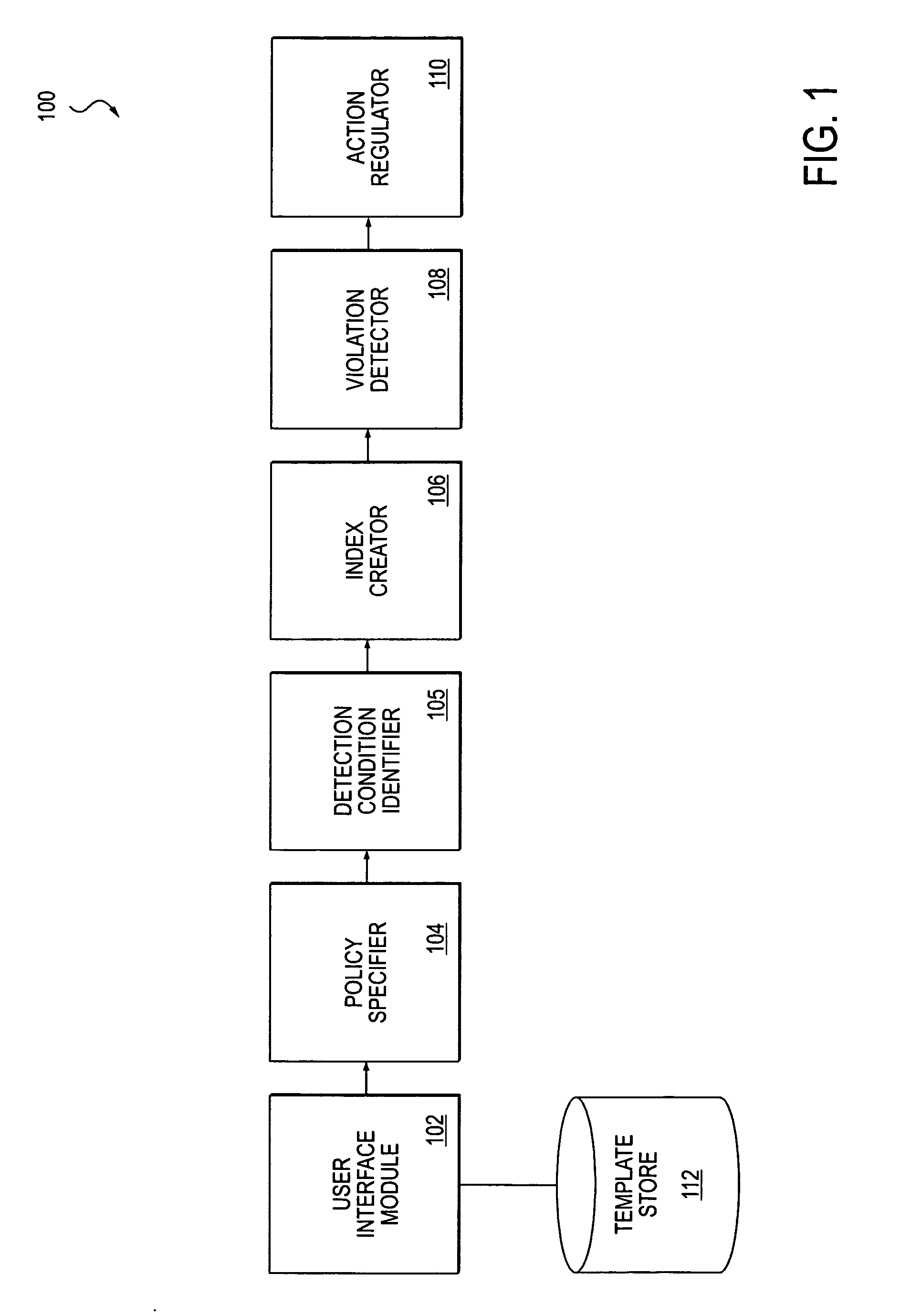
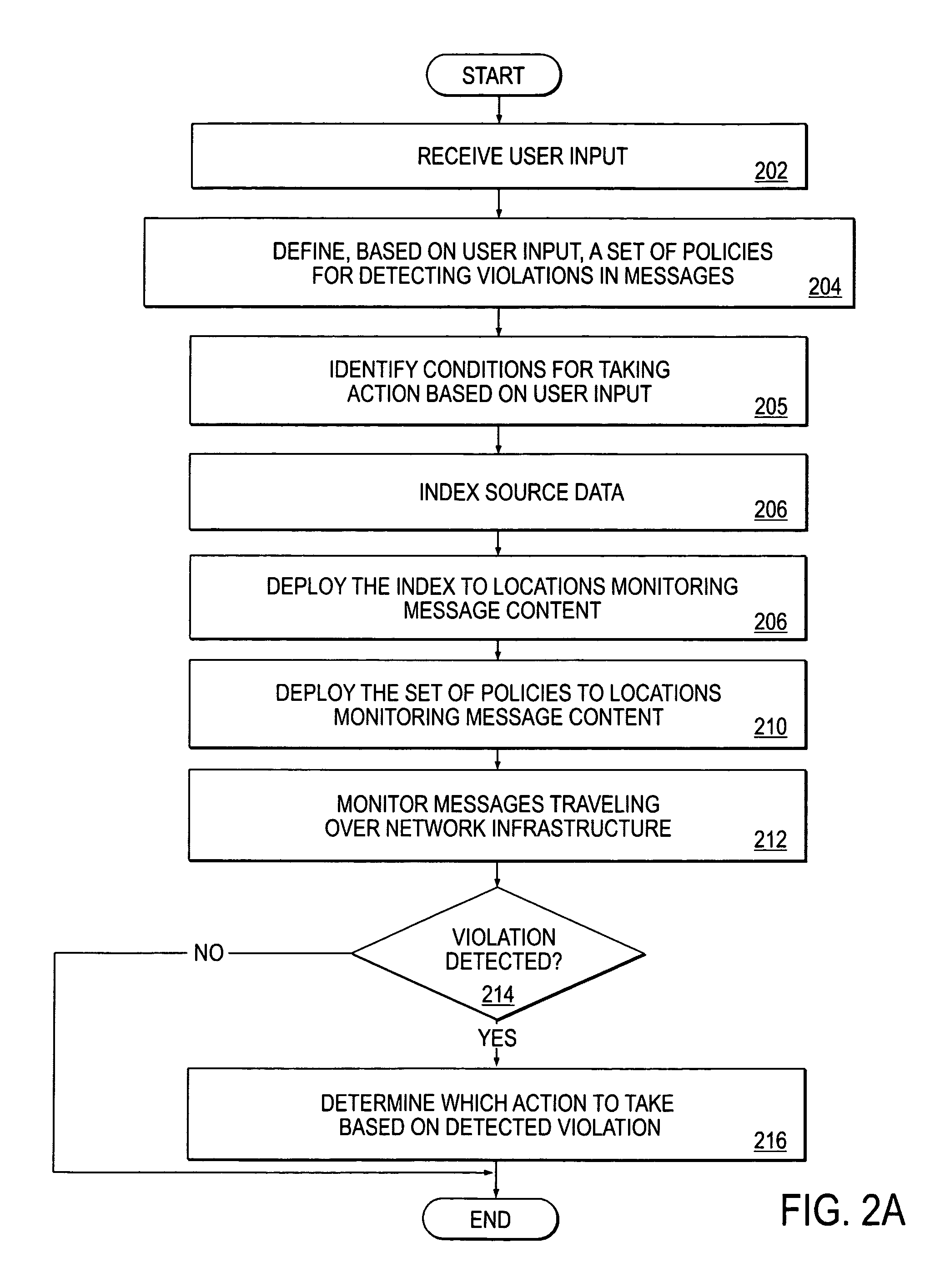
Method and apparatus for creating an information security policy based on a pre-configured template
ActiveUS20050086252A1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsInternet privacyInformation security policy
A method and apparatus for creating a policy based on a pre-configured template is described. In one embodiment, source data having a tabular structure is identified. Further, one of multiple policy templates is used to automatically create a policy for detecting information from any one or more rows within the tabular structure of the source data.
Owner:CA TECH INC
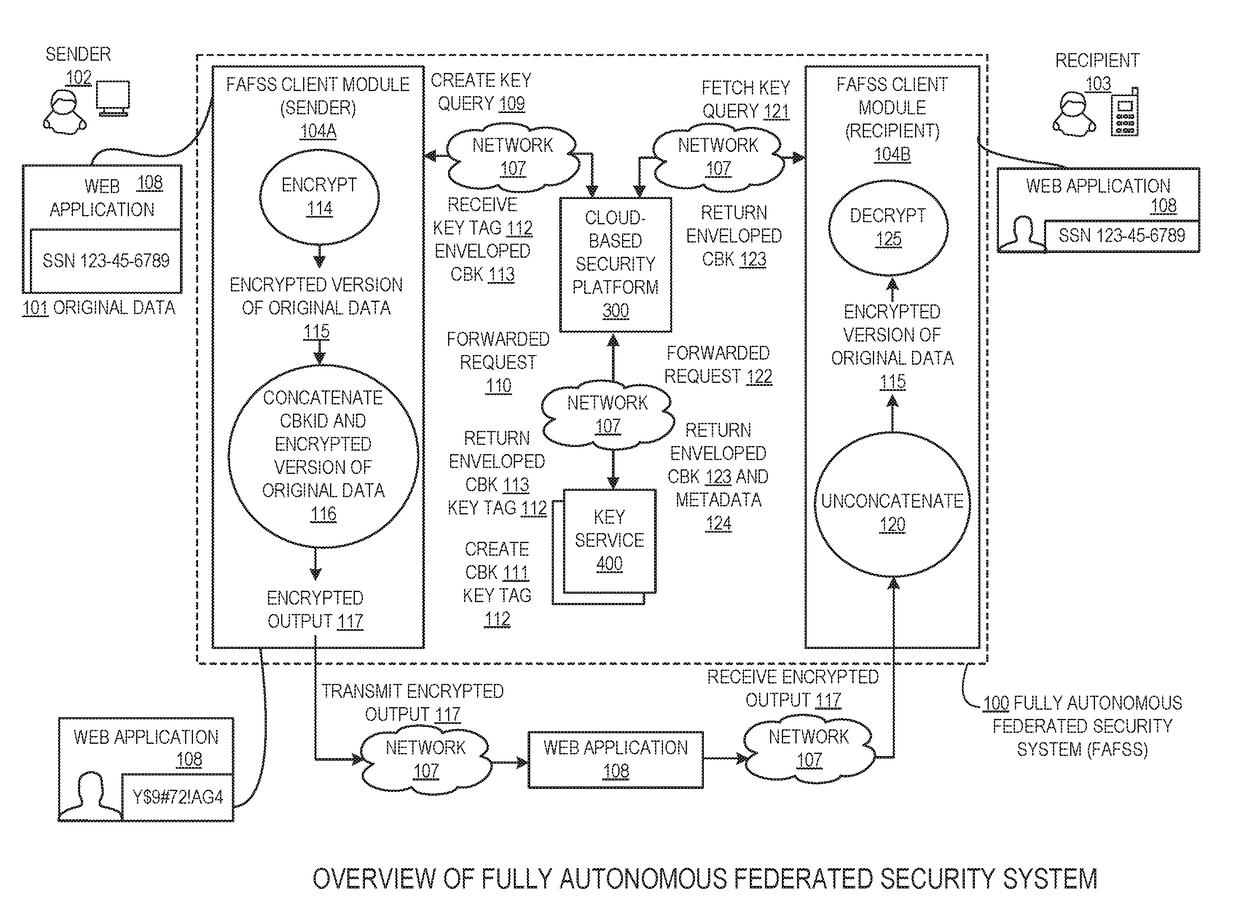
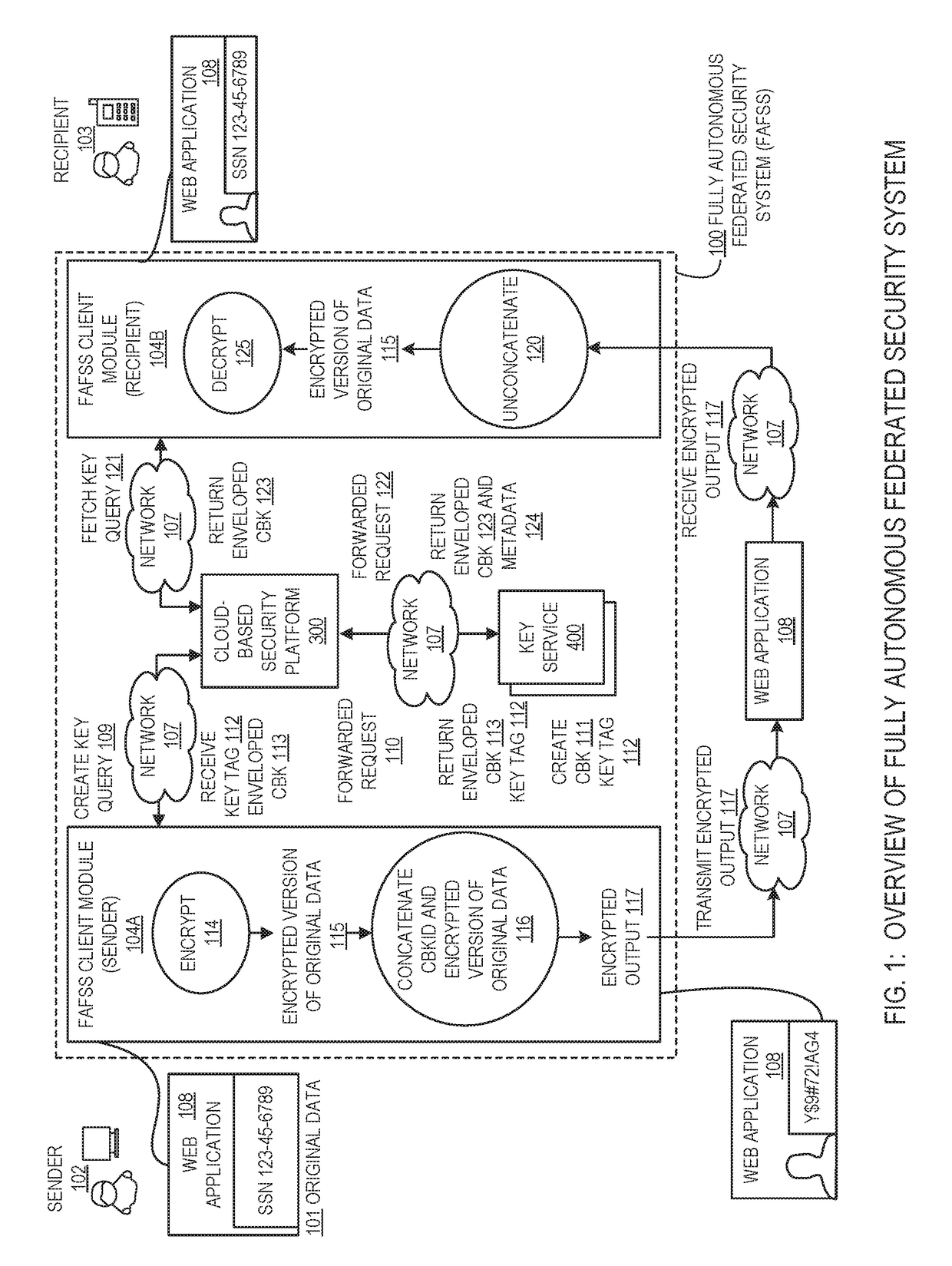
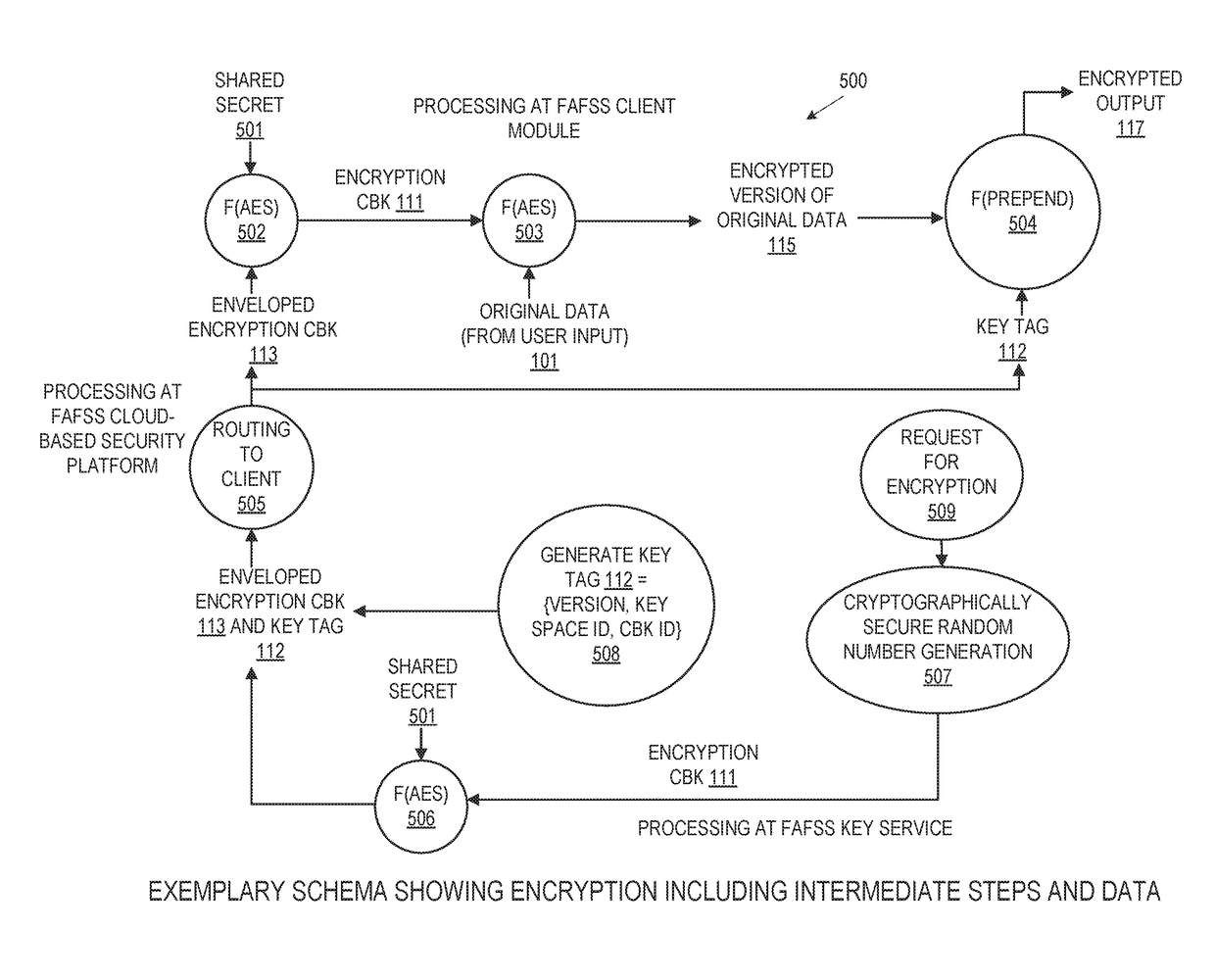
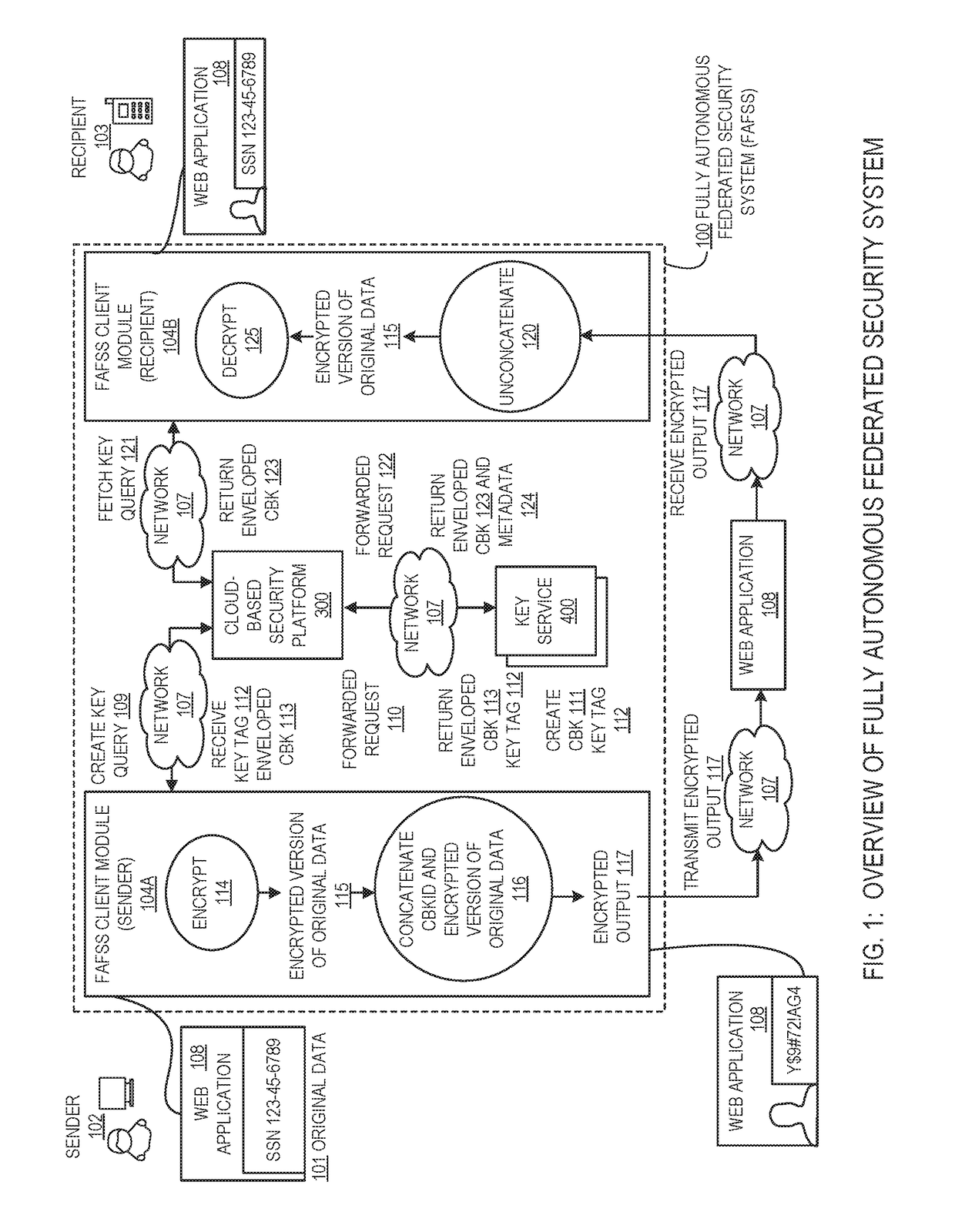
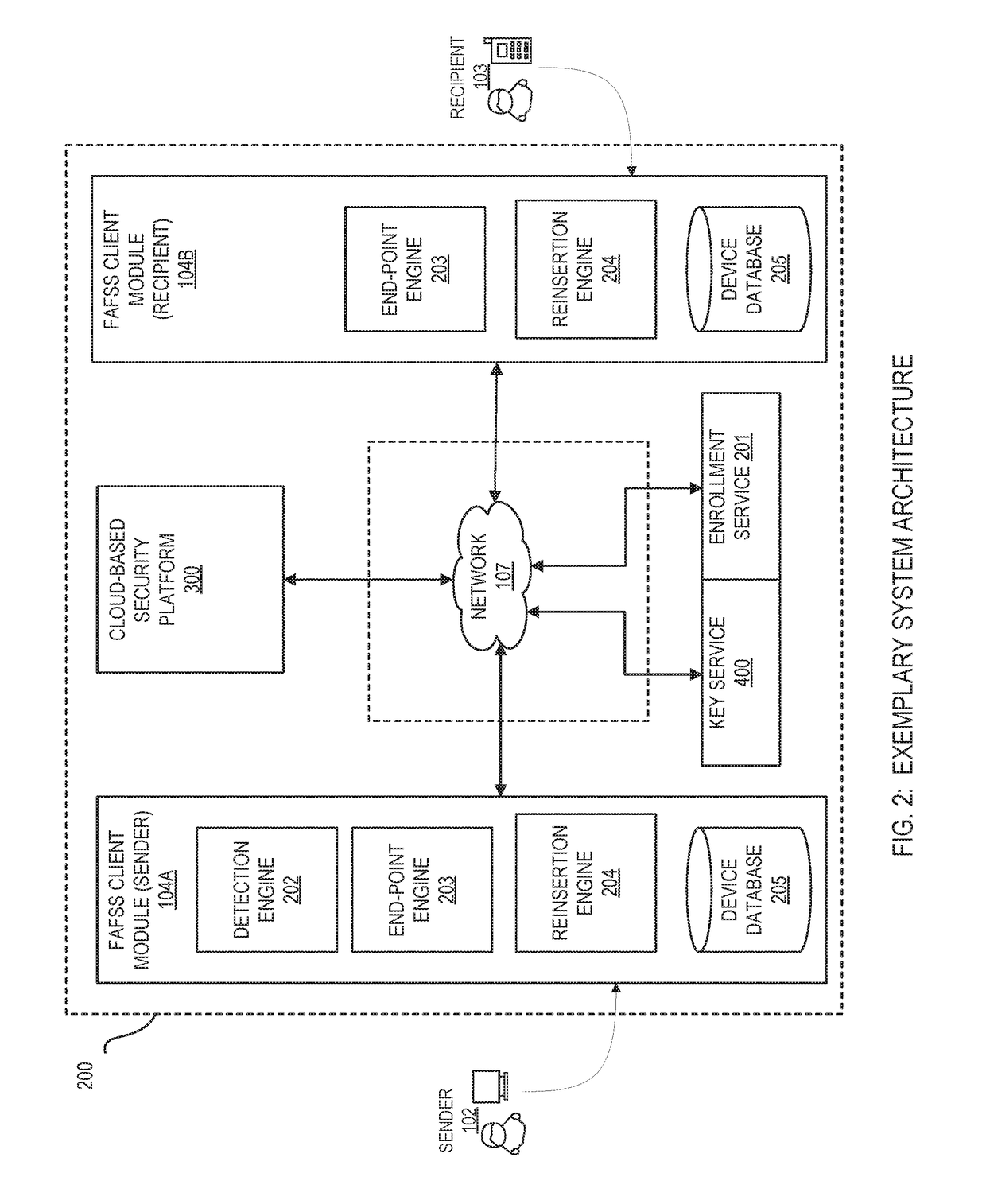
Systems and methods for encryption and provision of information security using platform services
ActiveUS9608809B1Enhanced interactionOptimizationKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data protectionCiphertextOriginal data
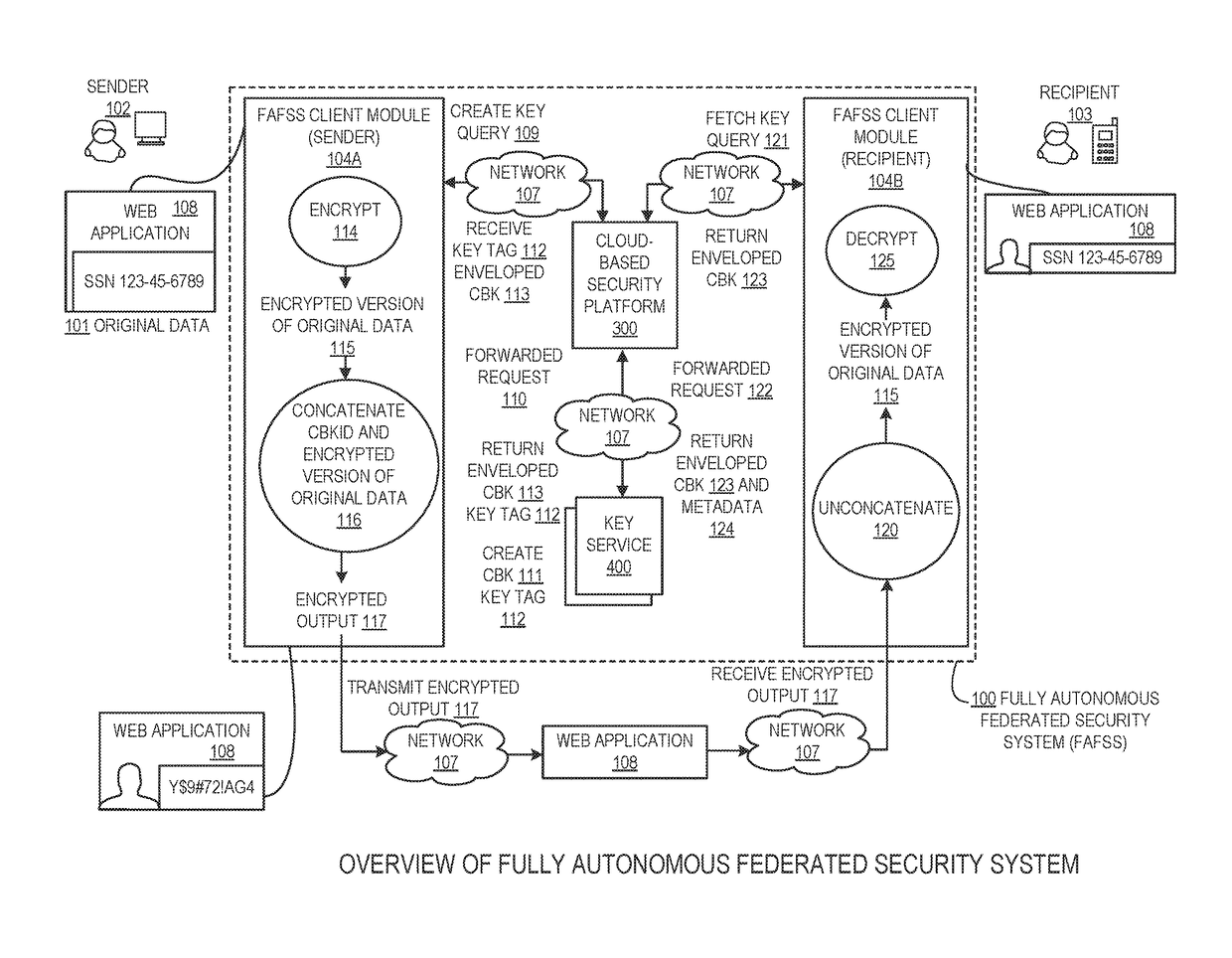
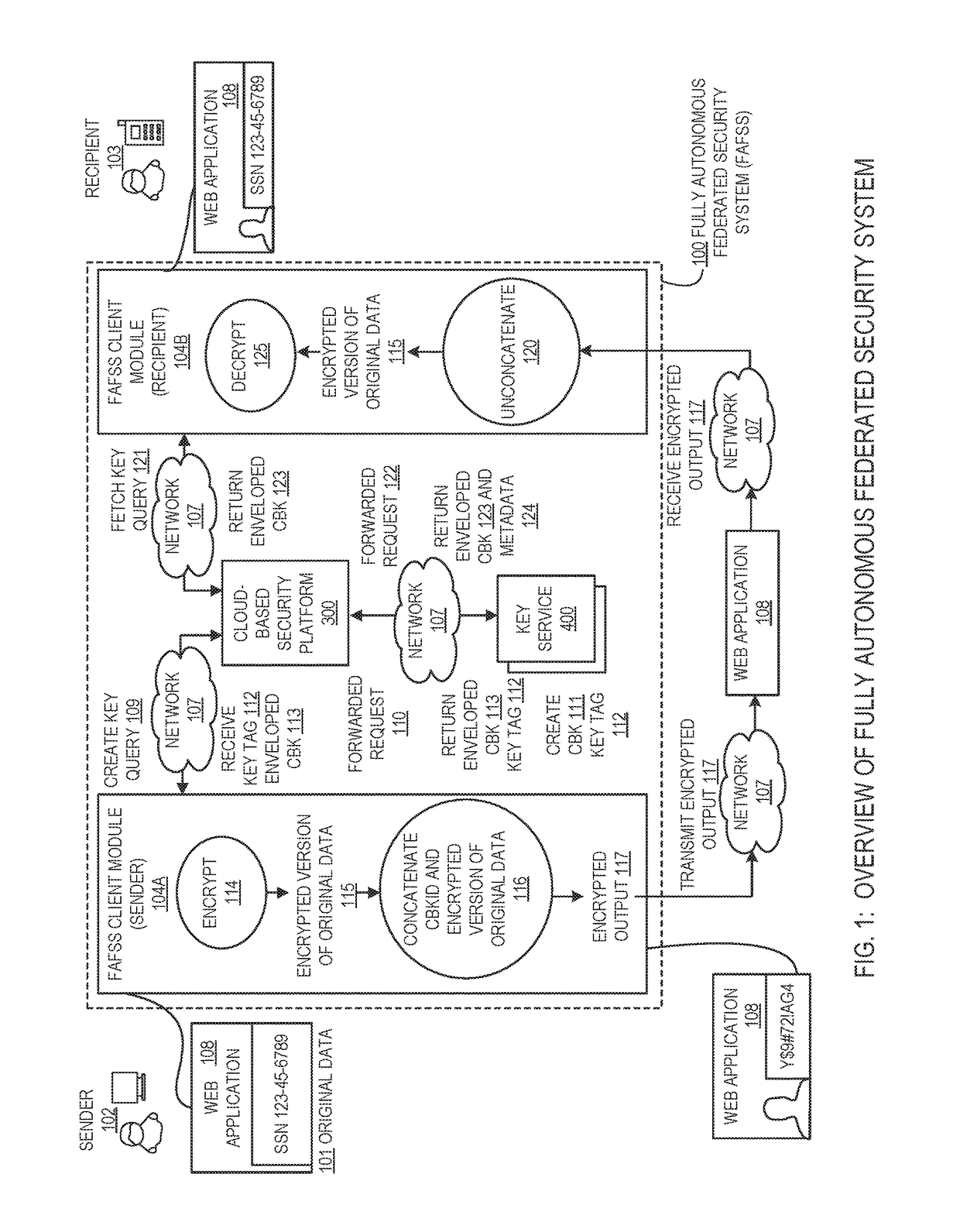
Systems and methods for securing or encrypting data or other information arising from a user's interaction with software and / or hardware, resulting in transformation of original data into ciphertext. Generally, the ciphertext is generated using context-based keys that depend on the environment in which the original data originated and / or was accessed. The ciphertext can be stored in a user's storage device or in an enterprise database (e.g., at-rest encryption) or shared with other users (e.g., cryptographic communication). The system generally allows for secure federation across organizations, including mechanisms to ensure that the system itself and any other actor with pervasive access to the network cannot compromise the confidentially of the protected data.
Owner:IONIC SECURITY
Method and apparatus for creating an information security policy based on a pre-configured template
ActiveUS8225371B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalInternet privacyInformation security policy
A method and apparatus for creating a policy based on a pre-configured template is described. In one embodiment, source data having a tabular structure is identified. Further, one of multiple policy templates is used to automatically create a policy for detecting information from any one or more rows within the tabular structure of the source data.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Systems and methods for encryption and provision of information security using platform services
ActiveUS9608810B1Enhanced interactionOptimizationKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data protectionCiphertextOriginal data
Systems and methods for securing or encrypting data or other information arising from a user's interaction with software and / or hardware, resulting in transformation of original data into ciphertext. Generally, the ciphertext is generated using context-based keys that depend on the environment in which the original data originated and / or was accessed. The ciphertext can be stored in a user's storage device or in an enterprise database (e.g., at-rest encryption) or shared with other users (e.g., cryptographic communication). The system generally allows for secure federation across organizations, including mechanisms to ensure that the system itself and any other actor with pervasive access to the network cannot compromise the confidentially of the protected data.
Owner:IONIC SECURITY
Information security policy evaluation system and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS7415728B2Efficiently and appropriately defined and operatedGuaranteed uptimeFinanceMemory loss protectionInformation processingEvaluation system
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Systems and methods for encryption and provision of information security using platform services
ActiveUS9614670B1Enhanced interactionOptimizationKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCiphertextOriginal data
Owner:IONIC SECURITY
Information security policy evaluation system and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS20050076243A1Guaranteed uptimeEfficiently and appropriately definedFinanceMemory loss protectionInformation processingInternet privacy
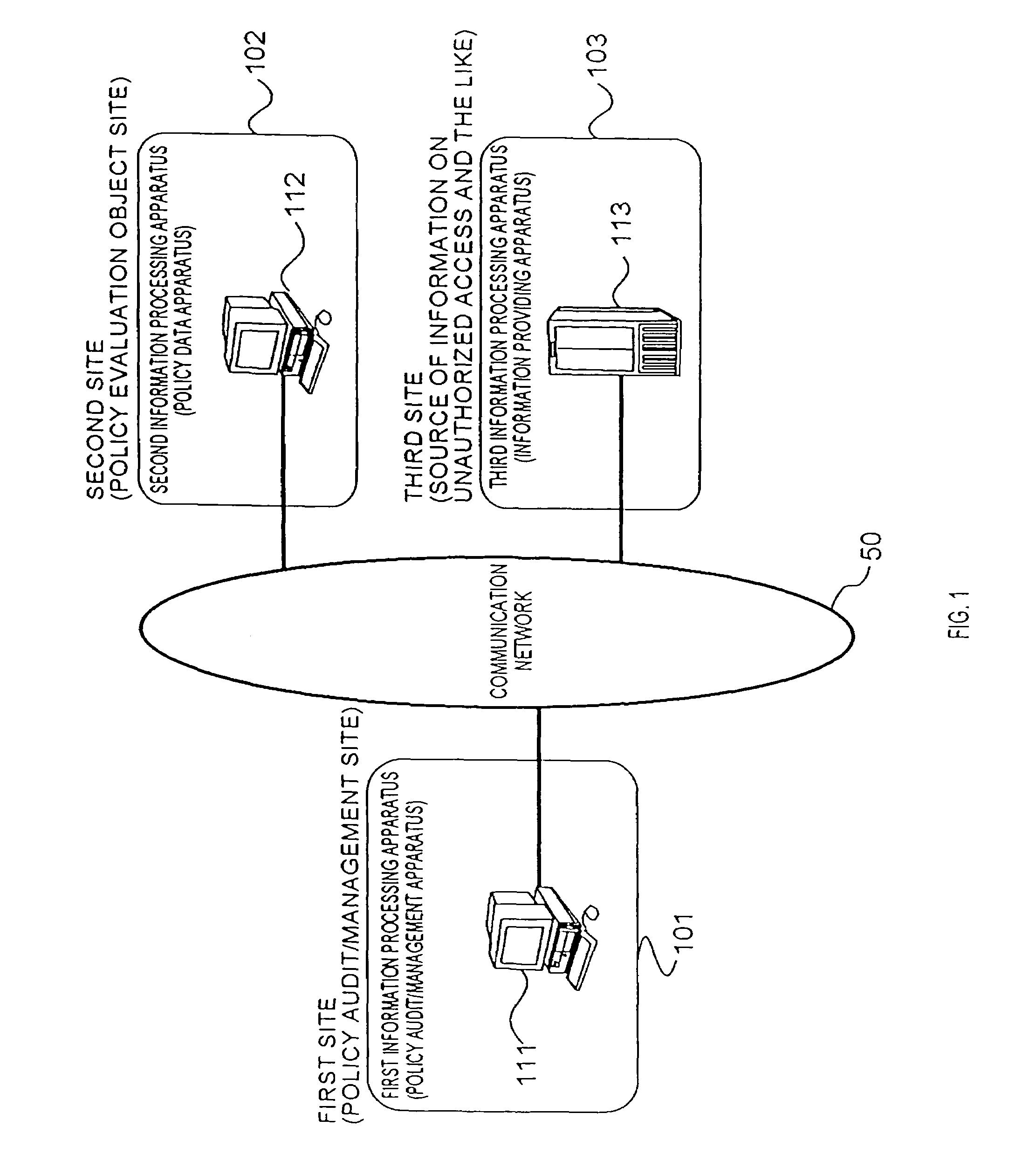
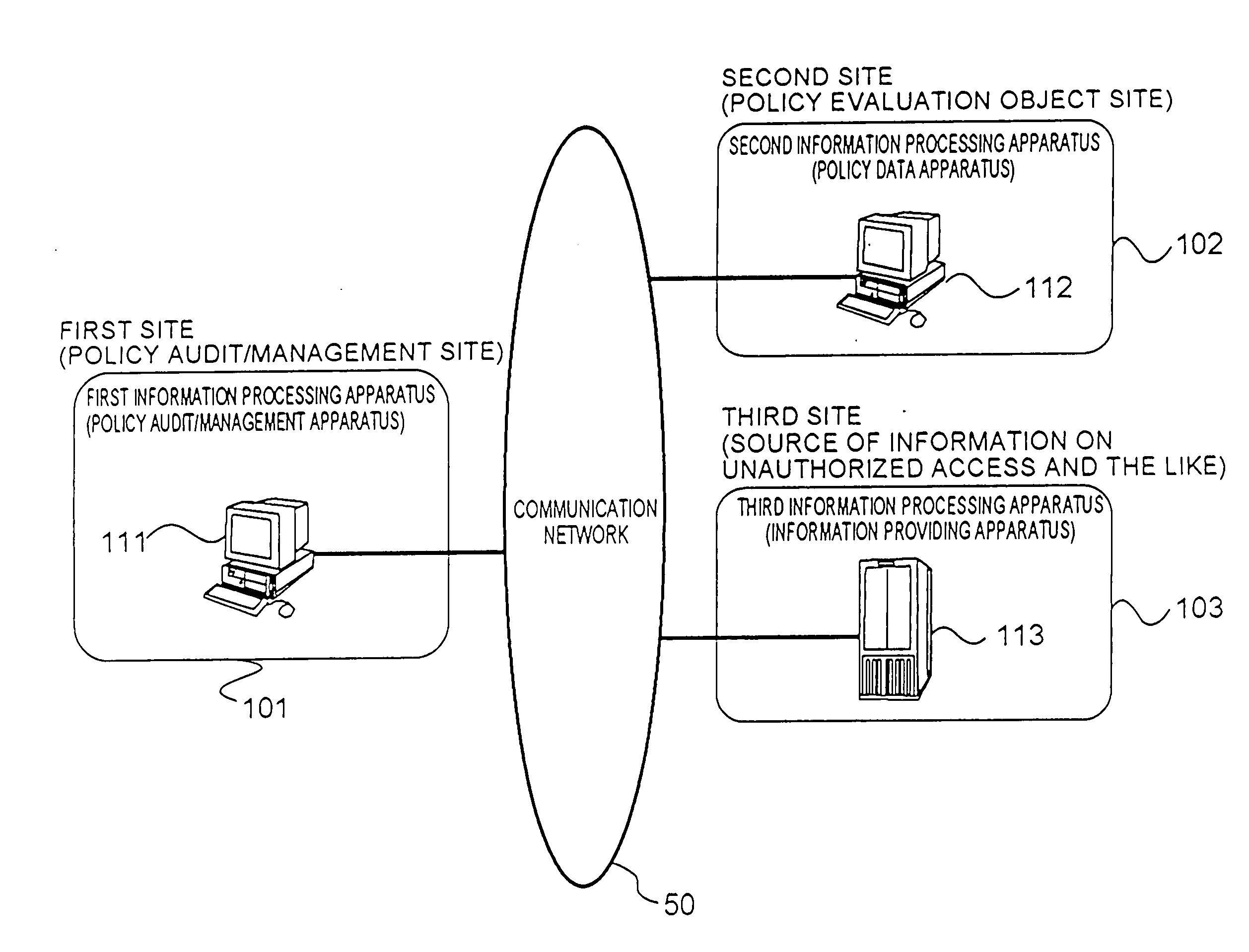
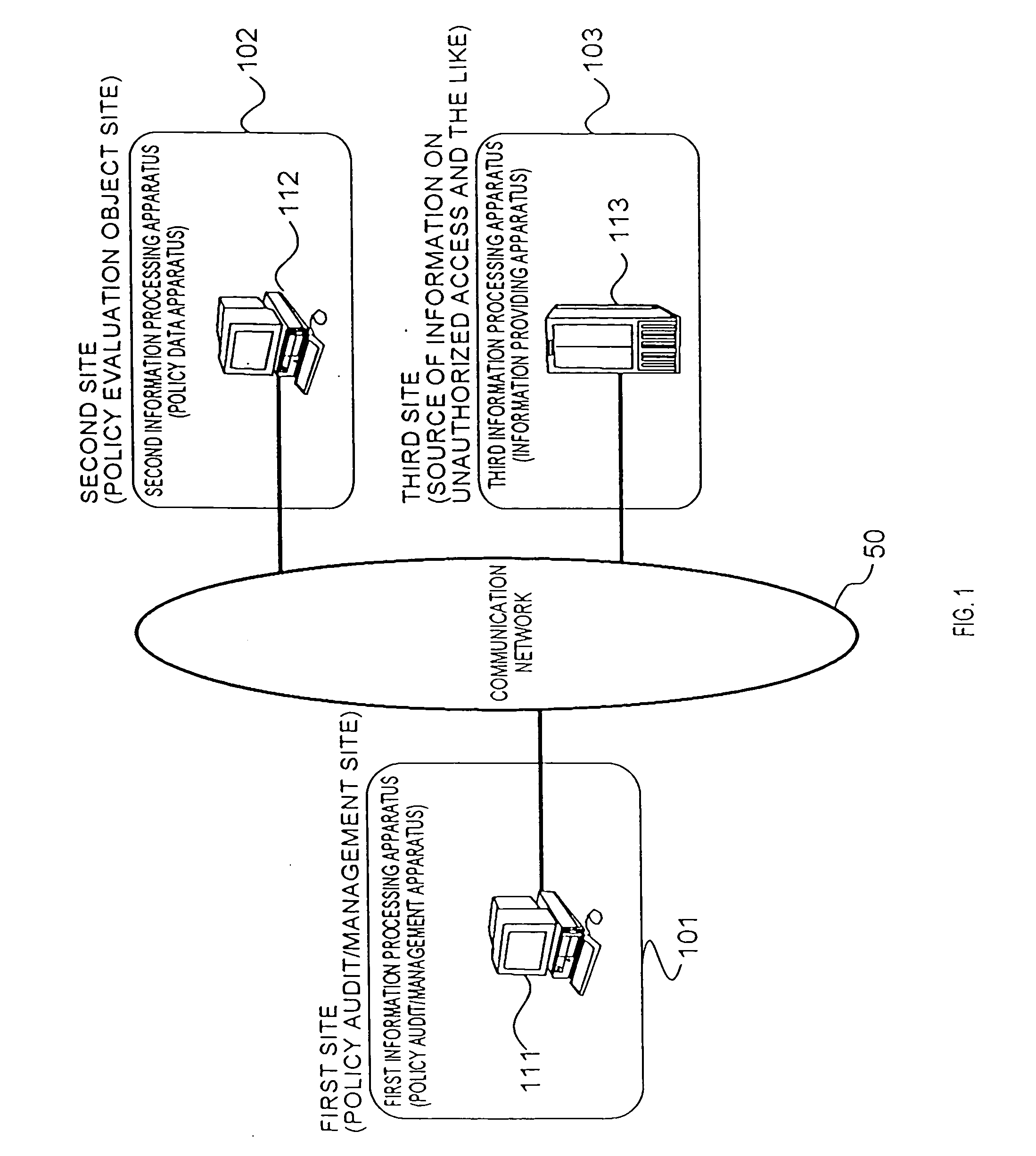
In order to provide an information security policy evaluation system in which information security policies can be efficiently and appropriately defined and operated in an organization, such as a corporation, treated threats operated on a second site 102 are transmitted from a second information processing apparatus 112 on the second site 102 to a first information processing apparatus 111 on a first site 101, threat information is transmitted from a third site 103 collecting information on threats to the first information processing apparatus 111 on the first site 101. The first information processing apparatus 111 extracts treated threats which have been effective for threats having occurred actually, and untreated threats, out of the received treated threat and generates an evaluation report in which these are described. Moreover, a compensation amount of insurance against threats is changed based on the generated evaluation report.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Industrial control system standard compliance evaluation system
InactiveCN107067179AReasonable designImprove the protective effectResourcesData switching networksTechnical standardUnit system
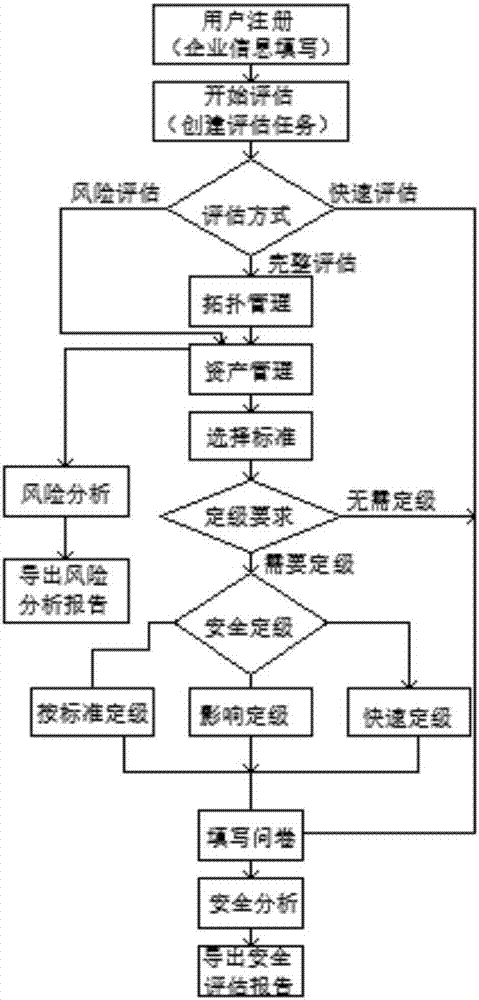
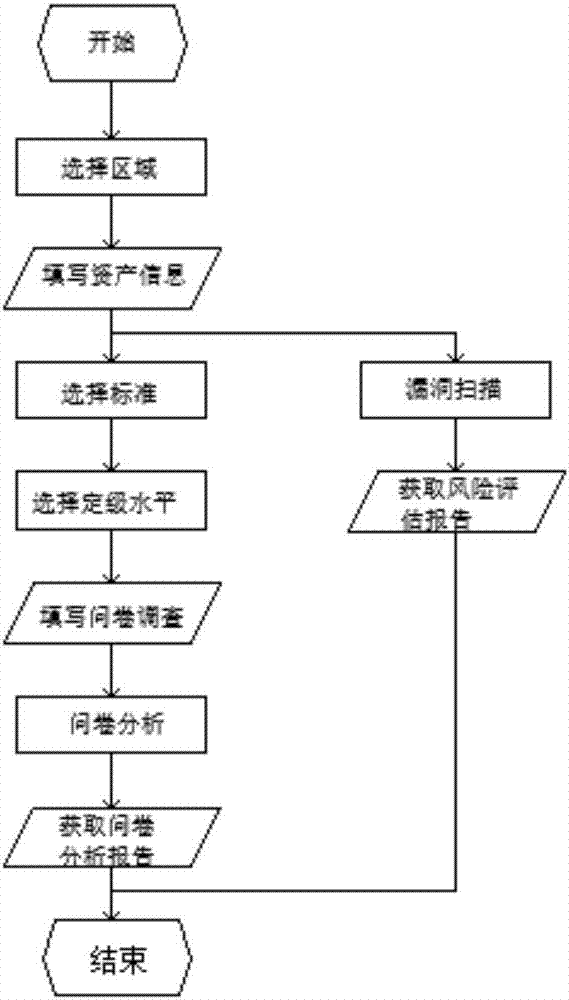
The invention discloses an industrial control system standard compliance evaluation system, which includes an evaluation module, a topology generation module, an asset management module and a report management module. The beneficial effect of the present invention is: carry out the conformity evaluation of relevant standards to the industrial control system, fully consider the particularity of the industrial control system and the safety requirements of different levels, carefully sort out the assets of the industrial control system system of the unit, and consider the environmental and human factors Analyze the threats faced by the industrial control system, analyze the vulnerability of the industrial control system from the aspects of technology and management, combine the existing security measures, analyze the existing risks of the industrial control system, balance the benefits and costs, formulate a risk treatment plan, and integrate the industrial The residual risk of the control system is controlled at an acceptable level, and the information security strategy is adjusted according to the evaluation results to help industrial enterprises improve their information security protection capabilities.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS STANDARDIZATION INST +1
Secret information transmission method based on instant messaging platform
ActiveCN105207900AGuaranteed privacyEnsure safetyData switching networksThird partyInformation transmission
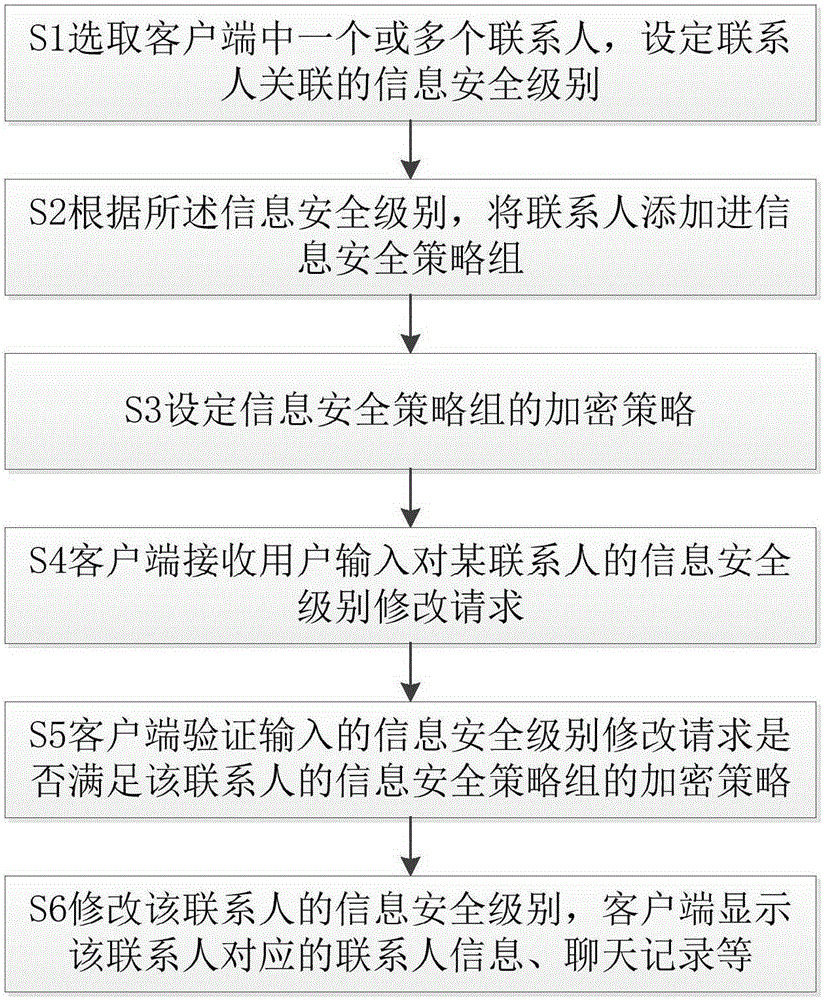
The invention provides a secret information transmission method based on an instant messaging platform. Through the method, a user can hide information of contacts at an instant messaging client, chatting records and a chatting process as required to prevent a third party from acquiring the secret information and the chatting records of the user under a condition that the instant messaging client logs in, so as to ensure the privacy and security of the instant messaging client. The method comprises the following steps: selecting one or more contacts at the client, setting a security level of information associated with the contacts; adding the contacts into an information security policy group according to the information safety level, wherein the information security policy group is used for hiding information of contacts corresponding to the contacts displayed on the client, the chatting records and the chatting process; setting an encrypted policy to the information security policy group, wherein the encrypted policy adopts a security certification manner to encrypt the security level of the information associated with the contacts.
Owner:上海掌信信息科技有限公司
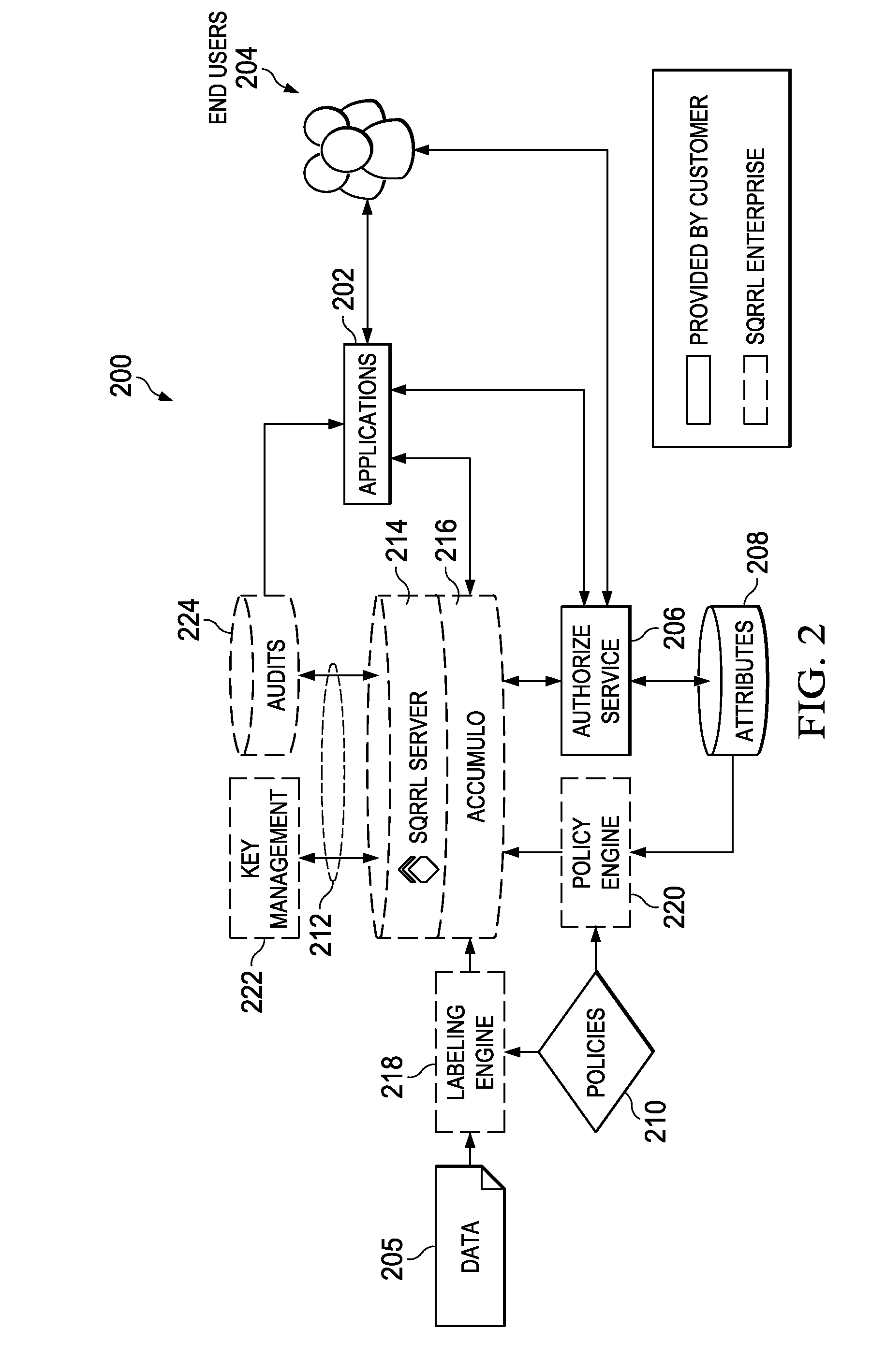
Policy-based data-centric access control in a sorted, distributed key-value data store
InactiveUS8914323B1Digital data processing detailsDigital data protectionData memoryMedia access control
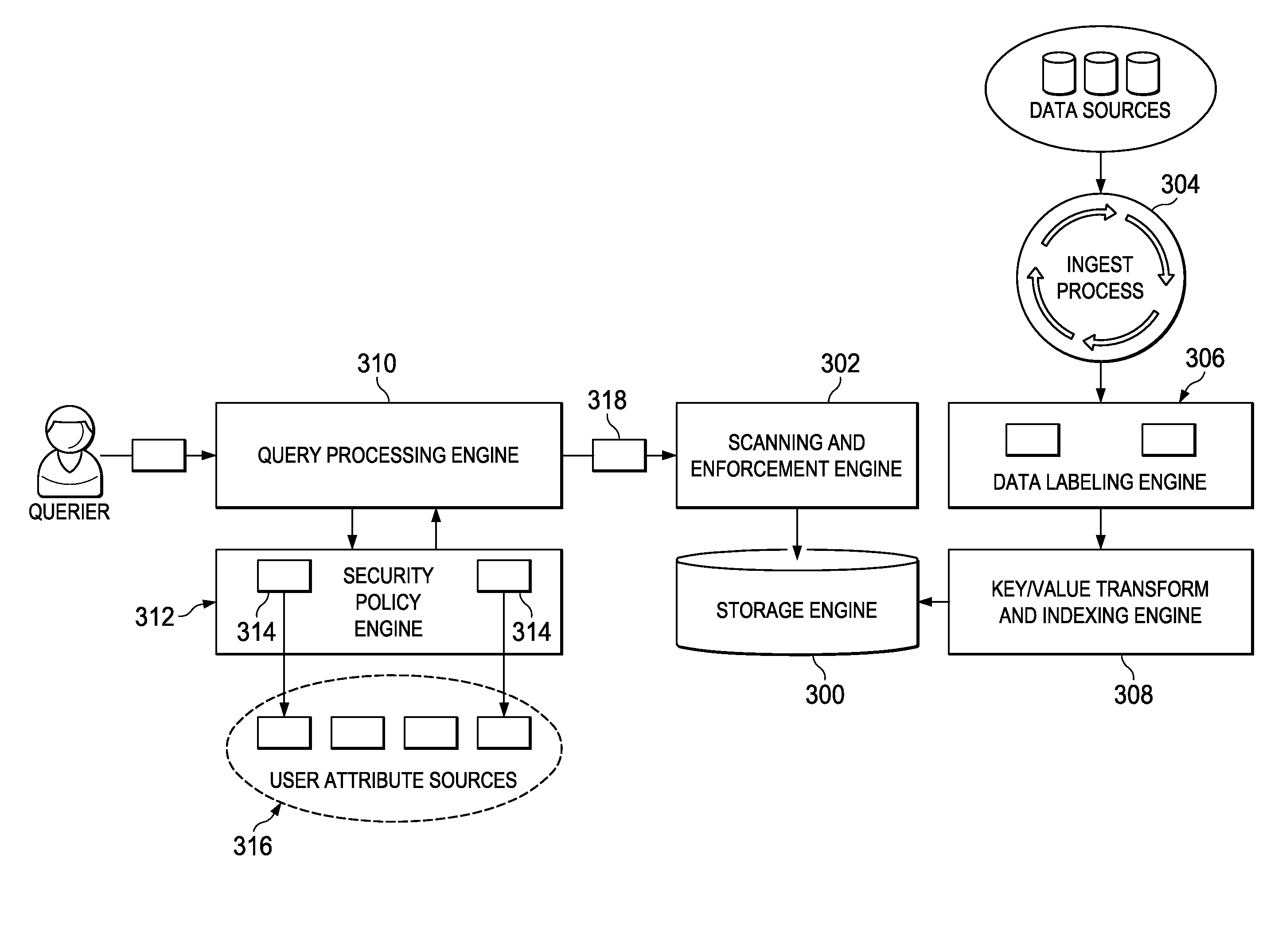
A method, apparatus and computer program product for policy-based access control in association with a sorted, distributed key-value data store in which keys comprise a cell-level access control. In this approach, an information security policy is used to create a set of pluggable policies. A pluggable policy may be used during data ingest time, when data is being ingested into the data store, and a pluggable policy may be used during query time, when a query to the data store is received for processing against data stored therein. Generally, a pluggable policy associates one or more user-centric attributes (or some function thereof), to a particular set of data-centric attributes. By using pluggable policies, preferably at both ingest time and query time, the data store is enhanced to provide a seamless and secure policy-based access control mechanism in association with the cell-level access control enabled by the data store.
Owner:A9 COM INC
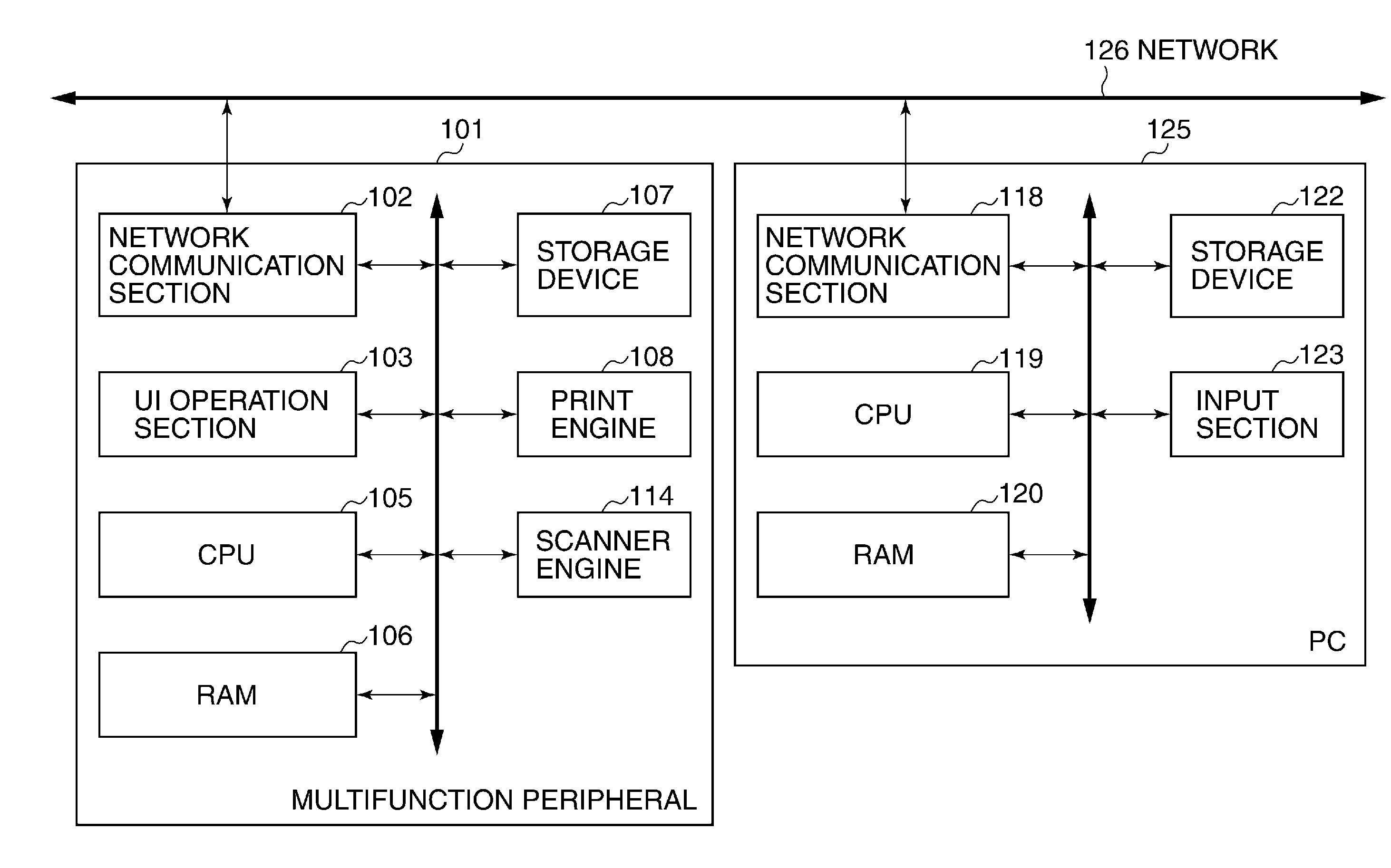
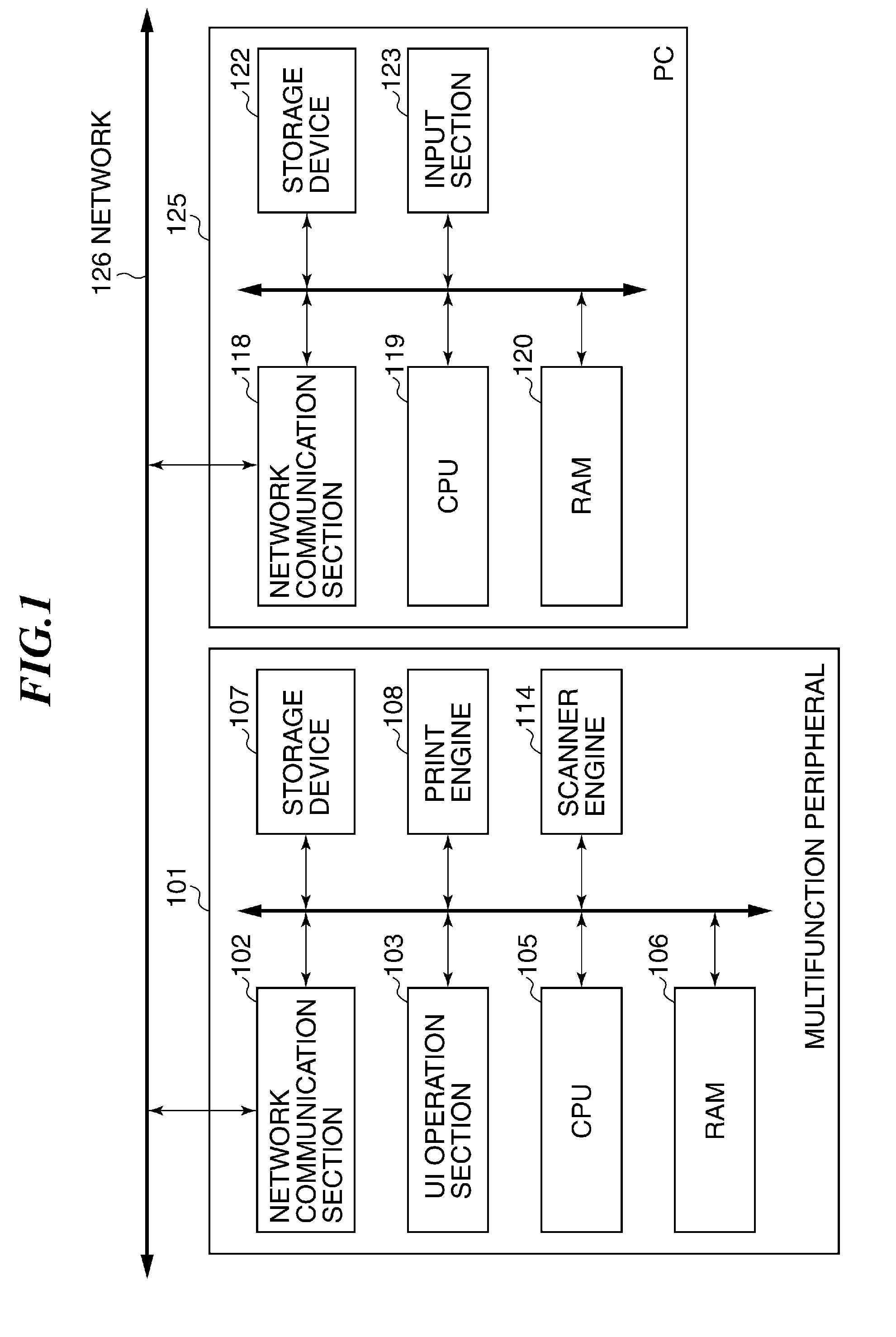
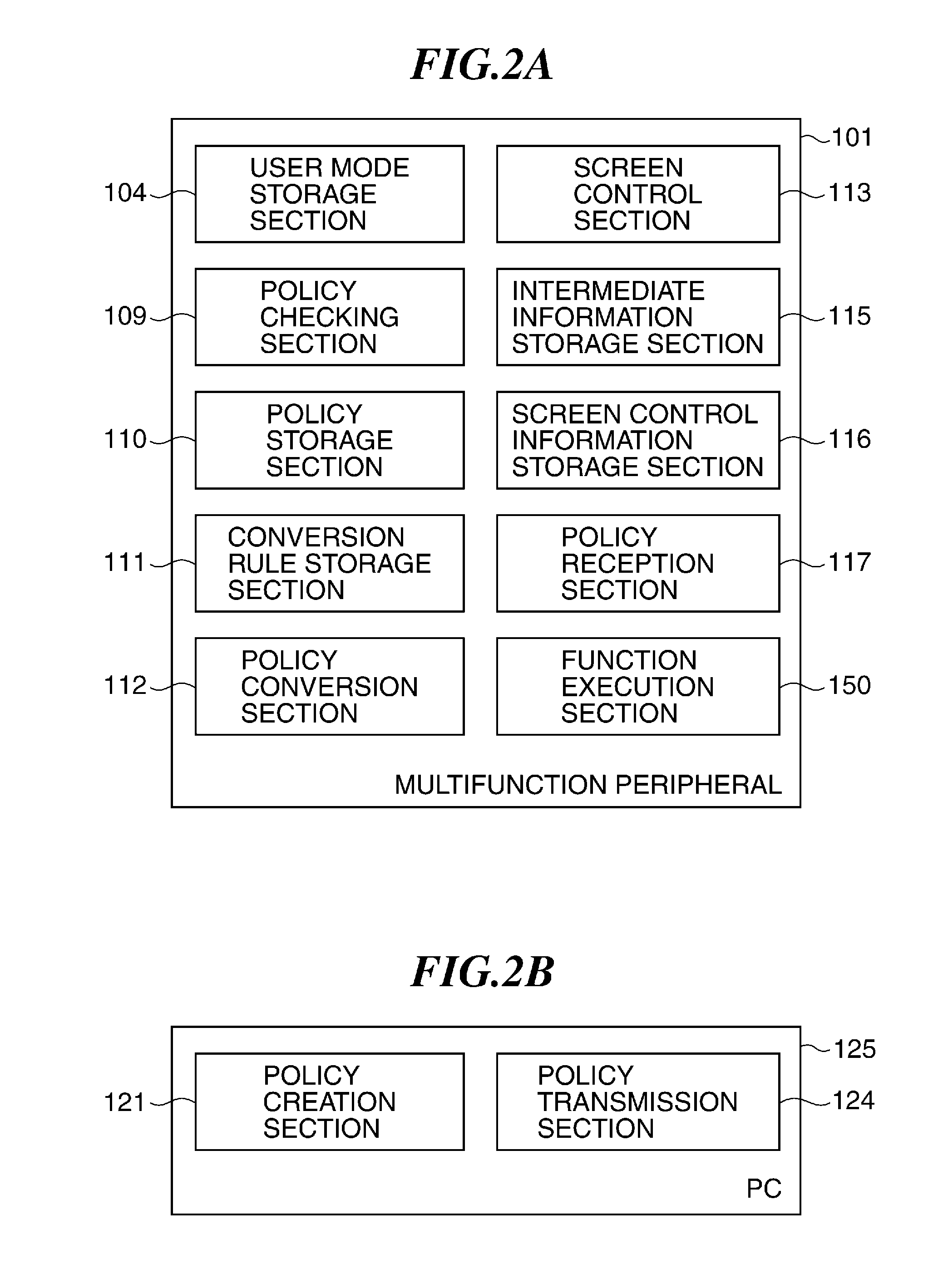
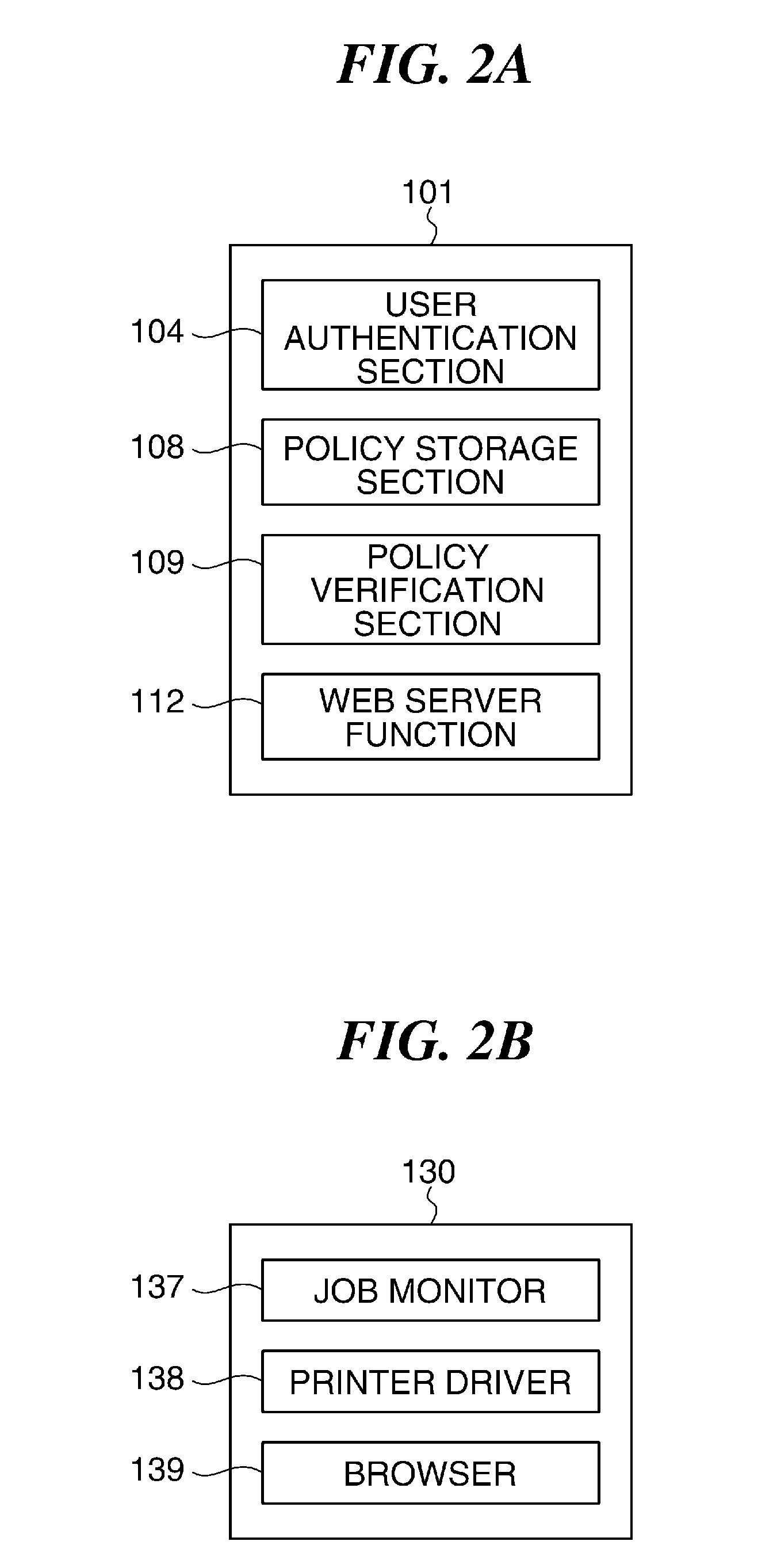
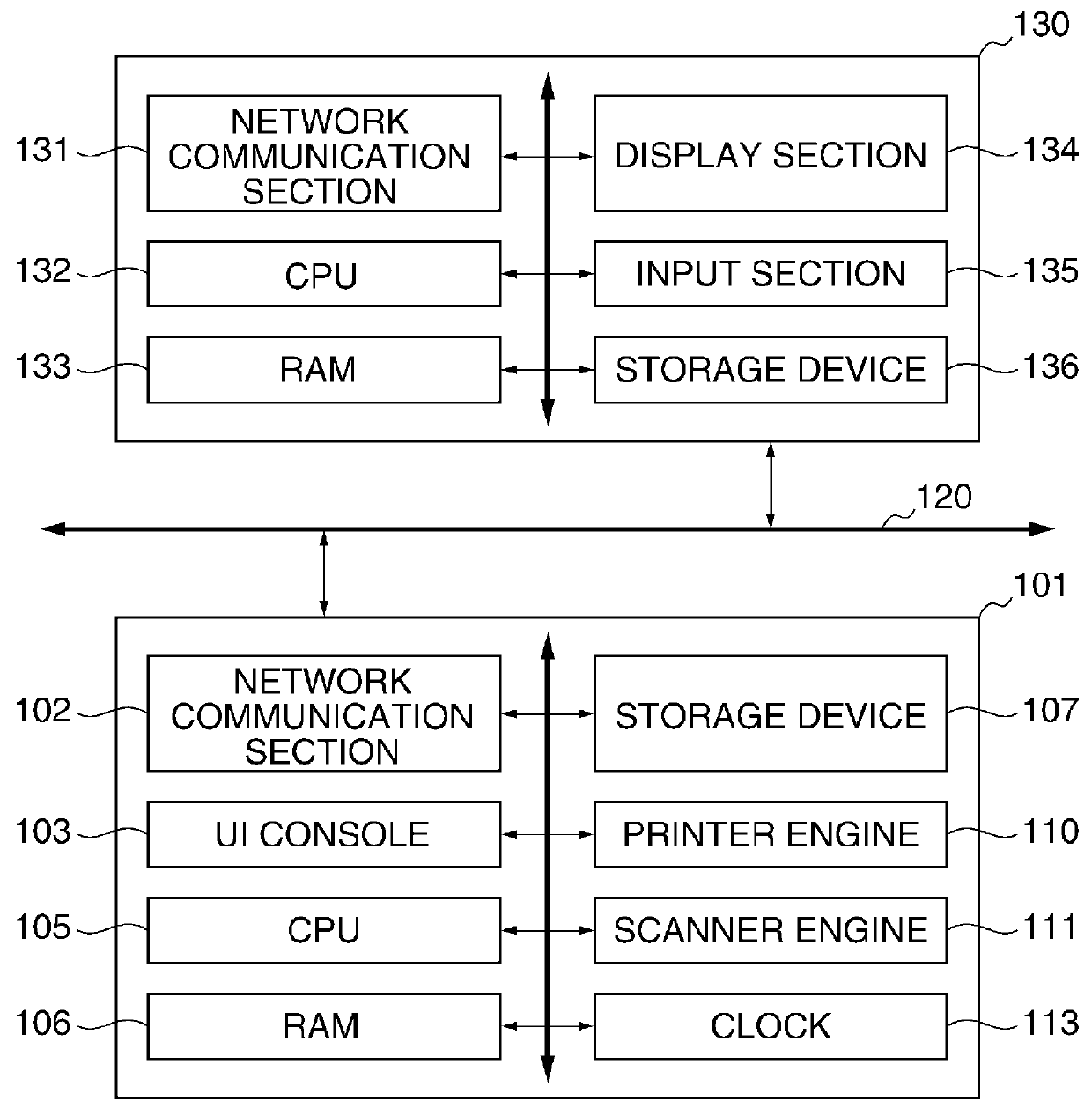
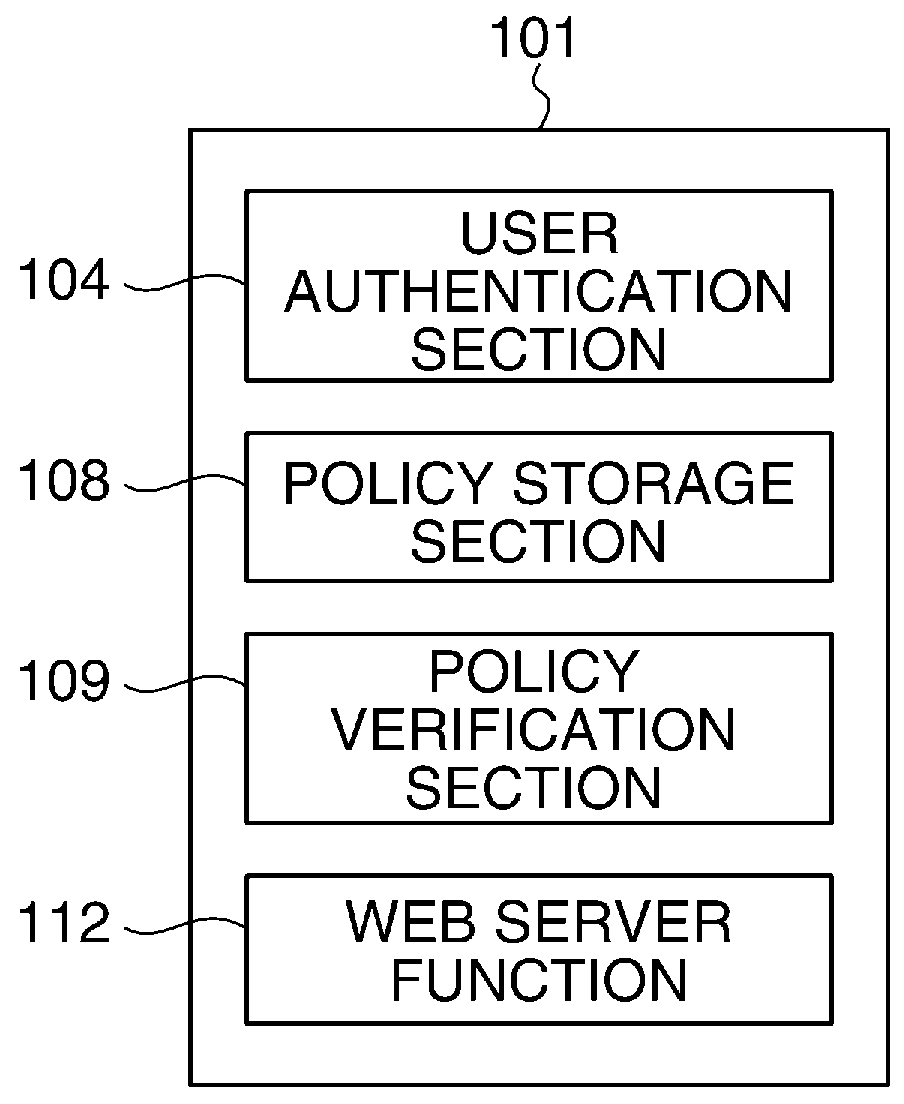
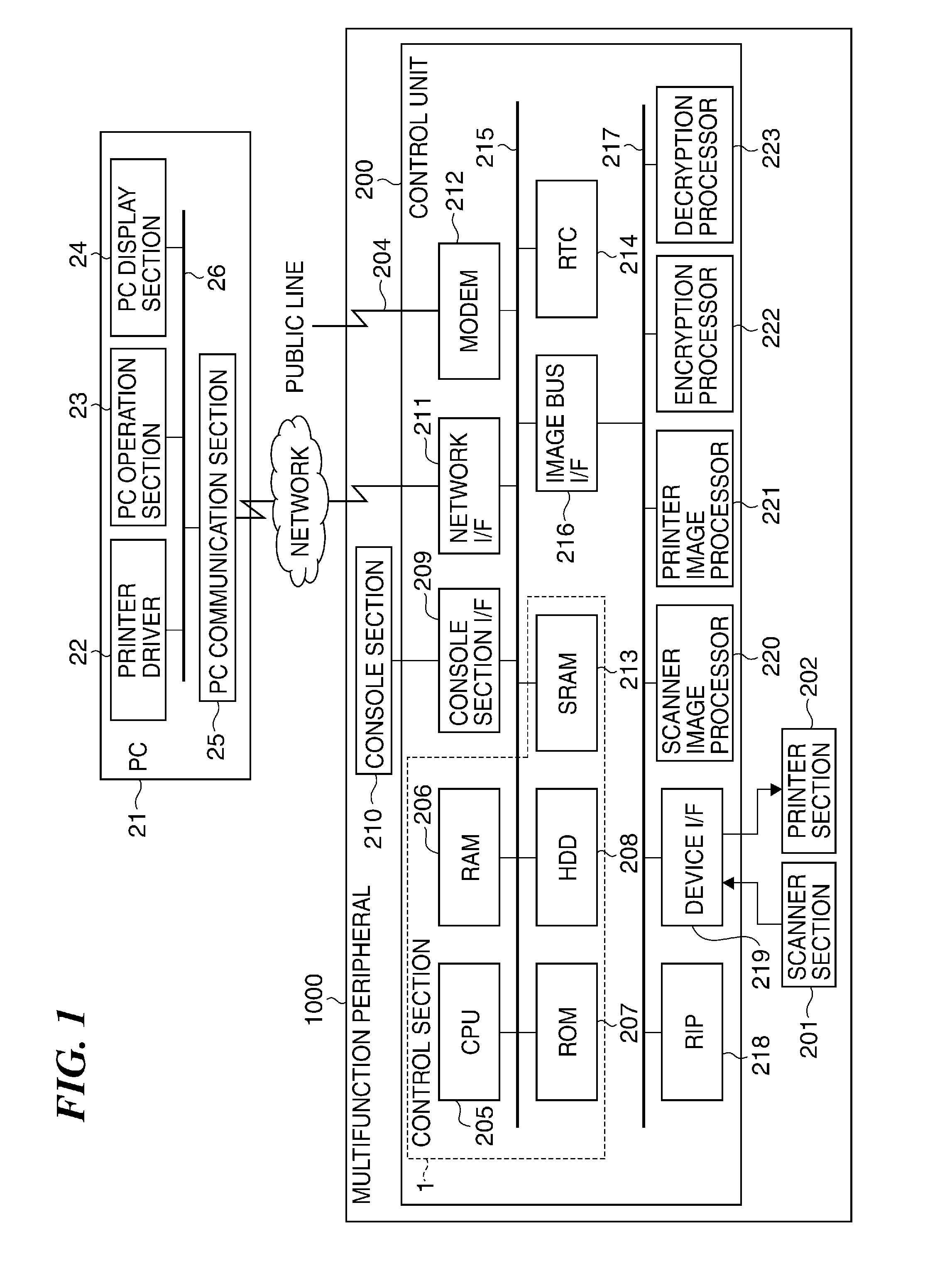
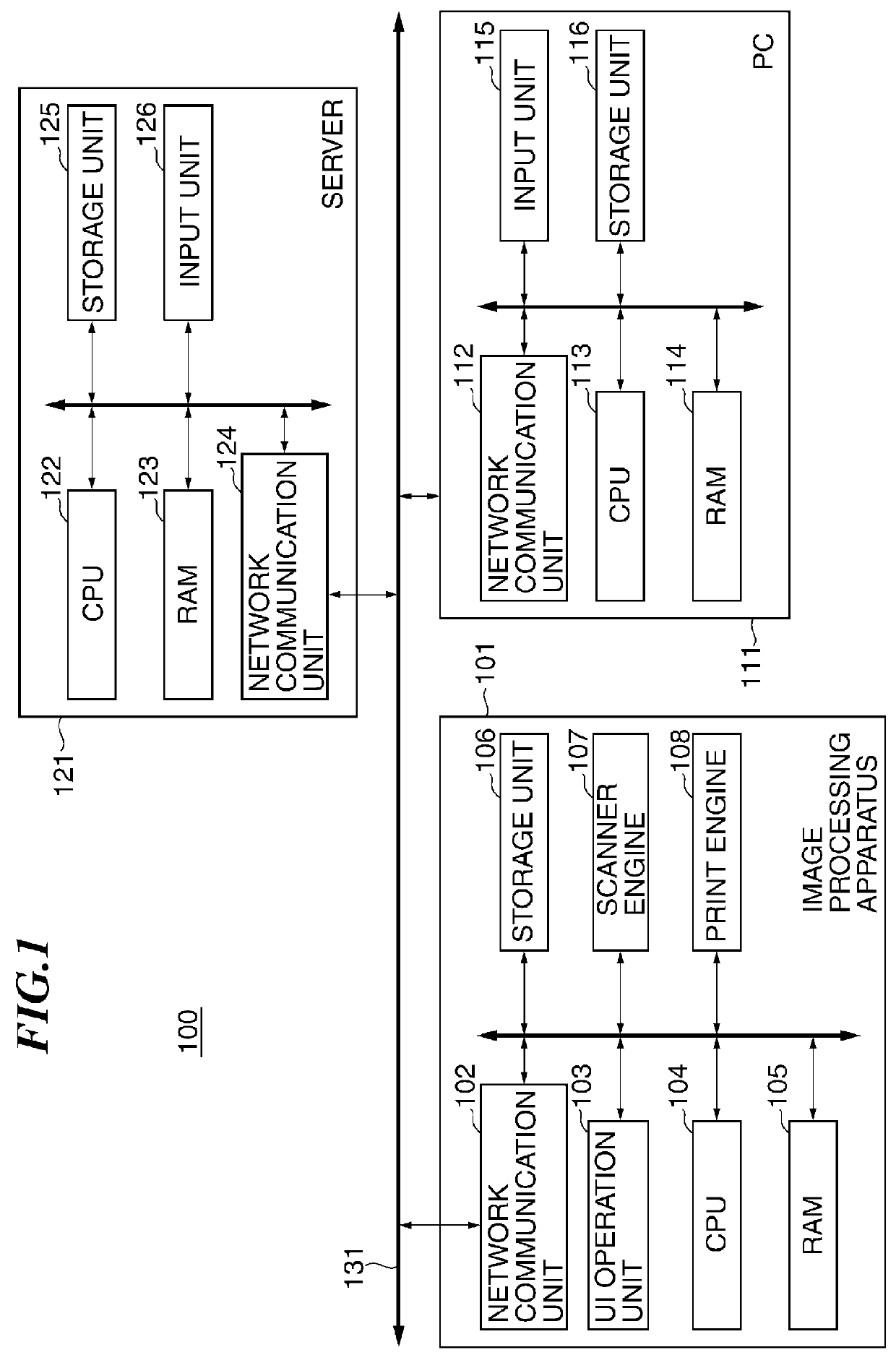
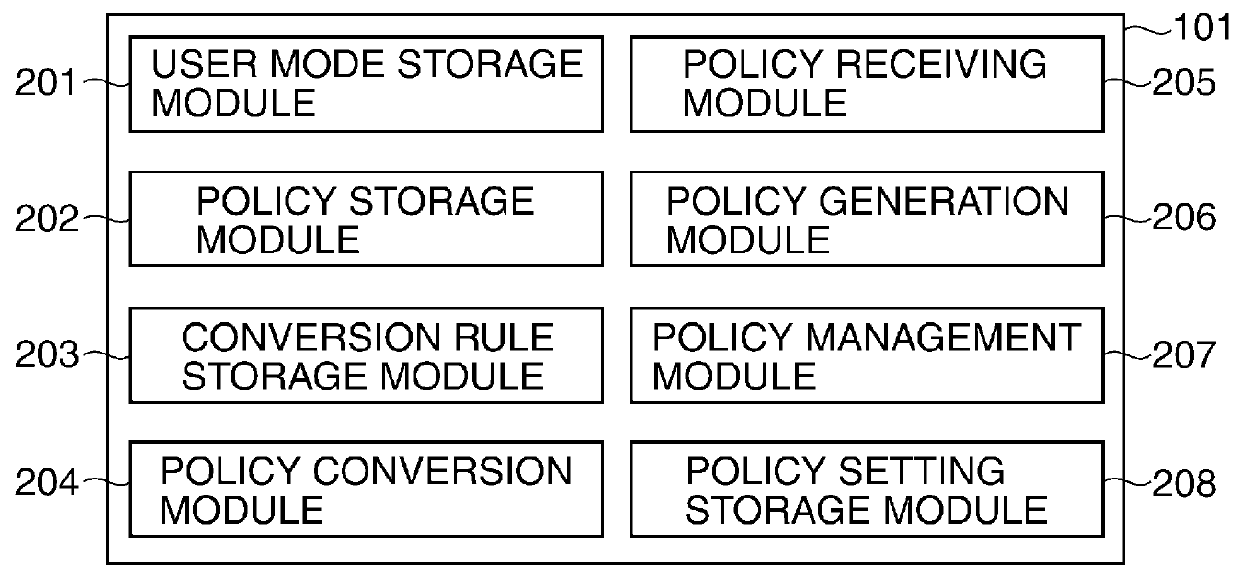
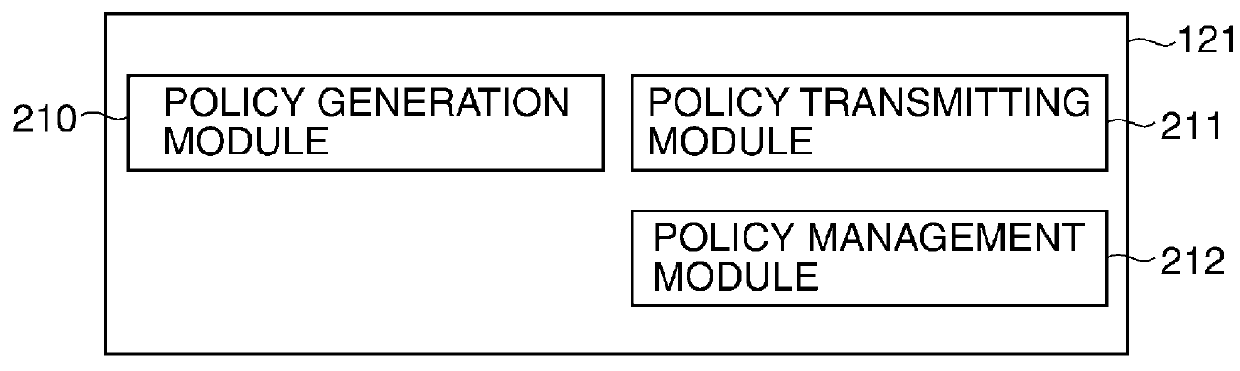
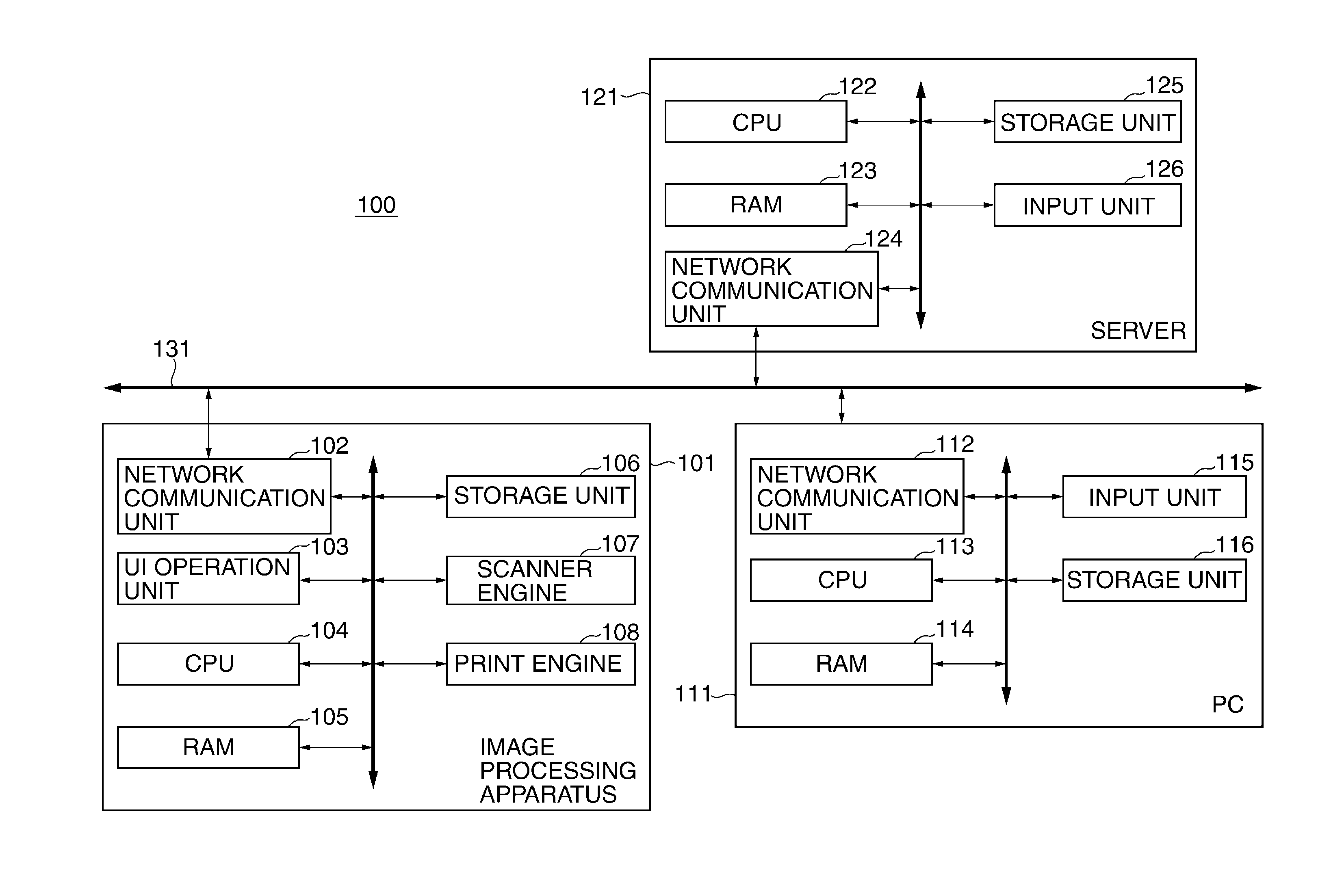
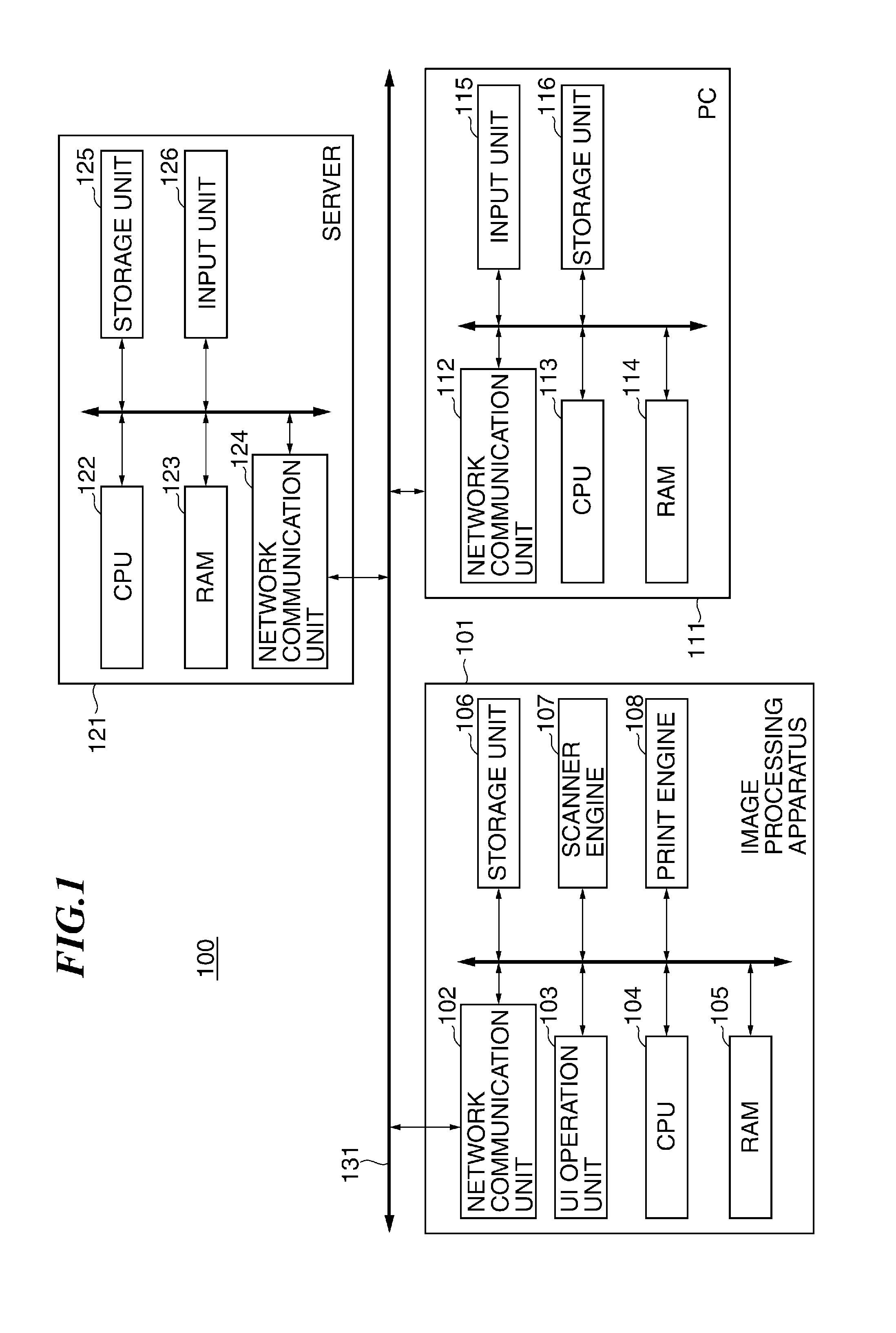
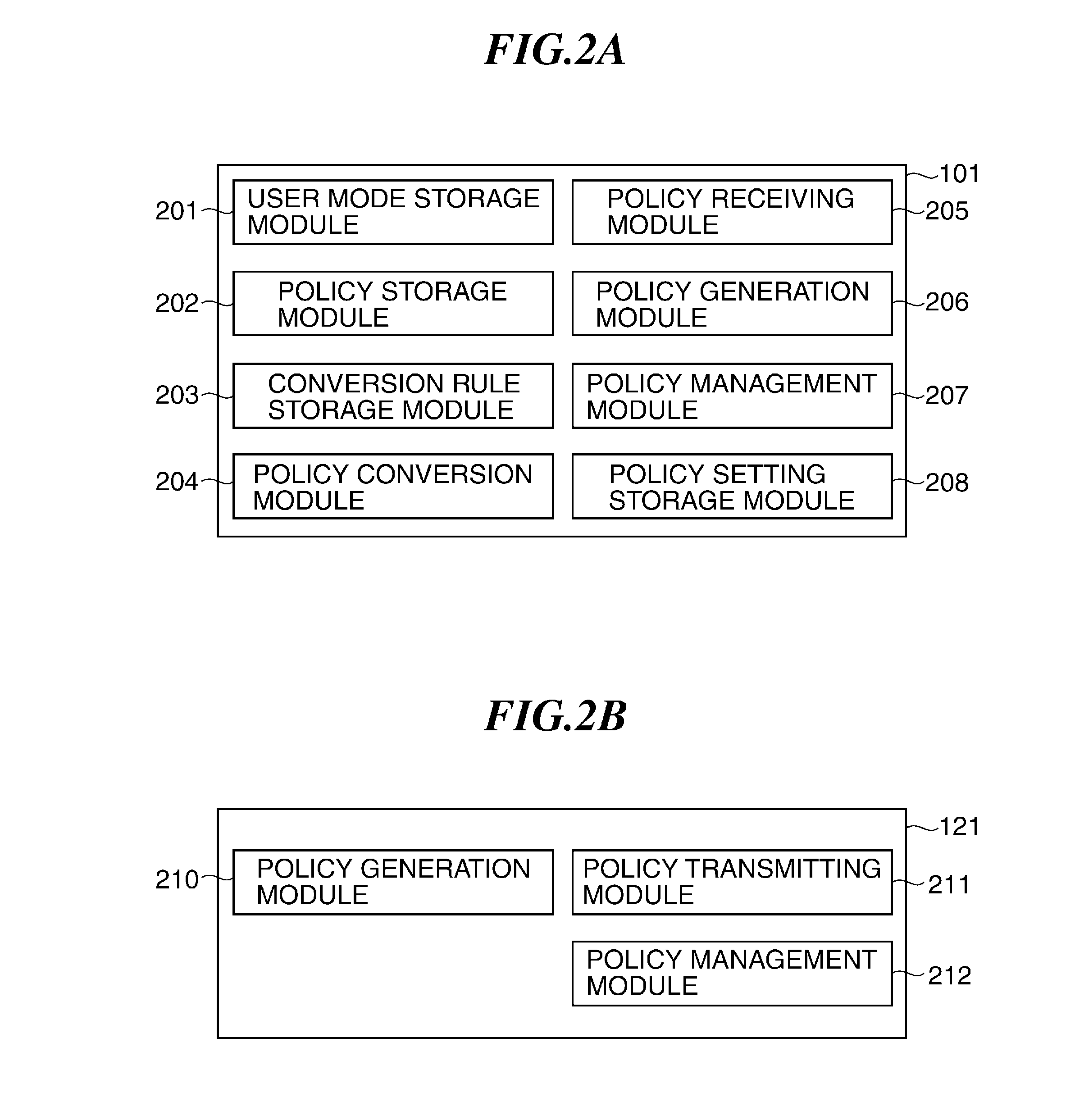
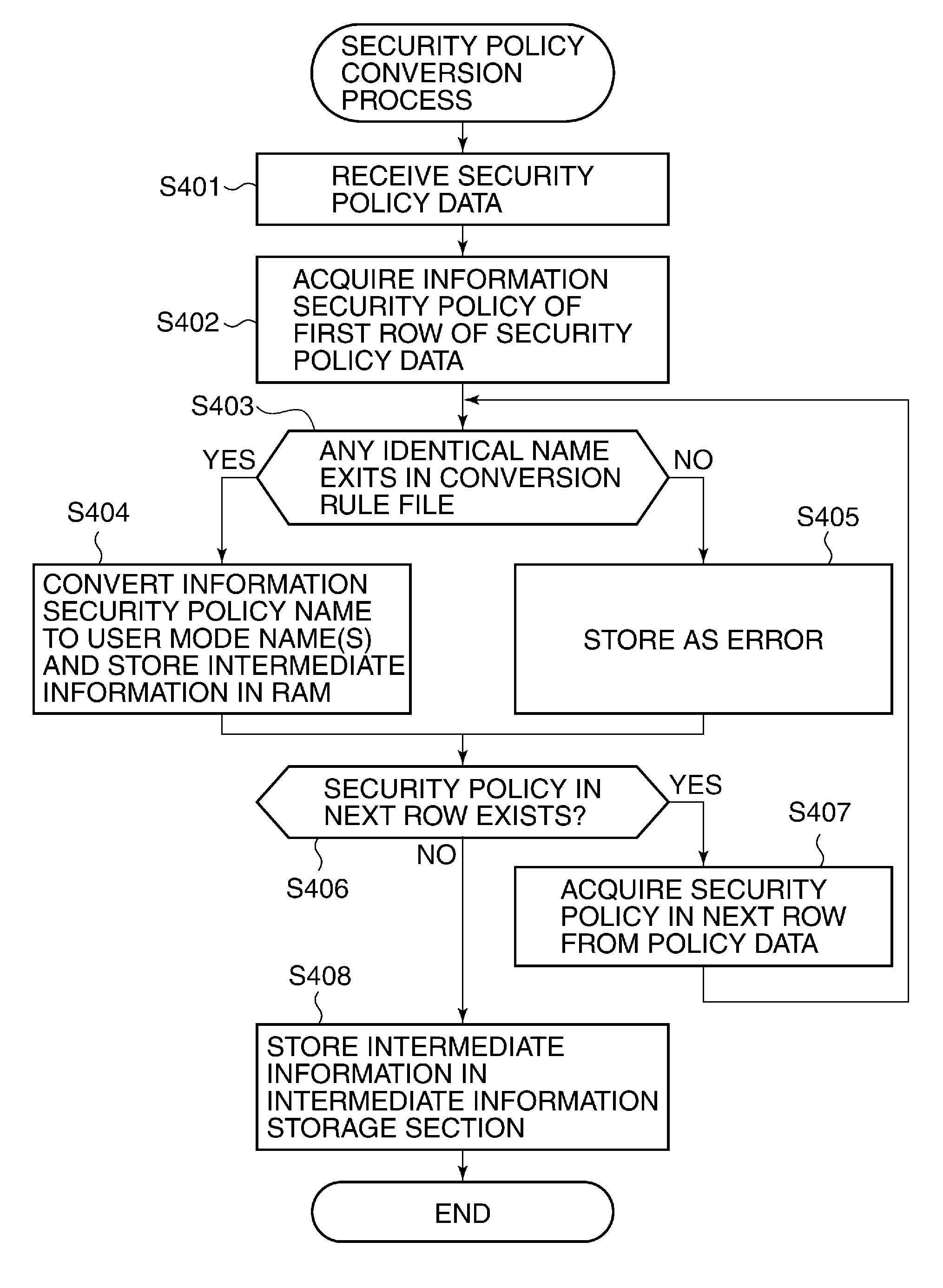
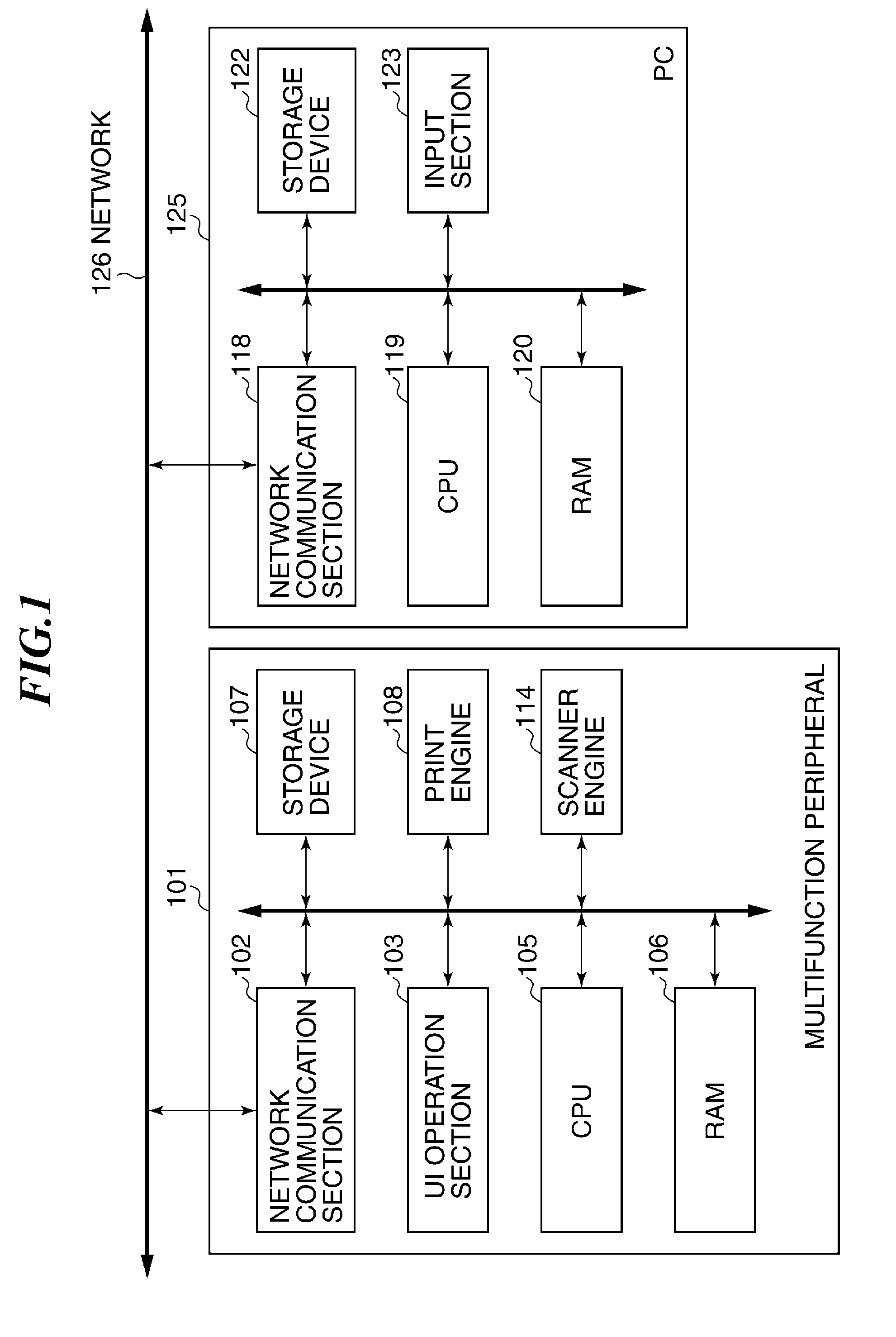
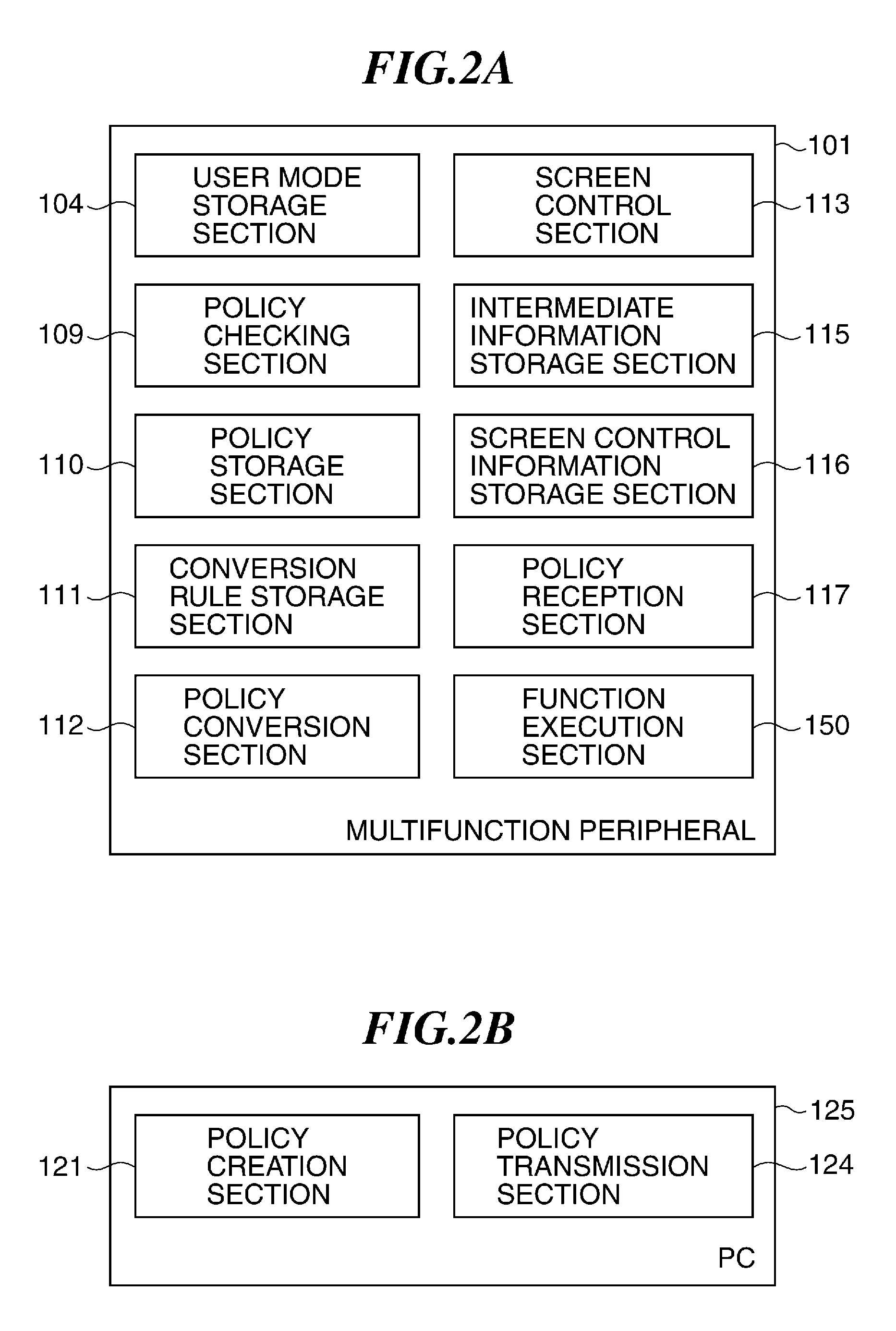
Image processing apparatus that configures settings of information security policy, method of controlling the same, program, and storage medium
ActiveUS20150046970A1Set changeComputer security arrangementsTransmissionImaging processingImage manipulation
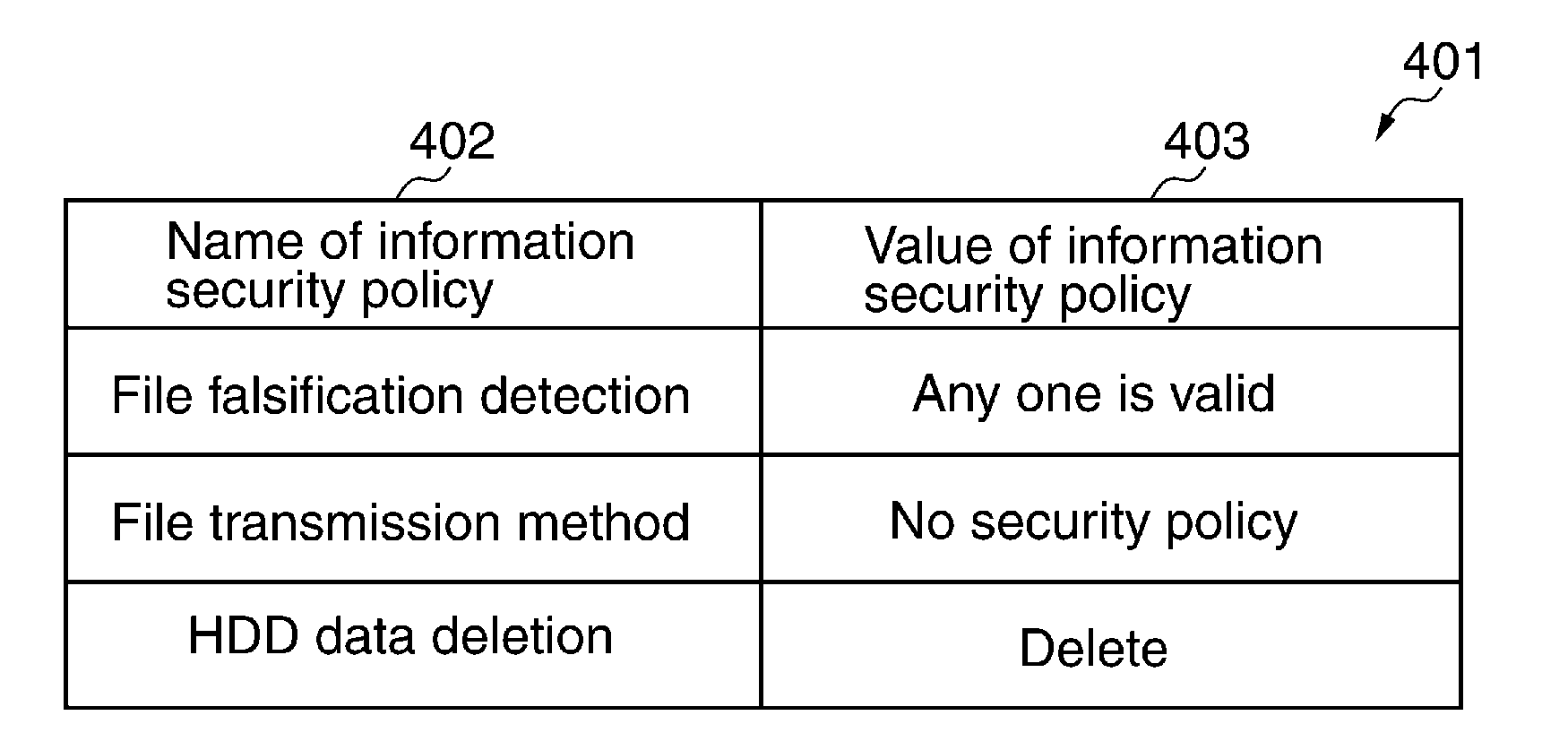
An image processing apparatus which enables a user to change the user mode while maintaining the state compliant with the information security policy. A network communication section receives security policy data in which information security policy is described from an external apparatus. A CPU identifies an operation mode of the image processing apparatus based on the received security policy. The CPU configures the identified operation mode such that the information security policy is satisfied.
Owner:CANON KK
Image forming apparatus capable of making user aware of security policy violation, method of controlling the image forming apparatus, and storage medium
An image forming apparatus which is capable of making a user aware of a violation of an information security policy. A network communication unit receives data having a user ID attached thereto from an external apparatus. A printing unit prints an image based on the data. A control unit executes user authentication using the user ID attached to the data and determines, when the user authentication is successful, whether or not a password expiration date of the user has passed. When it is determined that the password expiration date has passed, the control unit restricts printing of the image to be printed based on the data having the user ID attached thereto.
Owner:CANON KK
Systems and methods for encryption and provision of information security using platform services
ActiveUS10020936B1Enhanced interactionOptimizationKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCiphertextOriginal data
Systems and methods for securing or encrypting data or other information arising from a user's interaction with software and / or hardware, resulting in transformation of original data into ciphertext. Generally, the ciphertext is generated using context-based keys that depend on the environment in which the original data originated and / or was accessed. The ciphertext can be stored in a user's storage device or in an enterprise database (e.g., at-rest encryption) or shared with other users (e.g., cryptographic communication). The system generally allows for secure federation across organizations, including mechanisms to ensure that the system itself and any other actor with pervasive access to the network cannot compromise the confidentially of the protected data.
Owner:IONIC SECURITY
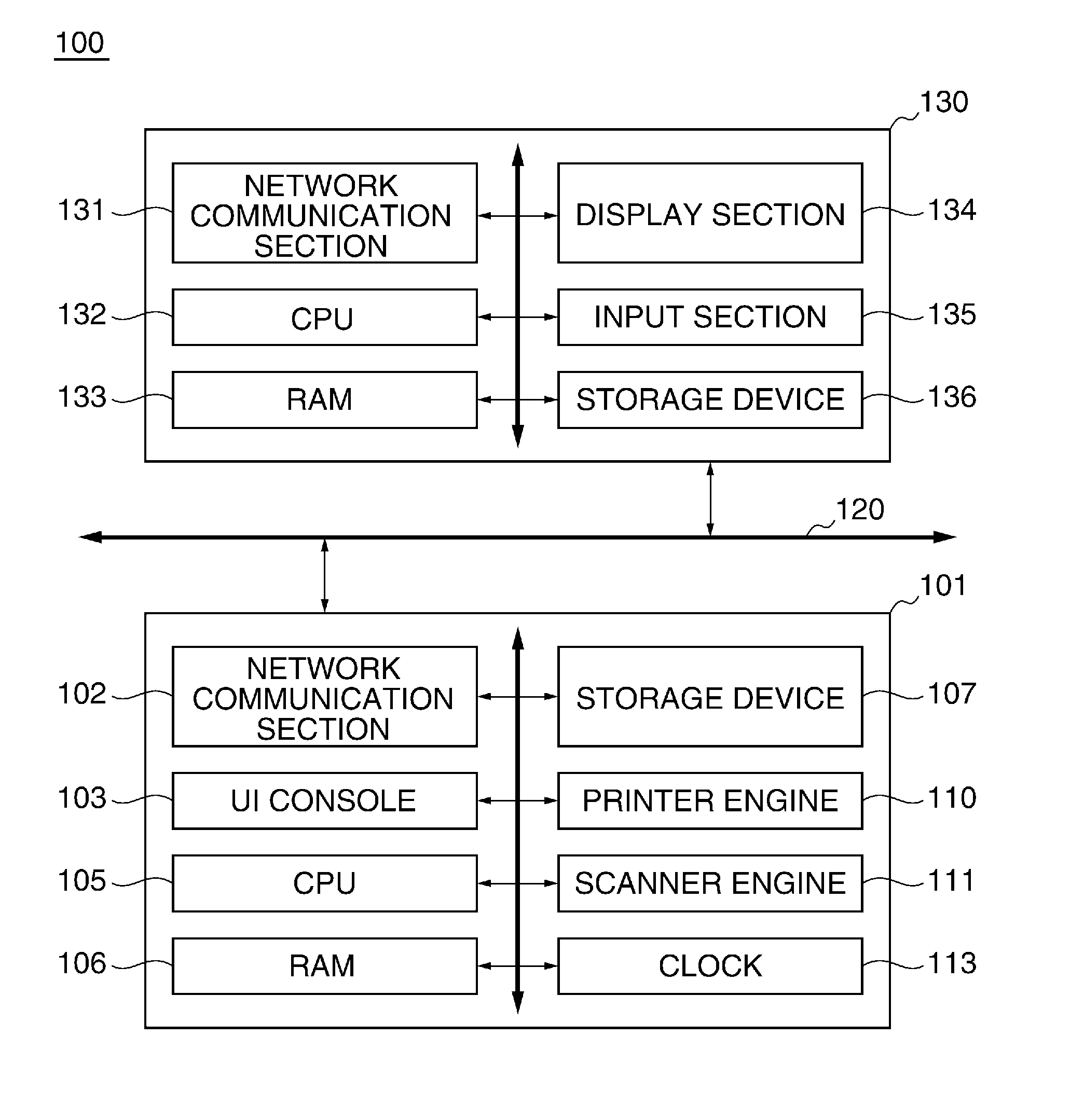
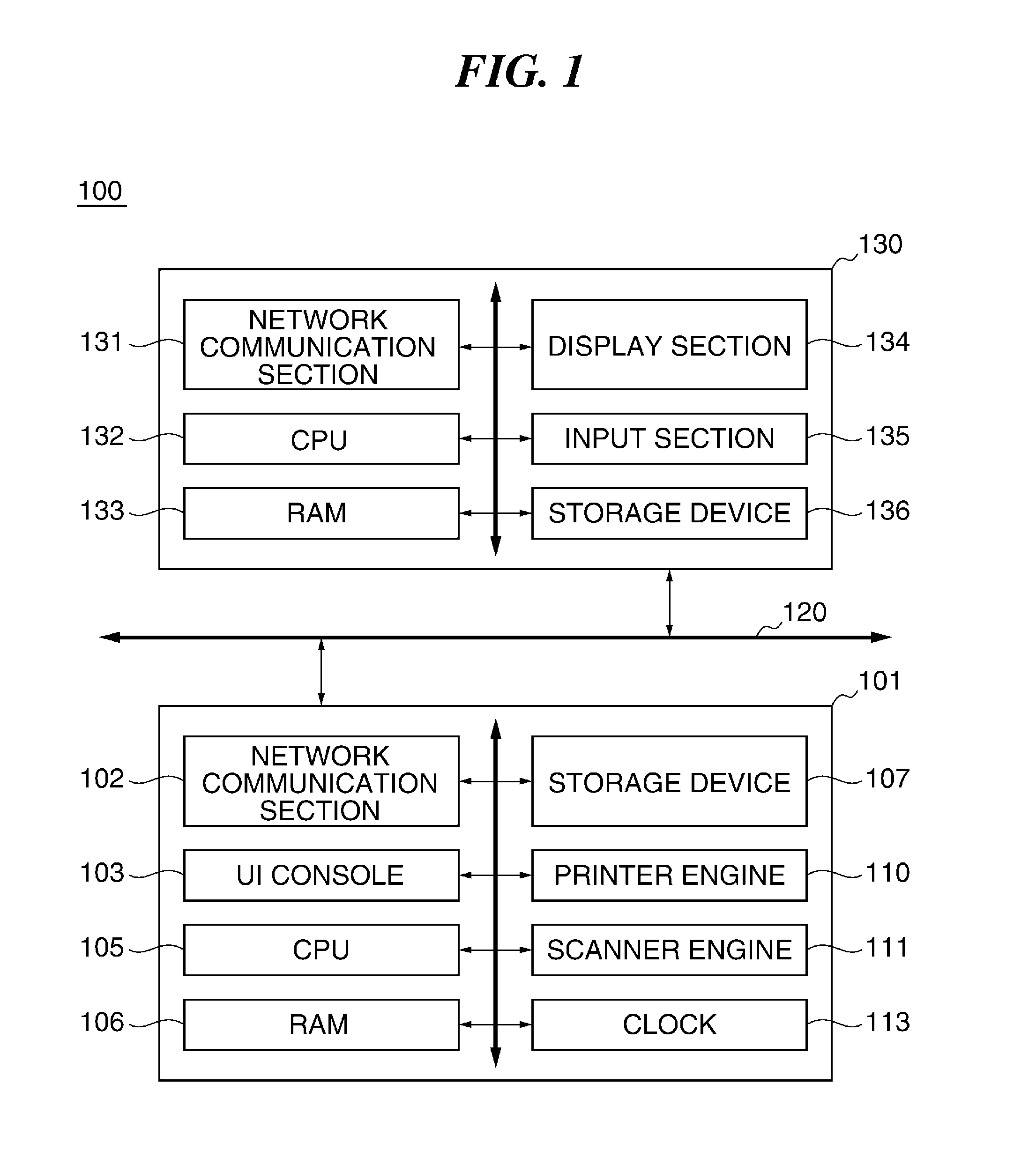
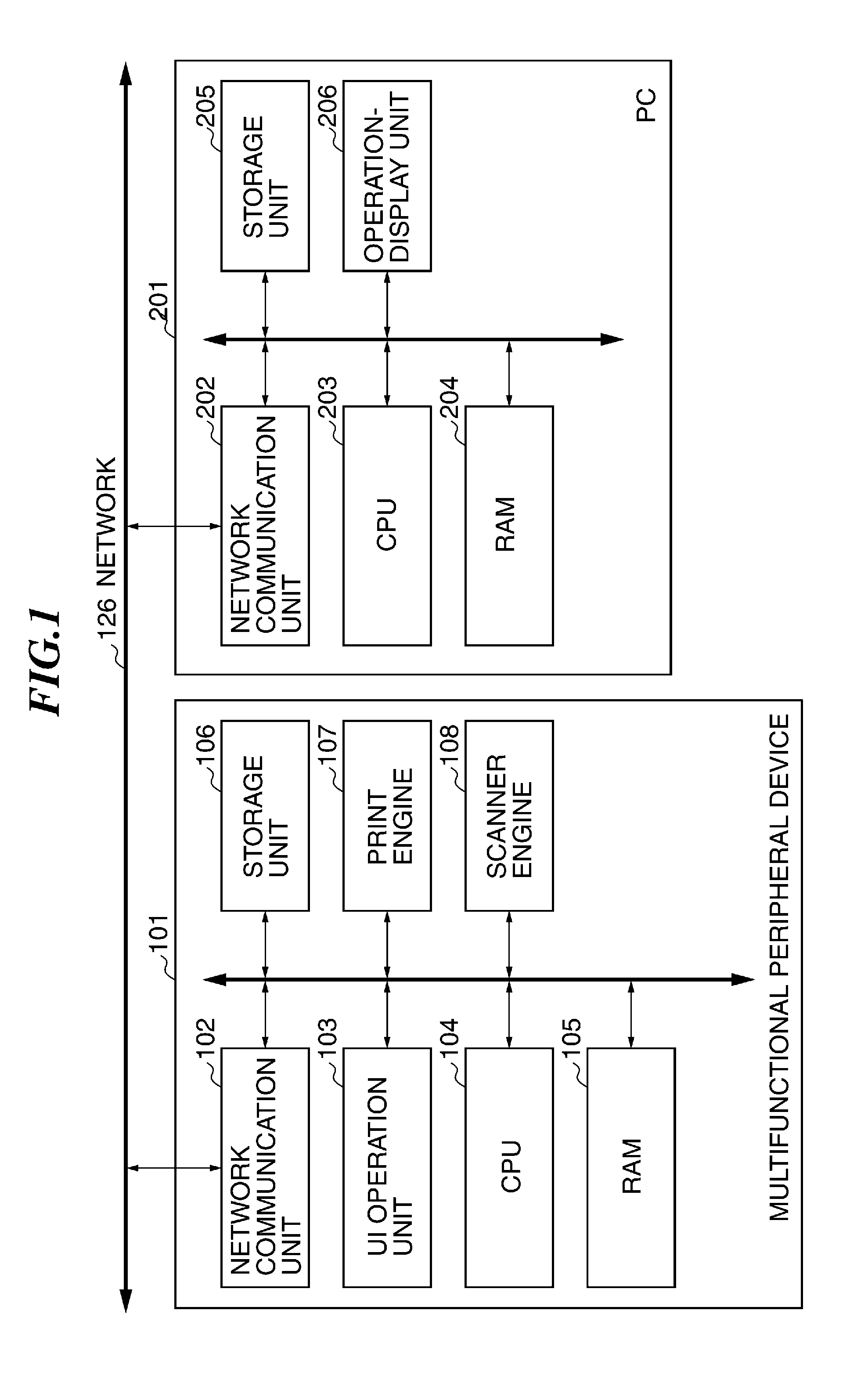
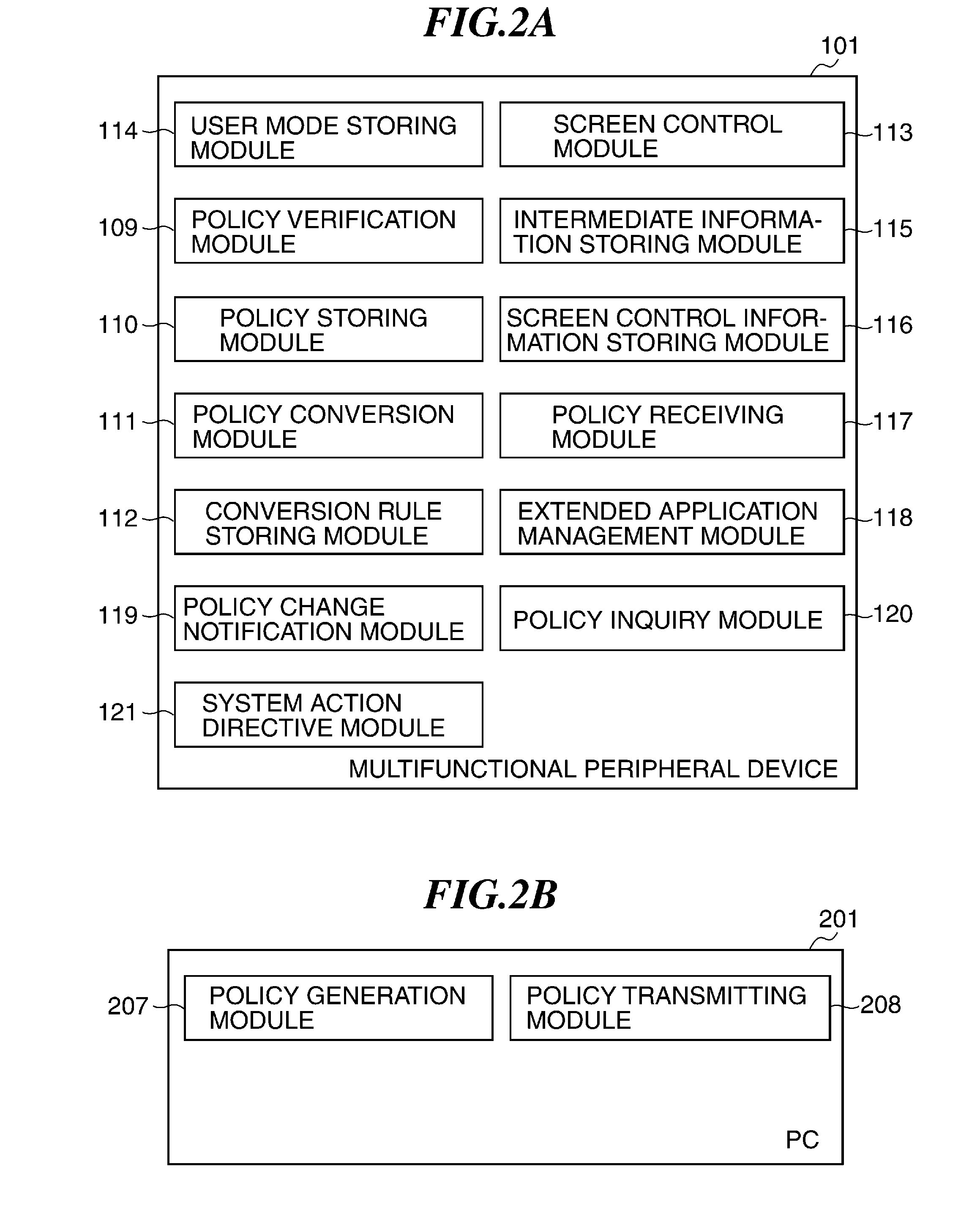
Image forming apparatus, control method therefor, and storage medium storing control program therefor
An image forming apparatus that facilitates management of information security policy even for an extended application installed from exterior. A scanning unit scans an original to generate image data of the original. A printing unit prints an image based on image data. A management unit manages applications dynamically installed. At least one of the applications executes a job using at least one of the scanning unit and the printing unit. A setting unit sets an operation mode for the image forming apparatus, based on security settings that are received from an external apparatus. A determination unit determines whether each of the applications supports the security settings. A control unit restricts an operation of an application that the determination unit determines that the application does not support the security settings.
Owner:CANON KK
Policy-based data-centric access control in a sorted, distributed key-value data store
InactiveUS20150294120A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data protectionData memoryMedia access control
A method, apparatus and computer program product for policy-based access control in association with a sorted, distributed key-value data store in which keys comprise n-tuple structure that includes a cell-level access control. In this approach, an information security policy is used to create a set of pluggable policies. A pluggable policy may be used during data ingest time, when data is being ingested into the data store, and a pluggable policy may be used during query time, when a query to the data store is received for processing against data stored therein. Generally, a pluggable policy associates one or more user-centric attributes (or some function thereof), to a particular data-centric label. By using pluggable policies, preferably at both ingest time and query time, the data store is enhanced to provide a seamless and secure policy-based access control mechanism in association with the cell-level access control enabled by the data store.
Owner:A9 COM INC
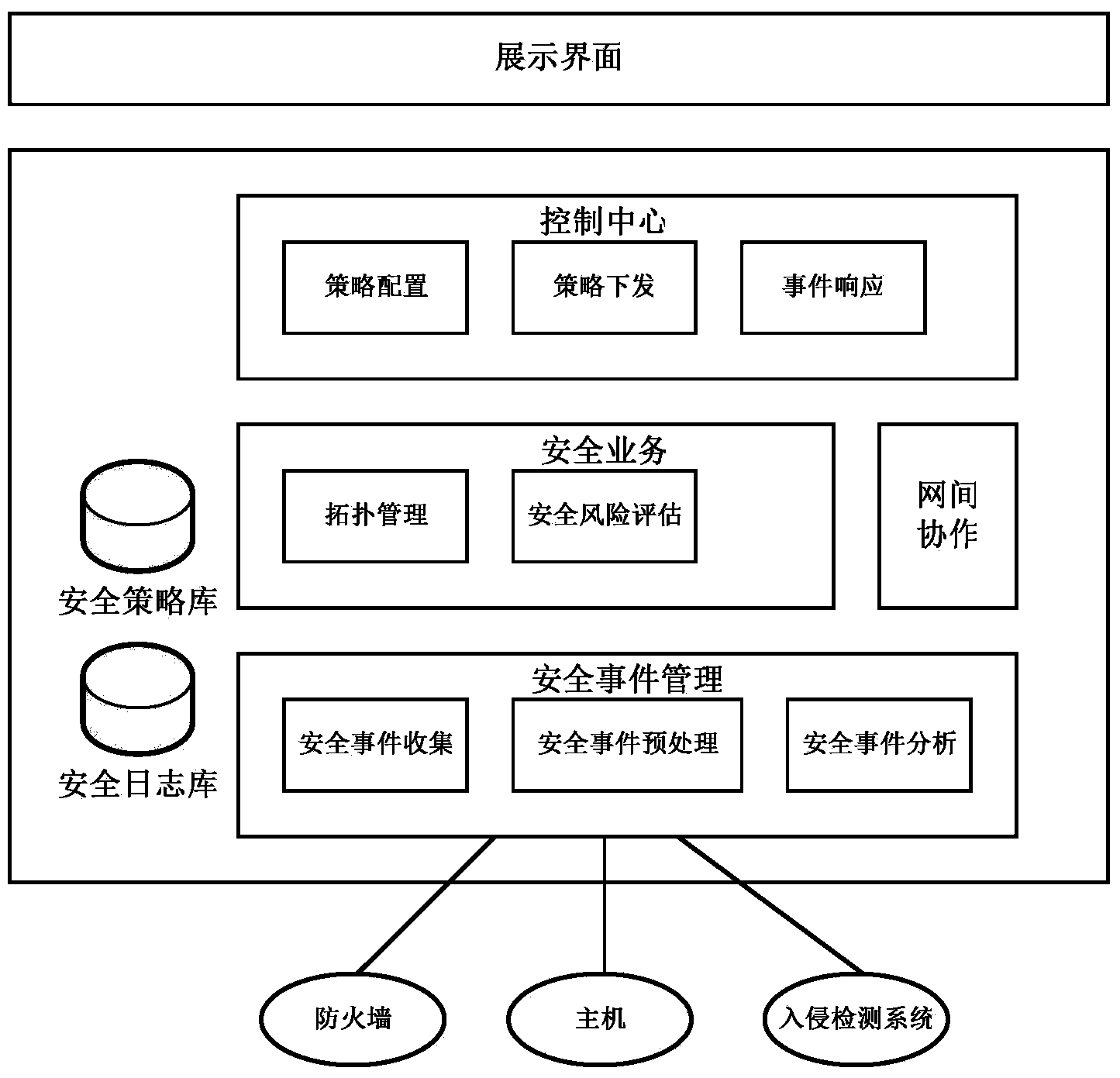
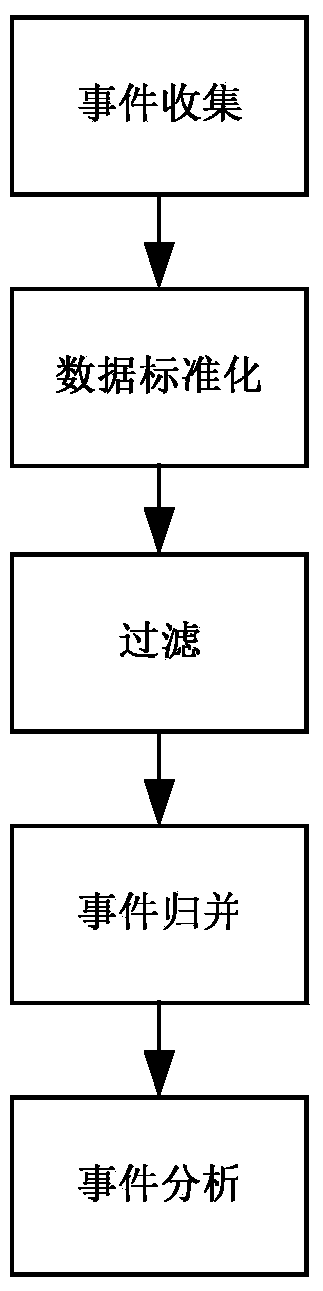
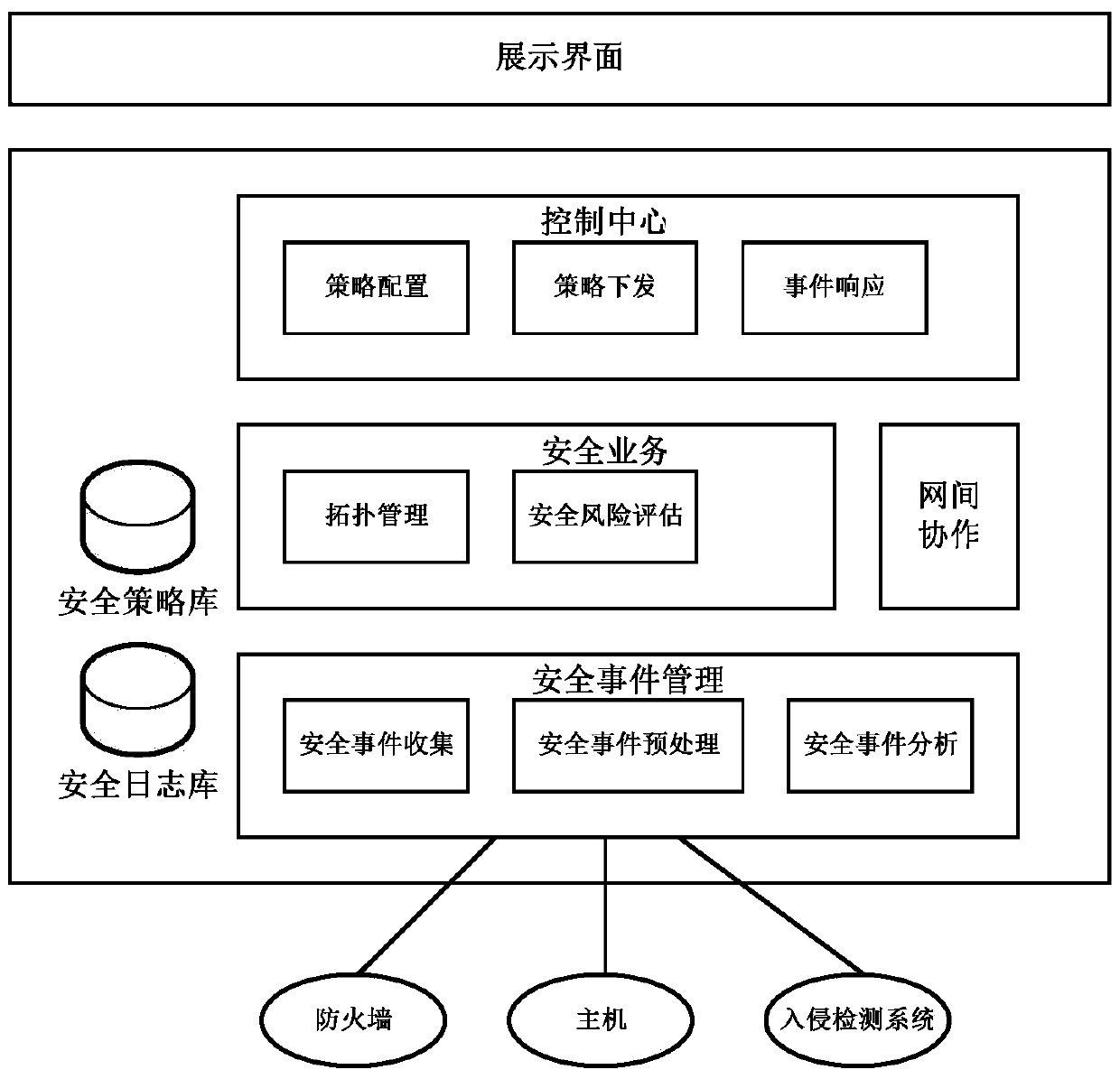
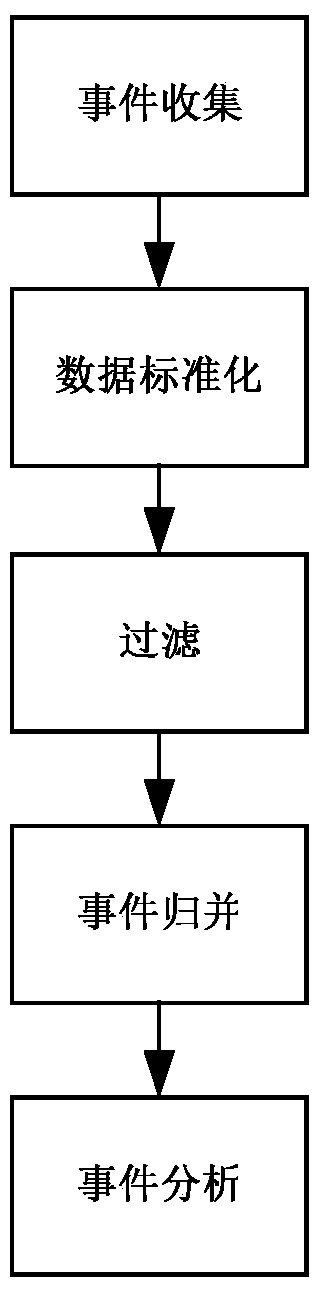
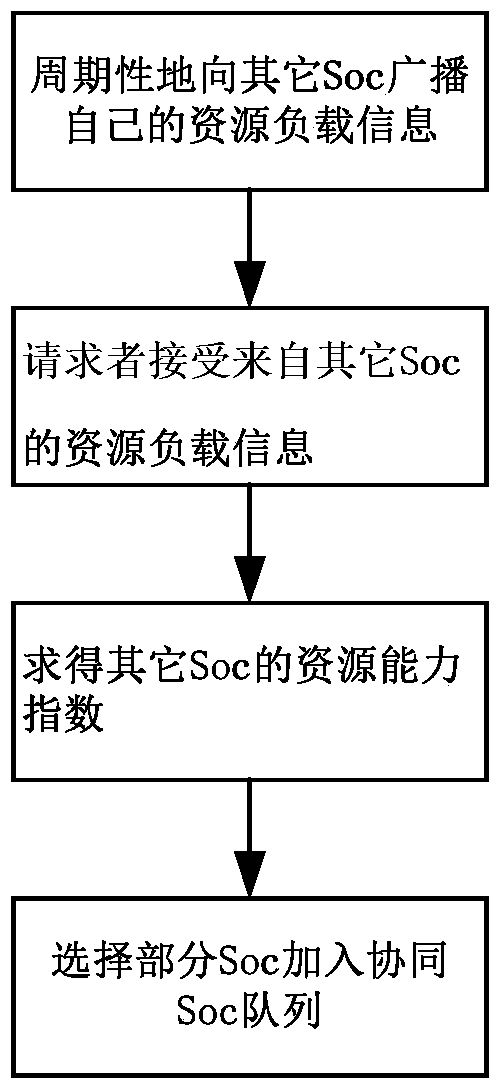
Collaborative analysis method of information security operation centers
ActiveCN104378364AComprehensive judgmentImprove accuracyTransmissionSecurity operations centerCorrelation analysis
The invention relates to the technical field of information safety, in particular to a collaborative analysis method of information security operation centers. An internetwork collaborative module of one of the security operation centers sends suspected threat information, then a safety event management module analyzes the suspected threat information, and it is determined that a threat is found if the threat meets the standard of a certain attack event; a receiver finding the threat informs a sender of the suspected threat and other security operation centers of confirmation information through the internetwork collaborative module; a requester takes corresponding measures through a safety strategy library; if the sender does not find the threat by himself, correlation analysis of the second stage is carried out by communication between the sender and other receivers; all the security operation centers take corresponding measures for response after receiving the information. The collaborative analysis method of the information security operation centers achieves the collaborative analysis of the information security operation centers and can be used for the security operation centers for information security operation.
Owner:GUANGDONG ELECTRONICS IND INST
System and method for detecting and mitigating the writing of sensitive data to memory
InactiveUS20090055889A1Internal/peripheral component protectionTransmissionInternet privacyApplication software
Disclosed is a system and method for detecting and mitigating the writing of sensitive or prohibited information to memory or communication media. The method includes detecting if an application is to write data to a memory, rerouting the writing of that data, and scanning the data for sensitive content or prohibited information. The scanning is done in accordance with one or more information security policies. If sensitive information is detected, the system has the option of issuing an alarm and / or preventing the sensitive information from being written, depending on the security policy. If the system permits the sensitive information to be written to memory, the system may spawn a file watcher object, which waits for a specified amount of time and then checks to see if the sensitive information has been deleted. If not, the system may issue an alarm or erase the sensitive information, depending on the security policy.
Owner:TRUSTWAVE HOLDINGS
Image forming apparatus capable of making user aware of security policy violation, method of controlling the image forming apparatus, and storage medium
ActiveUS9384434B2Digital data processing detailsVisual presentation using printersInternet privacyPassword
An image forming apparatus which is capable of making a user aware of a violation of an information security policy. A network communication unit receives data having a user ID attached thereto from an external apparatus. A printing unit prints an image based on the data. A control unit executes user authentication using the user ID attached to the data and determines, when the user authentication is successful, whether or not a password expiration date of the user has passed. When it is determined that the password expiration date has passed, the control unit restricts printing of the image to be printed based on the data having the user ID attached thereto.
Owner:CANON KK
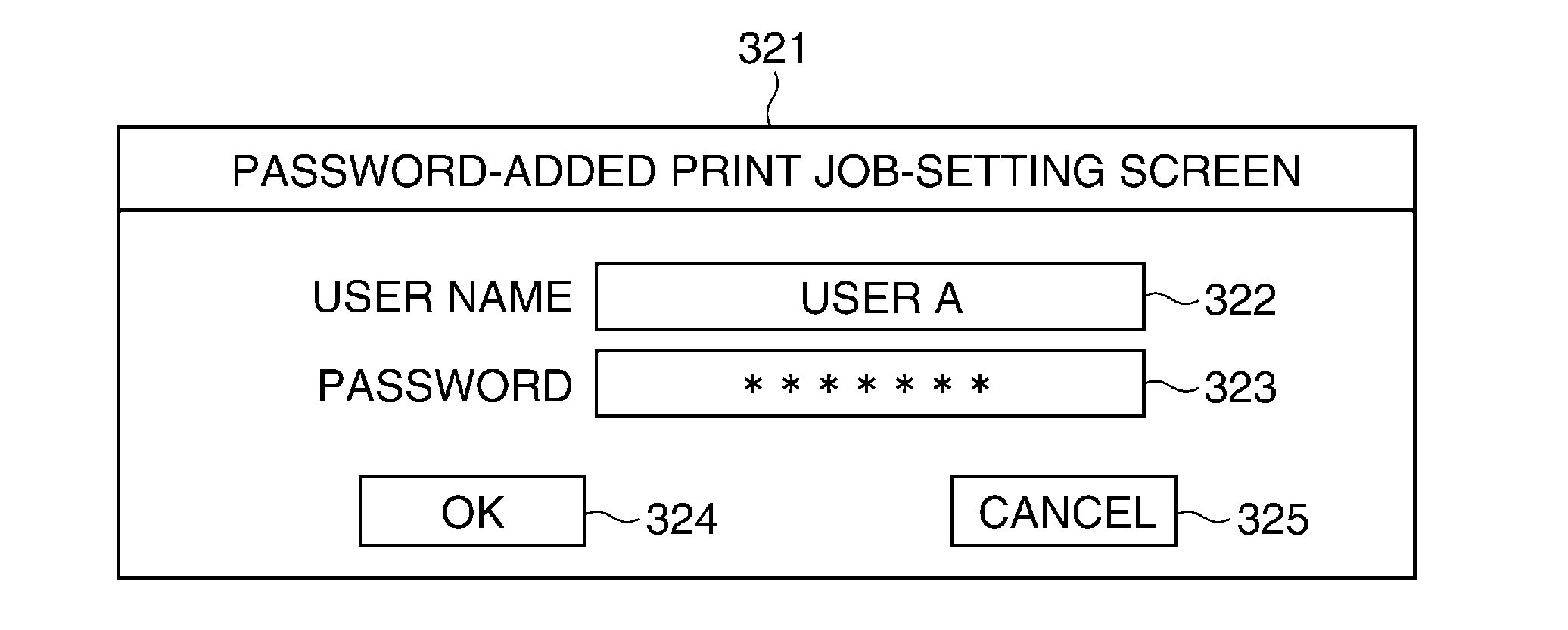
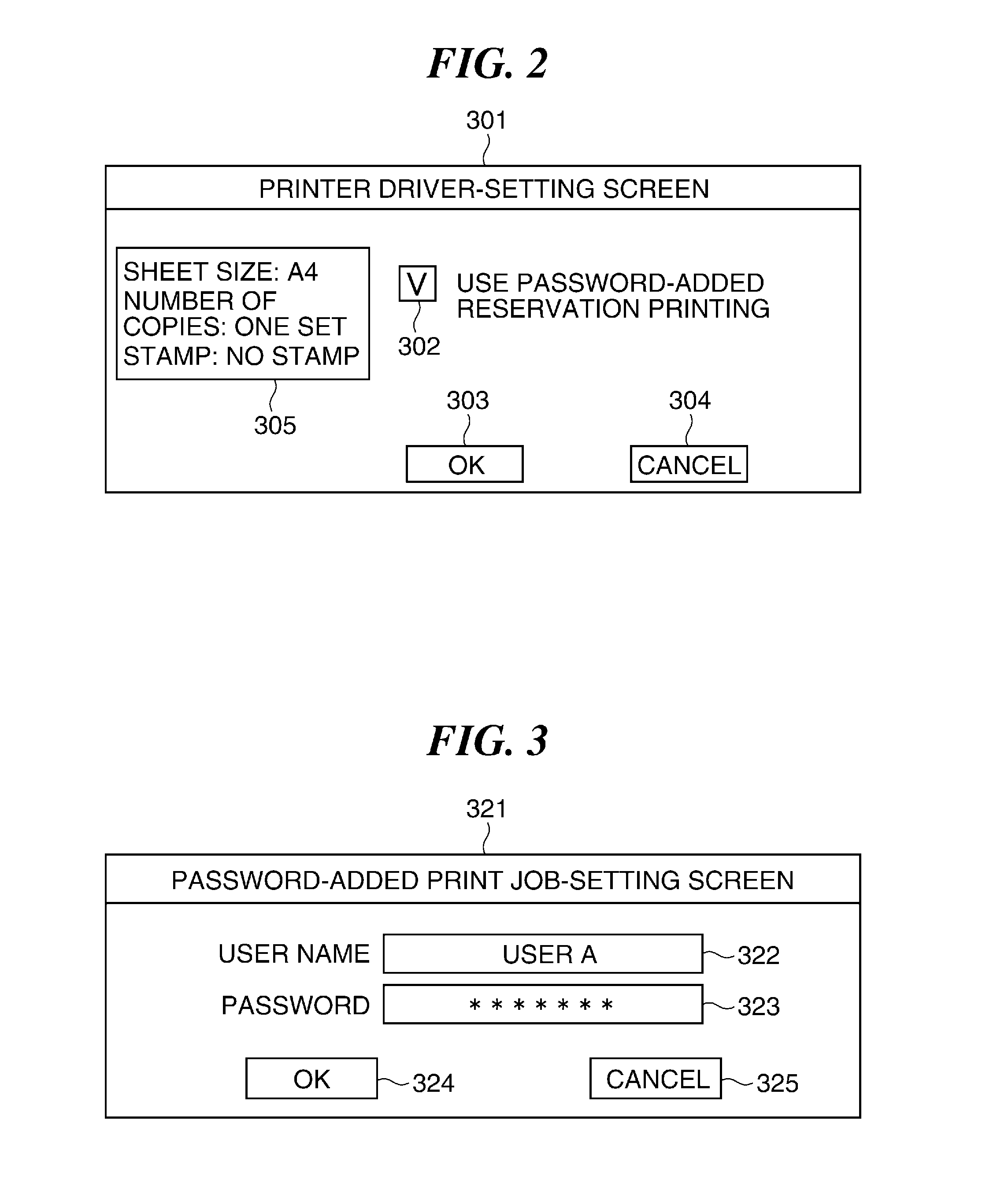
Image forming apparatus capable of reducing security risk, method of controlling image forming apparatus, system including image forming apparatus, and storage medium
ActiveUS20150128239A1Reduce security risksDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsPassword policyPassword
An image forming apparatus capable of notifying a user of violation of the information security policy or preventing execution of the job from being stopped. A password policy set via a password policy-setting screen. A password-added print job transmitted from a PC is stored in a storage device. A user inputs a password so as to execute processing of the password-added print job stored in the storage device. If the password input by the user matches the password added to the job, processing of the password-added print job is executed. It is determined whether or not the password added to the print job satisfies the password policy.
Owner:CANON KK
Low-overhead software transformation to enforce information security policies
ActiveUS10904291B1Reduce overheadAvoid passingTransformation of program codeSoftware testing/debuggingInformation transmissionSoftware analytics
Described is a system for enforcing software policies. The system transforms an original software by inserting additional instructions into the original software. The additional instructions have the effect of determining, at run-time, whether proceeding with execution of the original software is in accordance with a predefined policy. Transforming the original software relies on software analysis to determine whether any run-time checks normally inserted into the original software can be safely omitted. The transformed software prevents unauthorized information from passing to the network.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Image processing apparatus to which security policy is applicable, control method therefor, and storage medium storing control program therefor
ActiveUS9338326B2Appropriately appliedDigital data protectionVisual presentationSecurity policyImage processing
Owner:CANON KK
Image processing apparatus to which security policy is applicable, control method therefor, and storage medium storing control program therefor
ActiveUS20150092222A1Appropriately appliedDigital data protectionVisual presentationImaging processingApplication procedure
An image processing apparatus that is capable of appropriately applying security policy data based on an information security policy. Security policy data containing a policy name of a security policy and a security policy setting value corresponding to the policy name is applied to the image processing apparatus. An obtaining unit obtains updating security policy data for updating the security policy data. An application version determination unit determines whether the updating security policy data obtained by the obtaining unit will be applied according to a predetermined application version setting value, when a version of the updating security policy data differs from a version of security policy data that is being applied actually. An application unit applies the updating security policy data when the application version determination unit determines that the updating security policy data will be applied.
Owner:CANON KK
Image processing apparatus that configures settings of information security policy, method of controlling the same, program, and storage medium
An image processing apparatus which enables a user to change the user mode while maintaining the state compliant with the information security policy. A network communication section receives security policy data in which information security policy is described from an external apparatus. A CPU identifies an operation mode of the image processing apparatus based on the received security policy. The CPU configures the identified operation mode such that the information security policy is satisfied.
Owner:CANON KK
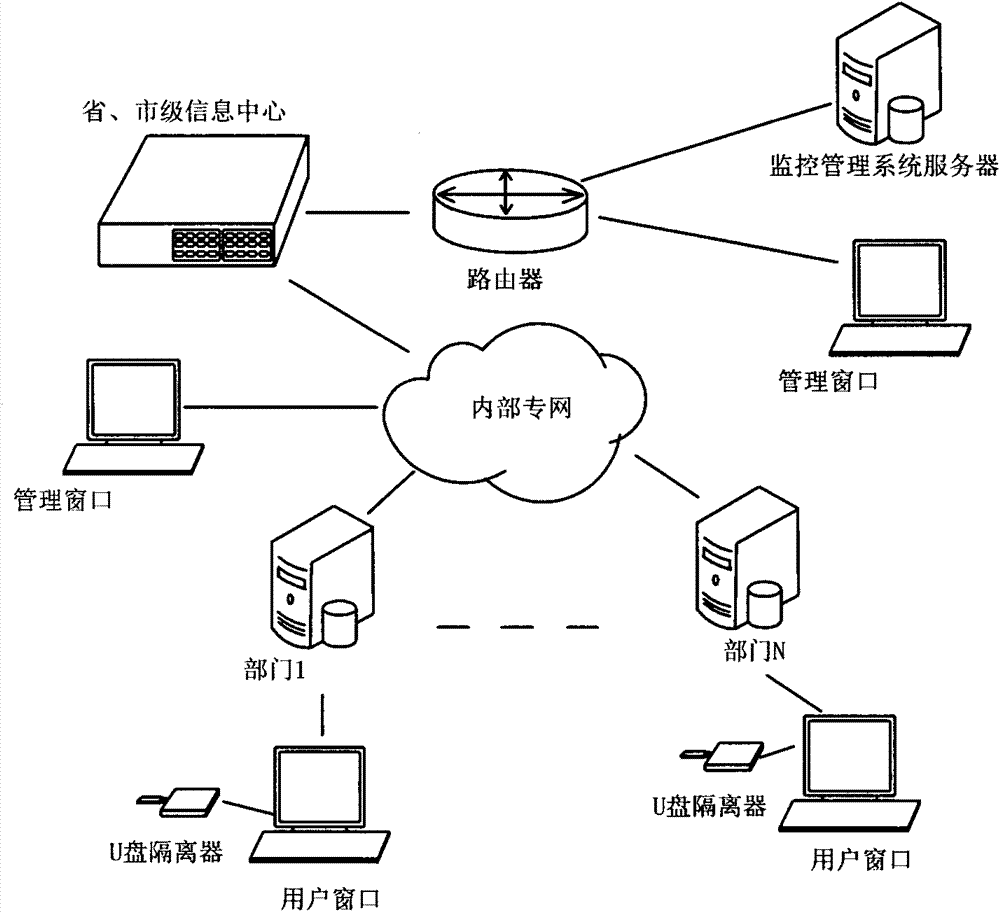
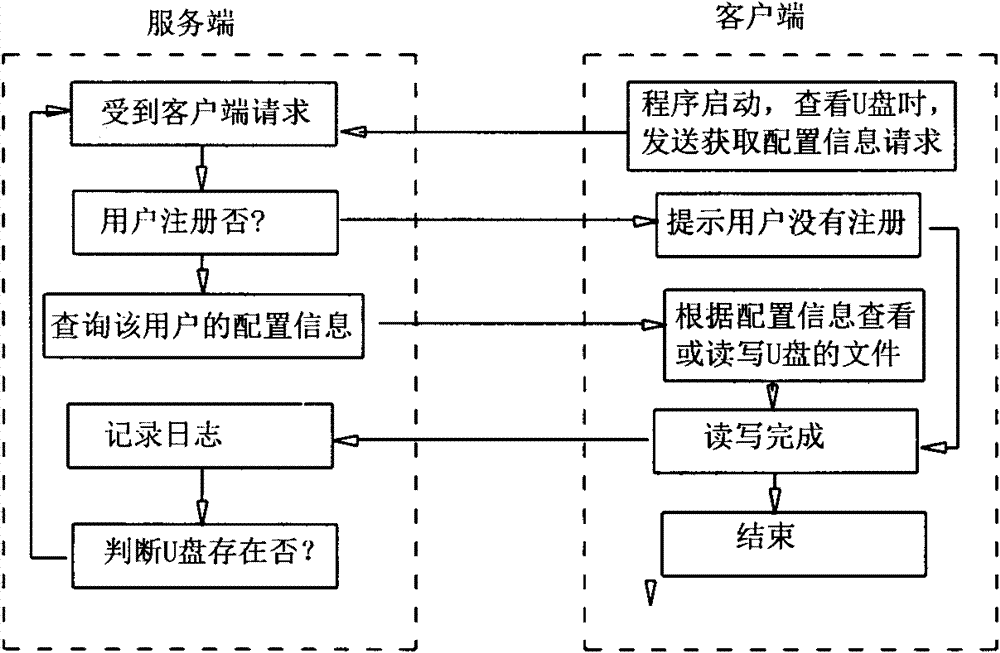
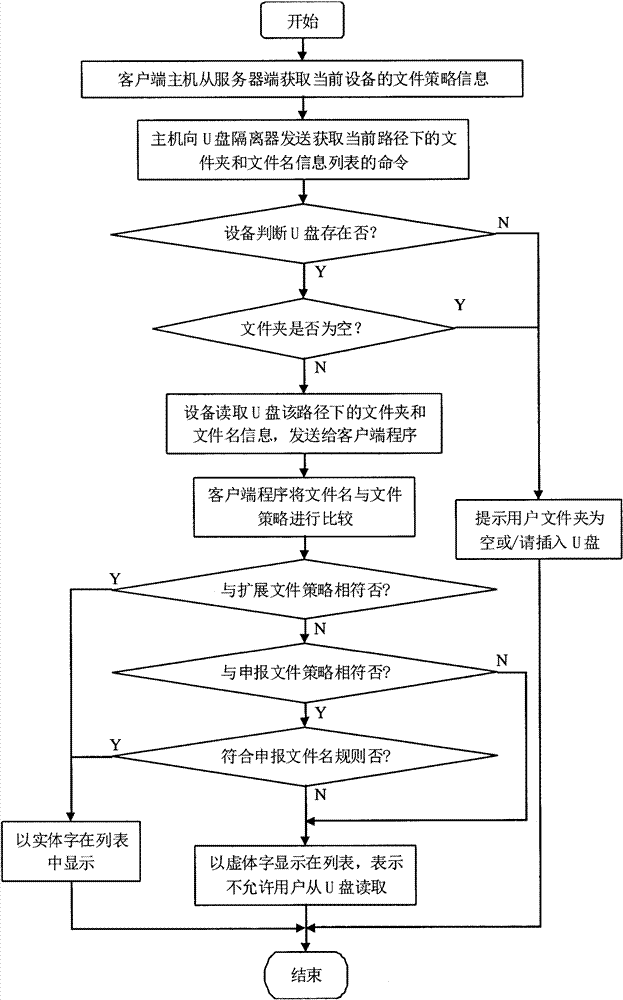
Security isolation and monitoring management method of USB mobile storage media
ActiveCN101901315BAchieve security isolationInternal/peripheral component protectionConfidentialityNetwork management
The invention provides a system of USB mobile storage medium security isolation and monitoring management. In the system, U disk isolator equipment is used for physically isolating the U disks of the users from hosts. Several file security policies are set and allocated for each equipment by a network management system. The files are only allowed to enter into the system or be copied onto the U disks as long as the files are in consistent with the security policies. Audit data are generated for each file access to the system so as to be convenient for tracing the information flow direction. Through the mode of software and hardware combination, the invention thoroughly solves the problem of security when the internal network system with information security and confidentiality requirements receives and acquires the mobile storage media data of the external network. Information security places emphasis on prevention and control, and the invention adopts the file security policy management mode, just embodying the emphasis, thus being a quite effective monitoring management means for the condition that the internal network system uses the USB mobile storage media.
Owner:INSPUR SOFTWARE TECH CO LTD
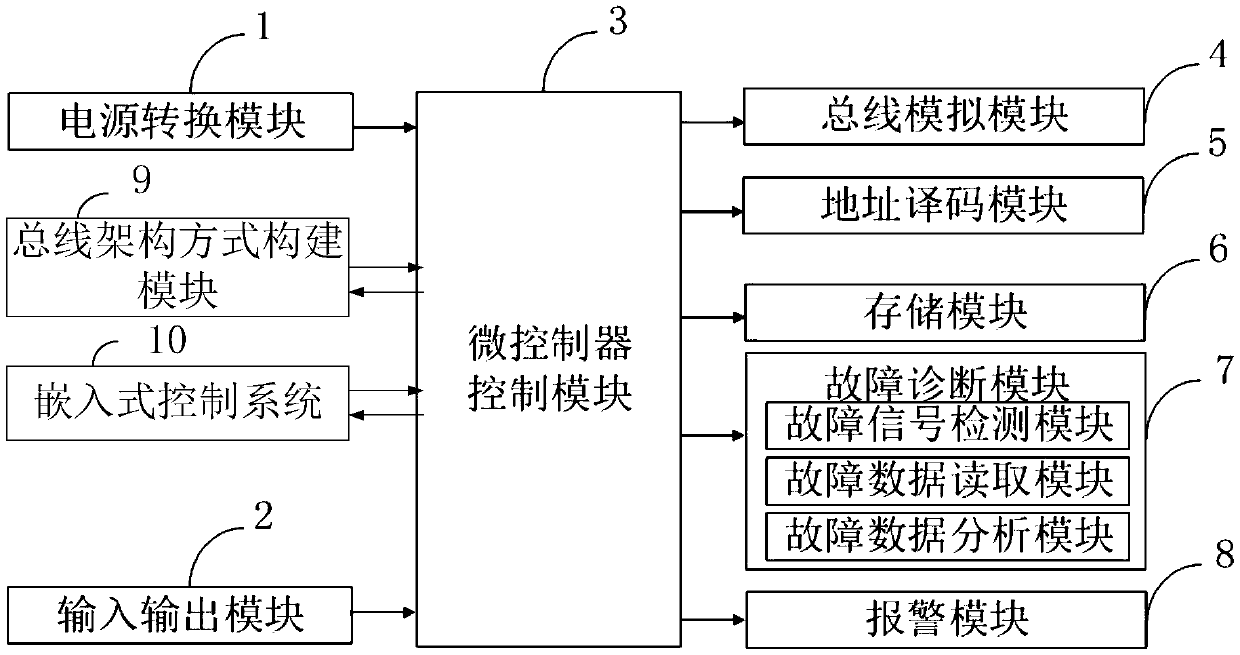
Industrial embedded control method and system for hybrid bus, and information processing terminal
InactiveCN108710352ARealize industrial embedded intelligent controlEffective frequency reuseTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlInformation processingMicrocontroller
The invention belongs to the technical field of industrial control, and discloses an industrial embedded control method and system of a hybrid bus, and an information processing terminal. A bus logiccontrol scheme, a motion control scheme, a CNC, a ROBOT composite control scheme, an XML control scheme, and an industrial information security policy scheme and an industrial network access scheme form a bus architecture mode; each control scheme has different distribution strategies in the bus, and different bus hybrid control methods are constructed; an integrated microcontroller, a Manchesterencoding and decoding device, a DMA memory and a bus simulator can perform different bus hybrid controls on different control schemes according to a certain algorithm. All the modules can share resources on the analog bus; a fault diagnosis module can read and analyze fault scene data if a main system crashes during operation of the embedded system, and the maintainability and the diagnosis of thewhole system can be improved.
Owner:广东盛哲科技有限公司
A Collaborative Analysis Method for Information Security Management Center
ActiveCN104378364BComprehensive judgmentImprove accuracyTransmissionInformation security risk managementSecurity operations center
The invention relates to the technical field of information safety, in particular to a collaborative analysis method of information security operation centers. An internetwork collaborative module of one of the security operation centers sends suspected threat information, then a safety event management module analyzes the suspected threat information, and it is determined that a threat is found if the threat meets the standard of a certain attack event; a receiver finding the threat informs a sender of the suspected threat and other security operation centers of confirmation information through the internetwork collaborative module; a requester takes corresponding measures through a safety strategy library; if the sender does not find the threat by himself, correlation analysis of the second stage is carried out by communication between the sender and other receivers; all the security operation centers take corresponding measures for response after receiving the information. The collaborative analysis method of the information security operation centers achieves the collaborative analysis of the information security operation centers and can be used for the security operation centers for information security operation.
Owner:GUANGDONG ELECTRONICS IND INST
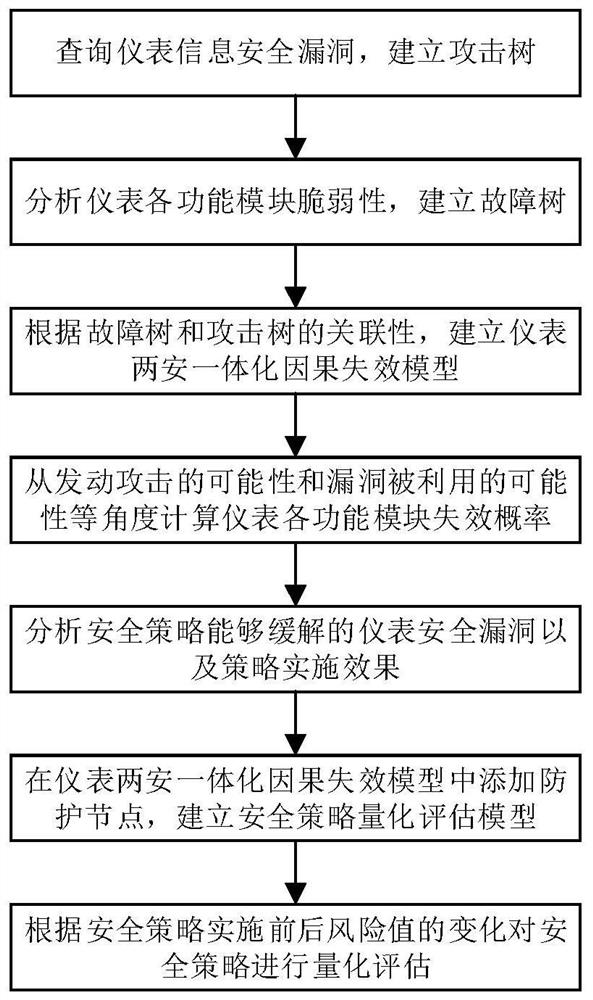
Unified Risk Quantitative Assessment Method for Instrument Functional Safety and Information Security Strategy
ActiveCN113434866BEffectively analyze the implementation effectOvercome limitationsDesign optimisation/simulationPlatform integrity maintainanceInstrument functionRisk quantification
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Computer network emergency response safety strategy generating system
InactiveCN100521625CQuick buildImprove survivabilityData switching networksStrategic analysisHandling system
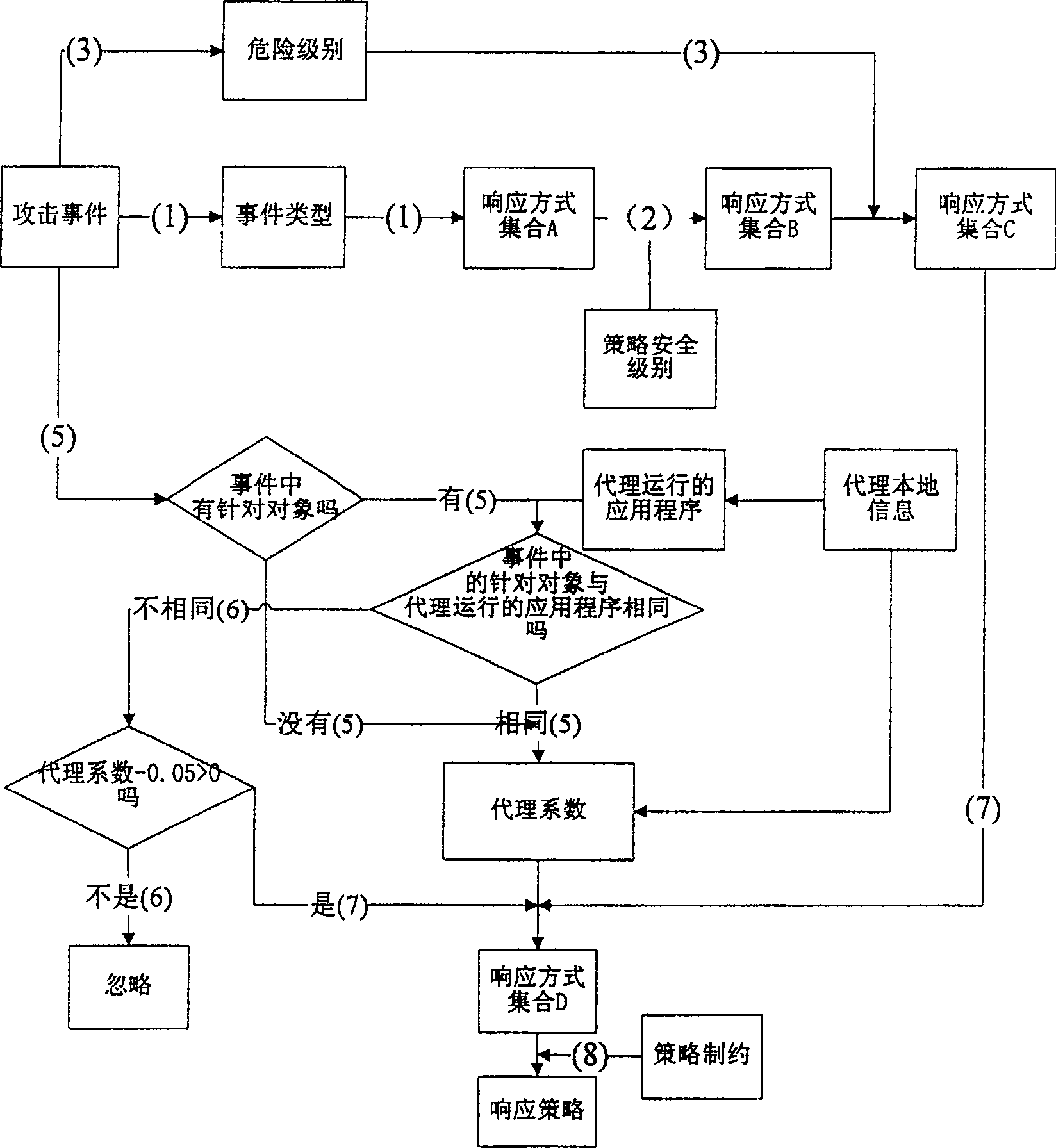
The invention discloses a security policy generation system for computer network emergency response, which is characterized in that: the security policy generation module starts and receives the attack event information, and the security policy generation module calls the preset definition information of the attack event in the database, and then Comparing the attack event information with the preset definition information of the attack event in the database, the security policy generation module will determine the corresponding response mode set A, and then the security policy generation module will perform policy analysis and screening on the determined corresponding response mode set A. After analysis and screening, a subset of response methods is obtained. Finally, the security policy generation module selects the response method with the highest comprehensive coefficient as the final response method according to the policy control principle. This system is a network that responds quickly, troubleshoots quickly, and recovers effectively. Emergency troubleshooting system.
Owner:上海三零卫士信息安全有限公司
Information environment security analysis method and system for mobile internet
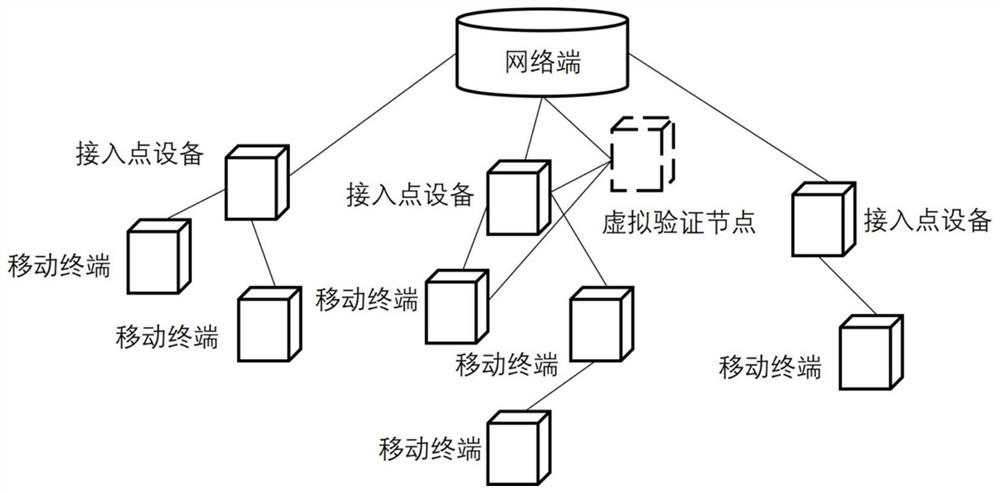
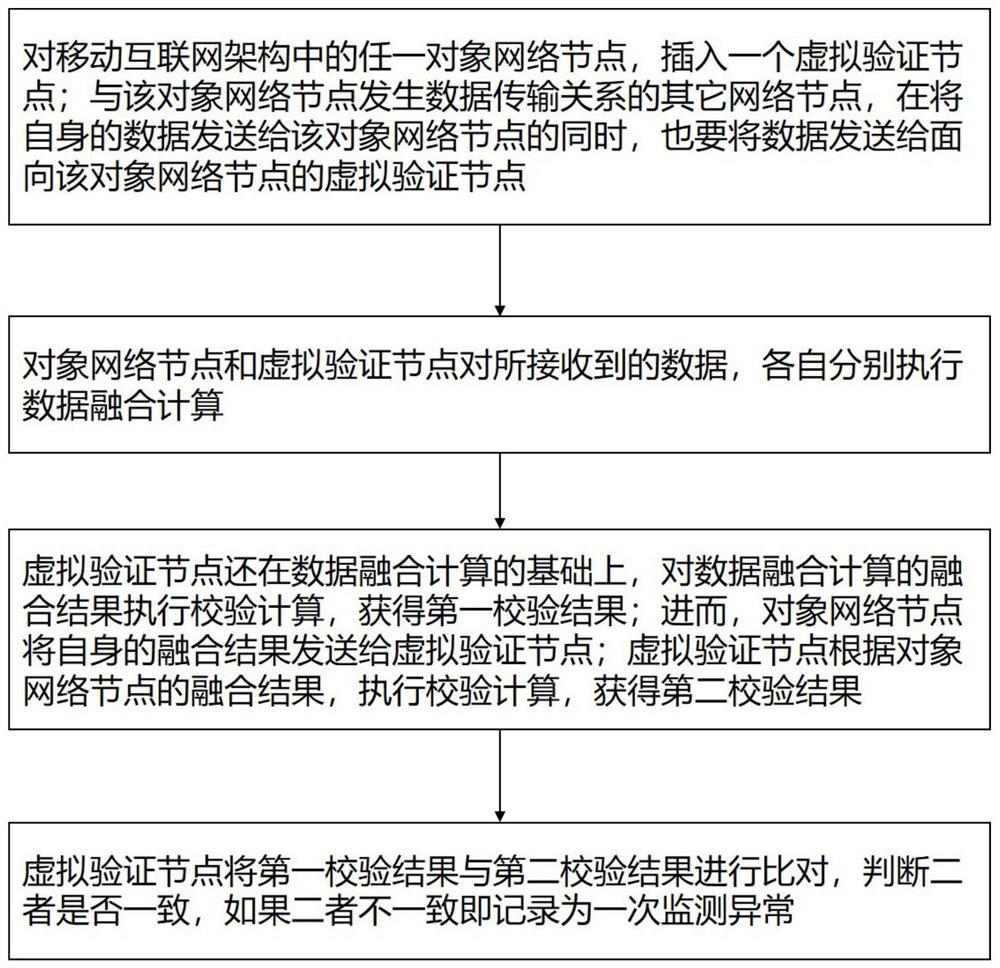
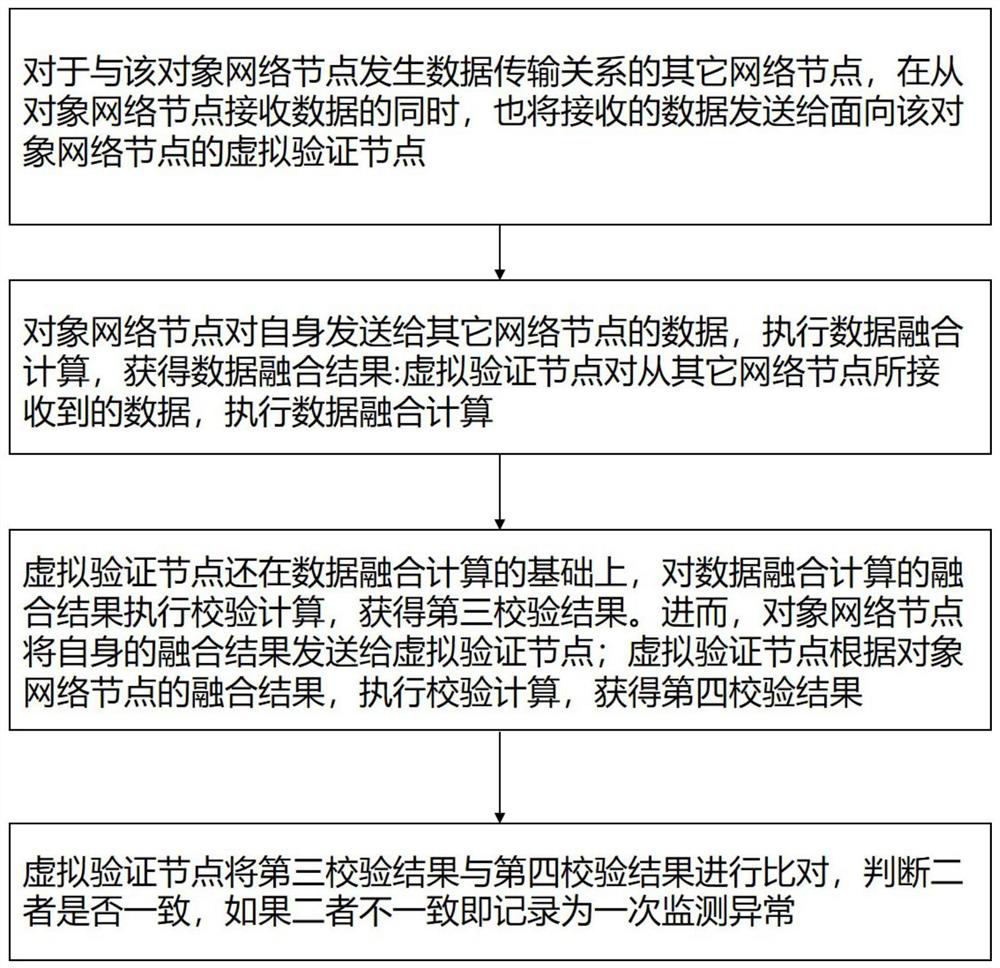
PendingCN112235802ACompatible with various changesStay flexibleSecurity arrangementHigh level techniquesNetwork architectureInformation environment
The embodiment of the invention provides an information environment security analysis method and system of a mobile internet. According to the application, a virtual verification node can be insertedinto any network node, especially a wireless access point, in a mobile internet architecture, information environment security monitoring and evaluation oriented to the network node is achieved through the virtual verification node, and according to the result of the information environment security monitoring and evaluation, an information security policy of the network node is set. According tothe invention, a monitoring analysis mechanism capable of being inserted and withdrawn instantly is achieved, the negative influence of information security environment monitoring analysis on the calculation amount and the energy consumption is reduced, the characteristic of various changes of a mobile internet network architecture is met, and the monitoring and analysis of the mobile internet information security environment can be achieved. Meanwhile, necessary flexibility and economization are kept.
Owner:深圳市众云网有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com