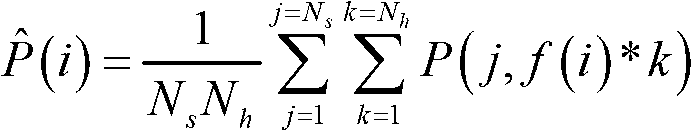Patents
Literature
99 results about "Steady state visually evoked potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
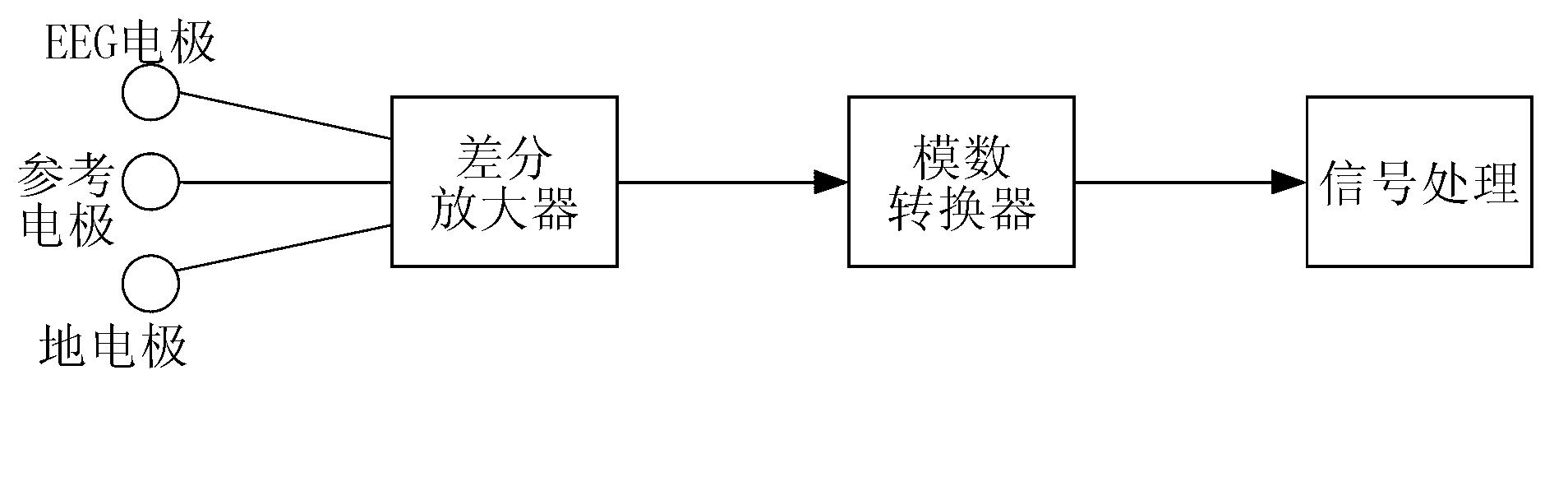
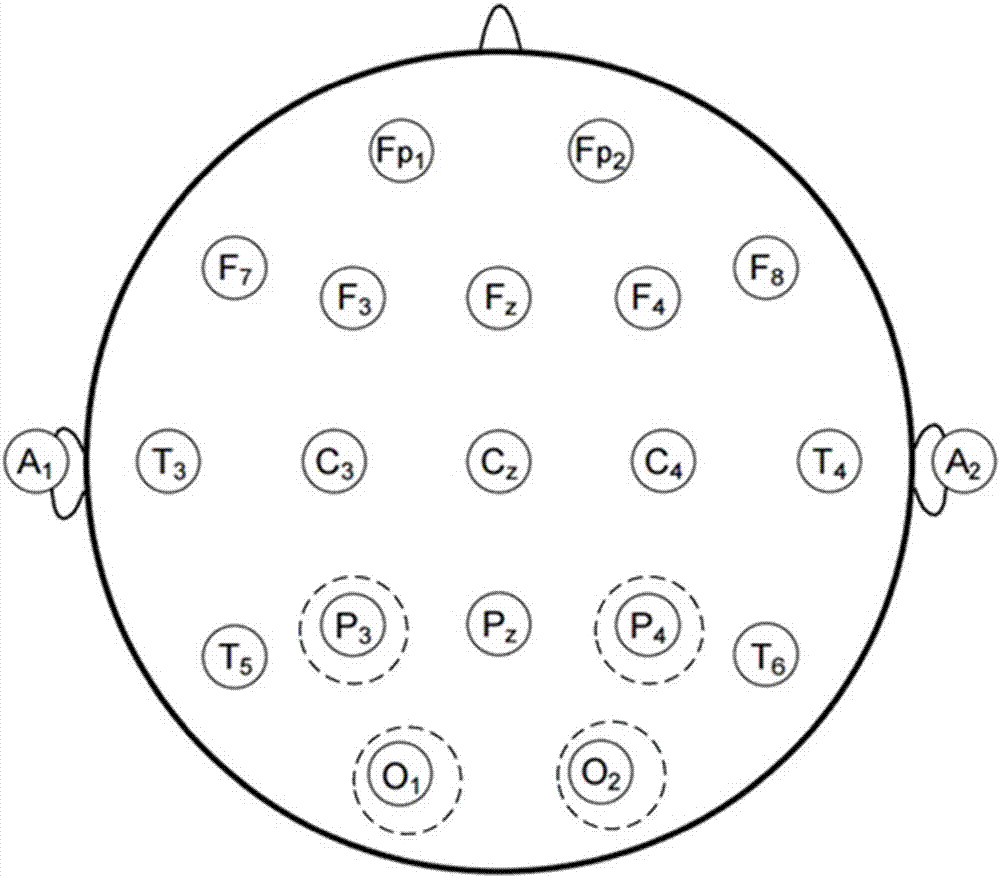
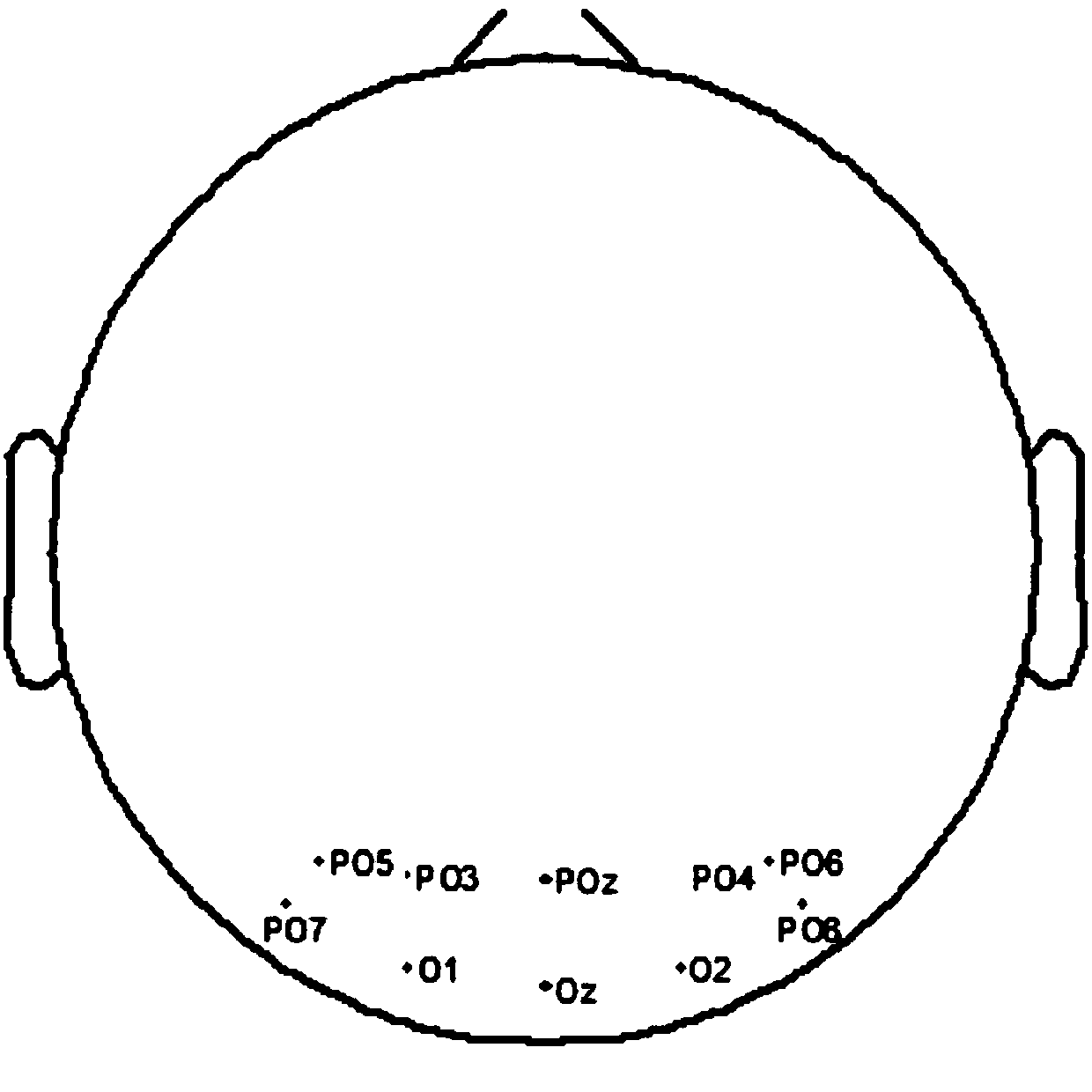
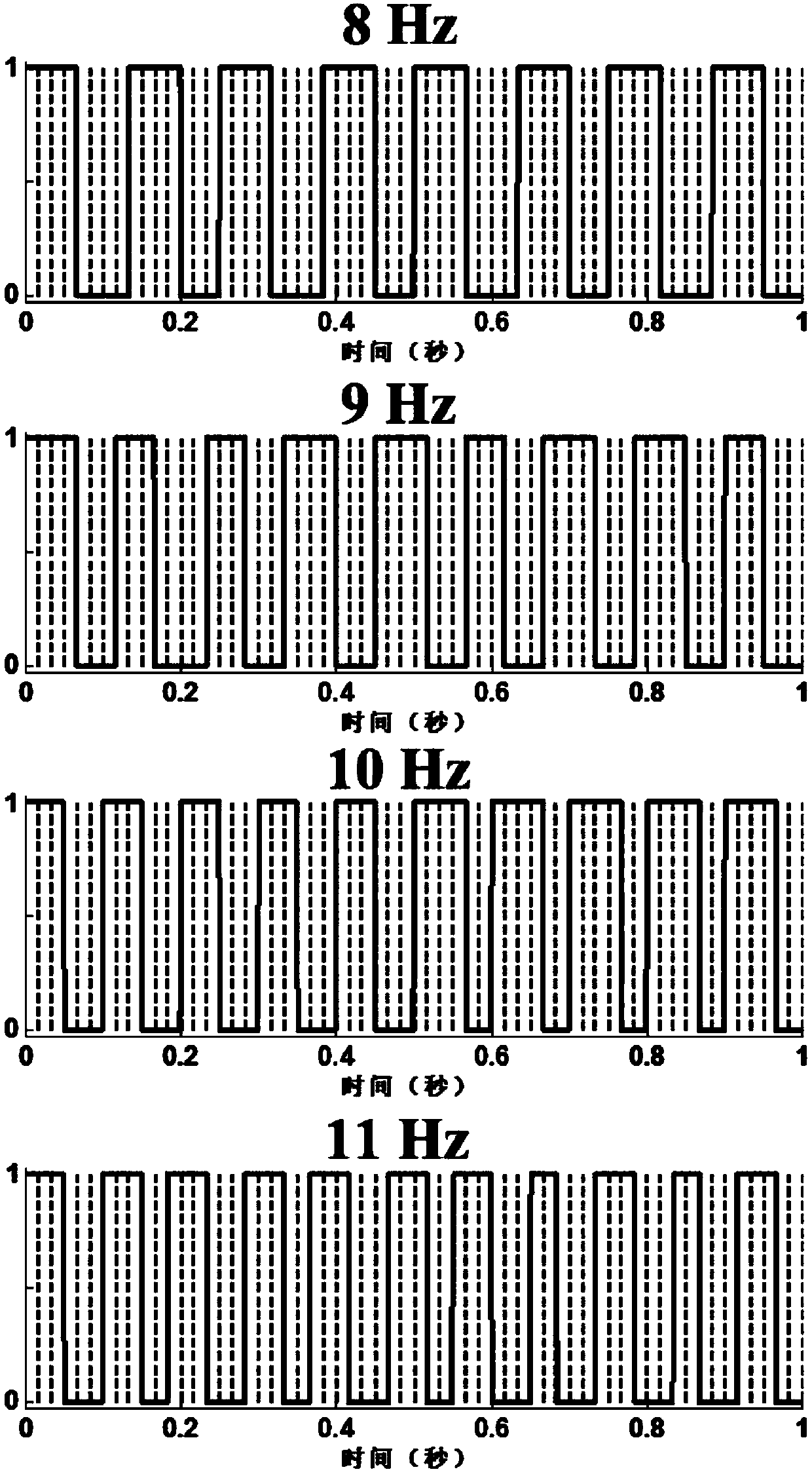
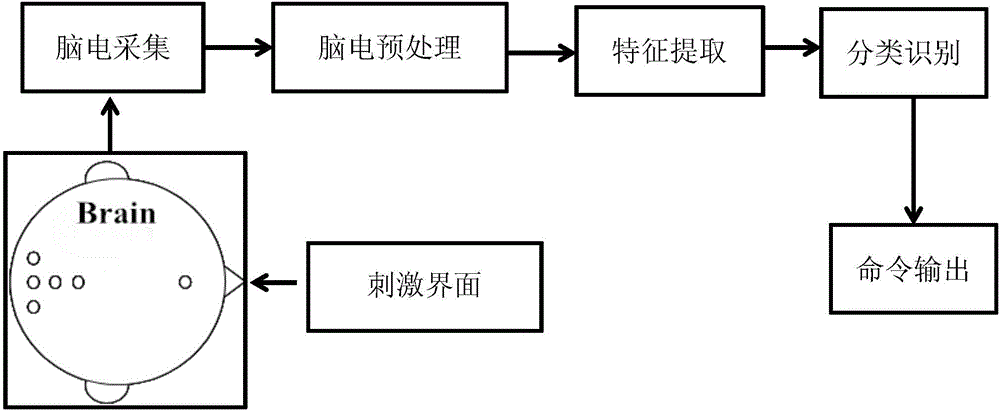
In neurology and neuroscience research, steady state visually evoked potentials (SSVEP) are signals that are natural responses to visual stimulation at specific frequencies. When the retina is excited by a visual stimulus ranging from 3.5 Hz to 75 Hz, the brain generates electrical activity at the same (or multiples of) frequency of the visual stimulus.
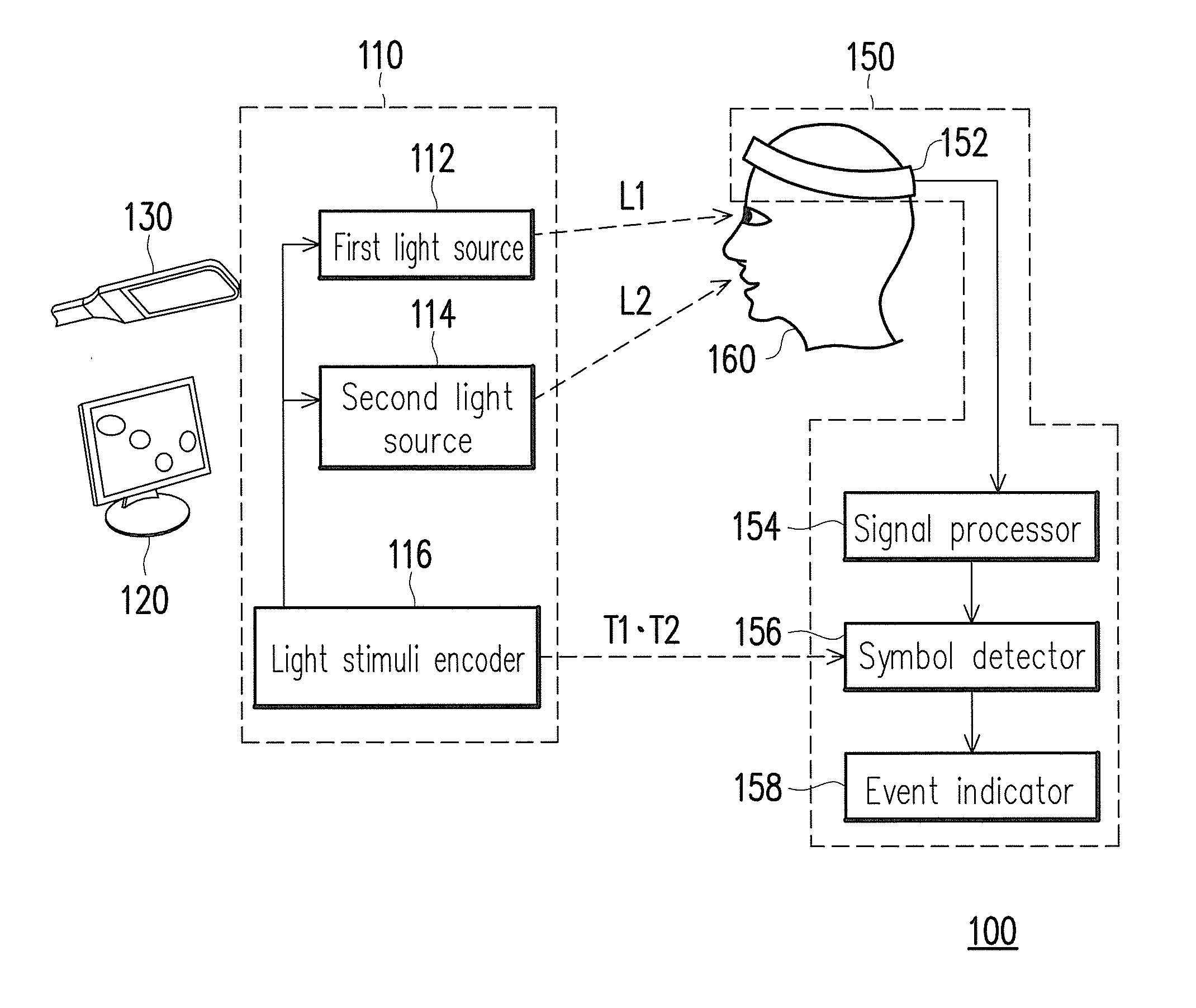
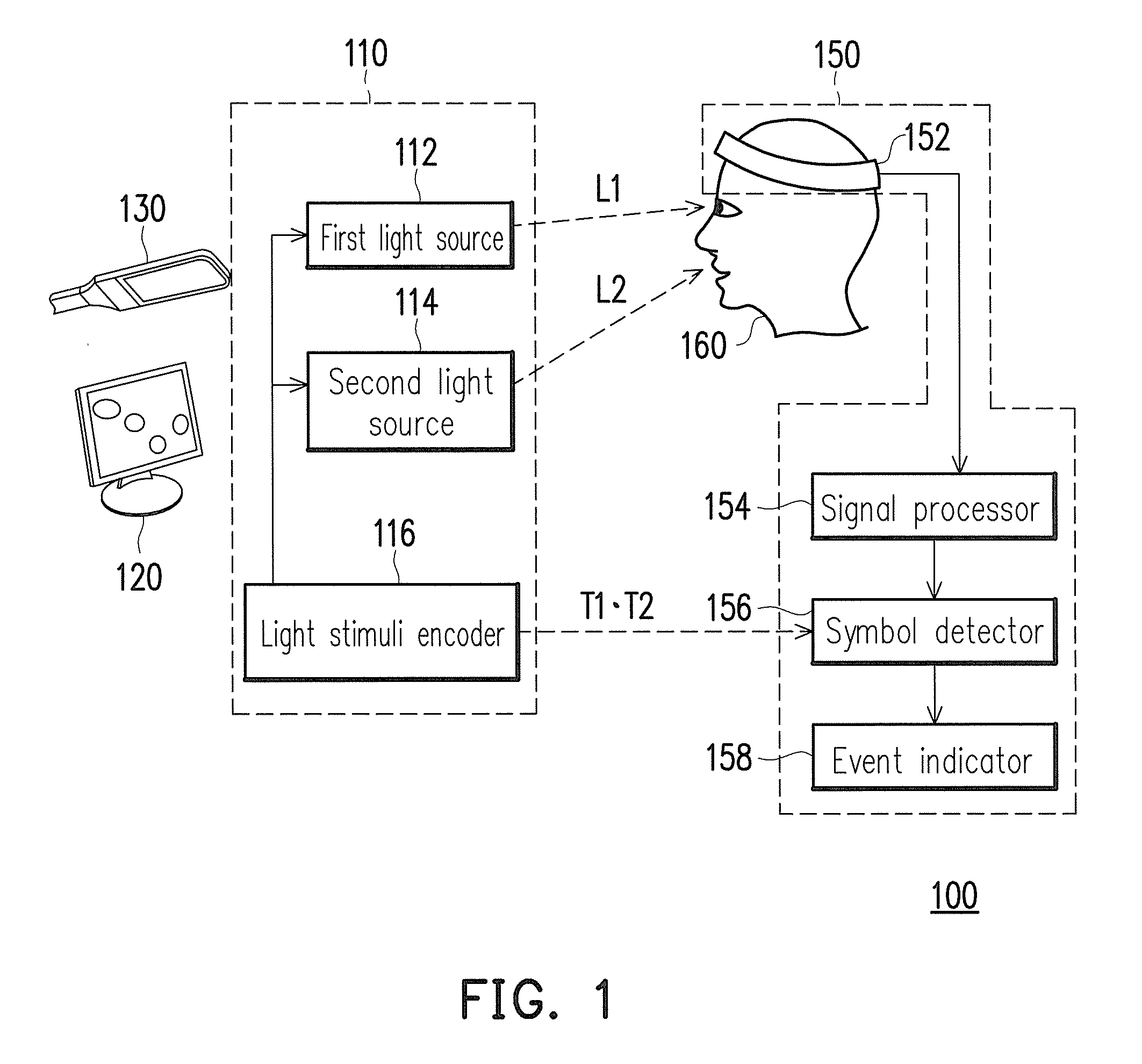
Stimuli generating methods, devices and control systems to induce visual evoked potentials using imperceptible flickering multi-color lights
ActiveUS20140058483A1Reduce riskMinimize sensationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFlickering lightHue
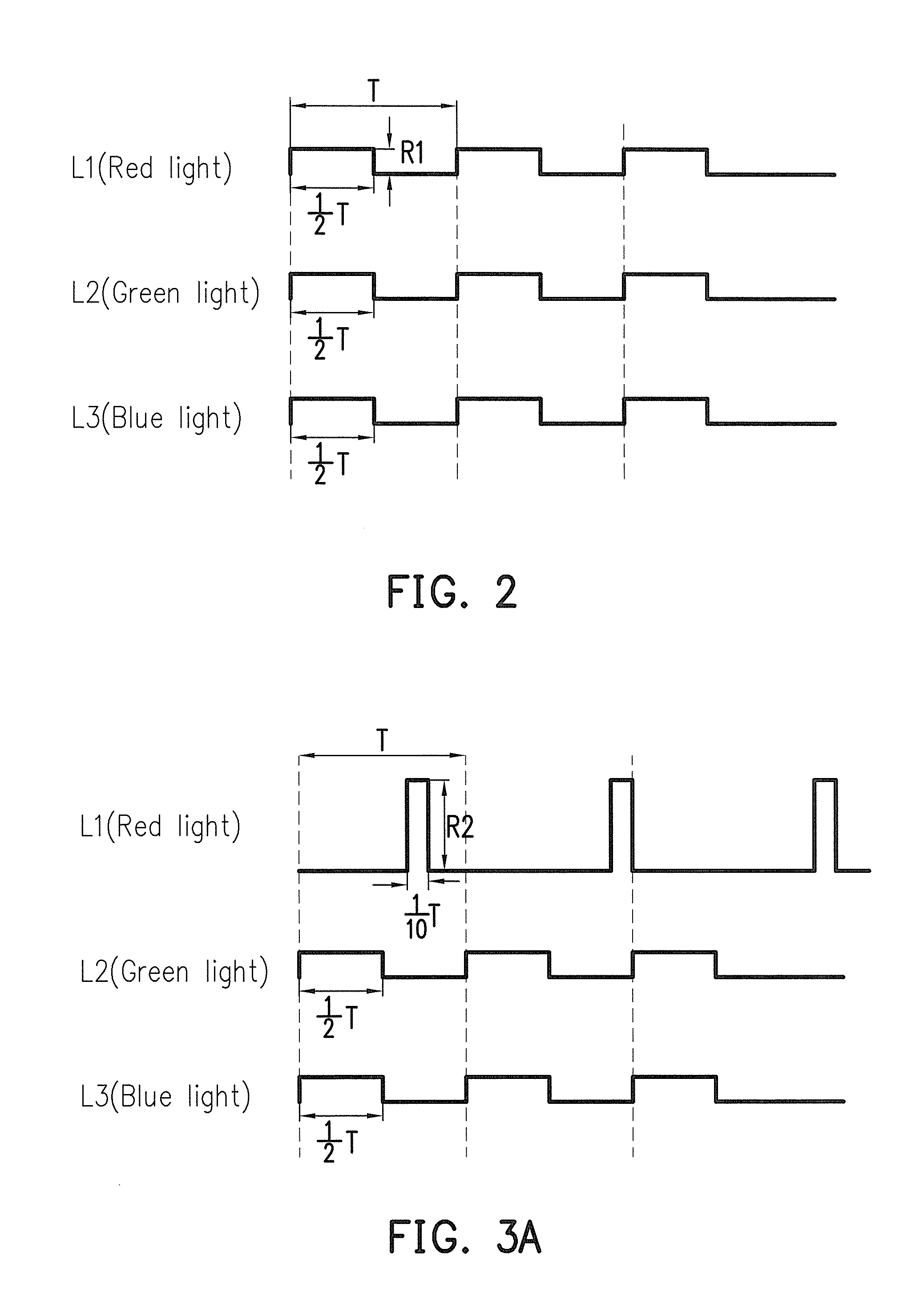
Visual or photic stimuli generating methods, devices and control systems for inducing steady-state visual evoked potential (SSVEP) from human viewers without causing discomfort to the viewers or distorting the embedding images are disclosed. The control system includes a stimuli-generating device and an electroencephalography (EEG) sensing device. The stimuli-generating device includes a first and a second light source. The first light source generates a flickering light with a first wavelength while a second light source generates another flickering light with one or more wavelength(s) differ from that of the first one. Together, the light sources generate visual / photic stimuli flickering above their critical flicker fusion threshold while maintaining the colorfulness and hue of the embedding images. At least one electrode of the EEG sensing device is connected to each viewer, configured to receive and analyze his / her EEG signals in order to detect and determine his / her responses to the stimuli.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
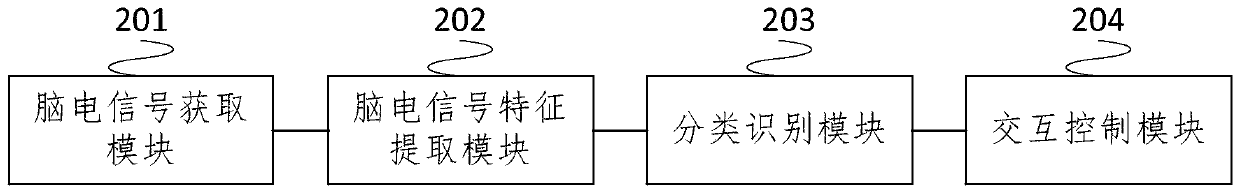
Robot system based on brain-computer interface and implementation method
InactiveCN105549743AFast and reliable handlingLow costInput/output for user-computer interactionInvalid friendly devicesLife qualityBrain computer interfacing
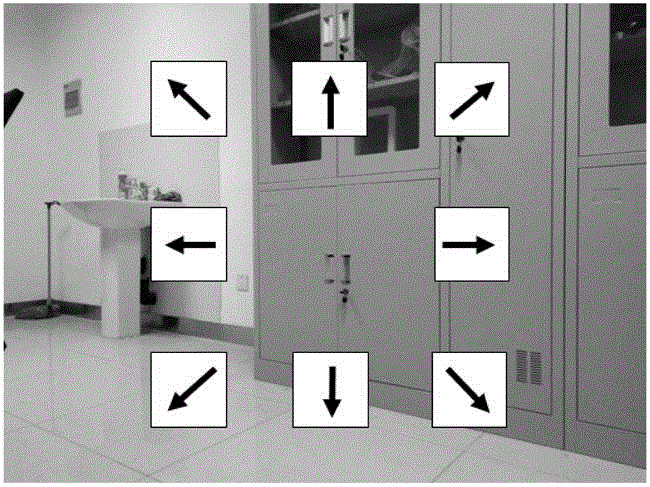
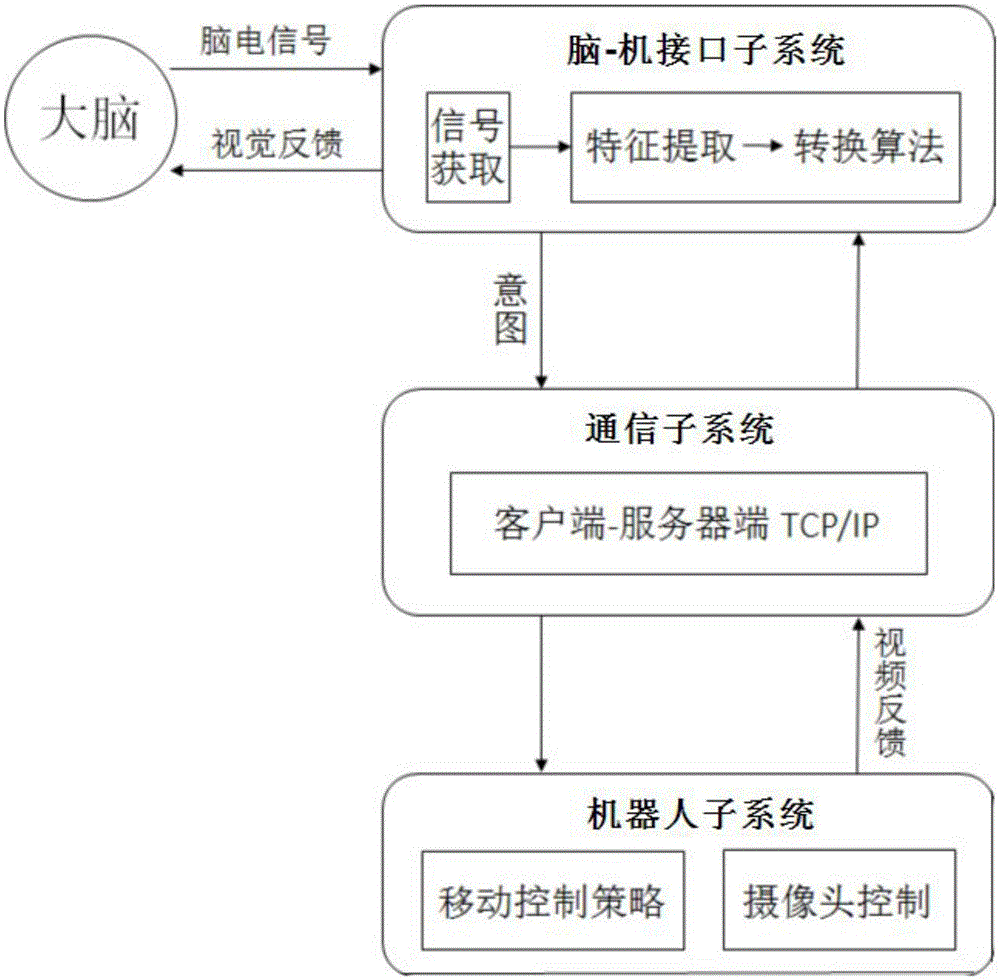
The invention relates to a robot system based on a brain-computer interface and an implementation method. The robot system is mainly characterized in that a brain-computer interface sub-system obtains a brain electrical signal through a measurement electrode and performs feature extraction of the brain electrical signal to obtain the intention of a user; the brain-computer interface sub-system converts the intention of the user into a control command and transmits the control command to a robot sub-system through a communication sub-system; the robot sub-system receives the control command of the brain-computer interface sub-system and controls a robot to move; the robot sub-system transmits video information acquired by self to the brain-computer interface sub-system; and the brain-computer interface sub-system forms a stimulation interface fed back to the user. According to the invention, mobility control of the robot in eight directions through the steady-state visual evoked potential brain-computer interface can be realized; furthermore, the system can control the robot rapidly and precisely without being trained; because the brain-computer interface is free from body movement participation, the user suffering from severe dyskinesia can move to an expected position; and thus, the living quality is increased.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI +1
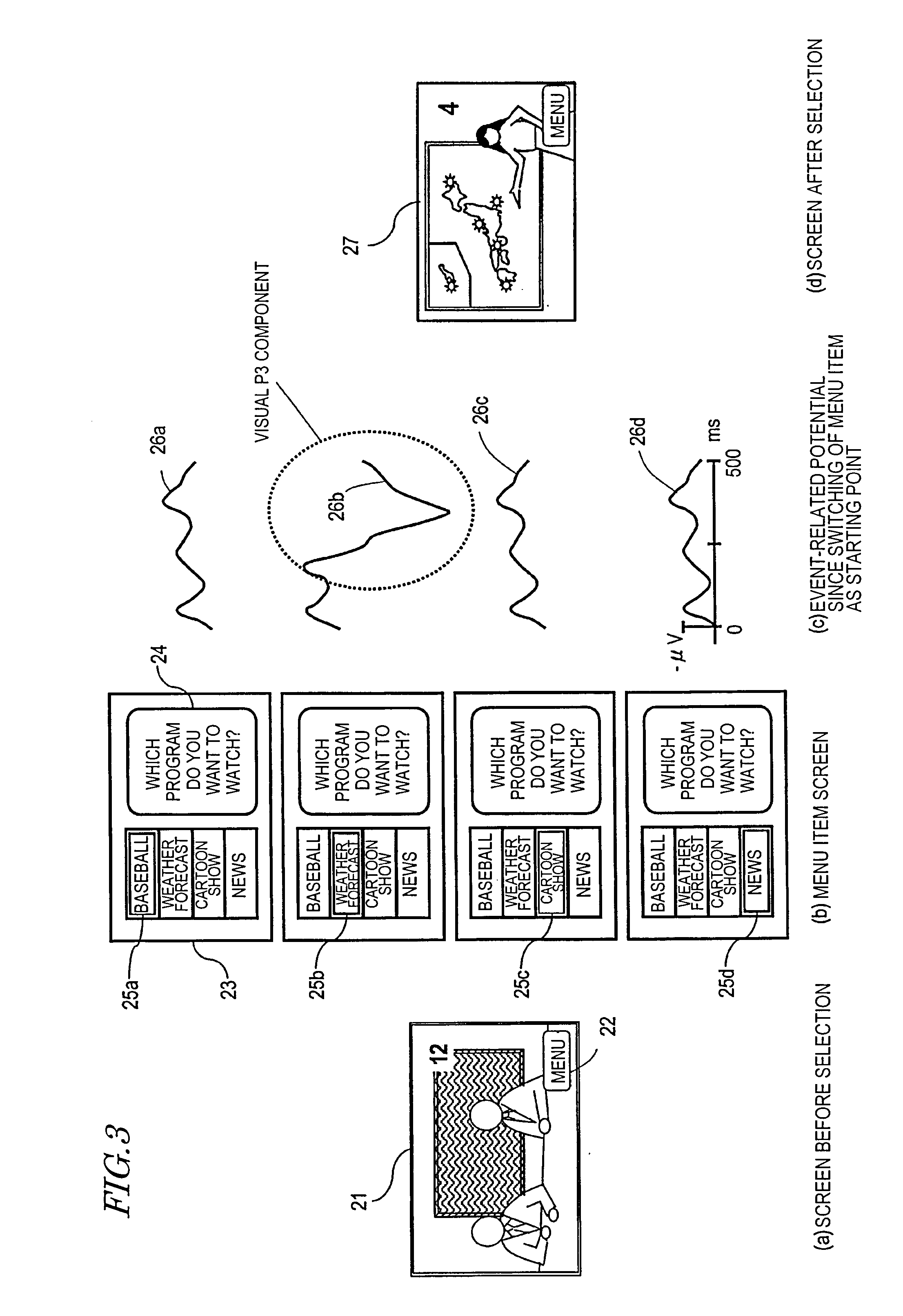
Electroencephalogram interface system and activation apparatus
ActiveUS20090187114A1Input/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsVisual evoked potentialsEngineering
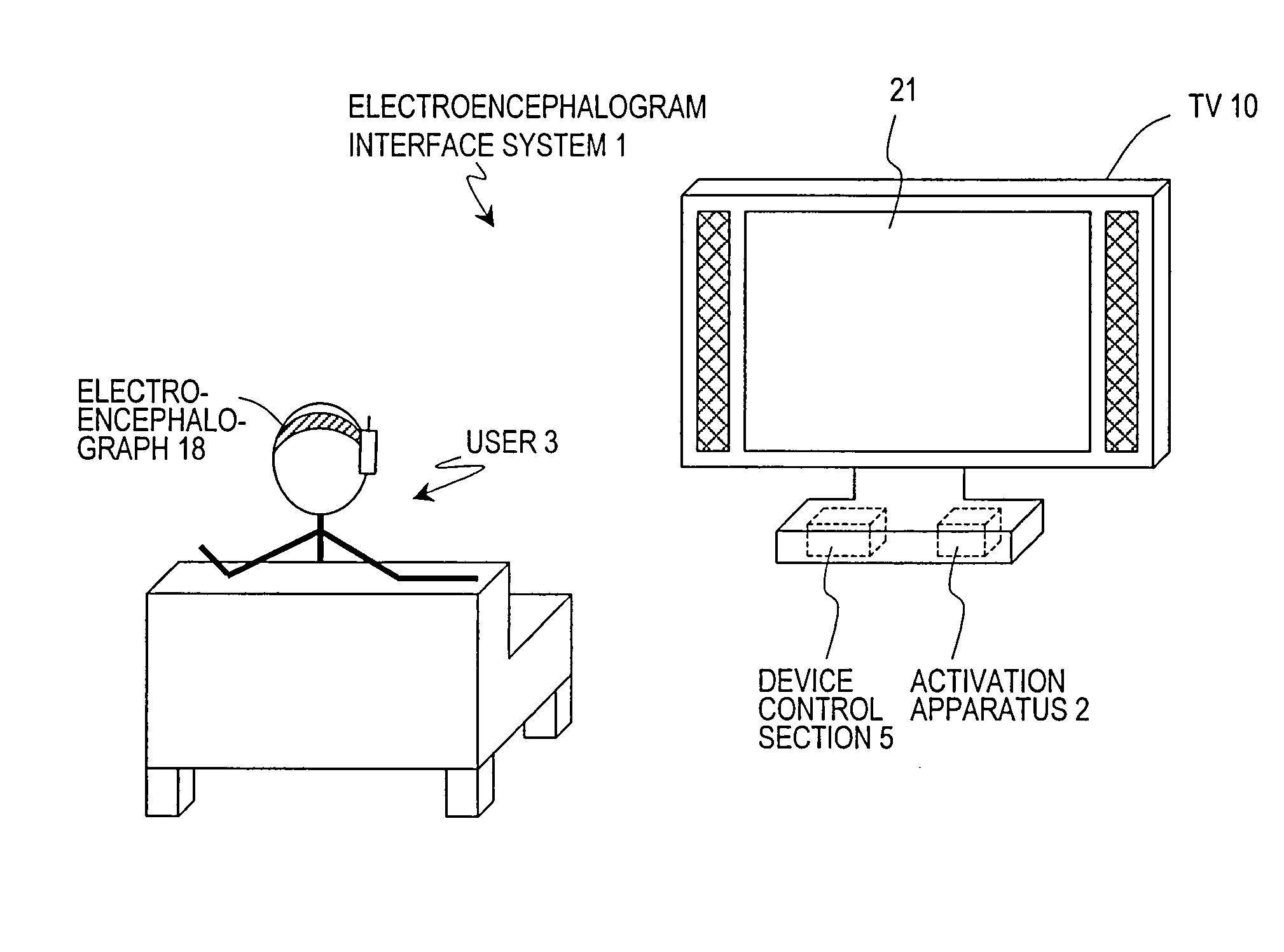
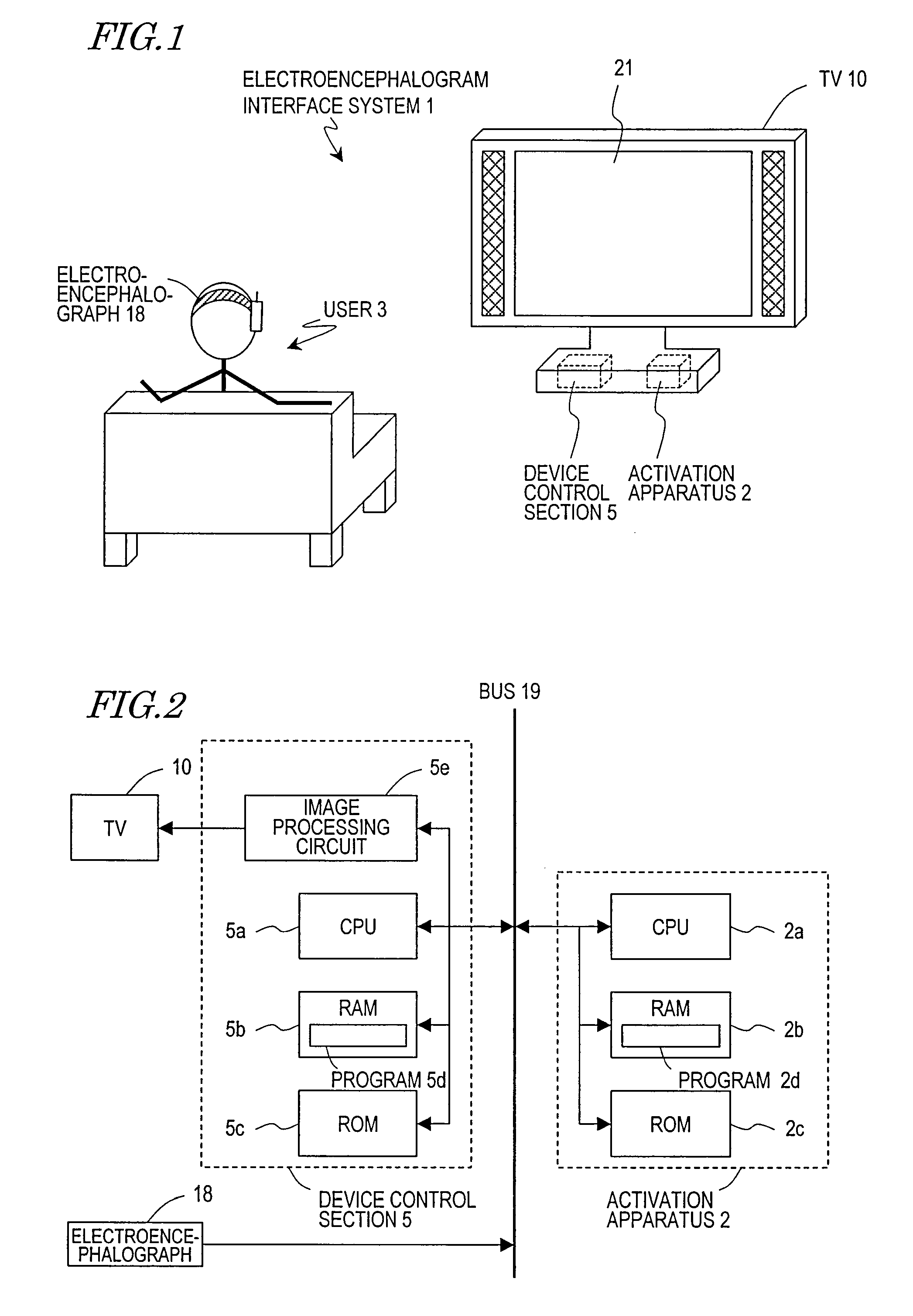
An electroencephalogram interface is activated by utilizing a biological signal, in particular a steady-state visual evoked potential, from a user.An electroencephalogram interface system (1) includes a biological signal detection section (4) for detecting an electroencephalogram signal from a user (3) and a control section (5) for distinguishing a component of an event-related potential which is contained in the electroencephalogram signal and causing a device to operate based on the distinguished event-related potential. The electroencephalogram interface system (1) further includes an activation apparatus (2) for activating the control section (5) and an output section (6) for presenting a visual stimulation which flickers with a predetermined frequency based on a signal from the activation apparatus (2). The activation apparatus (2) includes: a frequency analysis section (7) for analyzing a frequency component of the electroencephalogram signal detected by the biological signal detection section (4), and detecting an intensity corresponding to the predetermined frequency; and a determination section (8) for comparing the detected intensity of the predetermined frequency and a predetermined threshold, and if the intensity of the predetermined frequency is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold, determining that the user (3) has been paying attention to the visual stimulation and thus activating the control section (5).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
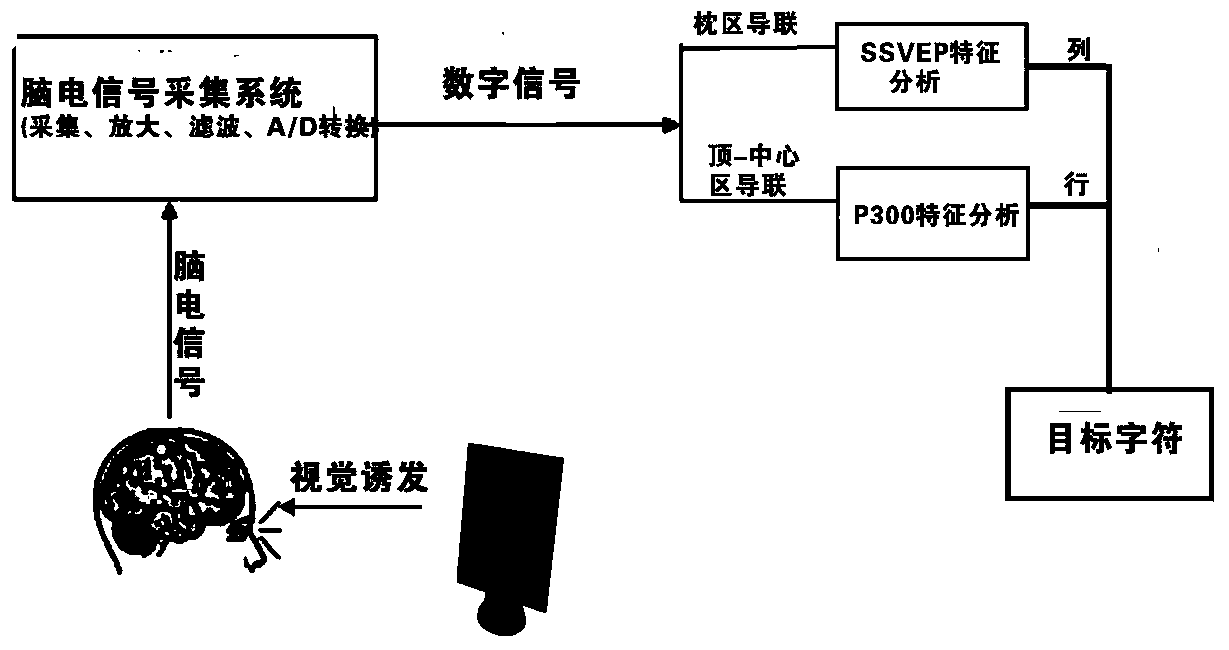
Combined brain-computer interface method and device based on SSVEP (Steady-State Visually Evoked Potentials) and P300
ActiveCN103399639AInput/output for user-computer interactionDiagnostic recording/measuringBrain computer interfacingSignal in space
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, and aims to provide a novel combined brain-computer interface normal form, which solves the technical difficult problem that two kinds of brain electrical signals are simultaneously evoked, separates the brain electrical signals in space and frequency domain and analyzes the signal features of the SSVEP and P300 so as to achieve the purpose of target identification. In order to achieve the purpose, the technical scheme adopted by the invention is that a combined brain-computer interface method based on the SSVEP and the P300 comprises the following steps: the SSVEP is evoked through line fixed frequency blinking, and the P300 is evoked through row color-frame highlighting; certain pre-processing is performed on the collected brain electrical signals, namely the SSVEP and P300; the lines in which the target characters are positioned are identified through analyzing the frequency features of the collected brain electrical signal SSVEP; the features of the P300 of the brain electrical signals are analyzed, the rows in which the target characters are positioned are identified. The combined brain-computer interface method and the combined brain-computer interface device are mainly applied to the brain-computer interface.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
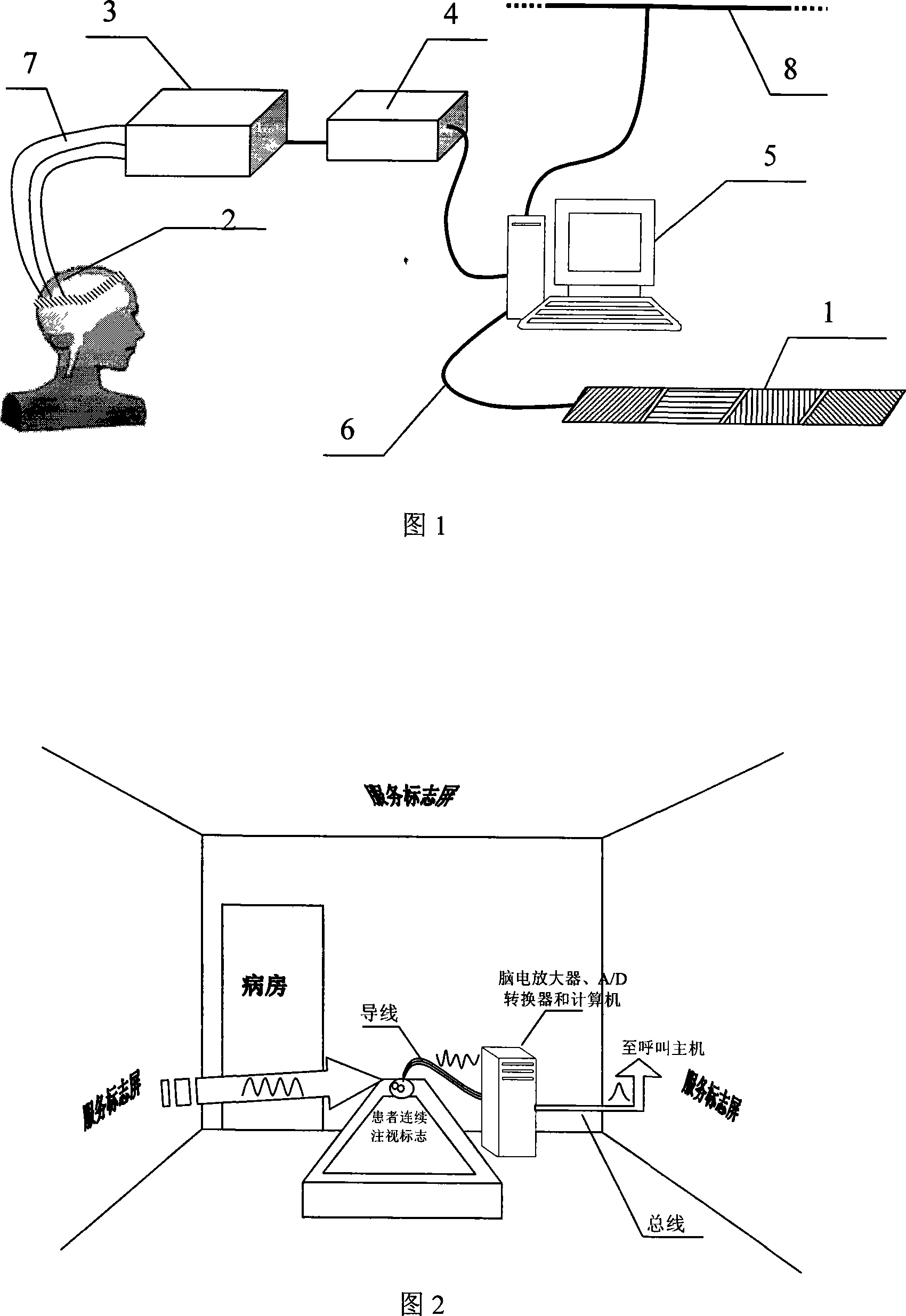
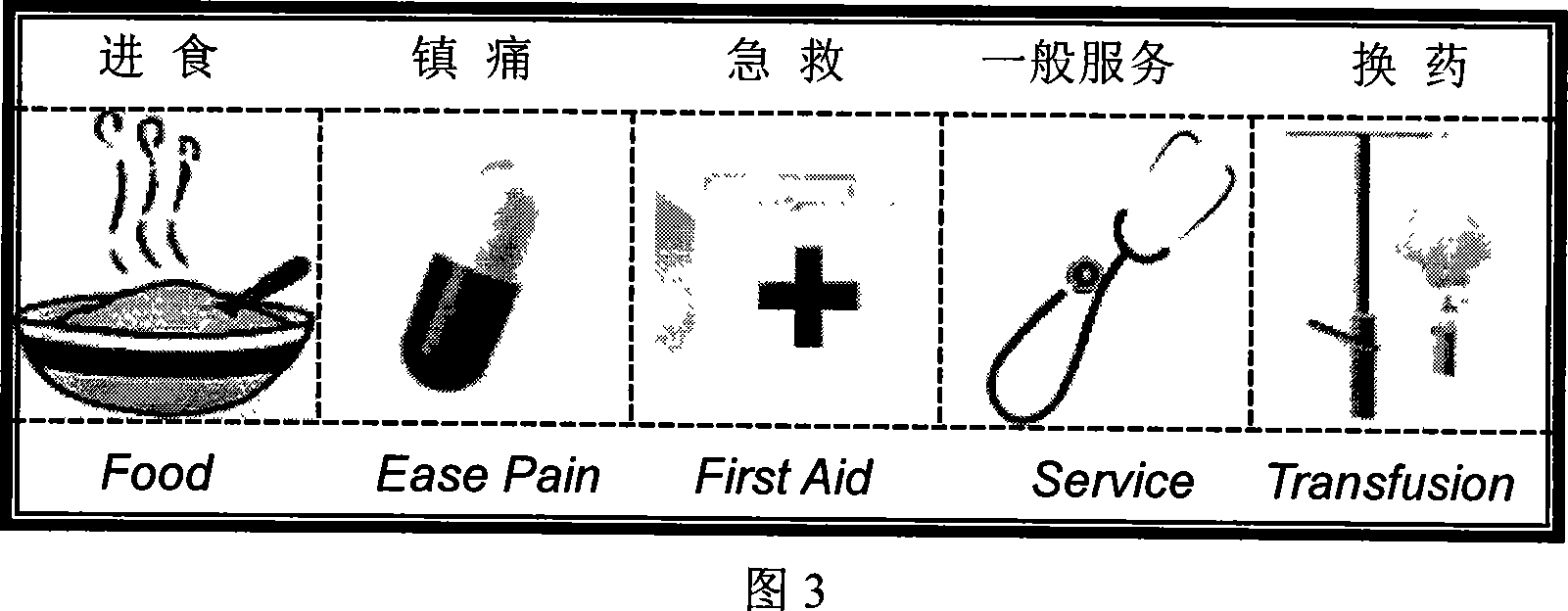
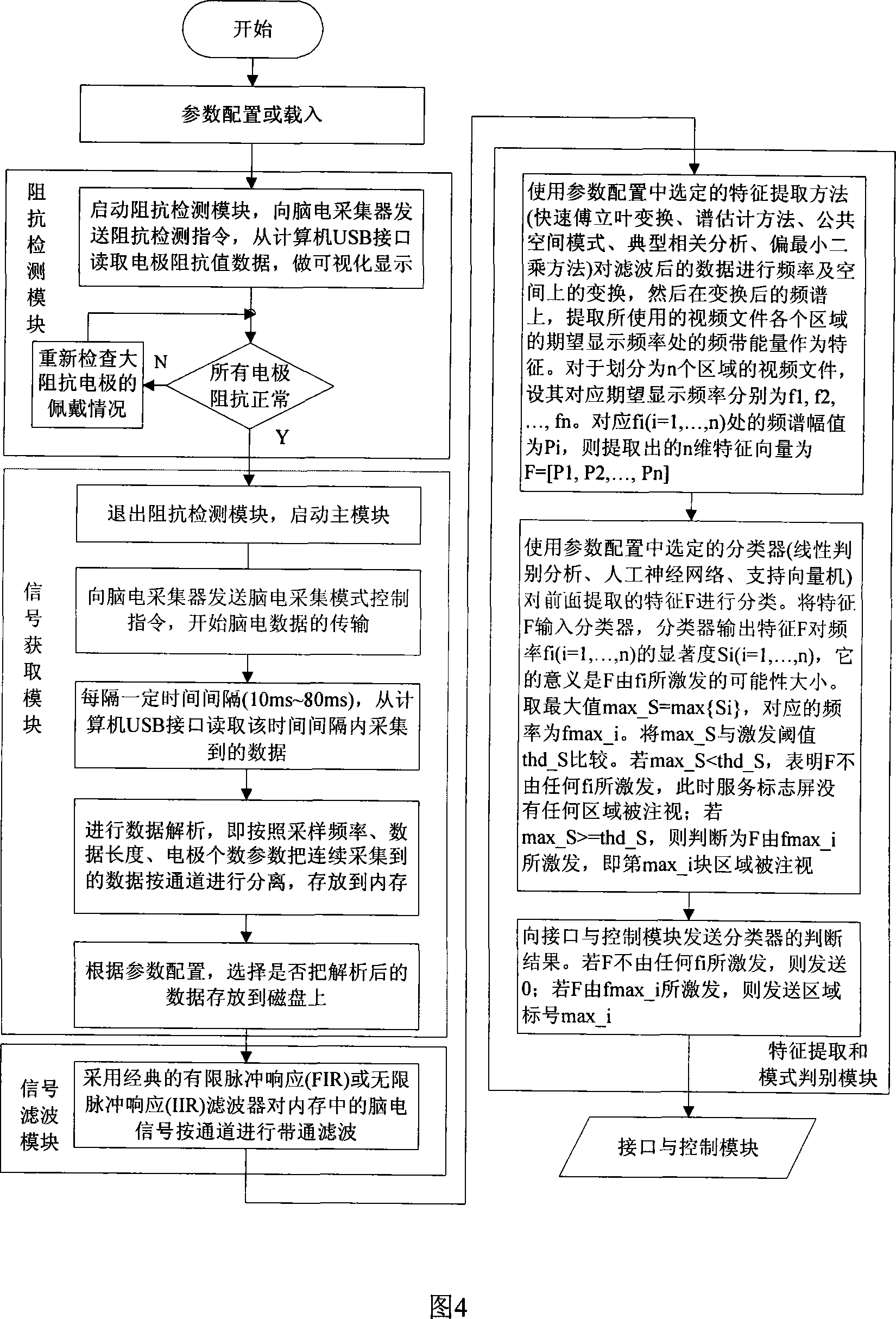
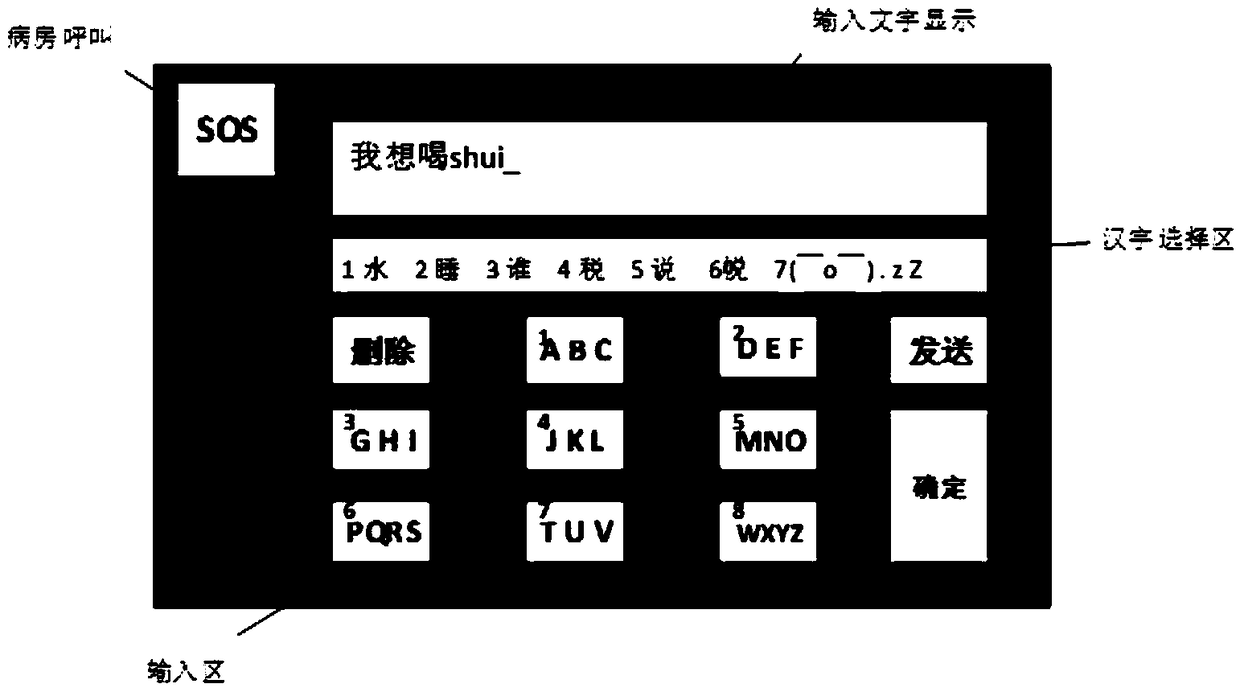
Calling device based on brain electric information demodulation
InactiveCN101159086AAvoid harmShort preparation timeAlarmsIdentification meansEngineeringVisual perception
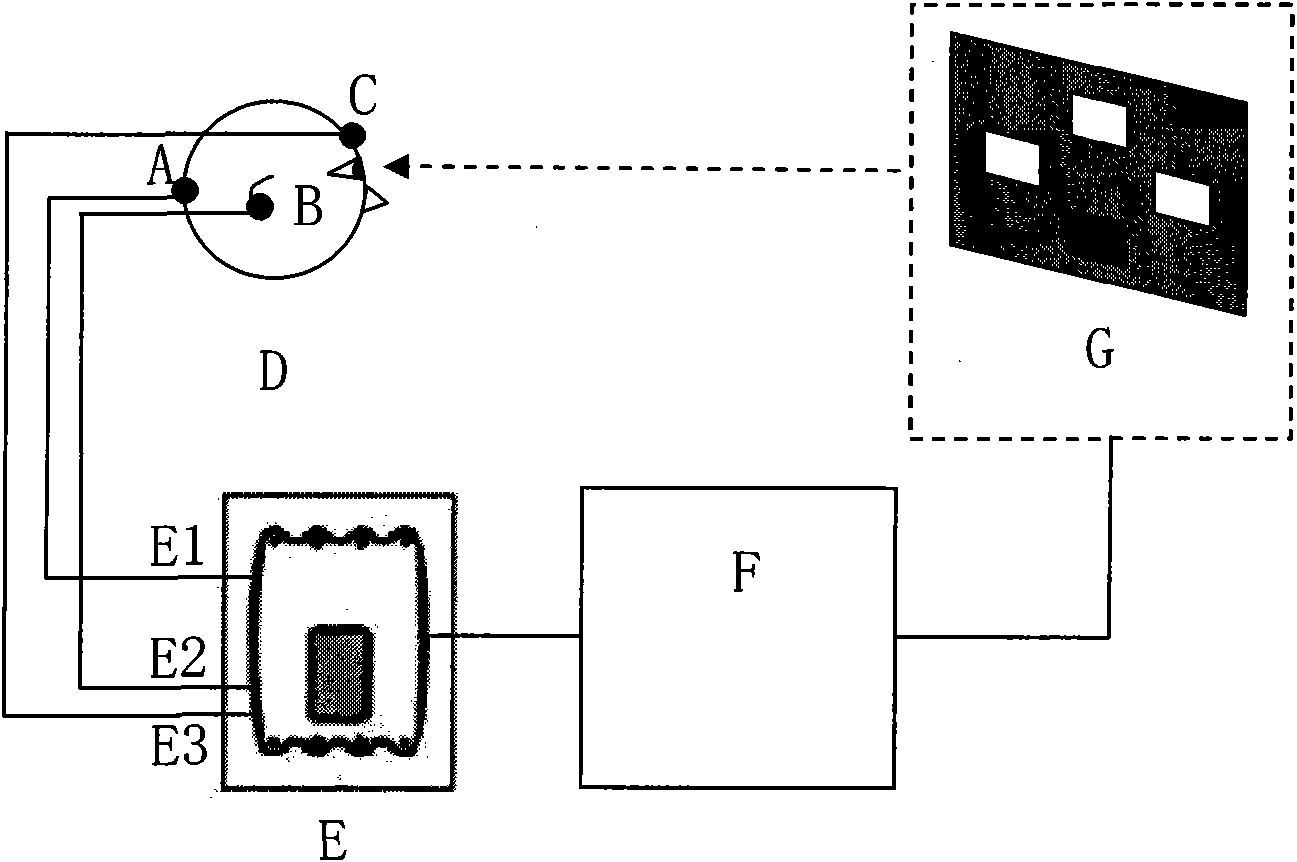
The invention discloses a calling device based on electrical brain information demodulation, which is to provide the calling device based on stable state visual induction electric potential demodulation for a ward calling system to substitute for a keypad type calling machine. The calling device consists of a service sign screen, an electrical brain collector, an electrical brain amplifier, an A / D converter and a calling extension machine; wherein the service sign screen is a LED display screen. The electric brain collector consists of 3-5 active electrodes, is fixed on the scalp on the position of occipital lobe of hind brain of a patient and is connected with the electric brain amplifier. Multi-lead electric brain signals are amplified by the electric brain amplifier and are transmitted to the A / D converter. The A / D converter transforms simulation signals into digital signals and transmits the digital signals to the calling extension machine. LED display control software and electric brain processing and analyzing software are arranged on the calling extension machine. The LED display control software controls the display of the service sign screen. The electric brain processing and analyzing software processes and analyzes the electric brain data in real time and transmits calling information to a host machine. The invention can substitute non-contact and non-action type fixation operation for keypad type operation.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
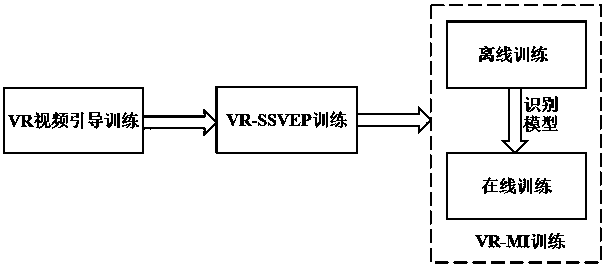
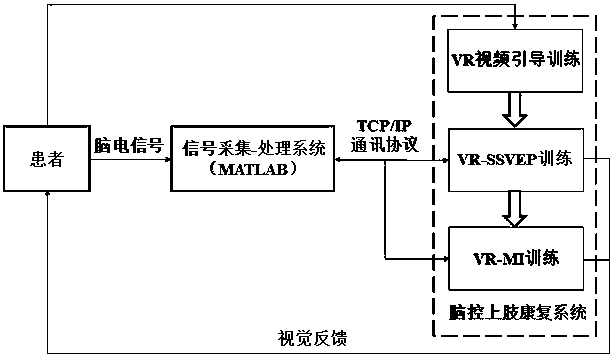
Three-stage brain-controlled upper limb rehabilitation method combining steady-state visual evoked potential and mental imagery
InactiveCN108597584AImprove securityImprove immersion effectMedical simulationMental therapiesPatient needUpper limb rehabilitation
The invention relates to a three-stage brain-controlled upper limb rehabilitation method combining steady-state visual evoked potential and mental imagery (MI). The method comprises the following steps: (1) the first stage of VR video guidance training: a patient is made to be familiar with upper limb rehabilitation movements through VR video guidance; (2) the second stage of VR-SSVEP training: the patient needs to concentrate to observe pictures that represent different upper limb movements and flicker with a specific frequency, EEG signals of the patient are collected in real-time to analyzeintentions of the patient, and visual feedback is provided to the patient through VR animation to make the patient learn to concentrate; and (3) the third stage of VR-MI training: EEG signals of theleft and right upper limbs of the patient during MI are collected during off-line training, and a mental imagery intention recognition model is established. The EEG signals of mental imagery of the patient are analyzed according to the model during online training, movement intentions of the patient are recognized, and movements of a 3D character in an interface are controlled in real time, so that brain central nerve remodeling is facilitated through MI. The method exhibits a good immersion property, enables active rehabilitation to be realized, enables rehabilitation to proceed step by step,and is a new method for upper limb rehabilitation of a cerebral stoke patient.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
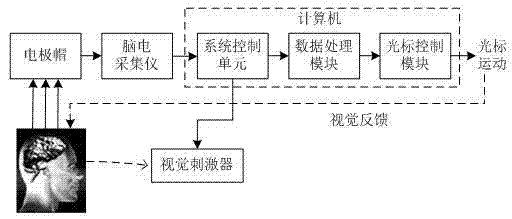
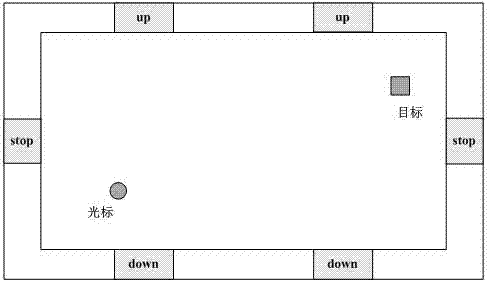
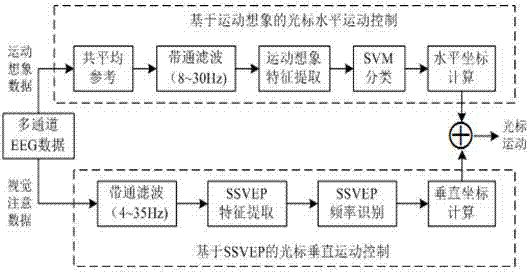
Two-dimensional cursor motion control system and method based on motor imagery and steady-state visual evoked potential
InactiveCN103699217AEasy to operateDisadvantages of Avoiding Jumping ExercisesInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingVisual perceptionSteady state
The invention discloses a two-dimensional cursor motion control system and method based on motor imagery and steady-state visual evoked potential. The system comprises an electrode cap, an electroencephalogram acquisition instrument, a system control unit, a data processing module, a cursor control module and a visual stimulator, wherein the visual stimulator is provided for a user in an interface display way. The method comprises the following steps that the user executes motor imagery and visual attention tasks simultaneously according to a working interface instruction; the electrode cap acquires an electroencephalogram signal; the electroencephalogram acquisition instrument performs amplifying, filtering and analog-digital conversion on the electroencephalogram signal; the system control unit separates electroencephalogram data generated by motor imagery and visual attention and saving; the data processing module performs preprocessing, feature extraction and classification and identification on two kinds of electroencephalogram data in sequence; the cursor control module controls a cursor to perform continuous two-dimensional motion according to a classification and identification result. The system has the advantage of high control accuracy, high robustness, capability of realizing two-dimensional cursor continuous motion and the like, and can be used for performing motion control on a computer mouse.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
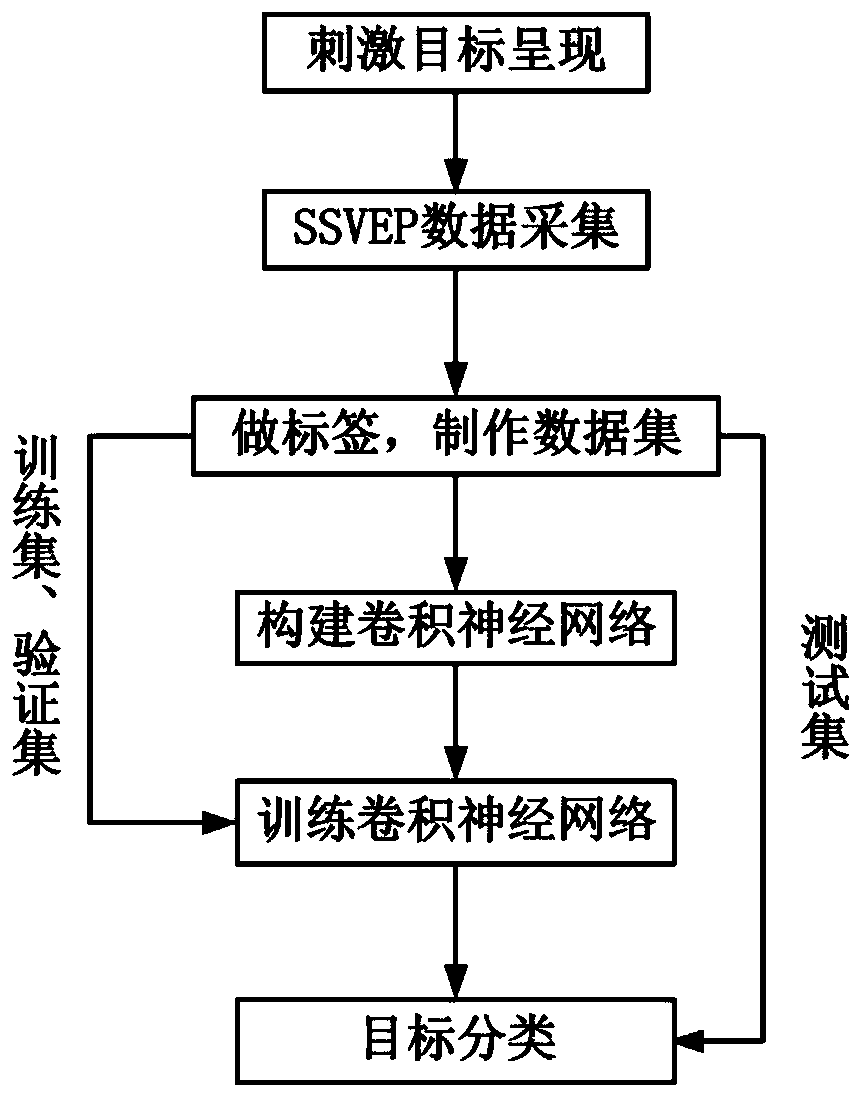
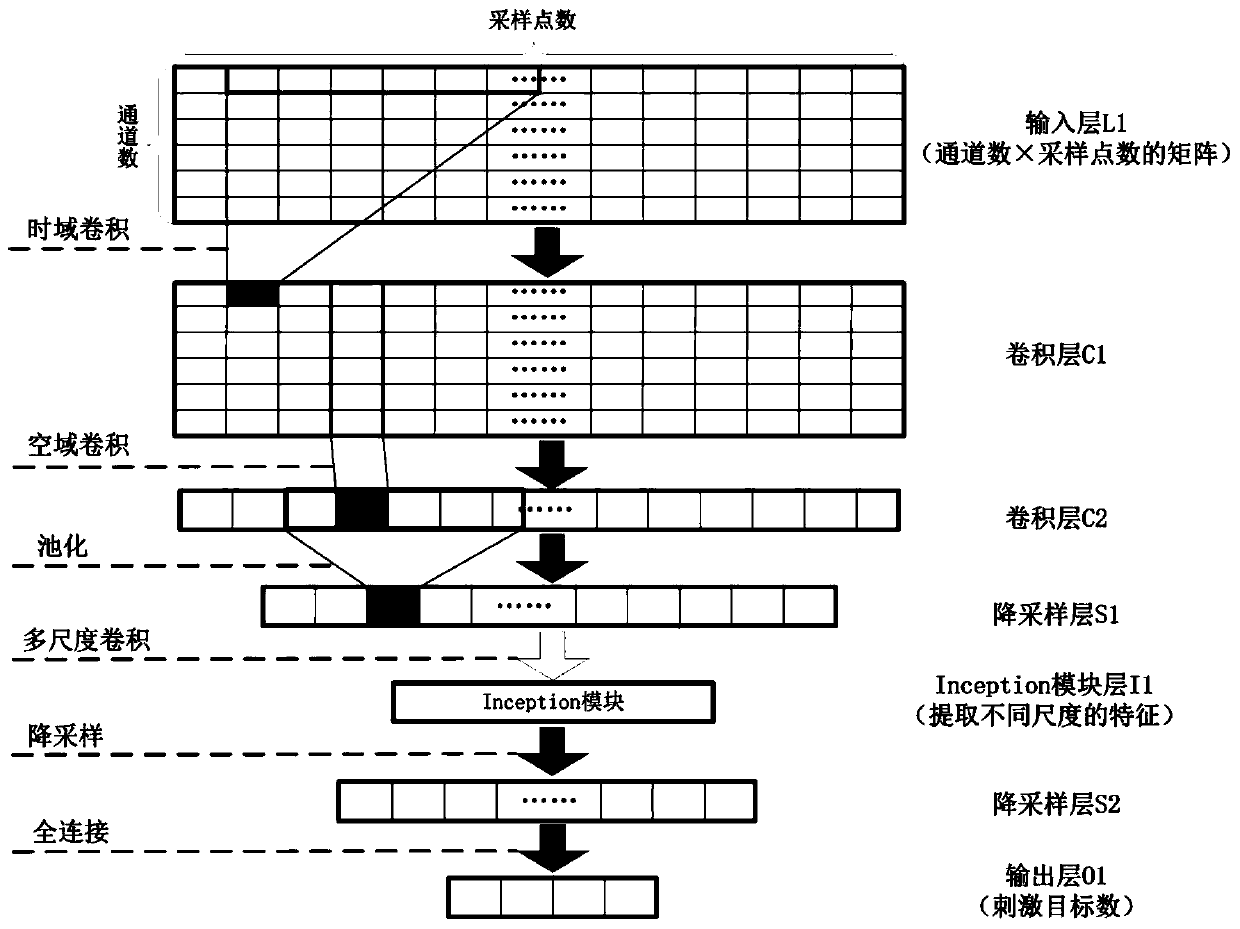
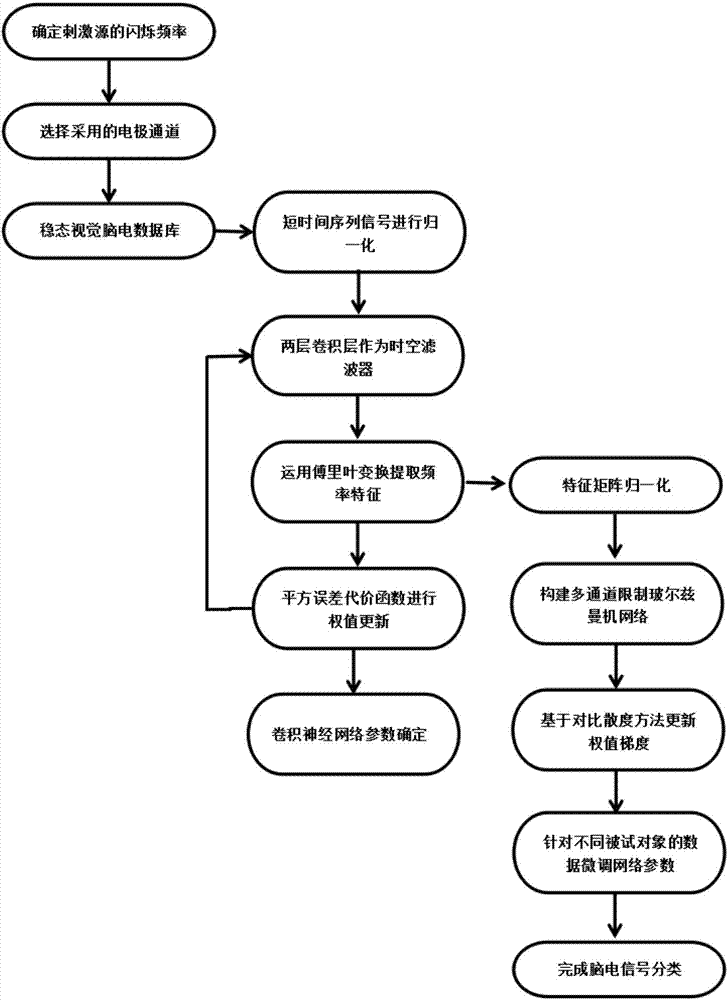
Steady-state visual evoked potential signal classification method based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN110222643ARealize precise identificationGood application effectCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringData setSignal classification
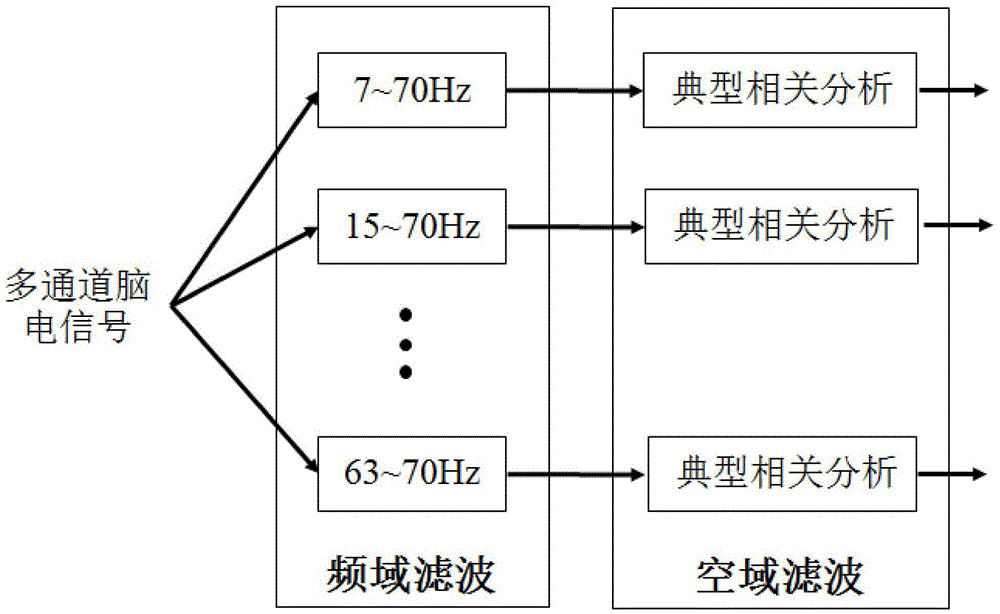
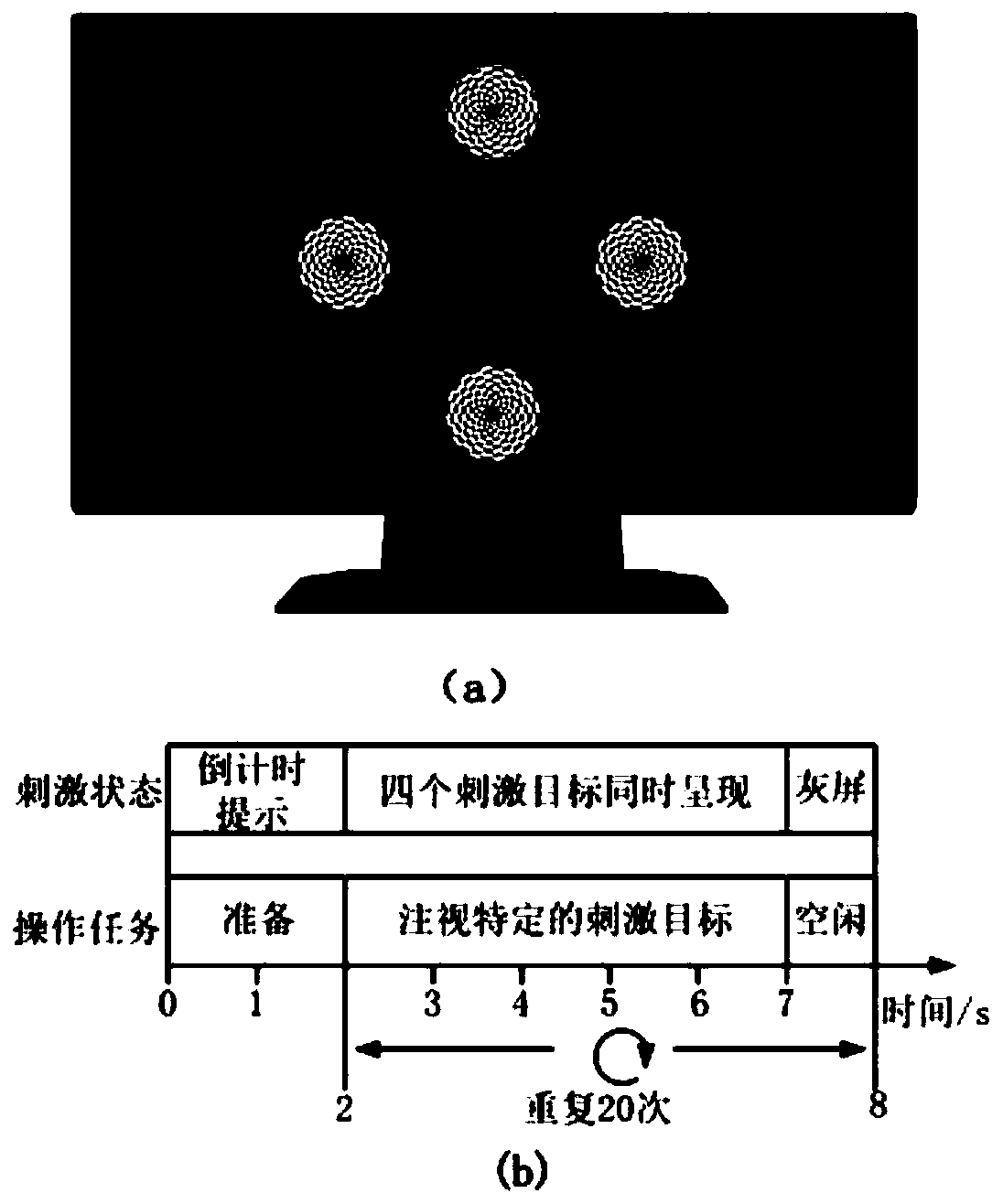
A steady-state visual evoked potential signal classification method based on a convolutional neural network comprises the following steps: firstly, presenting checkerboard stimuli flipped at differentfrequencies to a user at the same time, and acquiring an electroencephalogram signal when the user watches a specific target by using an electroencephalogram acquisition device; making original multi-channel electroencephalogram signals when the user watches different stimulation targets into a data set with labels, and dividing the data set into a training set, a verification set and a test set;inputting the training set into a designed deep convolutional neural network model for training, performing network optimal parameter selection by using a verification set, and finally inputting thetest set into the trained deep convolutional neural network model to complete the recognition of the stimulation target. Accurate identification of steady-state visual evoked potential signals can beachieved, the characteristic of adaptively extracting signal characteristics is achieved, manual preprocessing is not needed, and meanwhile individual difference can be better adapted through data learning.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Multi-frequency time sequence combined steady-stage visual evoked potential brain-computer interface method
InactiveCN101887307AImprove information transfer rateStrong specificityInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingPattern recognitionBrain computer interfacing
The invention discloses a multi-frequency time sequence combined steady-stage visual evoked potential brain-computer interface method. The method comprises the following steps of: putting a measurement electrode on the head of a subject and connecting the measurement electrode with an electroencephalogram amplifier, a computer and a computer screen; and forming n different representation targets by using n stimulus frequencies, wherein n is an integer more than 1; and realizing the representation of the visual targets and the visual feedback of the subject by using the computer screen. The method improves the information transmission rate of the brain-computer interface by constructing a plurality of representation targets from a few stimulus frequencies, has the advantages of multiple representation targets and high specificity of the detection result, can realize communication between the disabled having normal mind but suffering from paralysis of the neuromuscular system and an external apparatus, and is suitable for a normal person on occasions that the limbs are inconvenient to control.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
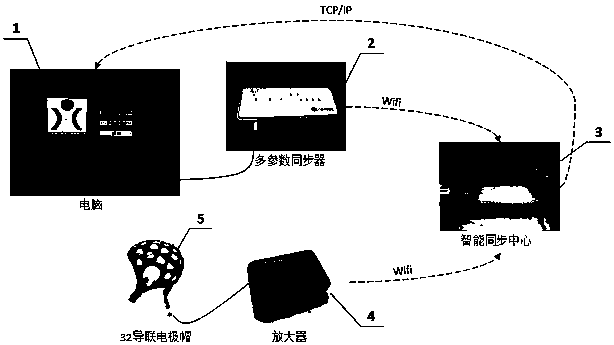
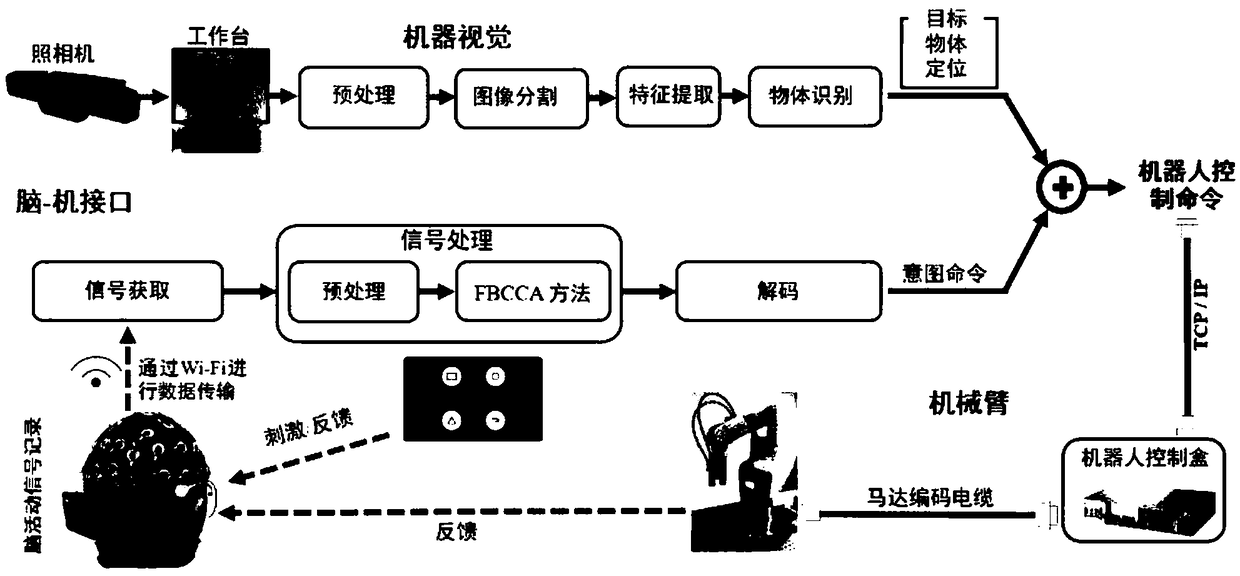
Advanced mechanical arm control system based on BCI and implementation method
InactiveCN109366508APrecise Control FunctionHigh stimulation frequencyInput/output for user-computer interactionProgramme-controlled manipulatorVisual evoked potentialsBrain computer interfacing
The invention relates to an advanced mechanical arm control system based on BCI and an implementation method thereof. The system comprises a machine vision subsystem, a brain-computer interface subsystem and a mechanical arm subsystem; the brain-computer interface subsystem and the machine vision subsystem are connected to the mechanical arm subsystem through a TCP / IP for communication, and the machine vision subsystem recognizes and positions coordinates of a target object in a photographing mode; and the brain-computer interface subsystem is used for acquiring scalp electroencephalogram signals generated by steady-state visual evoked potentials and performing real-time analysis and feature extraction on the scalp electroencephalogram signals, the control intention of a person is online decoded and a computer-recognizable control command is generated, and the machine arm subsystem operates according to the control command. According to the system, the design is reasonable, the controlintention of the person can be decoded online and the computer-recognizable control command is generated to control the mechanical arm to operate, the accurate multi-objective control function is realized, and the system has the characteristics of being safe, efficient and reliable.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
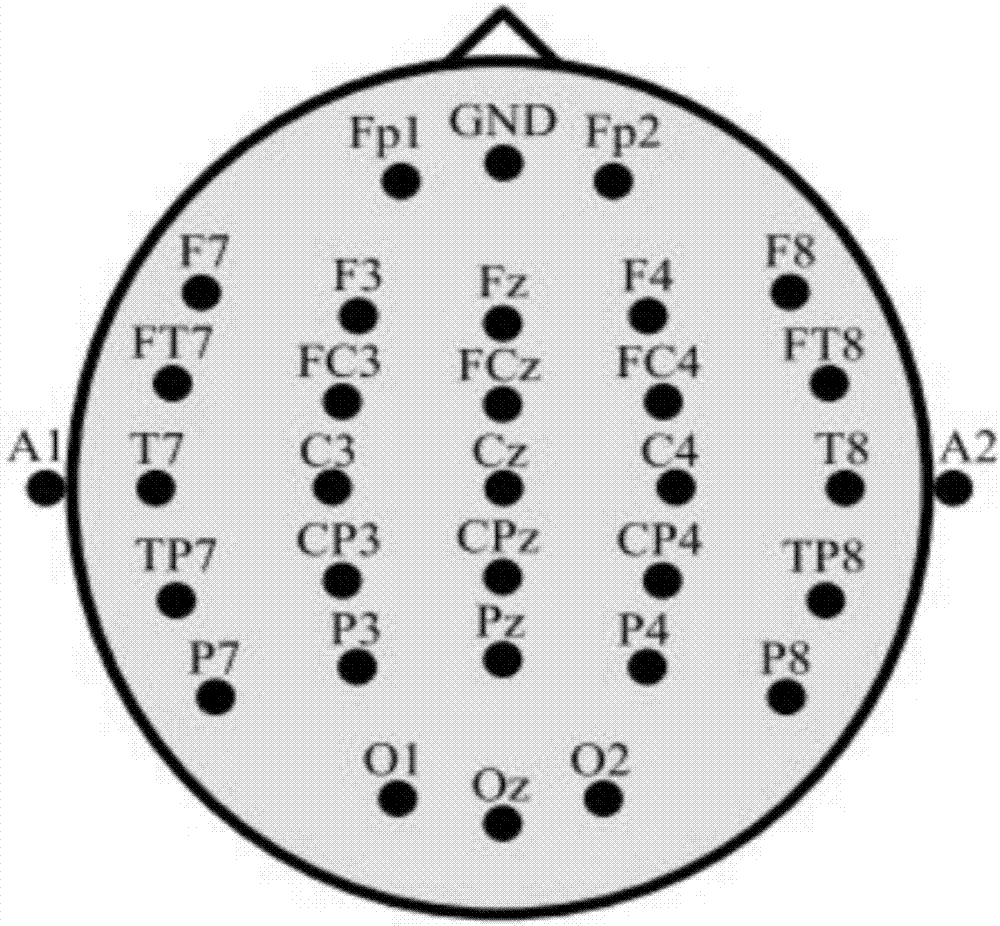
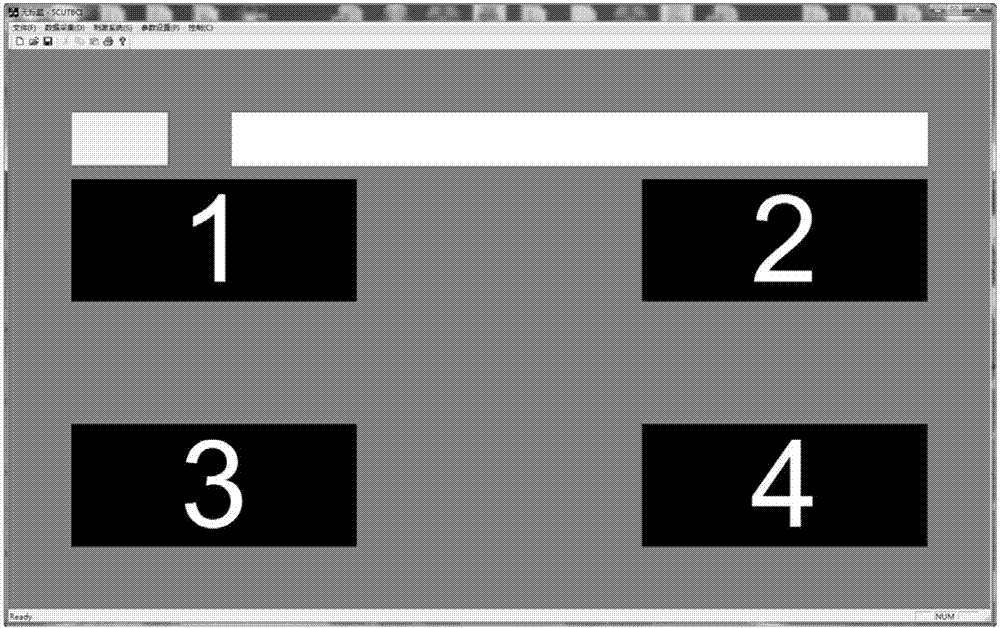
Deep learning mixed model-based steady state visual evoked potential classification method
ActiveCN107168524ARealize automatic extractionPreserve frequency domain featuresInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionSignal classificationClassification methods
The invention discloses a deep learning mixed model-based steady state visual evoked potential classification method. The method comprises the steps of 1, adopting an LCD display as a stimulation source, determining a flicker frequency, selecting an electrode channel for electroencephalogram collection, carrying out an experiment for multiple different testees, and performing collection to obtain a steady state visual electroencephalogram signal database; 2, based on short-time-sequence electroencephalogram signals in the database, training and determining parameters of a convolutional neural network model, and finishing automatic extraction of features of the electroencephalogram signals; and 3, adopting an output of a convolutional deep learning network as an input of a Boltzmann machine network, performing fine adjustment on parameters of a classification network model for the different testees, and determining parameters of a Boltzmann machine network model. According to the method, the extraction of the generalization features of the electroencephalogram signals can be well realized; the influence of electroencephalogram signal distortion on signal classification is reduced; and the short-time-length electroencephalogram signals can be utilized to well finish the signal classification.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GUANGDA INNOVATION TECH CO LTD
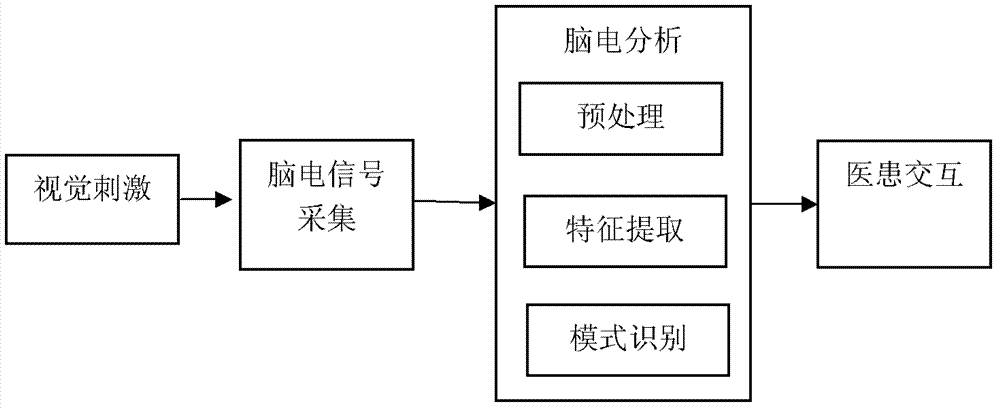
Brain-computer interface based doctor-patient interaction method
InactiveCN102708288AAchieve interactionRealize classification recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsInteraction systemsBrain computer interfacing
The invention provides a brain-computer interface based doctor-patient interaction method, which adopts a brain-computer interface based doctor-patient interaction system comprising an electroencephalographic collection module and an electroencephalographic analysis and doctor-patient interaction module. The method comprises the following steps of: setting visual stimulation signals with different frequencies, displaying the signals on a display, and mapping into controls of four commands through different combined codes (00, 01, 10 and 11) of 0 and 1; collecting an electroencephalographic signal of a subject by an electrode in real time, sending into a computer after the signal is amplified; analyzing the electroencephalographic signal; and broadcasting a voice prompt corresponding to the identification result through a speaker, and displaying the result on the display. Therefore, medical staff can carry out corresponding rescue according to the display and voice. The brain state can be identified by the brain-computer interface technology, and external equipment is accurately driven in time, so that communication and control can be realized. Brain can be effectively excited to generate steady state visual evoked potential by visual stimulations in different frequencies, the electroencephalographic signal can be accurately identified under stimulations in different frequencies through signal calculation and processing functions of the computer, and real doctor-patient interaction can be realized in the result display and voice prompt mode.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Steady state visual evoked potential brain-computer interface signal identification method
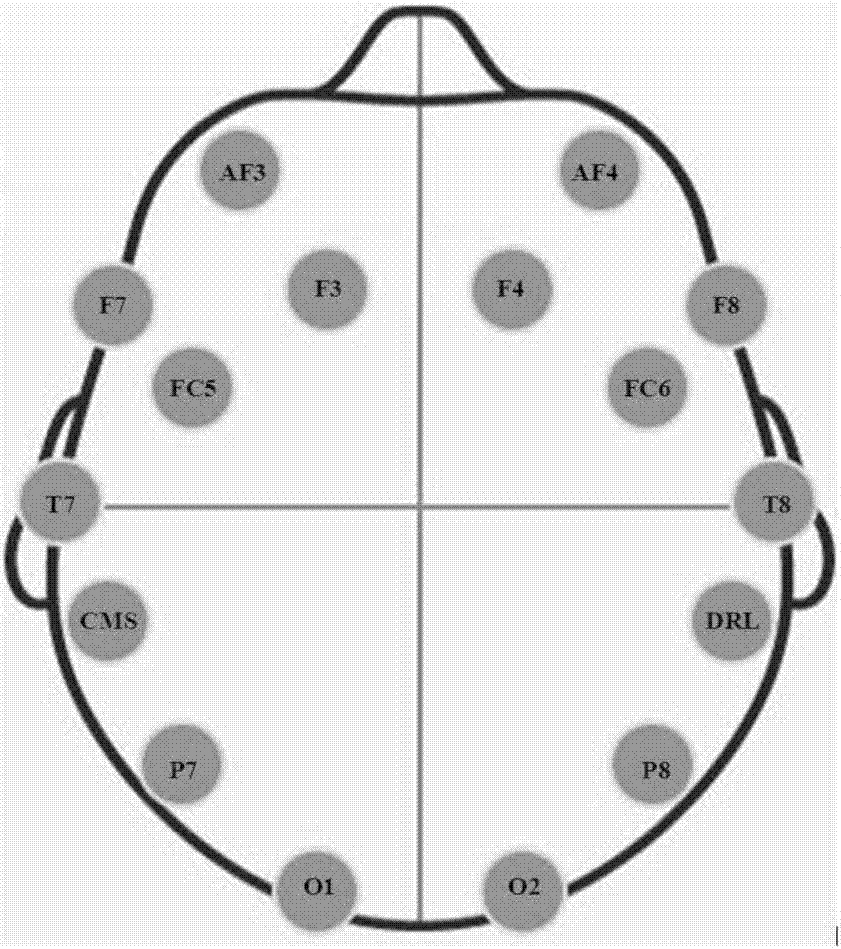
ActiveCN103019383AImprove transfer rateShort training timeInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingVisual evoked potentialsBrain computer interfacing
The invention discloses a steady state visual evoked potential brain-computer interface signal identification method, which comprises the following steps of: (1) simultaneously displaying a plurality of different pictures with different flicker frequencies through a visual stimulation unit and acquiring electroencephalogram signals of a testee who stares at the visual stimulation unit; (2) carrying out noise estimation and noise suppression on the electroencephalogram signals by a data processing unit, and then carrying out characteristic extraction and judgment on the processed electroencephalogram signals to primarily determine the picture at which the testee stares; and (3) upsetting the flicker frequencies of the displayed pictures, acquiring the electroencephalogram signals, then carrying out noise estimation and noise suppression on the currently acquired electroencephalogram signals, then carrying out characteristic extraction and judgment on the processed electroencephalogram signals to determine the picture at which the testee stares, if the currently determined picture is the same as the picture determined in the step 2, taking the picture as finally determined identification information to output, and if not, judging that the testee does not stare at any picture displayed by the visual stimulation unit. According to the steady state visual evoked potential brain-computer interface signal identification method, the electroencephalogram signal identification accuracy can be effectively improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
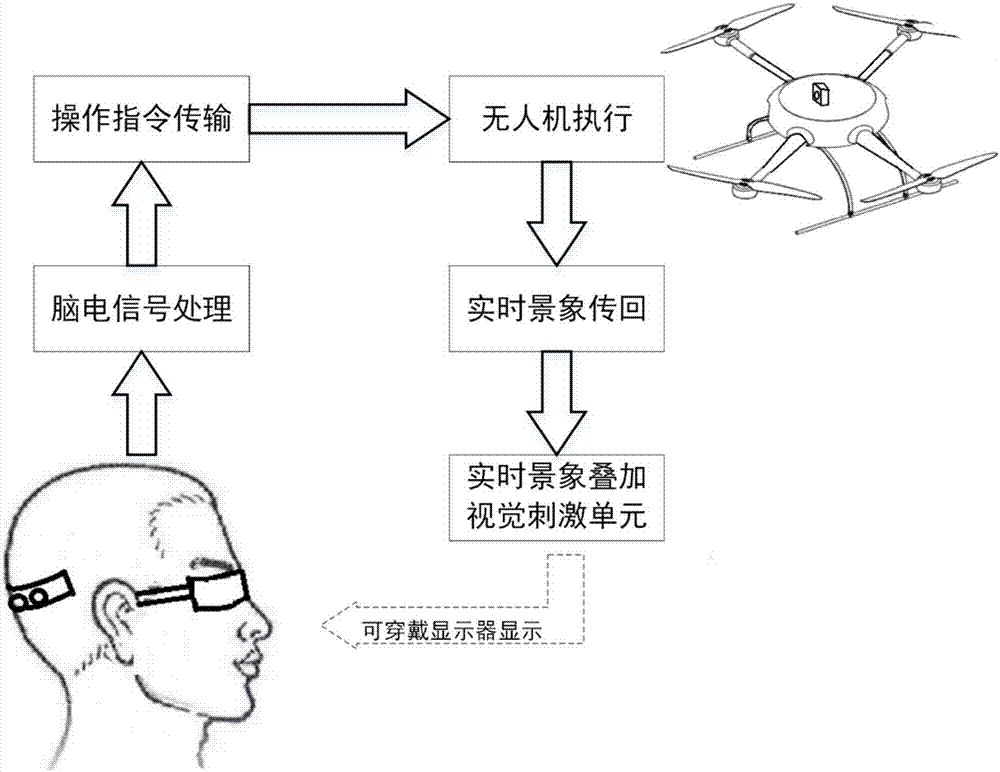
Wearable display-based asynchronous type brain-controlled unmanned aerial vehicle system
InactiveCN107168346AStrong flickeringStrong fatigueInput/output for user-computer interactionAttitude controlBrain computer interfacingSuperimposition
The present invention discloses a wearable display-based asynchronous type brain-controlled unmanned aerial vehicle system. A wearable display is utilized to display a group of visual stimulation units which flick with different frequencies; the visual stimulation units are corresponding to one group of different operation instructions of an unmanned aerial vehicle; a user gazes at different visual stimulation units, so that brain electrical signals can be generated, and the brain electrical signals are processed, so that the visual stimulation units which are gazed by the user and operation instructions corresponding to the visual stimulation units are identified; identification results are sent to the unmanned aerial vehicle end so as to be executed; the real-time scene pictures of the unmanned aerial vehicle are transmitted to the ground and are superimposed with the visual stimulation units, and superimposition results are displayed on the wearable display; and therefore, first-person perspective feedback can be provided for the user, and the portability of a steady-state vision-induced electric potential brain-computer interface system can be improved. According to the wearable display-based asynchronous type brain-controlled unmanned aerial vehicle system of the invention, an idle state can be fully utilized to perform decoding, and therefore, operational burden and fatigue feeling caused by using a brain-computer interface to control flight can be greatly decreased, and more free flight experience can be brought to the user.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Steady visual induction paradigm design and identification method for introducing continuous action of object
ActiveCN106951064AImprove recognition accuracyIncrease the differenceInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionBrain computer interfacingUser - individual
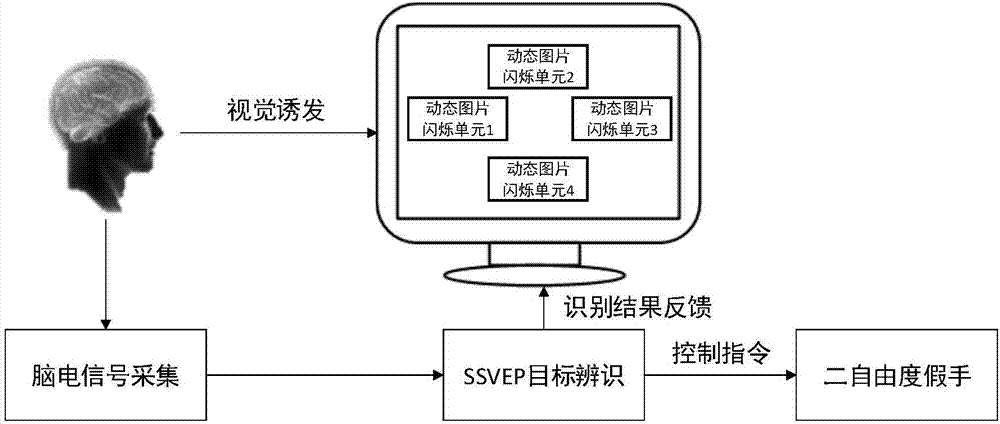
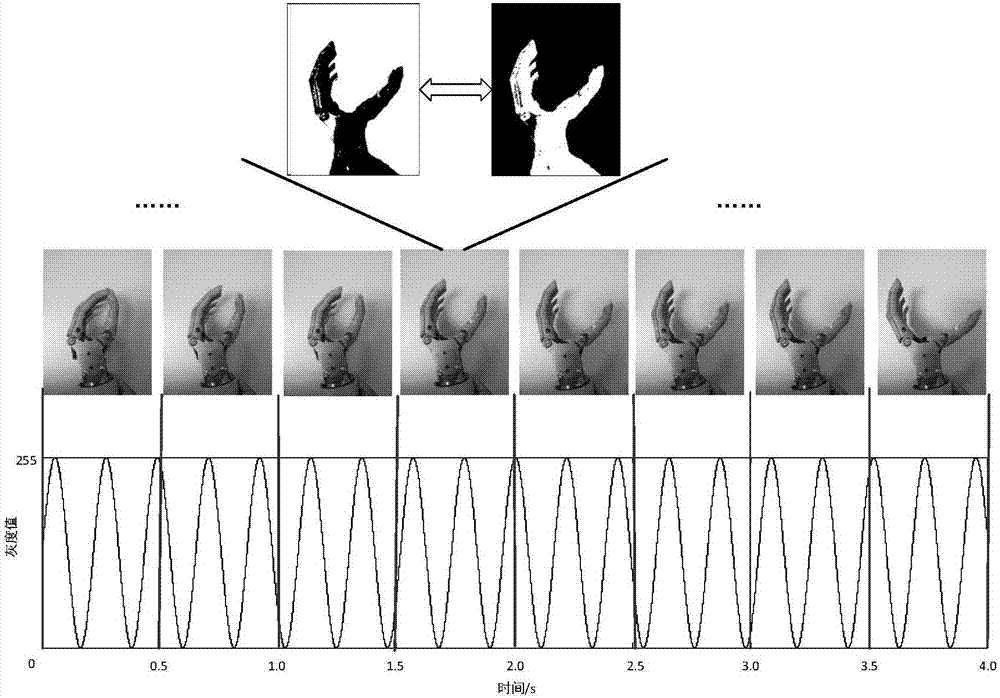
The invention discloses a steady visual induction paradigm design and identification method for introducing a continuous action of an object. During paradigm design, one continuous action of the object is introduced, the continuous action of the object is disintegrated into a plurality of pictures, continuous black and white flashing is performed according to a time sequence, dynamic picture flashing units are formed, the dynamic picture flashing units are displayed on a computer to stimulate a user to generate a steady visual induction potential, a brain wave signal of the user staring at a certain flashing unit is collected and transmitted to the computer for processing, a canonical correlation analysis algorithm based on personal characteristic correction is adopted to perform target identification, the result is fed back to the user, the object is controlled to complete a corresponding action at the same time, and then target identification is performed for the next time. Through the method, corresponding steady visual induction paradigms can be designed according to different application objects, the control effect of "what you see is what you obtain" is achieved, the difference between user individuals is relieved, the correct rate of identification is increased, and the method can be widely applied to all types of brain-computer interface systems based on steady visual induction paradigms.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Brain-computer interface-based telephone system for double-upper limb disabled people
InactiveCN103607519ATroubleshoot phone communication issuesHigh dialing accuracyTelephone sets with user guidance/featuresDisplay deviceVisual expression
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Human face perception-based steady-state visual evoked potential brain-computer interface method
InactiveCN107748622APrecise Brightness ControlQuick responseInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingBrain computer interfacingPattern perception
The invention relates to a human face perception-based steady-state visual evoked potential brain-computer interface method. The method is technically characterized by comprising the steps of recording an electroencephalogram signal of a user by using an electroencephalogram collection device, and transmitting the electroencephalogram signal to a calculation computer in real time; adopting a humanface perception coding method as a steady-state visual evoked potential evoking mode by a stimulation computer and generating a stimulation sequence; according to the stimulation sequence, generatingmultiple different stimulation frequencies, and performing coding by using the stimulation frequencies to obtain multiple different target blocks; preprocessing the obtained electroencephalogram signal by the calculation computer, and performing frequency identification on the preprocessed electroencephalogram signal by adopting an electroencephalogram decoding algorithm; and outputting a controlcommand corresponding to an identified frequency component to a feedback computer. According to the method, human face information of happy expressions is introduced in visual stimulation, so that the user visual attention can be enhanced, the signal-to-noise ratio of an evoked response is increased, the performance of a steady-state visual evoked potential brain-computer interface is improved, and a foundation is laid for promoting a practical process of the brain-computer interface.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
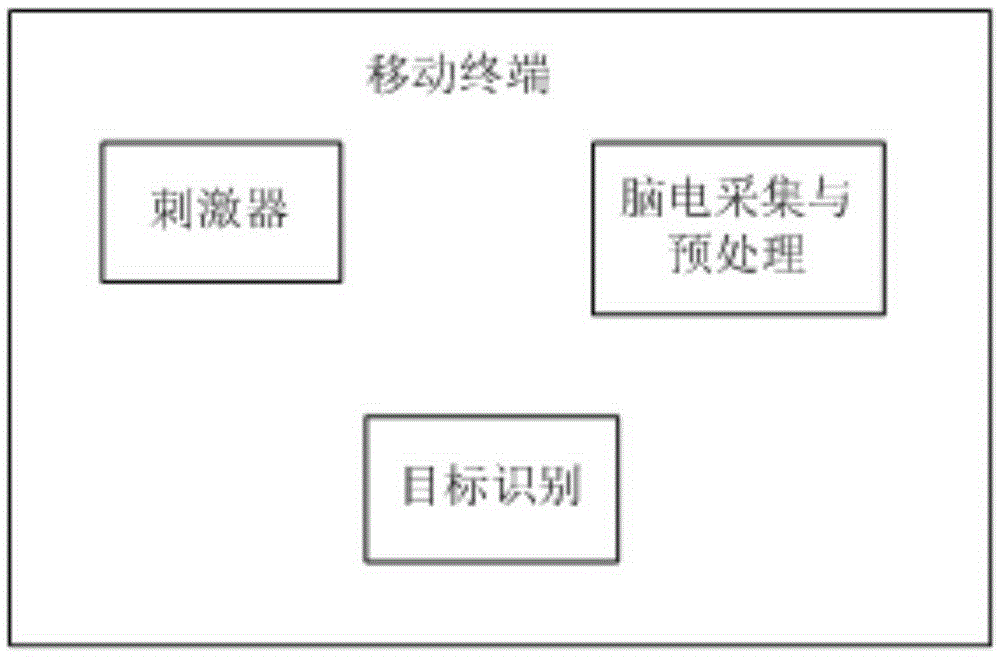
Mobile terminal based steady-state visual evoked potential brain computer interface system
InactiveCN105260025AThe flashing frequency is accurateEasy to carryInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingVisual evoked potentialsBrain computer interfacing
The present invention belongs to the technical field of bio-crossing, particularly relates to a mobile terminal based steady-state visual evoked potential (SSVEP) brain computer interface system, and aims to solve the problem in use of SSVEP on a mobile terminal. The system is characterized by comprising three modules: a stimulator module, an electroencephalogram collection module and a target identification module, wherein the stimulator module is used to generate electroencephalogram stimulation signals visually; the electroencephalogram collection and pre-processing module is used to collect brain waves and perform noise reduction; and the target identification module is used to identify processed brain wave signals. According to the mobile terminal based SSVEP brain computer interface system provided by the present invention, the flicker frequency is accurate, the carrying is convenient, and relatively good results can be achieved without the need for training. The system is suitable for occasions with relatively small target number and frequently changing application places, such as wheelchair controlling, mouse controlling, commercial entertainment development and the like. The system further expands the application range of brain computer interfaces and has a certain practical value.
Owner:中国兵器科学研究院
Brain-computer interface method based on high-frequency flicker emotional simulation
ActiveCN104536573AQuick responseImprove reliabilityInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingEnergy variationBrain computer interfacing
The invention discloses a brain-computer interface method based on high-frequency flicker emotional simulation. The method comprises the following steps of extracting phase features and energy features from preprocessed steady-state visual evoked potentials, conducting classification and recognition on the extracted phase features and energy features, finally outputting a control instruction, and controlling a mouse to move up and down and move left and right; measuring wavelet energy changes; measuring phase lock value changes; avoiding possible false positive operations through wavelet energy changes and phase lock value changes. According to the method, flickering emotional pictures are used for replacing a neutral checkerboard, and therefore the SSVEP response capable of being measured by the brain can be enhanced to a large extent; when a user uses the improved evoked simulation, the BCI reliability, speed and information transmission rate are greatly improved, and the fatigue degree of the user can be lowered according to behavioral analysis.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
VR head display visual evoked potential-based brain-machine interface system and control method
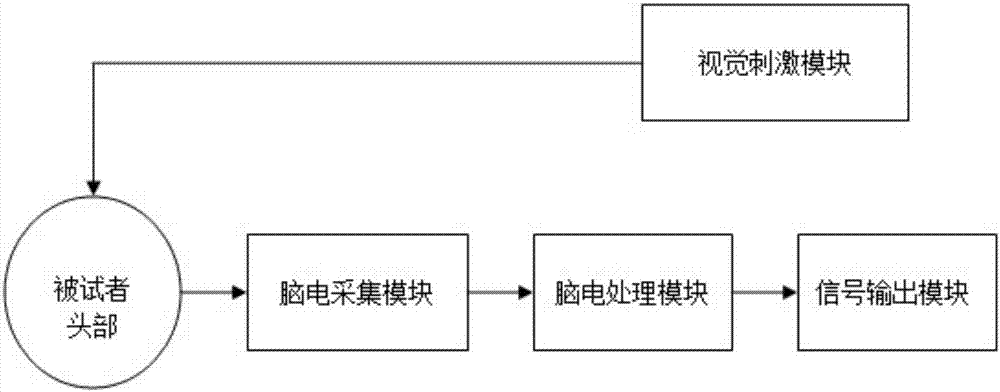
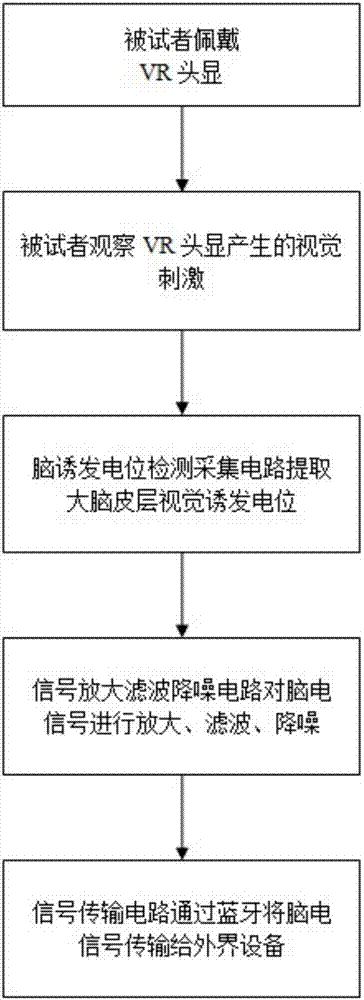
InactiveCN107463249AReduce volumeIncrease flexibilityInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingHuman–machine interfaceFiltration
The invention discloses a VR head display visual evoked potential-based brain-machine interface system and a control method. The system comprises visual stimulation module, an electroencephalogram acquisition module, an electroencephalogram processing module and a signal output module, wherein the visual stimulation module is used for providing visual stimulation capable of evoking all the visual invoked potentials such as event-related potentials or steady-state visual evoked potentials; the electroencephalogram acquisition module is used for acquiring evoked potentials generated by cerebral cortex under the visual stimulation; the electroencephalogram processing module is used for carrying out processing such as amplification, filtration and denoising on acquired electroencephalograms so as to obtain electroencephalogram signals with relatively good performance; and the signal output module is used for transmitting the processed electroencephalogram signals to external equipment through Bluetooth. According to the system, virtual reality head-mounted display equipment is adopted to provide visual stimulation so as to generate evoked potentials, so that visual stimulation systems which must be displayed through non-portable equipment such as computer screens and the like, in traditional brain-machine interface systems are changed, visual display equipment is more light and convenient, the volumes of the brain-machine interface systems are greatly decreased, and the flexibility and practical value of the brain-machine interface systems are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Virtual reality game interaction method and system based on brain-computer interface
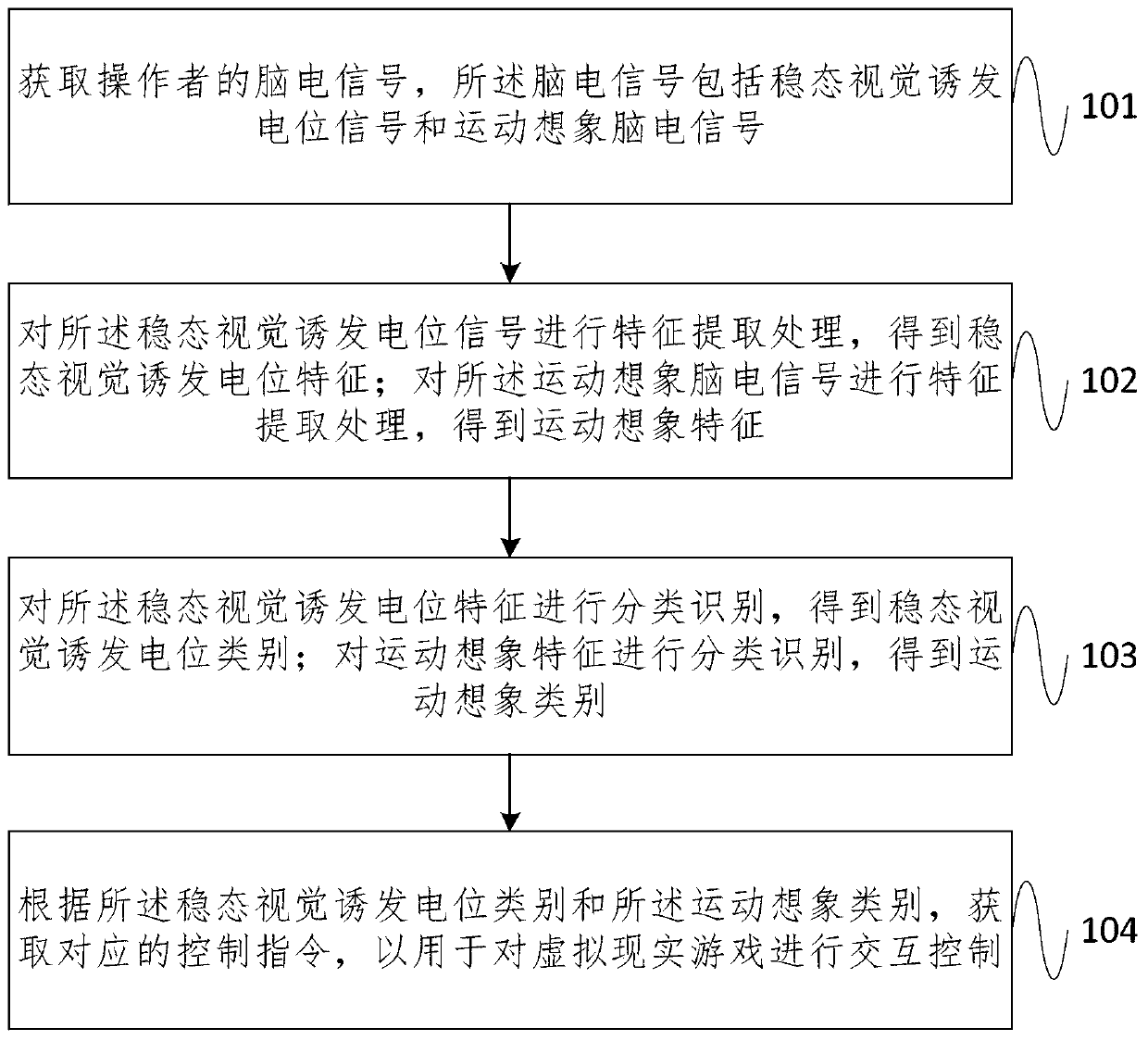
InactiveCN110442244AEasy to operateInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual evoked potentialsBrain computer interfacing
The embodiment of the invention provides a virtual reality game interaction method and system based on a brain-computer interface, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining an electroencephalogramsignal of an operator, and the electroencephalogram signal comprising a steady-state visual evoked potential signal and a motor imagery electroencephalogram signal; performing feature extraction processing on the steady-state visual evoked potential signal to obtain steady-state visual evoked potential features; performing feature extraction processing on the motor imagery electroencephalogram signal to obtain motor imagery features; classifying and identifying the steady-state visual evoked potential features to obtain steady-state visual evoked potential categories; carrying out classification and identification on the motor imagery features to obtain motor imagery categories; and according to the steady-state visual evoked potential category and the motor imagery category, obtaining acorresponding control instruction for performing interactive control on the virtual reality game. According to the embodiment of the invention, the operability of the virtual reality game is improved,and meanwhile, the application range of the brain-computer interface is expanded.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
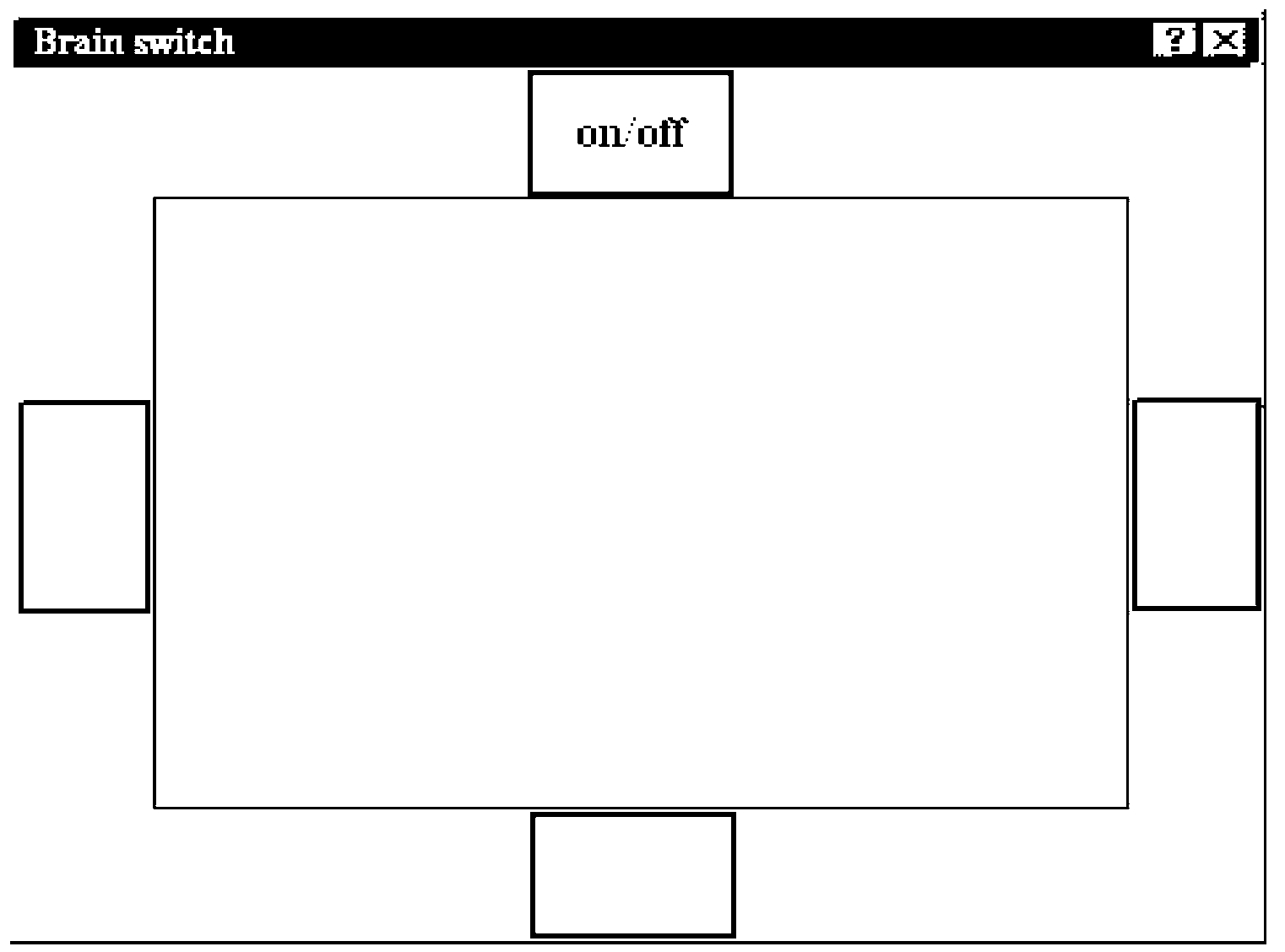
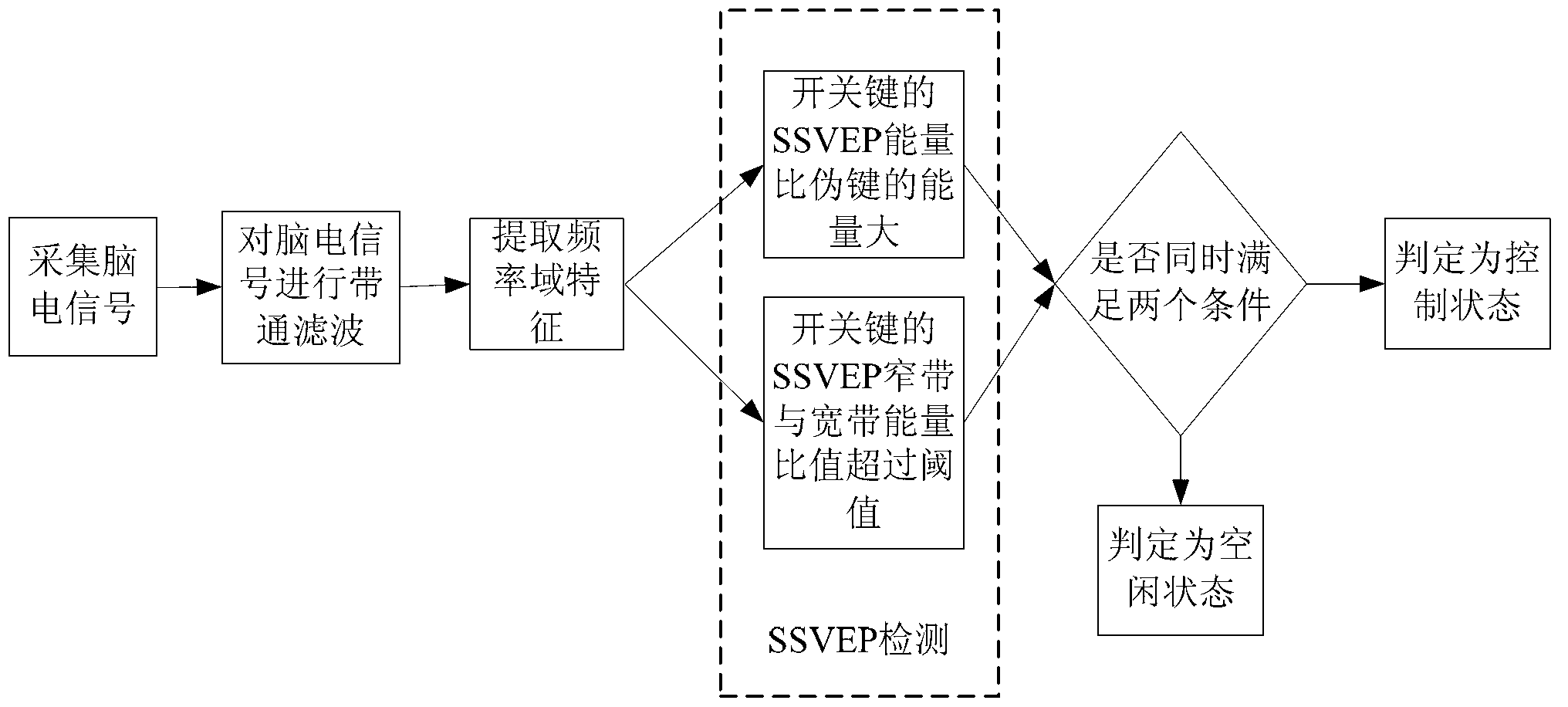
Method of asynchronous brain switch based on steady state visual evoked potentials
ActiveCN102799274AImprove the quality of lifeEffectively distinguish the control stateInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingVisual perceptionSteady state
The invention discloses a method of an asynchronous brain switch based on steady state visual evoked potentials. A twinkling on-off key and three twinkling pseudo-keys are arranged on the brain switch; and the states of a user comprise a control state and a leisure state. When the user wants to enter the control state, the user watches the on-off key; and when the user wants to enter the leisure state, the user neglects the on-off switch. The scalp brain electrical signals of the user are collected through an electrode cap; after filtering, SSVEP (Steady State Visual Evoked Potential) detection is performed to classify the two states of the user. If the SSVEP energy of the on-off switch is greater than that of other pseudo-keys and the ratio of the narrowband energy to the broadband energy of the on-off switch exceeds a predetermined threshold, the control state is determined; otherwise, the leisure state is determined. The method of the asynchronous brain switch improves the accuracy of leisure state monitoring and meets the performance requirements of the user through the arrangement of combining the on-off key with the pseudo-keys based on the steady state visual evoked potentials.
Owner:华南脑控(广东)智能科技有限公司
Brain-controlled input method based on steady state visual evoked potential and motor imagination
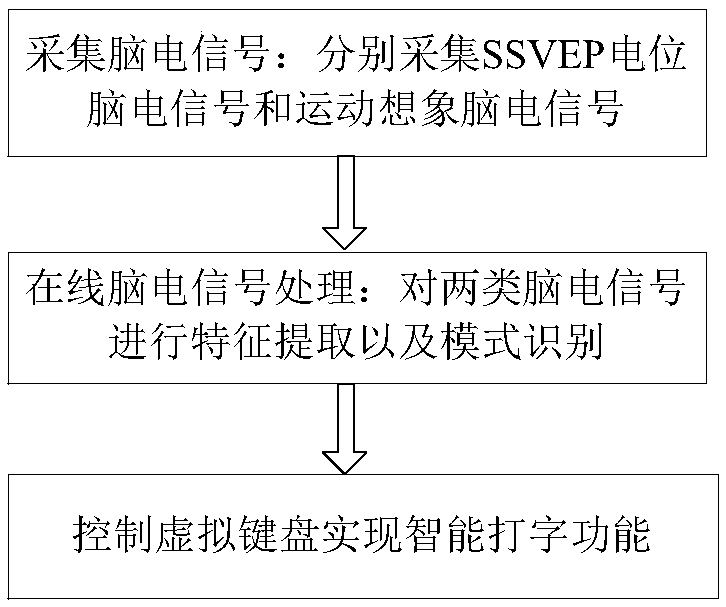
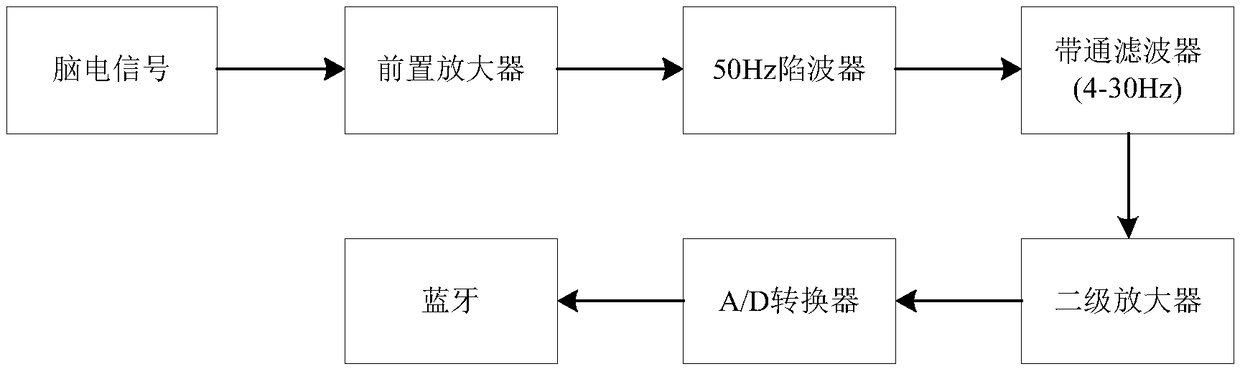
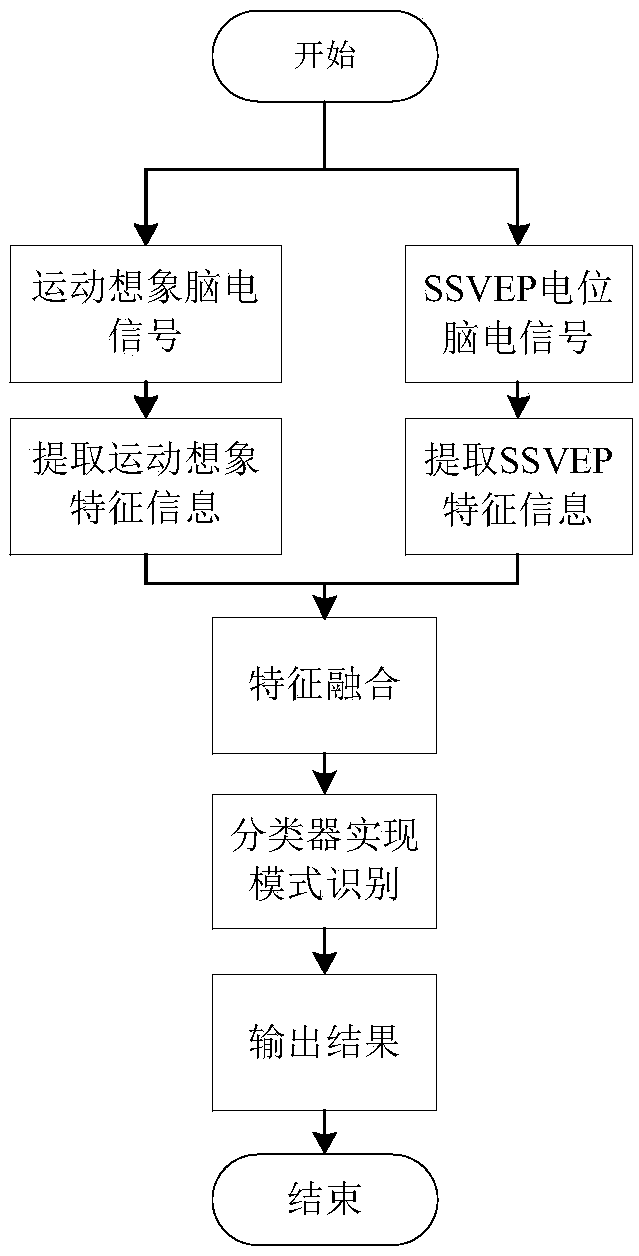
InactiveCN109471530ARealize smart typing functionRealize the function of shift left and rightInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionHand movementsVisual perception
The invention discloses a brain-controlled input method based on steady-state visual evoked potential and motor imagination. In order to overcome the problem of singleness and limitation of the function realization of the existing control method, the method comprises the following steps: 1) collecting EEG signals; (1) generating EEG signals; (2) EEG signal acquisition; 2) on-line EEG signal processing; 3) control that virtual keyboard to realize the intelligent typing function: the virtual keyboard interface is divide into: (1) a display interface: a. A character display area, wherein the character display area is used for displaying the input character; (b) vocabulary association area: that vocabulary association area can be use for users to quickly select character-related vocabulary andcan be selected whether to open or not; (2) Visual evoked input interface: All the 13 flashing keys in the visual evoked input interface can stimulate human brain to produce SSVEP potential. The movement of virtual keys is controlled by left and right hand movement imagination, and the selection of virtual keys is controlled by stimulating cerebral cortex to produce SSVEP signal by fixing virtualkeys.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Steady-state visual evoked potential brain-computer interface method based on cross modulation frequency
ActiveCN105242784AStable Cross Modulation FrequencyIncrease the number of targetsInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingVisual evoked potentialsBrain computer interfacing
The present invention relates to a steady-state visual evoked potential brain-computer interface method based on cross modulation frequency. The method has the technical characteristics that a cross modulation frequency encoding method is used as an evoking manner for a steady-state visual evoked potential; an alternating frequency is introduced on the basis of obtaining a stimulation with frequency of F by frequency division of a screen refresh rate; and different cross modulation frequency components F+ / -fi (i = 1, ..., 2xF-1) are generated by changing the alternating frequency fi = F / (i + 1) so as to realize the effect of encoding 2xF-1 different targets by using one stimulation. Compared with a conventional target presentation mode, the number of the targets that can be achieved by the method is improved by 2xF-1 times and the disadvantage that the previous alternative flicker frequency points are restricted is overcome so as to lay a foundation for promoting the utility process of the brain-computer interface; and compared with the existing multi-frequency combined encoding mode, the method is easier to implement, and has important theoretical study and practical application significance.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
MI and SSVEP dual paradigm-based few-channel asynchronous control brain computer interface system
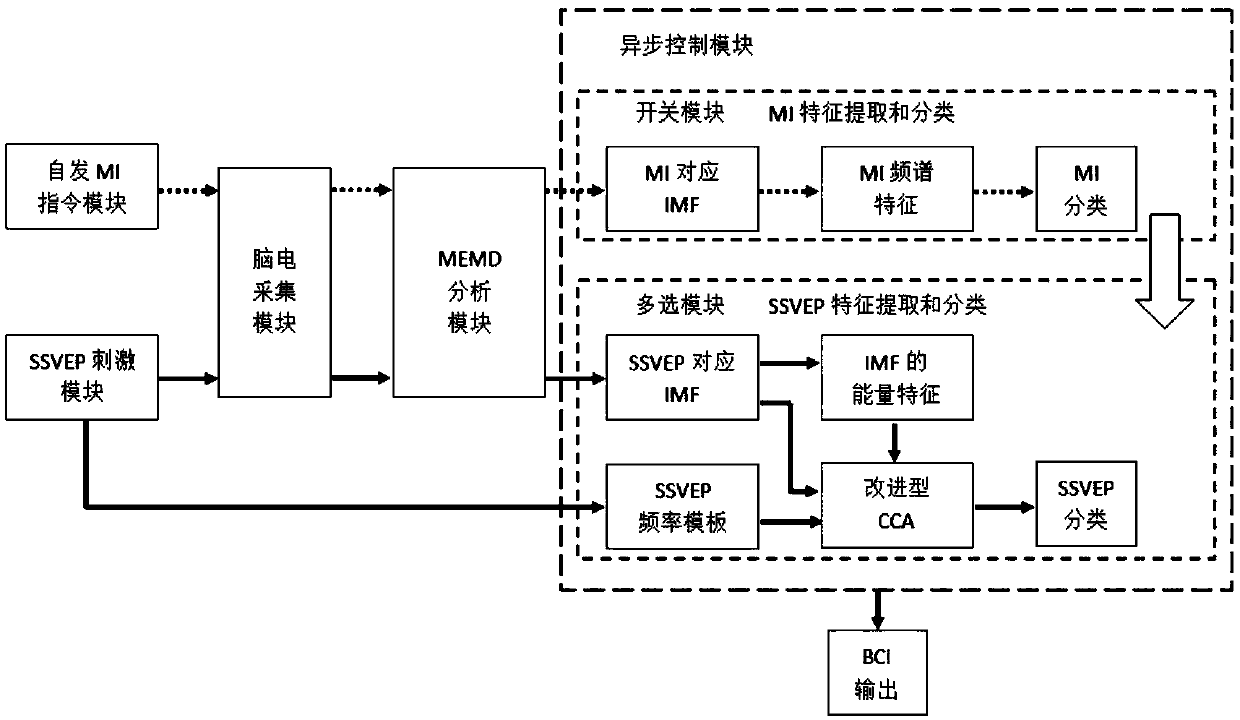
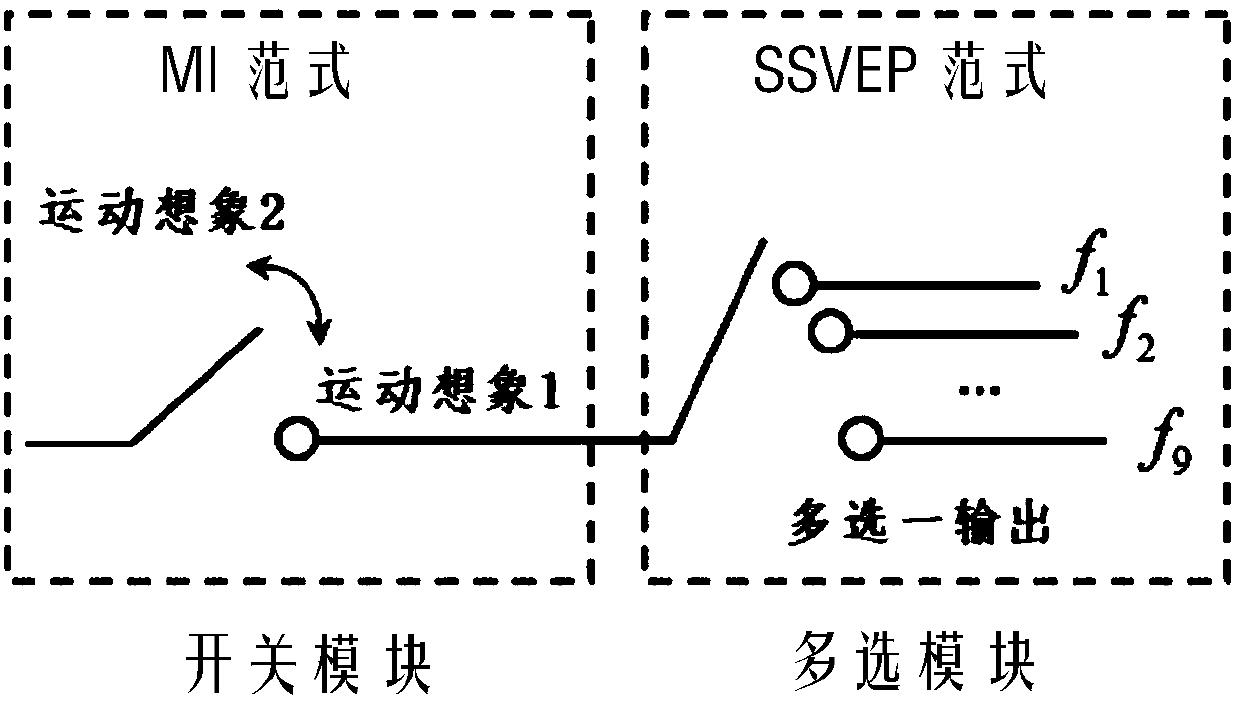
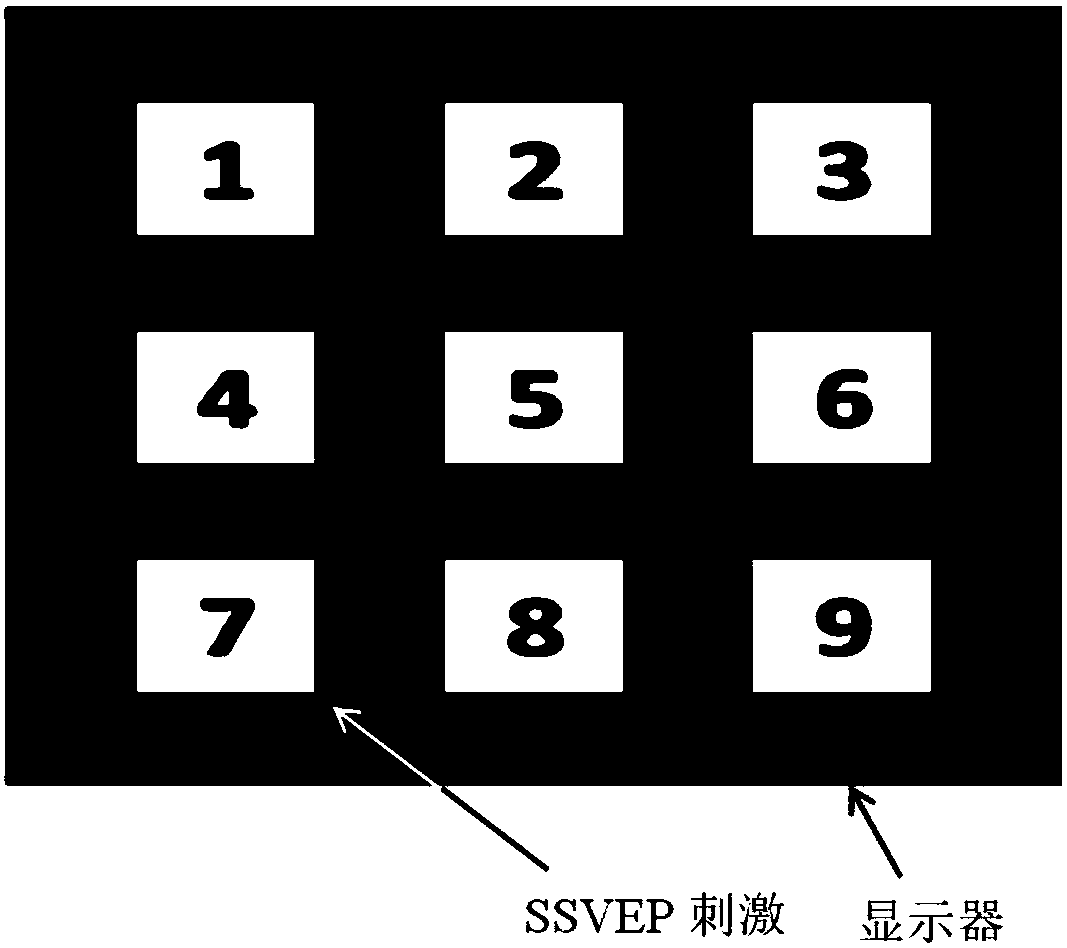
ActiveCN108459714AImprove classification accuracyEfficient extractionInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingInformation processingBrain computer interfacing
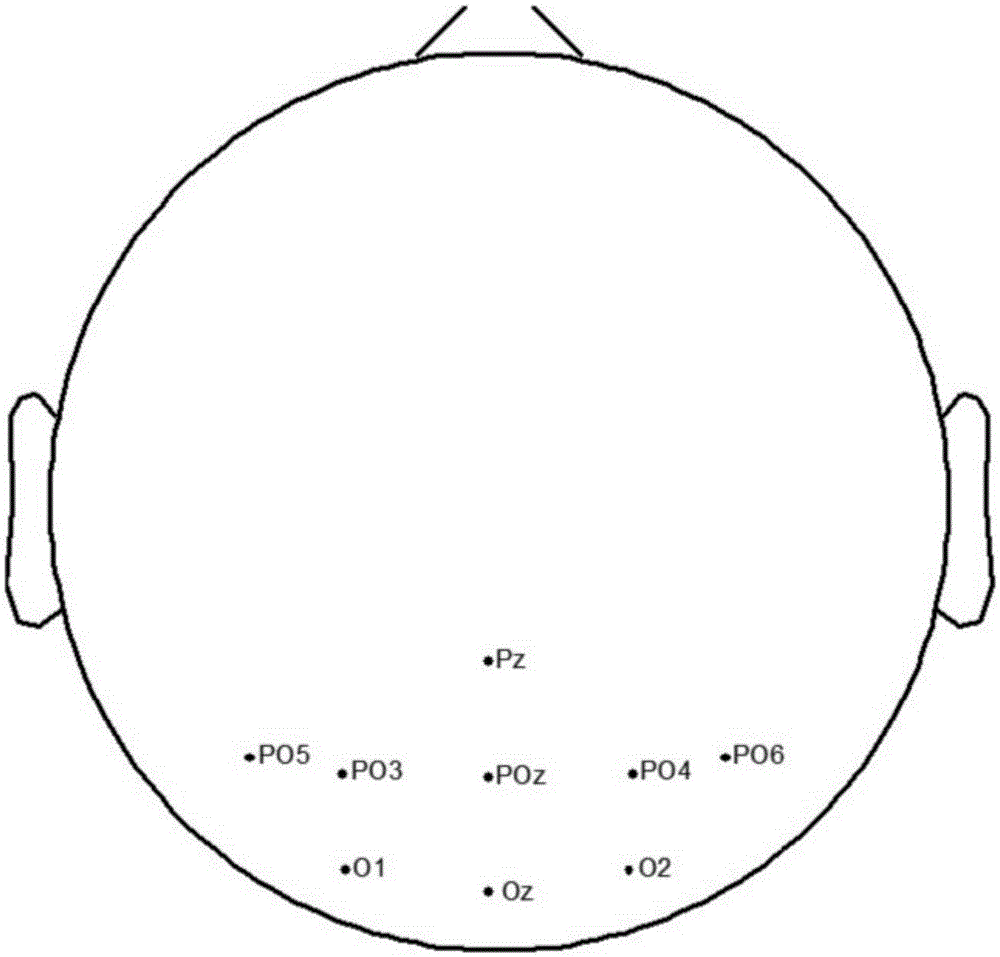
The invention discloses an MI and SSVEP dual paradigm-based few-channel asynchronous control brain computer interface system, and belongs to the technical field of cognitive neural science, information processing and automation control crossing. For a few-channel electroencephalogram signal BCI system, an MI paradigm is adopted as a switch module of the BCI system; an SSVEP paradigm is adopted asa BCI multi-choice module; the two modules are connected in series to form the asynchronous control BCI system; a few-channel EEG signal is decomposed into multiple intrinsic mode functions by utilizing a multi-variable empirical mode decomposition algorithm; based on a spectrum distribution characteristic of MI, the IMFs are preferentially selected as characteristics for realizing MI classification; an improved canonical correlation analysis method is proposed for calculating canonical correlation coefficients between the IMFs and SSVEP frequency templates; the optimal canonical correlation coefficient is preferentially selected out for realizing SSVEP classification; and therefore, the control effect and the classification accuracy of the few-channel BCI system can be improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Stroke patient voice communication care control system and method based on brain-computer interface
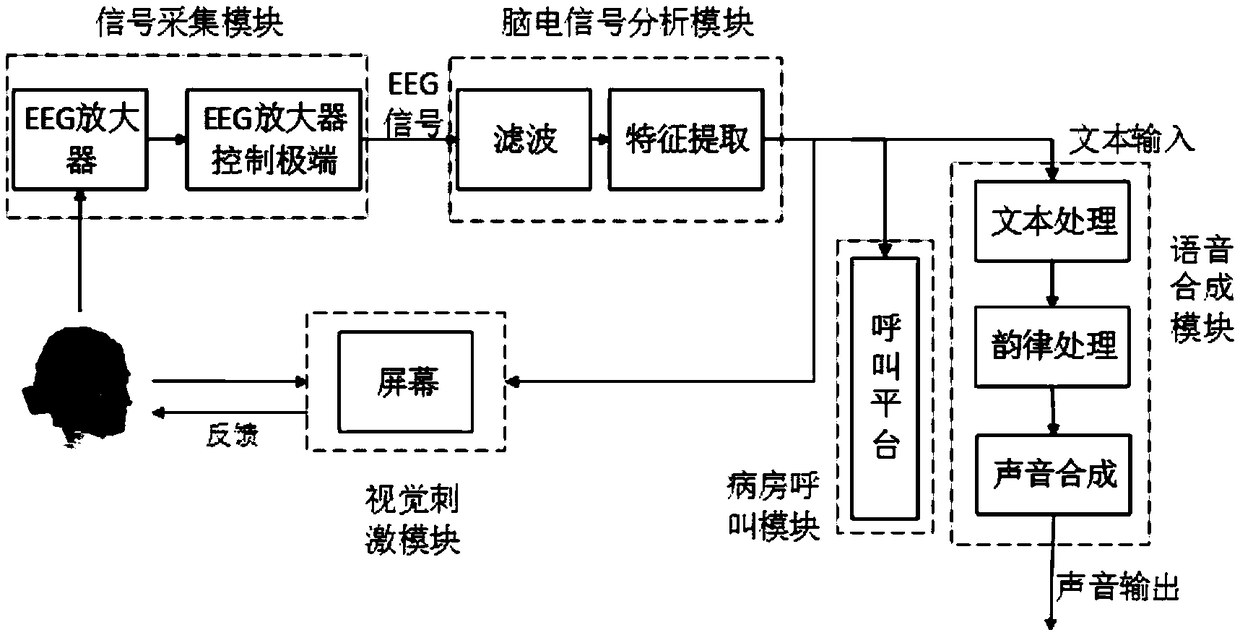
ActiveCN109065184AEasy to carry outTimely communicationMedical communicationHealthcare resources and facilitiesBrain computer interfacingVoice communication
The invention discloses a stroke patient voice communication care control system and method based on a brain-computer interface. The system comprises a visual stimulation module, an EEG signal collection module used for collecting an EEG signal in real time and transmitting the EEG signal to an EEG signal analysis module, the EEG signal analysis module used for performing steady state visual evoked potential analysis and extracting EEG signal characteristics for the received EEG signal after a patient is determined to pay attention to the flashing region, transmitting the EEG signal characteristics to a voice synthesis module, forming a calling signal and transmitting the calling signal to a ward calling module, and the voice synthesis module used for synthesizing the voice and outputtingthe voice, wherein the visual stimulation module is divided into multiple flashing regions, the flashing frequency of each flashing region is different, and each flashing region is constantly bright and is used for stimulating the stroke patient to generate the EEG signal.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
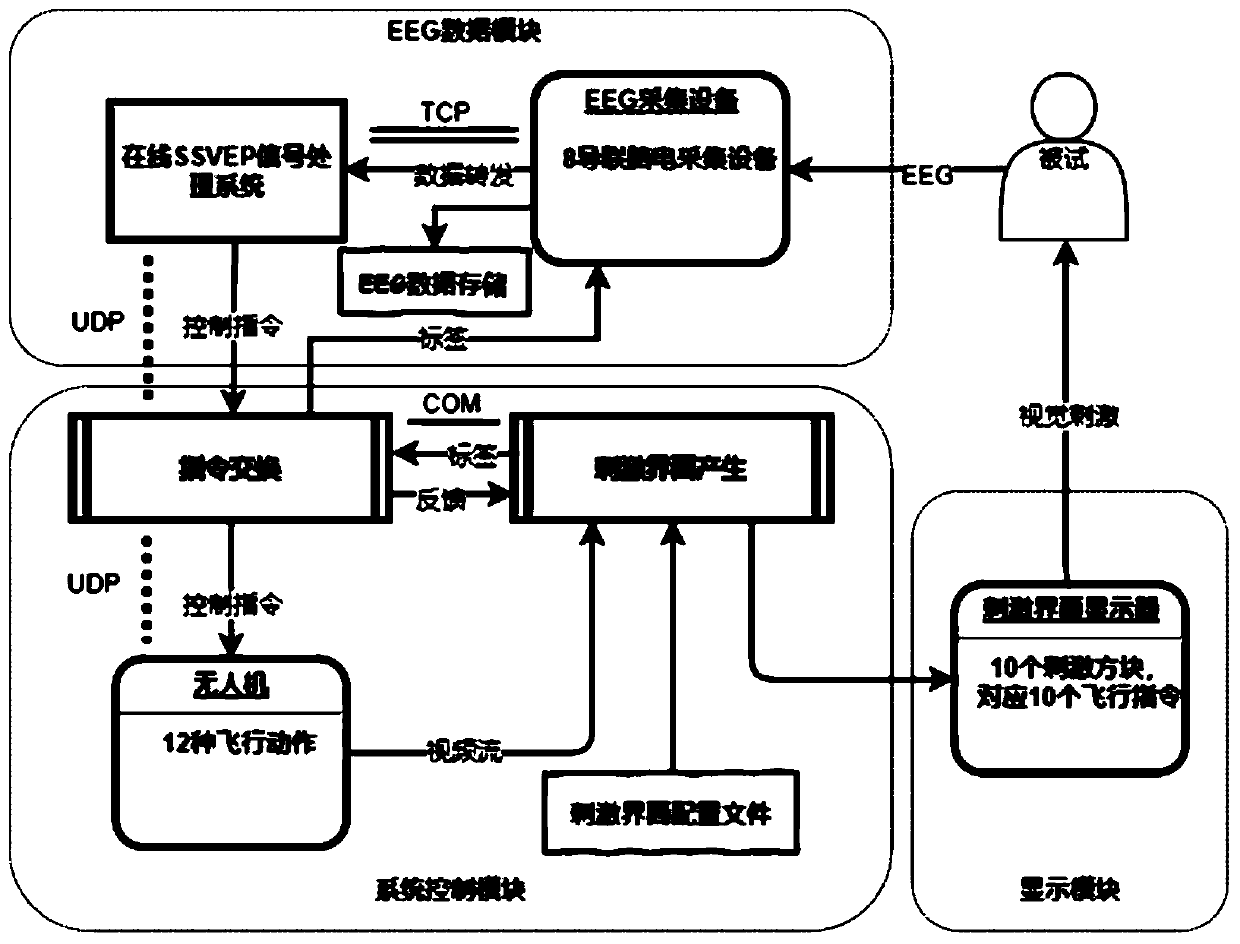
Brain-controlled unmanned aerial vehicle method based on steady-state visual evoked potential brain-computer interface
ActiveCN111487988AIncrease flexibilityImprove stabilityInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingEeg dataSimulation
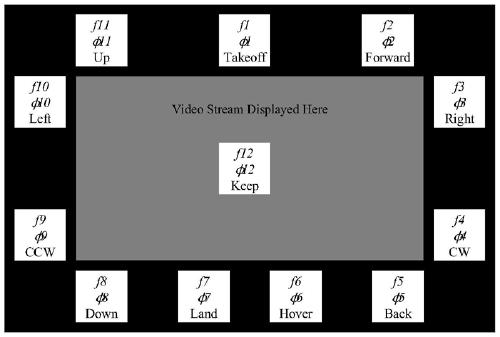
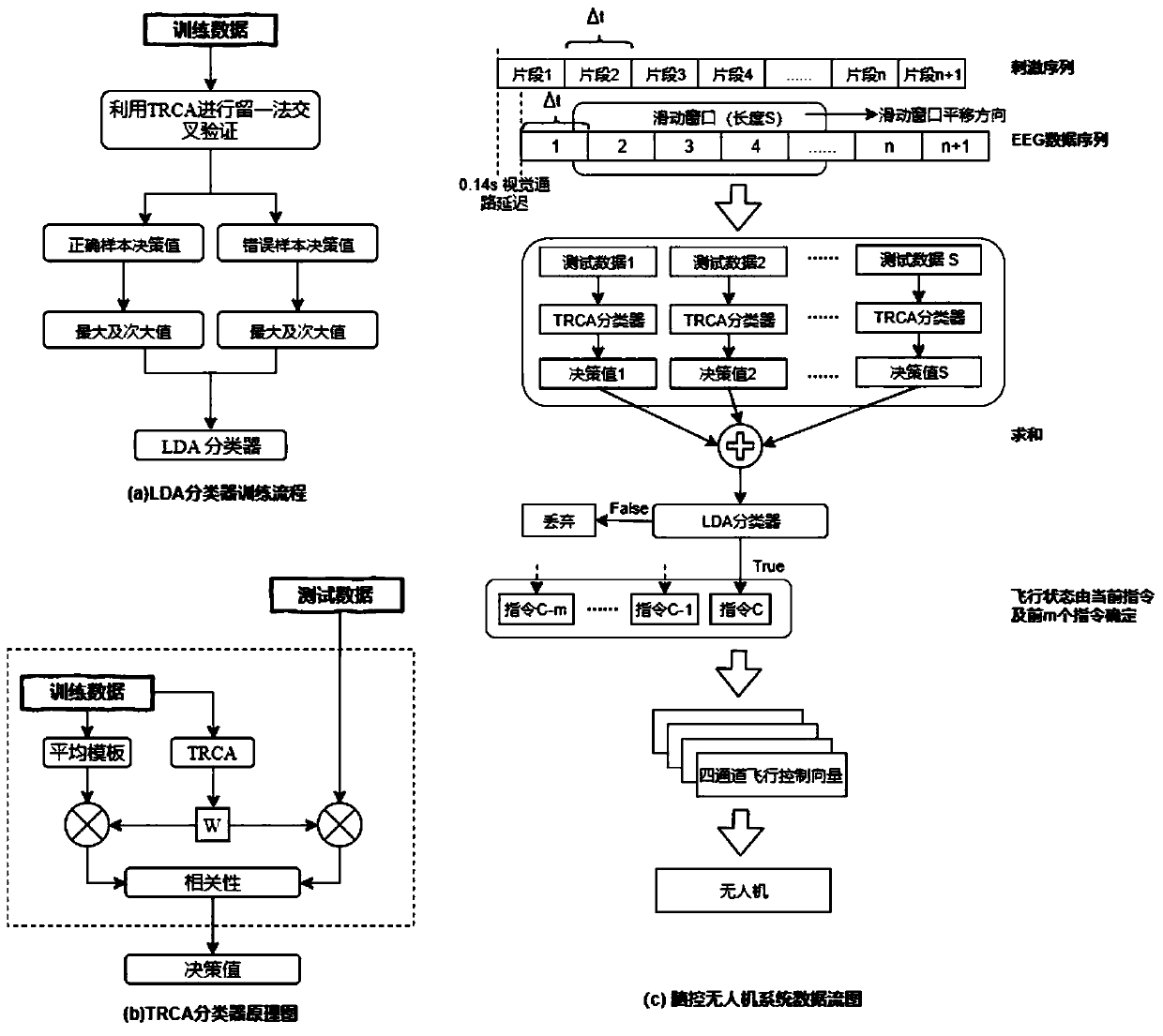
The invention discloses a brain-controlled unmanned aerial vehicle method based on a steady-state visual evoked potential brain-computer interface. The method comprises the steps that an SSVEP stimulation interface is constructed, a Keep instruction is set to be arranged in the center of the stimulation interface and used for keeping the flight state of an unmanned aerial vehicle and achieving a pseudo-asynchronous control effect, and when the stimulation interface works in an online mode, an SSVEP stimulation fragment with the duration [delta]t continuously flickers till the process that a user controls the unmanned aerial vehicle is finished; an EEG data module processes the acquired electroencephalogram signals of the duration[delta]t based on task related component analysis and a sliding time window method of a linear discrimination model, and maps classification results to different unmanned aerial vehicle flight control instruction vectors; and an unmanned aerial vehicle flight control module fuses the control instruction vectors output by the m+1 EEG data modules and transmits the fused instruction vectors to the unmanned aerial vehicle to realize flight control of the unmanned aerial vehicle. Flexible, stable and robust control over the unmanned aerial vehicle is achieved through the brain-computer interface, and a user does not depend on two hands any more when controlling the unmanned aerial vehicle.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
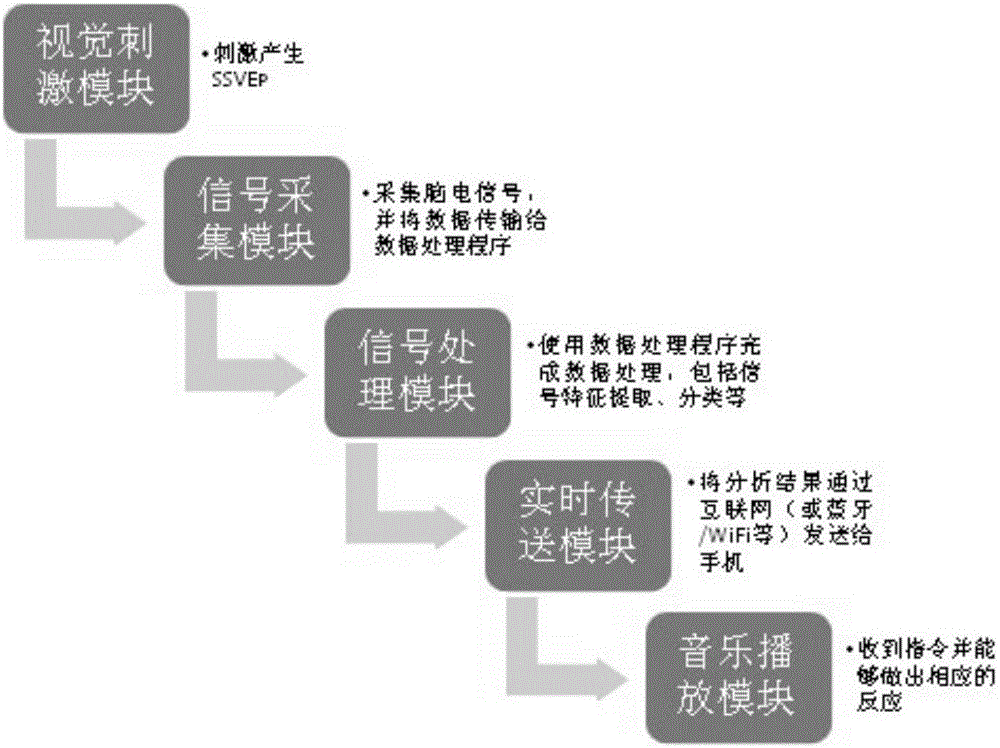
Mobile phone music playing system based on steady-state visual evoked potential (SSVEP)
InactiveCN105929937AEasy to controlHigh speedInput/output for user-computer interactionSubstation equipmentThe InternetMusic player
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
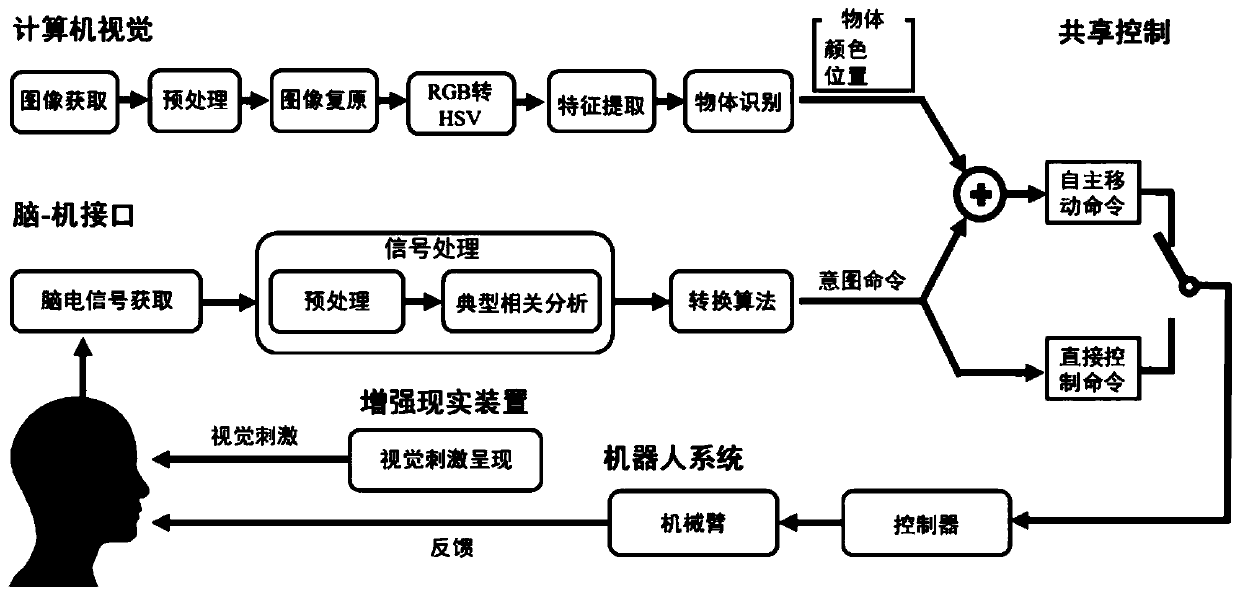
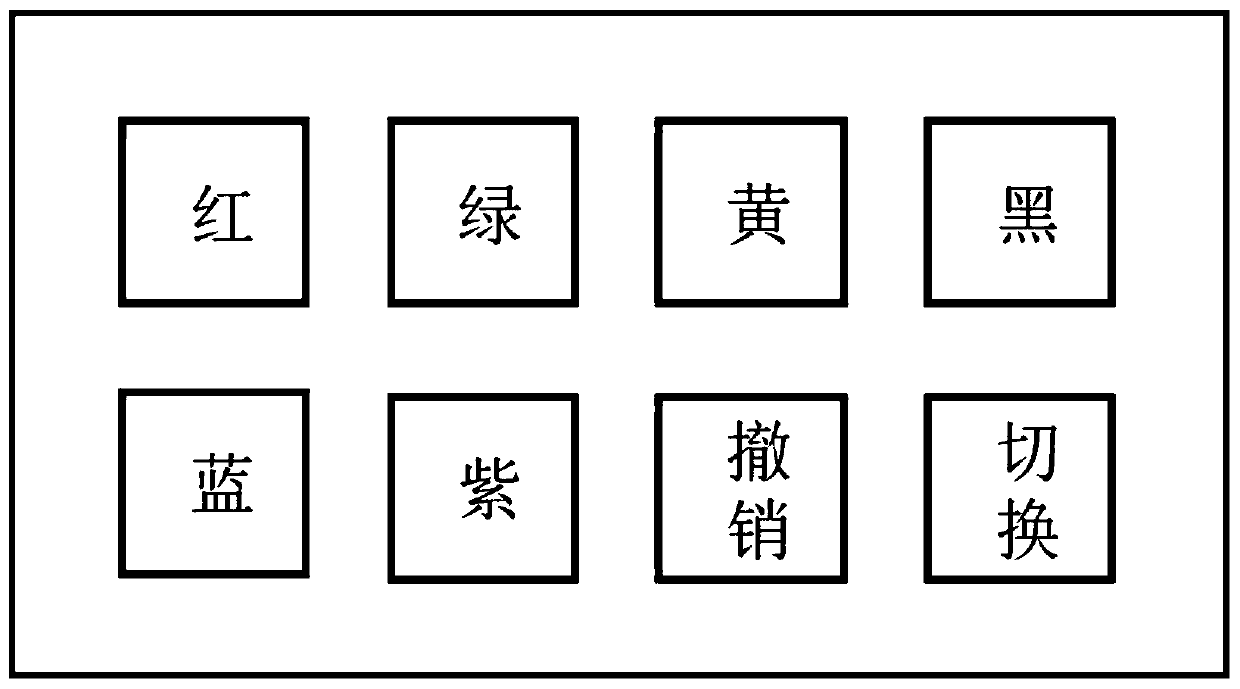
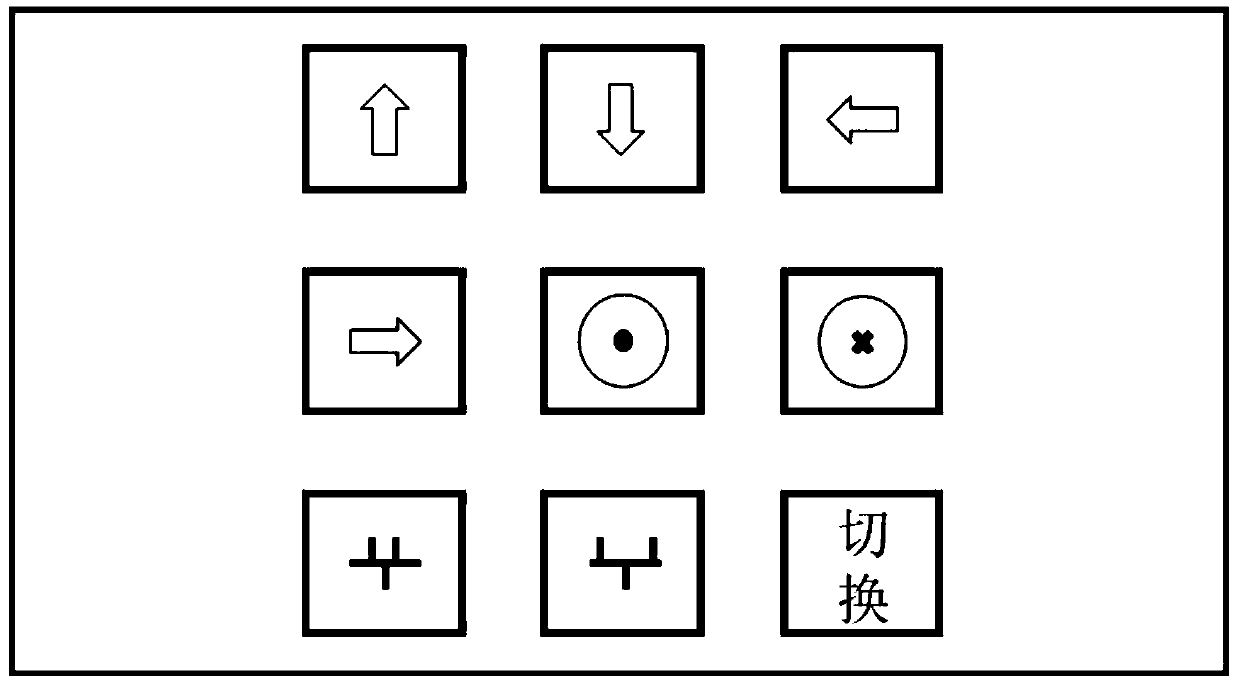
Brain-controlled mechanical arm sharing control system based on augmented reality and method thereof
InactiveCN110134243AReduce psychological burdenImprove applicabilityInput/output for user-computer interactionProgramme-controlled manipulatorBrain computer interfacingVisual perception
The invention relates to a brain-controlled mechanical arm sharing control system and method based on augmented reality. The system comprises a computer vision device, a steady-state visual evoked potential brain-computer interface device, a sharing control device, an augmented reality device and a mechanical arm, wherein the computer vision device is used for identifying the color and position information of an object in a working space; the augmented reality device is used for generating a visual stimulation signal and acting on a user; the steady-state visual evoked potential brain-computerinterface device obtains an electroencephalogram signal of the user and converts the electroencephalogram signal into a visual human brain control command; the sharing control device adopts a sharingcontrol strategy to control the mechanical arm; and the mechanical arm grabs the target object under the control of the sharing control device. The control function is achieved by combining the humanbrain control command with the mechanical arm autonomous control based on the computer vision, more natural human-computer interaction is achieved, the psychological burden of a user is reduced, theapplicability of the mechanical arm in a complex environment is enhanced, and therefore the practicability and reliability of the whole system are improved.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Brain-computer interface system based on steady-state visual evoked potential physiological characteristics
ActiveCN107957780ASolve the problem that the classification accuracy rate needs to be improved due to the lack of consideration of the physiological characteristics of SSVEPImprove classification accuracyInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionInformation processingAutomatic control
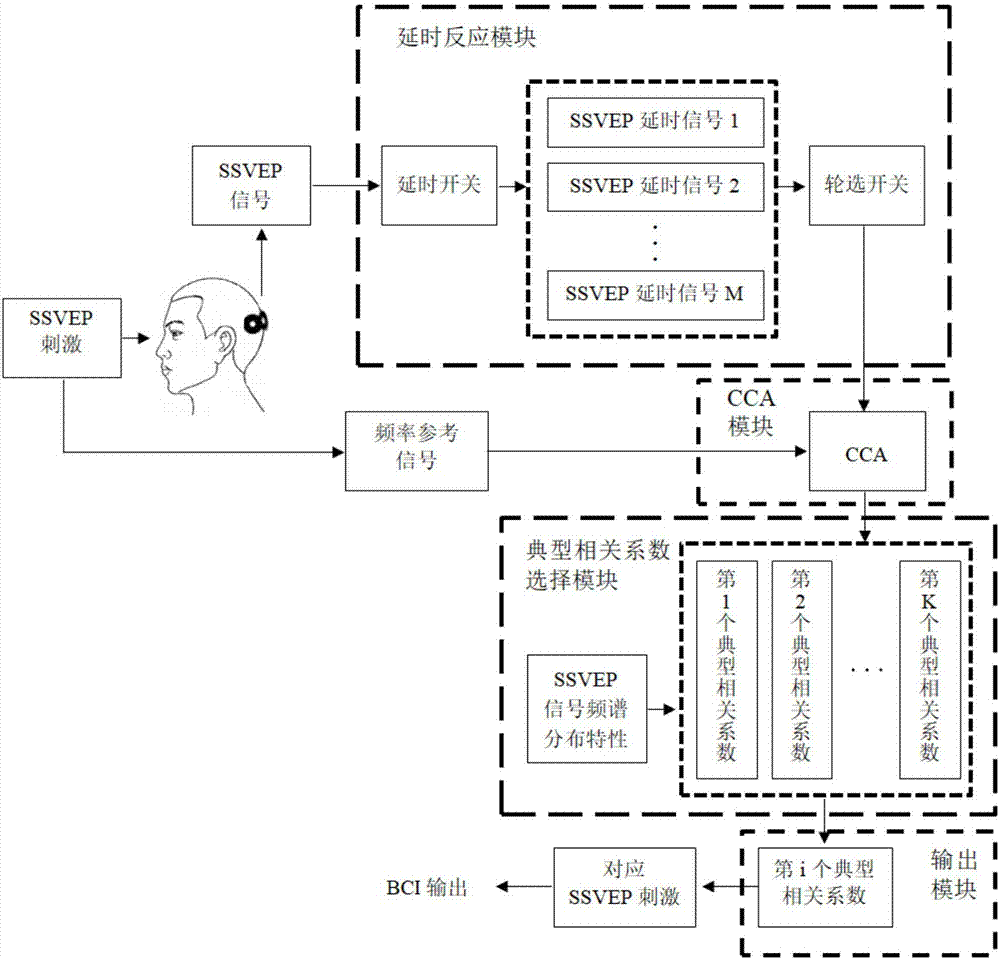
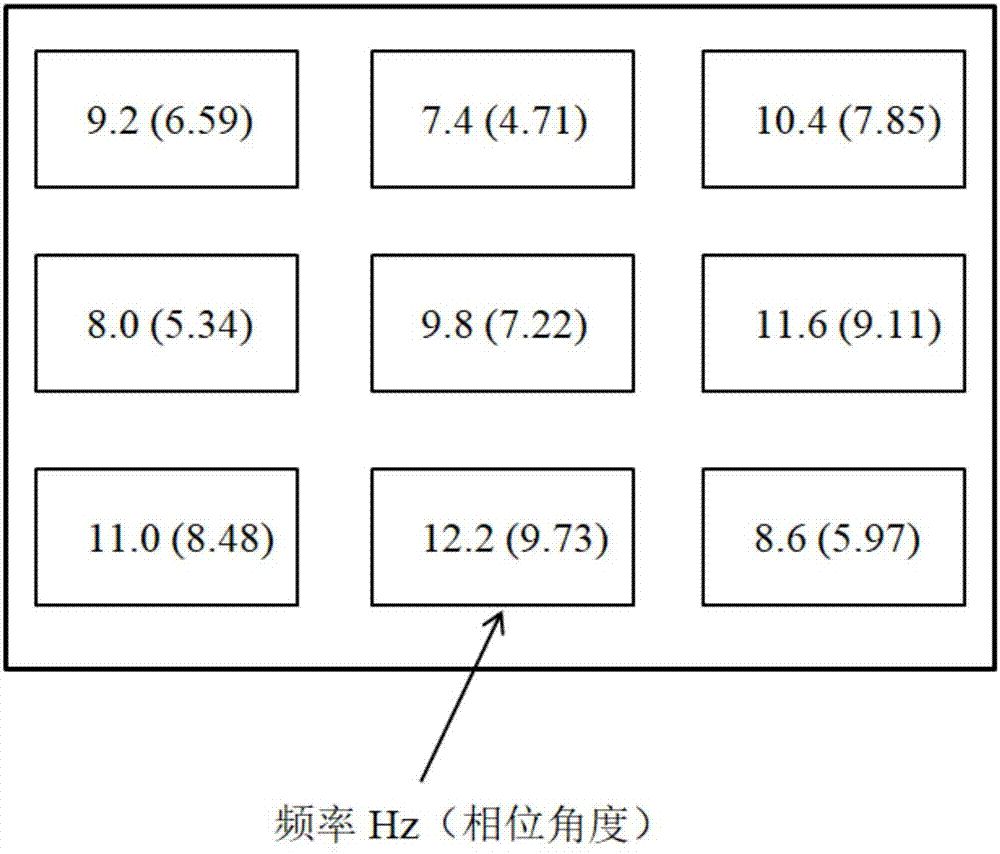
The invention discloses a brain-computer interface system based on steady-state visual evoked potential physiological characteristics, and belongs to the cross technical field of cognitive neural science, information processing and automatic control. The brain-computer interface system comprises a time delay reaction module, a CCA module, a typical correlation coefficient selection module and an output module. A delay reaction of SSVEP is modeled, a characteristic frequency point capable of reflecting the frequency spectrum energy change is selected as a frequency reference signal of SSVEP stimulation, all components of the frequency reference signal are linearly combined to obtain a spectral energy distribution model, and an analysis result of a CCA is optimized under the constraint of the ratio of the components of the frequency reference signal. The quality of SSVEP signals can be improved, the characteristics can be effectively extracted, the analysis capability of the CCA is improved, and finally the classification accuracy of a BCI system is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com