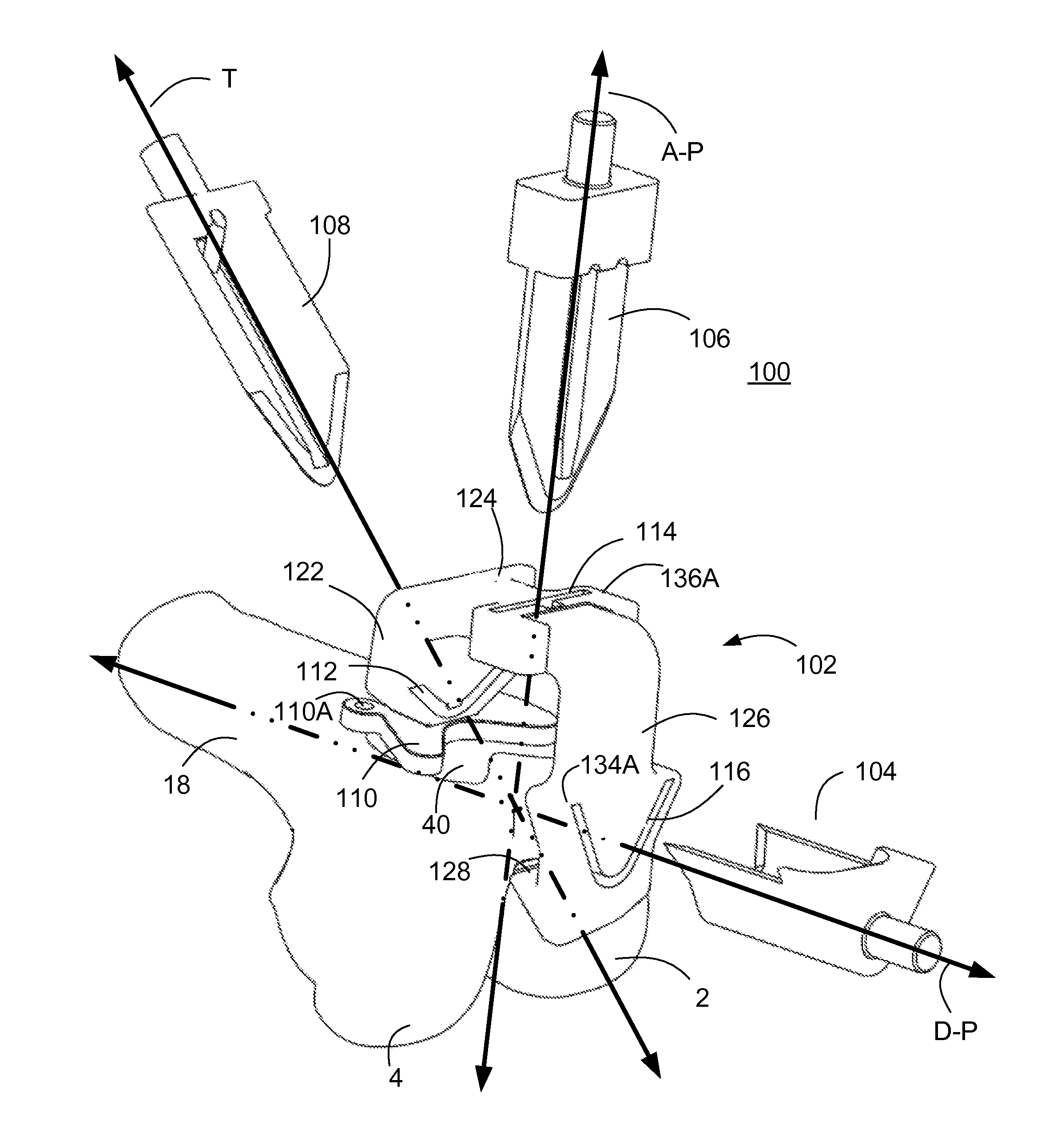
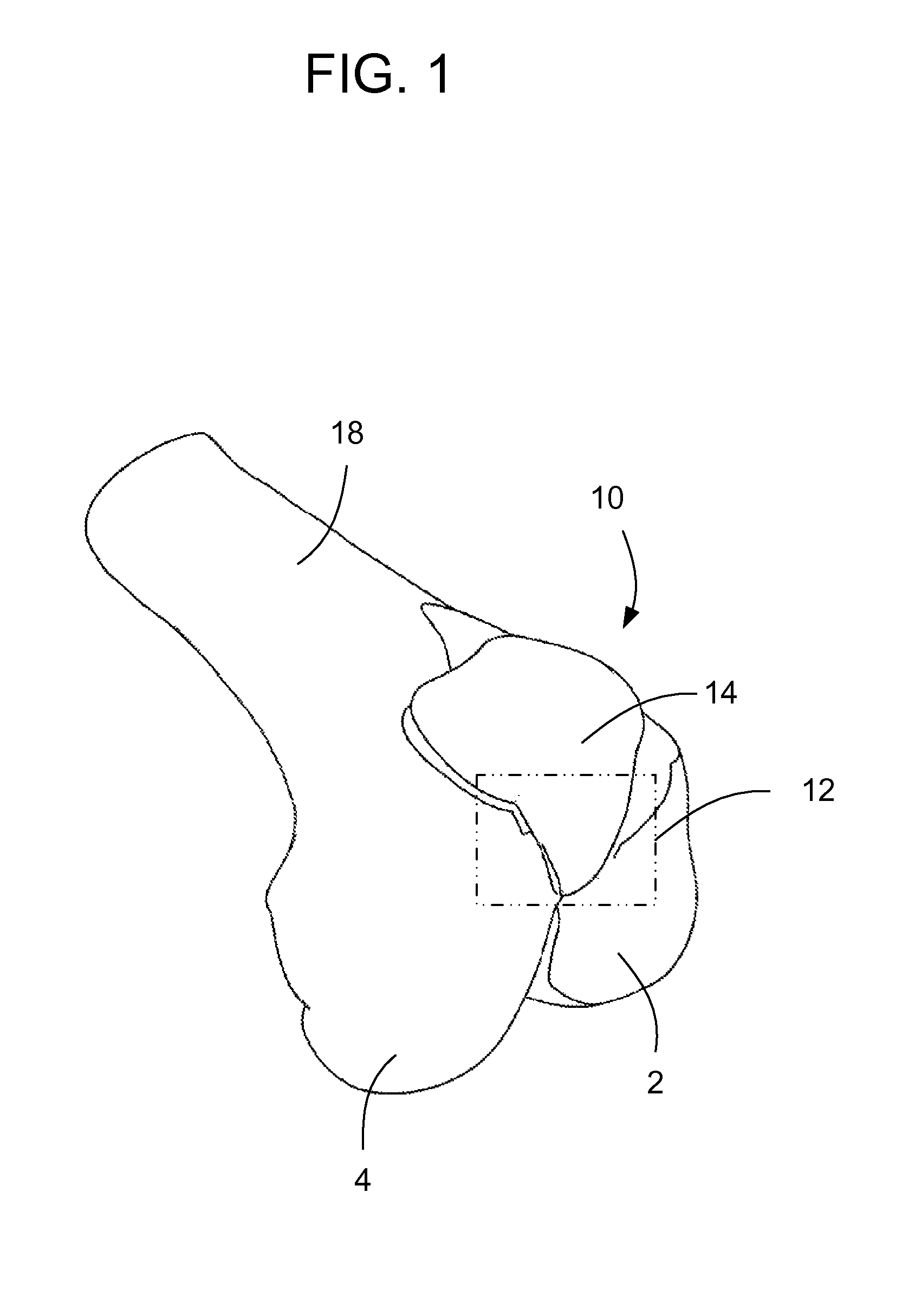
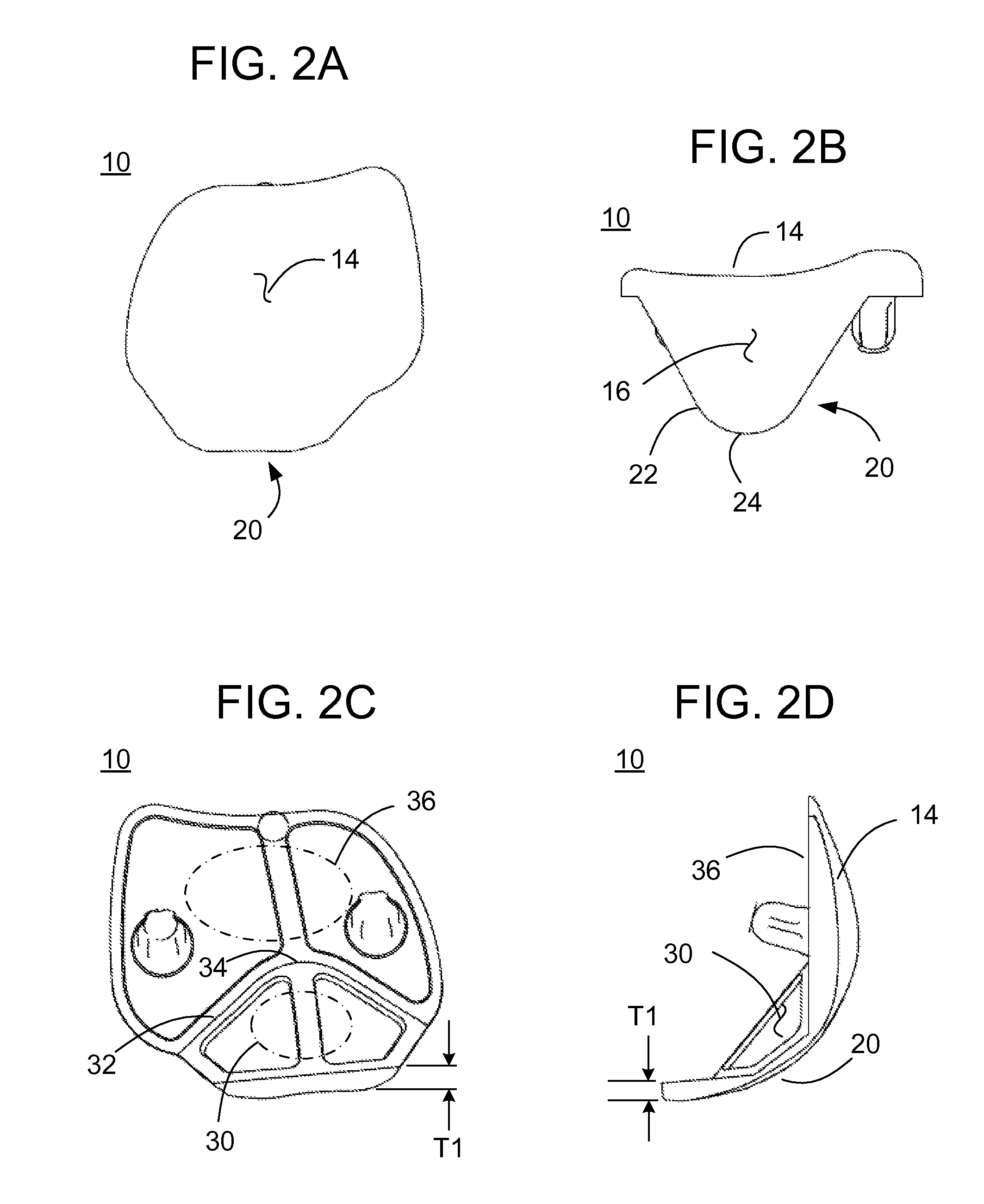
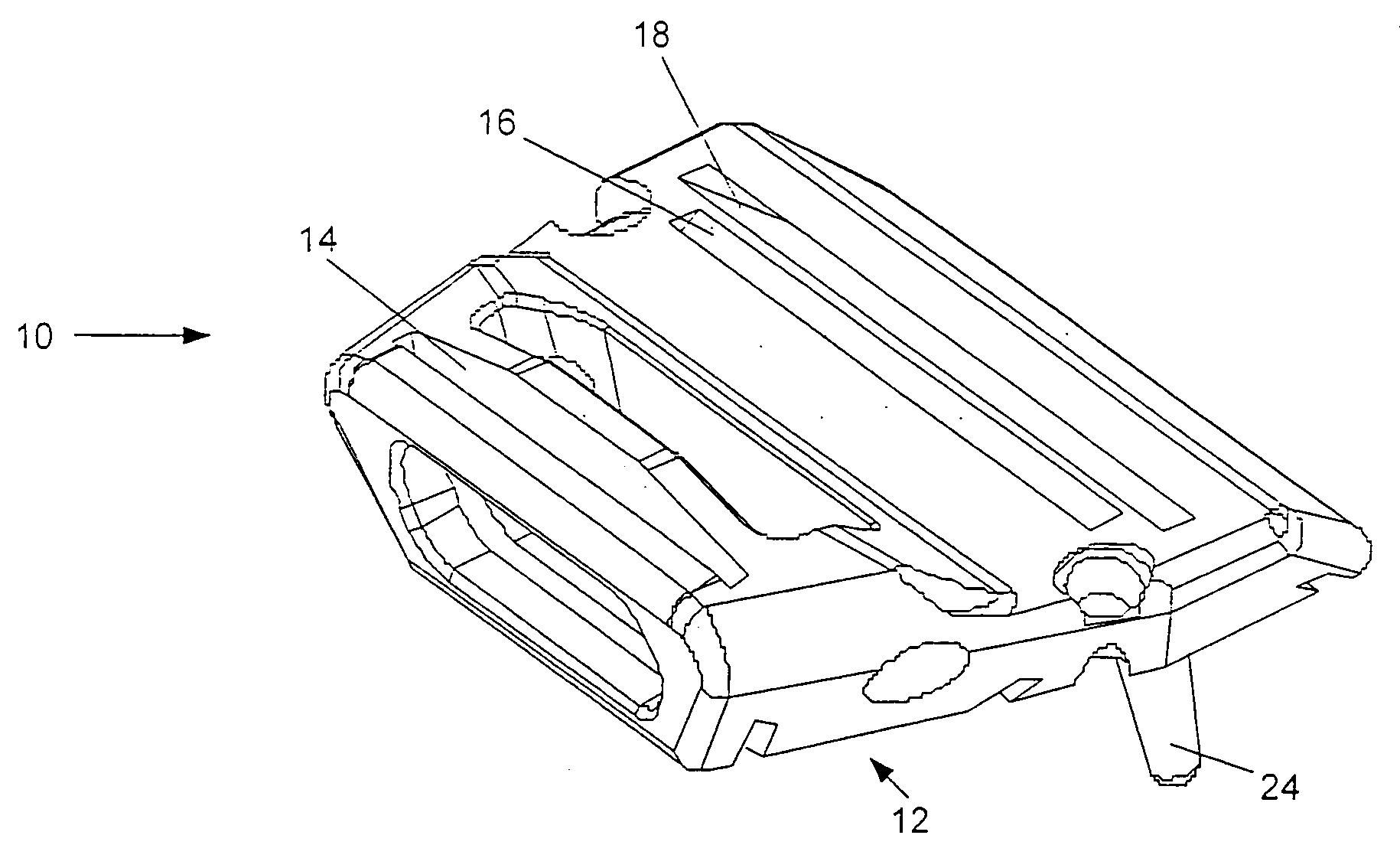
Patents
Literature
172 results about "Total knee arthroplasty" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A Total Knee Replacement (TKR) or Total Knee Arthroplasty is a surgery that replaces an arthritic knee joint with artificial metal or plastic replacement parts called the ‘prostheses’.
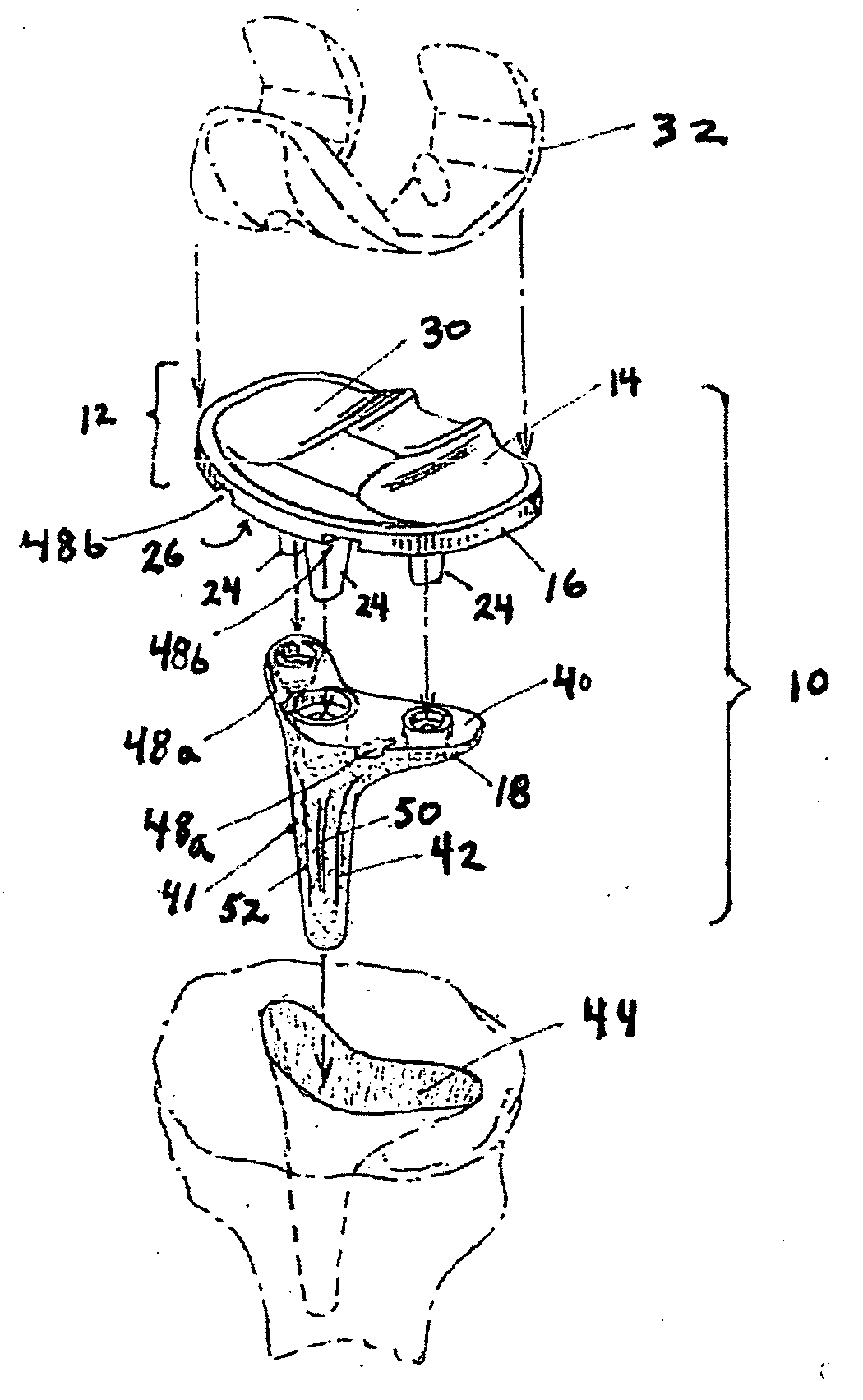
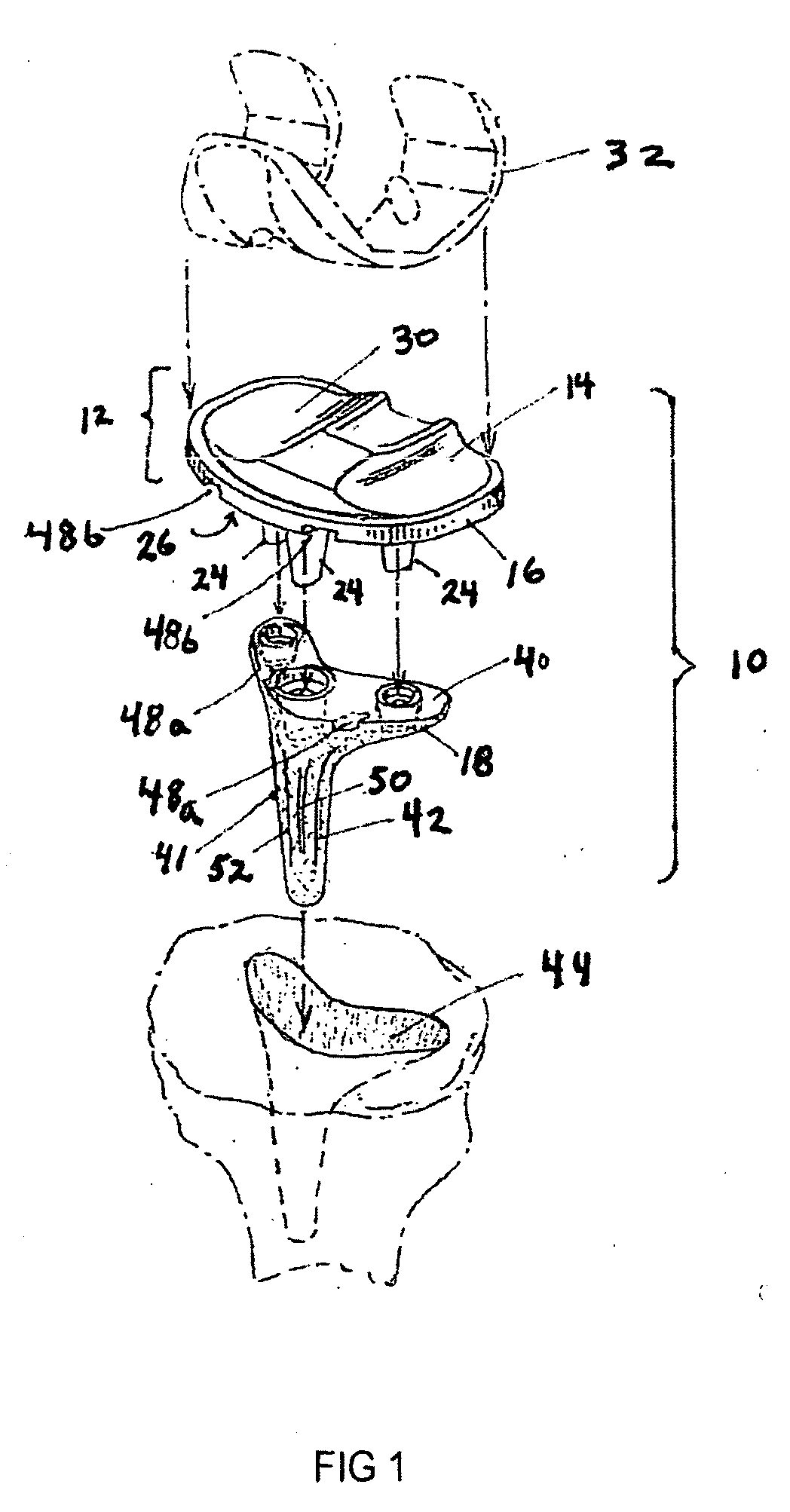
Total joint arthroplasty system
ActiveUS20090131941A1Precise alignmentImprove visualizationMedical simulationProgramme controlJoint arthroplastyTotal hip arthroplasty
A method and system for performing a total joint arthroplasty procedure on a patient's damaged bone region. A CT image or other suitable image is formed of the damaged bone surfaces, and location coordinate values (xn,yn,zn) are determined for a selected sequence of bone surface locations using the CT image data. A mathematical model z=f(x,y) of a surface that accurately matches the bone surface coordinates at the selected bone spice locations, or matches surface normal vector components at selected bone surface locations, is determined. The model provides a production file from which a cutting jig and an implant device (optional), each patient-specific and having controllable alignment, are fabricated for the damaged bone by automated processing. At this point, the patient is cut open (once), the cutting jig and a cutting instrument are used to remove a selected portion of the bone and to provide an exposed planar surface, the implant device is optionally secured to and aligned with the remainder of the bone, and the patient's incision is promptly repaired.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Cutting guide apparatus and surgical method for use in knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS7104997B2Avoiding minimizing errorPrecise alignmentSurgical sawsProsthesisSurgical approachSurgical incision
Novel cutting guides and surgical methods for use in knee arthroplasty are described. Embodiments of the inventive cutting guide apparatus include fixed and adjustable cutting guide blocks having a series of slots designed to accommodate a cutting saw. The cutting guides and surgical method are designed to allow for the provision of all desired surgical cuts upon the distal end of the femur, for subsequent implantation of a prosthesis thereto, without having to remove the cutting guide block.
Owner:LIONBERGER DAVID +1
Dynamic knee balancer
ActiveUS20050177169A1Enhancing knee surgery procedureAccelerated programBone implantDiagnosticsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationRange of motion
Dynamic knee balancing devices, systems and methods provide for enhanced total knee arthroplasty (“TKA”) procedures. Devices generally include a stationary femoral member for removably attaching to a distal femur and an adjustable femoral member coupled with the stationary member for adjusting ligament tension of the knee. The adjustable femoral member includes at least one positioning feature for providing positional and / or orientation information for facilitating the TKA procedure. Additionally, the adjustable femoral member is movably couplable with a tibial member engaged with the proximal tibia to allow movement of the knee through a range of motion without removing the device from the joint space. When the adjustable femoral member is adjusted, the positional feature(s) move relative to the distal femur to provide positional information.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
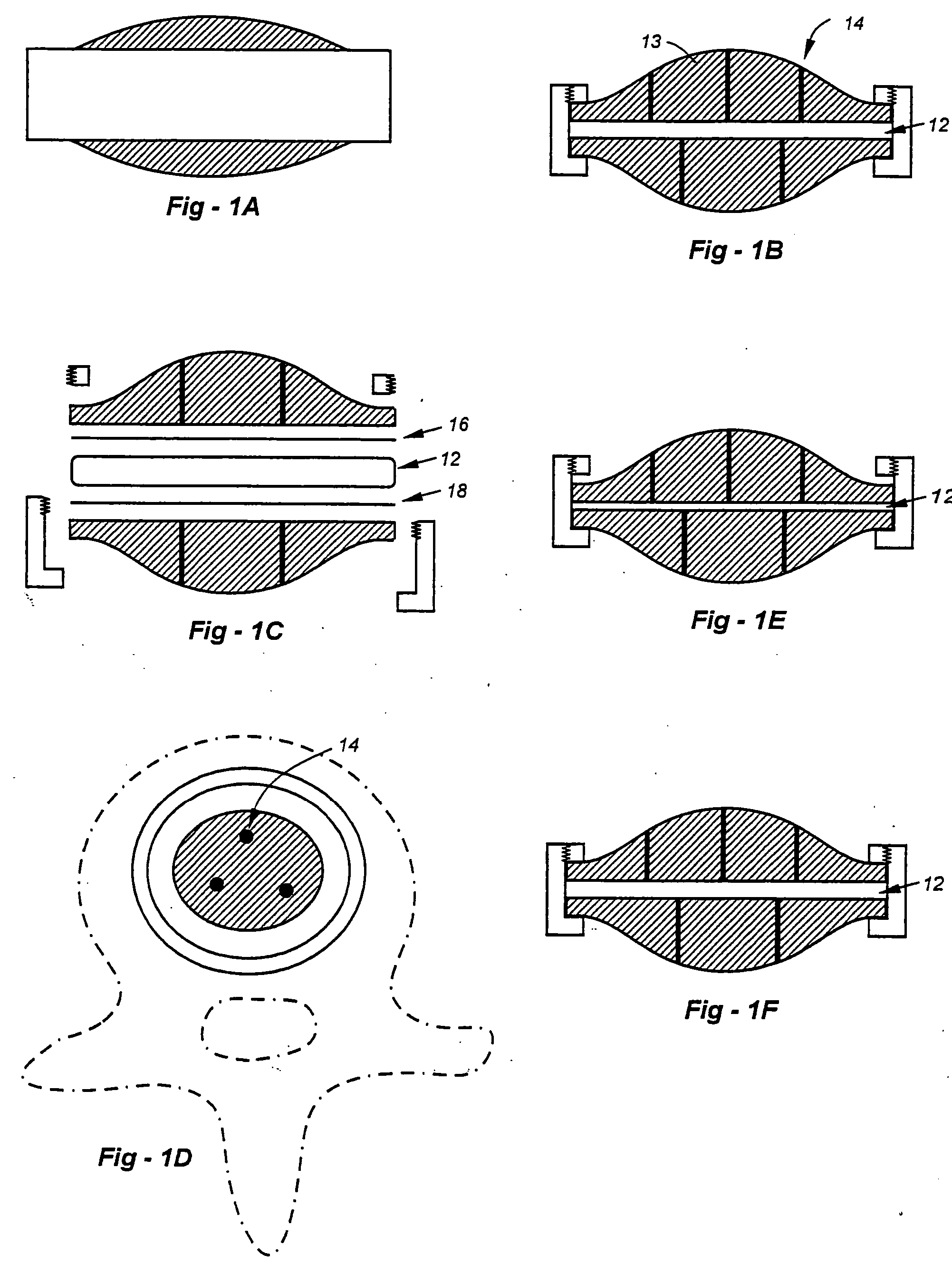
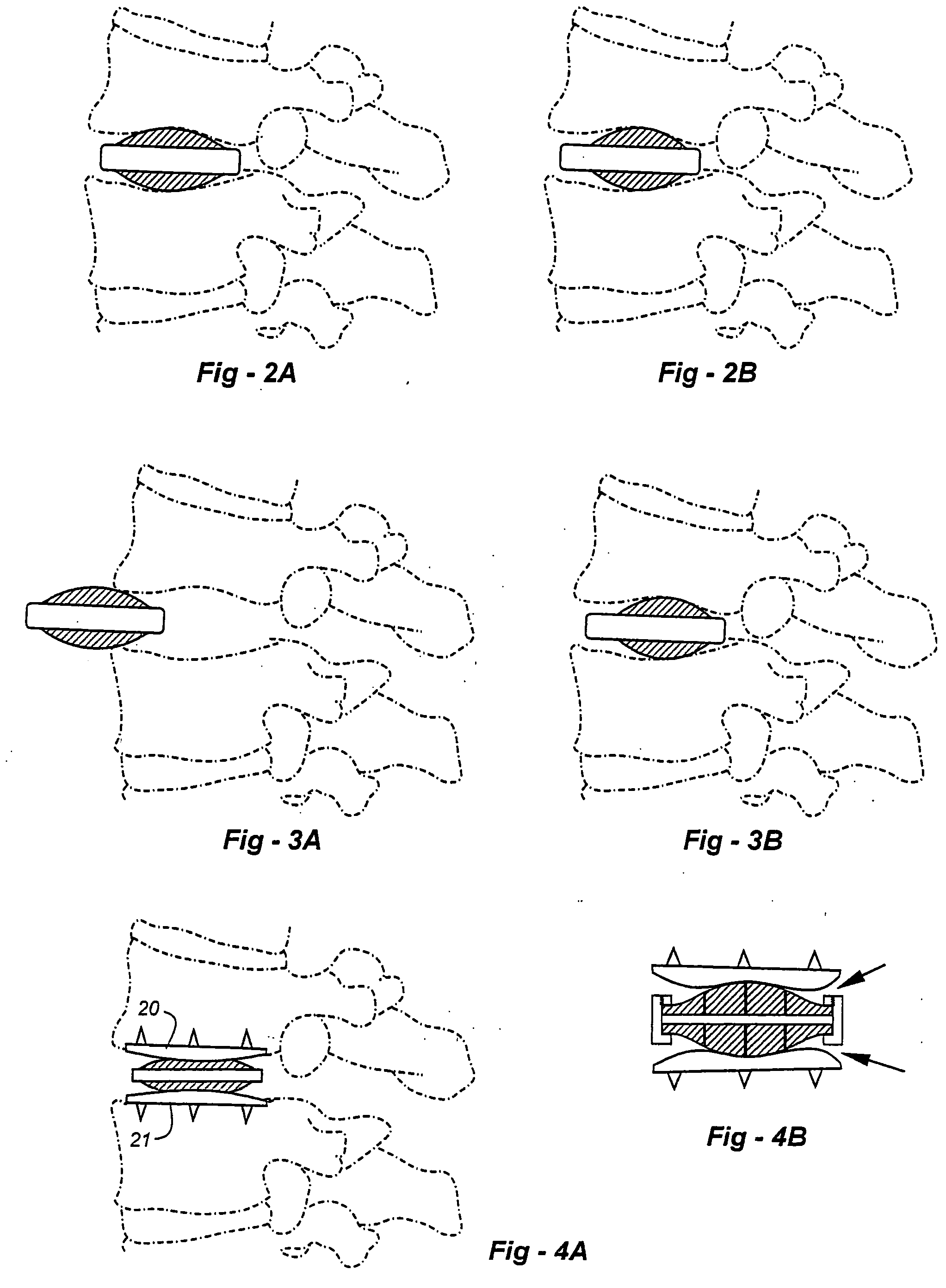
Dynamic spacer for total knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS20050020941A1Easy to useEasy constructionSurgeryPerson identificationPhysical medicine and rehabilitationSurgical instrumentation
A dynamic spacer is provided for measuring flexion-extension gap during total knee arthroplasty. The dynamic spacer is an improved surgical instrumentation system that it easy to use, simple in construction, and accurately measures flexion-extension gaps under repeatable soft tissue tension. The dynamic spacer generally comprises a first planar member having a lower tissue engaging surface, a second planar member having an upper tissue engaging surface. A tensioner is disposed between the first planar member and the second planar member for applying a tensile force acting upon the first and second planar members. The tensioner is fixedly attached to the first and second planar members, such that the first planar member is held substantially parallel to the second planar member in the absence of compressive load. The dynamic spacer allows for accurately measuring flexion-extension gaps and angular deviation in flexion indicating the appropriateness of femoral rotation.
Owner:TARABICHI SAMIH
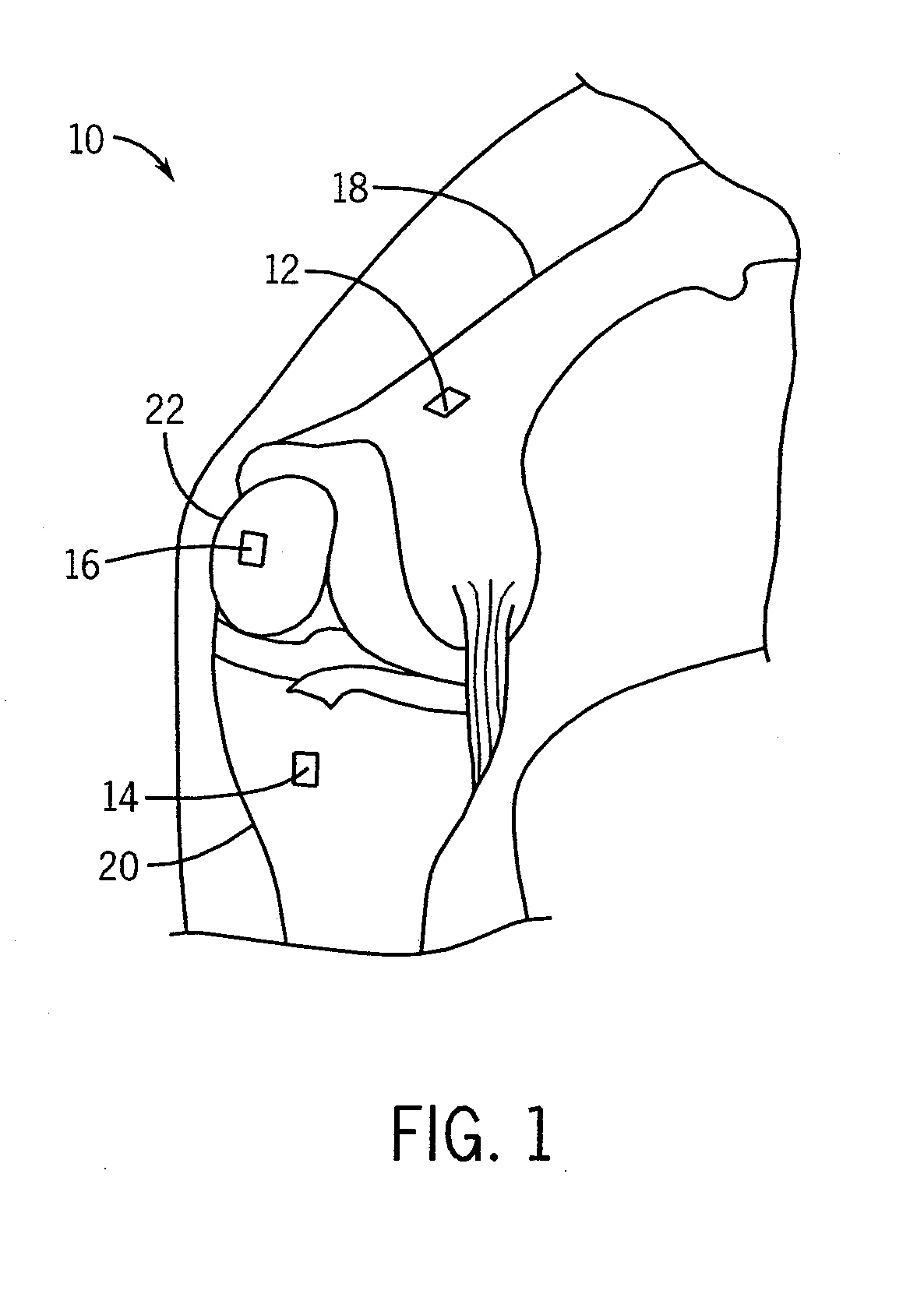
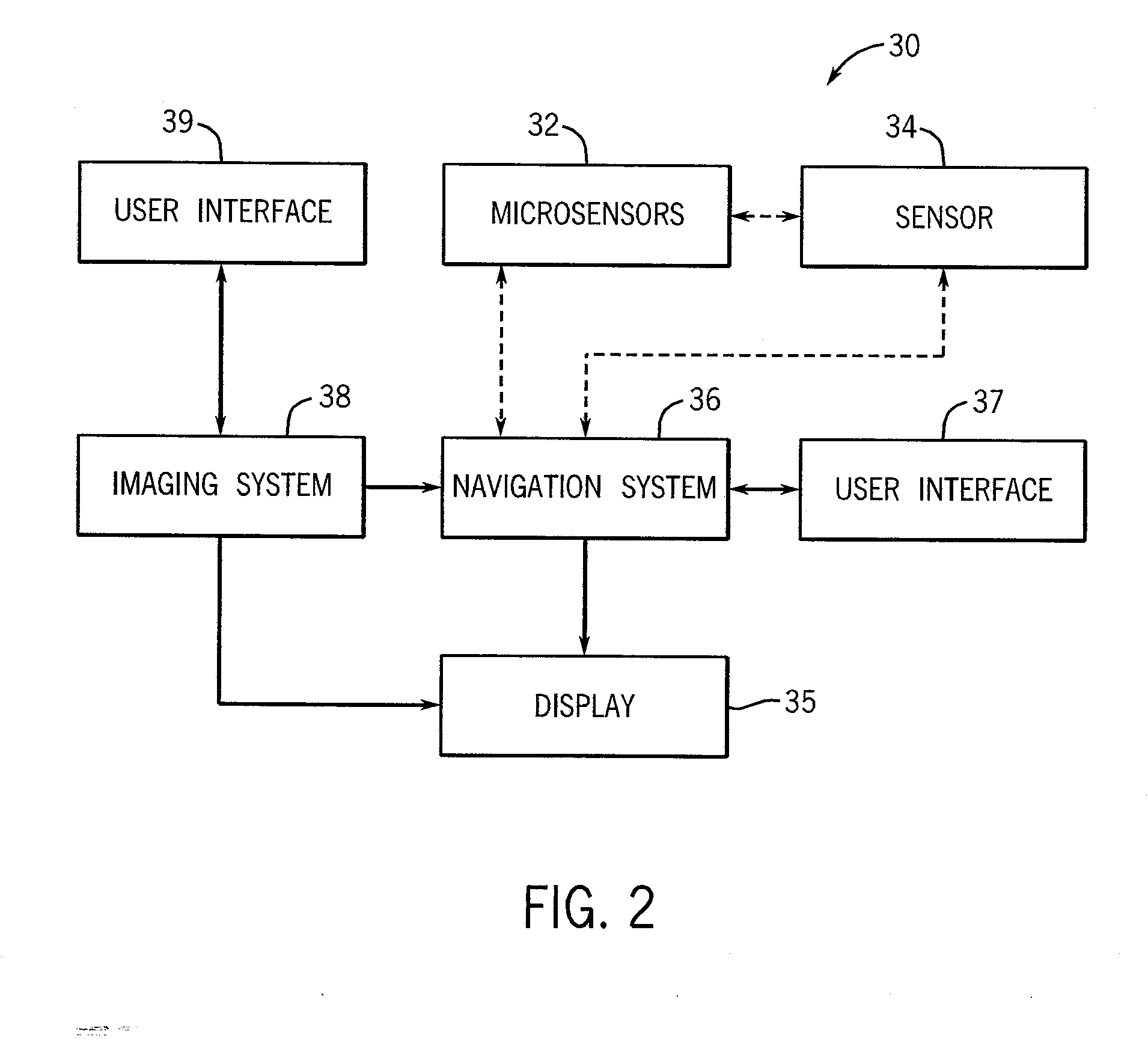
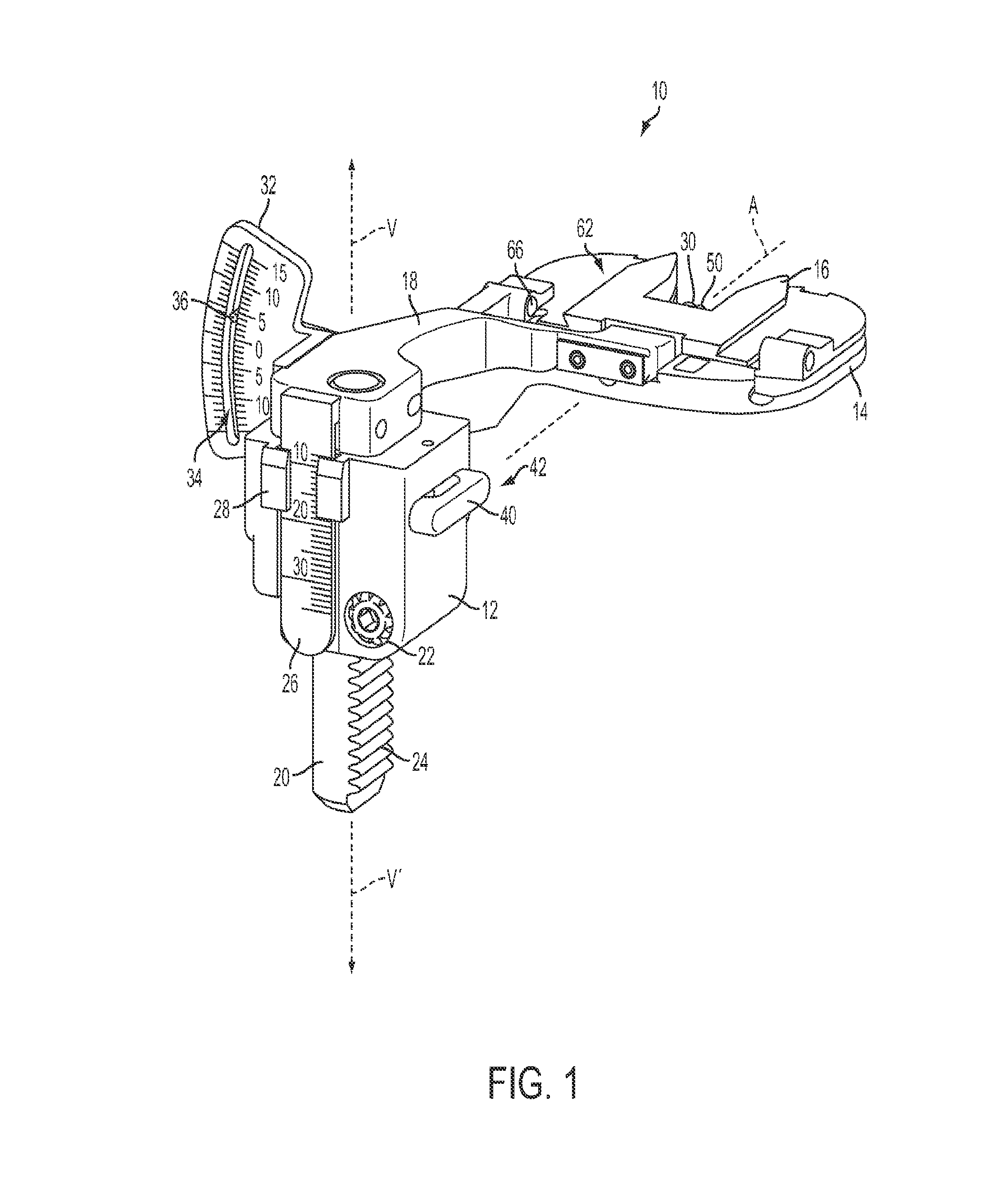
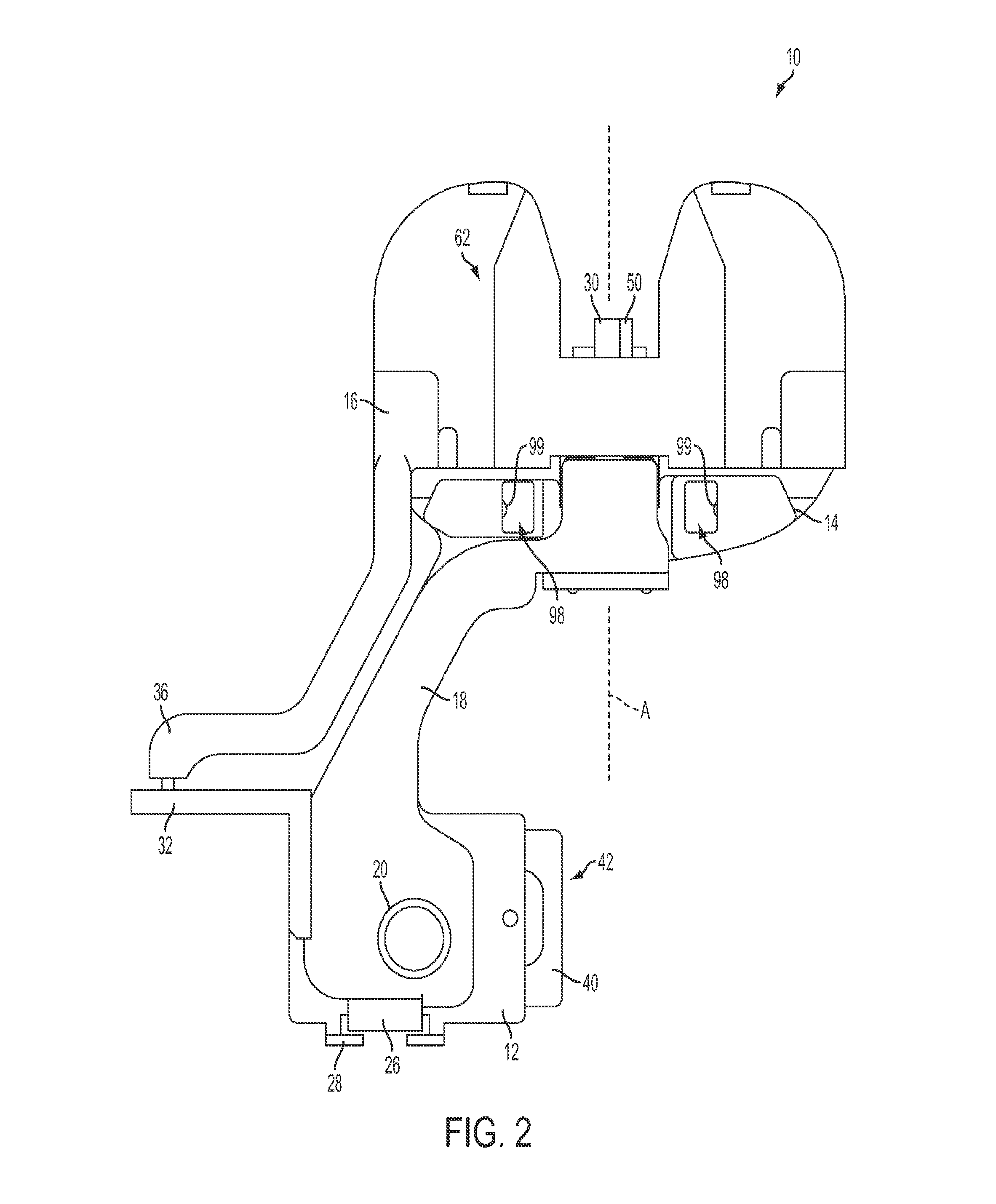
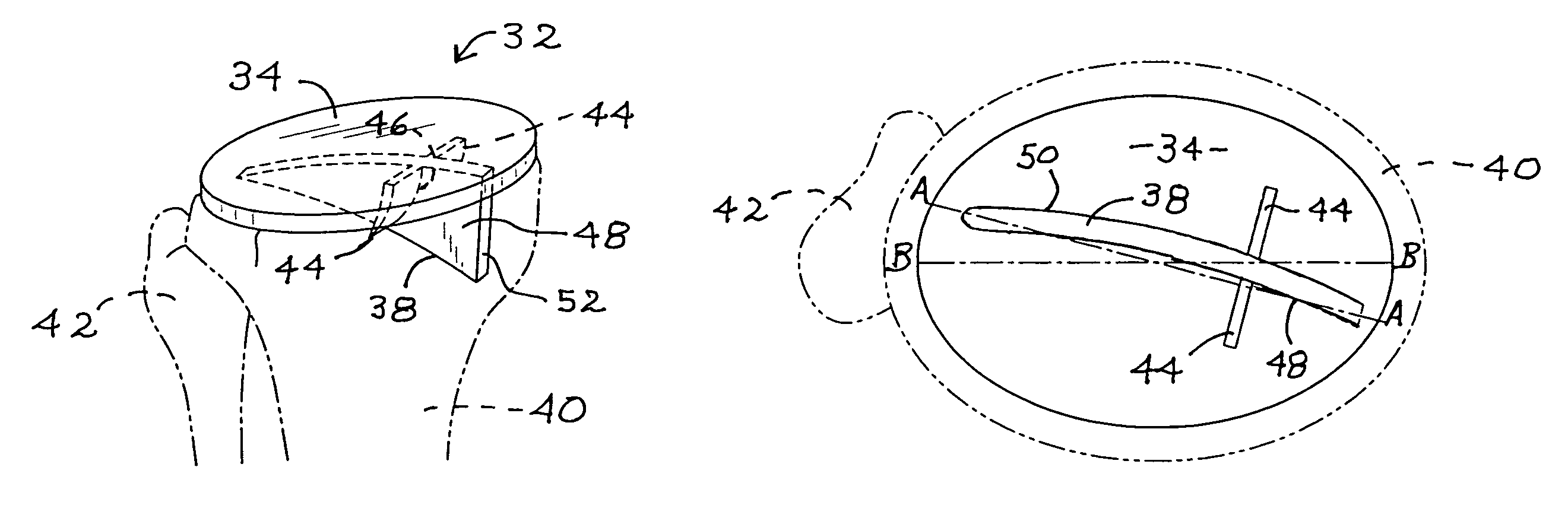
System and method for measurement of clinical parameters of the knee for use during knee replacement surgery
A system and method for measuring biomechanical parameters of a knee prior to total knee replacement (TKR) surgery includes a plurality of microsensors removably attached to the femur, tibia and patella; at least one sensor communicating with the plurality of microsensors; a navigation system coupled to the at least one sensor; an imaging system coupled to the navigation system for performing imaging of the joint; and at least one display for displaying imaging and tracking data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Total elbow arthroplasty system
A total elbow arthroplasty system, incorporating a humeral component, a radial component and a ball component, may be used as a total elbow replacement in the canine, as well as in other species. The implant of the present invention has an isometric humeral component and an isometric radial component. An isometric ball component having an isometric articular surface is mounted on the radial component. The humeral and radial components have stems for mounting in the medullary canals of the respective bones, which are angled so as to approximate the configuration of the original humerus and radius. The components work together to form a nonconstrained ball and socket joint. The invention is also directed to methods for implanting the novel endoprosthesis of the present invention in a canine elbow joint. The apparatus and methods of the present invention are useful in the treatment of elbow osteoarthritis in canines, as well as in other species, including other quadrupeds and humans.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
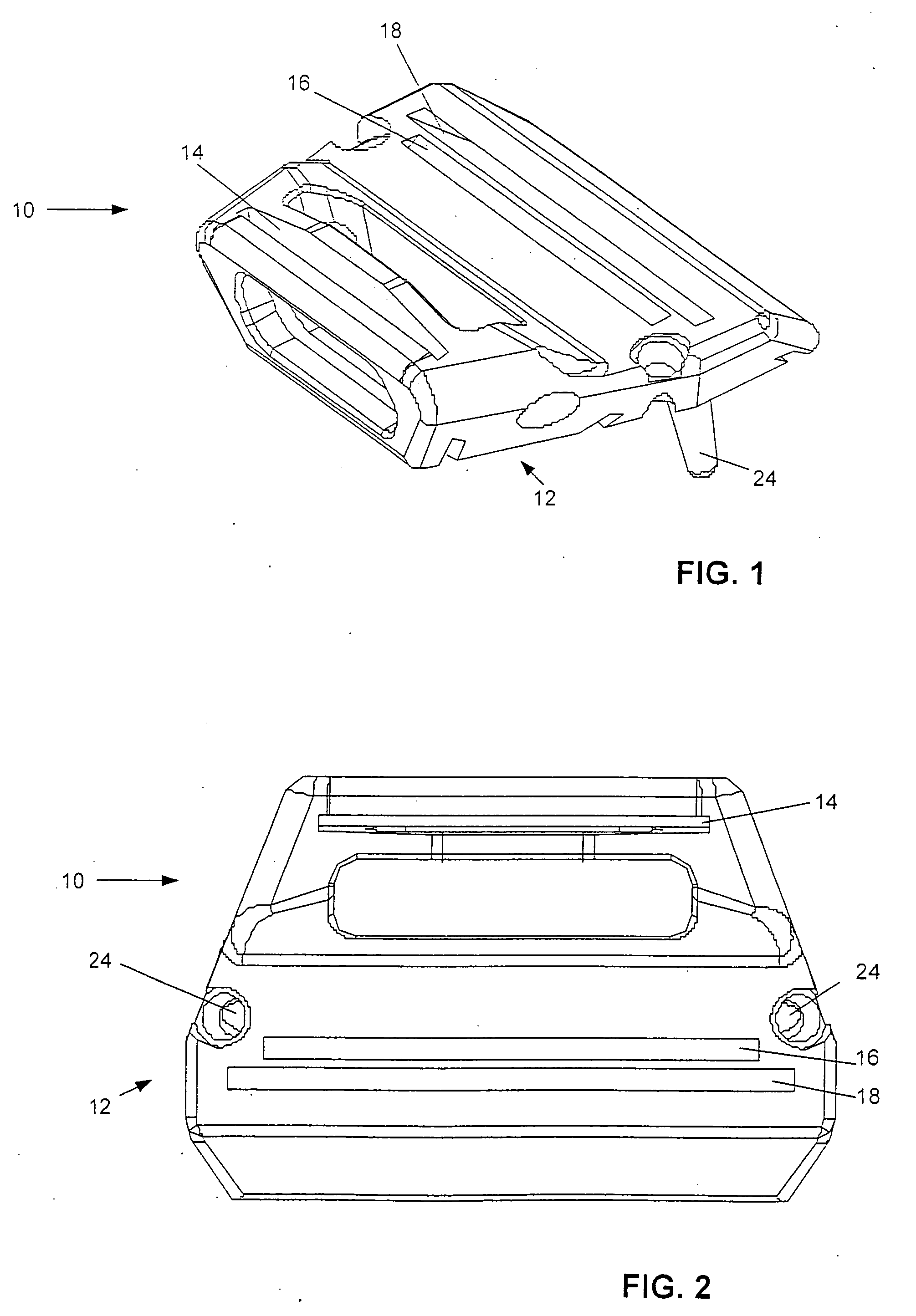
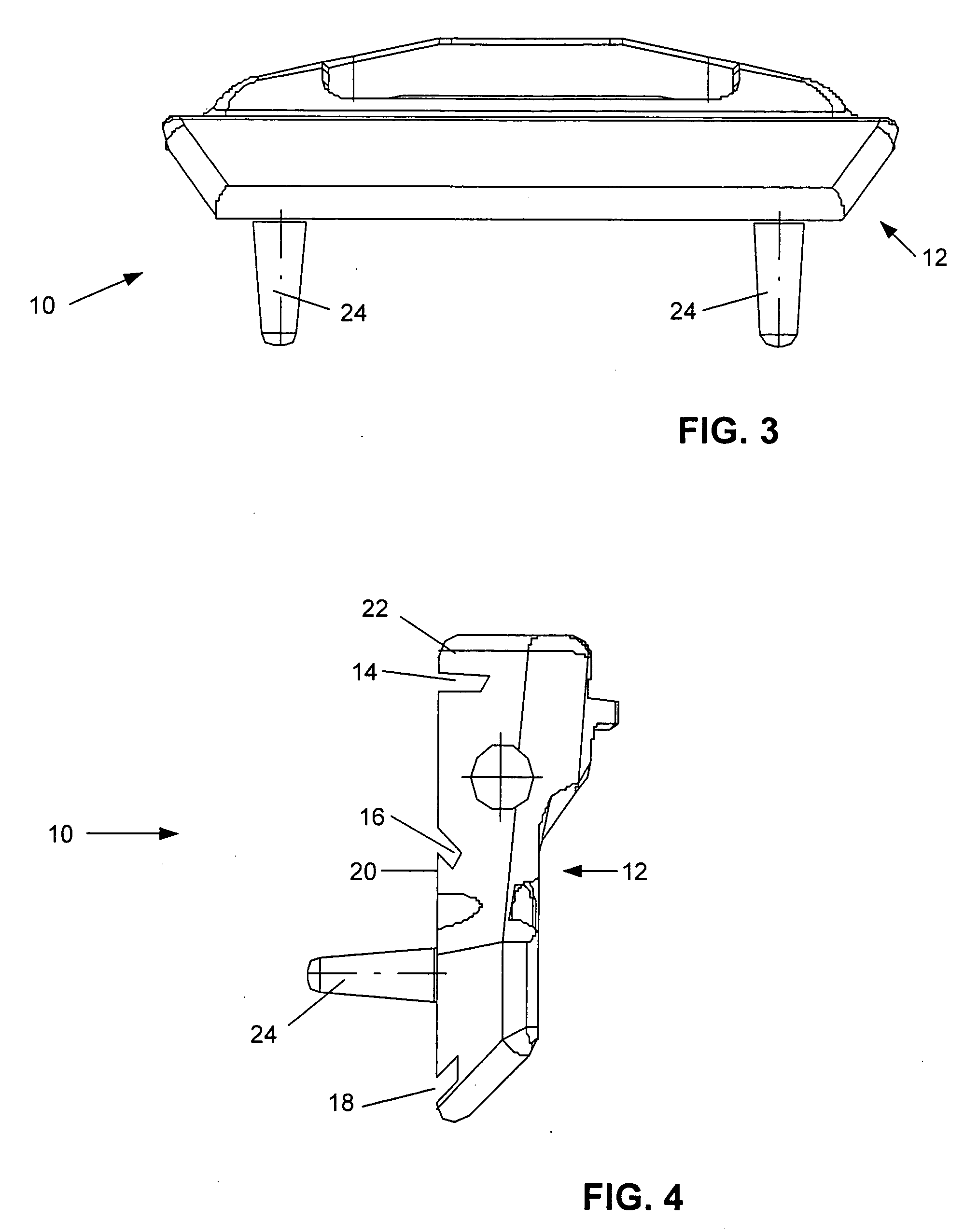
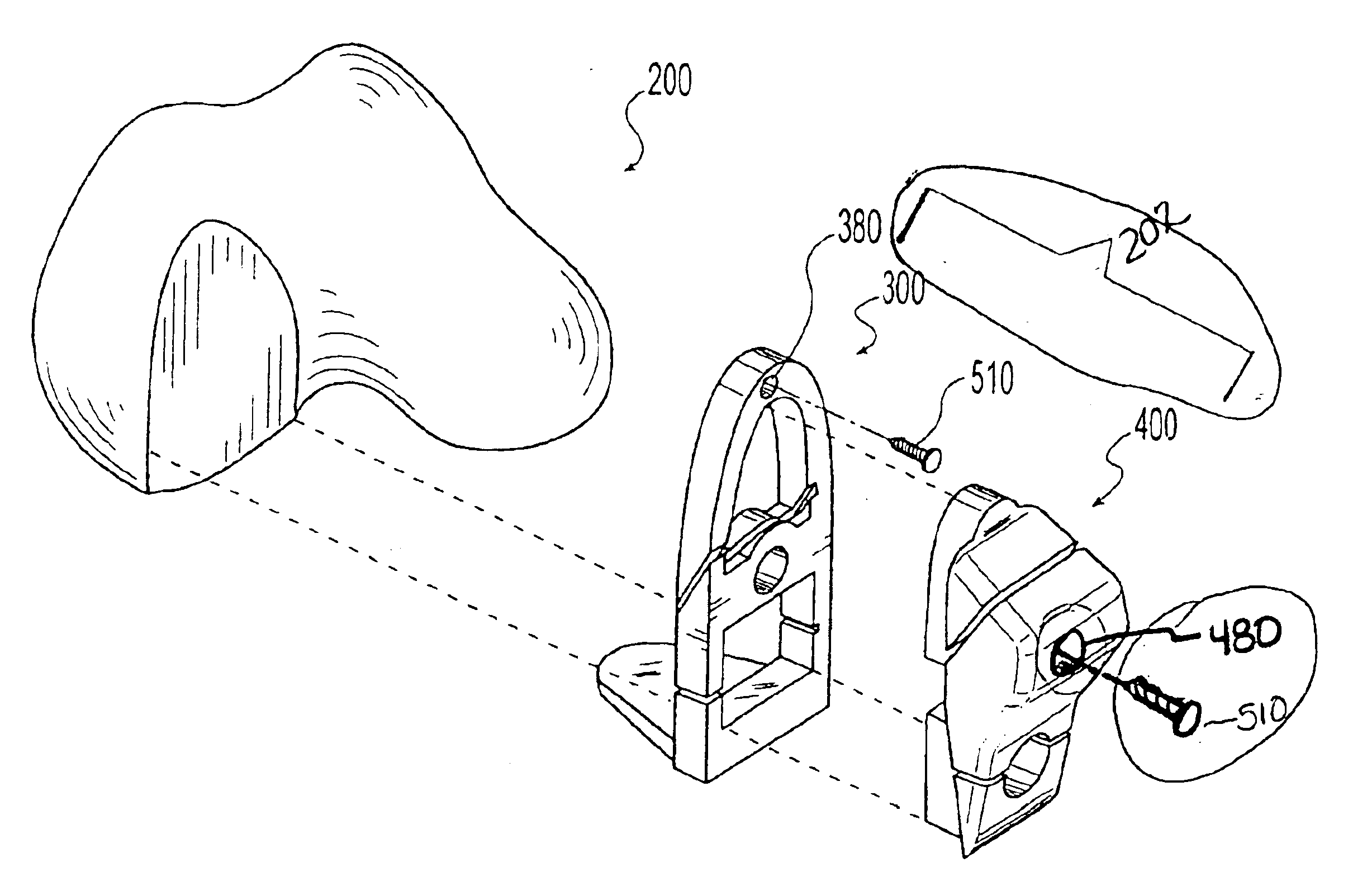
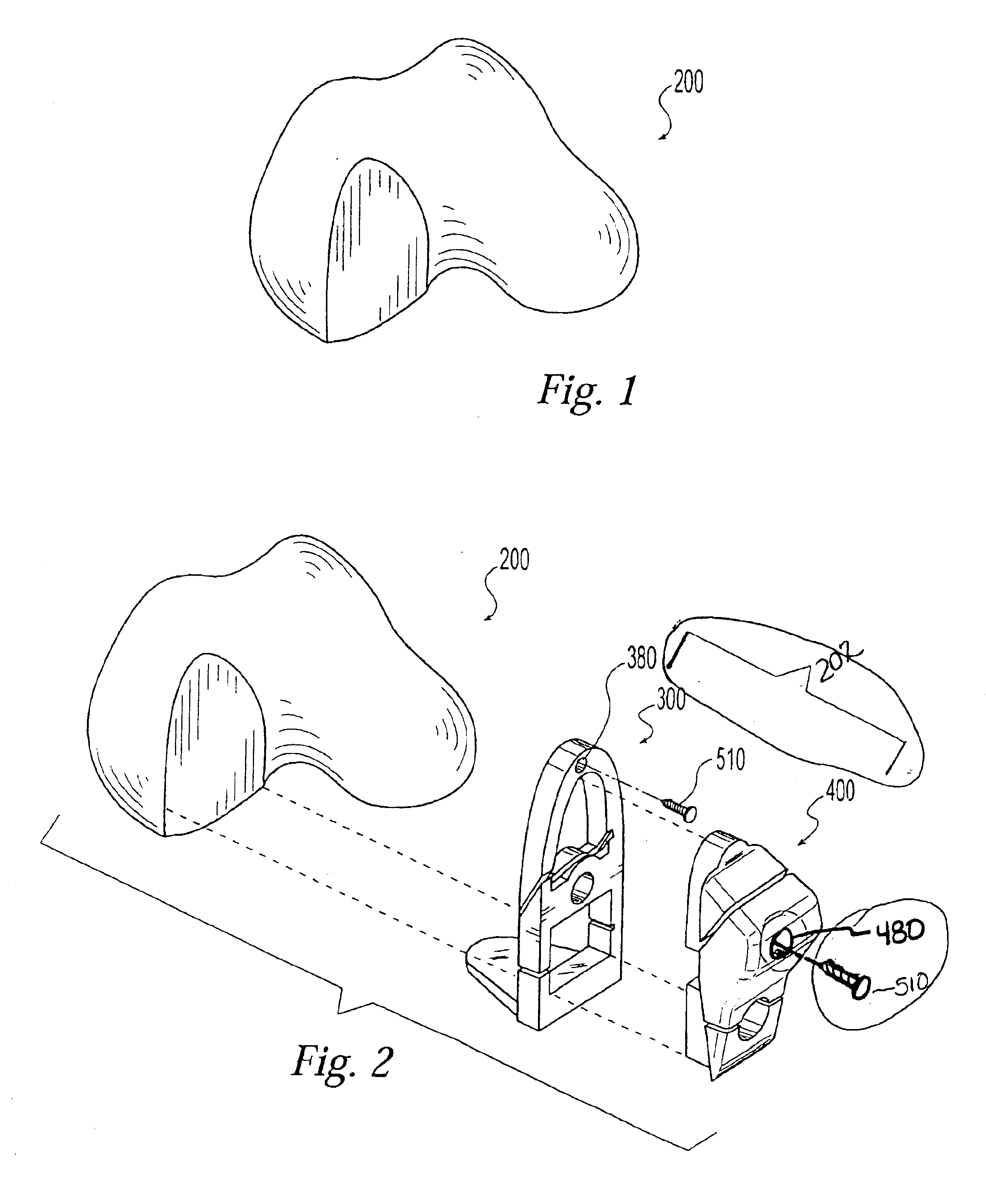
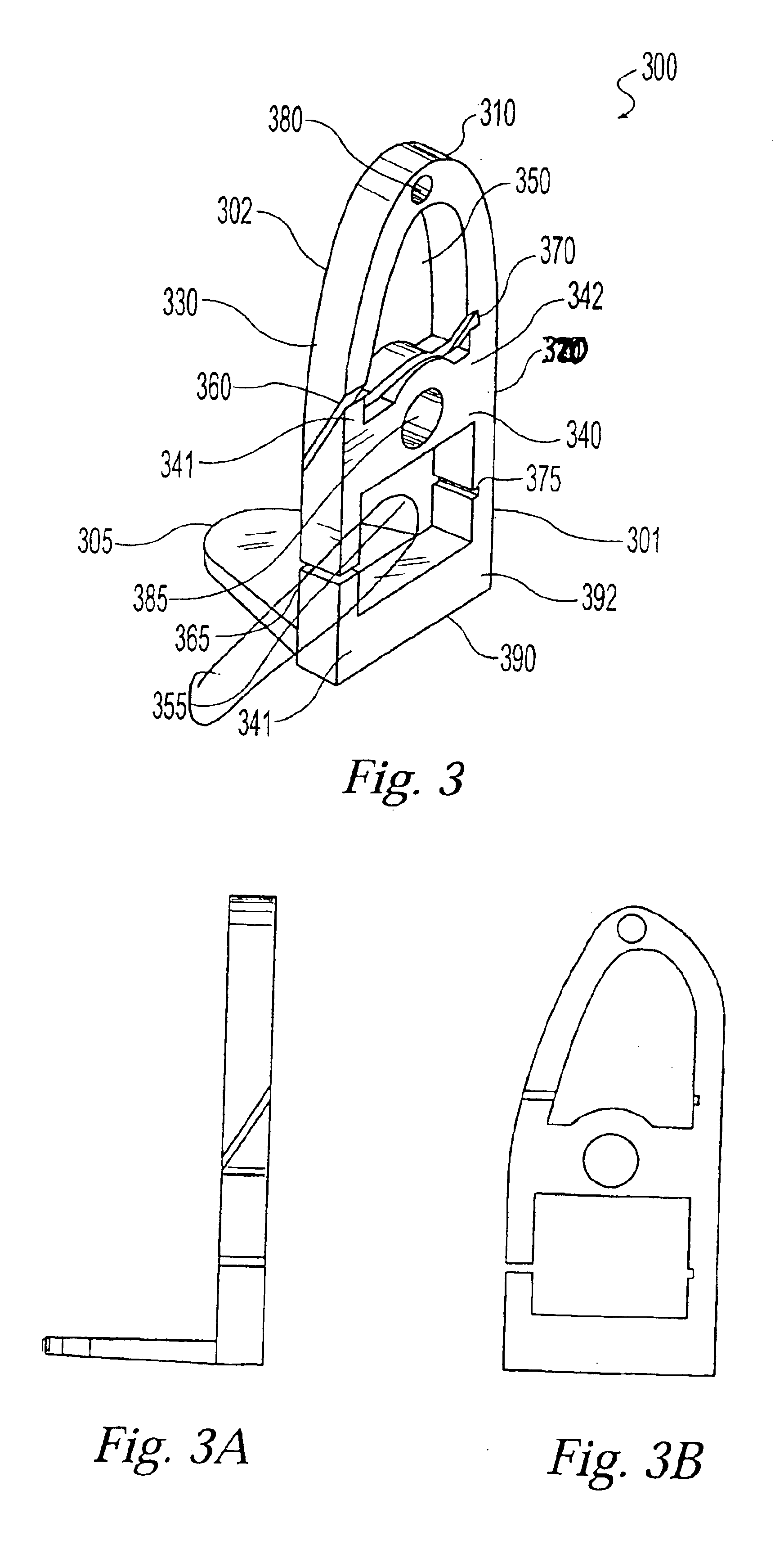
Surgical tool assembly for total knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS20080097451A1More convenienceMinimize damageJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTotal hip arthroplastyCutting guide
A surgical tool assembly for Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) including a femoral intra-medullary (IM) rod, a femoral intra-medullary (IM) alignment guide, a distal femoral alignment guide, and a distal femoral cutting guide. After the femoral IM alignment guide is selected to fit the valgus angle and utilized with the femoral IM rod with respect to the distal femur, the distal femoral alignment guide is integrated to the complex. Then, the distal femoral cutting guide is slid to the distal femoral alignment guide in the orientation from distal to proximal through the sliding concave integrated with the sliding track.
Owner:UNITED ORTHOPEDIC CORP +1
Prosthetic joints with contained compressible resilient members
InactiveUS20050192674A1Improve protectionEliminate shear stressInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsElastomerTotal knee replacement
In a total knee replacement (TKR), the use of a cushion element provides better wear characteristics than polyethylene (“poly”) alone. Since a metal-on-metal, metal-on-ceramic, or ceramic-on-ceramic articulating surface has better wear characteristics than metal on poly, the invention essentially provides cushioning for metal / ceramic-on-metal / ceramic joint replacements. It also allows the use of elastomers for their cushioning properties rather than their surface wear and tensile strength characteristics. The contained compressible elements could also be used as a cushion below polyethylene components, polyethylene over metal components, unicondylar knee replacements, patellar components, and prosthetic components for other parts of the body, including the hip, elbow, shoulder, wrist, and ankle.
Owner:ANOVA
Customized process for facilitating successful total knee arthroplasty with outcomes analysis
InactiveUS20140013565A1Address bad outcomesMedical data miningMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesBone morphologyTotal hip arthroplasty
A method for producing a custom resection jig for a current patient scheduled to receive total knee arthroplasty using outcomes analysis comprising the steps of maintaining a database on a computer system of (1) prior patient bone morphology, (2) along with anatomical and mechanical bone alignment data and (3) data defining a custom resection jig design with a generally transverse resection window operable to guide a surgeon's transverse bone cut for prior patients that have received total knee arthroplasty and a post-surgery medically recognized scoring register greater or equal to a predetermined highly successful score value for a total knee arthroplasty procedure using prior success data to guide production of a current patient custom jig resection windows.
Owner:MACDONALD M D JAMES
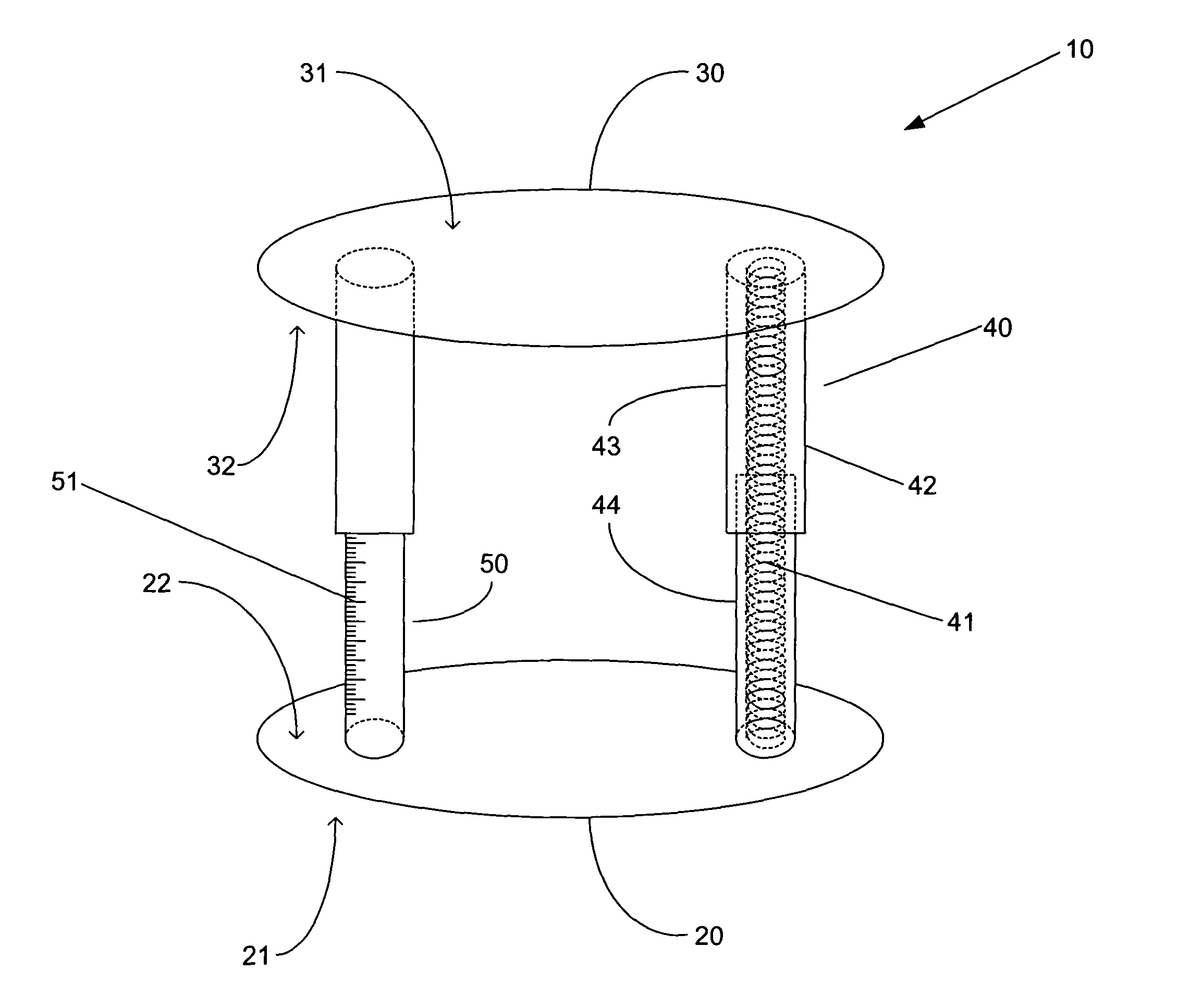
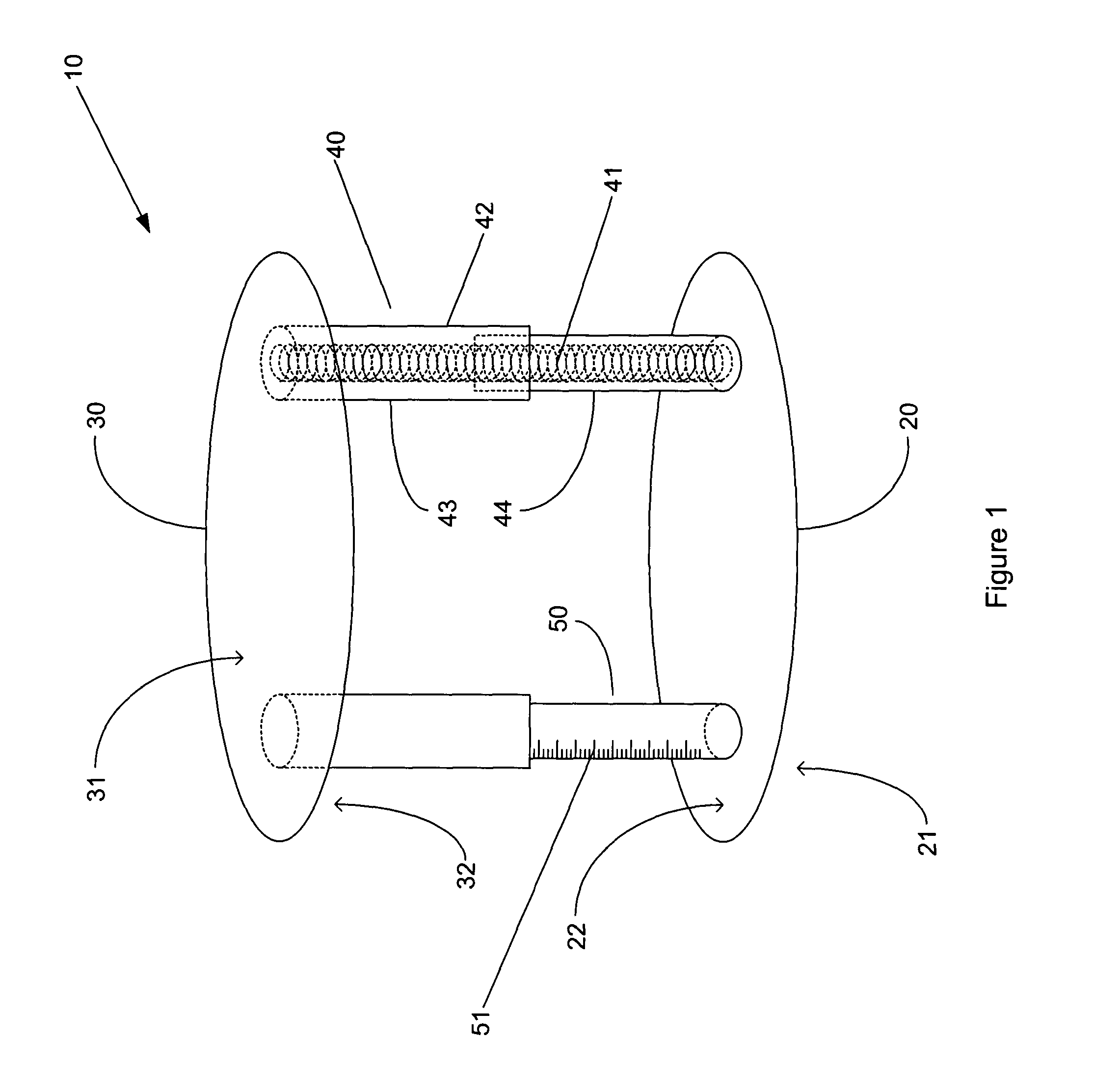
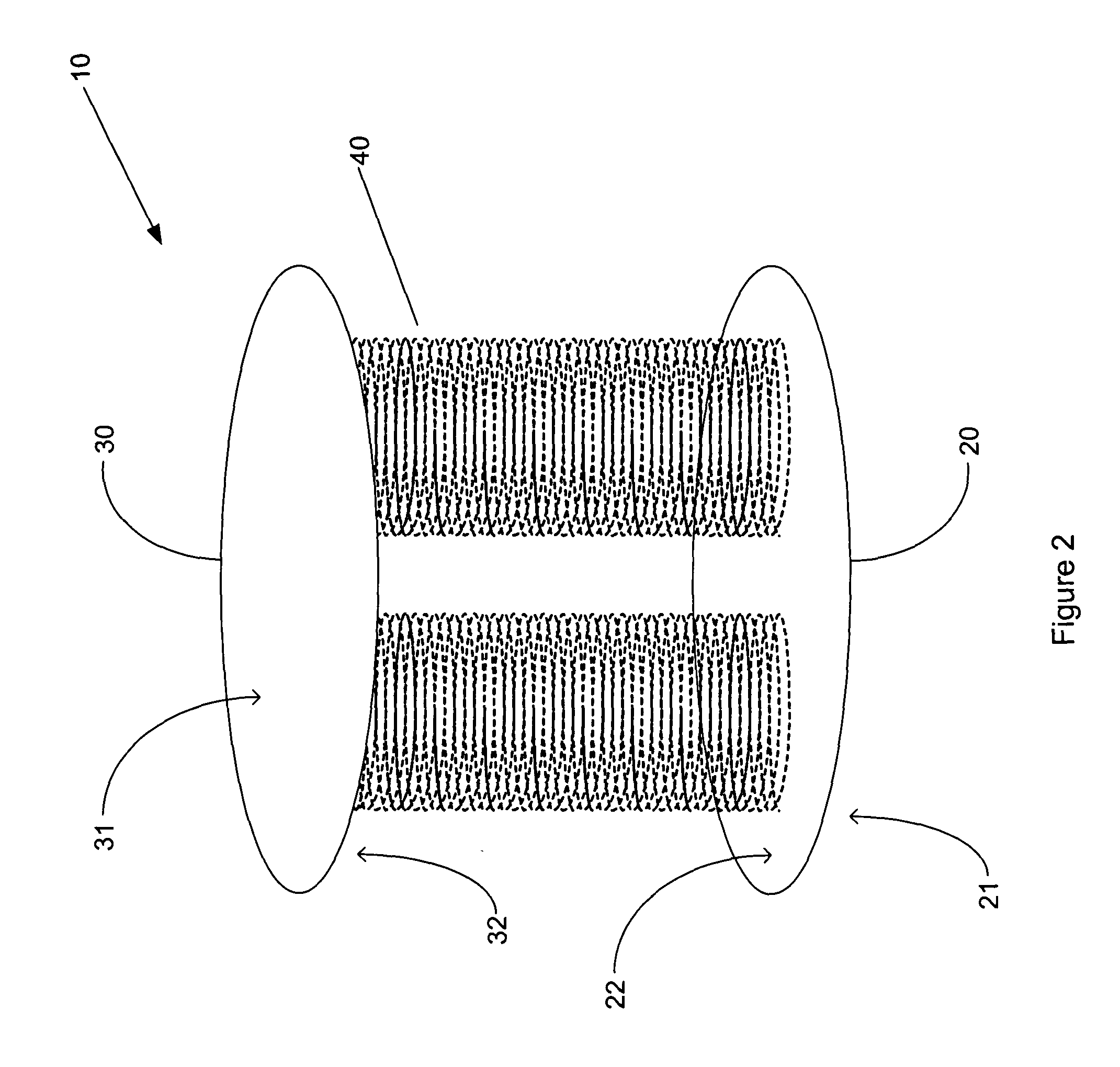
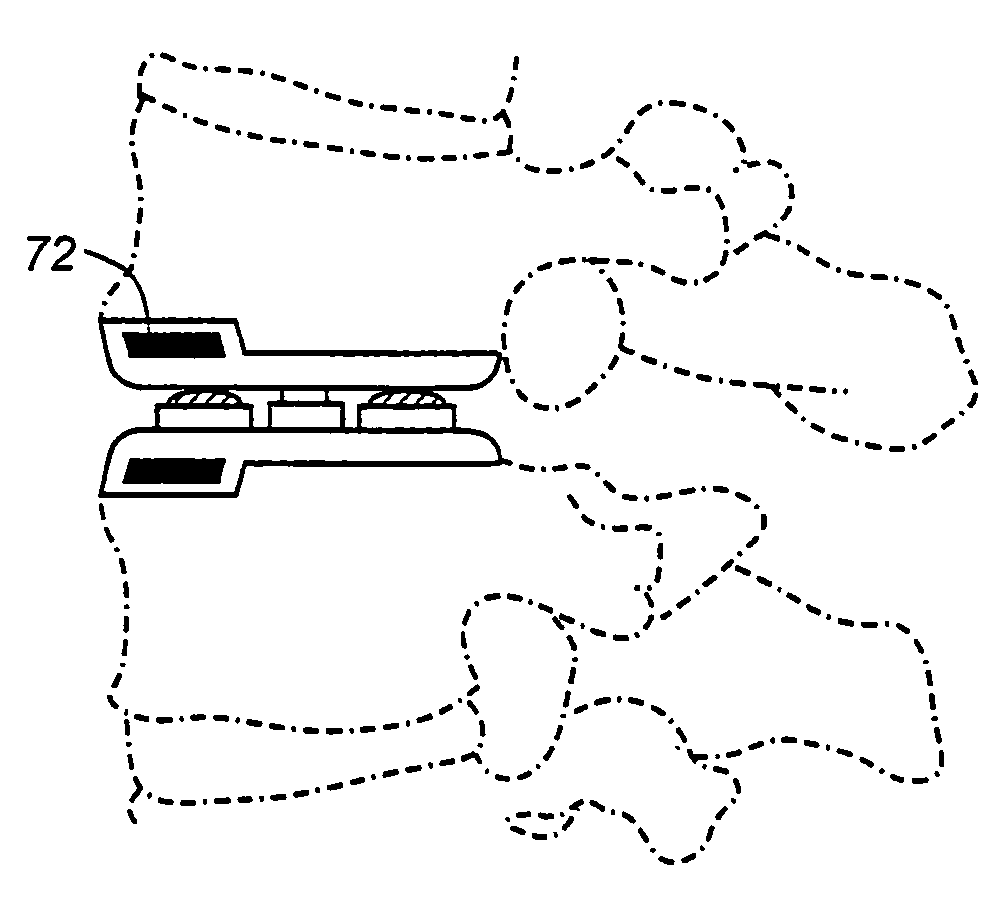
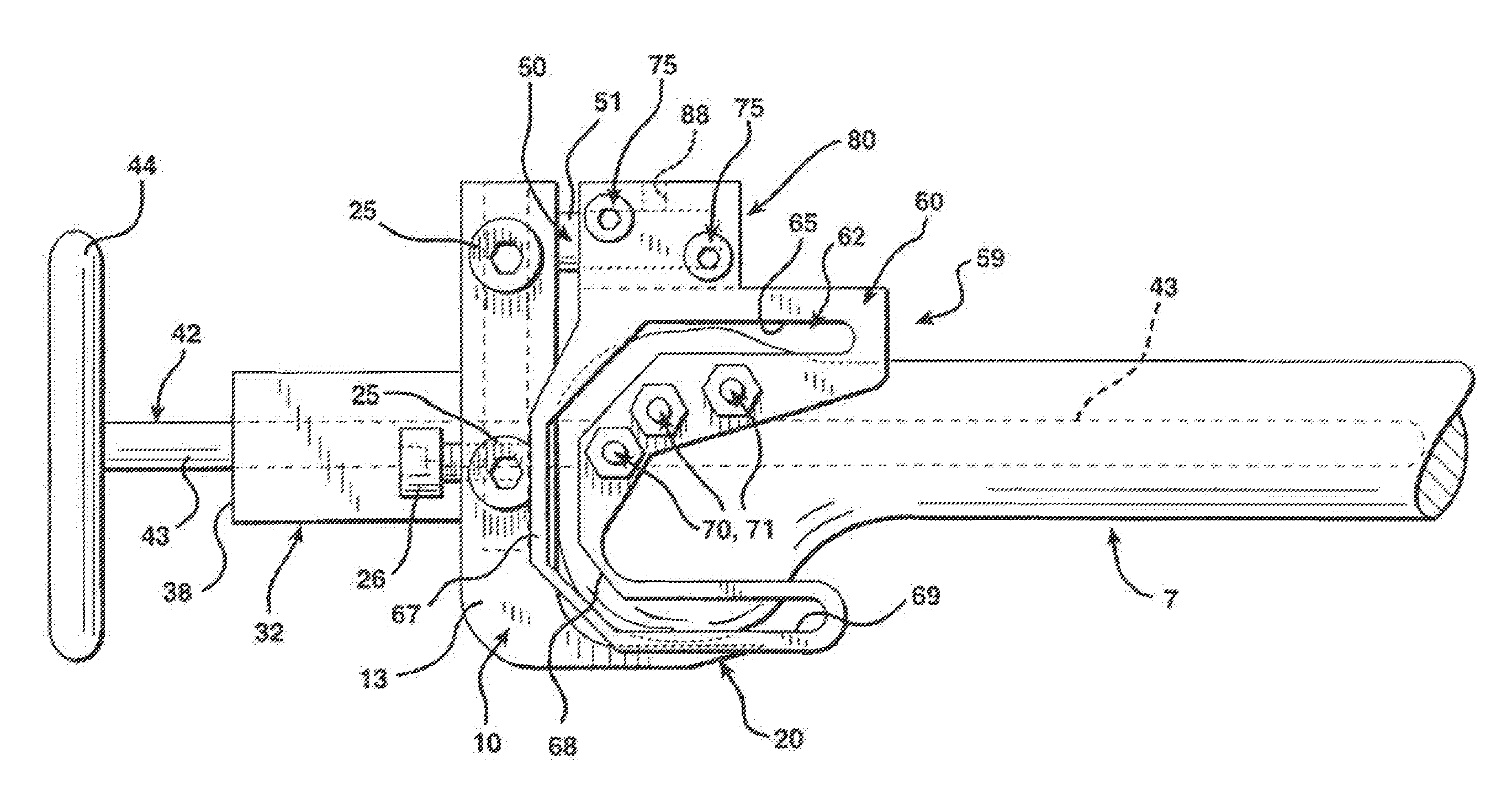
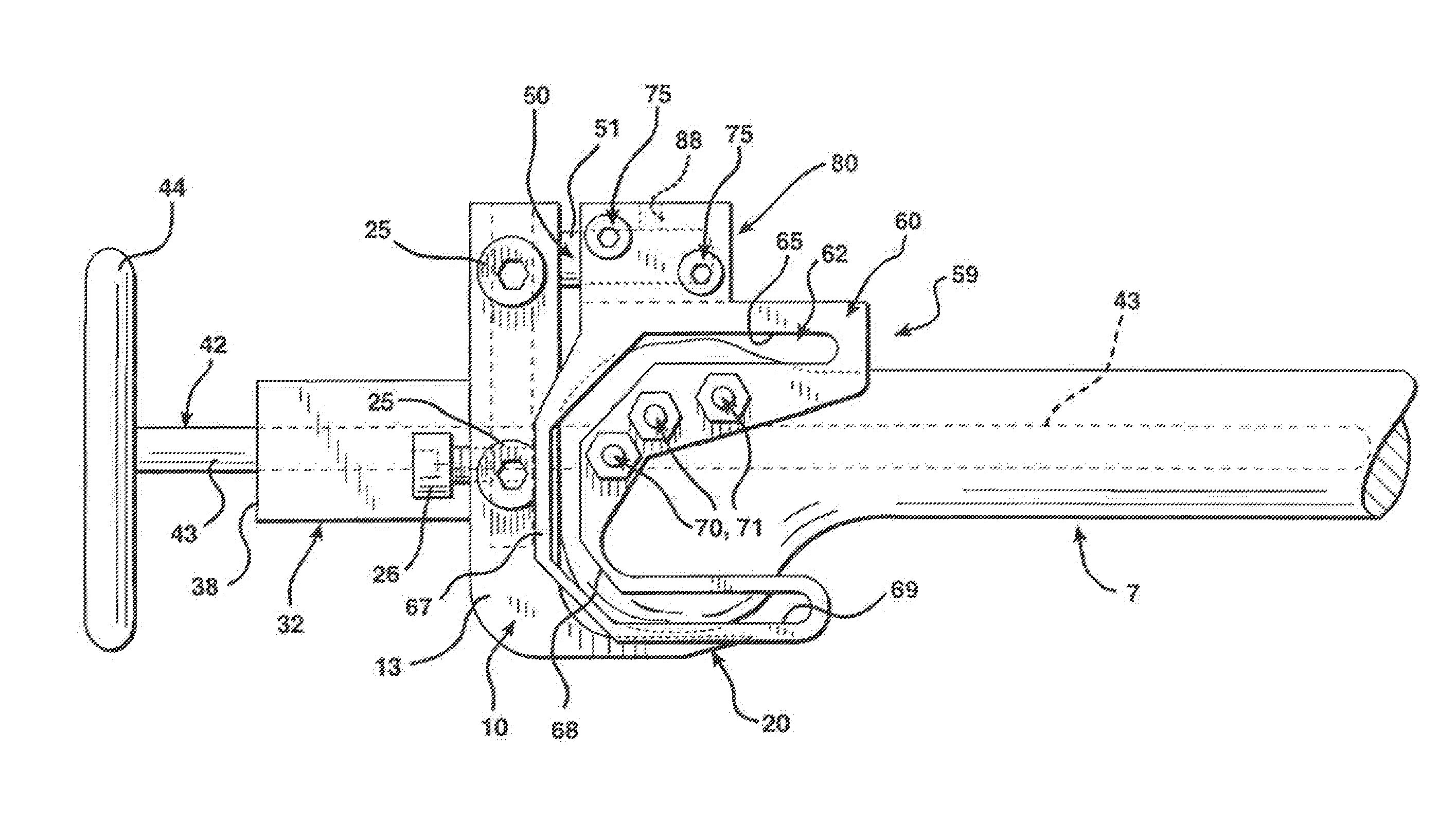
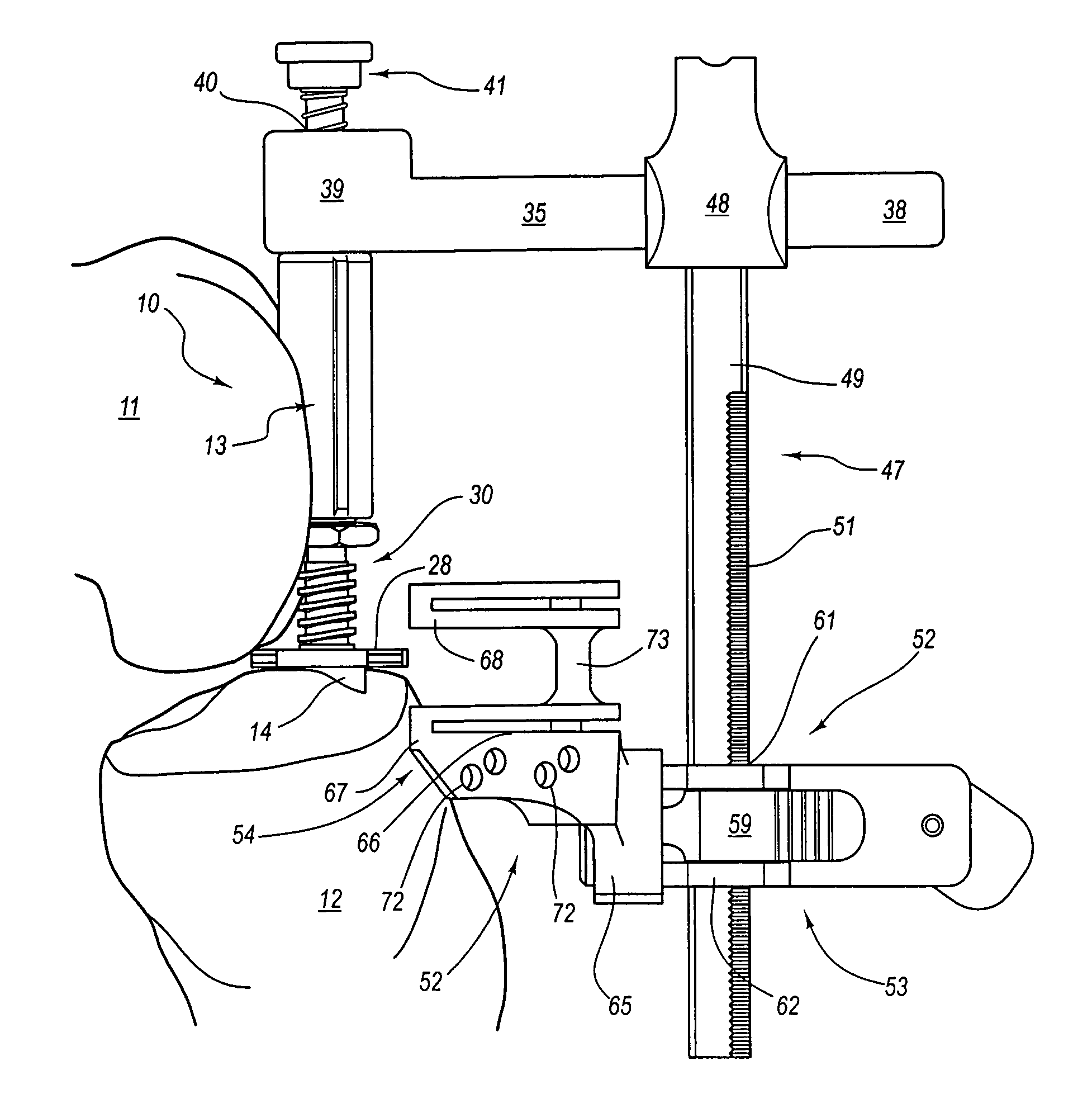
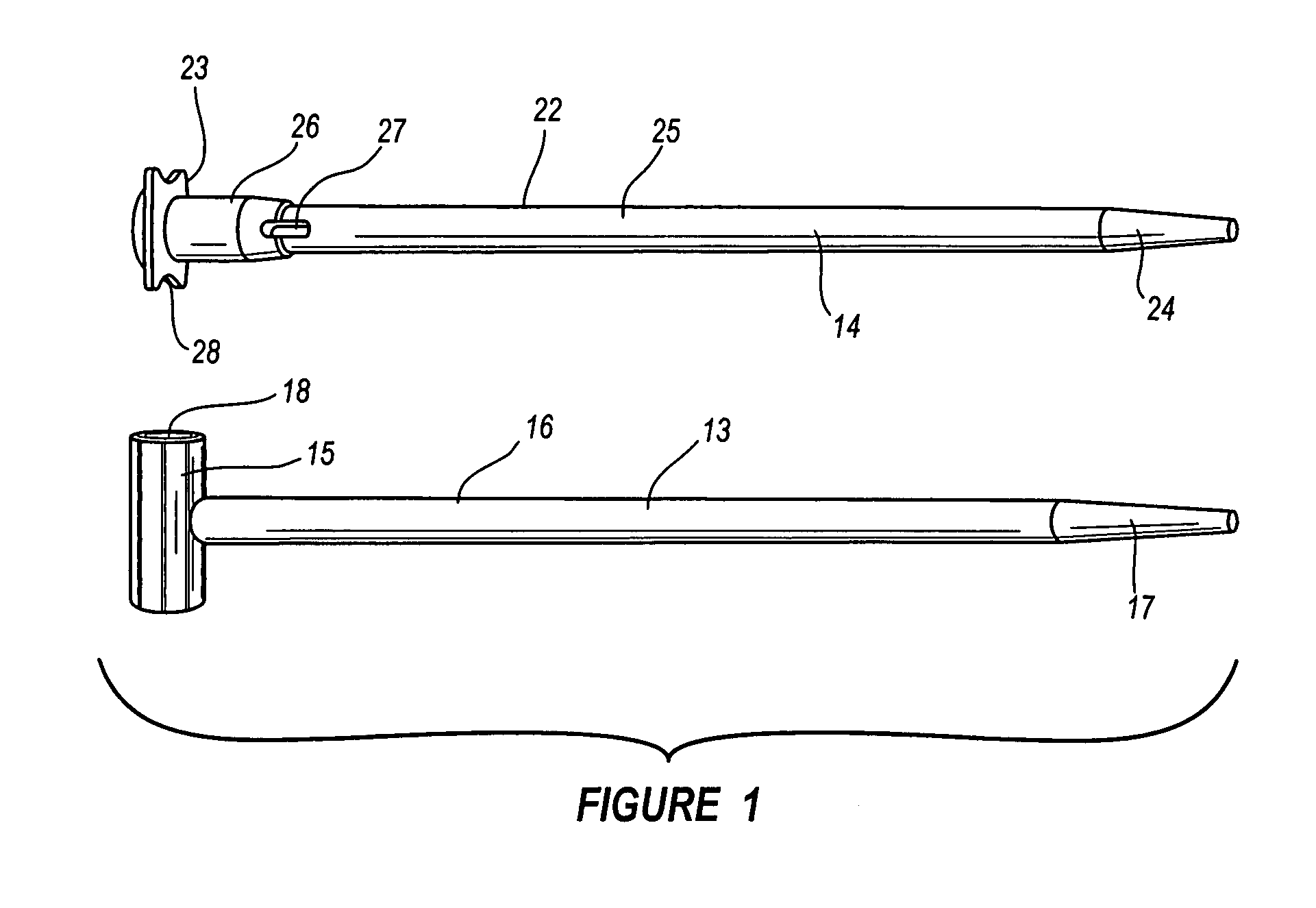
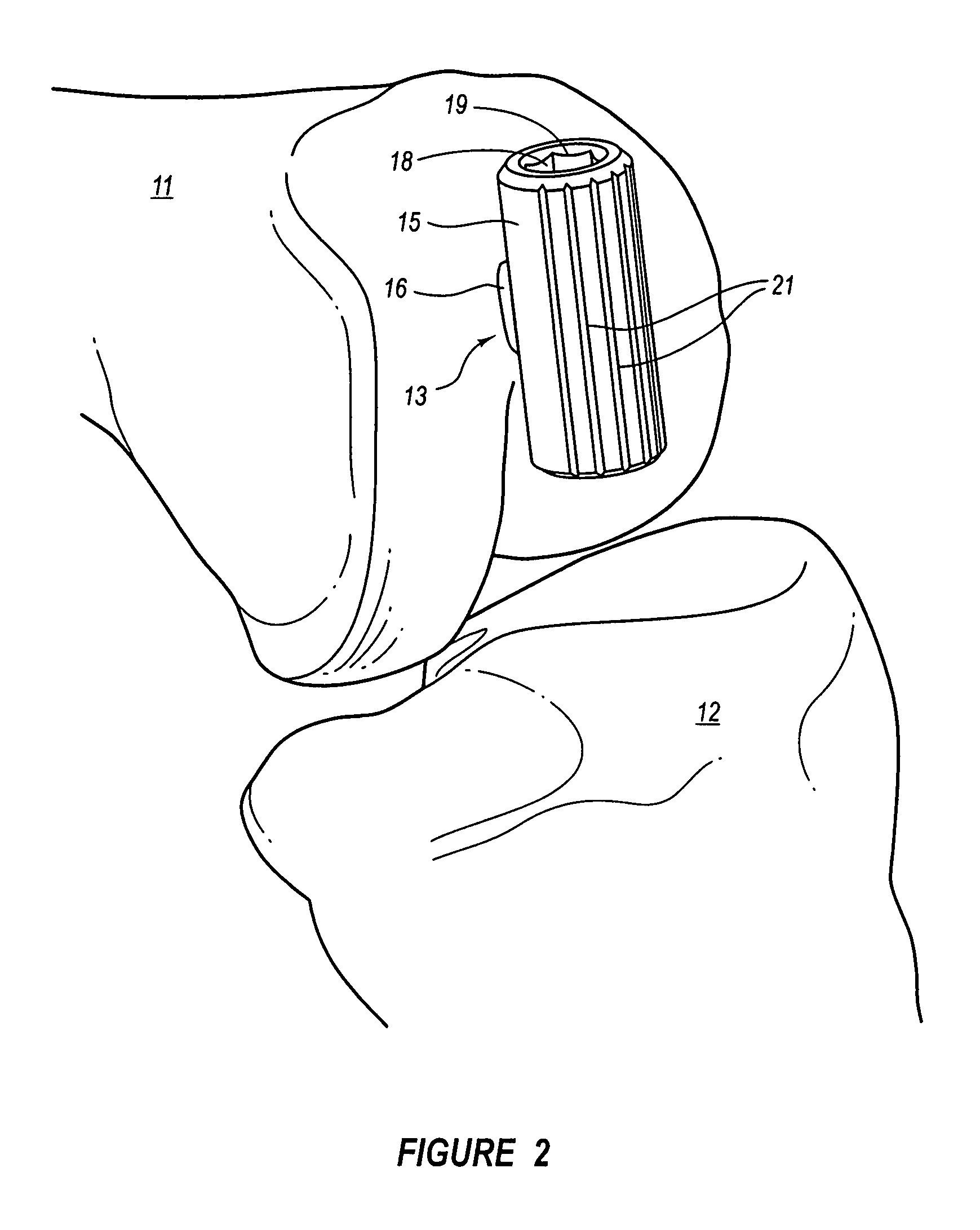
Device for measuring tibio-femoral force amplitudes and force locations in total knee arthroplasty
ActiveUS7412897B2Improve balanceImprove ergonomicsSurgeryForce measurementTotal hip arthroplastyPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A probe used during a total knee arthroplasty for measuring forces and locations of their points of application and thereby moments includes two load sensitive plates t to be inserted in one joint-compartment of a knee joint each and each being provided with a top surface and a bottom surface. At least two load sensors may be situated on the top surfaces and / or the bottom surface of each load sensitive plate.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
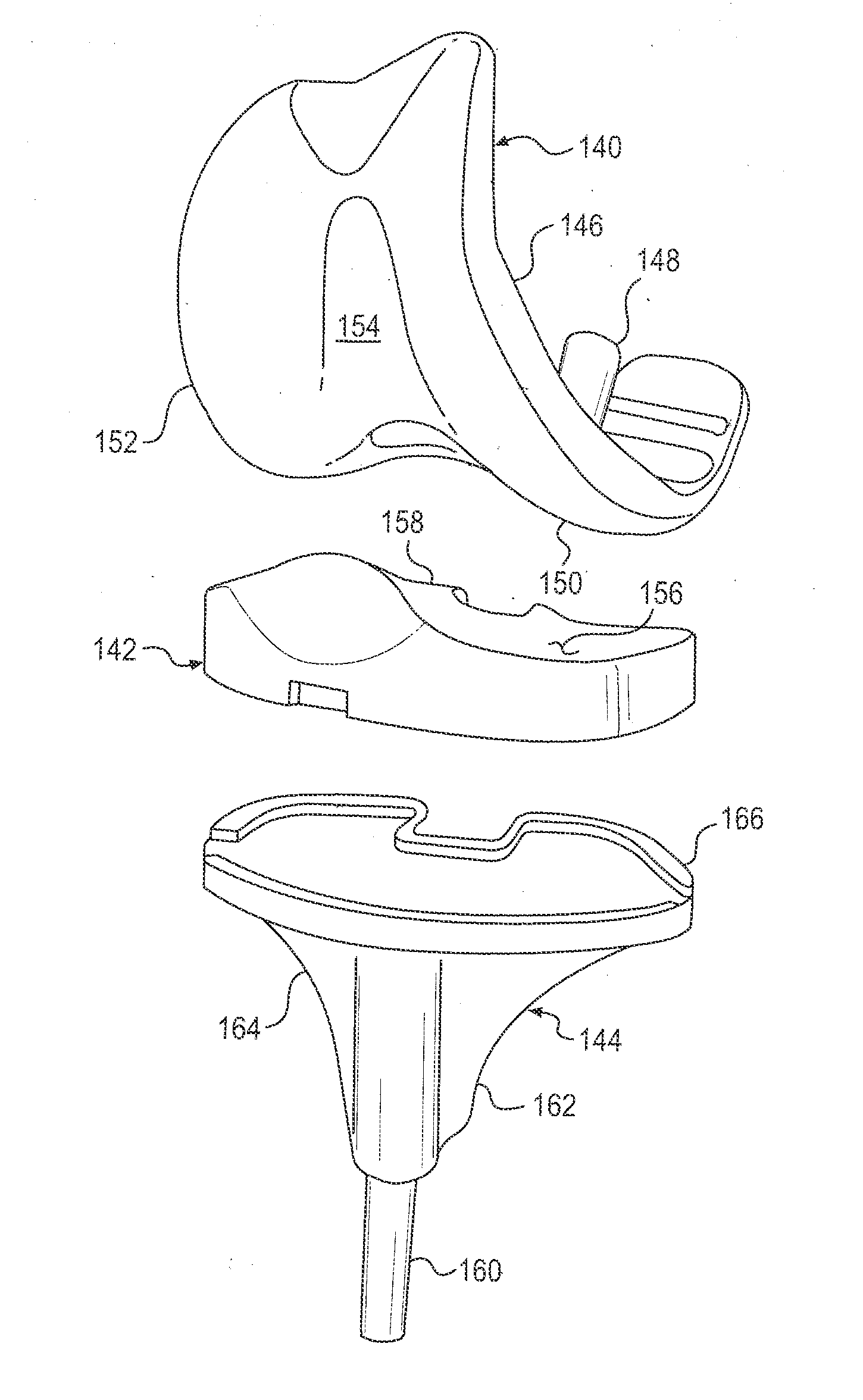
Dual-radius glenoid prosthetic component for total shoulder arthroplasty
InactiveUS6875234B2Reduce loadPowerfulJoint implantsShoulder jointsArticular surfacesTotal hip arthroplasty
A dual-radius glenoid component of a shoulder joint prosthesis for use in total shoulder arthroplasty has two radii of curvature. At substantially the center of the articulating surface a first non-conforming radius of curvature is provided, while a second conforming radius of curvature, smaller than that of the first radius of curvature and more closely conforming to the curvature of the humeral component, is disposed about the periphery of the articulating surface. The central non-conforming radius of curvature provides reduced constraint of the humeral component. In contrast, the conforming peripheral radius of curvature provides maximum constraint of the humeral component. When the humeral component is substantially centered on the articulating surface reduced constraint is placed on the prosthesis and less load is transferred to the bone-implant interface. As the humeral component translates towards the periphery, constraint on the prosthesis increases to prevent dislocation.
Owner:NEW YORK SOC FOR THE RUPTURED & CRIPPLED MAINTAINING THE HOSPITAL FOR SPECIAL SURGERY
Instruments for minimally invasive surgery total knee arthroplasty
ActiveUS20060241634A1Improve easeImprove accuracyDiagnosticsJoint implantsLess invasive surgeryIntramedullary rod
An anti-backout stylus comprising a stylus and a locking stylus holder. The locking stylus holder engages the stylus at a series of discrete positions during insertion of the stylus into the holder. The locking stylus holder prevents inadvertent backing out of the stylus by preventing the stylus from being withdrawn to a previous one of the discrete positions. The locking stylus holder can preferably be selectively disengaged from the stylus to allow for selective withdrawal of the stylus. Each engagement of one of the discrete positions by the locking stylus holder preferably indicates a femoral size. The discrete positions are preferably defmed by detents formed on the stylus and a stop member on the locking stylus holder. The locking stylus holder can be provided on an anterior rough cut guide, with the anterior rough cut guide preferably mountable on an intramedullary rod.
Owner:MICROPORT ORTHOPEDICS HLDG INC
Methods and devices for patient-specific acetabular component alignment in total hip arthroplasty
InactiveUS20120172884A1Comparably inexpensiveImprove accuracyJoint implantsAcetabular cupsAcetabular componentMedicine
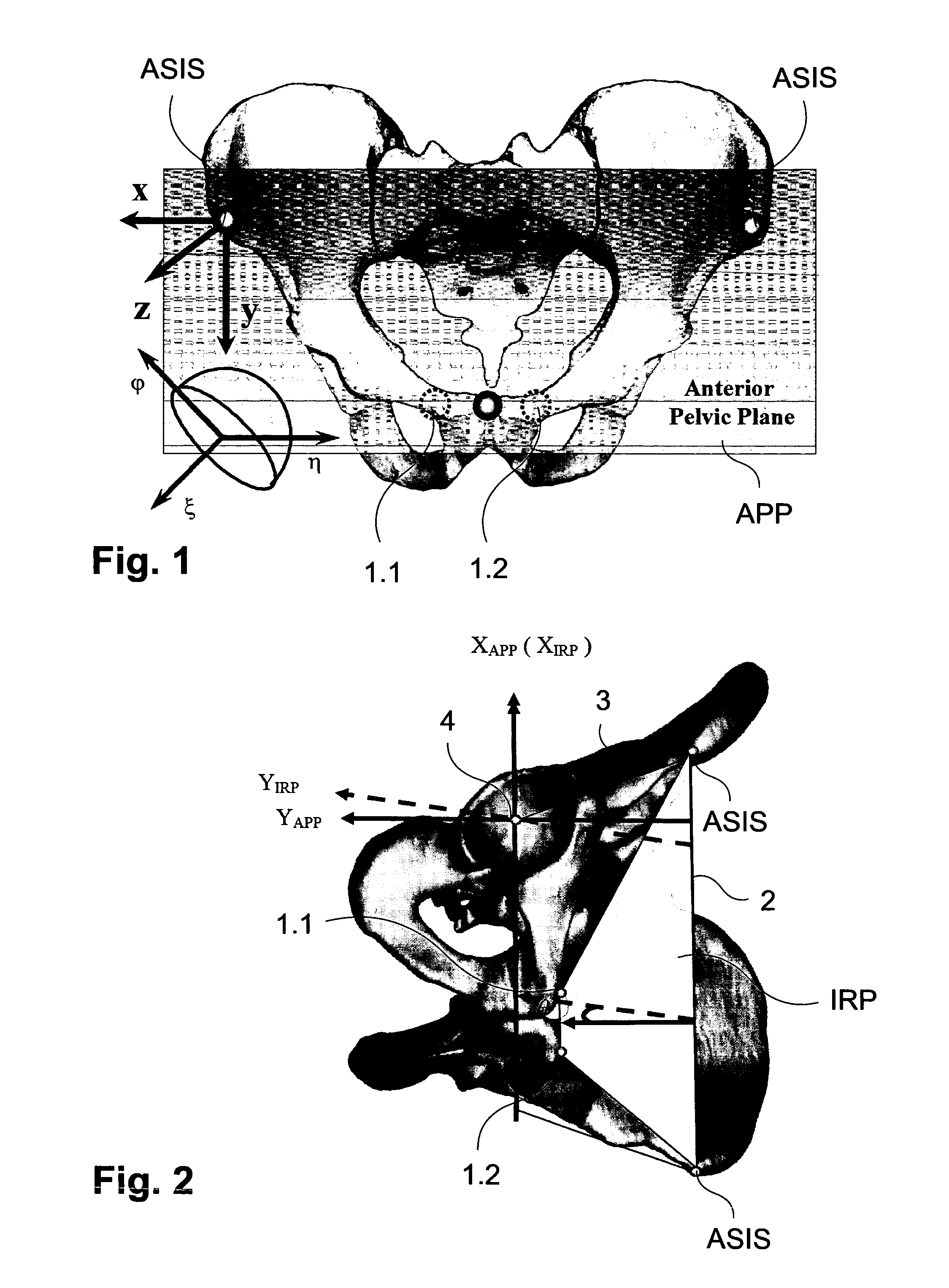
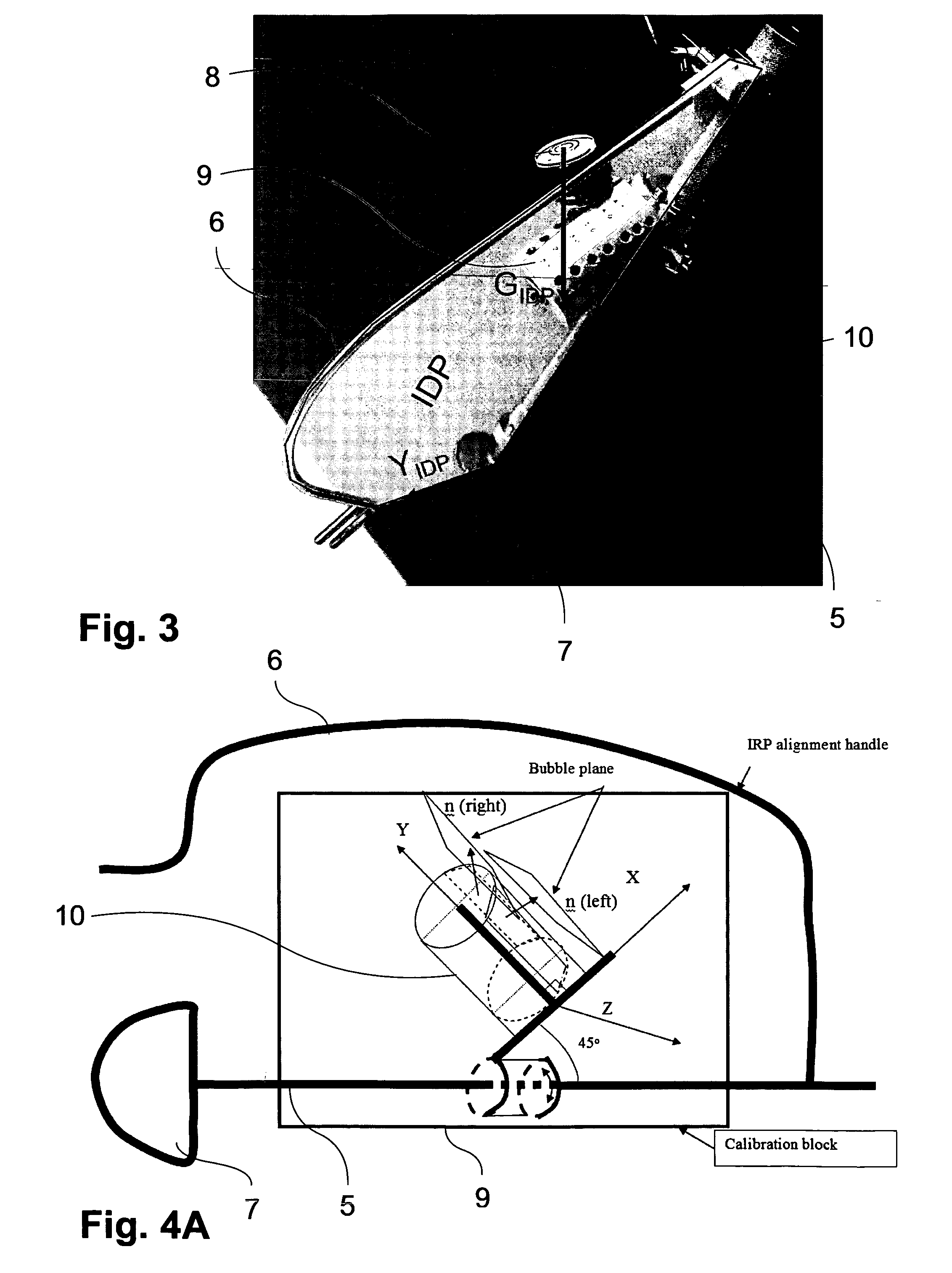
An acetabular component alignment device for total hip arthroplasty comprises a calibration component (9) allowing for aligning a main instrument axis (5) of the acetabular component depending on a set of two patient specific calibration parameters relating to rotational offsets of the acetabular component, whereas the device is constructed in such a way that calibration parameters may be chosen such that a second parameter of the set of calibration parameters is adjustable independently from a first parameter of the set of calibration parameters by rotating the acetabular component around the main instrument axis (5) of the acetabular component. A method for obtaining patient specific calibration parameters for alignment of an acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty, comprises the steps of determining patient specific morphology information relating to a geometry of the patient's pelvis; and processing the patient specific morphology information for obtaining a set of two patient specific calibration parameters relating to rotational offsets of the acetabular component. The calibration parameters are chosen such that a second parameter of the set of calibration parameters may be adjusted independently from a first parameter of the set of calibration parameters by rotating the acetabular component around a main instrument axis of the acetabular component.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BERN
Method for improved rotational alignment in joint arthroplasty
InactiveUS20080249394A1Improve accuracySurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringTibiaJoint arthroplasty
A method for improved rotational alignment of the bones in joint surgery is described. The method involves the tracking of the relative motion of a third bone in with respect to the movement of the first and second bone. In one aspect of the invention, the motion of the patella is used to derive the axis of rotation of the femoral and tibial components in total knee arthroplasty, either alone or in combination with other techniques.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
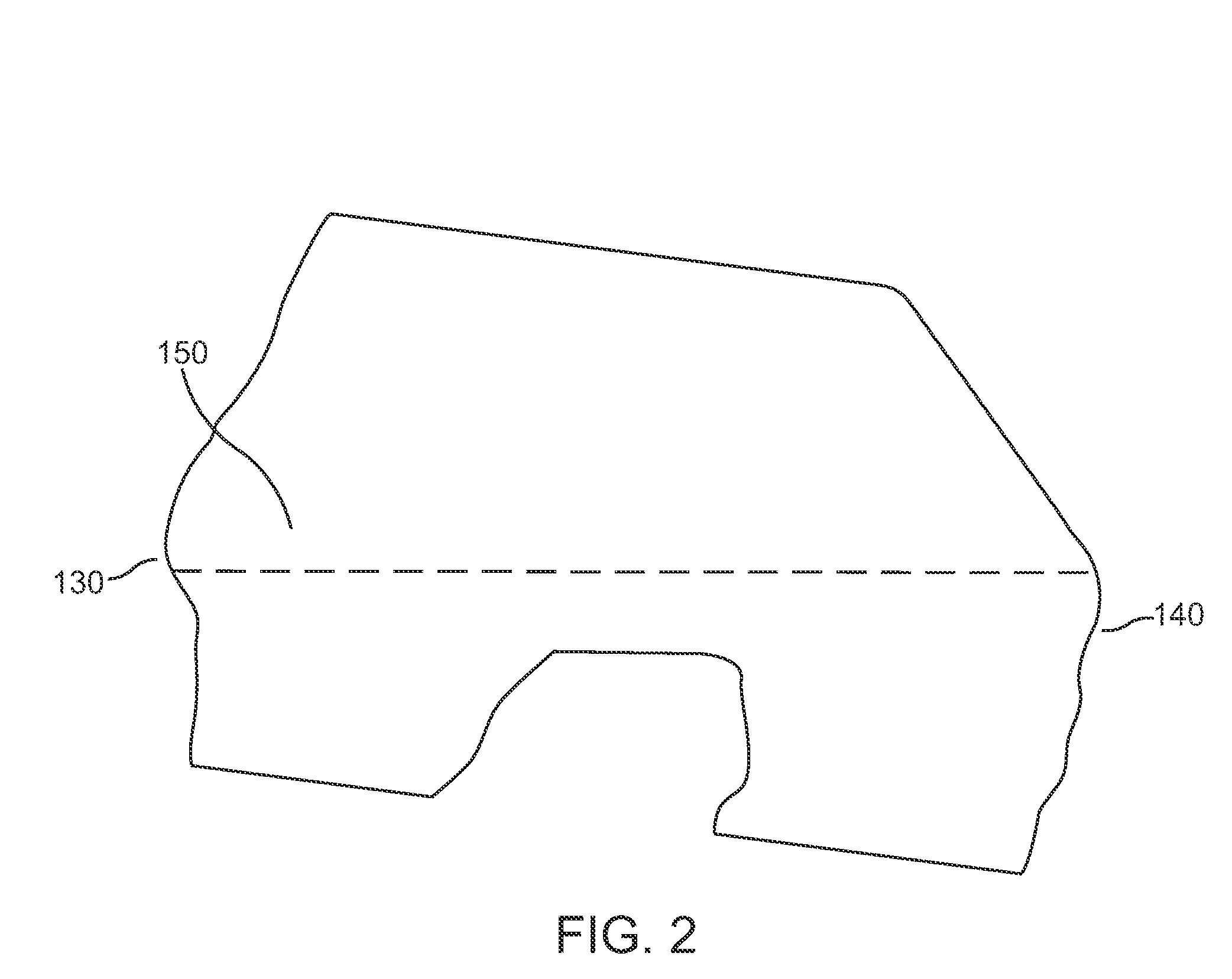
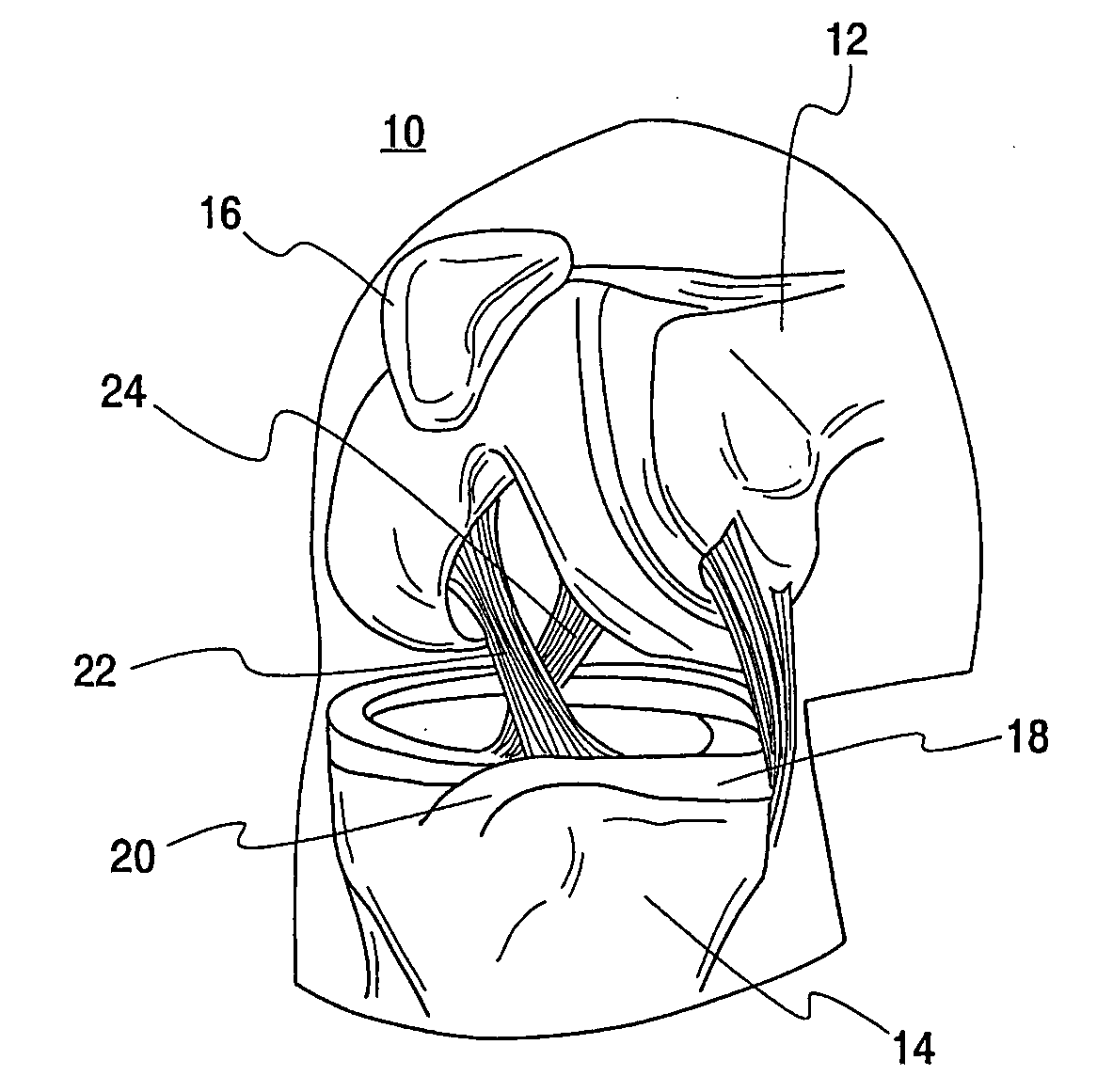
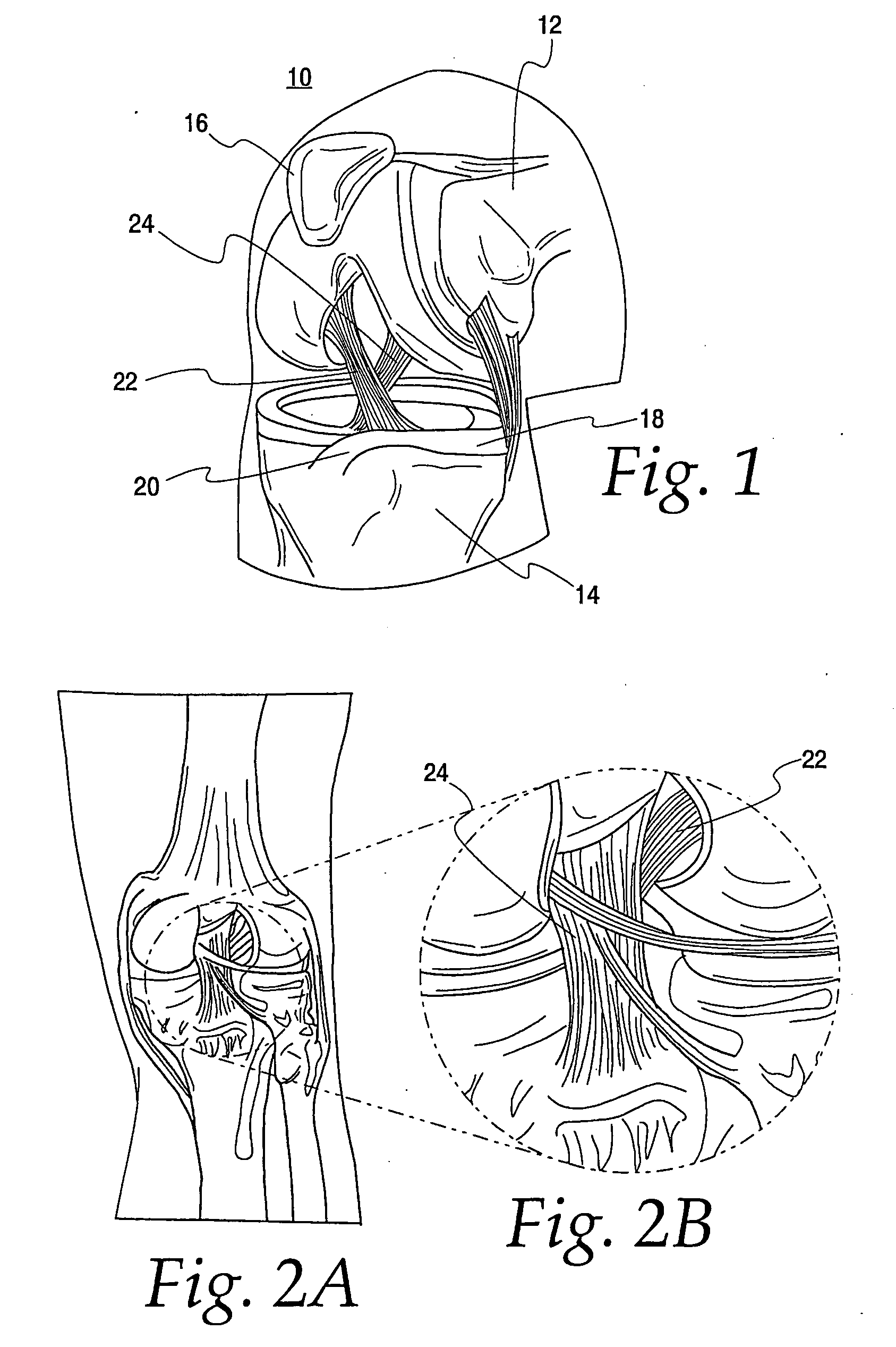
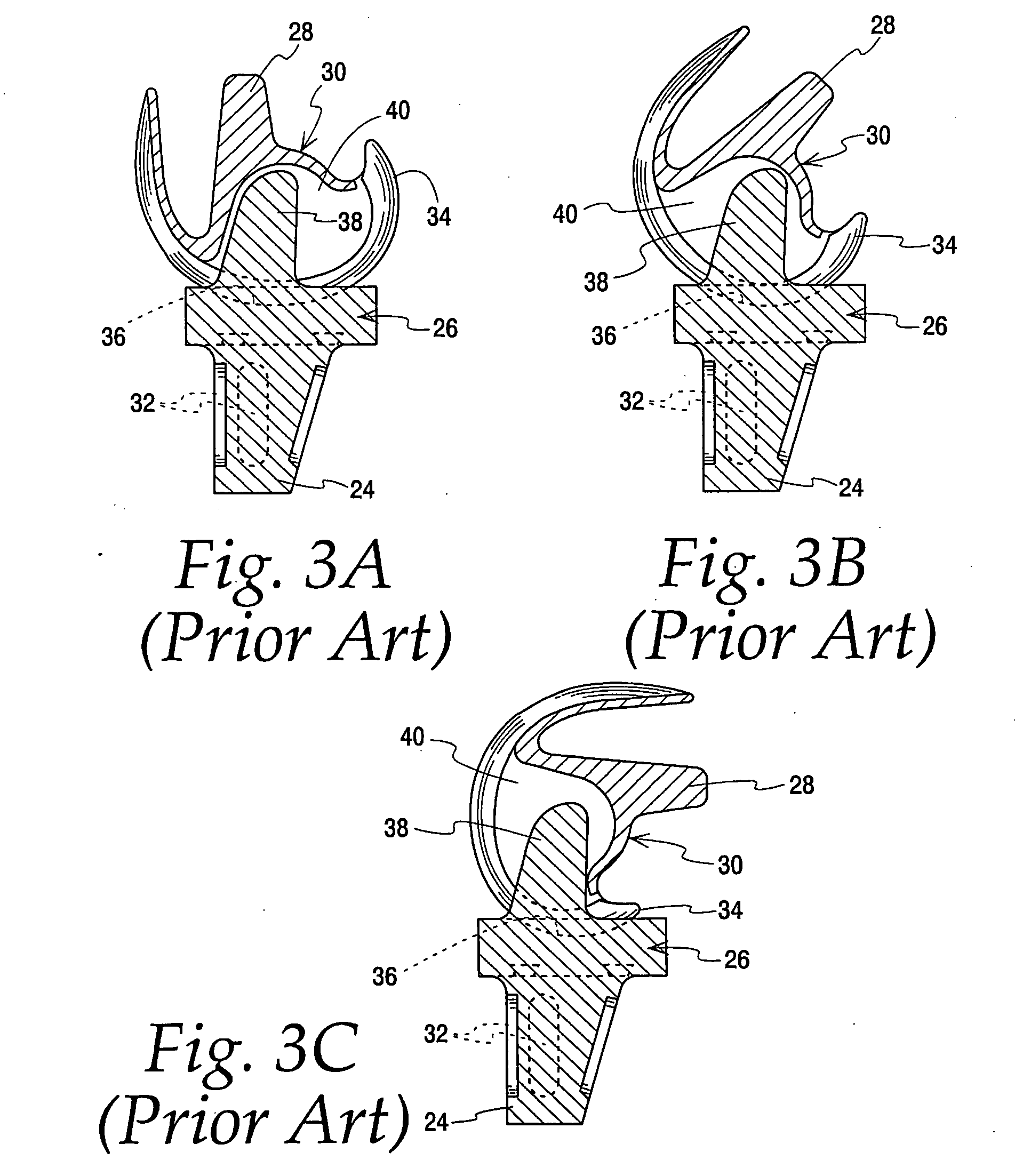
Pcl retaining acl substituting tka apparatus and method
A new class of total knee replacement includes a posterior cruciate ligament retaining anterior cruciate ligament substituting apparatus and method. Particular design considerations include: 1) a specific extension surface separate from the flexion surface, 2) rotational control in full extension to create the so-called screw-home mechanism, 3) translation restraints that will substitute for ACL function including a CAM-post or other abutment mechanism while allowing normal PCL function which should improve natural proprioception, 4) a modified femoral component with separate radii of curvature for the flexion and extension arcs of at least one condyle, and 5) a tibial component with slope built into the posterior aspect of its bone contacting surface on both sides of the PCL.
Owner:MASINI MICHAEL A
Methods and apparatus for knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS20080154270A1Appropriate balanceQuick and safe and accurateJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTibiaKnee Joint
Methods and apparatus for knee arthroplasty, including implants, positioning and alignment guides, cutting guides, cutting tools and techniques for the femur and / or tibia.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Apparatuses for femoral and tibial resection
Systems for use in total knee arthroplasty include a cutting guide having only a single slot. The single slot is configured to be positioned adjacent an anterior side of the medial compartment of the knee joint with no portion positioned adjacent an anterior side of the lateral compartment of the knee joint. The single slot is adapted to guide an oscillating saw blade across the knee bone from the medial compartment to resect at least a portion of the lateral compartment. The system also includes a total knee arthroplasty implant adapted to be implanted on the resected surface.
Owner:PUGET BIOVENTURES
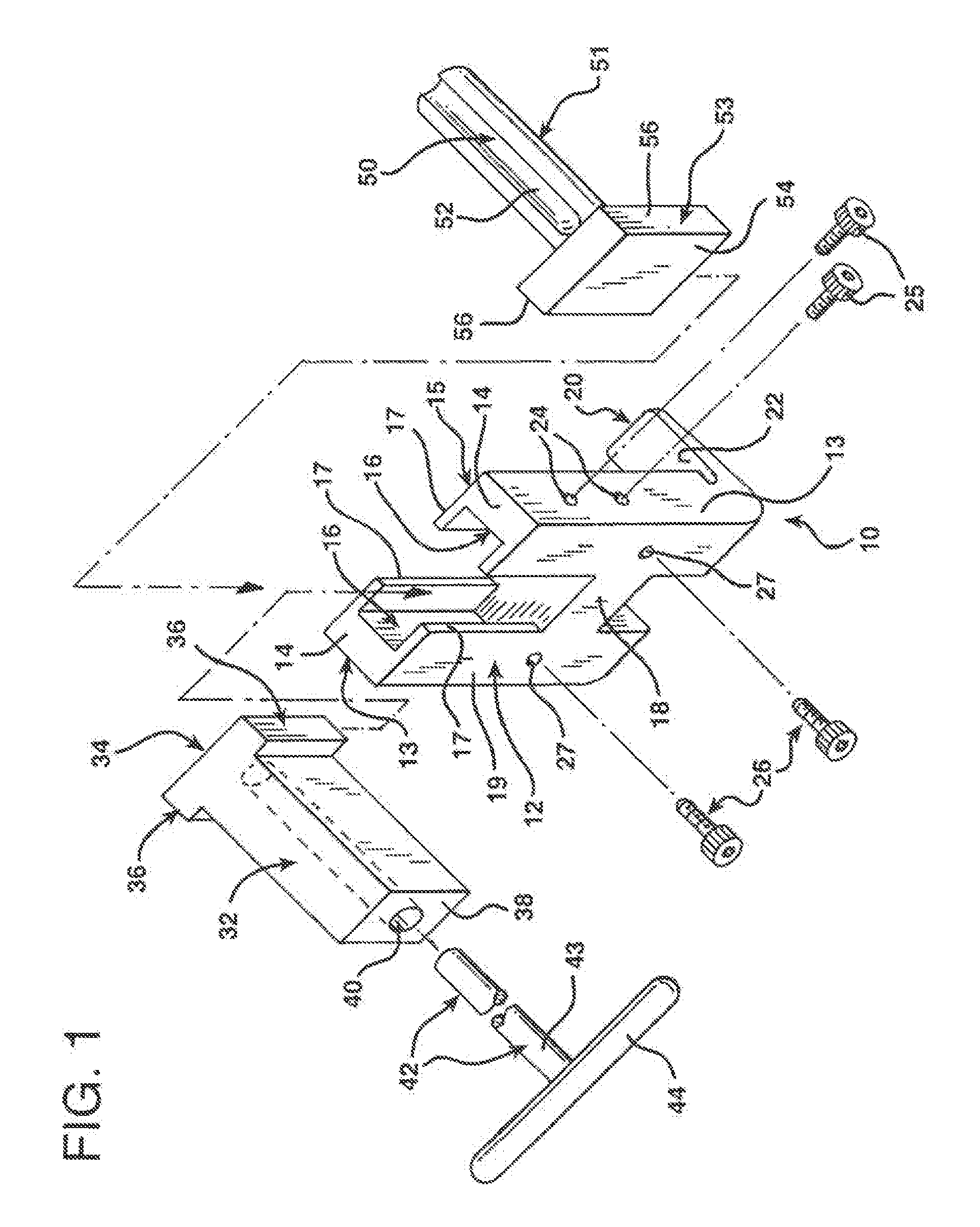
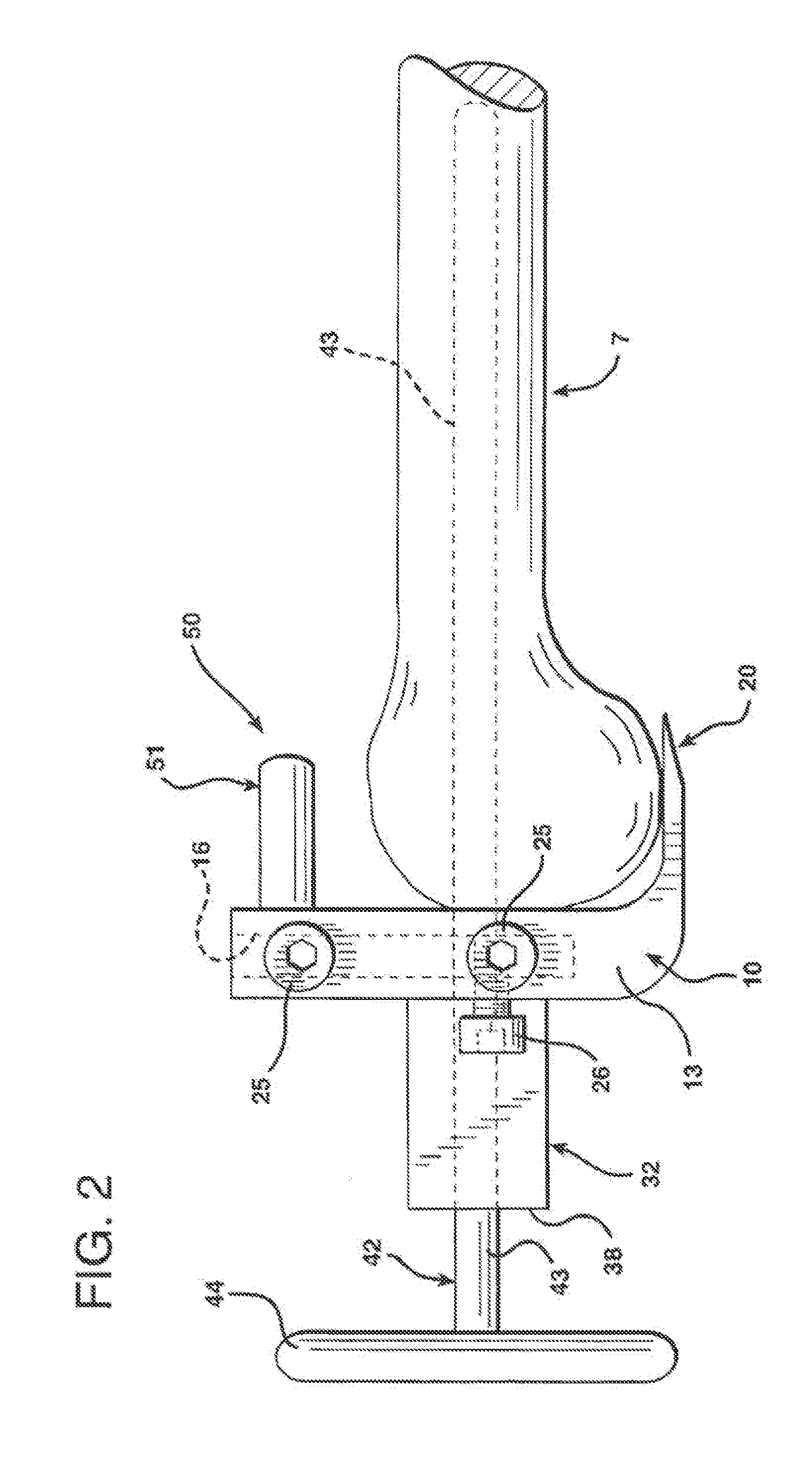
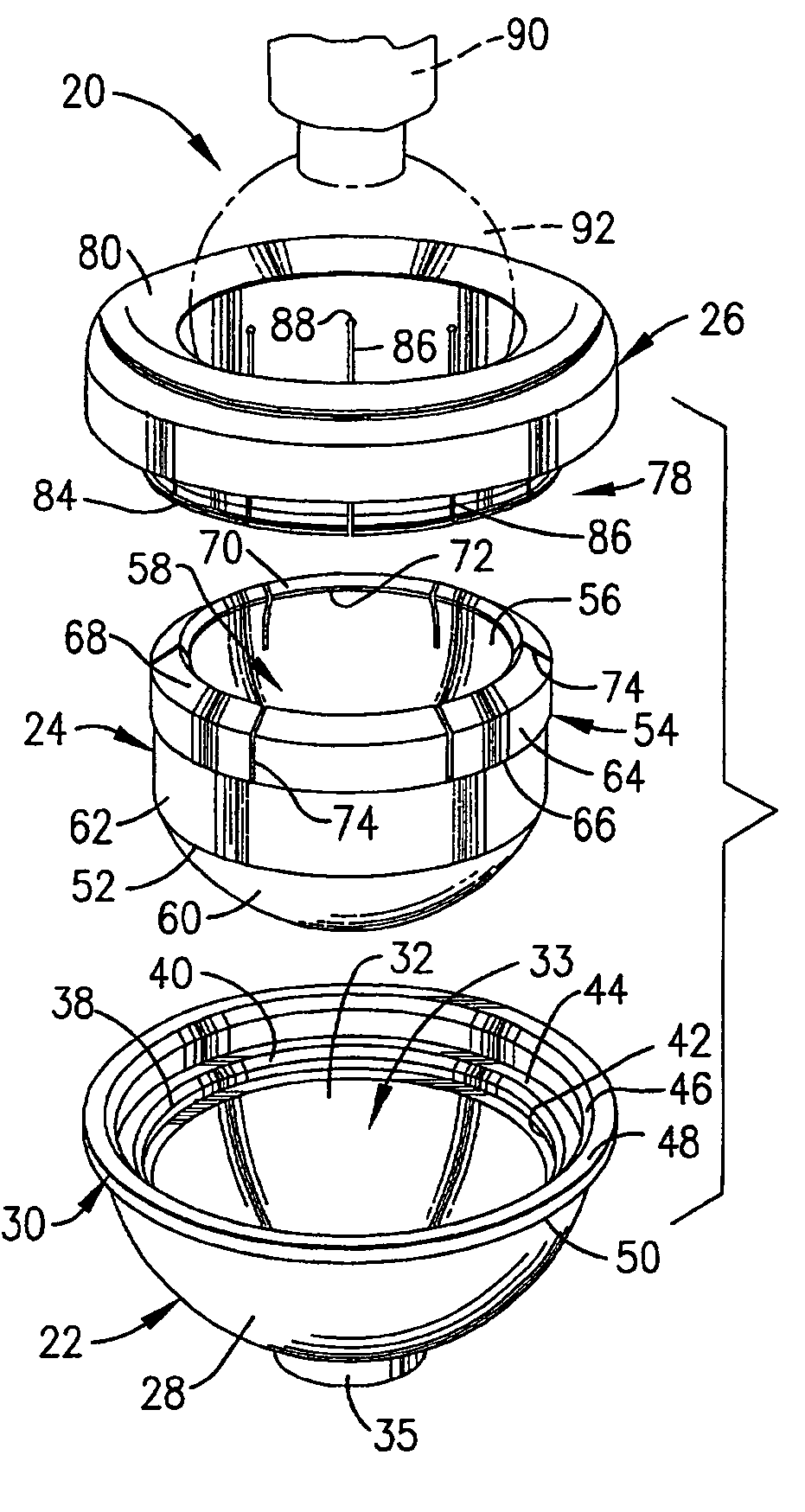
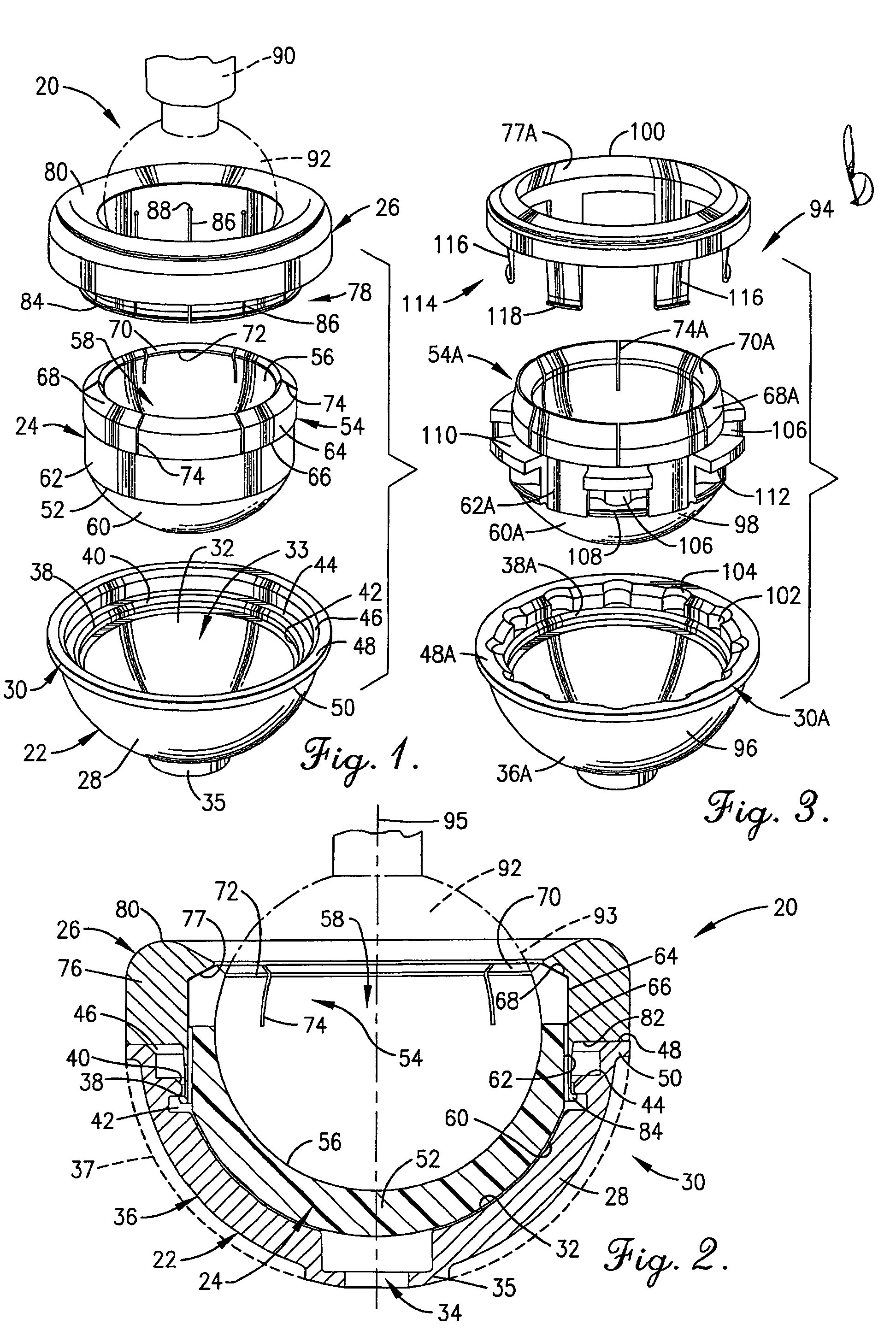
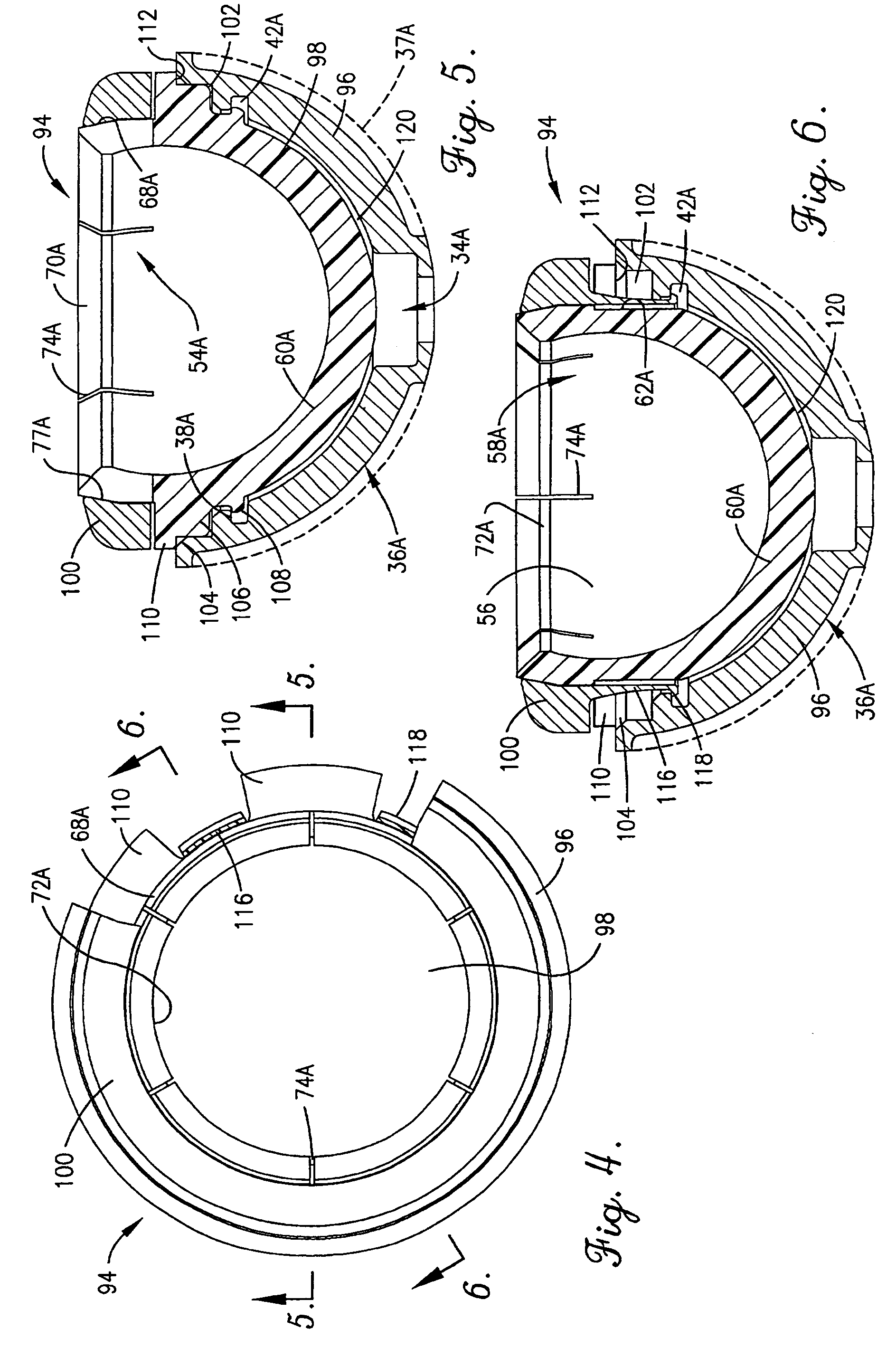
Constrained acetabular insert for total hip arthroplasty
A hip prosthesis (20) having a shell (22), liner (24), and retainer ring (26) is utilized for hip arthroplasty. The liner (24) fits inside the shell (22), which is attached to a patient's pelvis, and the retainer ring (26) engages a terminal liner margin (54) to inhibit expansion of and decrease the size of a restricted liner opening (72) defined by the liner margin (54). By inhibiting expansion of the liner opening (72), the ball (92) of a patient's femur (90) is securely held in the liner (24). In one embodiment, the liner (98) is inhibited from rotation relative to the shell (96) by a plurality of protrusions (106) which mate with recesses (102) in the shell (96). In that embodiment, the liner (98) is provided with catch lips (108) to hold the liner (98) in the shell (96) and a positioning flange (110) which operates to form a relief gap (120) between the shell (96) and the liner (98). In another embodiment, the retainer ring comprises an attachment portion (128) and a retainer portion (130) with a threaded connection (132) between the attachment portion (128) and the retainer portion (130).
Owner:ORTHOPAEDIC RES INST
Modular radial component for a total wrist arthroplasty
A radial component of a total wrist arthroplasty prosthesis includes a platform having a stem configured to be implanted within the radius bone. The platform carries an insert that provides the radial articulating component for the wrist joint. The platform and insert include mating features that allow for ready engagement or disengagement of the insert to the platform when the platform is implanted to the radius bone.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Methods and apparatus for preparing a patient's femur for patellofemoral knee arthroplasty
Methods and apparatus provide for modifying a patient's femur to receive a patellofemoral prosthesis, including: a distal punch, an anterior punch and a trochlear punch which are used in well defined orientations to remove material from the femur to accommodate complex geometries of a patellofemoral prosthesis; and optionally a guide operating to engage a distal end of the femur, the guide including a distal slot, an anterior slot and a transverse slot, which ensure that the punches achieve the desired orientations.
Owner:ARTHREX
Cutting blocks for a surgical procedure and methods for using cutting blocks
Two cutting blocks are provided for preparing a femur for total knee arthroplasty. A first cutting block comprises a block body positionable on a resected distal end of the femur. A first slot is provided in the block body for guiding a saw blade when making an anterior femoral cut. A second slot is provided for guiding a saw blade when making an anterior chamfer cut. A third slot is provided for guiding a saw blade when making a posterior chamfer cut. The second cutting block comprises a block body positionable on the resected distal end of the femur after making the anterior femoral cut, the anterior chamfer cut, and the posterior chamfer cut. A slot is provided in the block body of the second cutting block for guiding a saw blade when making a posterior femoral cut.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
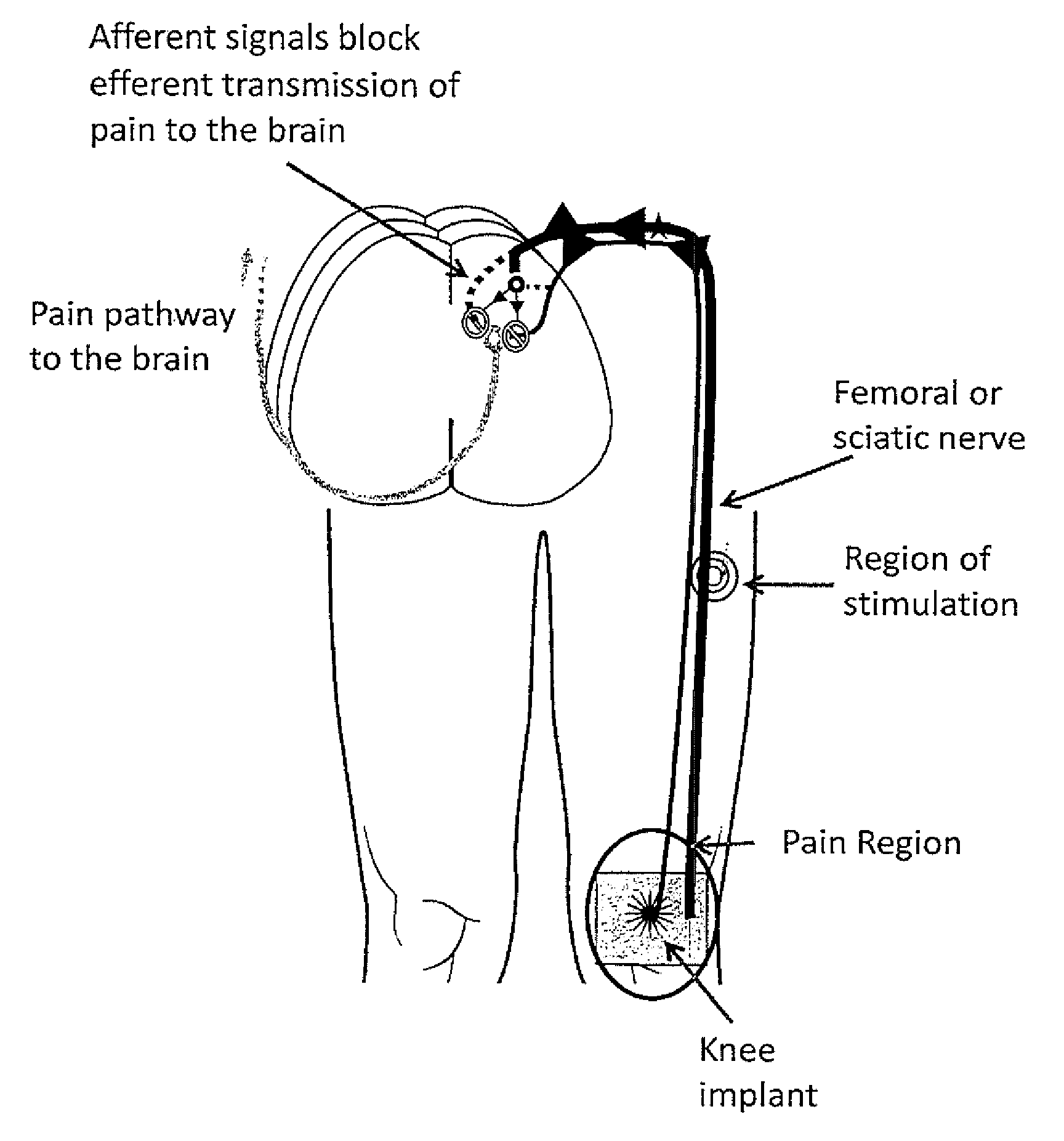
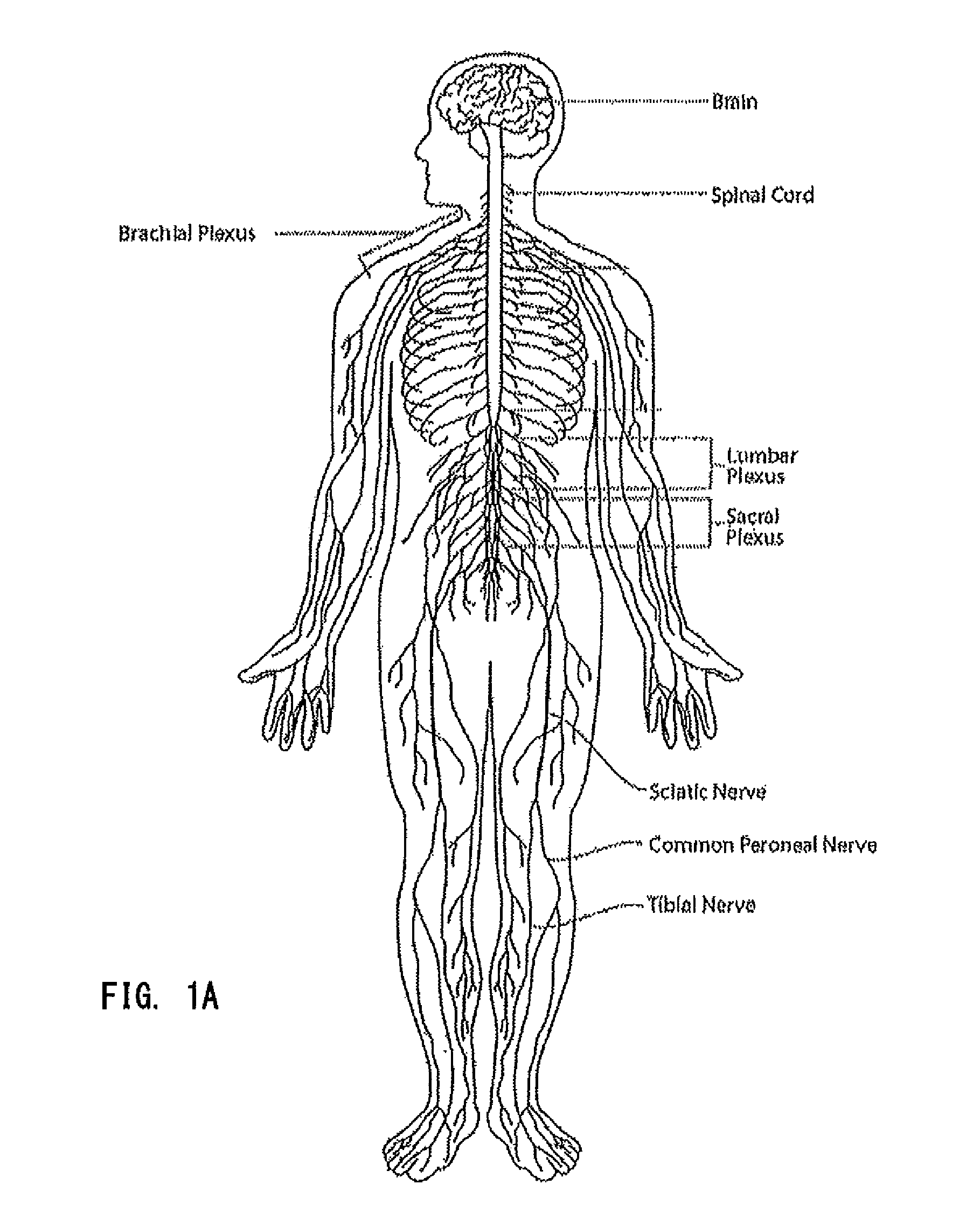
System and method for treatment of pain related to limb joint replacement surgery
It has been discovered that pain felt in a given region of the body can be treated by stimulating a peripheral nerve at a therapeutically effective distance from the region where pain is felt to generate a comfortable sensation (i.e., paresthesia) overlapping the regions of pain. A method has been developed to reduce pain in a painful region following limb joint replacement by stimulating a peripheral nerve innervating the painful region with an electrode inserted into tissue and spaced from the peripheral nerve. This method may be used to help alleviate postoperative pain in patients following total knee arthroplasty surgery or other limb joint replacement surgeries.
Owner:SPR THERAPEUTICS
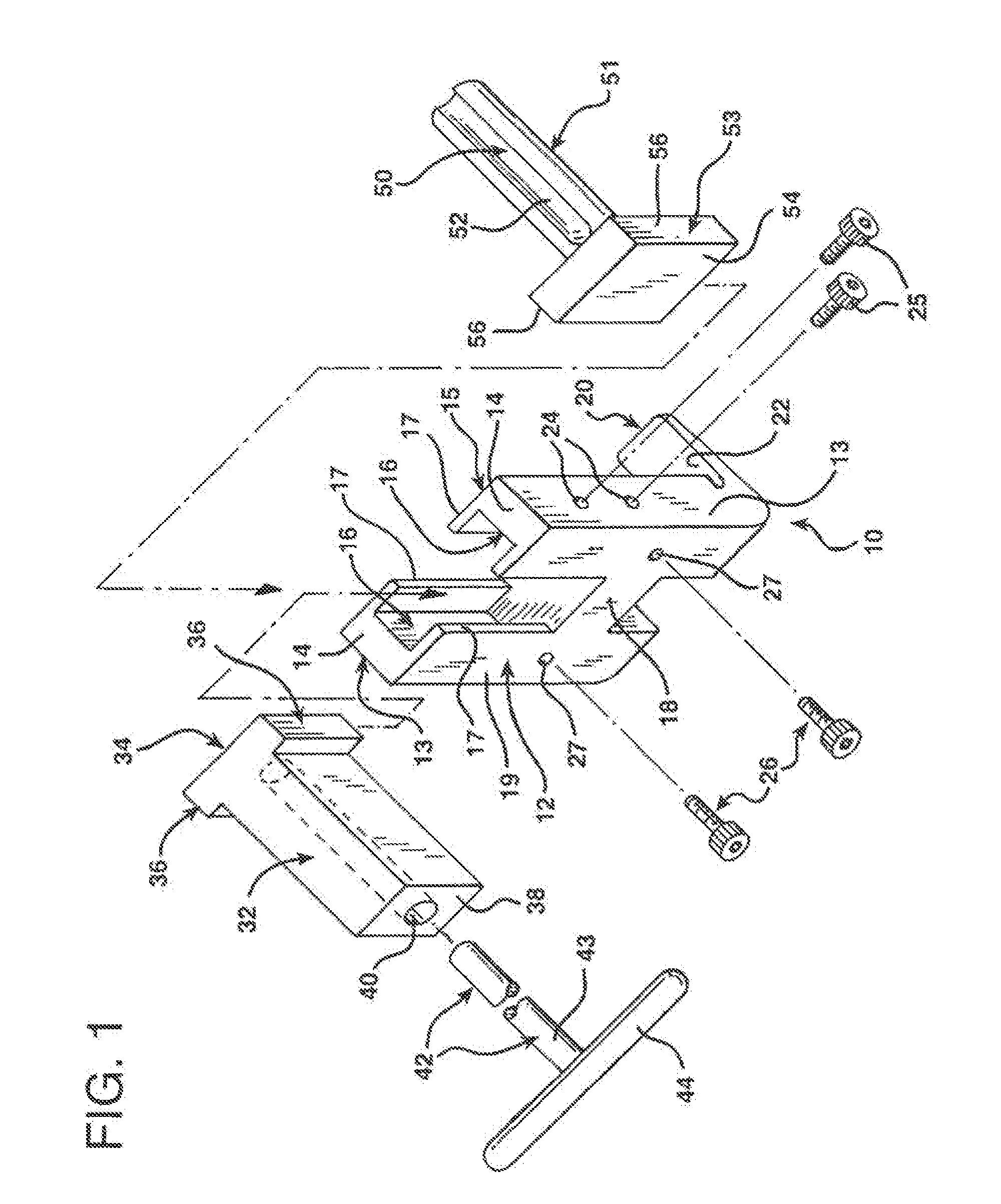
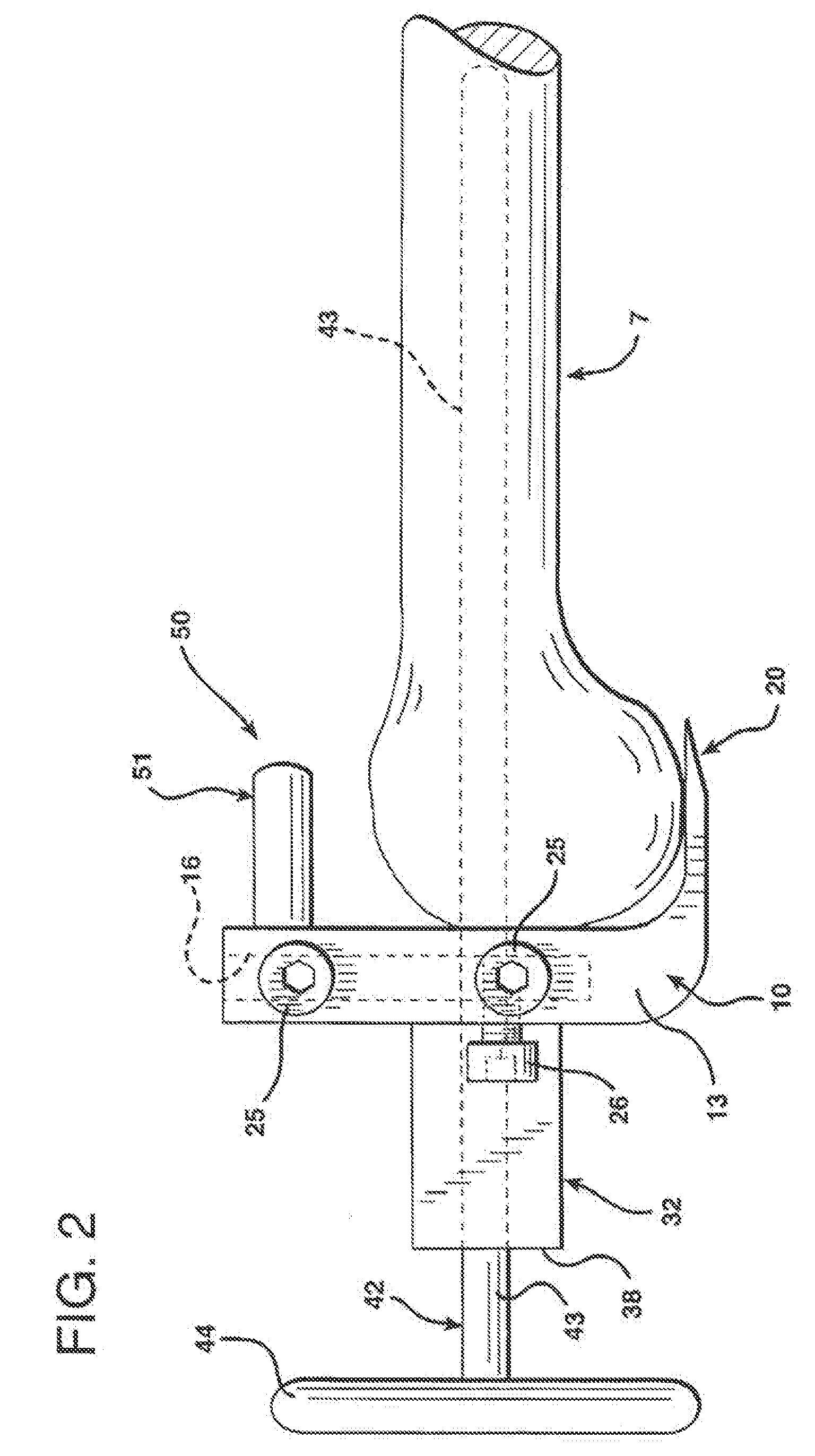
Guide assembly for guiding cuts to a femur and tibia during a knee arthroplasty
ActiveUS7927336B2Small and noninvasive approachPromote resultsInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsDistractionTibia
An assembly for guiding resection of a femur and tibia of a knee joint in preparation for installing a femoral and tibial knee components. For example, the assembly can include tibial and femoral IM rods to which are connected through a torque bolt that allows controlled adjustment of the distraction of the tibia and femur during cut positioning in a range of flexion angles. Also, the assembly is usable with relatively small, noninvasive approaches to the knee joint by way of relatively narrow, low profile components that attach to tibial and femoral IM rods. Further, the assembly includes several quick-release components to allow fast assembly and disassembly in a surgical setting. Each of these aspects, along with the ability of the assembly to accurately guide initial reference cuts to the tibia and femur, promotes an improved outcome for the patient.
Owner:RASMUSSEN INSTR LLC
Devices and methods for knee arthroplasty
The present invention provides, in certain embodiments, a device for positioning and orienting the femoral cutting block. The present invention also provides a device for setting rotation of sagittal resection for unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. The present invention further provides methods for setting the rotation of the tibial implant by kinematic measurements.
Owner:ORTHALIGN
Knee arthroplasty instrument
An instrument (10) and method are provided for total knee arthroplasty (TKA). The instrument separates a patient's tibia and femur, in both extension and flexion, to measure a gap and an angle therebetween. The instrument includes various modular accessories (16, 54, 70, 80, 90, 100) that provide flexibility of usage throughout the TKA procedure and that accommodate different surgical philosophies.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Precision Total Knee Arthroplasty
Owner:UNGER ANTHONY S
Conically-shaped glenoid implant with a prosthetic glenoid insert used in total shoulder arthroplasty and method
InactiveUS20070260321A1Promote ingrowthIncrease surface areaJoint implantsShoulder jointsTotal hip arthroplastyKeel
A conically-shaped glenoid implant (1) having a fastening means for the acceptance of a conventional prosthetic glenoid insert (7) and a hole (9) located thereon for the acceptance of a locking means. The fastening means are preferably notches (11) while the locking means is preferably reverse barbs (13). An optional screw (3) or keels (19) may be located on the exterior surface of the cone (2) for additional securement of the conically-shaped glenoid implant (1) in the glenoid (6) and to prevent rotation of the cone (27). By using the present invention, bone ingrowth is achieved because sheer forces are converted to compressive forces and surface area for ingrowth is significantly increased.
Owner:STCHUR ROBERT P
Two-piece cut block for minimally invasive surgical procedure
InactiveUS6962593B2Less initial traumaFast recovery timeJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTotal hip arthroplastyLess invasive surgery
A two-piece cut block for performing a minimally invasive partial or total knee arthroplasty. The present invention comprises a cut block that can be inserted into an incision in two parts then assembled in vivo. The two-piece design allows the relatively large surgical instrument to fit into a small, minimally invasive, surgical incision
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Tibial tray for total knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS7524334B2Improve usabilityProvide stabilitySurgeryJoint implantsTotal hip arthroplastyKeel
An improved one piece tibial tray uniquely characterized by its construction including an asymmetric keel extending from the bottom of the tibial tray base plate, whereby insertion of the tray during arthroplasty may be accomplished with a smaller than normal incision, enhancing the efficacy and safety of the surgical procedure. A fin on either or both sides of the asymmetric fin may be provided for enhanced stability of the tray.
Owner:HAIDUKEWYCH GEORGE J
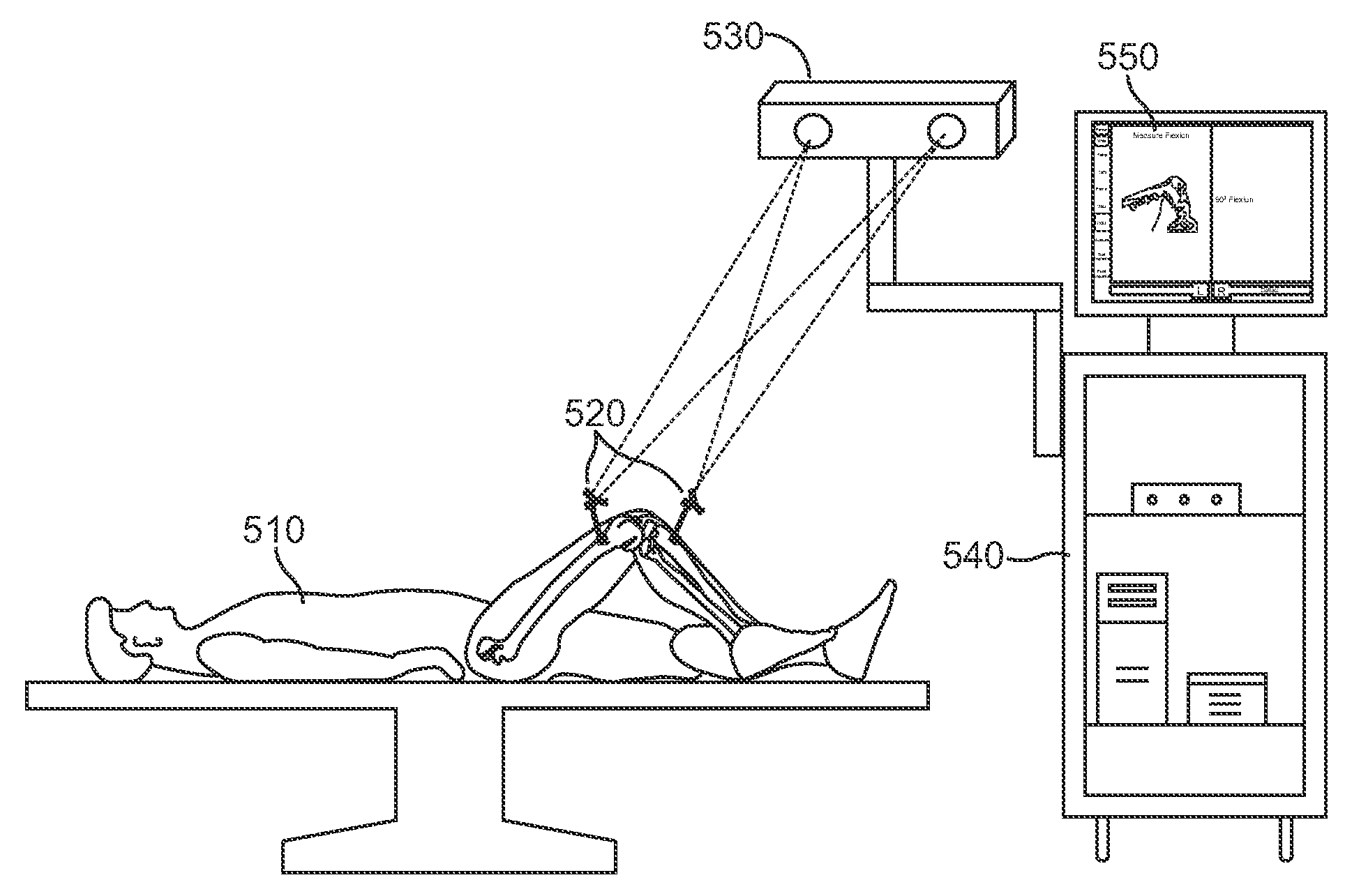
Systems and methods for providing alignment in total knee arthroplasty
ActiveUS20140276864A1Accurate and precise alignmentEfficiently and more accurately completingJoint implantsKnee jointsTotal hip arthroplastyMedicine
Systems and methods for providing alignment in total knee arthroplasty operations are provided herein. The systems and methods generally include a plurality of sensors coupled to a patient's bones or other surgical tools, the sensors detect their position and orientation in space and communicate this information to a processor. The processor can utilize the information to display data to a surgeon or other user regarding the position, angle, and alignment of a patient's bones, surgical tools, and the reconstructed knee joint.
Owner:ARTHROMEDA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com