Patents
Literature
1162results about "External condition output parameters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
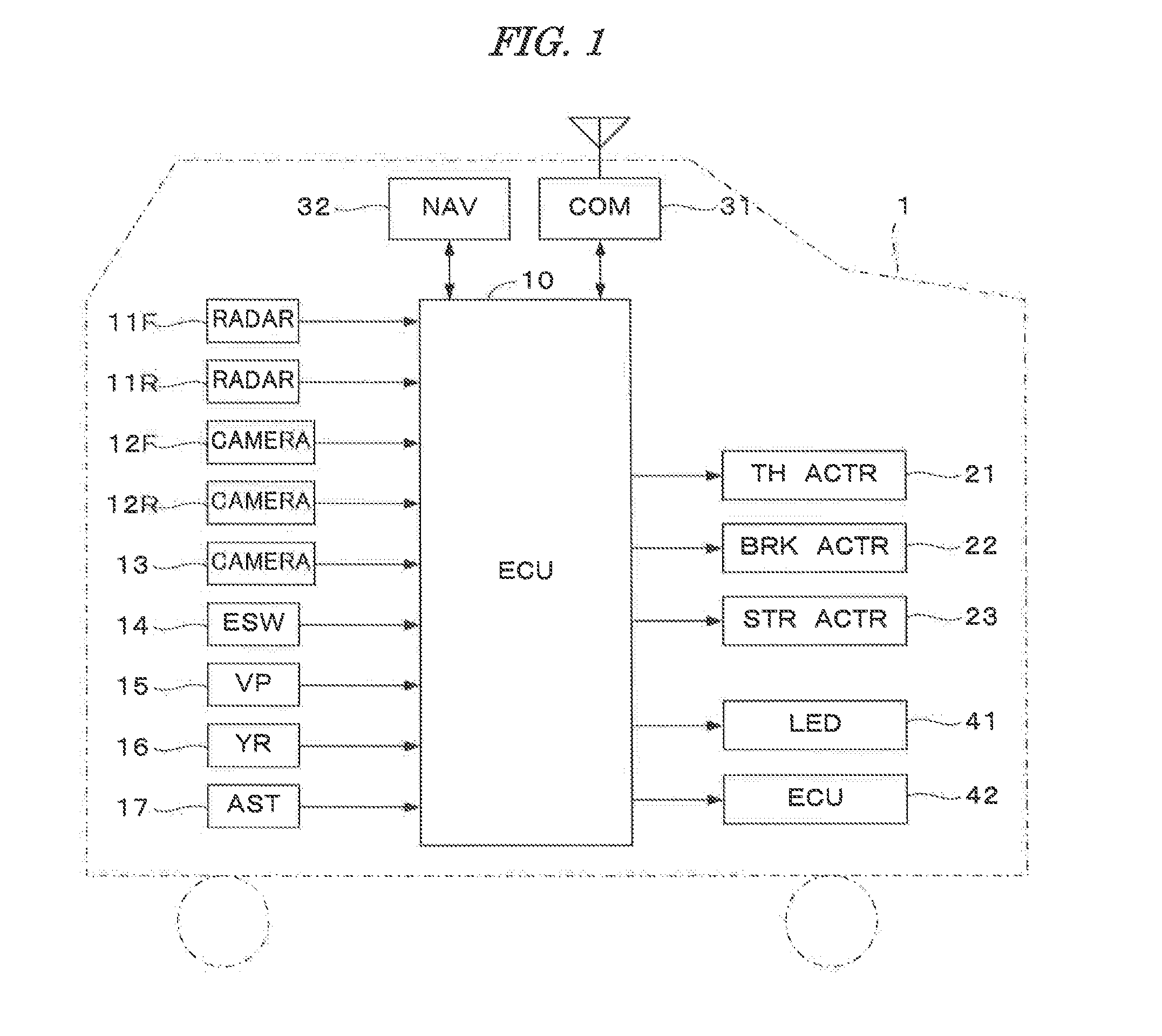
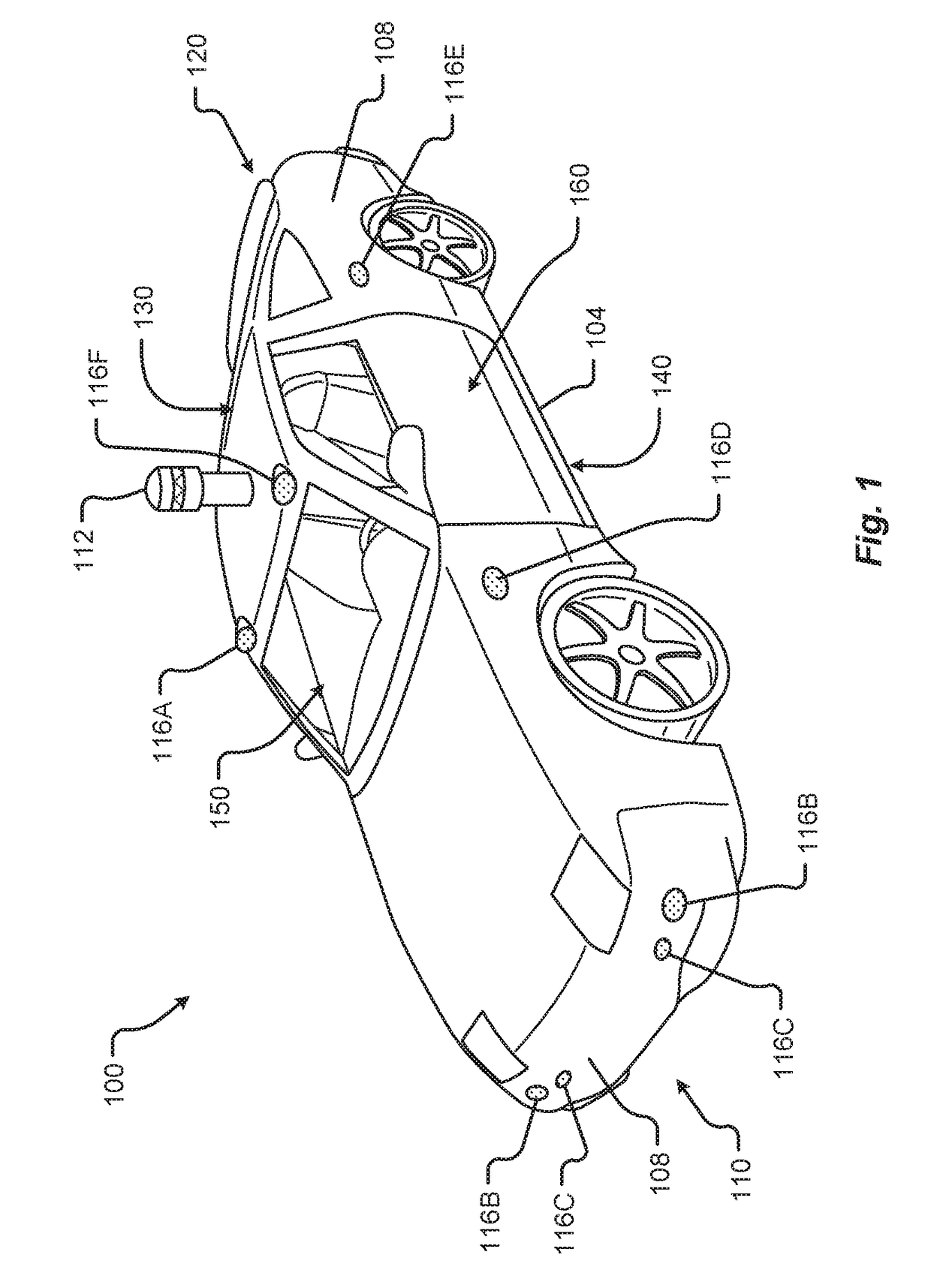
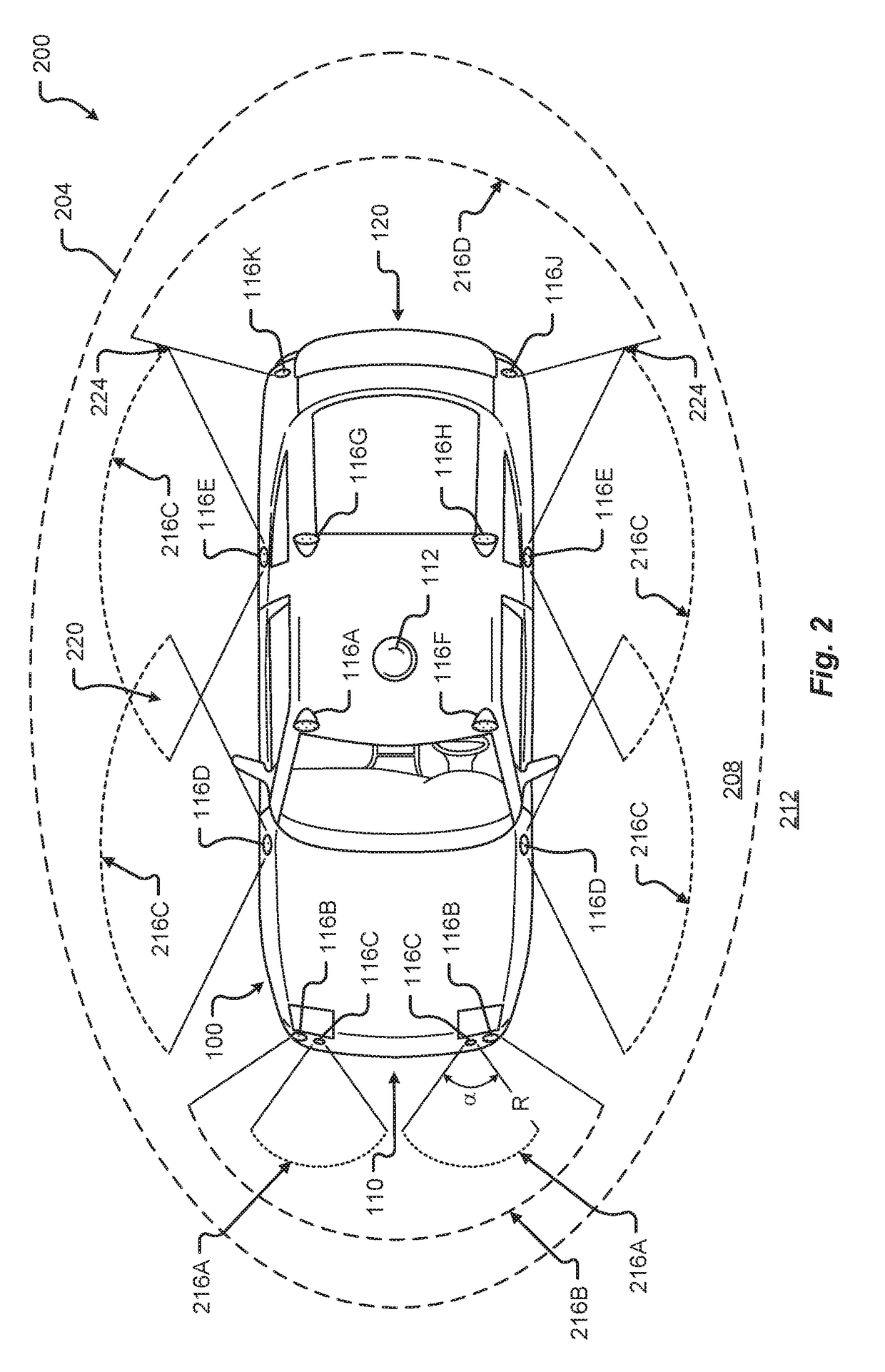
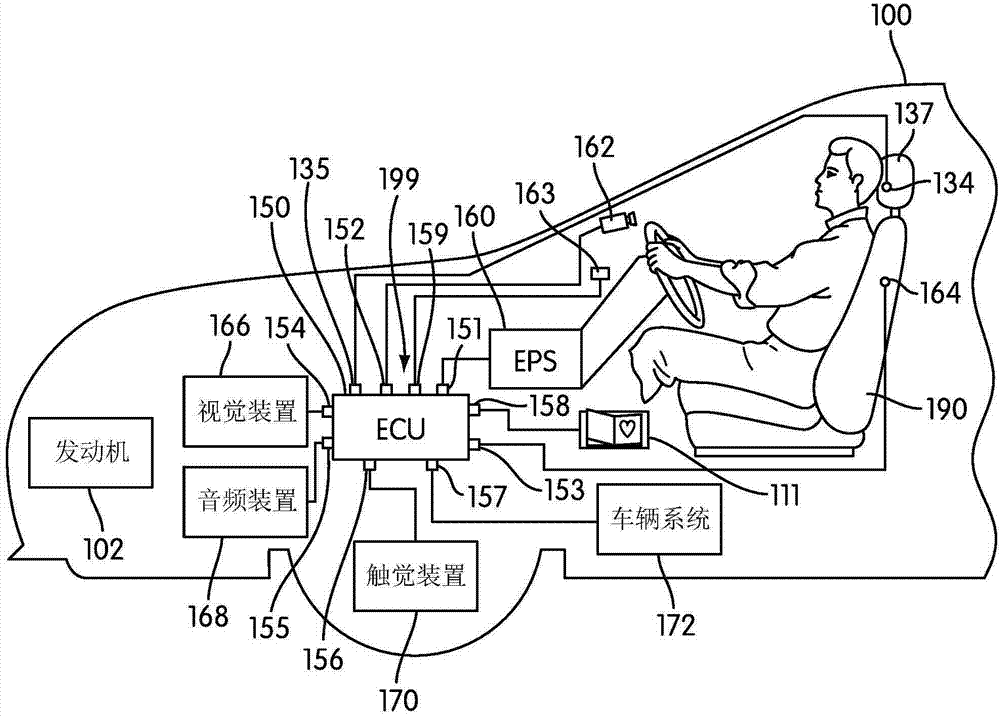
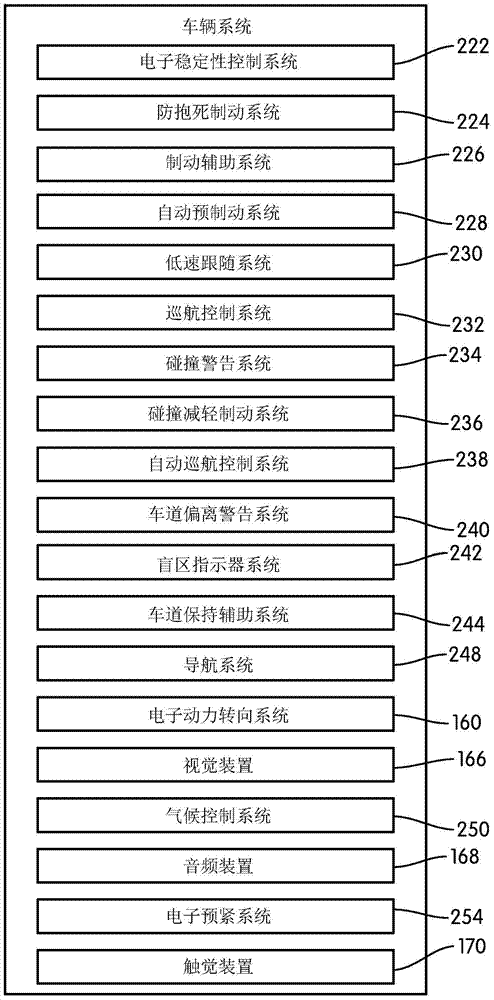
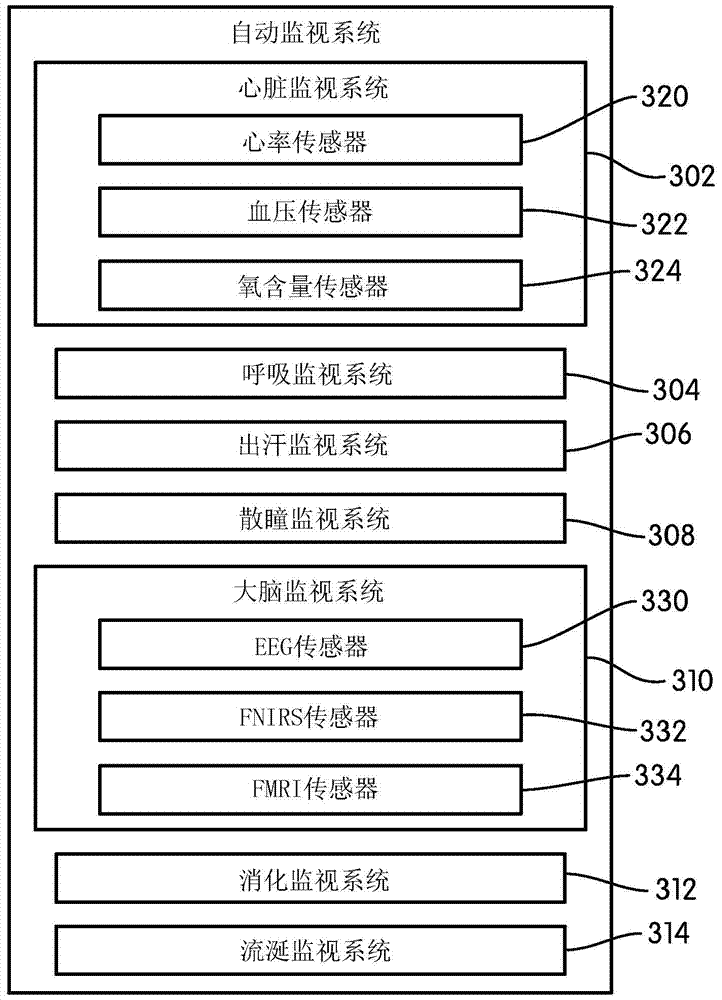
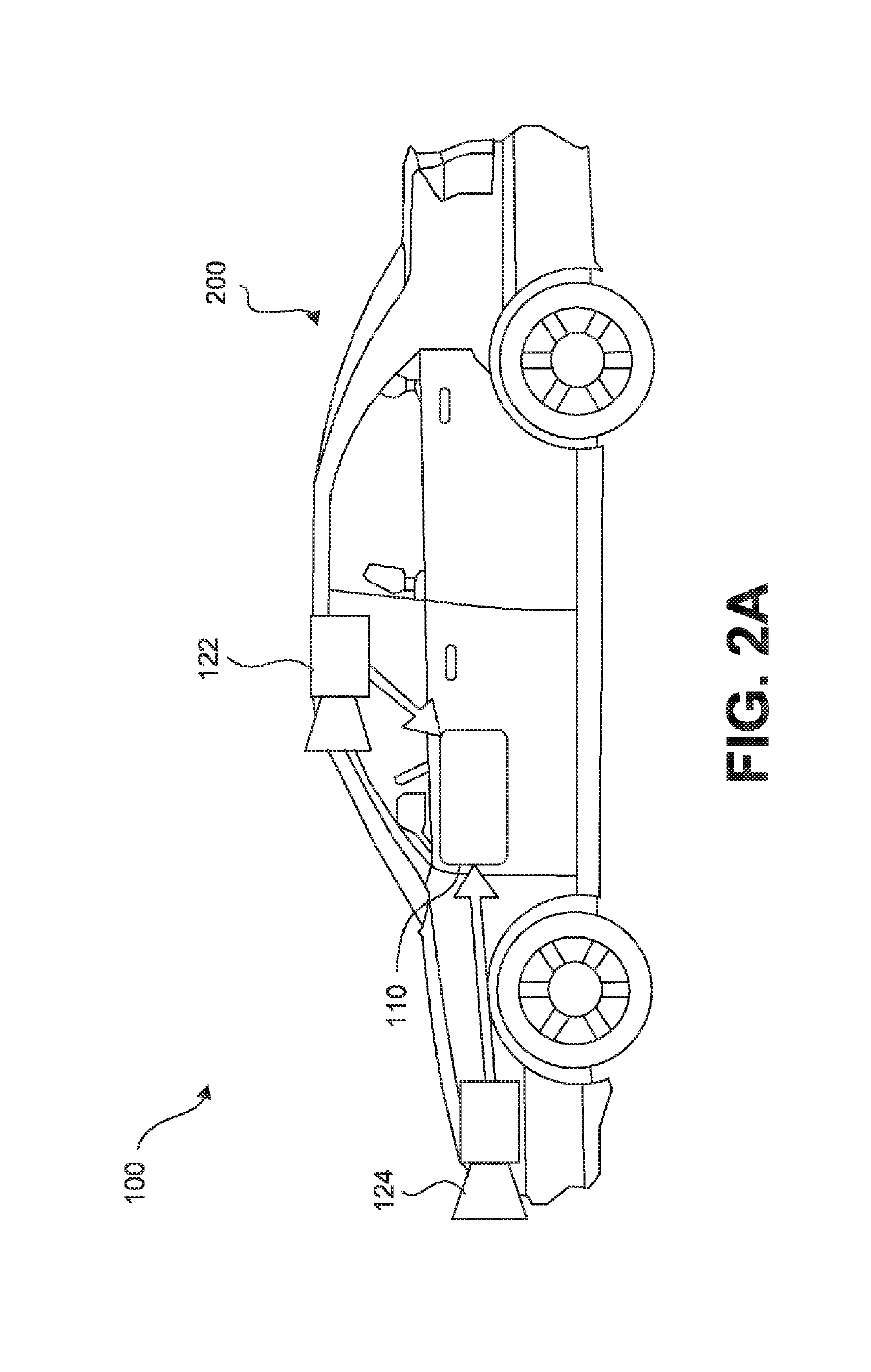
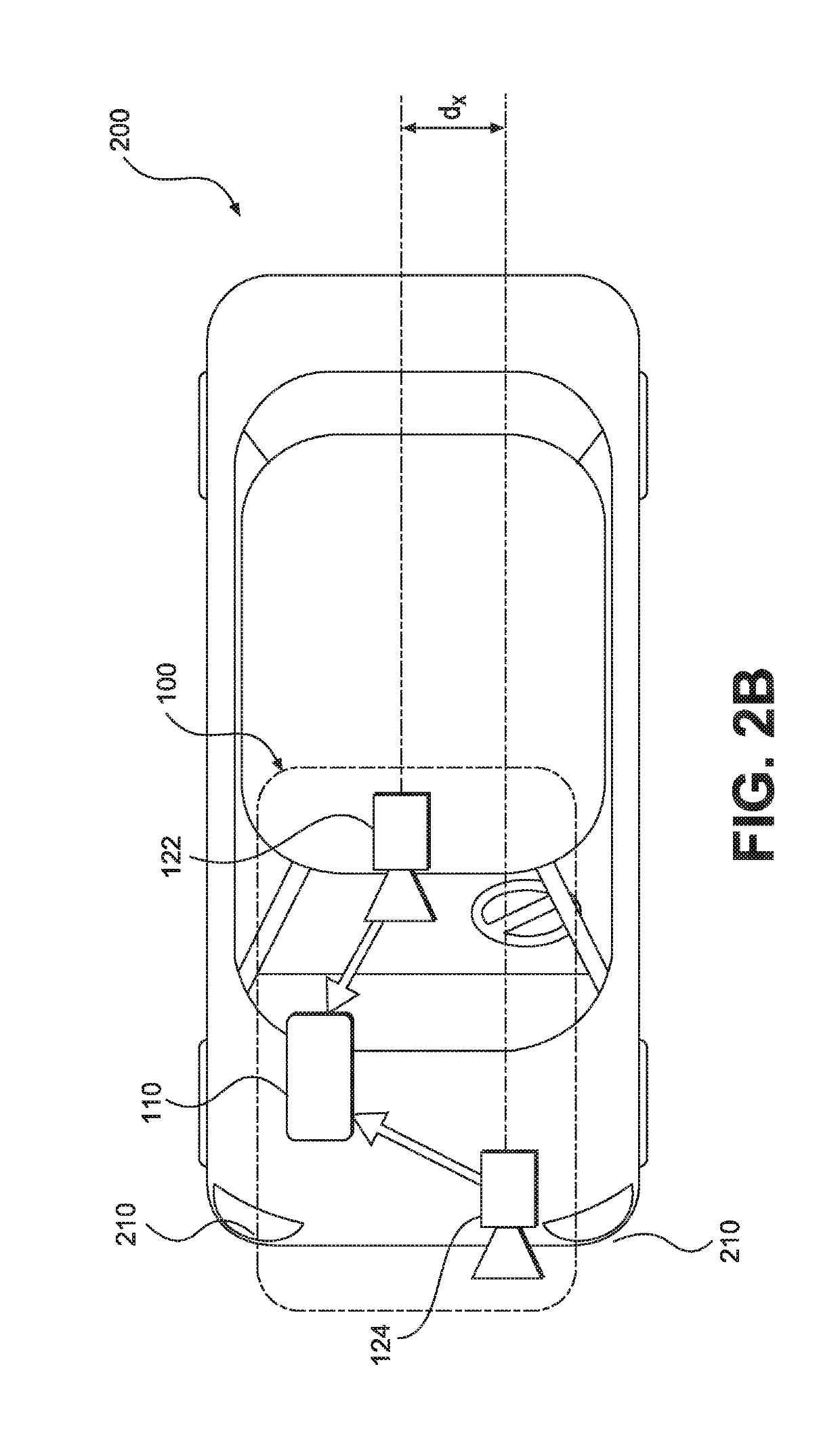
Autonomous vehicle with driver presence and physiological monitoring
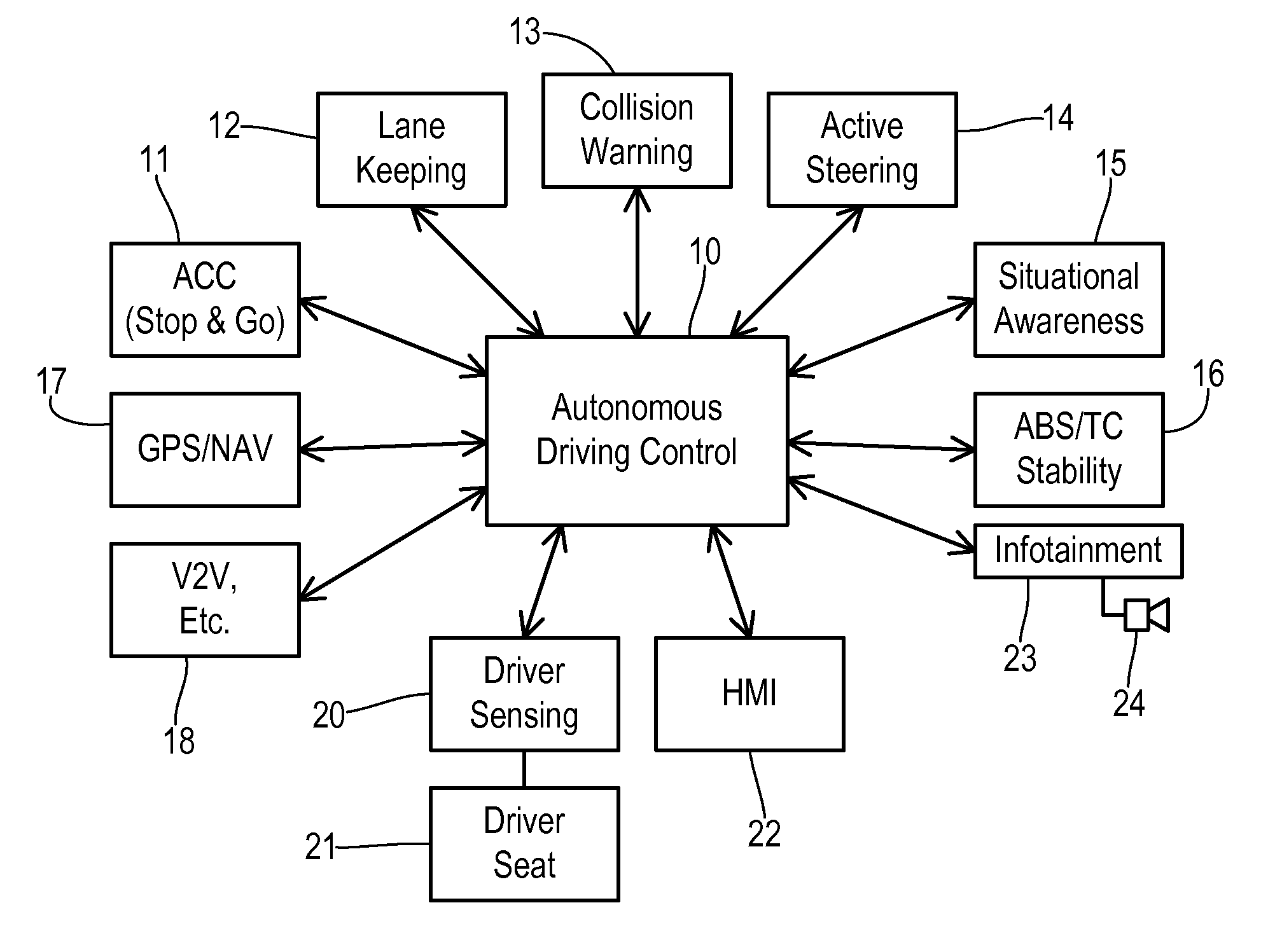
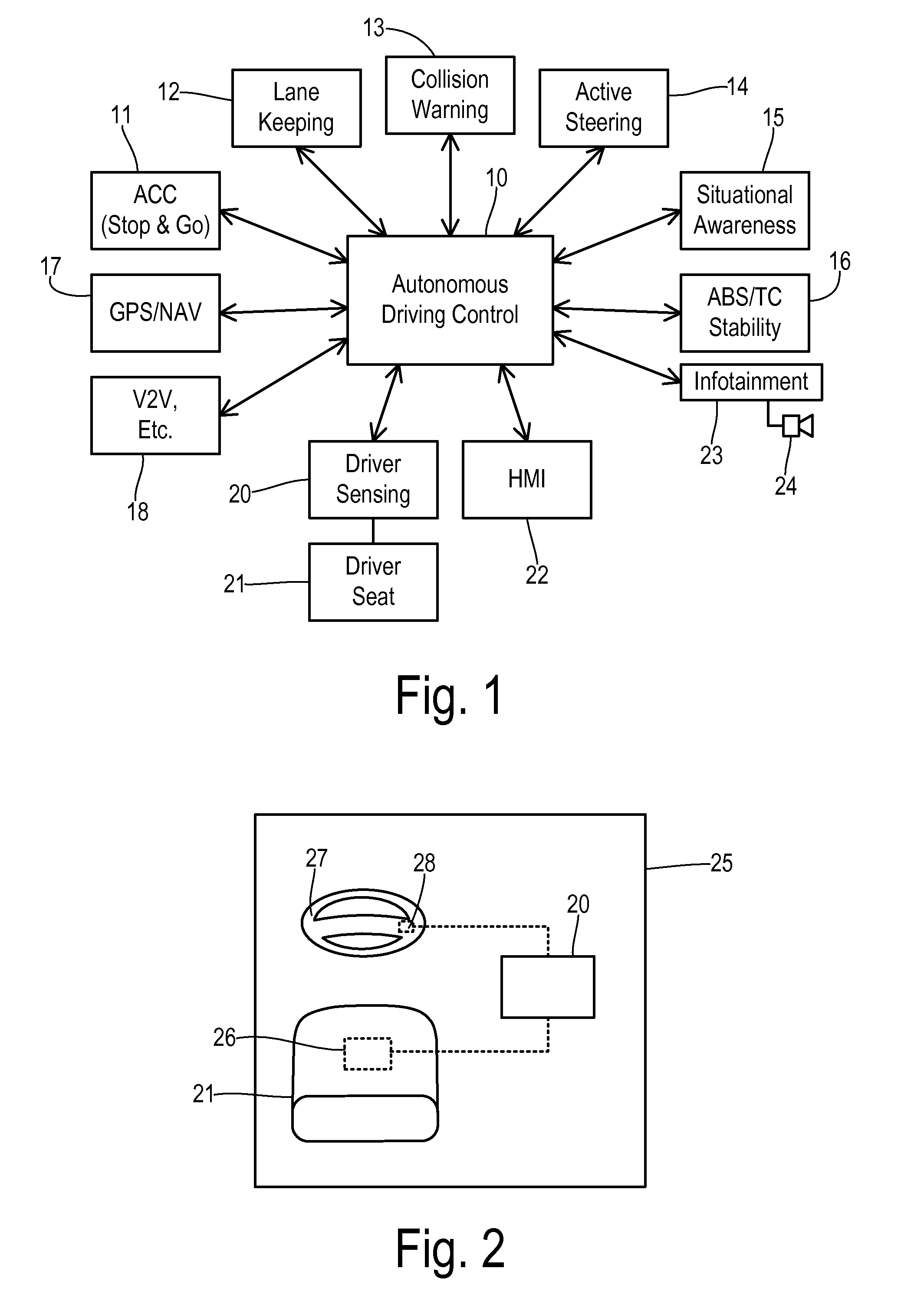
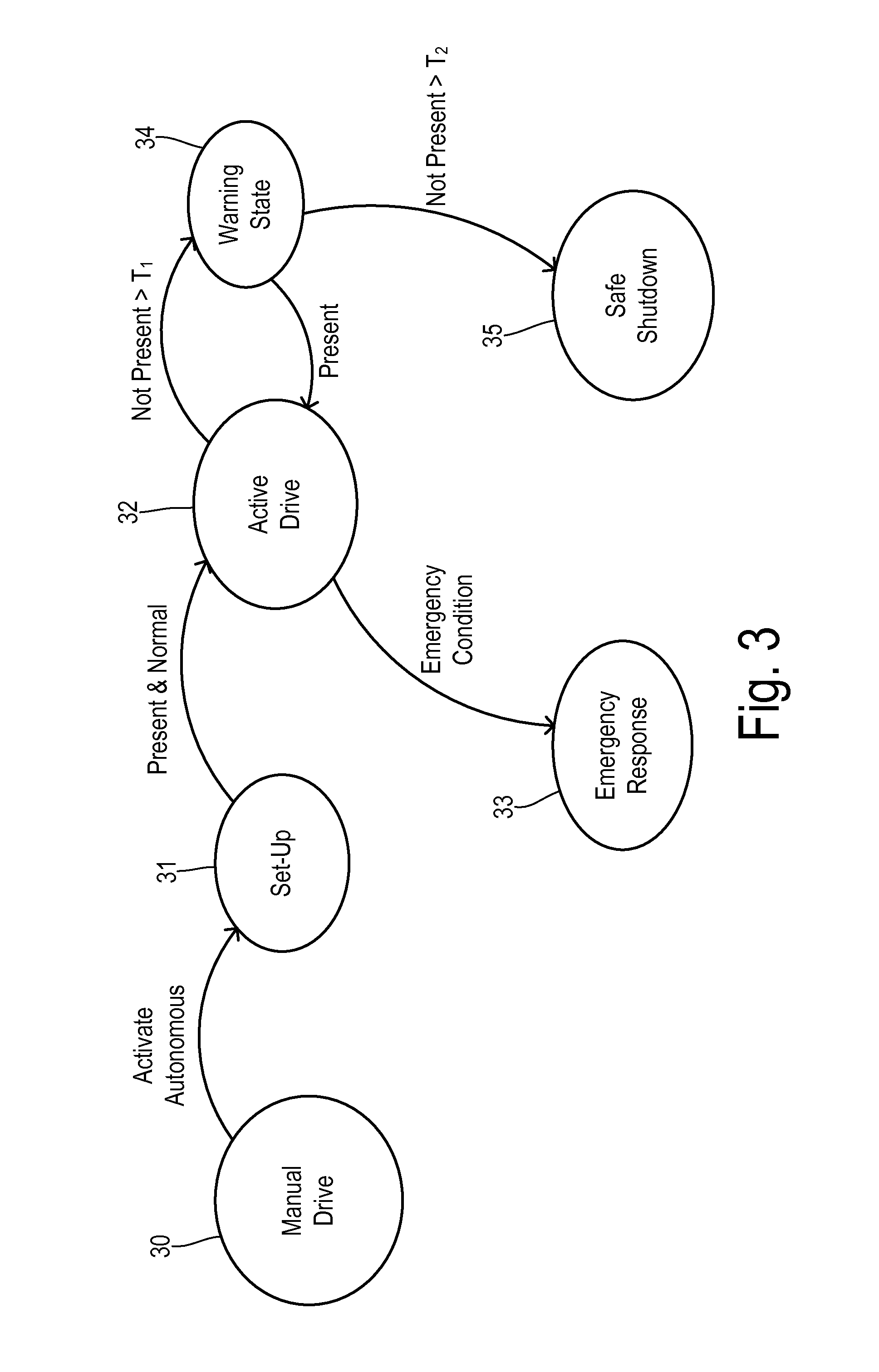
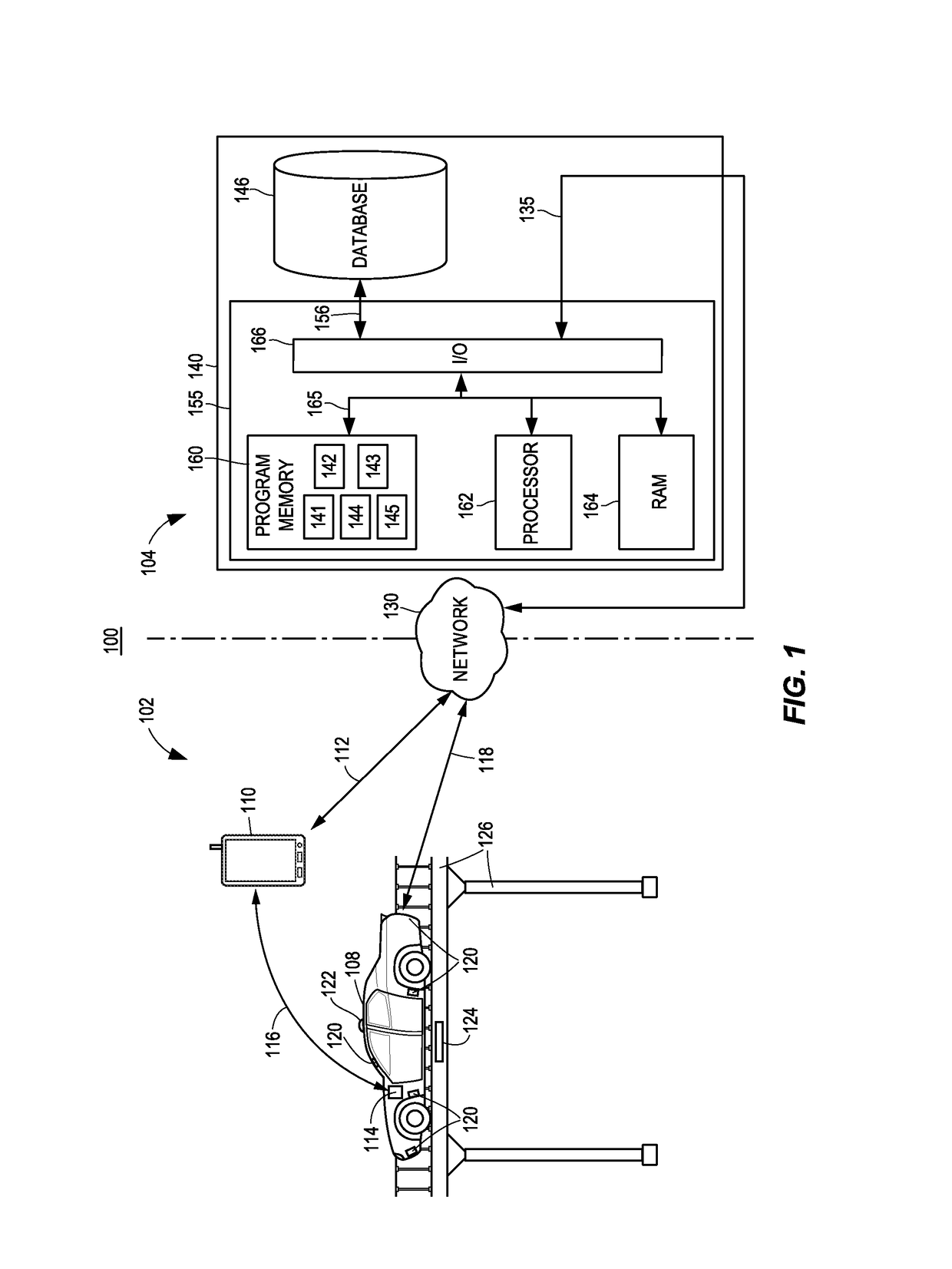
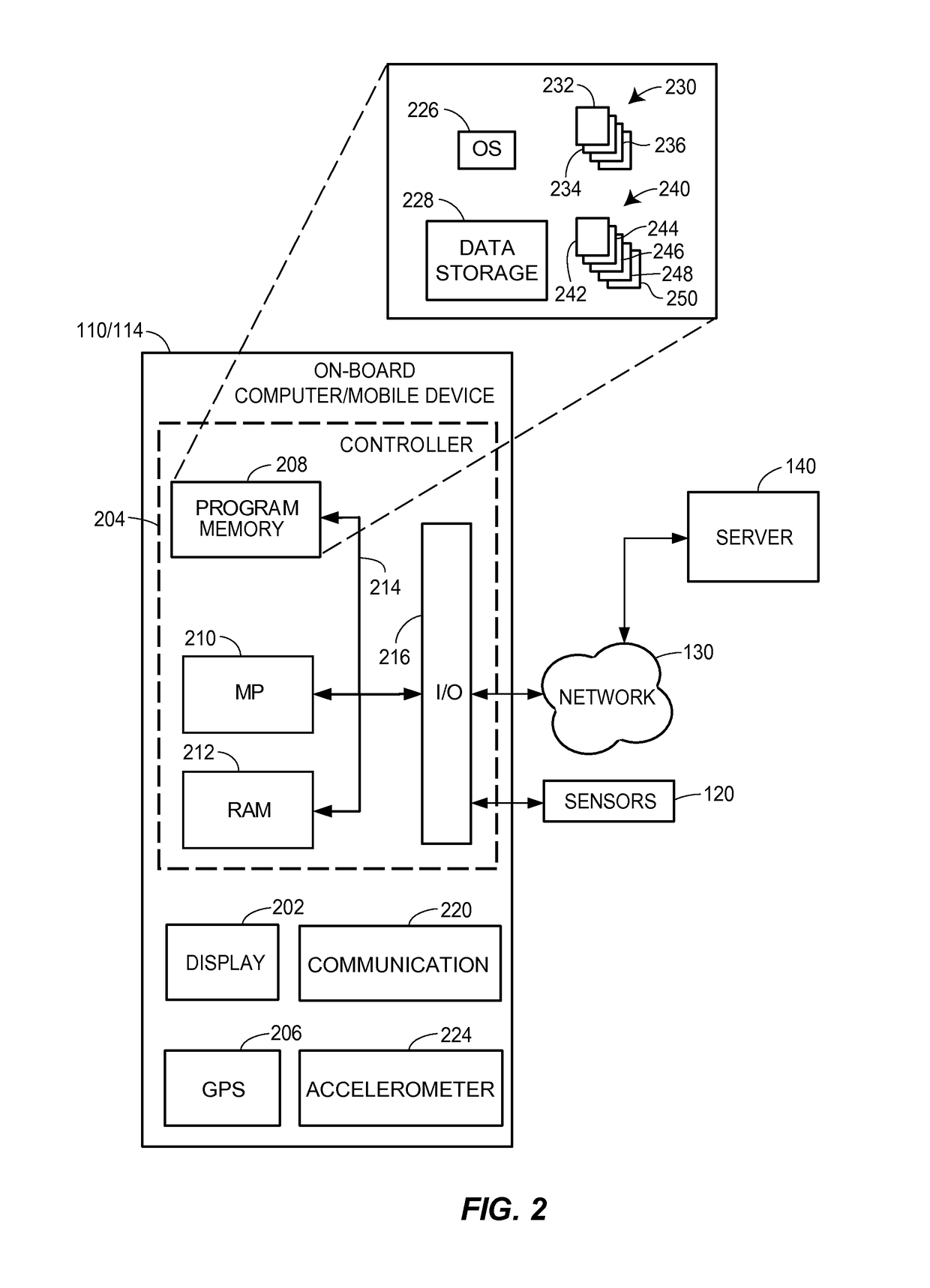
A transportation vehicle with an autonomous driving control has a set-up mode, an active drive mode, a safe shutdown mode, and an emergency response mode. The active drive mode autonomously navigates along a driving route specified in the set-up mode. A driver sensing system senses a driver presence in the driver seat and a driver's physiological state. Active drive mode is not entered from set-up mode unless the driver is present in the driver seat and the physiological state matches a normal condition. While in active driving mode, an elapsed time period is measured whenever the driver presence is not detected. If the time period increases above a first threshold then a notice is given to the driver that the active drive mode may be interrupted. If the time period increases above a second threshold then the active drive mode is terminated and the safe shutdown mode is initiated. A sensed physiological state is compared to a predetermined emergency condition and if a match is found then the autonomous driving control terminates the active drive mode and the emergency response mode is initiated.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Apparatus and method for cooperative autonomous driving between vehicle and driver
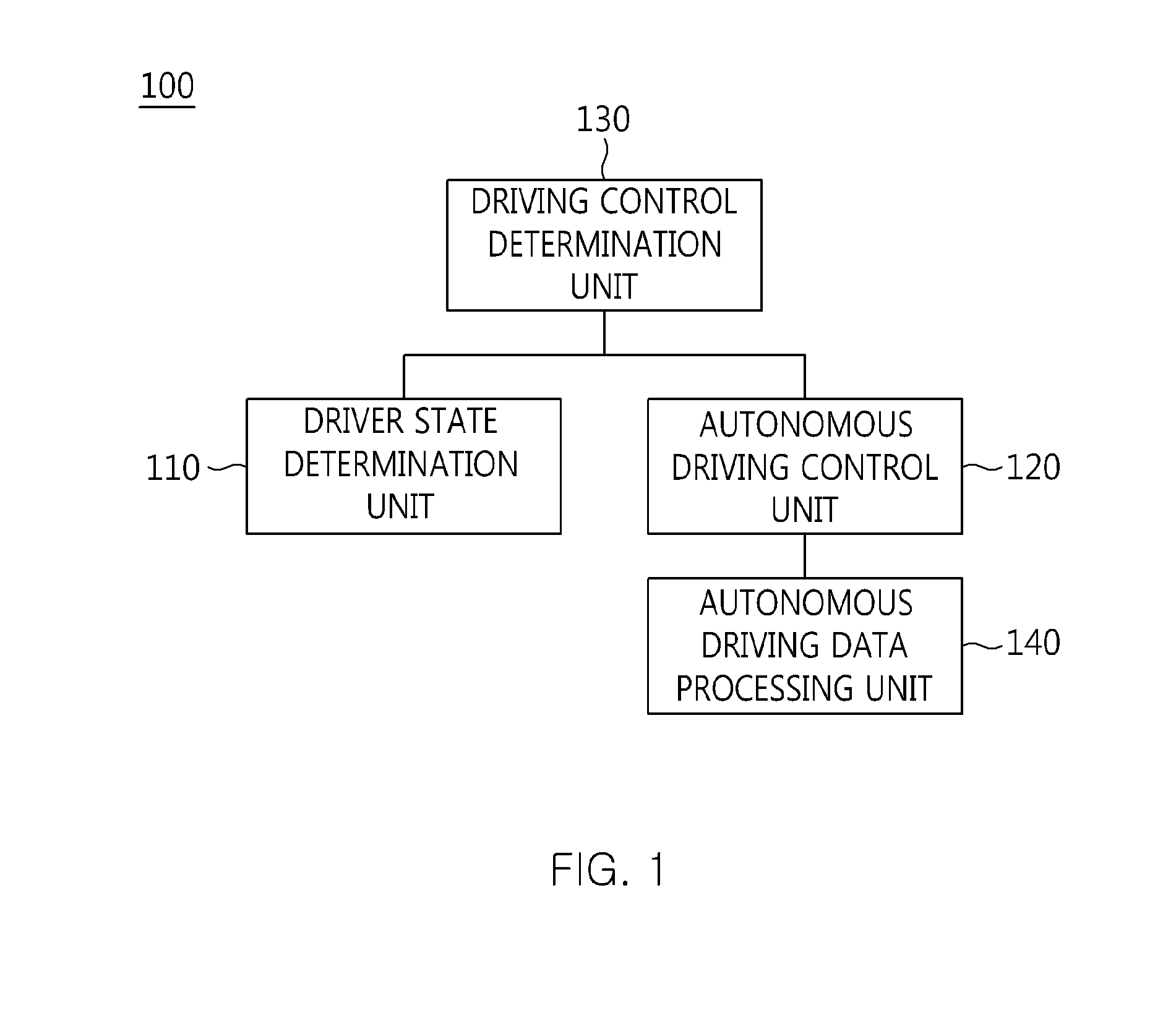
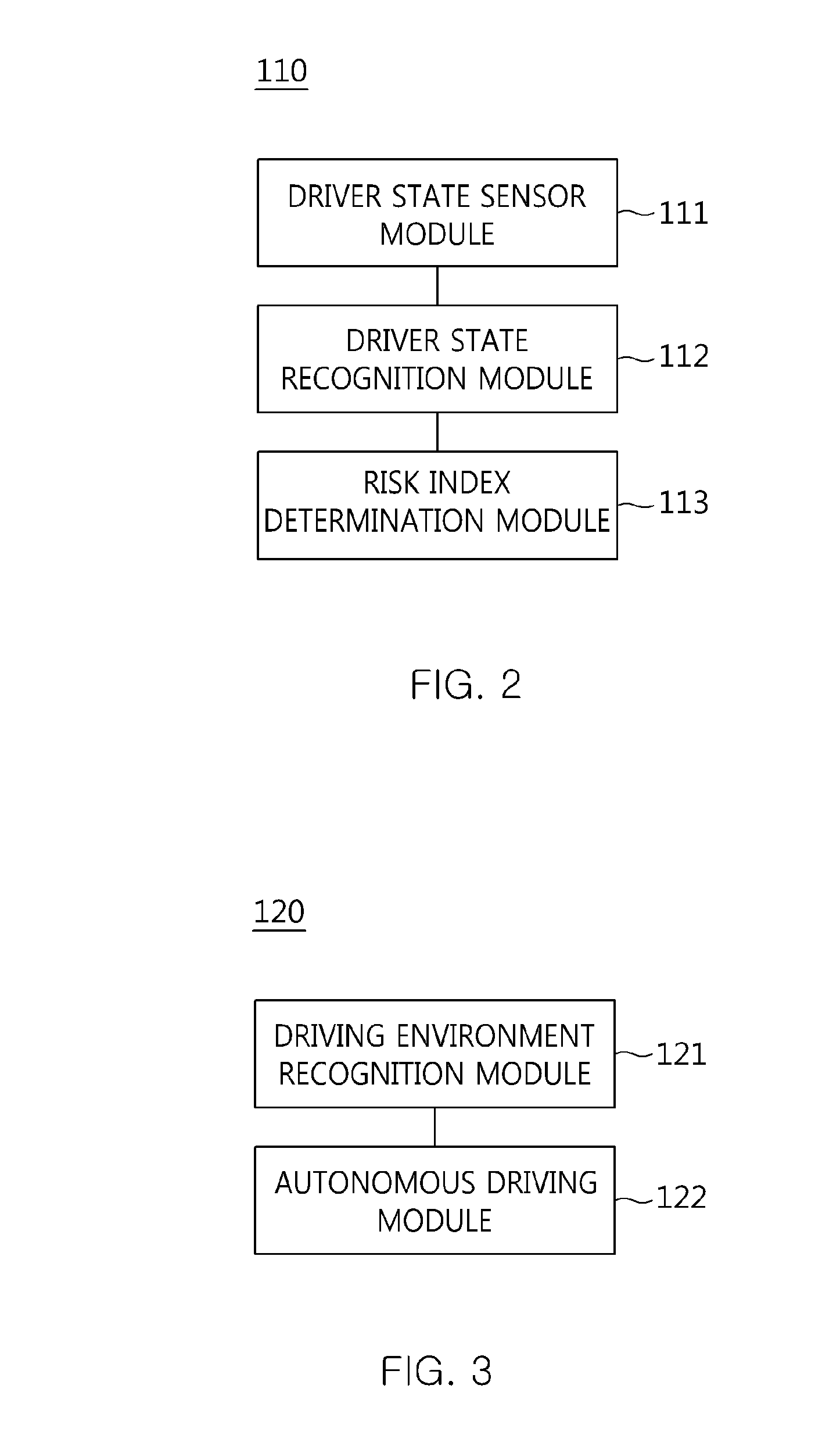
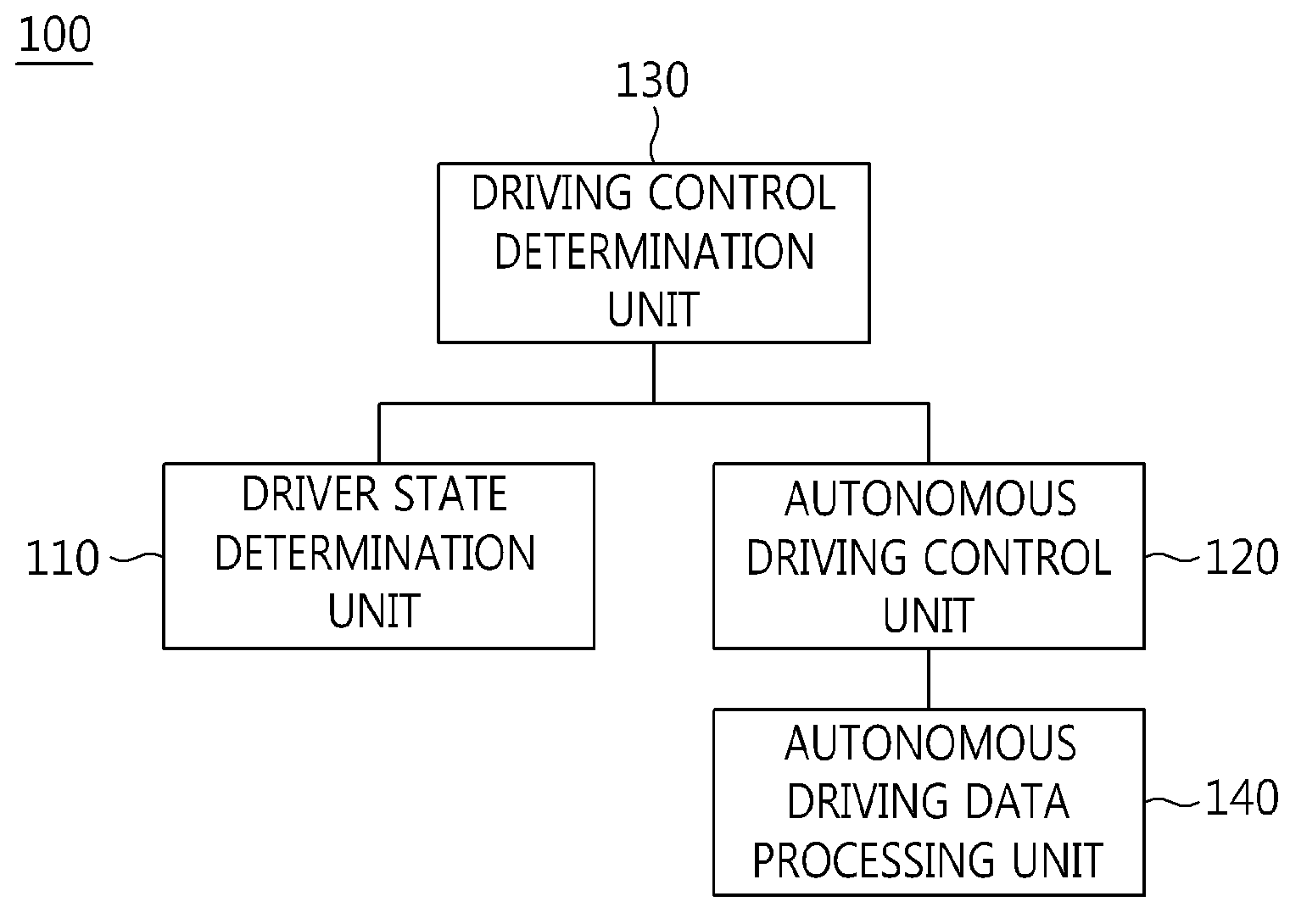
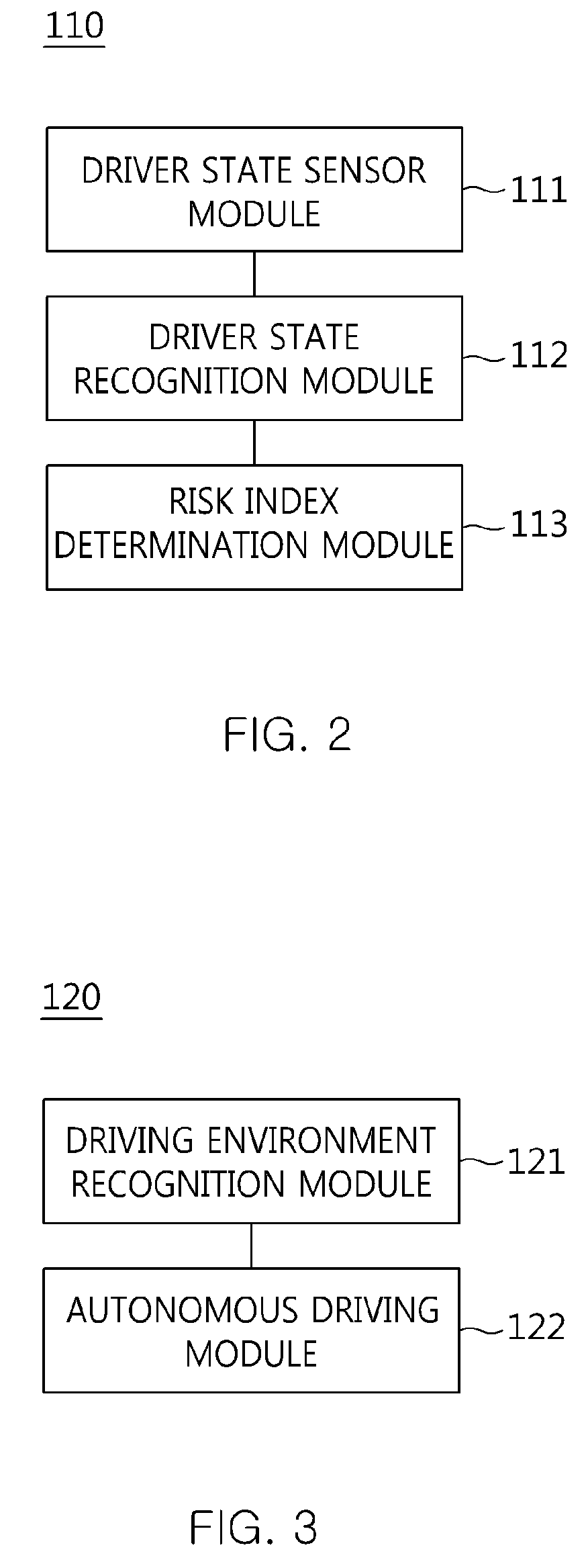
ActiveUS20140244096A1Improve driving performanceImprove performanceControl safety arrangementsExternal condition input parametersEngineeringData storing
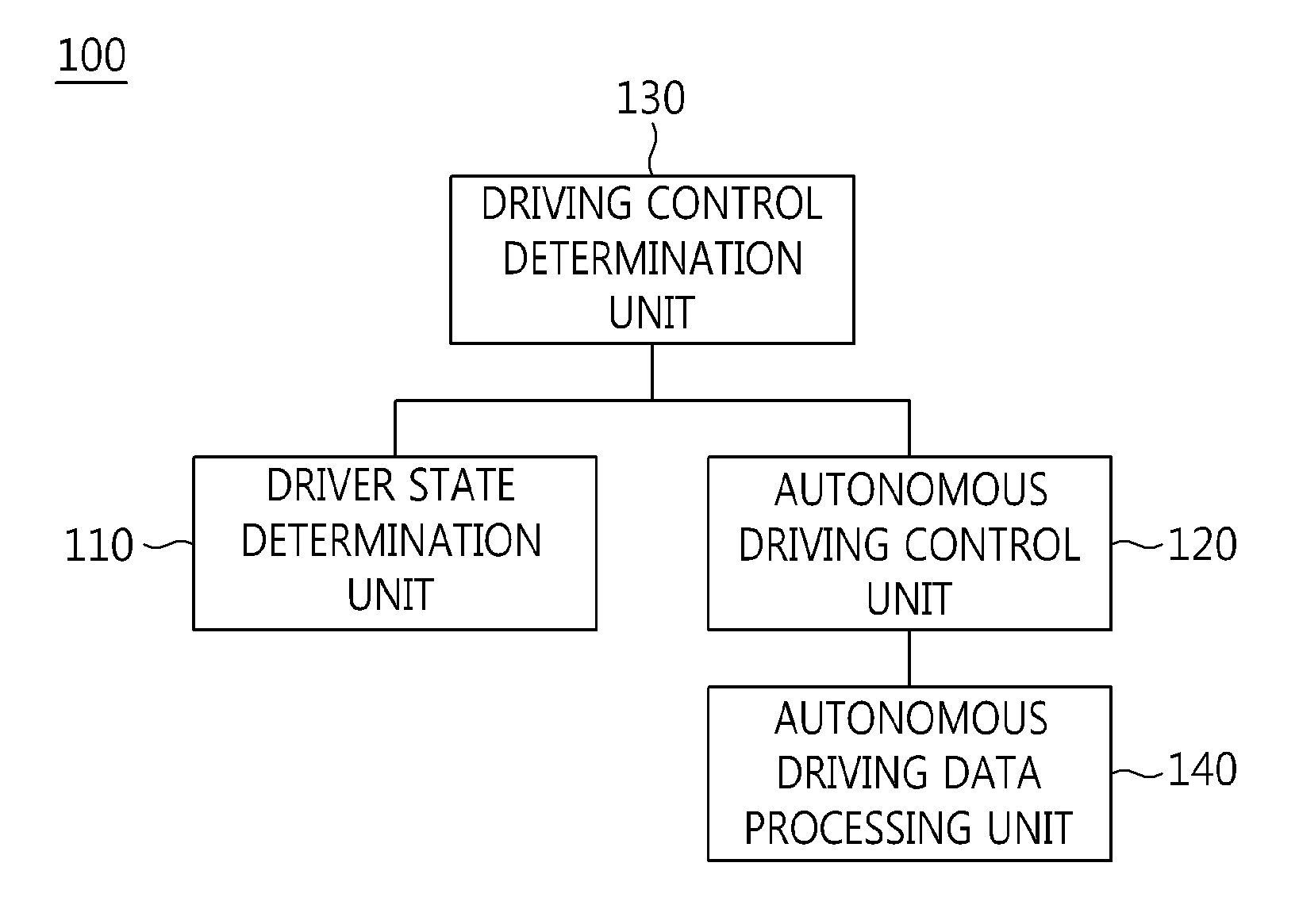
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for performing cooperative autonomous driving between a vehicle and a driver. For this, a cooperative autonomous driving apparatus according to the present invention includes a driver state determination unit for determining a state of a driver and calculating the state of the driver as a risk index. An autonomous driving control unit classifies section characteristics of respective sections included in a path to a destination corresponding to the driver based on section data stored in a database (DB), and controls autonomous driving of a vehicle in which the driver is riding, based on a driving environment recognized for the path to the destination corresponding to the driver. A driving control determination unit determines driving modes of the respective sections included in the path based on the state of the driver and the section characteristics.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Systems and methods for hazard mitigation
ActiveUS9701307B1Quality improvementImprove system reliabilitySteering linkagesAnti-collision systemsDriver/operatorPost collision
A system and method to avoid collisions on highways, and to minimize the fatalities, injury, and damage when a collision is unavoidable. The system includes sensors to detect other vehicles, and computing environments programmed to evaluate when a collision is imminent and to determine whether the collision is avoidable. If the collision is avoidable by a sequence of controlled accelerations and decelerations and steering, the system implements that sequence of actions automatically. If the collision is unavoidable, a different sequence is implemented to minimize the overall harm of the unavoidable collision. The system further includes indirect mitigation steps such as flashing the brake lights automatically. An optional post-collision strategy is implemented to prevent secondary collisions, particularly if the driver is incapacitated. Adjustment devices are provided to enable the driver to set the type and timing of automatic interventions.
Owner:AUTONOMOUS ROADWAY INTELLIGENCE LLC
Autonomous vehicle software version assessment
ActiveUS9946531B1Facilitate risk assessment and premium determinationOperation moreControl safety arrangementsMarket predictionsAssessment methodsSoftware update
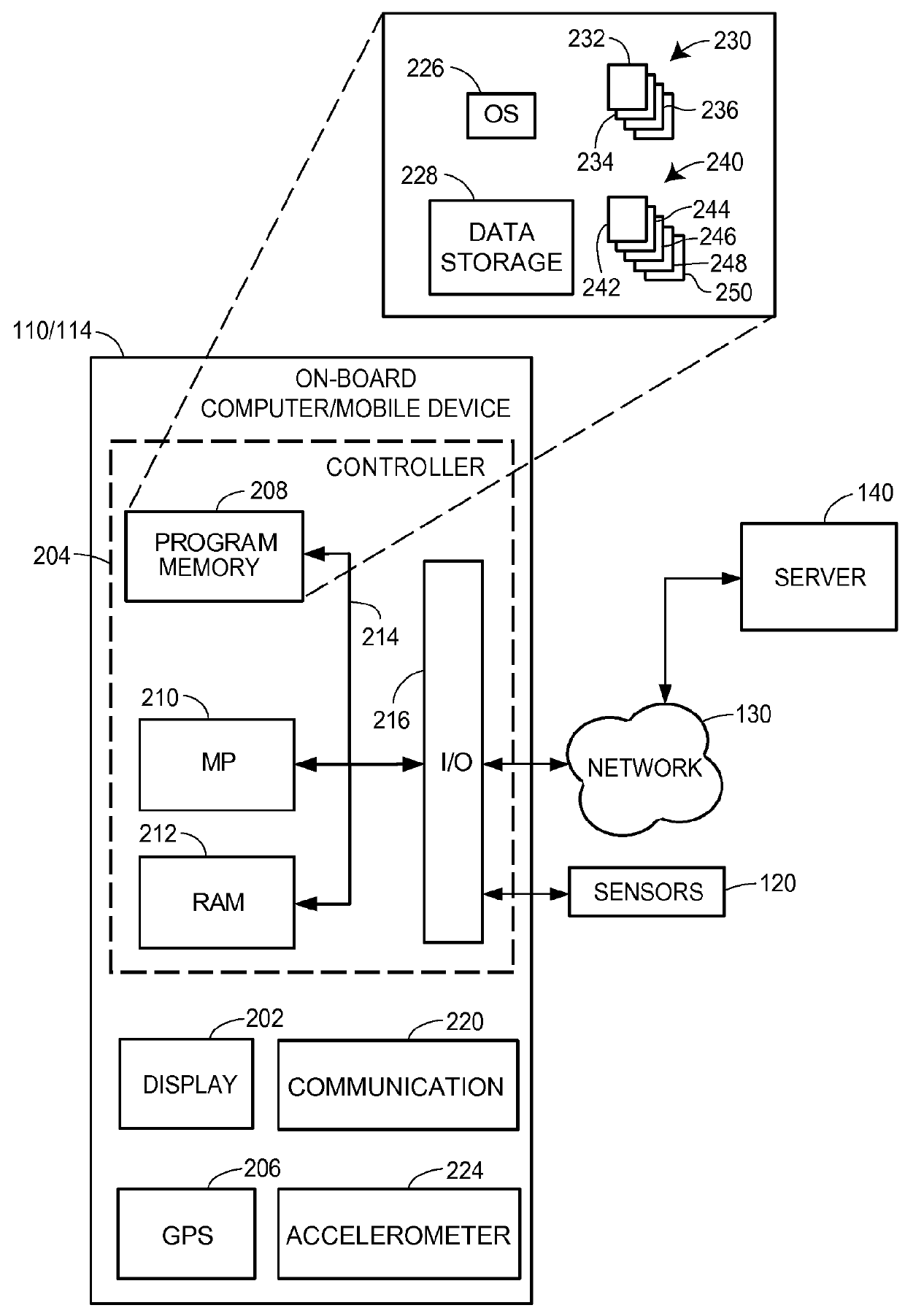
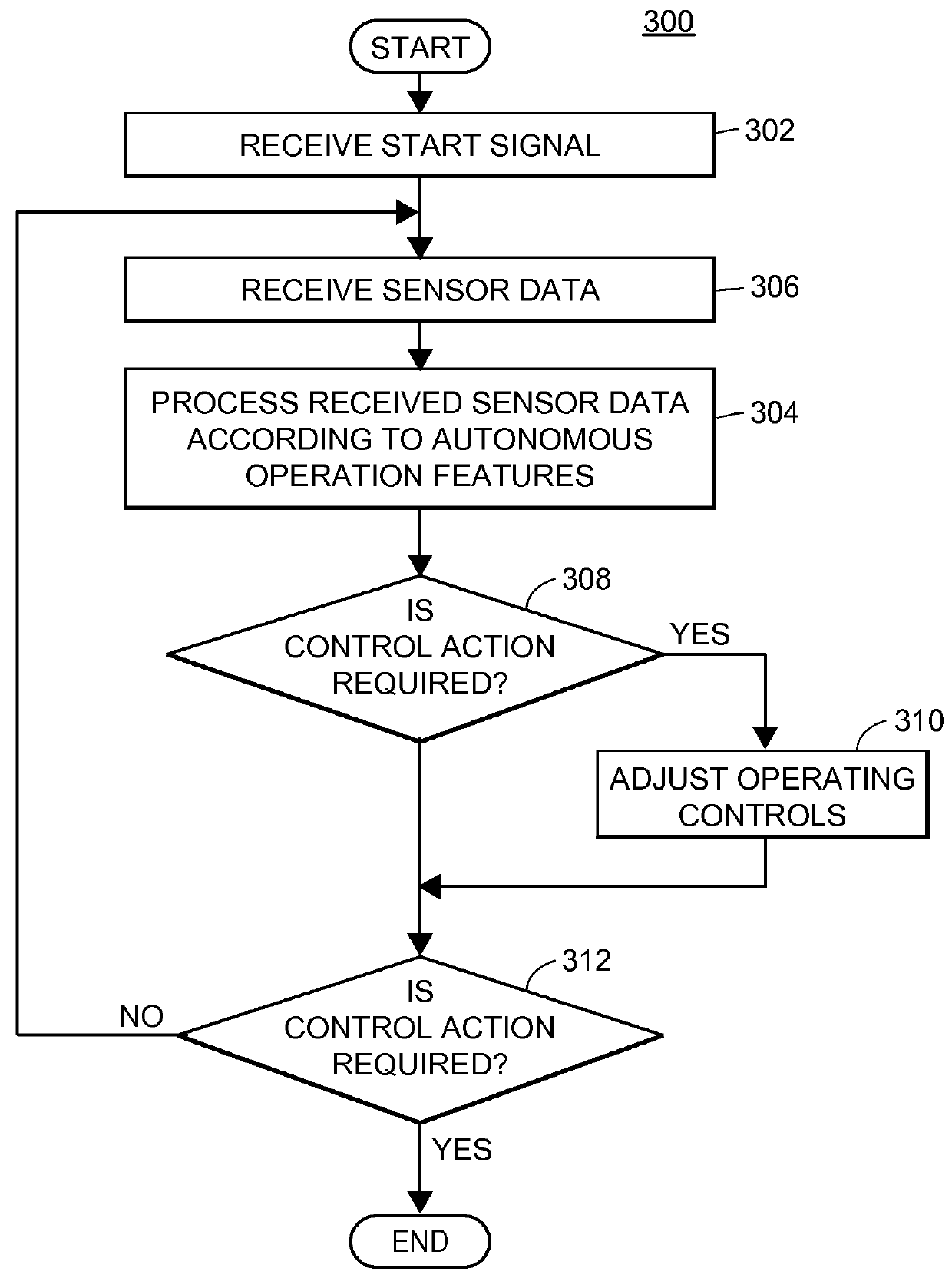
Methods and systems for monitoring use, determining risk, and pricing insurance policies for a vehicle having autonomous or semi-autonomous operation features are provided. In certain aspects, with the customer's permission, a computer-implemented method for updating an autonomous operation feature may be provided. An indication of a software update associated with the autonomous operation feature may be received, and several autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicles having the feature may be identified. The update may be installed within the several vehicles, such as via wireless communication. Also, a change in a risk level associated with the update to the autonomous operation feature may be determined, and an insurance discount may be determined or adjusted. As a result, an insurance discount may be provided to risk averse customers that affirmatively share their vehicle data with an insurance provider, and promptly and remotely receive new versions of software that operate autonomous vehicle safety features.
Owner:STATE FARM MUTUAL AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE
Control apparatus of vehicle
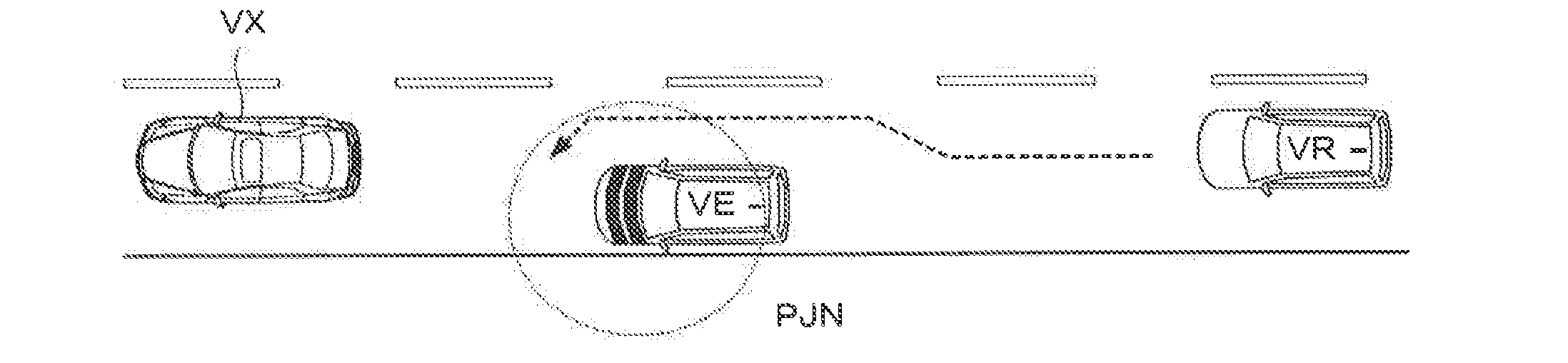
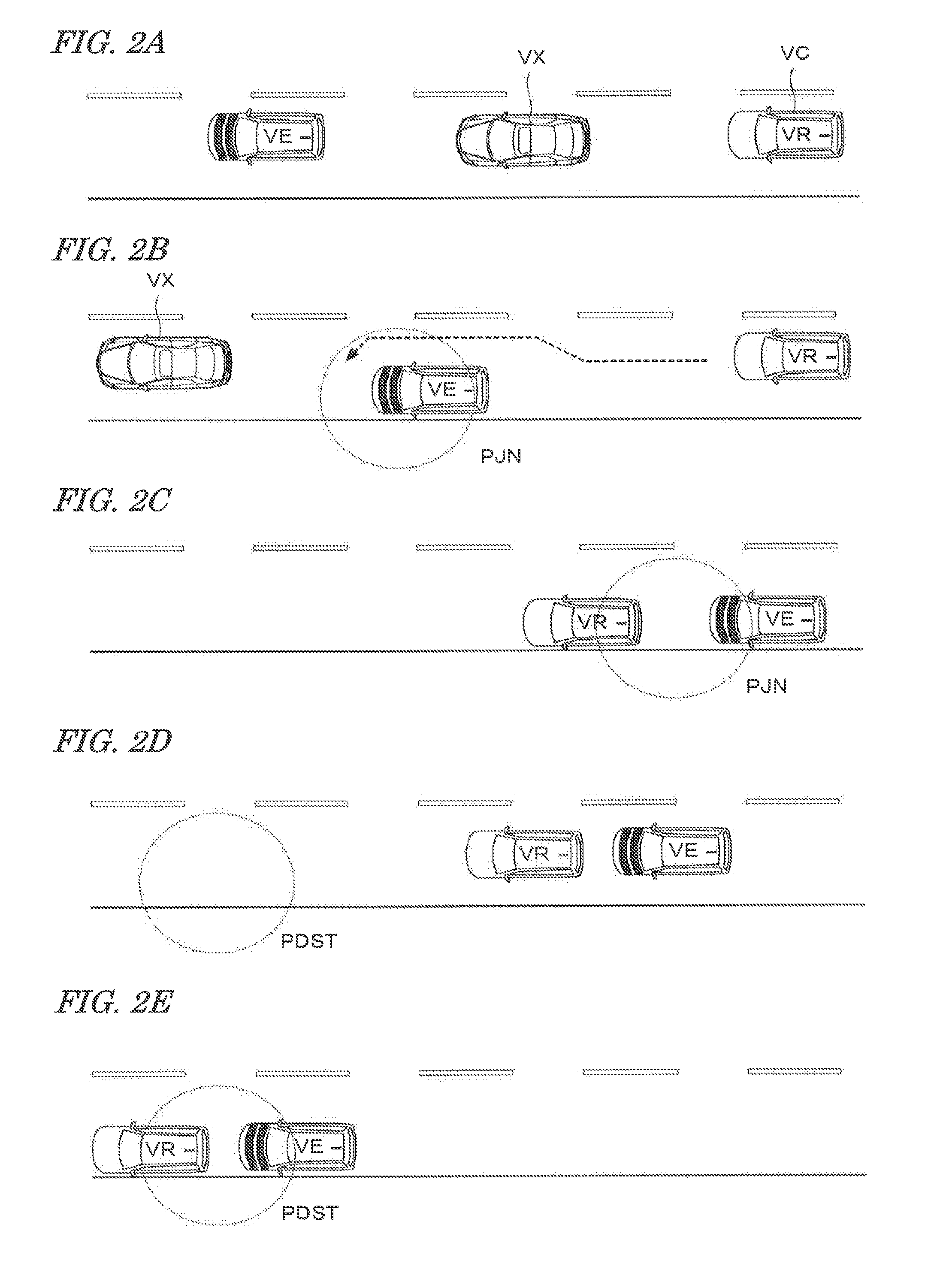
InactiveUS20150153733A1Avoid runningImprove performanceAutonomous decision making processExternal condition input parametersDriver/operatorVehicle driving
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Autonomous vehicle automatic parking
ActiveUS9944282B1Operation moreFacilitate risk assessmentControl safety arrangementsMarket predictionsDriver/operatorParking space
A computer-implemented method of enhancing safe vehicle operation may include, one or more processors, (1) determining a preferred parking spot for an autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicle; (2) determining a route to the preferred parking spot from a driver drop off point; and (3) causing the autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicle to travel from the driver drop off point to the preferred parking spot following the route controlled by one or more autonomous operation features. The preferred parking spot may be a covered parking spot, a parking spot in a parking structure, or a parking spot in a residential garage. An autonomous vehicle owner may remotely direct the autonomous vehicle to autonomously return to the driver drop off point, such as via their mobile device. Insurance discounts may be provided to autonomous vehicle owners having the self-parking functionality that mitigates or prevents risk of damage to, or theft of, the vehicle.
Owner:STATE FARM MUTUAL AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE
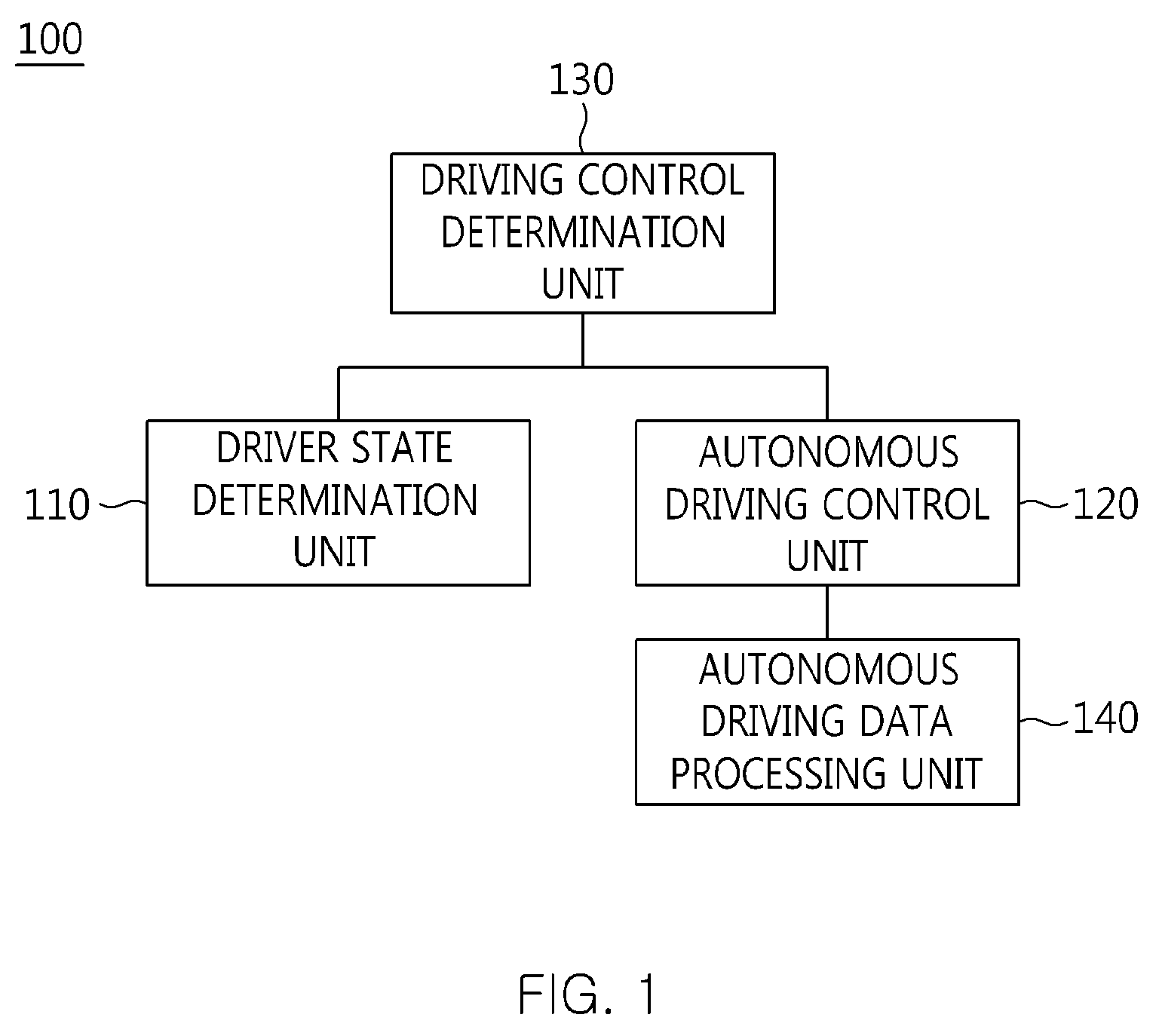
Apparatus and method for cooperative autonomous driving between vehicle and driver
ActiveUS9063543B2Improve performanceControl safety arrangementsExternal condition input parametersDriver/operatorEngineering
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for performing cooperative autonomous driving between a vehicle and a driver. For this, a cooperative autonomous driving apparatus according to the present invention includes a driver state determination unit for determining a state of a driver and calculating the state of the driver as a risk index. An autonomous driving control unit classifies section characteristics of respective sections included in a path to a destination corresponding to the driver based on section data stored in a database (DB), and controls autonomous driving of a vehicle in which the driver is riding, based on a driving environment recognized for the path to the destination corresponding to the driver. A driving control determination unit determines driving modes of the respective sections included in the path based on the state of the driver and the section characteristics.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Efficient data flow algorithms for autonomous lane changing, passing and overtaking behaviors
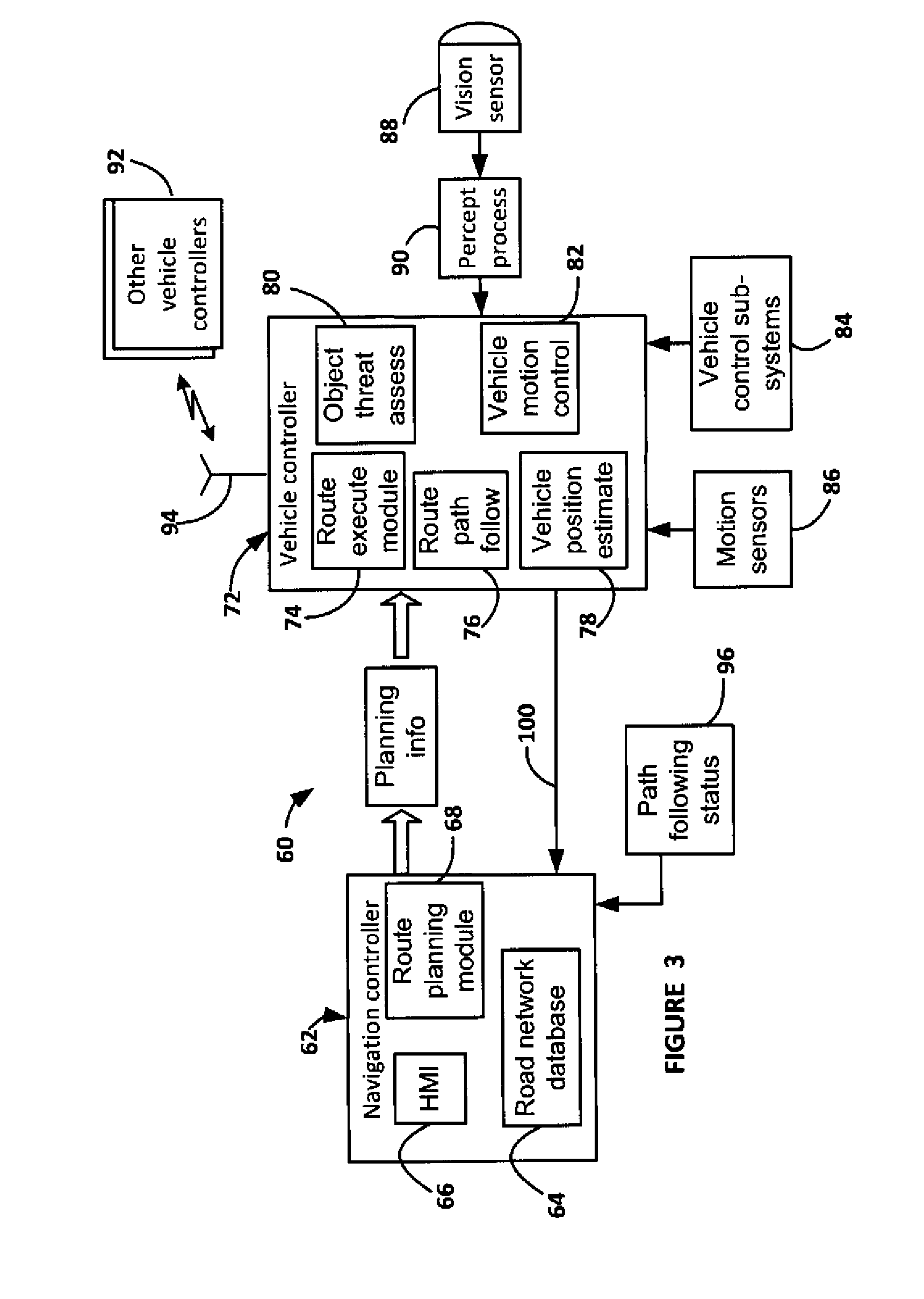
A system and method for providing lane changing maneuvers in an autonomously driven vehicle. The vehicle includes a navigation controller that provides a planned route for the vehicle to follow and a vehicle controller that receives route information from the navigation controller and provides steering, braking and throttle control for the vehicle to follow the route. Either the navigation controller or the vehicle controller may initiate a lane change maneuver to cause the vehicle to be steered from a travel lane to an adjacent lane. In response to the lane change requirement, the navigation controller provides a route segment to the vehicle controller and a lane-change zone so that the vehicle controller can steer the vehicle to the adjacent lane while in the lane-change zone.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
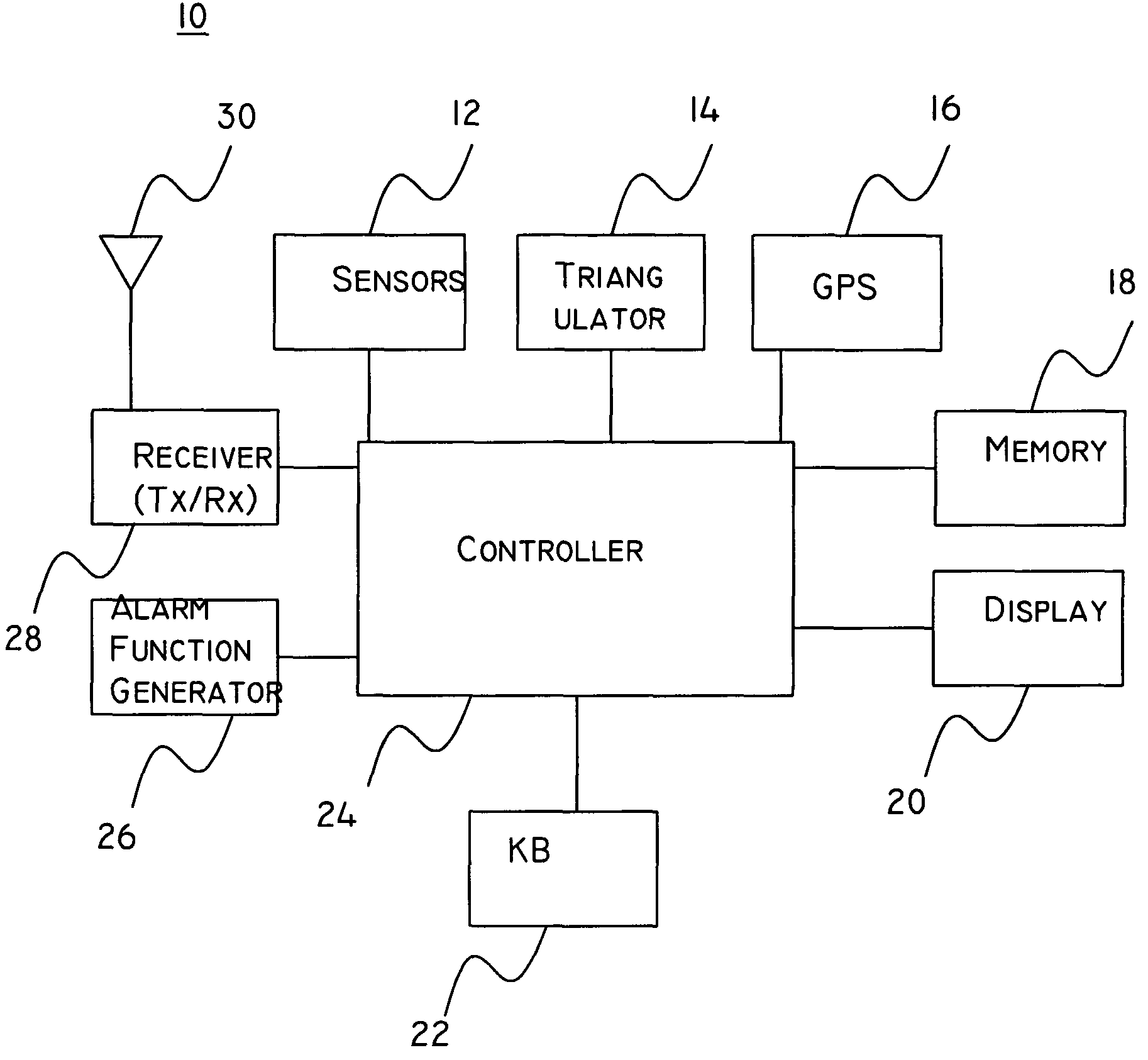
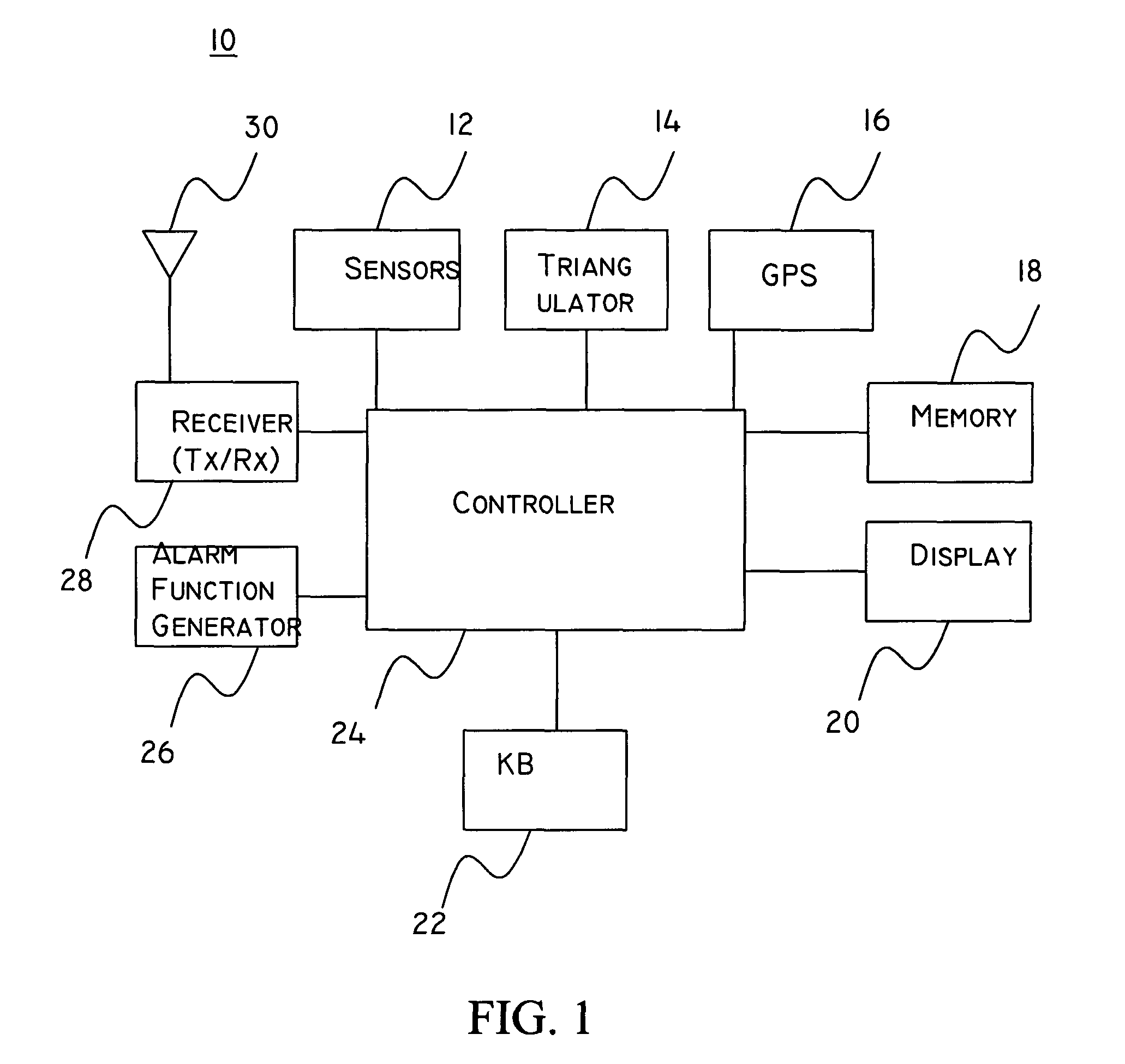
System and method for setting functions according to location
InactiveUS7755472B2Input/output for user-computer interactionRoad vehicles traffic controlCellular telephoneComputer science
An apparatus, system, and method for controlling functions of a vehicular alarm. The method includes receiving one or more signals including location information, determining a location of the vehicle using the location information, setting one or more functions based on the location information, determining whether an alarm function is activated, and activating the one or more functions according to the setting upon determining that an alarm has been activated. The method may further include using GPS data or signals transmitted from one or more base stations (e.g., from cellular telephone base stations, computer networks, proprietary transmitters, etc.) to determine the position of the apparatus (e.g., installed in the vehicle). The apparatus may also inform a user of regulations relating to an area dependent upon its location.
Owner:GROSSMAN VICTOR A
Autonomous vehicle accident and emergency response
ActiveUS10007263B1Operation moreFacilitate risk assessment and premium determinationControl safety arrangementsInstruments for road network navigationEngineeringAutomatic guidance
Methods and systems for monitoring use, determining risk, and pricing insurance policies for a vehicle having one or more autonomous or semi-autonomous operation features are provided. According to certain aspects, with the customer's permission, it may be detected by sensors that an occupant of the autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicle is experiencing a medical emergency. A nearby medical facility may be determined based upon the vehicle location and the detected medical emergency. A route from the current vehicle location to the medical facility may be determined, and the autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicle may be automatically directed or routed to the medical facility. A message may also be generated and transmitted to the medical facility to alert them that a person in need of timely medical assistance is on the way. Life and auto insurance discounts may be generated for risk averse customers based upon their vehicles having the emergency response functionality.
Owner:STATE FARM MUTUAL AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE
Systems and methods for navigating a vehicle
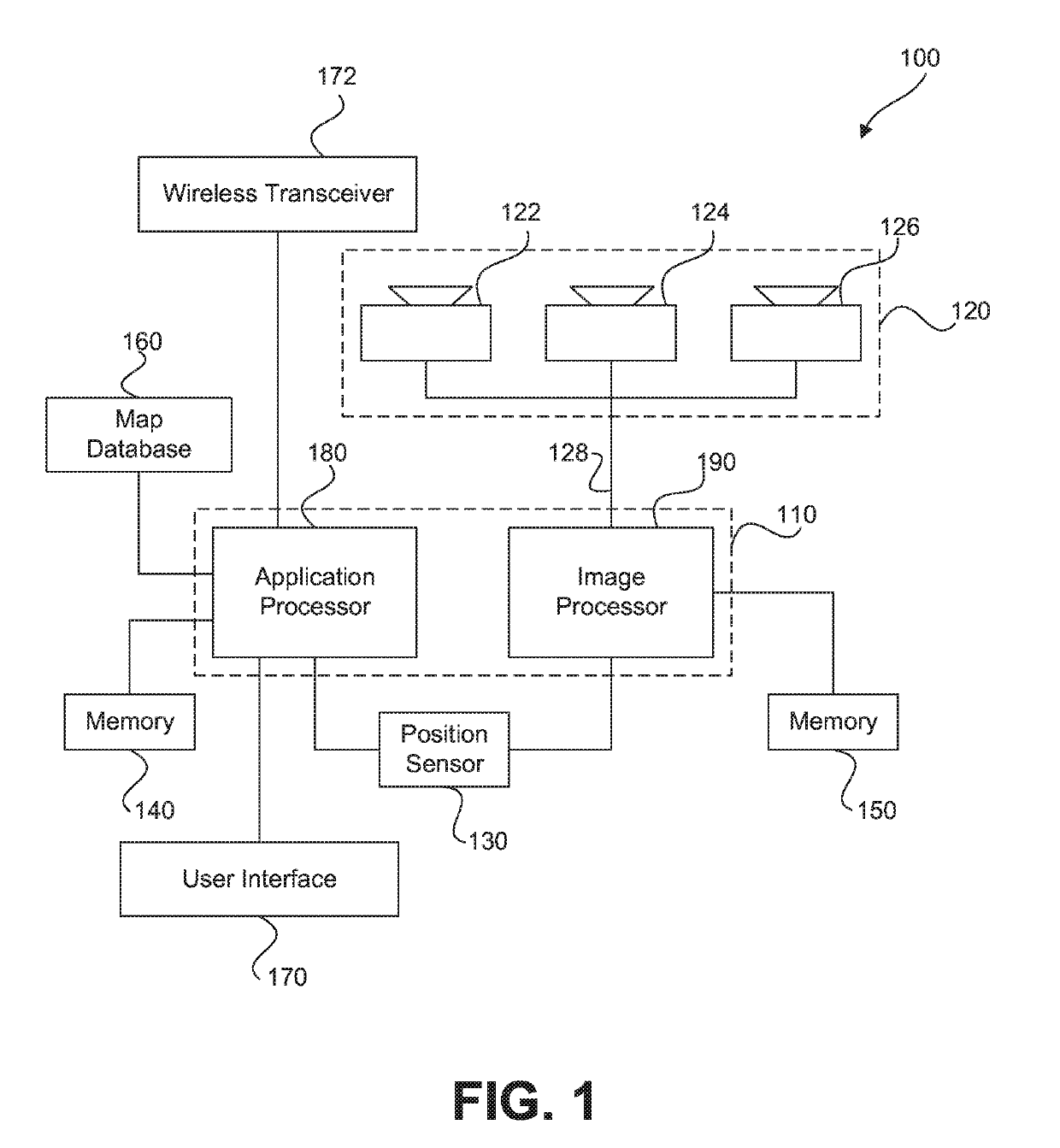
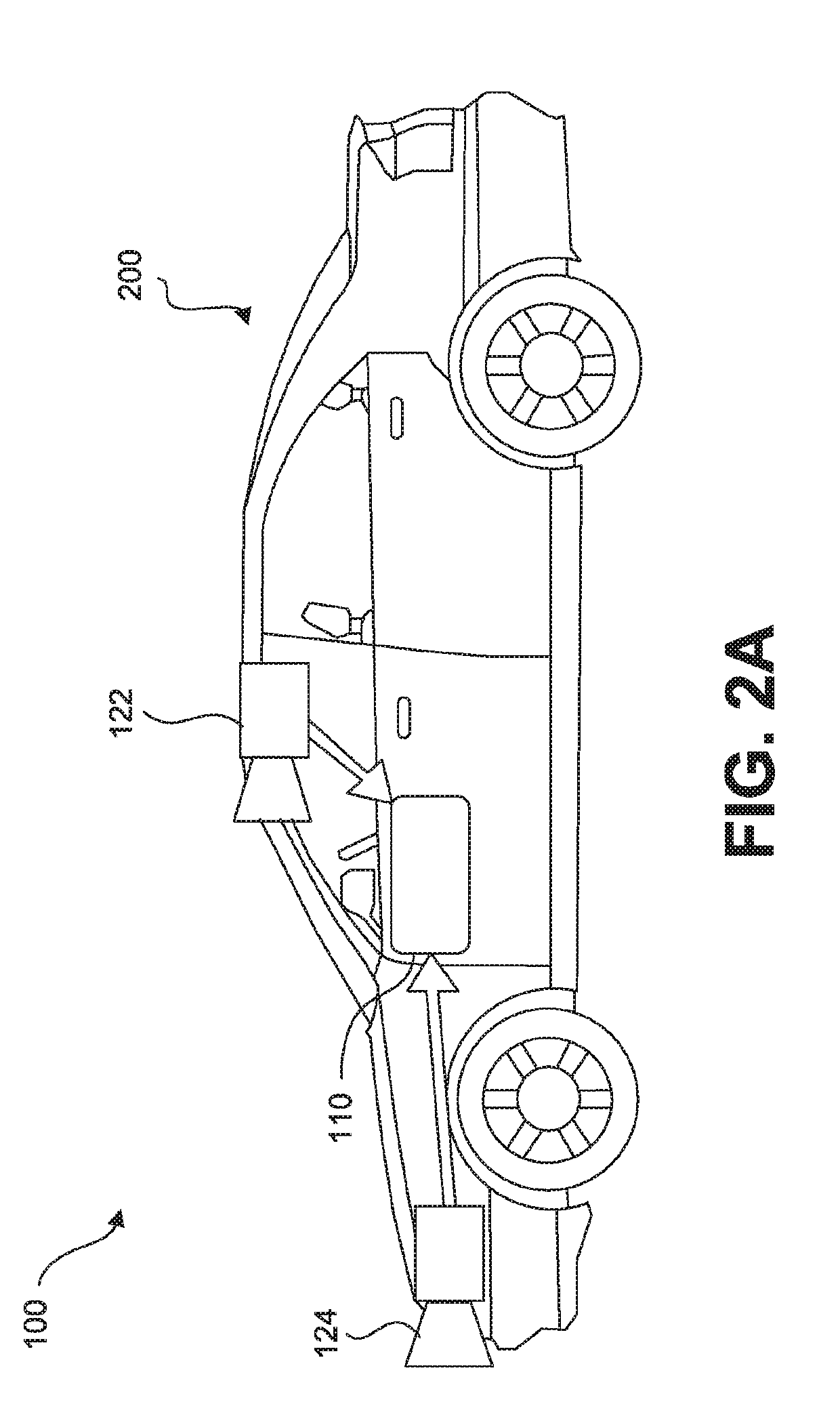
An autonomous system includes a processing device programmed to receive, from an image capture device, an image of an environment of the host vehicle; detect an obstacle in the environment, based on an analysis of the image; monitor a driver input to at least one of a throttle control, a brake control, or a steering control associated with the host vehicle; determine whether the driver input results in the host vehicle navigating within a proximity buffer relative to the obstacle; allow the driver input to cause a corresponding change in one or more host vehicle motion control systems, if the processing device determines that the driver input would not result in the host vehicle navigating within the proximity buffer relative to the obstacle; and prevent the driver input to cause the change if the driver input results in the host vehicle navigating within the proximity buffer relative to the obstacle.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
Autonomous vehicle operating style and mode monitoring
ActiveUS10157423B1Operation moreFacilitate risk assessment and premium determinationControl safety arrangementsMarket predictionsRisk levelComputer science
Methods and systems for monitoring use, determining risk, and pricing insurance policies for a vehicle having autonomous or semi-autonomous operation features are provided. According to certain aspects, with the insurance customer's permission, operation of an autonomous (or semi-autonomous vehicle) by a vehicle operator may be monitored. Based upon vehicle and / or other data analysis, an identity of the operator may be determined, and operating data regarding the autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicle while the operator at least partially controls the autonomous vehicle may be monitored. A vehicle operator profile that includes information regarding an operating style of the vehicle operator based upon the operating data may be determined. Risk levels associated with operation of the autonomous vehicle based upon the information regarding the vehicle operator's operating style may be determined. Insurance discounts may be provided to risk averse vehicle owners and / or operators, or those that utilize vehicle risk mitigation or prevention technology.
Owner:STATE FARM MUTAL AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE COMPANY
Combined vehicle-to-vehicle communication and object detection sensing
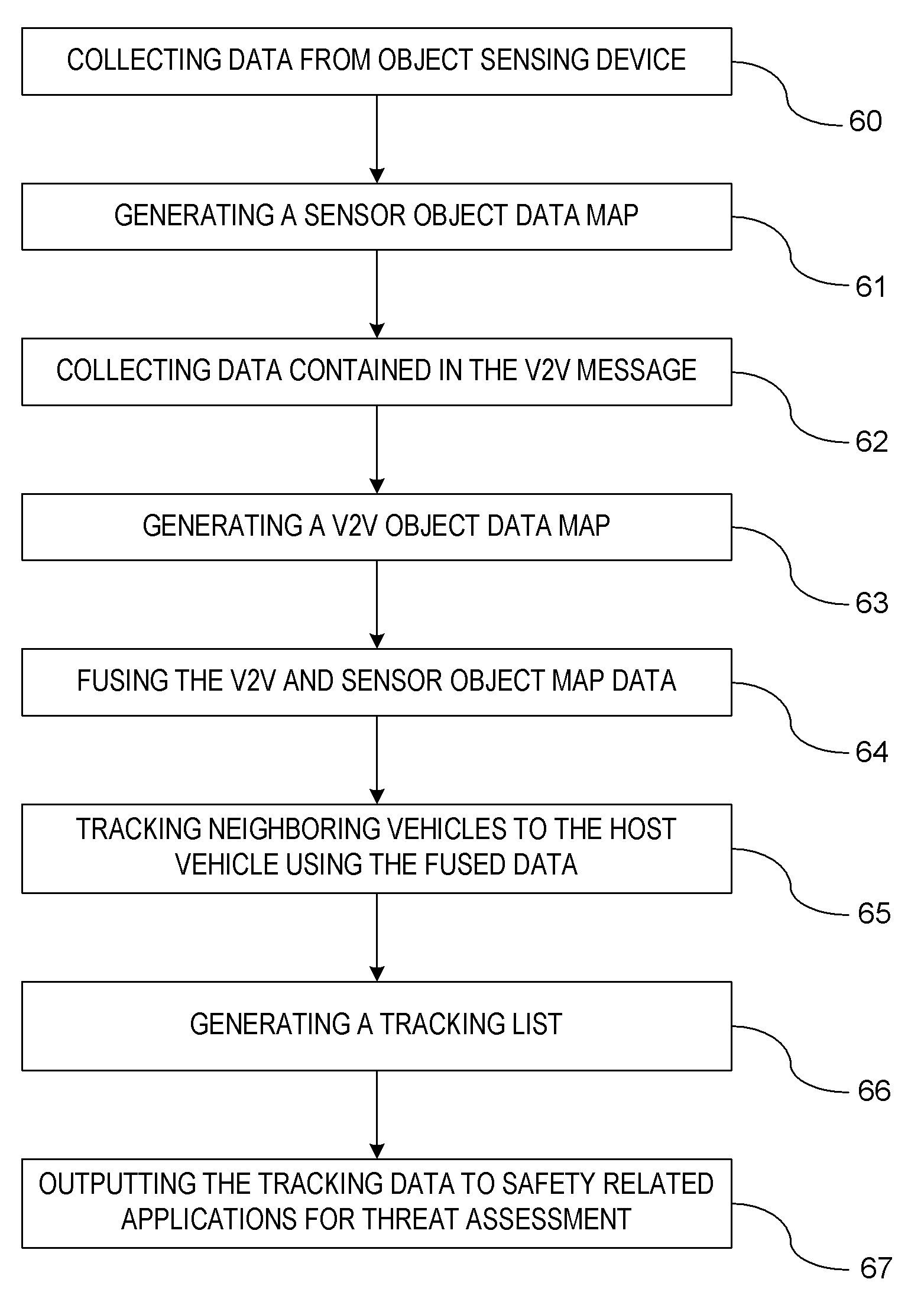
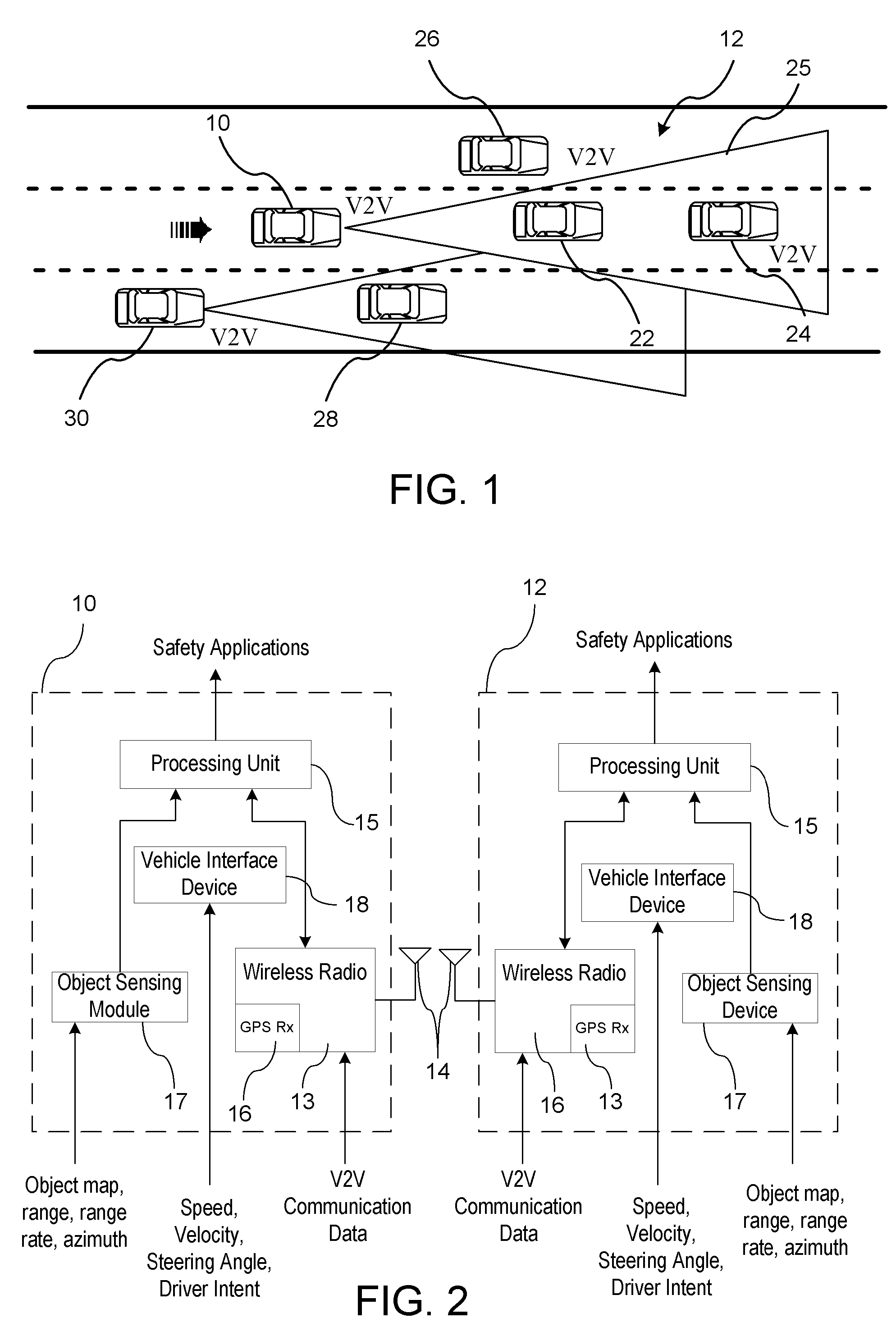
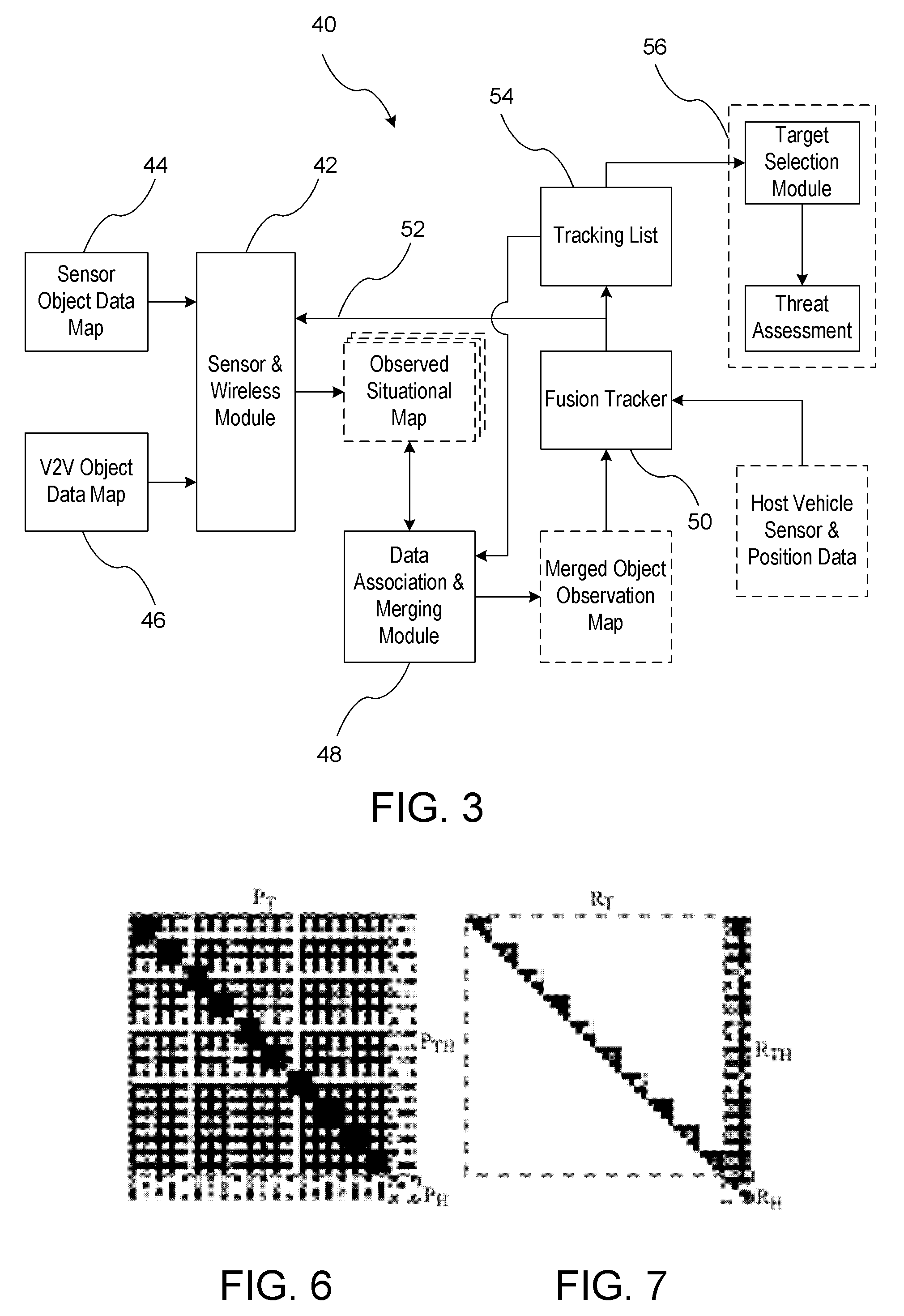
ActiveUS8229663B2Expand the scope of monitoringIncrease rangeArrangements for variable traffic instructionsDetection of traffic movementData acquisition moduleCommunication device
A vehicle awareness system for monitoring remote vehicles relative to a host vehicle. The vehicle awareness system includes at least one object sensing device and a vehicle-to-vehicle communication device. A data collection module is provided for obtaining a sensor object data map and vehicle-to-vehicle object data map. A fusion module merges the sensor object data map and vehicle-to-vehicle object data map for generating a cumulative object data map. A tracking module estimates the relative position of the remote vehicles to the host vehicle.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
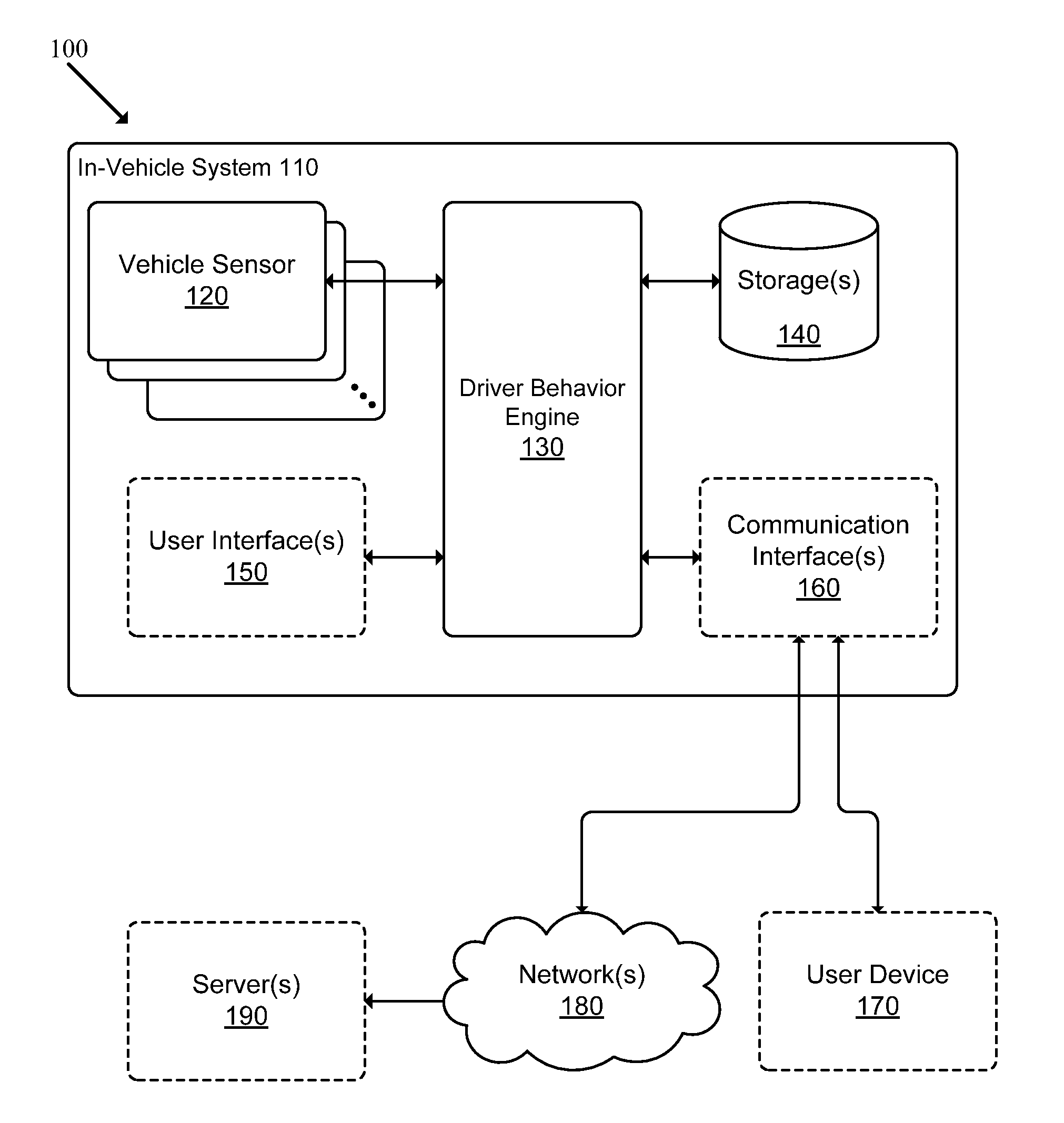
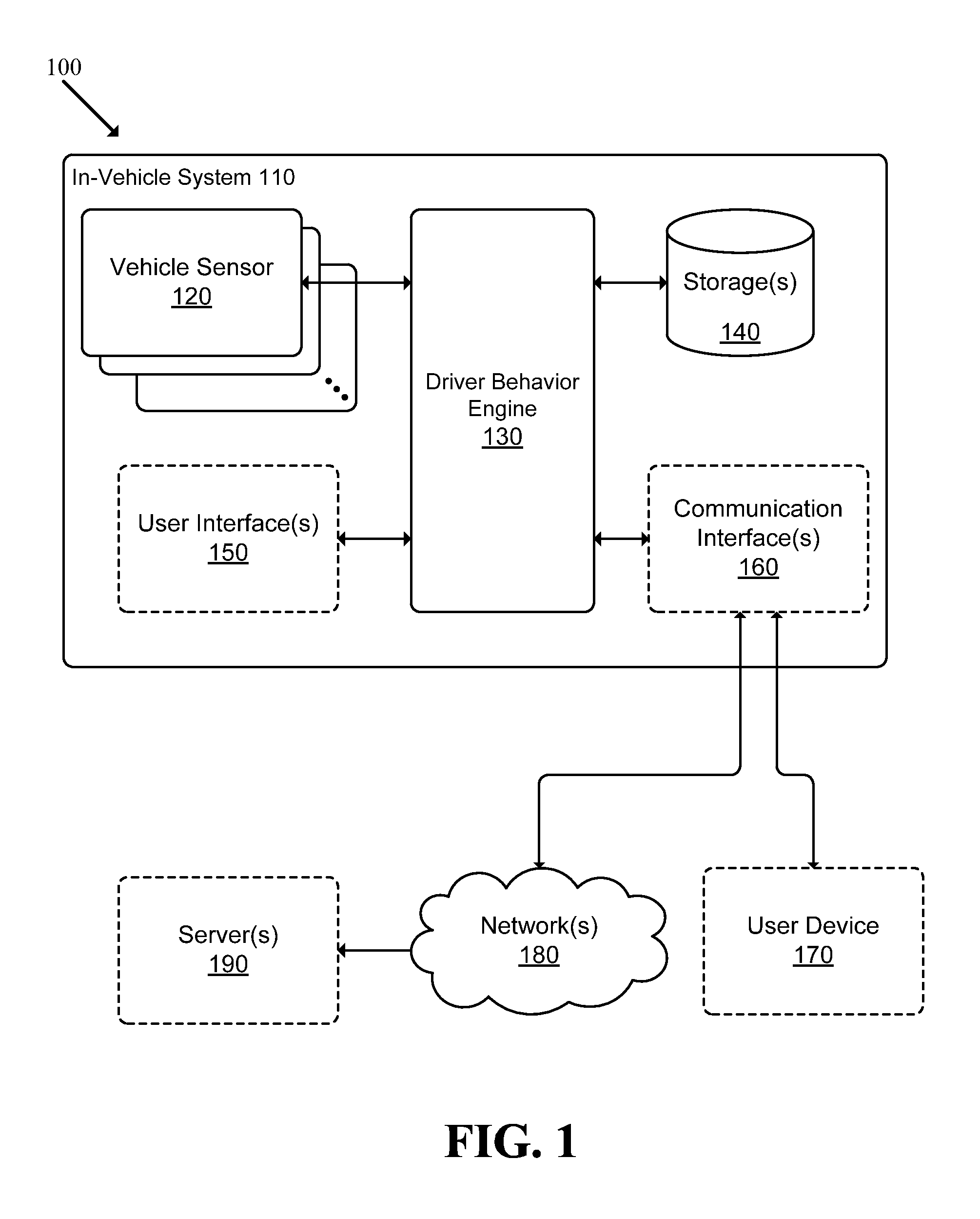
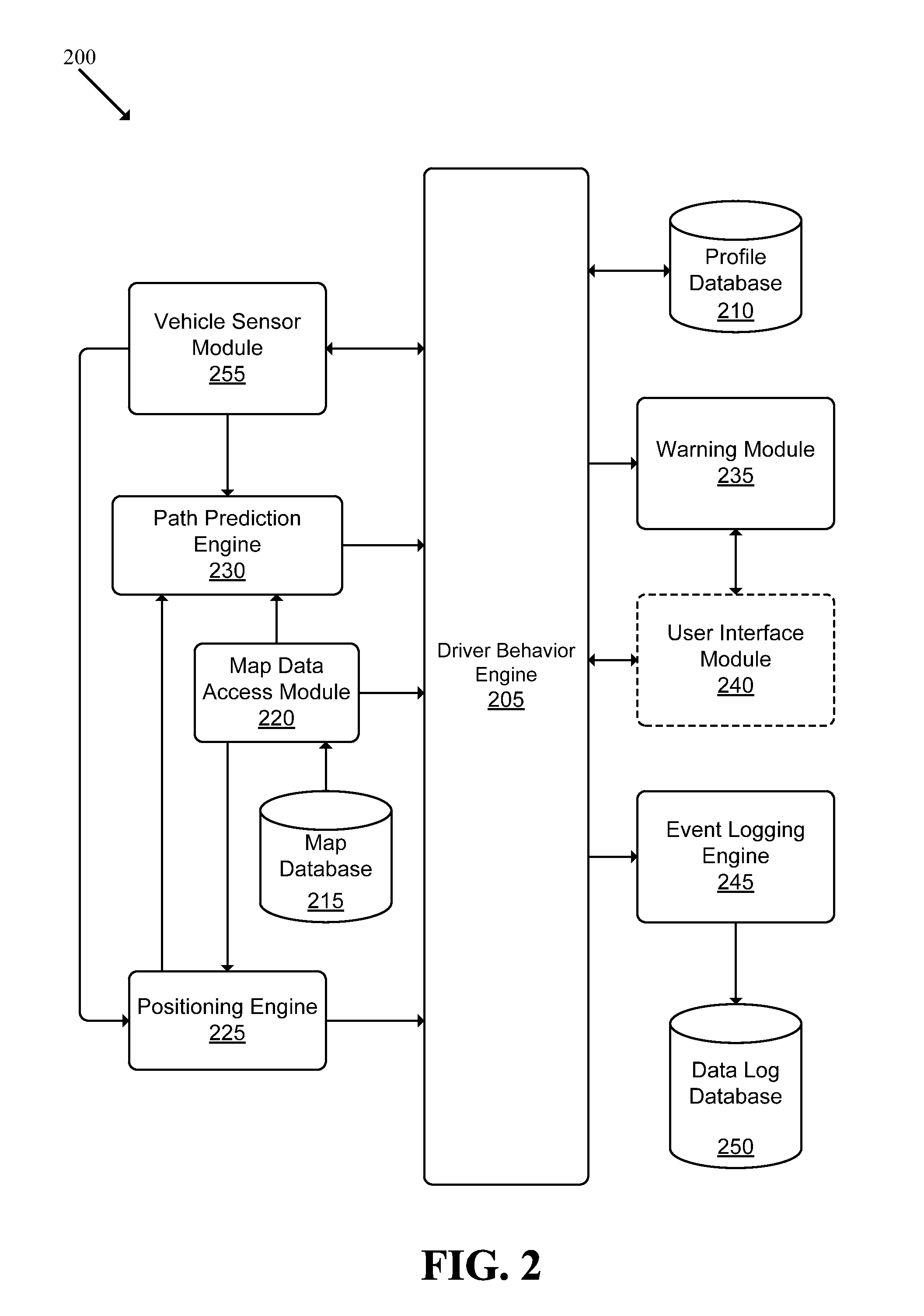
Recording, Monitoring, and Analyzing Driver Behavior
A system adapted to monitor, record and analyze driver performance is described. The system includes: a vehicle sensor module adapted to receive data from a set of sensors that each measure a driving characteristic associated with a vehicle; a map data access module adapted to retrieve, from a map database, map data elements indicating various features associated with at least one path of the vehicle; and a driver behavior engine adapted to receive information from the vehicle sensor module and the map data access module, and to monitor and evaluate driver performance based on the received information.
Owner:ABALTA TECH
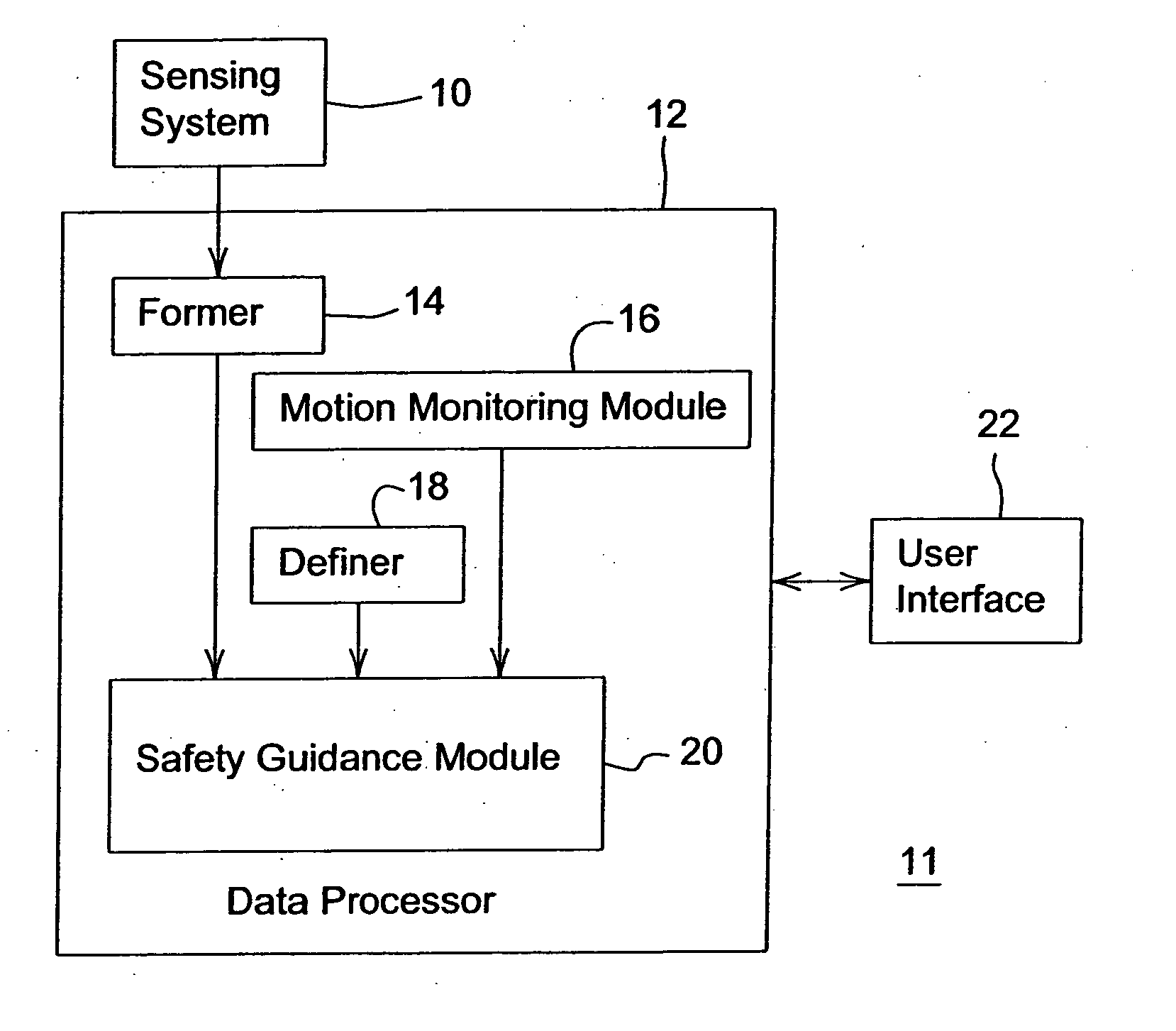
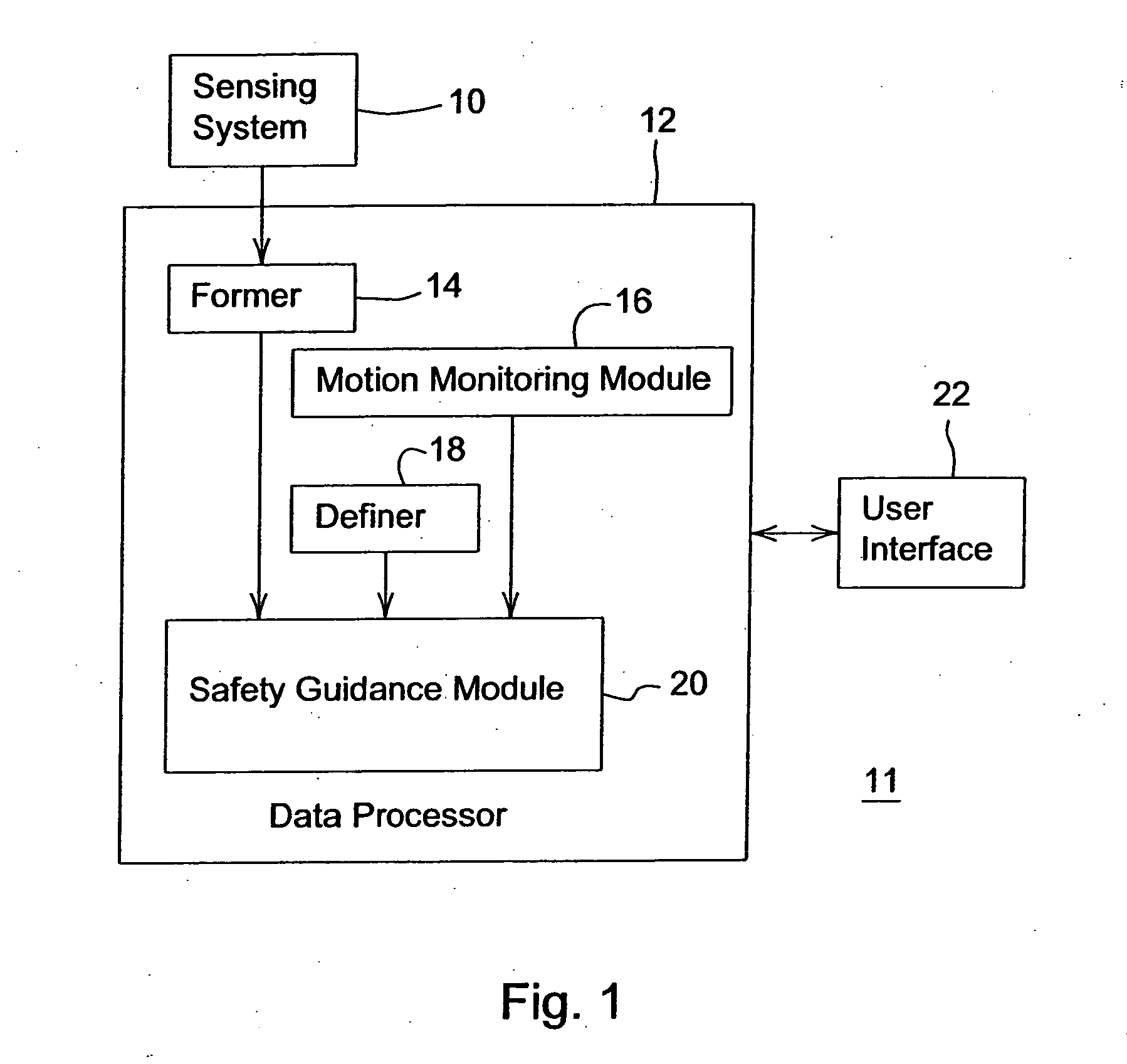
System and method for providing a safety zone associated with a vehicle
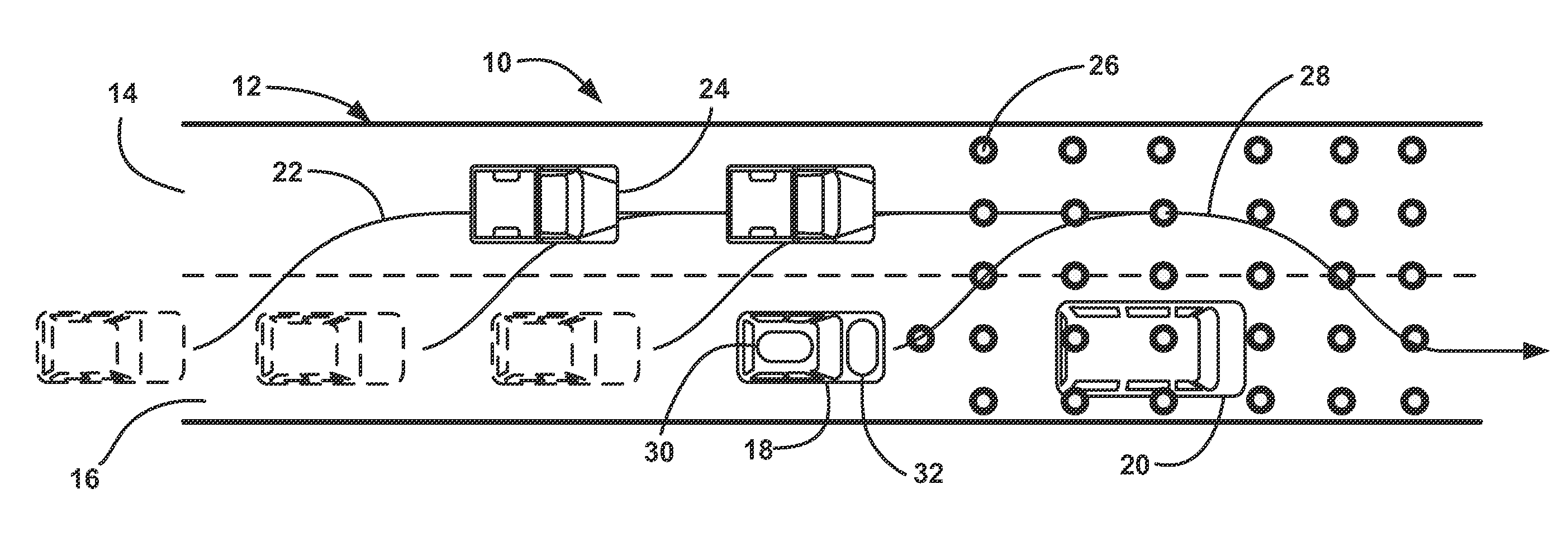
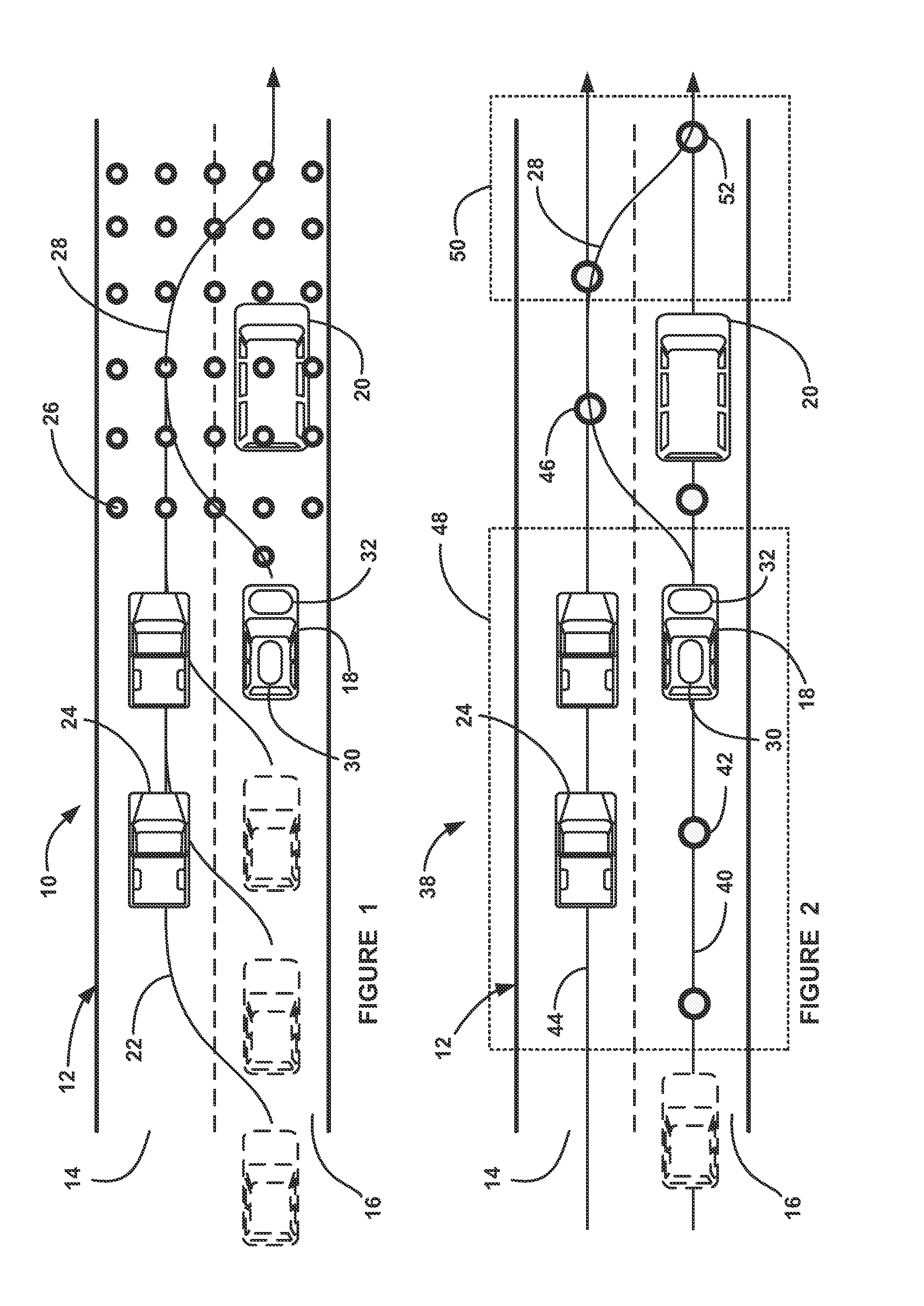
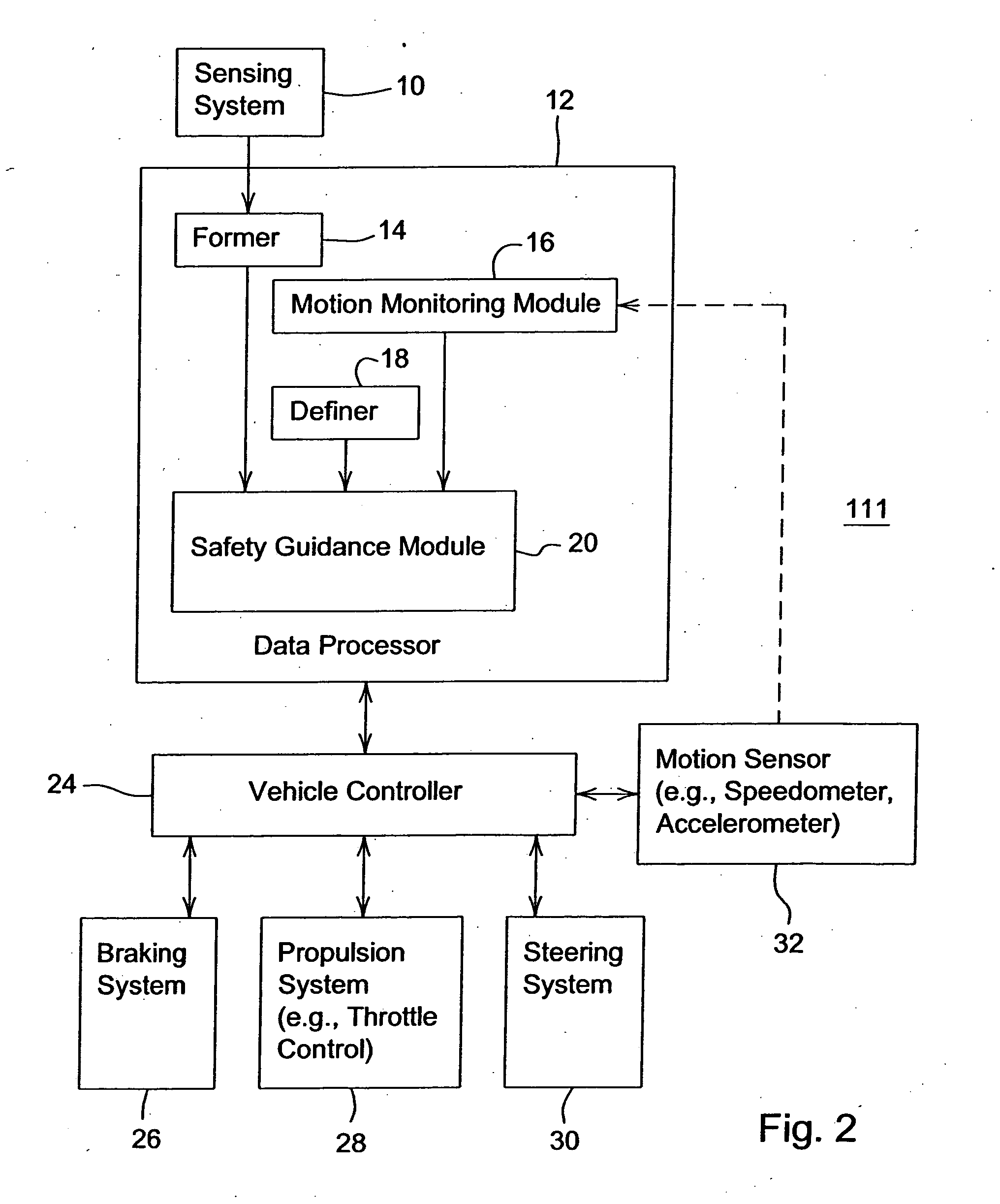
ActiveUS20060293856A1Facilitating collision avoidanceAnti-collision systemsExternal condition input parametersGrid basedEngineering
A sensing system collects position data associated with one or more obstacles within a certain range of a vehicle. A former establishes an occupancy grid based on the collected position data. A motion monitoring module determines a reaction distance and a deceleration distance associated with a vehicle at a regular time interval during an operational state. A safety guidance module establishes a safety zone (e.g., safety zone grid) for the regular time interval based on the occupancy grid, the determined reaction distance, and the deceleration distance.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Processing apparatus, processing system, and processing method
InactiveUS20150334269A1Solve problemsImage enhancementTelevision system detailsComputer visionObject detector
A processing apparatus includes a distance image acquirer, a moving-object detector, and a danger-level determining unit. The distance image acquirer acquires a distance image containing distance information of each pixel. The moving-object detector detects a moving object from the distance image. The danger-level determining unit determines a danger level of the moving object by use of the distance image, and outputs the danger level to a controller that controls a controlled unit in accordance with the danger level.
Owner:RICOH KK
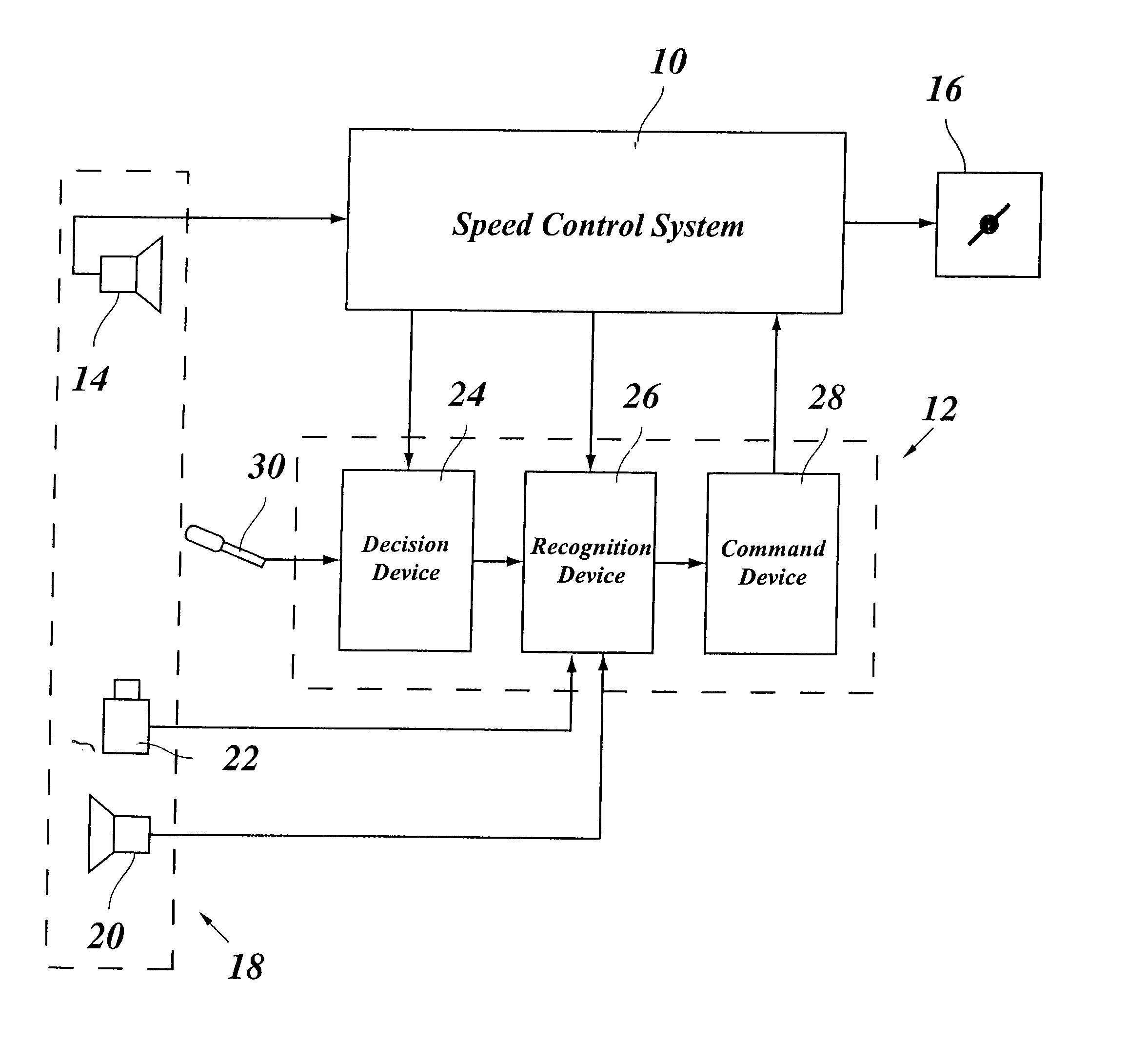
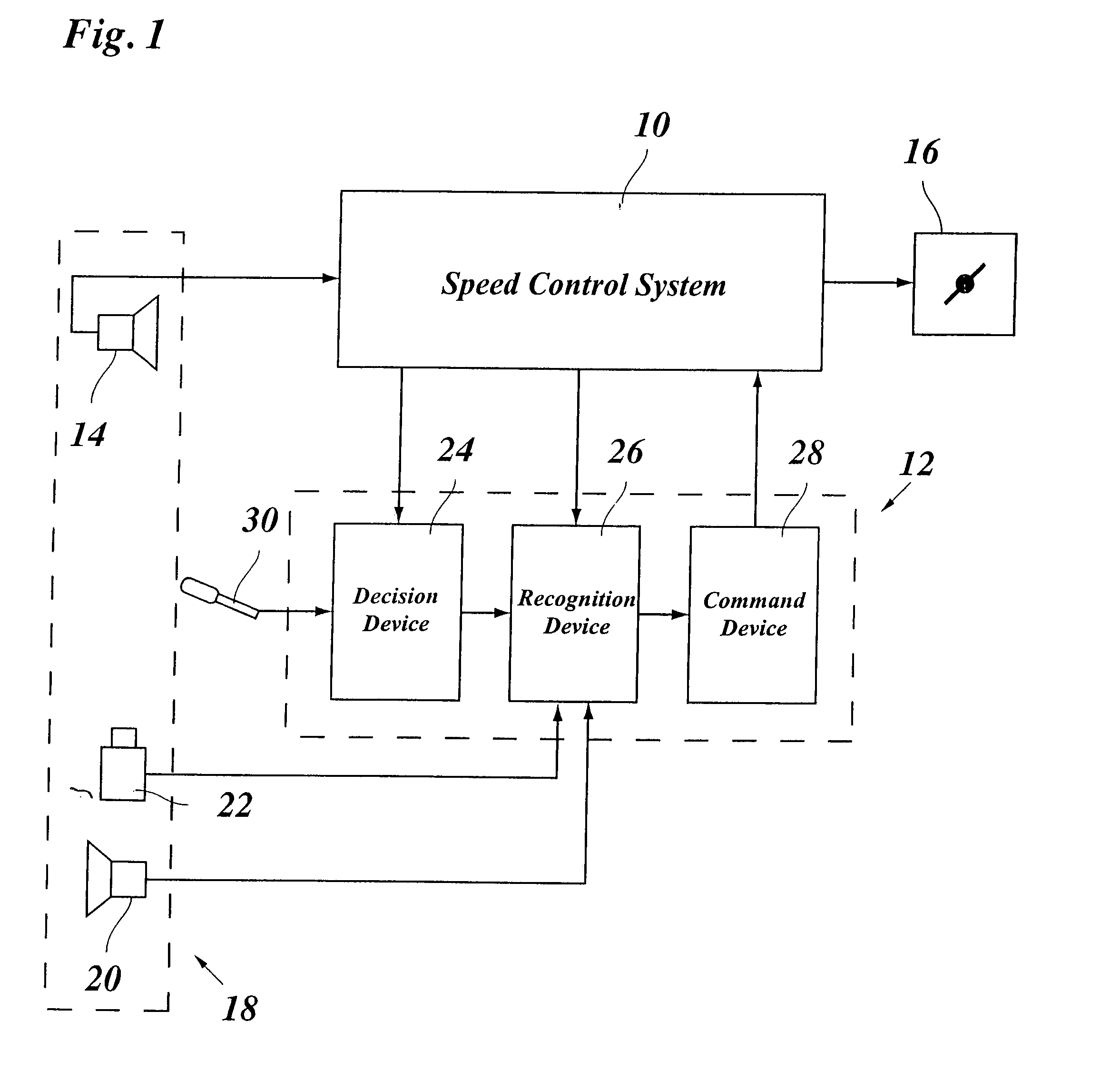
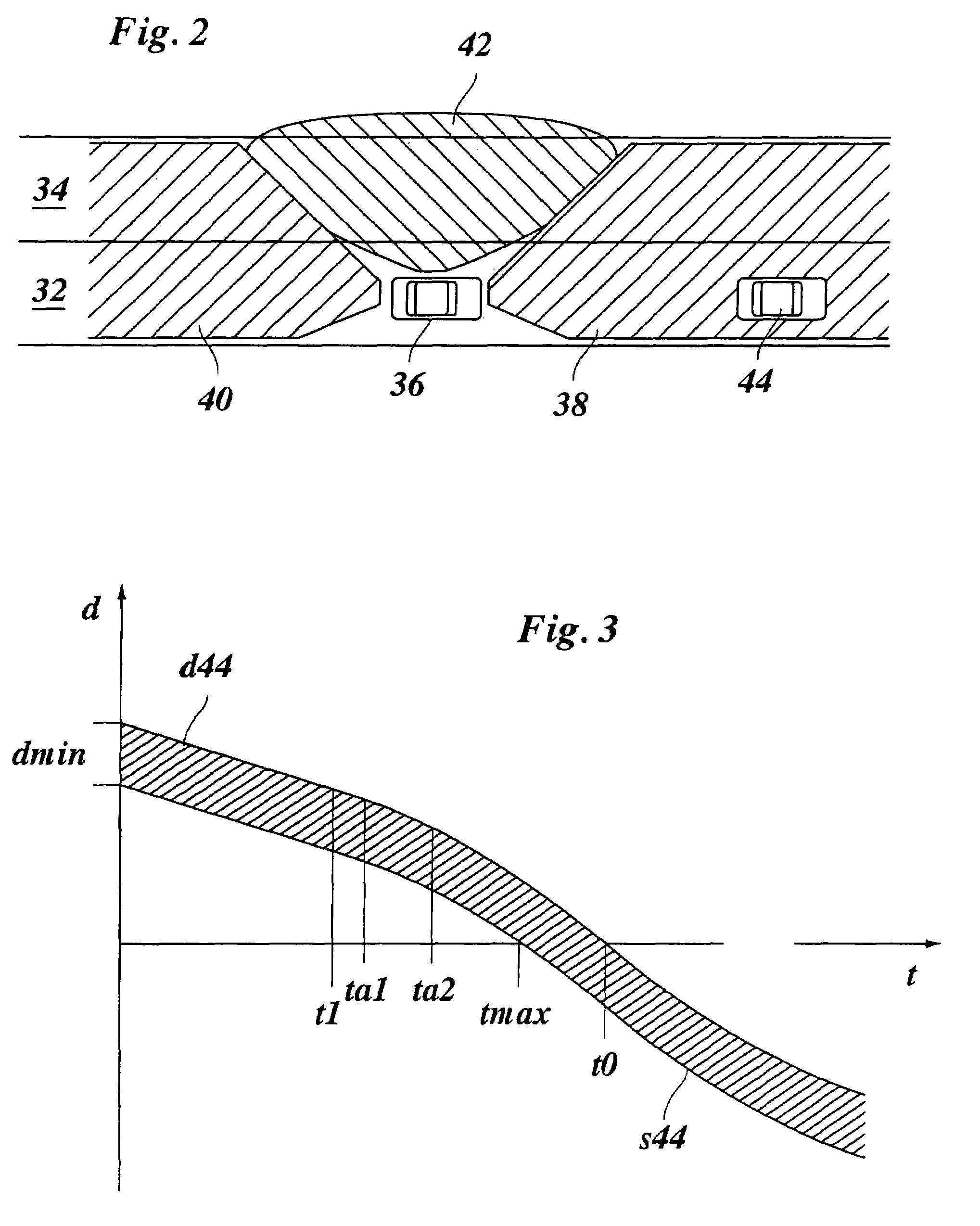
Lane changing assistant for motor vehicles
ActiveUS20060009910A1Easy to changeAvoid stimulationVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsDriver/operatorControl system
A lane changing assistant for motor vehicles, having a speed control system and a surroundings sensor system for recording the traffic environment including the traffic in an adjacent lane, having a decision device for deciding whether a lane changing request of the driver is to be accepted, and having a command device for issuing an acceleration command to the speed control system in the case of a lane changing request, wherein a recognition device is developed to recognize a window for swinging into the adjacent lane without danger, in the light of the data of the surroundings sensor system; and the command device is developed to compute an acceleration strategy adjusted to the window, including a point in time for the beginning of the acceleration.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Feedback Performance Control and Tracking
ActiveUS20180127001A1Instruments for road network navigationAutonomous decision making processDriver/operatorEngineering
A method is provided for optimizing the use of autonomous features of advanced driver assistance systems and the tracking thereof. For example, a vehicle may be equipped with several driver assistance systems in which a driver of the vehicle may be assisted. The vehicle may automatically change the number of active assistance systems or suggest to the driver one or more assistance systems to activate based on several factors, including poor driving on behalf of the driver or poor driving conditions due to weather or road quality. Statistics regarding the use of such advanced driver assistance systems may be monitored and tracked and stored on an onboard database or transmitted continuously or periodically to various entities. For example, the system may operate to allow an insurance company to track the driving performance and the use of the advanced driver assistance systems to update actuarial models to more accurately adjust rates.
Owner:NIO TECH ANHUI CO LTD
System and method for responding to driver behavior
Methods of assessing driver behavior include monitoring vehicle systems and driver monitoring systems to accommodate for a driver's slow reaction time, attention lapse and / or alertness. When it is determined that a driver is drowsy, for example, the response system may modify the operation of one or more vehicle systems. The systems that may be modified include: visual devices, audio devices, tactile devices, antilock brake systems, automatic brake prefill systems, brake assist systems, auto cruise control systems, electronic stability control systems, collision warning systems, lane keep assist systems, blind spot indicator systems, electronic pretensioning systems and climate control systems.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Lane changing assistant for motor vehicles
ActiveUS7363140B2Easy to changeAvoid stimulationVehicle fittingsAnalogue computers for trafficMobile vehicleDriver/operator
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
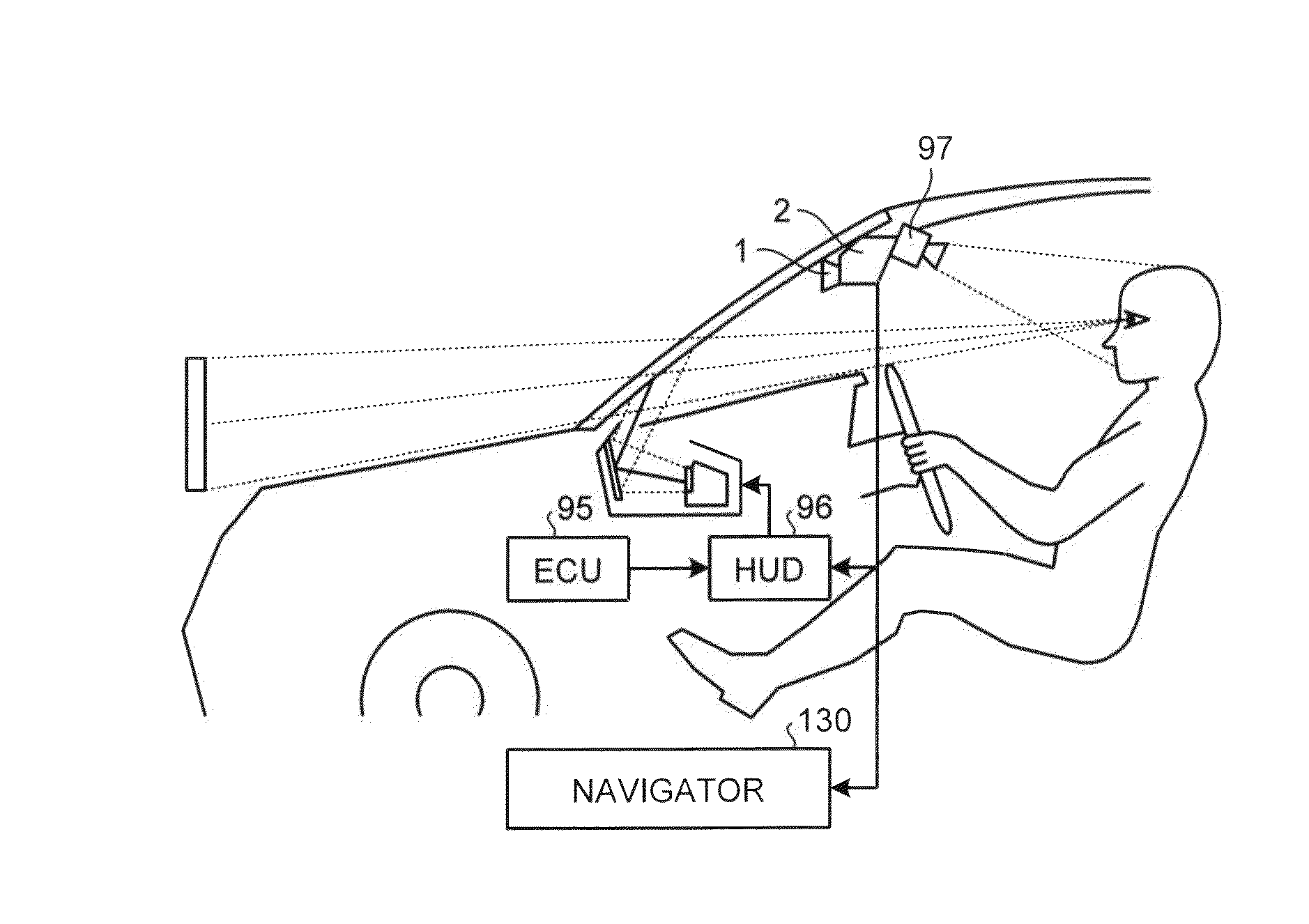
Driving support device, driving support system and driving support method
ActiveUS20170203763A1Efficient methodResistor terminals/electrodesRoad vehicles traffic controlSupporting systemSupport system
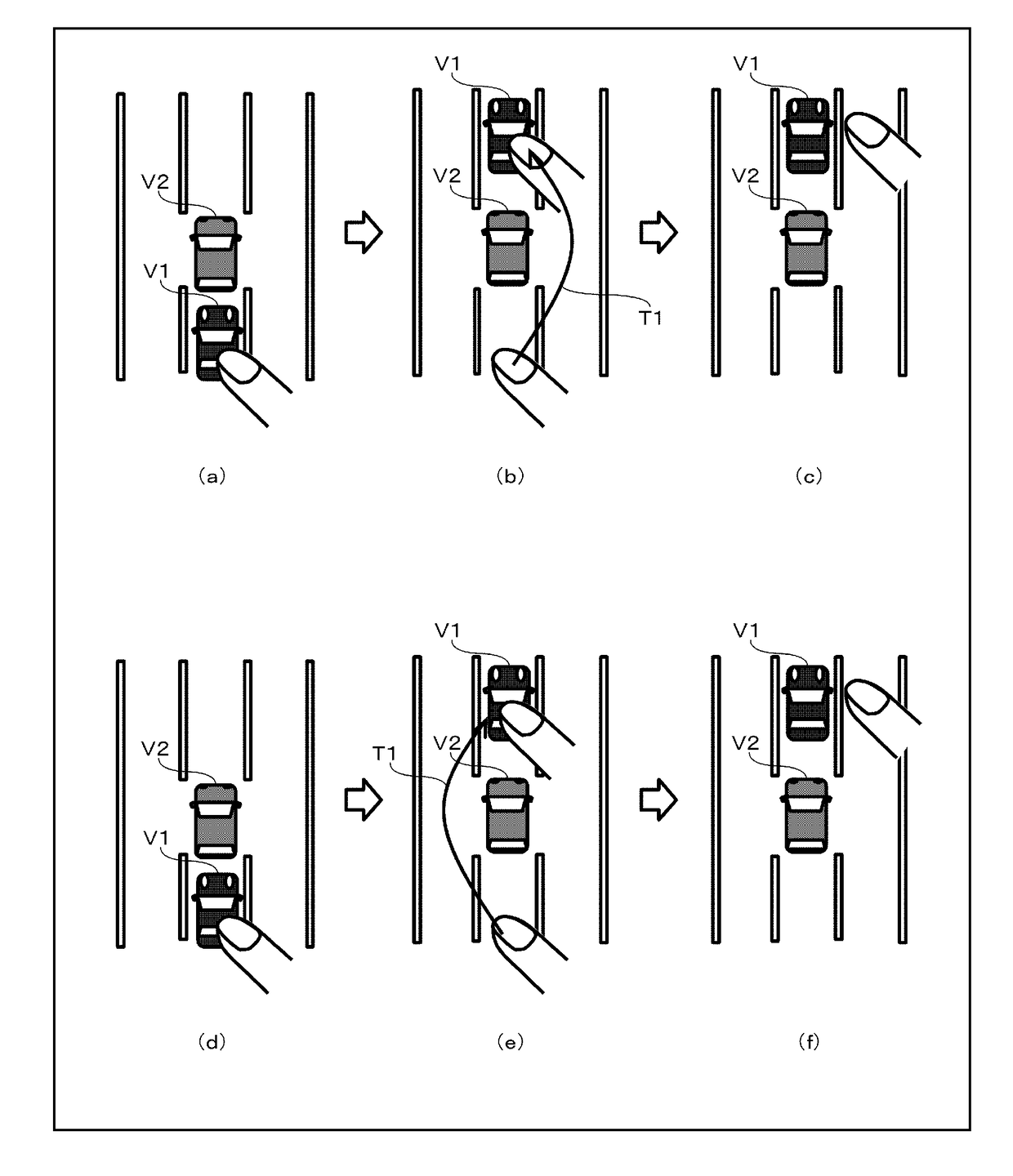
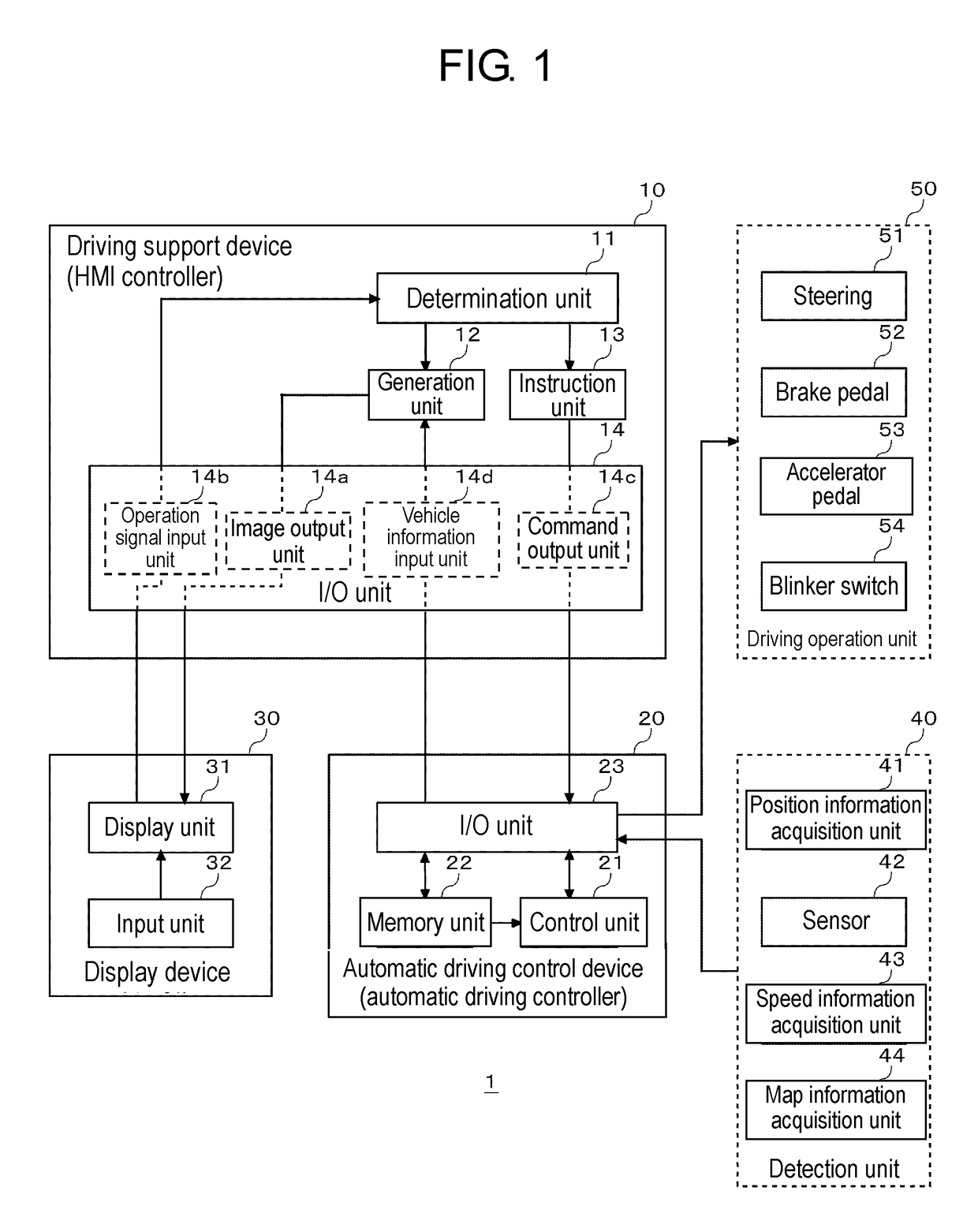
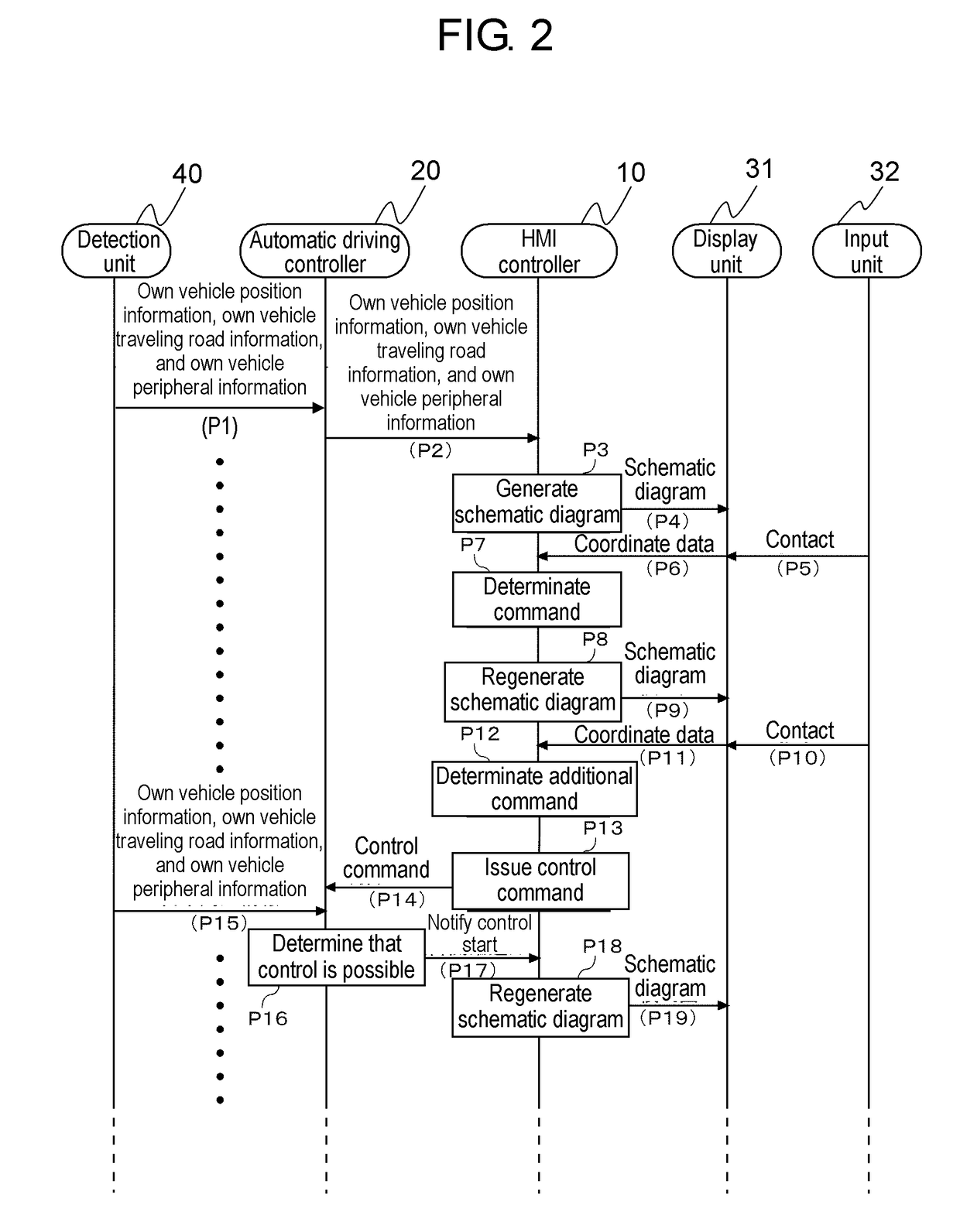
A driver can intuitively and conveniently perform an operation for instructing passing to a vehicle. In a driving support device 10, an image output unit 14a outputs, to a display unit 31, an image containing an own vehicle object representing an own vehicle and an another vehicle object representing another vehicle in front of the own vehicle object. An operation signal input unit 14b receives an operation of a user for changing the positional relationship between the own vehicle object and the another vehicle object in the image displayed on the display unit 31. A command output unit 14c outputs, to an automatic driving control unit 20, a command for instructing the own vehicle to pass the another vehicle when the positional relationship between the own vehicle object and the another vehicle object is changed such that the own vehicle object is positioned in front of the another vehicle object.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Systems and methods for navigating a vehicle
A system for navigating a host vehicle may receive an image representative of an environment of the host vehicle and determine a planned navigational action for accomplishing a navigational goal of the host vehicle. The system may identify a target vehicle, determine a current speed of the target vehicle, and assume a maximum braking rate capability of the target vehicle. The system may determine a next-state distance between the host vehicle and the target vehicle that would result if the planned navigational action was taken. The system may implement the planned navigational action if the host vehicle may be stopped using a predetermined sub-maximal braking rate within a distance that is less than the determined next-state distance summed together with a target vehicle travel distance determined based on the current speed of the target vehicle and the maximum braking rate capability of the target vehicle.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
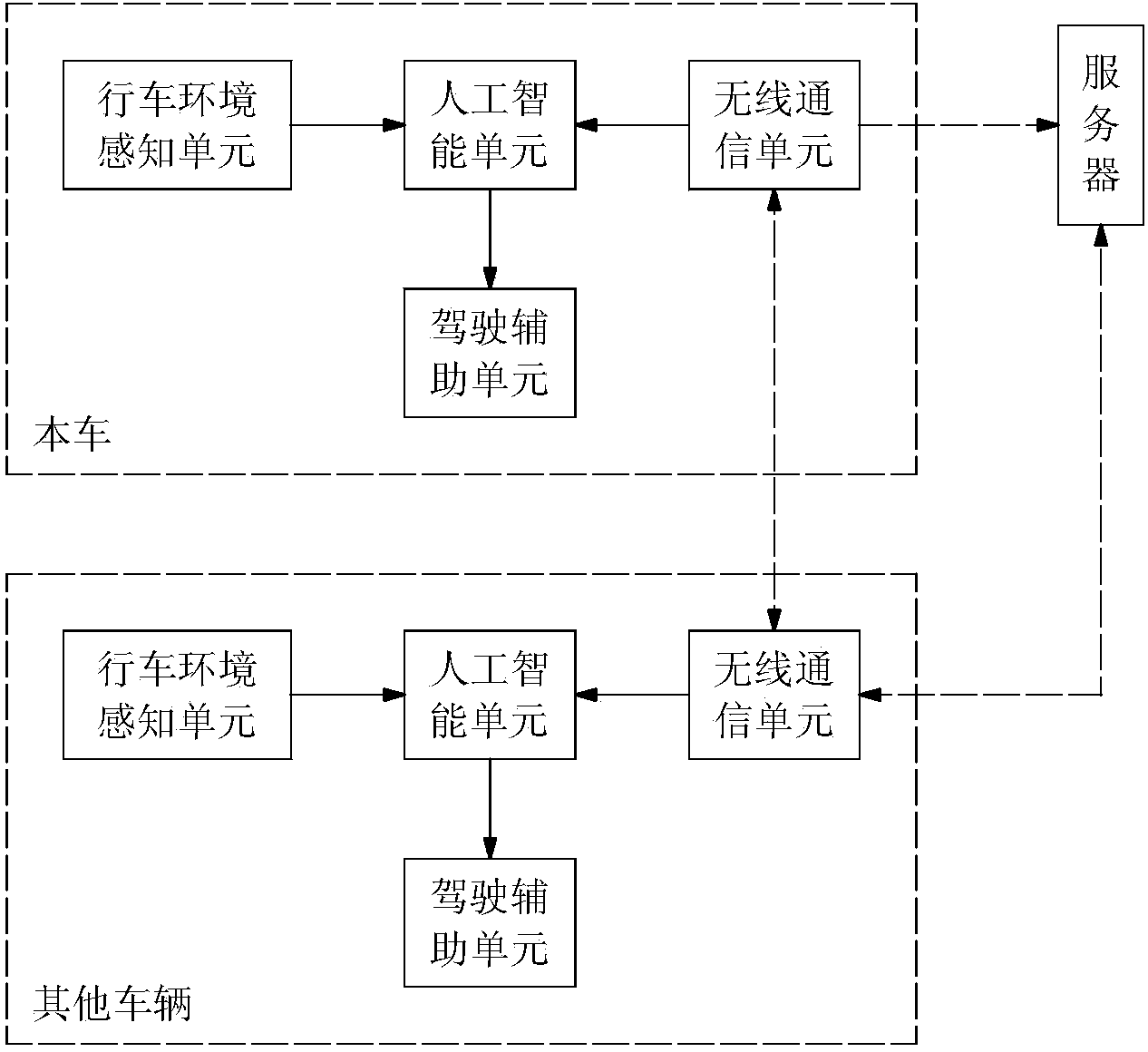
Driving assistance system based on artificial intelligence
ActiveCN104386063AReduce driving fatigueImprove securityExternal condition input parametersSignalling/lighting devicesIntelligent designDriver/operator
The invention belongs to the field of vehicle intelligence design, and in particular relates to a driving assistance system based on artificial intelligence. The system comprises a driving environment sensing unit and a wireless communication unit, wherein the driving environment sensing unit is used for identifying the ambient environment of a vehicle; the wire communication unit is used for communicating between the vehicle and surrounding vehicles and a server terminal; information acquired by the driving environment sensing unit and the wireless communication unit is output to an artificial intelligence unit for processing; and a driving assistance unit realizes the functions of vehicle speed adjustment, vehicle distance adjustment, lane change, overtaking and parking according to processed output control signals. The system can realize the functions of self-adaptive cruise control and automatic parking to relieve the driving fatigue of drivers, and can monitor the ambient environment of the vehicle to actively evade dangers so as to improve the driving safety.
Owner:WUHU LION AUTOMOTIVE TECH CO LTD
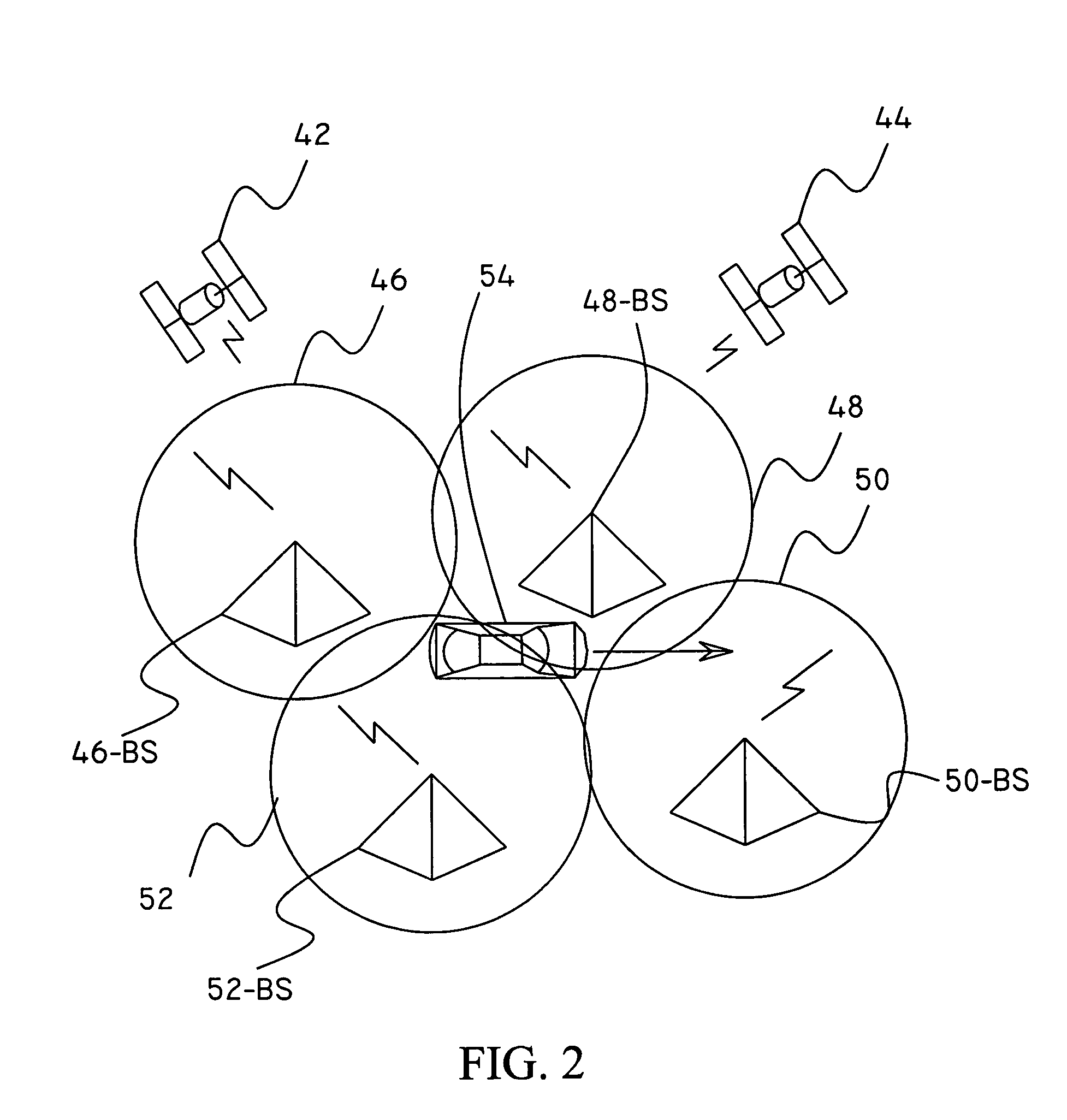
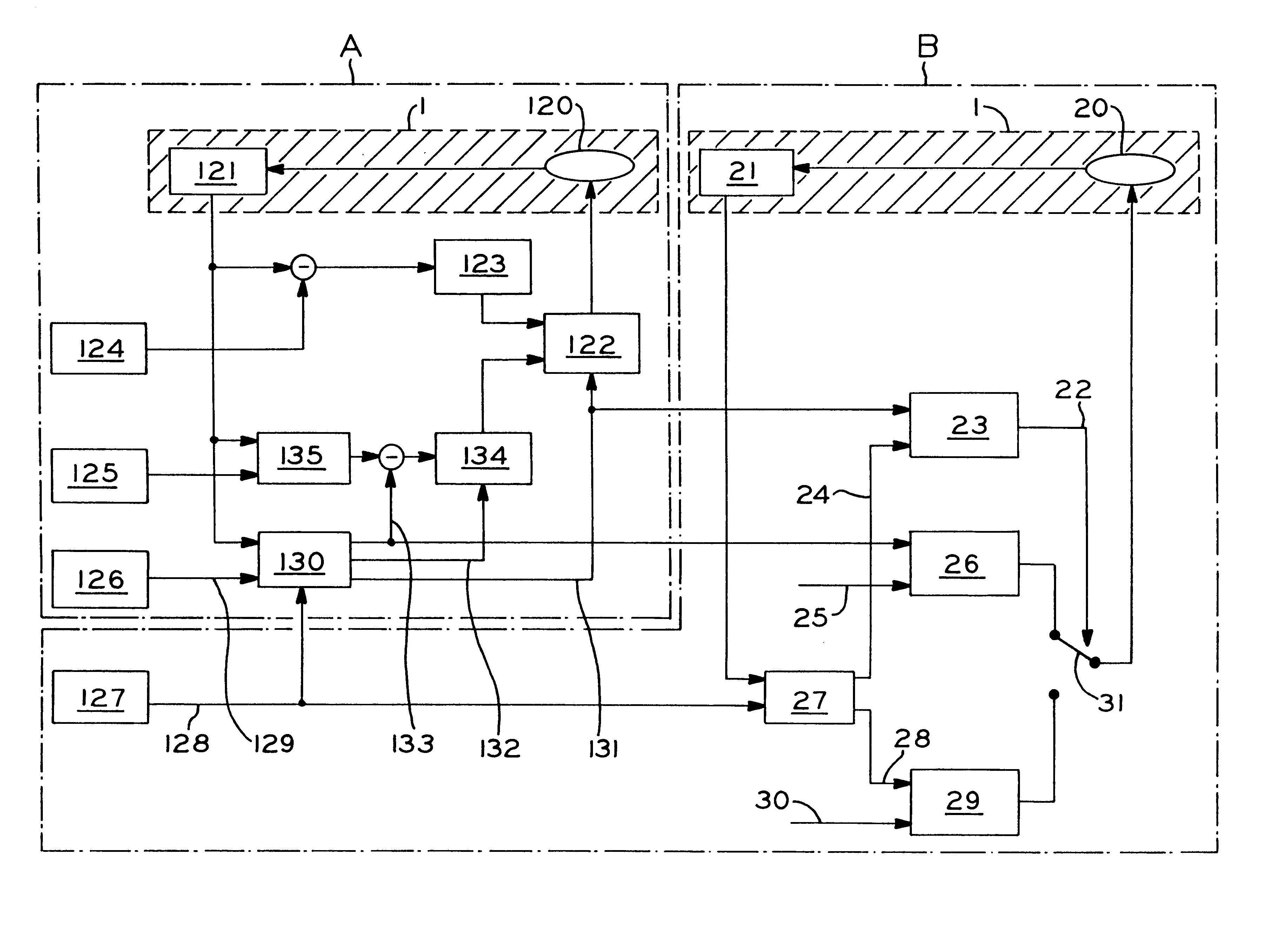
Automatic following guidance system for motor vehicles
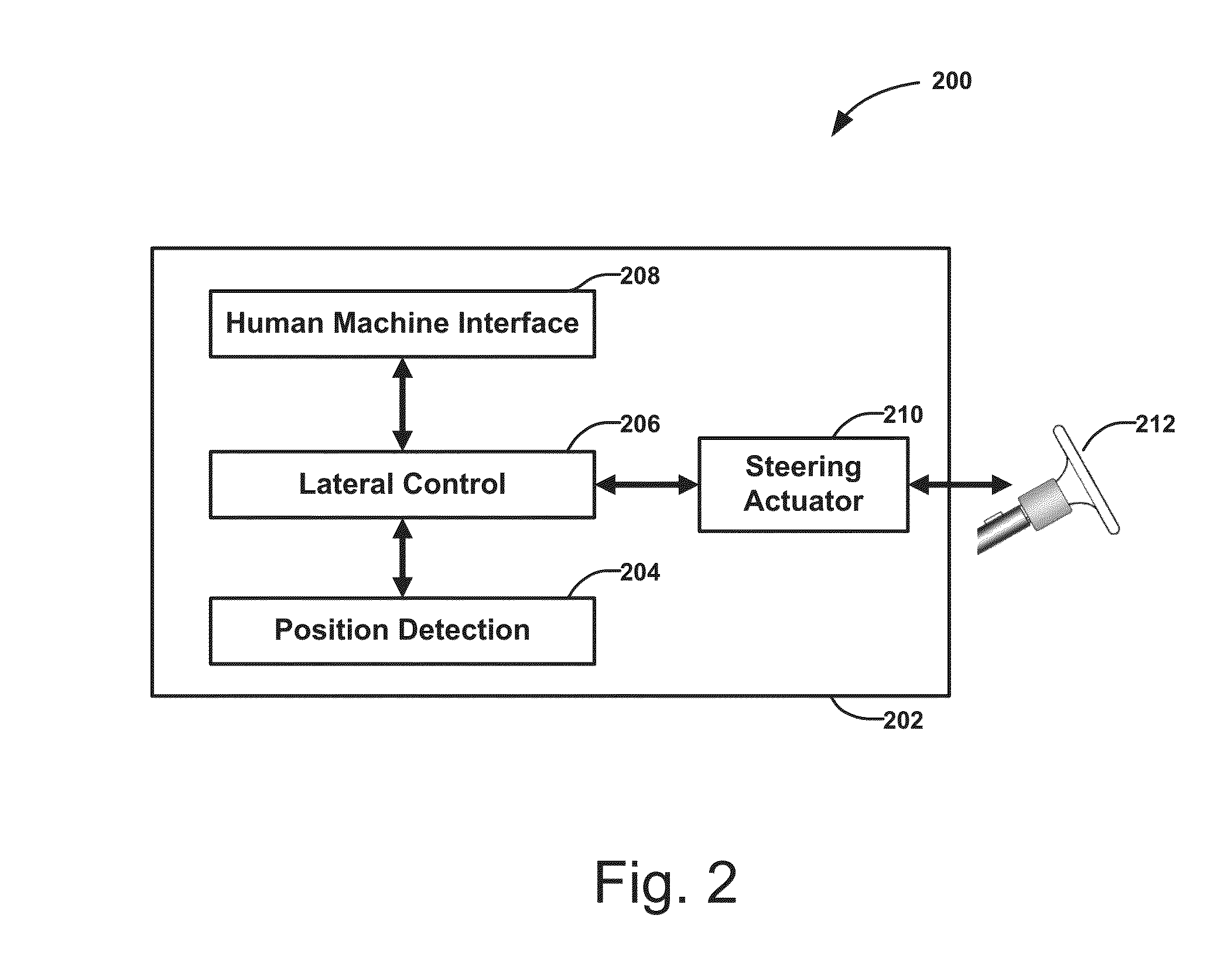
InactiveUS6370471B1Reduce the burden onVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsGuidance systemLevel iv
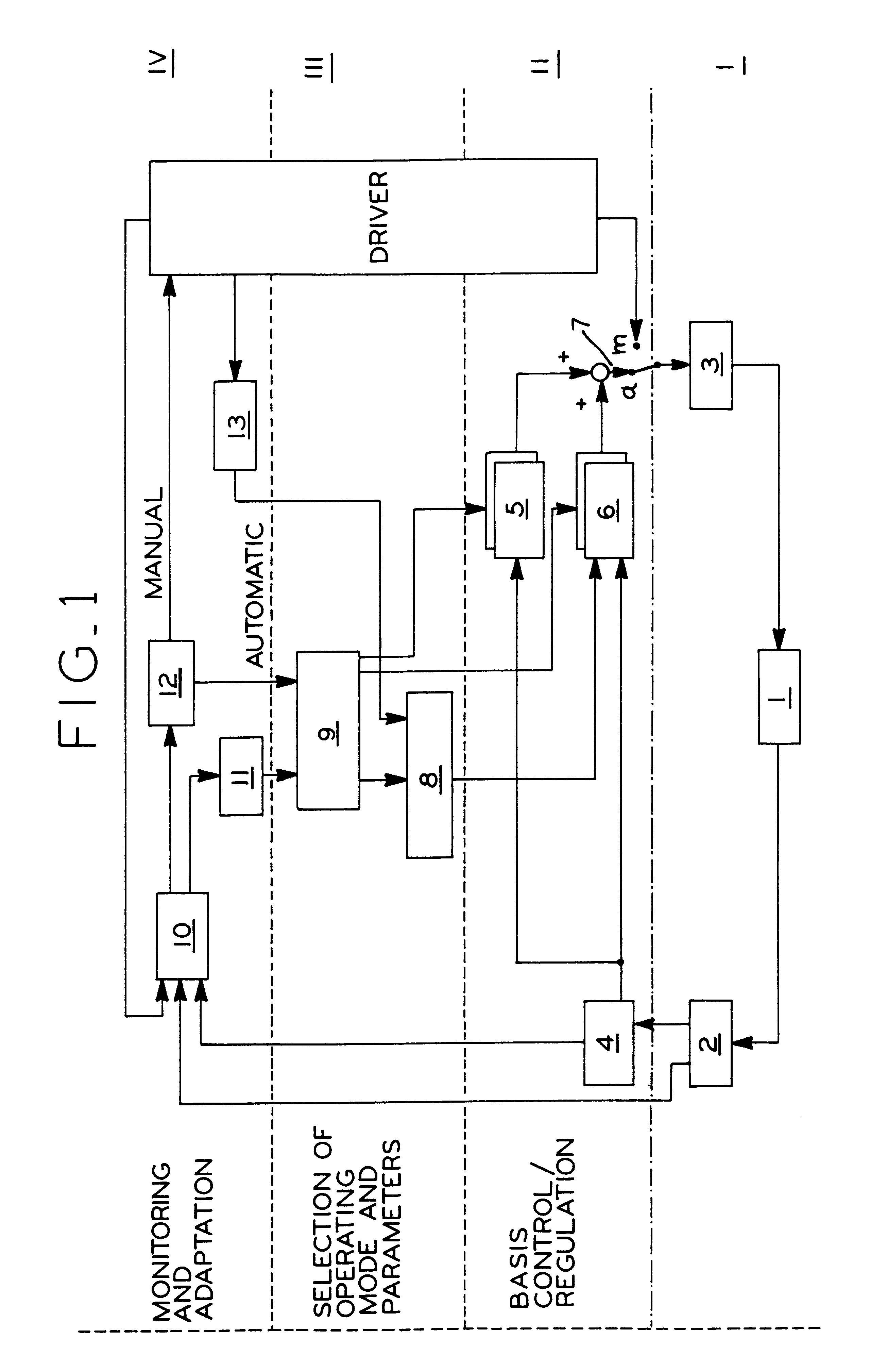
The invention concerns a system for automatic following guidance, particularly for heavy-traffic automatic following guidance, of a motor vehicle (1), designed to ease the burden on the driver in heavy-traffic situations both by taking over lateral guidance by means of an automatic steering regulation system and by maintaining a set distance from a leading vehicle. The latter function requires an adaptive cruise and braking regulation system with "stop" and "go" function. According to the invention, selection and decision means (5, 6, 7, 8, 9) are provided that select both the regulating parameters and the types of controllers [sic], e.g., following guidance of the motor vehicle (1) on the basis of lane markings recognized by means of a video camera or on the basis of a recognized leading vehicle. The system is divided into hierarchical levels I-IV, the driver always being in the monitoring and adaptation loop assigned to the top level IV of the hierarchy, so that he has the highest priority and can override the system at any time.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Autonomous Navigation System
ActiveUS20170363430A1Instruments for road network navigationExternal condition input parametersAutonomous Navigation SystemRemote system
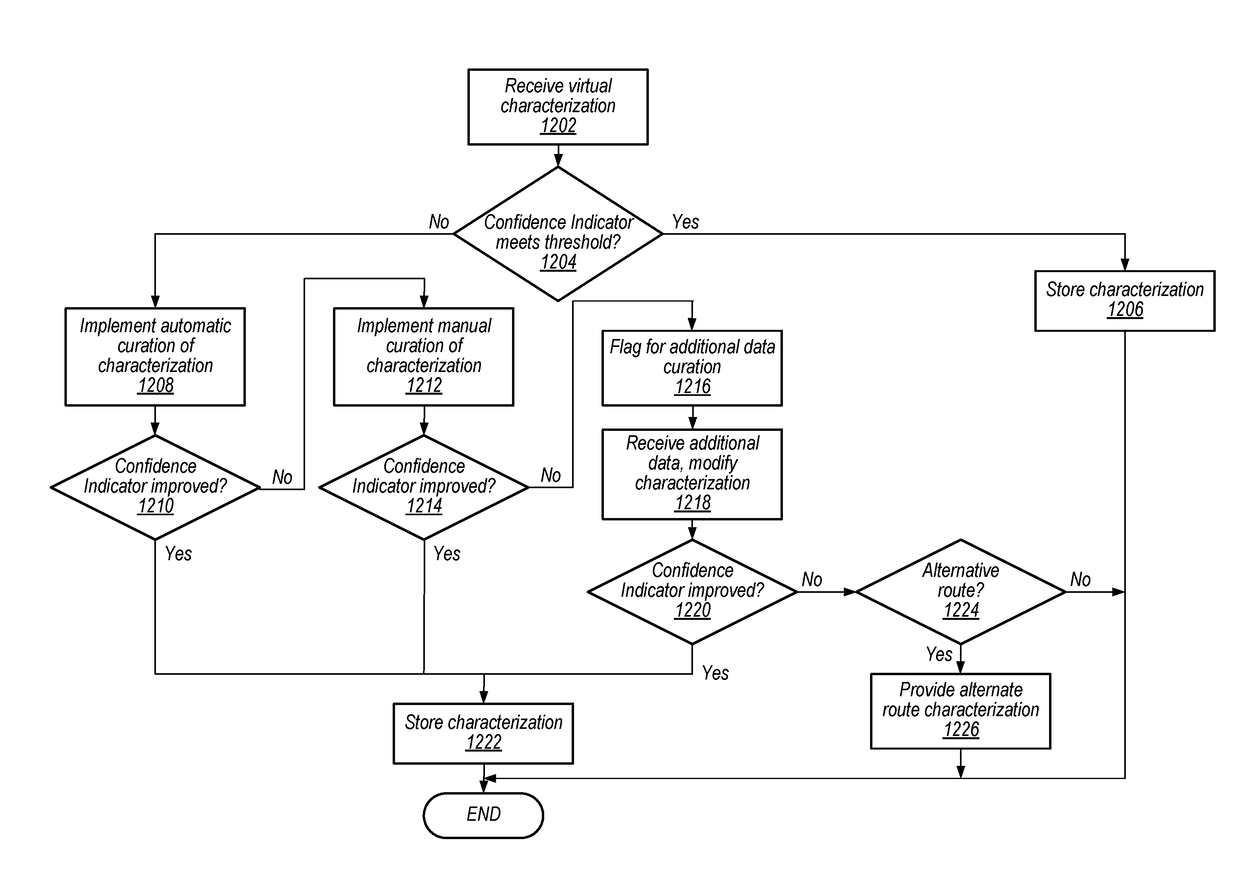
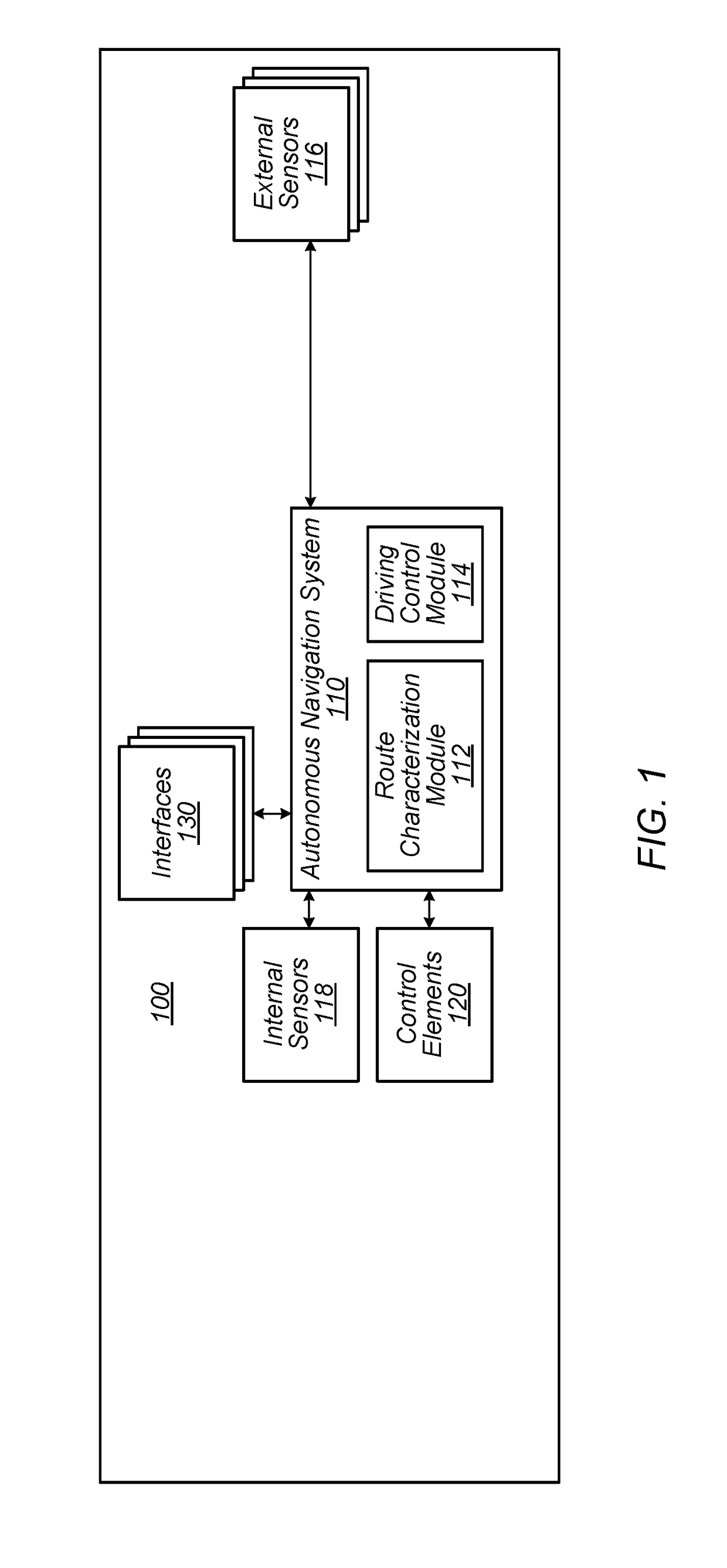
Some embodiments provide an autonomous navigation system which enables autonomous navigation of a vehicle along one or more portions of a driving route based on monitoring, at the vehicle, various features of the route as the vehicle is manually navigated along the route to develop a characterization of the route. The characterization is progressively updated with repeated manual navigations along the route, and autonomous navigation of the route is enabled when a confidence indicator of the characterization meets a threshold indication. Characterizations can be updated in response to the vehicle encountering changes in the route and can include a set of driving rules associated with the route, where the driving rules are developed based on monitoring the navigation of one or more vehicles of the route. Characterizations can be uploaded to a remote system which processes data to develop and refine route characterizations and provide characterizations to one or more vehicles.
Owner:APPLE INC
Highly Assisted Driving Platform
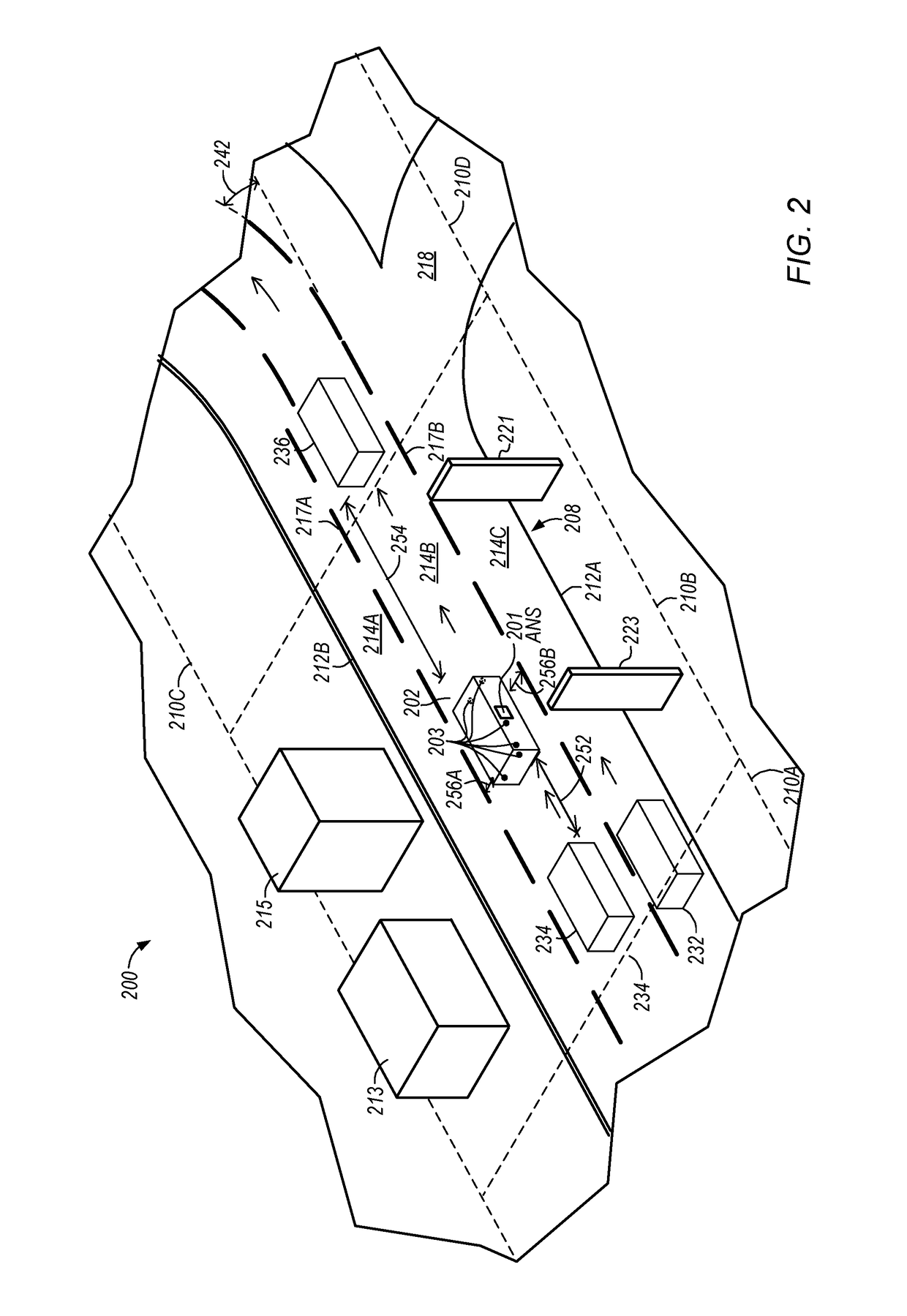
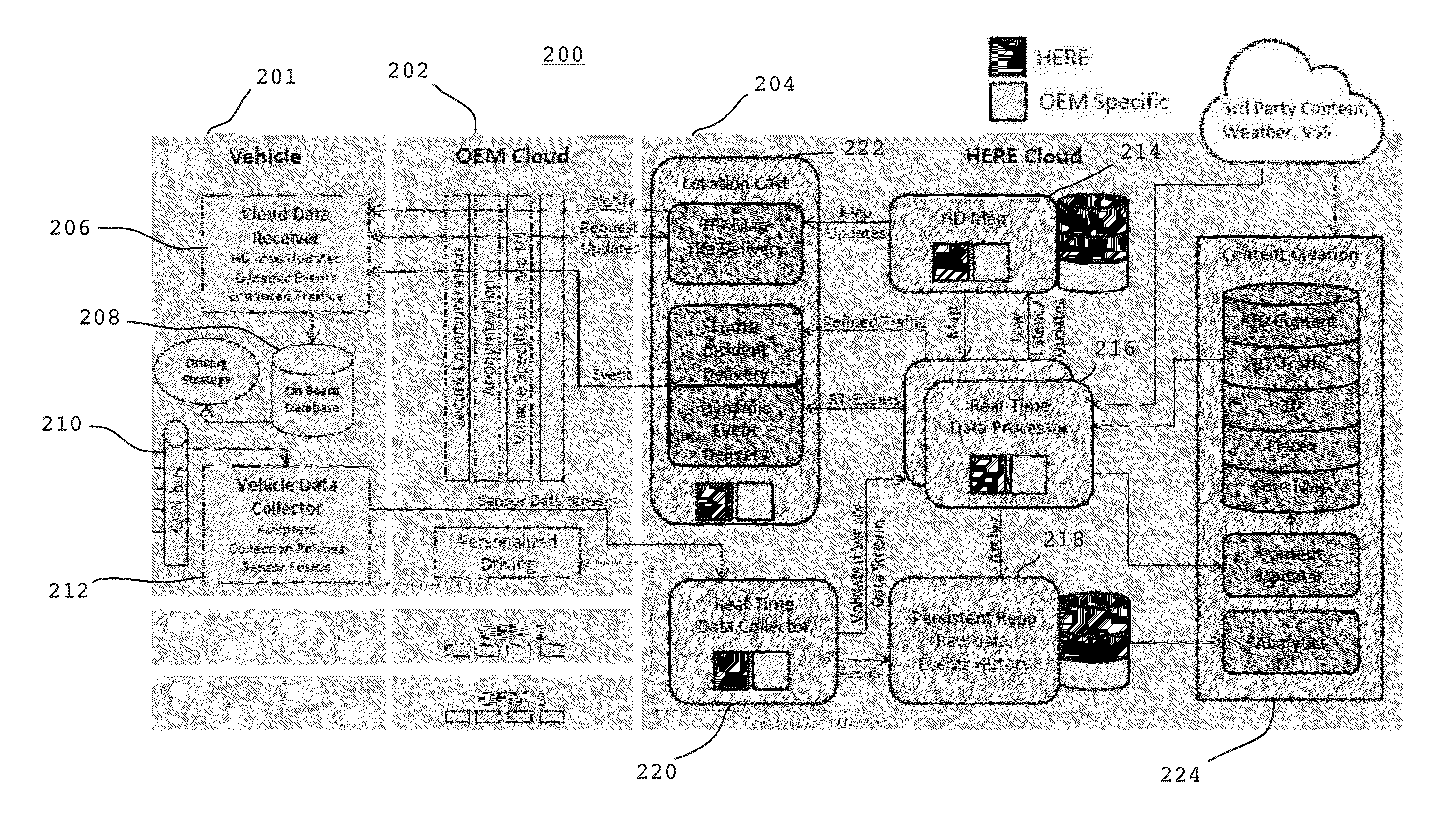
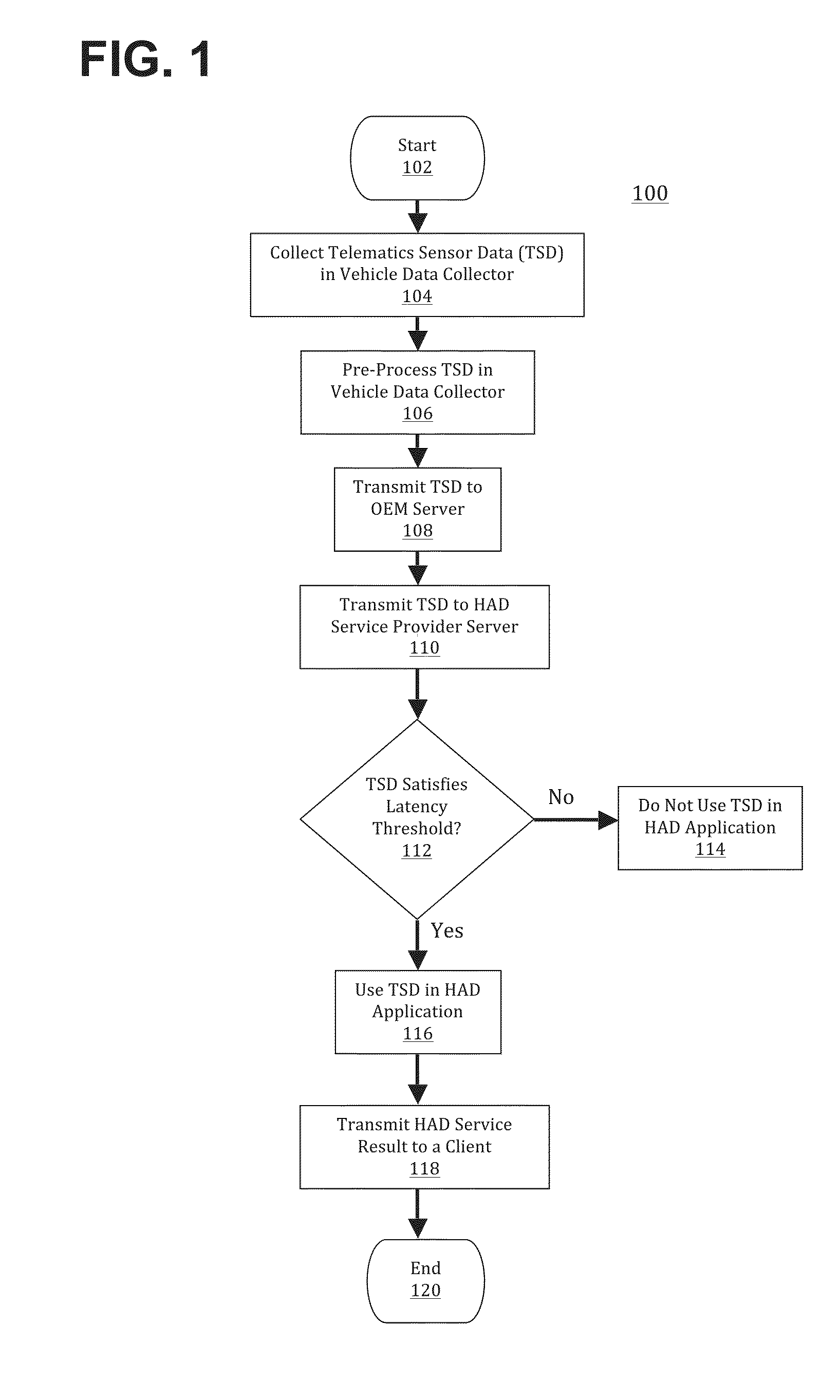
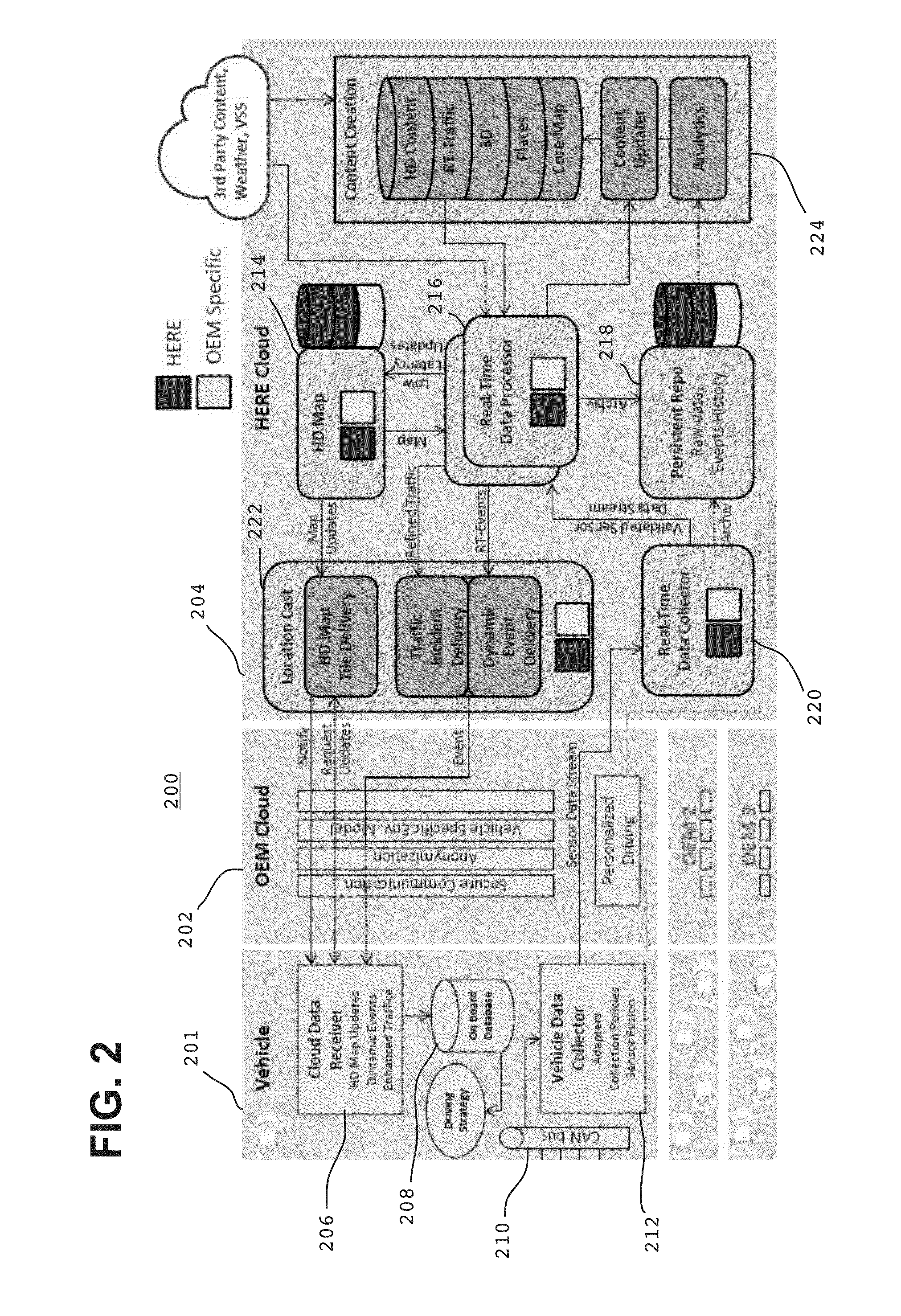
ActiveUS20160028824A1Autonomous decision making processRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesClient-sideComputer science
Methods for providing a highly assisted driving (HAD) service include: (a) transmitting telematics sensor data from a vehicle to a remote first server; (b) transmitting at least a portion of the telematics sensor data from the remote first server to a remote second server, wherein the remote second server is configured to execute a HAD application using received telematics sensor data, and wherein the HAD application is configured to output a HAD service result; and (c) transmitting the HAD service result from the remote second server to a client. Apparatuses for providing a HAD service are described.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
Dynamic dispatching and schedule management methods for an intelligent transit system with electronic guided buses
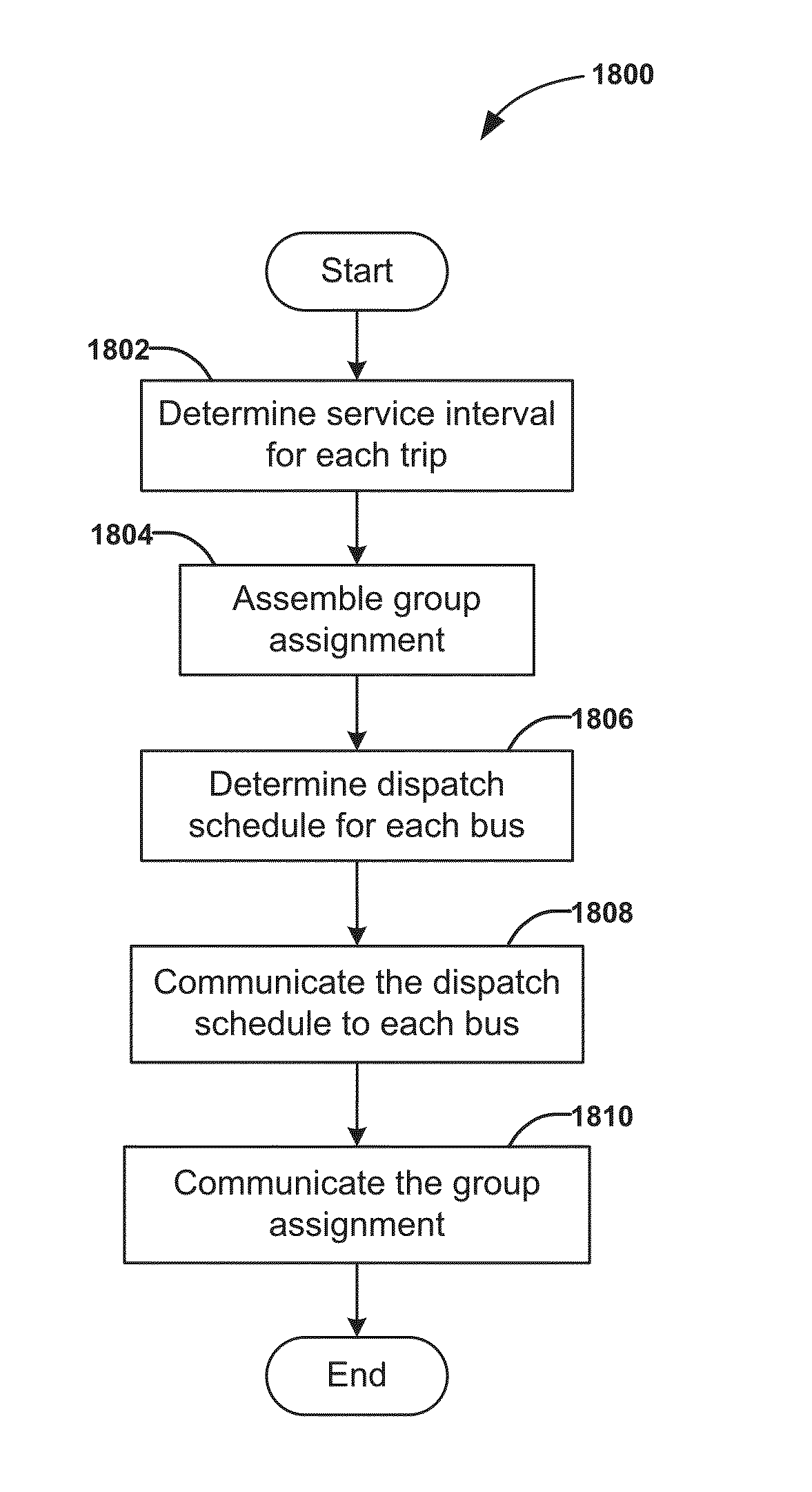
InactiveUS20150294430A1Increasing driver workloadIncreasing transit operational costDigital data processing detailsExternal condition input parametersGuided busTransit system
A method for dispatching buses in groups for a bus transit system comprising determining a service interval for each trip of the bus transit system, assembling group assignments based on the service interval for each trip, determining a dispatch schedule for each bus based on the service interval and the group assignment, communicating the dispatch schedule to each bus, and communicating group assignment information to each of a plurality of the buses in a group. The group assignment assigns a plurality of the buses into a group on a segment of the trip shared by the plurality of buses such that multiple buses for different trips can dock at a station at the same time like a train to facilitate transferring passengers.
Owner:TOMORROWS TRANSPORTATION TODAY
Vehicle multi-target coordinating lane changing assisting adaptive cruise control method
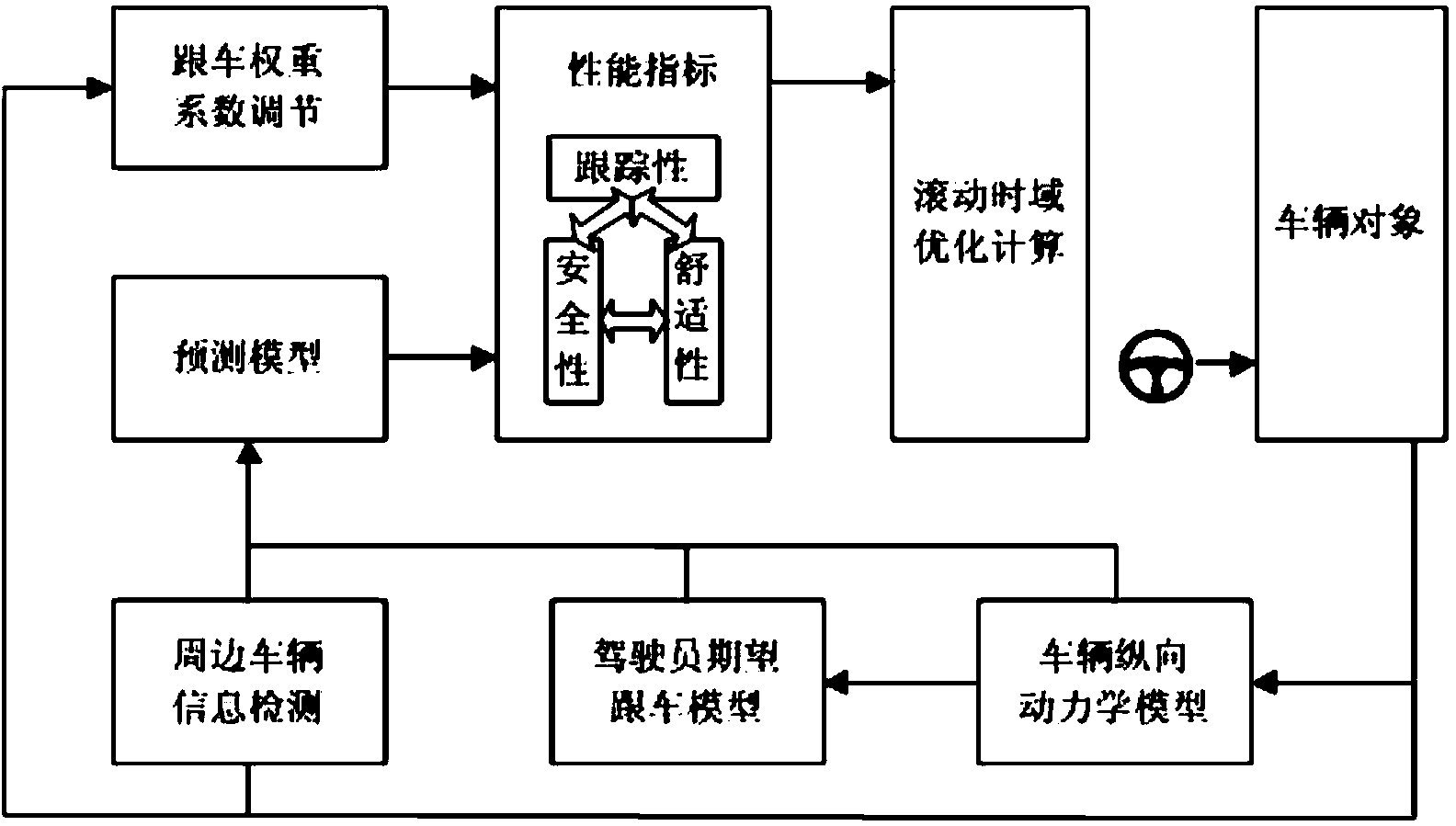
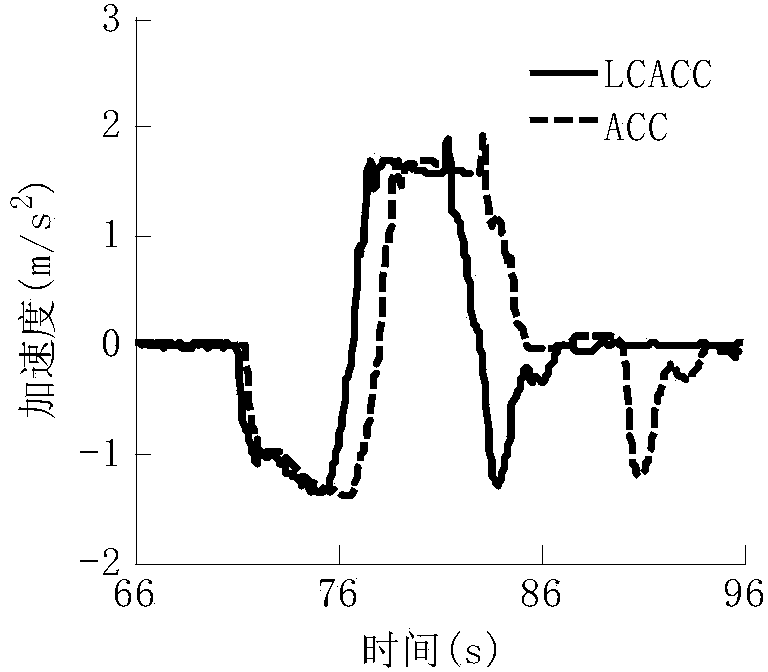
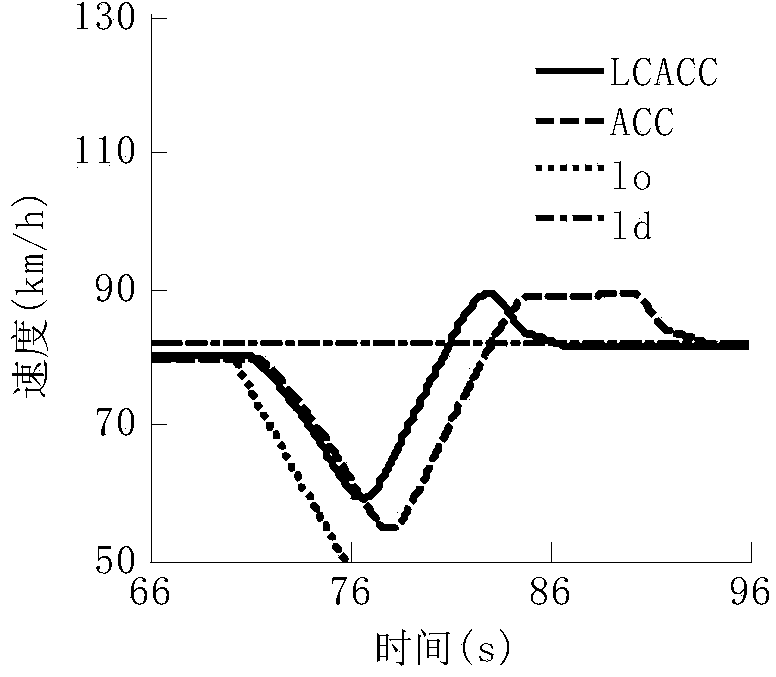
ActiveCN103754224AEnsuring the safety of changing lanesEnsure lane change safetyExternal condition input parametersExternal condition output parametersTime domainDriver/operator
The invention relates to a vehicle multi-target coordinating lane changing assisting adaptive cruise control method. The method comprises the following steps that 1) LCACC combination property indexes are set according to two-front-vehicle traceability, multi-vehicle movement safety and longitudinal driving comfort requirements, and the LCACC combination property indexes comprise a cost function and I / O constraints; 2) a multi-target coordinating optimal control problem is built, solving is carried out through a rolling time domain optimization algorithm, the optimal control quantity is obtained, and optimal control is achieved. The LCACC cost function is set according to the following steps that a) a traceability cost function is built through a two-norm linear combination of the vehicle distance errors and vehicle speed errors of the own vehicle and two front vehicles; b) a comfort cost function is built by restraining longitudinal acceleration. The LCACC I / O constraints are set according to the steps that a) in the respect of tracking performance, vehicle following error constraints which are used for limiting the vehicle speed errors and the vehicle distance errors and allowed by a driver are obtained through driver experimental data in a statistic mode; b) in the respect of safety performance, the safety distance between the own vehicle and multiple surrounding vehicles is restrained in the view of vehicle following and collision avoidance; c) in the respect of comfort performance, the expected longitudinal acceleration data range is restrained.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
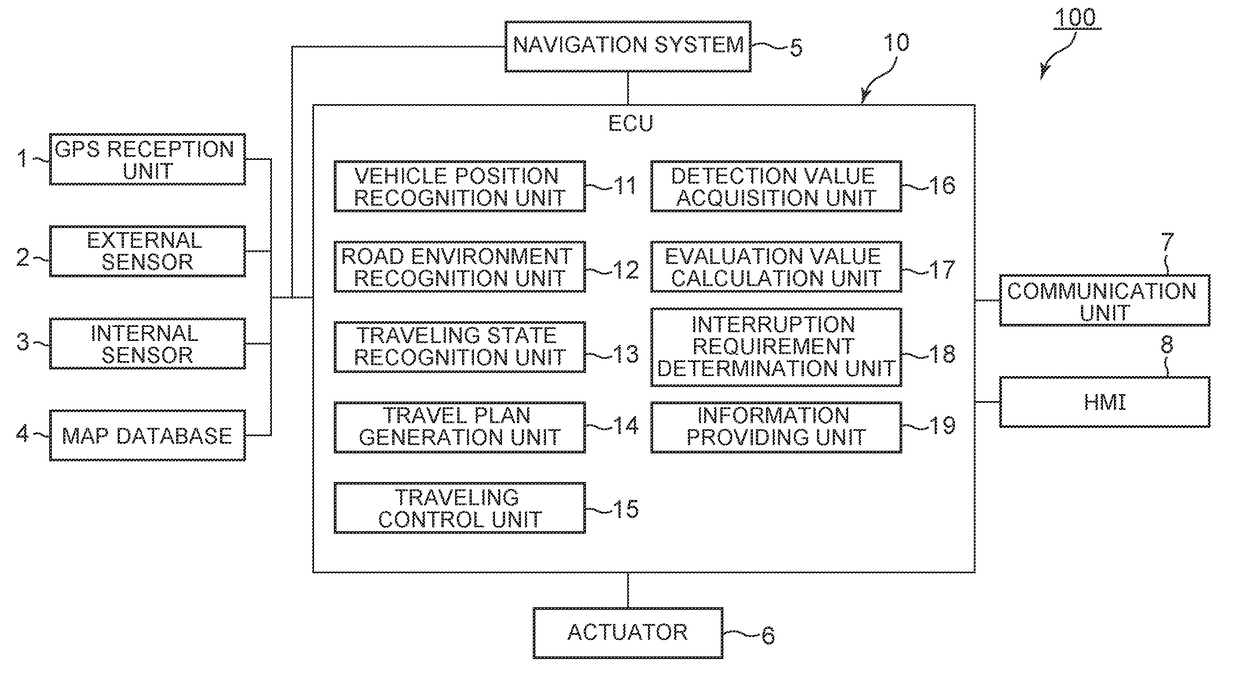
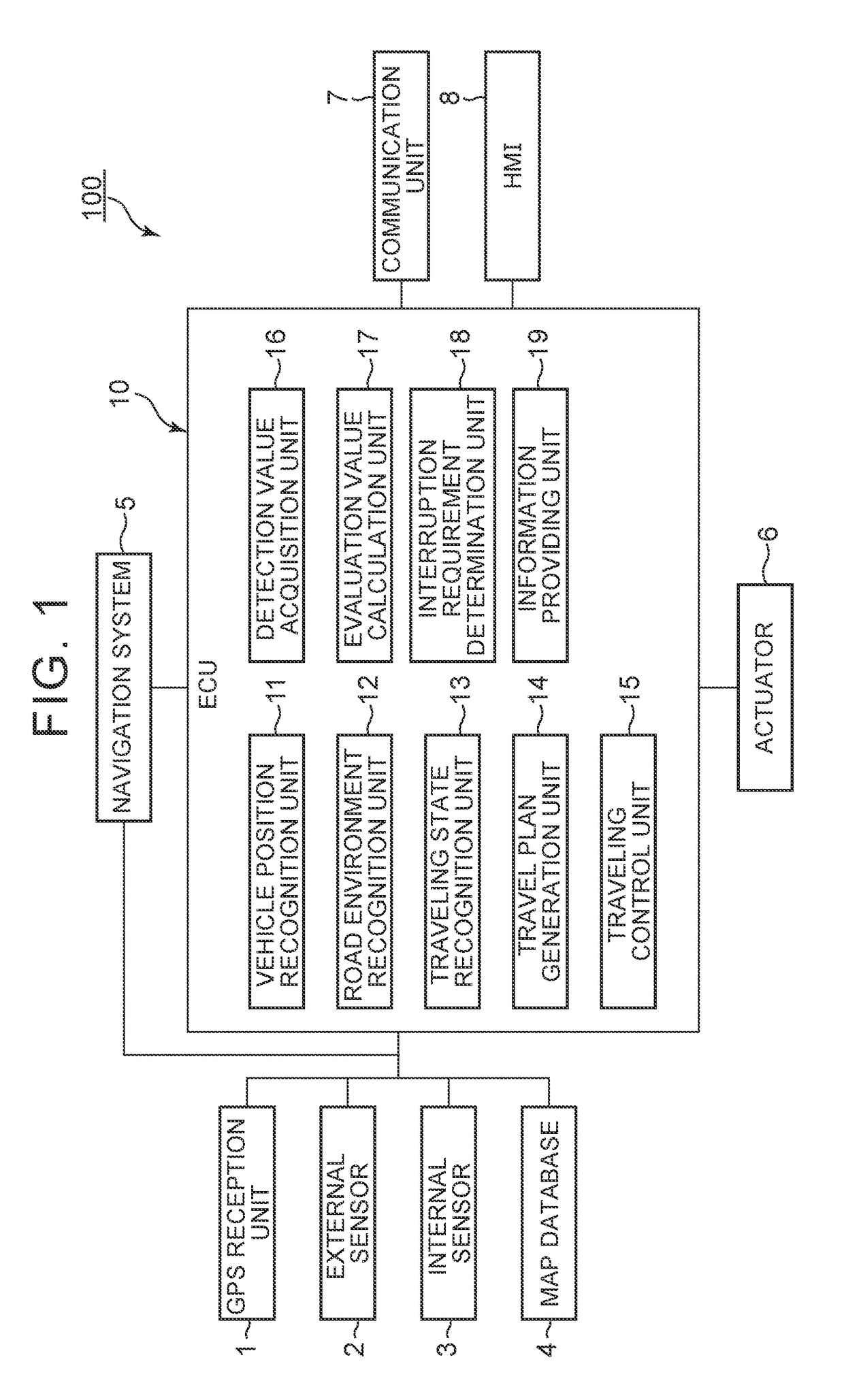
Autonomous driving system
ActiveUS20170123434A1Improve information accuracyConvenient and accurateInstruments for road network navigationAutonomous decision making processProgram planningEngineering
An autonomous driving system includes a travel plan generation unit that generates a travel plan of a vehicle, a traveling control unit that performs autonomous driving control of the vehicle b, a detection value acquisition unit that acquires a control-result detection value detected during the autonomous driving control, an evaluation value calculation unit that calculates an evaluation value of the travel plan based on a result of comparison between the control target value and the control-result detection value, an interruption requirement determination unit that determines whether an interruption of the autonomous driving control is required based on the evaluation value of the travel plan and an evaluation threshold, and an information providing unit that provides interruption information on the autonomous driving control to an occupant of the vehicle and to other vehicles around the vehicle if it is determined that the interruption of the autonomous driving control is required.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
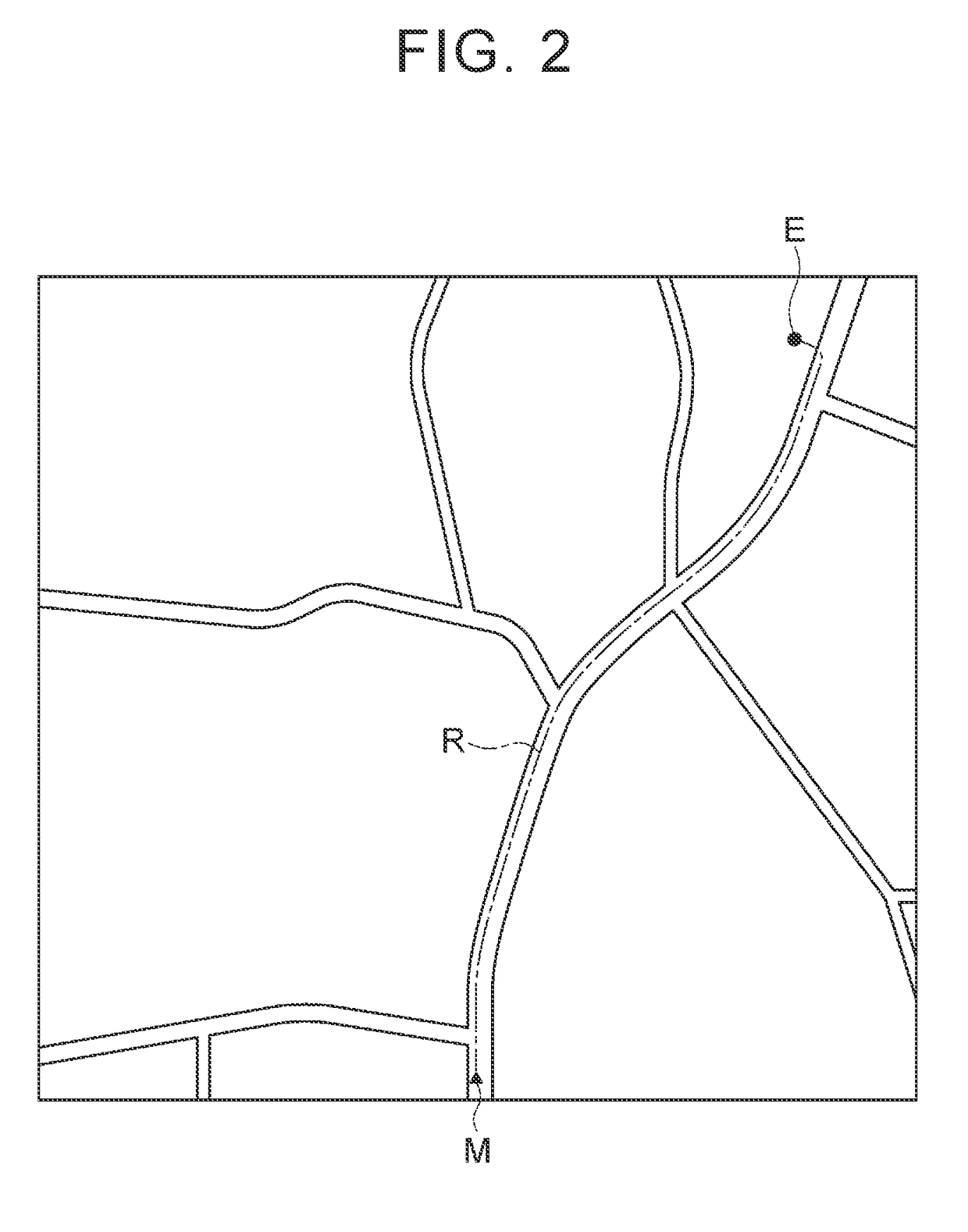
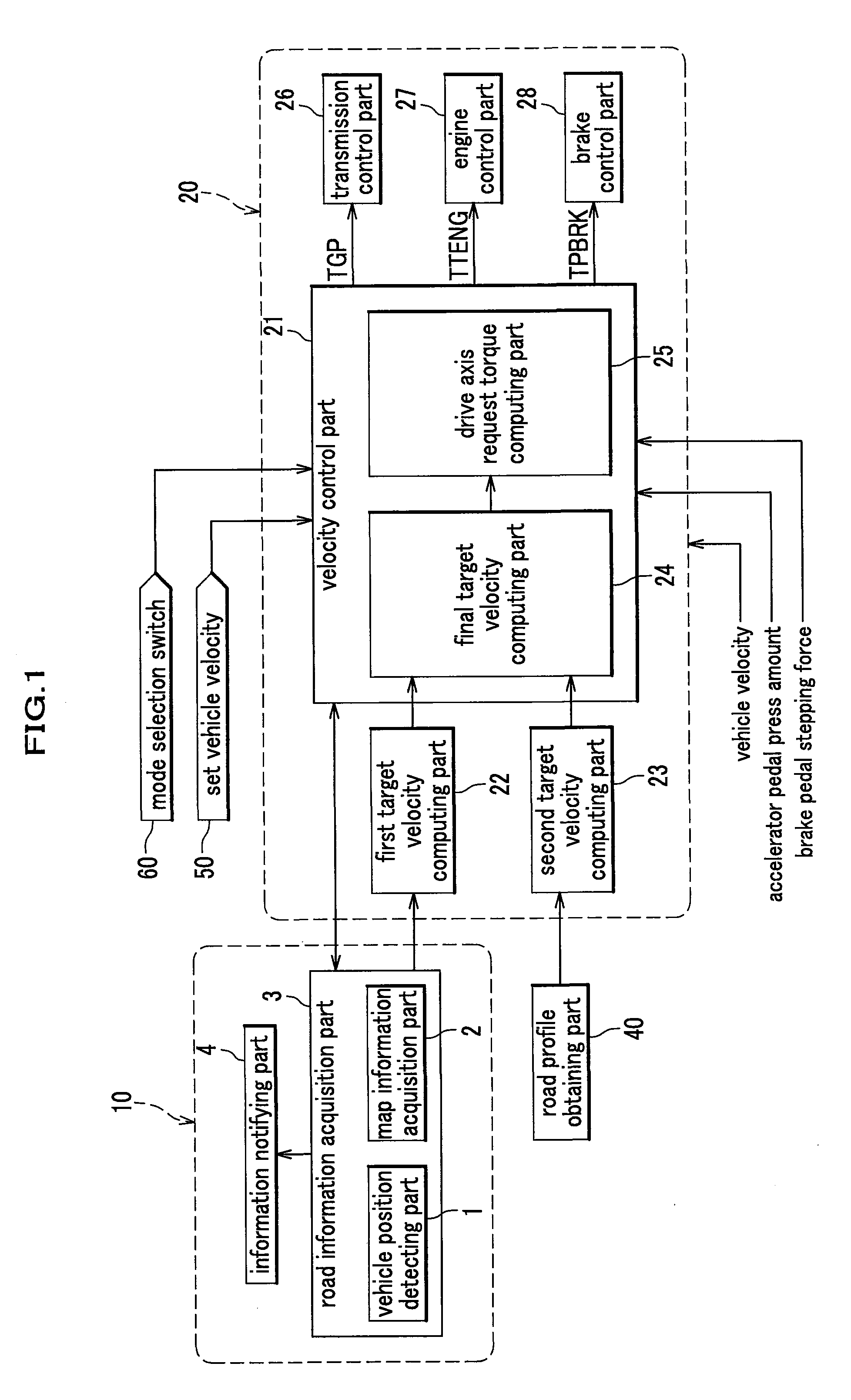
Vehicle Speed Control System
InactiveUS20080059036A1Stable speed controlFeel goodAnalogue computers for trafficAnti-collision systemsSpeed control systemControl system
A vehicle speed control system includes: a unit for computing a first target velocity based on map information; a unit for computing a second target velocity based on a road profile obtained from other information than the map information (such as lane recognition using a camera); a unit for comparing the first target velocity and the second target velocity; a unit for selecting a lower target velocity therefrom; and a unit for controlling a vehicle velocity in accordance with the selected target velocity.
Owner:CLARION CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com