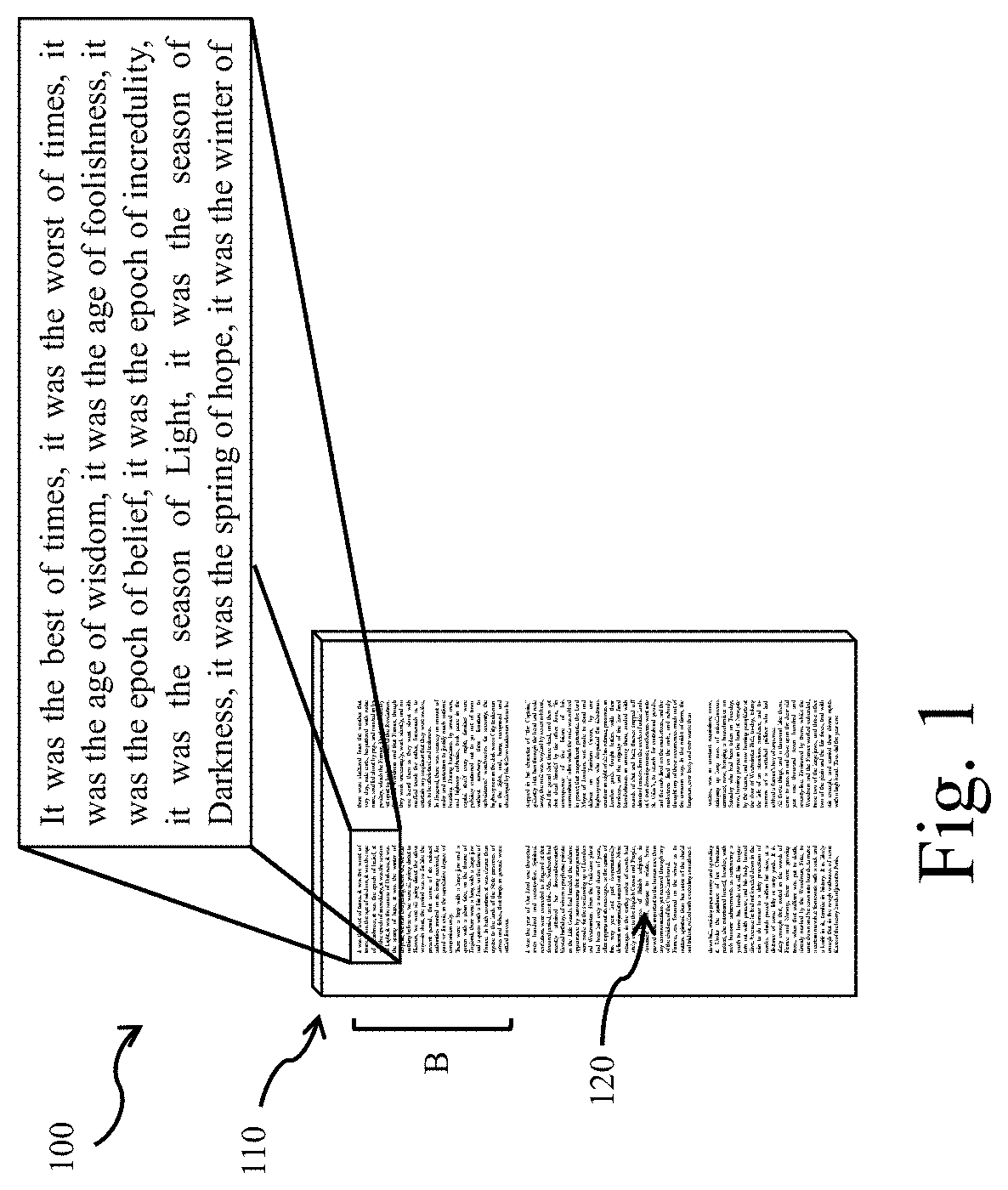
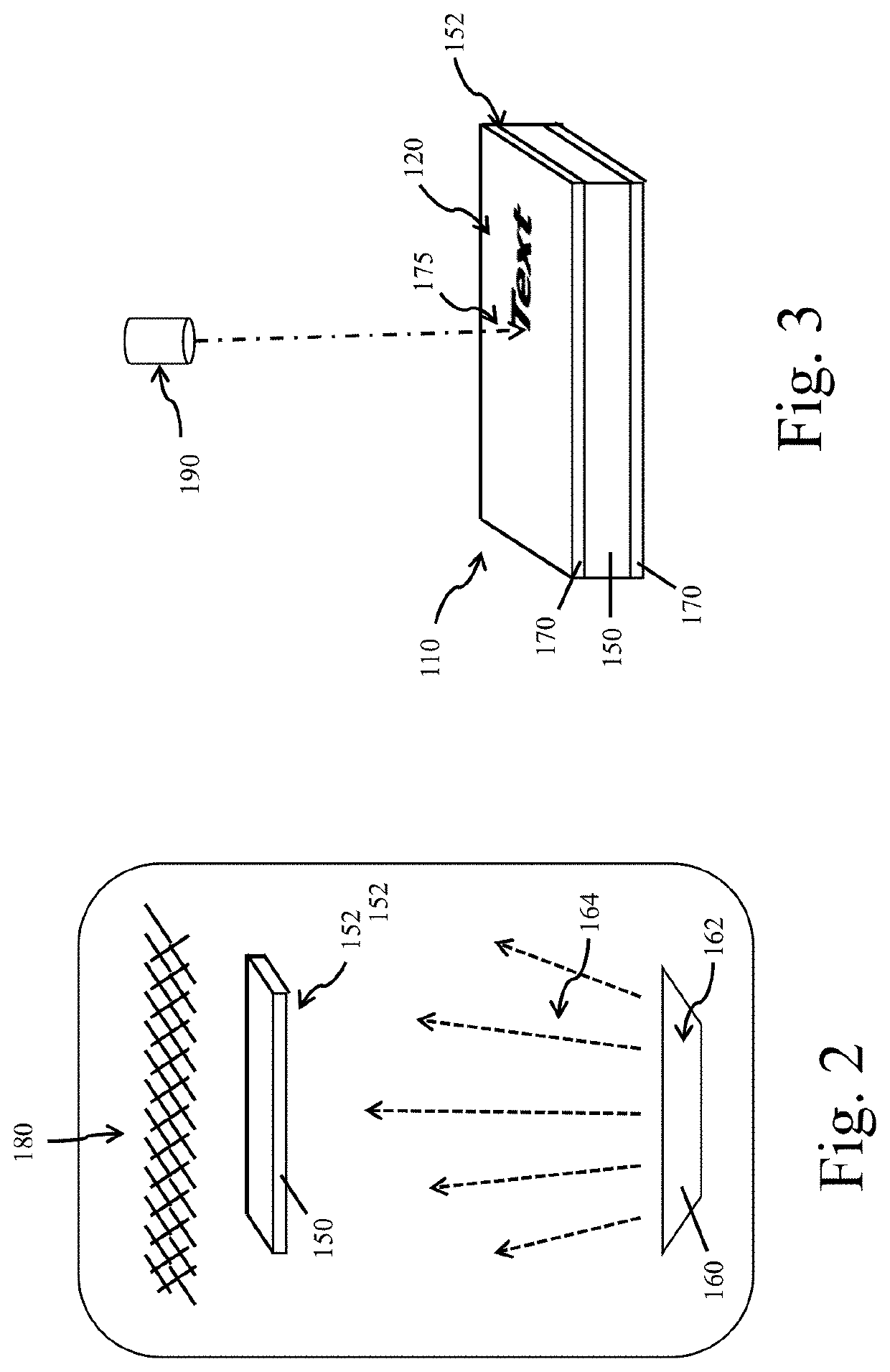
Patents
Literature
76results about "Recording involving layer ablation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
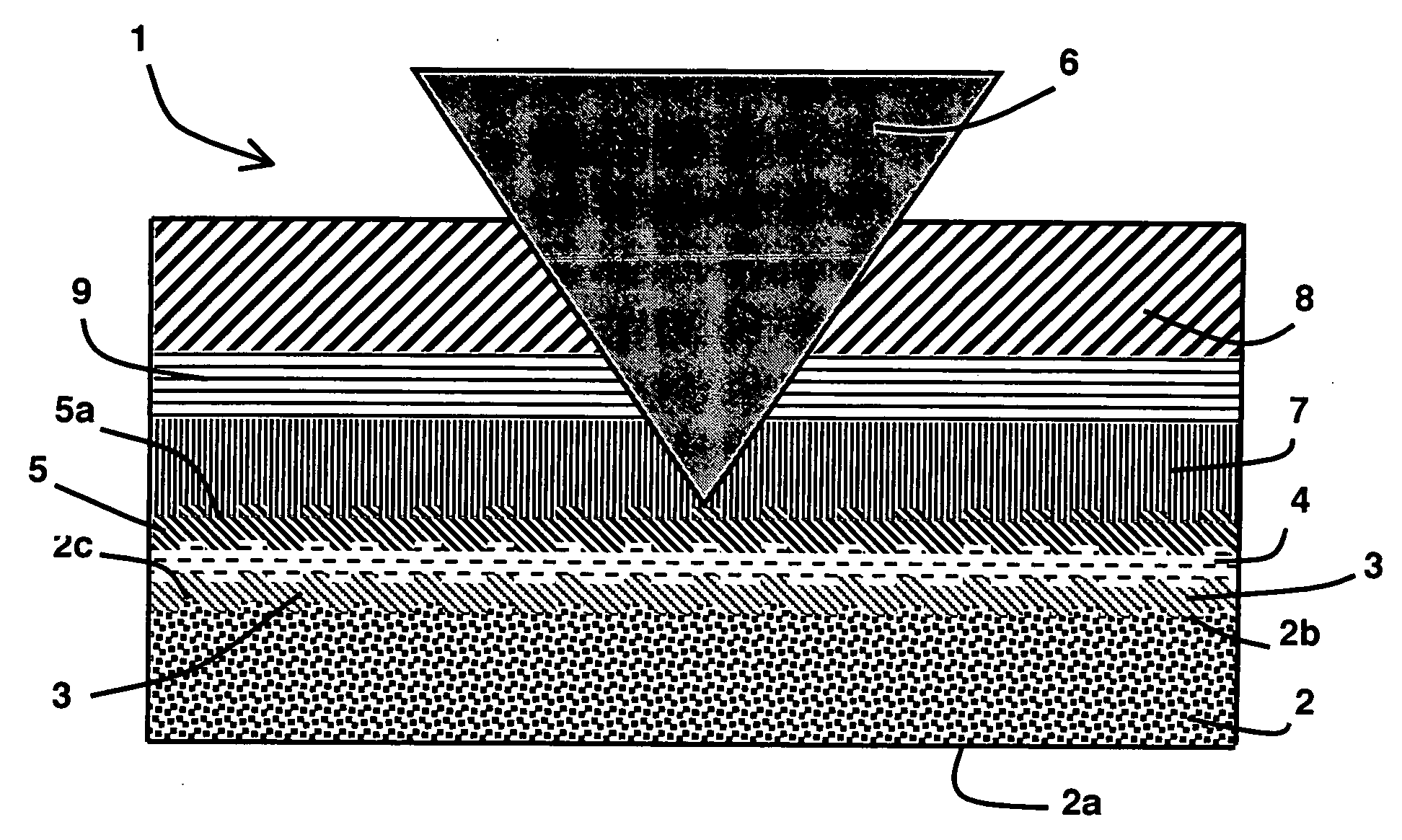
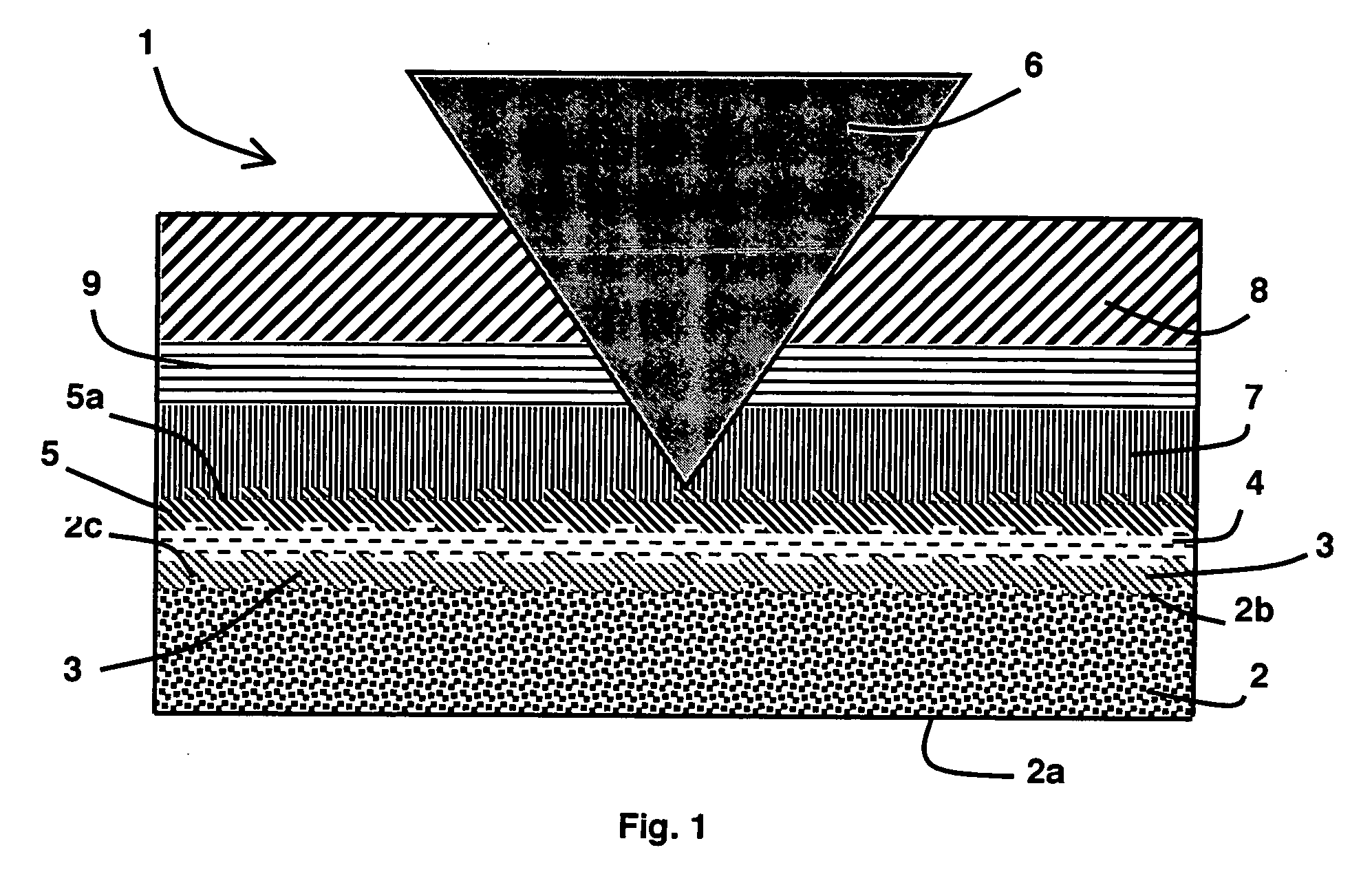
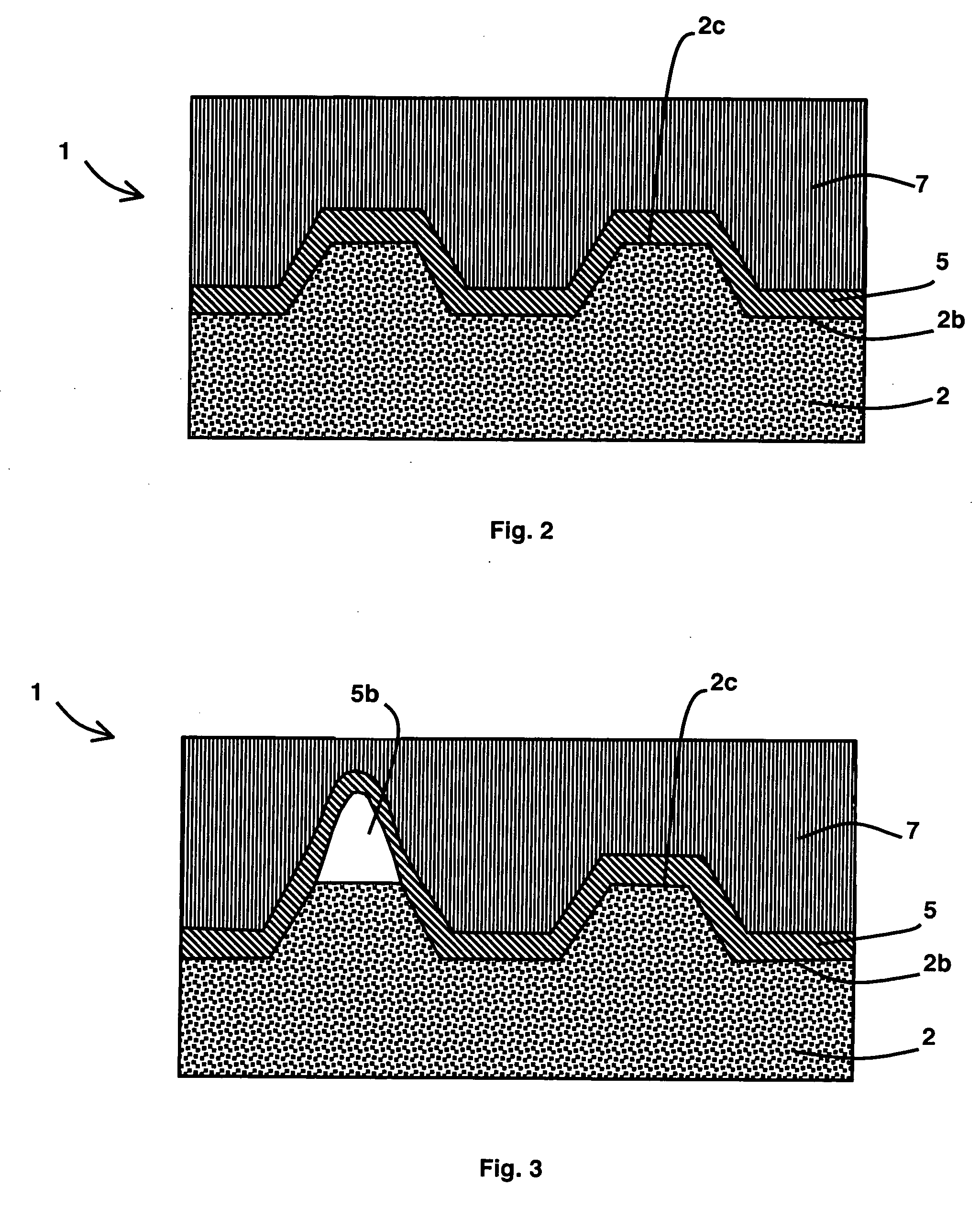
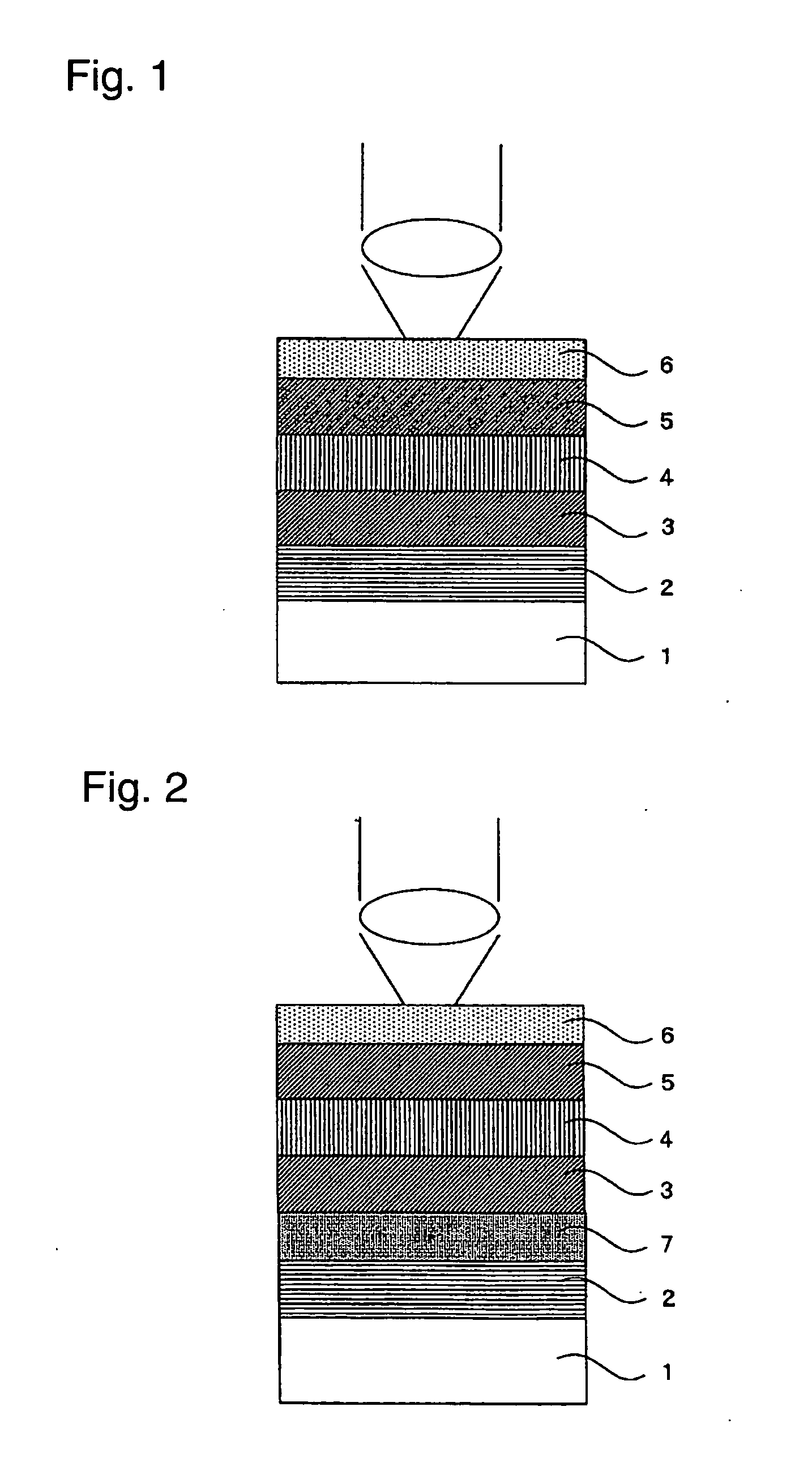
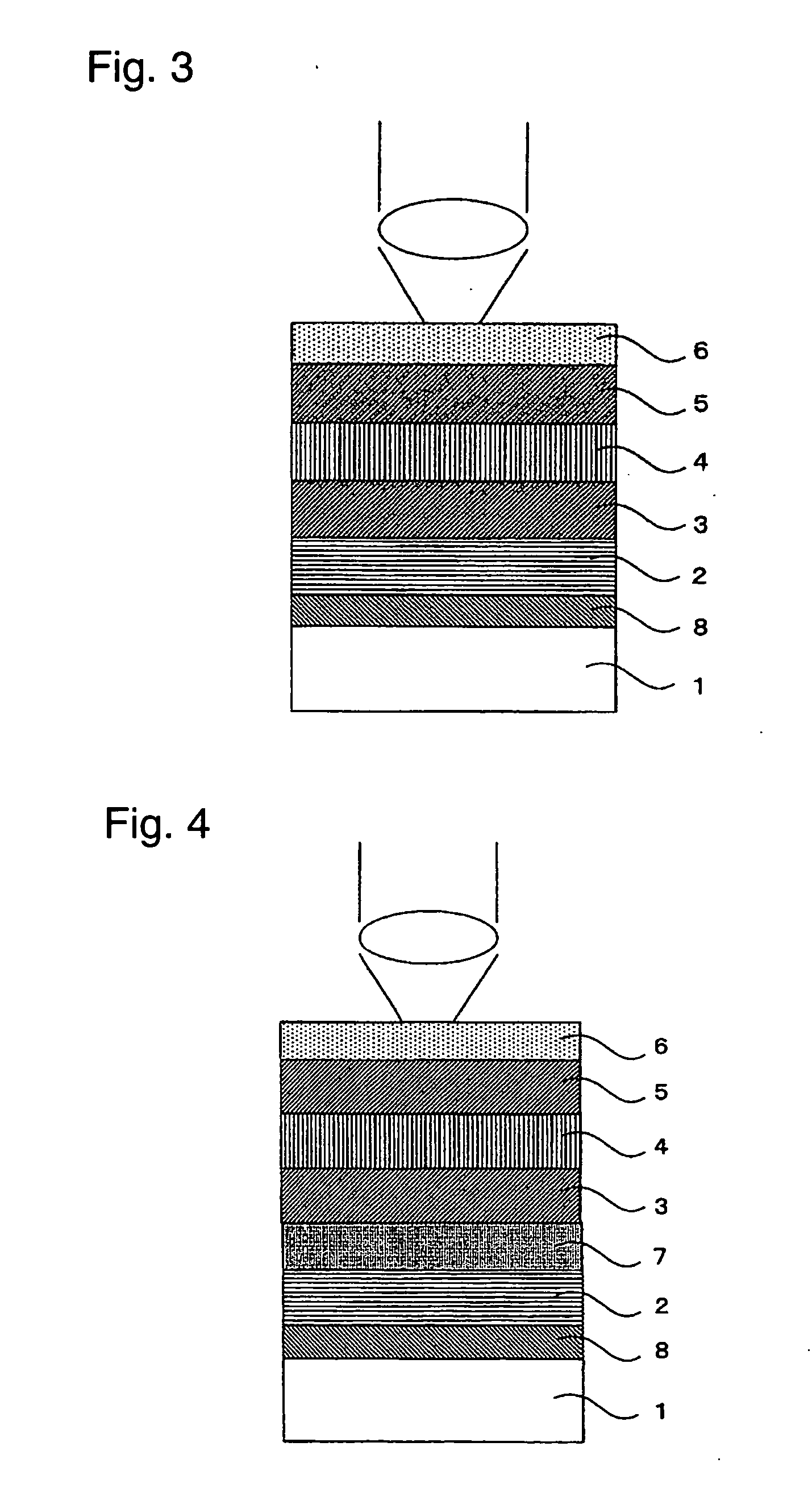
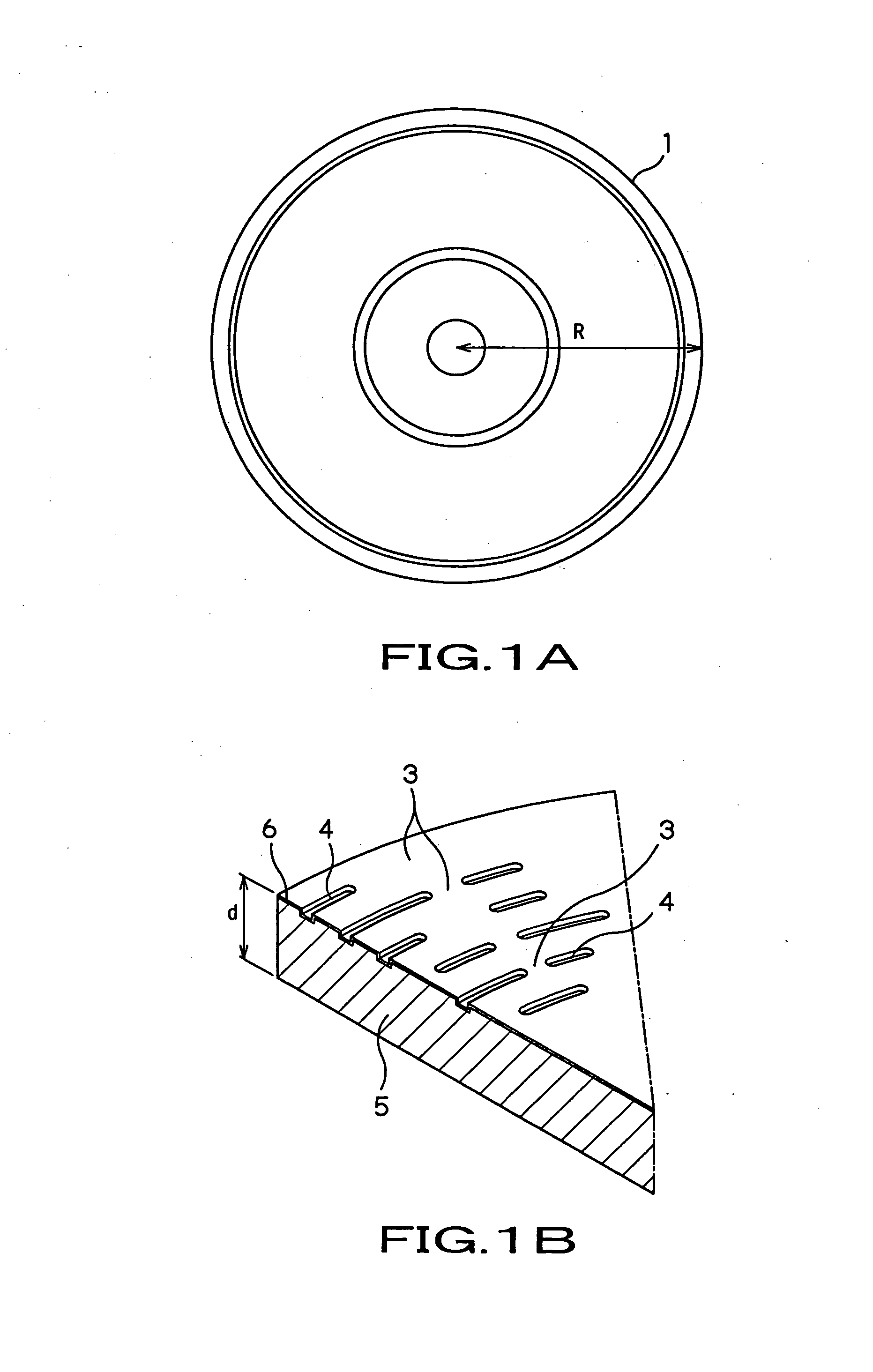
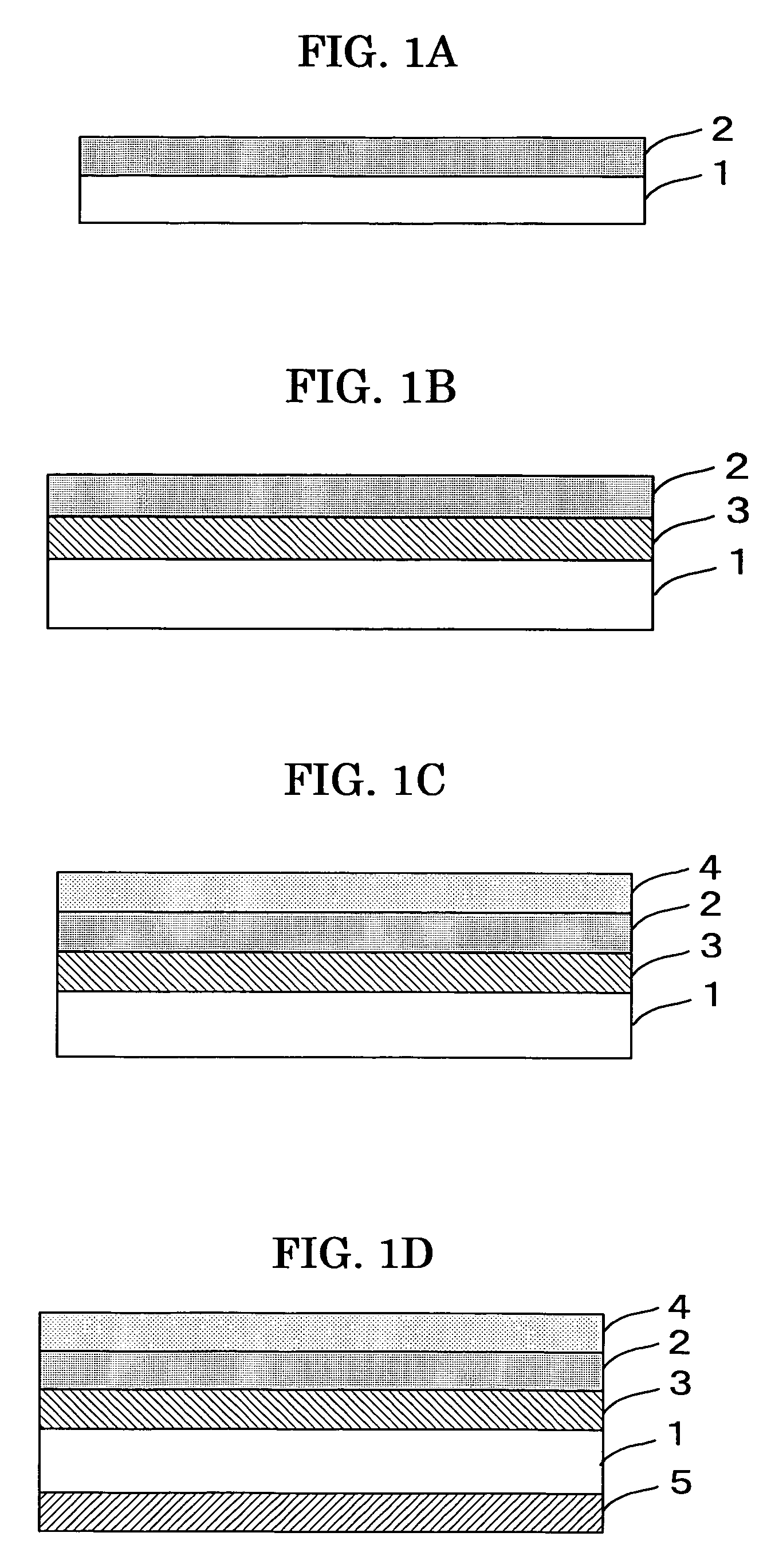
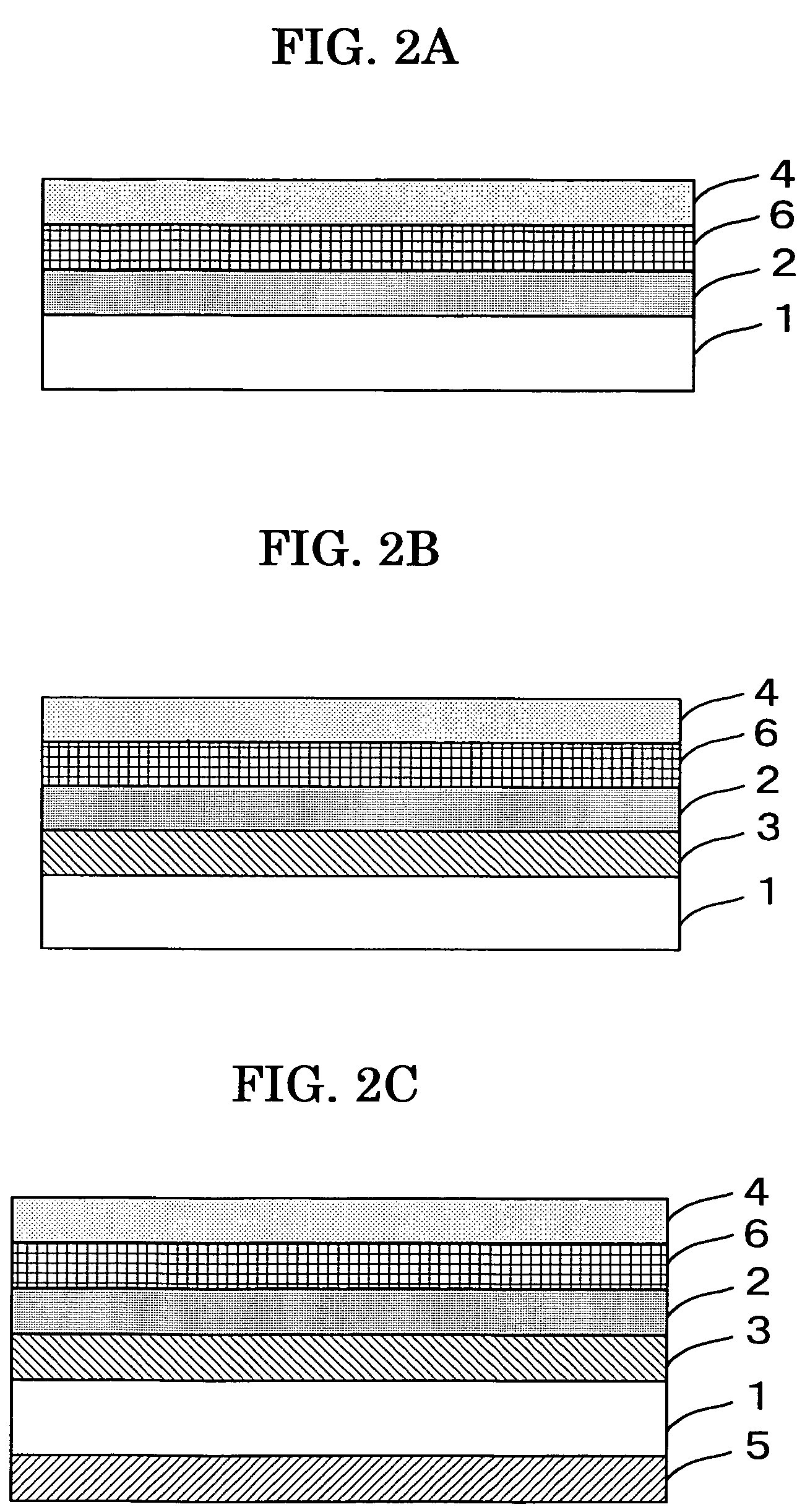
Optical data recording medium provided with at least one photosensitive layer and one deformable layer
InactiveUS20060182924A1High densityLayered productsRecording involving bubble/bump formingOptical radiationMonitoring system
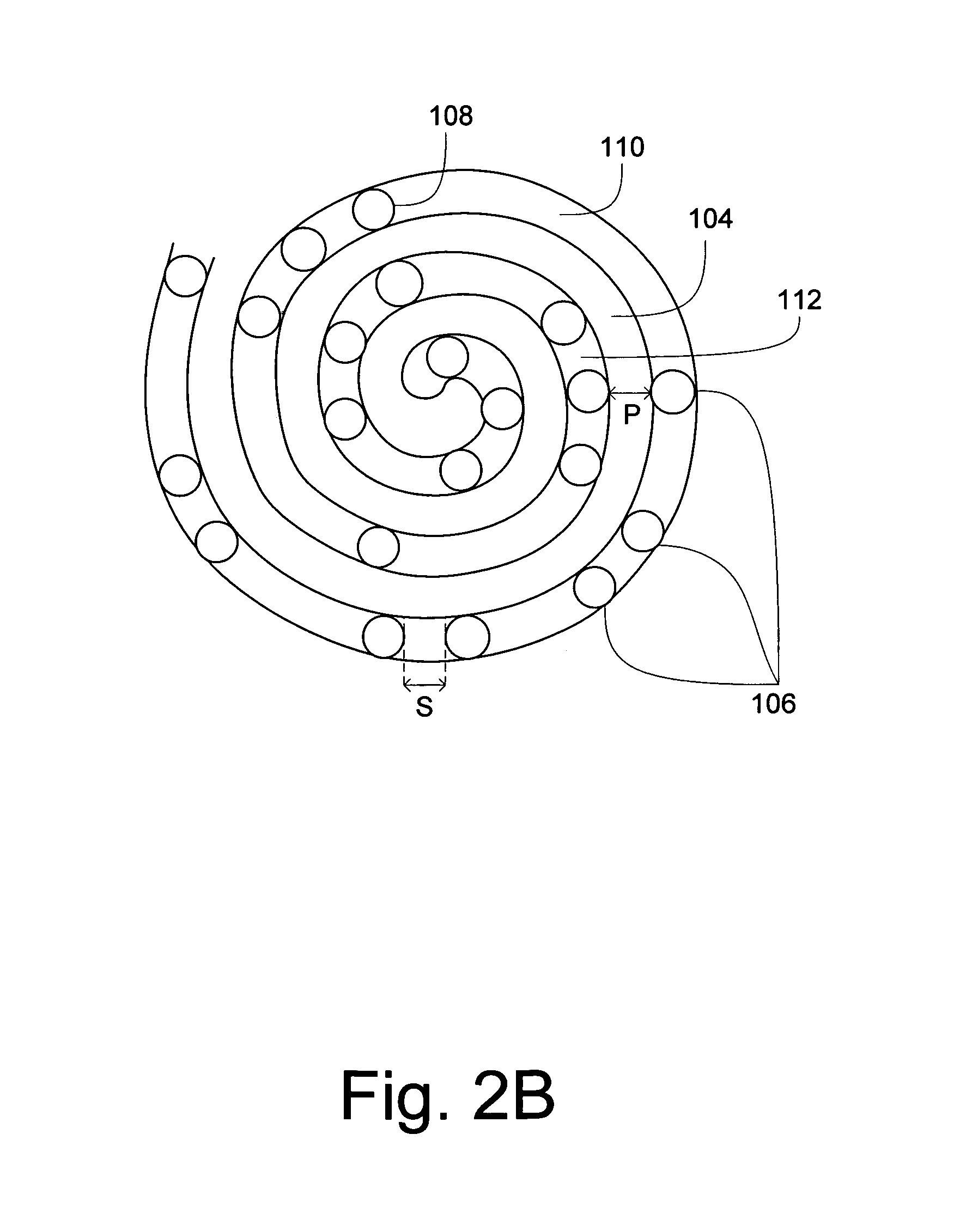
An optical recording medium comprises first and second substrates wherebetween there is arranged at least one first photosensitive layer, preferably made of inorganic material. The first photosensitive layer comprises a front face for receiving optical radiation, by means of the second substrate, during data writing and / or reading operations. A first deformable layer, transparent to the optical radiation, is arranged between the first photosensitive layer and the second substrate. The first substrate comprises a patterned front face, so as to form a preferably spiral-shaped groove enabling precise data writing and / or reading to be performed by means of an automatic focusing control and track monitoring system.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Recording medium
ActiveUS20060120262A1Improve compactnessWide power rangeLayered productsMechanical record carriersChemical reactionOptical recording
The main object of the present invention is to provide a recording medium which makes high densification of information possible, particularly a write-once-read-many optical recording medium having good recording signal characteristics to a wide range of recording powers. The present invention is one to accomplish the above object by providing a recording medium having a recording layer, whereby recording is carried out by heating the recording layer, characterized in that the recording layer contains a substance A which decomposes at a temperature which the recording layer reaches when heated for recording, and a substance B which does not undergo a chemical reaction or phase change at a temperature which the recording layer reaches when heated for recording.
Owner:CMC MAGNETICS CORPORATION
Device and method for optical data storage having multiple optical states
InactiveUS6115344APhotography auxillary processesMechanical record carriersPolymer substrateOptical storage
PCT No. PCT / NO96 / 00125 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 20, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 20, 1997 PCT Filed May 22, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 37888 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 28, 1996The optical storage device and method includes a fluorescent layer arranged on a substrate and having a surface. The fluorescent layer is composed of fluorescent dye molecules embedded in a transparent polymeric base material. A group of data-carrying structures are arranged in the fluorescent layer. Each of the data-carrying structures has more than two optical states represented by a specific degree of quenching of fluorescence emitted from the data-carrying structure when irradiated with a fluorescence exciting radiation.
Owner:THIN FILM ELECTRONICS ASA +1
Apparatus for recording dye based recordable DVD media and process for recording the same
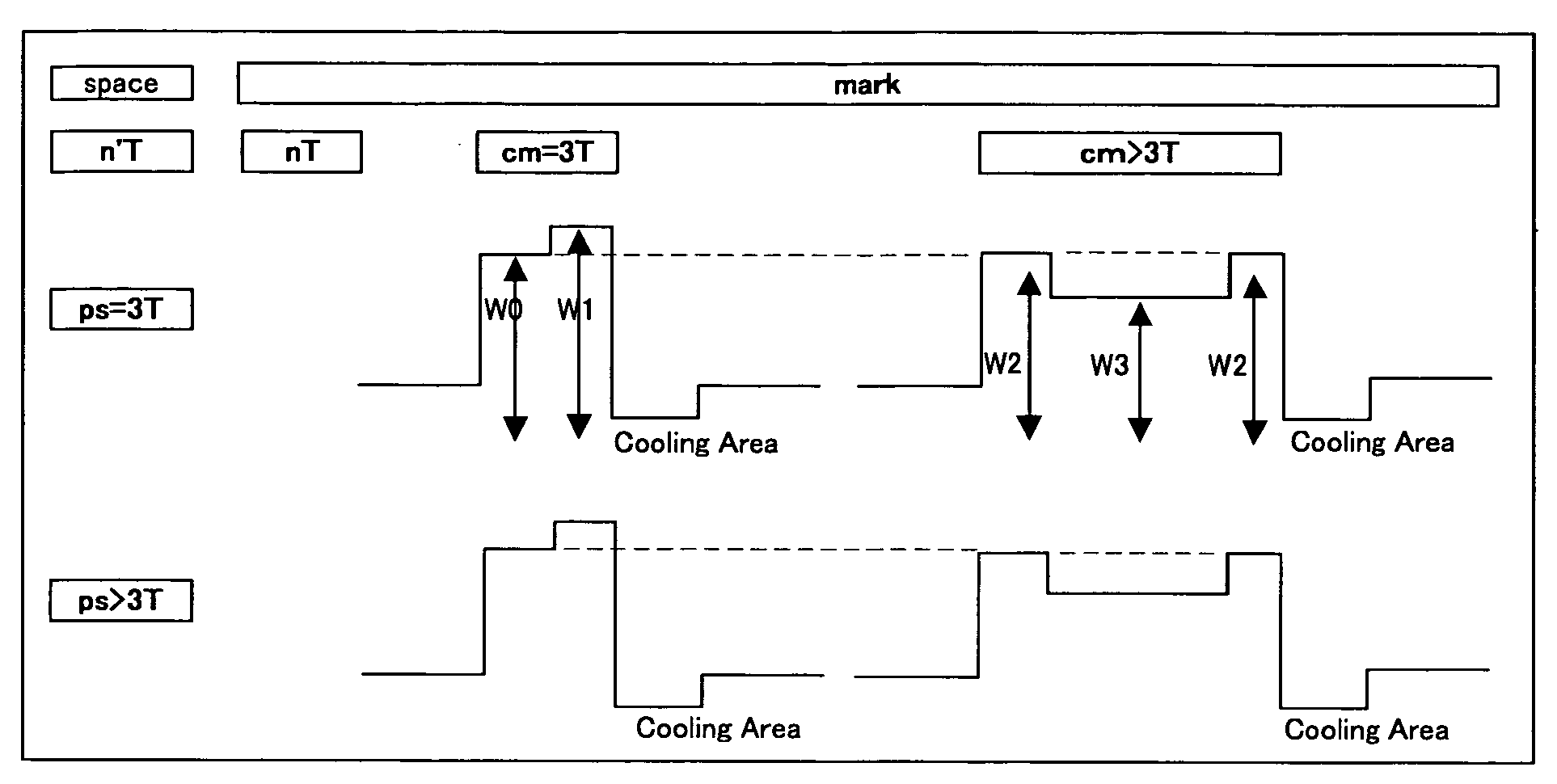
InactiveUS20050201243A1Avoid it happening againQuality improvementTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesPulse beamOrganic dye
The present invention relates to apparatuses and processes for recording dye-based recordable DVD media in higher quality at higher linear recording velocity, and provides an apparatus for recording a dye-based recordable DVD medium comprising a shortest mark recording unit, a second mark recording unit, and a cooling pulse irradiating unit, wherein the dye-based recordable DVD medium comprises a substrate and a recording layer formed on the substrate, the substrate comprises a guide groove to which wobble is formed, and the recording layer comprises at least an organic dye, the shortest mark recording unit is configured to record each of the shortest marks by use of one pulse beam of which the rear edge is more energized than the front edge, the second mark recording unit is configured to record each of the marks other than the shortest marks by use of one pulse beam of which the two sites of front and rear edges are energized, the cooling pulse irradiating unit is configured to irradiate cooling pulse laser beams onto the backwards of the respective pulse beams at 0.1 mW / pulse or less of optical energy, and the recording of marks is performed on the recording layer at a recording linear velocity of 42 m / sec or more.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical recording medium
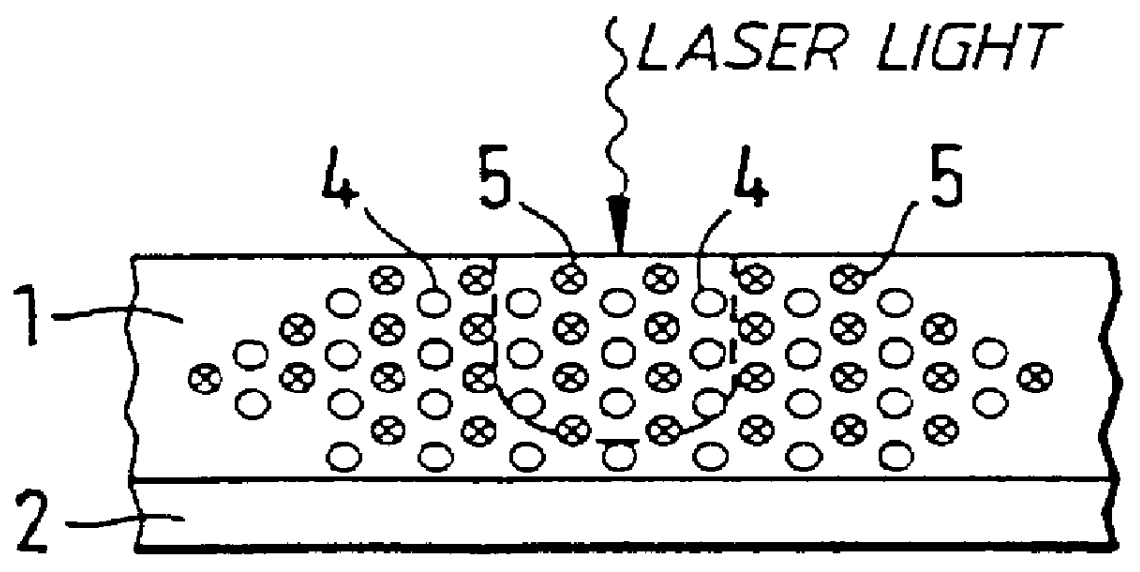
InactiveUS6844044B2High outputImprove reproductive characteristicsInformation arrangementLayered productsRefractive indexLaser light
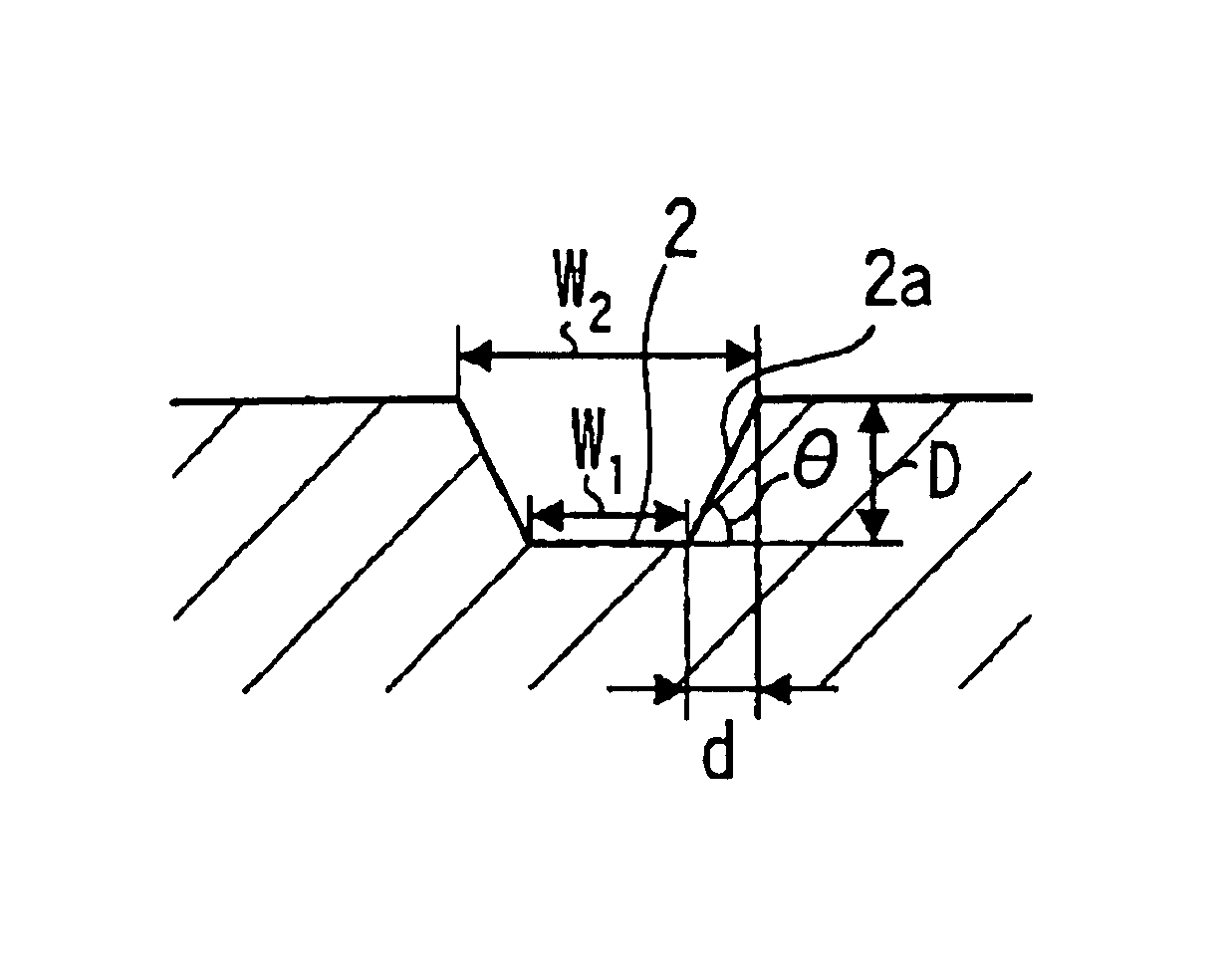
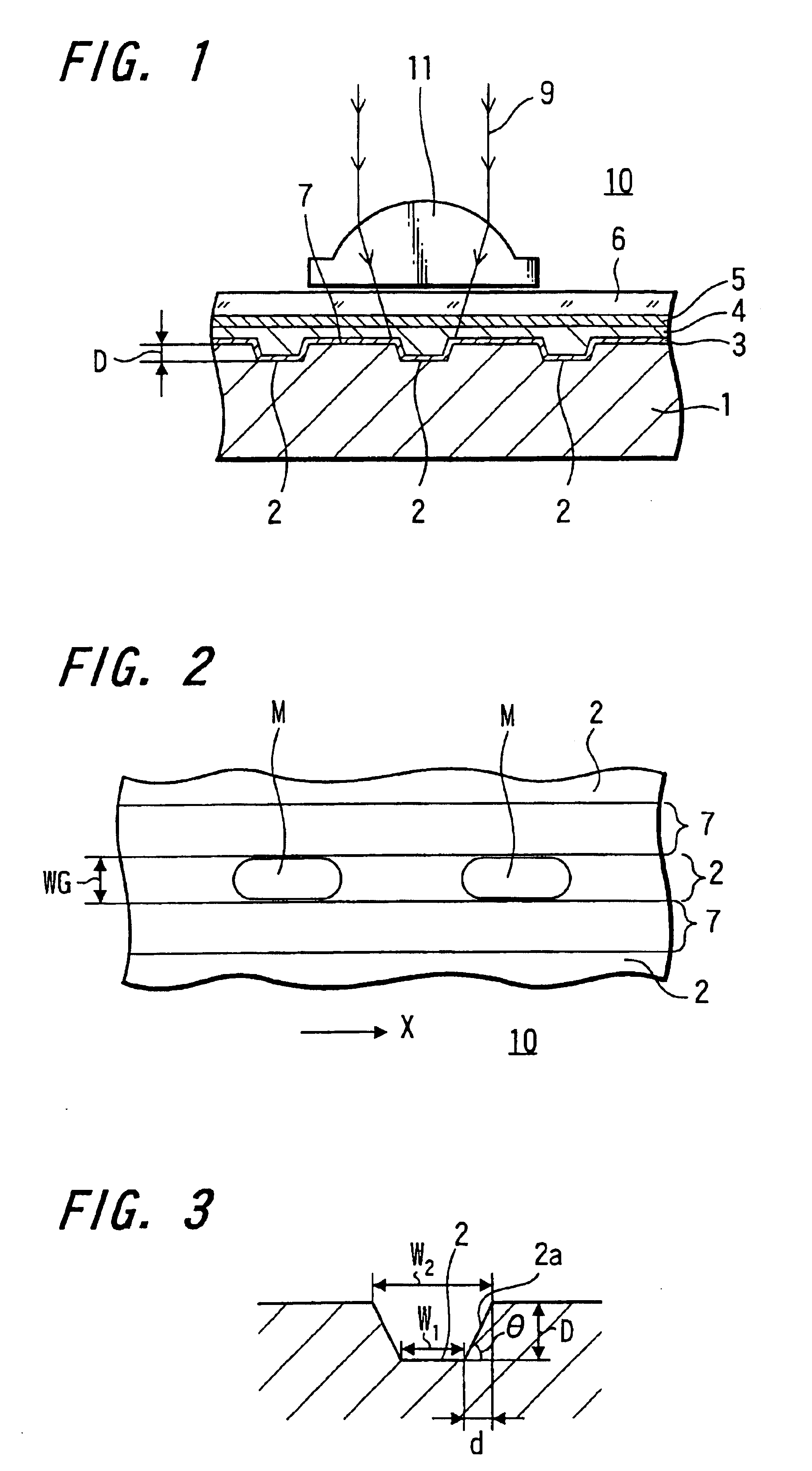
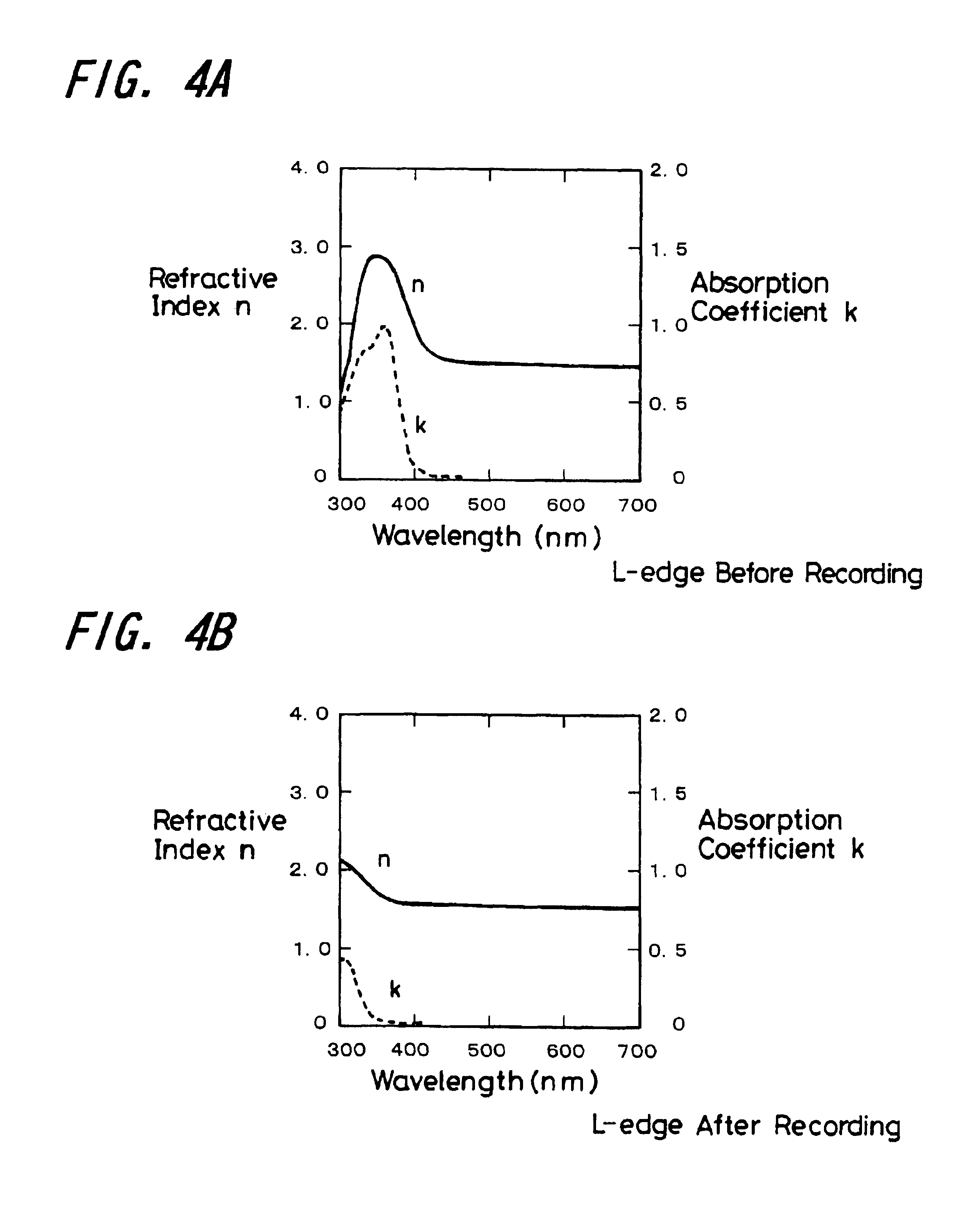
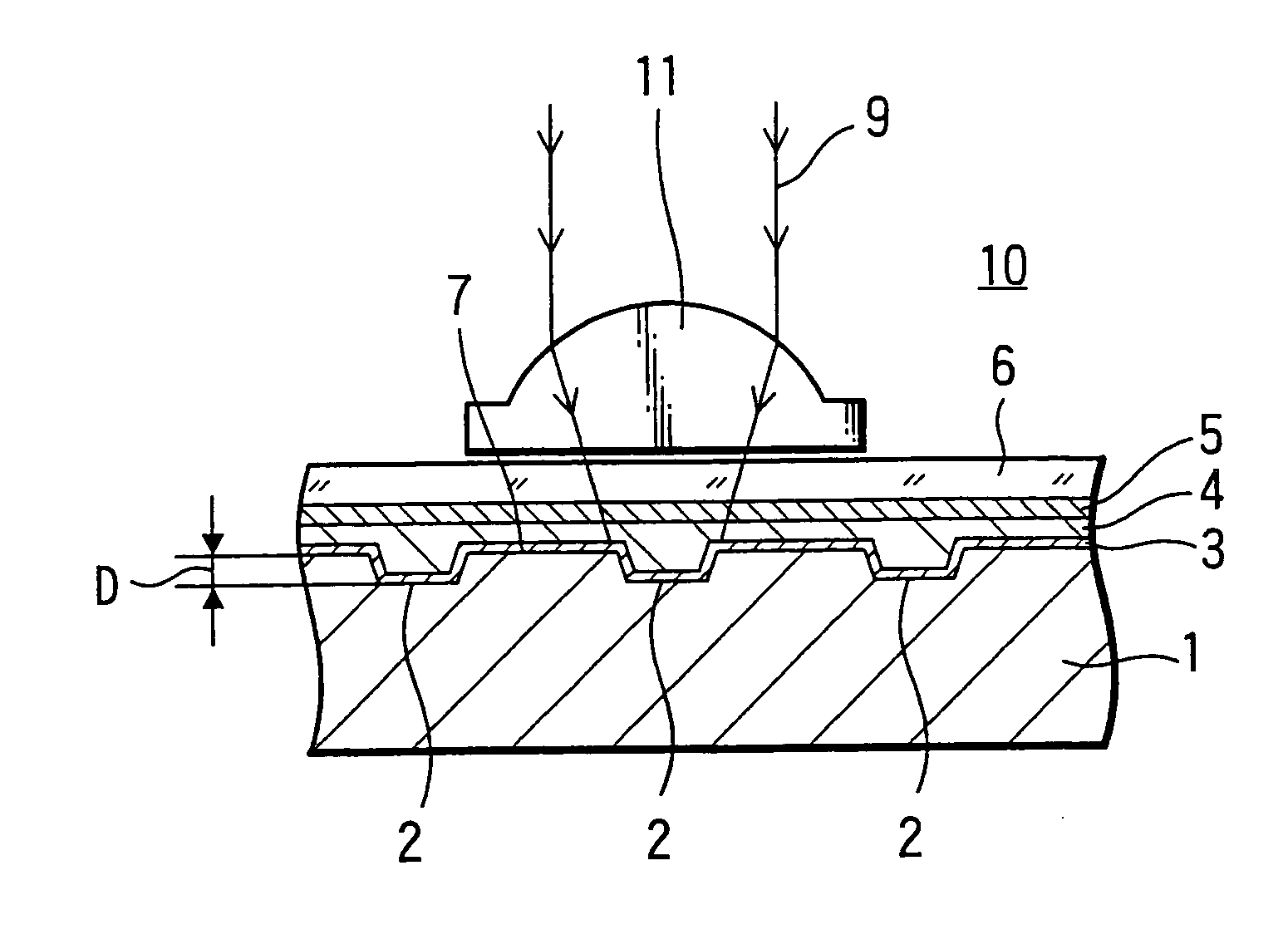
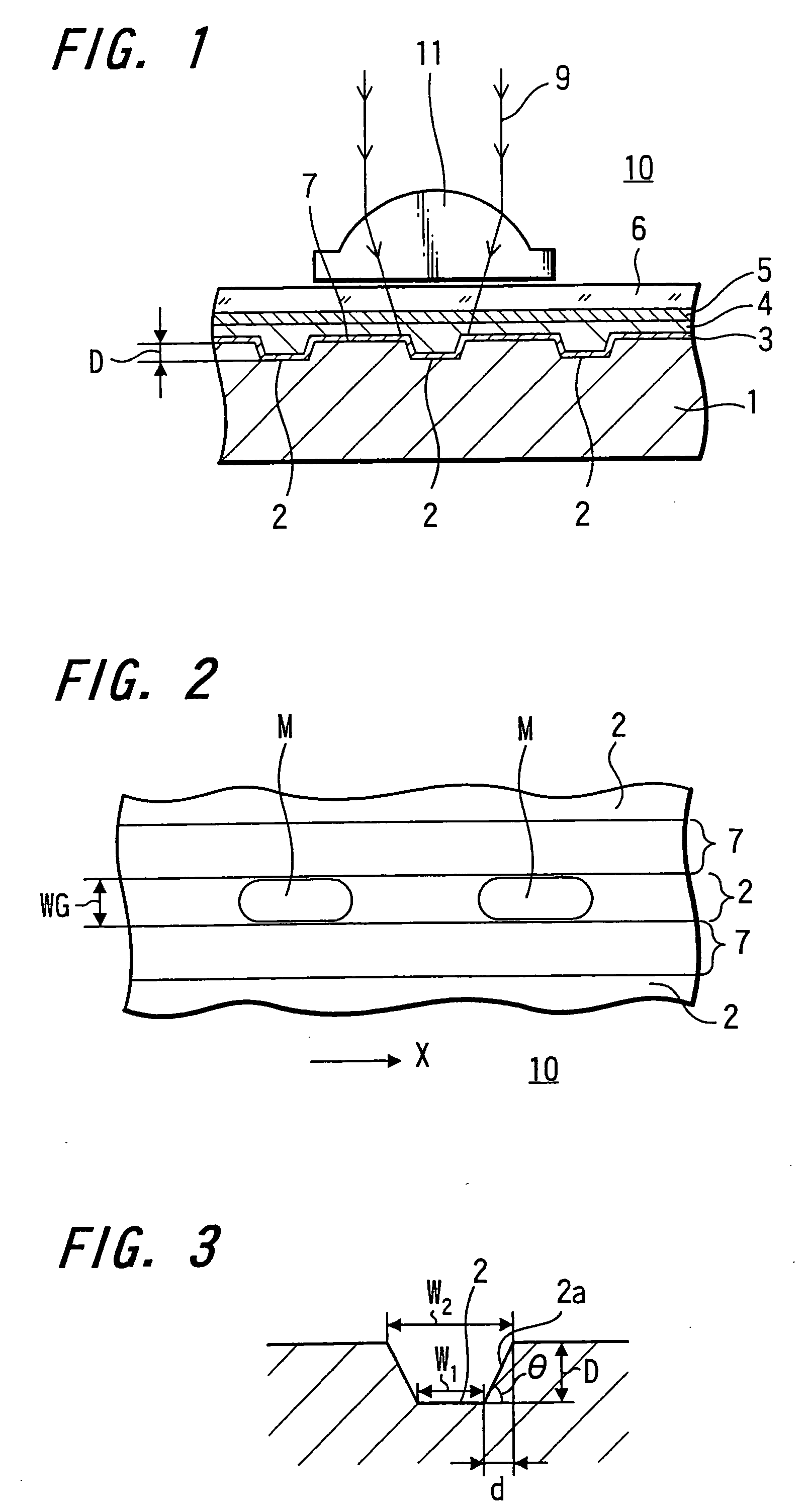
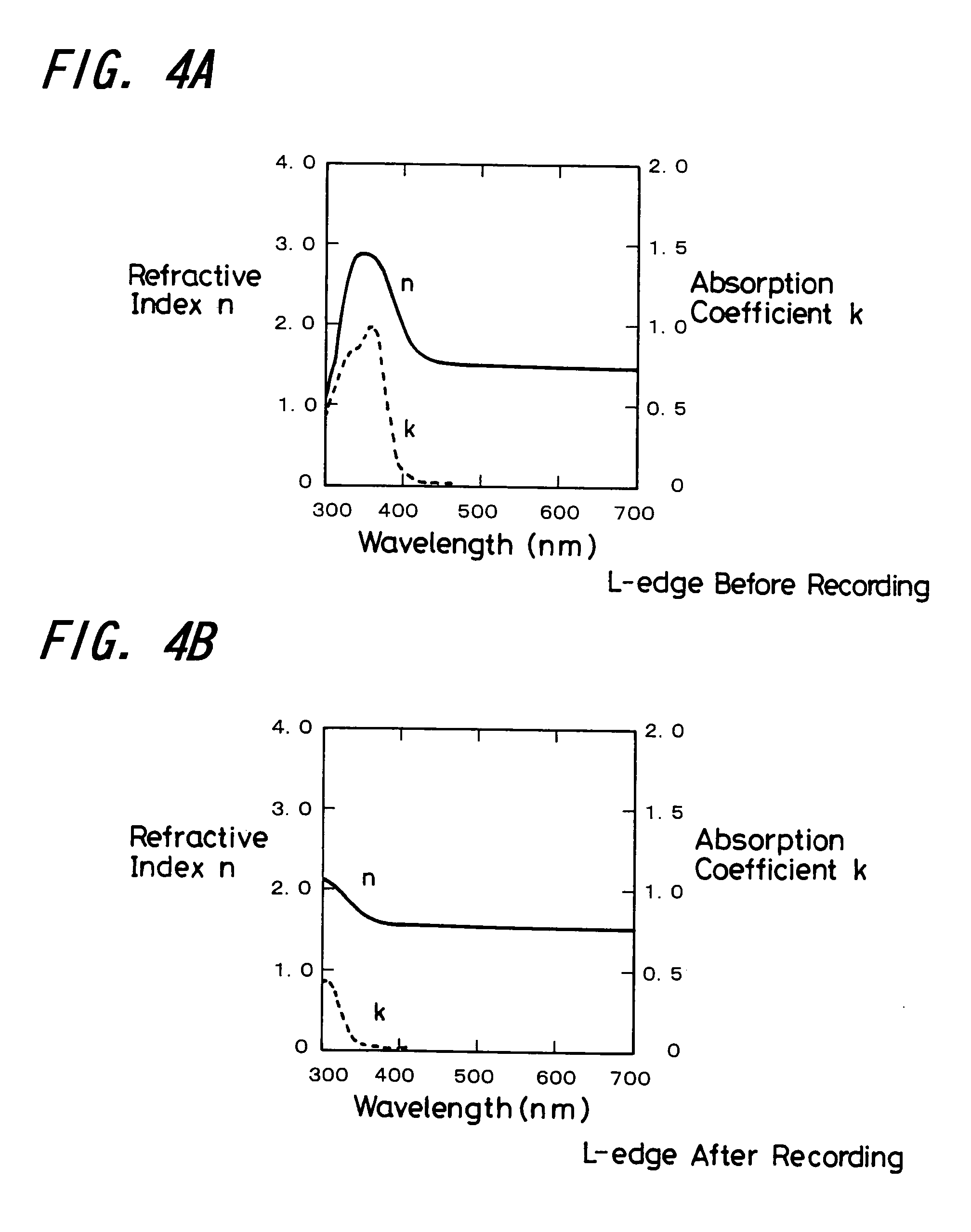
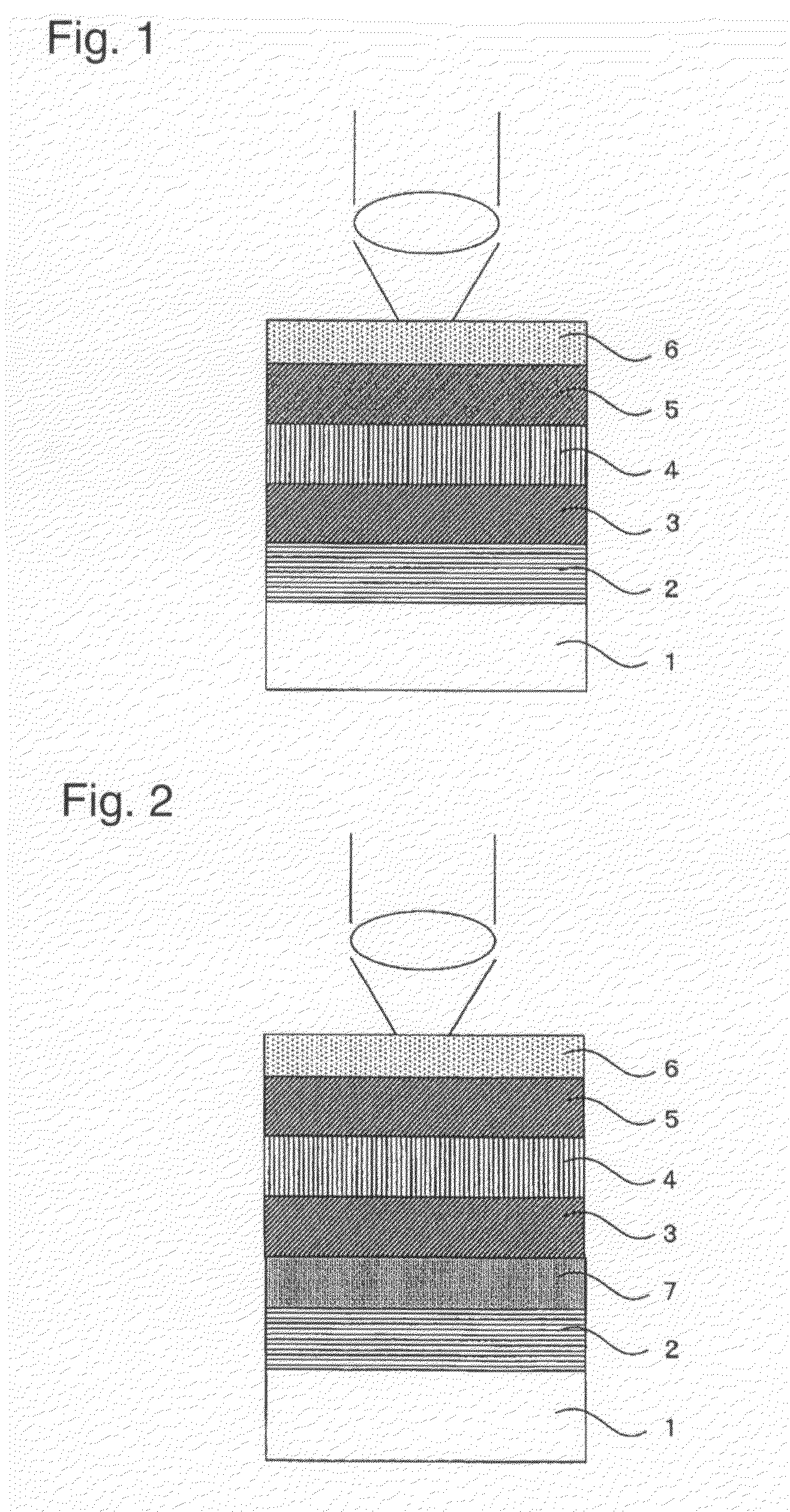
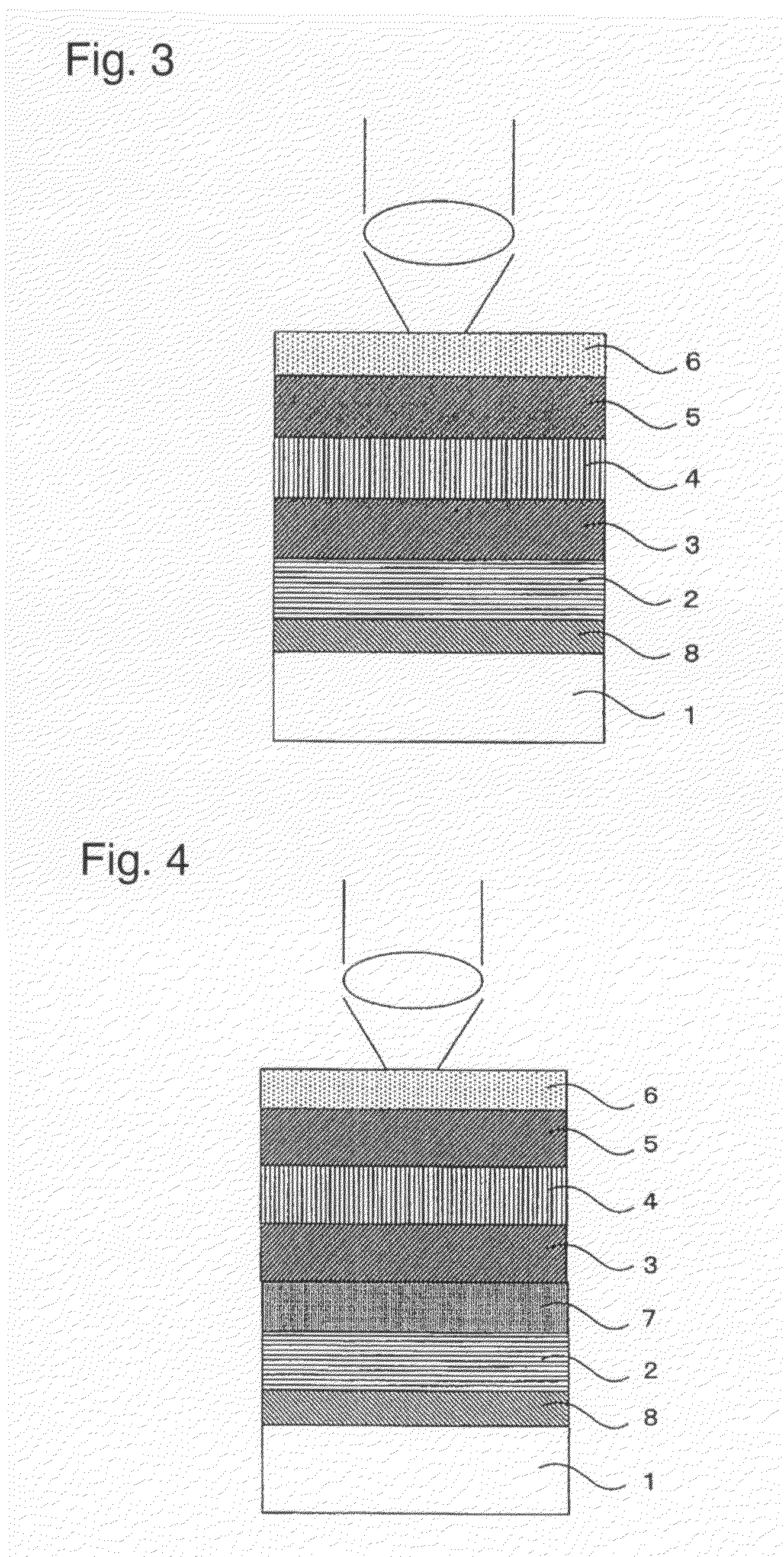
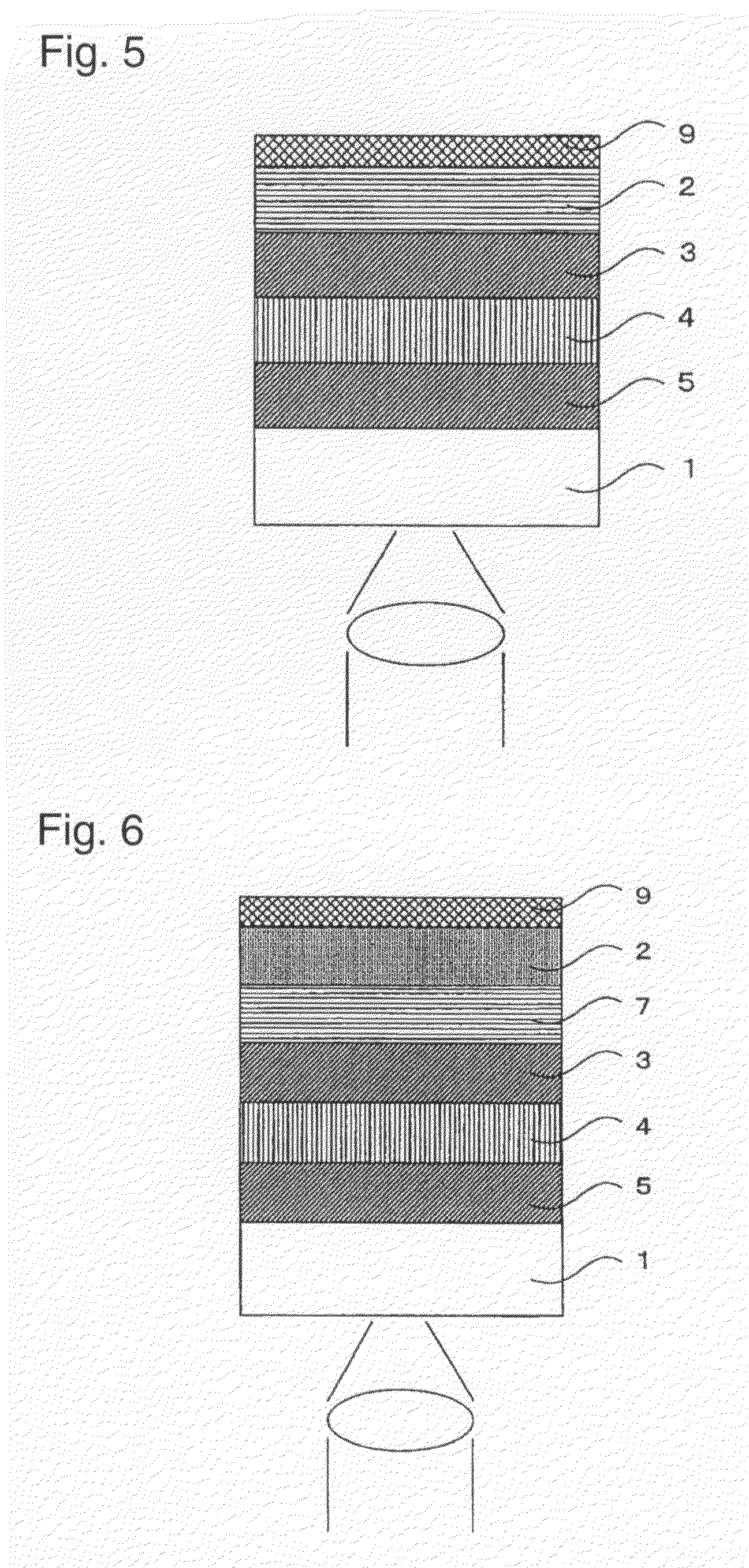
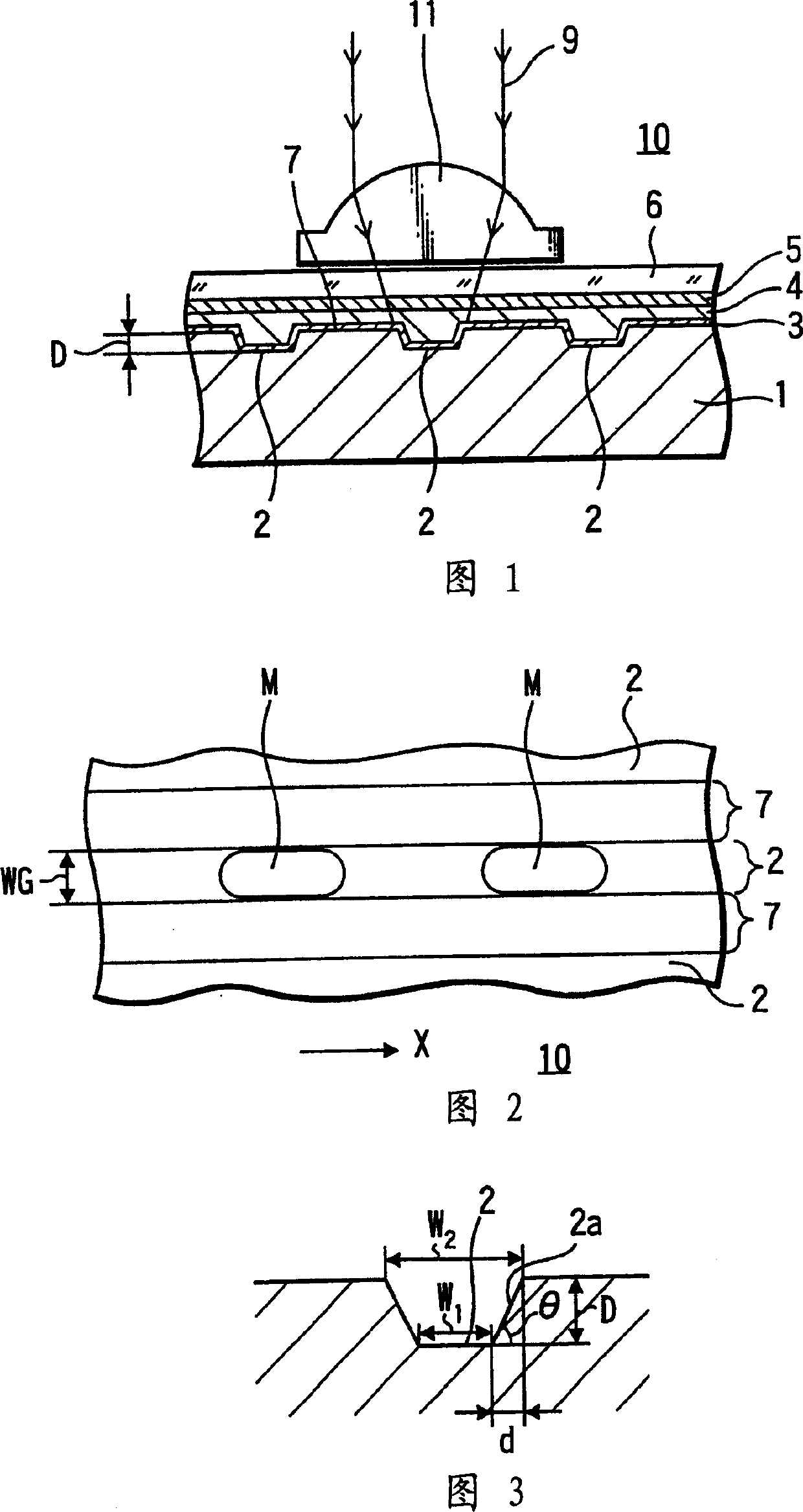
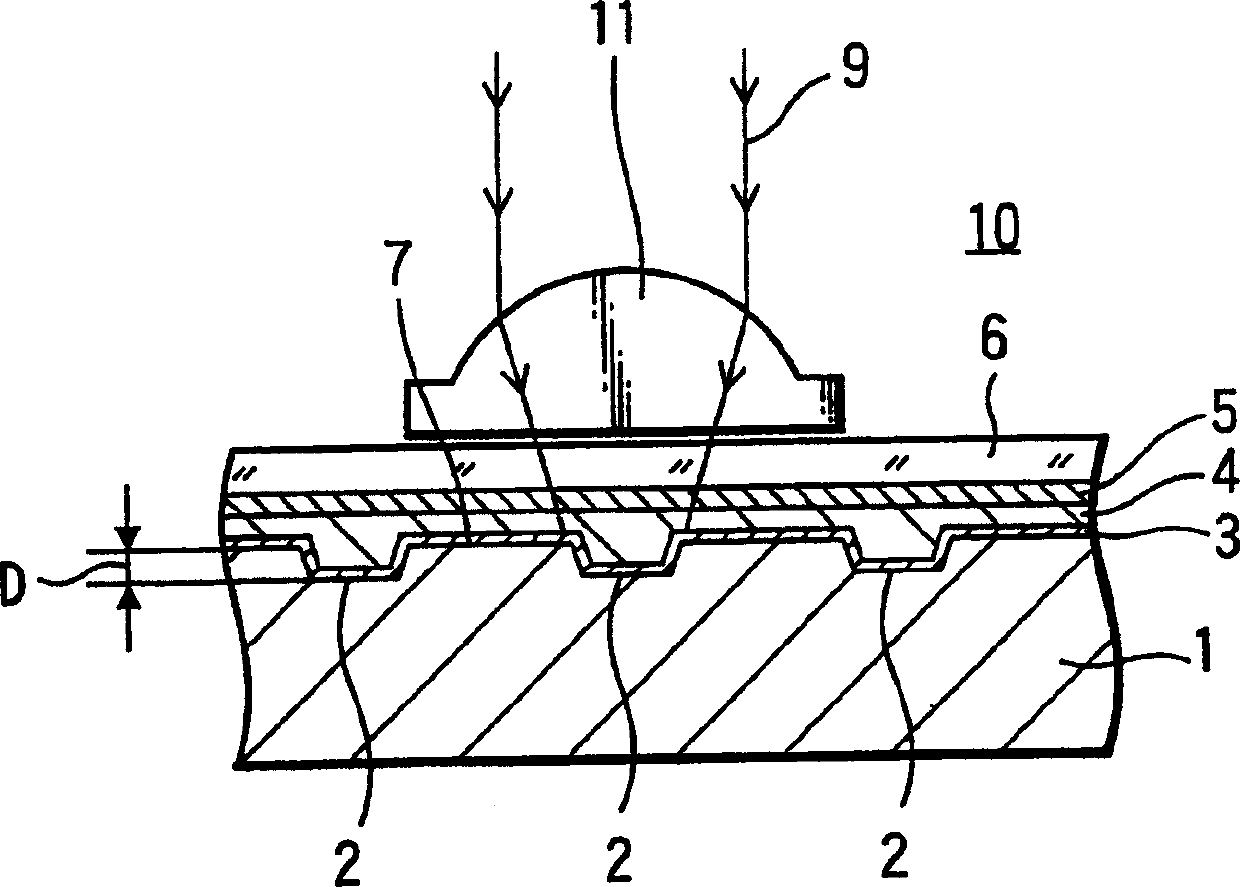
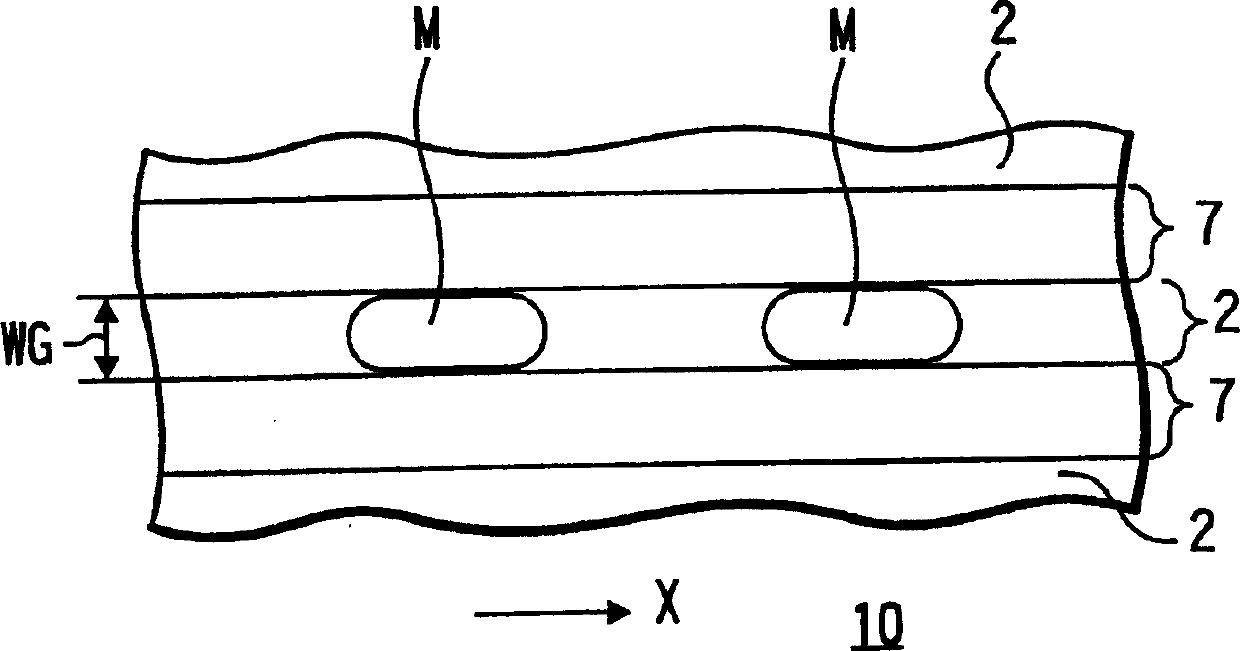
A phase modulation type optical recording medium has at least one layer of recording film 4 and at least one layer of metal film 3 on a substrate 1 having recessed portions formed therein, wherein one or more layers constituting the recording film include organic material that decomposes upon absorption of laser light to change its refractive index, and width of the recessed portions 2 is set to 0.10 μm˜0.21 μm, thereby providing an optical recording medium of write once type with high recording density capable of high reproduction output.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical recording medium
InactiveUS20040008610A1High outputImprove reproductive characteristicsInformation arrangementLayered productsRefractive indexLaser light
A phase modulation type optical recording medium has at least one layer of recording film 4 and at least one layer of metal film 3 on a substrate 1 having recessed portions formed therein, wherein one or more layers constituting the recording film include organic material that decomposes upon absorption of laser light to change its refractive index, and width of the recessed portions 2 is set to 0.10 mum-0.21 mum, thereby providing an optical recording medium of write once type with high recording density capable of high reproduction output.
Owner:SONY CORP
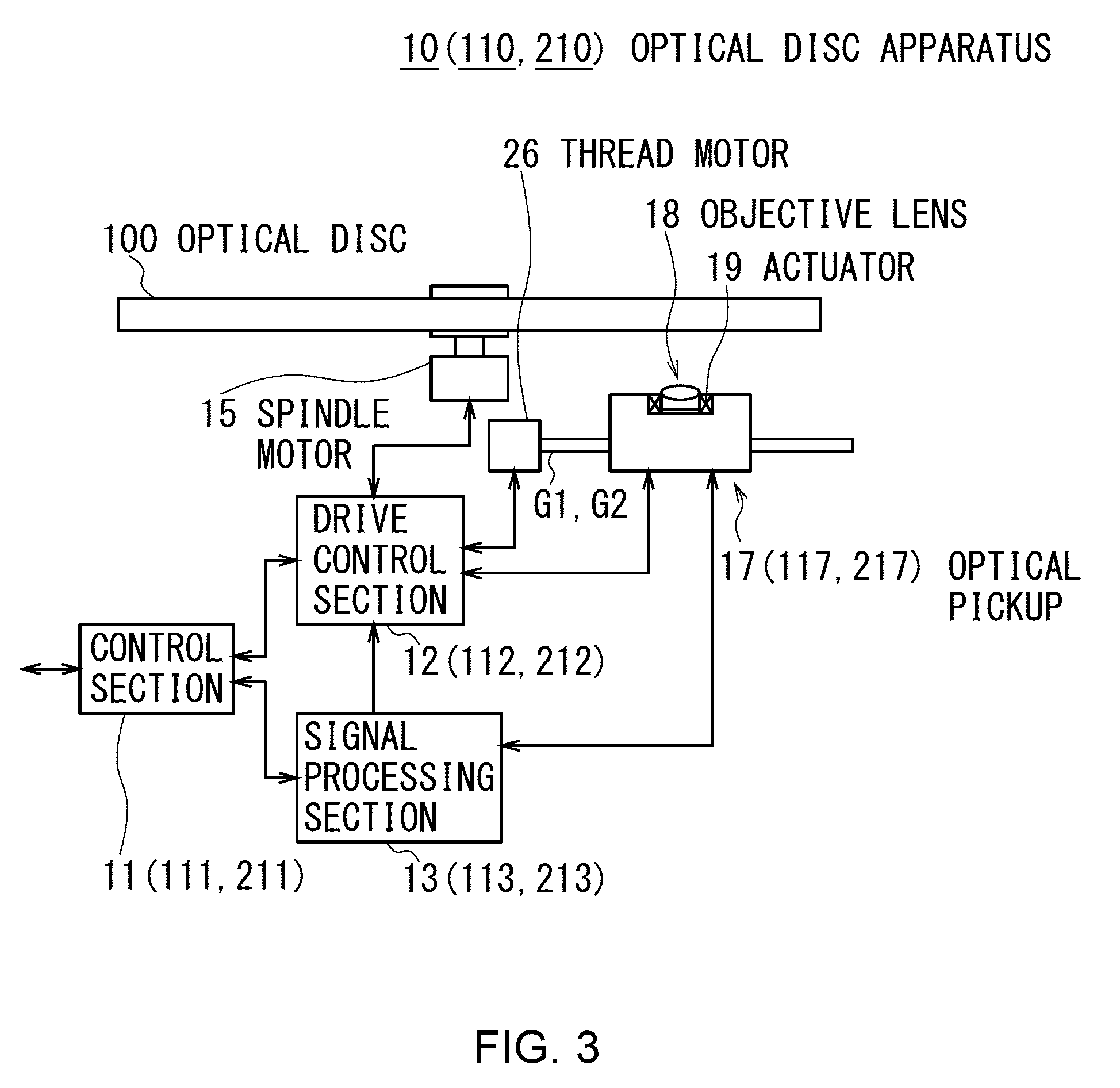
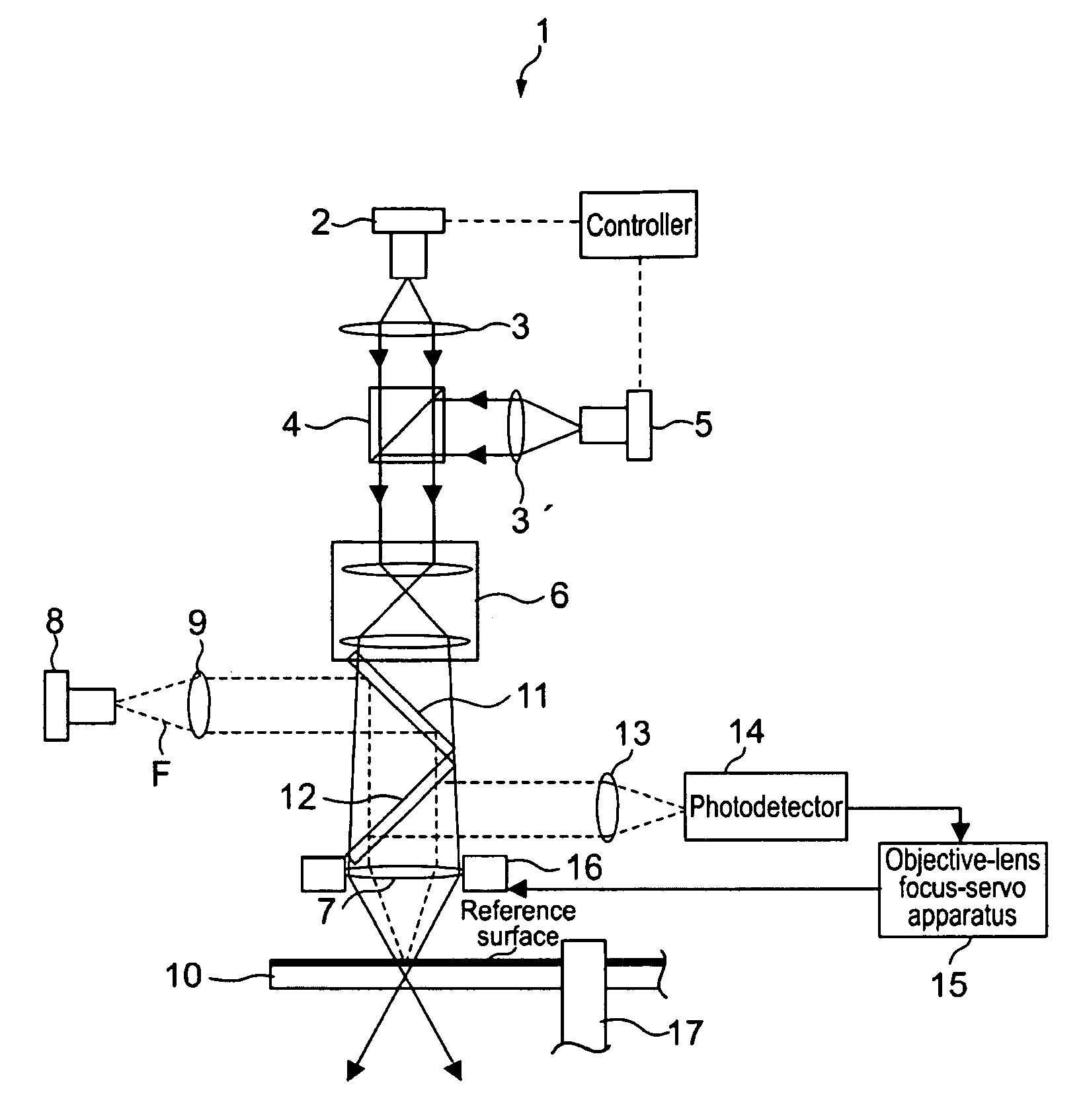
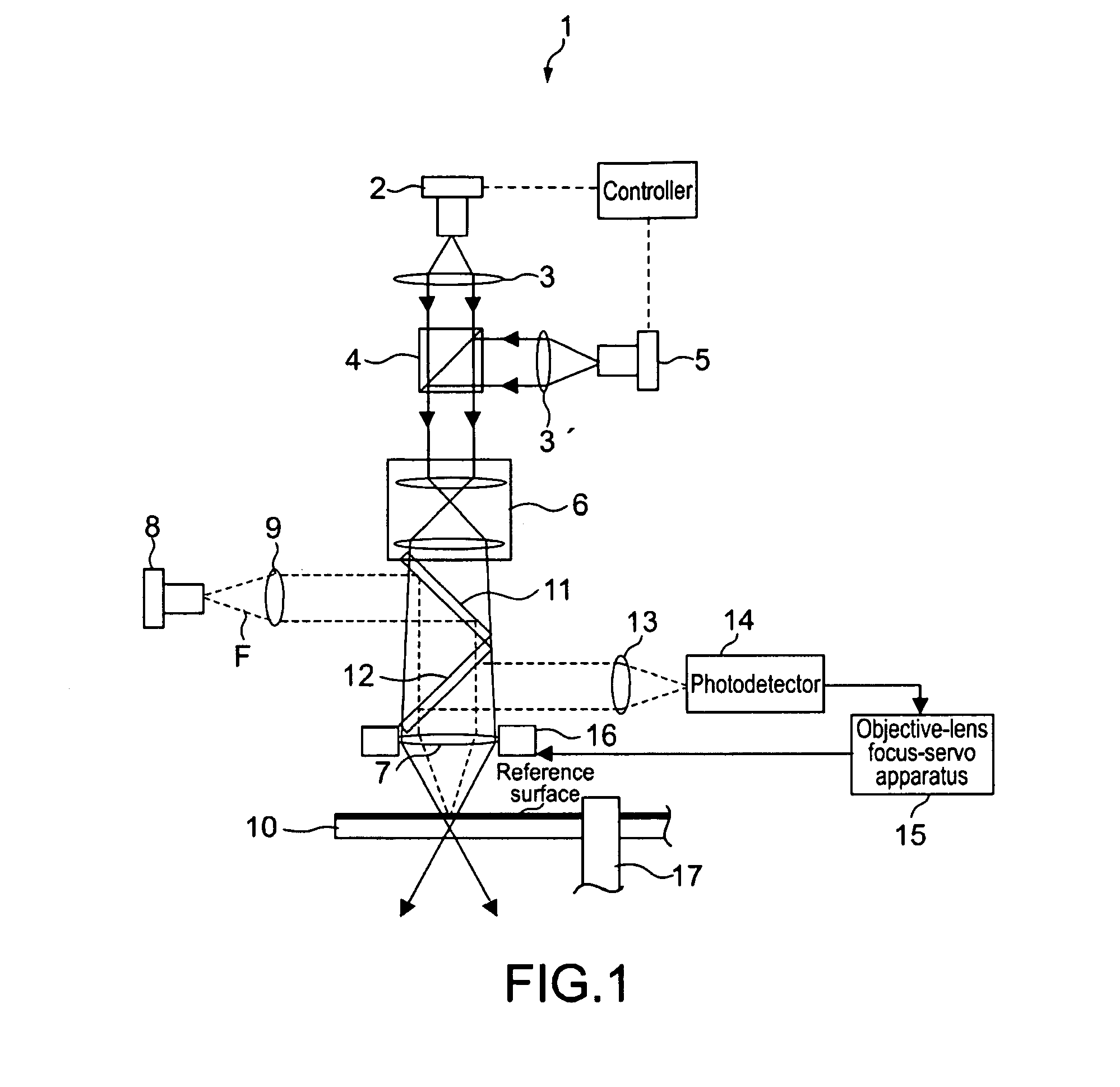
Optical disc apparatus and optical disc replay method
InactiveUS20090262633A1Simple configurationAccurately reproduce informationCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsLight beamRegion detection
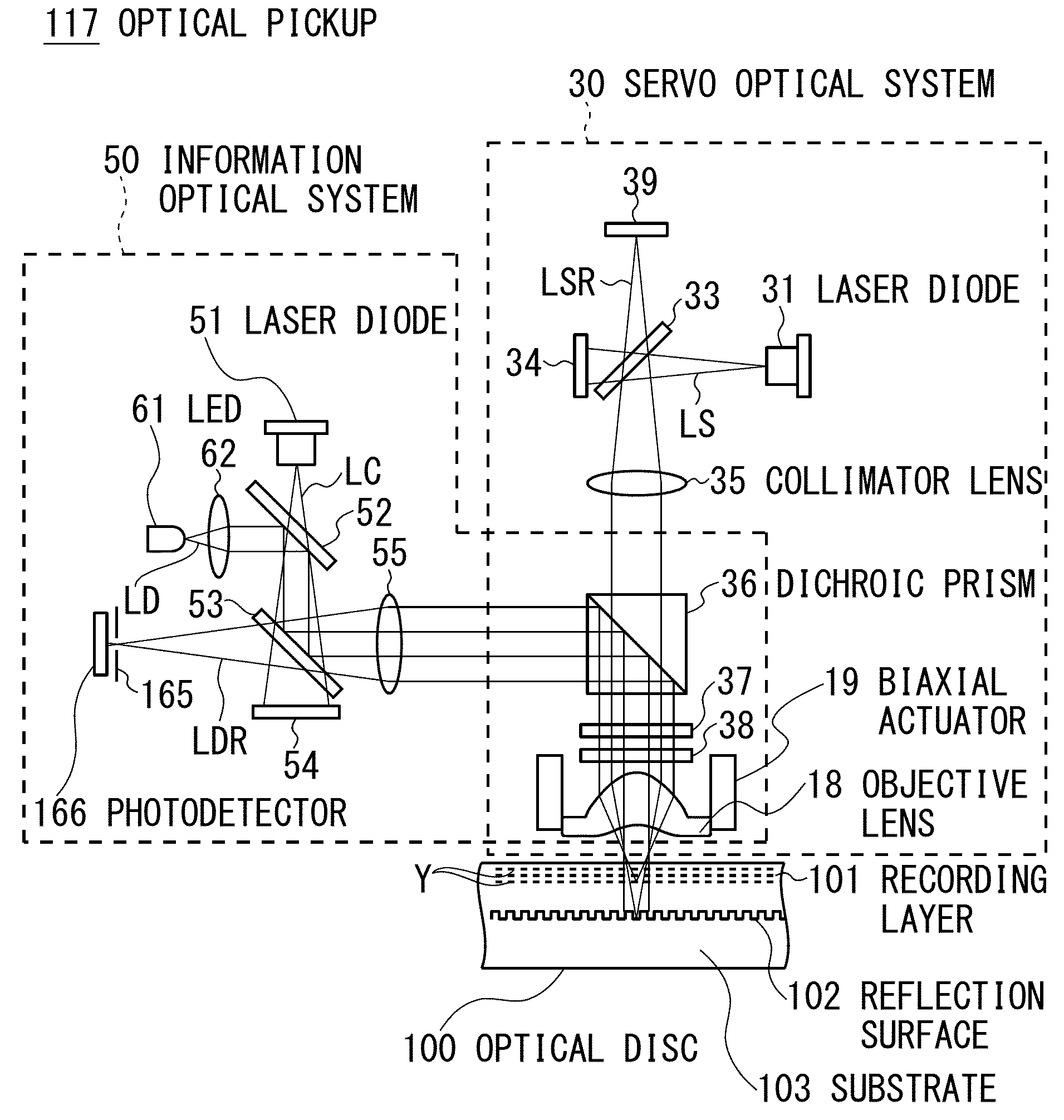
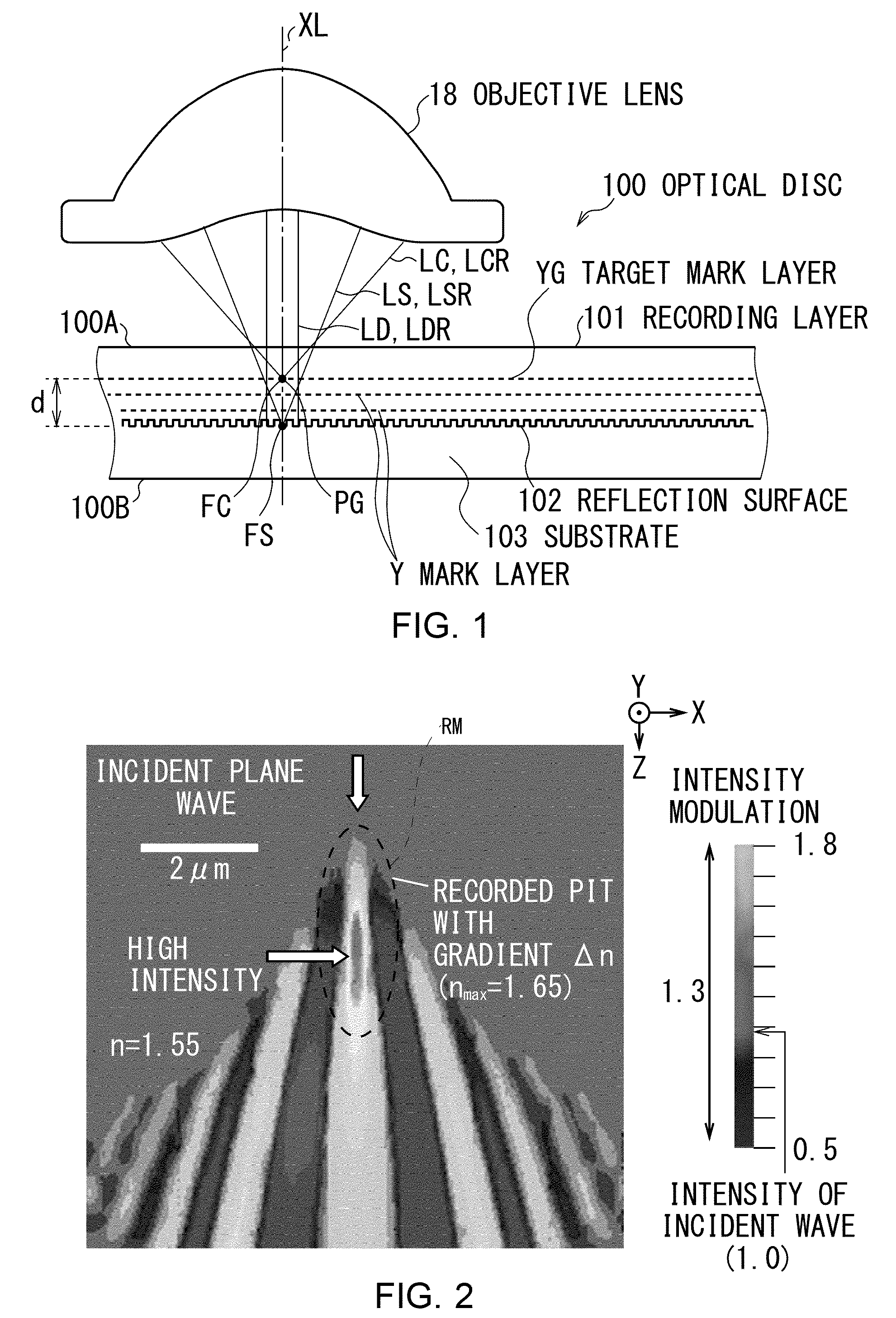
When an optical disc apparatus reproduces information from an optical disc, it converges a reading light beam emitted from an LED to substantially collimated light and projects it to the optical disc to cause it to be reflected by reflection surface thereof so as to make it become a reading reflected light beam. Then, the apparatus converges the reading reflected light beam by a mark layer selection lens, detects the reading reflected light beam passing through the target position by a detection region located at the confocal point of the target position and generates a detection signal. Subsequently, the apparatus recognizes the presence or absence of a recording mark based on the detection signal to reproduce the information. Thus, the apparatus can detect the state of the reading reflected light beam observed when it passes the target position and can recognize the presence or absence of a recording mark.
Owner:SONY CORP
Recording medium
ActiveUS7381458B2Improve compactnessWide power rangeLayered productsMechanical record carriersChemical reactionOptical recording
The main object of the present invention is to provide a recording medium which makes high densification of information possible, particularly a write-once-read-many optical recording medium having good recording signal characteristics to a wide range of recording powers.The present invention is one to accomplish the above object by providing a recording medium having a recording layer, whereby recording is carried out by heating the recording layer, characterized in that the recording layer contains a substance A which decomposes at a temperature which the recording layer reaches when heated for recording, and a substance B which does not undergo a chemical reaction or phase change at a temperature which the recording layer reaches when heated for recording.
Owner:CMC MAGNETICS CORPORATION
Optical information recording method and optical information recording medium
InactiveUS20070122747A1High densityStable recordInformation arrangementLayered productsLaser lightRecording layer
The present invention provides an optical information recording medium including a substrate with an on-groove and an in-groove, having successively disposed thereon a dye recording layer and a transparent sheet, wherein a width of the on-groove ranges from 50 to 140 nm, and a barrier layer is formed between the recording layer and the transparent sheet. The invention also provides an optical information recording method including irradiating the optical information recording medium with laser light from the side of the medium provided with a cover layer to form a void at a signal pit portion in the dye recording layer and thereby carrying out recording of information as well as an optical information recording medium on which information has been recorded by the method.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Read-only optical recording medium on which unique identification information is written
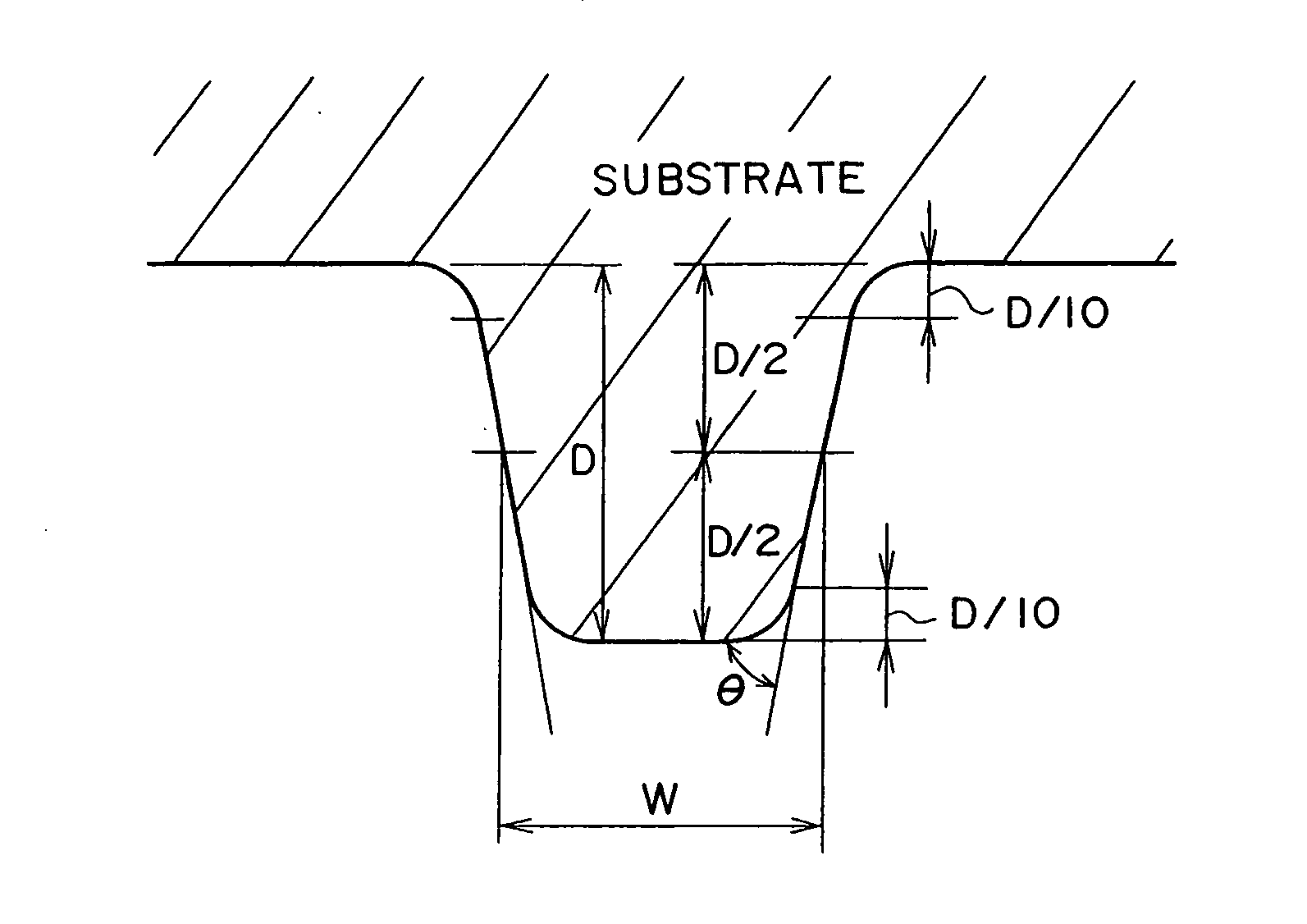
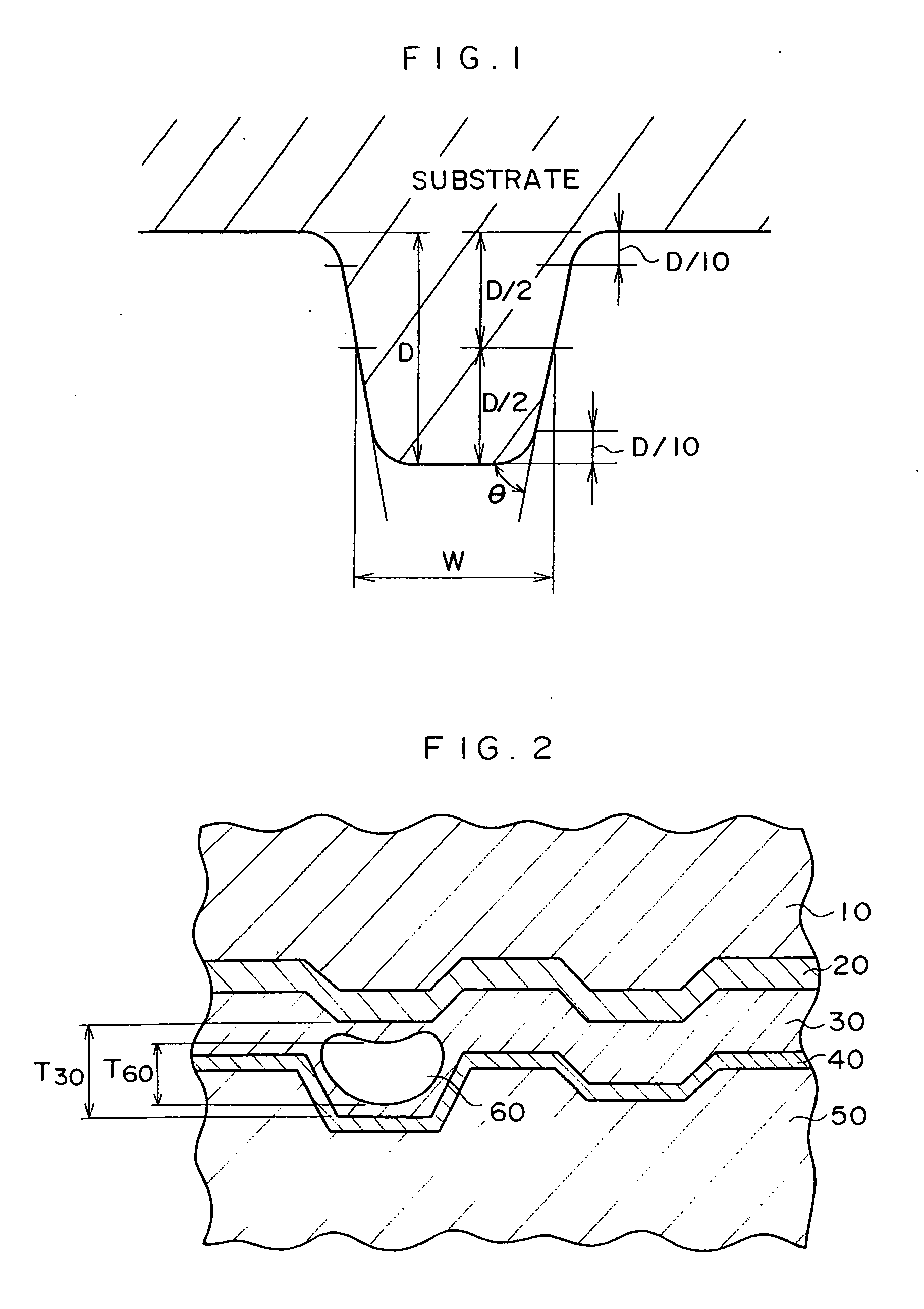
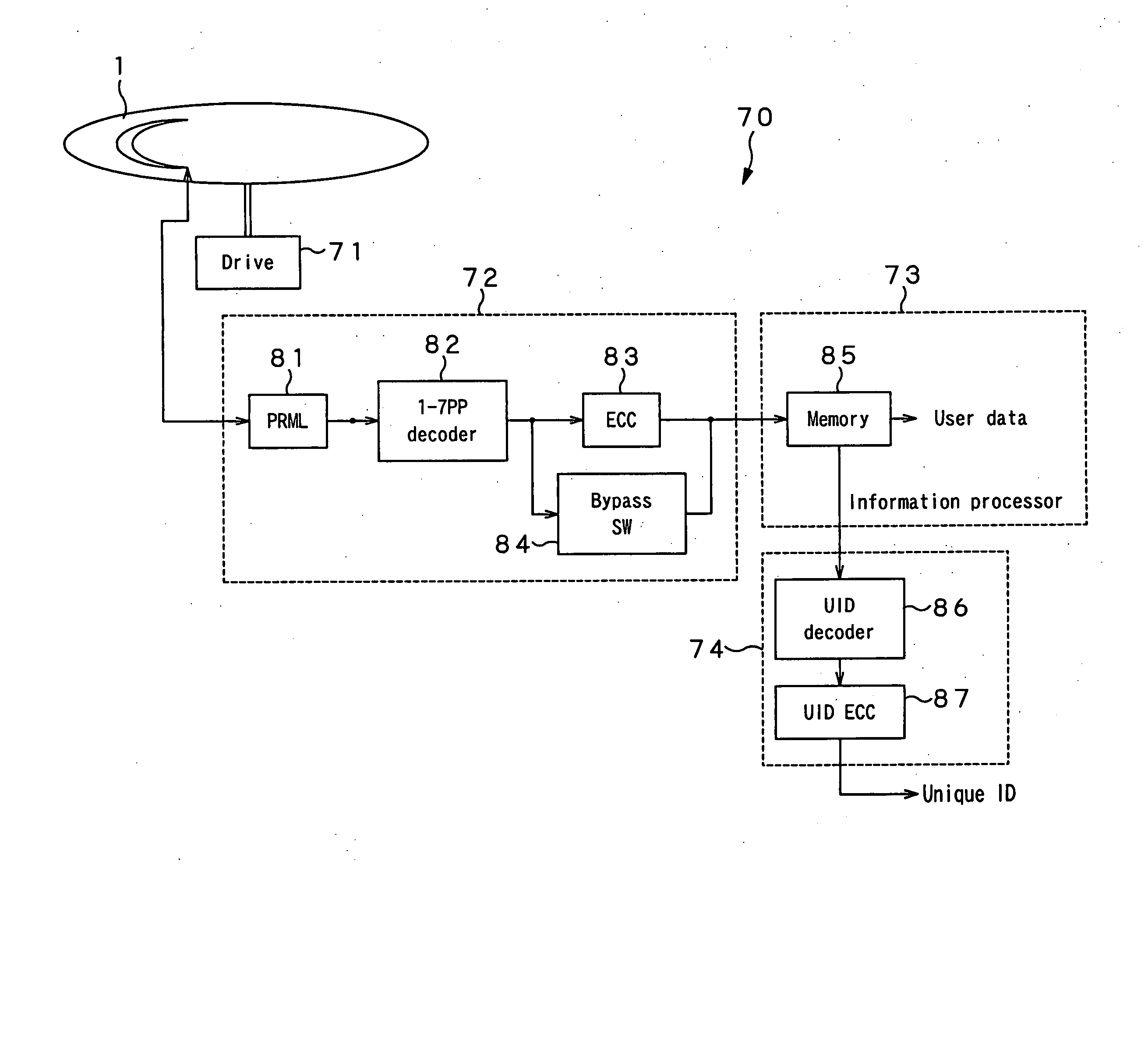
InactiveUS20070274177A1Clear messageIllegally copiedRecording strategiesFilamentary/web record carriersReading levelLaser light
There is provided a method for recording an unique ID to a read-only optical disk (1) adopting the 1-7 PP modulation technique and having provided in a plurality of predetermined positions postscript areas each having a predetermined postscript pattern formed therein. The postscript pattern takes a form of 3T (pit)-2T (land)-3T (pit) and has a length of 8T (largest code length of a modulated bit string). Modulated bit strings before and after the 3T-2T-3T postscript pattern are formed so that the pit-land-pit postscript pattern complies with the rule of the variable-length modulation even when it is replaced as a whole with a pit-only pattern. Further, the land in the middle of the pit-land-pit postscript pattern is formed from a material which will not physically change when irradiated with laser light having a reading-level power but will be melted when irradiated with laser light having a power higher than the reading-level one. Further, the postscript pattern is recorded at such a rate that any error can be corrected by the error correction.
Owner:SONY CORP
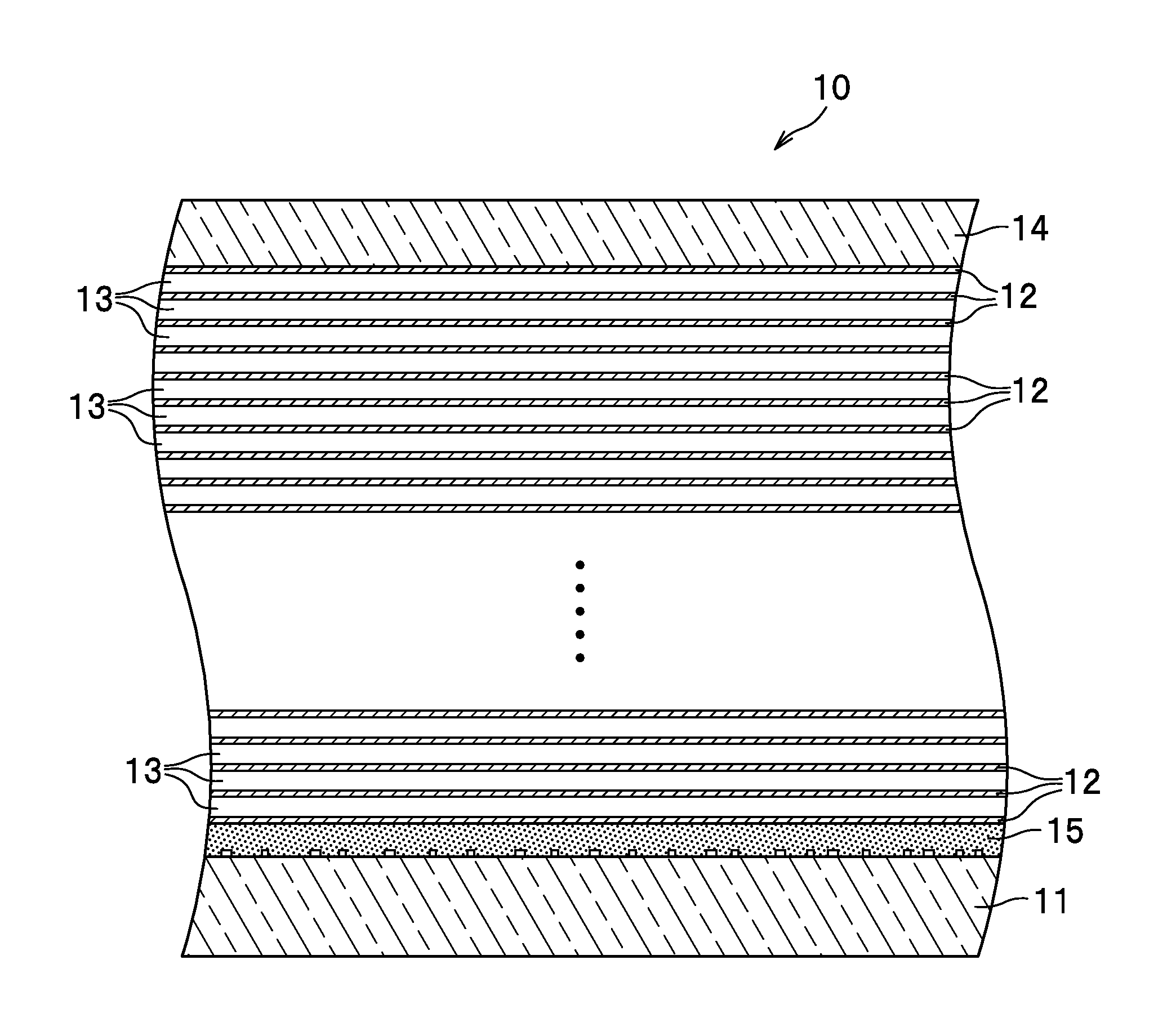
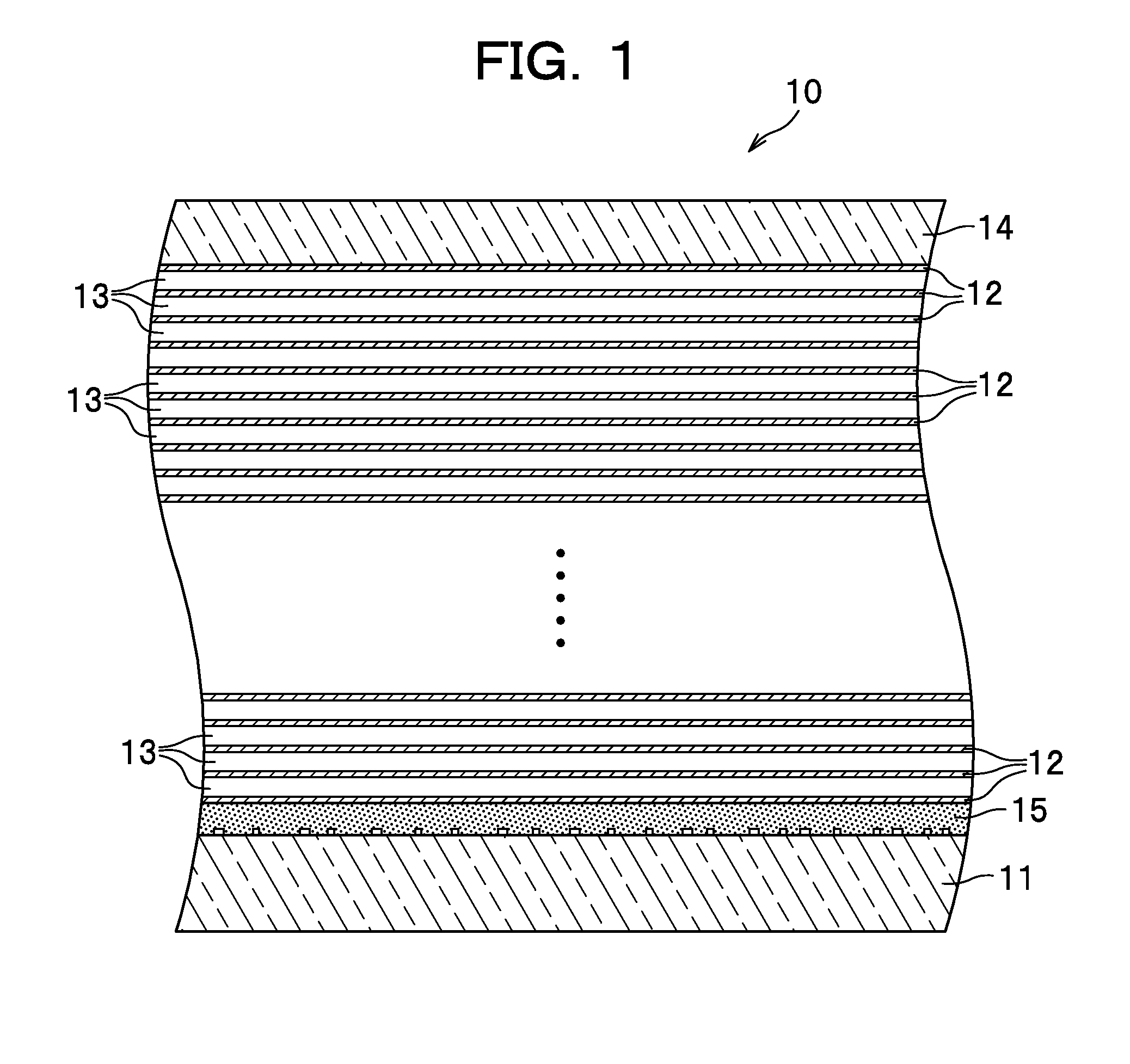
Optical information recording medium and optical information recording method
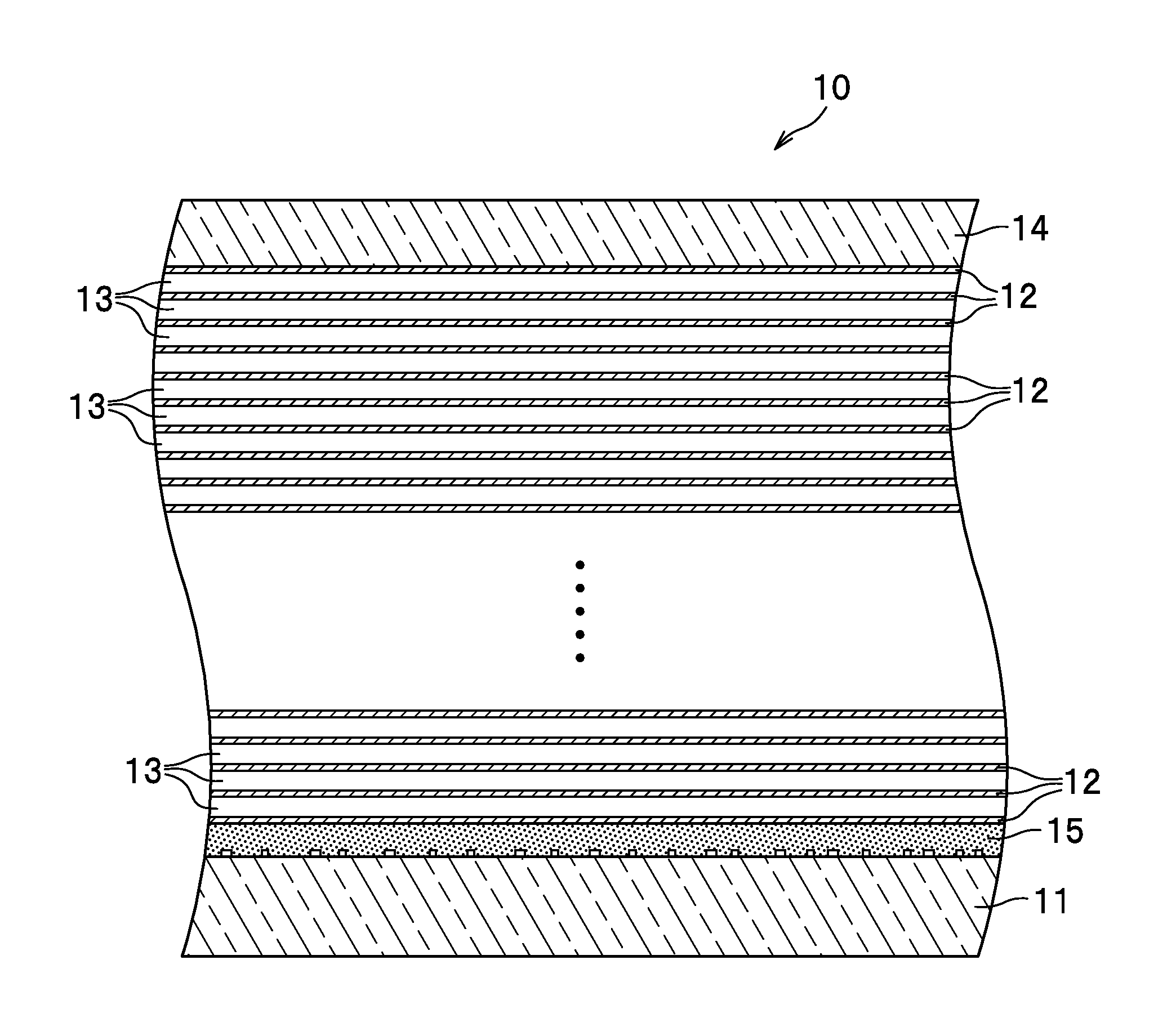
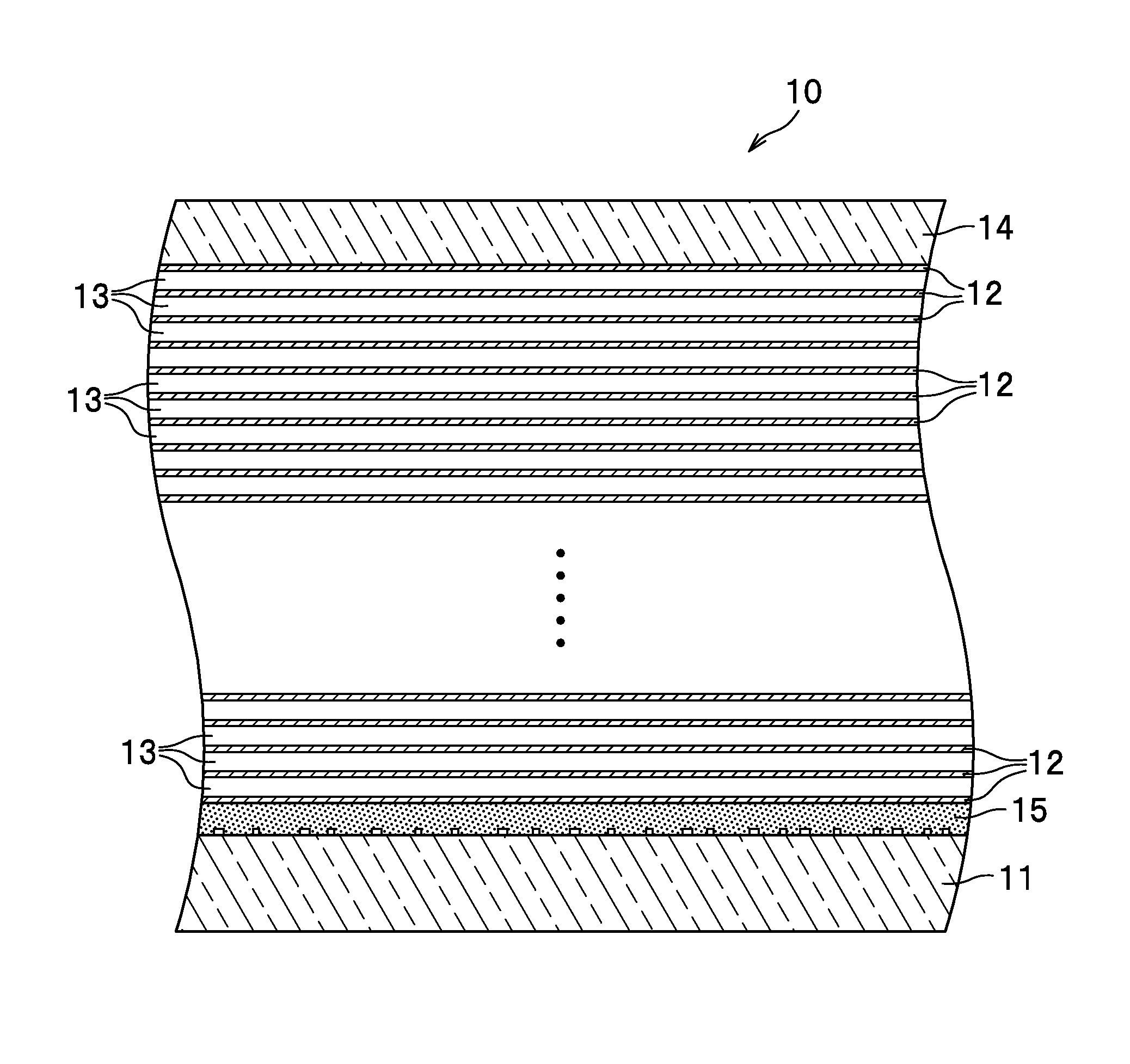
ActiveUS20130100791A1Evenly eraseInformation is easilyRecording carrier detailsLayered productsRecording layerComputer science
An optical information recording medium includes: a recording layer 12 comprising a multi-photon absorption compound and a one-photon absorption compound; and a supporting member (base layer 11) configured to support the recording layer 12. In this optical information recording medium, absorption of multiple photons by the multi-photon absorption compound and absorption of one photon by the one-photon absorption compound cause a void to be generated in the recording layer, whereby information is recordable by modulation based on a presence or absence of a void.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Optical disc recording method and device
InactiveCN1340810AReduce recording jitterImprove recording qualityRecording strategiesOptical discsLaser lightLaser beams
A method for recording on a write-once type optical disc. A laser light beam excited to light emission by a recording pulse having a pulse width corresponding to the length of a pit formed, with the recording power of substantially the leading end o the pulse being stepped over plural stages, is illuminated on a write-once type optical disc for recording. This enables recording with an optimal pit shape at a speed faster than a quadrupled speed, such as at an octupled speed or a duo-deca-tupled speed.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus for recording dye based recordable DVD media and process for recording the same
InactiveUS7646692B2Data error is hardlyAvoid it happening againRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsPulse beamOrganic dye
The present invention relates to apparatuses and processes for recording dye-based recordable DVD media in higher quality at higher linear recording velocity, and provides an apparatus for recording a dye-based recordable DVD medium comprising a shortest mark recording unit, a second mark recording unit, and a cooling pulse irradiating unit, wherein the dye-based recordable DVD medium comprises a substrate and a recording layer formed on the substrate, the substrate comprises a guide groove to which wobble is formed, and the recording layer comprises at least an organic dye, the shortest mark recording unit is configured to record each of the shortest marks by use of one pulse beam of which the rear edge is more energized than the front edge, the second mark recording unit is configured to record each of the marks other than the shortest marks by use of one pulse beam of which the two sites of front and rear edges are energized, the cooling pulse irradiating unit is configured to irradiate cooling pulse laser beams onto the backwards of the respective pulse beams at 0.1 mW / pulse or less of optical energy, and the recording of marks is performed on the recording layer at a recording linear velocity of 42 m / sec or more.
Owner:RICOH KK
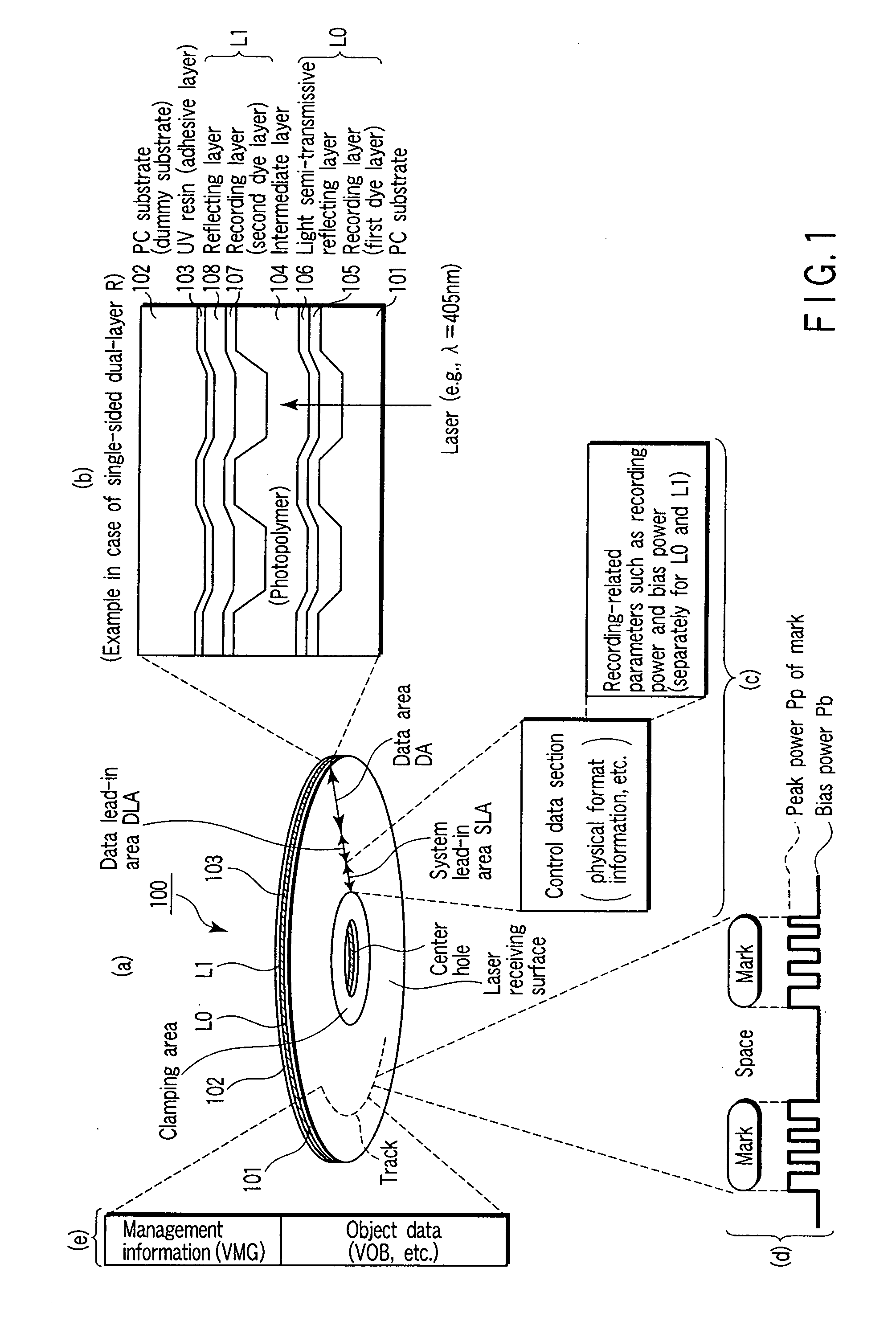
Write-once type multilayer optical disc, recording method, reproducing method, and recording device
InactiveUS20070286980A1Layered productsRecording involving reflectivity/absorption/color-changeOrganic dyeLight beam
Manufacturing of a higher quality write-once type multilayer optical disc is facilitated. The optical disc includes a plurality of recording layers in which recording or reproduction is carried out by a blue or blue-violet laser beam of a wavelength of about 405 nm. Each of the recording layers includes a recording layer which uses an organic dye. The plurality of recording layers includes a layer in which a groove pattern around a recording mark is deformed when information is recorded, and a layer in which the groove pattern around the recording mark is not deformed when information is recorded.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
High capacity digital data storage by transmission of radiant energy through arrays of small diameter holes
InactiveUS7054256B2Reduce distractionsReduce in quantityMechanical record carriersOptical detectorsLength waveData storing
Owner:WORLD THEATRE INC
Secure optical data card system
InactiveUS20080267047A1Solve insufficient capacityShorten the lengthInformation arrangementCard-like record carriersComputer hardwareOptical recording
A method of producing data storage card for storage of machine-readable information includes an optical memory area subjected to optical information recording and reproduction, comprising, a card-like card body, an optical recording portion provided on the card body. A method of combining a file access system with a write once optical data card produces a secure portable database system.
Owner:DCARD
Method for Long-Term Storage of Information and Storage Medium Therefor
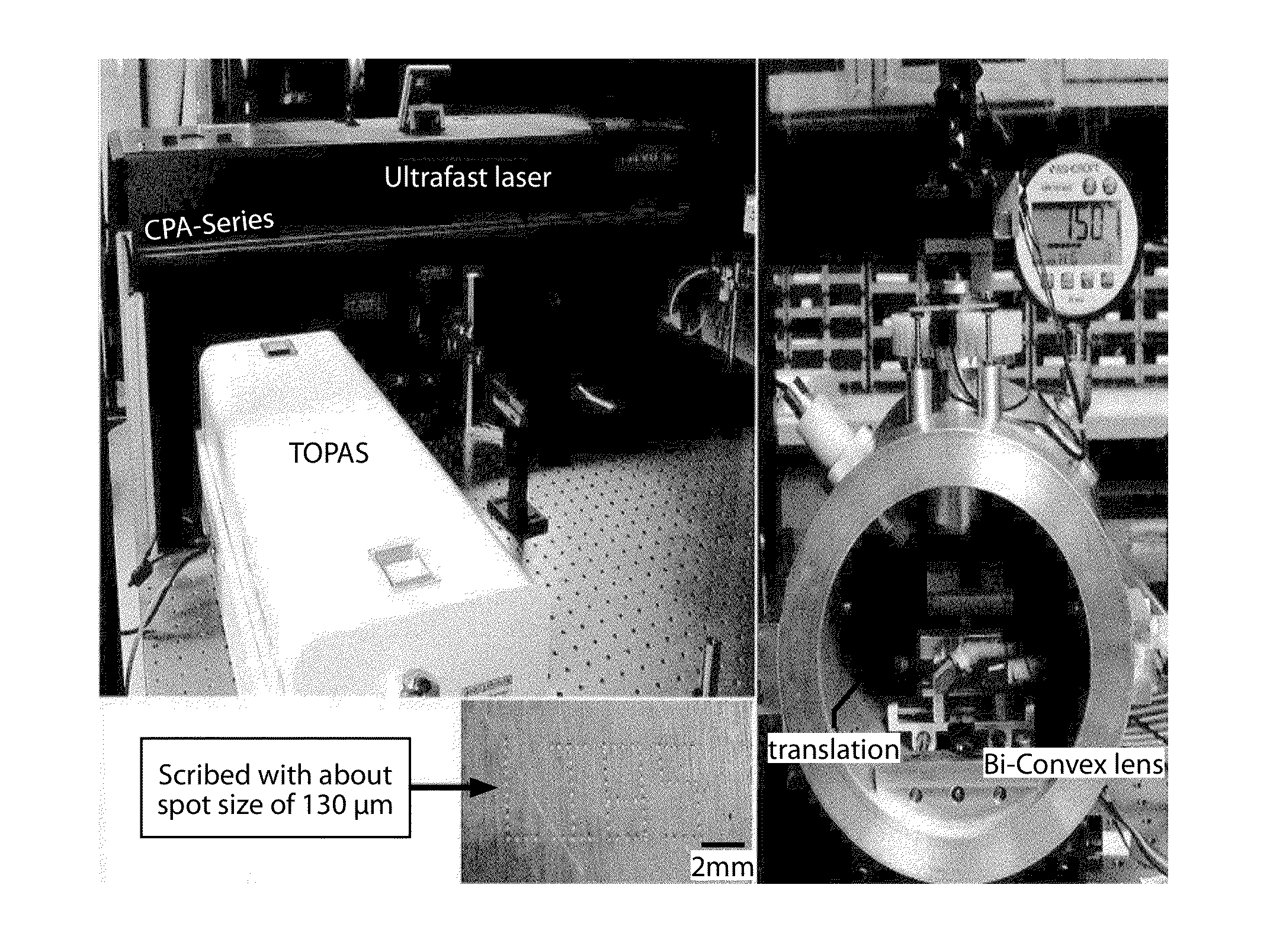
ActiveUS20210046588A1Cheap and efficient information storage systems has been acuteEasy to degradeElectron beam carrier recordingVacuum evaporation coatingParticle beamCeramic substrate
The present invention relates to an information storage medium and a method for long-term storage of information comprising the steps of: providing a ceramic substrate; coating the ceramic substrate with a layer of a second material different from the material of the ceramic substrate, the layer having a thickness no greater than 10 μm; tempering the coated ceramic substrate to form a writable plate or disc; encoding information on the writable plate or disc by using a laser and / or a focused particle beam to manipulate localized areas of the writable plate or disc.
Owner:CERAMIC DATA SOLUTIONS GMBH
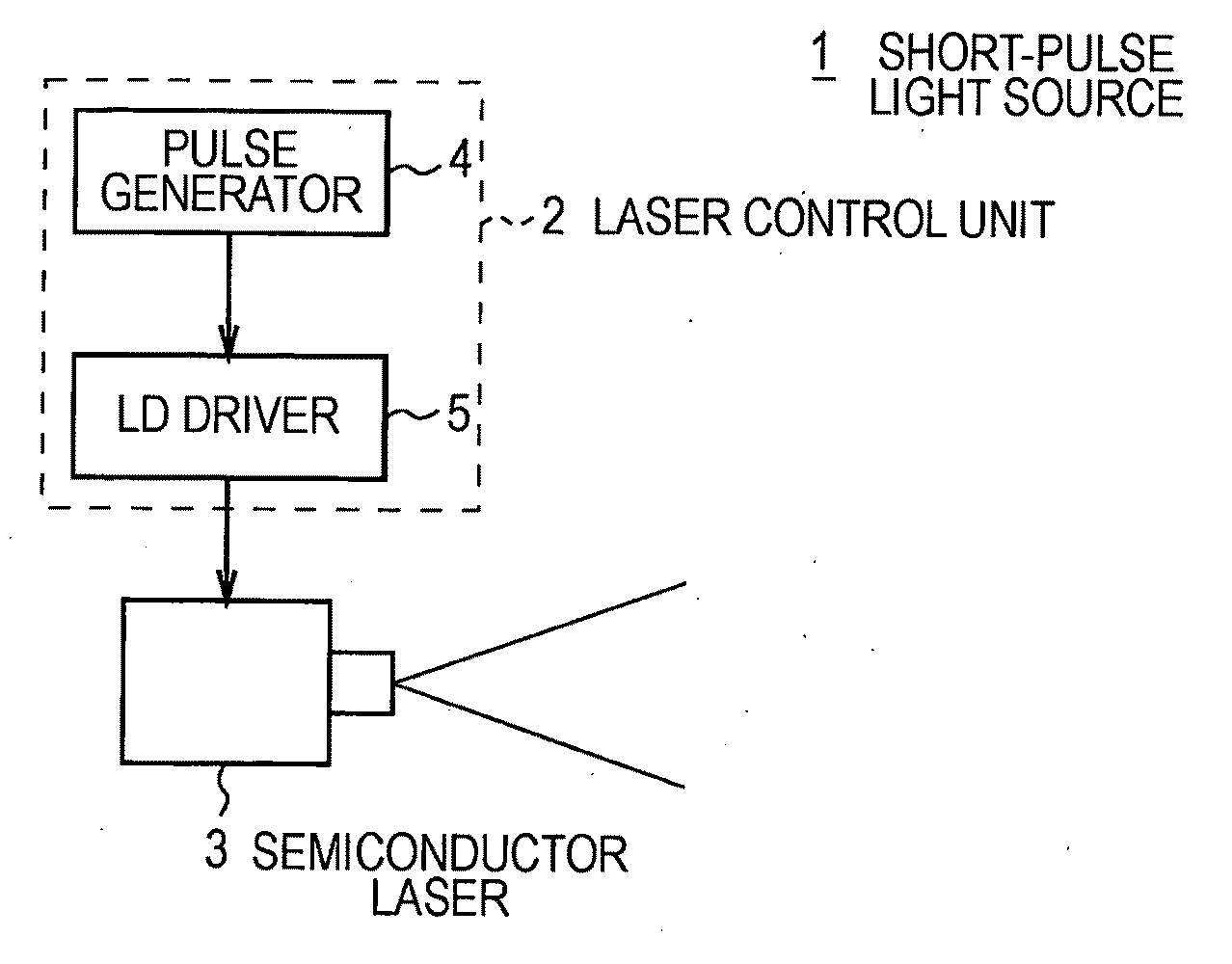
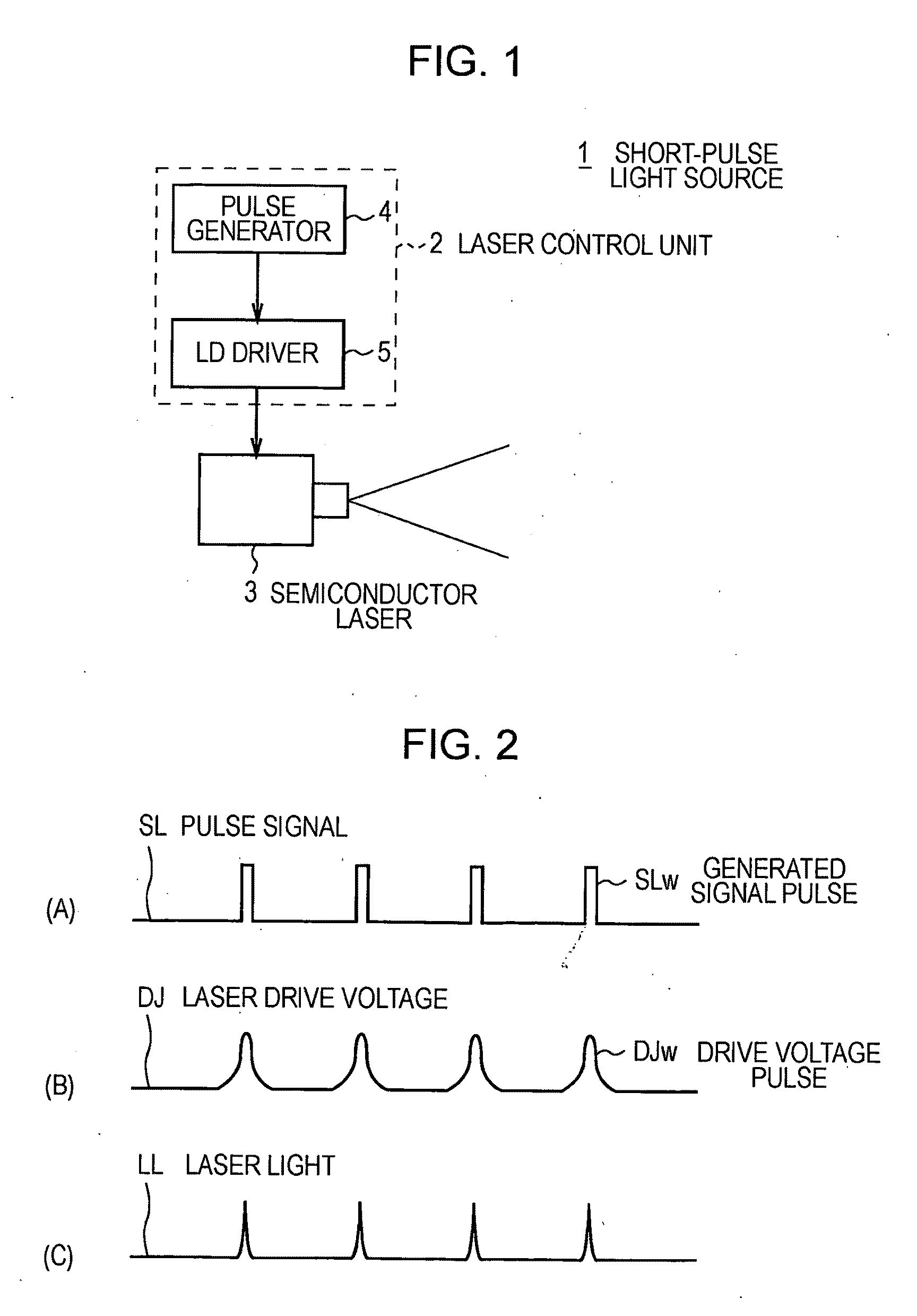
Short-pulse light source, laser light emitting method, optical device, optical disk device, and light pickup
The present invention can control output of pulses from a semiconductor laser.In the present invention, a short-pulse light source (1) applies a laser drive voltage (DJ) having a pulse-shaped drive voltage pulse (DJw) to a semiconductor laser (3), thereby causing the semiconductor laser (3) to emit specific output light (LAp), as laser light (LL), having a pulse-shaped specific peak (APK) and a specific slope (ASP), an emission intensity of the specific slope (ASP) being lower than an emission intensity of the specific peak (APK). The short-pulse light source (1) controls a voltage pulse half-width (Thalf), which is a pulse width of the drive voltage pulse (DJw), by setting a pulse width (Ws) of a set pulse (SLs), thereby adjusting a ratio between the specific peak (APK) and the specific slope (ASP).
Owner:SONY CORP
High capacity digital data storage by transmission of radiant energy through arrays of small diameter holes
ActiveUS20020126616A1Reduce distractionsReduce in quantityMechanical record carriersOptical detectorsLength waveData storing
A storage media for storage of data thereon is provided. The storage media including: a first layer, the first layer being substantially transparent to a predetermined radiant energy used for reading the data; and a second layer formed on the first layer and being substantially opaque to the radiant energy, the second layer having a pattern comprising a plurality of holes, each of the holes having a largest dimension which is greater than a wavelength of the radiant energy, the data being stored as the presence or absence of a hole in the pattern. Also provided are a method for fabricating the storage media as well as an apparatus and method for reading the data stored on the storage media.
Owner:WORLD THEATRE INC
Optical recording medium, optical recording apparatus, and system to prepare contents-recorded optical recording medium
InactiveUS20100027393A1Excellent recording sensitivityHigh sensitivityLayered productsRecord information storageLaser lightOptical recording
An optical recording medium, comprising a dye recording layer, wherein a recording mark portion is formed at the dye recording layer by use of a laser light having a wavelength of 640 nm to 680 nm, and a reflectance after recording with respect to the laser light at the recording mark portion is increased compared to a reflectance before recording.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical recording medium
A phase-modulation type optical recording medium comprising at least one layer of recording film (4) and at least one layer of metal film (3) on a recesses-formed substrate (1), wherein at least one layer of constituent film constituting the recording film consists of an organic matter that absorbs and breaks down a laser beam to have its refractive index changed, and the width of a recess (2) is 0.10 [mu]m-0.21 [mu]m, whereby providing a WORM type, high-density-recording optical recording medium capable of producing a high reproducing output.
Owner:SONY GRP CORP
Planetary compact disc recorder
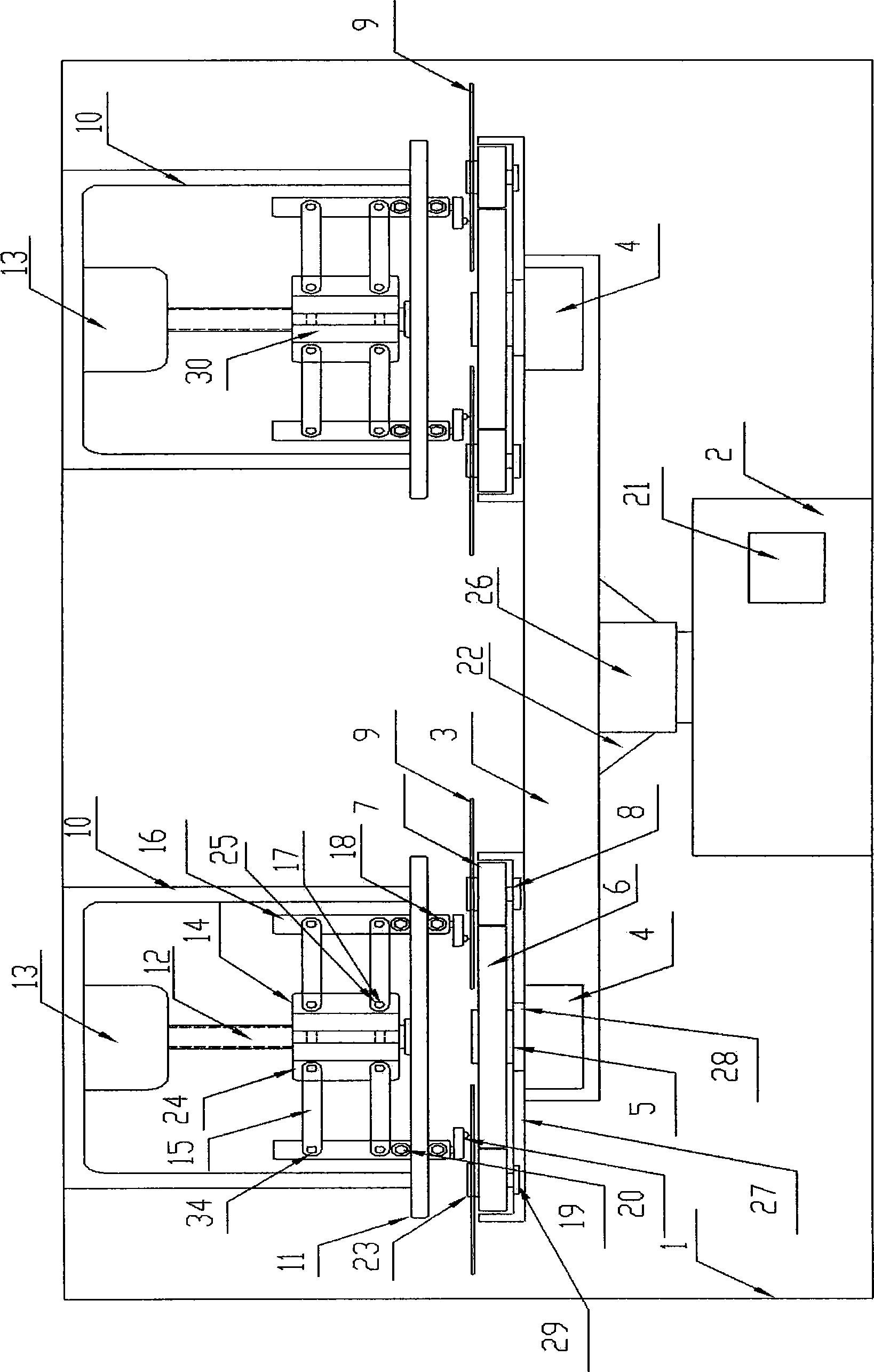
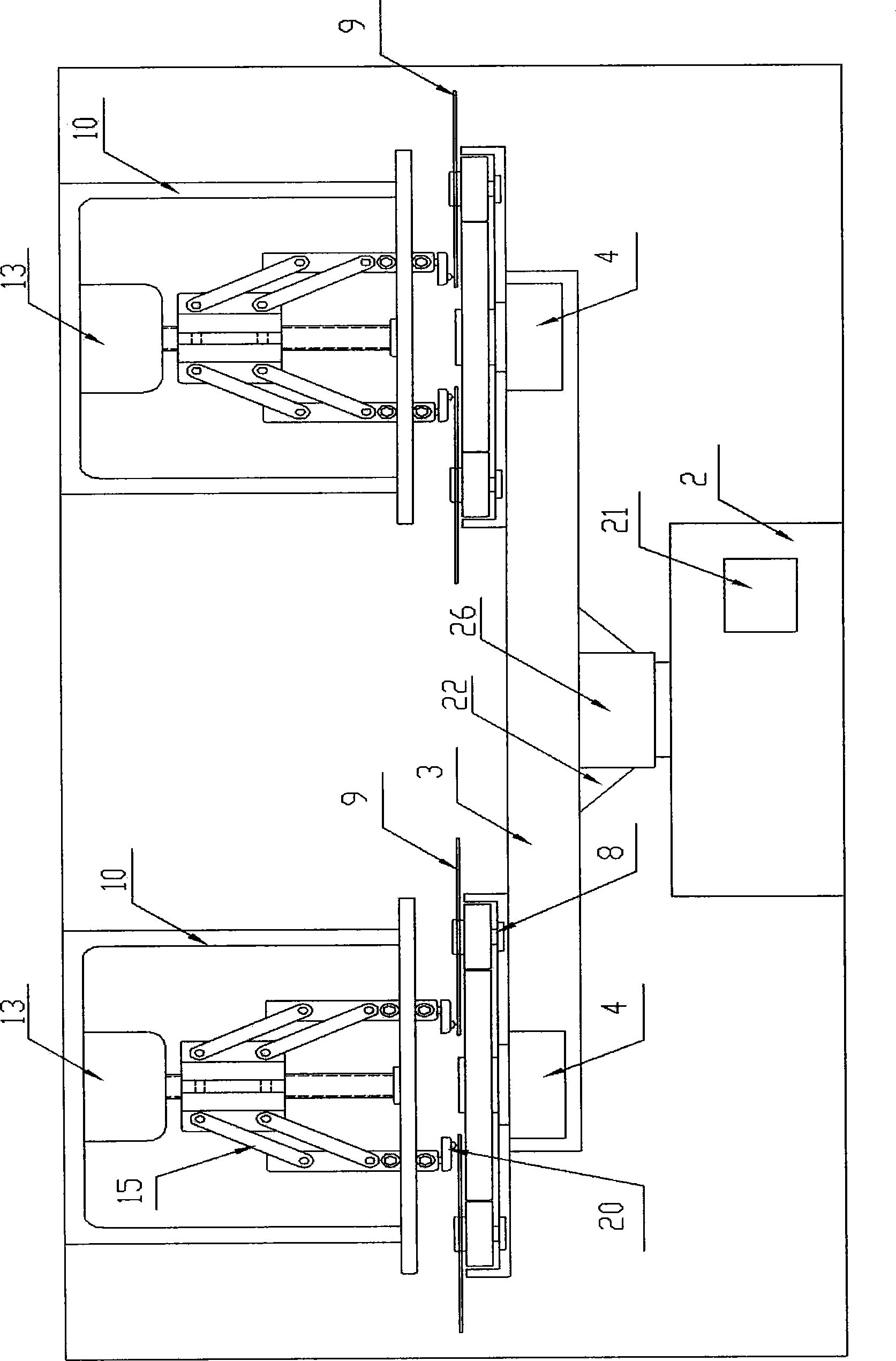
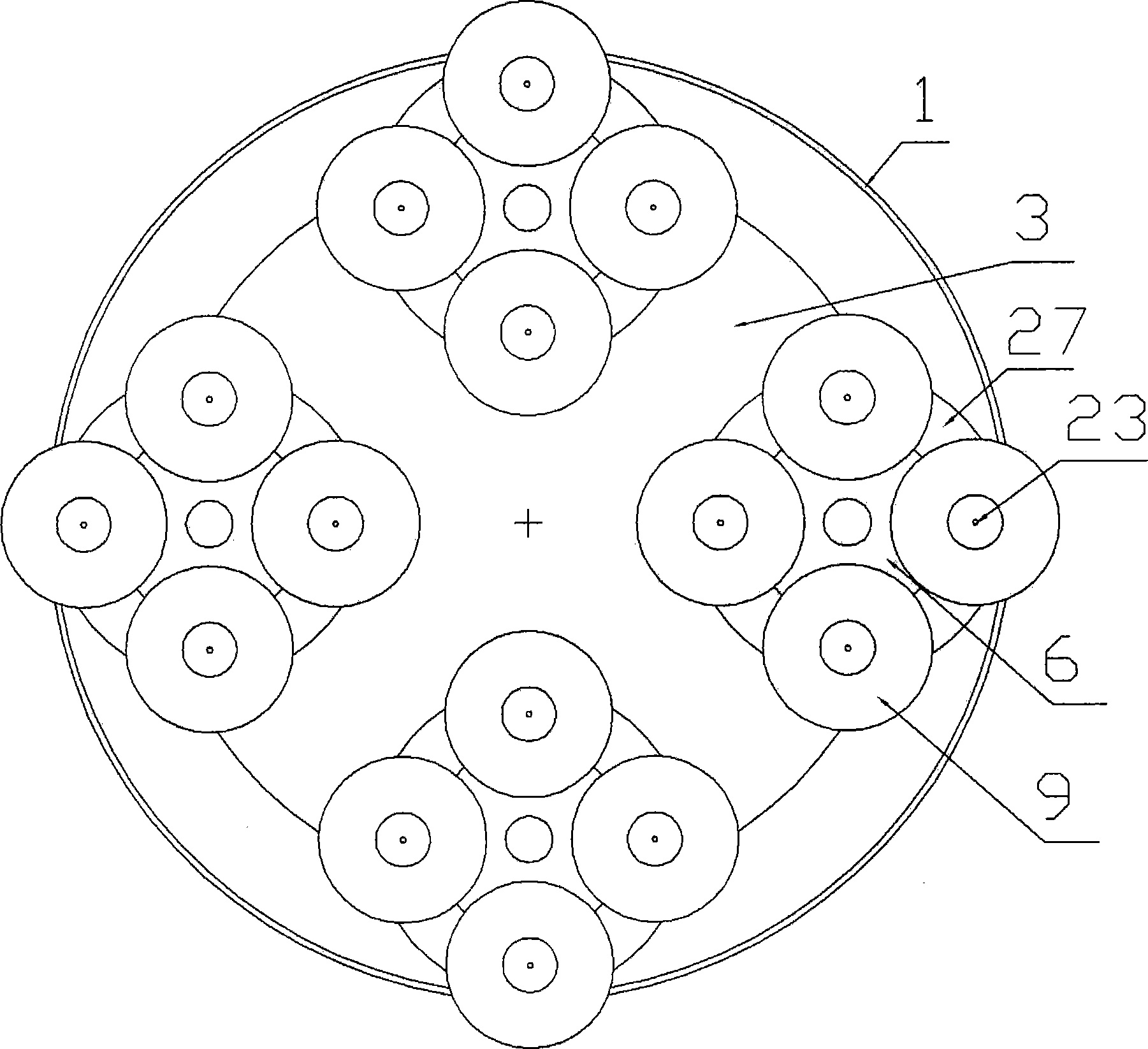
ActiveCN104269181ARealize the effect of simultaneous continuous recordingRecord information storageRecording involving layer ablationCompact discGear drive
The invention relates to the field of computers, in particular to a planetary compact disc recorder. Four drive assemblies in the planetary compact disc recorder are evenly distributed on a rotary disc and sequentially drive sun gears and planetary gears through speed regulating drive motors, and the sun gears and the planetary gears drive compact discs on compact disc clamp shaft heads to rotate at a constant speed so as to complete compact disc recording. Linear servo stepping motors rotate to drive helical lead screws to move upwards, then the helical lead screws drive hinge joint seats connected onto the helical lead screws in a sleeving mode to move upwards, and laser heads complete the whole recording work from inner circles to outer circles and complete simultaneous recording of a plurality of compact discs due to accurate motions of the linear servo stepping motors. Track seeking mechanism assemblies are switched to other drive assemblies in position each time cam indexing unit and a main power motor rotate at 90 degrees, the compact discs completely recorded on the drive assemblies are replaced while recording, the time for arranging compact discs to be recorded is not needed, and the effect of simultaneously recording a plurality of compact discs is really achieved.
Owner:河南万创技术服务有限公司
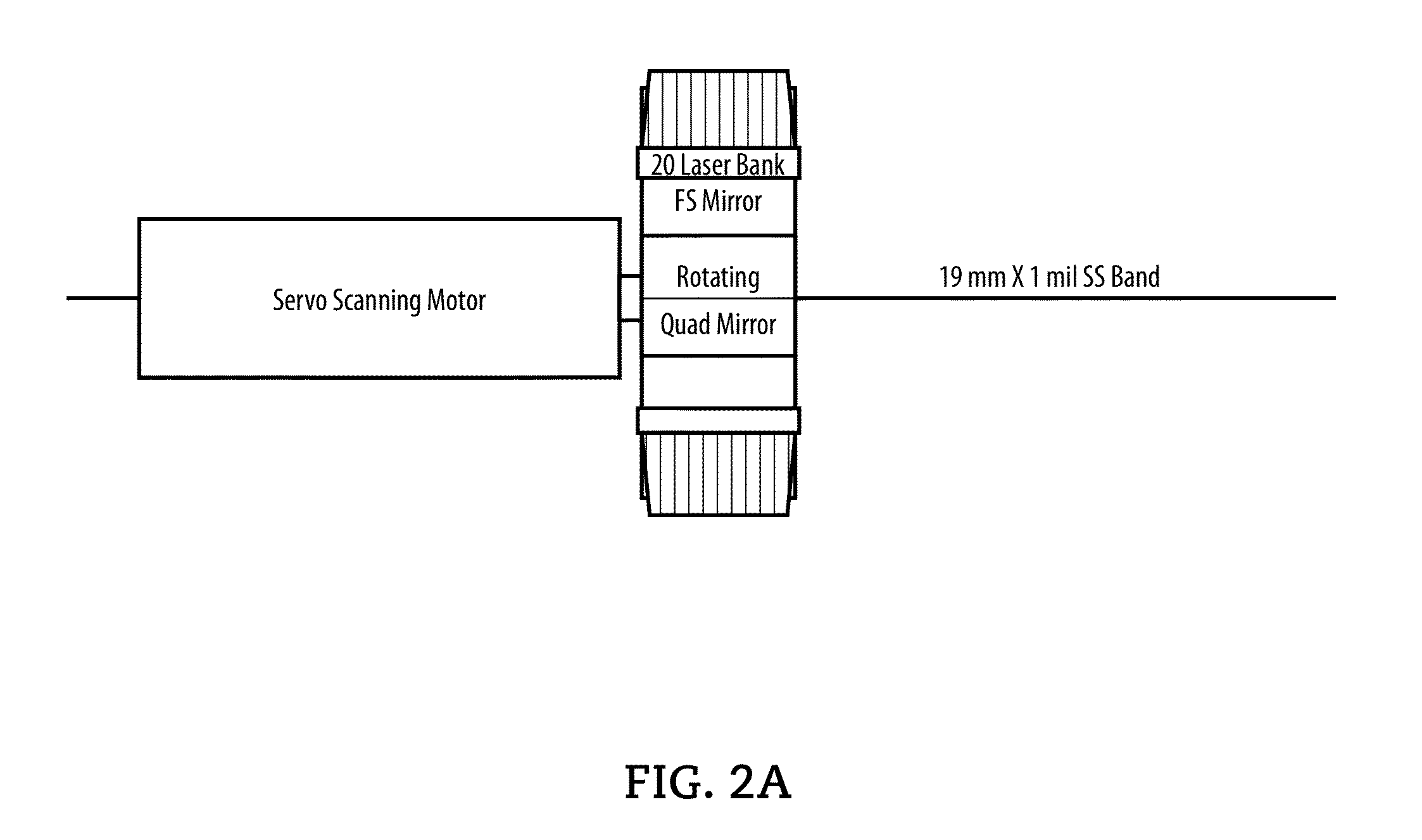
System and method for using stainless steel as a data archiving medium
An apparatus, method, and computer readable medium for writing data on a highly indestructible material is disclosed. A laser may write data on a first side of a highly indestructible material. The data may then be marked as non-rewriteable. The data may also be written on a second side of the highly indestructible material, with the second side being opposite the first side. The highly indestructible material may comprise a stainless steel storage medium.
Owner:LACEY STEVEN MICHAEL +3
Optical information recording medium
InactiveCN102237102ASmall sizeAvoid deformationTwo photon recordingRecord information storageOptoelectronicsRecording layer
An optical information recording medium includes a recording layer, wherein the recording layer includes a thermoplastic resin and inorganic oxide particles dispersed in the thermoplastic resin.
Owner:SONY CORP
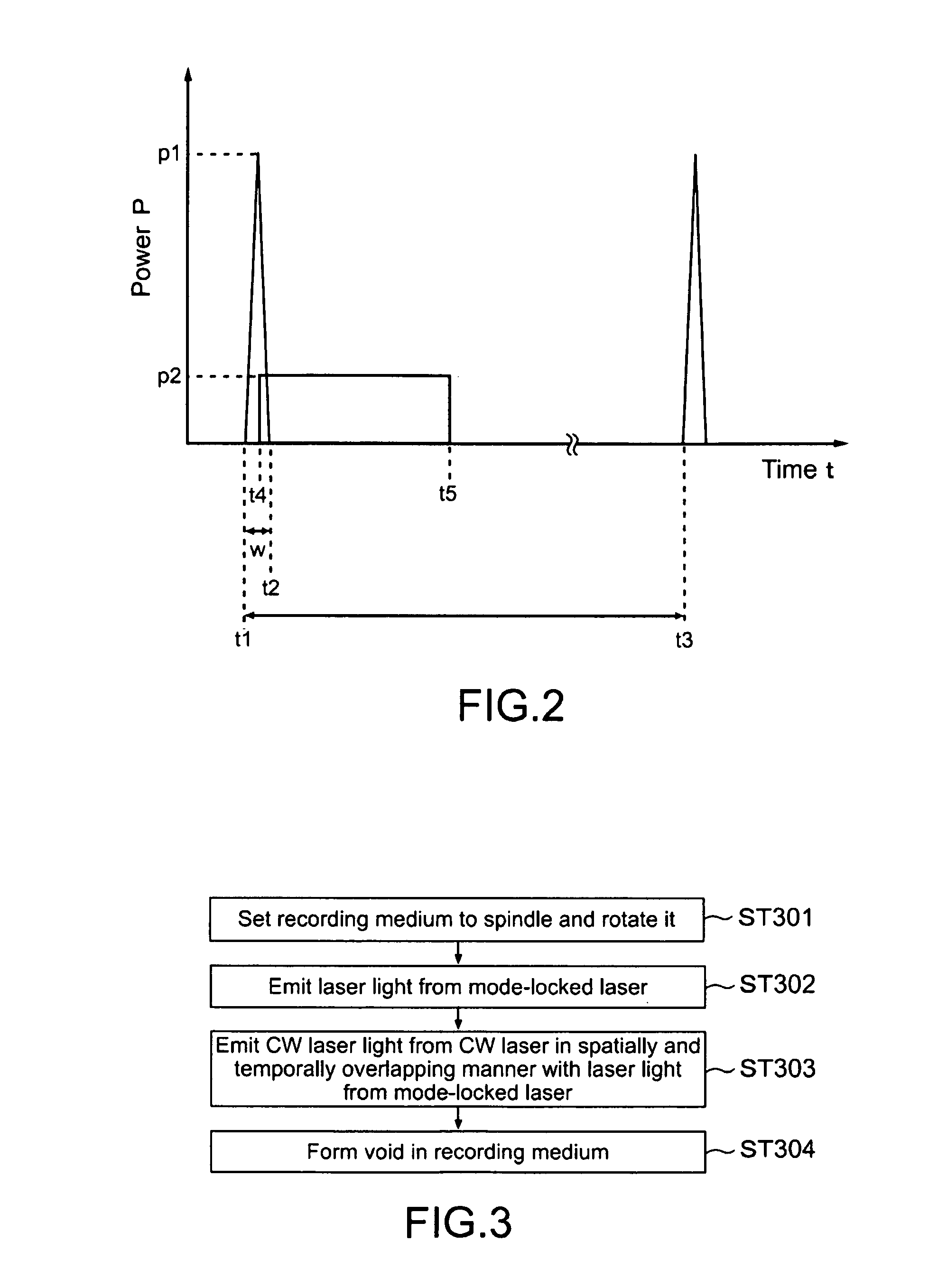
Optical recording method and optical recording apparatus
InactiveUS8165005B2Easy to produceEnhanced light absorptionOptical beam sourcesRecord information storagePhoto irradiationEngineering
Disclosed is an optical recording method. The optical recording method includes irradiating an area where a recording mark is formed in a medium with a pulse train of laser light, and irradiating the area where the recording mark is formed with continuous-wave laser light that is continuously output.
Owner:SONY CORP
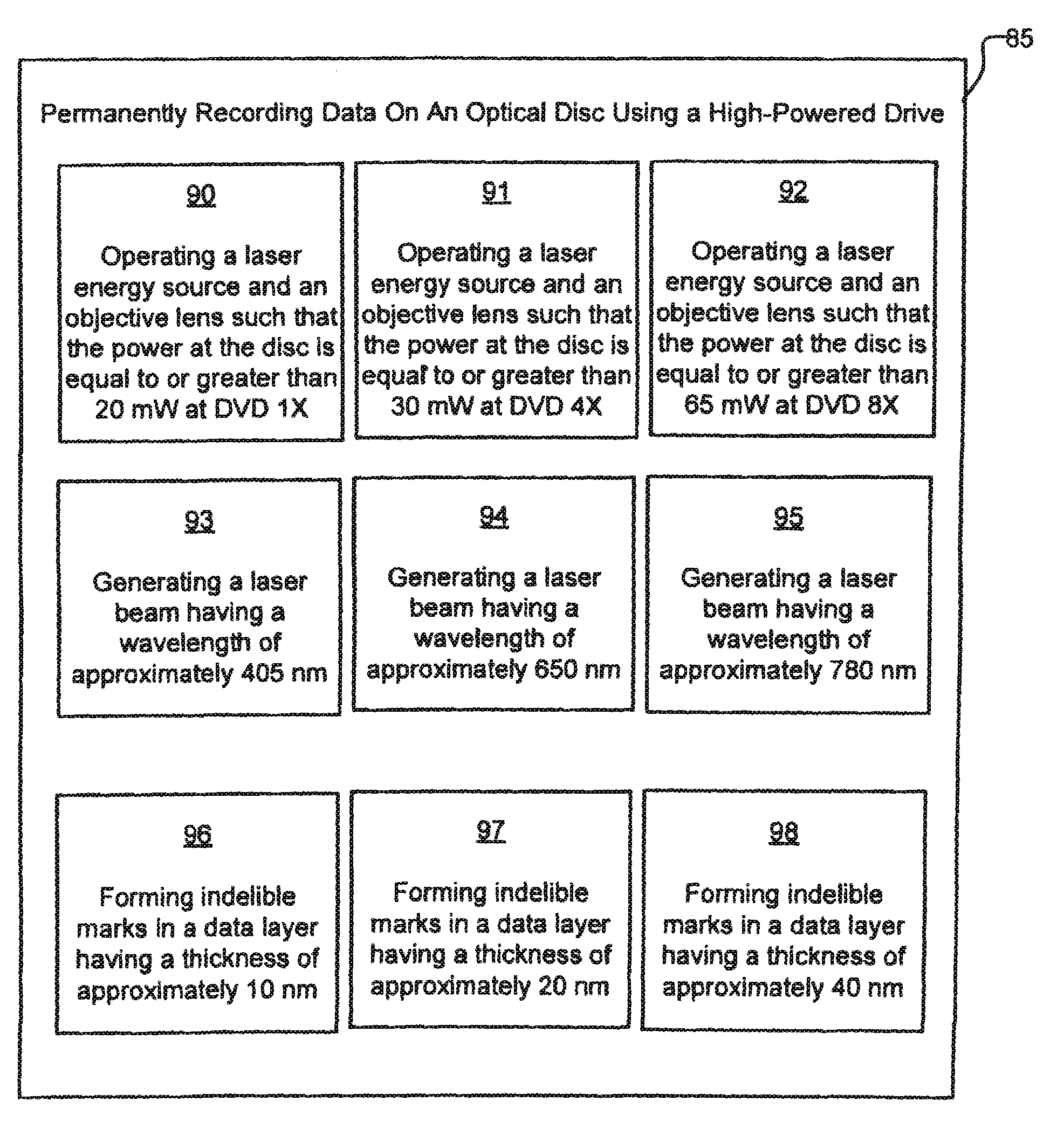
High power optical disc drives
ActiveUS20100135147A1Increase powerOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageEngineeringOptical disc drive
High power optical disc drives are disclosed. The drives are configured to deliver laser energy having a power of at least about 25 mW as measured at DVD 1X write speed upon first contact with the surface of an optical disc.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
Fluorescent dark-state optical disc information reading and writing methods and devices based on nano photoetching
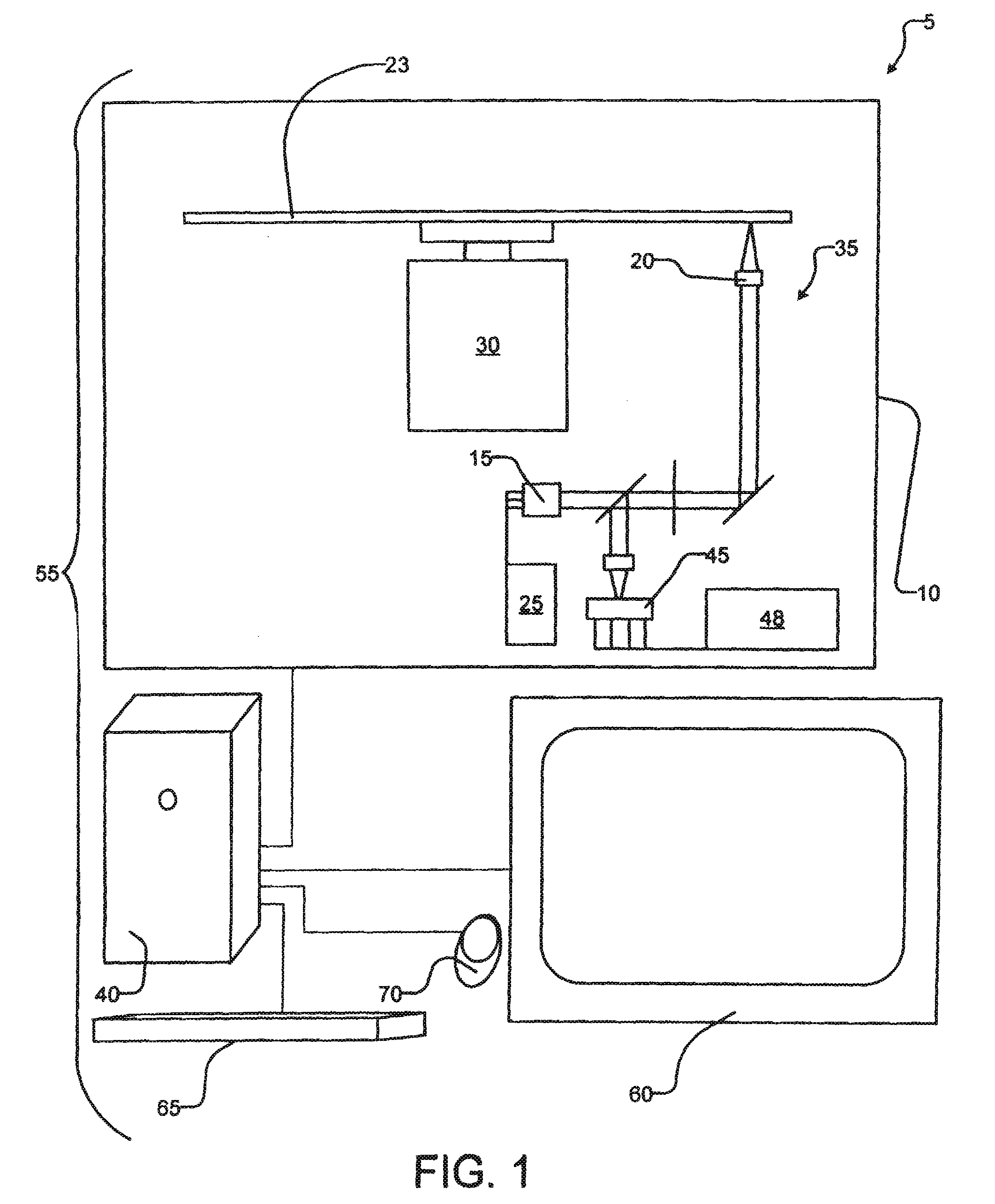
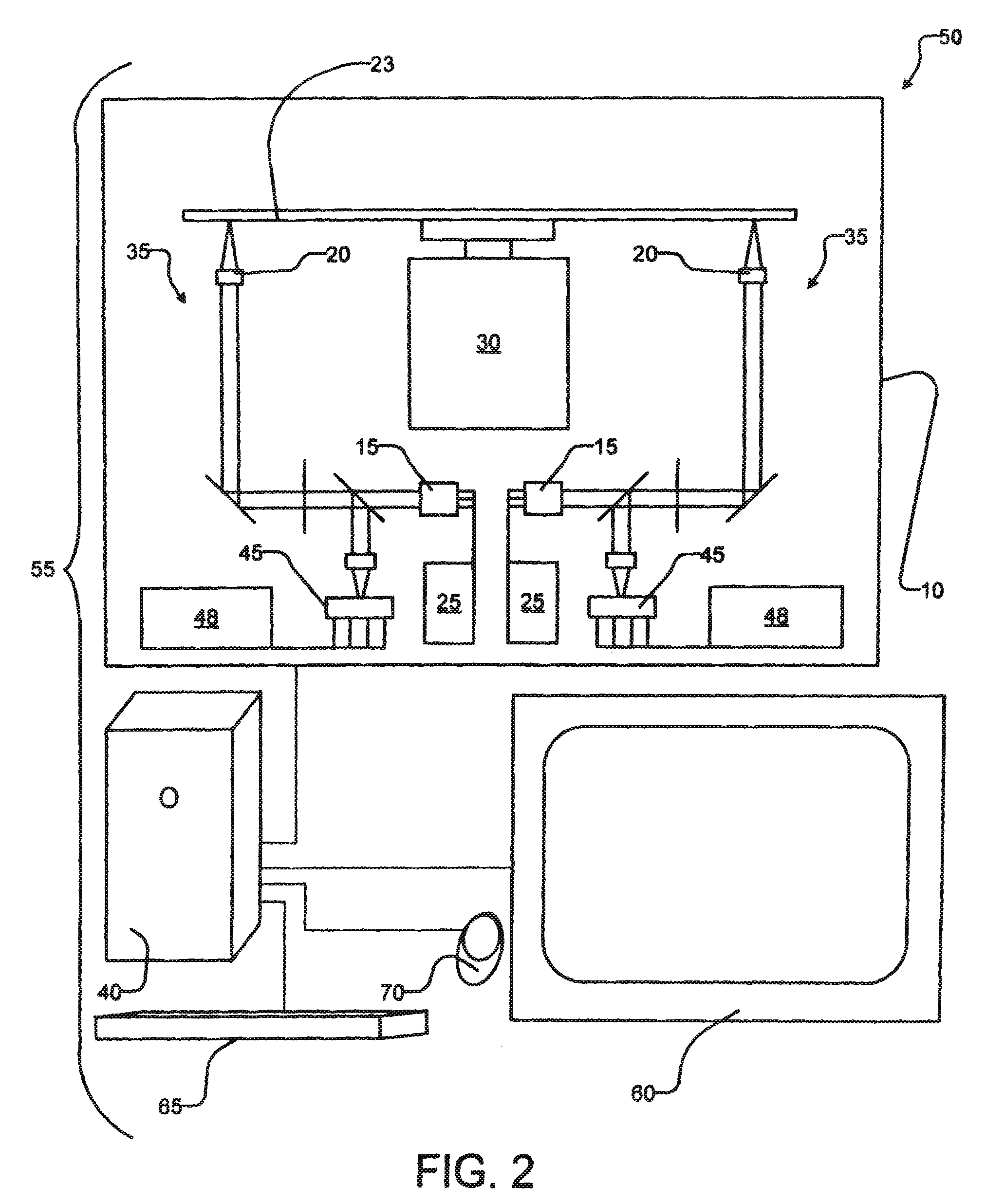
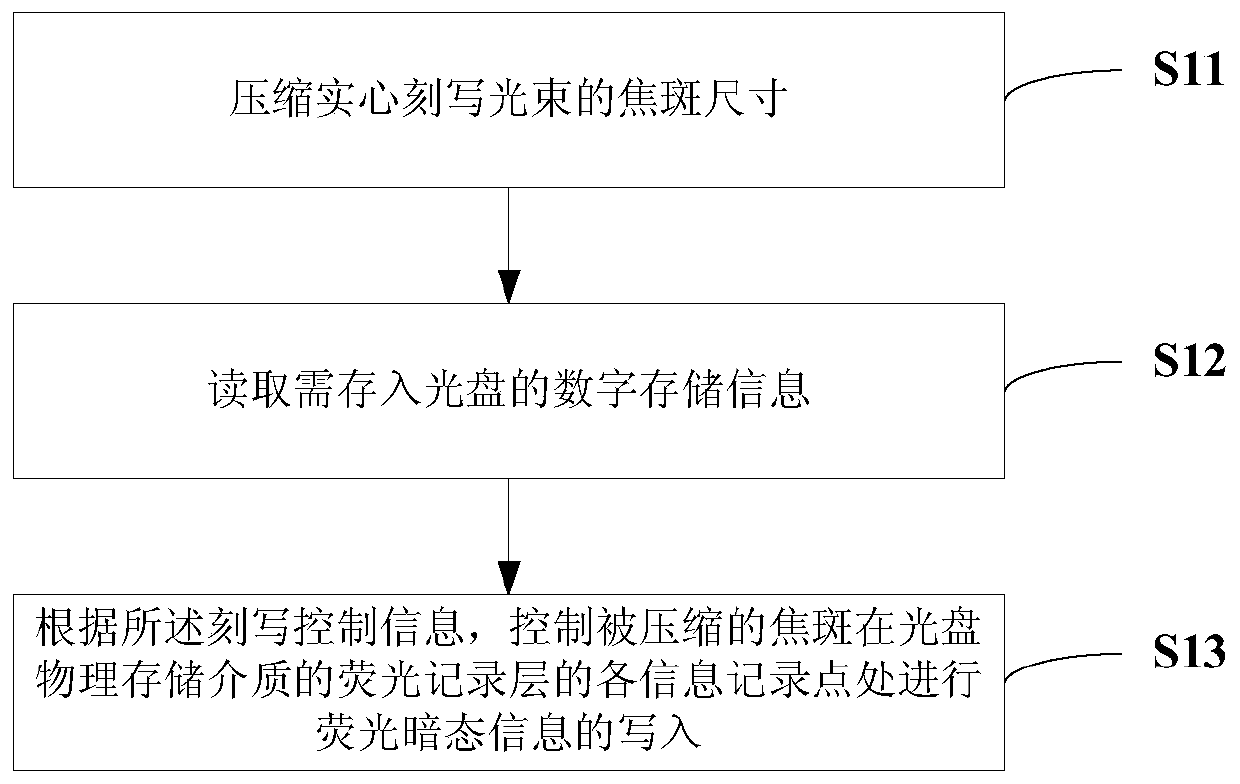
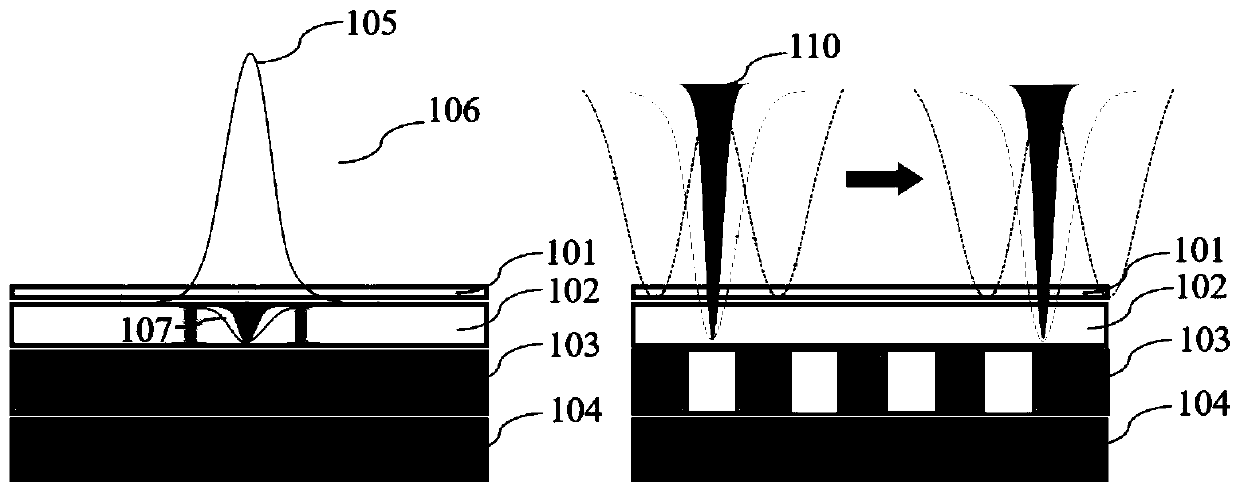
ActiveCN111462780AImprove storage densityIncrease storage capacityRecording strategiesTwo photon recordingTwo-photon absorptionHigh density
The invention provides optical disc information reading and writing methods and devices based on nano photoetching, and the writing method comprises: carrying out the writing of the storage information of an ultrahigh-density optical disc through a nano photoetching method, carrying out information storage by adopting a fluorescent dark state method, and achieving multi-layer optical disc information inscribing storage by utilizing a two-photon absorption characteristic. The reading method comprises: reading optical disc information by a super-resolution digital information reading method; byadopting a 'confocal chromatography' reading method, multilayer storage information reading of the optical disc can be realized. According to the invention, the size and spacing of the information recording points can be reduced, the stable and long-term storage of the ultra-high density information of the optical disc can be realized, and the effective and high-speed extraction of the storage information of the ultra-high density optical disc can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Long-term digital data storage
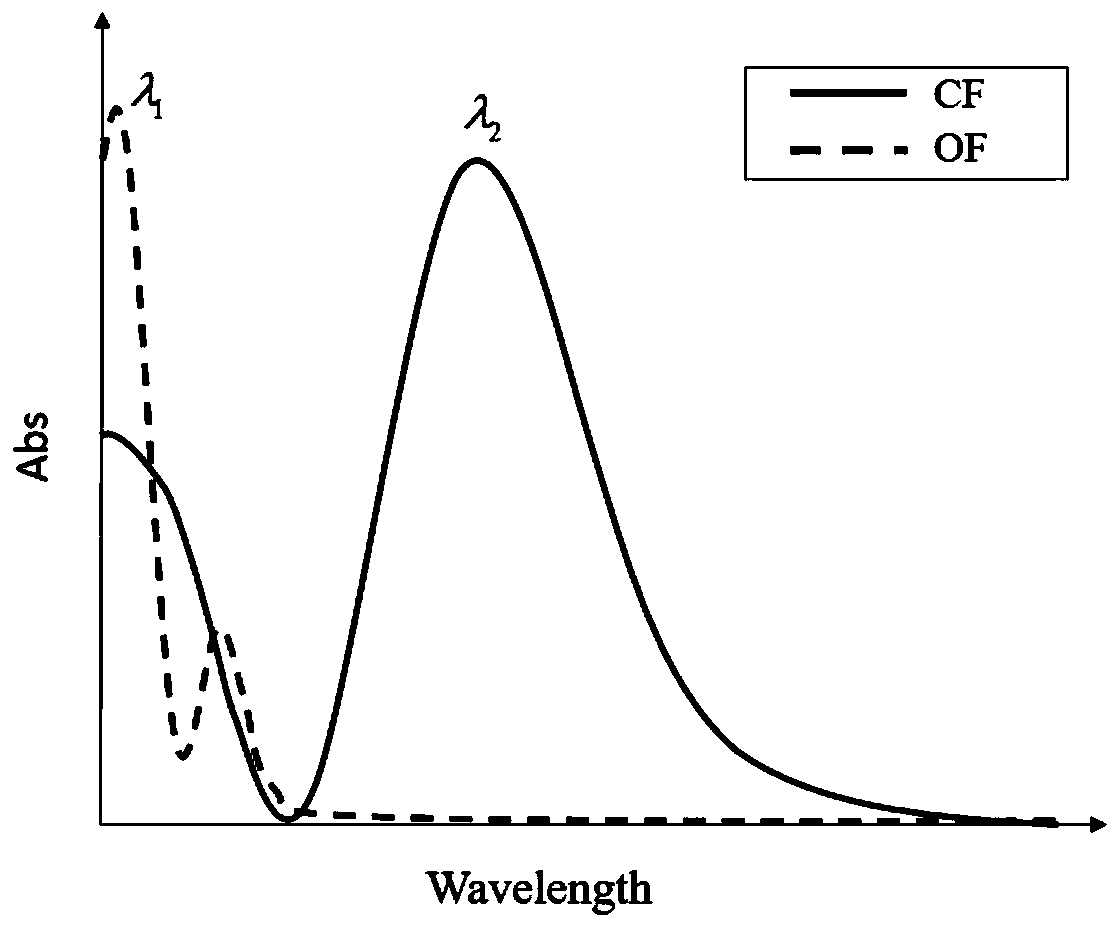
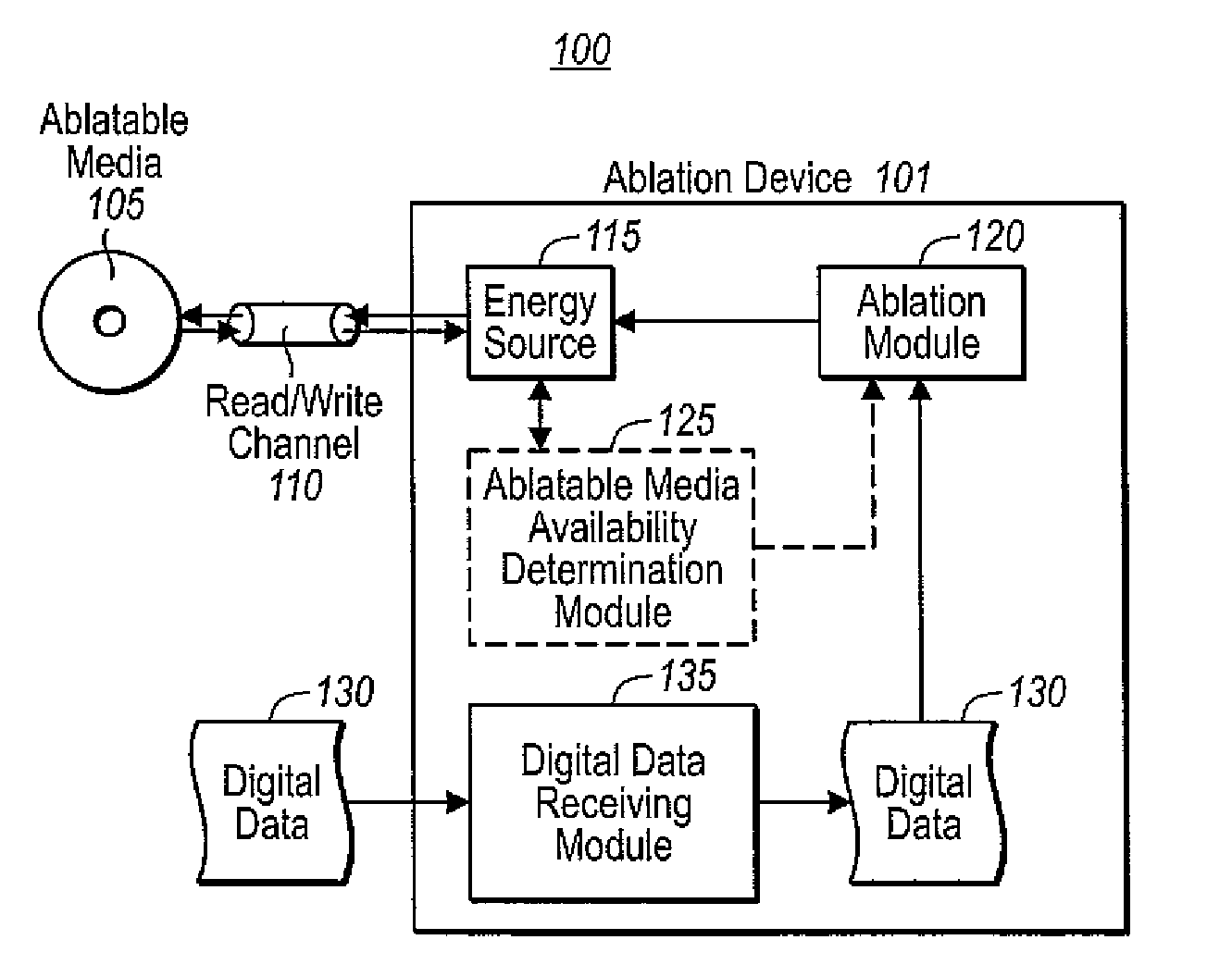
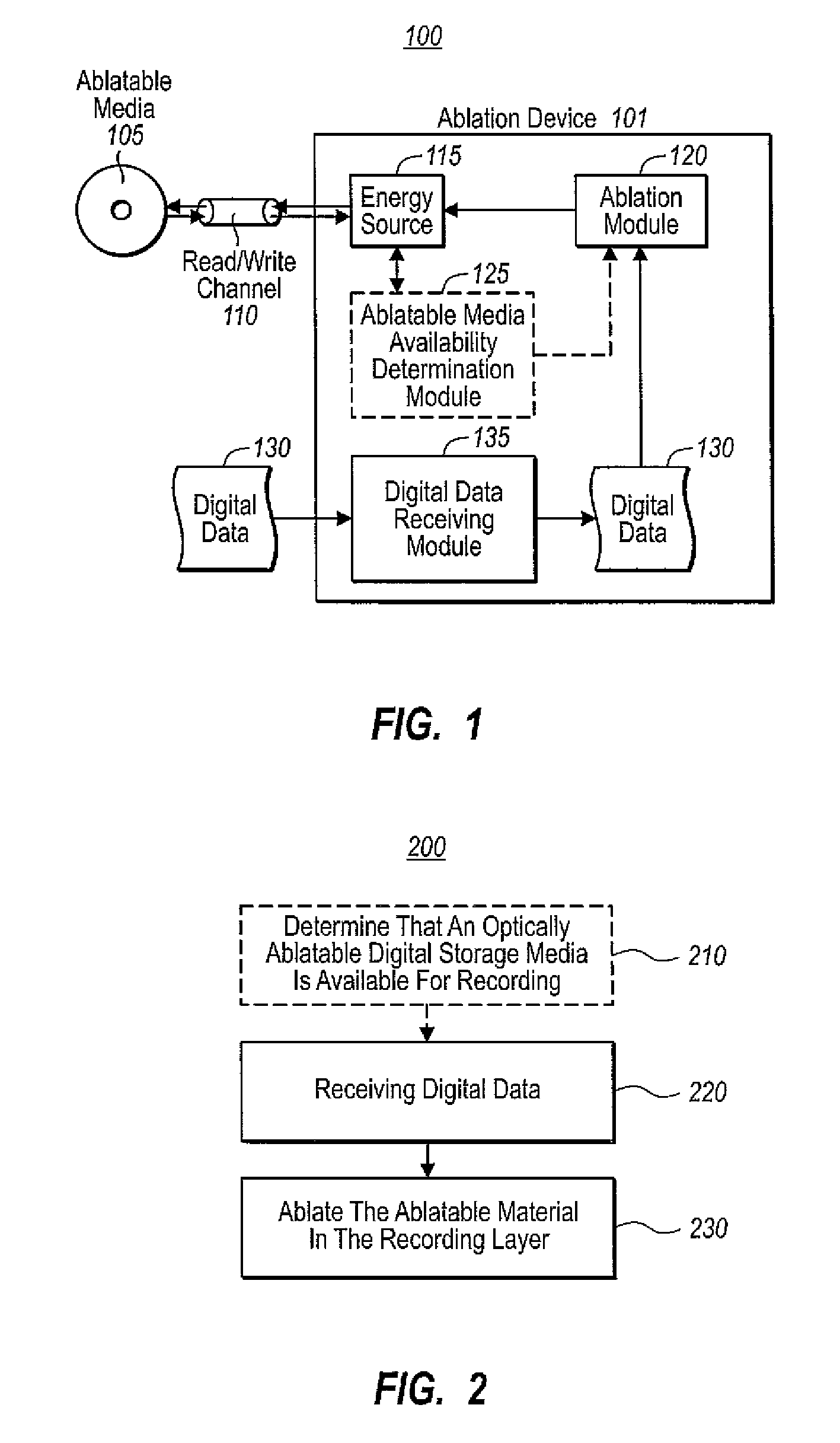
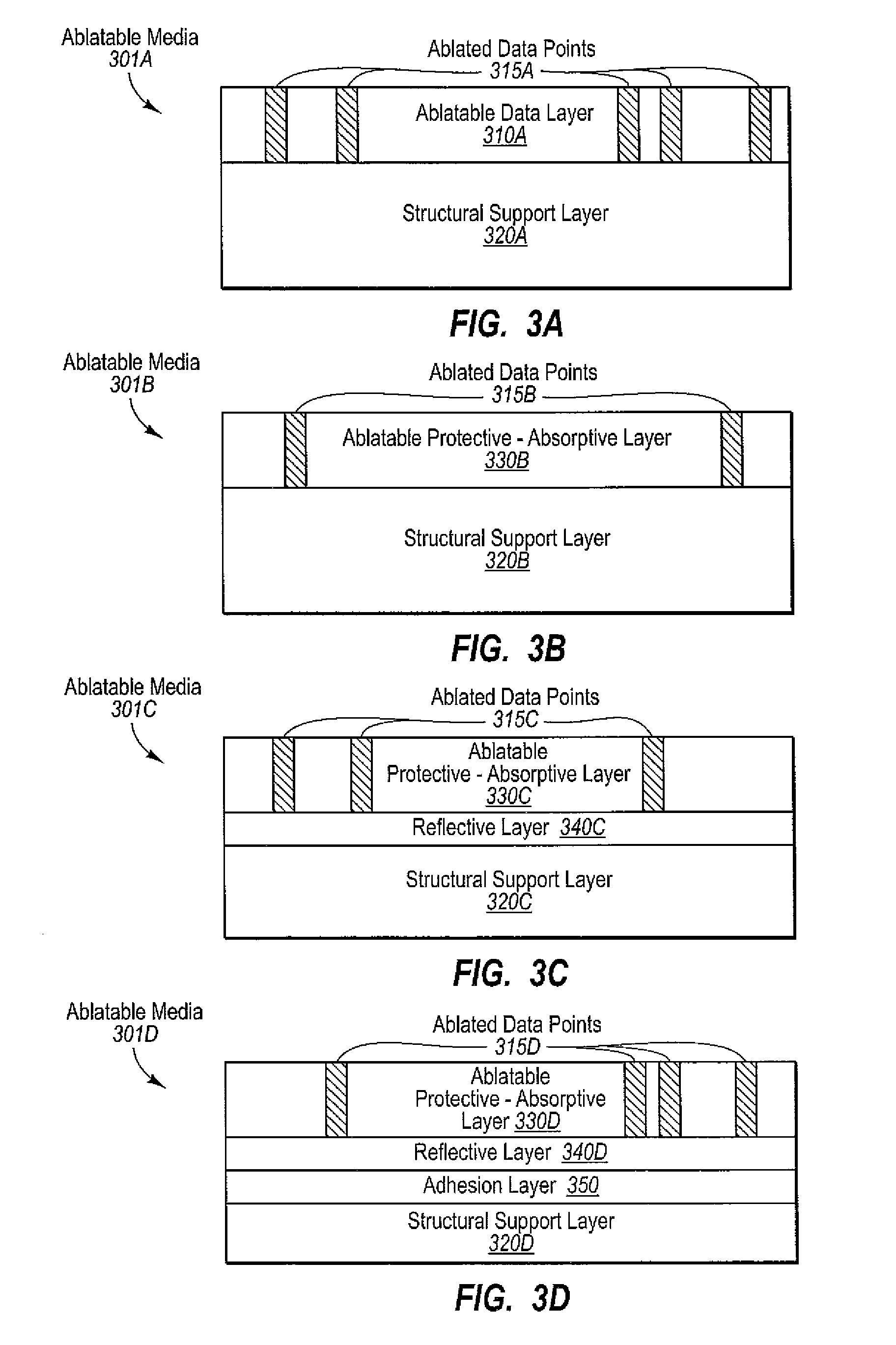
InactiveUS20090231978A1Well formedAdhesive processesRadiation applicationsDigital dataDigital storage
Embodiments are directed to recording digital data on an optically ablatable digital storage media. In one embodiment, a device configured to ablate portions of ablatable material on an optically ablatable digital storage media receives digital data that is to be recorded on a recording layer of an optically ablatable digital storage media. The recording layer is formed on a substrate with zero or more intervening layers between the recording layer and the substrate. The recording layer includes ablatable material capable of storing digital data. The device ablates the ablatable material in the recording layer according to a sequence defined by the received digital data such that the ablated portions correspond to data points of the received digital data.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
Optical information recording medium and optical information recording method
ActiveUS8670296B2High sensitivityIncrease speedNanoinformaticsMechanical record carriersRecording layerComputer science
An optical information recording medium includes: a recording layer 12 comprising a multi-photon absorption compound and a one-photon absorption compound; and a supporting member (base layer 11) configured to support the recording layer 12. In this optical information recording medium, absorption of multiple photons by the multi-photon absorption compound and absorption of one photon by the one-photon absorption compound cause a void to be generated in the recording layer, whereby information is recordable by modulation based on a presence or absence of a void.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for long-term storage of information and storage medium therefor
ActiveUS11007606B2Cheap and efficient information storage systems has been acuteEasy to degradeElectron beam carrier recordingVacuum evaporation coatingParticle beamCeramic substrate
The present invention relates to an information storage medium and a method for long-term storage of information comprising the steps of: providing a ceramic substrate; coating the ceramic substrate with a layer of a second material different from the material of the ceramic substrate, the layer having a thickness no greater than 10 μm; tempering the coated ceramic substrate to form a writable plate or disc; encoding information on the writable plate or disc by using a laser and / or a focused particle beam to manipulate localized areas of the writable plate or disc.
Owner:CERAMIC DATA SOLUTIONS GMBH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com