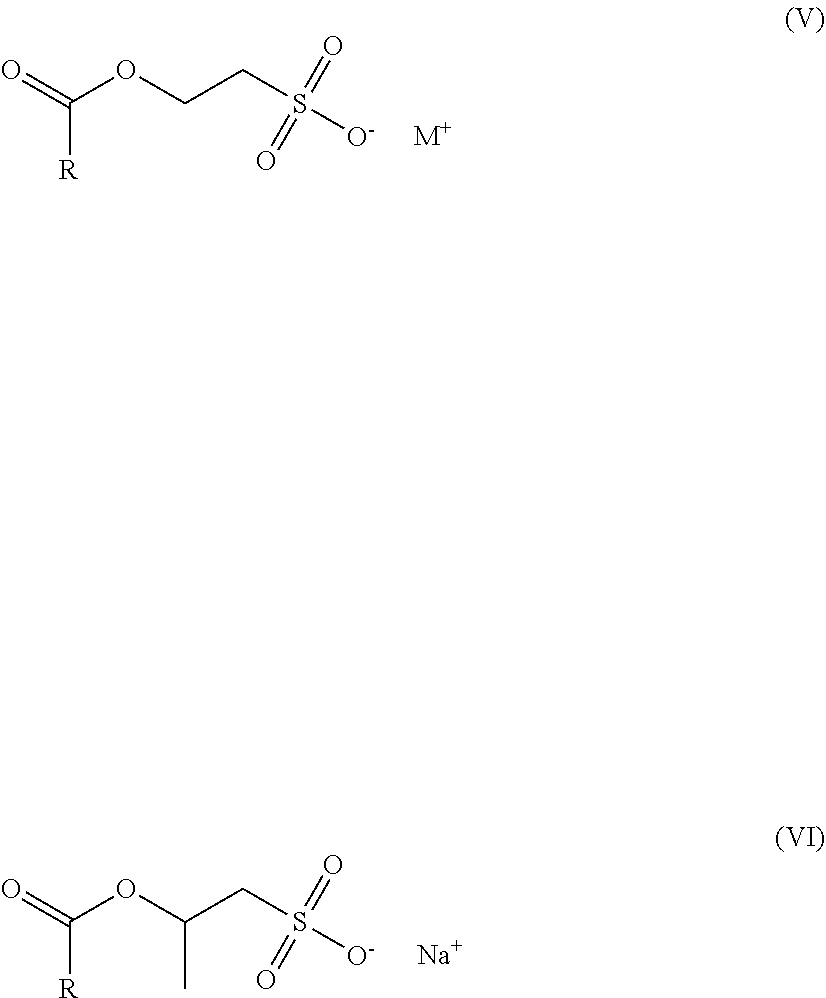
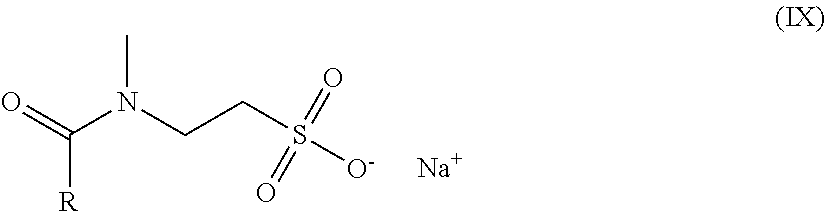
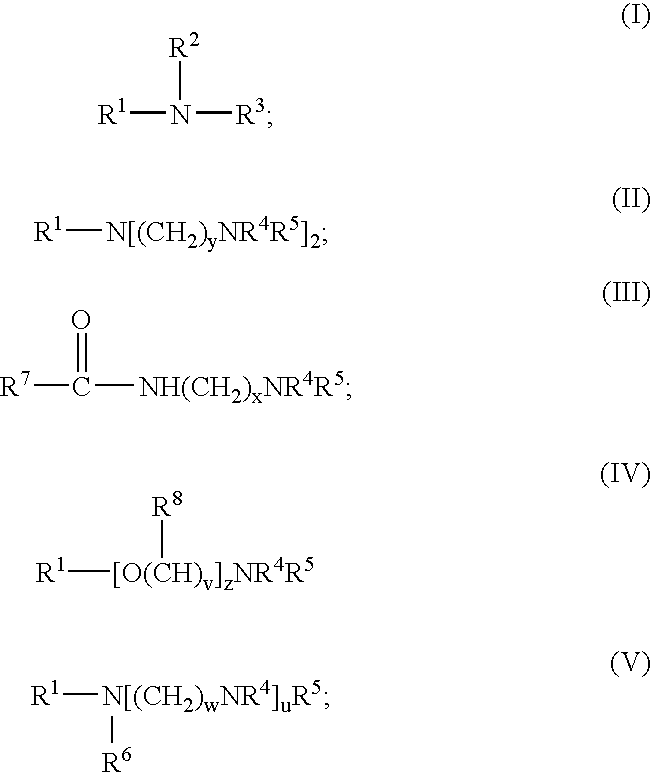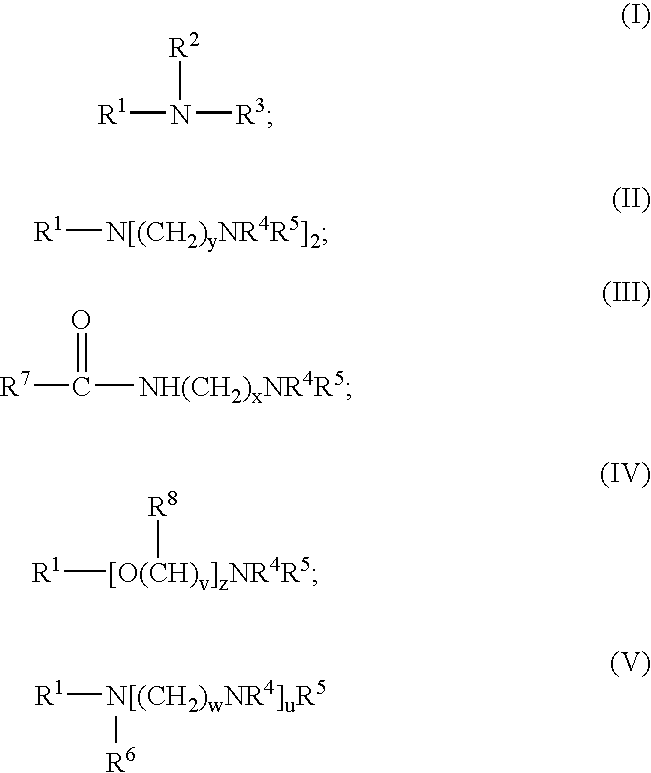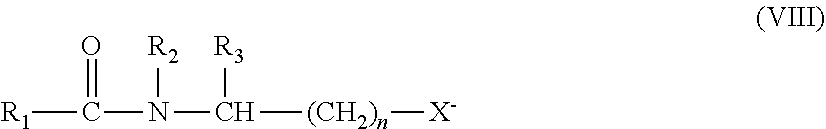Patents
Literature
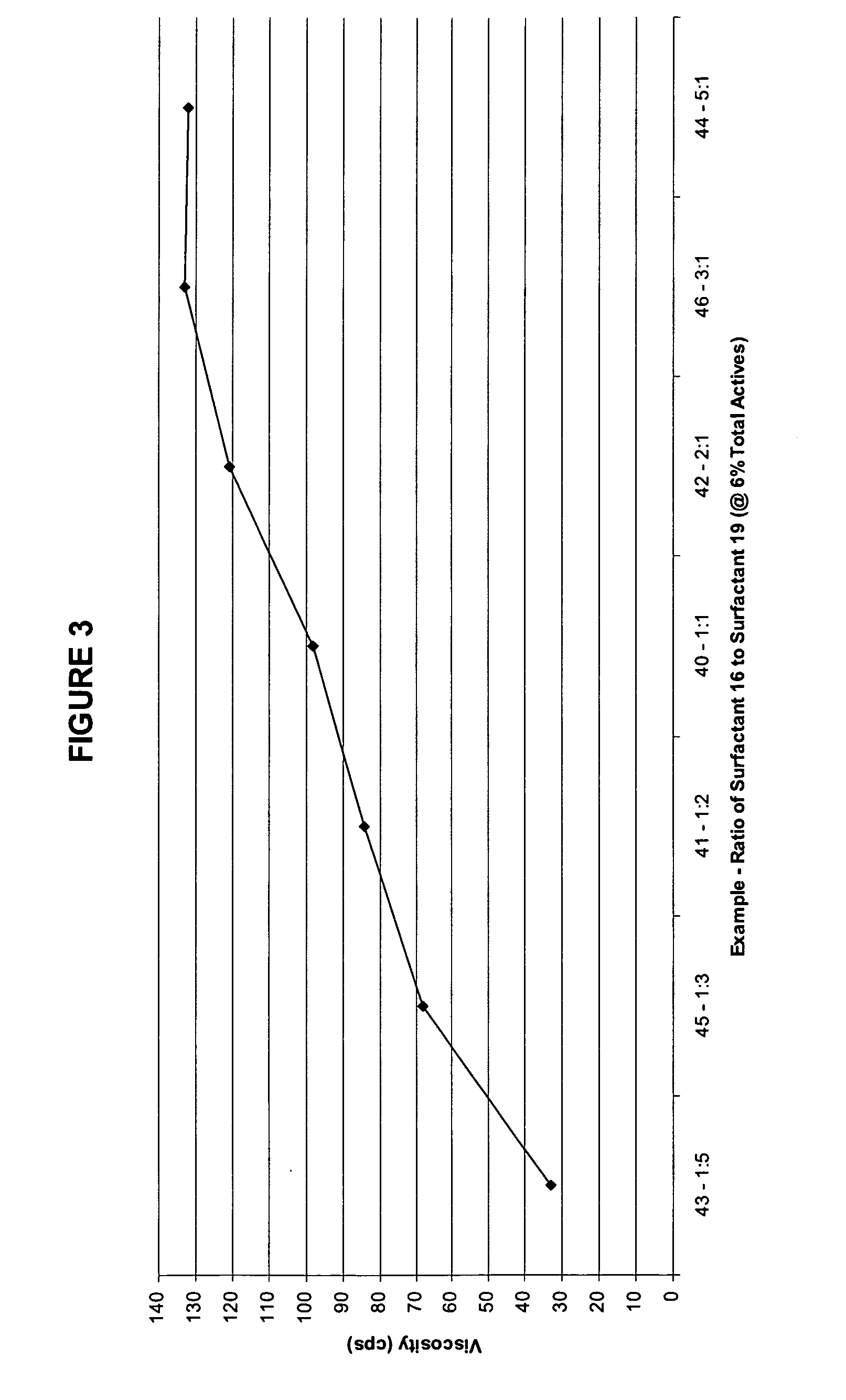
34results about How to "Desirable viscosity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Low solids, high viscosity fabric softener compositions and process for making the same
InactiveUS20060264352A1Improve propertiesImprove stabilityCationic surface-active compoundsDetergent mixture composition preparationViscosityOrganic chemistry
Disclosed are low solids and high viscosity fabric softener compositions and processes for preparing them. The composition contains from about 0.05% to about 10% by weight of a rheology modifying fabric softening active comprising at least one long chain amine of the present technology, a derivative thereof, or a mixture thereof, and from about 0% to 10% by weight of an additional fabric softening active dispersed in water.
Owner:STEPAN COMPANY
Process for preparing polyurethane polyol and rigid foams therefrom from cardanol
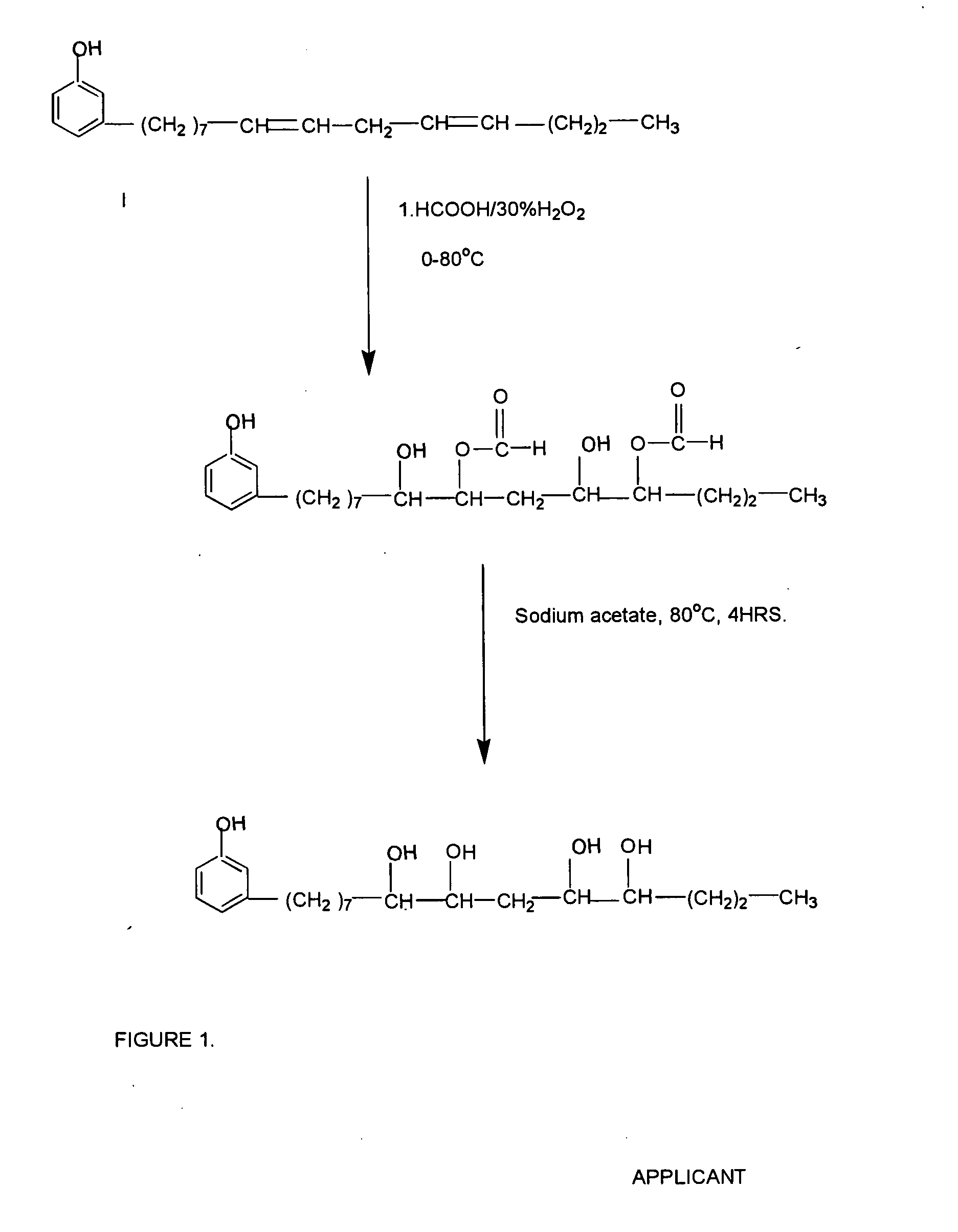
InactiveUS20060004115A1Desirable viscosityHigh contentOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound separation/purificationOrganic acidCardanol
The present invention provides a process for the preparation of polyurethane polyol from cardanol, derived from cashew nut shell liquid, a renewable resource material. The polyol is made by oxidation with peroxy acid generated in-situ to give epoxidised cardanol and the said epoxy derivative is converted to the polyol in the presence of the organic acid. According to another aspect of the present invention the cardanol-based polyol formed by the novel method of this invention may be reacted with isocyanate to form polyurethane. Alternatively blowing agents are included with the cardanol-based polyol before it is reacted with the isocyanate. These polyols are especially suitable for making rigid foams of very low density and high compressive strength.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Fluoropolymer composition
InactiveUS20070117929A1Increase melt viscosityImprove the extrusion effectTetrafluoroethyleneMolten state
A melt-mixed composition of non-melt flowable polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and melt-fabricable perfluoropolymer is provided that exhibits thixotropy at increasing shear rate in the molten state and high elongation at break even at PTFE concentrations well above 4 wt %, based on the combined weight of the PTFE and the perfluoropolymer, e.g. at least 200% up to at least 30 wt % PTFE, the composition also exhibiting the structure of a dispersion of submicrometer-size particles of the PTFE in a continuous phase of the melt-fabricable perfluoropolymer.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Dental adhesive composition
InactiveUS20060069181A1Optimized rheological behaviorEasy to handleImpression capsMedical preparationsAdhesiveAcid derivative
The present invention relates to a dental composition with optimized viscosity and / or rheological behavior. The present invention provides a dental composition comprising: (d) at least one carboxylic acid functional polymer, (e) at least one acid derivative with stronger acidity than the carboxylic acid functional polymer (a), substituted with at least one polymerizable ethylenically unsaturated group, (f) 0.1 to 10 weight % of water, wherein the carboxylic acid functional polymer (a) and the acid derivative (b) are present at least in an amount effective that the dental composition exhibit shear thinning and / or a viscosity from 1.0 to 20 Pa·s, when measured with a plate / plate geometry and at a shear rate of 0.5 to 1 s−1. It further relates to the use of this dental composition and to a method for preparing a dental adhesive.
Owner:3M ESPE
Silica-reinforced rubber compounded with an alkoxysilane and a catalytic alkyl tin compound
ActiveUS7119150B2Long scorch timeFast curingFilm/foil adhesivesSpecial tyresElastomerPolymer science
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
High recycle content polyester polyols
ActiveUS20160053050A1Nice appearanceDesirable functionalityPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsParticulatesPolyester
Polyester polyols made from thermoplastic polyesters are disclosed. The polyols are reaction products of a thermoplastic polyester, a glycol, and a hydrophobe selected from ricinoleic acid, ethoxylated castor oil, saturated or unsaturated C9-C18 dicarboxylic acids, tung oil, soybean oil, sunflower oil, cardanol-based products, recycled cooking oil, isostearyl alcohol, hydroxy-functional materials derived from epoxidized, ozonized, or hydroformylated fatty esters or fatty acids, and mixtures thereof. In one process, the polyols are made by reacting the thermoplastic polyester with a glycol to give a digested intermediate, which is then reacted with the hydrophobe. In another process, the thermoplastic polyester, glycol, and hydrophobe are combined and reacted in a single step. These hydrophobes facilitate the production from recycled thermoplastics of polyols that have good transparency and little or no particulate settling or phase separation. High-recycle-content polyols having desirable properties and attributes for formulating polyurethane products, including aqueous polyurethane dispersions, can be made. The polyols provide a sustainable alternative to bio- or petrochemical-based polyols.
Owner:RESINATE MATERIALS GRP
Polyester polyols from thermoplastic polyesters and dimer fatty acids
ActiveUS20150344622A1Nice appearanceDesirable hydroxyl numberOrganic compound preparationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionPolyesterPolyurethane dispersion
Polyester polyols made from thermoplastic polyesters are disclosed. The polyols can be made by heating a thermoplastic polyester such as virgin PET, recycled PET, or mixtures thereof, with a glycol to give a digested intermediate, which is then condensed with a dimer fatty acid to give the polyol. The invention includes a polyester polyol comprising recurring units of a glycol-digested thermoplastic polyester and a dimer fatty acid. The polyester polyol can also be made in a single step by reacting the thermoplastic polyester, glycol, and dimer acid under conditions effective to produce the polyol. High-recycle-content polyols having desirable properties and attributes for formulating polyurethane products, including aqueous polyurethane dispersions, can be made. The polyols provide a sustainable alternative to bio- or petrochemical-based polyols.
Owner:RESINATE MATERIALS GRP
Light duty liquid detergent composition
InactiveUS20060074004A1Easy to cleanMaintaining desirable foamingCationic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsSulfonateFatty amine
A light duty liquid detergent composition having improved greasy and baked-on soil removal properties is disclosed which comprises at least one of certain described fatty amine derivatives and an anionic surfactant formulation comprising an alkylbenzene sulfonate having a C6-C22 alkyl group. Methods for making and using a light duty liquid detergent composition are also disclosed.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL NV
Cleaning Composition And Method Of Forming The Same
InactiveUS20080188396A1Excellent detergency characteristicDesirable viscosity profileNon-ionic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsAliphatic hydrocarbonSURFACTANT BLEND
A cleaning composition comprises a first surfactant and a second surfactant. The first surfactant is of the general formula R1-O-(A)mH, wherein R1 is an aliphatic hydrocarbon having from 10 to 16 carbon atoms, A is an alkyleneoxy group, and subscript m is a positive number. The second surfactant is of the general formula R2 -O-(B)nH, wherein R2 is an aliphatic hydrocarbon having from 12 to 15 carbon atoms, B is an alkyleneoxy group, and subscript n is a positive number. The cleaning composition has an average degree of alkoxylation of from about 3 to about 8 moles and an excess of the first surfactant relative to said second surfactant. The cleaning composition can further comprise a third surfactant in addition to the first and second surfactants. If employed, the third surfactant typically can comprise a linear alkyl sulfonate (LAS) and / or an alkyl ether sulfate (AES).
Owner:BASF AG
Polyester polyols from recycled polymers and waste streams
ActiveUS20170029561A1Nice appearanceDesirable hydroxyl numberPlastic recyclingPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyesterPolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The present invention relates to polyester polyols made from aromatic polyacid sources such as thermoplastic polyesters. The polyols can be made by heating a thermoplastic polyester such as virgin polyethylene terephthalate, recycled polyethylene terephthalate, or mixtures thereof, with a glycol to give a digested intermediate which is then reacted with a digestible polymer, which can be obtained from various recycle waste streams. The polyester polyols comprise a glycol-digested polyacid source and a further digestible polymer. The polyester polyols provide a sustainable alternative to petrochemical or biochemical based polyester polyols.
Owner:RESINATE MATERIALS GRP
High recycle content polyols from thermoplastic polyesters and lignin or tannin
ActiveUS20160208044A1Easy to produceNice appearancePlastic recyclingLignin derivativesPolyesterPolyol
Polyester polyols, processes for making them, and applications for the polyols are disclosed. In some aspects, the polyols comprise recurring units from a thermoplastic polyester or an aromatic polyacid source, a glycol, and a lignin, tannin, or mixture thereof. Optionally, the polyols incorporate recurring units of a hydrophobe. The polyols are made in one or multiple steps; in some aspects, the thermoplastic polyester or aromatic polyacid source and the glycol are reacted first, followed by reaction with the lignin, tannin, or mixture thereof. High-recycle-content polyols having desirable properties and attributes for formulating polyurethane products, including two-component polyurethane coatings, can be made. The polyols provide a sustainable alternative to bio- or petrochemical-based polyols.
Owner:RESINATE MATERIALS GRP
Conditioning compositions for keratinous substrates
InactiveUS20140186284A1Easy to shapeGood/sleek feelCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsAqueous mediumPolymer
The present invention is directed towards a conditioning composition comprising, in an aqueous medium, at least one nonionic film forming polymer; at least one viscosity modifying agent; at least one cationic polymer; at least one cationic surfactant; and wherein the composition is free of silicones. Preferably, the composition is clear in appearance. The present invention also relates to a process for conditioning keratinous substrates.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Multi-phase personal care composition comprising a depositing perfume
A personal care composition and multi-phase personal care composition are described that comprise 3% or less, by weight of the personal care composition, of a perfume. The personal care composition comprises at least 0.27%, by weight of the personal care composition, of the perfume raw materials having a Kovat's Index of greater than 1700.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Cycloaliphatic polyester polyols from thermoplastic polyesters
Cycloaliphatic polyester polyols and processes for making them from thermoplastic polyesters are disclosed. One process comprises heating a thermoplastic polyester with a glycol to give a digested intermediate and hydrogenating aromatic rings in the digested intermediate to produce the cycloaliphatic polyester polyol. Optionally, the digested intermediate is reacted with a hydrophobe to give a modified polyol prior to hydrogenation, and the modified polyol is hydrogenated to give the cycloaliphatic polyester polyol. The high-recycle-content cycloaliphatic polyester polyols have desirable attributes for formulating polyurethane dispersions, two-component polyurethane coatings, mono- or poly(meth)acrylates, polyisocyanurates, flexible and rigid foams, coatings, adhesives, sealants, and elastomers, and they provide a sustainable alternative to petrochemical-based polyols.
Owner:RESINATE MATERIALS GRP
Cycloaliphatic polyester polyols from thermoplastic polyesters
ActiveUS20160272756A1Nice appearanceDesirable hydroxyl numberPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsElastomerPolyester
Cycloaliphatic polyester polyols and processes for making them from thermoplastic polyesters are disclosed. One process comprises heating a thermoplastic polyester with a glycol to give a digested intermediate and hydrogenating aromatic rings in the digested intermediate to produce the cycloaliphatic polyester polyol. Optionally, the digested intermediate is reacted with a hydrophobe to give a modified polyol prior to hydrogenation, and the modified polyol is hydrogenated to give the cycloaliphatic polyester polyol. The high-recycle-content cycloaliphatic polyester polyols have desirable attributes for formulating polyurethane dispersions, two-component polyurethane coatings, mono- or poly(meth)acrylates, polyisocyanurates, flexible and rigid foams, coatings, adhesives, sealants, and elastomers, and they provide a sustainable alternative to petrochemical-based polyols.
Owner:RESINATE MATERIALS GRP
High recycle content polyols from thermoplastic polyesters and lignin or tannin
ActiveUS9481760B2Nice appearanceDesirable functionalityPlastic recyclingLignin derivativesPolyesterPolymer science
Polyester polyols, processes for making them, and applications for the polyols are disclosed. In some aspects, the polyols comprise recurring units from a thermoplastic polyester or an aromatic polyacid source, a glycol, and a lignin, tannin, or mixture thereof. Optionally, the polyols incorporate recurring units of a hydrophobe. The polyols are made in one or multiple steps; in some aspects, the thermoplastic polyester or aromatic polyacid source and the glycol are reacted first, followed by reaction with the lignin, tannin, or mixture thereof. High-recycle-content polyols having desirable properties and attributes for formulating polyurethane products, including two-component polyurethane coatings, can be made. The polyols provide a sustainable alternative to bio- or petrochemical-based polyols.
Owner:RESINATE MATERIALS GRP
High recycle content polyester polyols from hydroxy-functional ketal acids, esters or amides
InactiveUS20170335057A1Easy to produceHigh transparencyPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPlastic recyclingParticulatesPolyester
Polyester polyols, processes for making them, and applications for the polyols are disclosed. In some aspects, the polyols comprise recurring units from a thermoplastic polyester or an aromatic polyacid source, a glycol, and a hydroxy-functional ketal acid, ester or amide. Optionally, the polyols incorporate recurring units of a hydrophobe. The polyols are made in one or multiple steps; in some aspects, the thermoplastic polyester or aromatic polyacid source and the glycol are reacted first, followed by reaction with the hydroxy-functional ketal acid, ester or amide. The resulting polyols have good transparency and little or no particulate settling or phase separation. High-recycle-content polyols having desirable properties and attributes for formulating polyurethane products, including aqueous polyurethane dispersions, flexible and rigid foams, coatings, adhesives, sealants, and elastomers can be made. The polyols provide a sustainable alternative to bio- or petrochemical-based polyols.
Owner:RESINATE MATERIALS GRP
Cleansing compositions free of sodium chloride and sulfate-based surfactants
ActiveUS20200078284A1Less runnyEasy to spreadCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsPolymer scienceMeth-
The present disclosure relates to cleansing compositions that are free of sulfate-based surfactants and free of sodium chloride. The cleansing compositions include: (a) one or more non-sulfate anionic surfactants; one or more amphoteric surfactants; one or more nonionic surfactants; (d) one or more hydrophobically modified poly(meth)acrylates; one or more silicones; and water. The cleansing compositions are particularly useful for cleansing hair and providing conditioning benefits to the hair.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Polyester polyols from thermoplastic polyesters and dimer fatty acids
ActiveUS9840584B2Nice appearanceDesirable numberOrganic compound preparationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionPolyesterPolyurethane dispersion
Polyester polyols made from thermoplastic polyesters are disclosed. The polyols can be made by heating a thermoplastic polyester such as virgin PET, recycled PET, or mixtures thereof, with a glycol to give a digested intermediate, which is then condensed with a dimer fatty acid to give the polyol. The invention includes a polyester polyol comprising recurring units of a glycol-digested thermoplastic polyester and a dimer fatty acid. The polyester polyol can also be made in a single step by reacting the thermoplastic polyester, glycol, and dimer acid under conditions effective to produce the polyol. High-recycle-content polyols having desirable properties and attributes for formulating polyurethane products, including aqueous polyurethane dispersions, can be made. The polyols provide a sustainable alternative to bio- or petrochemical-based polyols.
Owner:RESINATE MATERIALS GRP
Low Solids, High Viscosity Fabric Softener Compositions and Process for Making the Same
ActiveUS20110028381A1Improve propertiesImprove stabilityCationic surface-active compoundsDetergent mixture composition preparationOrganic chemistryViscosity
Disclosed are low solids and high viscosity fabric softener compositions and processes for preparing them. The composition contains from about 0.05% to about 10% by weight of a rheology modifying fabric softening active comprising at least one long chain amine of the present technology, a derivative thereof, or a mixture thereof, and from about 1% to 10% by weight of an additional fabric softening active dispersed in water.
Owner:STEPAN COMPANY
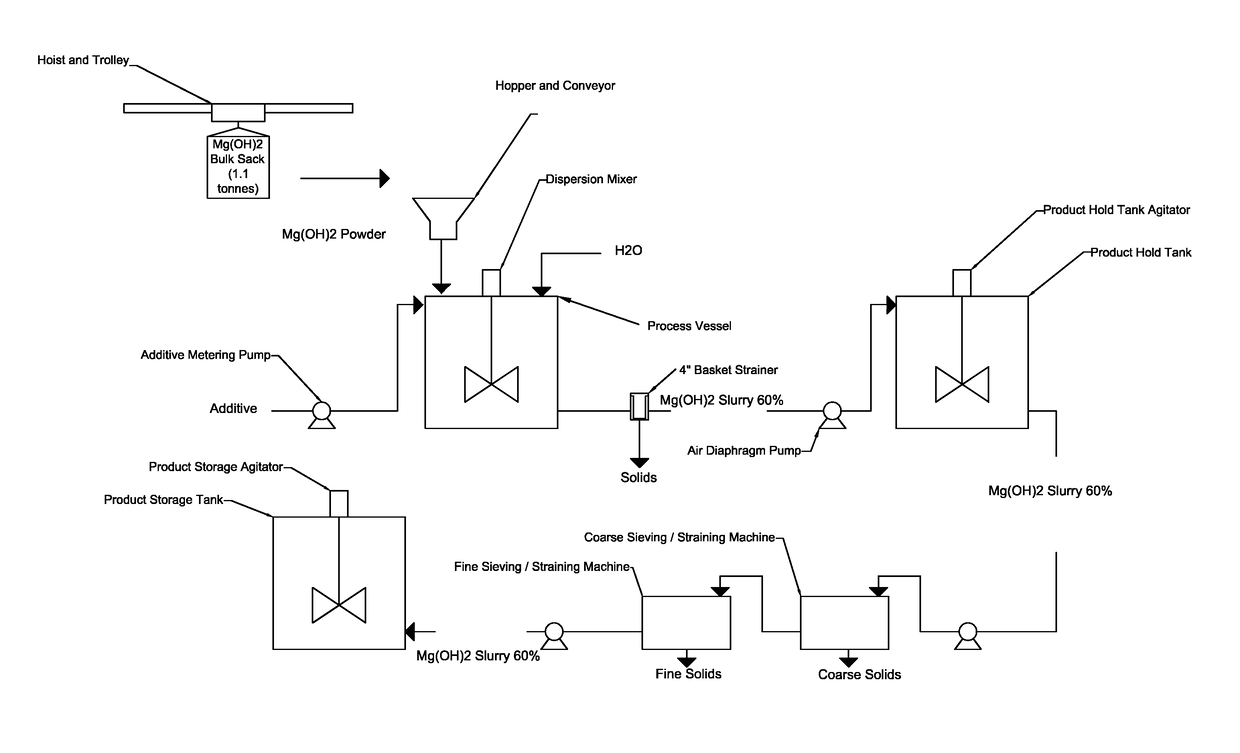
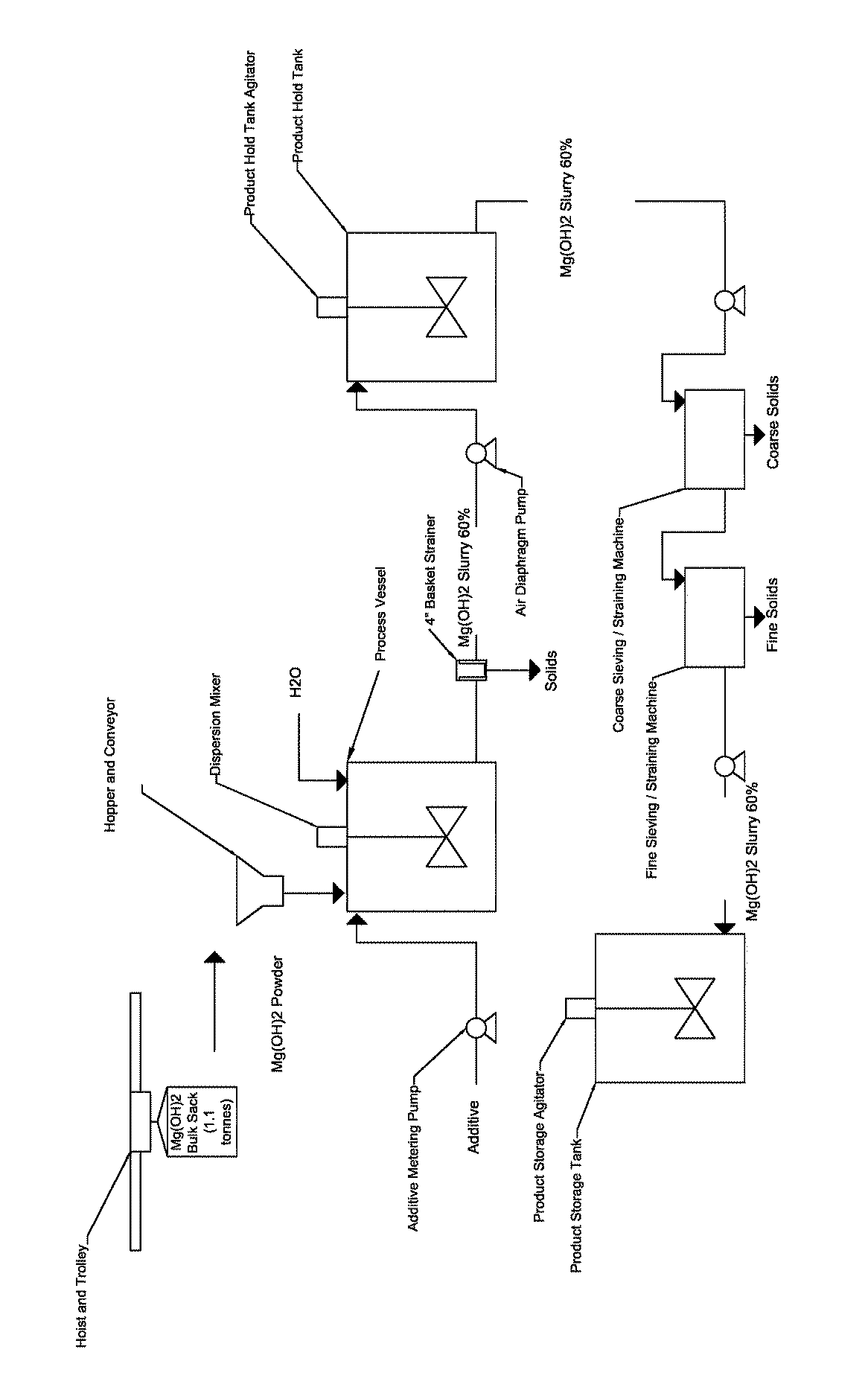
Process for producing a stabilized magnesium hydroxide slurry
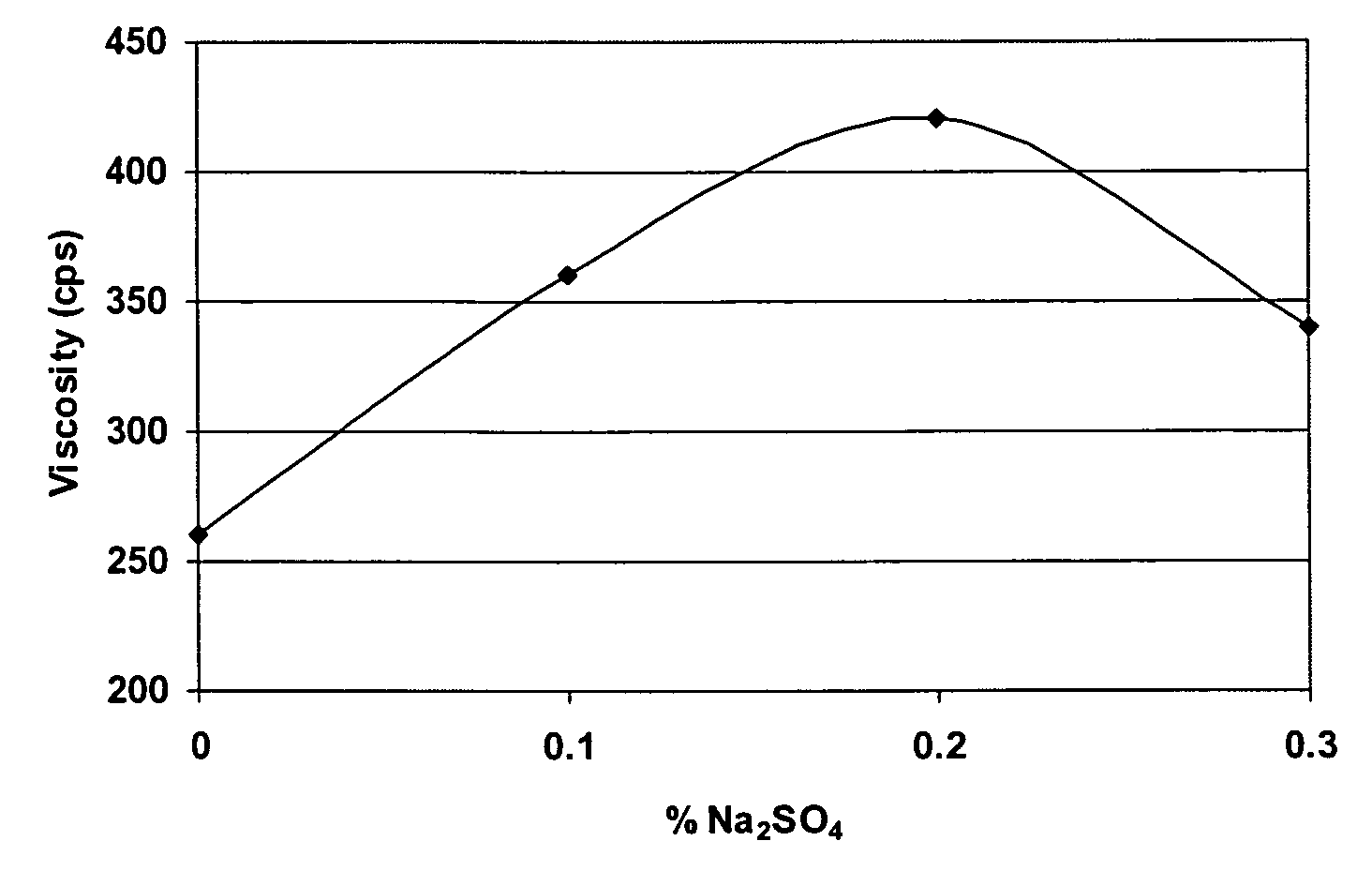
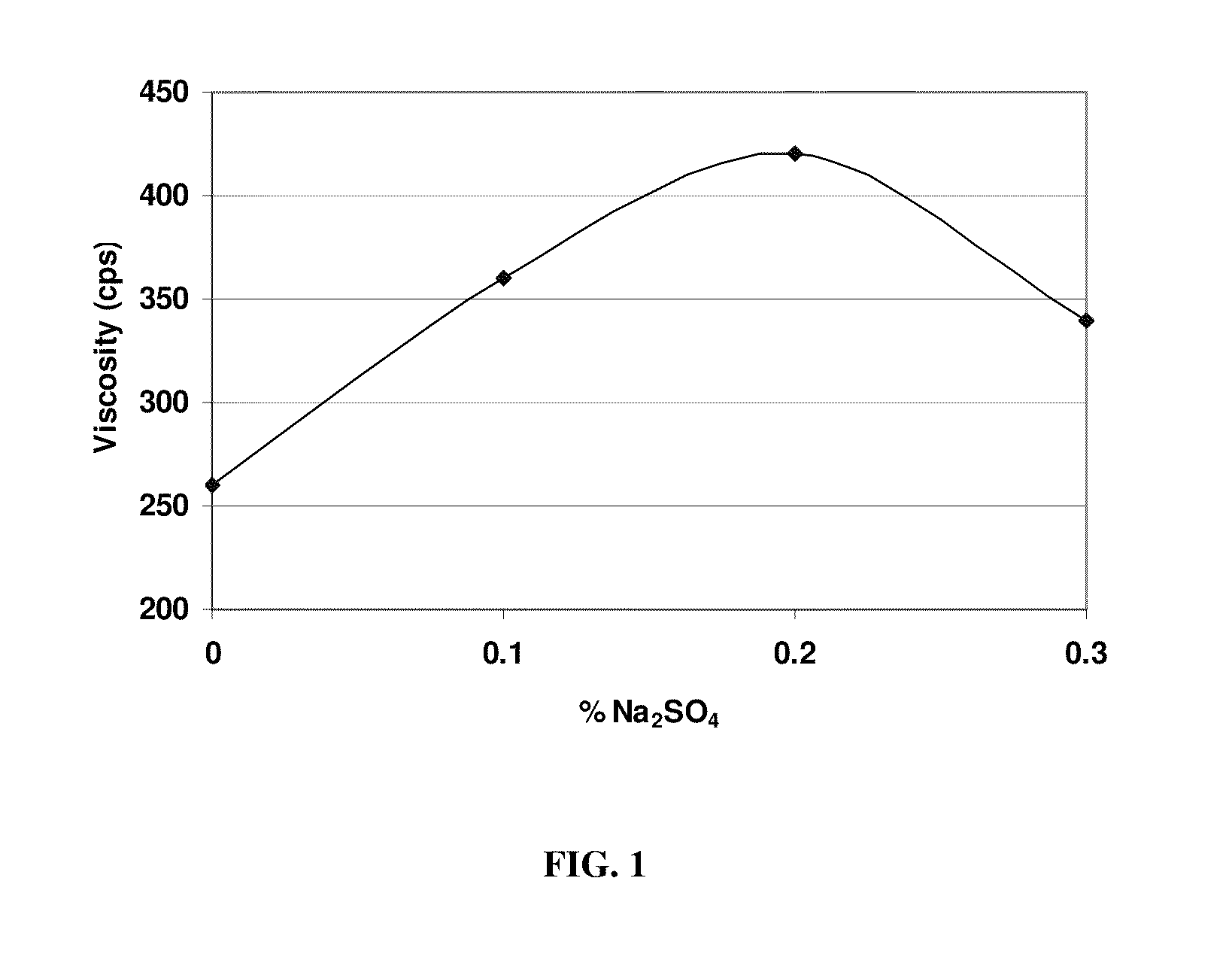
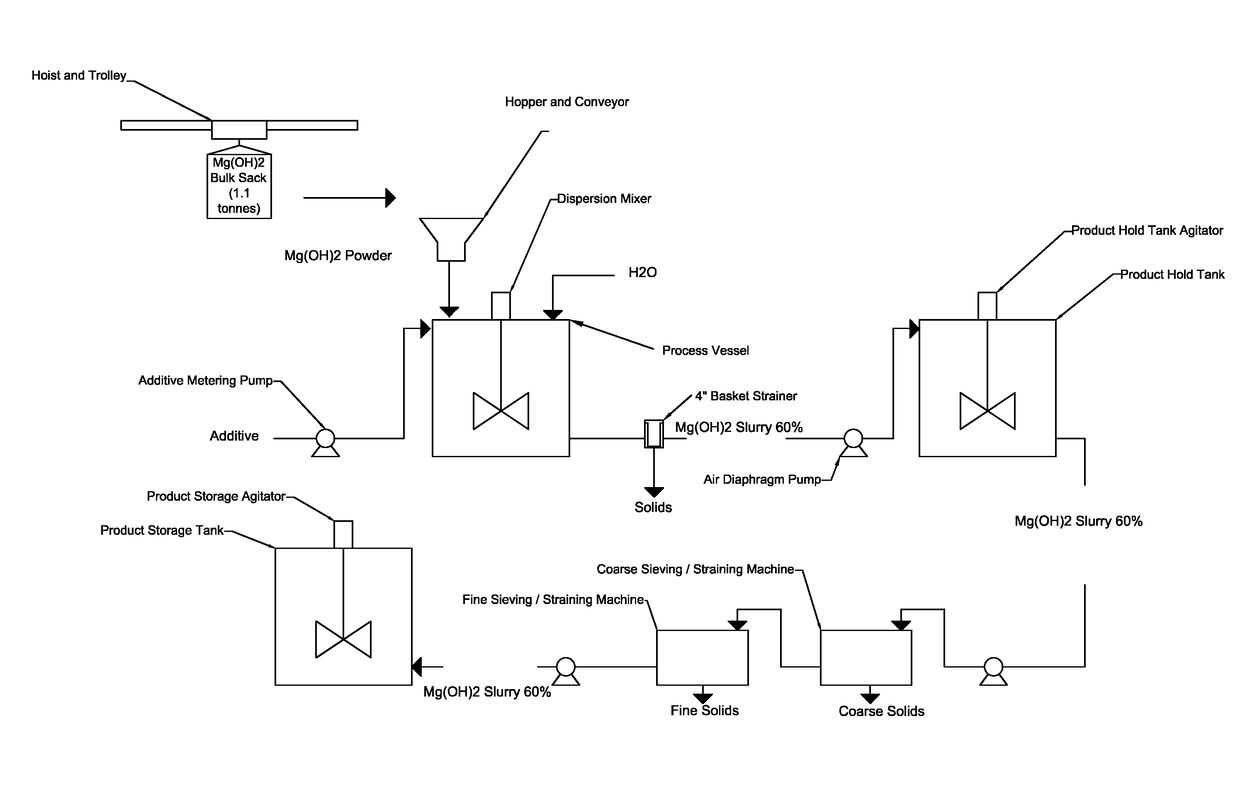
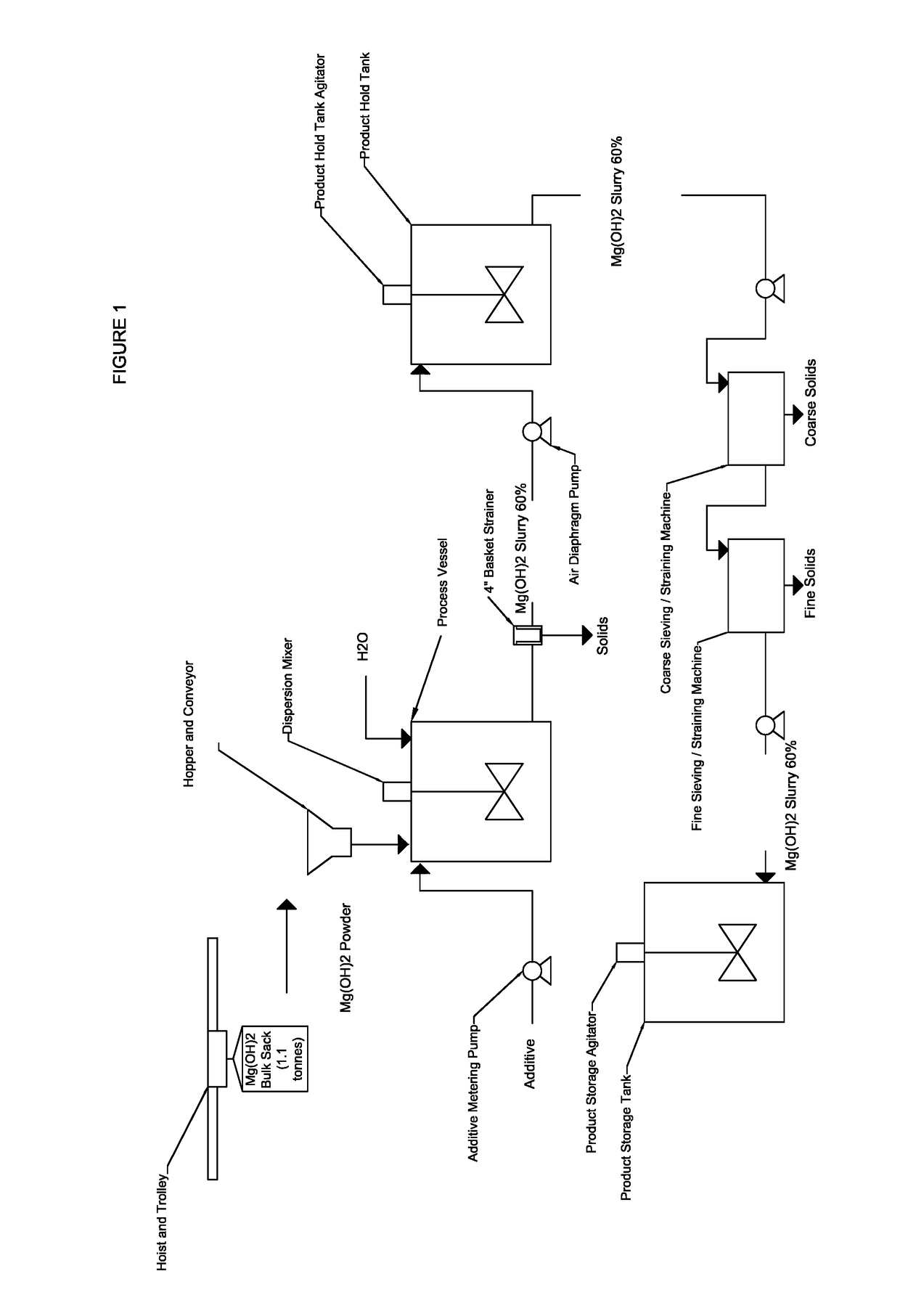
ActiveUS20170225961A1Desirable viscosityImprove stabilityMagnesium hydroxideChemical inhibitorsSlurryViscosity
The present disclosure provides stable magnesium hydroxide slurry compositions and methods for producing stable magnesium hydroxide slurry compositions. The stable magnesium hydroxide slurries of the disclosure comprise magnesium hydroxide at about 50 to about 70% solids by weight in the slurry, a viscosity of less than about 1000 centipoise, and a 7-day pour test of 90% or greater.
Owner:MARTIN MARIETTA MAGNESIA SPECIALTIES
High recycle content polyester polyols
ActiveUS10414859B2Nice appearanceDesirable functionalityPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyesterParticulates
Polyester polyols made from thermoplastic polyesters are disclosed. The polyols are reaction products of a thermoplastic polyester, a glycol, and a hydrophobe selected from ricinoleic acid, ethoxylated castor oil, saturated or unsaturated C9-C18 dicarboxylic acids, tung oil, soybean oil, sunflower oil, cardanol-based products, recycled cooking oil, isostearyl alcohol, hydroxy-functional materials derived from epoxidized, ozonized, or hydroformylated fatty esters or fatty acids, and mixtures thereof. In one process, the polyols are made by reacting the thermoplastic polyester with a glycol to give a digested intermediate, which is then reacted with the hydrophobe. In another process, the thermoplastic polyester, glycol, and hydrophobe are combined and reacted in a single step. These hydrophobes facilitate the production from recycled thermoplastics of polyols that have good transparency and little or no particulate settling or phase separation. High-recycle-content polyols having desirable properties and attributes for formulating polyurethane products, including aqueous polyurethane dispersions, can be made. The polyols provide a sustainable alternative to bio- or petrochemical-based polyols.
Owner:RESINATE MATERIALS GRP
Hot melt adhesive composition for bookbinding
ActiveUS20160376479A1Good ink resistance performanceEasy to processMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesMixingWaxHot-melt adhesive
The present invention provides a hot melt adhesive composition for bookbinding comprising a base polymer, a wax and / or an oil, a tackifier, a stabilizer and optionally a filler; wherein the base polymer comprises a propylene-based elastomer, an amorphous poly-α-olefin (APAO), and optionally, an ethylene-based or propylene-based plastomer.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Fluoropolymer Composition
A melt-mixed composition of non-melt flowable polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and melt-fabricable perfluoropolymer is provided that exhibits thixotropy at increasing shear rate in the molten state and high elongation at break even at PTFE concentrations well above 4 wt %, based on the combined weight of the PTFE and the perfluoropolymer, e.g. at least 200% up to at least 30 wt % PTFE, the composition also exhibiting the structure of a dispersion of submicrometer-size particles of the PTFE in a continuous phase of the melt-fabricable perfluoropolymer.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Digestion of keratin
InactiveUS20160052844A1Desirable hydroxyl numberDesirable viscosityOrganic compound preparationOther chemical processesSolventChemistry
The present invention relates to the chemical digestion of keratin, such as avian feathers and wool. The digestion product is made by heating the feathers or wool with a solvent selected from glycols, alkanolamines, polyamines, and combinations thereof. The resulting digested keratin product is a keratin-derived polyol useful for making polymeric materials such as polyurethanes. The digestion products provide a sustainable alternative to petrochemical based intermediates.
Owner:RESINATE MATERIALS GRP
Hot melt adhesive composition for bookbinding
InactiveUS10227509B2Easy to processLess odorMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesBookbinding adhesiveElastomerWax
The present invention provides a hot melt adhesive composition for bookbinding comprising a base polymer, a wax and / or an oil, a tackifier, a stabilizer and optionally a filler; wherein the base polymer comprises a propylene-based elastomer, an amorphous poly-α-olefin (APAO), and optionally, an ethylene-based or propylene-based plastomer.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Fluoropolymer composition
A melt-mixed composition of non-melt flowable polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and melt-fabricable perfluoropolymer is provided that exhibits thixotropy at increasing shear rate in the molten state and high elongation at break even at PTFE concentrations well above 4 wt %, based on the combined weight of the PTFE and the perfluoropolymer, e.g. at least 200% up to at least 30 wt % PTFE, the composition also exhibiting the structure of a dispersion of submicrometer-size particles of the PTFE in a continuous phase of the melt-fabricable perfluoropolymer.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Digestion of keratin
InactiveUS20170029551A1Desirable hydroxyl numberDesirable viscosityPlastic recyclingPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPetrochemicalDigestion
The present invention relates to the chemical digestion of keratin, such as avian feathers and wool. The digestion product is made by heating the feathers or wool with a solvent selected from glycols, alkanolamines, polyamines, and combinations thereof. The resulting digested keratin product is a keratin-derived polyol useful for making polymeric materials such as polyurethanes. The digestion products provide a sustainable alternative to petrochemical based intermediates.
Owner:RESINATE MATERIALS GRP
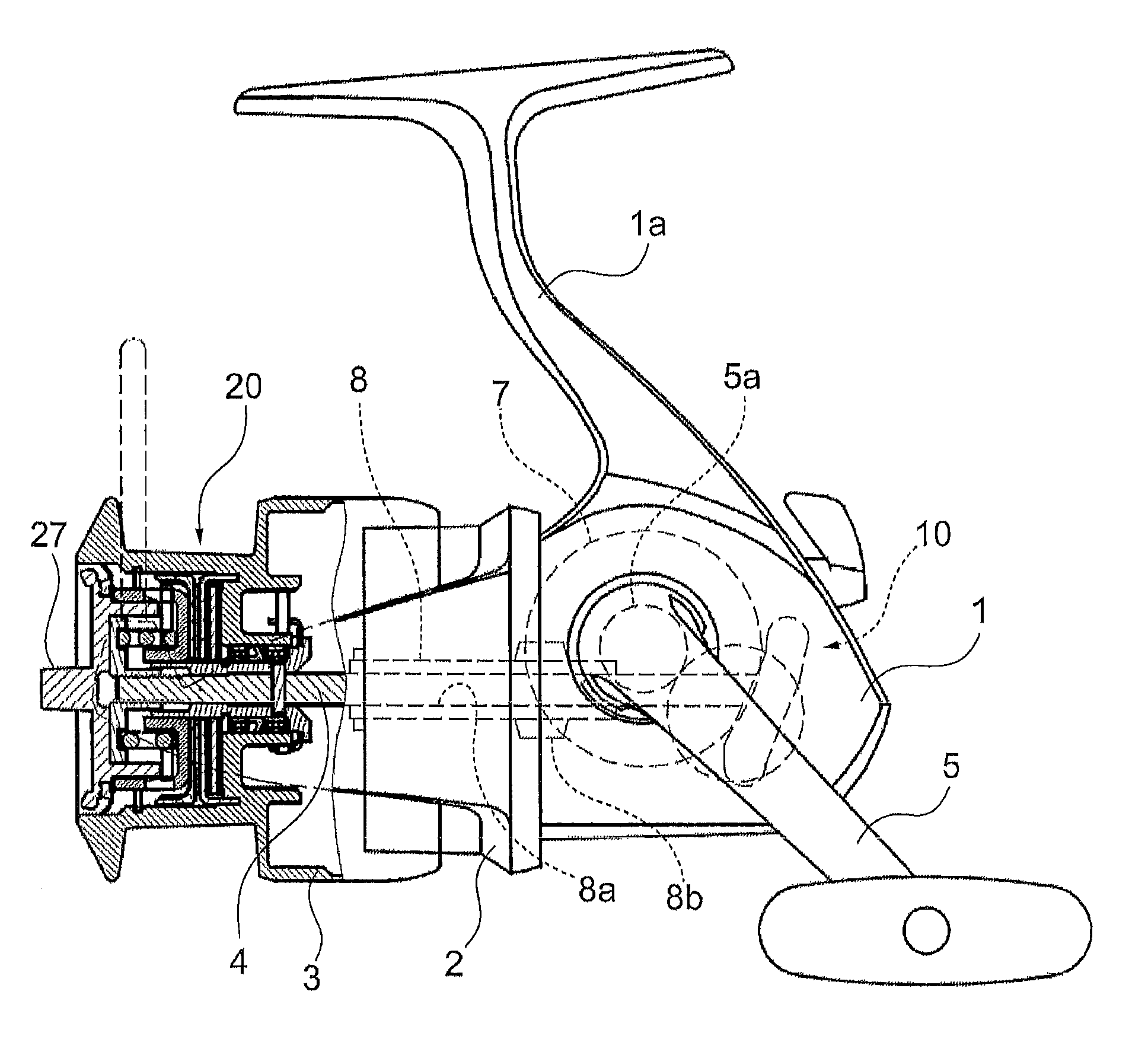
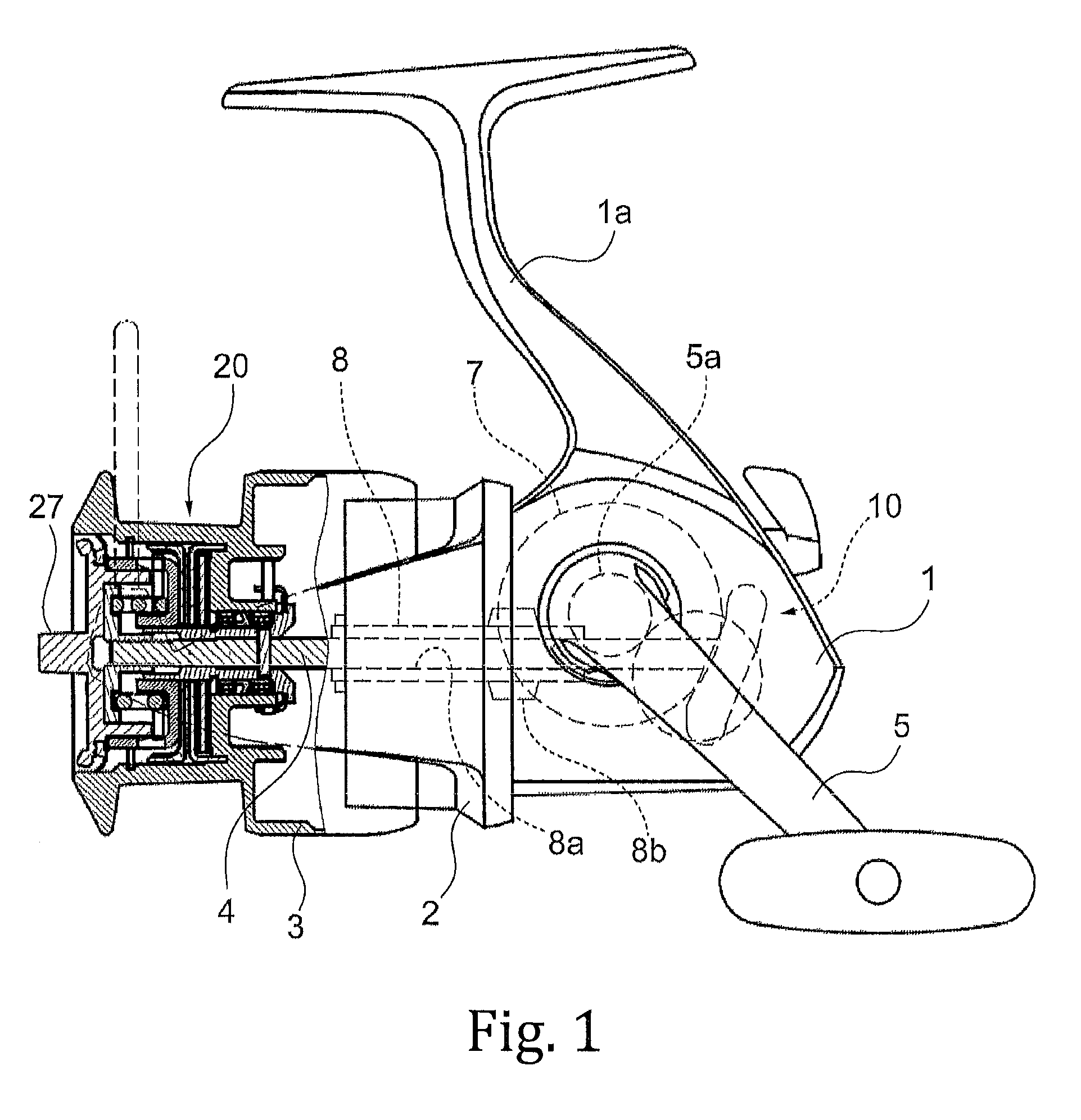
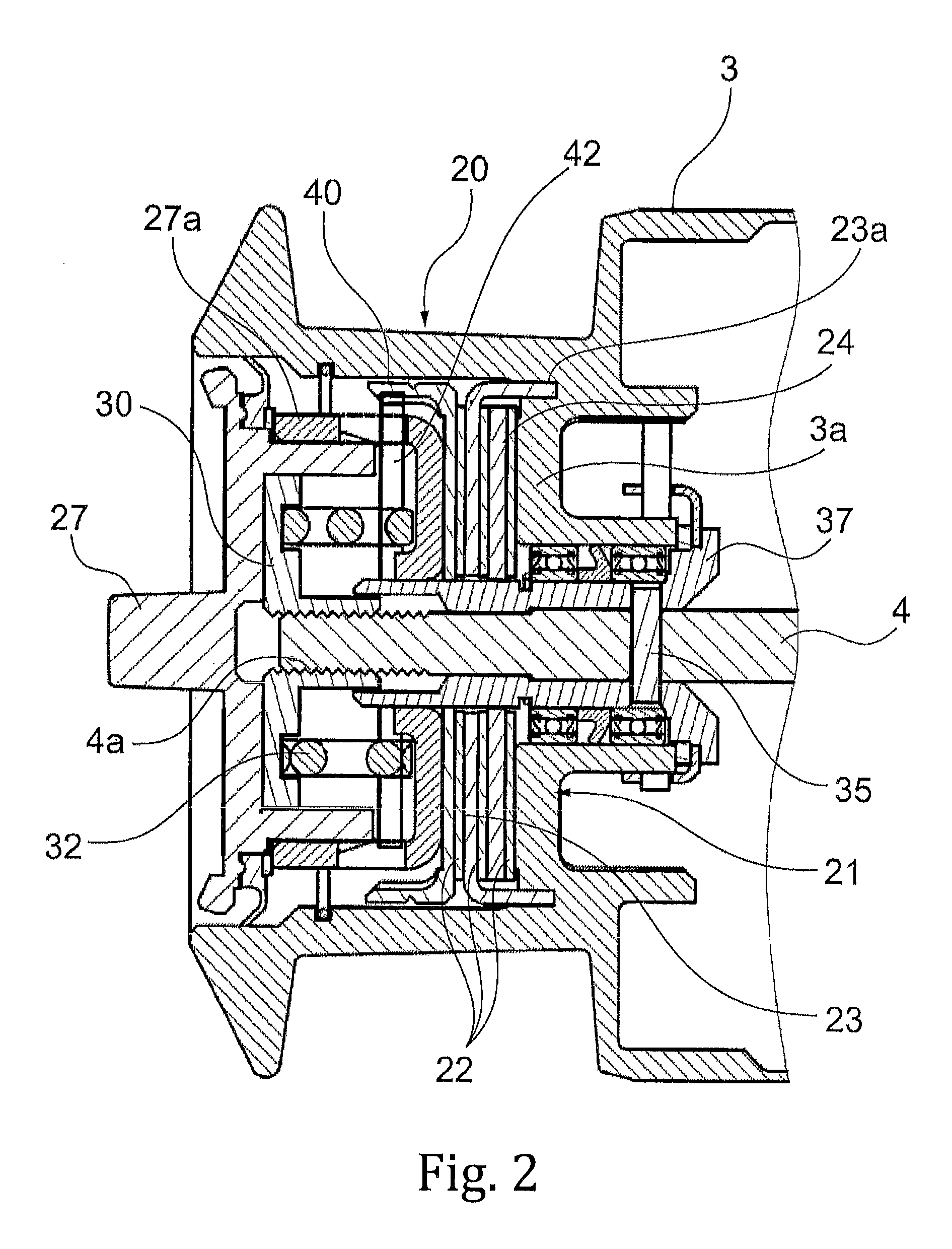
Fishing reel
One object is to provide a fishing reel including a drag device achieving stable drag performance. A fishing reel of the present invention includes: a spool around which a fishing line is to be wound by rotational operation of a handle; and a drag device configured to apply a braking force to the spool, wherein the drag device includes one or more drag washers, one or more lining washers in surface contact with the drag washers, and an operation member for adjusting a pressing force of the drag washers on the lining washers, and wherein the lining washers are provided with a grease having a viscosity of 800 mm2 / s or higher.
Owner:DAIWA SEIKO CORPORATION
Process for producing a stabilized magnesium hydroxide slurry
ActiveUS9890054B2Expensive to shipLong durationMagnesium hydroxideChemical inhibitorsSlurryViscosity
The present disclosure provides stable magnesium hydroxide slurry compositions and methods for producing stable magnesium hydroxide slurry compositions. The stable magnesium hydroxide slurries of the disclosure comprise magnesium hydroxide at about 50 to about 70% solids by weight in the slurry, a viscosity of less than about 1000 centipoise, and a 7-day pour test of 90% or greater.
Owner:MARTIN MARIETTA MAGNESIA SPECIALTIES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com