Patents
Literature
34results about How to "Unnecessary time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
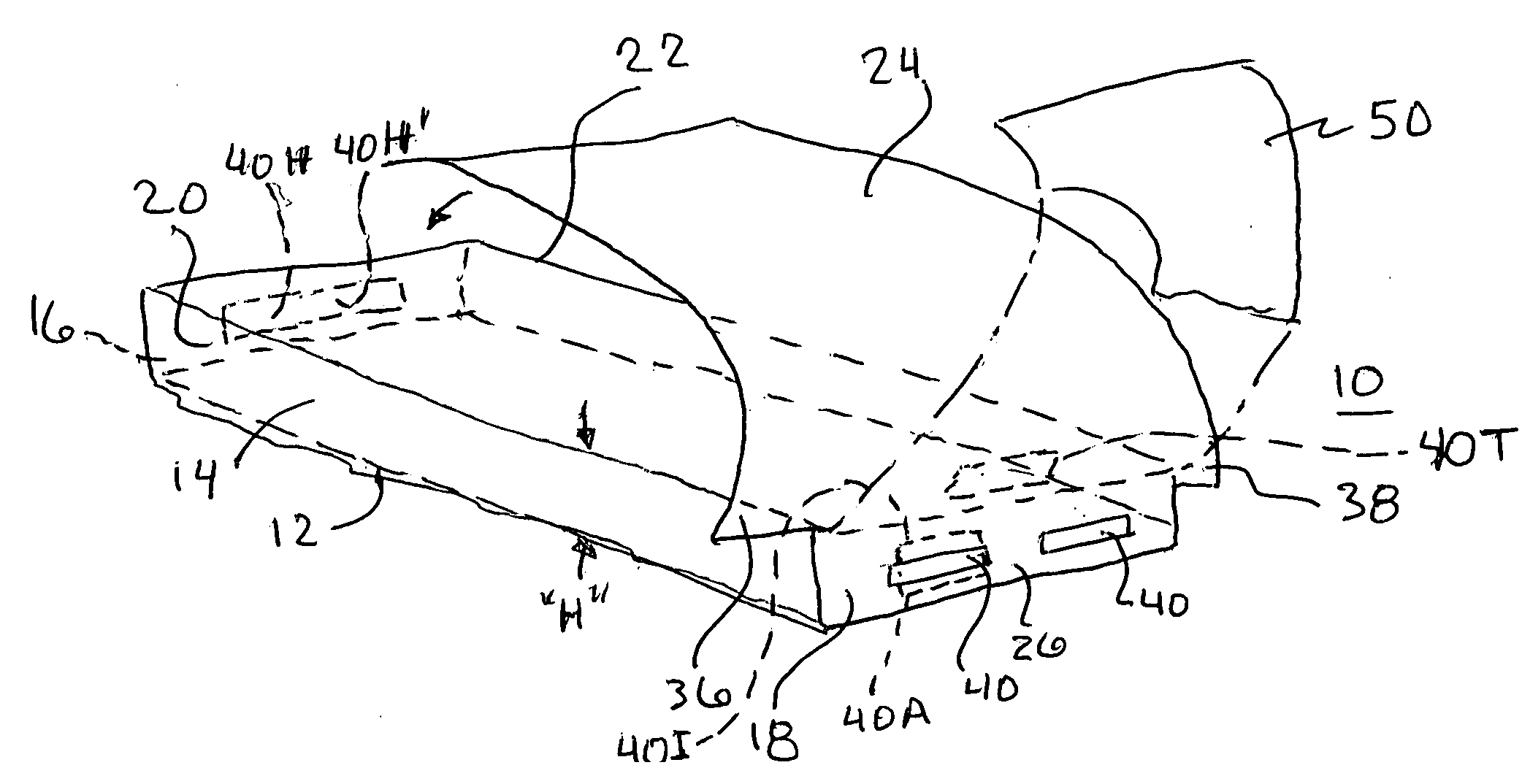
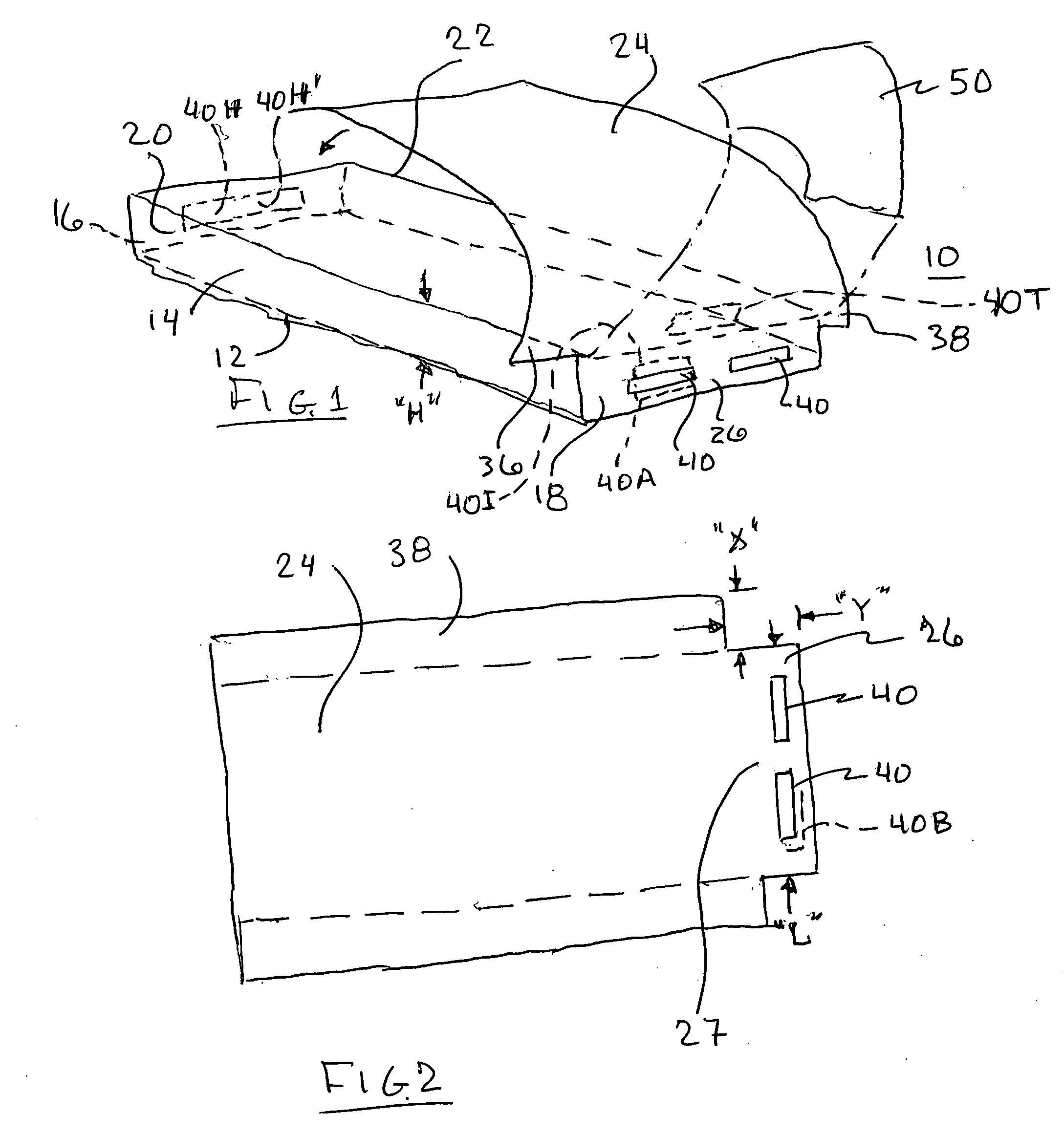
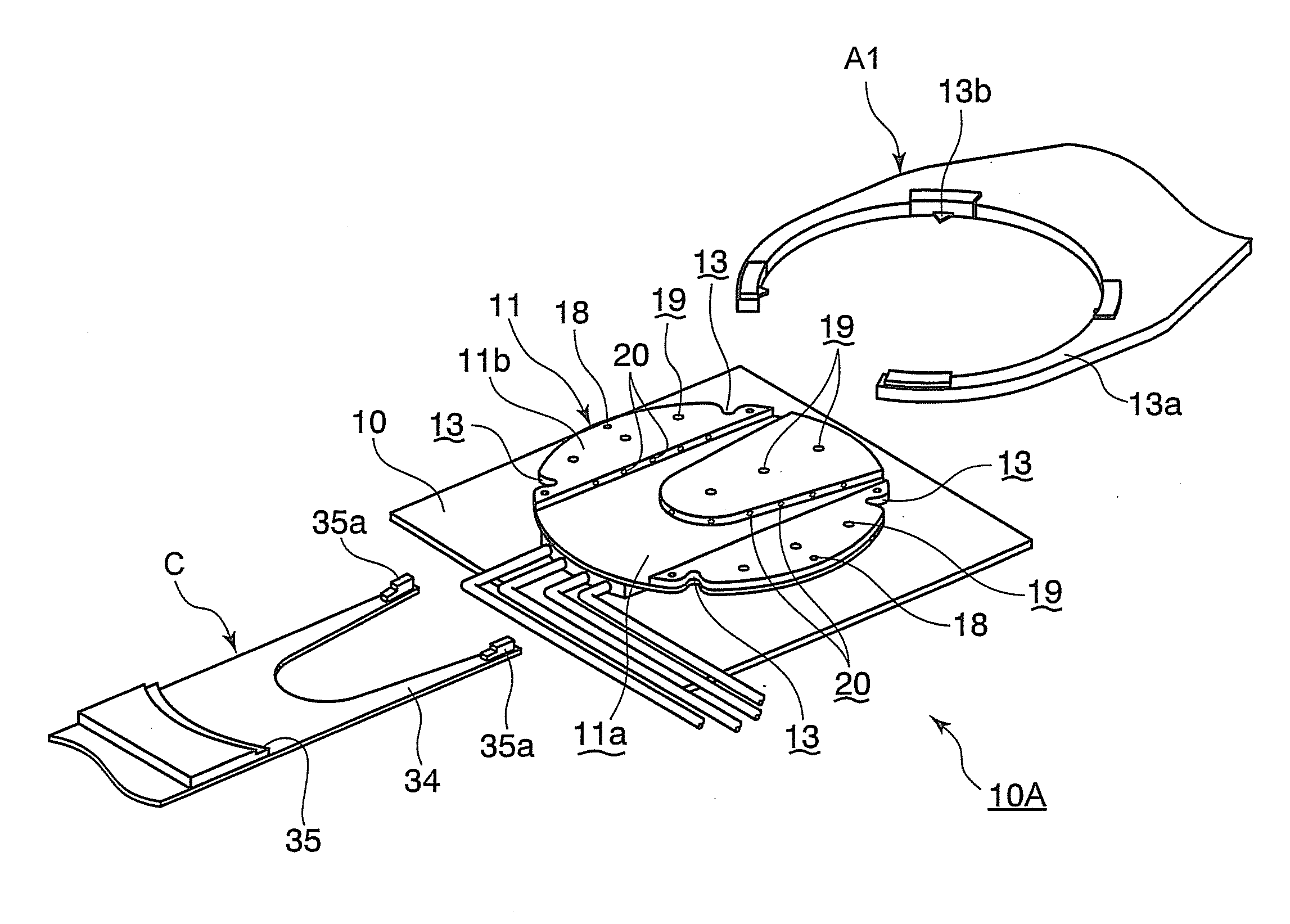
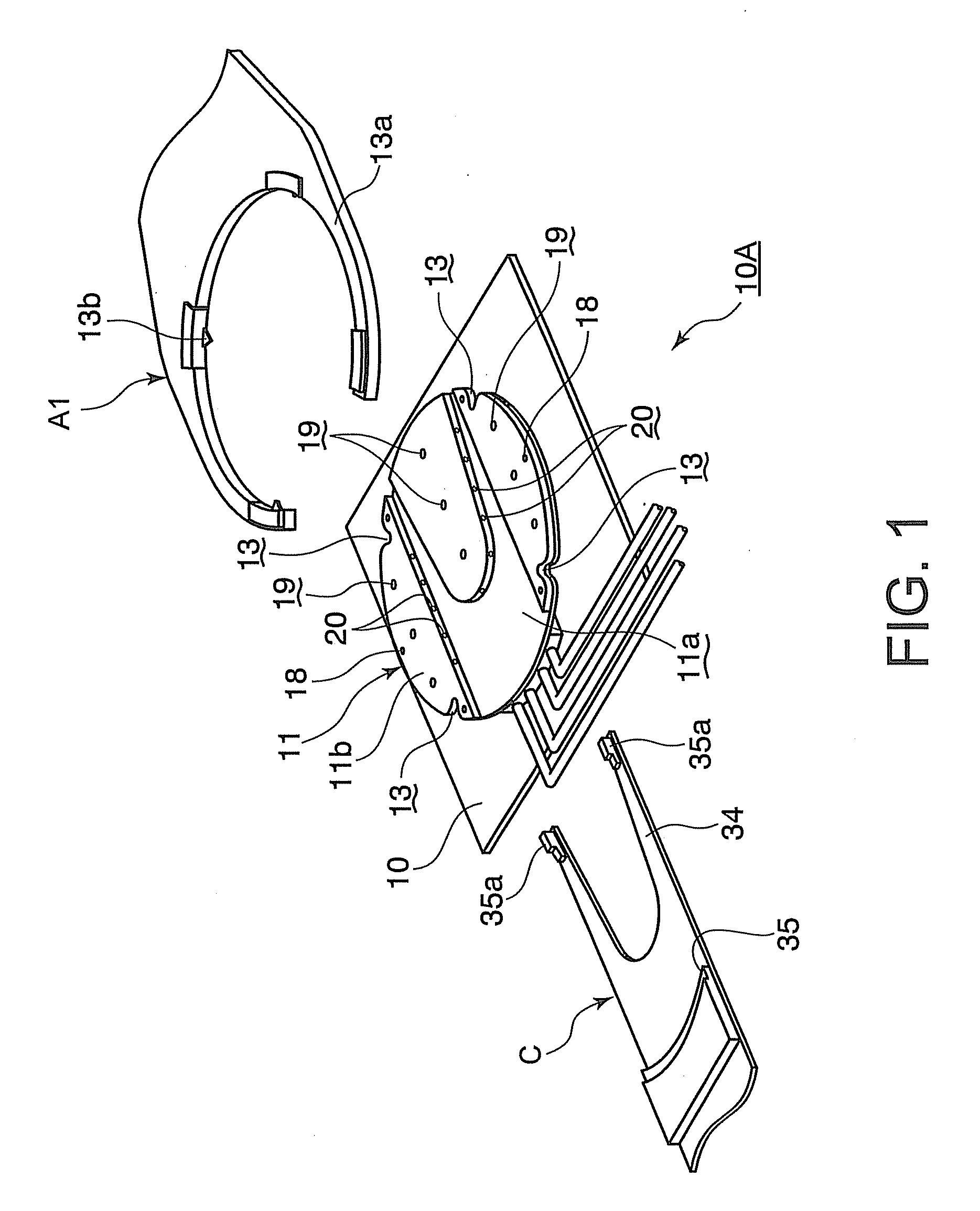
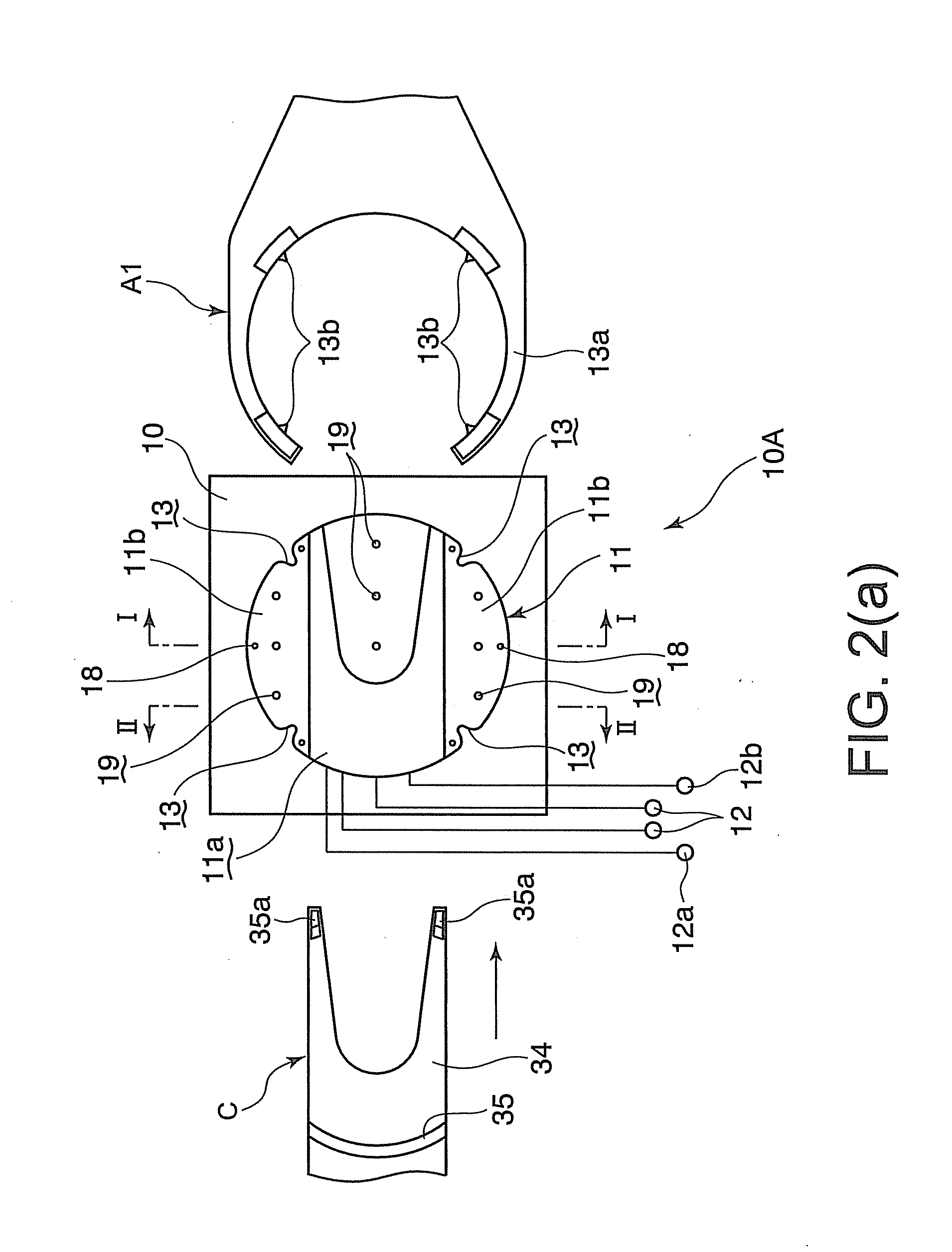
Conformable bedding arrangement
A bed sheet construction assembly utilized in the “making” of a bed mattress while eliminating unnecessary time and confusion therewith, comprising a lower mattress-fitted sheet having a first and a second side portion and a head and a foot portion thereon. The first and second side portions are longer than the head and foot portions. An upper or top sheet has a first and a second side portion and a head and a head and a foot portion thereon. The first and second side portions are longer than the head and foot portions. A notched-out corner is arranged on each side of the foot end of the top sheet. An attachment means is arranged between the lower fitted sheet and the upper or top sheet along their respective foot ends.
Owner:SACCHETTI WILLIAM B
Method of driving organic electroluminescence emission portion
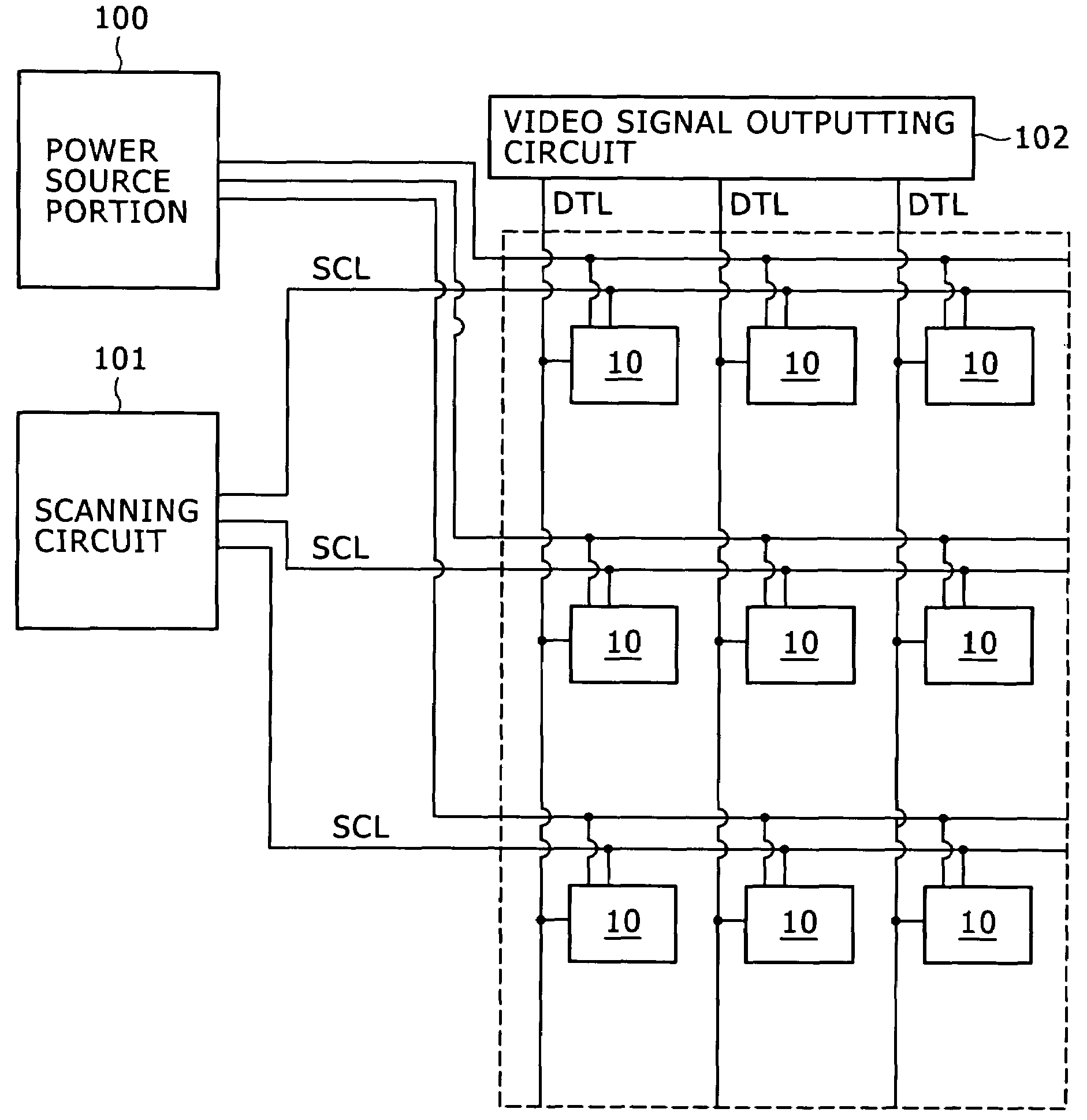
ActiveUS20090058771A1Short timeUnnecessary timeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingOrganic electroluminescenceTransistor
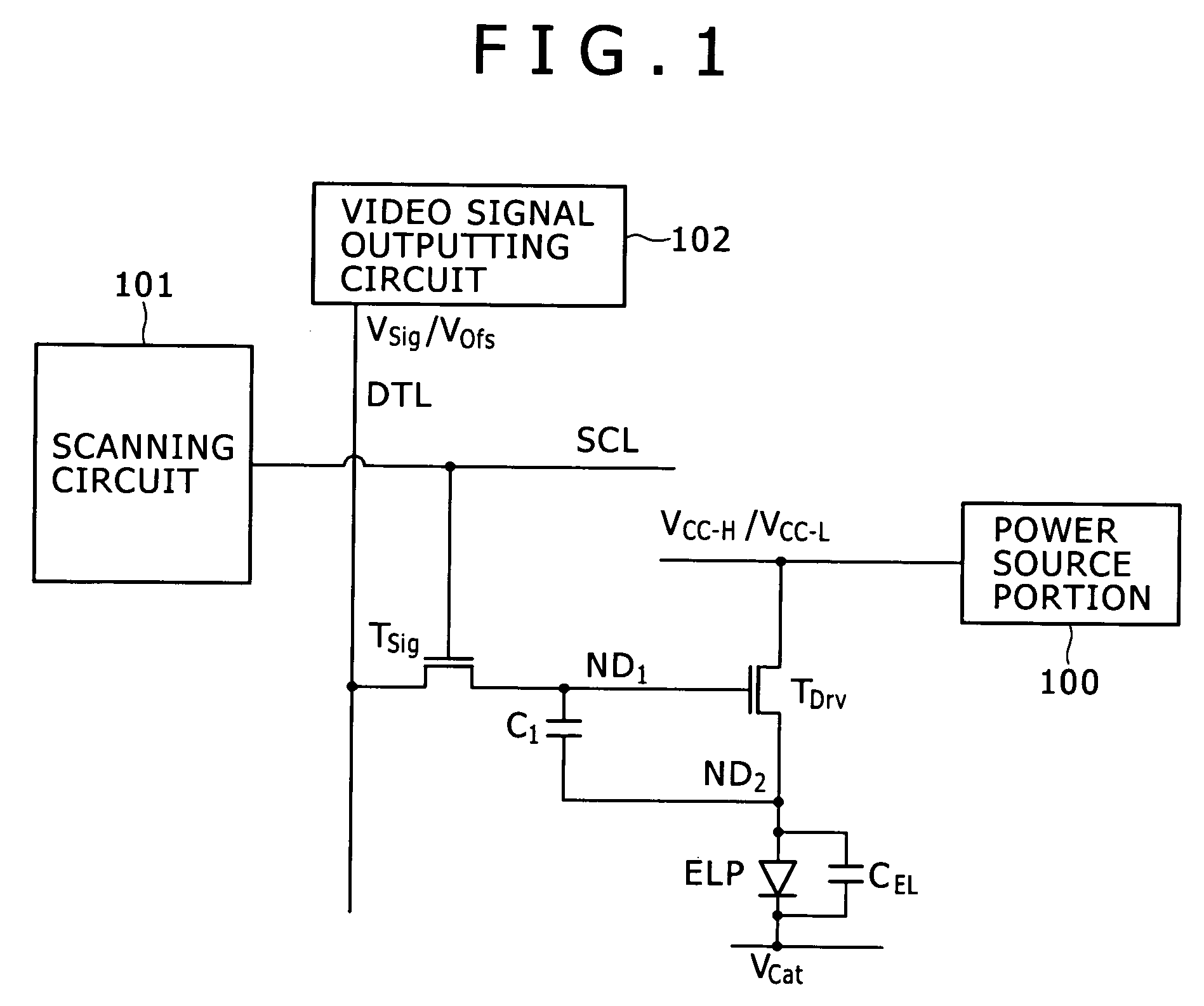
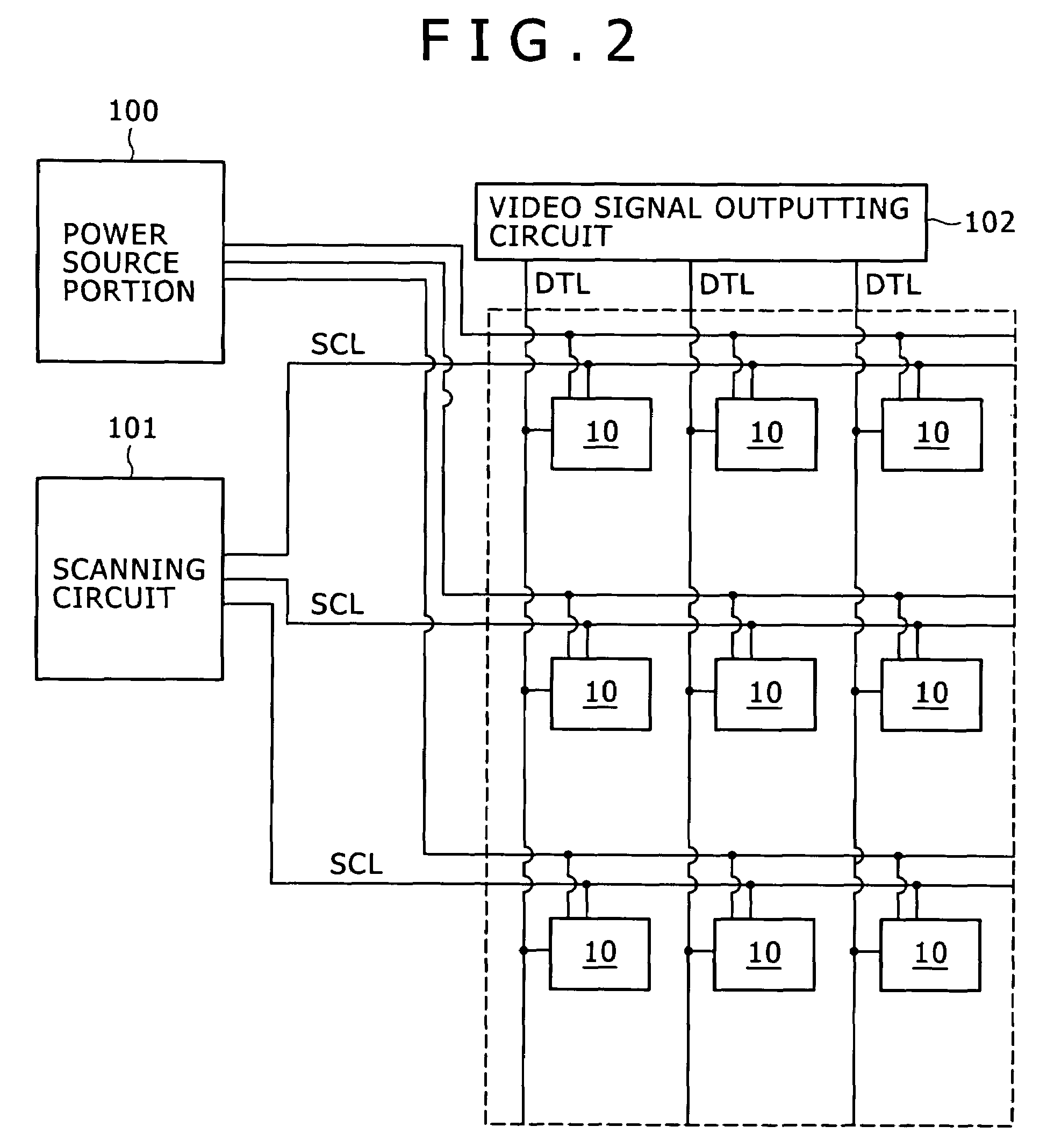
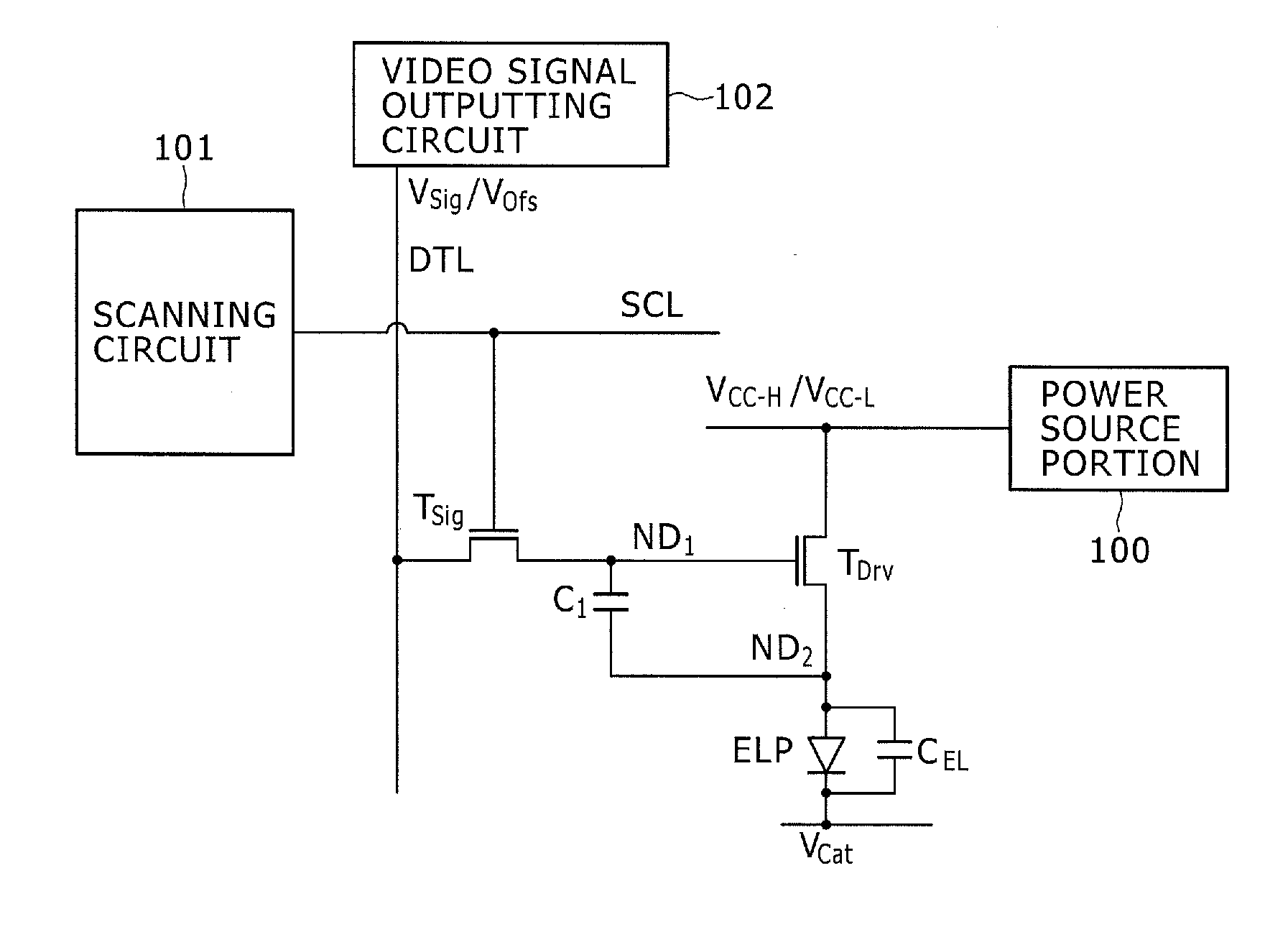
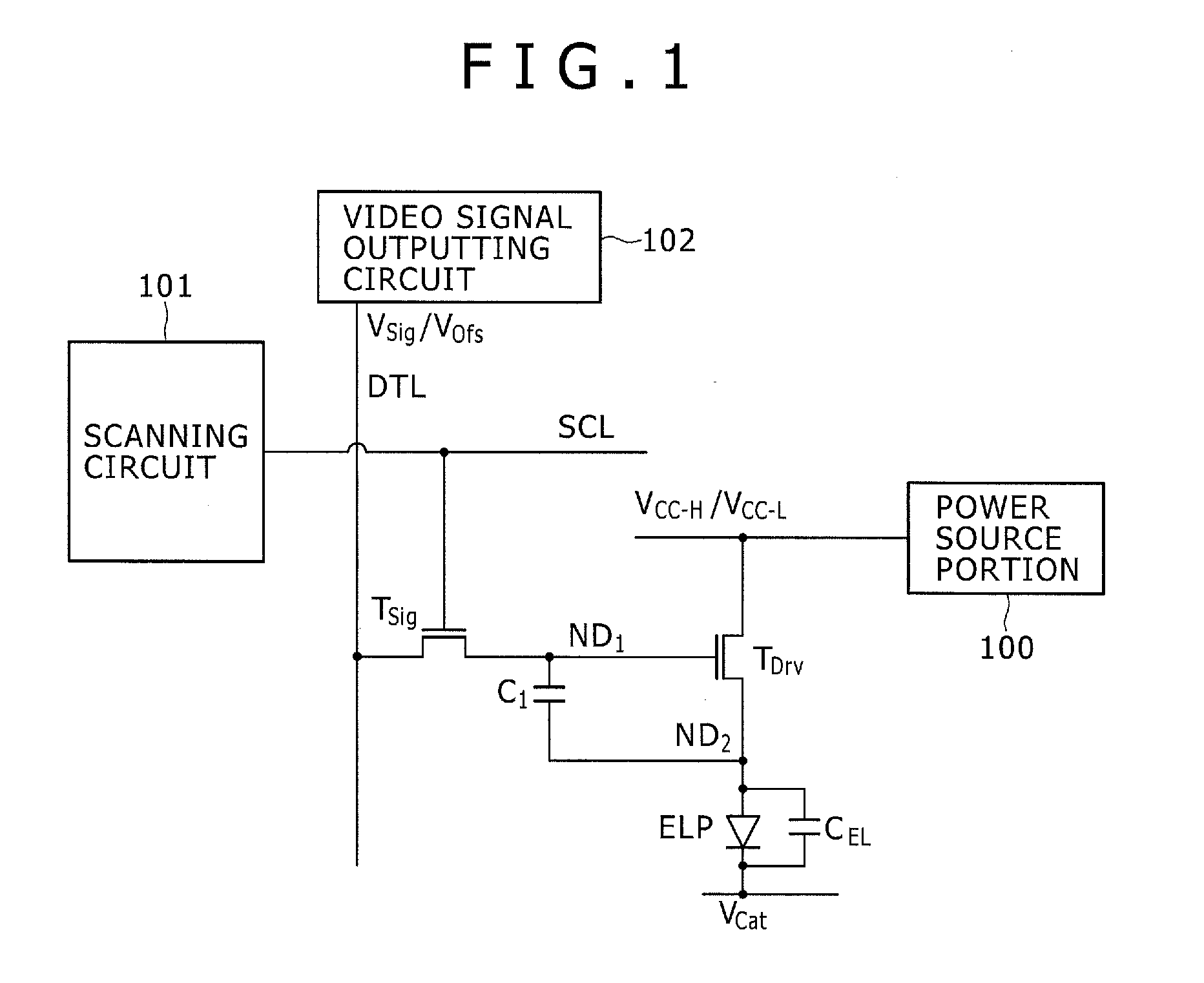
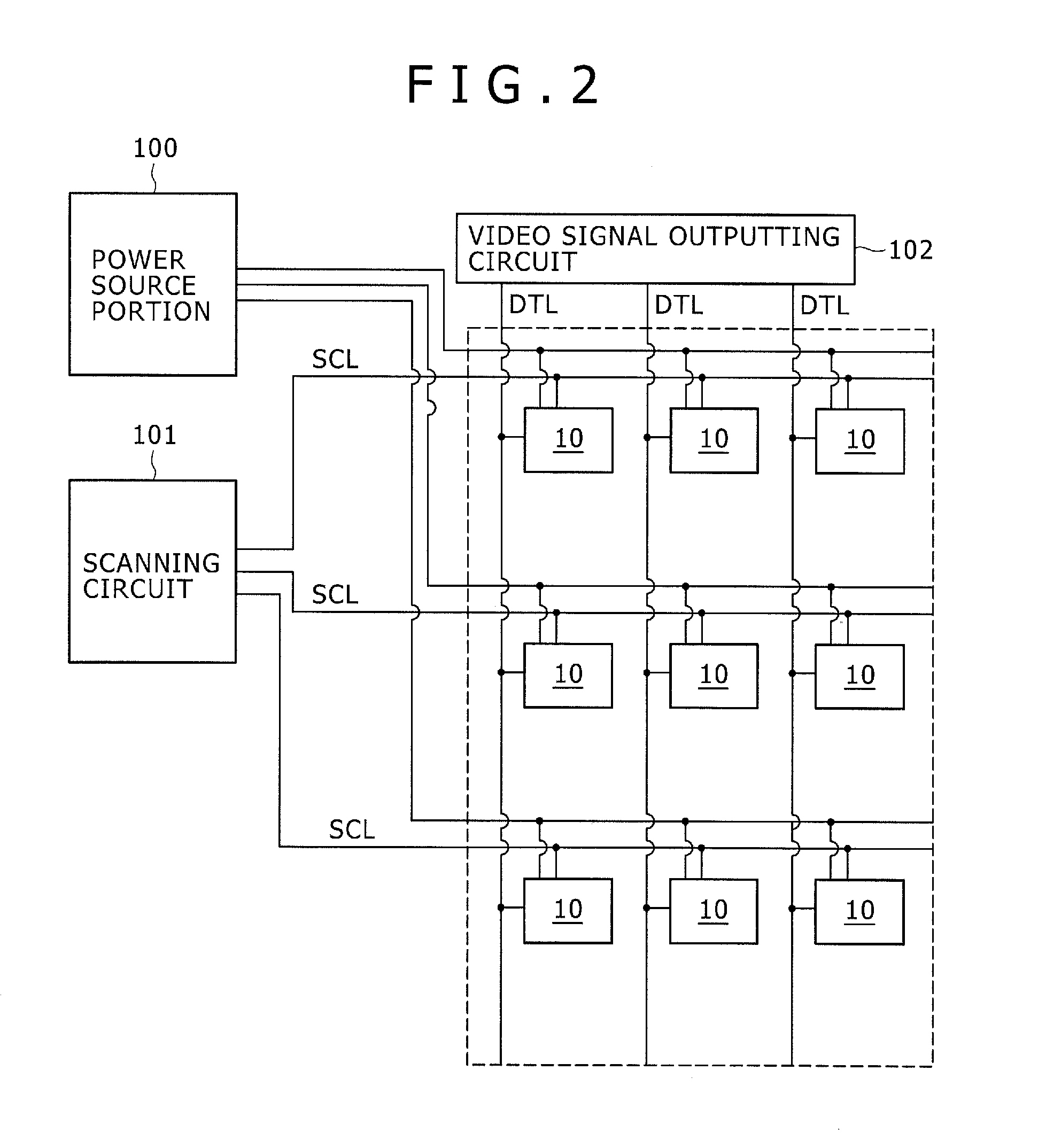
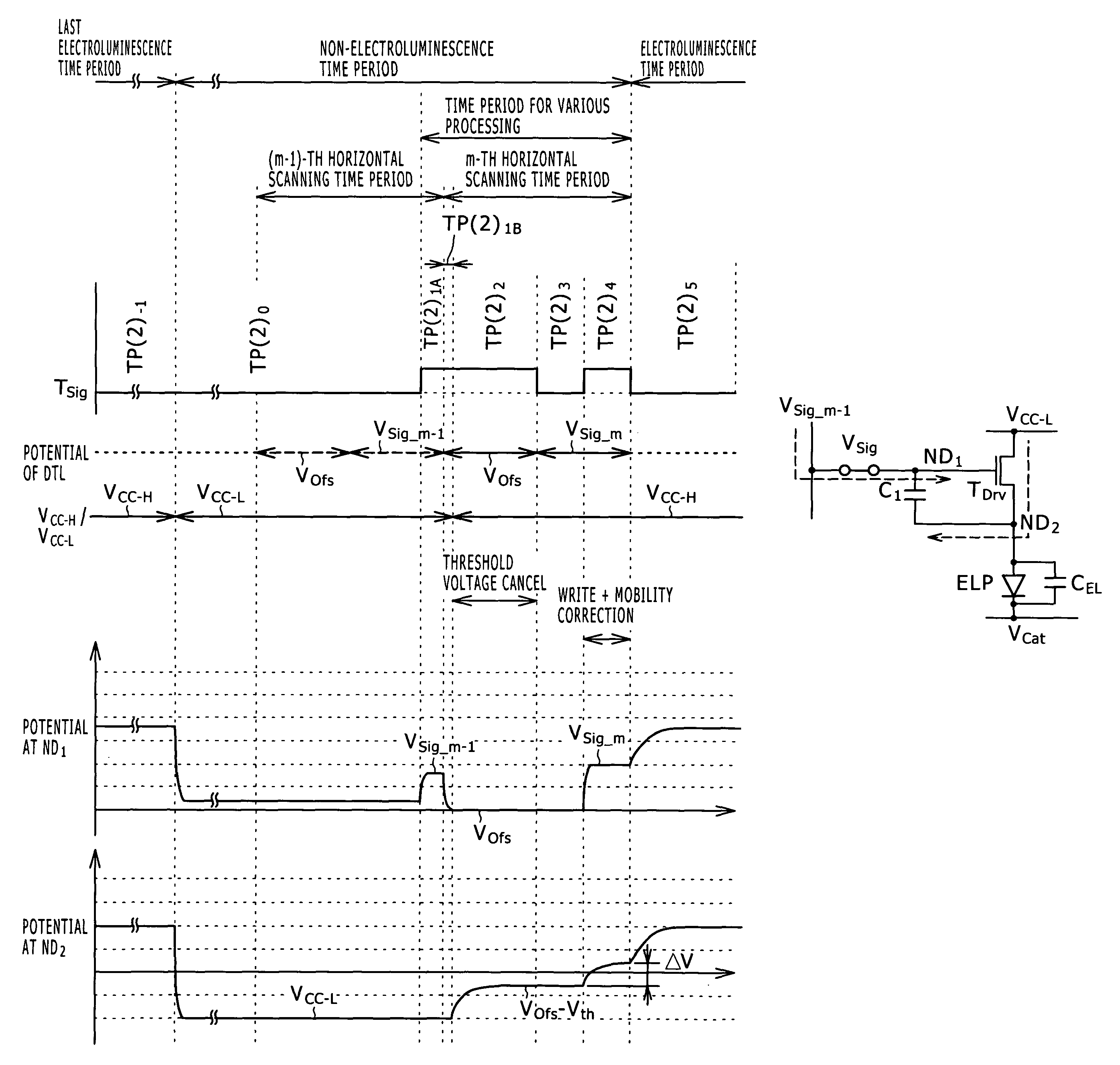
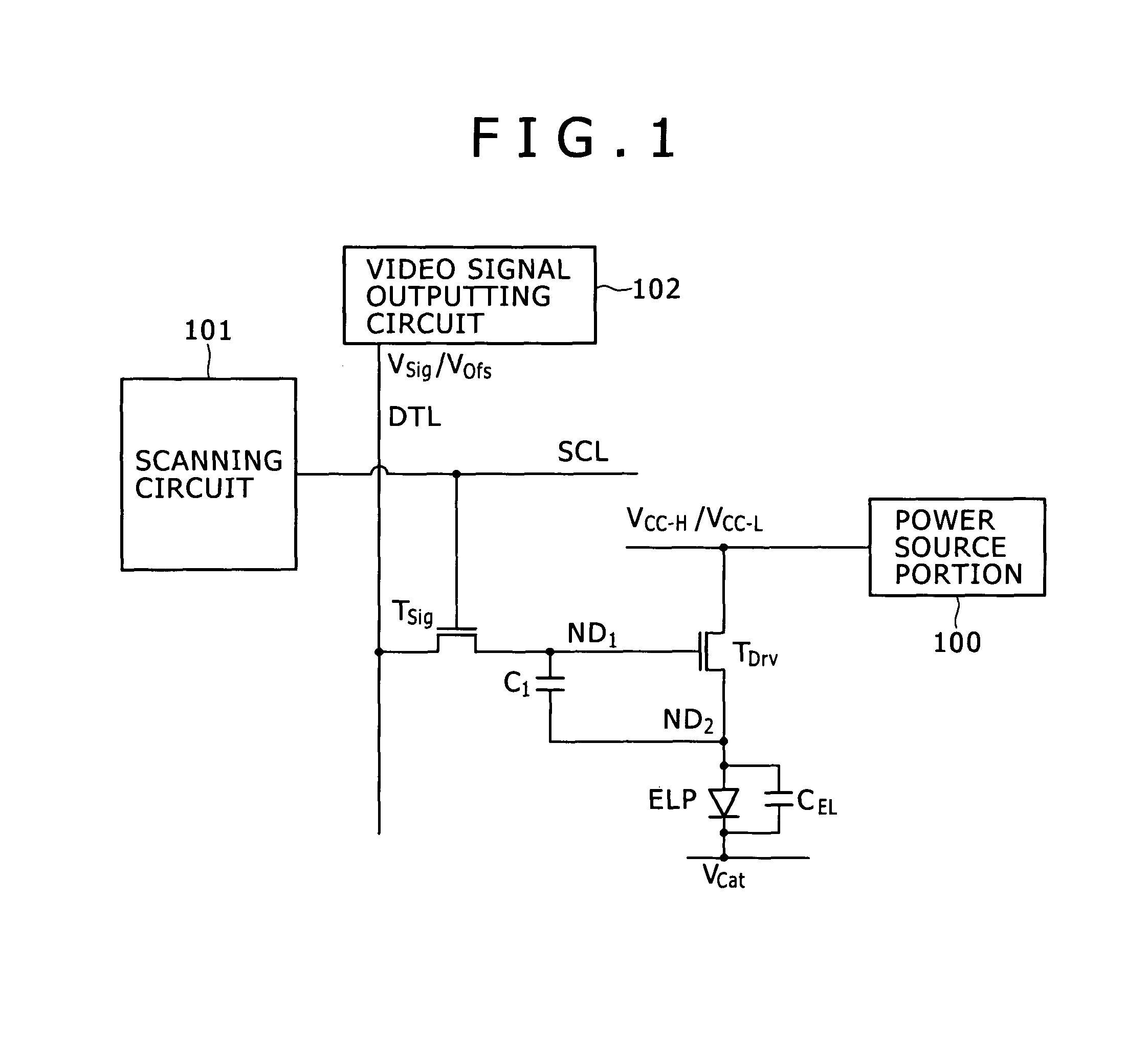
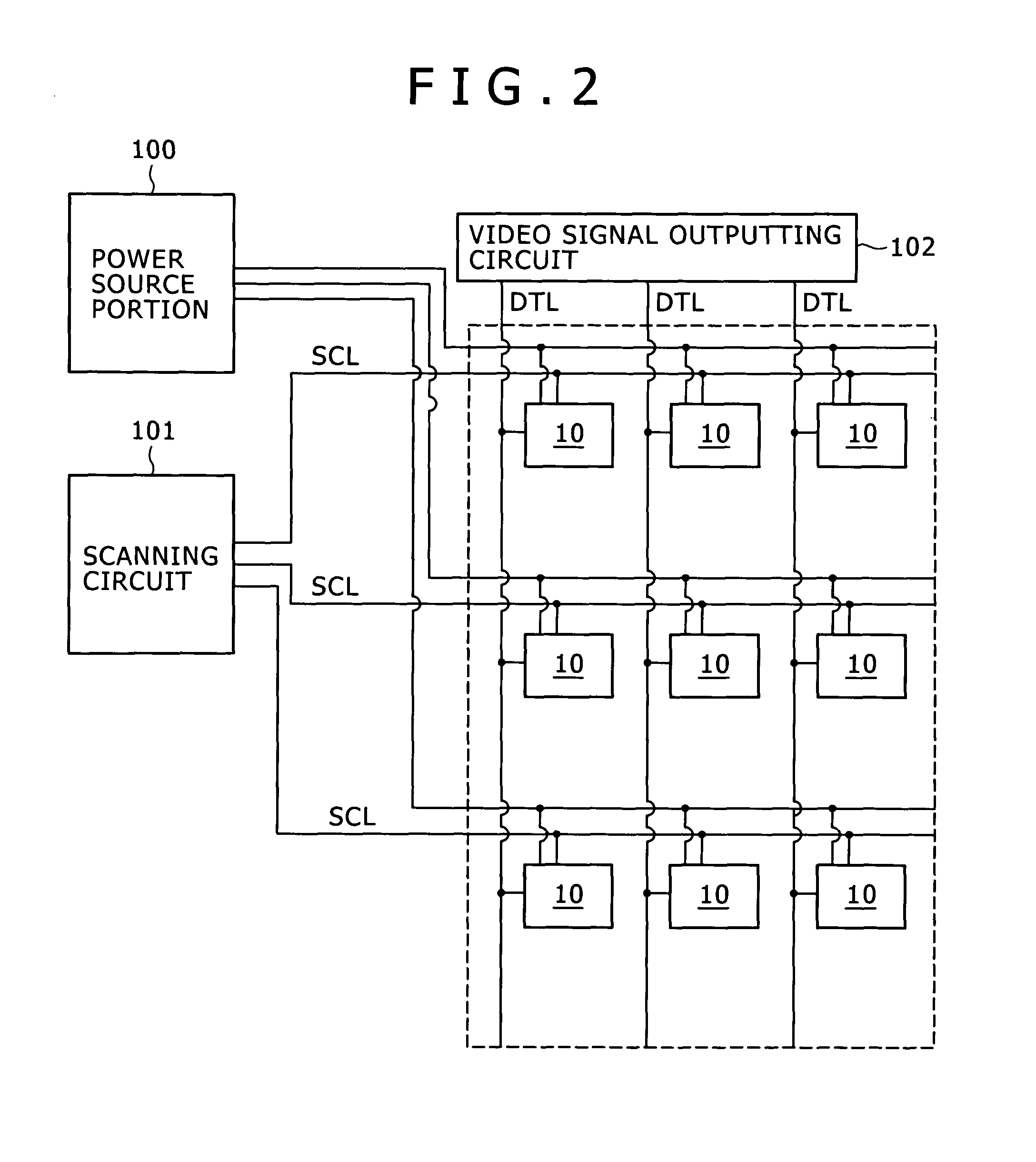
Disclosed herein is a method of driving an organic electroluminescence emission portion, the method including the steps of: applying a first node initialization voltage to corresponding one of the data lines, and supplying the video signal instead of the first node initialization voltage for a predetermined scanning time period, applying the first node initialization voltage from the corresponding one of the data lines to the first node through the write transistor held in an ON state for initializing the potential at the first node, and holding a state of applying the first node initialization voltage from the corresponding one of the data lines to the first node through the write transistor held in an ON state for holding the potential at the first node.
Owner:JOLED INC
Calibration device, calibration method, and computer readable medium for visual sensor
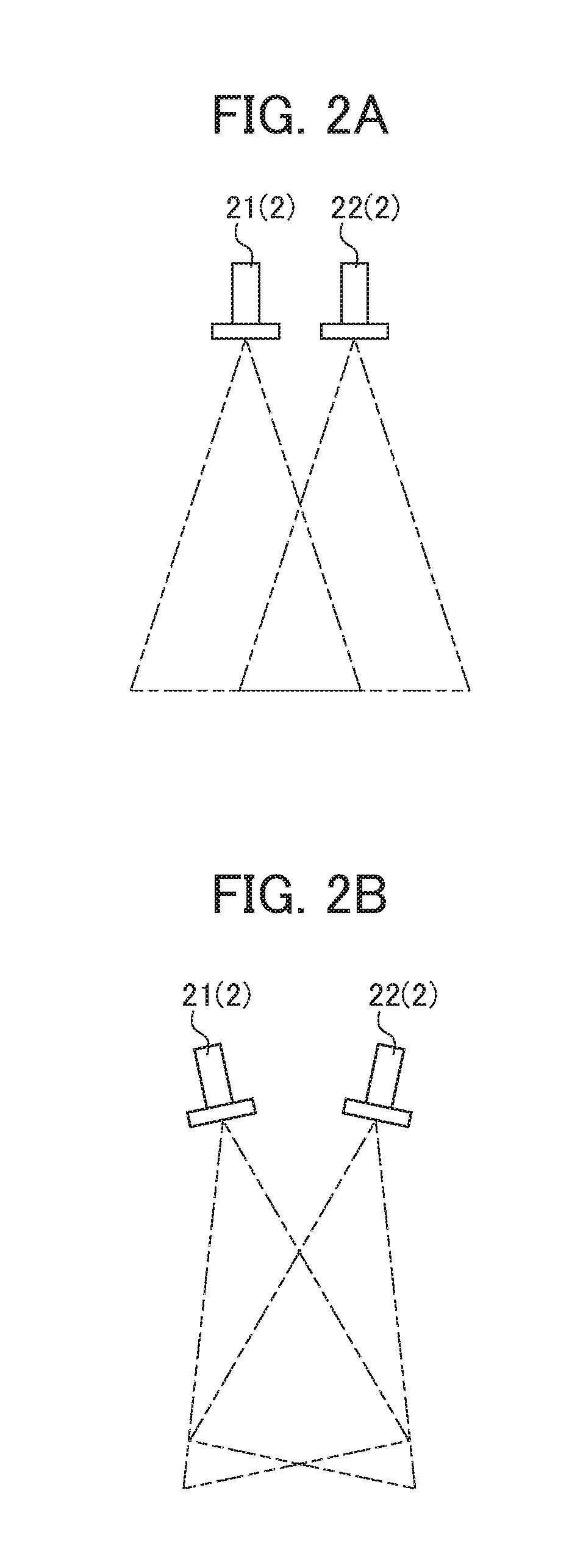
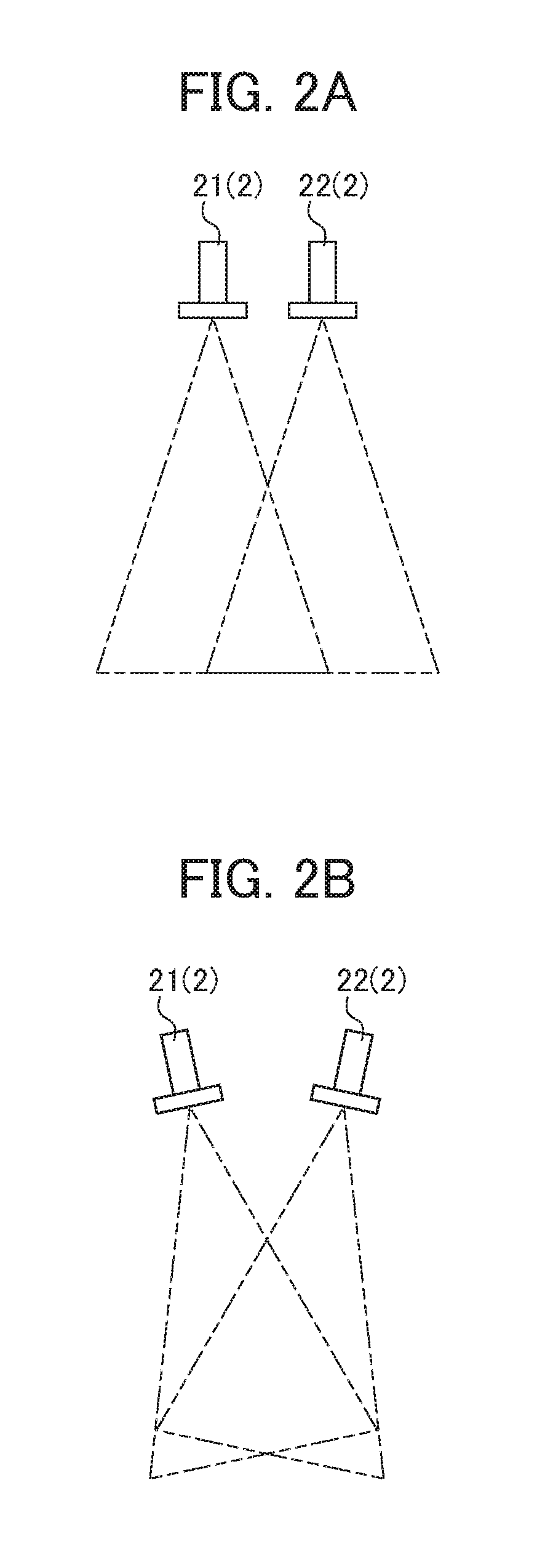
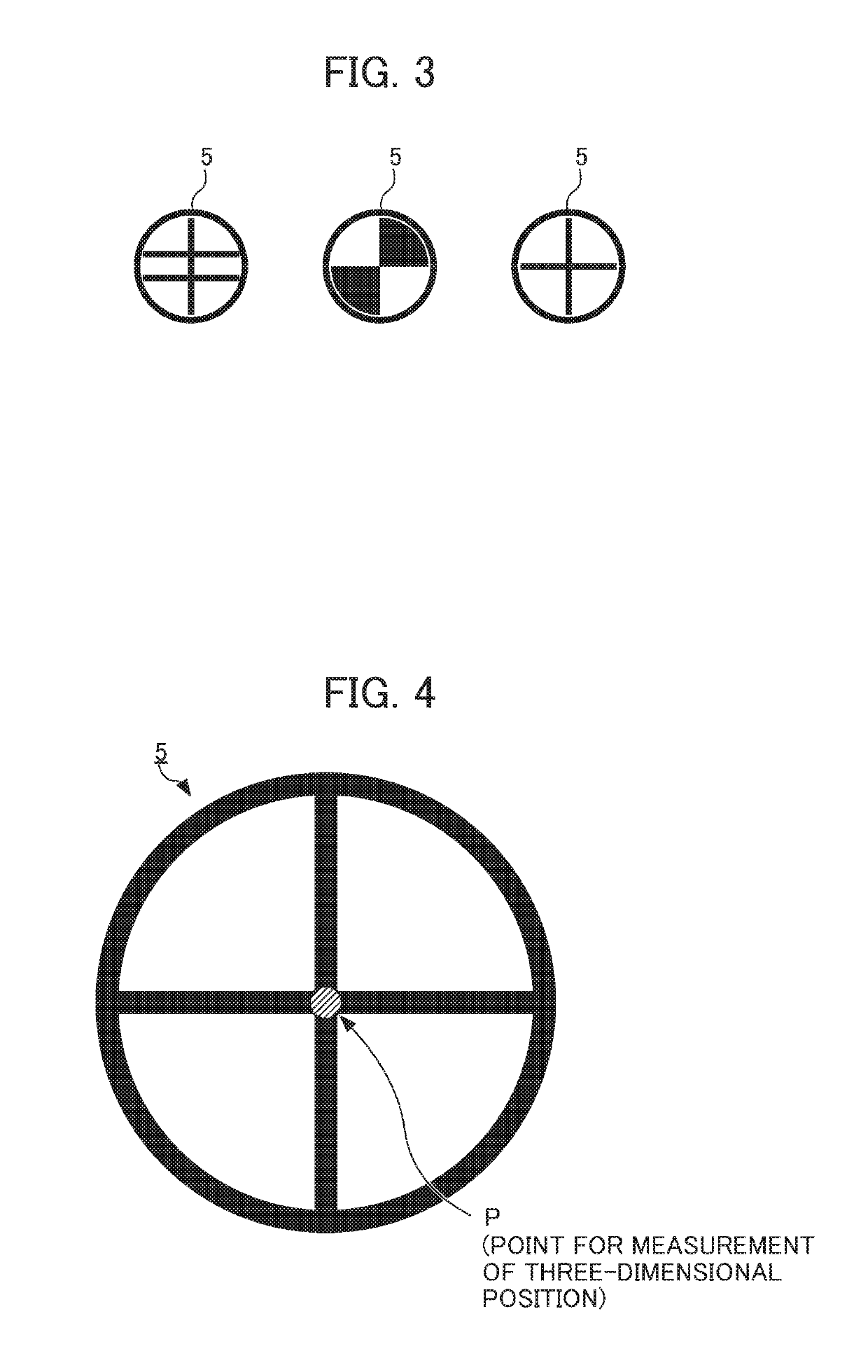
ActiveUS20180194007A1Eliminate generationAffect operabilityImage enhancementProgramme-controlled manipulatorStereo cameraVision sensor
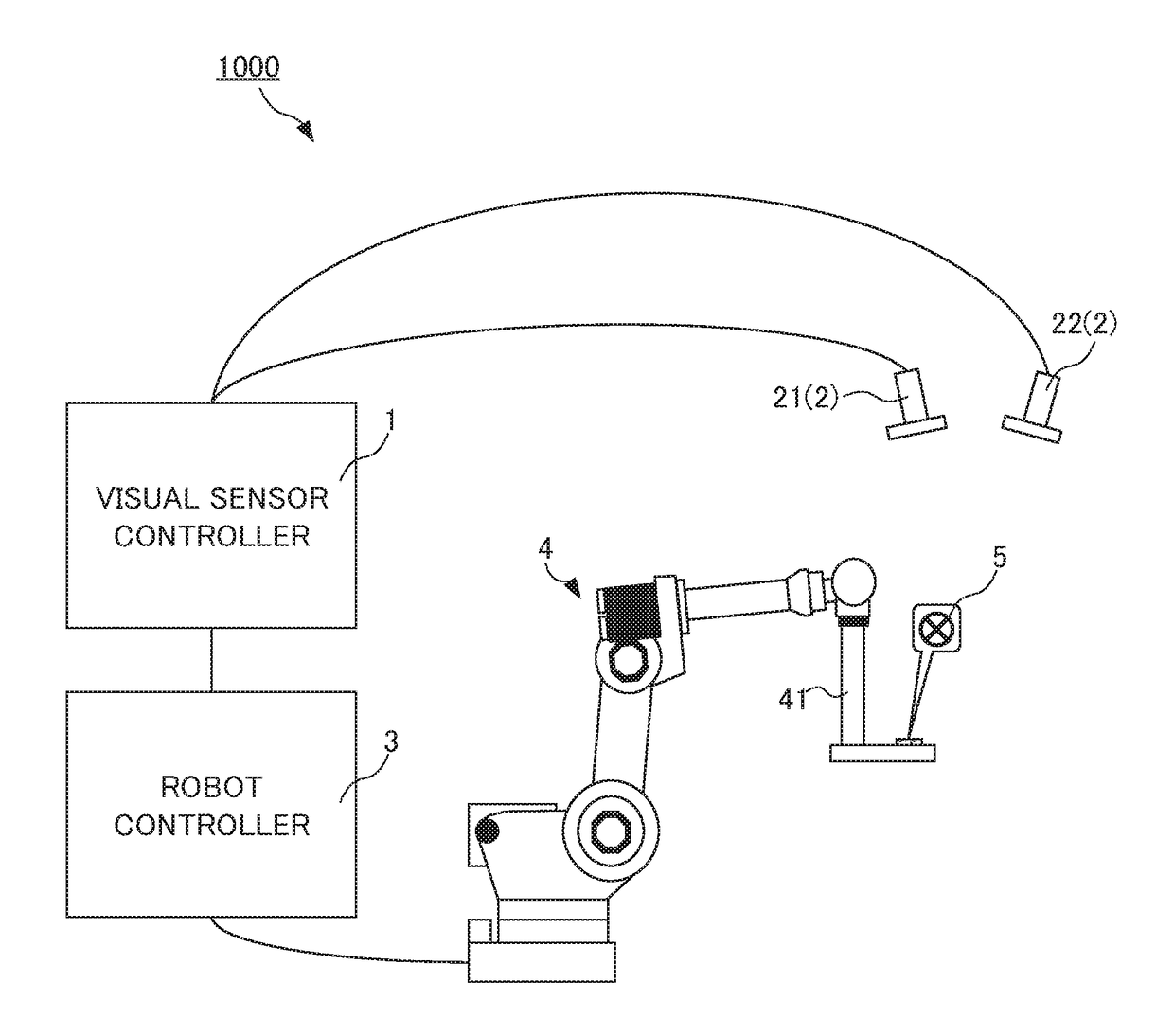
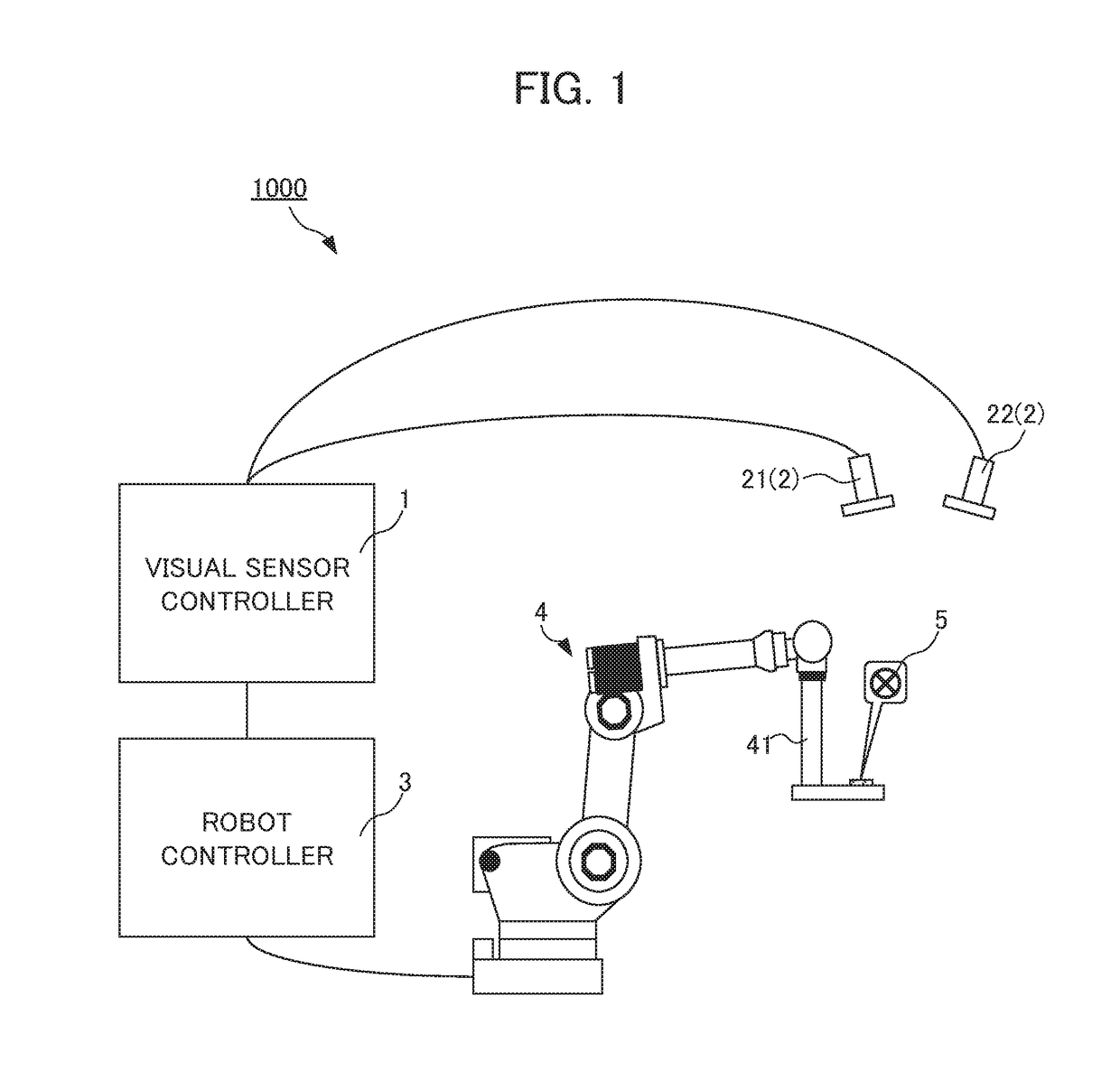
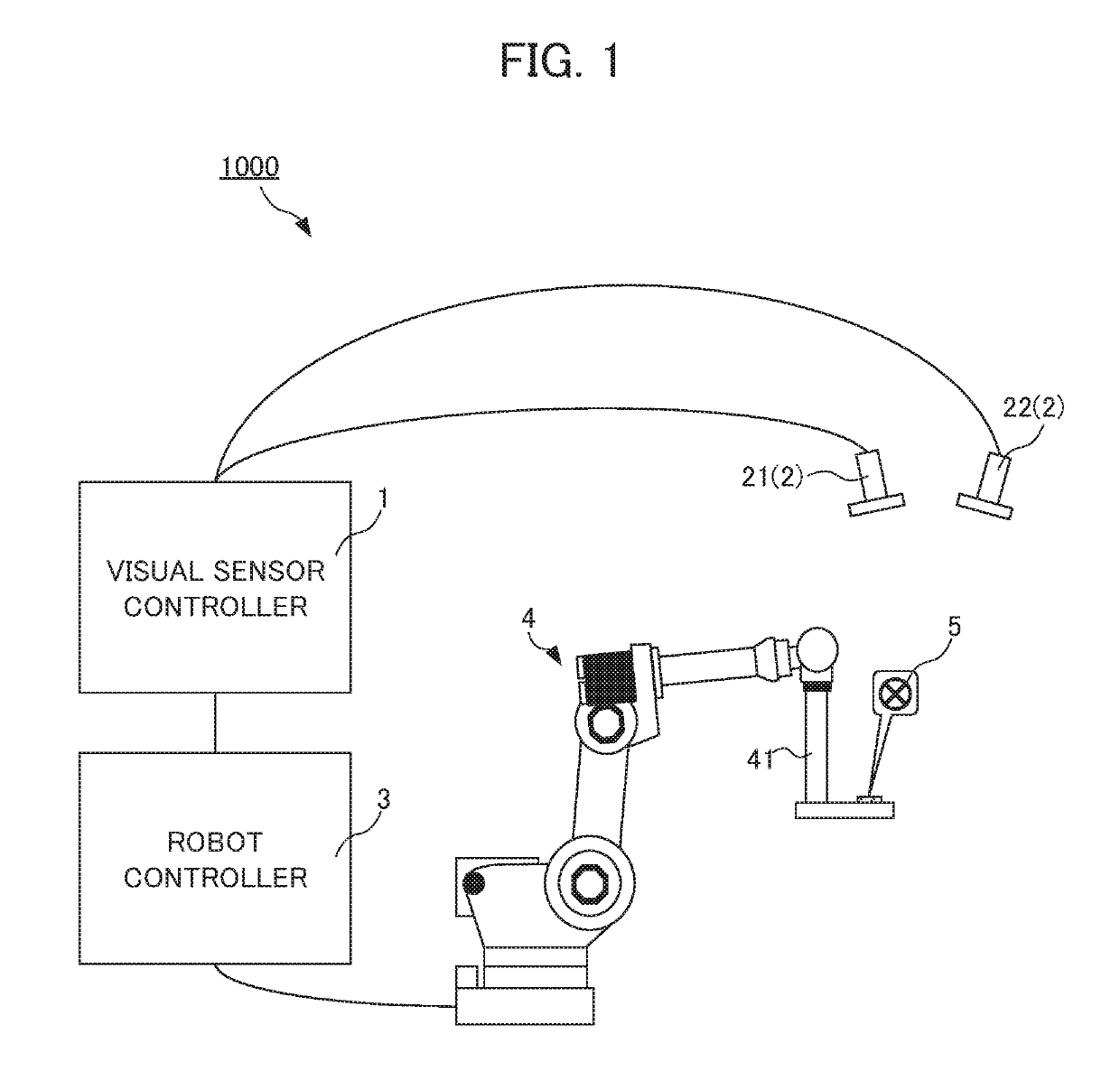
A parameter for detecting a target mark 5 is not required to be set for each camera repeatedly while a stereo camera 2 is calibrated. A calibration device 1 associates position information in an image coordinate system at a first camera 21 of a stereo camera 2, position information in an image coordinate system at a second camera 22 of the stereo camera 2, and position information in a robot coordinate system at a robot 4. The calibration device comprises: first parameter setting unit 102 that sets a first parameter for detecting a target mark 5 attached to the robot 4 from data about an image captured by the first camera 21; and a second parameter setting unit 104 that sets a second parameter for detecting the target mark 5 from data about an image captured by the second camera 22 based on the first parameter.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Silver indicator methods and test kit
InactiveUS6145468AEasily employedReliable and sensitive resultAnalysis using chemical indicatorsTesting metalsCopperColor changes
A method for determining silver concentration in a solution is disclosed. This method generally comprises immersing a substantially pure, elemental, copper strip in a sample of the solution to be tested, agitating the strip in the sample, removing the strip from the sample, and observing the color change, if any, of the strip. These strips are generally greater than 99% pure copper, and have been coated with a metal ion layer. An alternative embodiment provides for removal of the metal ion layer immediately before testing the silver concentration of the solution. A test kit comprising the active copper strips is also disclosed.
Owner:WOOG MANFRED J
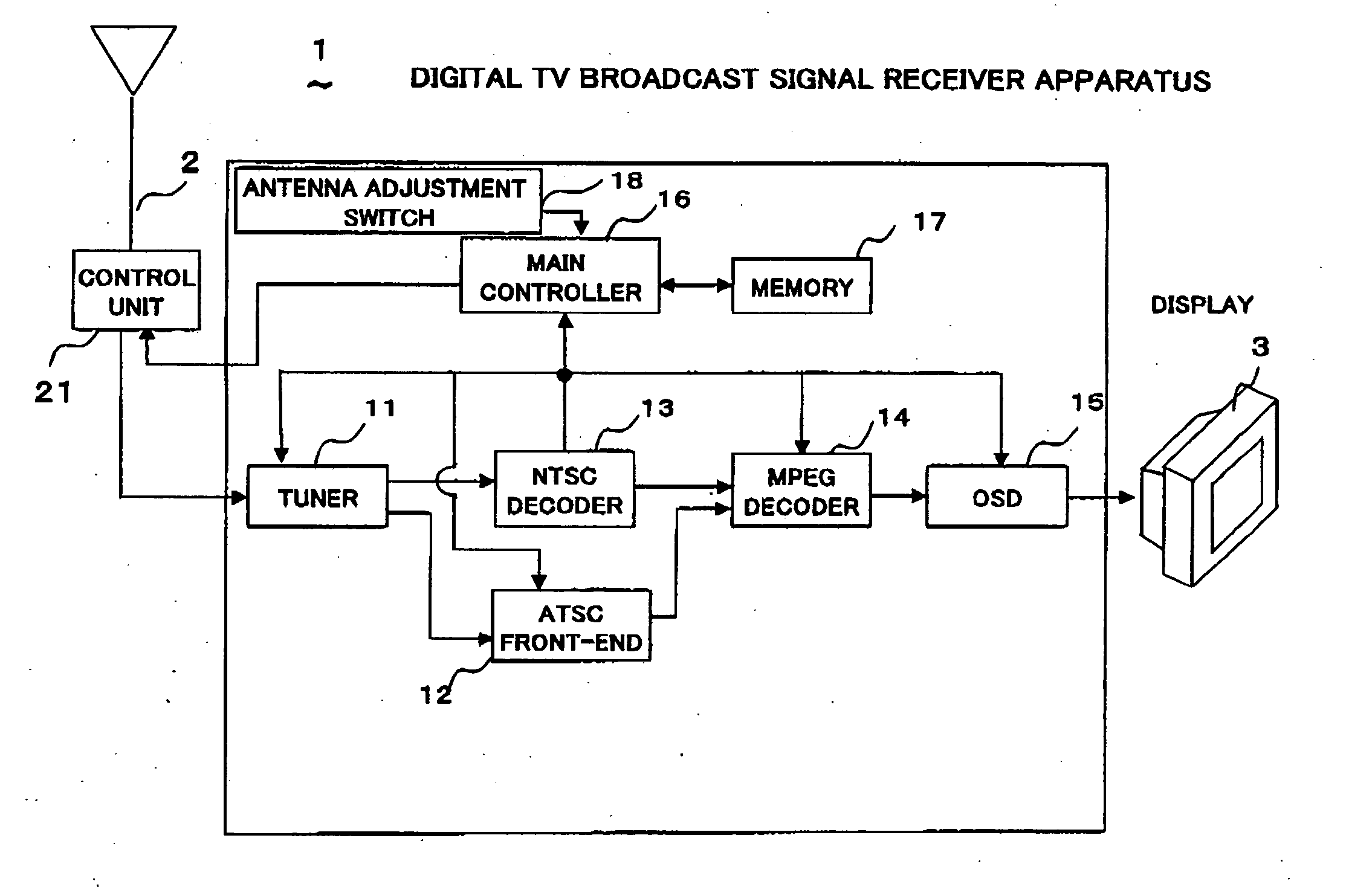
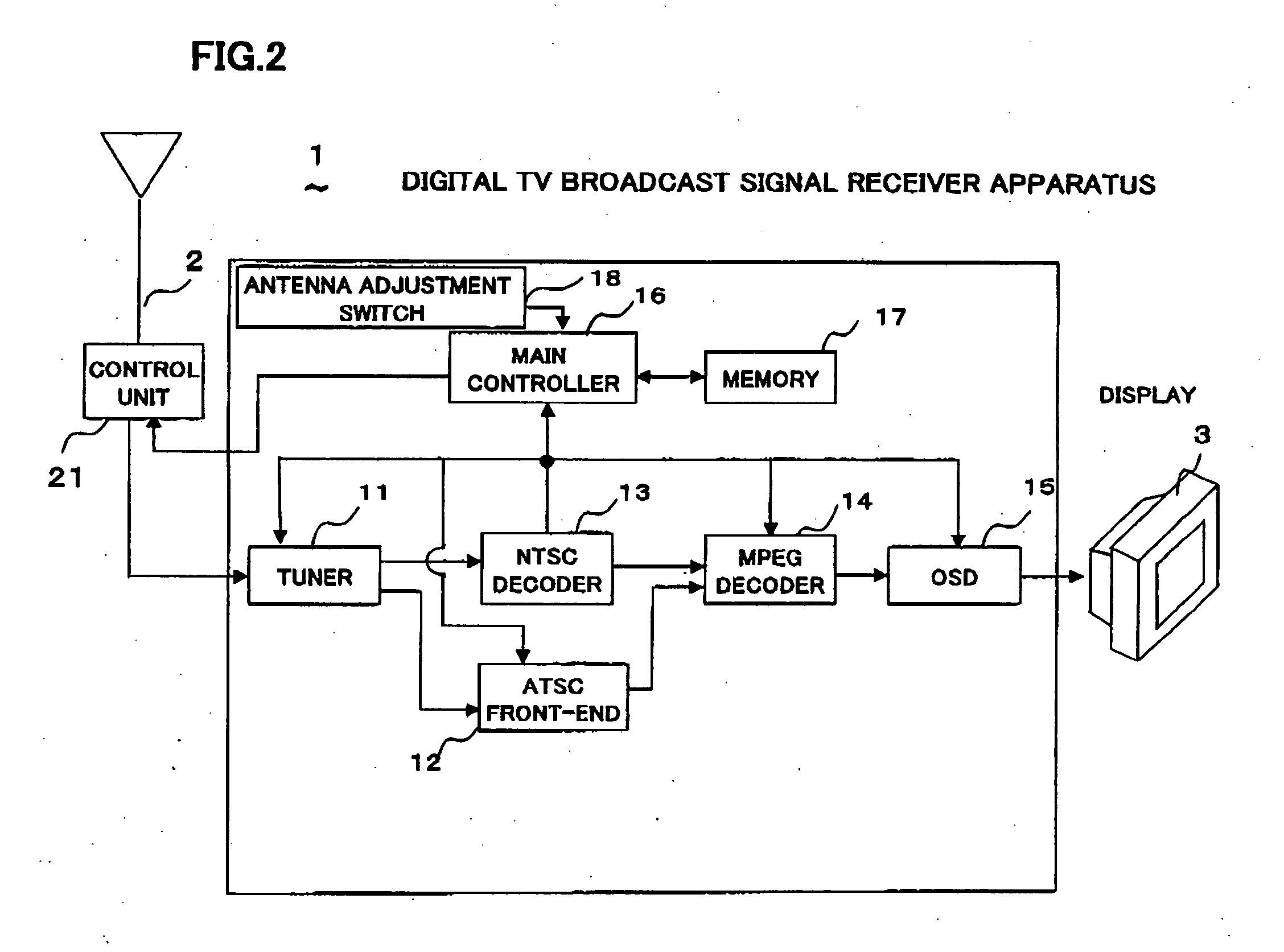
Digital television broadcast signal receiver
InactiveUS20050287968A1Prevent unnecessary scanning rotationShorten the timeTelevision system detailsSpatial transmit diversityOmni directionalData storing
A TV receiver preliminarily measures and stores, in a memory, data of best receiving directions, each giving maximum signal intensity, of a multi-directional antenna for receivable channels. When the antenna rotationally shifts physically for some reason, one channel is selected and subjected to measurements by an omni-directional scanning again to determine a new best receiving direction. A receiving direction number difference between the stored best receiving direction and the new best receiving direction of the same channel is determined. Using the receiving direction number difference for the one channel, all data stored in the memory are renewed at one time, the data being the best receiving direction numbers and the signal intensities therefor for all the channels. The antenna direction can be quickly adjusted to the rotational shift by new measurements for one channel, without requiring time to make unnecessary measurements for all channels, achieving a best receiving condition steadily.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
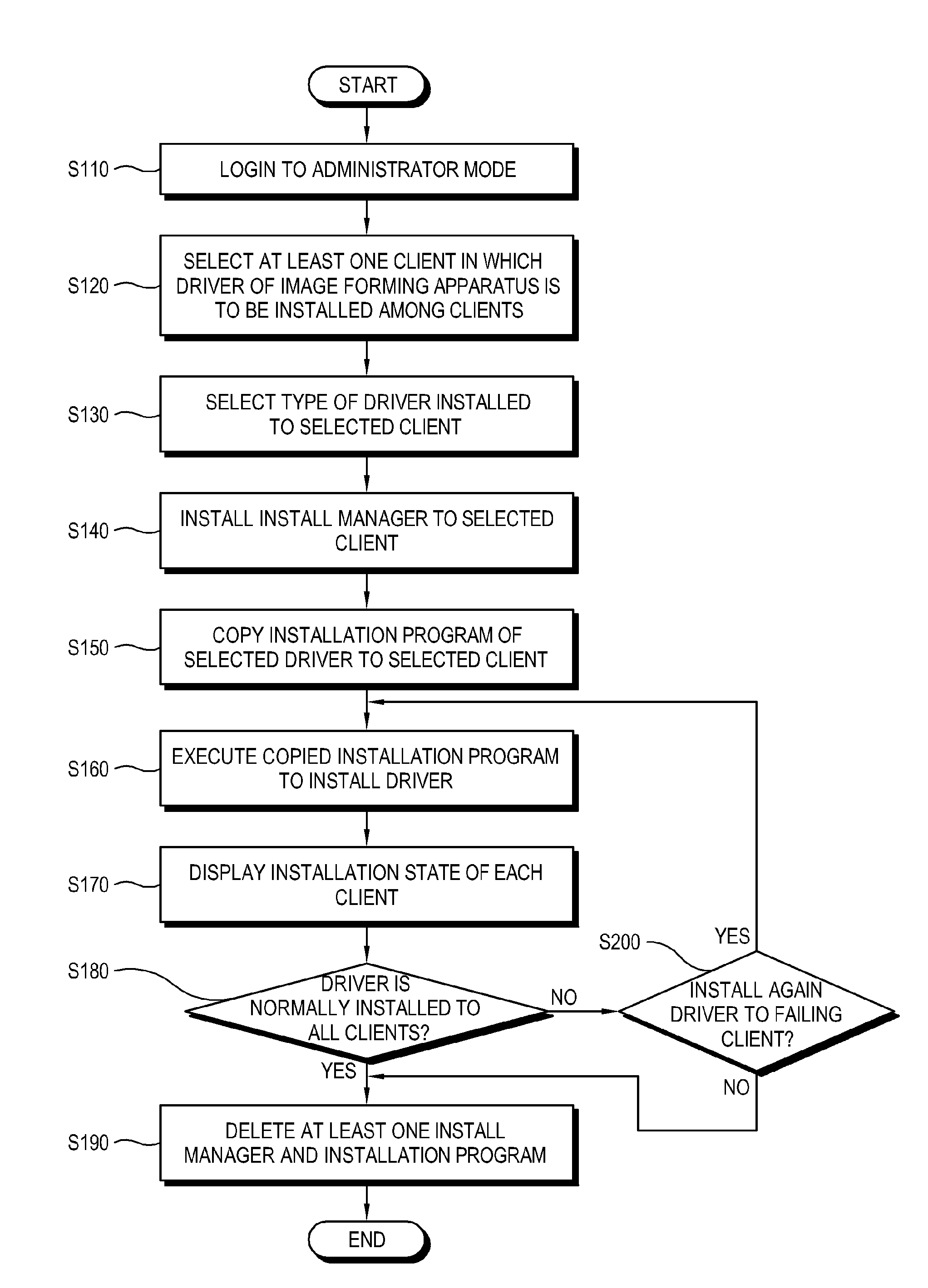
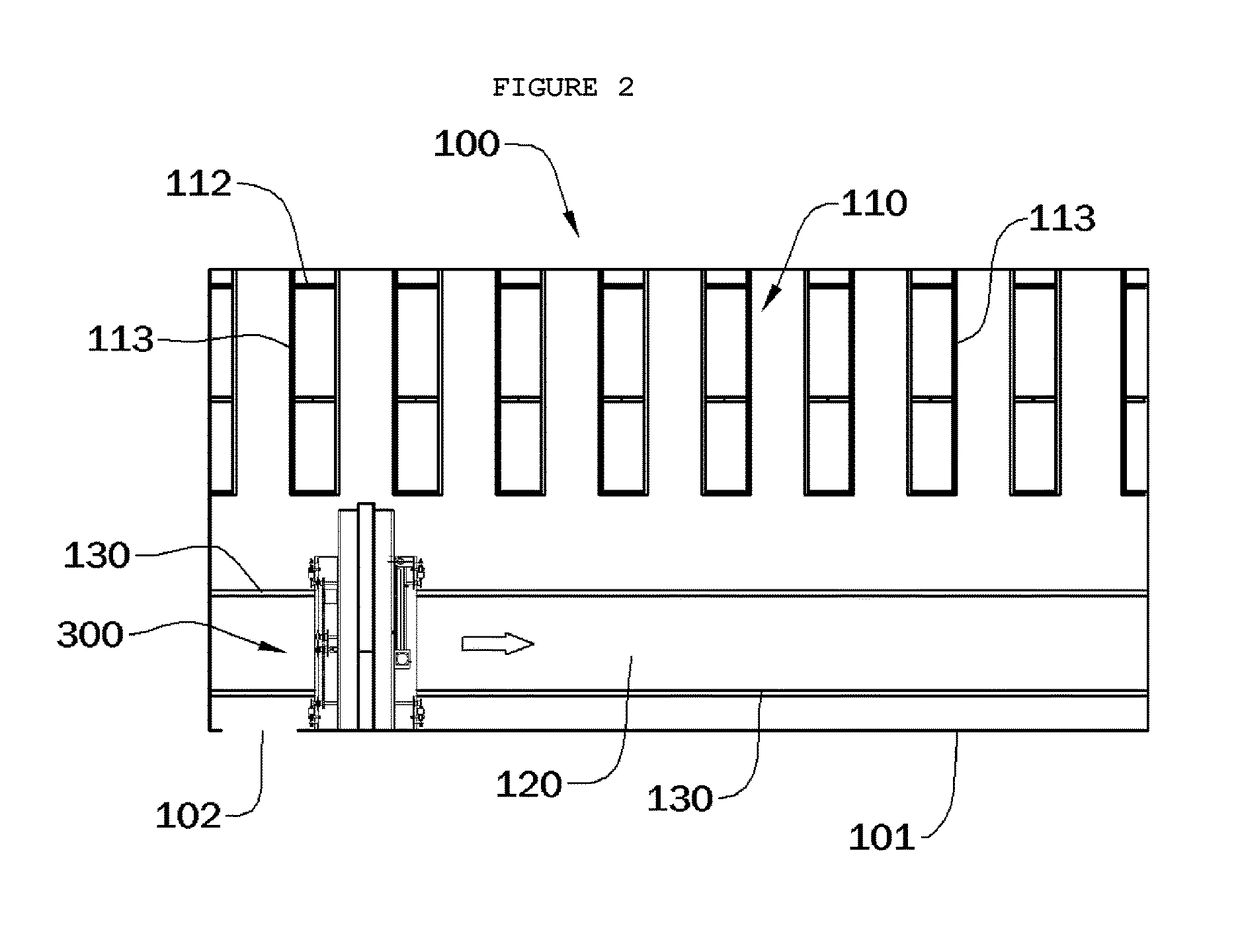
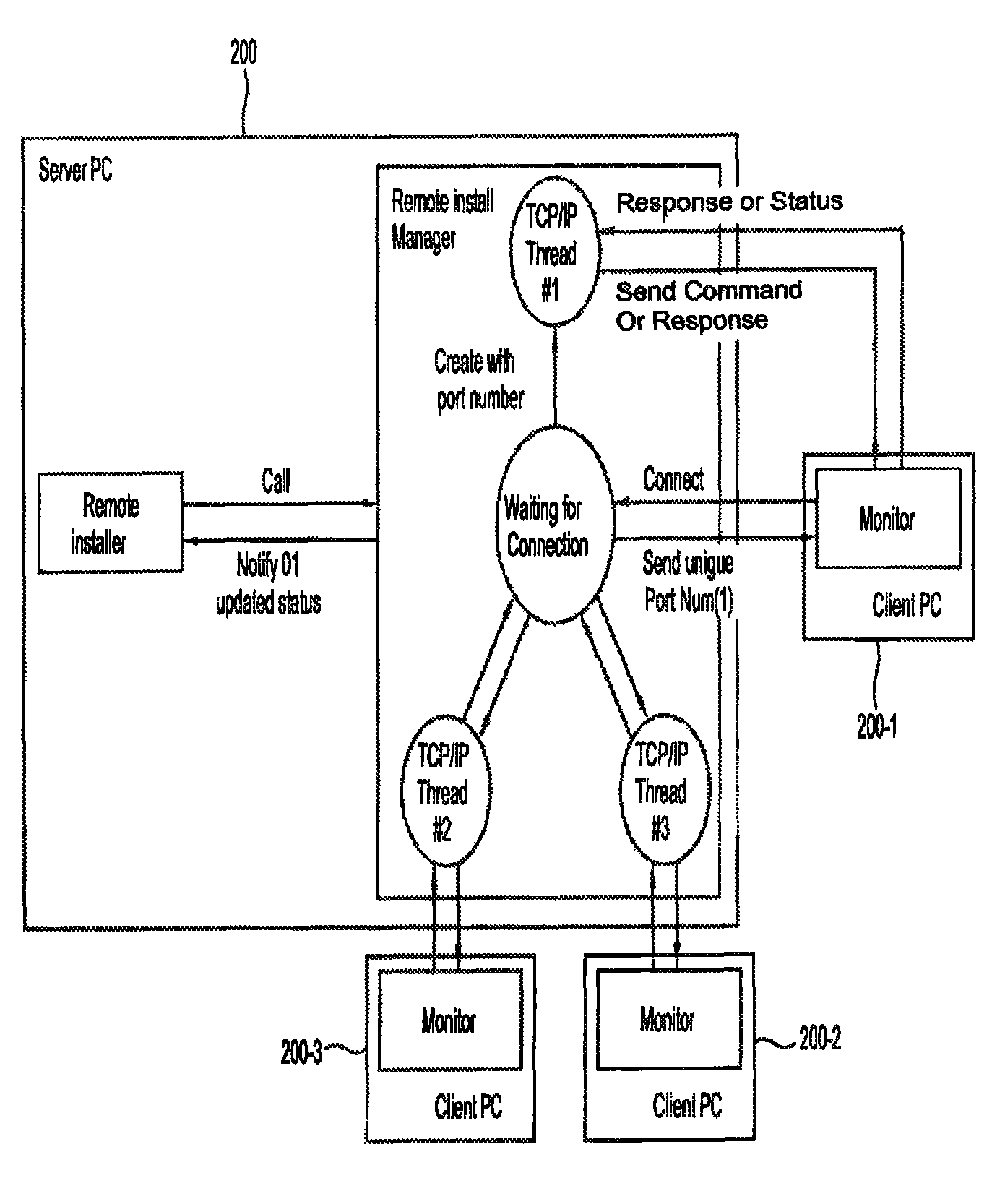
Server connected with image forming apparatus and client, image forming system having the same, and driver remote installation method of image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20100107157A1Save unnecessary timeLow costProgram loading/initiatingExecution paradigmsImage formationMethod of images
A server connected with an image forming apparatus and a client, an image forming system having the same and a driver remote installation method of an image forming apparatus, the method including selecting at least one client in which a driver of the image forming apparatus is to be installed by the server; selecting a type of the driver to be installed in the at least one selected client; installing an install manager to install the driver in the at least one selected client; and installing the selected driver in the at least one selected client using the install manager.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
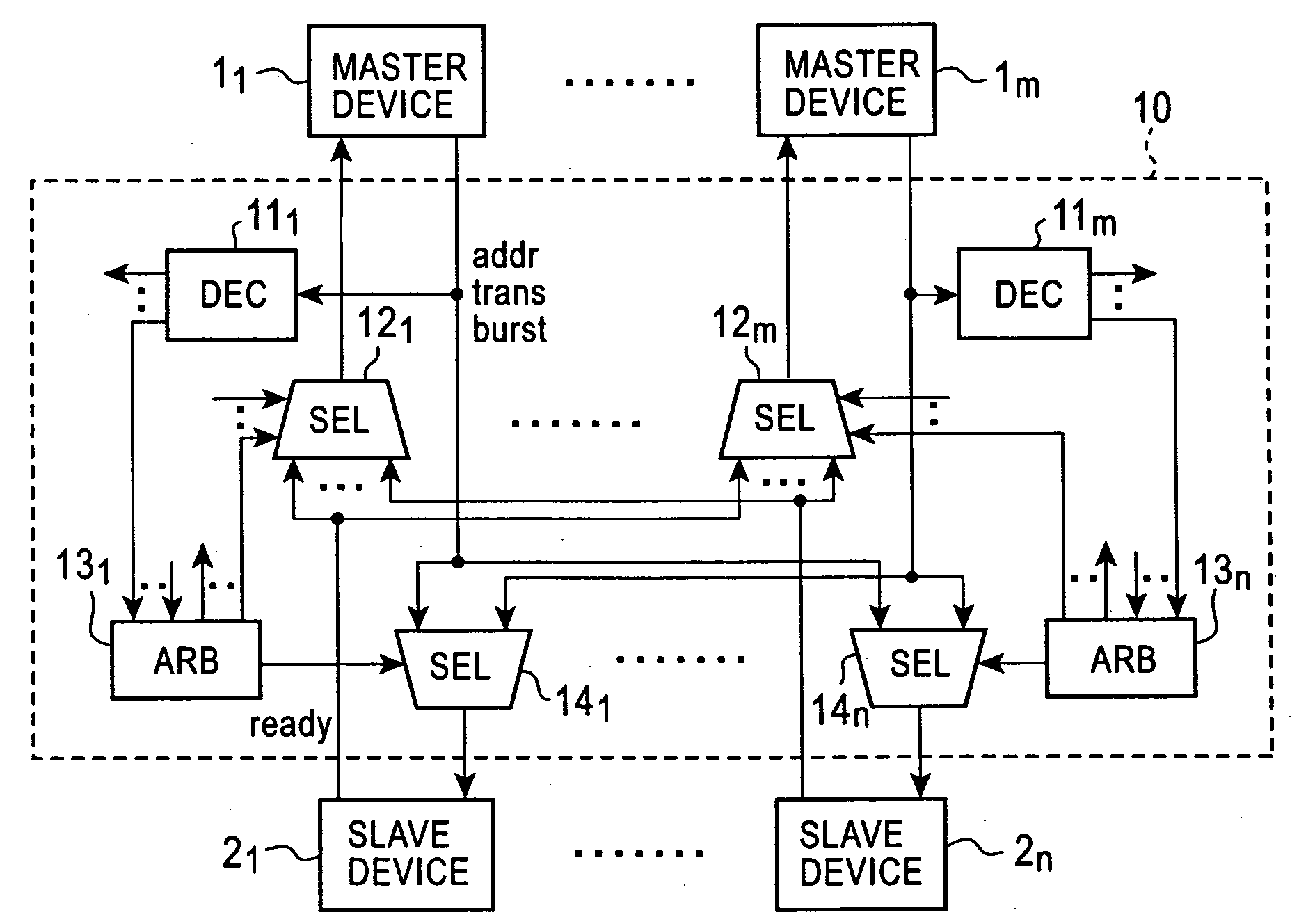
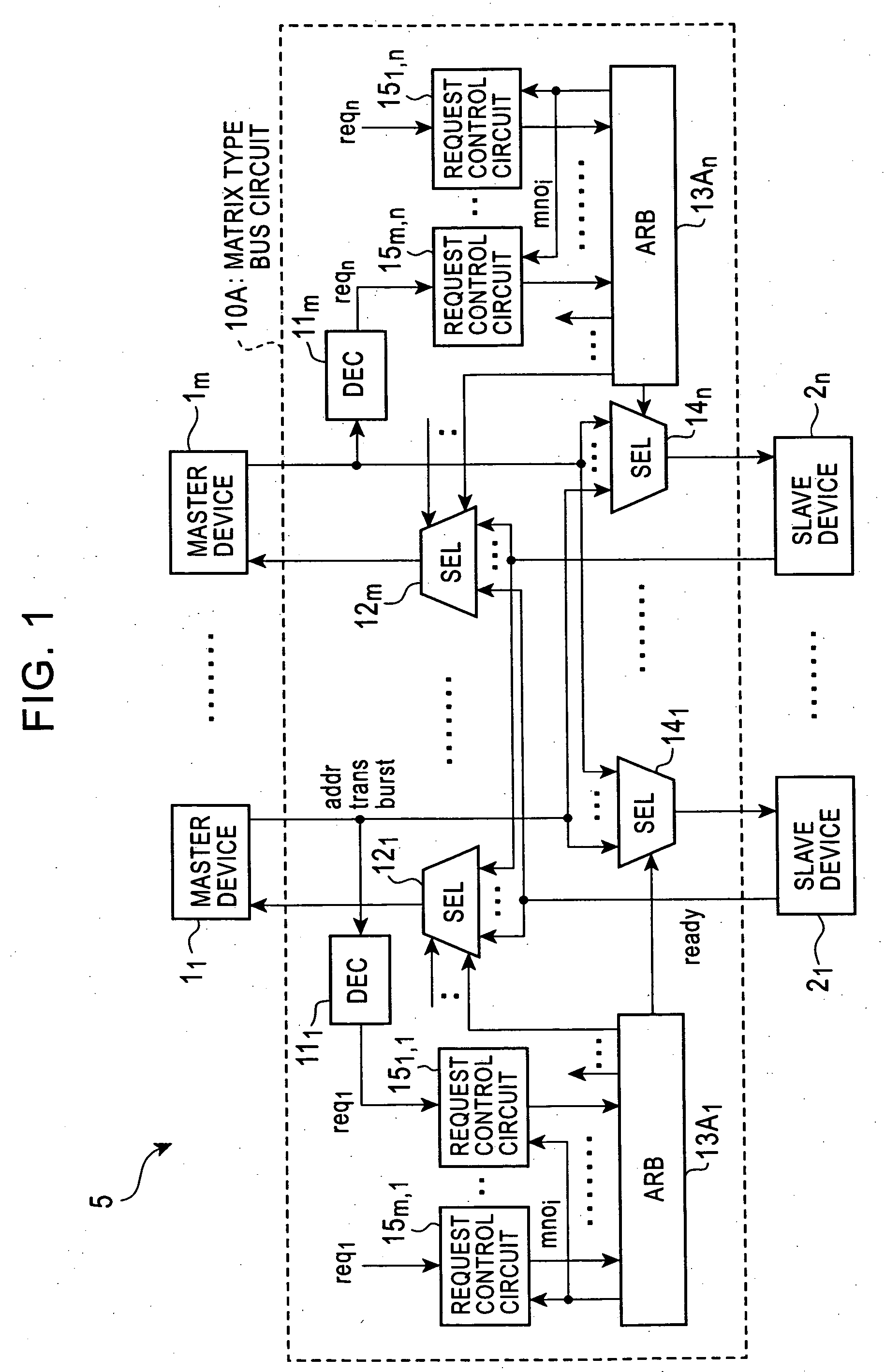
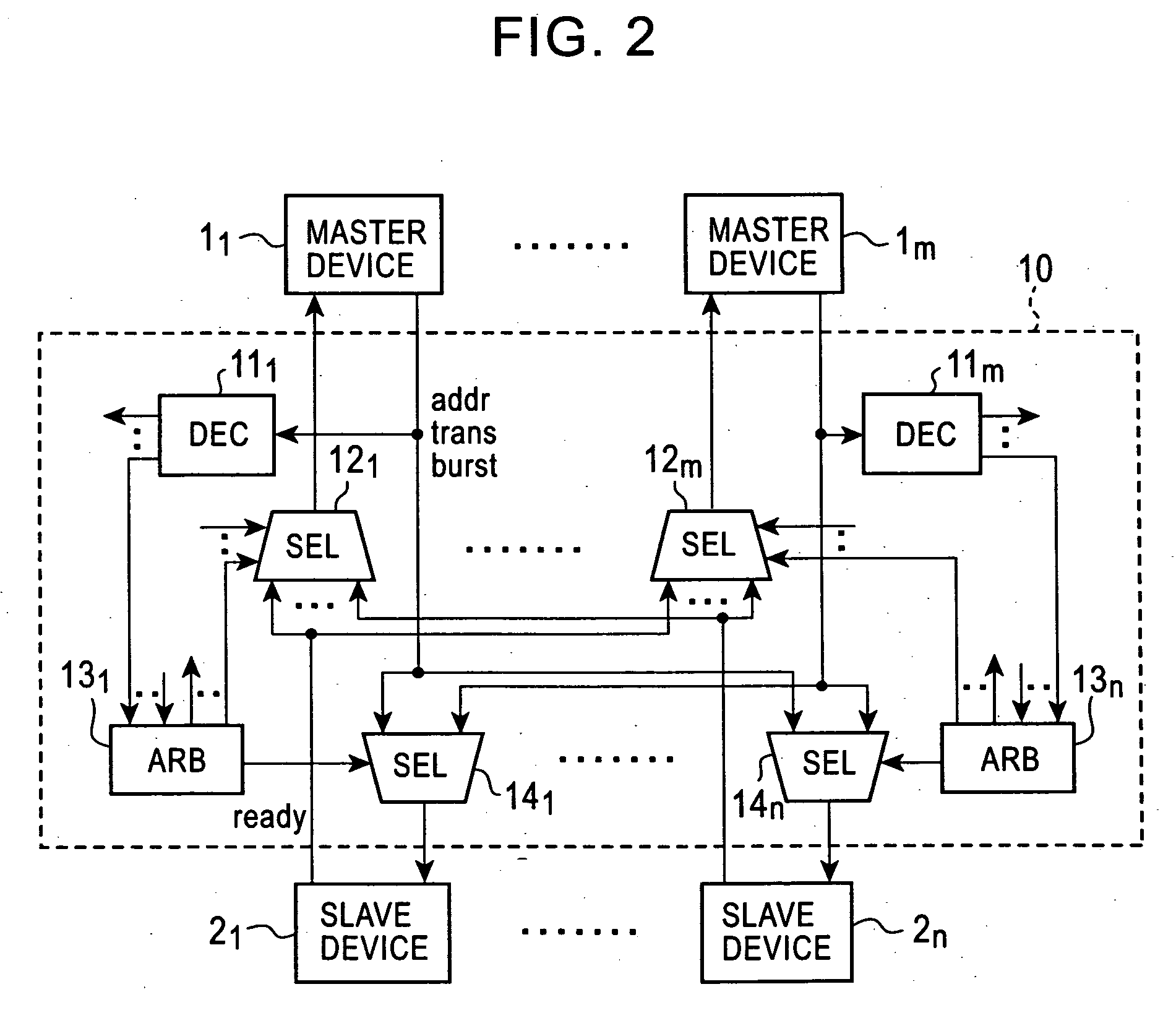
Matrix type bus connection system
InactiveUS20050228914A1Eliminate delaysUnnecessary timeData switching networksElectric digital data processingConnection controlComputer engineering
A matrix type bus connection system has a plurality of master devices and a plurality of slave devices. Each slave device has an arbitration circuit. The arbitration circuit stores an address of a master device that made the access the last time, and continues holding a select signal to a selector when access ends. If a new connection request is received, the arbitration circuit compares the address of the master device that is now making the access request with the address of the master device that made the access the last time. If the connection request is from the same master device, a connection control is not performed. The previous connection status is maintained. Thus, the master device can be connected to the slave device without a delay.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
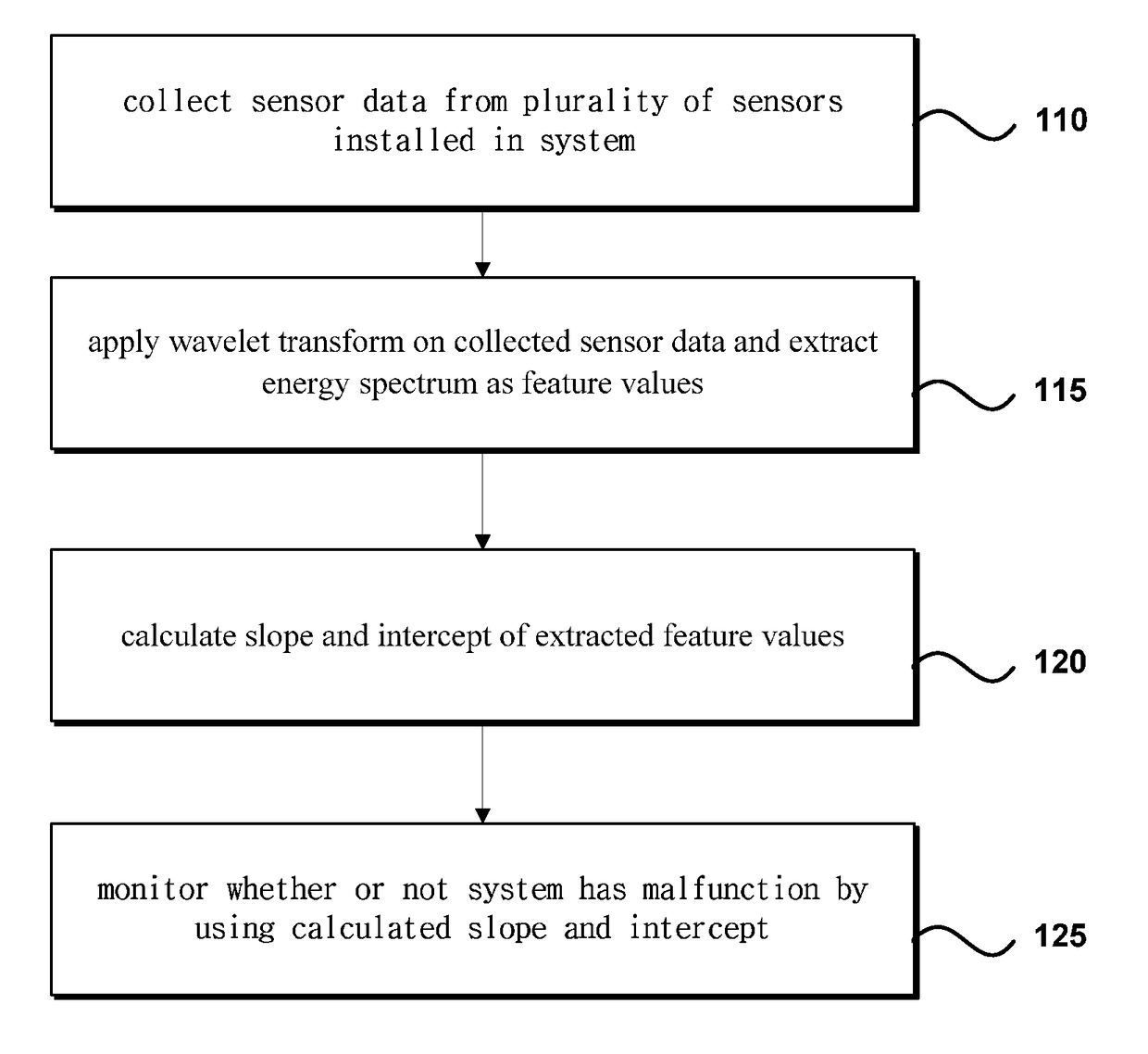
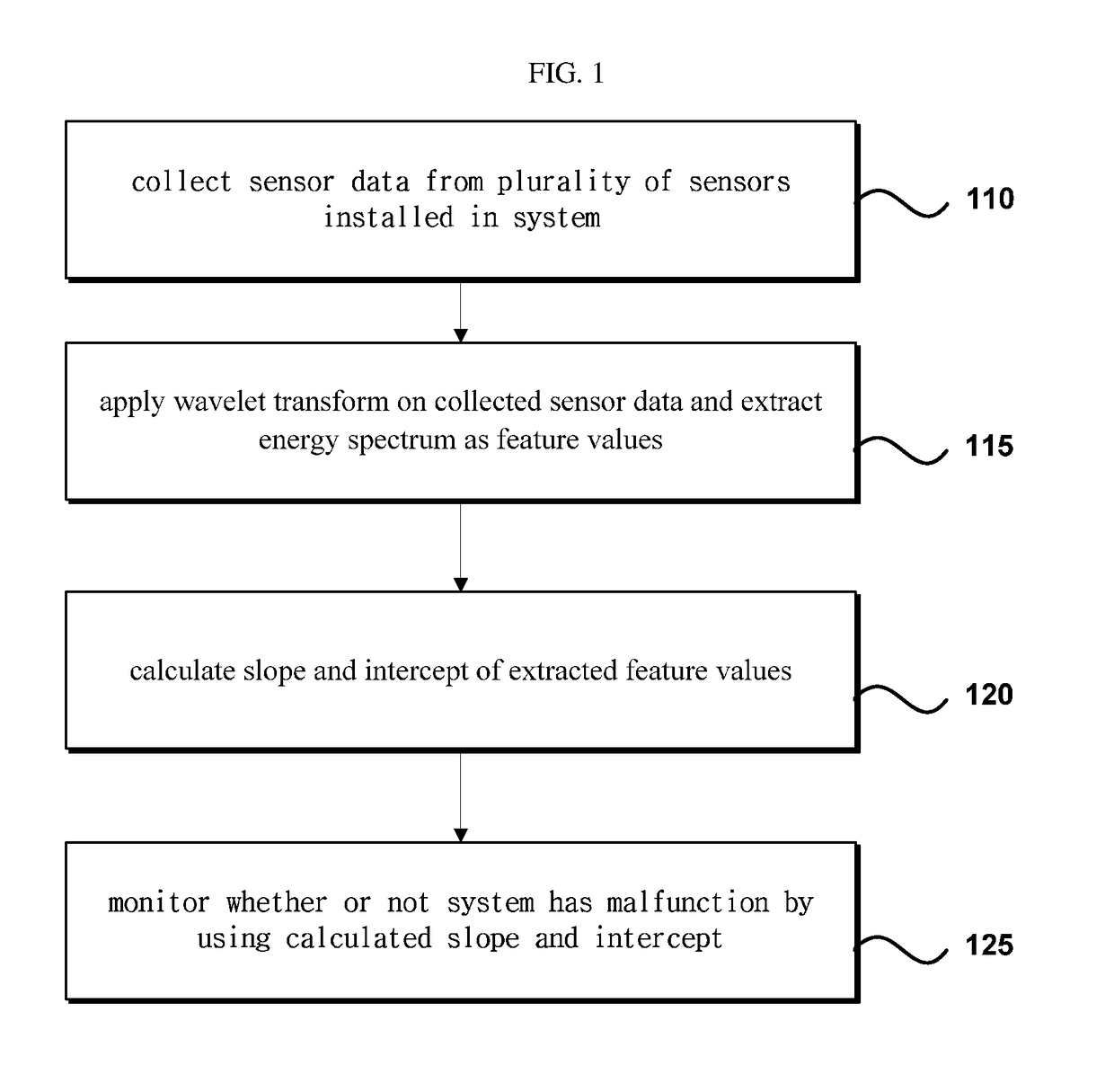
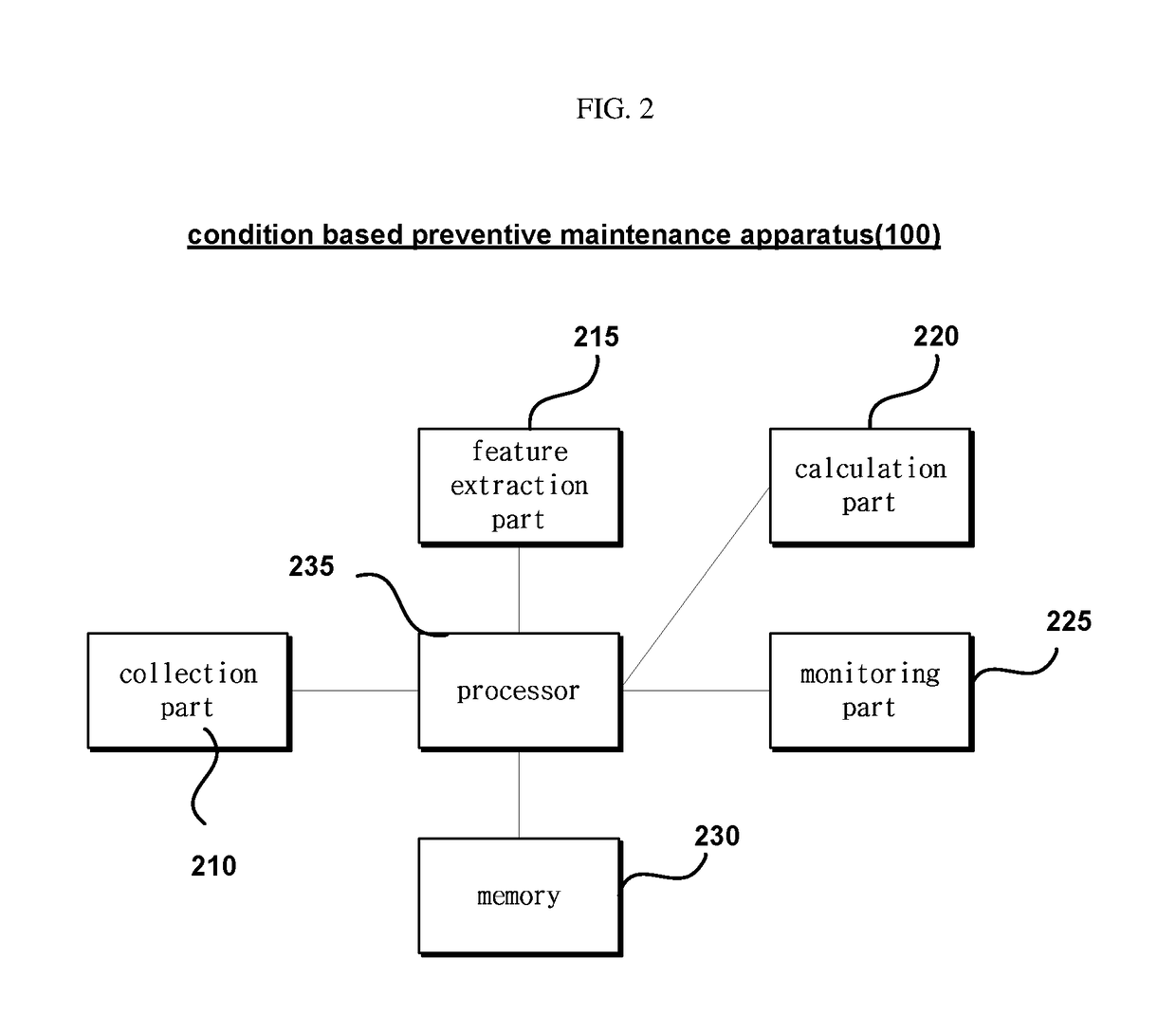
Condition based preventive maintenance apparatus and method for large operation system
ActiveUS20180130032A1Detection malfunctionUnnecessary costTesting/monitoring control systemsProbabilistic networksFeature extractionOperational system
Disclosed are a condition based preventive maintenance apparatus and method for a large operation system. The condition based preventive maintenance apparatus for a large operation system comprises: a collection part for collecting sensor data from a plurality of sensors installed in a system; a feature extraction part for wavelet-transforming the collected sensor data and extracting an energy spectrum as a feature value; a calculation part for calculating a slope and an intercept of the extracted feature value; and a monitoring part for monitoring whether the system is broken or not using the calculated slope and intercept.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
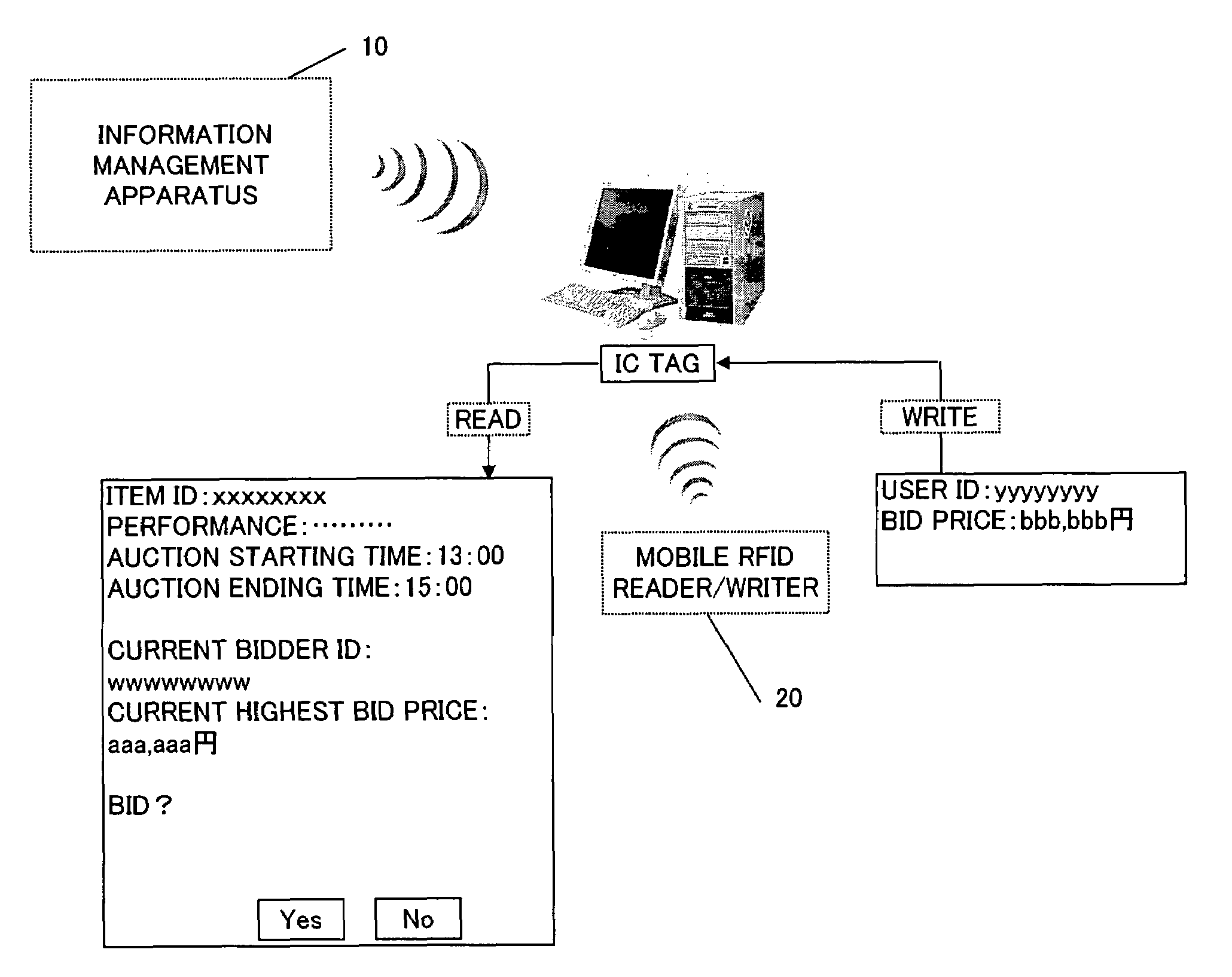
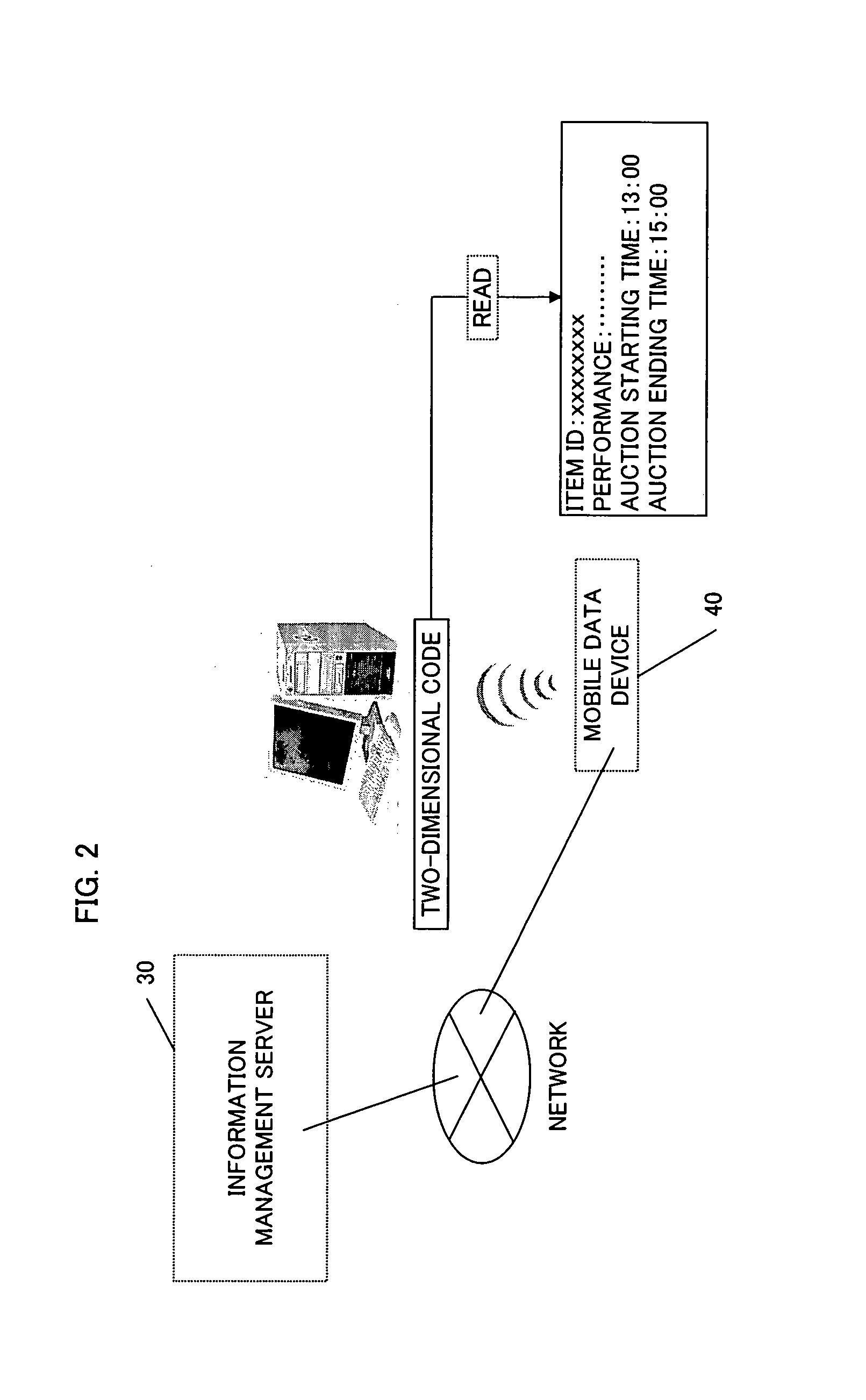
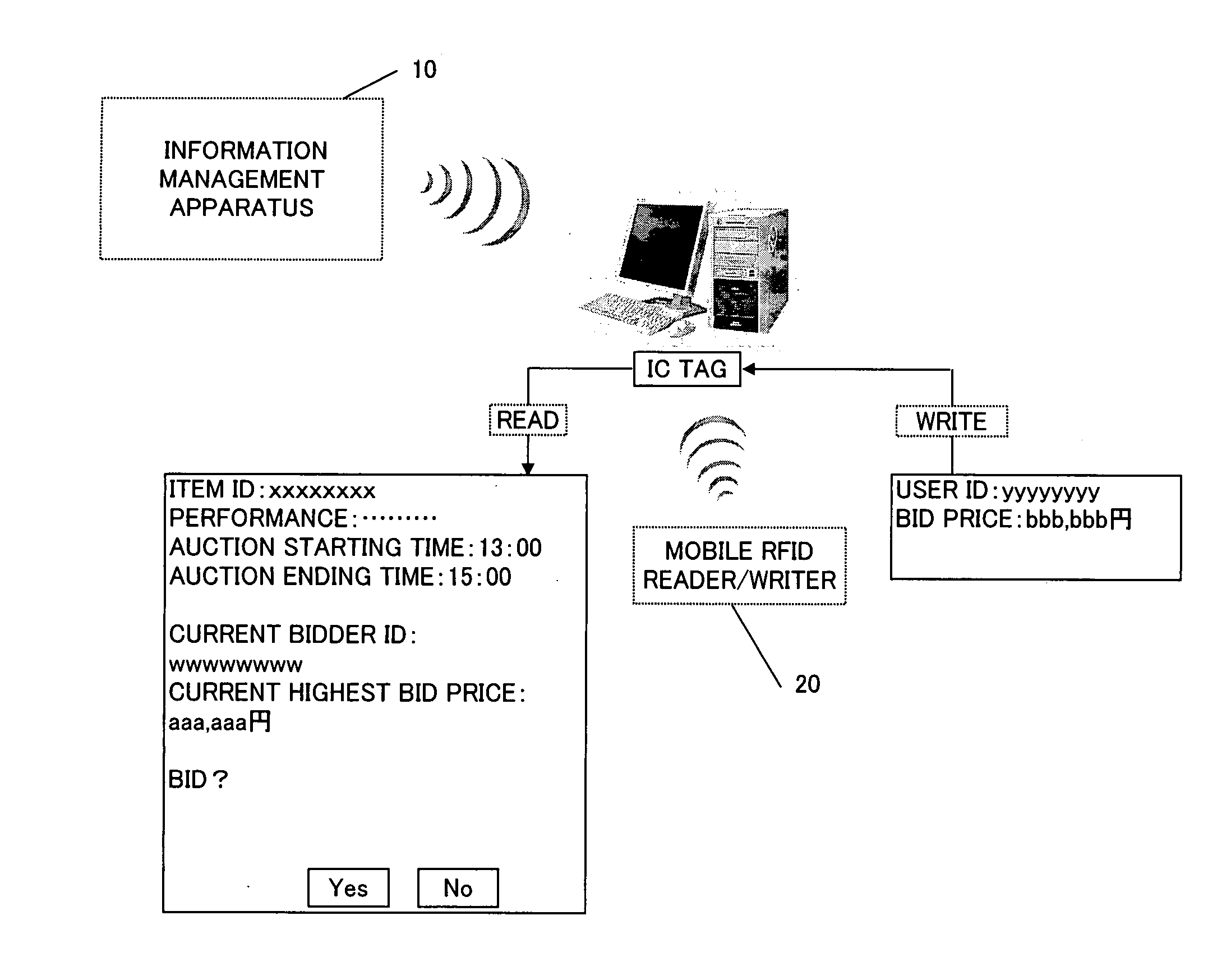
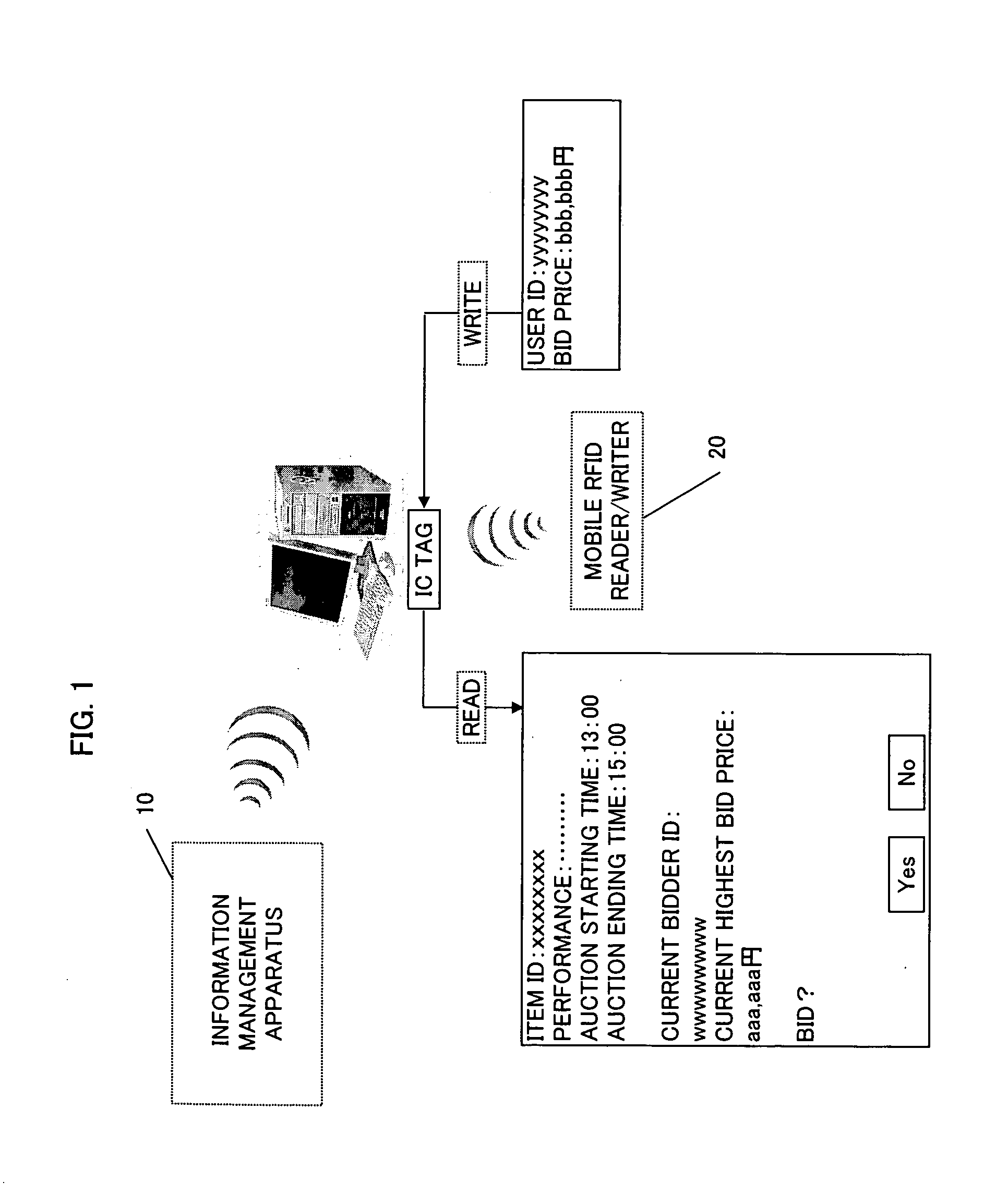
Auction system
InactiveUS7711608B2Unnecessary effortUnnecessary timeBuying/selling/leasing transactionsMobile deviceComputer science
An auction system for use in auctions is provided. In the auction system, a recording medium is attached to an auction item. An auction participant reads information about the auction item out of the recording medium using a mobile data device. In order to place a bid on the auction item, the auction participant writes a bid price to the recording medium using the mobile data device.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
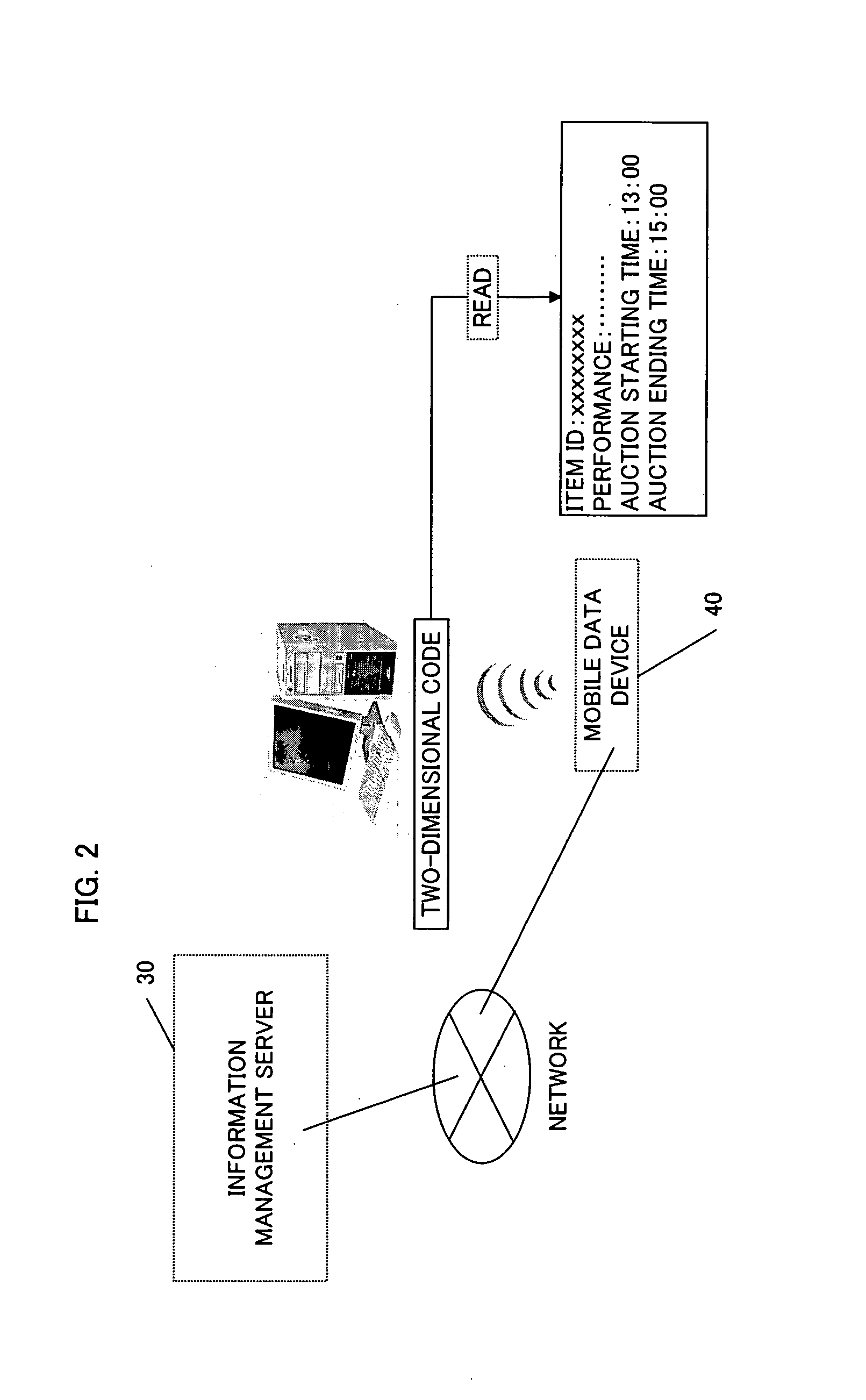
Auction system
InactiveUS20070168258A1Without spending unnecessary timeWithout effortBuying/selling/leasing transactionsMobile deviceComputer science
An auction system for use in auctions is provided. In the auction system, a recording medium is attached to an auction item. An auction participant reads information about the auction item out of the recording medium using a mobile data device. In order to place a bid on the auction item, the auction participant writes a bid price to the recording medium using the mobile data device.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Substrate processing apparatus
ActiveUS8375884B2Improve productivityUnnecessary timeLiquid surface applicatorsDigital data processing detailsElectrical and Electronics engineeringEngineering
A substrate processing apparatus including: a heating part for heating a wafer; a transport part through which a wafer is transported; a first transfer arm that receives a wafer from the heating part and places the wafer on the transport part; and a second transfer arm including a pair of plate-like tweezers that receives the wafer placed on the transport part from the transport part and transfers the wafer. The transport part includes a cooling plate having a cooling surface on which a wafer is placed. The cooling plate includes a temperature-adjusting channel through which a temperature-adjusting water is circulated for cooling the cooling plate to a temperature lower than a temperature of the heating process of the heating part. The cooling surface is provided with a recess that is similar in shape to and slightly larger than a planar shape of the pair of tweezers.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
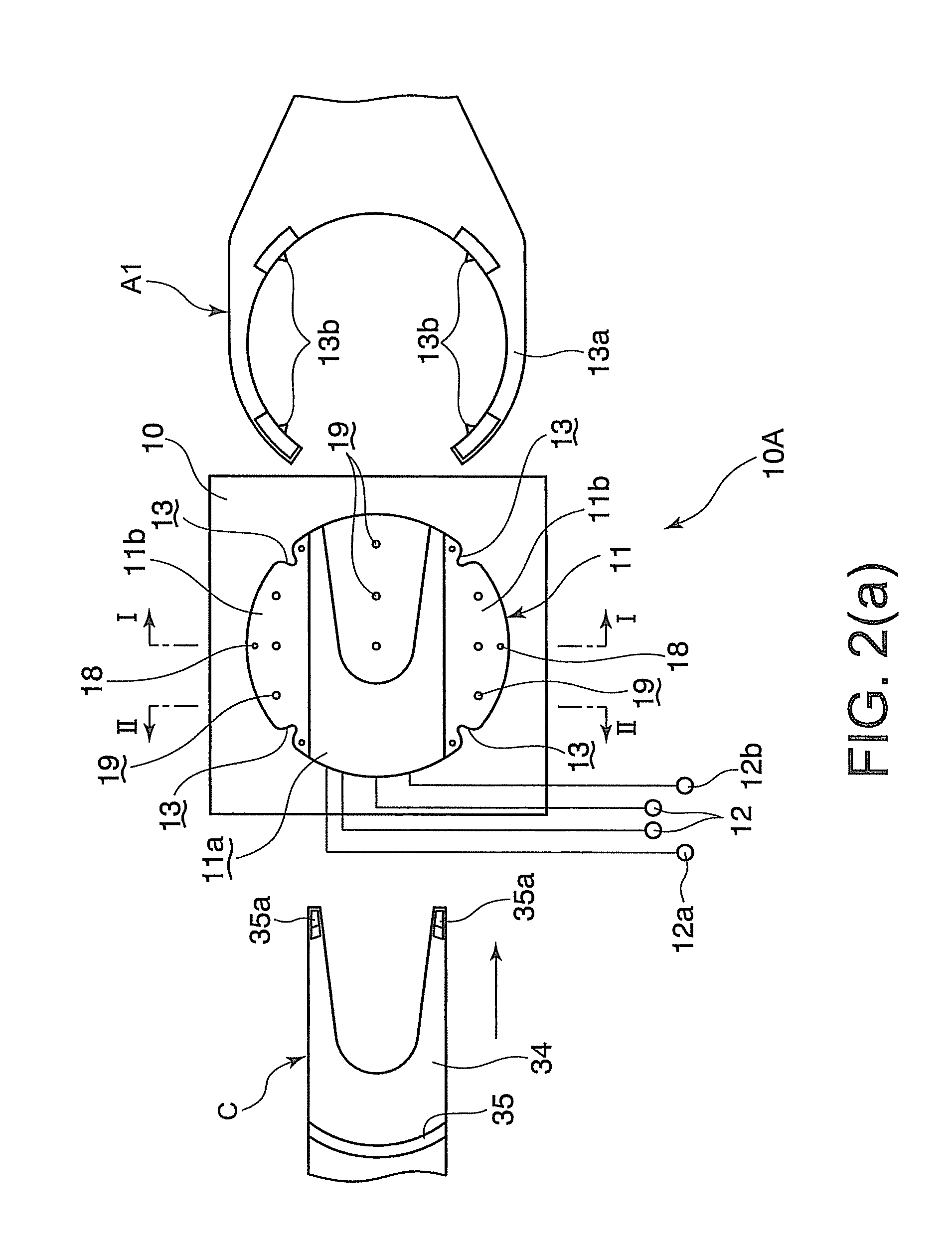
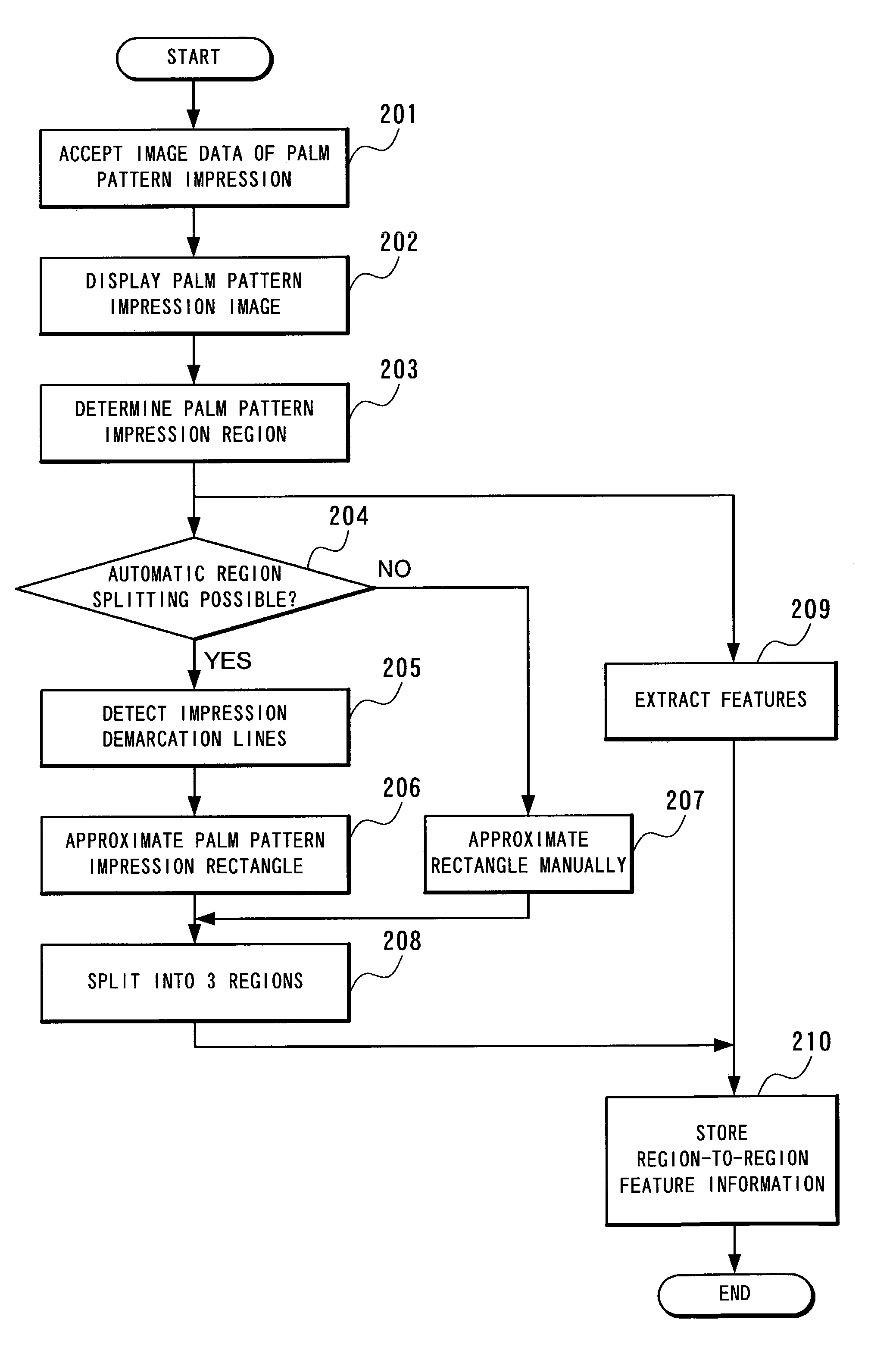
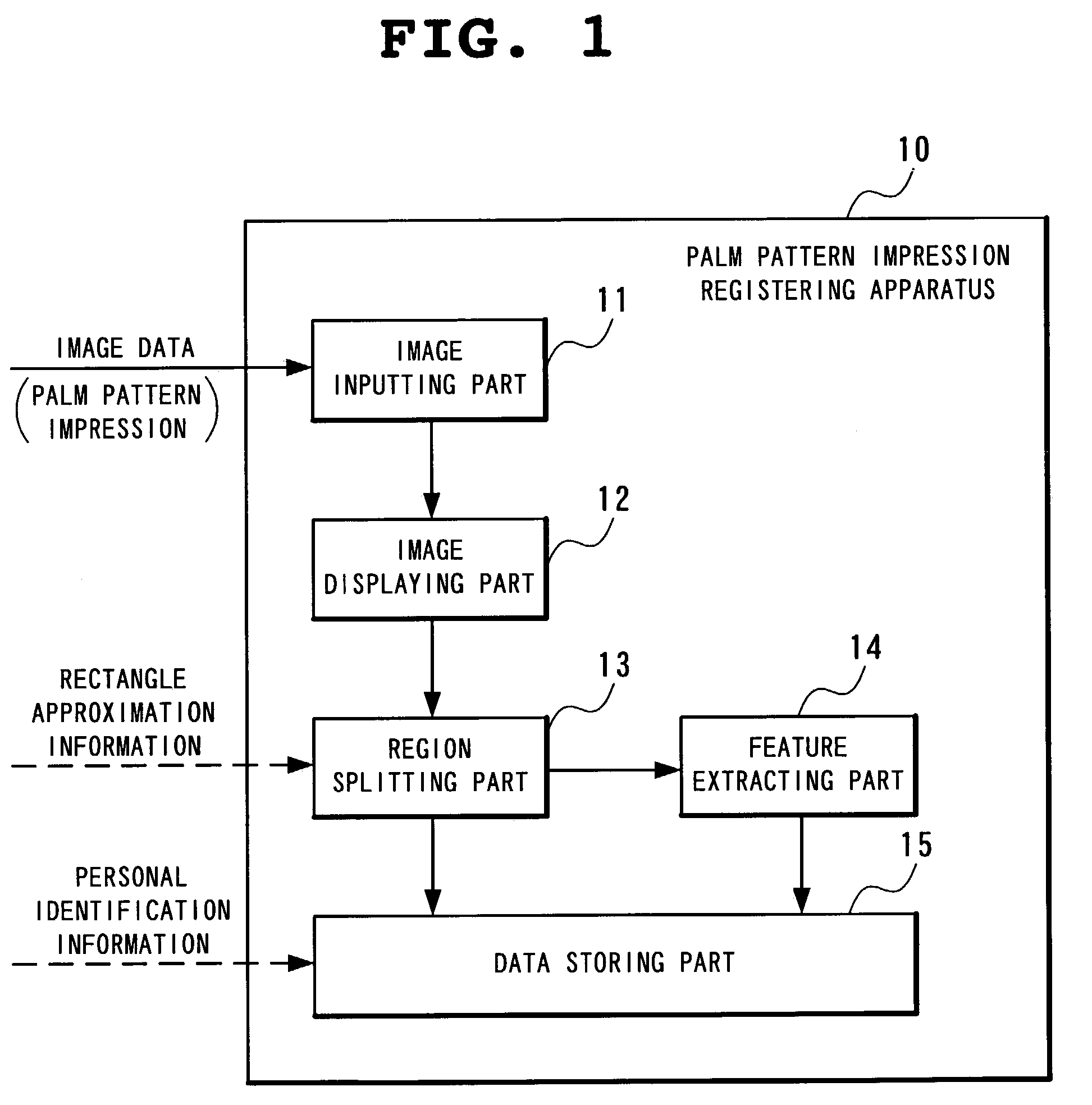
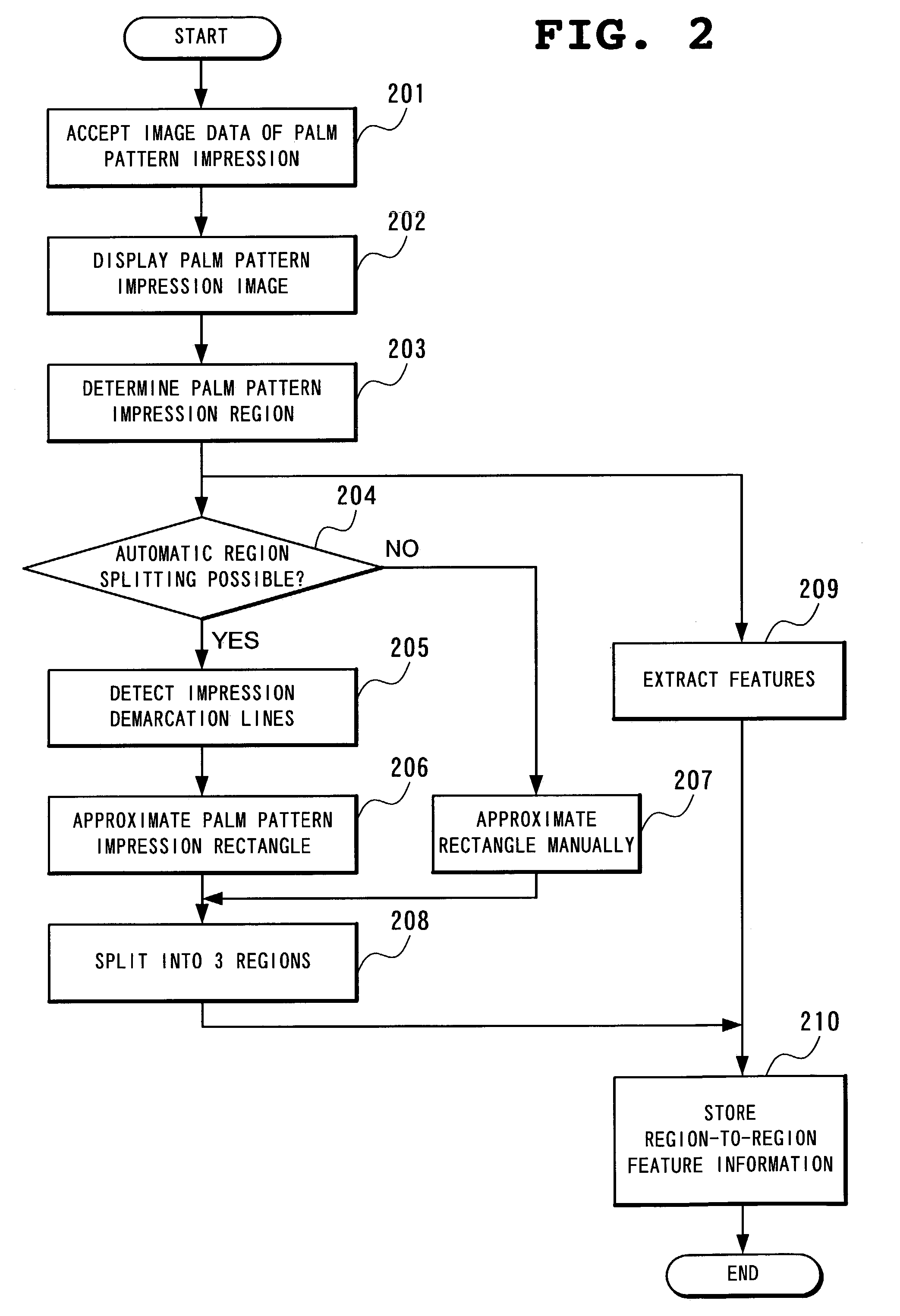
Method and apparatus for registering palm pattern impression
InactiveUS7215796B2Simple processReduce time required for collationElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisLittle fingerEngineering
A method detecting a rectangle enclosed by a pair of parallel horizontal lines that are demarcation lines between the palm pattern impression and the background in wrist-side and fingertip-side, and a pair of parallel vertical lines are orthogonal to the horizontal lines and are demarcation lines between the palm pattern impression and the background in thumb-side and little-finger-side. The method splits the rectangle into, three segments horizontally by four segments vertically, and then splits the palm pattern impression into three regions, the first being a combination of three segments horizontally by two segments vertically located toward the fingertip among the segments, the second being a combination of two segments horizontally by three segments vertically located toward the thumb and the wrist among the segments, and the third region being a combination of two segments horizontally by three segments vertically located toward the little finger and the wrist among the segments.
Owner:NEC CORP
Substrate processing apparatus
ActiveUS20100199911A1Improve throughputIncrease temperatureLiquid surface applicatorsDigital data processing detailsElectrical and Electronics engineering
A substrate processing apparatus including: a heating part for heating a wafer; a transport part through which a wafer is transported; a first transfer arm that receives a wafer from the heating part and places the wafer on the transport part; and a second transfer arm including a pair of plate-like tweezers that receives the wafer placed on the transport part from the transport part and transfers the wafer. The transport part includes a cooling plate having a cooling surface on which a wafer is placed. The cooling plate includes a temperature-adjusting channel through which a temperature-adjusting water is circulated for cooling the cooling plate to a temperature lower than a temperature of the heating process of the heating part. The cooling surface is provided with a recess that is similar in shape to and slightly larger than a planar shape of the pair of tweezers.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
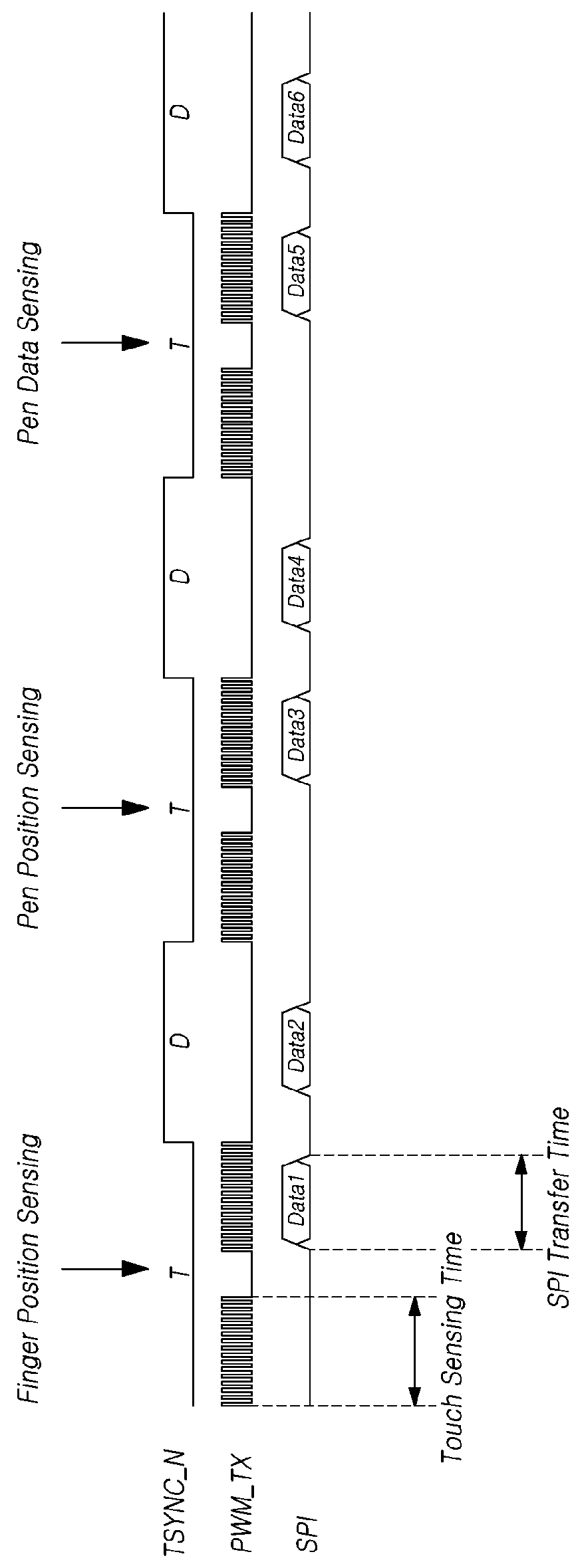
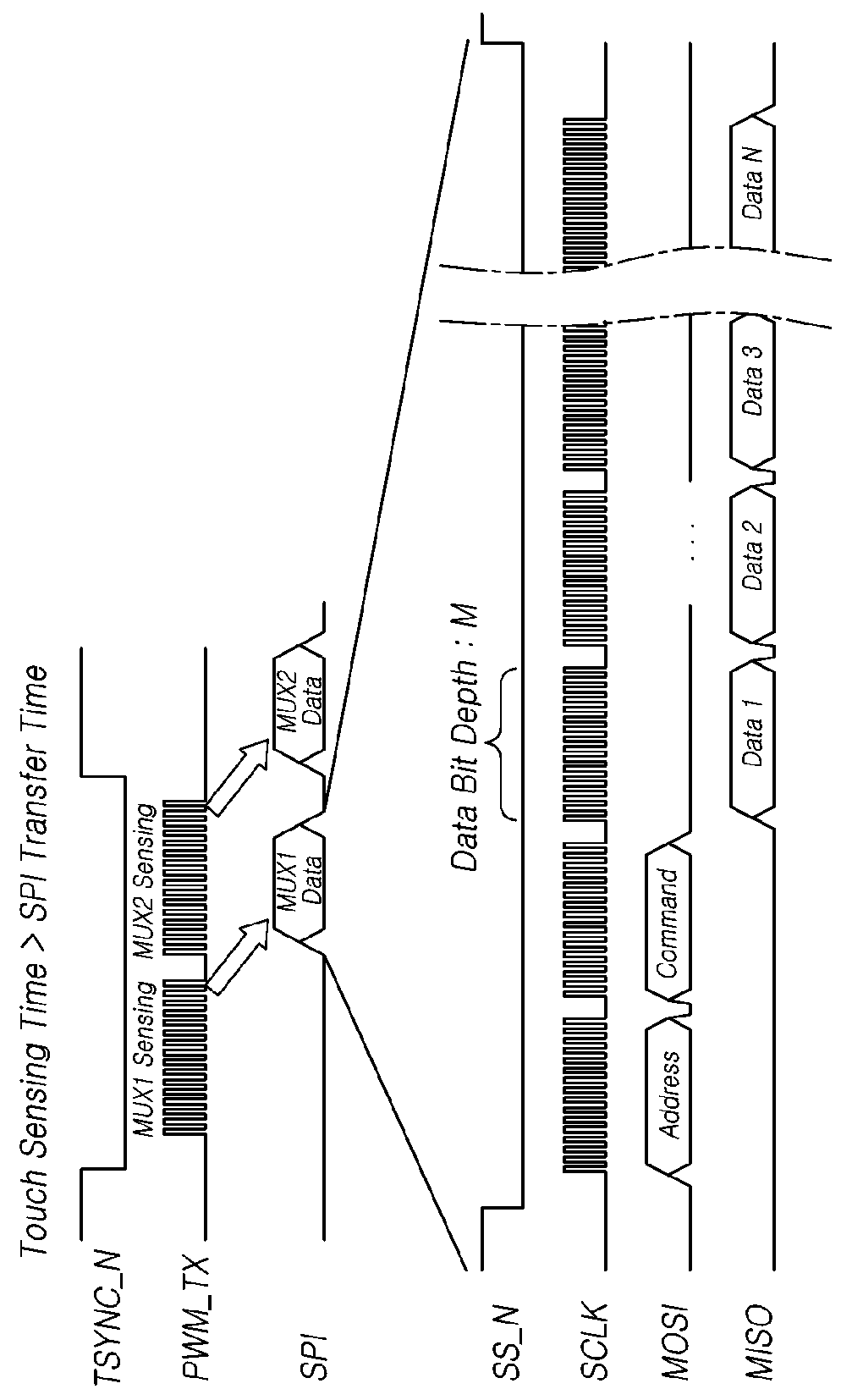
Touch display device, and touch driving circuit and method of driving same
ActiveUS20180107292A1Unnecessary timeImprove sensing data transmission efficiencyInput/output processes for data processingSensing dataActive pen
The present disclosure provides a touch display device and a touch driving circuit which support touch sensing of an active pen, and a method of driving the same. Sensing data acquired during a first sensing time period in a pen position sensing section may be transmitted as one data packet, and a plurality of pieces of sensing data acquired during a second sensing time period shorter than the first sensing time period in a pen data sensing section may be transmitted as one data packet, so that it is possible to reduce an unnecessary sensing time period when pen data is sensed, while preventing sensing data transmission sections from overlapping each other. In addition, information about a Most Significant Bit (MSB) of the sensing data to be transmitted when the sensing data is transmitted may be transmitted in the pen data sensing section, so that it is possible to easily restore the sensing data while minimizing a loss of the sensing data.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
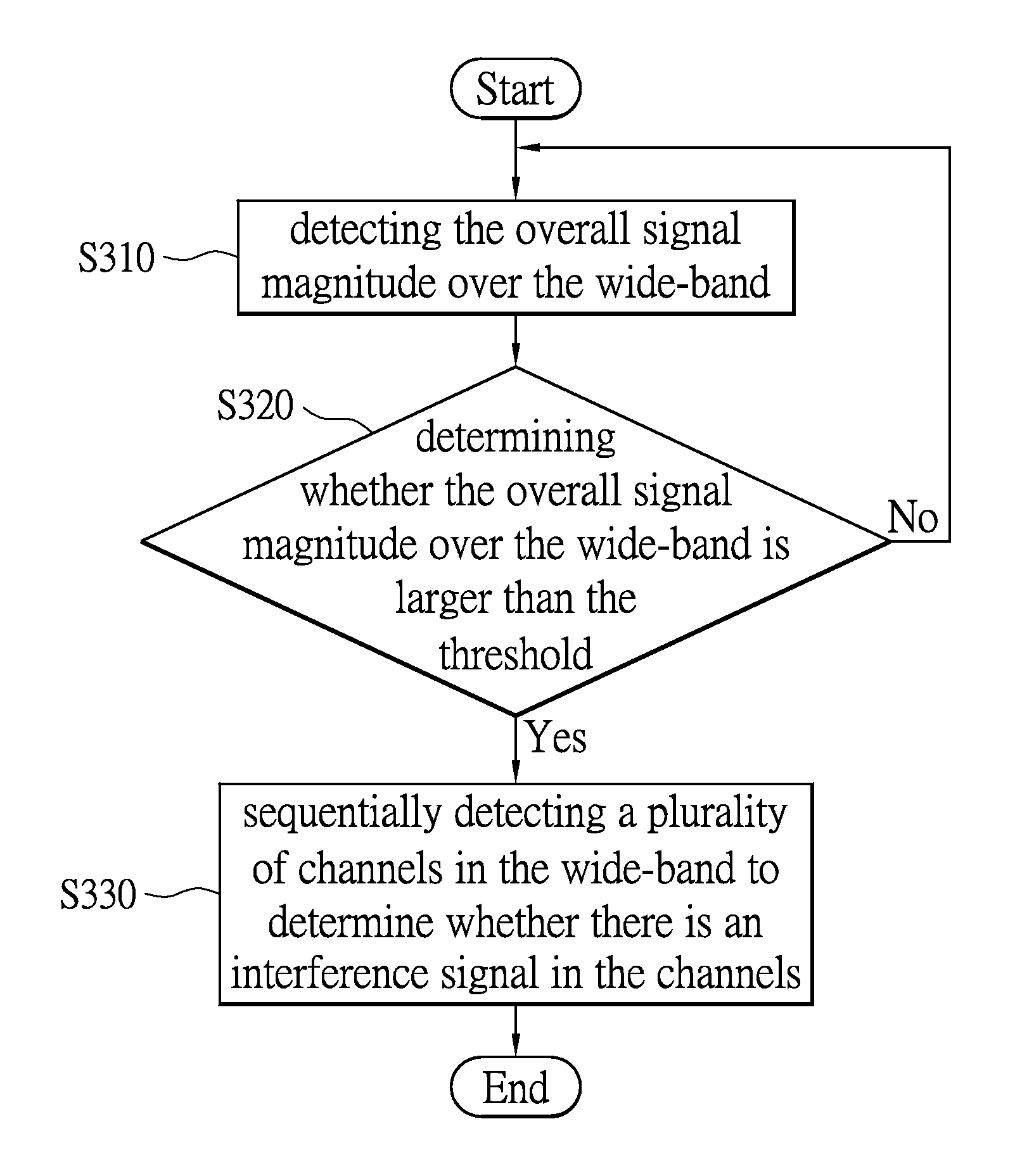
Wireless interference scanning method and device for adaptive frequency hopping
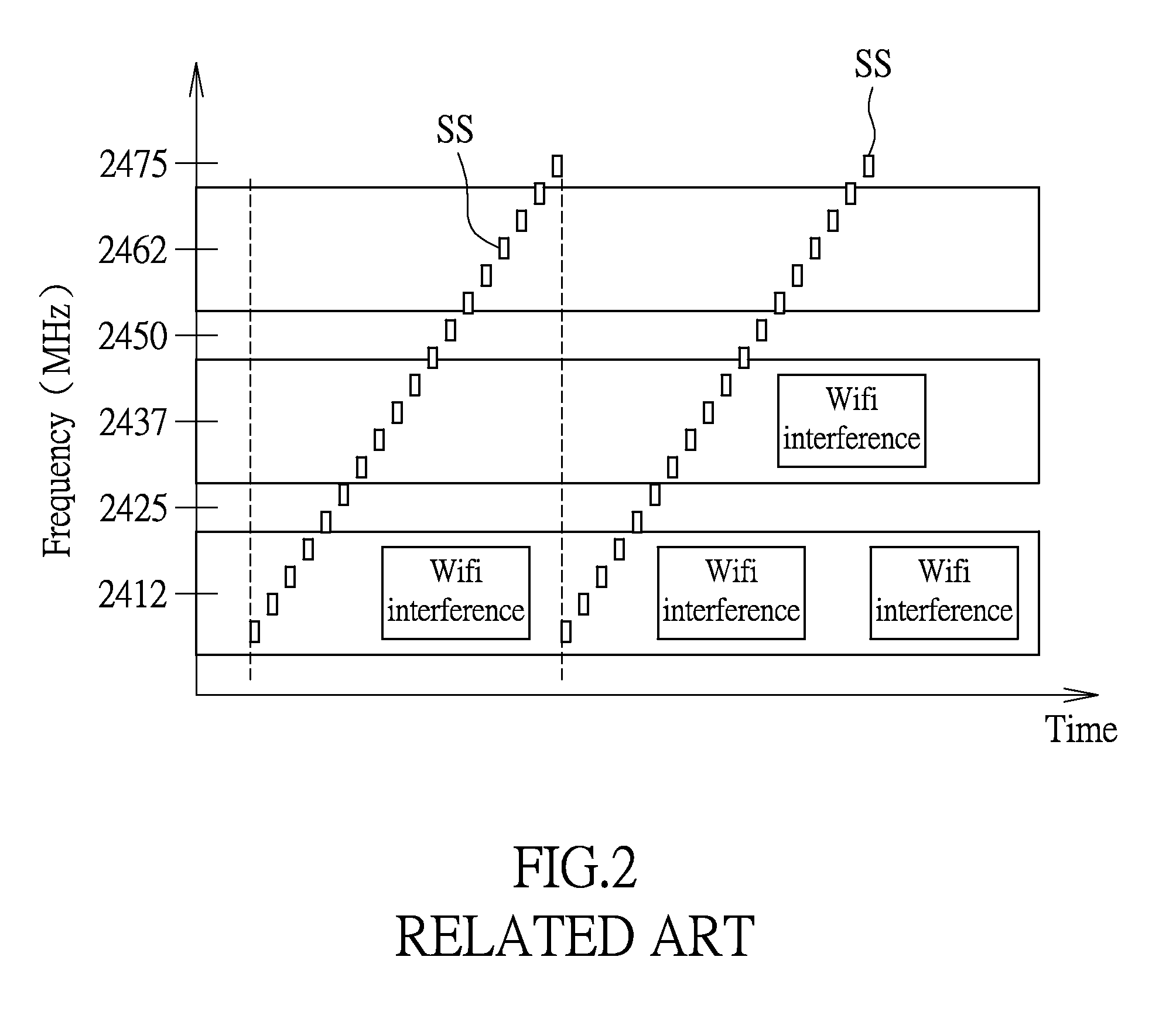
InactiveUS20150303990A1Reduce unnecessary scanning timeReduce power consumptionTransmission monitoringEngineeringWide band
The present disclosure provides a wireless interference scanning method and device for adaptive frequency hopping. The wireless interference scanning method comprise detecting the overall signal magnitude over a wide-band; determining whether the overall signal magnitude over the wide-band is larger than a threshold; sequentially detecting a plurality of channels in the wide-band to determine whether there is an interference signal in the channels when the overall signal magnitude over the wide-band is larger than the threshold; and redetecting the overall signal magnitude over the wide-band for determining whether the overall signal magnitude over the wide-band is larger than the threshold when the overall signal magnitude over the wide-band is not larger than the threshold.
Owner:INTEGRATED SYST SOLUTION
Optical disk recording apparatus and program
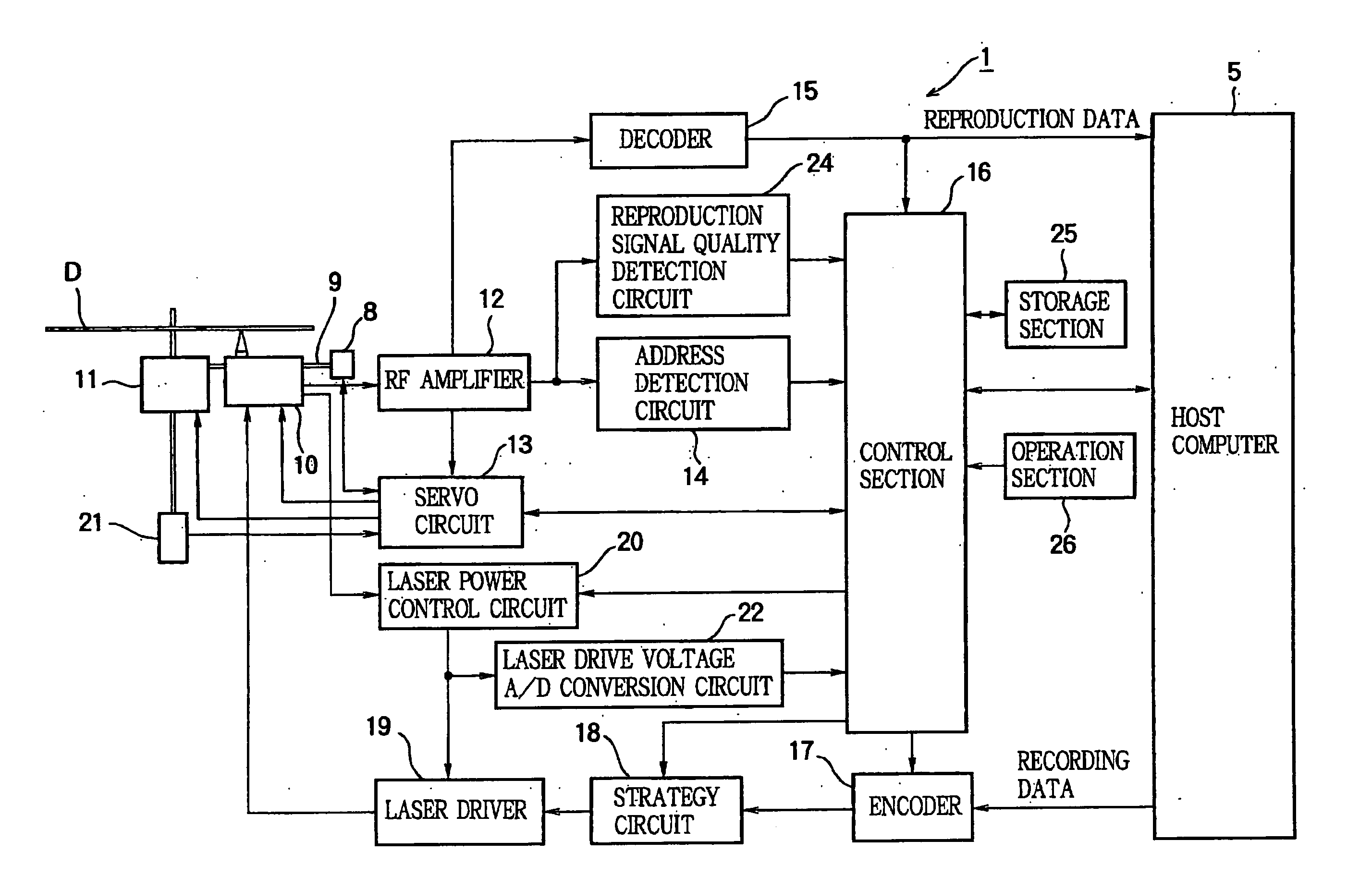
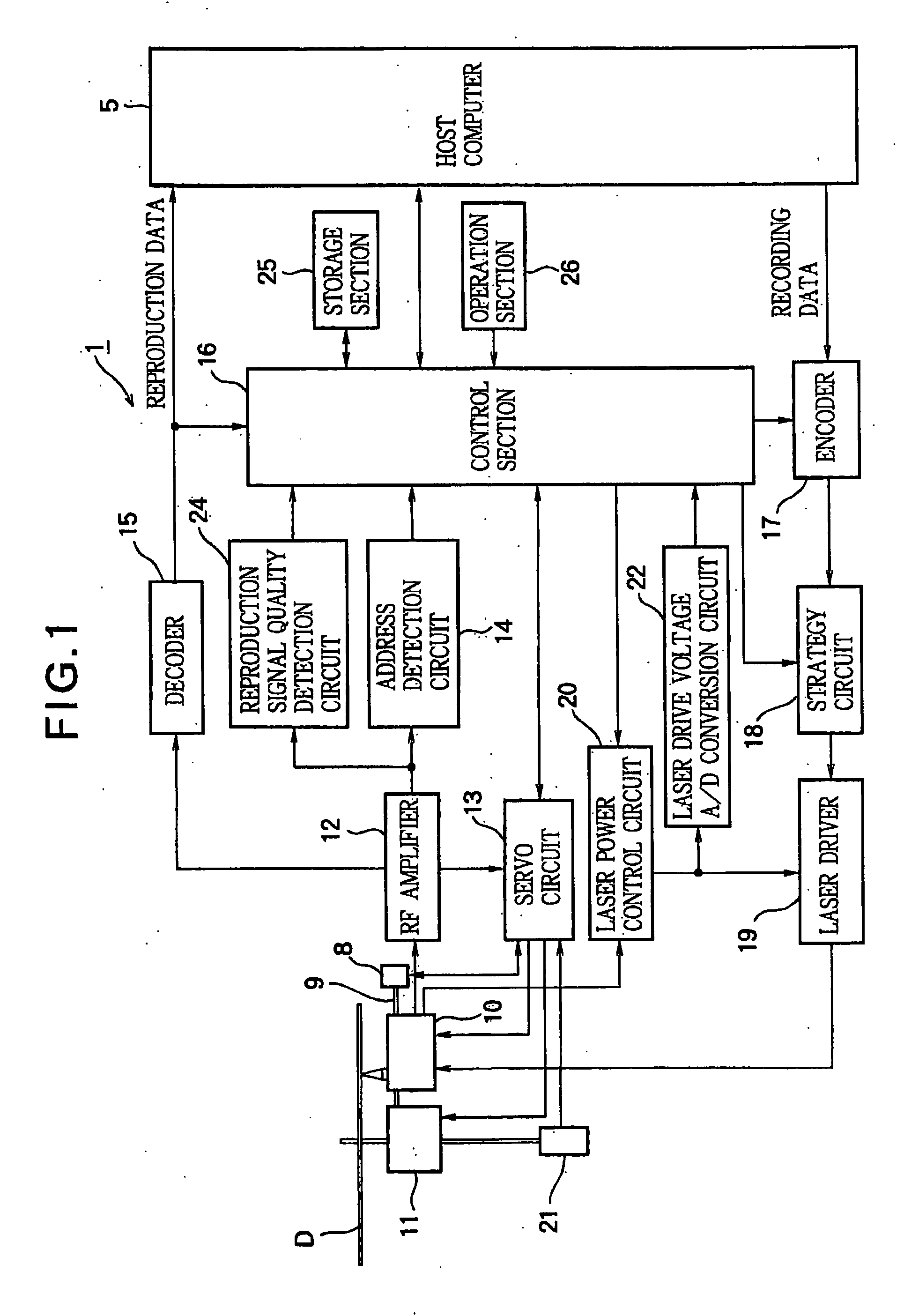
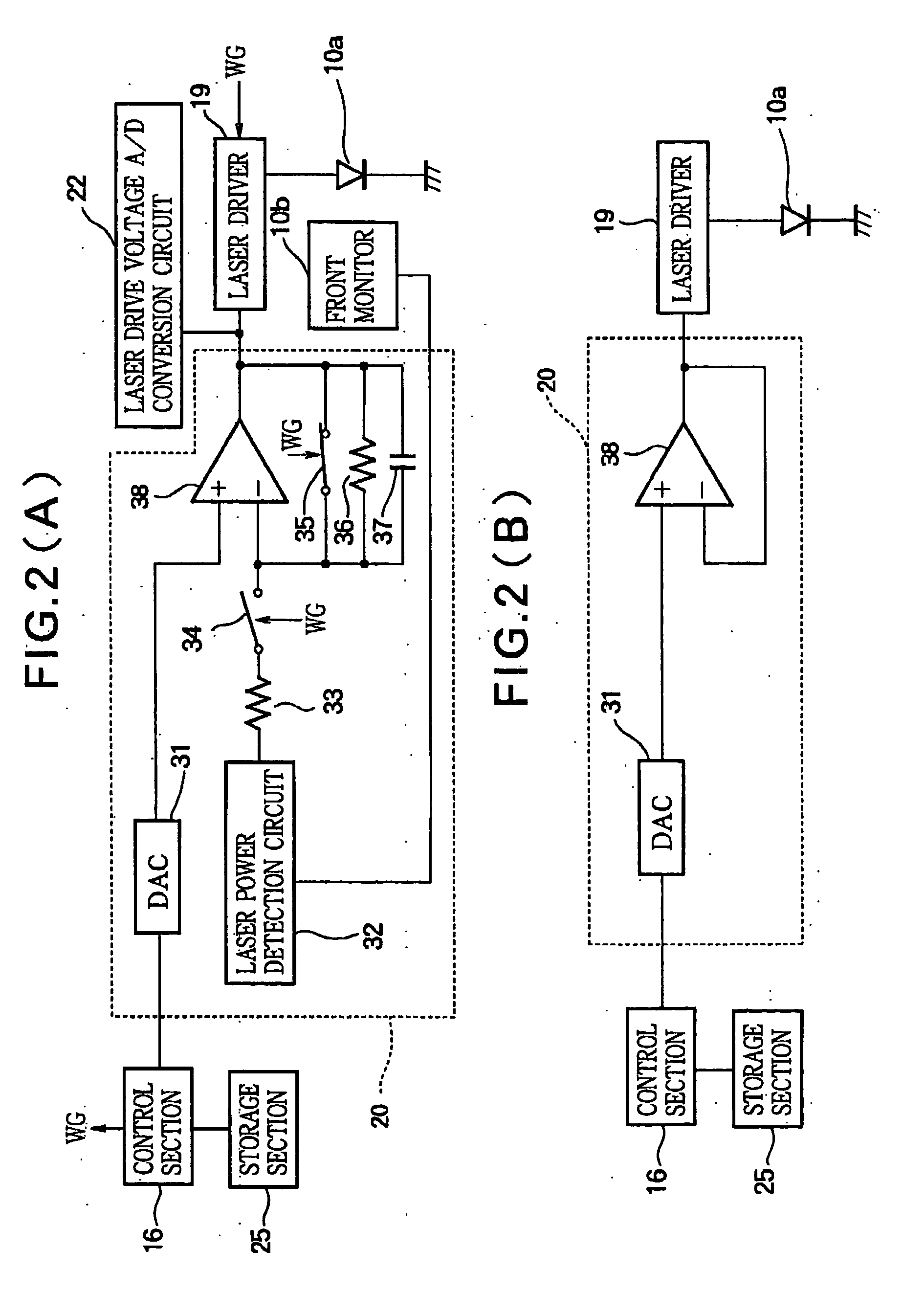
InactiveUS20050213450A1Accurate valueUnnecessary timeCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsLaser lightMaster controller
In an optical disk recording apparatus, a monitor monitors a recording power of a laser light. A laser control circuit enables a laser diode to perform test recording while using the monitor to monitor the recording power of the laser light and while controlling a laser drive voltage, so that the monitored recording power reaches a given reference value during the test recording. A voltage measurement section measures the laser drive voltage when the recording power of the laser light reaches the reference value. A calculation section calculates an initial laser drive voltage from the reference value of the recording power and the measured laser drive voltage corresponding to the reference value. A main controller allows the laser control circuit to set the calculated initial laser drive voltage and to start the recording while supplying the laser control circuit with the target value so that an actual recording power of the laser light promptly reaches the target value during the course of the recording.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Device and method for controlling switchover of broadcasting channel in digital multimedia broadcasting receiver
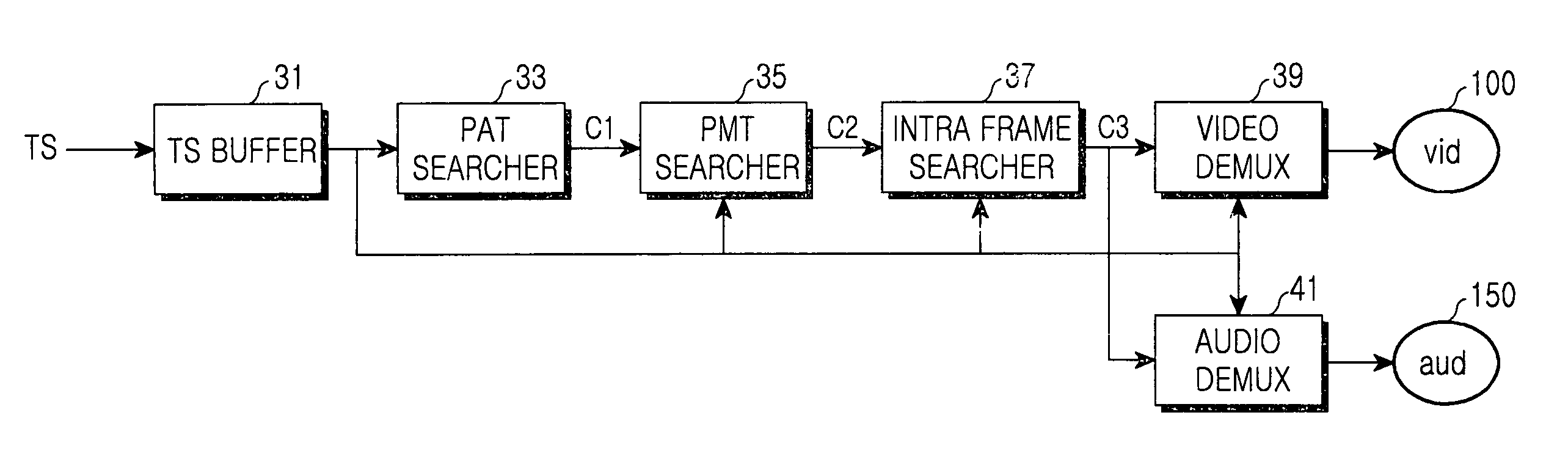
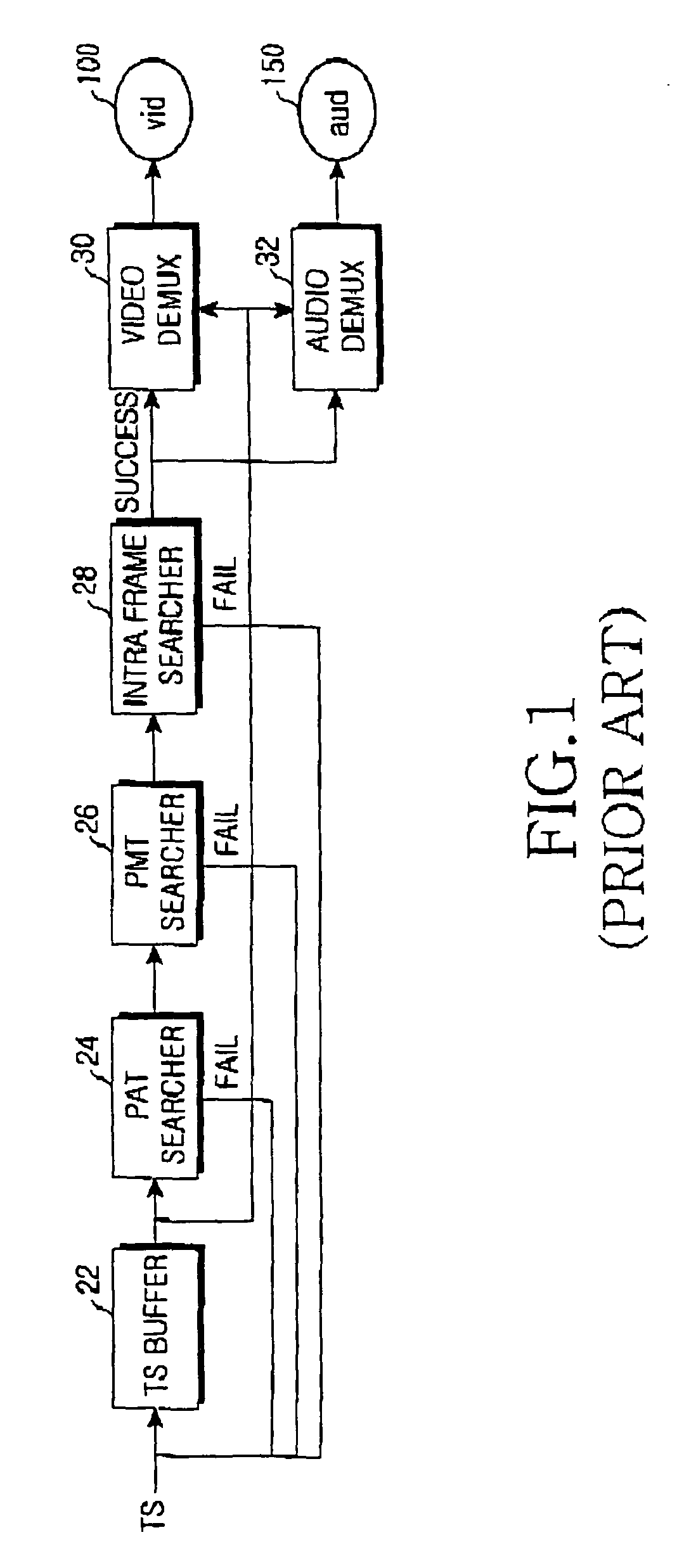
InactiveUS7933299B2Unnecessary timeMinimize timeTelevision system detailsTime-division multiplexBroadcast channelsVideo transmission
Provided is a device and method for controlling switchover of a broadcasting channel in a digital multimedia broadcasting receiver. The device includes a first demultiplexing unit for firstly buffering transport stream packets, searching the buffered transport stream packets for a PAT (program association table), a PMT (program map table), and an intra frame, and obtaining program information on the broadcasting channel to be switched over; and a second demultiplexing unit for secondly buffering the transport stream packets and, on the basis of the obtained program information, searching the secondly buffered transport stream packets for an audio or video transport stream packet of the corresponding broadcasting channel, and performing audio or video demultiplexing for the searched audio or video transport stream packet.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of driving organic electroluminescence emission portion
ActiveUS20120249517A1Short timeUnnecessary timeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringOrganic electroluminescence
A pixel circuit and driving method are disclosed, wherein the pixel circuit comprises a first transistor, a second transistor, and a capacitor. The first transistor is connected between a power source and a light emission portion, and the second transistor is connected to a data line. The capacitor is initialized according to a potential, and a video signal is applied from the data line to the capacitor through the second transistor. For driving, an initialization voltage is applied to the data line and the video signal is supplied to the data line, with the second transistor being turned ON prior to applying the initialization voltage to the data line.
Owner:JDI DESIGN & DEV GK
Mask inspection method, mask defect inspection system, and method of production of mask
InactiveUS7167582B2Accurate repairImprove throughputImage enhancementImage analysisMask inspectionDefect size
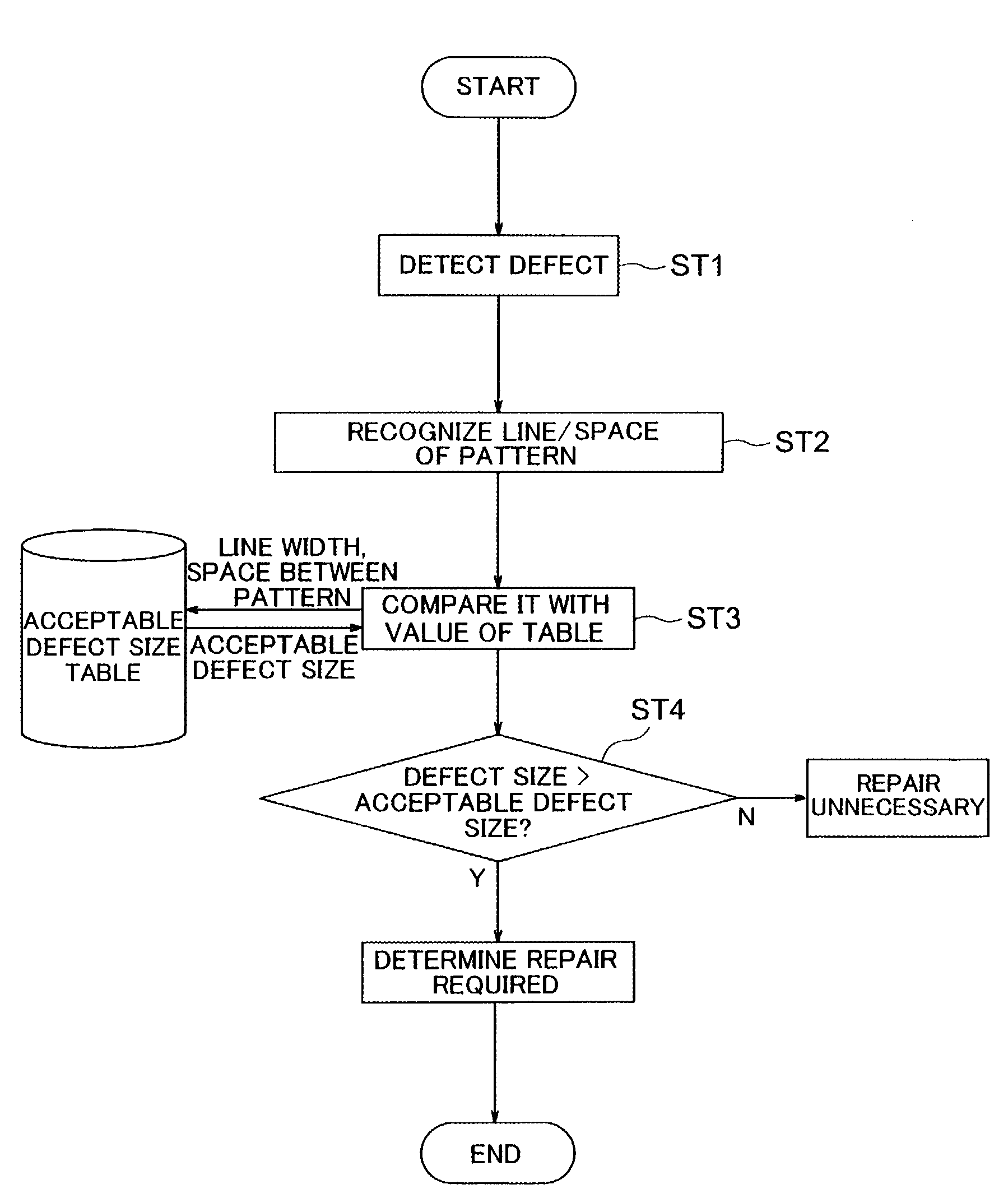
A method of inspection for detecting pattern defects in a mask used for transferring a predetermined pattern of regions passing and blocking an exposure beam, comprising the steps of presetting different acceptable defect sizes for a plurality of conditions different in the line and / or space of the pattern, detecting a defect and recognizing the line and space of the pattern at the defect part, selecting an acceptable defect size corresponding to the line and space of the pattern recognized at the defect part and comparing it with the size of the detected defect, and determining a defect larger than the acceptable defect size as a defect requiring repair; a mask defect inspection system for inspection according to the method, and a mask production method including a step of the inspection.
Owner:SONY CORP
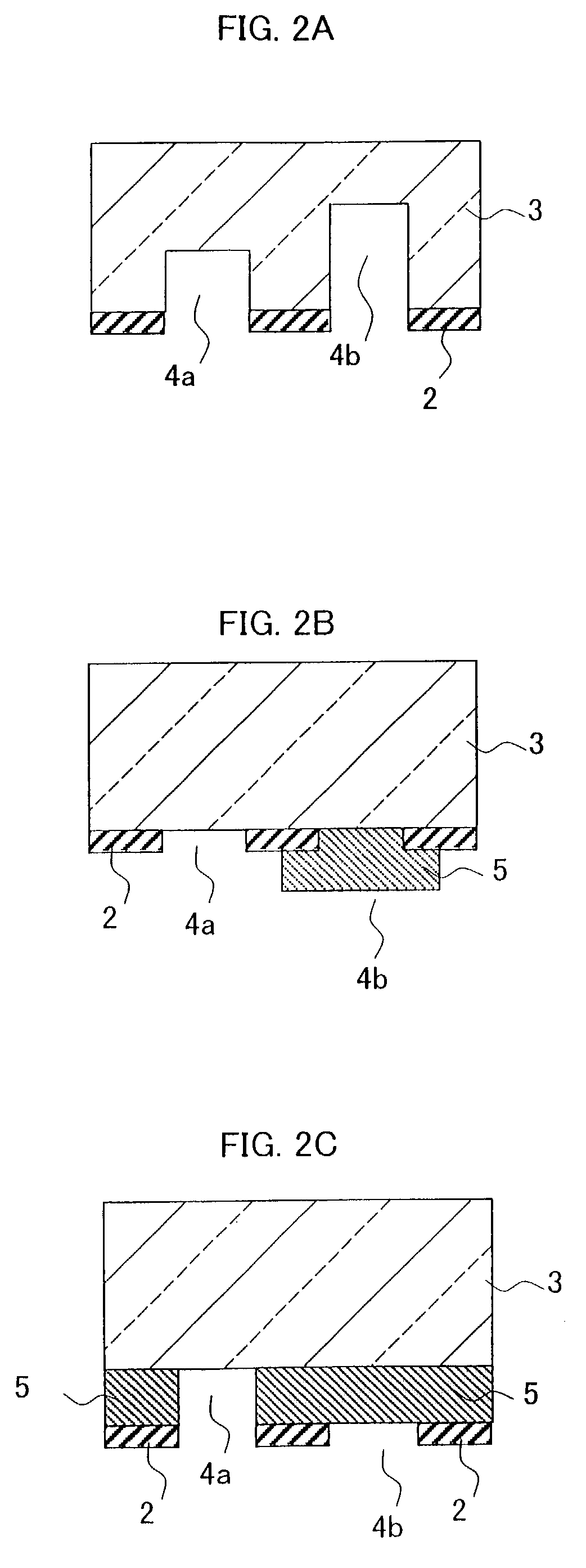
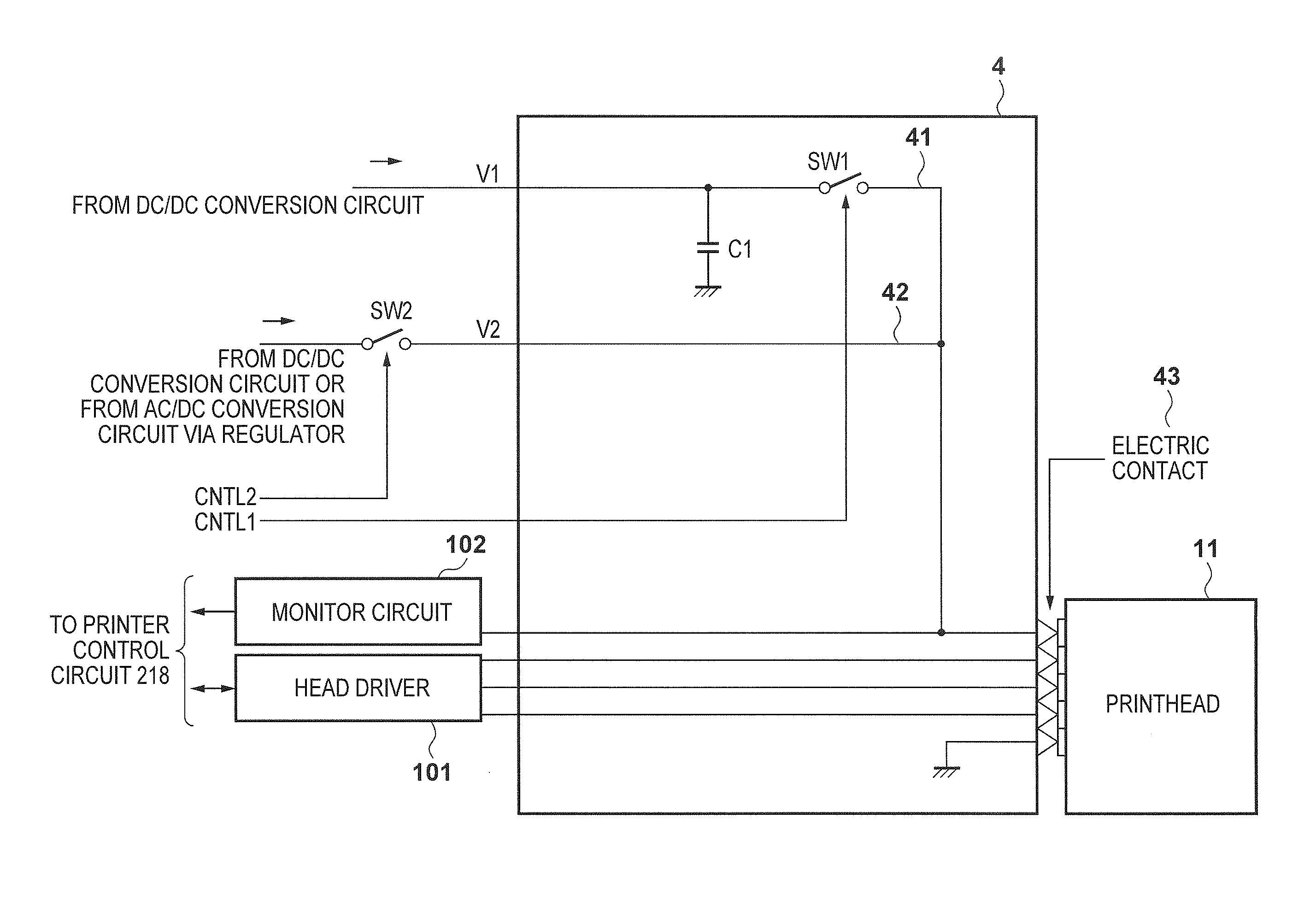
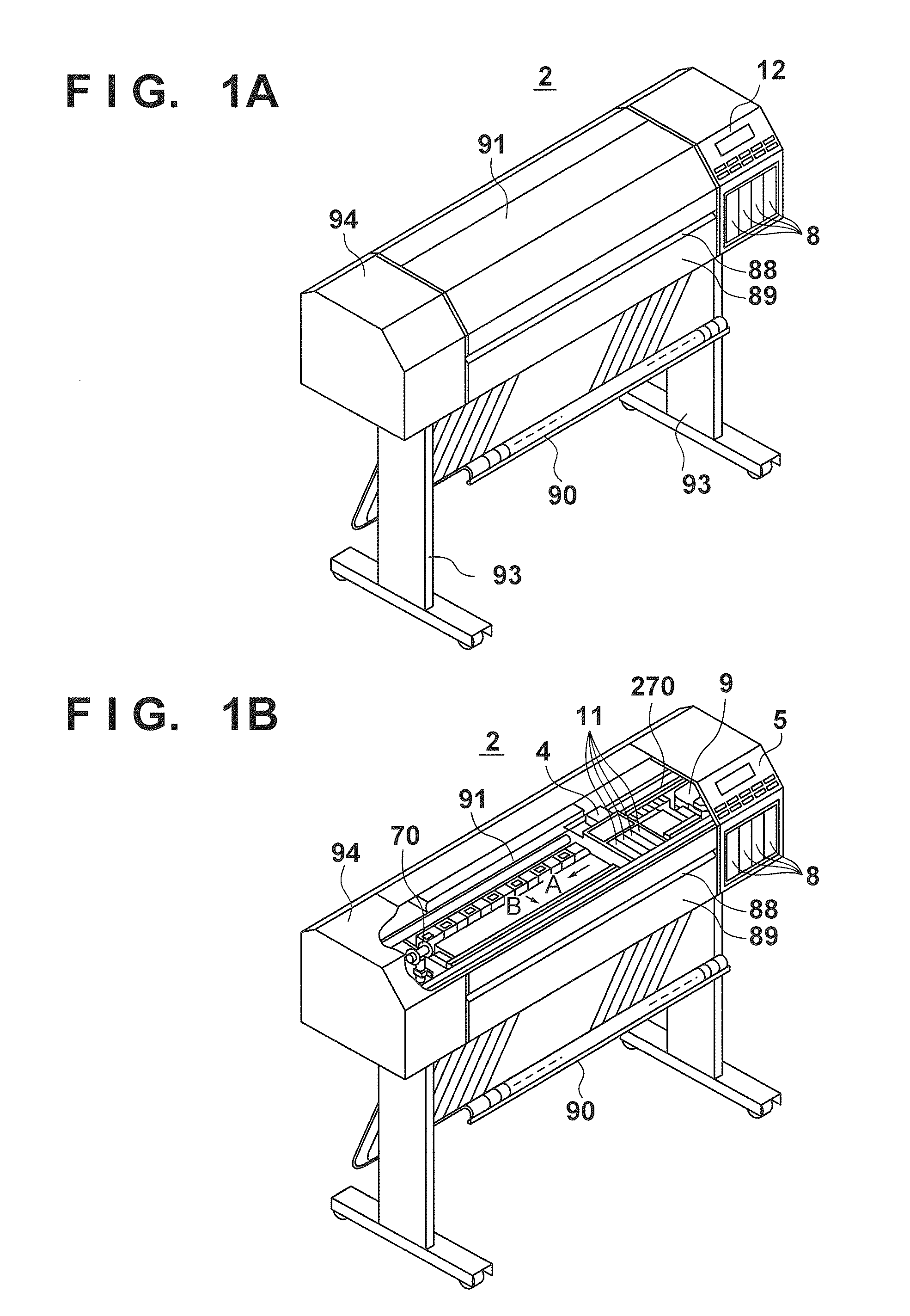
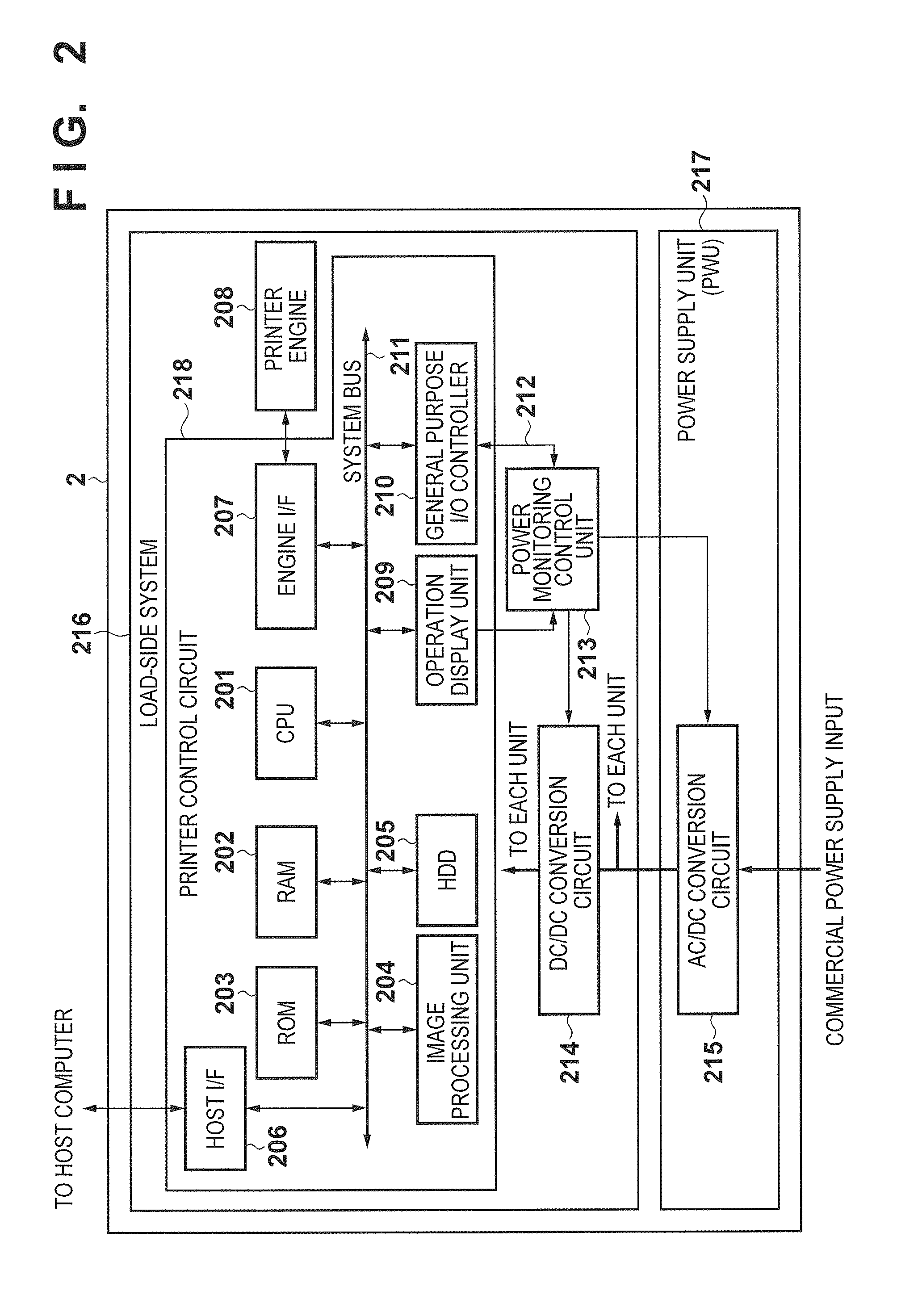
Printing apparatus
Disclosed is a printing apparatus capable of safe high-speed leakage detection and contact detection of a printhead. The leakage detection and contact detection are executed in the apparatus which prints on a printing medium by scanning a removable printhead mounted to a carriage. When the printhead is mounted, connection with a capacitor used in normal printing is disconnected, a lower voltage is applied to drive a printing element and monitor the voltage. If the monitored voltage is not less than a predetermined threshold, occurrence of a poor contact is determined. This is performed for electric contacts one by one. During the operation, a lower voltage is applied at a predetermined timing to drive a printing element and monitor the voltage. If the monitor voltage is not higher than a predetermined threshold, occurrence of current leakage is determined.
Owner:CANON KK
Method of driving organic electroluminescence emission portion
ActiveUS8248334B2Short timeUnnecessary timeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringOrganic electroluminescence
Disclosed herein is a method of driving an organic electroluminescence emission portion, the method including the steps of: applying a first node initialization voltage to corresponding one of the data lines, and supplying the video signal instead of the first node initialization voltage for a predetermined scanning time period, applying the first node initialization voltage from the corresponding one of the data lines to the first node through the write transistor held in an ON state for initializing the potential at the first node, and holding a state of applying the first node initialization voltage from the corresponding one of the data lines to the first node through the write transistor held in an ON state for holding the potential at the first node.
Owner:JOLED INC
Calibration device, calibration method, and computer readable medium for visual sensor
ActiveUS10434654B2Affect operabilityUnnecessary timeImage enhancementProgramme-controlled manipulatorStereo cameraVision sensor
A parameter for detecting a target mark 5 is not required to be set for each camera repeatedly while a stereo camera 2 is calibrated. A calibration device 1 associates position information in an image coordinate system at a first camera 21 of a stereo camera 2, position information in an image coordinate system at a second camera 22 of the stereo camera 2, and position information in a robot coordinate system at a robot 4. The calibration device comprises: first parameter setting unit 102 that sets a first parameter for detecting a target mark 5 attached to the robot 4 from data about an image captured by the first camera 21; and a second parameter setting unit 104 that sets a second parameter for detecting the target mark 5 from data about an image captured by the second camera 22 based on the first parameter.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Height extensible container-type warehouse
InactiveUS9776790B2Quick installationUnnecessary timeLarge containersStorage devicesTelecommunicationsRoad traffic
The present invention relates to a height-extensible container-type warehouse that is manufactured in a container type at a factory, can be transported to a desired place, and can be increased in height at the place by coupling a section, which exceeds a height limit under the Road Traffic Act and is separately manufactured, to an opening of the warehouse in order to increase the height thereof.
Owner:KWON YEONG JONG +1
Server connected with image forming apparatus and client, image forming system having the same, and driver remote installation method of image forming apparatus
ActiveUS8769527B2Unnecessary costUnnecessary timeProgram loading/initiatingExecution paradigmsImage formationMethod of images
A server connected with an image forming apparatus and a client, an image forming system having the same and a driver remote installation method of an image forming apparatus, the method including selecting at least one client in which a driver of the image forming apparatus is to be installed by the server; selecting a type of the driver to be installed in the at least one selected client; installing an install manager to install the driver in the at least one selected client; and installing the selected driver in the at least one selected client using the install manager.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
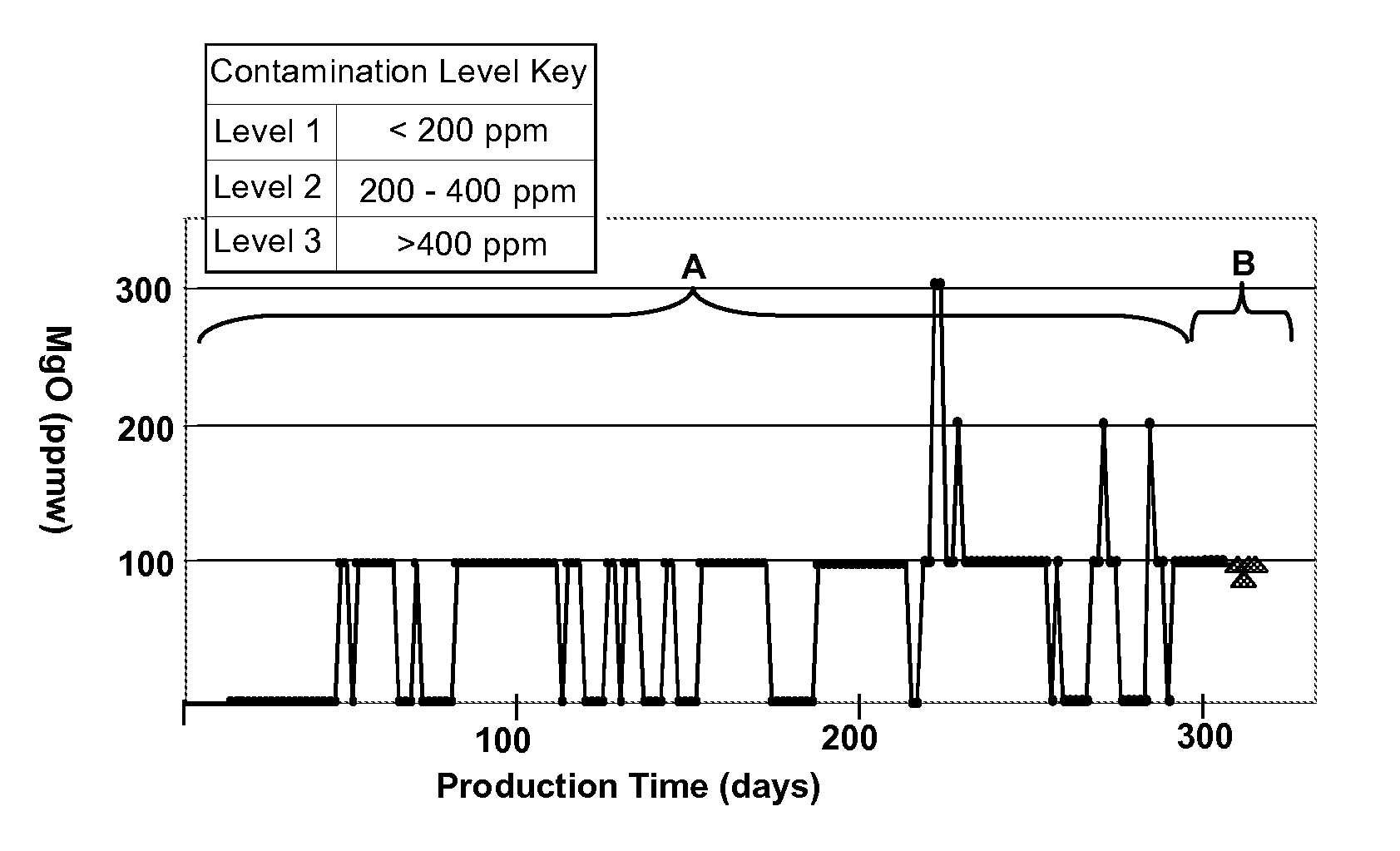
Ceramic contamination control processes
InactiveUS20100217424A1Reduce riskUnnecessary expenseHollow article cleaningAuxillary shaping apparatusProduction linePowder mixture
Trace cross-contamination in mixtures or preforms of plasticized ceramic-forming powder mixtures, arising for example in manufacturing facilities where components of one ceramic product being manufactured can contaminate mixtures for another product to be manufactured, are controlled by one or more of: the targeted decontamination of shared production lines, rapid trace analysis of the mixtures to establish the presence and / or concentration levels of contaminants, the application of statistical models to project final product properties based on the analyzed concentrations, and decisional analysis of appropriate corrective actions based on the statistical projections.
Owner:CORNING INC
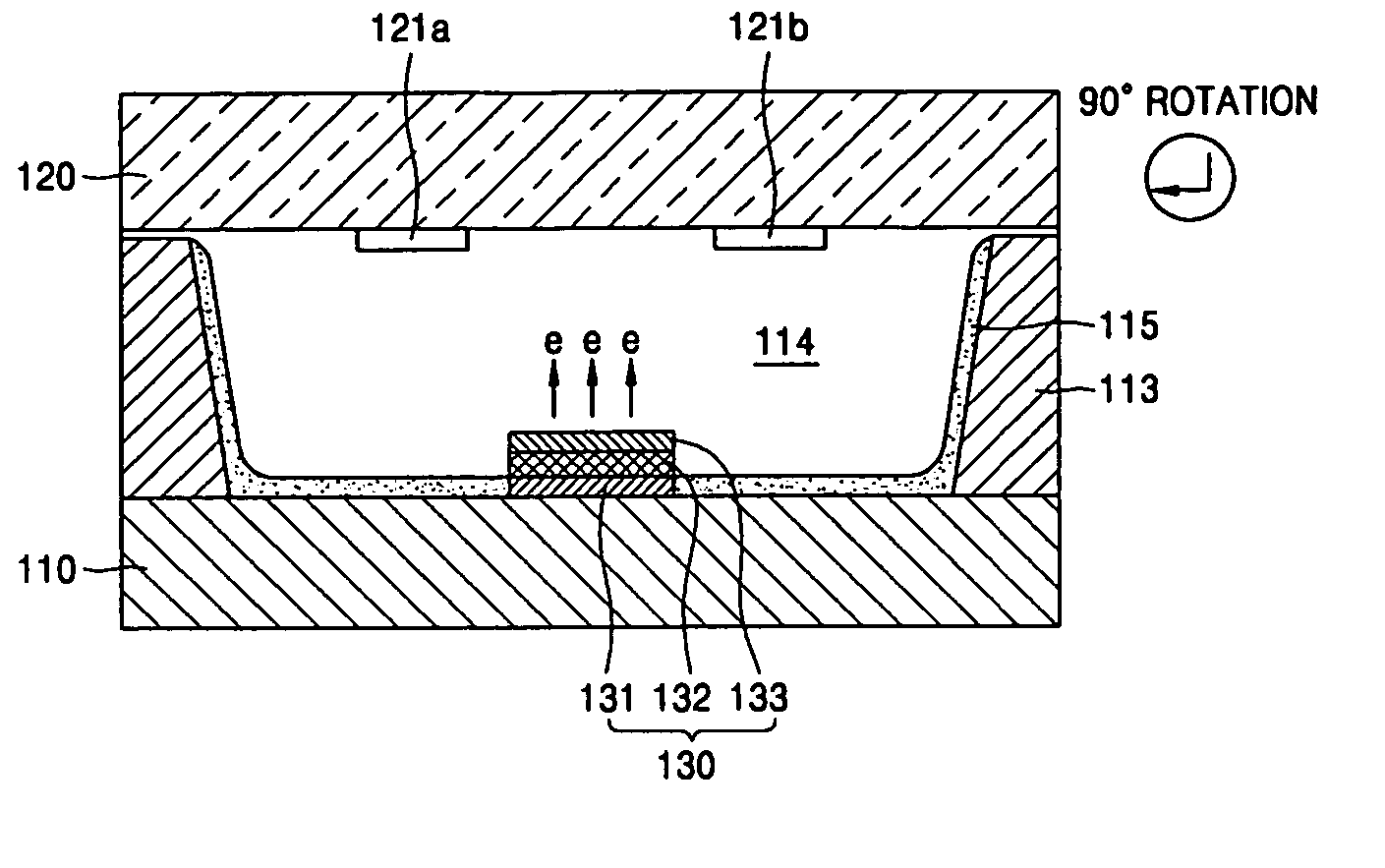
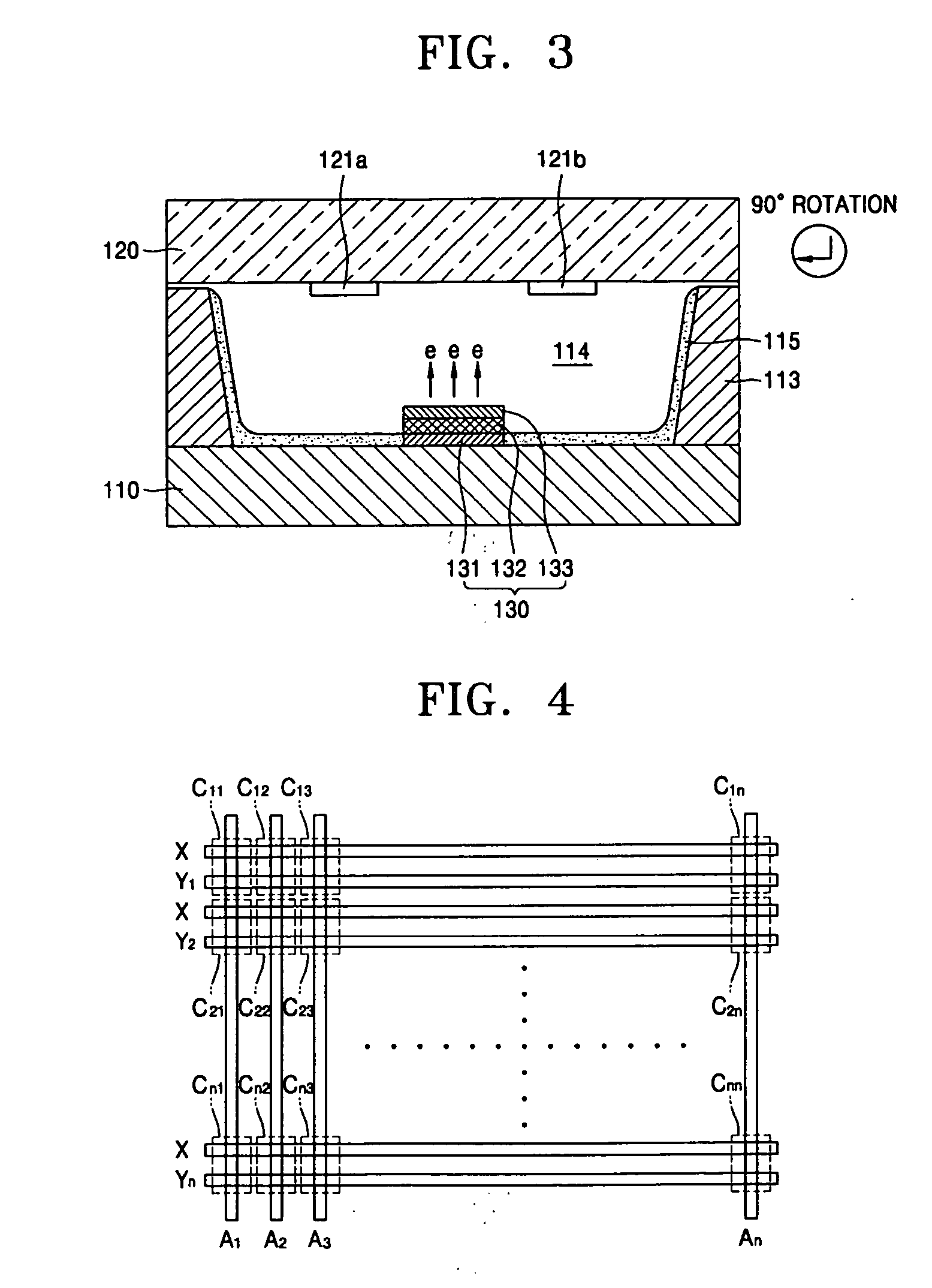
Plasma display panel and method of driving the same
InactiveUS20060220996A1Reduce unnecessary timeReduce power consumptionAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesEngineeringElectron
A plasma display panel (PDP) and a method of driving the same, and the PDP includes a lower substrate and an upper substrate facing each other with a discharge space therebetween, a plurality of barrier ribs arranged between the lower substrate and the upper substrate to partition the discharge space and define a plurality of discharge cells, a pair of first and second sustain electrodes corresponding to the discharge cells electron emission sources that correspond to the discharge cells, emit electrons into the discharge cells to address the discharge cells and simultaneously cause a sustain discharge between the first and second sustain electrodes, and a florescent layer coated on inner walls of the discharge cells.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
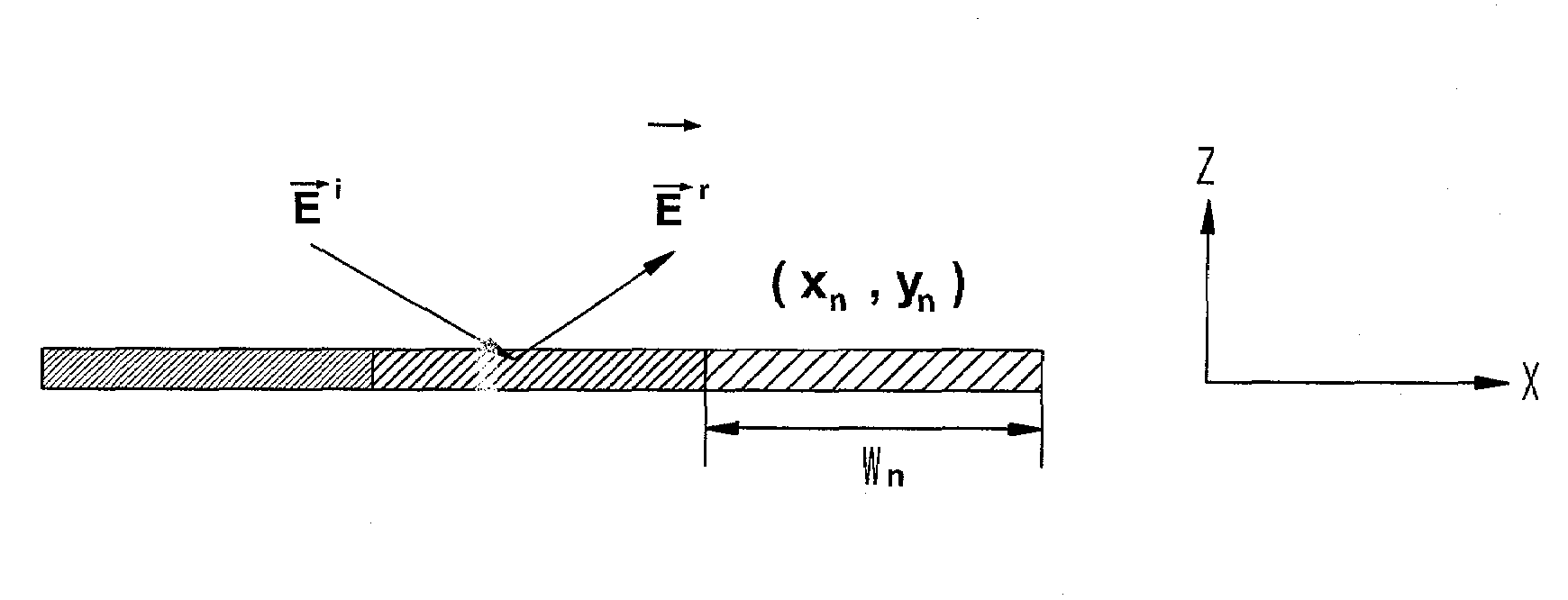
Method of analyzing reflection waves using effective impedance
InactiveUS20100010760A1Simple modelReduce the amount of calculationDigital variable/waveform displayTransmission monitoringReflected wavesElectrical impedance
Provided is a method for analyzing a reflection wave using effective impedance. The method includes the steps of: a) modeling a reflection surface of a building two-dimensionally; and b) obtaining a reflection wave by radiating a radio wave to the modeled reflection surface and analyzing the obtained reflection wave through making medium uniform.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Mobile communication terminal and mobile communication control method
InactiveUS20090305692A1Reduce battery consumptionNetwork degradationAssess restrictionWireless commuication servicesTelecommunicationsCell search
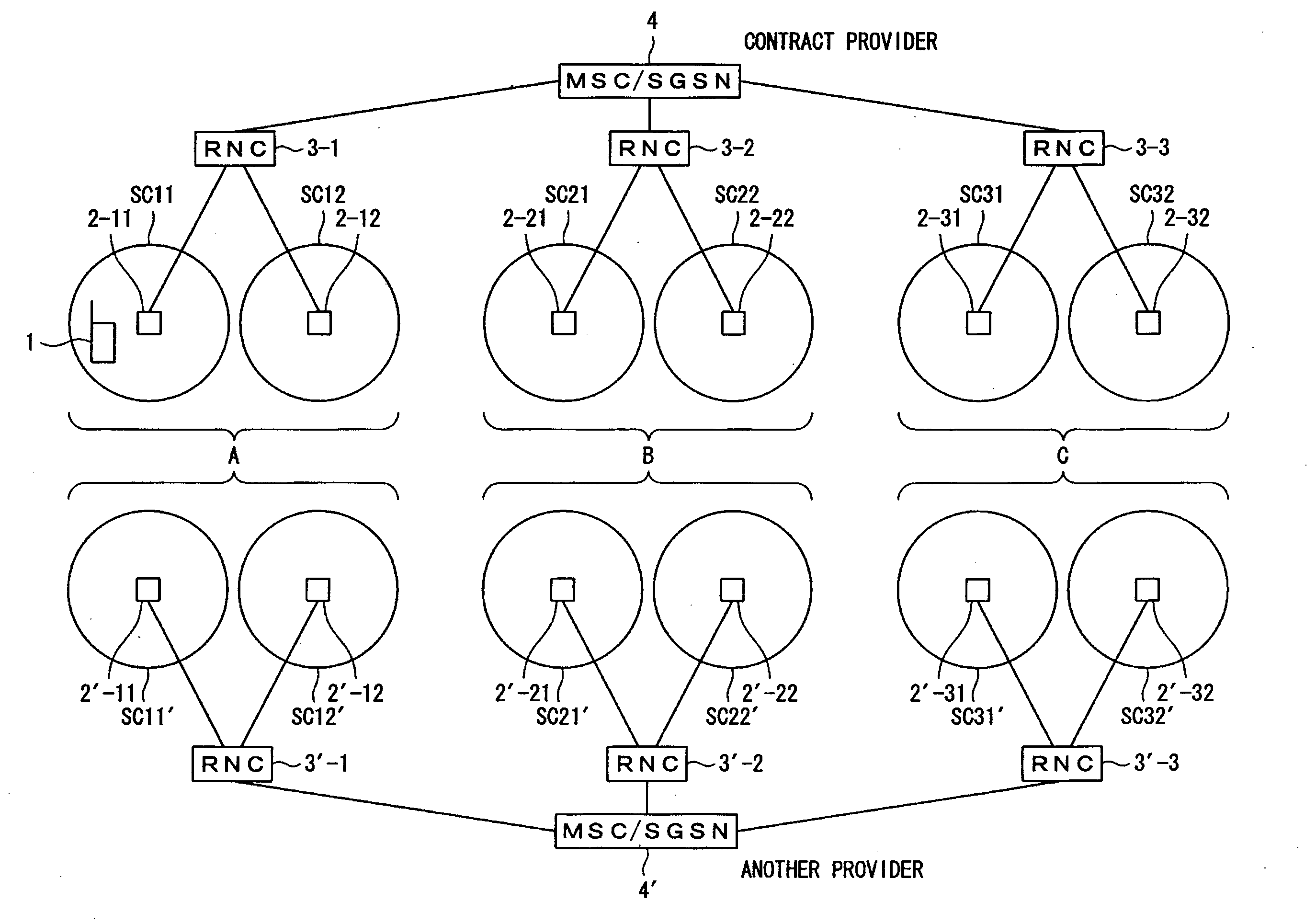
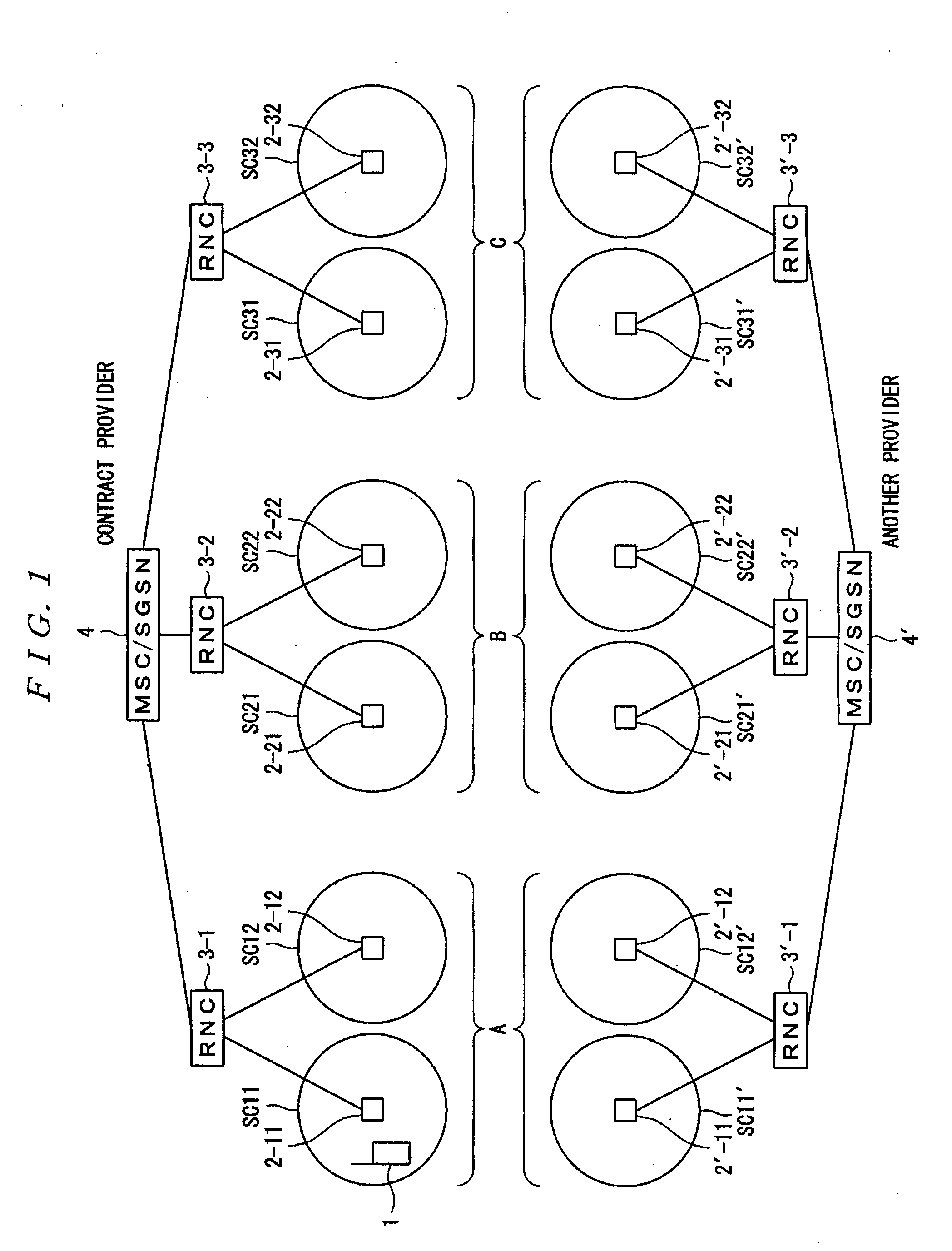
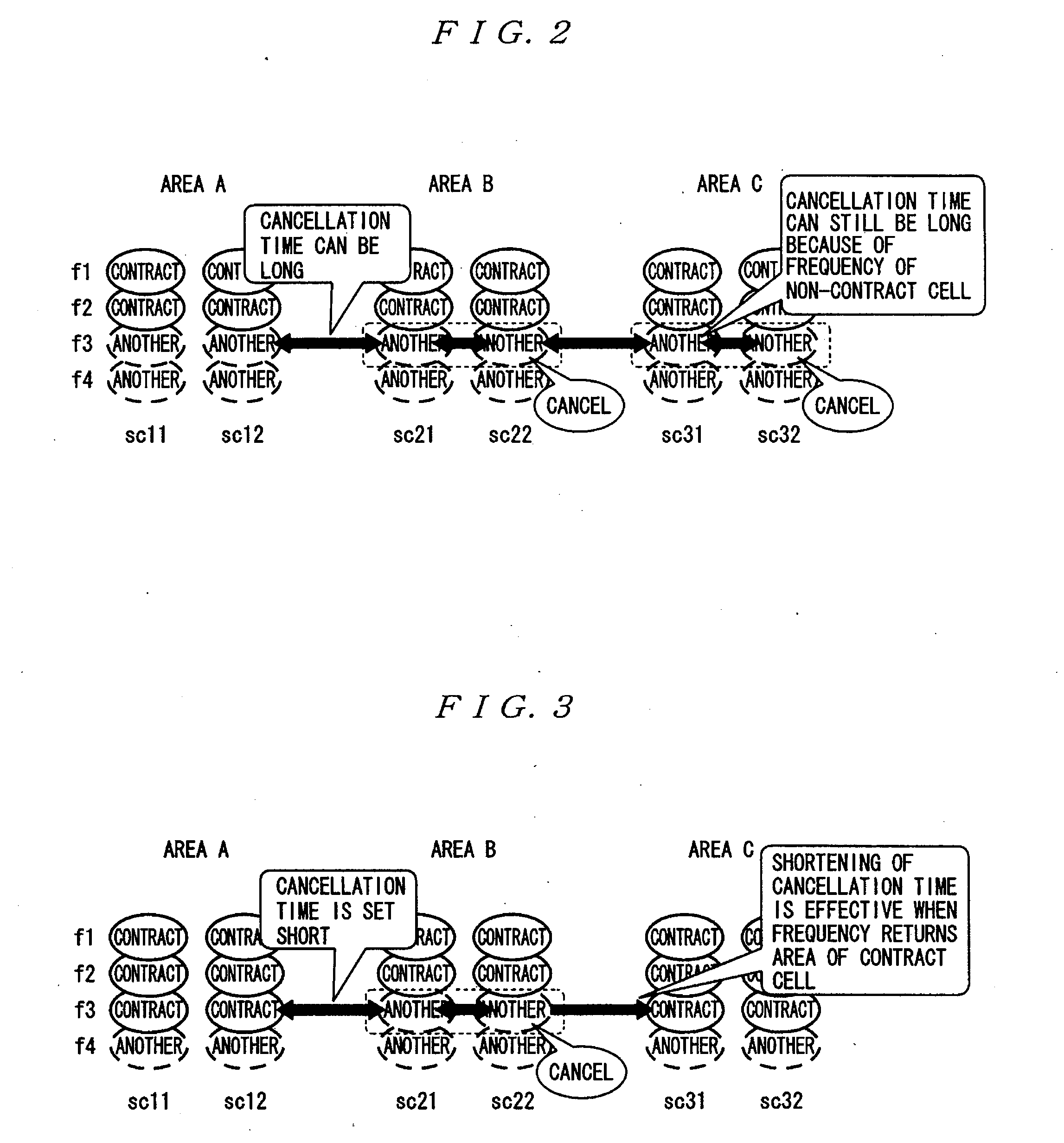
A mobile communication terminal holds a frequency cancellation list that is information related to cells that cannot be connected, and controls execution / non-execution (frequency cancellation) of the cell search according to the content of the cancellation list. In a case where a frequency is not assigned in a unified manner (when a frequency is assigned to different communication providers in some cells), a frequency cancellation time is set shorter than a case where the frequency is assigned in a unified manner. For example, a frequency f3 is rejected in a cell represented by “another” surrounded by a broken line when the mobile communication terminal moves from an area A to an area B. When the mobile communication terminal further moves to an area C, the frequency cancellation process initiated in the area B terminates. This is because a short frequency cancellation time is set. Therefore, the frequency cancellation time expires while the mobile communication terminal is moving from the area B to the area C. The frequency cancellation terminates, so as to be connectable in the area C of the frequency f3.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
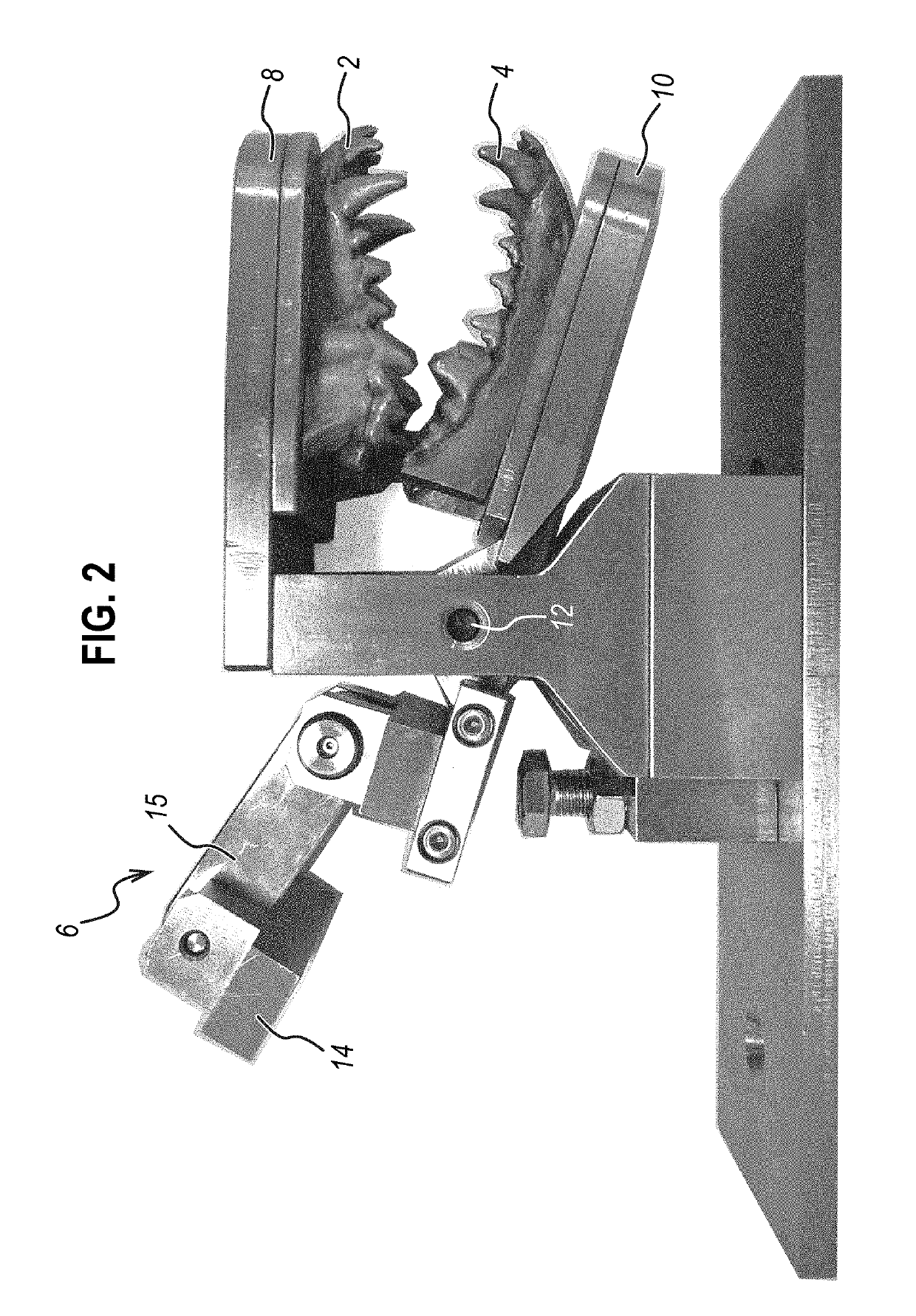
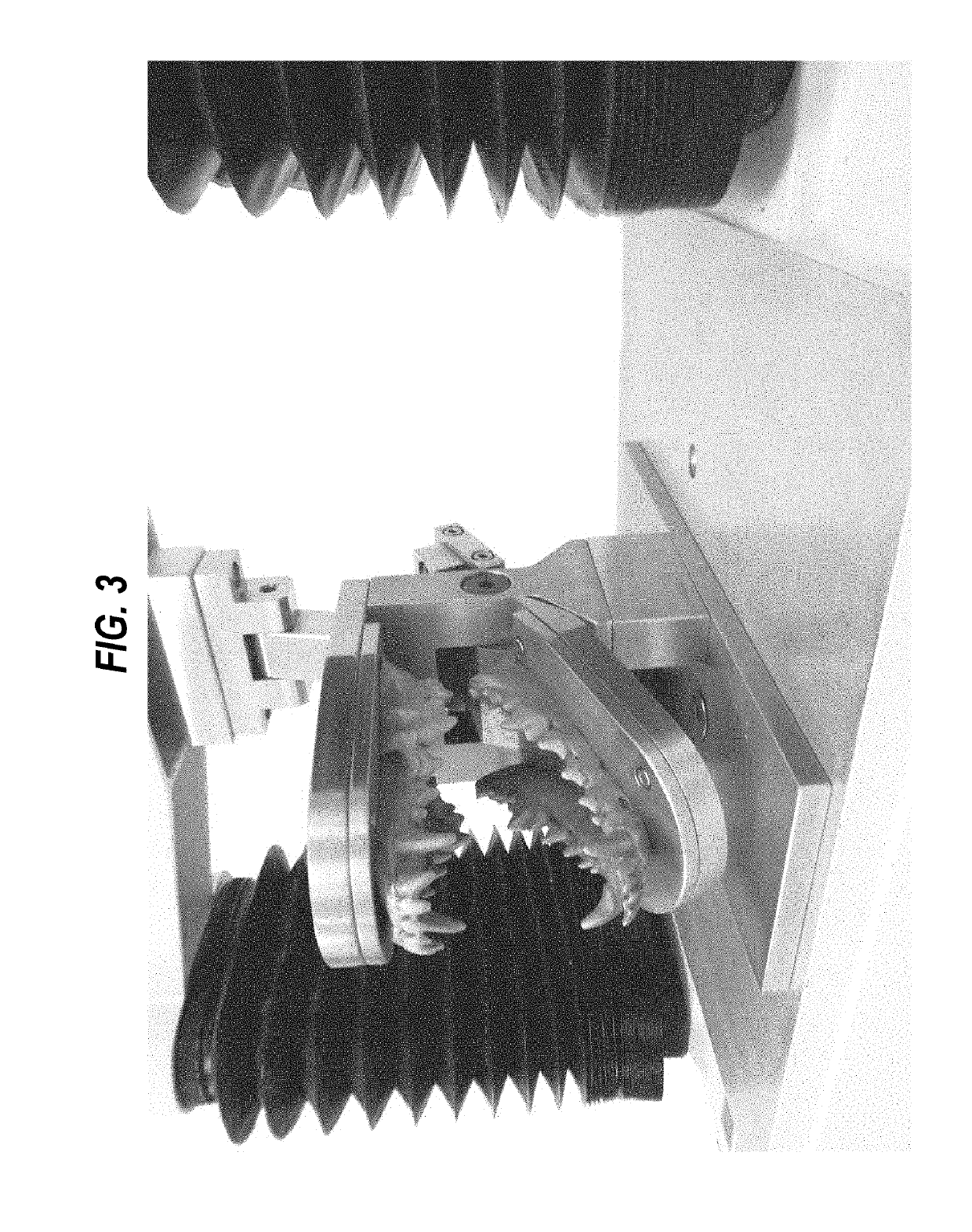
Animal dentistry apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20190090994A1Accurate assessmentUnnecessary costAnimal teeth treatmentDental articulatorsChewable ProductChewing food
An animal dentistry apparatus is provided and comprises a jaw assembly. The jaw assembly comprises a lower jaw and an upper jaw, and is configured such that the lower jaw and the upper jaw can move apart and together in a mastication action. The upper and lower jaw comprise at least one tooth. The apparatus further comprises a means, such as a motor, to effect the mastication action. The animal dentistry apparatus may be used to assess a chewable product, and such methods are also provided.
Owner:MARS INC
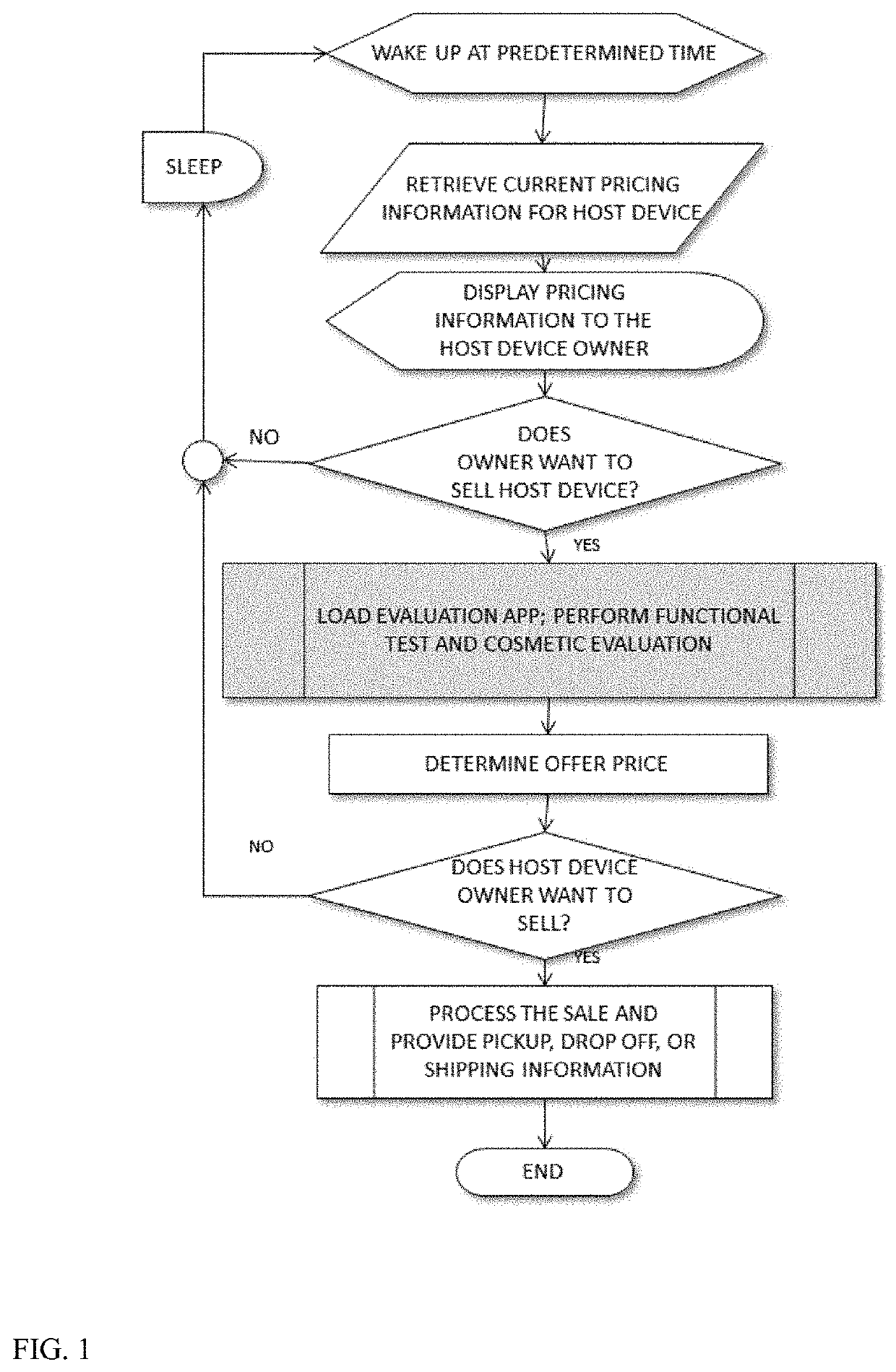
System and Method for Remote Valuation and Resale of a Used Electronic Device
InactiveUS20210312509A1Easy to seeUnnecessary timeMarket predictionsProduct appraisalEngineeringProcess engineering
A method for determining and continuously updating the price of a used electronic device and for enabling the consumer to easily resell the used electronic device when desired.
Owner:NGUYEN TU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com