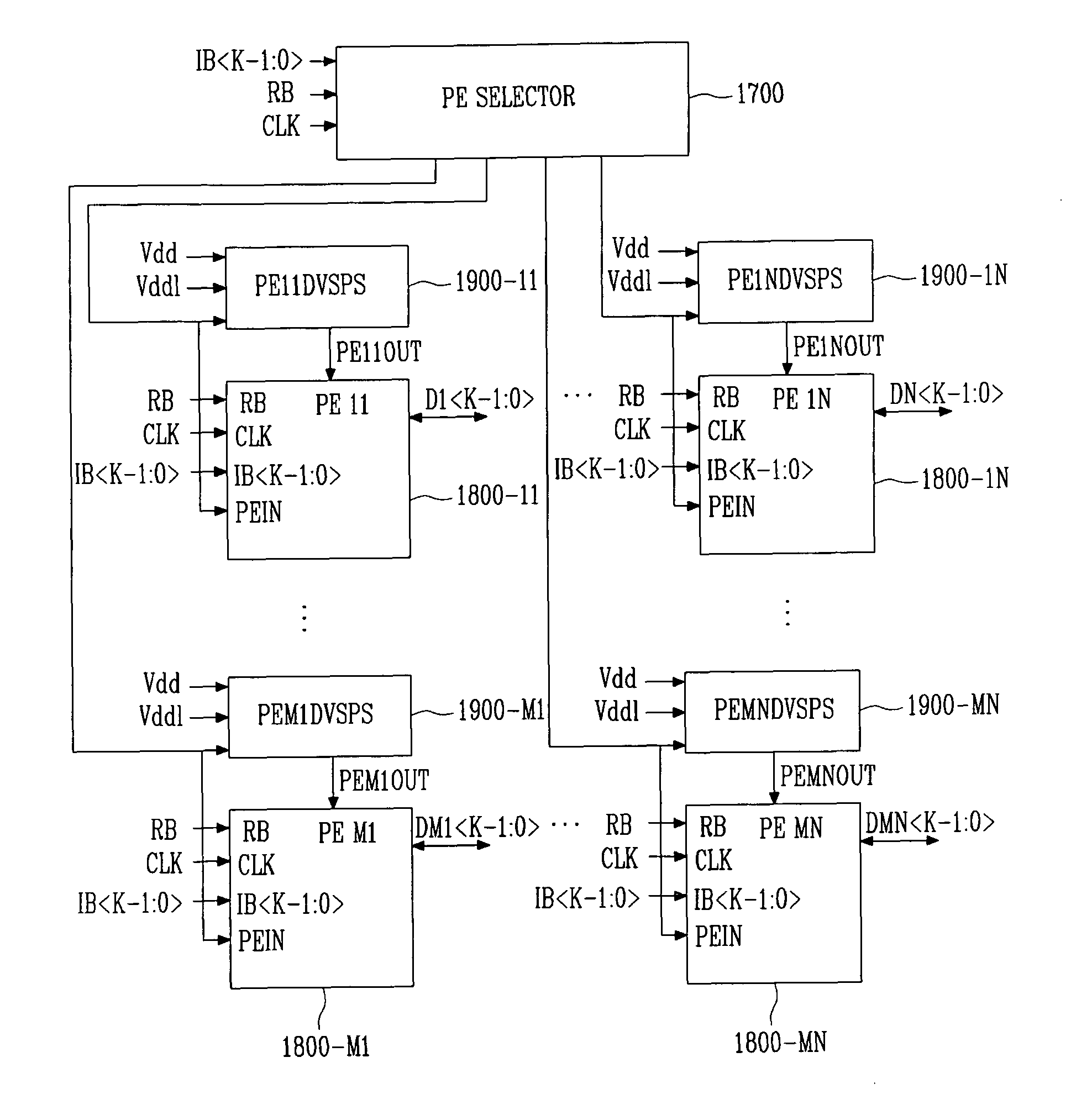Patents
Literature
59 results about "Adaptive voltage scaling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
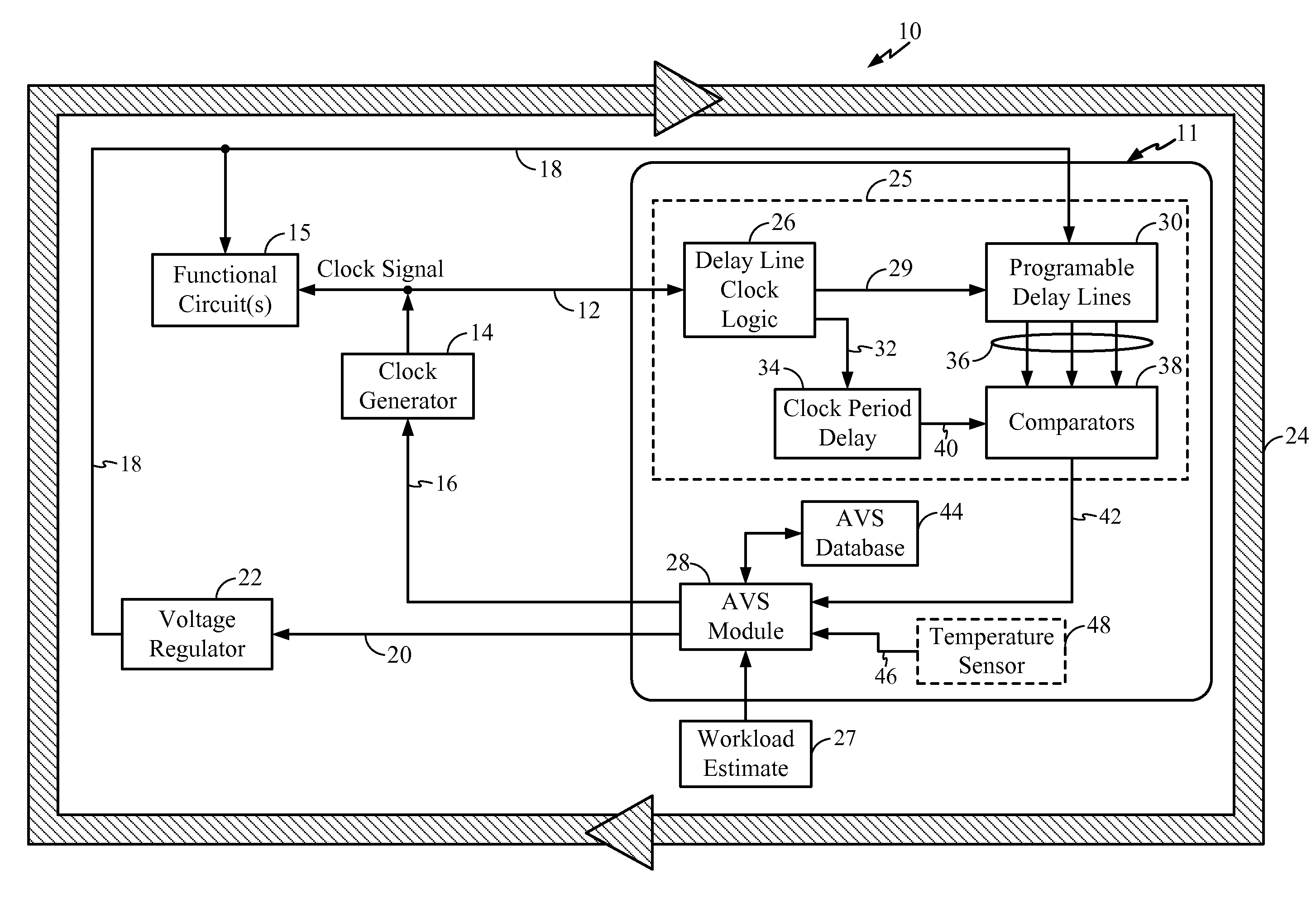
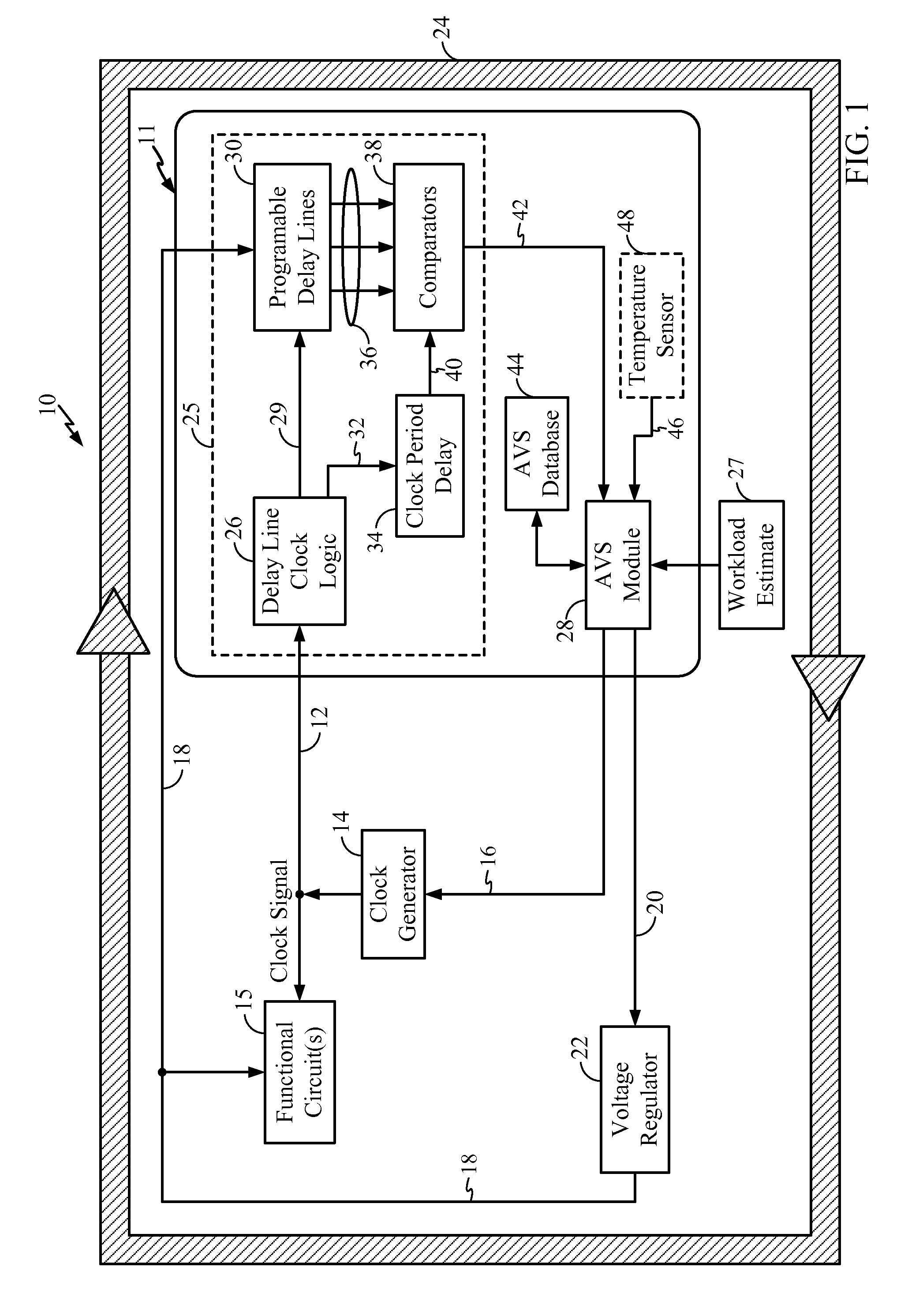
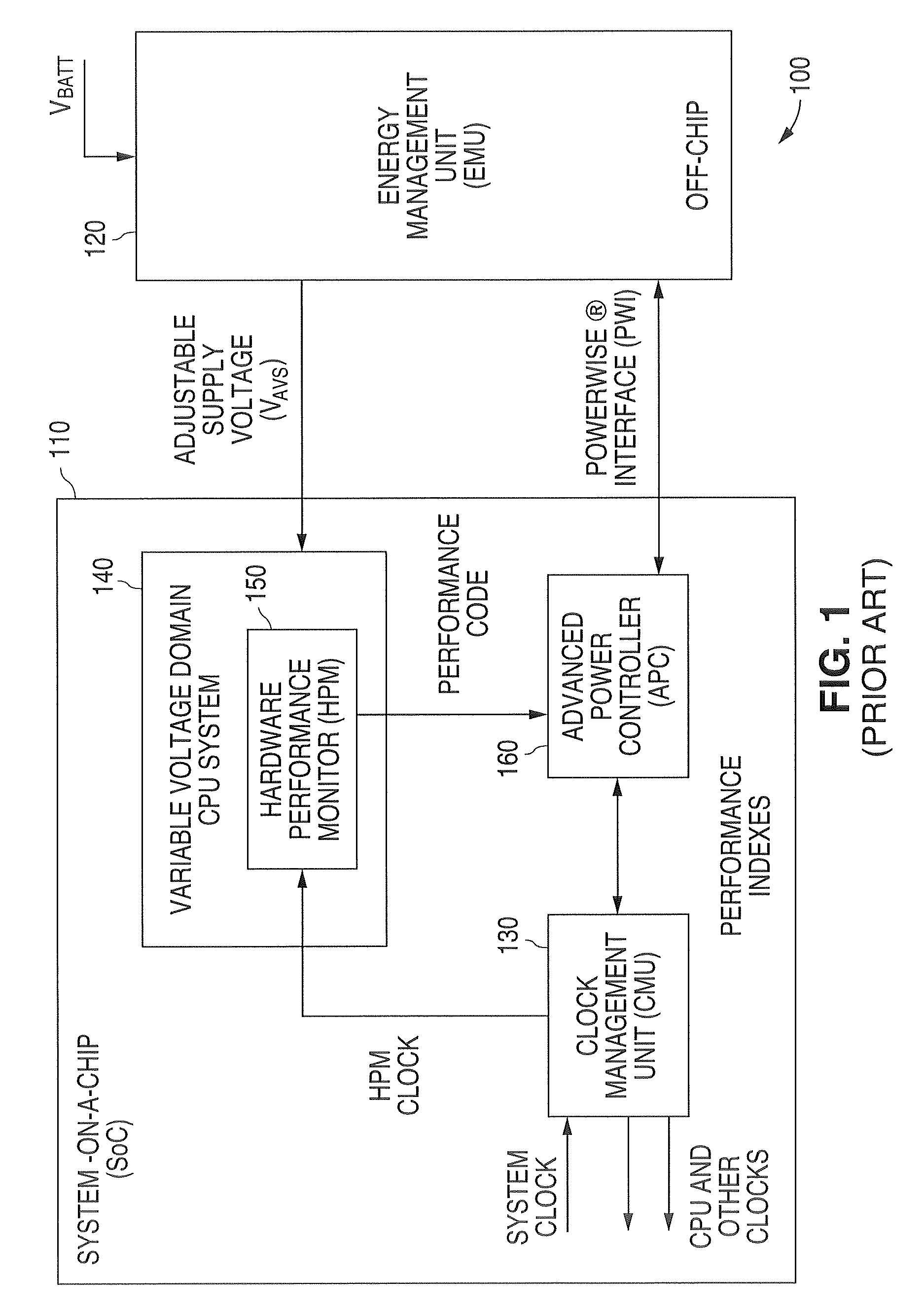
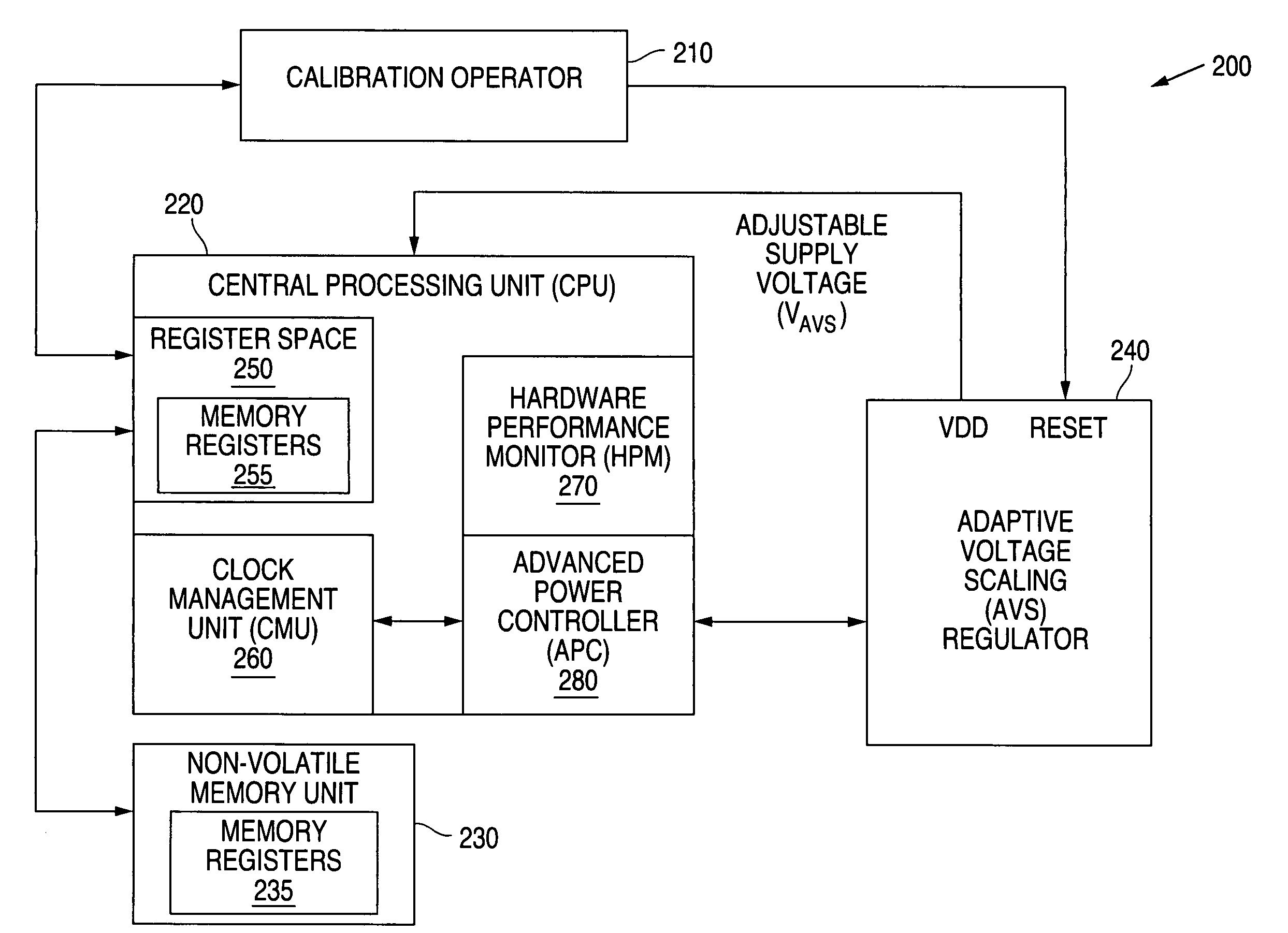
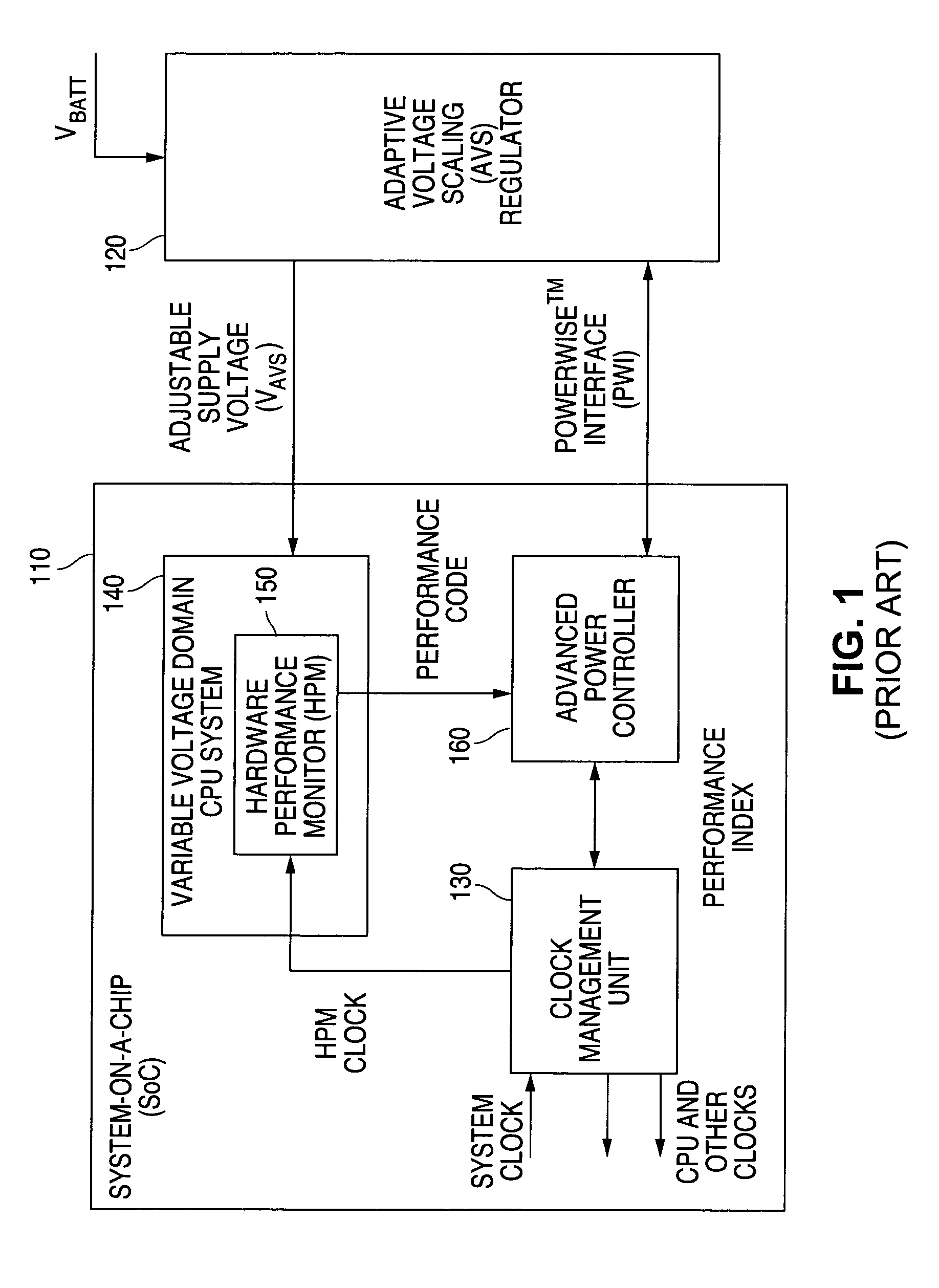
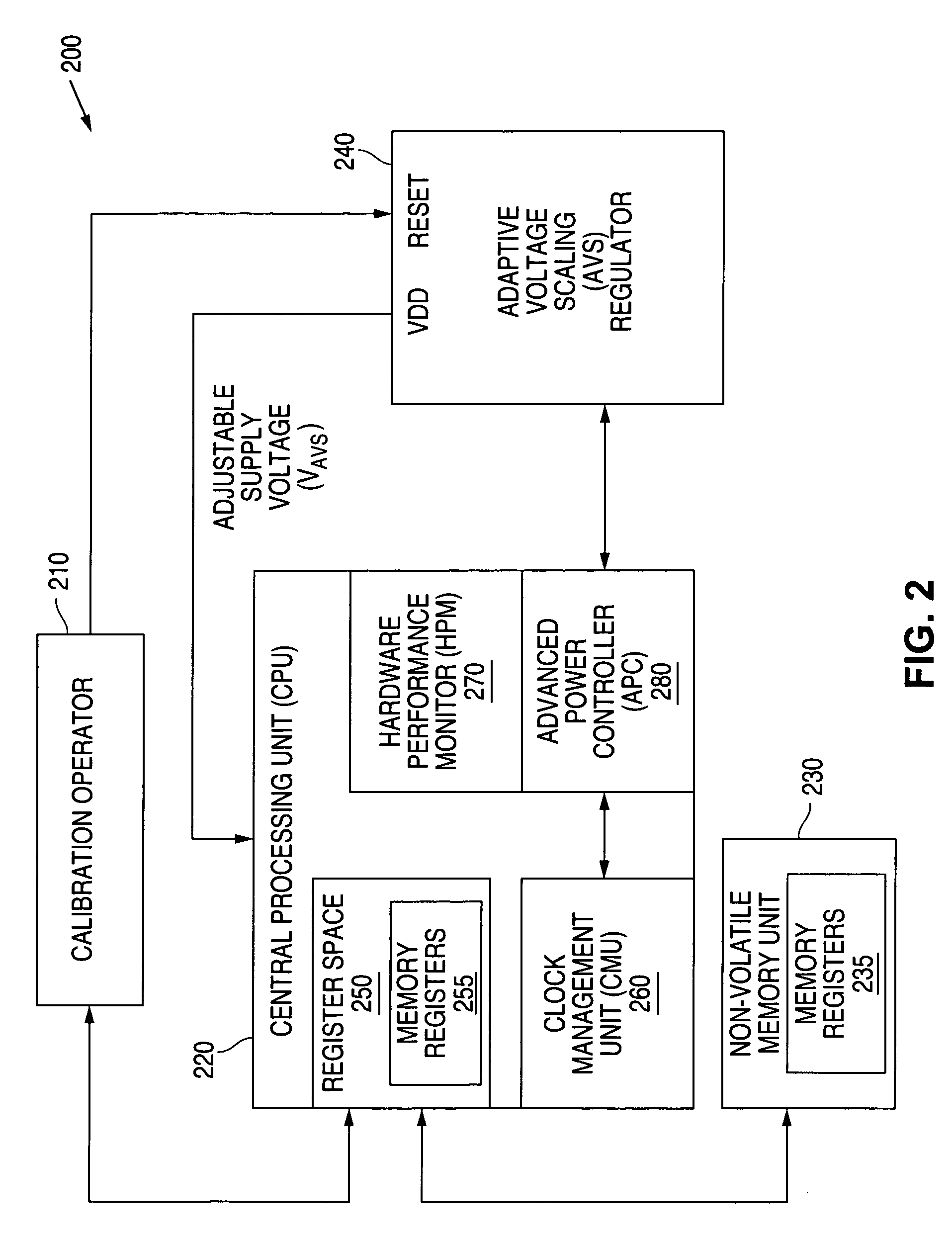
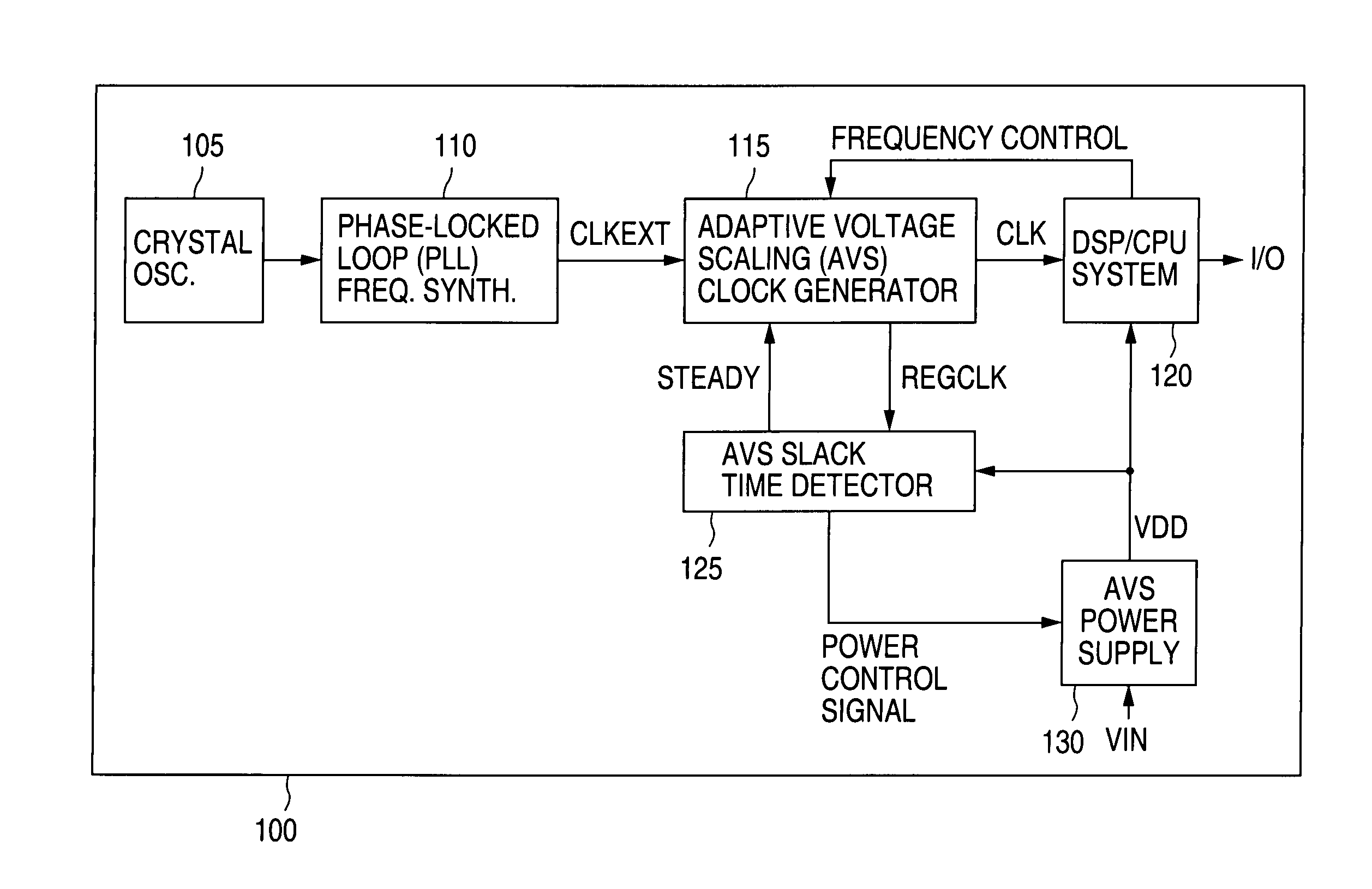
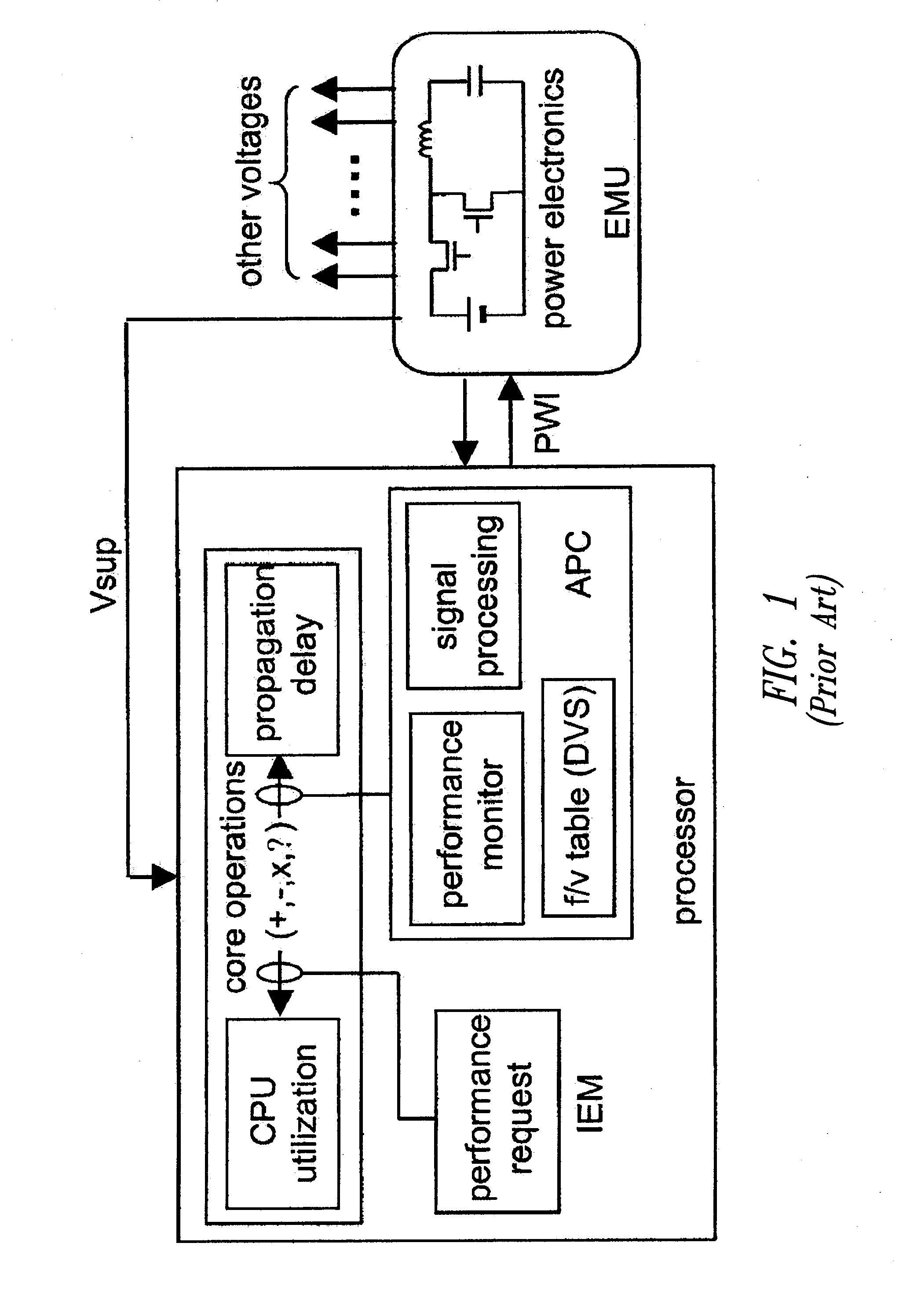
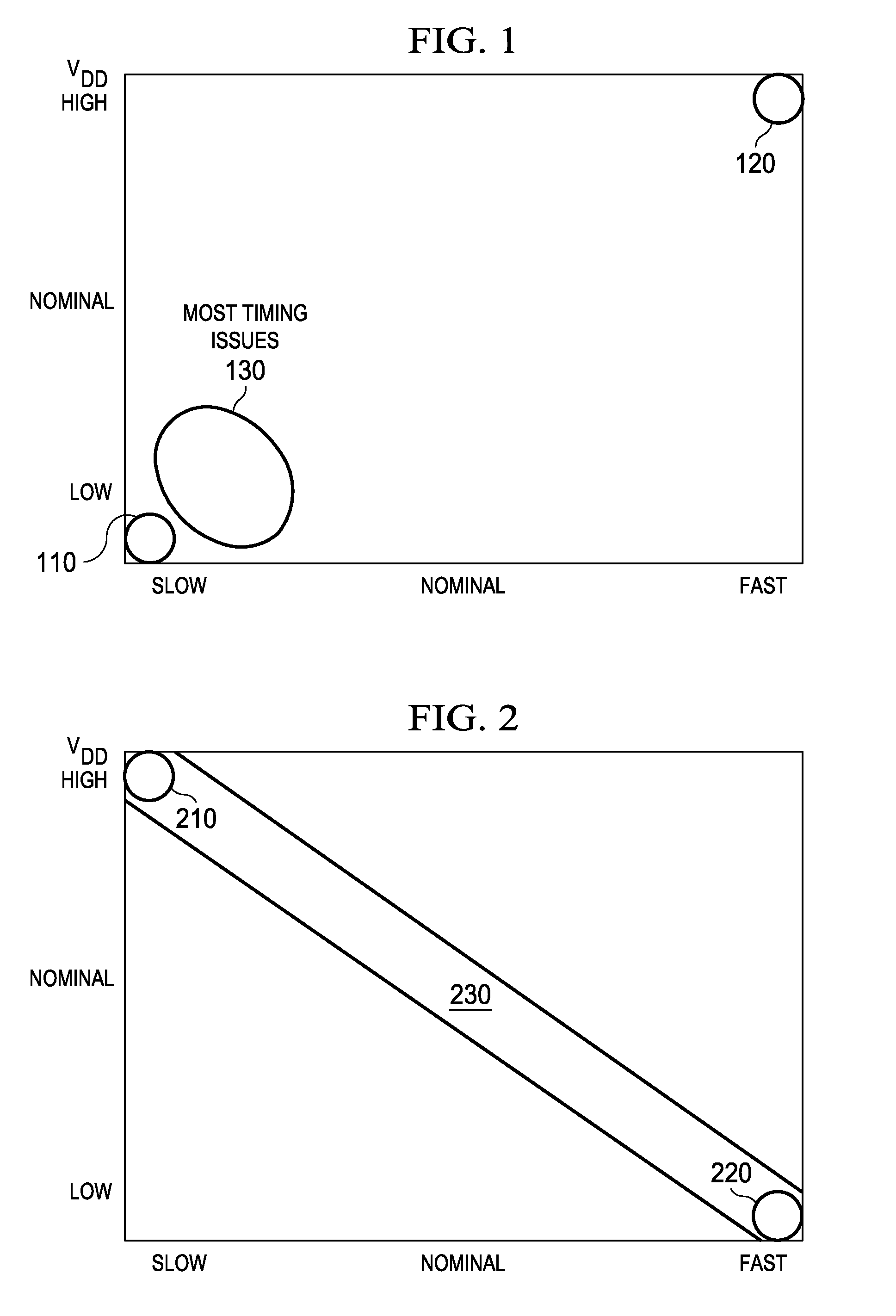
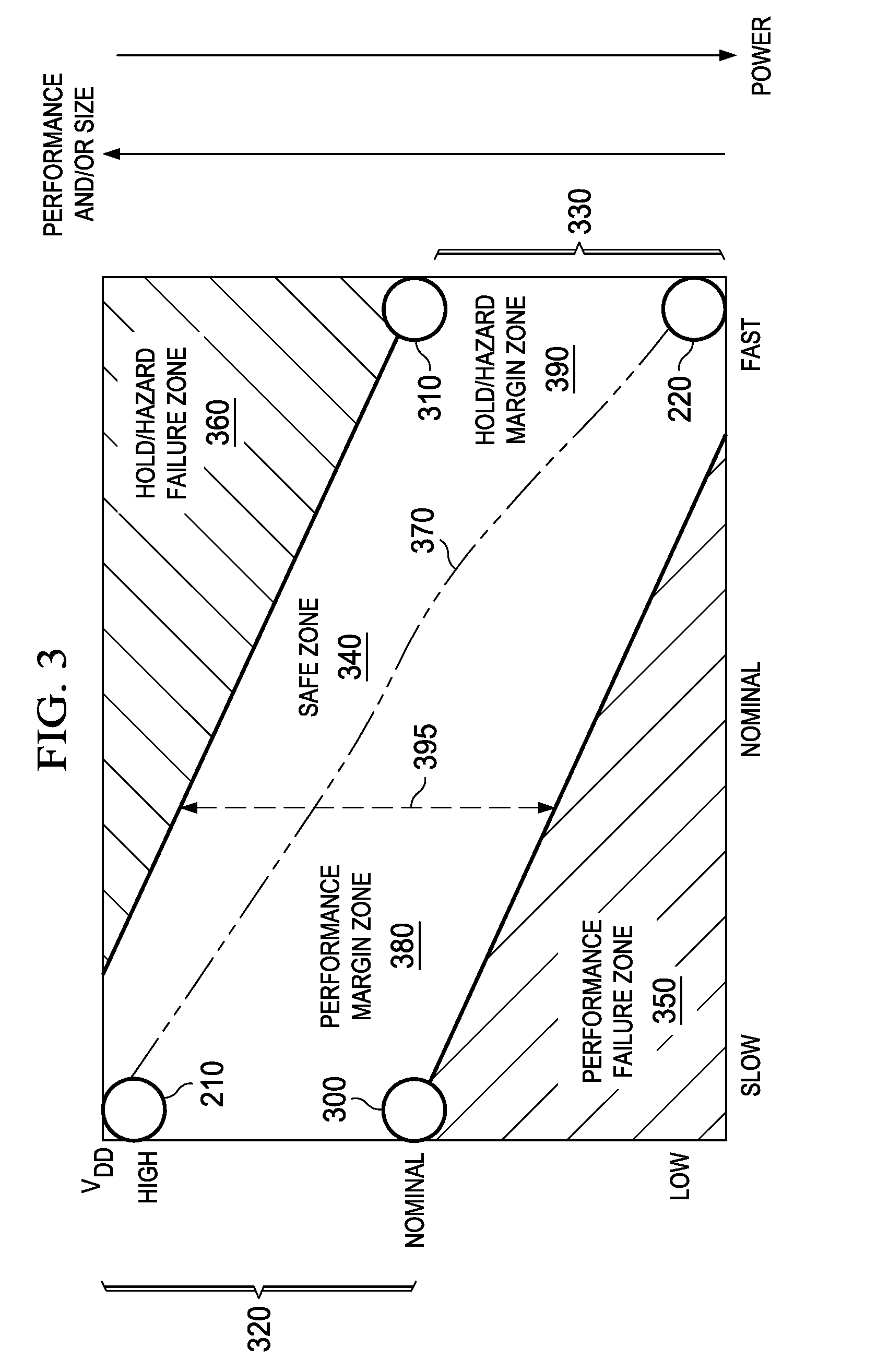
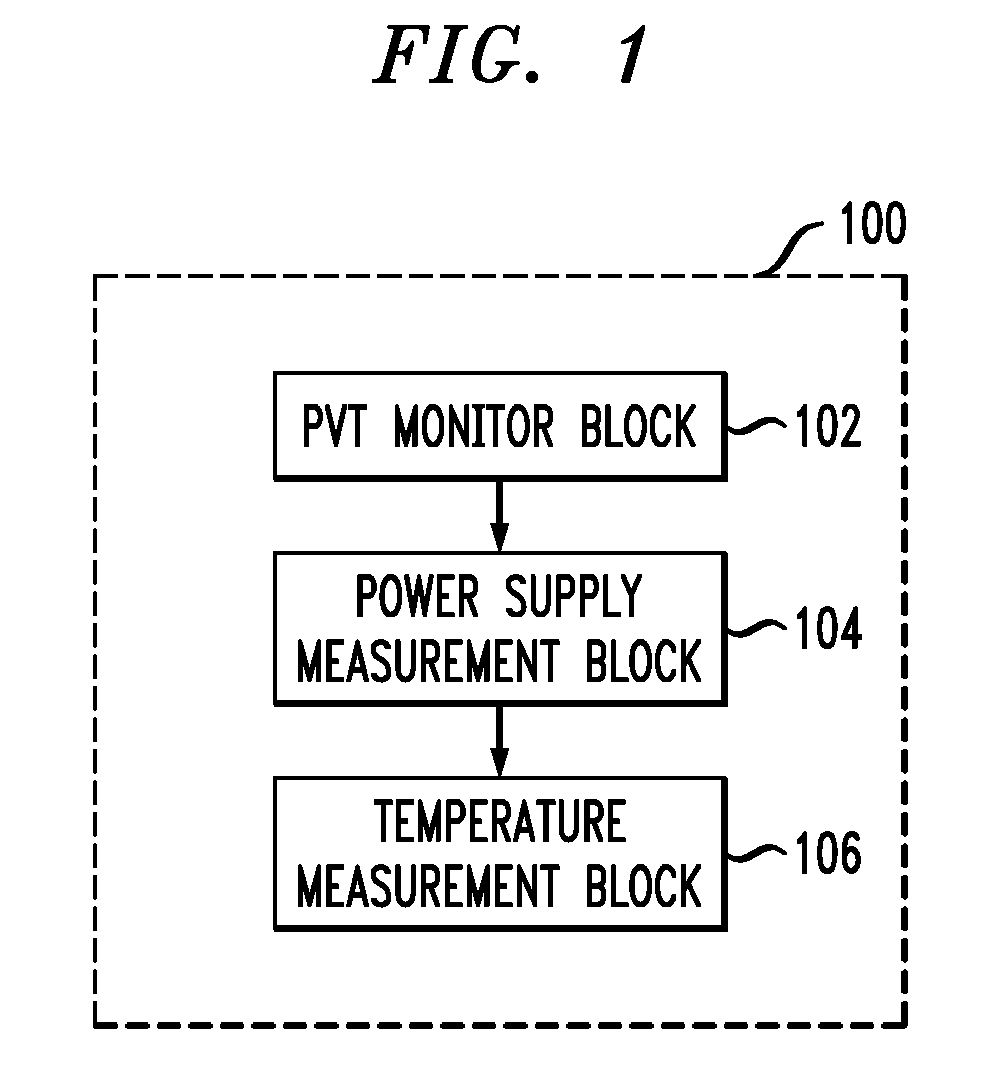
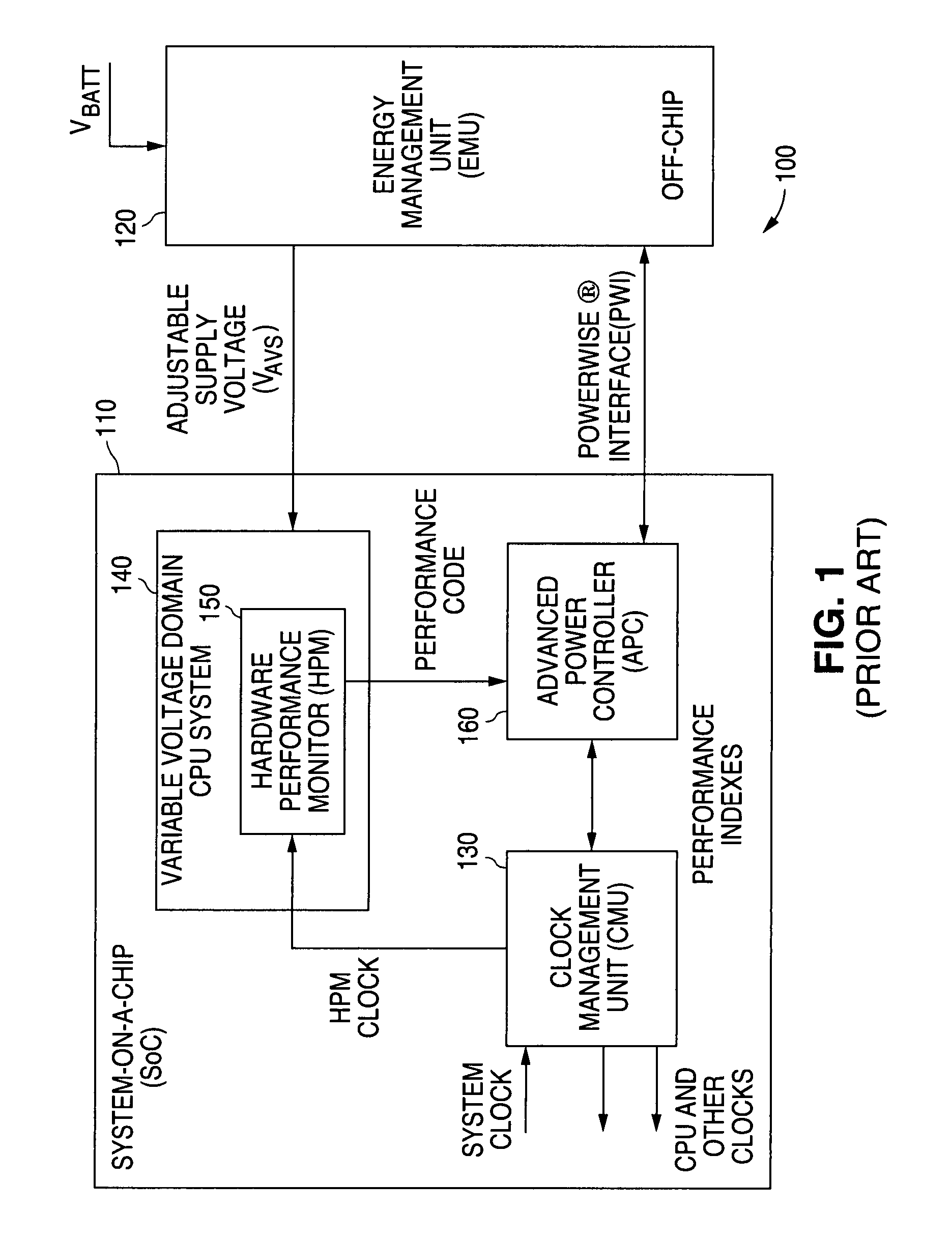
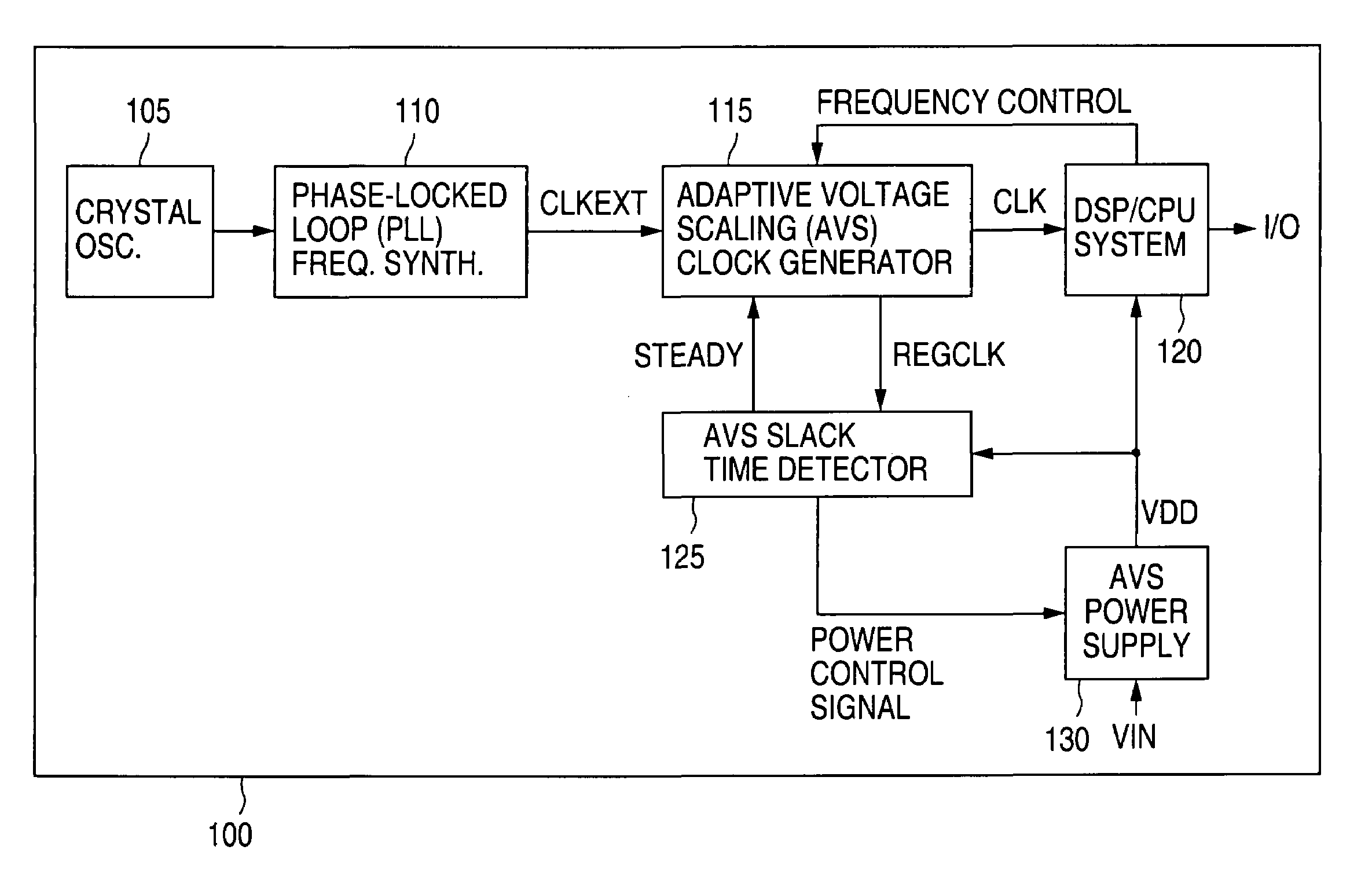
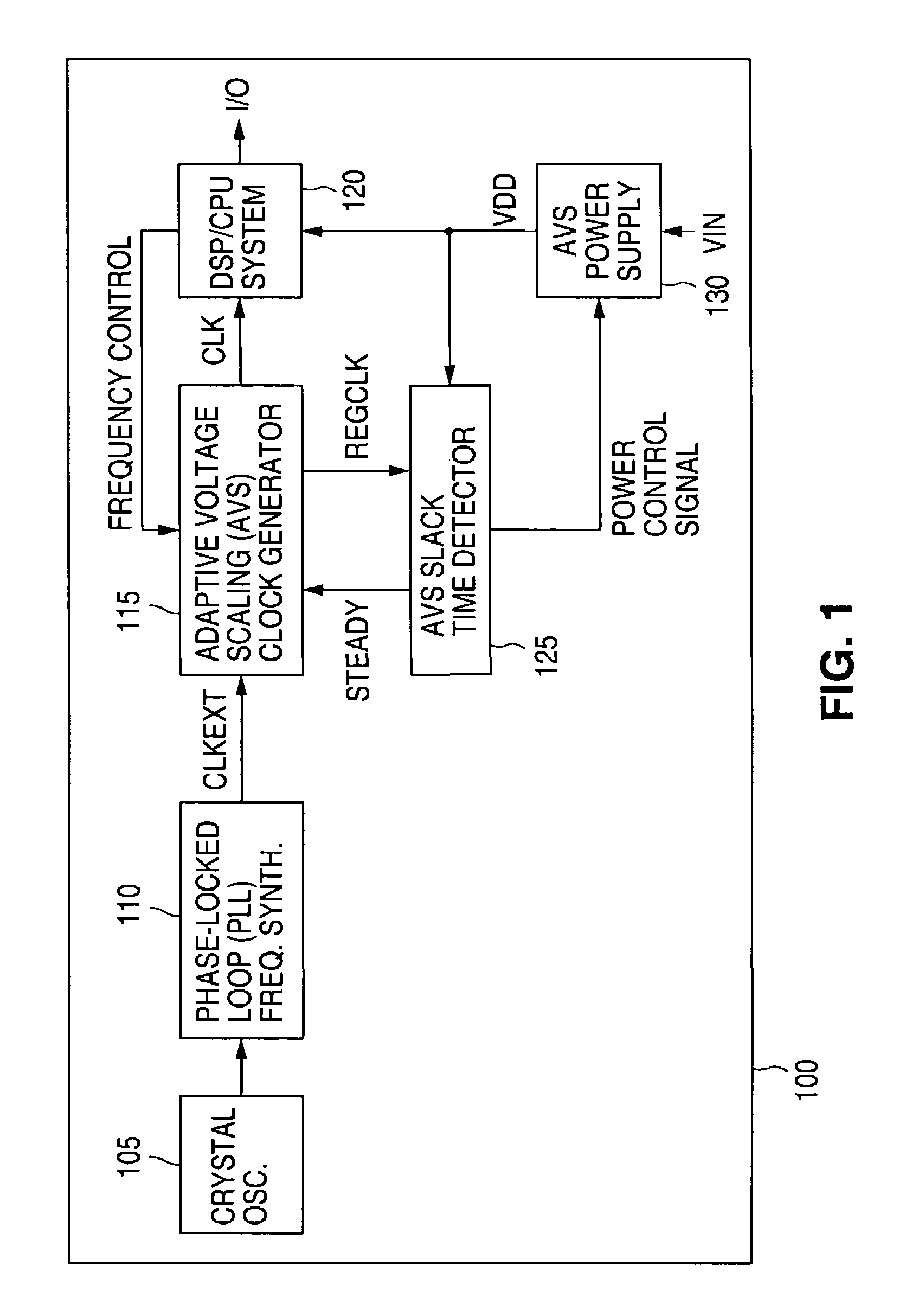
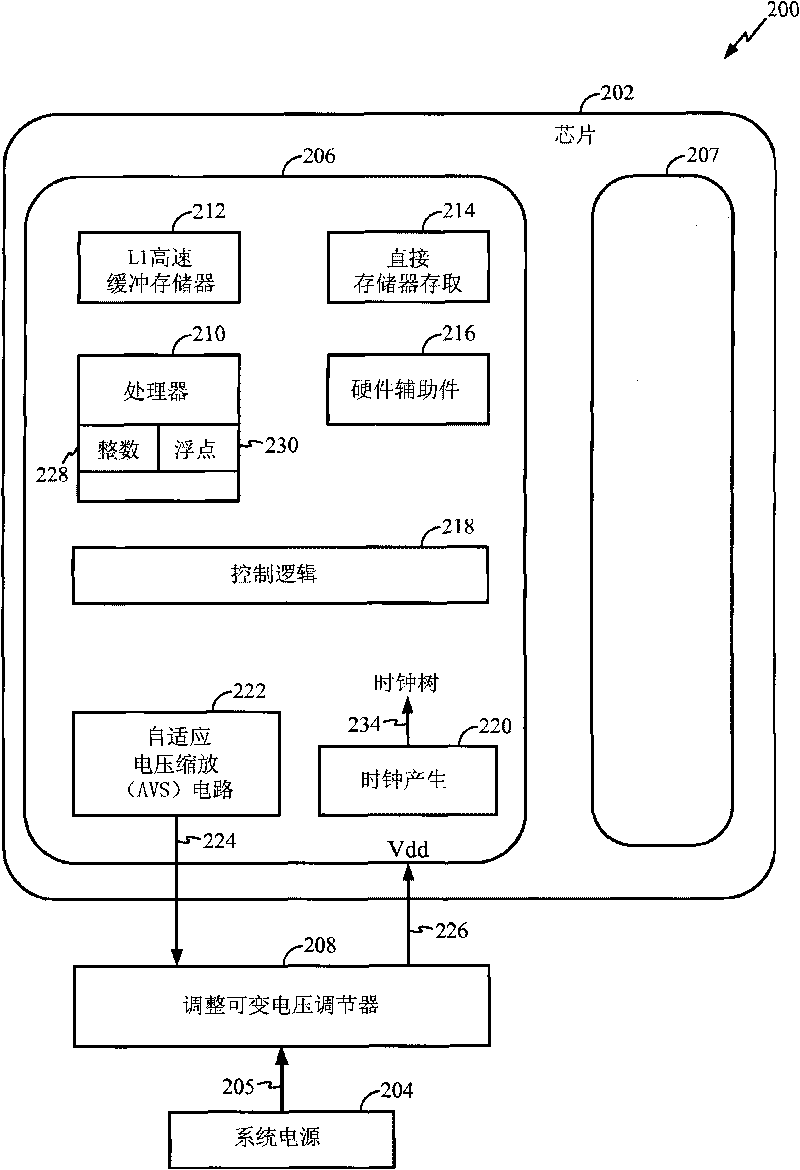
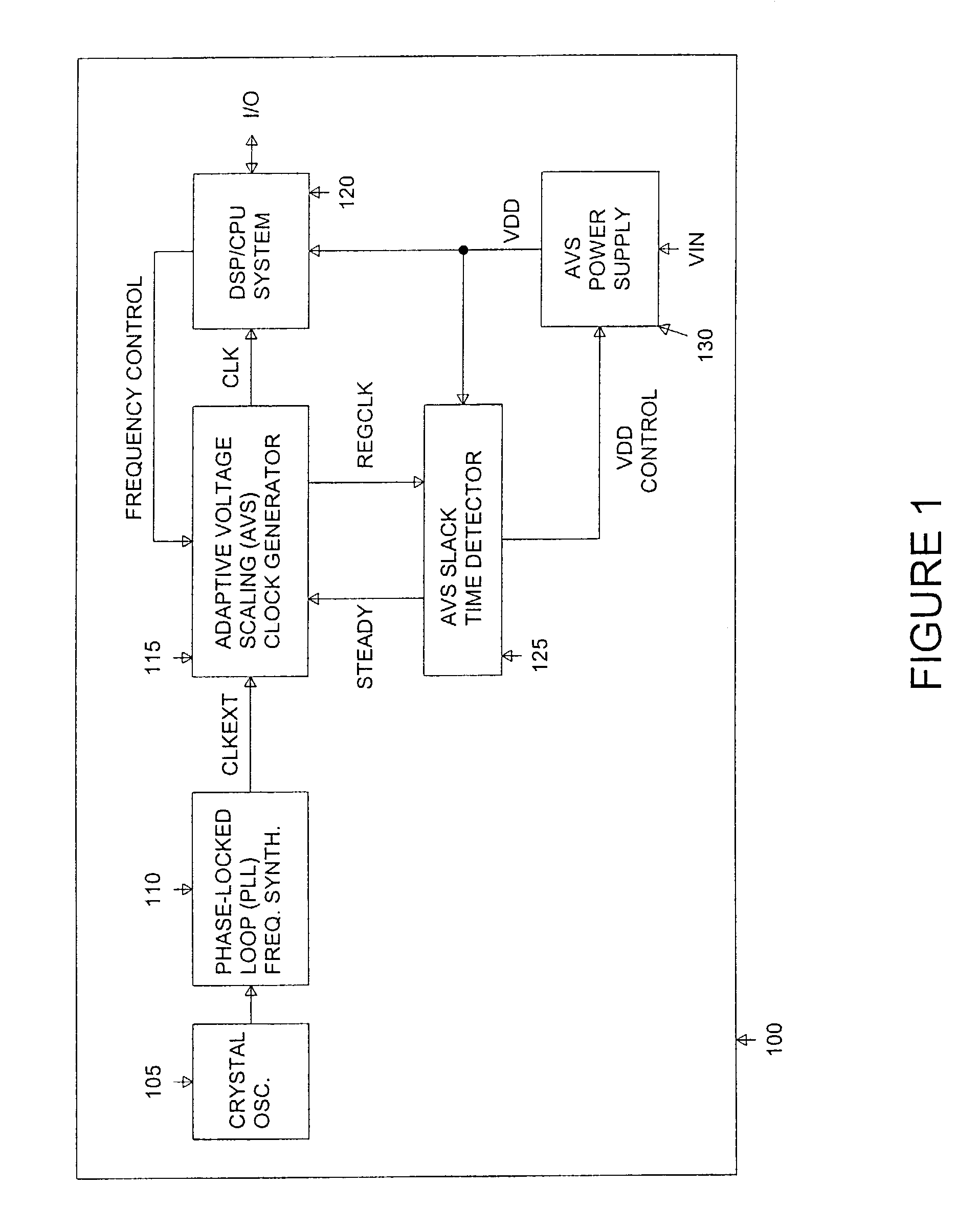
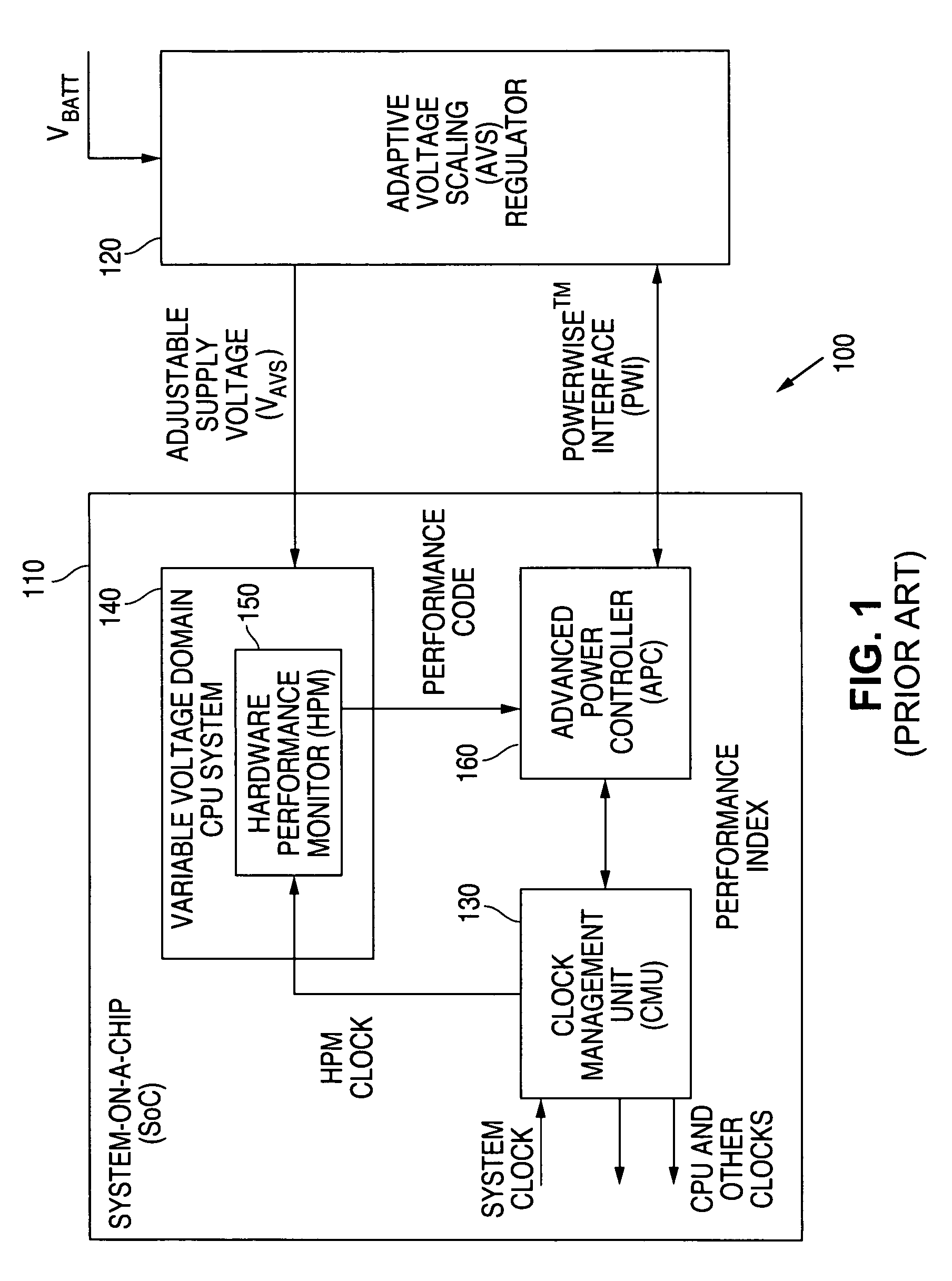
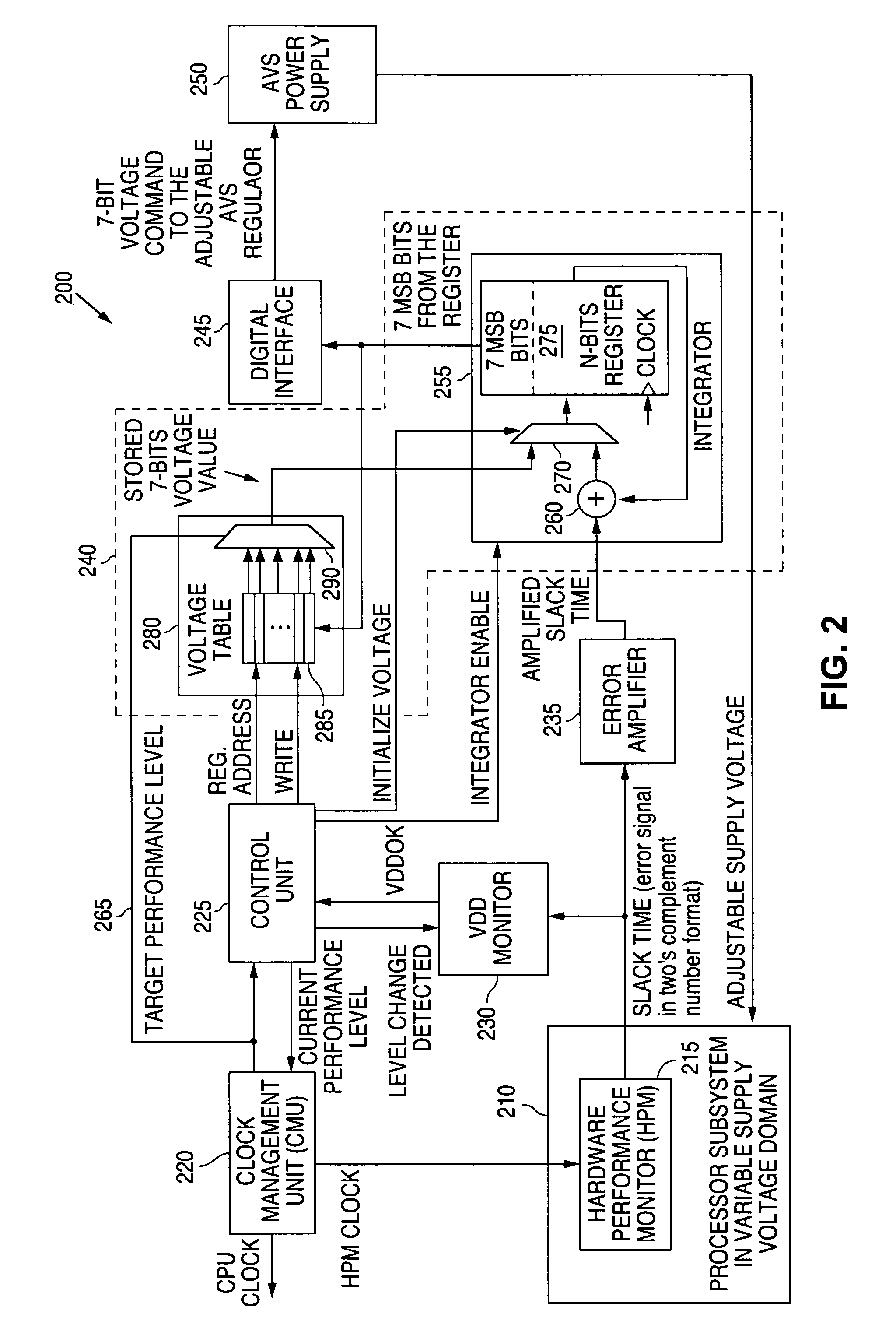
Adaptive Voltage Scaling (AVS) is a closed-loop dynamic power minimization technique that adjusts the voltage supplied to a computer chip to match the chip's power needs during operation. Many computer chips, especially those in mobile devices or Internet of things devices are constrained by the power available (for example, they are limited to the power stored in a battery) and face varying workloads. In other situations a chip may be constrained by the amount of heat it is allowed to generate. In addition, individual chips can vary in their efficiency due to many factors, including minor differences in manufacturing conditions. AVS allows the voltage supplied to the chip, and therefore its power consumption, to be continuously adjusted to be appropriate to the workload and the parameters of the specific chip. This is accomplished by integrating a device that monitors the performance of the chip (a hardware performance manager) into the chip, which then provides information to a power controller.
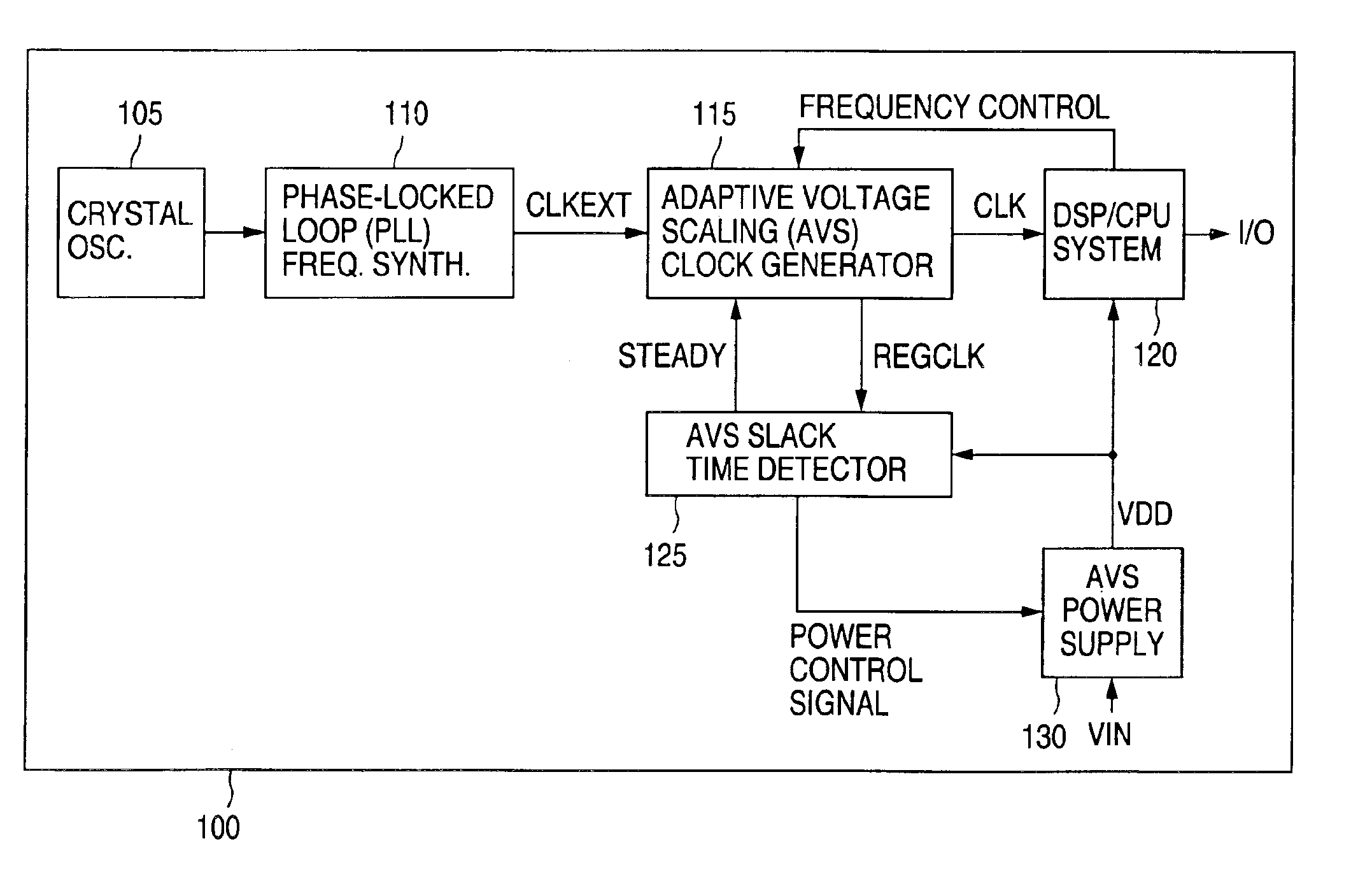
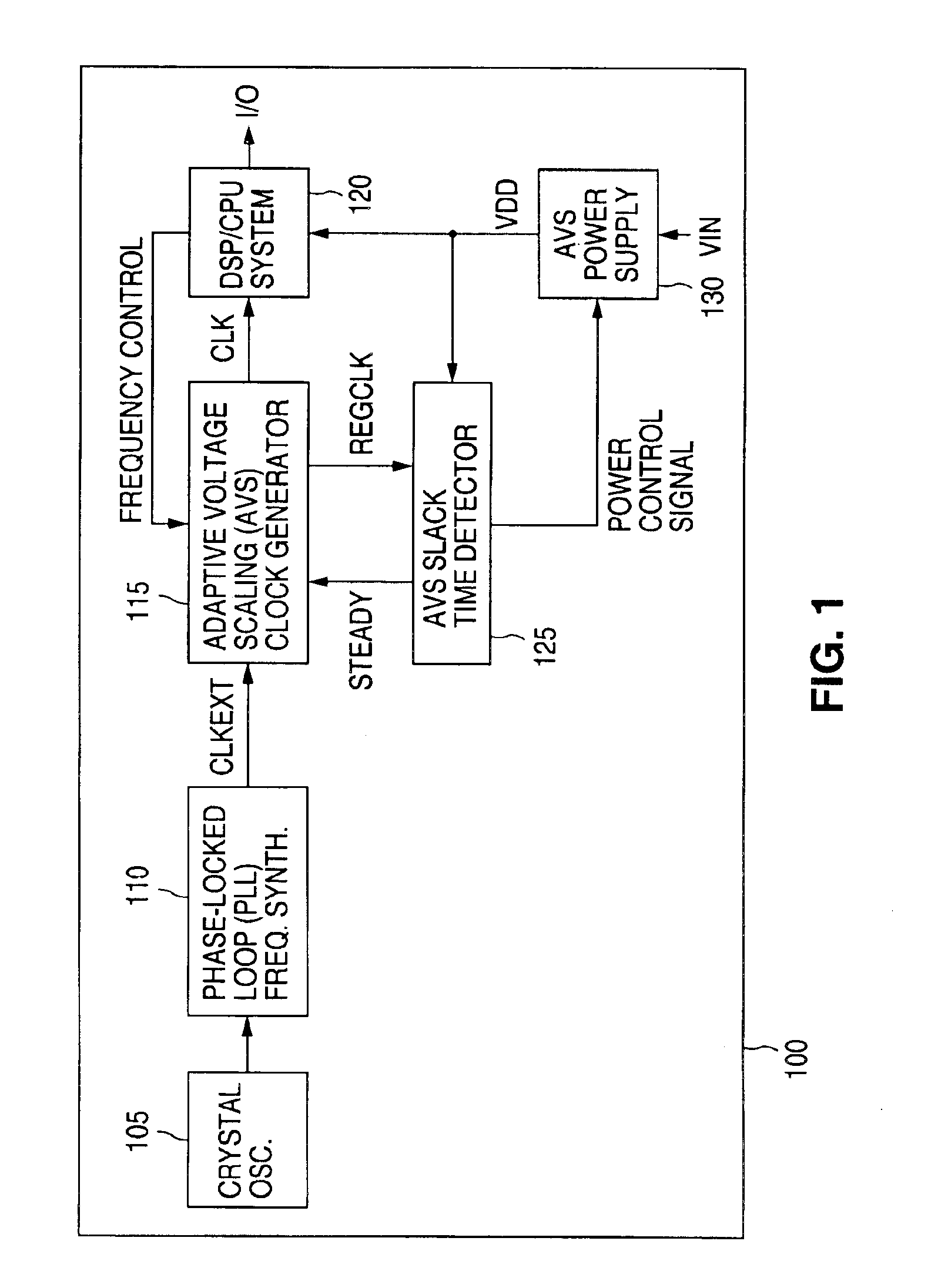
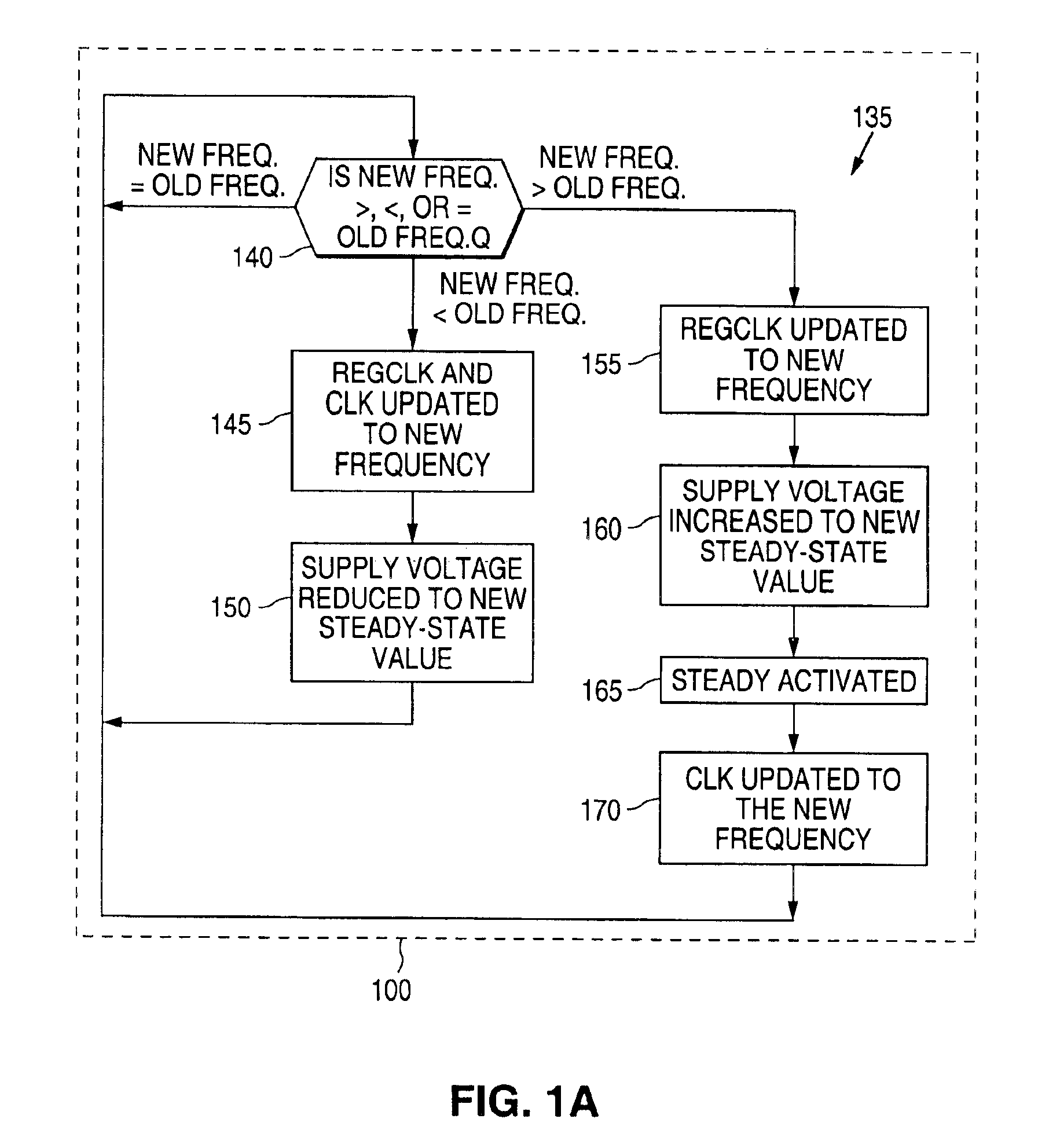
Adaptive voltage scaling digital processing component and method of operating the same
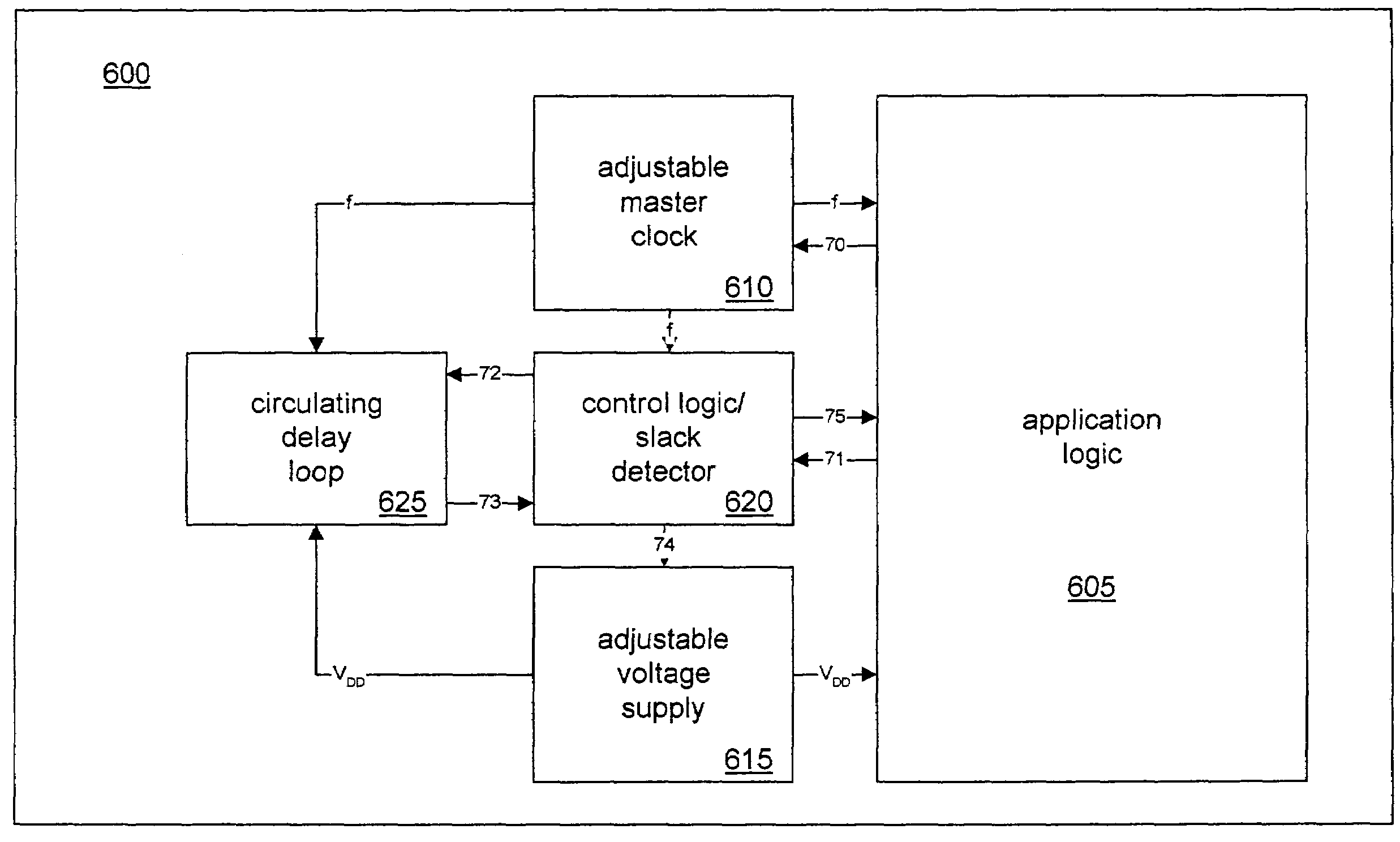
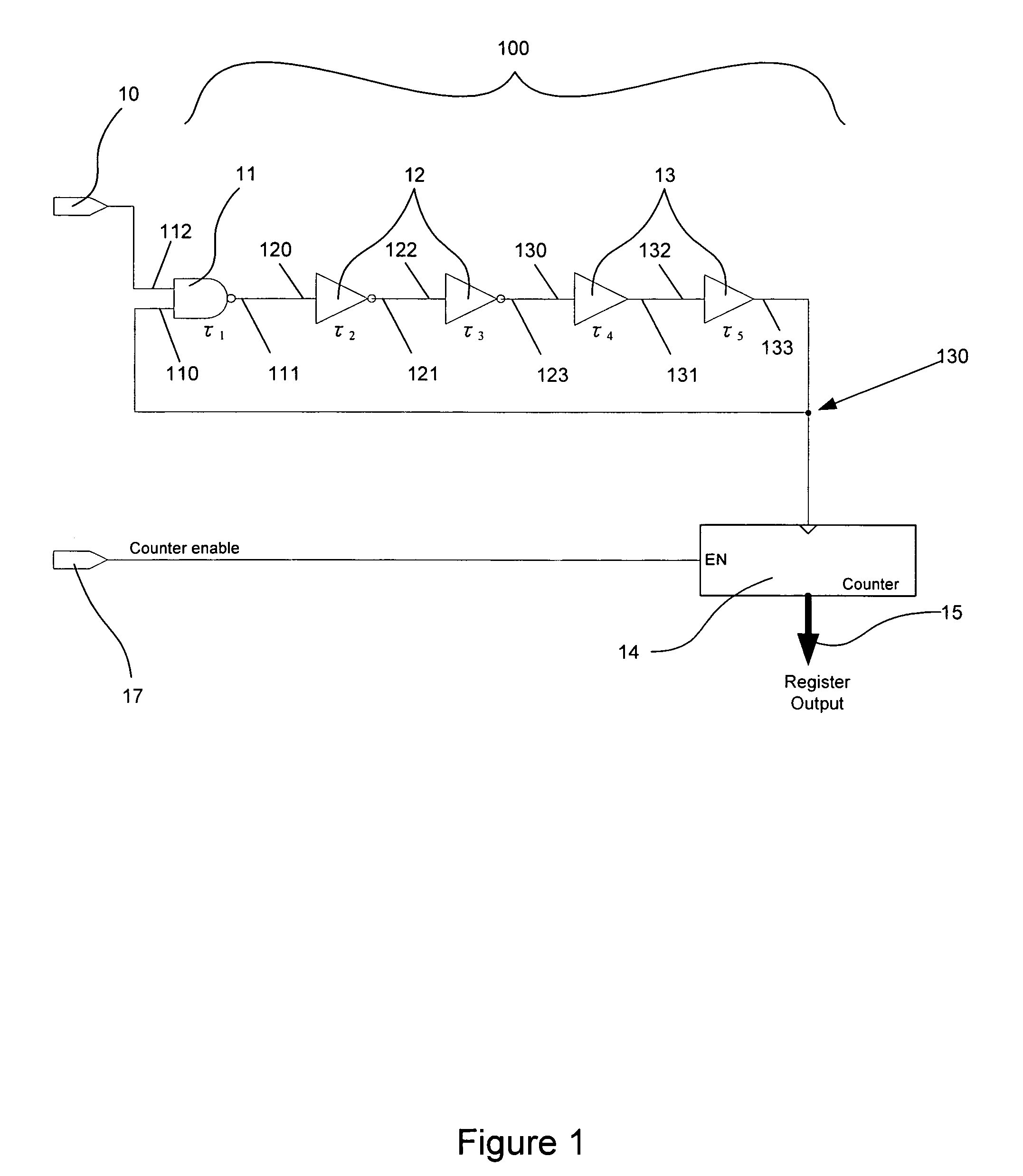
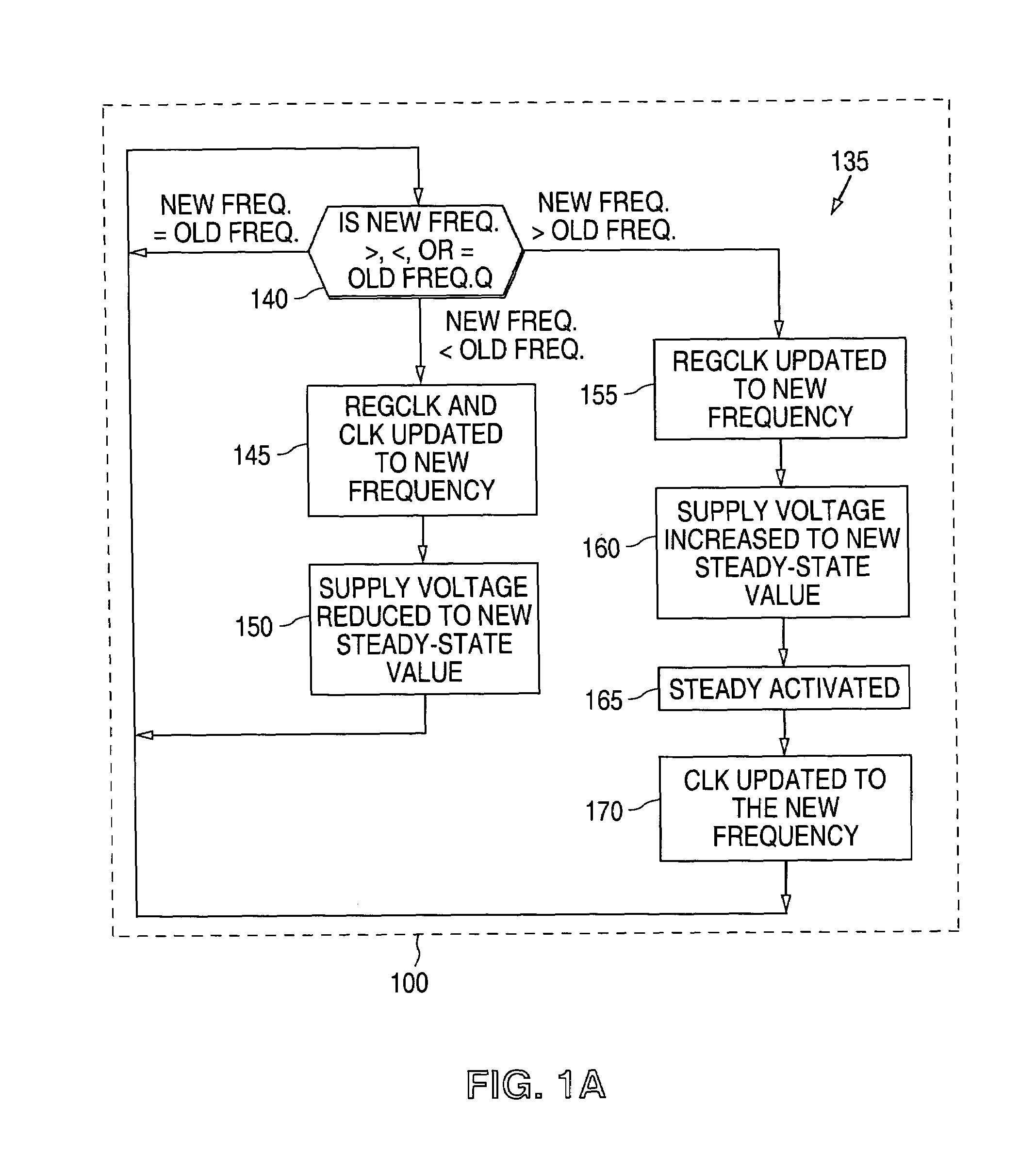
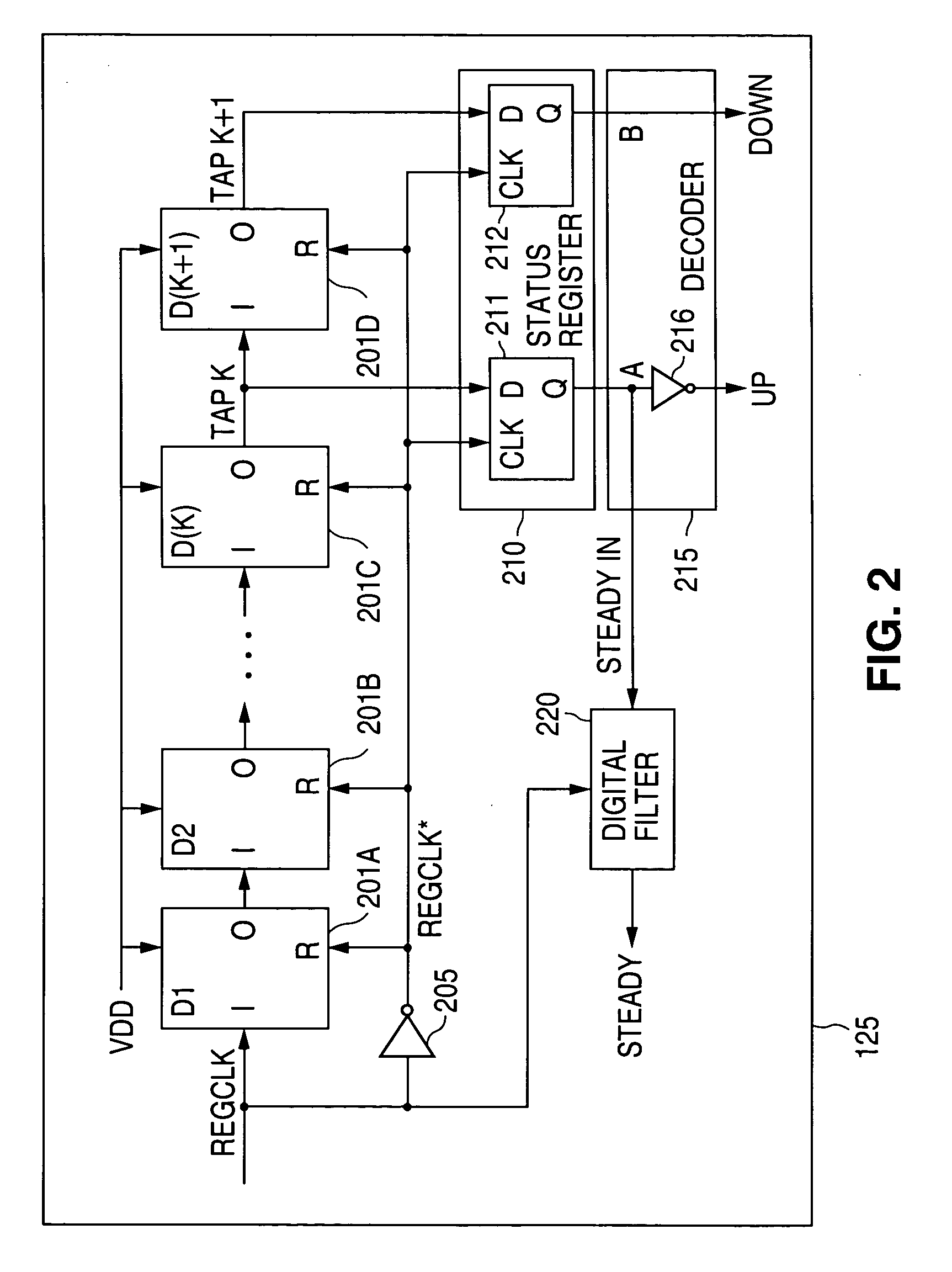
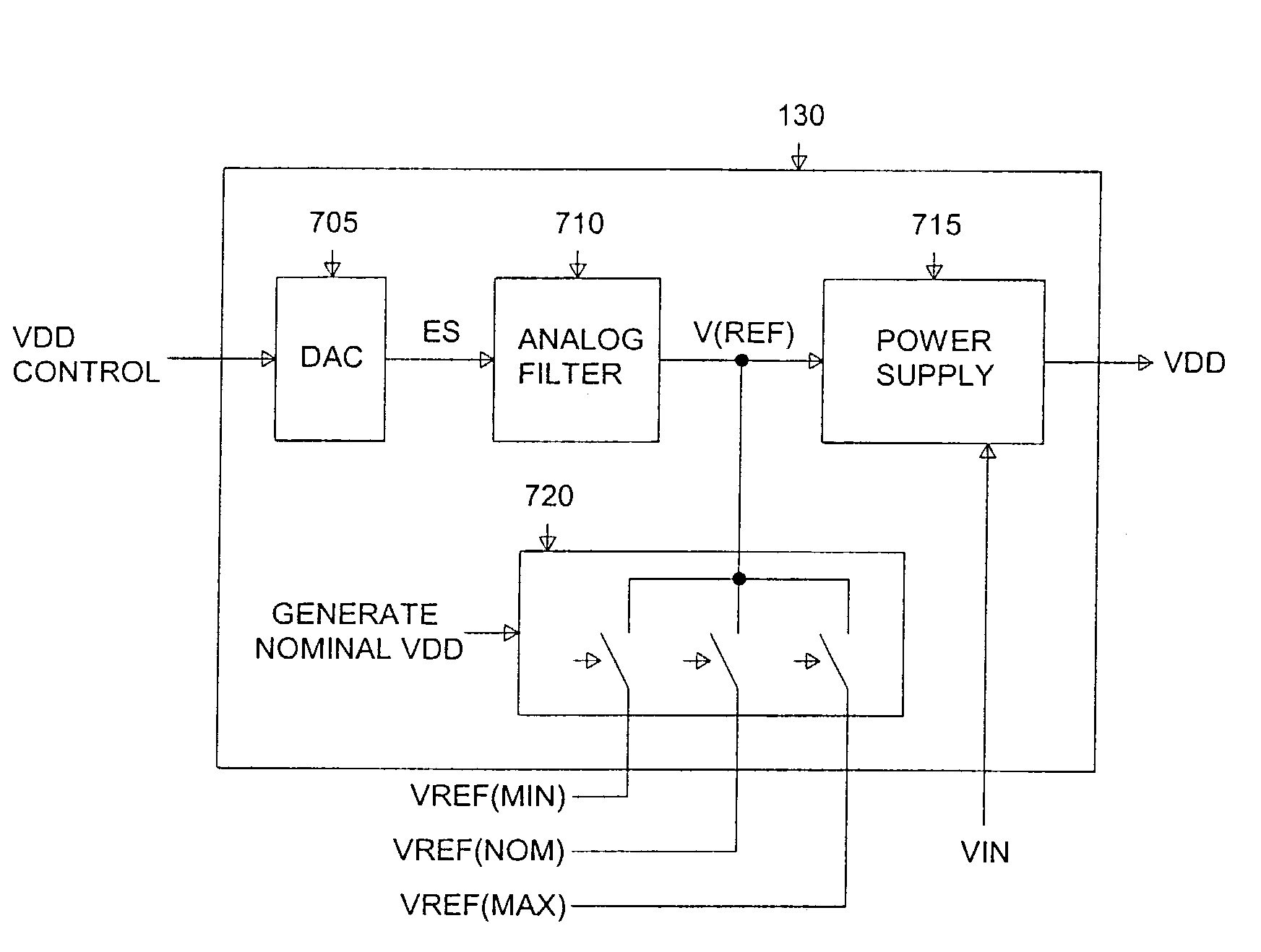
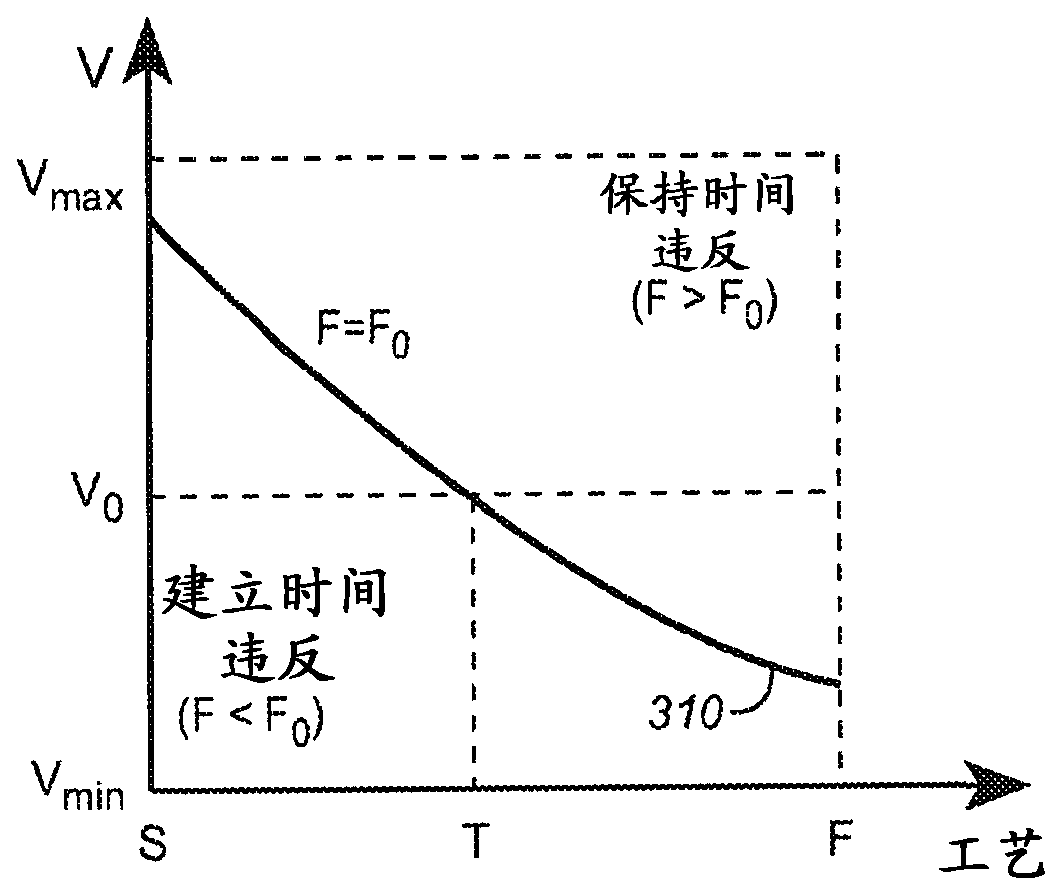
There is disclosed a digital circuit comprising a digital processing component, an adjustable power supply and power supply adjustment circuitry. The digital processing component is capable of operating at a plurality of selected clock frequencies, wherein a maximum delay time of a critical path in the digital processing component is determined by a level of a power supply, VDD, of the digital processing component. The adjustable power supply is capable of supplying VDD to the digital processing component. The power supply adjustment circuitry is operable to receive a first selected clock signal and adjusts the level of VDD such that the maximum delay time of the critical path of the digital processing component is less than a pulse-width duration between a first clock edge of the first selected clock signal and a second clock edge of the first selected clock signal immediately following the first clock edge.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
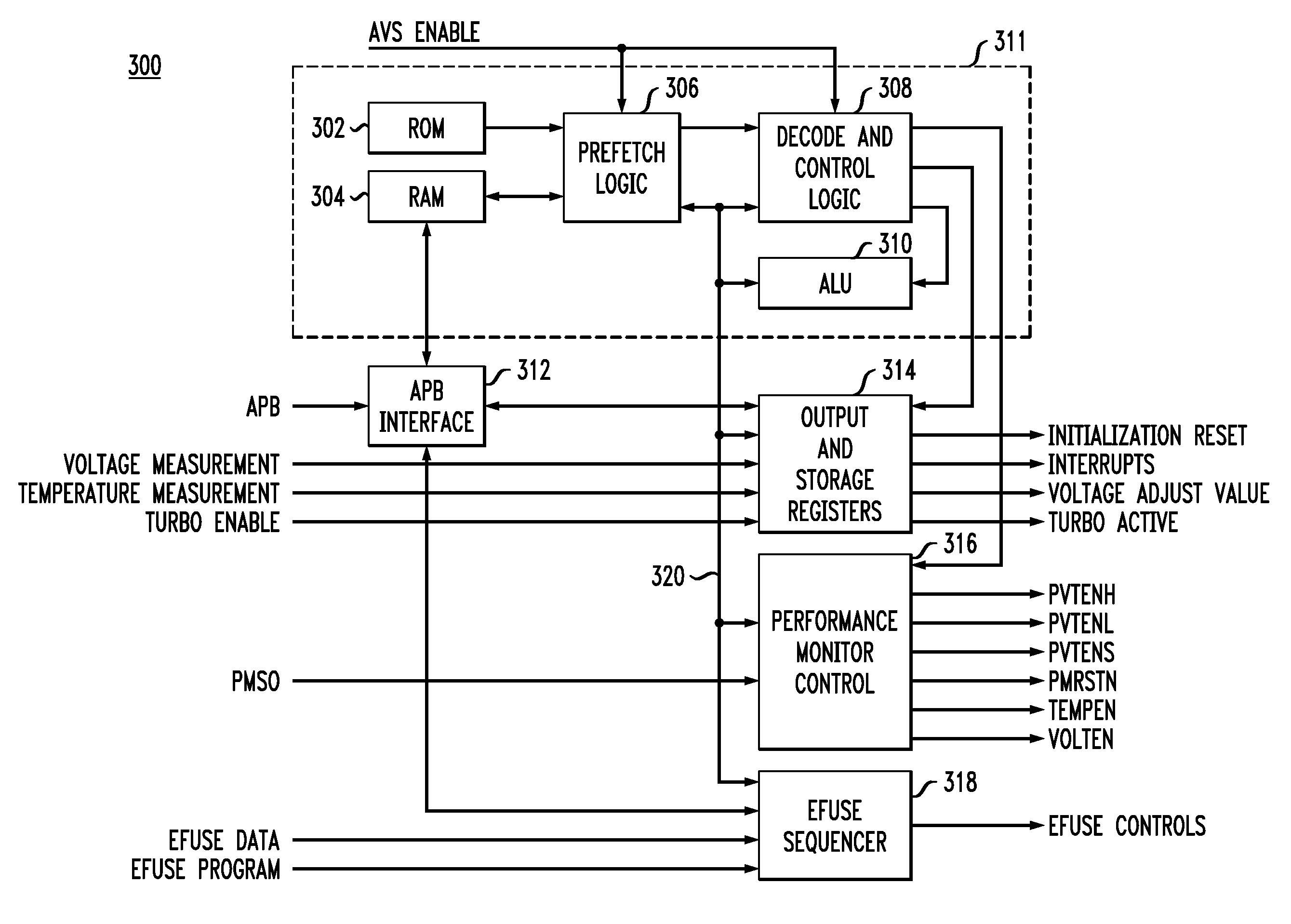
ADAPTIVE VOLTAGE SCALERS (AVSs), SYSTEMS, AND RELATED METHODS
ActiveUS20110080202A1Avoid and reduce tolerance voltage marginAvoid and reduce voltage marginPower supply for data processingElectric pulse generatorSelf adaptiveOperating frequency
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Memory device with adaptive voltage scaling based on error information
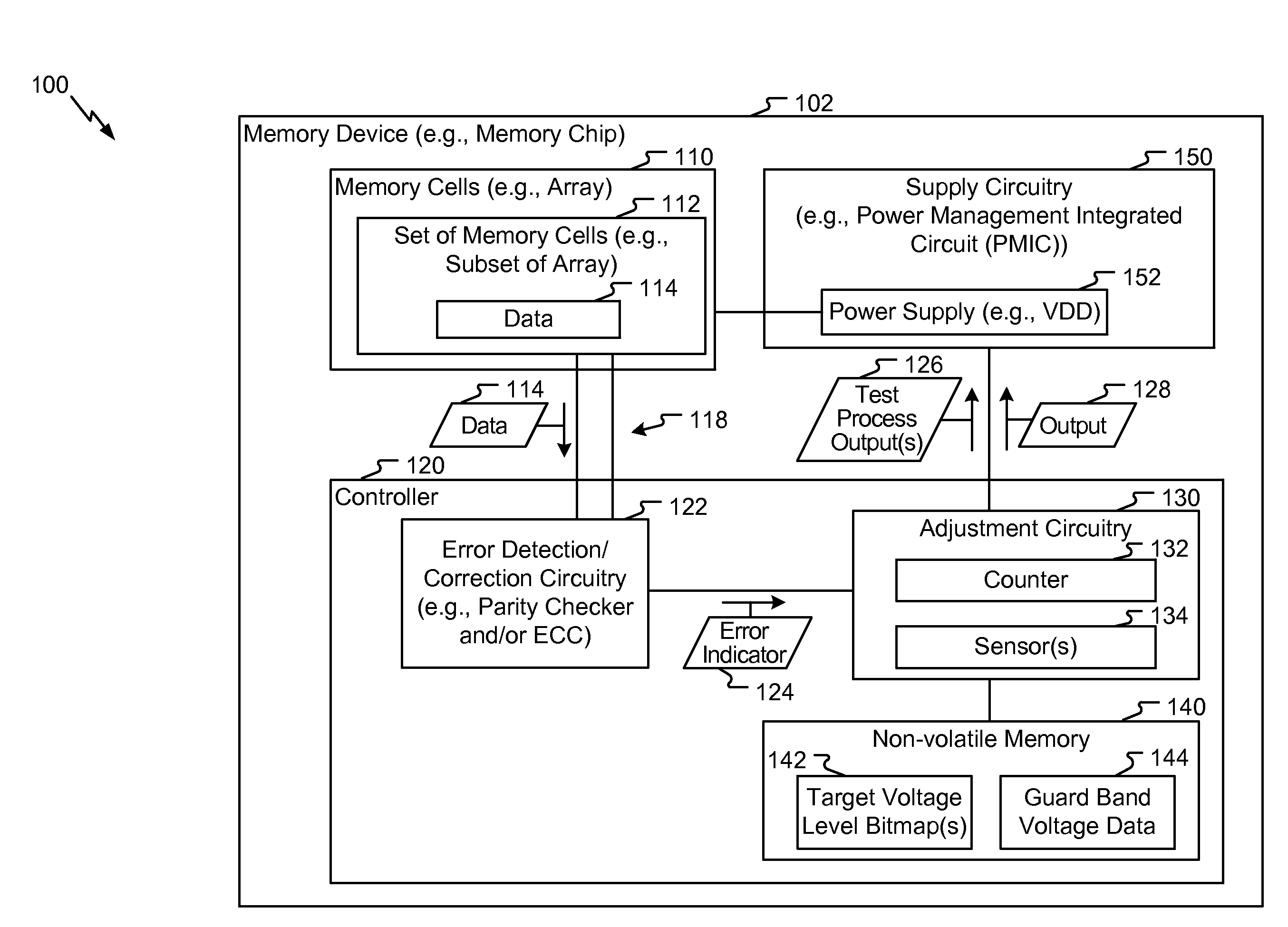
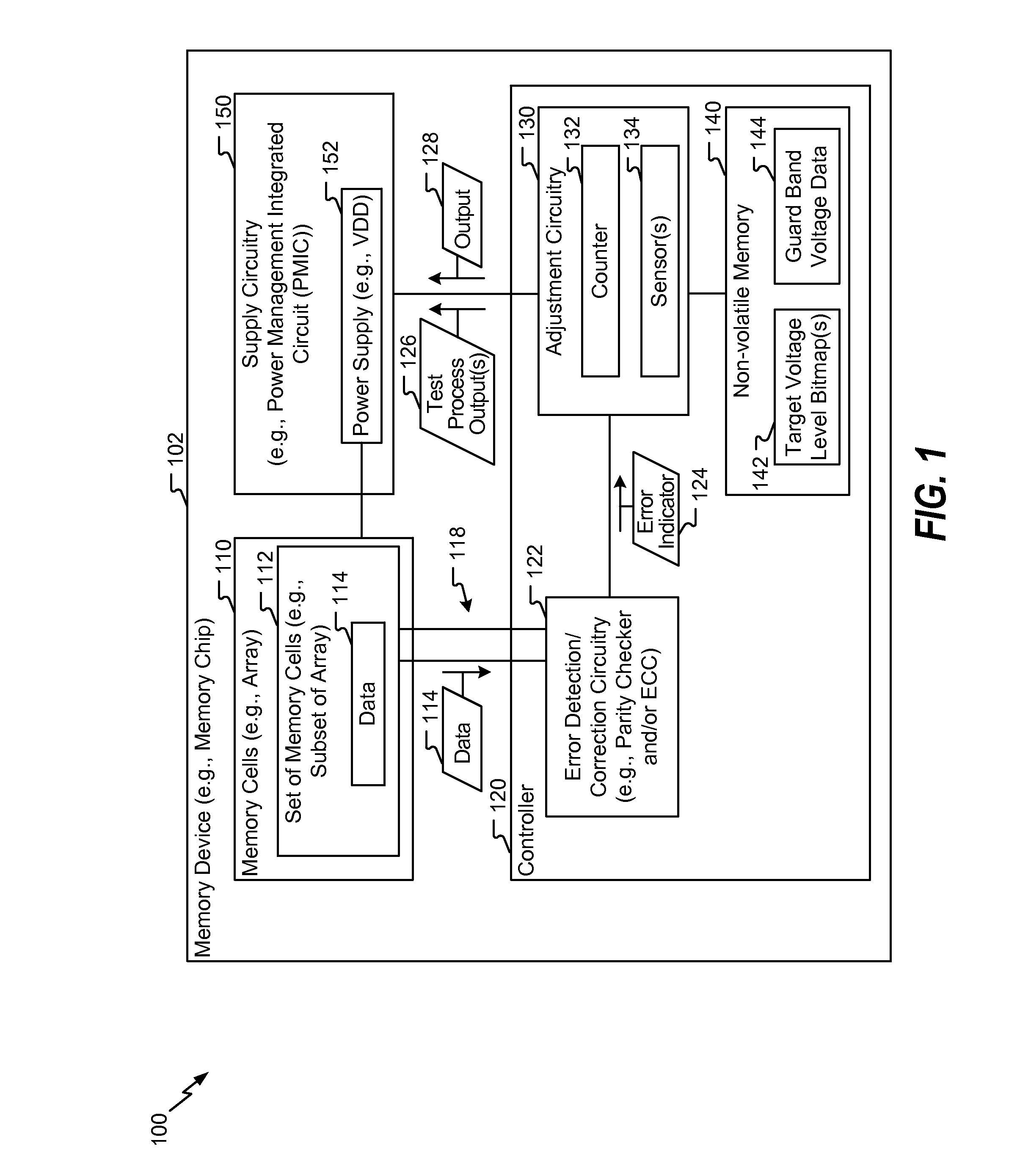
ActiveUS20160225436A1Reduce impactOperation margin is reducedDigital storageNon-redundant fault processingEngineeringSelf adaptive
A method of operation of a memory device includes, for each operating frequency of multiple operating frequencies, determining a target voltage level of a supply voltage. For example, a first target voltage level for a first operating frequency of the multiple operating frequencies is determined. The method includes accessing first data from the memory device while the memory device is operating at the first operating frequency and is powered by the supply voltage having a first voltage level. The method includes determining a first number of errors associated with the first data. The method further includes, in response to the first number of errors satisfying a threshold, adjusting the supply voltage to a second voltage level that is greater than the first voltage level.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
System and method for signal delay in an adaptive voltage scaling slack detector
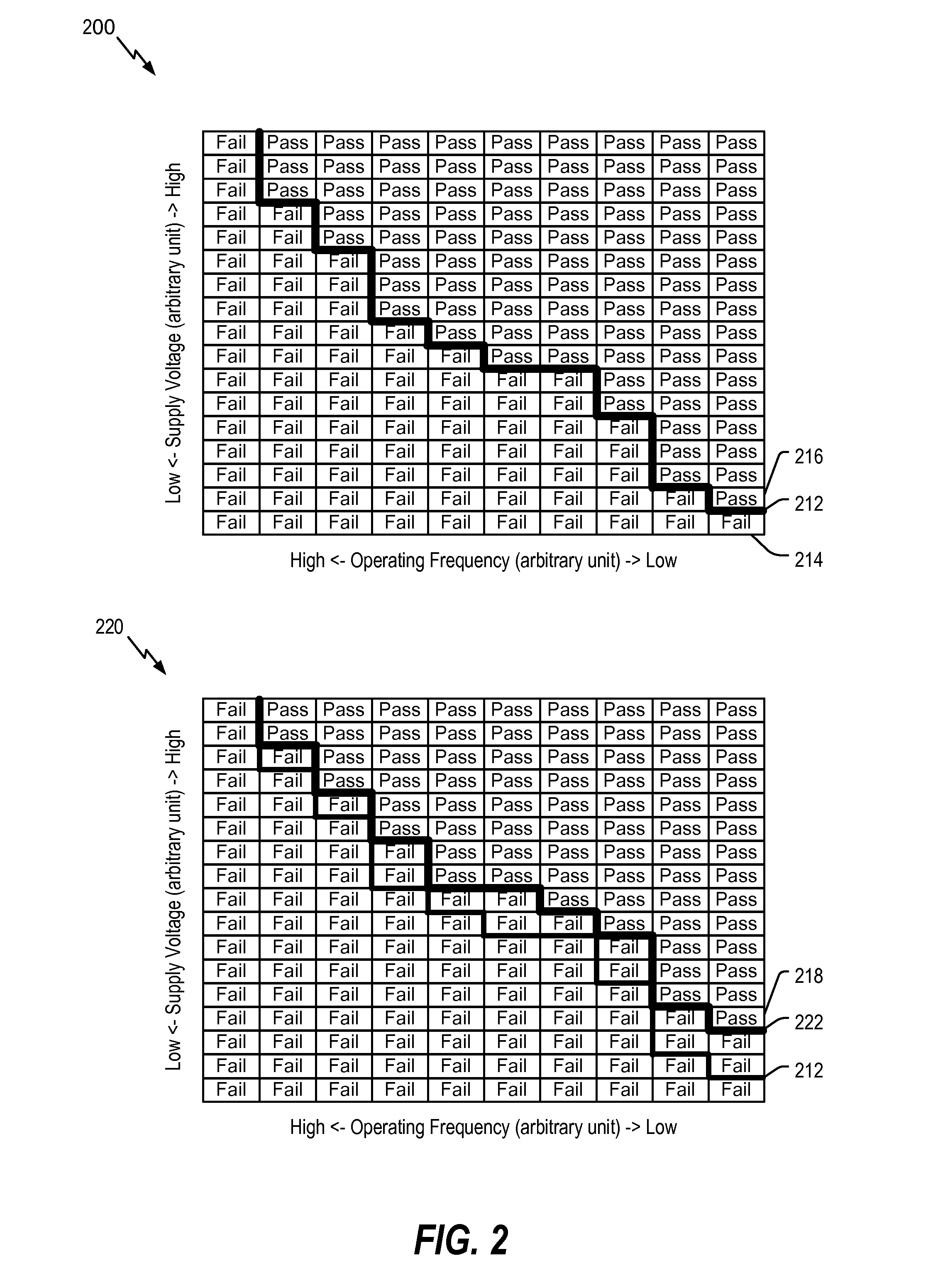
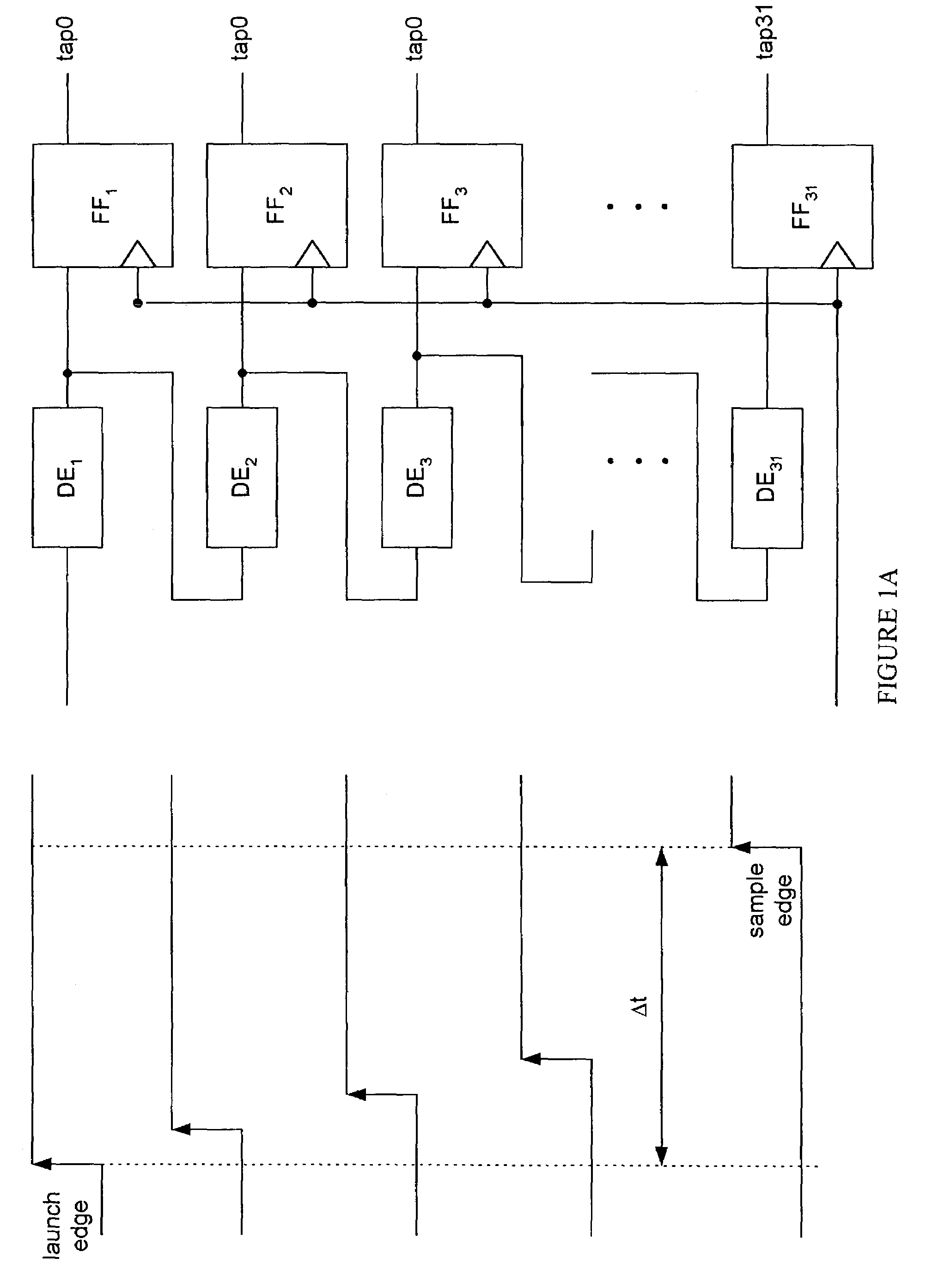
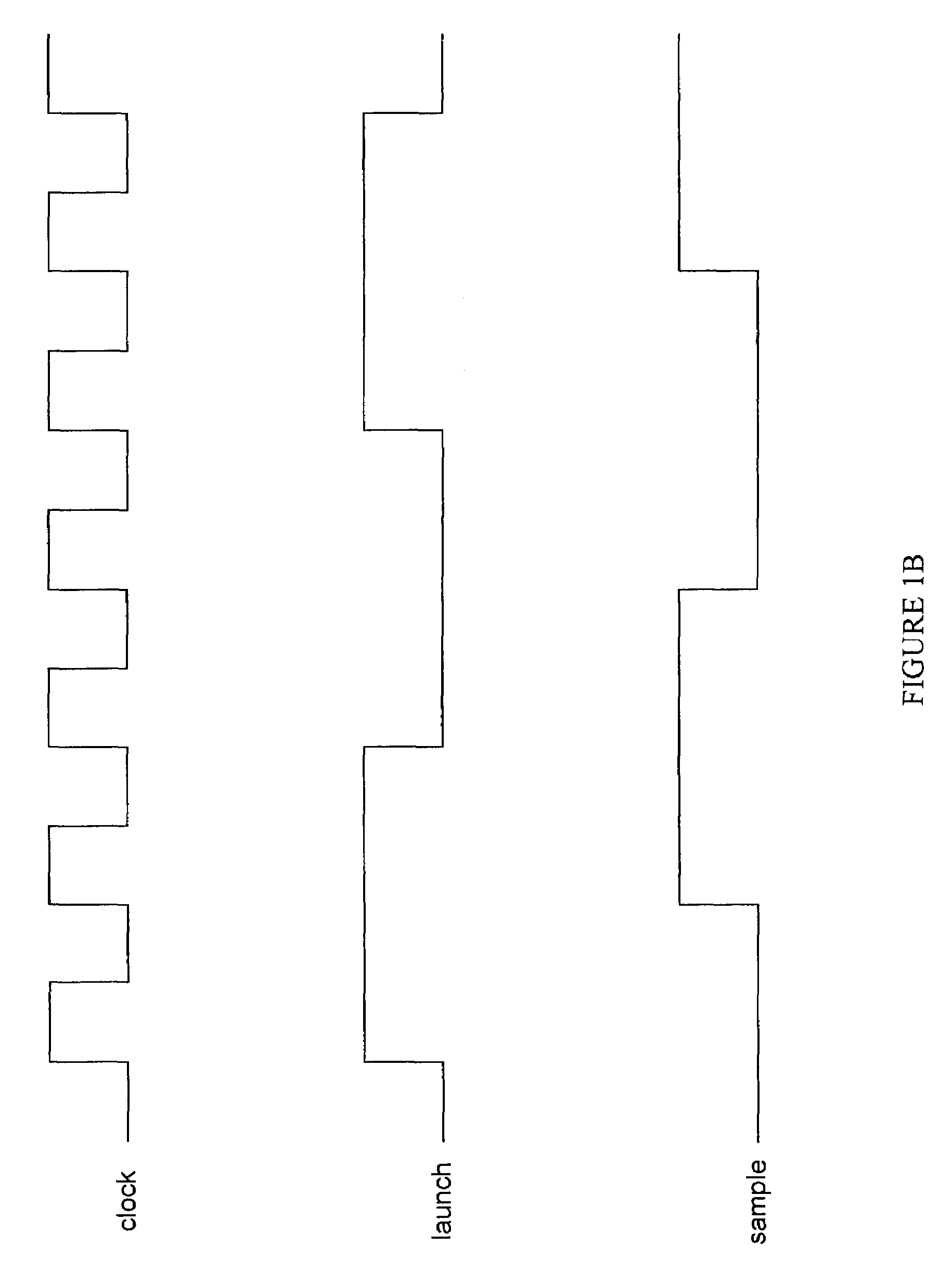
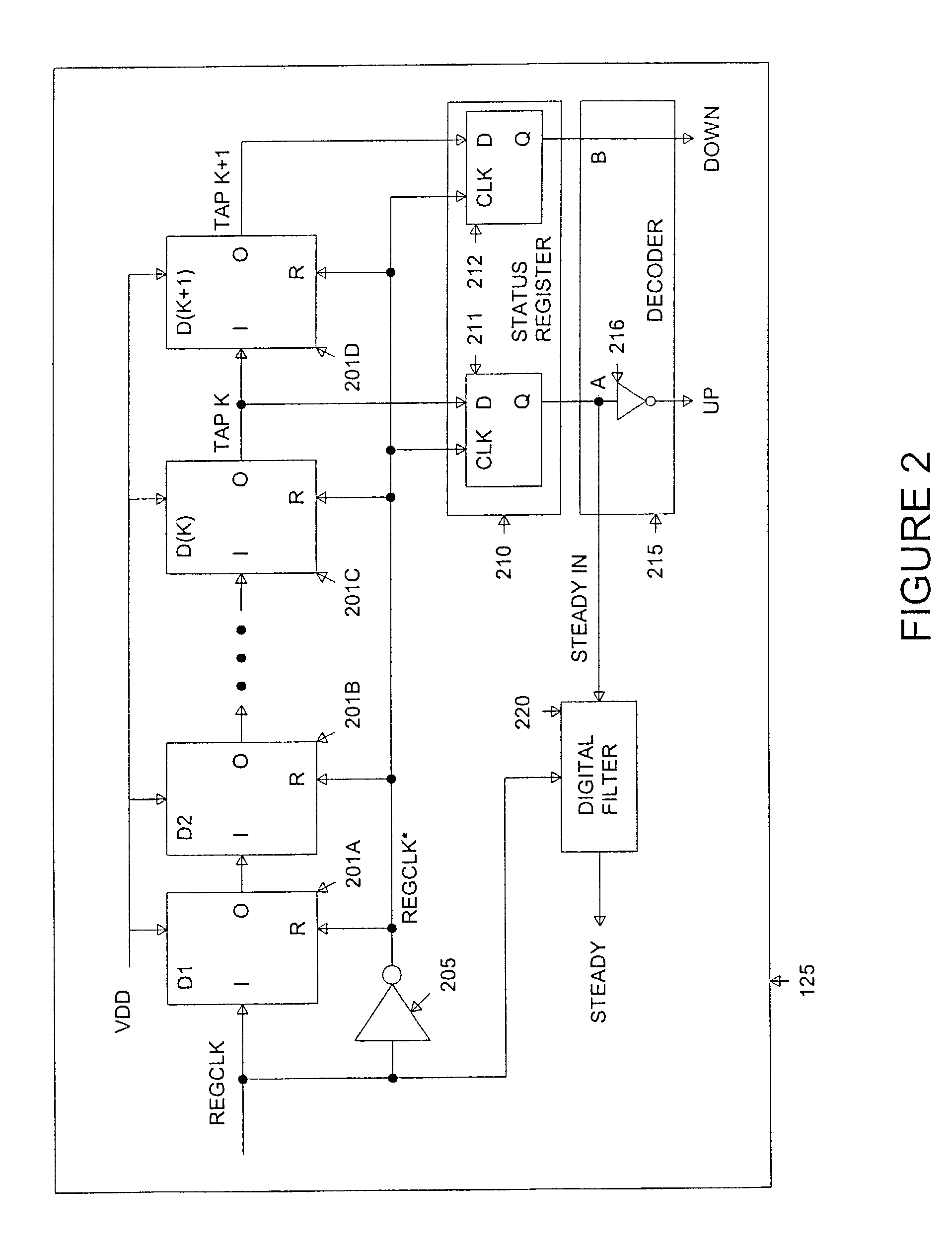
ActiveUS7149903B1Easy maintenanceContinuously circulated pulse countersVolume/mass flow measurementLeading edgeSelf adaptive
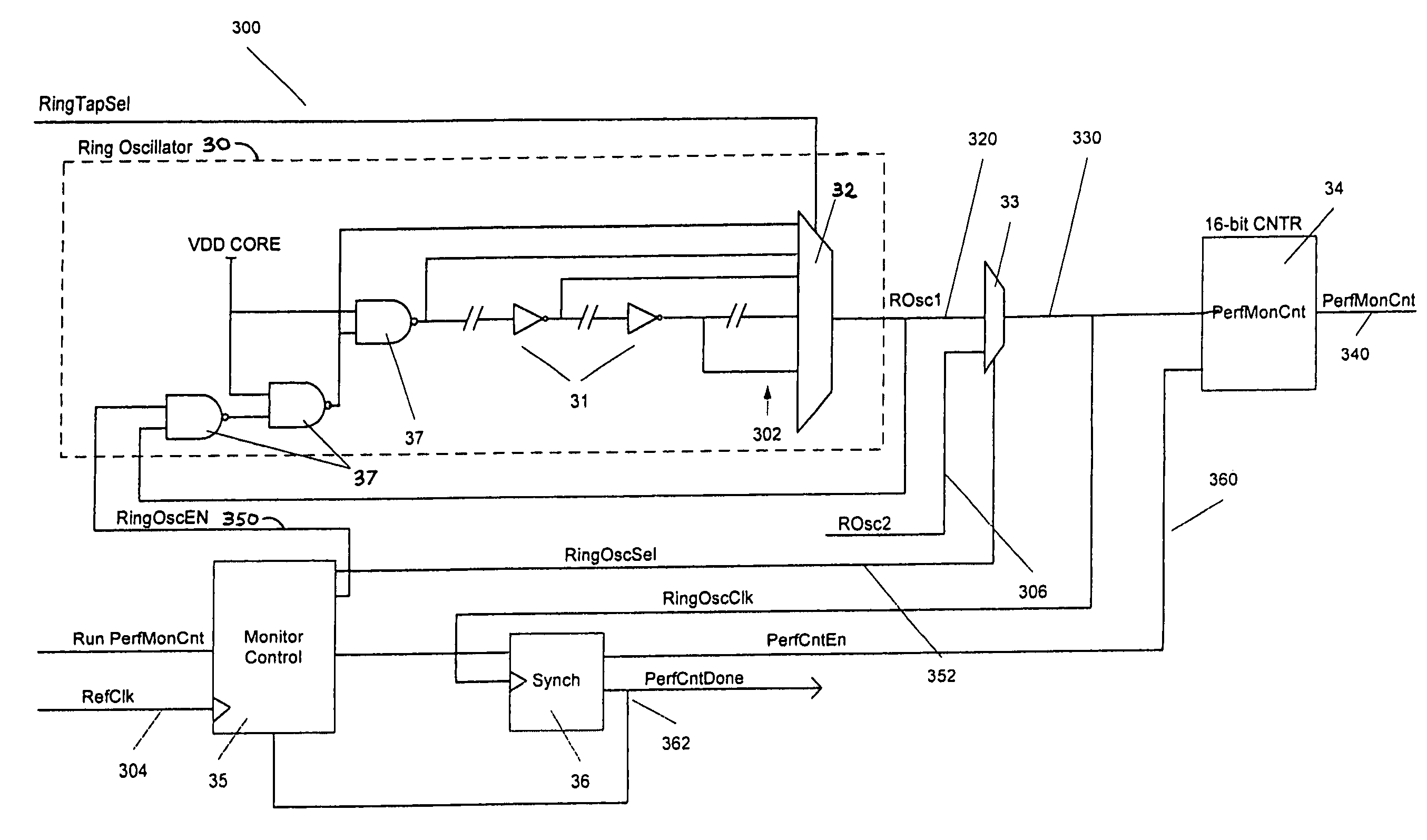
A system and method for slack determination in a logic integrated circuit. A launch pulse is input to a circular delay loop circuit. The leading edge of the launch pulse causes a pulse to circulate around the circular delay loop. The number of passes made through the loop by the circulating pulse is counted by a latch / counter circuit. A sample pulse is input to the latch / counter circuit to latch the number of pulse circulations at the leading edge of the sample pulse. The pulse circulation count provides delay information in the circuit that may subsequently be used to adjust a supply voltage in the integrated circuit.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Temperature Compensating Adaptive Voltage Scalers (AVSs), Systems, and Methods
ActiveUS20110004774A1Avoid and reduce voltage marginAvoiding and reducing voltage marginEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringOperating frequency
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
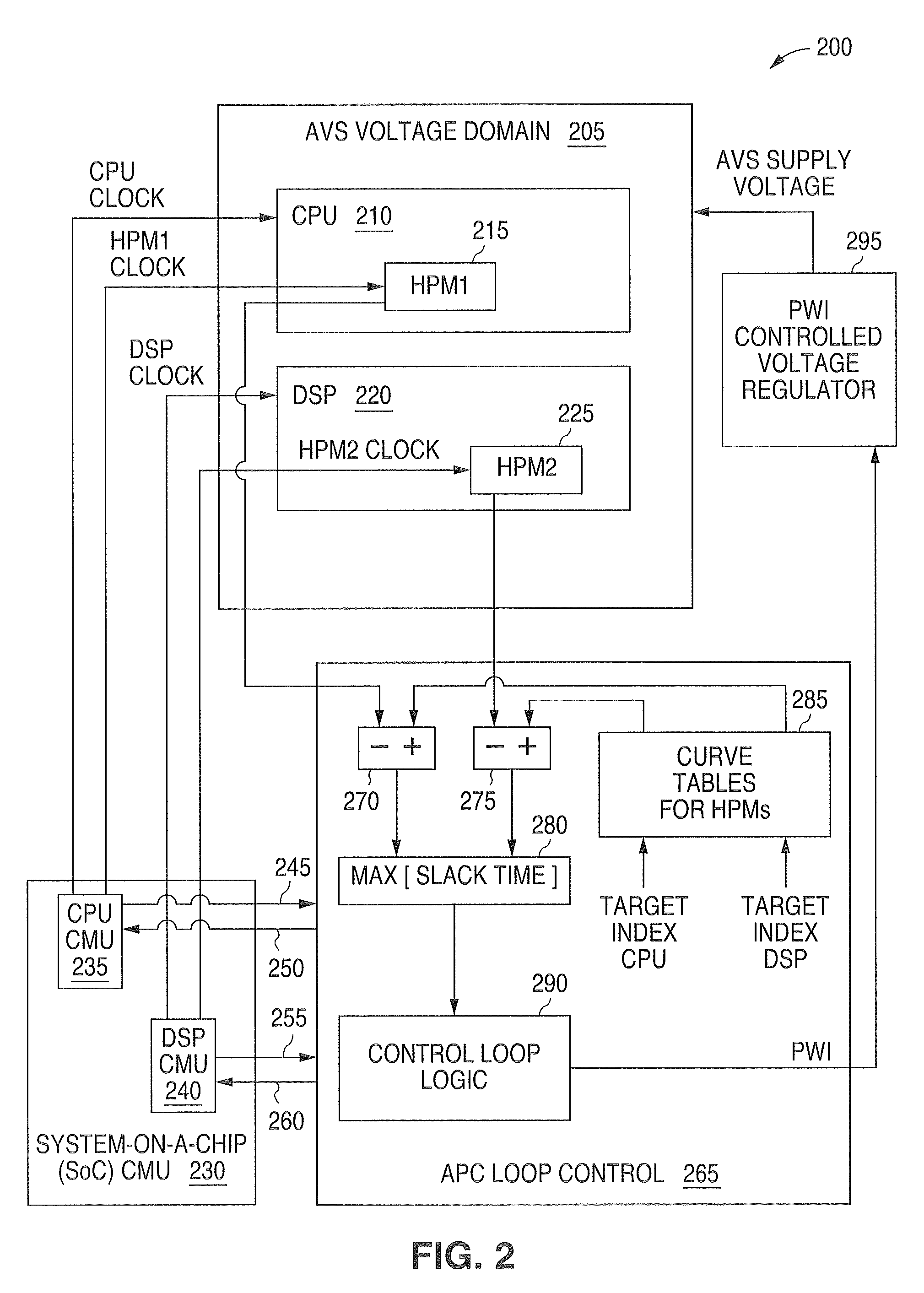
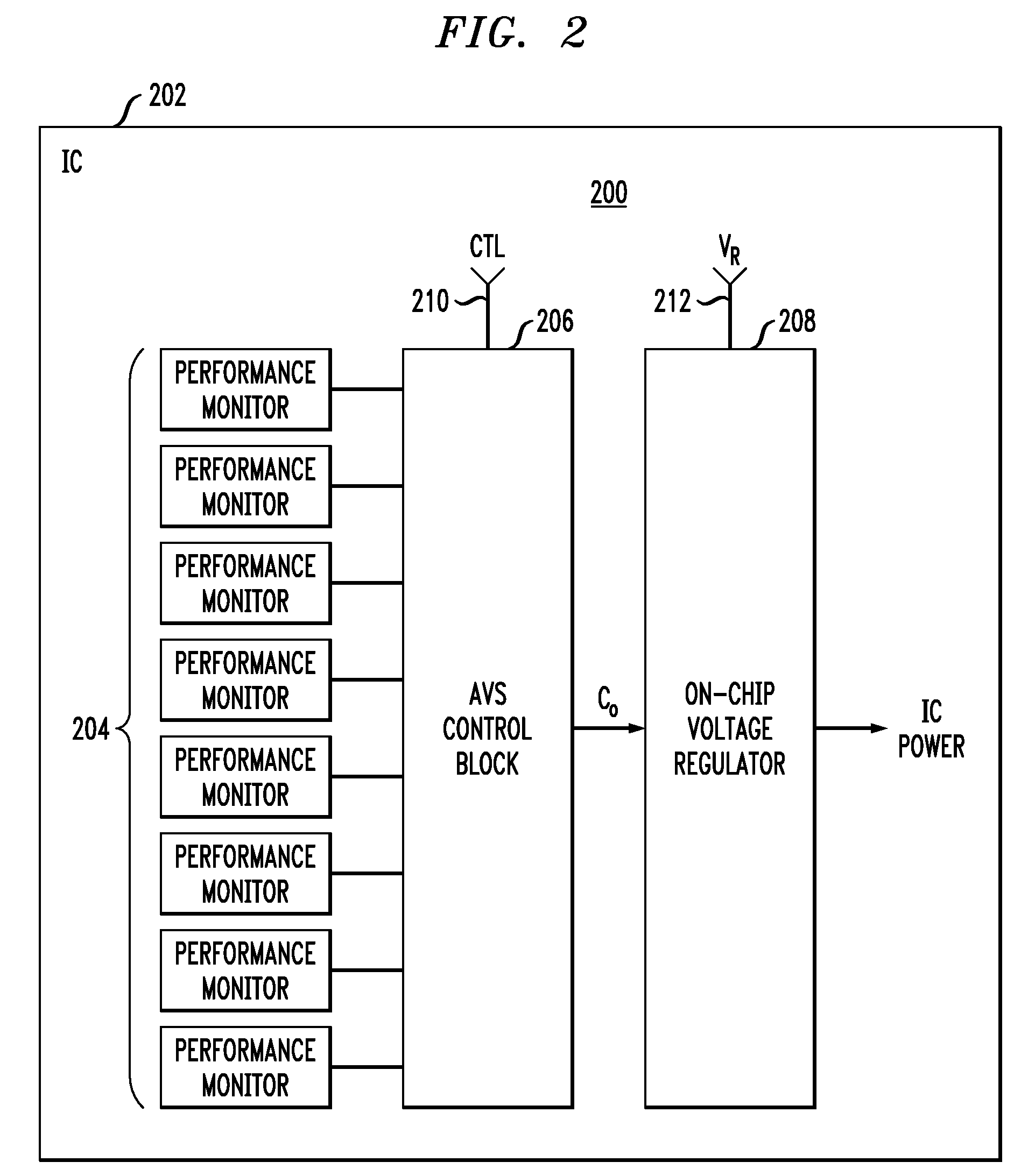
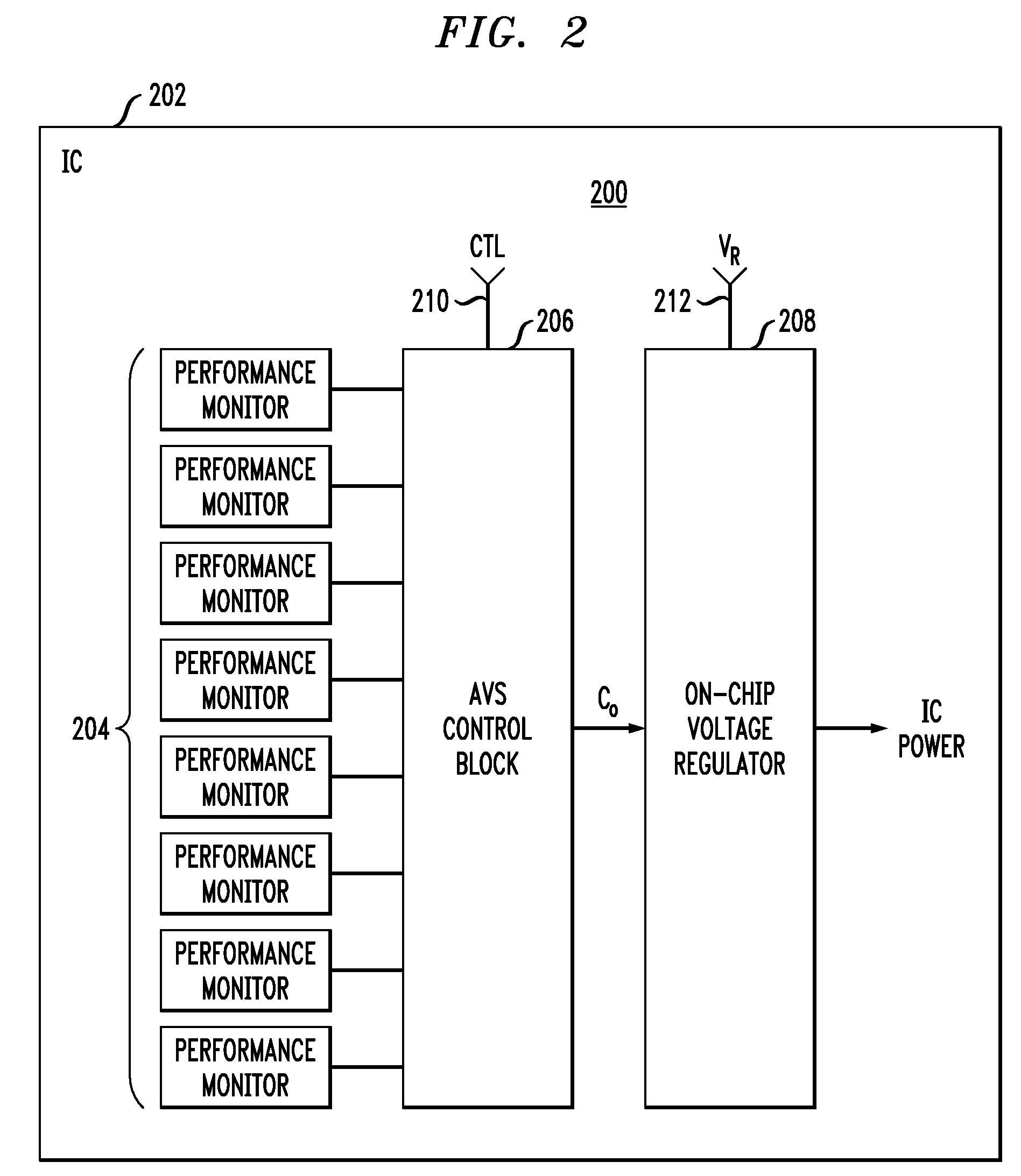
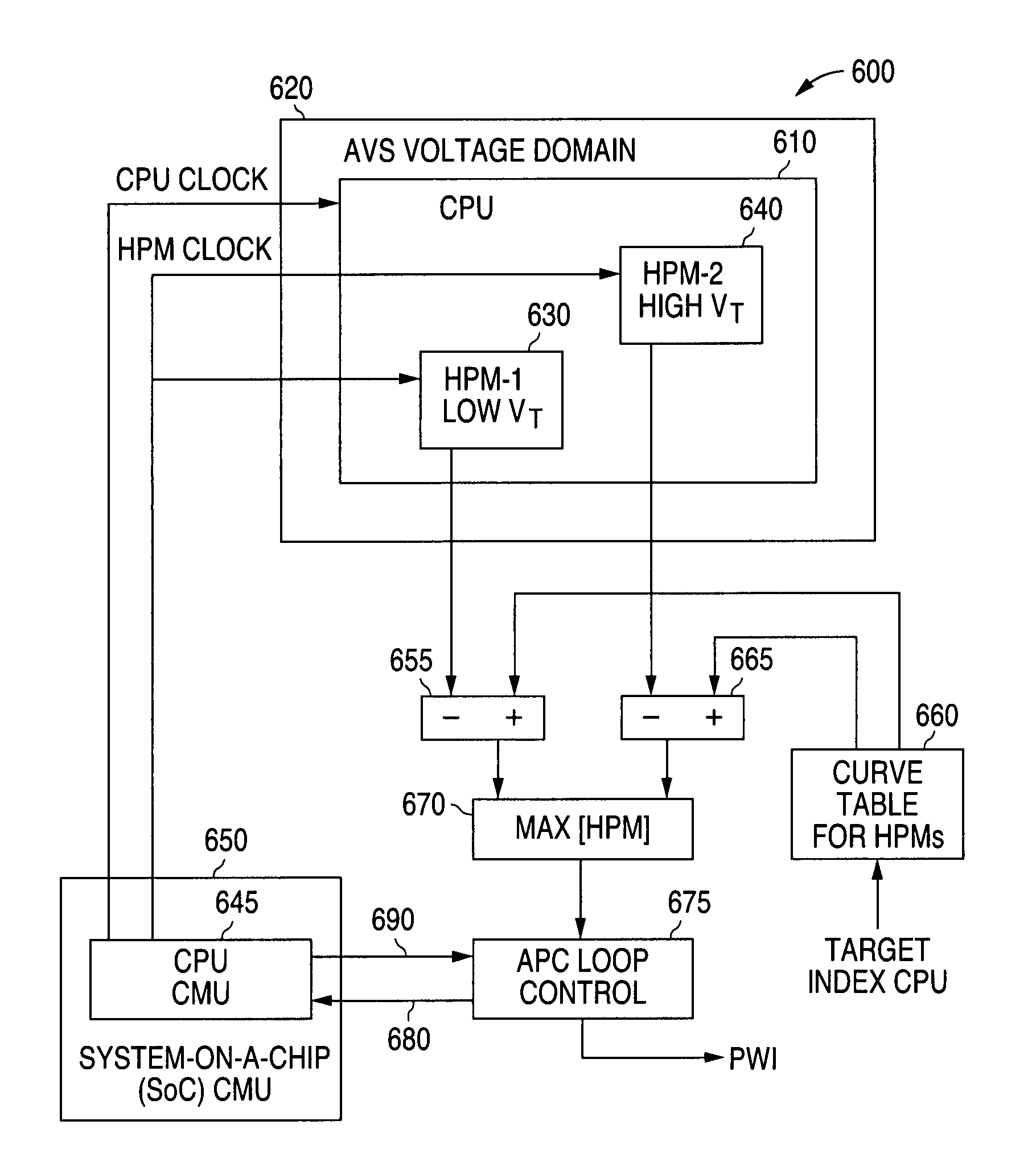
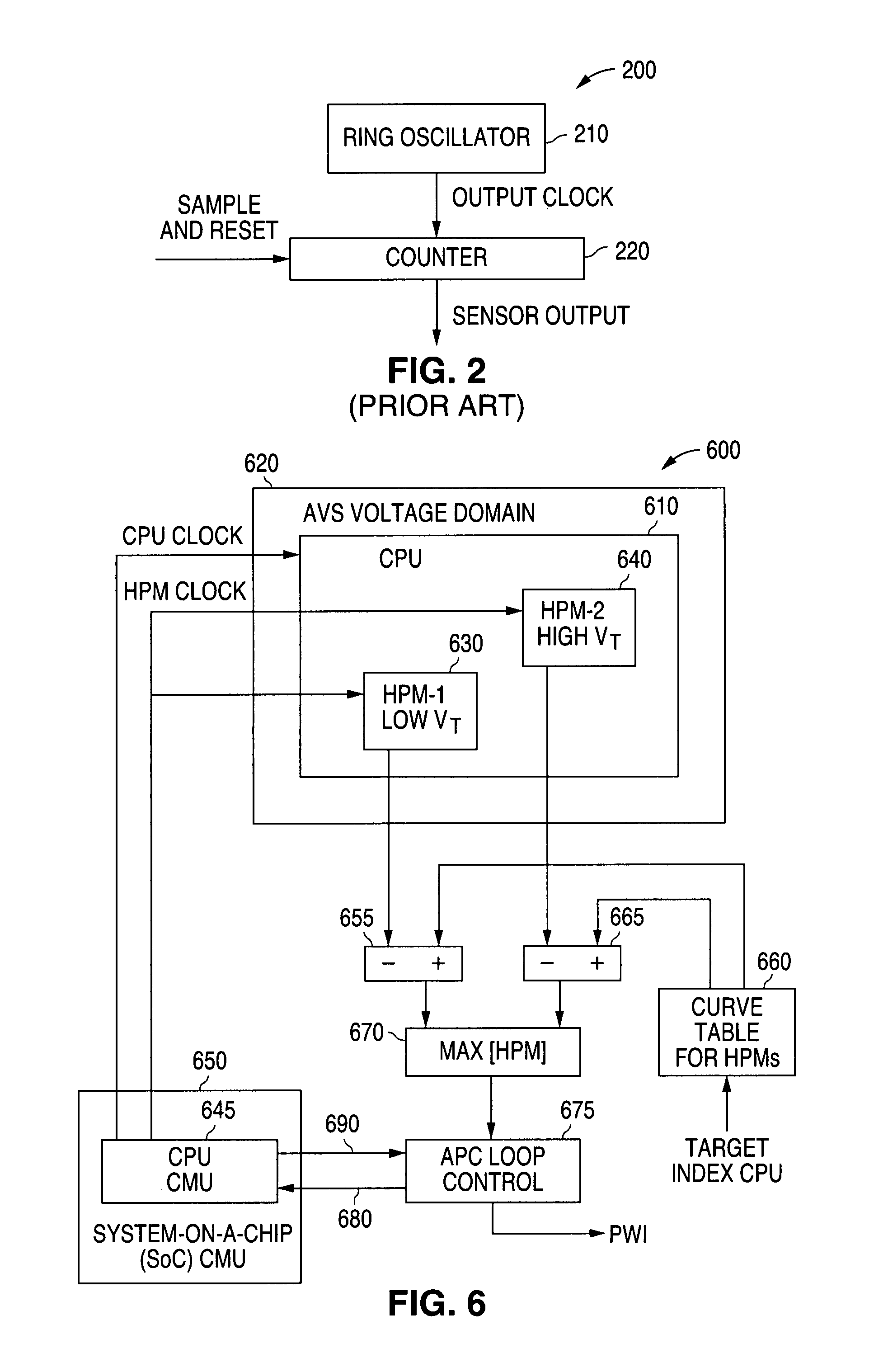
System and method for providing adaptive voltage scaling with multiple clock domains inside a single voltage domain
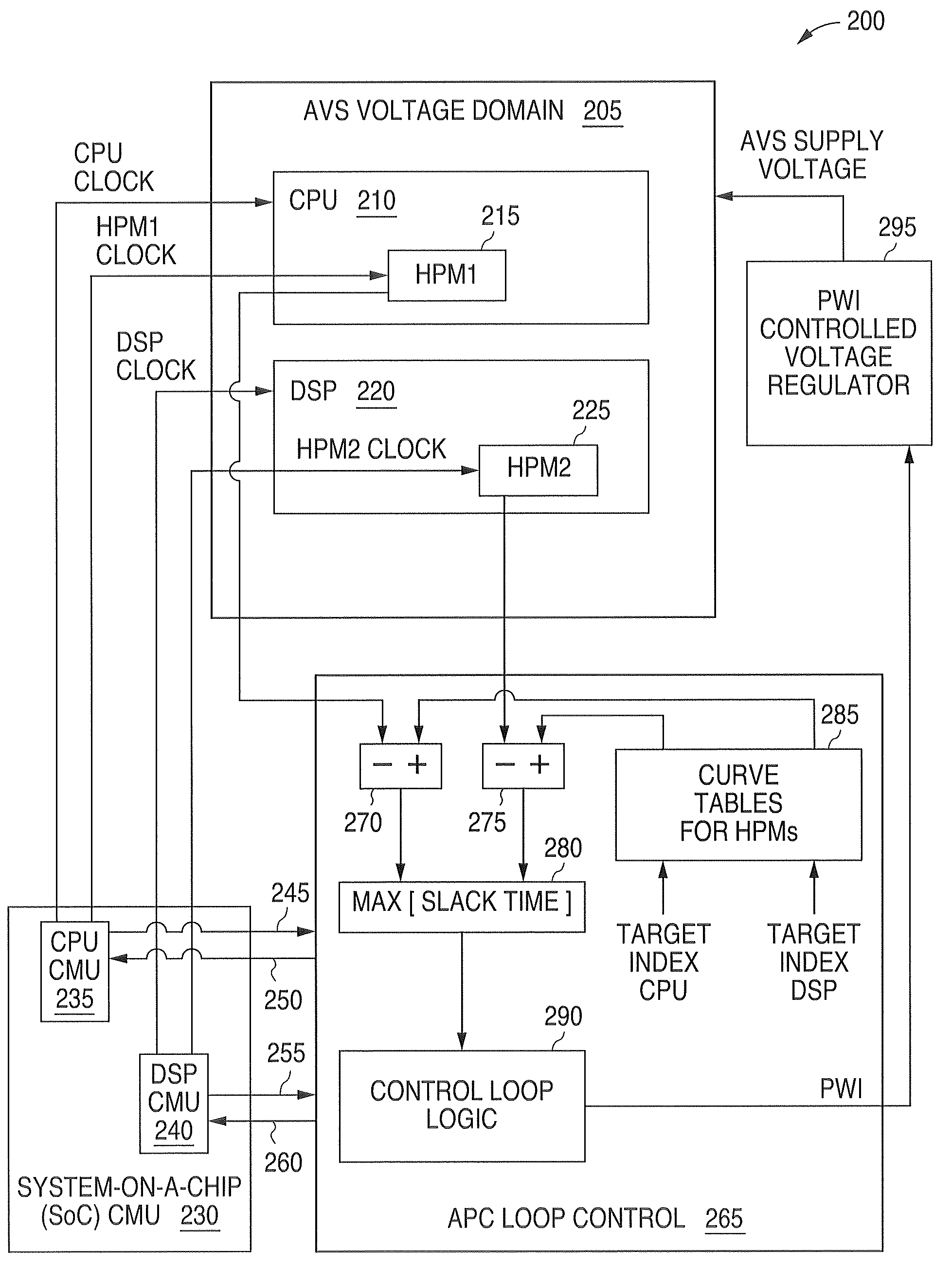
ActiveUS7921312B1Accurate scaleEnergy efficient ICTImpedence convertorsPower controllerSoftware engineering
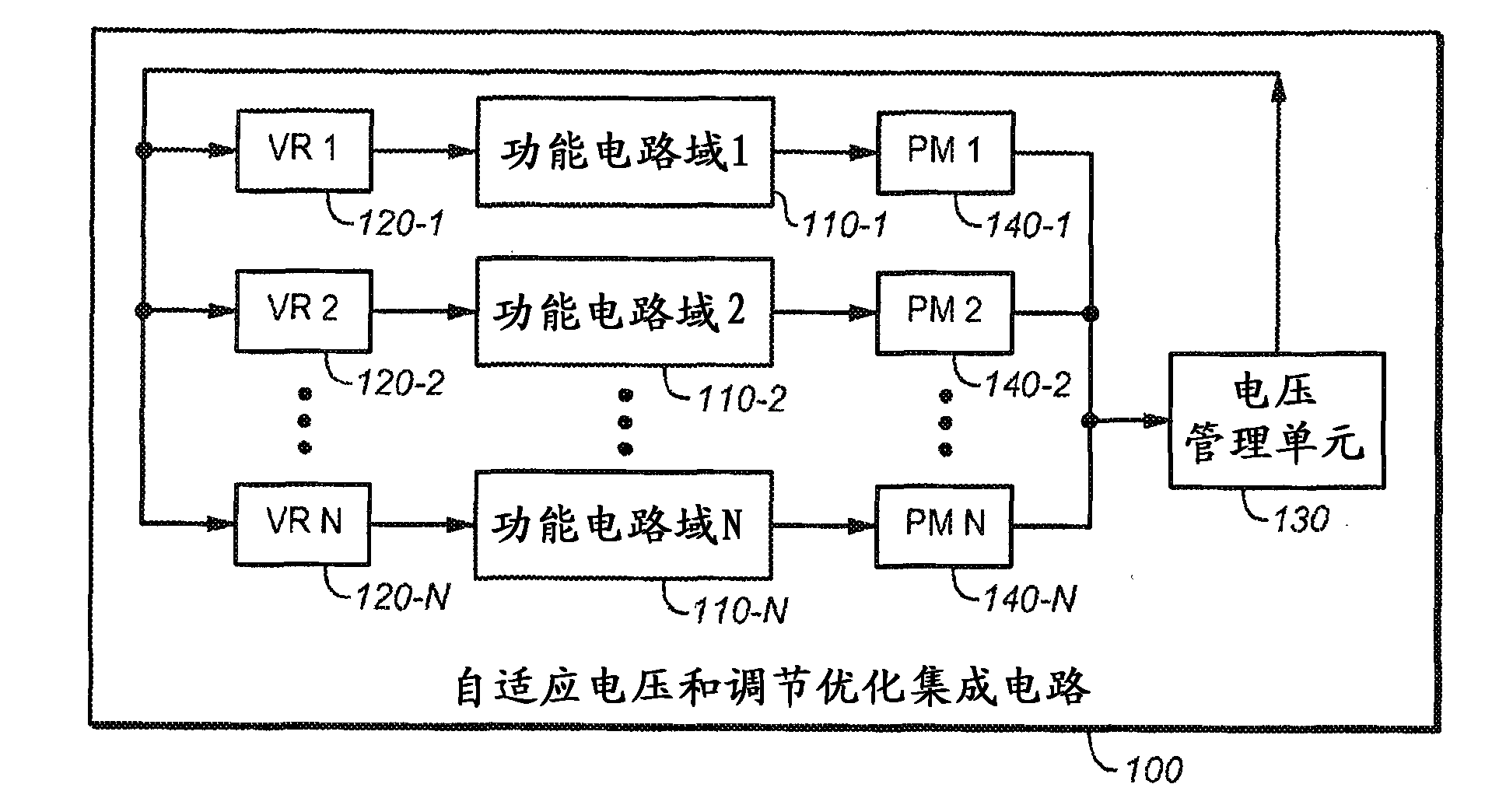
A system and method is disclosed for providing a plurality of hardware performance monitors for adaptive voltage scaling in an integrated circuit system that comprises a plurality of clock domains. Each hardware performance monitor is associated with one of the plurality of clock domains and provides a signal that measures a performance of its respective clock domain temperature, process corner and supply voltage. The difference between the measured performance and a nominal expected performance for each hardware performance monitor is determined. The largest of the plurality of difference signals is selected and used in an advanced power controller to provide adaptive voltage scaling for the integrated circuit system.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
System and method for providing multi-point calibration of an adaptive voltage scaling system
ActiveUS7581120B1Efficiently provideEfficiently providedEnergy efficient ICTPulse automatic controlOperating pointClock rate
A system and method is disclosed for providing multi-point calibration of an adaptive voltage scaling (AVS) system. A plurality of Reference Calibration Codes (RCCs) within a multi-point calibration table is provided. Each code is associated with one of the clock frequencies of the adaptive voltage scaling (AVS) system. The present invention provides multi-point calibration by calibrating a Reference Calibration Code (RCC) for each operating point (clock frequency) of the adaptive voltage scaling (AVS) system.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Dynamic voltage scaling
ActiveUS7739531B1Minimize power consumptionPacked tightlyEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringDynamic voltage scaling
An apparatus and method for dynamically controlling the maximum frequency of operation of the IC is provided. The invention optimizes power consumption in a device by measuring a current maximum frequency of operation and adjusting IC operating voltage to provide a desired maximum operating frequency. The invention provides an apparatus and method for controlling multiple voltages in an IC to independently adjust maximum operating frequencies for a plurality of separate portions of the IC. The invention may equally be applied to a group of ICs. The invention further provides a method for calibrating an IC. Thus, the apparatus facilitates the operation of an IC at a minimum voltage for a selected maximum frequency, thereby minimizing power consumption overall a wide range of operating frequencies.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
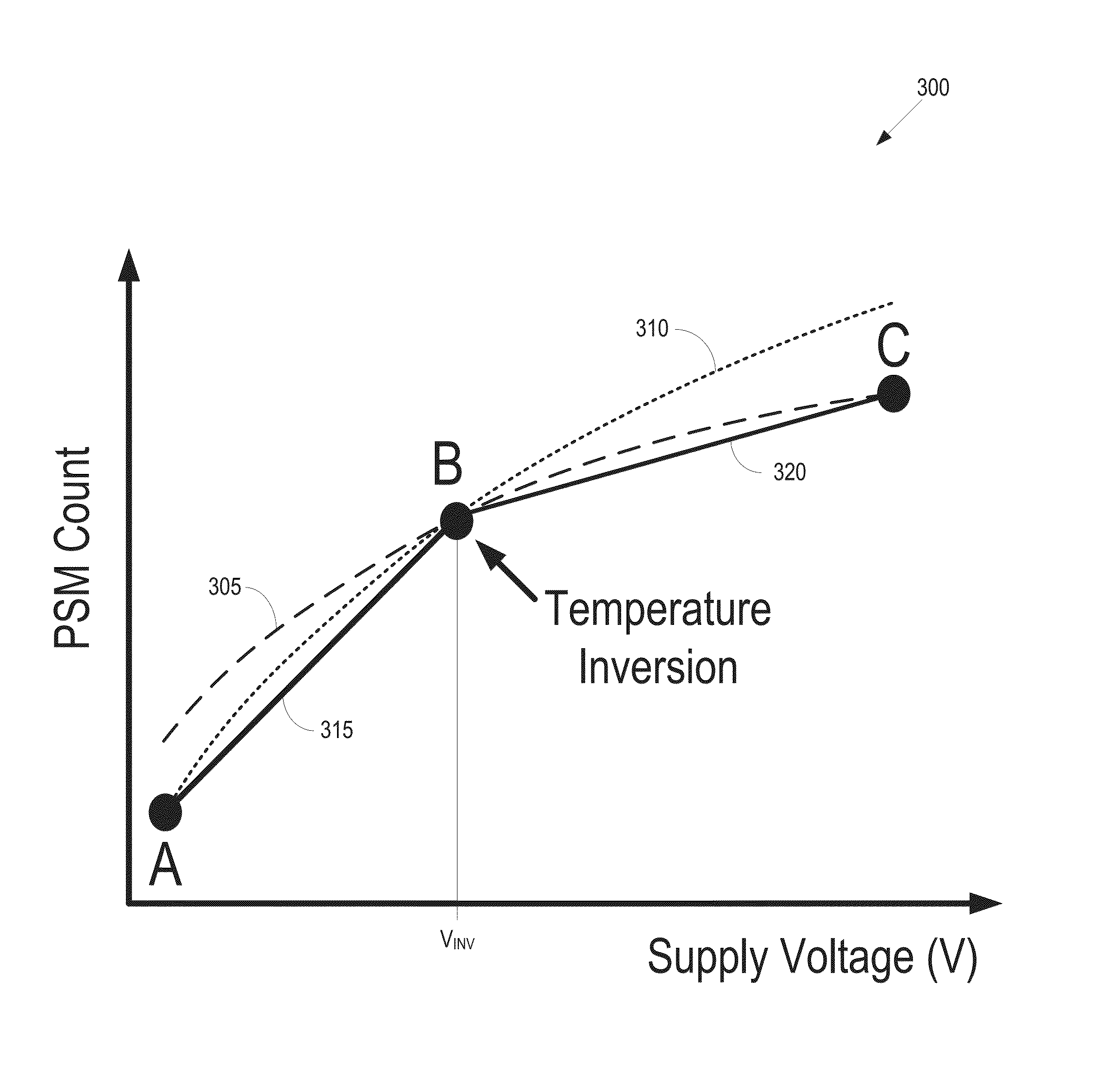
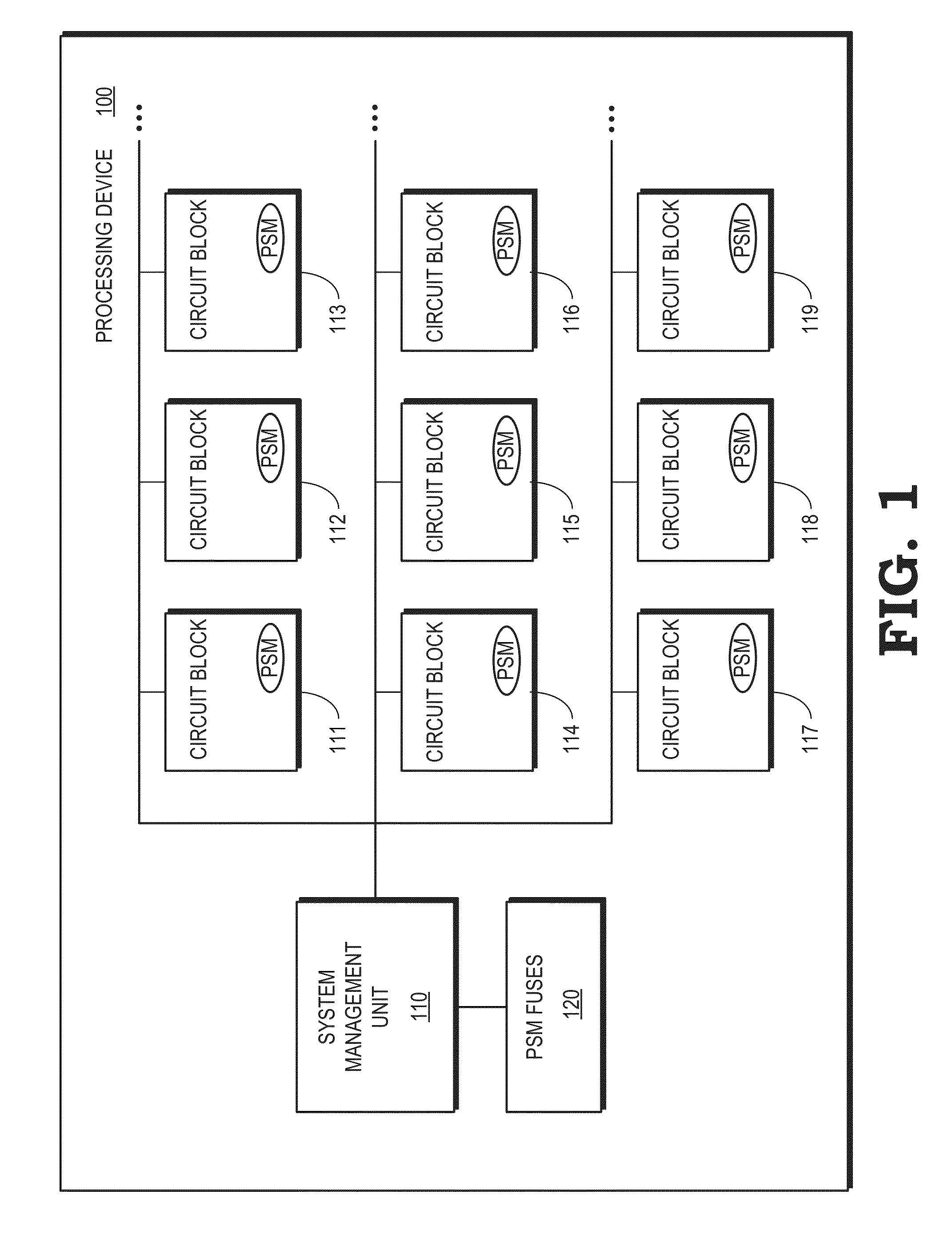
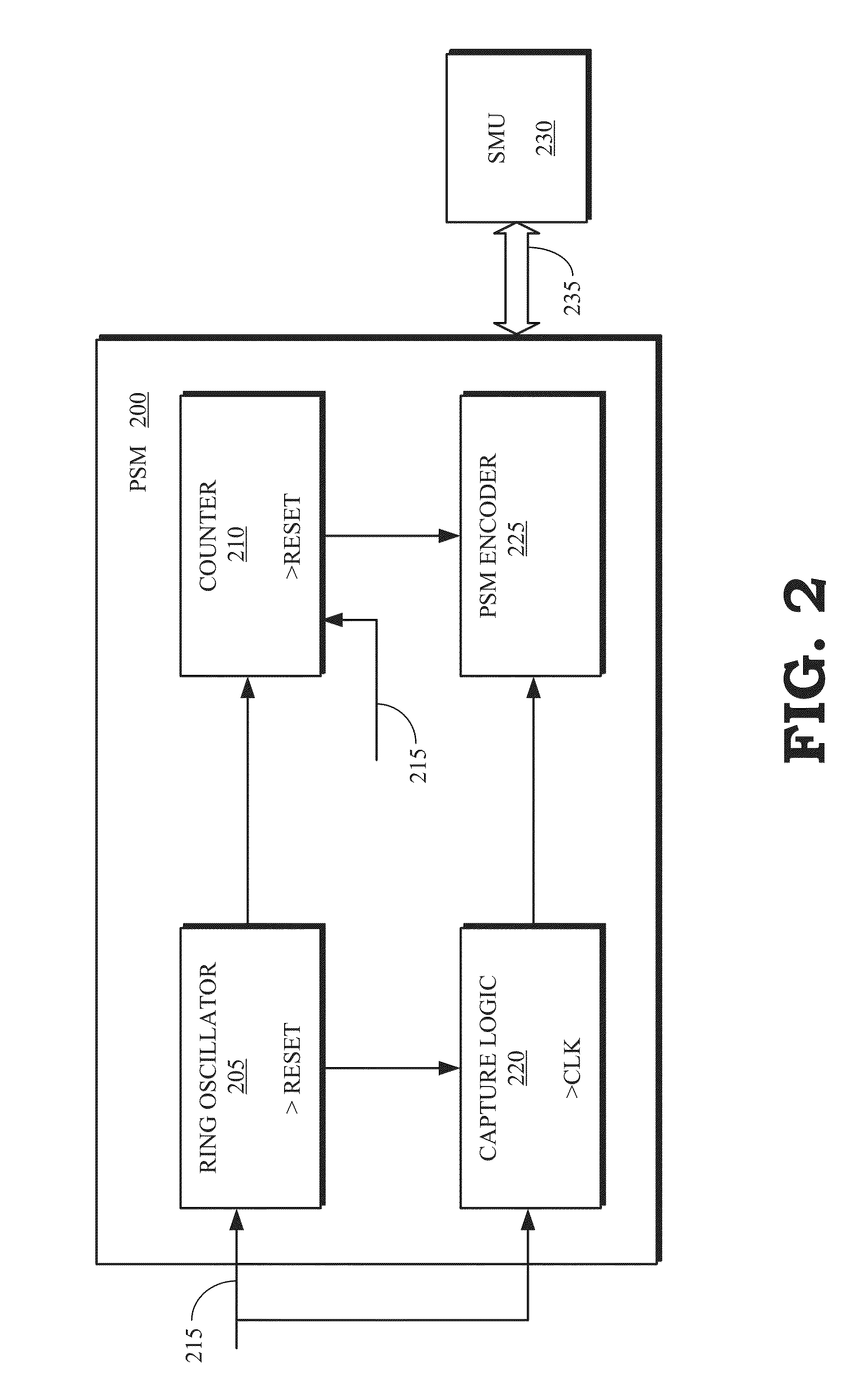
Adaptive voltage scaling
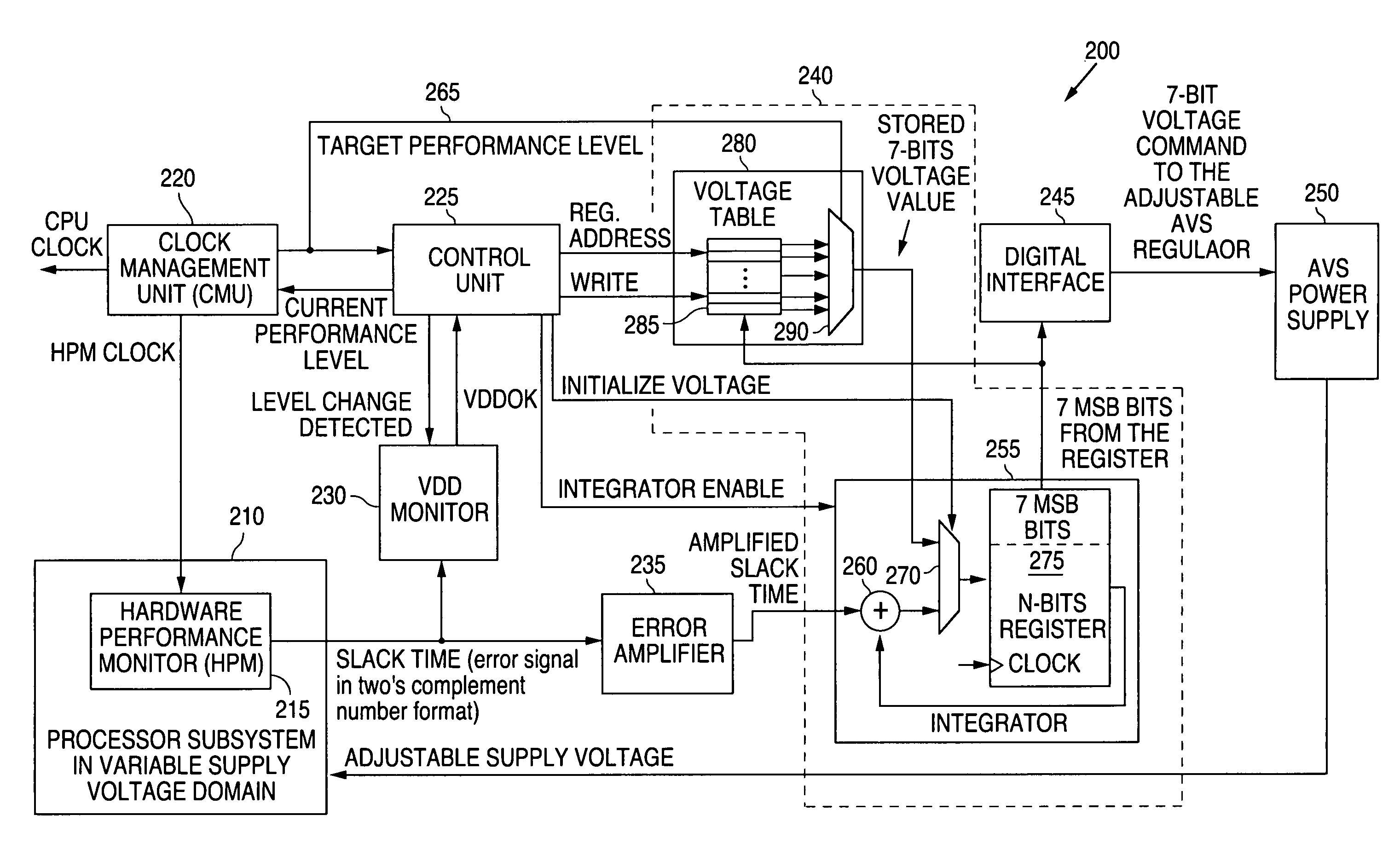
ActiveUS20150241955A1Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingElectricitySystems management
Some embodiments of a processing device include one or more power supply monitors to provide one or more counts representative of one or more operating frequencies of one or more circuit blocks based on a voltage supplied to the circuit block(s). Some embodiments of the processing device also include a system management unit to determine an initial voltage supplied to the circuit block(s) based on a target count and to reduce the voltage supplied to the circuit block(s) from the initial voltage in response to the count(s) generated by the power supply monitor(s) exceeding the target count.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
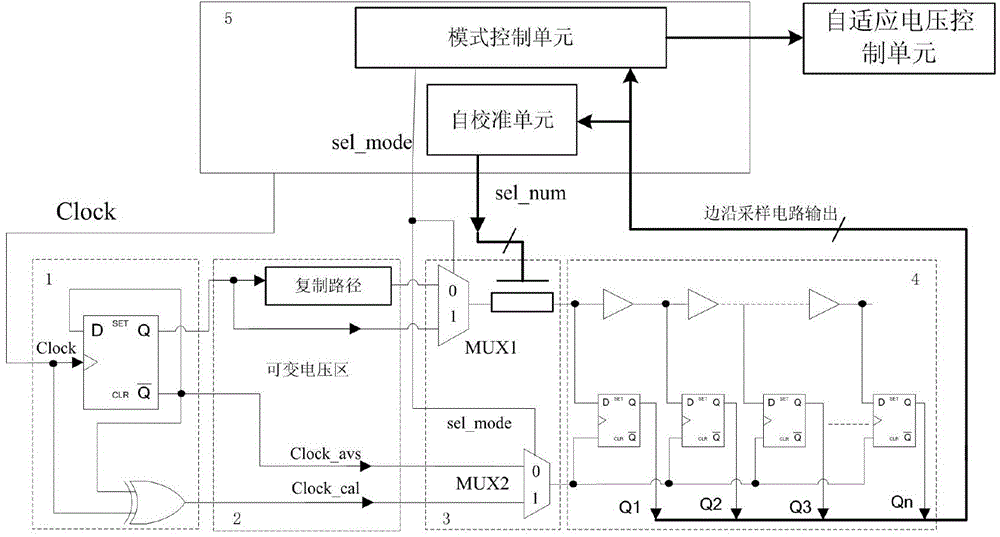
A delay sampling circuit having self-calibration function
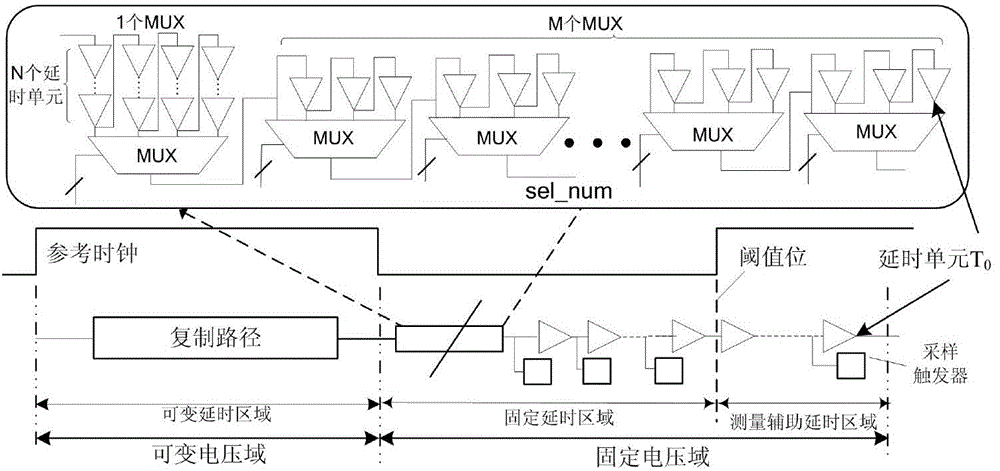
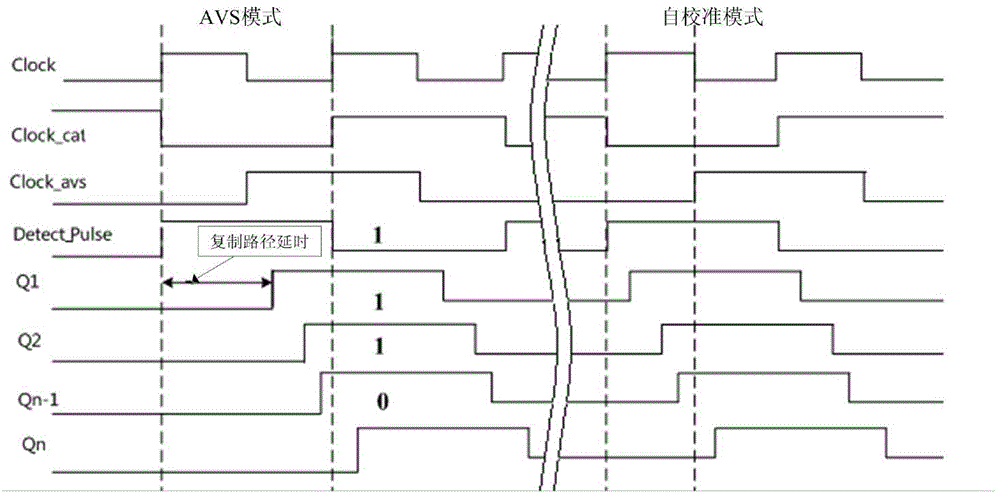
ActiveCN104135256AAvoid accumulationImprove Sampling AccuracyElectronic switchingLow voltageVoltage regulation
The invention discloses a delay sampling circuit having self-calibration function. The delay sampling circuit includes a pulse generation circuit, a replication path unit, a calibration delay circuit, an edge sampling circuit, and a delay sampling control module, wherein, the replication path unit is in a variable voltage area, and other parts are in a fixed voltage area. The invention can be applied to reflect a time sequence condition of a chip and to guide voltage scaling of the chip. Two operation modes of a self-calibration mode and an adaptive voltage scaling mode are provided according to the delay sampling circuit, and cooperate with adaptive voltage scaling to operate together, which can prevent measurement deviation of the chip that results from environment change during operation, thus simultaneously giving consideration to real-time performance and reliability, and can allow the monitored circuit to operate in the required lowest voltage, thus reducing power consumption of the circuit effectively.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Adaptive voltage scaling digital processing component and method of operating the same
There is disclosed a digital circuit comprising a digital processing component, an adjustable power supply and power supply adjustment circuitry. The digital processing component is capable of operating at a plurality of selected clock frequencies, wherein a maximum delay time of a critical path in the digital processing component is determined by a level of a power supply, VDD, of the digital processing component. The adjustable power supply is capable of supplying VDD to the digital processing component. The power supply adjustment circuitry is operable to receive a first selected clock signal and adjusts the level of VDD such that the maximum delay time of the critical path of the digital processing component is less than a pulse-width duration between a first clock edge of the first selected clock signal and a second clock edge of the first selected clock signal immediately following the first clock edge.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
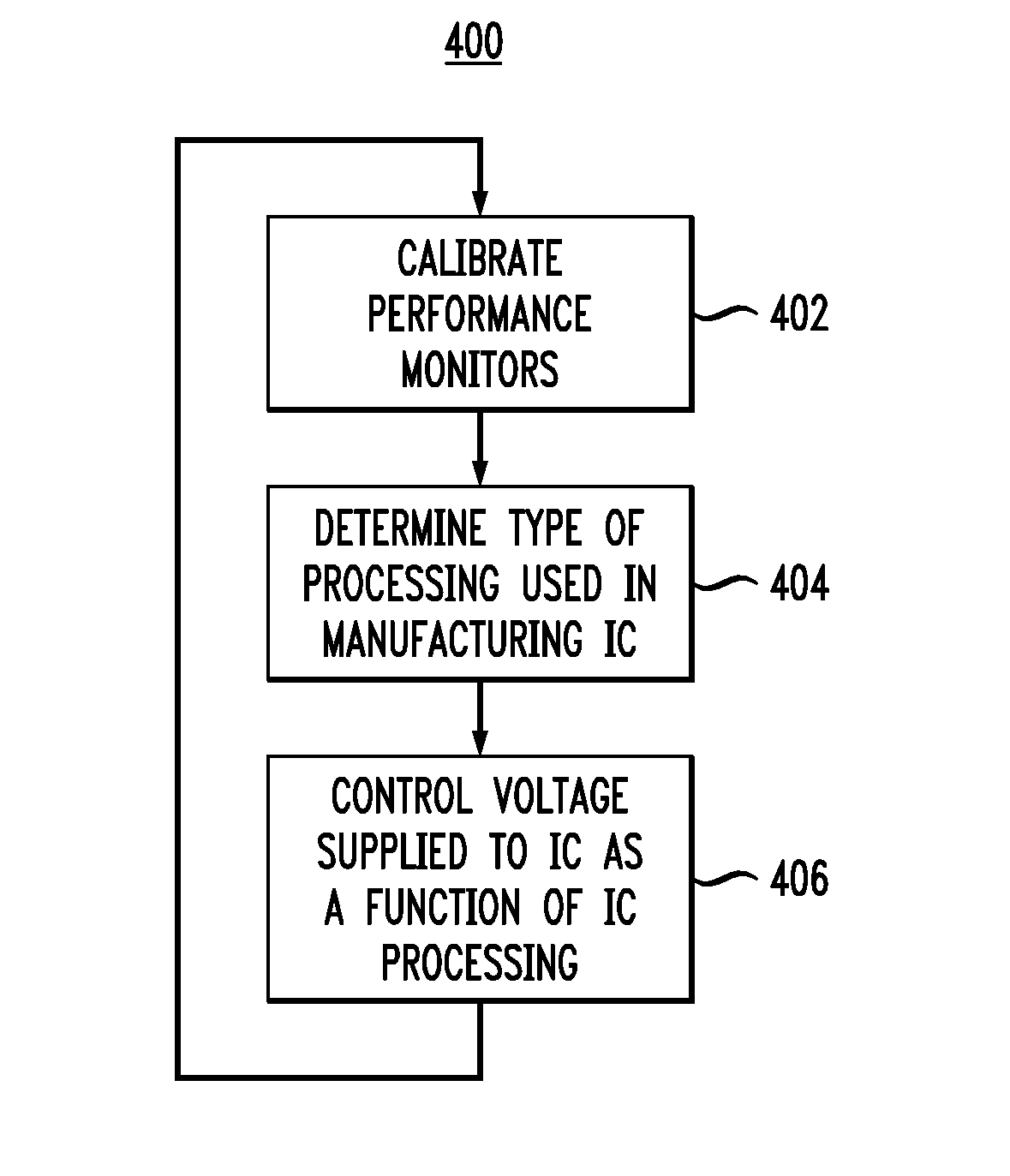
Integrated circuit performance enhancement using on-chip adaptive voltage scaling
InactiveUS8161431B2Reduce power consumptionImprove performanceThermometer detailsVolume/mass flow measurementProcessing typePerformance enhancement
Techniques for enhancing the performance of an IC are provided. A method of enhancing IC performance includes the steps of: associating at least one performance result of at least one performance monitor, formed on the IC, with deterministic combinations of IC performance and a processing parameter, a supply voltage, and / or a temperature of the IC; determining an IC processing characterization of the IC as a function of the performance result for at least one prescribed supply voltage and temperature of the IC, the IC processing characterization being indicative of a type of processing received by the IC during fabrication of the IC; and controlling a voltage supplied to at least a portion of the IC, the voltage being controlled as a function of the IC processing characterization and / or the temperature of the IC so as to satisfy at least one prescribed performance parameter of the IC.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Semi-adaptive voltage scaling for low-energy digital vlsi-design
InactiveUS20100289553A1Reduce power consumptionSave powerSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementWelding electric supplyClosed loopEngineering
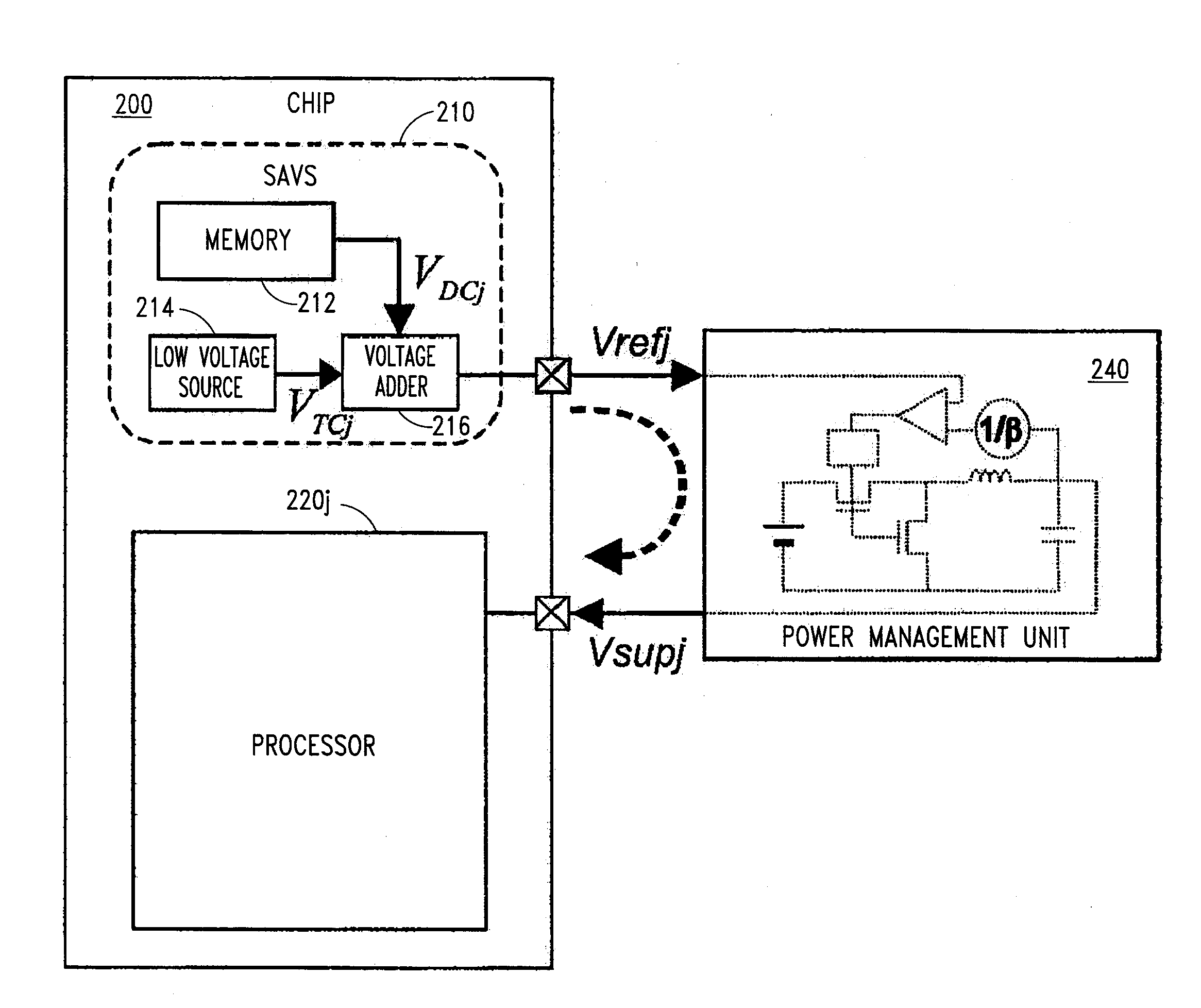
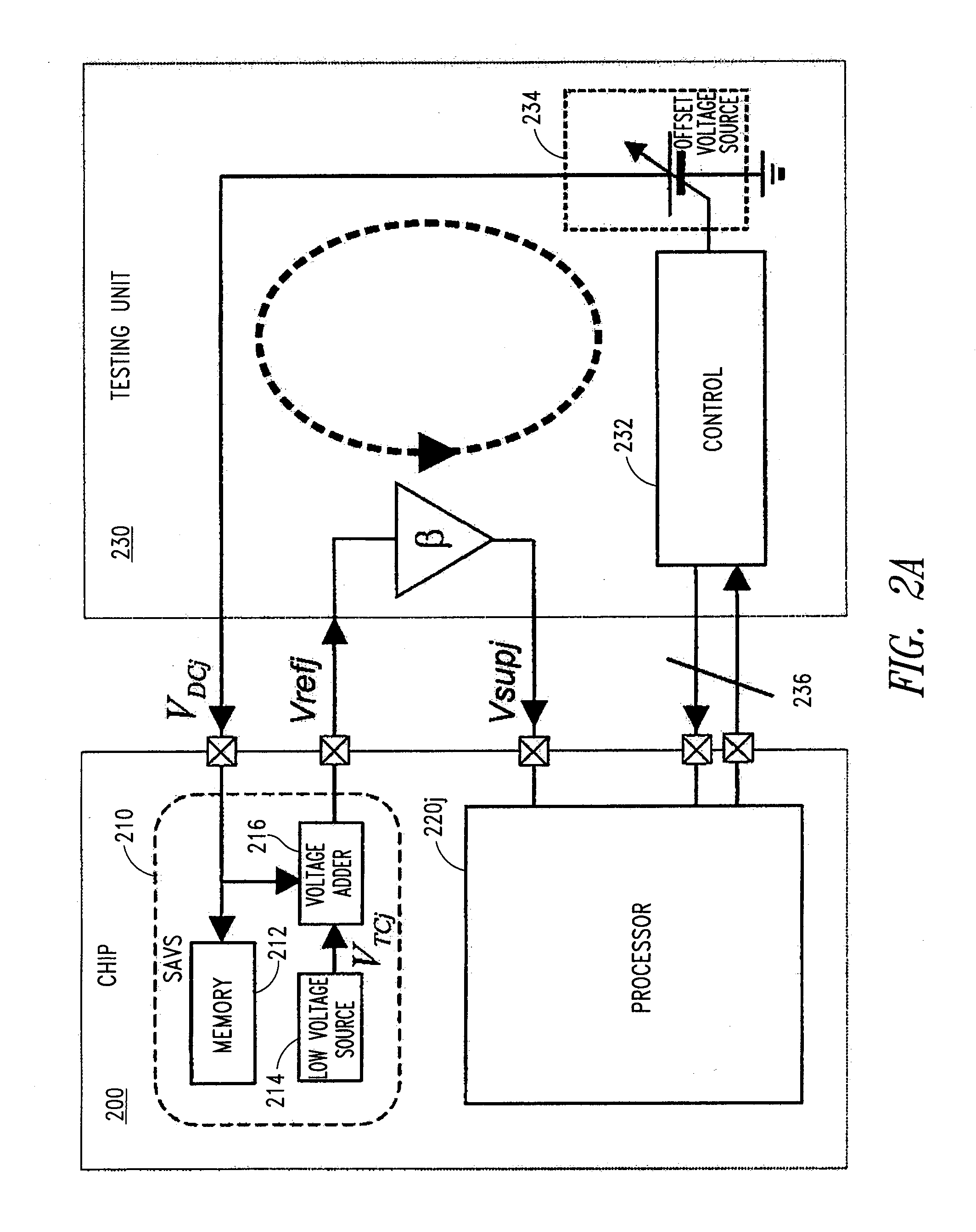
A semi-adaptive voltage scaling method and device for determining minimal supply voltages for digital electronic semiconductor circuitry, e.g., microprocessors, of electronic devices under production testing and “real” operating conditions. The SAVS operates in a closed-loop during a production test phase of the circuitry and in an open-loop mode in an application (operation) phase of the semiconductor circuitry. During production testing, a lowermost level of the supply voltage for the semiconductor circuitry is determined at one single defined temperature at which operating specifications of the circuit are met. The lowermost level is stored in a dedicated electronic memory of the circuitry together with temperature dependent parameters. Afterwards, when the digital electronic circuitry is operated in a “real” application, e.g., a mobile phone, the device and method reads the previously measured and proven data from the memory and regenerates the minimum level of supply voltage for the circuitry, taking into account the actual temperature of the application. As a result, the digital semiconductor circuitry in the “real” application is supplied with a minimum level of supply voltage, whereby specified parameters of the circuitry are met. Thus, a power consumption of the circuitry is advantageously reduced to a minimum.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Systematic, normalized metric for analyzing and comparing optimization techniques for integrated circuits employing voltage scaling and integrated circuits designed thereby
InactiveUS20100037188A1Electrical testingPower supply for data processingIntegrated circuit layoutEngineering
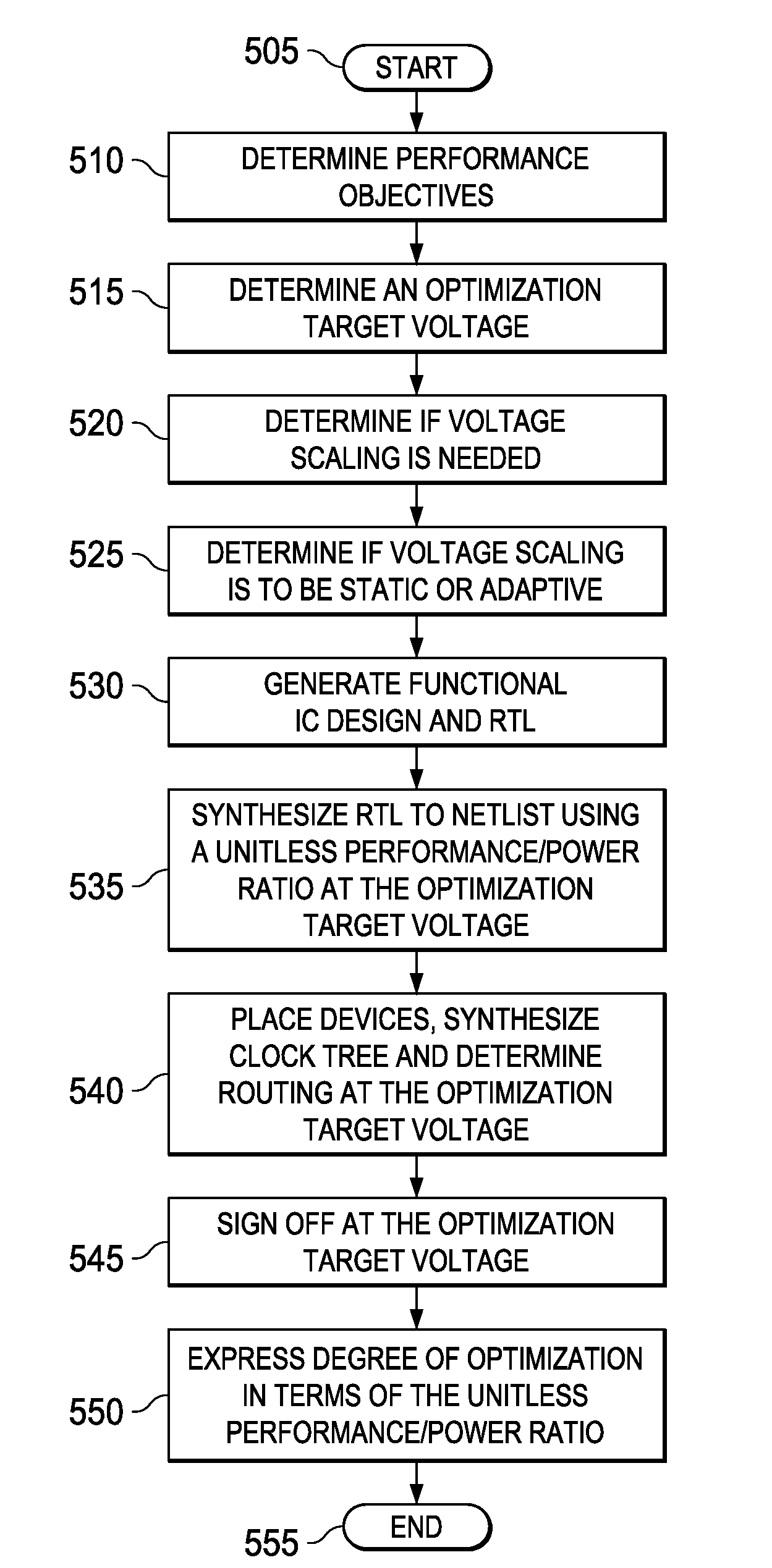
Various embodiments of methods of designing an integrated circuit (IC). One embodiment of one such method includes: (1) generating a functional design for the IC, (2) determining performance objectives for the IC, (3) determining an optimization target voltage for the IC, (4) determining whether the IC needs voltage scaling to achieve the performance objectives at the optimization target voltage and, if so, whether the IC is to employ static voltage scaling or adaptive voltage scaling, (5) using the optimization target voltage to synthesize a layout from the functional IC design that meets the performance objectives by employing a unitless performance / power quantifier as a metric to gauge a degree of optimization thereof and (6) performing a timing signoff of the layout at the optimization target voltage.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
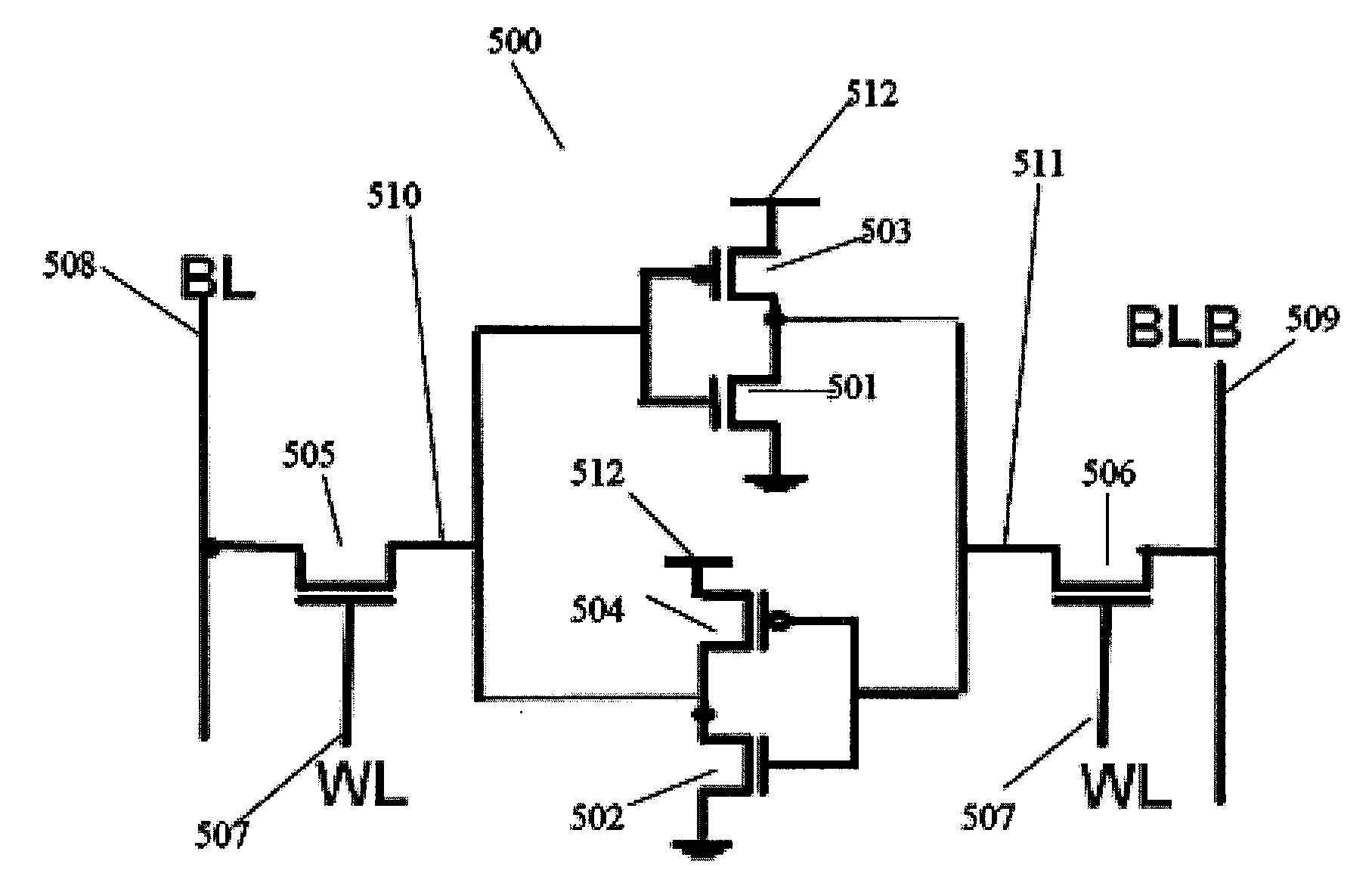
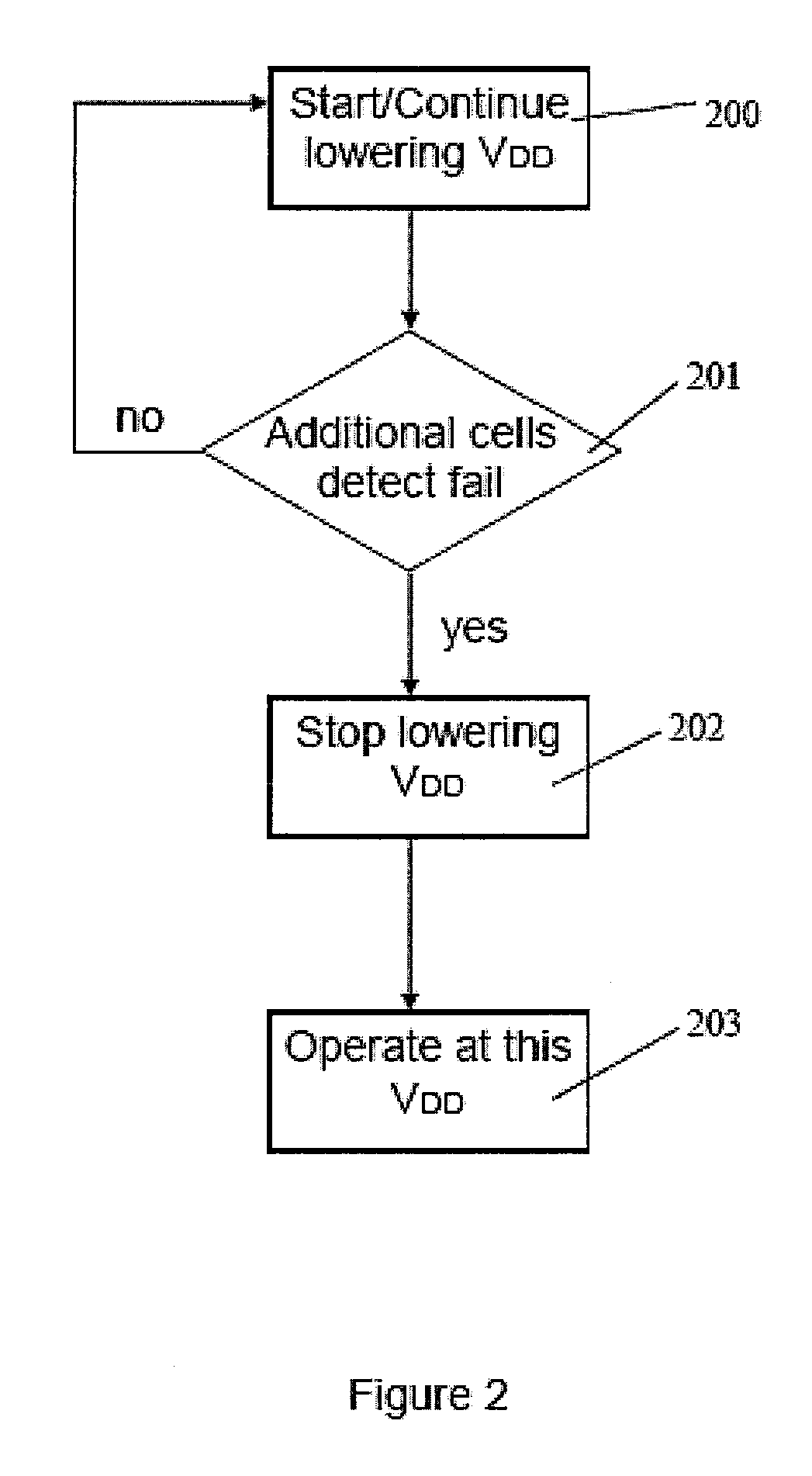
Canary based SRAM adaptive voltage scaling (AVS) architecture and canary cells for the same
A memory bank includes memory cells and an additional cell to determine an operating voltage of the memory bank. The additional cell has an operating margin that is less than a corresponding operating margin of the other memory cells in the memory bank.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Integrated Circuit Performance Enhancement Using On-Chip Adaptive Voltage Scaling
InactiveUS20100115475A1Reduce power consumptionIncrease productionThermometer detailsVolume/mass flow measurementTemperature controlPerformance enhancement
Techniques for enhancing the performance of an IC are provided. A method of enhancing IC performance includes the steps of: associating at least one performance result of at least one performance monitor, formed on the IC, with deterministic combinations of IC performance and a processing parameter, a supply voltage, and / or a temperature of the IC; determining an IC processing characterization of the IC as a function of the performance result for at least one prescribed supply voltage and temperature of the IC, the IC processing characterization being indicative of a type of processing received by the IC during fabrication of the IC; and controlling a voltage supplied to at least a portion of the IC, the voltage being controlled as a function of the IC processing characterization and / or the temperature of the IC so as to satisfy at least one prescribed performance parameter of the IC.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
System and method for providing hardware performance monitors for adaptive voltage scaling with a plurality of VT logic libraries
ActiveUS8010317B1Accurate scaleEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsPower controllerEngineering
A system and method is disclosed for providing a plurality of hardware performance monitors for adaptive voltage scaling in an integrated circuit system that comprises a plurality of threshold voltage VT logic libraries. Each hardware performance monitor is associated with one of the plurality of threshold voltage VT logic libraries and provides a signal that measures a performance of its respective threshold voltage VT logic library die temperature, process corner and supply voltage. The difference between the measured performance and a nominal expected performance for each hardware performance monitor is determined. The largest of the plurality of difference signals is selected and provided to an advanced power controller for use in providing adaptive voltage scaling for the integrated circuit system.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
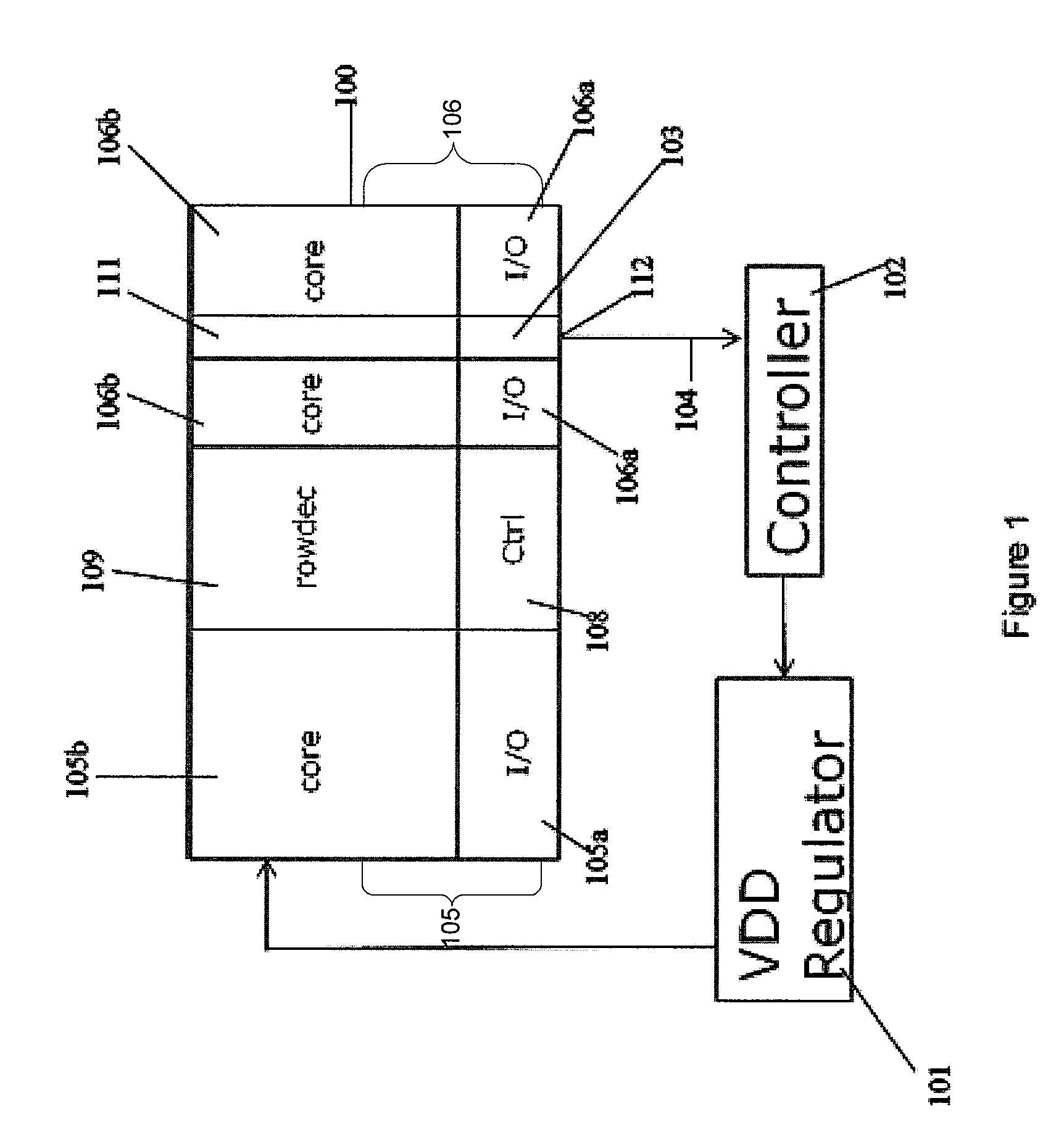
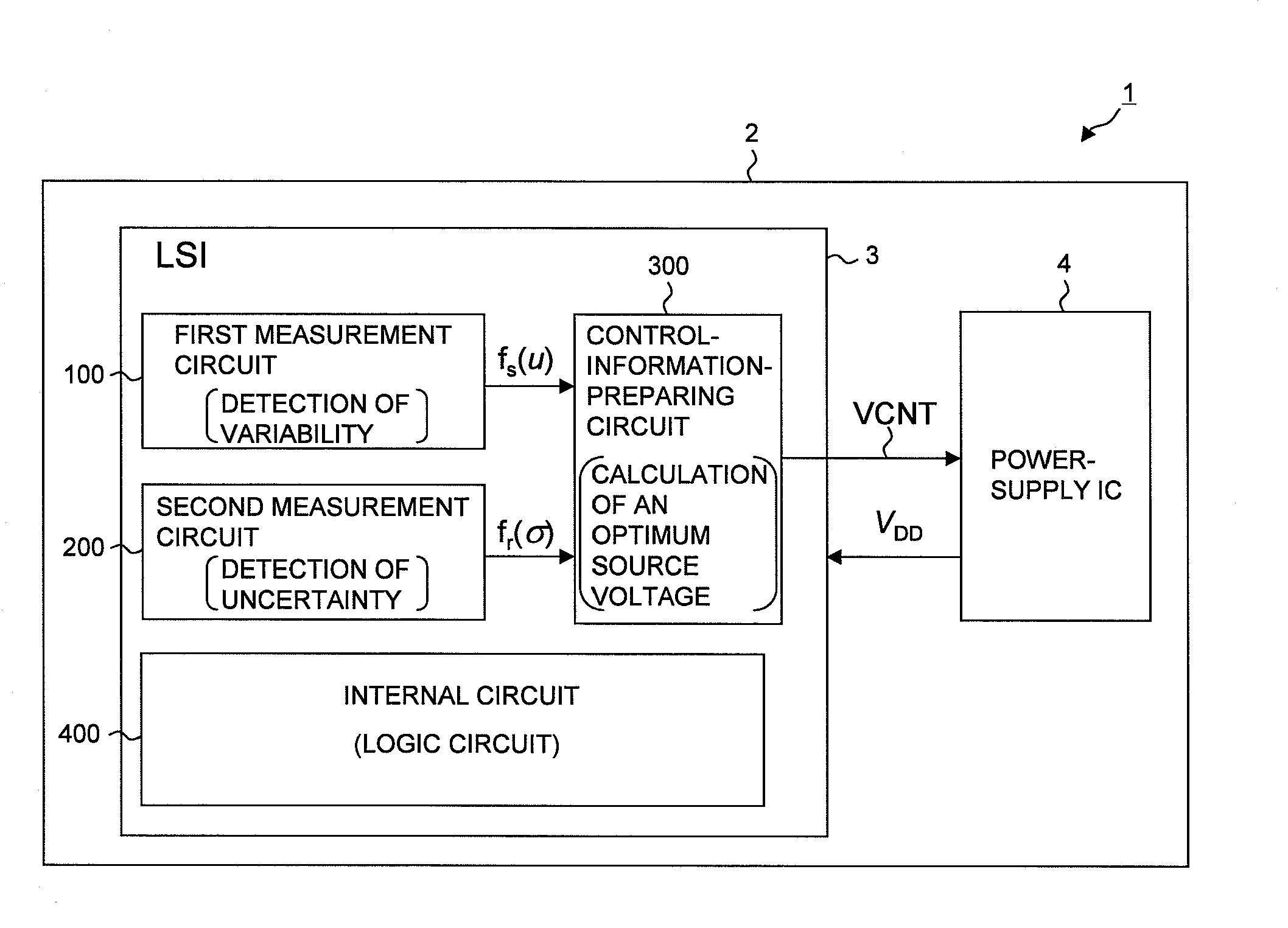
Semiconductor integrated circuit and electronic device
ActiveUS20110181337A1Easy to prepareAccurate detectionPulse automatic controlSolid-state devicesSemiconductorIntegrated circuit
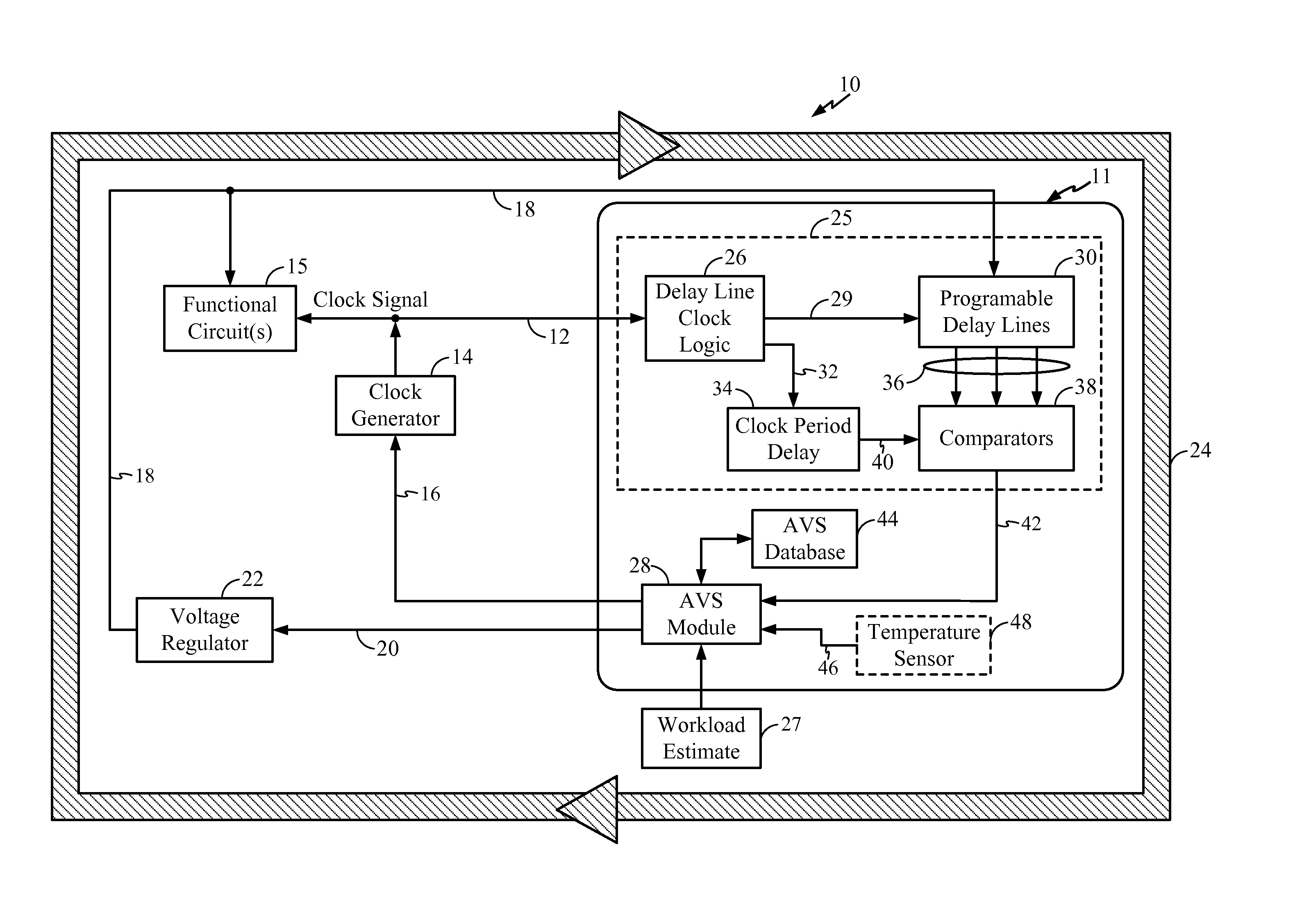
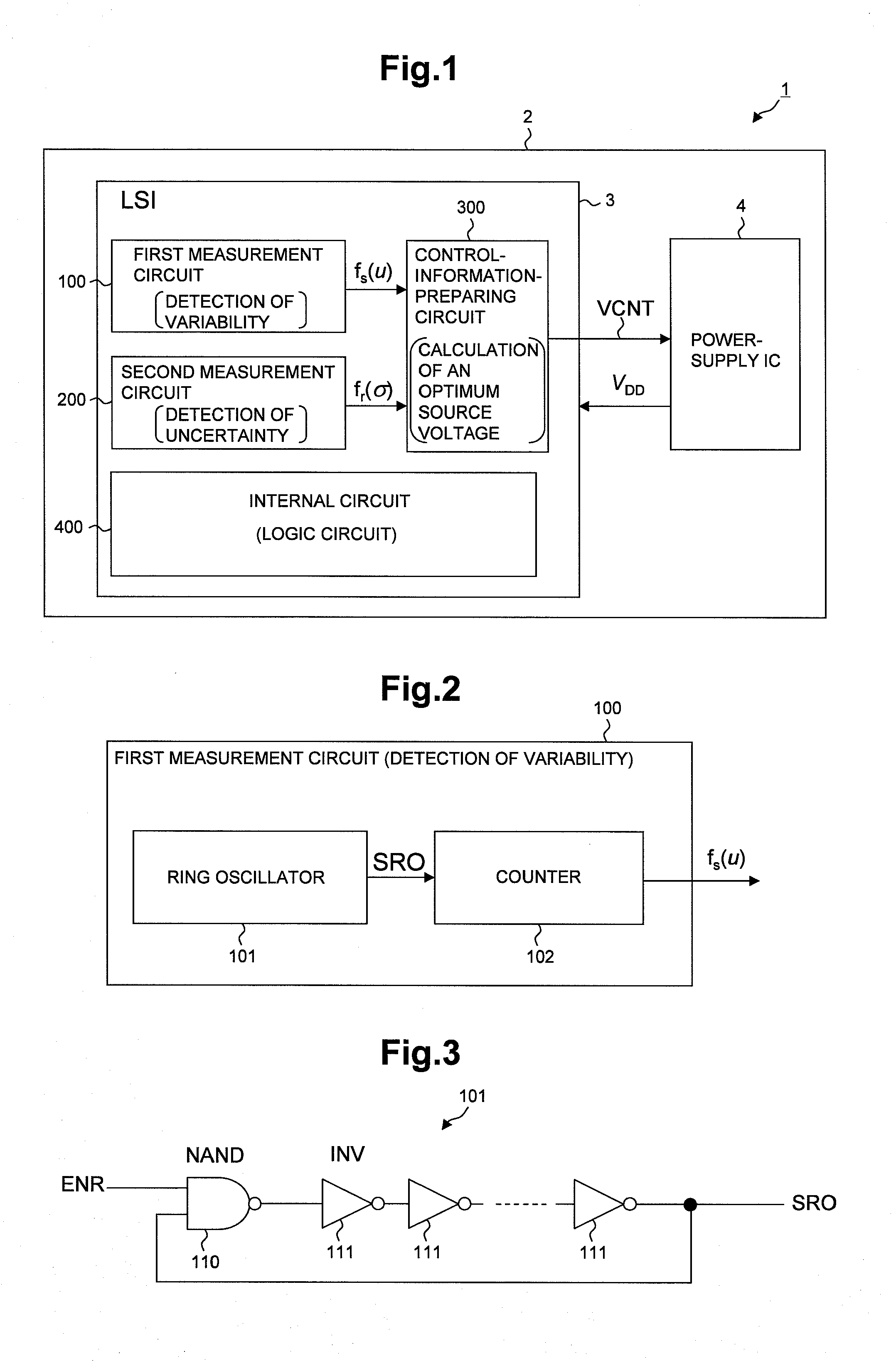
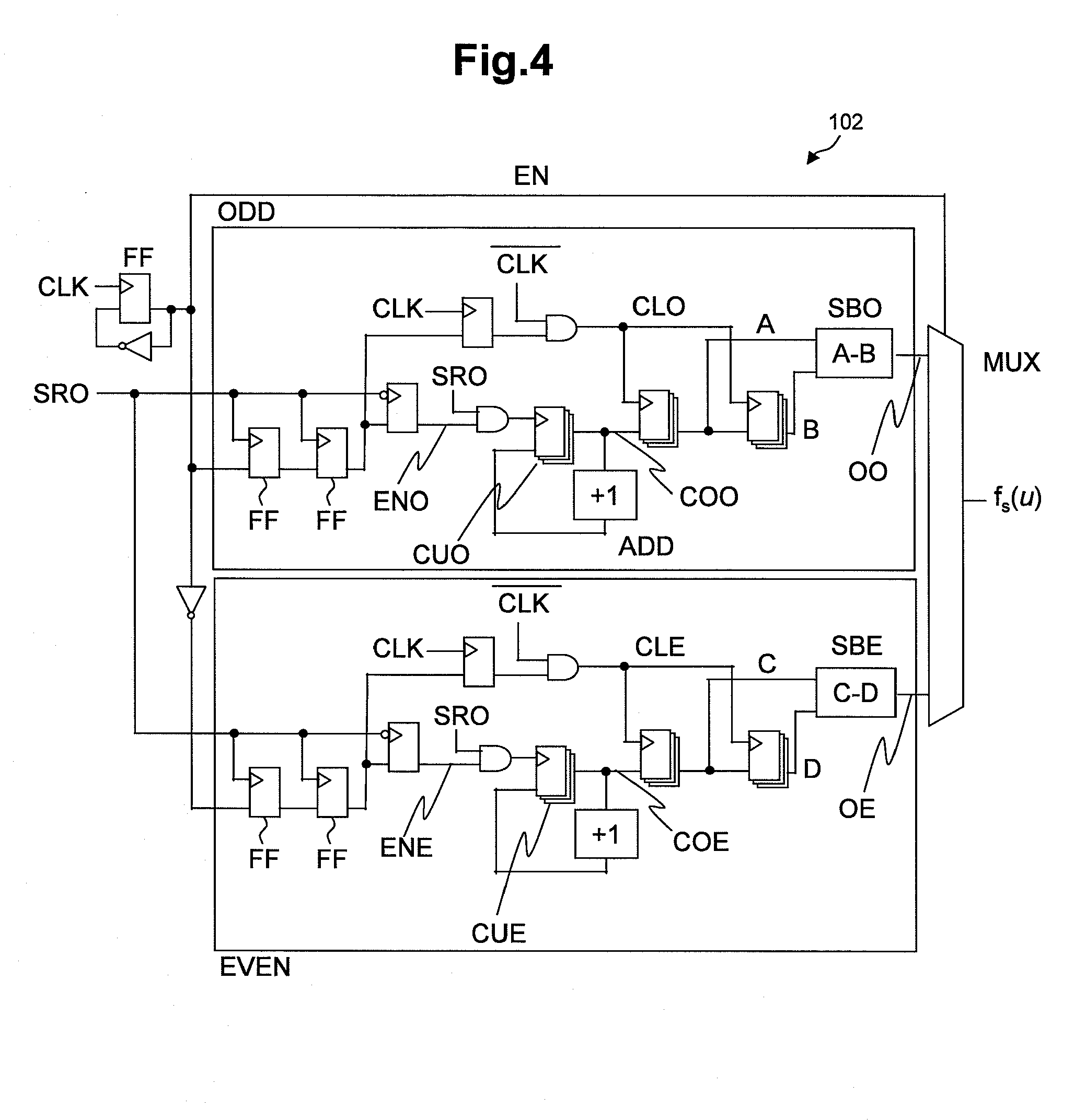
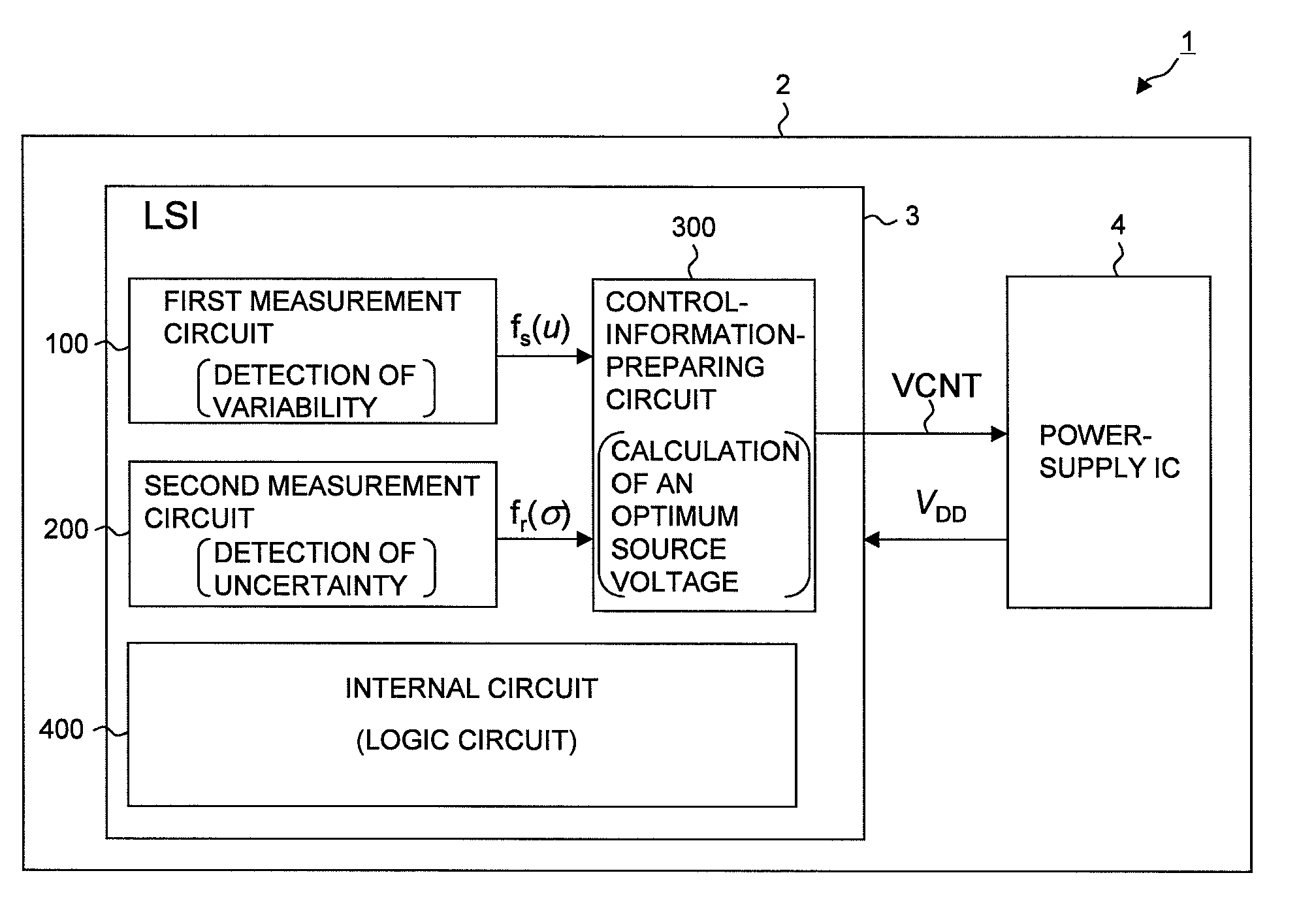
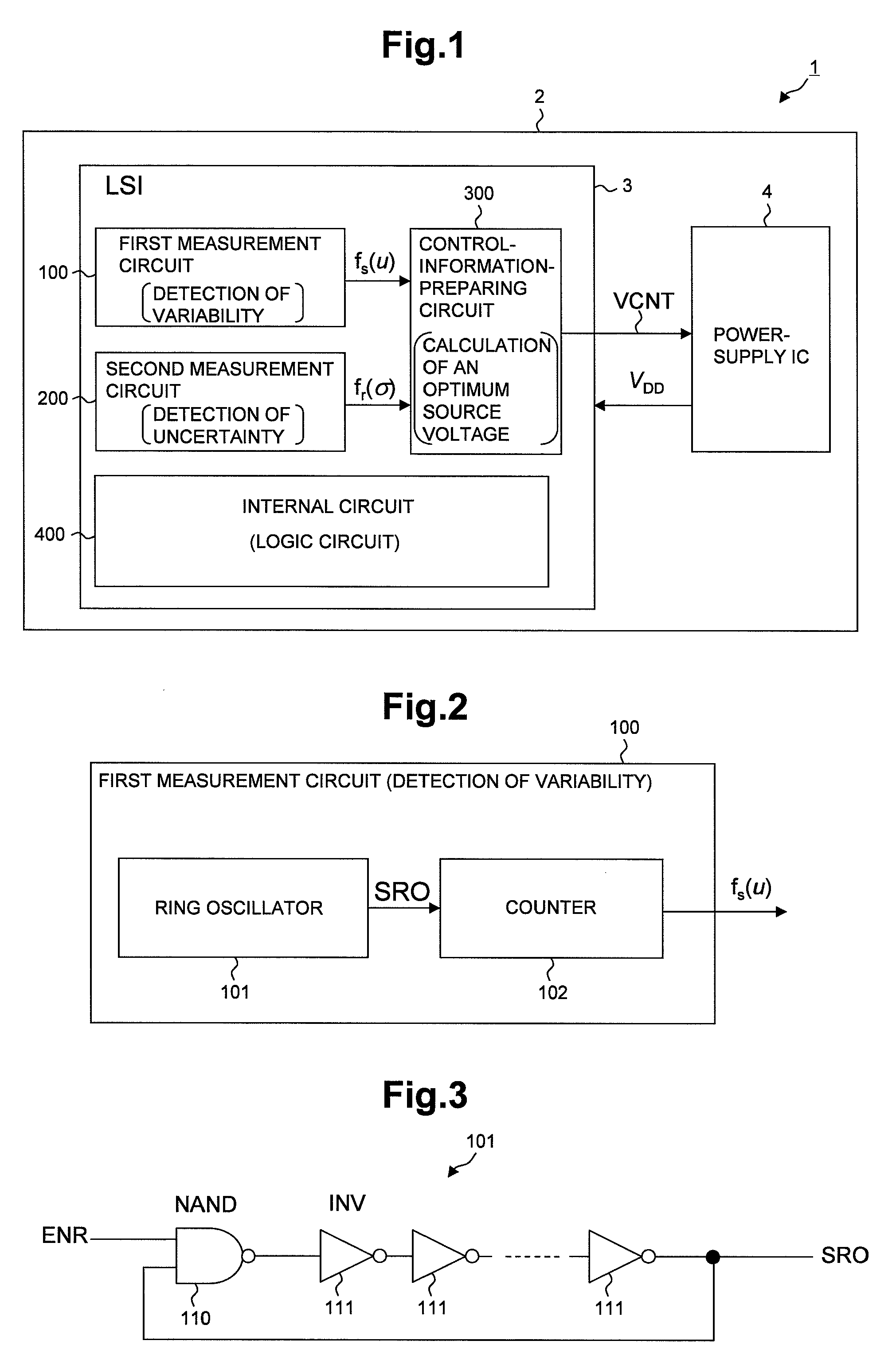
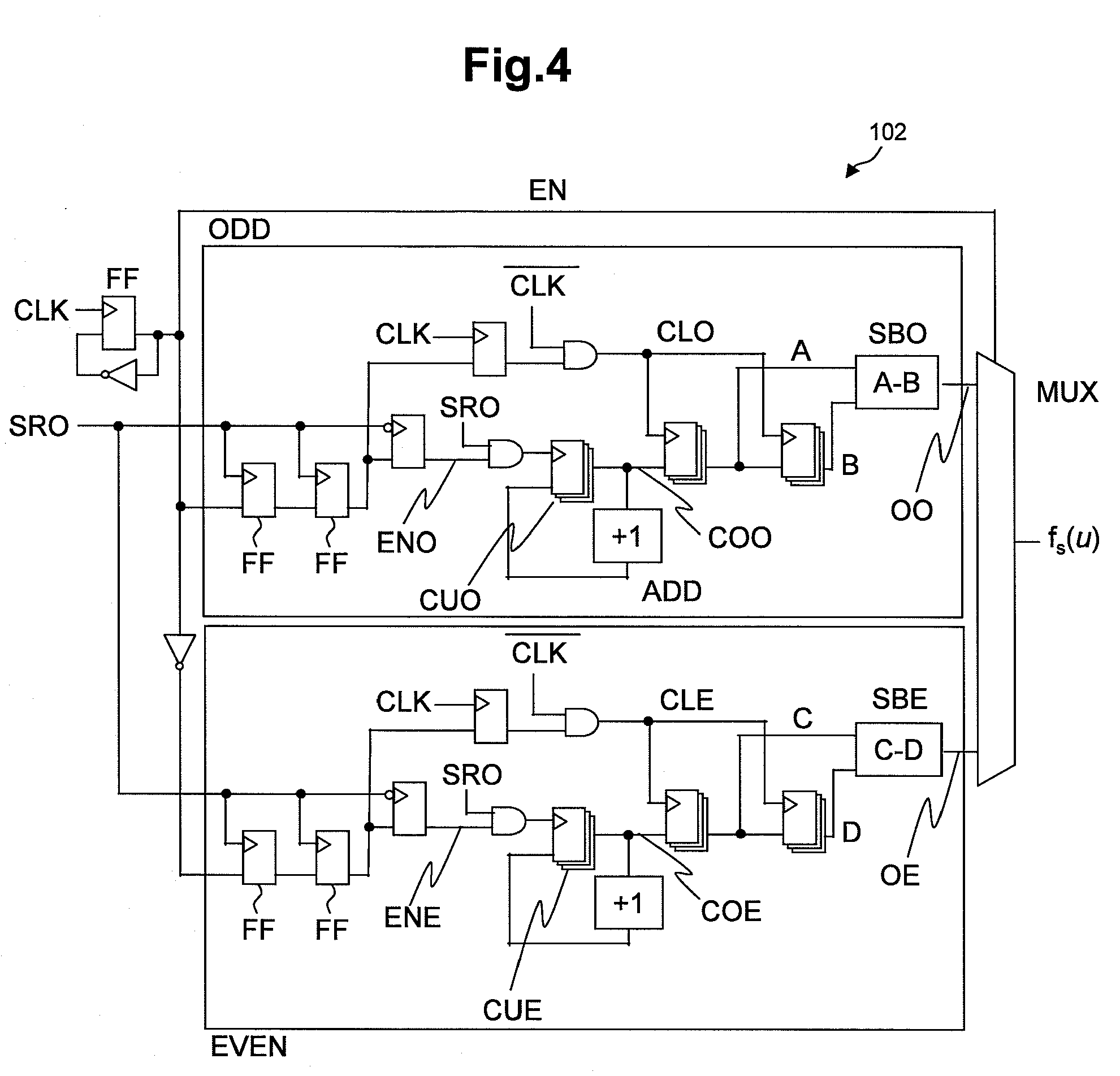
AVS (Adaptive Voltage Scaling) technique, by which variability and uncertainty are both taken into account. In the system arranged for AVS technique, a detection circuit optimum for each type of process variation is set. Examples of the detection circuit so arranged include a first measurement circuit for detection of variability, which produces a relative value with respect to the gate delay mean value, and a second measurement circuit for detection of uncertainty, which produces a relative value related to the gate delay standard deviation. The first and second measurement circuits are provided separately from each other. The control information for deciding the supply voltage is prepared based on relative values produced by the detection circuits. When preparing the control information, reference is made to e.g. a table data.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Adaptive voltage scaling clock generator for use in a digital processing component and method of operating the same
ActiveUS6944780B1Accurate operationImprove utilizationEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingEngineeringClock generator
There is disclosed clock control circuitry for selectively applying a clock signal to a digital processing component wherein the clock signal is capable of being changed to a plurality of operating frequencies. The clock control circuitry is operable to (i) receive a command to change a first operating frequency to a second operating frequency, (ii) in response to the command, disable the applied clock signal, (iii) generate a test clock signal having the second operating frequency, (iv) apply the test clock signal to a power supply adjustment circuit, and (v) sense a status signal from the power supply adjustment circuit. The status signal indicates that a power supply level of the digital processing component has been adjusted to an optimum value suitable for the second operating frequency.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
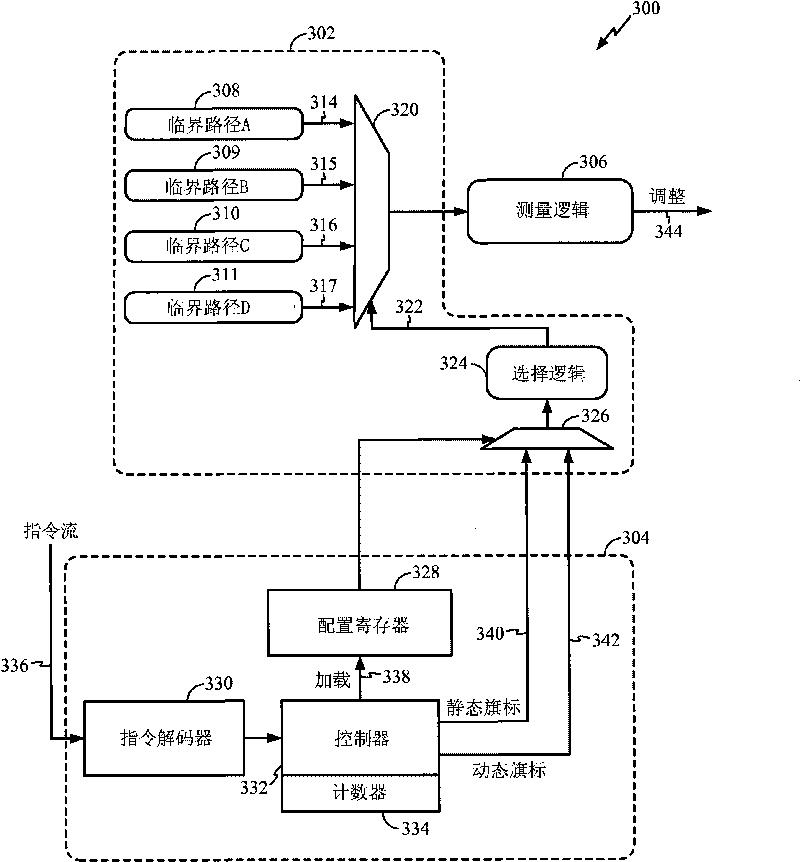
Method and apparatus for adaptive voltage scaling based on instruction usage
InactiveCN101765822AReduced Power RequirementsReduce electricity usageEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingClock rateLife time
Different software applications may use a set of instructions having critical timing paths less than a worst case critical timing path of a processor complex. For such applications, a supply voltage may be reduced while still maintaining the clock frequency necessary to meet the application's performance requirements. In order to reduce the supply voltage, an adaptive voltage scaling method is used. A critical path is selected from a plurality of critical paths for analysis on emulation logic to determine an attribute of the selected critical path during on chip functional operations. The selected critical path is representative of the worst case critical path to be in operation during a program execution. During on-chip functional operations, a voltage is controlled in response to the attribute, wherein the voltage supplies power to a power domain associated with the plurality of critical paths. The reduction in voltage reduces power drain based on instruction set usage allowing battery life to be extended.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Adaptive voltage scaling power supply for use in a digital processing component and method of operating the same
InactiveUS7106040B1Easy to adjustIncreasing reference voltageElectric variable regulationControl signalEngineering
There is disclosed an adaptive voltage power supply that finely adjusts VDD to an optimum level. The adaptive voltage power supply comprises: 1) a first charging circuit capable of increasing a reference voltage on a charge capacitor in response to receipt of a first VDD control signal; 2) a second charging circuit capable of decreasing the reference voltage on the charge capacitor in response to receipt of a second VDD control signal; and 3) a power supply capable of receiving the reference voltage on the charge capacitor and generating an output power level, VDD, determined by a level of the reference voltage.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
System and method for rapidly increasing a rising slew rate of an adjustable supply voltage in adaptive voltage scaling
ActiveUS7788508B1Increase conversion rateImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingClosed loopEngineering
A system and method is disclosed for rapidly increasing a rising slew rate of an adjustable power supply signal in an adaptive voltage scaling system. When a central processing unit of an adaptive voltage scaling system requests an increase in a performance level, a closed loop control mode of the adaptive voltage scaling system is disabled. Then a value of voltage that corresponds to the requested increased performance level is provided as a voltage change command to an adaptive voltage scaling regulator. The adaptive voltage scaling system is then operated at a maximum slew rate that can be achieved by the adaptive voltage scaling regulator. The closed loop mode is enabled after the adjustable power supply voltage reaches the requested voltage value.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
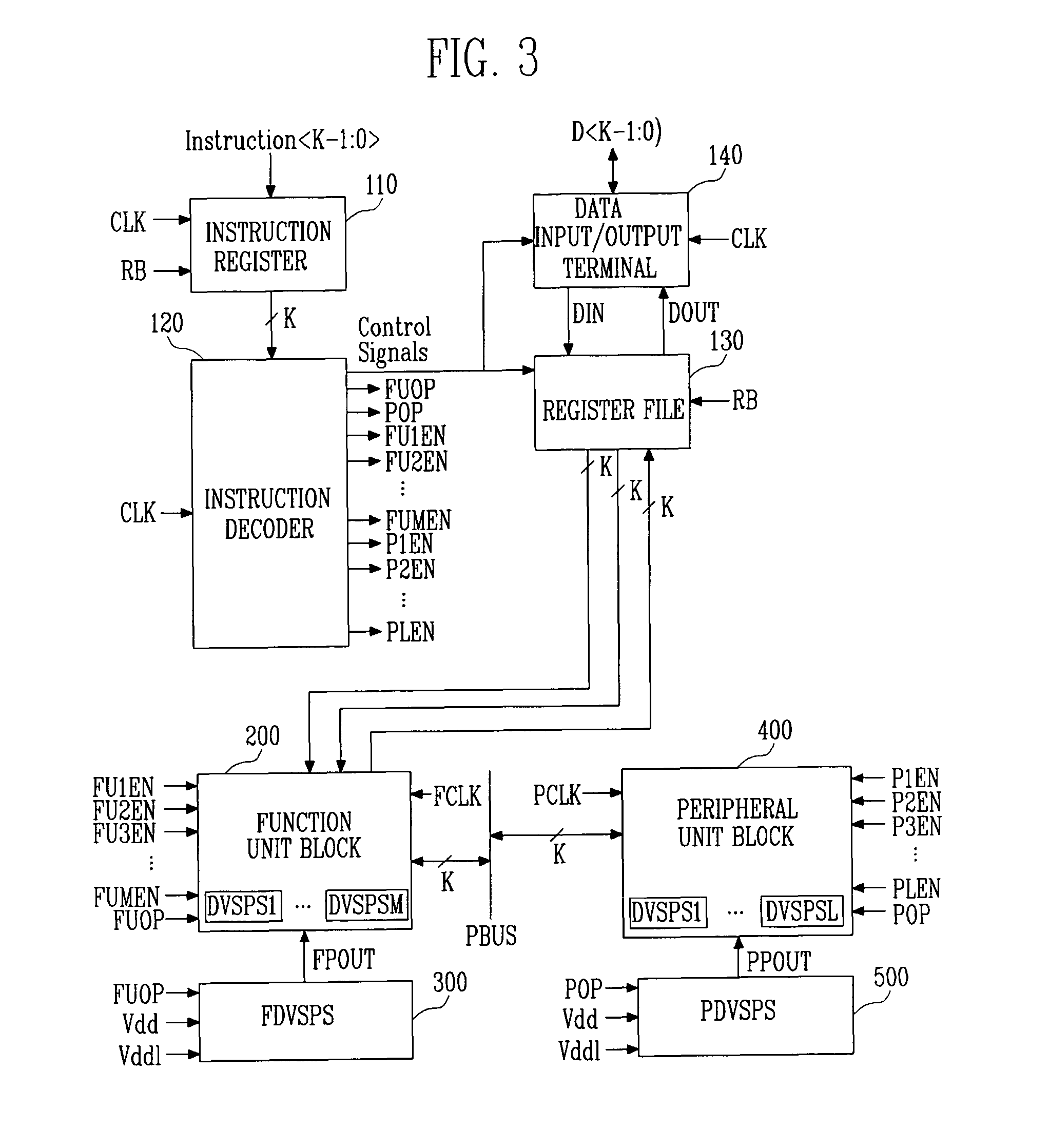
Highly energy-efficient processor employing dynamic voltage scaling
ActiveUS7805620B2Simple structureMaximize energy efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingHigh energyParallel computing
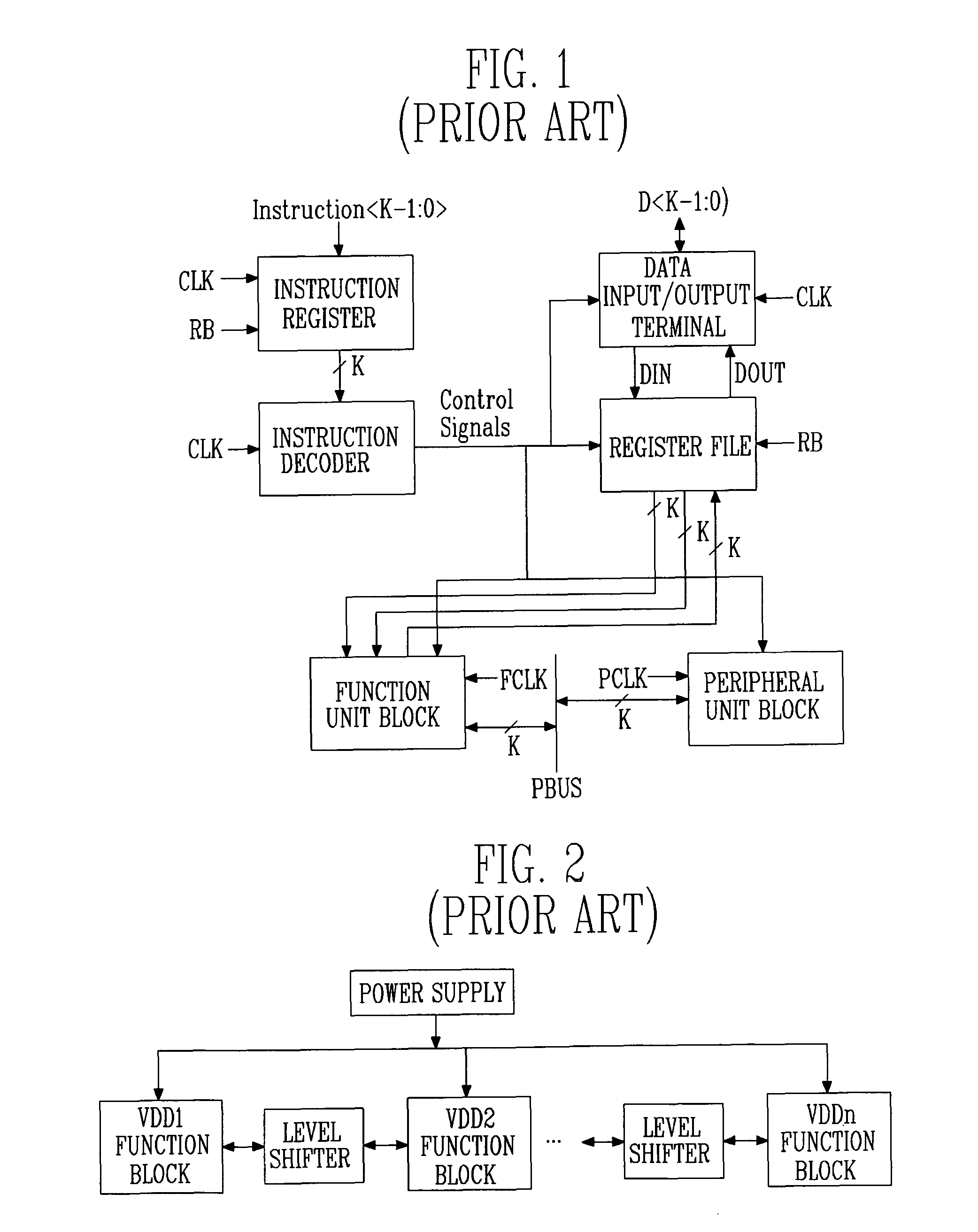
Provided is a highly energy-efficient processor architecture. The architecture employs 2-stage dynamic voltage scaling (DVS) and a sleep mode for high energy efficiency, dynamically controls the power supply voltage and activation of an embedded processor with instructions, and thus can prevent performance deterioration while reducing power consumption.A highly energy-efficient processor employing the processor architecture includes: a function unit block for performing an operation according to instructions input from the outside; at least one peripheral unit block for performing data communication with an external device; an instruction decoder for interpreting the input instructions and determining operation modes of the function unit block and peripheral unit block required for executing the interpreted instructions; a function unit block driver for applying a different power supply voltage according to the operation mode of the function unit block to the function unit block; and a peripheral unit block driver for applying a different power supply voltage according to the operation mode of the peripheral unit block to the peripheral unit block.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Temperature compensating adaptive voltage scalers (AVSs), systems, and methods
ActiveUS8661274B2Avoid and reduce voltage marginLower levelEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringOperating frequency
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Fast adaptive voltage scaling
InactiveUS20090265572A1Fast voltage scalingReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementClock rateEngineering
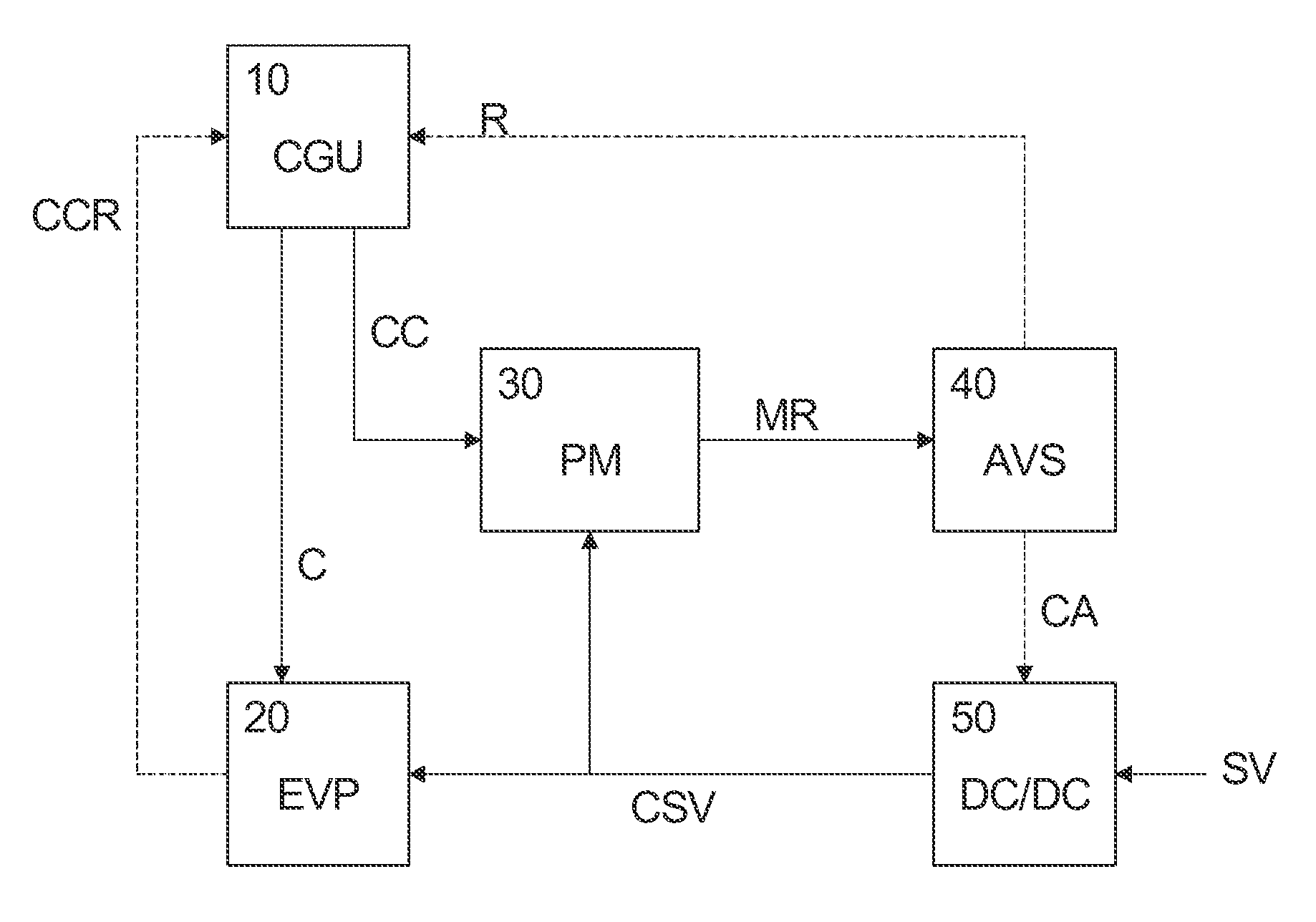
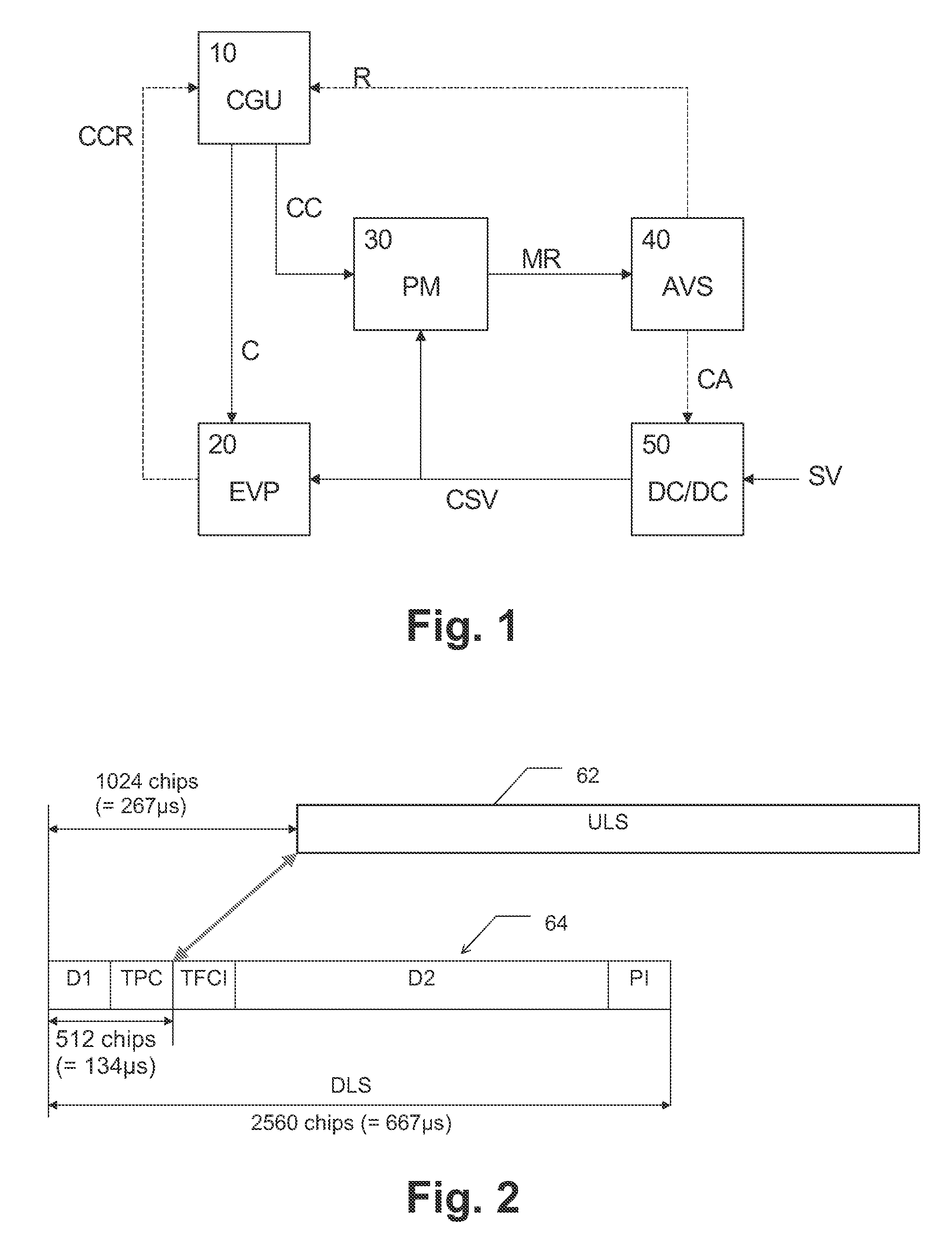
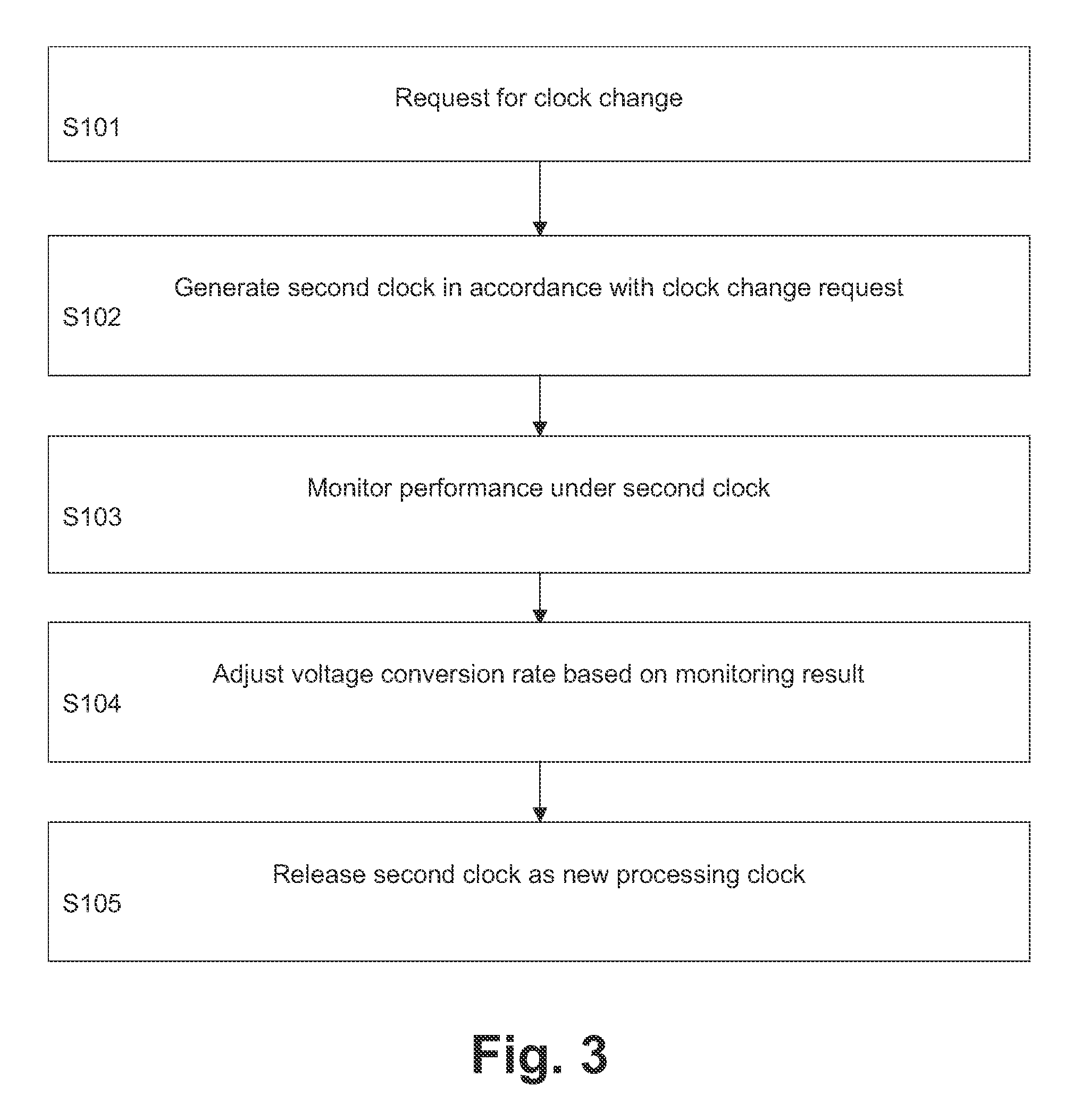
A method, digital circuit, and computer program product control a supply voltage of a processing circuit based on a processing clock of the processing circuit. A first clock frequency and at least one second clock frequency are generated, wherein the first clock frequency is used as the processing clock and the second clock frequency is adjusted based on a clock control information issued by the processing circuit. A voltage conversion ratio for converting the supply voltage to a scaled supply voltage applied to the processing circuit is directly controlled in response to the result of a monitored performance under said second clock frequency. Thereby, a new fast automatic voltage scaling approach can be provided which allows to meet critical timing requirements of portable systems and to reduce power consumption significantly.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Method for performing adaptive voltage scaling (AVS) and integrated circuit configured to perform avs
ActiveUS20140191794A1Avoid performanceDigital data processing detailsElectronic switchingEngineeringSelf adaptive
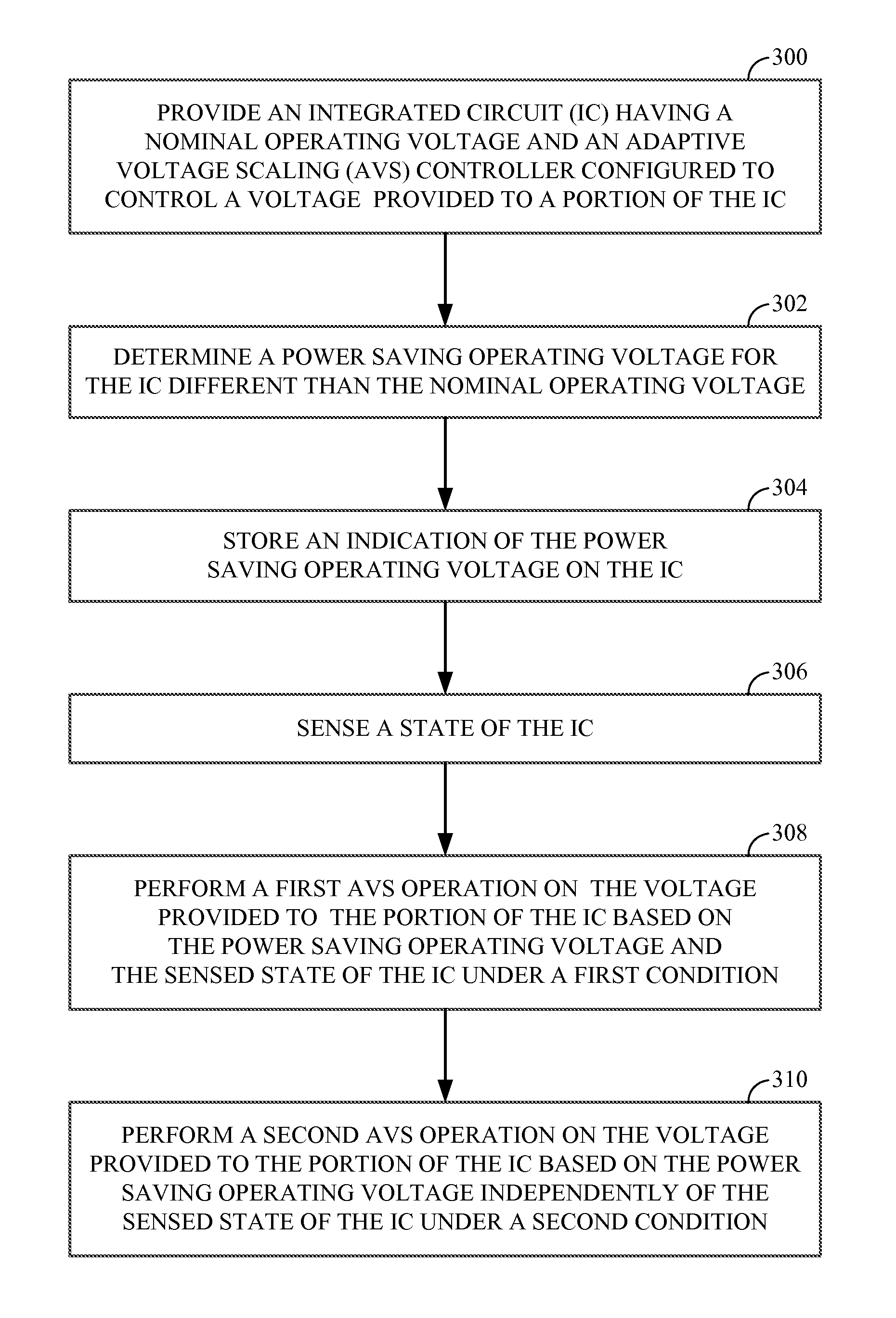
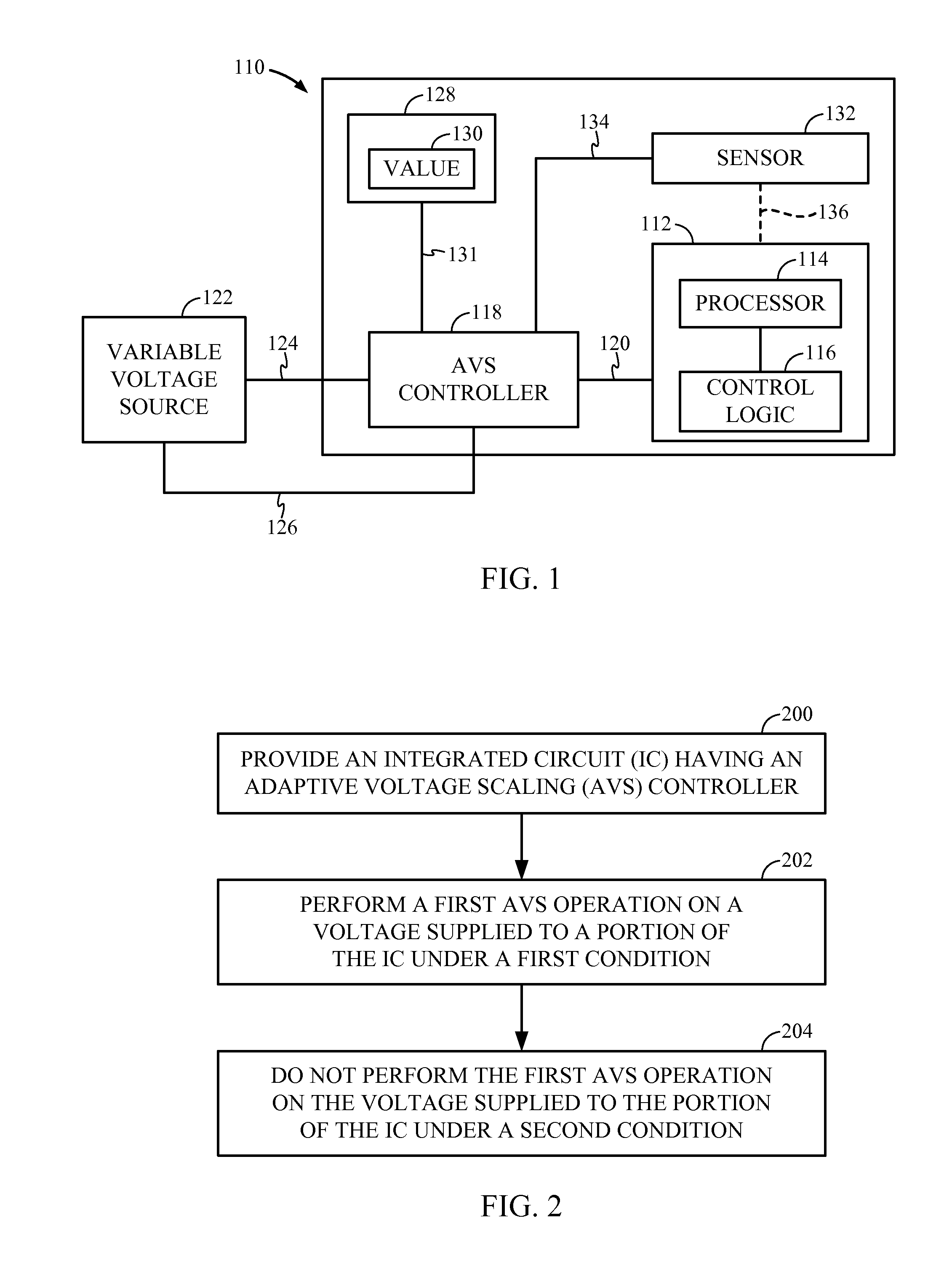
An integrated circuit (IC) includes an adaptive voltage scaling (AVS) controller configured to control a voltage supplied to a portion of the IC and at least one sensor configured to sense at least one state of the IC and to provide an output signal indicative of the at least one sensed state to the AVS controller, the IC having a first setting and a second setting, the AVS controller being configured to use the output signal to control the voltage in the first setting and the AVS controller being configured to control the voltage independently of the output signal in the second setting. Also a method of performing AVS is provided.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
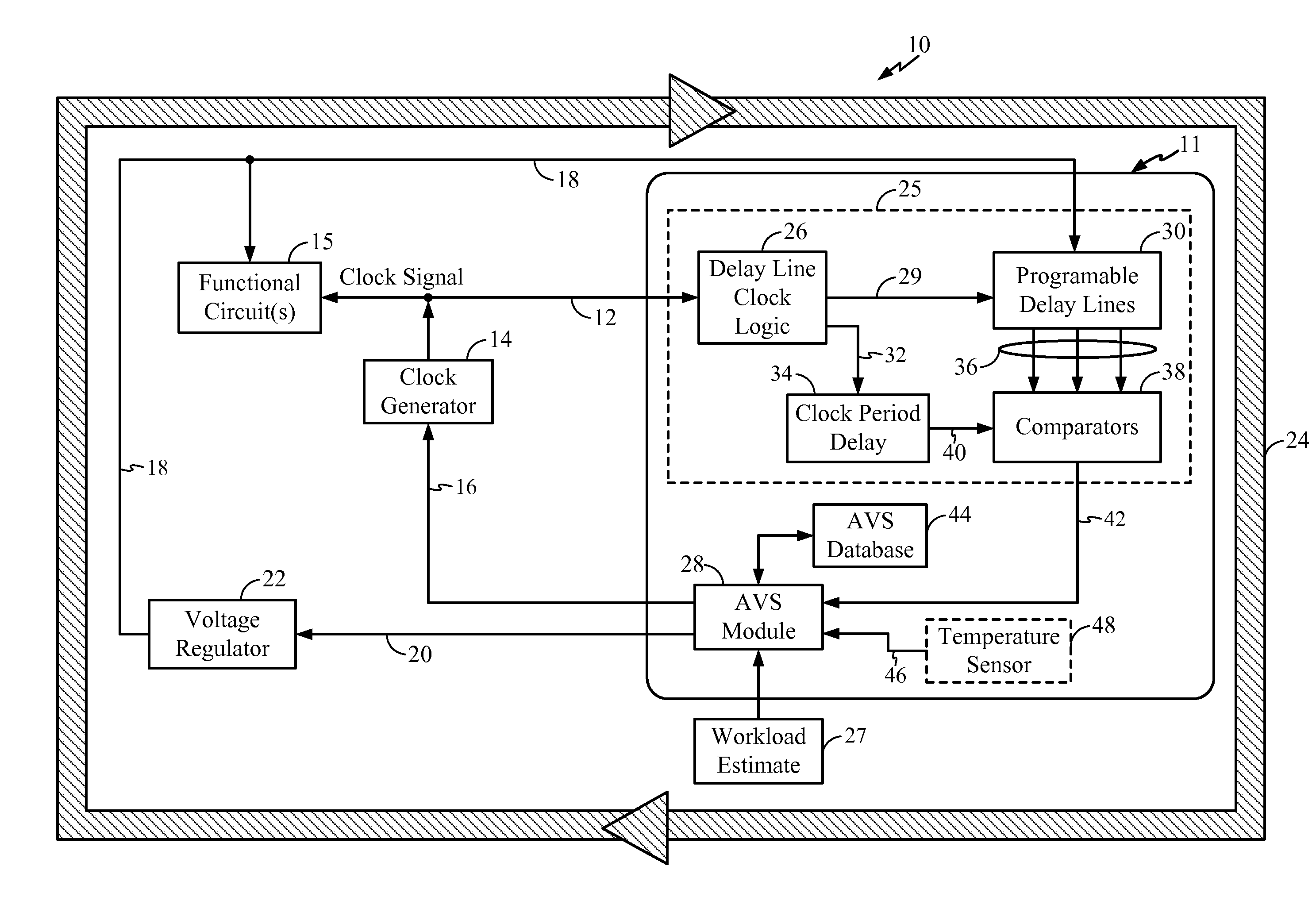
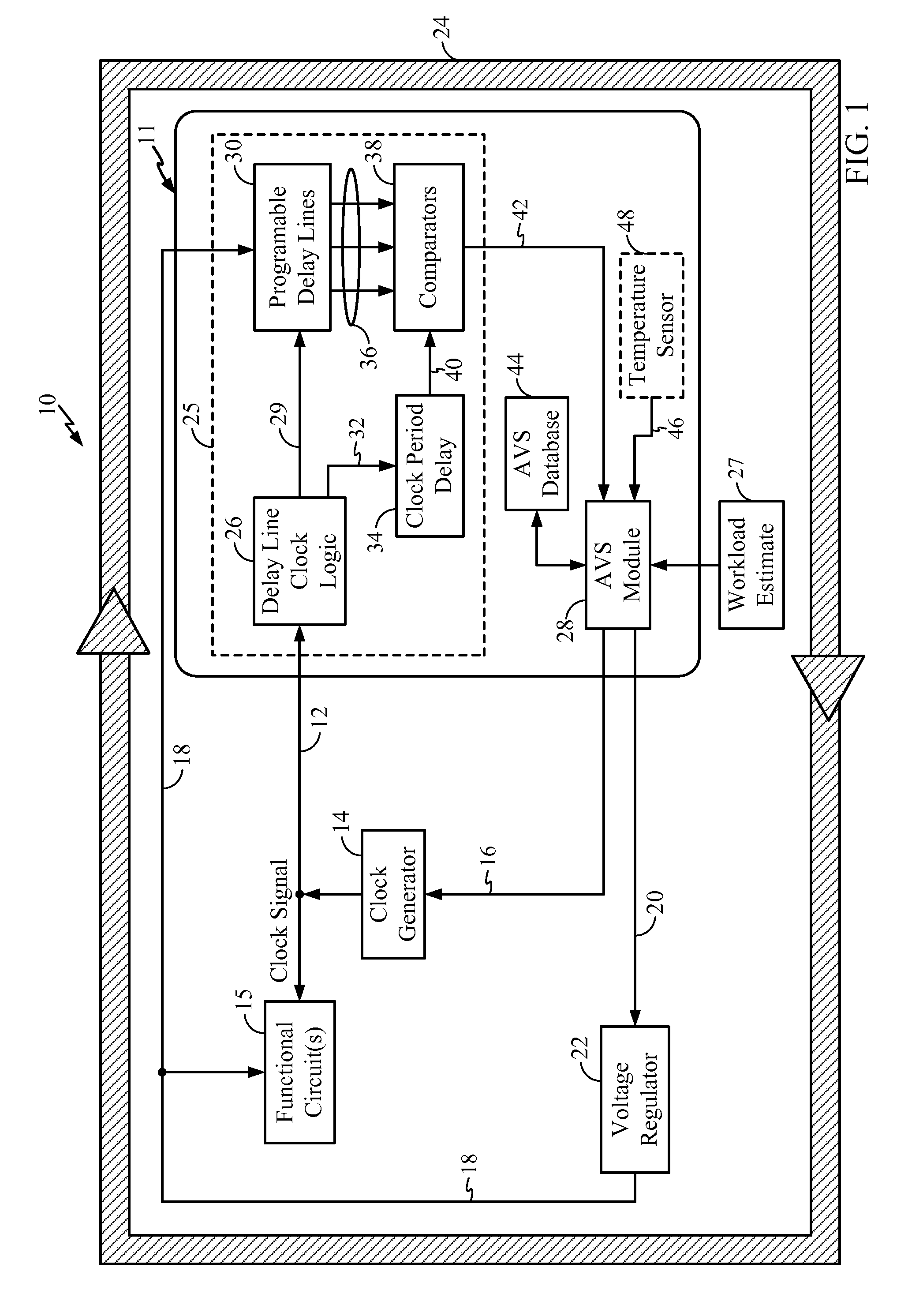
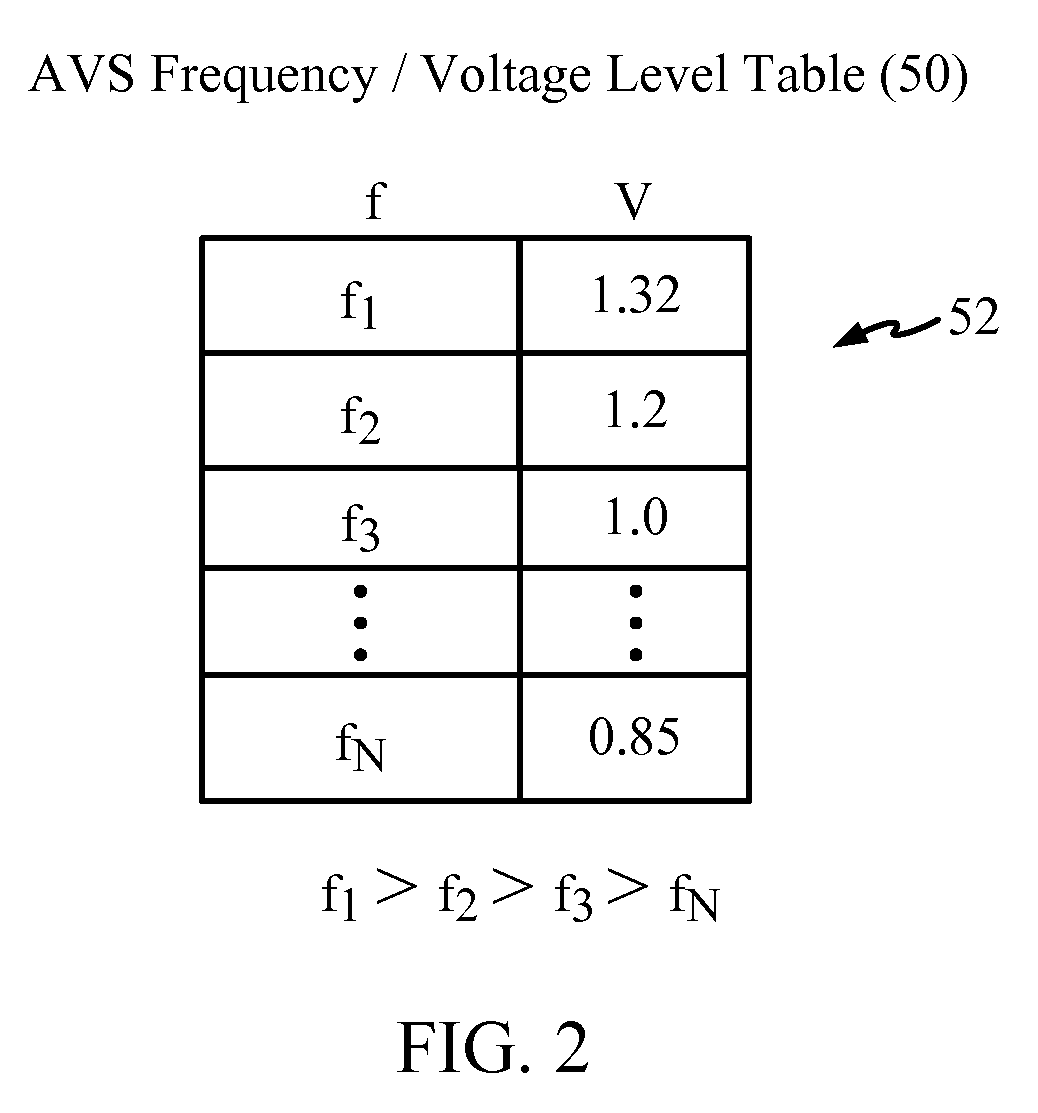
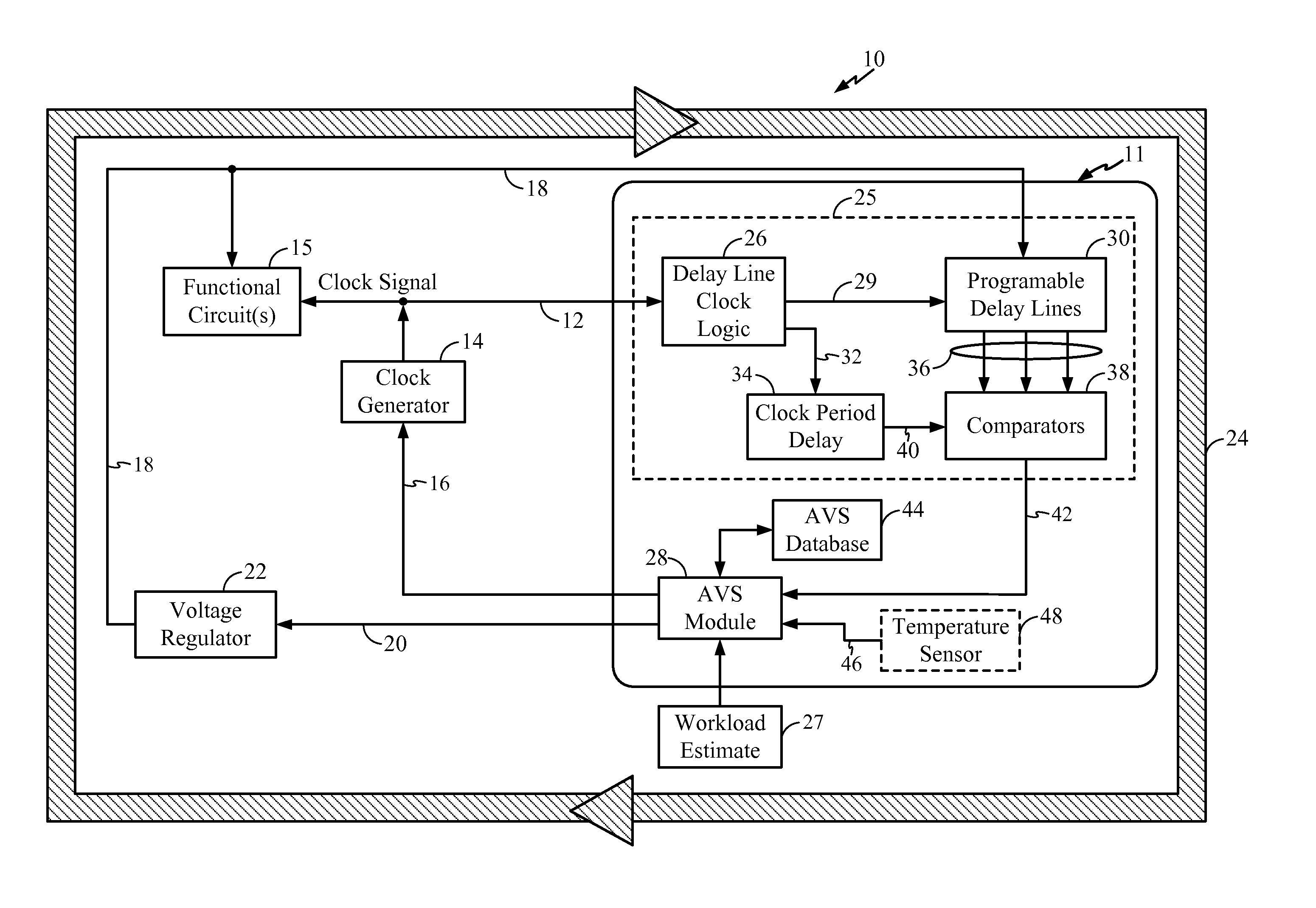
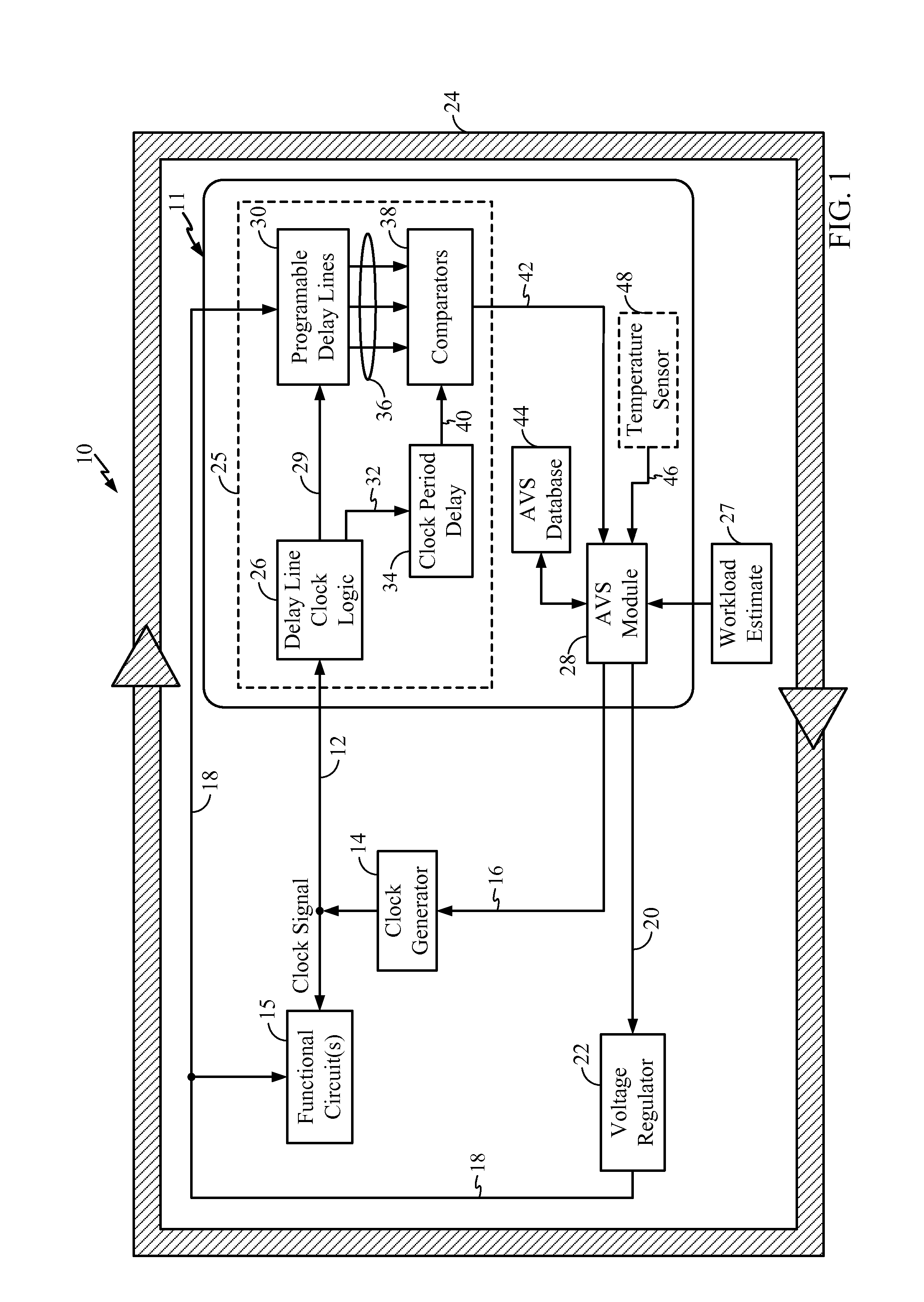
Adaptive voltage scalers (AVS), systems, and related methods
ActiveUS8797095B2Avoid and reduce voltage marginIncrease delayEnergy efficient ICTElectric pulse generatorSelf adaptiveOperating frequency
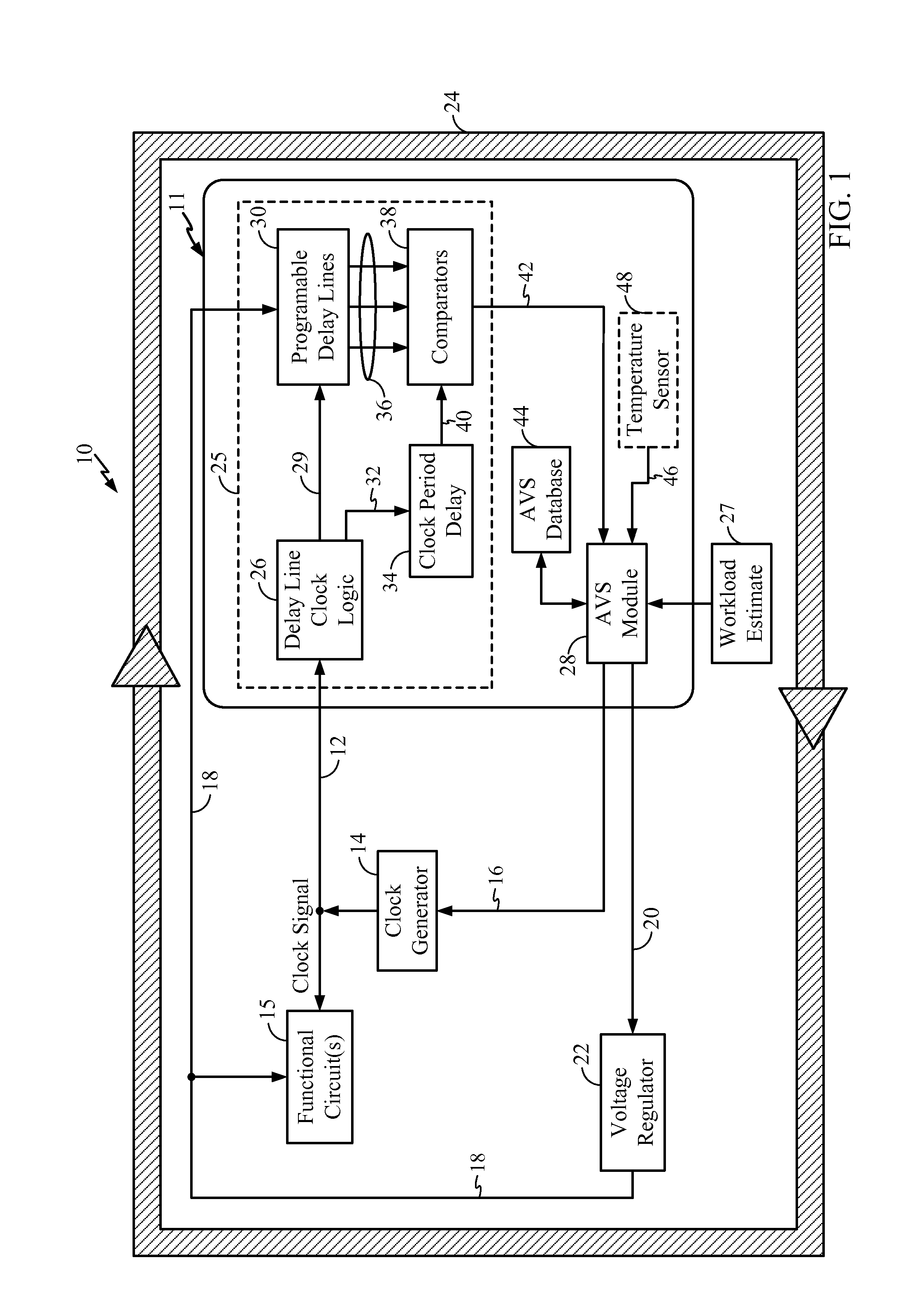
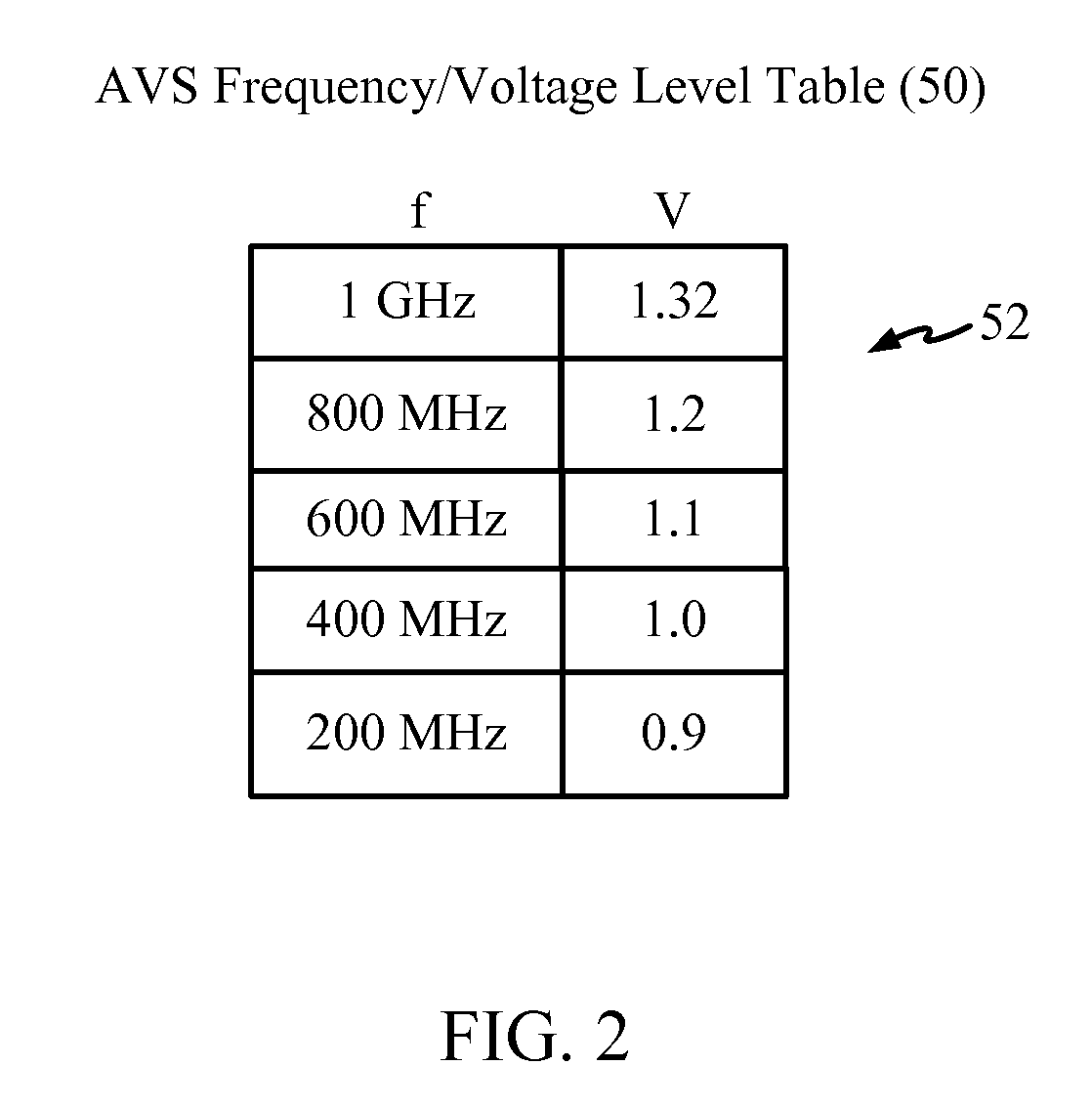
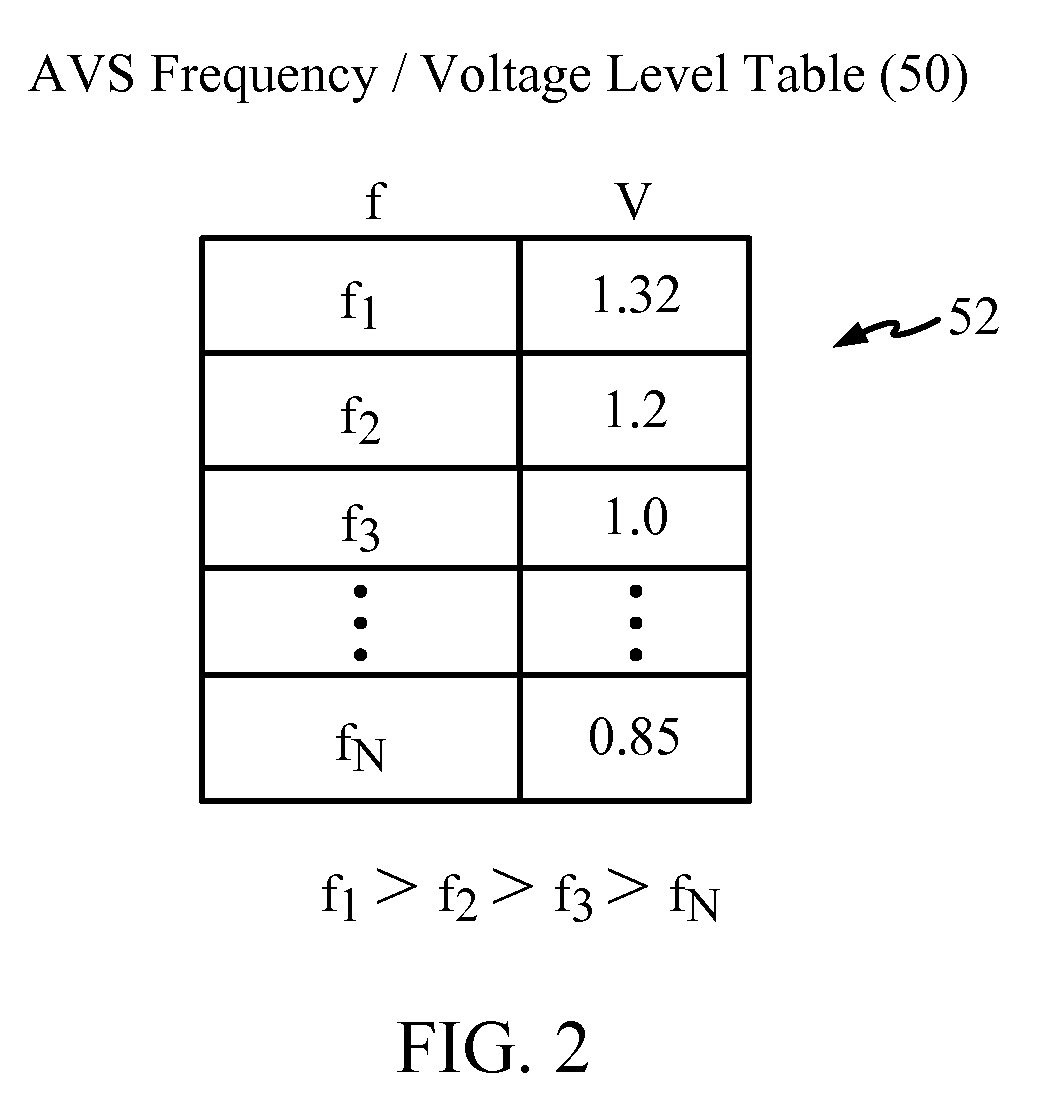
Adaptive voltage scalers (AVSs), systems, and related methods are disclosed. The AVSs are configured to adaptively adjust voltage levels powering a functional circuit(s) based on target operating frequencies and delay variation conditions to avoid or reduce voltage margin. In one embodiment, the AVS includes an AVS database. The AVS database can be configured to store voltage levels for various operating frequencies of a functional circuit(s) to avoid or reduce voltage margin. The AVS database allows rapid voltage level decisions. The voltage levels stored in the AVS database may be initial, minimum, learned, populated, explored, backed out, temperature-based, and / or age-based voltage levels according to disclosed embodiments to further avoid or reduce voltage margin. An AVS module may be a software-based module that consults the AVS database to make voltage level decisions. Providing the AVS module as a software-based module may allow flexibility in configuring the AVS module and / or the AVS database.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
System and method for designing integrated circuits that employ adaptive voltage scaling optimization
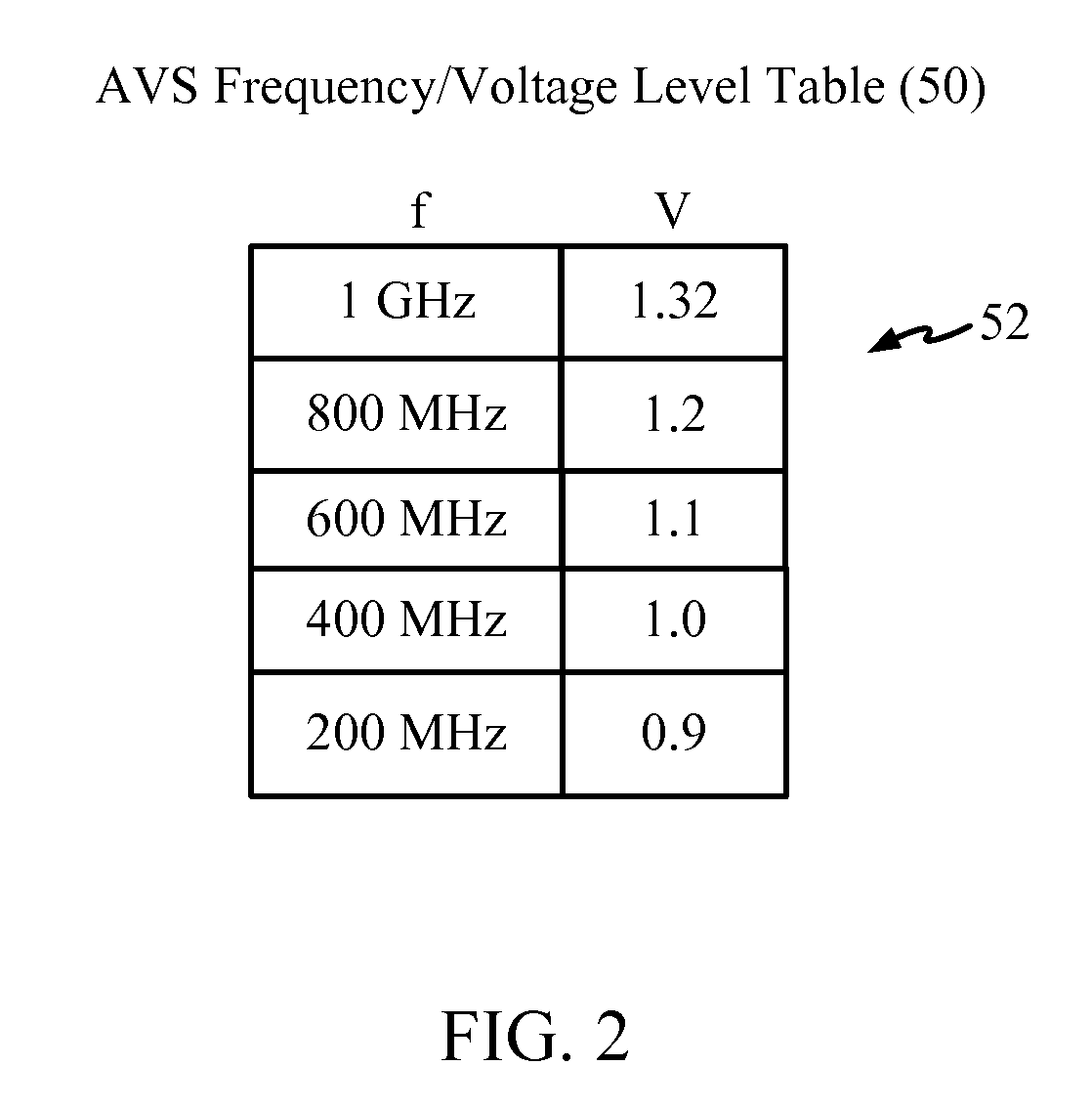
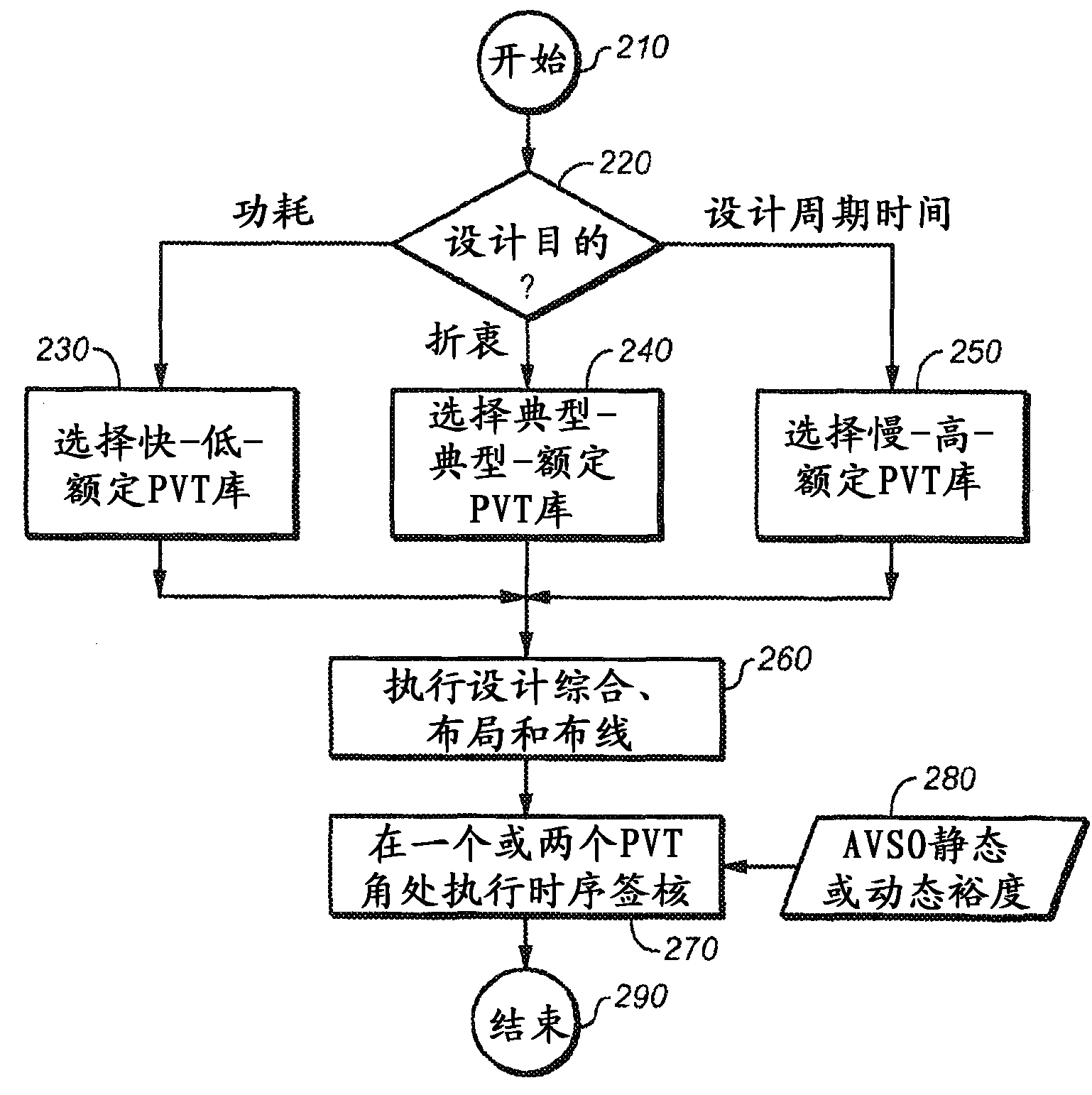
ActiveCN102160054AEasy to understandEasy to useComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsProcess optimizationAdaptive voltage scaling
The represent invention relates to a design process optimization system and method for designing a circuit which may be an integrated circuit (IC) employing adaptive voltage and scaling optimization (AVSO). In one embodiment, the system includes: (1) a process-voltage-temperature (PVT) libraries database configured to contain PVT libraries of PVT characterizations of devices of cells from which the circuit is to be constructed, and (2) a PVT library selector coupled to the PVT libraries database and configured to receive a selection indicating a supplemental objective and respond to the selection by selecting one of the PVT libraries from the PVT libraries database, a timing signoff tool later employing at most two corners from the one of the PVT libraries to perform a timing signoff with respect to the circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Semiconductor integrated circuit and electronic device
AVS (Adaptive Voltage Scaling) technique, by which variability and uncertainty are both taken into account. In the system arranged for AVS technique, a detection circuit optimum for each type of process variation is set. Examples of the detection circuit so arranged include a first measurement circuit for detection of variability, which produces a relative value with respect to the gate delay mean value, and a second measurement circuit for detection of uncertainty, which produces a relative value related to the gate delay standard deviation. The first and second measurement circuits are provided separately from each other. The control information for deciding the supply voltage is prepared based on relative values produced by the detection circuits. When preparing the control information, reference is made to e.g. a table data.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
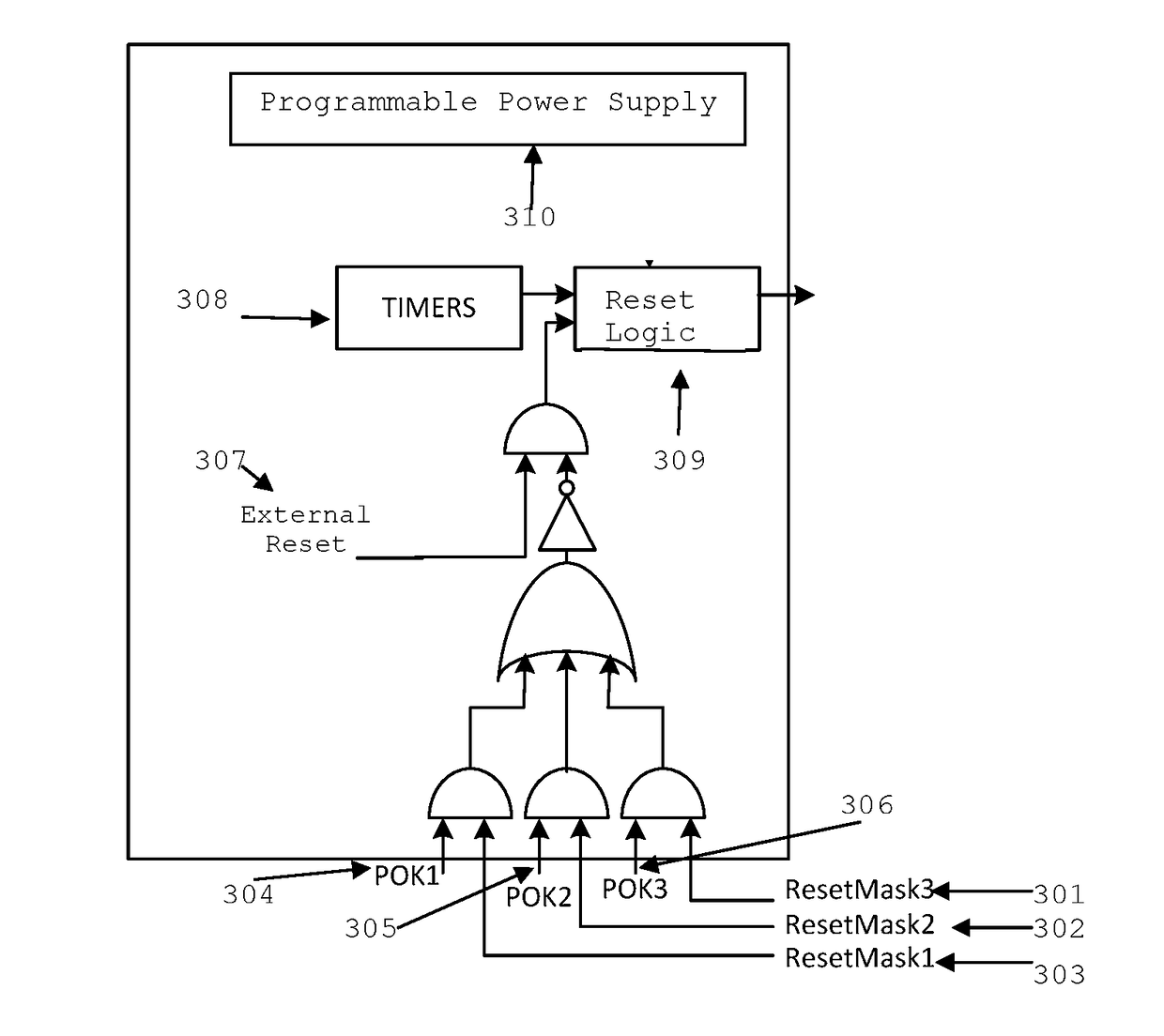
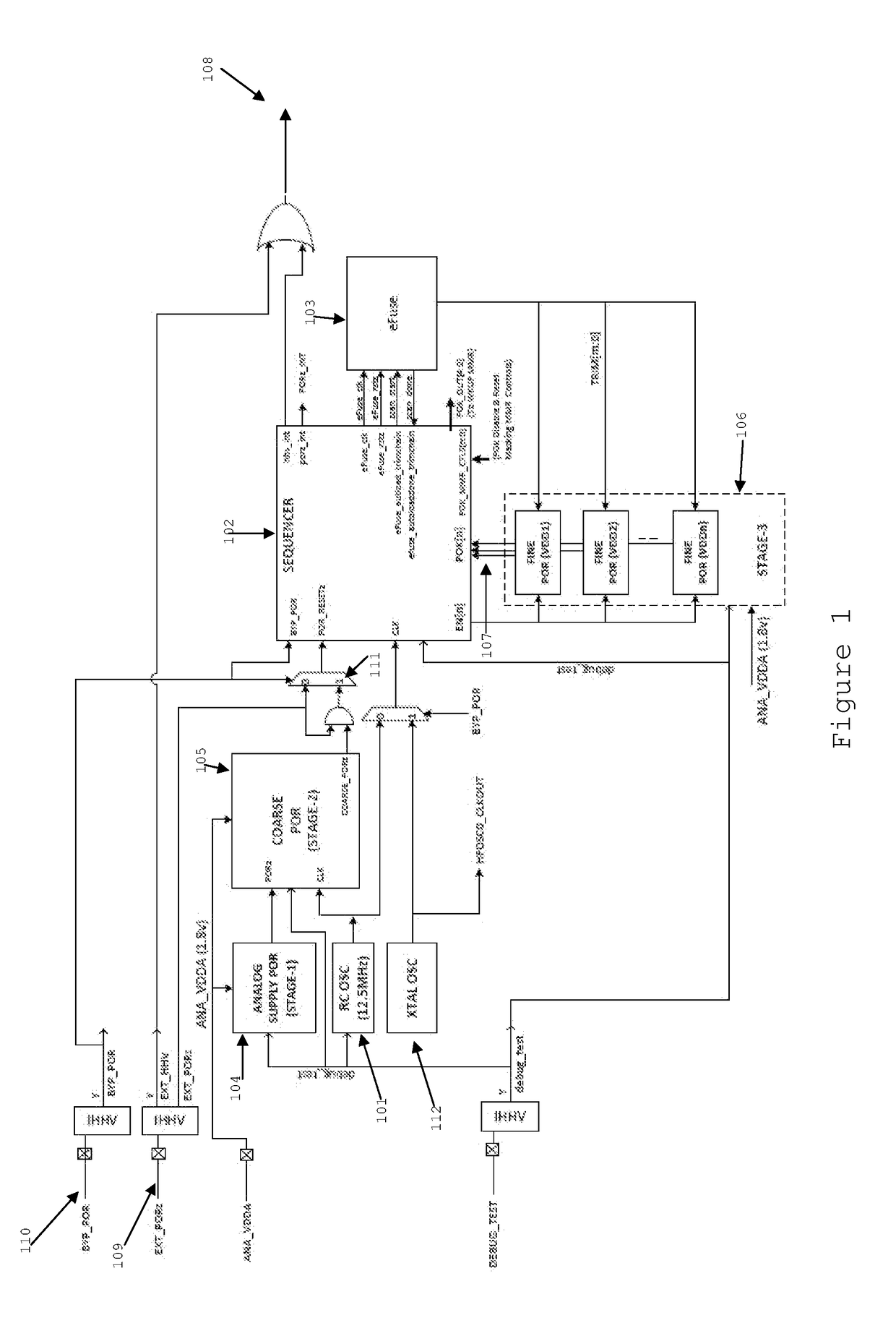
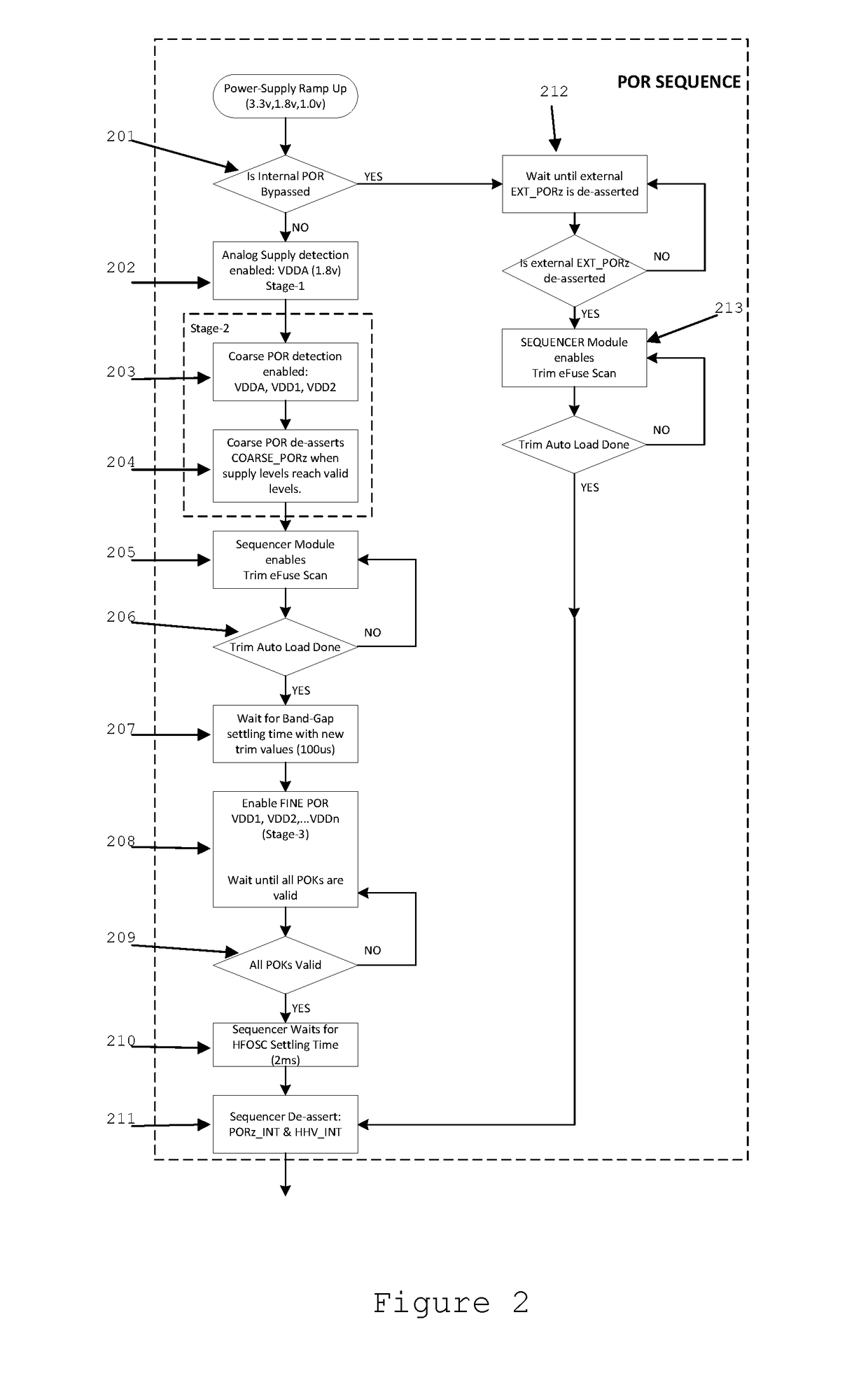
ADAPTIVE VOLTAGE SCALING SYSTEM FOR OUT OF CONTEXT FUNCTIONAL SAFETY SoC
The optimal operating voltage of a complex SoC may be influenced by process variations. The operating voltages may be dynamically adjusted for optimal performance. These adjustments require a dynamic reconfiguration of the voltage monitoring thresholds in the power on reset circuitry of the SoC.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com