Patents
Literature
50 results about "Circuit Switched Data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
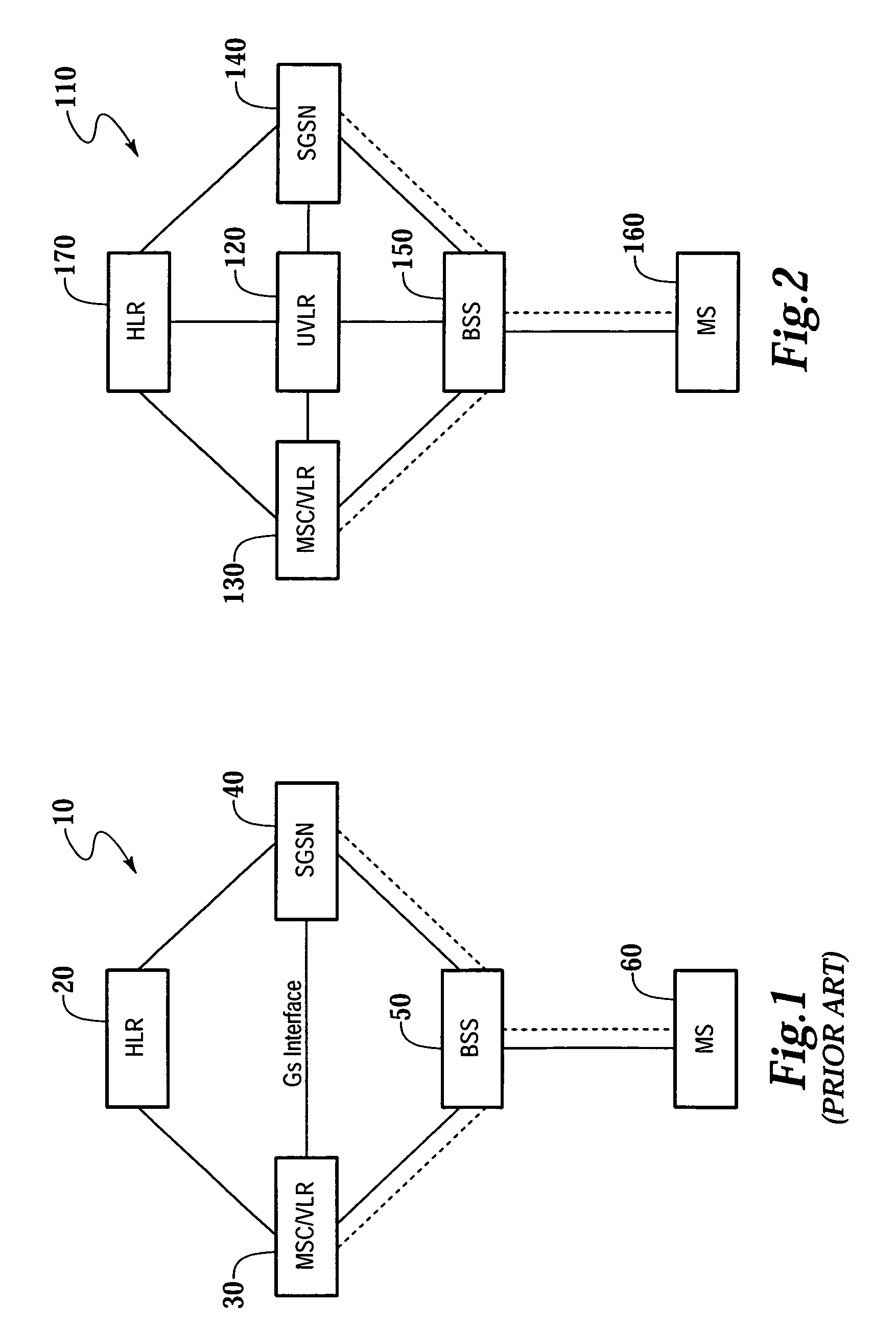
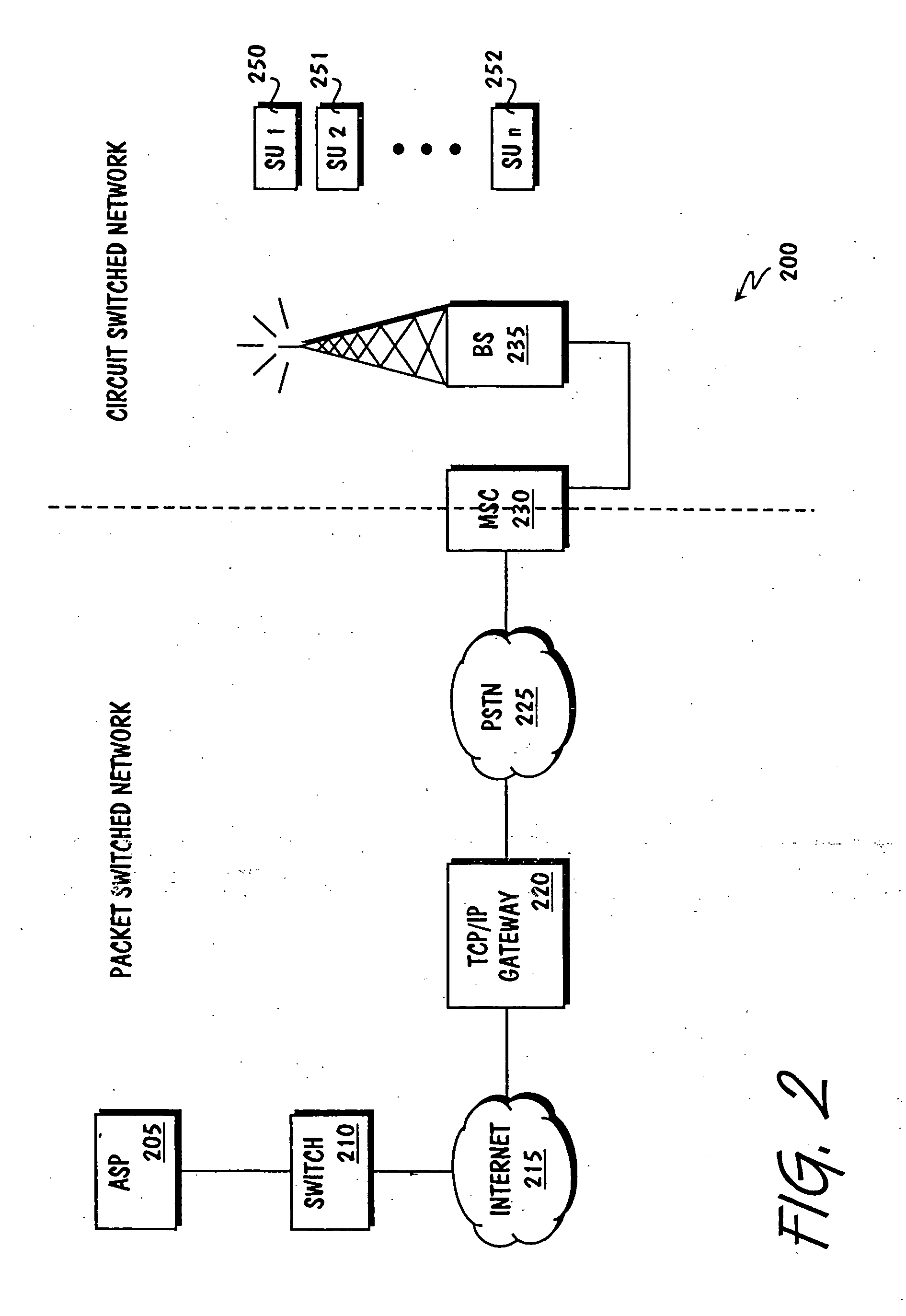
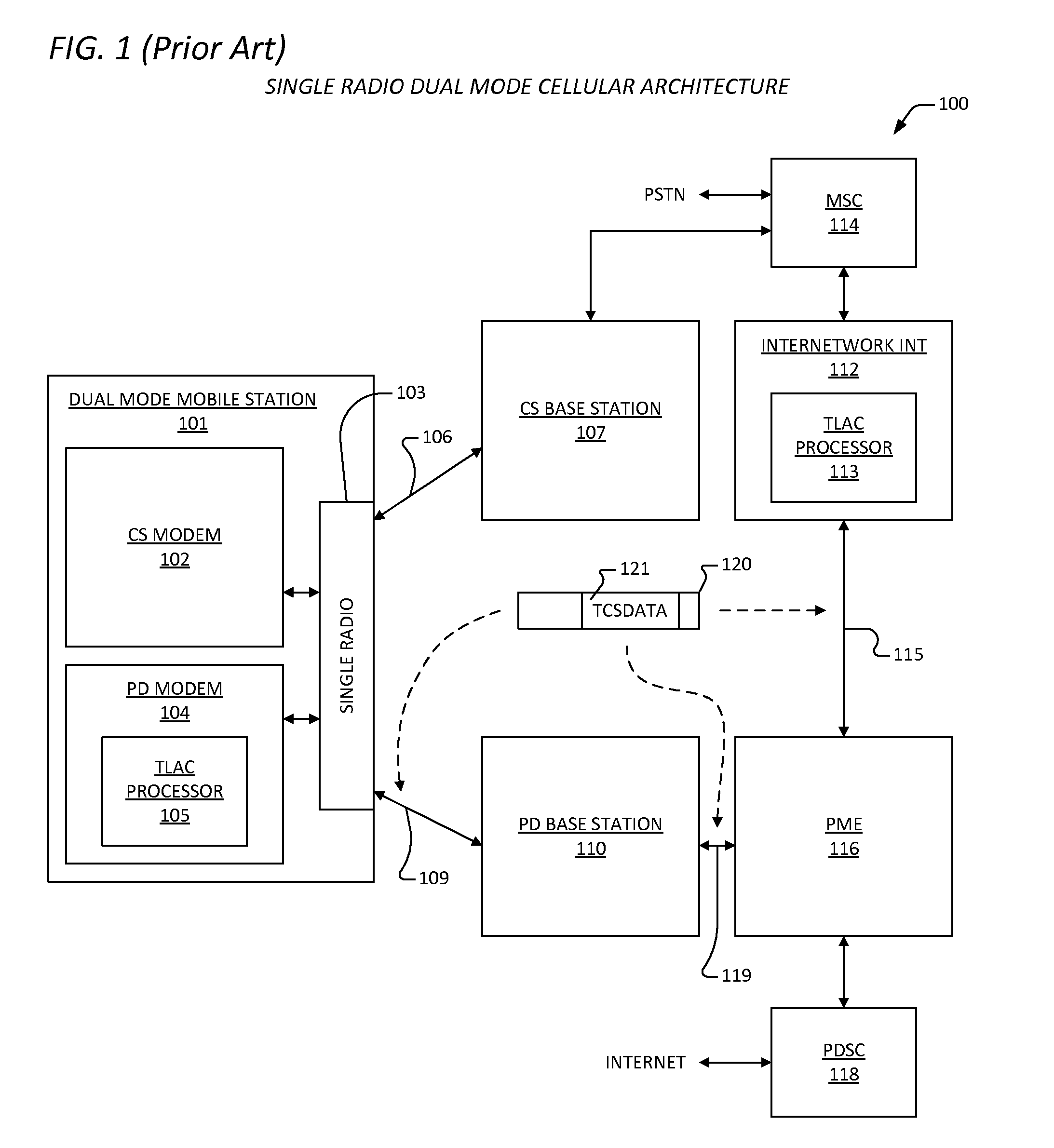
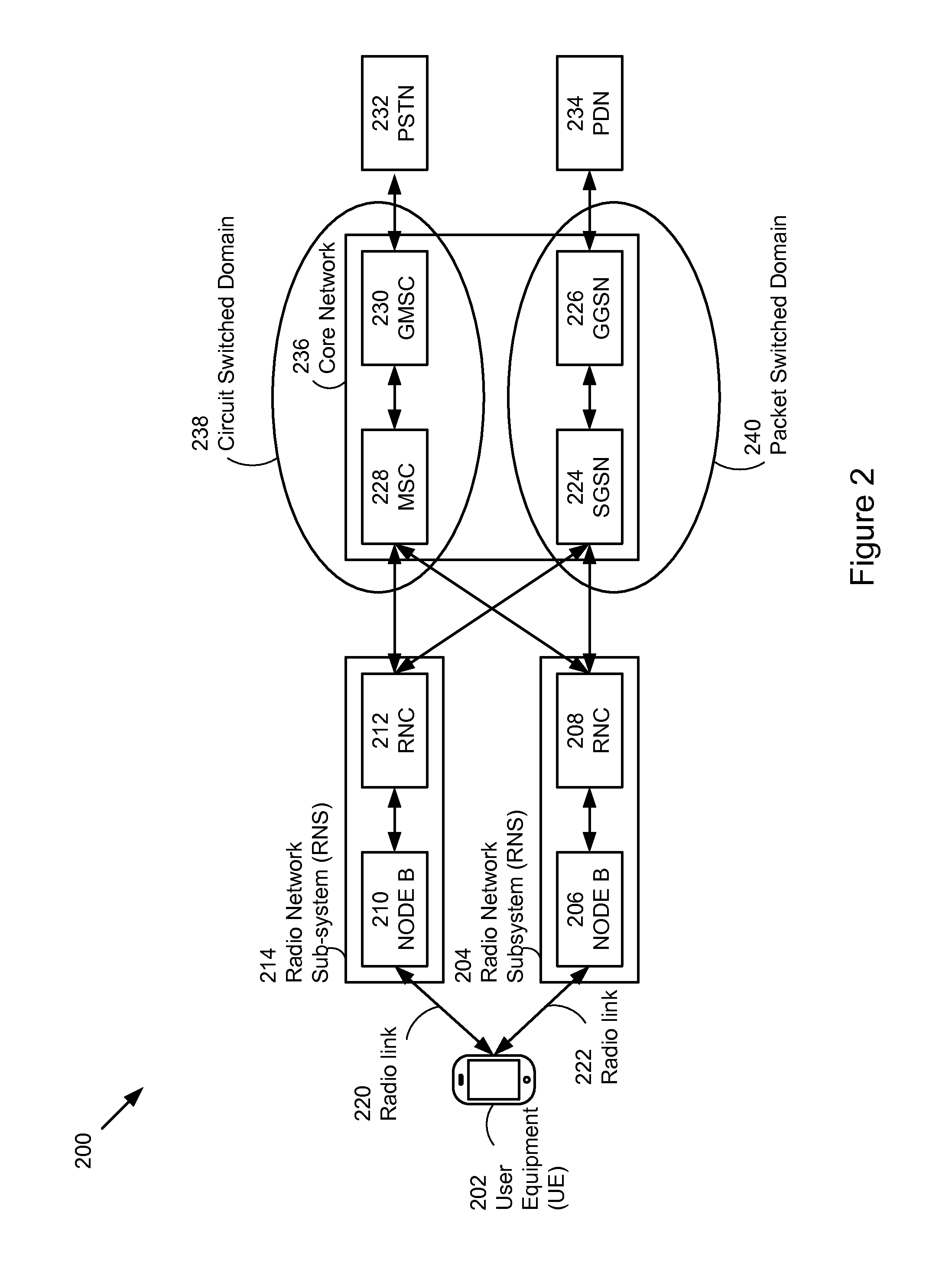
In communications, Circuit Switched Data (CSD) is the original form of data transmission developed for the time-division multiple access (TDMA)-based mobile phone systems like Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM). After 2010 many telecommunication carriers dropped support for CSD, and CSD has been superseded by GPRS and EDGE (E-GPRS).
Mobile originated interactive menus via short messaging services
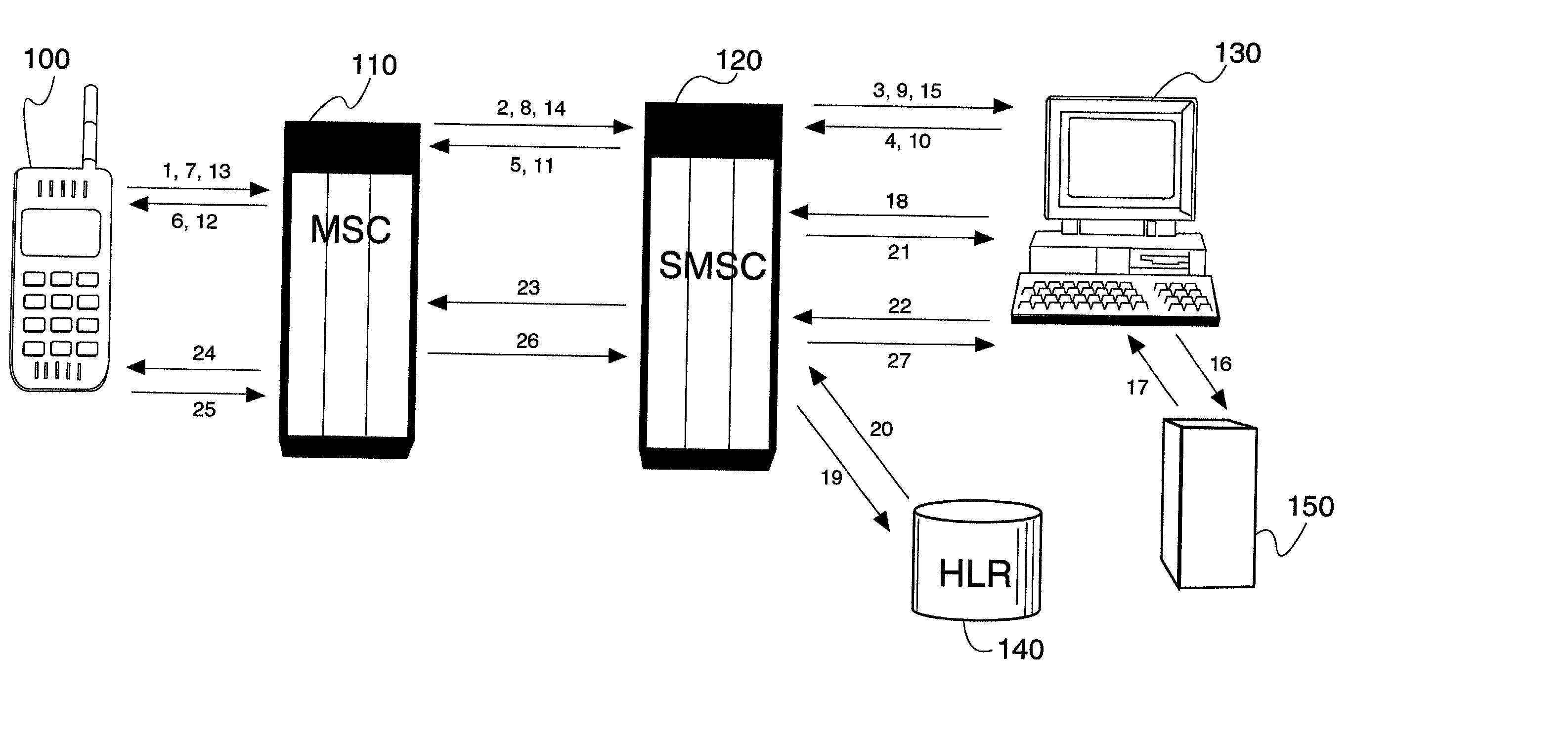
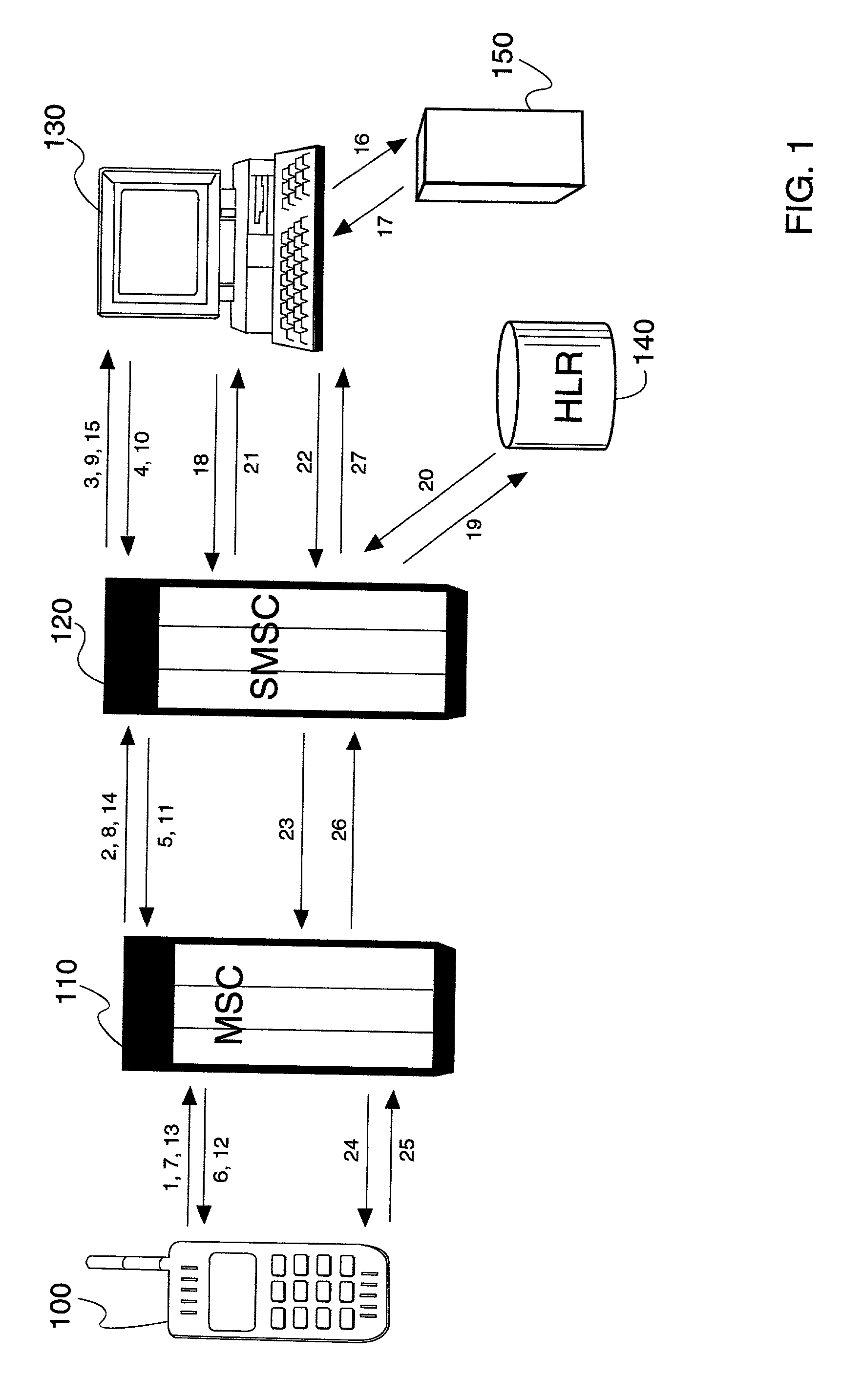
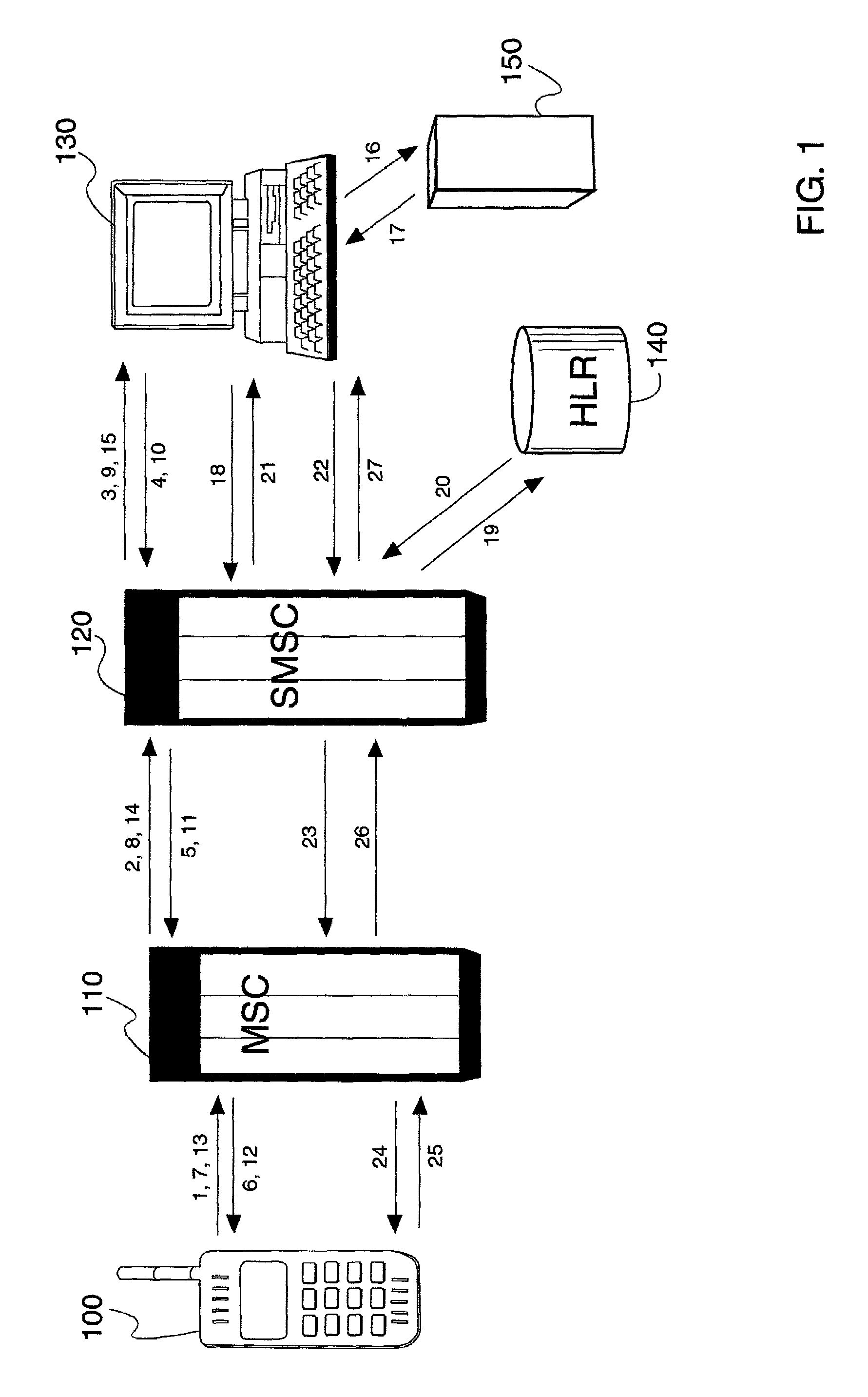
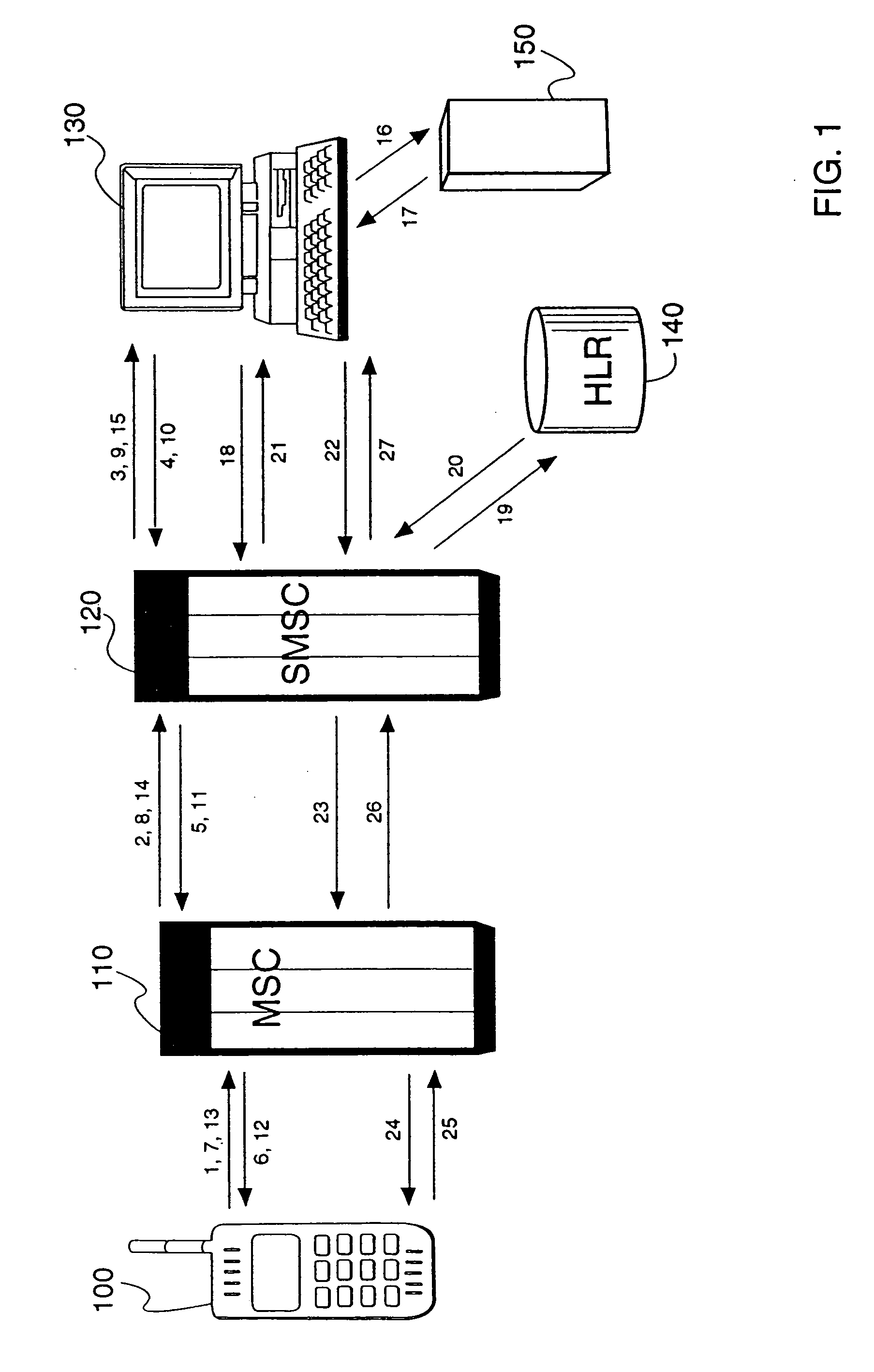
InactiveUS20020119793A1Substation equipmentMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsCircuit Switched DataGSM
A method and apparatus for providing 2-way interactive short message system menus to a mobile device using text-based short messaging rather than WAP techniques. This provides the ability to provide WAP like services at a fraction of the cost of CSD. Mobile Originated Interactive Menus are implemented as a feature of a Short Message Service Center (SMSC). Each option guides either to the next menu level, or to a final action to be executed according to the path followed by the subscriber. Importantly, the mobile originated interactive menus use SMS communications instead of circuit switched data (CSD) (e.g., instead of WAP communications), thus leaving traffic channels available for voice calls. Interactive SMS menus allow service providers to offer their subscribers personalized messaging menus with multiple options for quick and easy access to Web-based content. Users may define the content and frequency they want, whether it is a scheduled delivery or on-demand. The interactive SMS menu options offer customers a simple-to-use technique and apparatus for checking, e.g., stock quotes, local weather, and / or other Web-based news and information when they want it. The interactive nature of the service allows the wireless network to poll the user for their next response, with multiple menued options offered, making it highly intuitive. Replacement of messages in TDMA and GSM mobile devices allow for heavy usage without filling up the user's phone buffer, i.e., prior messages may be overwritten, to assure that only the latest information is all that is being displayed and read. The flexibility of Interactive SMS Menus can allow service providers to define their own base offering of menus, depending upon their targeted customer segments.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Mobile originated interactive menus via short messaging services
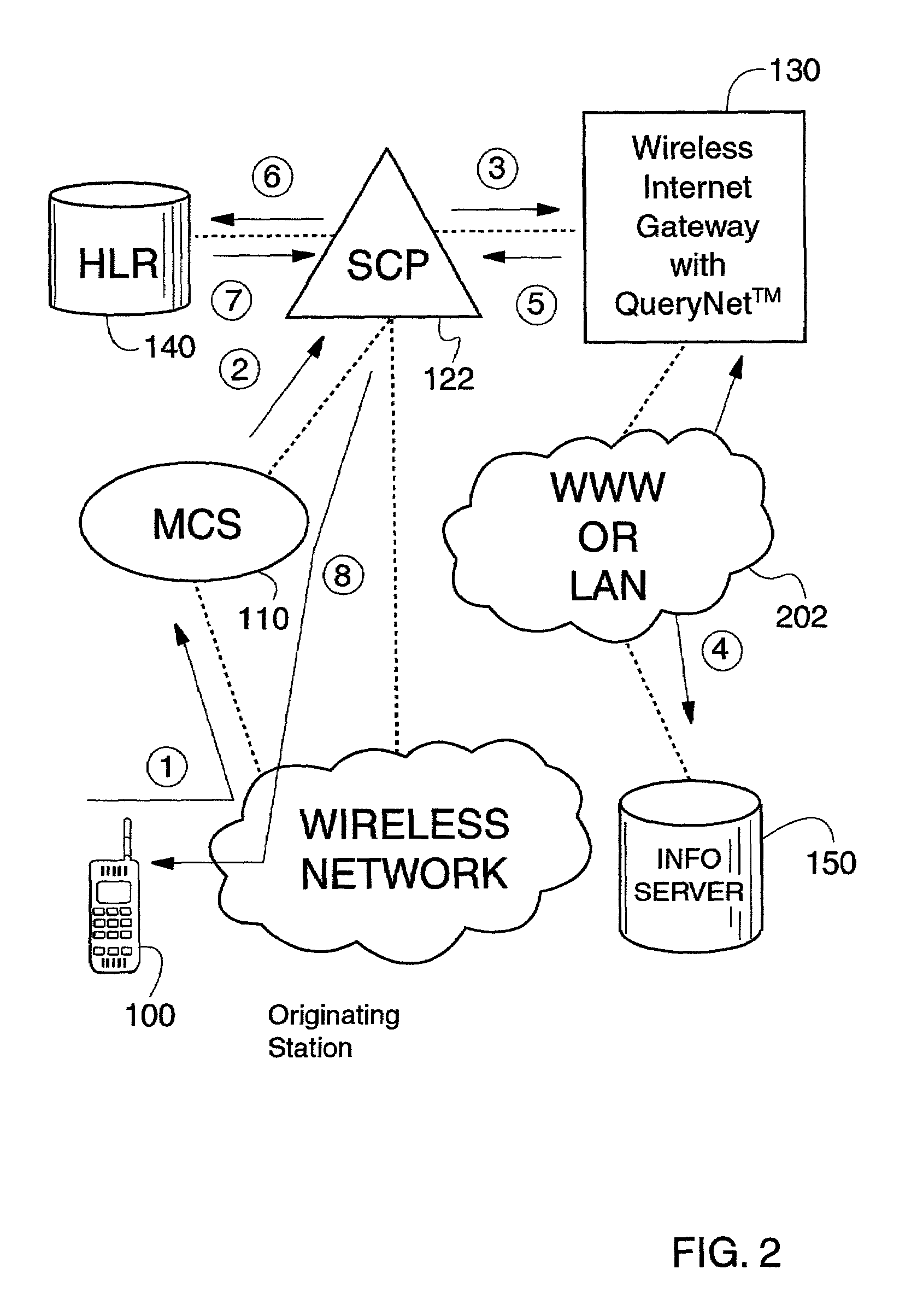
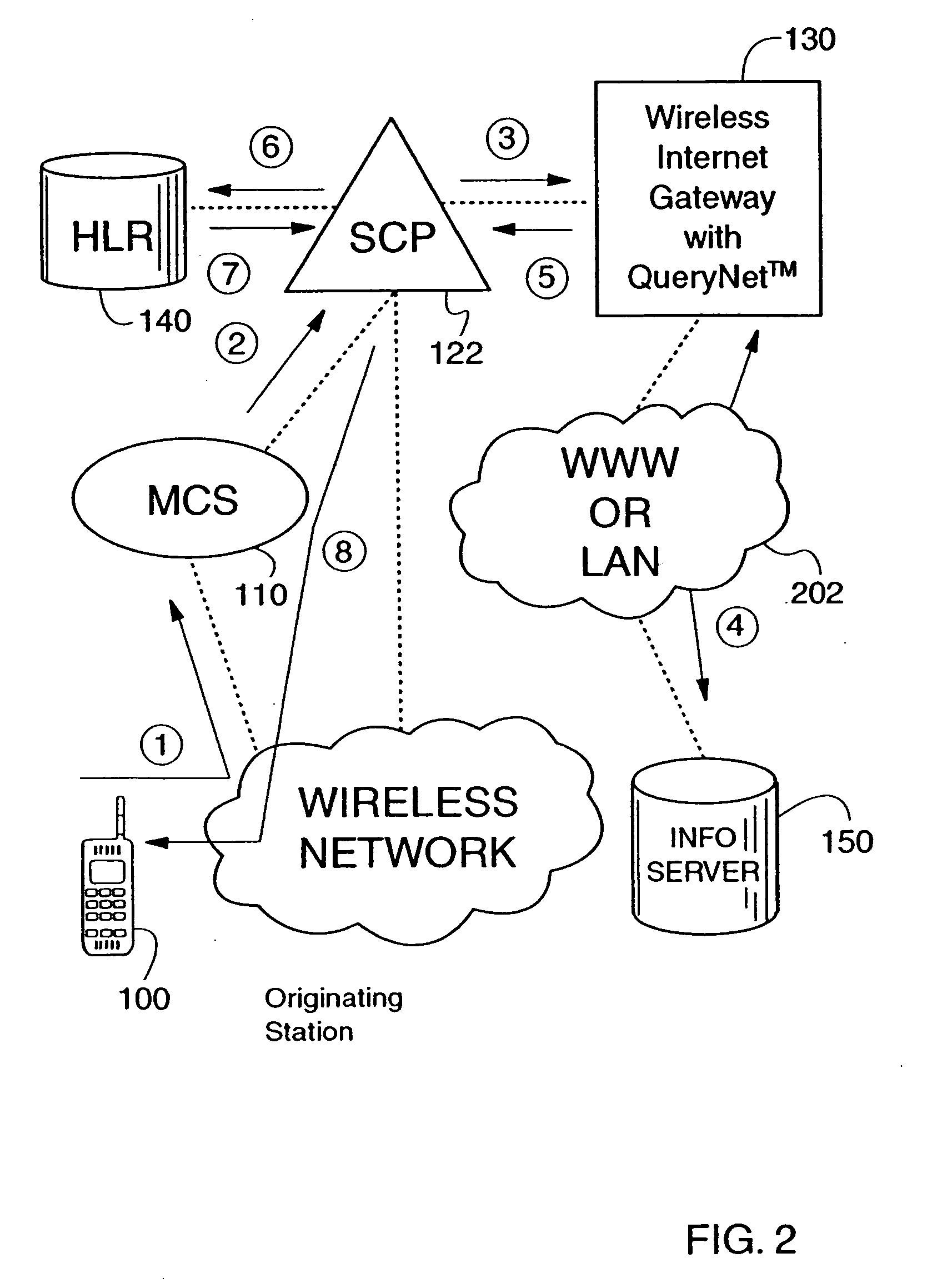
InactiveUS7127264B2Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPersonalizationCircuit Switched Data
Two-way interactive short message system with personalized messaging menus that provide WAP like services at less cost than CSD. Mobile Originated Interactive Menus are implemented as a feature of a Short Message Service Center (SMSC). Each option guides either to the next menu level, or to a final action to be executed according to the path followed by the subscriber. Importantly, the mobile originated interactive menus use SMS communications instead of circuit switched data (CSD) (e.g., instead of WAP communications), thus leaving traffic channels available for voice calls. Users may define the content and frequency they want. Replacement of messages in TDMA and GSM mobile devices allow for heavy usage without filling up the user's phone buffer, i.e., prior messages may be overwritten, to assure that only the latest information is all that is being displayed and read.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
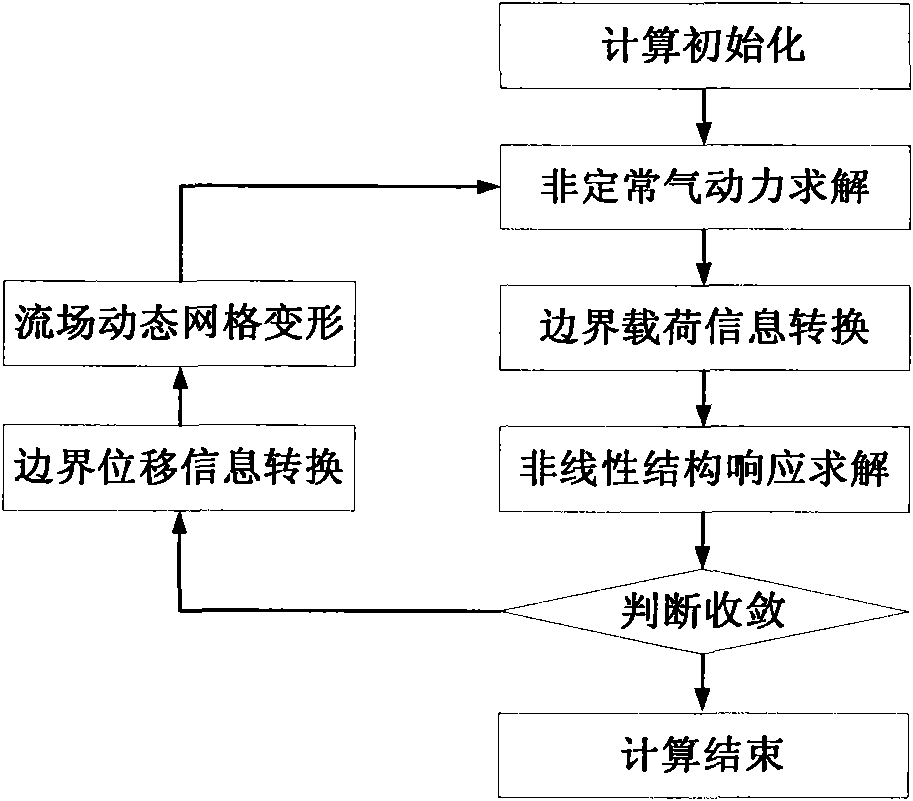
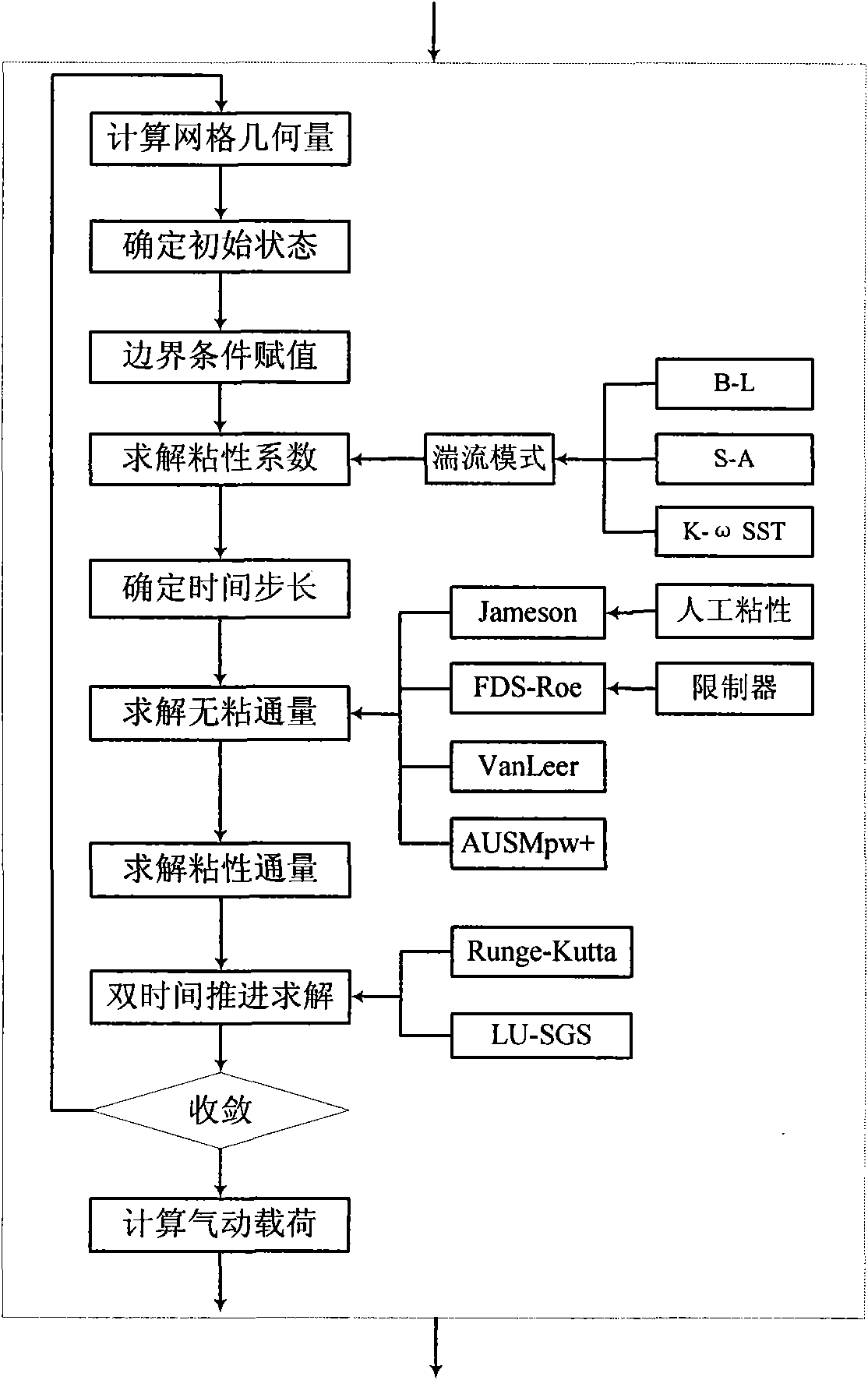
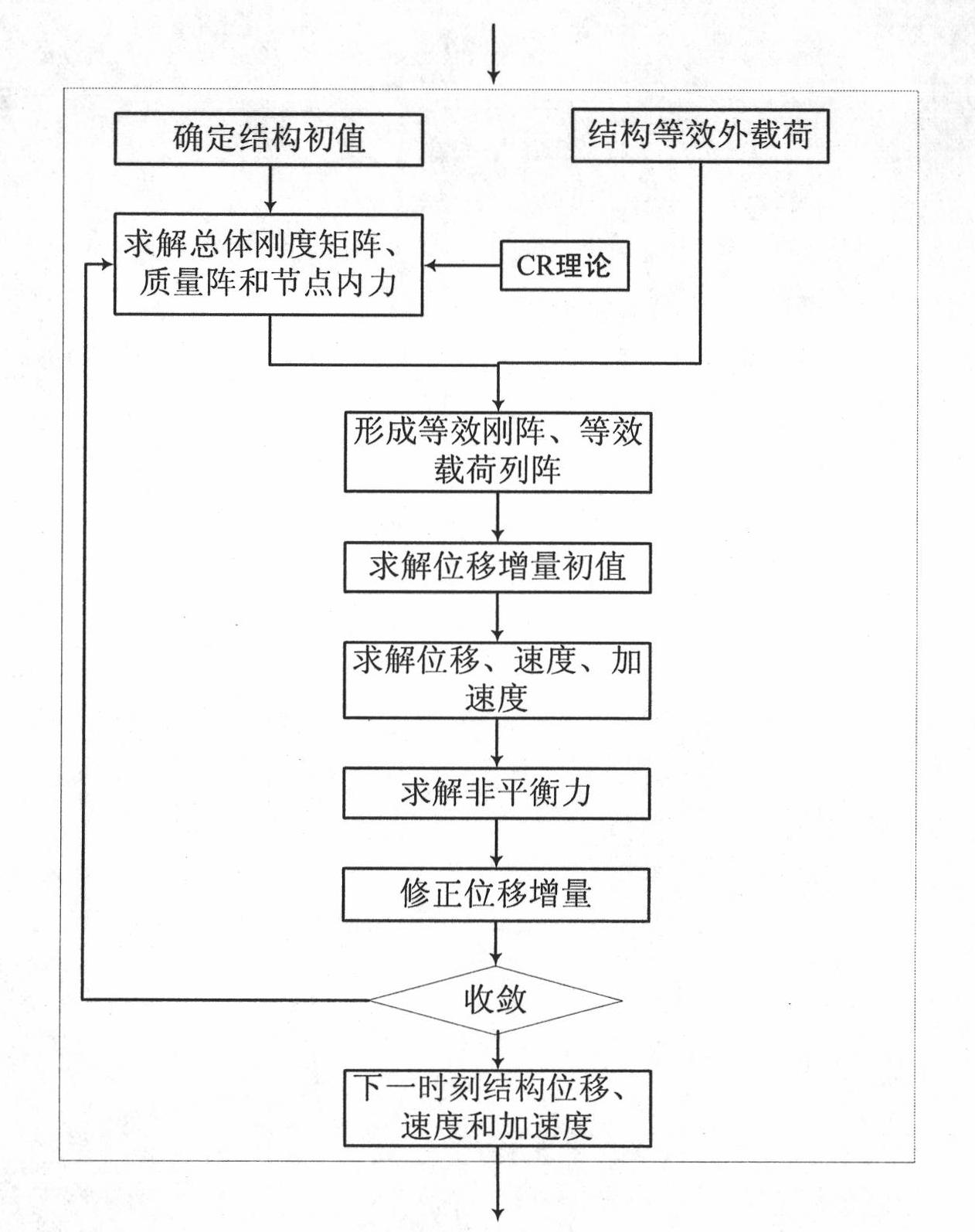
CFD (computational fluid dynamics)/CSD (circuit switch data) coupled solving nonlinear aeroelasticity simulation method
InactiveCN102012953ACapable of nonlinear couplingSpecial data processing applicationsAviationCircuit Switched Data
The invention discloses a CFD (computational fluid dynamics) / CSD (circuit switch data) coupled solving nonlinear aeroelasticity simulation method, comprising: firstly, carrying out calculation initialization; then solving the CFD of unsteady aerodynamic force; converting boundary load information; solving the CSD of nonlinear structure dynamic response; judging whether to exist computation or notby taking the response of structural finite-element mesh point displacement as a convergence criteria; if not exiting, carrying out the dynamic mesh deformation of a flow field after the surface displacement information of a computation model is converted; and then, continuing to compute until the convergence criteria is satisfied, thus finishing computation. By means of the simulation method disclosed by the invention, the problem of pneumatic nonlinearity and structural nonlinearity coupling and the problem of geometric large deformation dynamic mesh can be solved; and the simulation methoddisclosed by the invention can be applied on the nonlinear aeroelasticity analysis of aerospace aircrafts and the nonlinear aeroelasticity analysis of civil high-rise buildings and bridges.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
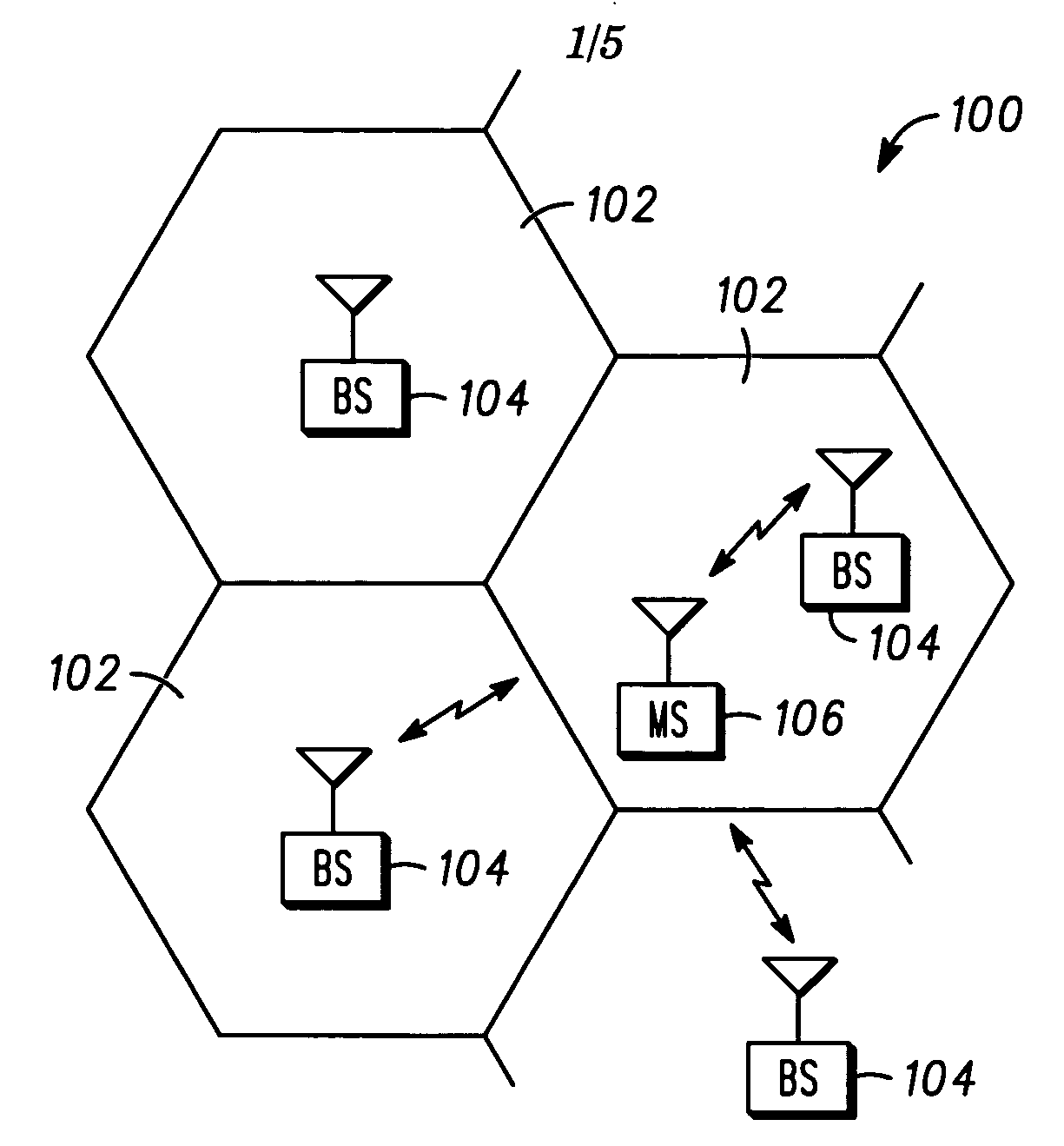
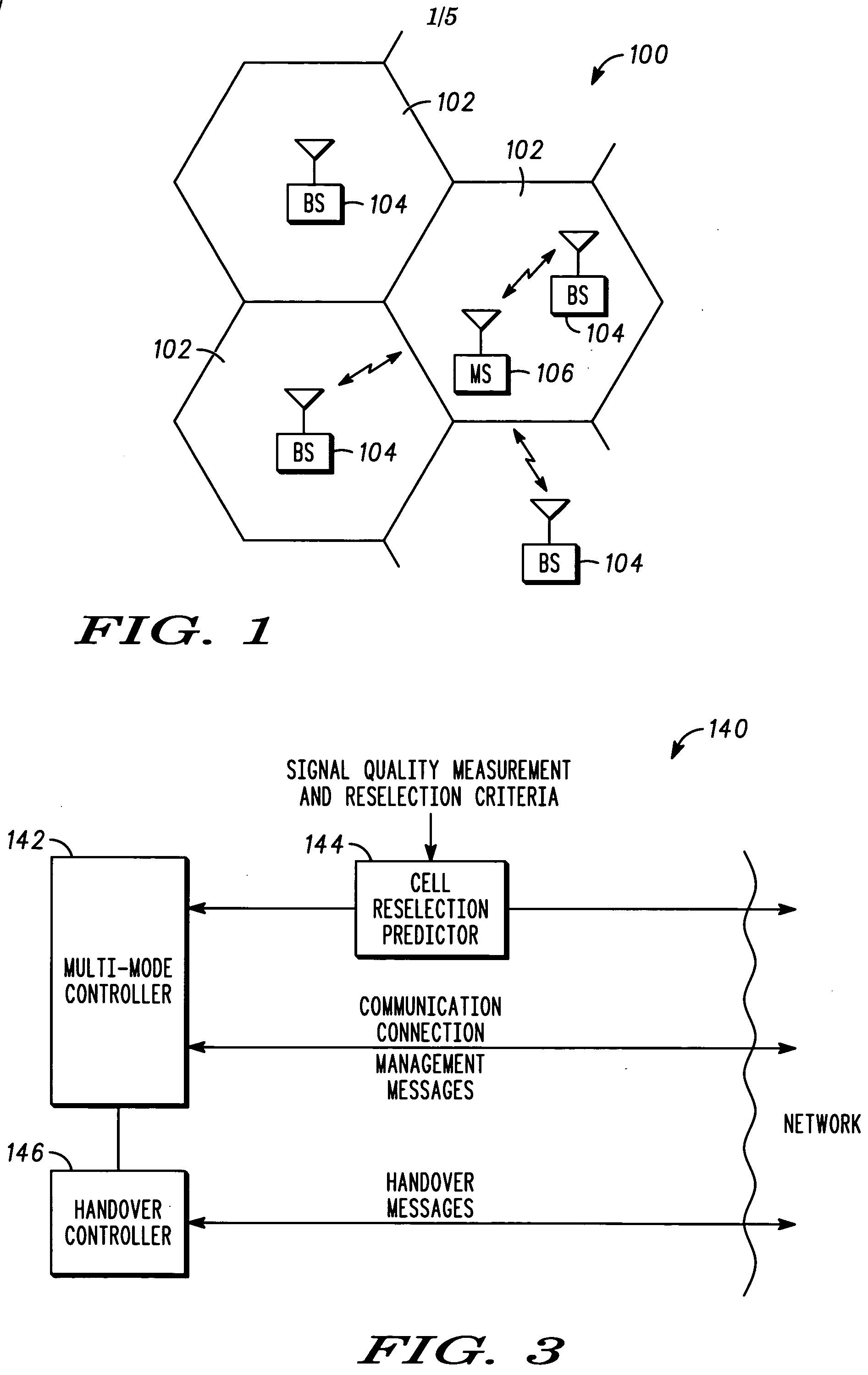
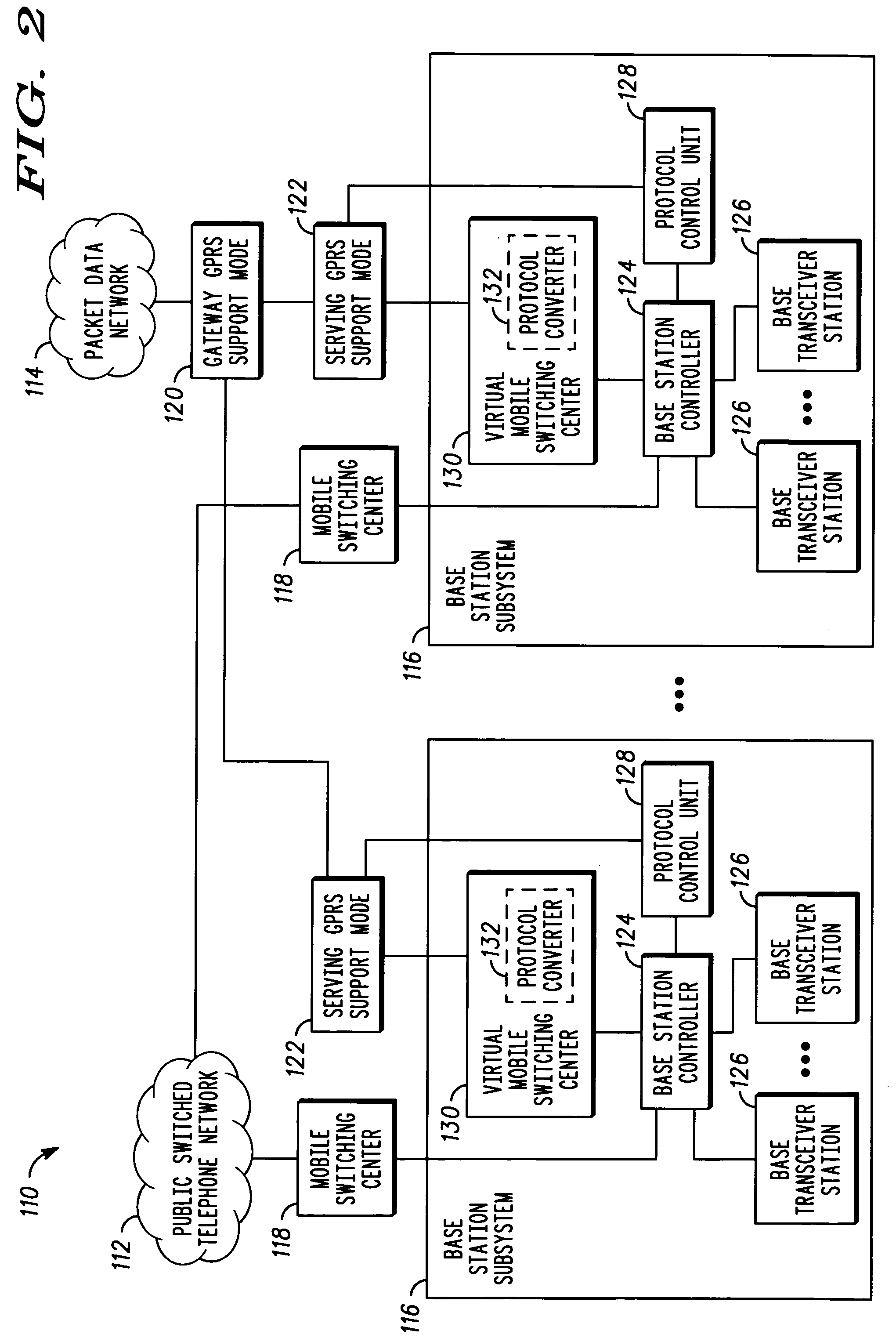
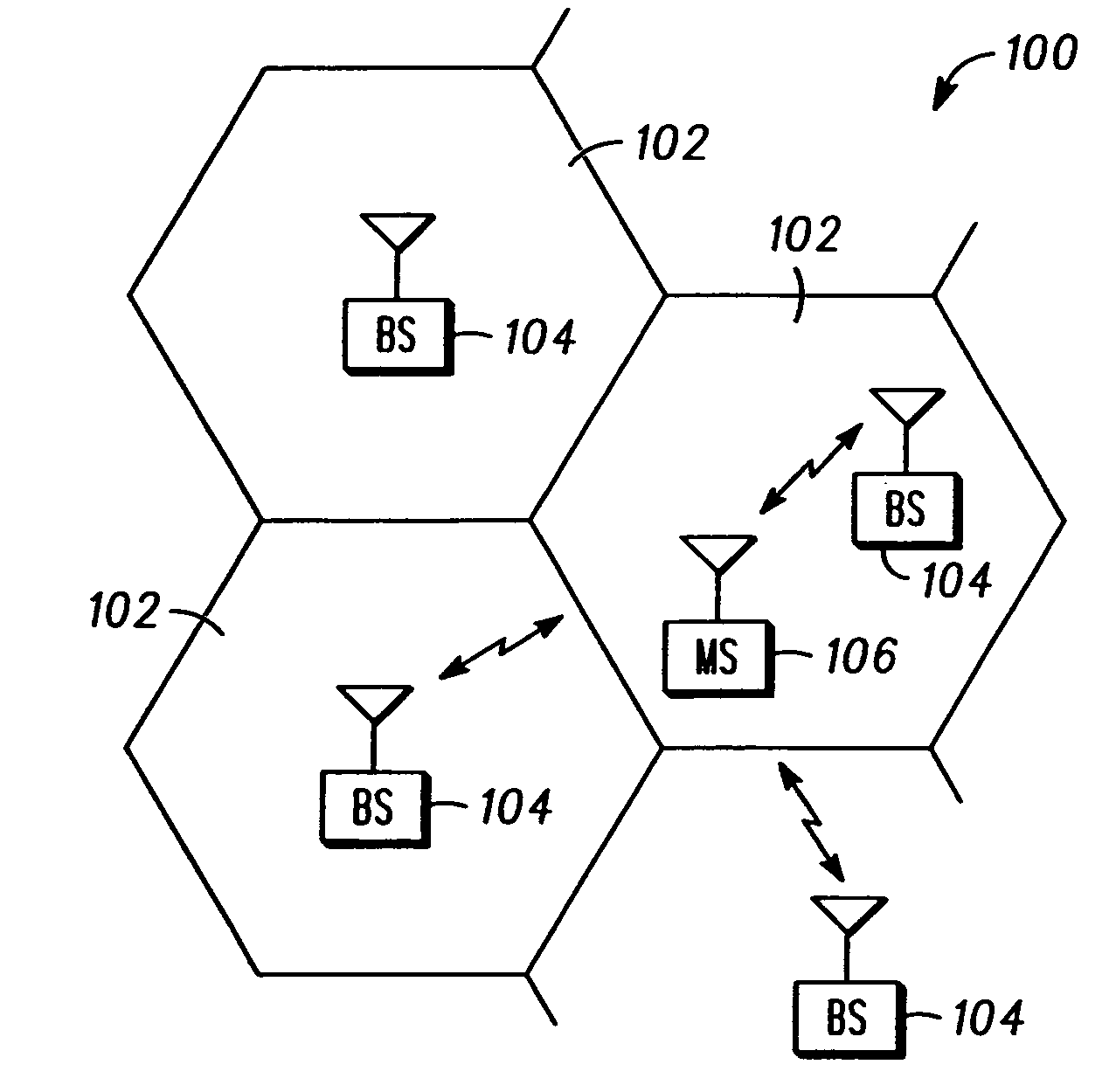
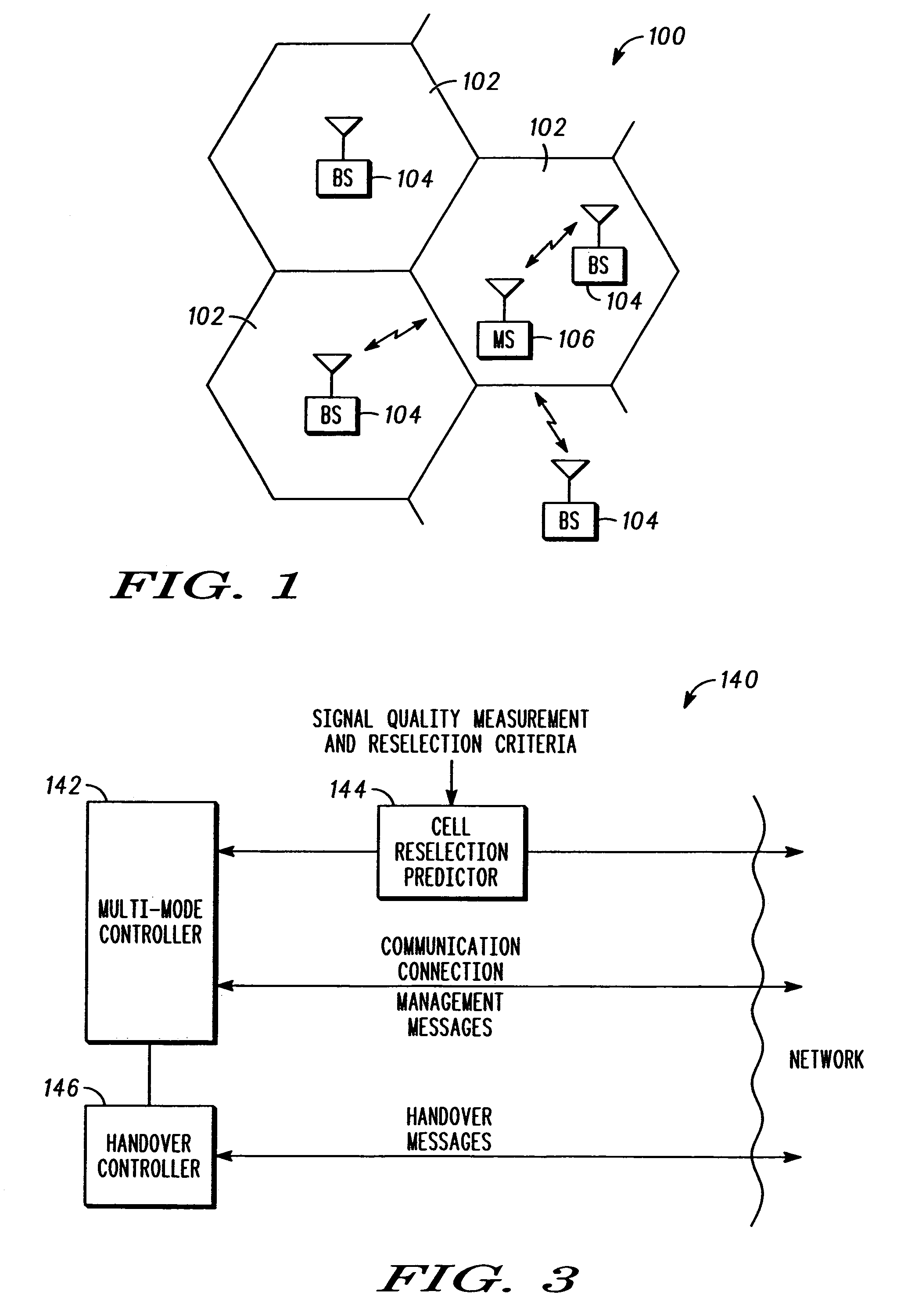
Communication controller and method for maintaining a communication connection during a cell reselection
ActiveUS20050049000A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationCircuit Switched DataOperation mode
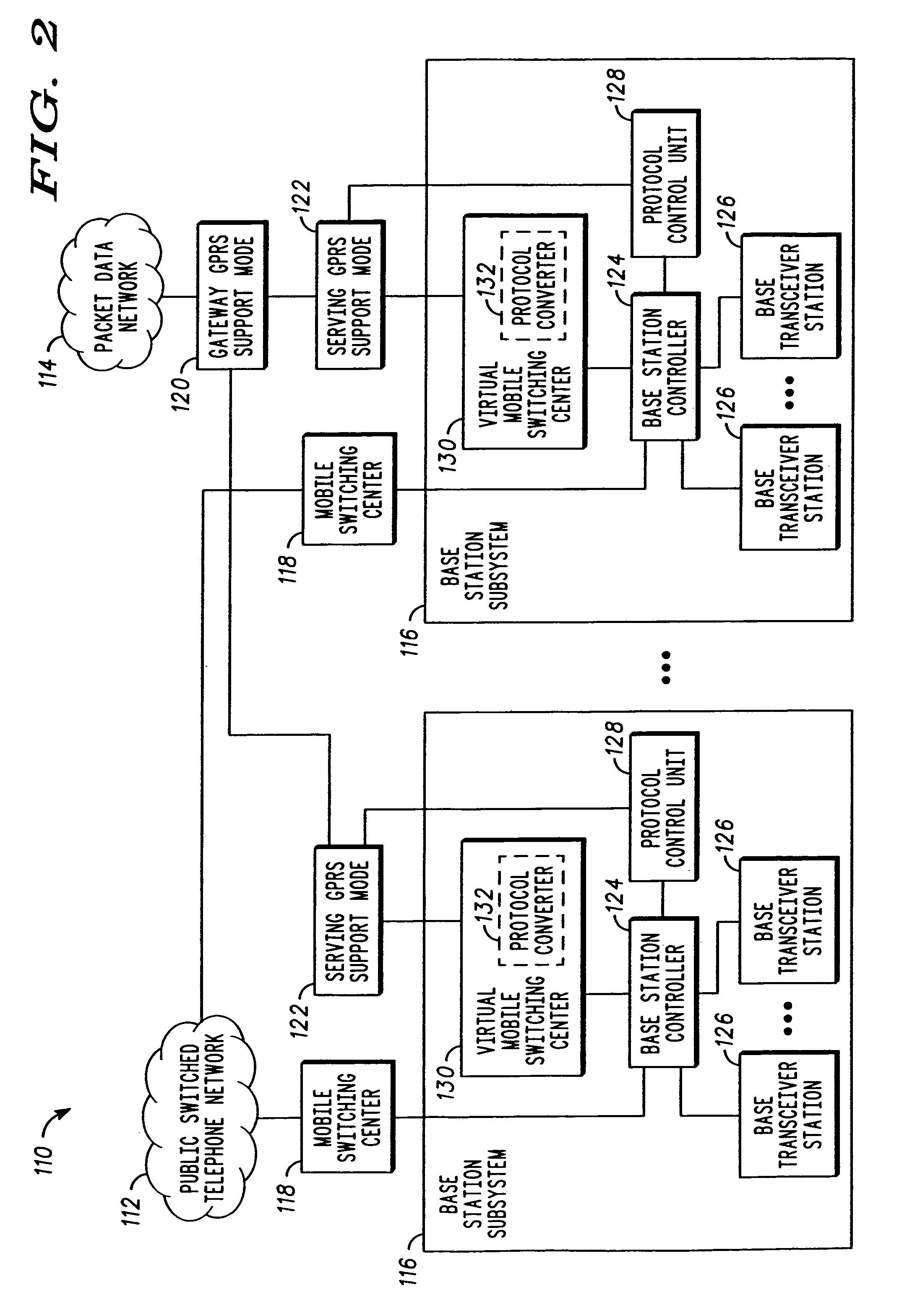
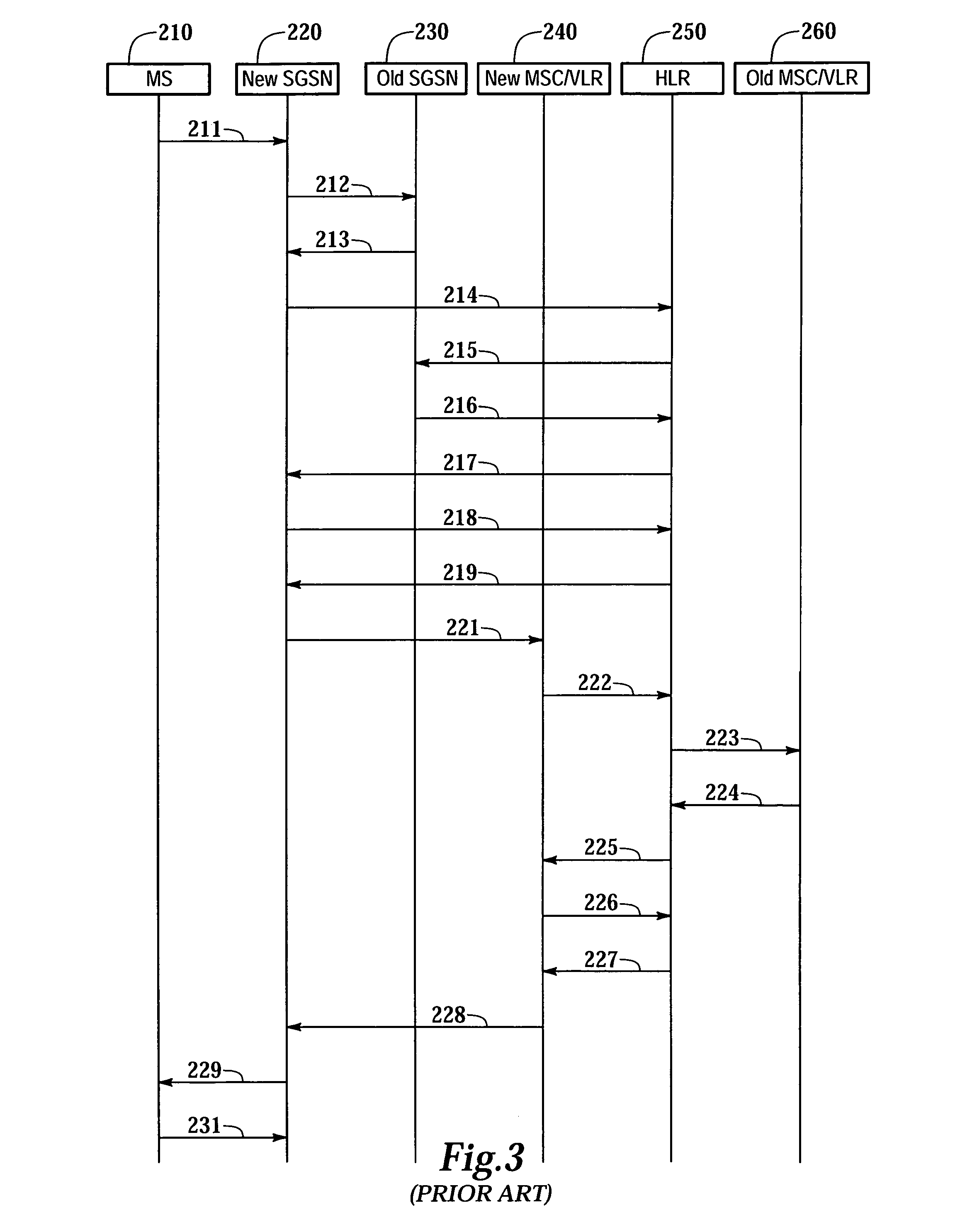
The present invention provides a communication controller and a method for maintaining a communication connection during a cell reselection. The communication connection is maintained by changing between a first operating mode, such as a packet data mode, which does not support the maintenance of a communication connection throughout a cell reselection, and a second operating mode, such as a circuit switched mode, which does support maintenance of a communication connection during a handover. Use of a virtual mobile switching center in the base station subsystem facilitates the conversion and routing of circuit switched data, transmitted between the mobile subscriber and the base transceiver station, to the packet data network while in a circuit switched mode.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Communication controller and method for maintaining a communication connection during a cell reselection
InactiveUS6975881B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationCircuit Switched DataOperation mode
The present invention provides a communication controller and a method for maintaining a communication connection during a cell reselection. The communication connection is maintained by changing between a first operating mode, such as a packet data mode, which does not support the maintenance of a communication connection throughout a cell reselection, and a second operating mode, such as a circuit switched mode, which does support maintenance of a communication connection during a handover. Use of a virtual mobile switching center in the base station subsystem facilitates the conversion and routing of circuit switched data, transmitted between the mobile subscriber and the base transceiver station, to the packet data network while in a circuit switched mode.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
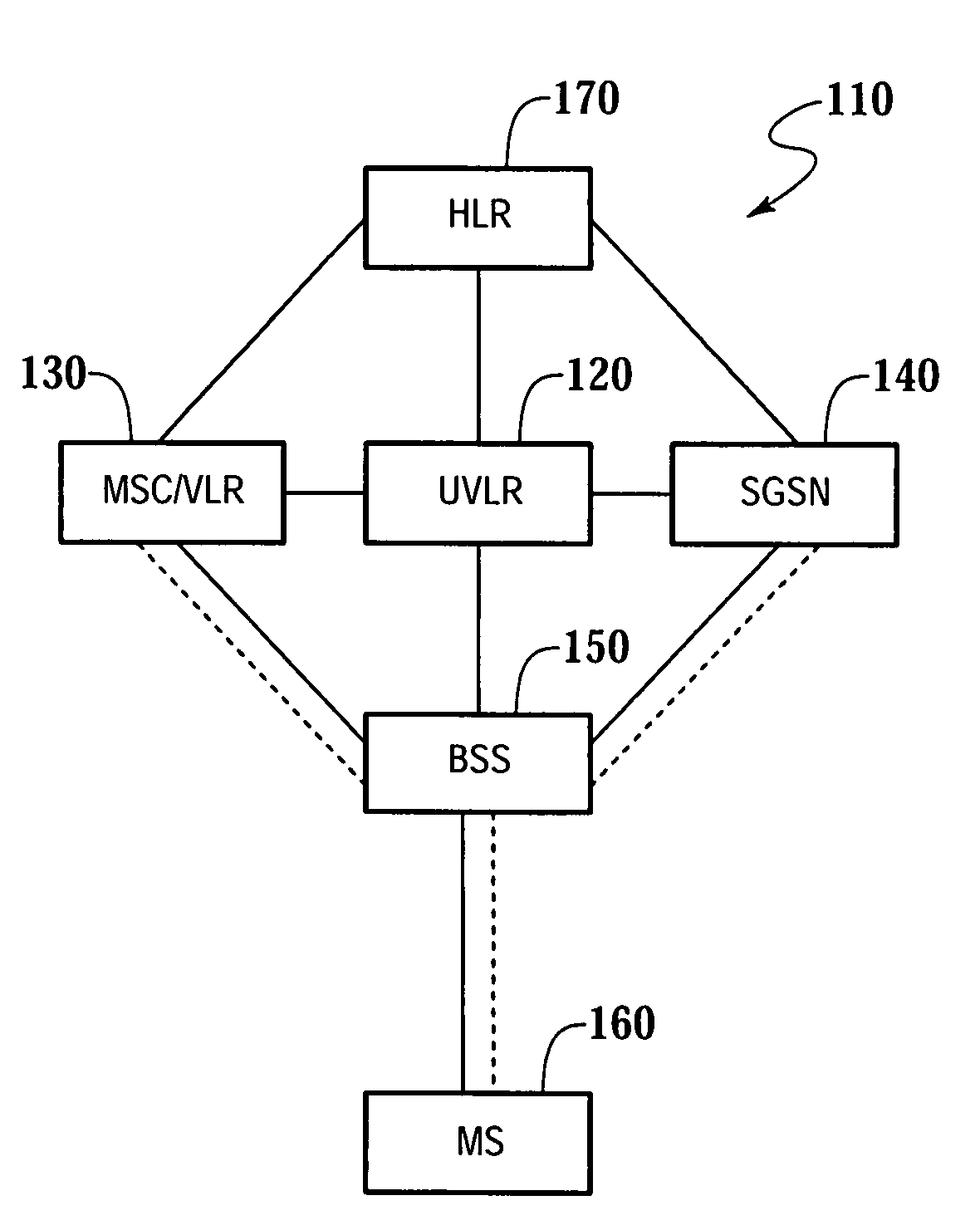
Method, apparatus and system for managing subscriber data
ActiveUS7054307B2Reduce signaling trafficSignalingDigital data processing detailsWireless commuication servicesCircuit Switched DataProcessor register
The present invention provides a method, apparatus and system for managing subscriber data in a telecommunications system. The present invention receives one or more messages from a mobile station. The one or more messages received may be a routing area update request signal. Subsequently, the present invention requests the subscriber data from a home location register. The subscriber data contains circuit switching data, packet switching data, or circuit switching data and packet switching data. Then, the subscriber data is stored in the new universal visitor location register. The present invention may request the subscriber data from the home location register by sending an update location signal to the home location register.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
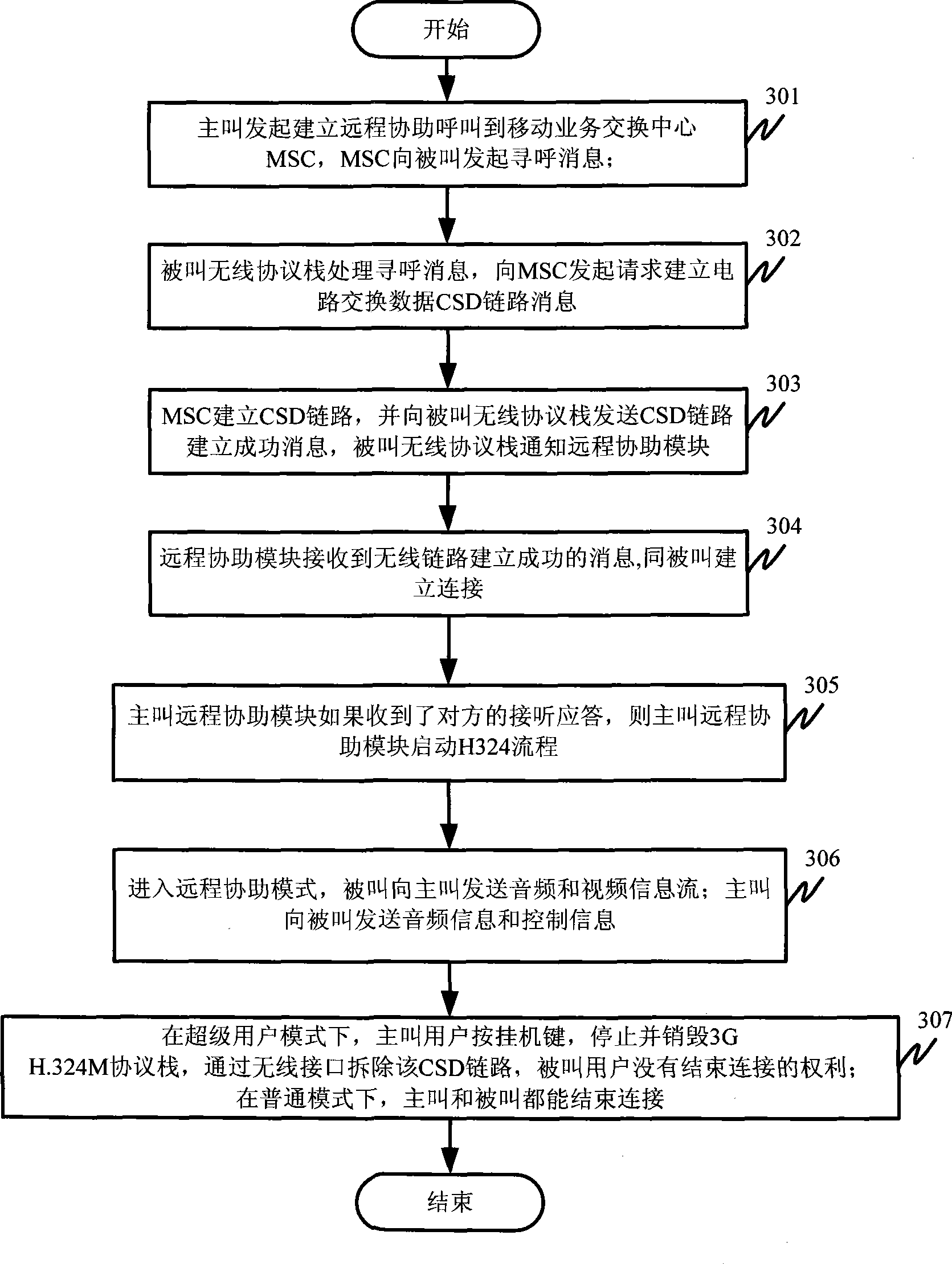
System and method for realizing remote assistance by mobile terminal
InactiveCN101400149AIncrease selling pointConnection managementWireless network protocolsCircuit Switched DataMobile business
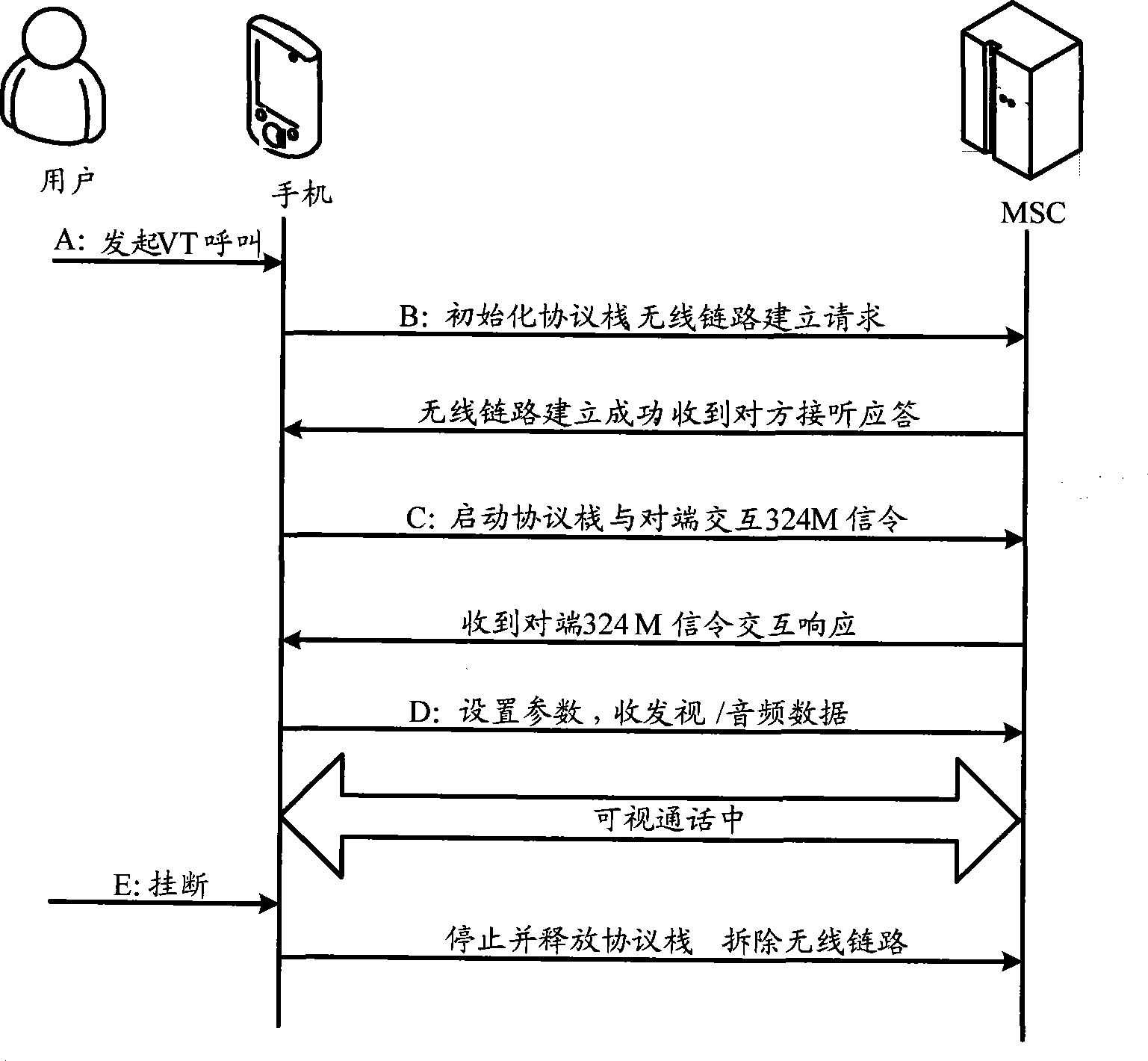
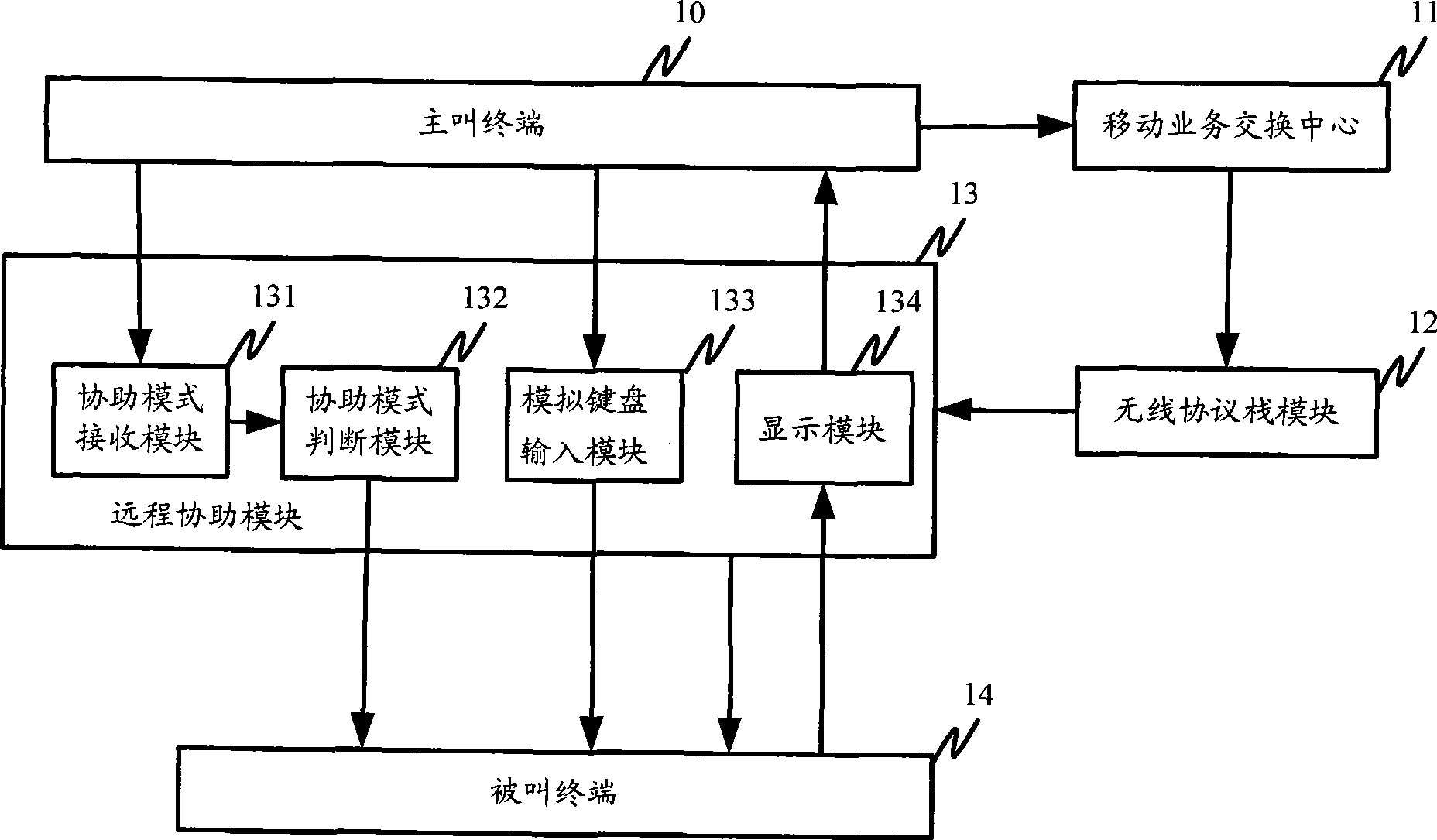
The invention provides a system of a mobile terminal to realize remote assistance, comprising that: (1) a calling terminal transmits information of building remote assistance information to a mobile service exchange center, which initiates paging information to the called terminal; (2) a called wireless protocol stack receives paging information, transmits request information to the mobile service exchange center after processing, requires to build a circuit switched data link; (3) the mobile service exchange center informs the called terminal after building the circuit switched data link, the called wireless protocol stack transmits the successful building of the circut circuit switched data link to a remote assistance module; (4) the remote assistance module builds remote assistance connection between the calling terminal and the called terminal after receiving the information. The invention causes the remote assistance technology to be applied on the mobile terminal, better satisfying user requirement, meanwhile obtaining larger economic benefit for the terminal makers and operators.
Owner:ZTE CORP
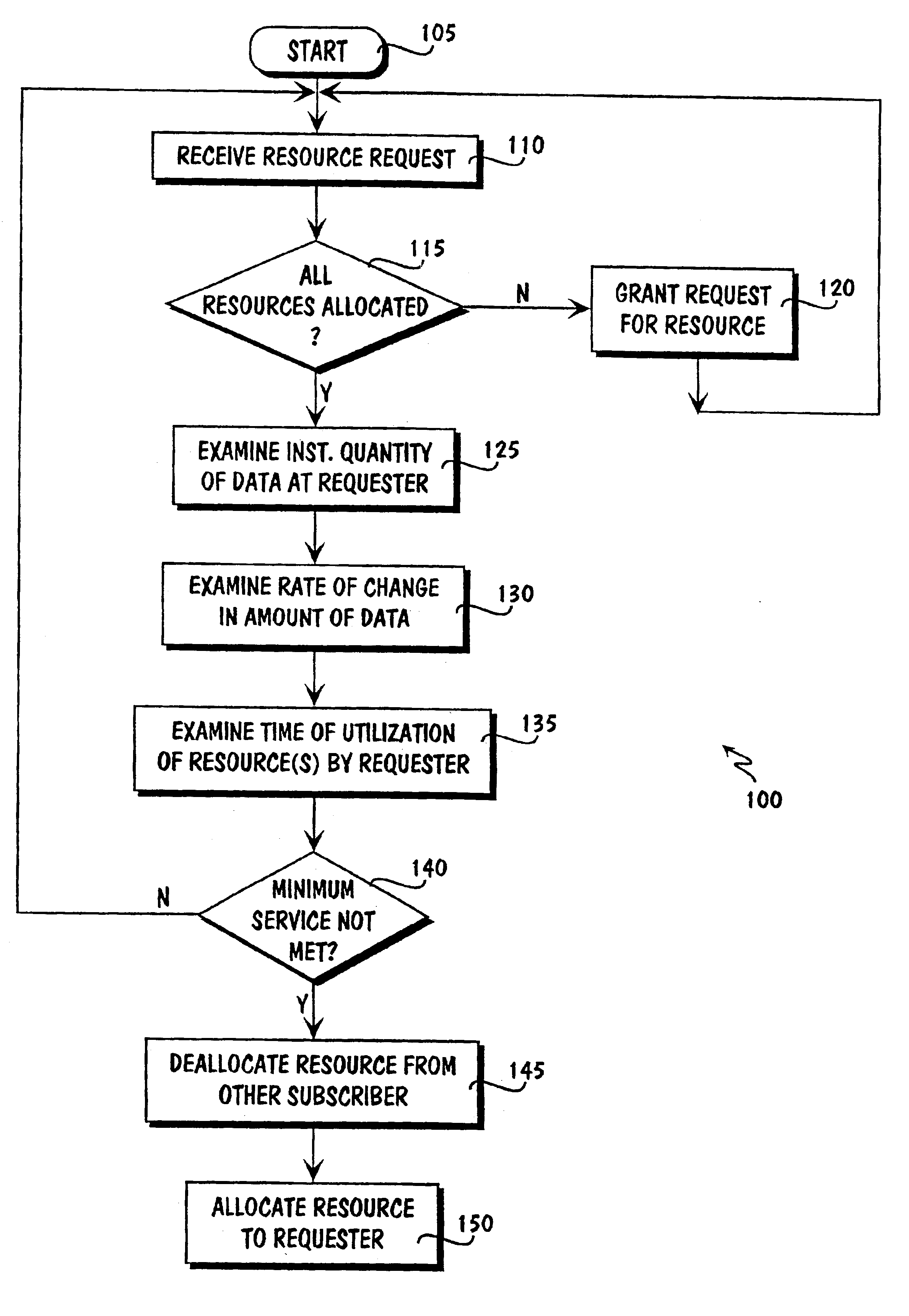
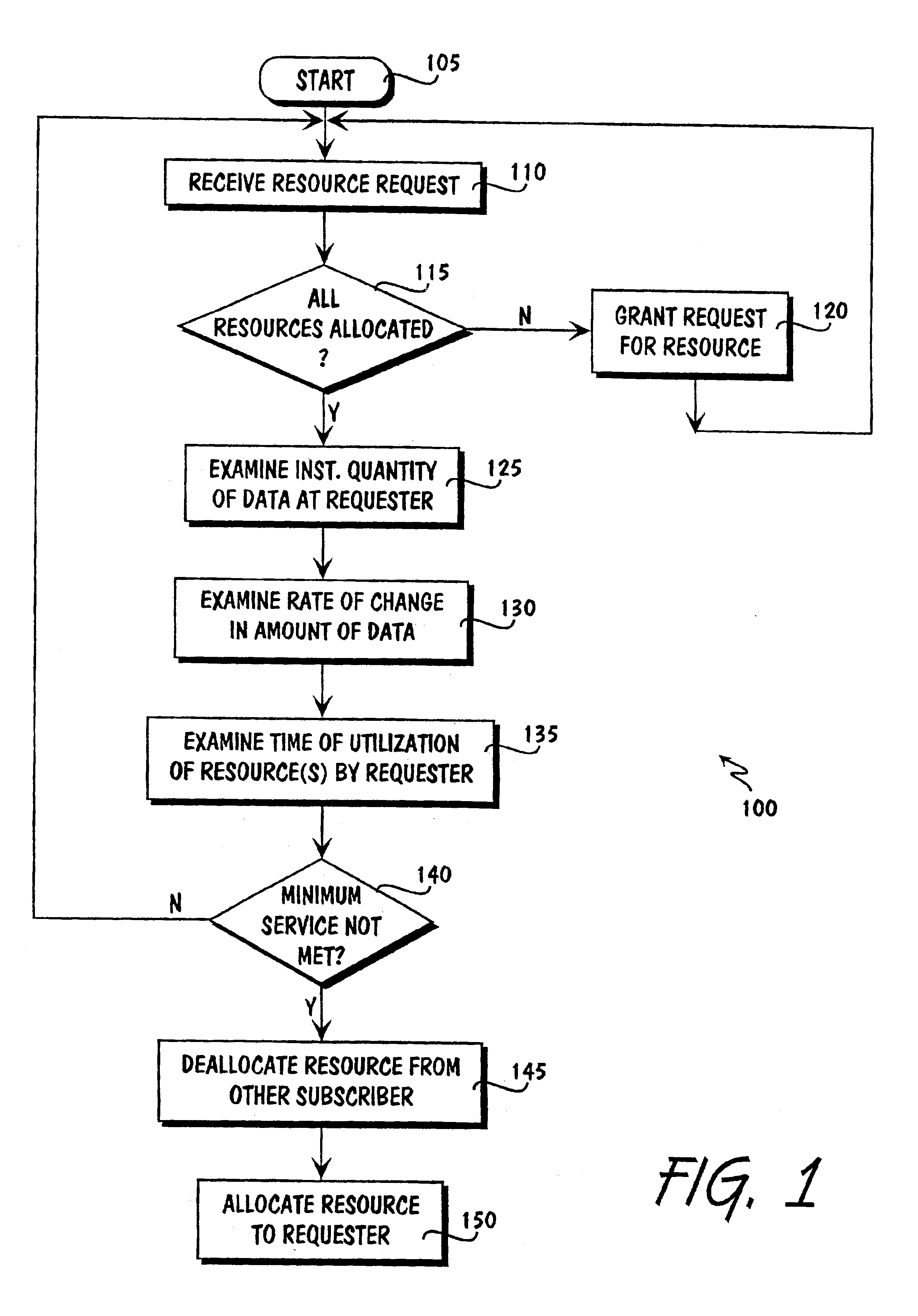
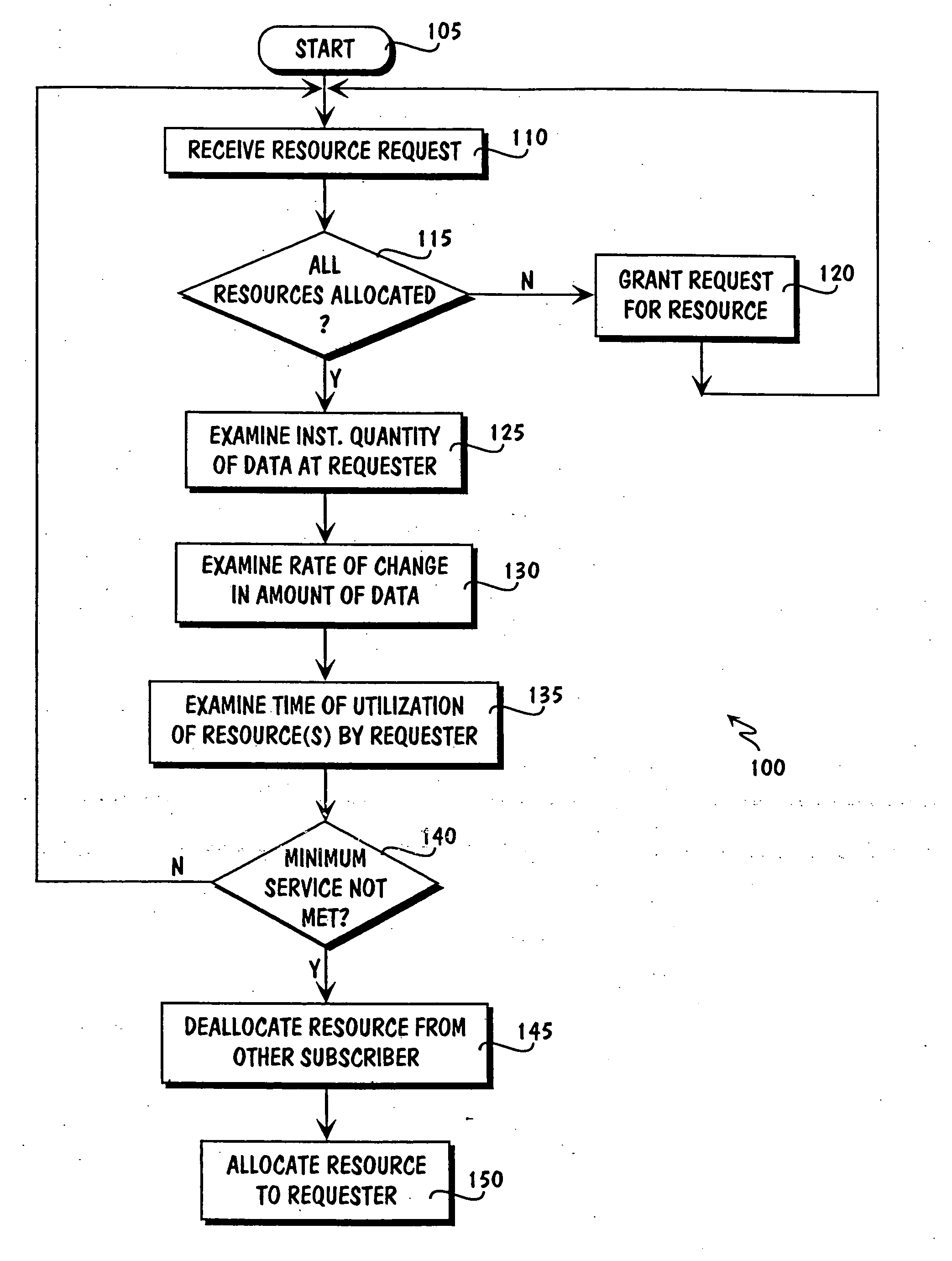
Resource allocation in a circuit switched network
Allocating resources in a circuit switched data network, comprising receiving a request for a resource from a device coupled to the circuit switched data network and granting the resource to the requesting device if the resource is available. If the resource is not available, then examining the instantaneous quantity of data to be transmitted by the requesting device; the rate of change in the instantaneous quantity of data to be transmitted by the requesting device; and the time of utilization of the resource by the requesting device, and granting the resource to the requesting device based on the examination of the three factors.
Owner:CDN INNOVATIONS LLC
Design method of detecting system for telecontrol remote terminal unit (RTU) and information channel
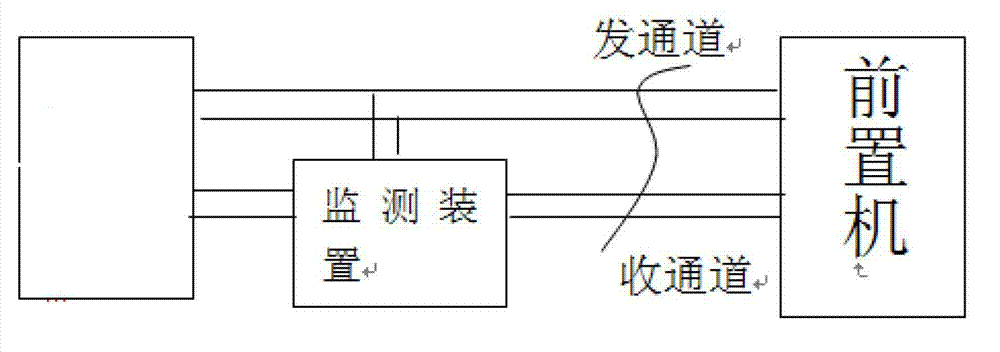
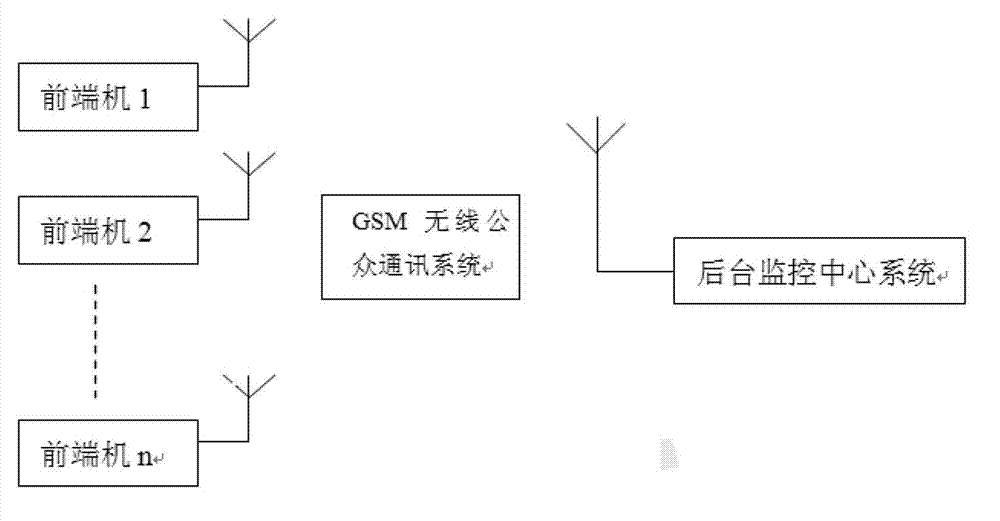
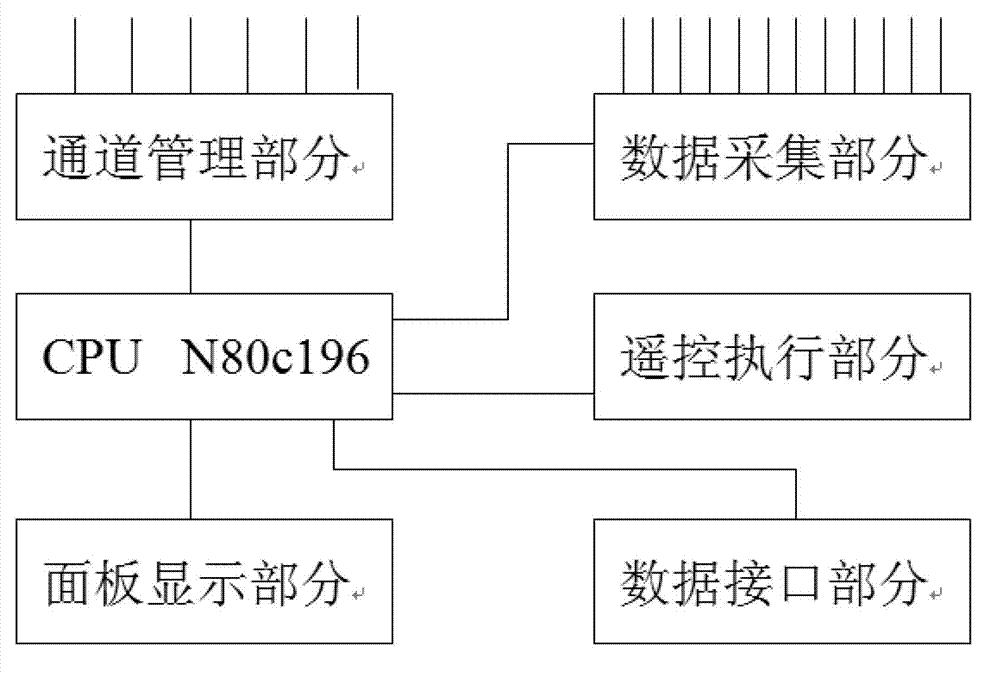
InactiveCN103036625AMonitor voltage and current conditionsWith remote signaling functionElectric signal transmission systemsNon-electrical signal transmission systemsCircuit Switched DataStructure of Management Information
In a design method of a detecting system for a telecontrol remote terminal unit (RTU) and an information channel, a structure of the detecting system for the telecontrol RTU and the information channel is confirmed to be a distributed control system, each converting station is provided with a front terminal machine, one industrial control computer is used for centralized management control in an electric power dispatching center, a circuit switched data (CSD) communication mode of a global system for mobile communications (GSM) is applied, bidirectional data communication between a field main control unit and a monitoring center is achieved, and alarm information is transmitted to a mobile phone of a manager through a short message. After a central processing unit (CPU) is first initiated, information channel data of telemetering, remote signaling and carrier frequency are respectively collected, and then malfunction distinguishing is operated according to related principles, if the system is abnormal, a GSM module is started to send malfunction information to a background monitoring center. The design method of the detecting system for the telecontrol remote terminal unit (RTU) and the information channel has the advantages that the detecting system for the telecontrol RTU and the information channel is used for monitoring conditions of voltages and currents of the RTU and other devices, functions of the remote signaling and the remote control are achieved, remote operations to the RTU and other devices are available, and data used in the process of operations is stored in a data base for future reference.
Owner:YINGKOU ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID LIAONING ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY +1
Mobile originated interactive menus via short messaging services
InactiveUS20090191904A1Substation equipmentMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsCircuit Switched DataGSM
A method and apparatus for providing 2-way interactive short message system menus to a mobile device using text-based short messaging rather than WAP techniques. This provides the ability to provide WAP like services at a fraction of the cost of CSD. Mobile Originated Interactive Menus are implemented as a feature of a Short Message Service Center (SMSC). Each option guides either to the next menu level, or to a final action to be executed according to the path followed by the subscriber. Importantly, the mobile originated interactive menus use SMS communications instead of circuit switched data (CSD) (e.g., instead of WAP communications), thus leaving traffic channels available for voice calls. Interactive SMS menus allow service providers to offer their subscribers personalized messaging menus with multiple options for quick and easy access to Web-based content. Users may define the content and frequency they want, whether it is a scheduled delivery or on-demand. The interactive SMS menu options offer customers a simple-to-use technique and apparatus for checking, e.g., stock quotes, local weather, and / or other Web-based news and information when they want it. The interactive nature of the service allows the wireless network to poll the user for their next response, with multiple menued options offered, making it highly intuitive. Replacement of messages in TDMA and GSM mobile devices allow for heavy usage without filling up the user's phone buffer, i.e., prior messages may be overwritten, to assure that only the latest information is all that is being displayed and read. The flexibility of Interactive SMS Menus can allow service providers to define their own base offering of menus, depending upon their targeted customer segments.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
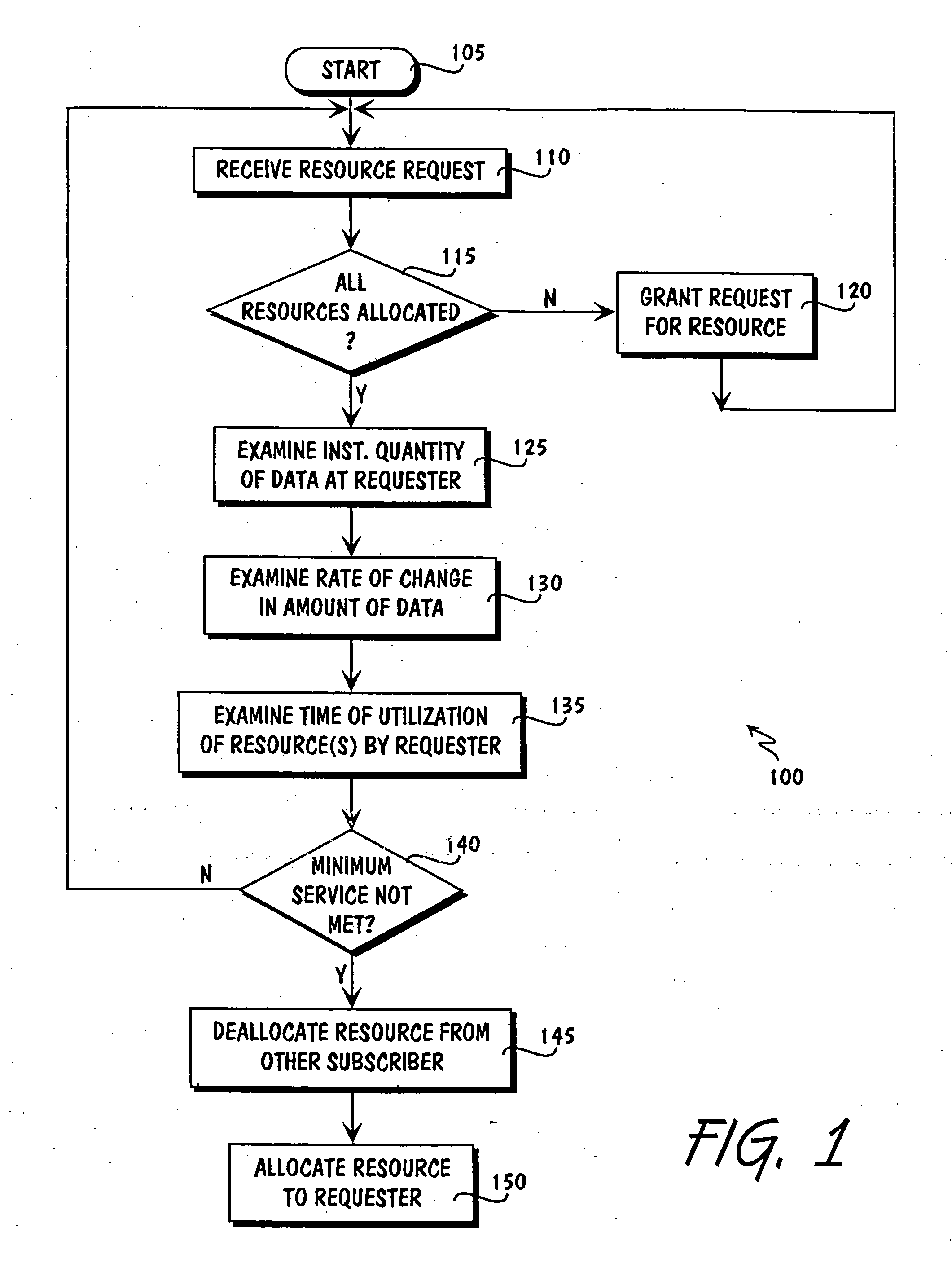
Resource allocation in a circuit switched network
InactiveUS20050169178A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCircuit Switched DataResource allocation
Allocating resources in a circuit switched data network, comprising receiving a request for a resource from a device coupled to the circuit switched data network and granting the resource to the requesting device if the resource is available. If the resource is not available, then examining the instantaneous quantity of data to be transmitted by the requesting device; the rate of change in the instantaneous quantity of data to be transmitted by the requesting device; and the time of utilization of the resource by the requesting device, and granting the resource to the requesting device based on the examination of the three factors.
Owner:CDN INNOVATIONS LLC
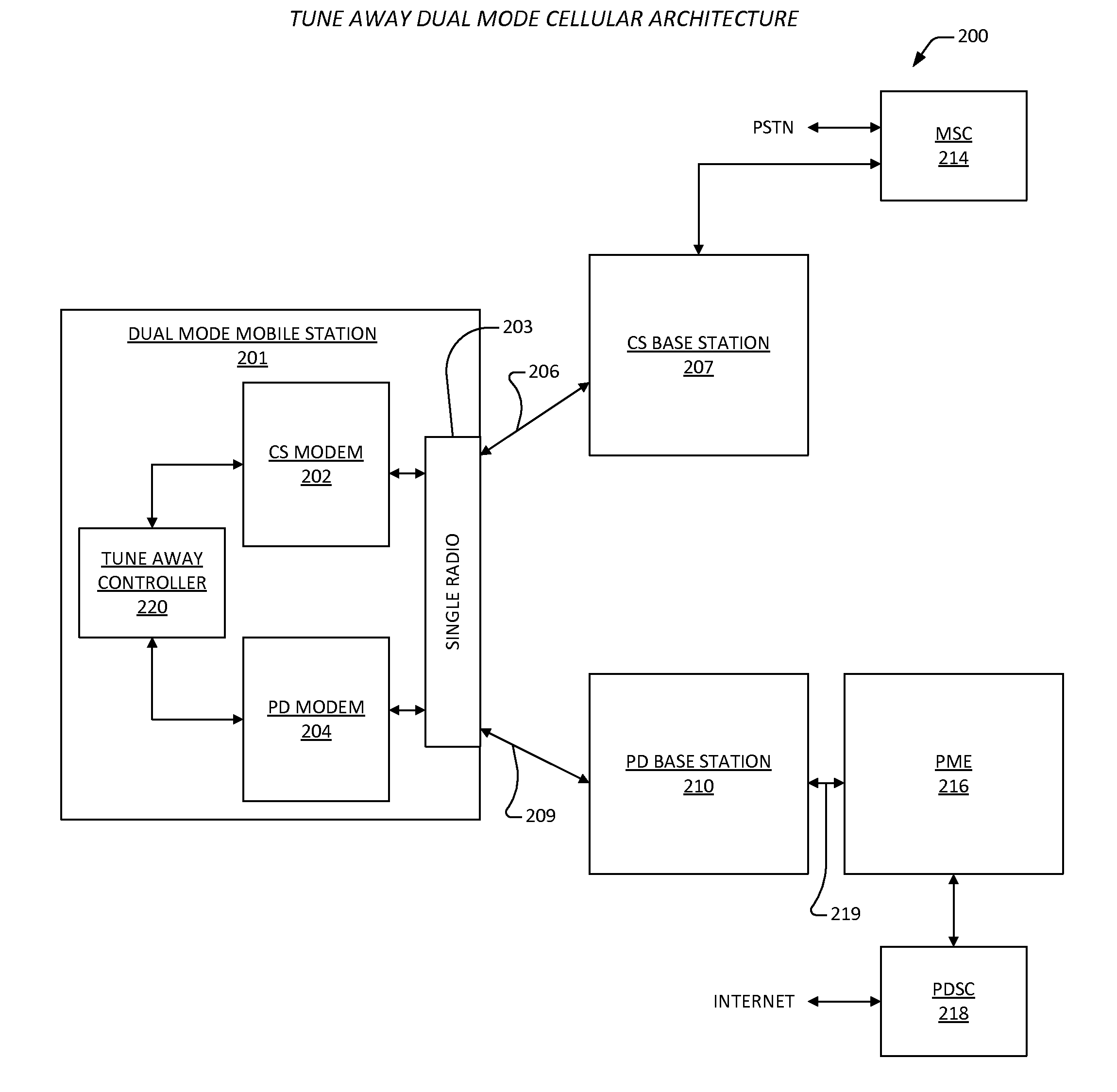
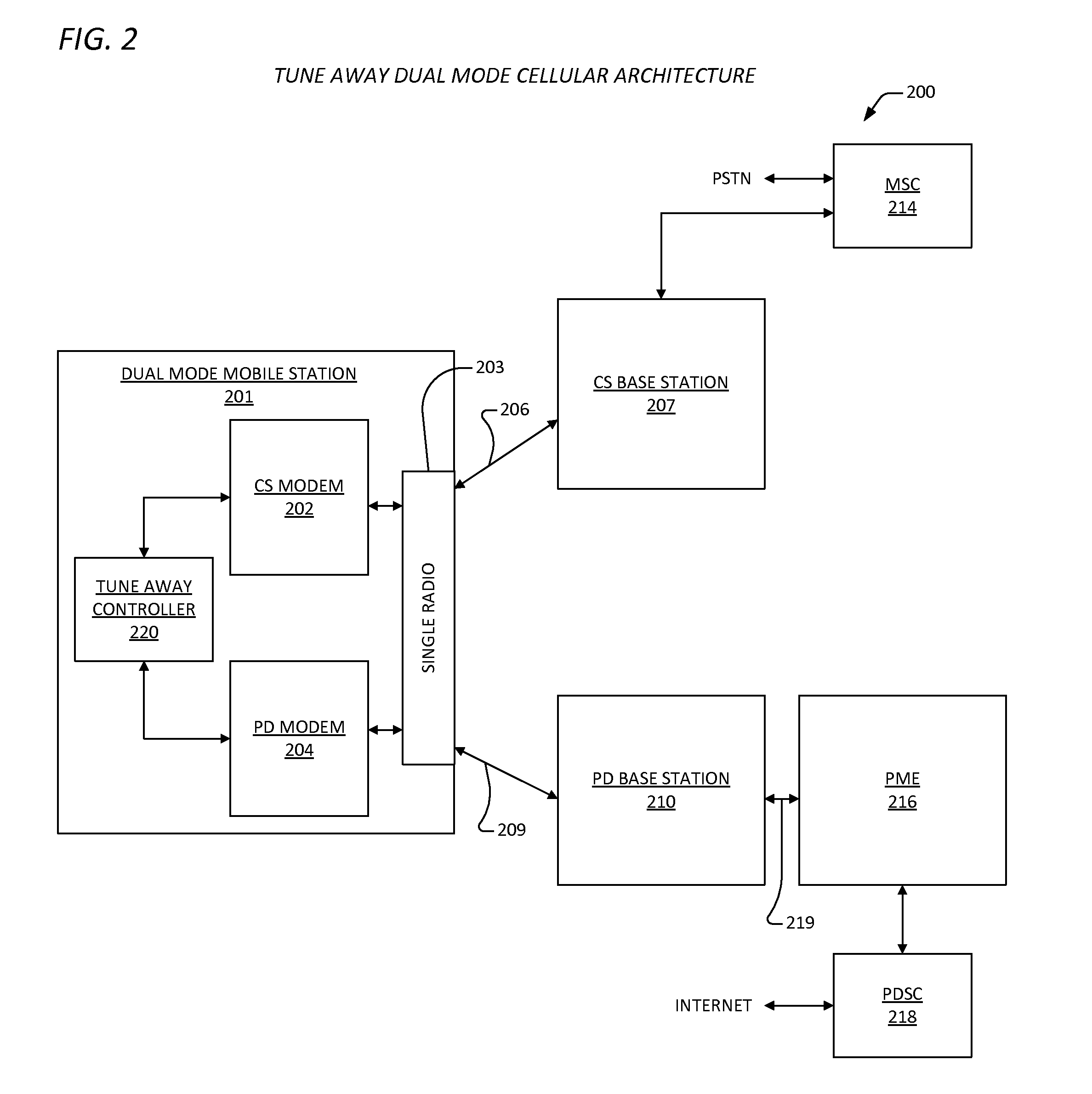
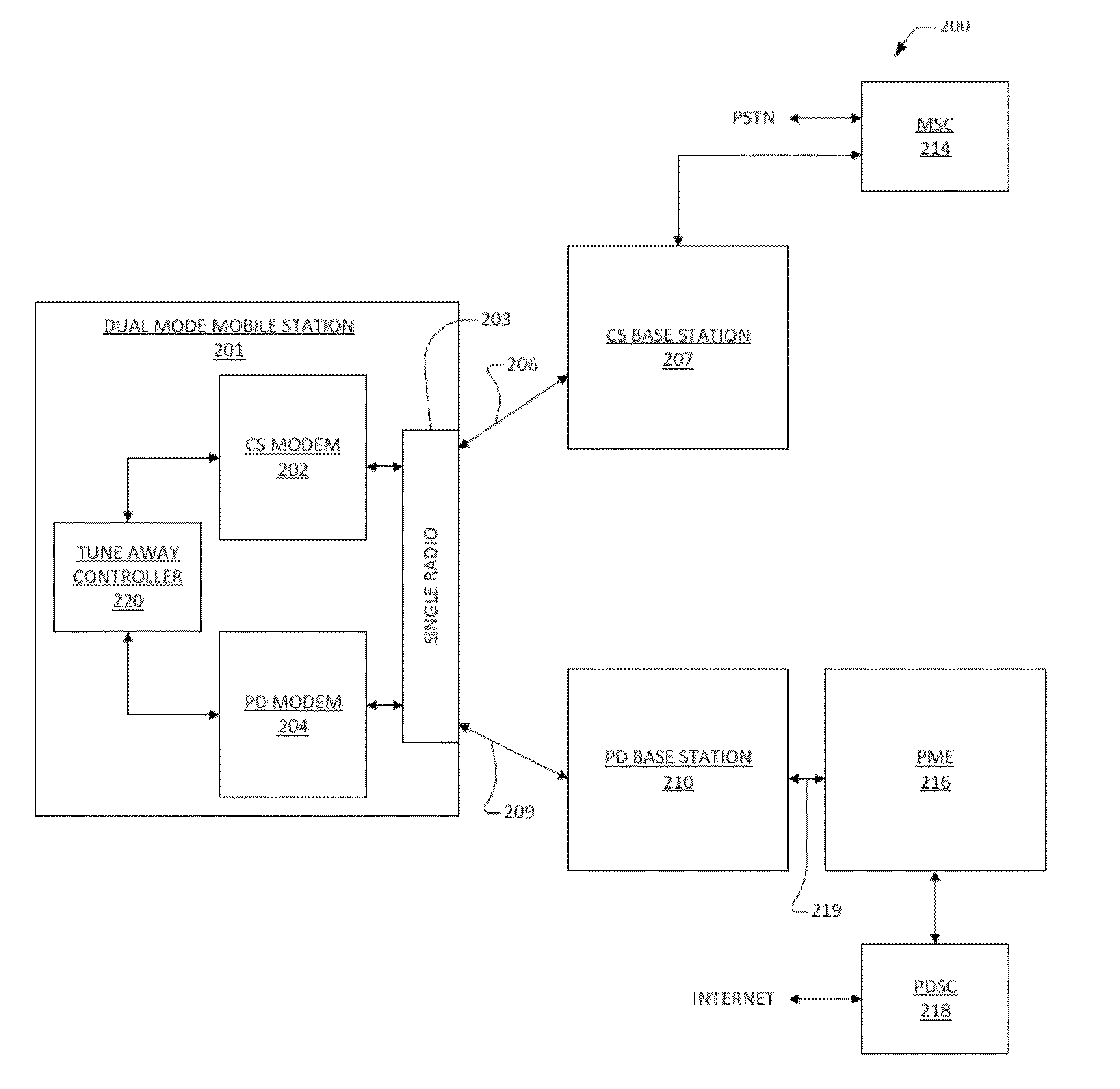
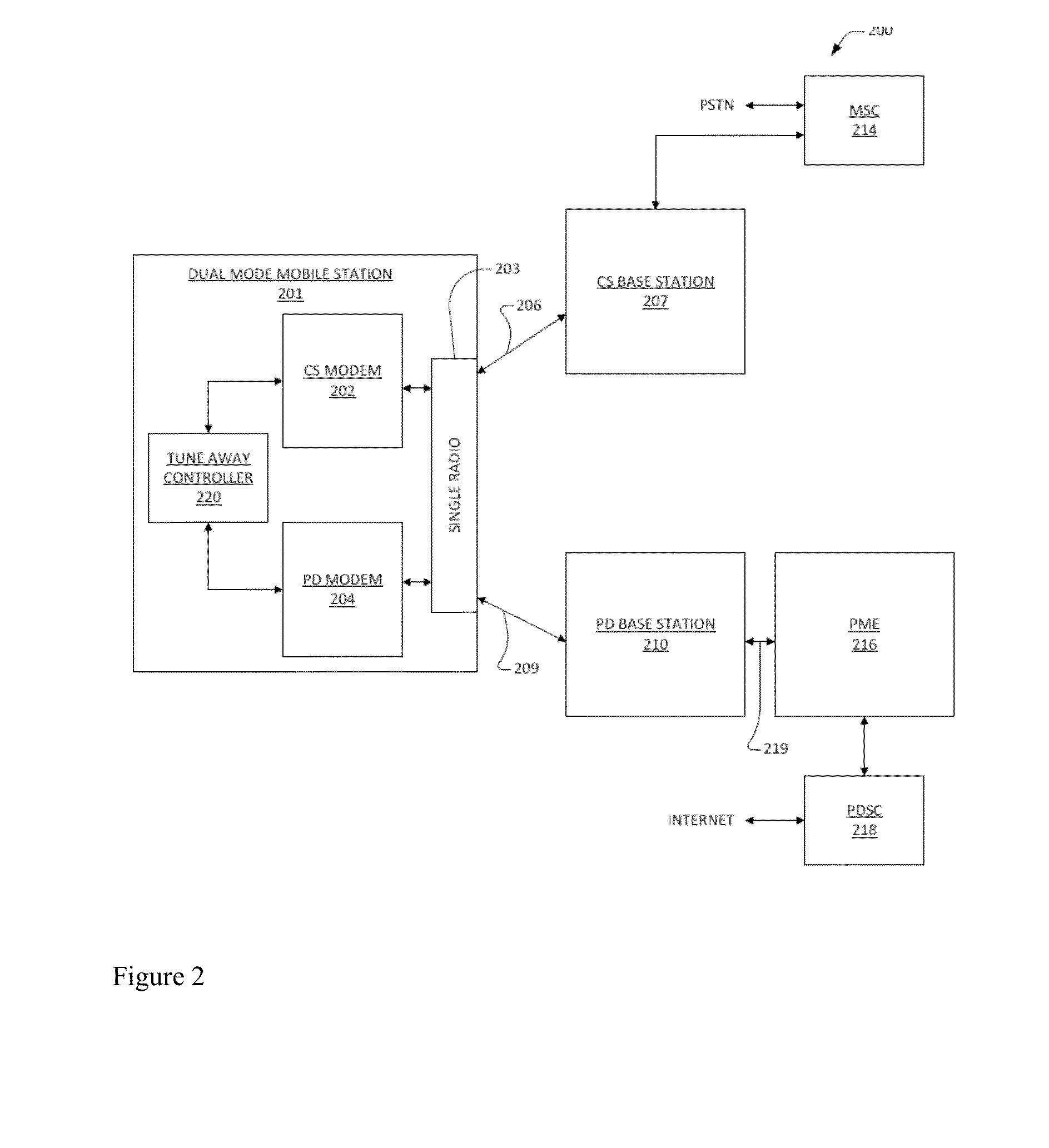
Ue based csfb enhancement
ActiveUS20130250854A1Good techniqueSynchronisation arrangementConnection managementCircuit Switched DataModem device
A mobile station for notification of a circuit switched event. The mobile station includes a circuit switched modem, a packetized data modem, a radio, and a tune away controller. The circuit switched communicates circuit switched data over a circuit switched network. The packetized data modem communicates packetized data over a packetized data network. The radio couples the packetized data modem to the packetized data network via a packetized data radio link, and couples the circuit switched modem to the circuit switched network via a circuit switched radio link. Only one of the links may be active at a time. The tune away controller is coupled to the circuit switched modem and to the packetized data modem, and indicates tune away events over the packetized data network so that the circuit switched event is processed by the mobile station. The tune away controller directs switching between the links.
Owner:C W INVESTMENT SERVICES
Apparatus and method for implementing data safety transmission of mobile communication apparatus
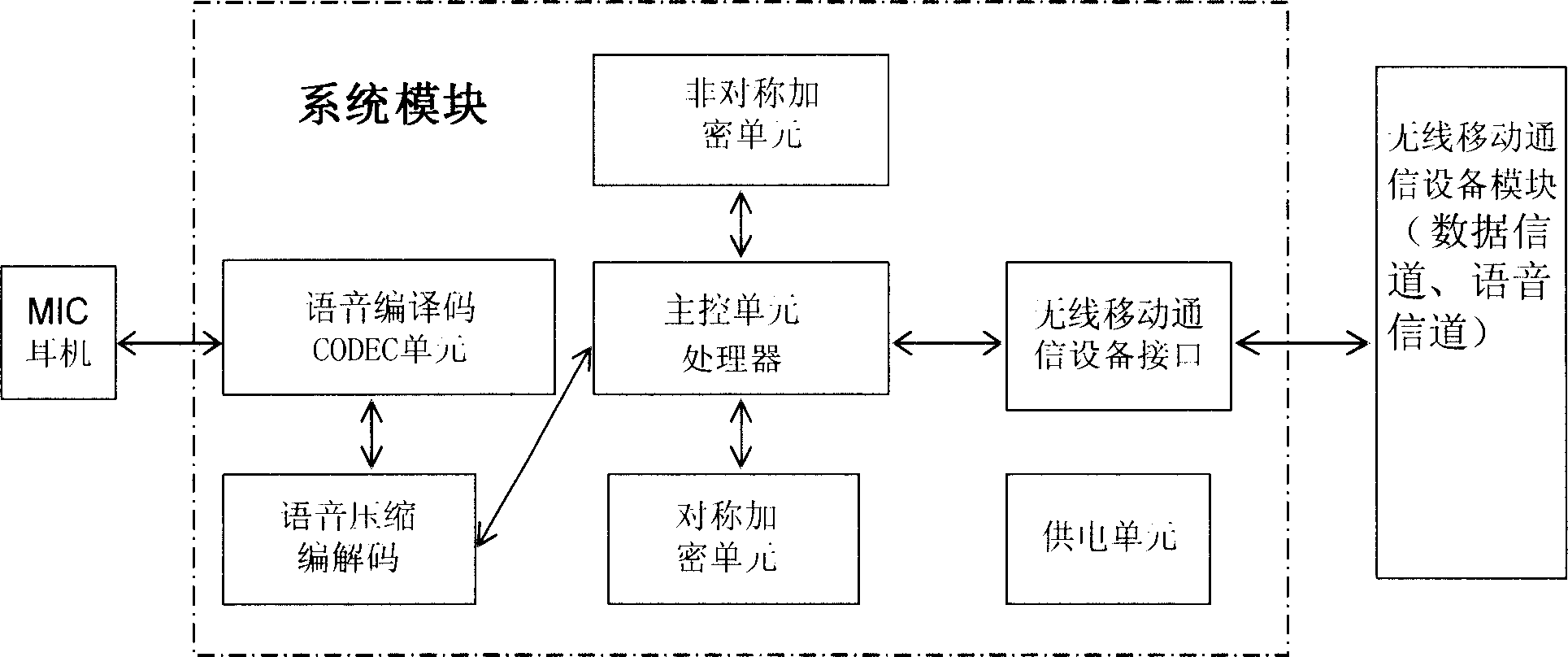
ActiveCN1688171AFlexible and convenient to useWill not affect the useUser identity/authority verificationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCircuit Switched DataData compression
This invention discloses a safety transmitting device and a method for mobile communication devices. Said device can be connected on radio mobile communication devices of GSM or CDMA network detachably via their interface units including seven parts: a master control unit, a CODEC unit, a data compression code / decode unit, an asymmetrical ciphering unit, a symmetrical ciphering unit, a power supply unit and an interface unit. Said device utilizes the current GSM or CDMA network to carry out identity certification and session cryptographic key transfered by the improved PK1 asymmetric ciphered code system without CA and ciphers the data by session cryptographic key to be transmitted by the circuit exchange data service supported by network and carries out inverse process at the receive end to realize end-to end cipher communication function.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SPACEFLIGHT HAITE SYST ENG
High-speed audio and video magnitude storage method and device for vehicular environment
InactiveCN101237546AIncrease storage bandwidthImprove scalabilityTelevision system detailsInput/output to record carriersCircuit Switched DataLow speed
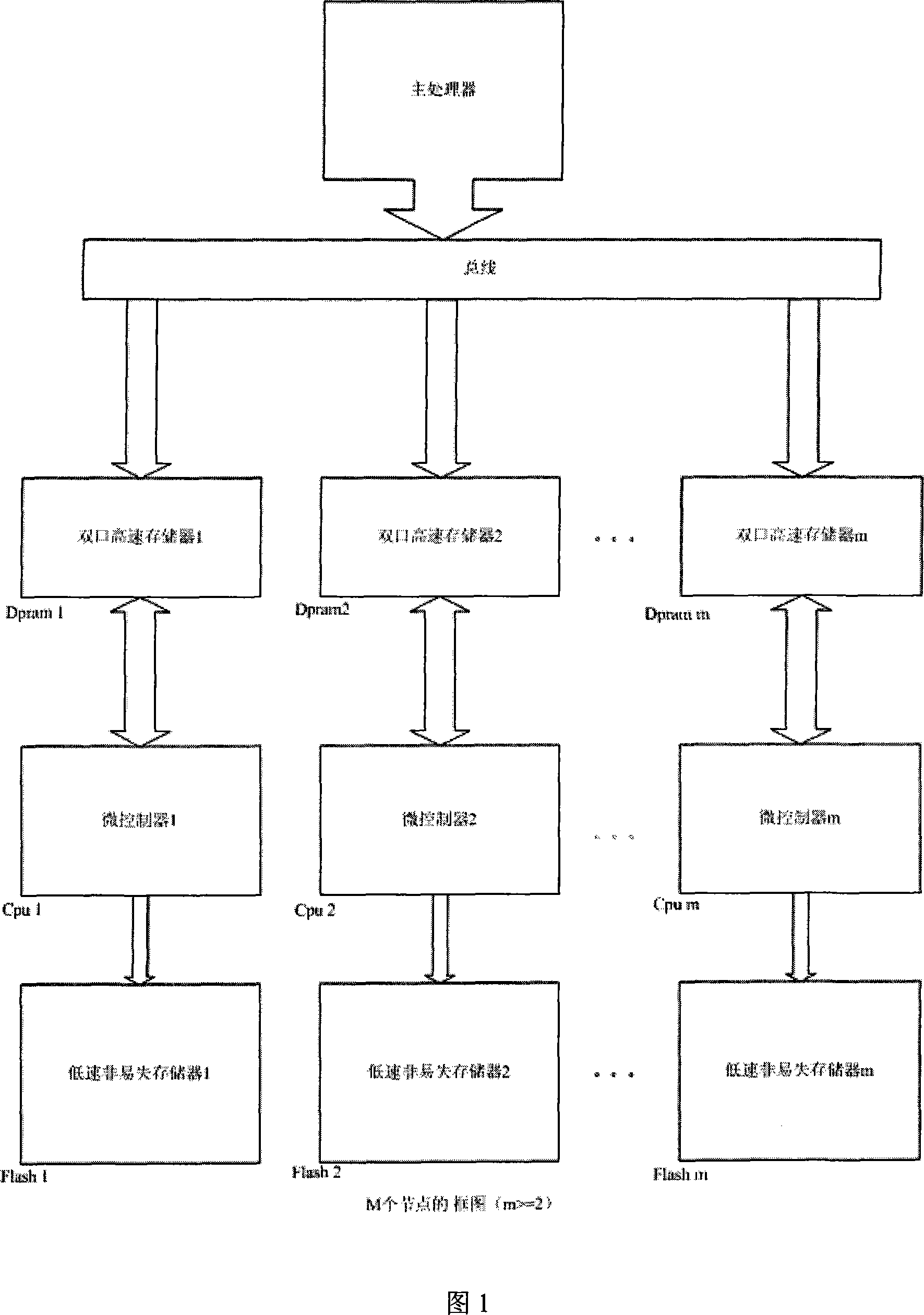
A high-speed audio-video mass storing method used in vehicular environment comprises the following steps: through adopting a plurality of parallel-operation intelligent nodes to increase bandwidth, data is stored in a high-speed volatile memory unit at first; then, a plurality of intelligent nodes respectively writes the data block in the high-speed volatile memory unit belonging to each intelligent node in the low-speed nonvolatile memory unit controlled by a corresponding intelligent node. A high-speed audio-video mass storing device, which is used in vehicular environment and is designed according to the method, is provided with a main processor circuit, a volatile cache circuit, an embedded intelligent node circuit and a low-speed nonvolatile memory circuit, wherein the volatile cache circuit which adopts a duplex interface is respectively connected with the main processor circuit and the embedded intelligent node circuit; the main processor circuit exchanges data and commands with the embedded intelligent node circuit through the volatile cache circuit; moreover, the embedded intelligent node circuit reads out data from the volatile cache circuit and writes the data in the low-speed nonvolatile memory circuit.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and device for assigning cell data units to sequential storage positions of data frames using a pointer position estimation
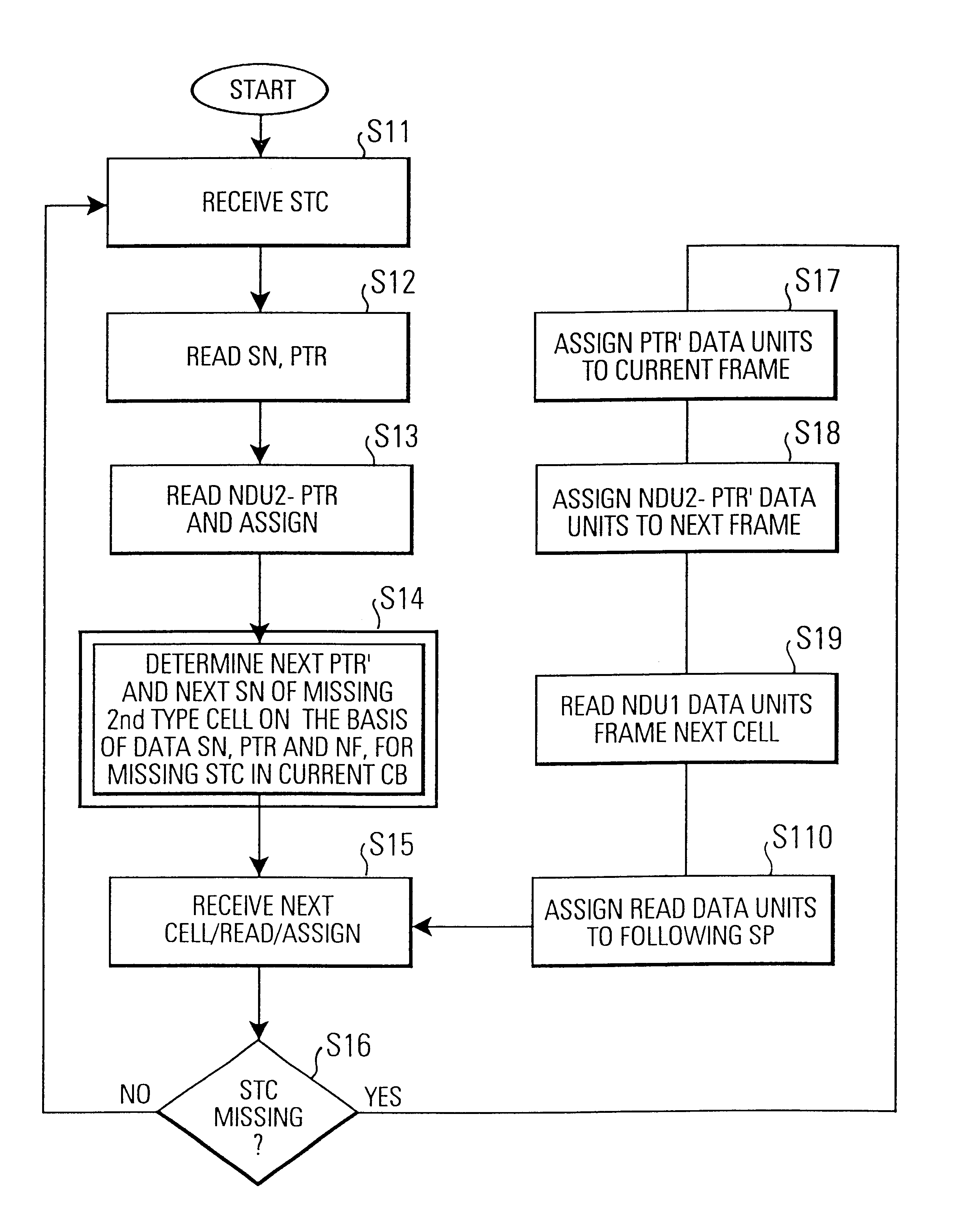
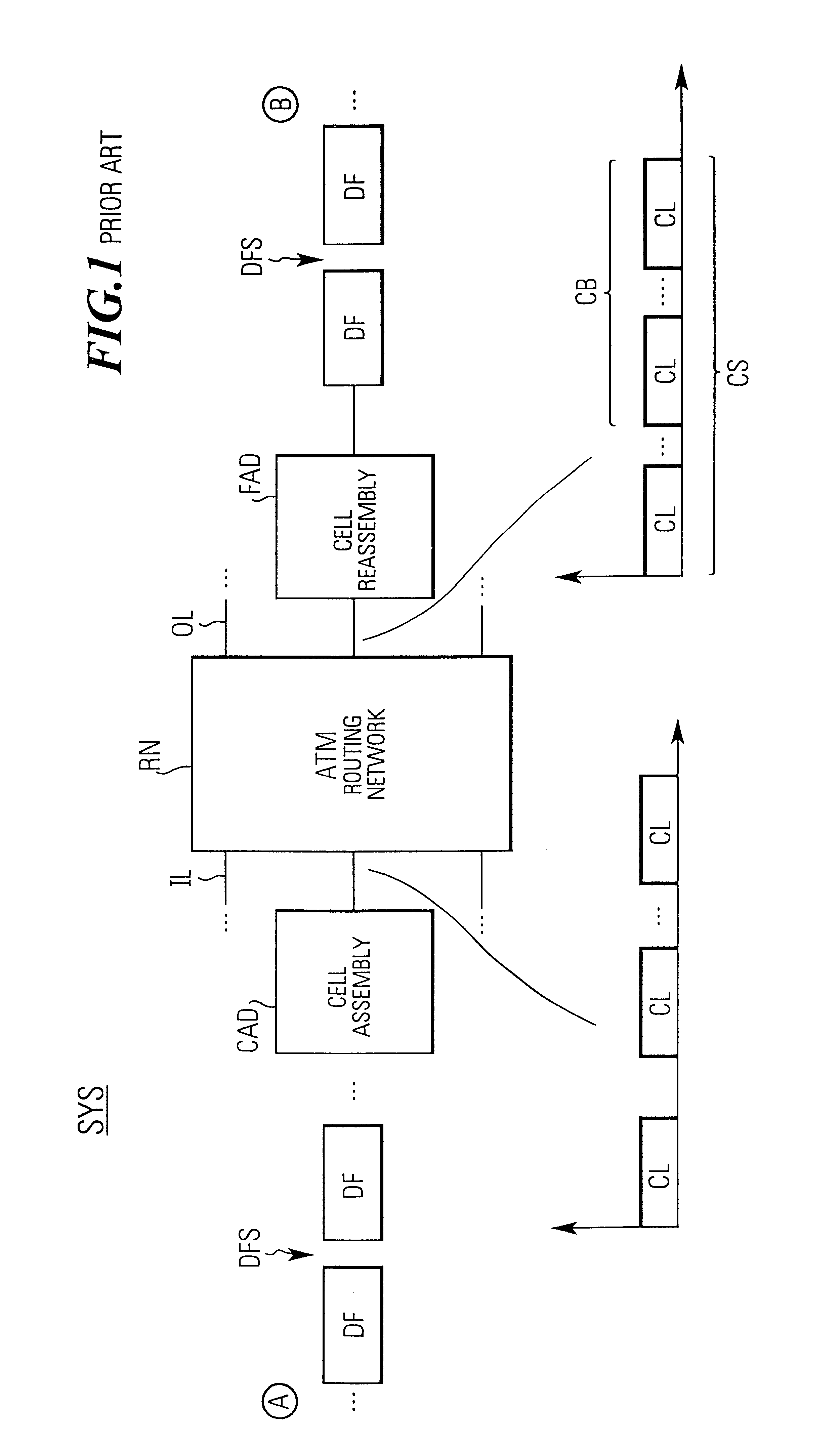
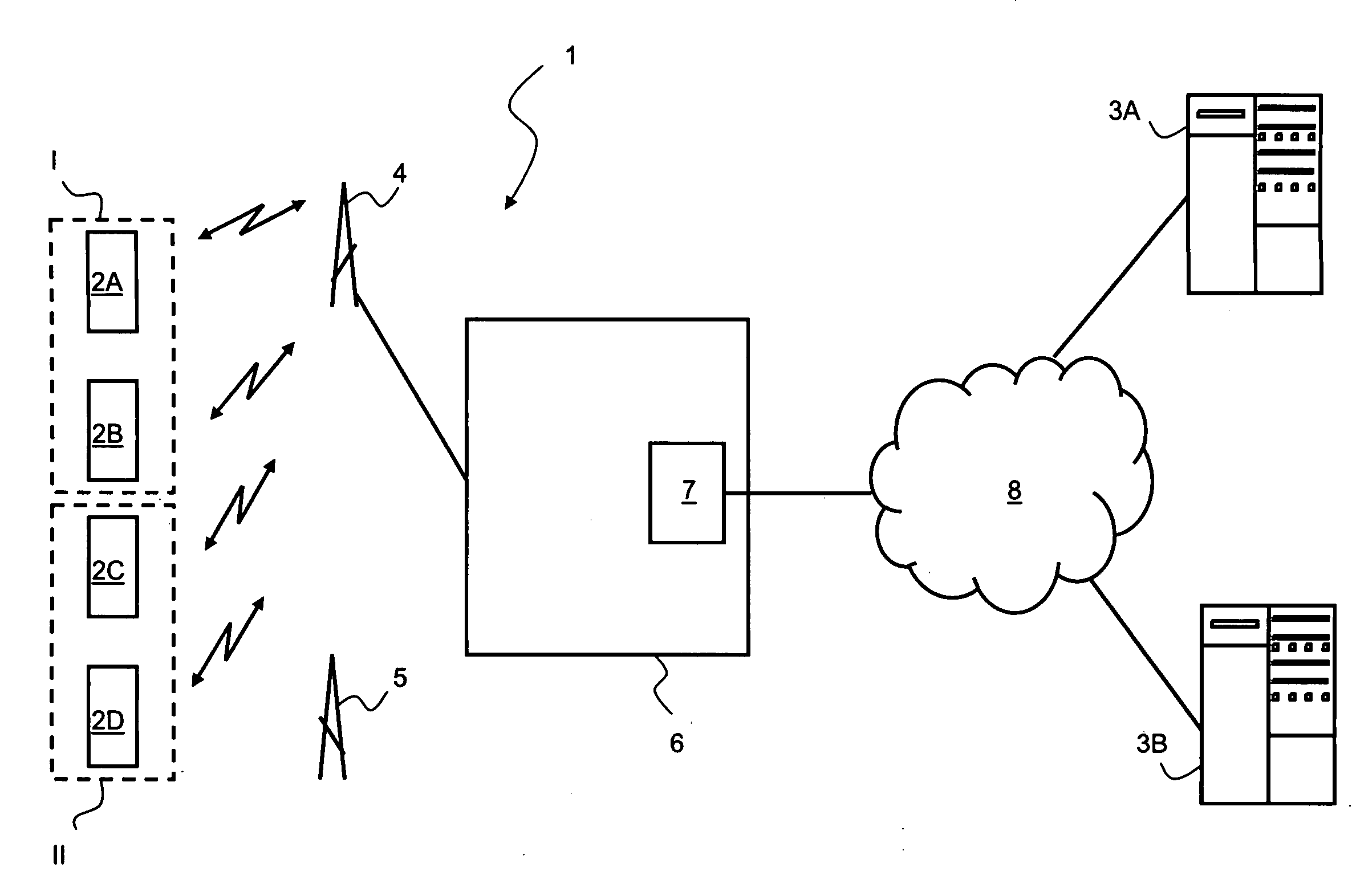
InactiveUS6944161B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComplete dataCircuit Switched Data
In a communication system (SYS) circuit switched data frames (DF) are disassembled into ATM cells (CL), routed through an ATM routing network (RN) and cell data is reassembled into data frames (DF) by a frame assembly device (FAD). Second type cells including a pointer value (PTR) are normally included in the cell stream (CS) received from the ATM routing network (RN). This pointer value (PTR) indicates the delimitation position, i.e. the number of data units belonging to a current frame (DF) and to a next frame (DF′). In order to avoid a loss of data units of a complete frame when such a second type cell (STC) is lost during the transmission, the invention estimates the sequence number of the missing second type cell as well as the pointer value (PTR′). The pre-estimation of the pointer value (PTR′) can be done by continuously updating a respective counter assigned to a respective sequence number (SN) of a cell block (CB). Thus, instead of losing the complete data of a whole frame, due to lack of information of where the delimitation occurs, in accordance with the invention only the data units of the missing second type cell are replaced with dummy data units (AIS) in the data frame (DF, DF′).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
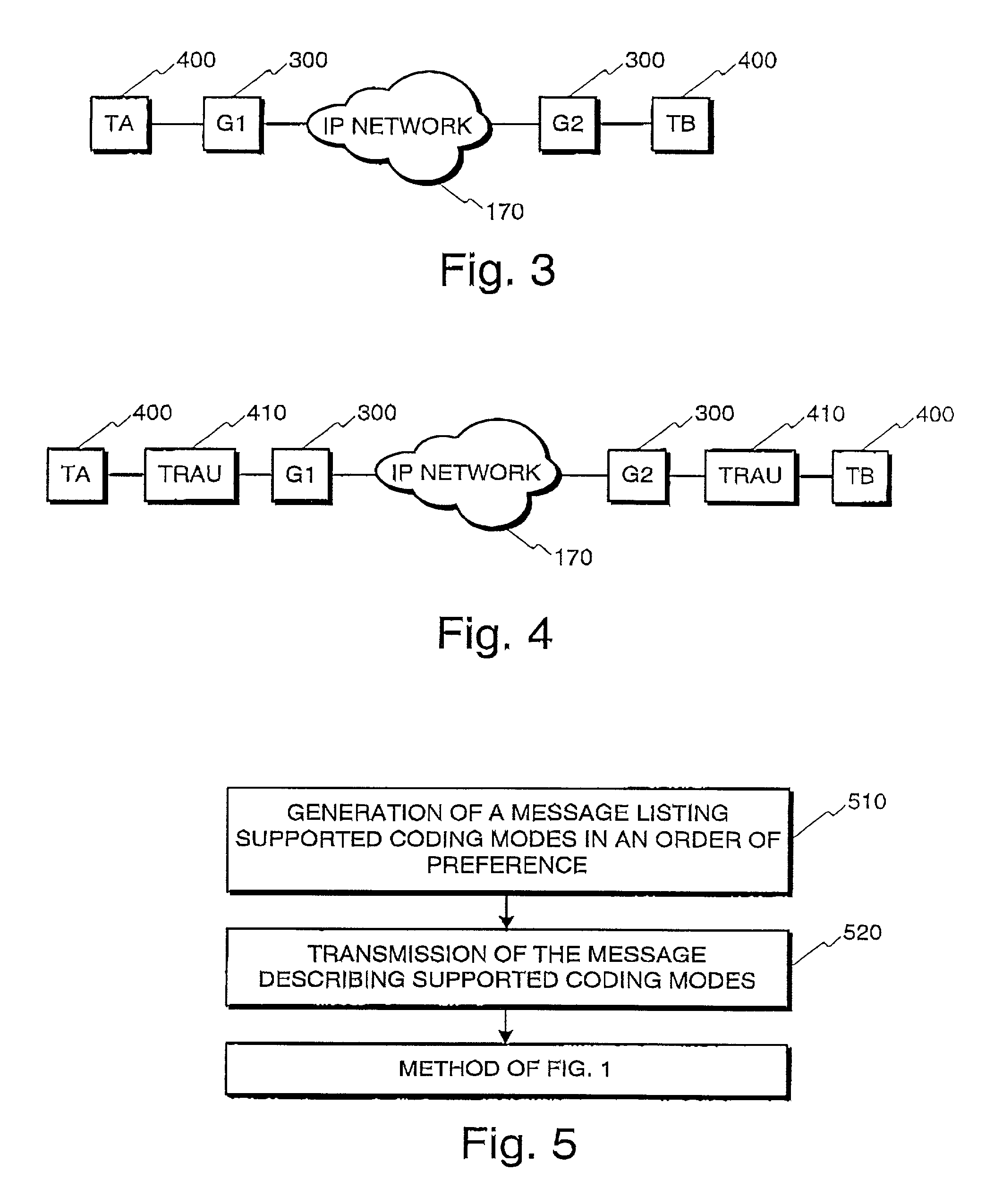
Data transmission method and a network element
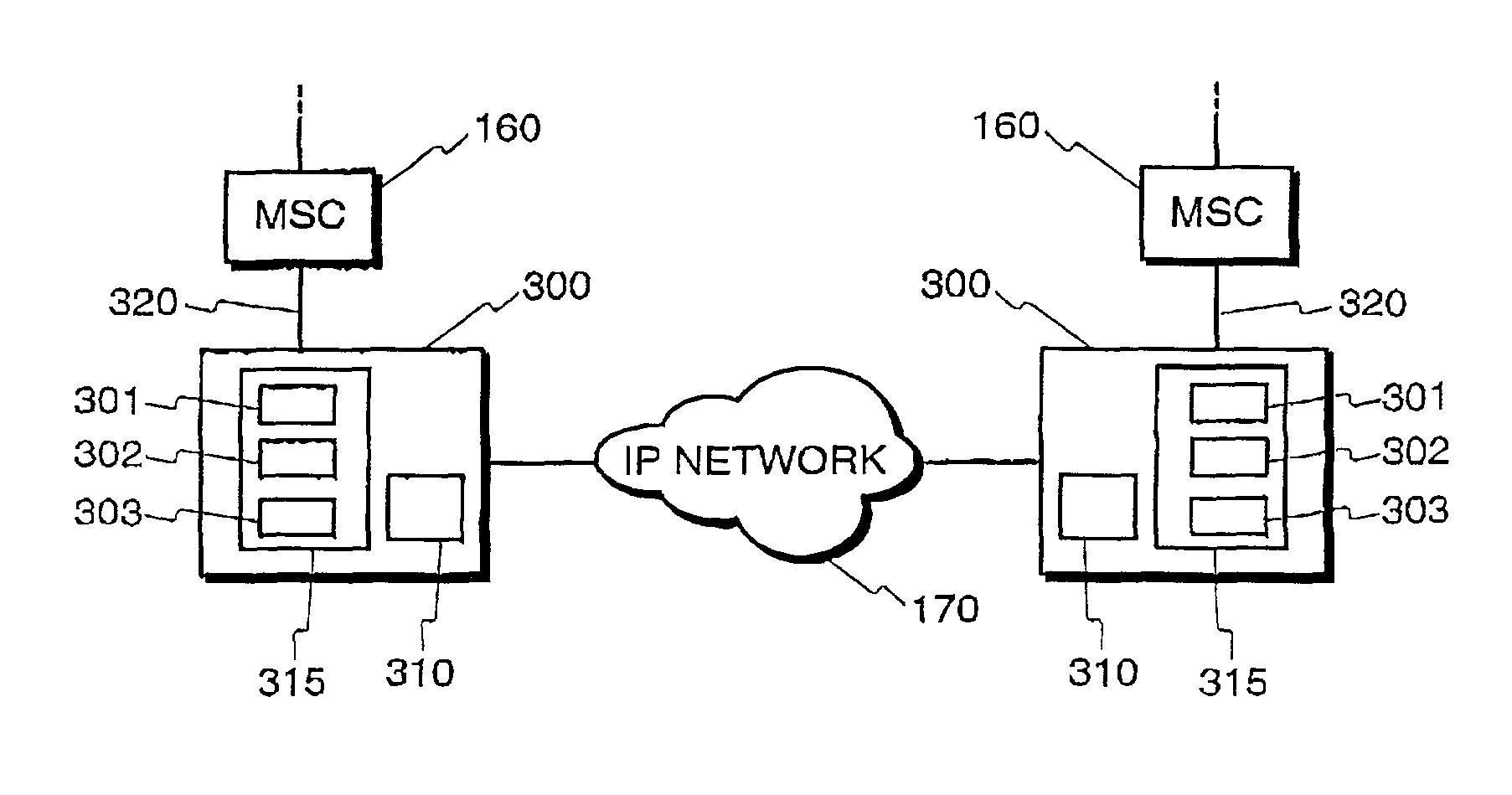
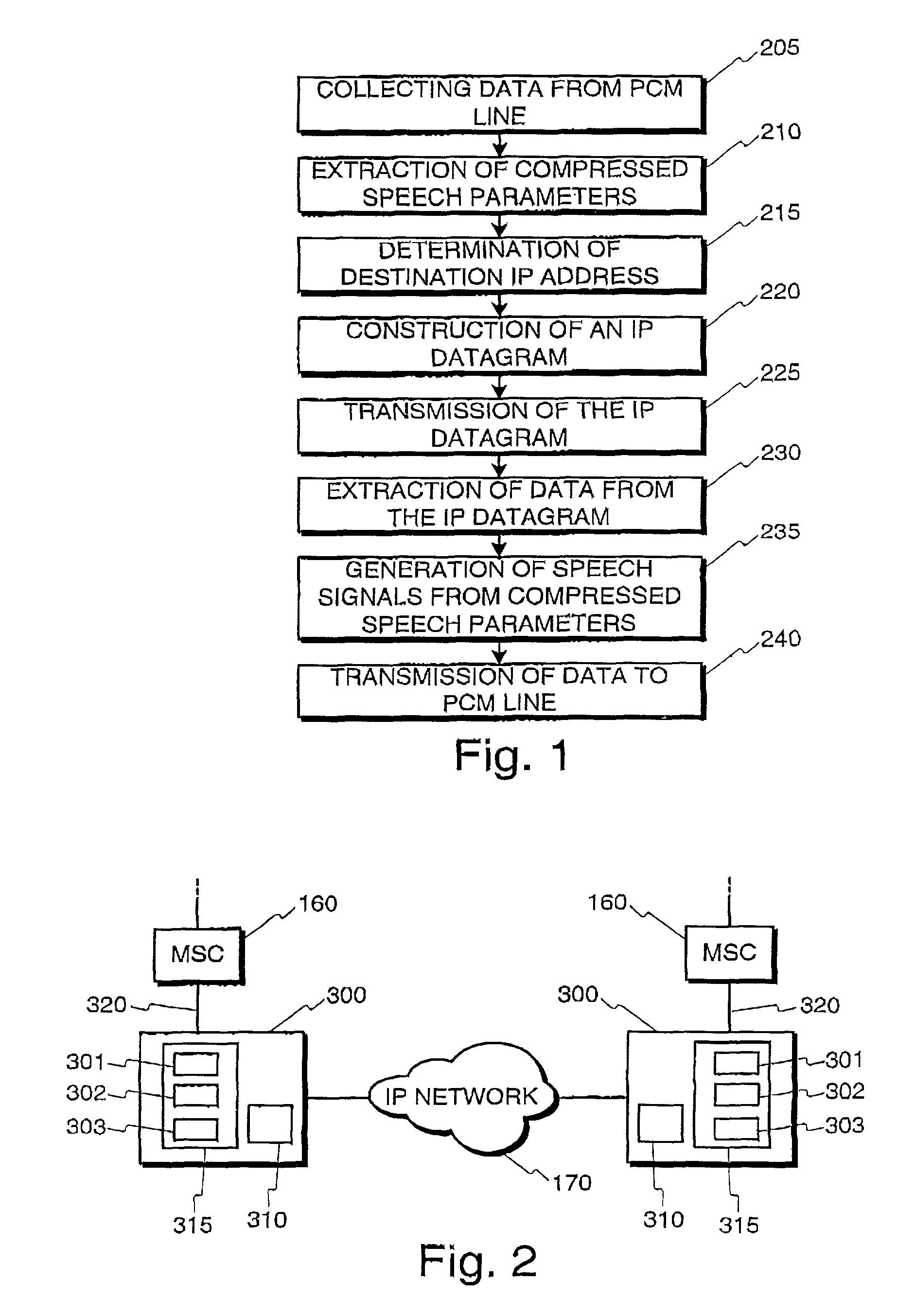
InactiveUS7792092B1Telephone data network interconnectionsHybrid transportCircuit Switched DataData transmission
The invention is concerned with transmission of speech information over mixed networks, particularly over a segment using packet transmission in an otherwise circuit switched data transmission network. According to the invention, PCM transmission lines are connected with a packet based network such as an IP network in such a way, that data from one or more channels of a first PCM transmission line is collected in the payload part of a data packet. Further, the destination address of the data packet is constructed in such a way, that the packet network entity being connected to the second PCM transmission line can determine based on the destination address of the packet, to which channel or channels of the second PCM transmission line the data should be transmitted.
Owner:VRINGO INFRASTRUCTURE +1
LTE-1x Hybrid Device and System
An apparatus for notification of a circuit switched event in a mobile station. The apparatus comprising a circuit switched modem, a packetized data modem and a radio. The circuit switched modem, configured to communicate circuit switched data over a circuit switched network. The packetized data modem, configured to communicate packetized data over a packetized data network. The radio, configured to couple the packetized data modem to the packetized data network via a packetized data radio link, and configured to couple the circuit switched modem to the circuit switched network via a circuit switched radio link, wherein said radio comprise one transmitter and two receivers.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method for Transferring Data from a Plurality of SIM-Less Communication Modules
InactiveUS20130130644A1Low costIncrease flexibilityUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsCircuit Switched DataData connection
Owner:KONINK KPN NV +1
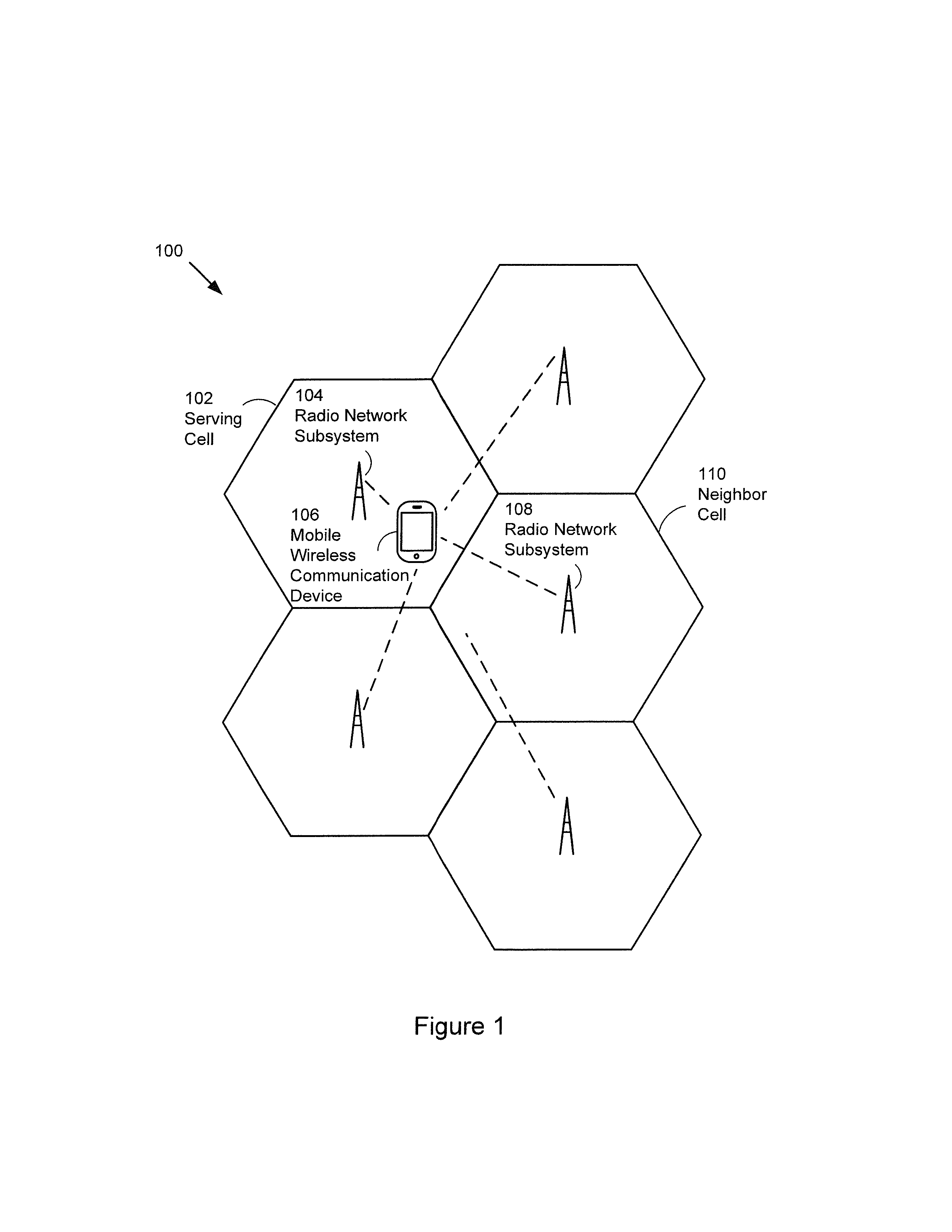
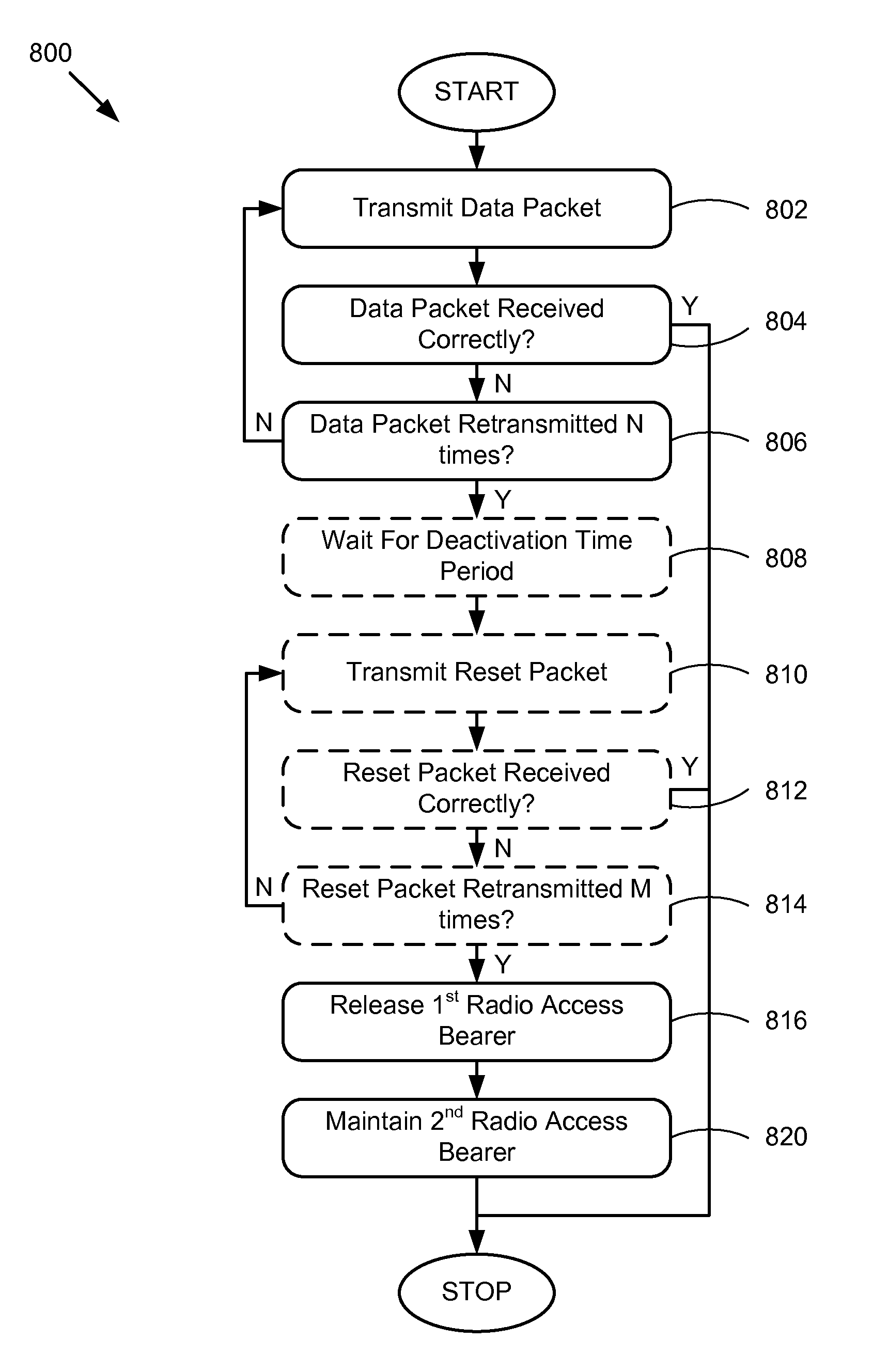
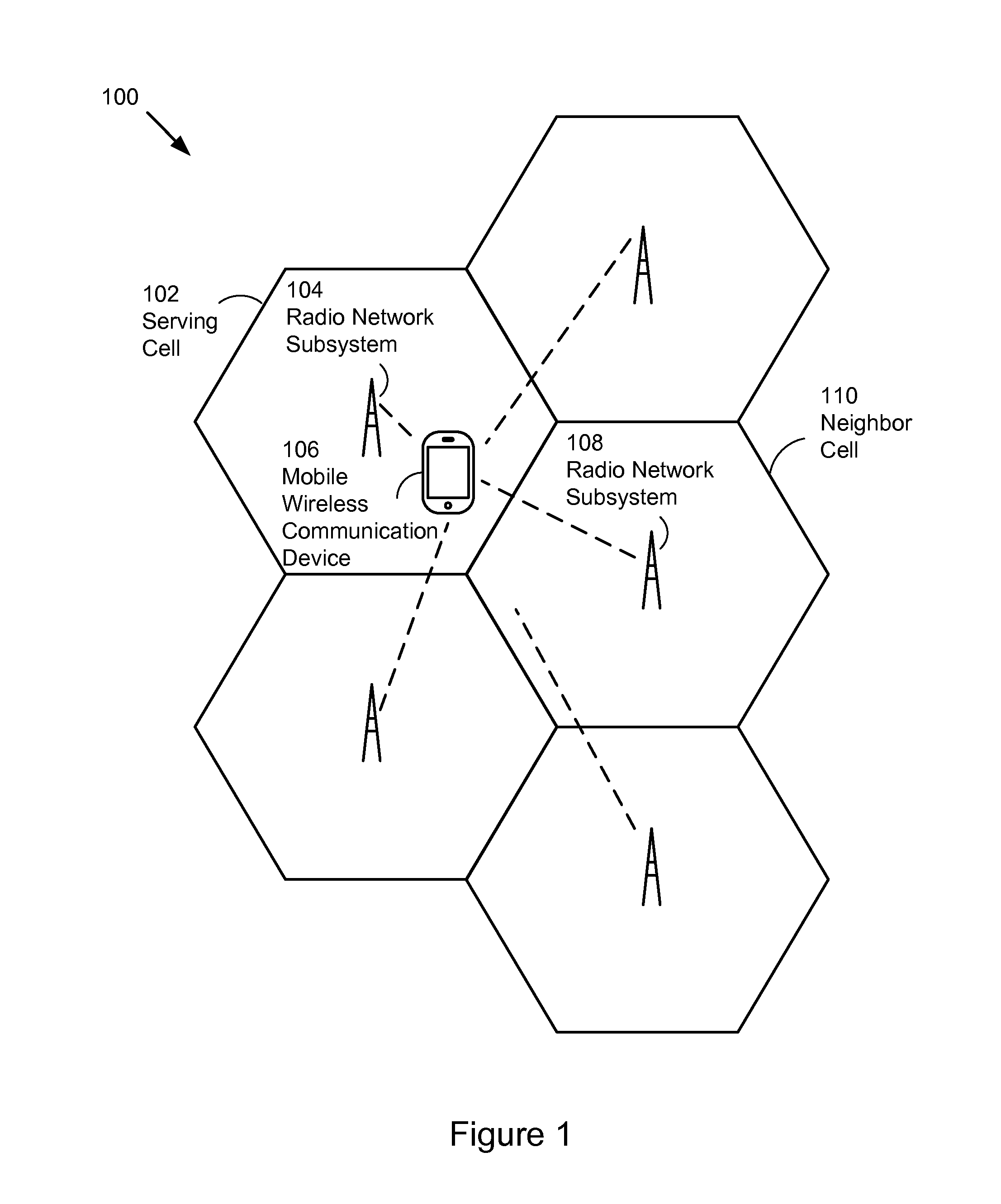
Methods to control multiple radio access bearers in a wireless device
ActiveUS20130182681A1Connection managementWireless commuication servicesCircuit Switched DataRadio networks
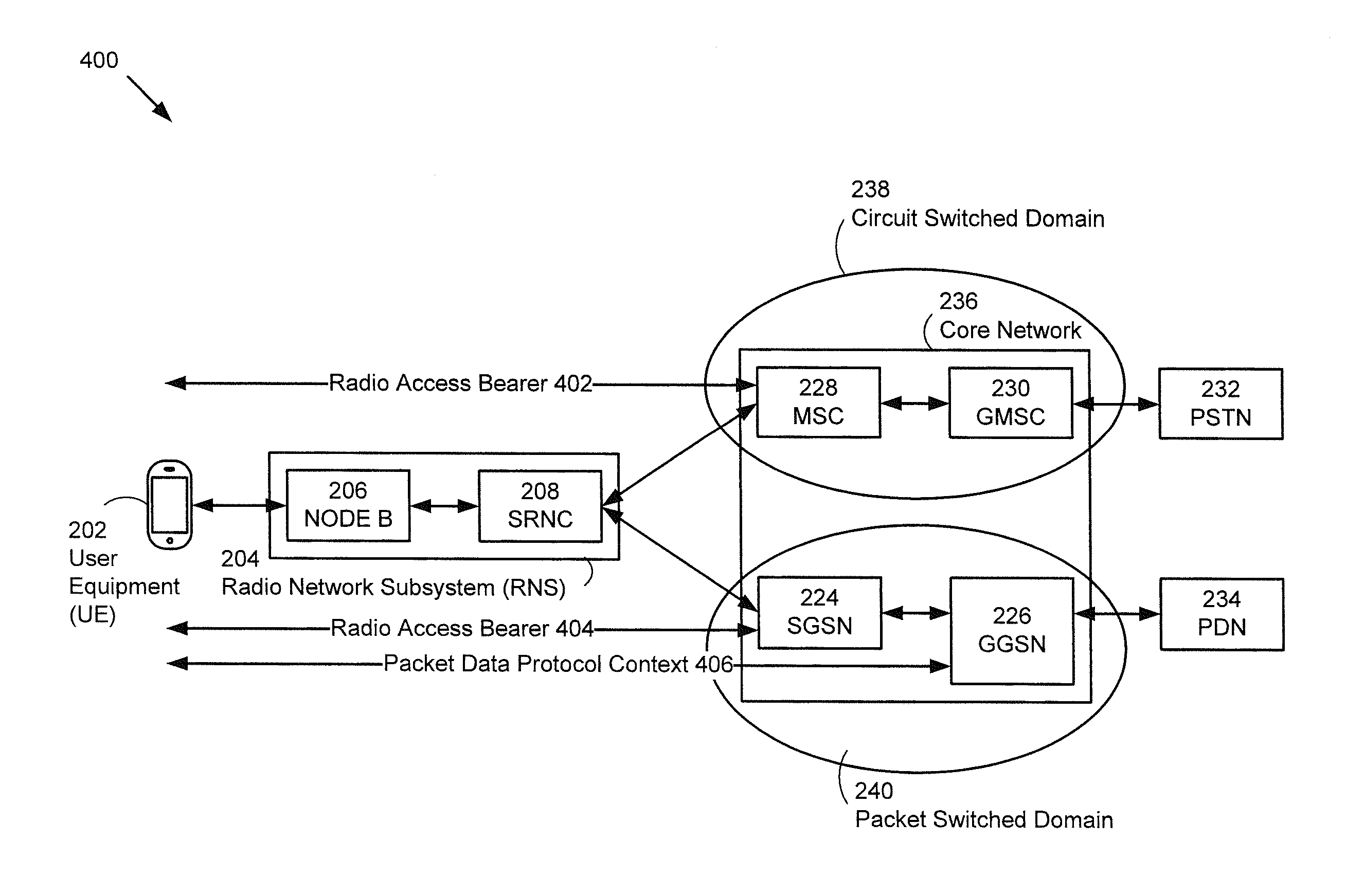
A method to control multiple radio access bearers is performed at a mobile wireless communication device when the mobile wireless communication device is connected to a radio network subsystem in a wireless communication network by first and second bidirectional radio access bearers. The mobile wireless communication device transmits a data packet on an uplink of the first bidirectional radio access bearer to the radio network subsystem. When the data packet is not correctly received by the radio network subsystem, the mobile wireless communication device retransmits the data packet repeatedly. After N retransmissions of the data packet, the mobile wireless communication device releases the first bidirectional radio access bearer while maintaining the second bidirectional radio access bearer. The first bidirectional radio access bearer provides a channel to transport packet switched data, and the second bidirectional radio access bearer provides a channel to transport circuit switched data.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method to control multiple radio access bearers in a wireless device
ActiveUS8346274B2Connection managementWireless commuication servicesCircuit Switched DataRadio networks
A method to control multiple radio access bearers is performed at a mobile wireless communication device when the mobile wireless communication device is connected to a radio network subsystem in a wireless communication network by first and second bidirectional radio access bearers. The mobile wireless communication device transmits a data packet on an uplink of the first bidirectional radio access bearer to the radio network subsystem. When the data packet is not correctly received by the radio network subsystem, the mobile wireless communication device retransmits the data packet repeatedly. After N retransmissions of the data packet, the mobile wireless communication device releases the first bidirectional radio access bearer while maintaining the second bidirectional radio access bearer. The first bidirectional radio access bearer provides a channel to transport packet switched data, and the second bidirectional radio access bearer provides a channel to transport circuit switched data.
Owner:APPLE INC
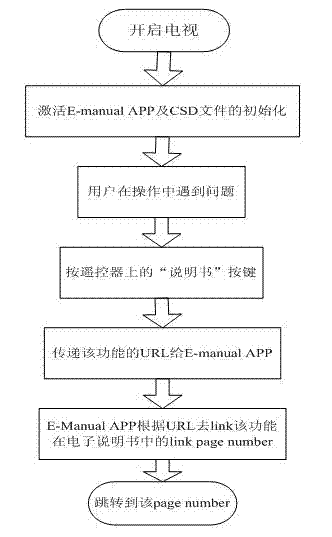
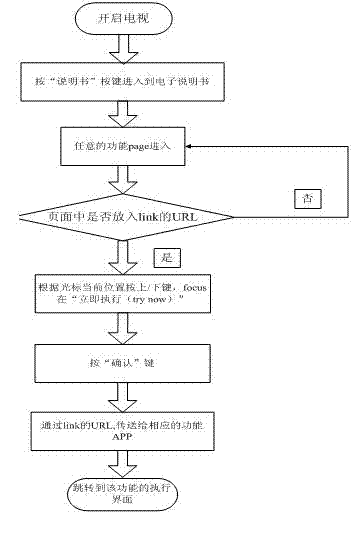
Method for learning about TV functions in real time
The invention discloses a method for learning about TV functions in real time and overcomes the defects that in the prior art, searching by a paper instruction book and an electronic instruction book is time-consuming and labor-consuming, and detailed and rich solutions cannot be provided quickly and in real time. According to the technical scheme, a PBA (printed board assembly) circuit board of a TV is provided with a USB port used for upgrading an intelligent electronic instruction book, and flash on the PBA circuit board is used for storing CSD (circuit switched data) files of the upgraded electronic instruction book. A skip function is provided for a user, the user can directly skip to a corresponding function interface in the instruction book by pressing an 'instruction book' button when problems occur in operation and can return the function interface by performing 'try now' from the function interface of the instruction book, an 'index' function is provided for the user in the electronic instruction book to arrange some commonly-used functions in order according to Pinyin of Chinese characters, and accordingly the user can find out the function that he wants to learn about quickly by the index and switch to the interface of the instruction book of the function.
Owner:TIANJIN SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for Transferring Data from a Plurality of SIM-less Communication Modules
InactiveUS20090298518A1Low costIncrease flexibilityUser identity/authority verificationTelephonic communicationCircuit Switched DataData connection
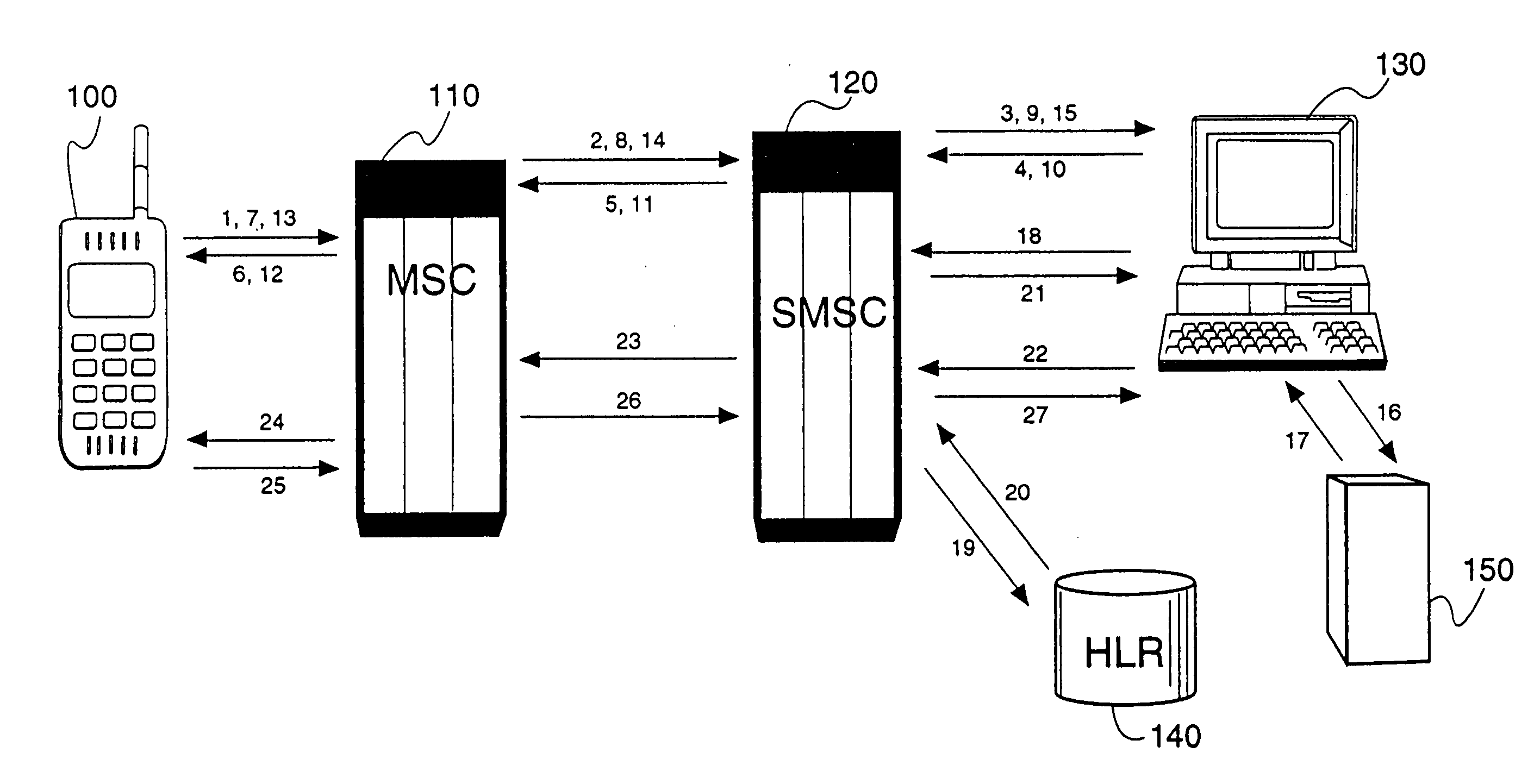
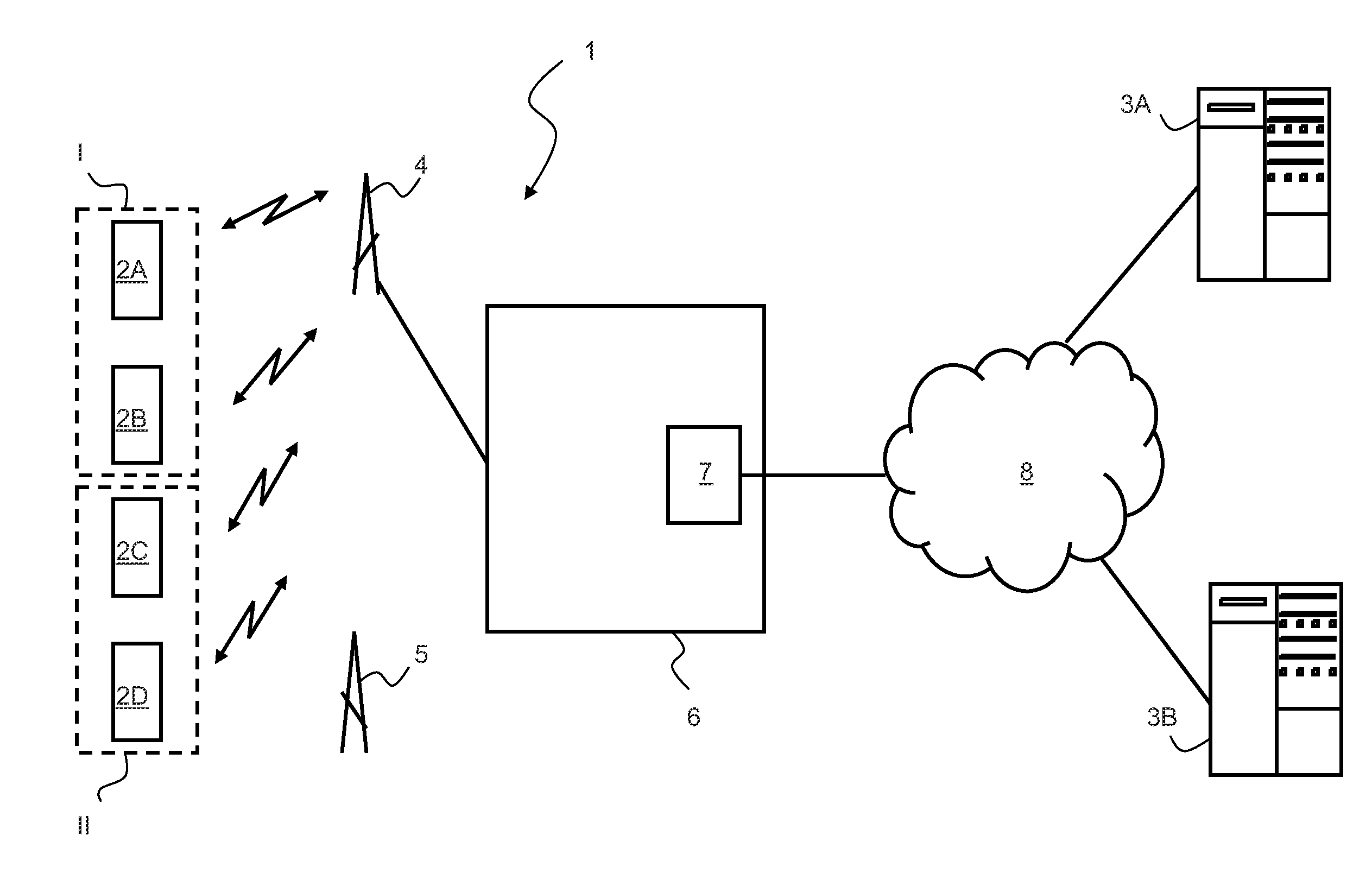
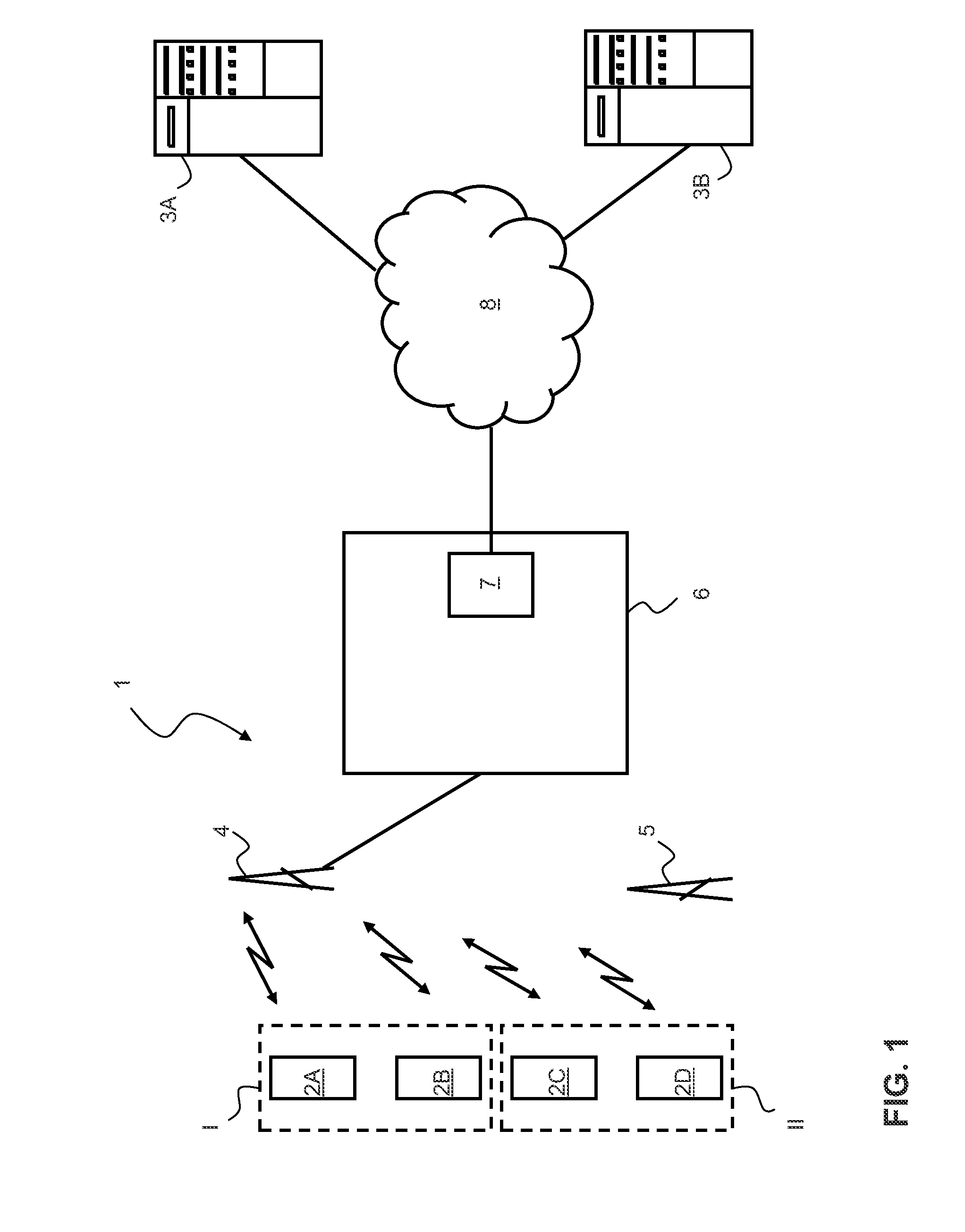
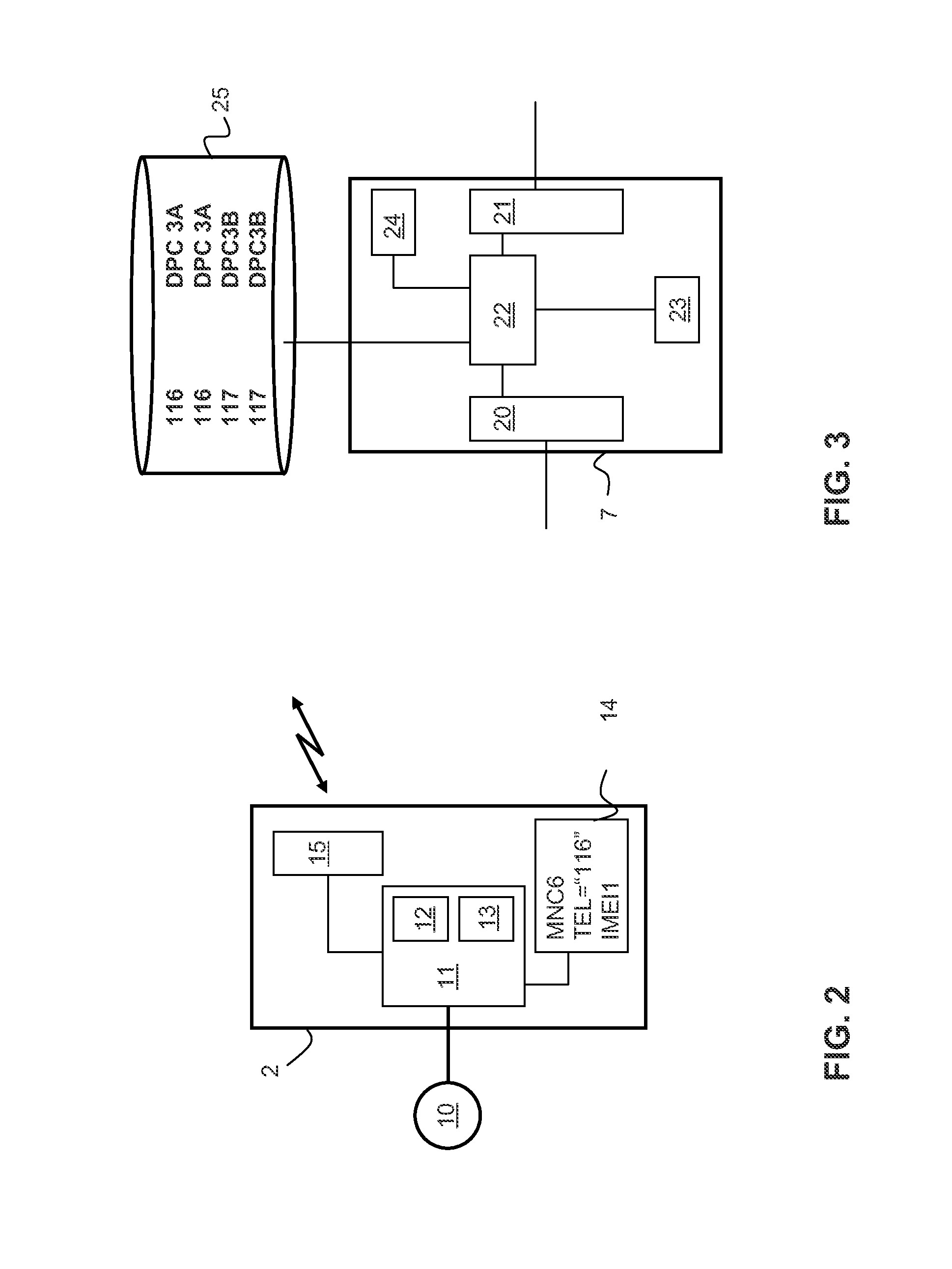
The invention relates to a method of transferring data from at least a first communication module and a second communication module to, respectively, a first data processing centre and a second data processing centre via a circuit switched telecommunications network. A first and second connection request containing respective first and second pre-provisioned telephone numbers from the first and second communication modules are received in the network. The first and second telephone numbers are processed such that the network refrains from authenticating the first and second communication modules. Subsequently first and a second circuit switched data connections are established with the first and second communication modules for receiving data. The data can be routed from the first communication module to the first data processing centre and from the second communication module to the second data processing centre in accordance with the first and second telephone numbers, respectively.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO) +1
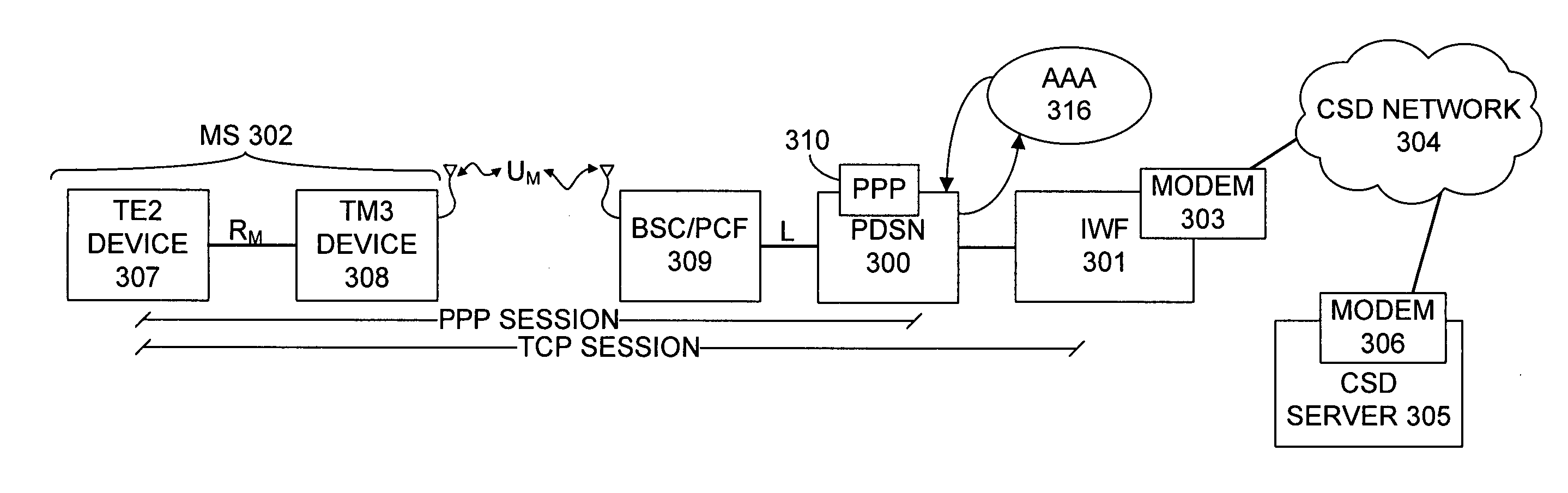
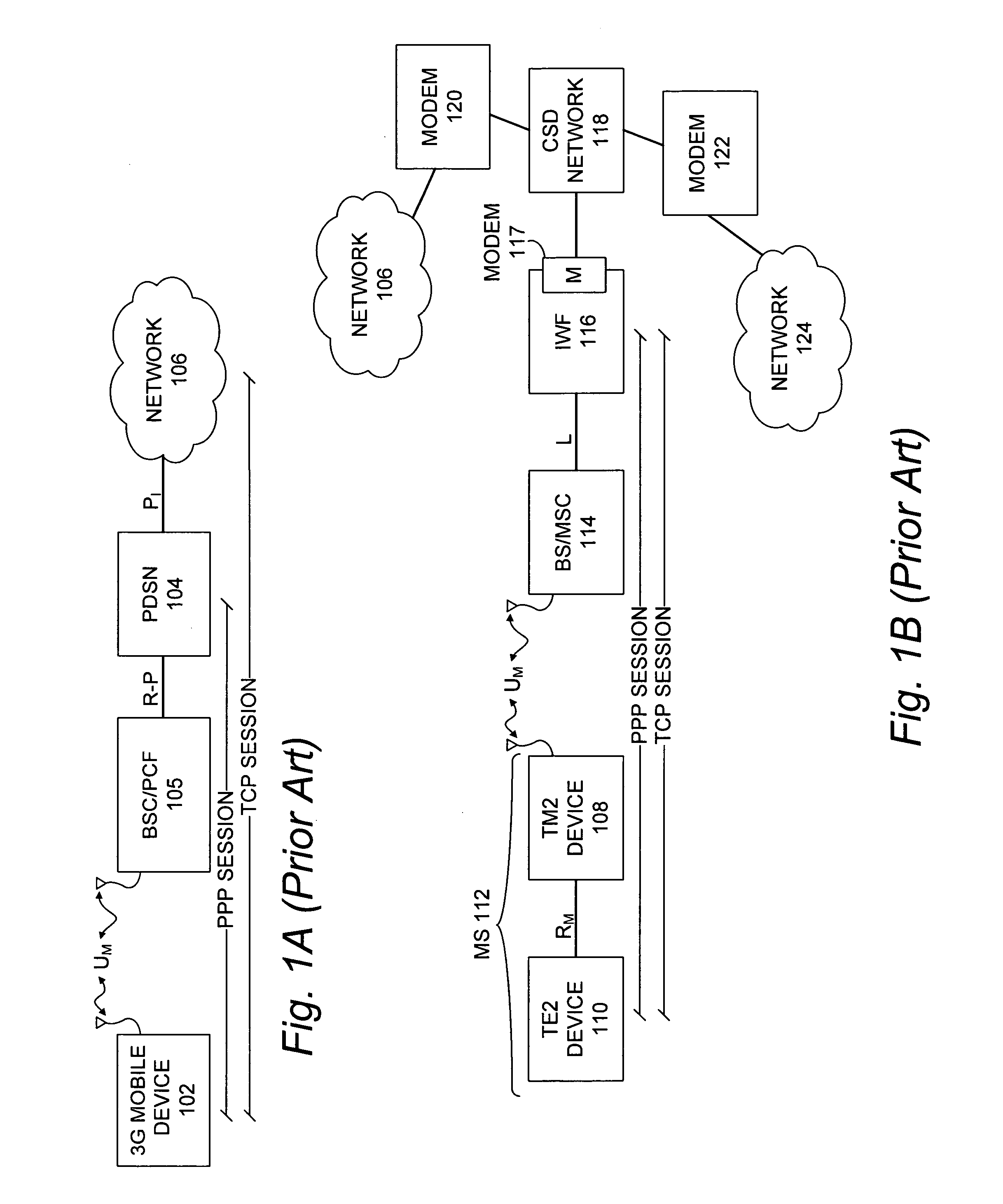
Method of establishing a PPP session over an air interface
InactiveUS20070211752A1Easy to set upNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexPacket data serving nodeCircuit Switched Data
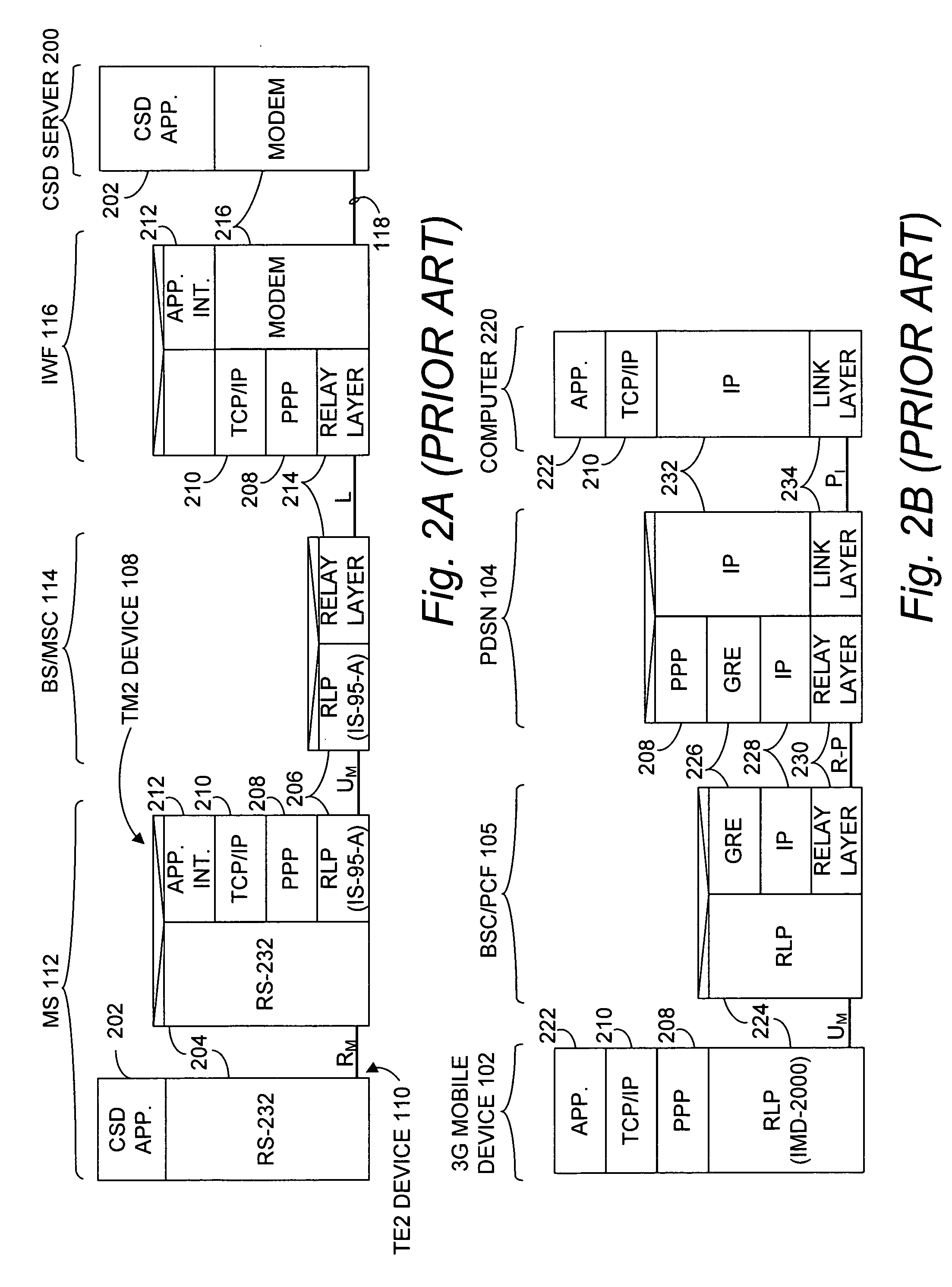
A method of establishing a Point-to-Point (PPP) session over an air interface is described. In order to provide access to a Circuit Switched Data (CSD) server on a CSD network, a Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) establishes a PPP session on behalf of an InterWorking Function (IWF). This establishment of the PPP session allows a mobile 3G device to setup a TCP session with the IWF. The mobile 3G device may communicate modem emulation data to the IWF and thereby use a modem in the IWF to communicate over the CSD network with the CSD server.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
Data transmission method and apparatus
InactiveUS7768994B2Good network serviceNarrow bandwidthAccounting/billing servicesTime-division multiplexCircuit Switched DataTelecommunications network
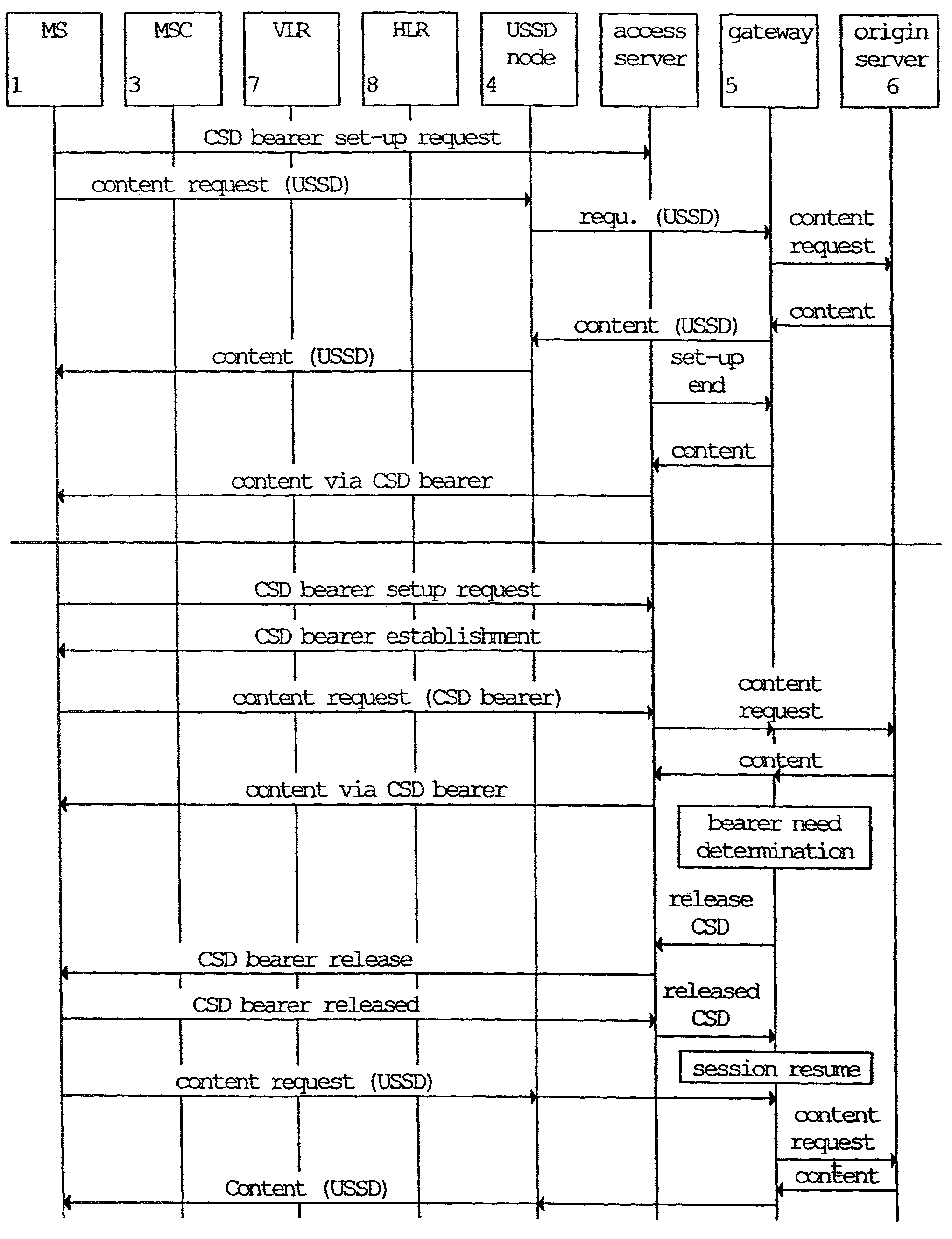
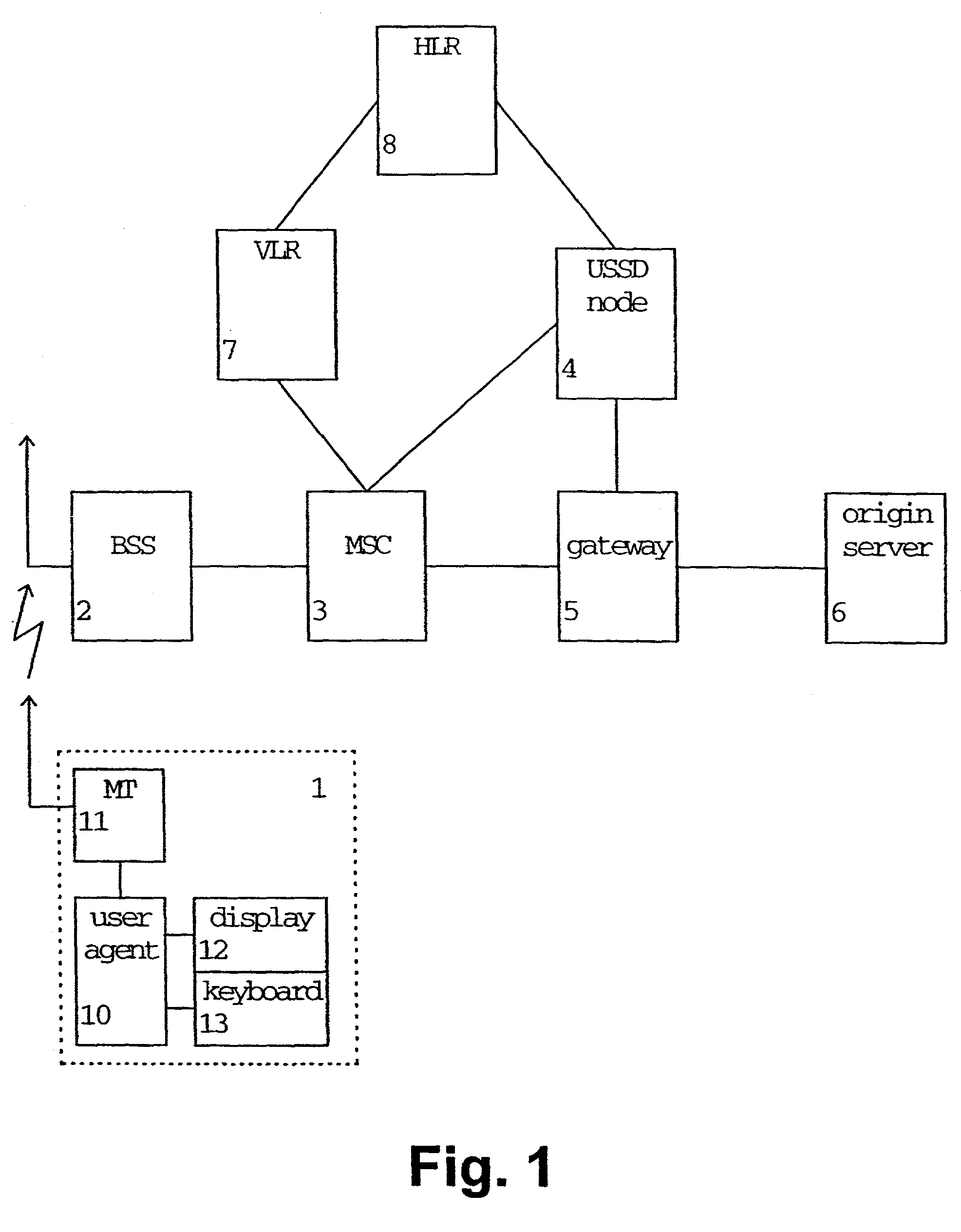
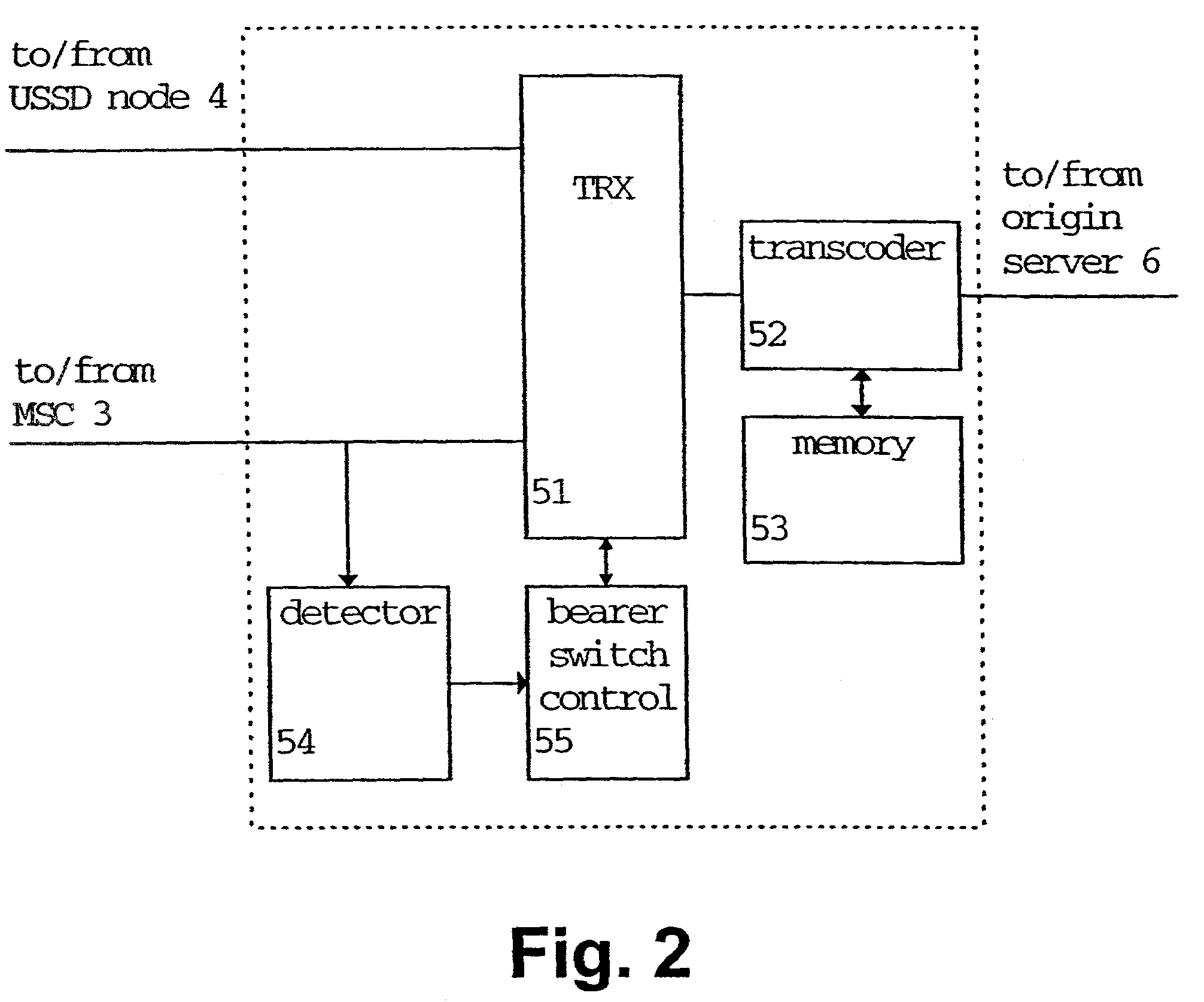
A data transmission method and apparatus for performing a data transmission between end terminals of a telecommunication network, where the data is transmitted from at least one of the end terminals using the first data bearer. Then, data transmission is switched from the first to the second data bearer, if a predetermined bearer need condition has been determined or in order to obtain a subscriber identity used for gathering charging data. The network service provided by the operator can be improved, since the bearer switching allows an increase of the overall speed of the data transmission, an adaptation of the bearer bandwidth to the data amount, and a provision of the subscriber identity. The first data bearer may be a USSD or SMS data bearer, and the second data bearer may be a circuit-switched data bearer or a GPRS bearer, or vice versa.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
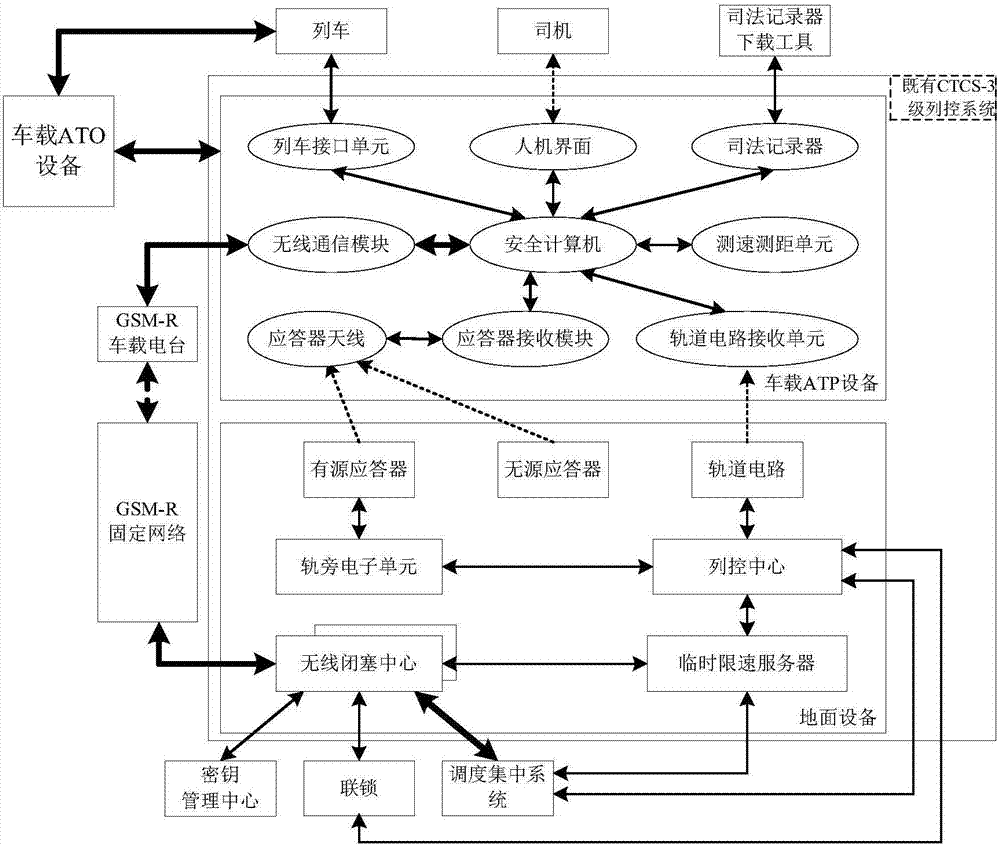
Automatic driving system applied to high speed railway
InactiveCN107215343AReduce labor intensityHigh degree of automationAutomatic systemsLocomotivesCircuit Switched DataEmbedded system
The invention discloses an automatic driving system applied to a high speed railway. The automatic driving system comprises a vehicle-mounted ATP device, a vehicle-mounted ATO device, a ground device, an interlocking device and a centralized traffic control system, wherein the vehicle-mounted ATP device is respectively connected with the ground device and the vehicle-mounted ATO device, and the vehicle-ground bidirectional transmission between the vehicle-mounted ATP device and the ground device is realized by virtue of data exchange service of a GSM-R network circuit; the ground device is also respectively connected with the interlocking device and the centralized traffic control system; and the ground device comprises a precise positioning responder, and a radio block center in the ground device has a function for processing ATO relevant information so as to realize the transmission of the ATO relevant information. By adopting the system, the automatic driving of trains in the high speed railway can be realized, so that the labor intensity of a driver can be alleviated, and the automation degree and transportation efficiency of the device can be improved.
Owner:SIGNAL & COMM RES INST OF CHINA ACAD OF RAILWAY SCI +3
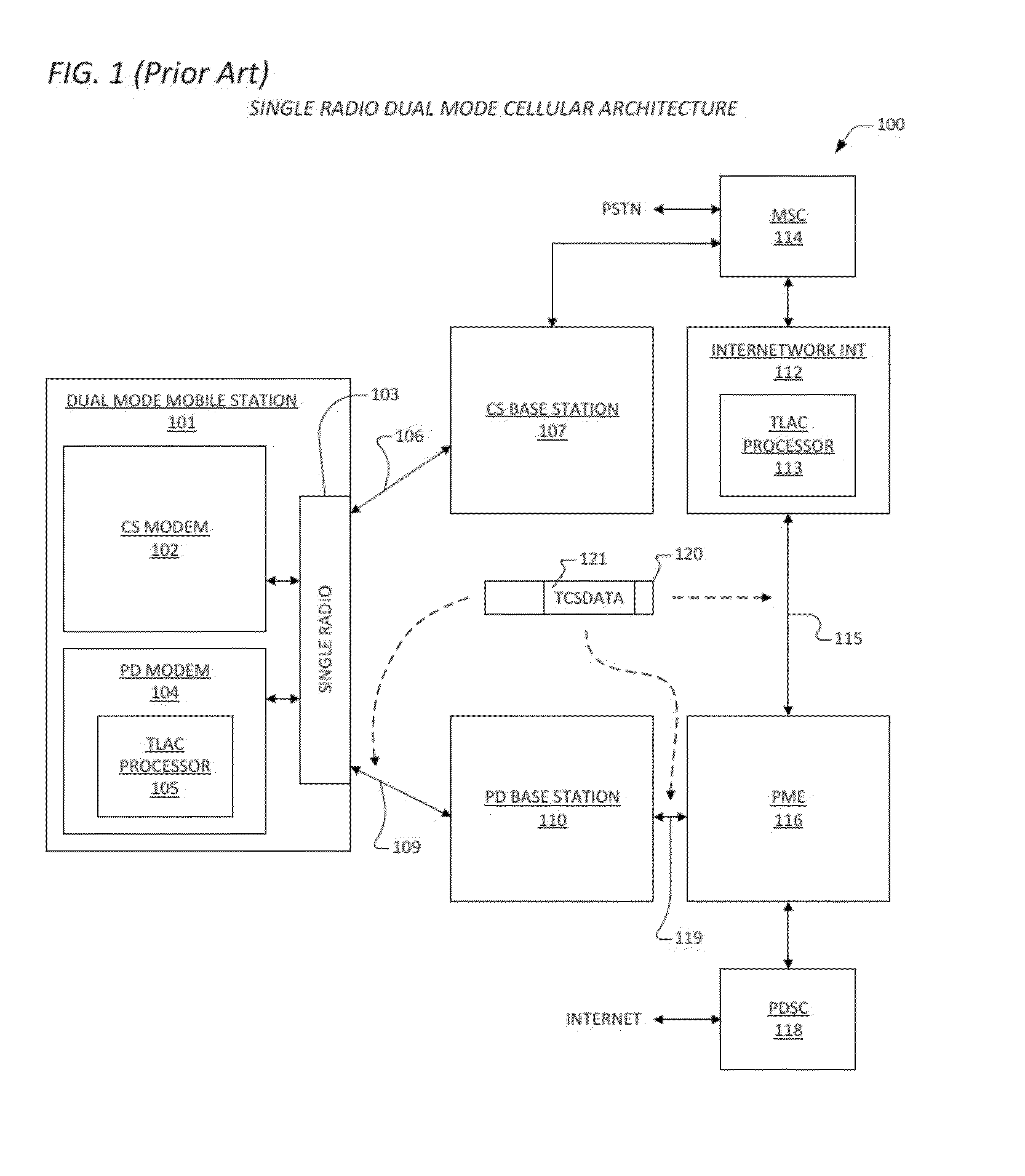
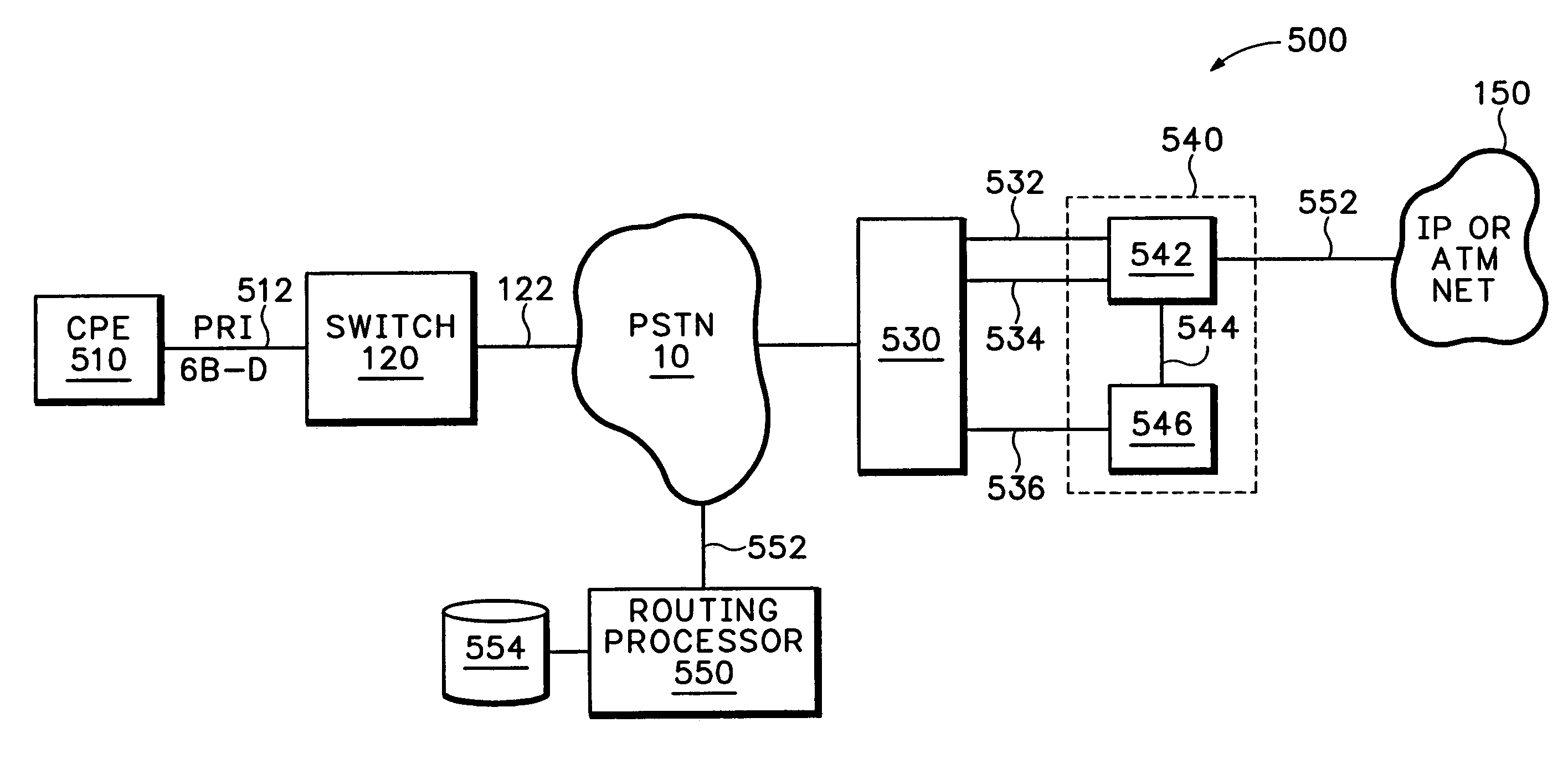
Call control system and method for automatic routing of circuit switched data connections based upon stored communication link information
InactiveUS7493411B1Readily apparentDigital computer detailsData switching networksData connectionCircuit Switched Data
A method and apparatus for automatic routing of multi-link circuit switched connections are shown. A routing processor monitors the behavioral characteristics of a previous connection from an originating client and stores data relating to the characteristics of the previous connection. In particular, data is stored regarding the previous connection which is not available until after call completion of the previous connection. When the originating client initiates a subsequent connection, the routing processor retrieves the data relating to the behavioral characteristics of the previous connection and efficiently routes the subsequent based upon the behavioral characteristics.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Device for data communications between wireless application protocol terminal and wireless application server, and method thereof
InactiveUS6937604B2Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexCircuit Switched DataWireless data
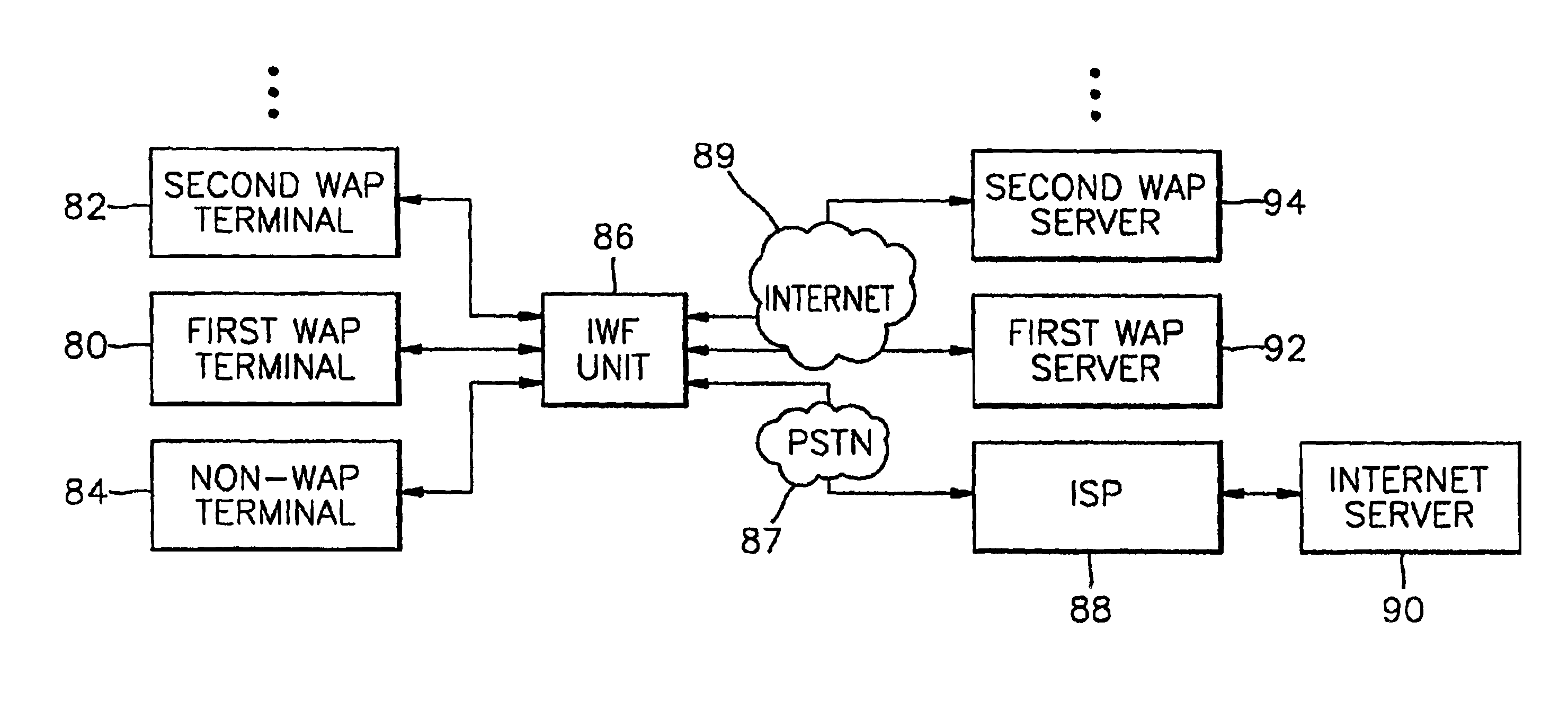
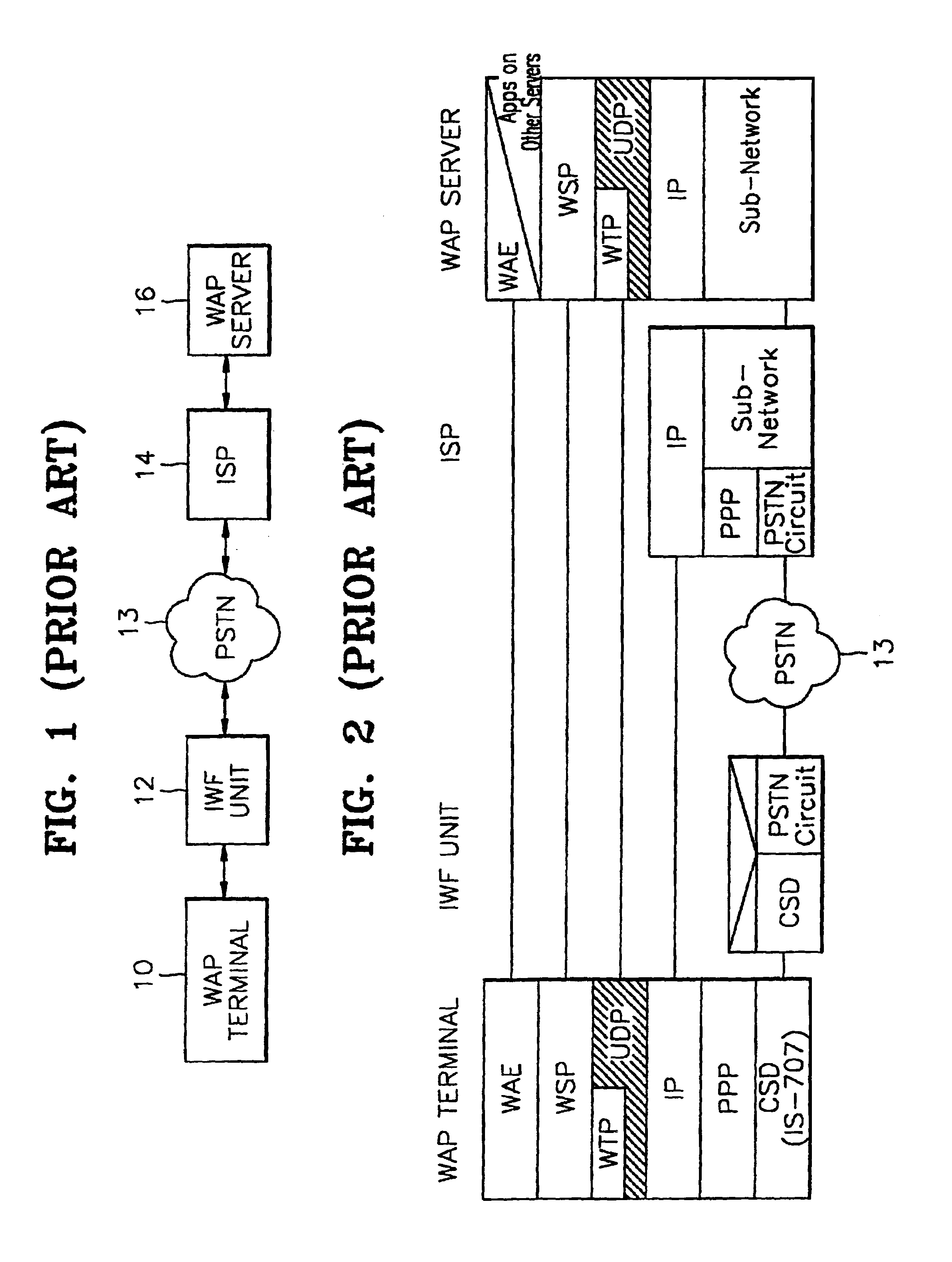
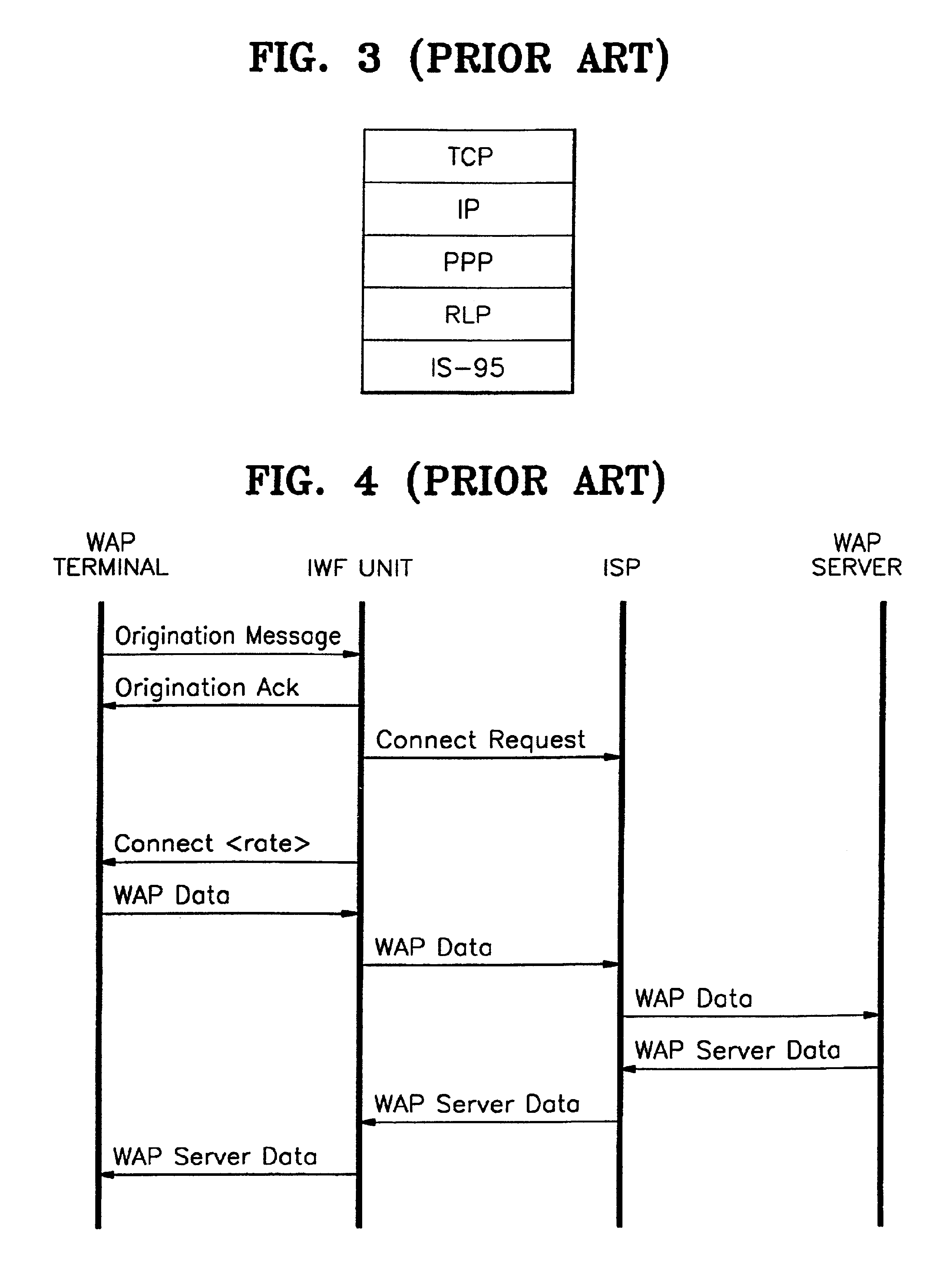
A device for data communications between a Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) terminal and a WAP server, and a data communication method thereof. The data communications device includes: a plurality of WAP terminals each having a protocol stack in which a Circuit Switch Data service (CSD) protocol layer is laid under a Wireless Transaction Protocol (WTP) layer and a Wireless Datagram Protocol (WDP) layer, for generating WAP data which is service request data; a plurality of WAP servers each having a protocol stack in which a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) layer and an Internet Protocol (IP) layer are laid under a WTP layer and a WDP layer, for providing the WAP terminals with WAP server data according to the WAP data; and an interworking function (IWF) unit having a CSD protocol layer connected to the CSD protocol layers of each WAP terminal, and a TCP layer and an IP layer which are connected to the TCP and IP layers of each WAP server, for mapping the WAP terminals to the corresponding WAP servers, wherein each WAP terminal communicates with the IWF unit though a single Internet Protocol / Peer-to-Peer Protocol (IP / PPP) layer included in its own CSD protocol layer, and the IWF unit communicates through the Internet with each WAP server. Because there is no redundancy of IP / PPP protocol layers in the WAP terminal, overhead is considerably reduced. Also, the IWF unit is directly connected through the Internet to the WAP server, not through the PSTN and the ISP, so that connection time and costs can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Providing wireless data services via public telephones
InactiveUS20050041645A1Accounting/billing servicesNetwork topologiesCircuit Switched DataWireless data services
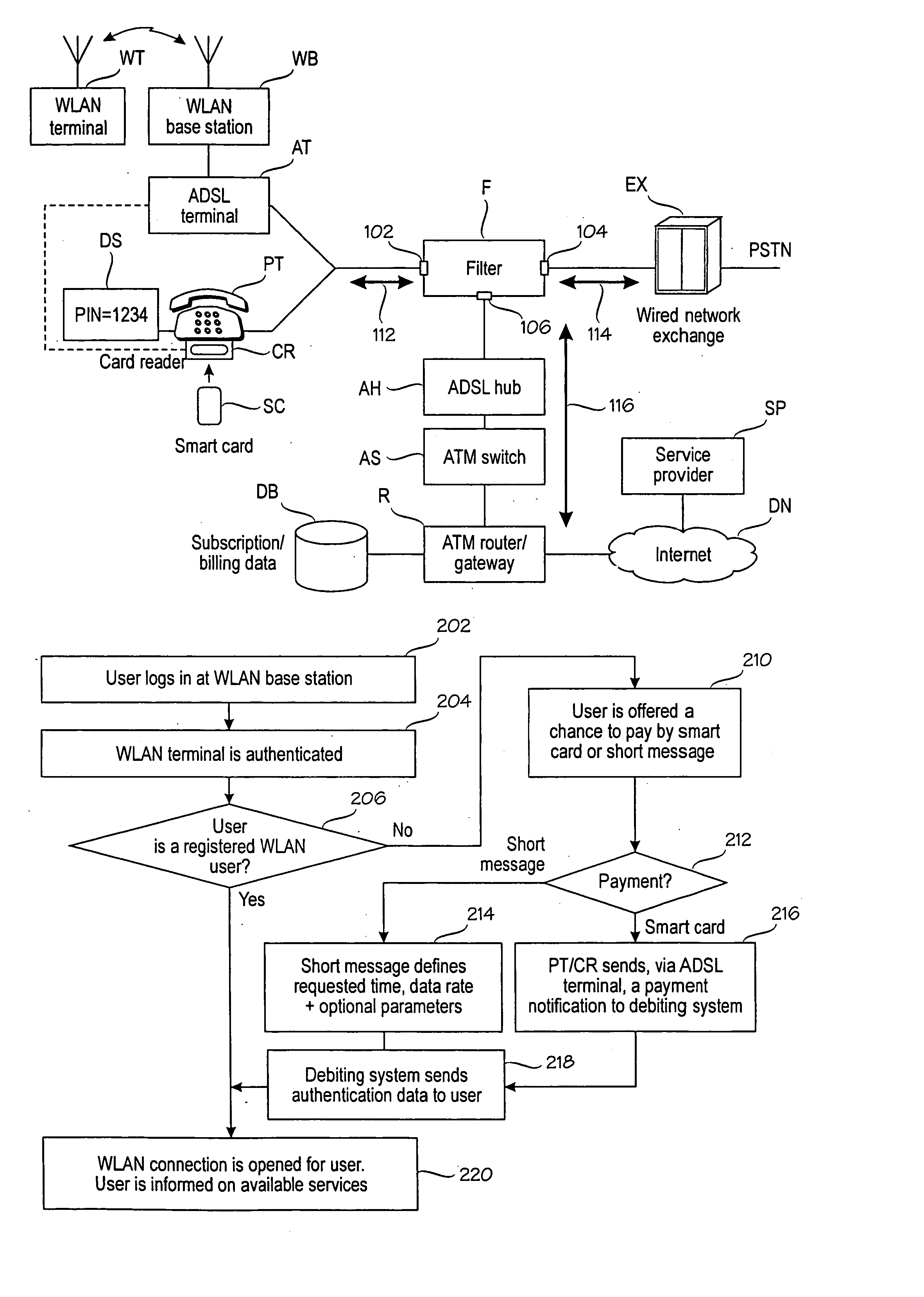
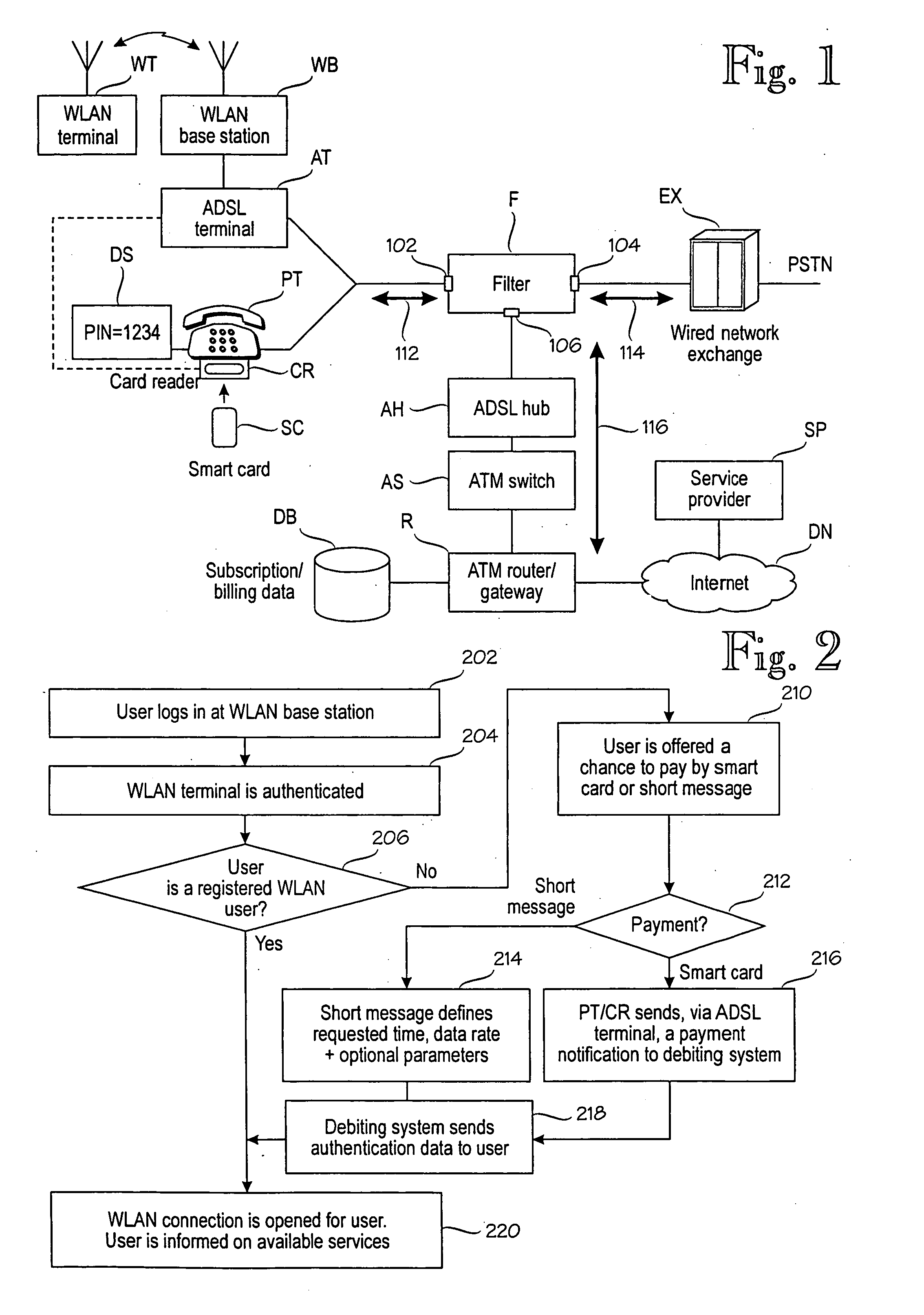
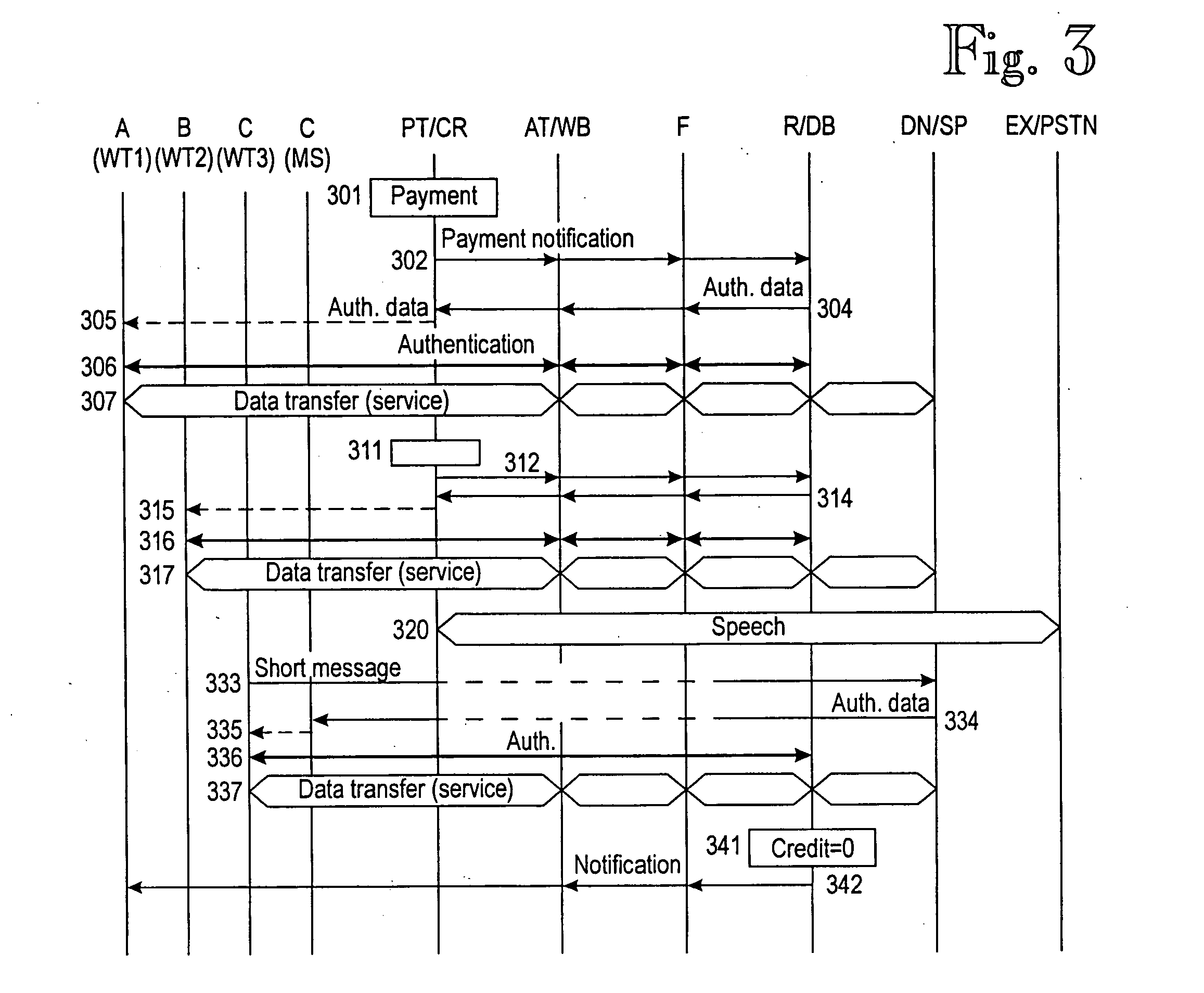
An arrangement for providing a wireless data service from a service provider (SP) to a wireless terminal (WT). The arrangement comprises a public telephone (PT). In order to provide packet-switched connection, which can be shared among multiple terminals, the arrangement comprises a filter (F) that directs voice traffic to a circuit-switched data path (114) between an exchange (EX) and the filter, and data services to a packet-switched data path (116) between the a network (DN) and the filter. Voice traffic and data services share a common data path (112) between the public telephone (PT) and the filter. There are wireless communication means, such as a WLAN base station (WB) and an ADSL terminal (AT), operationally coupled to the filter, for conveying the wireless data service to the wireless terminal (WT). Debiting means (R, DB) control debiting of the wireless terminal for the use of the wireless data service.
Owner:SONERA
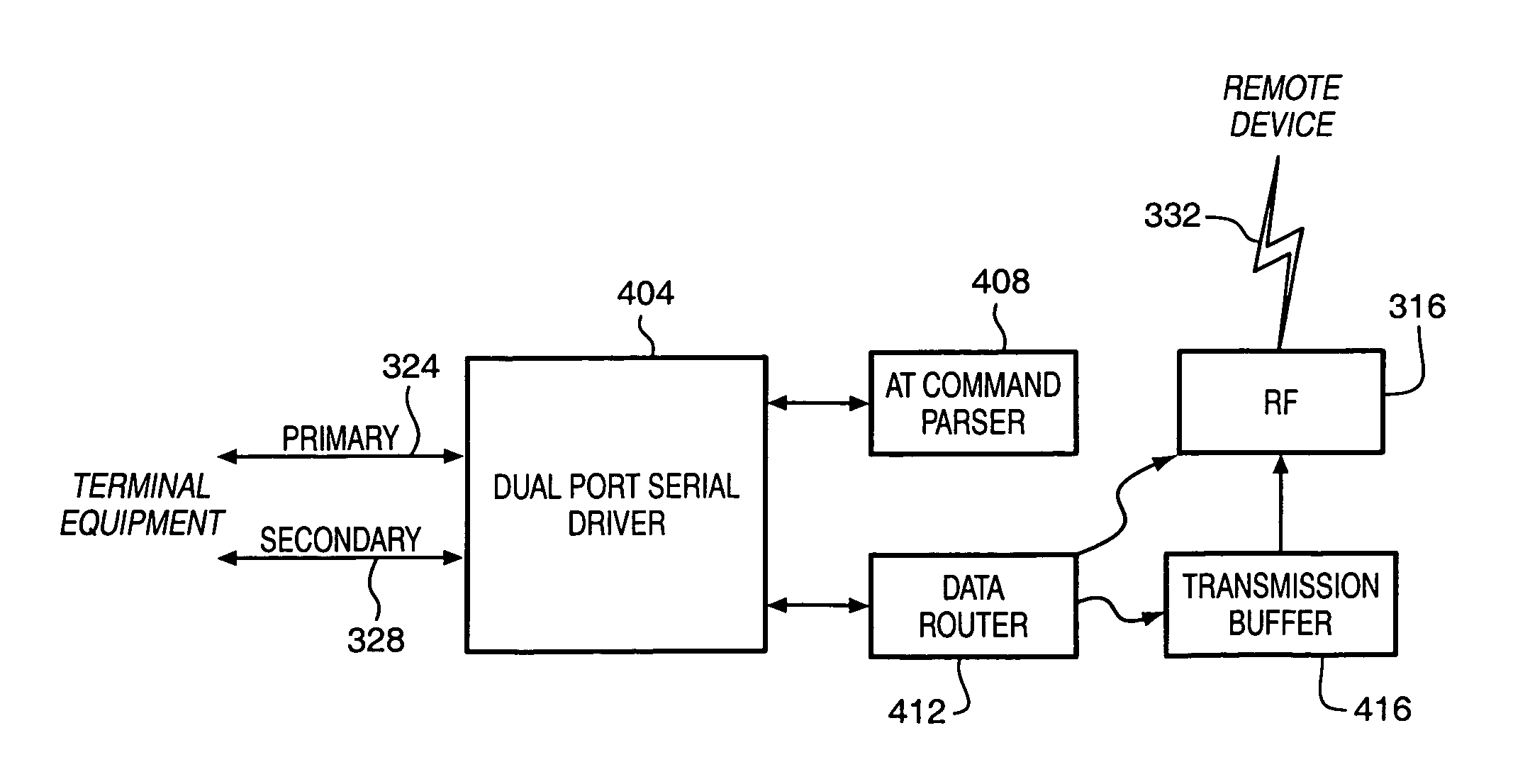
Dual port wireless modem for circuit switched and packet switched data transfer
InactiveCN1677963ANetwork traffic/resource managementHybrid switching systemsCircuit Switched DataModem device
A dual port external wireless modem is disclosed. According to one embodiment, the external wireless modem receives command and control information over a primary serial port, and real-time data over a secondary serial port. The primary serial port is further configured to receive packet switched data, such as short message service messages, while the secondary serial port is configured to receive circuit switched data. An RF transceiver in the wireless modem modulates data and control received over the respective serial ports, preferably using a GSM protocol stack. According to an embodiment, the circuit switched and packet switched data received at the wireless modem can be simultaneously transmitted by the RF transceiver without interrupting the circuit switched data transfer, thereby avoiding a context switch and a loss of throughput.
Owner:捷迅无线公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com