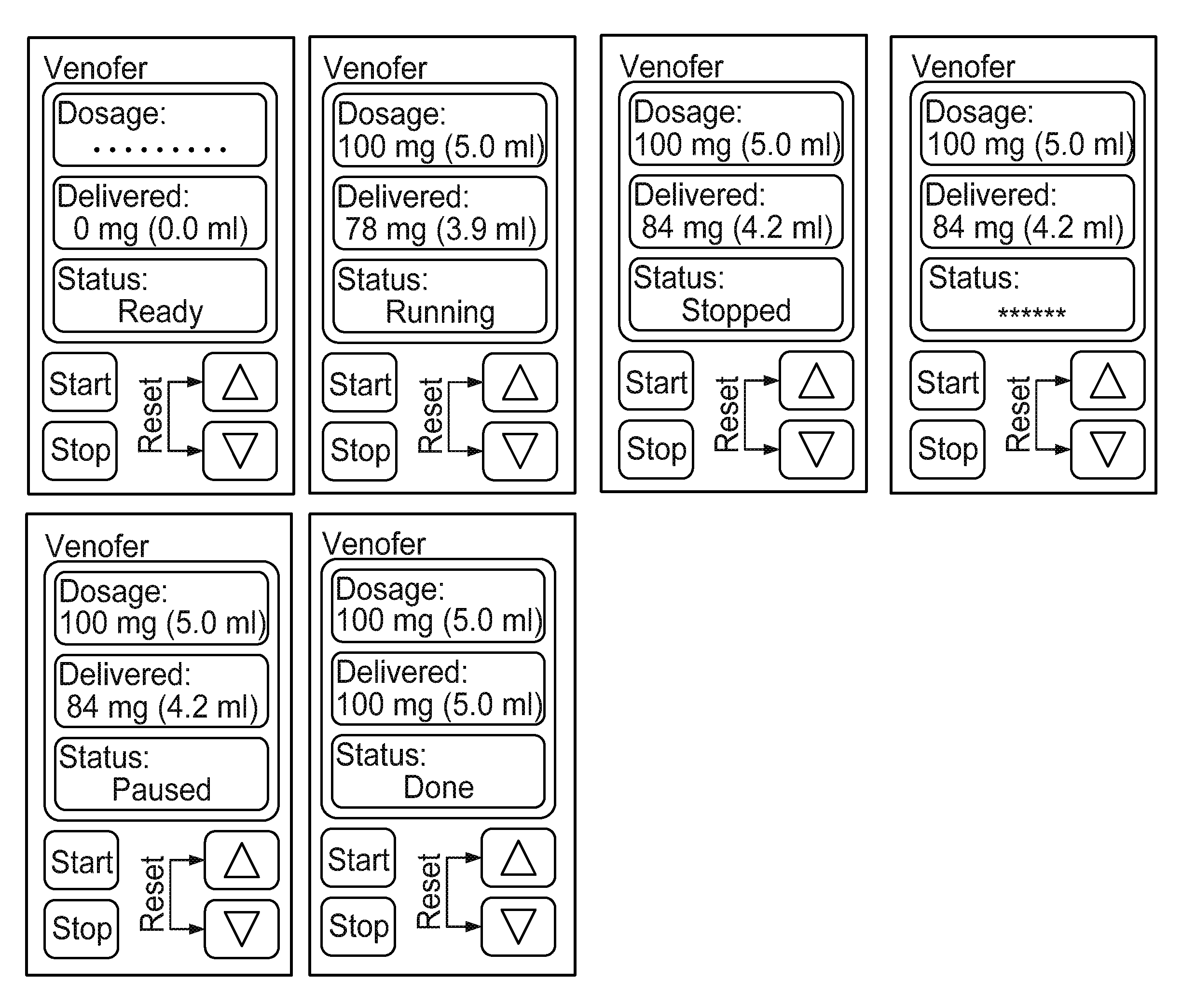
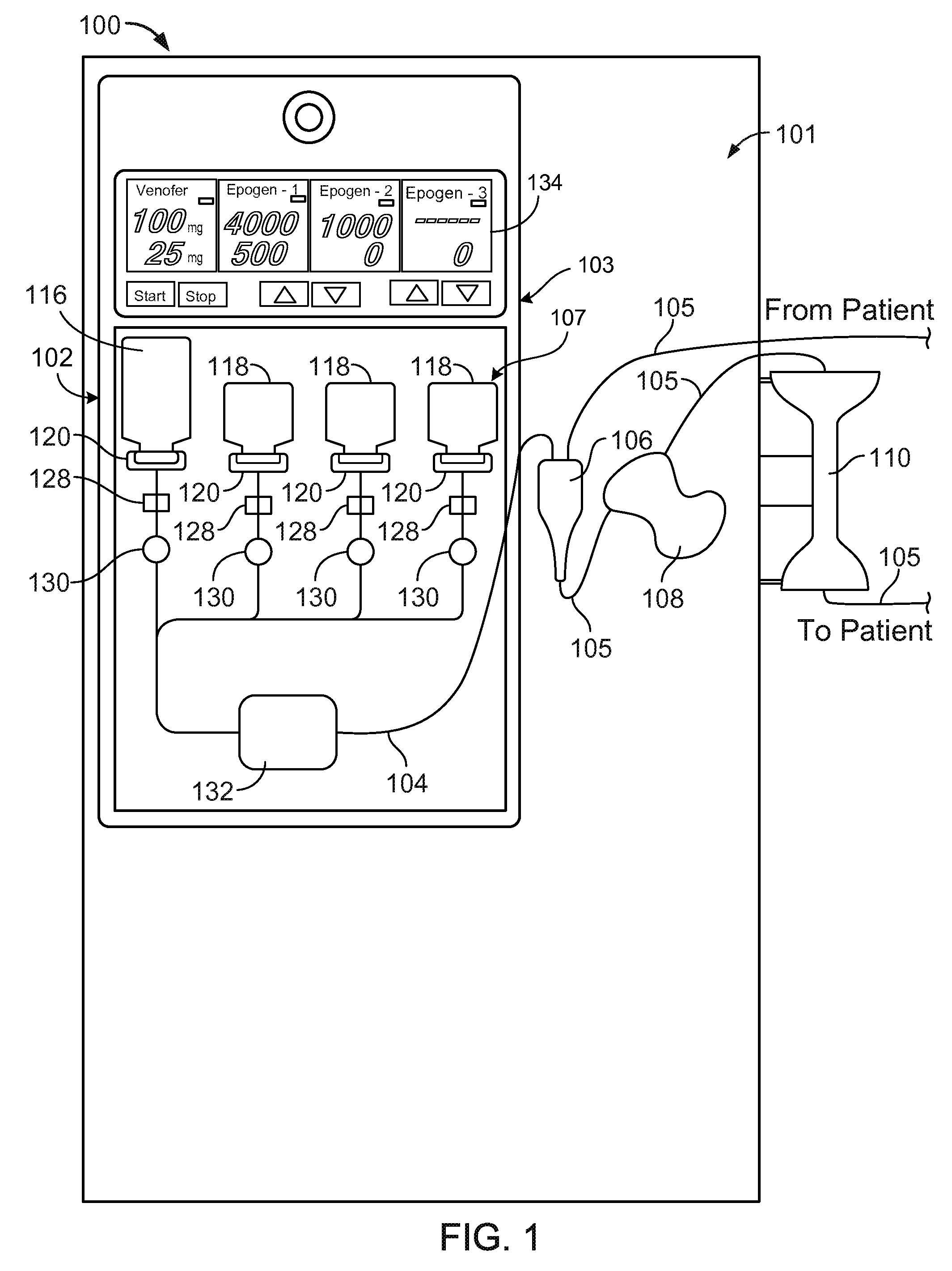
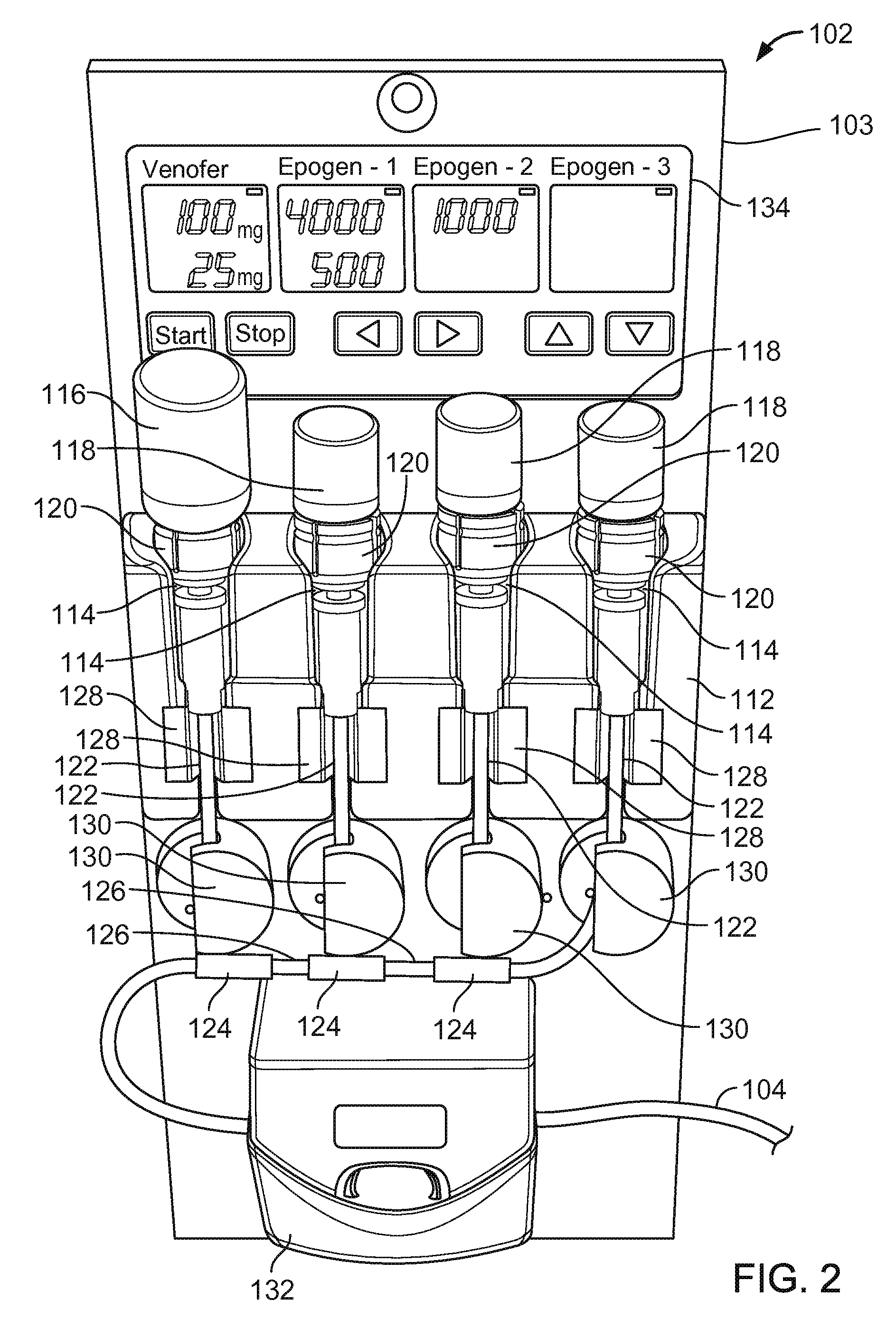
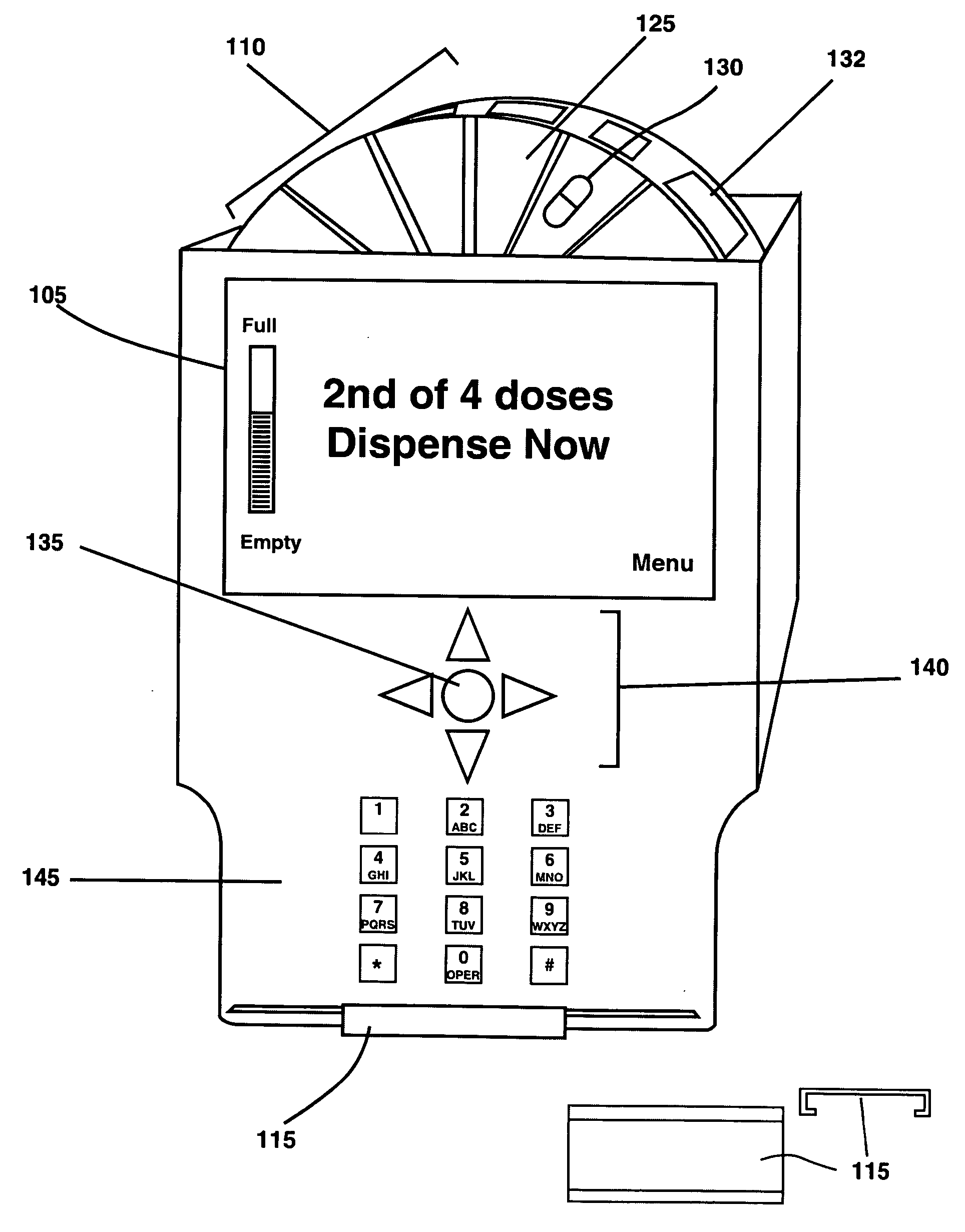
Patents
Literature
91 results about "Dosing schedules" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
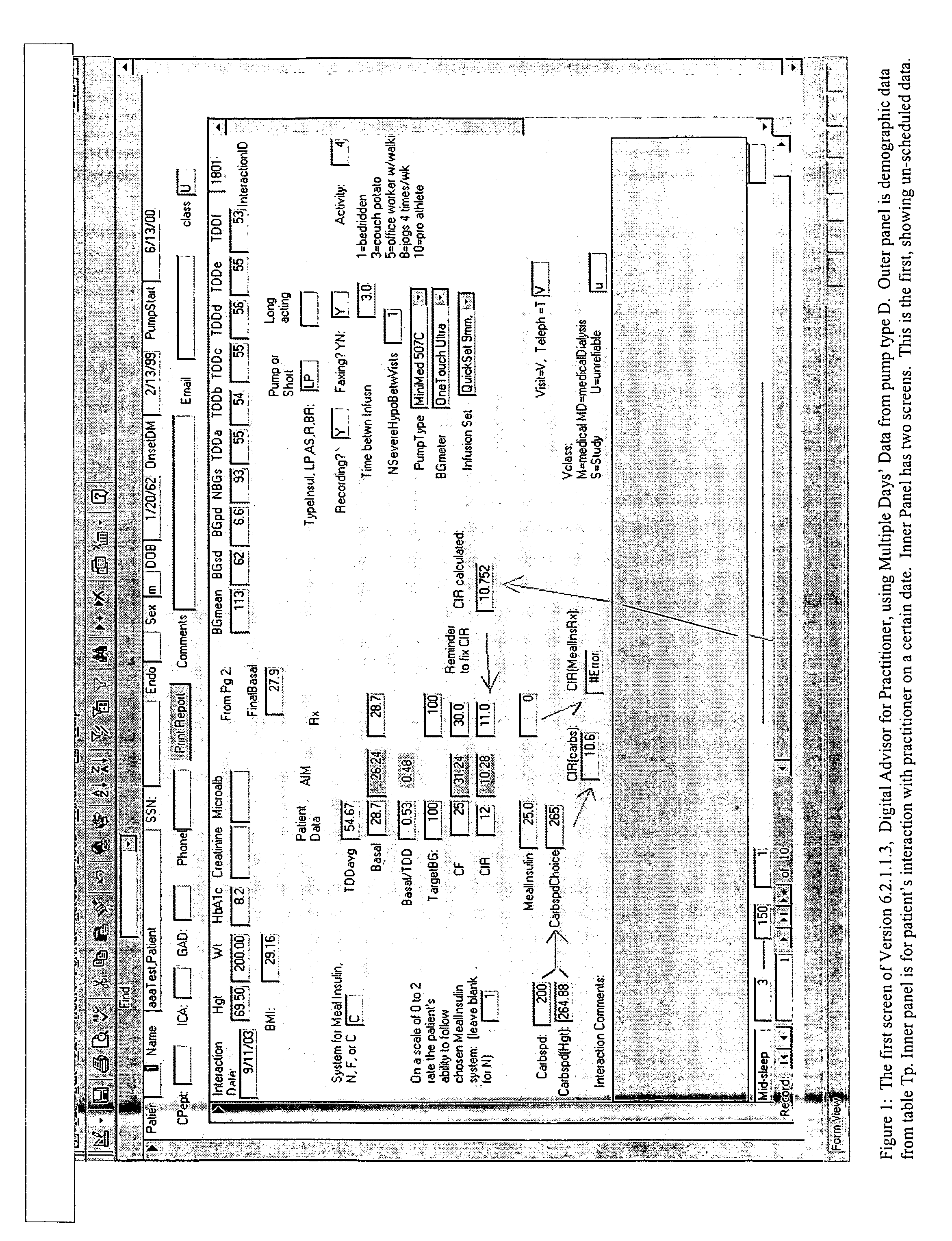
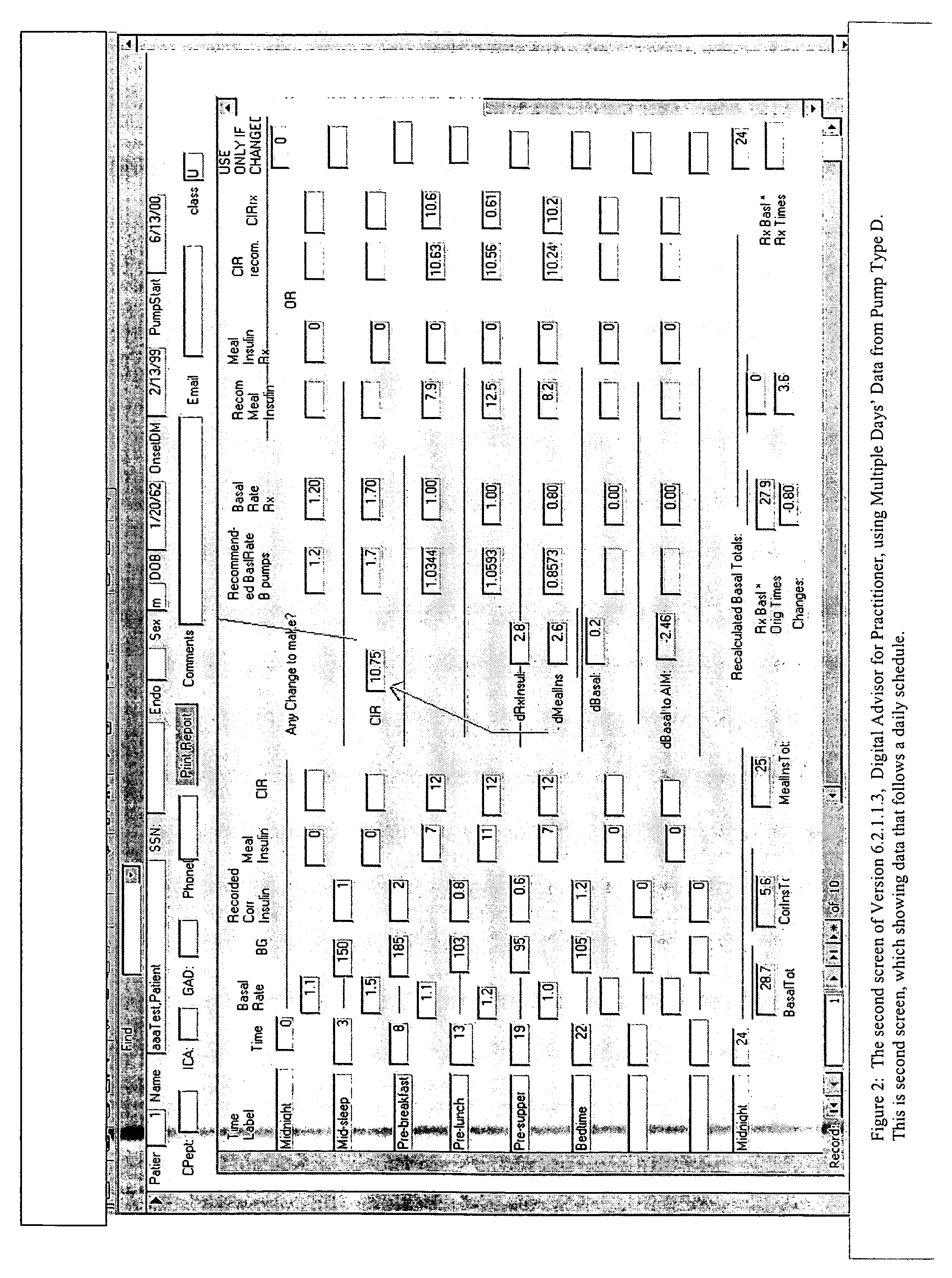
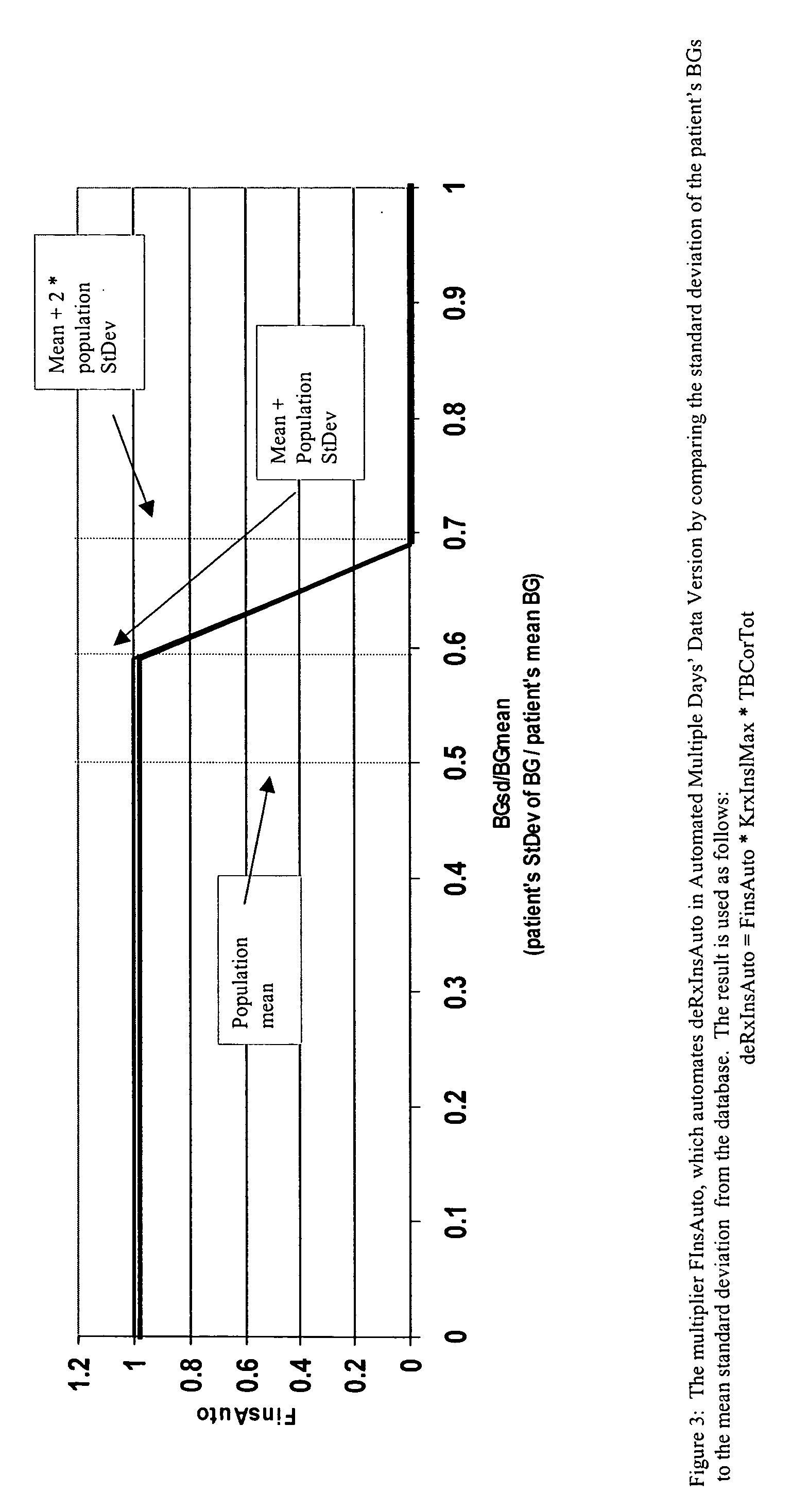
Method and system for determining insulin dosing schedules and carbohydrate-to-insulin ratios in diabetic patients
ActiveUS20050049179A1Prevent overshootPeptide/protein ingredientsAutomatic syringesInsulin regimenCompound (substance)
Method for digitally determining the daily insulin regimen for a diabetic patient. The invention divides the patient's day into adjustable time intervals containing basal insulin dosage rates and Carbohydrate-to-Insulin Ratio(s) (for determining meal insulin doses). The invention identifies the Corrective Insulin doses over a time interval as an “error” in the Prescription Insulin (Basal Insulin+Meal Insulin). Methods involve first estimating the change to one of these two components of Prescription Insulin, and then determining the change to the other by subtracting from the error. One method estimates Change in Meal Insulin distributed among intervals proportional to old Meal Insulin. Another method lumps After-Meal Corrective Insulin together with Meal Insulin. Another method splits the interval at the After-Meal Corrective Dose and determines Basal from Time-Boundary Corrective Dose. Data may be obtained from the previous day, and a small fraction of error applied, leading to asymptotic reduction of error. Data may be obtained from recent history, and a larger fraction of error applied by doctor or automatic method.
Owner:ASEKO
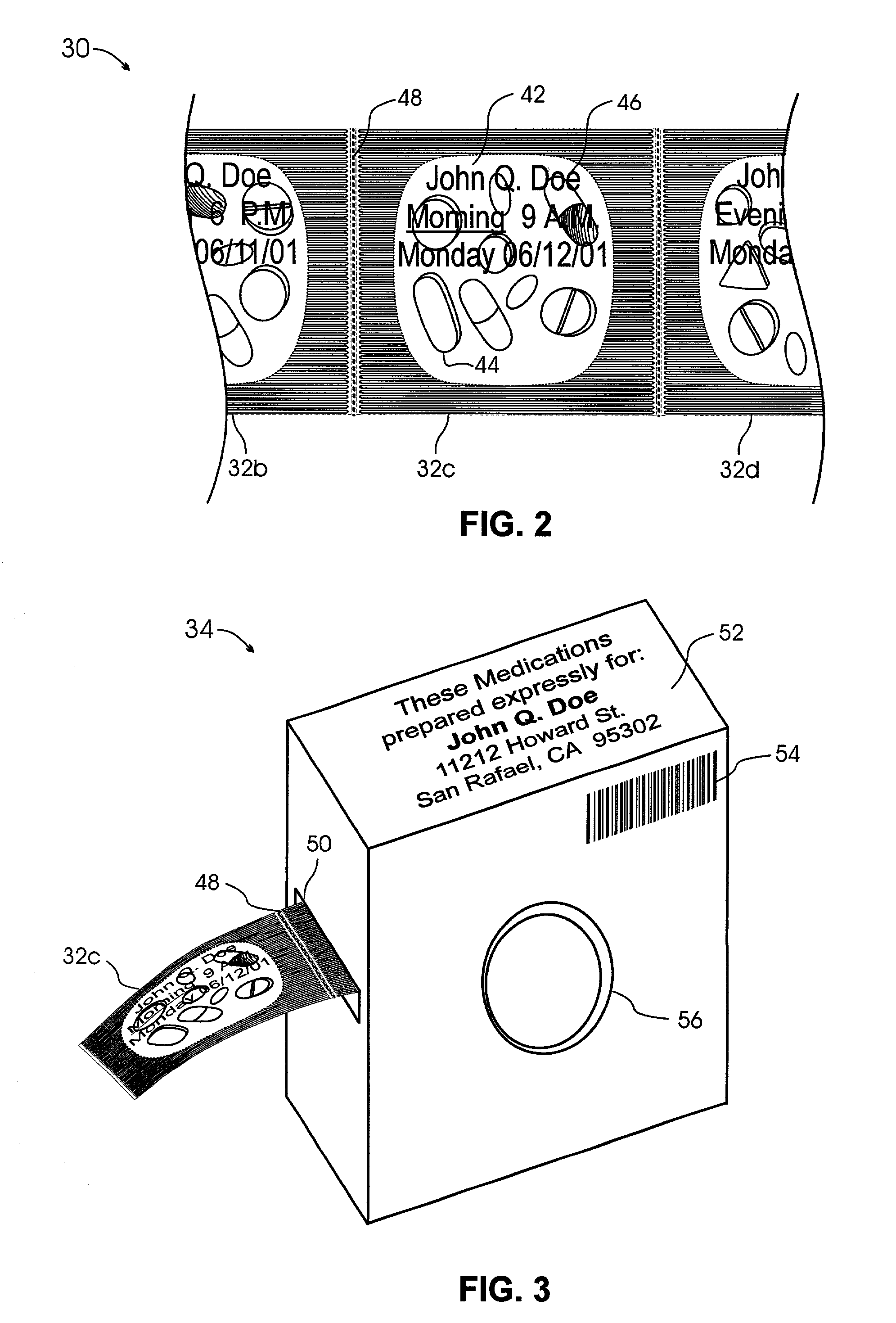
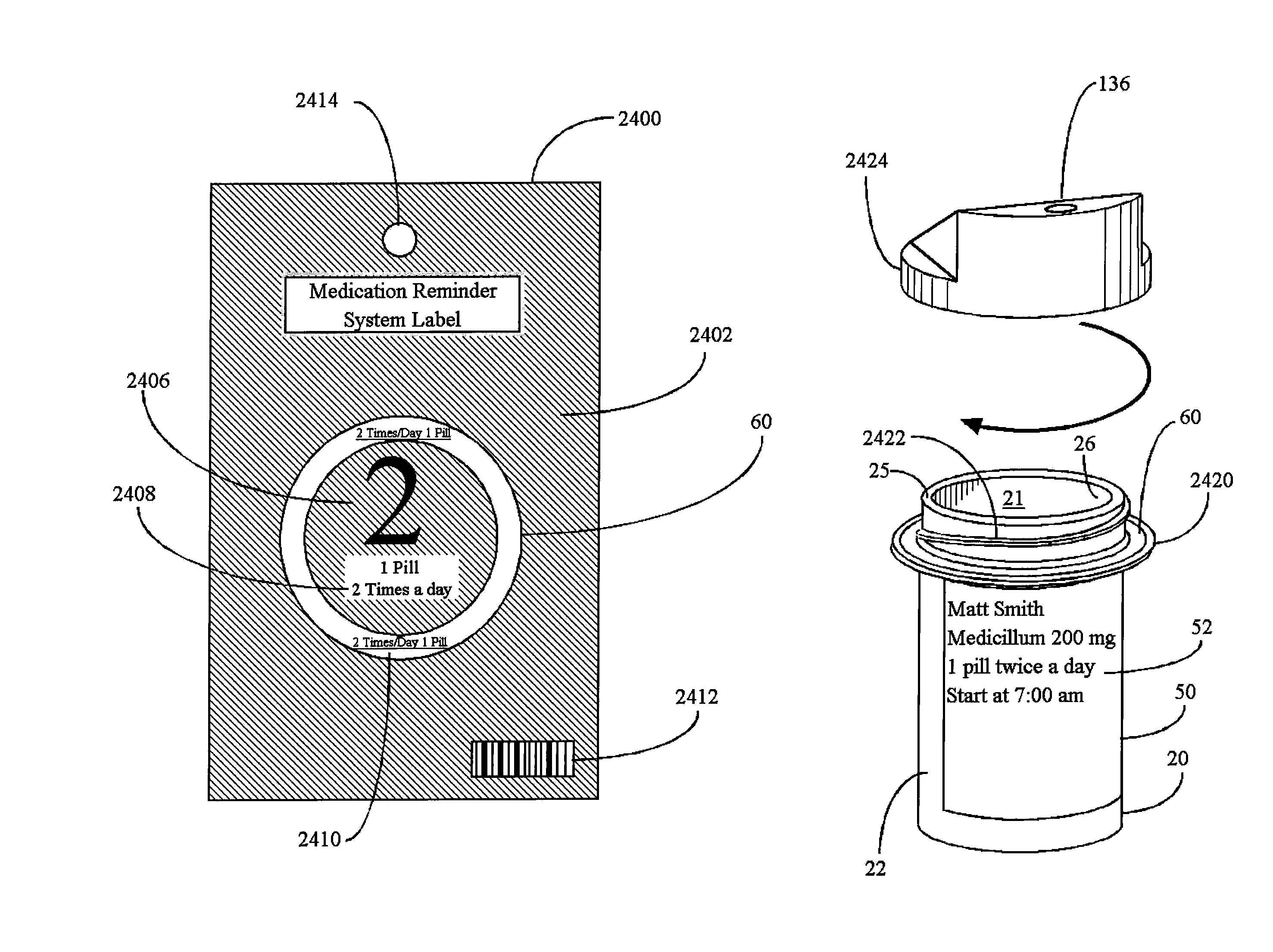
Interactive medication container labeling
InactiveUS20090294521A1Food safetyMechanical clocksDrug and medicationsMedication nameBiomedical engineering
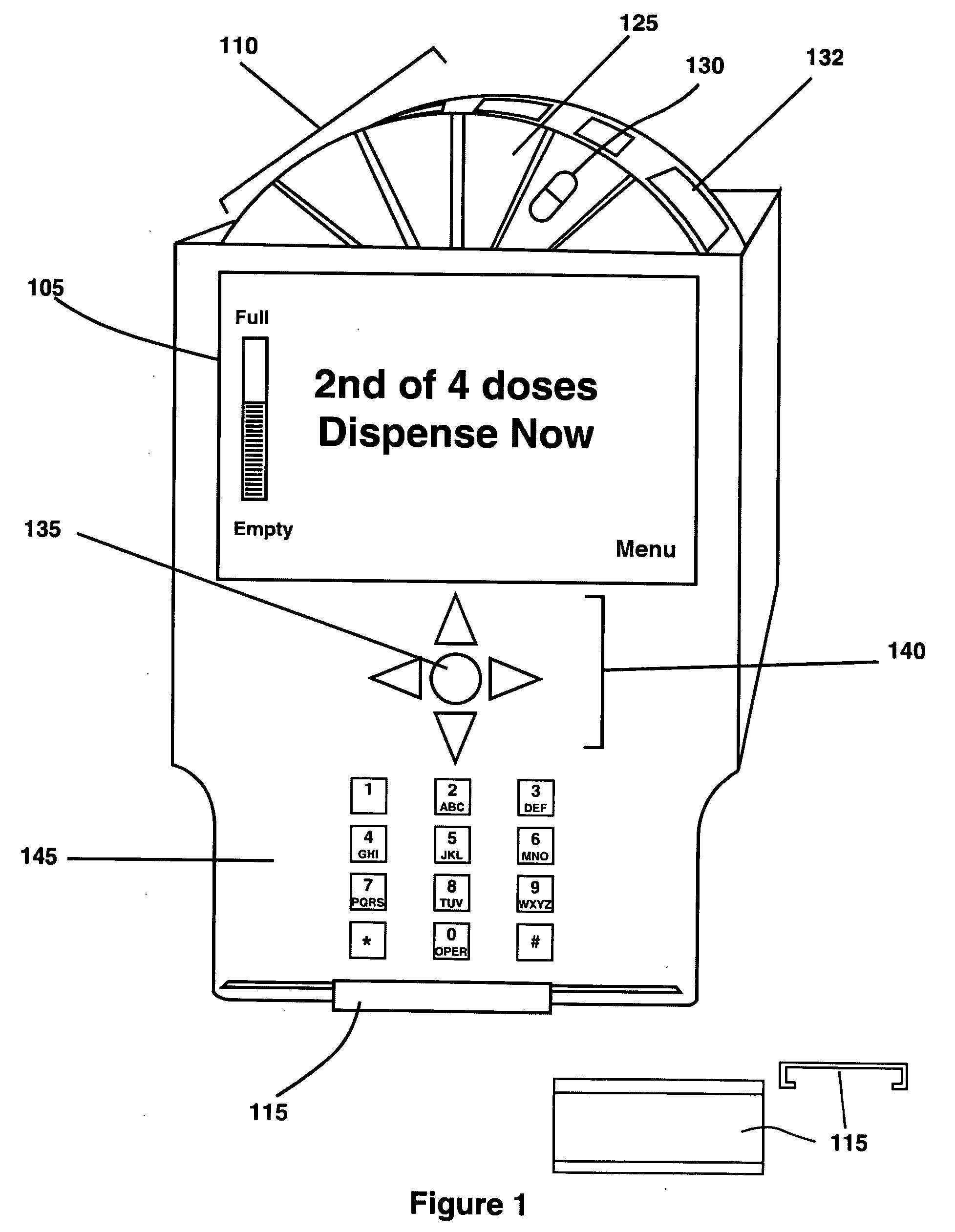
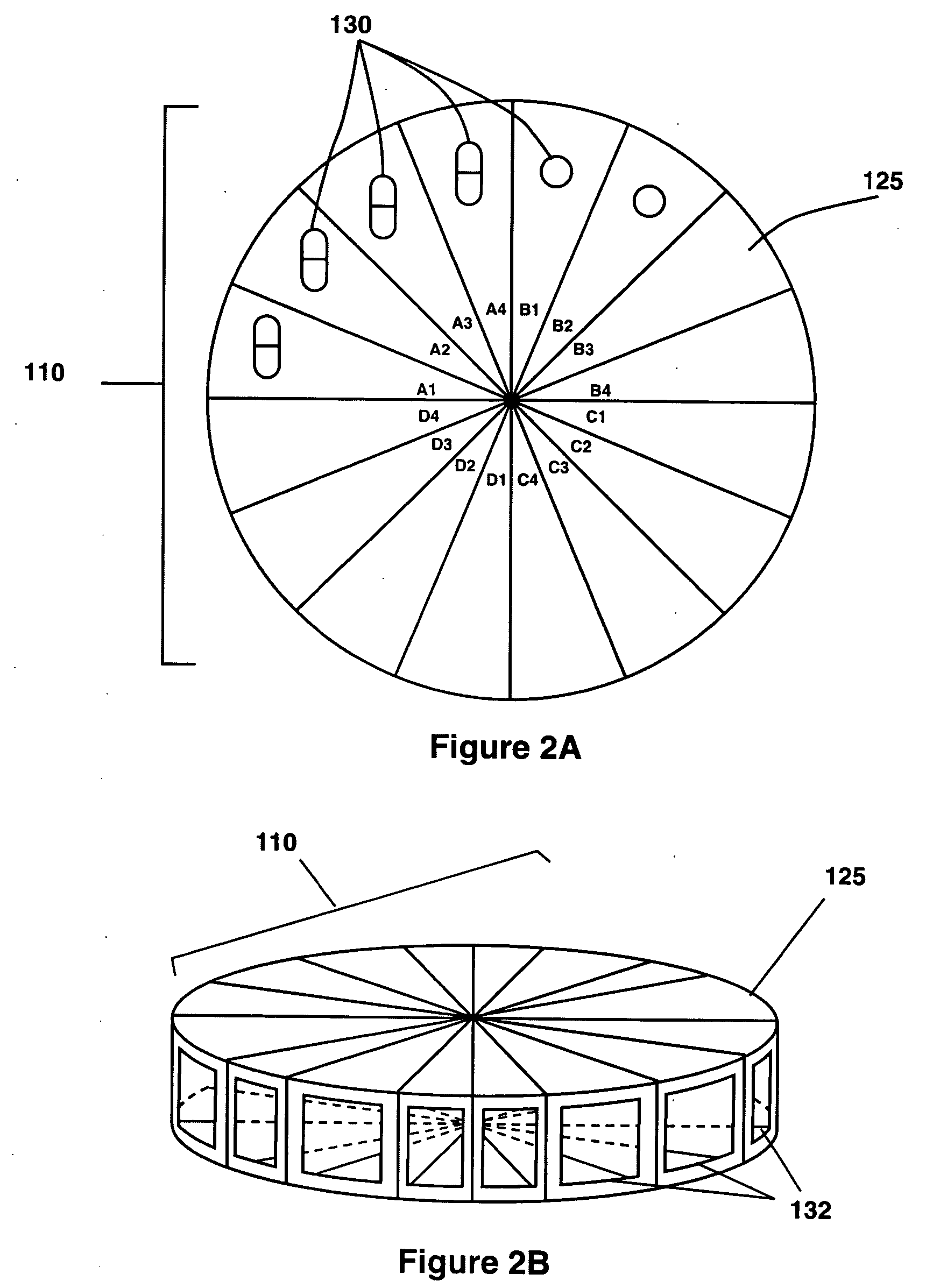
This invention relates to the dispensing, creation, and selecting of memory devices that are used with interactive medication containers, dispensers, reminders, or consoles that hold or otherwise organize one or more medication vials or containers. The memory device is attached or adhered to a medication container or vial and has information corresponding to medication and prescription information. The memory device can be prepared when a standard medication label is printed by a pharmacist and can be part of the standard printed label. In other instances the memory device is separate from the medication label. When separate, the memory device has a printed section that identifies the dosing schedule or medication name that corresponds to the reminder schedule the memory device is associated with. The pharmacist or the customer / patient can match the text printed on the memory device with the text of the medical container label to ensure the memory device is only attached to the correct medication container.
Owner:SOUTHWEST TECH INNOVATIONS
System and method for providing temporal patient dosing
InactiveUS20030200726A1Improve securityImprove reliabilityDrug and medicationsCoin-freed apparatusPersonalizationTime table
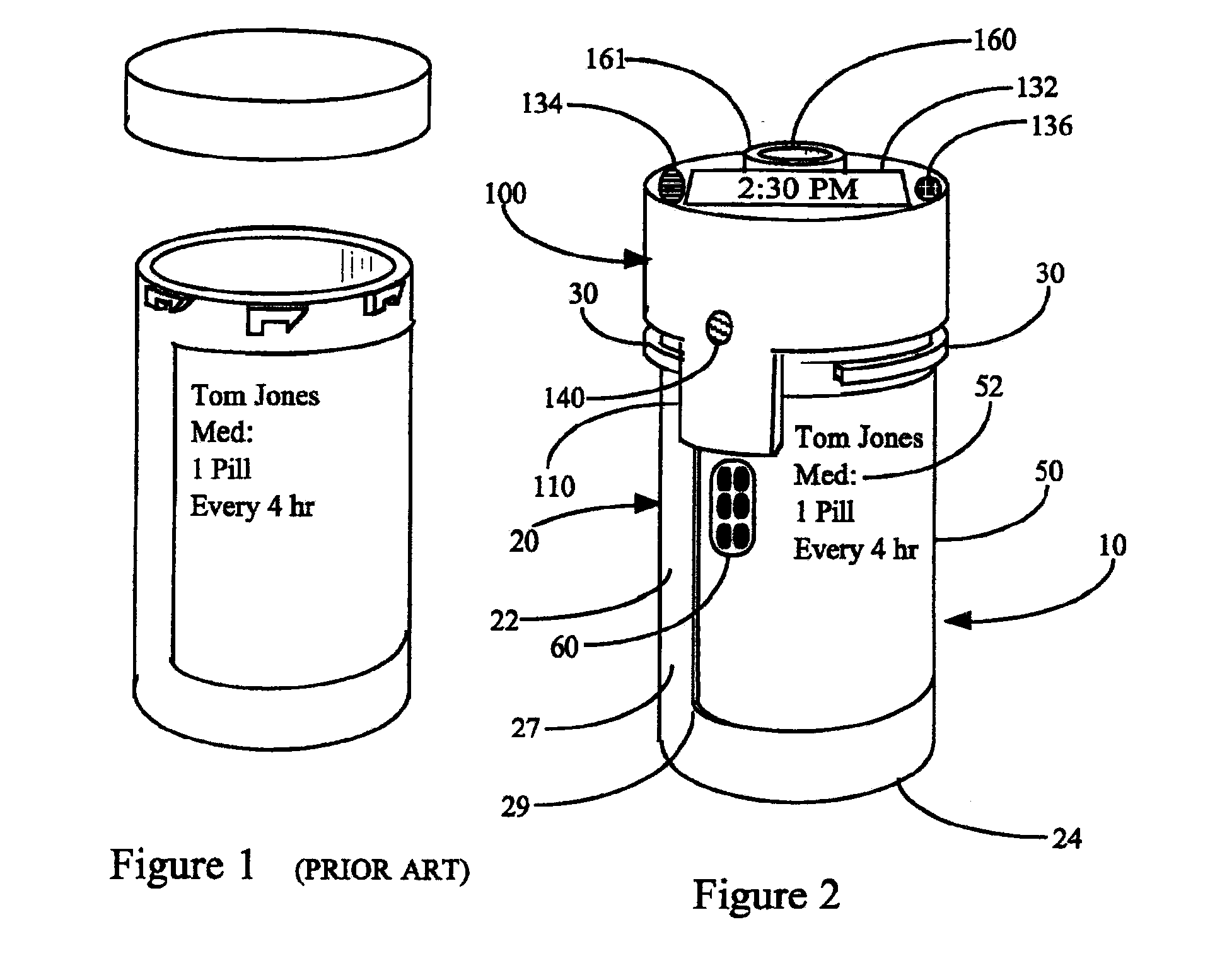
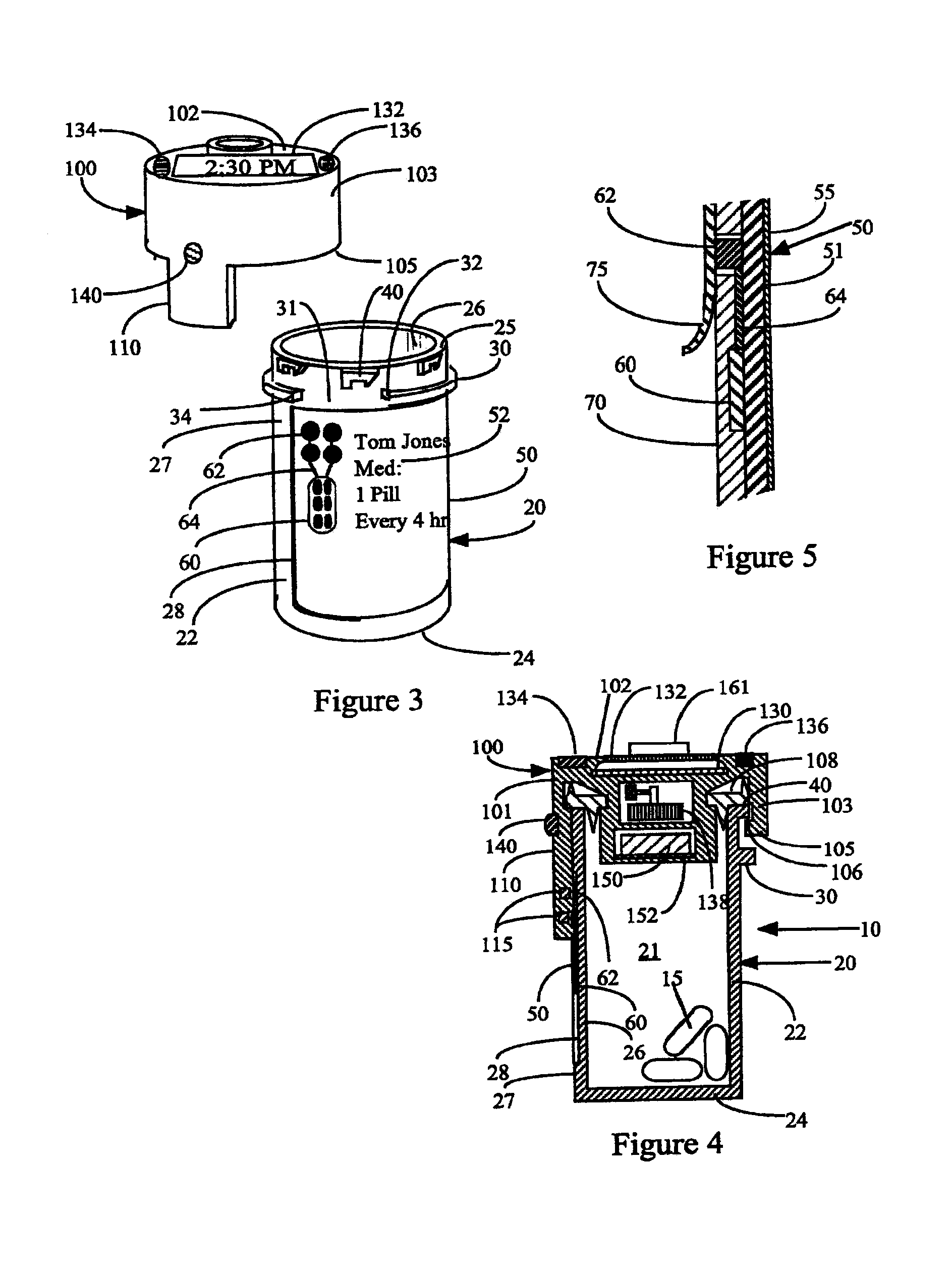
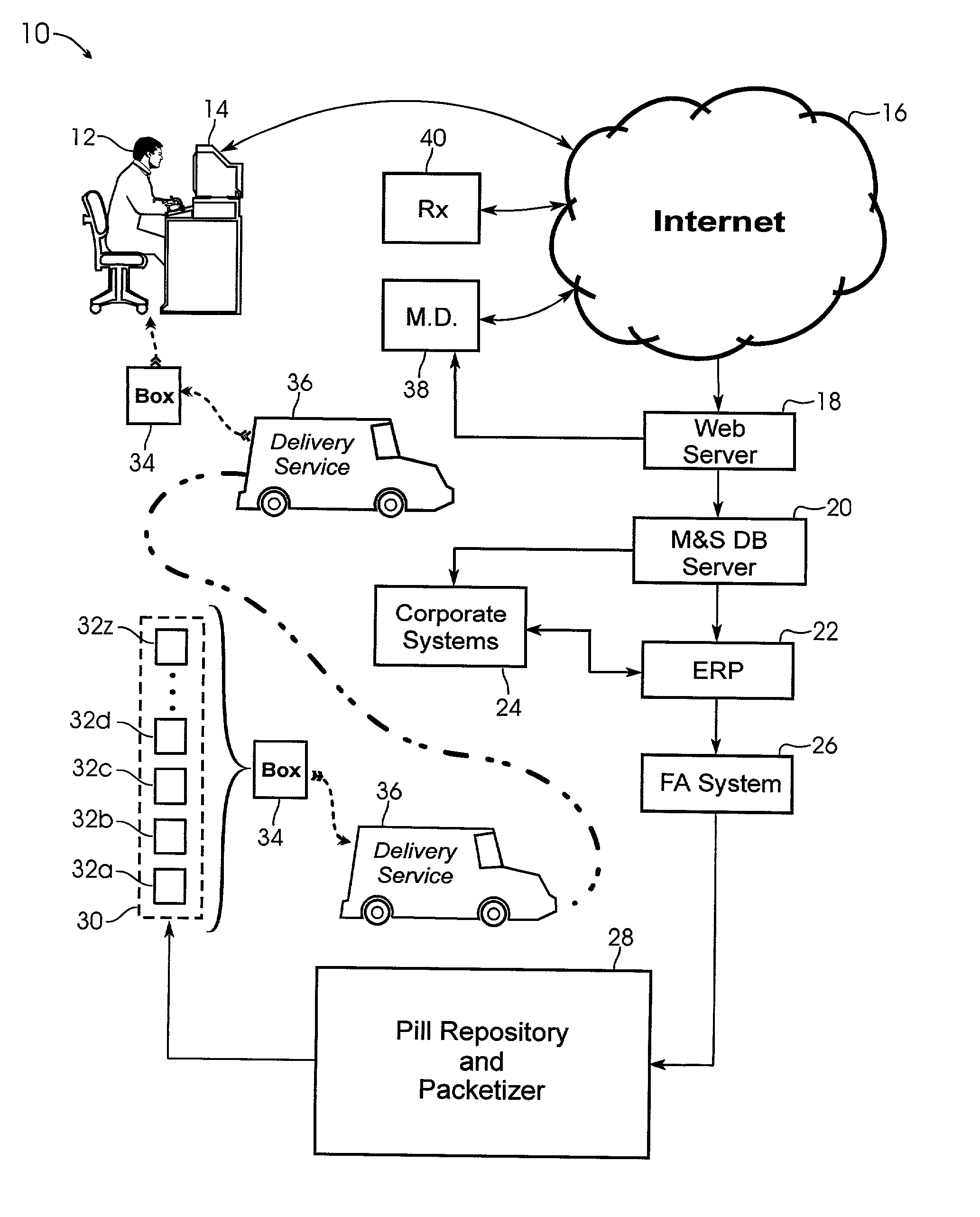
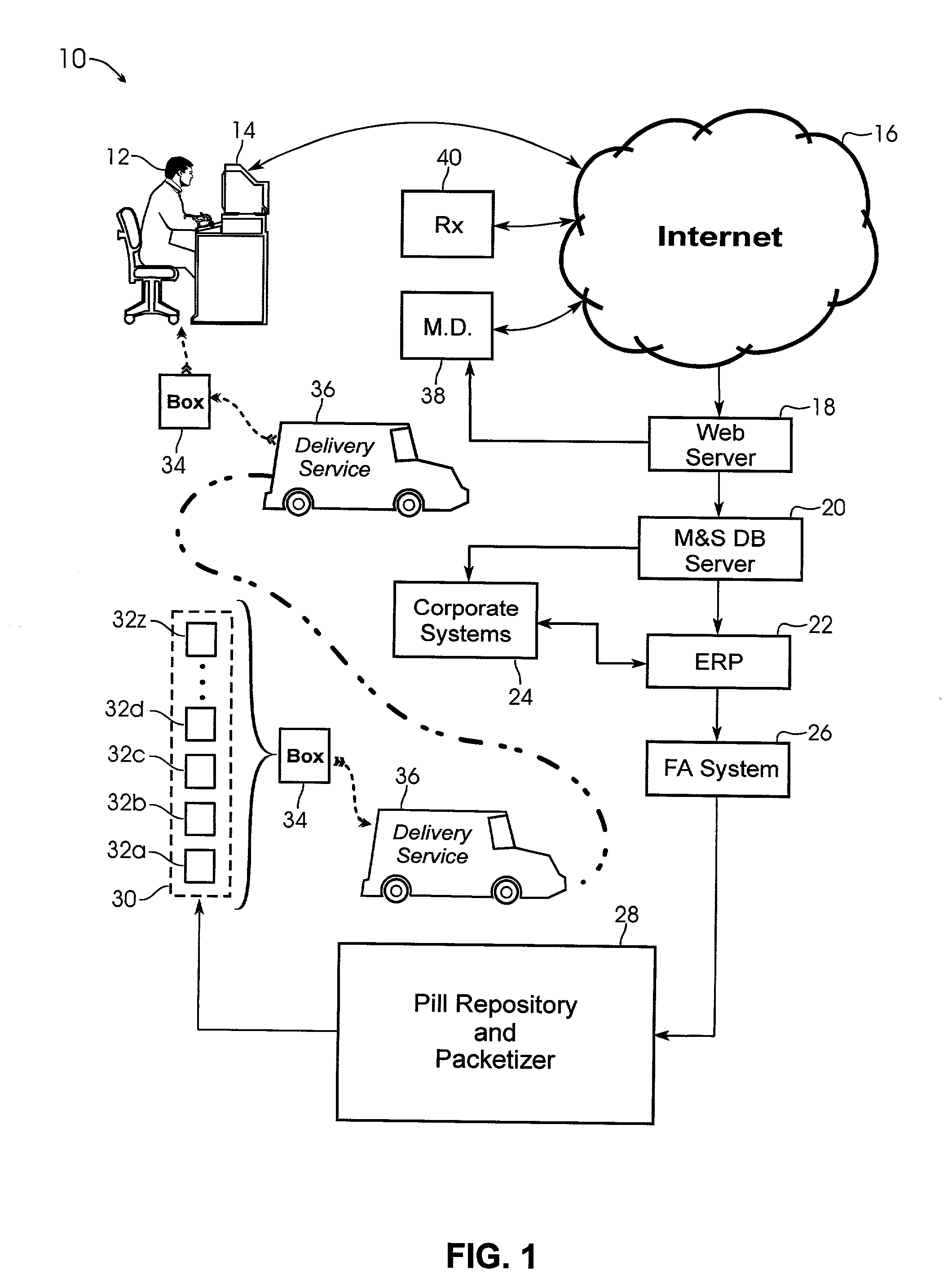
A system and method for creating a series of individualized custom doses for a consumer. The individualized doses being delivered in a package or packages, such that each individualized custom dose, comprising a plurality of medications and / or supplements, is individually separable from the remaining doses within the series. By way of example, and not of limitation, a system is described having a web based front-end interface within which the user may establish a dosing schedule, select supplements and / or medications (MS) from an MS database, elect which MS are to be included in each dose, and communicate the order to be processed by a packetizing system. The packetizing system utilizes a conveyance device which interconnects a series of pill dispensing bins. The conveyance device has compartments for collecting a series of doses which are then packetized and shipped for use by the consumer.
Owner:RAST RODGER H
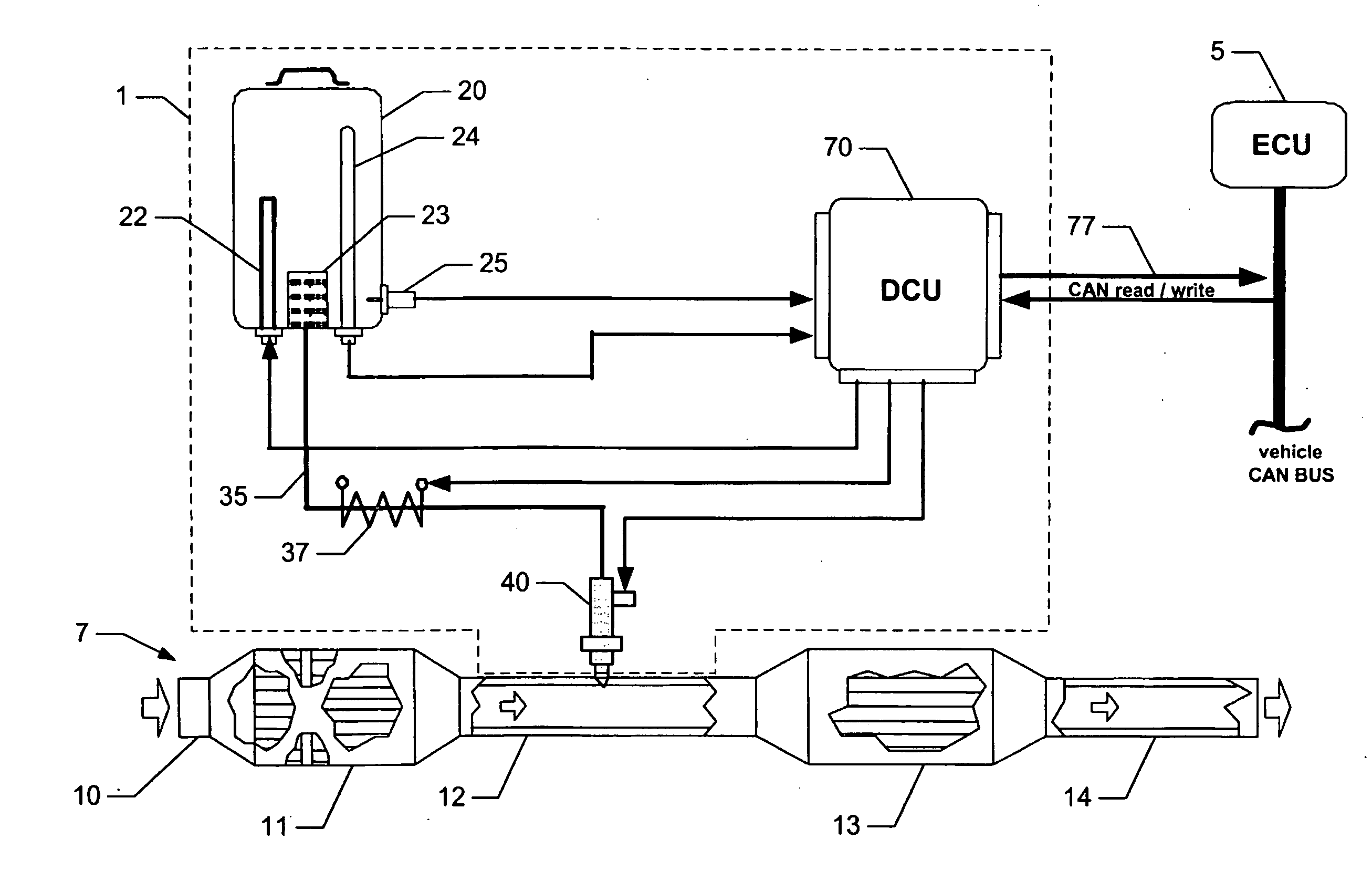
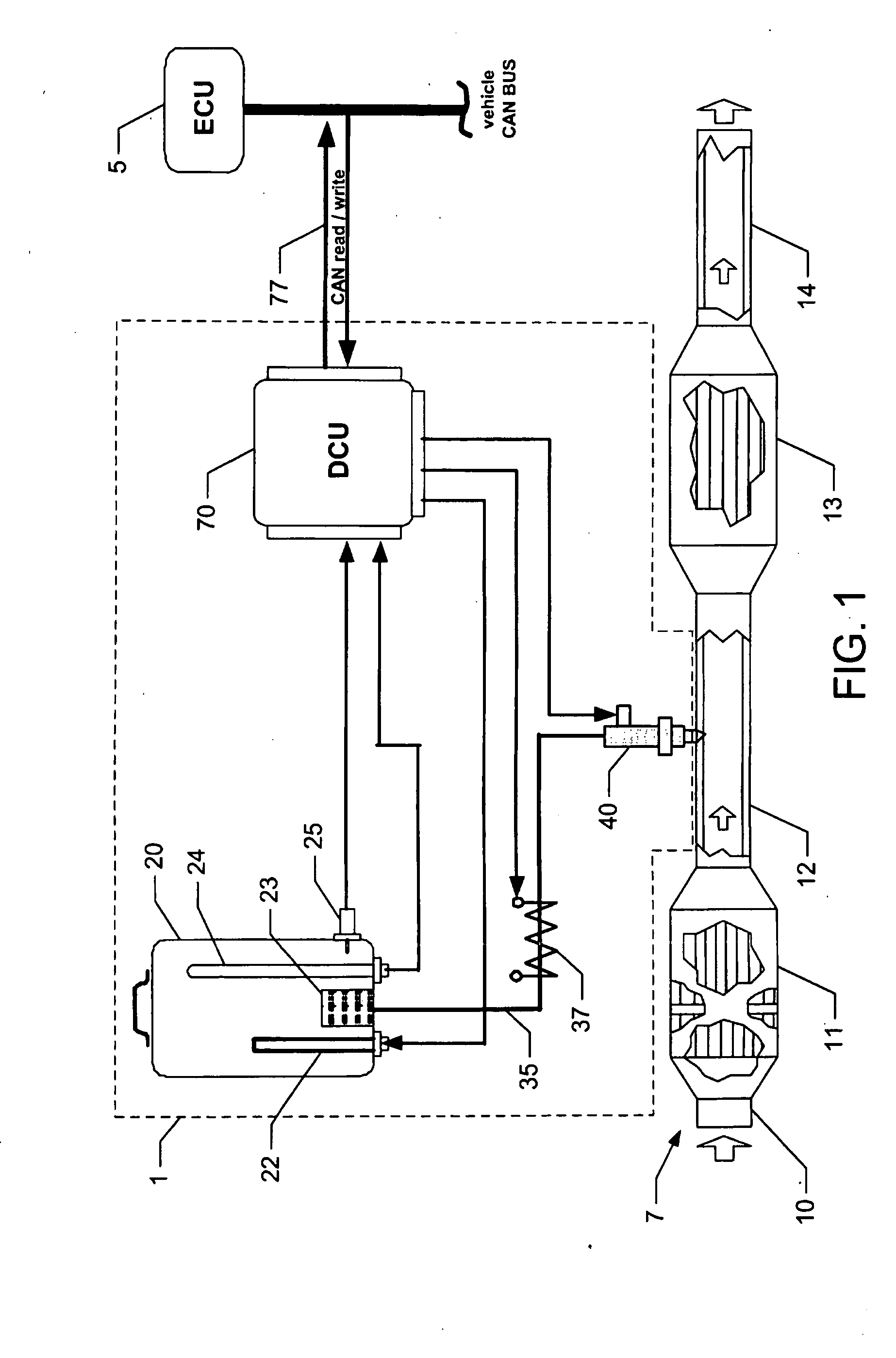
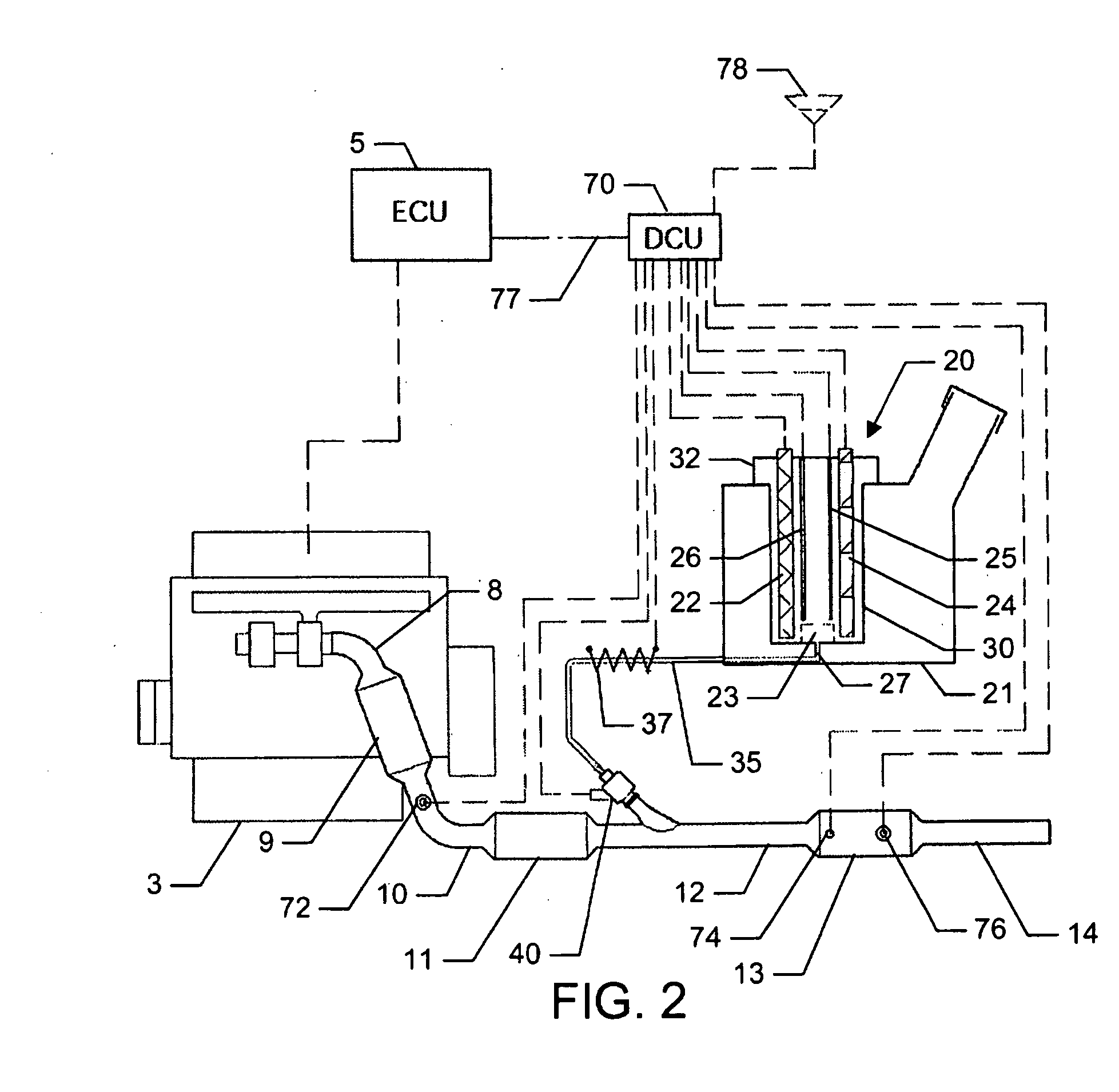
Reagent dosing system and method of dosing reagent
InactiveUS20090301067A1Well mixedInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusEngineeringInternal combustion engine
A method of dosing a reagent into an exhaust gas stream of an internal combustion engine having an SCR catalyst, the method comprising injecting reagent from a reagent tank into the exhaust gas stream at a position upstream of the SCR catalyst using a reagent injector in accordance with a first dosing schedule in order to remediate a predetermined proportion of NOx in the exhaust gas stream, the first dosing schedule being associated with a first range of engine operating conditions; and injecting reagent from the reagent tank into the exhaust gas stream at a position upstream of the SCR catalyst using a reagent injector in accordance with a second dosing schedule in order to enable heat transfer between the reagent injector and said injected reagent, the second dosing schedule being associated with a second range of engine operating conditions.Dosing in accordance with said first or said second dosing schedule is carried out in dependence on whether engine operating conditions lie within said first or said second range of engine operating conditions, and the proportion of NOx in the exhaust gas stream which is remediated by dosing using said second dosing schedule is less than said predetermined portion. A reagent dosing system is also provided for dosing a reagent into the exhaust gas stream of an internal combustion engine, comprising a reagent tank for storing a supply of reagent, an injector module comprising an atomising dispenser and a positive-displacement metering pump which draws reagent from the reagent tank and delivers it to the dispenser a supply line coupling the reagent tank to the injector module, and a dosing control unit operable to control the injector module to inject reagent into the exhaust gas stream. A priming pump is provided to urge reagent along the supply line toward the injector module under selected conditions.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Interactive medication container labeling
This invention relates to the dispensing, creation, and selecting of memory devices that are used with interactive medication containers, dispensers, reminders, or consoles that hold or otherwise organize one or more medication vials or containers. The memory device is attached or adhered to a medication container or vial and has information corresponding to medication and prescription information. The memory device can be prepared when a standard medication label is printed by a pharmacist and can be part of the standard printed label. In other instances the memory device is separate from the medication label. When separate, the memory device has a printed section that identifies the dosing schedule or medication name that corresponds to the reminder schedule the memory device is associated with. The pharmacist or the customer / patient can match the text printed on the memory device with the text of the medical container label to ensure the memory device is only attached to the correct medication container.
Owner:SOUTHWEST TECH INNOVATIONS
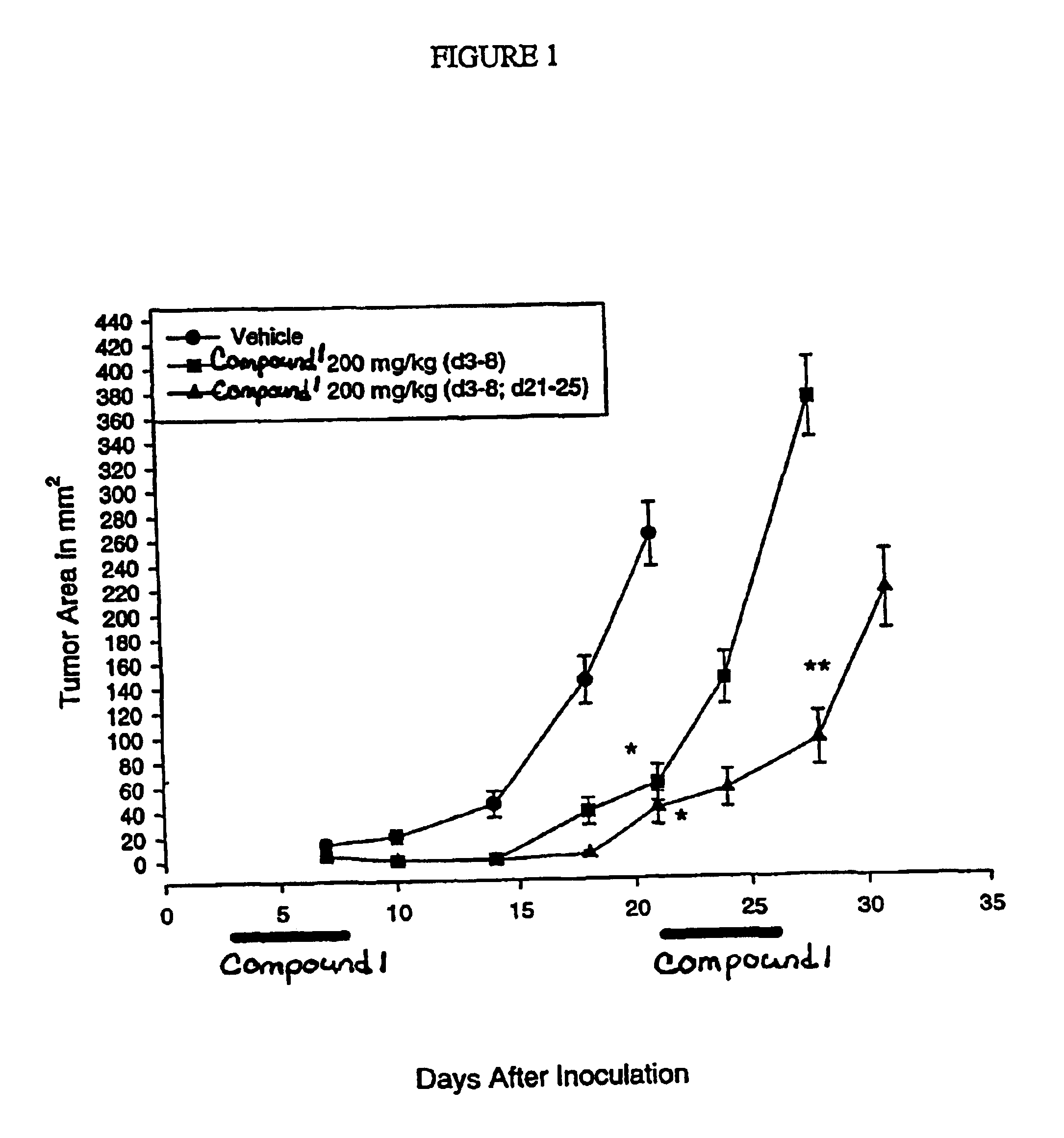
Dosing regimen
InactiveUS6838467B2Inhibit tumor growthSustained antitumor effectBiocideOrganic chemistryDosing regimenFarnesyl Transferase Inhibitor
This invention relates to a method of treatment and dosing regimen for treating mammalian tumors by the discontinuous administration of a farnesyl transferase inhibitor over an abbreviated one to five day dosing schedule.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Methods of treating chronic disorders with complement inhibitors
ActiveUS20140371133A1Organic active ingredientsSenses disorderObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesDisease cause
In some aspects, the invention provides methods of treating a subject in need of treatment for a chronic complement-mediated disorder. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of treating a subject in need of treatment for a Th17-associated disorder. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of treating a subject in need of treatment for a chronic respiratory system disorder. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of administering a complement inhibitor to a subject. In some embodiments, a method of treating a subject comprises administering multiple doses of a complement inhibitor to the subject according to a dosing schedule that leverages the prolonged effect of complement inhibition in chronic respiratory disorders. In some embodiments, a subject has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In some embodiments, a subject has asthma.
Owner:APELLIS PHARMA
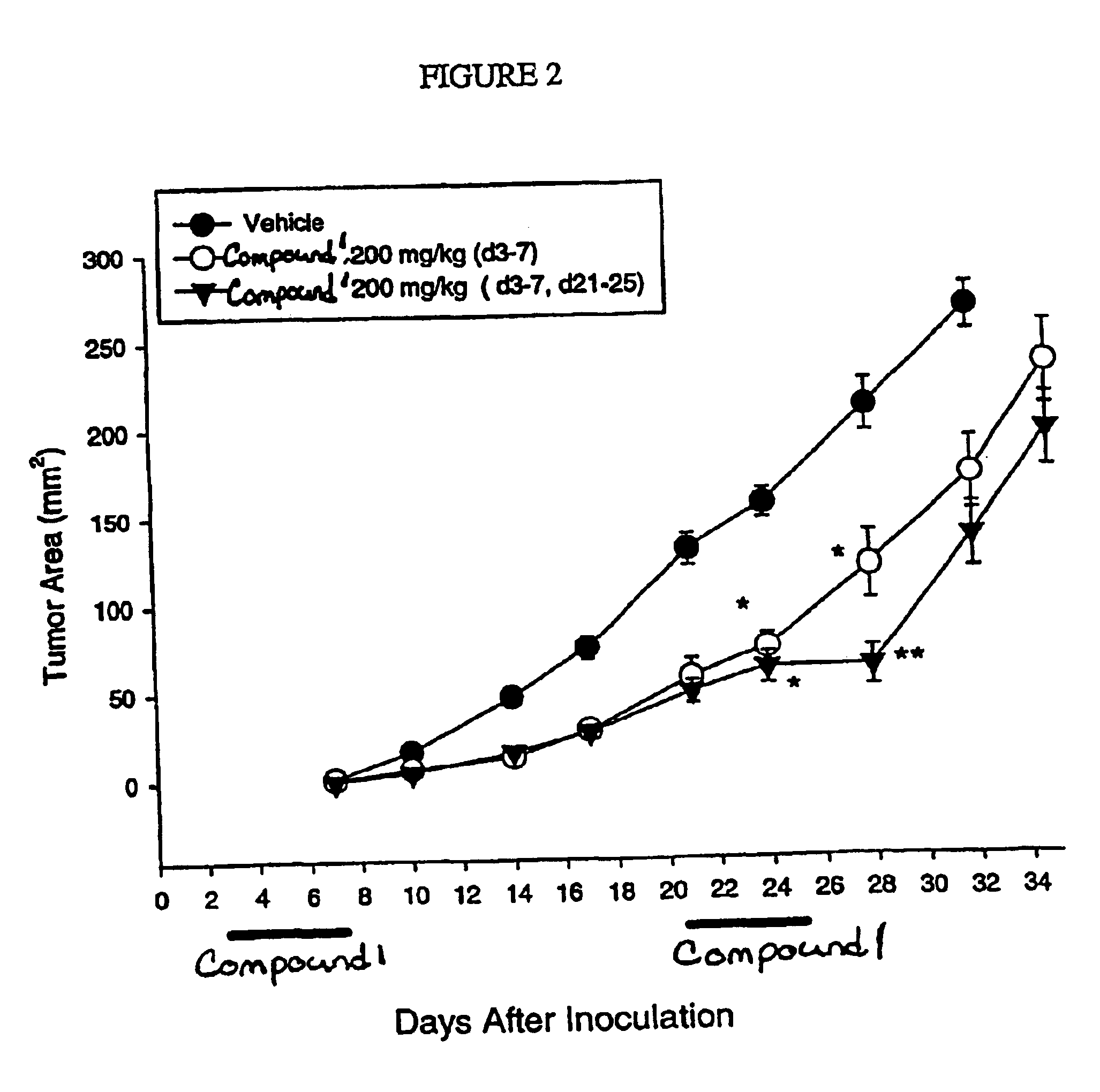
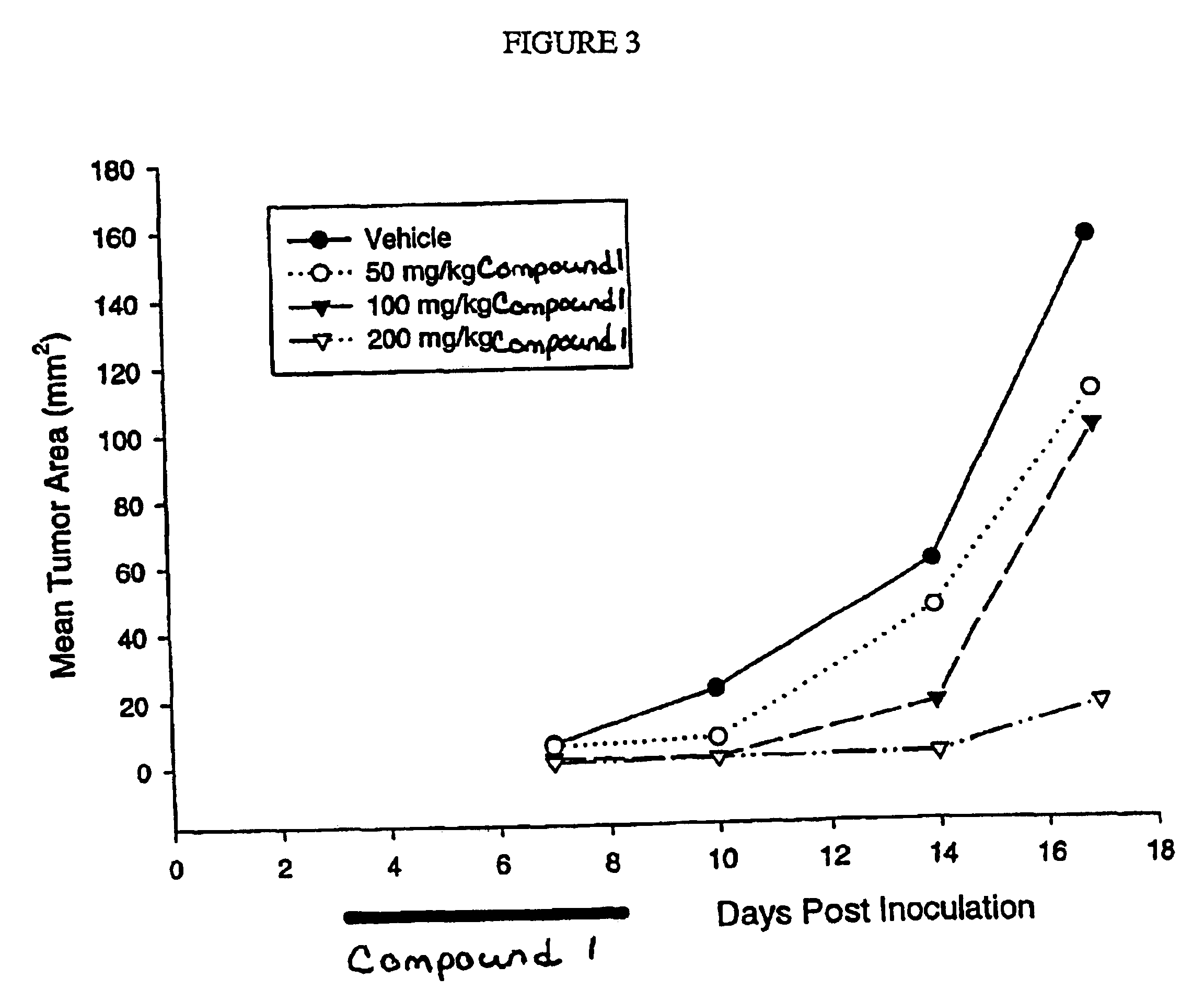
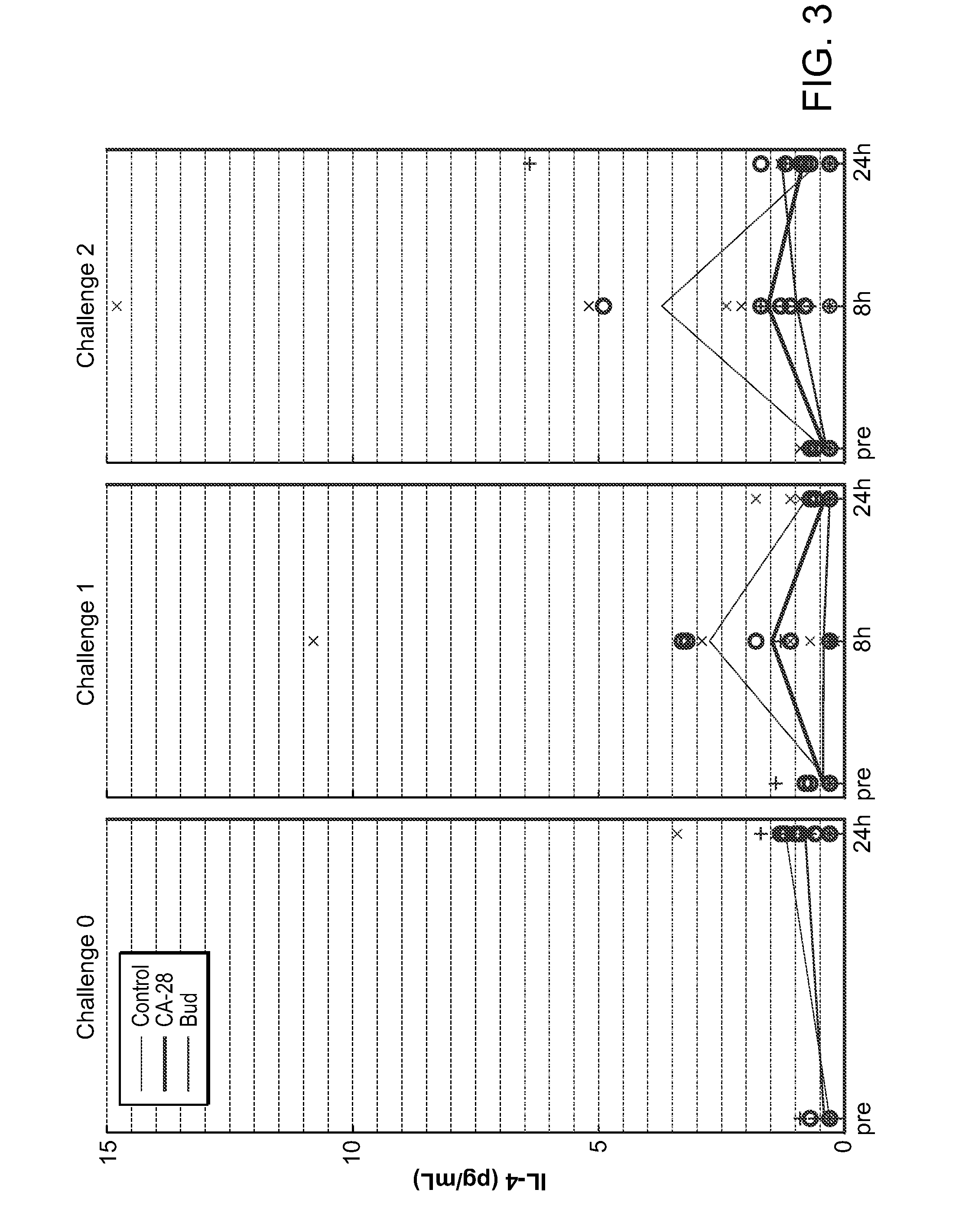
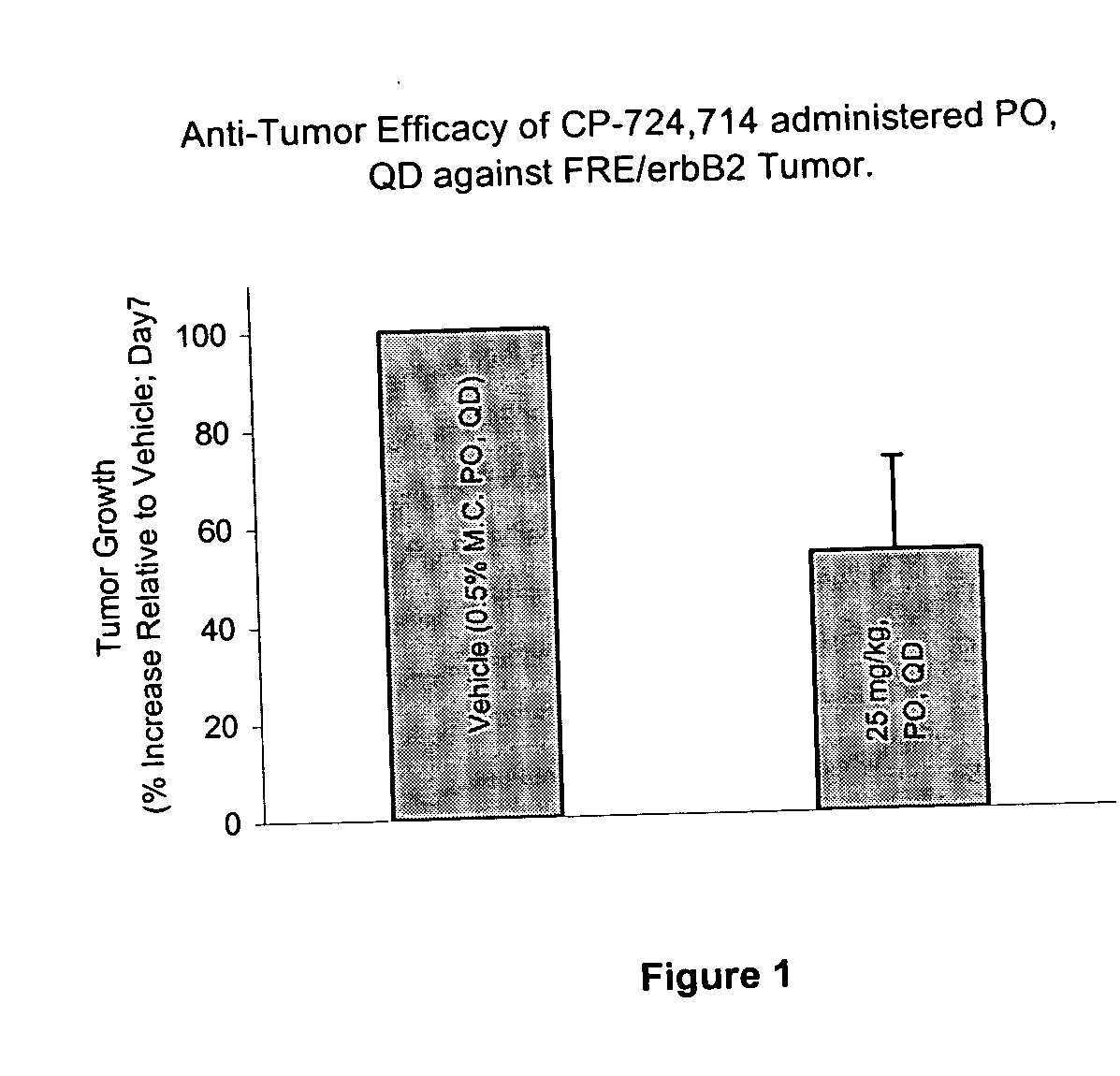
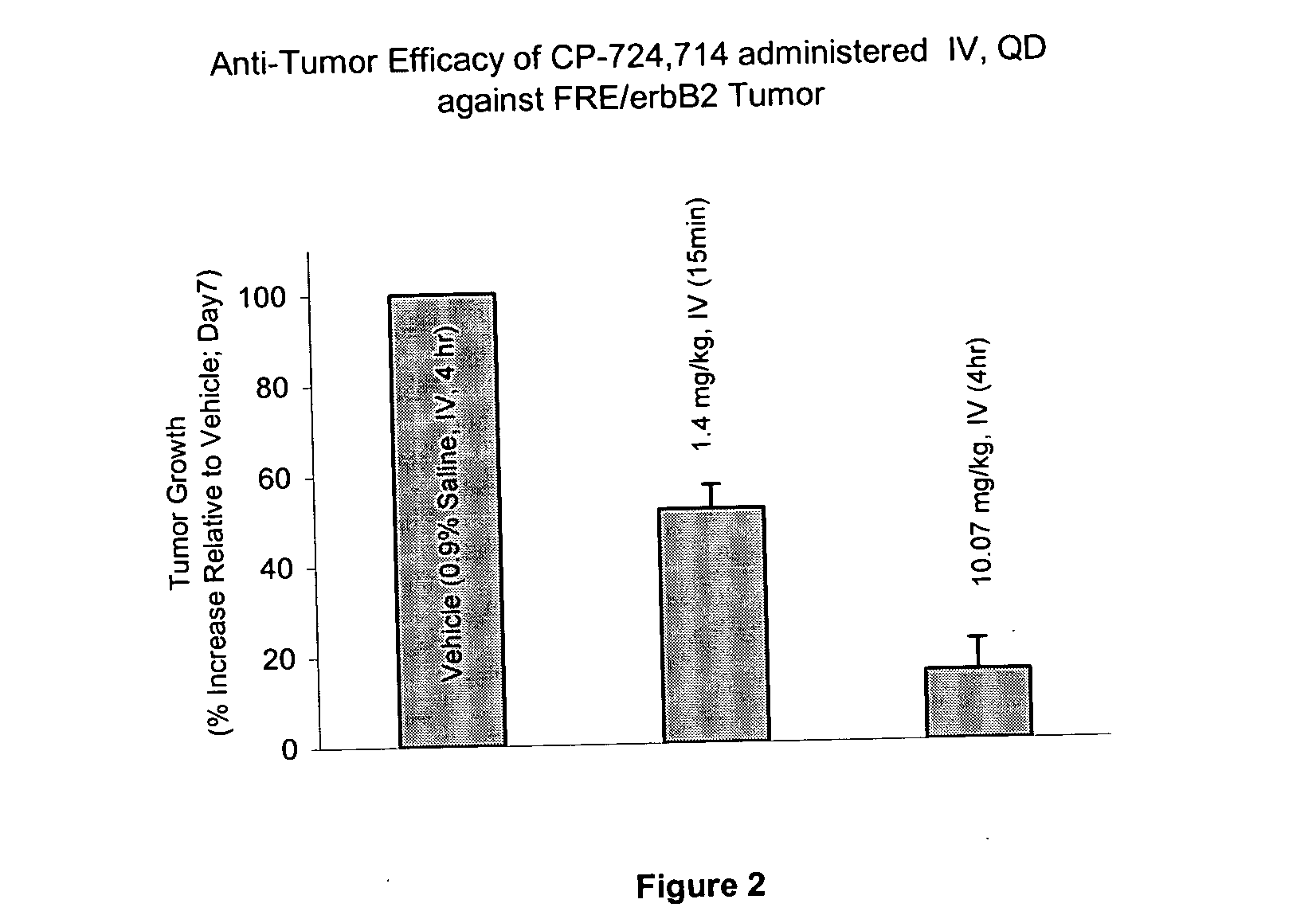
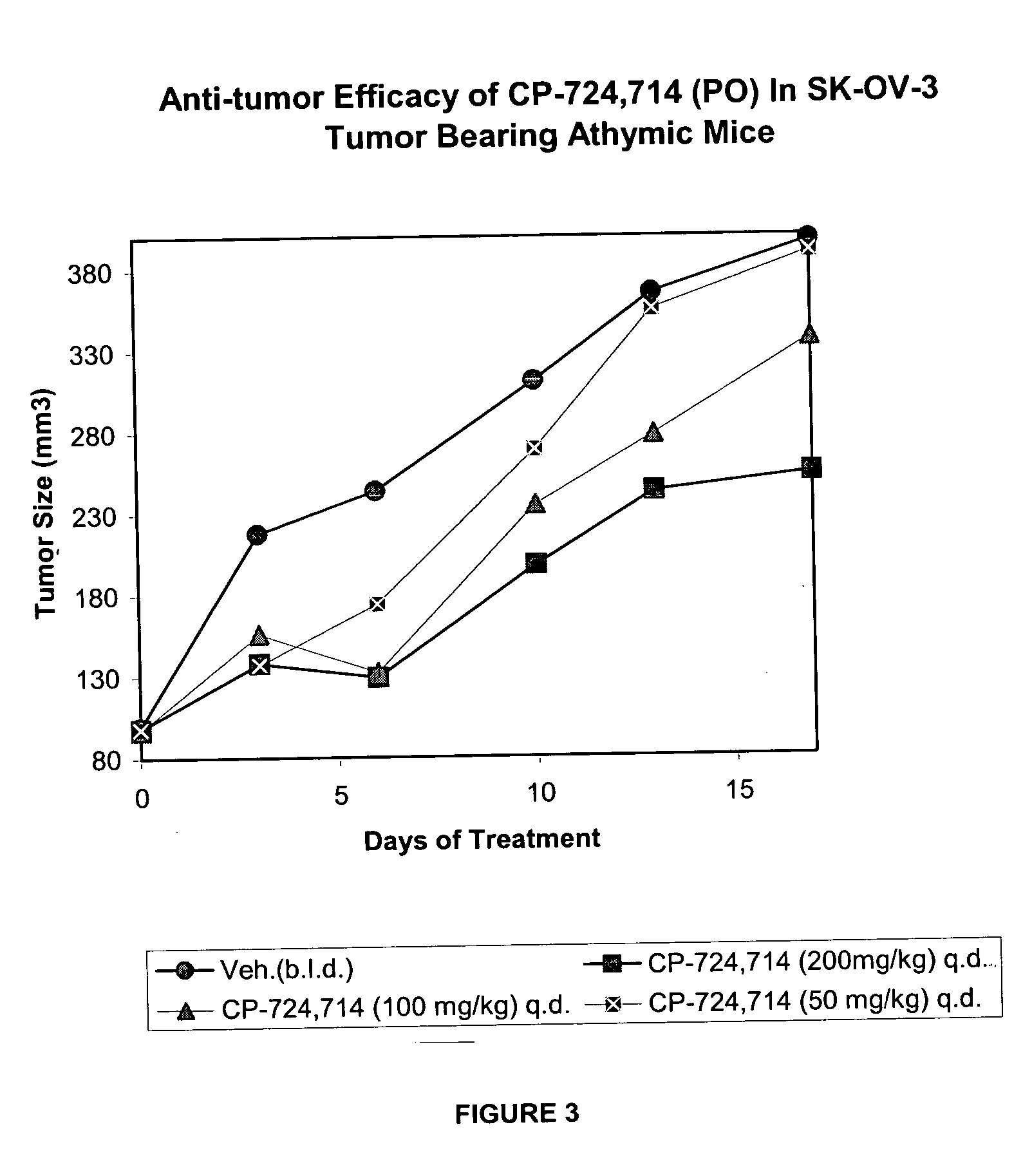
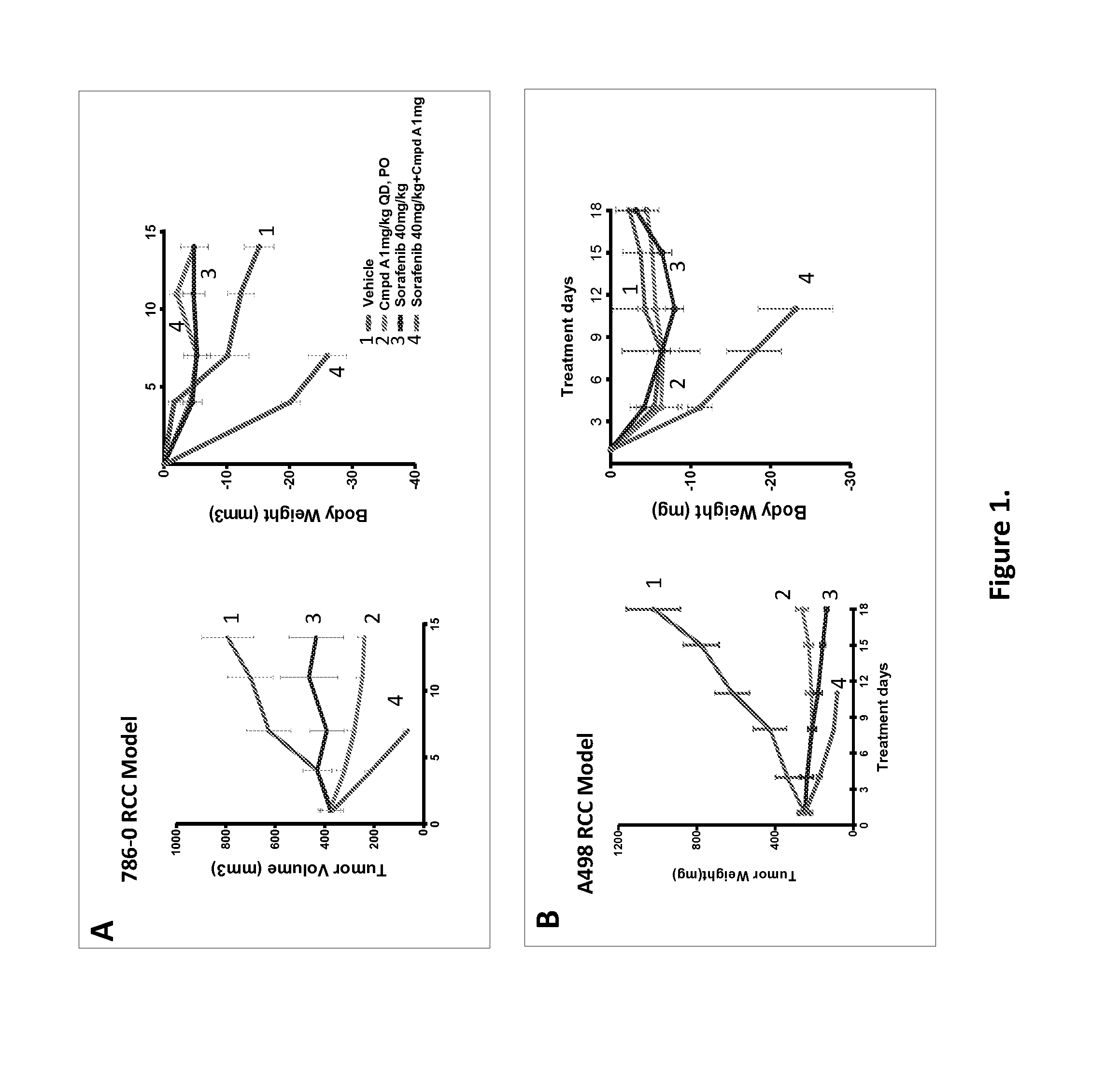
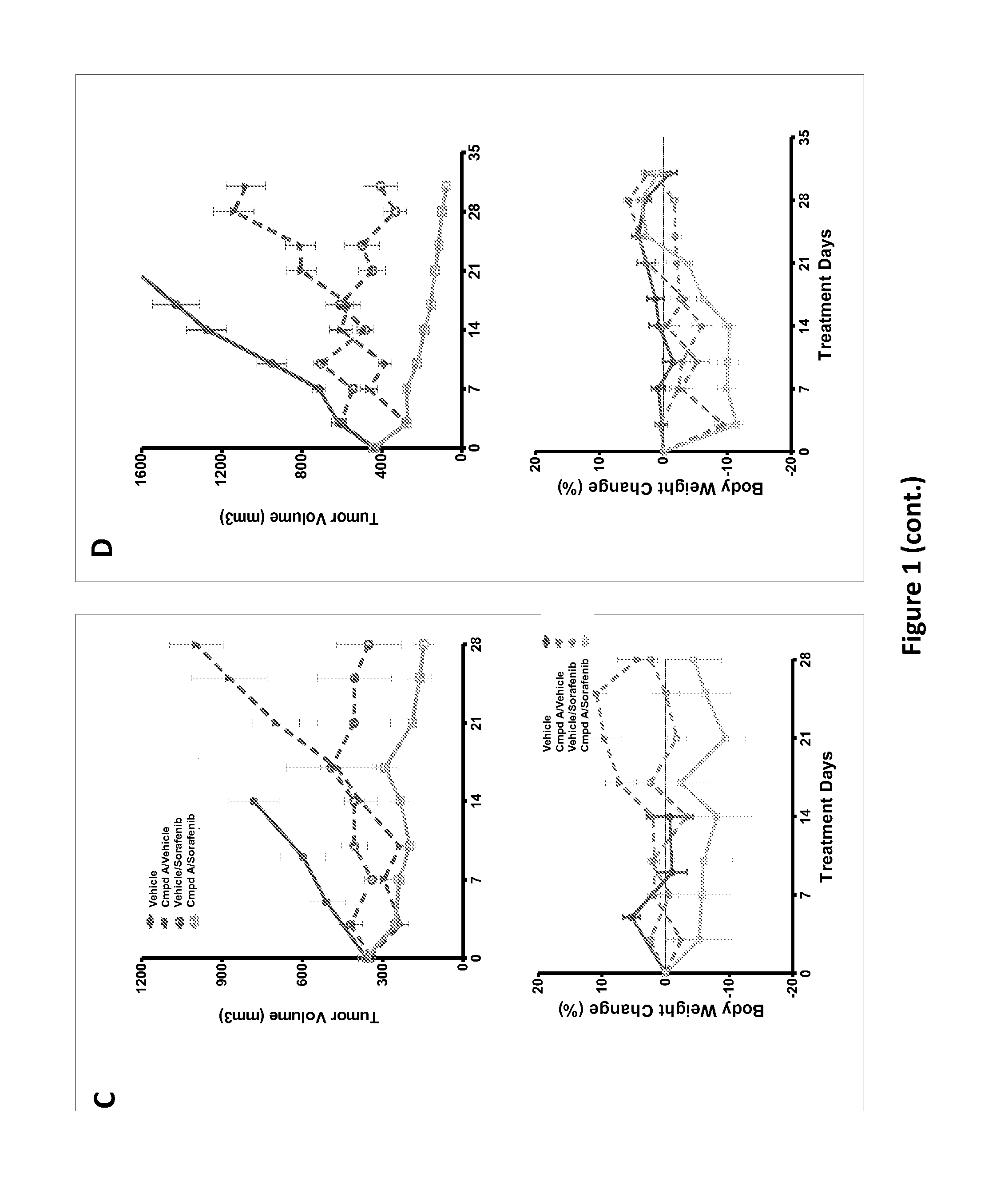
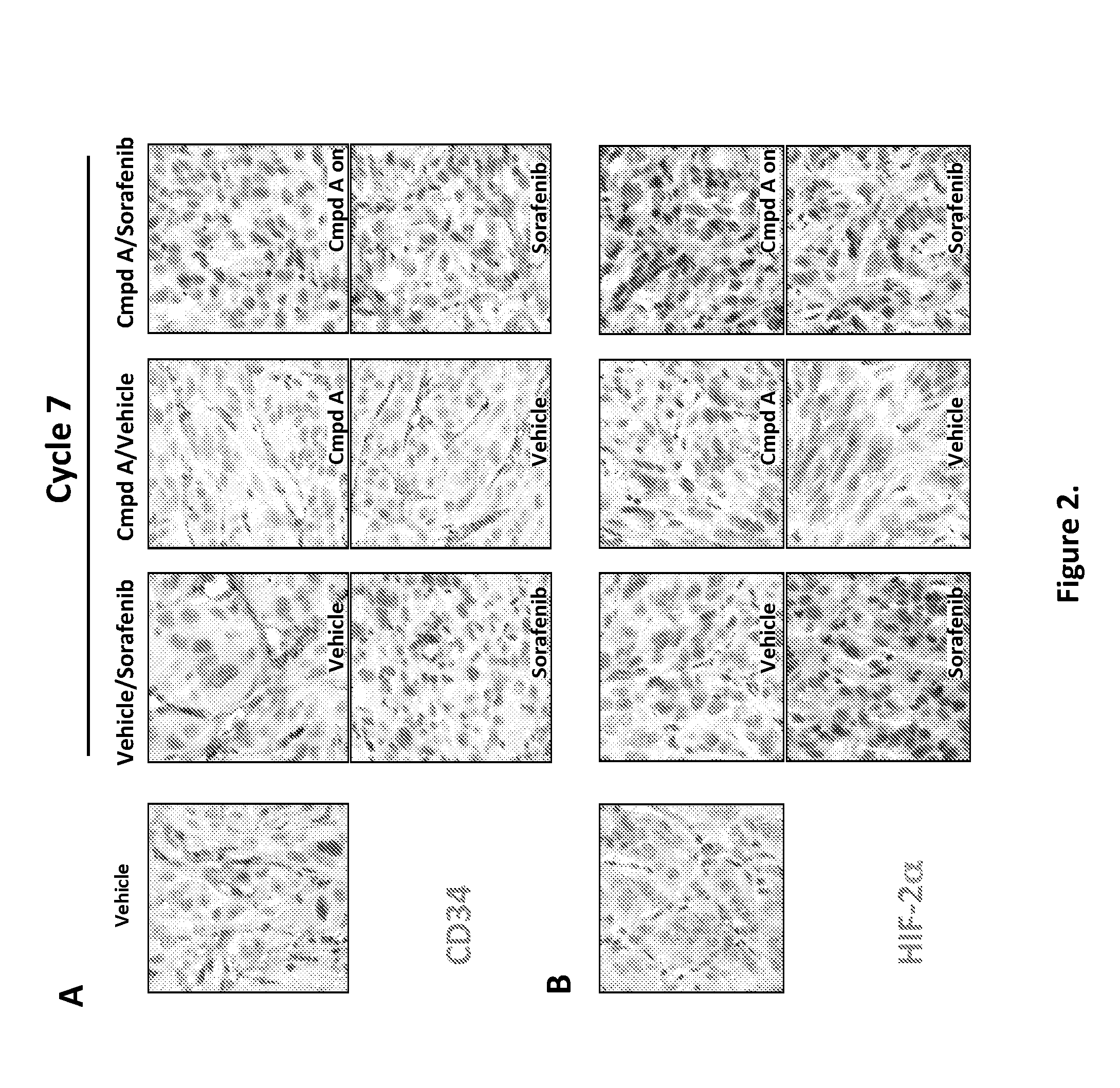
Dosing schedule for a novel anticancer agent
InactiveUS20050119288A1Low affinityMinimize consequencesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAnticarcinogenMedicine
The invention is directed to methods for the a method for treating overexpression of the erbB2 in a mammal in need of treatment by administering to the mammal a therapeutically effective amount of a first inhibitor of an erbB2 receptor and then, after an interval of less than 24 hours, administering to the mammal from one to six therapeutically effective amounts of the same or different inhibitor of the erbB2 receptor. The invention is also directed to a slow daily infusion of the erbB2 inhibitor. The overexpression of the erbB2 receptor can result in abnormal cell growth and lead to cancer. By the methods of the invention, the efficacy and safety of the inhibitors is increased. The invention is also directed to kits for facilitating the dose administration method of the invention.
Owner:PFIZER INC
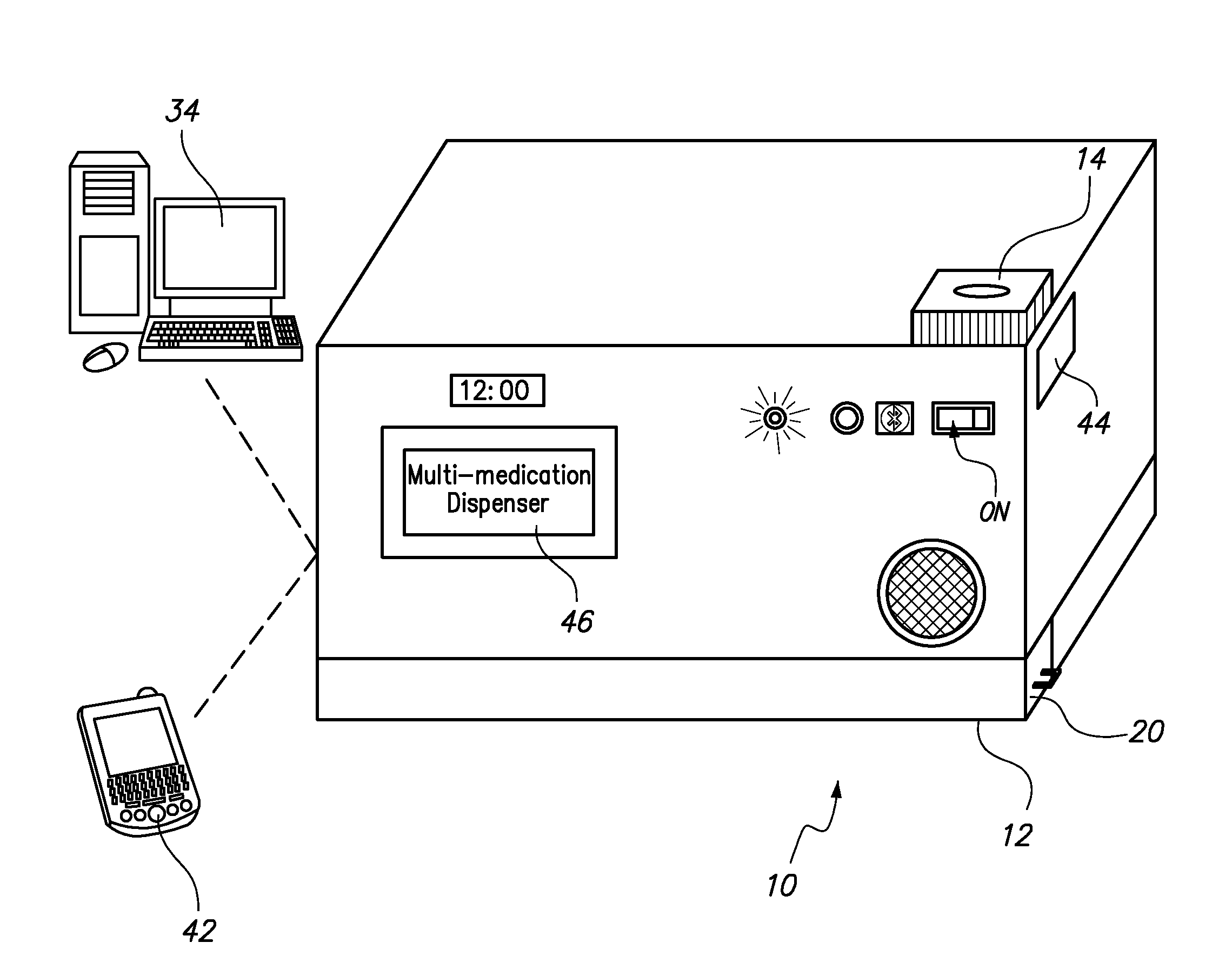
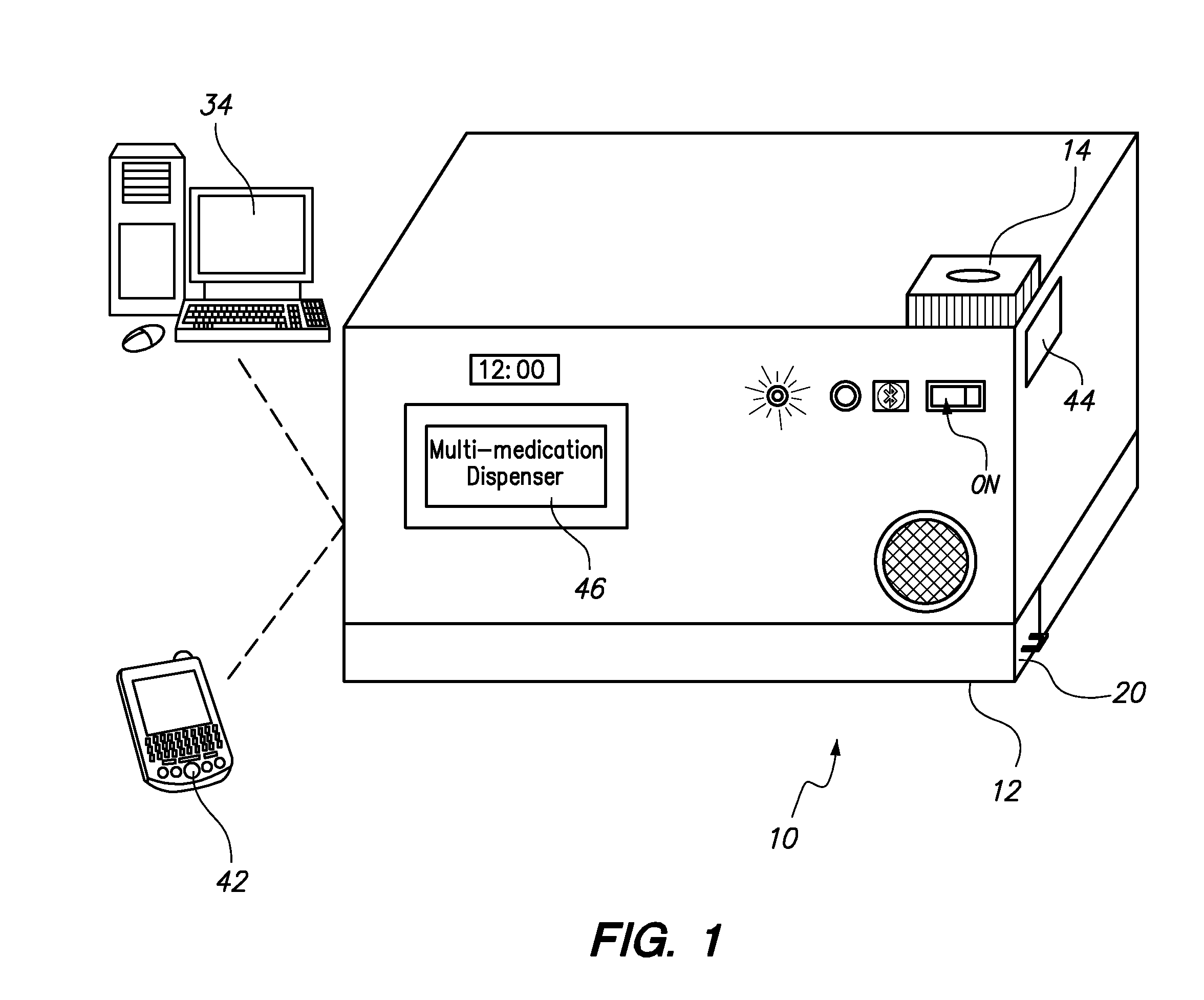
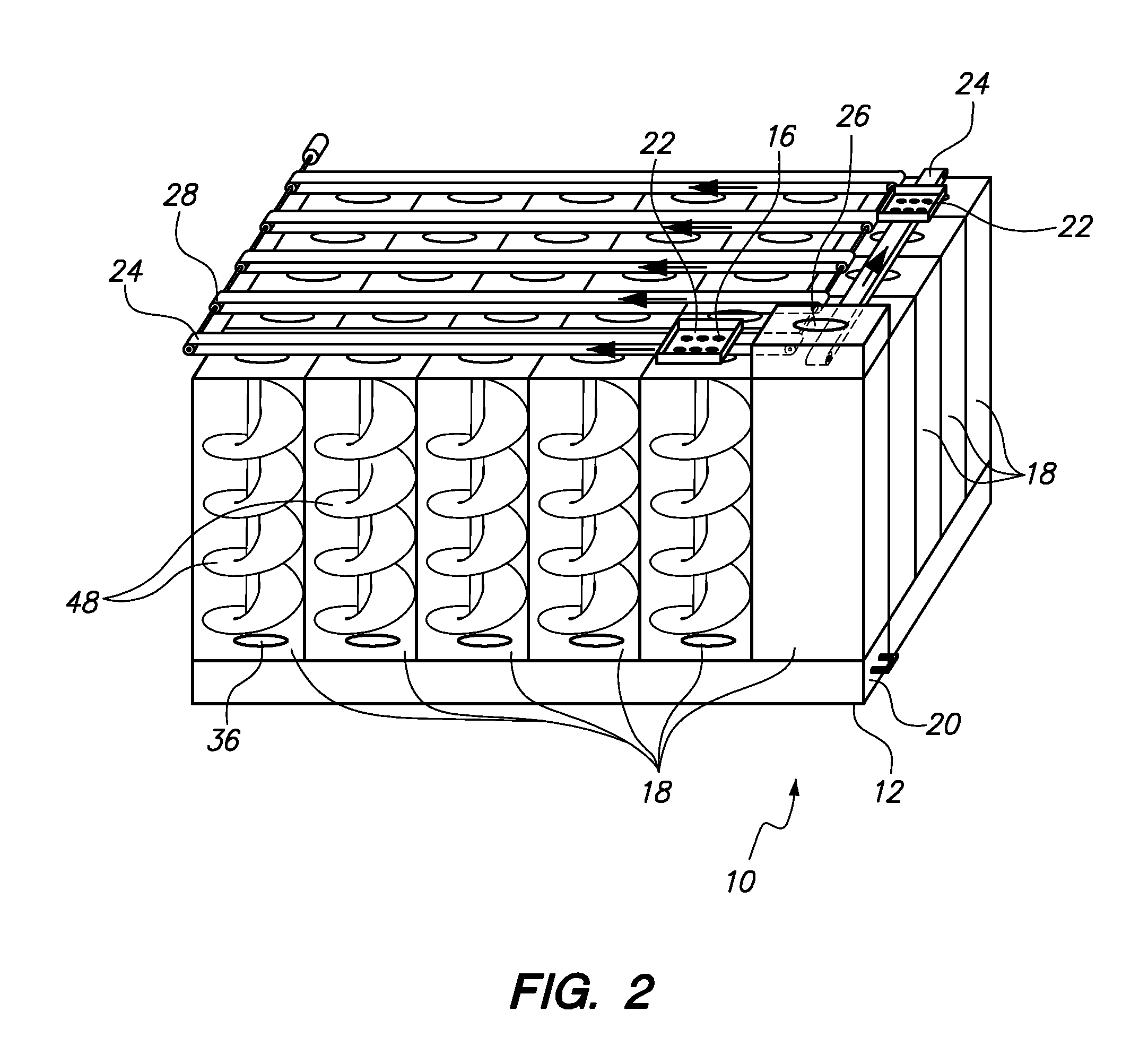
Automated Multi-Medication Dispenser
InactiveUS20140244033A1Drug and medicationsCoin-freed apparatus detailsMedication DispenserEngineering
An automated medication dispenser which includes a storage container having a plurality of storage columns configured to store a plurality of pills, an input slot, an output slot, automated means for delivering pills from the input slot to the storage columns, and automated means for delivering pills from the storage columns to the output slot on a time-based or meal-based dosing schedule.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
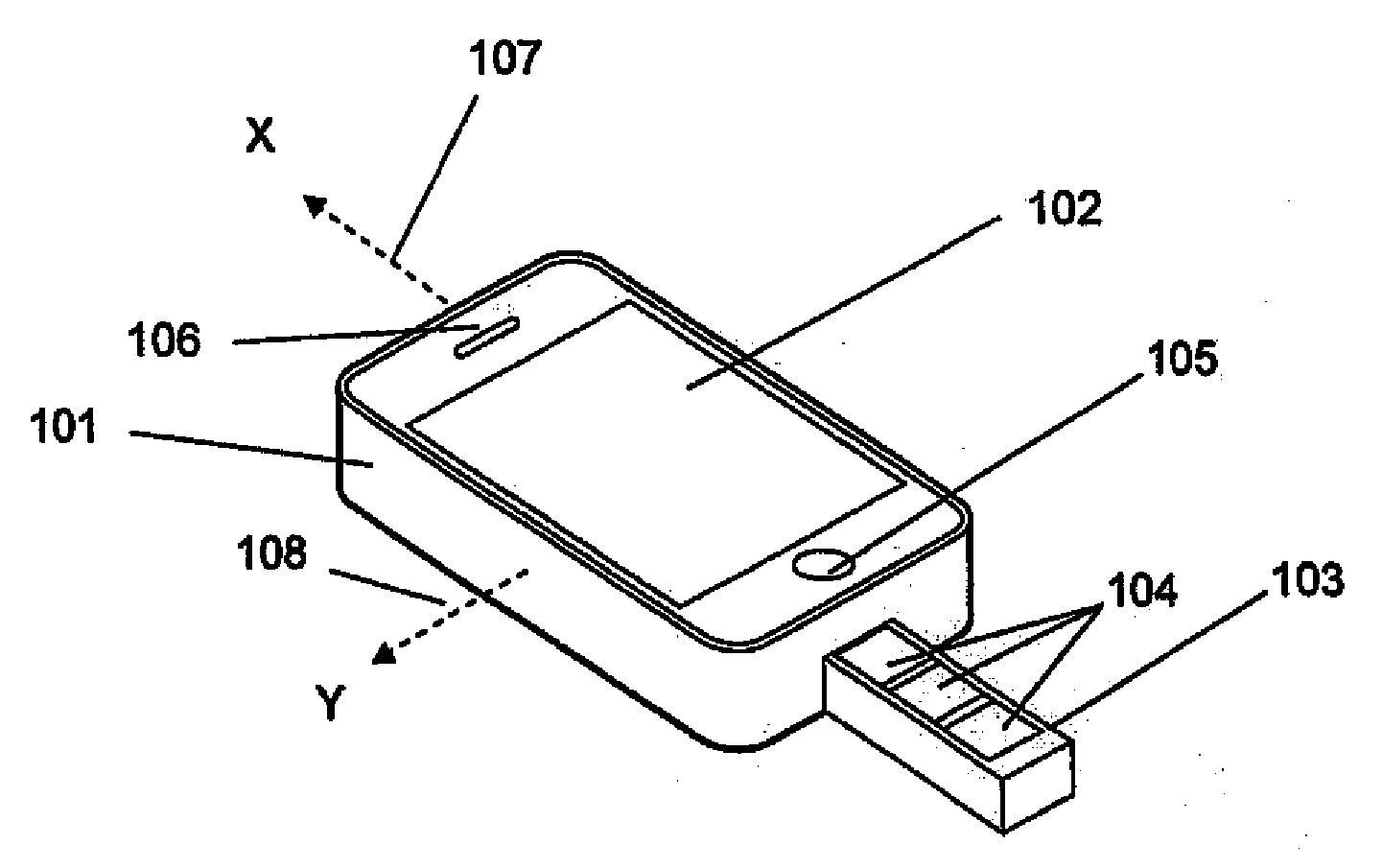
Portable medication management system
InactiveUS20120160716A1Pharmaceutical containersMedical packagingTablet computerProgrammable logic device
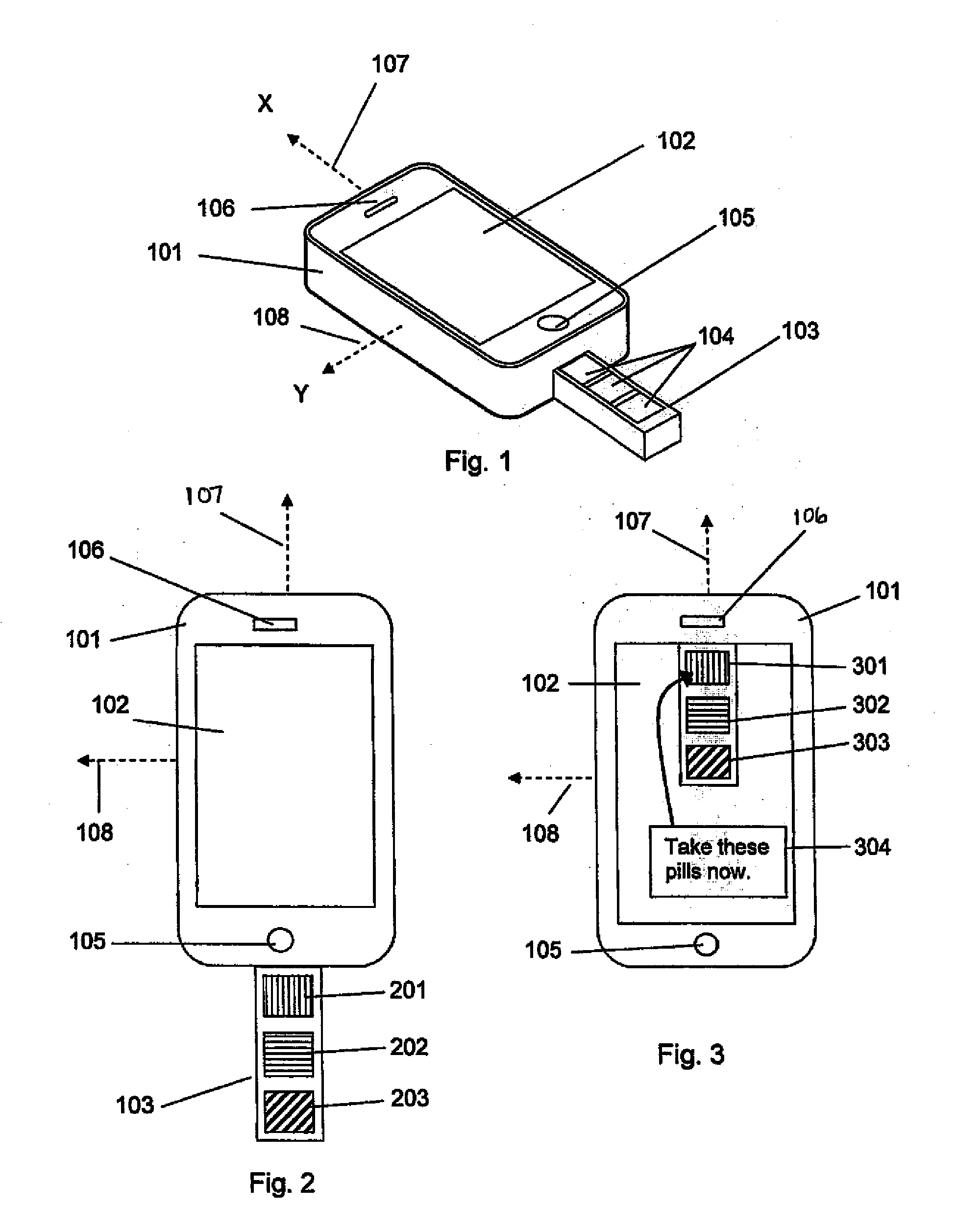
The present invention is a medication management system for use with a programmable mobile device, such as a cell phone, smart phone, or a tablet computer. The invention consists of a case that encases or attaches to the mobile device, with a pill container attached to the case, and software for execution by the mobile device to manage the use of medication, generally in the form of pills, by the user of the mobile device. The pill container slideably engages the case so that doses of pills in the container may be removed by sliding the container out far enough to expose the next dose of pills and turning the mobile device and case over. The software allows the user to program a dosing schedule into it and then alerts the user when it is time to take doses of pills.
Owner:CHAN CHUN KONG JOSEPH +3
Use of antitumoral compound in cancer therapy
InactiveUS20050004018A1Shorten infusion timeAvoid toxicityHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsTumor therapyCancer therapy
Owner:PHARMA MAR U
Patch pump training device
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
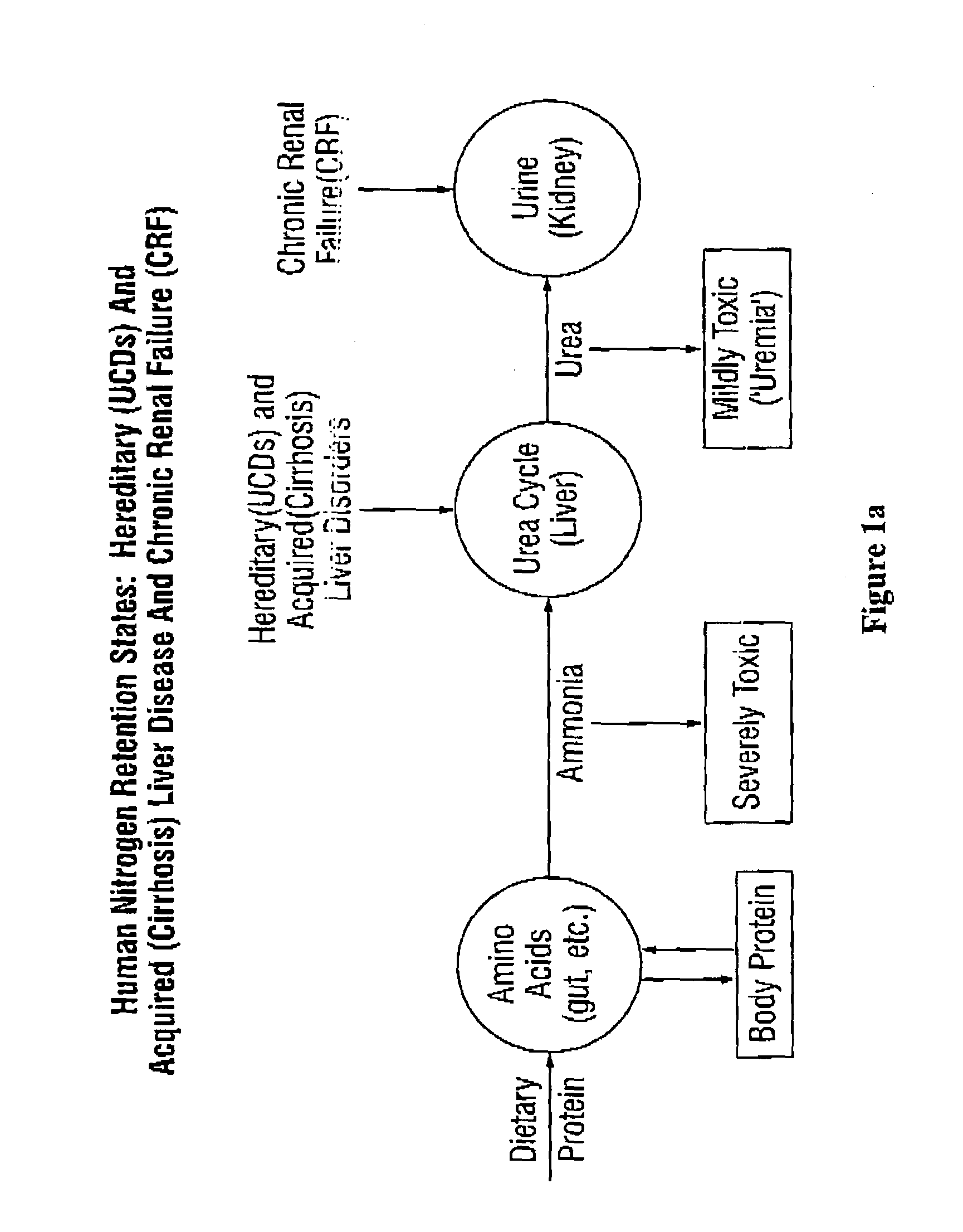
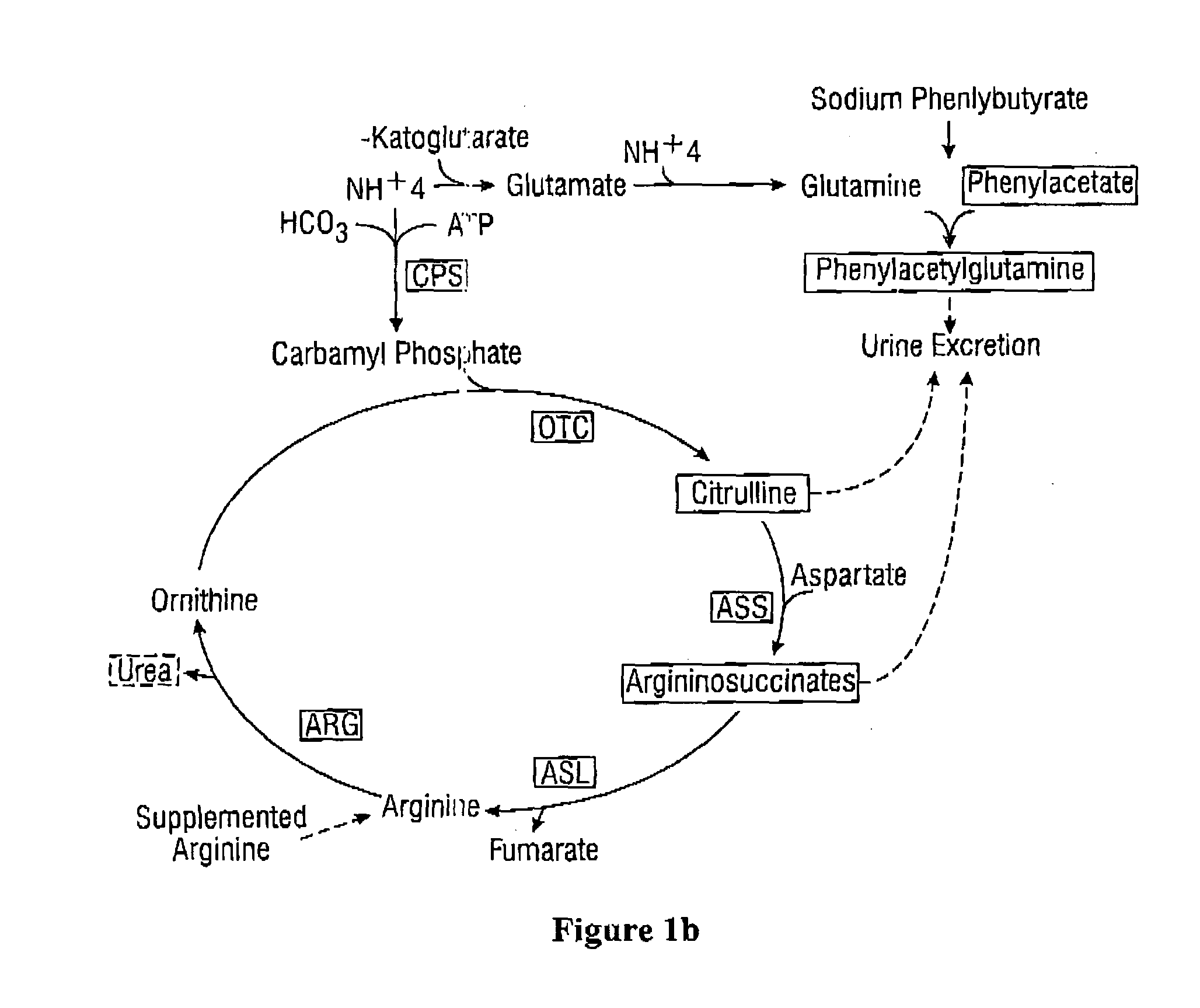
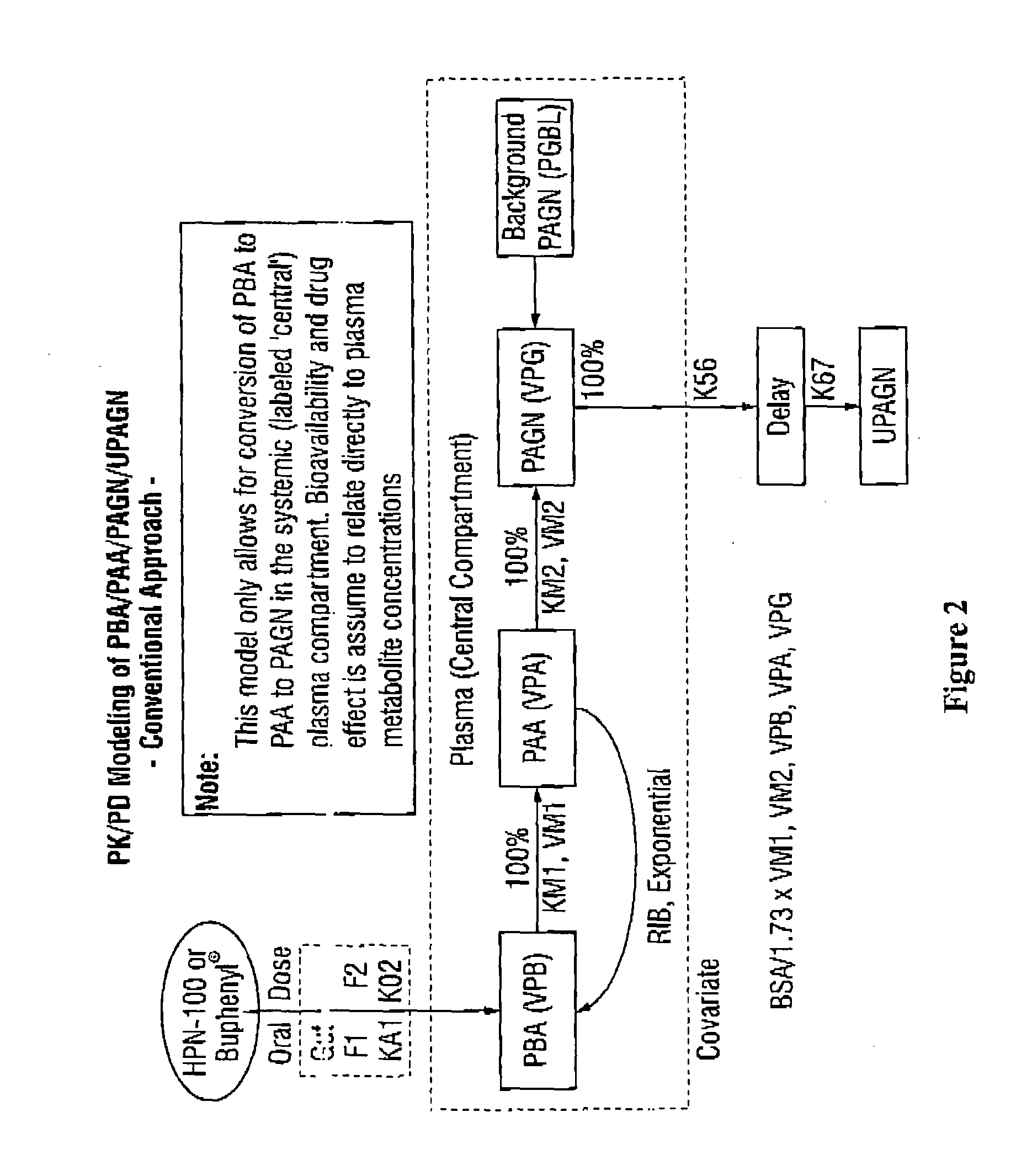
Dosing and monitoring patients on nitrogen-scavenging drugs
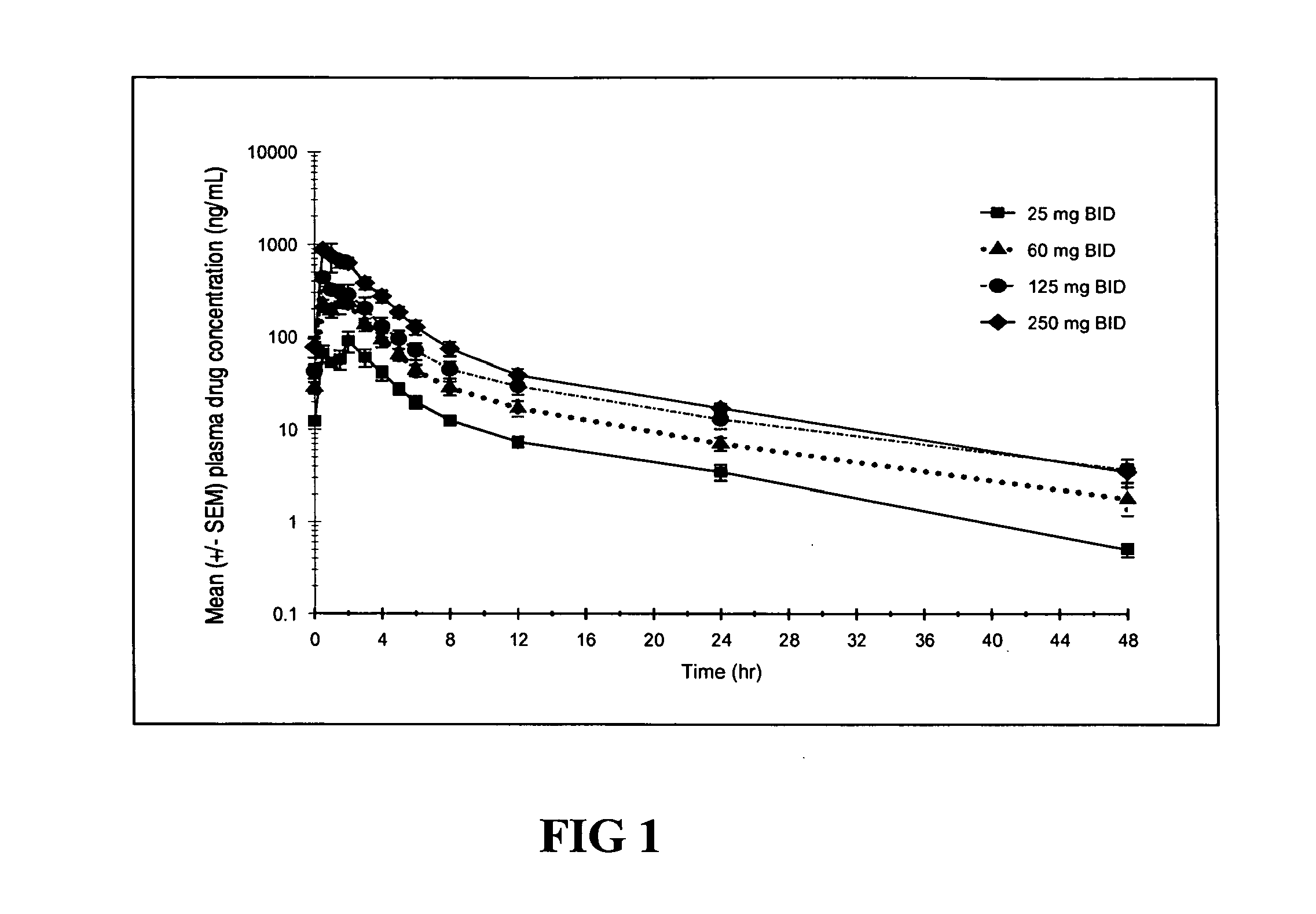
The invention provides a method for determining a dose and dosing schedule, and making dose adjustments of patients taking PBA prodrugs as nitrogen scavengers to treat nitrogen retention states, including ammonia accumulation disorders as well as chronic renal failure, by measuring urinary excretion of phenylacetylglutamine and / or total urinary nitrogen. The invention provides methods to select an appropriate dosage of a PBA prodrug based on the patient's dietary protein intake, or based on previous treatments administered to the patient. The methods are applicable to selecting or modifying a dosing regimen for a subject receiving an orally administered waste nitrogen scavenging drug, and to monitoring patients receiving such drugs.
Owner:HYPERION THERAPEUTICS
Treatment regimens using multiple pharmaceutical agents
InactiveUS20140377285A1Lower toxicity levelGood curative effectBiocideMetabolism disorderTreatment regimenReduced toxicity
The present invention provides for methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treating disorders using treatment regimens involving multiple agents. In one aspect, a method of treatment is provided resulting in reduced toxicity and / or synergistic effect by administration according to a described dosing schedule.
Owner:INTELLIKINE
Drug Delivery Methods And Related Products
ActiveUS20110004187A1Easy loadingAvoid pollutionMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDrug and medicationsPrescribed drugsDrug delivery
This disclosure relates to drug delivery methods and related products. In some aspects, a method includes selecting a drug vial combination by comparing a prescribed drug dosage to a dosing schedule, and delivering substantially all of the first drug from each of the selected drug vials to a patient by operating a pump of a drug delivery device to which the drug vials are connected.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
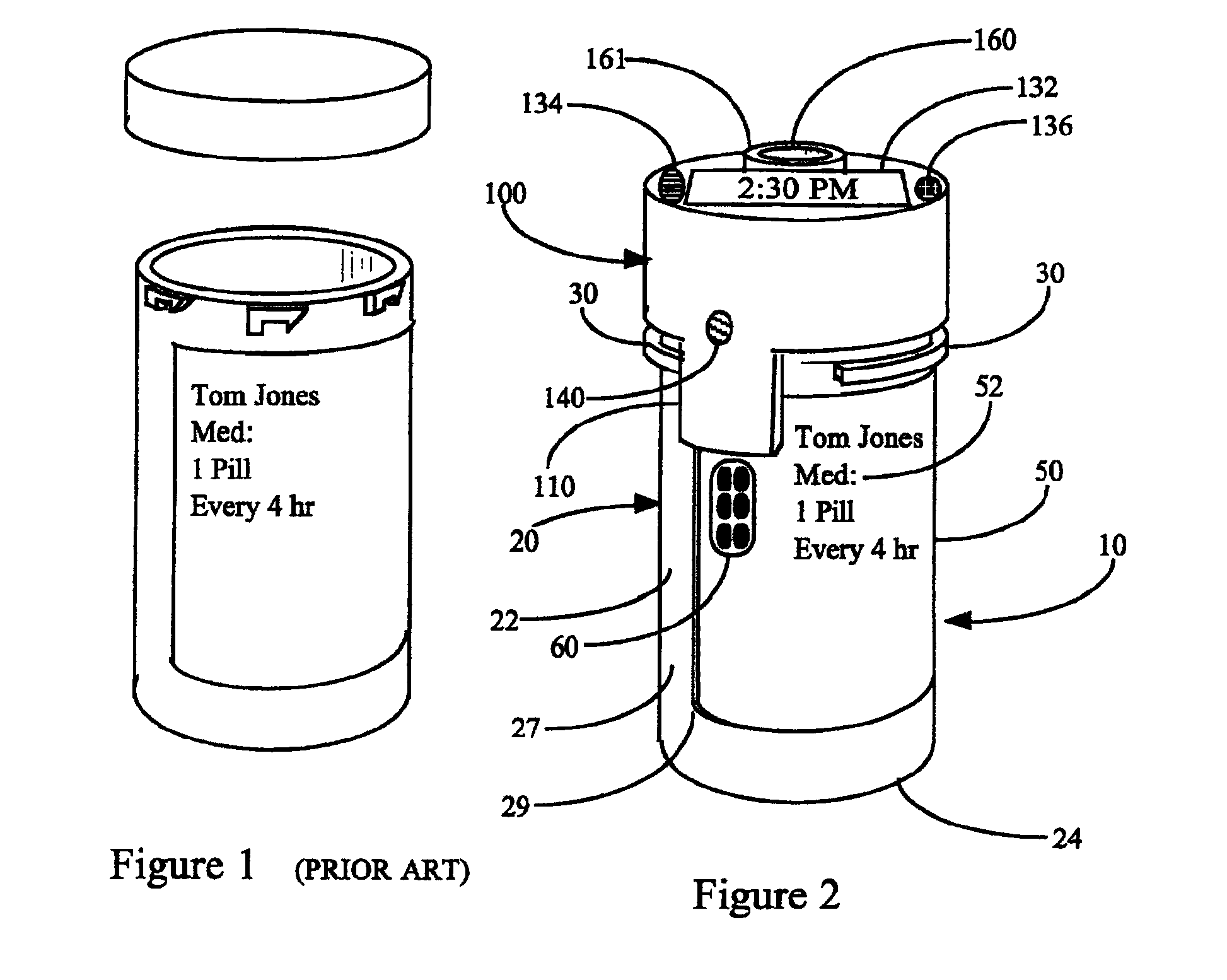
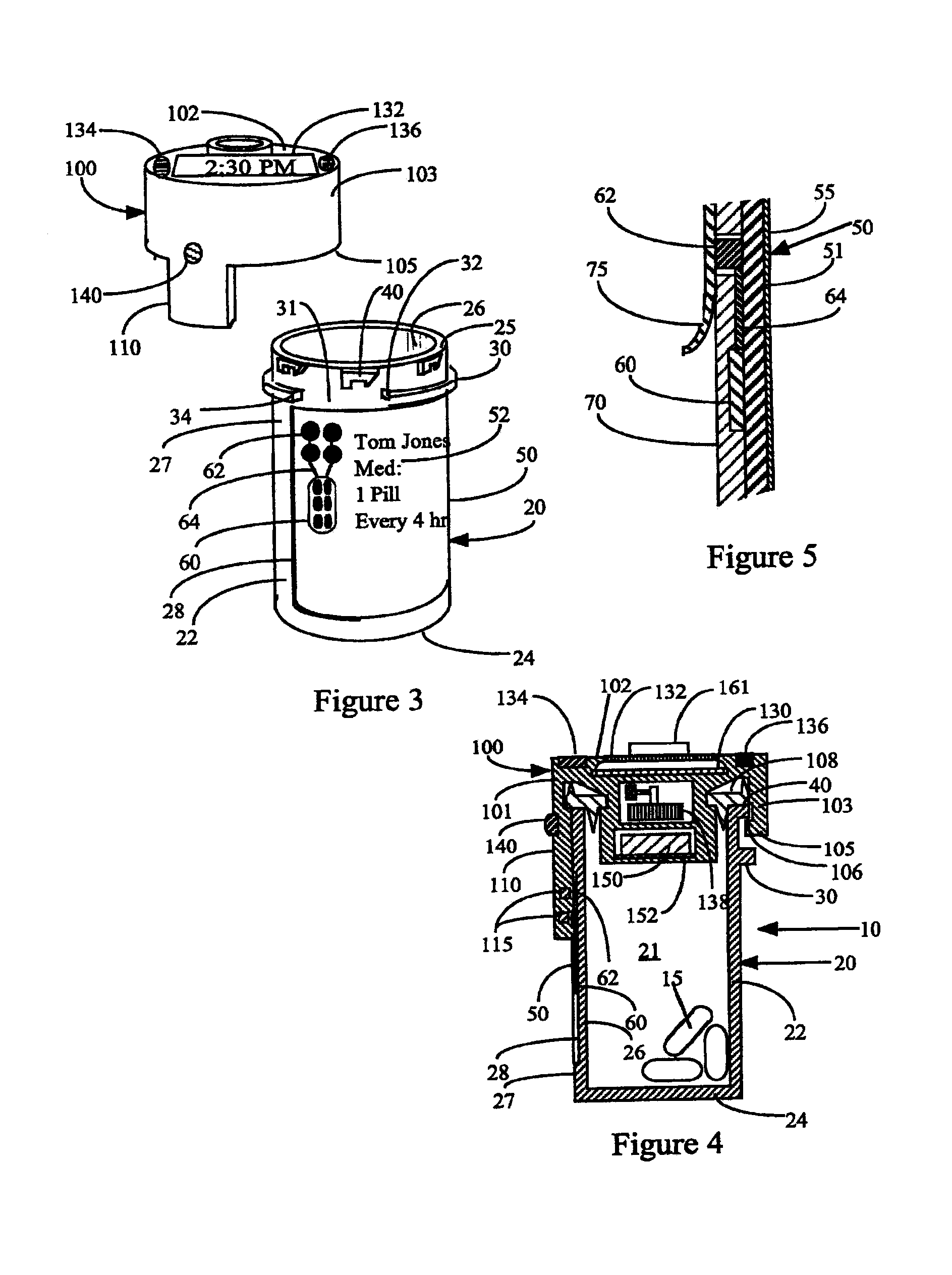
Automated prescription reminder, dispenser, and monitor
InactiveUS20060180600A1Coin-freed apparatus detailsOral administration deviceCaregiver personDisplay device
A medication dispensing device is provided. The device has a storage compartment which stores the user's medication, a programming means whereby a caregiver can input dosage schedules and dosage instructions, and a display which shows the users dosage information. The device can be equipped with communication devices which will allow caregivers to monitor dosing schedules and dosage levels.
Owner:TALYOR SHANNON
Methods for treating ocular diseases
ActiveUS20160130337A1Senses disorderImmunoglobulins against growth factorsVascular diseaseTreatment burden
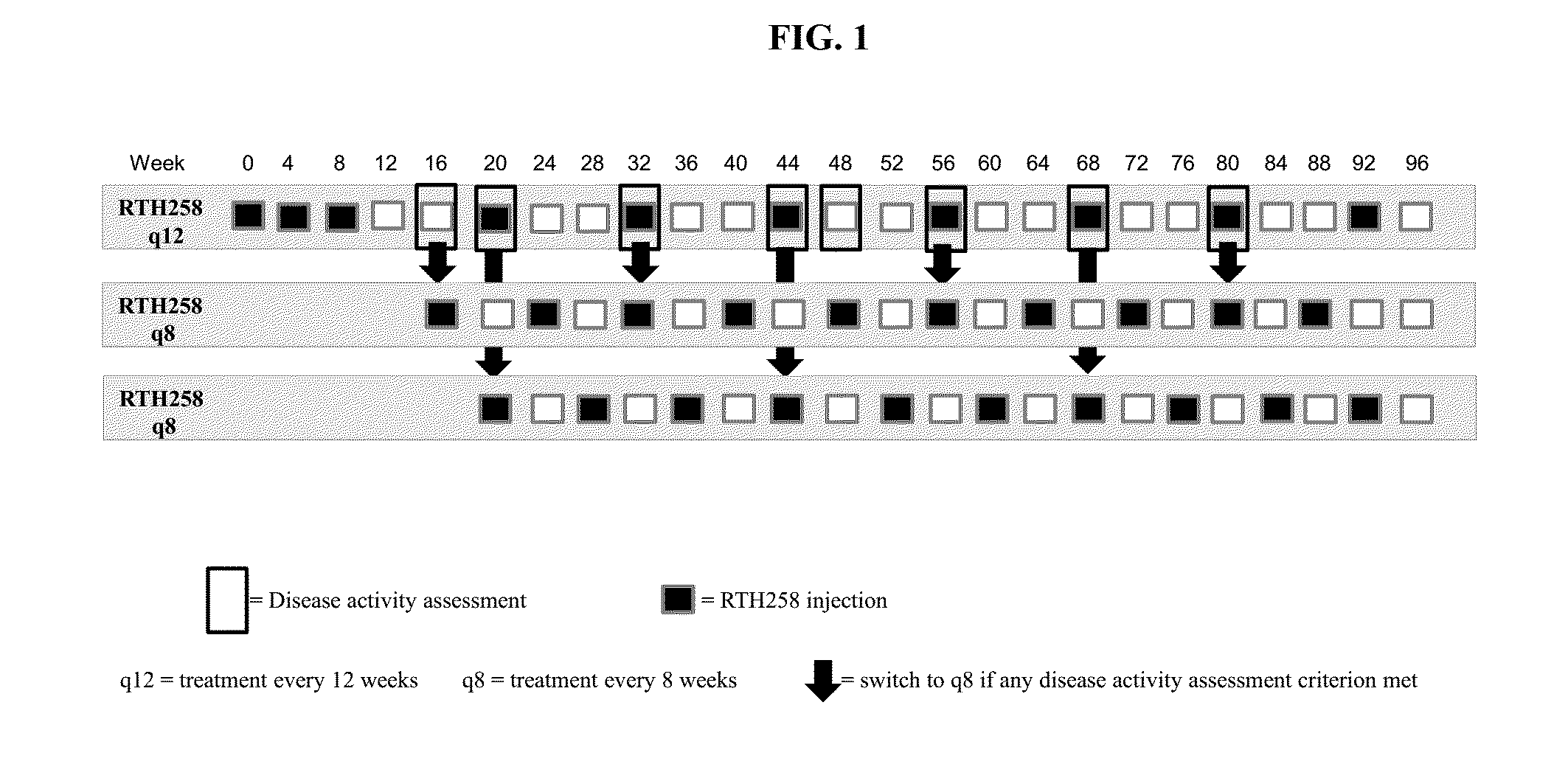
A method is provided for reducing the treatment burden for patients who have an intraocular neovascular disorder, the method comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of VEGF antagonist on a dosing schedule that includes treatment intervals of 8 and / or 12 weeks.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Method and system for enrolling in a medication compliance packaging program
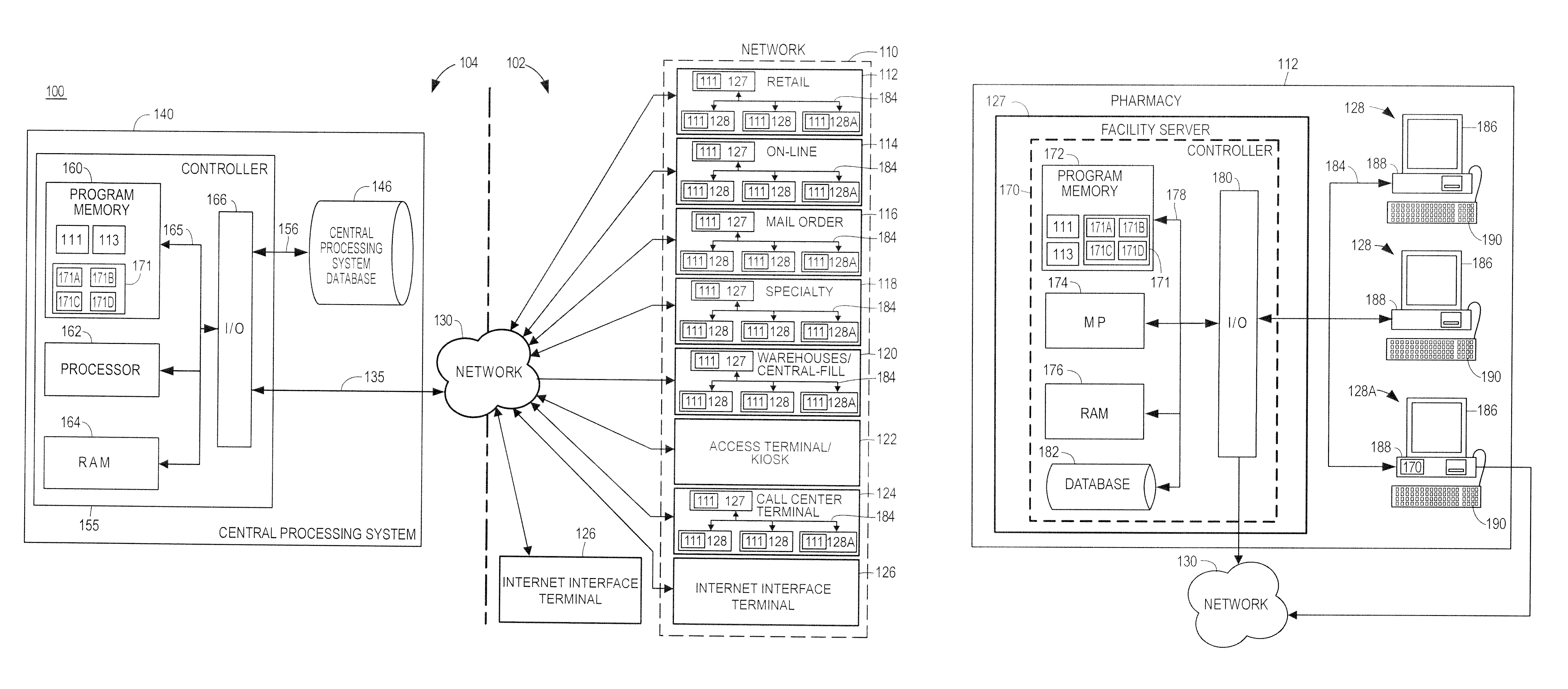
A method and system facilitate enrollment of a customer in a medication compliance packaging program. The medication compliance packaging program facilitates proper dosing of each included medication dispensing each medication in a customized package and thereby serving as a personalized, prepackaged pill organizer. The compliance package groups all of the customer's daily pills, separated by the day and time of day that the customer takes each dose. The disclosed method and system provide a convenient means for a customer to enroll in the program, select prescription medications to include in the medication compliance packaging, and set up a dose schedule for each medication.
Owner:WALGREEN CO
Pharmaceutical formulation for oral delivery of bisphosphates
InactiveUS20050182028A1Minimizing potential esophageal irritationMinimize irritationBiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsDosing regimenPharmacy
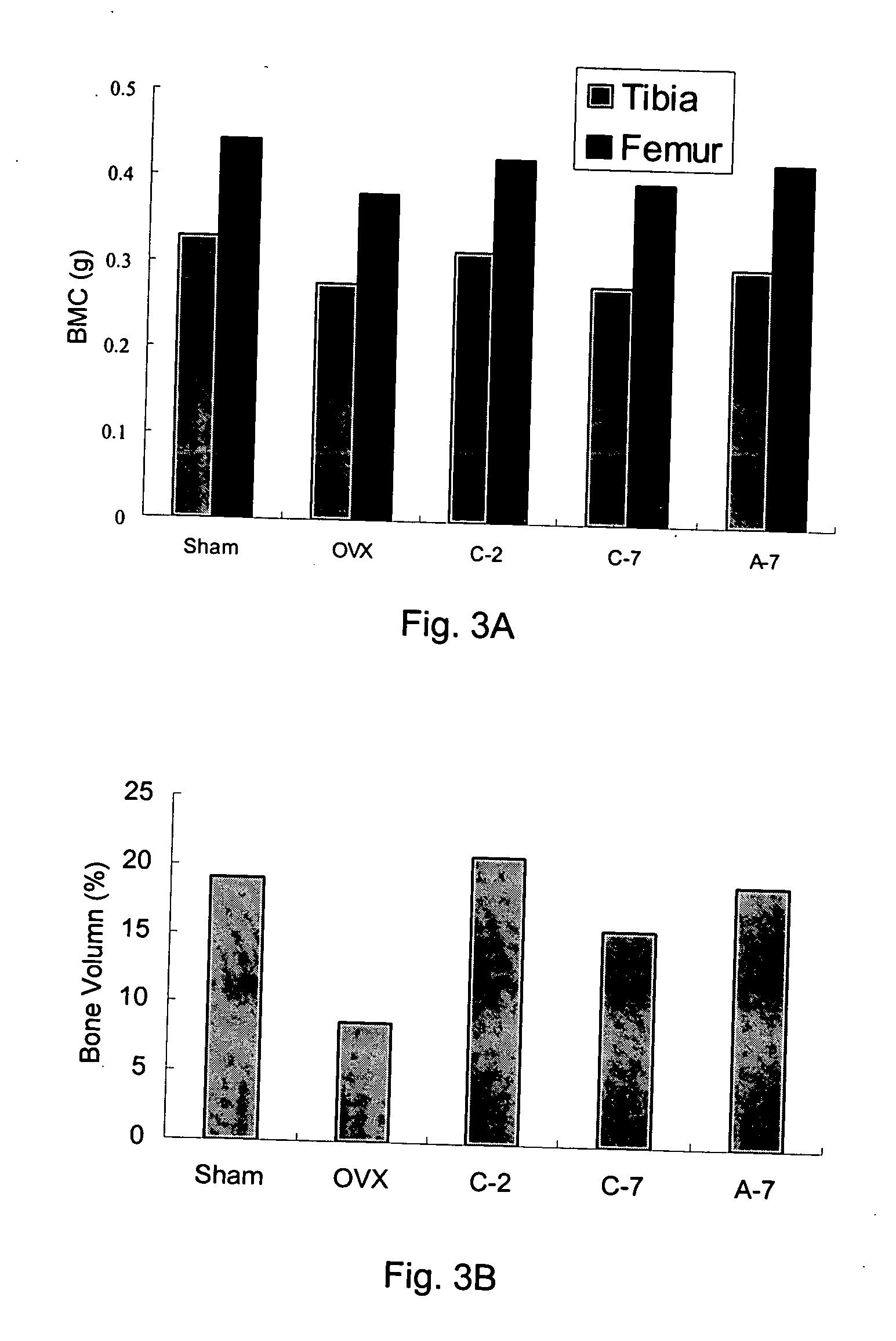
The present invention discloses a method for treating or preventing a bone disorder in a mammal in need thereof comprising orally administering to said mammal a pharmaceutically effective amount of a pharmaceutical composition of at least one bisphosphonate, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or esters thereof, and at least one aminoalky methacrylate copolymer, according to a dosing schedule having a dosing interval selected from once-weekly dosing, twice-monthly dosing, once-monthly, once-quarterly and once-annually dosing. The present invention further discloses a method for treating or preventing a bone disorder in a mammal in need thereof comprising continuously orally administering a unit dosage per-day to said mammal in a short time for a long time therapy.
Owner:CHEN CHIH MING JAMES
Oral administration of peripherally-acting opioid antagonists
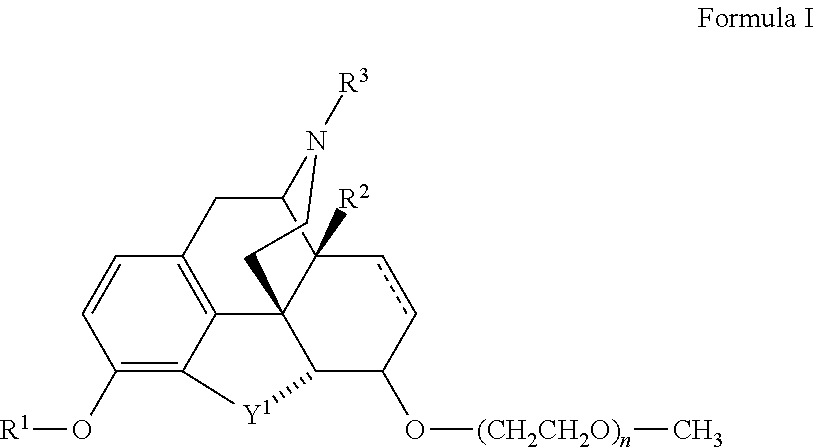
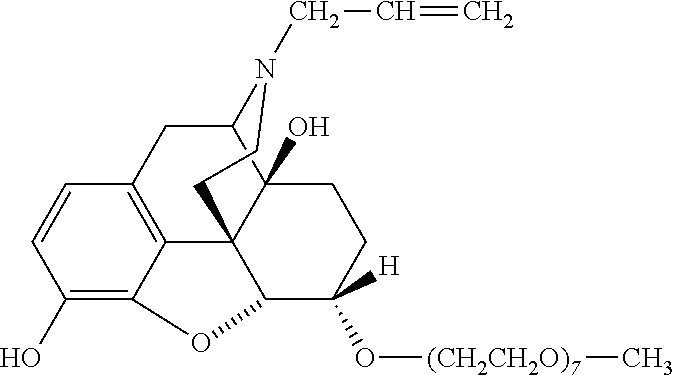
InactiveUS20110160239A1Inhibition becomes largerAvoid dysfunctionBiocideNervous disorderOpioid antagonistSide effect
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Orally dispersible multi-micronutrient dietary supplement composition and methods of using same
InactiveUS20130323350A1Acceptable mouth feelGood for healthMilk preparationVitamin food ingredientsDietary supplementBioavailability
The present invention is directed to a novel orally dispersible multi-micronutrient dietary supplement in a tablet dosage form. Use of lipid encapsulated substrates, flavorings, sweeteners and bitter masking agents provides for a dosage that suppresses unpleasant tastes or aftertastes and imparts a pleasant mouth feel when the tablet disperses after being sucked or chewed for several minutes. The combination of lipid encapsulated substrates, oral disintegration and multiple daily dosing schedule provides for improved bioavailability of several crucial micronutrients.
Owner:SELIGSON ALLEN
Arthropod trapping apparatus and method
An arthropod trap with an aerosol dispenser that is remotely controllable to dispense spray doses of an active ingredient such as a pheromone or other semiochemical. Images are captured of trapping media within the trap and are wirelessly communicated to a remote server or application. The dispenser is preferably upside down with the nozzle near the lower extremity of the inverted dispenser. An actuation mechanism controls the spray dose according to a schedule or according to individual sprays commands, each of which may be received wirelessly by the trap. Images of the trapping media may be used as feedback for verifying or modifying the metered dosing schedule.
Owner:SEMIOSBIO TECH
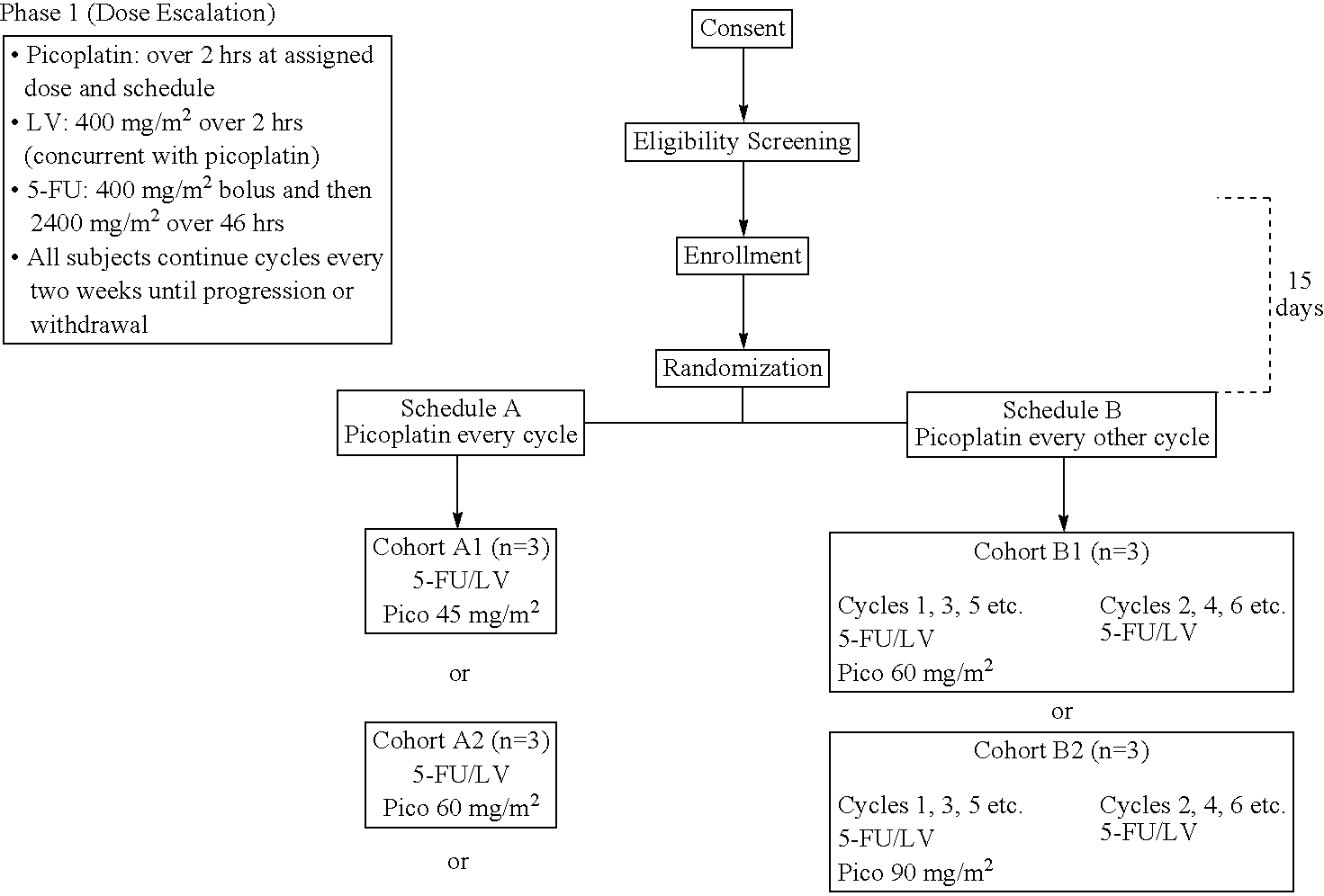
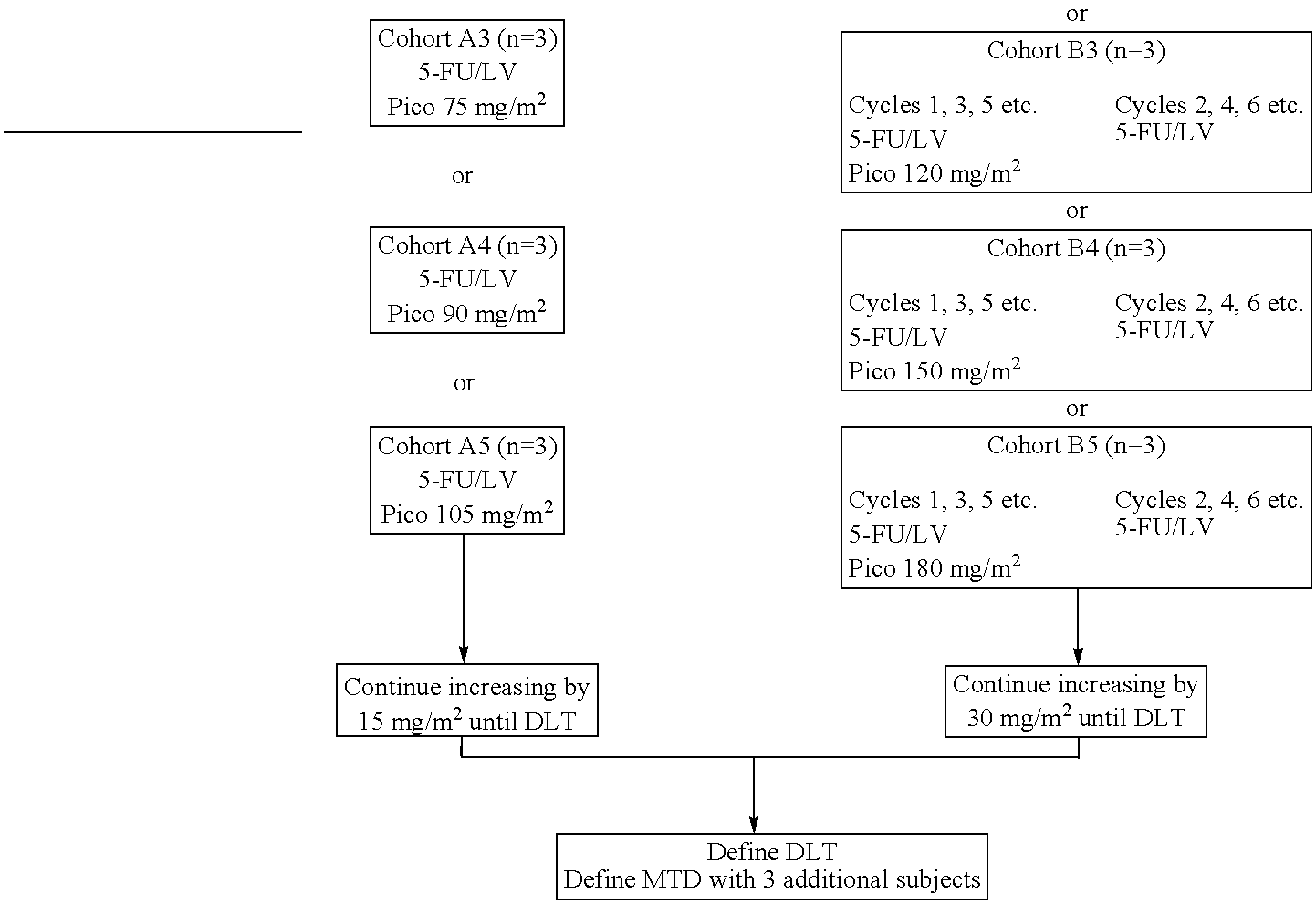
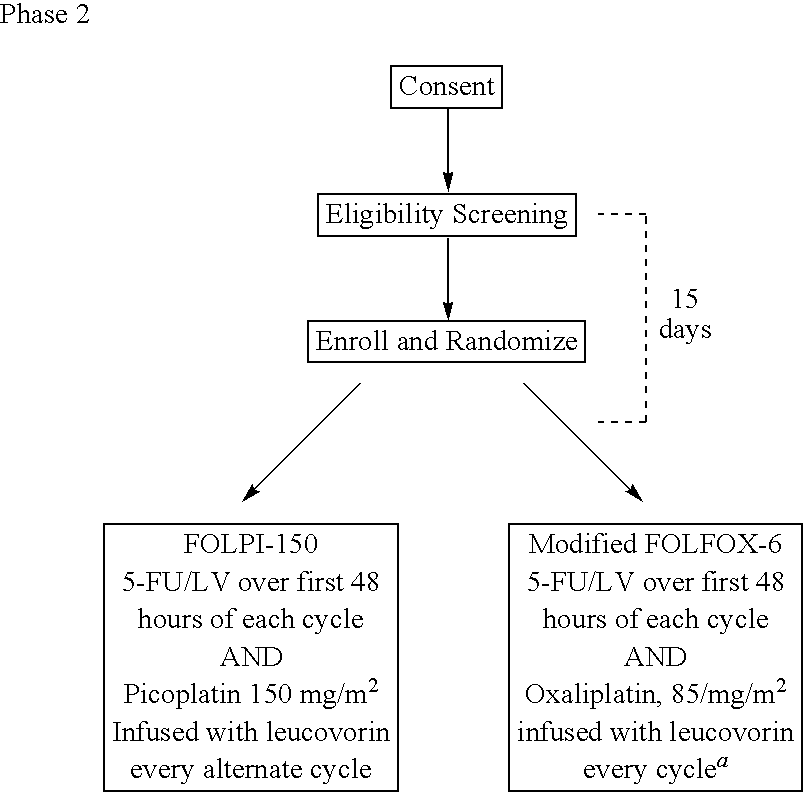
Use of picoplatin to treat colorectal cancer
The invention provides a method of treatment of colorectal cancer by administration of the anti-cancer platinum drug picoplatin in conjunction with 5-FU and leucovorin in a variety of treatment regimens. Dosages, dosing schedules, and ancillary treatments are described.
Owner:ACCELERATED PHARMA
Treatment of cancer in pediatric patients
Compositions comprising a cancer drug, a continuous oral dosing schedule with a drug which binds to the colchicine site of tubulin β-subunits, and methods of treating cancer in a pediatric patient using continuous dosing schedules are disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
System And Method For Secure Medication Dispensing, Monitoring, And Control
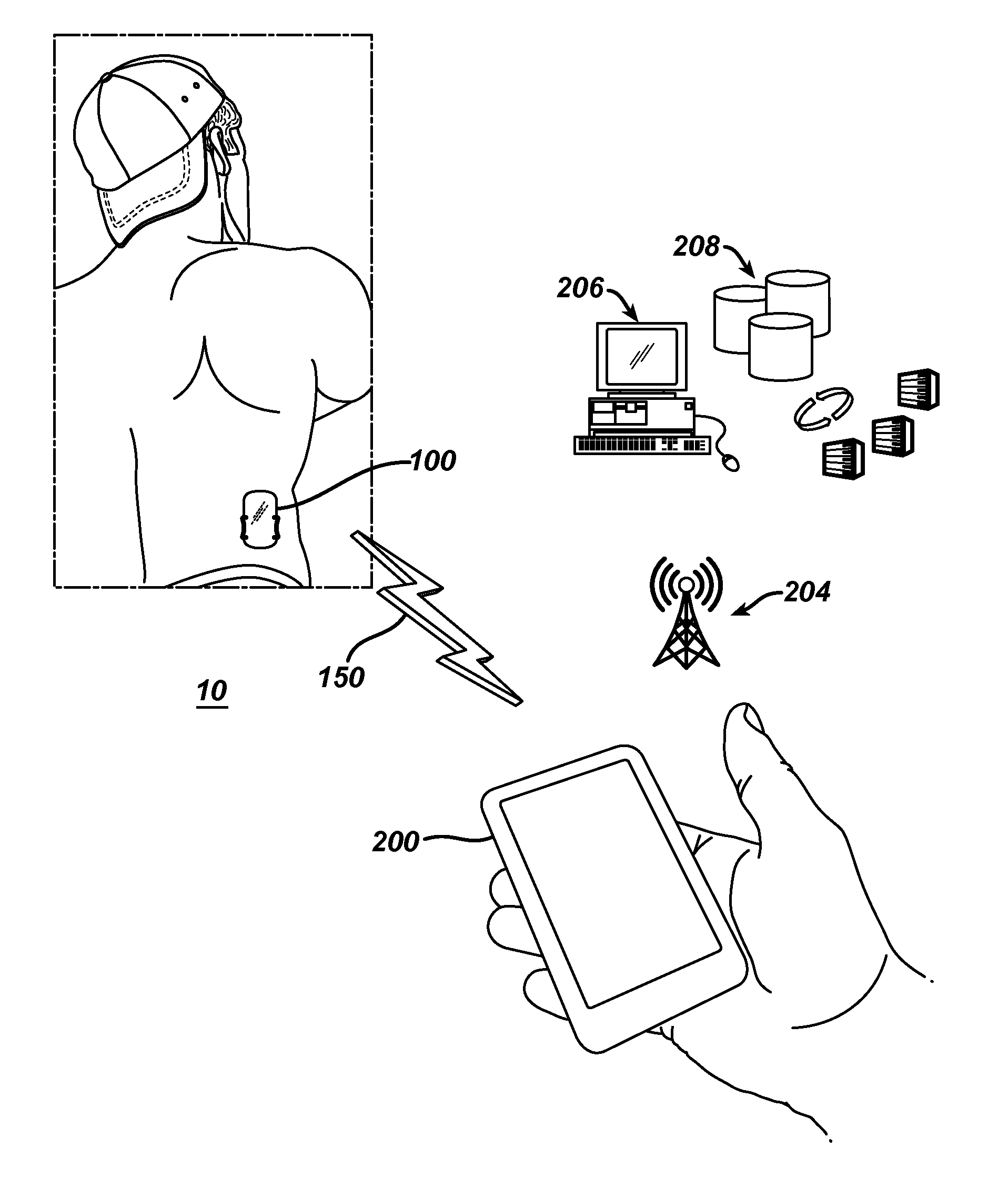
ActiveUS20190307647A1Mitigates risk of diversionMitigating risk of diversionDrug and medicationsSurgeryMedication DispenserComputer module
A programmable medication dispenser is provided to securely dispense medication to a patient and mitigate the risk of diversion of the medication to an unauthorized user. The programmable medication dispenser may include a processor, a memory, a housing, a biometric verification module, an inner receptacle having a plurality of compartments for storing the medication, and a gate for dispensing the medication from one of the compartments. A patient may access the medication stored within the medication dispenser according to a prescribed dosing schedule based on instructions executed by the processor after verifying his or her identify via the biometric verification module. A system is also provided for securely dispensing, monitoring, controlling medication for a patient using the programmable medication dispenser and for mitigating the risk of diversion of the medication to an unauthorized user. The system could be implemented in a cloud-based environment wherein centralized, cloud-based monitoring and control of a network of medication dispensing systems is provided, and the system could function as a centralized portal for allowing healthcare providers to access patient healthcare data, as well as for allowing insurers and other entities to access such data, as needed.
Owner:SBG MEDICAL TECH
Von willebrand factor specific binders and methods of use therefor
InactiveUS20110158996A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDosing regimenVon willebrand
The invention provides new uses for specific binders to the Al domain of the von Willebrand Factor (vWF), in particular the use in patients with stable angina undergoing elective percutaneous coronary intervention. Furthermore, dosing schedules and use of suitable assays such as RIPA and RICO in the particular disease settings are provided.
Owner:ABLYNX NV
Use of bisphosphonates for otosclerosis
InactiveUS20050049225A1Efficient responseSustained benefitBiocideSenses disorderOral medicationMedicine
A method of treating otosclerosis in a human in need thereof by administering a bisphosphonate in a defined dosing schedule. The invention demonstrates an effective response and sustained benefit in the treatment of otosclerosis. Particularly, the method involves administration of a bisphosphonate in a stepped-up dosage amount, e.g., in a dose that is at least one and a half times the recommended dose for osteoporosis. It also includes administration of a time-dependent dose of more than one bisphosphonate, specifically, alternating administration of a first bisphosphonate with a second bisphosphonate. The inventive method further includes intravenous administration of a bisphosphonate, and optionally oral administration of a bisphosponate. The present invention further contemplates a kit for facilitating the alternating bisphosphonate dosing schedule
Owner:BROOKLER KENNETH H
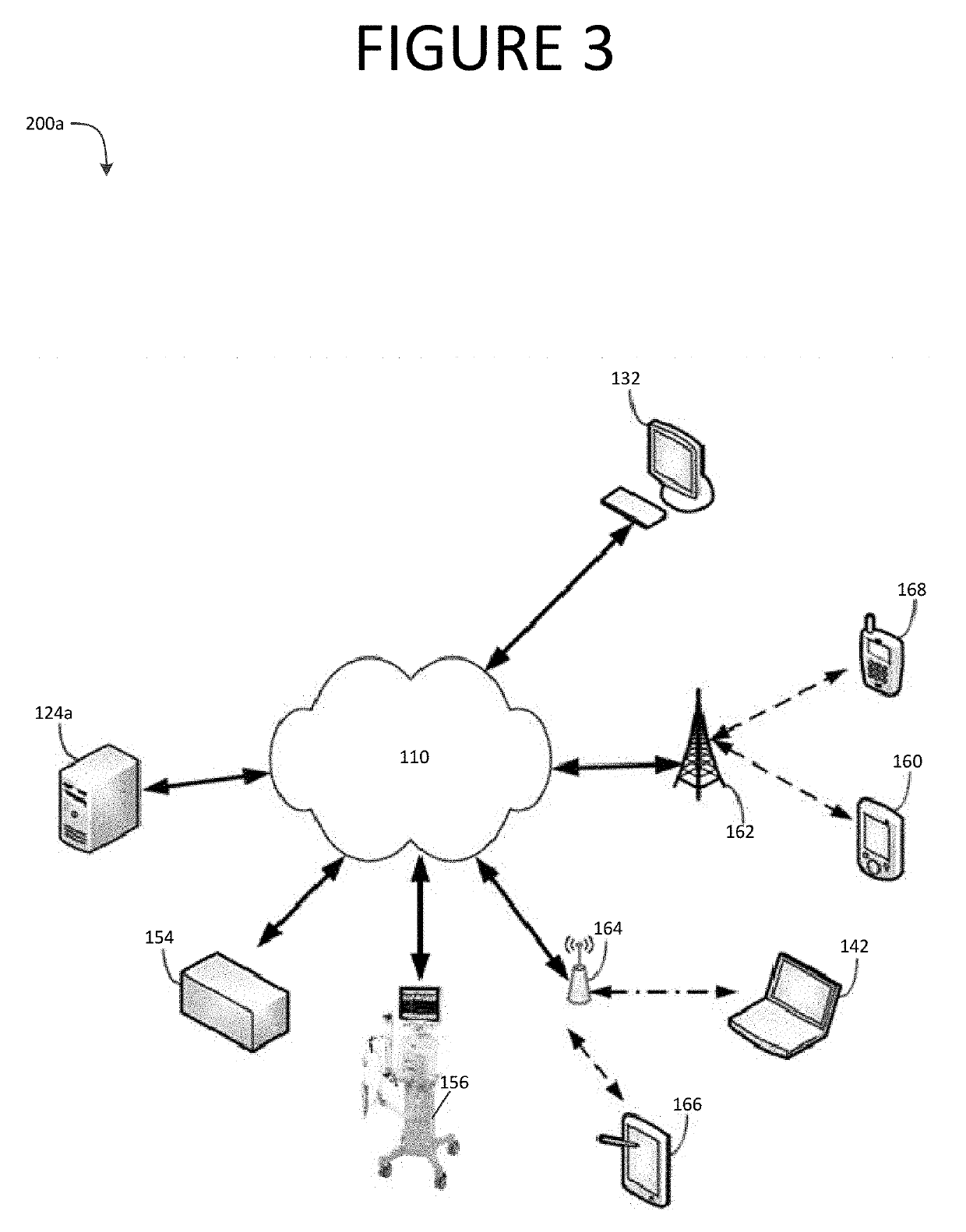
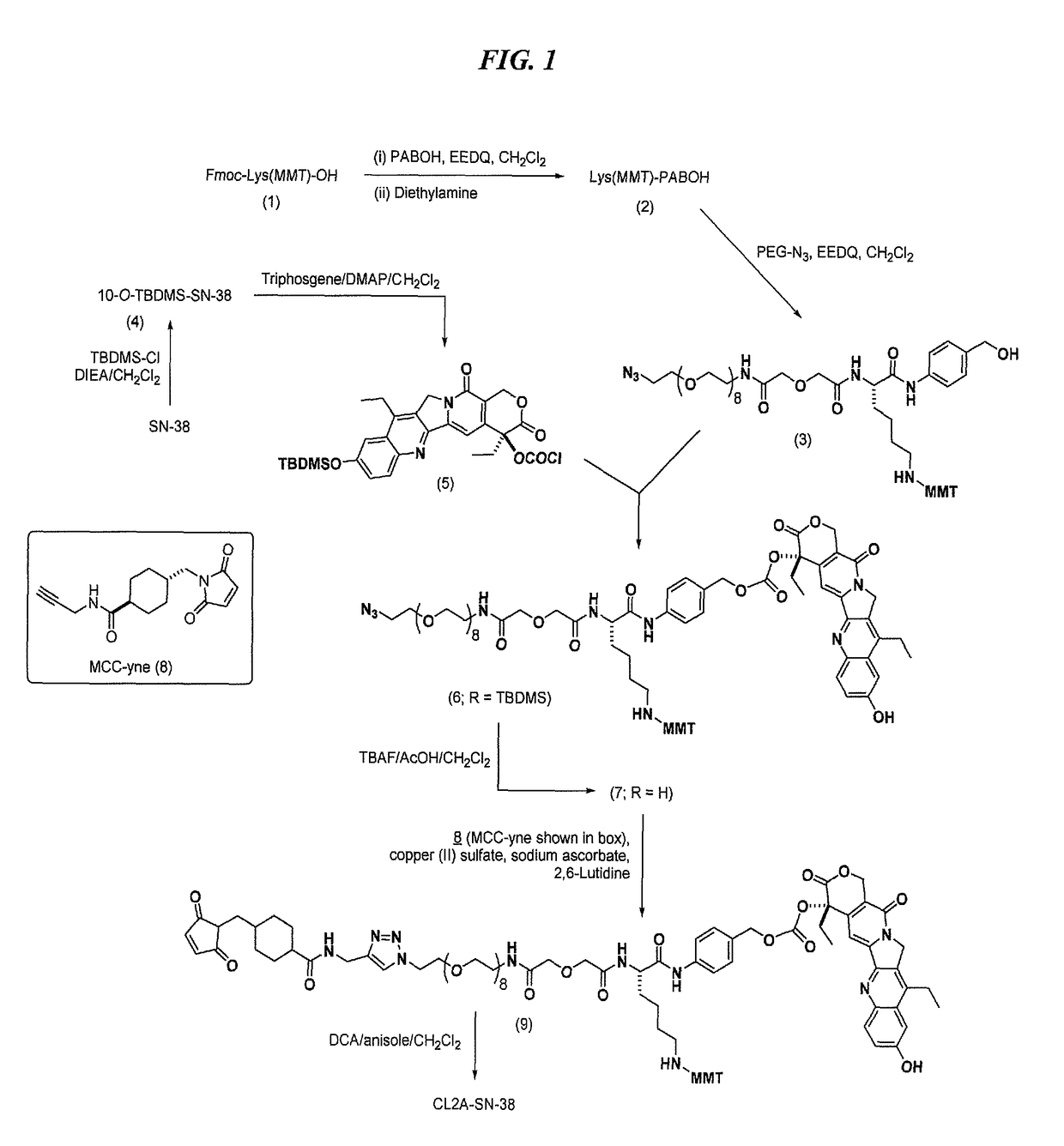
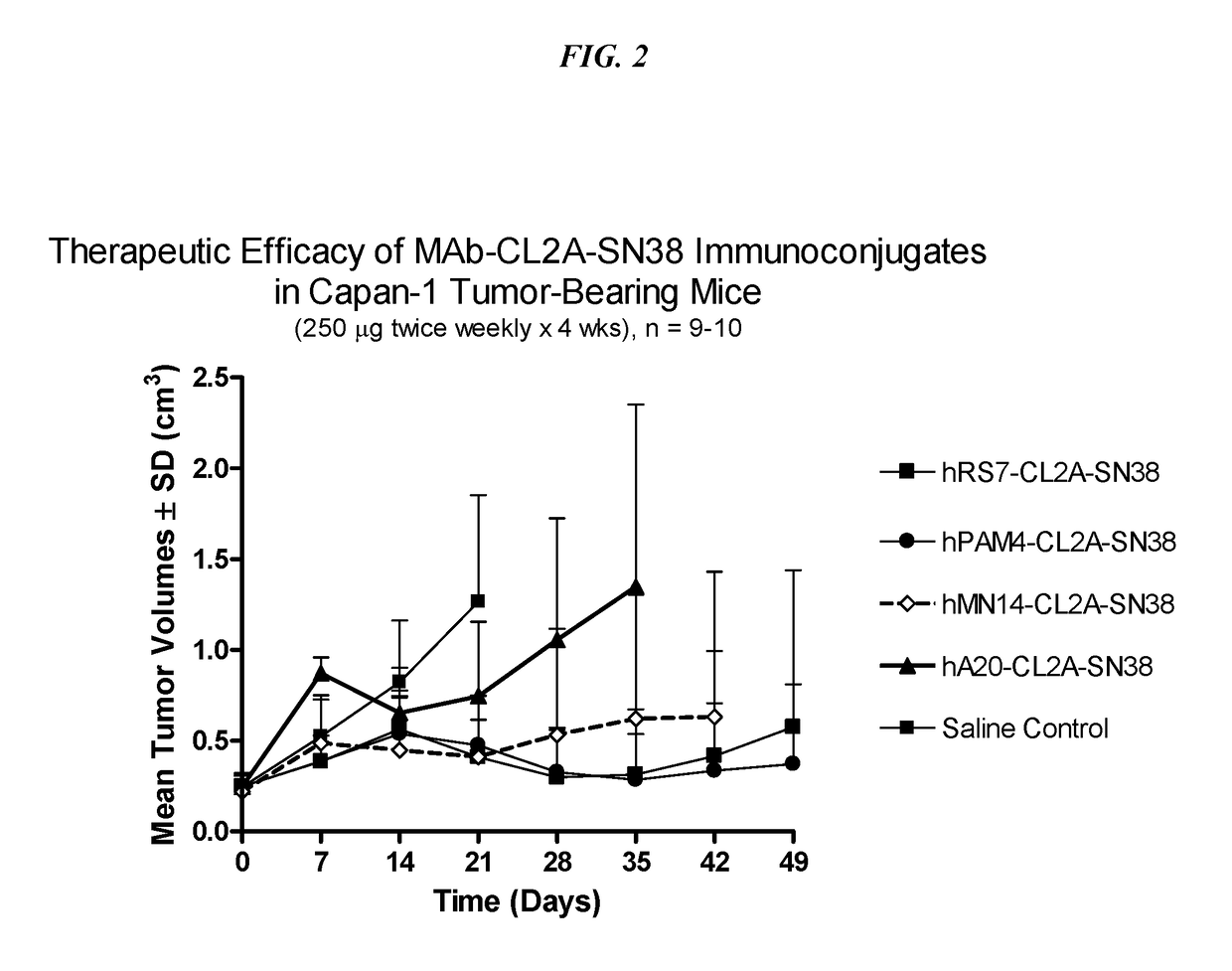
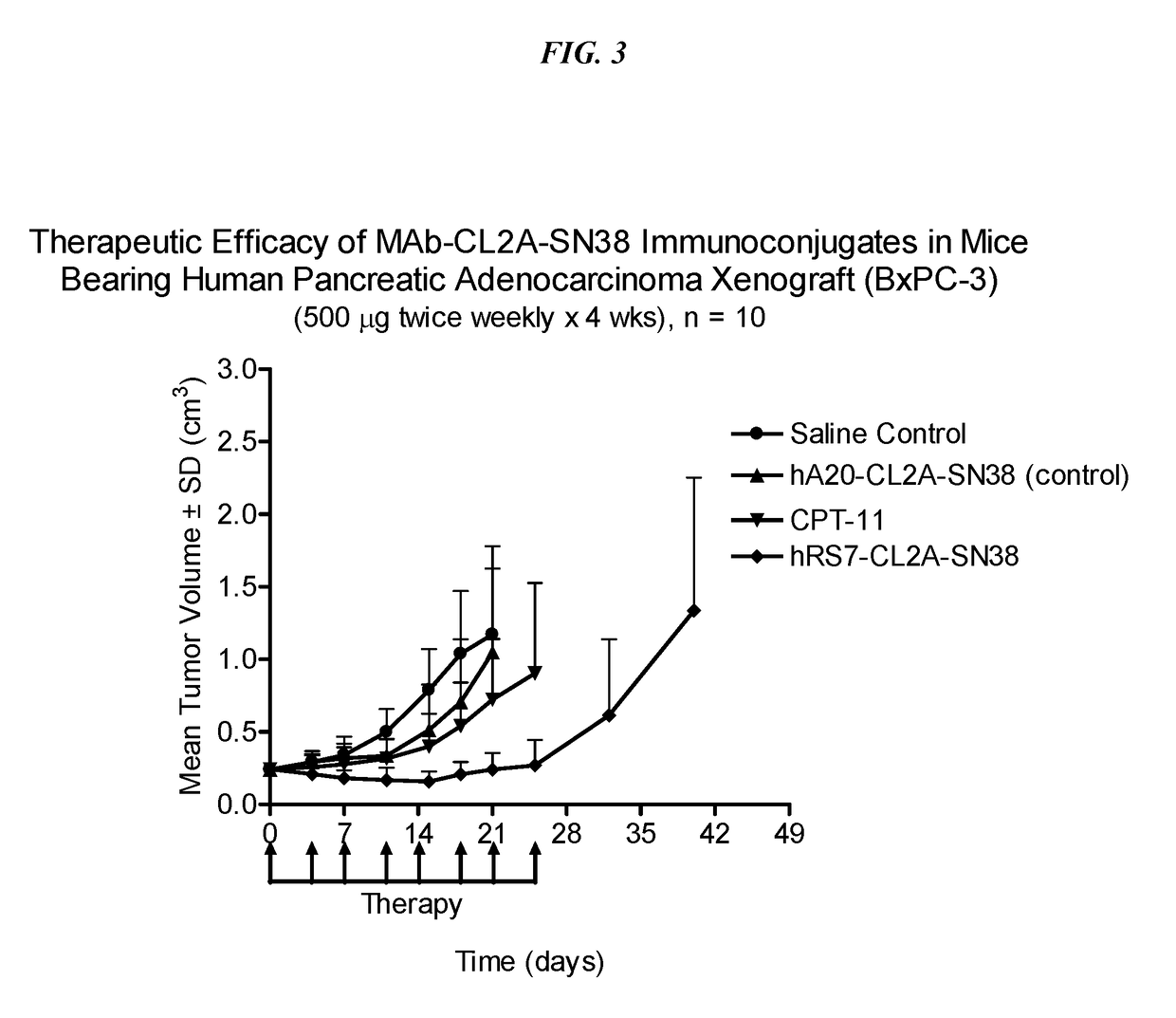
Antibody-SN-38 immunoconjugates with a CL2A linker
ActiveUS9931417B2Improve efficiency and yieldDecrease in levelPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseSide effect
The present invention concerns improved methods and compositions for preparing SN-38 conjugates of proteins or peptides, preferably immunoconjugates of antibodies or antigen-binding antibody fragments. More preferably, the SN-38 is attached to the antibody or antibody fragment using a CL2A linker, with 1-12, more preferably 6-8, alternatively 1-5 SN-38 moieties per antibody or antibody fragment. Most preferably, the immunoconjugate is prepared in large scale batches, with various modifications to the reaction scheme disclosed herein to optimize yield and recovery in large scale. Other embodiments concern optimized dosages and / or schedules of administration of immunoconjugate to maximize efficacy for disease treatment and minimize side effects of administration.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
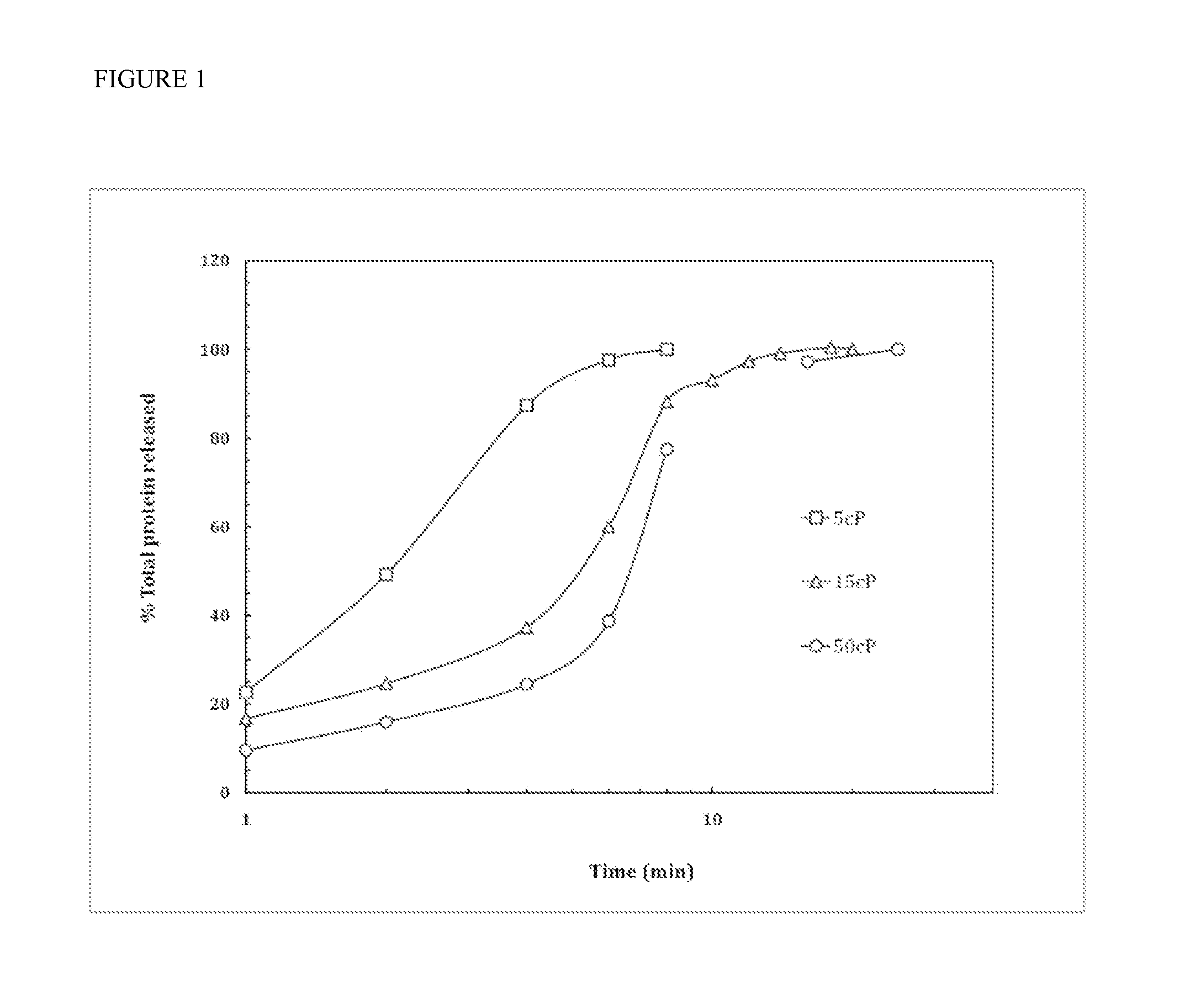
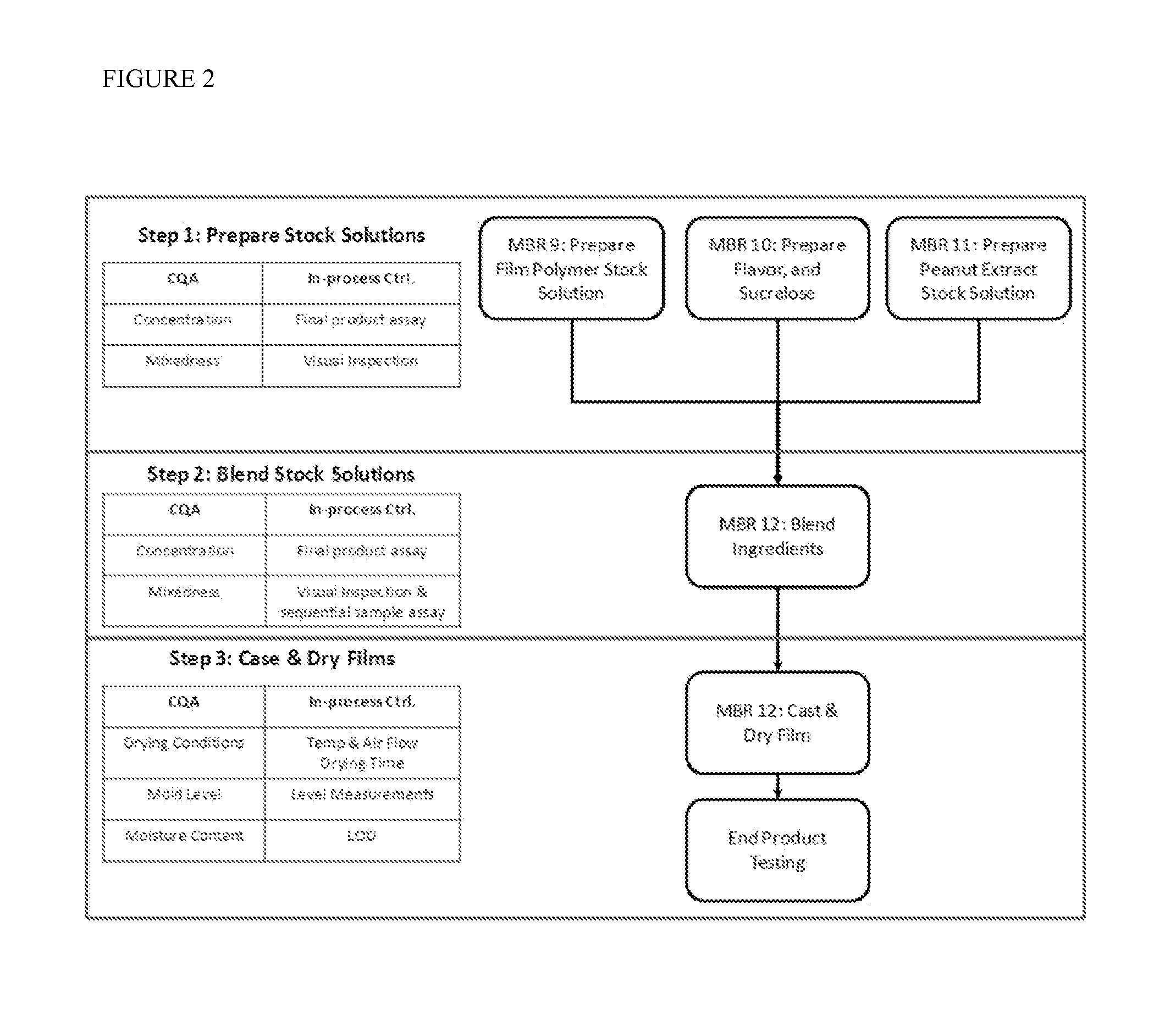
Orally dissolving thin films containing allergens and methods of making and use
The present invention provides a thin mucoadhesive sublingual film composition which provides improved allergen delivery and efficacy at a smaller dose while prolonging the contact time between the allergen and oral antigen presenting cells (APCs), and therefore minimizing the risk of systemic side effects. The thin film compositions of the present invention are also easier to standardize, and removes any need for measuring allergen doses at the physician's office, and which allows for a simplified dosing schedule. Methods of making the thin film compositions and methods for their use are also disclosed.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com