Patents
Literature
54 results about "Leased line" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
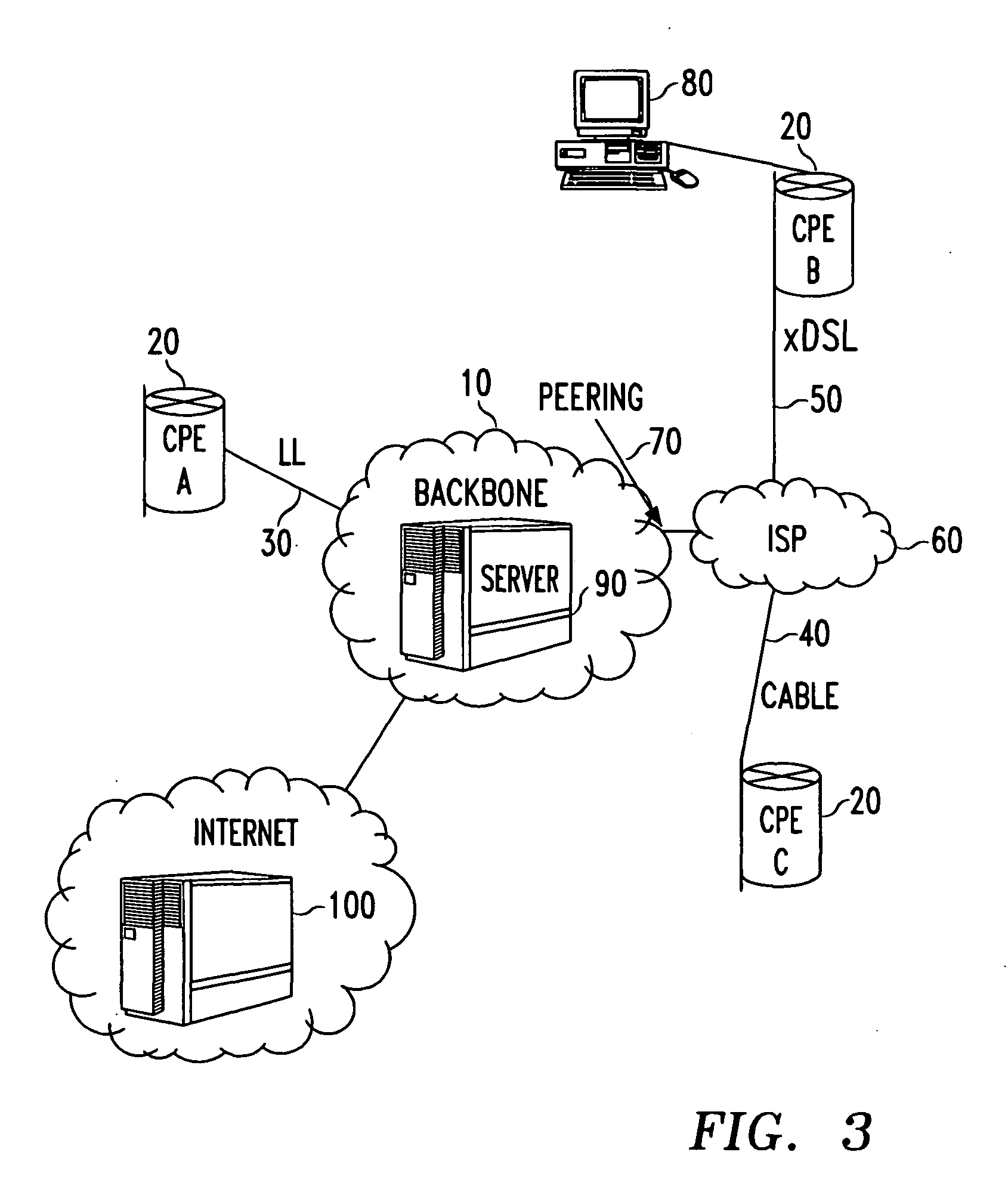
A leased line is a private bidirectional or symmetric telecommunications circuit between two or more locations provided according to a commercial contract. It is sometimes also known as a private circuit, and as a data line in the UK.
Integrated pharmaceutical accounts management system and method
InactiveUS20020002495A1Facilitate real-time adjudicationEasy to processHand manipulated computer devicesDrug and medicationsData warehouseDrug interaction
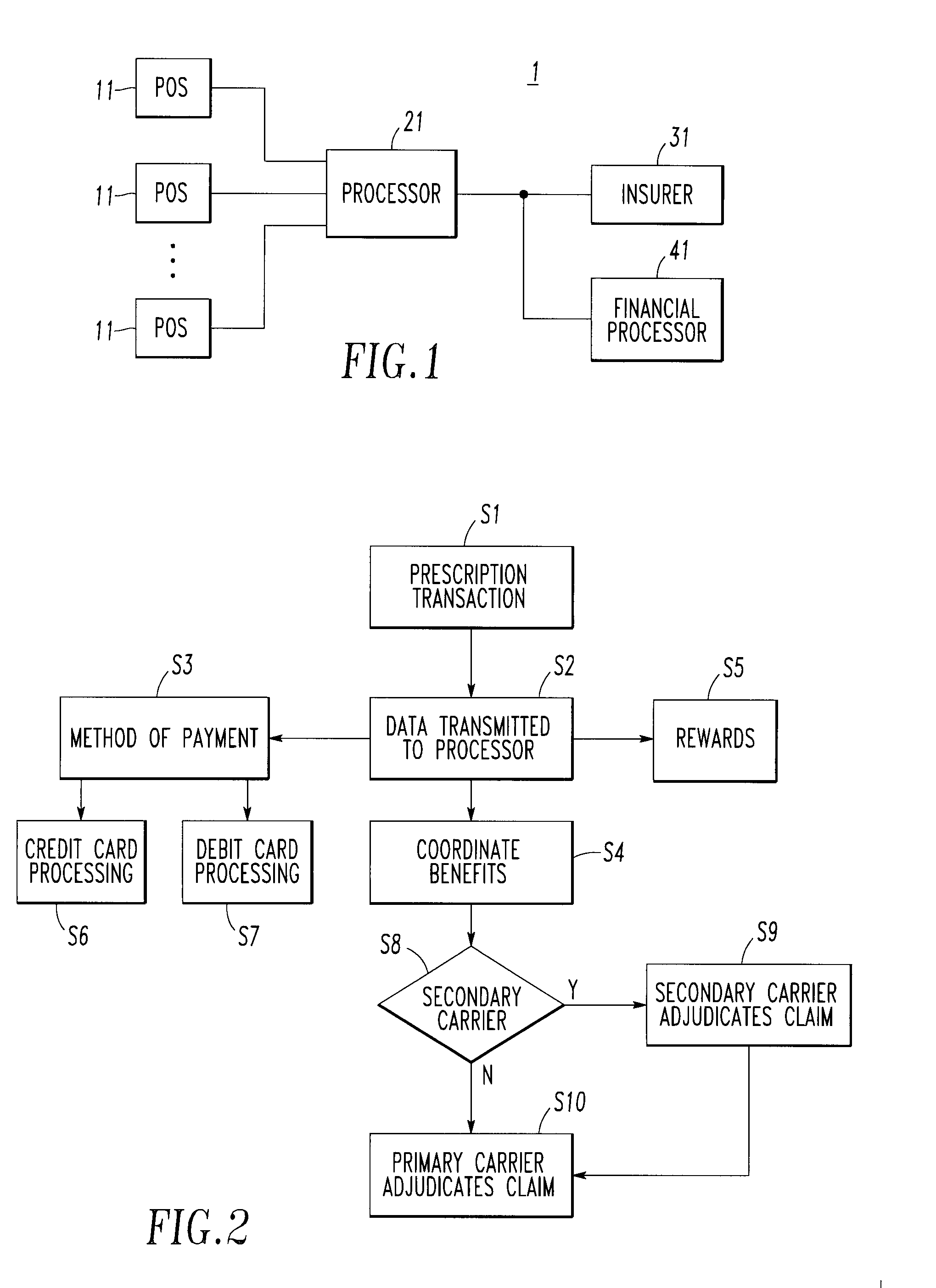
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> An integrated suite of services for consumers, service providers and manufacturers in the pharmaceutical industry is disclosed. The present invention utilizes one or more of the NCPDP standard formats and adopts the switch for an integrated system of, for example, instant adjudication of prescriptions, consumer data warehousing and / or incentive rewards for the consumer. A participating consumer with one card, can instantly purchase pharmaceuticals and charge the transaction to a credit card and earn and apply savings dollars redeemable for pharmaceutical purchases. For a participating service provider, instant adjudication and instant validation of consumer eligibility can be performed. Moreover, a service provider may receive messages related to the patient's medications. Significantly, data is recorded for consumers even when consumers make the pharmaceutical purchase with cash. The system includes a unique card issued to participating consumers. The card is adapted to encode conventional credit or debit card information specific to the participating consumer so that the consumer can consummate a transaction for the purchase of pharmaceuticals without possession of an additional credit card. The system further includes a host processor coupled to the point of sale at the service provider through a leased line or public switch network or the like. When a customer performs a pharmaceutical transaction at the point of sale of the service provider, the host processor coordinates any benefits and data with other prescription benefit management systems through messages transmitted and received from any primary or secondary carrier systems. The host processor further is adapted to facilitate real-time adjudication of claims and checks for any dangerous drug-to-drug interactions. The host processor additionally facilitates any financial processing including the accumulation and redemption of any bonus dollars earned by the consumer. Furthermore, since the card used by the consumer can be encoded with credit or debit card information, the host processor determines the desired payment method and performs the actual financial transaction. Even if the transaction at the point of sale is a cash purchase, the consumer may desire to use his unique card for the accrual of bonus dollars. Therefore, data concerning the transaction (i.e., pharmacy number, prescription number, etc.) can be recorded even for transactions conducted with cash.
Owner:NPAX
System and method for secure communications with a remote software program
ActiveUS7877783B1Communication securityAmount of timeDigital data processing detailsData switching networksSecure communicationLeased line
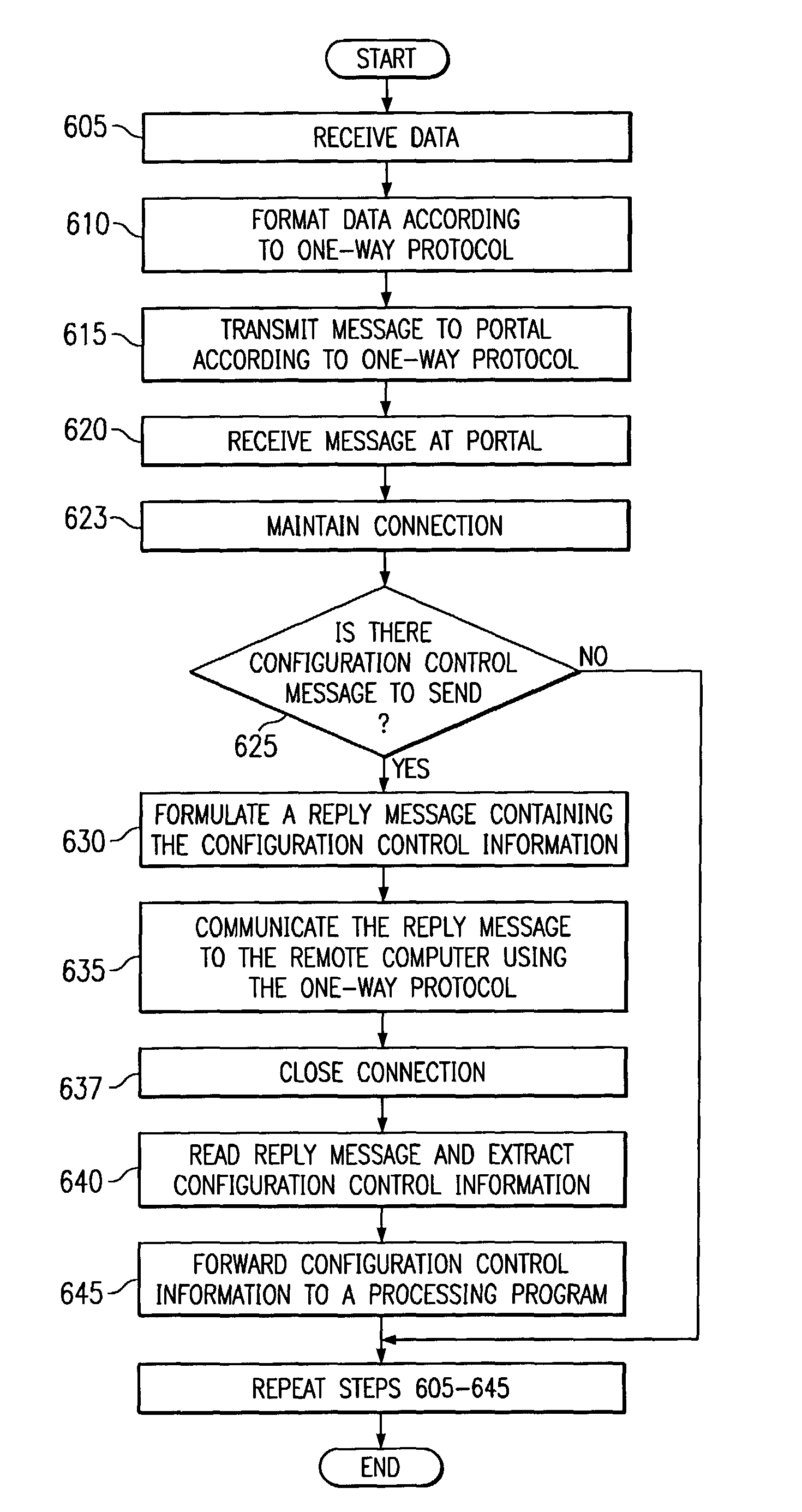
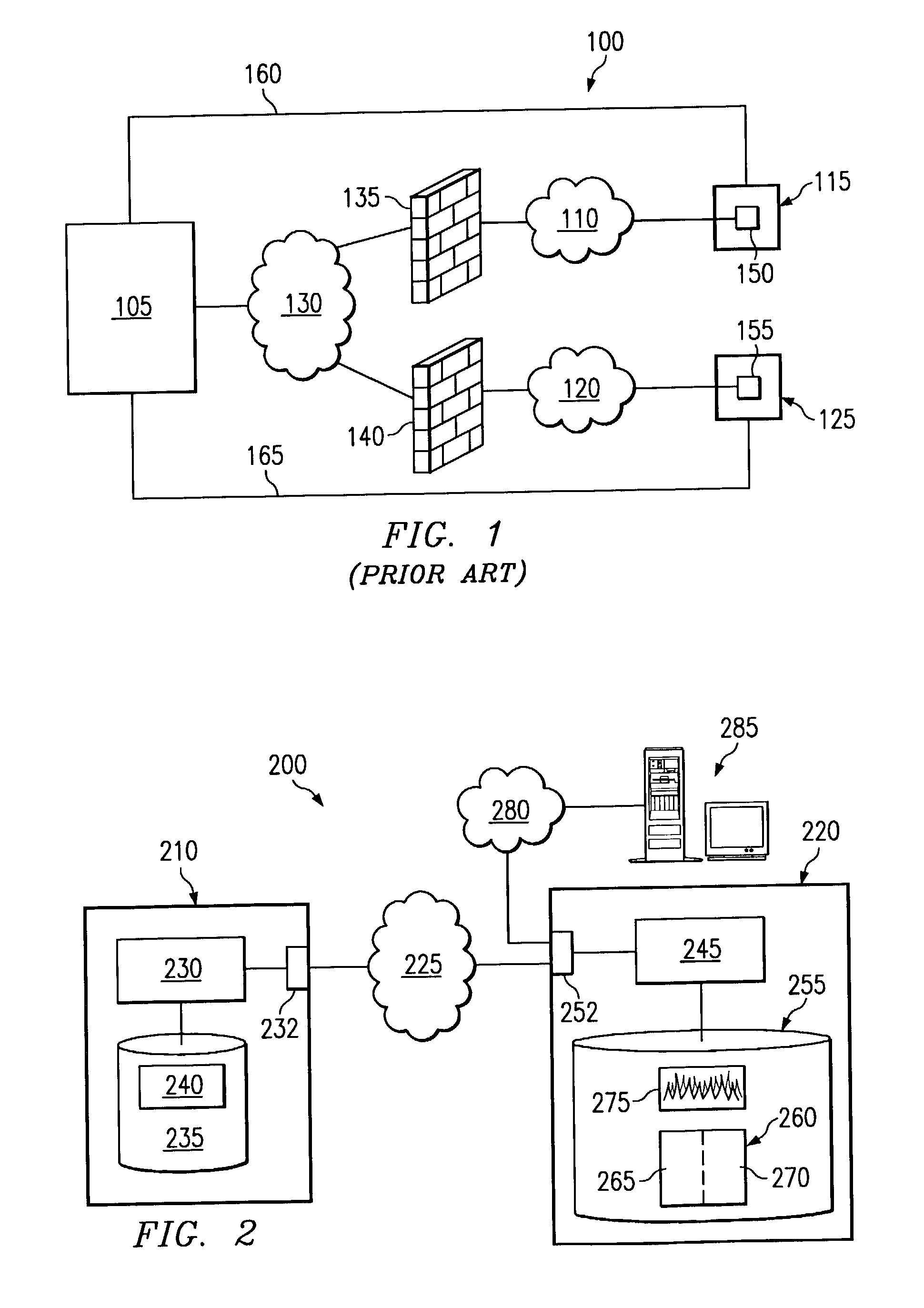
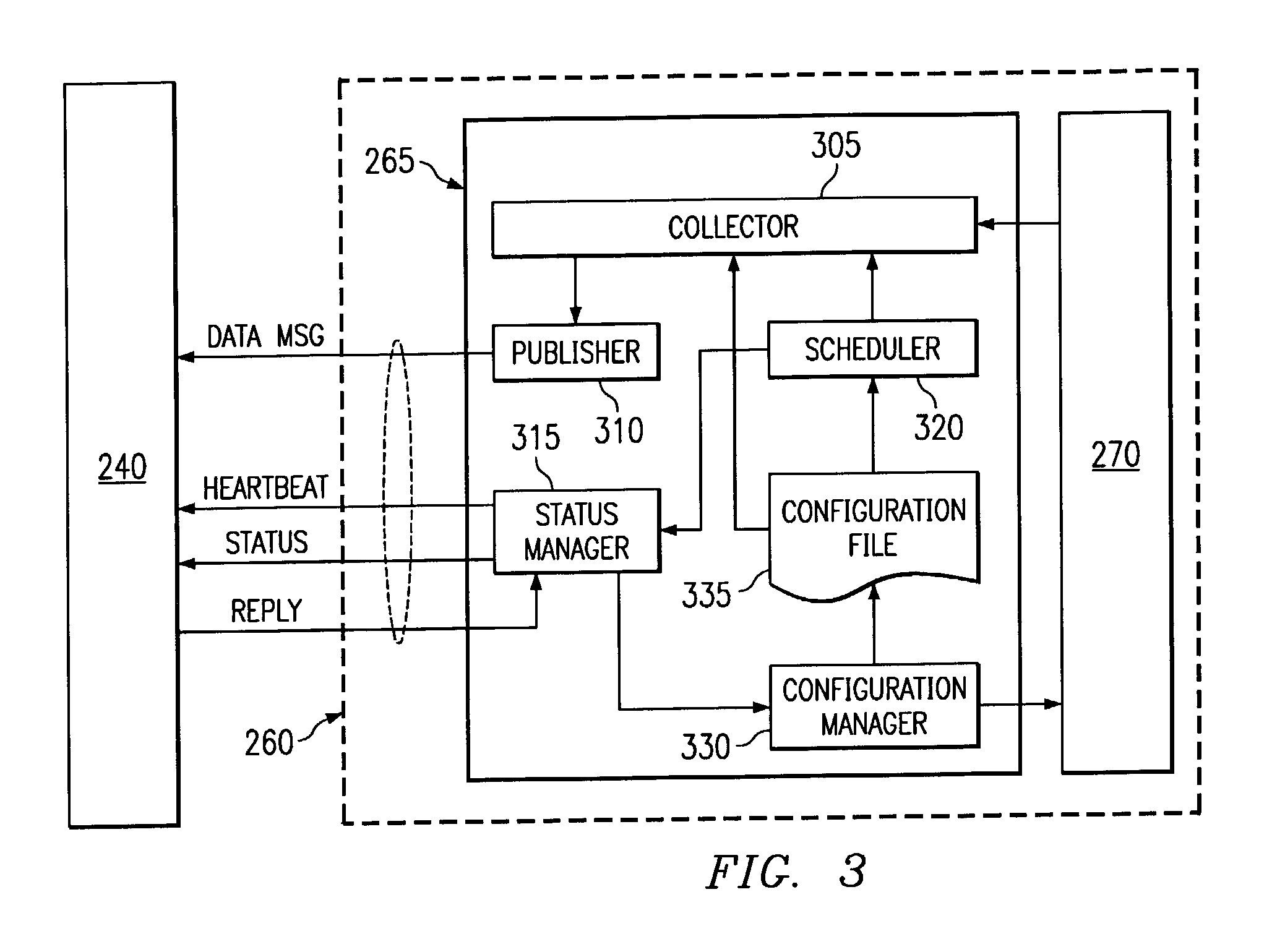
In one embodiment of the present invention, a messaging program at a remote computer can send a first message to a portal computer according to a one-way protocol such as HTTP. A portal program at the portal computer can receive the first message and determine if information should be sent to the portal computer. If so, the portal computer can generate a reply message that includes the information and send the reply message to remote computer on the same connection over which the first message was received. In this manner, the portal computer can send configuration control information and other information to the messaging program without requiring leased lines, dial-up connections or a VPN. Moreover, since the communication according to the one-way protocol was initiated at the remote computer, a firewall will allow the remote computer to receive the reply message.
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
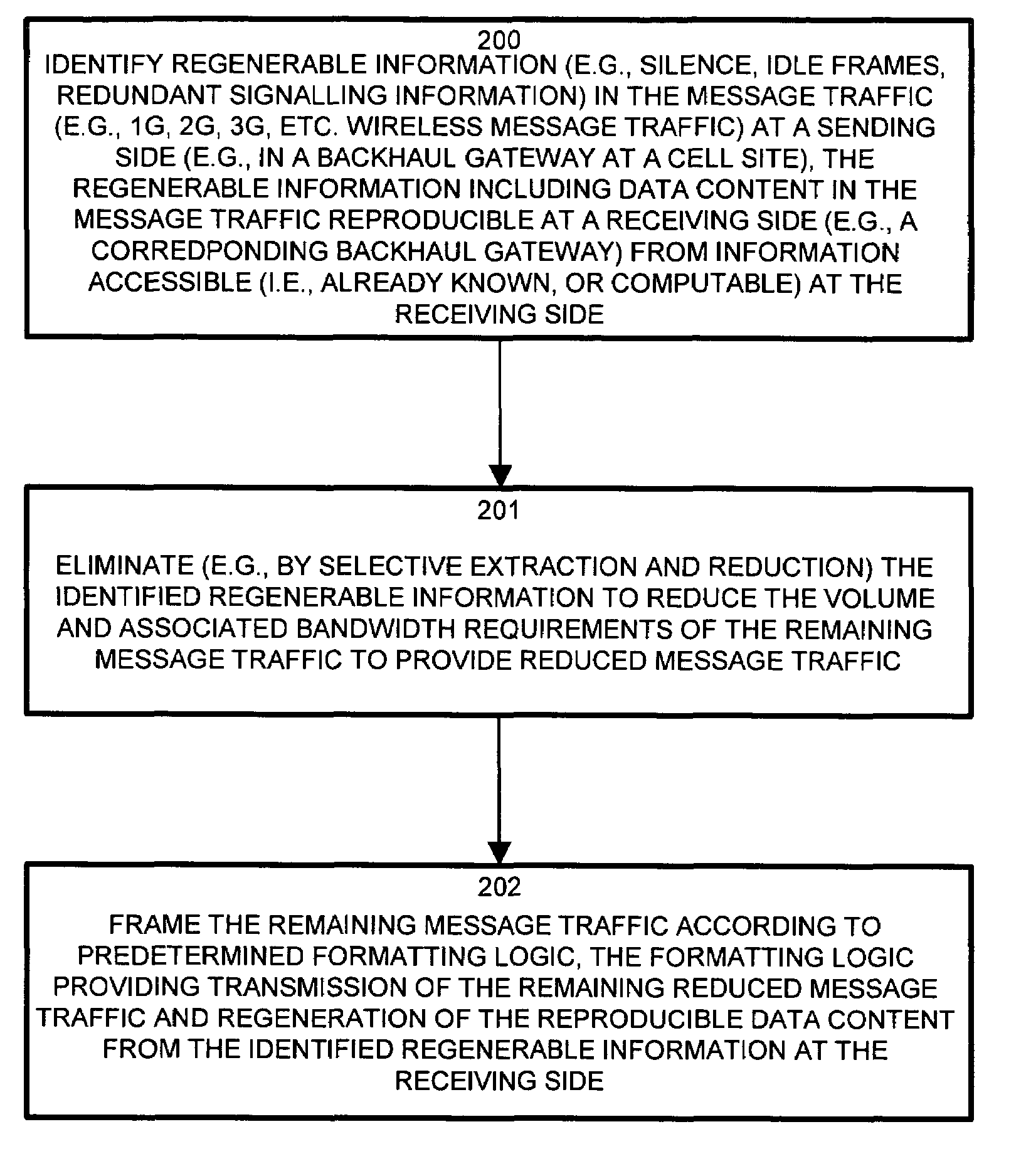
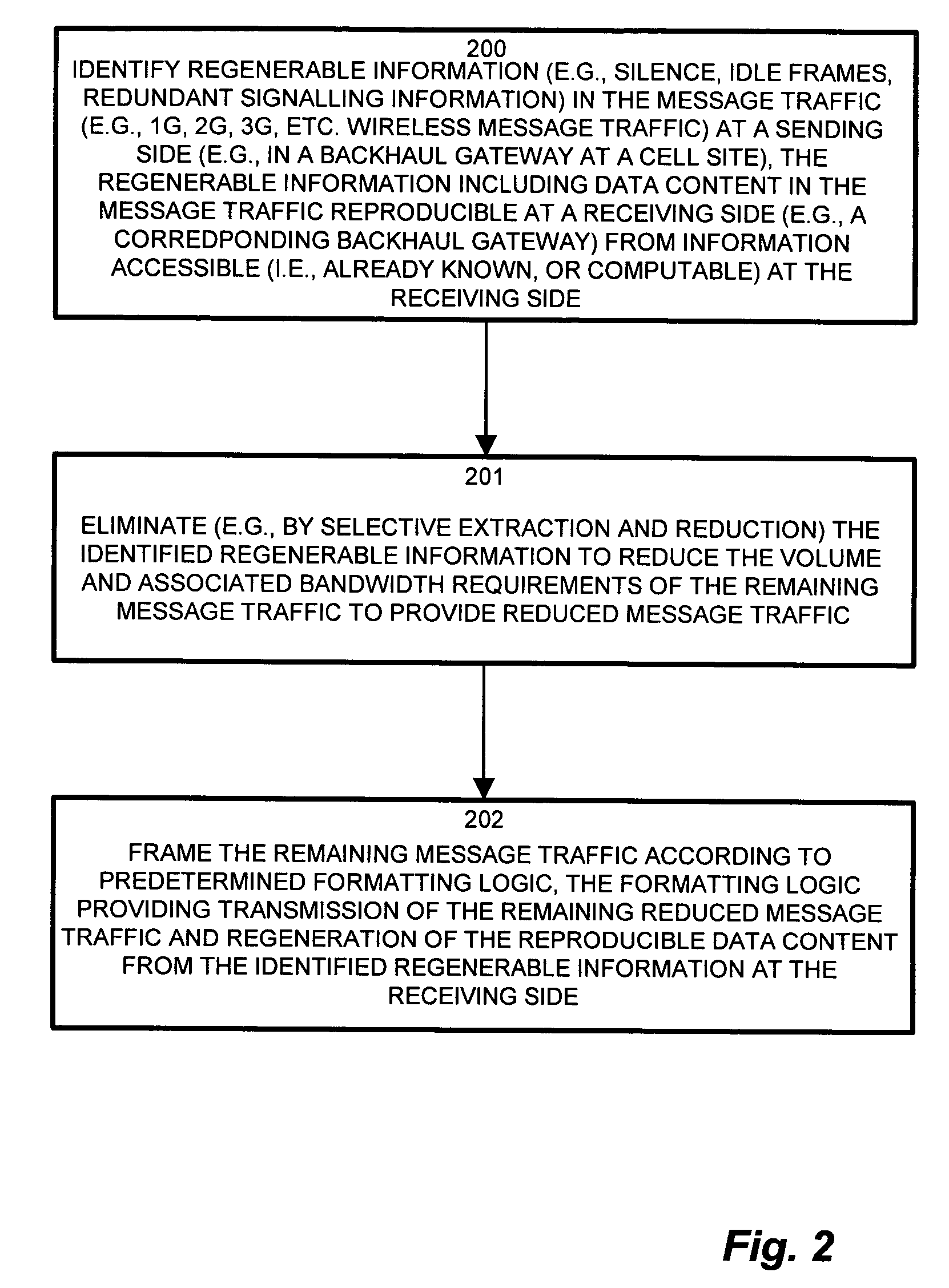
Methods and apparatus for low latency signal aggregation and bandwidth reduction
InactiveUS20070195815A1Minimize the numberFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementType specificService provision
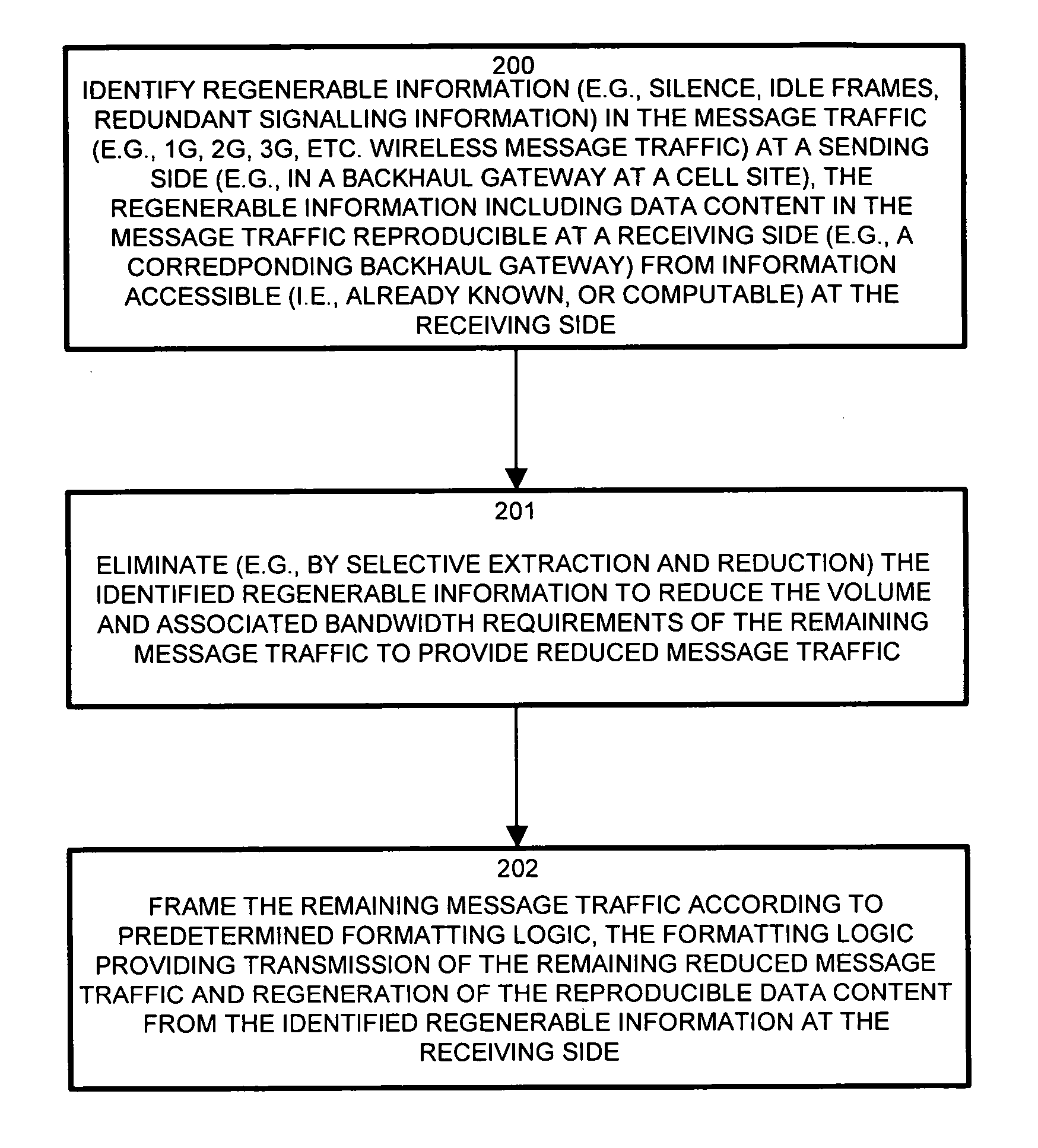
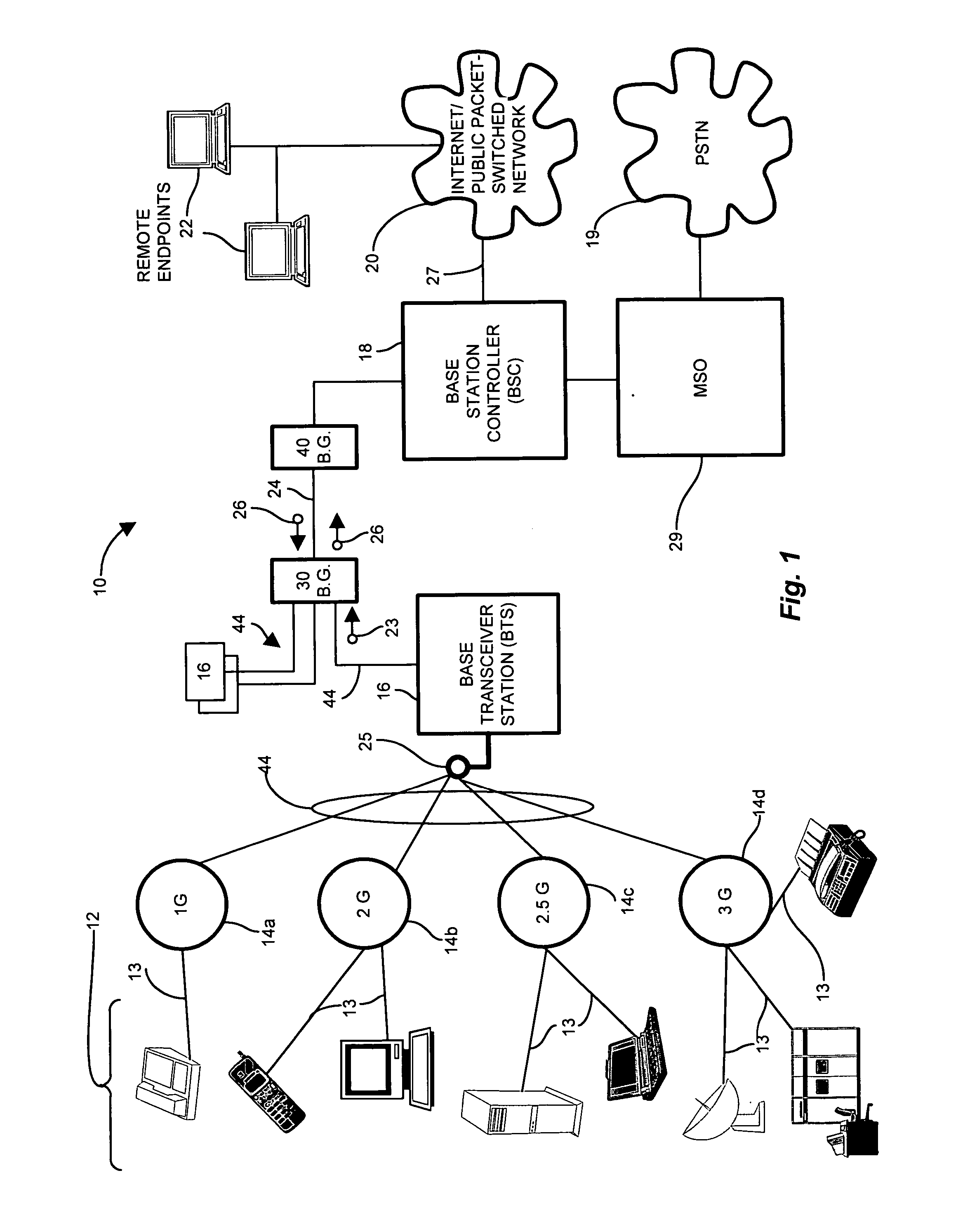
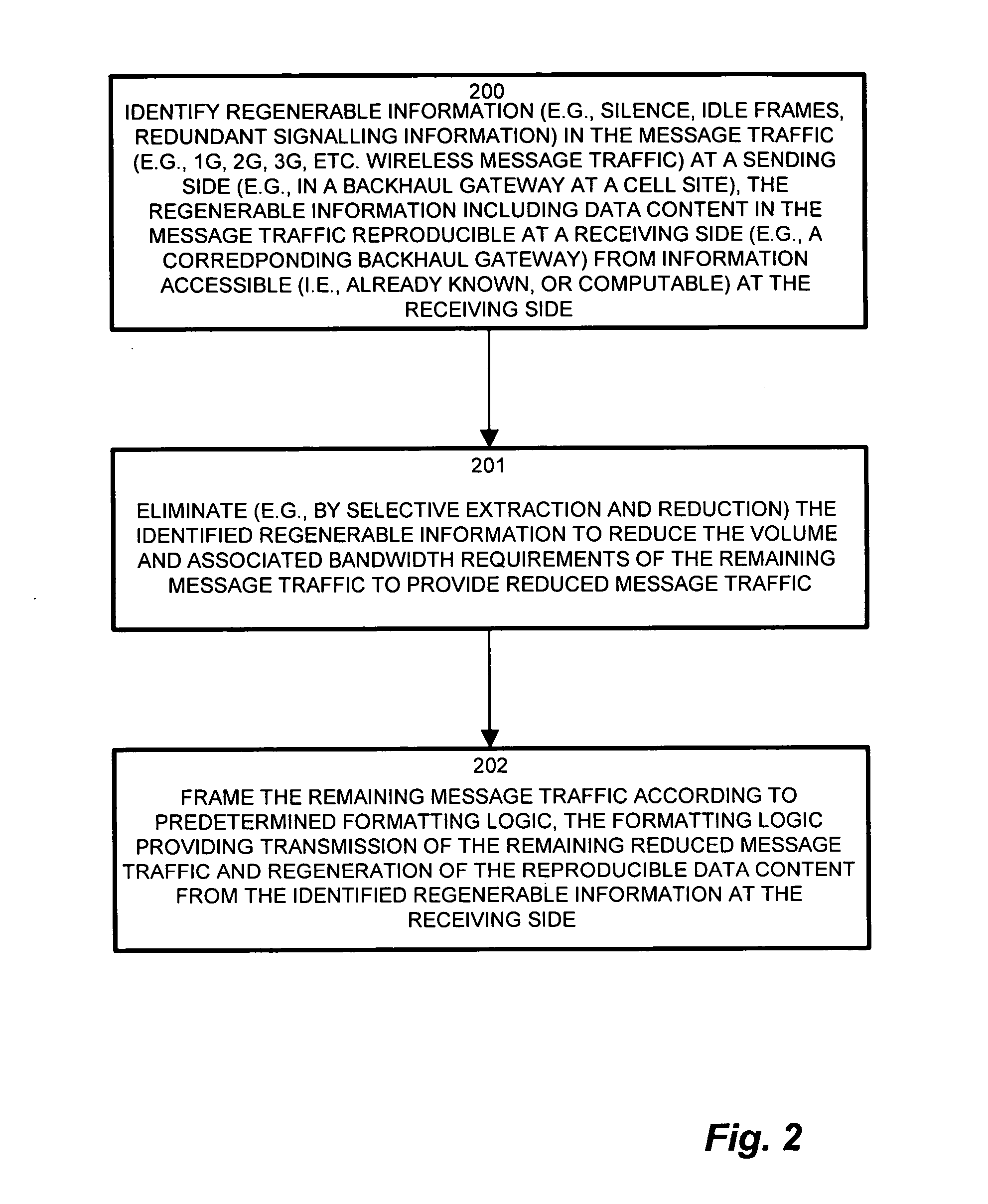
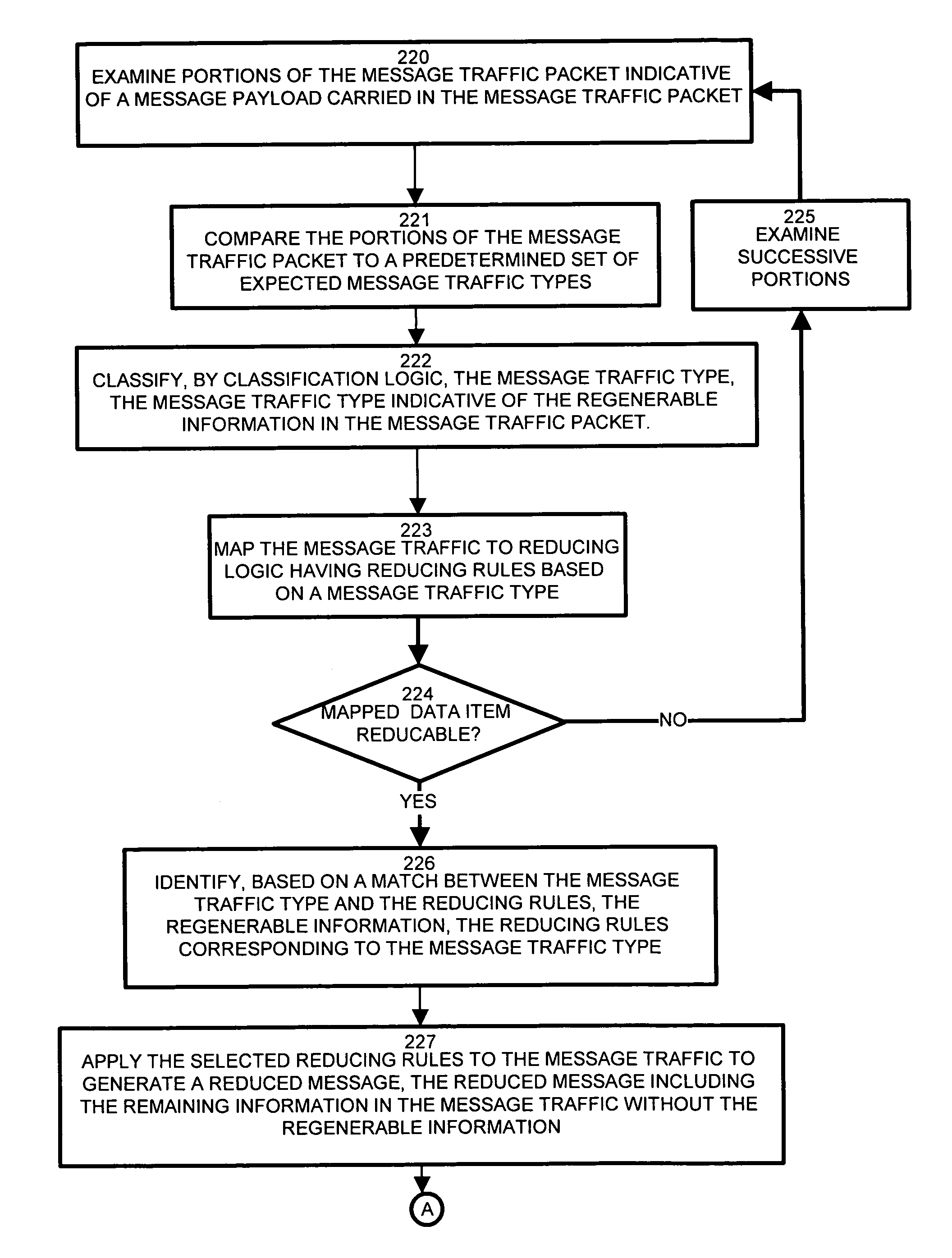
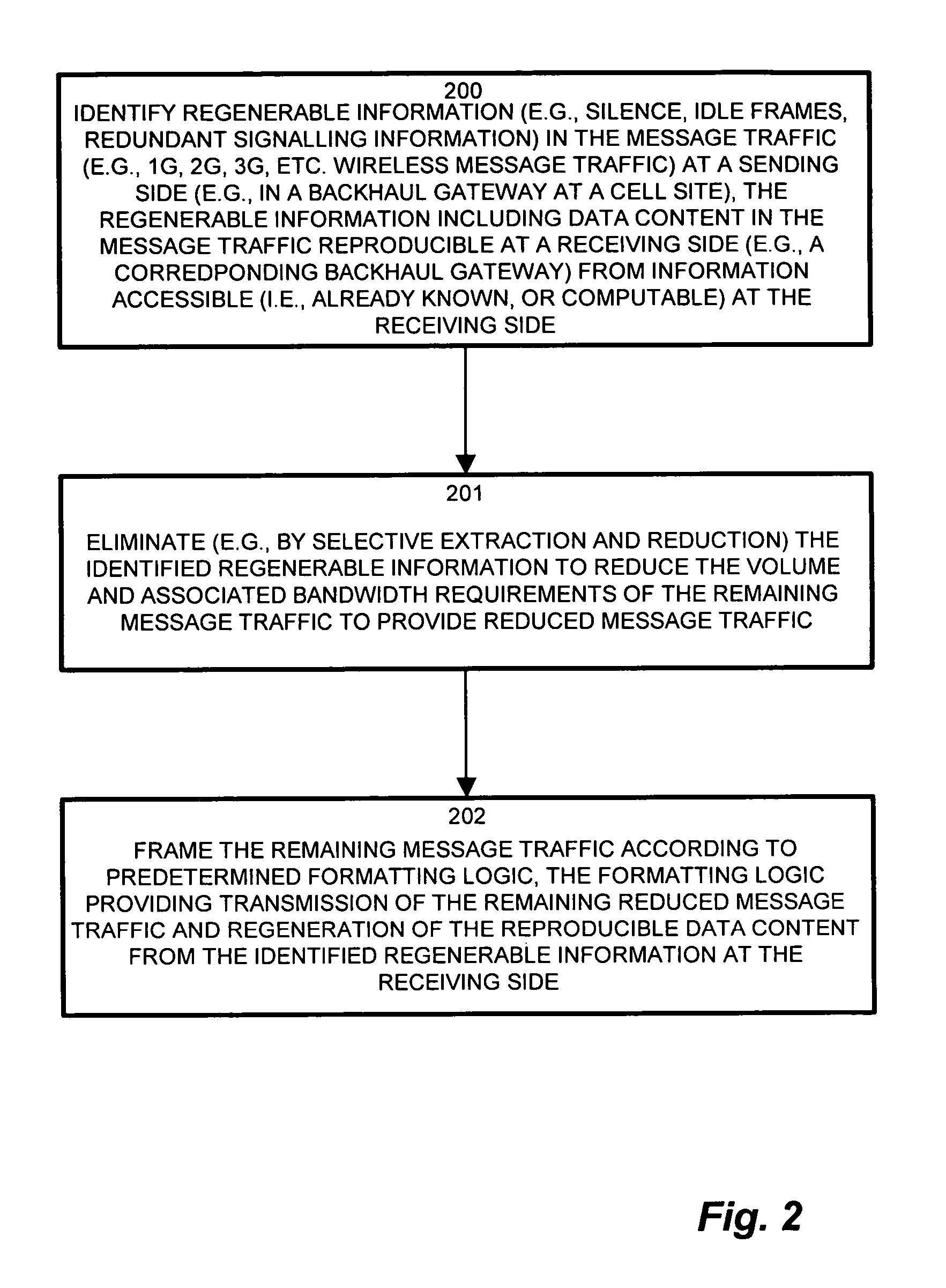
Wireless network demands continually increase as wireless service providers pursue additional service capabilities. In a cellular communication system, leased lines between remote cell sites and the corresponding Mobile Switching Offices (MSOs) remain a major operating cost. Bandwidth reduction by identification and elimination of payload data and control information which need not be fully replicated because it can be deduced from information accessible or previously transmitted allows fewer lines to support the same bandwidth. A wireless access gateway is operable to aggregate such redundant and regenerable data on a backhaul link between a wireless cell site and the corresponding mobile switching office (MSO) to provide low-latency, type specific lossless bandwidth reduction. The wireless access gateway identifies regenerable information and eliminates portions of the data which the device need not transmit because the data is redundant, or accessible or recreatable, at the receiving side. In this manner, the access device allows fewer lines to carry the reduced message traffic by transmitting only the non-recreatable data and eliminating message traffic for regenerable information.
Owner:VERSO BACKHAUL SOLUTIONS
Shared Radio Backhaul System
InactiveUS20080181183A1Small surface areaAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesData capacityTelecommunications network
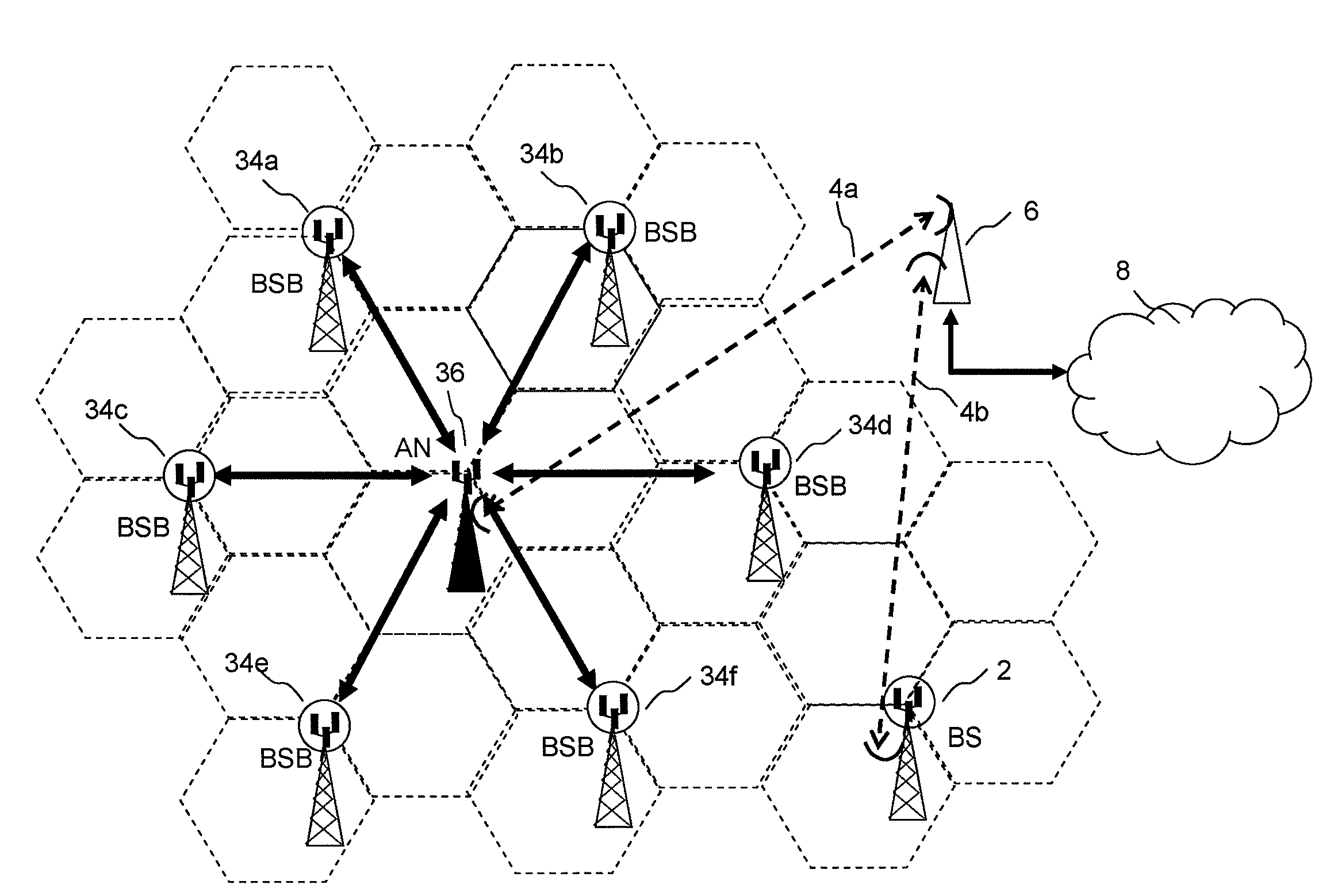
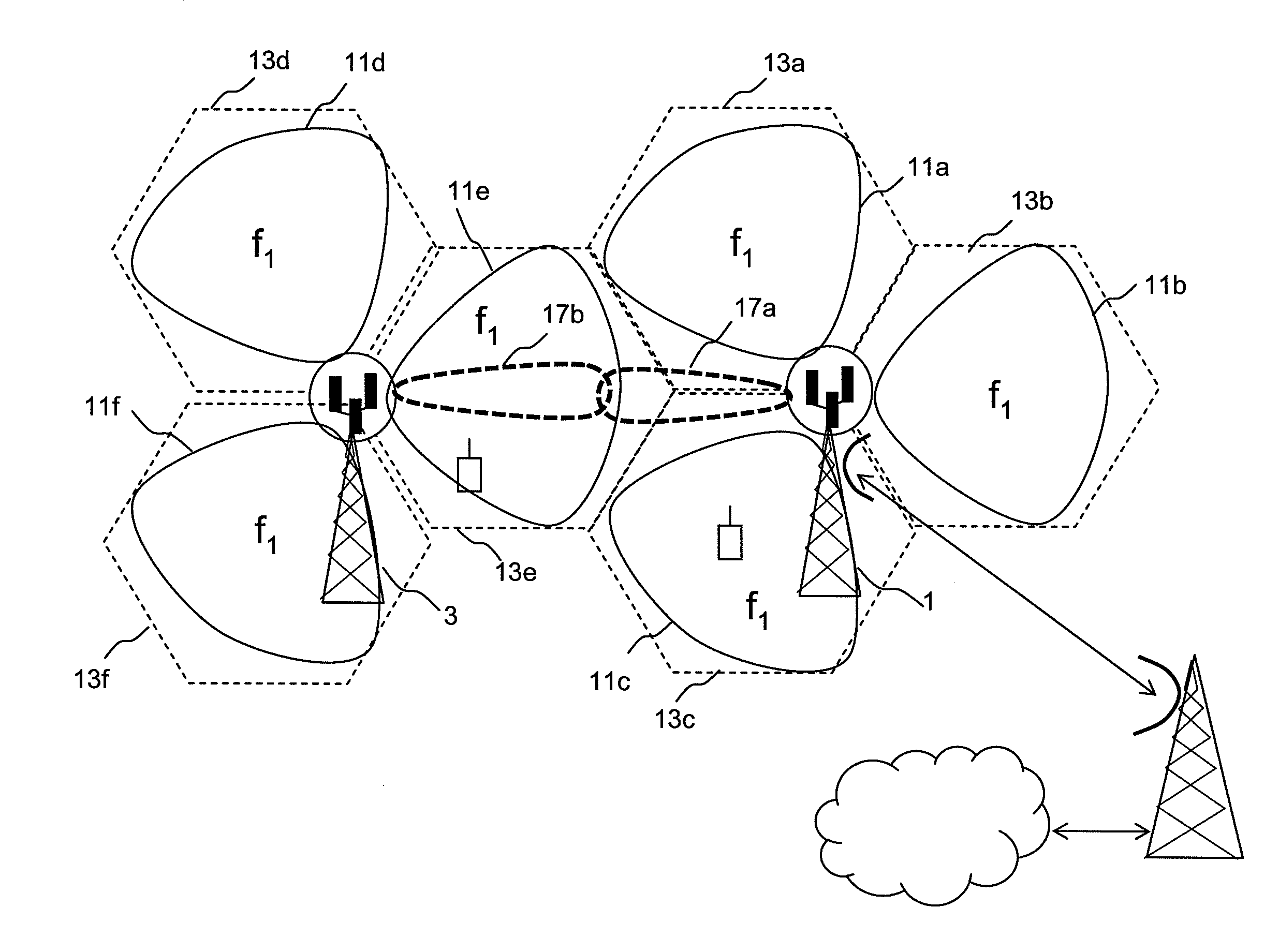
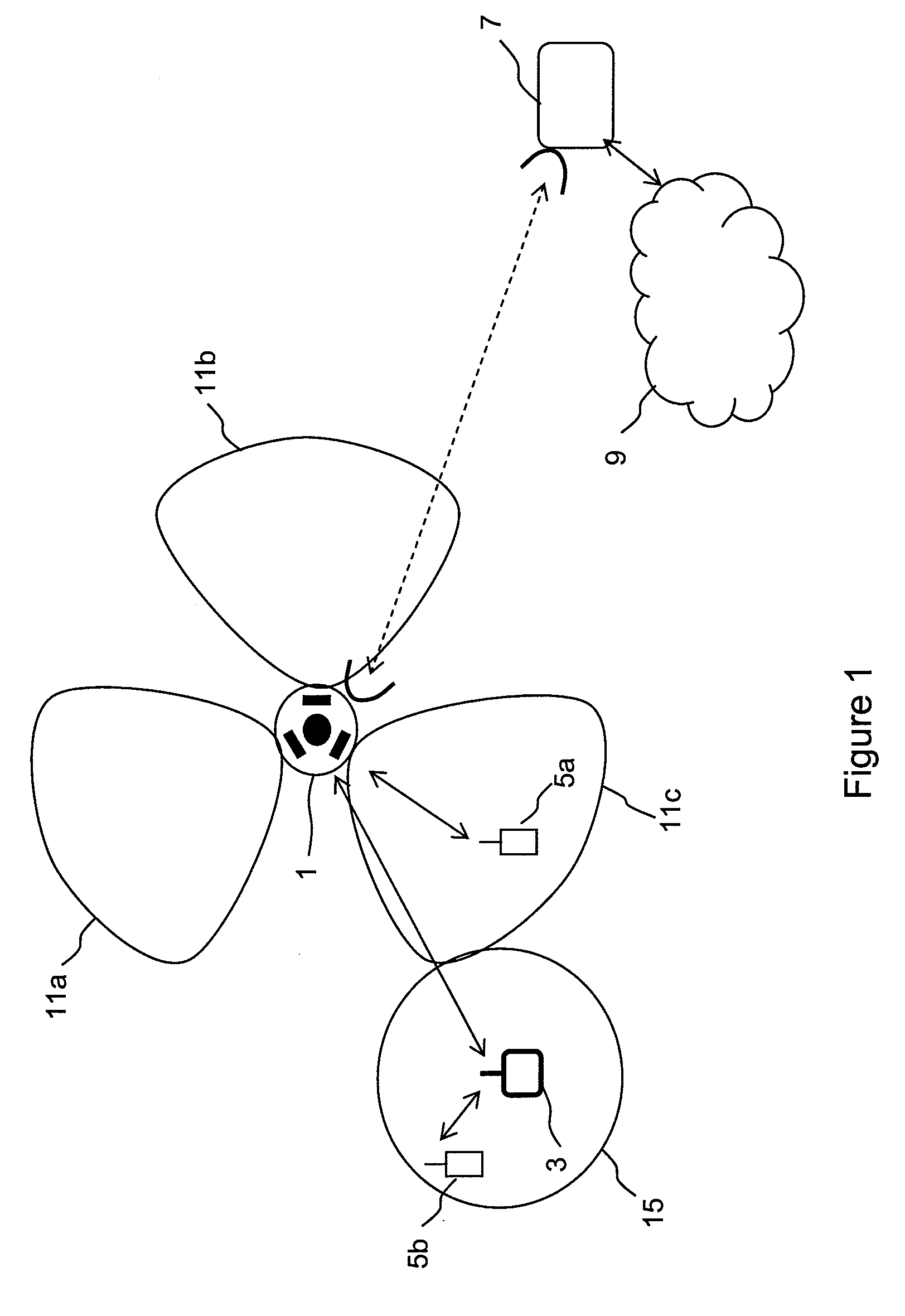
Embodiments of the invention relate to wireless communications networks, and more specifically to method and apparatus relating to wireless backhaul for cellular wireless systems. Increasing data capacity of cellular wireless systems places increasing demands on the capacity of the two way connection, known as backhaul, between a cellular base station and a telecommunications network such as the PSTN backhaul, since this is the connection that has to convey the wireless-originating traffic to its destination, often in an entirely different network. Known backhaul links include leased lines, microwave links, optical fibre links or radio resources for relaying backhaul traffic between base stations. The fixed line solutions are expensive to implement and maintain, while the radio solutions suffer from interference from transmissions between base stations with transmissions from user equipment to base stations which are not communicating with other base stations. In embodiments of the invention, the relaying of access data between base stations utilises radio resources other than radio resources used by transmissions from user equipment within an area of contiguous wireless coverage. The benefit of this approach is that it provides a means of avoiding interference between inter-base station transmissions and user equipment to base station transmissions.
Owner:APPLE INC
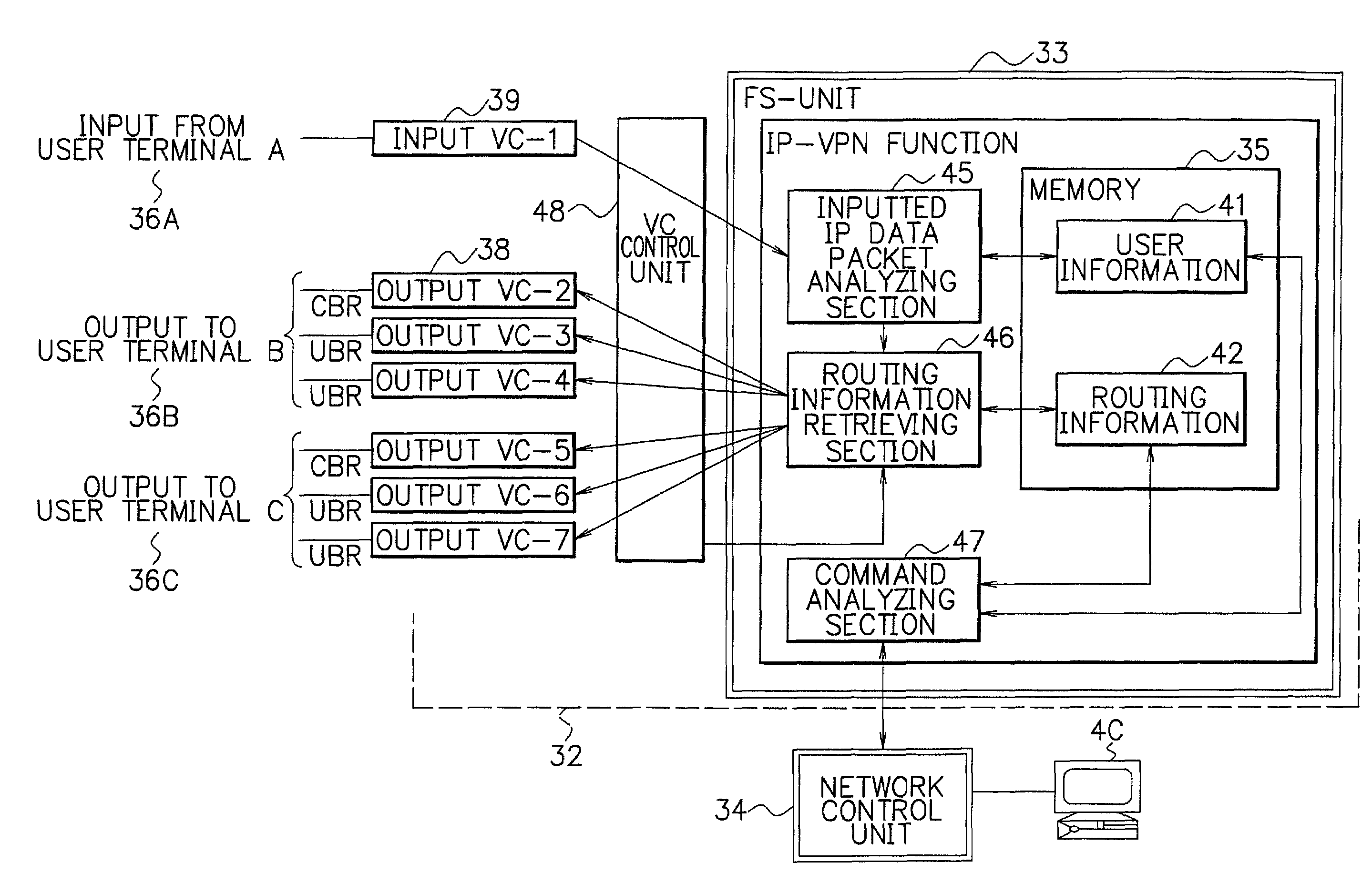
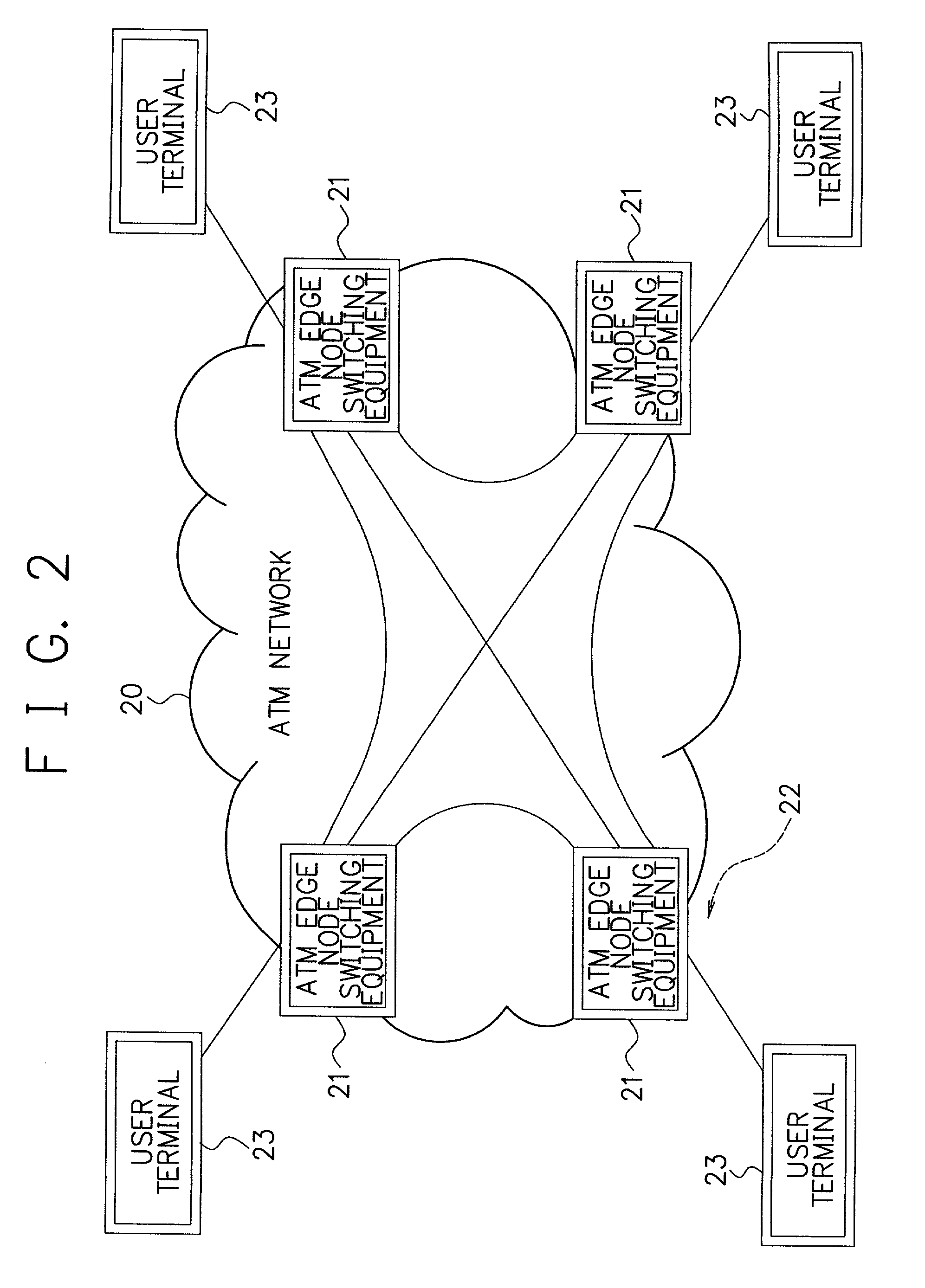
ATM edge node switching equipment utilized IP-VPN function
InactiveUS6967954B2Low costTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionQuality of serviceNetwork packet
ATM edge node switching equipment utilizes an IIP-VPN function, which can achieve a low cost VPN compared with an L2-VPN in which a user terminal is connected to the ATM edge node switching equipment by a mesh connection. This connection is provided, by connecting the user terminal and the ATM edge node switching equipment with one leased line. The ATM edge node switching equipment has an IP data packet distribution unit, which distributes each of IP data packets to each of the plural user terminals, by utilizing a IP-VPN unit using a destination IP address of each of the plural user terminals. The IP-VPN unit has an inputted IP data packet analyzing section that obtains an input VC (virtual channel) number and also obtains a VPN-ID (virtual private network-identifier) for distinguishing each of the user terminals and a QOS (quality of service) type set by QOS information from a header part of the IP data packet transferred from one of the user terminals. The IP-VPN device also has a routing information retrieving section that retrieves a routing of a VC for a destination address by using the destination IP address, the VPN-ID, and the QOS type, and sets the routing of the VC for the destination address.
Owner:NEC CORP
Methods and apparatus for network signal aggregation and bandwidth reduction
Wireless network demands continually increase as wireless service providers pursue additional service capabilities. In a cellular communication system, leased lines between remote cell sites and the corresponding Mobile Switching Offices (MSOs) remain a major operating cost. Bandwidth reduction by identification and elimination of payload data and control information which need not be fully replicated because it can be deduced from information accessible or previously transmitted allows fewer lines to support the same bandwidth. A wireless access gateway is operable to aggregate such redundant and regenerable data on a backhaul link between a wireless cell site and the corresponding mobile switching office (MSO) to provide low-latency, type specific lossless bandwidth reduction. The wireless access gateway identifies regenerable information and eliminates portions of the data which the device need not transmit because the data is redundant, or accessible or recreatable, at the receiving side. In this manner, the access device allows fewer lines to carry the reduced message traffic by transmitting only the non-recreatable data and eliminating message traffic for regenerable information.
Owner:VERSO BACKHAUL SOLUTIONS
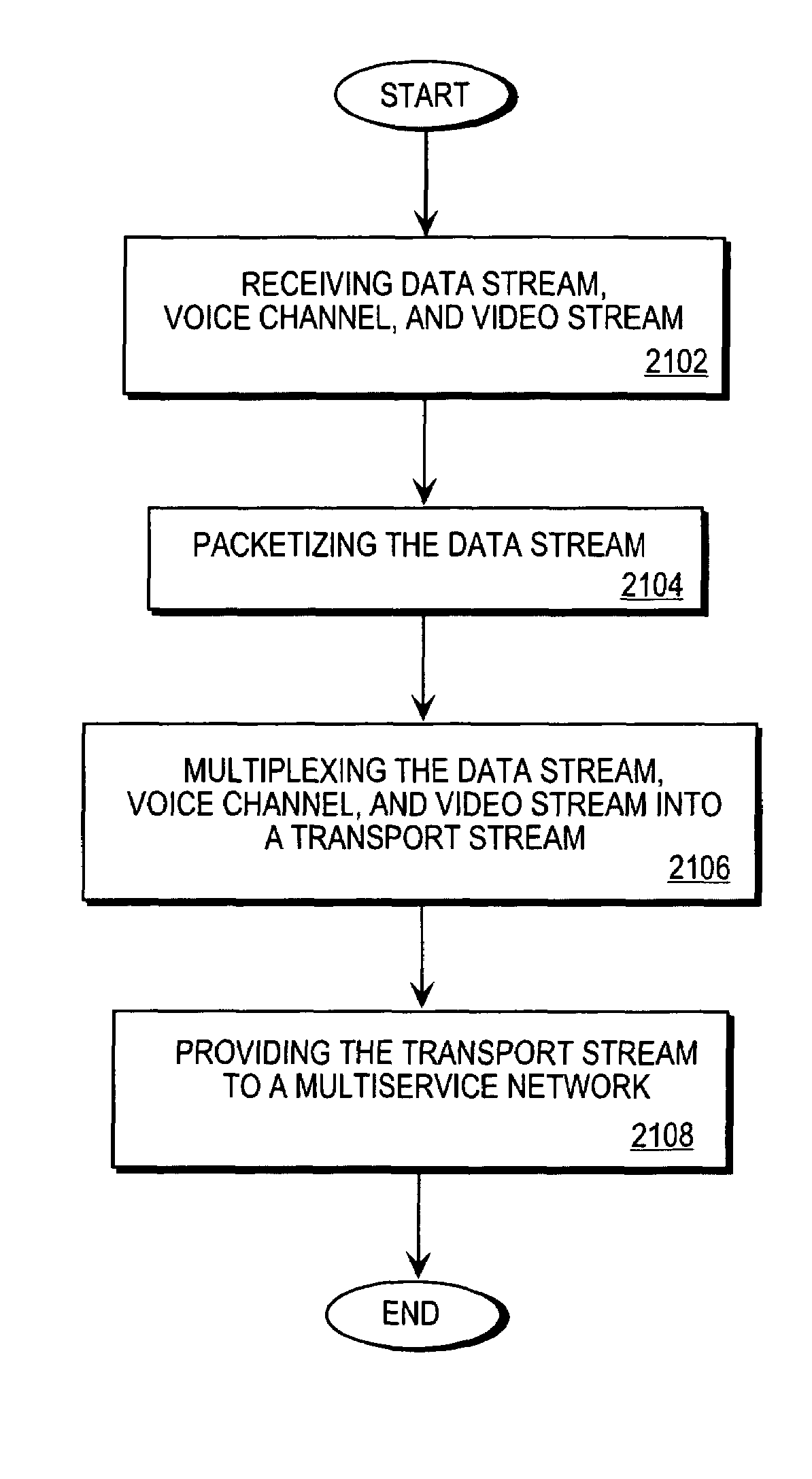
Method and apparatus for routing integrated data, voice, and video traffic
A Multiservice Access Concentrator (MAC) receives information comprising at least one data stream, at least one voice channel, at least one video stream, Local Area Network (LAN)-based traffic, and facsimile traffic. The received data stream is packetized, and the packetized data stream is multiplexed with the voice channel and the video stream to form an integrated transport stream. The voice channel comprises compressed and uncompressed voice information. The integrated transport stream is provided to at least one multi-service network using a software-configurable trunk. The multi-service network includes cell-based and packet-based networks comprising Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), Frame Relay, High-level Data Link Control (HDLC), Internet Protocol (IP), and Time Division Multiplex (TDM) networks, as well as leased-line carrier services. The trunk is configured at a physical level and a protocol level using at least one trunk option.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
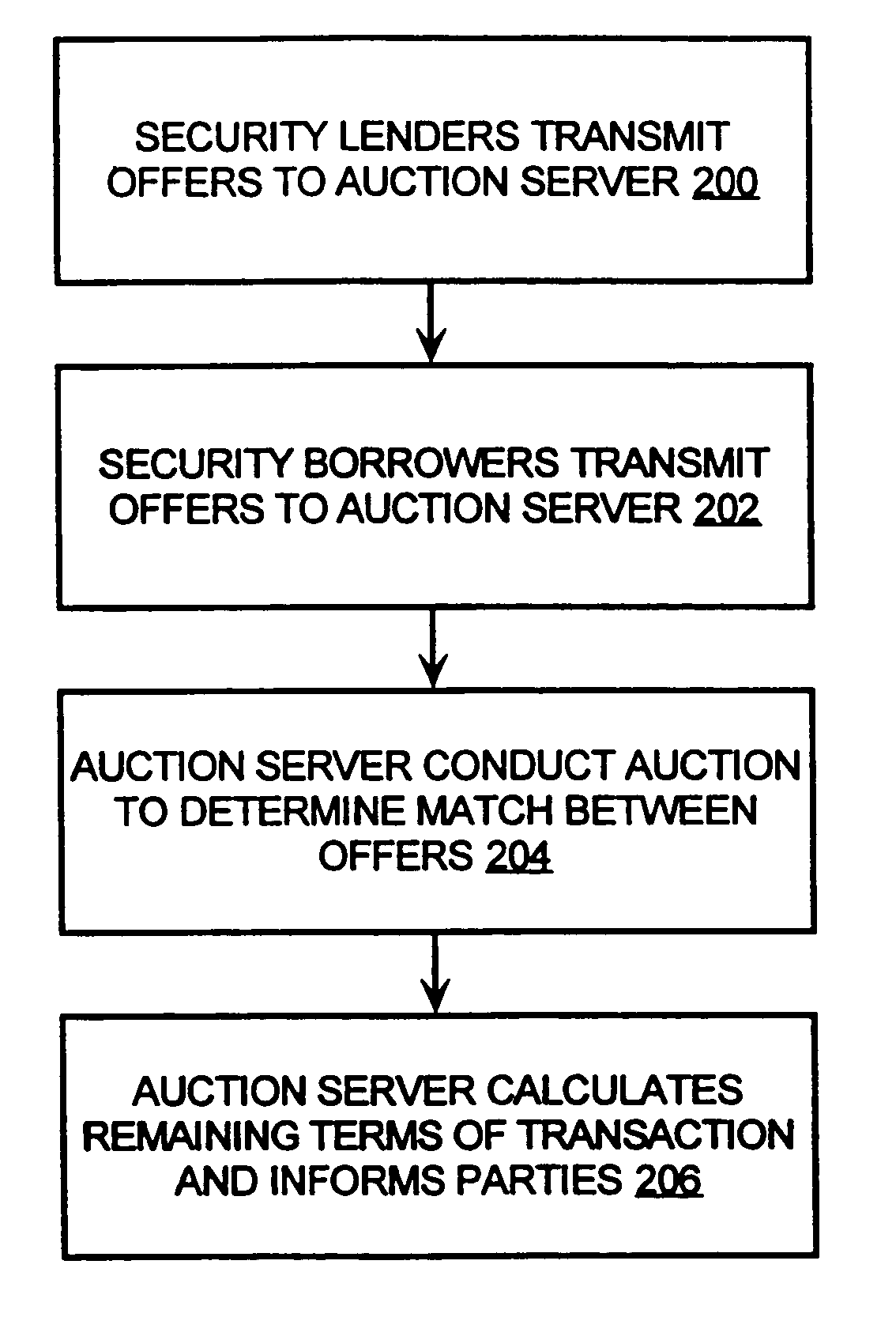
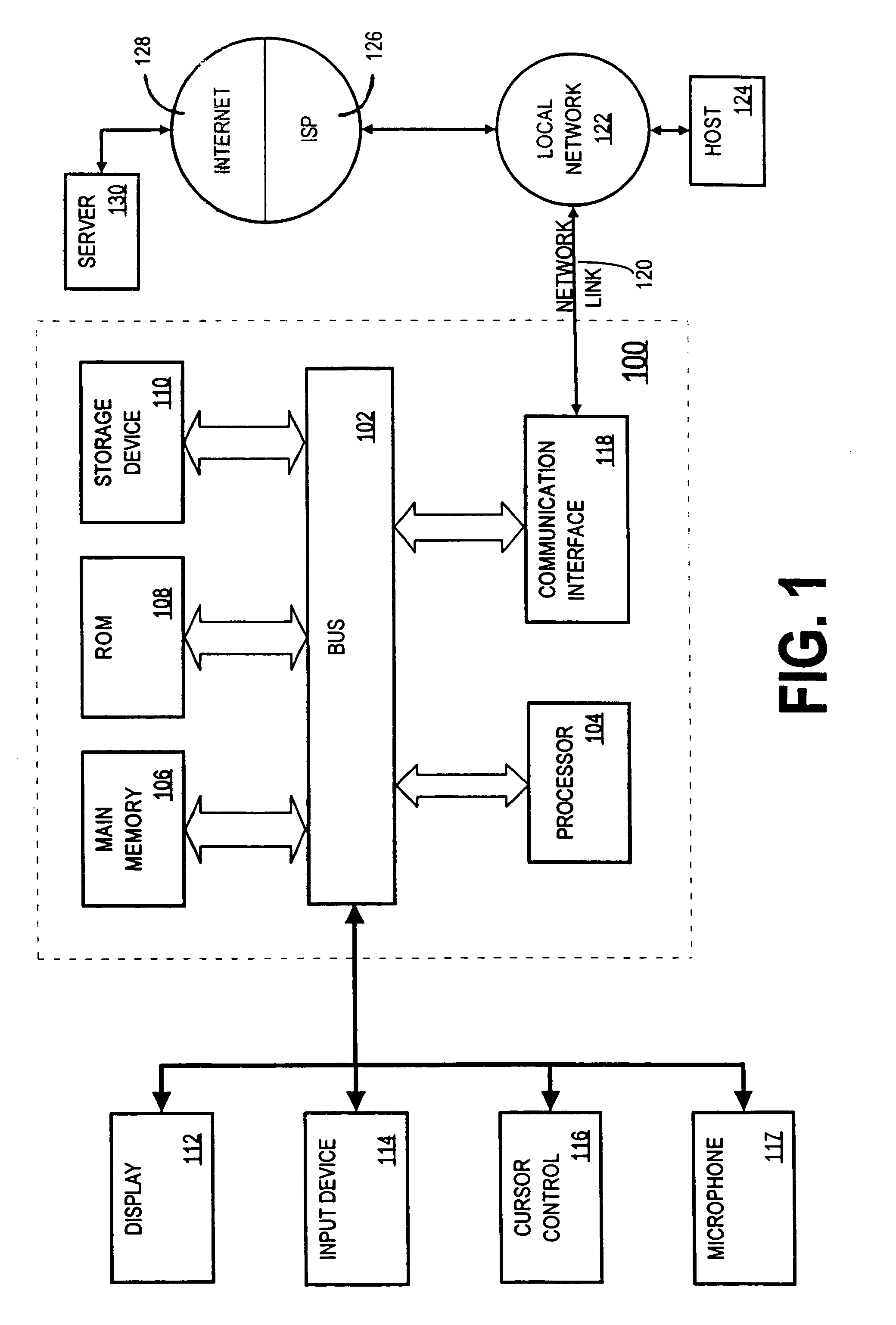
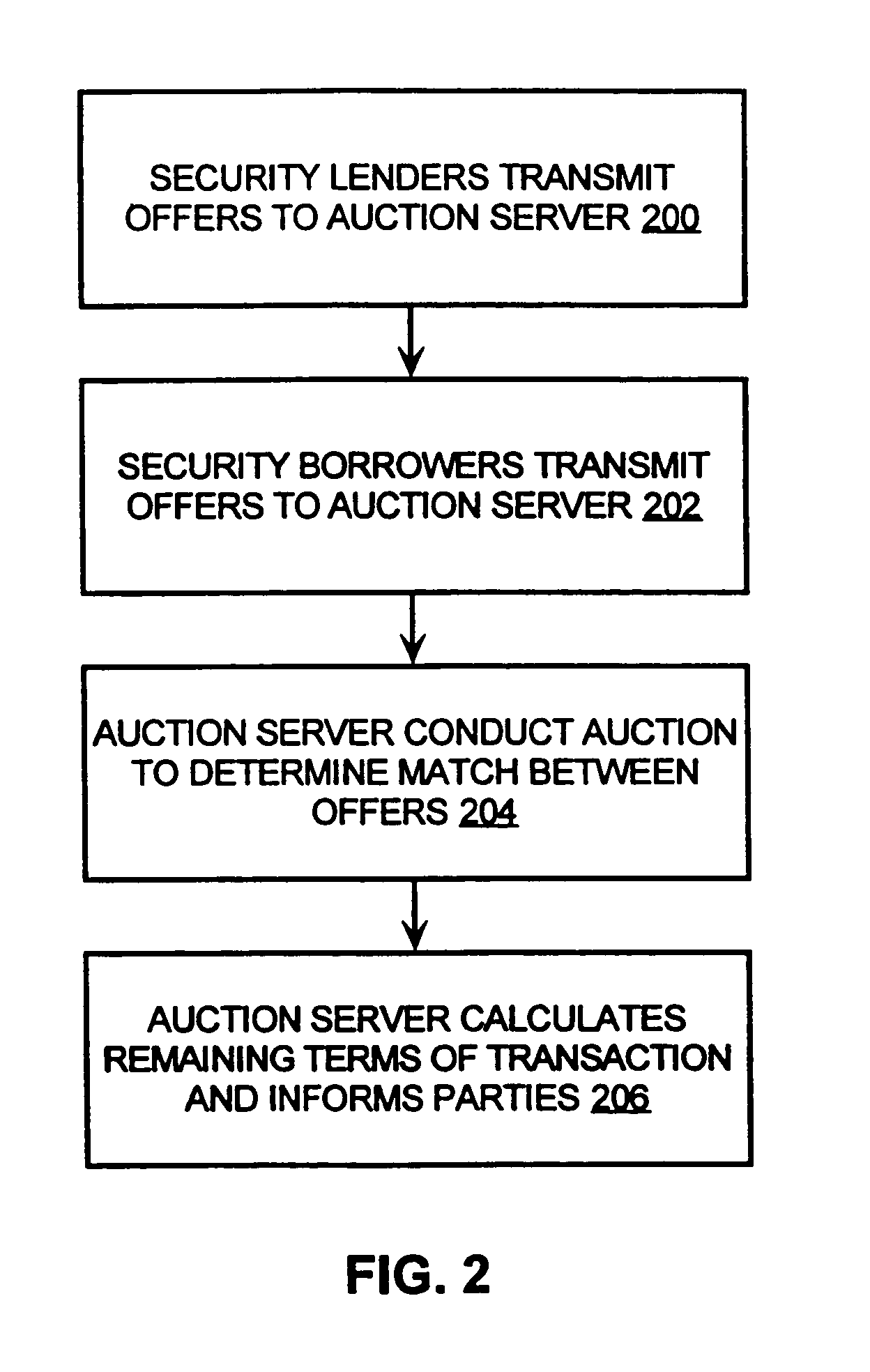
Computer borrow and loan securities auction system
ActiveUS7349881B1High transparencyLow costFinanceComputer security arrangementsLeased lineLarge size
An auction system is disclosed which allows users to participate using their own, or the exchanges, or a brokers, computers, suitably connected to the auction system. This connection may use the internet or a private leased line or an alternative network. The invention involves a method and system for providing auction mechanisms, including a wide variety of types of auctions as described below, and a central counterparty for assuming credit risk between borrowers and lenders, if the borrowers and lenders chose not to transact with each other. This method and auction system provides a means for borrowers and lenders of securities to meet more efficiently, to trade at a better price, to trade in larger size, to trade more rapidly, and, in some cases eliminate the role of the broker as an intermediary between borrower and lender. This mechanism facilitates not only a borrowing and subsequent short sale of securities but also the financing of securities.
Owner:LOCKWOOD DAVID
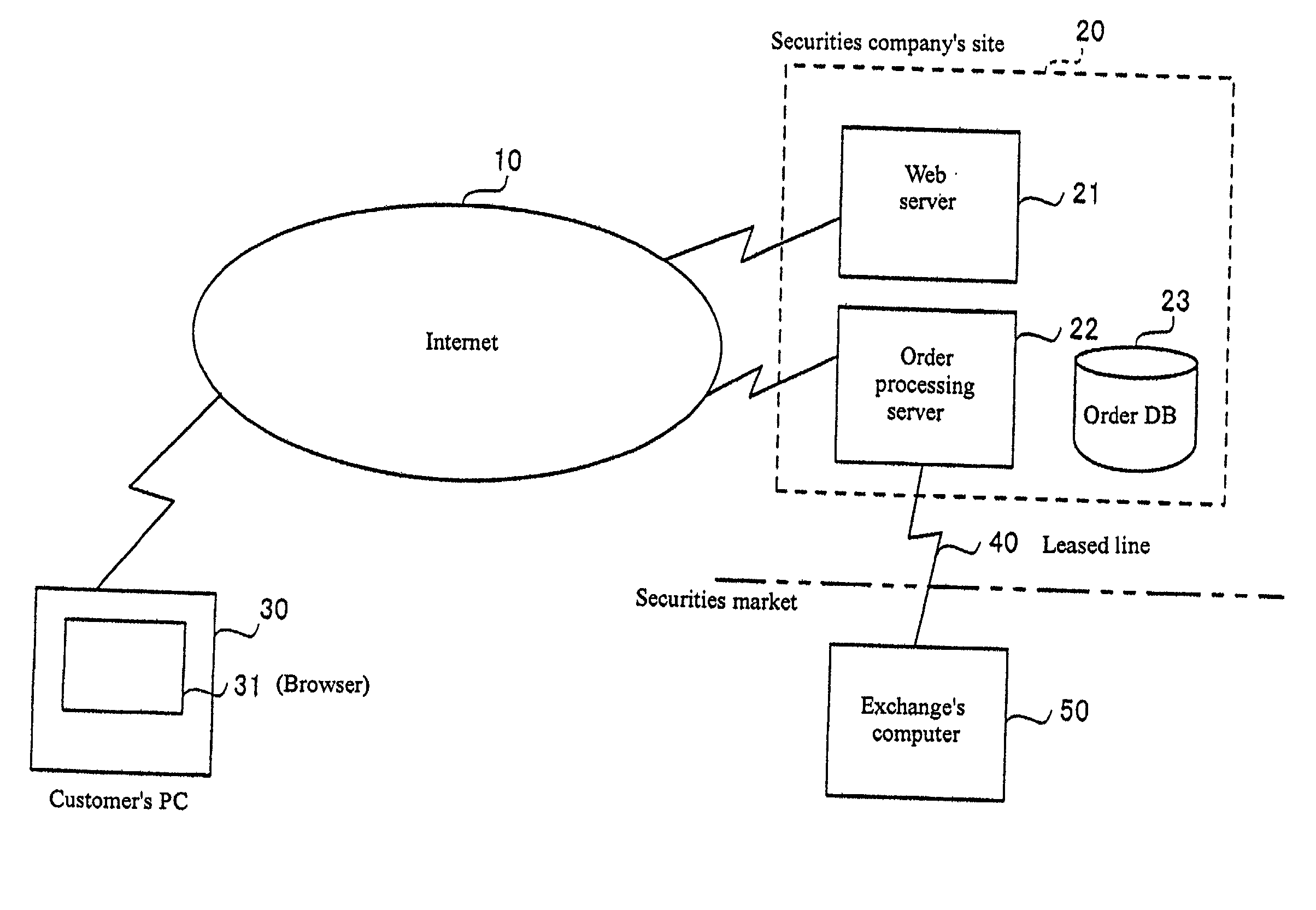
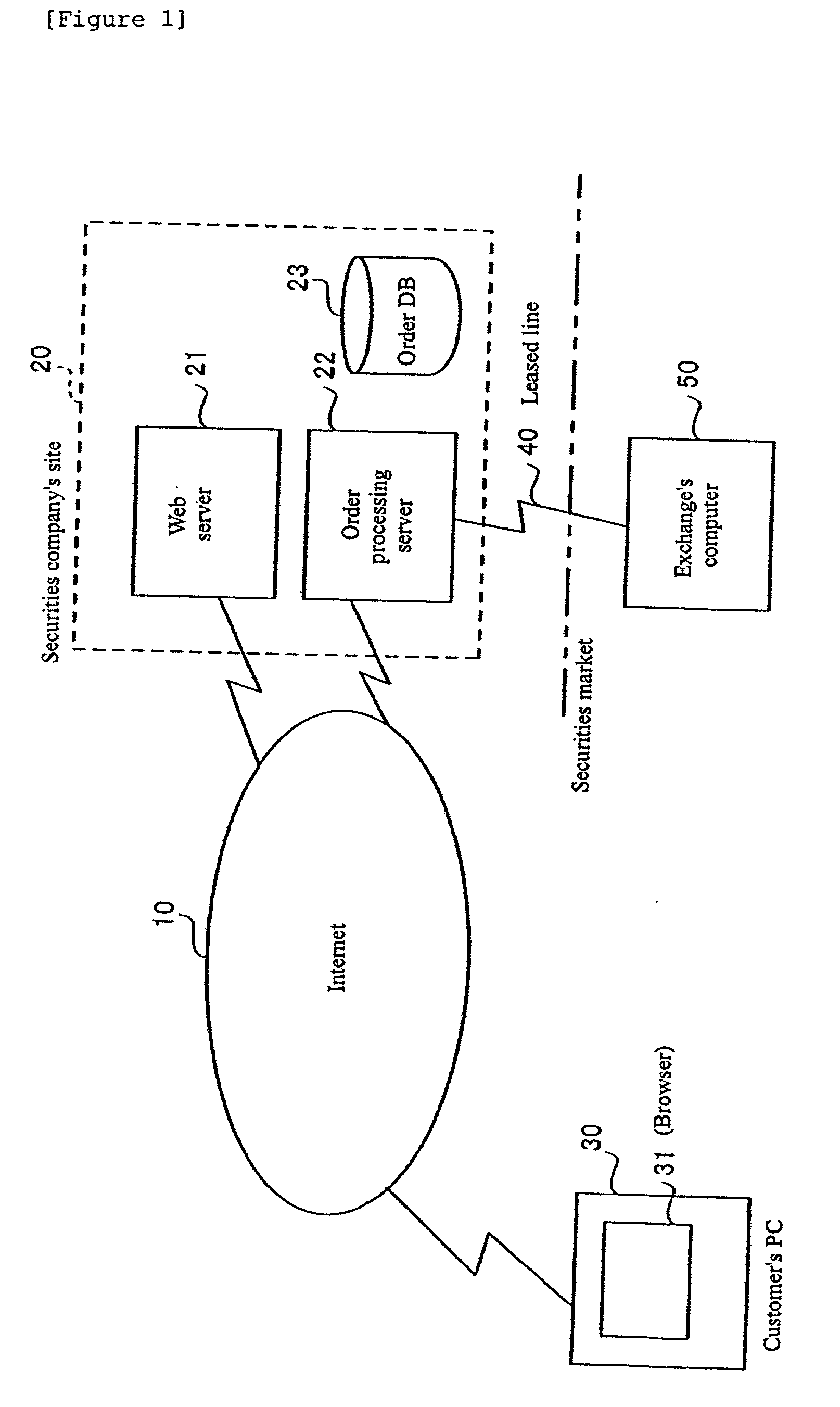
Securities trading system, computer system, buy/sell order placement method, buy/sell order processing method, and program
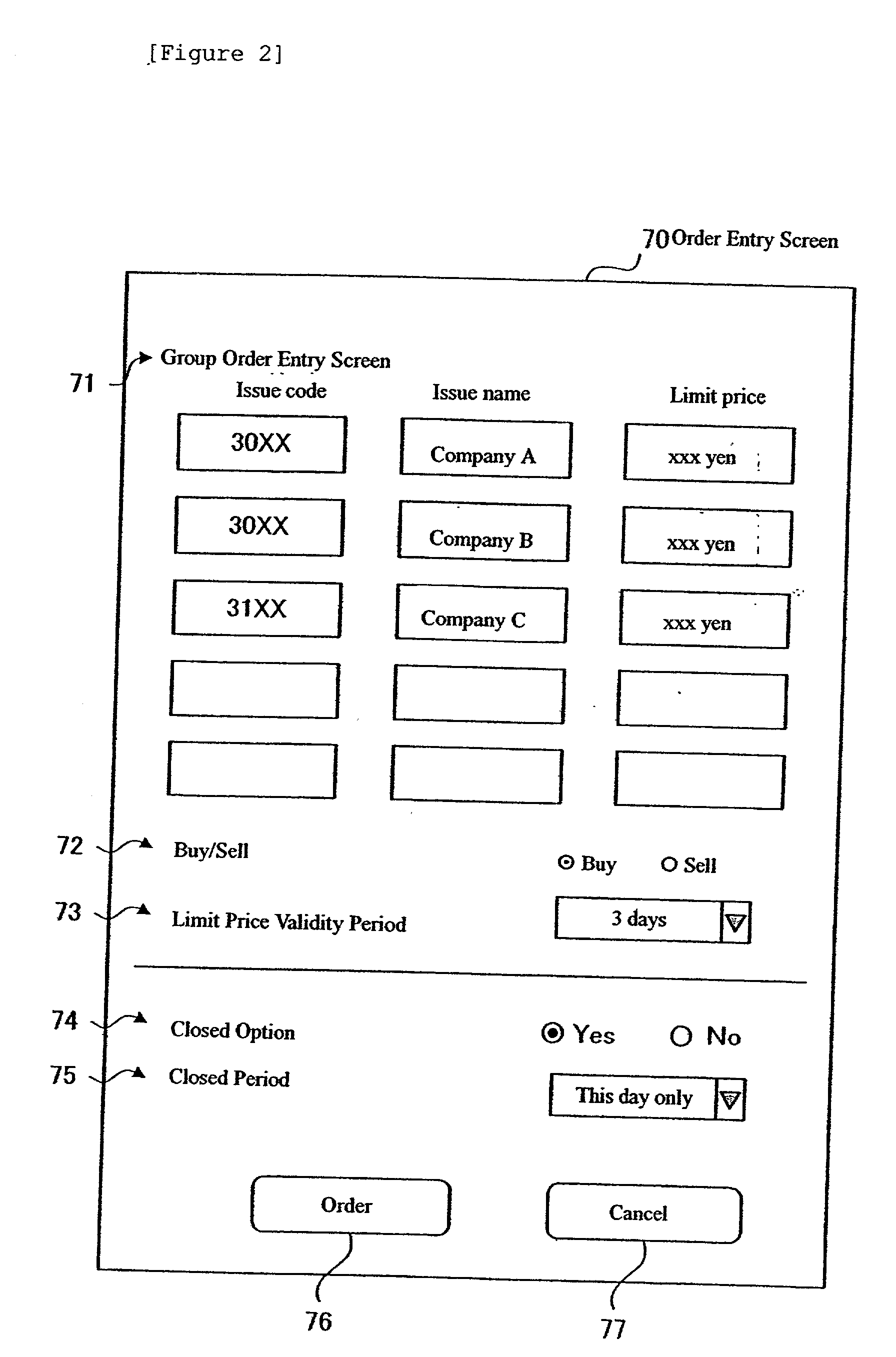
InactiveUS20020152153A1Increase opportunitiesFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsLeased lineComputerized system
A securities trading system including a customer's PC 30 connected to the Internet 10, a securities company's site 20 which is connected to the Internet 10 and processes securities trading orders from the customer's PC 30, and an exchange's computer 50 connected to the securities company's site 20 via a leased line 40, wherein the securities company's site 20 provides information of a group order entry screen for entering an order covering multiple issues and their respective limit prices specified as a group, to the customer's PC 30, and after displaying the group order entry screen information provided by the securities company's site 20 in a browser 31, the customer's PC 30 outputs a group order covering a group of issues for which respective limit prices are specified, through the Internet 10.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for implementing a remote mirroring data facility without employing a dedicated leased line to form the link between two remotely disposed storage devices
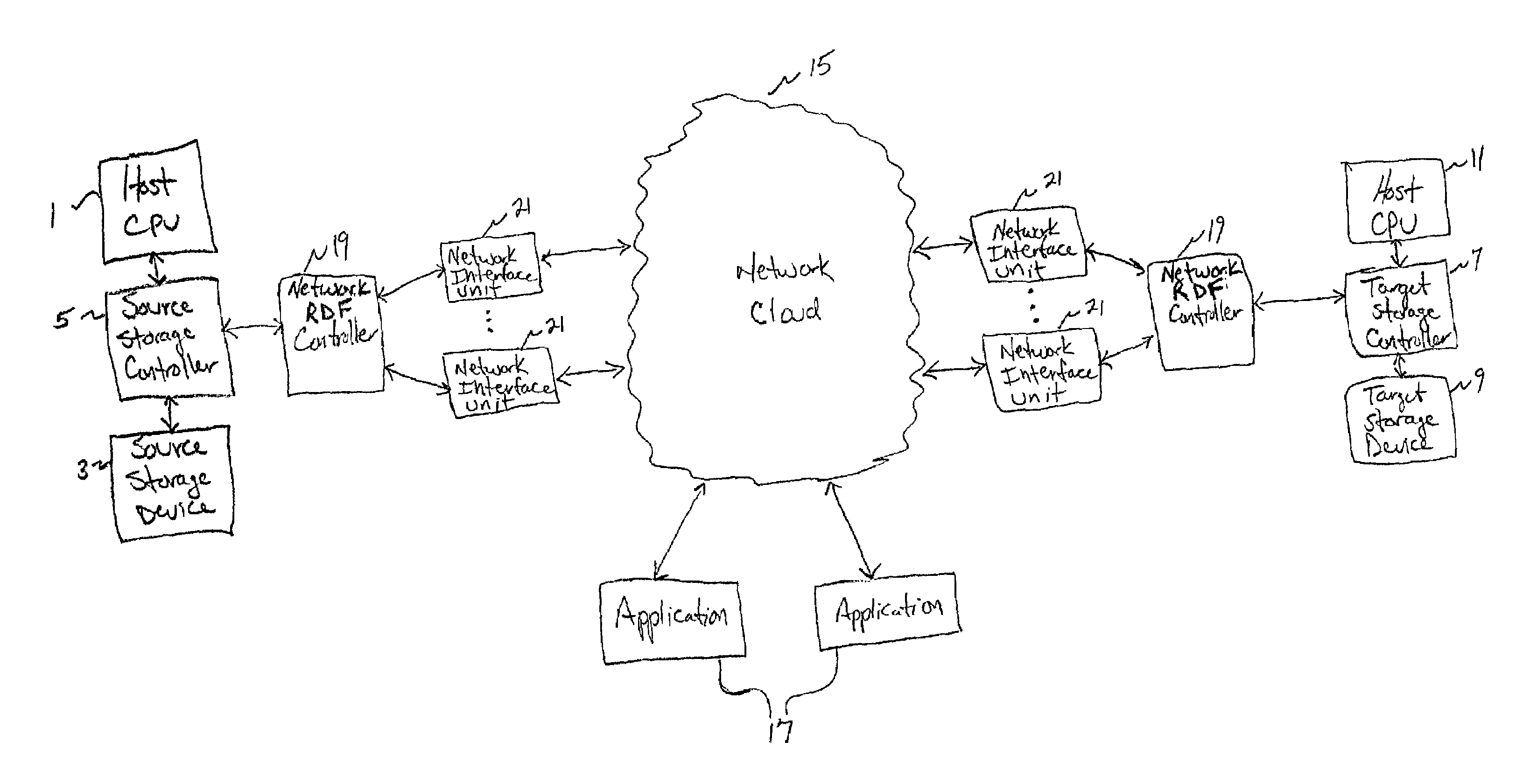
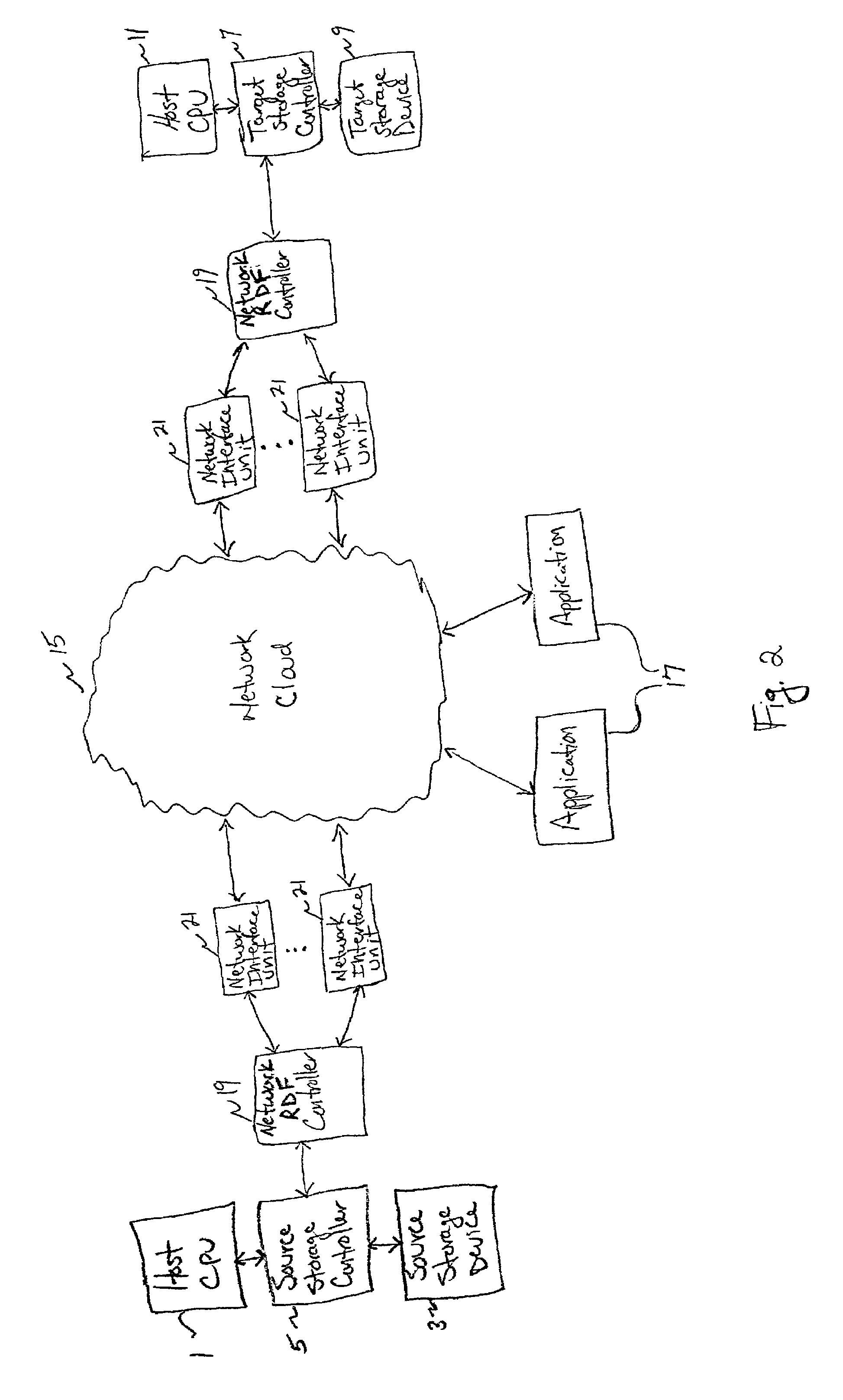
A method and apparatus for implementing a remote mirroring data facility for a computer system comprising a central processing unit (CPU); a first storage system that is coupled to the CPU so that the CPU can store information in the first storage system; a second storage system coupled to the CPU via a communication link; and a mirroring controller to mirror at least some of the information stored in the first storage system in the second storage system by transferring the at least some of the information over the communication link. The communication link can be implemented via a network cloud, which may be the Internet or an intranet. Multiple pipes can be used to pass data through the network cloud in parallel. Alternatively, the communication link can be implemented using wireless technology.
Owner:EMC CORP
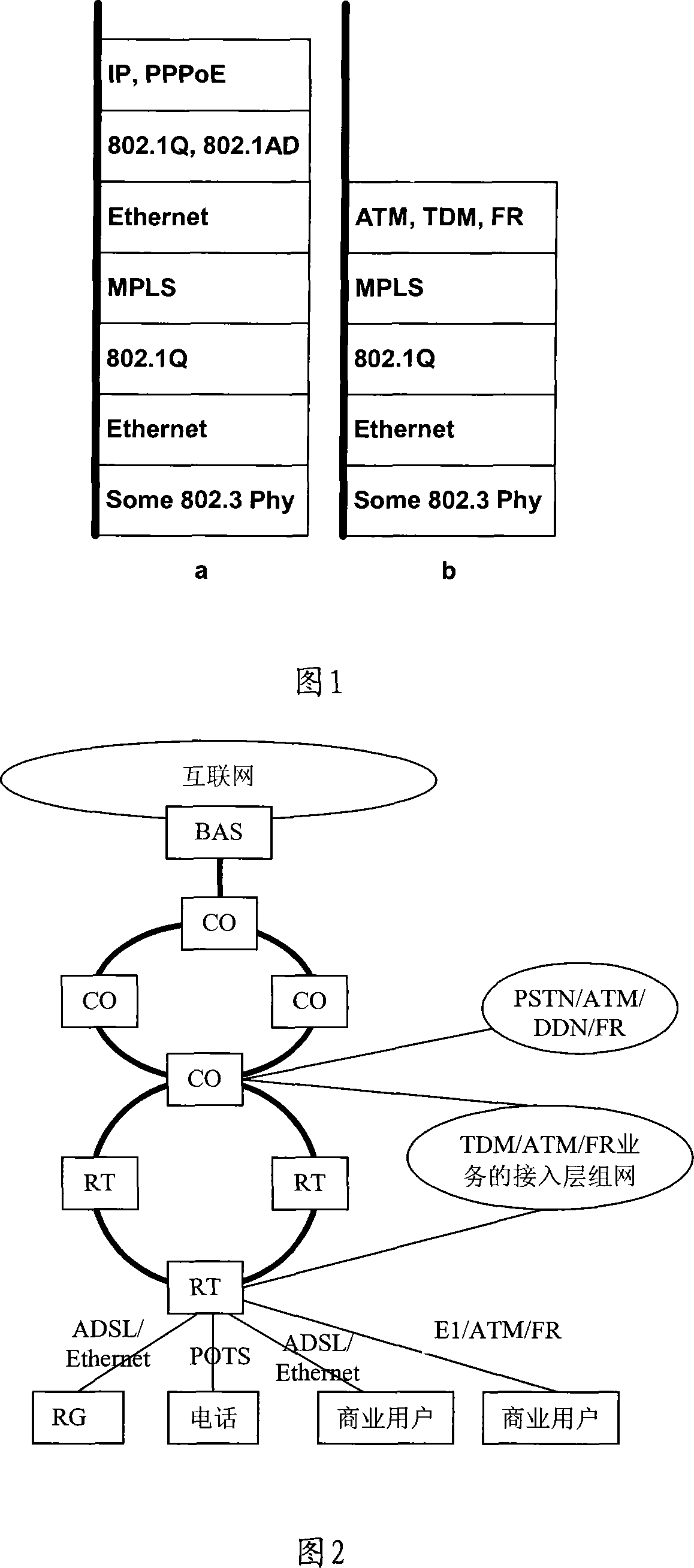
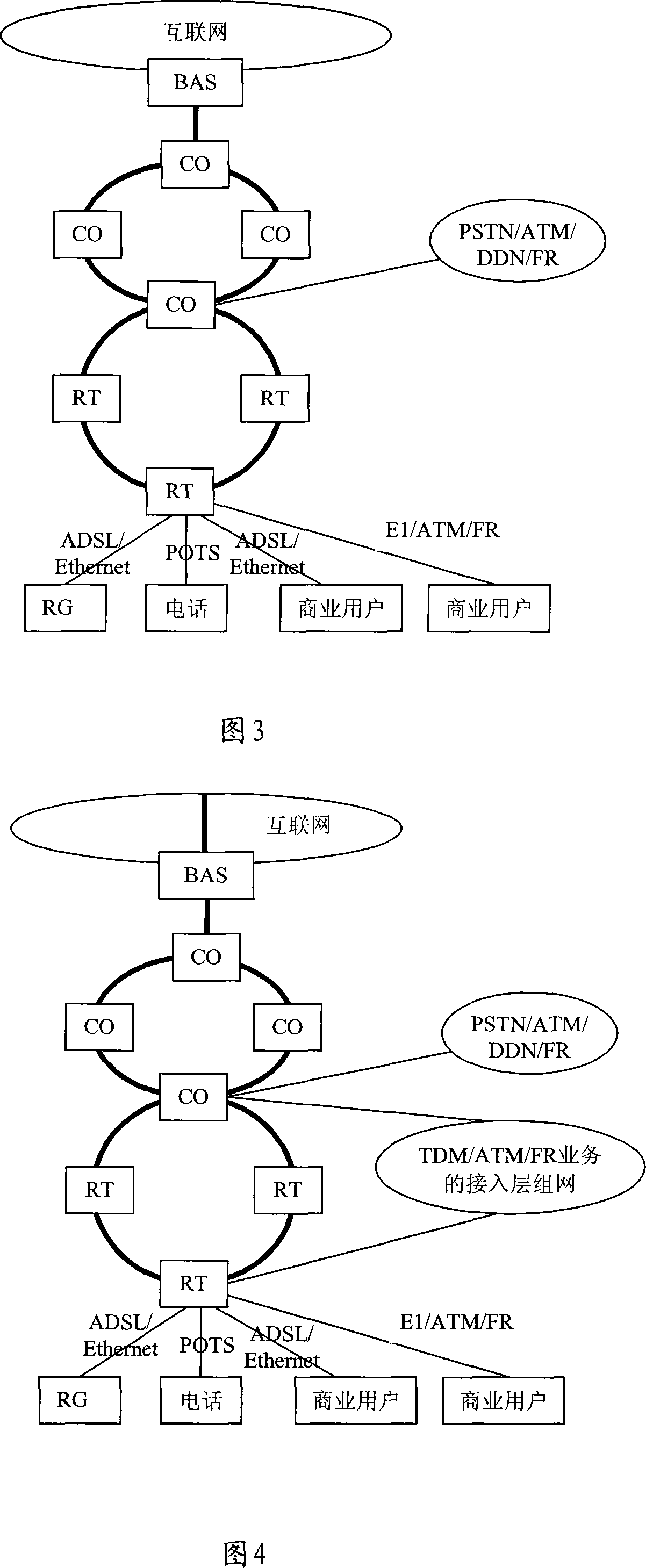
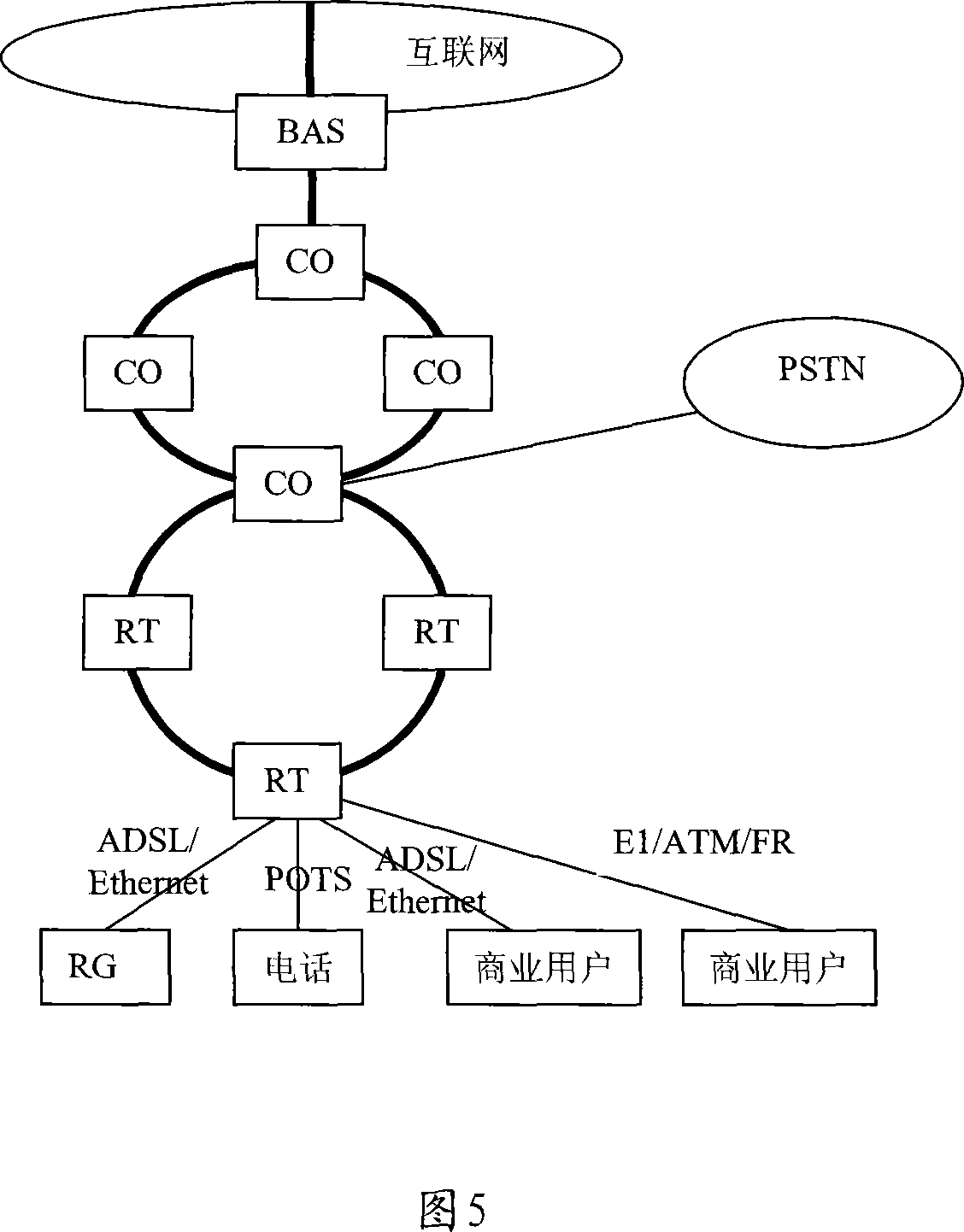
Method for access network to realize synthesis business access
InactiveCN101232460AImprove bandwidth utilizationIncrease incomeMultiplex system selection arrangementsNetworks interconnectionAccess networkLeased line
The invention relates to a broadband access network method for accessing integrated services. The invention includes the following steps: firstly, establishing at least one label switching path (LSP) in broadband access network based on multi-protocol label switching (MPLS); then, MPLS encapsulates the service to be transferred in the broadband access node equipment and transfer in the broadband access network through the LSP. As MPLS is a technology of providing a multi-level connection, the method, which takes MPLS as a private line means for broadband access network networking and traversing core network, can solve the problem faced by broadband access network as integrated services bearer network, thus realizing the bearing of integrated services like IP video, voice, data and private lines (including IP leased line and ATM private line of traditional asynchronous transmission mode, TDM private line and FR private line ).
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
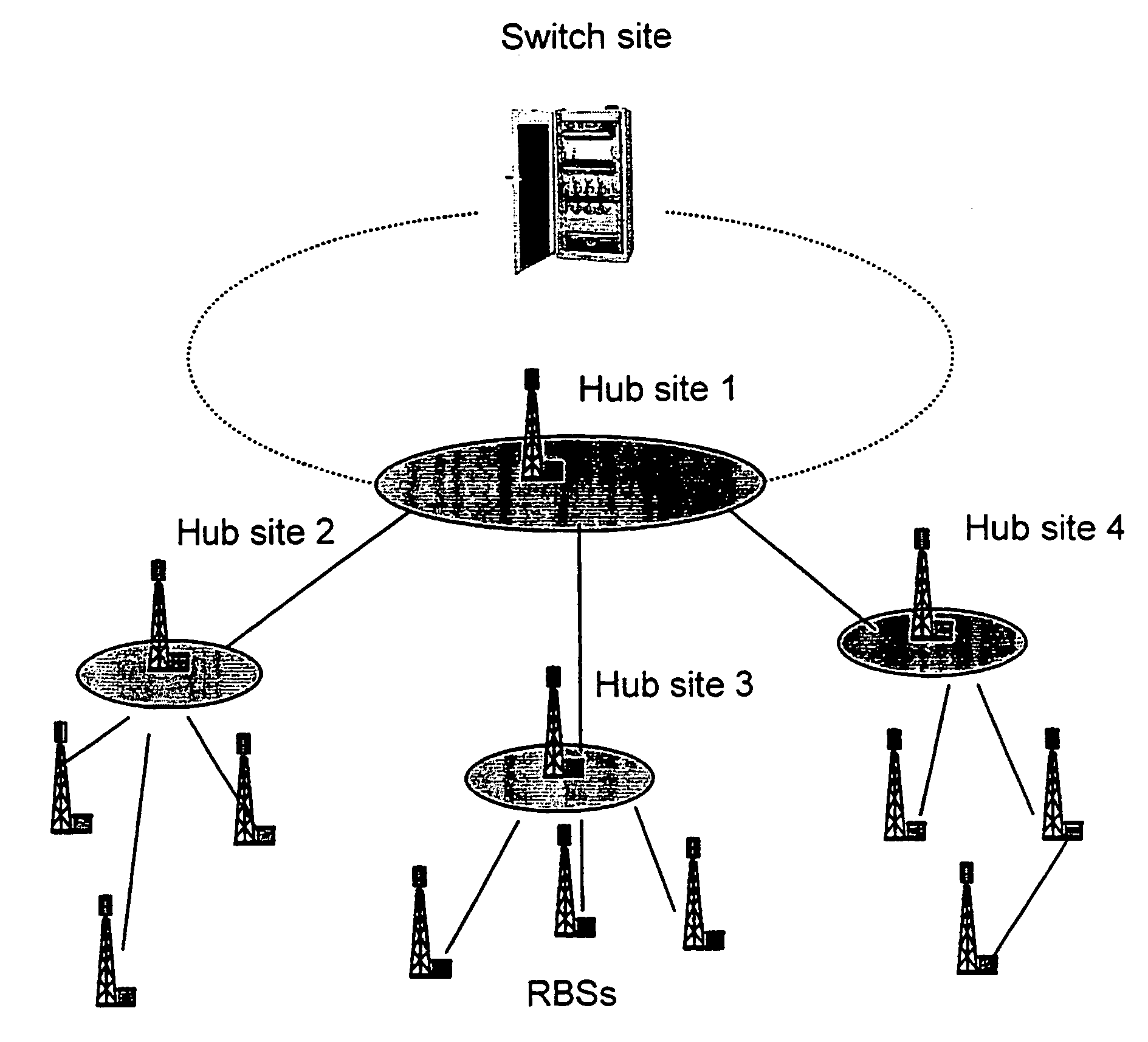
Optimisation mechanism for frequency reuse
InactiveUS20050245265A1Improve system qualityLess affectedNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSystem qualityFrequency reuse
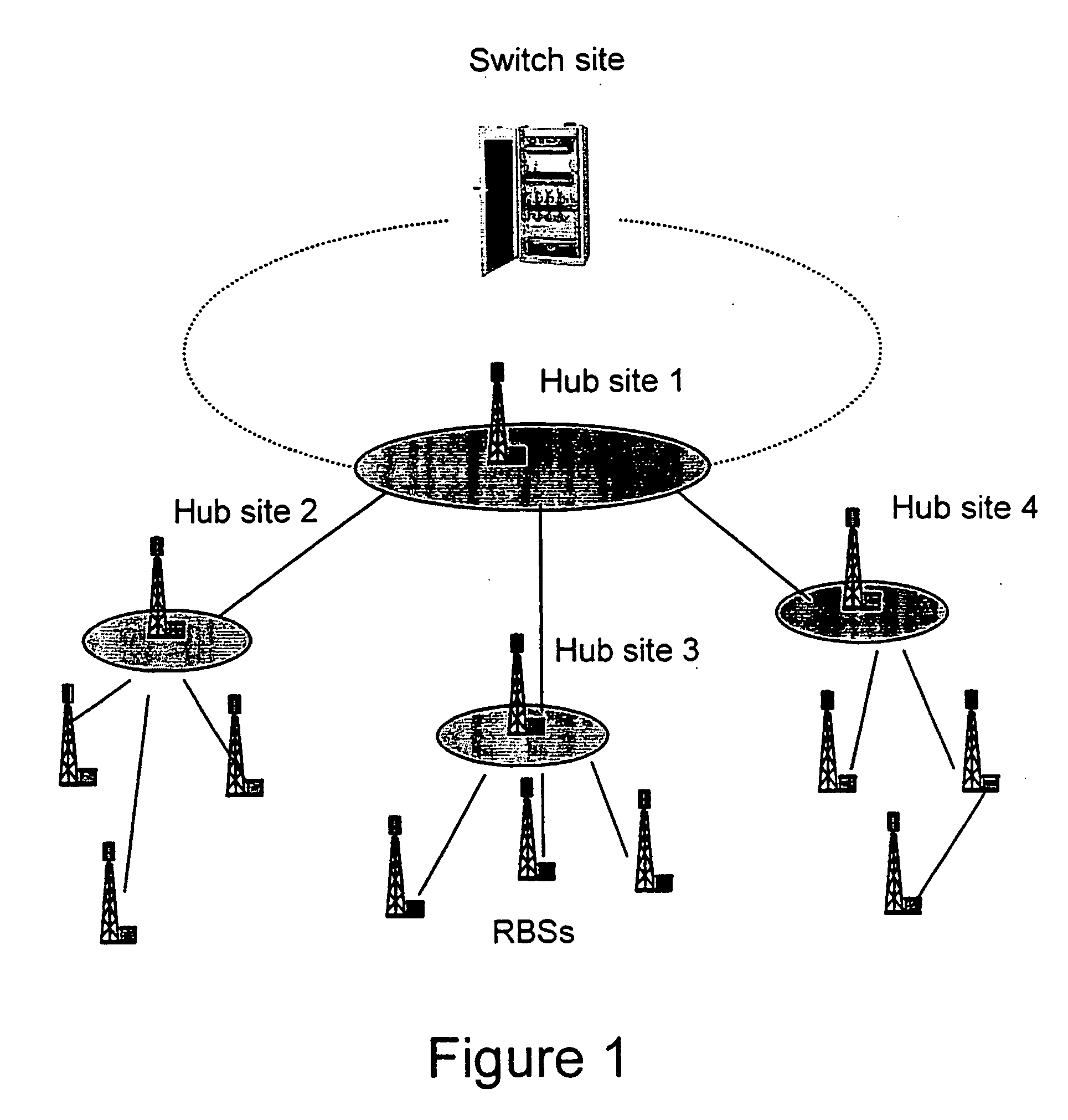
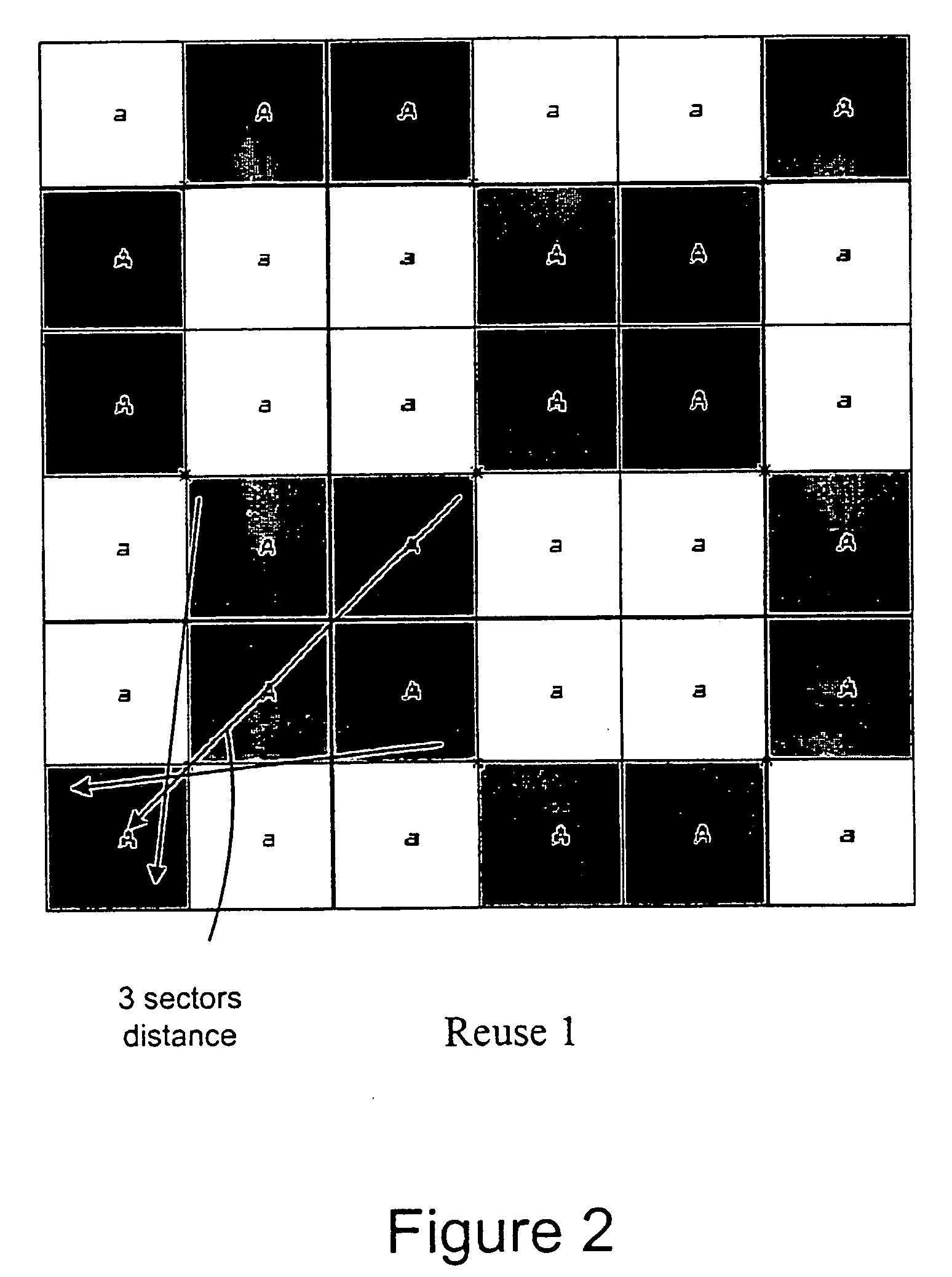
The present invention describes a network planning mechanism for the optimisation of system quality associated with frequency reuse for a mobile network infrastructure and business access applications, by using an intelligent combination of microwave point-to-point and point-to-multipoint links in Broadband Wireless Access Systems or LMDS, for example. In an embodiment of the invention, Radio Base Stations (RBSs) sites can be connected to the Switch site by a combination of fibre optics, leased lines, or preferably microwave radio links. The embodiment enables traffic from several end sites to be concentrated at selected hub sites (hub site 1-4). The system is optimised by minimizing the quality degradation that can be experienced due to excessive interference inside a certain portion of the point-to-multipoint covered sector by means of the combined point-to-multipoint and point-to point solutions. The RBS, which on the planning phase will experience excessive interference in the direction to the hub, is not directly connected the point-to-multipoint hub, but through a point-to-point link connecting to an access terminal, co-located with a different RBS or business user, in line of sight with the previous one. The access terminal in turn connects the point-to-multipoint hub allowing a frequency reuse factor of one to be deployed.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Methods and apparatus for low latency signal aggregation and bandwidth reduction
InactiveUS7720094B2Minimize the numberNetwork traffic/resource managementCode conversionType specificLeased line
Wireless network demands continually increase as wireless service providers pursue additional service capabilities. In a cellular communication system, leased lines between remote cell sites and the corresponding Mobile Switching Offices (MSOs) remain a major operating cost. Bandwidth reduction by identification and elimination of payload data and control information which need not be fully replicated because it can be deduced from information accessible or previously transmitted allows fewer lines to support the same bandwidth. A wireless access gateway is operable to aggregate such redundant and regenerable data on a backhaul link between a wireless cell site and the corresponding mobile switching office (MSO) to provide low-latency, type specific lossless bandwidth reduction. The wireless access gateway identifies regenerable information and eliminates portions of the data which the device need not transmit because the data is redundant, or accessible or recreatable, at the receiving side. In this manner, the access device allows fewer lines to carry the reduced message traffic by transmitting only the non-recreatable data and eliminating message traffic for regenerable information.
Owner:VERSO BACKHAUL SOLUTIONS
Internet protocol network alternate routing system
InactiveUS6888793B1Maintain service levelError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLeased lineCall control
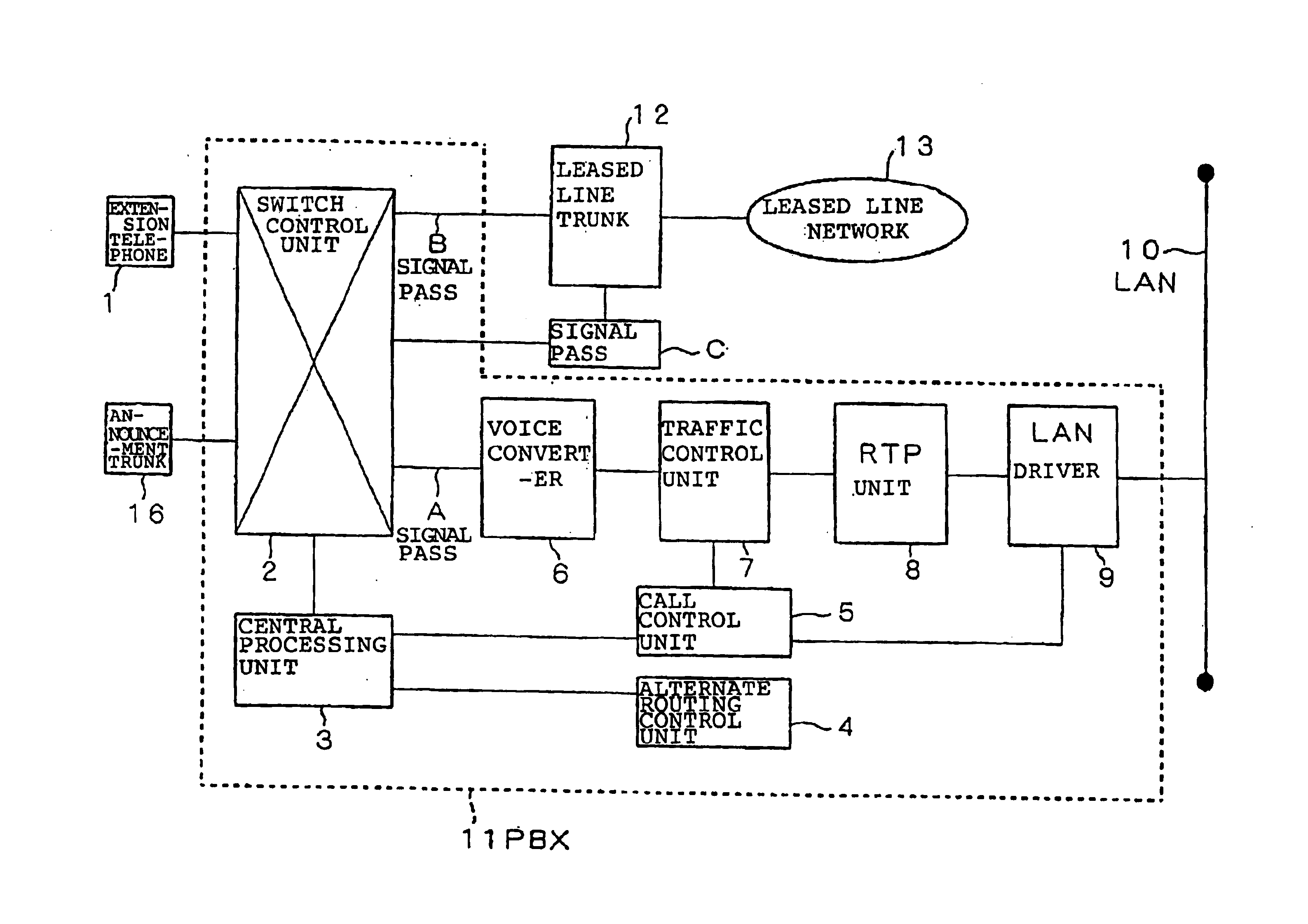
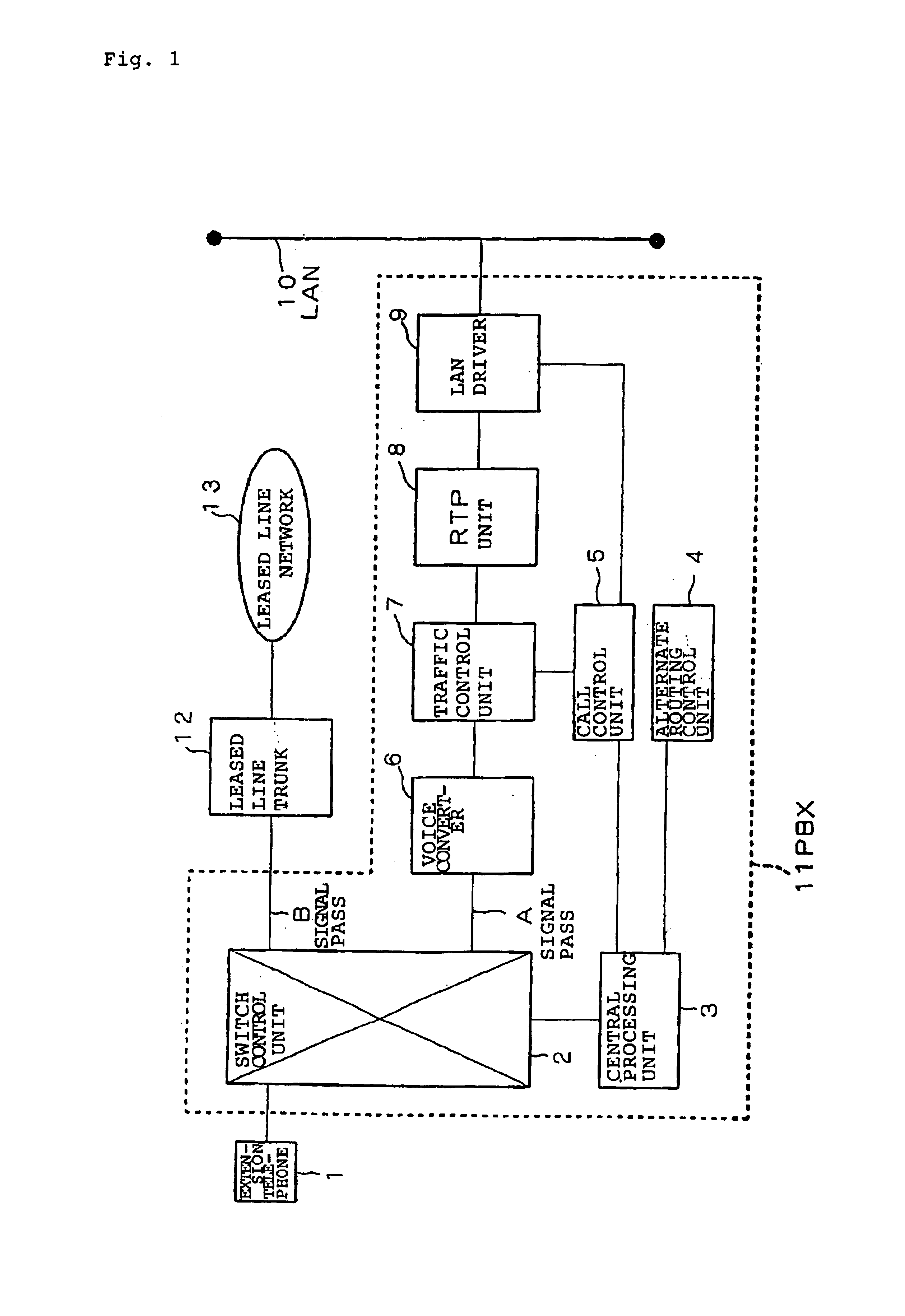
An Internet protocol network alternate routing system comprises: a traffic control unit for detecting the state of congestion of an LAN, which is an Internet protocol network; a call control unit for establishing a link between an extension telephone and the LAN based on the detection results of the traffic control unit; a central processing unit for designating the signal path of voice signals that are transmitted from the extension telephone based on the results of establishing a link in the call control unit; and a switch control unit for switching the signal path that connects a path to the extension telephone. In a case in which the call control unit does not establish a link, voice signals that are transmitted from the extension telephone are rerouted by switching performed by the switch control unit to a leased line network by way of a leased line trunk.
Owner:NEC INFRONTIA CORP
Antenna System
InactiveUS20100048218A1Increased gainSmall shareModulated-carrier systemsAssess restrictionData capacityMicrowave
Embodiments of the invention relate to wireless communications networks, and more specifically to an antenna apparatus for cellular wireless systems. Increasing data capacity of cellular wireless systems places increasing demands on the capacity of the two way connection, known as backhaul, between a cellular base station and a telecommunications network such as the PSTN backhaul, since this is the connection that has to convey the wireless-originating traffic to its destination, often in an entirely different network. Known backhaul links include leased lines, microwave links, optical fibre links or radio resources for relaying backhaul traffic between base stations. The fixed line solutions are expensive to implement and maintain, while the radio solutions antenna configurations that are not ideal for relaying data between base stations. In embodiments of the invention, communication between base stations occurs in a first timeslot by use of a first antenna system and communication between a given base station and a user equipment occurs in a second timeslot using a second antenna system. The benefit of this method is that the first antenna system can be optimised for use in communication between base stations, whereas the second antenna system can be optimised for communication with user equipment which preferably occurs within the area of cellular wireless coverage of the sector served by the second antenna system.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF BELFAST +2
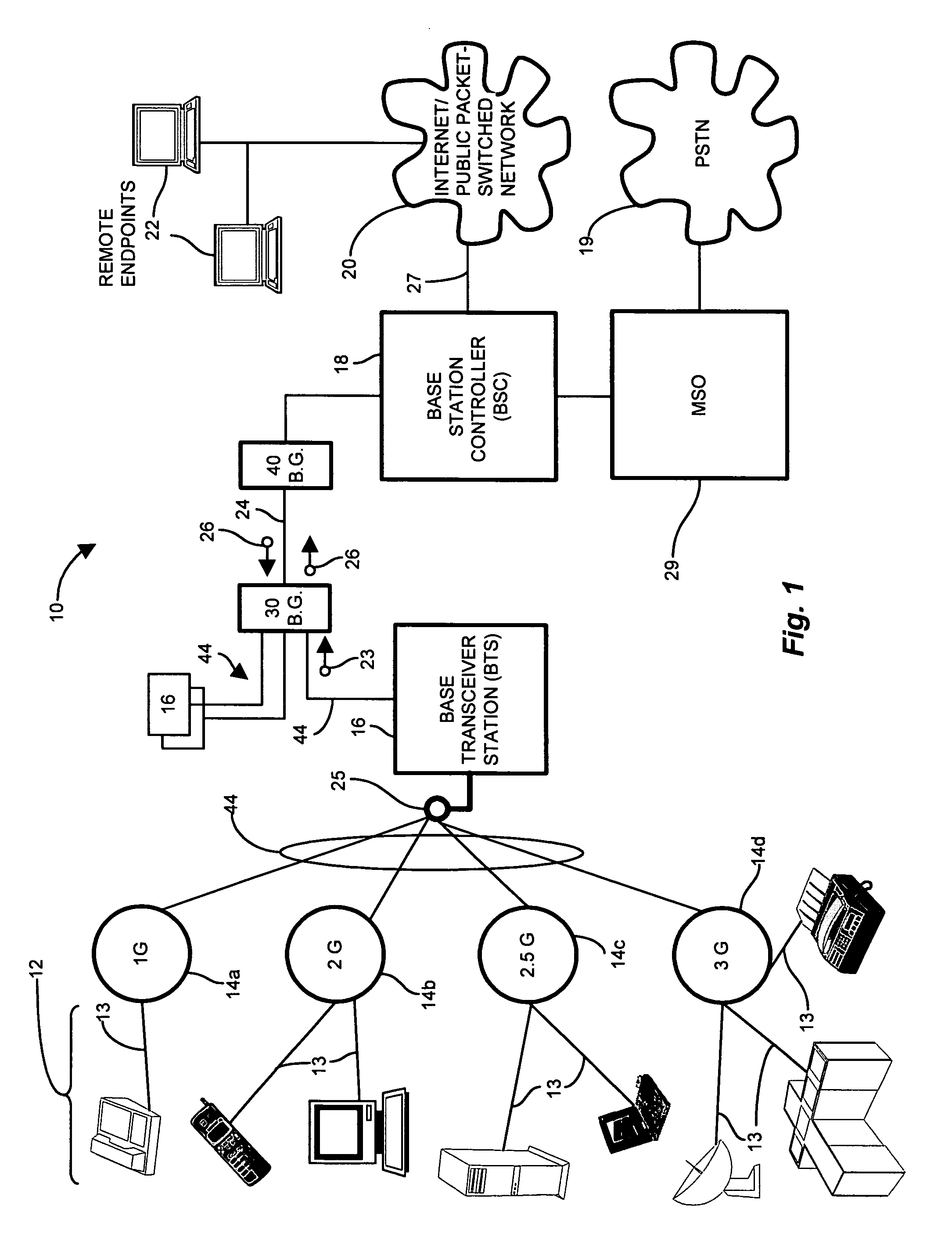
Mobile telephone system
InactiveUS6112076AAccounting/billing servicesNetwork traffic/resource managementMobile Telephone ServiceTelecommunications link
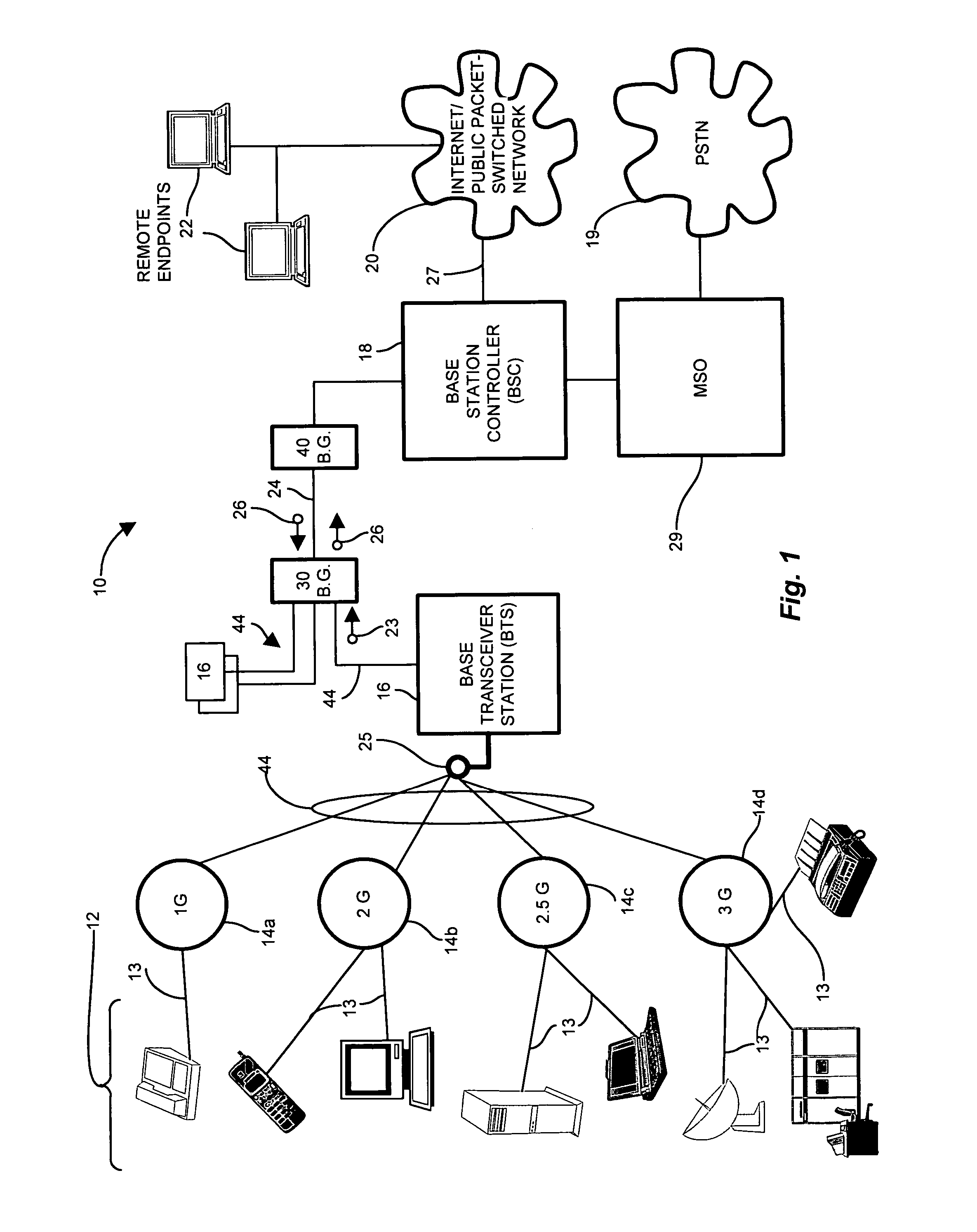
PCT No. PCT / GB96 / 01711 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 21, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 21, 1998 PCT Filed Jul. 17, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 04615 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 6, 1997A mobile telephone system has a base transceiver station (BTS) that provides radio communication with a mobile handset (MS) and also communicates with a control station (BSC) through a communication link in the form of a leased line which provides a first communication path with a predetermined bandwidth for signals communicated between the BTS and the BSC. A communication network in the form of an ISDN is used to provide a selectively connectable second communication path between the BTS and the BSC so as to augment the bandwidth available for the signals during periods of peak demand. In order to accommodate different call connection times in the system through the leased line and the ISDN, the BSC / BTS are arranged to produce all connection signals that initiate billing at the same time irrespective of the path used to make the call connection.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
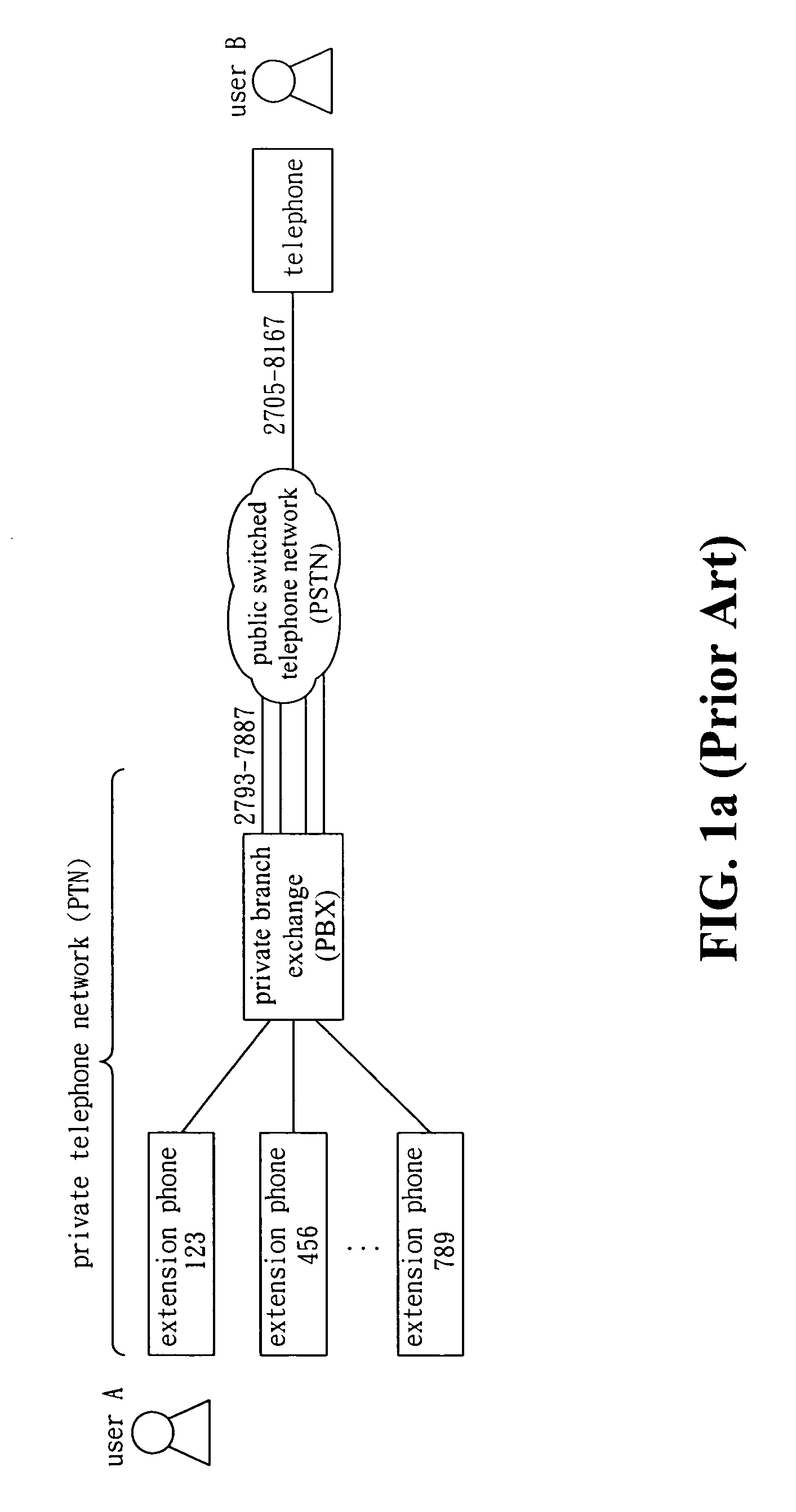
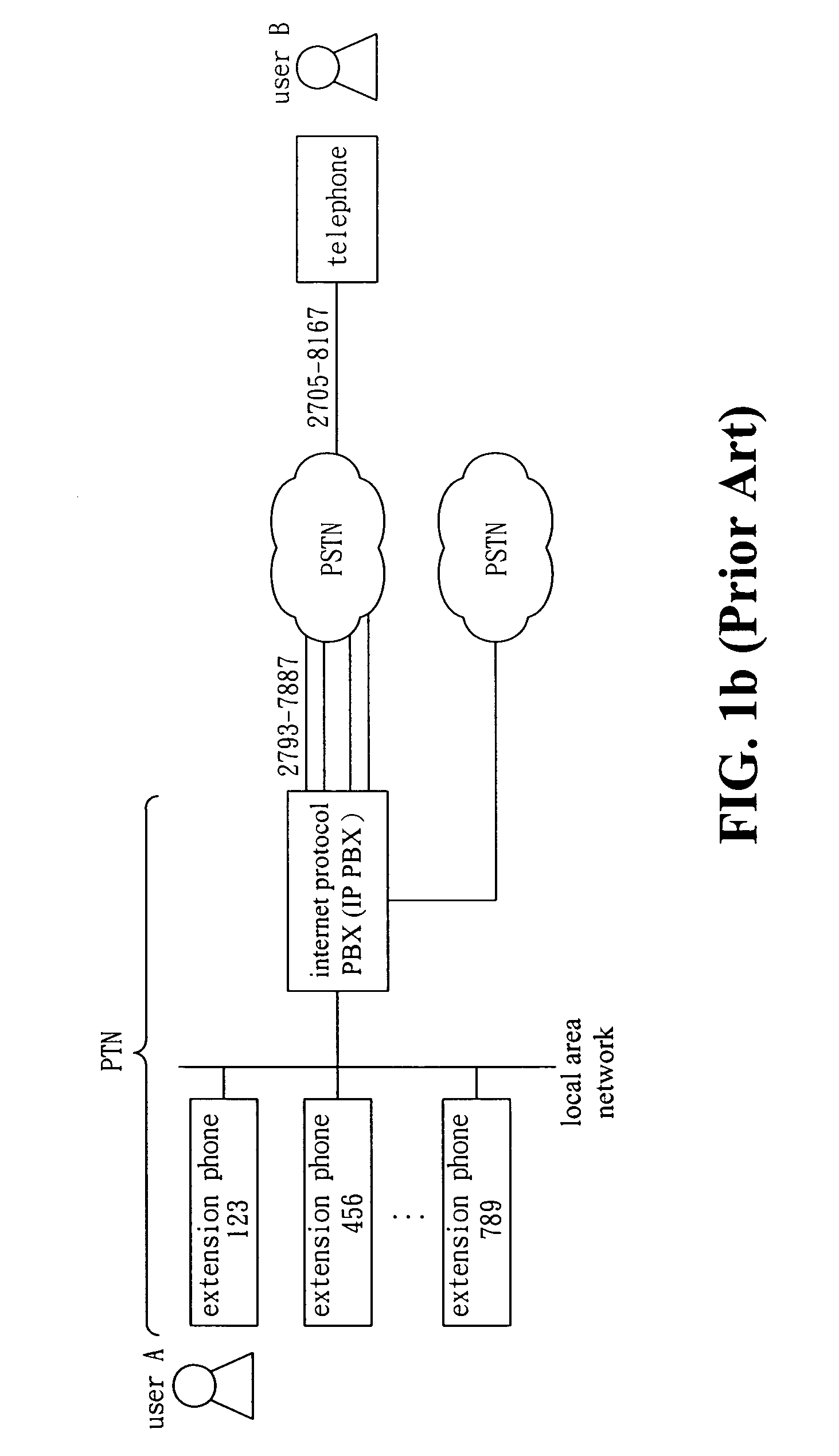
Method and apparatus for telephone routing between PTN and PSTN
ActiveUS7627101B2Interconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersRouting tableLeased line
Disclosed is a method and apparatus applicable to an interface between PSTN and PTN for telephone routing. The interface includes a branch switch, a key system, a network branch switch, and media gateway, etc. The telephone routing method and apparatus of the present invention creates, maintains, and utilizes a call-back routing table to enable a specified PSTN user to call the callback external leased line to reach a specified PTN user in a one-stage dialing manner. The process of one-stage dialing includes PTN call origination to PSTN, PSTN call origination to PTN, and callback tag insertion in the call-back routing table. The call-back routing table consists of a plurality of call-back tags. Each call-back tag consists of at least a data triple, i.e. PTN user identifier, PSTN called party telephone number, and callback leased line identifier.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST +1
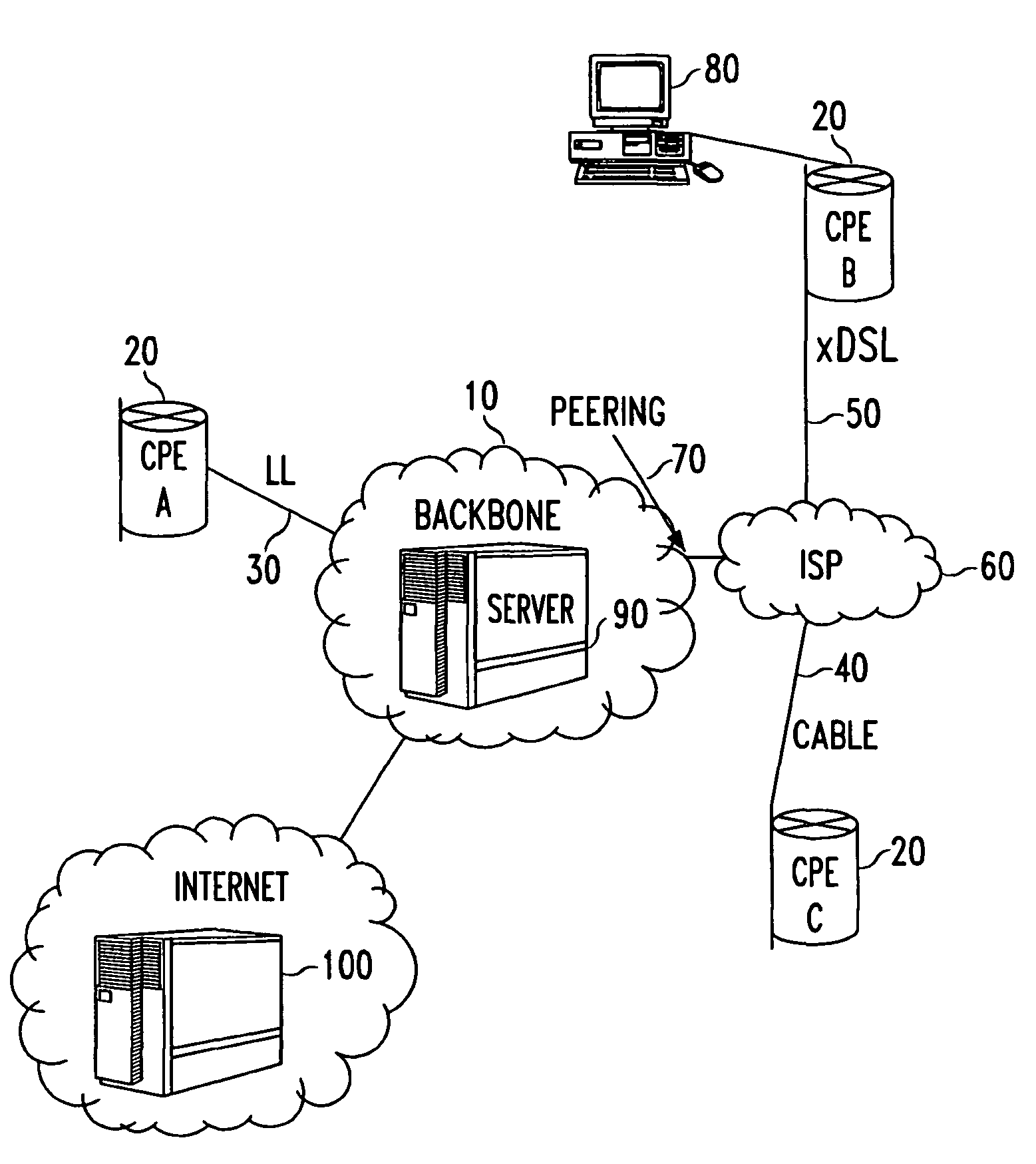
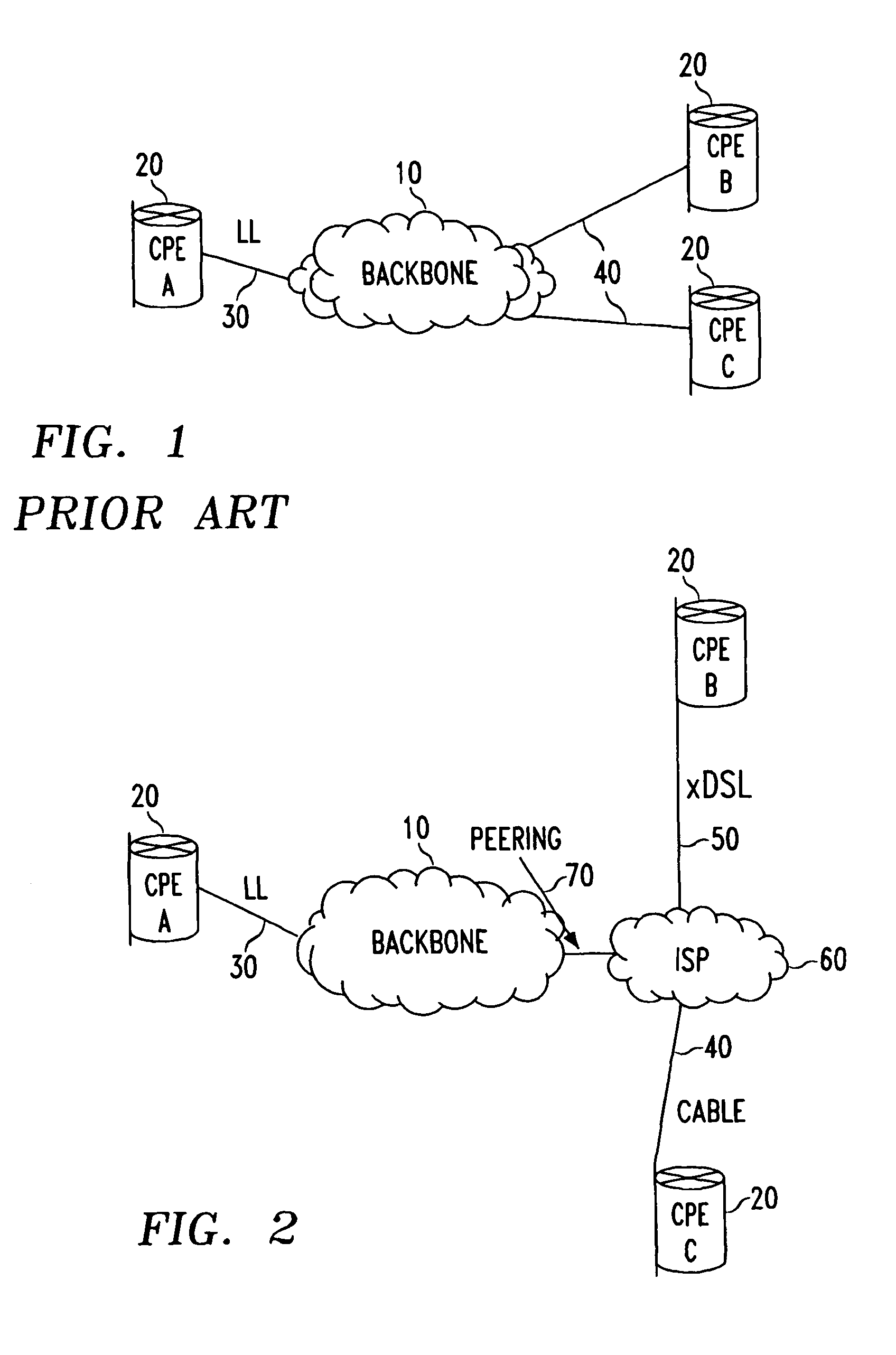
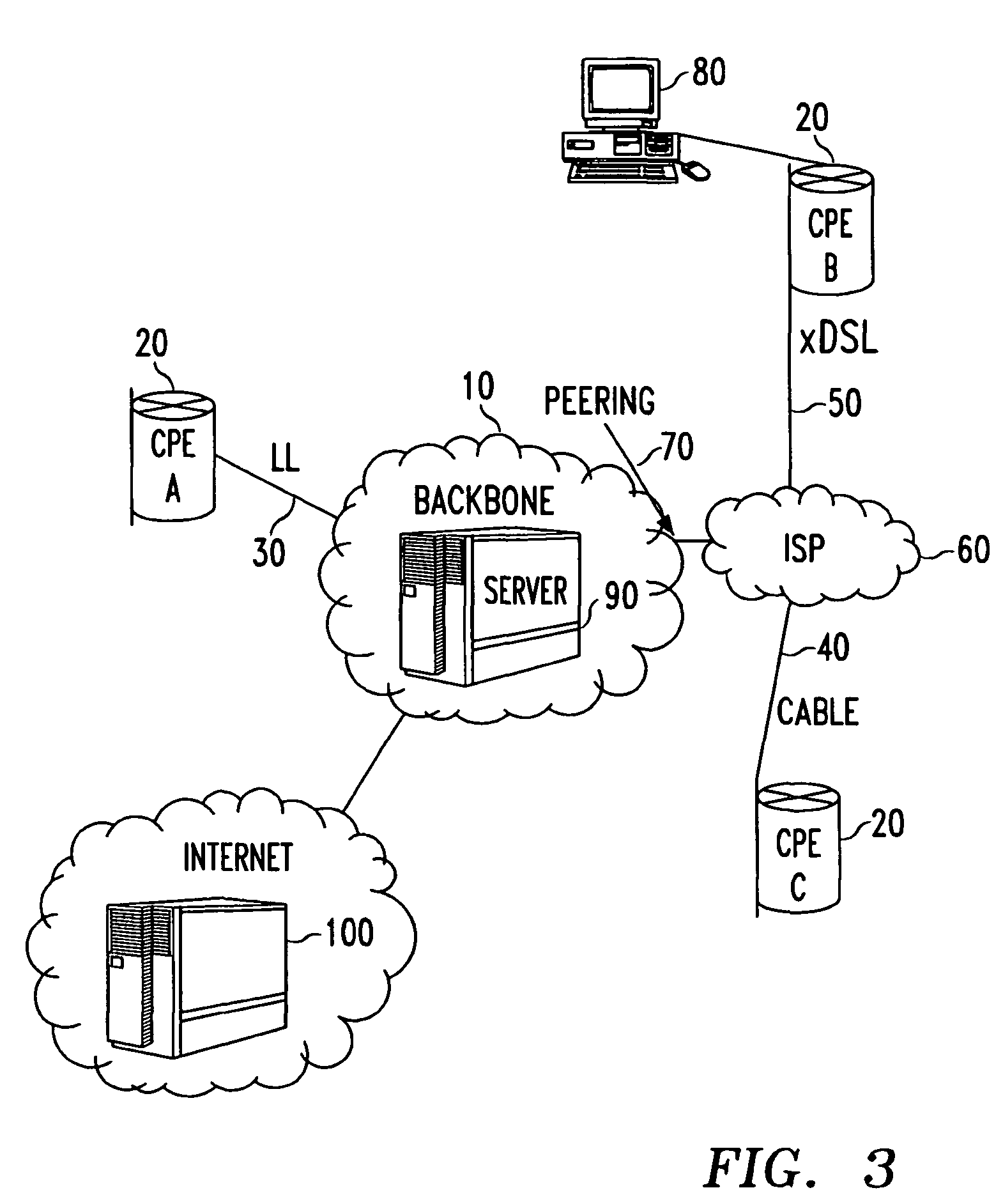
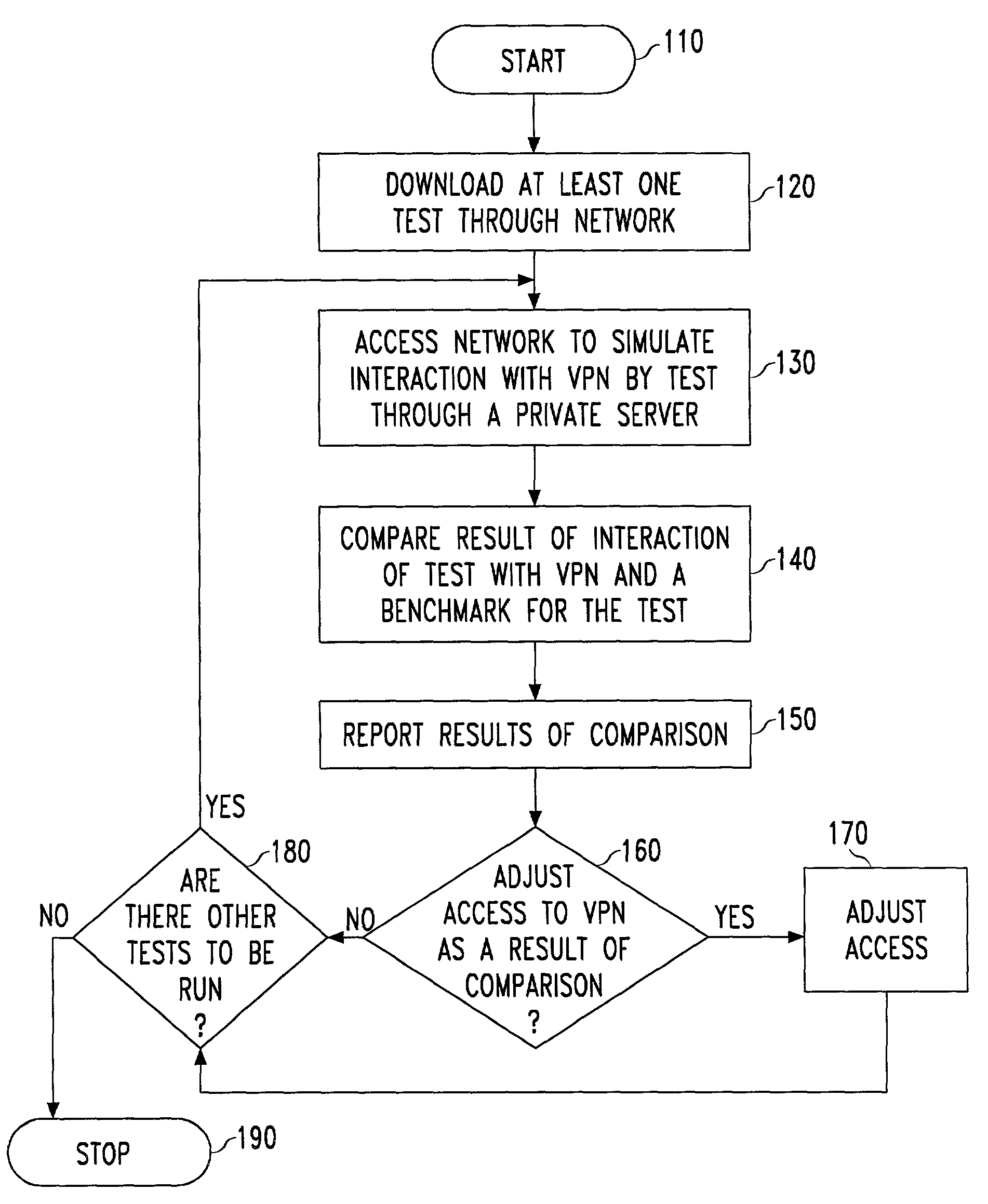
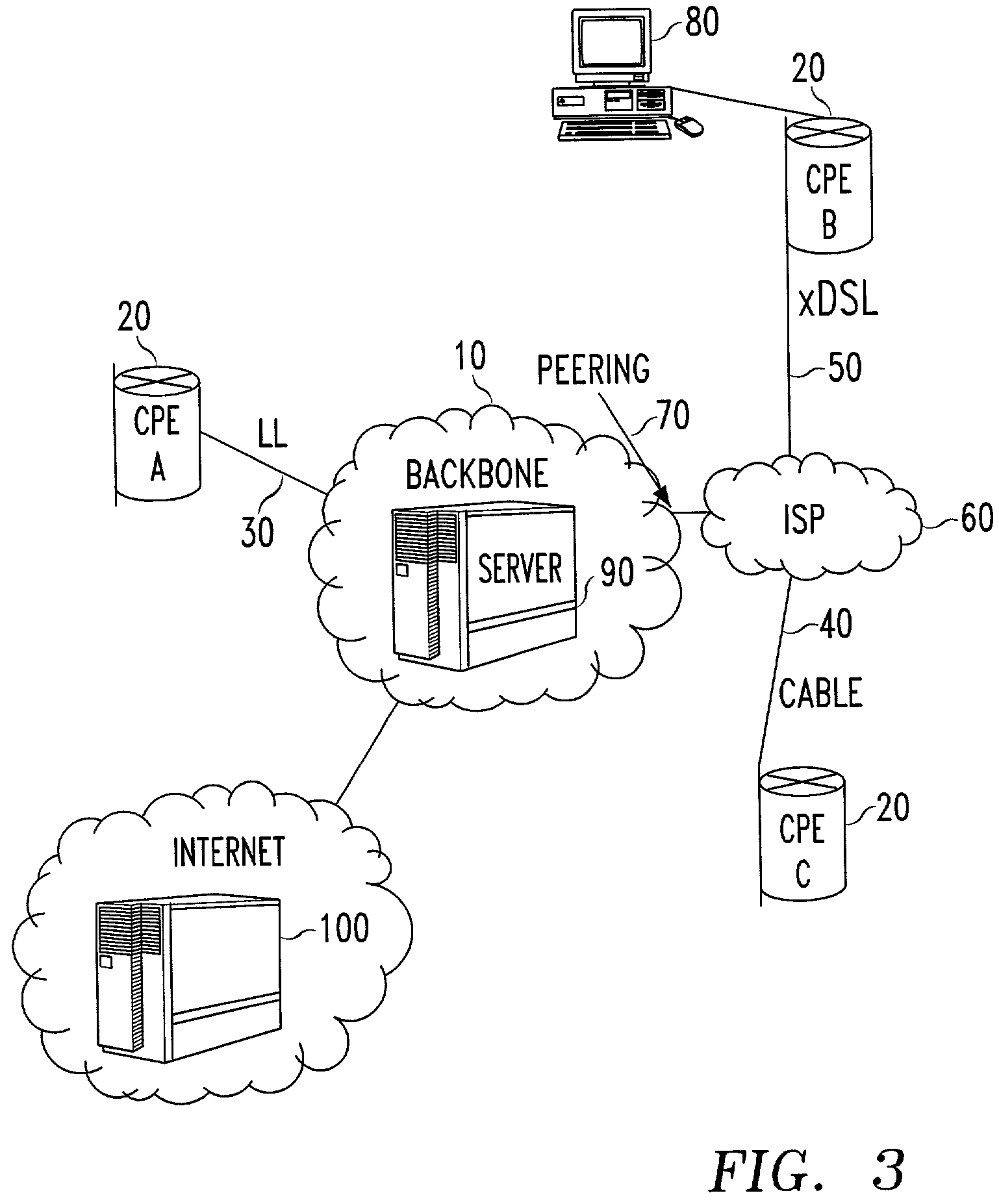
Methods for optimizing and evaluating network access techniques
InactiveUS7925281B2Expand accessImprove data throughputError preventionTransmission systemsModem devicePrivate network
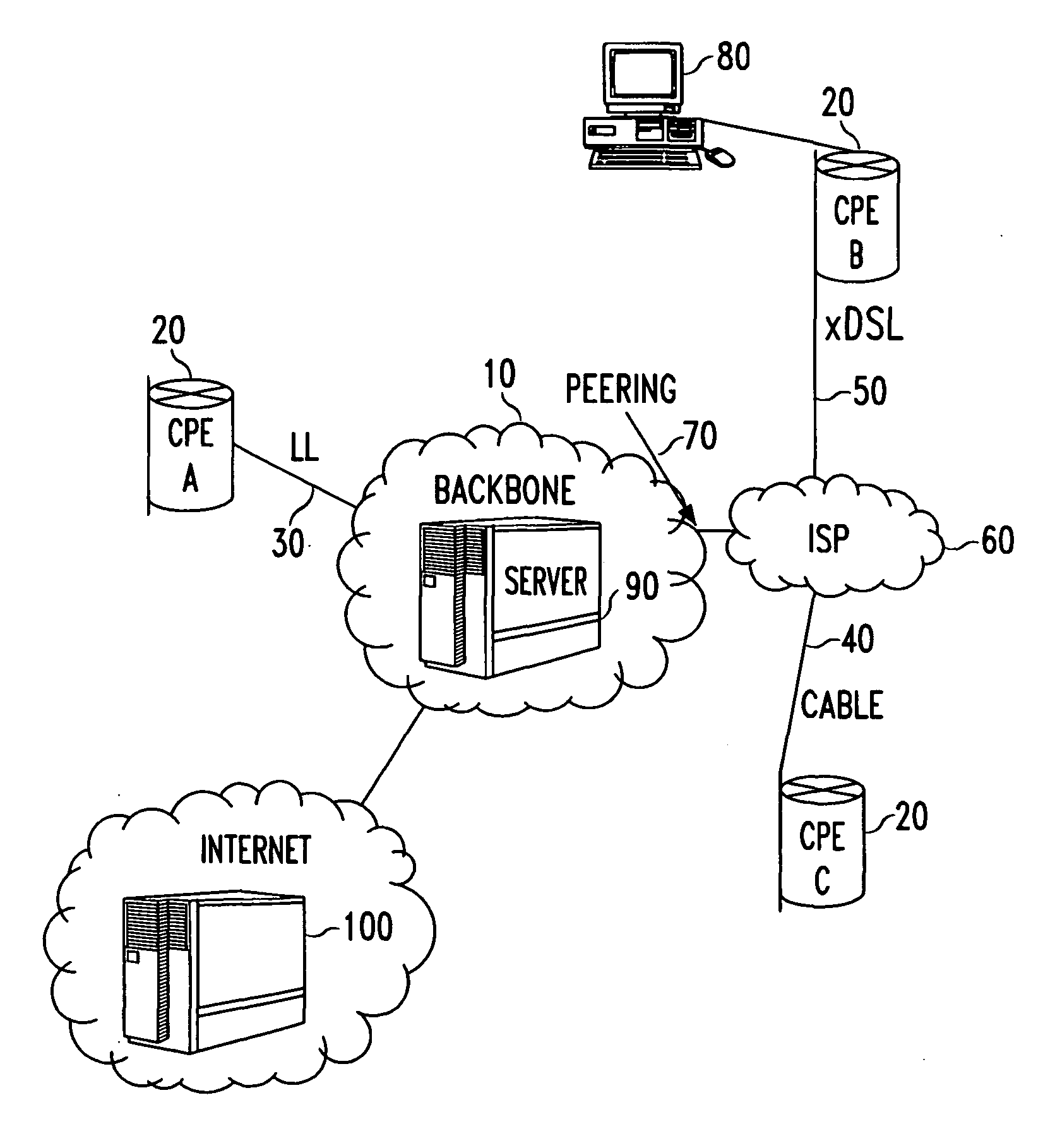
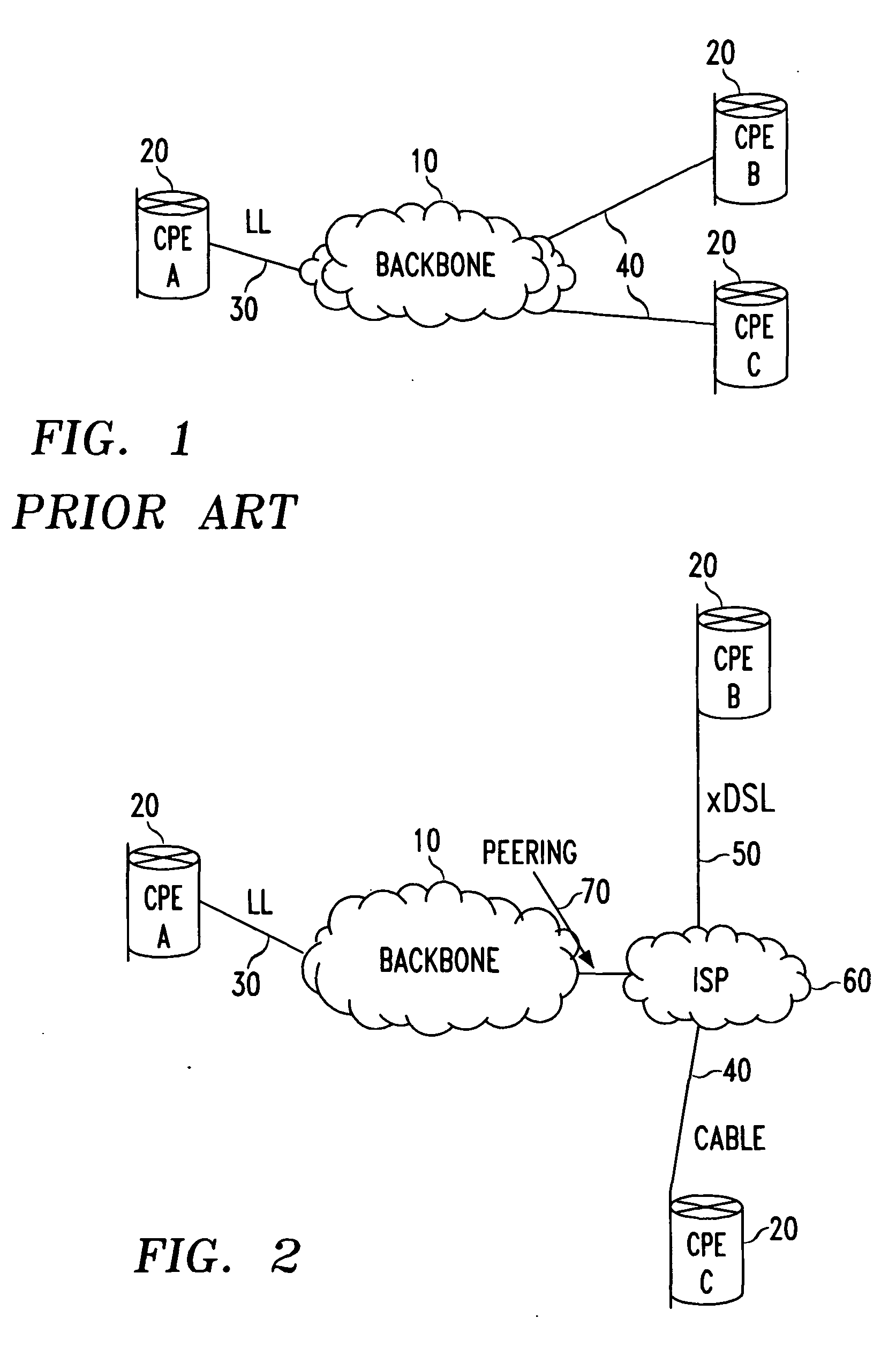
Methods of evaluating access to Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) from alternate access connections and for improving access to VPNs from alternate access connections such as ISPs. The methods include downloading a set of tests through a network backbone to simulate access to the VPN from the alternate access connection and comparing the results of the test to benchmarks for the test of access to the VPN from leased lines and modems. By obtaining comparisons of the tests and the benchmarks, it is possible to determine the throughput of data through the VPN and tell the customer how its access connections are affecting, among other things, the raw data throughput. This allows the customer and / or the network service provider to adjust the access connections to improve communications with the VPN.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
Methods for optimizing and evaluating network access techniques
InactiveUS7035222B2Expand accessImprove data throughputCorrect operation testingFrequency-division multiplex detailsModem devicePrivate network
Methods of evaluating access to Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) from alternate access connections and for improving access to VPNs from alternate access connections such as ISPs. The methods include downloading a set of tests through a network backbone to simulate access to the VPN from the alternate access connection and comparing the results of the test to benchmarks for the test of access to the VPN from leased lines and modems. By obtaining comparisons of the tests and the benchmarks, it is possible to determine the throughput of data through the VPN and tell the customer how its access connections are affecting, among other things, the raw data throughput. This allows the customer and / or the network service provider to adjust the access connections to improve communications with the VPN.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
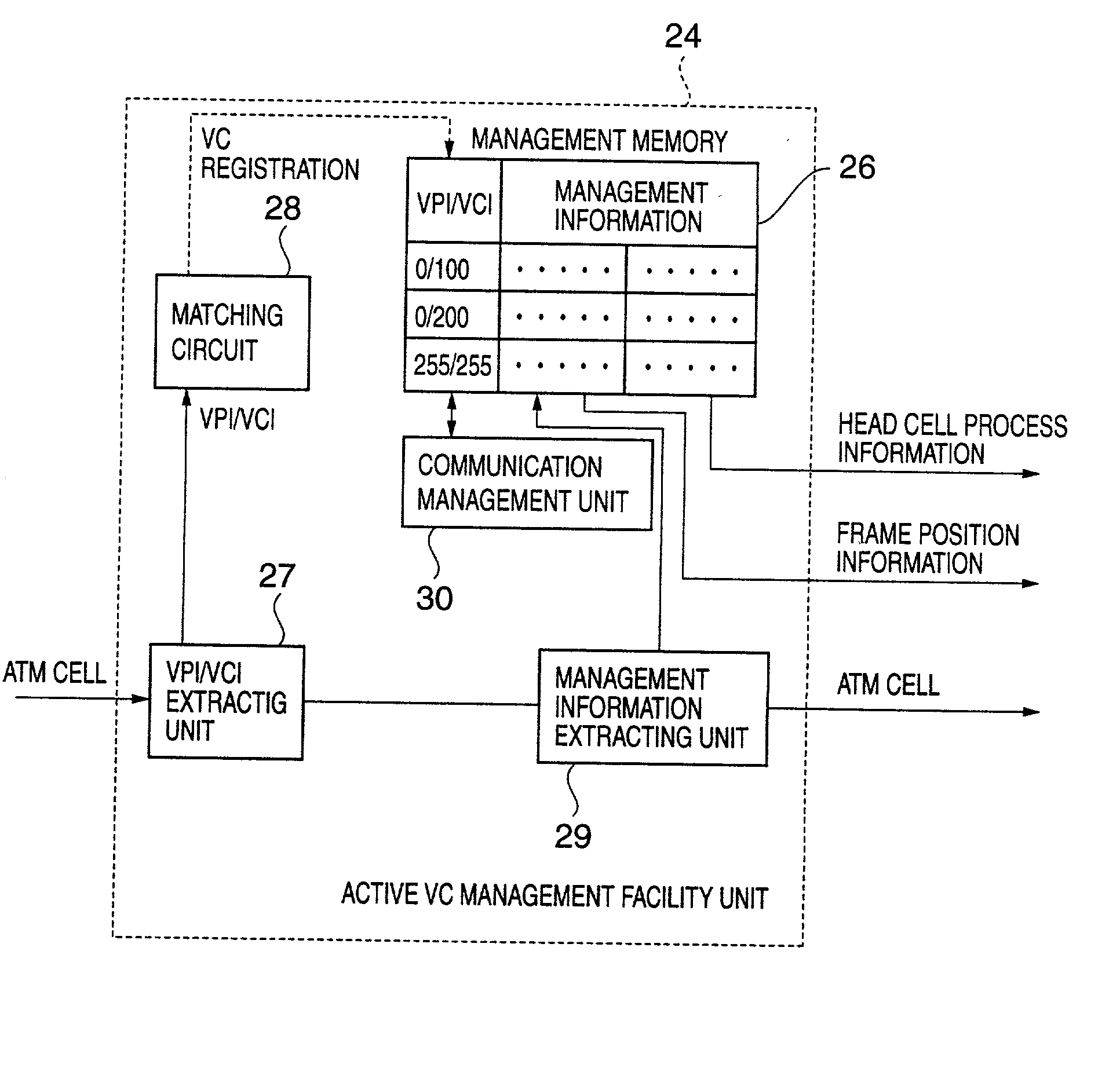
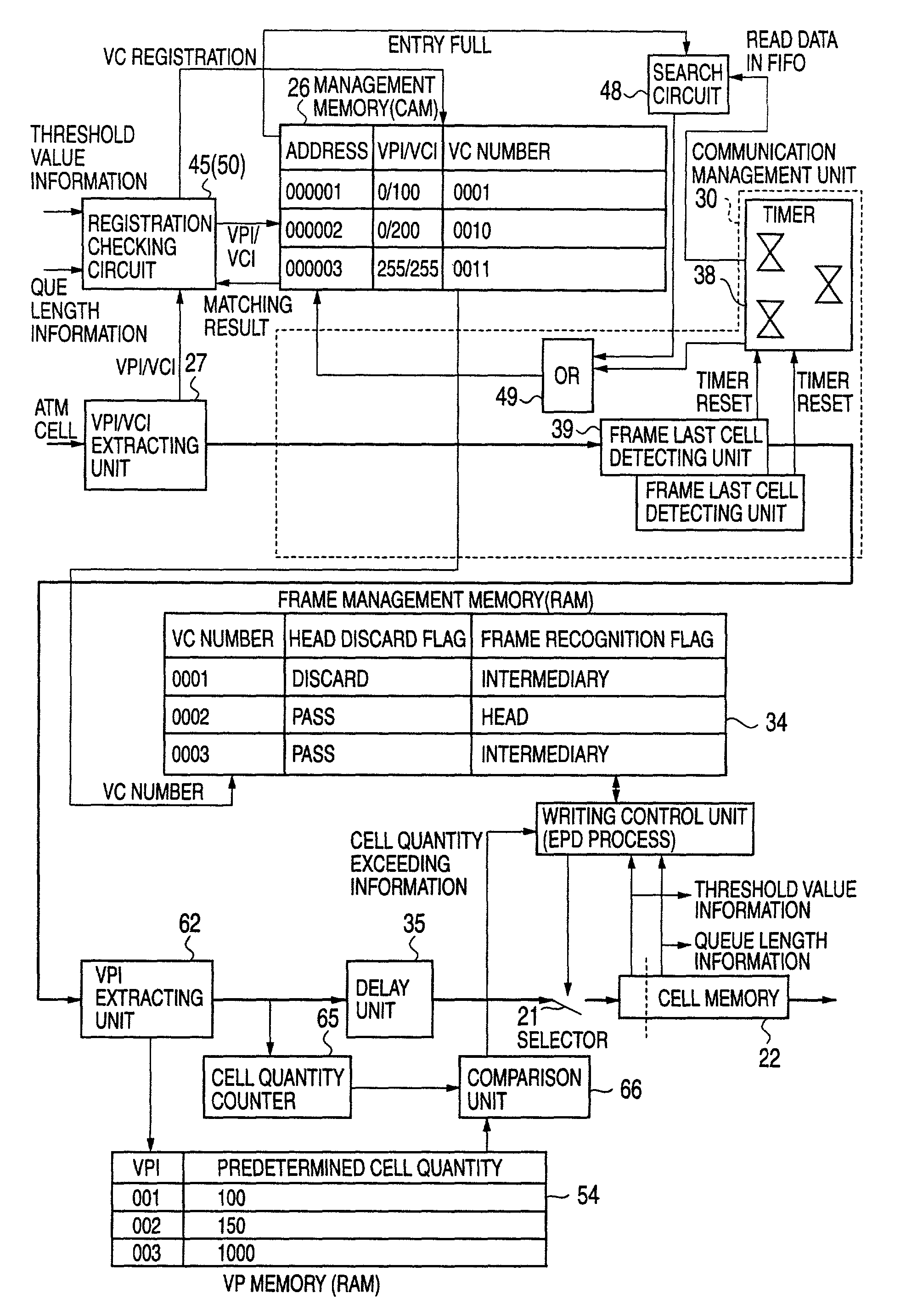
Dynamic virtual channel management apparatus
InactiveUS20020054600A1Data switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsLeased lineParallel computing
The present invention includes a detection unit for detecting an active virtual channel of arriving ATM cells, and a management memory unit for managing management information about the detected active virtual channel on a virtual-channel-to-virtual-channel basis, wherein a frame-by-frame process is performed on cells whose virtual channel identifier matches that of an active virtual channel managed by the management memory unit. In this manner, virtual-channel-by-virtual-channel processing is achieved in ATM leased line services that are provided on a virtual-path-by-virtual-path basis, thereby dispensing with needs to register a virtual channel into management memory in advance and allowing a large number of virtual channels to be accommodated.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
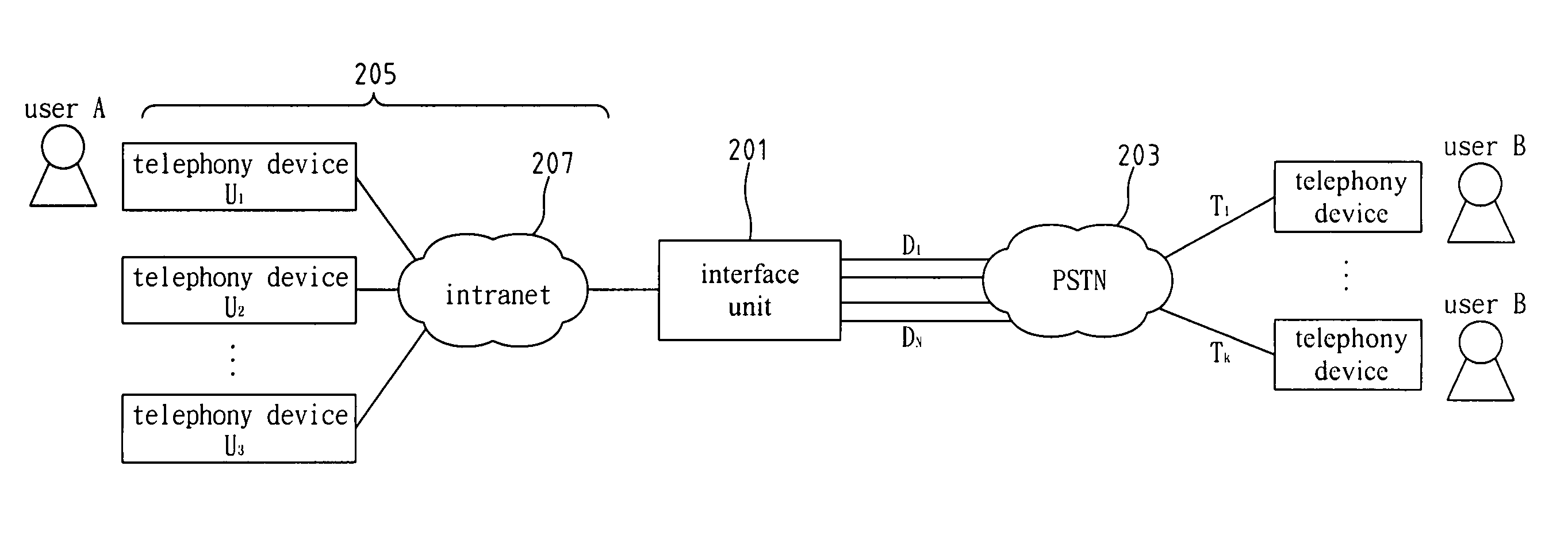
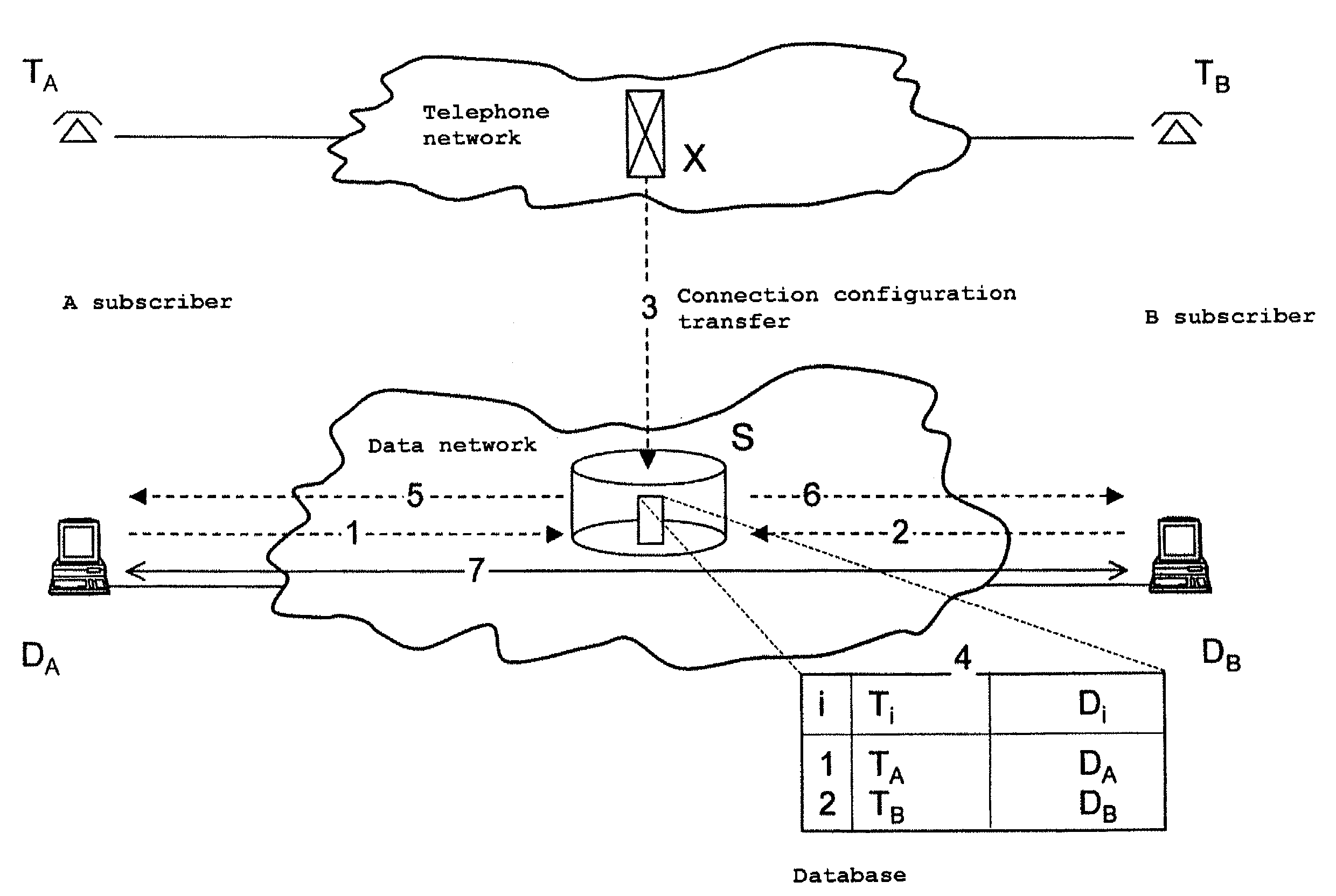
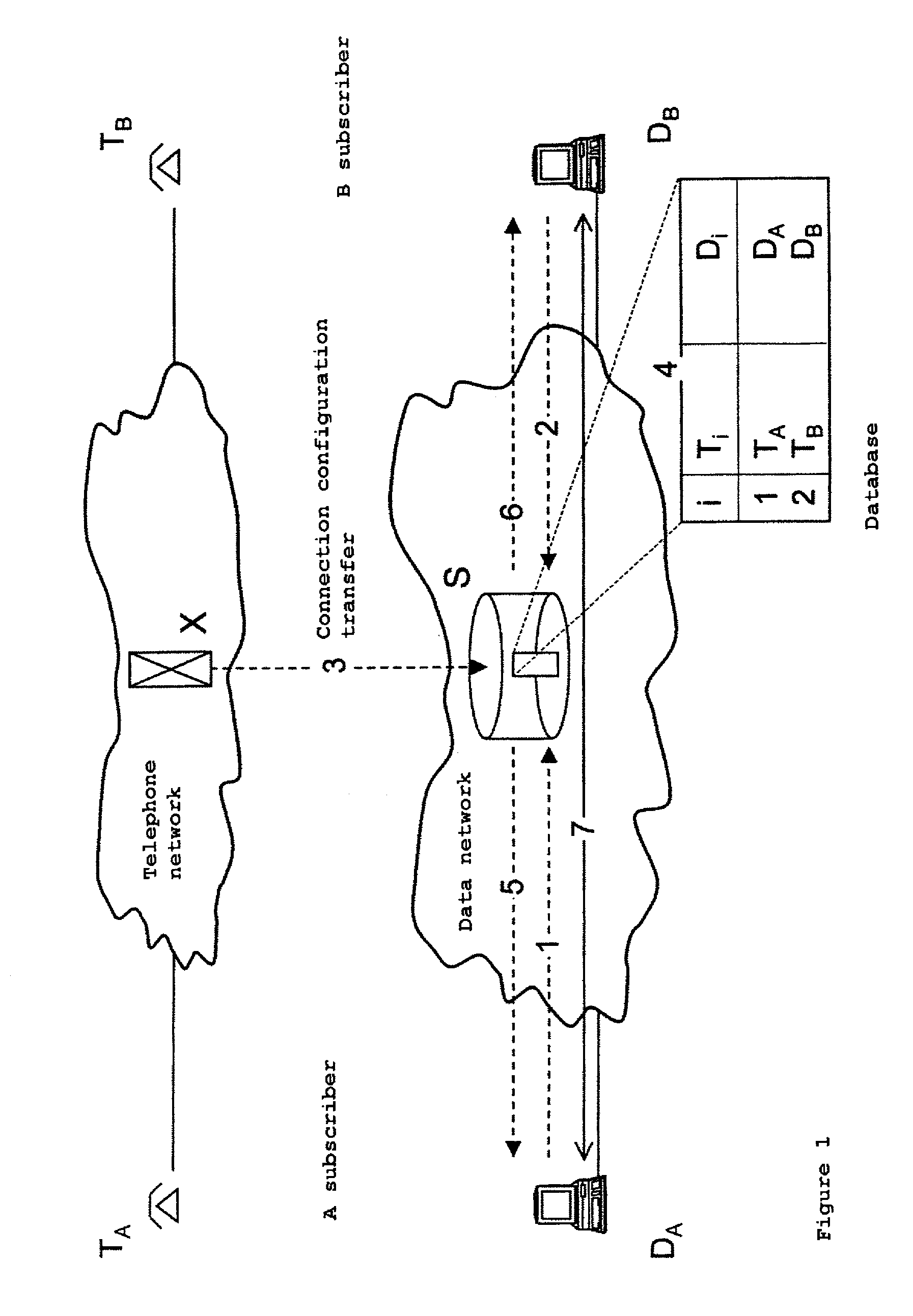
System and method for transferring connecting configurations from a telephone network to a data network
InactiveUS7177302B2Data switching by path configurationHybrid transportData connectionNetwork connection
Two subscribers A and B are each connected to a network, e.g. by means of a leased line or a dialup connection. Subscriber A sets up a telephone connection to subscriber B. In the course of the telephone connection, a data connection additionally needs to be set up. A service provided by the telephone network operator and an appropriate method taking place on the subscribers data terminal equipment automatically transfer the data network addresses of the subscribers involved in a connection and also the connection configuration of the telephone connection to the subscribers data terminal equipment. This means that a data network connection can automatically be set up for a telephone connection on request.
Owner:UNIFY GMBH & CO KG
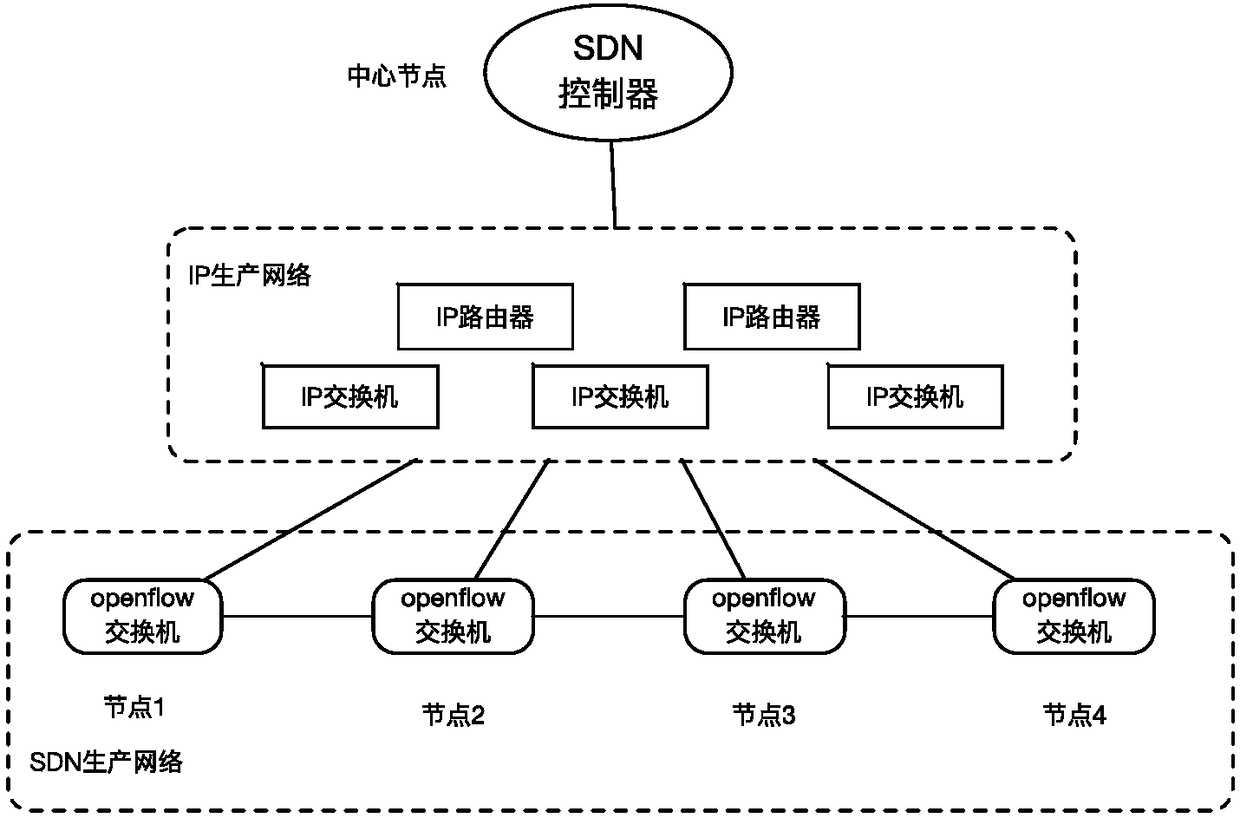
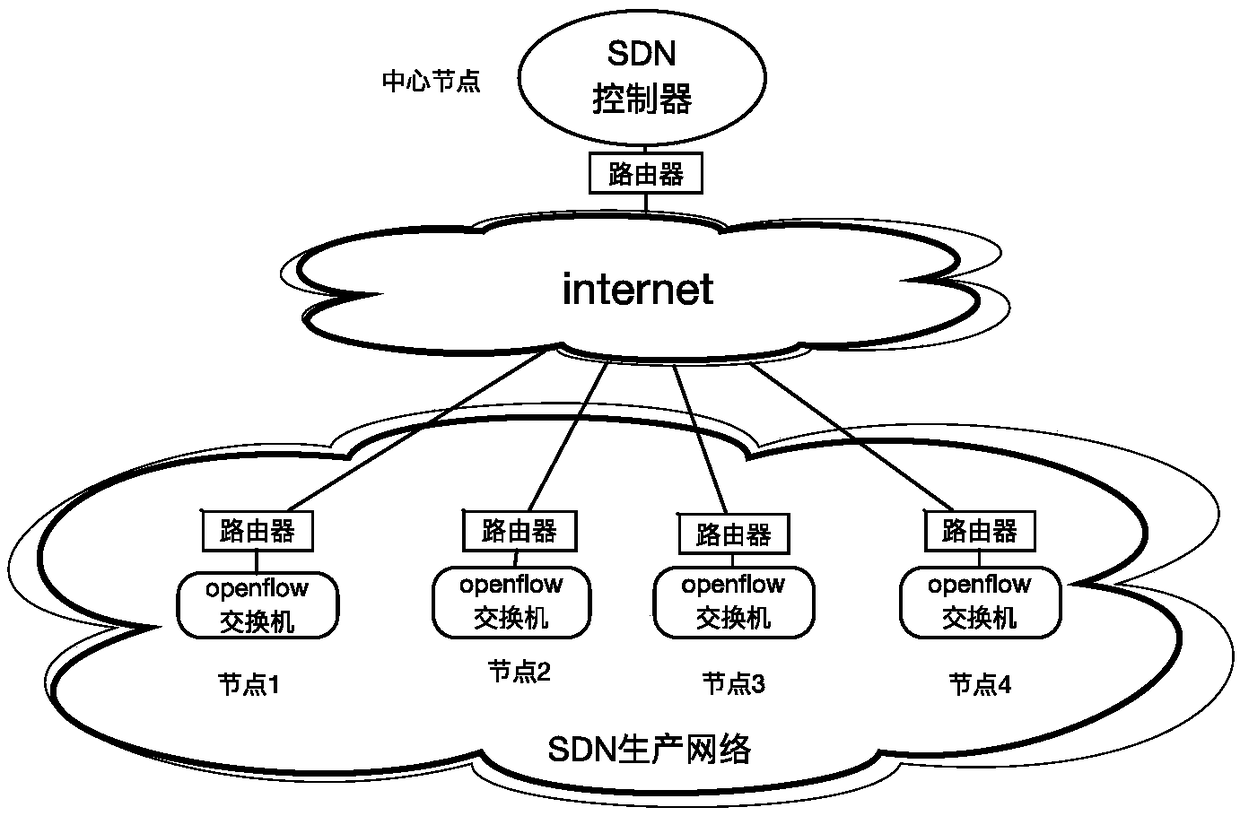
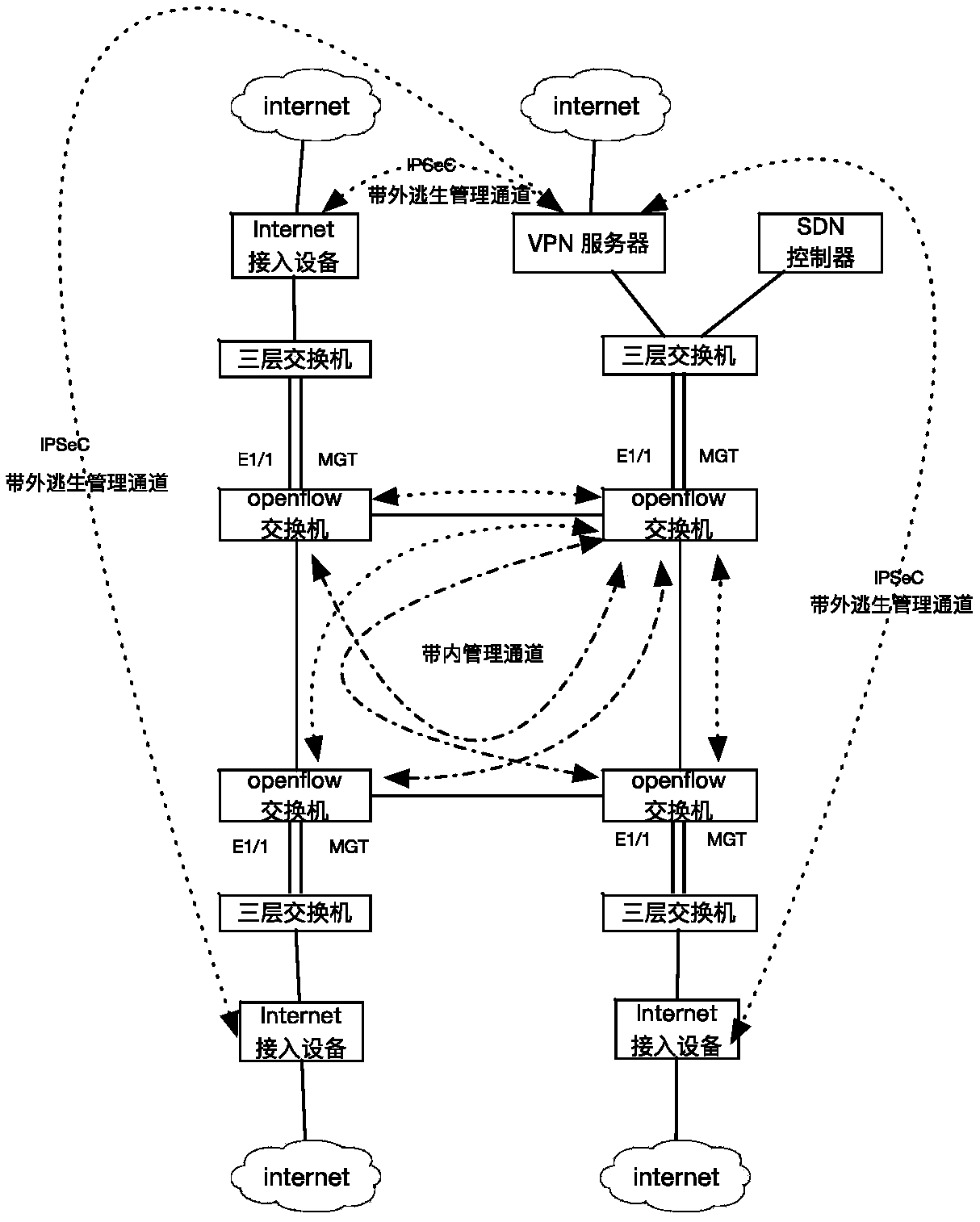
SDN management network architecture, method for establishing SDN management network and switching method for SDN management network
The invention discloses an SDN management network architecture, which comprises an SDN controller, a core node layer 3 switch, openflow switches, branch node layer 3 switches, a VPN server and internet access equipment, wherein the SDN controller is deployed at a core node of a network; the SDN controller is connected to the core node layer 3 switch; the branch node layer 3 switches and the openflow switches are deployed at branch nodes; a management port and a service port of each openflow switch are respectively connected to two ports of the corresponding branch node layer 3 switch; the VPNserver is deployed at the core node and is connected to internet through the internet access equipment; in-band management channels are established between the core node and the branch nodes based onan SDN service network, and the in-band management channels are virtual leased lines established by configuring an initialization flow table of the openflow switches; and VPN leased lines are established between the core node and the branch nodes through the internet and are taken as out-of-band escape management channels which have lower levels of usage than the in-band management channels.
Owner:上海层峰网络科技有限公司
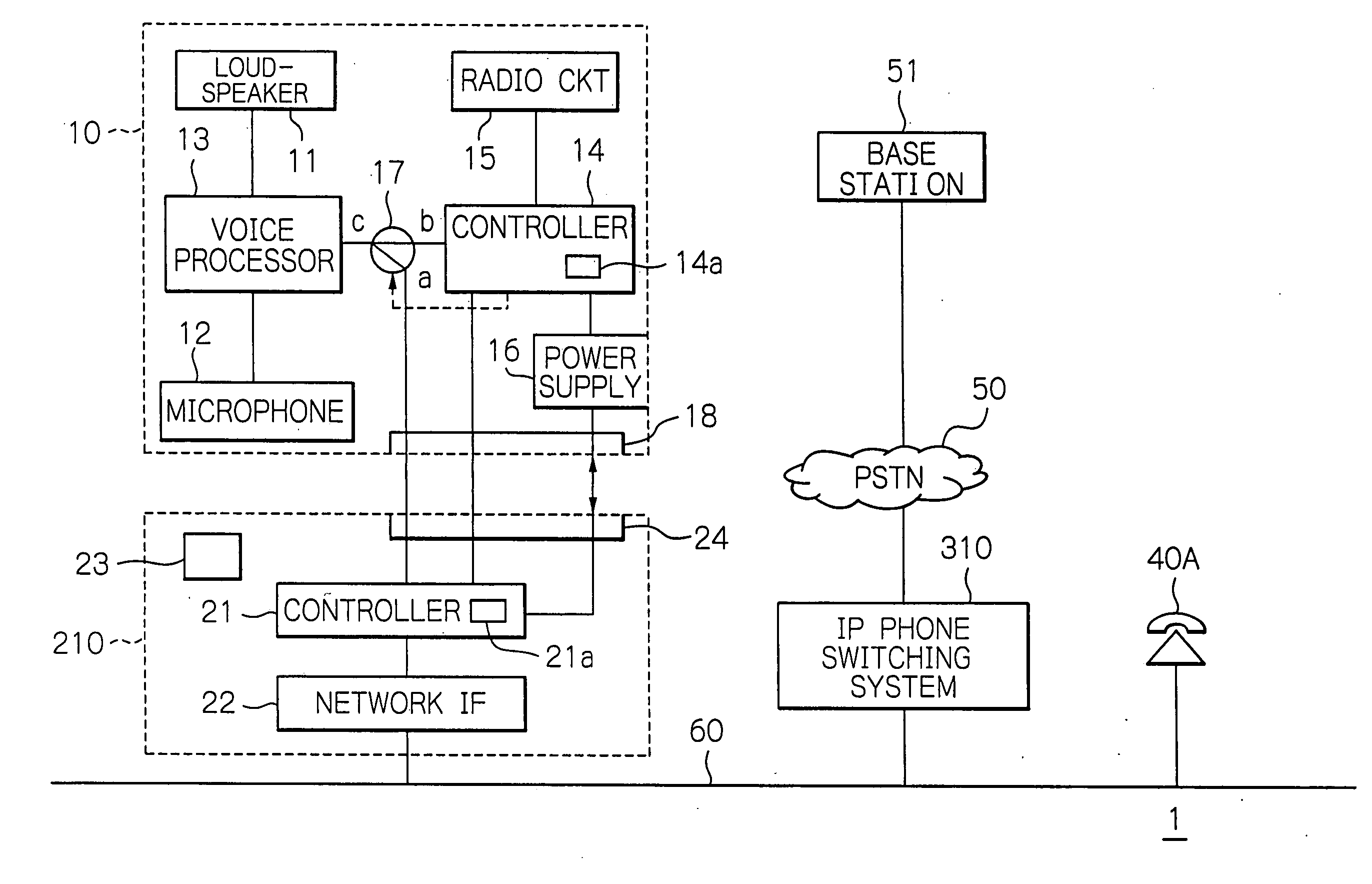
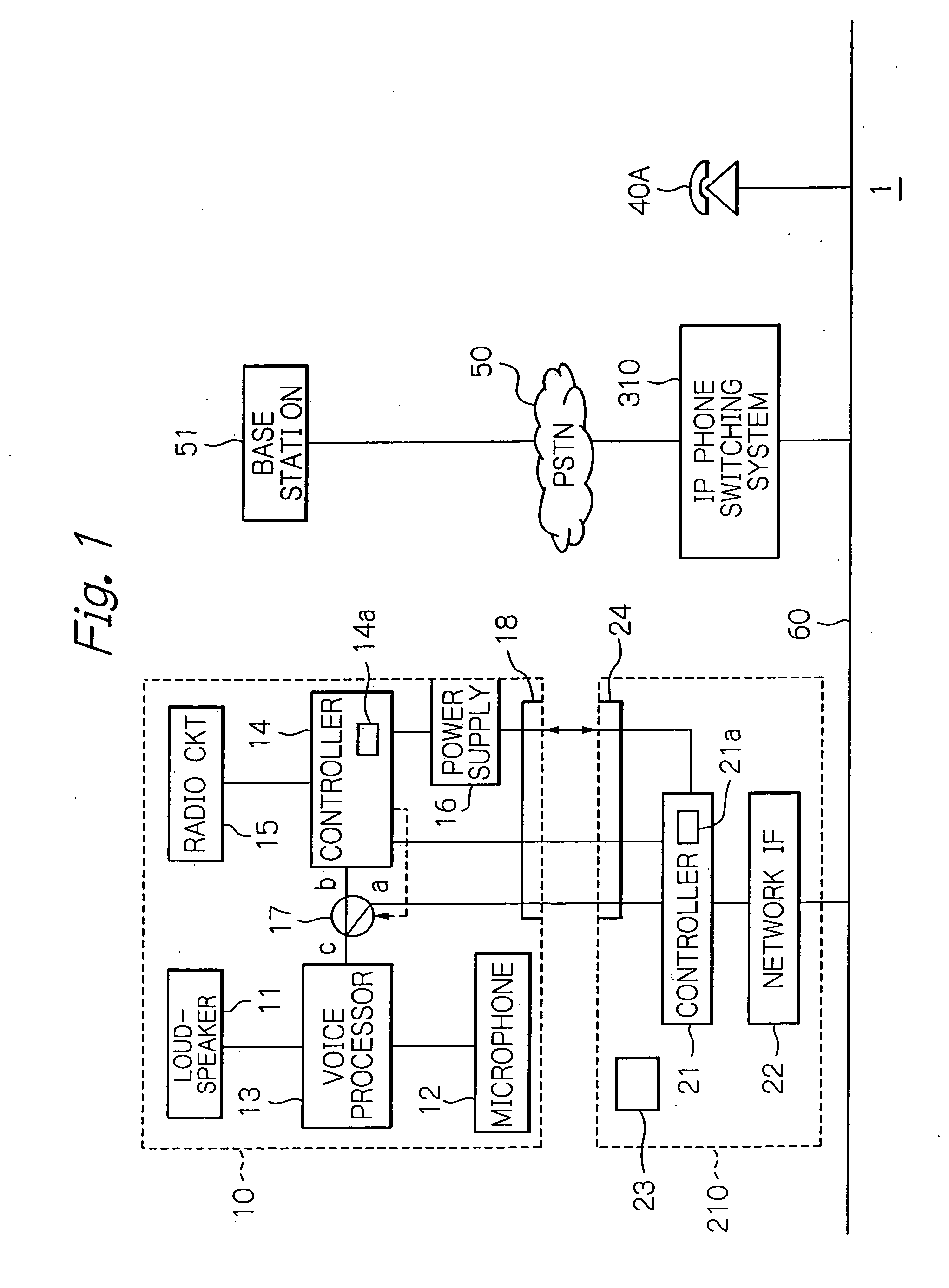
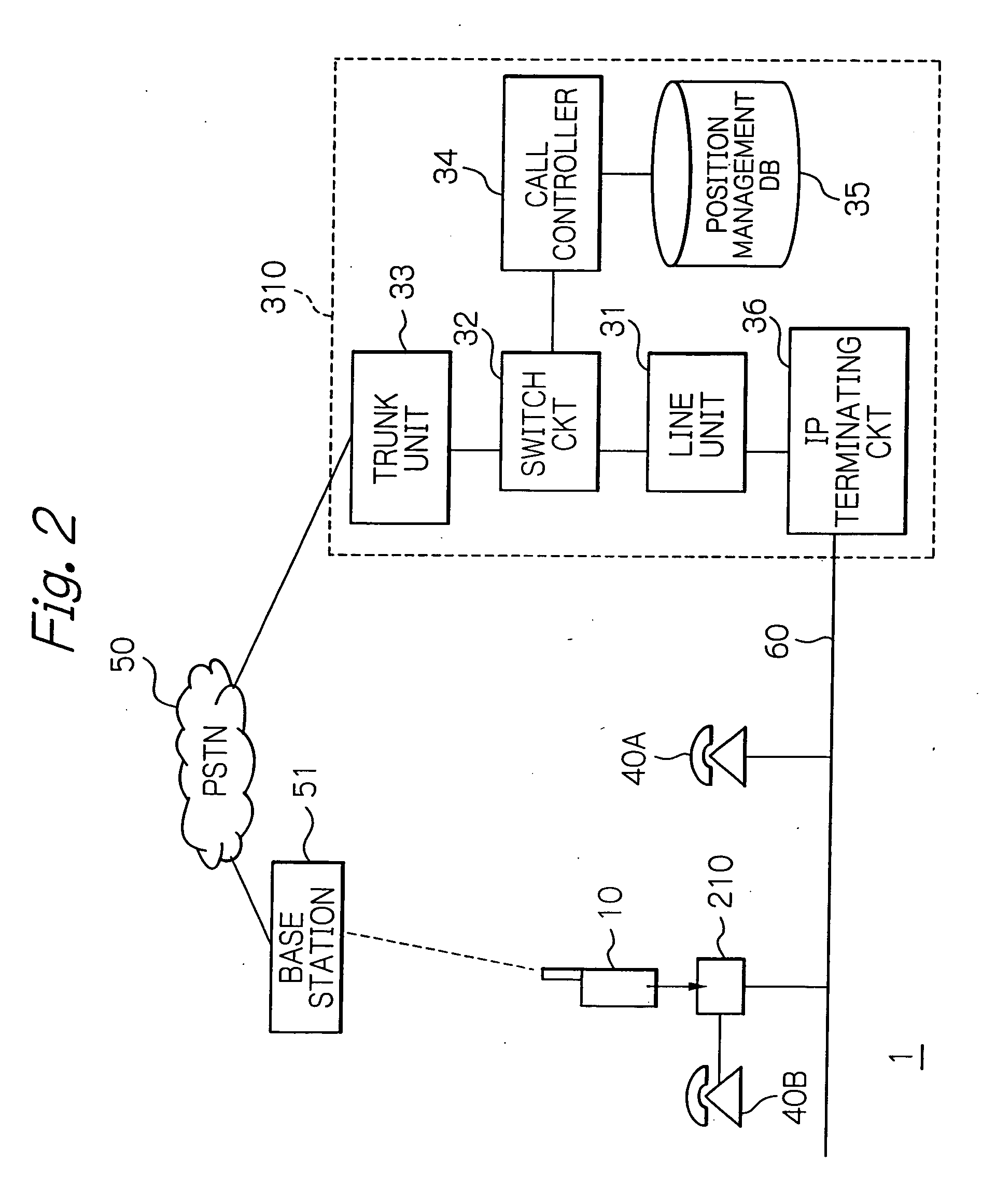
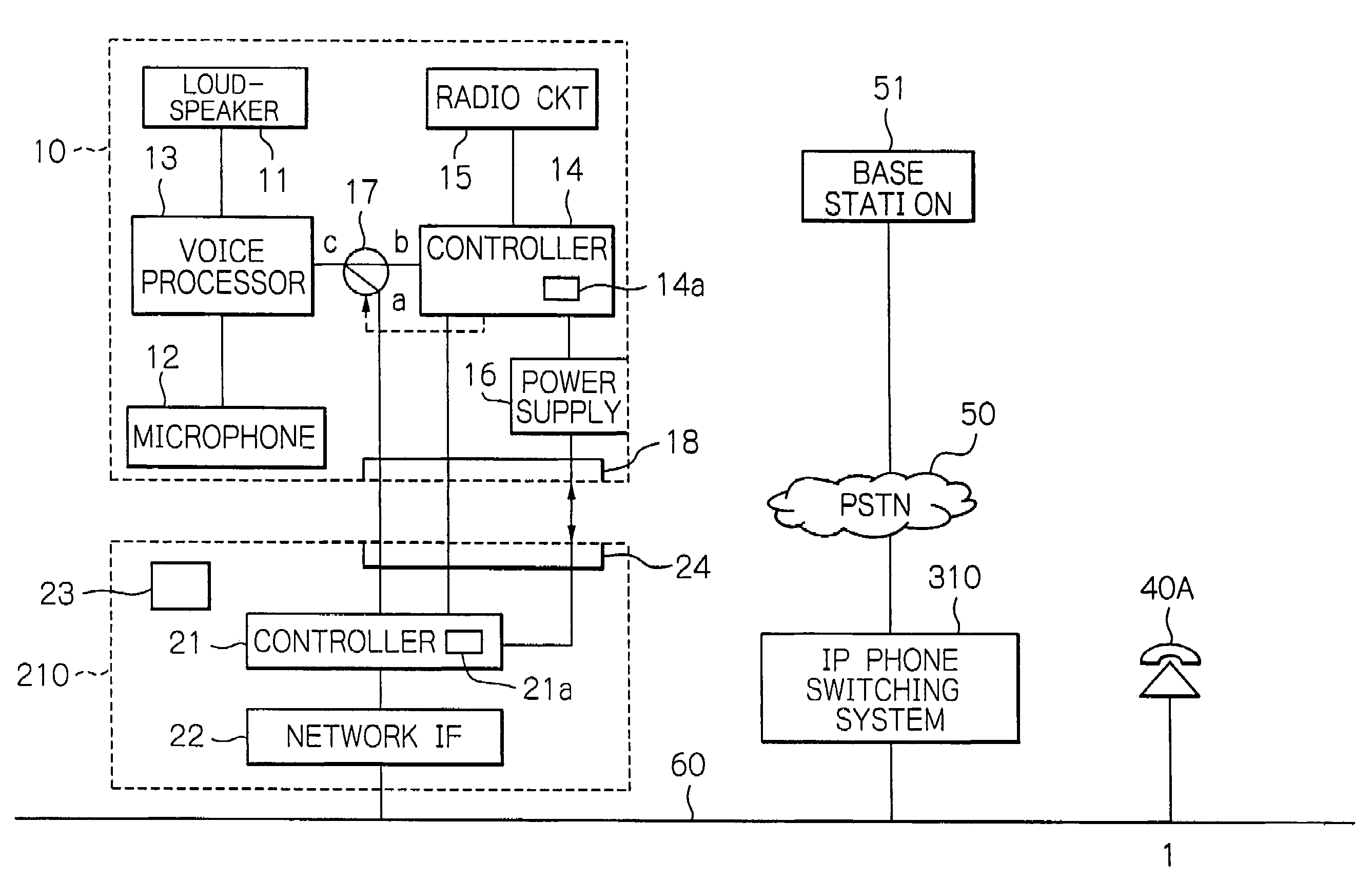
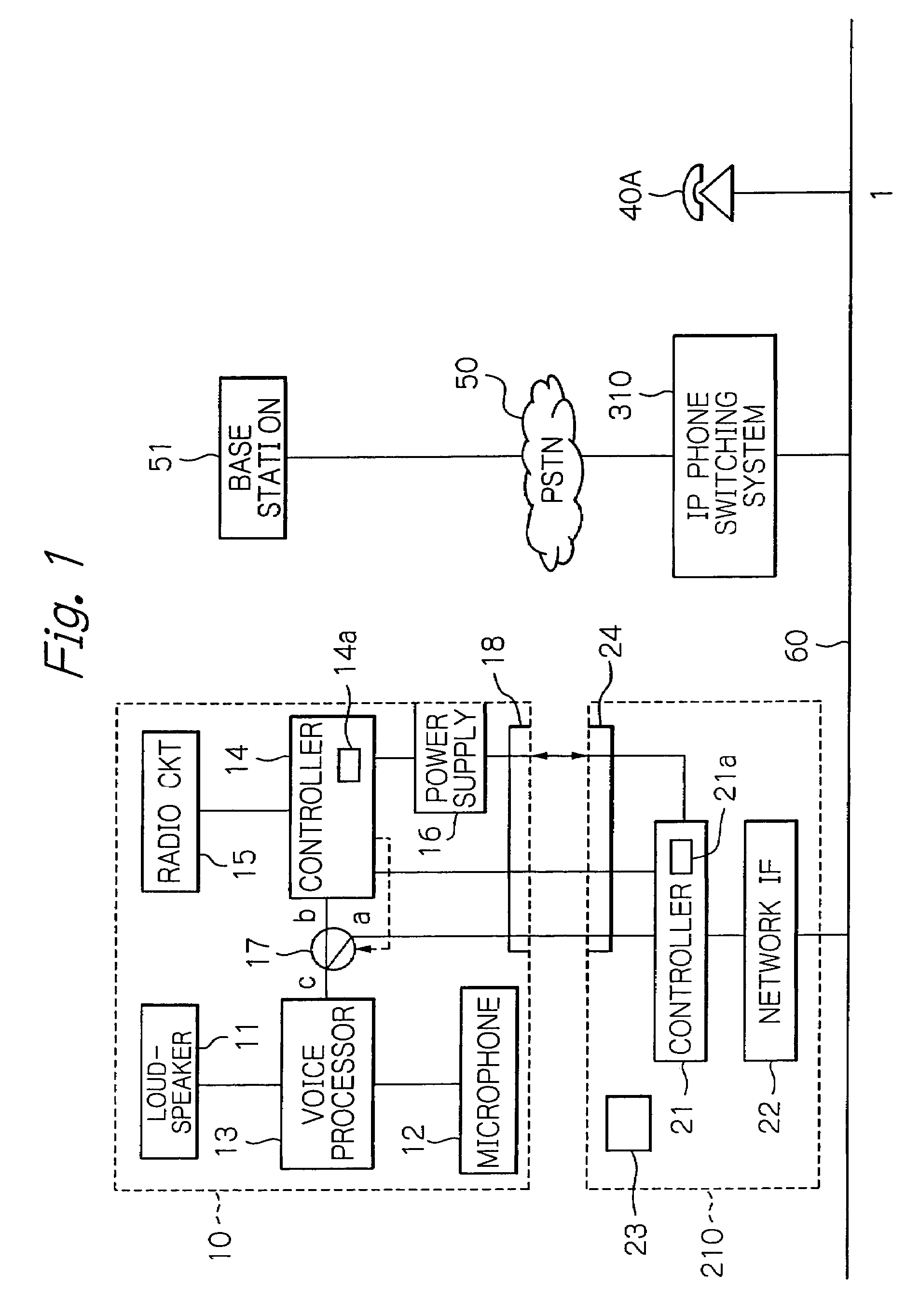
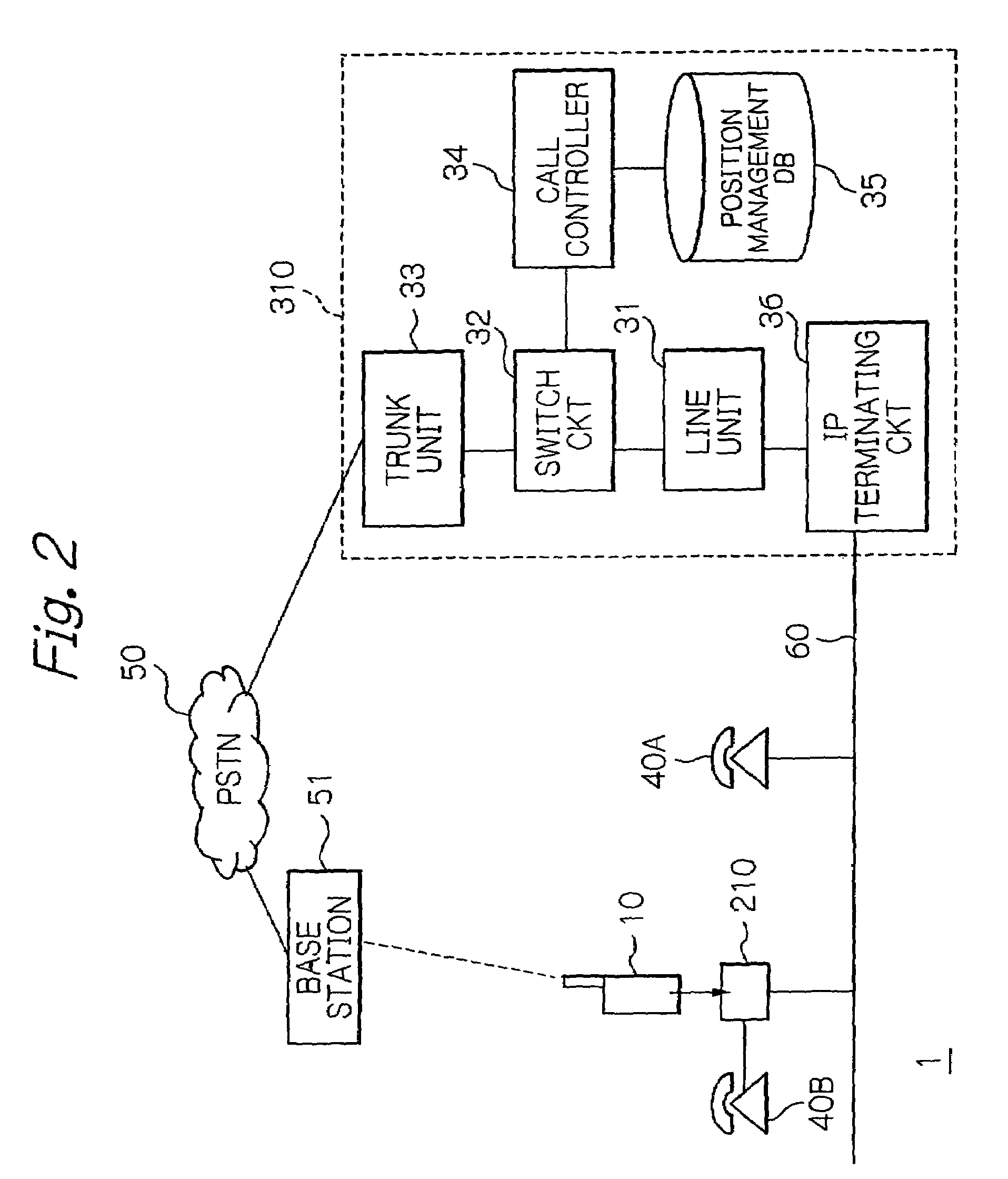
Switching system connecting a radio communication terminal via a LAN line to a public switched network or a leased line
ActiveUS20050143063A1Telephone data network interconnectionsNetwork topologiesVoice communicationLeased line
A telephone switching system includes a position information management database and a call conversion controller. On receiving number conversion information from an adapter having a radio communication terminal connected, the database registers an identification number assigned to the adapter and terminal information particular to the communication terminal in one-to-one correspondence, thereby managing the position of the communication terminal. When a call is originated on a telephone terminal interconnected thereto or a communication terminal having a voice communication function interconnected to its LAN system, the call conversion controller searches the database on the basis of a destination number and substitutes, if terminal information corresponding to the destination number is found out in the database, the identification number of the adapter corresponding to the terminal information for the destination number to process call switching.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Switching system connecting a radio communication terminal via a LAN line to a public switched network or a leased line
ActiveUS7321767B2Telephone data network interconnectionsNetwork topologiesVoice communicationLeased line
A telephone switching system includes a position information management database and a call conversion controller. On receiving number conversion information from an adapter having a radio communication terminal connected, the database registers an identification number assigned to the adapter and terminal information particular to the communication terminal in one-to-one correspondence, thereby managing the position of the communication terminal. When a call is originated on a telephone terminal interconnected thereto or a communication terminal having a voice communication function interconnected to its LAN system, the call conversion controller searches the database on the basis of a destination number and substitutes, if terminal information corresponding to the destination number is found out in the database, the identification number of the adapter corresponding to the terminal information for the destination number to process call switching.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
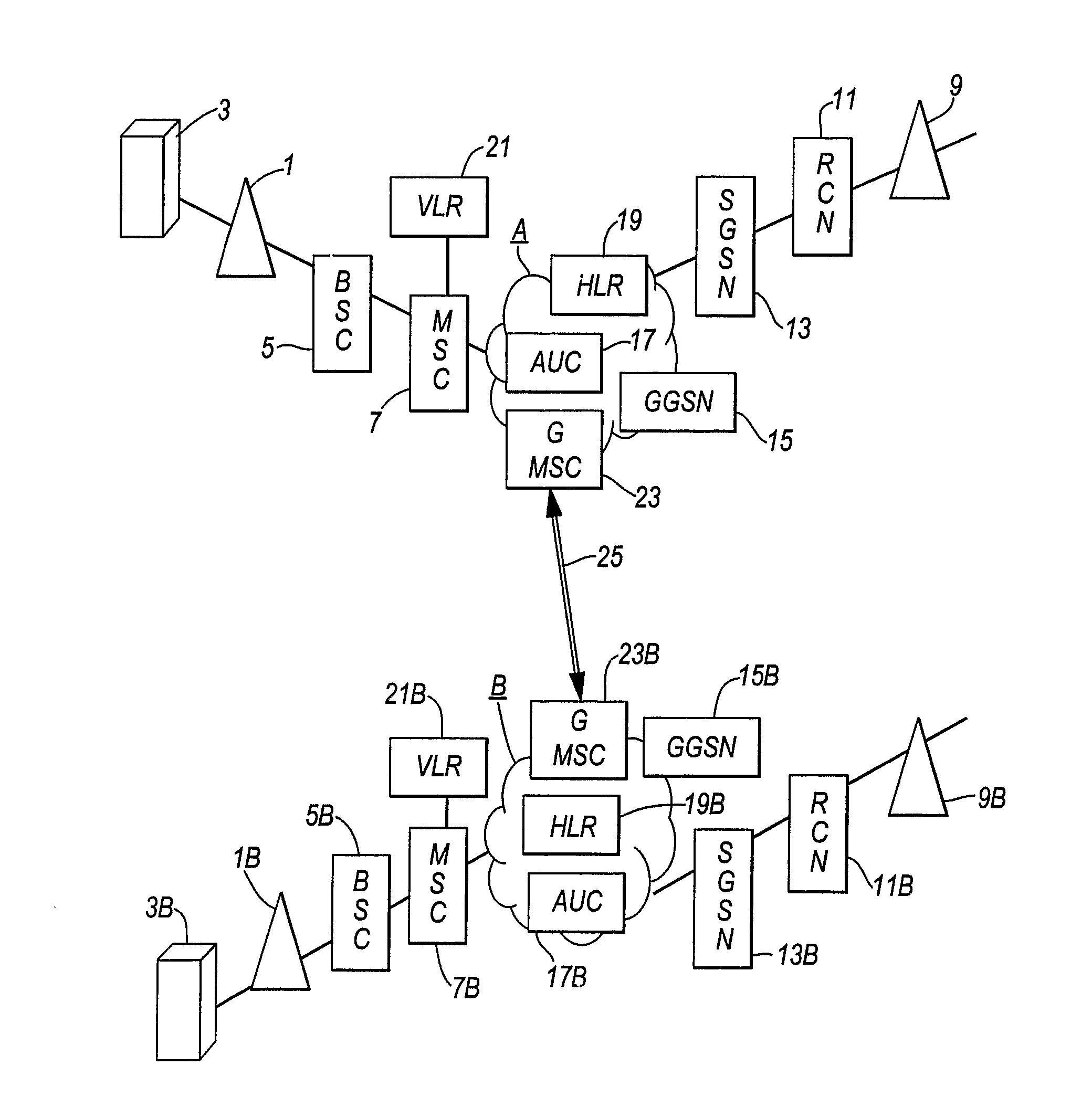
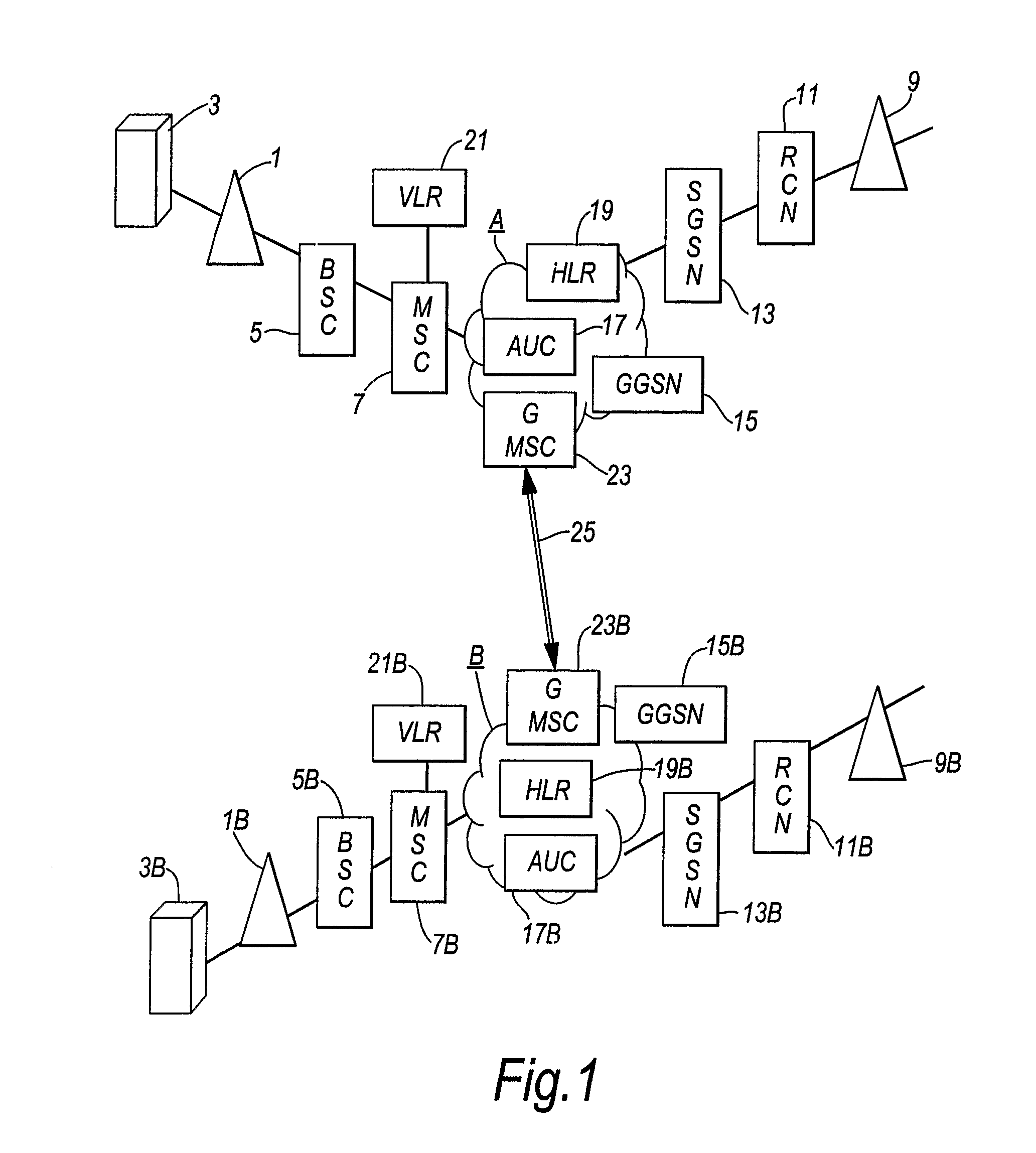
Routing communications between telecommunications networks
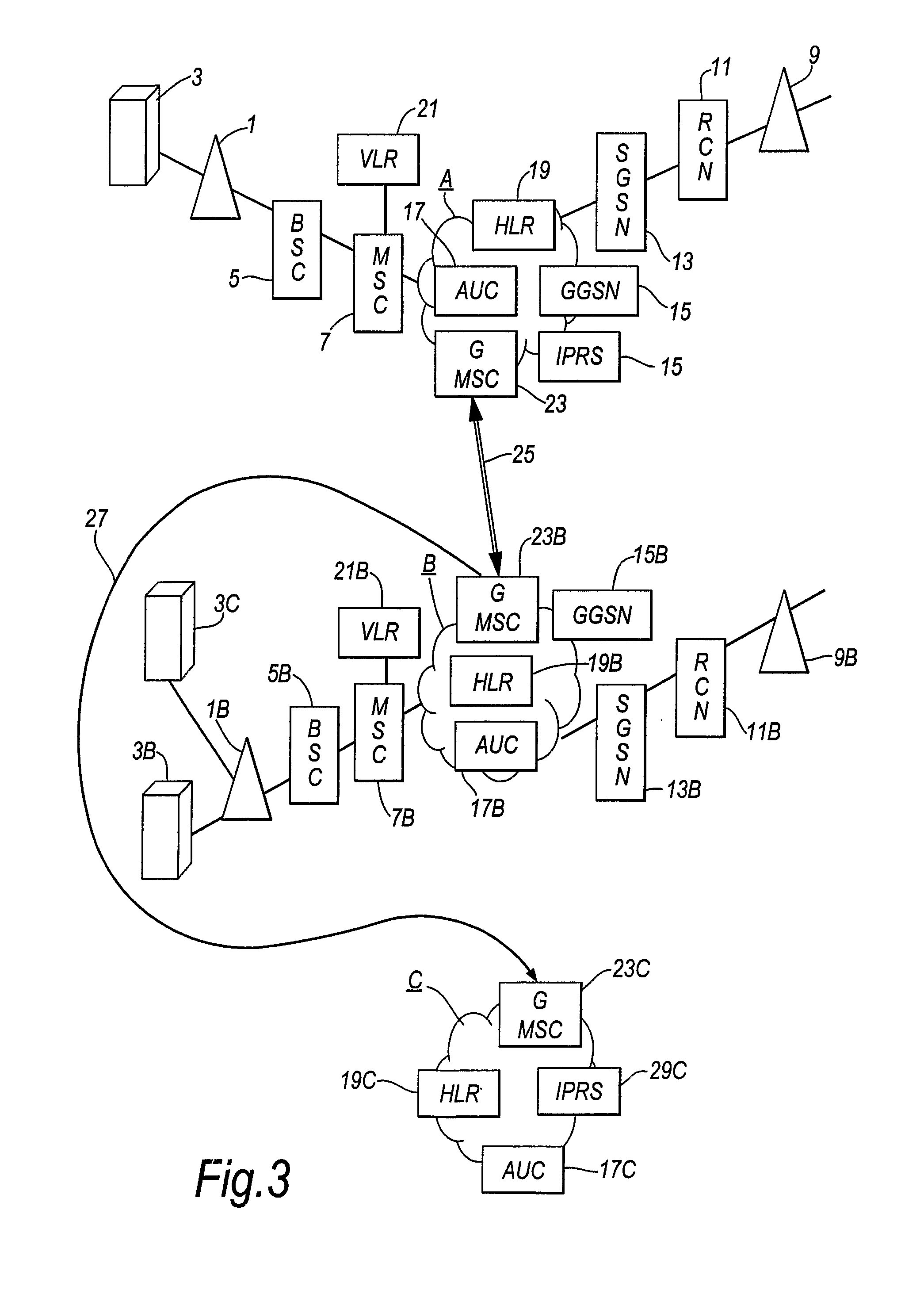
InactiveUS20130203408A1Reduce call costsLow costWireless commuication servicesNetwork data managementTelecommunications networkLeased line
A telecommunications system includes a first (home) mobile telecommunications network A5 second (roamed) mobile telecommunications network B and a third (virtual) mobile telecommunications network C. The virtual network C does not have its own radio access network but uses the radio access network of network B in accordance with a commercial contract between networks B and C. Network C is a MVNO. When a mobile telecommunications device that has network A as its home network roams to network B, the mobile telecommunications device initially registers with network B as the roamed network. Conventionally, communications between network A and network B would be transmitted via a fixed communication link (25) (such as a leased line). However, in the embodiment described, the network A transmits a command to the mobile telecommunications device, instructing that device to de-register from network B and to re-register with virtual network C. The home network A and the virtual network C include IP routing servers (29,29C) which enable voice over IP calls to be routed between the home network A and the virtual network C via the Internet (31). The calls can subsequently be routed from the virtual network C to the mobile device via the radio access network on network B. In this way, use of the fixed communication link (25) between network A and network B is reduced, thereby potentially reducing the cost of making and receiving calls while roaming.
Owner:VODAFONE IP LICENSING
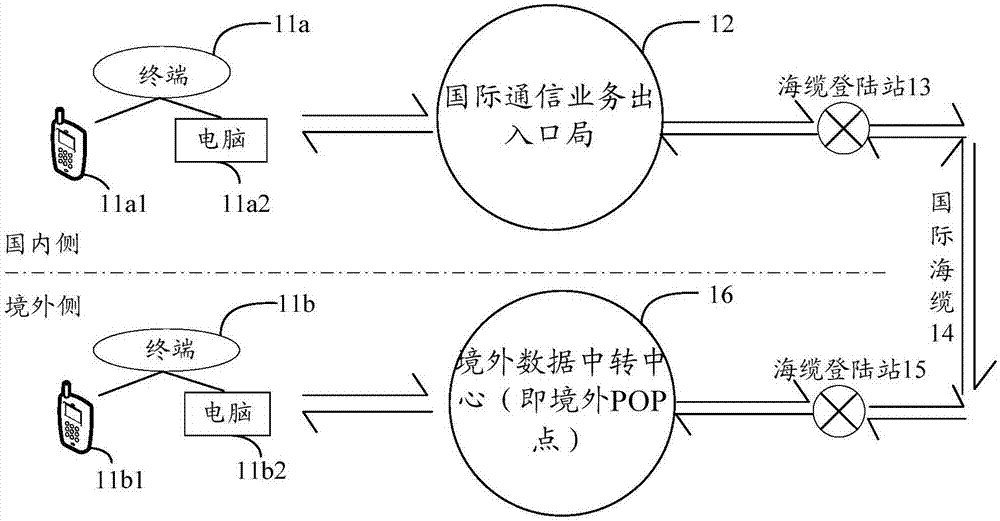
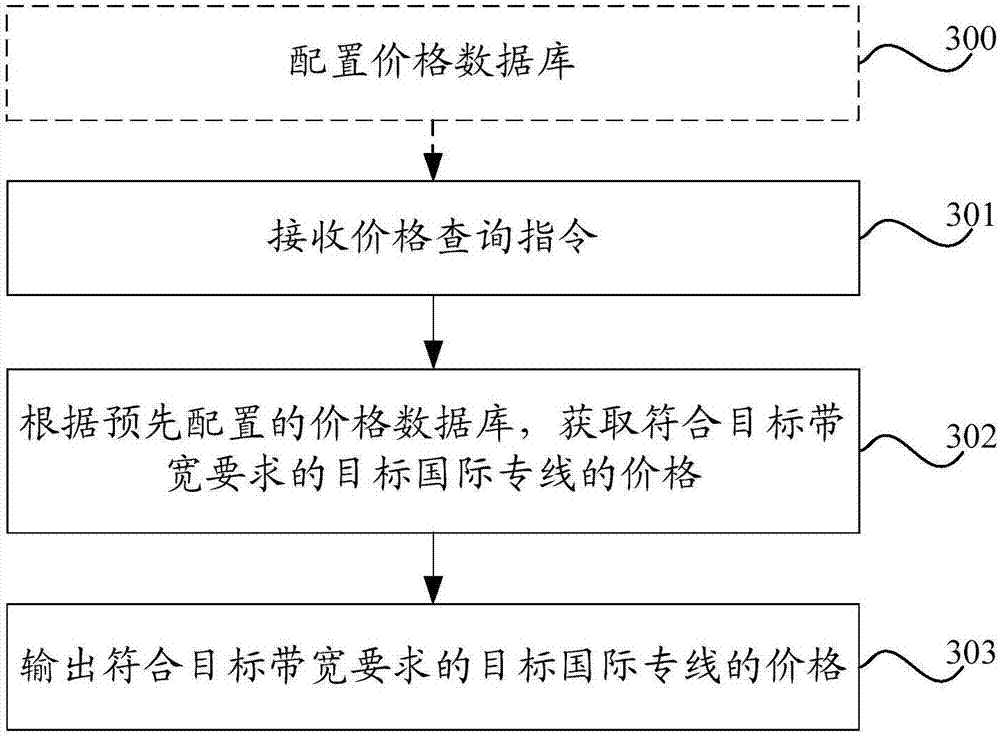
Price query method and device
InactiveCN107066610AShorten the determination timeFeedback as soon as possibleData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsLeased lineComputer science
Embodiments of the invention provide a price query method and device, relate to the technical field of communications, and aim to solve the problem of low efficiency of querying prices of international private leased line businesses. The method comprises the steps of receiving a price query instruction, wherein the price query instruction comprises an identifier of a target international private leased line and a target bandwidth, and the identifier of the target international private leased line includes a country / region identifier of an opposite end of the target international private leased line; then, according to a pre-configured price database, obtaining the price of the target international private leased line meeting the requirement of the target bandwidth, wherein the price database is used for storing prices of international private leased lines corresponding to identifiers of different international private leased lines under different bandwidths and / or prices of international private leased line sections; and finally, outputting the price of the target international private leased line meeting the requirement of the target bandwidth.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
Dynamic virtual channel management apparatus
InactiveUS7058061B2Process is performedData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsLeased lineParallel computing
The present invention includes a detection unit for detecting an active virtual channel of arriving ATM cells, and a management memory unit for managing management information about the detected active virtual channel on a virtual-channel-to-virtual-channel basis, wherein a frame-by-frame process is performed on cells whose virtual channel identifier matches that of an active virtual channel managed by the management memory unit. In this manner, virtual-channel-by-virtual-channel processing is achieved in ATM leased line services that are provided on a virtual-path-by-virtual-path basis, thereby dispensing with needs to register a virtual channel into management memory in advance and allowing a large number of virtual channels to be accommodated.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for establishing jewelry network leasing order
InactiveCN107730341AQuick buildApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingBuying/selling/leasing transactionsOrder formLeased line
The invention relates to a method for establishing a jewelry online rental order. The unique jewelry identification code is actively sent offline through a user terminal or a rental order is established on a server by first filling in a terminal for an offline order and then receiving it by a user terminal. The two methods for establishing online jewelry rental orders in the present invention are both offline-oriented. After users see a suitable jewelry style offline, they can quickly create a rental order on the server for subsequent rental processes.
Owner:秦伏尹 +1
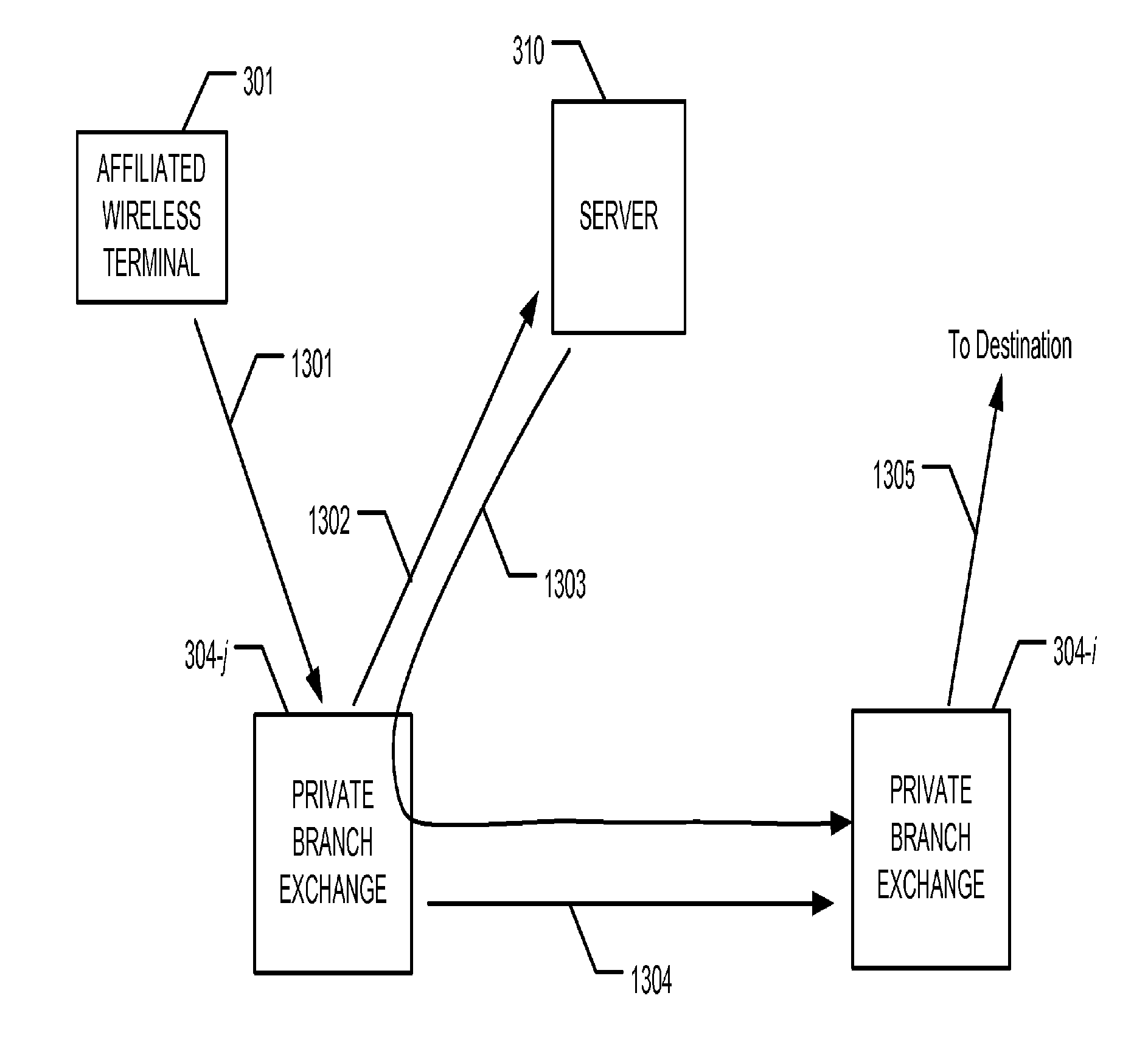
Reduction of Wireless Communication Costs in Enterprises
InactiveUS20130252619A1Reducing wireless telecommunication costLow costMultiplex system selection arrangementsNetwork topologiesPrivate networkLeased line
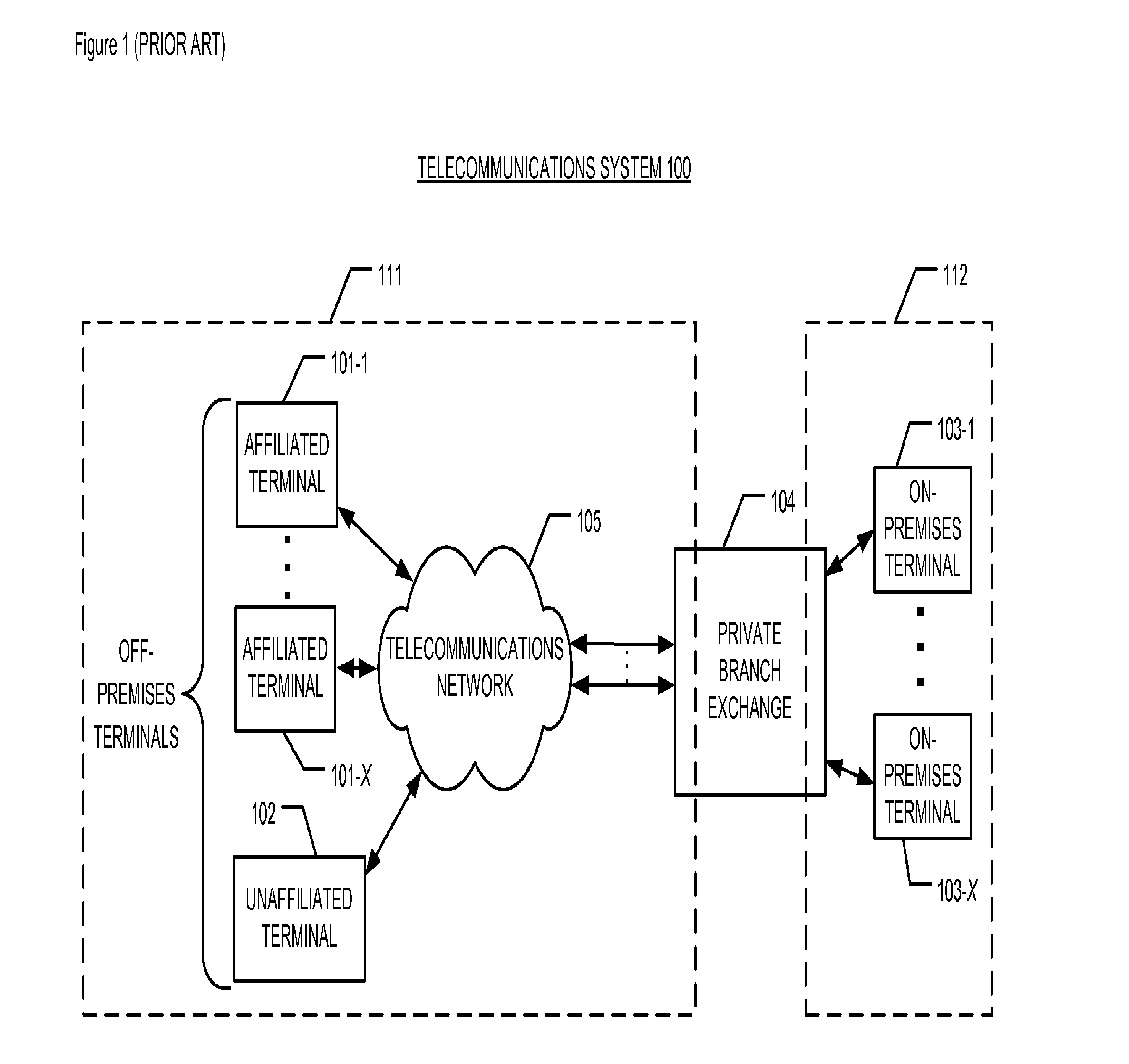
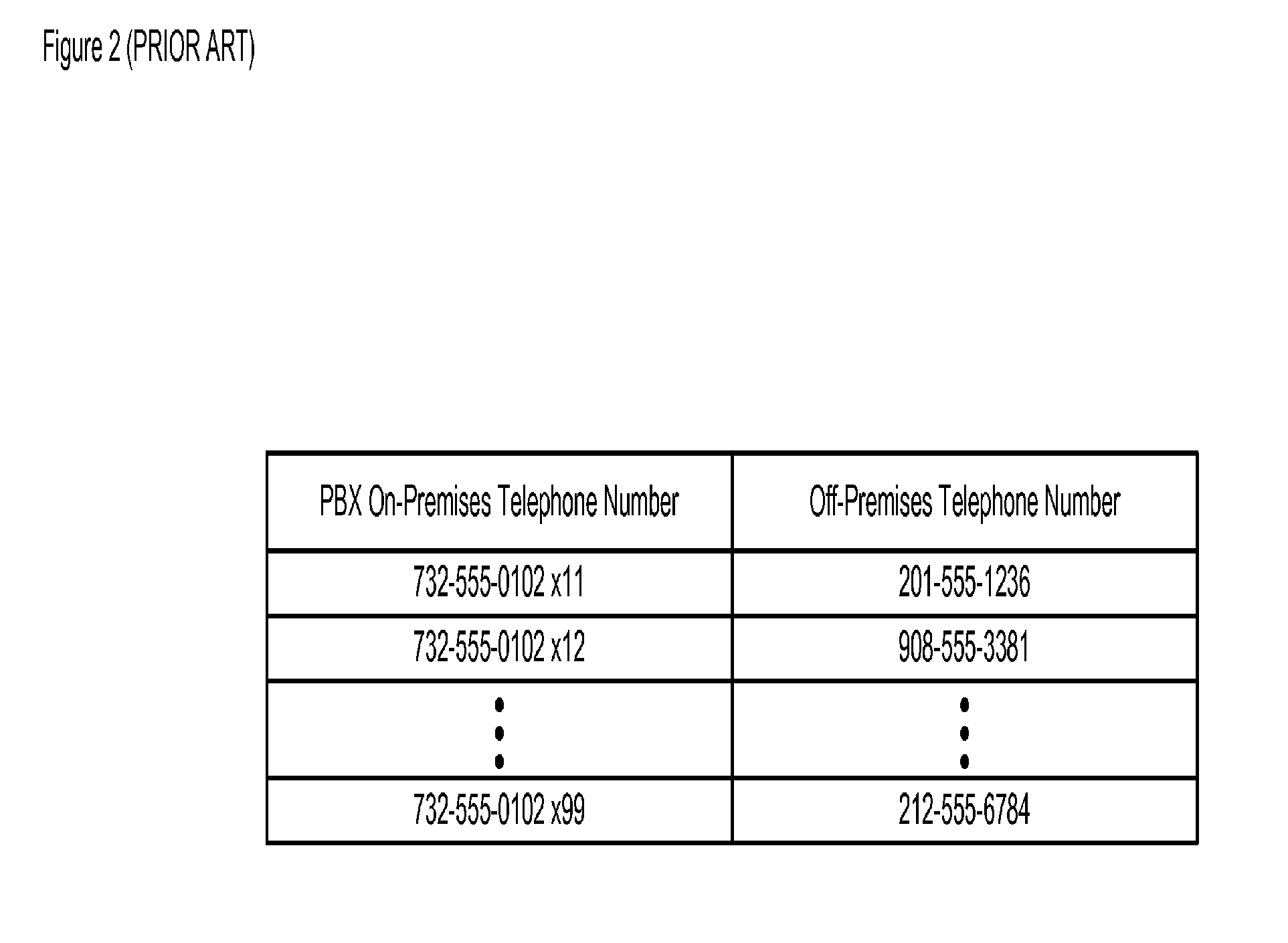
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for reducing wireless telecommunication costs for enterprises having a plurality of PBX-equipped sites, connected by either a public network (e.g., the PSTN, the Internet, etc.), a private network (e.g., leased lines, a virtual private network [VPN] over the Internet, etc.), or some combination of public and private networks. In particular, the illustrative embodiments of the present invention attempt to reduce telecommunication costs by advantageously routing calls from an off-premises wireless terminal belonging to the enterprise via one or more of the enterprise's private branch exchanges. The present invention is especially advantageous in that it can reduce telecommunication costs for calls from an off-premises wireless terminal to any type of destination: another cell phone, a wireline terminal, a private branch exchange, etc.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Methods for optimizing and evaluating network access techniques
InactiveUS20060140131A1Expand accessImprove data throughputCorrect operation testingFrequency-division multiplex detailsModem devicePrivate network
Methods of evaluating access to Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) from alternate access connections and for improving access to VPNs from alternate access connections such as ISPs. The methods include downloading a set of tests through a network backbone to simulate access to the VPN from the alternate access connection and comparing the results of the test to benchmarks for the test of access to the VPN from leased lines and modems. By obtaining comparisons of the tests and the benchmarks, it is possible to determine the throughput of data through the VPN and tell the customer how its access connections are affecting, among other things, the raw data throughput. This allows the customer and / or the network service provider to adjust the access connections to improve communications with the VPN.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com