Patents
Literature
56results about How to "Increased gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
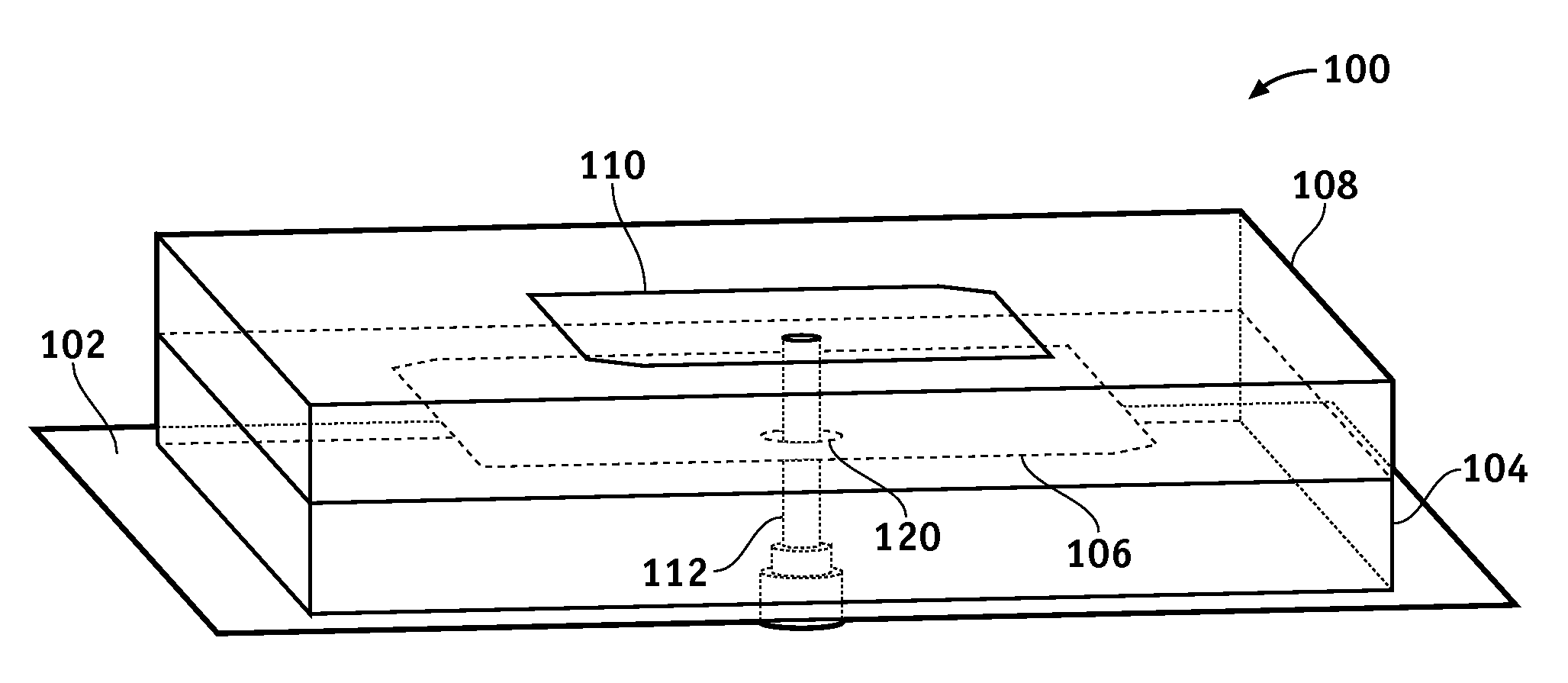
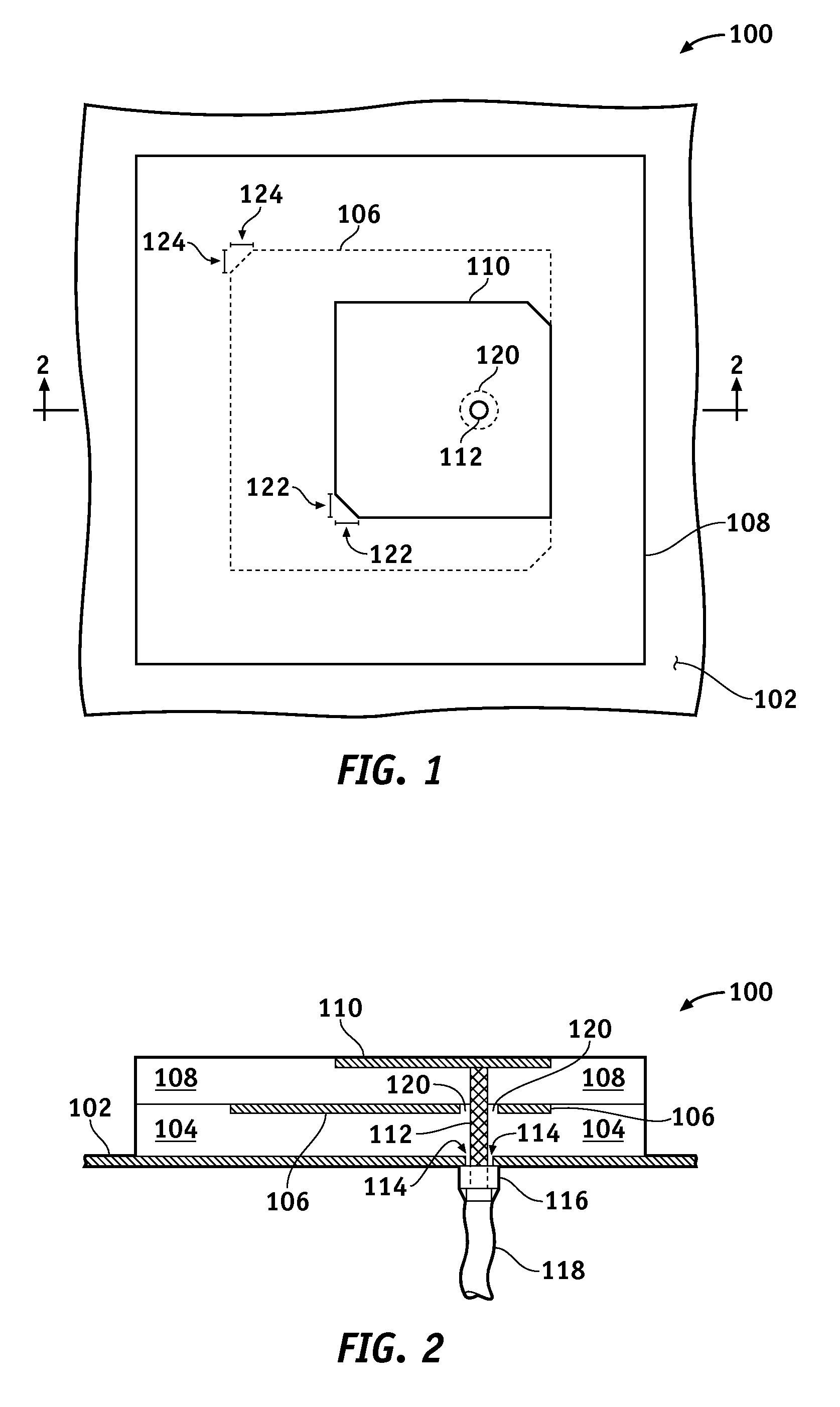
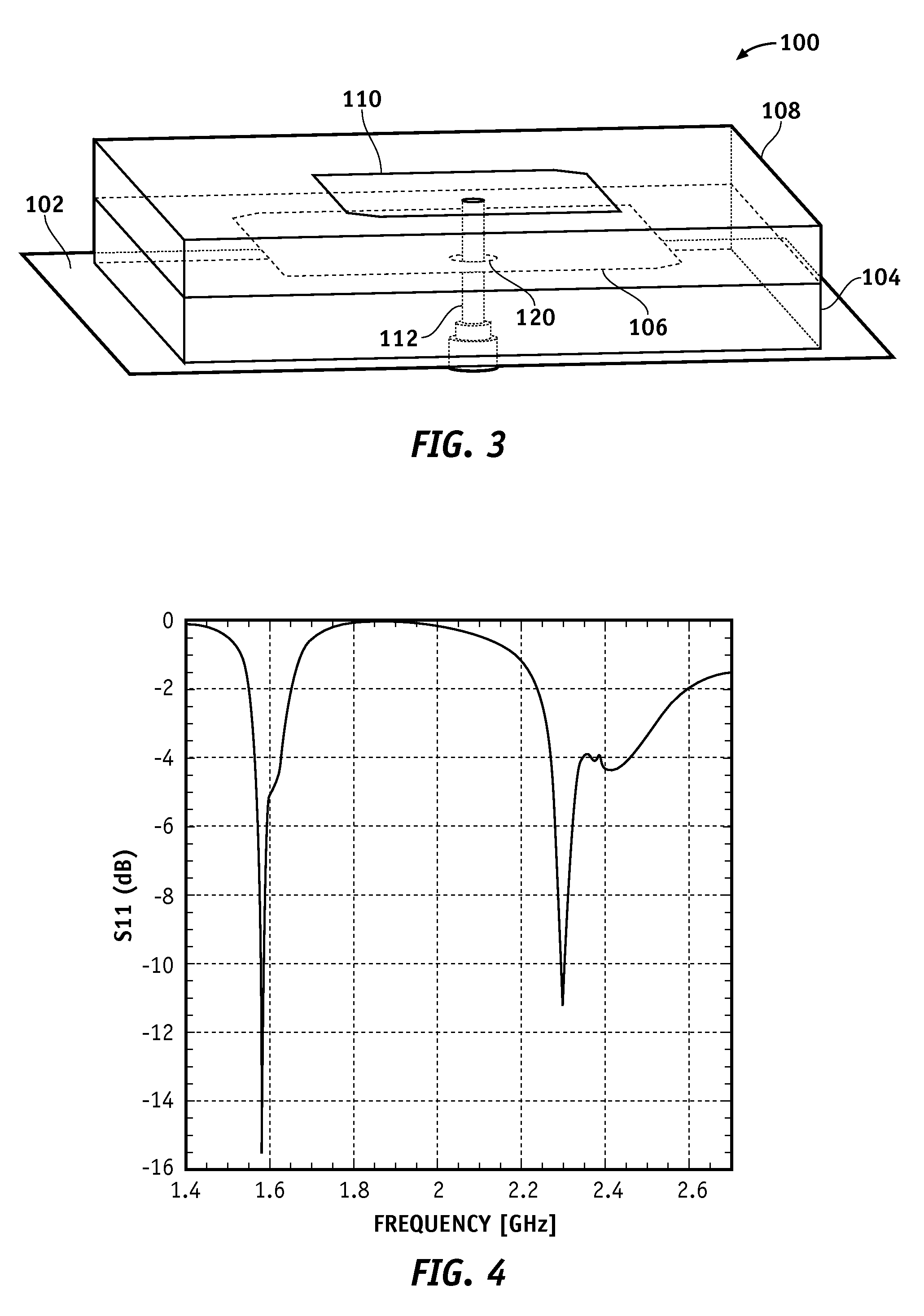
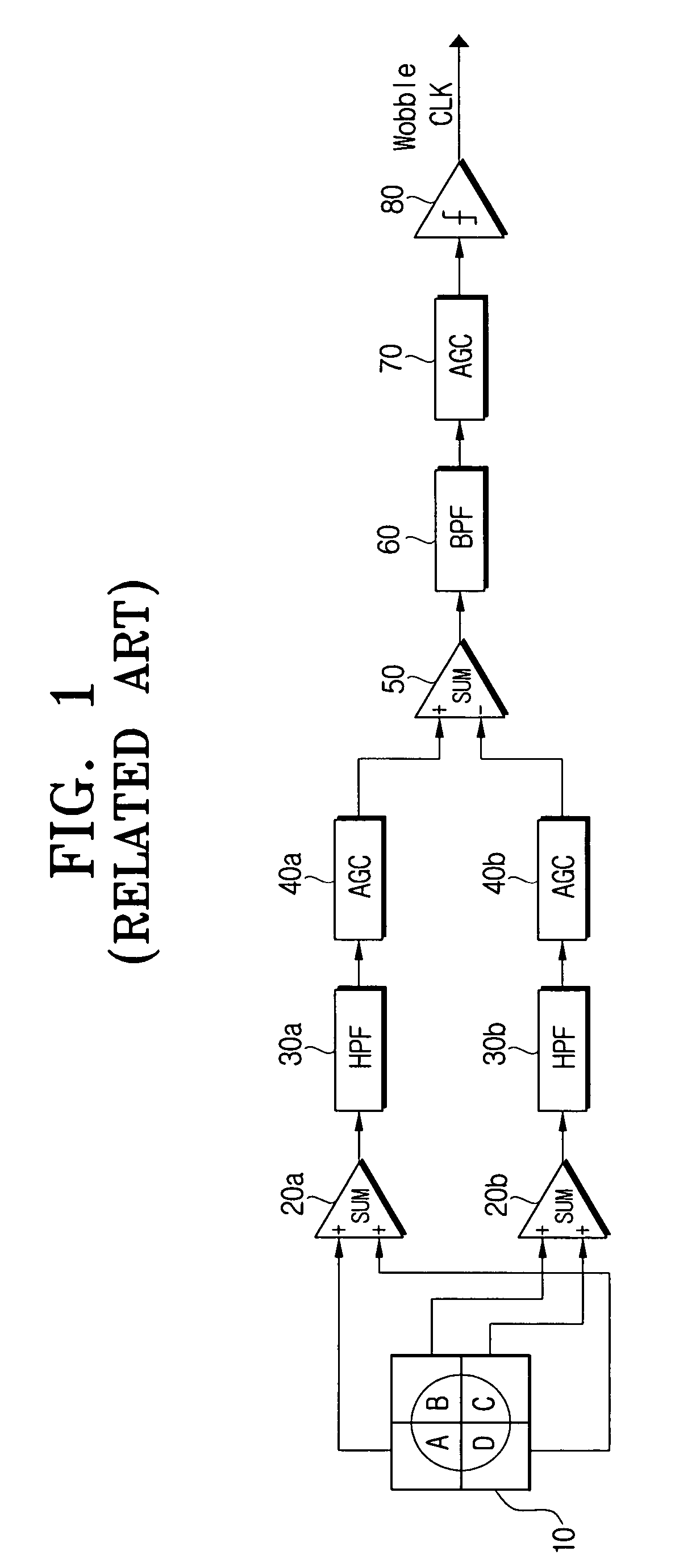
Dual Band Stacked Patch Antenna
InactiveUS20090058731A1Reduce manufacturing costHigh gainSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDual frequencyDual band antenna
One or more of the embodiments of a dual band stacked patch antenna described herein employ an integrated arrangement of a global positioning system (GPS) antenna and a satellite digital audio radio service (SDARS) antenna. The dual band antenna receives right hand circularly polarized GPS signals in a first frequency band, left hand circularly polarized SDARS signals in a second frequency band, and vertical linear polarized SDARS signals in the second band. The dual band antenna includes a ground plane element, an upper radiating element (which is primarily utilized to receive SDARS signals), dielectric material between the ground plane element and the upper radiating element, and a lower radiating element (which is primarily utilized to receive GPS signals) surrounded by the dielectric material. The dual band antenna uses only one conductive signal feed to receive both GPS and SDARS signals.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
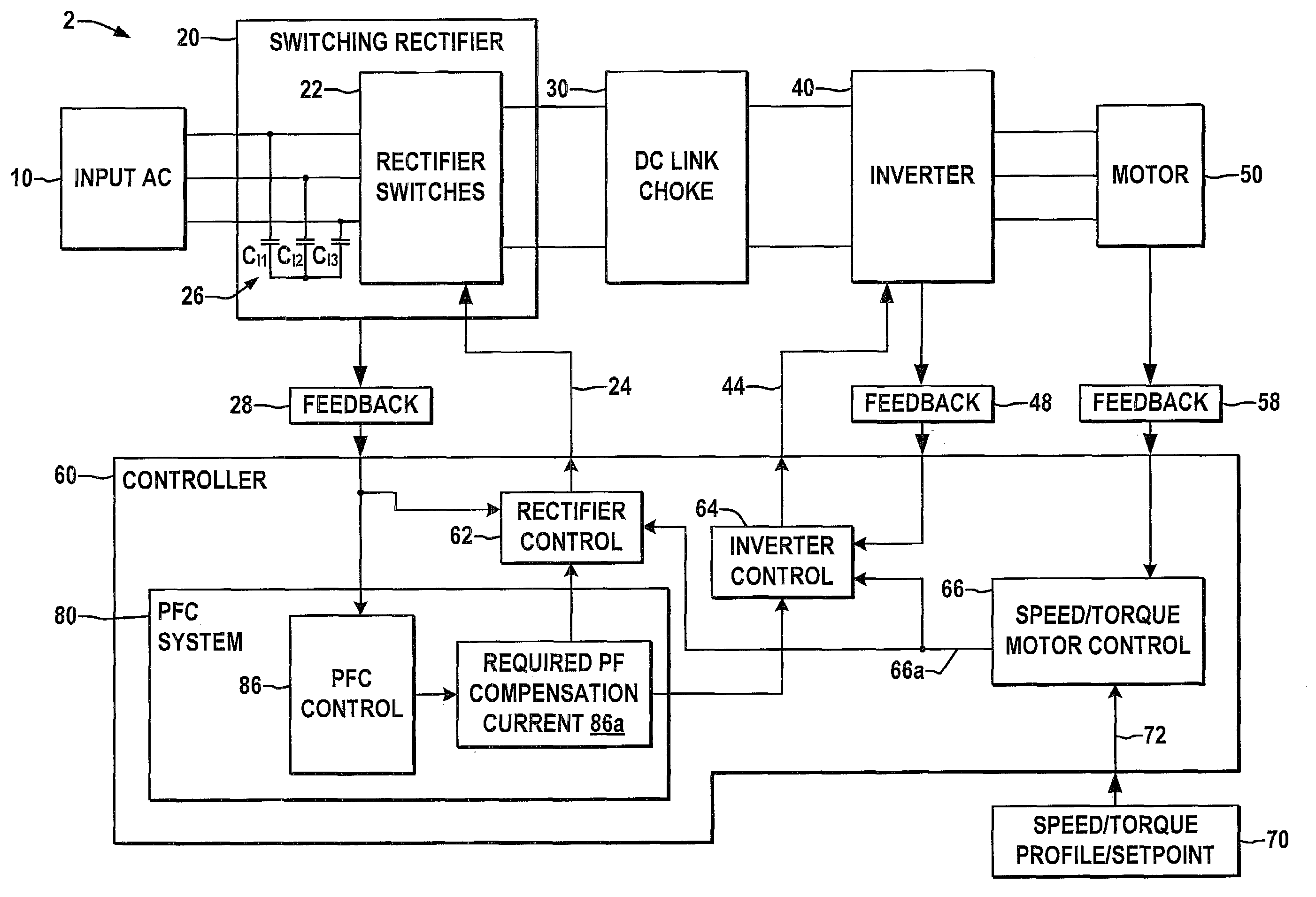
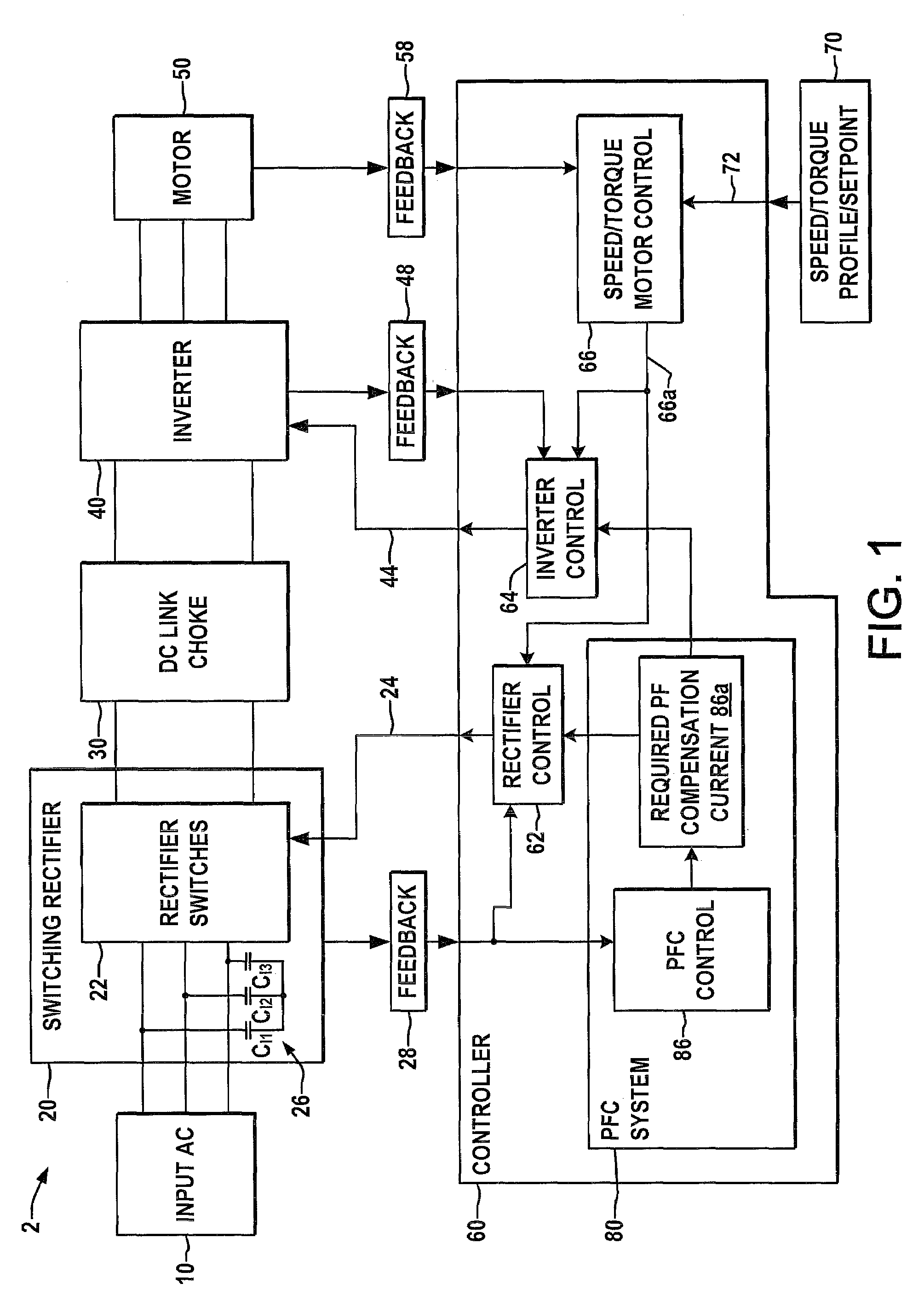
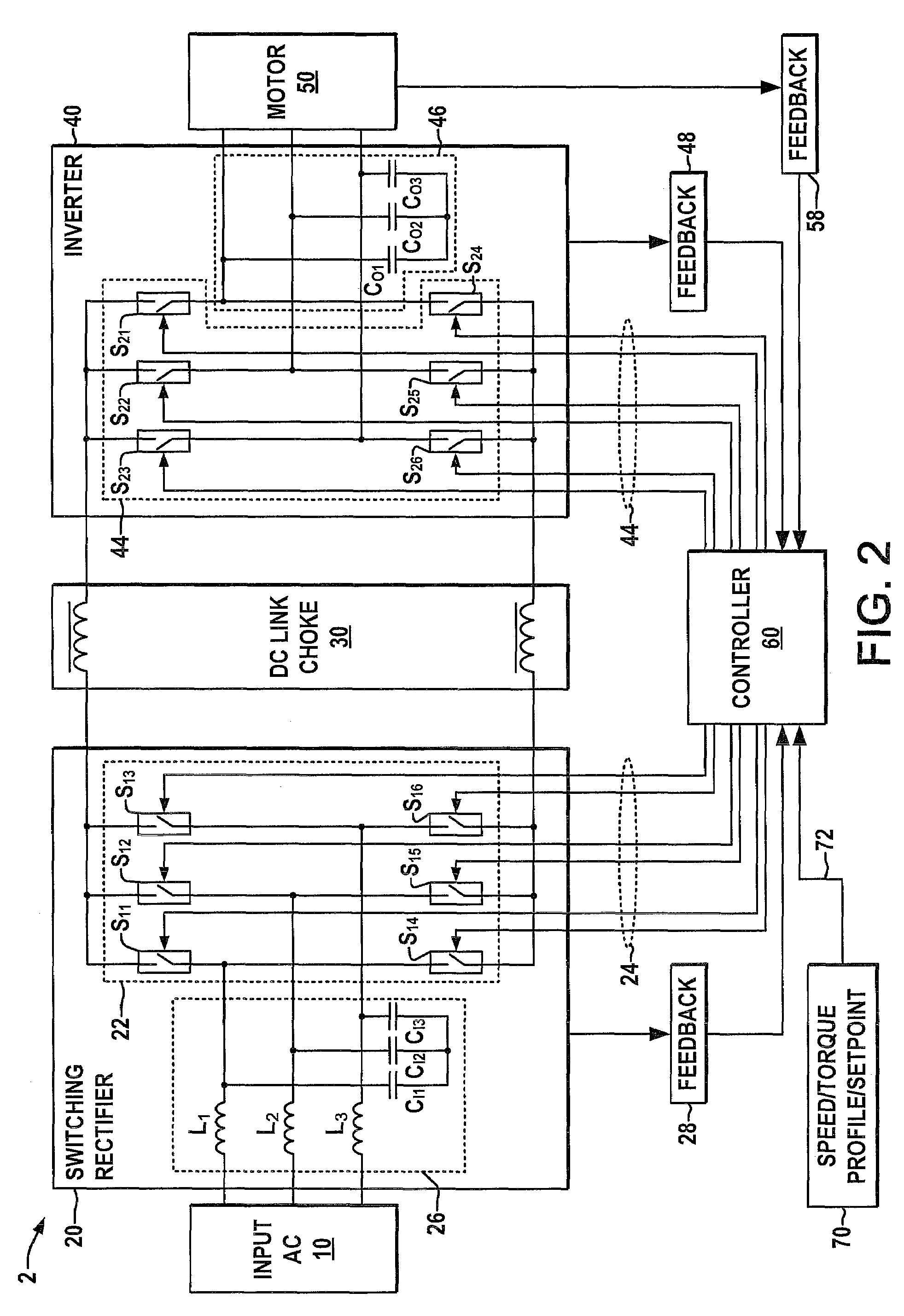
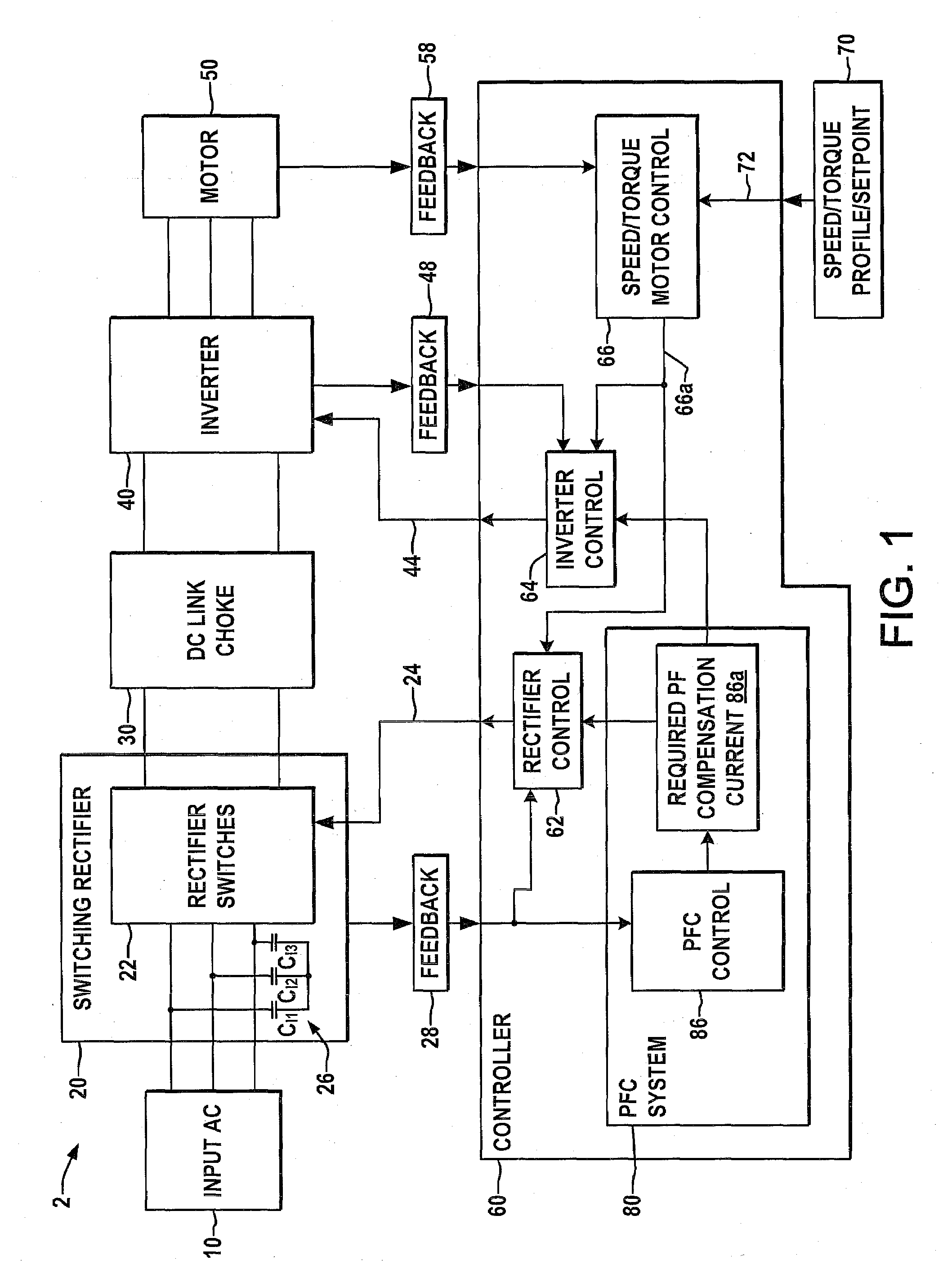
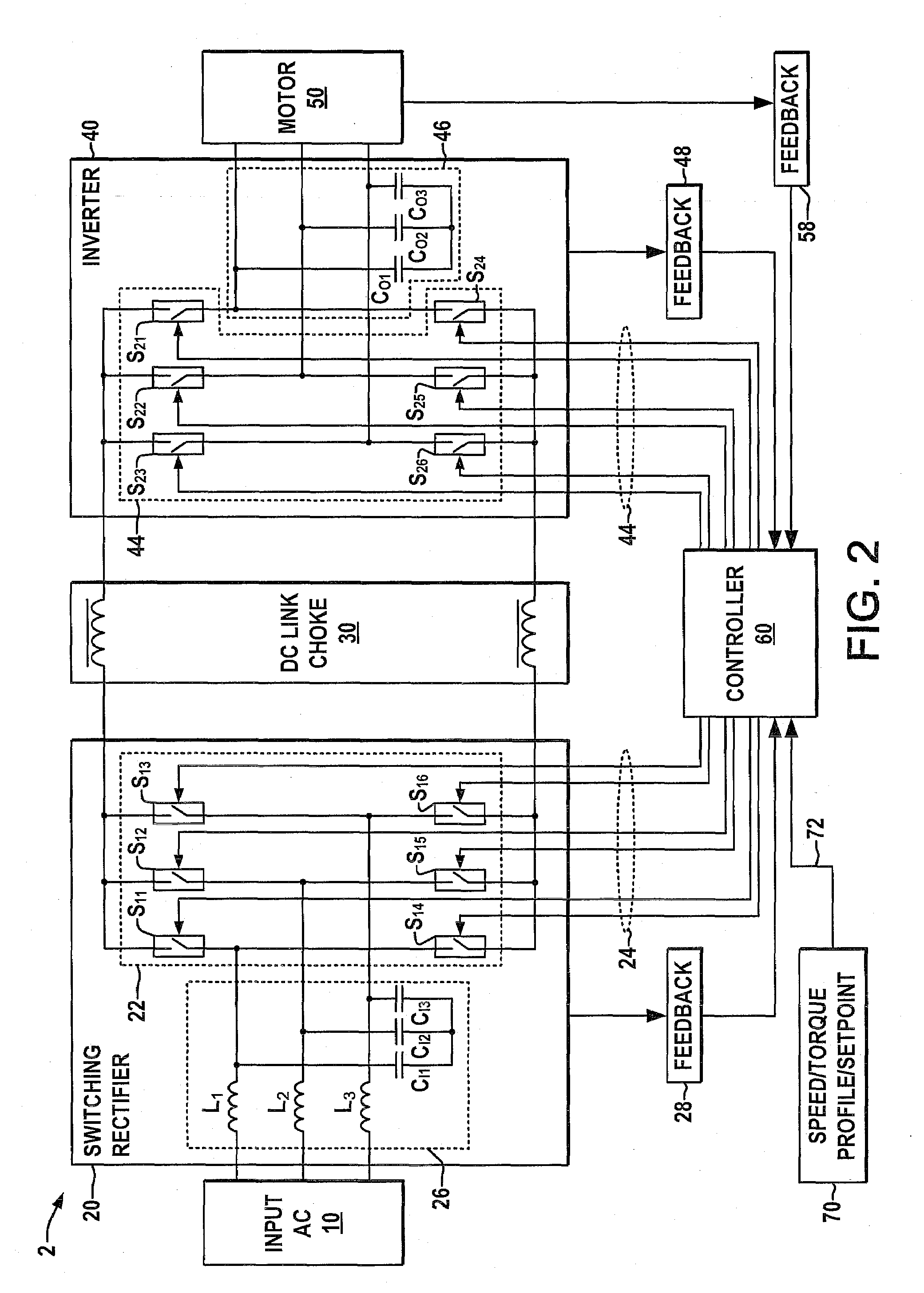
Systems and methods for improved motor drive power factor control
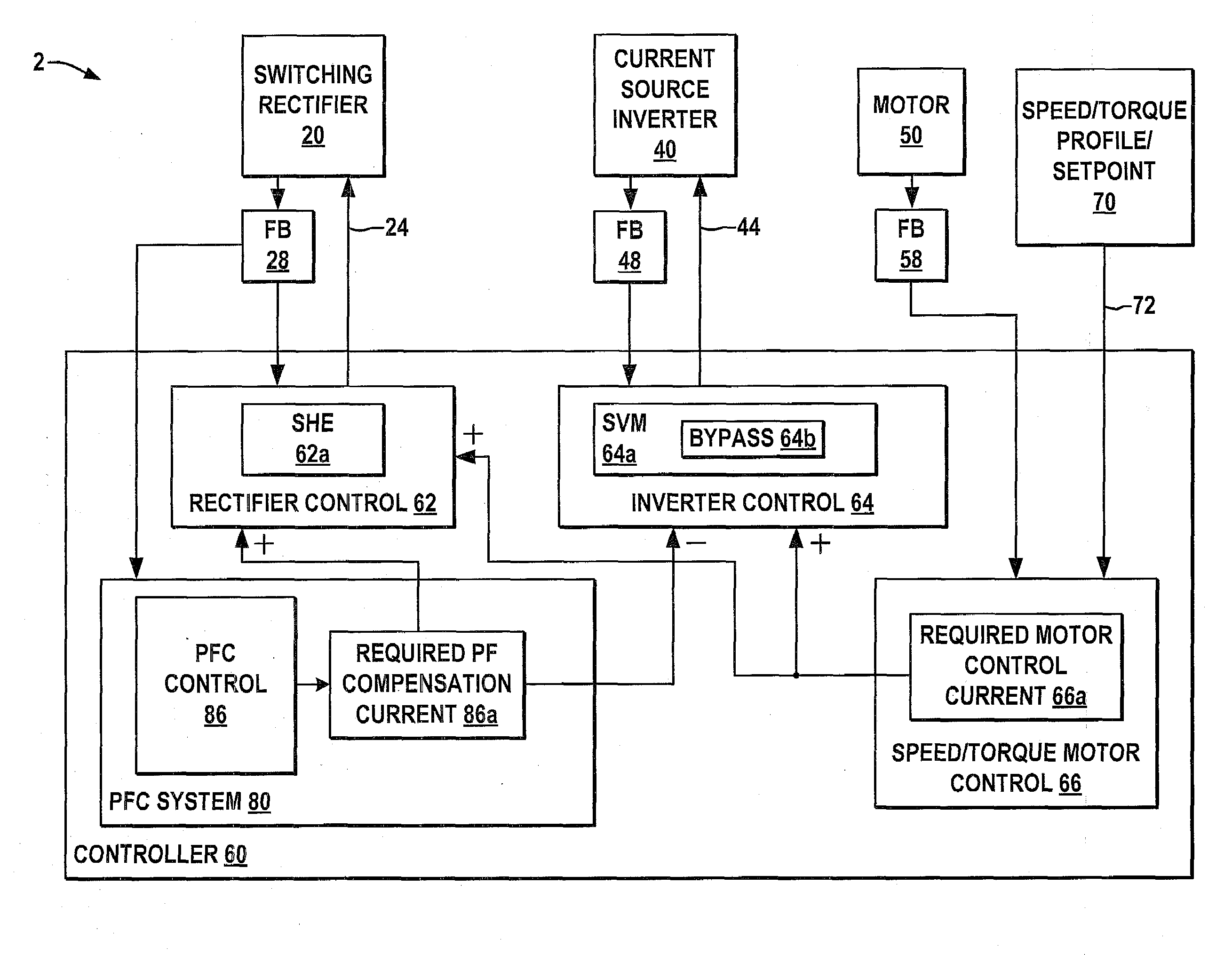
ActiveUS7495410B2Easy to understandReduce adverse effectsSingle-phase induction motor startersAc-dc conversion without reversalPower inverterMotor drive
Systems and methods are described for controlling power factor in motor drives having a switching rectifier providing a DC link current to an inverter in which the rectifier gain is increased to provide additional DC link current to correct the drive power factor based on current drawn by capacitors of the AC drive power input, and the inverter gain is decreased by introducing bypass states in the inverter switching control scheme or by reducing the motor flux to accommodate the increased DC link current.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
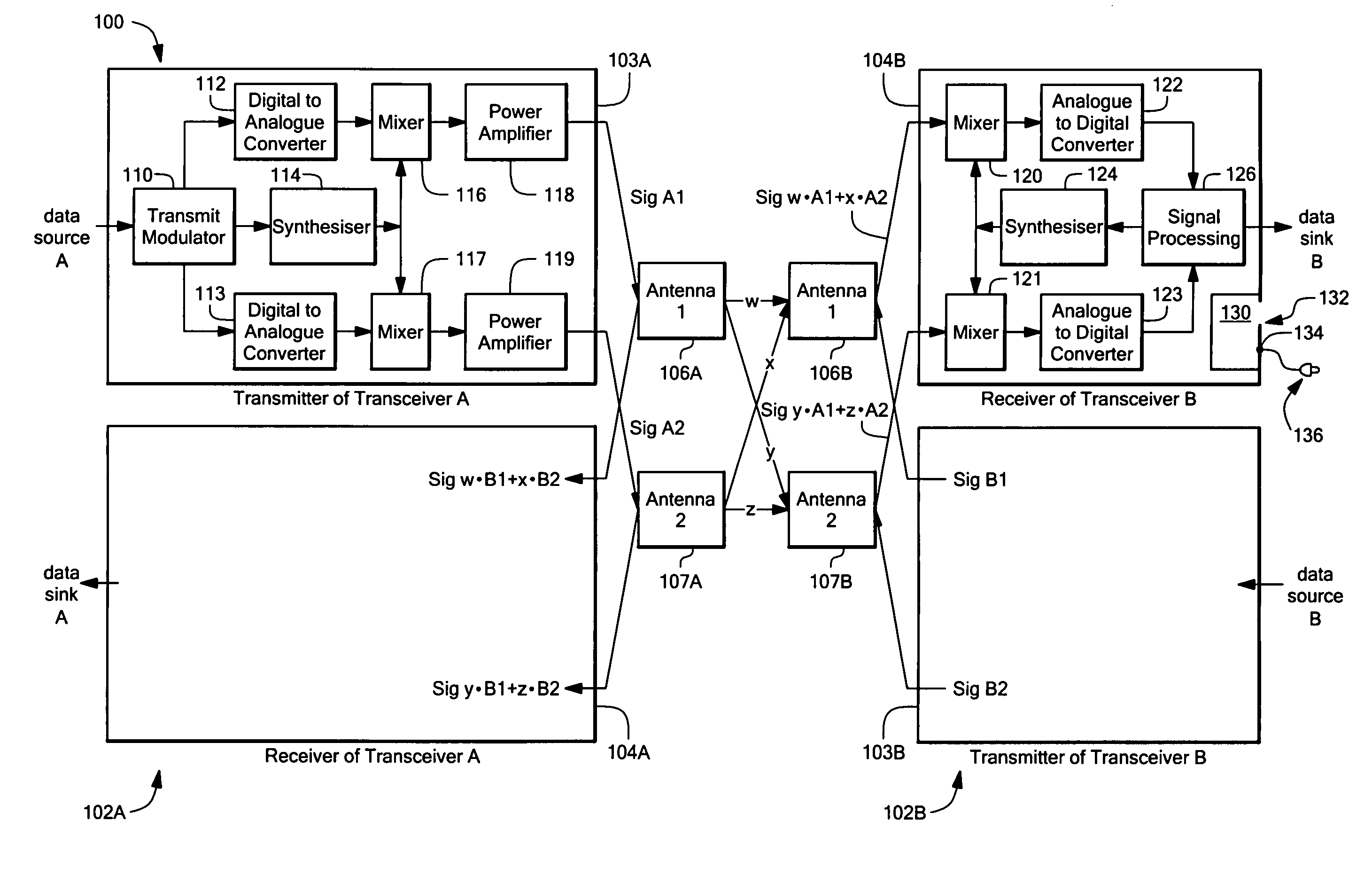
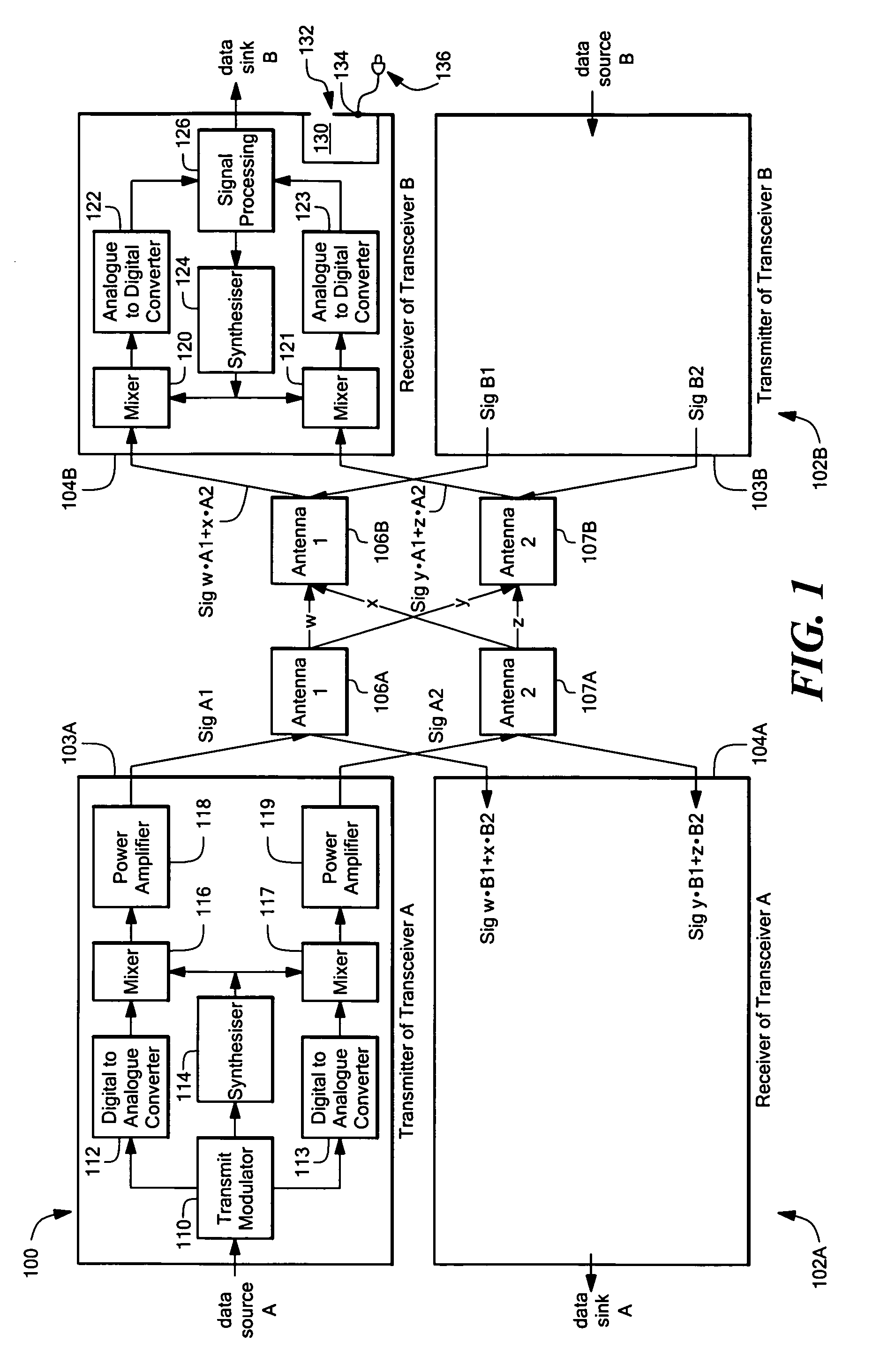
Intelligent adaptive modulation in a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) wireless communications system
ActiveUS7469013B1Reduce power levelIncreased de-correlationSpatial transmit diversityError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorOperational systemDynamic channel
A wireless broadband communications system that can maintain high data rates while taking into account channel interference resulting from operating in shared frequency bands, signal fading resulting from dynamic channel degradation, and signal distortion resulting from compliance with maximum power output regulations. In one mode of operation, the system performs adaptive modulation by transmitting a first signal over a selected channel using a first modulation mode having a level of distortion associated therewith resulting from operating the system at a predetermined maximum power output level. Next, a SINAD level is measured on the first channel. The level of distortion associated with the first modulation mode is then subtracted from the measured SINAD level to obtain a first noise level. In the event the first noise level is less than a noise level required to achieve an acceptable error rate in a next modulation mode, a second signal is transmitted over the selected channel using the next modulation mode.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
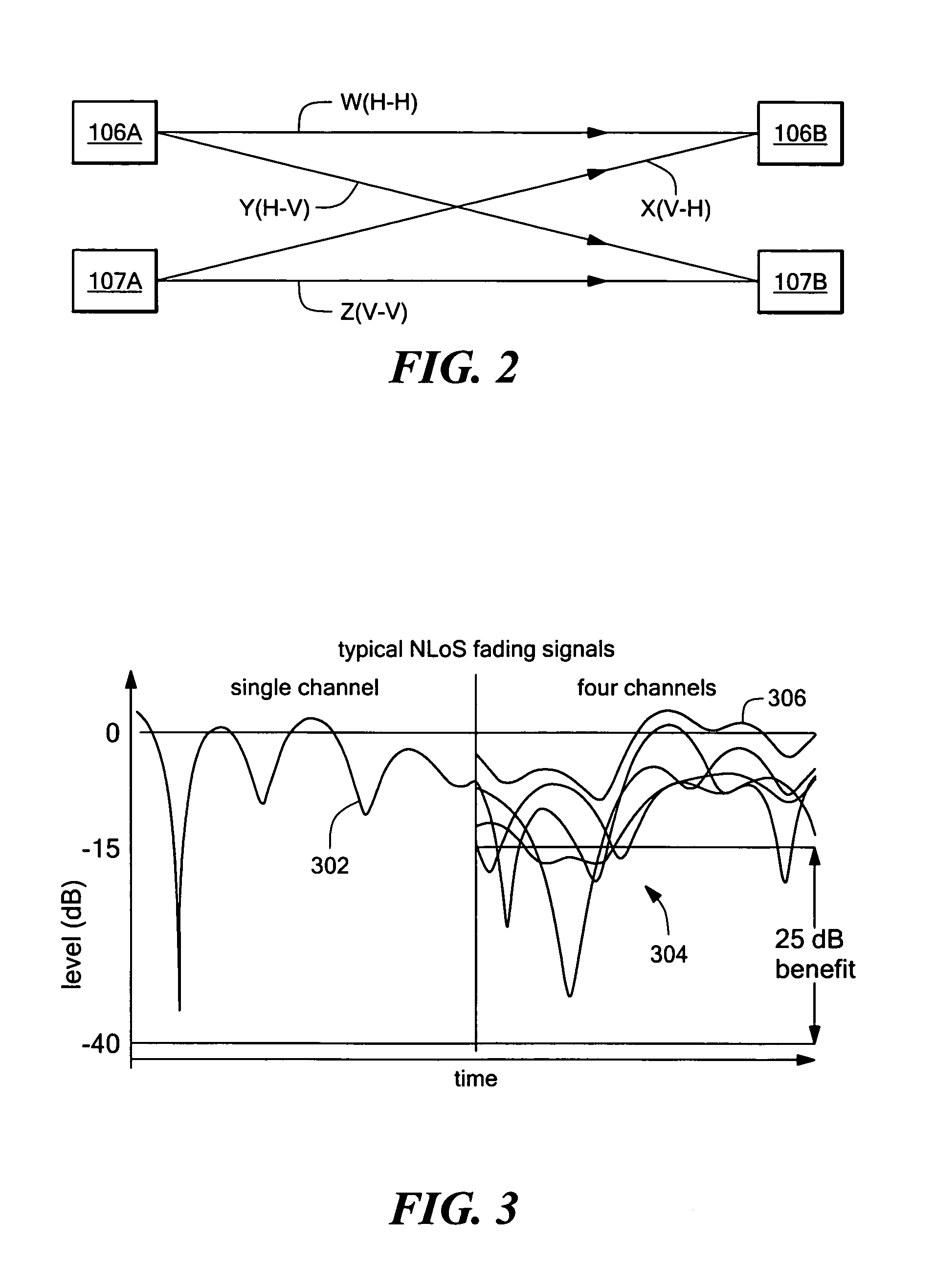
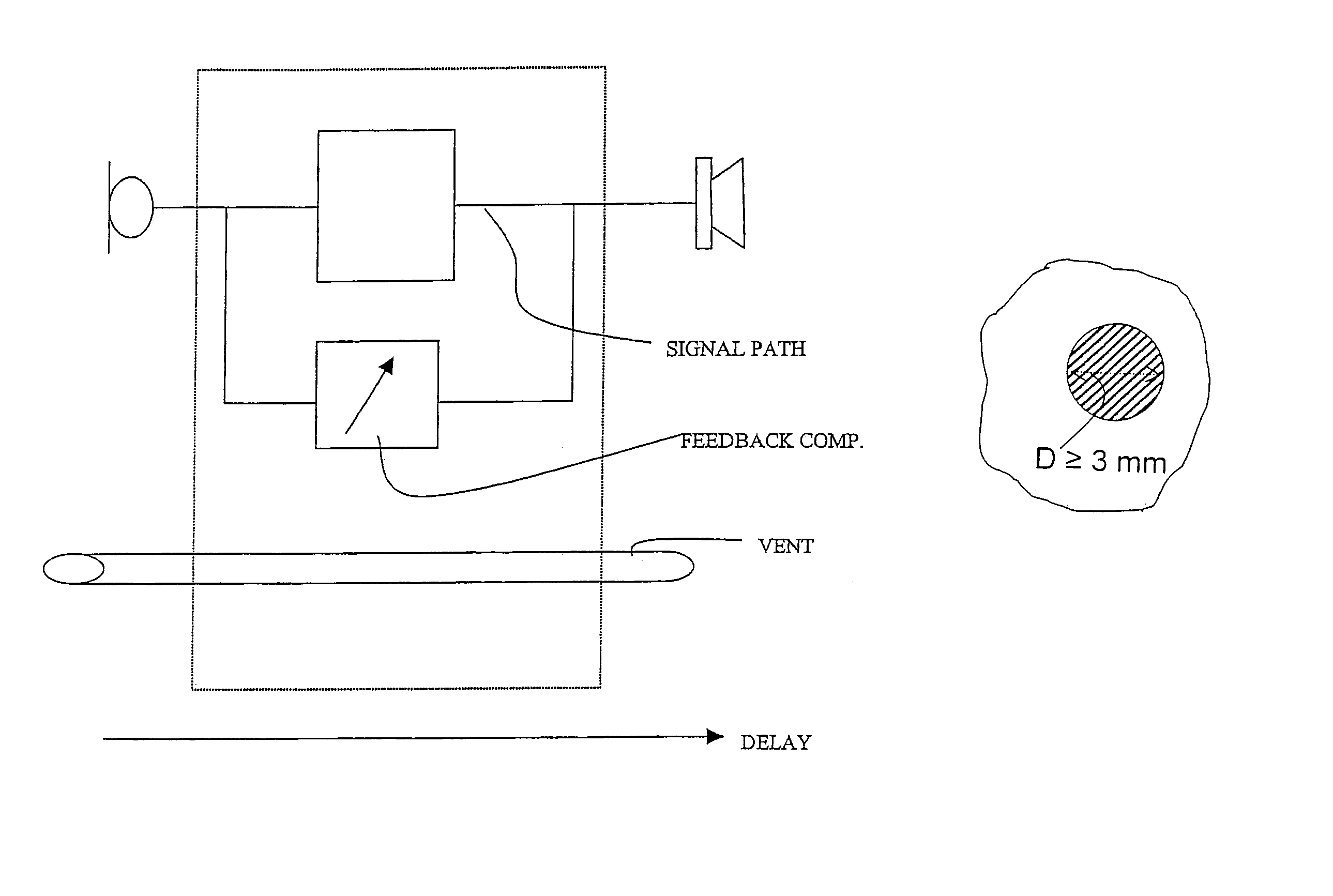
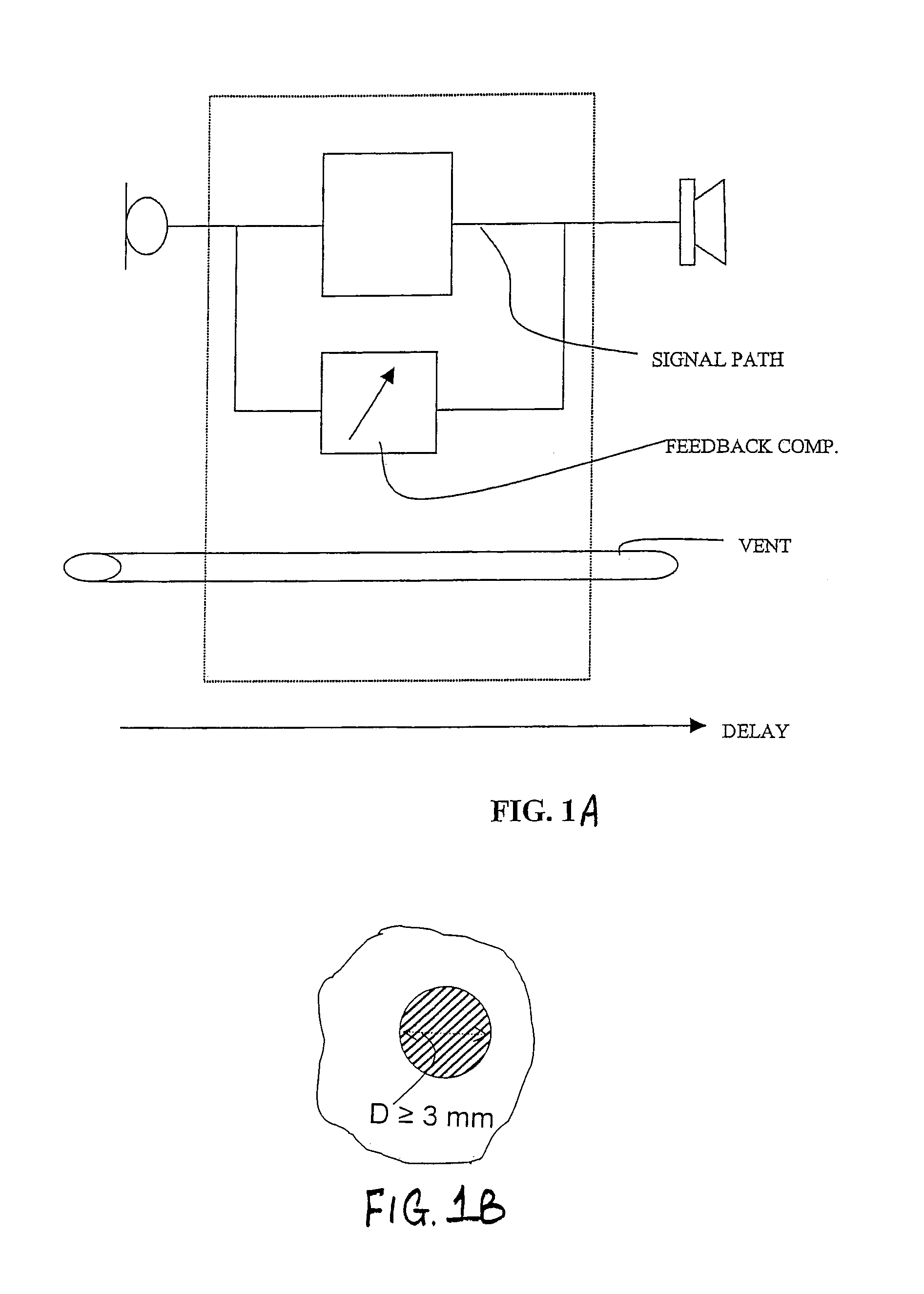
Hearing aid
A digital hearing aid system includes a signal path with an input transducer, a signal processor and an output transducer, a part of the system being intended for delivering sound into an ear canal of a hearing aid user leaving the ear canal with an unobstructed cross-sectional area corresponding to a vent channel with a diameter of at least 3 mm or a total area of at least 7.07 mm2. The signal path is designed to have a signal delay less than 15 ms. The hearing aid signal path furthermore preferably includes means for providing an adaptive feedback compensation. The signal processor is adjusted to provide increased gain in low frequency areas.
Owner:OTICON
Multi-access system and method using multi-sectored antenna
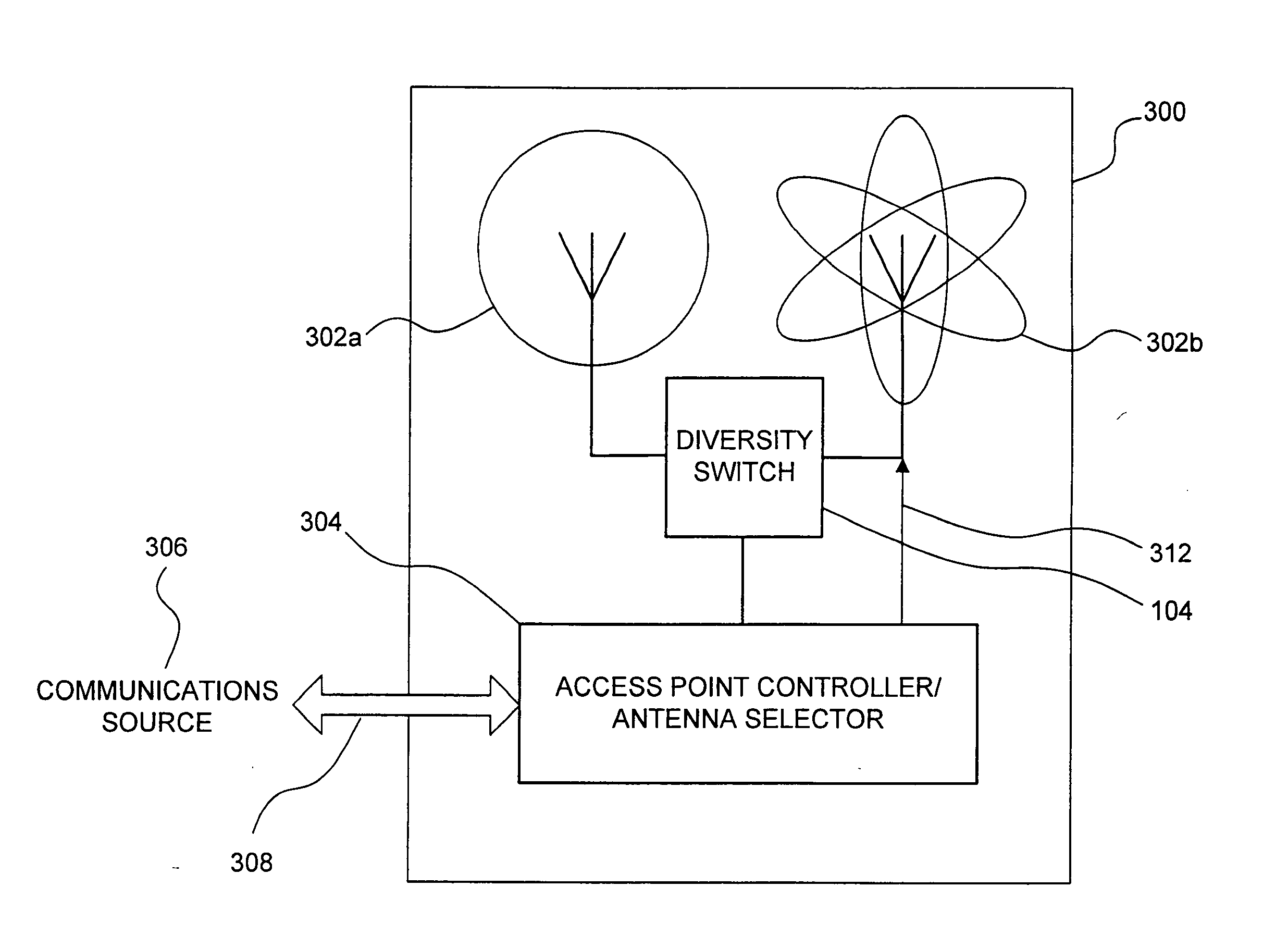
InactiveUS20060172711A1Increased gainFast communication rateDiversity/multi-antenna systemsTransmission noise suppressionOmnidirectional antennaClient-side
A wireless access point is equipped with both an omnidirectional antenna and a directable antenna that can be selectively directed to any of a plurality of directional spaces overlapping the network space served by the omnidirectional antenna. The directable antenna is directed to an optimal directional space for a client when the access point is communicating with the client at a high data rate. The access point can intermittently exchange information with other clients using the omnidirectional antenna. The omnidirectional antenna enables broadcast signals to be transmitted to any client in the entire network space, but at a lower data rate. A preferred data rate and an optimal client directional space are re-determined periodically or as necessary based on parameters such as the data rate, signal strength, and rate of success in communicating data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Systems and methods for improved motor drive power factor control
ActiveUS20080180055A1Reduce adverse effectsHigh gainSingle-phase induction motor startersAc-dc conversion without reversalControl powerMotor drive
Systems and methods are described for controlling power factor in motor drives having a switching rectifier providing a DC link current to an inverter in which the rectifier gain is increased to provide additional DC link current to correct the drive power factor based on current drawn by capacitors of the AC drive power input, and the inverter gain is decreased by introducing bypass states in the inverter switching control scheme or by reducing the motor flux to accommodate the increased DC link current.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
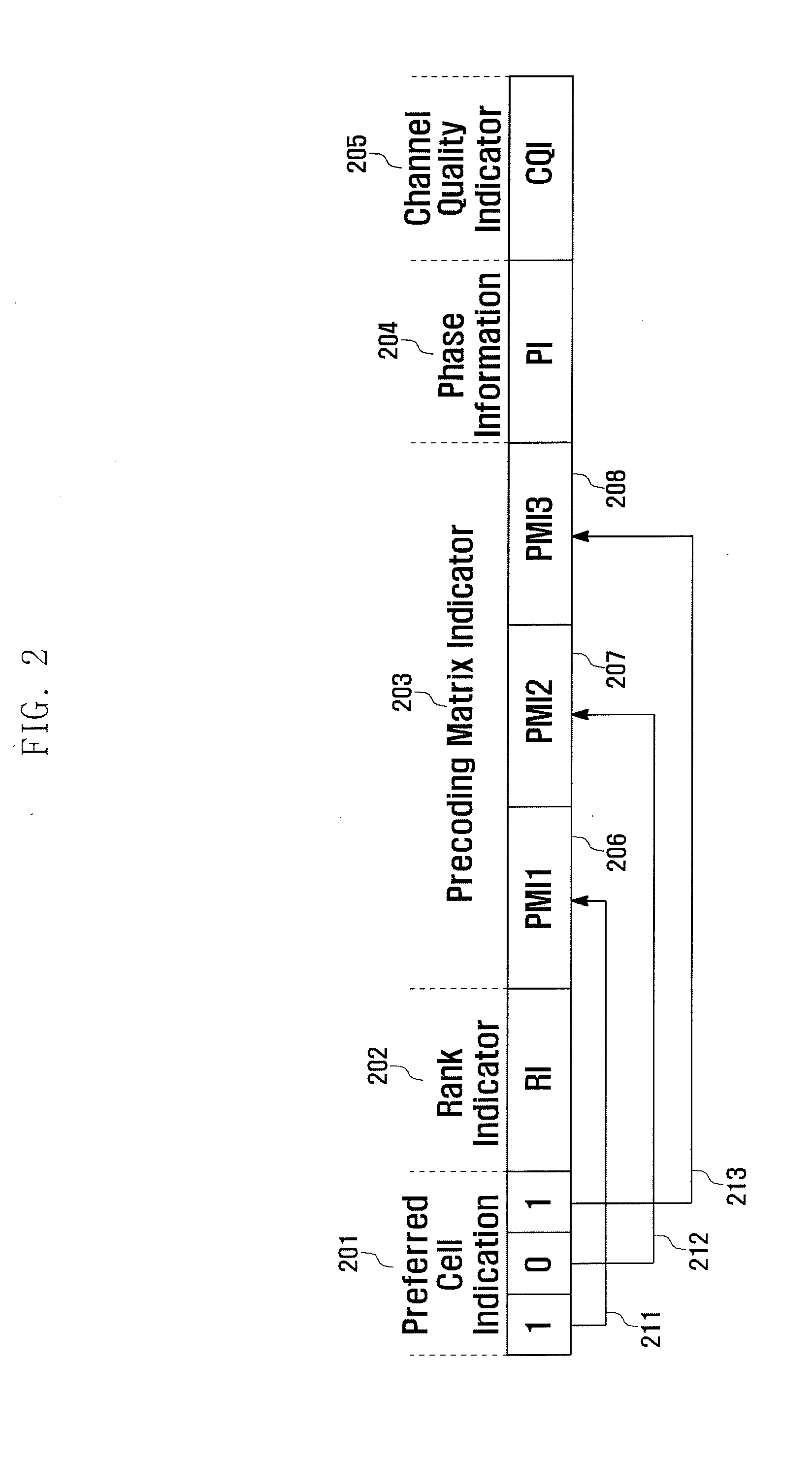
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving feedback information for inter-cell cooperative transmission in wireless communication cellular system
InactiveUS20120088514A1High gainEfficient managementSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityPhase correctionCode book
A method for transmitting feedback information for cooperative transmission in a wireless communication cellular system comprises: receiving information on cells that can be cooperatively transmitted from a base station; determining cells that prefer the cooperative transmission among the cells that can be cooperatively transmitted; generating feedback information, which includes a preference cell indicator representing preferred cells and non-preferred cells for the cooperative transmission among the cells that can be cooperatively transmitted, precoding matrix information for the respective cell that can be cooperatively transmitted, phase information representing a phase correction value of each of the preferred cells for the cooperative transmission, and a channel quality indicator; and transmitting the feedback information through a control channel or a data channel. Accordingly, the present invention provides a method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving a report of implicative feedback information on code books that can be designed for the gain improvement of a high-level inter-cell cooperative transmission.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
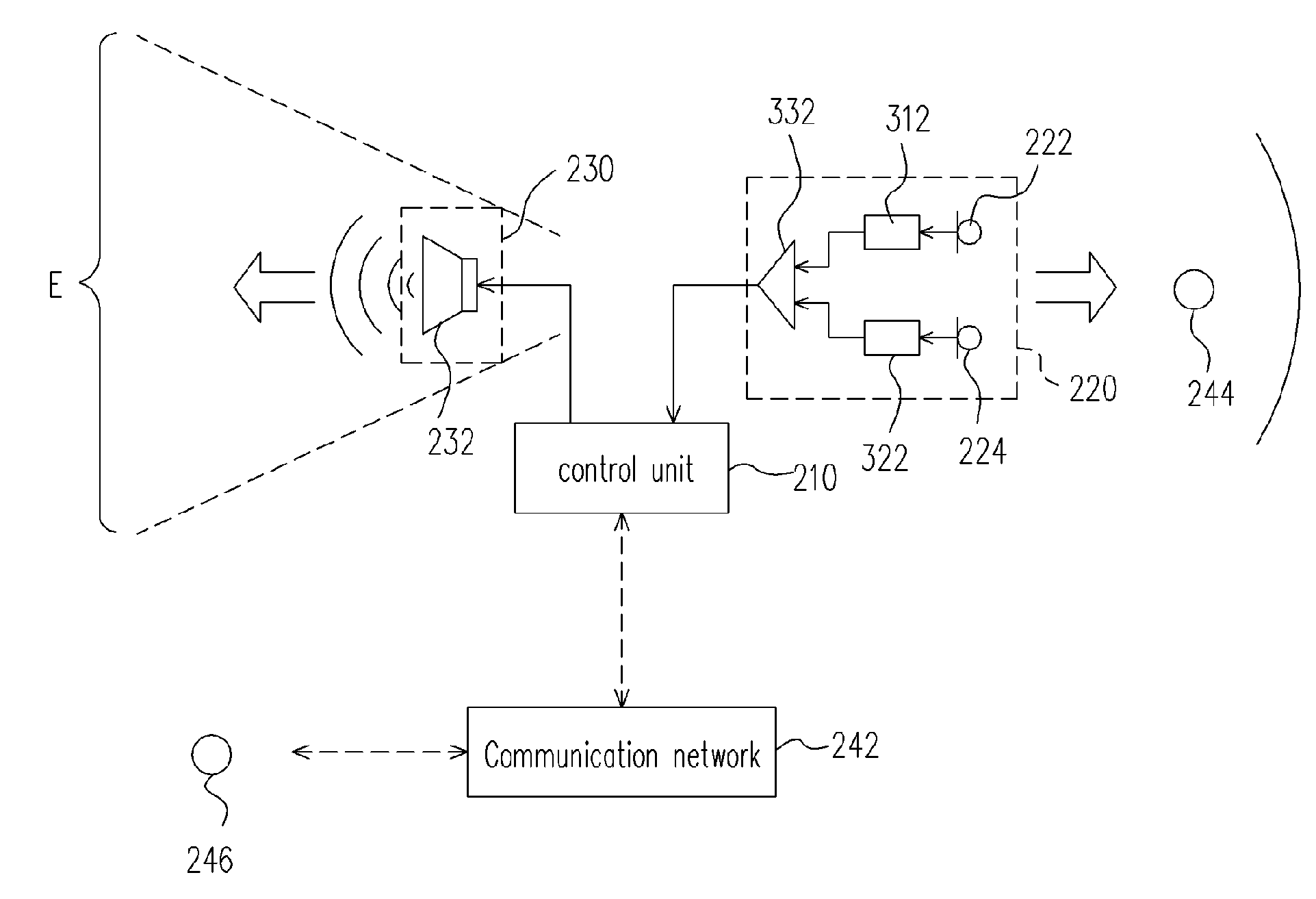
Dual microphone communication device for teleconference
InactiveUS20050175189A1Improve communication qualityHigh gainTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsMicrophonesPhase differenceFixed gain
A dual microphone communication device comprising a first microphone module, a second microphone module and a mixer circuit is provided. The first microphone module amplifies a near-end audio signal to produce a first audio signal. The second microphone module receives and amplifies the near-end audio signal by a fixed gain and a constant phase difference to produce a second audio signal. The mixer circuit subtracts the second audio signal from the first audio signal to produce a third audio signal so that interference resulting from echoes is significantly reduced while keeping, or enhance the near end voice level.
Owner:FORTEMEDIA
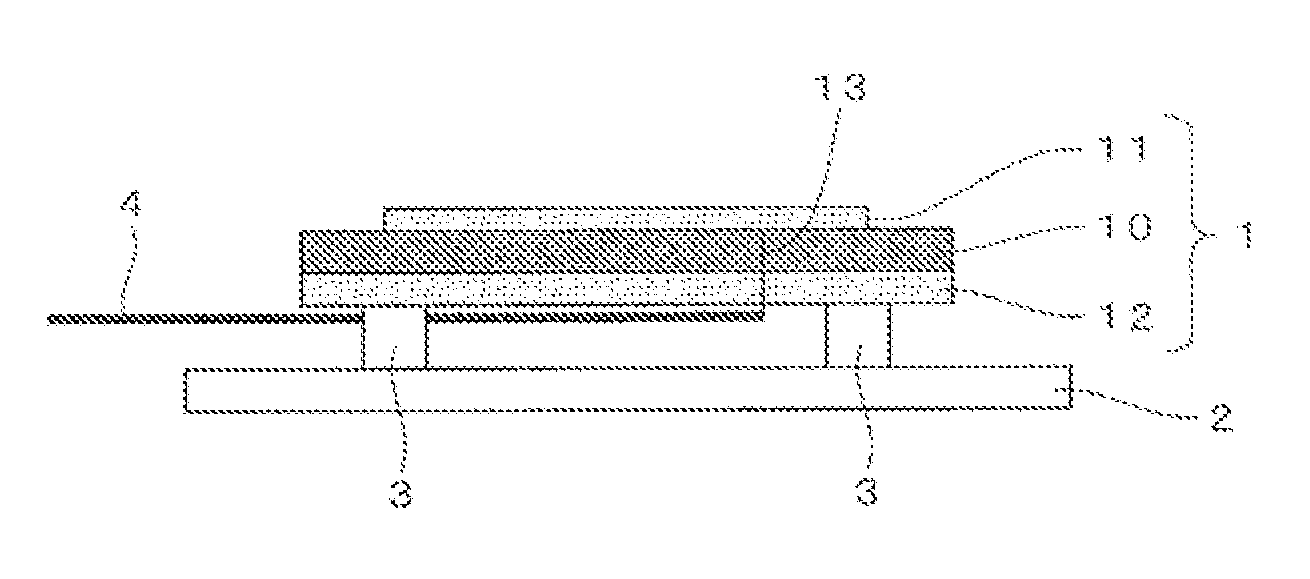
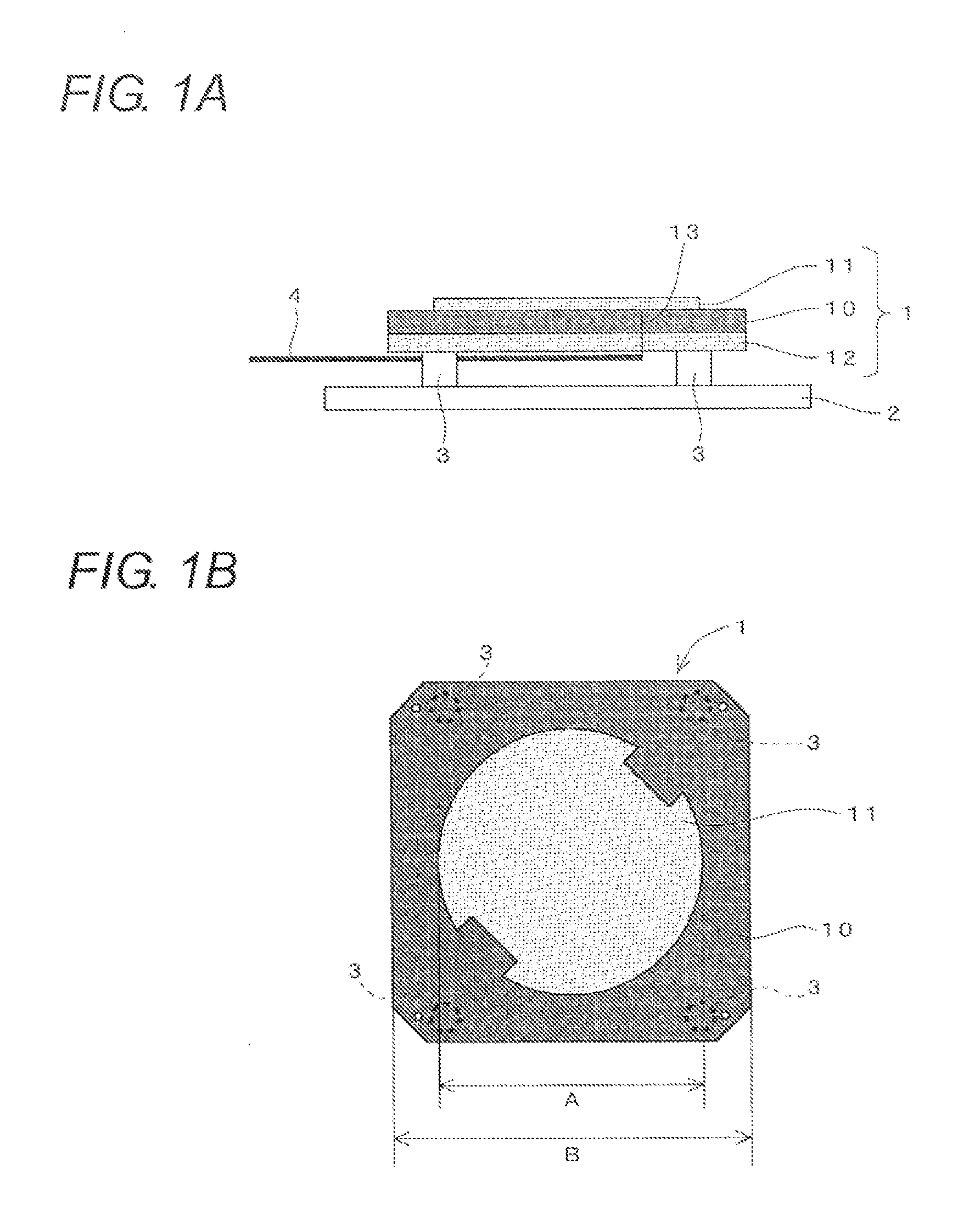
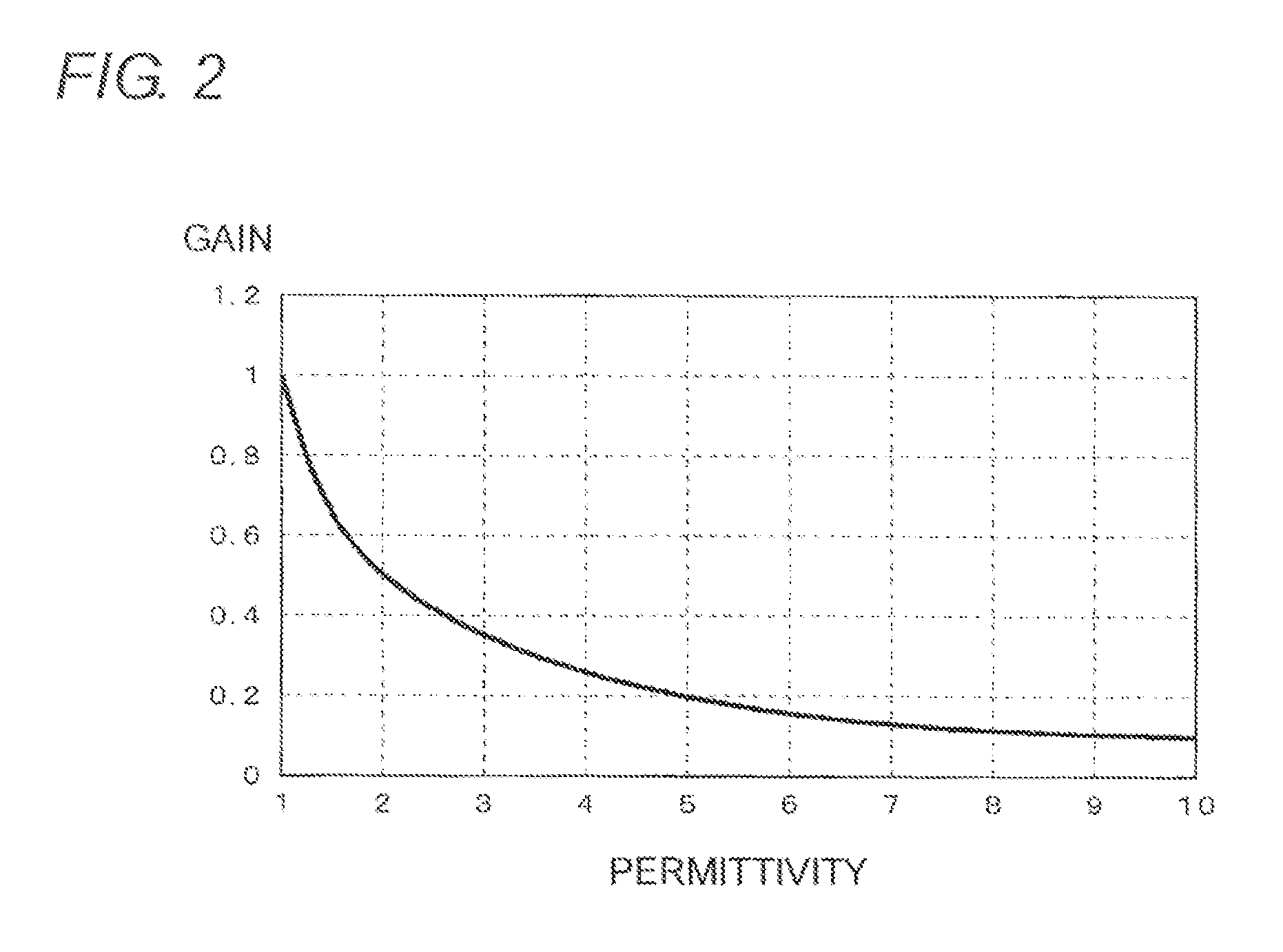
Pressure sensor device
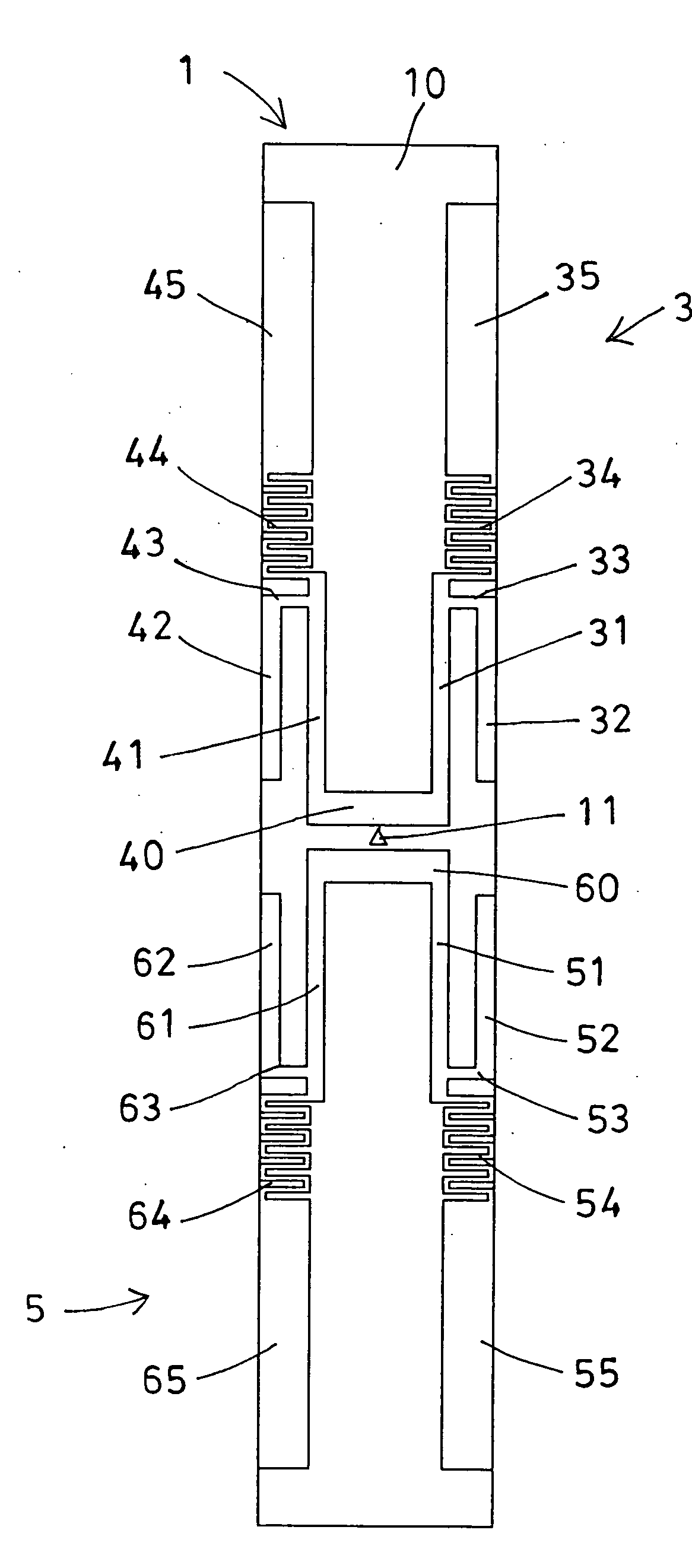
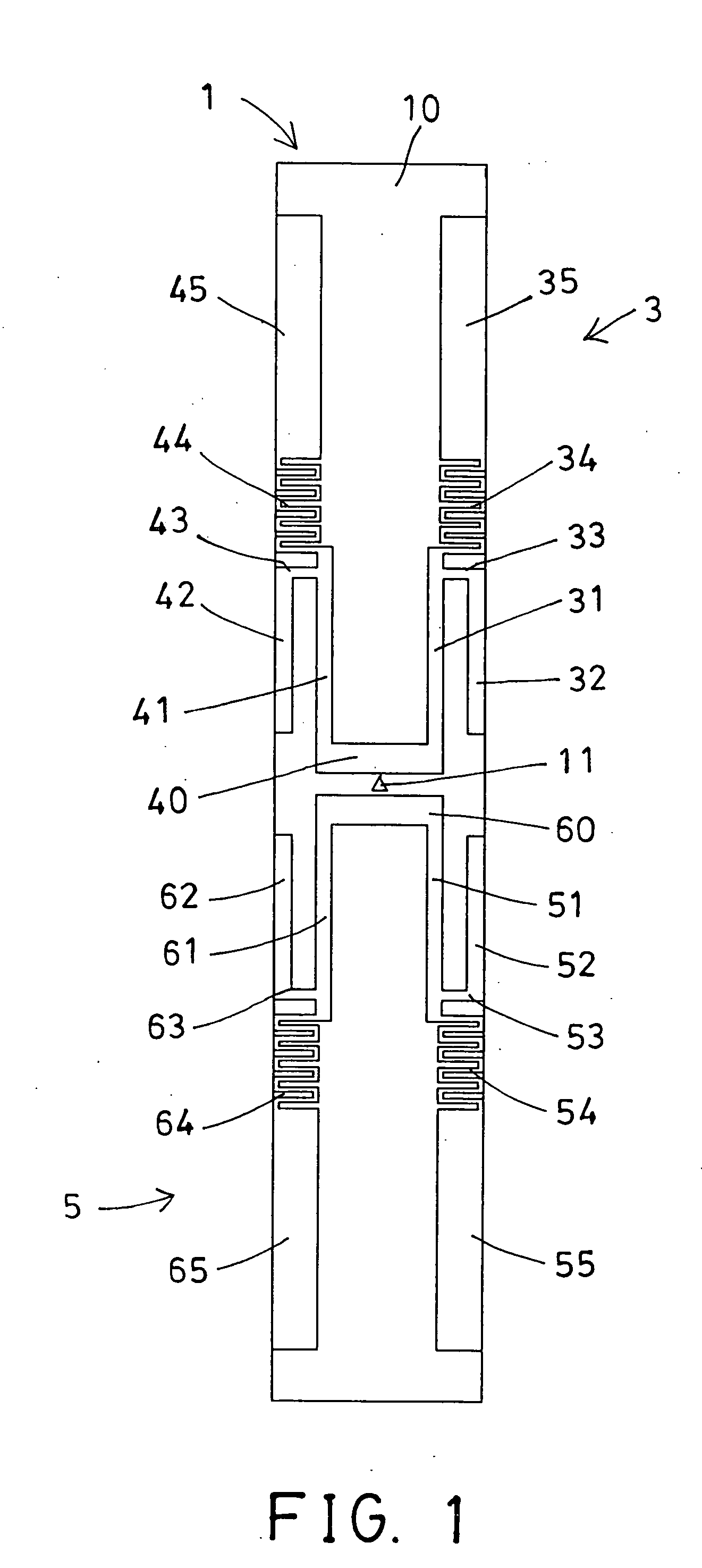
InactiveUS20070089525A1Increase effective lengthIncreased gainFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsEngineeringPressure sensor
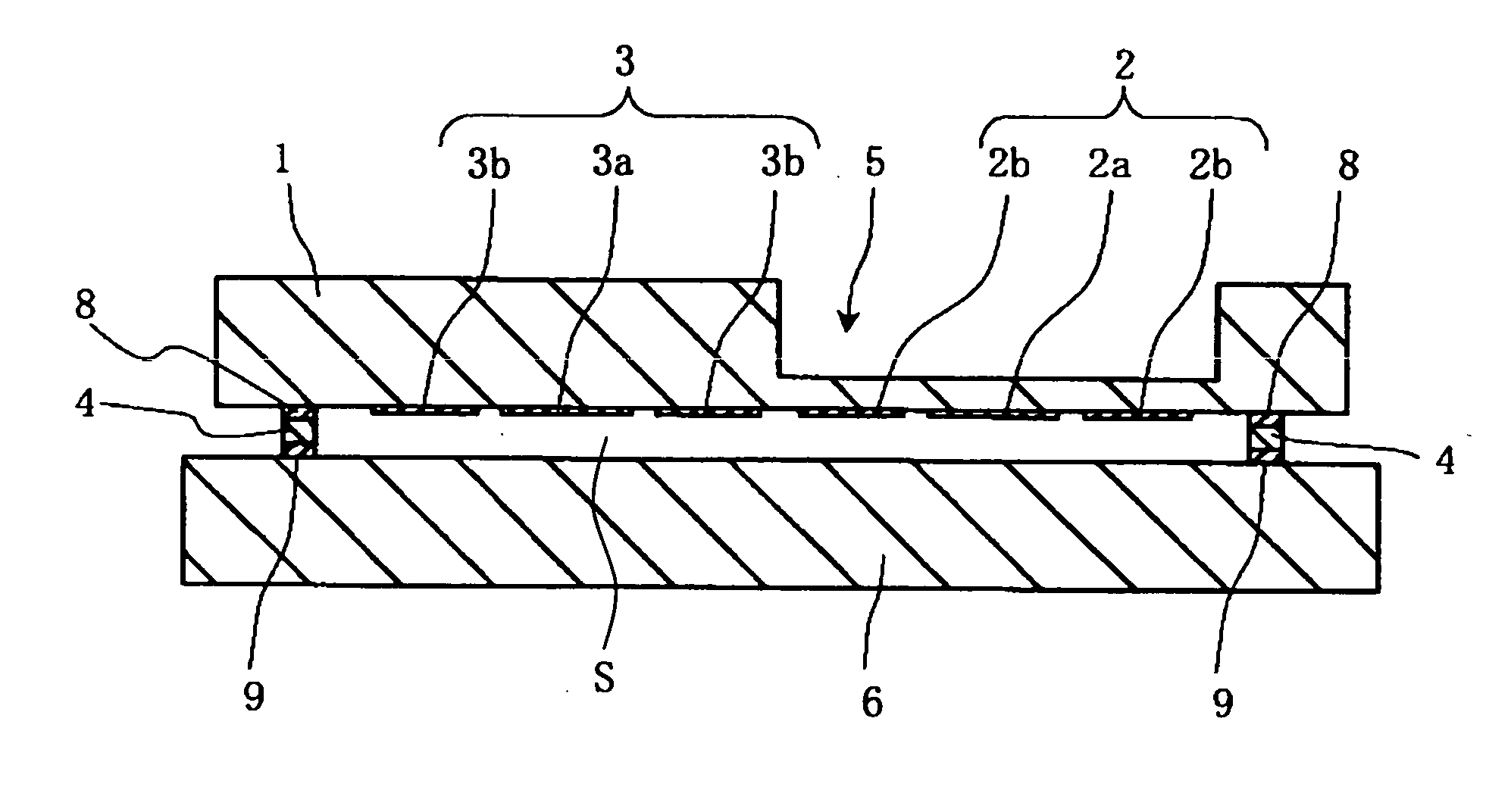
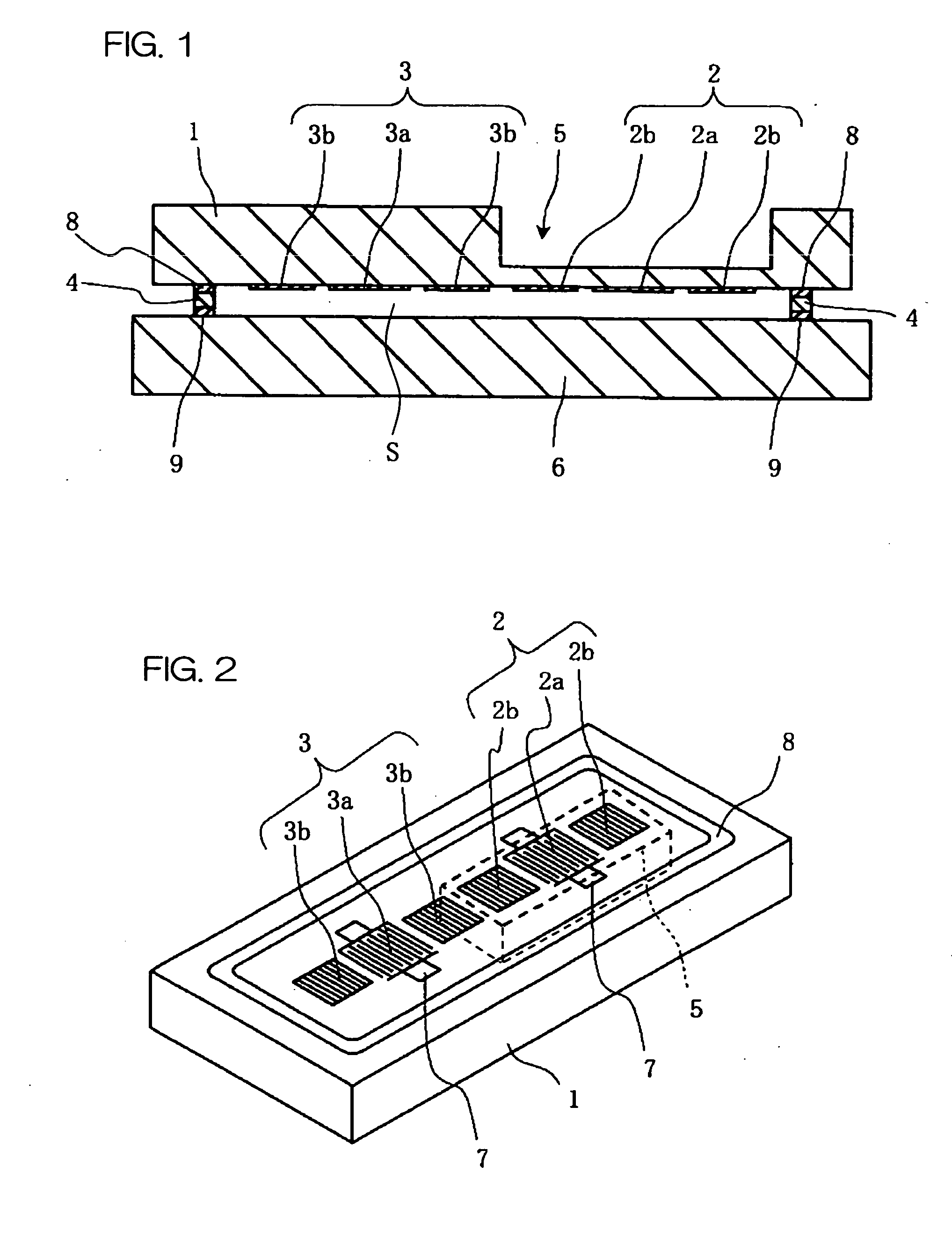
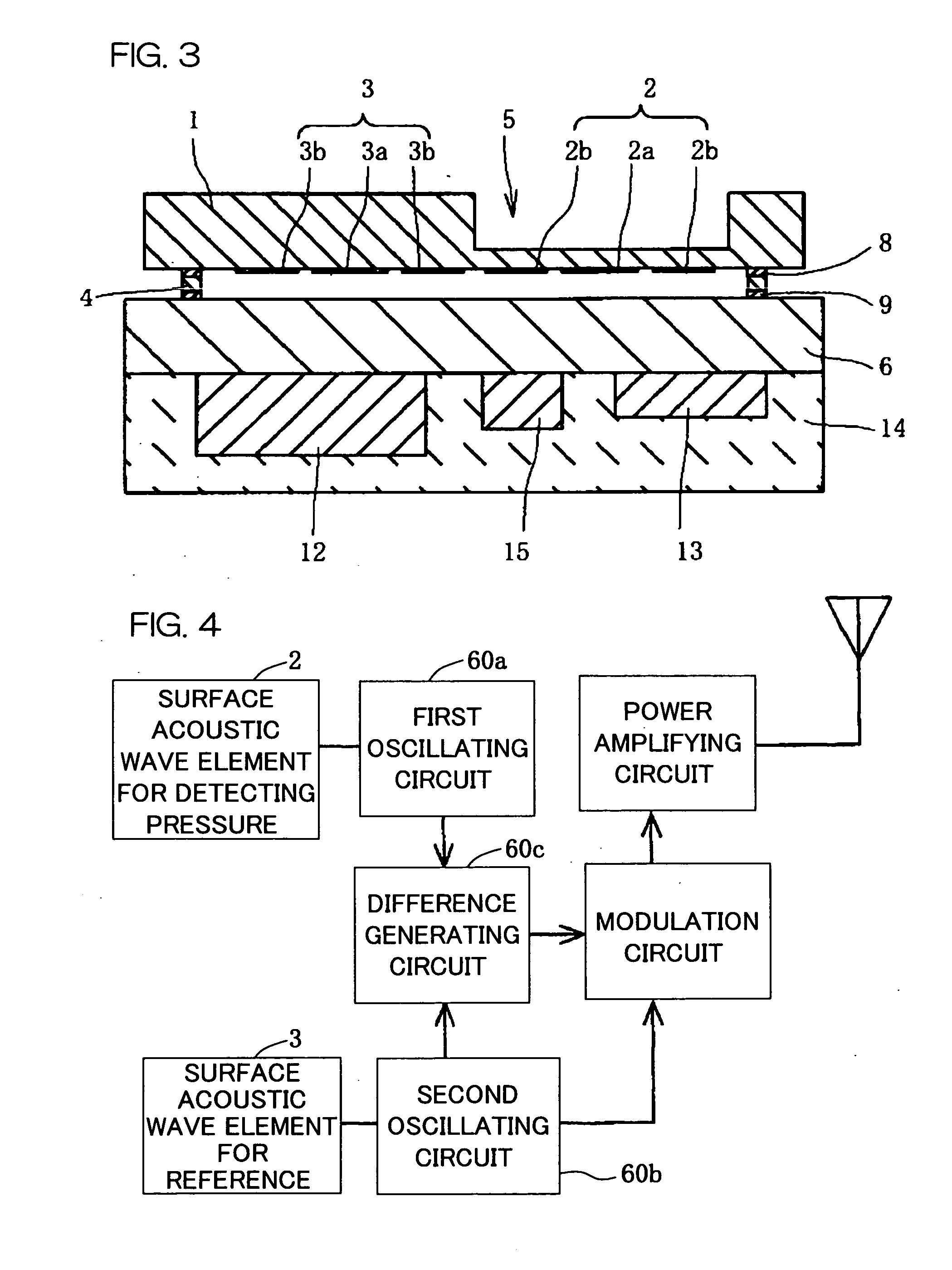
A sensor substrate 1 having on its lower surface a surface acoustic wave element 2 for detecting pressure is mounted on a supporting substrate 6 through a sealing member 4 surrounding a sensor section 2. A sealing space S is formed by the sensor substrate 1, the supporting substrate 6, and the sealing member 4, and the surface acoustic wave element 2 for detecting pressure is sealed hermetically in the sealing space S. Reliability can be enhanced by protecting the surface acoustic wave element 2 from the external environment.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Gravity-actuated submarine antenna
InactiveUS6859180B1Minimum interruptionIncreased gainAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesSubaqueous/subterranean adaptionOcean bottomResonant cavity
An antenna including a feed tube with radial fins and circular plates at the ends of the tube and fins thereby forming a boundary for a plurality of resonant cavities. Curved plates, connected to the tube by switches of a switching system, partially encompass and subtend to the length of the tube. Interior to the tube, a transmission line from an end plate terminus conducts radio-frequency energy from the terminus to a hub and onto a switch of the switching system in which the switch is mechanically reactive to and actuated by a righting action of the curved plates when the curved plates encounter a sea state. When actuated, energy from the switch distributes to a proximate resonant cavity and curved plate to form a radiation pattern based on the difference in phase of the resonant cavity and curved plate.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Gas detecting apparatus having condition monitoring means
InactiveUS6251243B1Increased gainEasy to detectMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical gas sensorPower flow
An operational amplifier (34) has its inverting input connected to a electrochemical gas sensor (38) for amplifying the current produced thereby in response to presence of a predetermined gas. In order to determine whether a sensor (38) is indeed present and that a sensor present is serviceable, a transient is applied to the non-inverting input of the operation amplifier (34). The presence or absence of the sensor (38) alters the transfer function of the operational amplifier (34) in respect of the test signal. If a serviceable sensor (38) is present, the gain of the operational amplifier (34) is high for the transient resulting at square pulse output. However, if a serviceable sensor (38) is not present, the gain of the operational amplifier (34) is relatively low and the transient retains its original form. Consequently the presence of a serviceable sensor (38) can be determined from the output of the operational amplifier (34) in response to the transient test signal.
Owner:ZELLWEGER ANALYTICS
Contactless integrated circuit card system
InactiveUS20090159657A1Setup easily and adjustablyAvoid influenceRecord carriers used with machinesSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringCard reader
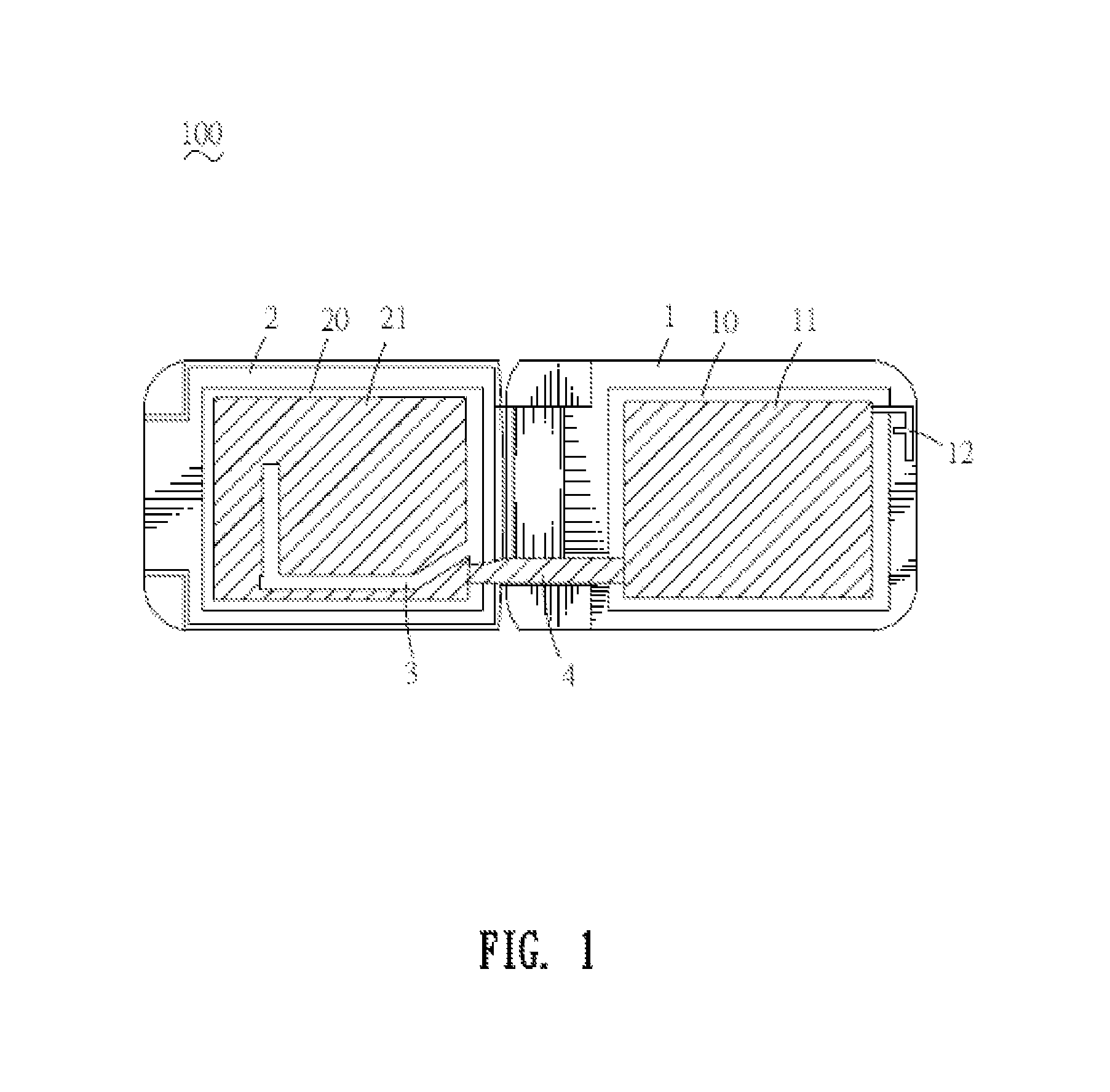
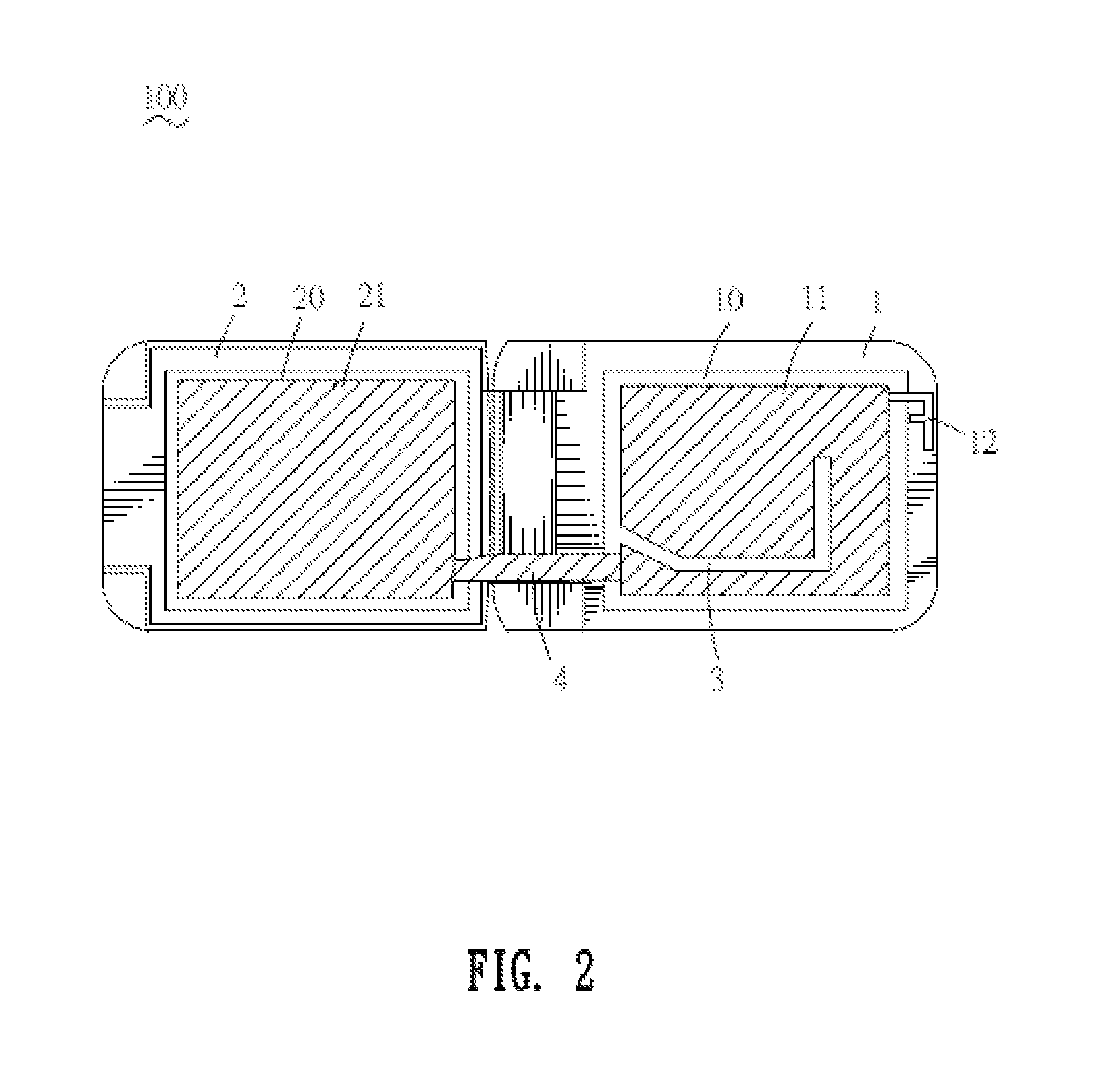
A contactless integrated circuit card system for communicating with a card reader is disclosed. The contactless integrated circuit card system includes an integrated circuit chip for performing contactless identification; a main antenna connected to the integrated circuit chip for transmitting signals to and from the card reader; and at least one open-circuit antenna disposed on the main antenna for increasing gain of the main antenna so that the electromagnetic induction of the main antenna is enhanced.
Owner:TAISYS TECH
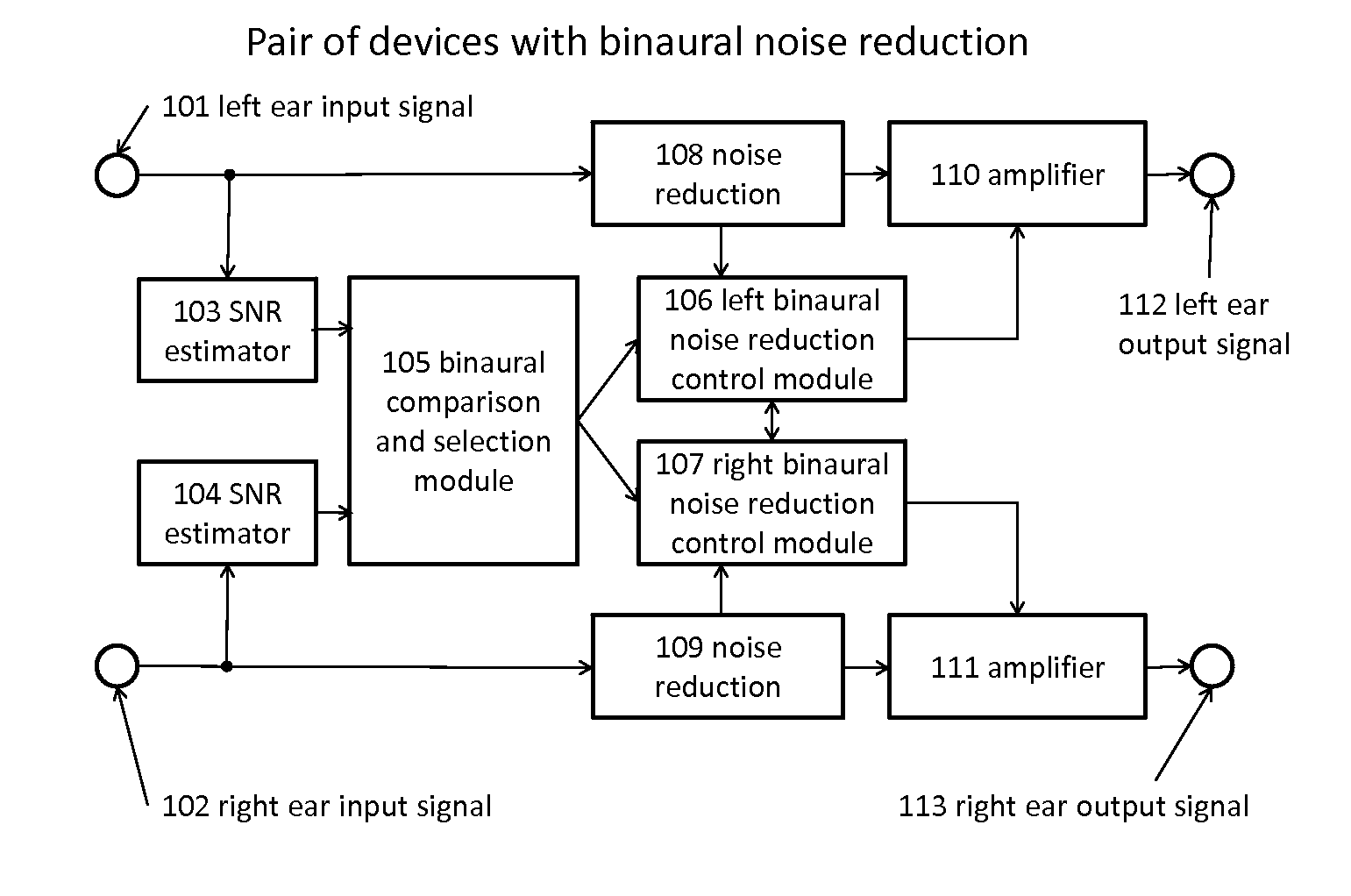
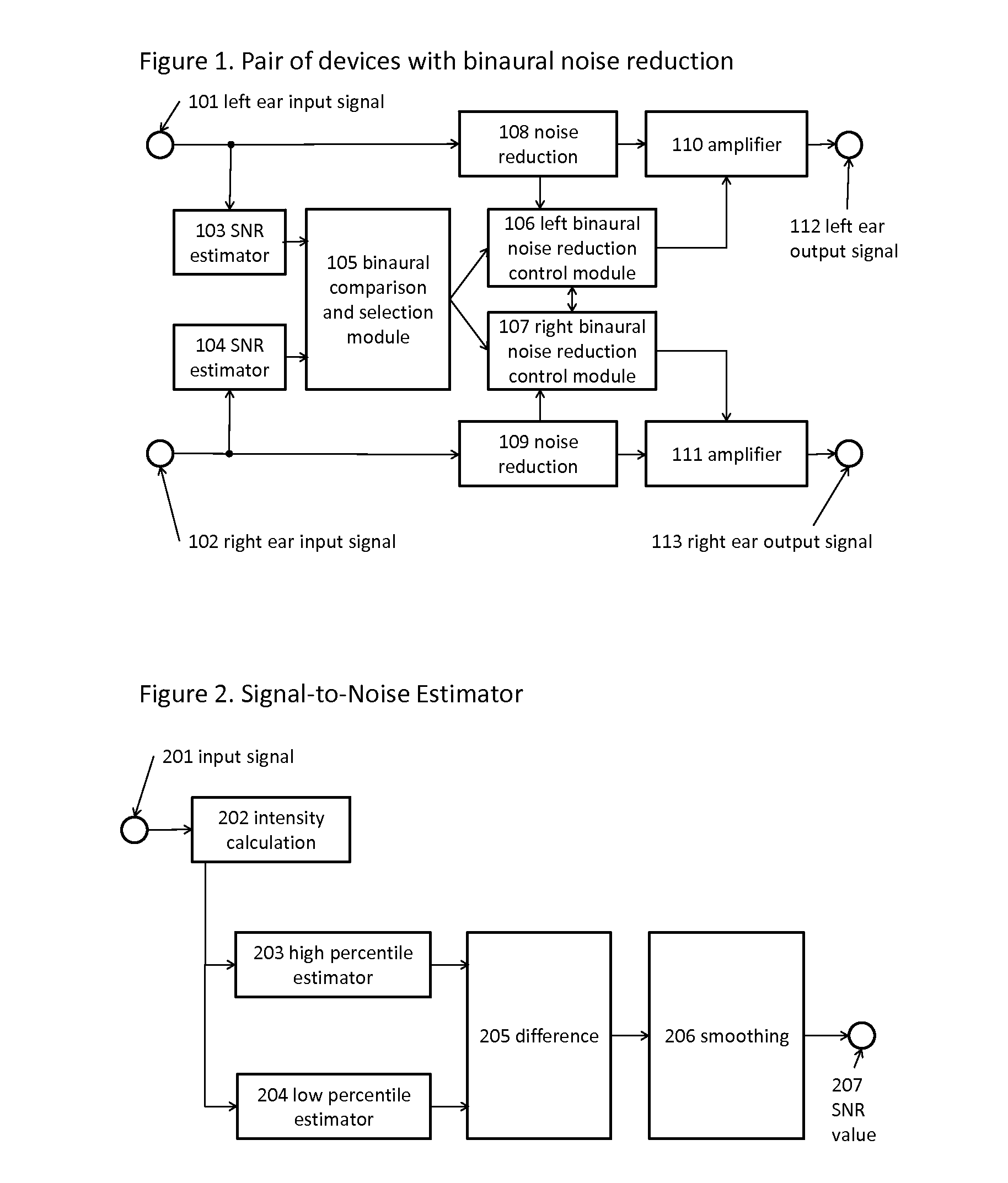
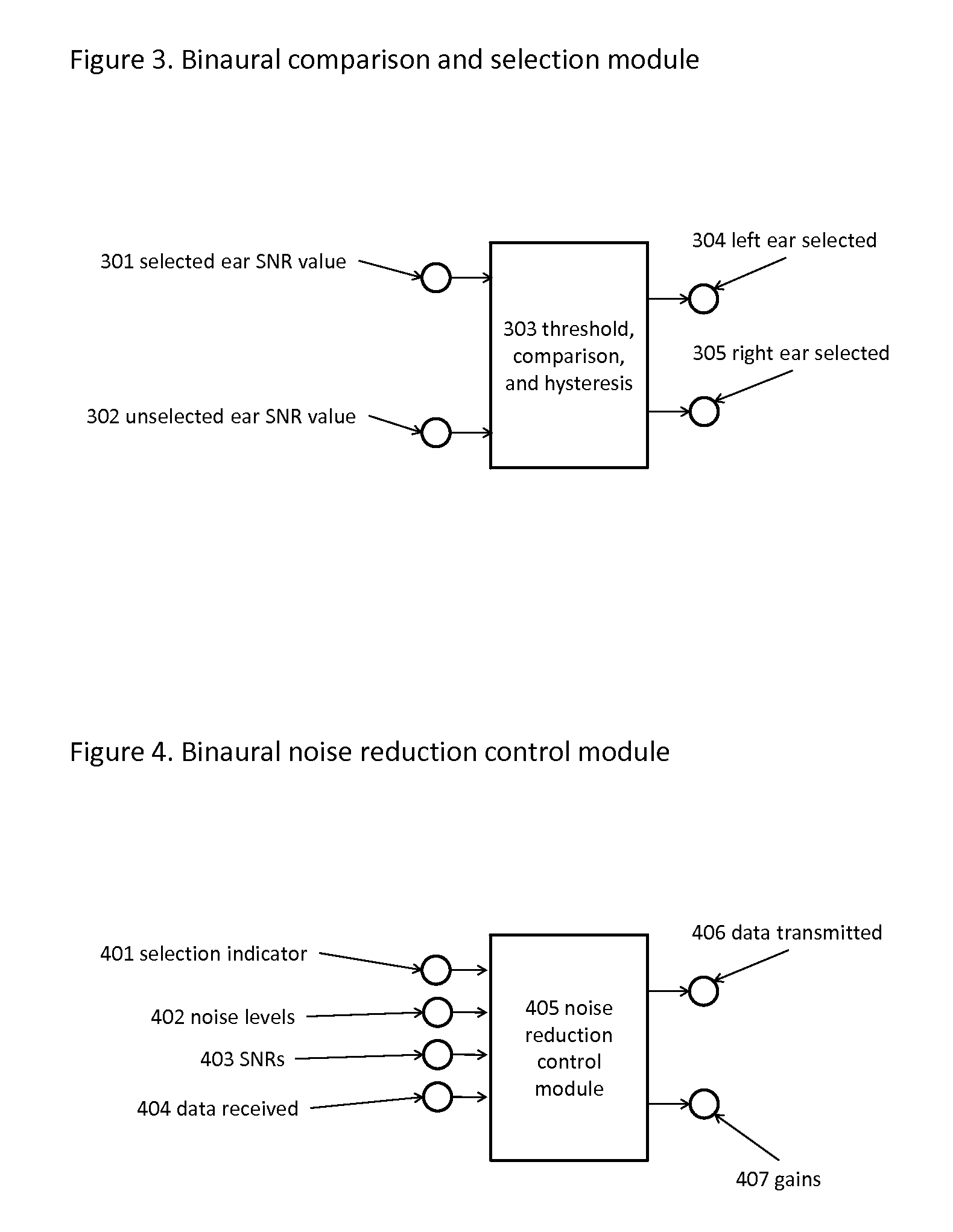
Binaural noise reduction
ActiveUS20120128164A1Save powerIncreased gainStereophonic circuit arrangementsTwo-channel systemsTemporal informationFrequency spectrum
In one embodiment, the present invention provides a sound processing device with a binaural input and binaural output, where “binaural input” means at least one microphone mounted in or near each ear of the device user, and “binaural output” means at least one output signal directed to each ear. The device may be comprised of two parts connected by a wired or wireless link. The device comprises: at least one microphone in or near each ear for the transduction of the sound at each ear; a signal-to-noise estimation module to estimate the signal-to-noise ratio present at each ear; a comparison and selection module to compare the signal-to-noise ratios present at the two ears and select the ear with the greater signal-to-noise ratio; a noise reduction control module that uses the spectral and temporal information from the selected ear signal to control two identical noise reduc tion modules; two identical noise reduction modules that process the signals from the two ears, under the control of the control module; and two output modules that amplify the output signals from the noise reduction modules appropriately for each ear and present the amplified signals as sound or other signals to each ear of the device user. The device may be implemented in dedicated hardware embodiment or by software running on a microprocessor.
Owner:SONOVA AG
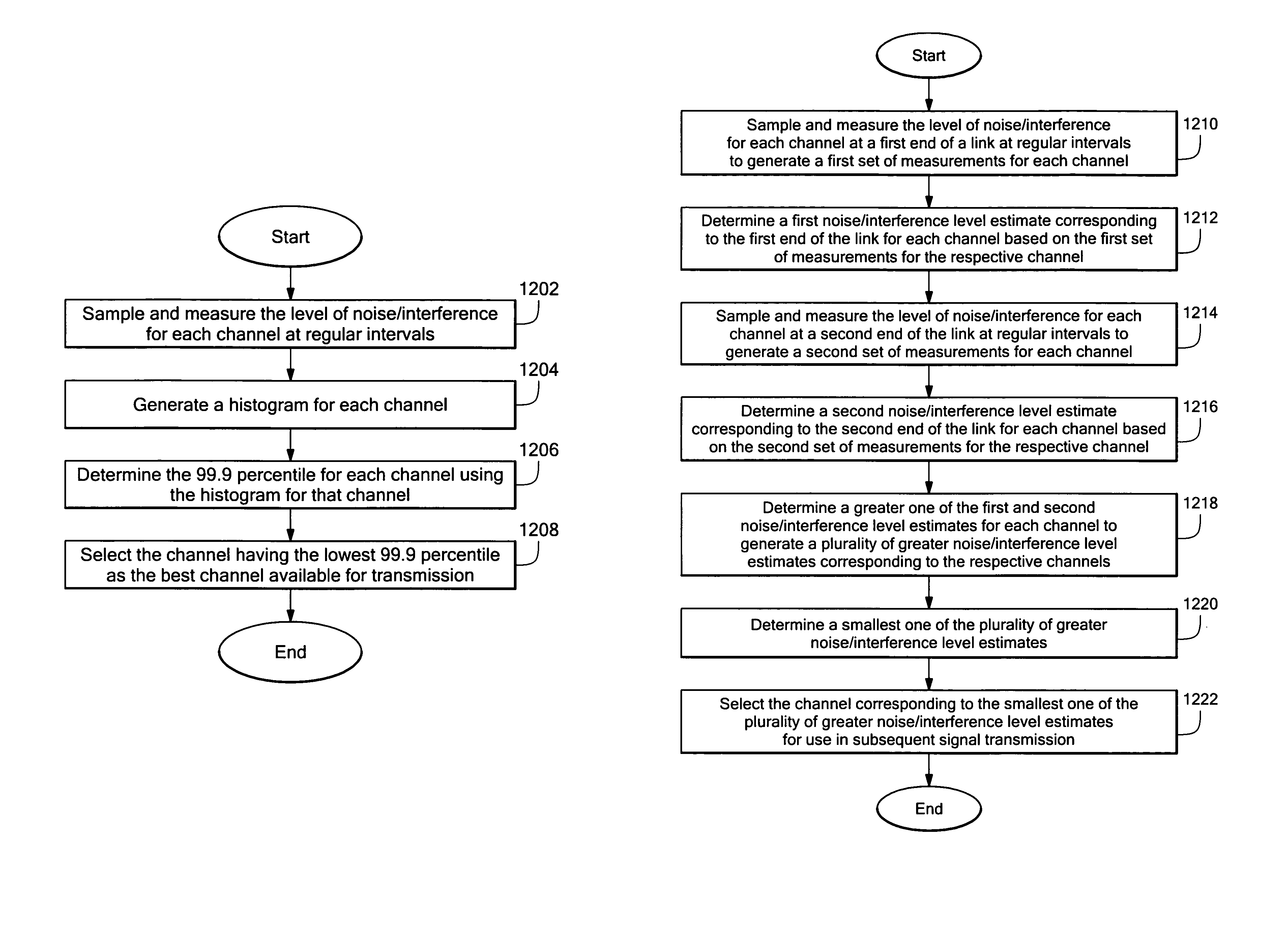
Intelligent spectrum management in a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) wireless communications system
ActiveUS7330698B1Increased de-correlationProvide diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringLow noiseFrequency spectrum
A wireless broadband communications system that increases data throughput and link availability through more efficient use of the electromagnetic spectrum allocated to the system. In one mode of operation, the system periodically measures a noise or interference level associated with each one of a plurality of communications channels, and generates a histogram of the measurements associated with each channel. Next, the system determines a noise / interference level estimate for each channel as a predetermined percentile of the histogram associated with the respective channel. The system then selects a respective one of the channels having the lowest noise / interference level estimate for subsequent signal transmission.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
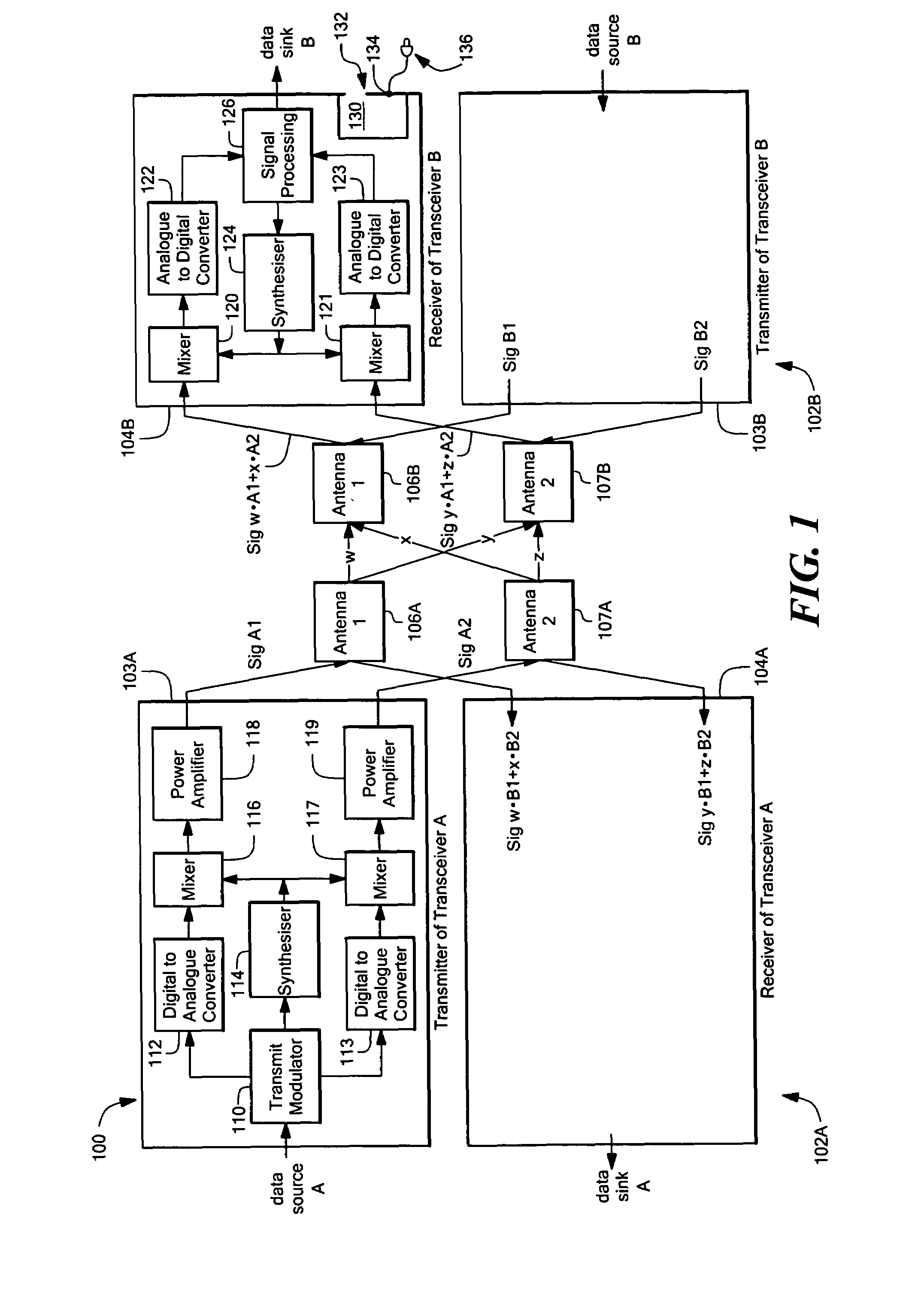
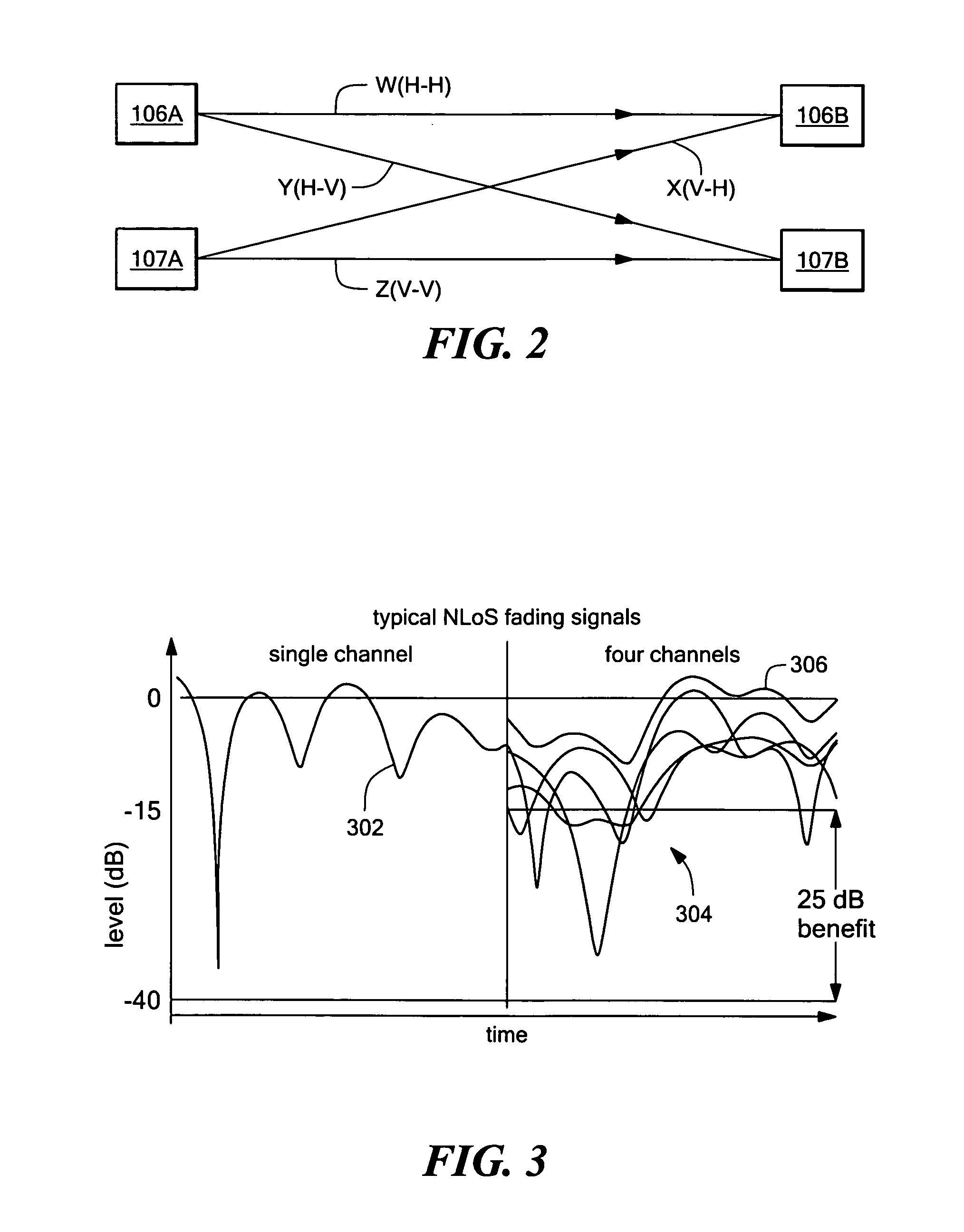
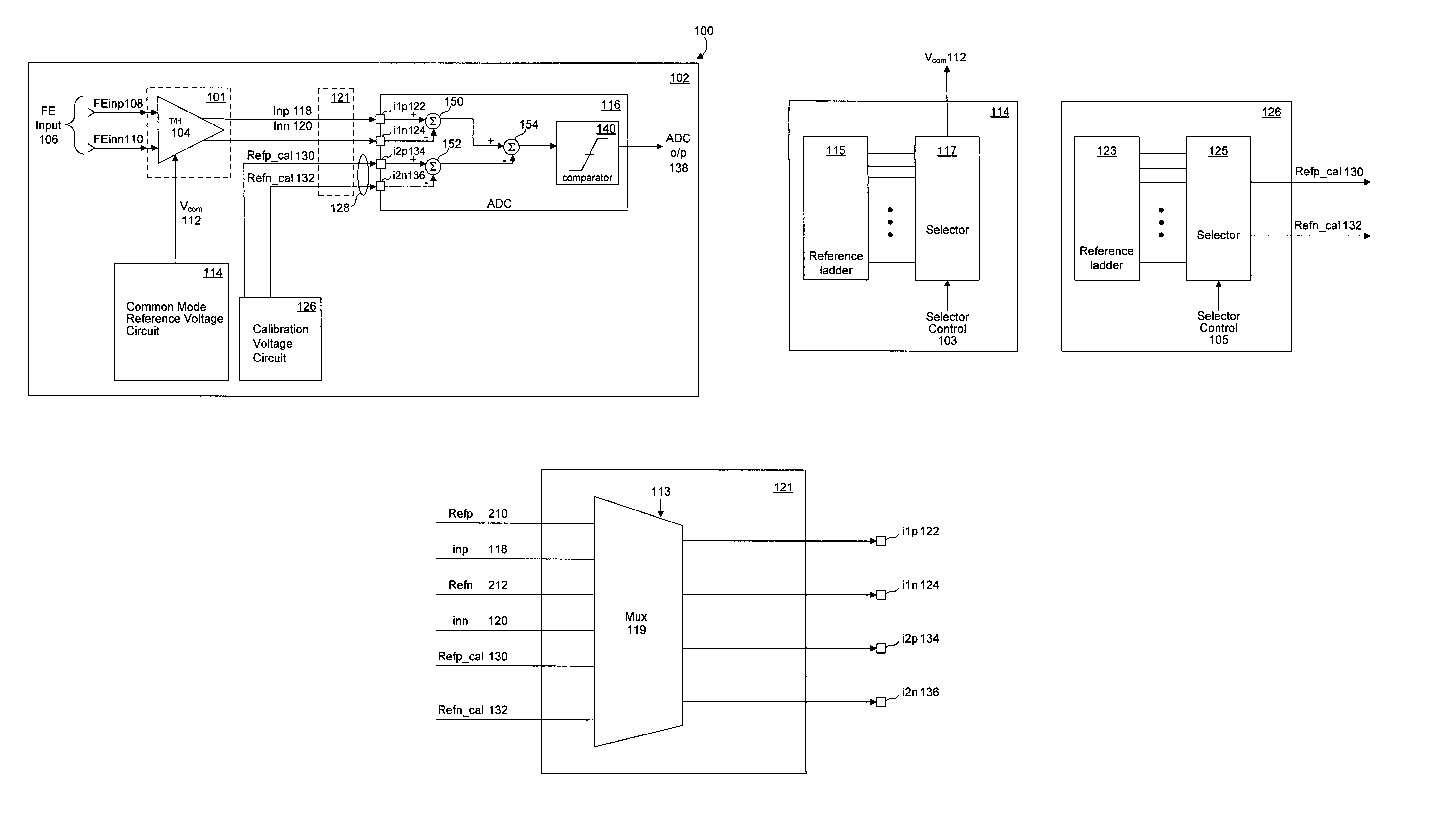
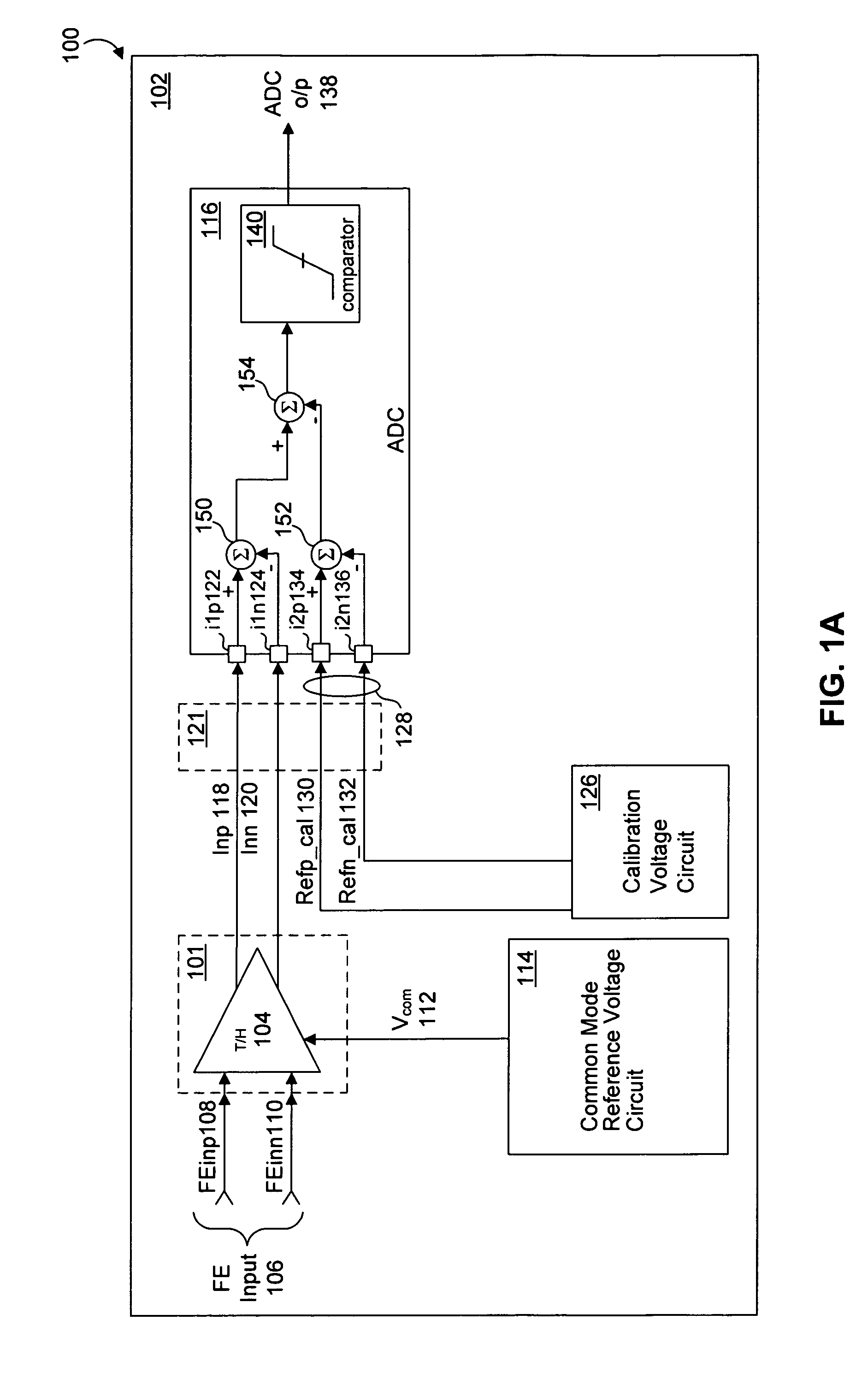
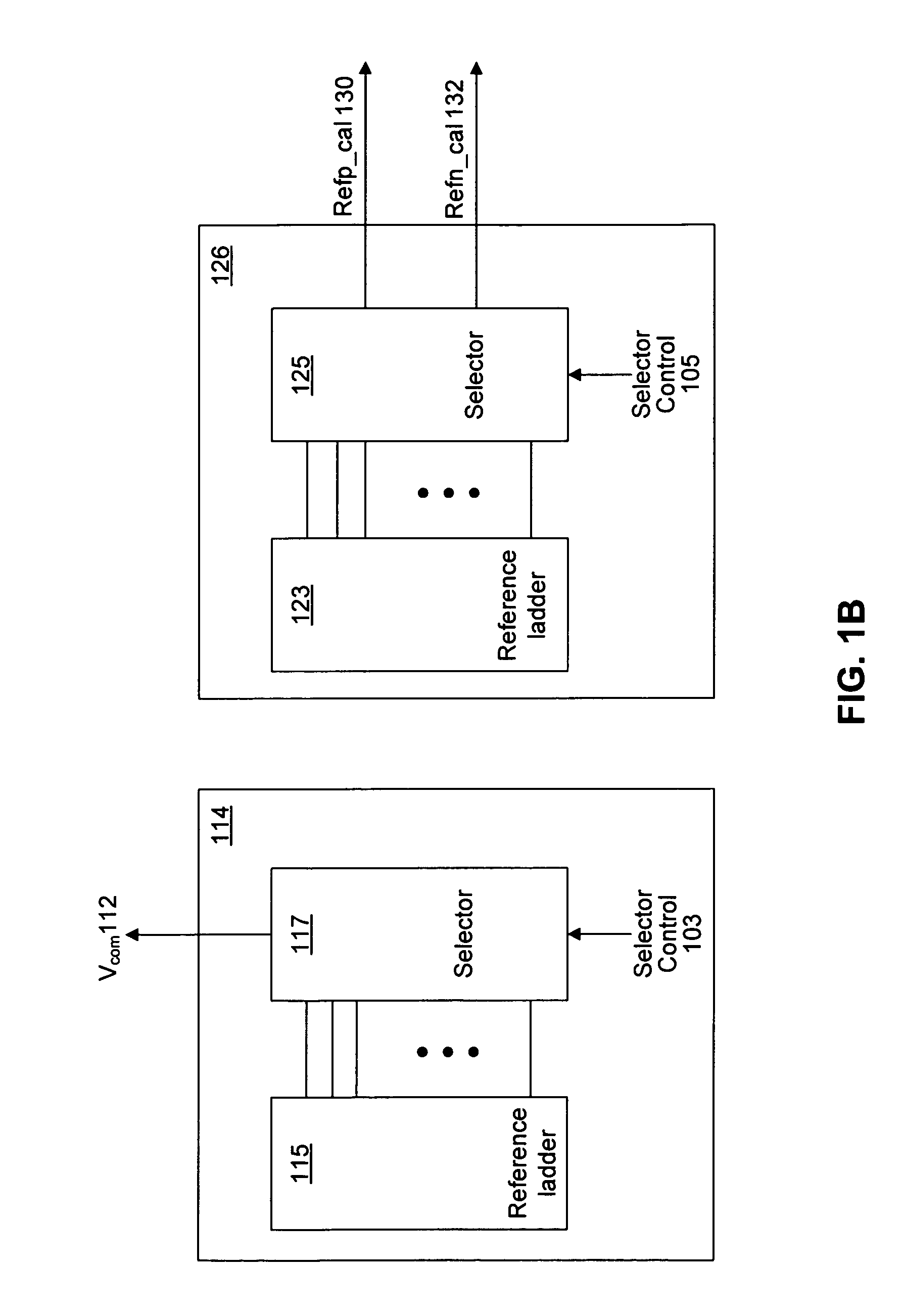
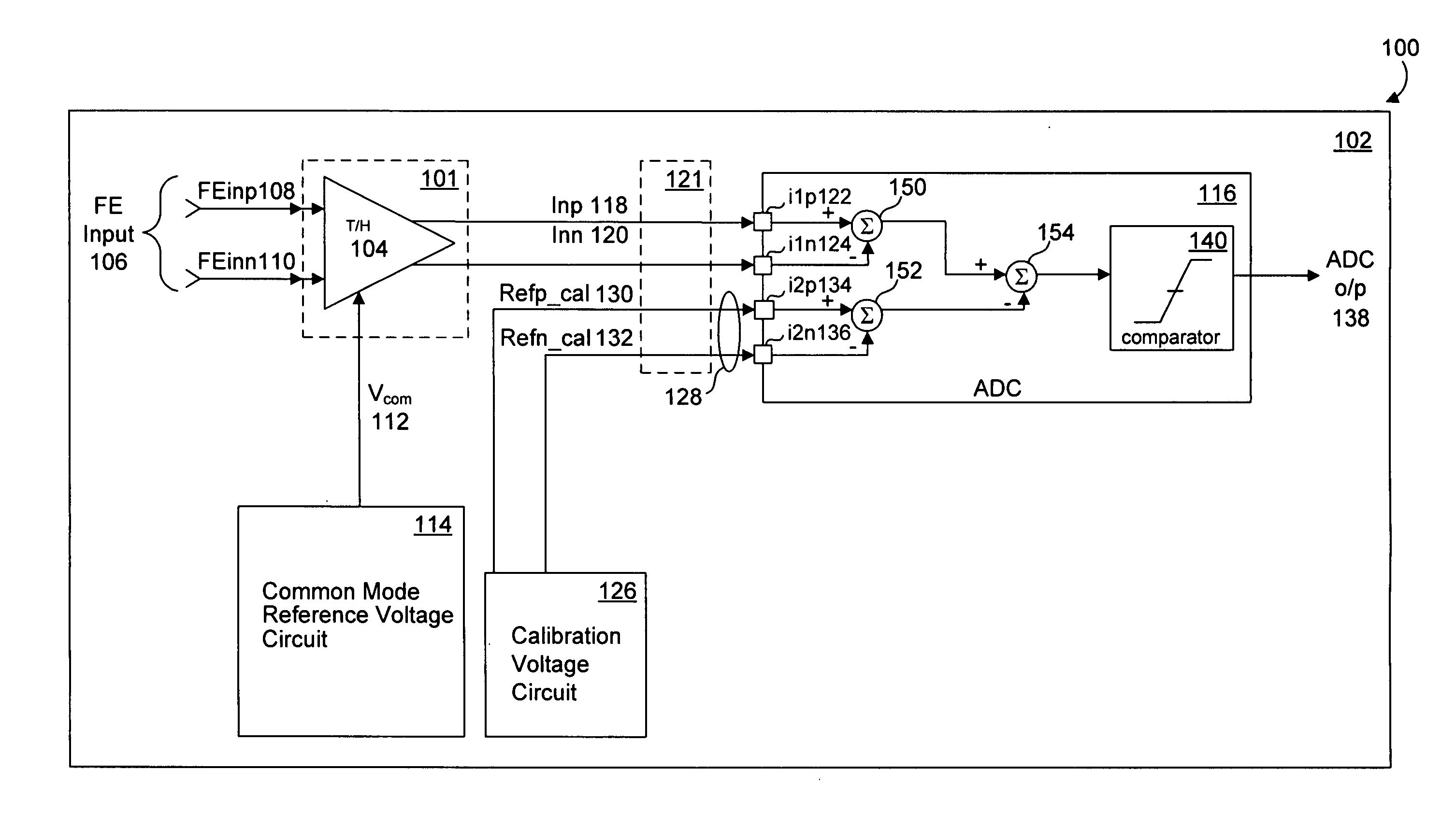
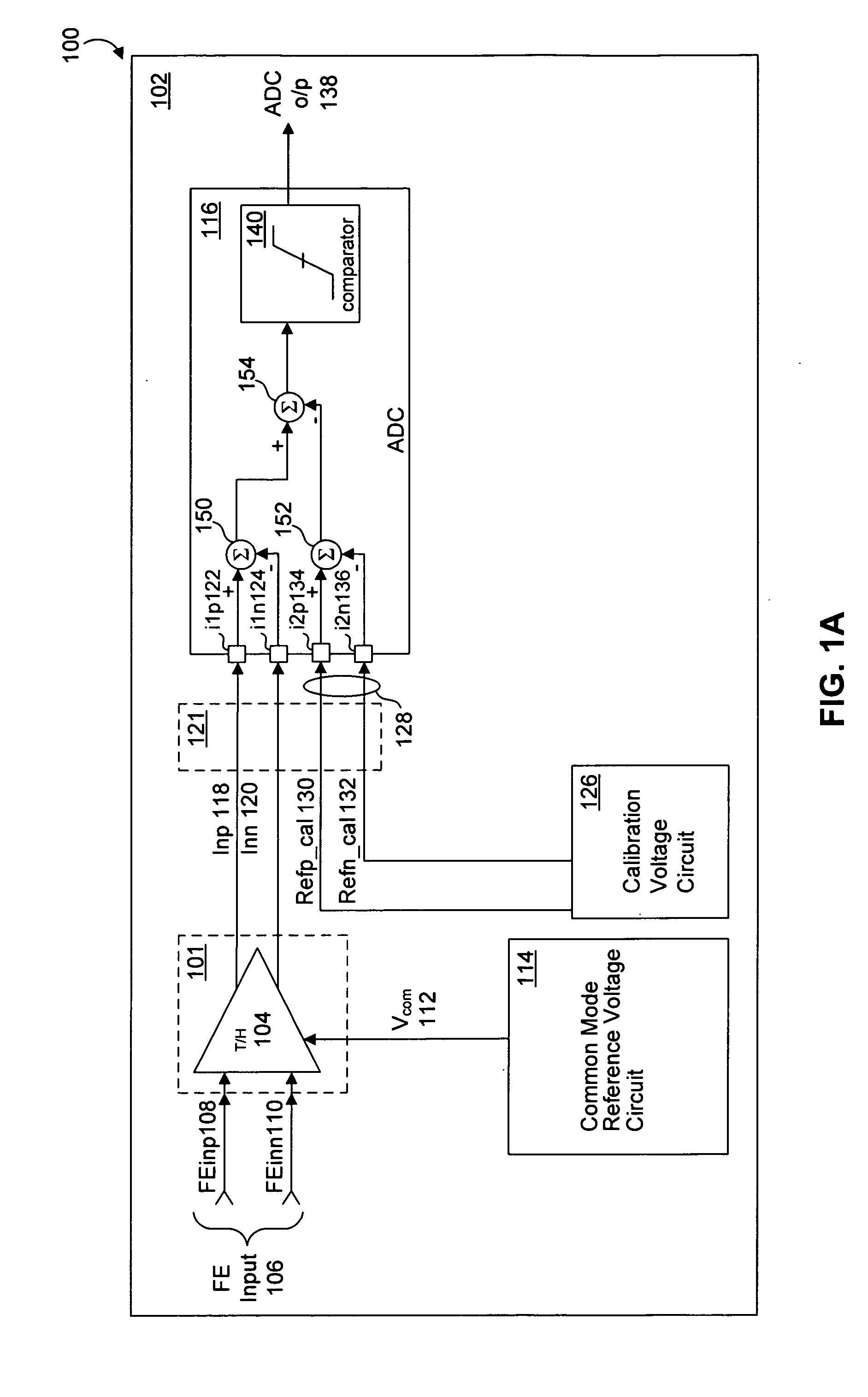
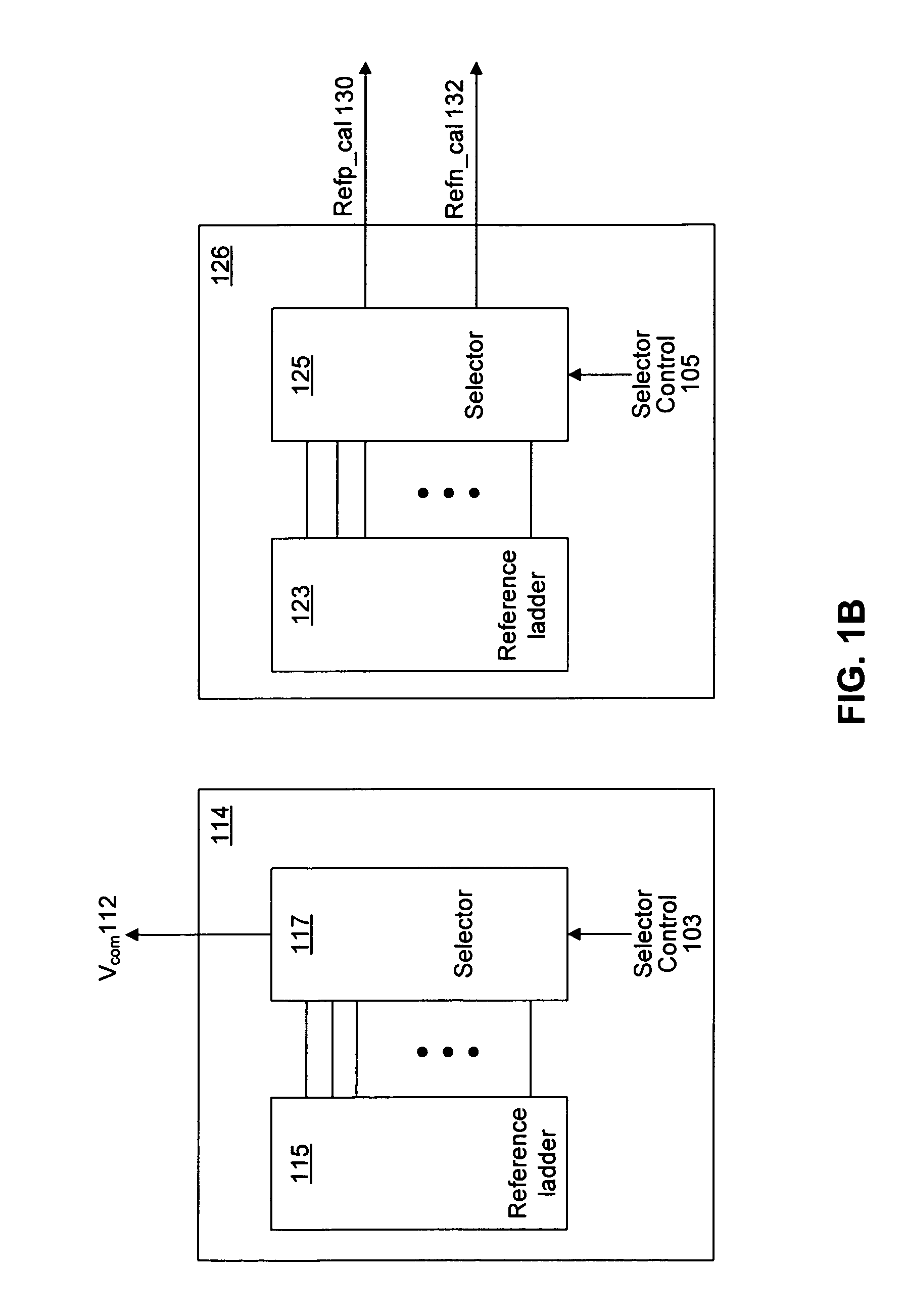
System and method for common mode calibration in an analog to digital converter
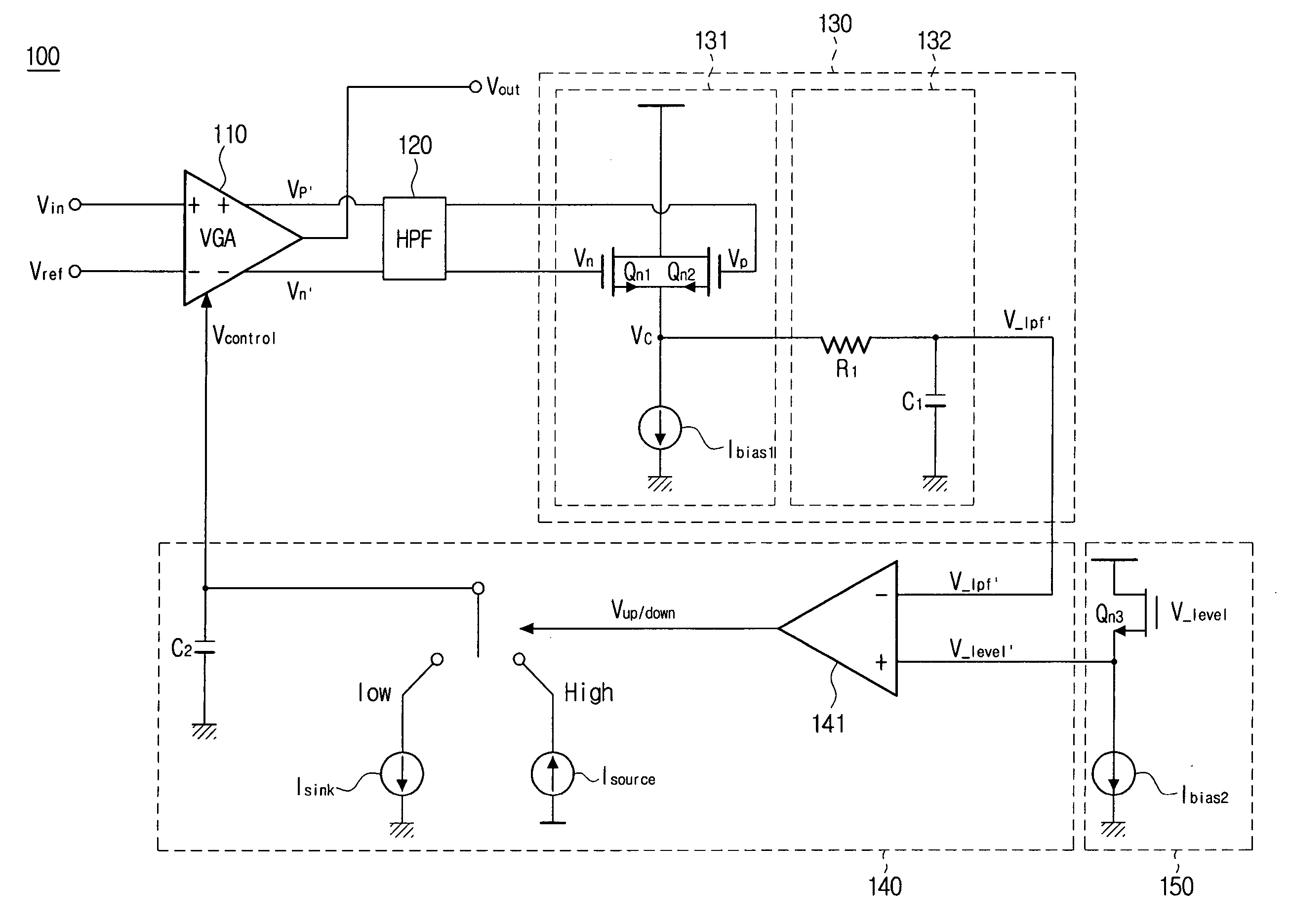
ActiveUS7466249B2Increased gainMinimize offsetElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersFeedback controllerAnalog-to-digital converter
A conversion circuit increases a gain of an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) preamplifier by minimizing a common mode offset voltage between an input signal and a reference signal. The feedback controller circuit calibrates an input common mode voltage to mitigate a common mode offset voltage. Reduction of the common mode offset voltage increases the gain of the ADC preamplifier. In an example, the method is executed during a hold phase of a track-and-hold circuit that transmits the input signal to the ADC.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Antenna device
ActiveUS20130050028A1Without degrading radiation efficiencyIncreased gainSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsPhysicsGround plane
An antenna device comprises an antenna board, wherein an antenna pattern is formed in or on a front surface of a dielectric layer, a ground layer is formed in or on a rear surface of the dielectric layer, and a feed pin is inserted into a thickness of the antenna board through the ground layer and the dielectic layer. The diameter of the antenna pattern is set to one half of the wavelength of an RF signal passed through the antenna pattern, and a length of one side of the dielectric plate is set shorter than the wavelength. A metallic plate is coupled to the ground layer with a plurality of metallic spacers interposed therebetween, whereby the metallic plate is electrically connected to the ground layer. .
Owner:ORMON CORP
Gas detecting apparatus having condition monitoring means
InactiveUS6123818AIncreased gainEasy to detectMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical gas sensorPower flow
An operational amplifier (34) has its inverting input connected to a electrochemical gas sensor (38) for amplifying the current produced thereby in response to presence of a predetermined gas. In order to determine whether a sensor (38) is indeed present and that a sensor present is serviceable, a transient is applied to the non-inverting input of the operation amplifier (34). The presence or absence of the sensor (38) alters the transfer function of the operational amplifier (34) in respect of the test signal. If a serviceable sensor (38) is present, the gain of the operational amplifier (34) is high for the transient resulting at square pulse output. However, if a serviceable sensor (38) is not present, the gain of the operational amplifier (34) is relatively low and the transient retains its original form. Consequently the presence of a serviceable sensor (38) can be determined from the output of the operational amplifier (34) in response to the transient test signal.
Owner:HONEYWELL ANALYTICS LTD
Wireless apparatus for increasing antenna gain
InactiveUS7417593B1High gainReduce parasitic effectsAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsAntenna gainMetallic materials
A wireless apparatus has a main housing, a movable housing relatively extended to the main housing. The main housing contains a first PCB with a first layer being fully laid metal material. The movable housing contains a second PCB with a second layer being fully laid metal material. An insulation route is laid on the second layer and led to the border of the second layer. A connection component electronically connects the first layer and the second layer. When the wireless apparatus is operated at wireless communication, the cooperation of the first layer, the second layer, the insulation route and the connection component adjusts the electrical characteristic of the first and second PCBs for eliminating a parasitic effect being caused of movement of the first and second PCBs and increasing gain of the antenna of the wireless apparatus.
Owner:CHENG UEI PRECISION IND CO LTD
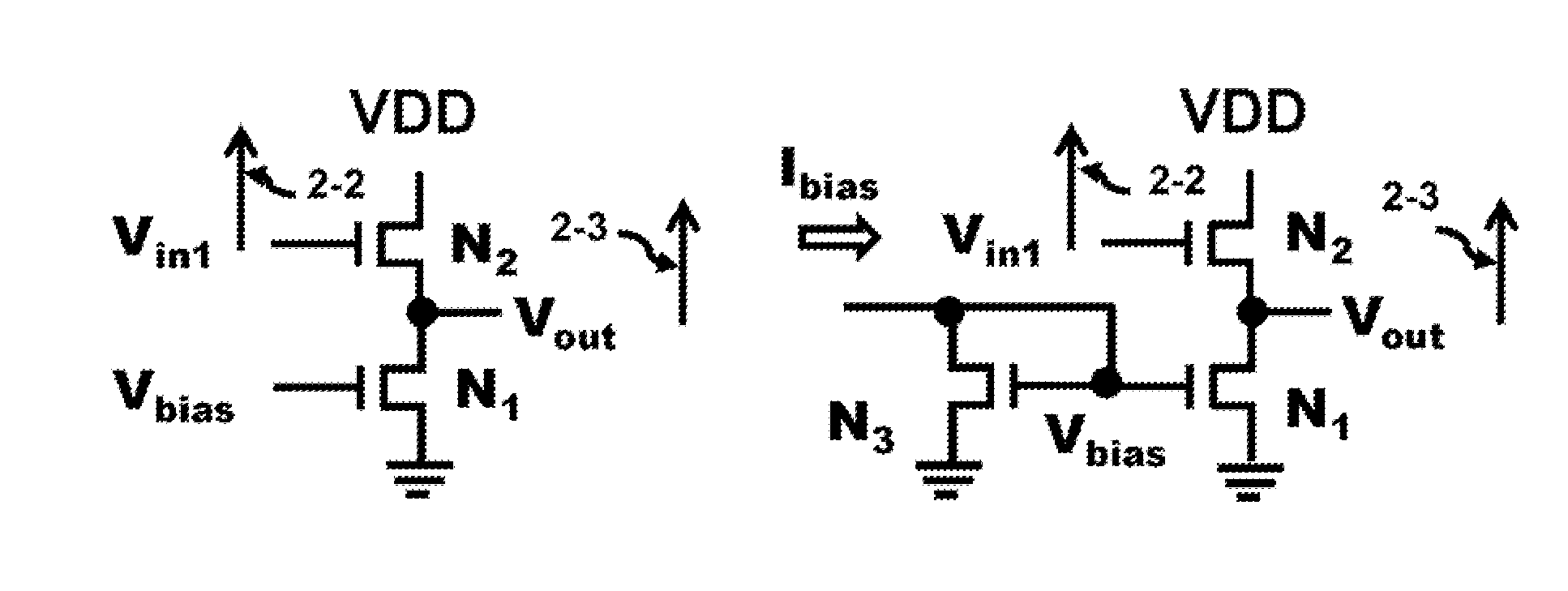
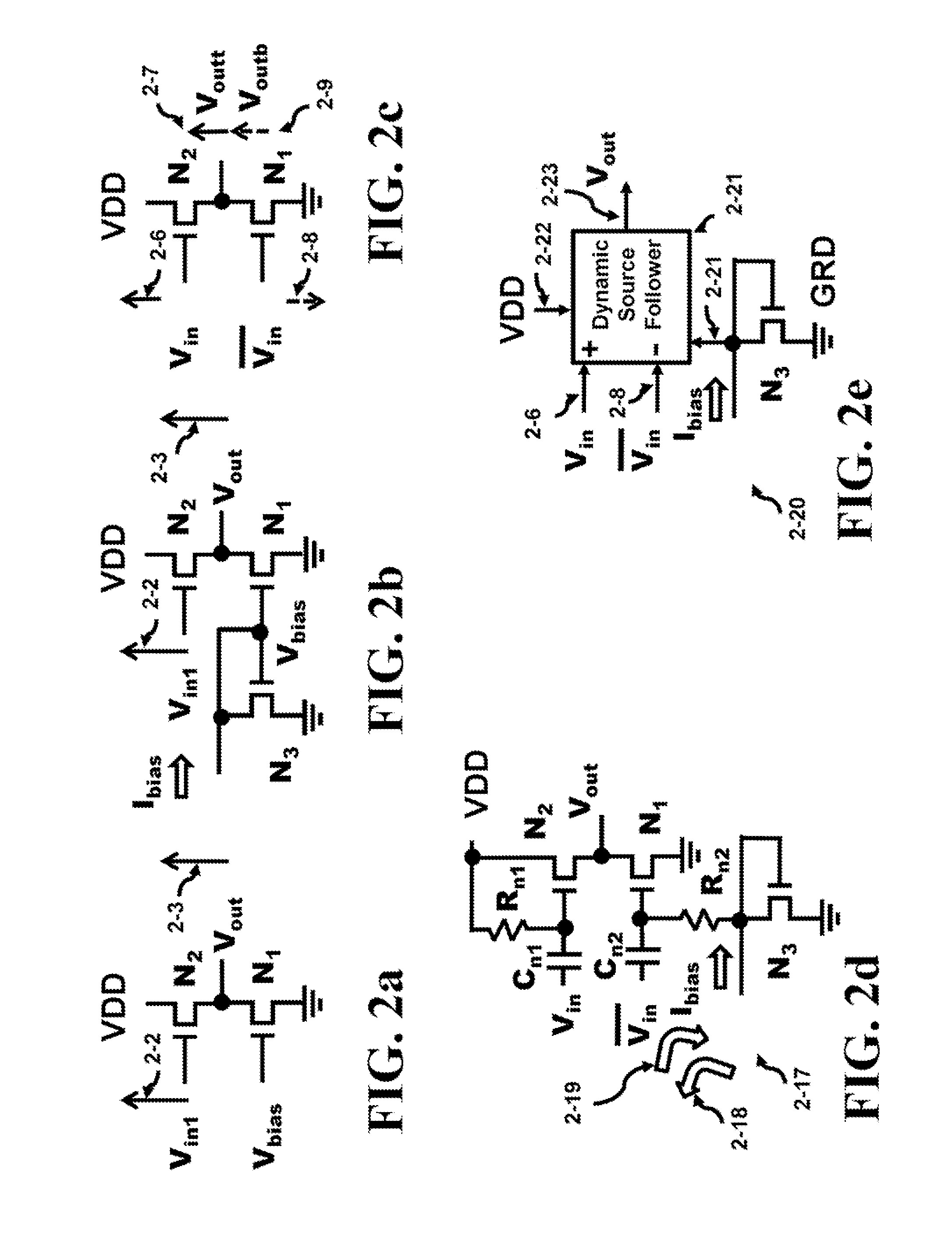
Differential Source Follower having 6dB Gain with Applications to WiGig Baseband Filters
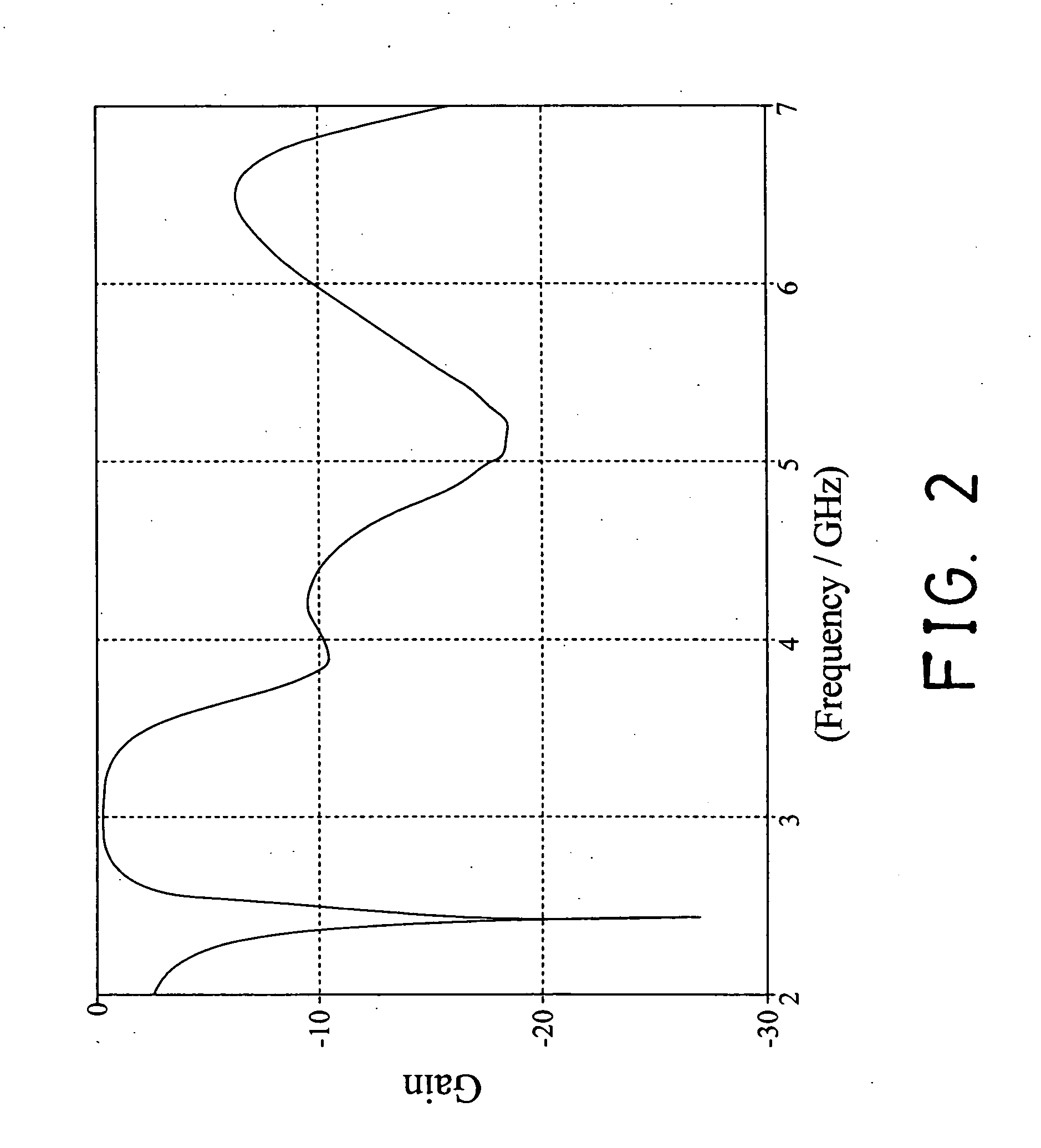
ActiveUS20130076434A1Increase capacitanceHigh input impedanceActive element networkDifferential amplifiersCMOSAudio power amplifier
A Sallen-Key filter requires an operational amplifier with a large input impedance and a small output impedance to meet the external filter characteristics. The operational amplifier requires an internal feedback path for stability that limits performance. This invention eliminates the need for internal feedback and increases the gain of a source follower which has characteristics matching the operational amplifier in the Sallen-Key filter. The source follower provides 6 dB of AC voltage gain and is substituted for the operational amplifier in the Sallen-Key filter. The Sallen-Key filter requires a differential configuration to generate all the required signals with their compliments and uses these signals in a feed forward path. Furthermore, since the source follower uses only two n-channel stacked devices, the headroom voltage is maximized to several hundred millivolts for a 1.2V voltage supply in a 40 nm CMOS technology. Thus, the required 880 MHz bandwidth of the Sallen-Key filter can be easily met using the innovative source follower.
Owner:TENSORCOM
System and method for common mode calibration in an analog to digital converter
ActiveUS20070132625A1Increased gainMinimize offsetElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAudio power amplifierFeedback controller
A conversion circuit increases a gain of an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) preamplifier by minimizing a common mode offset voltage between an input signal and a reference signal. The feedback controller circuit calibrates an input common mode voltage to mitigate a common mode offset voltage. Reduction of the common mode offset voltage increases the gain of the ADC preamplifier. In an example, the method is executed during a hold phase of a track-and-hold circuit that transmits the input signal to the ADC.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Time-to-digital converter and operation method thereof
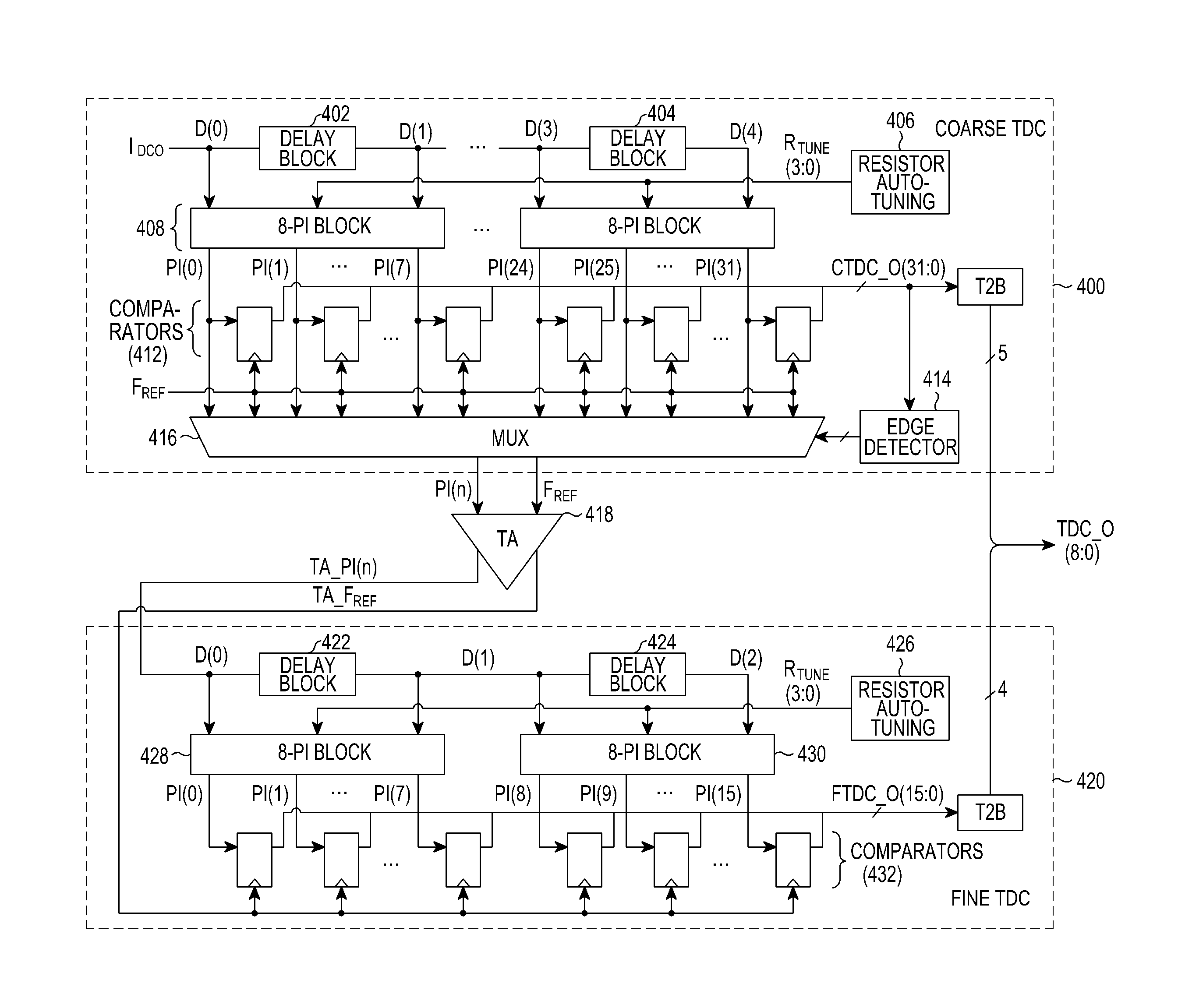
ActiveUS20110260902A1Increased gainHigh gainAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsSignal onSpecific time
A Time-to-Digital Converter (TDC) is provided. The TDC includes a first TDC unit for receiving a first input signal and a second input signal, delaying the first input signal on a specific time basis using each of first delay blocks, generating first phase-divided signals by performing first phase division on signals of input / output nodes for each of the first delay blocks on a predefined Phase-Interpolation (PI) delay time basis, and outputting the second input signal and a phase-divided signal closest to the second input signal, among the first phase-divided signals, a time amplifier for independently time-amplifying the second input signal and the phase-divided signal closest to the second input signal, and a second TDC unit for delaying a phase-divided signal closest to the time-amplified second input signal on a specific time basis using each of second delay blocks, and generating second phase-divided signals by performing second phase division on signals of input / output nodes for each of the second delay blocks on a predefined PI delay time basis.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Antenna System
InactiveUS20100048218A1Increased gainSmall shareModulated-carrier systemsAssess restrictionData capacityMicrowave
Embodiments of the invention relate to wireless communications networks, and more specifically to an antenna apparatus for cellular wireless systems. Increasing data capacity of cellular wireless systems places increasing demands on the capacity of the two way connection, known as backhaul, between a cellular base station and a telecommunications network such as the PSTN backhaul, since this is the connection that has to convey the wireless-originating traffic to its destination, often in an entirely different network. Known backhaul links include leased lines, microwave links, optical fibre links or radio resources for relaying backhaul traffic between base stations. The fixed line solutions are expensive to implement and maintain, while the radio solutions antenna configurations that are not ideal for relaying data between base stations. In embodiments of the invention, communication between base stations occurs in a first timeslot by use of a first antenna system and communication between a given base station and a user equipment occurs in a second timeslot using a second antenna system. The benefit of this method is that the first antenna system can be optimised for use in communication between base stations, whereas the second antenna system can be optimised for communication with user equipment which preferably occurs within the area of cellular wireless coverage of the sector served by the second antenna system.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF BELFAST +2
Directional antenna structure with dipole antenna element
ActiveUS20150042533A1High gainIncreased gainAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsElectrical conductorDirectional antenna
An antenna structure includes a dipole antenna element, a closed-loop conductor, and a reflection plane. The dipole antenna element is configured to transmit an electromagnetic signal. The closed-loop conductor is disposed adjacent to the dipole antenna element. The dipole antenna element is substantially between the closed-loop conductor and the reflection plane, or the closed-loop conductor is substantially between the dipole antenna element and the reflection plane. The reflection plane is configured to reflect the electromagnetic signal from the dipole antenna element so as to enhance the total gain of the antenna structure. The mutual coupling effect between the closed-loop conductor and the dipole antenna element effectively causes the distance between the dipole antenna element and the reflection plane to be shorter.
Owner:WISTRON NEWEB
Electronic camera having an automatic electric flash function
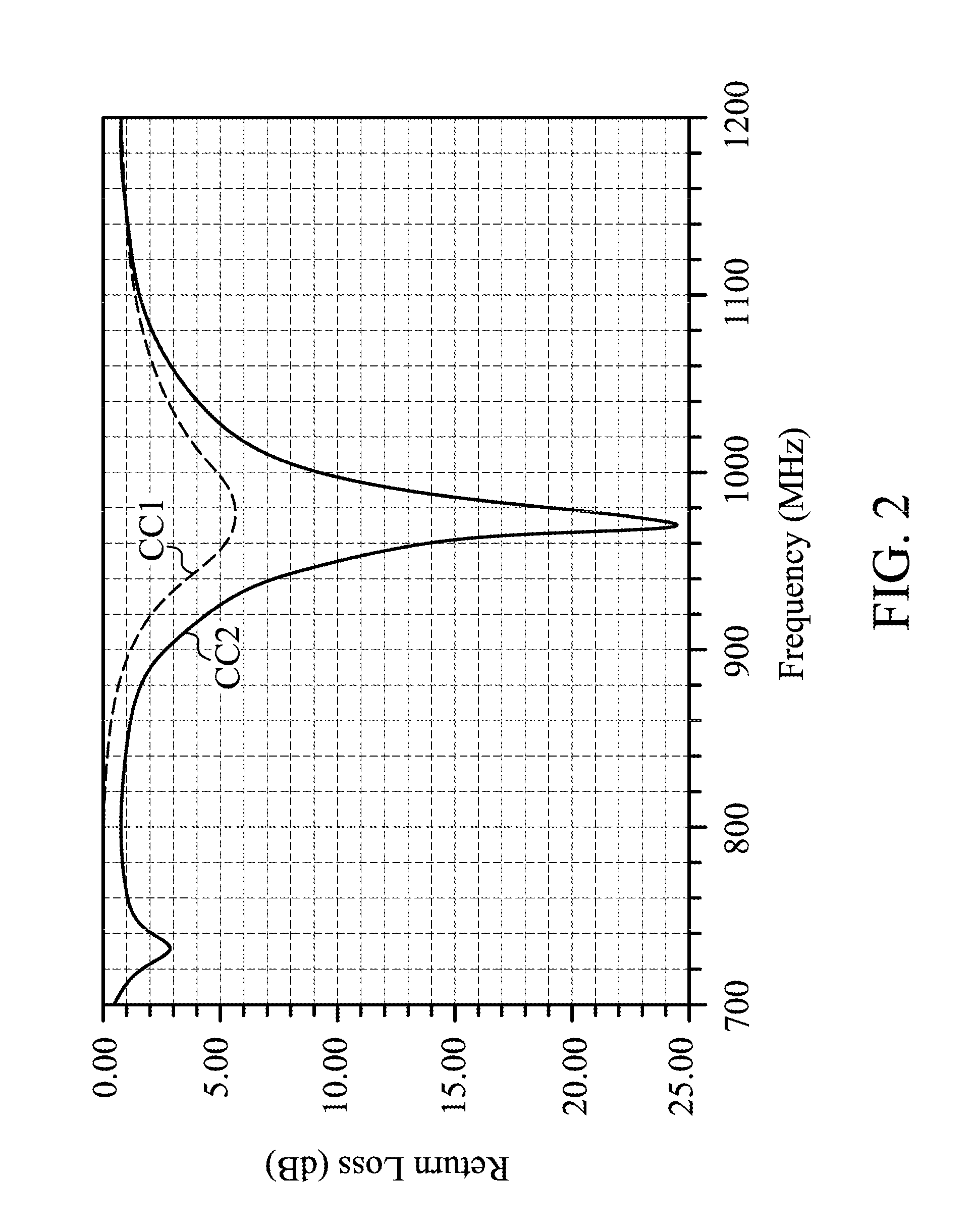
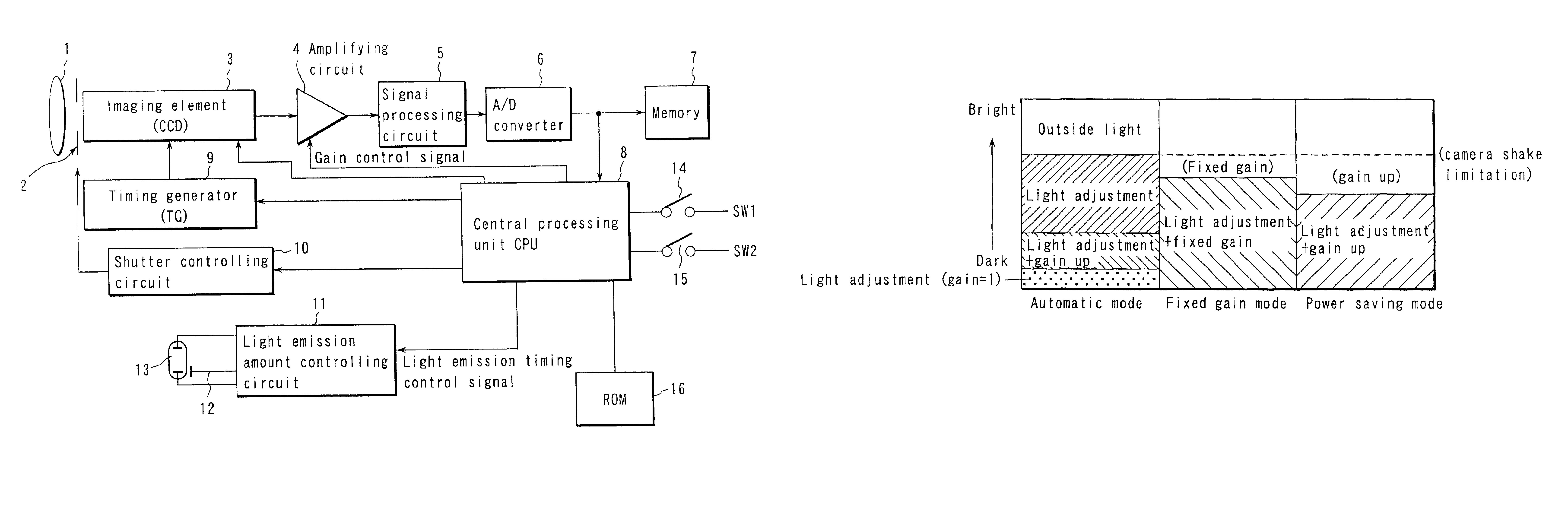
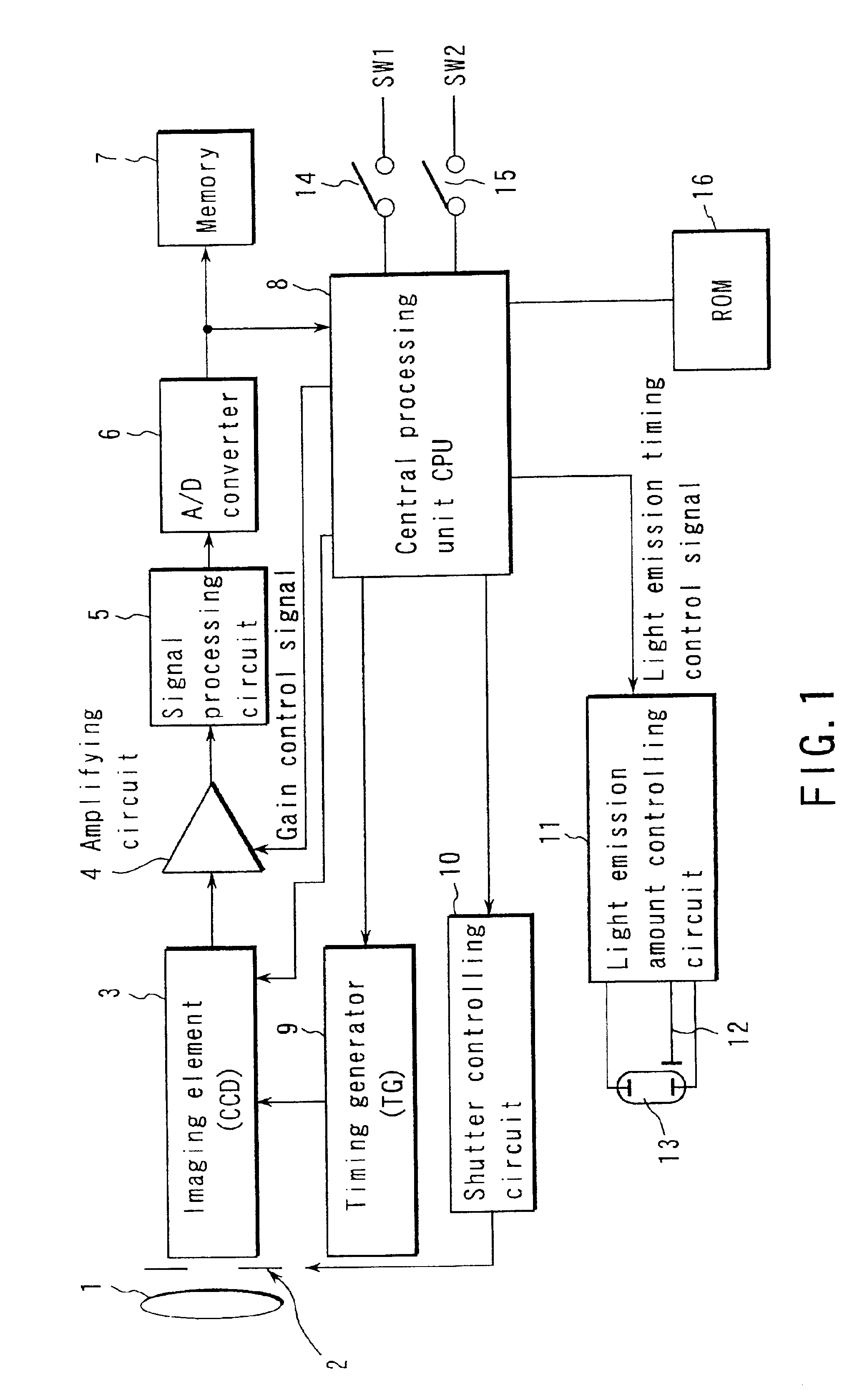
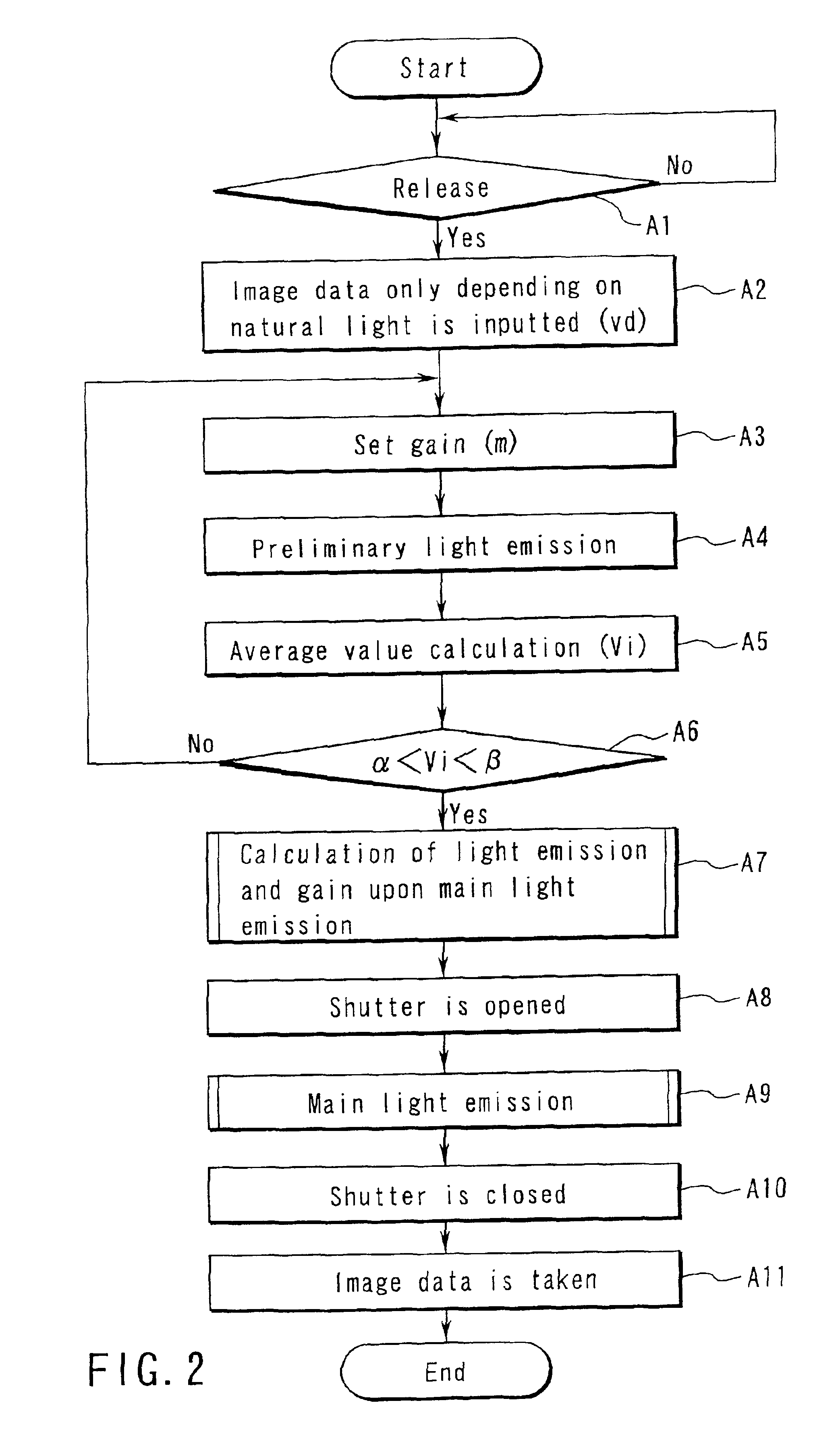
ActiveUS6961093B2Increase exposureIncreased gainTelevision system detailsPrintersElectricityLight emission
An electronic camera, which is capable of obtaining a more appropriate exposure even when taking a picture by an electric flash photograph, comprises a light emission section for emitting a preliminary light prior to a main photograph and emitting a main light upon taking a picture with respect to a object, a pickup device for receiving an object image in the preliminary light emission and converting a light into electricity to obtain a photograph signal, an amplifying section for amplifying the photograph signal which is obtained by the pickup device and a setting section for setting a gain of the amplifying section and a light emission amount in the main light emission on the basis of the photograph signal obtained in the preliminary light emission.
Owner:OM DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
Multiple frequency antenna assembly
InactiveUS20100321274A1High gainIncreased gainSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMultiple frequencyGSM
An antenna assembly includes a circuit board, a substrate extended from one side of the circuit board, a conductive member provided the other side of the circuit board, and a GPS antenna connected to the conductive member and arranged opposite to the second side of the substrate, one or more antenna devices and a GSM antenna are disposed on the circuit board and arranged opposite to the GPS antenna for preventing the GPS antenna and the antenna devices and the GSM antenna from being interfered or affected by each other and for allowing the antenna assembly to suitably transmit and receive the signals.
Owner:JOYMAX ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Automatic gain controller
InactiveUS20070040610A1Reduce gainIncreased gainModification of read/write signalsGain controlVoltage referenceAudio power amplifier
An automatic gain controller includes a variable gain amplifier for amplifying an input signal having a specified DC level on the basis of the DC level, and outputting a first differential signal having a specified gain α, a second differential signal having a 180° phase difference from the first differential signal, and an output signal obtained by subtracting the second differential signal from the first differential signal; a full-wave-rectifying unit for full-wave-rectifying the first differential signal and the second differential signal; a low-pass filter for extracting the DC component from the output signal of the full-wave-rectifying unit and outputting the extracted DC component; a reference voltage level adjustment unit for adjusting a DC level of a reference voltage; and a comparison unit for comparing the output signal of the low-pass filter with the output signal of the reference voltage level adjustment unit to adjust a gain of the variable gain amplifier.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
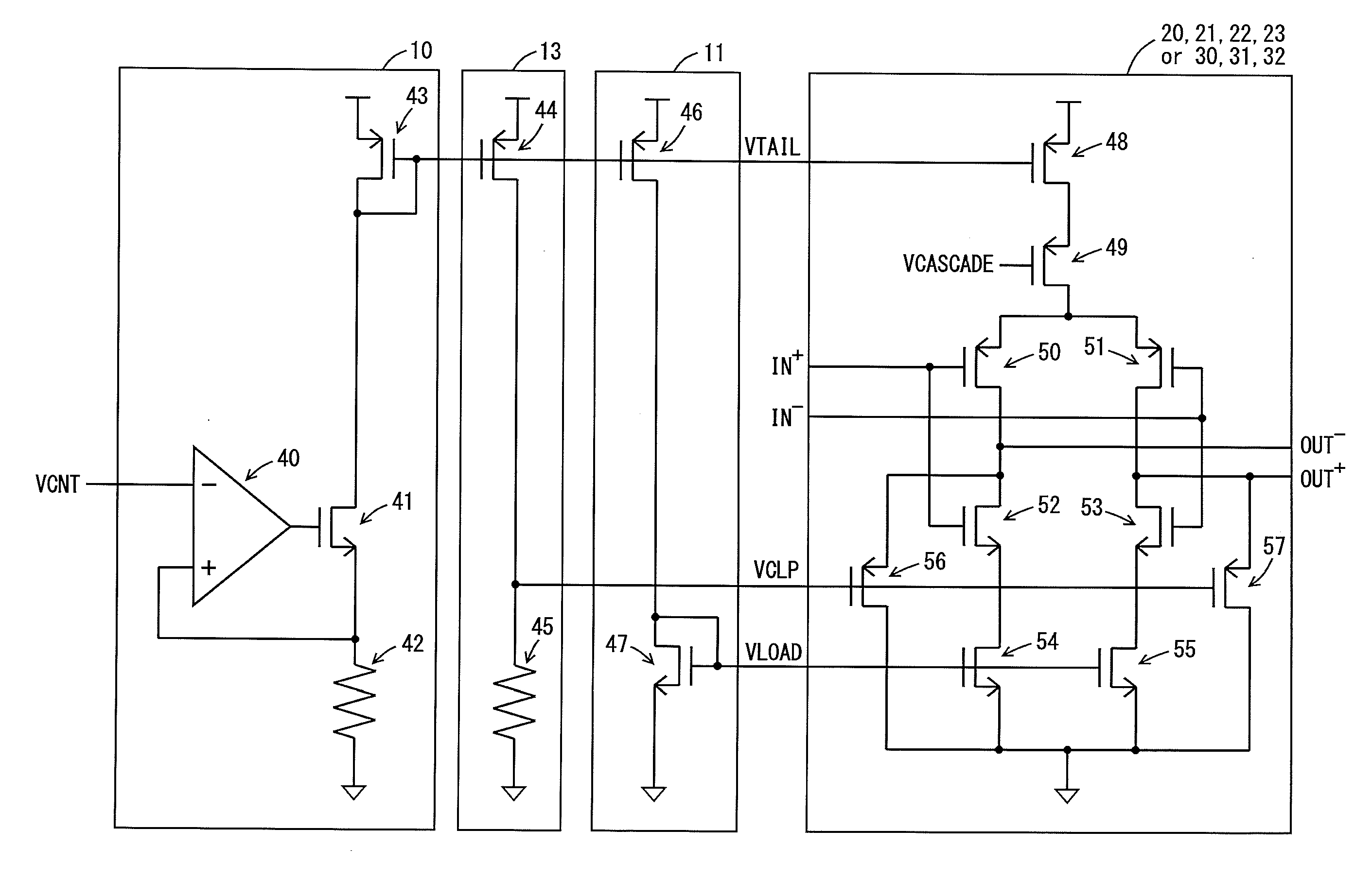
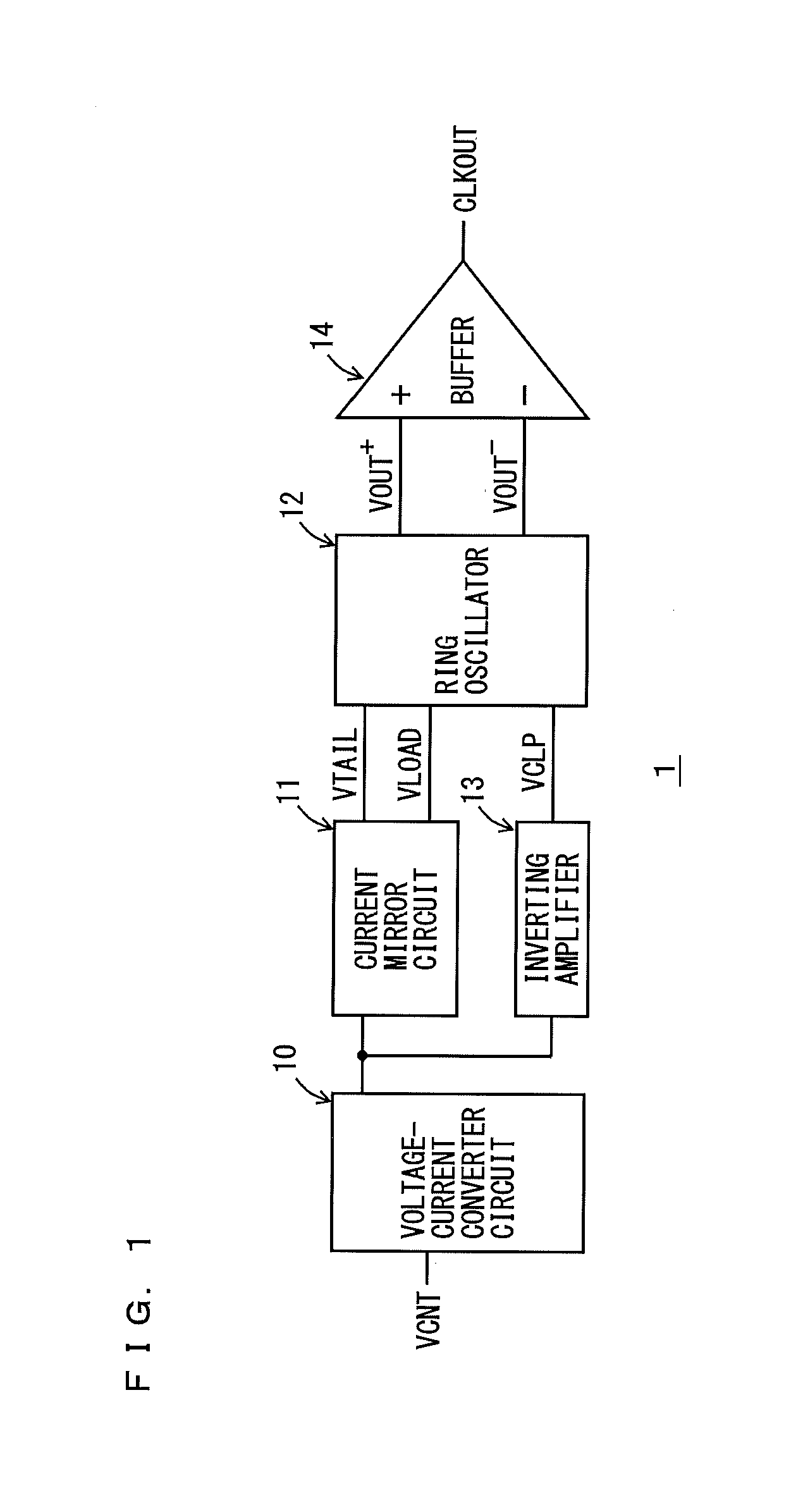
Differential ring oscillator-type voltage control oscillator
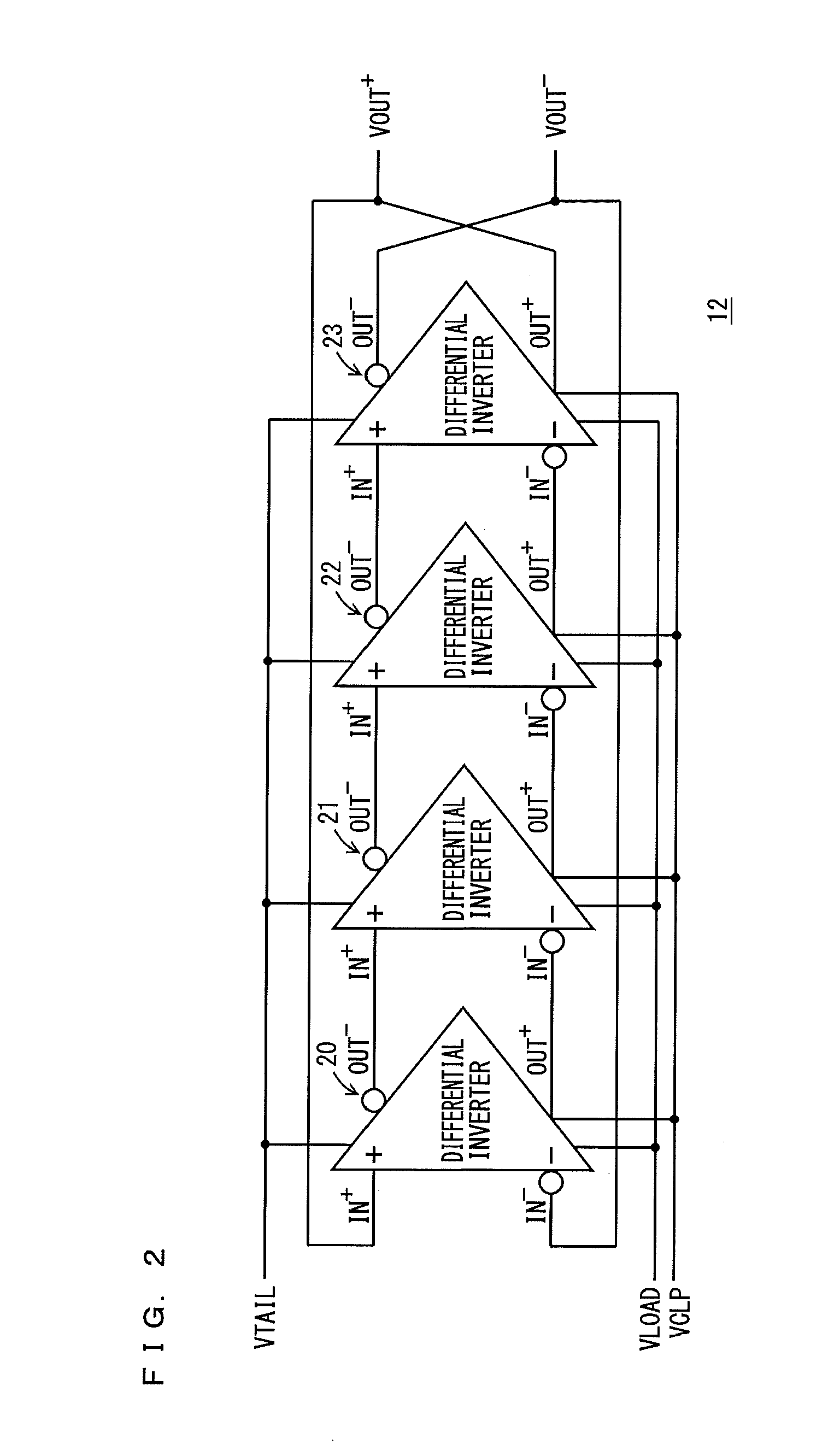
InactiveUS20130015894A1Shortened fall timeShorten rise timePulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsRC oscillatorAmplifier
A voltage control oscillator according to the present invention includes: a voltage-current converter circuit that converts an inputted voltage to a current according to the value of the voltage; a current mirror circuit; a ring oscillator including differential inverters connected in multiple stages; an inverting amplifier; and a buffer. The ring oscillator outputs, from each of the differential inverters, a signal amplitude-limited by a “current converted by the voltage-current converter circuit and the current mirror circuit” and a “voltage applied from the inverting amplifier” and the ring oscillator outputs an oscillatory frequency in response to the output signal.
Owner:KOUYAMA KUNIHIKO
Compact planar antenna assembly
InactiveUS20100001907A1Decreasing volume and size and dimensionIncreased gainSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsWave shapeCoupling
An antenna assembly includes a substrate having a feed line, and an antenna device having two inner radiators electrically coupled to the feed line and disposed at a distance from each other, and two outer radiators electrically coupled to the middle portions of the inner radiators for decreasing the dimension of the antenna assembly and for increasing the gain of the antenna assembly, the inner radiators each include an antenna segment disposed at a distance parallel to the inner radiators and disposed on an outer portion of the inner radiators, the inner radiators are electrically coupled to the outer radiators with a coupling element which includes either a zigzag shape or a wave-shaped structure.
Owner:JOYMAX ELECTRONICS CO LTD
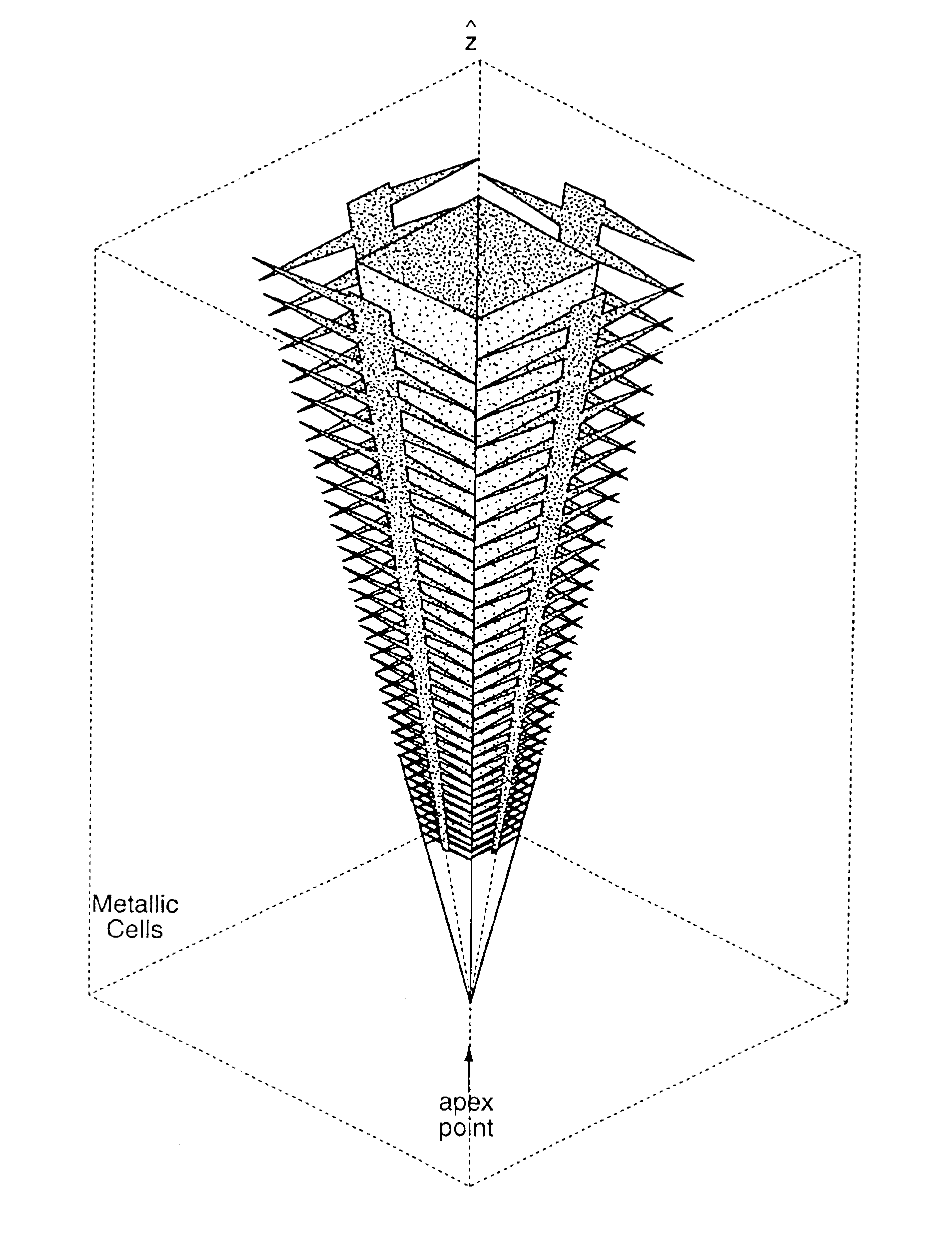
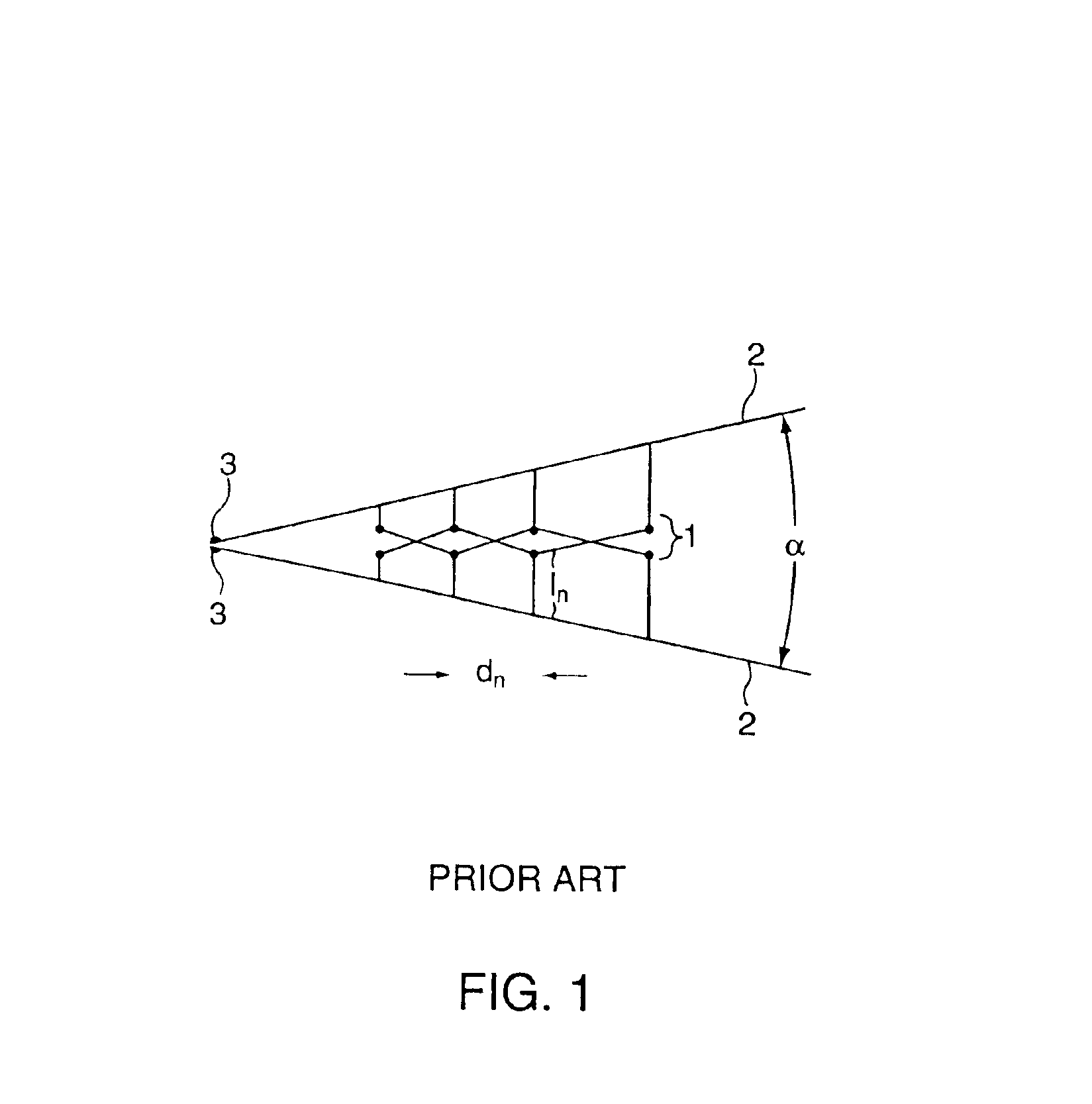
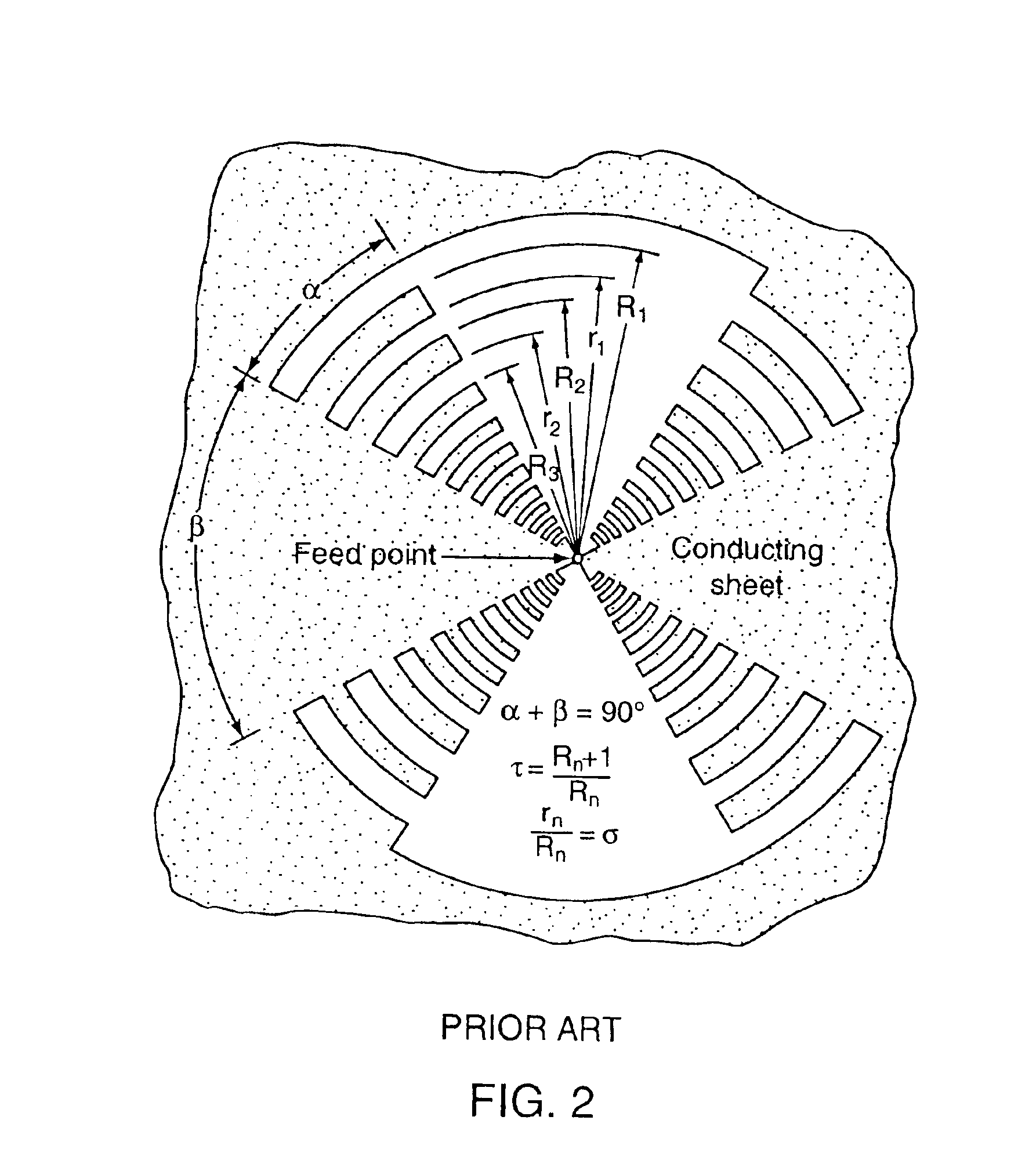
Log-periodic antenna
InactiveUS6952189B2Decreased cross-polarization couplingSimple designLogperiodic antennasAntenna arraysEngineeringElectromagnetic shielding
A self-similar log-periodic antenna is described comprising a plurality of substantially triangular conductive elements, 4, symmetrically disposed in either planar or curved configurations about a central conductive boom to form an antenna arm. Two or more antenna arms are assembled into an antenna by symmetrically locating such antenna arms substantially in the shape of a pyramid (for planar arms) or in a conical shape (for curved arms). Some embodiments include a conductive fin, 5, to reduce cross-polarization coupling between antenna arms. Some embodiments include a grounded conductive shield on the interior of the antenna providing electromagnetic shielding for the interior region of the antenna while preserving the self-similar geometry of the antenna and shield combination.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
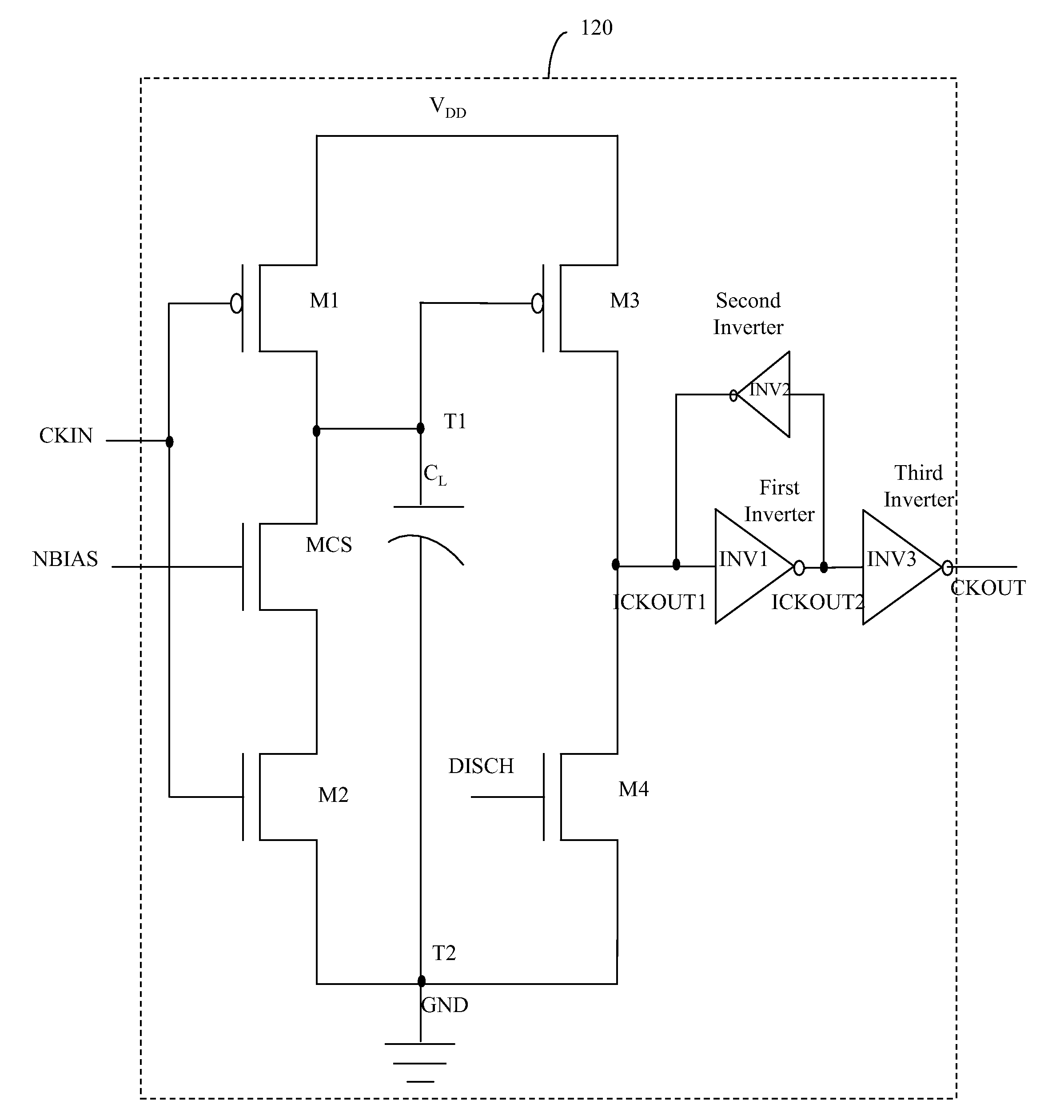
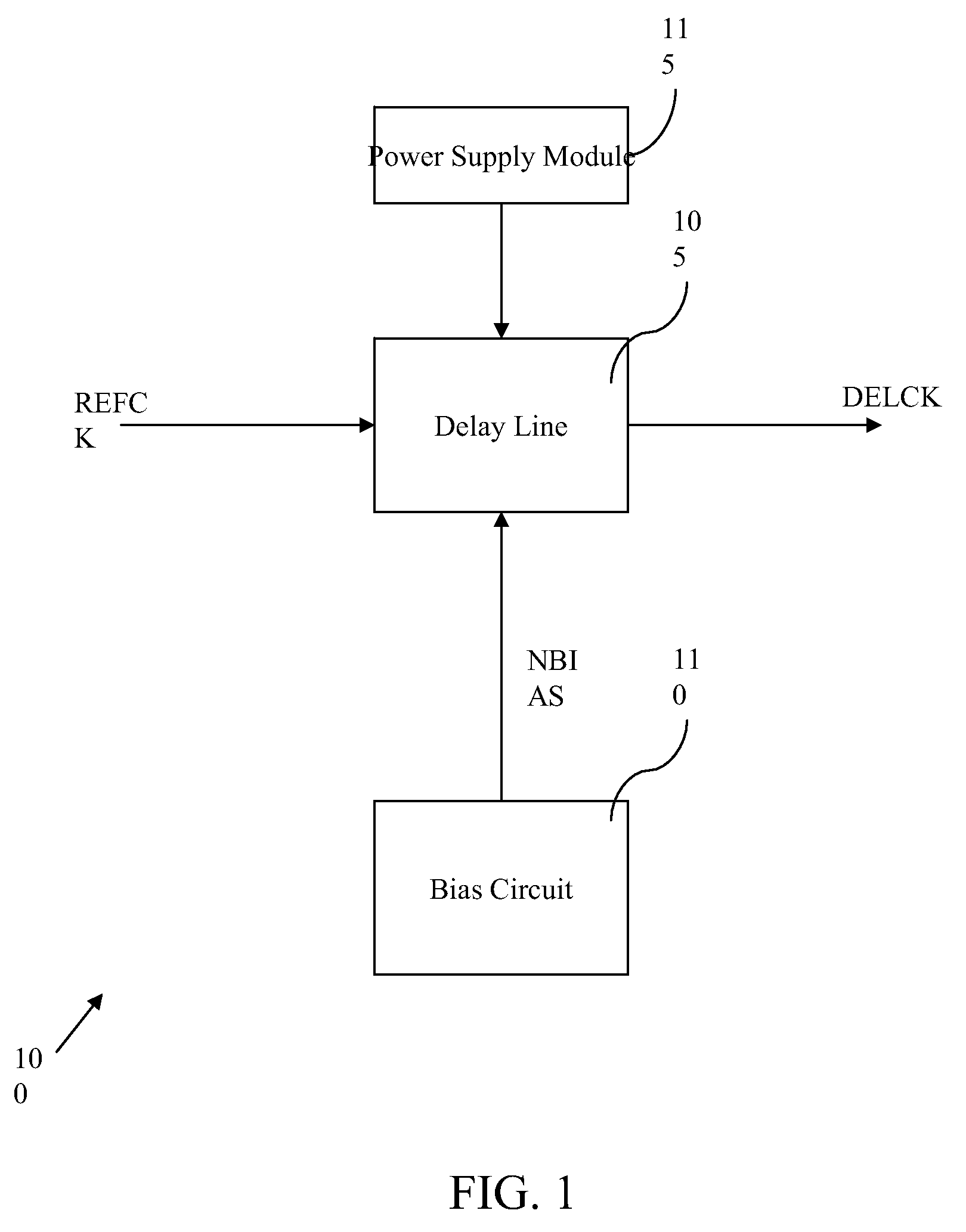
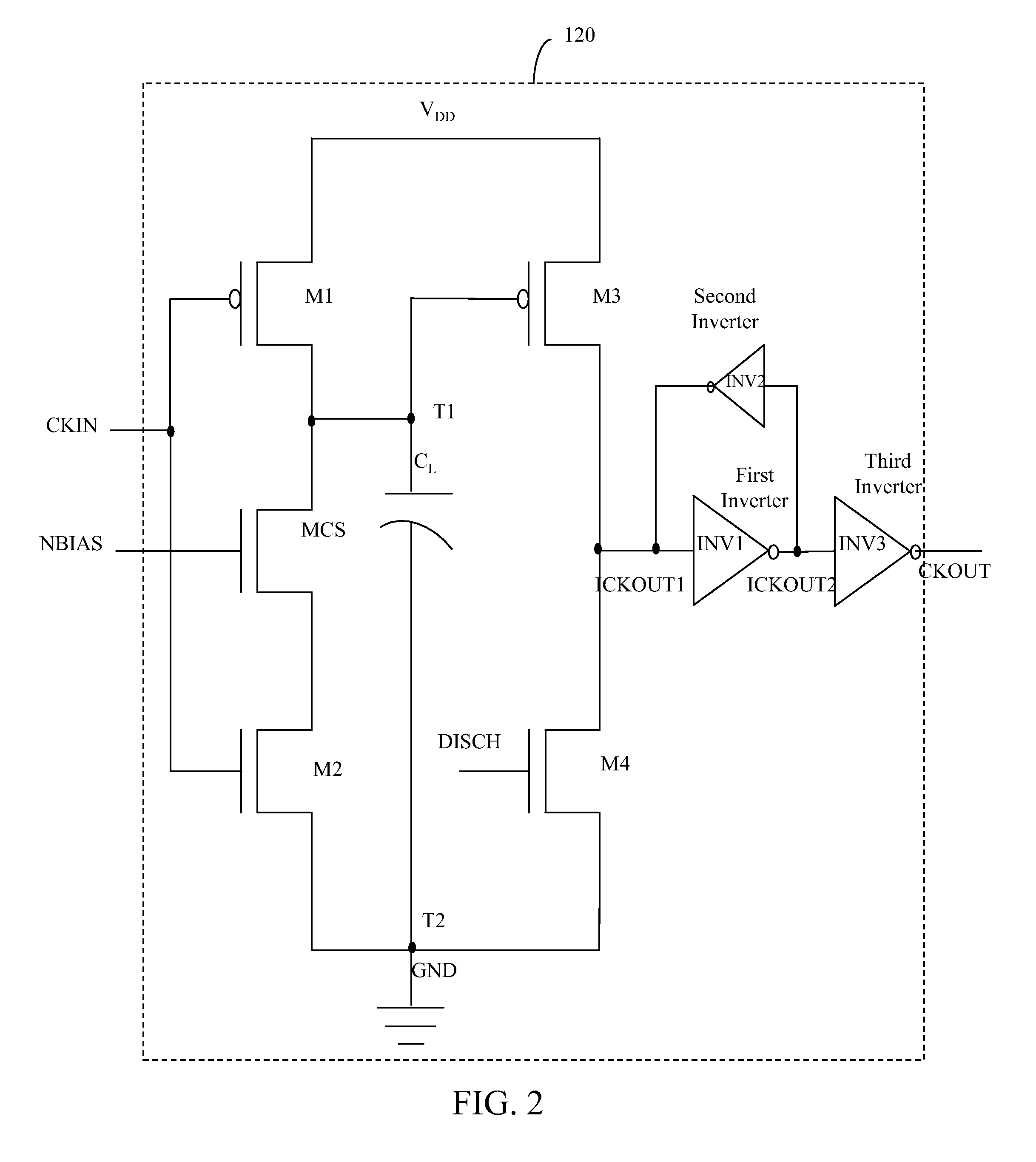
Delay line with delay cells having improved gain and in built duty cycle control and method thereof
InactiveUS20070285144A1Increased gainReduced duty cycle distortionPulse manipulationTime-delay networksDuty cycle distortionCurrent source
A delay line including a sequence of identical delay cells with improved gain and in built duty cycle distortion control and a method thereof is disclosed. Each delay cell of the sequence includes a current source, four transistors, and a load capacitor. A gate of the current source receives a voltage bias that controls a delay of the delay cell. A drain of the first transistor is connected to the drain of the current source. The first and second transistor gates receive an input clock signal. The second transistor drain is connected to the source of the current source. The third transistor gate and the load capacitor are also connected to the drain of the current source. The fourth transistor drain is connected to the third transistor drain. The fourth transistor gate is coupled to an output of a second consecutive delay cell for duty cycle distortion control.
Owner:COSMIC CIRCUITS PRIVATE LIMITED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com