Patents
Literature
41results about How to "Image is often very small" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
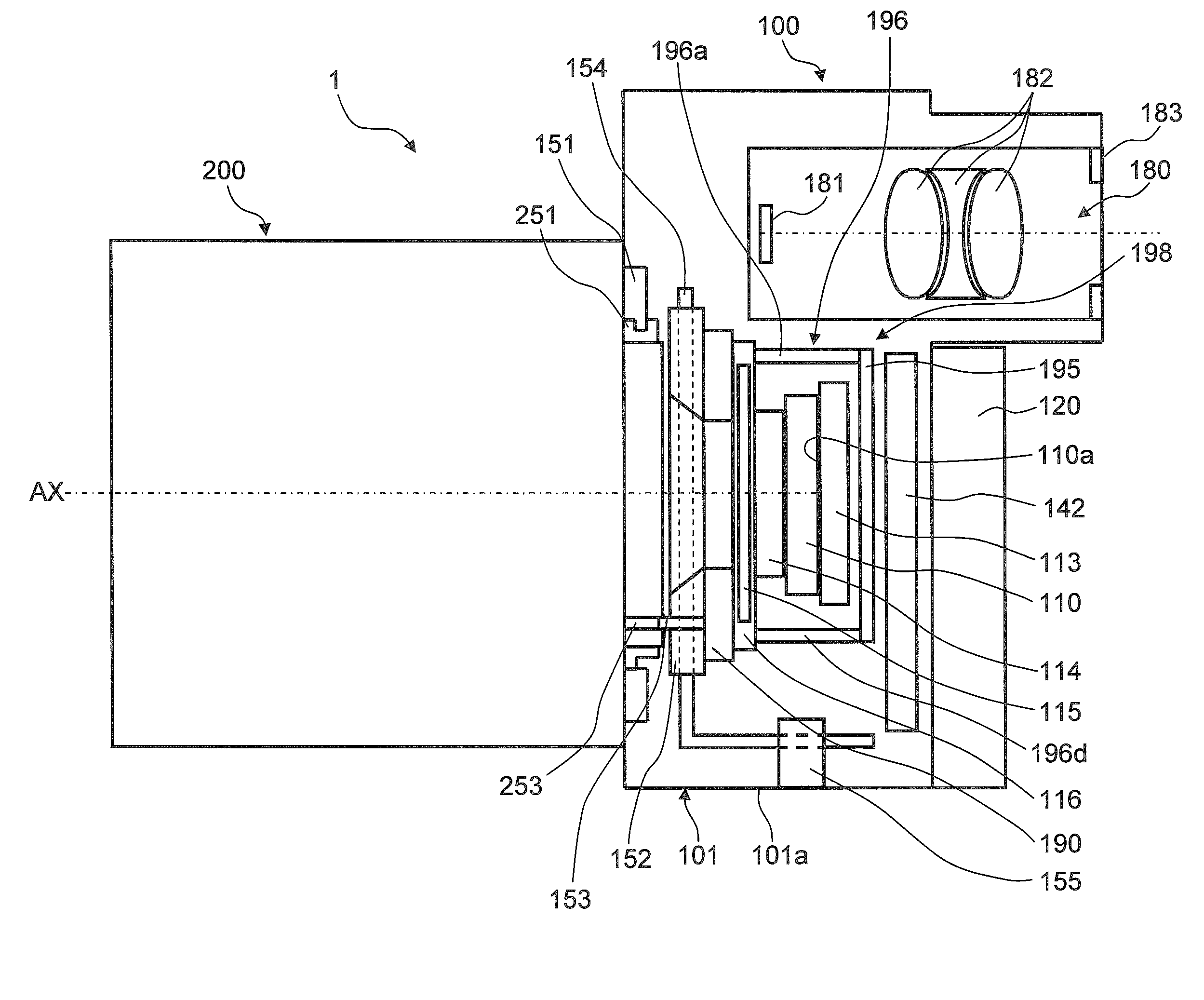
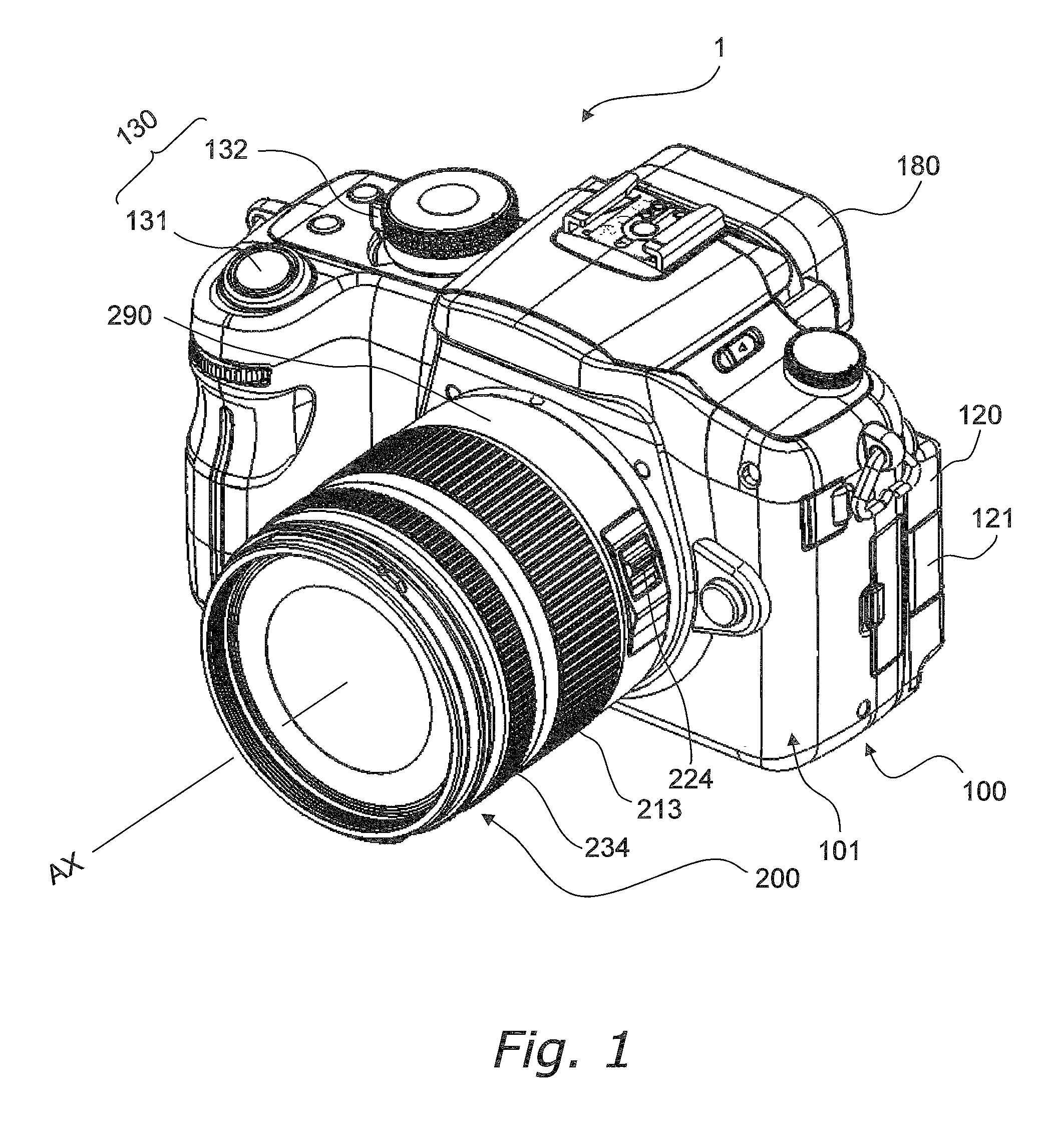
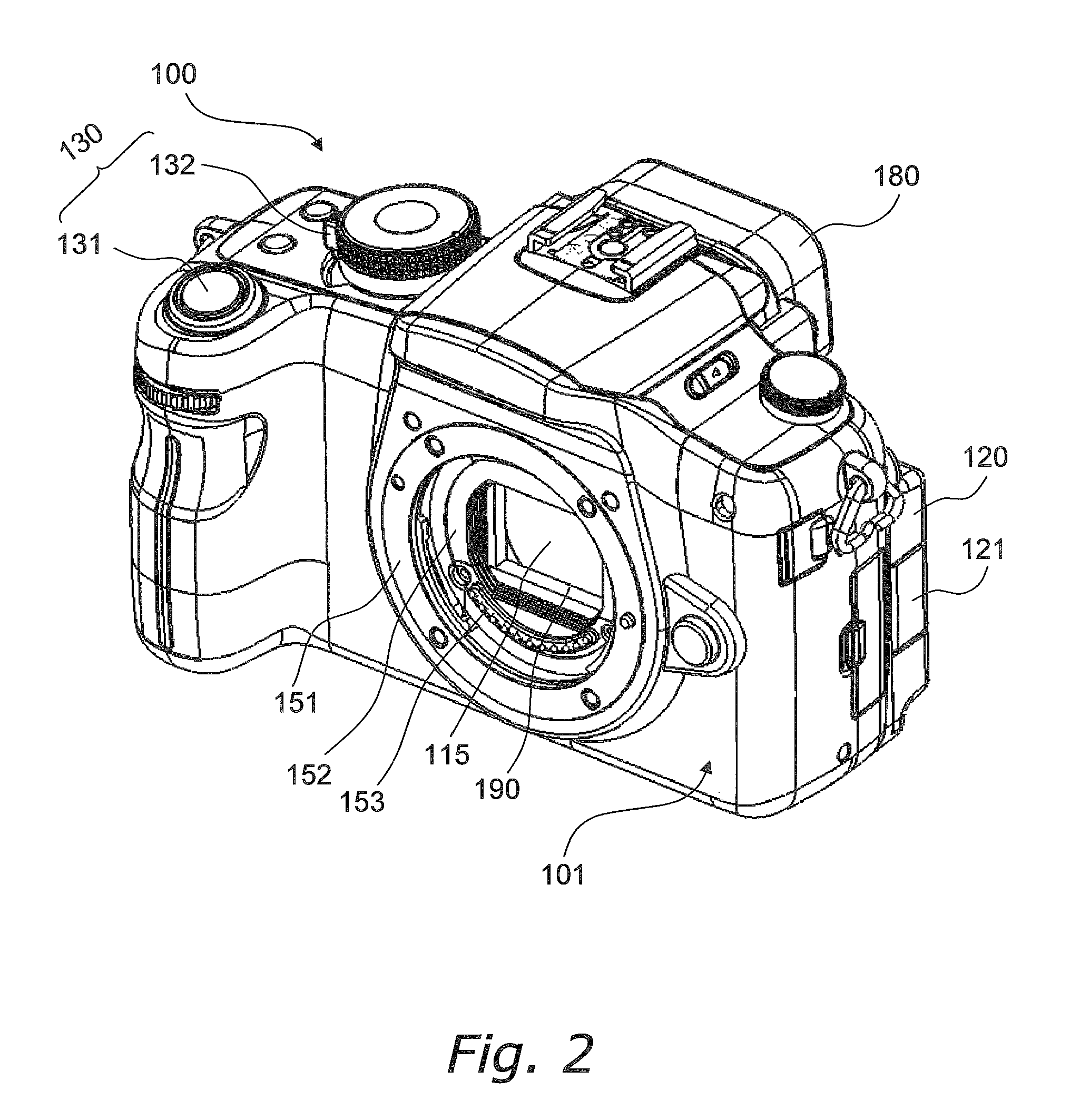
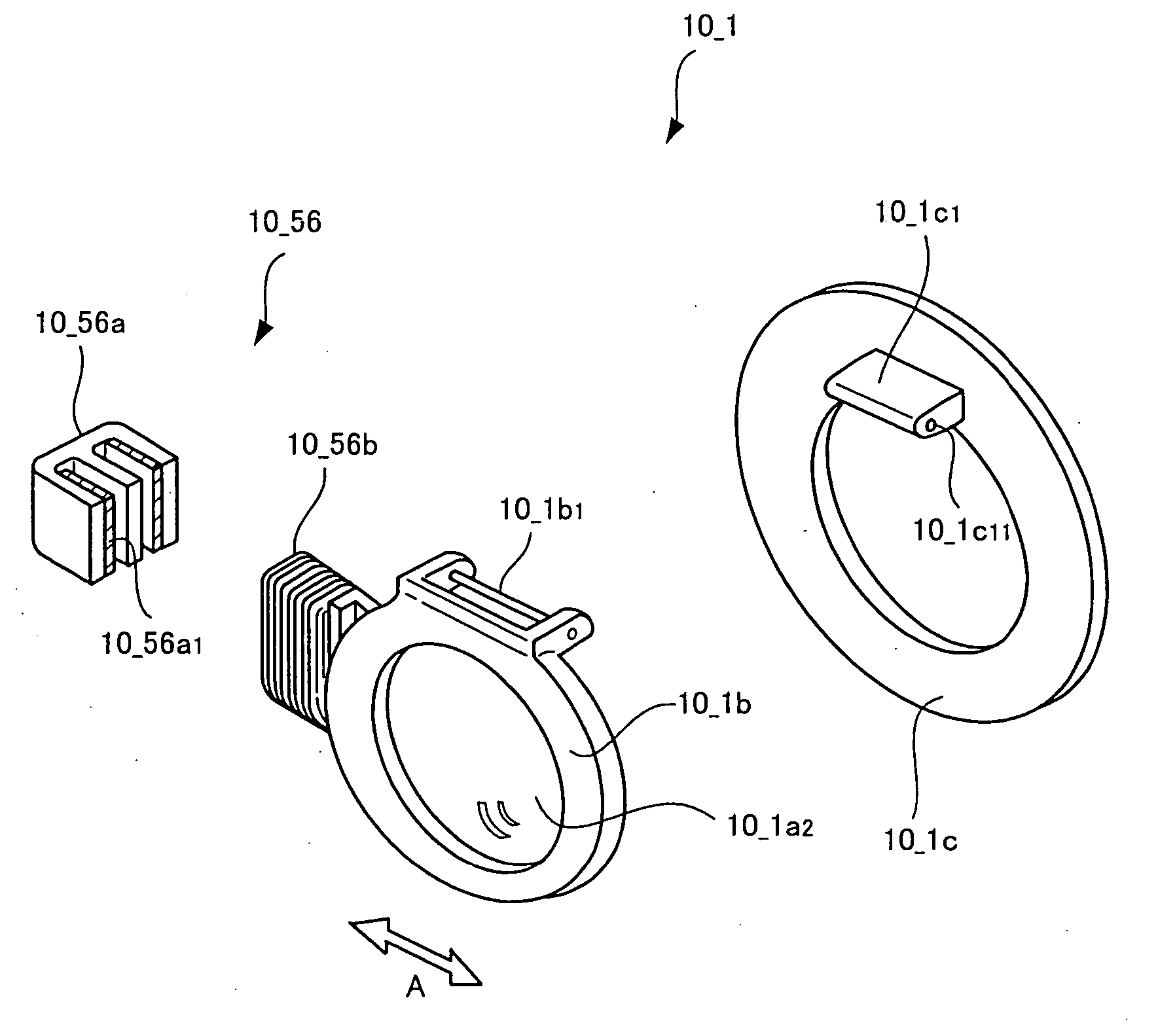
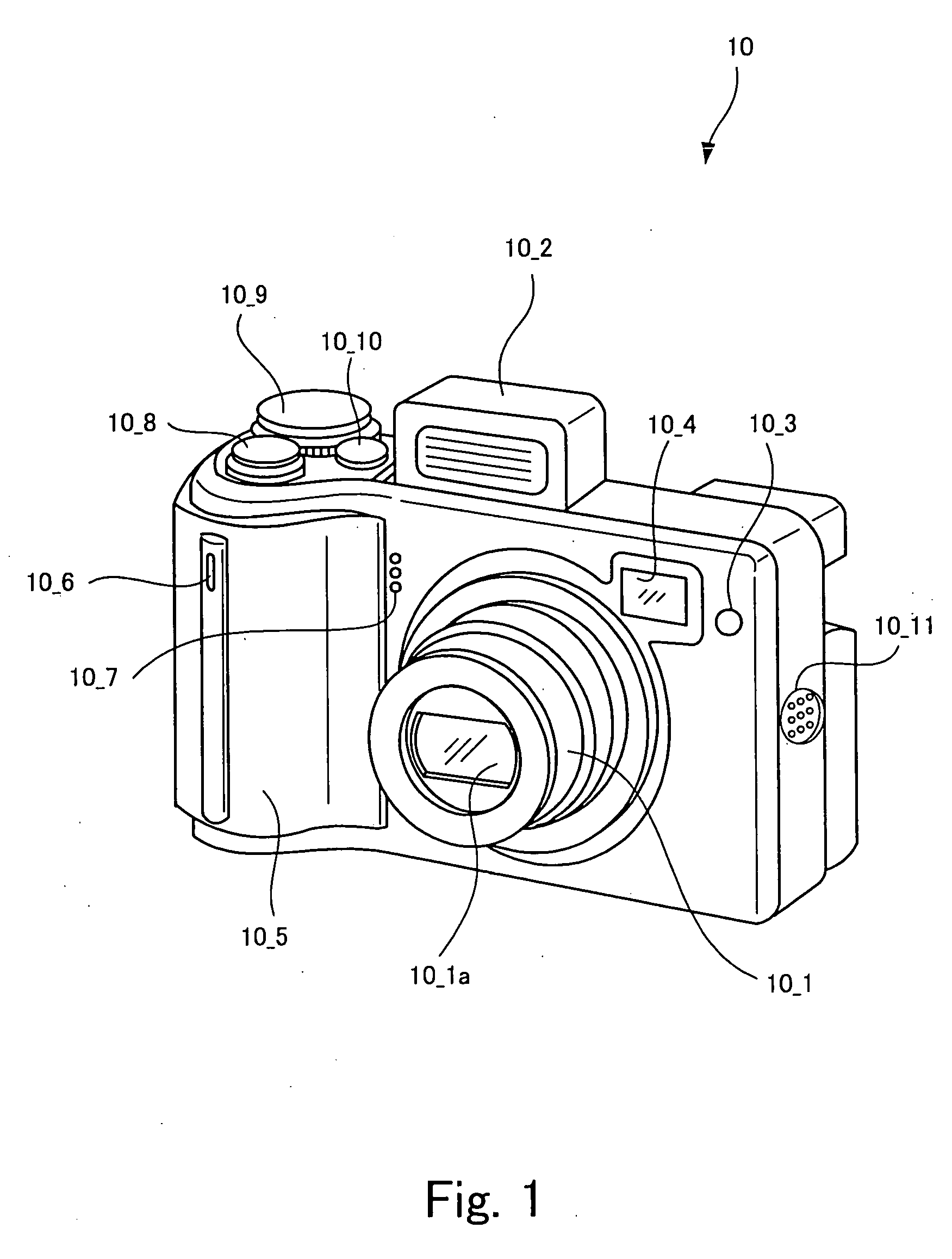
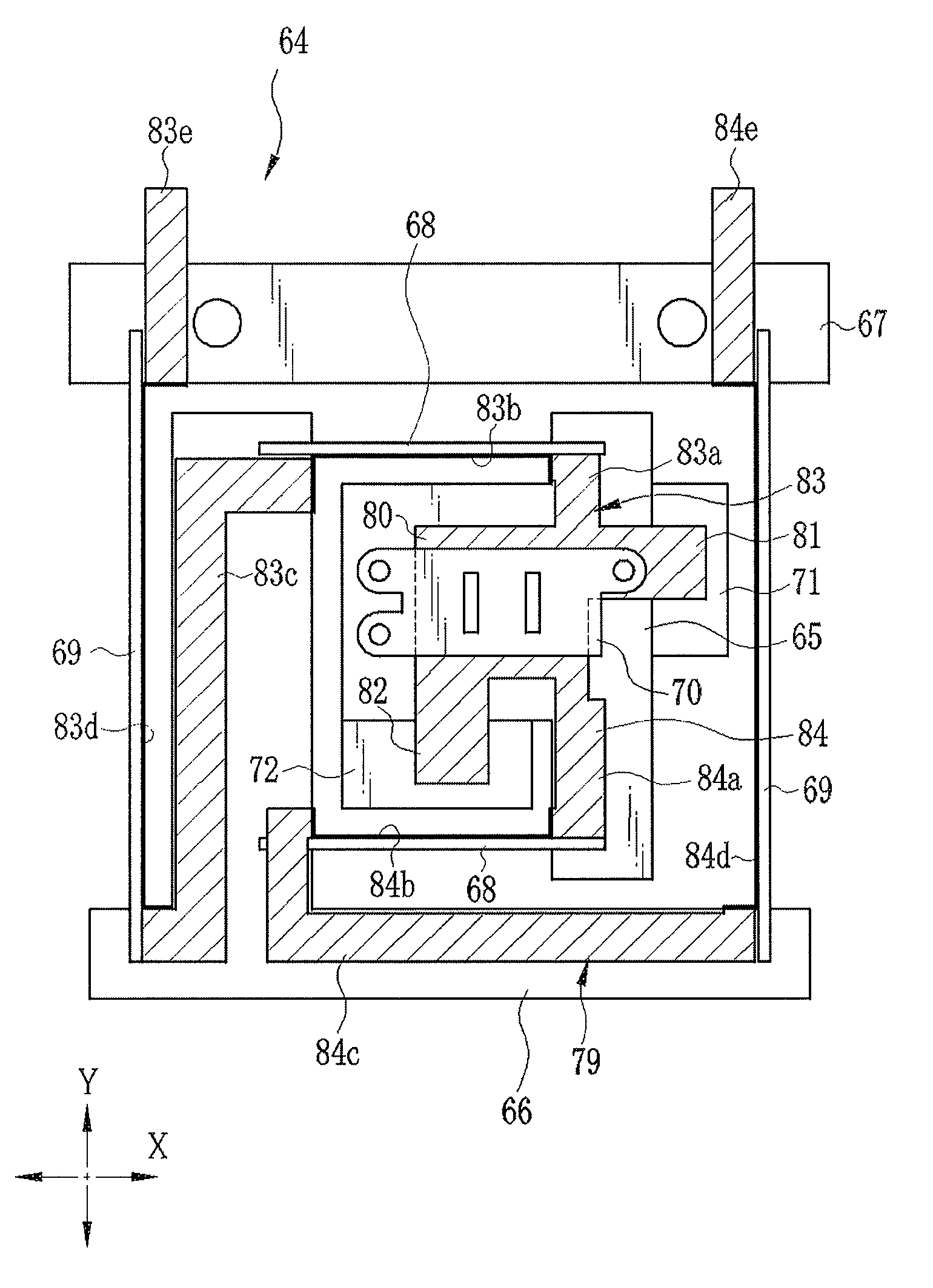
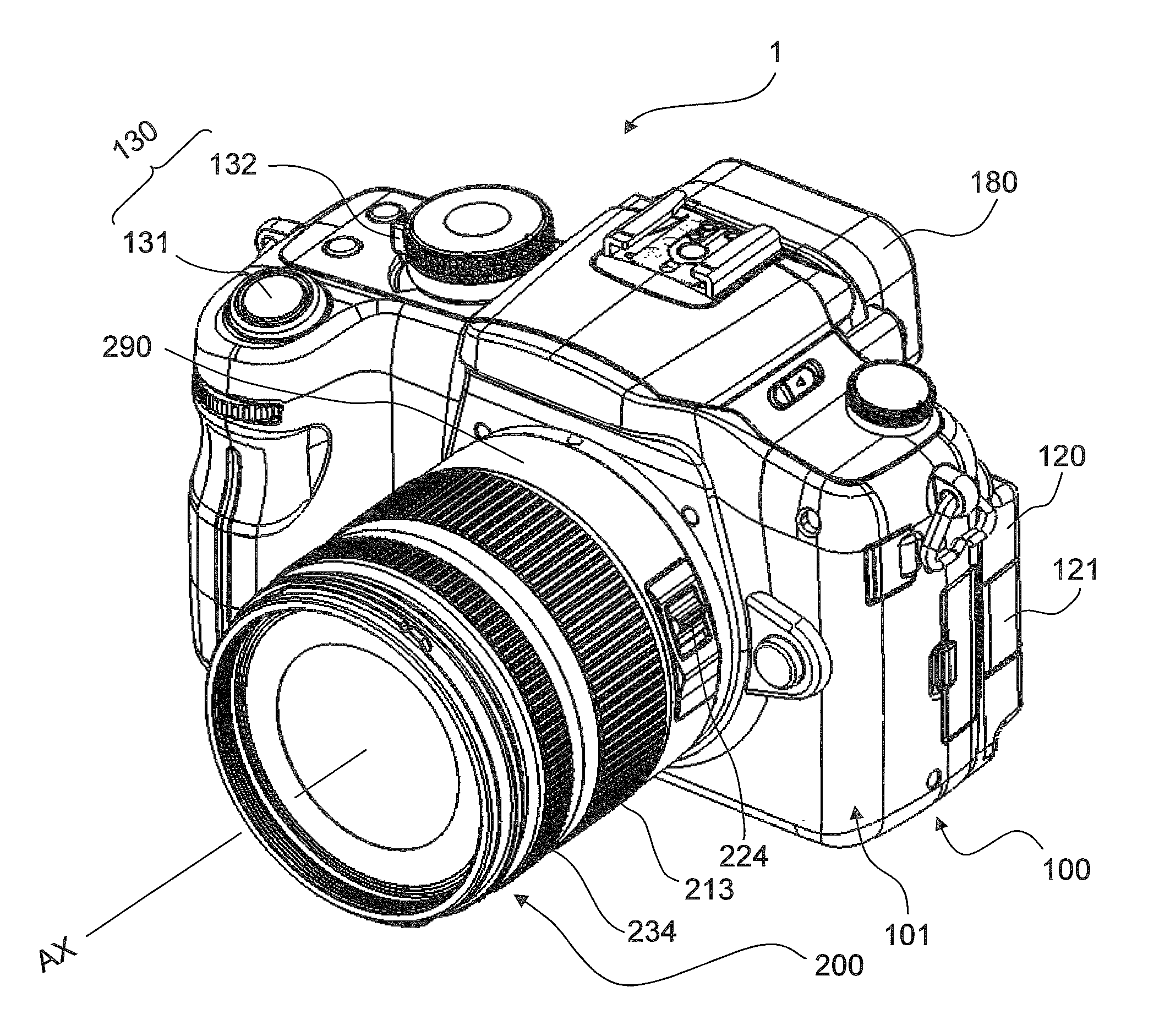
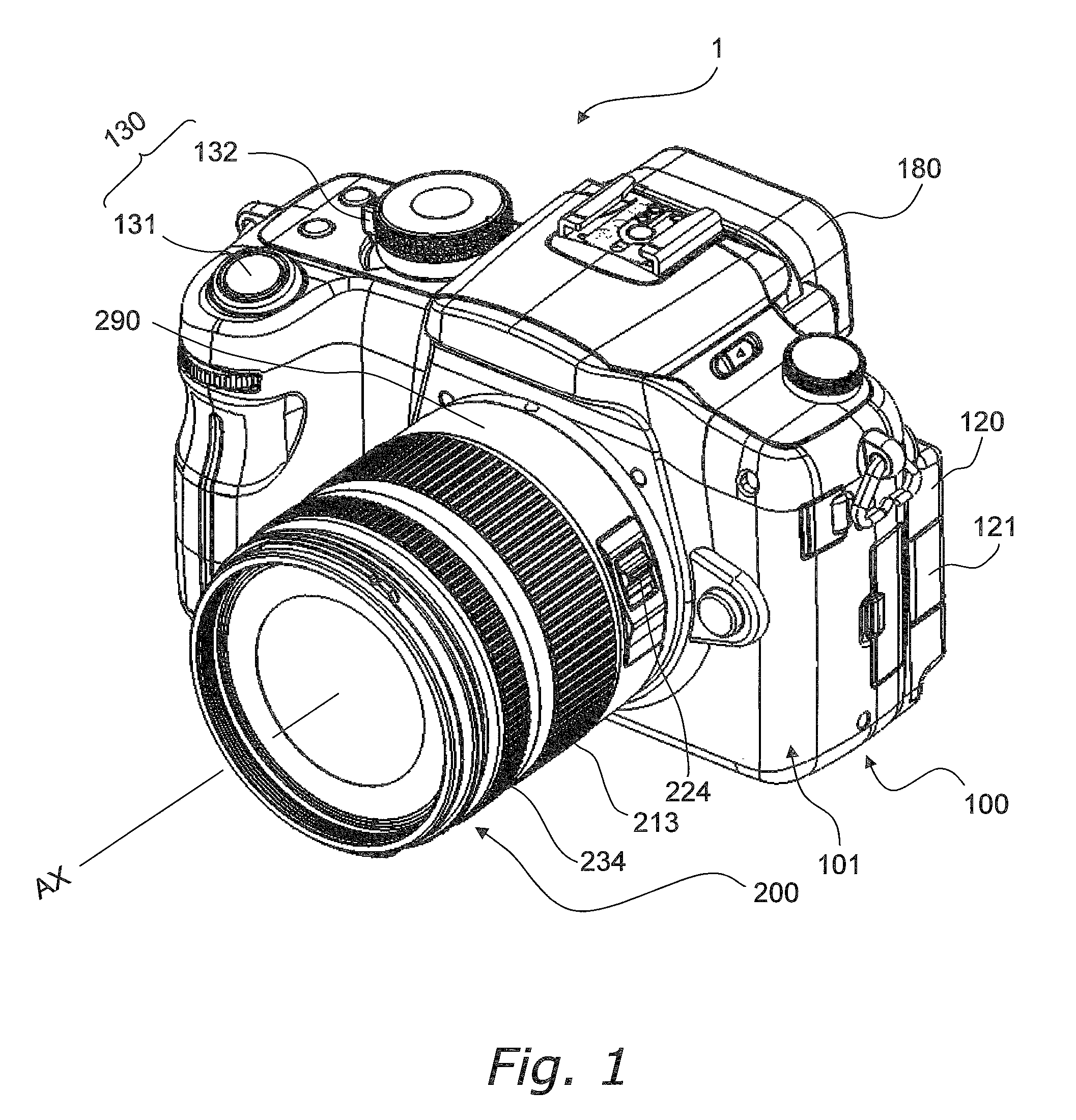
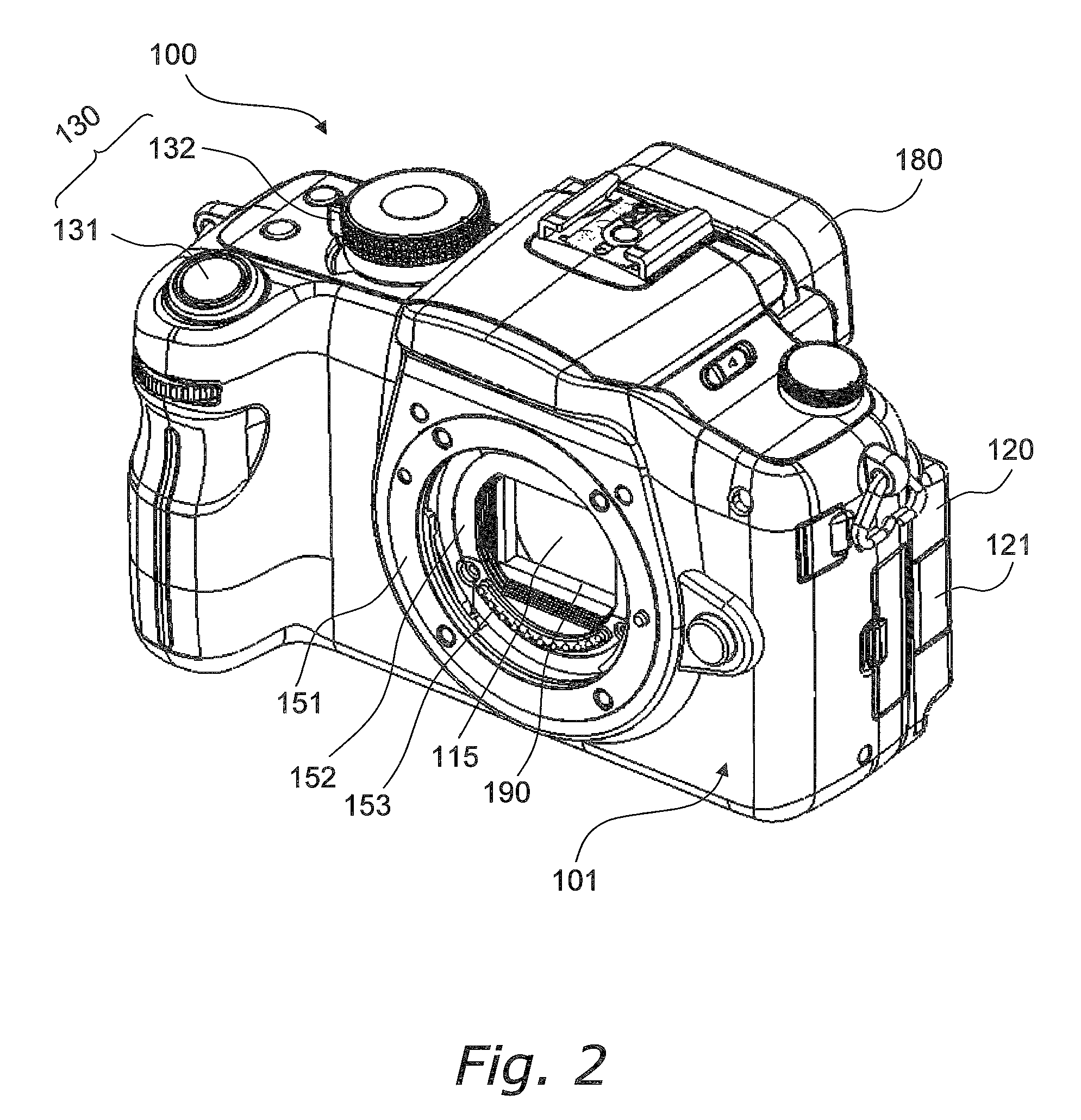
Image stabilizer and optical instrument therewith
ActiveUS20100165131A1Eliminate harmful effect of sagEliminate reaction forceTelevision system detailsPrintersHand heldEngineering
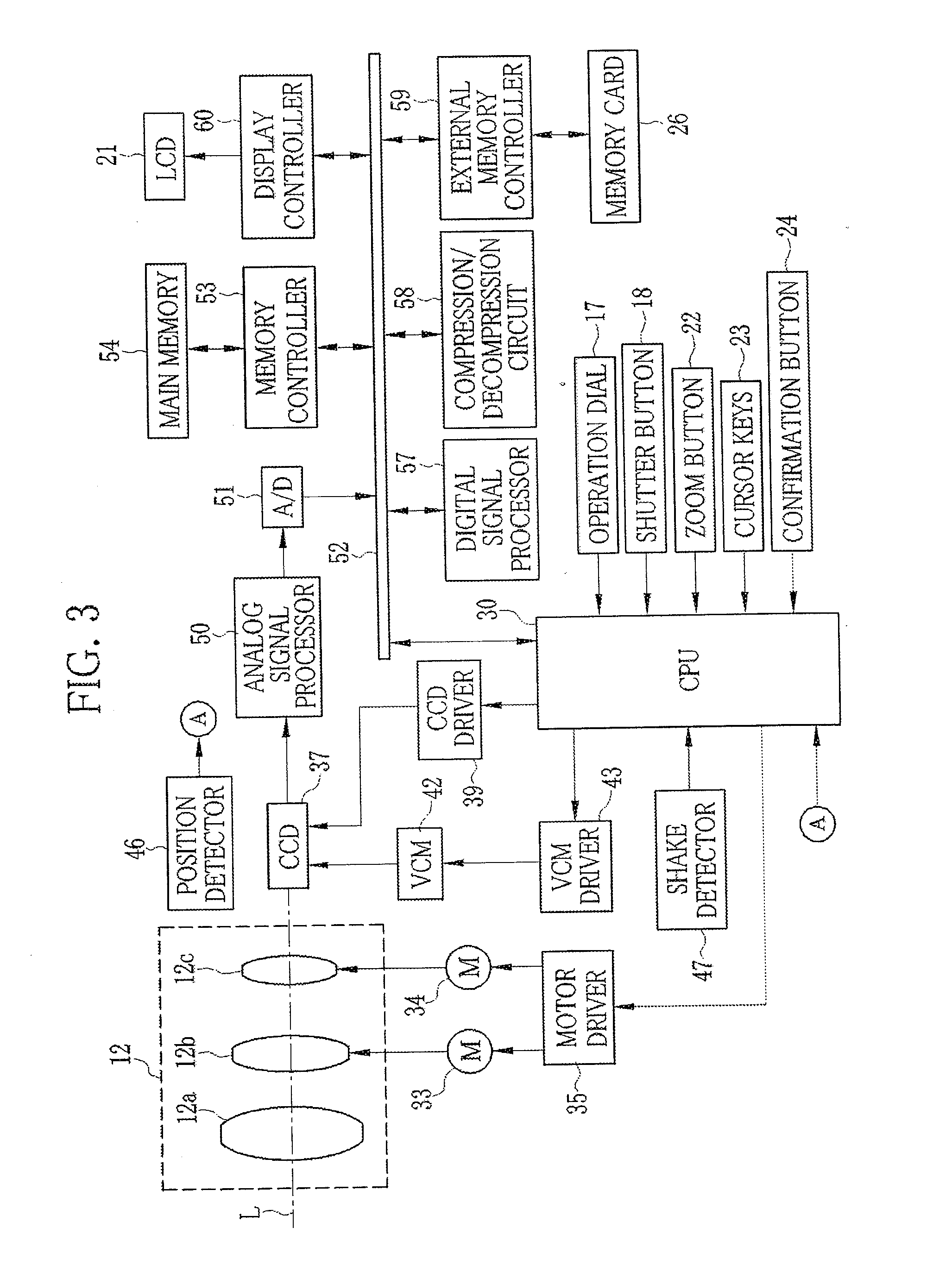
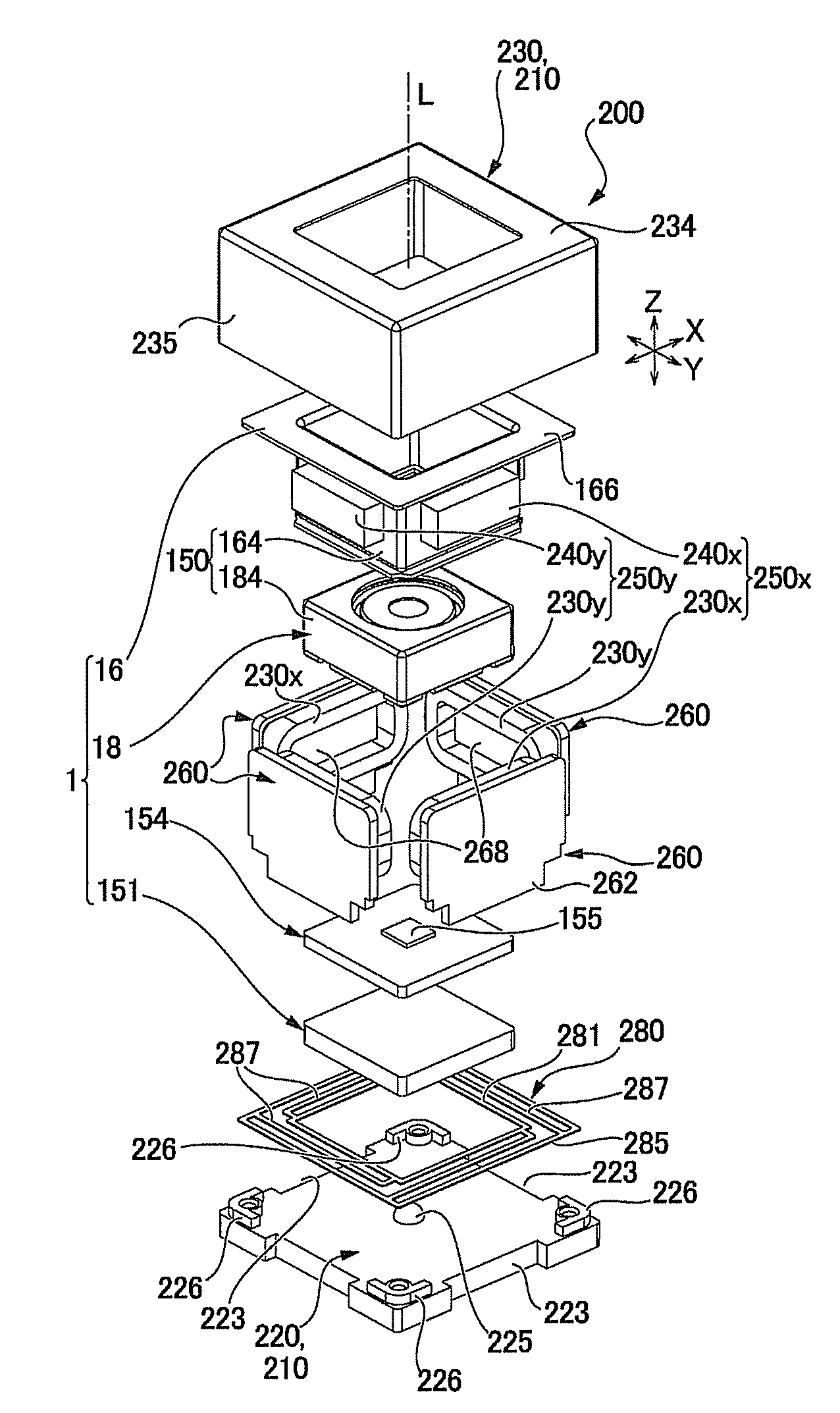
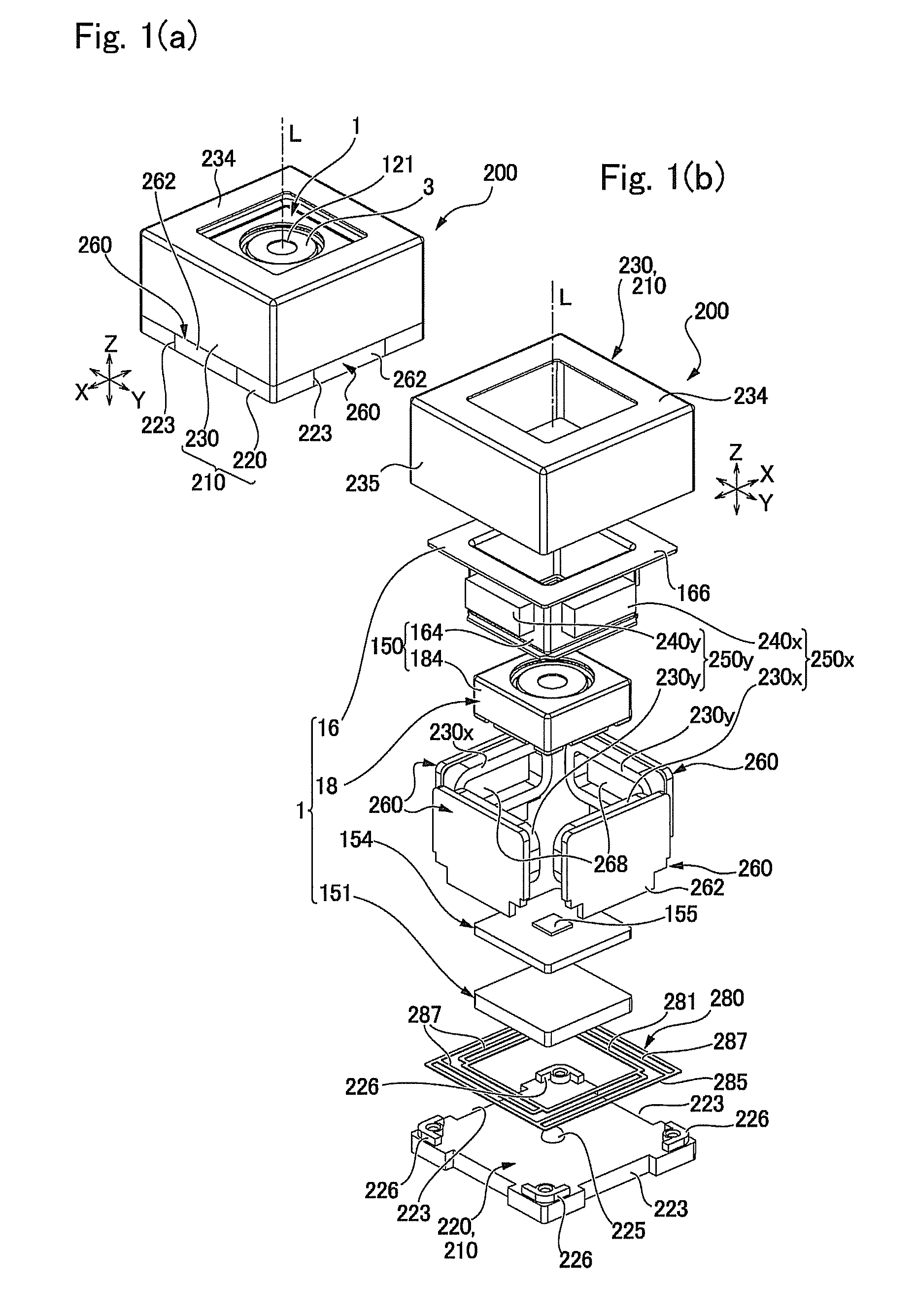
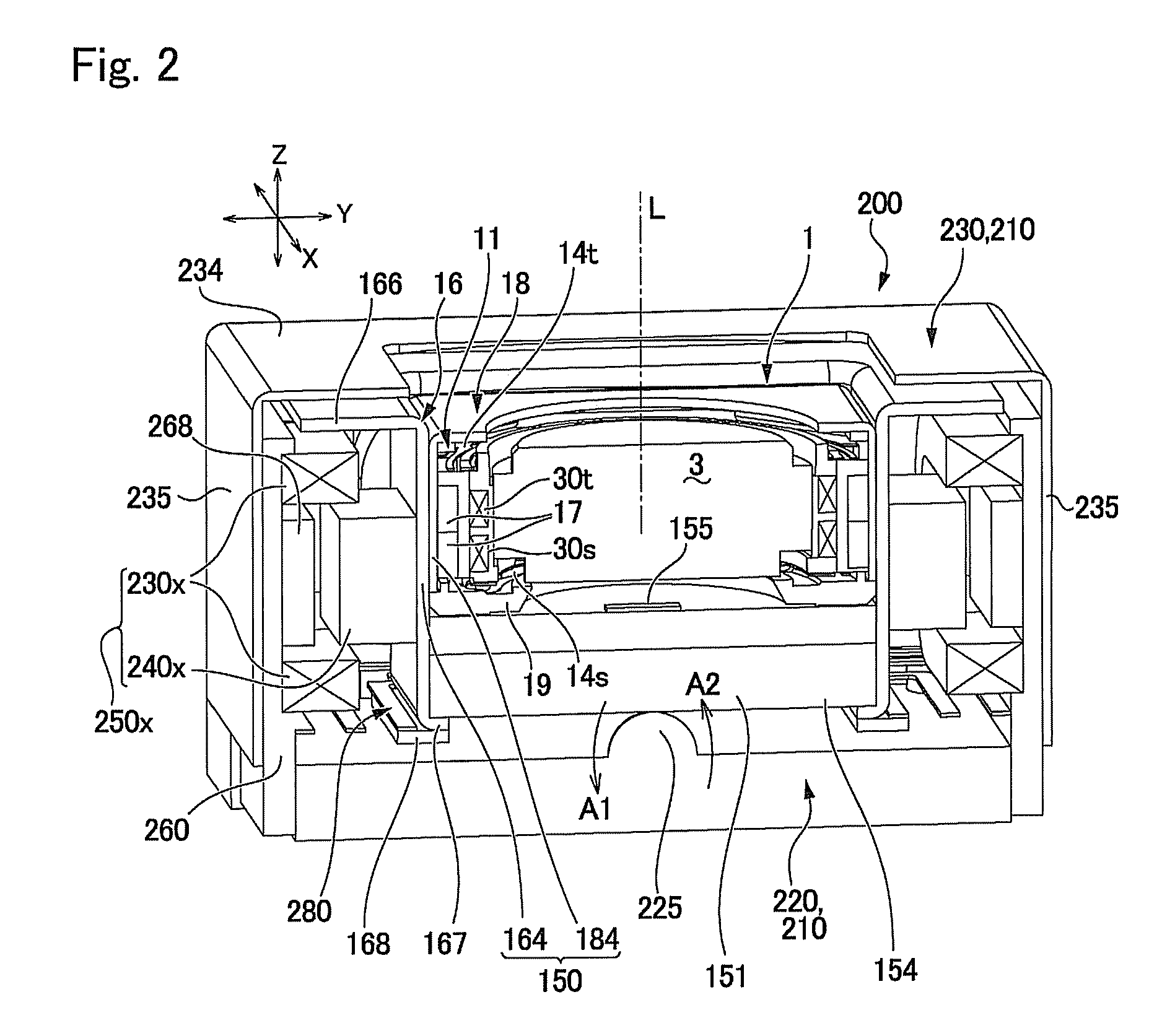
An image stabilizer has a base block, an inner frame for holding a CCD, an outer frame, a pair of horizontal leaf springs, a pair of vertical leaf springs, voice coil motors (VCMs) and a flexible printed circuit (FPC). Upon a shake of a digital still camera due to hand-held shooting, the VCMs shift the inner or outer frame while bending the horizontal or vertical leaf springs so that the CCD is shifted to counteract the camera shake. The FPC connected to the CCD and the VCMs is routed from the inner frame, through the horizontal leaf spring, the outer frame and the vertical leaf spring, and pulled out above the base block. The FPC is glued to the horizontal and vertical leaf springs, and elastically bent together with the horizontal and vertical leaf springs.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
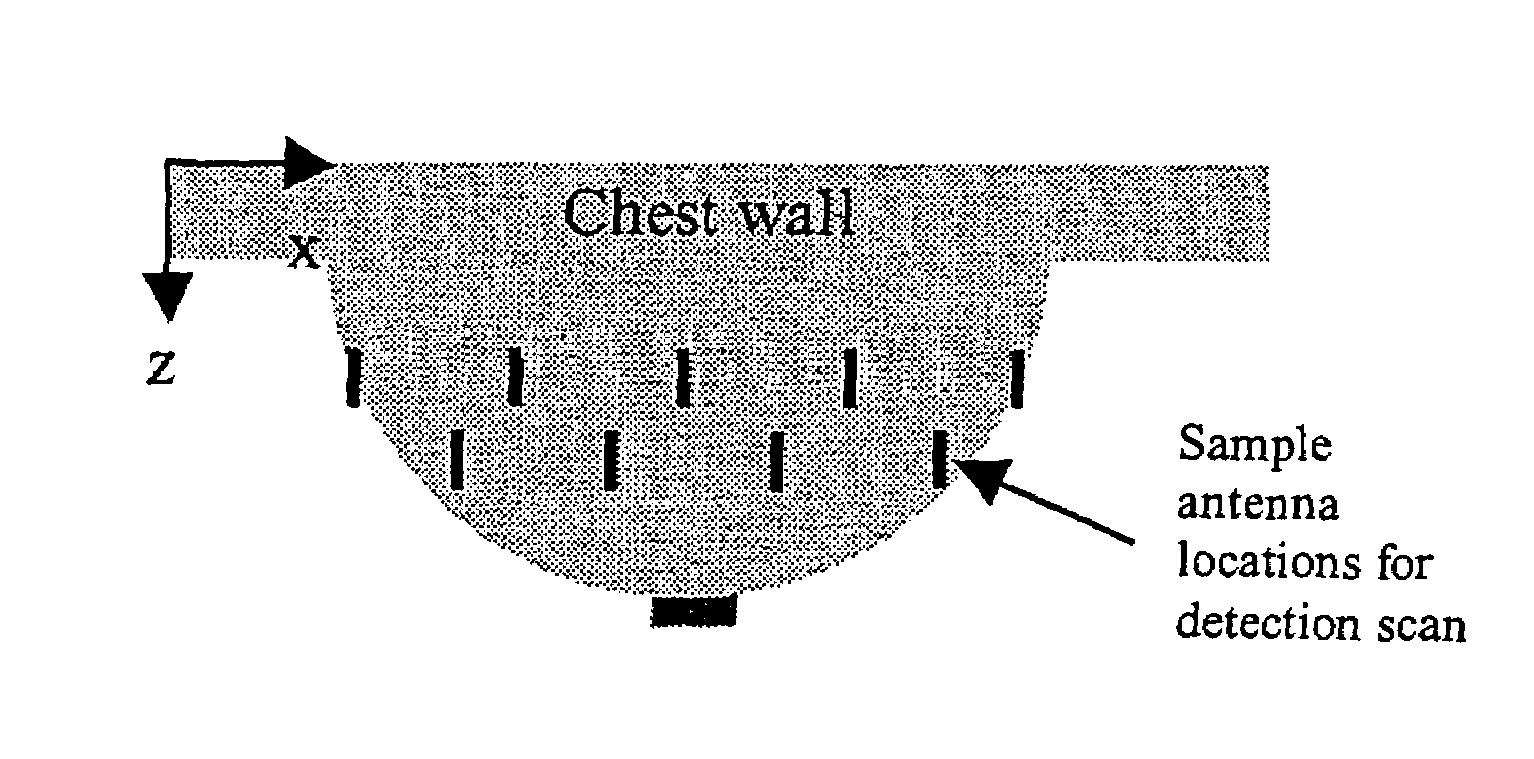
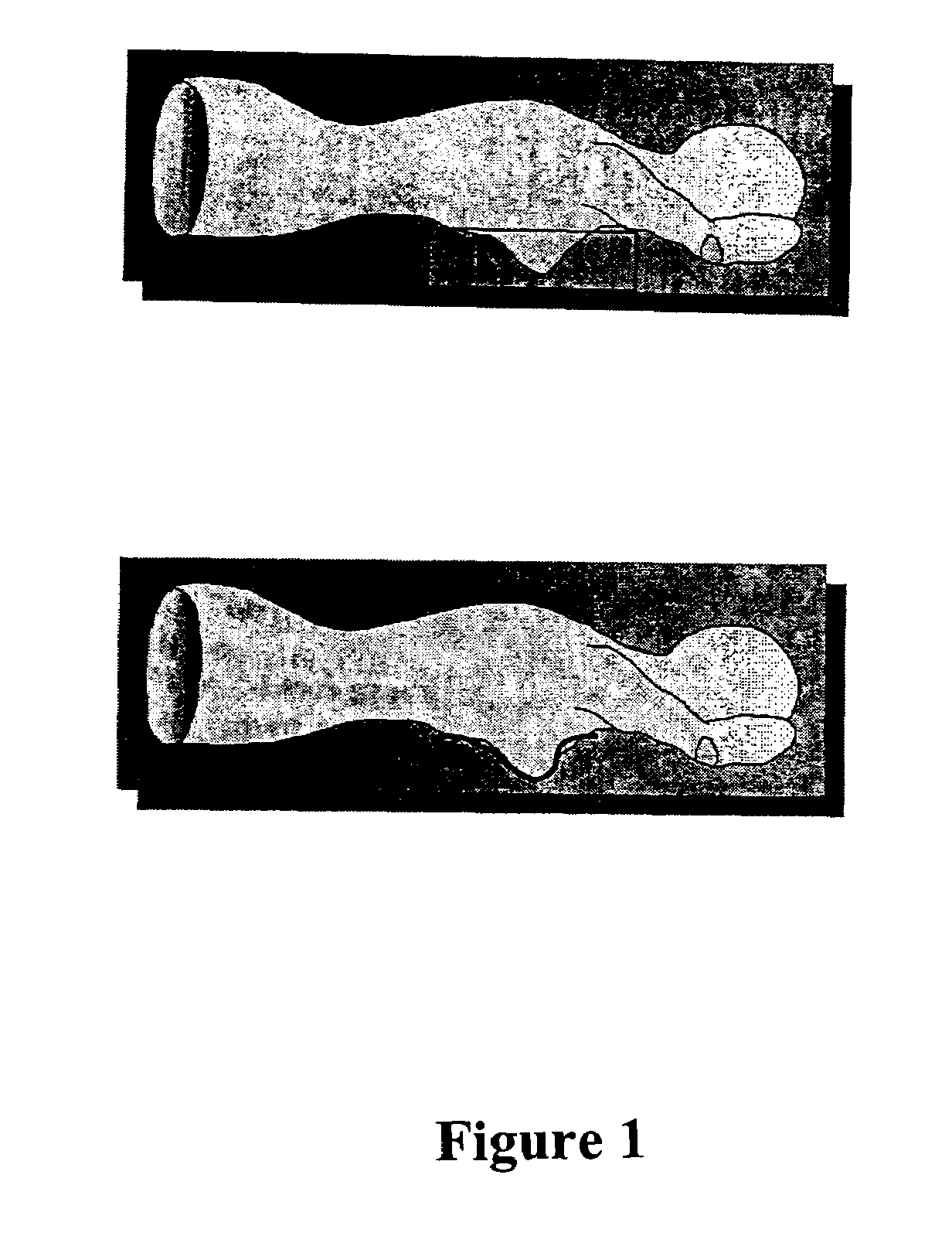
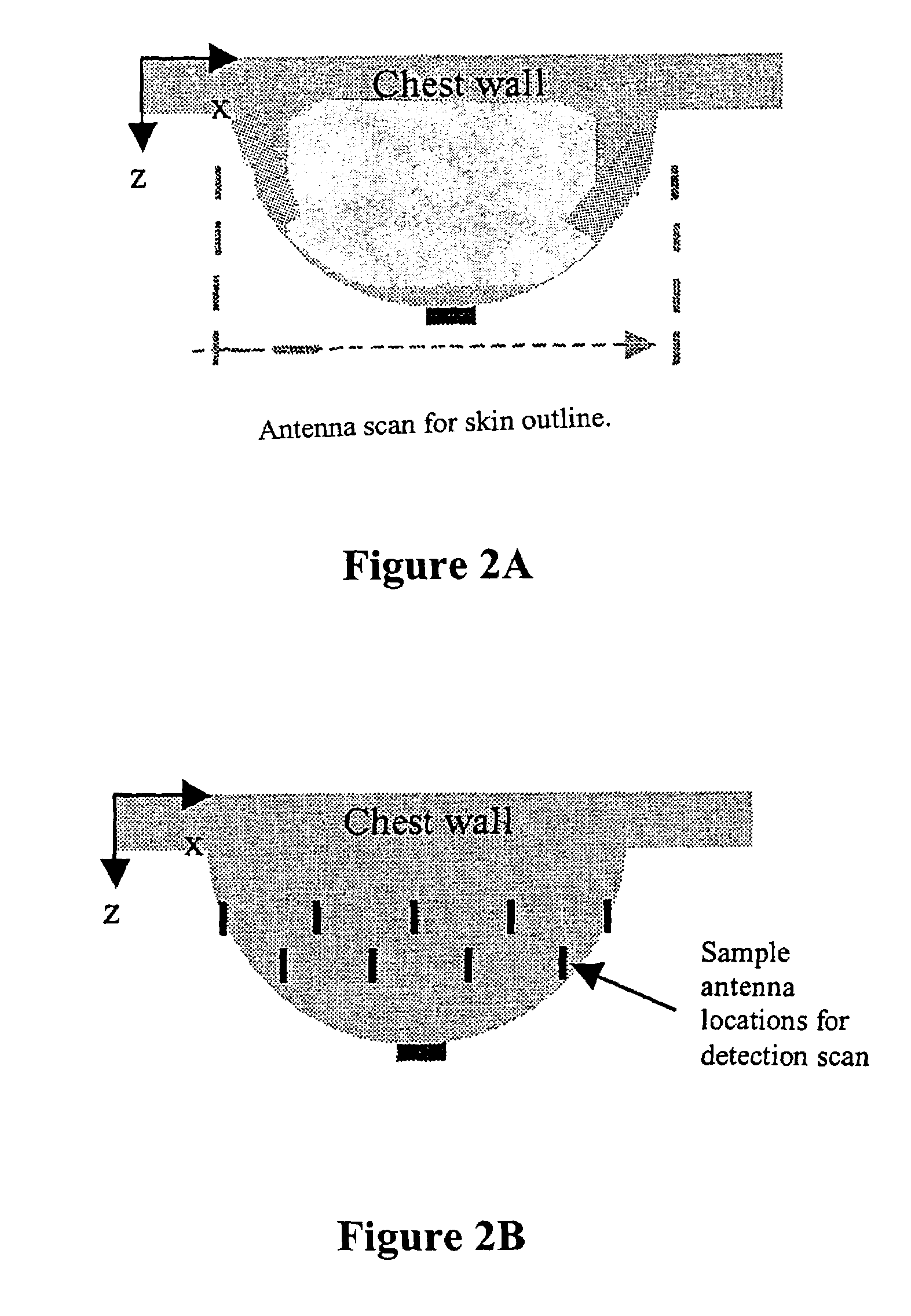
Tissue sensing adaptive radar imaging for breast tumor detection
InactiveUS7454242B2Big imageImage is often very smallElectrotherapyPolarisation/directional diversityMicrowaveRadar imaging
Owner:UTI LLP
System and method for custom-polarized photolithography illumination
ActiveUS20050128458A1Image is often very smallLarge spacingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolarising elementsPolarizerPhotolithography
In one embodiment, a system for custom-polarized photolithography illumination includes an illuminator operable to generate an illumination pattern of light, a polarizer unit operable to variably polarize the light, and a mask pattern defining photolithographic pattern features in two dimensions. The mask pattern is associated with a mask capable of transmitting at least a portion of the variably polarized light through the mask pattern.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Imaging lens and imaging apparatus
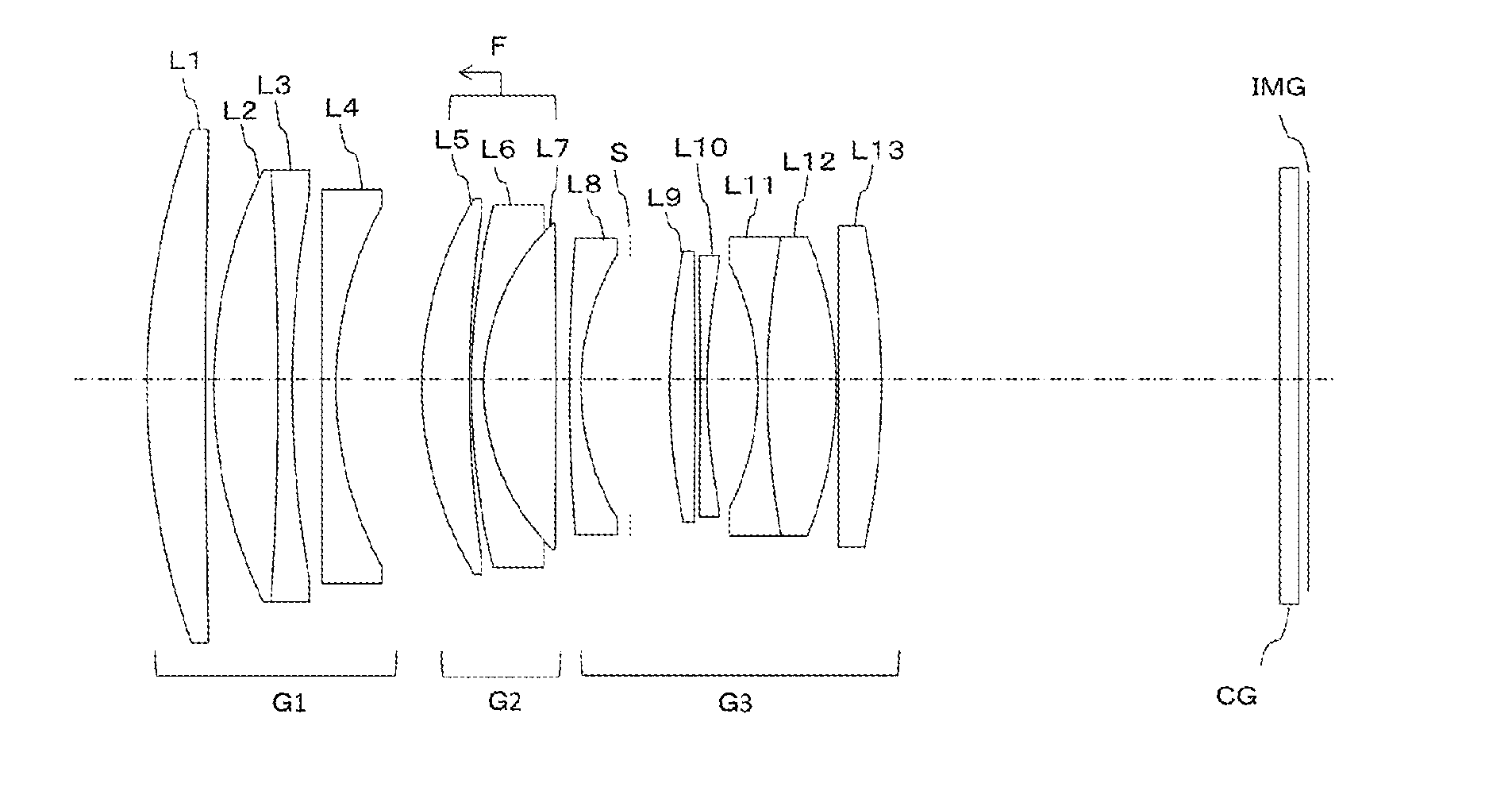
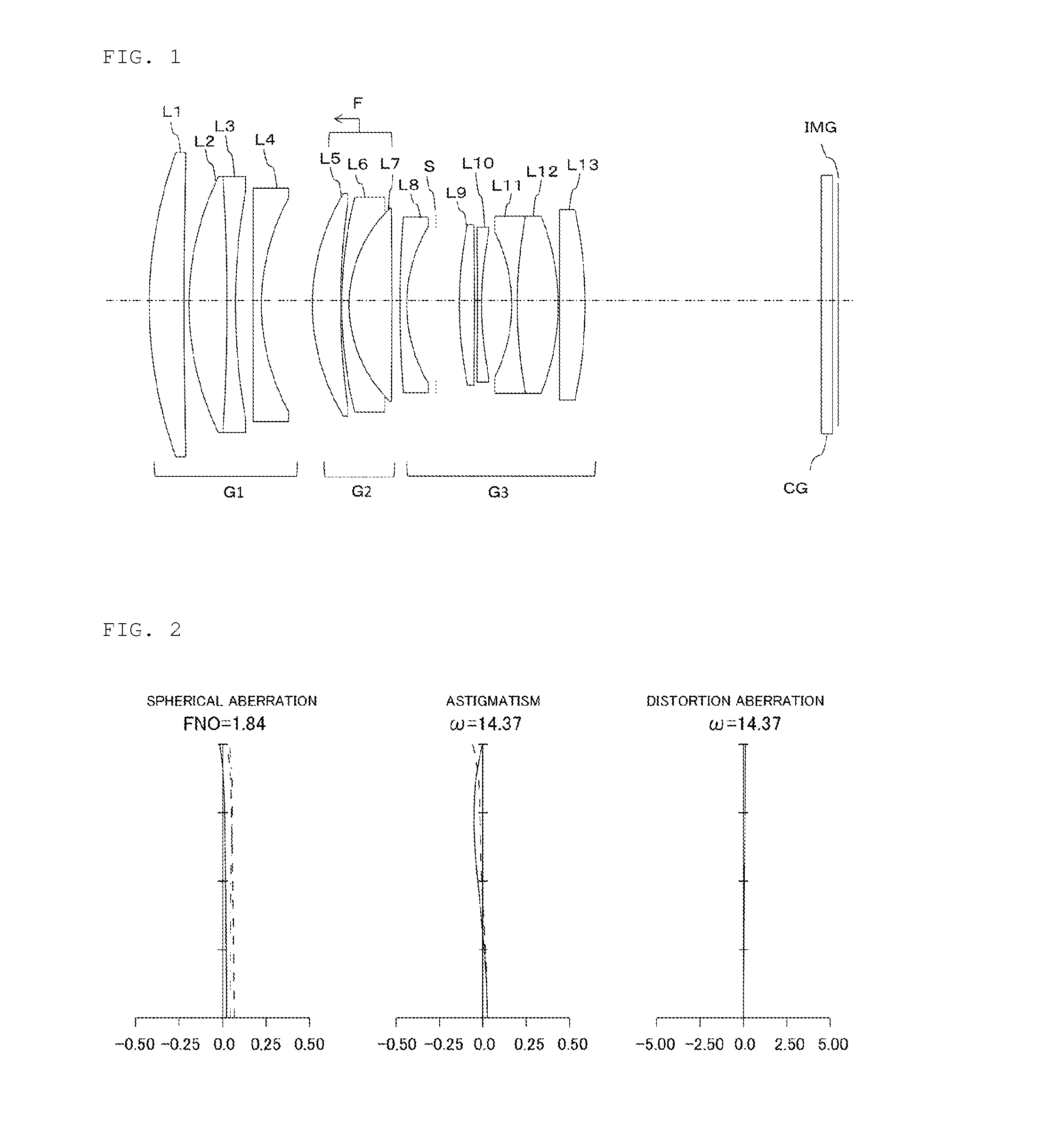
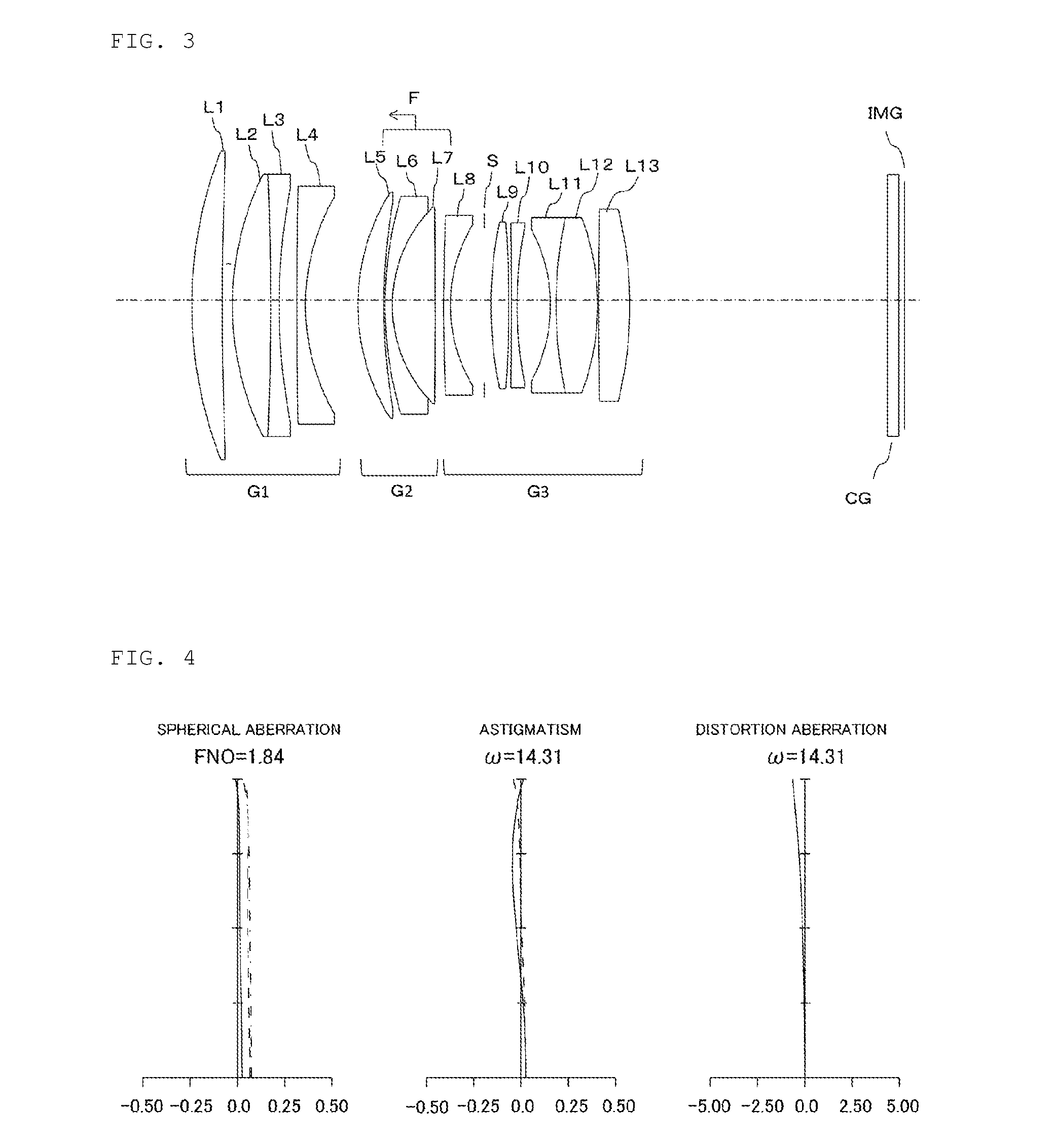
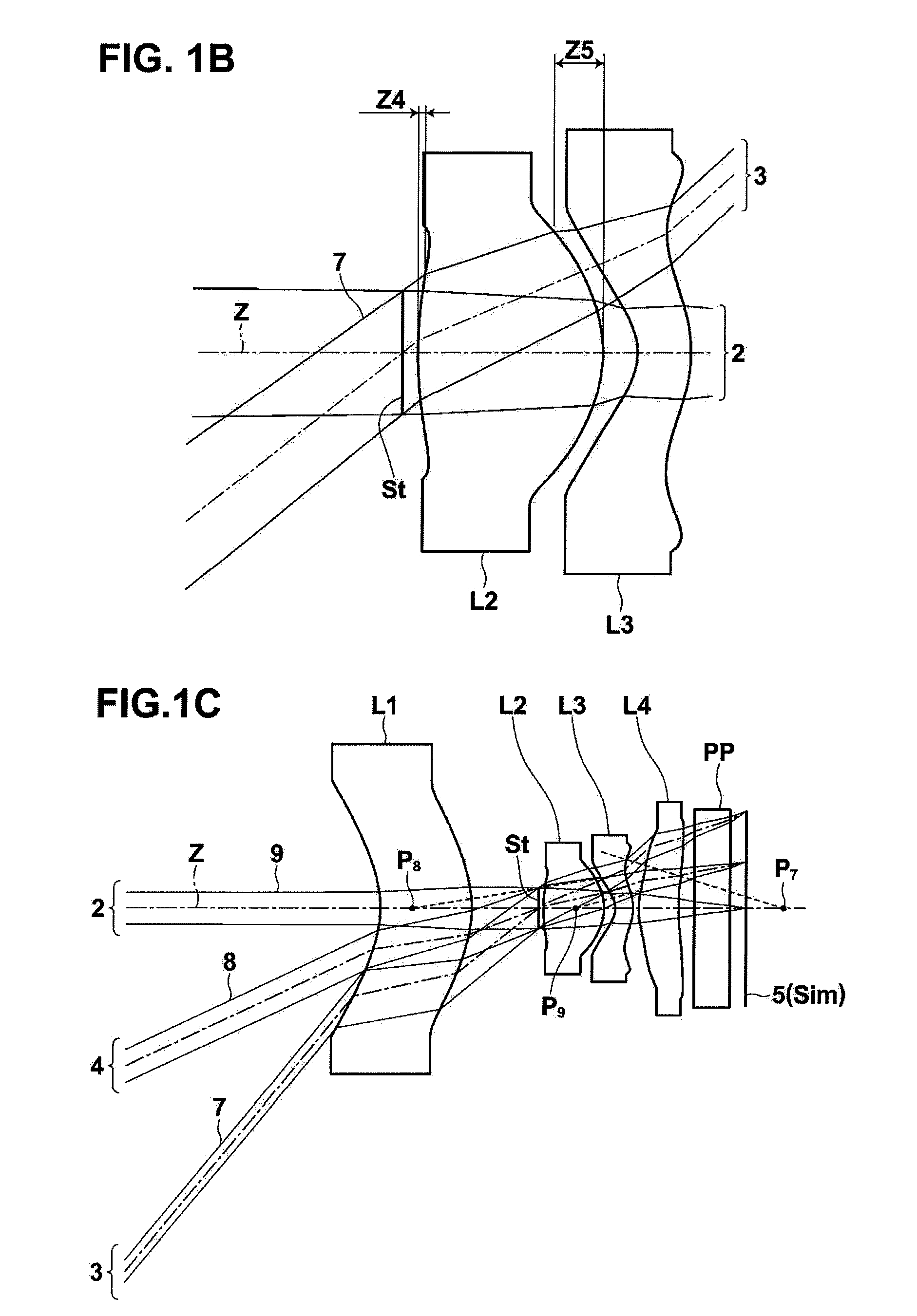
Disclosed is an imaging lens having a small F-number, high resolution, a sufficiently wide angle of view, and a small size.An imaging lens includes: a first lens with a meniscus shape having a concave surface facing an object side; a second positive lens; a third negative lens with a meniscus shape having a convex surface facing an image side; and a fourth lens having a convex surface facing the object side. The first to fourth lenses are arranged in this order from the object side. The imaging lens satisfies the following conditional expression:0.25<D / f<4.0(where D indicates the distance between the first lens and the second lens on the optical axis and f indicates the focal length of the entire system).
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
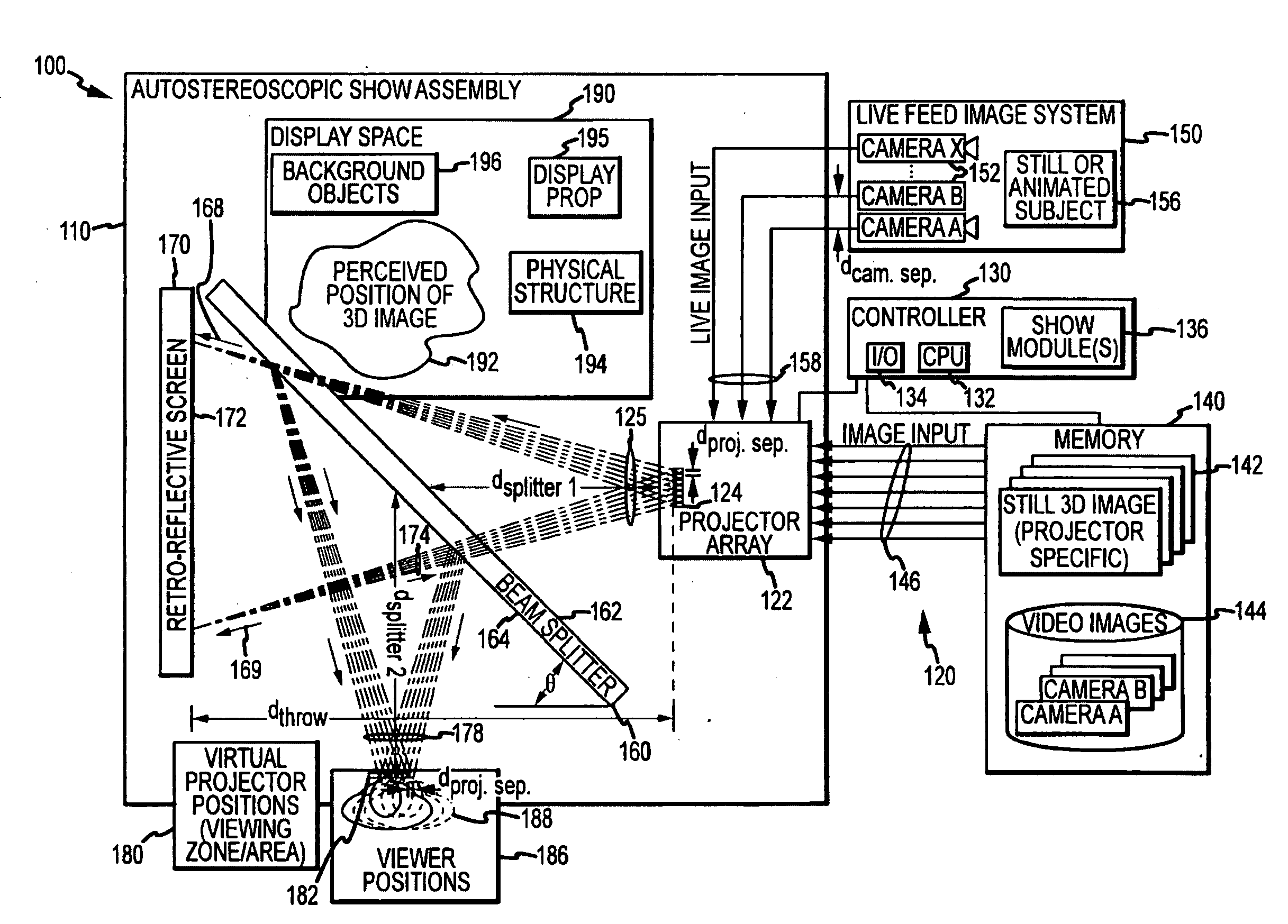
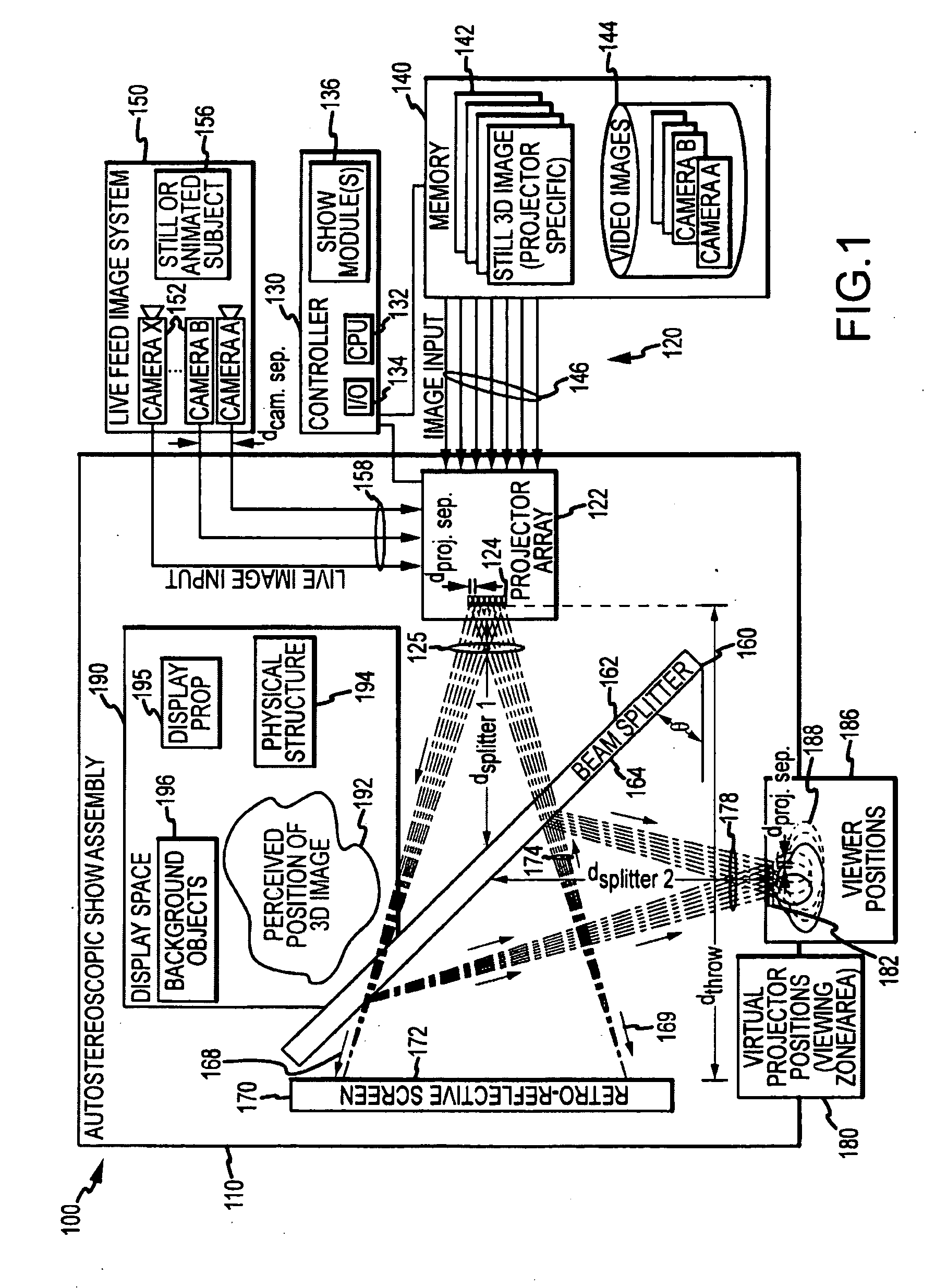
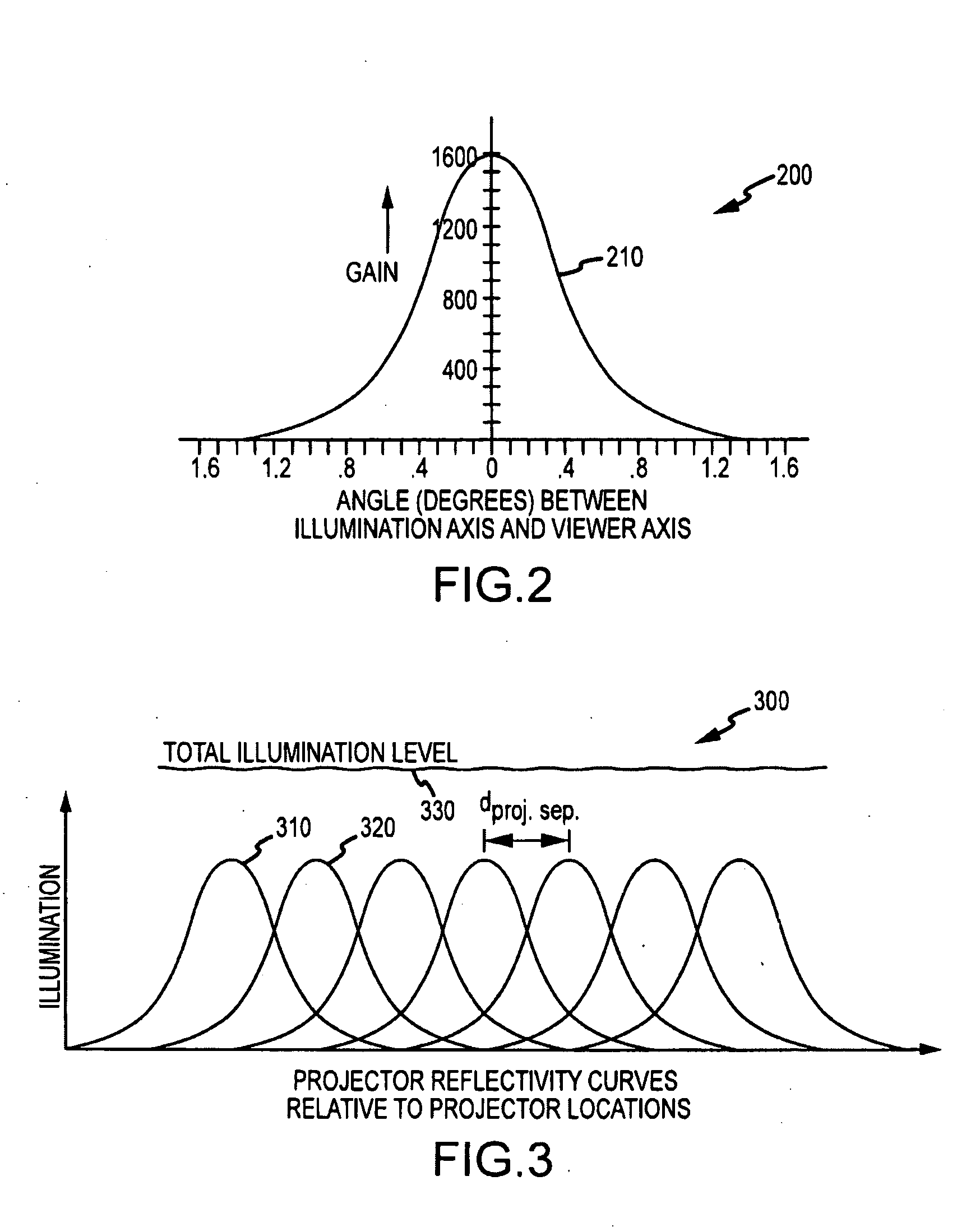
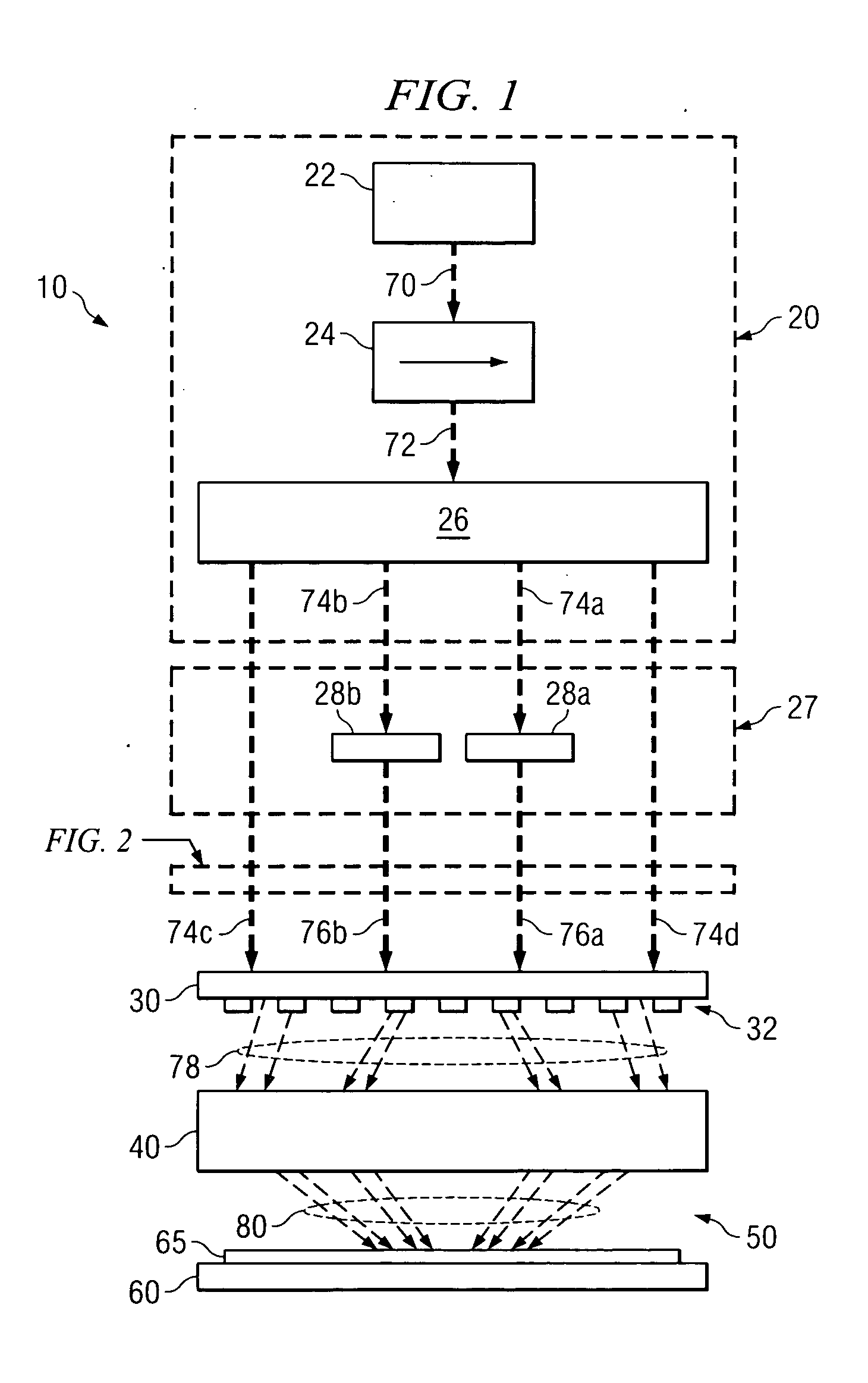
Autostereoscopic projection system
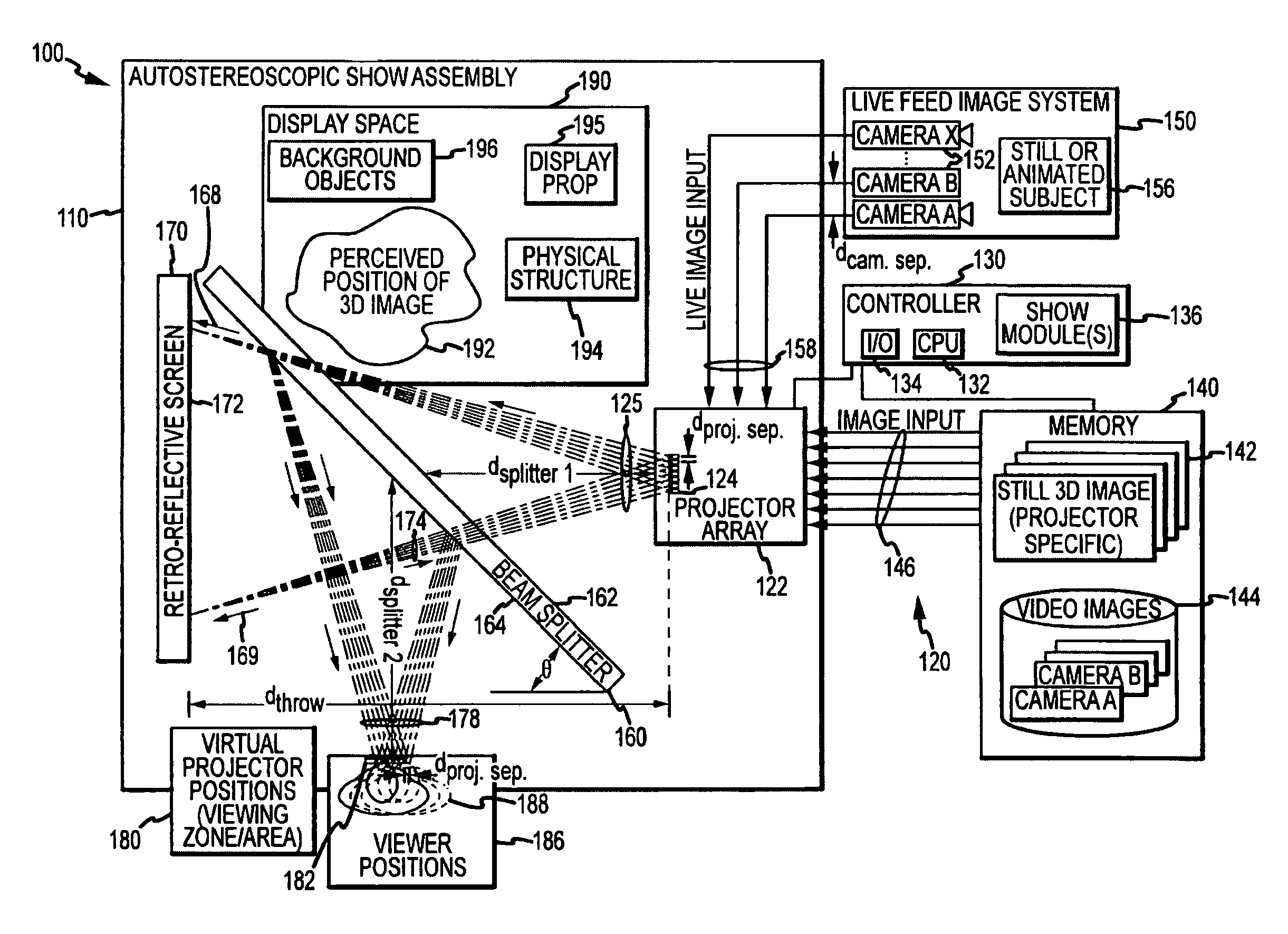
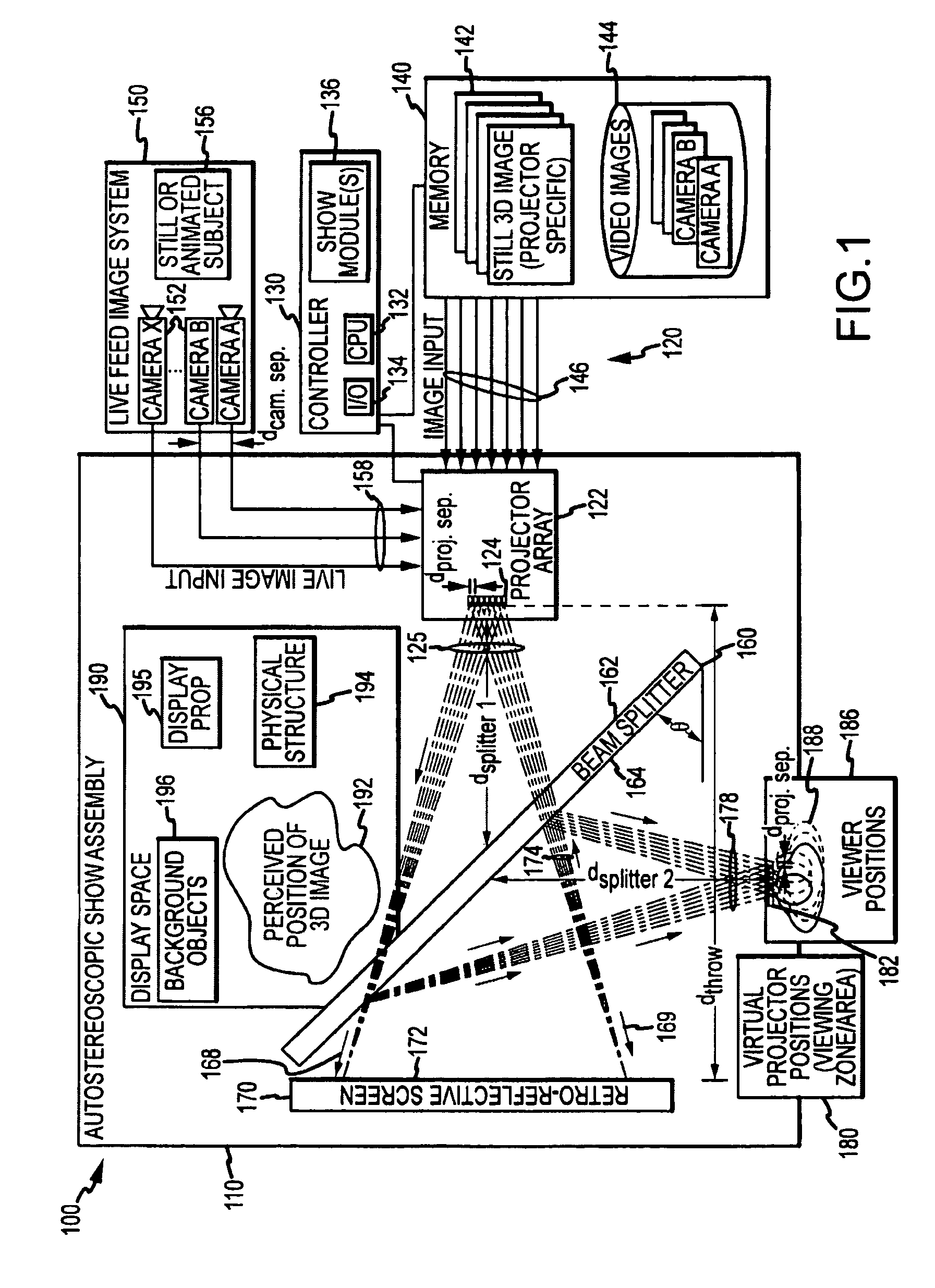
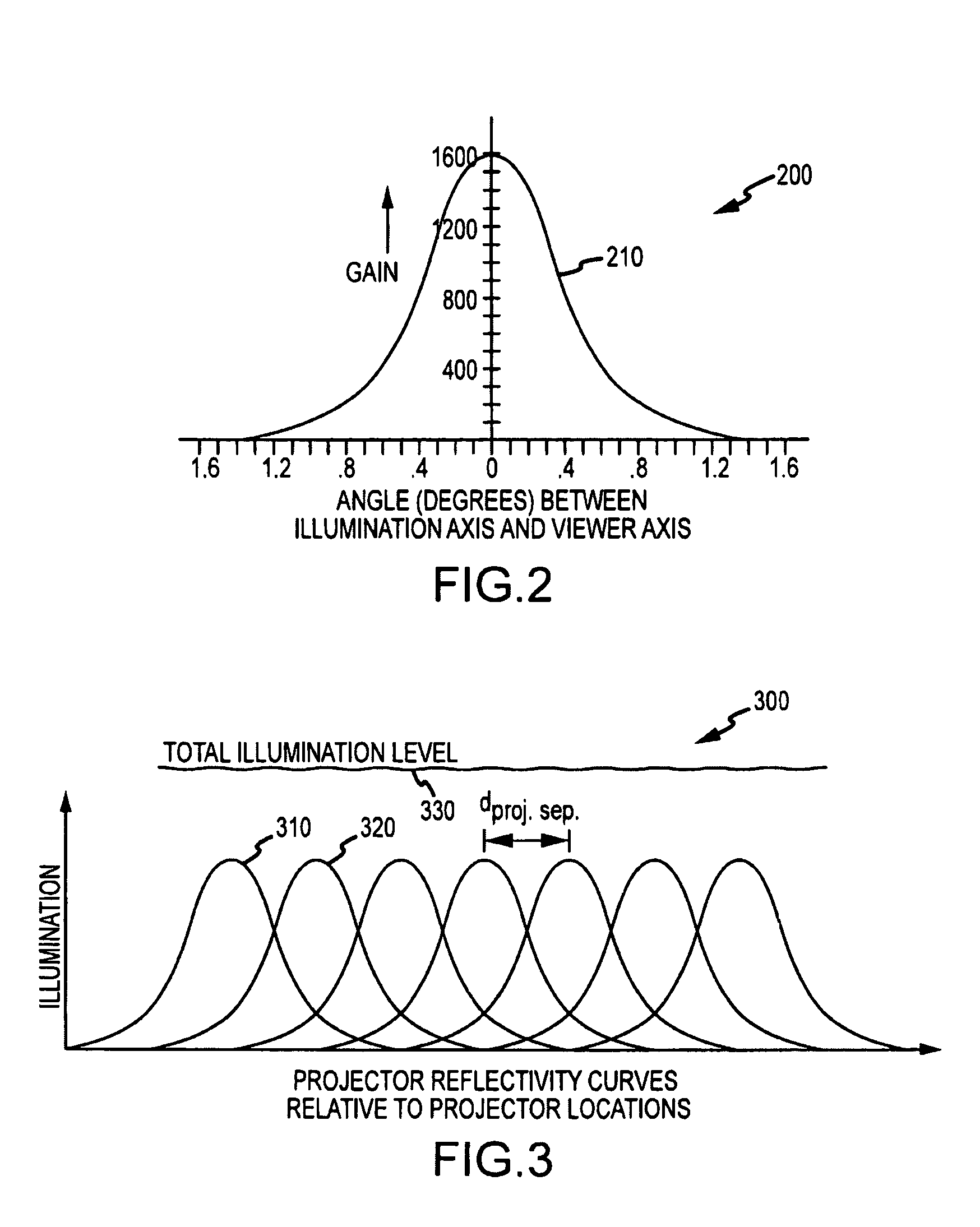
ActiveUS20100014053A1Reduce resolutionImage is often very smallProjectorsSteroscopic systemsDigital videoBeam splitter
An apparatus projecting 3D autostereoscopic images viewers. The apparatus includes a projector array with projectors each receiving an input image such as digital video and projecting an image based on the input image. A beam splitter with first and second surfaces is positioned such that the projected images strike the first surface and a portion (e.g., 50 to 95 percent) is transmitted through the beam splitter toward a screen with a retroreflective surface. The retroreflective surface reflects the splitter-transmitted portion back along the same path but with increased brightness. The light reflected from the retroreflective surface strikes the second surface of the beam splitter and is reflected toward a display viewing zone provided at about the focal points of the reflected projectors. A 3D image is perceivable to a viewer who positions his eyes at or near any of two or more viewing locations proximate to the projection surface.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
System and method for custom-polarized photolithography illumination
InactiveUS20050237509A1Image is often very smallLarge spacingTesting eggsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolarizerPhotolithography
In one embodiment, a system for custom-polarized photolithography illumination includes an illuminator operable to generate an illumination pattern of light, a polarizer unit operable to variably polarize the light, and a mask pattern defining photolithographic pattern features in two dimensions. The mask pattern is associated with a mask capable of transmitting at least a portion of the variably polarized light through the mask pattern.
Owner:BLATCHFORD JAMES W
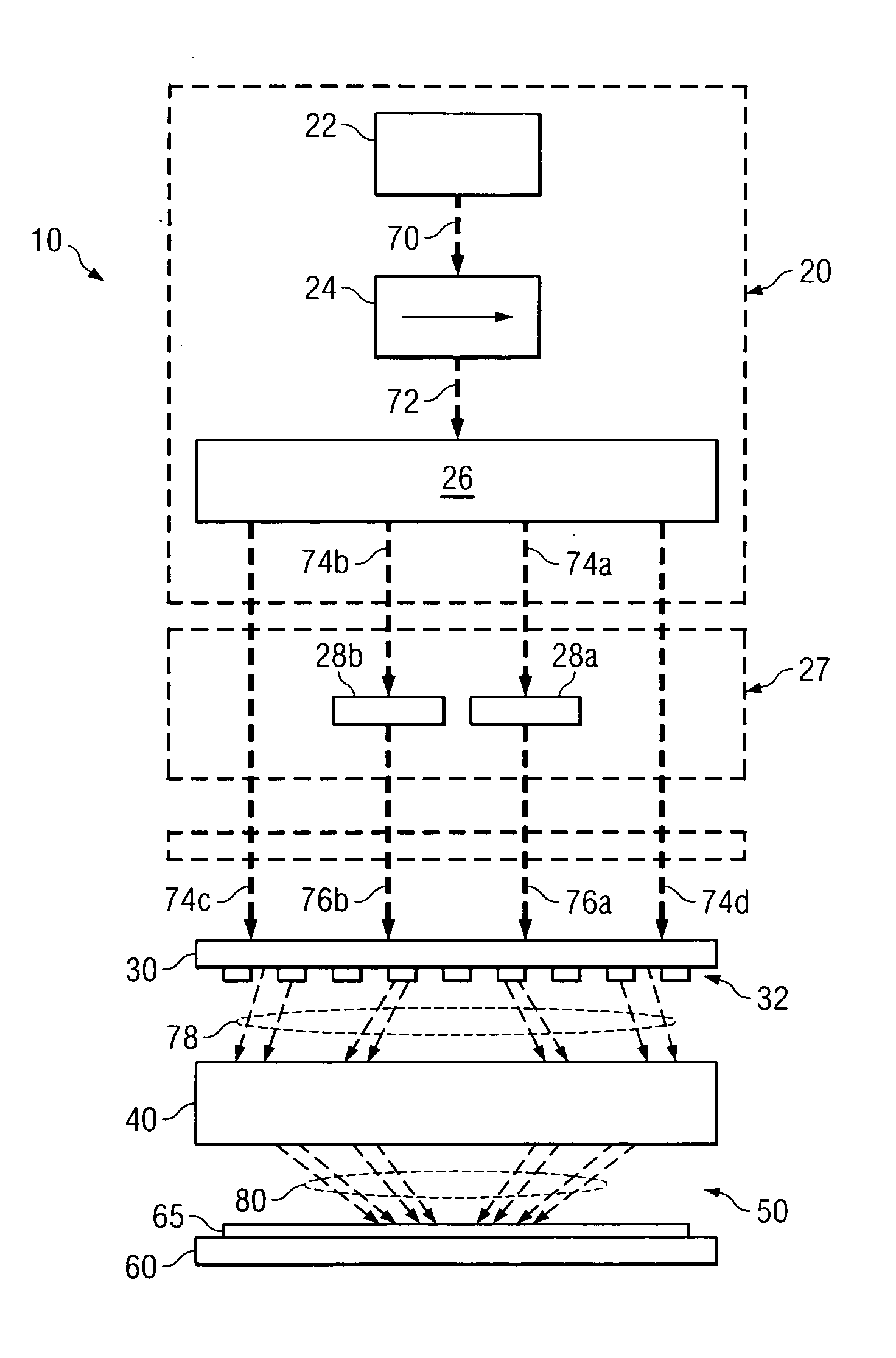
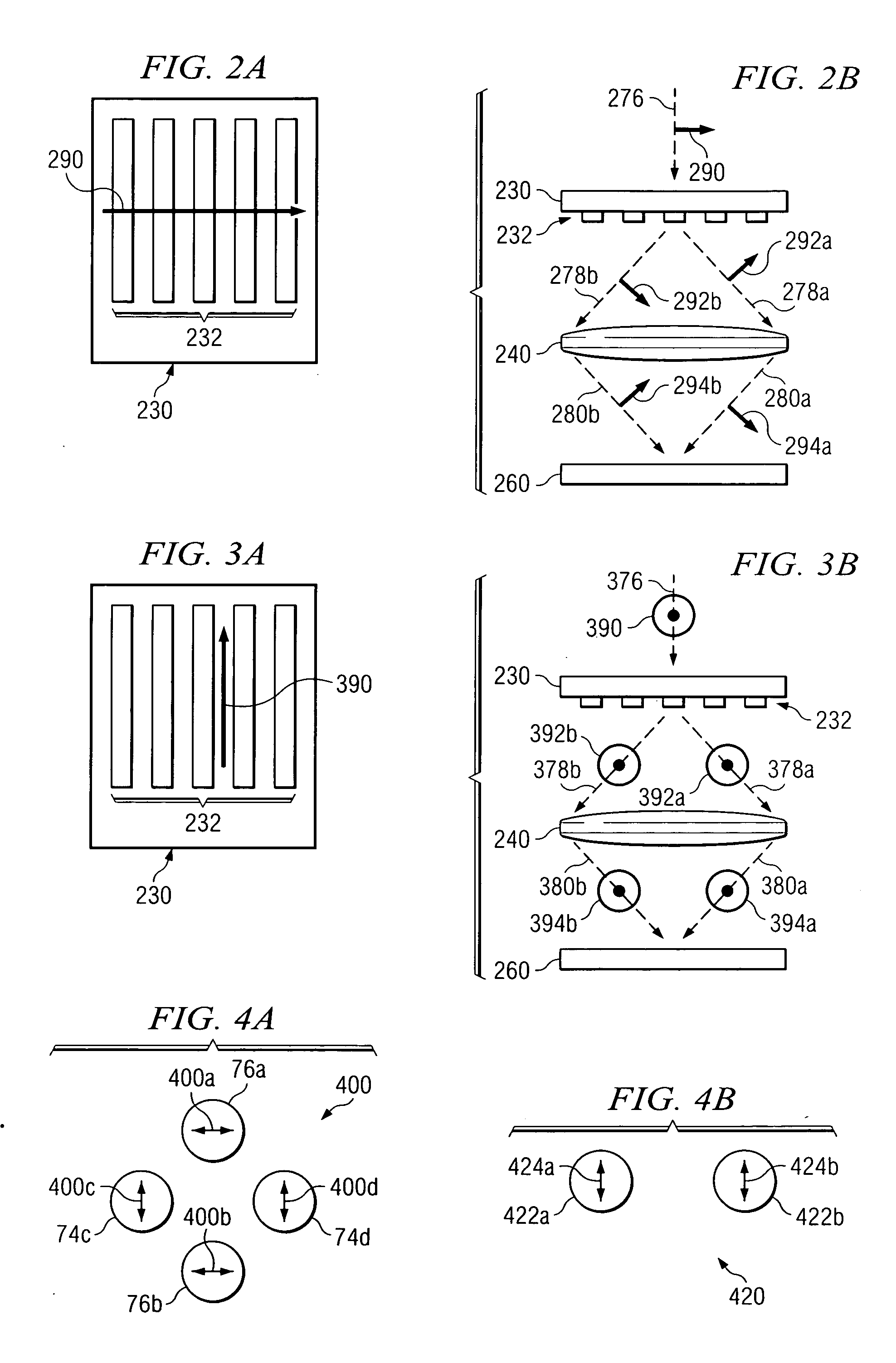
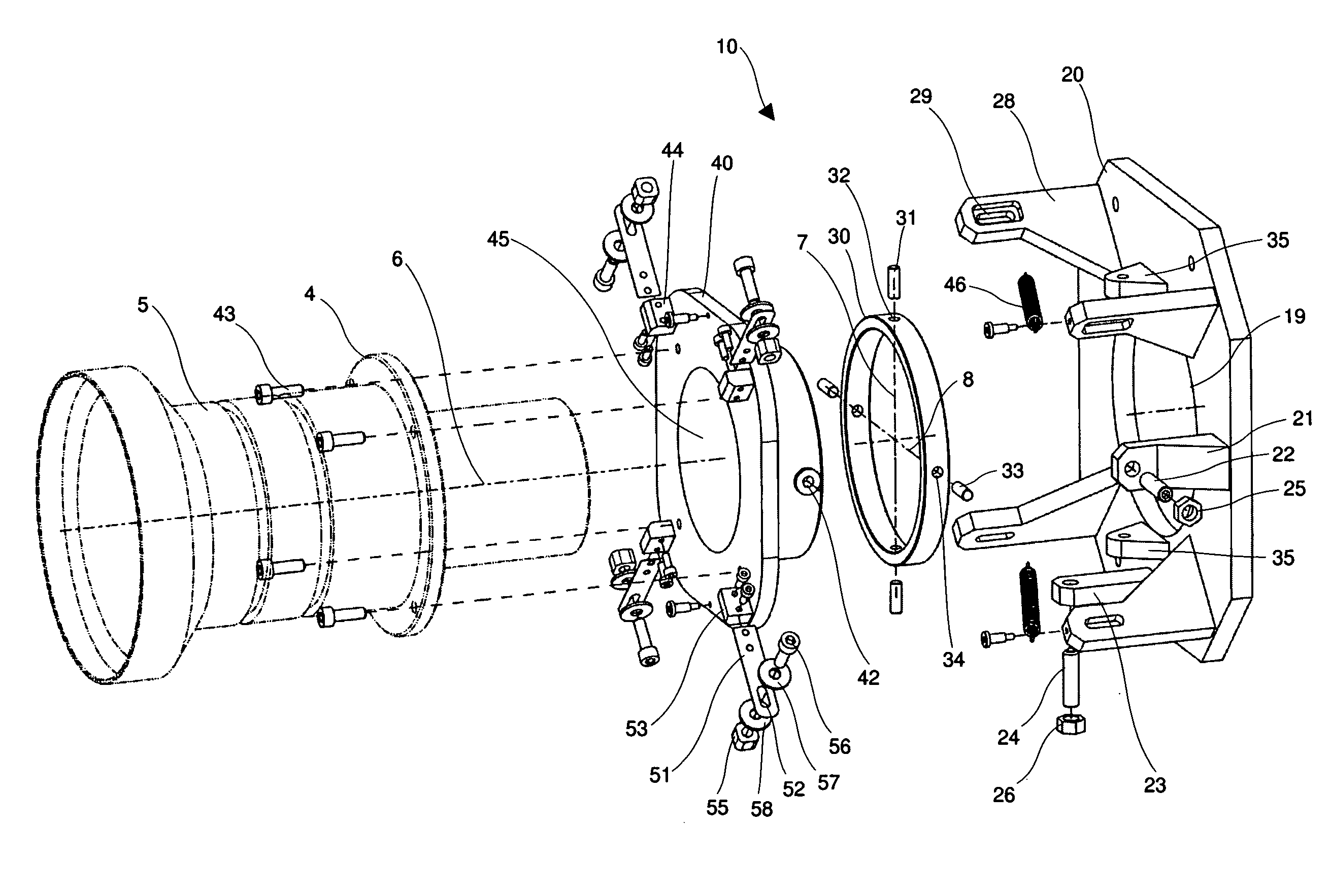
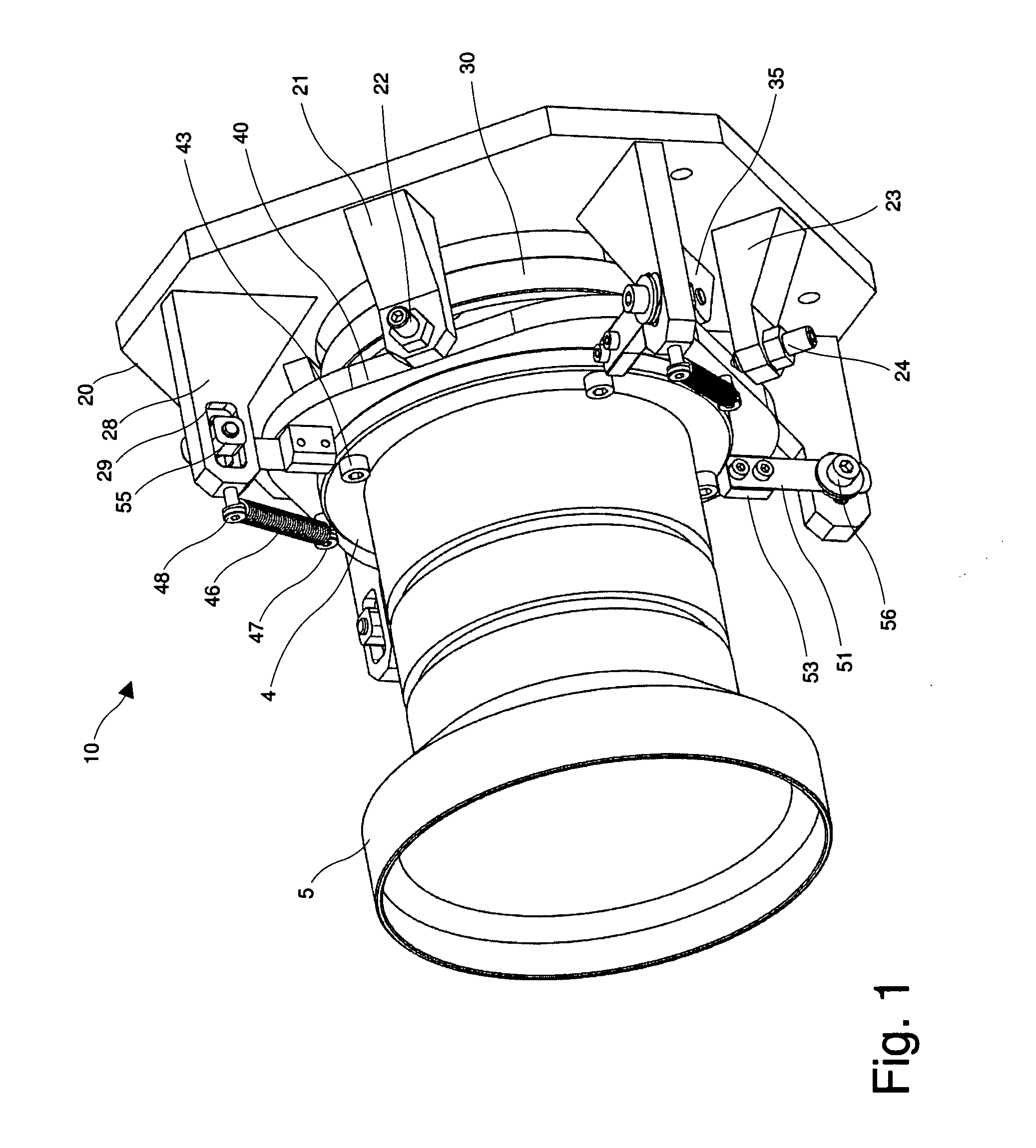
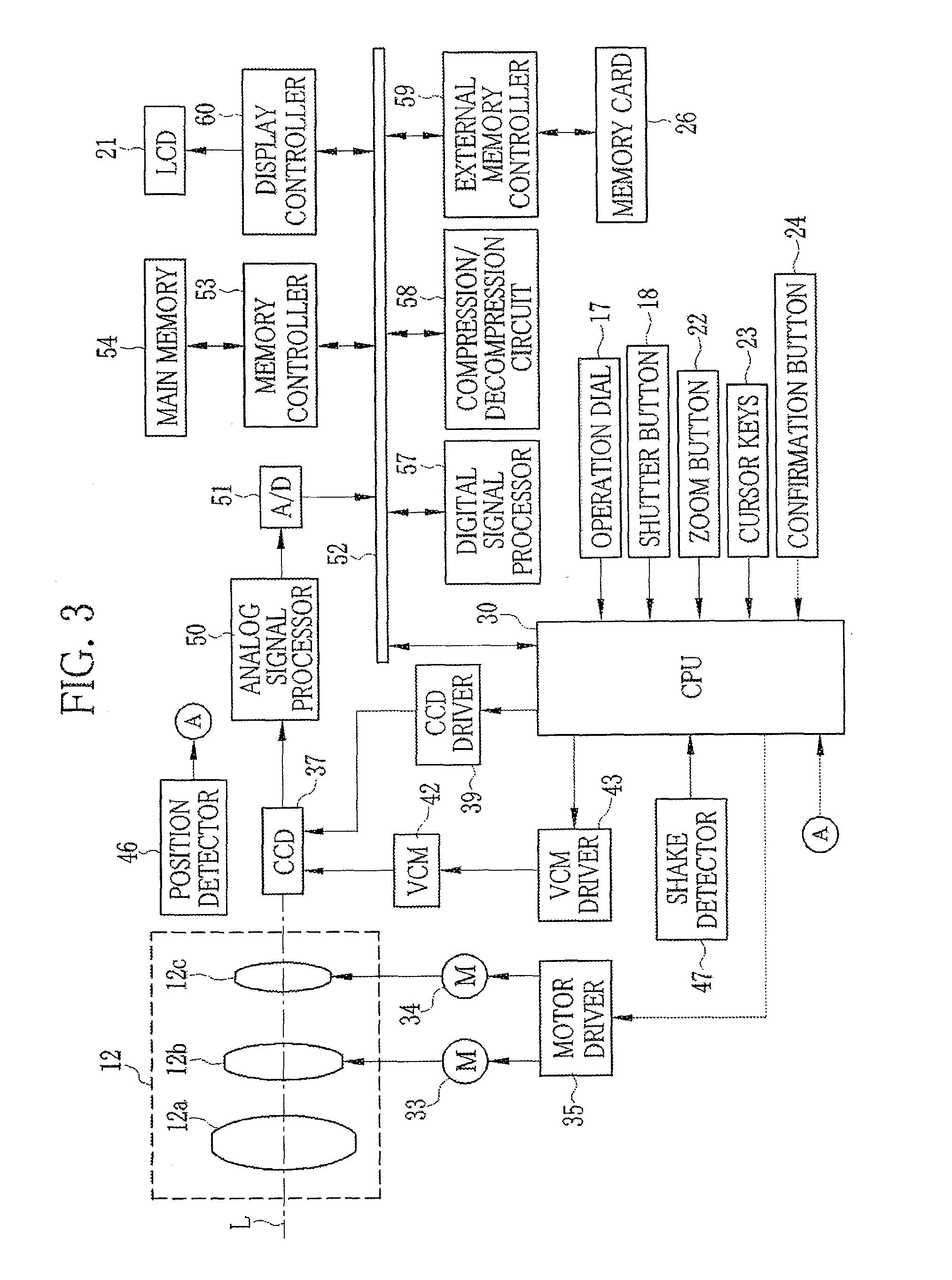
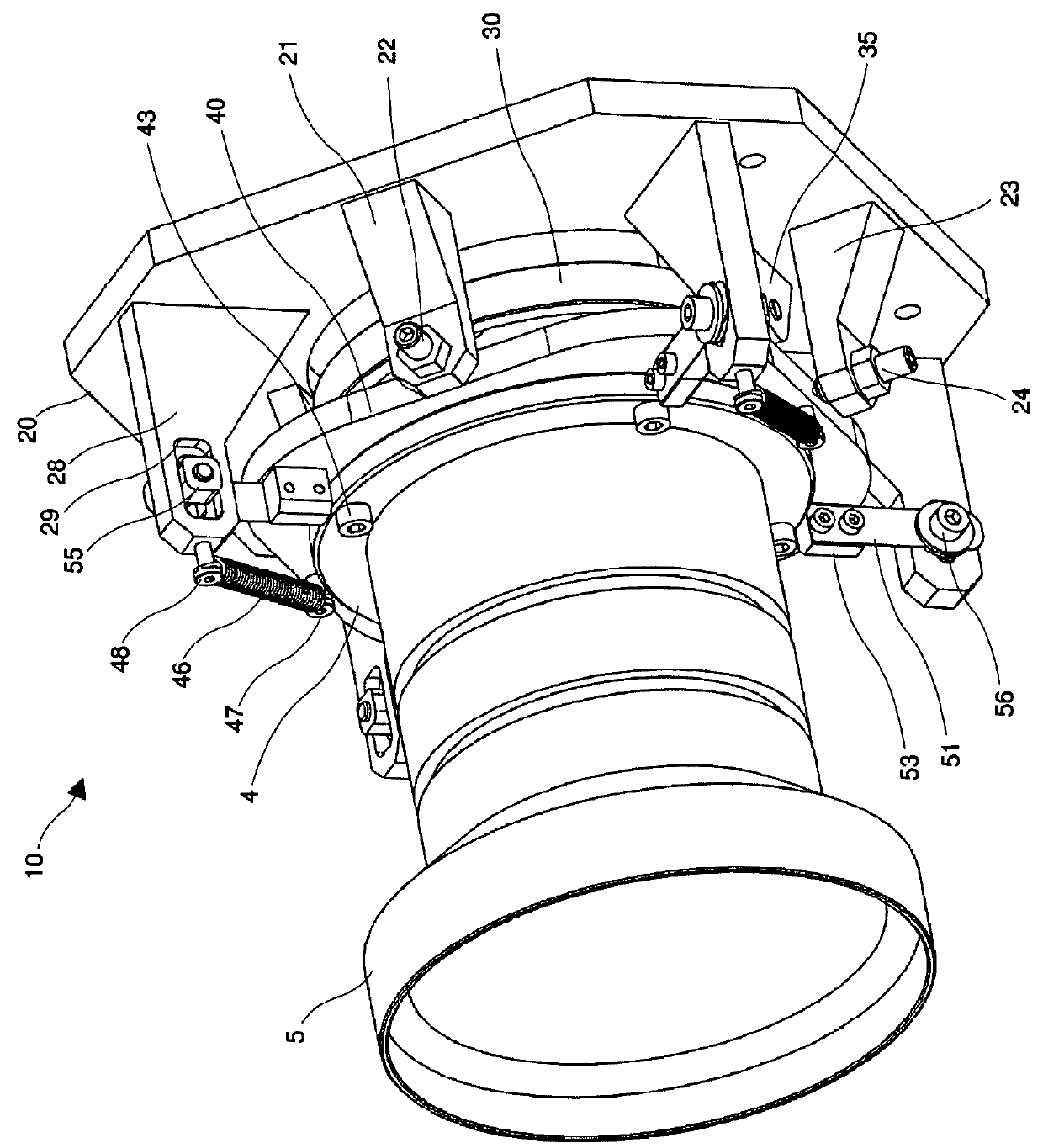
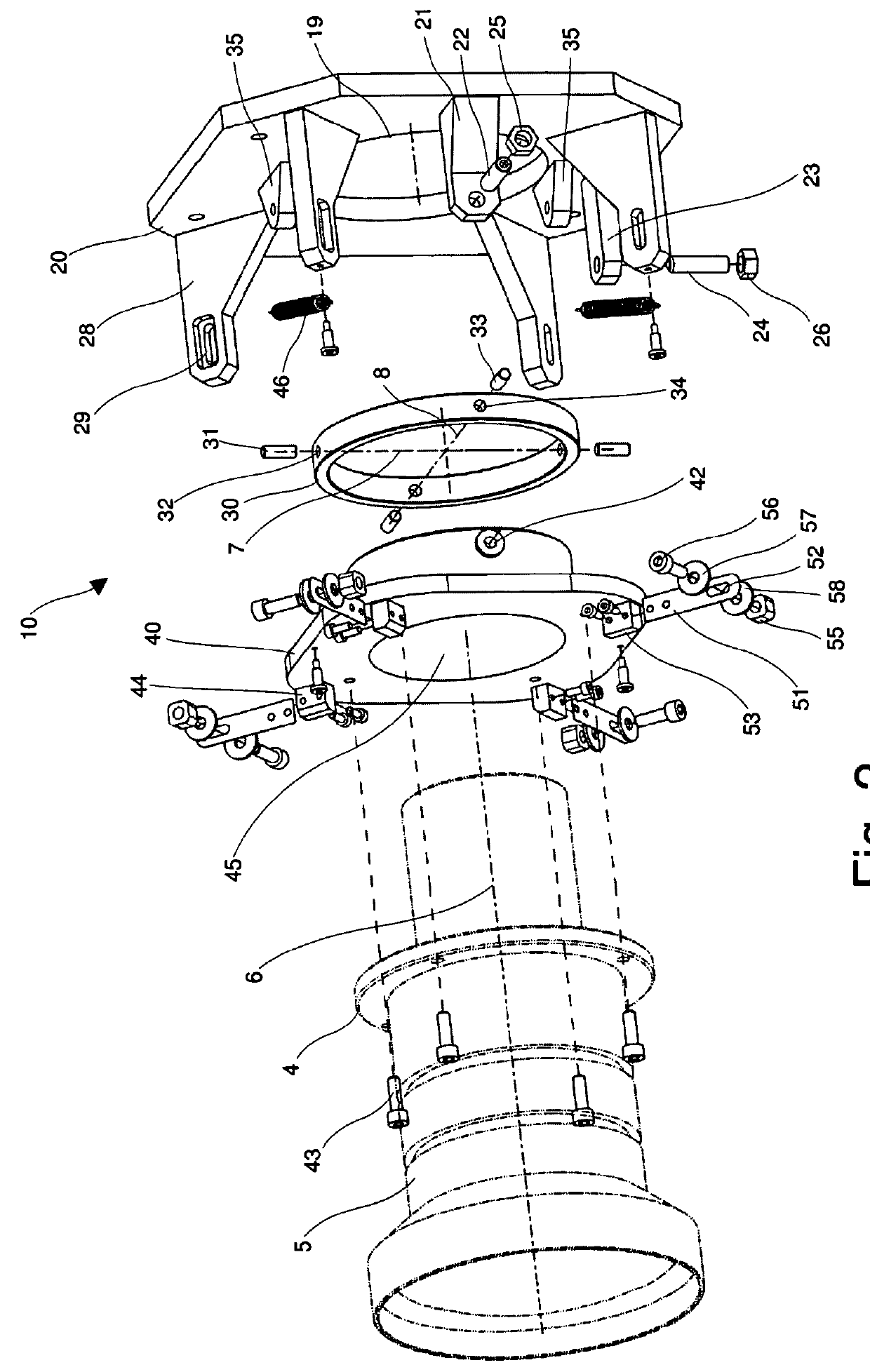
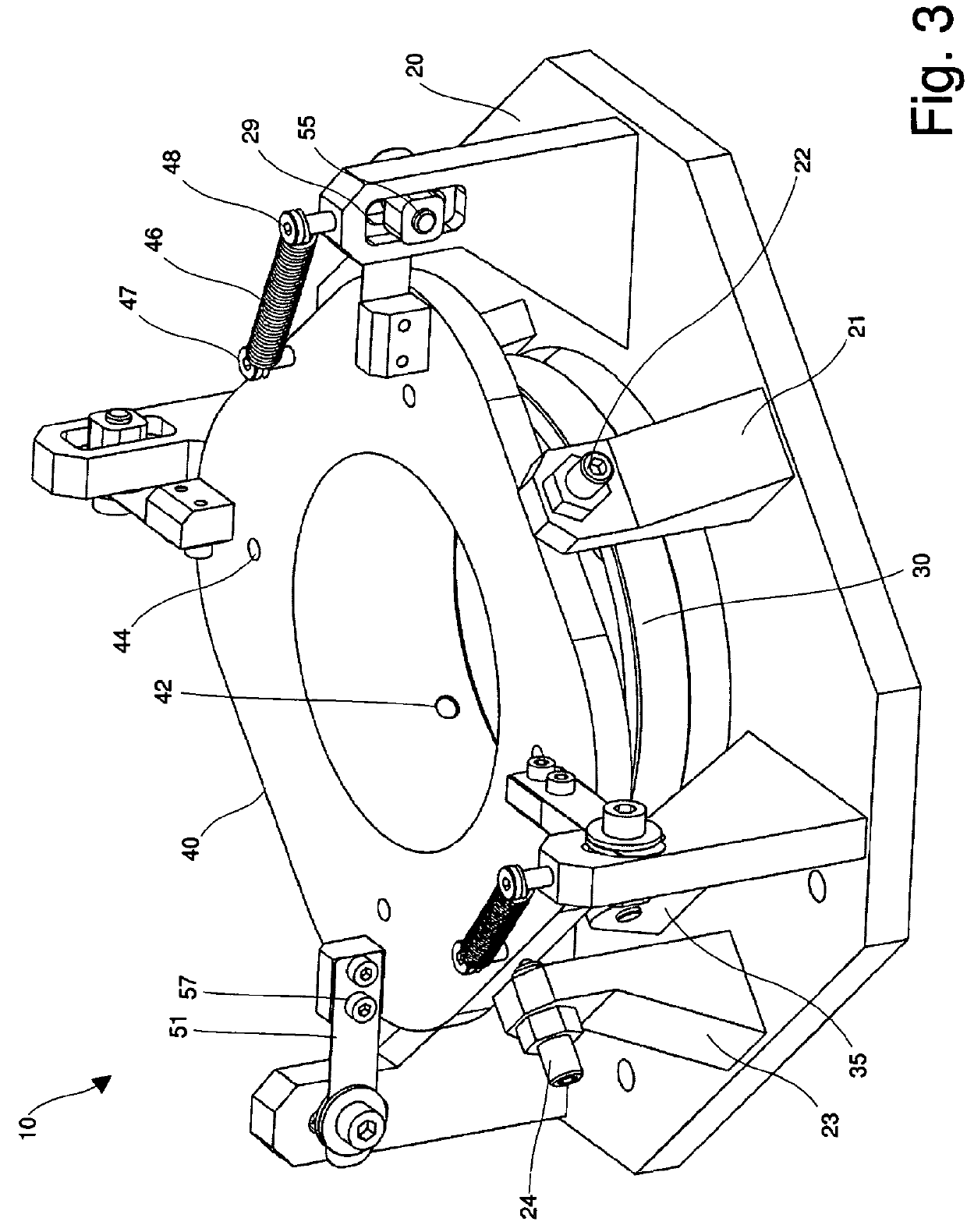
Position adjustment system for a projection lens
ActiveUS20130120720A1Permit adjustmentImage is often very smallProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensLocking mechanism
A lens position adjustment system (10) permits adjustment of the position of a projection lens (5) relative to a projector (100) for making a Scheimpflug adjustment. The projection lens (5) has an optical axis (6). The system (10) comprises: a first support part (20) for fitting to, or forming part of the projector (100); a second support part (40) for fitting to, or forming part of the projection lens (5); and a connecting part (30). The connecting part (30) is pivotally connected to the first support part (20) and pivotally connected to the second support part (40) and configured to permit independent adjustment of the second support part (40) relative to the first support part (20) about two axes of rotation (7, 8) which intersect, and are perpendicular to, the optical axis (6) of the projection lens (5). A locking mechanism (28, 29, 51-58) is provided for securing a position of the second support part (40) relative to the first support part (20).
Owner:BARCO NV
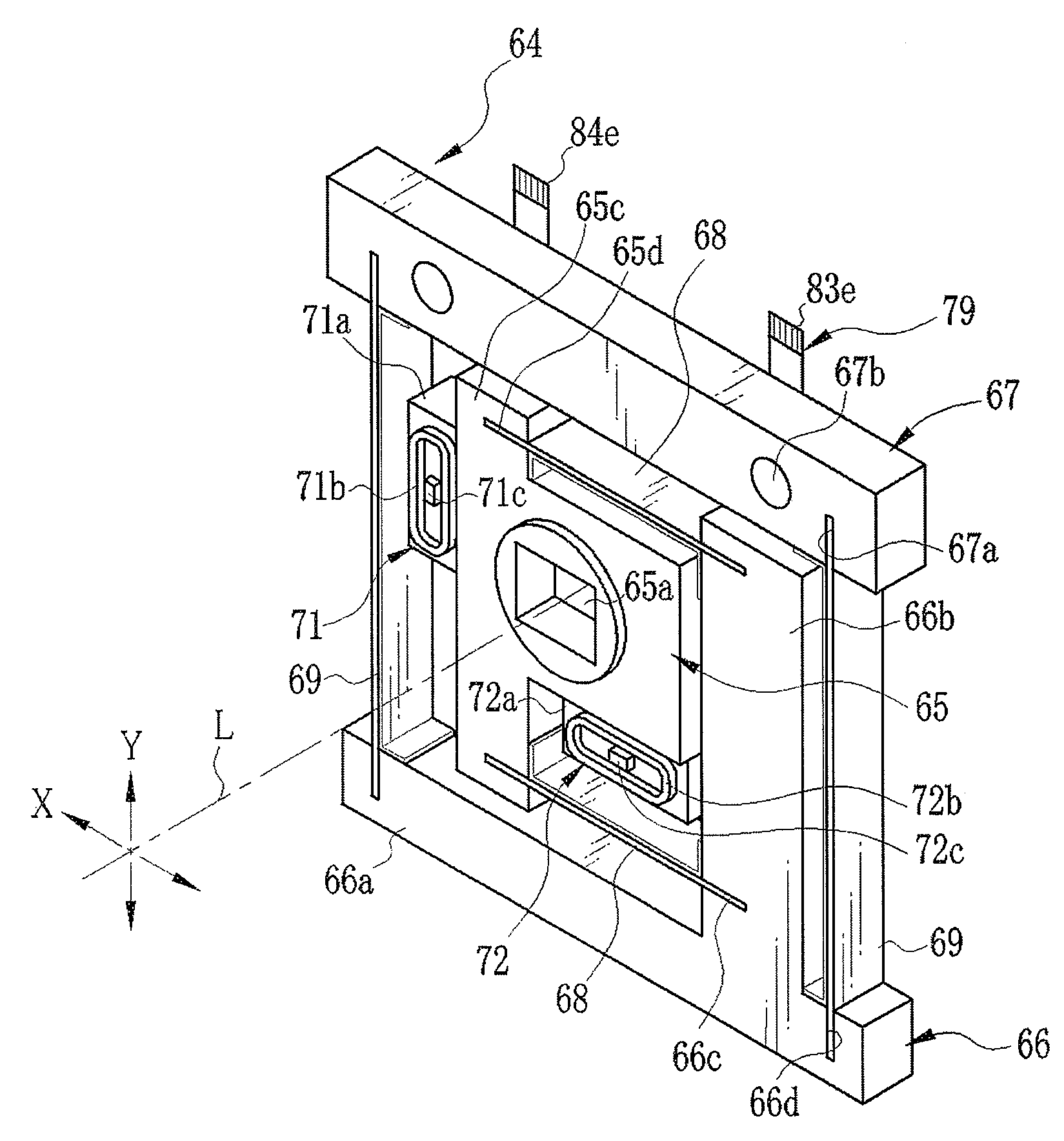
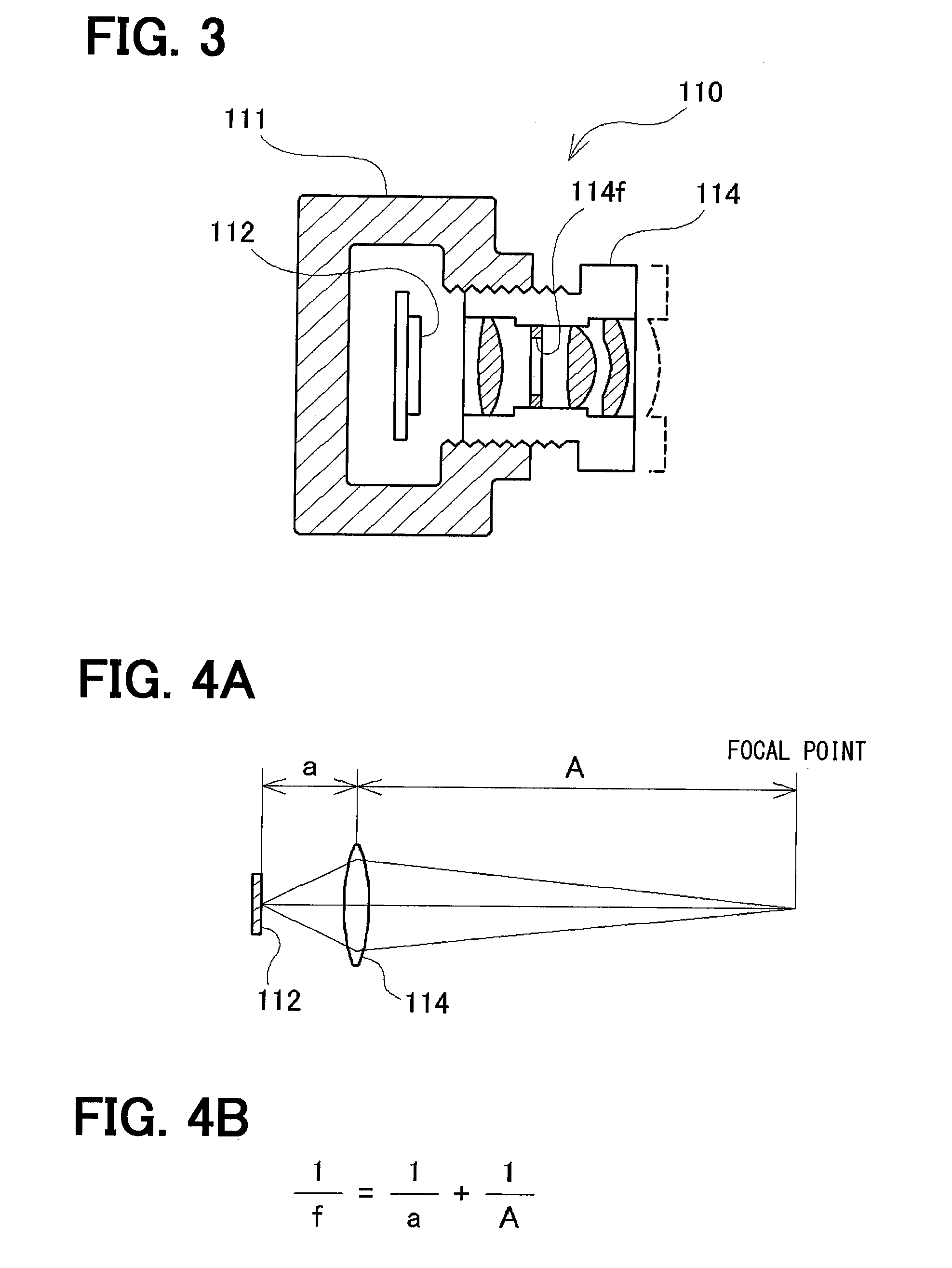
Image stabilizer and optical instrument therewith
A CCD support mechanism includes a CCD holder for holding a CCD, a first printed circuit board having a first printed coil, a second printed circuit board having a second printed coil, a pair of horizontal leaf springs, and a pair of vertical leaf springs. When a camera shake occurs by hand-held shooting, a VCM composed of the first printed coil and a first stationary magnet shifts the CCD, while bending the horizontal leaf springs, to counteract the camera shake in a Y-axis direction. A VCM composed of the second printed coil and a second stationary magnet shifts the CCD, while bending the vertical leaf springs, to counteract the camera shake in an X-axis direction. Current values of the VCMs are determined by feedback control by using an output signal from a shake detector as a target value and a present position from a position detector as a measurement value.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
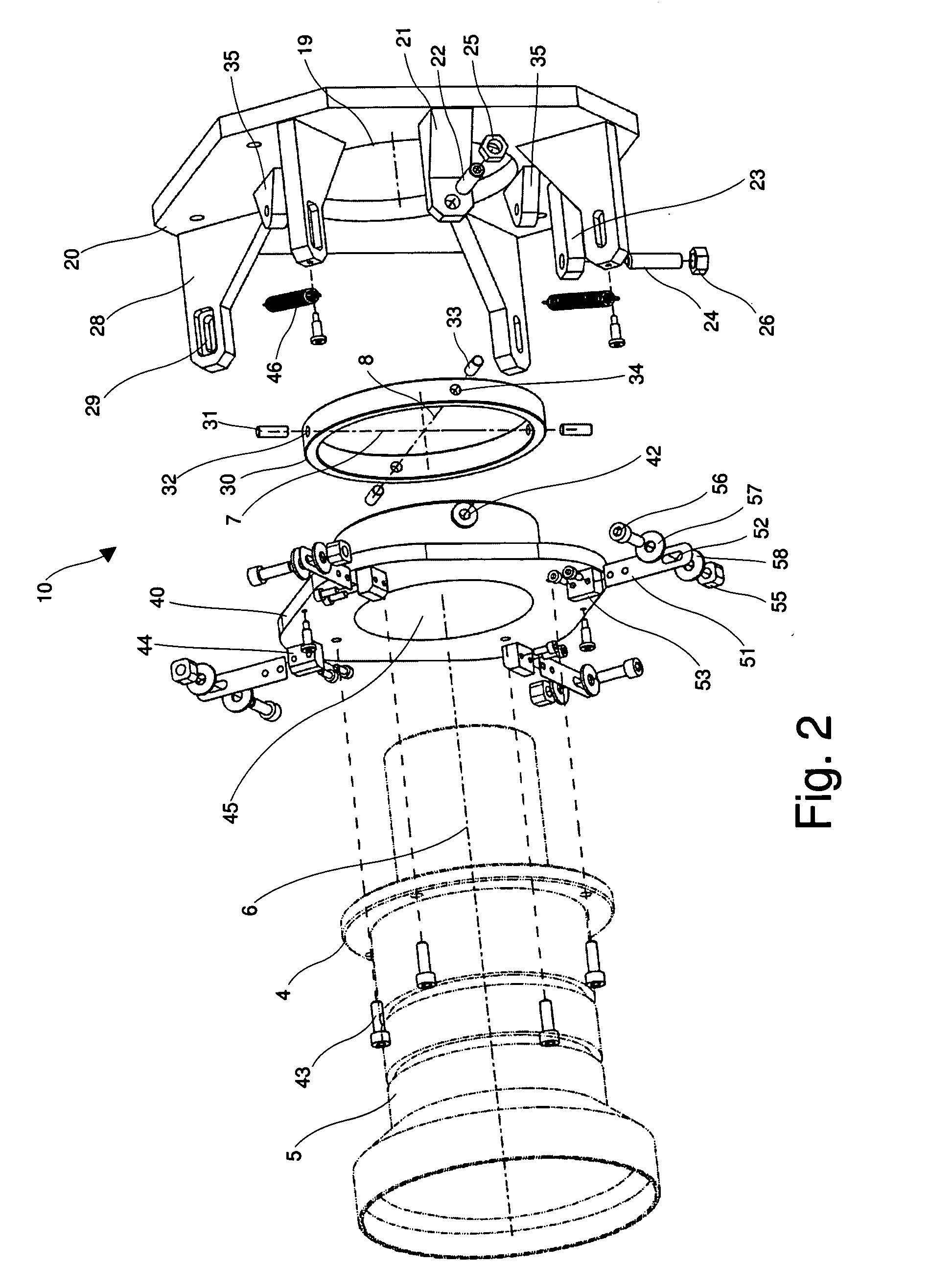
Optical unit with shake correcting function and photographic optical device
ActiveUS8238736B2Efficiently interlinkedHigh torqueTelevision system detailsPrintersEngineeringMagnet
Provided is a photographing optical device, which is able to reliably correct an unintentional movement by hand of a user by improving the constitution of a camera unit driving mechanism for correcting the deflection of a camera unit. In order that a camera unit is made to be rocked to correct the unintentional movement, a photographing optical device includes a first camera unit drive mechanism and a second camera unit drive mechanism, which are so disposed at two side portions sandwiching a pivot portion therebetween as to make a pair. In these camera unit drive mechanisms, camera unit driving magnets are held on the side of the camera unit as a movable body side, and camera unit driving coils are held on the side of a stationary body. The camera unit is pushed toward the pivot portion by a gimbal spring.
Owner:SANKYO SEIKI MFG CO LTD
Head-up display system with dynamic image field and brightness control
InactiveUS20140092481A1High resolutionIncrease and decrease sizeDiffusing elementsHead-up displayMagnification
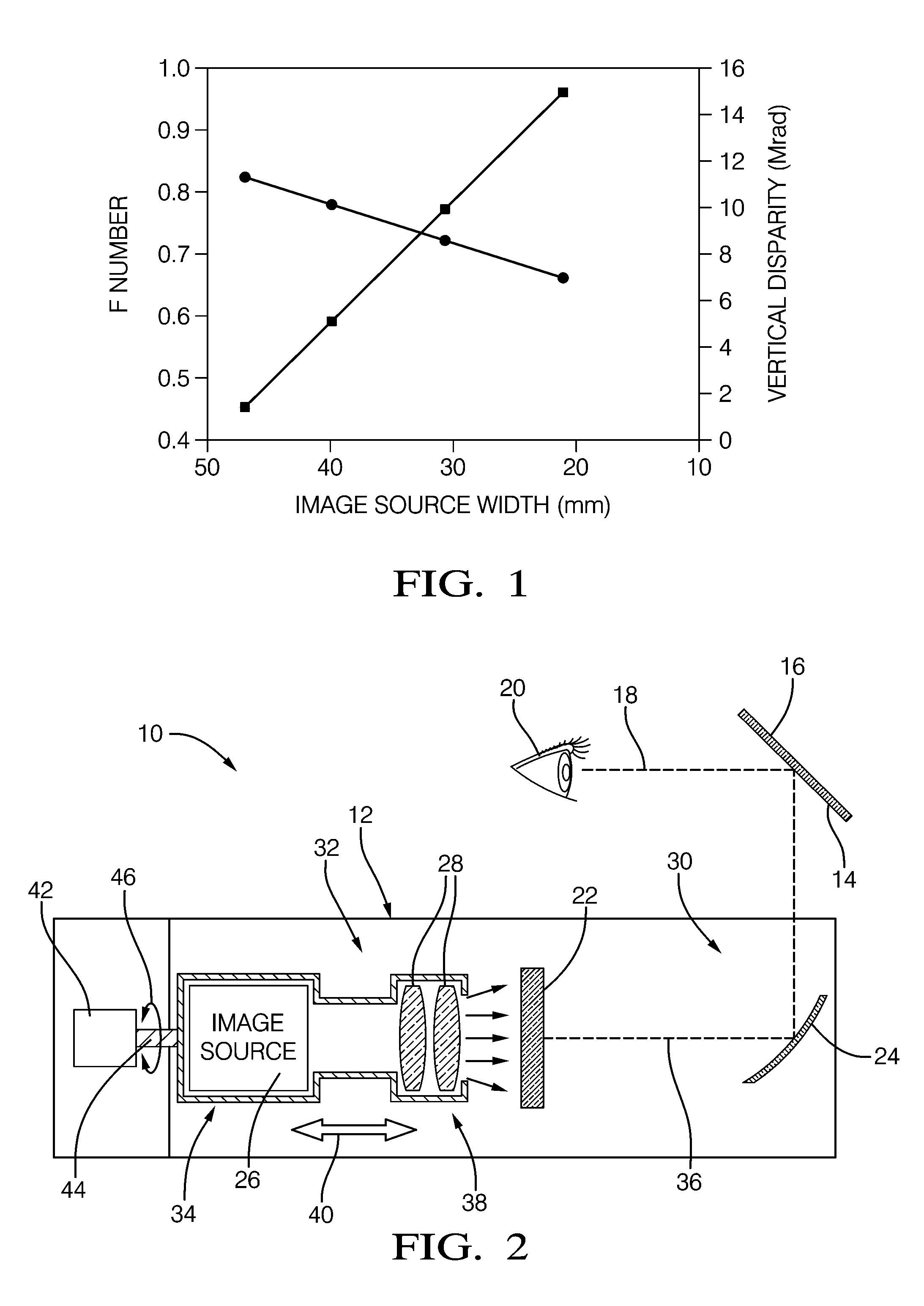
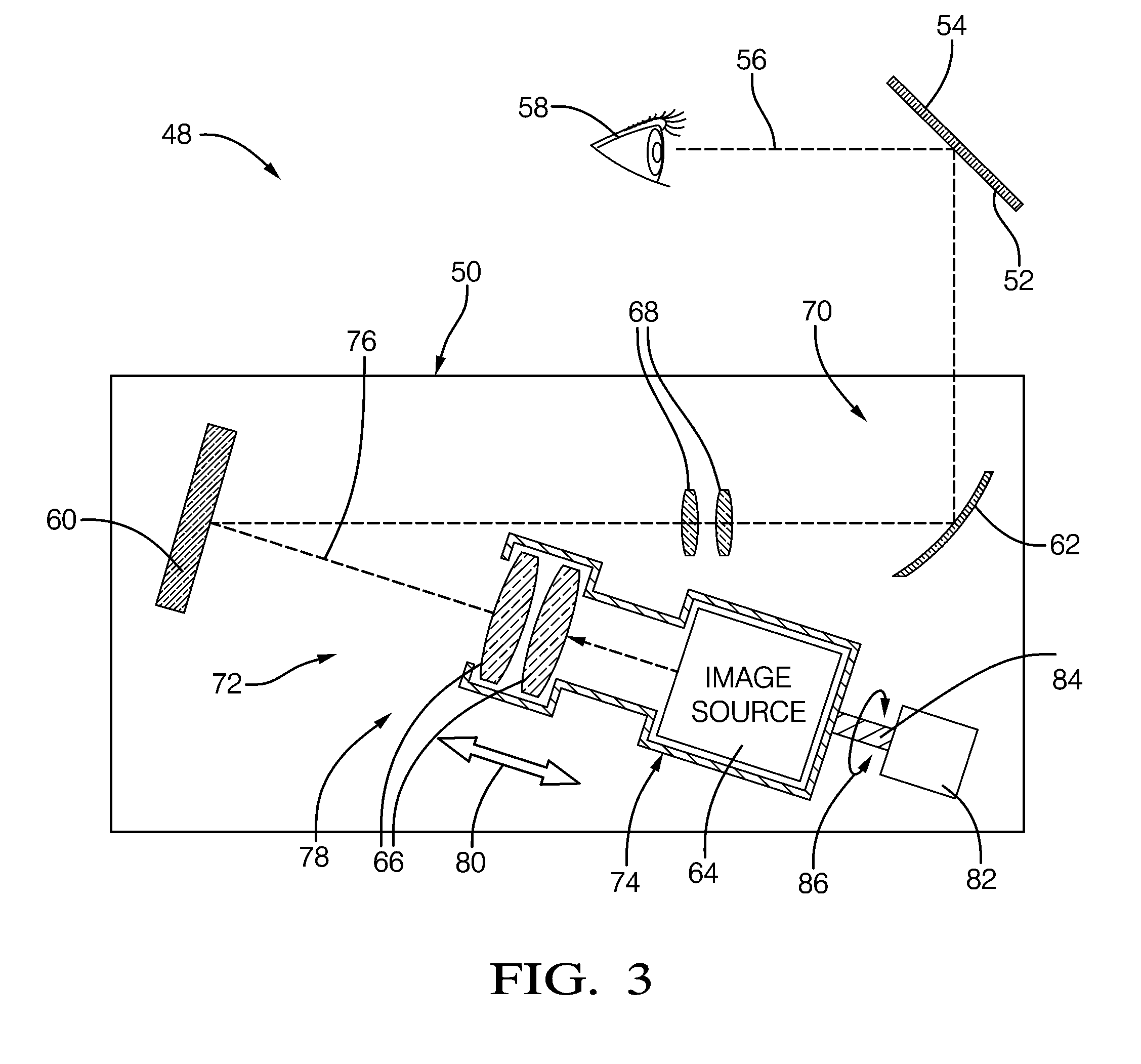
A head-up display system having a diffusing image plane or diffuser. The light output of a relatively small image source is imaged on the diffuser by way of imaging optics. A mirror is used to image light from the diffuser onto a windshield and correct for distortion caused by the windshield. The diffuser is advantageously used when a large field-of-view is desired, or sun load characteristics need to be addressed. The diffuser may be flat or curved in order to optimize the system for different applications. The magnification of the mirror may be made relatively low, and the solar emergency density that is made incident on the image source is reduced, providing for a low cost, high performance, color head-up display system. A drive mechanism allows selective operator controlled repositioning of the image source and imaging optics with respect to diffuser to vary image size, position and / or intensity.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Projection type display device, projection display method, and projection display program
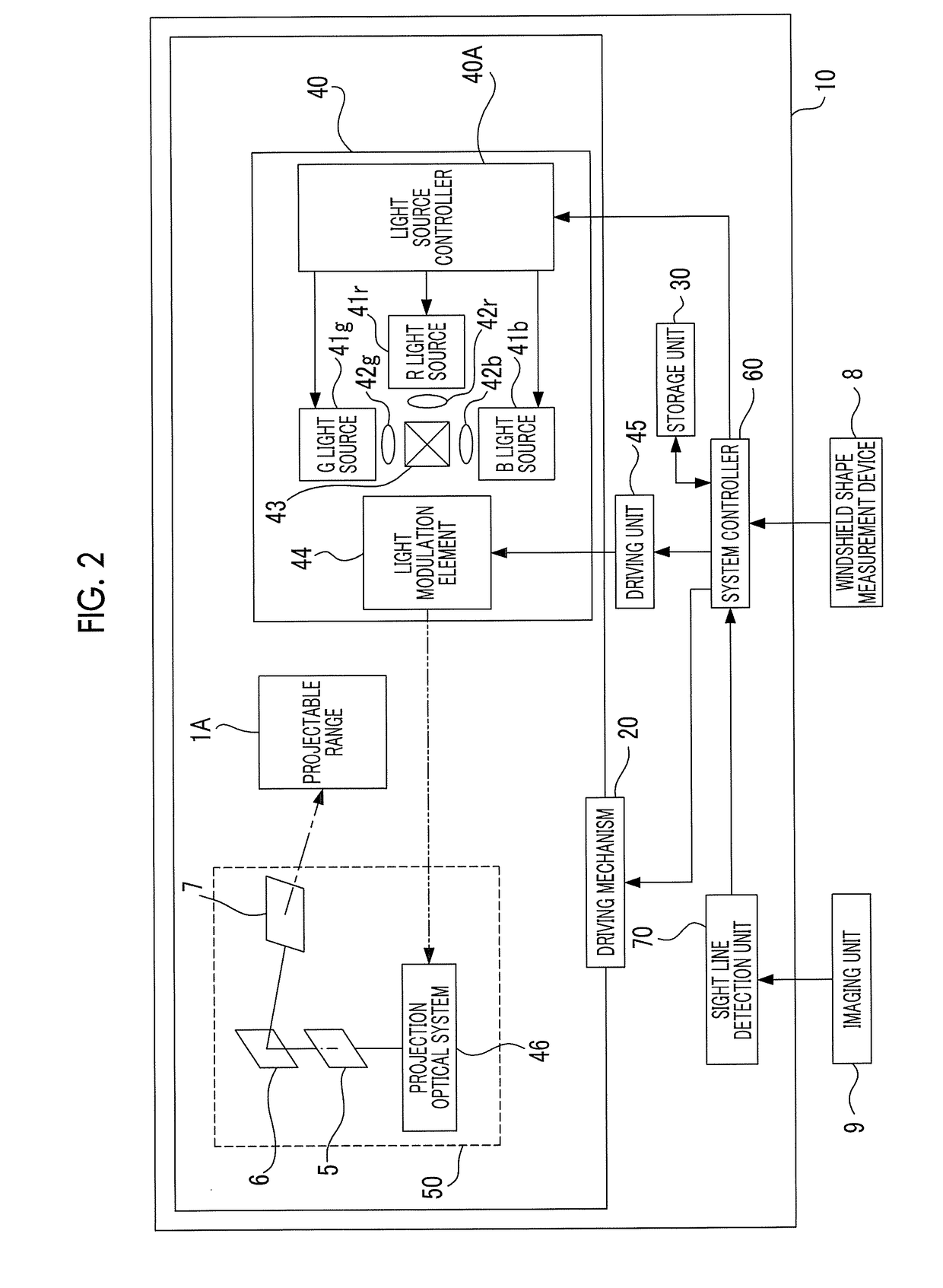
ActiveUS20180157035A1Easy to changeReduce distortion problemsProjectorsCharacter and pattern recognitionDisplay deviceSystem controller
An HUD includes a projection unit that projects image light that is spatially modulated on the basis of image data onto a windshield, a sight line detection unit that detects a line of sight of a driver of a vehicle, and a system controller that acquires measurement data on shape of a region including a point that intersects the line of sight of the driver in a projectable range of the image light in the windshield, generates correction data for correcting distortion of an image based on the image light projected onto the region on the basis of the acquired measurement data and the direction of the line of sight of the driver, and corrects the image data using the generated correction data.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Autostereoscopic projection system
ActiveUS7938540B2Image is often very smallReduce resolutionProjectorsSteroscopic systemsDigital videoBeam splitter
An apparatus projecting 3D autostereoscopic images viewers. The apparatus includes a projector array with projectors each receiving an input image such as digital video and projecting an image based on the input image. A beam splitter with first and second surfaces is positioned such that the projected images strike the first surface and a portion (e.g., 50 to 95 percent) is transmitted through the beam splitter toward a screen with a retroreflective surface. The retroreflective surface reflects the splitter-transmitted portion back along the same path but with increased brightness. The light reflected from the retroreflective surface strikes the second surface of the beam splitter and is reflected toward a display viewing zone provided at about the focal points of the reflected projectors. A 3D image is perceivable to a viewer who positions his eyes at or near any of two or more viewing locations proximate to the projection surface.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
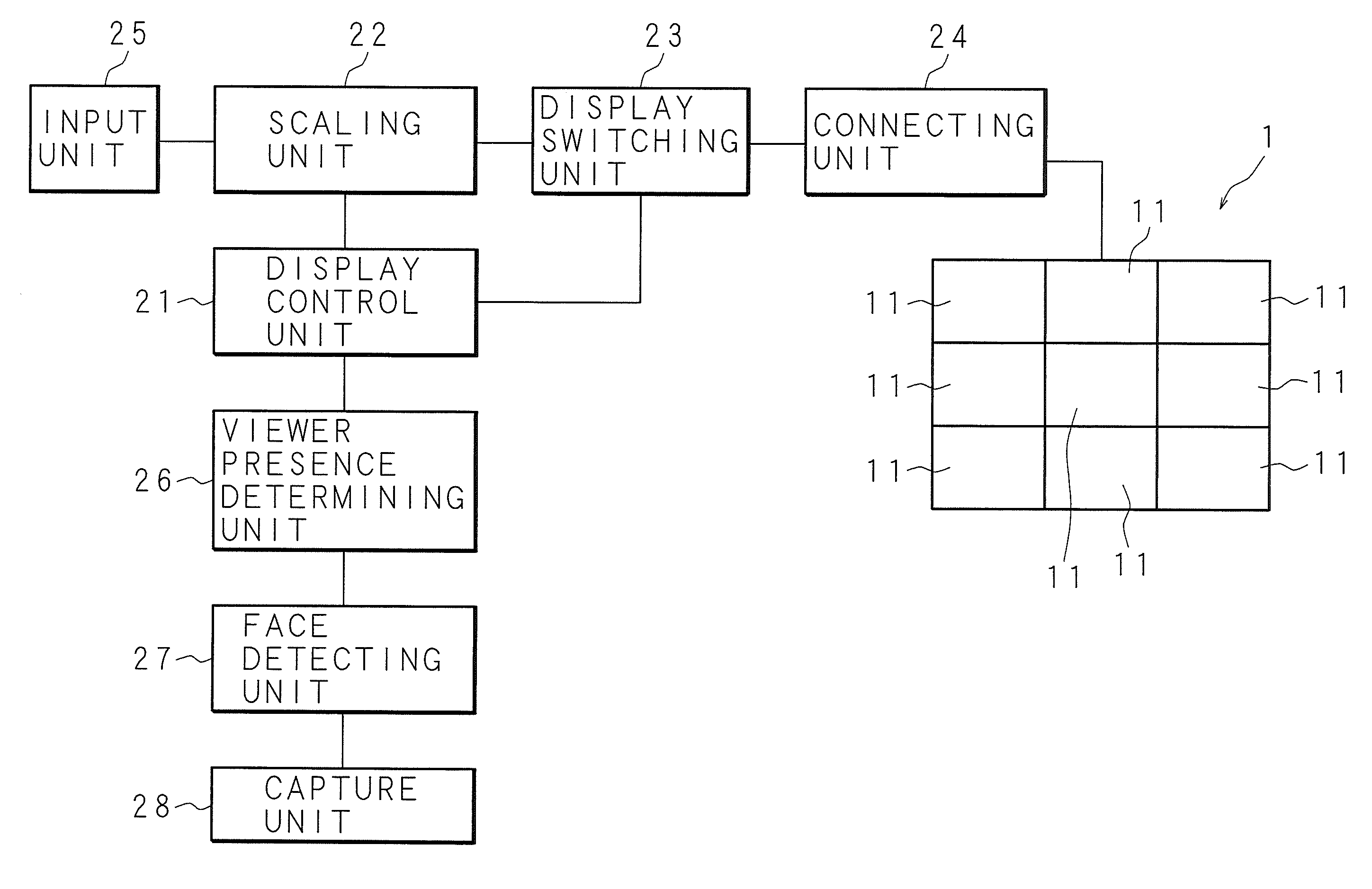
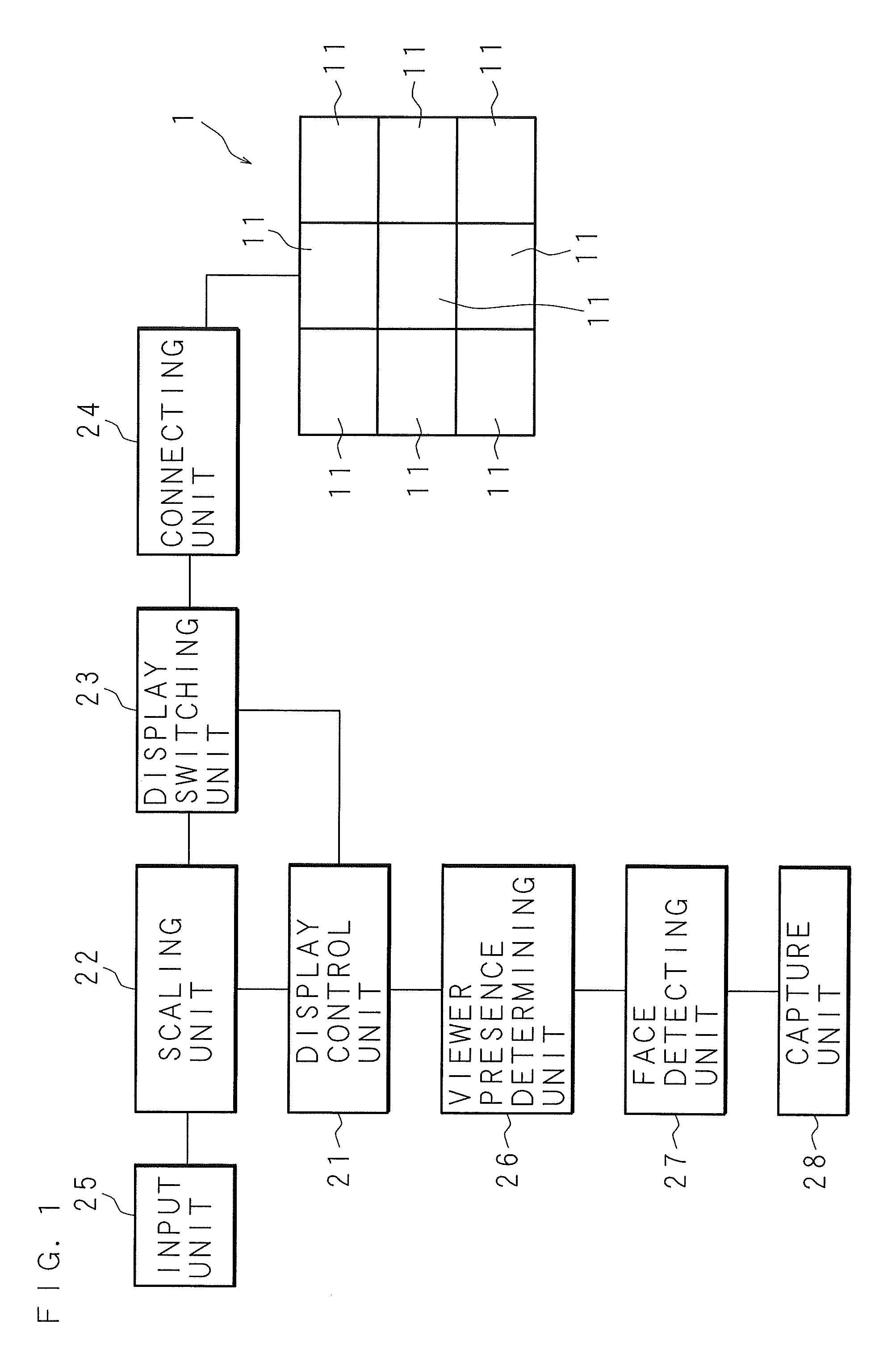
Multi-display apparatus
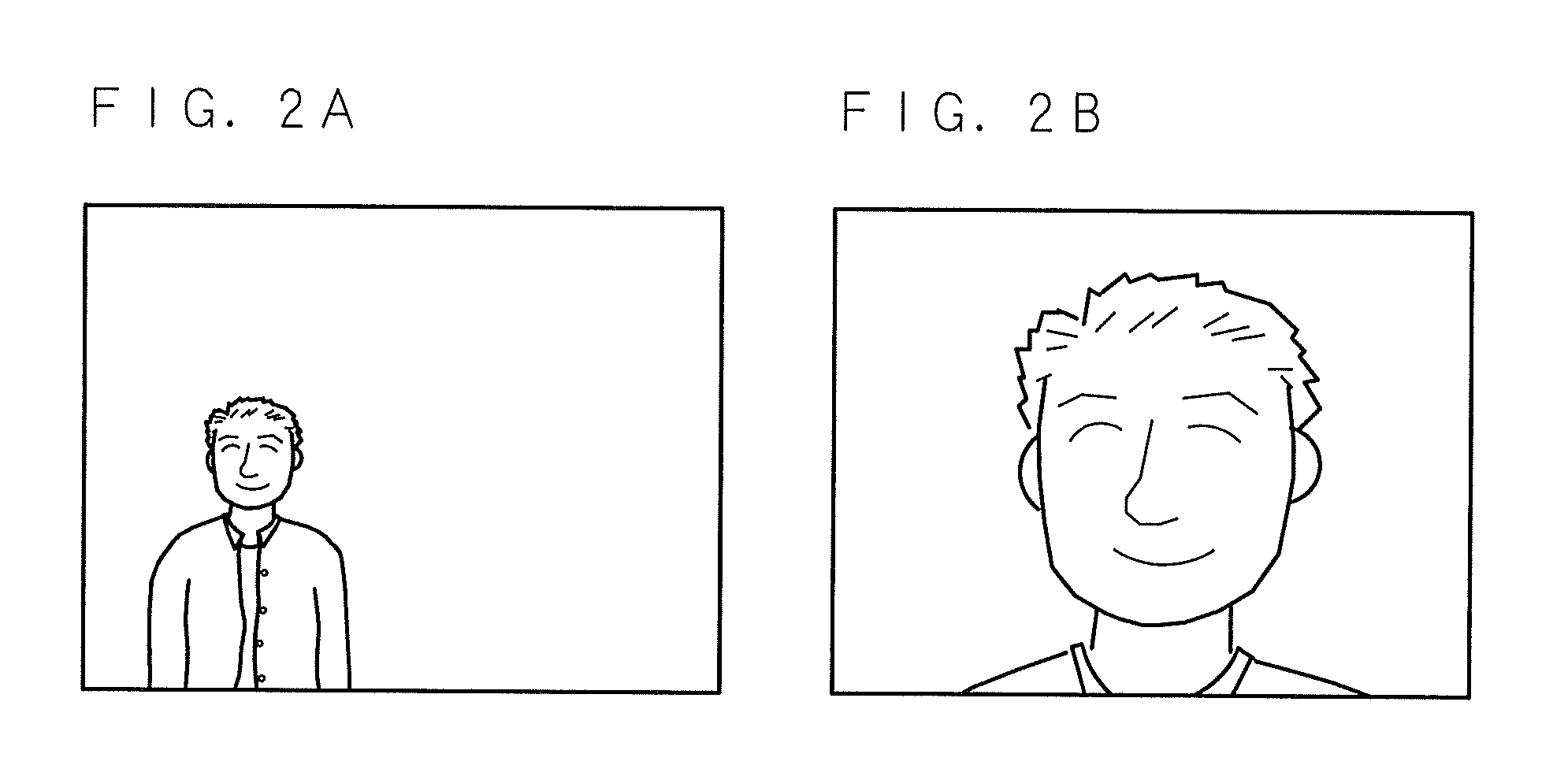
InactiveUS20120056902A1Adjustable sizeImage is often very smallCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer graphics (images)Display device
A multi-display apparatus including a display unit 1 constituted by plural displays 11 detects that a viewer who is watching an image showed on the display unit 1 is present in a near region, and shows an image with the size thereof adjusted based on the detected result on the display unit 1. For example, the multi-display apparatus shows a small image on the display unit 1 by reducing the number of displays 11 used for image display when a viewer is present in the near region, allowing the viewer in the near region to easily see the image. Moreover, the multi-display apparatus shows a large image on the display unit 1 when no viewer is present in the near region, allowing a viewer outside the near region to easily see the image.
Owner:SHARP KK
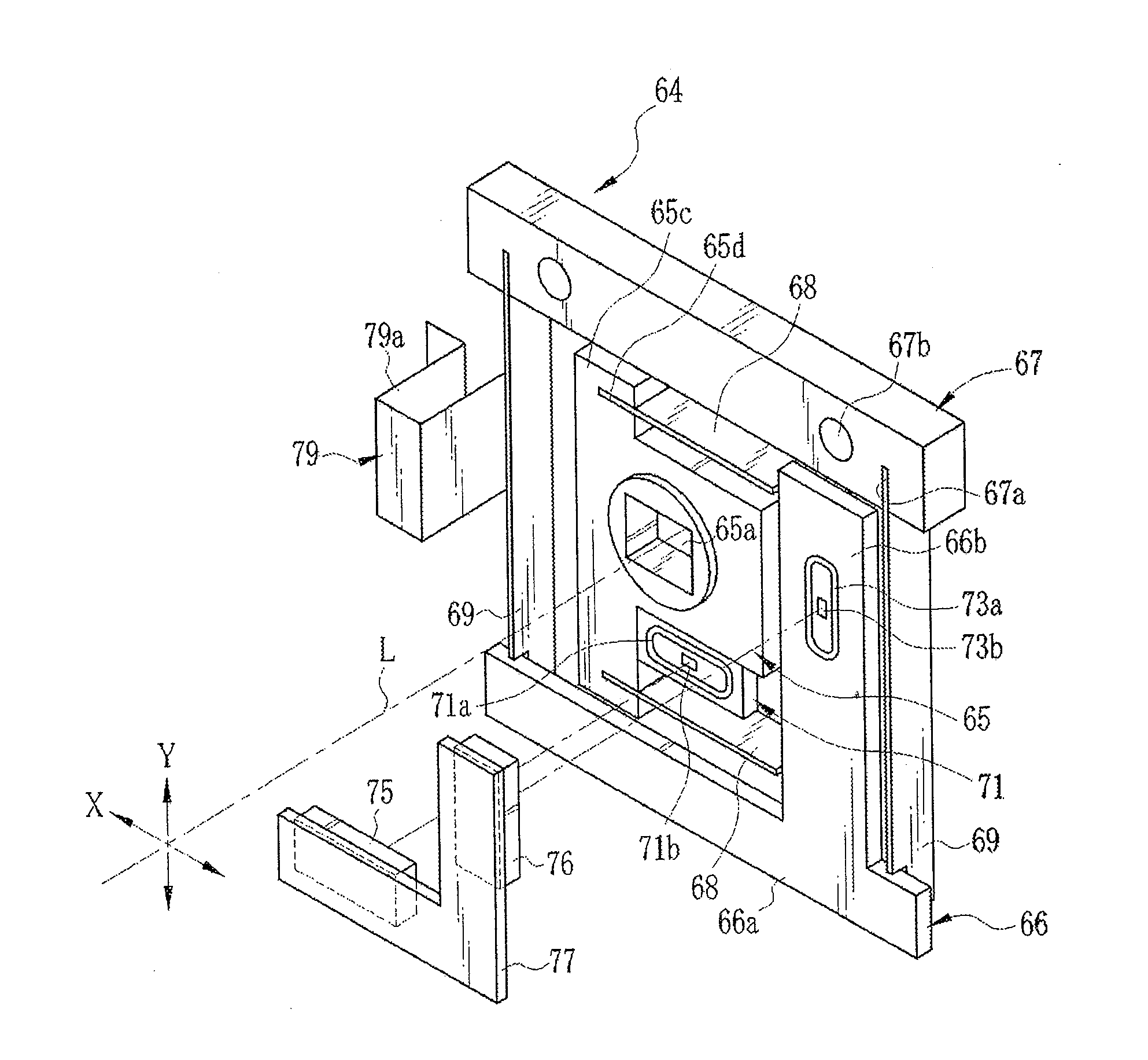
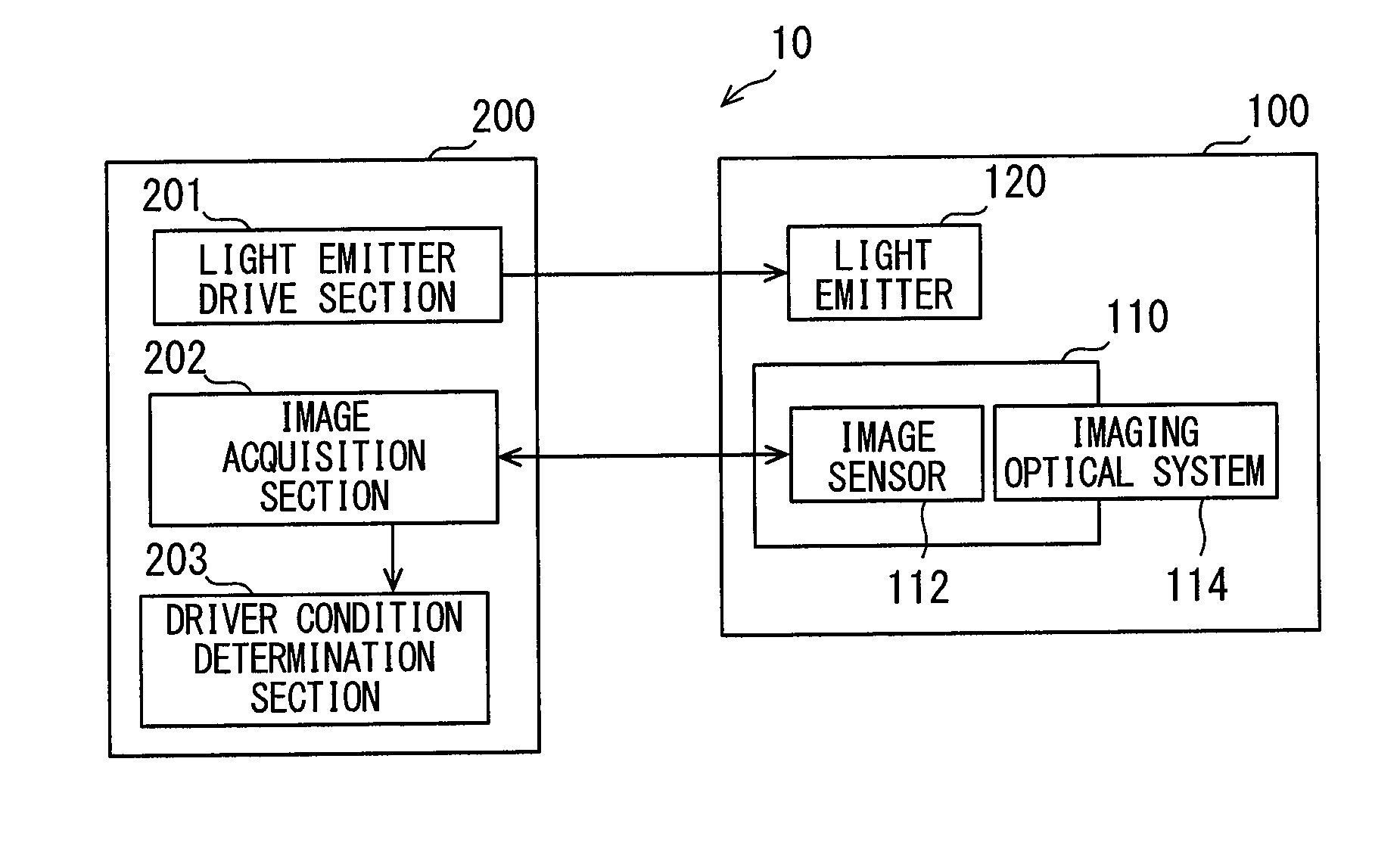
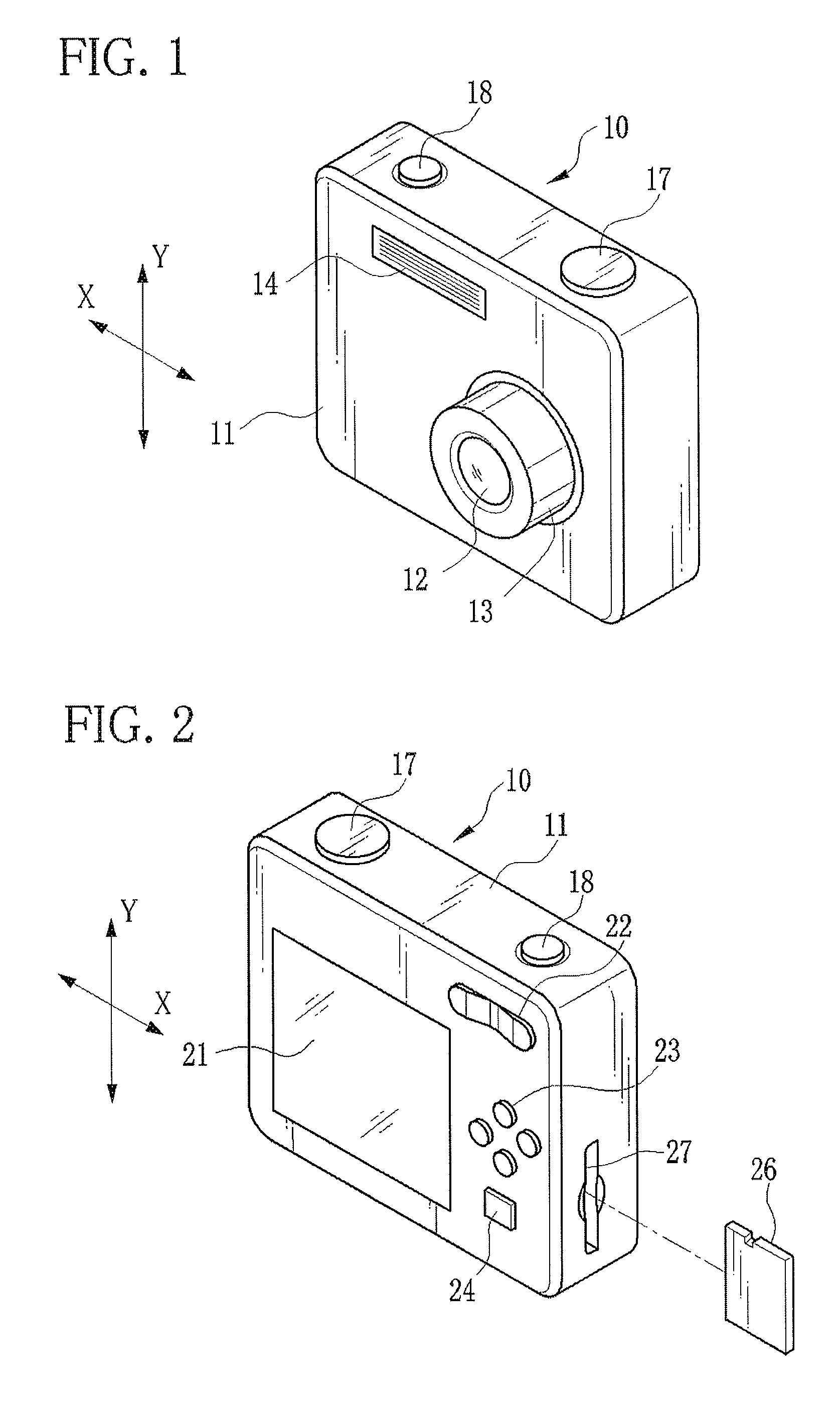
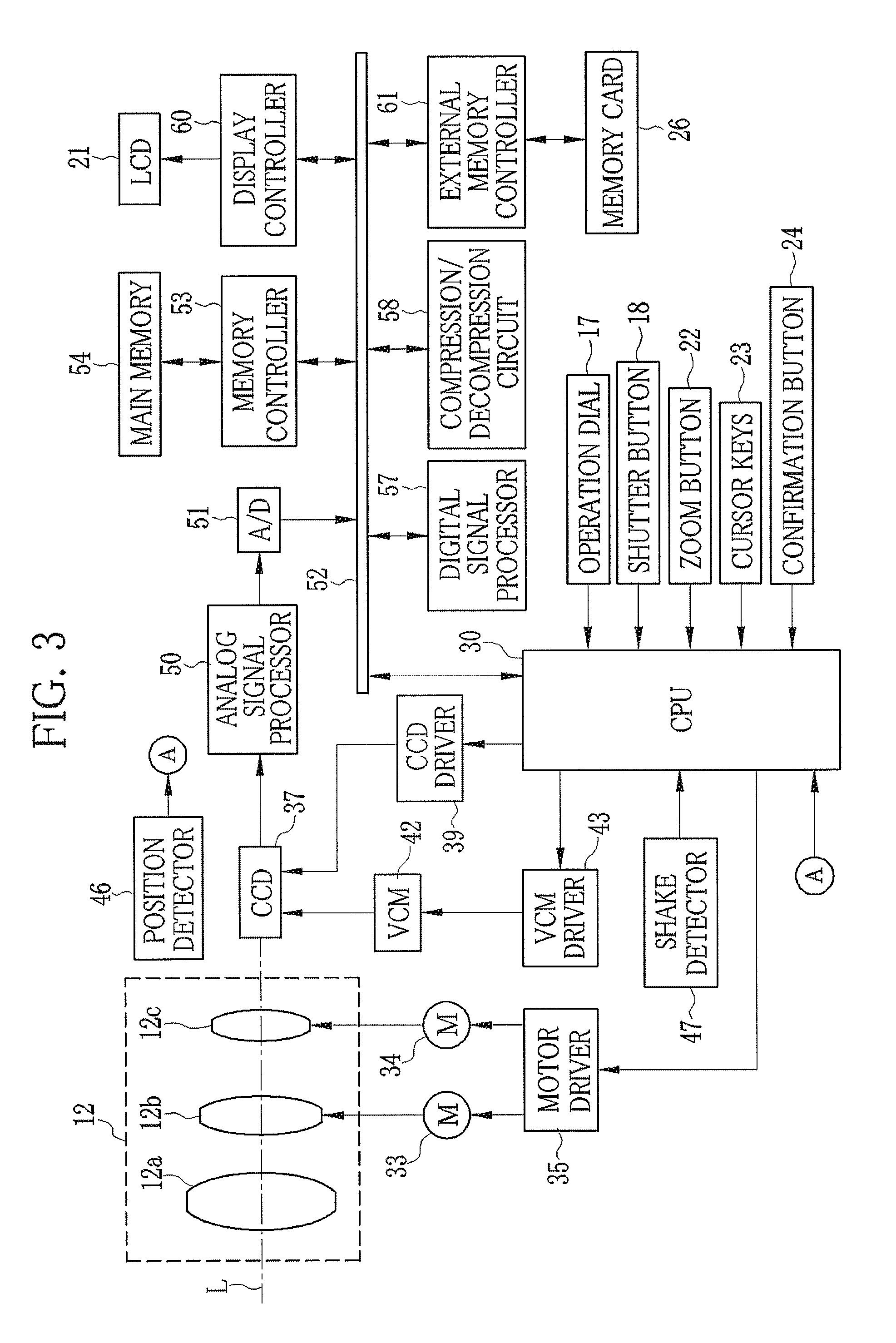
Camera body and imaging device equipped with same
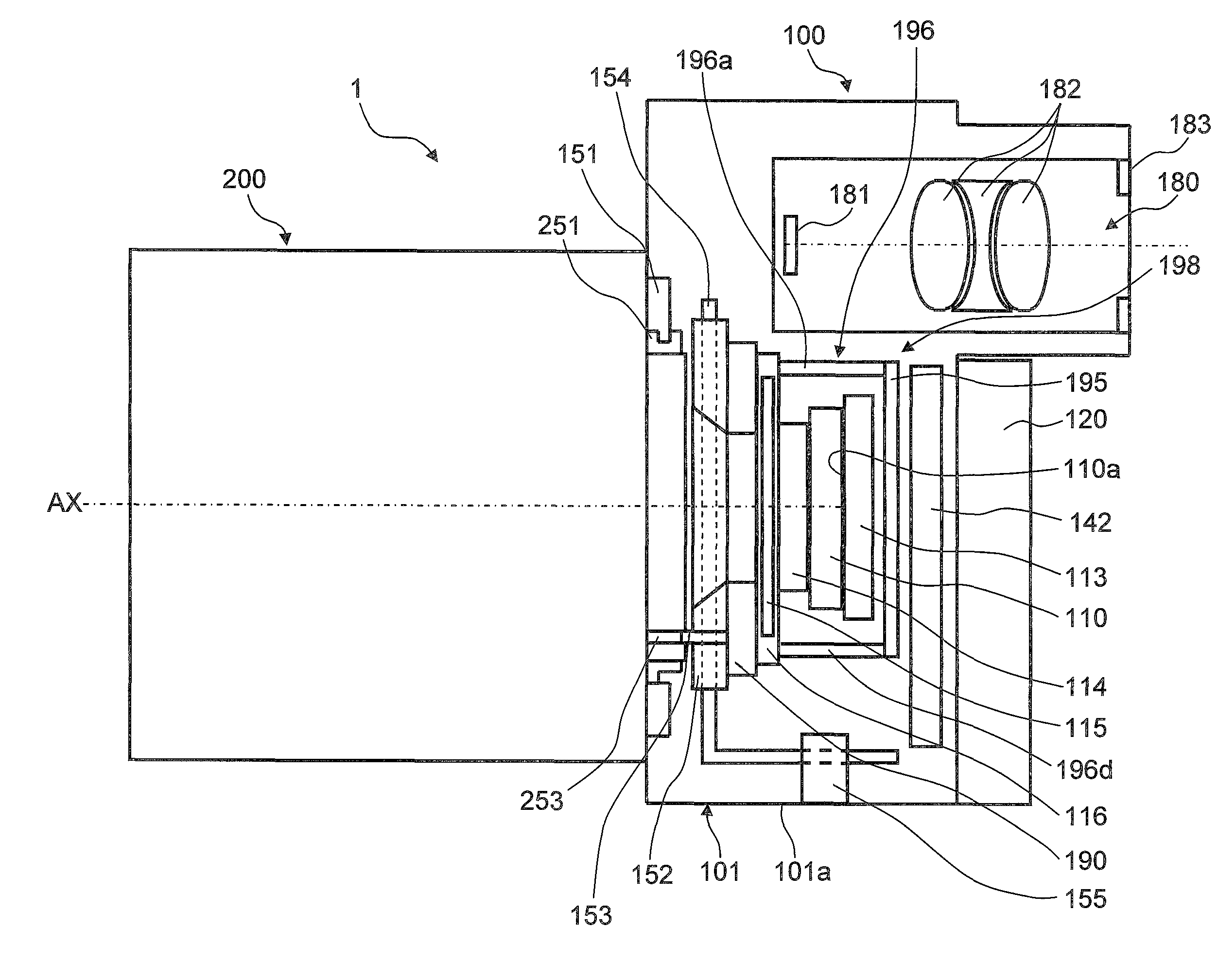
ActiveUS20100061716A1Increase temperatureSmall sizeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensEngineering
A camera body includes a body mount to which the lens unit can be mounted, a metal main frame supporting the body mount, an imaging element configured to convert an optical image of the subject into image data, an intermediate part disposed along a thermal conduction path formed between the main frame and the imaging element, and a metal heat radiating member connected to the intermediate part.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
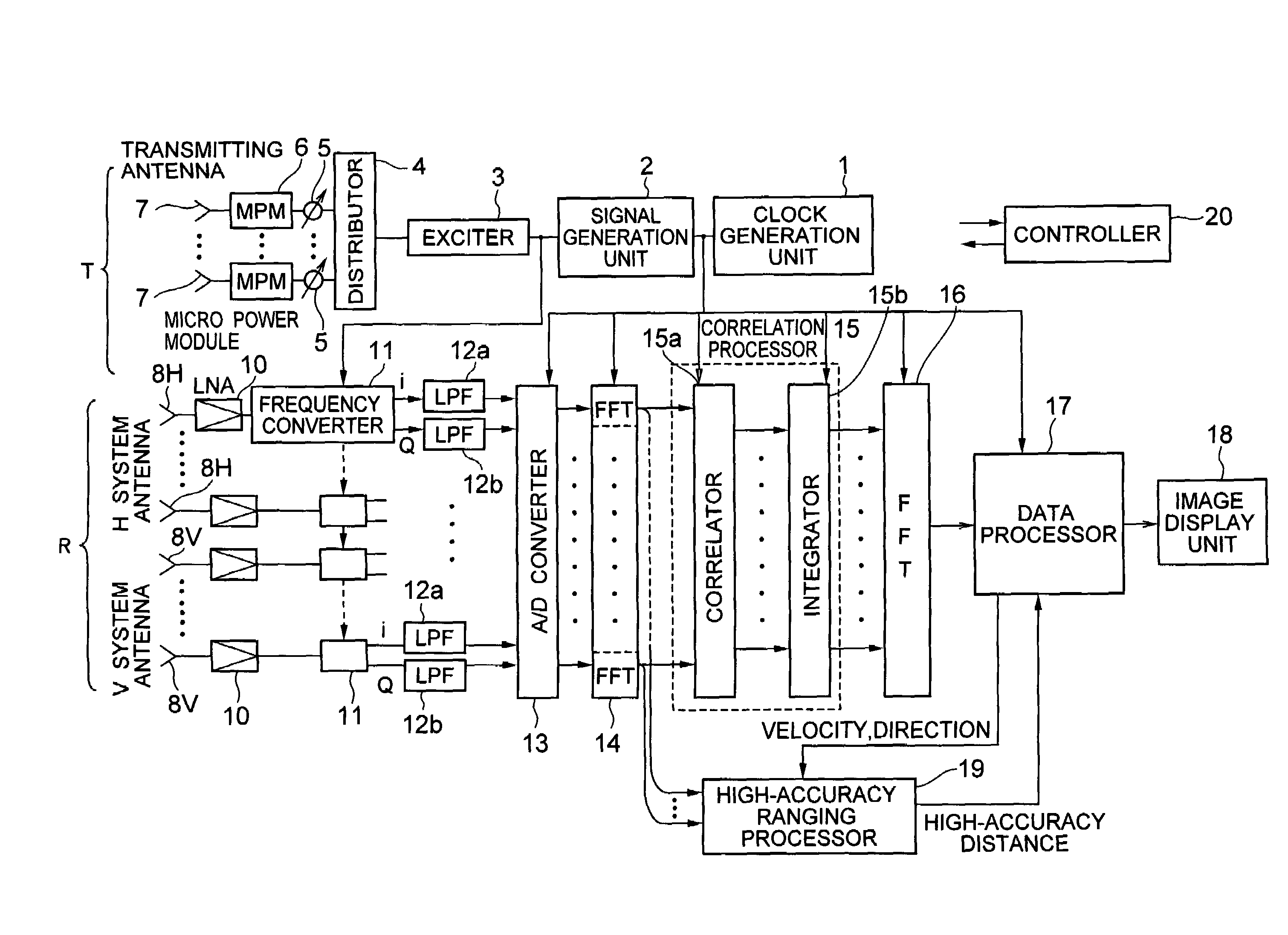
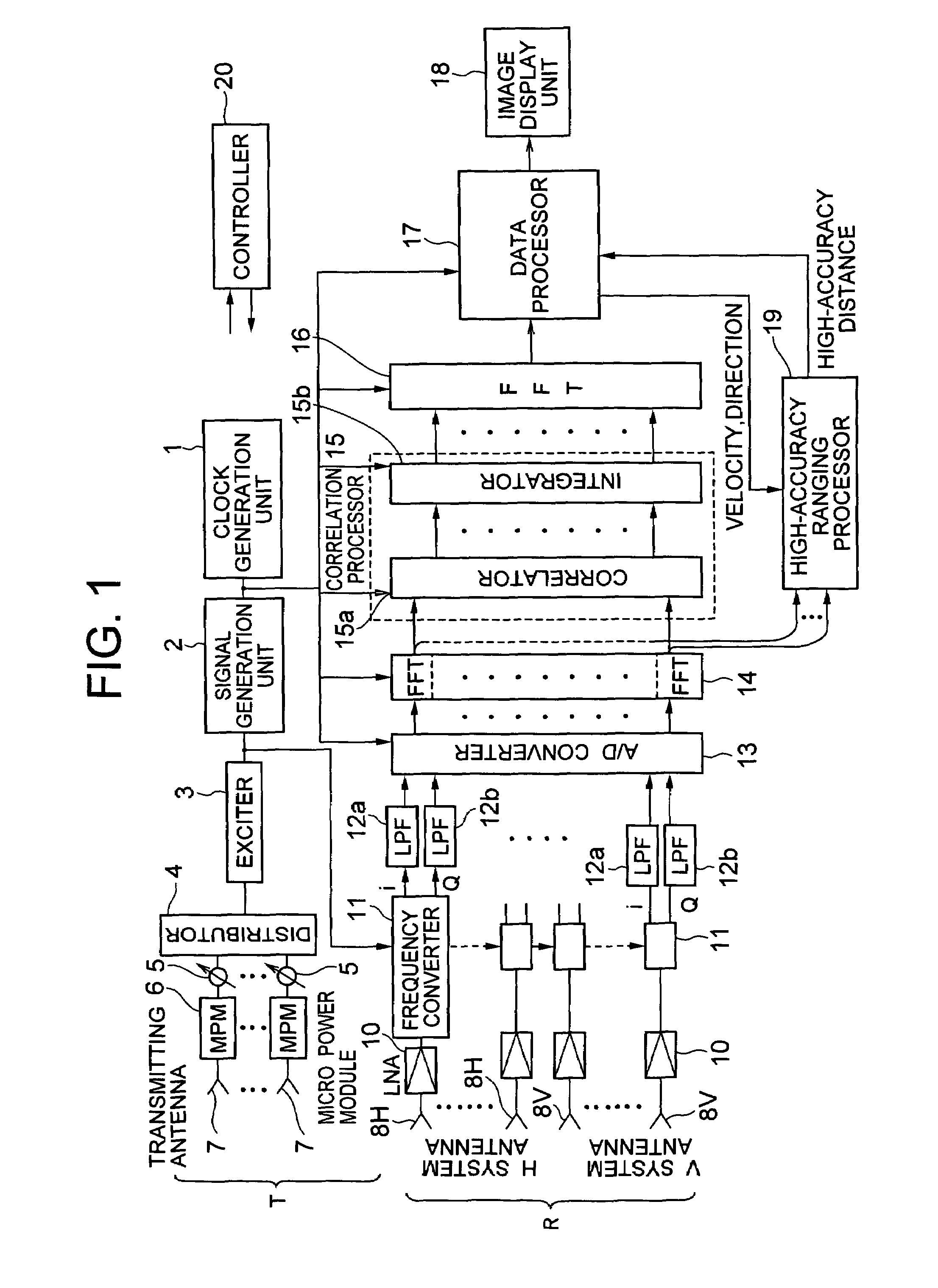
Interferometer-type radar
InactiveUS7394422B2Easily realizedImprove reliabilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarPhase difference
A transmitter for transmitting signals to targets and a receiver for receiving signals reflected from targets are included. The transmitter outputs CW signals for detecting direction and velocity of the target. The receiver performs: a function of receiving signals reflected from targets with a plurality of receiving antennas at the same time as transmitting from the transmitter, and performing spectral analysis with respect to receiving signals to thereby classify them by velocity component; a function of correlating signals of the receiving antenna systems; a function of integrating the signals correlation-processed; and a function of obtaining phase fronts of signals made incident on an antenna face from the phase differences of signals between receiving antennas, and performing two-dimensional FFT to the outputs to thereby measure the direction and velocity of the target.
Owner:NEC CORP
Camera body and imaging device equipped with same
ActiveUS20100061717A1Avoid heat damageSmall sizeTelevision system detailsCamera body detailsCamera controlCamera lens
A camera body includes a body mount, an imaging element, an imaging element circuit board, a main circuit board, and a metal heat radiating plate. The body mount allows the lens unit to be mounted. The imaging element is disposed on the opposite side of the body mount from the side where the lens unit is mounted, and converts an optical image of the subject into image data. The imaging element circuit board is electrically connected to the imaging element and controls the imaging element. The main circuit board is disposed on the opposite side of the imaging element from the body mount, and includes a camera controller. The heat radiating plate is disposed between the imaging element and the main circuit board.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
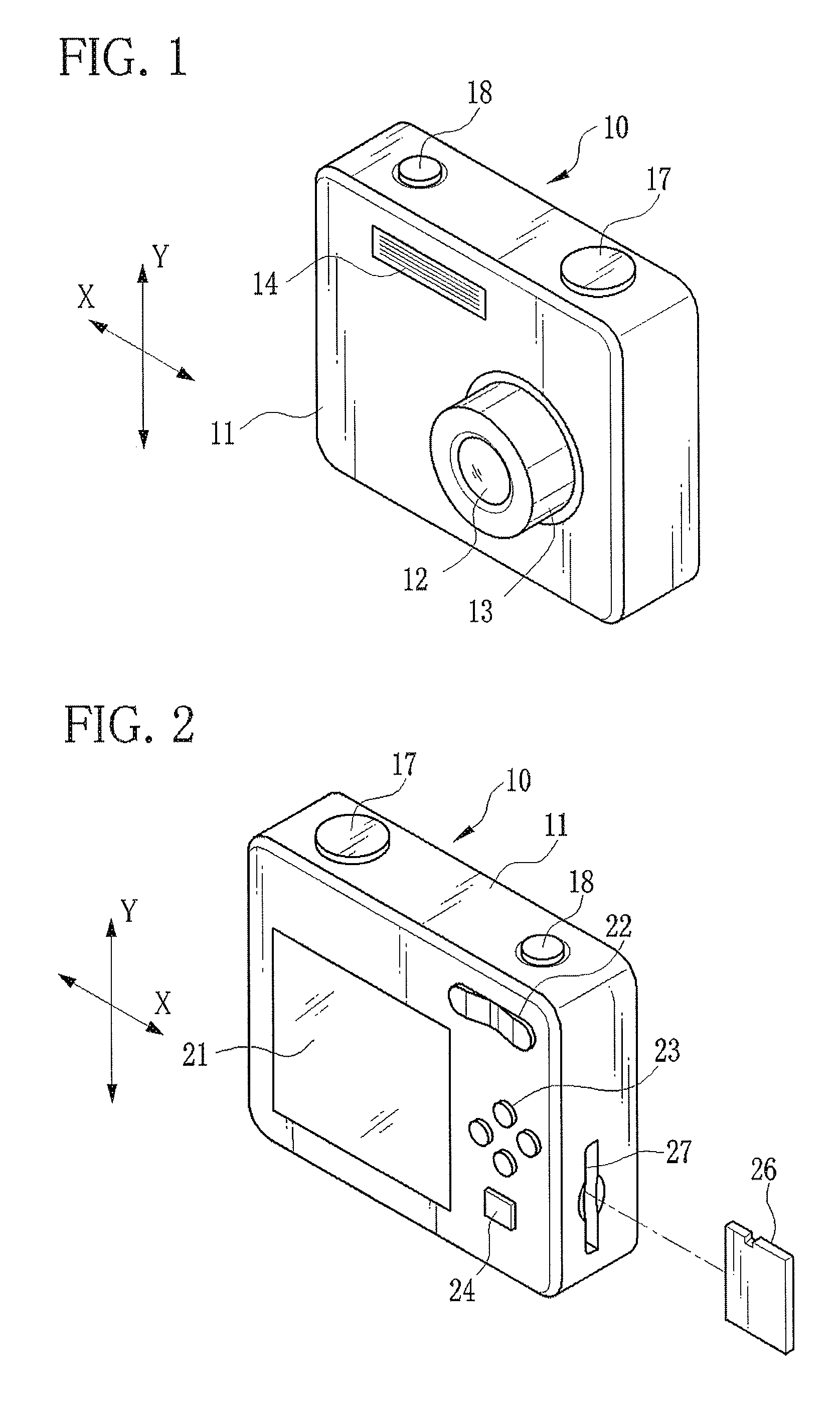
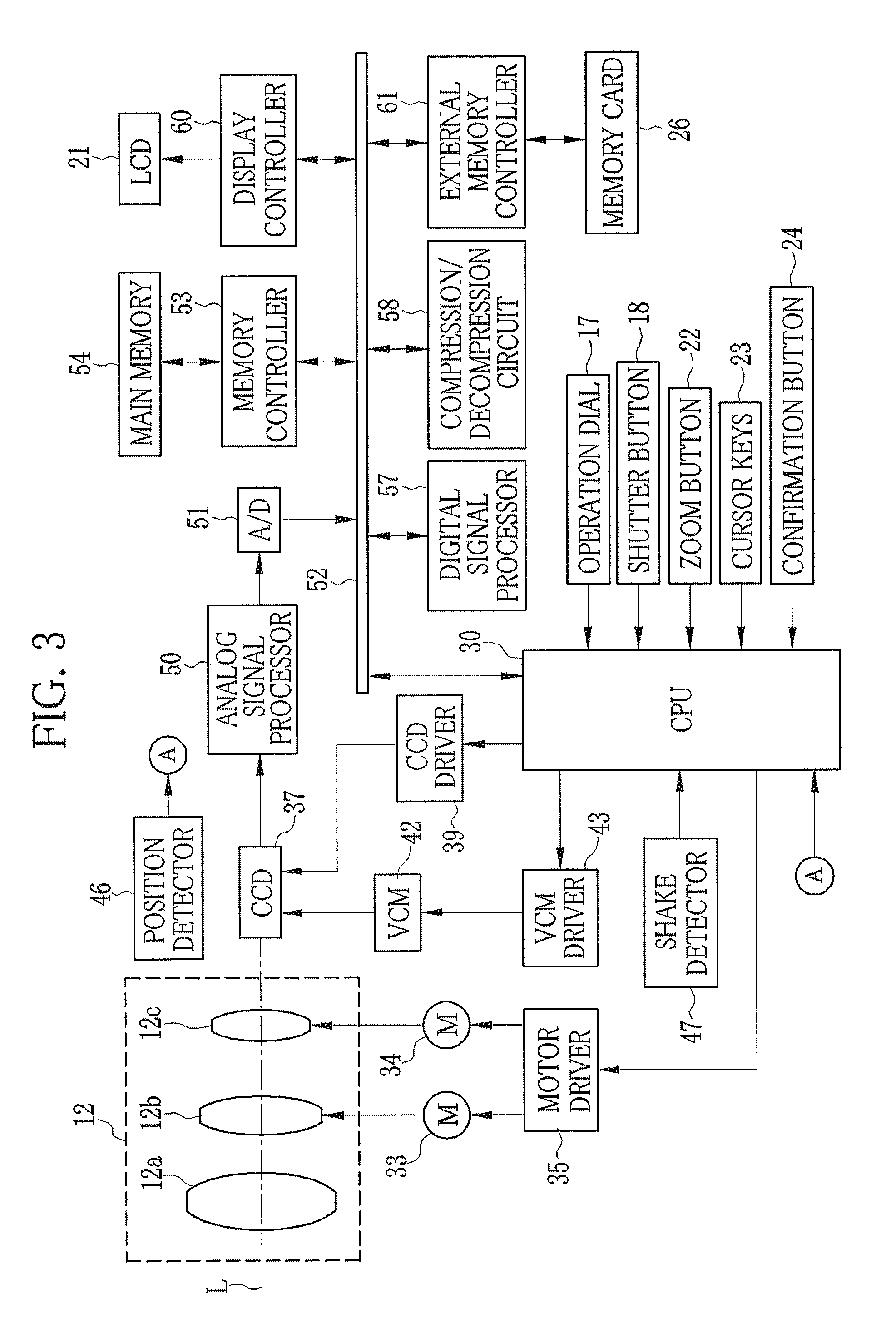
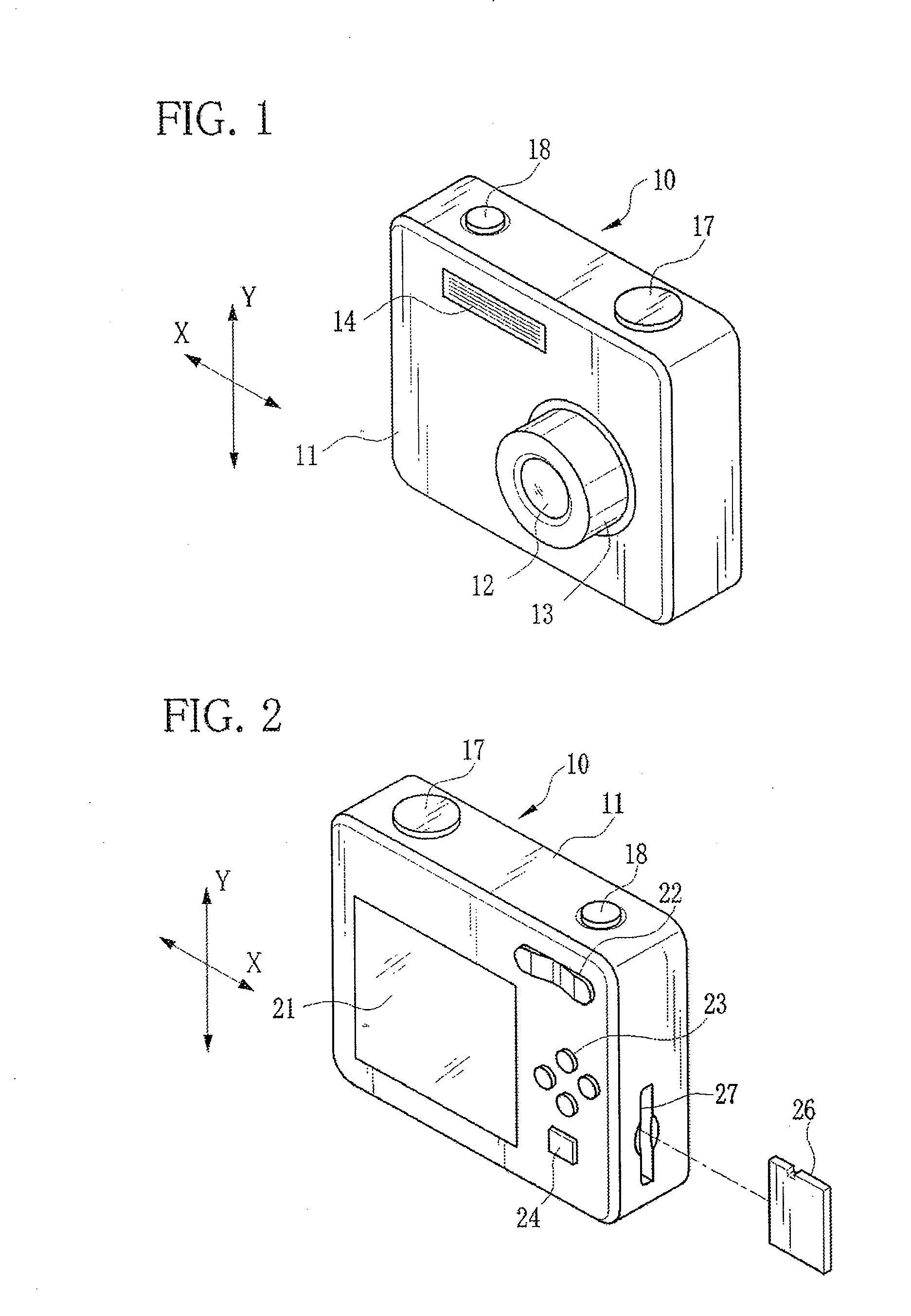
Image-taking device
InactiveUS20060153554A1Easy to useImage is often very smallPrintersProjectorsLiquid-crystal displayAngular rate sensor
An image-taking device is capable of effectively utilizing a shake correcting section and thereby shooting an image with little blur. The image-taking device includes: an angular rate sensor which detects a shake; a shift lens which travels within a predetermined moving range to correct the shake; a shift lens driving section which pulls the shift lens, which has moved to a biased position from a predetermined center, back to the center; a central processing unit which calculates a correction effect for the shake; and a liquid crystal monitor. The central processing unit calculates the correction effect based on a distance between the position of the moved shift lens and the center, and displays the correction effect on the liquid crystal monitor.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
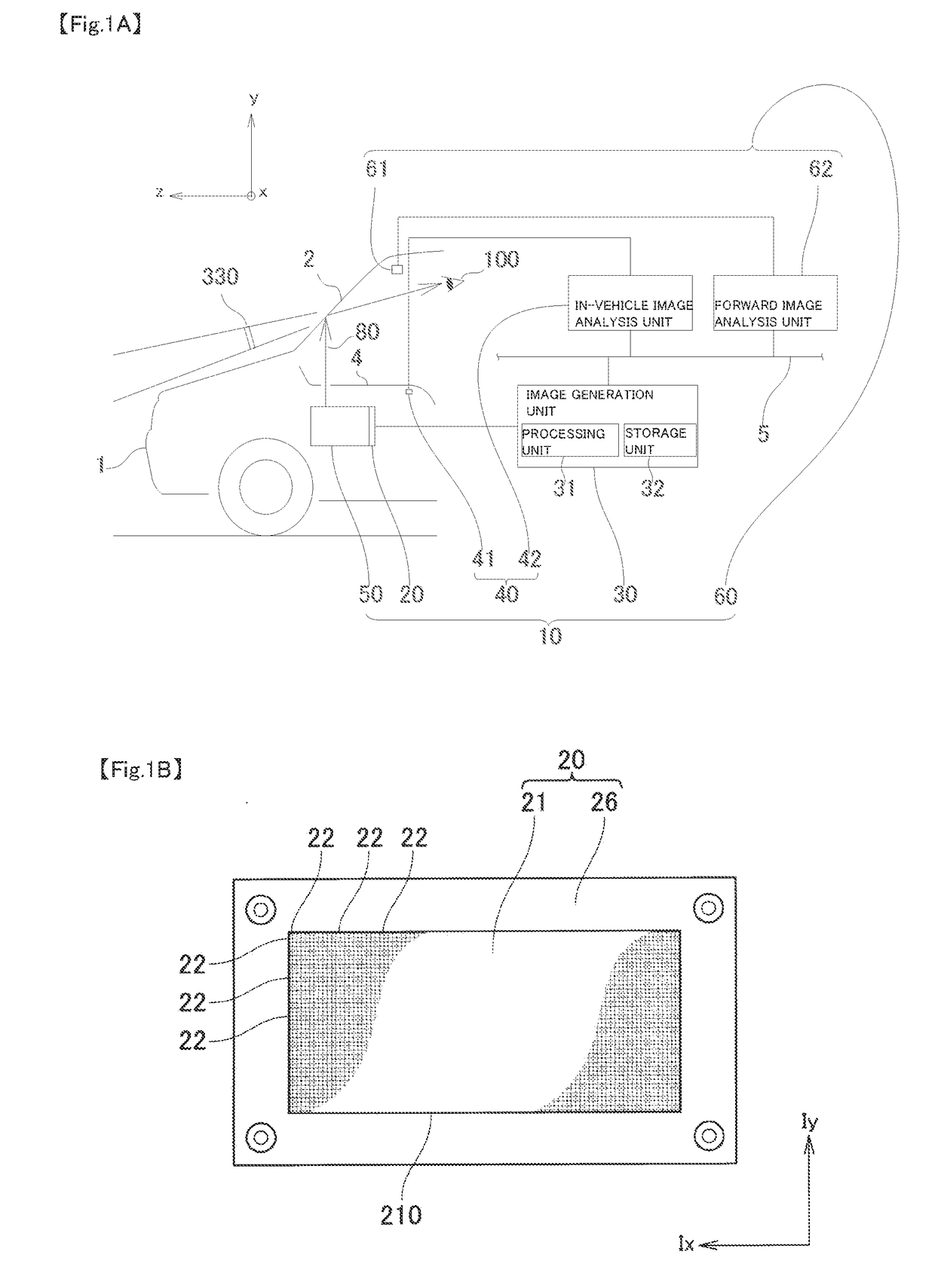
Vehicle display device
ActiveUS20180210210A1Less discomfortImage is often very smallNavigation instrumentsSteroscopic systemsDriver/operatorVirtual image
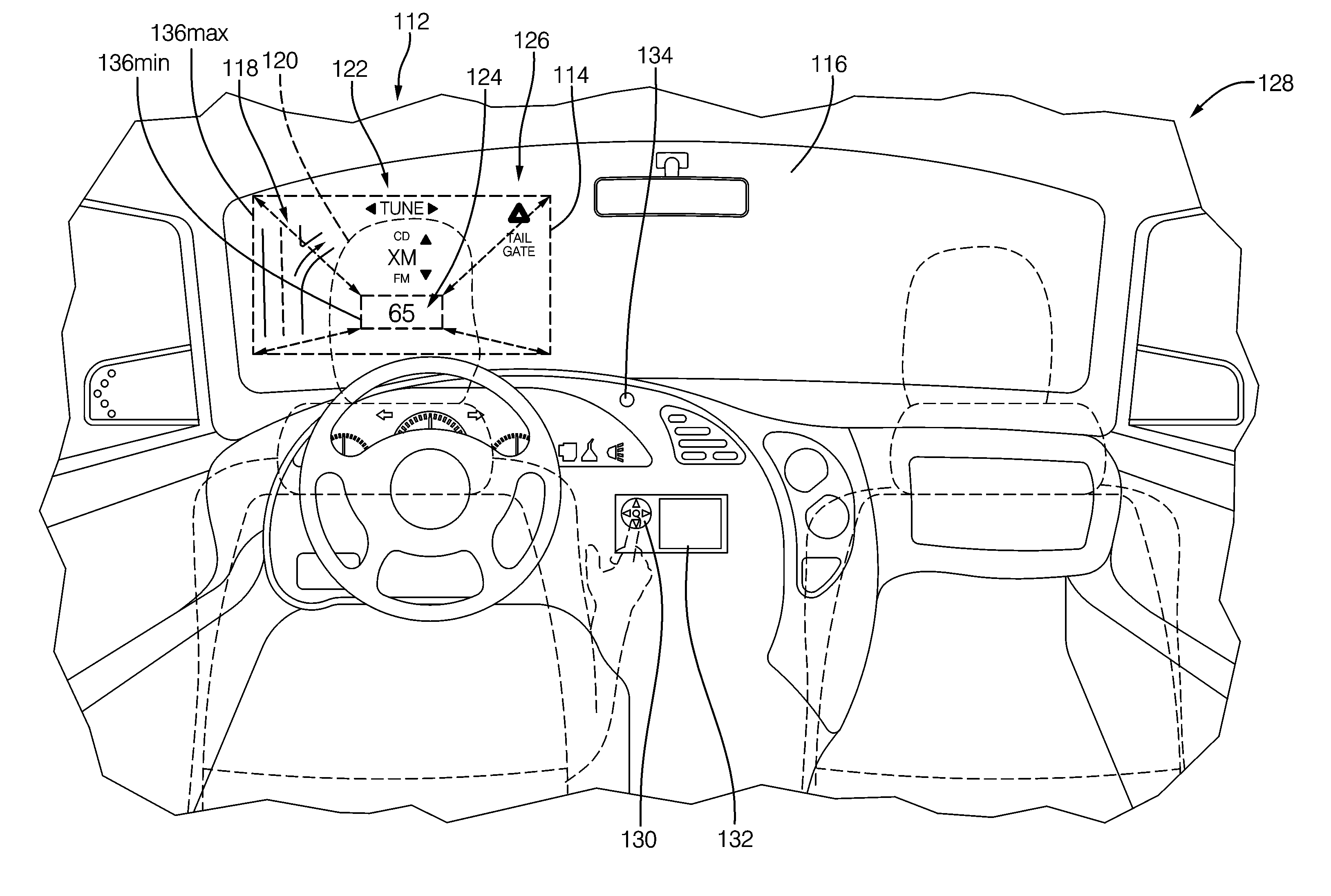
A vehicle display device includes: a viewpoint position acquisition unit acquiring a user viewpoint position of a user seated in a driver seat of a vehicle; a forward information acquisition unit acquiring forward information of the vehicle; an image generation unit generating an image obtained by reflecting the forward information included within a prescribed area among the forward information acquired by the forward information acquisition unit; an image display unit having a display surface capable of displaying the image generated; and a projection unit projecting the image toward a vehicle's translucent member such that a virtual image is visible to the user. The image generation unit determines the position and the size of a first image element to be displayed, among image elements included in the generated image, on the display surface, according to the user viewpoint position in the vertical direction acquired by the viewpoint position acquisition unit.
Owner:NIPPON SEIKI CO LTD
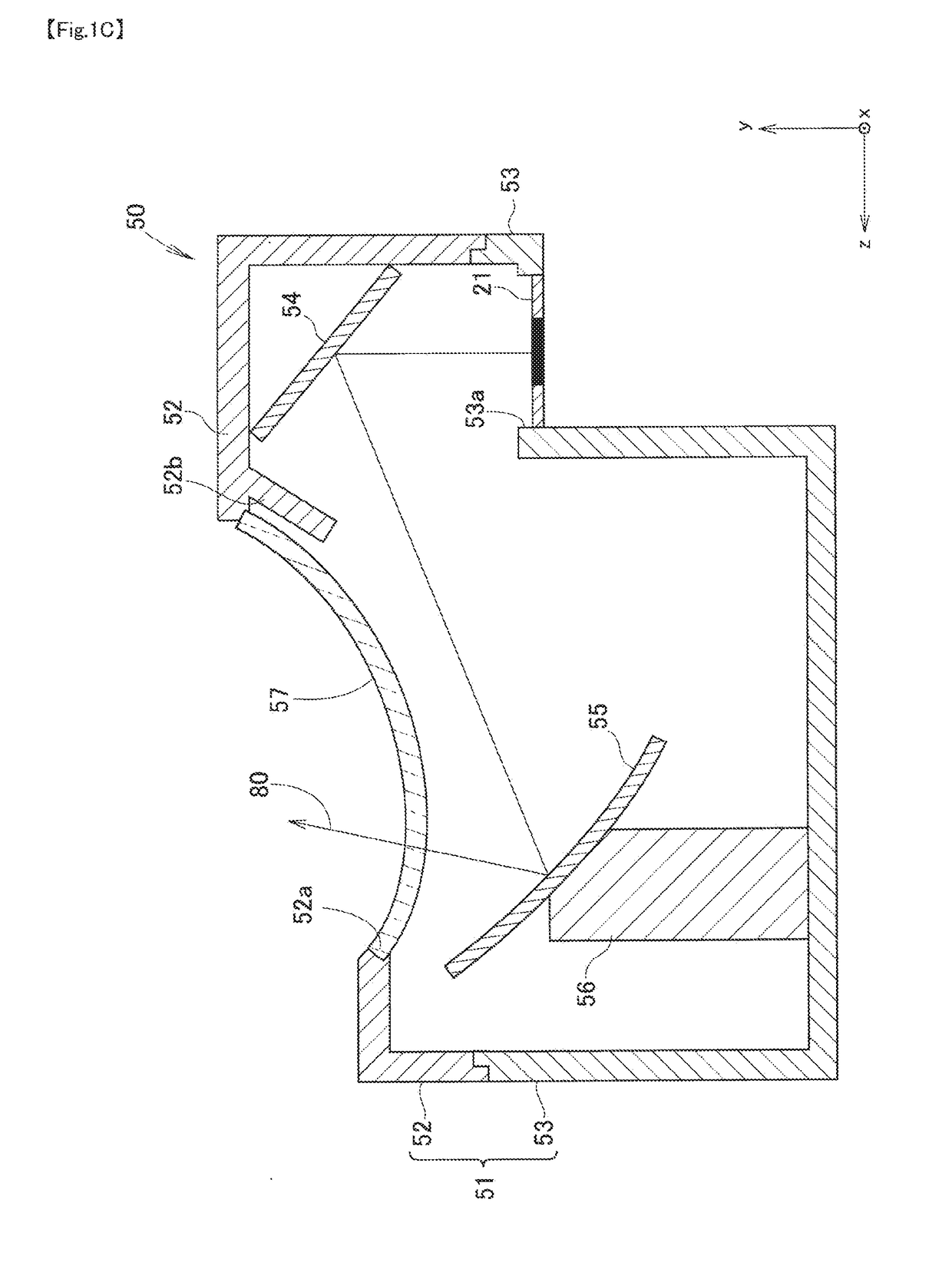
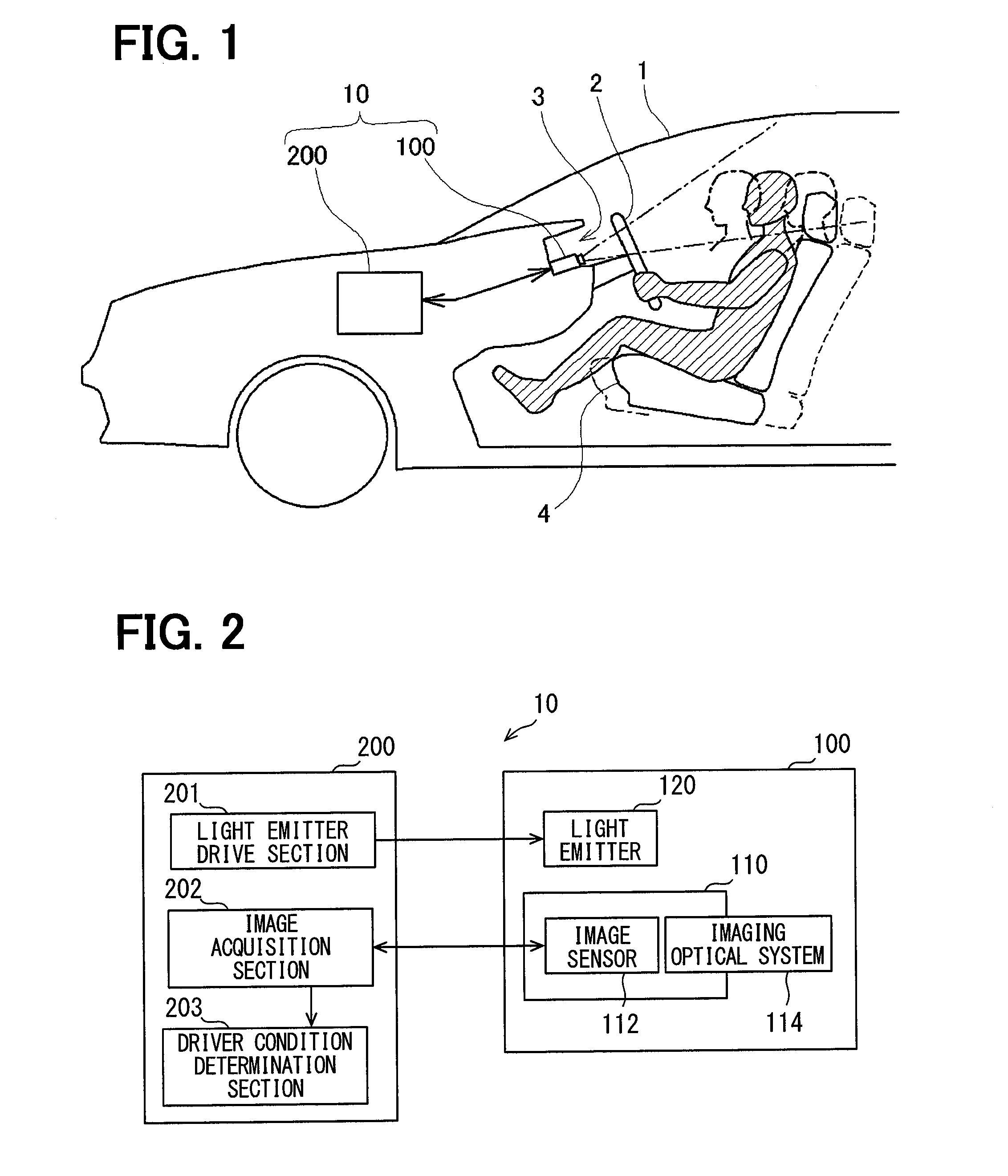
Face image capturing device and driver condition determination device
ActiveUS20160314366A1Accurate detectionSmall sizeTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementComputer graphics (images)In vehicle
In a face image capturing device, a focal point of a fixed-focus in-vehicle camera is set to a position where a circle of confusion with respect to a foremost face position is larger than the circle of confusion with respect to a rearmost face position. The rearmost face position is where the driver's face is positioned when a driver's seat is moved to the rearmost limit. The foremost face position is where the driver's face is positioned when the driver's seat is moved to the foremost limit. When the focal point of the in-vehicle camera is set to the above position, the focal point can be moved rearward to reduce the blurring of a face image at the rearmost face position. Even if the blurring of the face image at the rearmost face position is increased, a driver condition can be accurately determined at all times.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Image stabilizer and optical instrument therewith
ActiveUS8208031B2Eliminate saggingImage is often very smallTelevision system detailsPrintersEngineeringOptical instrument
An image stabilizer has a base block, an inner frame for holding a CCD, an outer frame, a pair of horizontal leaf springs, a pair of vertical leaf springs, voice coil motors (VCMs) and a flexible printed circuit (FPC). Upon a shake of a digital still camera due to hand-held shooting, the VCMs shift the inner or outer frame while bending the horizontal or vertical leaf springs so that the CCD is shifted to counteract the camera shake. The FPC connected to the CCD and the VCMs is routed from the inner frame, through the horizontal leaf spring, the outer frame and the vertical leaf spring, and pulled out above the base block. The FPC is glued to the horizontal and vertical leaf springs, and elastically bent together with the horizontal and vertical leaf springs.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Apparatus, method and computer program product for defect detection in work pieces
ActiveUS20160313257A1Increased signal noiseFast inspection solutionElectronic circuit testingOptically investigating flaws/contaminationCamera imageWavelength range
An apparatus, a method and a computer program product for defect detection in work pieces is disclosed. At least one light source is provided and the light source generates an illumination light of a wavelength range at which the work piece is transparent. A camera images the light from at least one face of the work piece on a detector of the camera by means of a lens. A stage is used for moving the work piece and for imaging the at least one face of the semiconductor device completely with the camera. The computer program product is disposed on a non-transitory, computer readable medium for defect detection in work pieces. A computer is used to execute the various process steps and to control the various means of the apparatus.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Image generating process
InactiveUS20070057089A1Good printing baseBig imageAircraft componentsVehicle fittingsAutomatic controlEngineering
Owner:IDEEUNDTECHN
Image stabilizer and optical instrument therewith
InactiveUS8111295B2Image is often very smallNegates needTelevision system detailsPrintersPhase detectorHand held
A CCD support mechanism includes a CCD holder for holding a CCD, a first printed circuit board having a first printed coil, a second printed circuit board having a second printed coil, a pair of horizontal leaf springs, and a pair of vertical leaf springs. When a camera shake occurs by hand-held shooting, a VCM composed of the first printed coil and a first stationary magnet shifts the CCD, while bending the horizontal leaf springs, to counteract the camera shake in a Y-axis direction. A VCM composed of the second printed coil and a second stationary magnet shifts the CCD, while bending the vertical leaf springs, to counteract the camera shake in an X-axis direction. Current values of the VCMs are determined by feedback control by using an output signal from a shake detector as a target value and a present position from a position detector as a measurement value.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Position adjustment system for a projection lens
ActiveUS9229300B2Image is often very smallEasy to correctProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensLocking mechanism
A lens position adjustment system (10) permits adjustment of the position of a projection lens (5) relative to a projector (100) for making a Scheimpflug adjustment. The projection lens (5) has an optical axis (6). The system (10) comprises: a first support part (20) for fitting to, or forming part of, the projector (100); a second support part (40) for fitting to, or forming part of, the projection lens (5); and a connecting part (30). The connecting part (30) is pivotally connected to the first support part (20) and pivotally connected to the second support part (40) and configured to permit independent adjustment of the second support part (40) relative to the first support part (20) about two axes of rotation (7, 8) which intersect, and are perpendicular to, the optical axis (6) of the projection lens (5). A locking mechanism (28, 29, 51-58) is provided for securing a position of the second support part (40) relative to the first support part (20).
Owner:BARCO NV
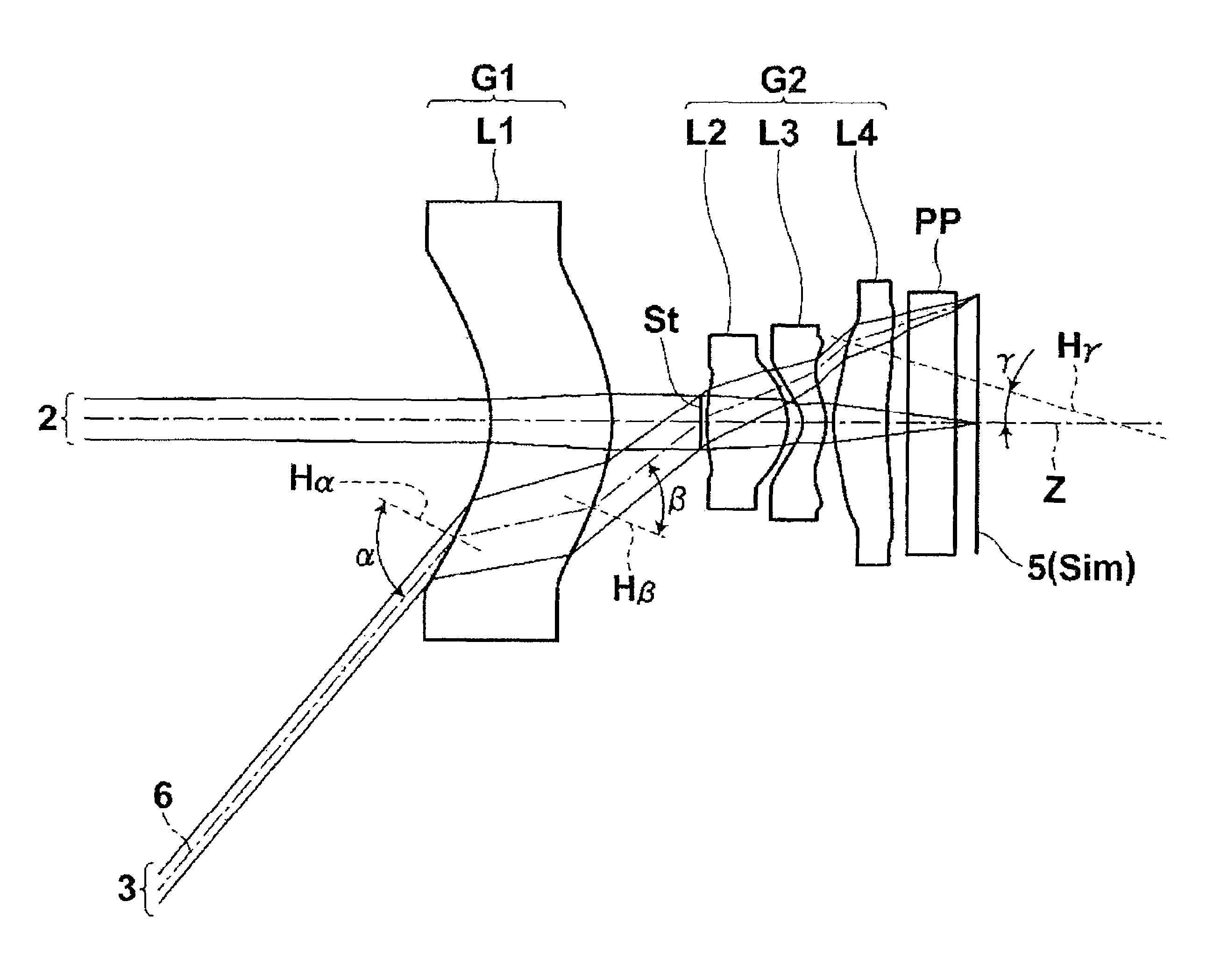
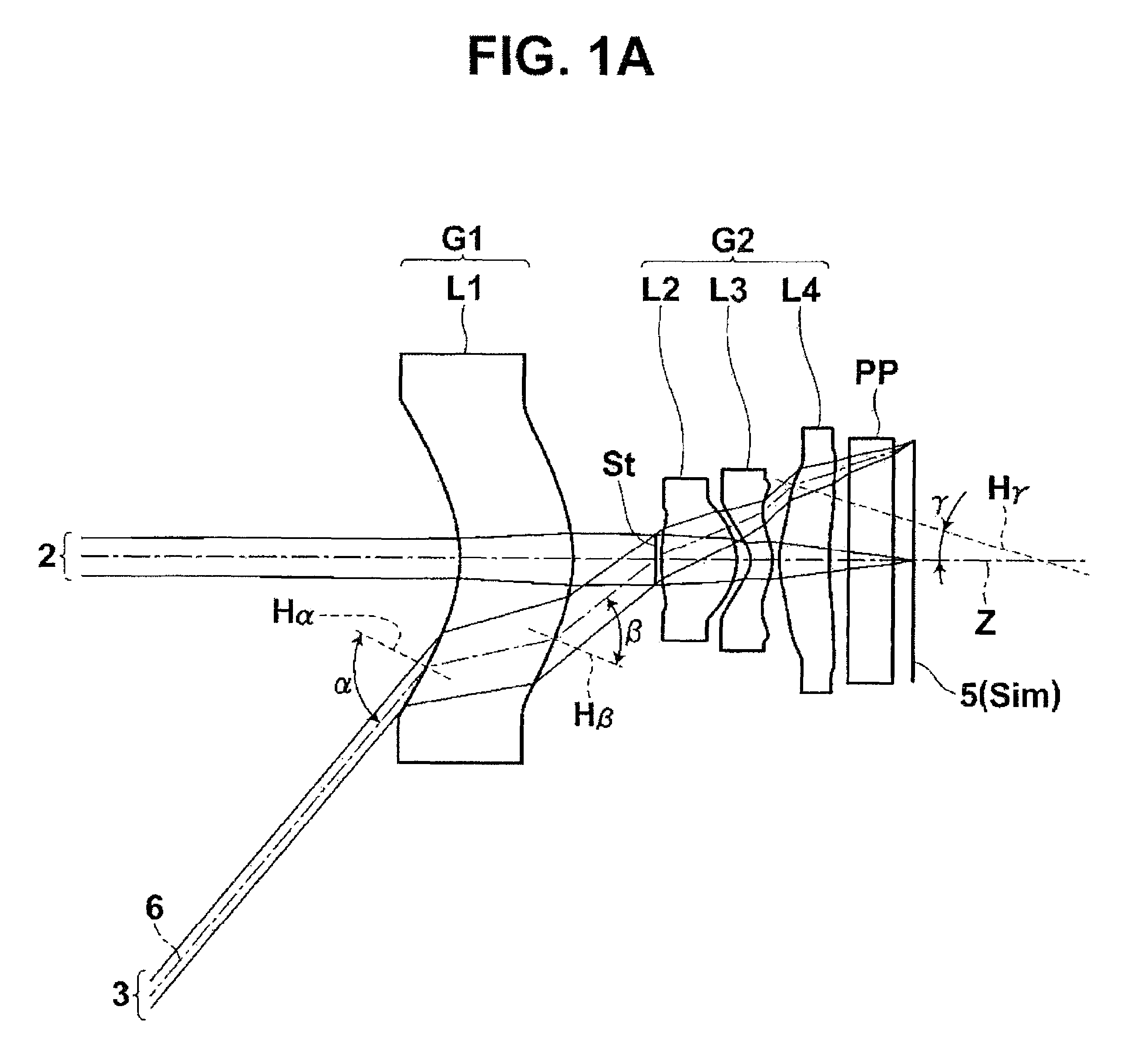
Optical System and Image Pickup Apparatus
An optical system of the present invention includes, in order from an object side: a first lens group G1; a second lens group G2 having positive refractive power; and a third lens group G3 having positive refractive power, wherein the first lens group G1 and the third lens group G3 are fixed in an optical axis direction while the second lens group G2 is moved in an optical axis direction to focus on from an object at infinity to an object at a finite distance, and specified conditions is satisfied.
Owner:TAMRON
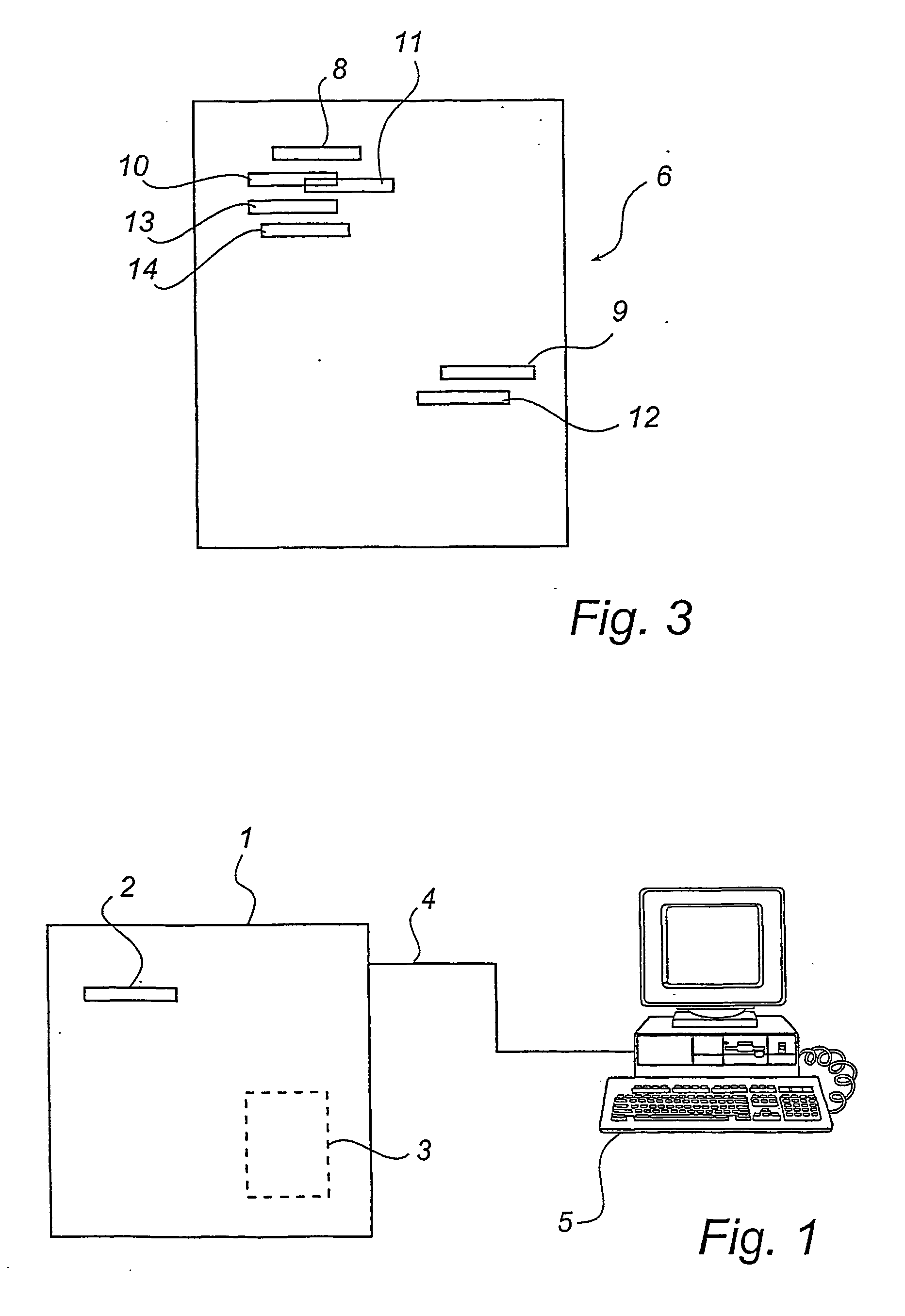
Device and method for fingerprints supervision
InactiveUS20040028261A1Simpler and cheaper device for checking fingerprintsReduce manufacturing costProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsFingerprintComputer hardware
A method and a device for checking fingerprints are described. The method comprises the steps of recording in succession at least two digital images of finger areas and comparing each of the recording images with a reference image that represents at least one previously recorded reference fingerprint from a reference finger areas. The device according to the invention is arranged to carry out the method.
Owner:PRECISE BIOMETRICS AB
Imaging lens and imaging apparatus
Disclosed is an imaging lens having a small F-number, high resolution, a sufficiently wide angle of view, and a small size. An imaging lens includes: a first lens with a meniscus shape having a concave surface facing an object side; a second positive lens; a third negative lens with a meniscus shape having a convex surface facing an image side; and a fourth lens having a convex surface facing the object side. The first to fourth lenses are arranged in this order from the object side. The imaging lens satisfies the following conditional expression: 0.25<D / f<4.0 (where D indicates the distance between the first lens and the second lens on the optical axis and f indicates the focal length of the entire system).
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Camera body and imaging device equipped with same
ActiveUS7933515B2Small sizeImage is often very smallTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensEngineering
A camera body includes a body mount to which the lens unit can be mounted, a metal main frame supporting the body mount, an imaging element configured to convert an optical image of the subject into image data, an intermediate part disposed along a thermal conduction path formed between the main frame and the imaging element, and a metal heat radiating member connected to the intermediate part.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Camera body and imaging device equipped with same
ActiveUS7933516B2Small sizeImage is often very smallTelevision system detailsCamera body detailsCamera lensEngineering
A camera body includes a body mount, an imaging element, an imaging element circuit board, a main circuit board, and a metal heat radiating plate. The body mount allows the lens unit to be mounted. The imaging element is disposed on the opposite side of the body mount from the side where the lens unit is mounted, and converts an optical image of the subject into image data. The imaging element circuit board is electrically connected to the imaging element and controls the imaging element. The main circuit board is disposed on the opposite side of the imaging element from the body mount, and includes a camera controller. The heat radiating plate is disposed between the imaging element and the main circuit board.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Light source arrangement for an illumination device of a medical-optical observation
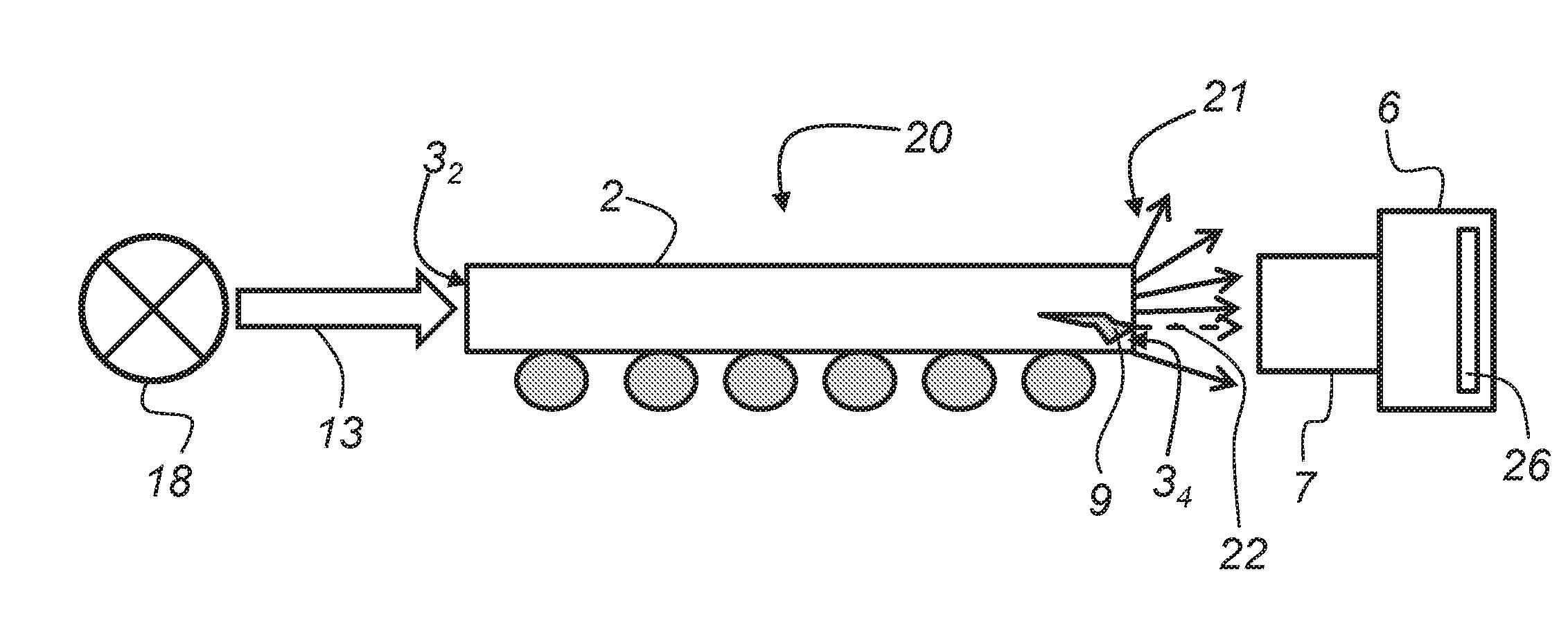
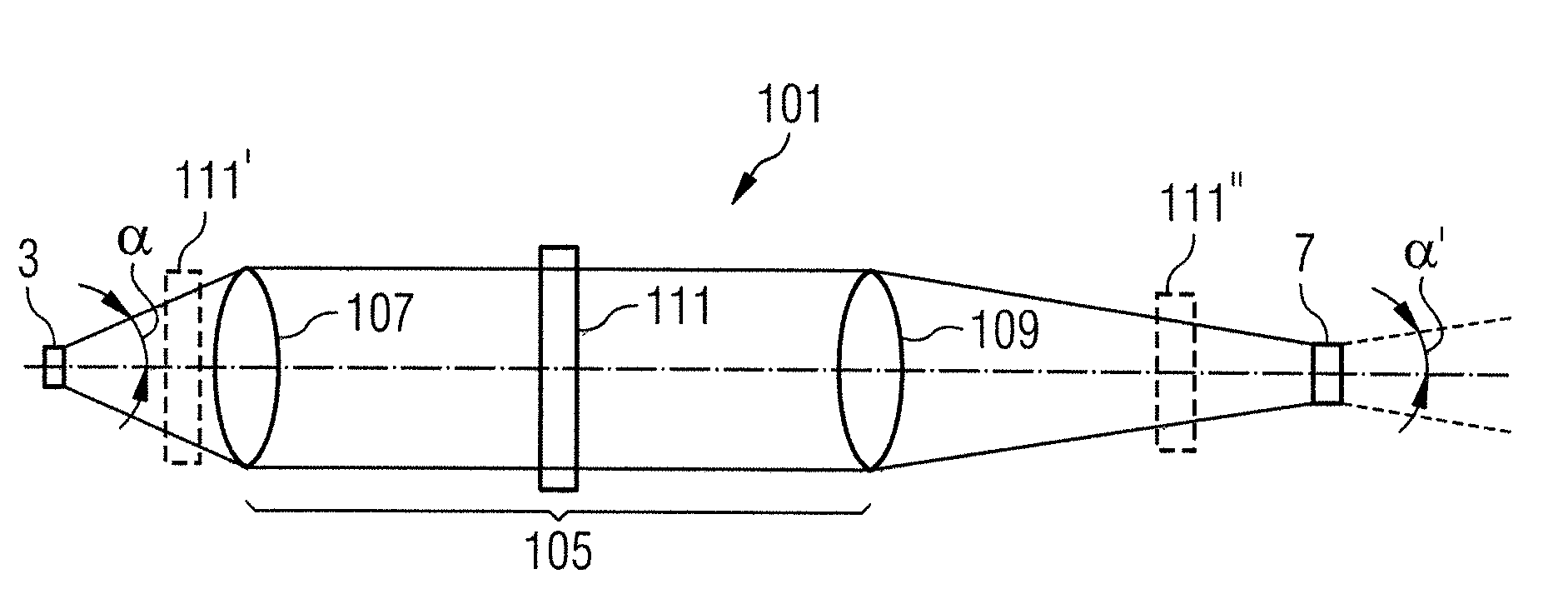
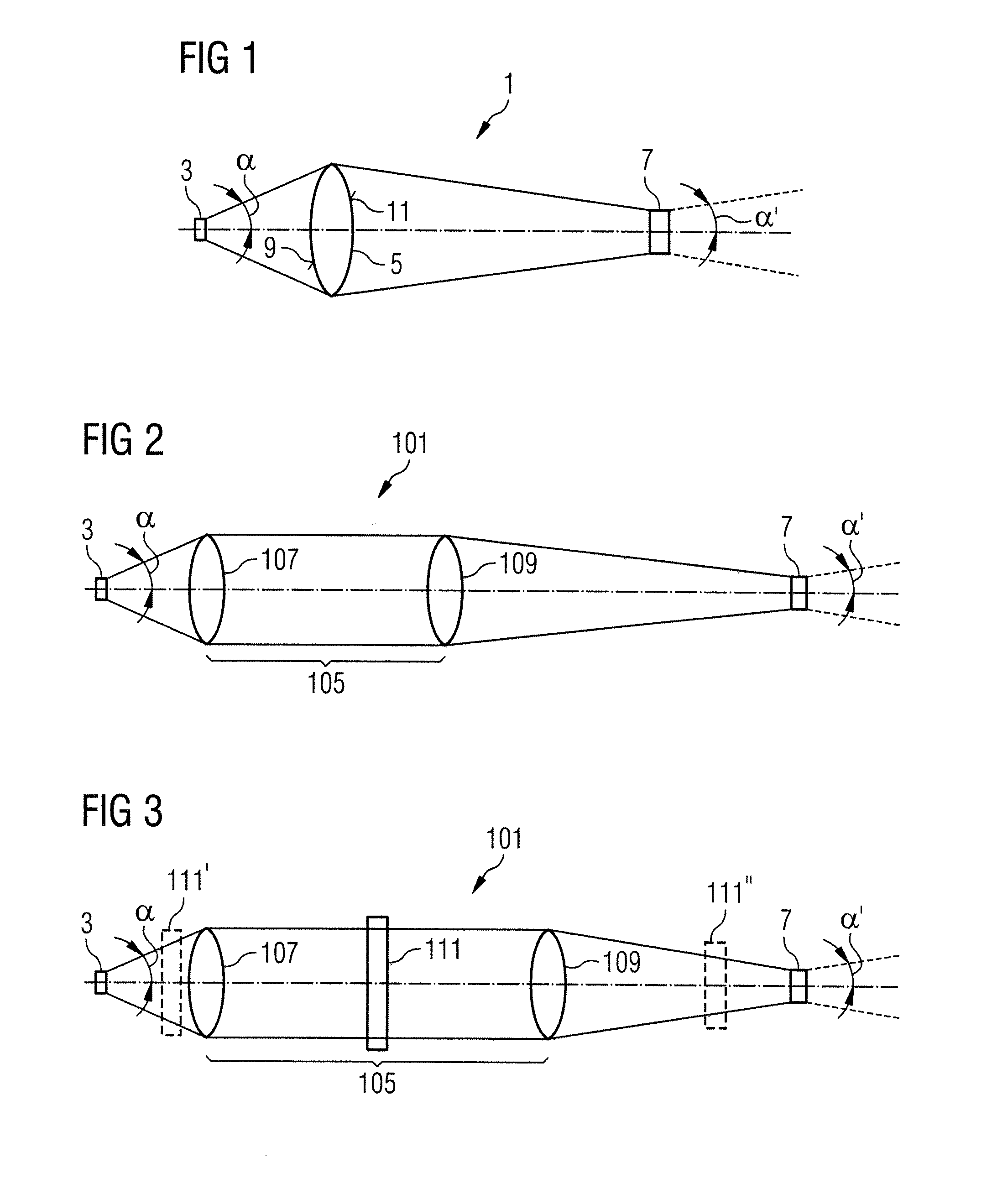
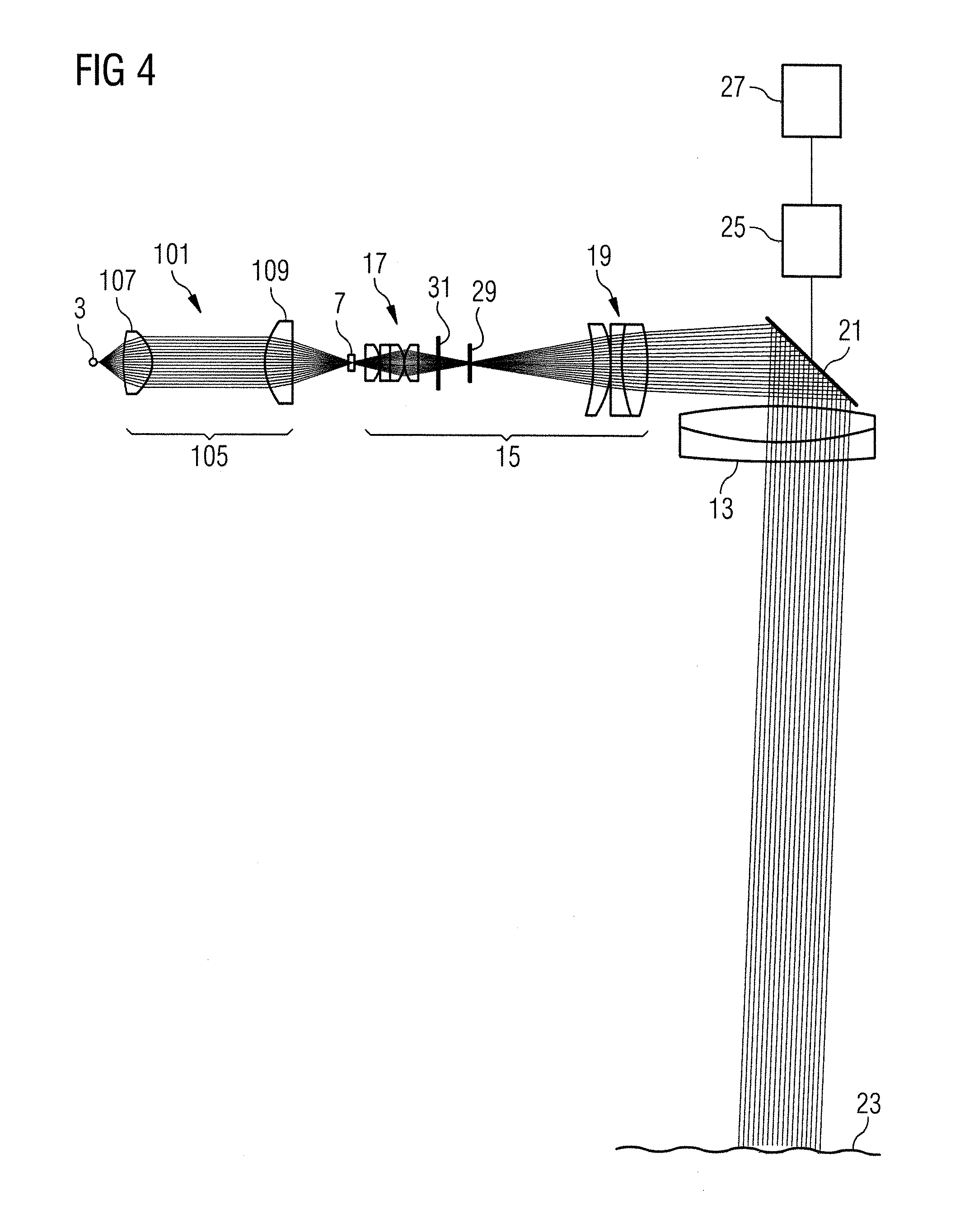
ActiveUS20100309549A1Improve image qualityConvenient distanceSurgeryEndoscopesMagnificationOptical observation
A light source arrangement (101) for an illumination device of a medical-optical observation apparatus has an illumination light source (7) and an illumination optical unit (15) for illuminating an observation object (23) with illumination light from the illumination light source (7). The light source arrangement (101) has at least one luminescence emitter (3) as light source and an imaging optical unit (105) that generates an image (7) of the at least one luminescence emitter (3) with a defined magnification scale, which image forms the illumination light source for the illumination device.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com