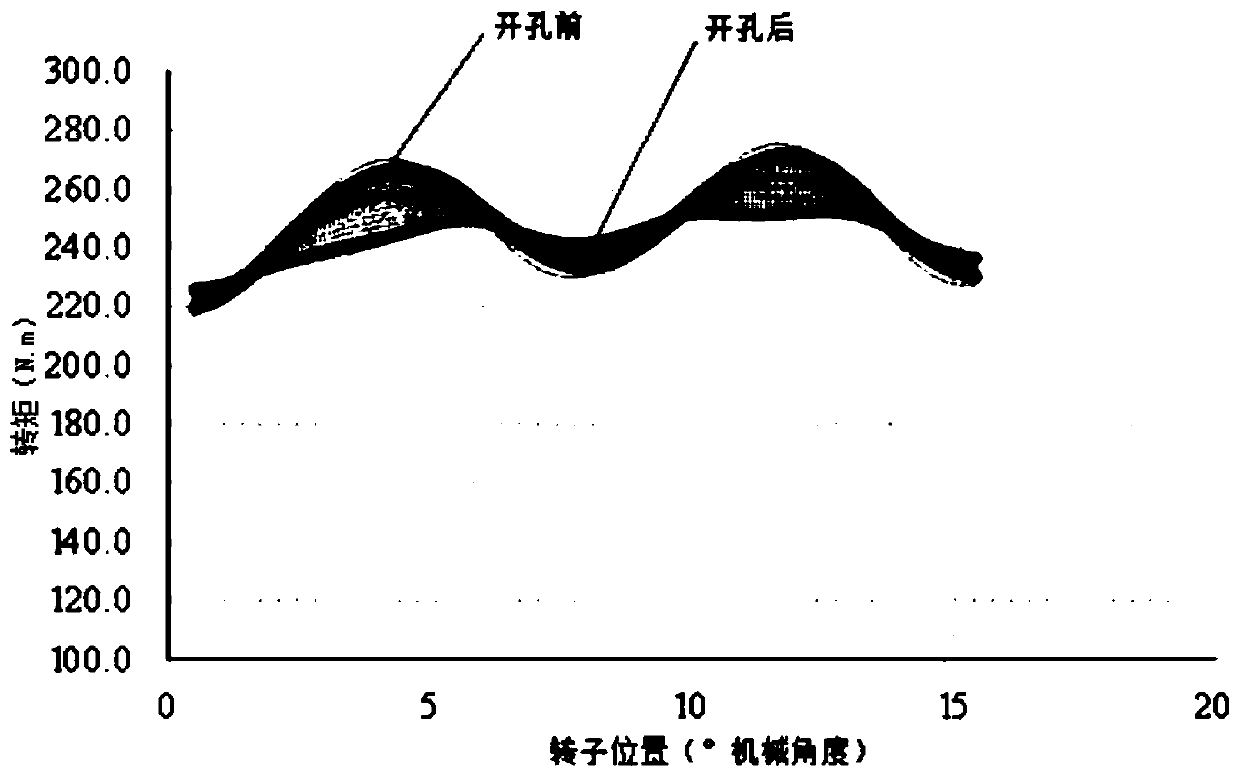
Patents
Literature
74results about How to "Reduce cogging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
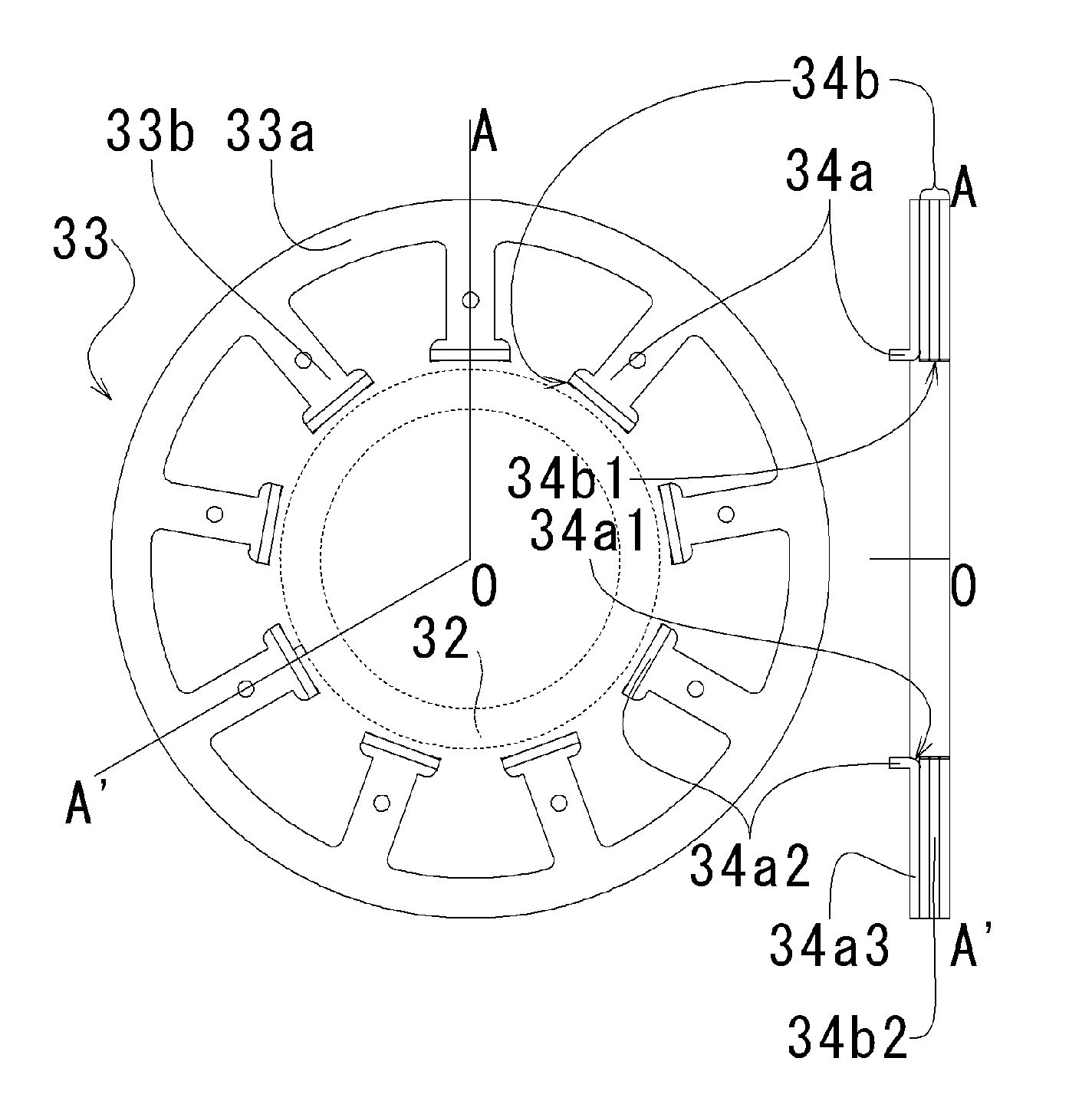
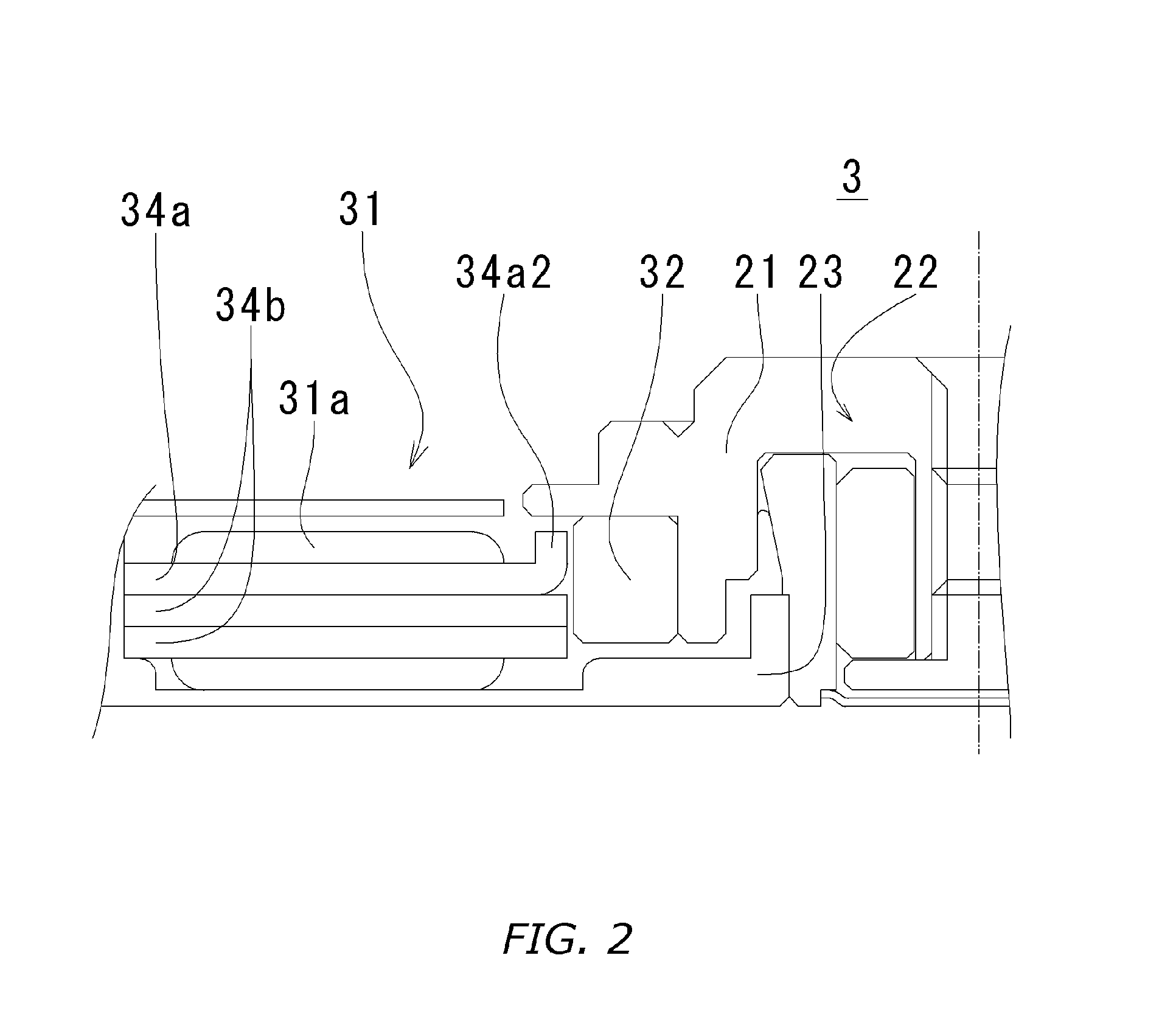
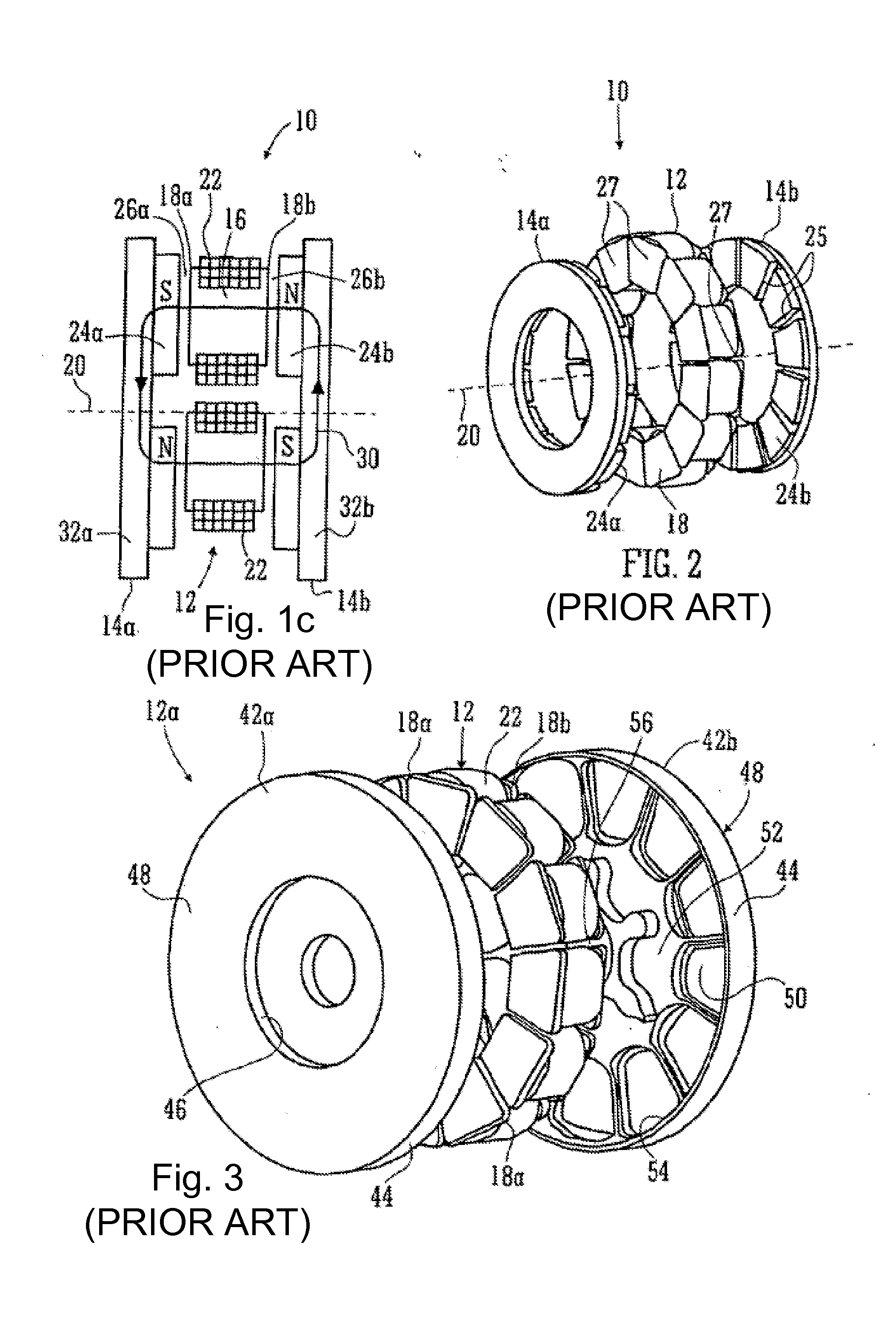
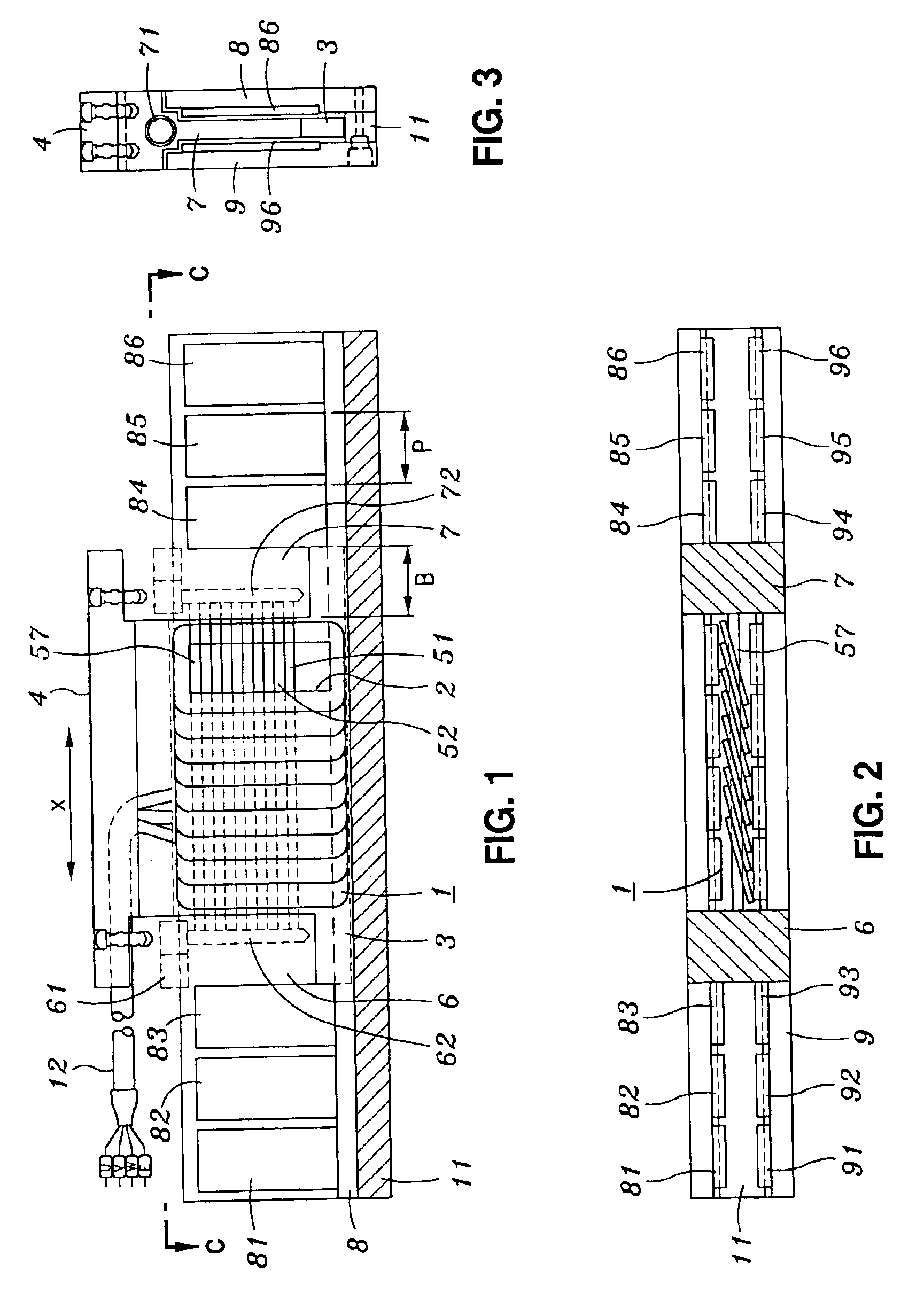
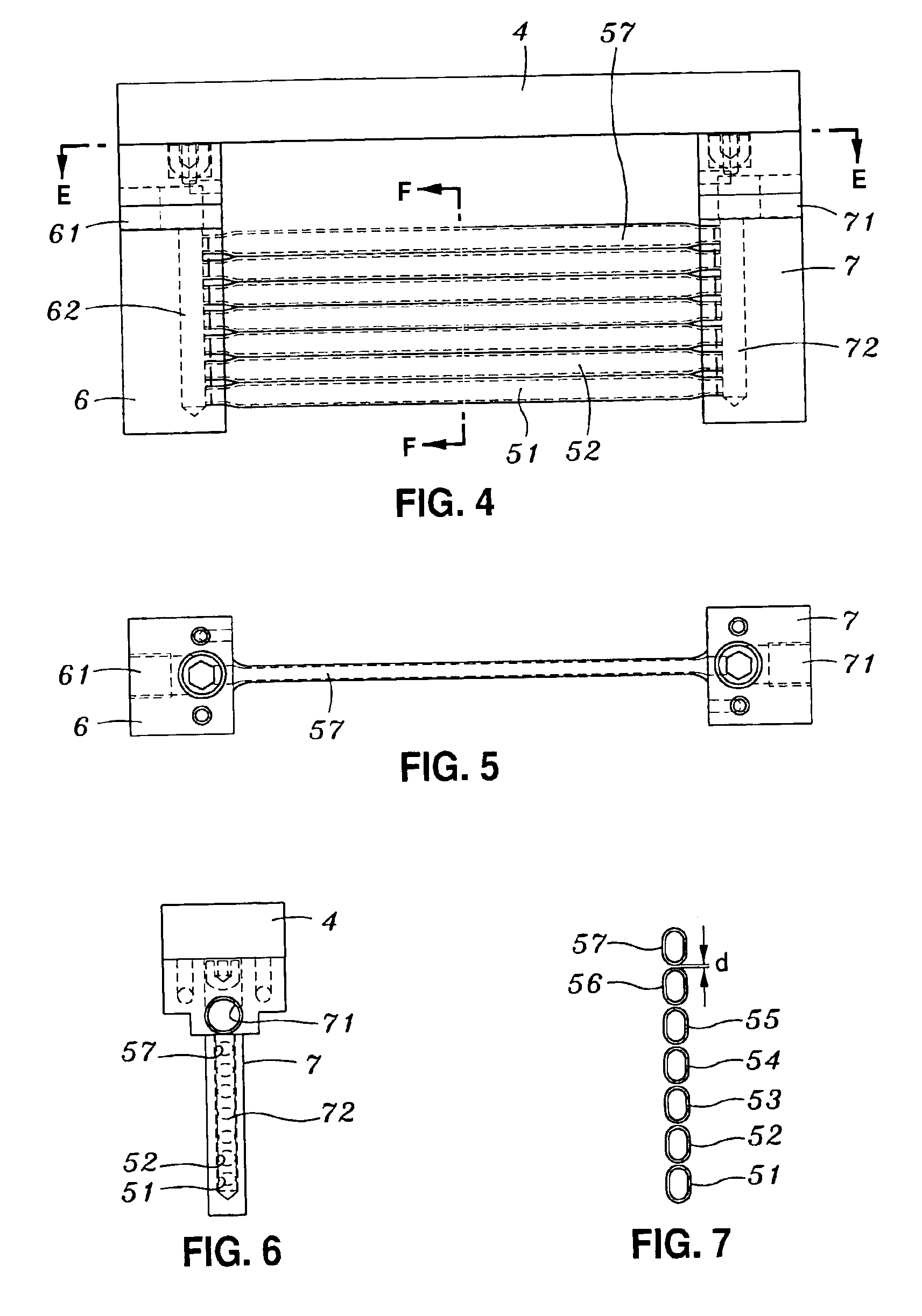
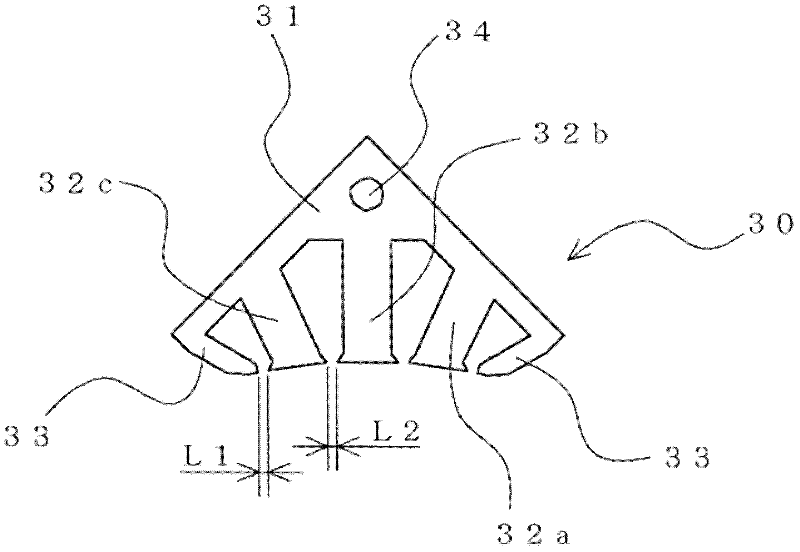
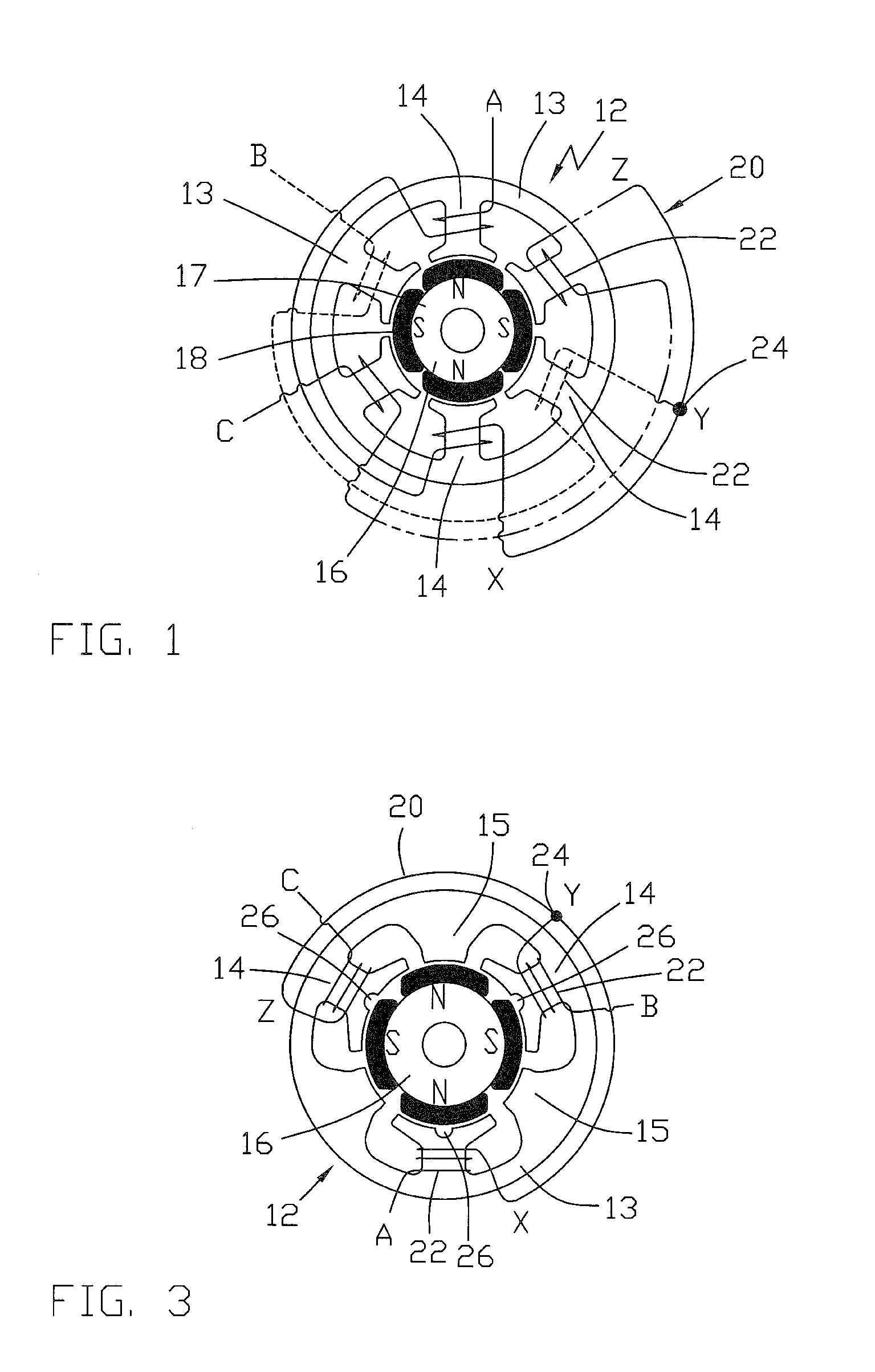
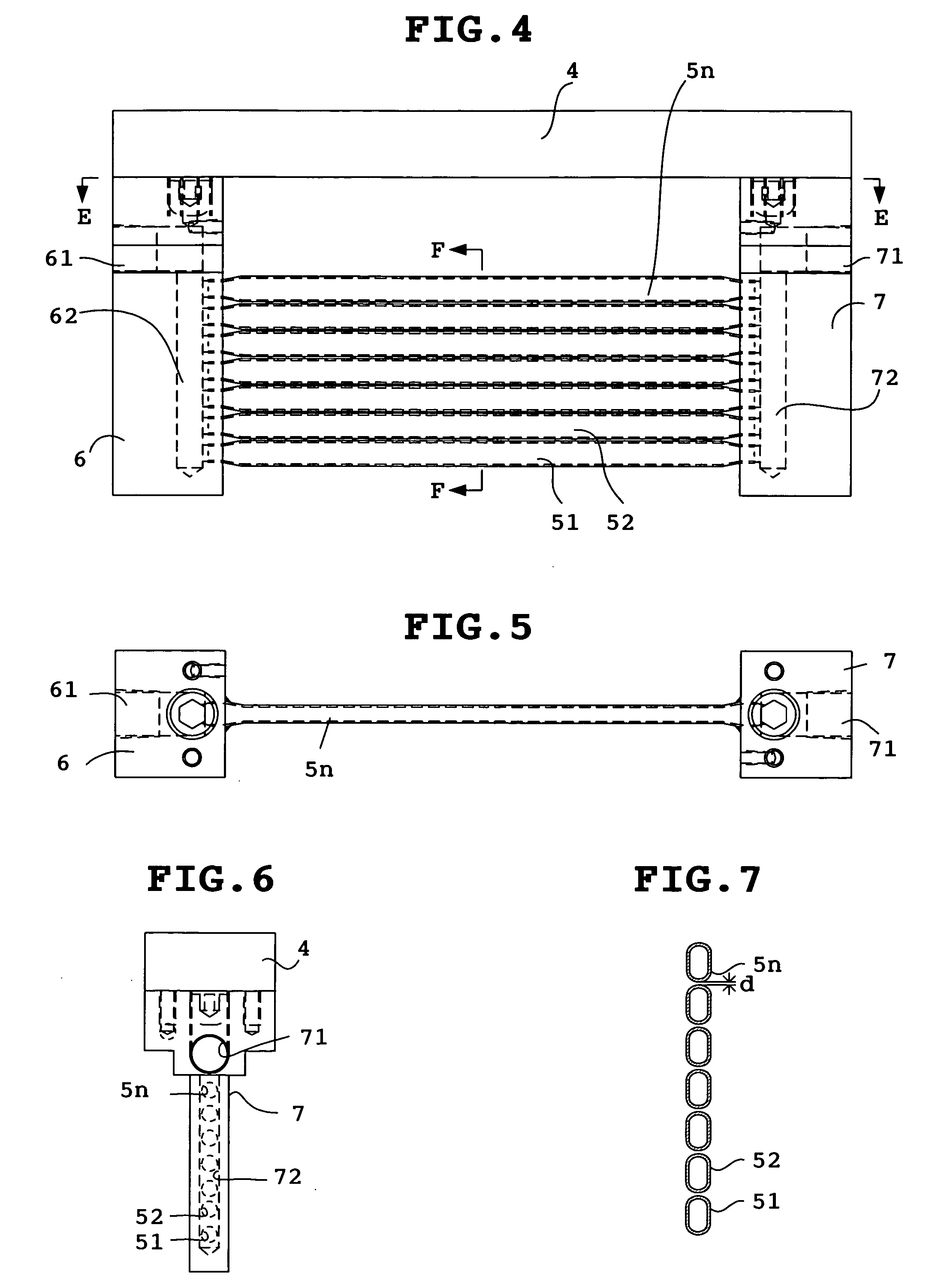
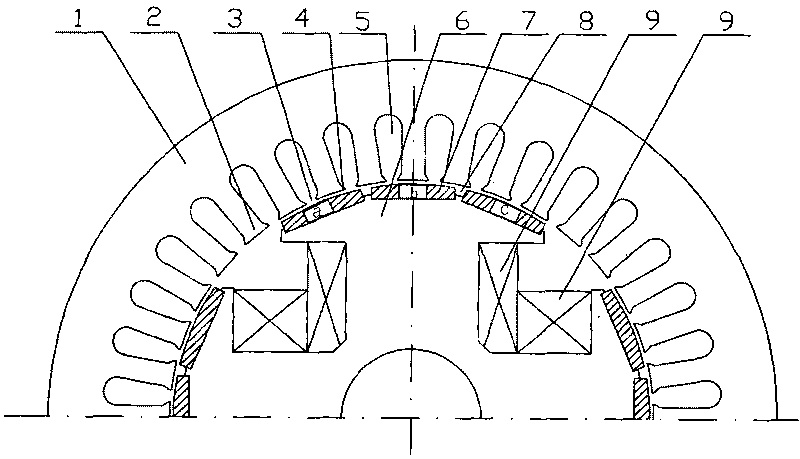
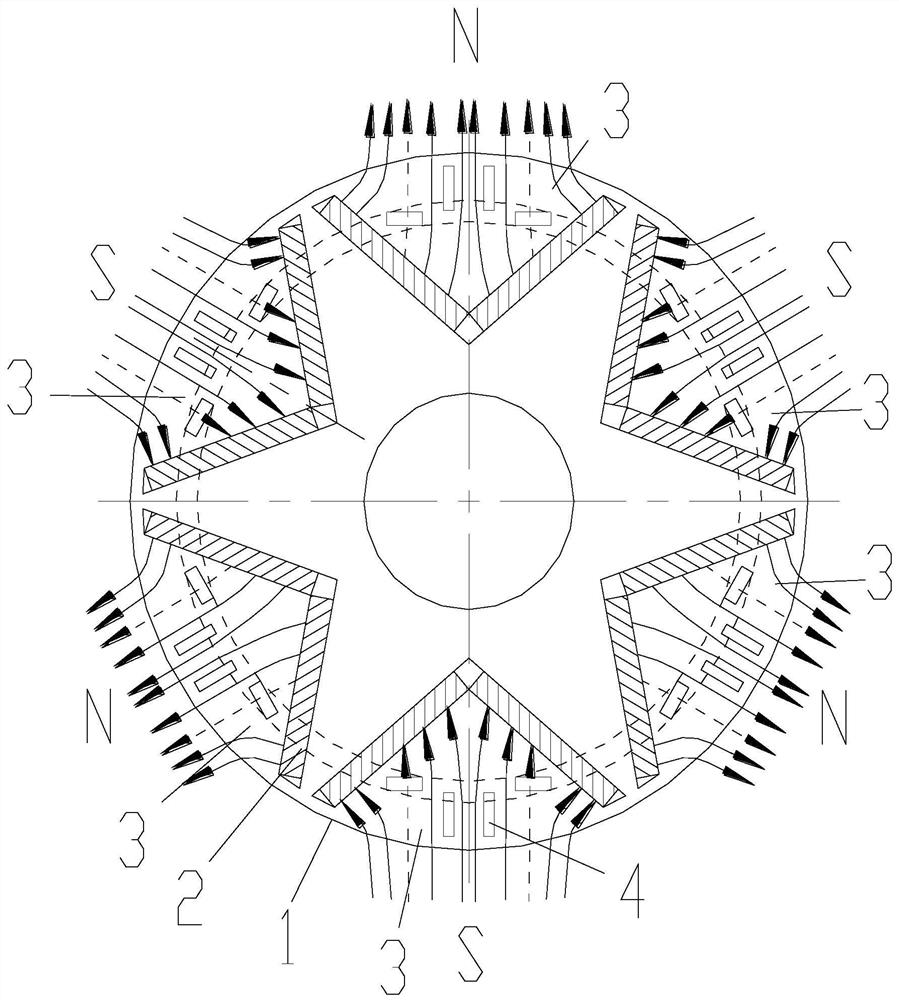
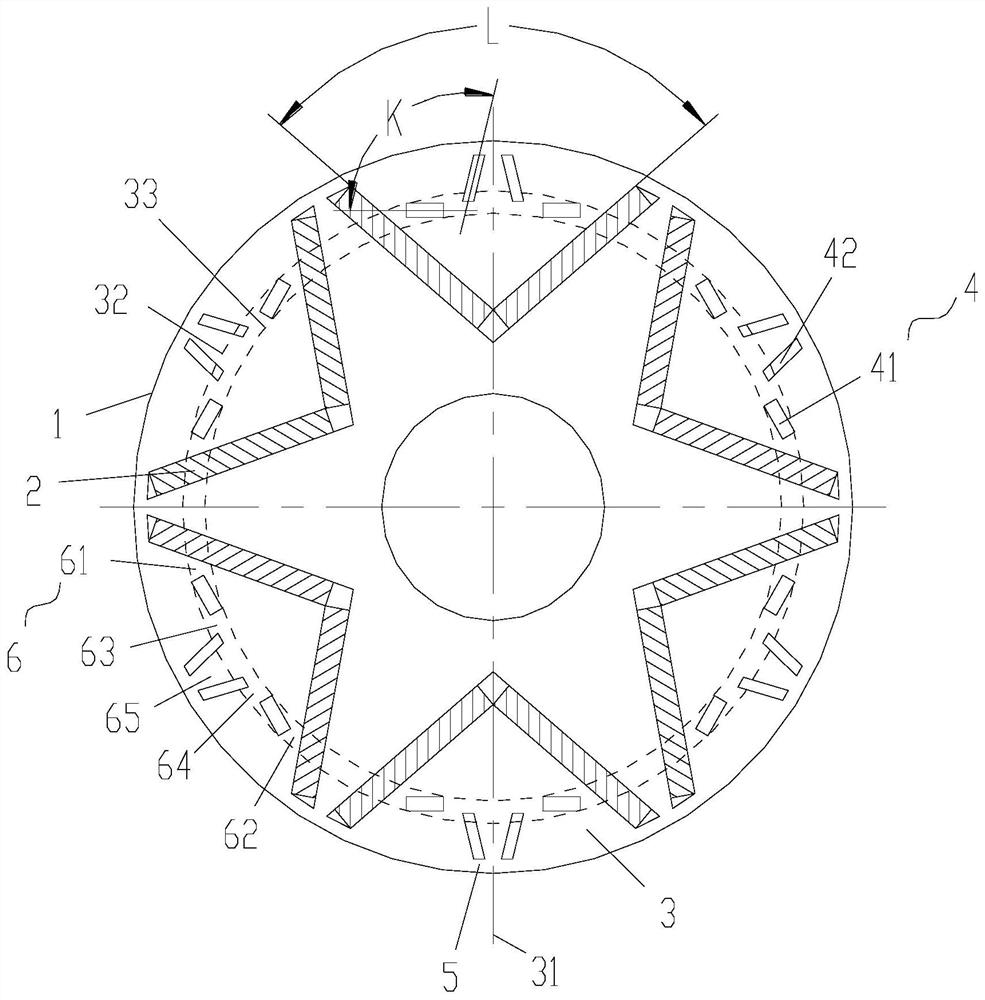
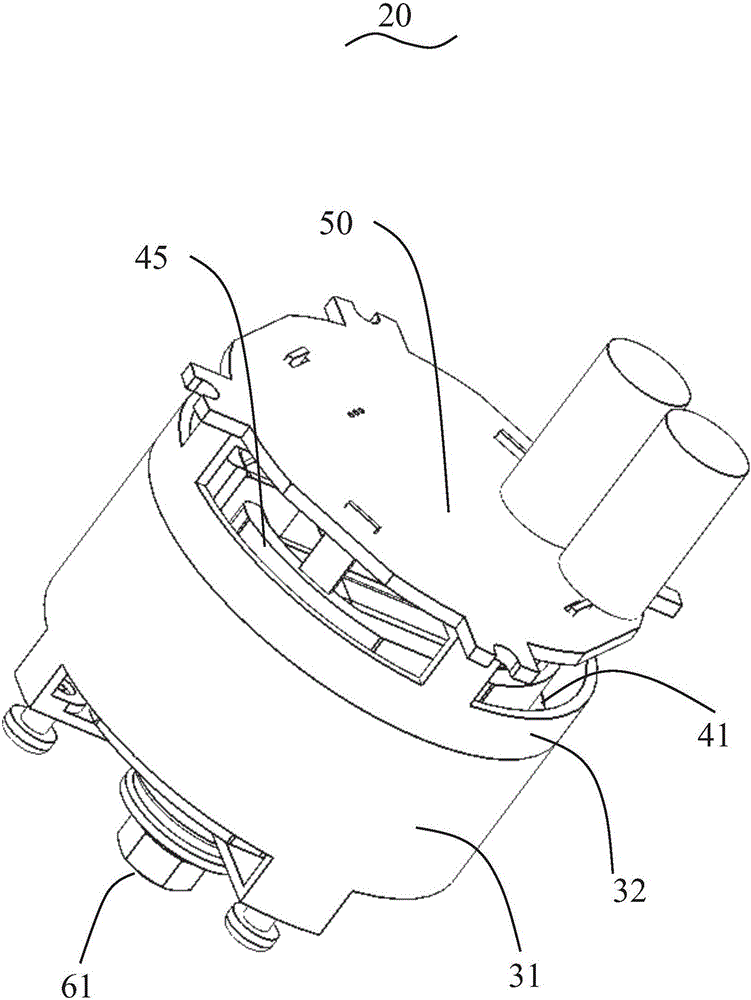
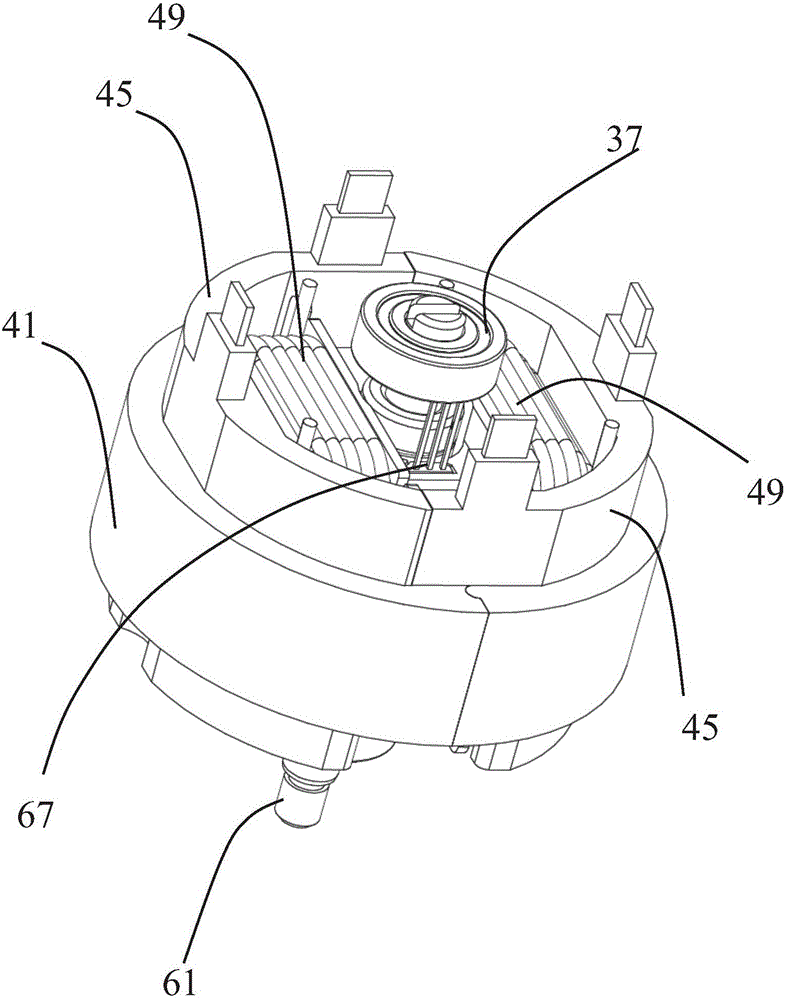
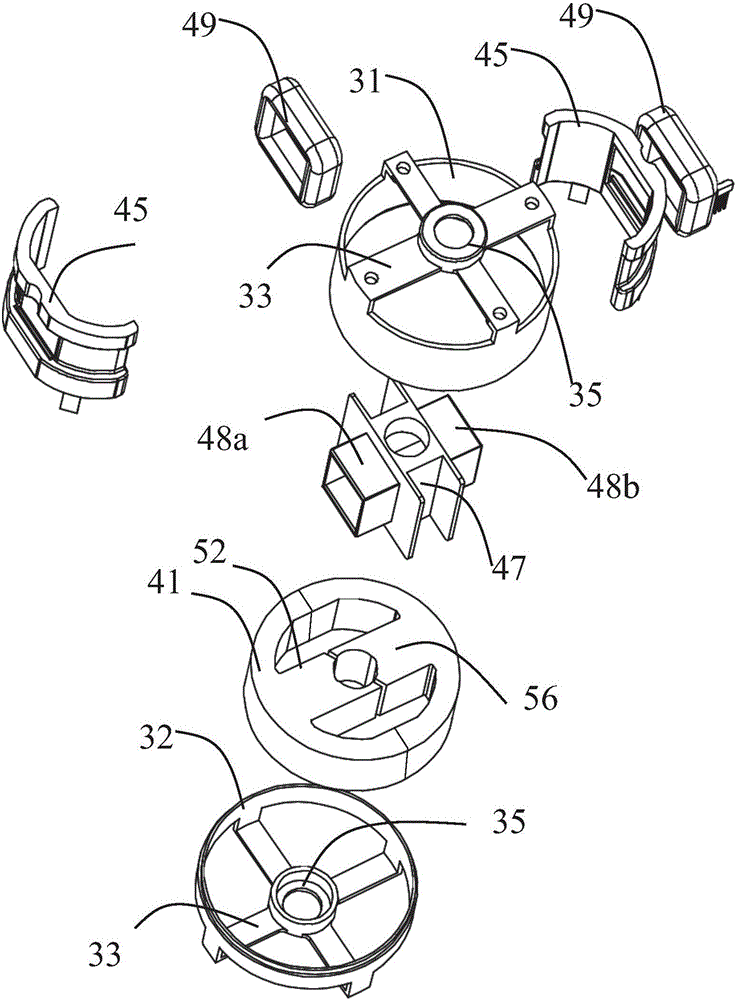
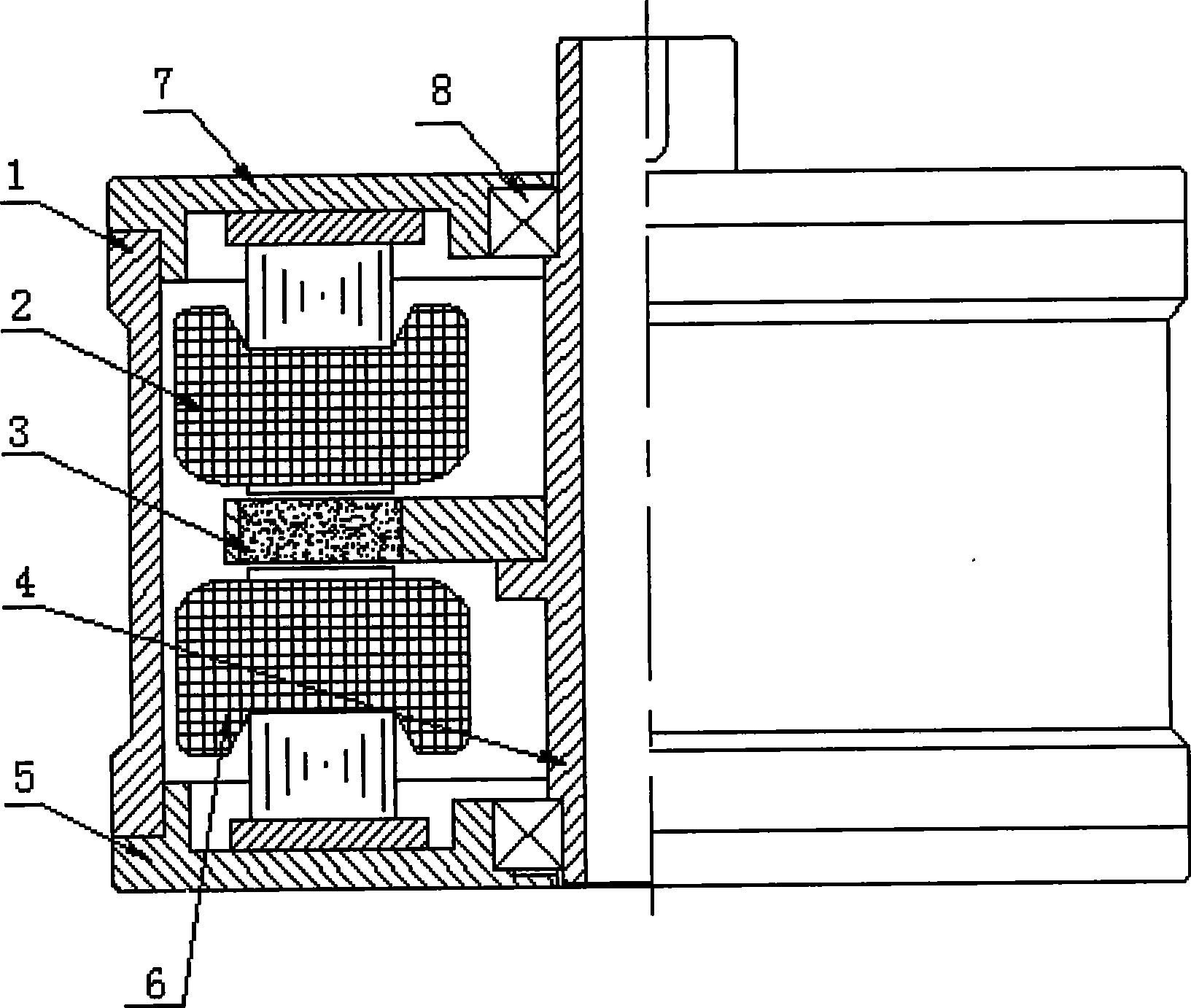
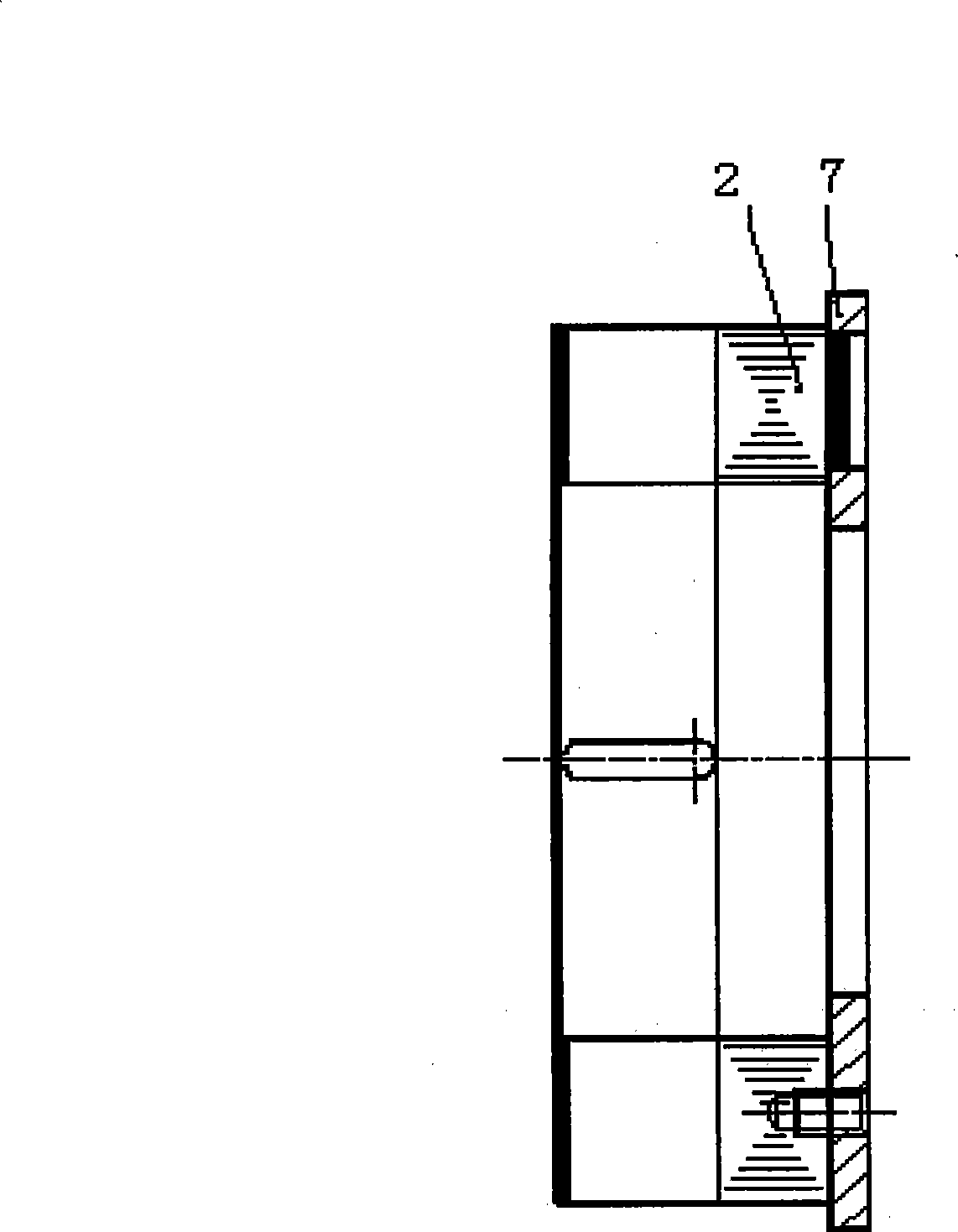
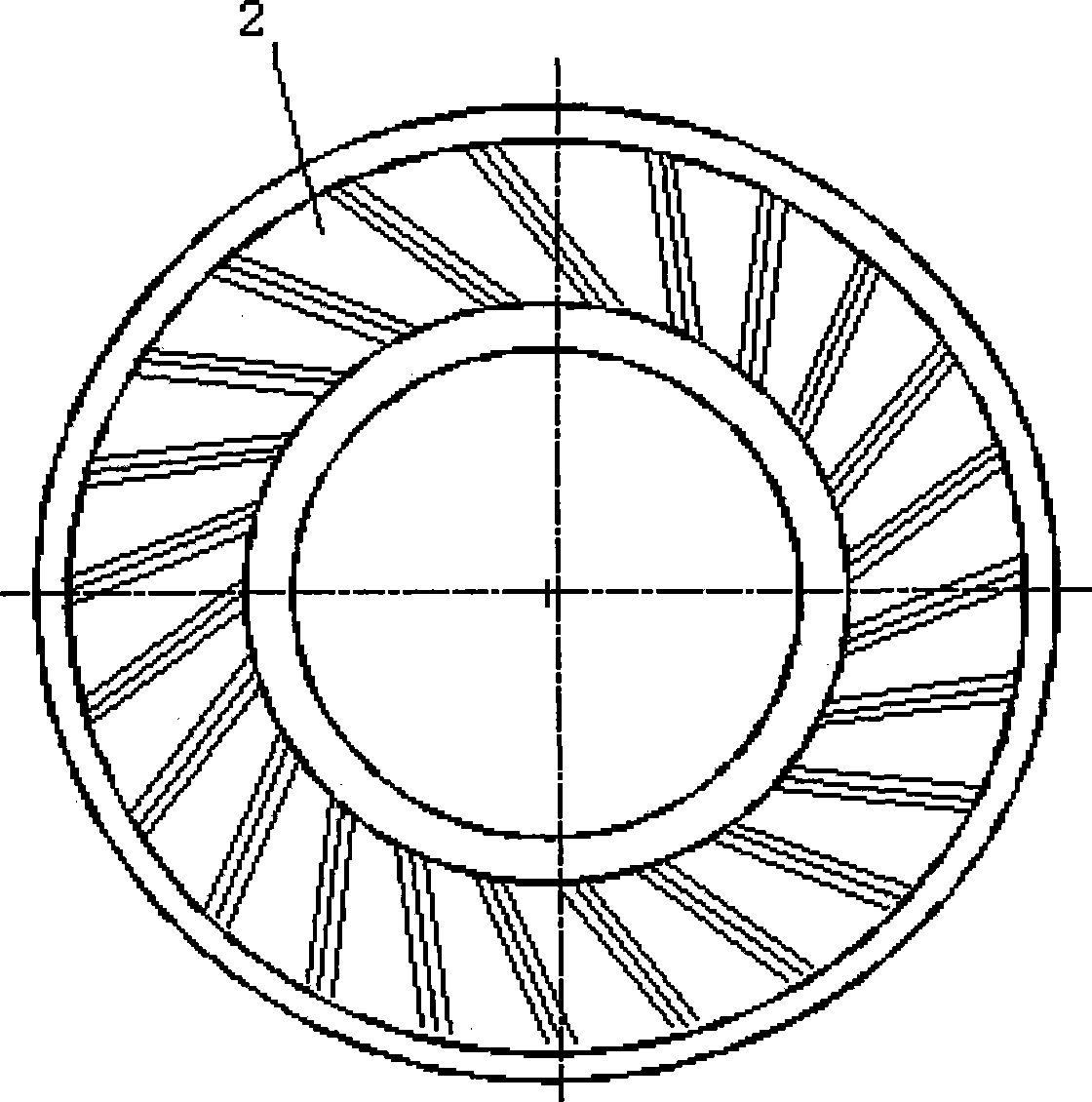
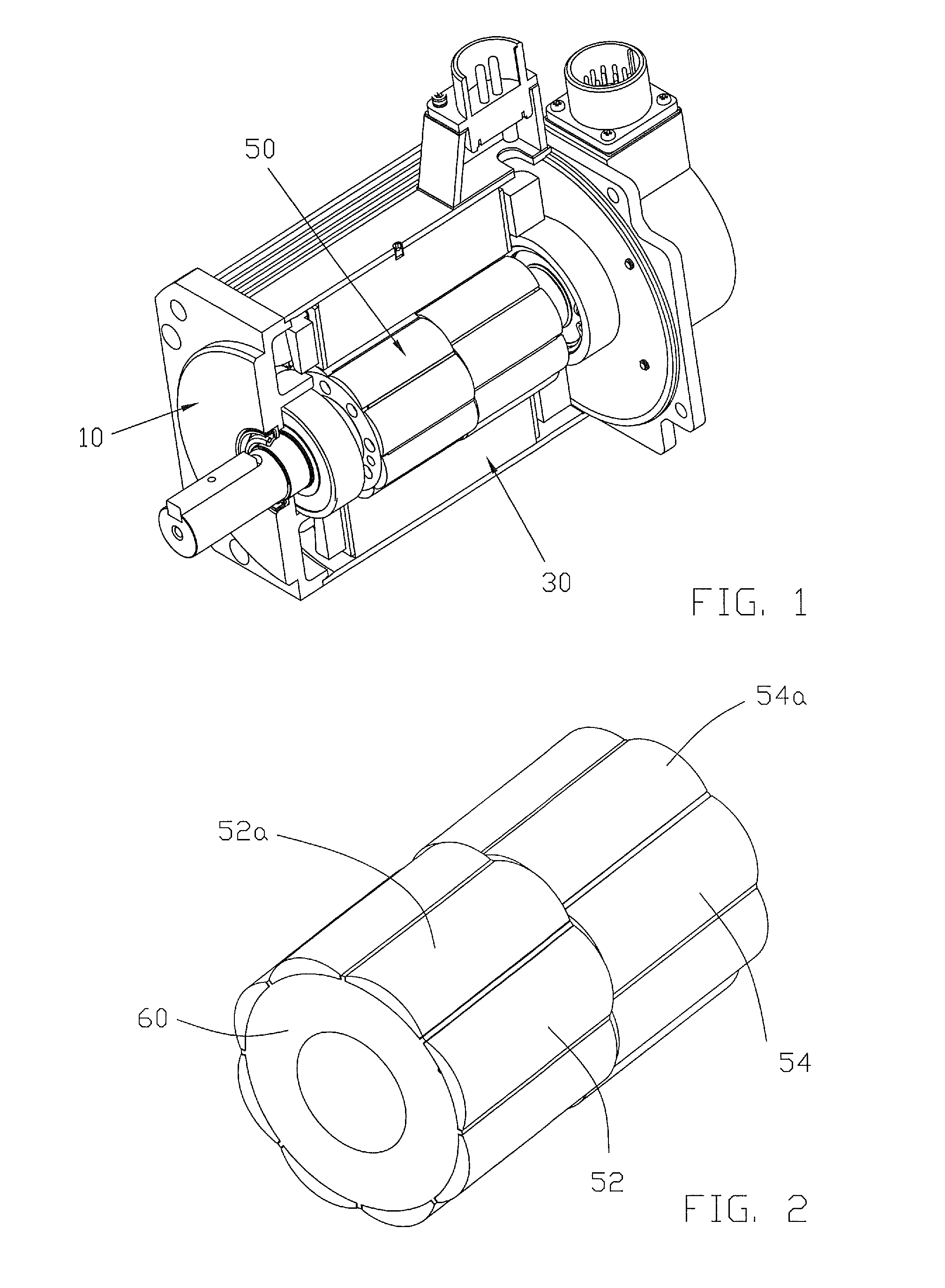
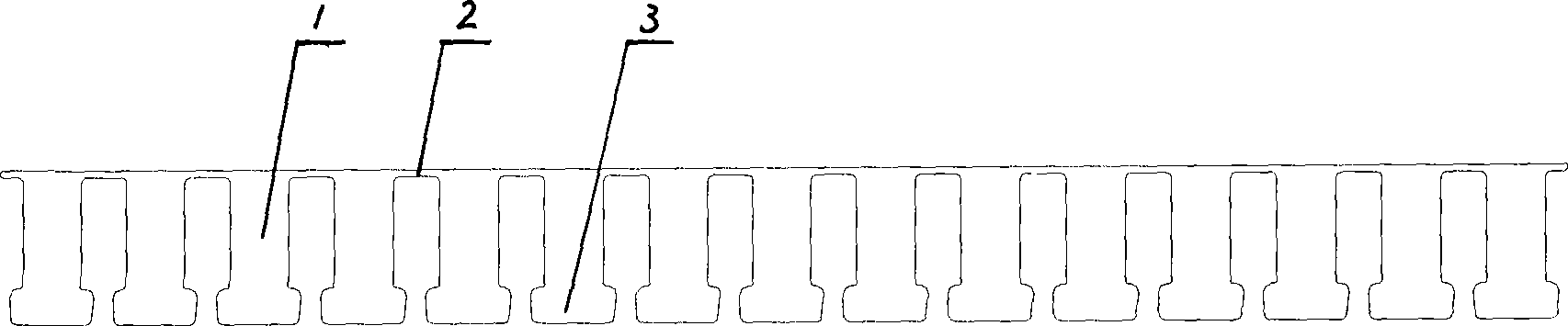
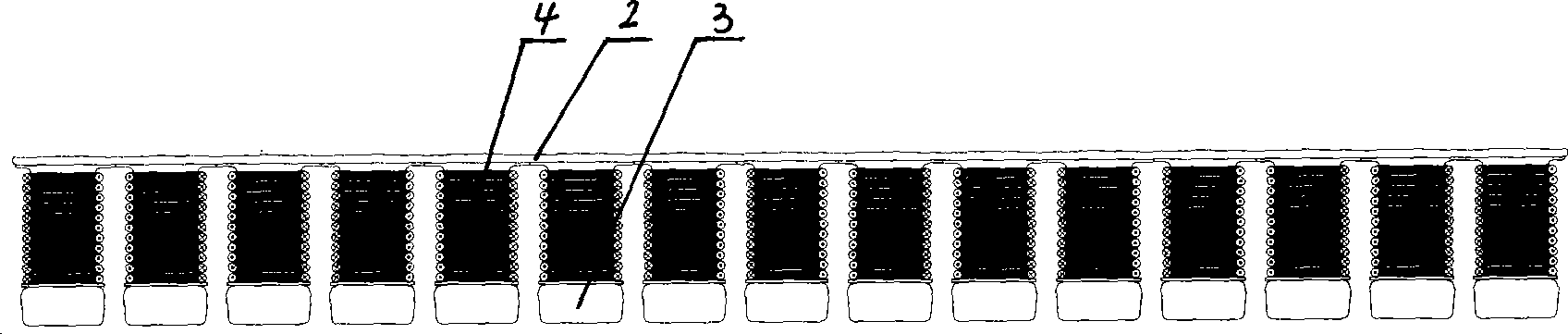
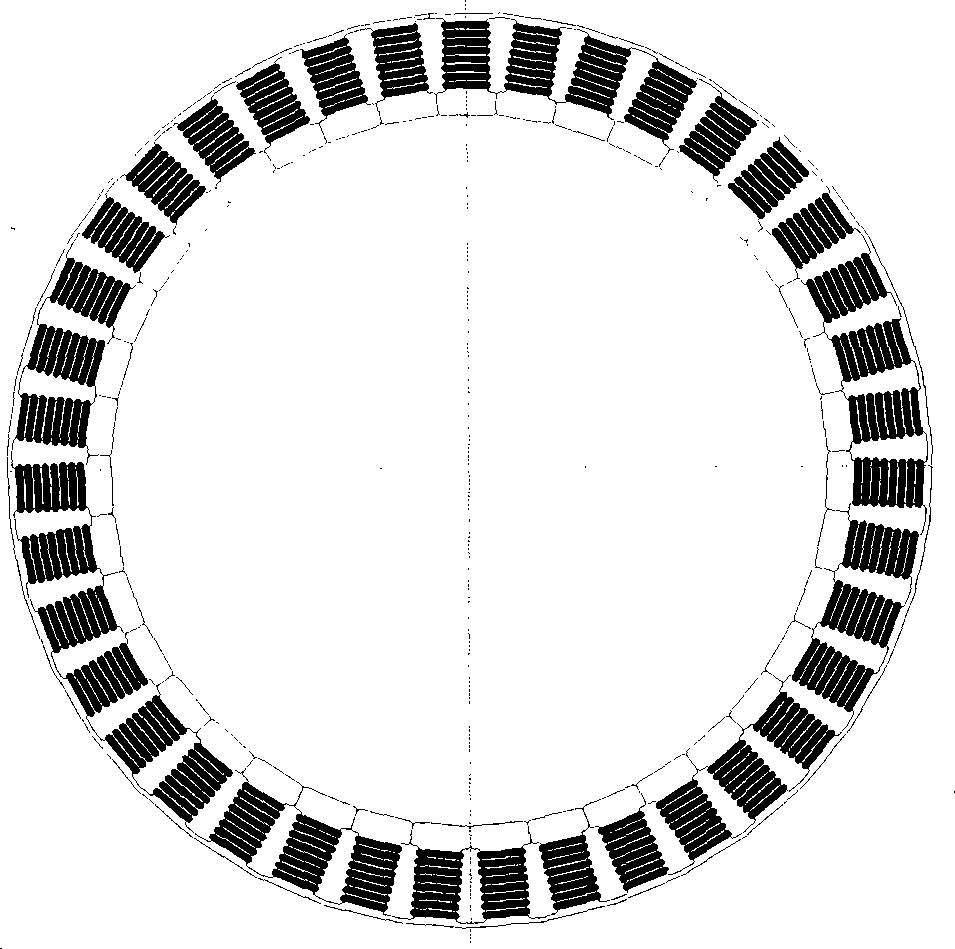
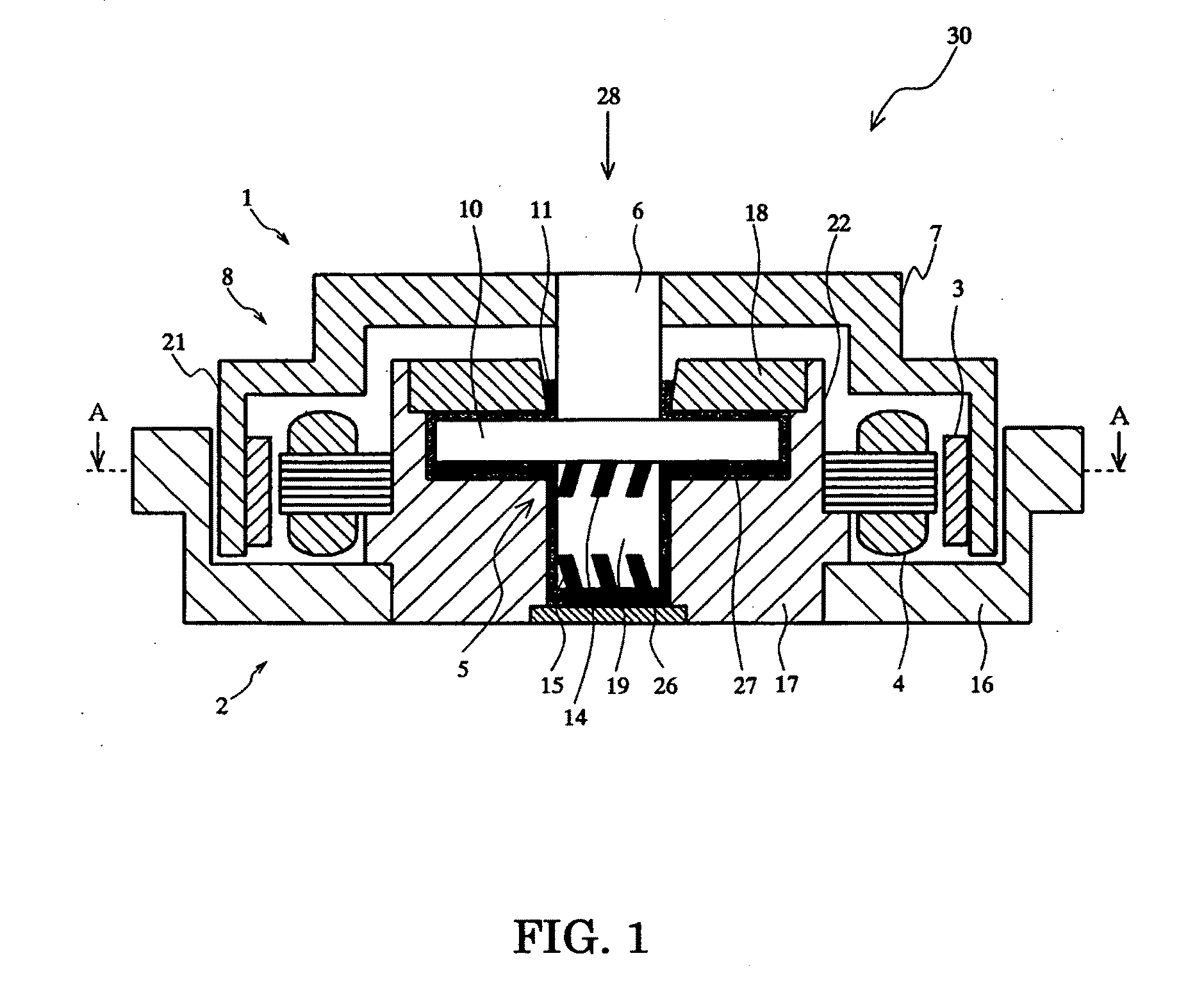
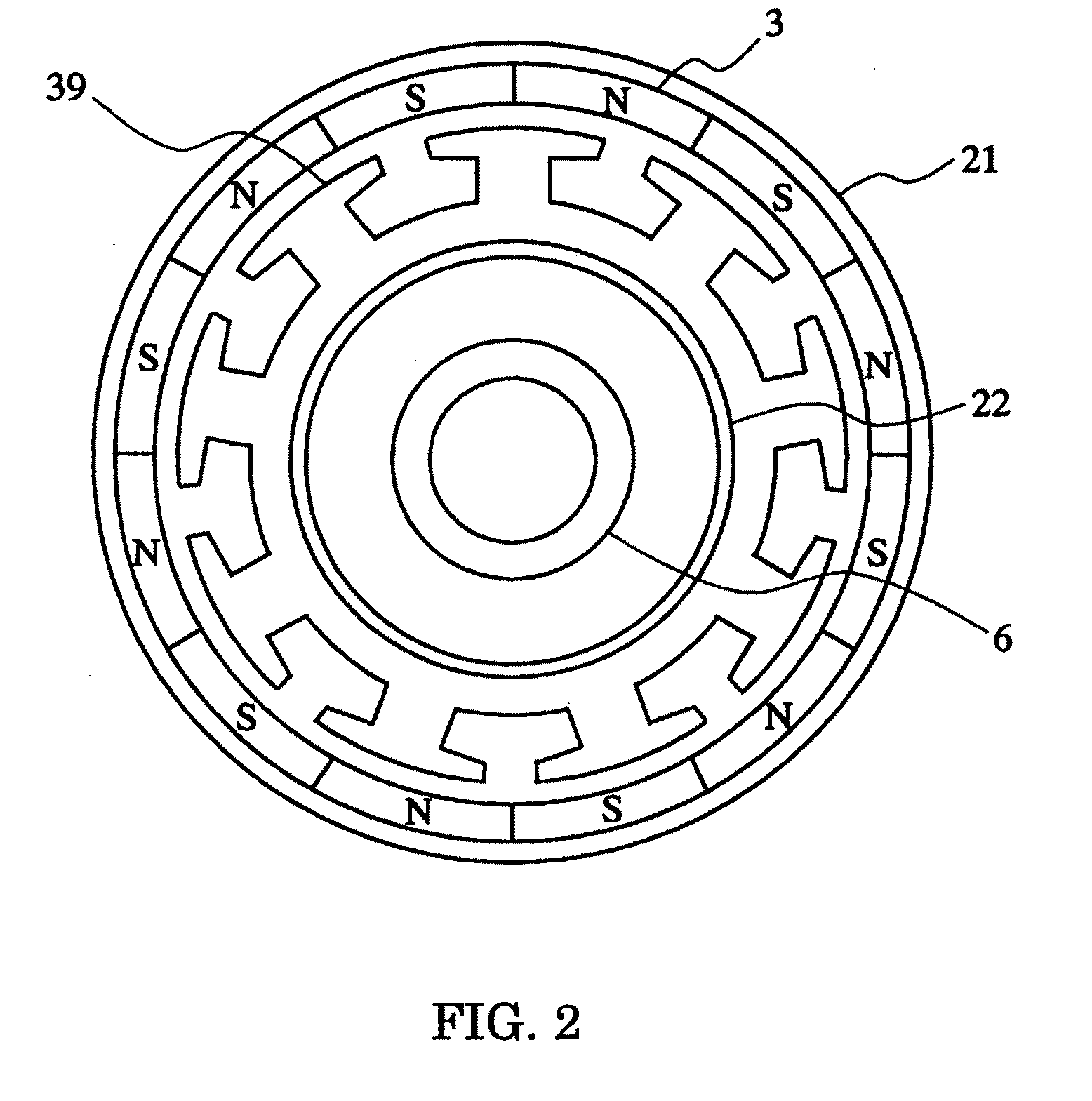
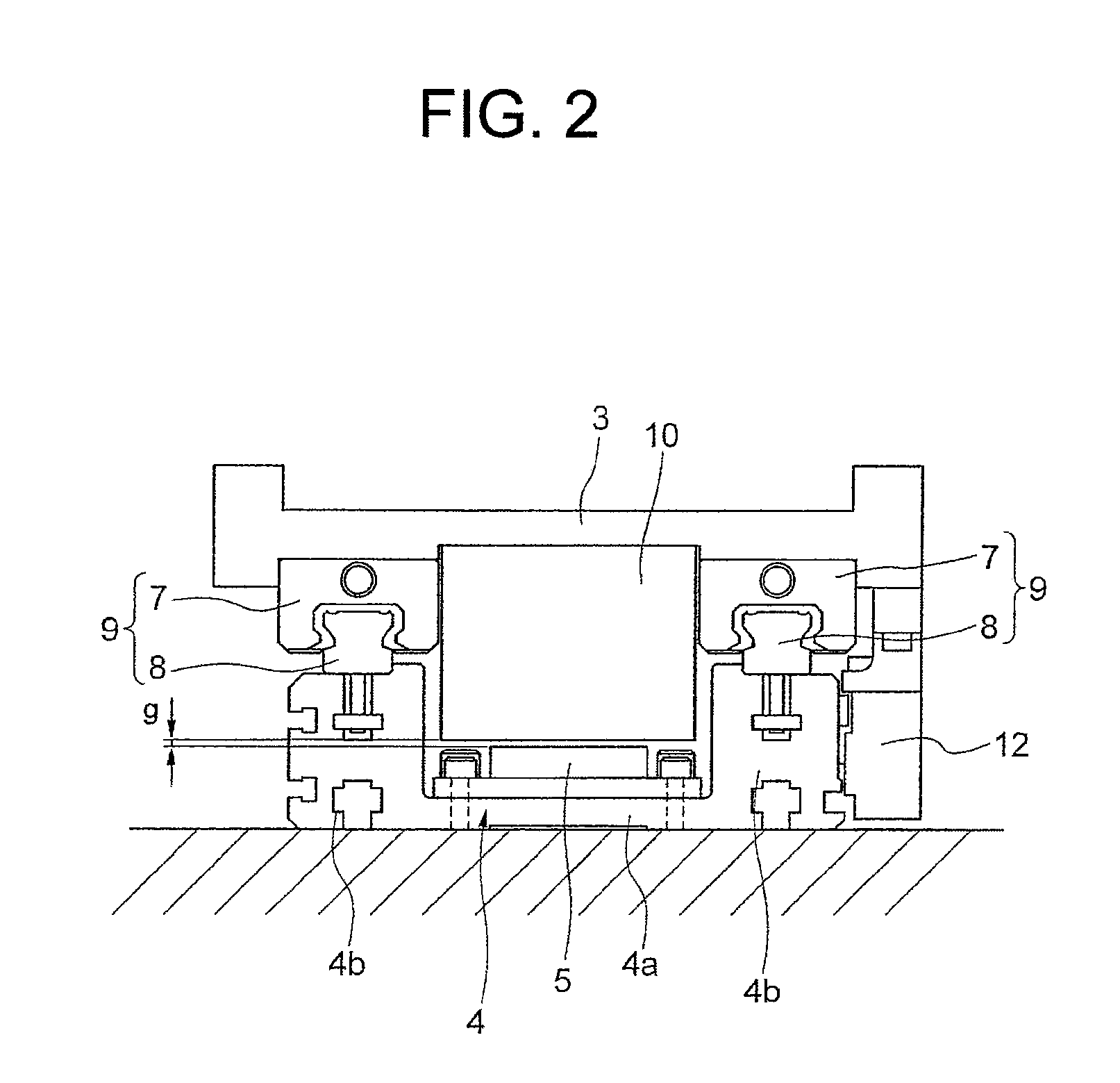
Motor and Recording Disk Drive Device Provided with the Same
InactiveUS20060197402A1Easy to adjustCombined cogging waveform can be reducedMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsRotor magnetsEngineering
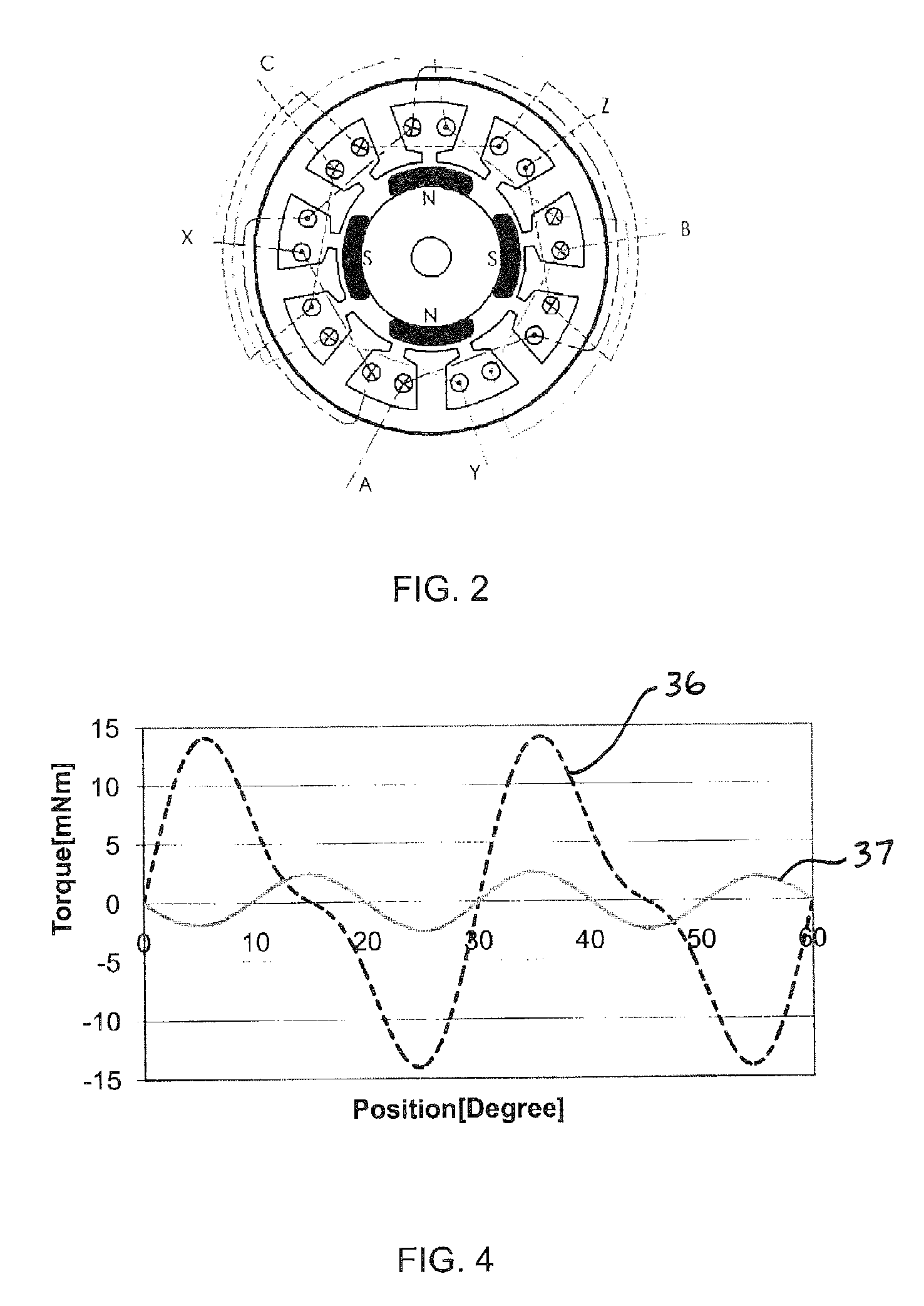
In a spindle motor, a core (33) includes a plurality of core plates (34), which are laminated one on another. The core (33) is constituted by laminating two cores, that is, a first core (34a) and a second core (34b), which are different from each other in shape of a surface facing to a rotor magnet (32). At least a part of a cogging torque generated at the second core (34b) can be cancelled by a cogging torque generated at the first core (34a).
Owner:NIPPON DENSAN CORP
Structure of motor stator core and cooling method for motor stator based on structure of motor stator core
ActiveCN103280903ALow ferromagnetic lossImprove efficiencyWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuit stationary partsWater coolingOil cooling
The invention relates to a structure of a motor stator core and a cooling method for a motor stator based on the structure of the motor stator core. The structure is characterized in that the stator core is formed by splicing and combining stator yoke units and stator tooth units, wherein the quantities of the stator yoke units and the stator tooth units are the same, and are equal to the slot number Z1 of a stator; the stator yoke units and the stator tooth units are formed by laminating oriented silicon steel sheets; a stator yoke unit is connected between every two adjacent tooth units; the tooth units and the stator yoke units are in joggle joint; the silicon steel sheets of the stator yoke units are oriented circumferentially; and the silicon steel sheets of the stator tooth units are oriented radially. The cooling method is selected from one of air cooling, water cooling and oil cooling. The structure has the advantage that the motor has the characteristics of low ferromagnetic loss, high efficiency, low torque pulsation, low slot effect, low running noise, low wind resistance, high slot fullness rate of a stator winding, high utilization ratio of a silicon steel sheet material, suitability of the stator for automatic mass production and the like.
Owner:曹宇轩
Brushless motor
InactiveUS20100054971A1Simple structureLow cogging torqueAsynchronous induction motorsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric energyEngineering
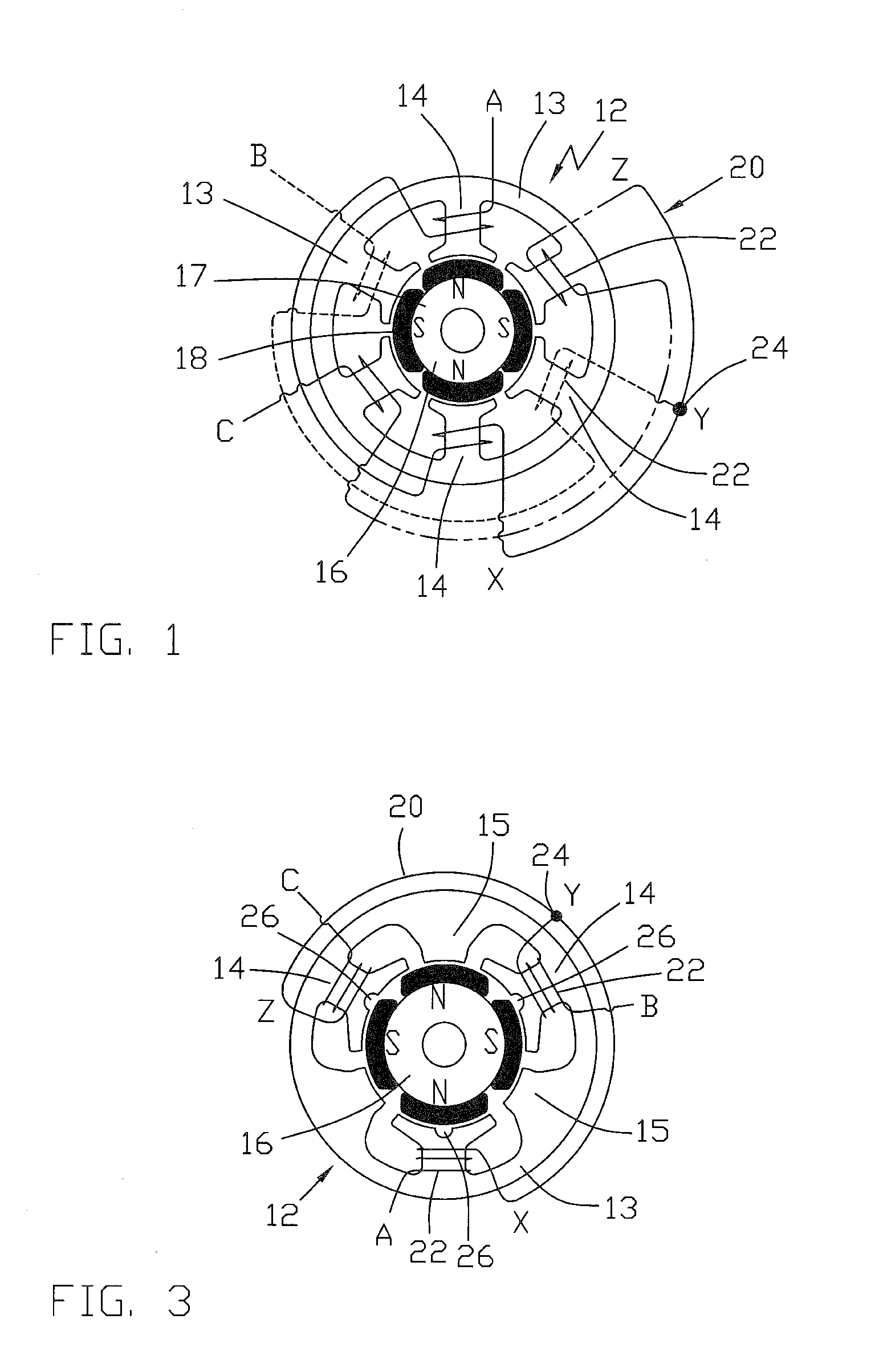
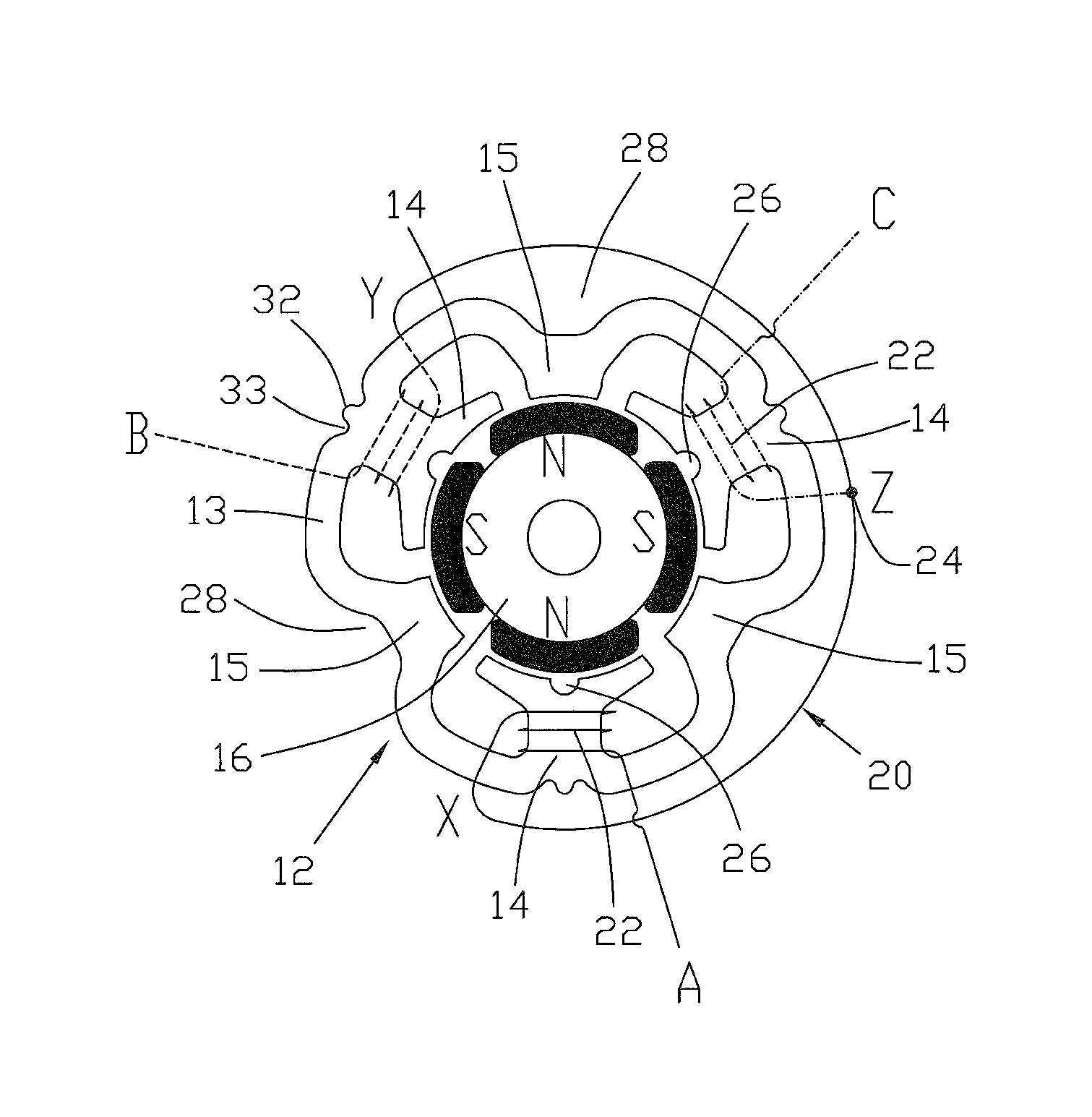
A brushless direct current (BLDC) motor has a 3-phase winding 20 and six stator teeth 14, 15 with alternate stator teeth 14 being wound and the remaining stator teeth 15 being left unwound. The winding 20 has three legs, one for each phase and each leg has one coil 22 wound about one of the stator teeth 14. Each leg has a first end A,B,C, arranged to receive electrical power and a second end X,Y,Z, which is connected to the second end of the other legs to form a star connection 24. Selected stator teeth have grooves in a face thereof dividing those teeth into a plurality of stator poles. The motor may be used to drive a fuel pump for an internal combustion engine, typically for a vehicle.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC INTERNATIONAL AG
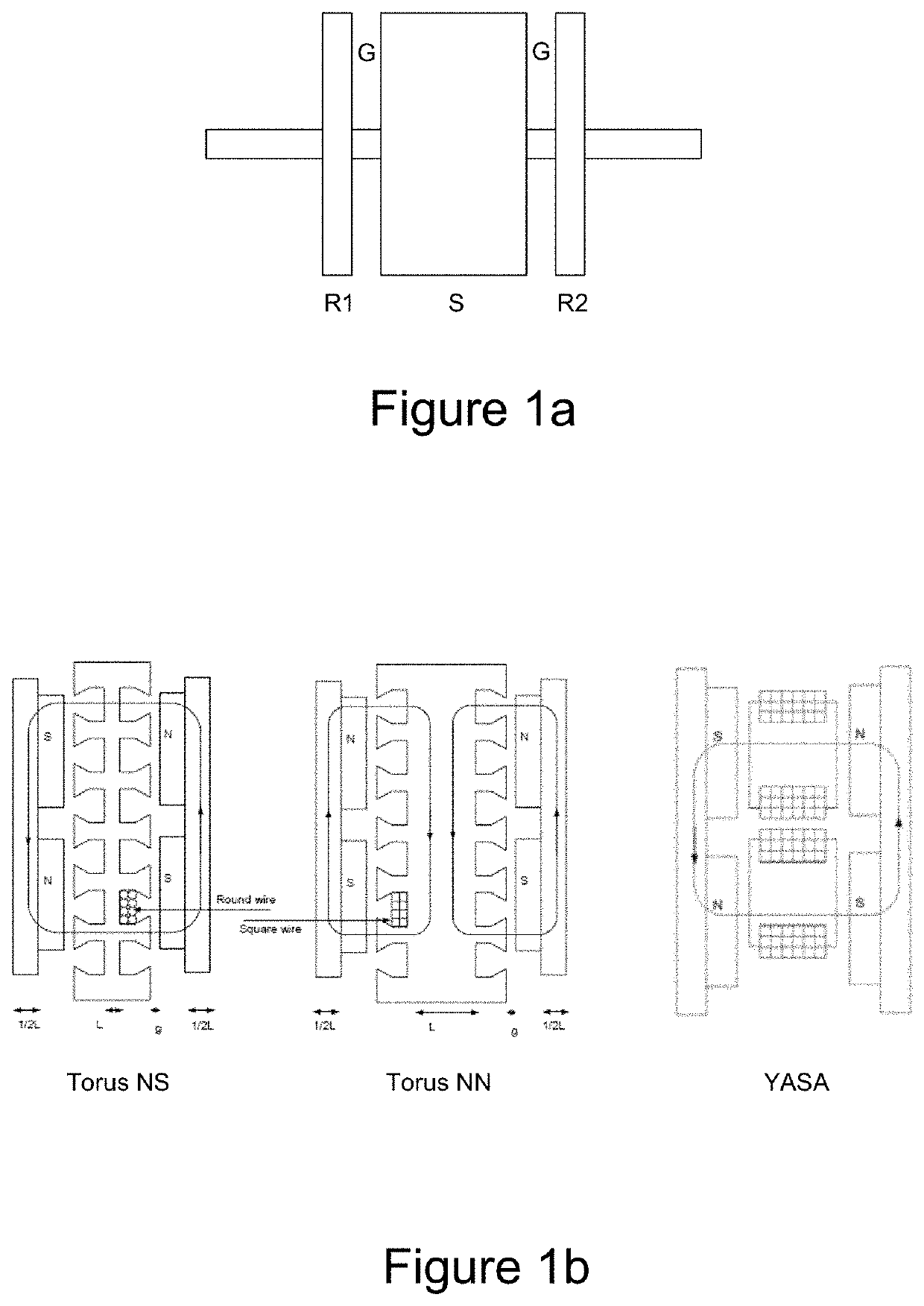
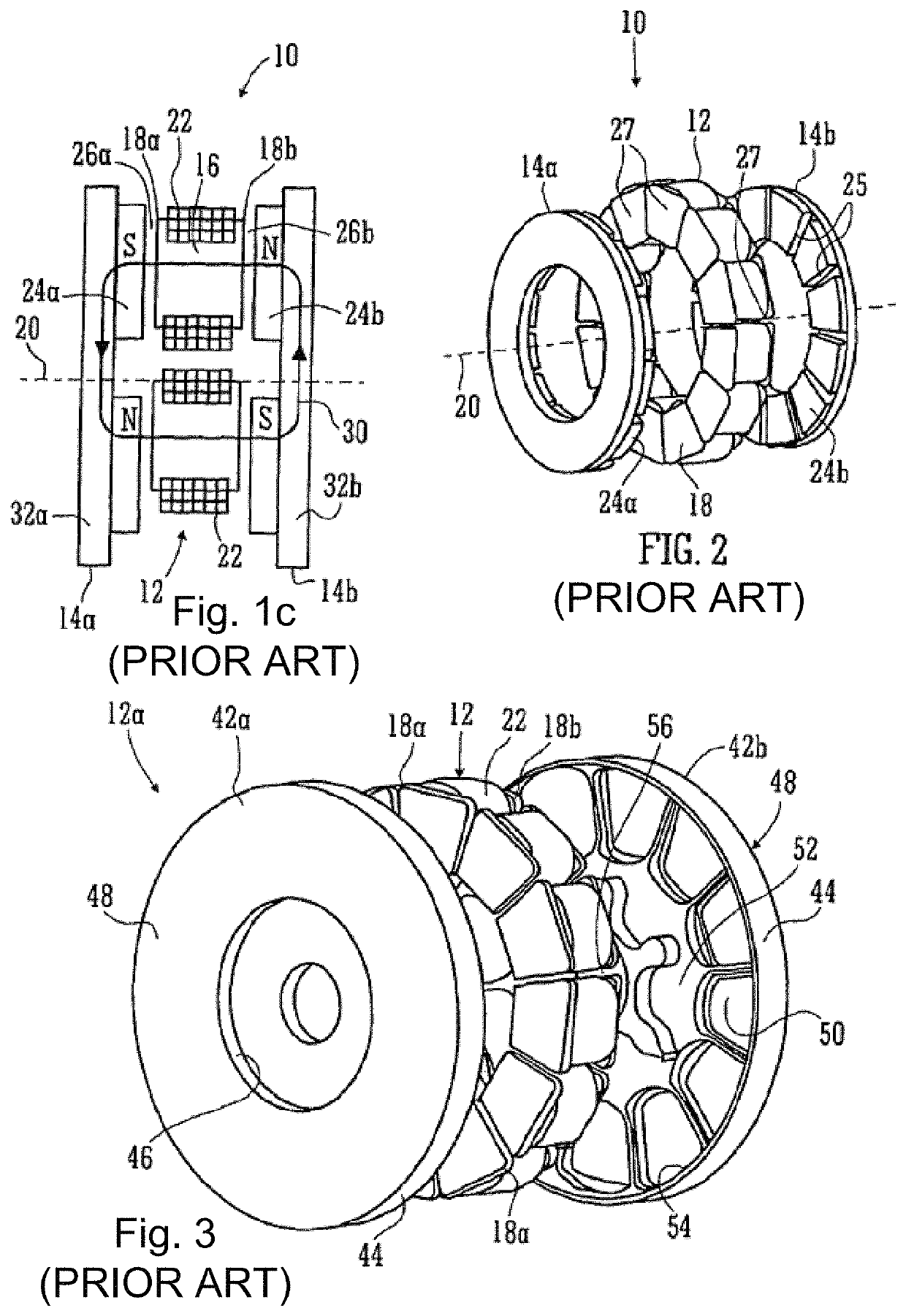
Asymmetric machines
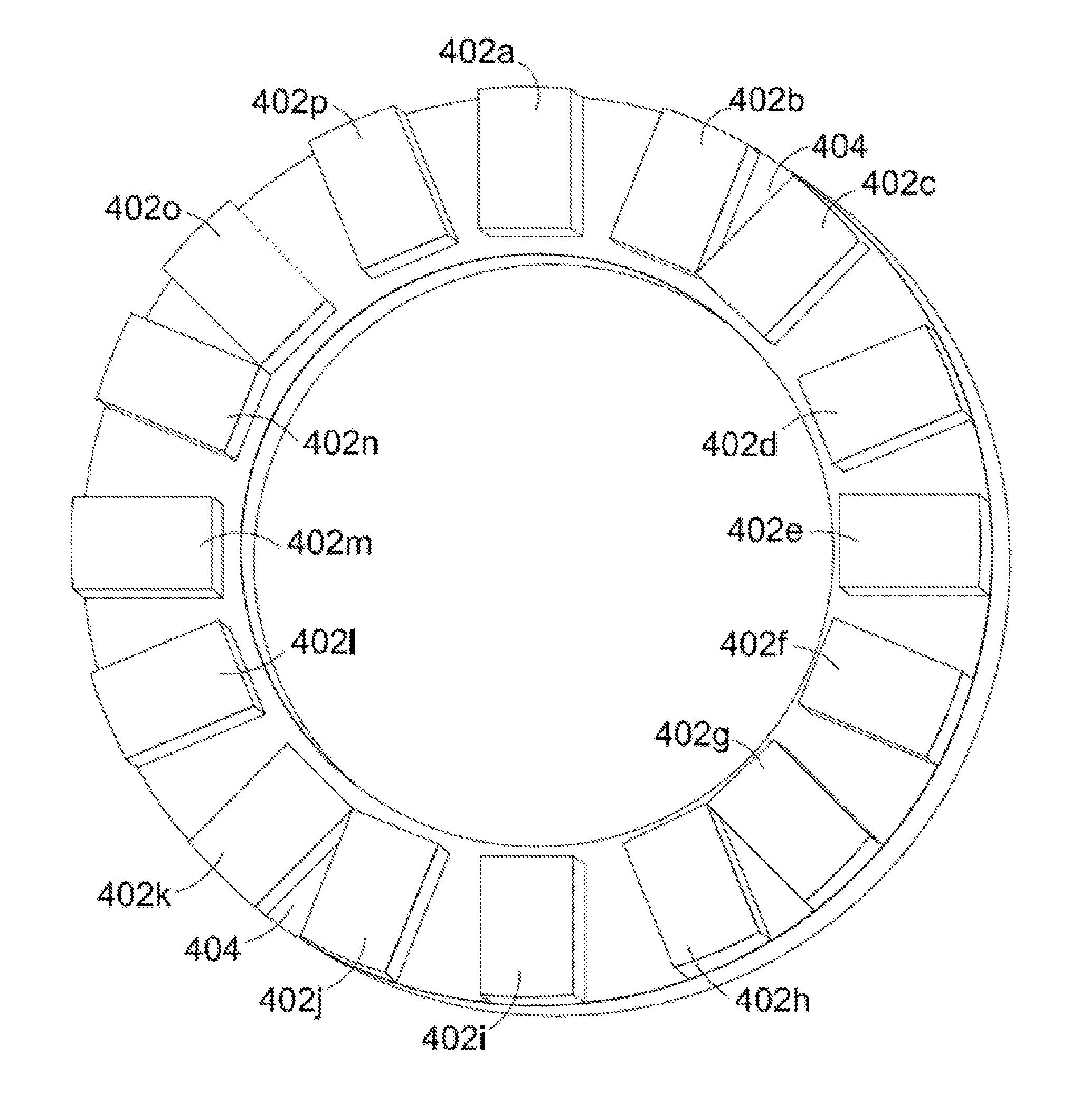
ActiveUS20150244219A1Conveniently manufacturedImprove connectivityMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPhysicsAxial flux
A rotor for an axial flux permanent magnet machine is described. The machine has a stator comprising a stator housing enclosing a set of coils wound on stator bars or teeth and disposed circumferentially at intervals about an axis on the machine, and a rotor bearing a set of permanent magnets and mounted for rotation about the said axis. The rotor and stator are spaced apart along said axis to define a gap therebetween in which magnet flux in the machine is generally in an axial direction. The magnets are disposed circumferentially around said rotor and define a plurality, n, of matching sets of magnets. Each set of magnets includes a plurality of magnets, wherein said n sets of magnets on said rotor have n-fold rotational symmetry. Within a said set, the magnets have different shapes and / or relative circumferential spacings of adjacent magnets within the set of magnets are irregular.
Owner:YASA LIMITED
Ironless AC linear motor
ActiveUS6977451B2Improve cooling efficiencyReduce coggingWindingsCooling/ventillation arrangementEngineeringLinear motor
Owner:SODICK CO LTD
Fan motor and air conditioner with same
InactiveCN102549883AIncreased Design FreedomReduce coggingPump componentsMagnetic circuit stationary partsDegrees of freedomAir conditioning
Provided are a fan motor having an increased degree of freedom in design obtained with an increase in the size of the fan motor minimized, and an air conditioner provided with the fan motor. A fan motor (100) provided with: a blade section (20); a motor (40) which has a rotor (10) provided on the outer periphery of the blade section (20) and also has a stator (30) provided on the outer peripheral side of the rotor (10) and having teeth (32) on the inner peripheral surface thereof; and a housing (50) which is provided so as to cover the outer peripheral side of the stator (30) and the rotor (10). The housing (50) is a polygon, the stator (30) is provided to at least one corner of the housing (50), and some or all of the stators (30) each have an auxiliary tooth (33) provided to an end thereof.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Servo motor and rotor thereof
InactiveUS20090267437A1Easy to shapeReducing cogging torqueMagnetic circuitSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetStator
A servo motor, comprising a stator and a rotor disposed within the stator. The rotor has a core and magnets, covering the periphery of the core, forming a plurality of axially extending rotor poles. The rotor poles comprise a plurality of the magnets arranged axially, and the centers of adjacent magnets of a rotor pole are staggered by a mechanical angle in the circumferential direction of the rotor.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SA
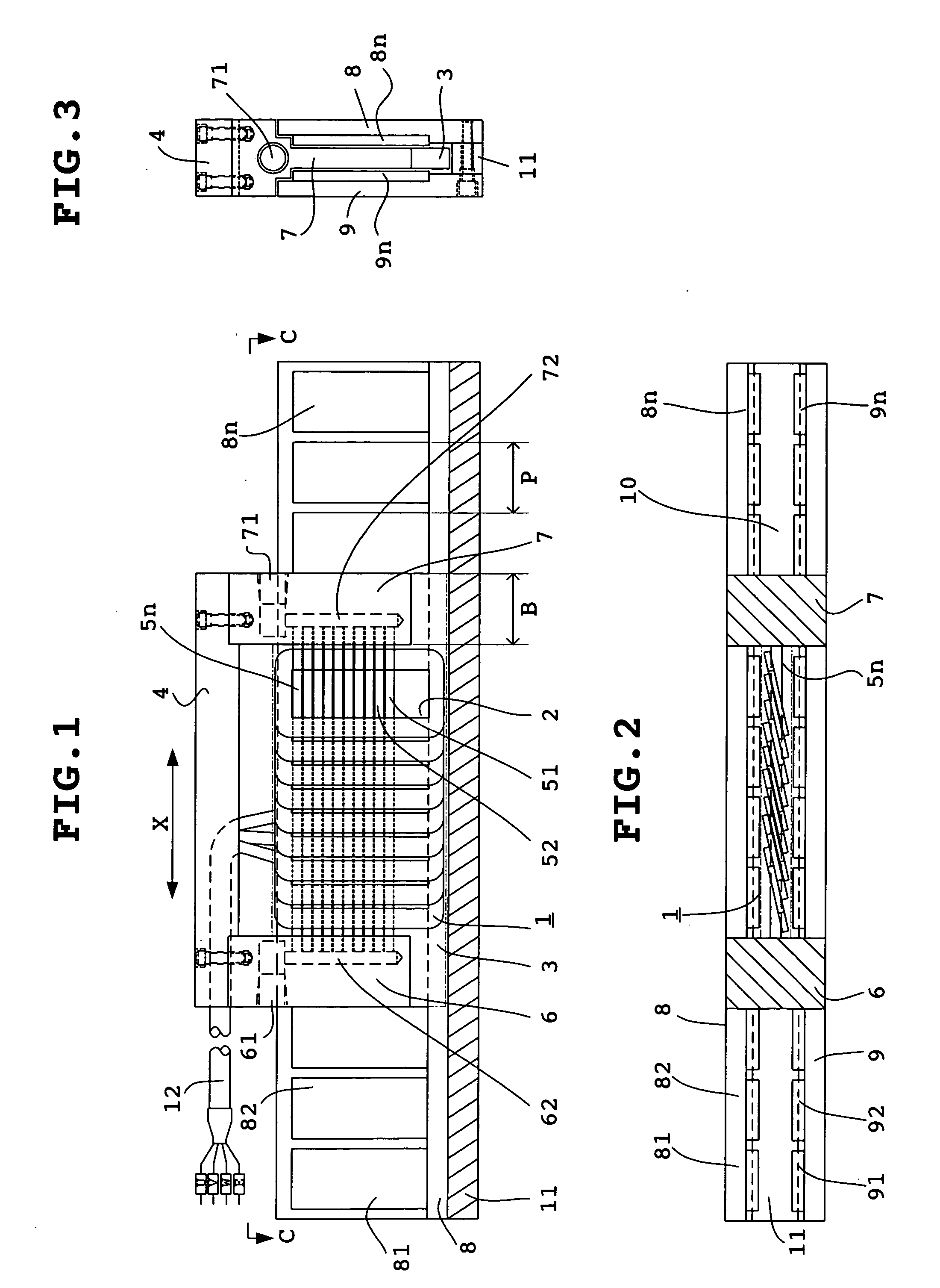
Linear motor and linear motor cogging reduction method
ActiveUS8030804B2Reduce coggingReduce impactMagnetic circuitPropulsion systemsMagnetic polesThree-phase
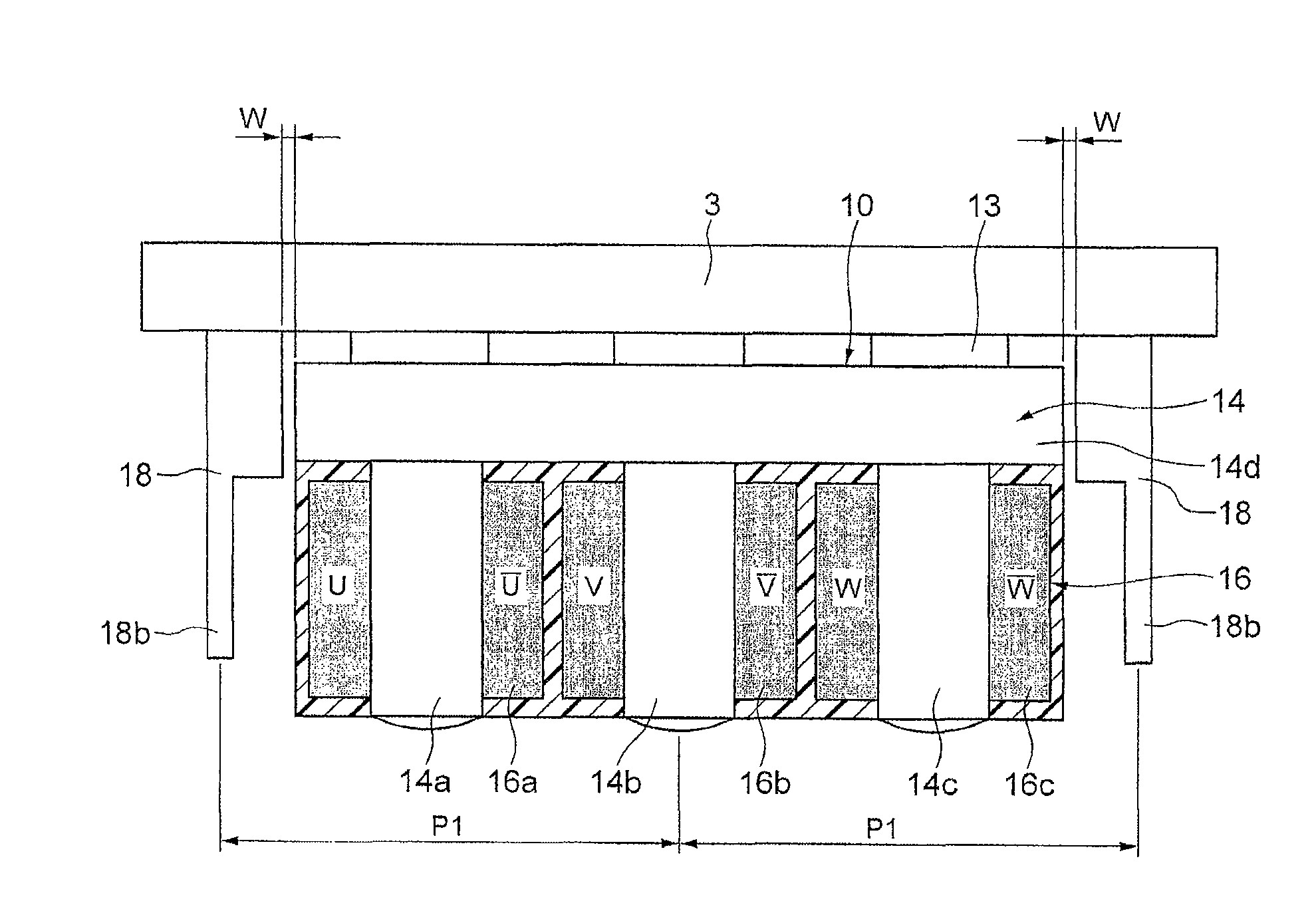
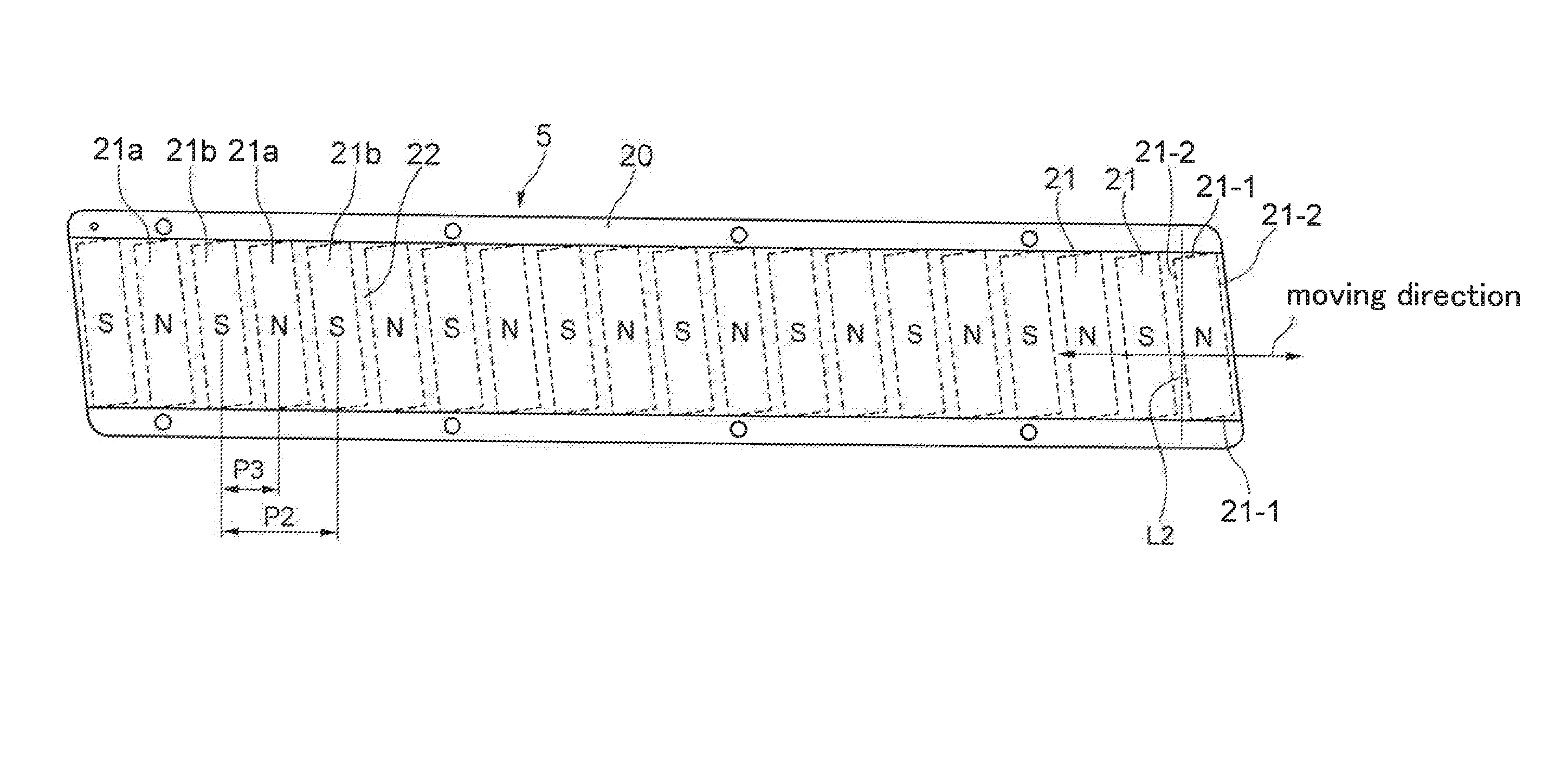
Provided is a linear motor capable of reducing cogging. The linear motor has a field magnet part 5 having a plurality of permanent magnets 21 arranged to form N and S poles alternately; a core 14 having a plurality of salient poles 14a, 14b and 14c arranged facing the field magnet part 5; and a three-phase coil 16 wound around the salient poles 14a, 14b and 14c of the core 14. At respective sides in the moving direction of an armature having the three-phase coil 16 and the core 14, auxiliary cores 18 made of a magnetic material are provided to sandwich the armature 10. The distance P1 between a center of each auxiliary core and a center of a center salient pole 14b is set to be substantially ¼×(2N+1)×a magnetic pole pitch between N poles of the field magnet part 5 (N: an integer equal to or greater than 1).
Owner:THK CO LTD
Brushless motor
InactiveUS8415855B2Simple winding structureReduce coggingMagnetic circuit rotating partsAsynchronous induction motorsBrushless motorsEngineering
A brushless direct current (BLDC) motor has a 3-phase winding 20 and six stator teeth 14, 15 with alternate stator teeth 14 being wound and the remaining stator teeth 15 being left unwound. The winding 20 has three legs, one for each phase and each leg has one coil 22 wound about one of the stator teeth 14. Each leg has a first end A,B,C, arranged to receive electrical power and a second end X,Y,Z, which is connected to the second end of the other legs to form a star connection 24. Selected stator teeth have grooves in a face thereof dividing those teeth into a plurality of stator poles. The motor may be used to drive a fuel pump for an internal combustion engine, typically for a vehicle.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SA
Ironless AC linear motor
ActiveUS20050012404A1Reduce coggingImprove cooling efficiencyWindingsCooling/ventillation arrangementLinear motorMagnet
An ironless AC linear motor for generating a thrust such that a carrier can move relative to a stator along a movement axis, includes parallel rows of permanent magnets arranged along the movement axis with a given magnet pitch to form a magnetic gap, a row of ironless coils having through holes and a manifold connected to the cooling tubes for distributing the coolant having a length equal to the magnet pitch in the direction of the movement axis.
Owner:SODICK CO LTD
Asymmetric axial permanent magnet machines having axial rotors with irregular magnets
ActiveUS10566866B2Reduce coggingLow energy stateMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machineryEngineering
A rotor for an axial flux permanent magnet machine is described. The machine has a stator comprising a stator housing enclosing a set of coils wound on stator bars or teeth and disposed circumferentially at intervals about an axis on the machine, and a rotor bearing a set of permanent magnets and mounted for rotation about the said axis. The rotor and stator are spaced apart along said axis to define a gap therebetween in which magnet flux in the machine is generally in an axial direction. The magnets are disposed circumferentially around said rotor and define a plurality, n, of matching sets of magnets. Each set of magnets includes a plurality of magnets, wherein said n sets of magnets on said rotor have n-fold rotational symmetry. Within a said set, the magnets have different shapes and / or relative circumferential spacings of adjacent magnets within the set of magnets are irregular.
Owner:YASA LIMITED
Stator chute machining tool and stator chute machining method
ActiveCN103219838ANovel ideaSimple structureManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesLaser beam welding apparatusScrew jointStator
The invention belongs to the field of machinery and particularly relates to a stator chute machining tool and a stator chute machining method. The stator chute machining tool comprises a stator iron core piece fixing device and a stator chute forming device. The stator iron core piece fixing device is composed of a base plate, a positioning mandrel and a pressing plate, wherein the positioning mandrel is arranged on the base plate in a screw joint mode, the pressing plate is arranged at the top end of the positioning mandrel in a screw joint mode, and stator iron core pieces are sleeved on the positioning mandrel. The stator chute forming device is composed of a fixing plate, an angle plate and a parallel positioning mandrel, wherein the fixing plate is fixedly arranged on the base plate, the parallel positioning mandrel is arranged in the center of the fixing plate in a rotating mode, a positioning rib which is matched with stator iron core piece grooves is arranged at one end, close to the stator iron core pieces, of the parallel positioning mandrel, and the other end of the parallel positioning mandrel penetrates through the fixing plate to be sleeved with and fix the angle plate. The stator chute machining tool rapidly and efficiently machines stator chutes, inclined angles of the chutes are controlled when a positioning pin is matched with a positioning pin stroke hole, and a stator chute iron core can effectively weaken the effect of teeth and slots of a motor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LINIX MOTOR
Hybrid excitation synchronous generator with low cogging effect
InactiveCN101719707AImprove load characteristicsReduce starting resistanceMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsExcitation currentMagnetic poles
The invention discloses a hybrid excitation synchronous generator with low cogging effect, relates to synchronous generators and solves the problems that the traditional generator has the disadvantages of high starting resistance, poor starting performance and poor effect; and the problems that a small hybrid excitation synchronous generator has a thick size of a permanent magnet on a magnetic pole and a high magnetic motive force, which affect the adjustment effect of a voltage. The rotor of a motor of the invention adopts a split-pole structure, wherein a plurality of magnets are arranged on the surface of a pole yoke of the rotor; the polarity of the magnets is the same; the distance between the magnets is kept in a certain proportion; and non-guide magnetic space is arranged between two neighbouring magnets. The hybrid excitation synchronous generator of the invention can weaken or eliminate the cogging effect in the synchronous generator, improves a whole moment coefficient of a stator winding of the generator, reduces the starting resistance and the running noise of the generator, can increase the main magnetic flux of the hybrid excitation synchronous generator when an excitation current is increased, and improves the load characteristic of the generator.
Owner:刘志新
Motor and recording disk drive device provided with the same
InactiveUS7327066B2Easy to adjustCombined cogging waveform can be reducedMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsRotor magnetsEngineering
In a spindle motor, a core (33) includes a plurality of core plates (34), which are laminated one on another. The core (33) is constituted by laminating two cores, that is, a first core (34a) and a second core (34b), which are different from each other in shape of a surface facing to a rotor magnet (32). At least a part of a cogging torque generated at the second core (34b) can be cancelled by a cogging torque generated at the first core (34a).
Owner:NIDEC CORP
Linear motor
ActiveUS20130082544A1Reduce variationReduce coggingWindingsMagnetic circuit stationary partsLinear motorMagnet
Provided is a linear motor capable of preventing an increase in length of the armature in the moving direction and also of reducing cogging. The linear motor has a magnetic field part having a plurality of permanent magnets arranged in a straight line in such a manner that N poles and S poles are formed alternately; and an armature having a core which has a plurality of teeth arranged opposite to the magnetic field part with a gap created therebetween and a plurality of coils wound on the teeth of the core. Among the teeth with the coils wound around, a width TW1 in a relative moving direction of each of teeth placed at both ends in the relative moving direction of the armature is smaller, from a base part to an end part thereof, than a width TW2 in the relative moving direction of each of other teeth.
Owner:THK CO LTD
Disc type motor rotor with embedded magnetic poles
ActiveCN108233568AIncrease inductanceGood magnetoresistance effectMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesEngineering
The invention provides a disc type motor rotor with embedded magnetic poles, which comprises a rotor back plate, magnetic poles and surface iron cores, wherein the rotor back plate is in the shape ofa circular ring, the upper surface of the rotor back plate is provided with a plurality of magnetic pole grooves which are formed in a continuous manner, and the longitudinal cross section of each magnetic pole groove in the direction perpendicular to the radial direction of the rotor back plate is bilaterally symmetrical; each magnetic pole groove is fixedly embedded with a magnetic pole, and themagnetic pole is of a groove shape corresponding to the shape of the magnetic pole groove; and the surface iron cores are fixed in the grooves of the magnetic poles, and the surface iron cores are ofa shape corresponding to an accommodating space of the grooves of the magnetic poles. The disc type motor rotor with the embedded magnetic poles is high in inductance and good in magnetoresistive effect, obtains a magnetic field with a better sine degree, improves the torque, and is high in speed and easy to perform field weakening control. In addition, the disc type motor rotor with the embeddedmagnetic poles is low in magnetic field loss and low in cogging effect.
Owner:姚常勤
Brushless direct current permanent magnet motor having characteristics of low noise, low vibration and low temperature rise and assembly technology thereof
ActiveCN102522835AIncrease speedEnsure vibrationMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsLow noisePunching
The invention relates to a brushless direct current permanent magnet motor having characteristics of low noise, low vibration and low temperature rise. The brushless direct current permanent magnet motor consists of a motor rotor, a motor stator, a front end cap, a motor housing and a rear end cap. The front end cap and the rear end cap are sealedly installed at two ends of the motor housing to form an integral motor housing; the motor stator is arranged inside the motor housing; and the motor rotor is installed inside the motor stator. The brushless direct current permanent magnet motor is characterized in that: an iron core of the motor stator is formed by lamination of a plurality of punching sheets that are manufactured by Fe-Ni soft magnetic alloy; the punching sheets are in a circular ring shape and grooves that are arranged regularly are made on inner circles. When the plurality of punching sheets are laminated, an angle is formed by staggering of the grooves of adjacent punching sheets, so that a chute is formed at a stator slot; and an enameled wire is wound in the chute. According to the invention, a heat dispersion performance, a stator lamination mode and a balancing performance are improved; therefore, the motor has characteristics of high rotating speed, low noise, low vibration and low temperature rise as well as is suitable for application to a special using occasion. When the motor that is assembled by the assembly technology in the invention works at 7000RPM, the temperature rise is not more than 12 DEG C and the noise is less than 60dB.
Owner:SHAANXI AEROSPACE TIMES NAVIGATION EQUIP CO LTD
Rotor chip, rotor and motor
PendingCN110022016AImprove the distribution of magnetic field linesReduce in quantityMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic lineStator
The invention discloses a rotor chip, a rotor and a motor. The rotor chip comprises a disc-shaped chip, wherein the chip is provided with 16 magnetic steel grooves, and every two adjacent magnetic steel grooves form a set of magnetic groove pairs; the two magnetic steel grooves in each group of magnetic groove pairs are arranged in a V shape, and the opening direction faces the outer side of the chip; the eight groups of magnetic groove pairs are symmetrically distributed around the center of the chip; the two magnetic steel grooves in the same group of magnetic groove pairs are symmetricallyarranged relative to the straight line n which passes through the center of a certain chip; the chip is provided with a group of magnetic separation holes in the V-shaped opening side of each group ofmagnetic grooves; the magnetic separation hole group comprises two first magnetic separation holes and two second magnetic separation holes which are symmetrically arranged relative to the straight line n; and the second magnetic separation holes are located in the two sides of the first magnetic separation holes. The distribution of magnetic force lines of the rotor adopting the rotor chip can be effectively improved, so that the tooth groove effect of the motor is weakened, and the purpose of improving the torque fluctuation is achieved; and in addition, the structure of a stator inclined groove and a rotor inclined groove does not need to be arranged, so that the production process is simplified, and the cost is lowered.
Owner:GUANGDONG JINBA INTELLIGENT TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
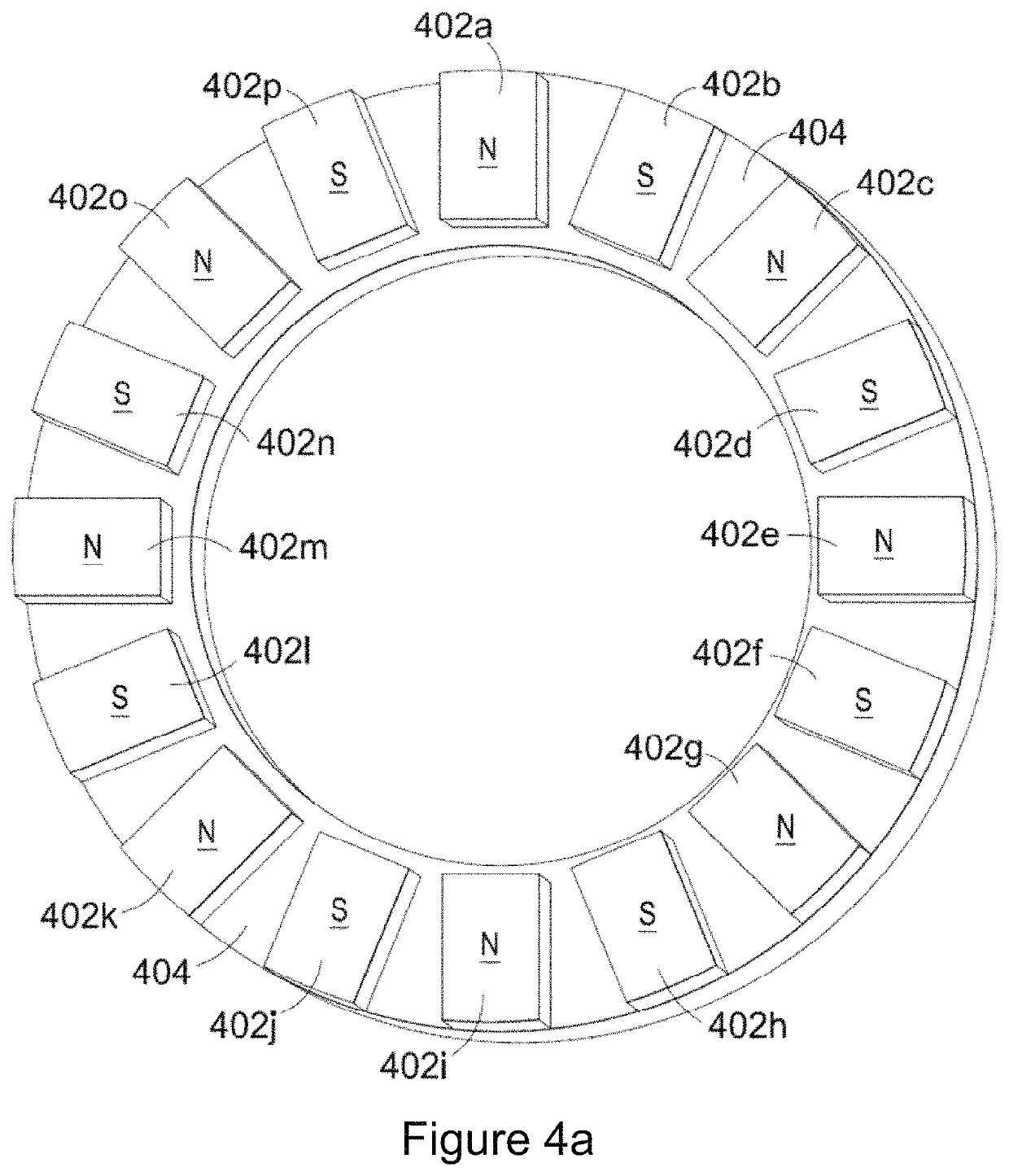
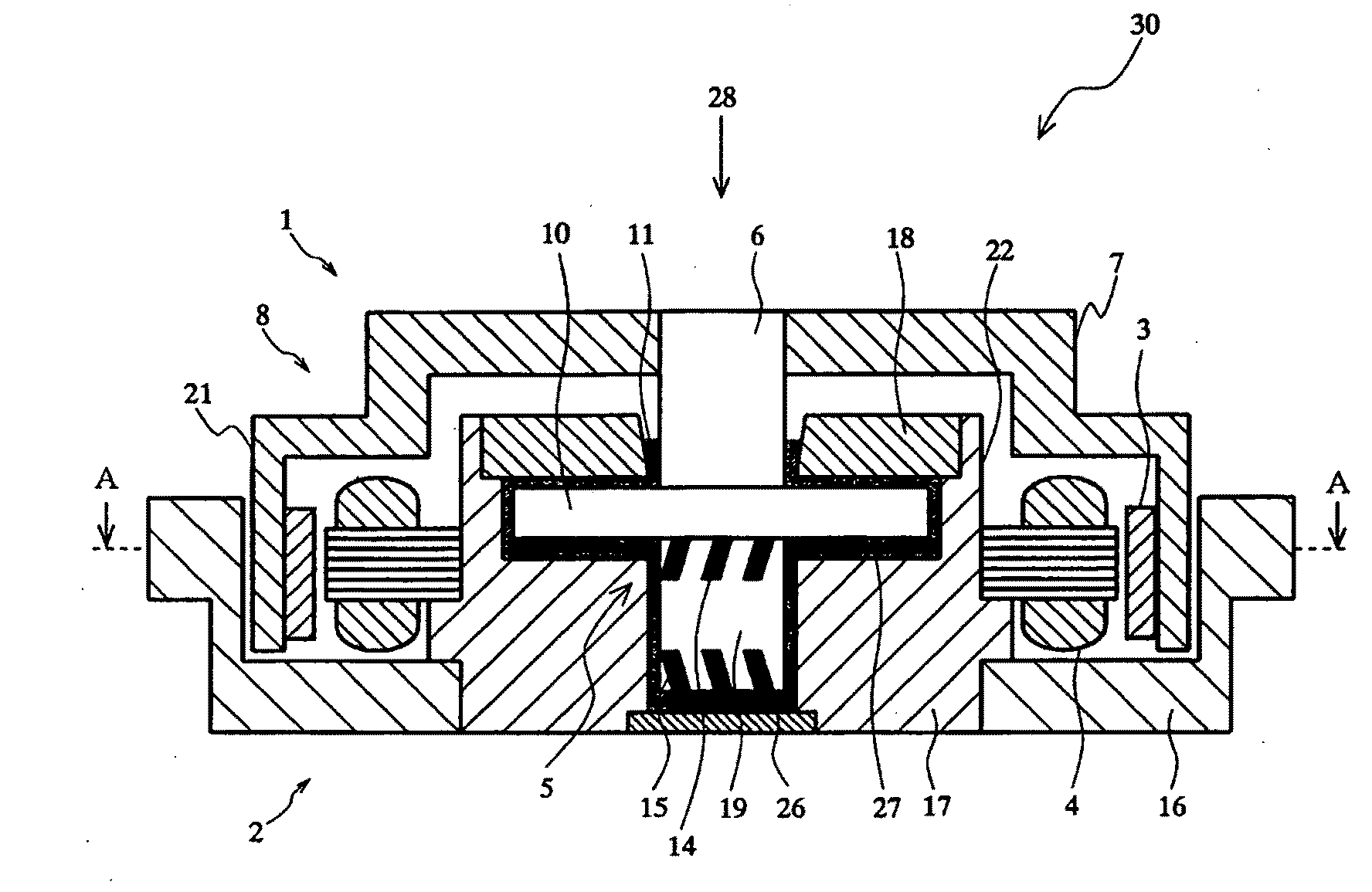
Electrical machines with reduced cogging
ActiveUS20100117476A1Weakening rangeOverall potential energy of the rotorMagnetic circuitSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machineConductor Coil
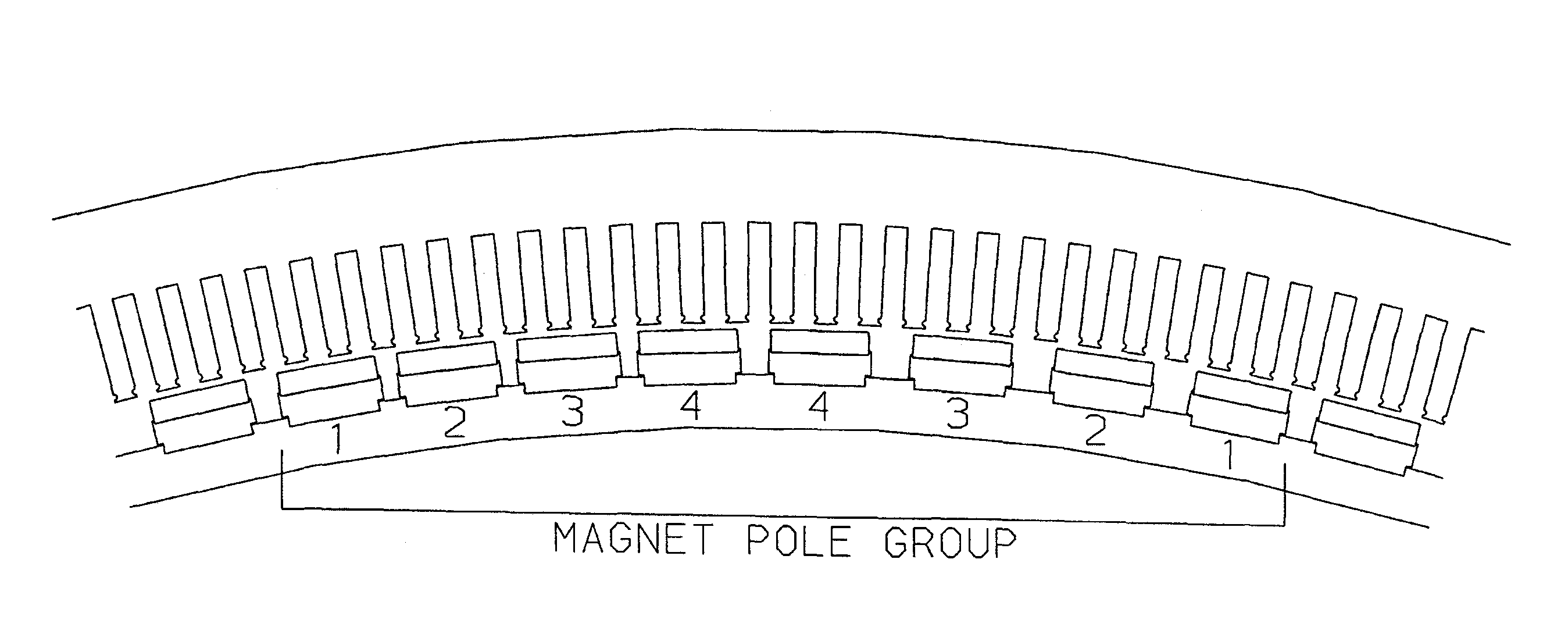
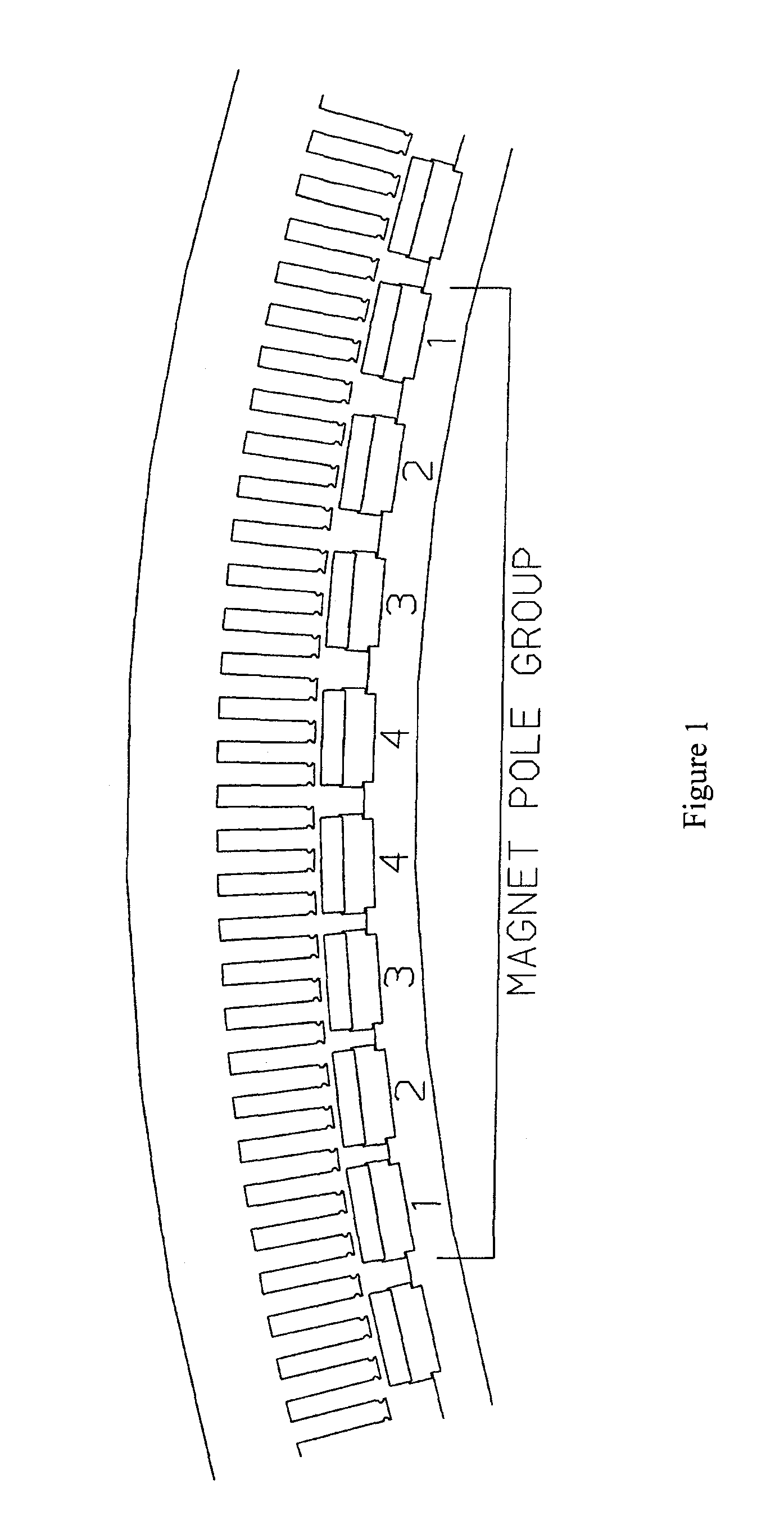
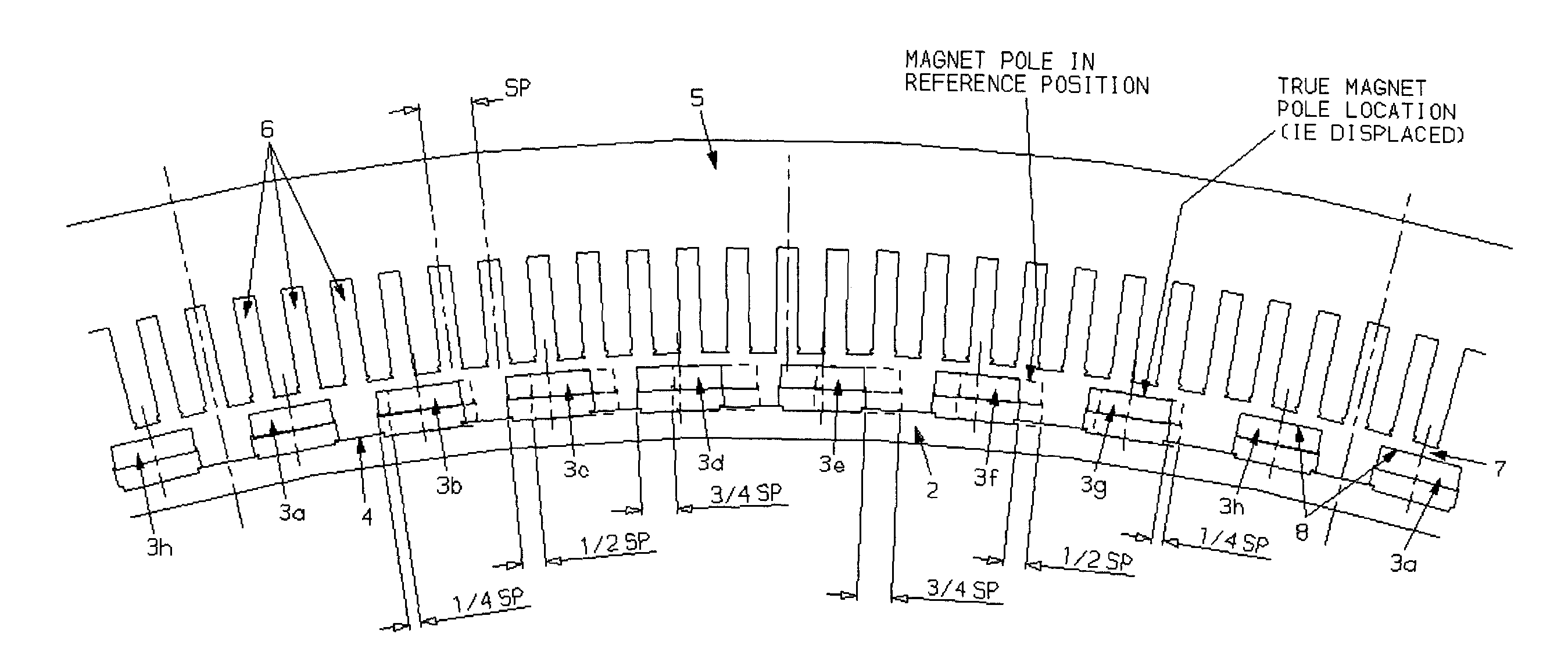
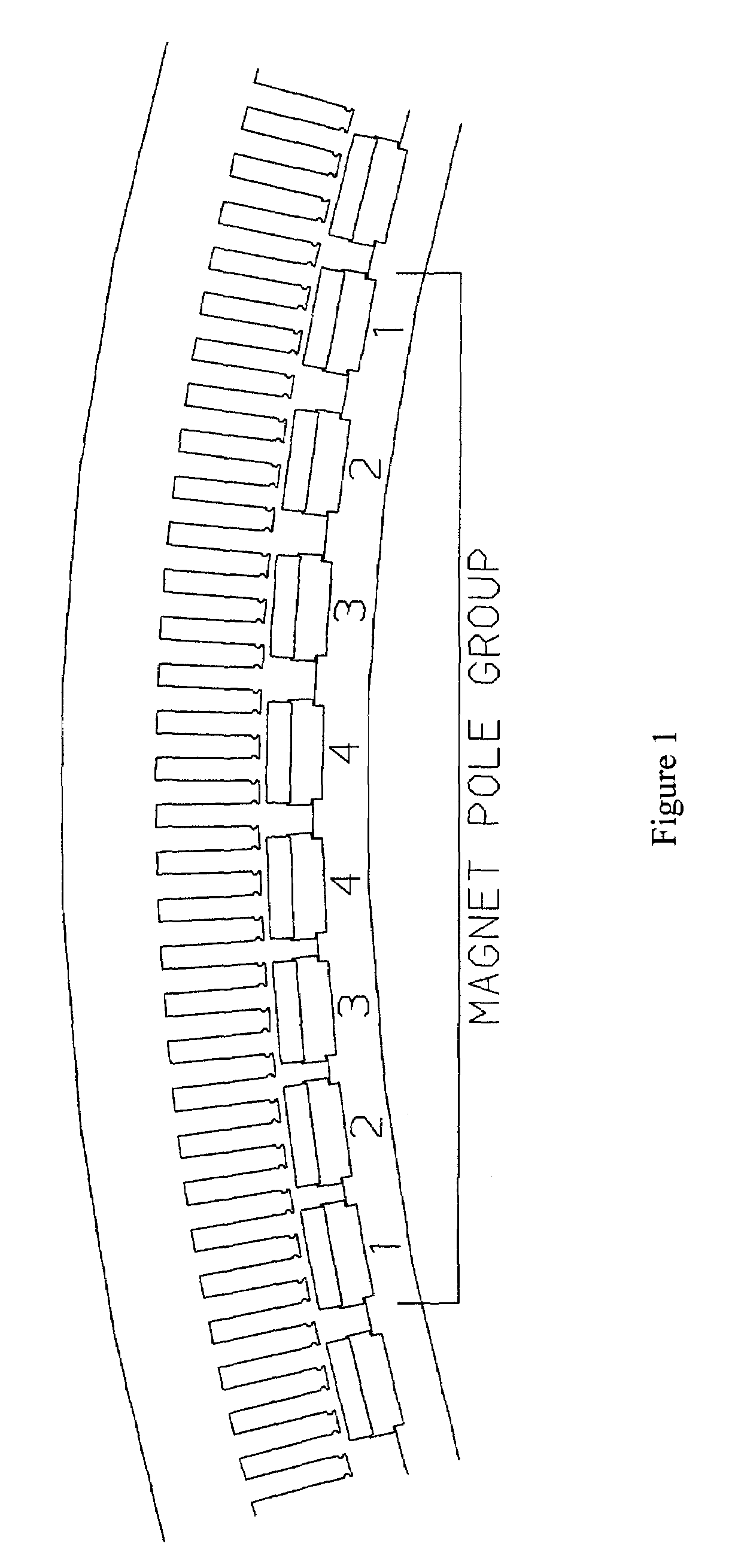
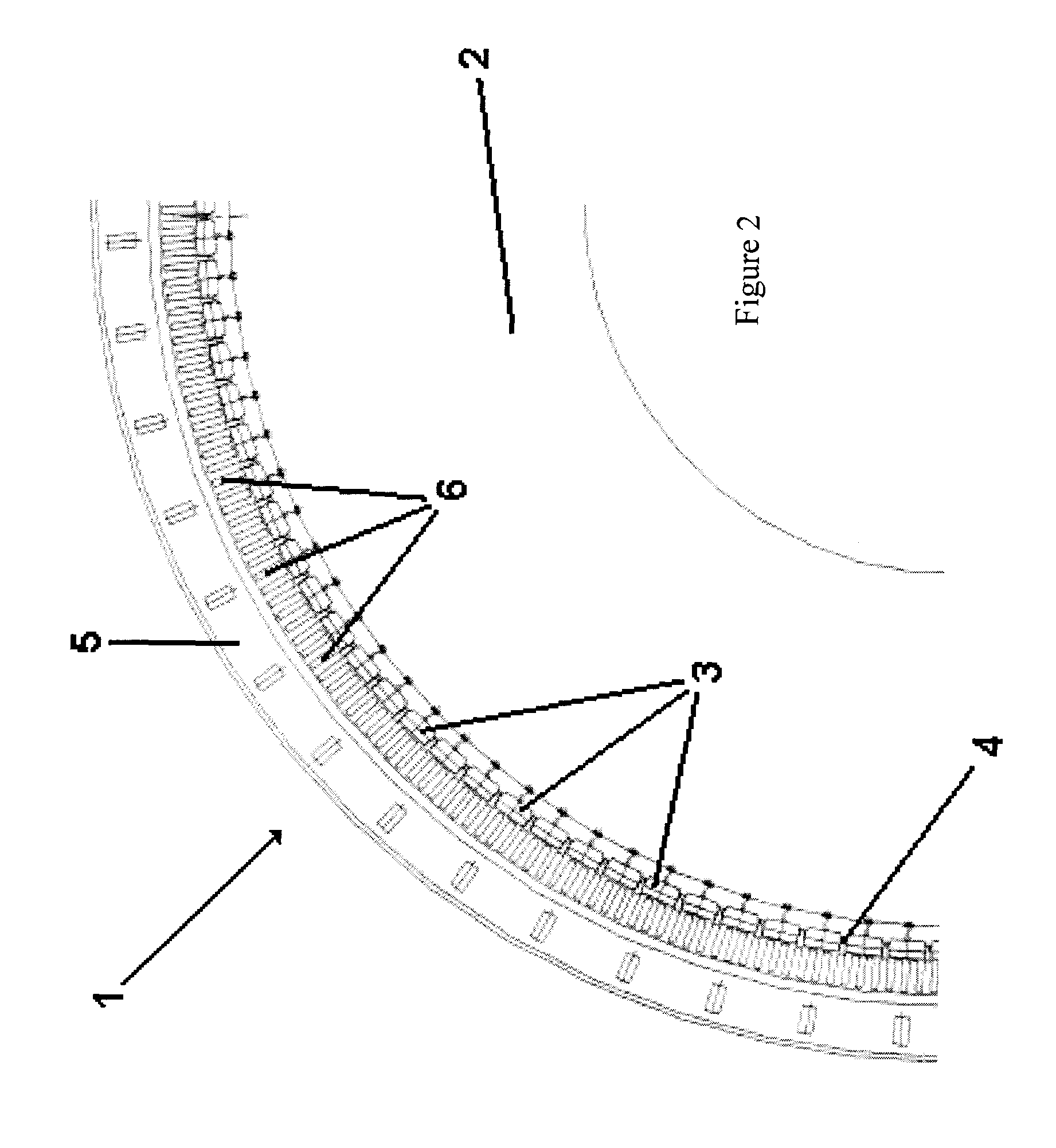
An electrical machine has at least two separate groups of at least two circumferentially adjacent magnet poles. One of the circumferentially outer magnet poles in one of the groups of magnet poles is defined as being in its reference position. The reference position of each other magnet pole is defined as the position each other magnet pole would occupy if all the magnet poles were equally circumferentially spaced around the first or second body and the one circumferentially outer pole was in its reference position. At least one of the circumferentially outer magnet poles in each group is sited in its reference position. At least one magnet pole in each group is a displaced magnet pole and is sited in a position that is displaced from its reference position by an amount that is not equal to an integral multiple of the reference angular pitch of the winding slots. The displacement of the magnet poles provides a pronounced reduction in cogging.
Owner:GE POWER CONVERSION
Rotor structure, motor and compressor
PendingCN111711292AImproved reluctance distributionImprove flux density waveformMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineMagnetic poles
The invention mainly aims to provide a rotor structure, a motor and a compressor. The rotor structure comprises a rotor iron core and a plurality of permanent magnets arranged on the rotor iron core so as to form a plurality of magnetic poles on the rotor iron core, wherein the plurality of magnetic poles comprise a plurality of N poles and a plurality of S poles which are alternately arranged along the circumferential direction of the rotor iron core, at least one magnetic pole of the rotor iron core is provided with a magnetic isolation hole group, the magnetic isolation hole group is provided with a first magnetic isolation hole and a second magnetic isolation hole which are arranged at an interval along the direction far away from the axis of the rotor iron core, and by using a plane perpendicular to the axis of the rotor iron core as a predetermined plane, the projection of the first magnetic isolation hole on the predetermined plane and the projection of the second magnetic isolation hole on the predetermined plane are strip-shaped, and the extension directions of the projections are crossed. By means of the arrangement, the problem that in the prior art, vibration noise of amotor is large is solved.
Owner:ZHUHAI GREE REFRIGERATION TECH CENT OF ENERGY SAVING & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Single-phase motor, fluid generation device and electrical equipment
InactiveCN106169819AReduce coggingSmall starting currentSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineElectric current
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SHENZHEN
IE5 three-phase asynchronous motor based on stator unequal-groove punching sheets and cast-aluminum rotor
ActiveCN111682665AIncrease profitImprove efficiencyMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsPunchingThree phase asynchronous motor
The invention discloses an IE5 three-phase asynchronous motor based on stator unequal-groove punching sheets and a cast-aluminum rotor. A rotor core of the motor is formed by laminating a plurality ofrotor punching sheets, each rotor punching sheet comprises an annular first substrate, a plurality of closed grooves are radially and uniformly formed in the outer annular surface of each first substrate along the circumferential direction of the first substrate, and aluminum conducting bars are cast in the closed grooves; a stator core of the motor is formed by laminating a plurality of stator unequal-groove punching sheets. Each stator unequal-slot punching sheet comprises a second substrate in a circular ring shape; stator groove groups used for placing copper wires are uniformly arrangedon the inner circular ring surface of the second substrate along the circumferential direction of the second substrate in a radial manner. The number of the stator slots of each pole and each phase ineach stator slot group is at least three, the stator slots comprise at least one large stator slot and at least two small stator slots, the large stator slot is arranged in the middle of the stator slot group, and the two sides of the large stator slot are respectively provided with one or more small stator slots; or at least one large stator slot, at least two middle stator slots and at least two small stator slots are included; the large stator slot is arranged in the middle of the stator slot group, two sides of the large stator slot are respectively provided with one or more small statorslots, one or more middle stator slots are respectively arranged between the large stator slot and the small stator slots, and concave slot wedges or convex slot wedges are plugged in the stator slotsembedded with the stator windings.
Owner:SHANXI ELECTRIC MOTOR MANUFACTURING CO LTD
Skewed slot dual-stator permanent magnetic disc type wind power generator
InactiveCN101442241AReduce wind resistanceReduce coggingSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet rotorEngineering
The invention discloses a permanent-magnet disk type wind generator with double chute stators, which comprises a left chute stator, a right chute stator, a permanent-magnet rotor, a hollow output shaft, a first chassis, a second chassis, a middle component and a control unit, wherein the left chute stator and the right chute stator are correspondingly arranged and fixed on the first chassis and the second chassis respectively, the permanent-magnet rotor is fixed on the hollow output shaft and positioned between the left chute stator and the right chute stator, the hollow output shaft is arranged in central through holes of the first chassis and the second chassis, and two ends of the first chassis and the second chassis are connected through the middle component. The permanent-magnet disk type wind generator with the double chute stators has the advantages of simple and compact structure, low cost, simple and convenient assembly, and wide application range.
Owner:CHANGSHA ANCHUAN ELECTRIC
Servo motor and rotor thereof
InactiveUS7965008B2Reduce coggingEasy to shapeMagnetic circuitSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsEngineeringMagnet
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SA
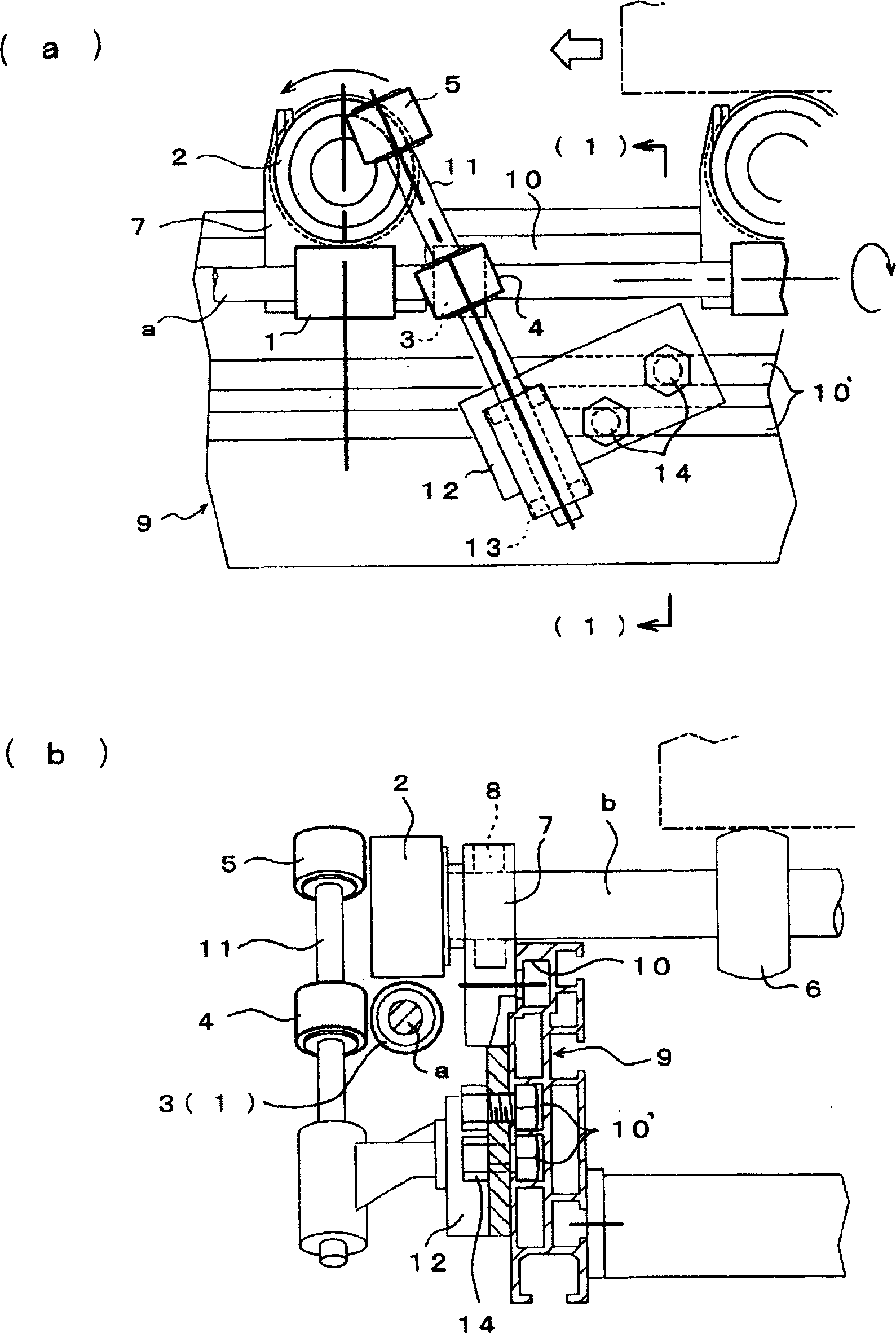
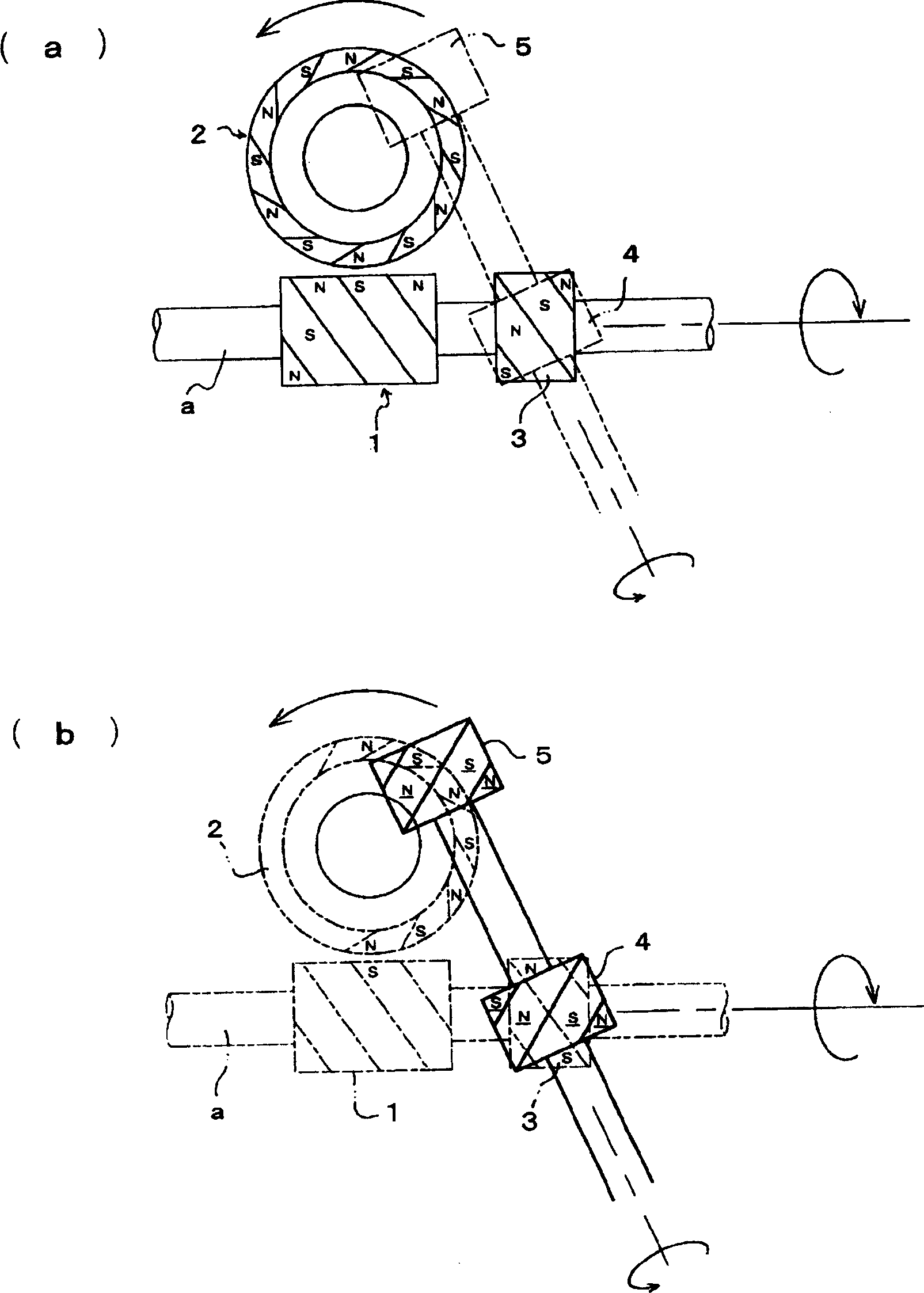
Driving device
InactiveCN1674419AReduce coggingEfficient assembly workManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesNon-mechanical conveyorsTransmission systemHigh torque
The present invention provided a drive unit utilizing magnetism which generates high torque and increases torque without enlarging the diameters of a driving magnetic wheel and a driven magnetic wheel. This driving unit, which rotates a shaft b to which a roller is attached by a power transmission mechanism in noncontact making use of magnetic force, transmits power from the driving magnetic wheel 1 to the driven magnetic wheel 2 to which the roller shaft b is attached, by means of two or more transmission systems, and totals the power to rotate the shaft to which the above roller is attached.
Owner:MARUYASU KIKAI KK
Electrical machines with reduced cogging
ActiveUS7714473B2Weakening rangeOverall potential energy of the rotorMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineEngineering
The present invention provides an electrical machine 1 with reduced cogging. The magnet poles 3 of the electrical machine are comprised of at least two separate groups of at least two circumferentially adjacent magnet poles. One of the circumferentially outer magnet poles 3 in one of the groups of magnet poles is defined as being in its reference position. The reference position of each other magnet pole 3 is defined as the position each other magnet pole would occupy if all the magnet poles were equally circumferentially spaced around the first or second body and the one circumferentially outer pole was in its reference position. At least one of the circumferentially outer magnet poles 3 in each group is sited in its reference position. At least one magnet pole 3 in each group is a displaced magnet pole and is sited in a position that is displaced from its reference position by an amount that is not equal to an integral multiple of the reference angular pitch of the winding slots. The displacement of the magnet poles 3 provides a pronounced reduction in cogging.
Owner:GE POWER CONVERSION
Stator iron core construction for outer rotor permanent magnet motor and stator winding contra-wound method
ActiveCN101459353AEliminate the influence of human factorsIncrease productivityMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesPermanent magnet motorEngineering
The invention relates to an outer rotor permanent magnet motor stator iron core structure and a roll-back method of a stator winding, wherein a stator iron core thereof is a multi-tooth strip structure of an reverse slot, the edges of notches of the air gap sides of adjacent tooth portions of the stator iron core are made into connecting strips which are mutually connected, adjacent stator yoke portions are made into opening gaps, the self-opened stator yoke portions of the winding are rolled reversely on a multi-tooth strip stator tooth portion, the stator yoke portions are closed after being bent to a round stator, and the air gap sides of the stator tooth portion are located in a connecting state to form a closed slot structure. The invention has simple process and scientific and reasonable design, creates a novel stator structure, and reduces the slot effect. All production links of an outer rotor permanent magnet motor can achieve mechanized production, the effects of human factors are effectively eliminated, the production efficiency and the consistency of products are greatly increased, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN NAVIGATION INSTR RES INST
Magnetic member, motor device, magnetizing method, and storage device
InactiveUS20100259122A1Cogging of a small permanent magnet can be reducedMaintain propertiesMagnetic circuitManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesMagnetizationMagnetic poles
A method of magnetizing a magnetic member for a rotor of a motor device. The magnetic member has a thickness t in the radial direction of the magnetic member satisfying the relation πD / (0.75MP−π)<t≦πD / (0.5MP−π), where D represents an inner diameter of the magnetic member having a value of 20 mm or less, P represents the number of magnetic poles, and M represents the number of alternating current phases for driving the motor device. The magnetic member is magnetized unidirectionally in the radial direction of the magnetic member. Thereafter, the unidirectionally magnetized magnetic member is magnetized in partitions at regular intervals in the radial direction so that a magnetization direction of the magnetic member is reversed and the magnetic poles are arranged at regular intervals in a circumferential direction.
Owner:TAKEHARA ISAMU +2
Linear motor and linear motor cogging reduction method
ActiveUS20100207464A1Reduce coggingReduce influenceMagnetic circuitPropulsion systemsPhysicsMagnetic core
Provided is a linear motor capable of reducing cogging.The linear motor has a field magnet part 5 having a plurality of permanent magnets 21 arranged to form N and S poles alternately; a core 14 having a plurality of salient poles 14a, 14b and 14c arranged facing the field magnet part 5; and a three-phase coil 16 wounded around the salient poles 14a, 14b and 14c of the core 14. At respective sides in the moving direction of an armature having the three-phase coil 16 and the core 14, auxiliary cores 18 of magnetic body are provided to sandwich the armature 10. The distance P1 between a center of each auxiliary core and a center of a center salient pole 14b is set to be substantially ¼×(2N+1)×a magnetic pole pitch between N-N poles of the field magnet part 5 (N: an integer equal to or greater than 1).
Owner:THK CO LTD
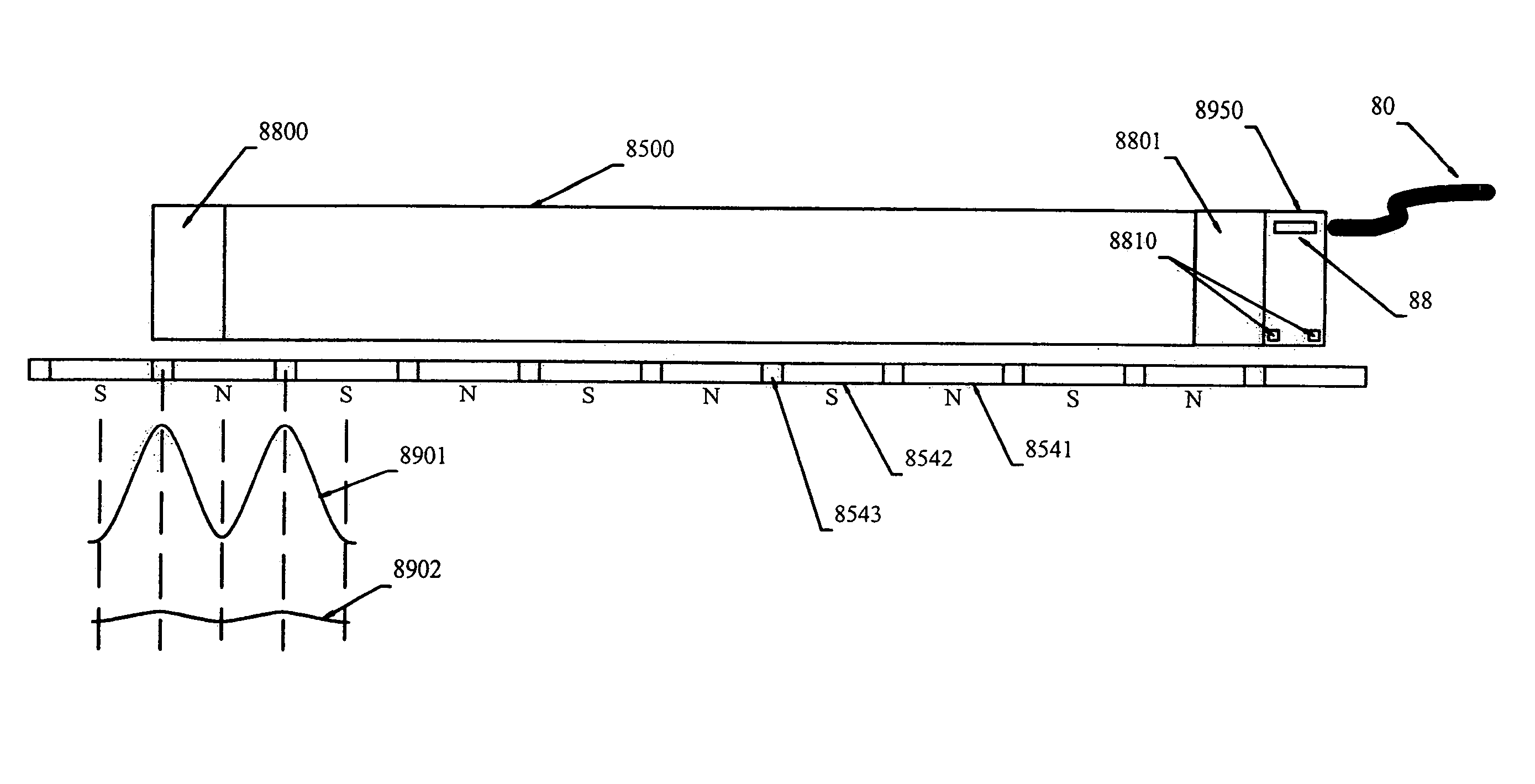
Anti-cogging method and apparatus for a linear motor
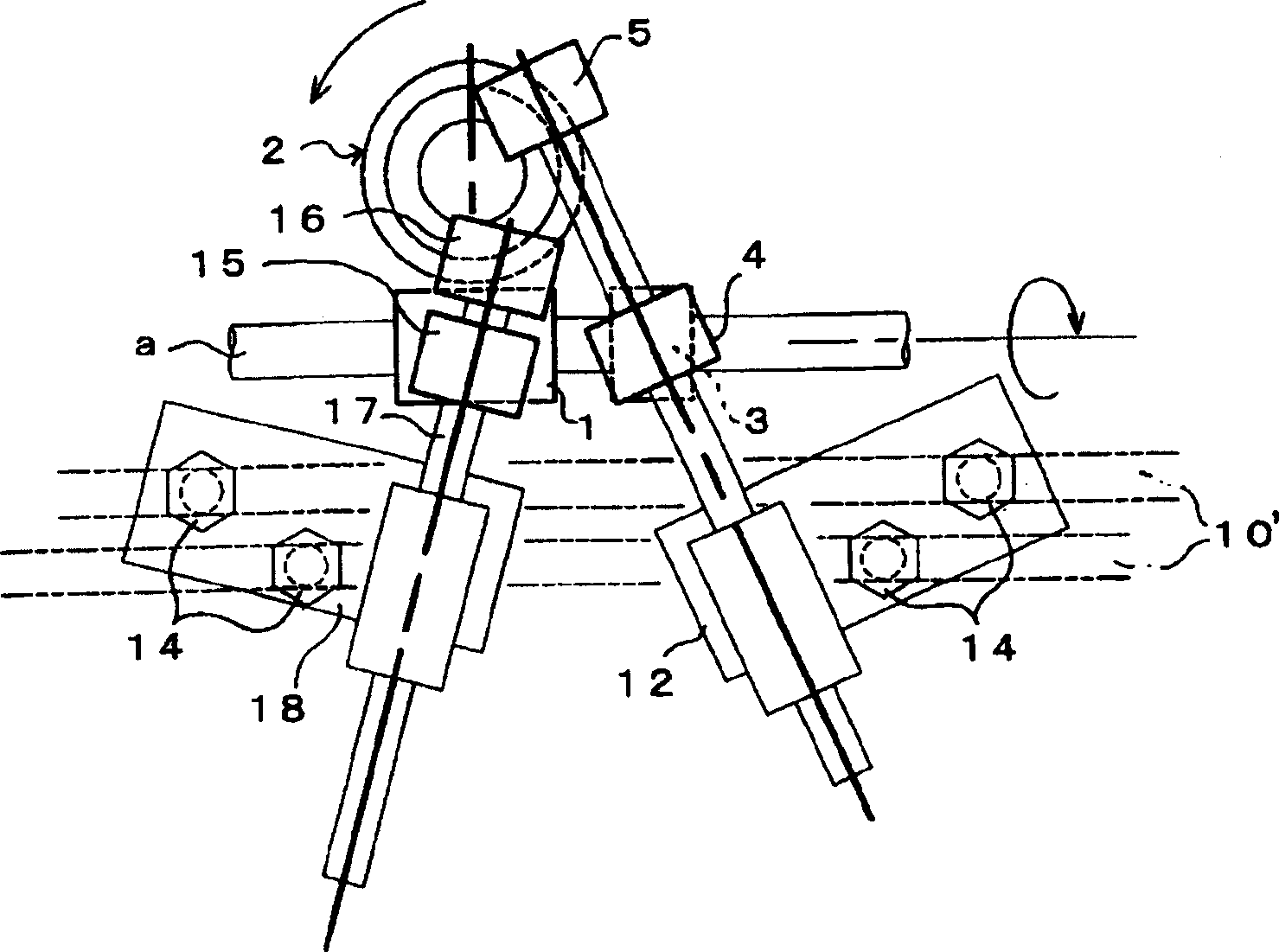
ActiveUS7317266B2Substantial reduction of cogging in a linear motorLow implementation costPropulsion systemsLinear motor
The present invention provides a method for reducing cogging in a linear motor and for mounting sensors to determine motion of the motor.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com