Patents
Literature
44 results about "Constrained-layer damping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
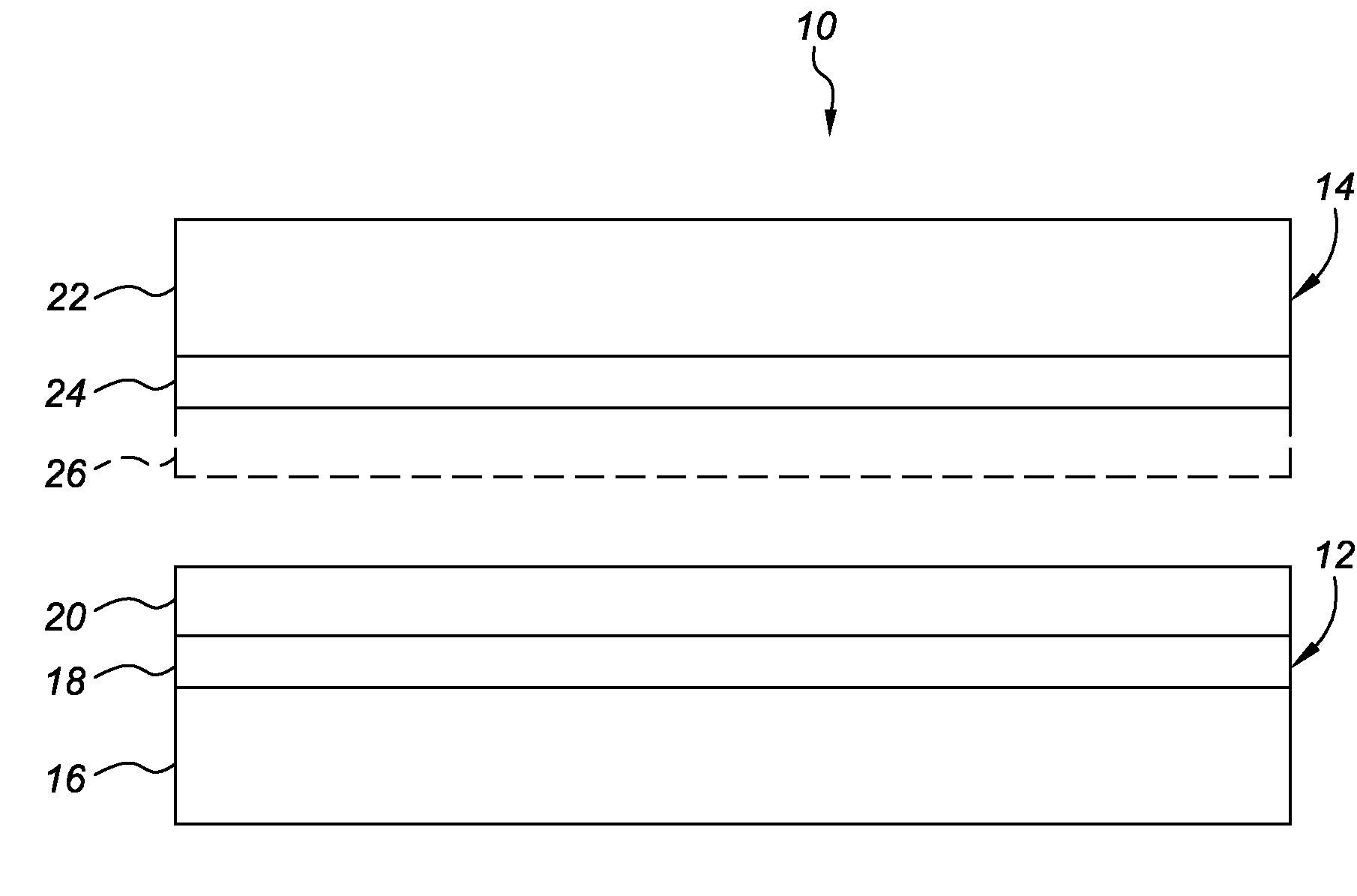
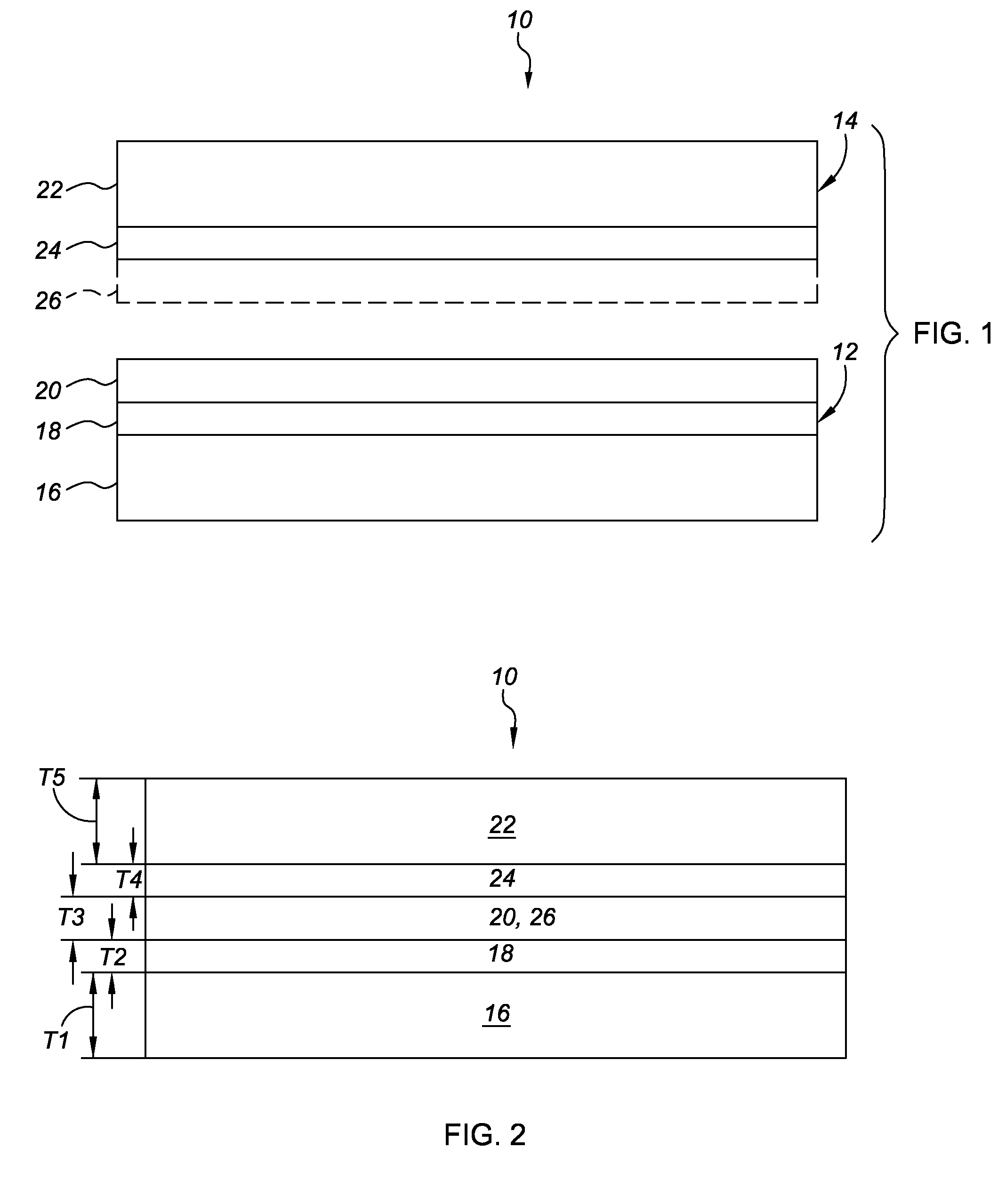
Constrained-layer damping is a mechanical engineering technique for suppression of vibration. Typically a viscoelastic or other damping material, is sandwiched between two sheets of stiff materials that lack sufficient damping by themselves. The ending result is, any vibration made on either side of the constraining materials (the two stiffer materials on the sides) are trapped and evidently dissipated in the viscoelastic or middle layer.
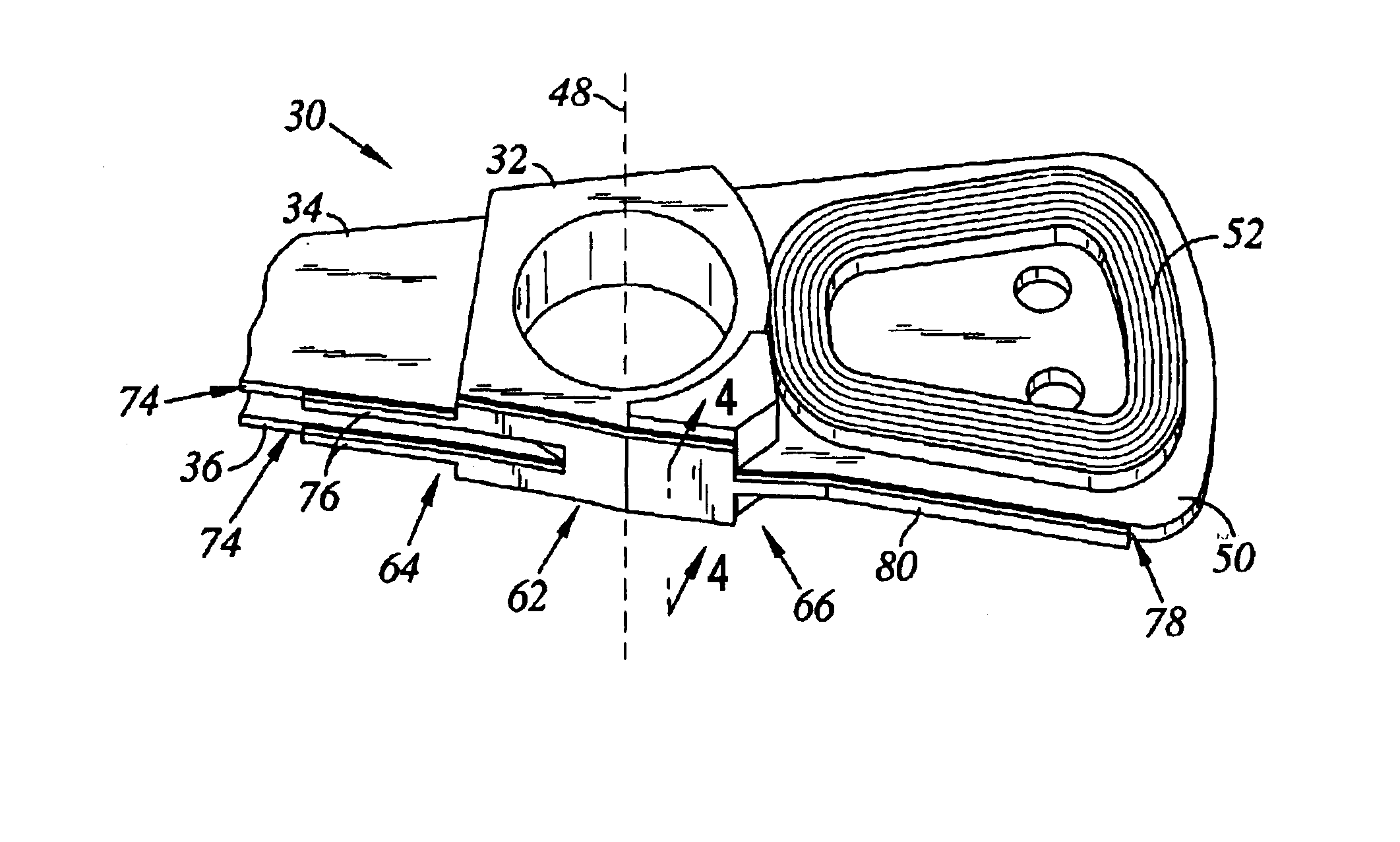
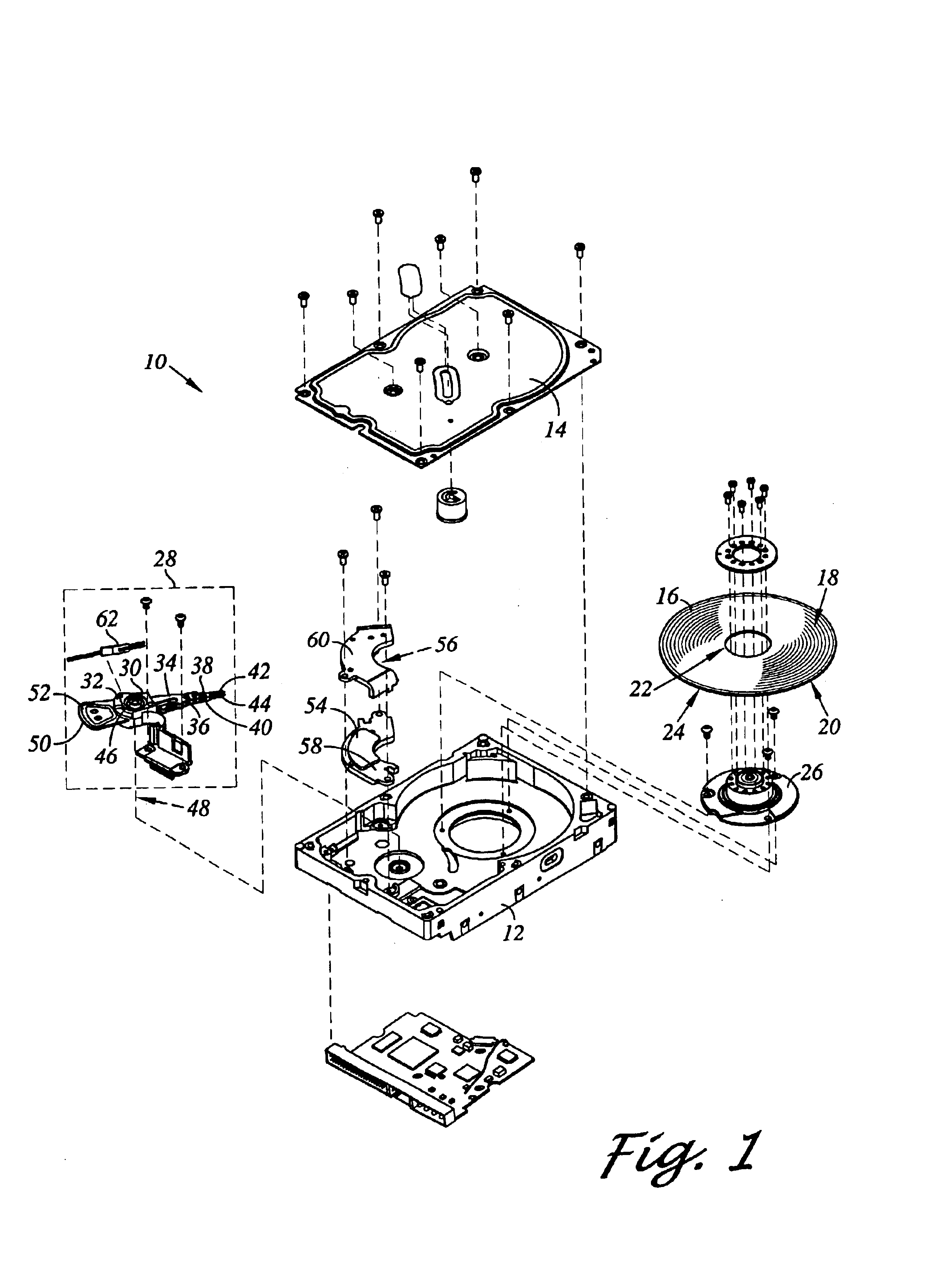
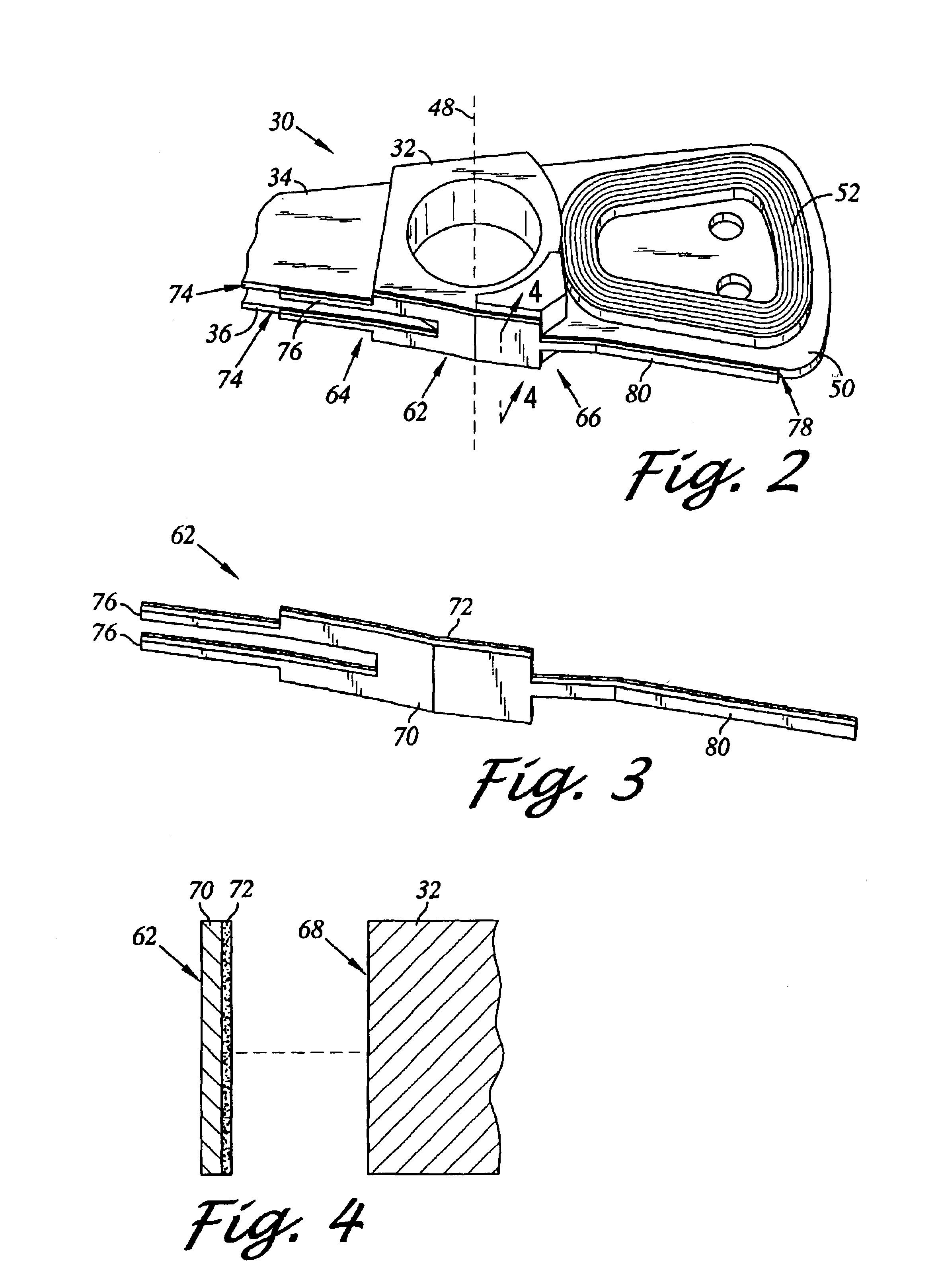
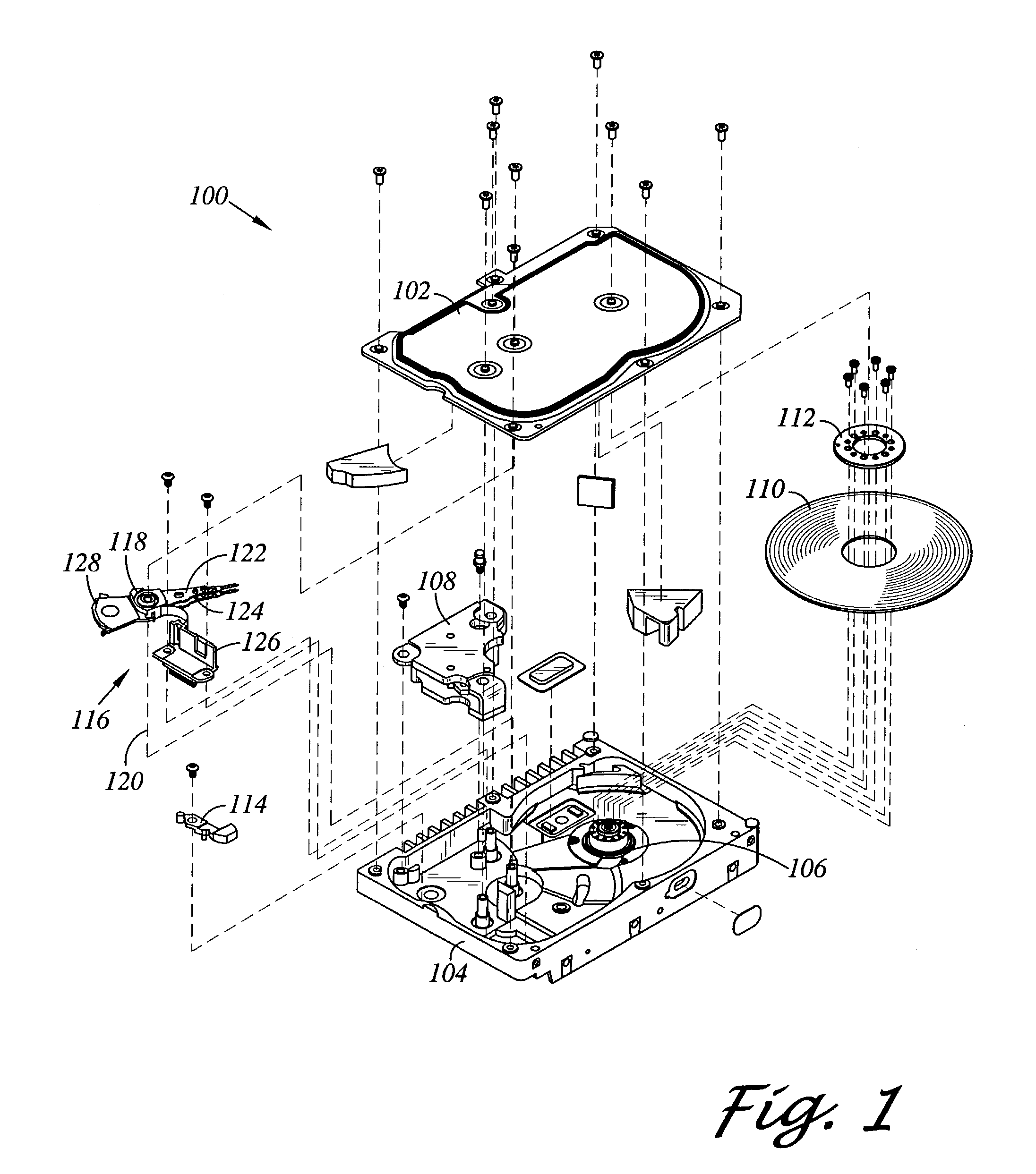
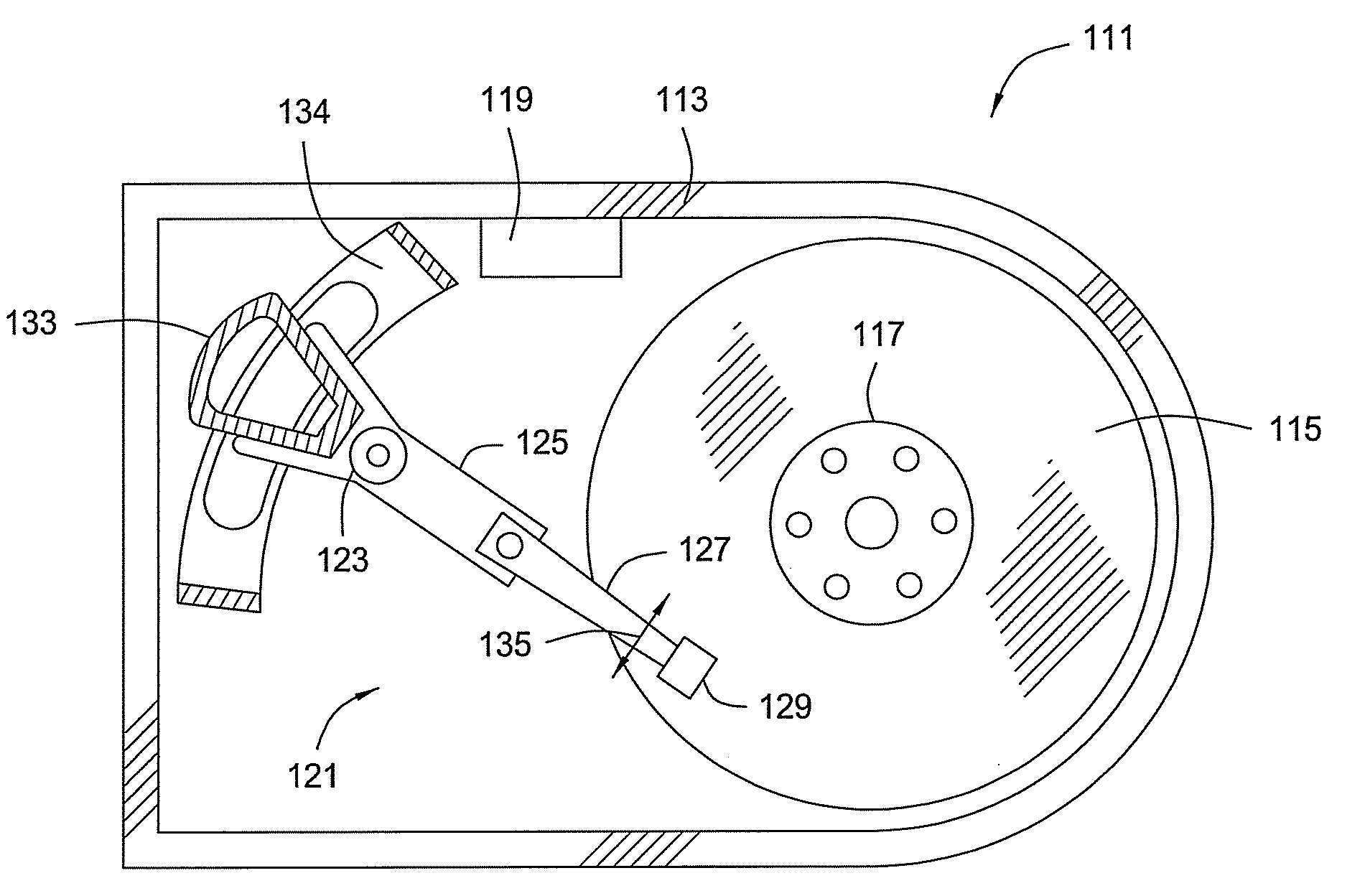
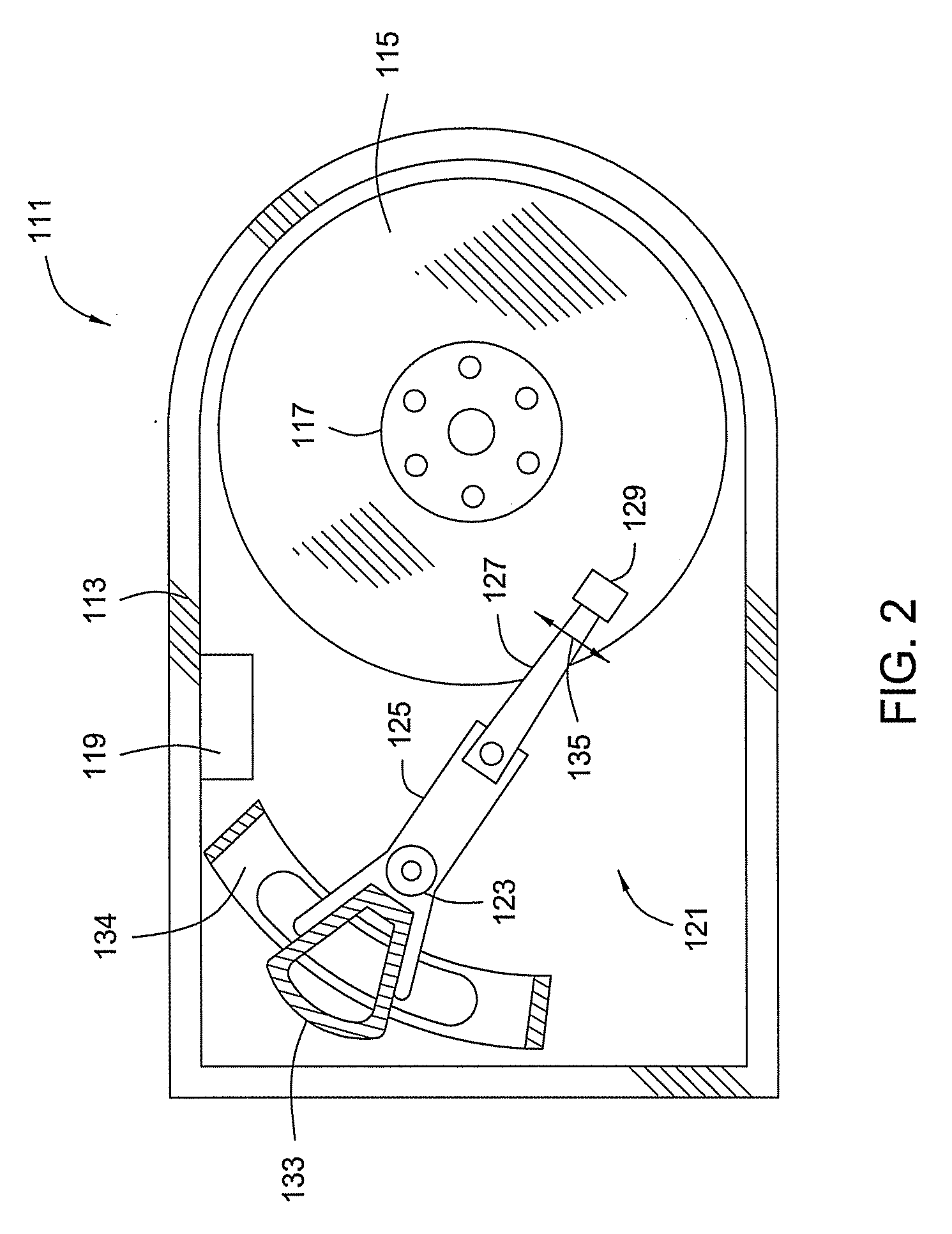
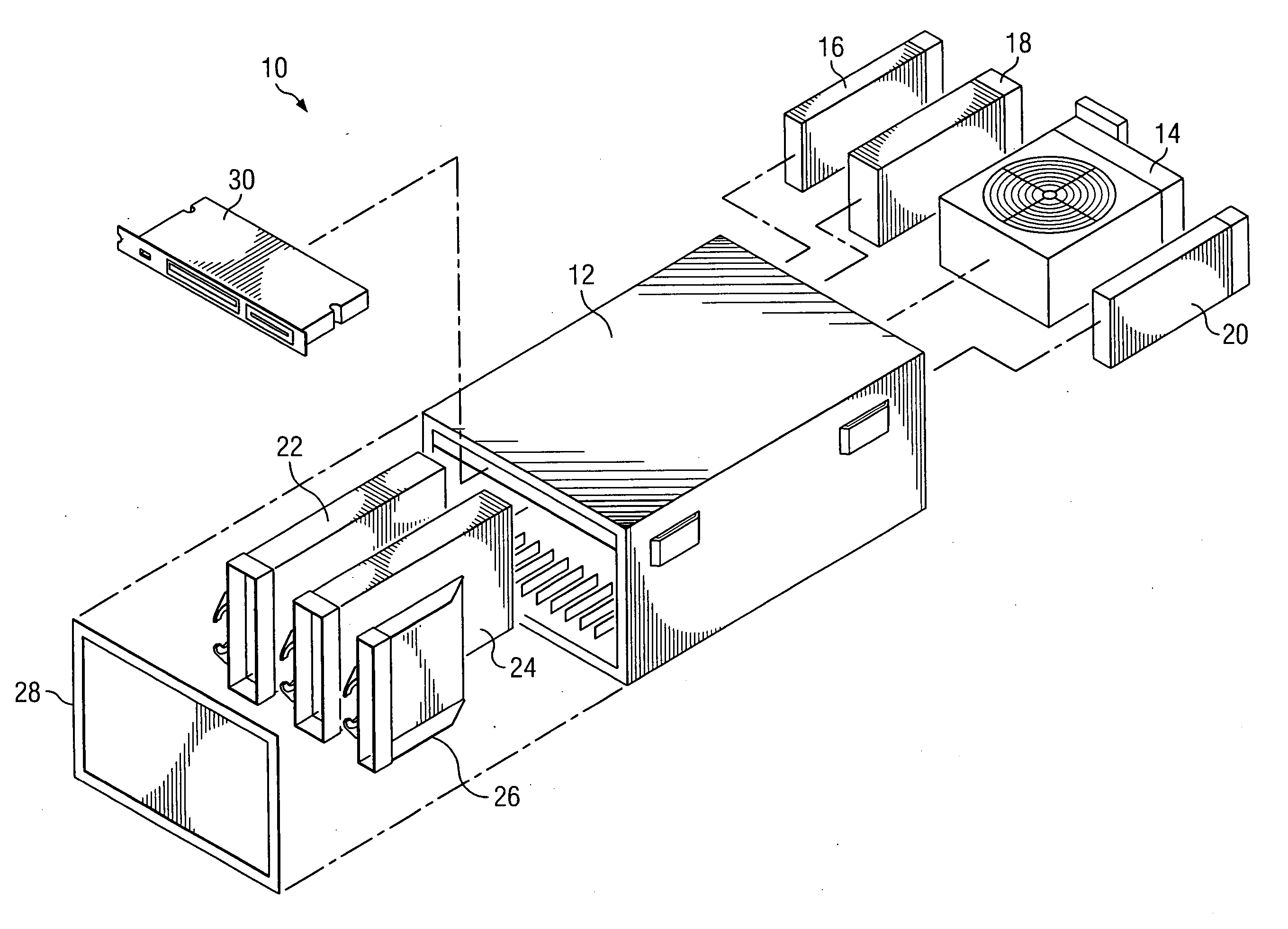
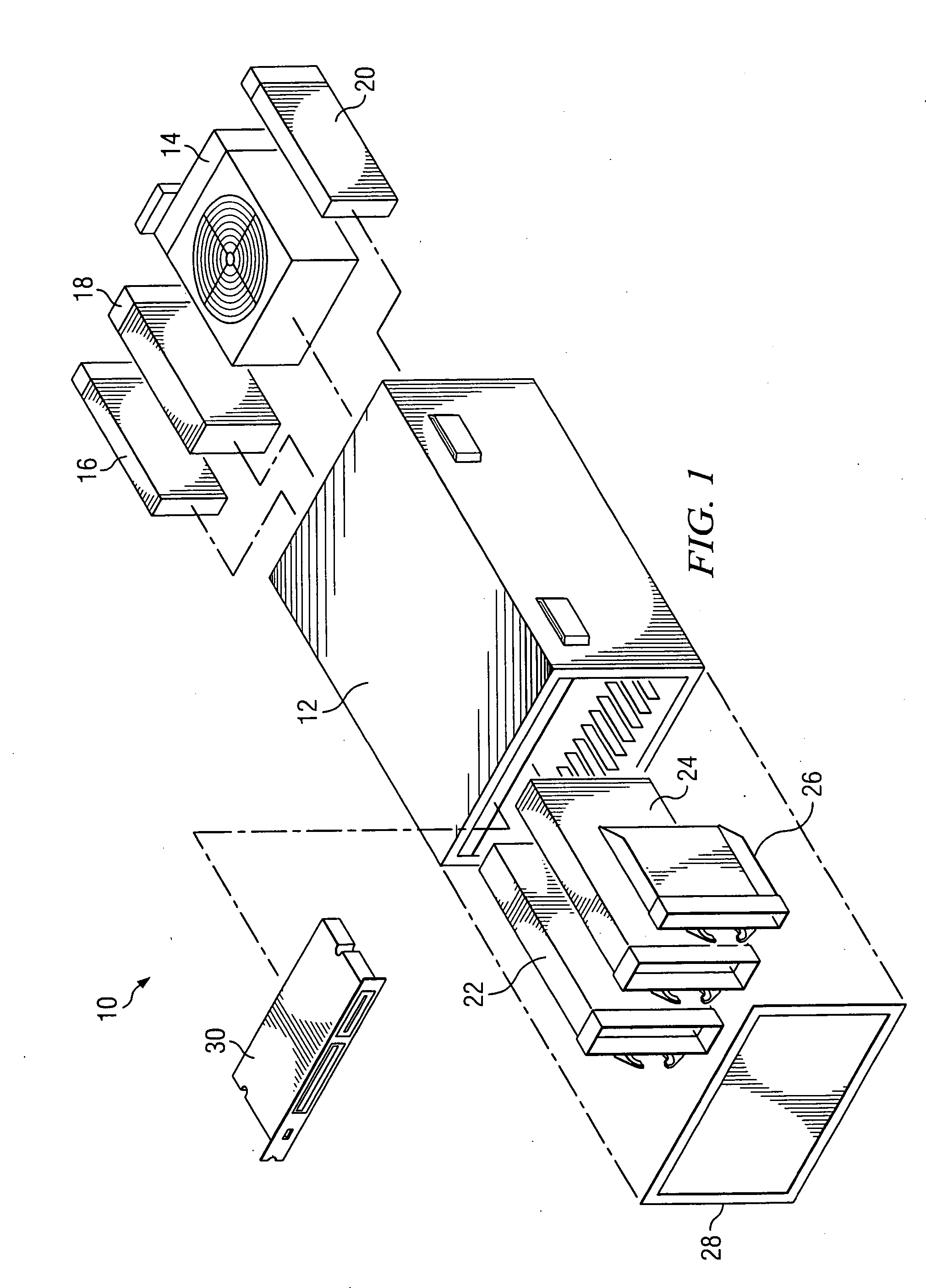
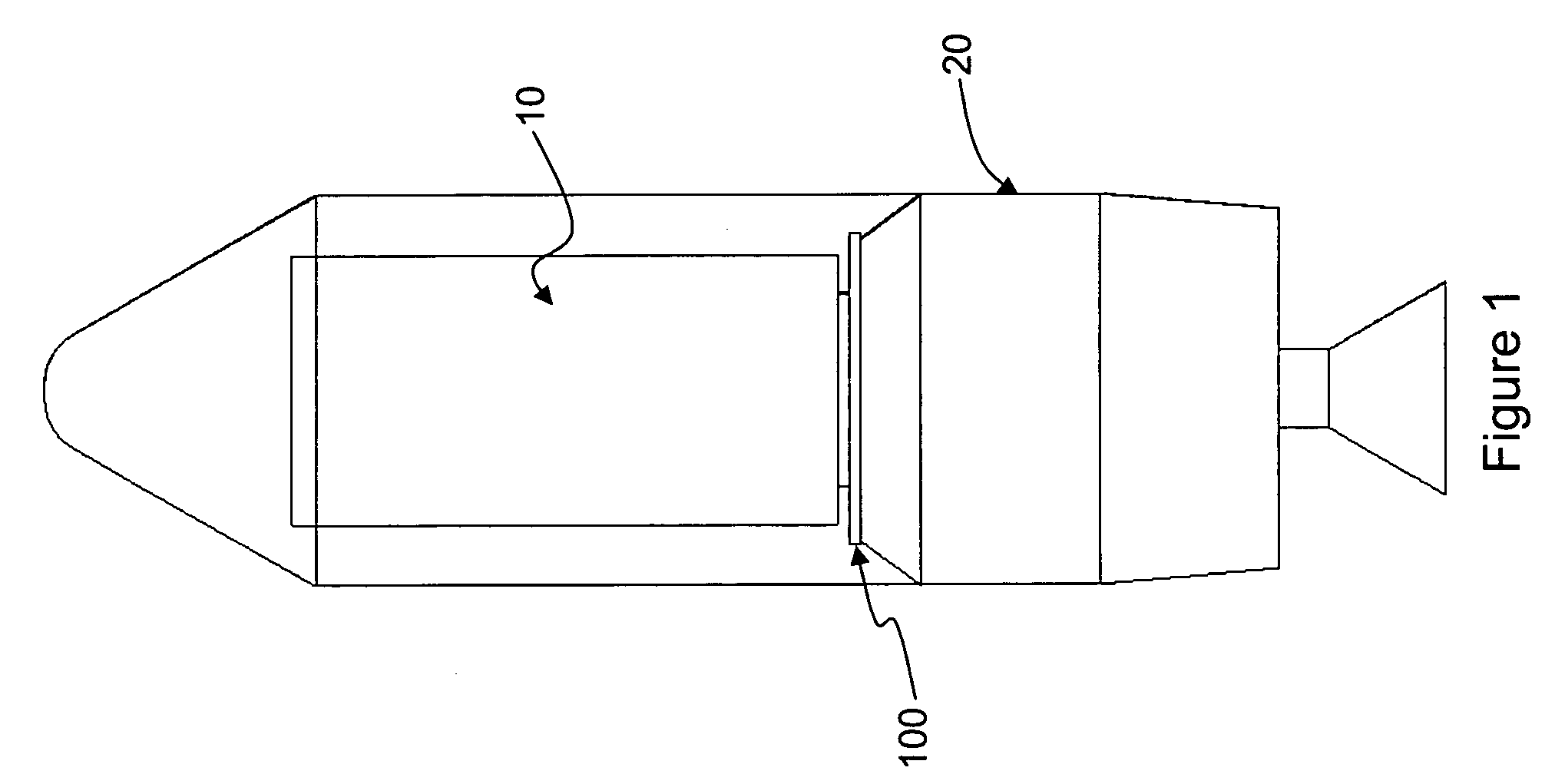
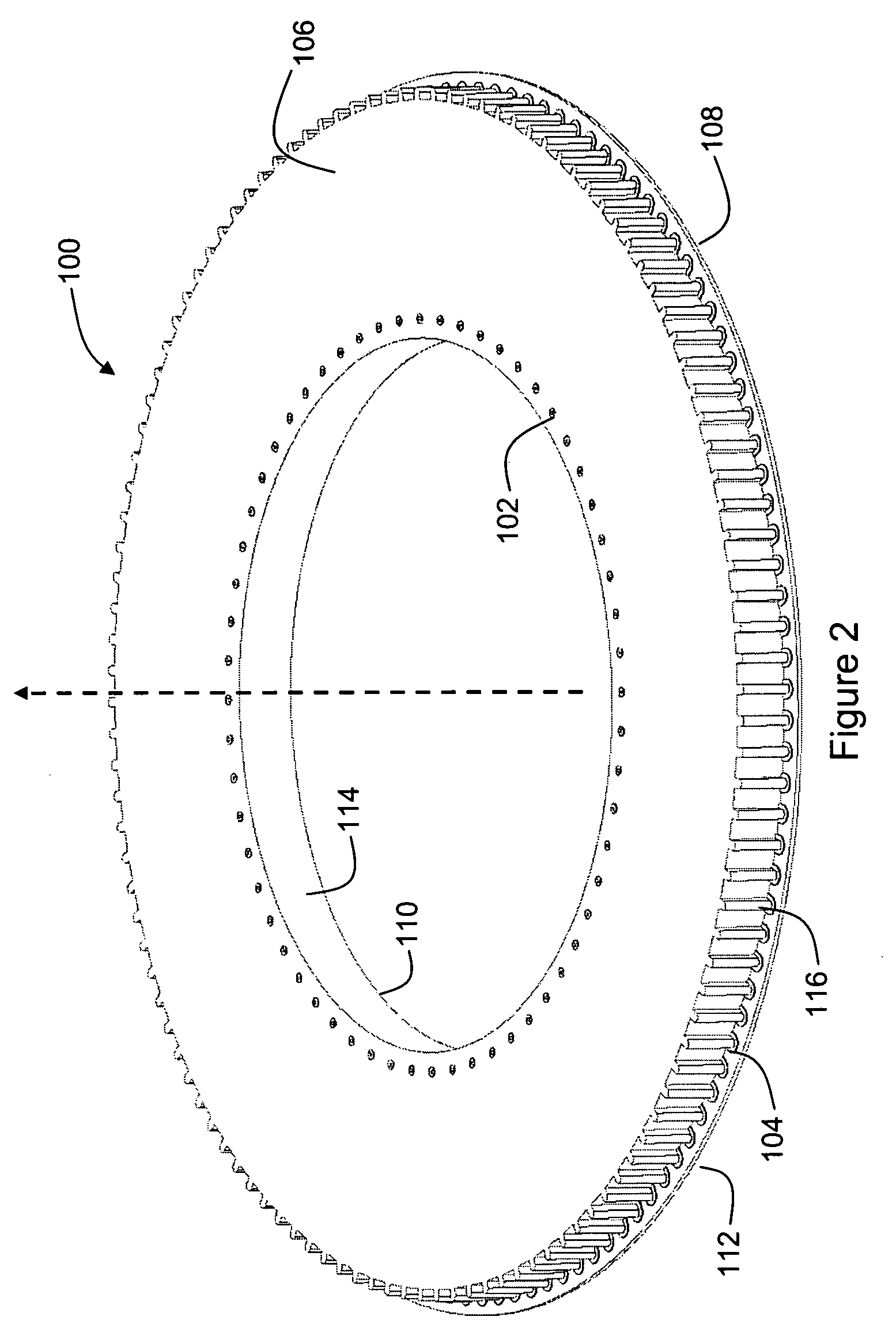
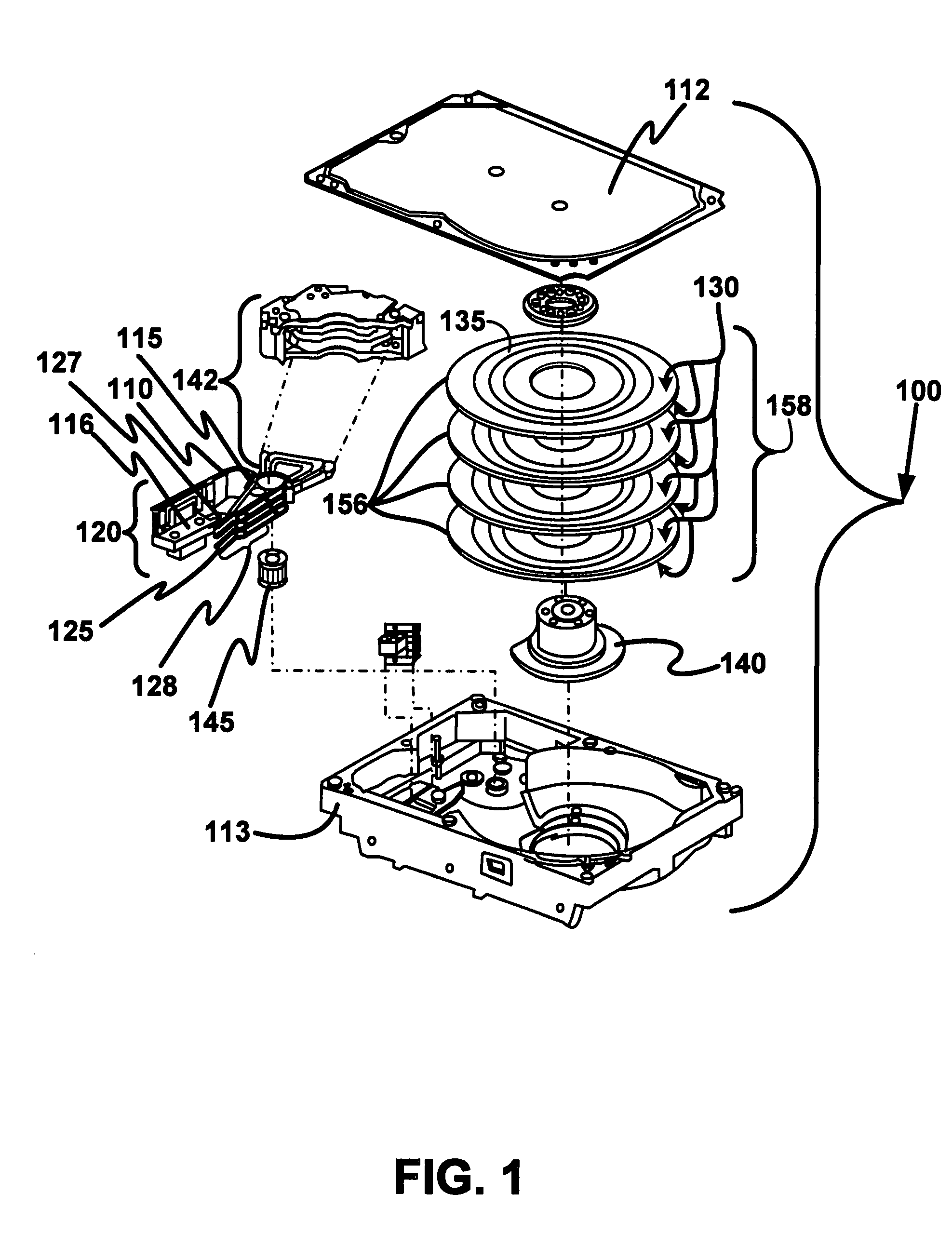
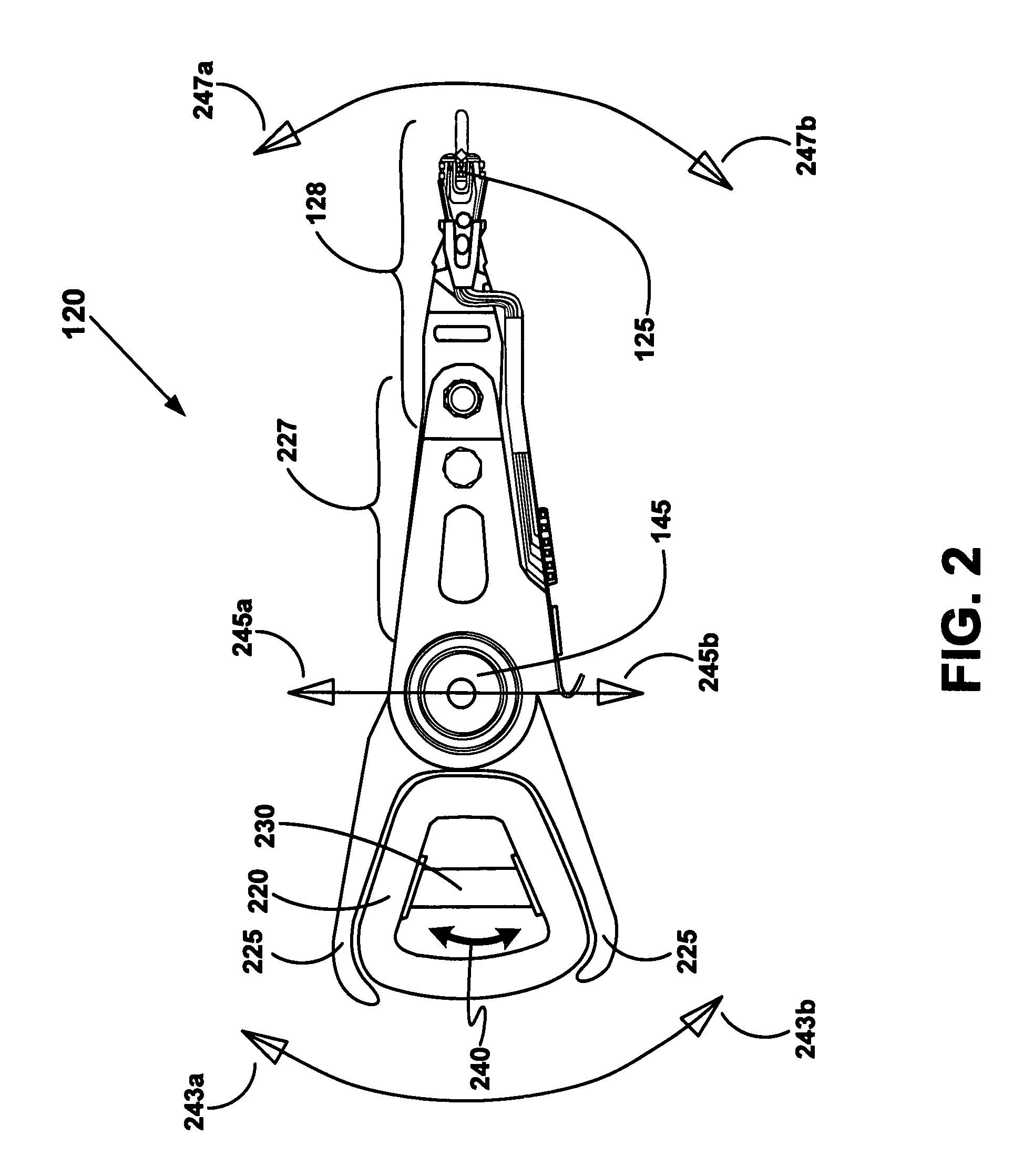
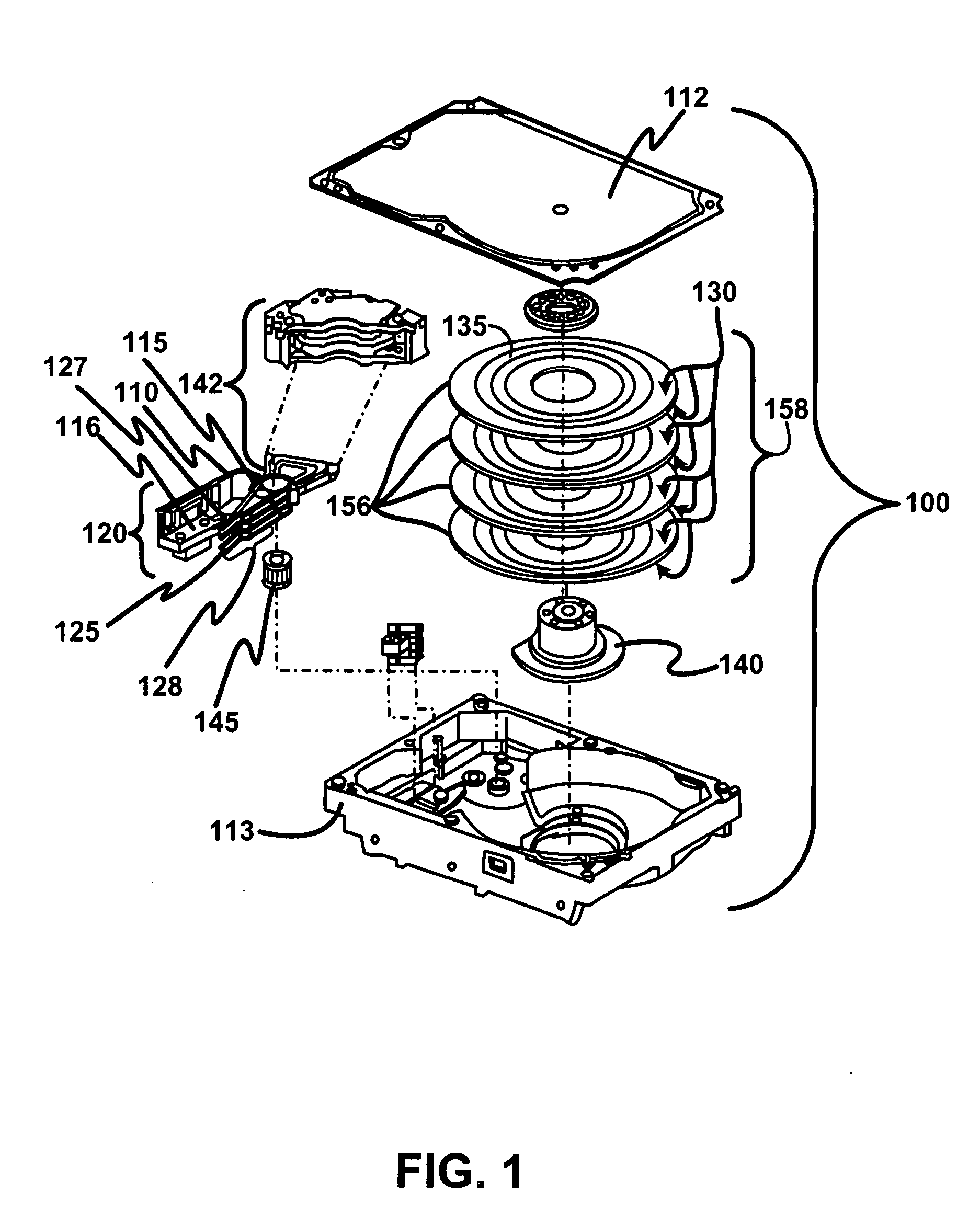
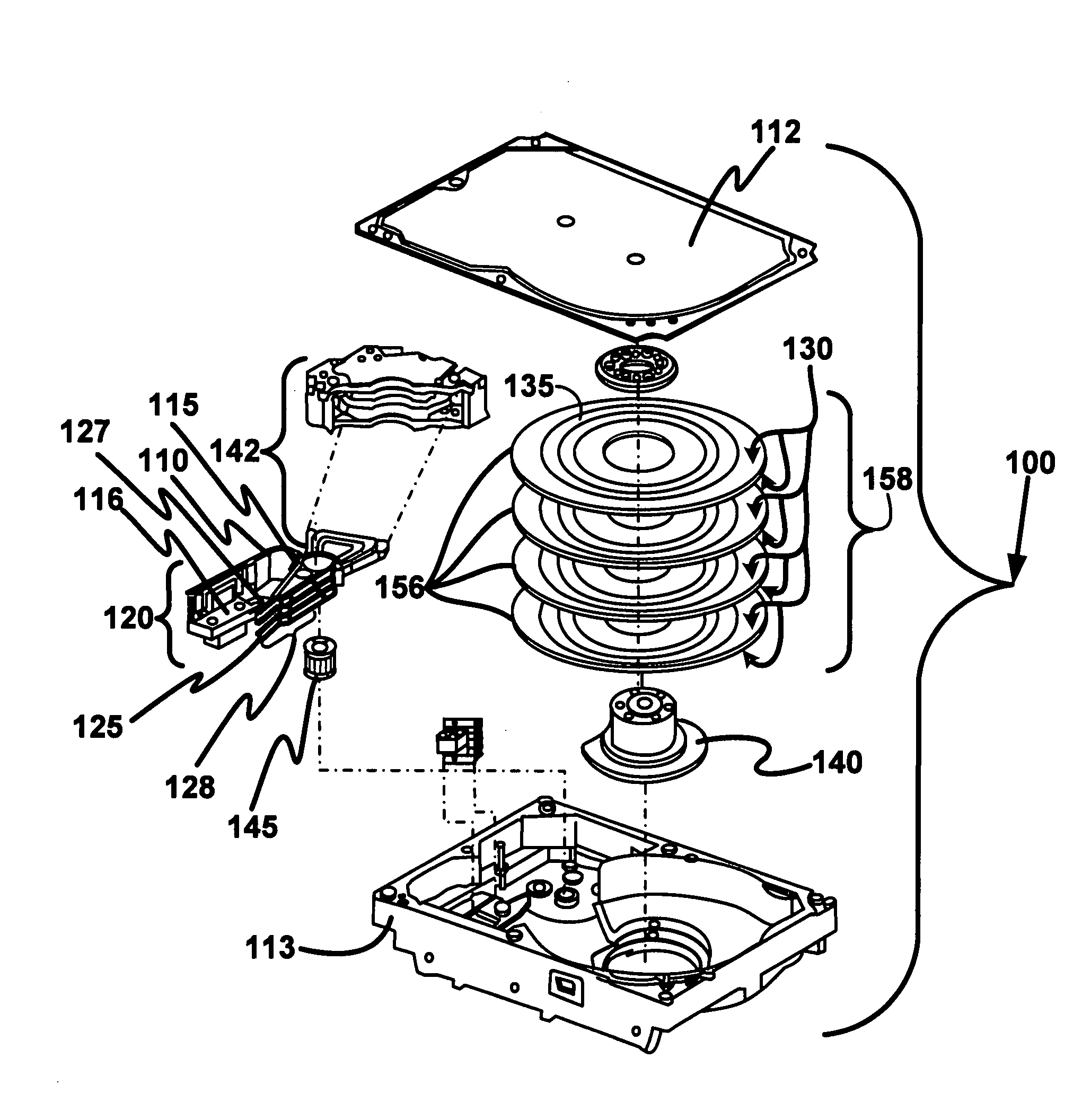
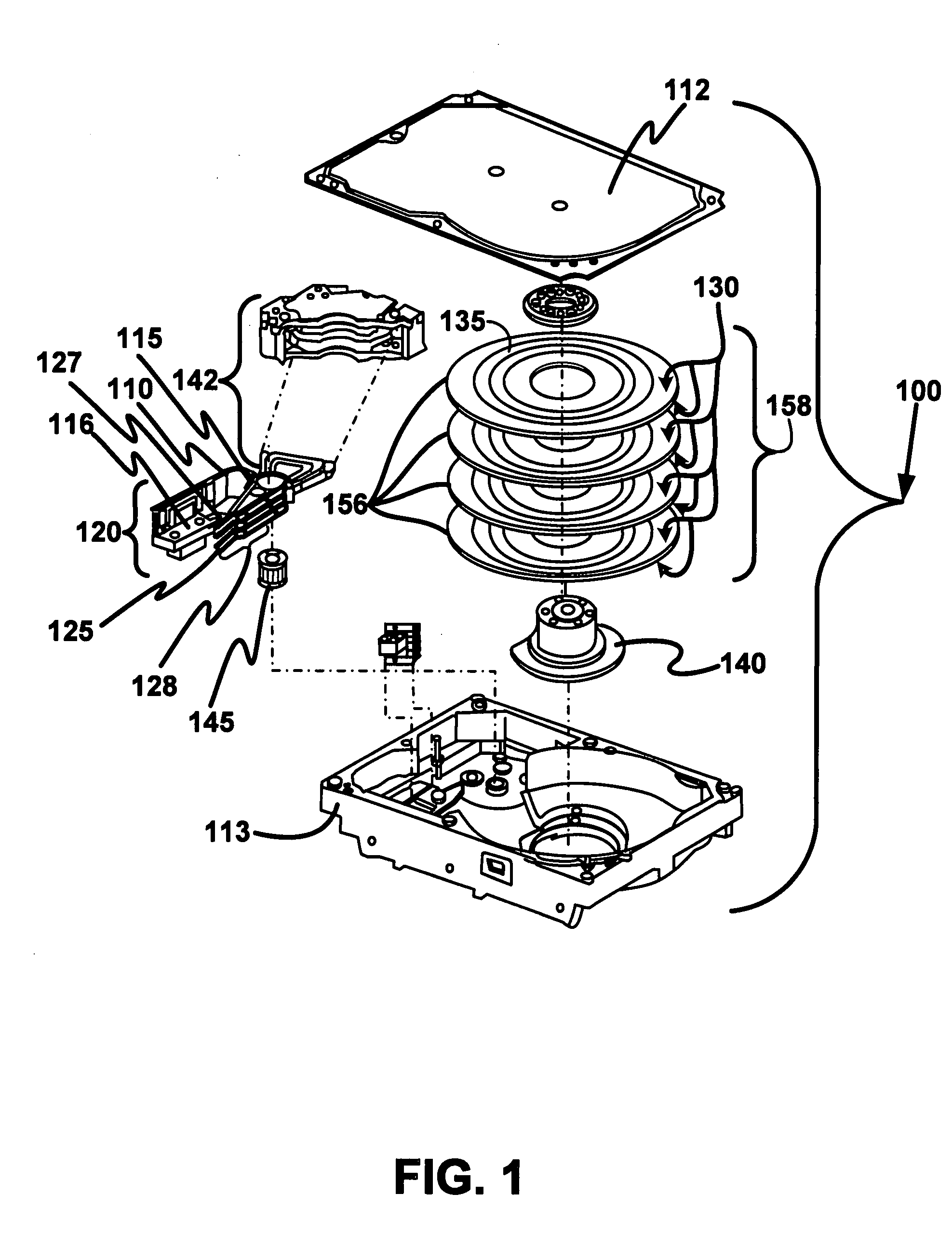
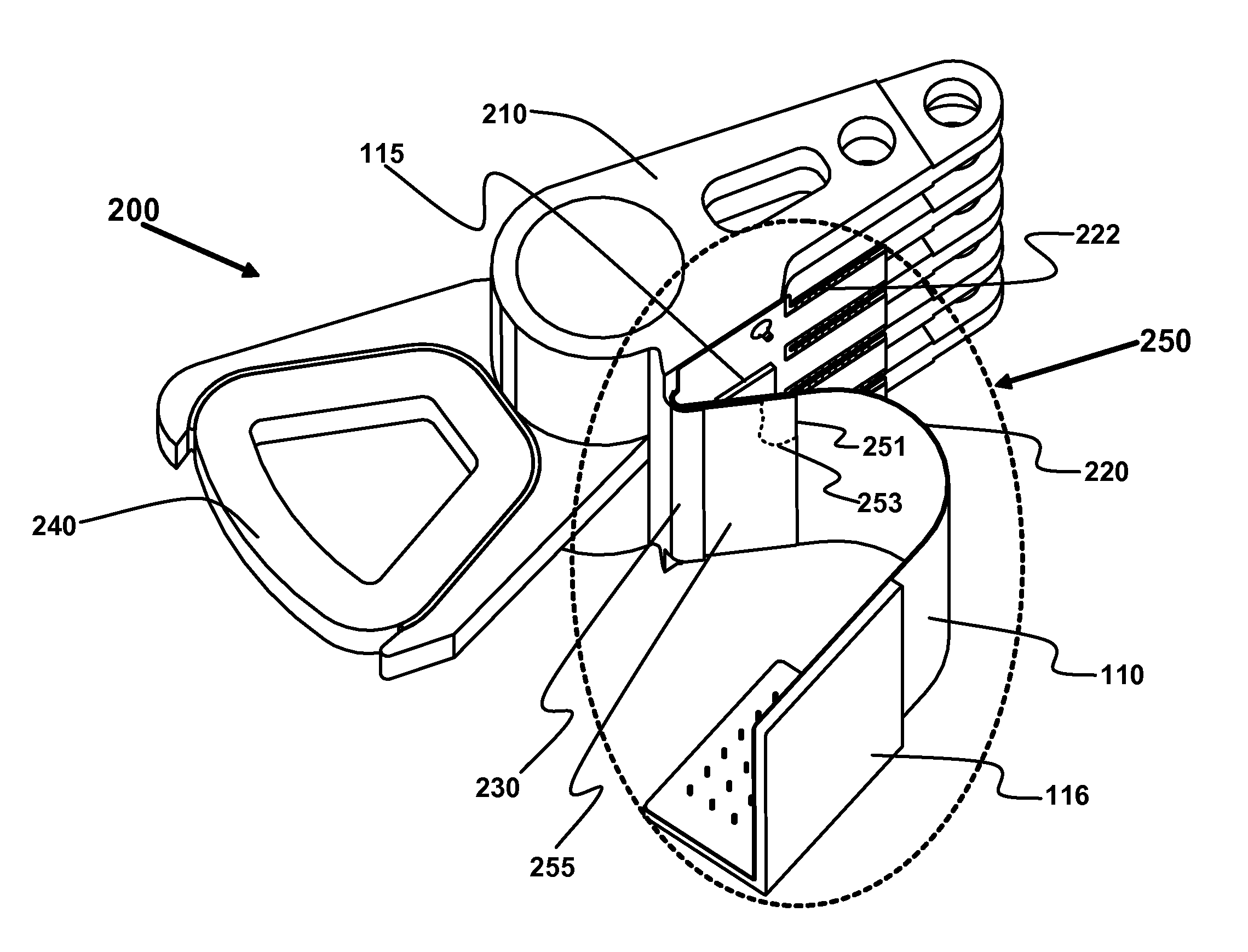
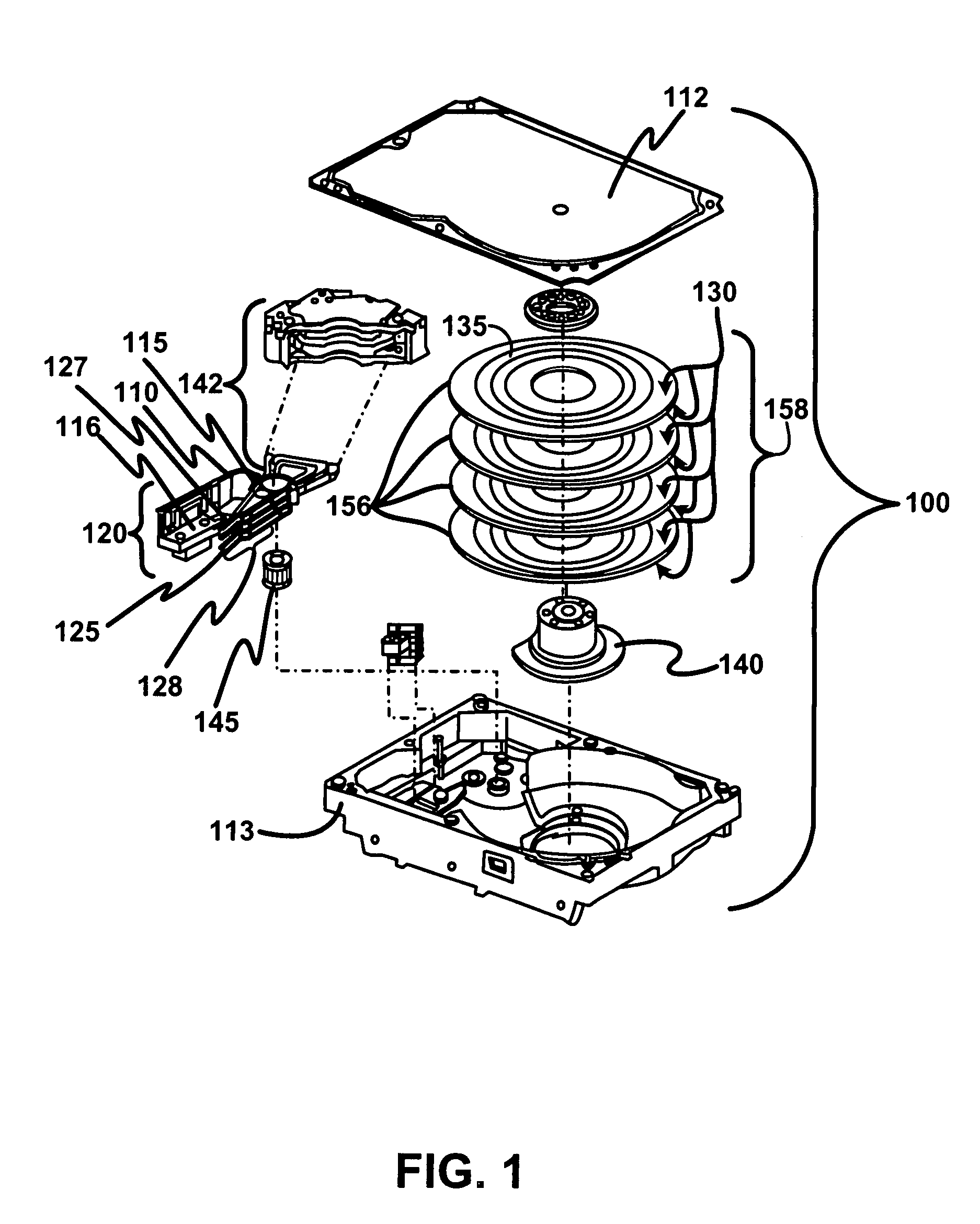
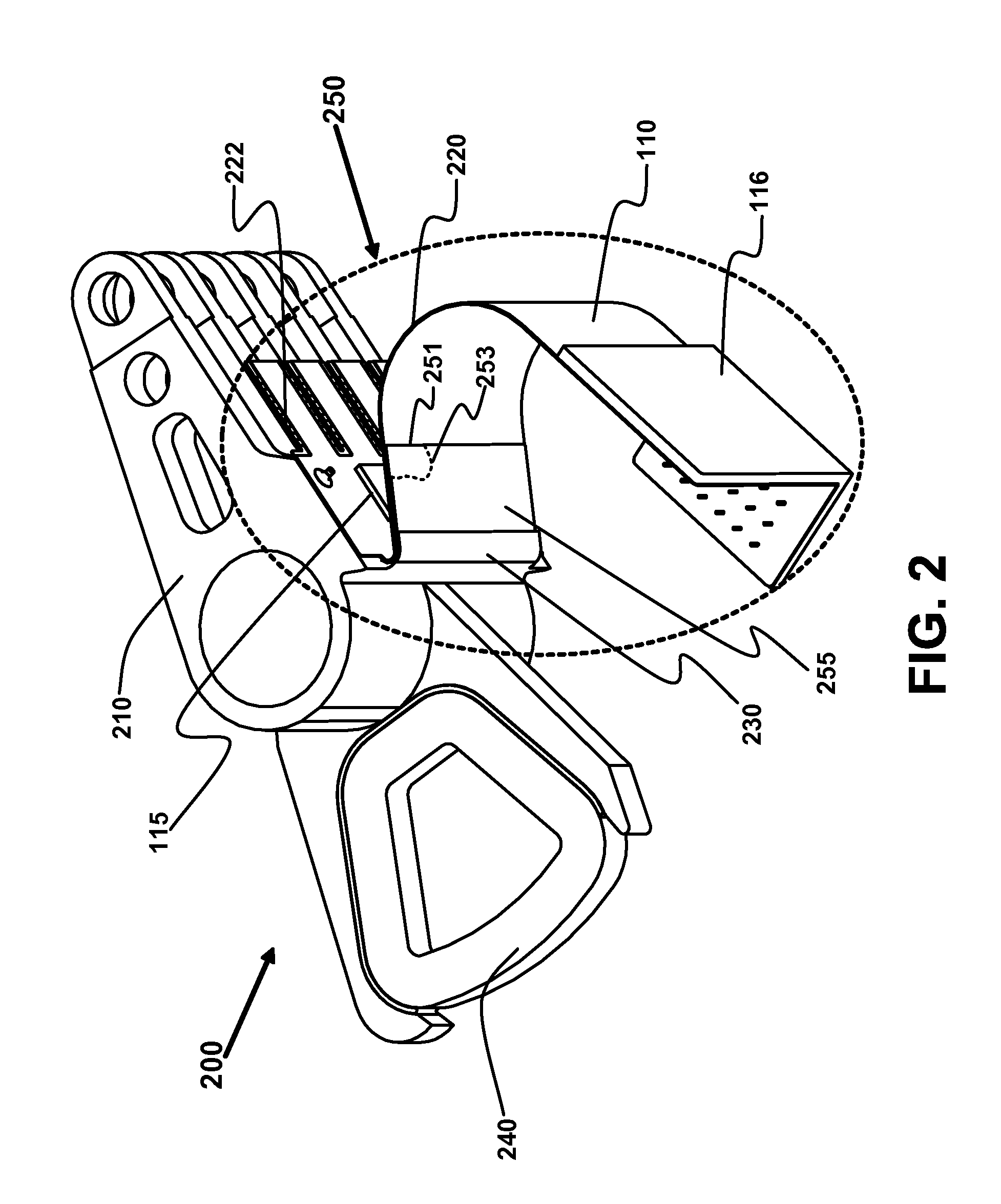
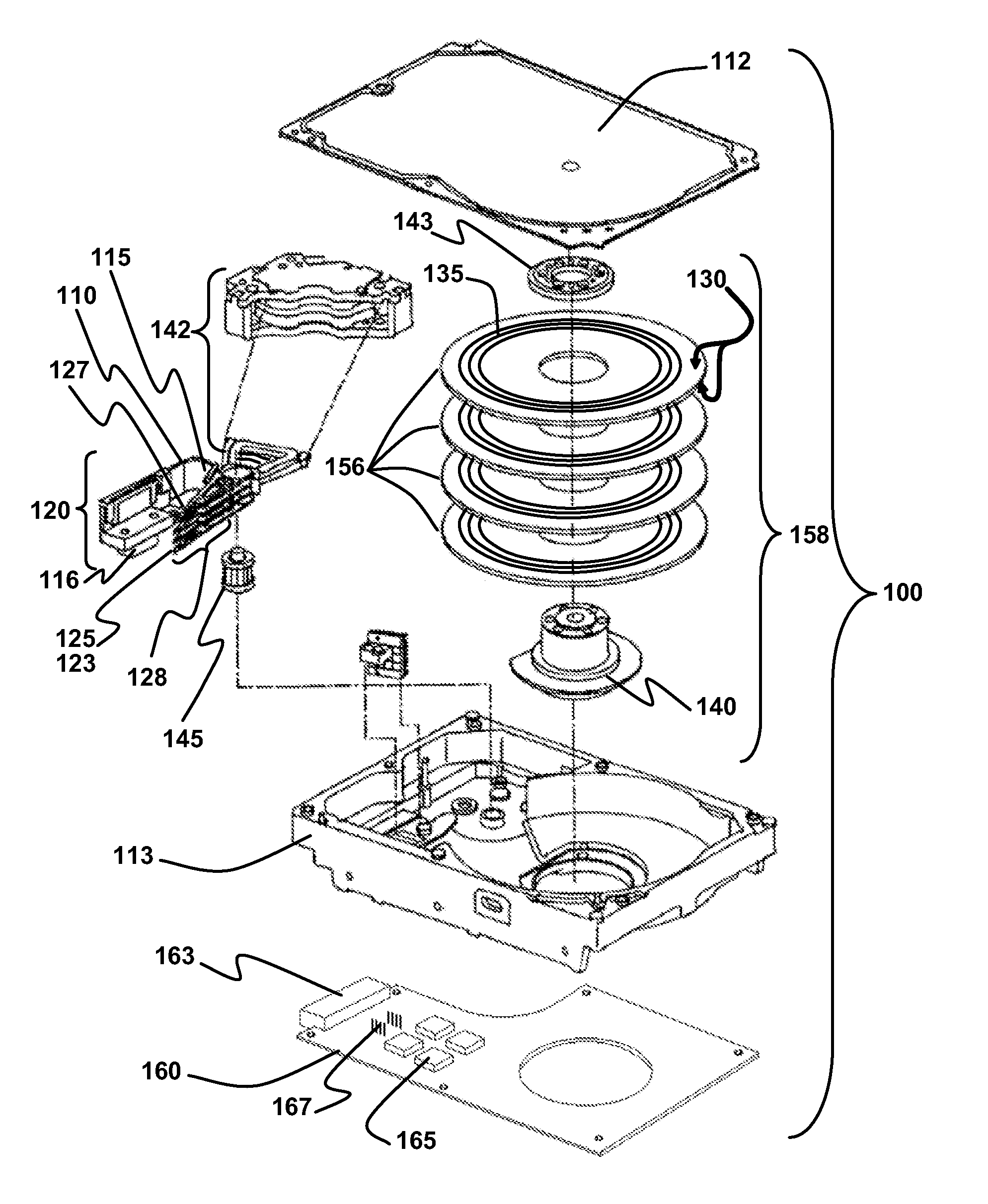
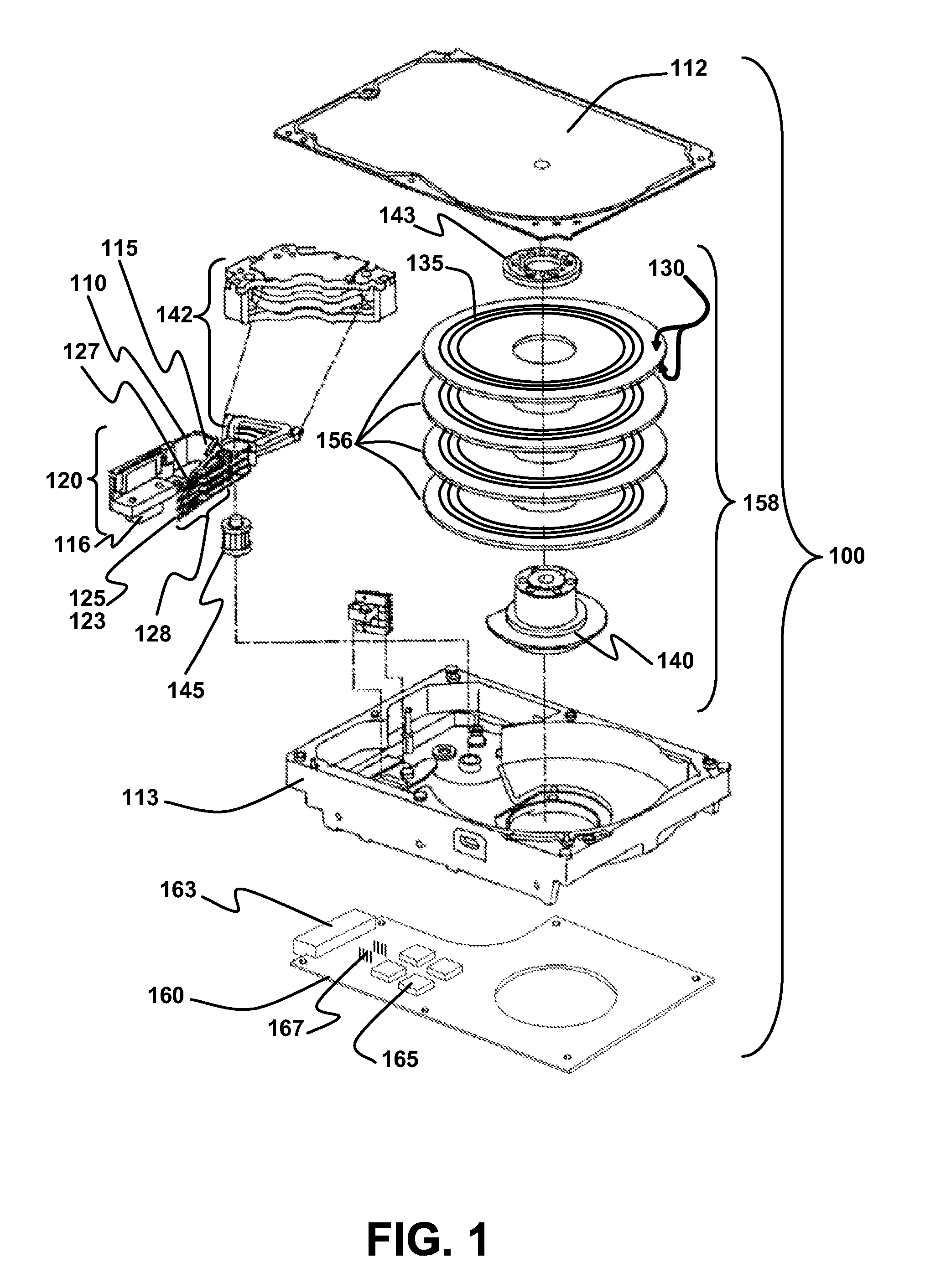
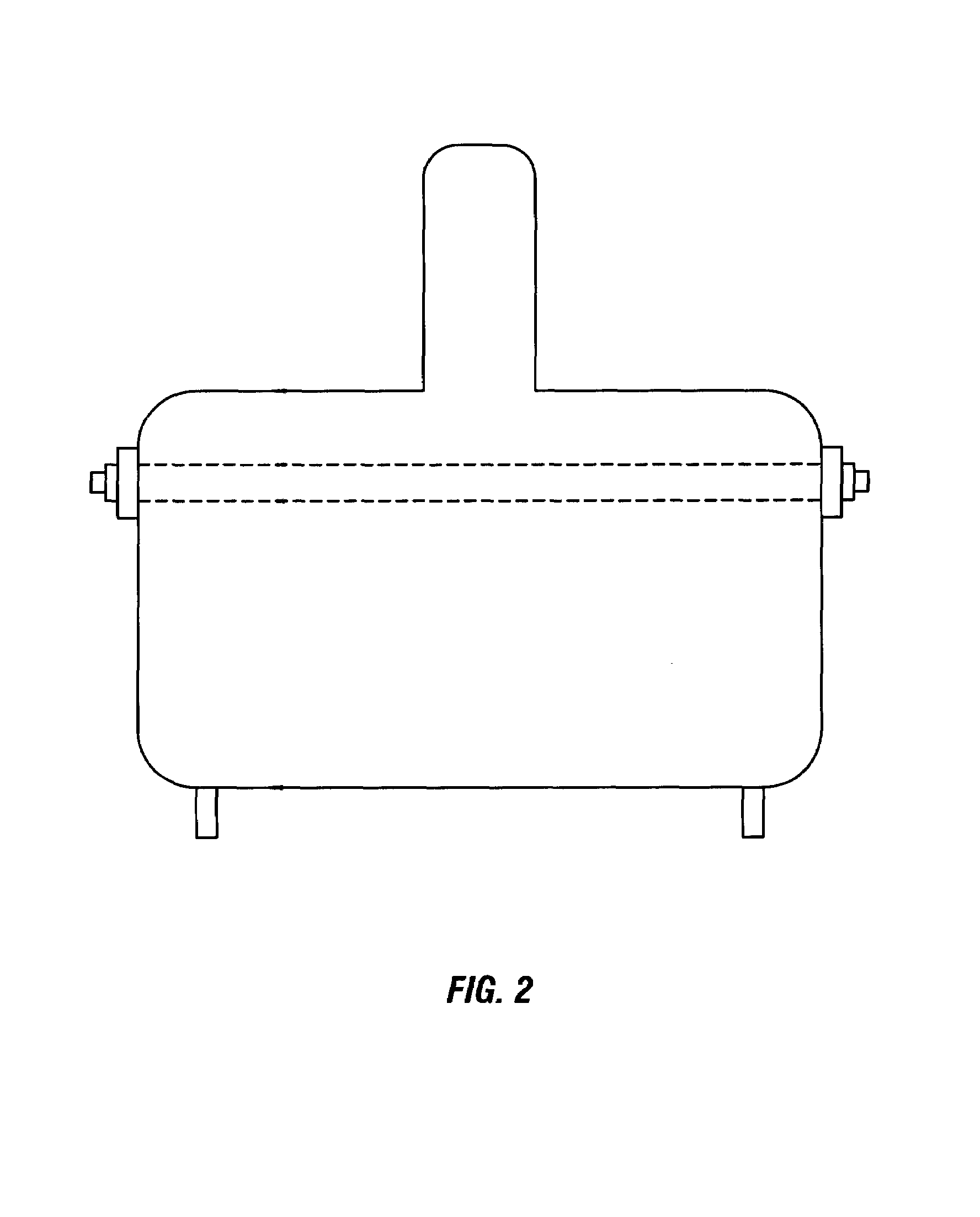
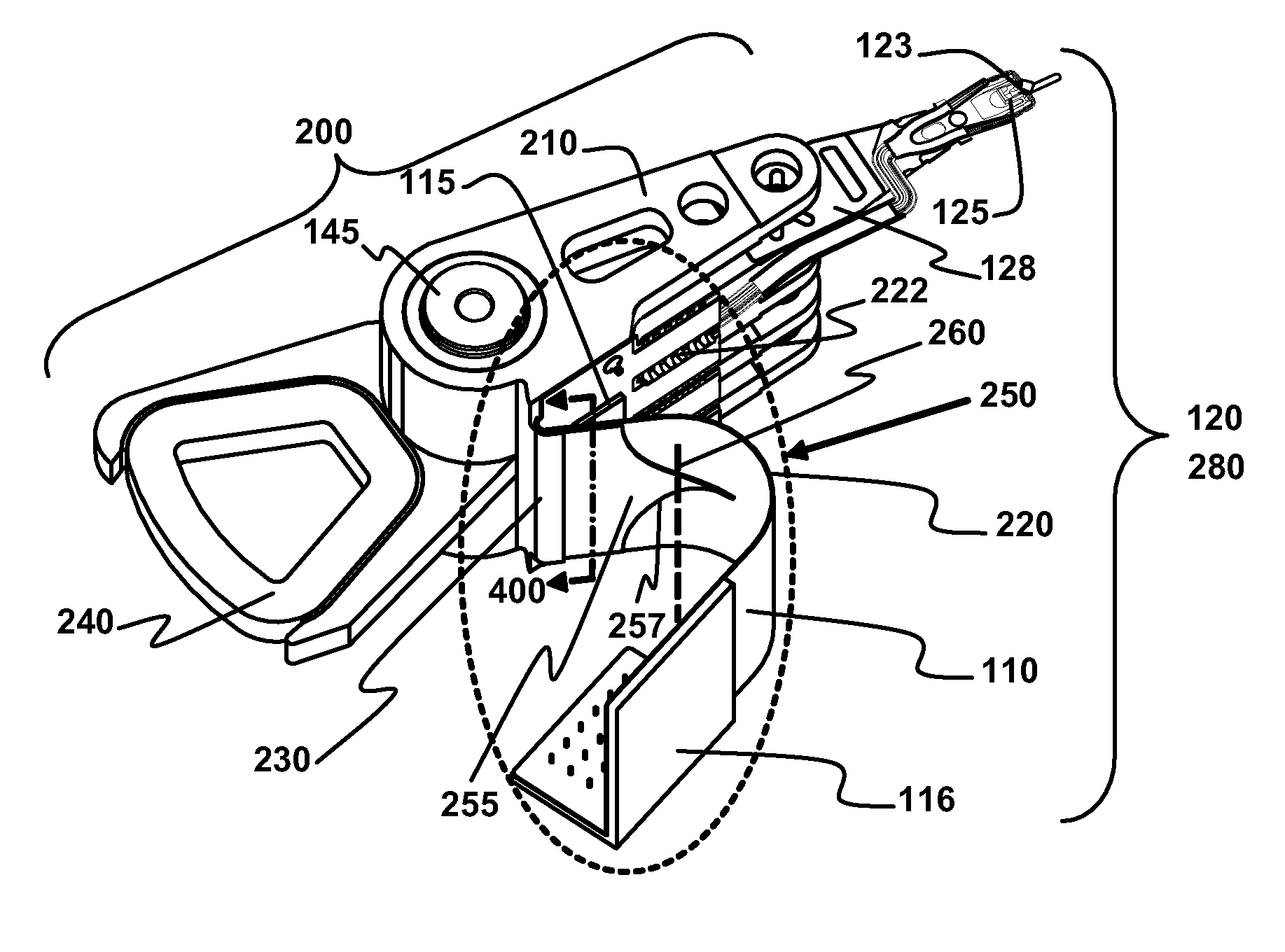
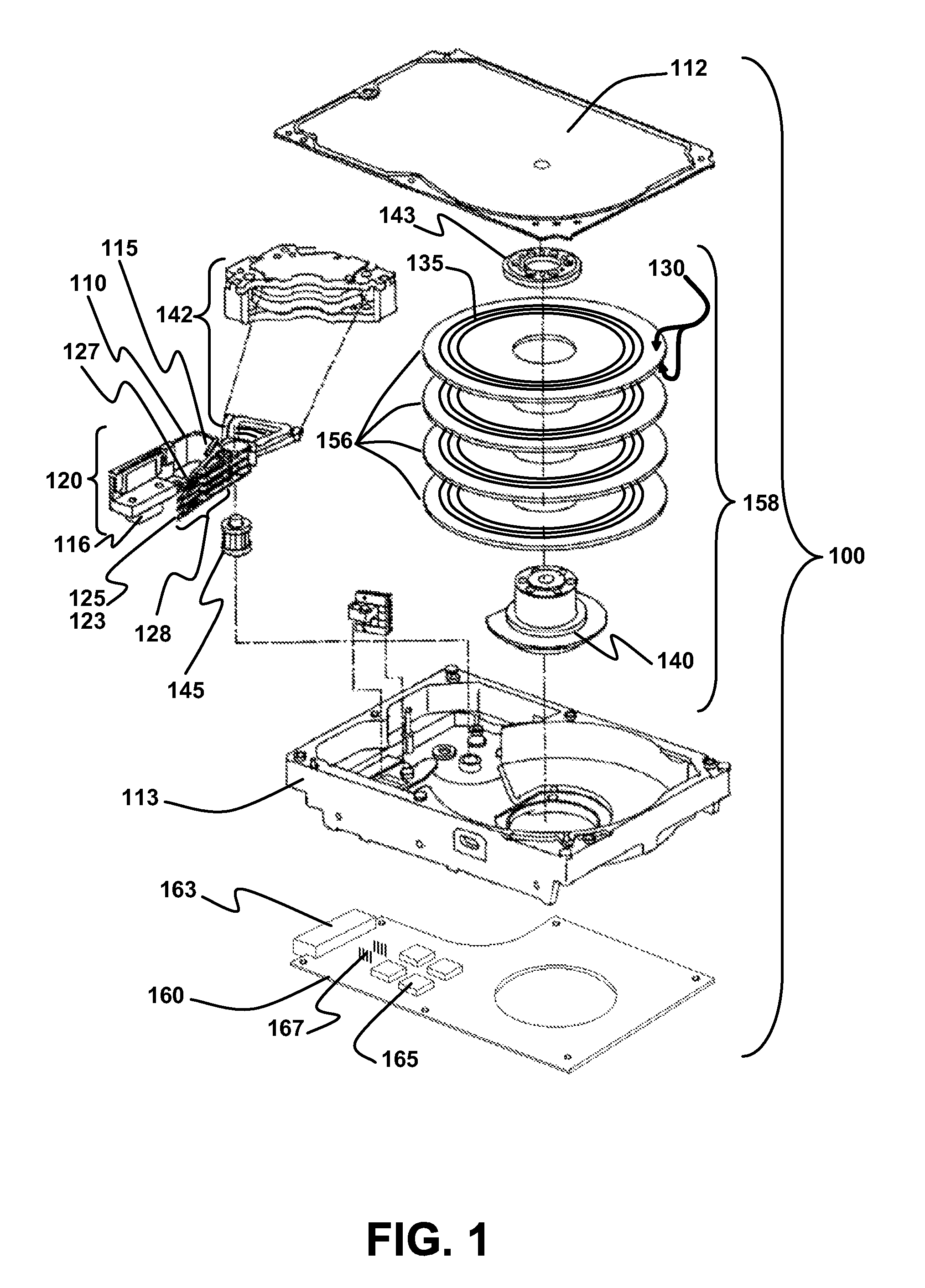
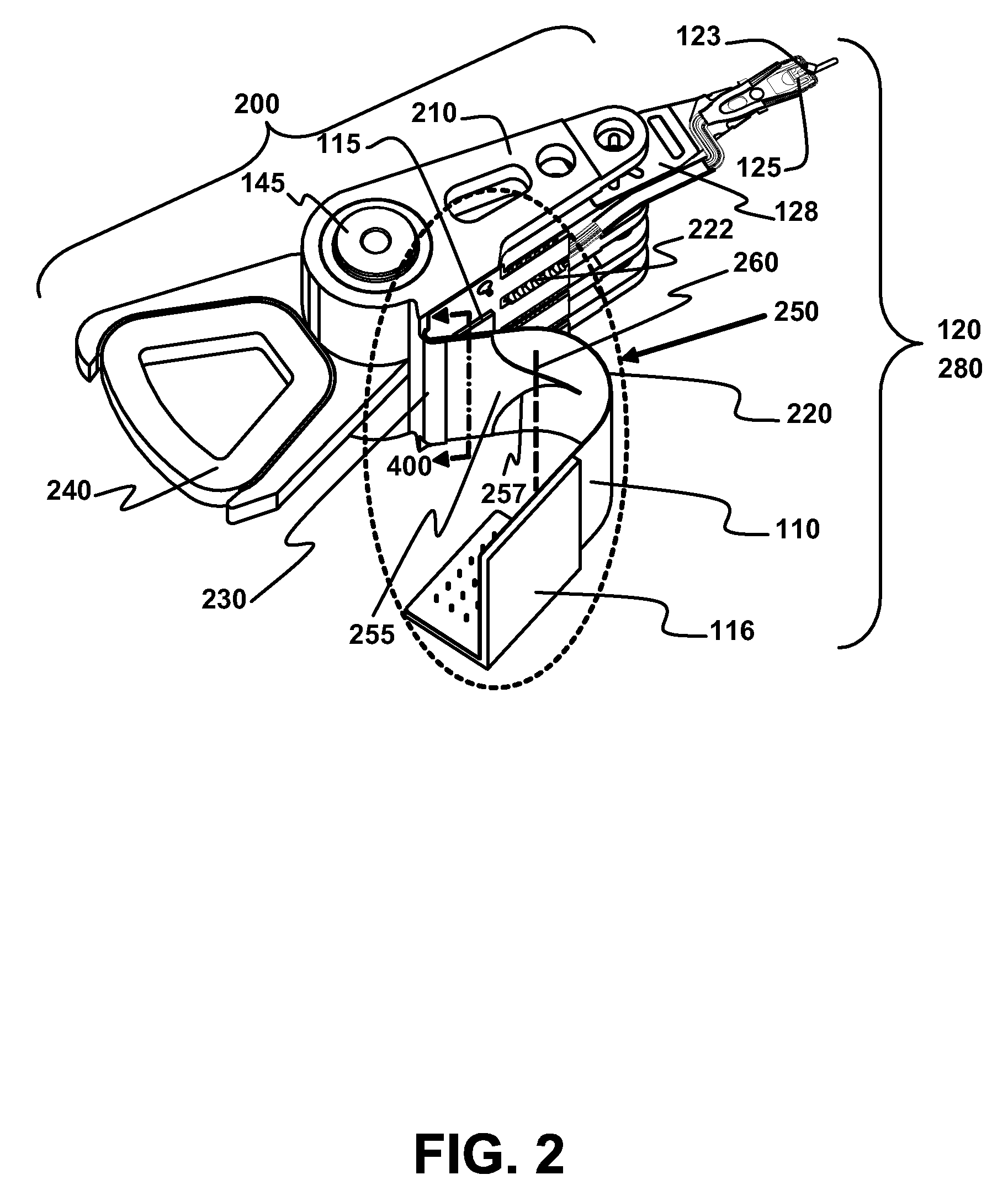
Disk drive including an actuator with a constrained layer damper disposed upon an actuator body lateral surface
ActiveUS6879466B1Reduce resonanceApparatus modification to store record carriersUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionSnubberActuator
An actuator for a disk drive. The actuator includes an actuator body defining an axis of rotation and including a body lateral surface disposed generally parallel to the axis of rotation. The actuator further includes an actuator arm extending from the actuator body. The actuator arm includes an arm base disposed adjacent the actuator body. The actuator further includes a coil support extending from the actuator body opposite the actuator arm. The coil support includes a coil support base disposed adjacent the actuator body. The actuator further includes a constrained layer damper disposed upon the body lateral surface extending from the arm base to the coil support base for mitigation of resonant vibration of the actuator arm and the coil support.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
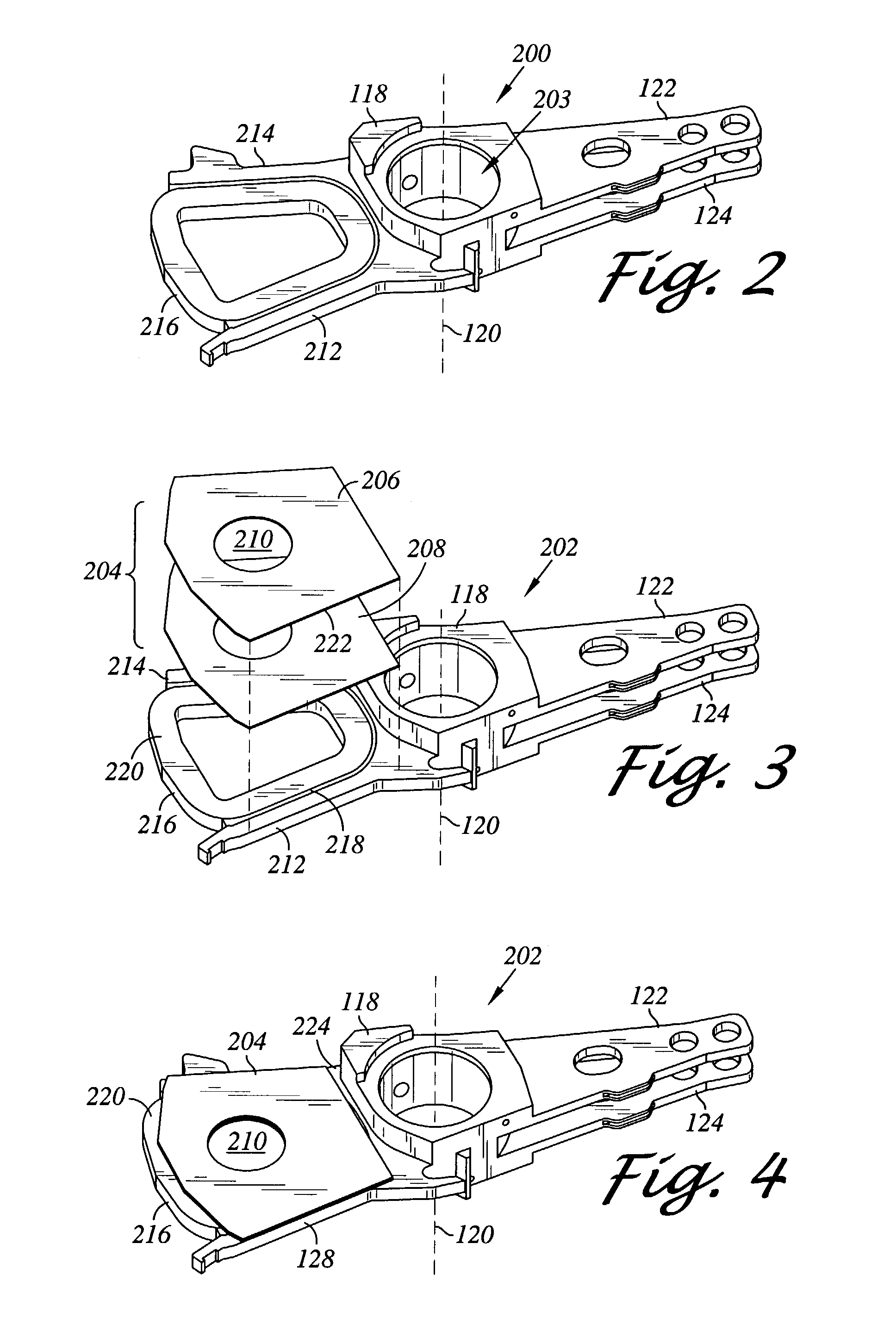
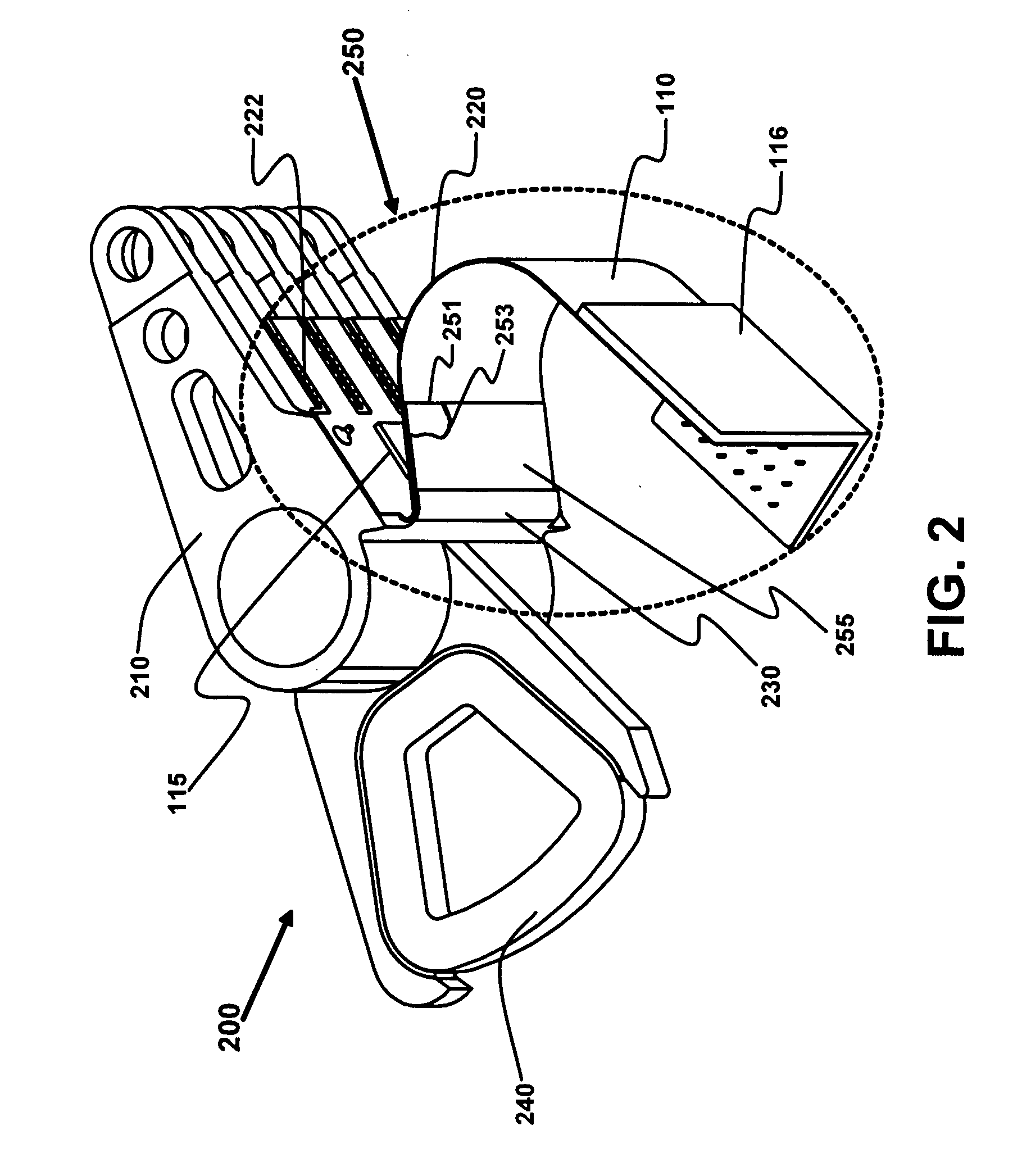
Disk drive rotary actuator assembly having a constrained layer damper attached to a flat actuator coil
InactiveUS6937444B1Disposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageSnubberCantilever
A head stack assembly for a disk drive includes a rotary actuator assembly. The rotary actuator assembly includes an actuator body having a bore defining a pivot axis, an actuator arm cantilevered from the actuator body, and a coil portion cantilevered from the actuator body in a direction opposite from the actuator arm. The coil portion includes a coil support, a flat coil supported by the coil support, the flat coil including a coil surface generally perpendicular to the pivot axis, and a constrained layer damper attached to the coil surface. The constrained layer damper includes a stiffening layer having a coil-facing planar surface generally perpendicular to the pivot axis and an adhesive layer positioned between the coil-facing planar surface and the coil surface.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Low-profile, multi-axis, highly passively damped, vibration isolation mount
ActiveUS7249756B1High passive dampingIncrease of longitudinal profilePortable framesCosmonautic vehiclesEngineeringMulti axis
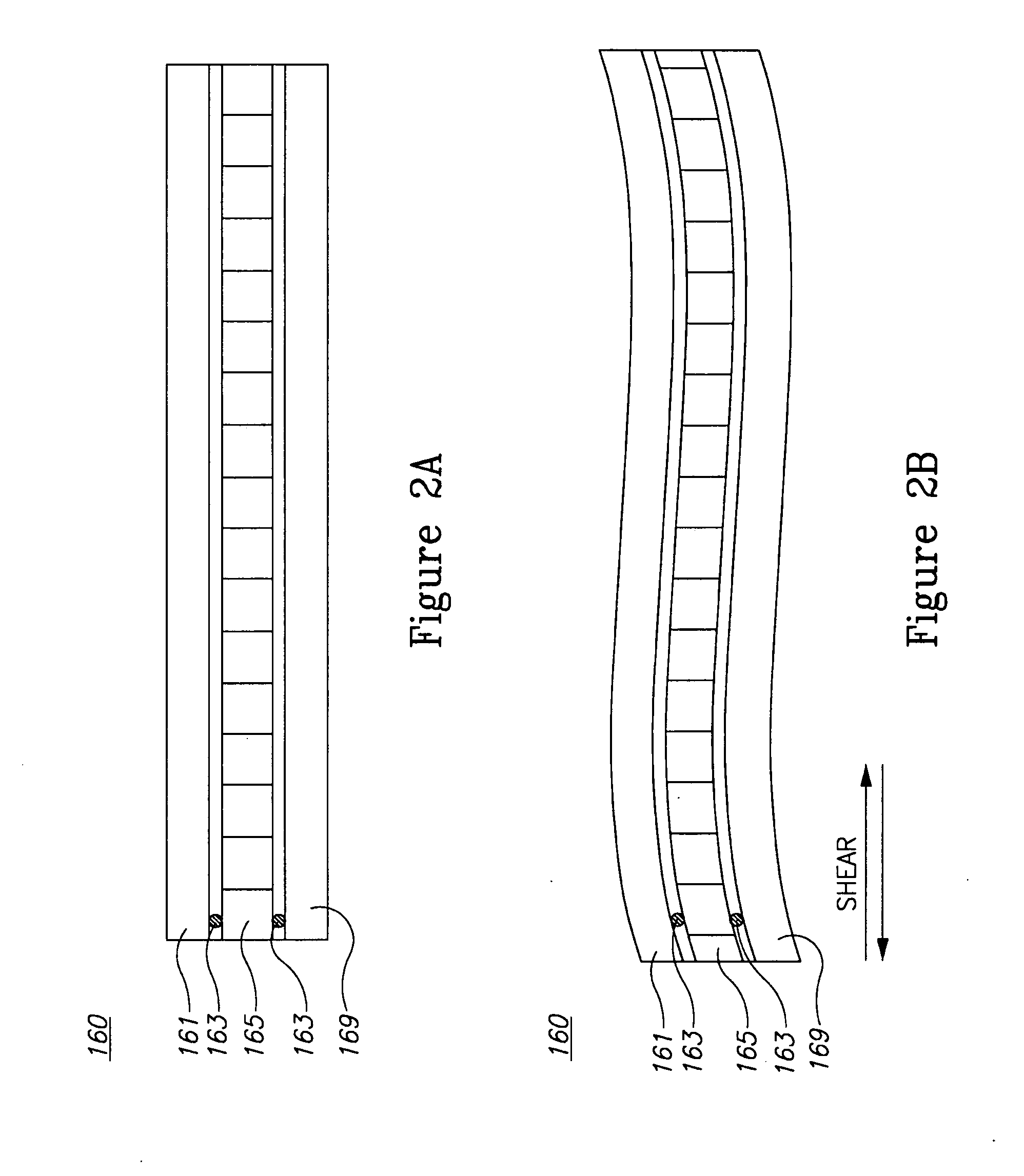
The invention disclosed is a low-profile, multi-axis, highly passively damped, vibration isolation mount which when used in multiplicity provides a complete vibration load isolation mounting system. The device provides in unique fashion a very low profile interface in combination with independently determinable compliance in all directions of vibration loading. Substantial passive damping is afforded without sacrifice to strength and linearity of behavior through adaptation of a shear wall type constrained layer damping. The result is a highly passively damped vibration isolation device that provides a very low profile interface, wide ranging longitudinal and lateral compliance management, in a durable, reliable, lightweight, and compact form.
Owner:MOOG INC
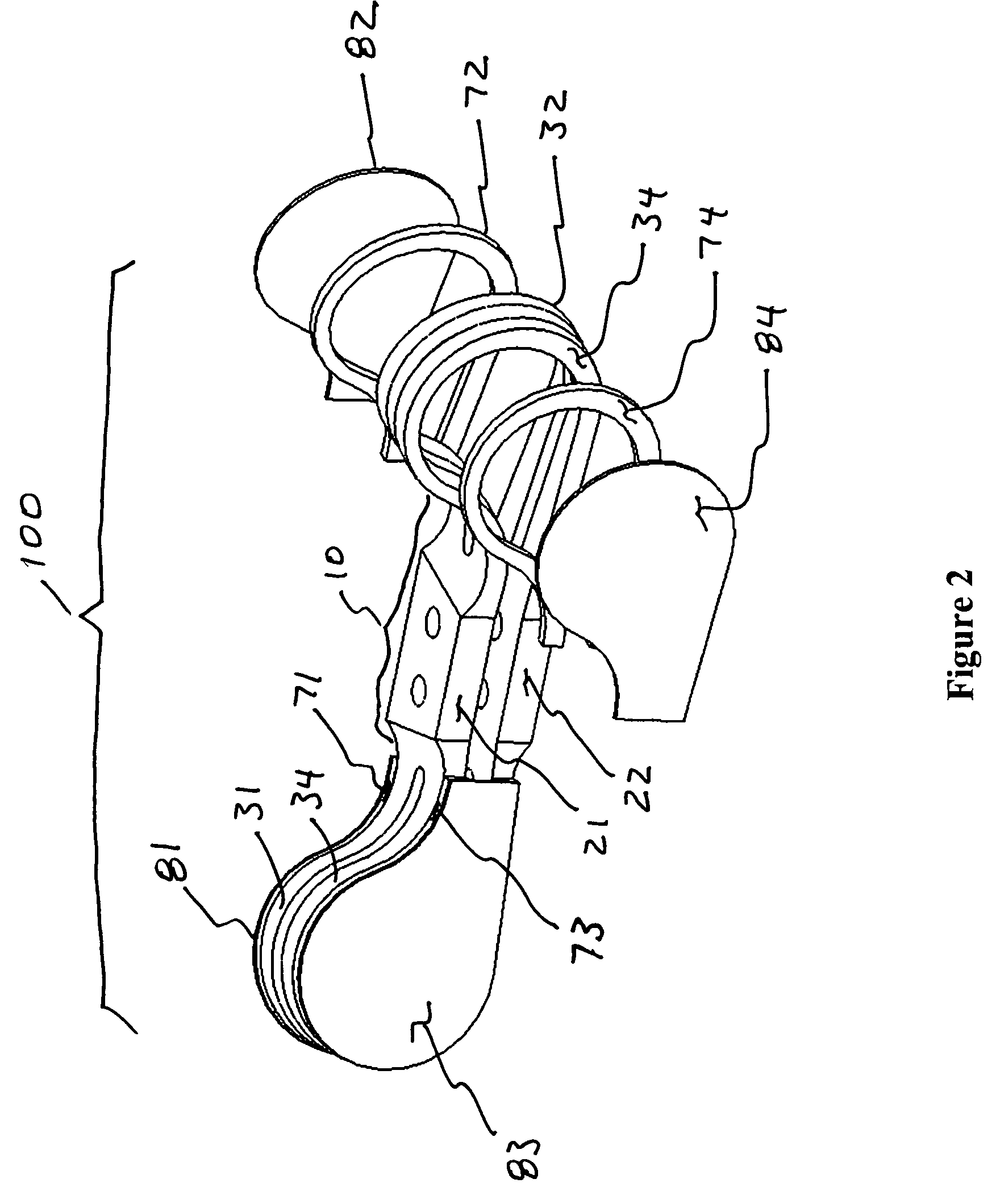
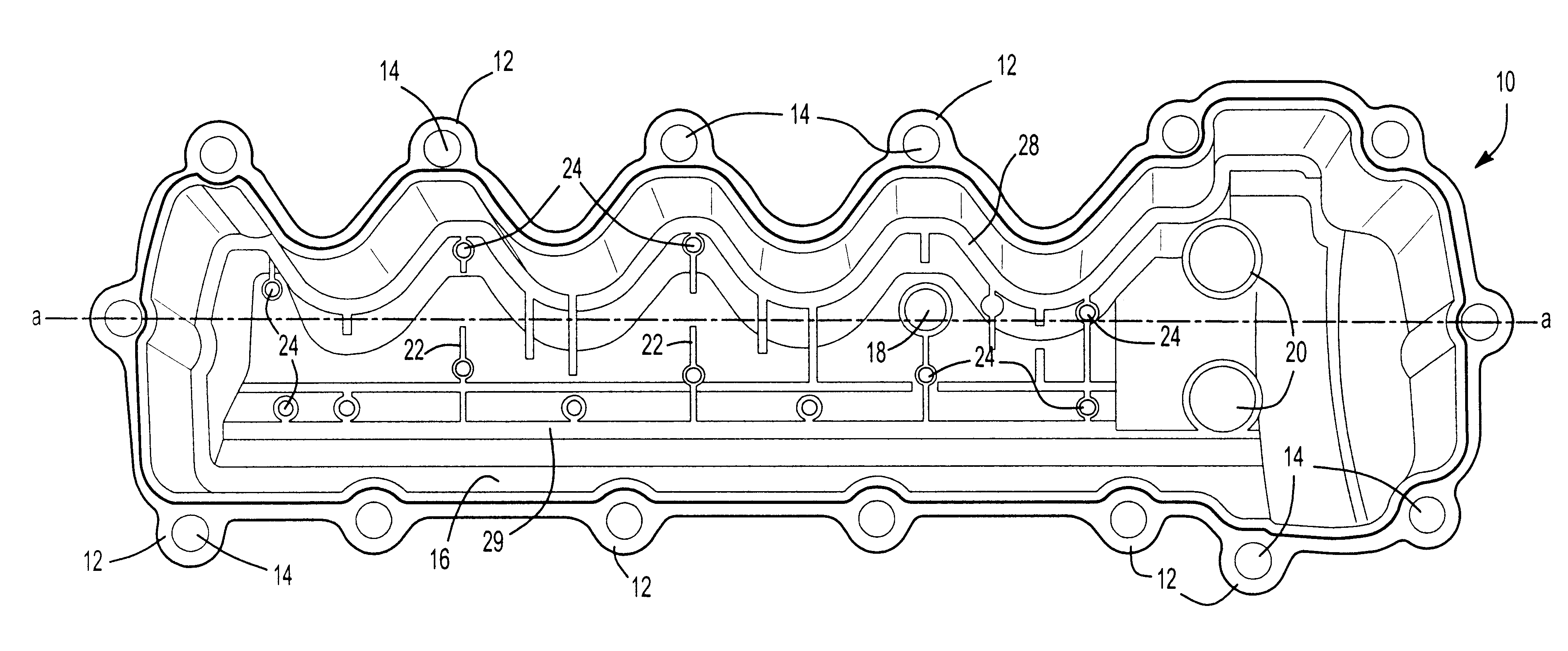
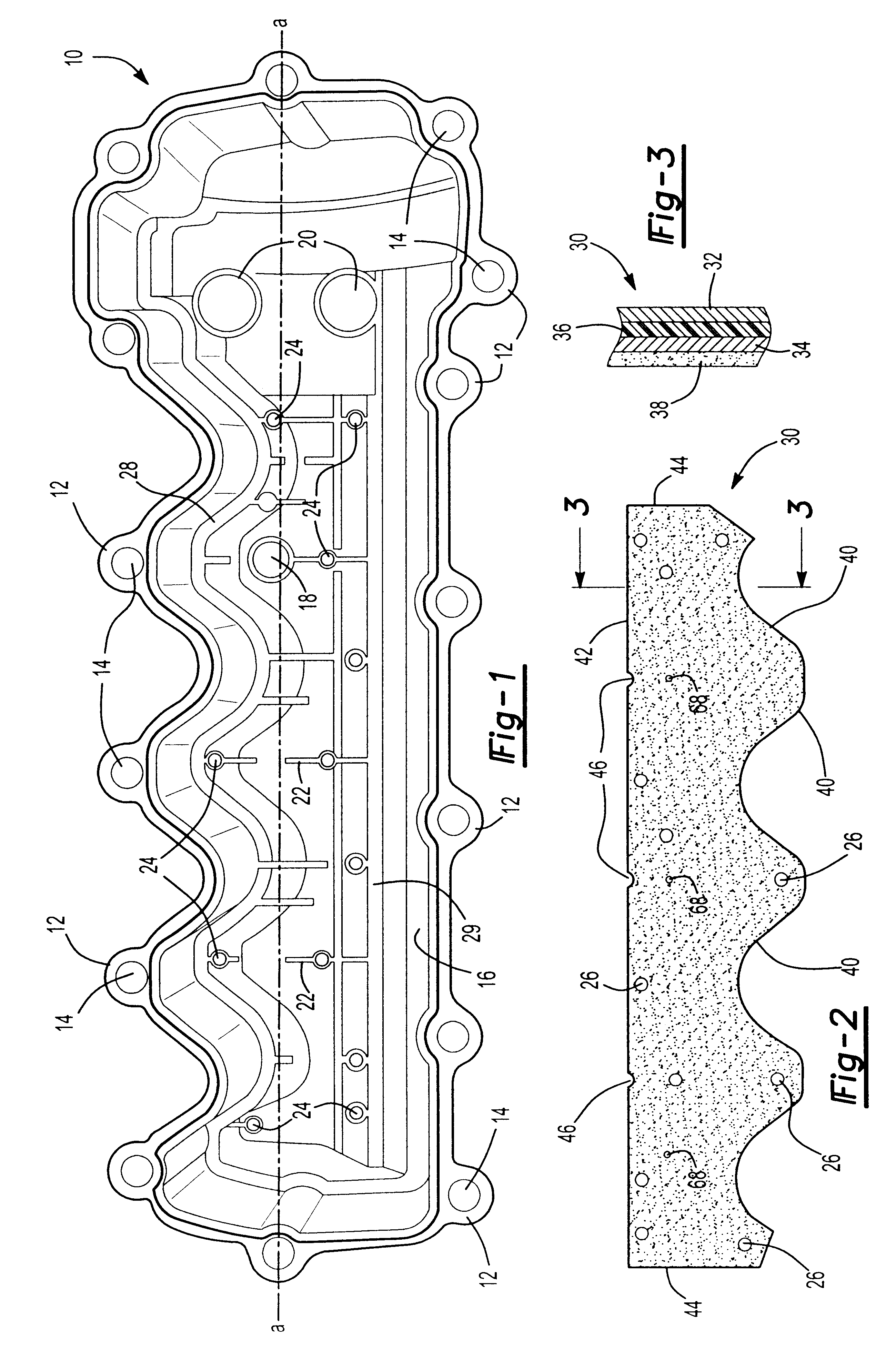
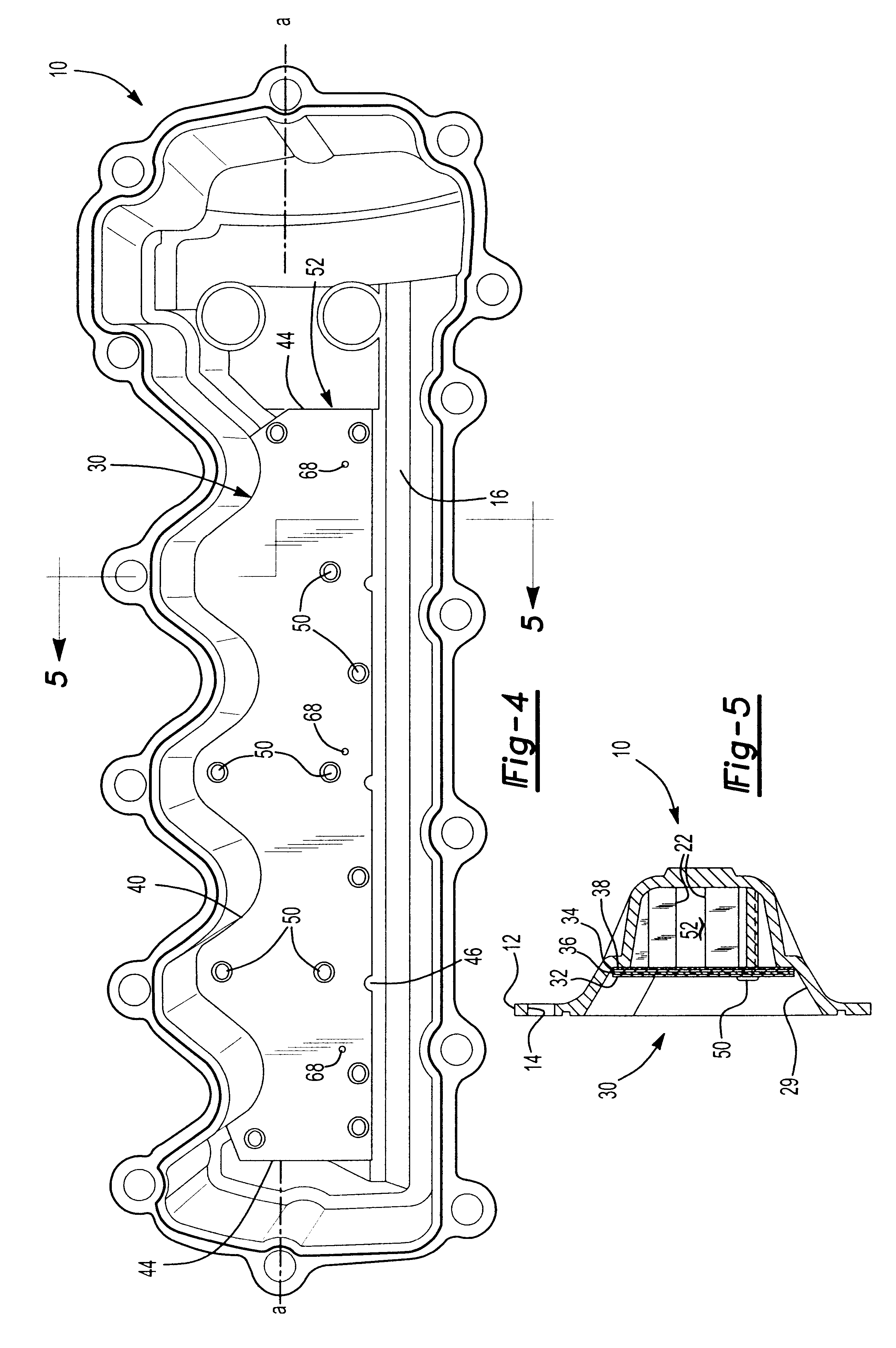
Constrained layer damped steel baffle
A damped steel baffle for an engine cam cover aids in separation of oil mist entrained in a flow of crankcase air vented through the cam cover, and directs the air to a PCV valve atop the cover. The baffle forms a channel for the air, and effectively absorbs noise generated within the cover. Oil droplets condense on channel and baffle surfaces, and drain to an engine oil sump. The interface between baffle and cam cover is sealed with a foam gasket layer or RTV sealant. The baffle is constructed of two metal layers joined together by a thin layer of viscoelastic adhesive that converts vibrational energy into heat to dampen resonant vibrations. Amplitudes of vibration are significantly lower than for plain steel baffles, hence lower sound radiation is achieved. The individual steel layers are 0.2 to 0.6 mm thick; the viscoelastic layer has a thickness up to 0.15 mm.
Owner:DANA AUTOMOTIVE SYST GRP LLC
System and apparatus for vibration damping of integrated lead suspensions in high density magnetic storage devices
ActiveUS20080253028A1Reducing level of excitationReduce vibrationDisposition/mounting of recording headsUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionHigh densityElectrical conductor
An integrated lead suspension (ILS) has a constrained layer damper (CLD) that attenuates vibration of the ILS. The CLD may be applied over an already assembled ILS such that the CLD is applied to the cover layer, to the base layer, or to both. Alternatively, the ILS may be encapsulated via a deposition process such that a damping layer is sandwiched between the conductor layer and the cover layer of the ILS, between the conductor layer and the dielectric layer of the ILS, or both.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
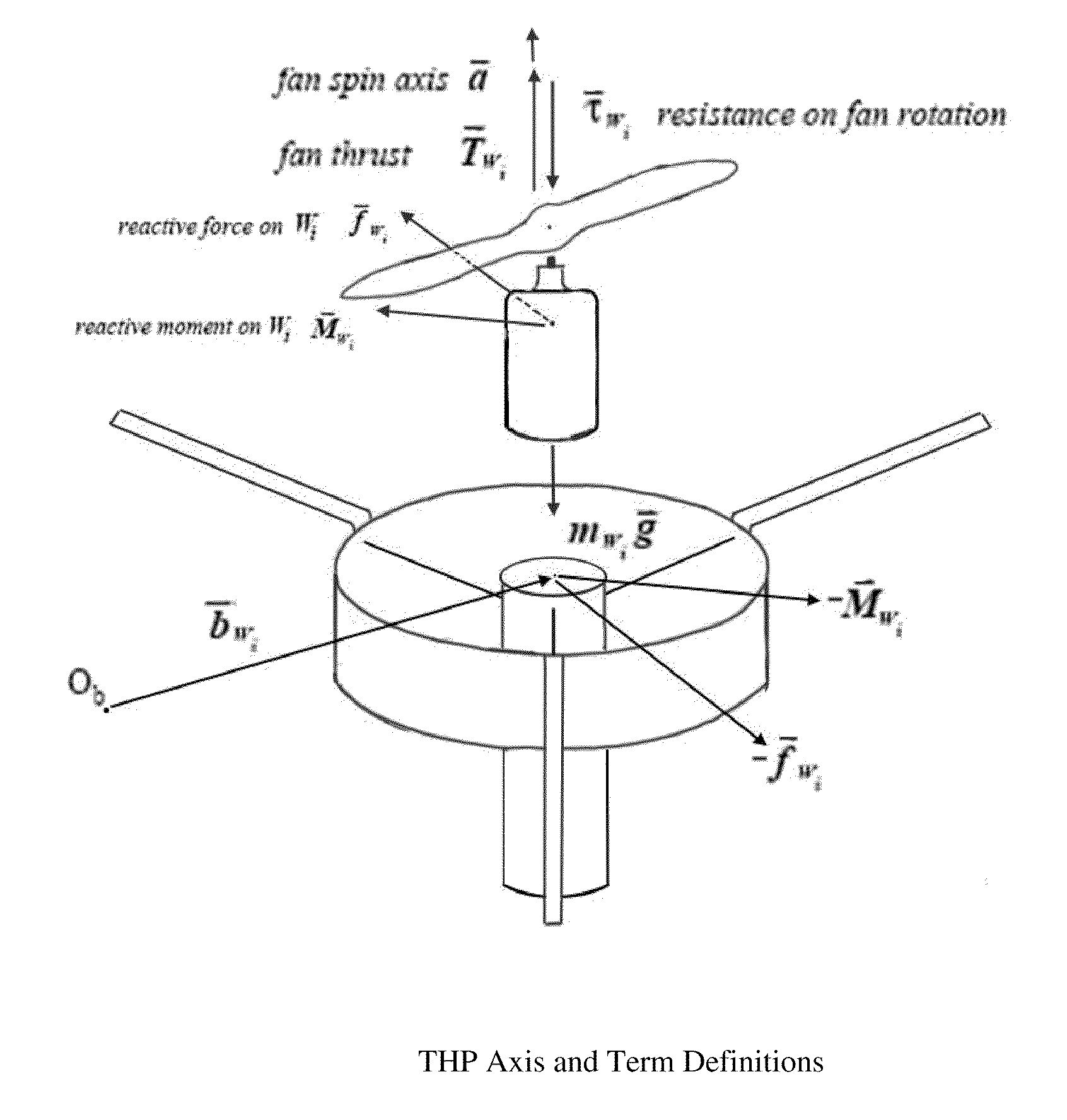
Tethered hovering platform
ActiveUS20100108807A1Easy to deployMinimal human interactionIrregular area designTethered aircraftInstabilityPropeller
The design and refinement of a tethered hovering platform into a feasible working system is presented. To determine a starting point for the design, a detailed historical search was conducted to find the history and the current state of such technology. Real world current needs are analyzed to produce a mission specification and to drive the preliminary vehicle design. Analysis of environmental conditions and decisions about an initial payload package are made in conjunction with motor and propeller sizing. Initial concept testing to discover feasibility and operational issues was performed; from this, instability issues were discovered. Analyzing these instability issues using known rotorcraft and momentum effects, in conjunction with flight testing, yields possible solutions to the problem. The use of constrained layer dampers as a means of passive stabilization is addressed and suggested as the preferred solution. Testing of passive constrained layer damping verifies the stability of the solution. The system components and manufacturing cost is presented in comparison to current systems using active stabilization
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Constrained layer damping assembly
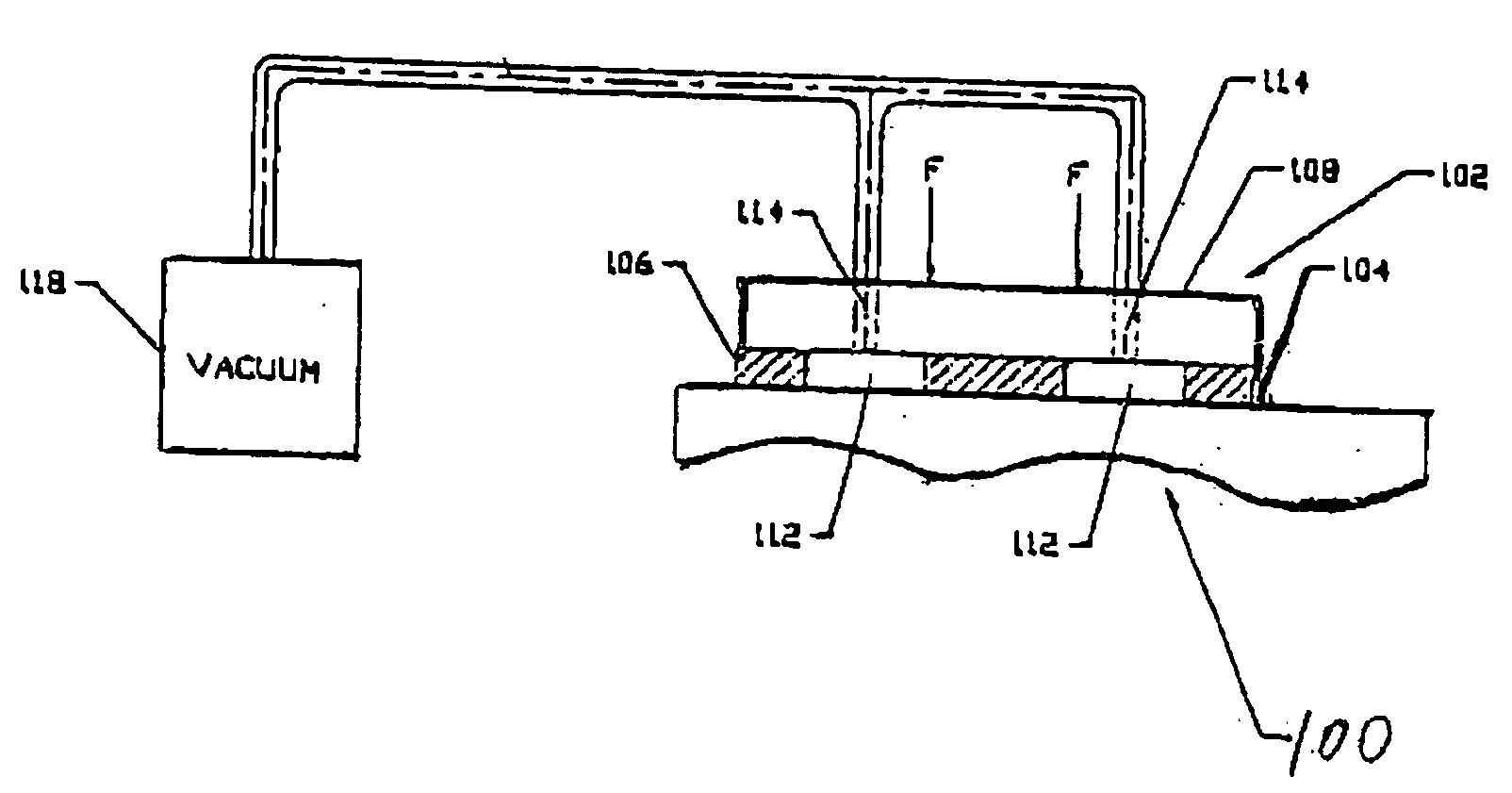
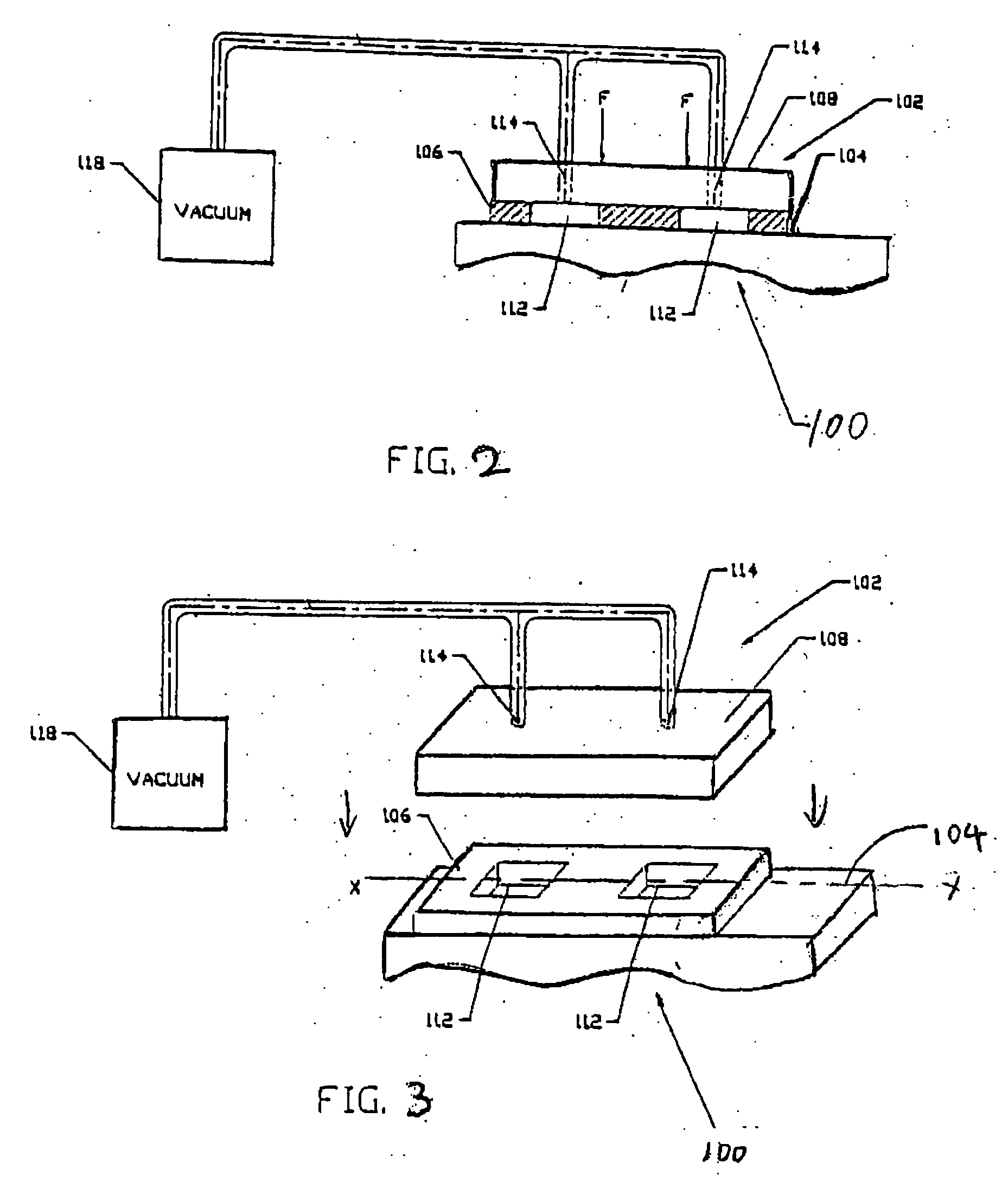
InactiveUS20060033249A1Minimizing amplitudeMachine framesLiquid springsEngineeringConstrained-layer damping
A constrained layer damping assembly for a rigid base member having a substantially planar surface comprises a gas impervious damping layer disposed on the substantially planar surface of the base member, and a load element disposed on the damping layer. The damping layer defines at least one void region extending between the planar surface and the load element, and the load element defines at least one channel for coupling a low pressure to the void region relative to the pressure external to the constrained layer damping assembly to establish a pressure differential between the inside of the void region and the outside of the constrained layer damping assembly. The pressure differential keeps the damping layer under compression and secures the load element and the damping layer onto the base member.
Owner:GUZIK TECHN ENTERPRISES
Tethered hovering platform
ActiveUS8777157B2Easy to useEasy to deployAircraft navigation controlTethered aircraftInstabilityPropeller
The design and refinement of a tethered hovering platform into a feasible working system is presented. To determine a starting point for the design, a detailed historical search was conducted to find the history and the current state of such technology. Real world current needs are analyzed to produce a mission specification and to drive the preliminary vehicle design. Analysis of environmental conditions and decisions about an initial payload package are made in conjunction with motor and propeller sizing. Initial concept testing to discover feasibility and operational issues was performed; from this, instability issues were discovered. Analyzing these instability issues using known rotorcraft and momentum effects, in conjunction with flight testing, yields possible solutions to the problem. The use of constrained layer dampers as a means of passive stabilization is addressed and suggested as the preferred solution. Testing of passive constrained layer damping verifies the stability of the solution. The system components and manufacturing cost is presented in comparison to current systems using active stabilization.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Method of forming a panel constrained layer damper treatment
A method of forming a panel constrained layer damper treatment from a laminate, having a panel and a visco-elastic layer attached thereto, by forming a panel constrained layer damper from the laminate to a predetermined shape is provided. Additionally, the method of the present invention includes attaching the panel constrained layer damper to a substrate to form the panel constrained layer damper treatment. The method may also include subjecting the panel constrained layer damper to heat energy to bond the visco-elastic layer to the substrate. In addition, various methods of attaching the panel constrained layer damper to the substrate are provided.
Owner:MATERIALS SCI CORP
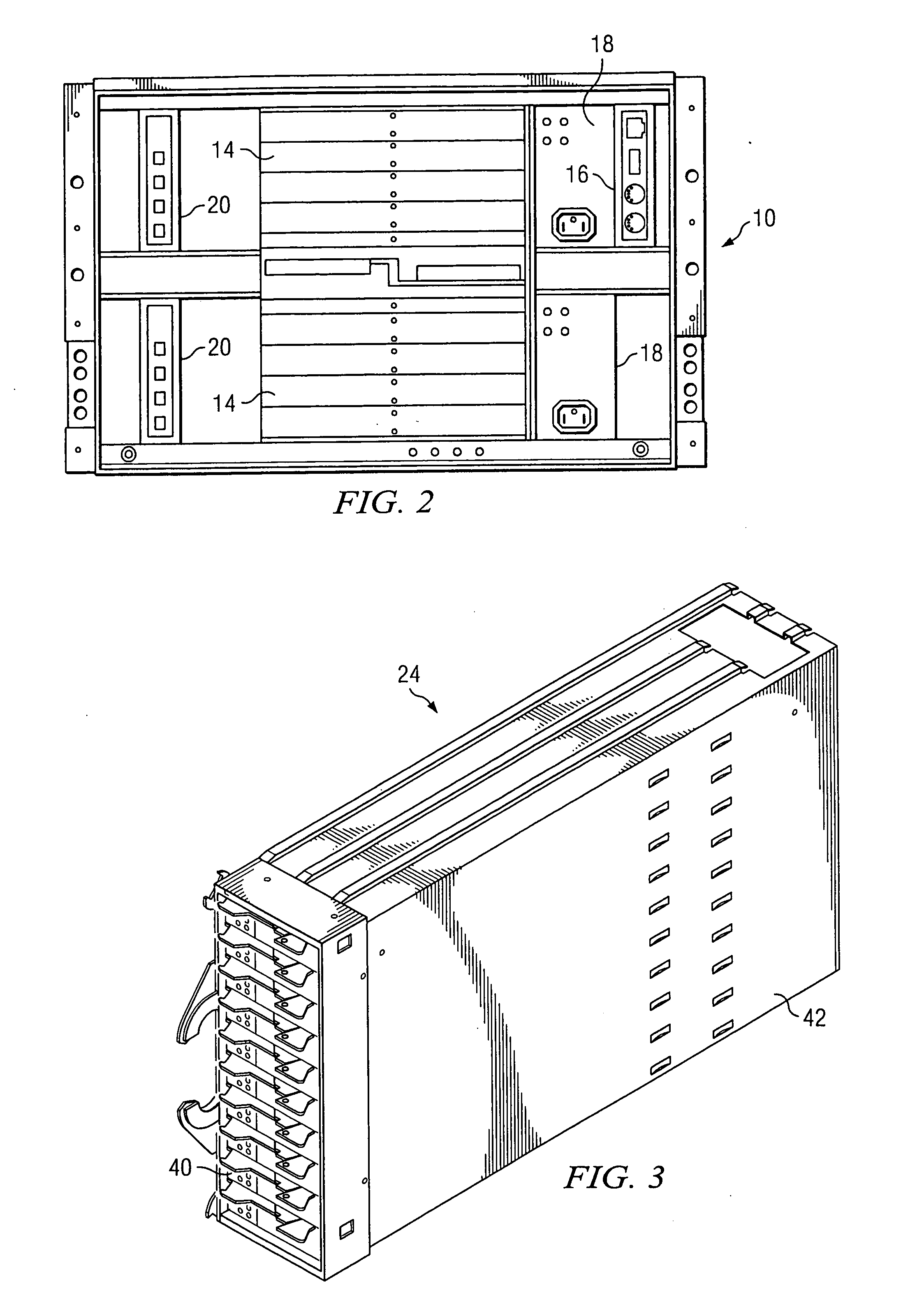
Damping rotational vibration in a multi-drive tray
InactiveUS20070098281A1Minimizing transferReduce vibrationUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionRecord information storageRotational vibrationExternal rotation
One or more layers of constrained layer damping material is strategically placed within a data storage library having one or more sources of rotational vibration energy. Data storage devices, such as disk drives, are isolated from each other and from a drive tray by a first layer of constrained layer damping material. The drive trays are isolated from drive enclosure bays by a second layer of constrained layer damping material. A third layer of constrained layer damping material isolates each drive enclosure bay from the housing of the data storage library. The net effect is a significant reduction of the amount of rotational vibration energy arriving at each data storage device from other system components, such as a blower module. Additionally, the amount of rotational vibration energy arriving at each data storage device from other data storage devices is also reduced. By mounting the data storage devices to the drive trays in a single plane, the rigidity and mass of the drive tray is increased, reducing its susceptibility to external rotational vibration energy.
Owner:IBM CORP
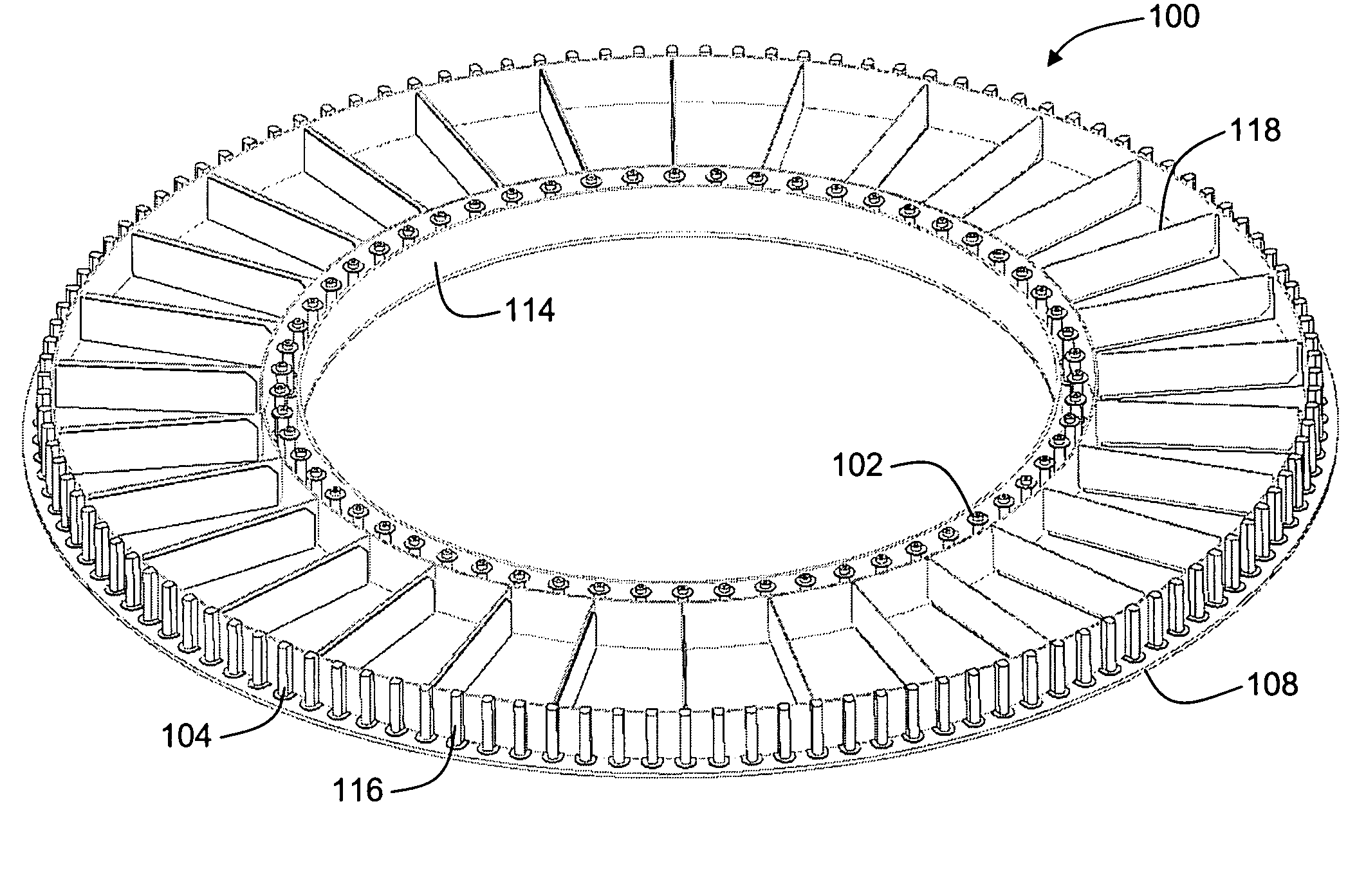
Payload adapter
InactiveUS7222823B2Minimizing ratioCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsVibration attenuationEngineering
A payload adapter consists of a body that when hollow includes a plurality of stiffeners—radial and / or circumferential—or alternatively a core for carrying shear loads. The body may include a first annular face sheet, a second annular face sheet and a plurality of stiffeners connecting between the first annular face sheet and the second annular face sheet. The combination of the annular hollow body and the plurality of stiffeners or the same face sheets combined with an in-filled core results in an axial frequency and a lateral (pitch) frequency for the payload adapter that provides superior vibration isolation. Constrained layer damping is incorporated into the design for additional vibration attenuation.
Owner:ATA ENG
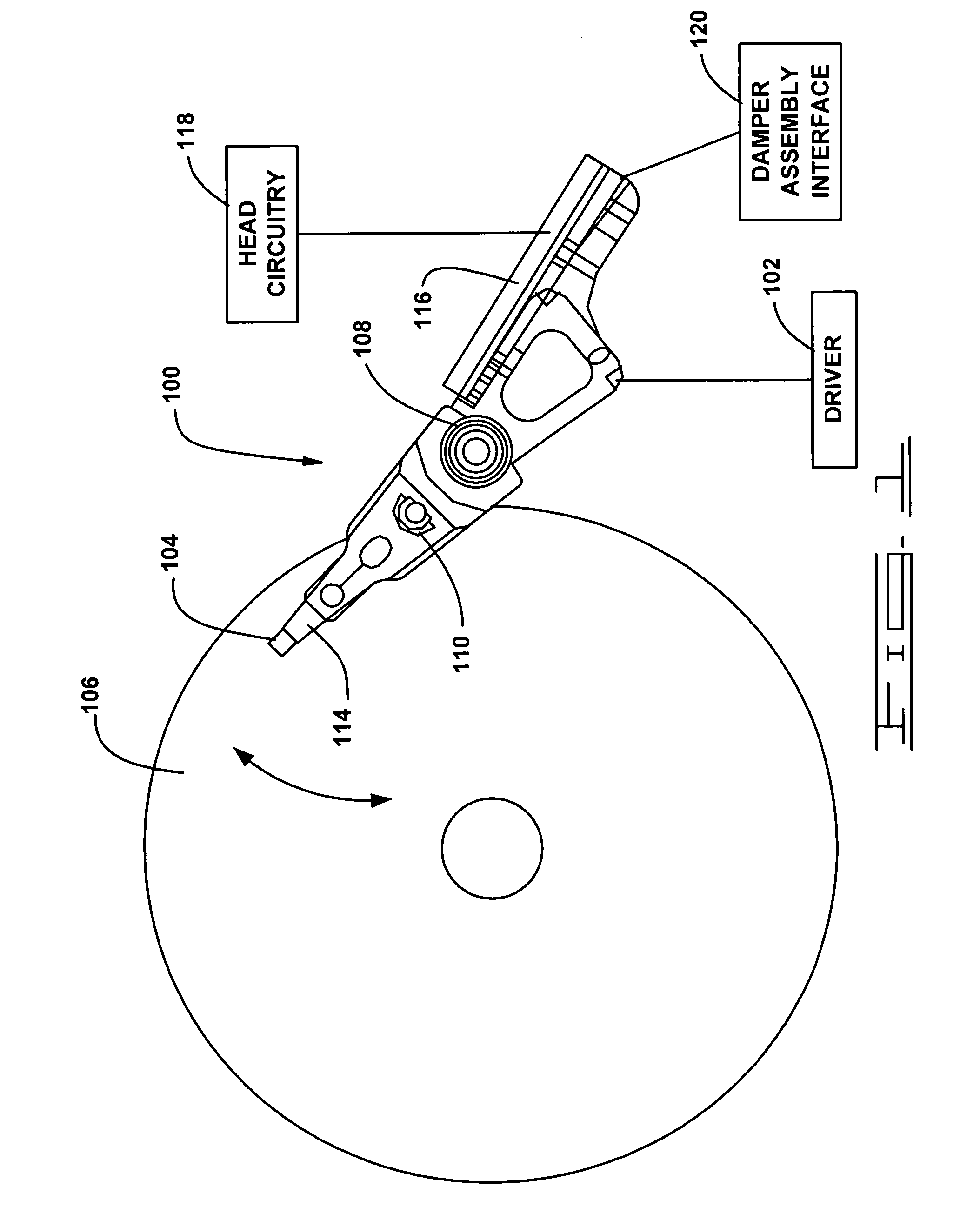
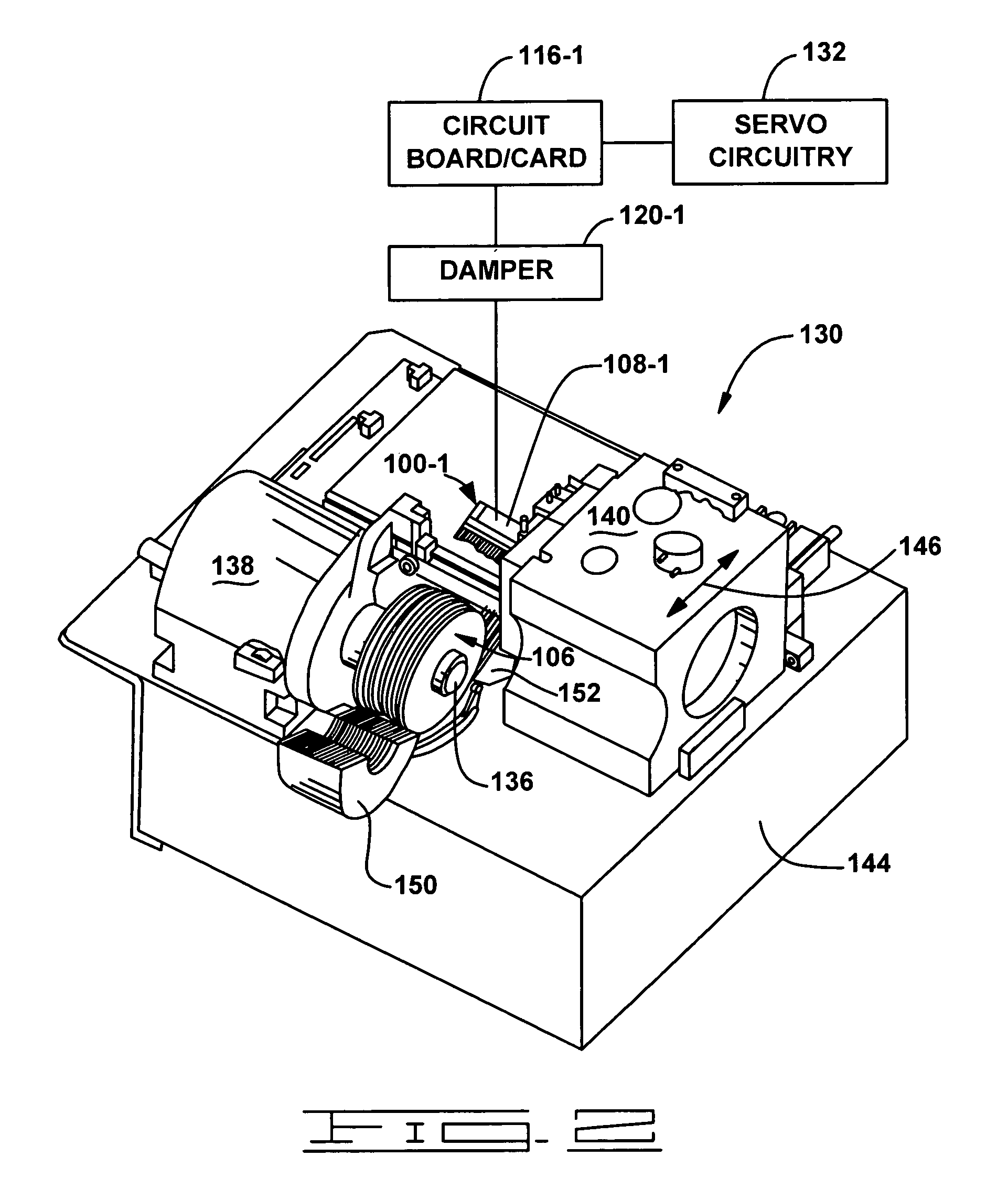
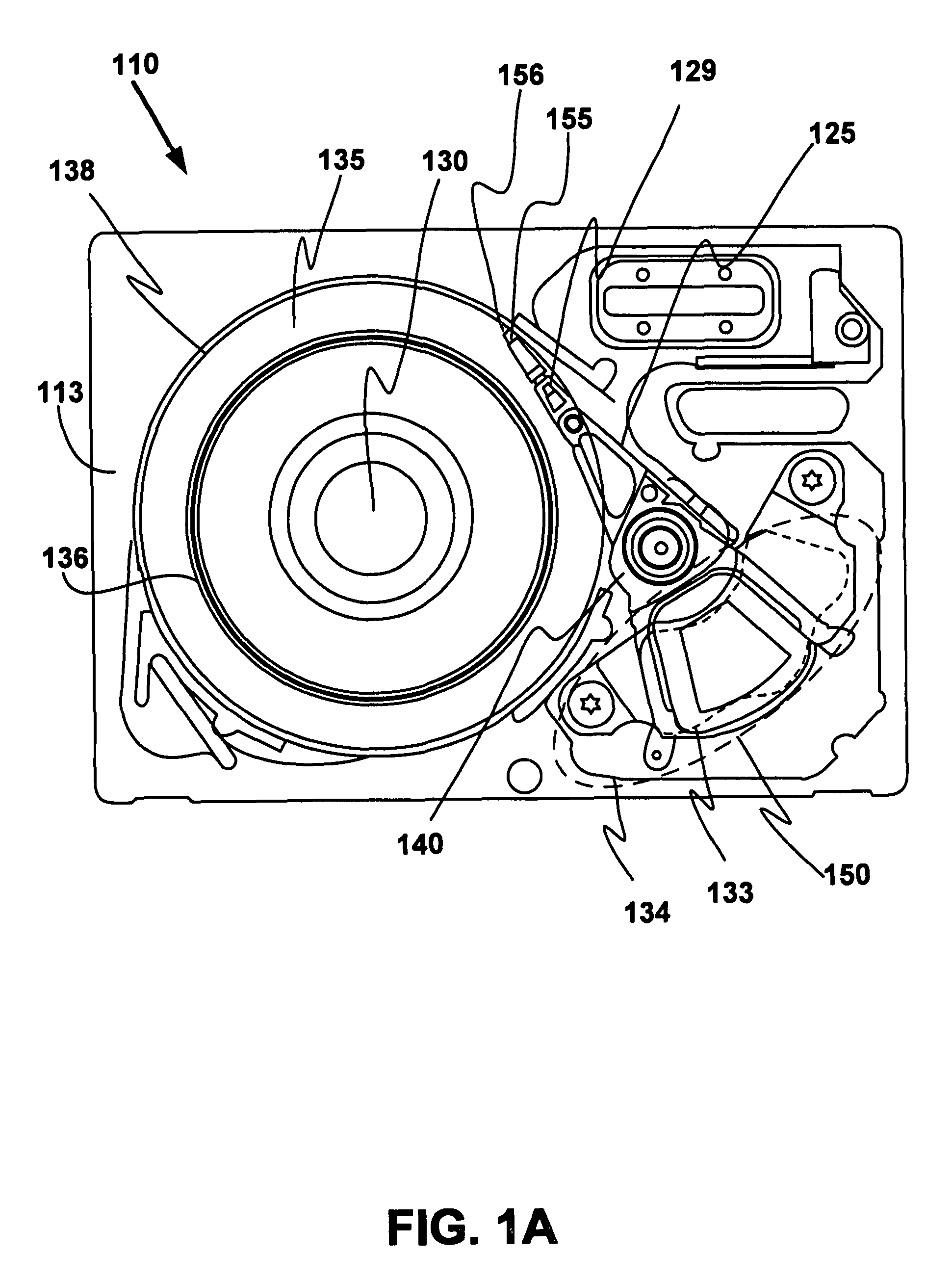
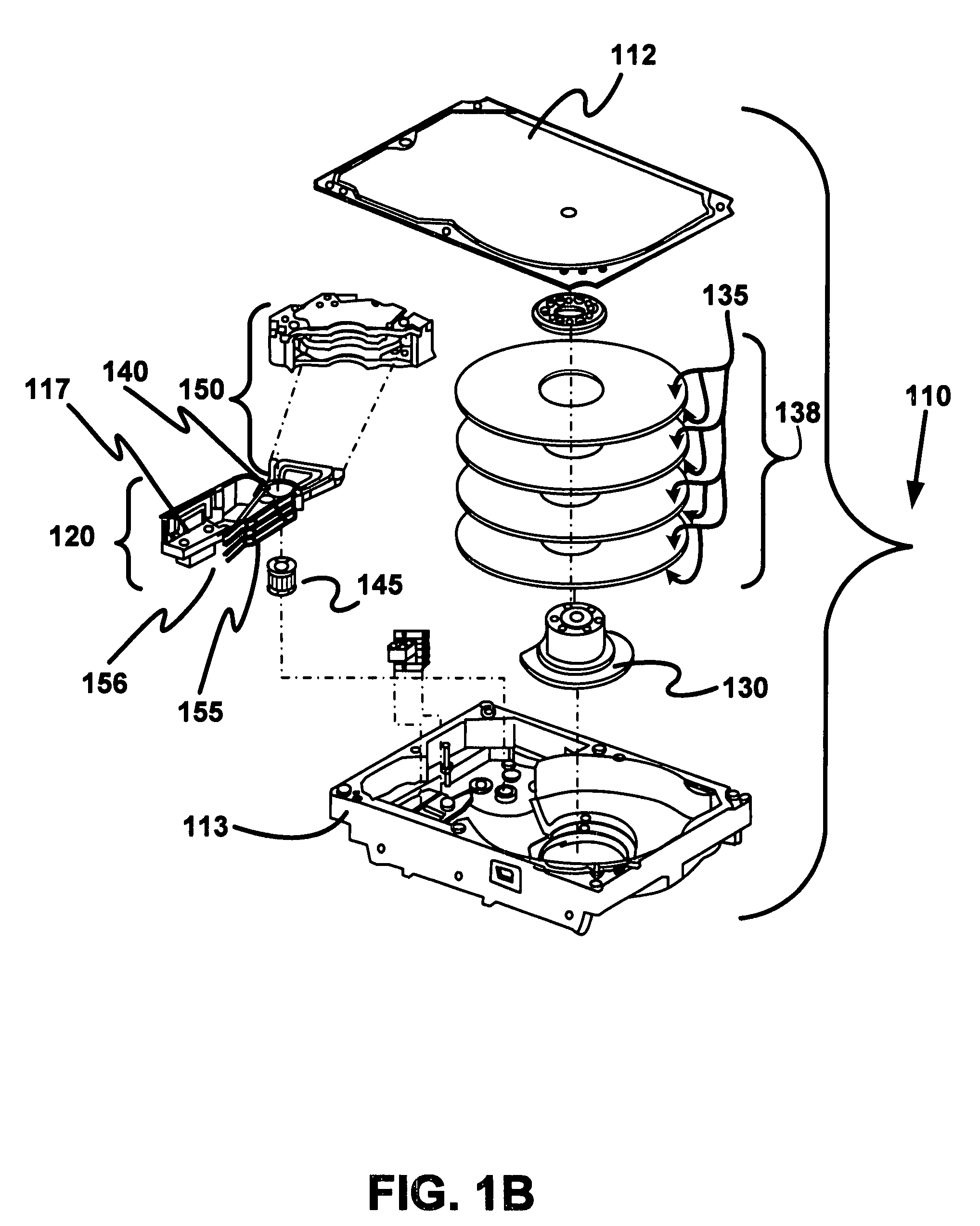
Actuator assembly including a circuit assembly and a damper therefor
Apparatus and method for damping operational vibration modes of an actuator assembly. The actuator assembly preferably supports a data transducing head adjacent a storage medium in a servo track writing environment. The actuator assembly further supports a circuit assembly comprising circuit board, card or other circuit portion to facilitate electrical communication with the data transducing head. A damping assembly is interposed between the circuit assembly and the actuator assembly to mechanically decouple the circuit assembly from the actuator assembly. Preferably, the damper assembly comprises one or more rigid damper plates and one or more viscoelastic layers therebetween to provide constrain layer damping. As desired, the plates can be provided with progressively larger thickness dimensions in a direction away from the actuator assembly.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
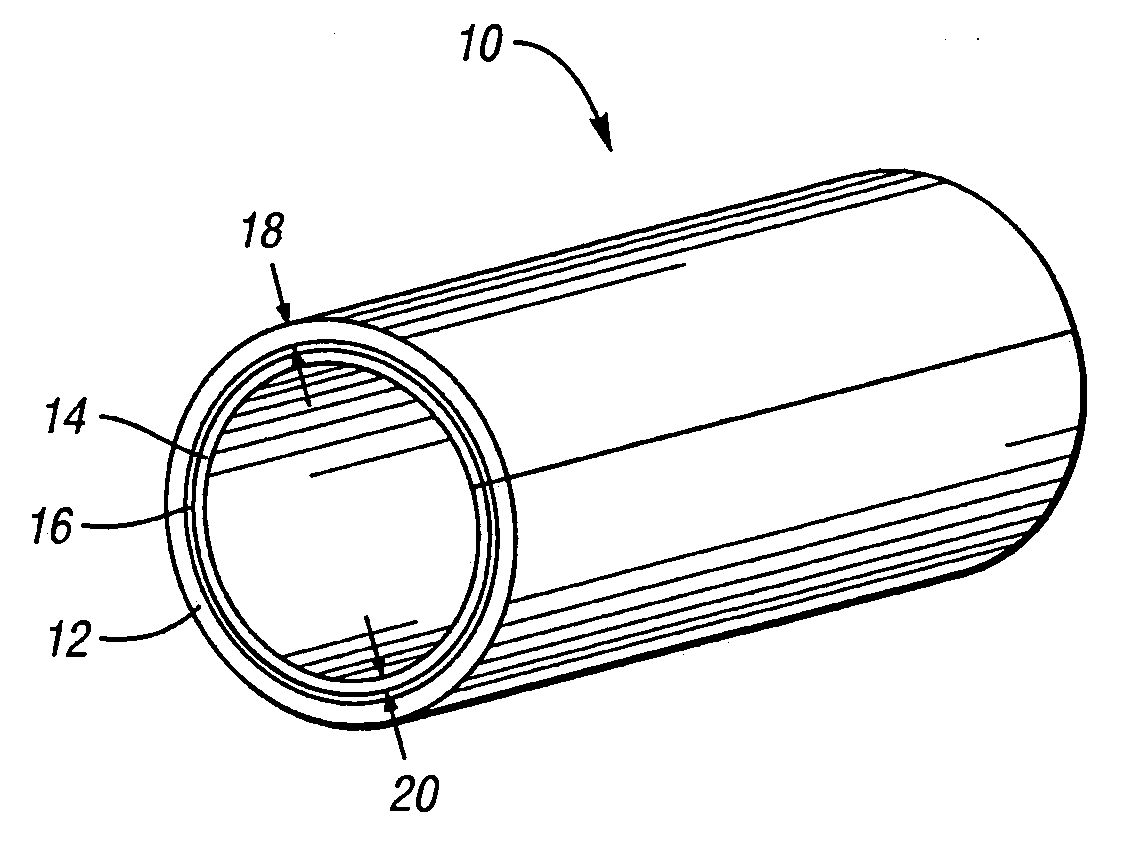
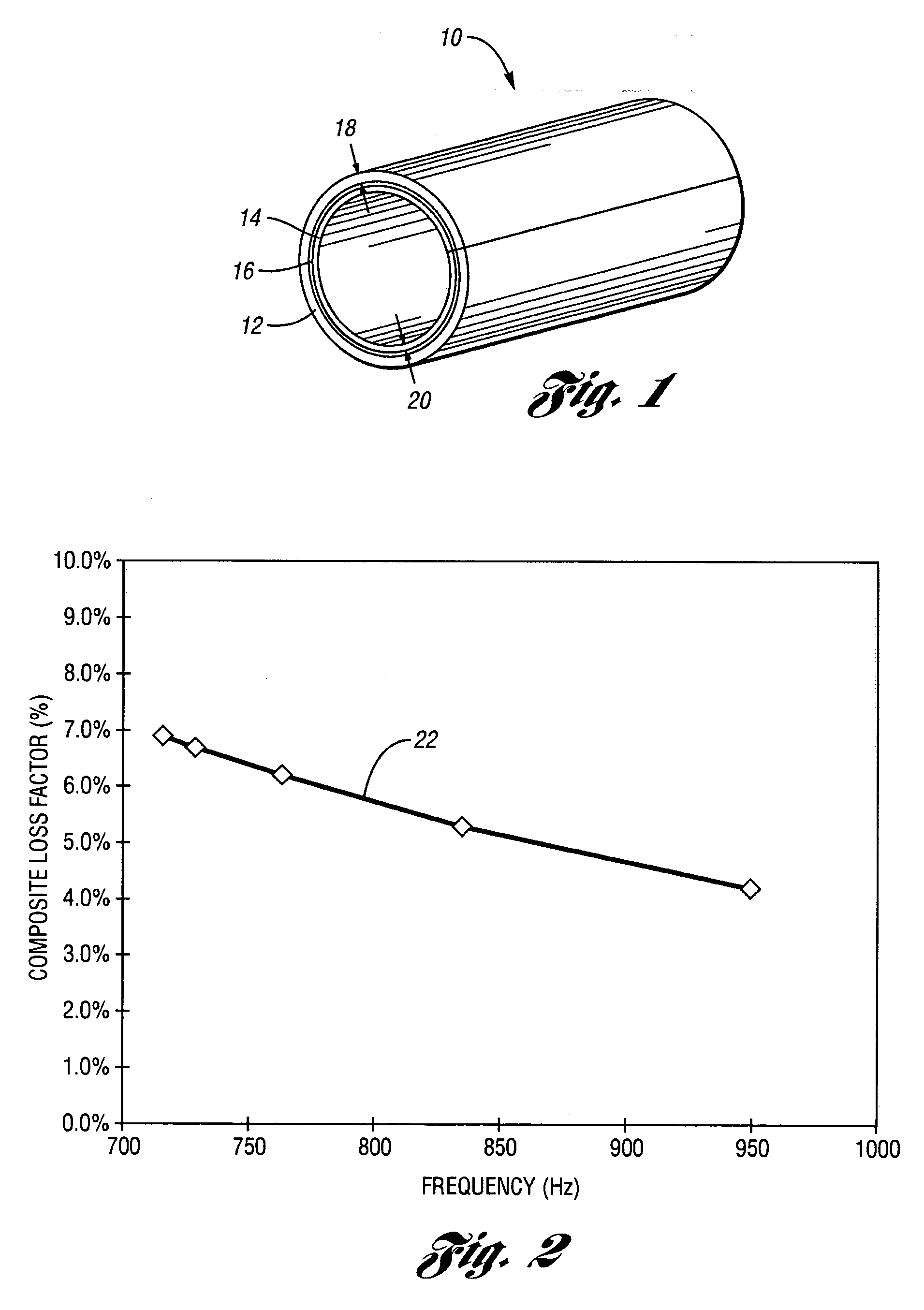
Internally damped laminated tube
An internally damped laminated tube comprises an outer layer and an inner layer, with a viscoelastic layer disposed therebetween. The outer and inner layers constrain the viscoelastic layer, thereby providing noise and vibration reduction through constrained-layer damping. While both the outer and inner layers act as constraining layers, the outer layer also preferably provides structural support for the tube, thus necessitating a thicker outer layer. Preferably, the outer and inner layers comprise steel. The internally damped tube according to the present invention exhibits a composite loss factor greater than four percent for ring modes occurring at vibrational frequencies between 700 and 950 Hz.
Owner:MATERIAL SCIENCES CORPORATION
Constrained layer damping system and method of making the same
InactiveUS20090183821A1Synthetic resin layered productsLaminationEngineeringConstrained-layer damping
A method of producing a constrained layer damping system including a constraining layer, a damping layer, a viscous thermally-activated decoupler (VTAD) layer and a base blank layer. The method includes the steps of blanking a constraining layer, applying a damping layer to the constraining layer to form a constraining / damping construct. A VTAD layer can be applied onto the damping layer to form a layered constraining / damping / VTAD construct in which the VTAD layer has at least one exposed surface. The exposed surface of the VTAD layer on the constraining / damping / VTAD construct is pressed onto a cleansed side of a base blank layer to form a constrained layer damping system.
Owner:INTPROP HLDG
Payload adapter
InactiveUS20060016928A1Minimizing ratioCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsVibration attenuationFace sheet
A payload adapter consists of a body that when hollow includes a plurality of stiffeners—radial and / or circumferential—or alternatively a core for carrying shear loads. The body may include a first annular face sheet, a second annular face sheet and a plurality of stiffeners connecting between the first annular face sheet and the second annular face sheet. The combination of the annular hollow body and the plurality of stiffeners or the same face sheets combined with an in-filled core results in an axial frequency and a lateral (pitch) frequency for the payload adapter that provides superior vibration isolation. Constrained layer damping is incorporated into the design for additional vibration attenuation.
Owner:ATA ENG
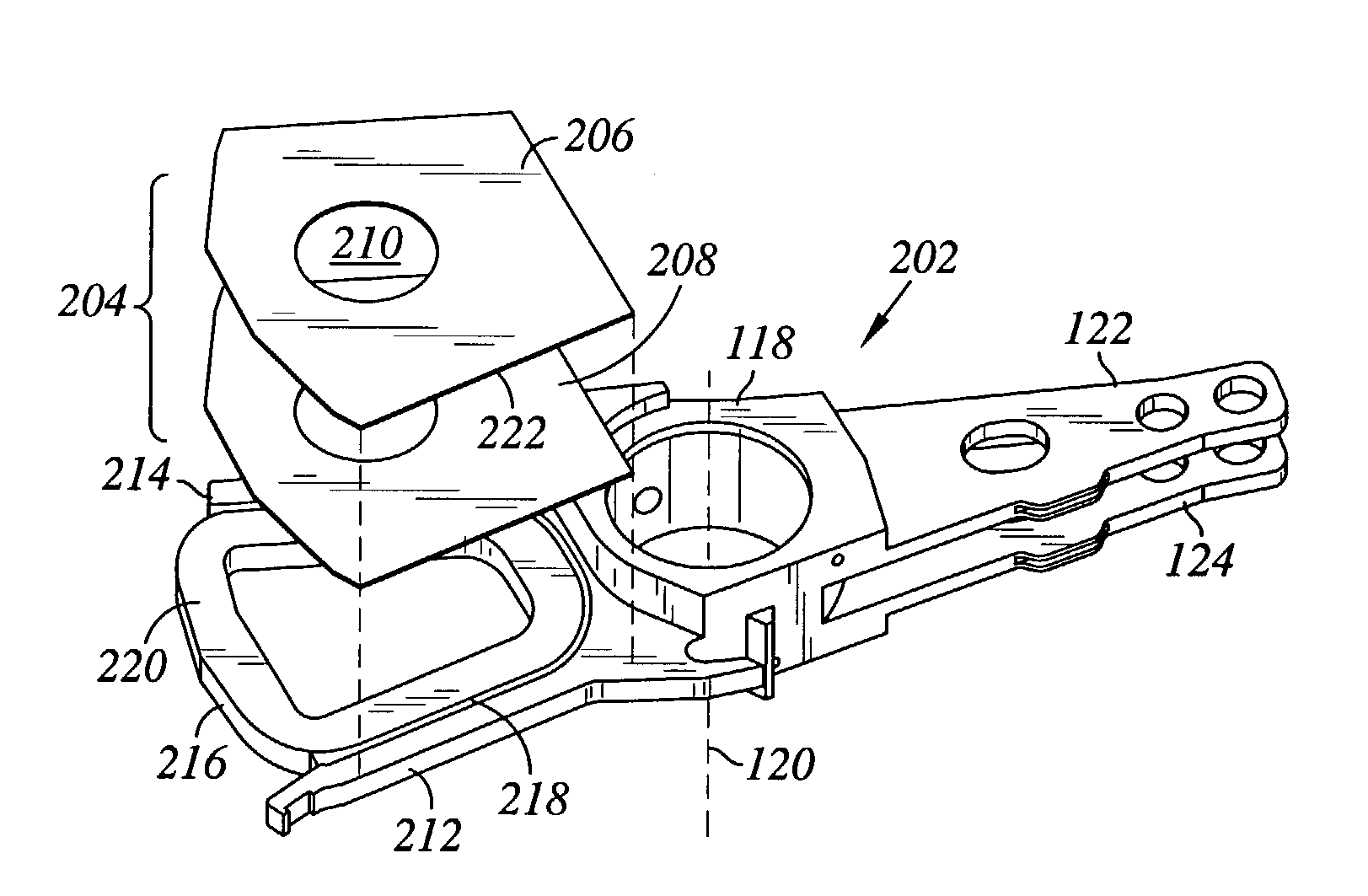
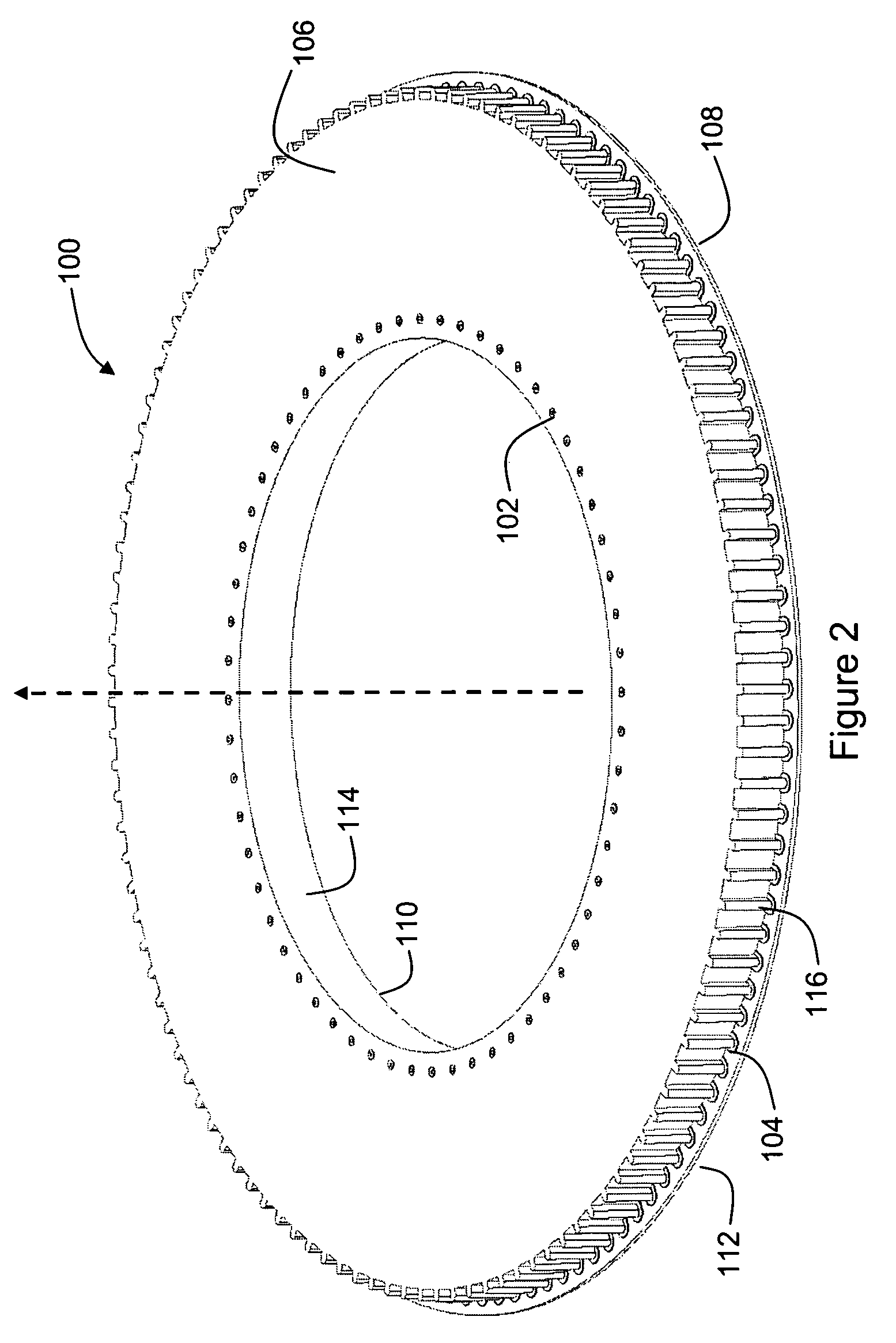
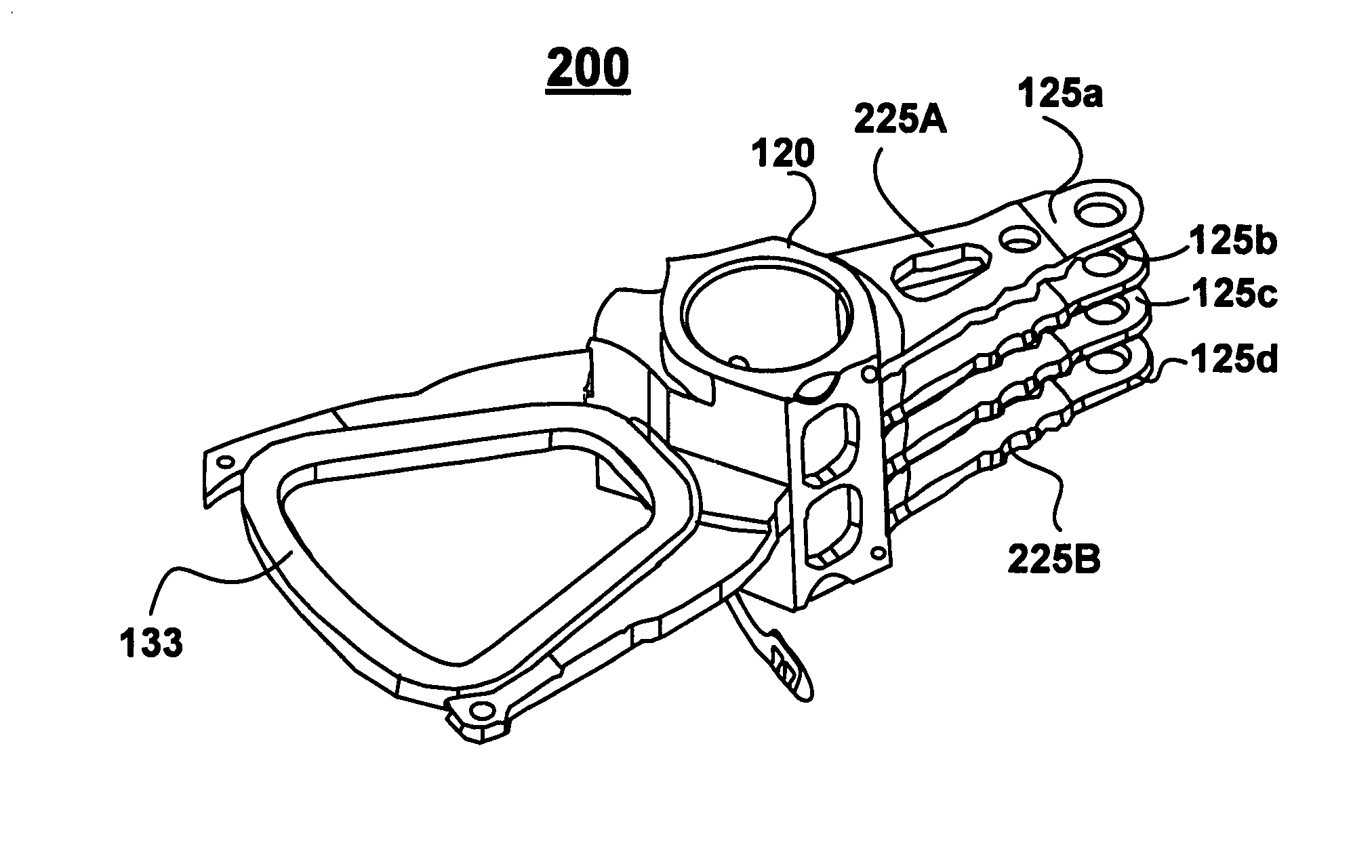
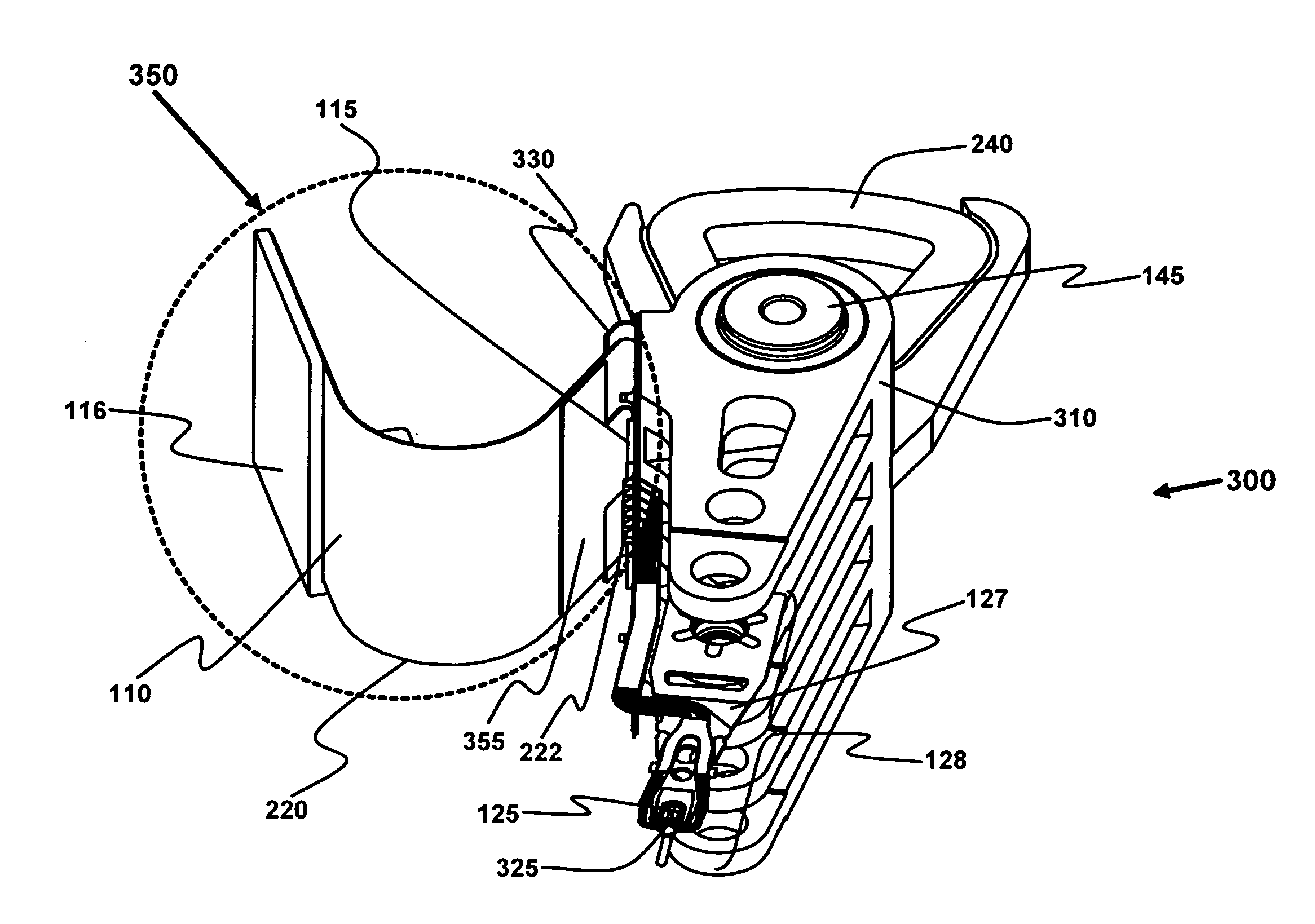
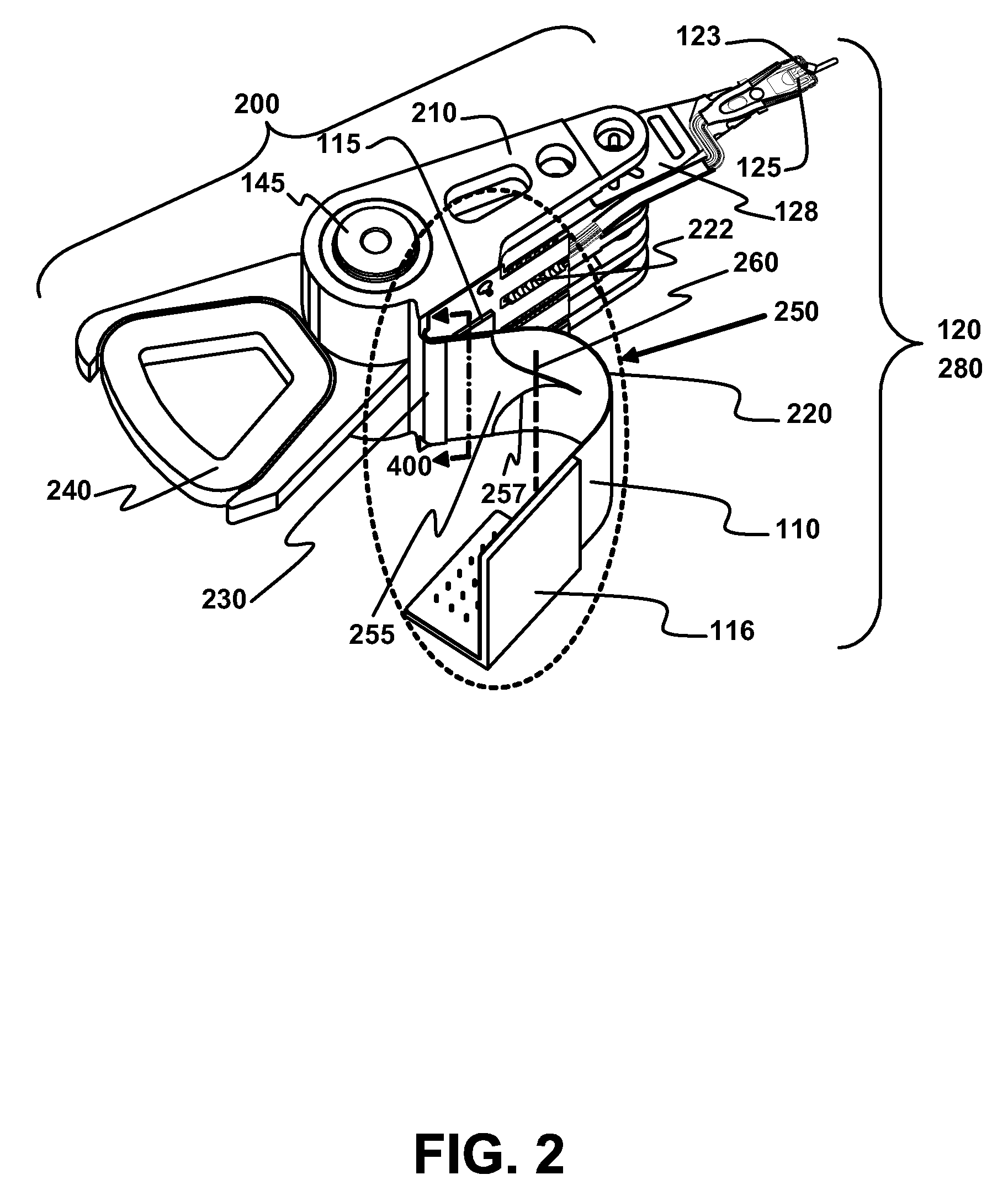
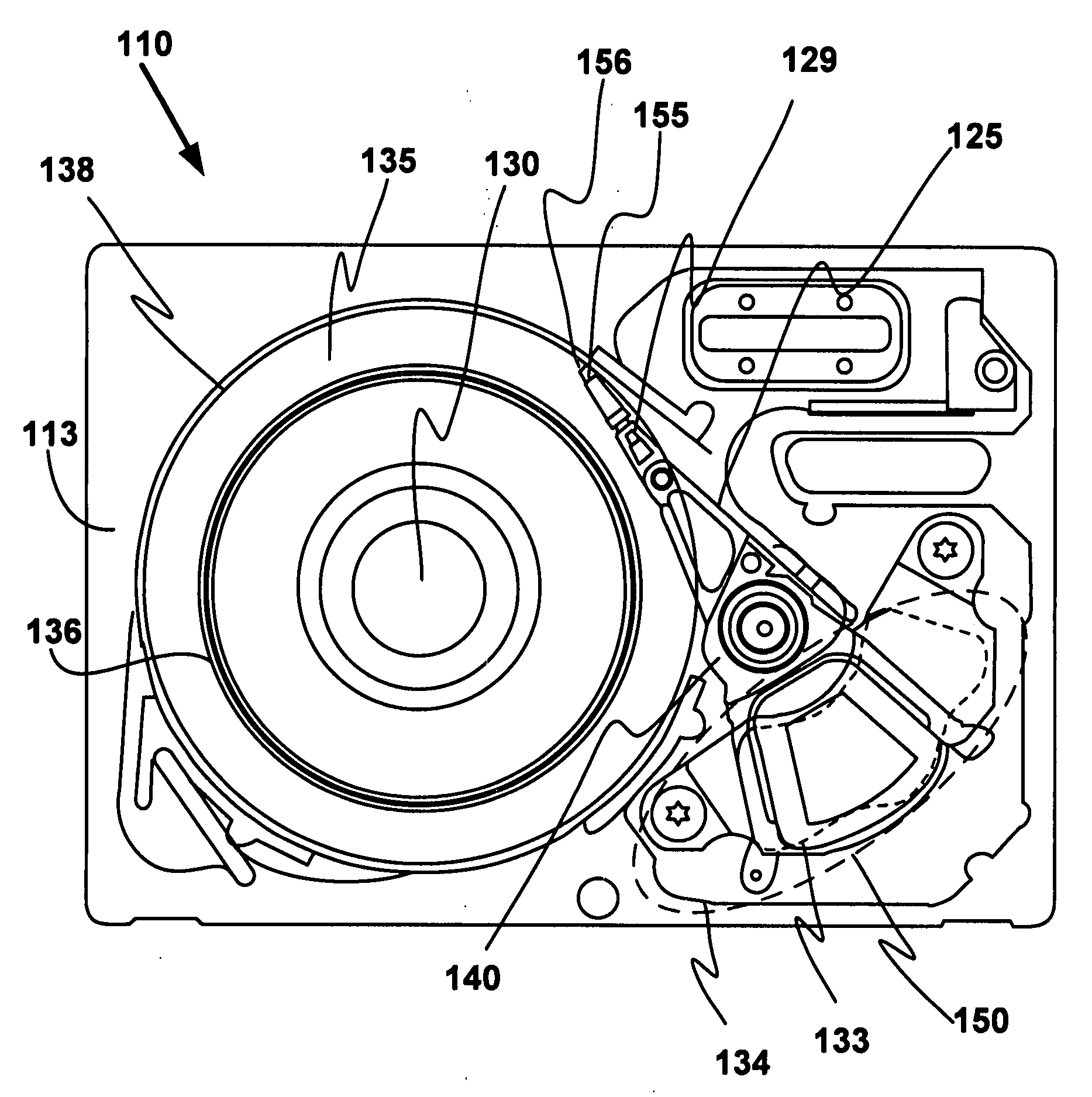
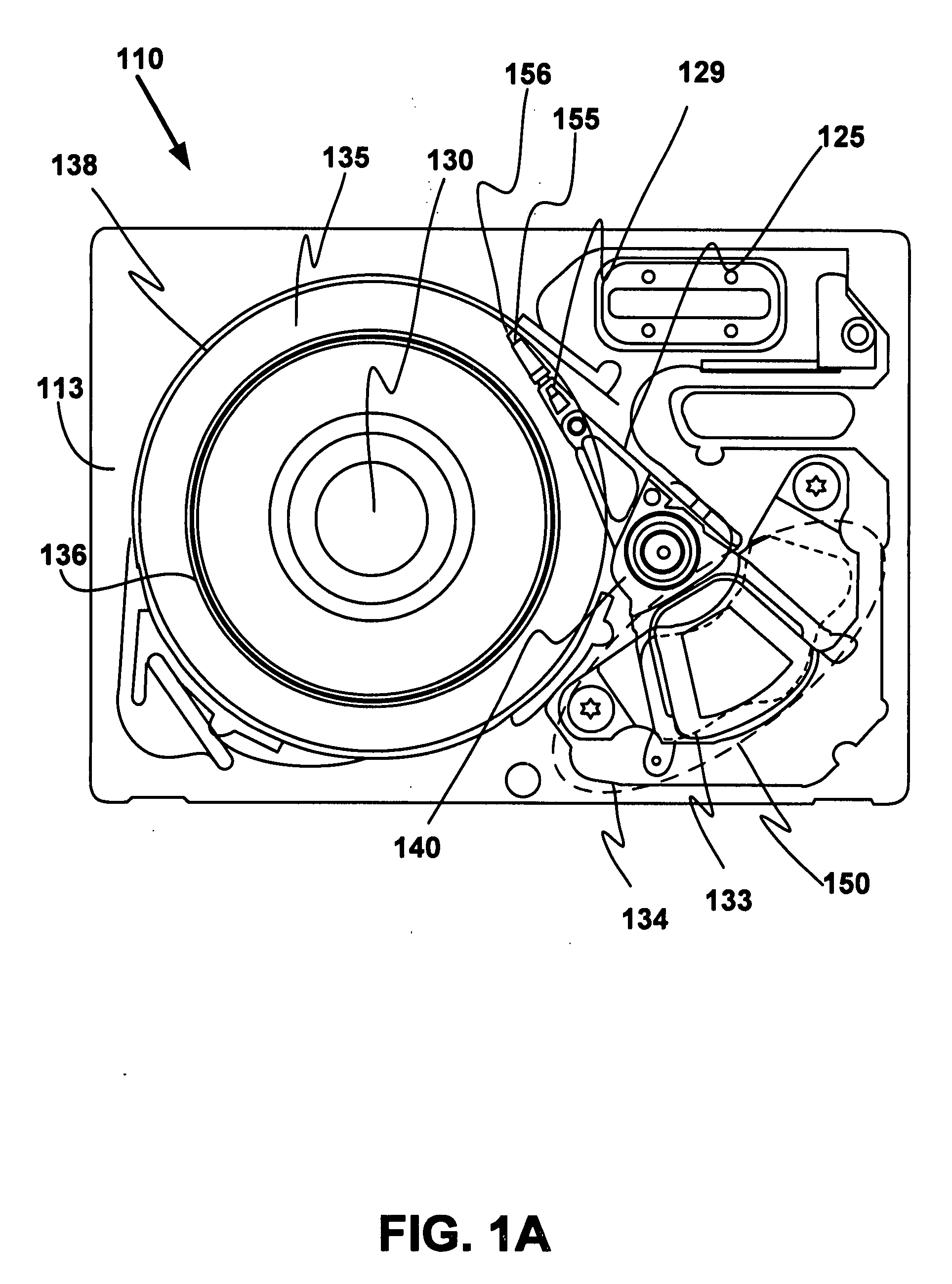
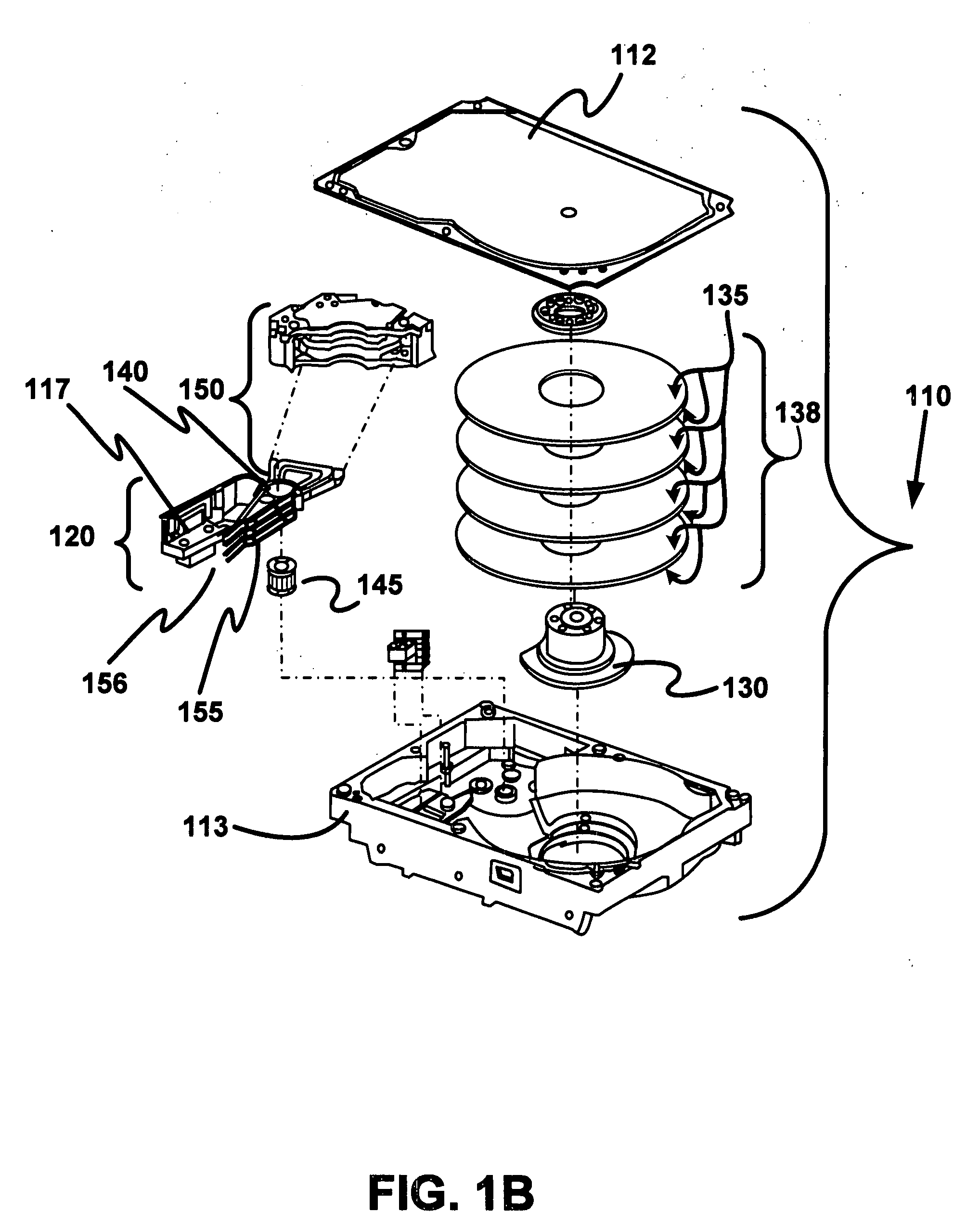
Outer actuator arm constrained layer dampers
ActiveUS7859795B2Disposition/mounting of recording headsUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionSnubberActuator
Outer arm constrained layer dampers to improve actuator dynamics are disclosed. One embodiment provides a housing and disk pack mounted to the housing and having a plurality of disks that are rotatable relative to the housing. In addition, an actuator is coupled to the housing, the actuator having a plurality of suspensions arms for reaching over the plurality of disks. A first damper is coupled with an outside (or inside) portion of a top outside suspension arm of the plurality of suspensions arms. In addition, a second damper is coupled with an outside (or inside) portion of a bottom suspension arm of the plurality of suspensions arms. In so doing, vibration modes involving deformation of the top suspension arm and the bottom suspension arm are damped.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
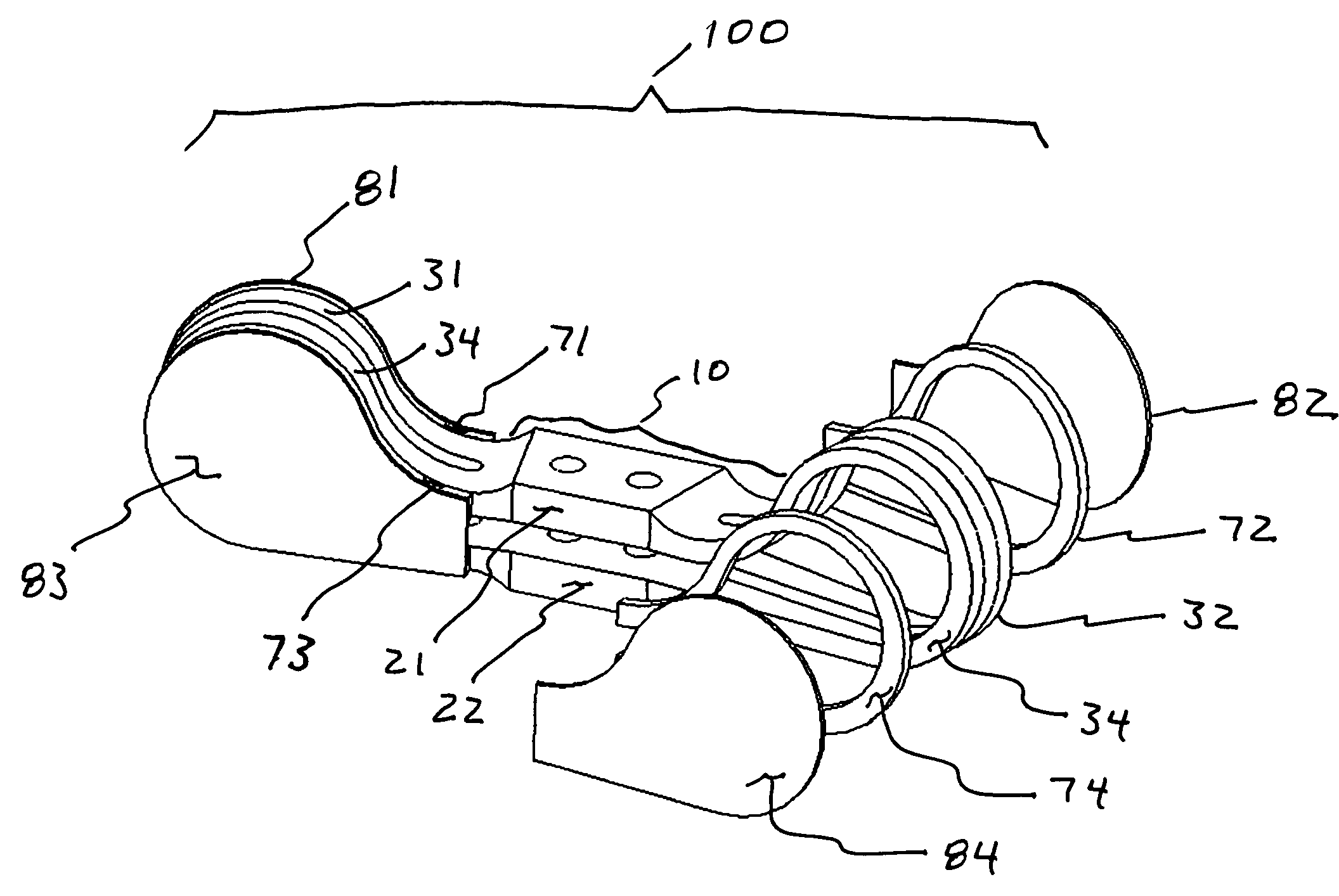
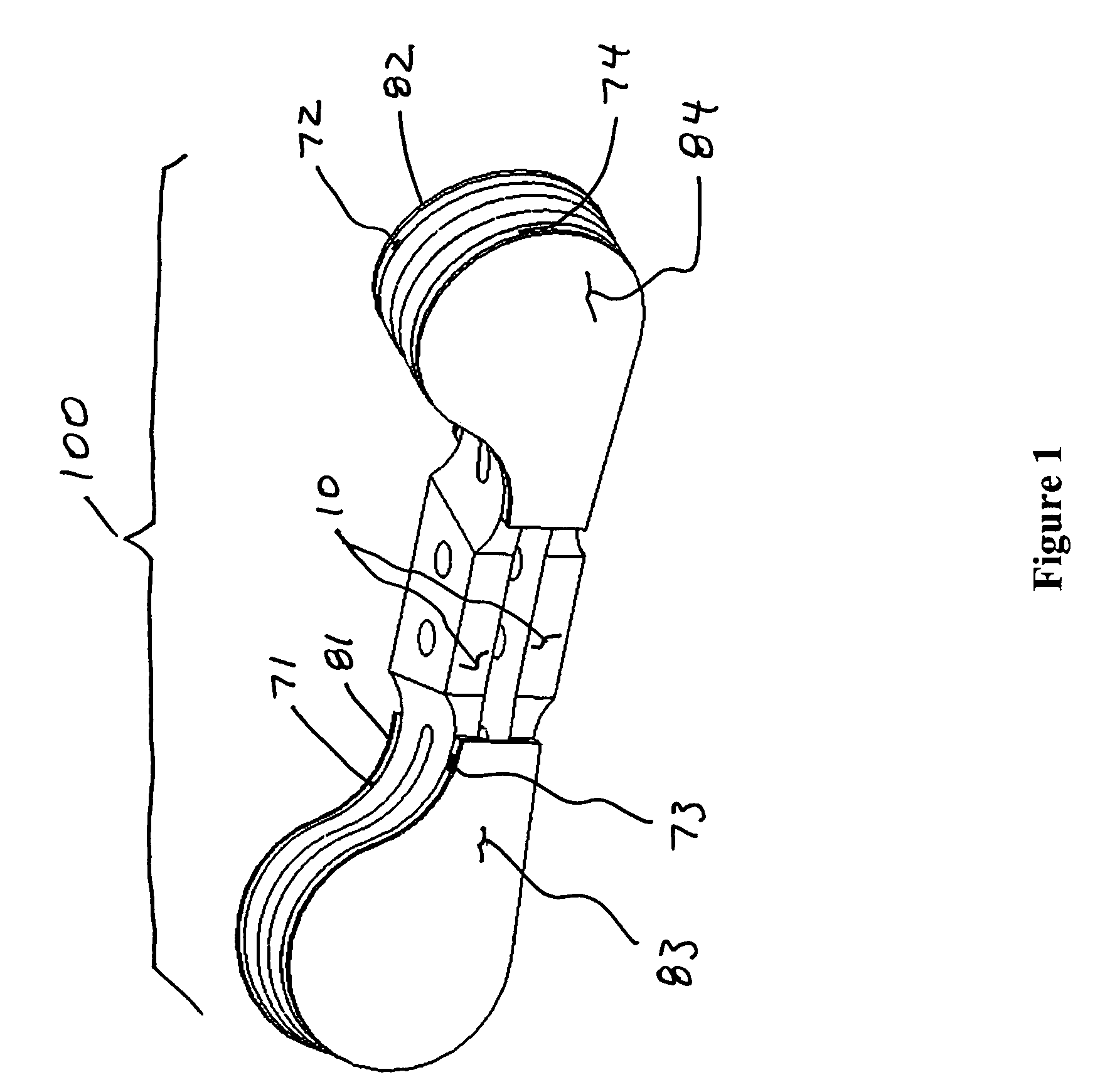
Voice coil damper
ActiveUS7848058B2Disposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageViscoelastic dampingHard disc drive
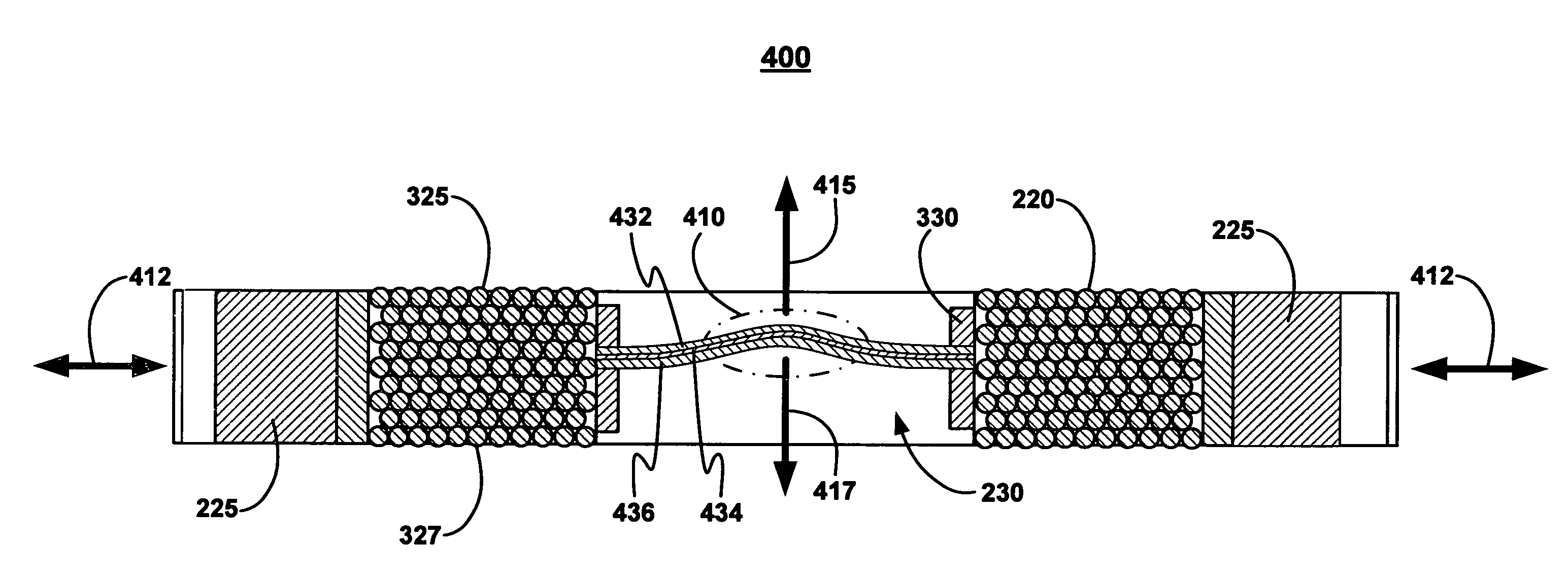
A voice coil for a voice coil motor of a hard disk drive comprises an inner surface of the voice coil, which bounds a central space of the voice coil. A first outer surface of the voice coil is substantially parallel to a second outer surface of the voice coil. A constrained layer damper is attached to the inner surface of the voice coil by a coupler. The constrained layer damper comprises a first constraining layer coupled to a first surface of a viscoelastic damping layer. A second constraining layer is coupled to a second surface of the viscoelastic damping layer. The constrained layer damper is curved in a direction that is substantially perpendicular to the first outer surface of the voice coil and the second outer surface of the voice coil.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
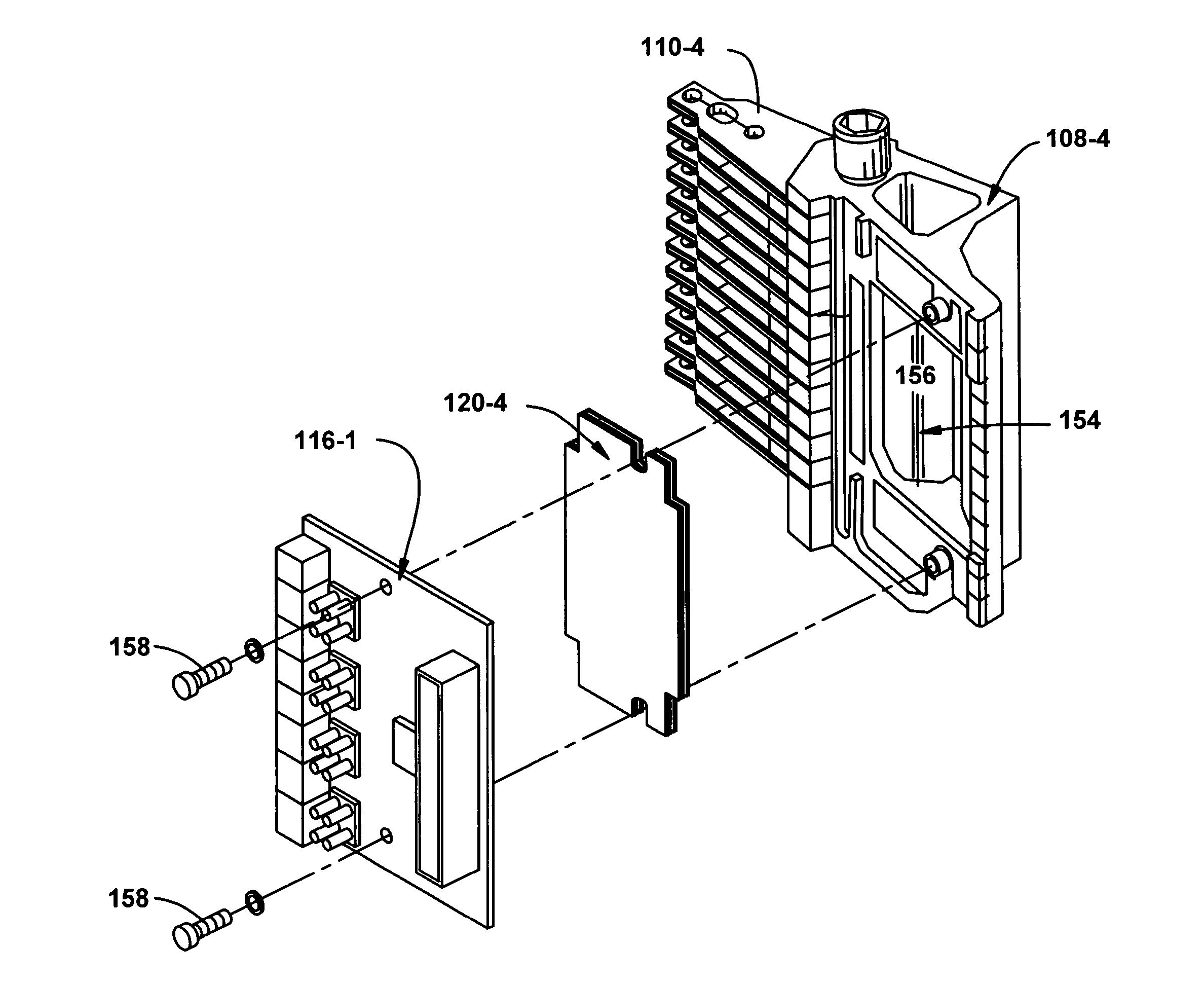
Flex cable assembly damper
ActiveUS20090141404A1Record information storageElectrical connection between arm and supportHard disc driveEngineering
A flex cable assembly for a head stack assembly of a hard disk drive comprises a flex cable for conducting data signals from the head stack assembly to a connector. The flex cable comprises a dynamic loop section between a termination for the head stack assembly and the connector. A constrained layer damper is attached adjacently to an area of the flex cable that is configured to receive the coupler. The constrained layer damper extends into the dynamic loop section of the flex cable.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Voice coil damper
ActiveUS20090059435A1Disposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageViscoelastic dampingHard disc drive
A voice coil for a voice coil motor of a hard disk drive comprises an inner surface of the voice coil, which bounds a central space of the voice coil. A first outer surface of the voice coil is substantially parallel to a second outer surface of the voice coil. A constrained layer damper is attached to the inner surface of the voice coil by a coupler. The constrained layer damper comprises a first constraining layer coupled to a first surface of a viscoelastic damping layer. A second constraining layer is coupled to a second surface of the viscoelastic damping layer. The constrained layer damper is curved in a direction that is substantially perpendicular to the first outer surface of the voice coil and the second outer surface of the voice coil.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
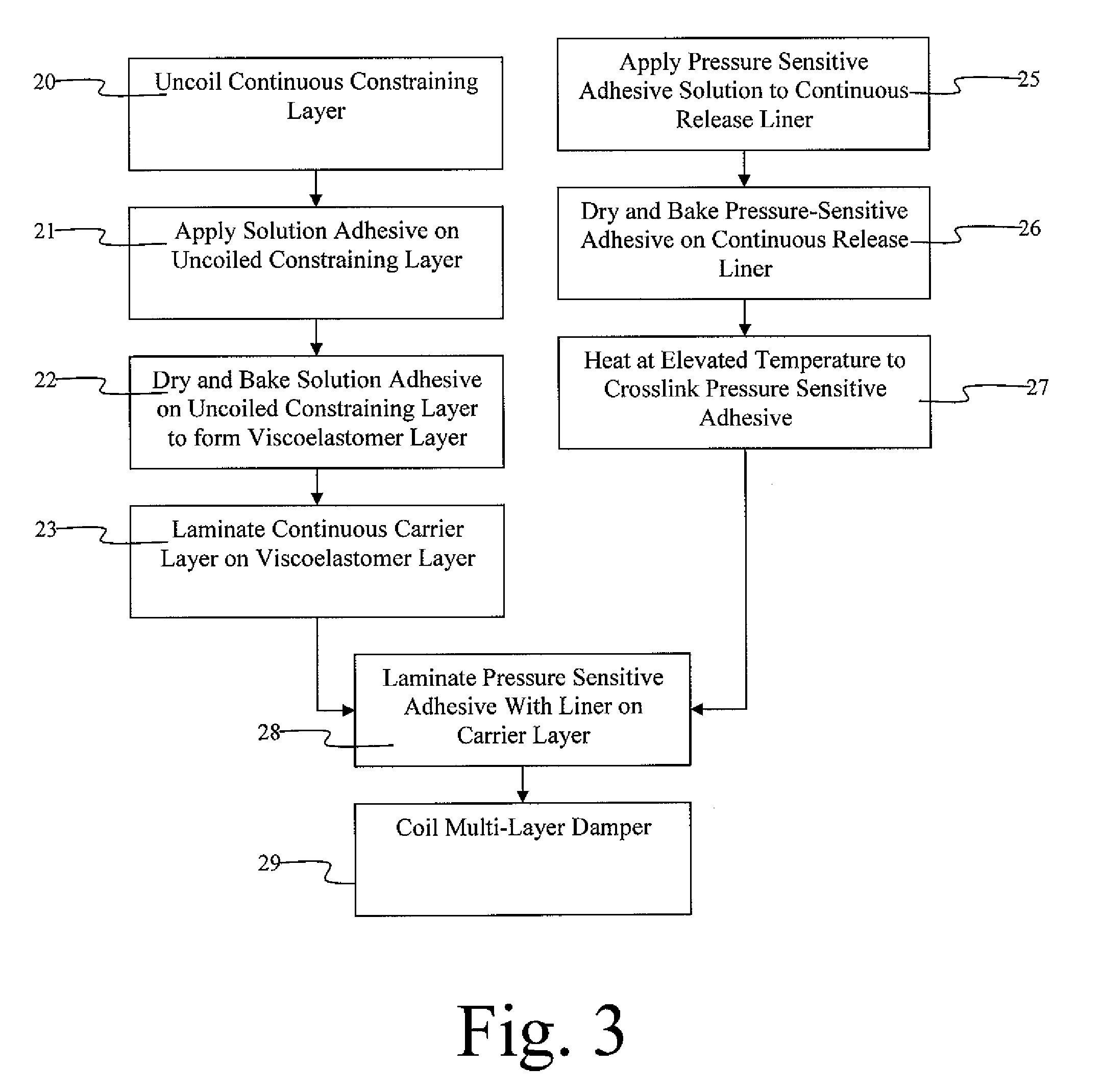
Method of manufacturing laminated damping structure with vulcanized rubber as viscoelastic core
ActiveUS20090249627A1High bonding strengthImprove soundElectrical transducersRecord carriersAdhesiveEngineering
The present invention provides an improved method of manufacturing constrained layer dampers with a vulcanized rubber viscoelastic core. The method includes the steps of: applying a first layer of adhesive to a first constraining layer; applying a layer of unvulcanized rubber solved in a solvent to the first layer of adhesive to form a first laminate structure; applying a second layer of adhesive to a second constraining layer to form a second laminate structure; laminating the first laminate structure with the second laminate structure; coiling the laminated first and second laminate structures; and increasing the temperature of the coiled first and second laminate structures to thereby vulcanize the layer of rubber.
Owner:WOLVERINE ADVANCED MATERIALS
Flex cable assembly damper
ActiveUS8270120B2Record information storageElectrical connection between arm and supportHard disc driveEngineering
A flex cable assembly for a head stack assembly of a hard disk drive comprises a flex cable for conducting data signals from the head stack assembly to a connector. The flex cable comprises a dynamic loop section between a termination for the head stack assembly and the connector. A constrained layer damper is attached adjacently to an area of the flex cable that is configured to receive the coupler. The constrained layer damper extends into the dynamic loop section of the flex cable.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Symmetrically tapered constrained layer damper for a flex cable assembly for a hard disk drive
ActiveUS20100027165A1Reduce stress concentrationReduce transient vibrationUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionRecord information storageHard disc driveStress concentration
A flex cable assembly for a head stack assembly of a hard disk drive comprises a flex cable for conducting data signals from the head stack assembly to a connector. The flex cable has a dynamic loop section between a termination for the head stack assembly and the connector. The flex cable has a constrained layer damper for attenuating random transient vibration. The constrained layer damper has a symmetrically tapered shape for reducing stress concentration and is coupled with the dynamic loop section of the flex cable adjacent to an area of the flex cable configured for receiving a coupler for coupling the flex cable assembly with the head stack assembly.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Resonant frequency adjustment using tunable damping rods
InactiveUS7212644B2Prevent and minimize undesirable resonancePrevent or minimize undesirable resonanceFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsEngineeringConstrained-layer damping
A mechanical device is tuned using a tunable damping rod. The tunable damping rod can have its tension increased between its respective engines, to in order to increase the resonant frequency of the mechanical device. Different aspects may also be included; the mechanical device may include a constrained layer damping material, which constraints certain mechanical vibrations. The tuning may tuned the mechanical device to reach that vibration.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Outer actuator arm constrained layer dampers
ActiveUS20090002894A1Disposition/mounting of recording headsUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionSnubberActuator
Outer arm constrained layer dampers to improve actuator dynamics are disclosed. One embodiment provides a housing and disk pack mounted to the housing and having a plurality of disks that are rotatable relative to the housing. In addition, an actuator is coupled to the housing, the actuator having a plurality of suspensions arms for reaching over the plurality of disks. A first damper is coupled with an outside (or inside) portion of a top outside suspension arm of the plurality of suspensions arms. In addition, a second damper is coupled with an outside (or inside) portion of a bottom suspension arm of the plurality of suspensions arms. In so doing, vibration modes involving deformation of the top suspension arm and the bottom suspension arm are damped.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Symmetrically tapered constrained layer damper for a flex cable assembly for a hard disk drive
ActiveUS8228639B2Undesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionRecord information storageHard disc driveData signal
A flex cable assembly for a head stack assembly of a hard disk drive comprises a flex cable for conducting data signals from the head stack assembly to a connector. The flex cable has a dynamic loop section between a termination for the head stack assembly and the connector. The flex cable has a constrained layer damper for attenuating random transient vibration. The constrained layer damper has a symmetrically tapered shape for reducing stress concentration and is coupled with the dynamic loop section of the flex cable adjacent to an area of the flex cable configured for receiving a coupler for coupling the flex cable assembly with the head stack assembly.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
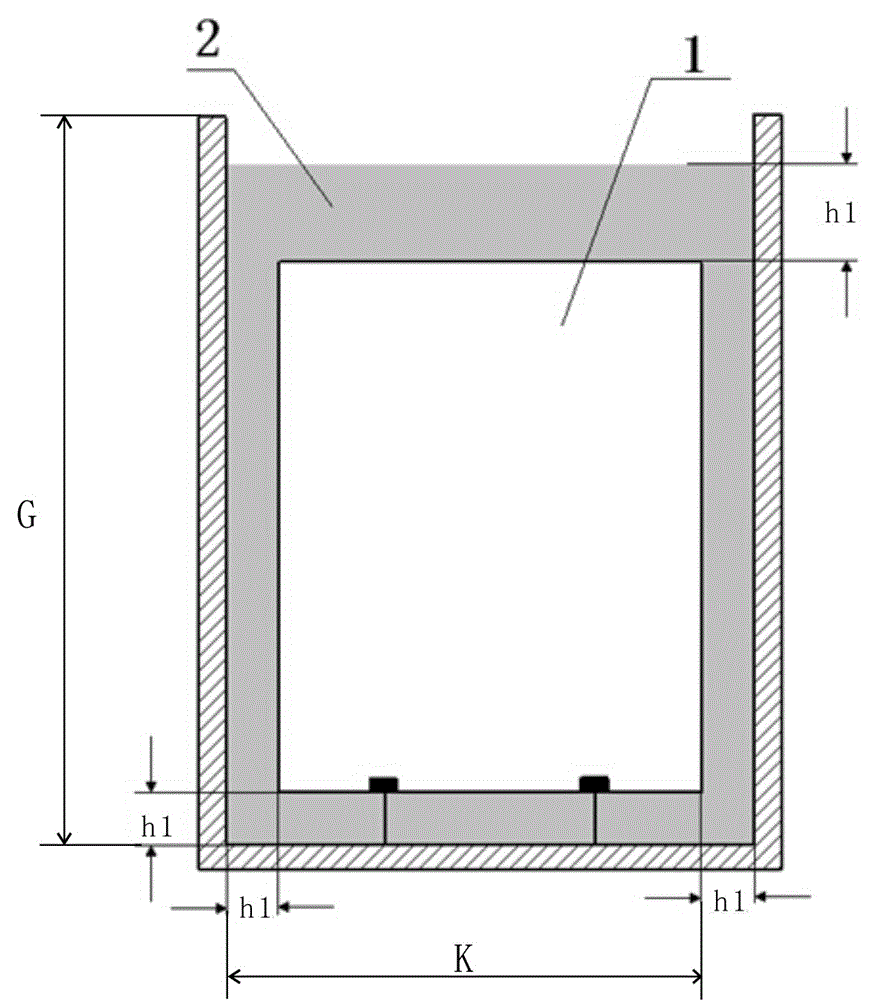
Manufacturing and damping enhancing method for pouring type active constrained damping structure
InactiveCN105041963ASimple control systemReduce difficultyRotating vibration suppressionVibration dampersAudio power amplifierControl system
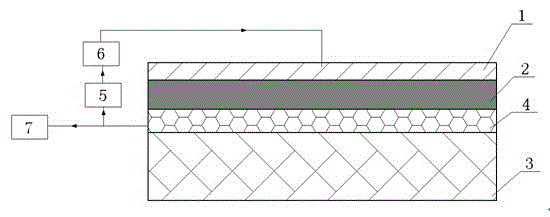
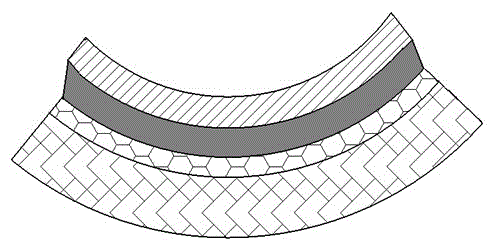
Disclosed is a manufacturing and damping enhancing method for a pouring type active constrained damping structure. The pouring type active constrained damping structure comprises actuating material layer (1), a damping material layer (2), a sensing material layer (4) and a controlled material layer (3). The actuating material layer and the sensing material layer are poured into a whole by the damping material layer by means of a U-shaped mold and then the active constrained damping structure is manufactured by sticking the controlled material layer. Damping of the active constrained damping structure is enhanced under the effects of a control module (5), an oscilloscope (6) and an amplifier (7). No matter whether the controlled material layer is in the compressed state or the stretched state, the damping material layer can generate the larger shearing deformation amount; the shearing deformation amount can further increase energy dissipation of the damping material layer and enhance the damping effect; the active constrained layer damping structure is simple, and the stability is good; and the corresponding control system is simple, molding can be achieved through pouring at a time, and the damping effect is obvious.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Design method for sensitive restraint layer damping plate structural modal state observer
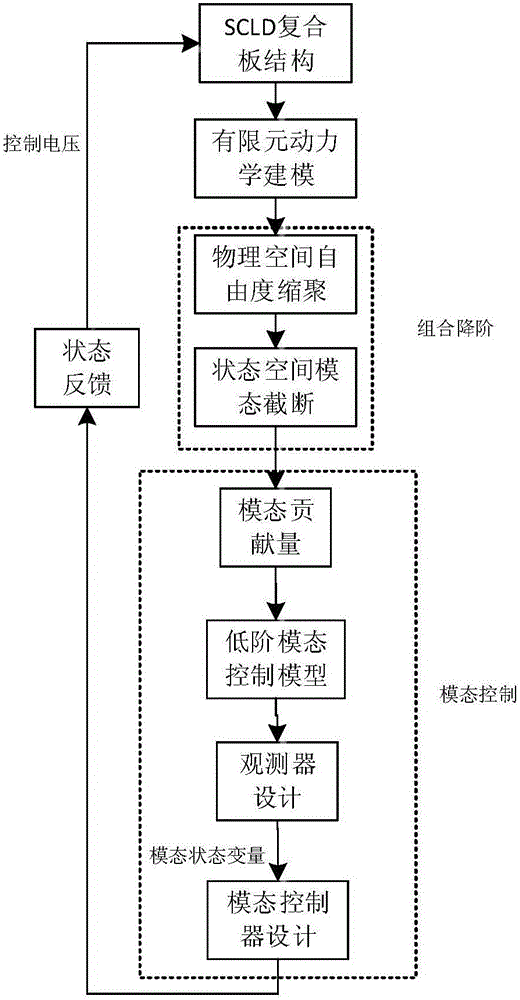
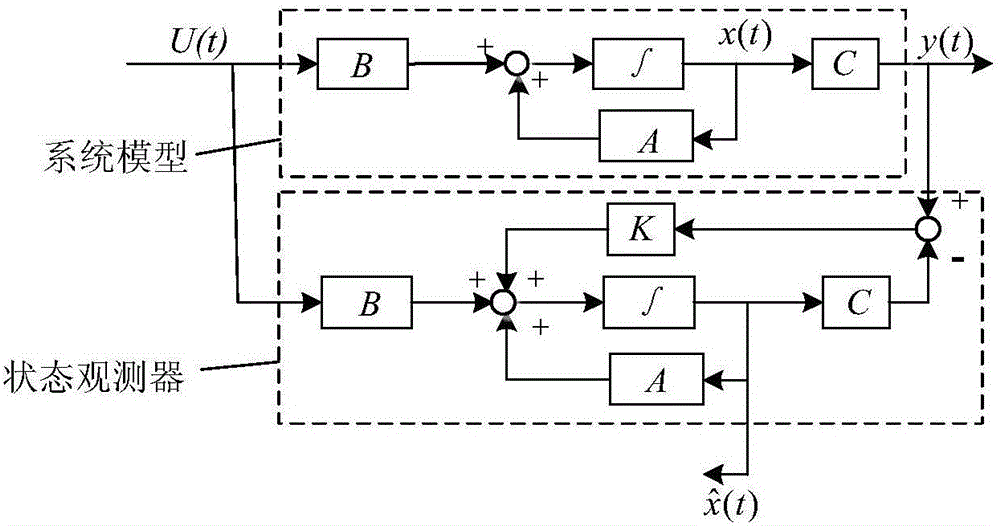
InactiveCN105956213AEasy to observeObserver design is easyDesign optimisation/simulationCAD circuit designPhysical spaceResearch Object
The invention relates to a design method for sensitive restraint layer damping plate structural modal state observer, and belongs to the technical field of modal control. The design method includes the following steps: S1, establishing a structural dynamical model of a sensitive restraint layer damping plate structure; S2, writing out a state equation of a system, and performing combination and dimensionality reduction on a physical space and a state space; S3, achieving mapping from a complex number space to a real number space to obtain a lower dimension real modal control model; S4, selecting a main control mode of a research object through the modal rate of contribution; S5, determining the structure of the sensitive restraint layer damping plate structural modal state observer; and S6, solving a feedback gain matrix of the sensitive restraint layer damping plate structural modal state observer through a pole assignment method. The method can be applied to design of the sensitive restraint layer damping plate structural vibration modal state observer, can observe modal state variation of the sensitive restraint layer damping plate structure during vibration, is simple in principle, is easy to implement, and has high application value.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
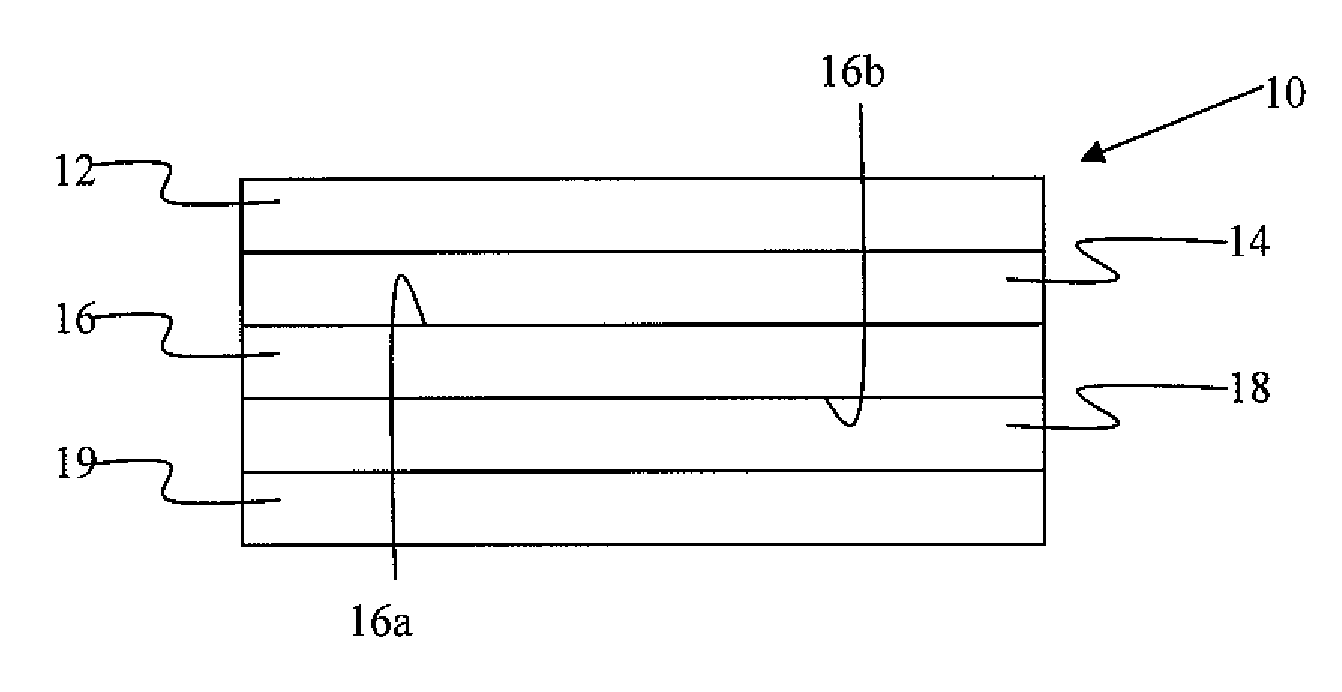
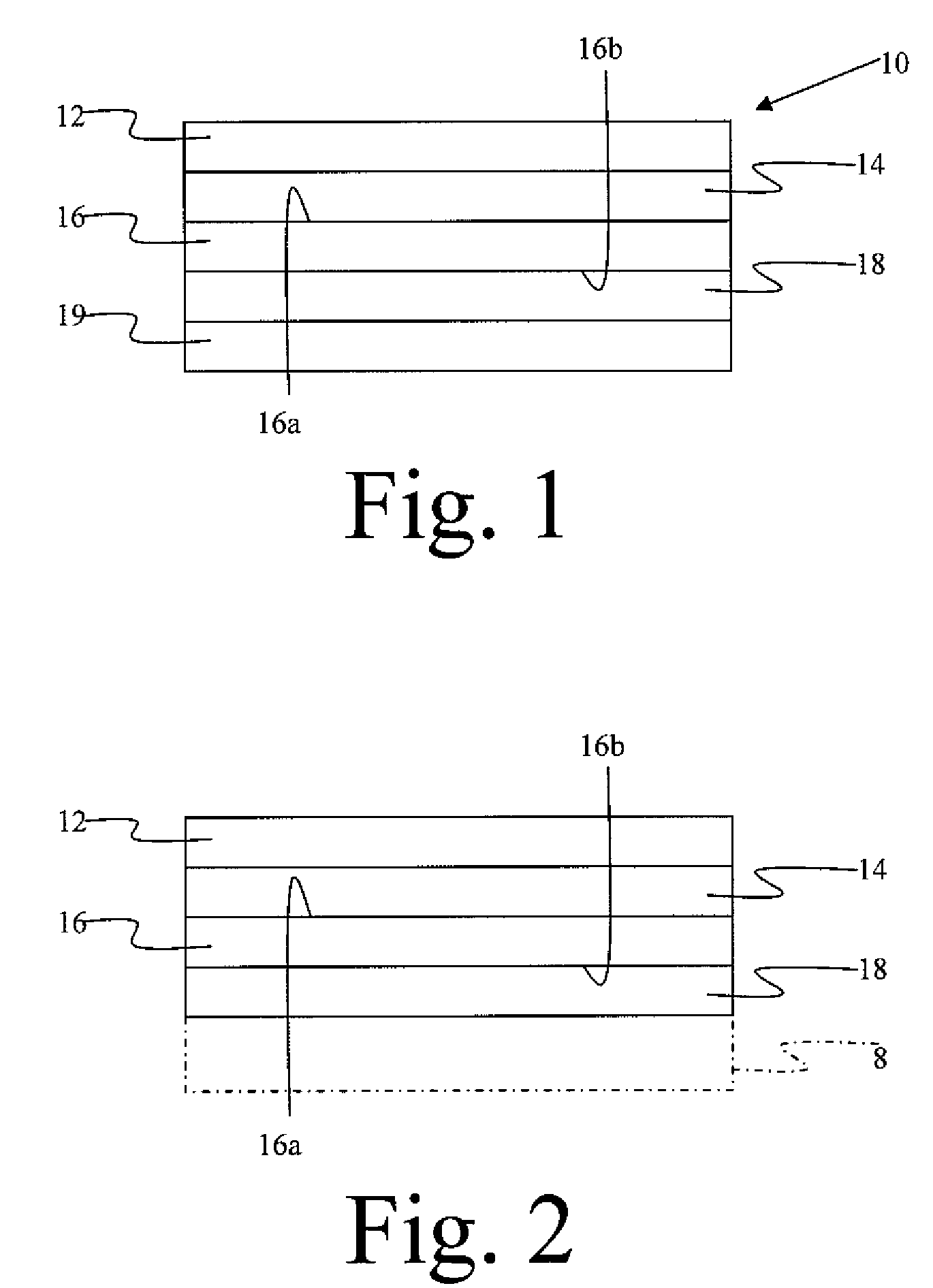
Constrained layer damper, and related methods
A constrained layer damper having a multilayer damping material is provided, as are related methods for making and using the damper. The constrained layer damper features a constraining layer, a carrier layer, a release liner, a viscoelastic layer interposed between the constraining layer and a first surface of the carrier layer, and a silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive interposed between the release liner and a second surface of the carrier layer. The silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive has sufficient tackiness at room temperature to adhere the constrained layer damper, with the release liner removed, to a substrate, such as a metallic substrate. The constrained layer damper has a peak damping temperature value in a range of about 50° C. to about 100° C.
Owner:MATERIALS SCI CORP
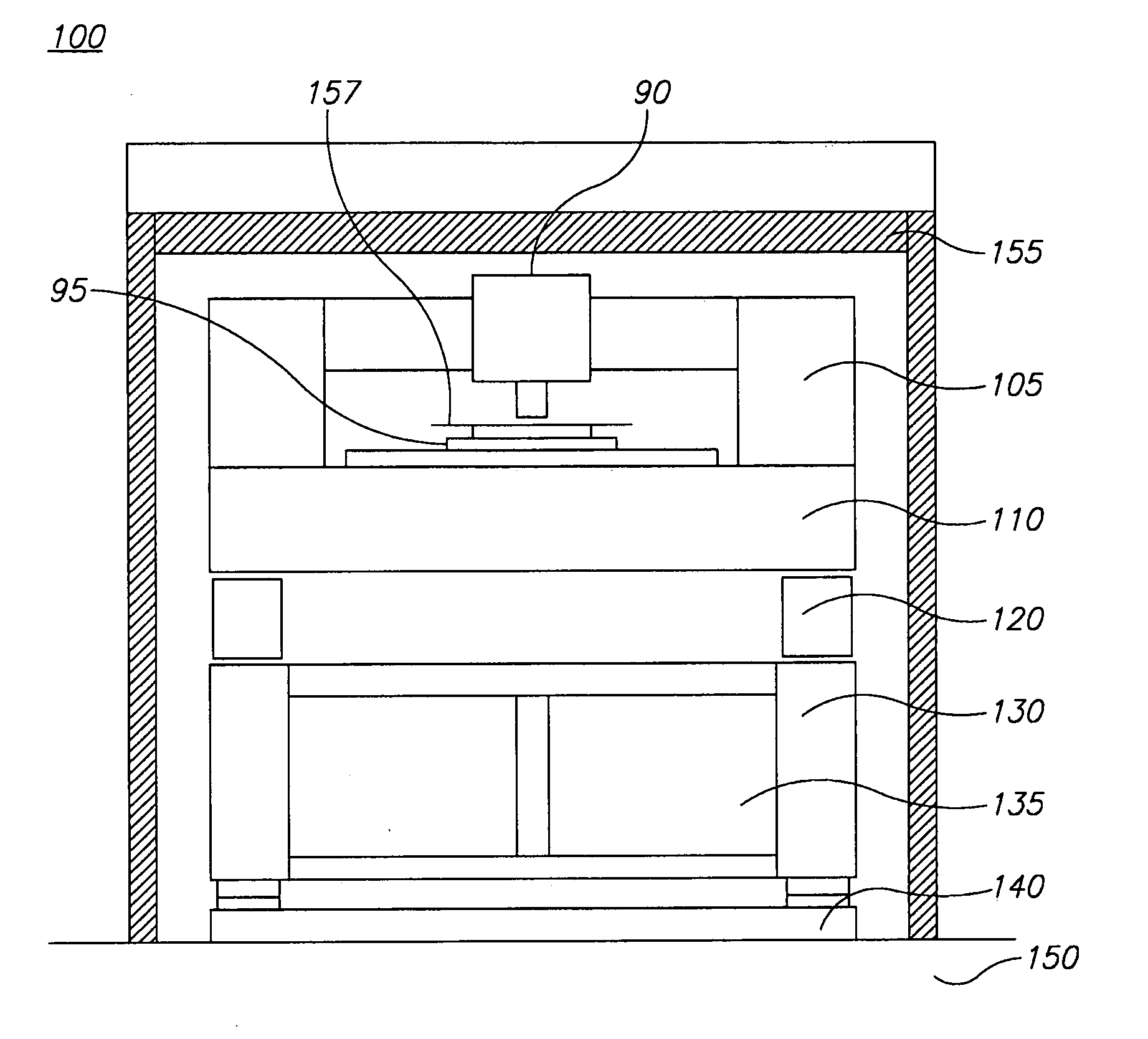
Metrology target indentification, design and verification
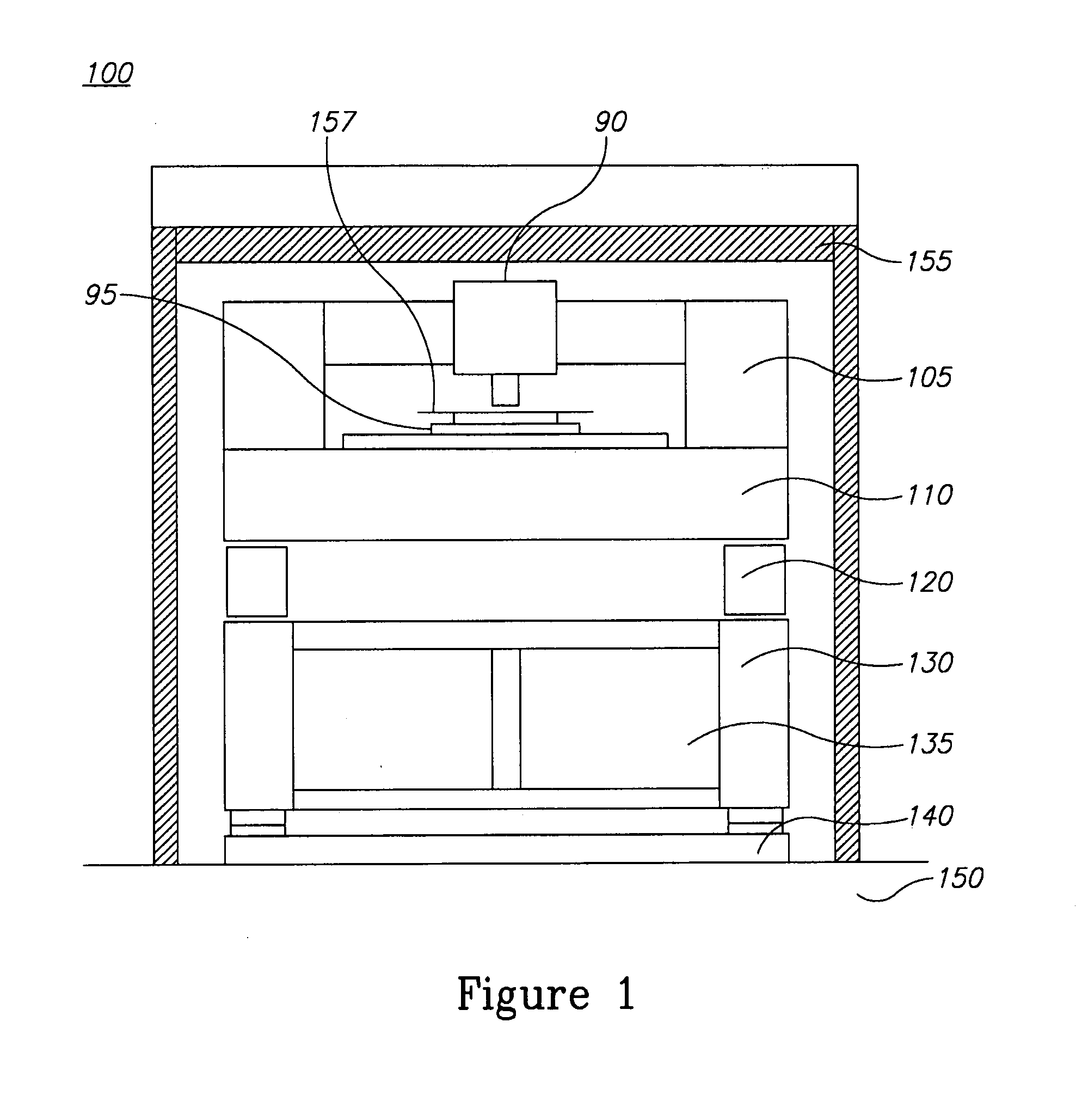
Metrology tools are provided, which comprise both active and passive vibration isolation devices, passive or active isolation systems such as constrained layer dampers, particle impact dampers or liquid impact dampers, and / or noise cancellation transducers, combined in different supporting structures of the metrology tool to dampen and reduce vibrations at a wide range of frequencies and intensities, and to which frequency range spectral analysis and optimization may be applied to determine specific tool configurations according to the provided principles.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
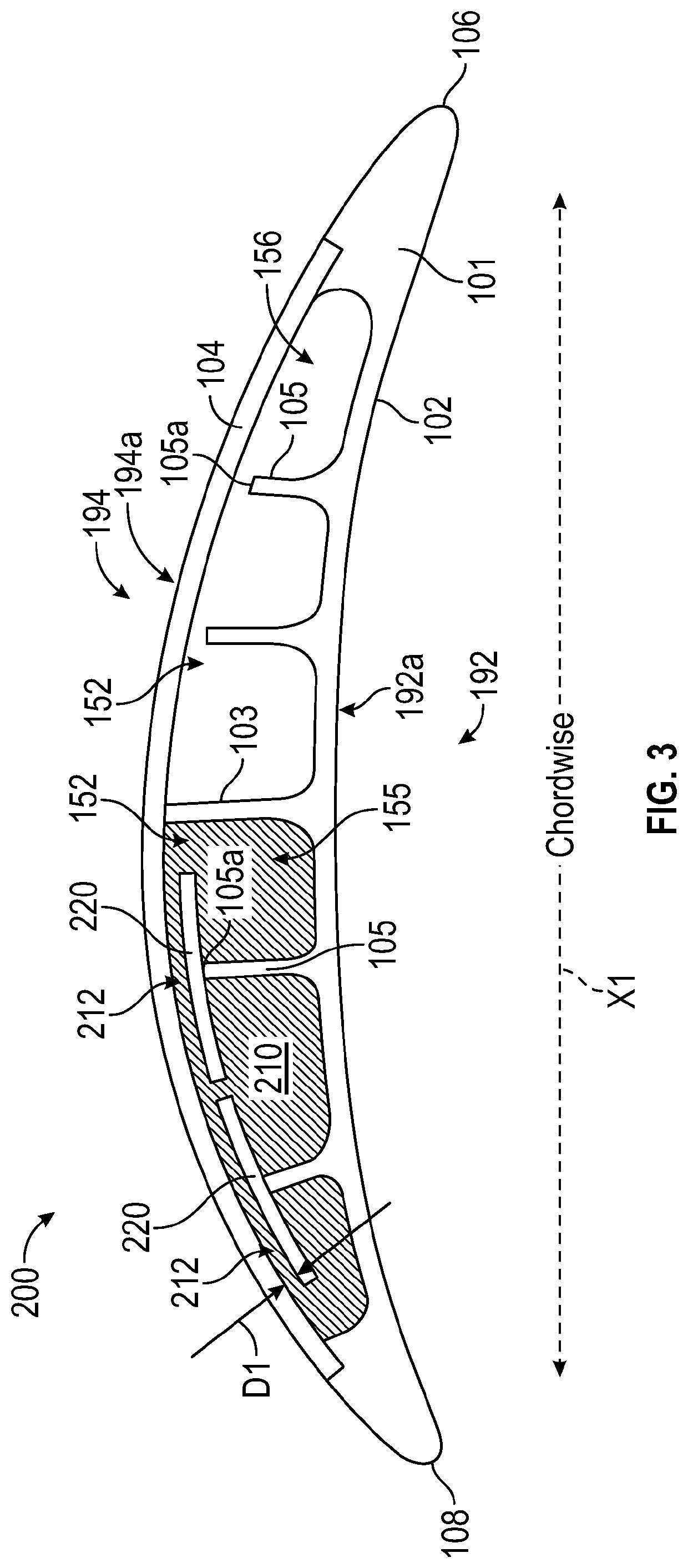
Hollow fan blade constrained layer damper
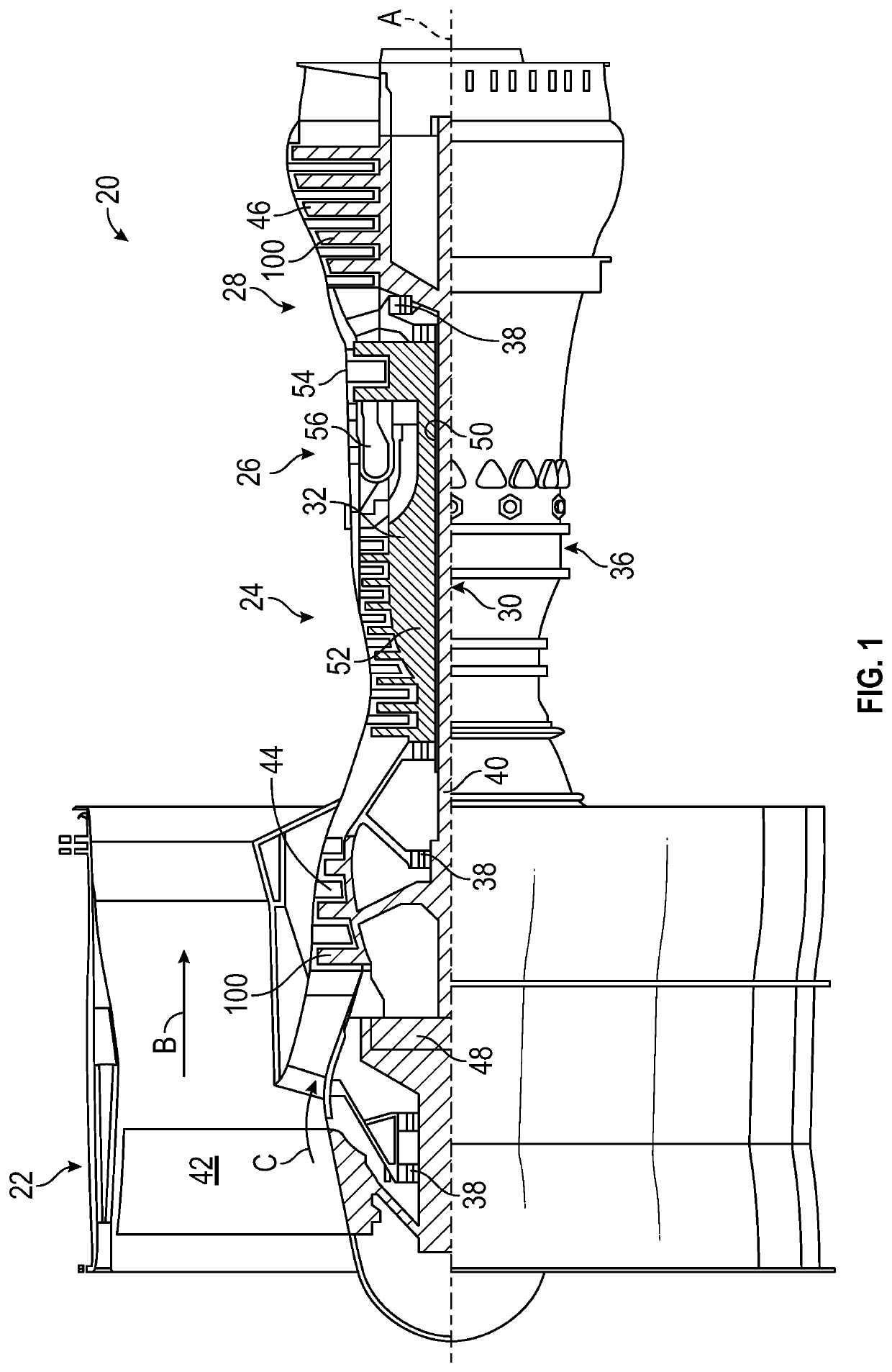
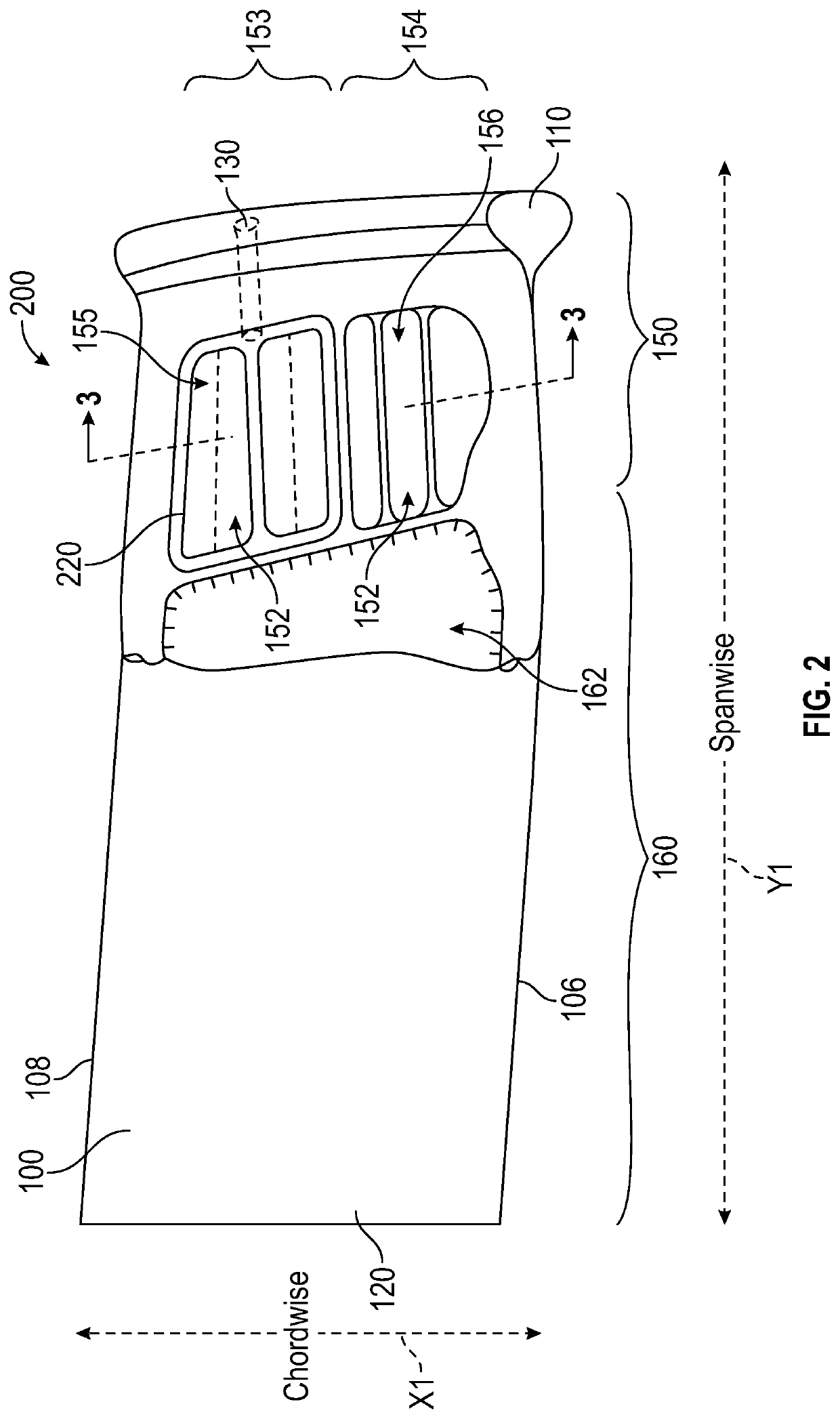
A fan blade having a damping system is provided. The fan blade comprising: a fan blade body having one or more compartments within the fan blade body; a damping material located within at least one of the one or more compartments; one or more partial ribs originating at the fan blade body and extending into at least one of the one or more compartments, wherein each of the one or more partial ribs terminate at a distal end; and one or more damping plates, wherein each of the one or more damping plates are attached to a distal end of a partial rib, wherein the damping material is located between the damping plate and the fan blade body.
Owner:RTX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com