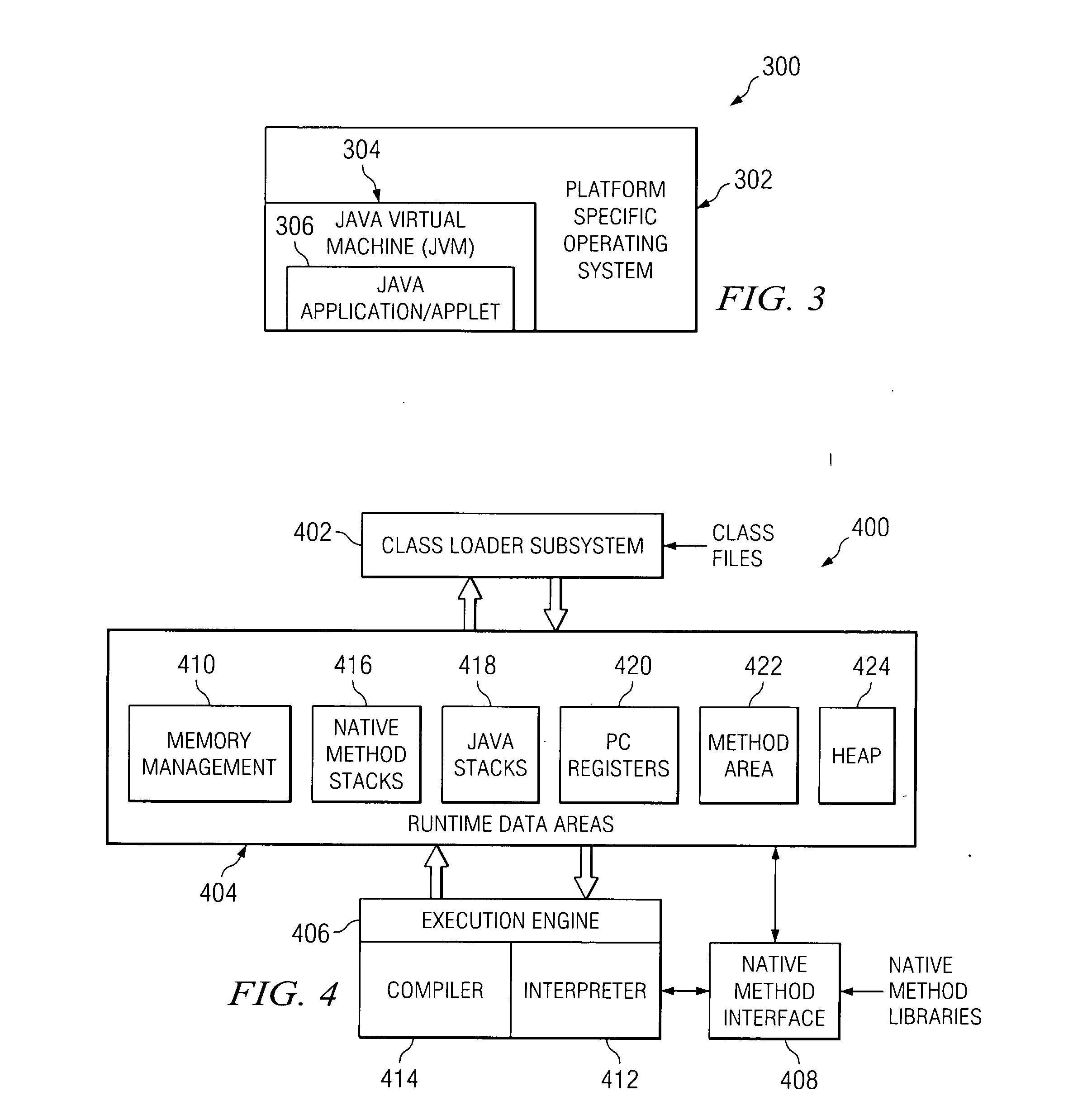
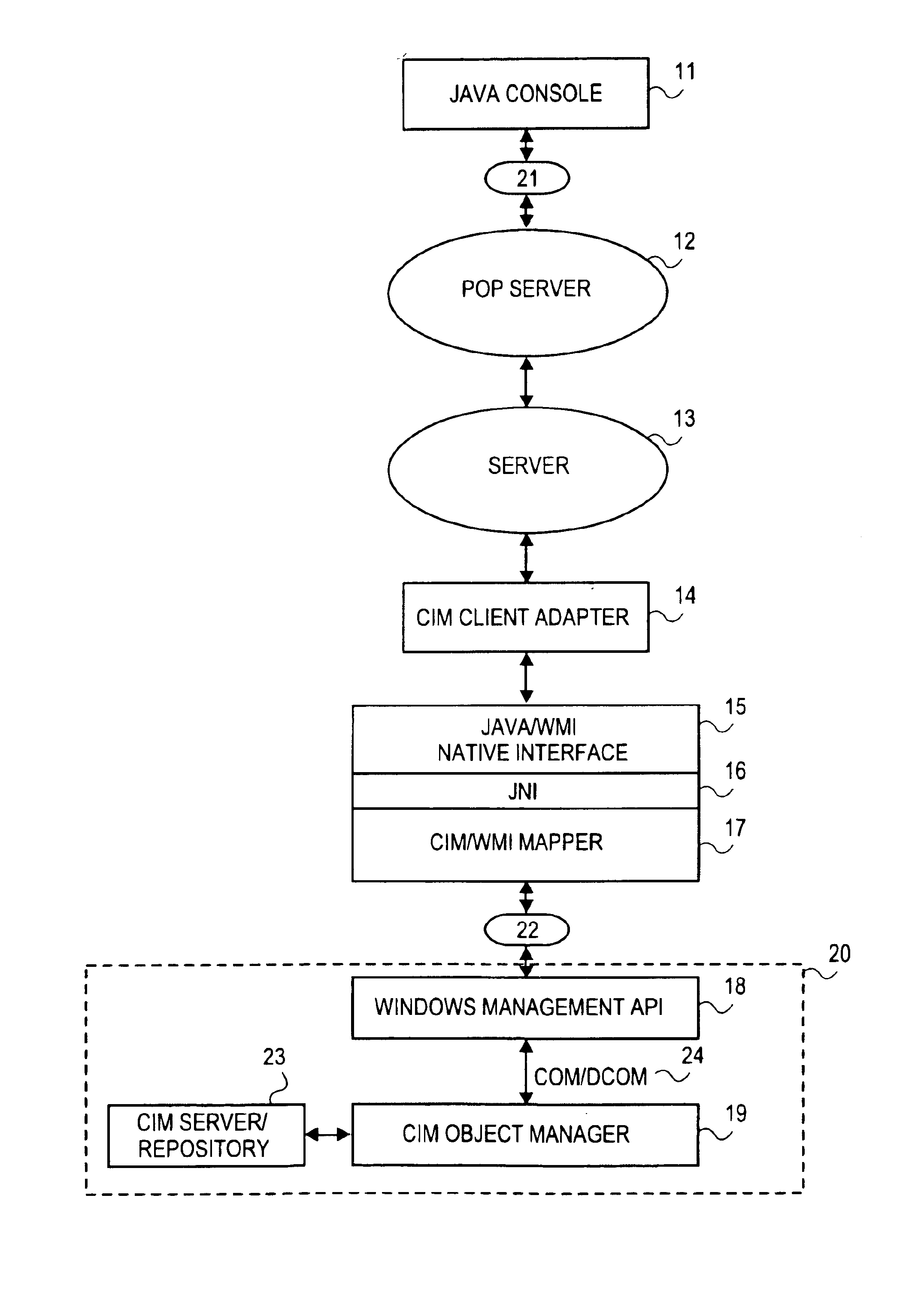
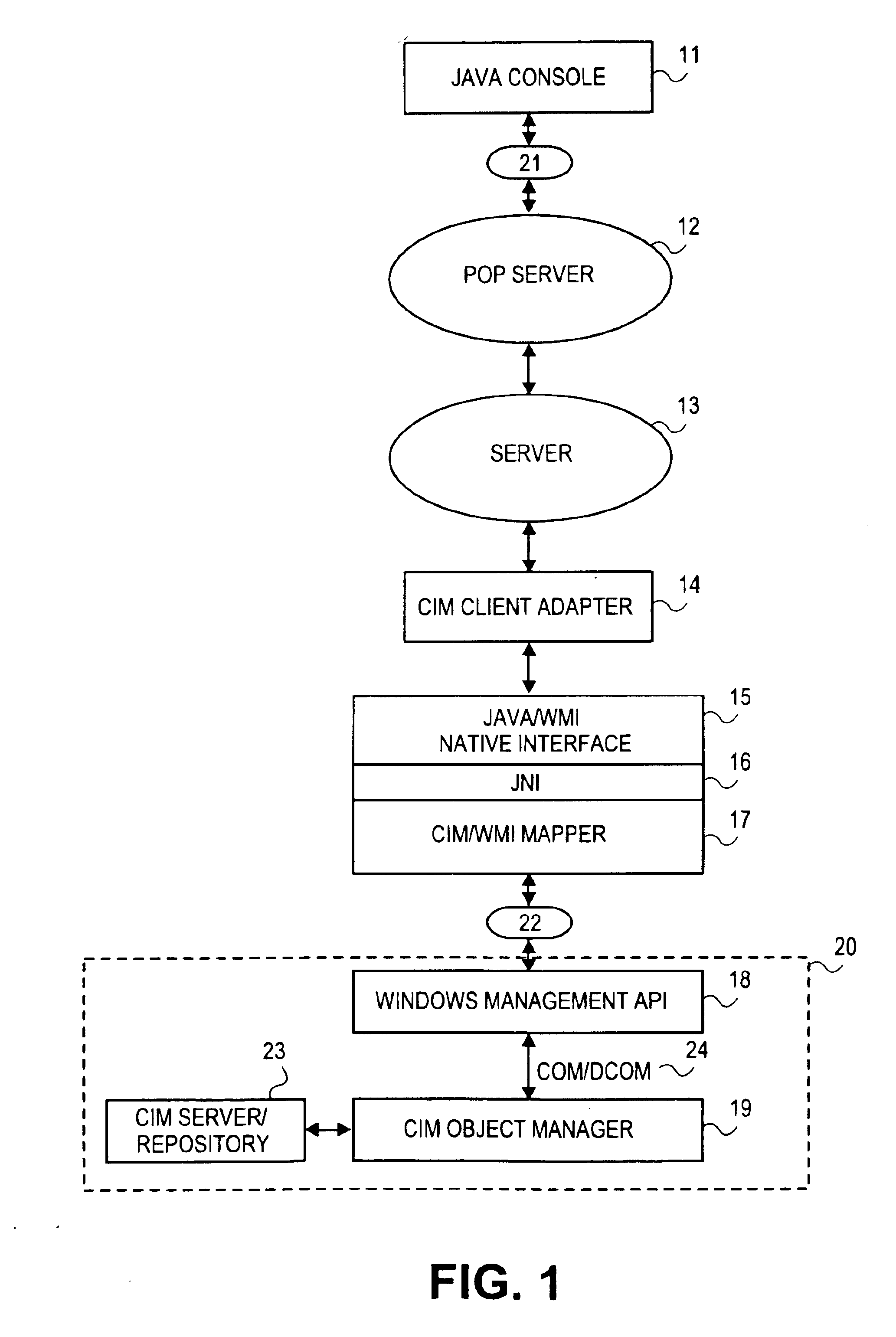
Patents
Literature
49 results about "Java Native Interface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
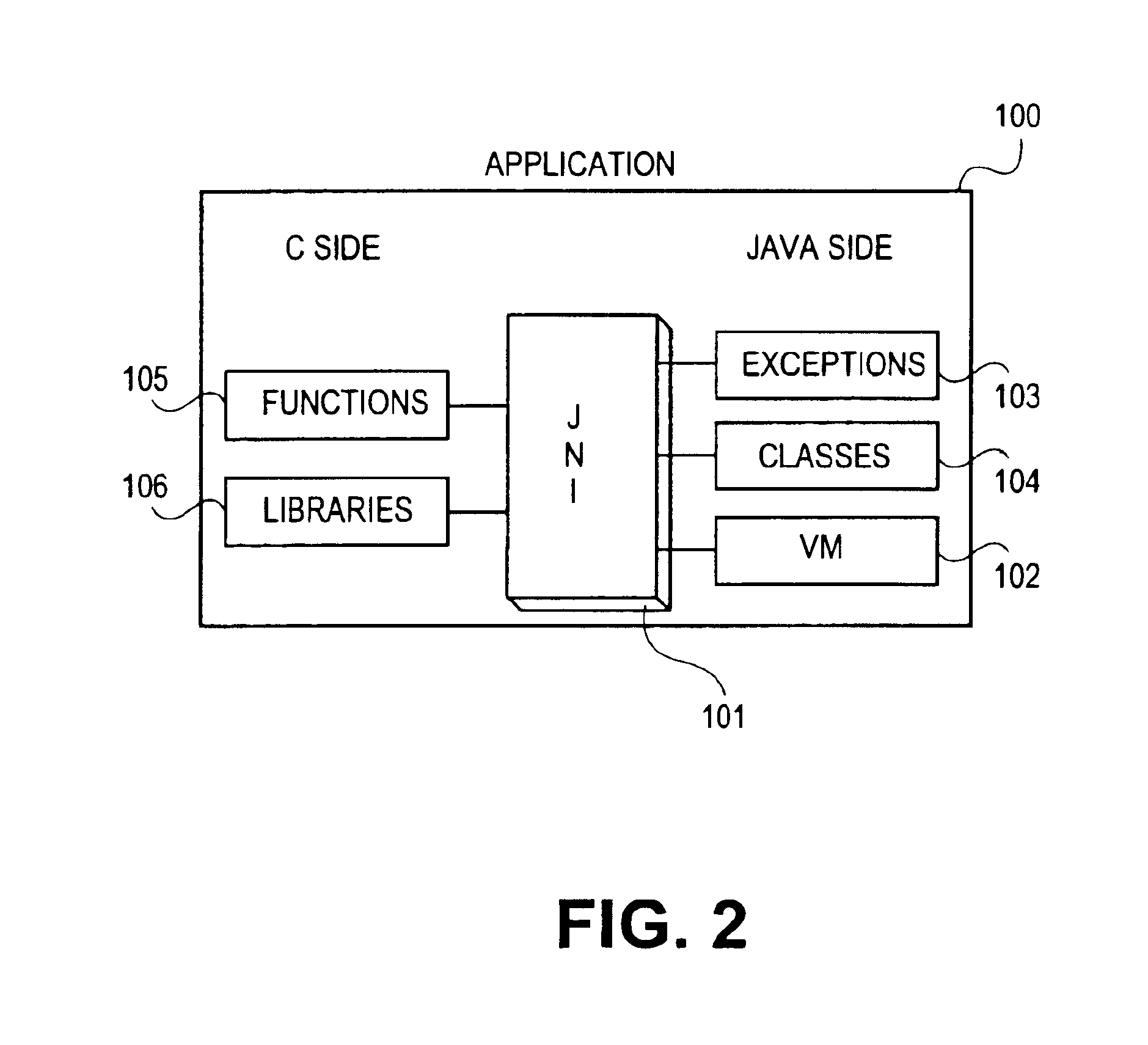
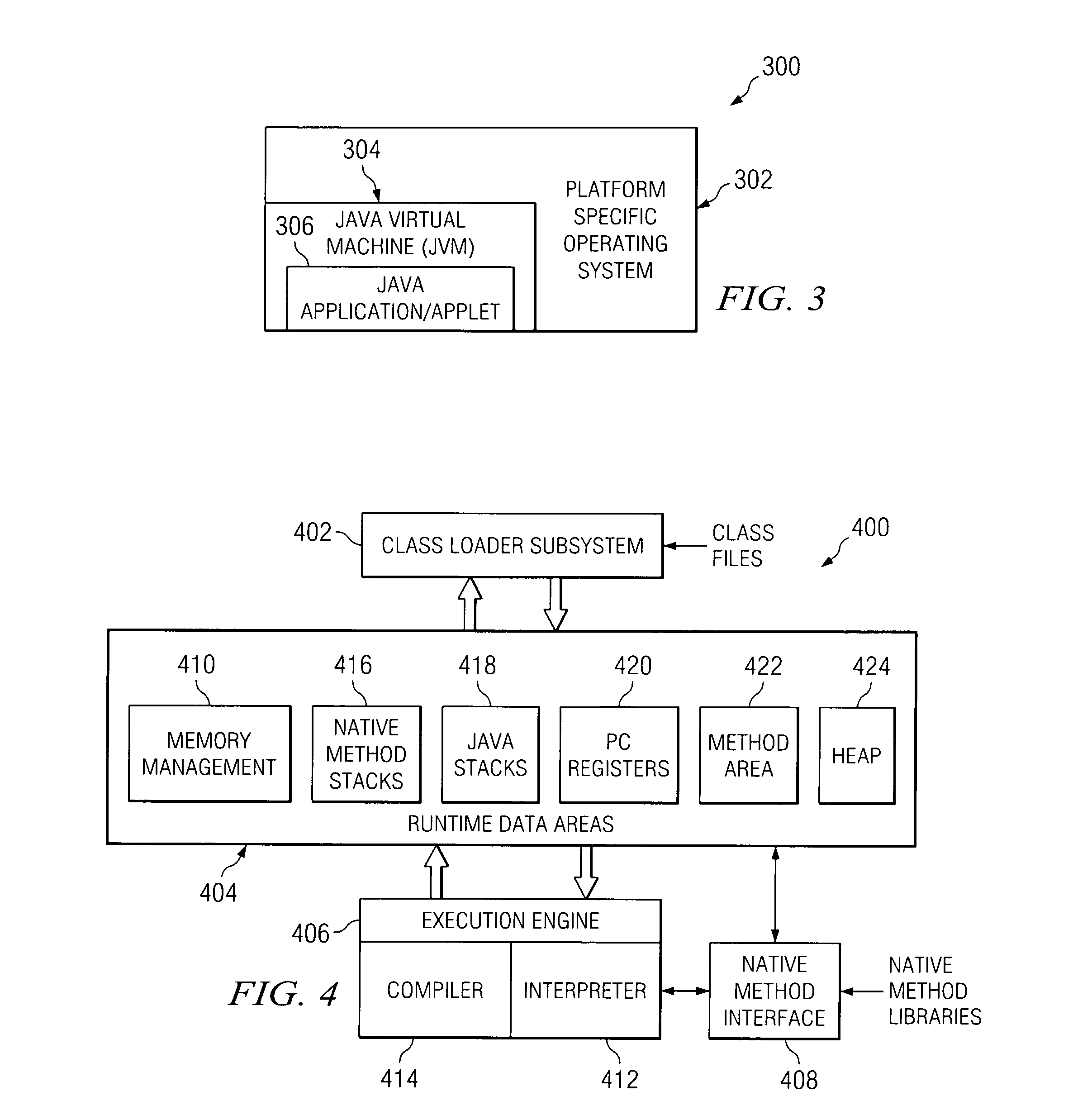
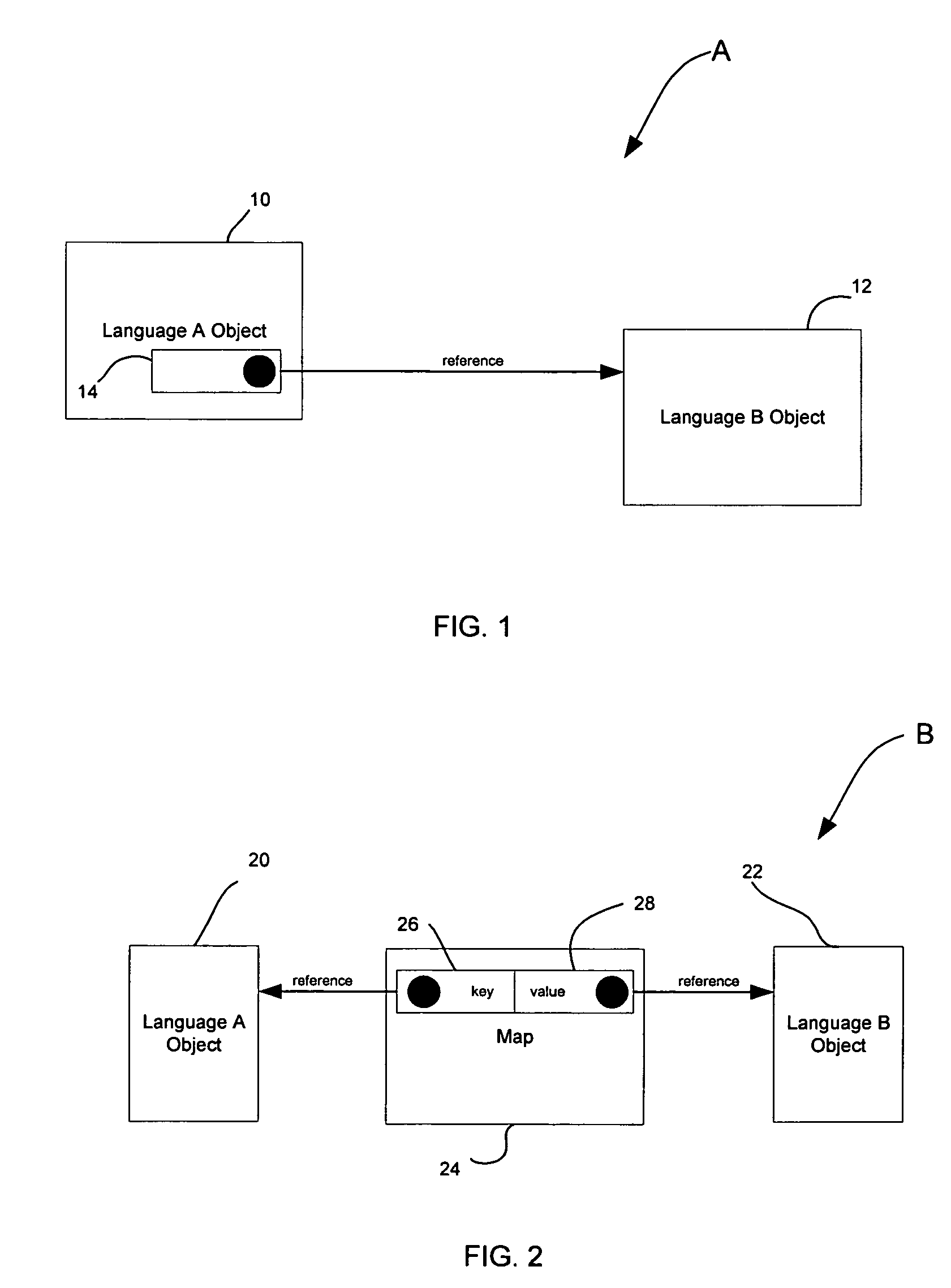
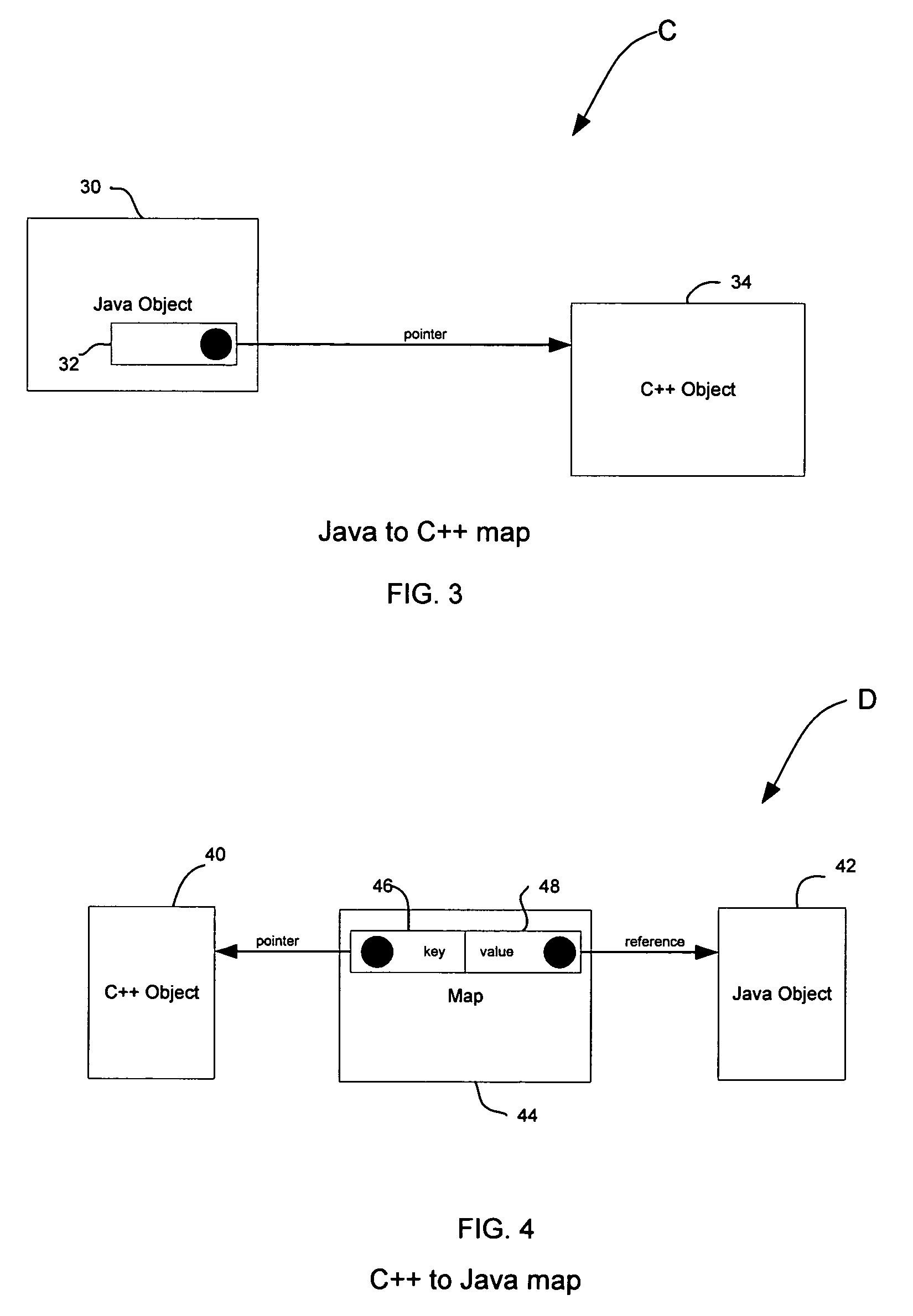
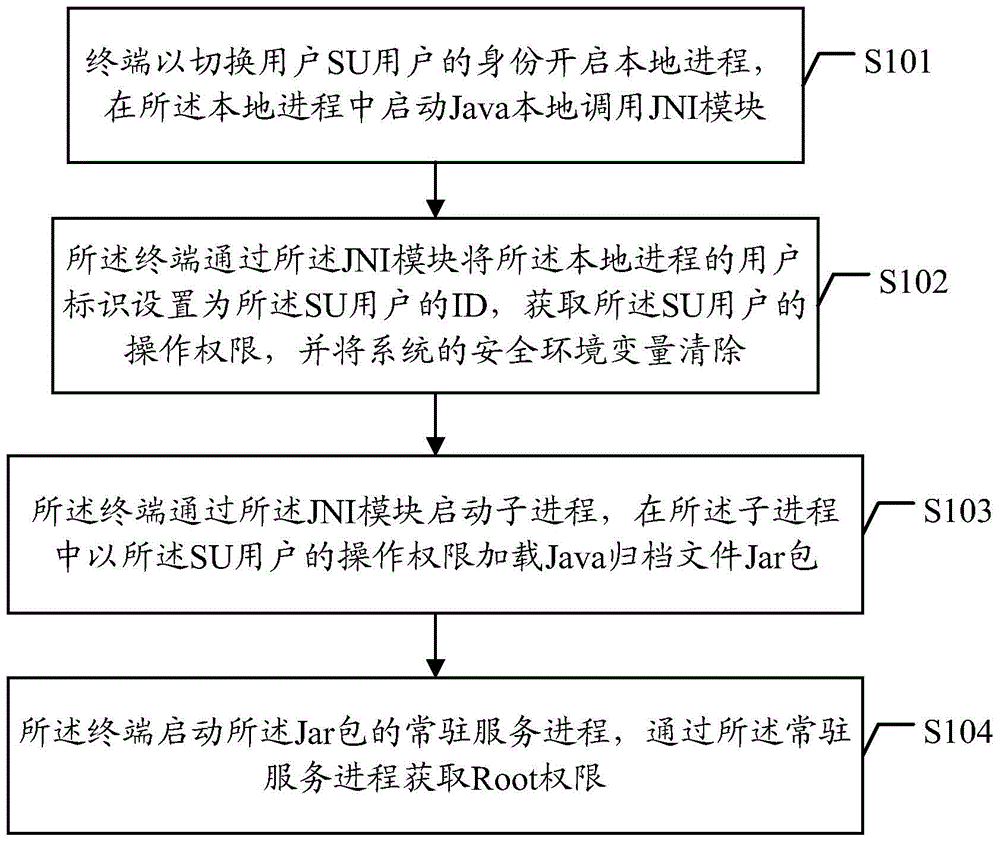
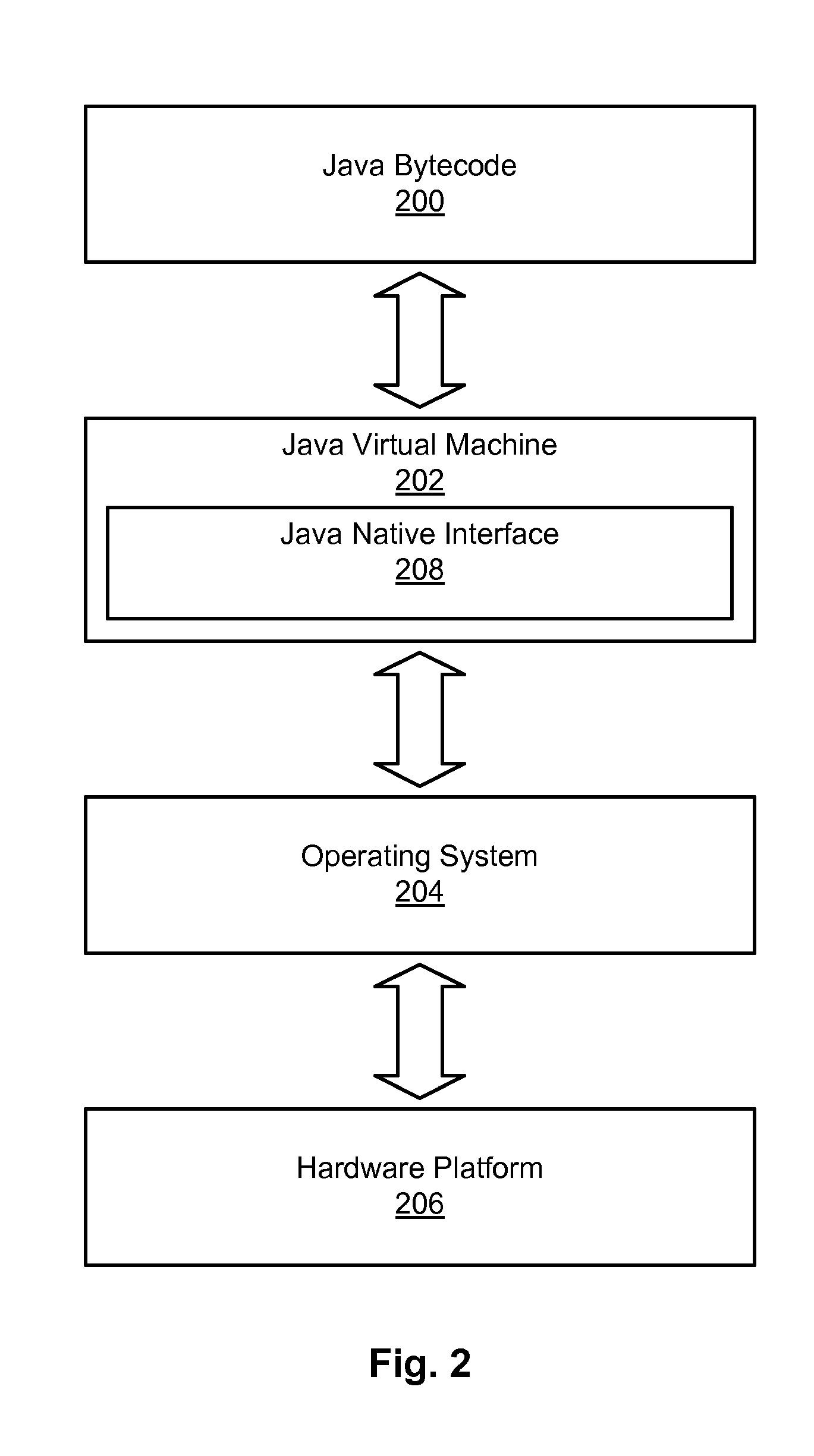
The Java Native Interface (JNI) is a foreign function interface programming framework that enables Java code running in a Java virtual machine (JVM) to call and be called by native applications (programs specific to a hardware and operating system platform) and libraries written in other languages such as C, C++ and assembly.
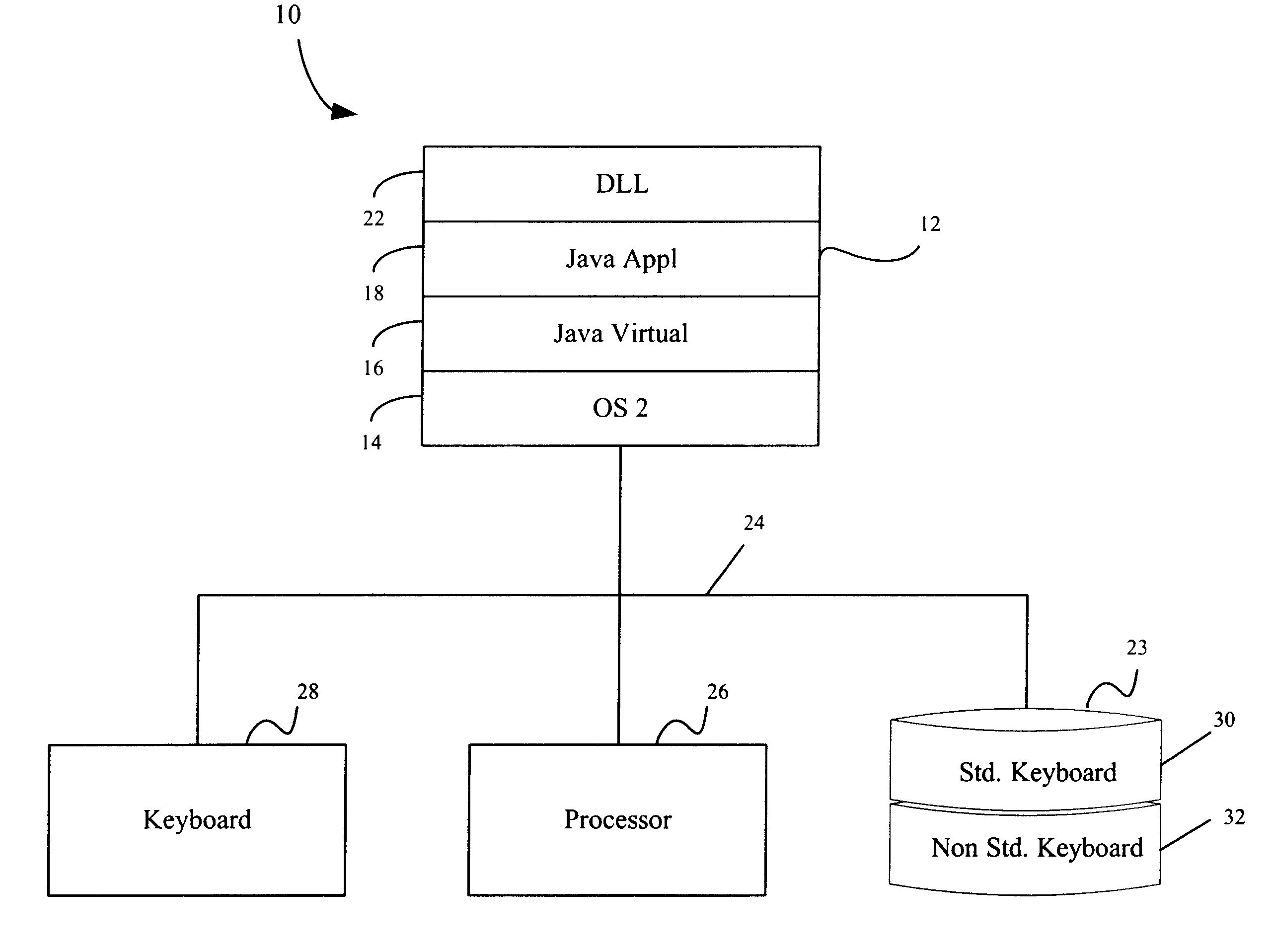
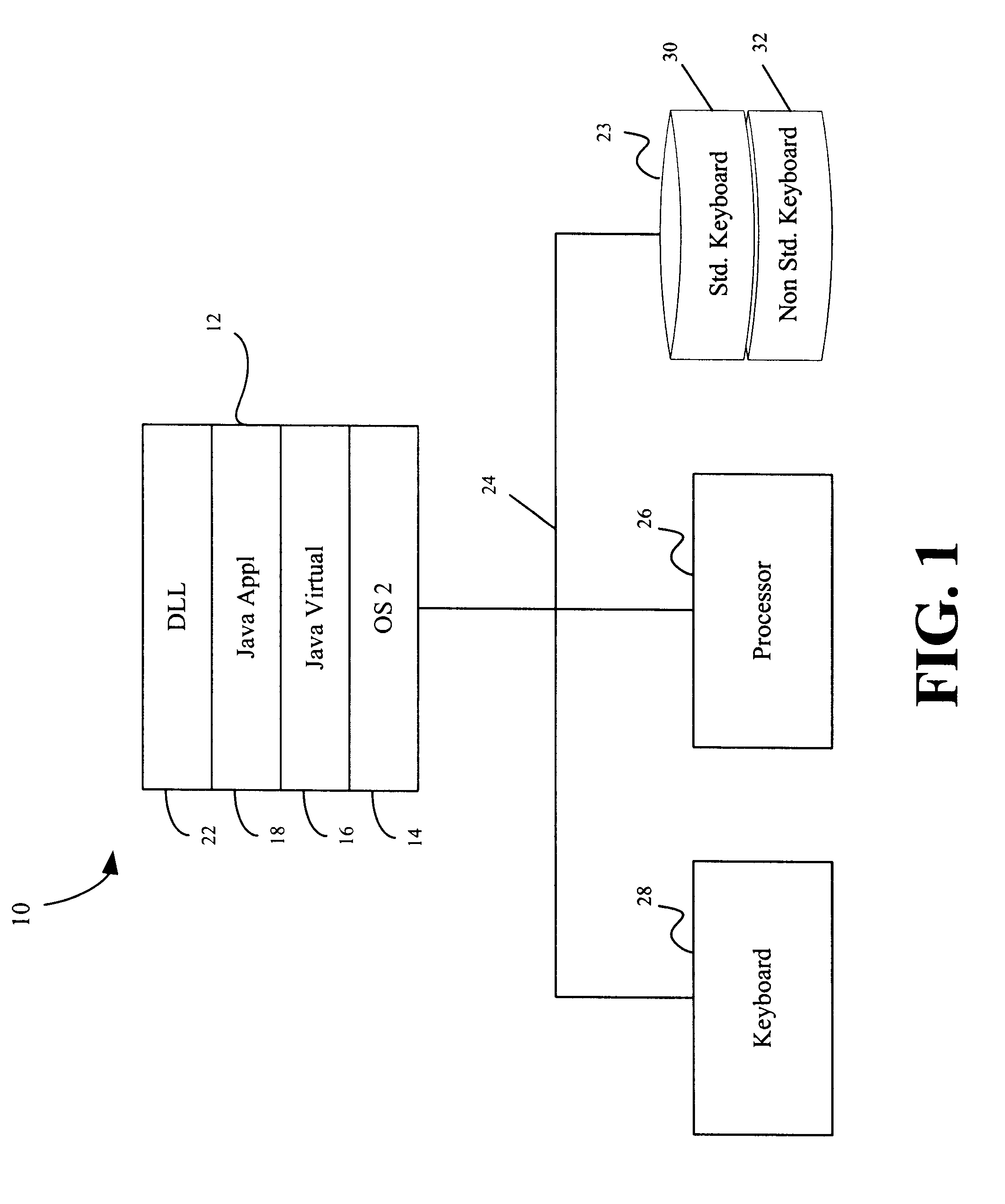
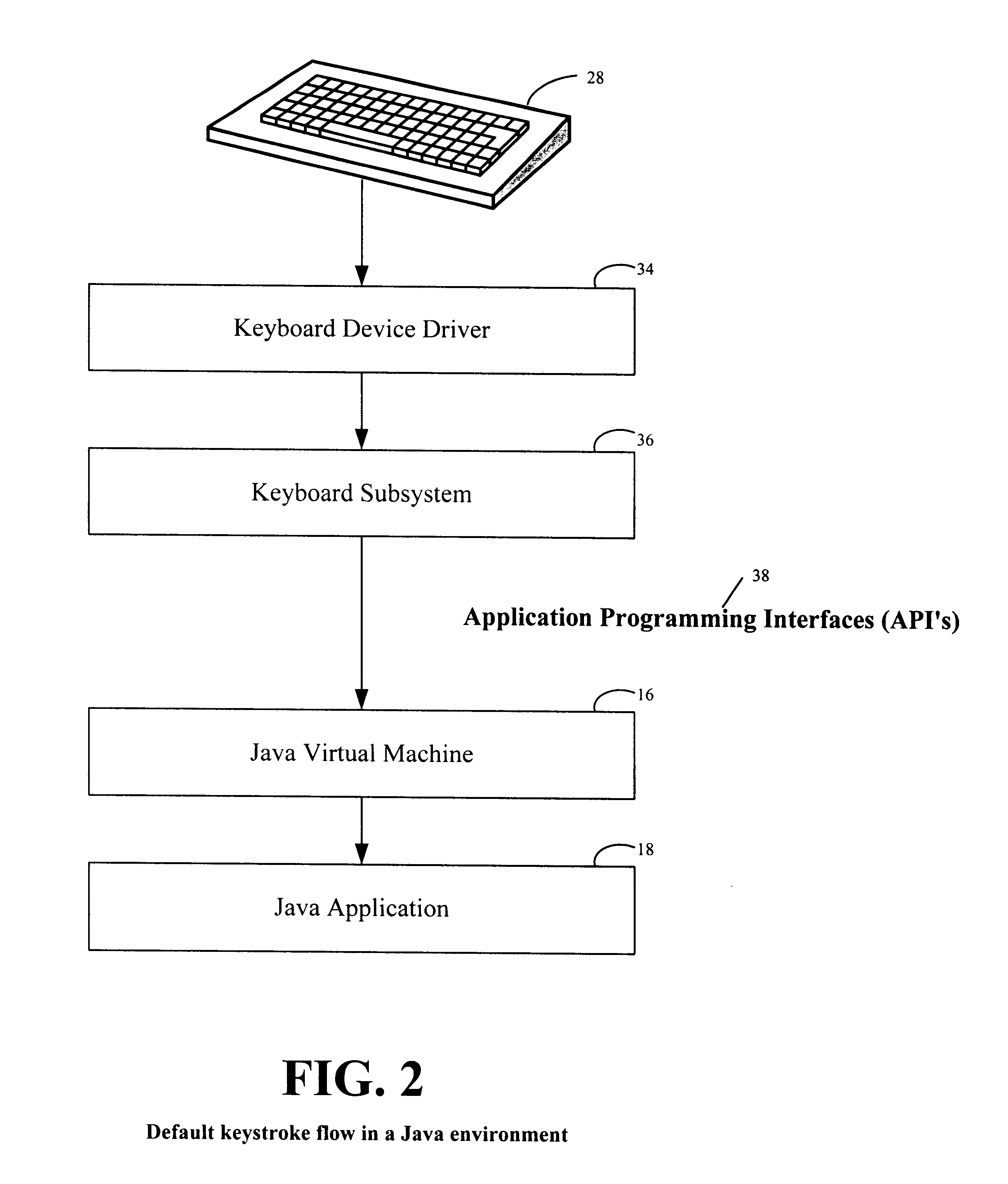
Extended keyboard support in a run time environment for keys not recognizable on standard or non-standard keyboards
InactiveUS6535931B1Easy to identifySimple methodInput/output processes for data processingProgramming languageProgram instruction
A keyboard is programmatically adapted to enable an application in a run time environment to distinguish operator keys (ALT / CTRL), not otherwise recognizable on a standard keyboard and special keys not otherwise recognizable on a non-standard keyboard by the application, when actuated. In one embodiment, a native Dynamic Link Library (DLL) is created in memory to capture the keystroke stream and maintain state information about the keyboard. A Java Native Interface (JNI) is created in the DLL and provided to a Java application. At initialization time, the Java application loads the native DLL with extended program instructions relating to key recognition in its static constructor. The Java application receives notification when an ALT or CTRL key is actuated. At that time the Java application calls the native DLL to receive the extended program instruction to determine whether the right or left ALT or CTRL key was actuated. The DLL programmatically determines whether the right or left ALT or CTRL key was struck. The DLL provides the Java application a flag that allows the application to determine if a "right" or a "left" (ALT / CTRL) key was actuated. On a non-standard keyboard, the Java application calls the native DLL to receive the necessary information on the key that was actuated. Again, the DLL programmatically provides a flag and extended keystroke data that allows the Java application to determine if a special key was actuated.
Owner:IBM CORP
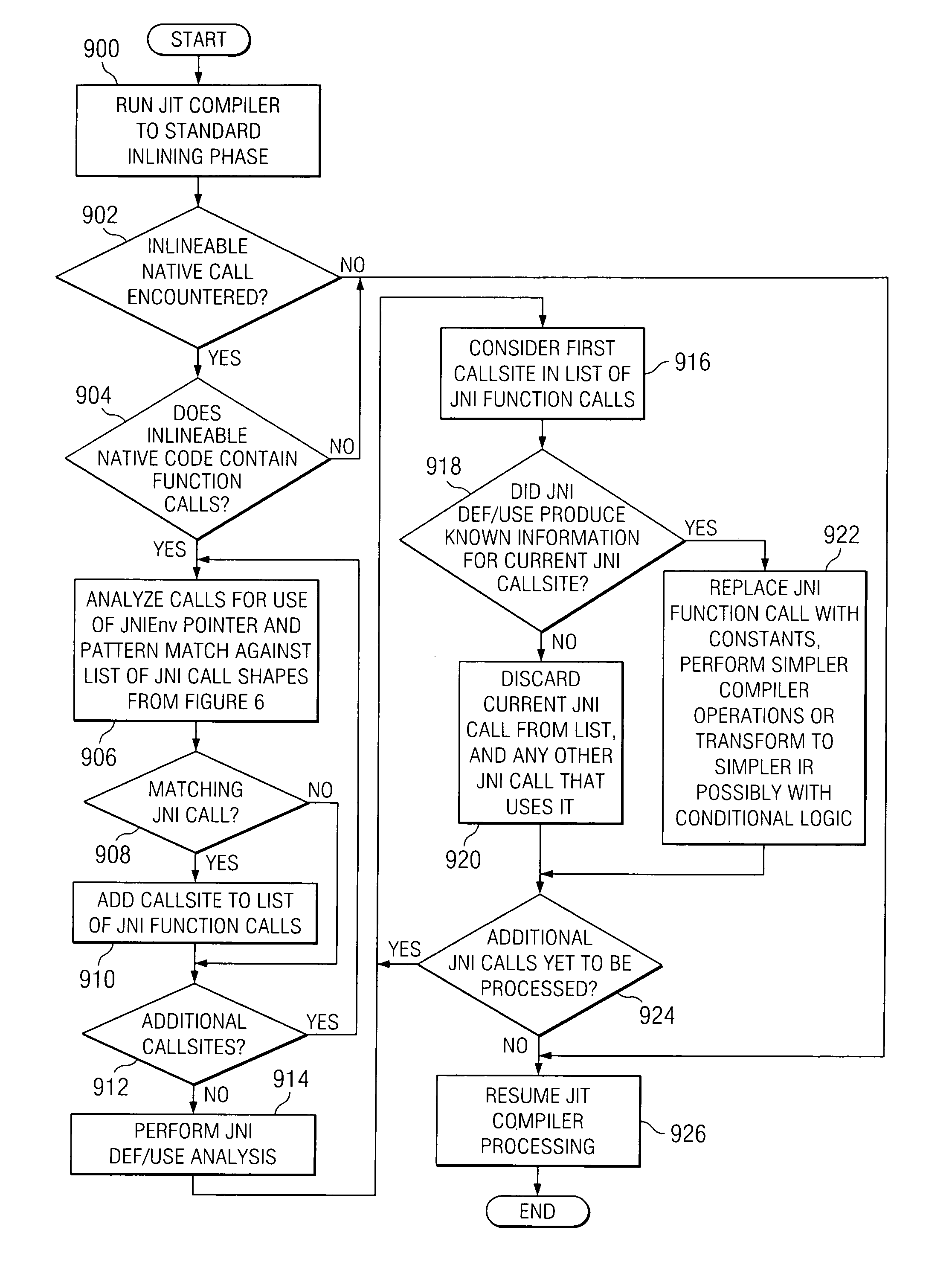
Method and apparatus for transforming Java native interface function calls into simpler operations during just-in-time compilation
InactiveUS20060190935A1Specific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsJust-in-time compilationIntermediate language
A method, apparatus, and computer instructions are provided for transforming Java Native Interface function calls to constants, internal just-in-time compiler operations or simpler intermediate representation. A compiler generates a plurality of intermediate representations for a plurality of native interface function calls. During inlining of native code, matching is performed on each native function call (against this list) and a list of native interface function calls is generated. For each native interface function call, a JIT call transformer attempts to replace the native interface function call with a constant, internal just-in-time compiler operation or a simpler intermediate representation depending on the type of native interface function call.
Owner:IBM CORP
Java common information model interface for windows management instrumentation via COM/DCOM
InactiveUS6854122B1Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsOperational systemWindows management instrumentation
A system and method are disclosed for utilizing a computer with a first operating system to access and perform operations on a second computer having a different operating system, using a web-based adapter routine. A Java console accesses a web based adapter routine to implement a set of Java based APIs to perform CIM operations. The adapter routine, in conjunction with a Java Native Interface and a CIM to WMI mapper enables CIM operations to be performed on a managed server having for example, a Microsoft Operating System or XML based communications.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for transforming Java Native Interface function calls into simpler operations during just-in-time compilation
InactiveUS7490320B2Software simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsJust-in-time compilationIntermediate language
A method and apparatus for transforming JAVA Native Interface function calls to constants, internal just-in-time (JIT) compiler operations or simpler intermediate representation. A compiler generates a plurality of intermediate representations for a plurality of native interface function calls. During inlining of native code, matching is performed on each native function call (against this list) and a list of native interface function calls is generated. For each native interface function call, a (JIT) call transformer attempts to replace the native interface function call with a constant, internal JIT compiler operation or a simpler intermediate representation depending on the type of native interface function call.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for preventing Java program from being decompiled
ActiveCN102043932AKeep it cross-platformGuaranteed versatilityProgram/content distribution protectionJava bytecodeJava virtual machine
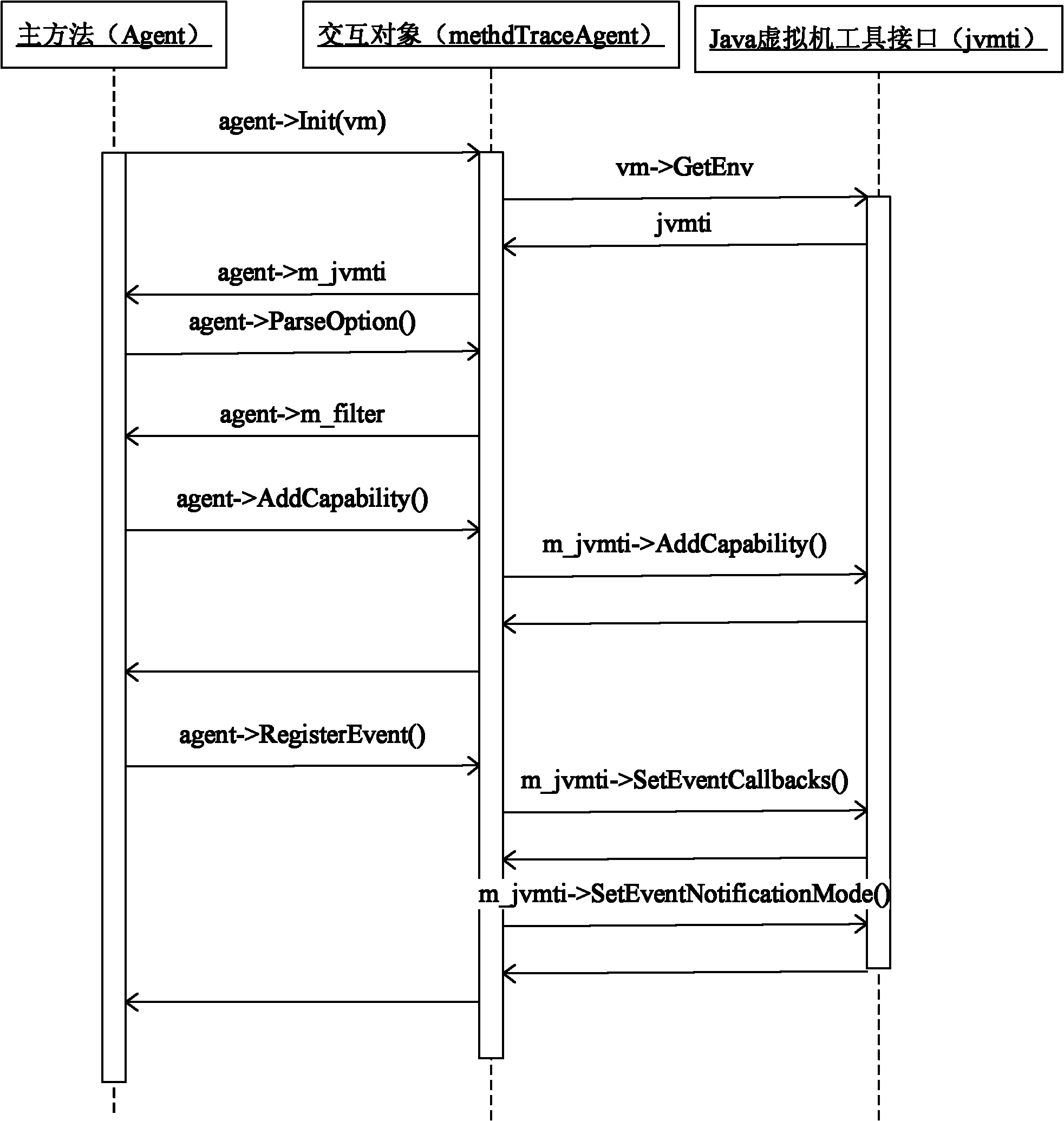
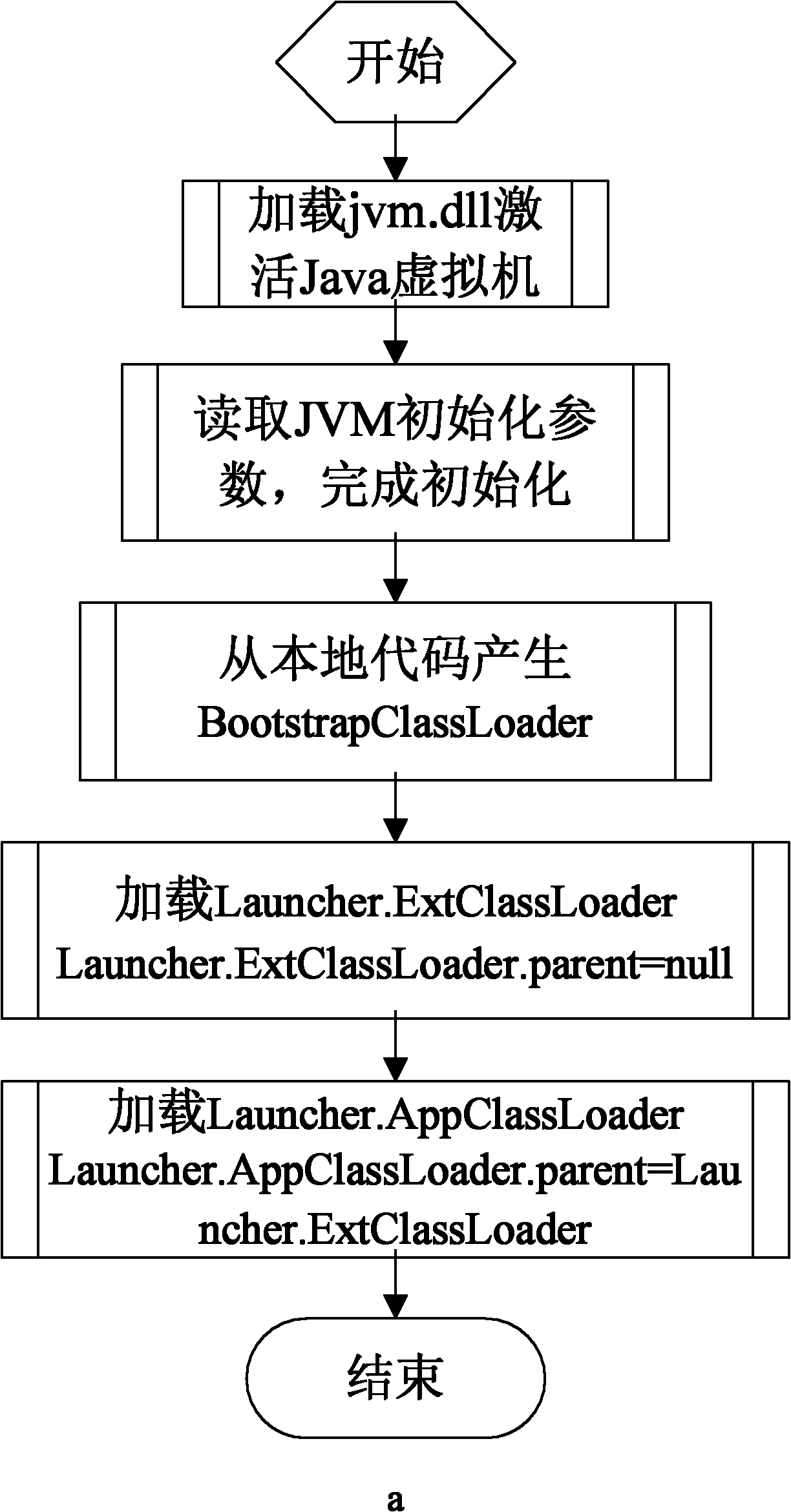
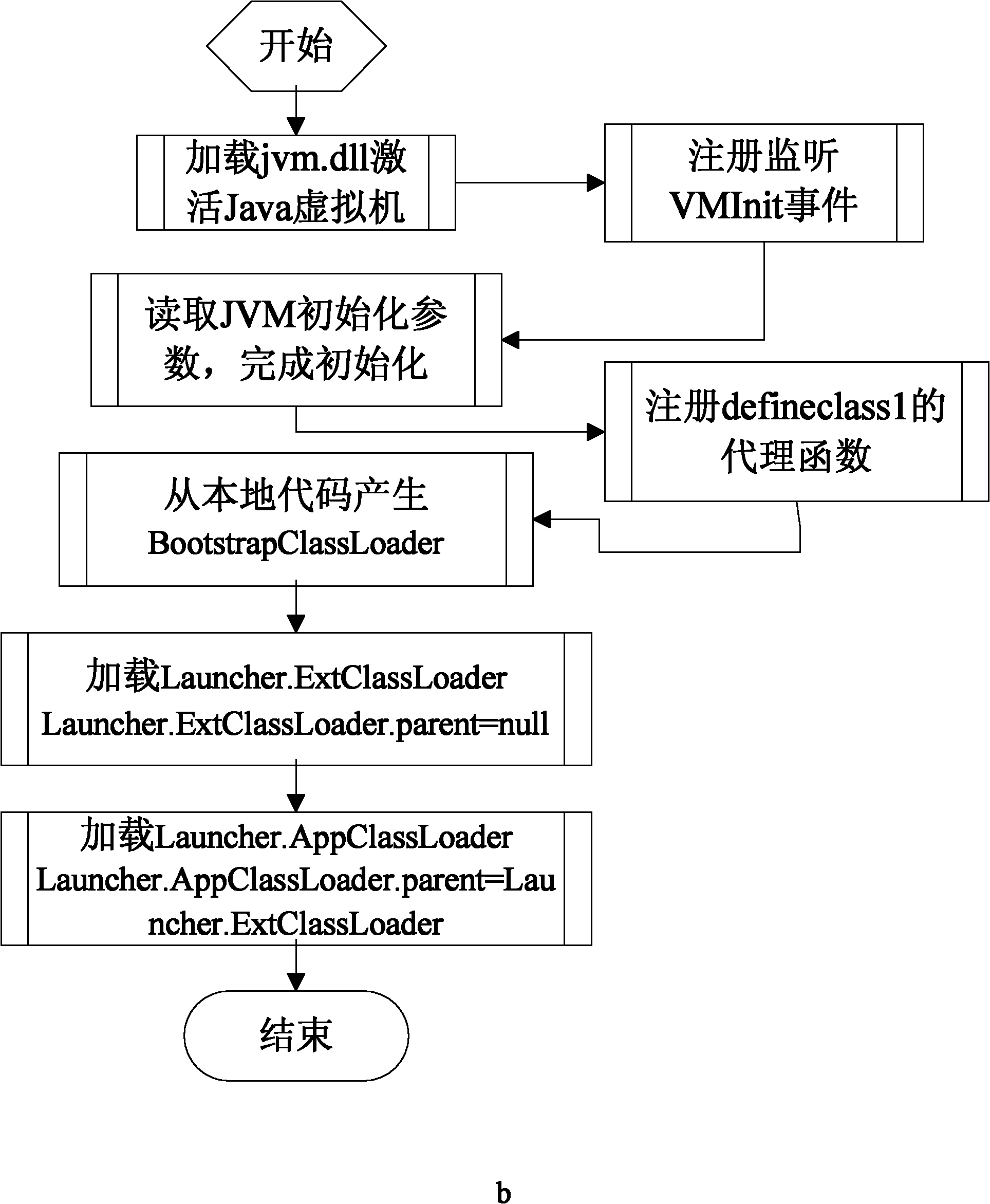
The invention relates to a method for preventing a Java program from being decompiled, which comprises the following steps: 1) encrypting a Java bytecode file to be issued; 2) using a Java virtual machine tool interface to monitor an initialization event of a Java virtual machine; 3) designating a Hook function for the initialization event of the Java virtual machine; 4) when the initialization of the Java virtual machine is finished, automatically calling the Hook function, and using a Java local interface in the Hook function to register a function called by the Java virtual machine for generating class objects as a self-defined agent function; 5) when the Java virtual machine generates a certain class object, calling the self-defined agent function, and decrypting the encrypted Java bytecode file in the self-defined agent function; and 6) generating a class object corresponding to the decrypted Java bytecode file, and returning to the Java virtual machine. The invention solves the technical problem of the limited application range of the method for preventing a Java bytecode file from being decompiled in the prior art, keeps the cross-platform characteristics of the Java program and maintains the universality of the Java virtual machine.
Owner:AVIC NO 631 RES INST
Universal serial device communication module based on Android system
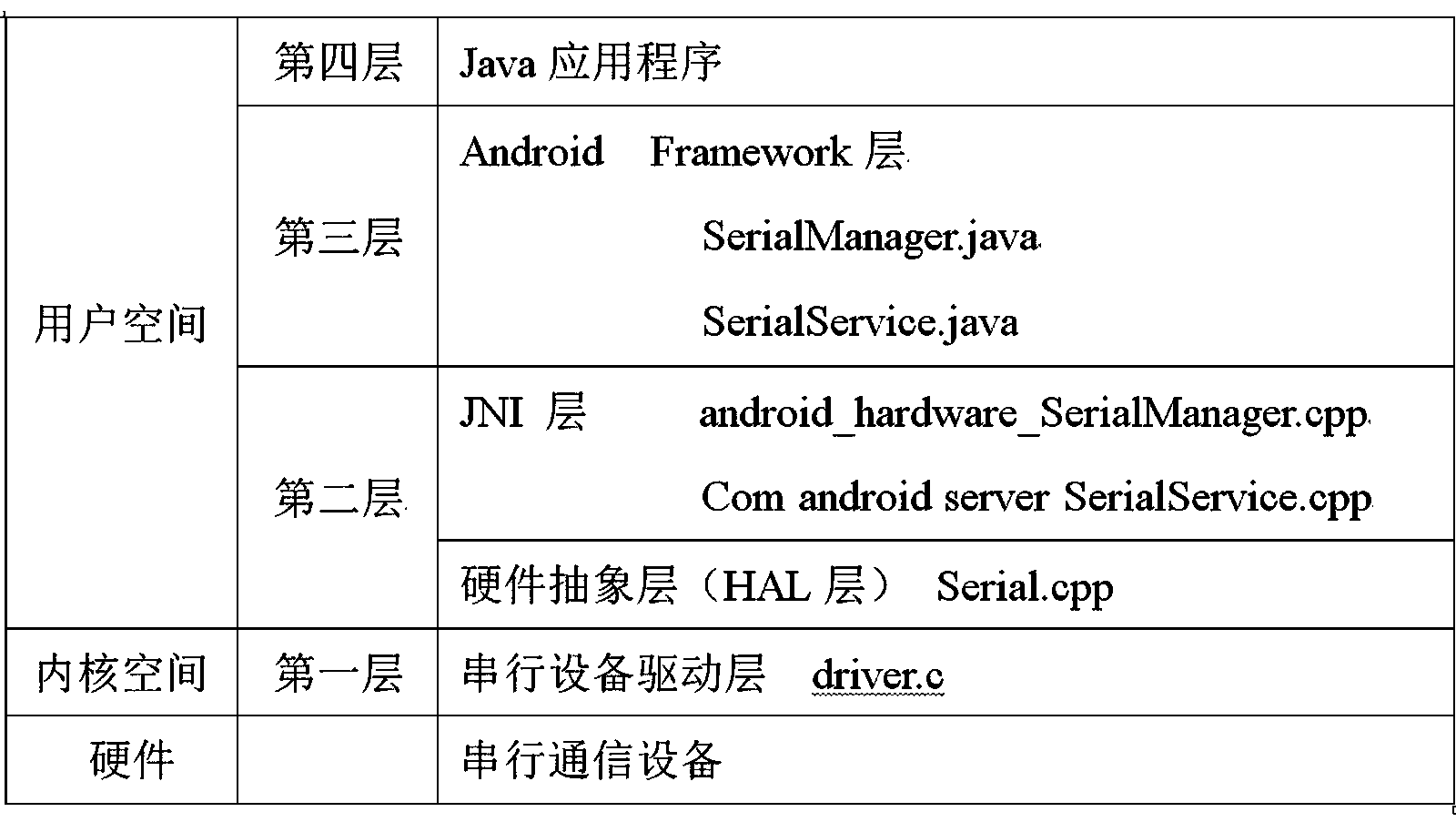
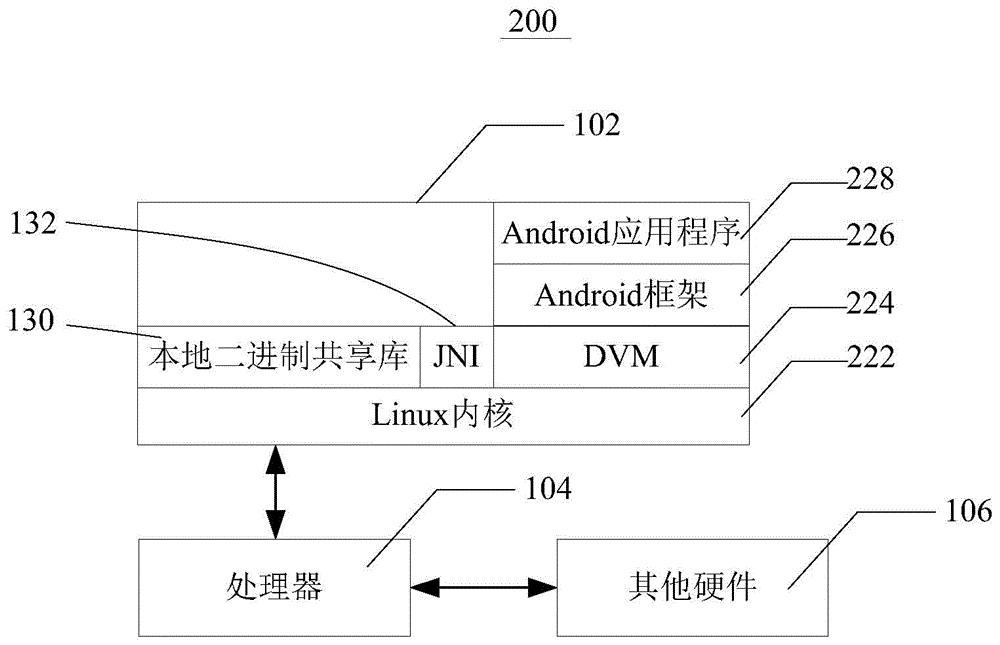
InactiveCN103353839AApplied to the convenience of calling devices with serial portsEasy to callSpecific program execution arrangementsLinux kernelApplication software
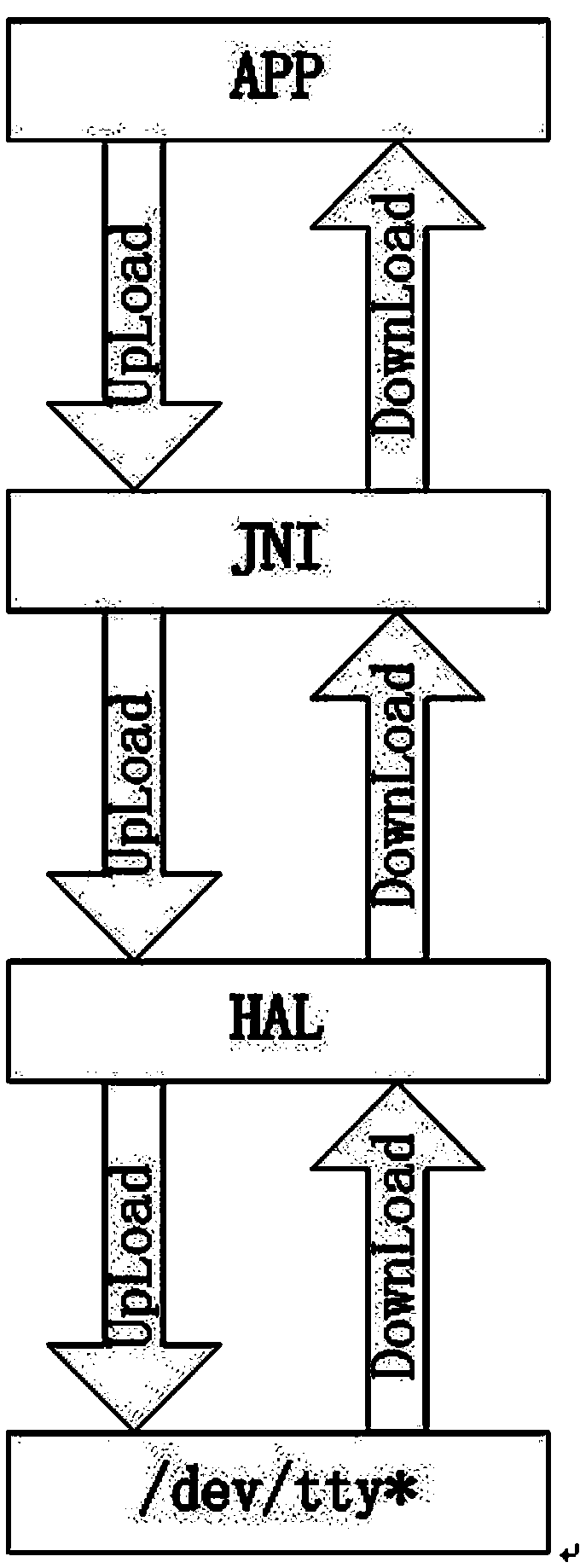
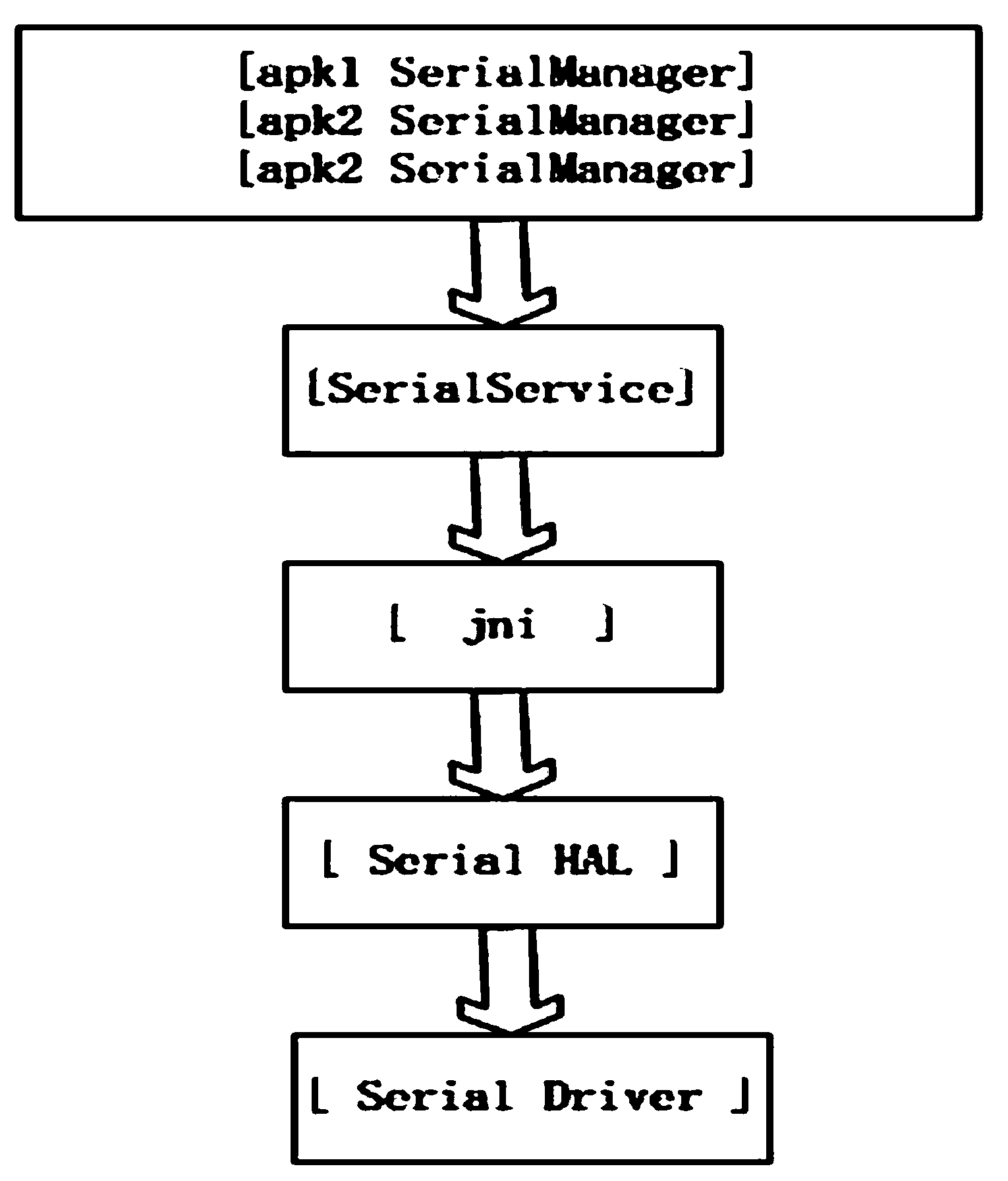
The invention provides a universal serial device communication module based on an Android system, which can realize calling to various serial devices under the Android system, and provides a solution for mutual exclusion produced when various (APK) application processes access to the same serial device at the same time. The universal serial device communication module is in operation on a Linux kernel and under an Android frame, and comprises a serial device drive layer, a hardware abstraction layer, a Framework layer and a JNI (Java Native Interface) layer. The universal serial device communication module provides convenience for the Android system to be applied in industries needing to call the serial devices.
Owner:杭州竞航科技股份有限公司
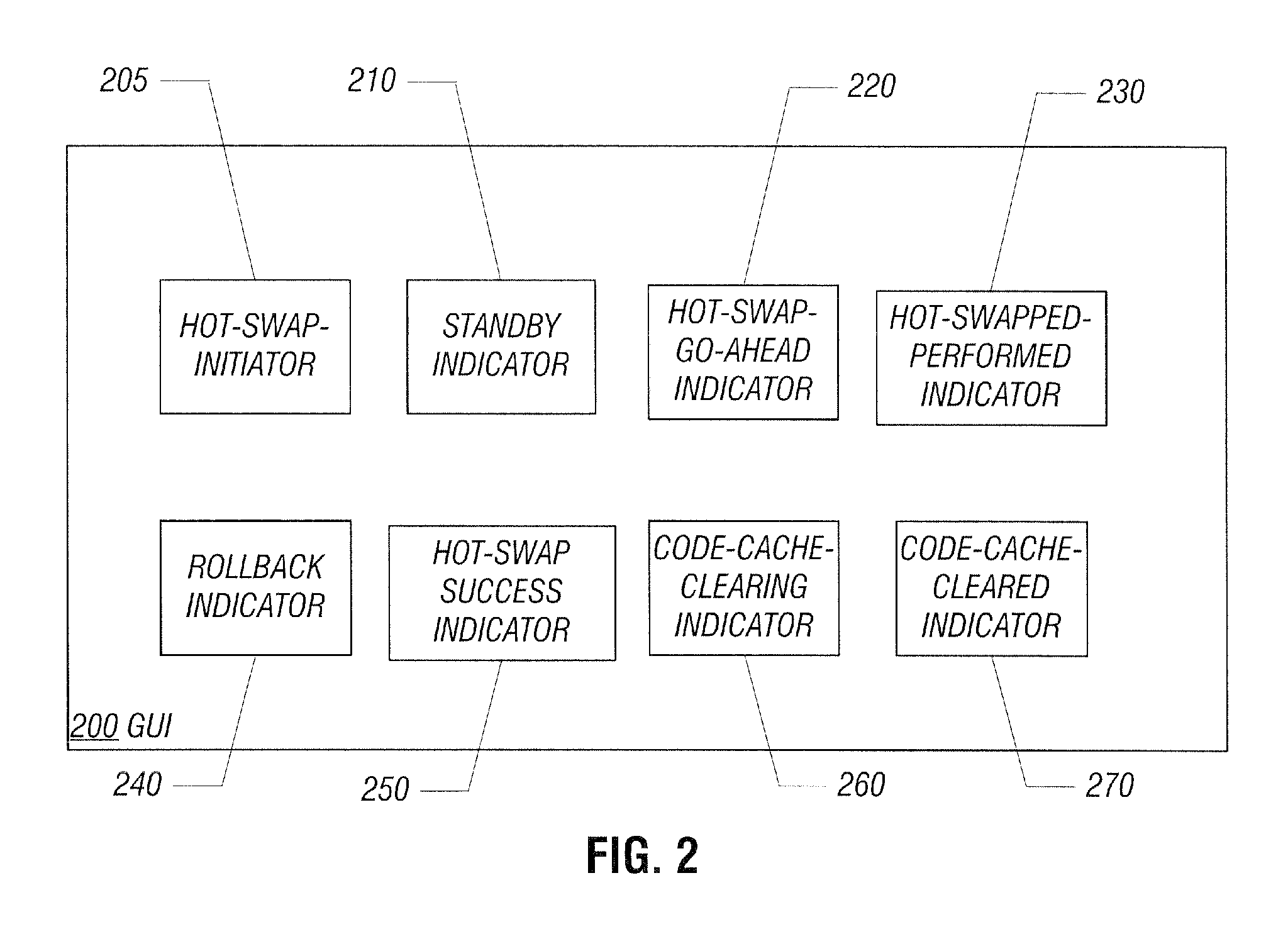
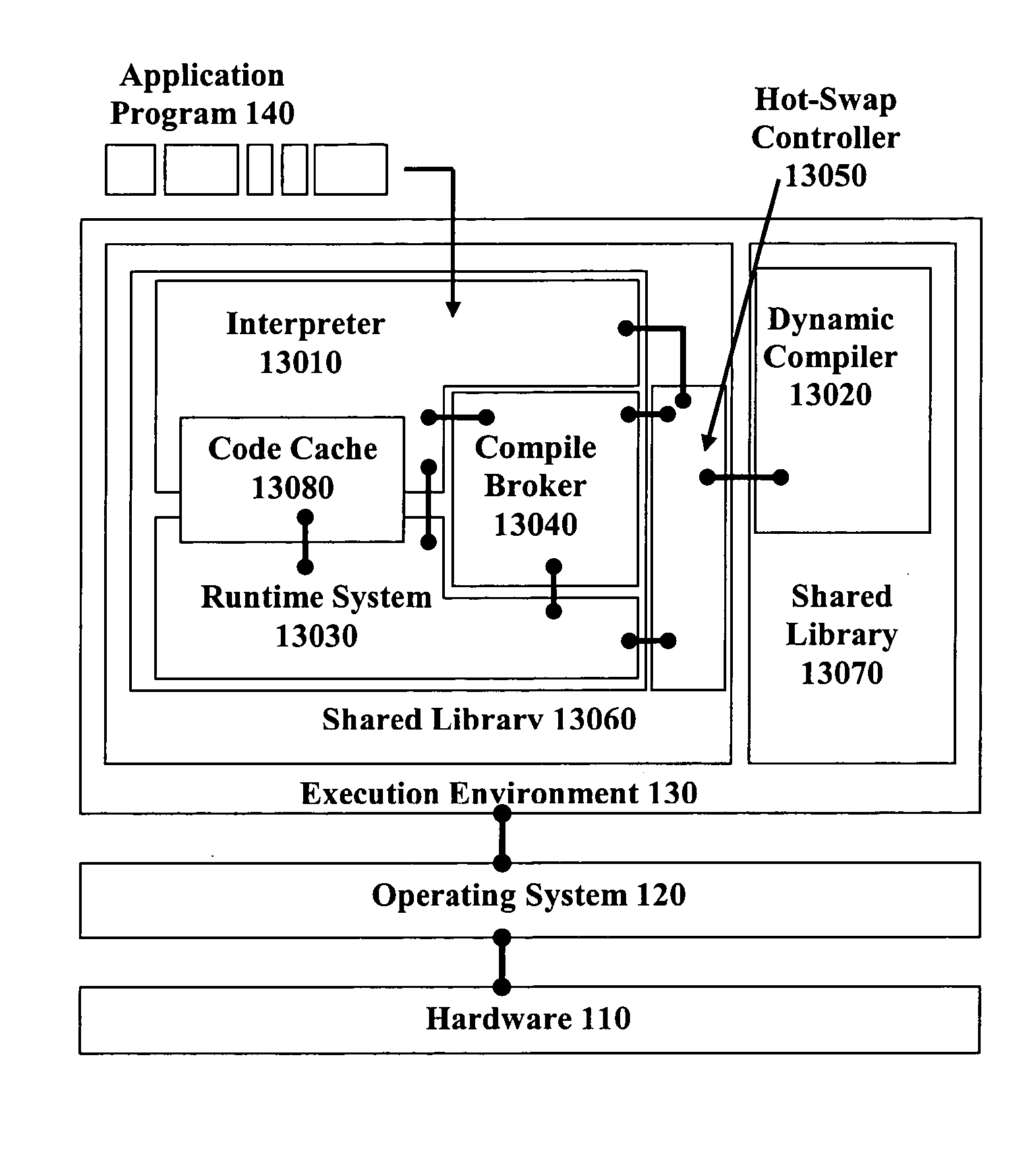
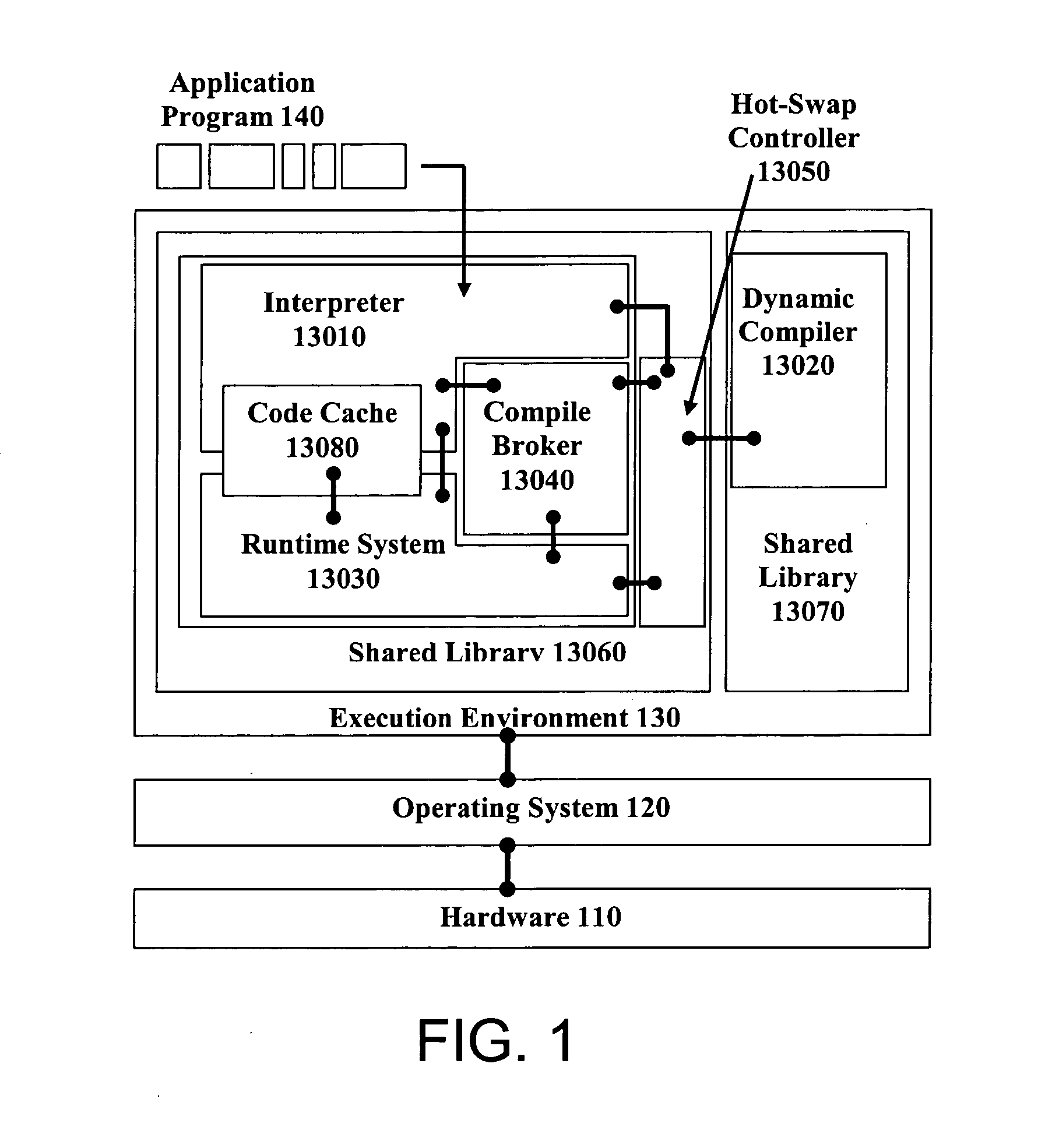
Hot-swapping a dynamic code generator
ActiveUS7853934B2Software engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsGraphicsGraphical user interface
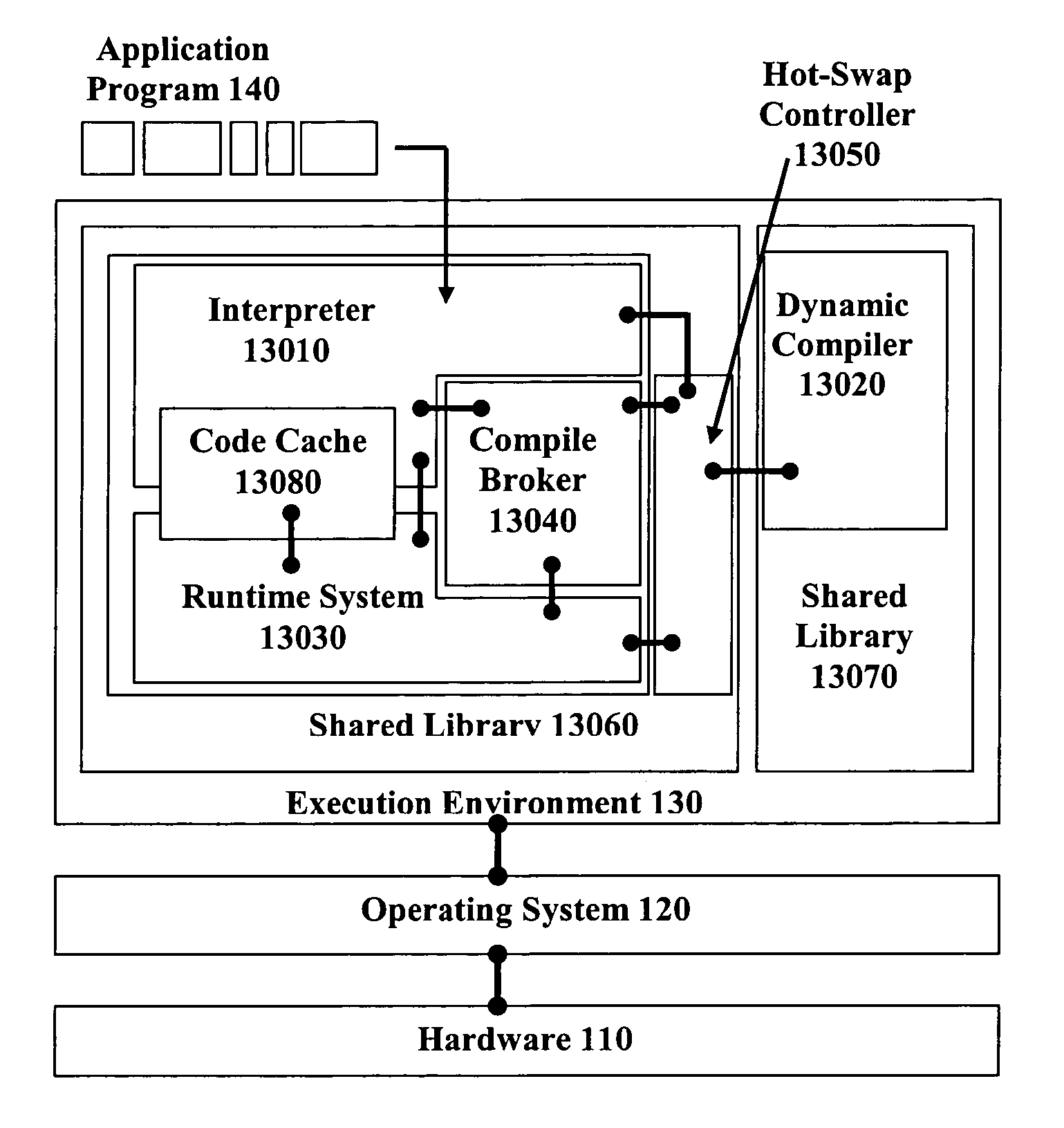
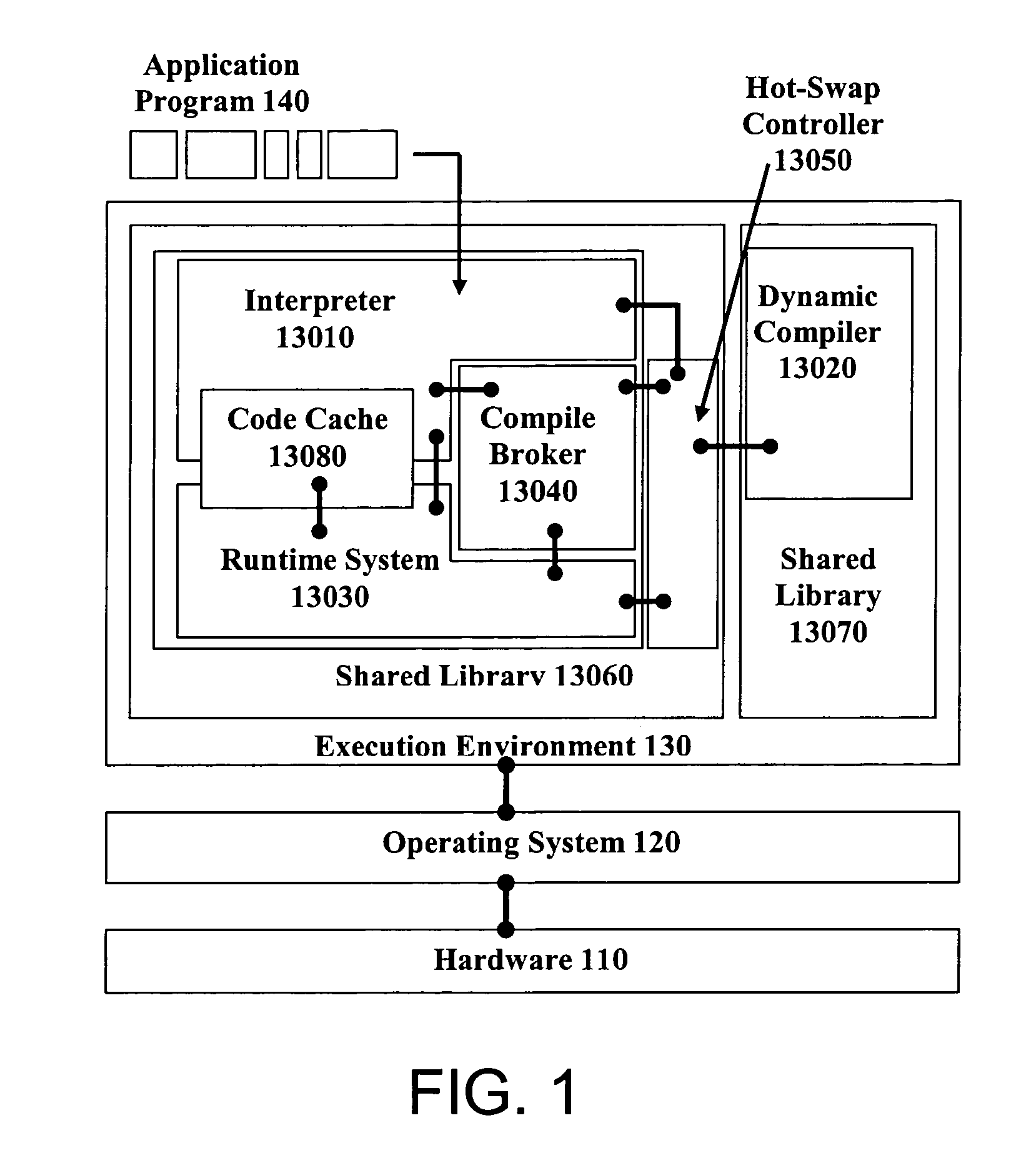
Embodiments of the invention relate to hot-swapping a live dynamic code generator. In an embodiment, hot-swapping is done in the Java execution environment. The dynamic code generator to be hot-swapped is stored in a module of a shared library separated from other components of the Java environment such as the garbage collector, the class loader, the Java Native Interface, the threading and synchronization package, etc. A graphical user interface (GUI) is provided so that the user can interact with the execution environment to control and perform hot-swapping.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
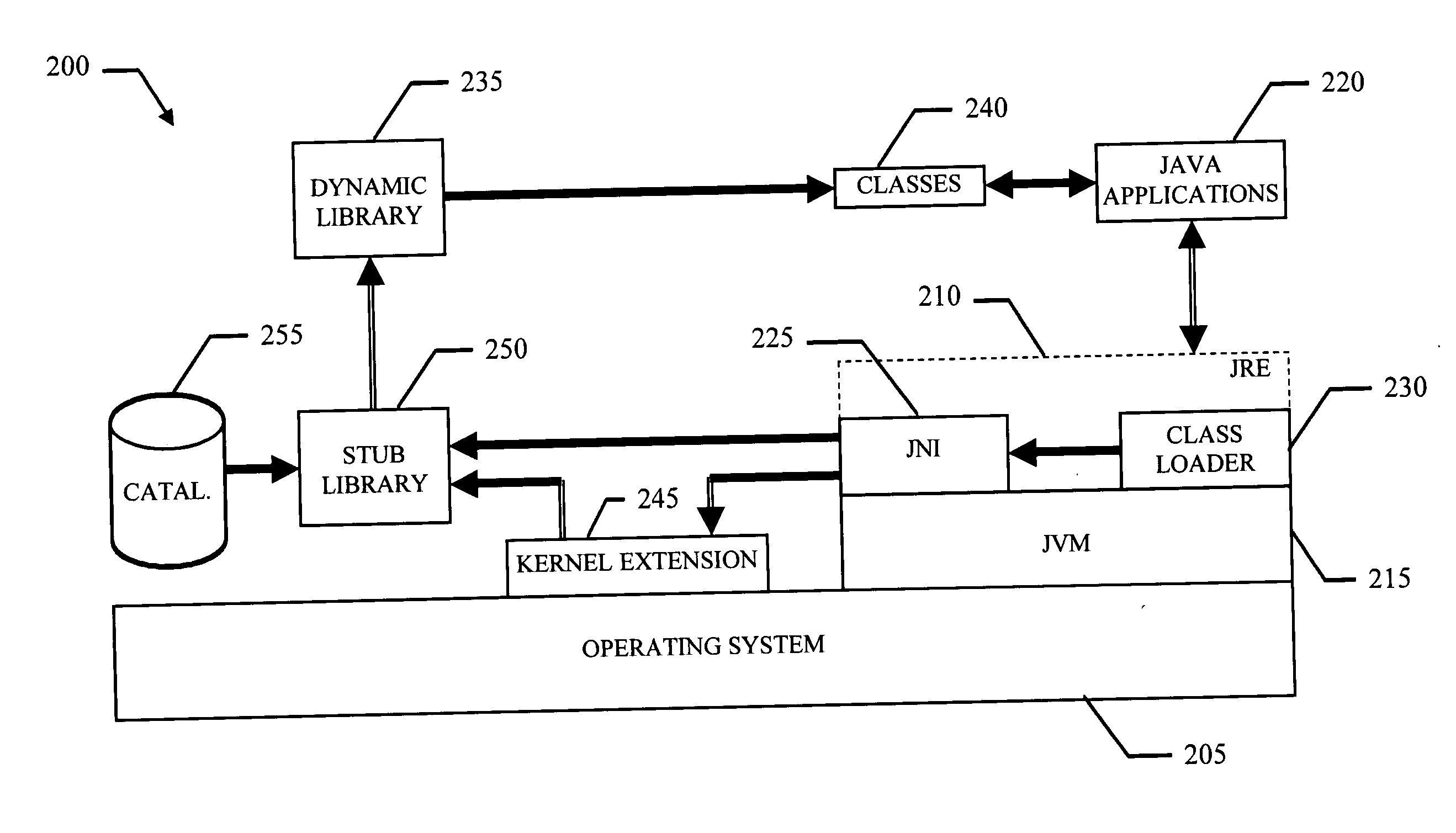
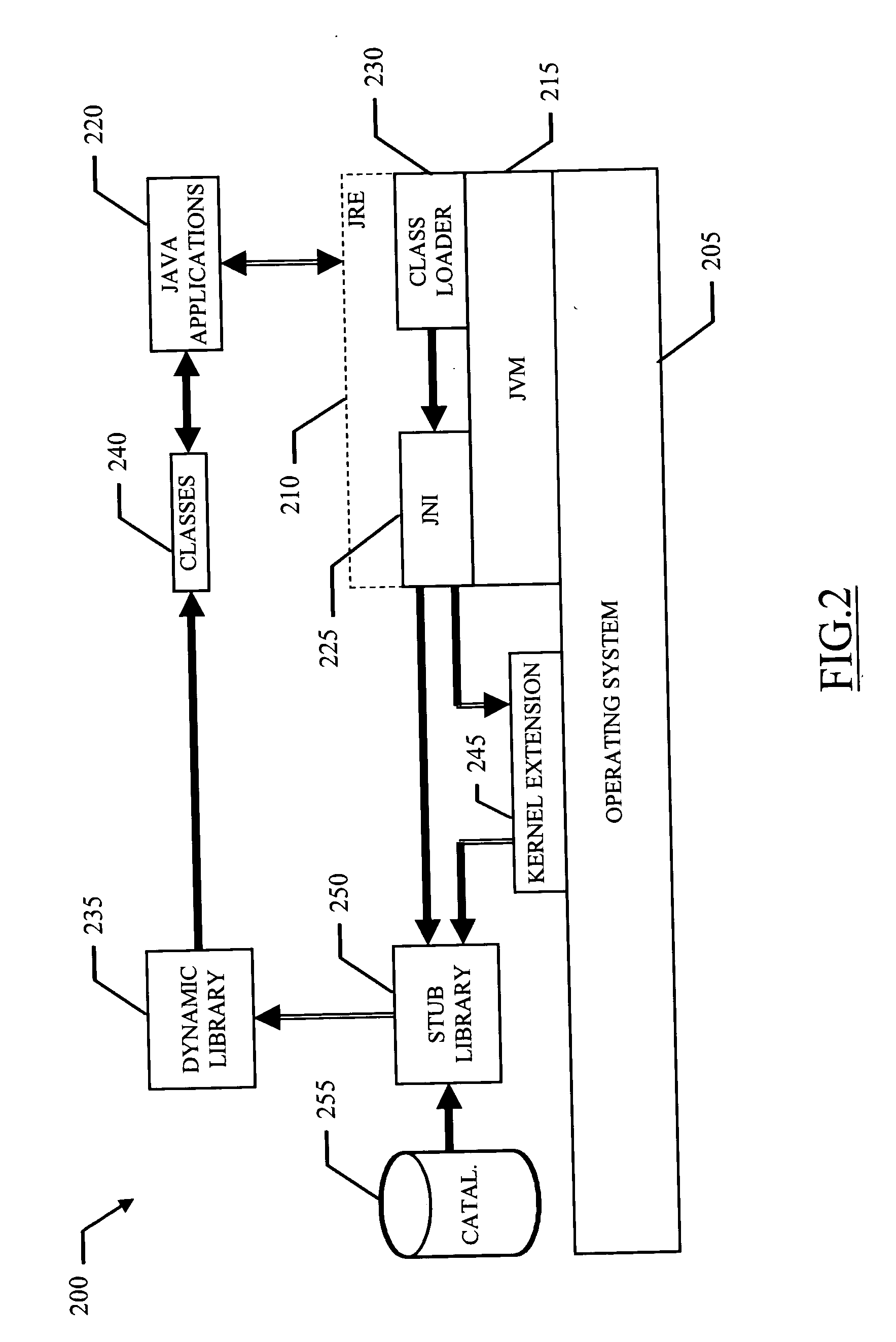
Method and system for metering execution of interpreted programs
InactiveUS20050268290A1Process controlInterference minimizationComputer security arrangementsProgram loading/initiatingJava virtual machineSoftware
A method and a corresponding system (200) for metering execution of interpreted programs (220) are proposed. Typically, an interpreter, such as the Java Virtual Machine (215), lacks built-in capabilities for communicating with the hardware and software platform of the computer directly; for this purpose, the virtual machine invokes external native functions through the Java Native Interface (225). The solution of the invention is based on the idea of stubbing the dynamic libraries (235) that implement those native functions. Therefore, when the virtual machine needs a native function (for example, to load a new class), a stub library (250) is loaded in place of the required dynamic library. As soon as the virtual machine calls the desired command, the stub library takes control and identifies the interpreted program that is run by the virtual machine; preferably, this operation is performed by querying a catalogue that associates the new class with the corresponding interpreted program. The stub library then loads the dynamic library and forwards the required command. In a different embodiment, the class loader is replaced with a stub module. In this case, the stub class loader detects the loading of the class including a main method of the interpreted program; the main method is then updated by inserting a call to a licensing agent, in order to identify the interpreted program when the main method is actually executed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Hot-swapping a dynamic code generator
ActiveUS20060294498A1Software engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsGraphicsGraphical user interface
Embodiments of the invention relate to hot-swapping a live dynamic code generator. In an embodiment, hot-swapping is done in the Java execution environment. The dynamic code generator to be hot-swapped is stored in a module of a shared library separated from other components of the Java environment such as the garbage collector, the class loader, the Java Native Interface, the threading and synchronization package, etc. A graphical user interface (GUI) is provided so that the user can interact with the execution environment to control and perform hot-swapping.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
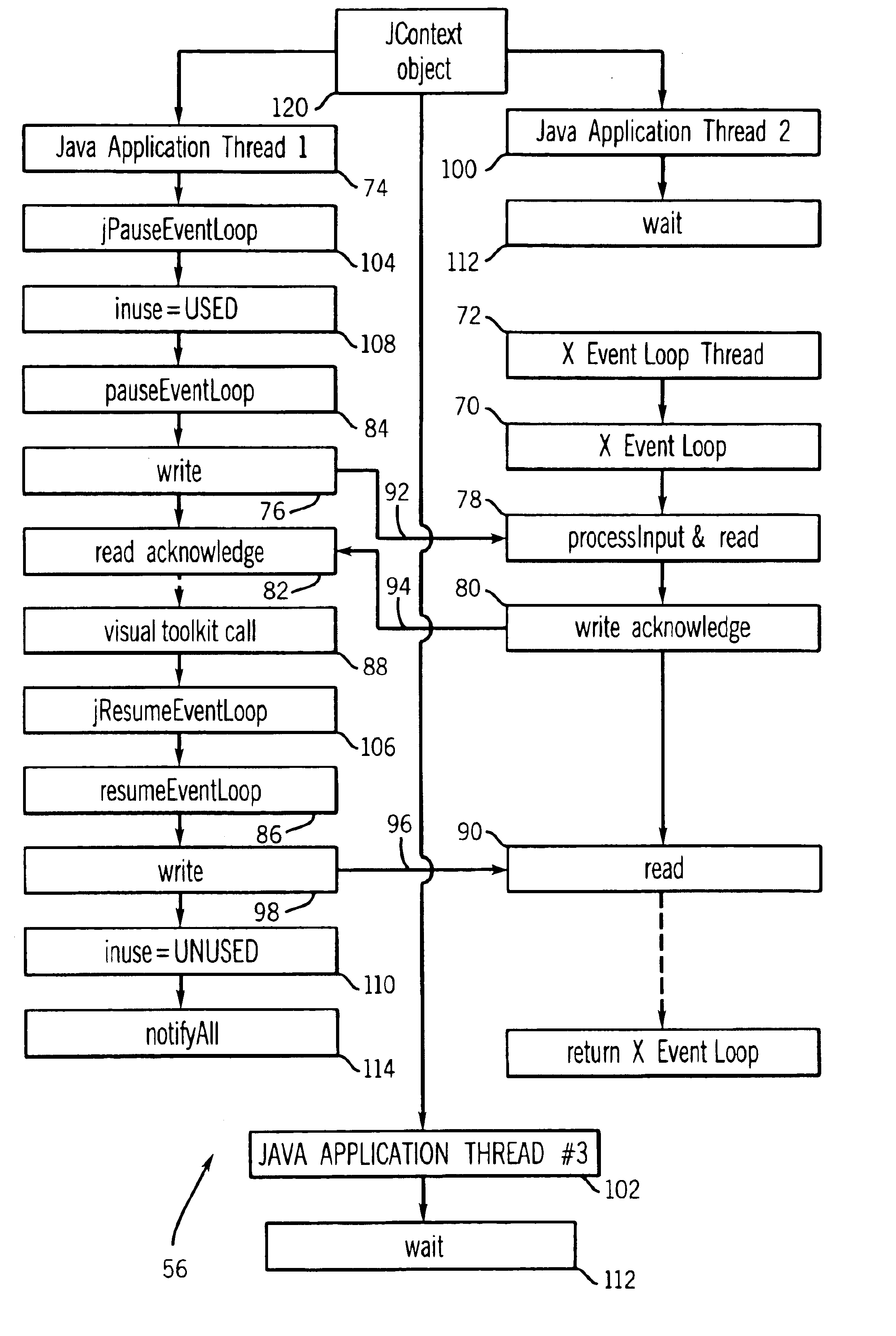
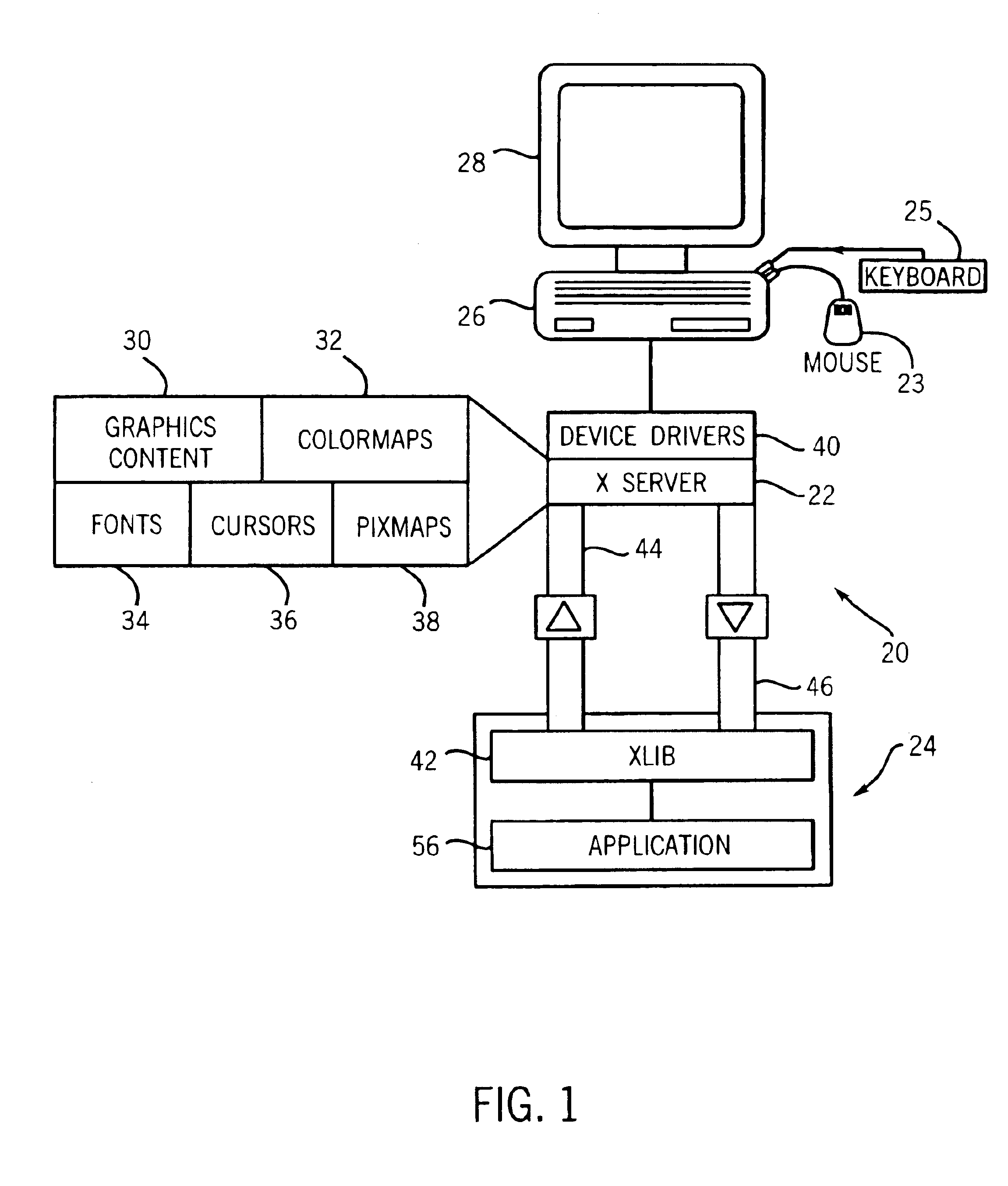
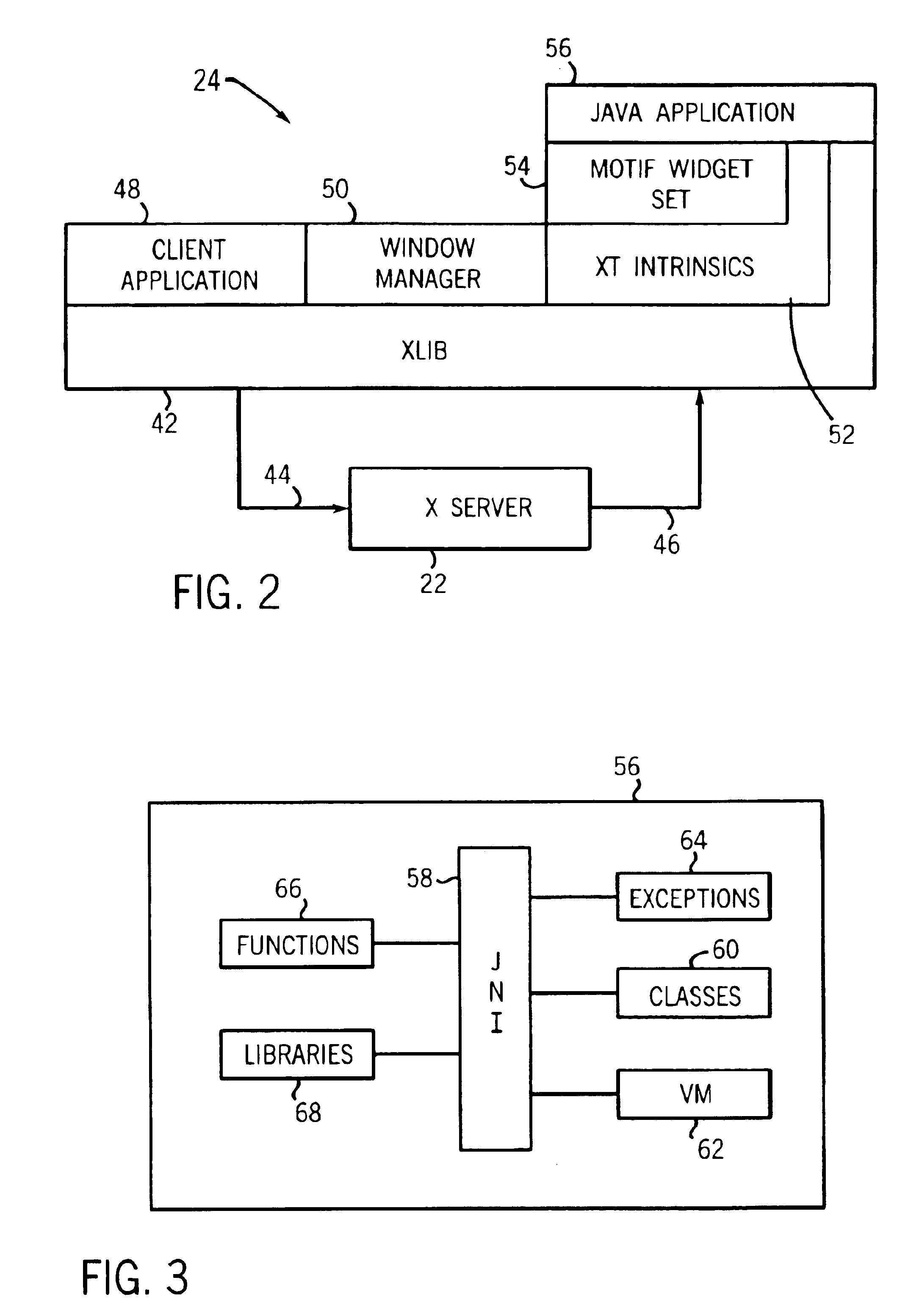
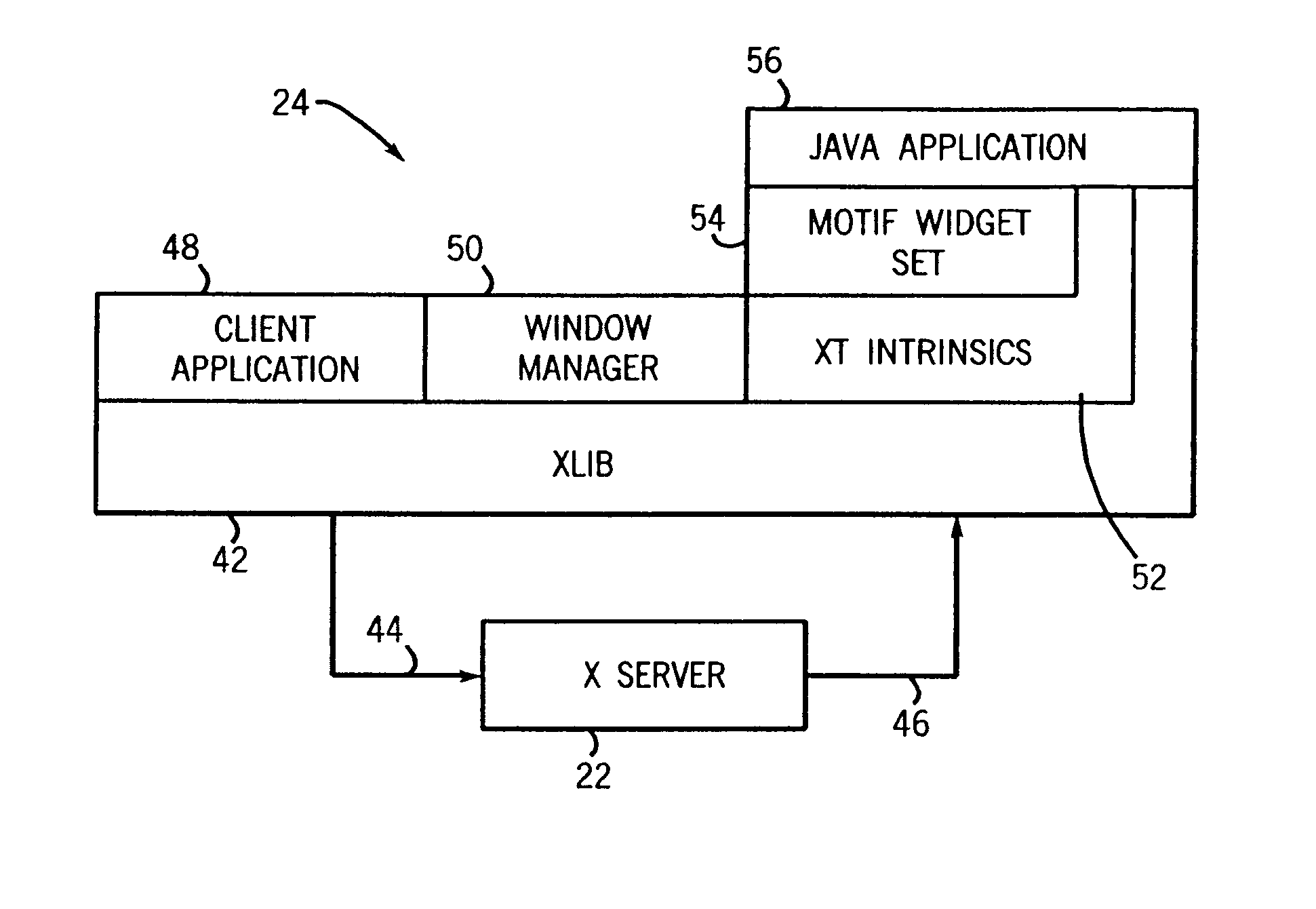
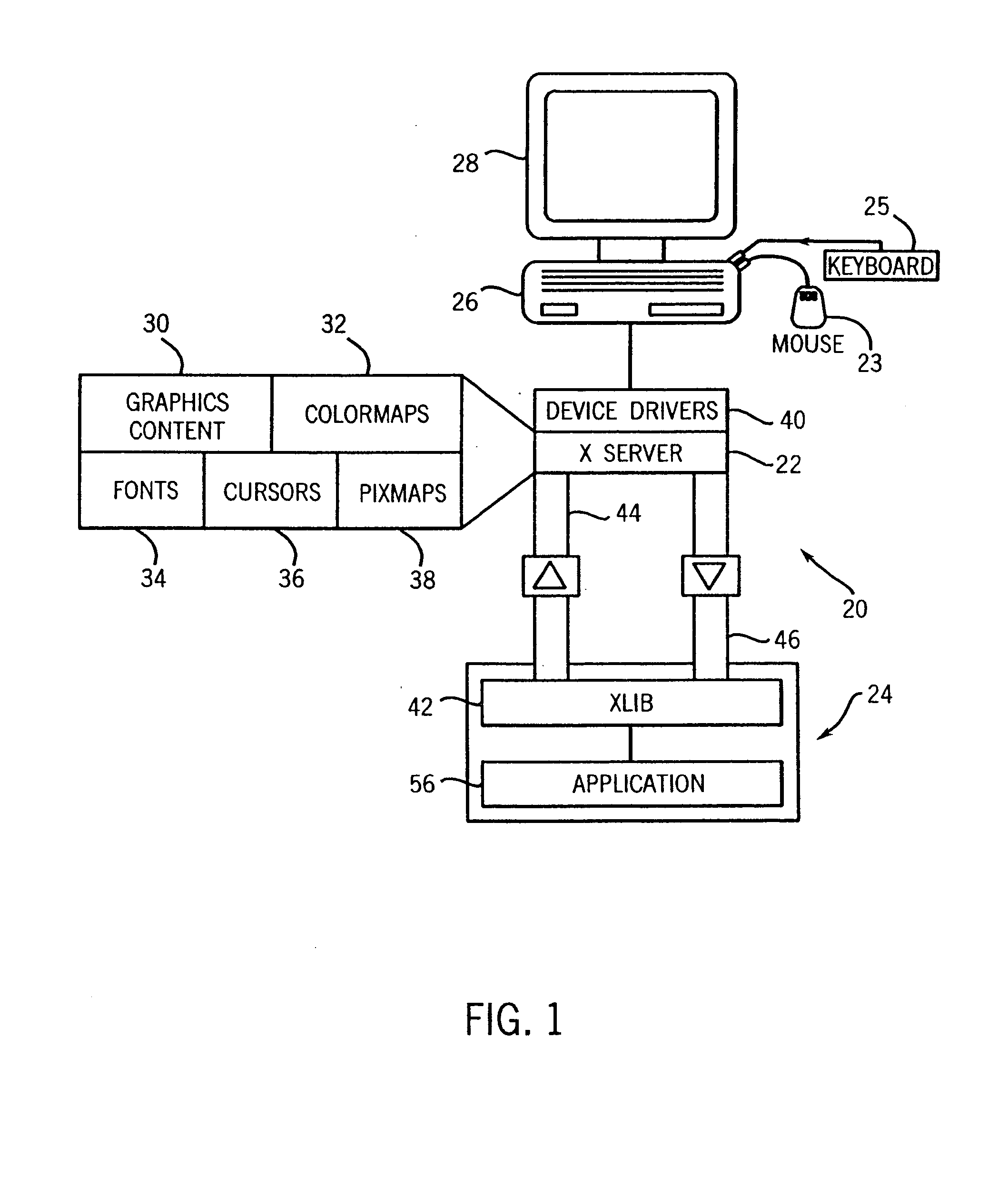
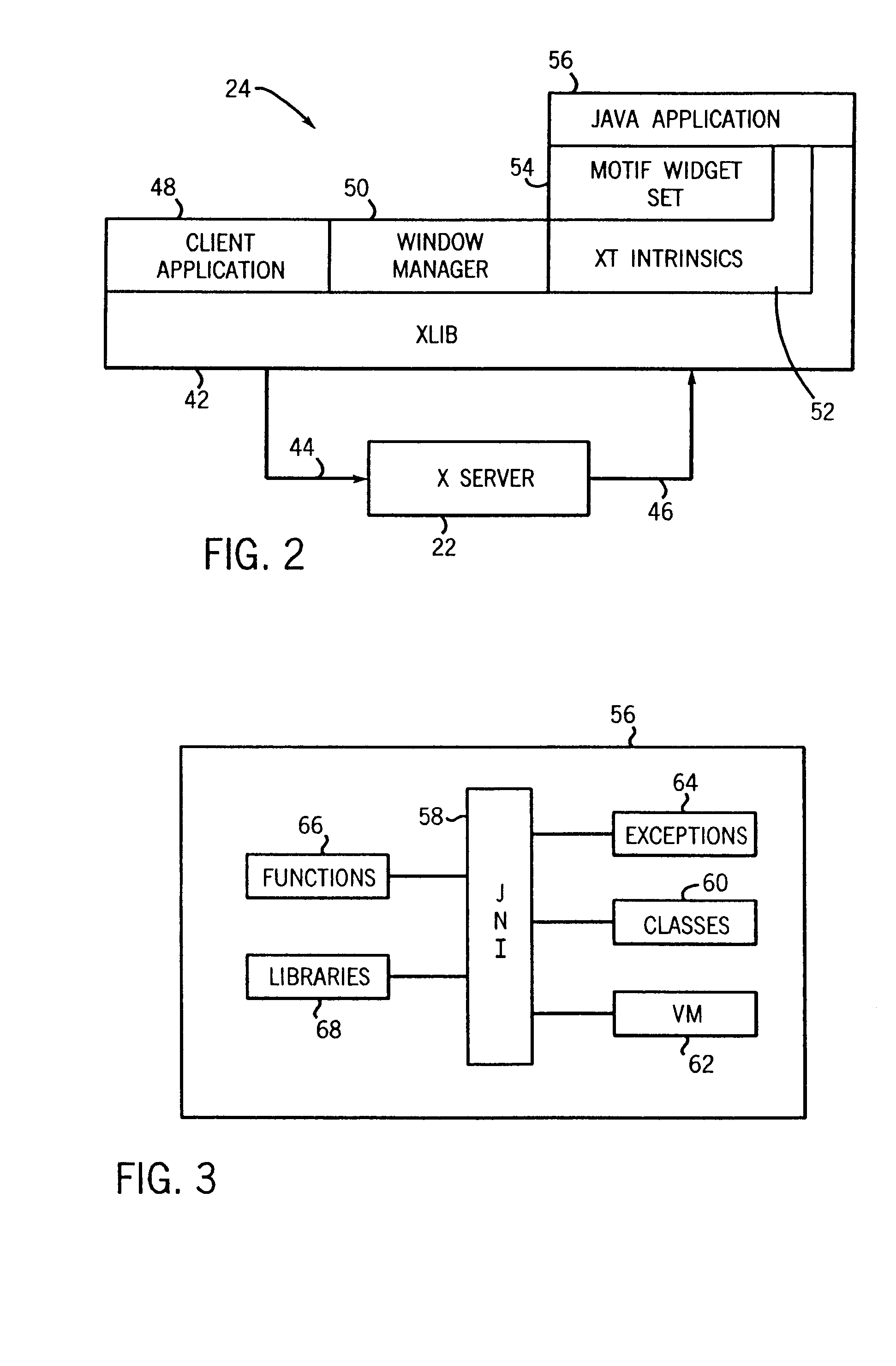
Method of integrating X window intrinsics based toolkits and widgets with java
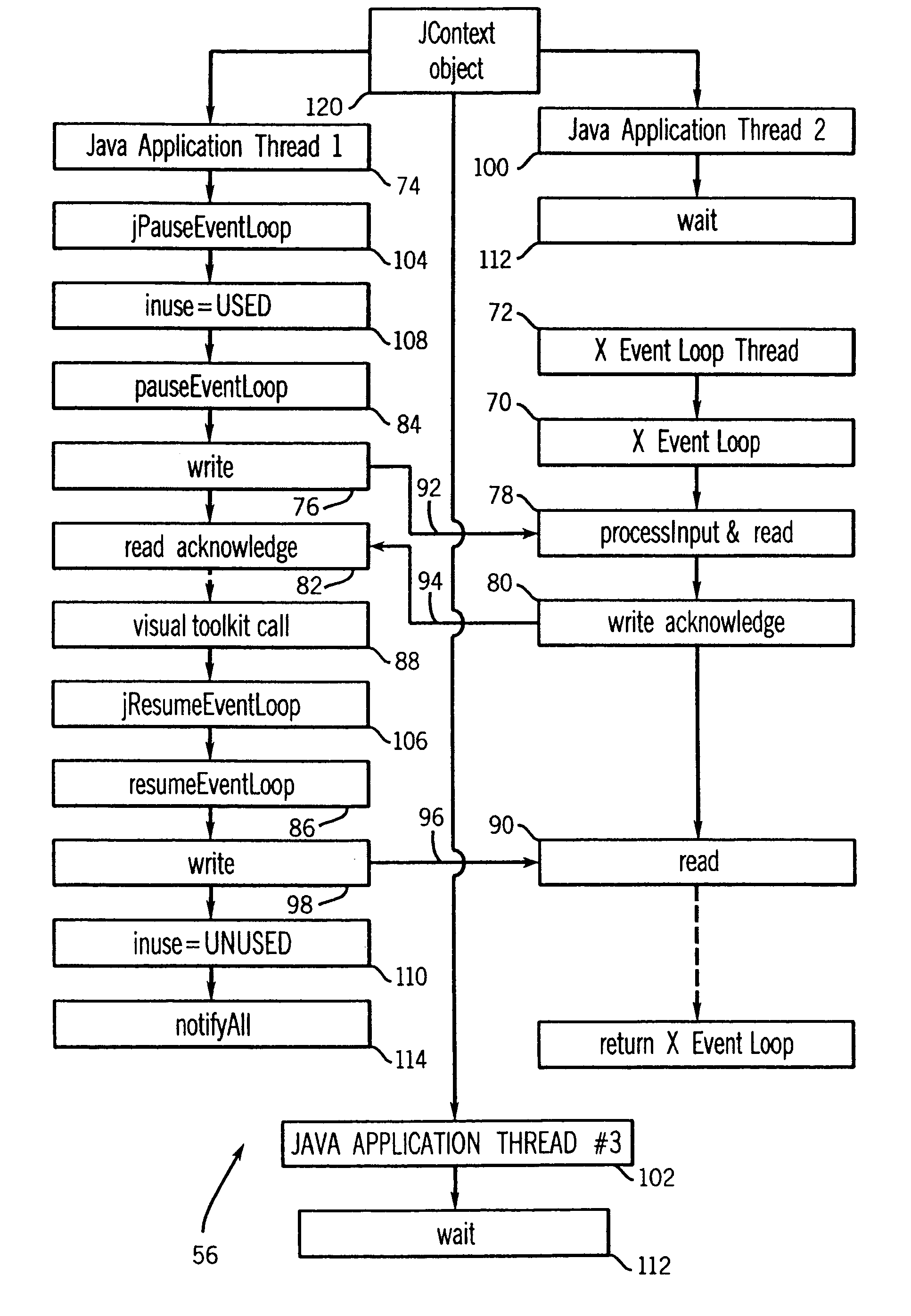
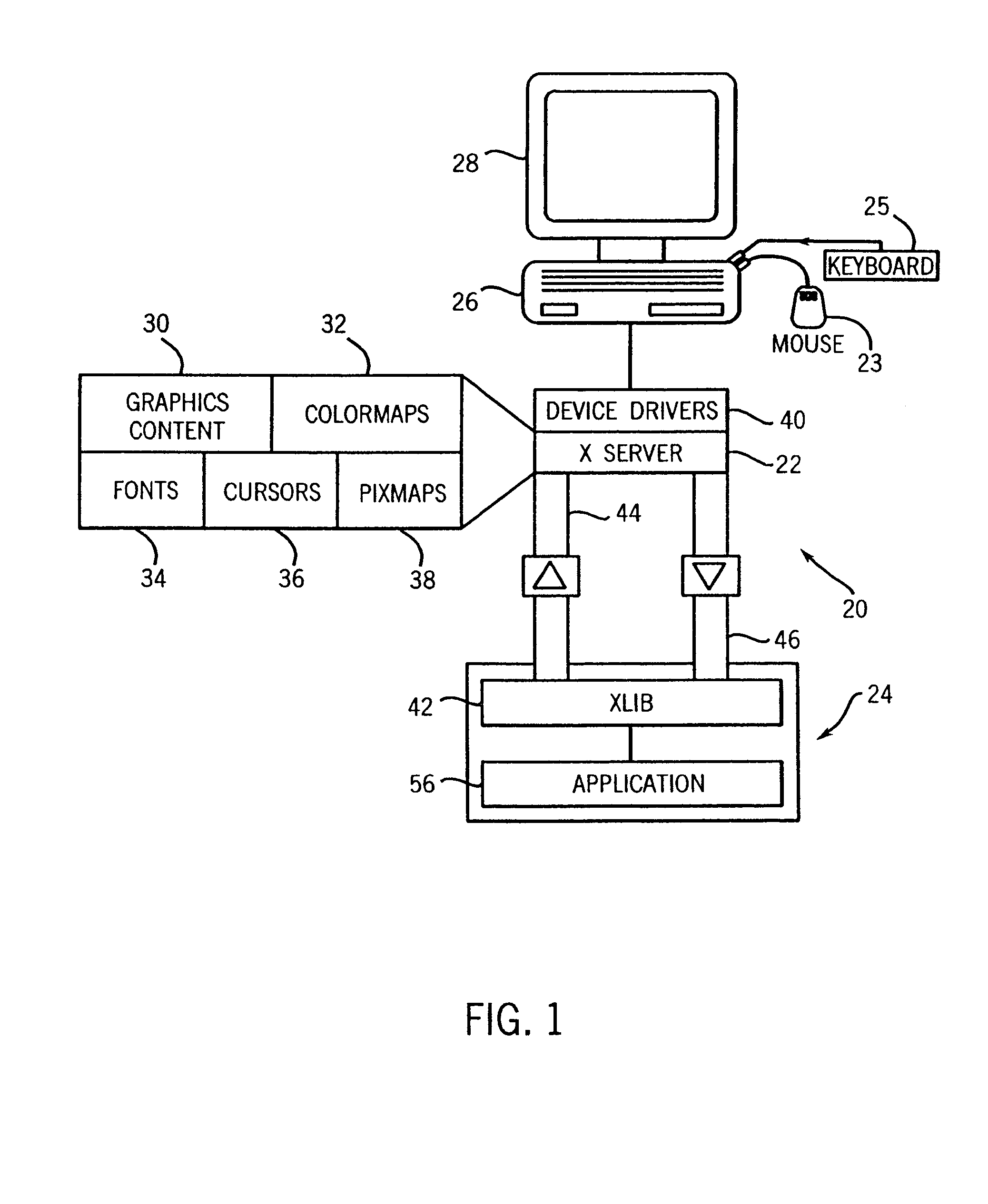
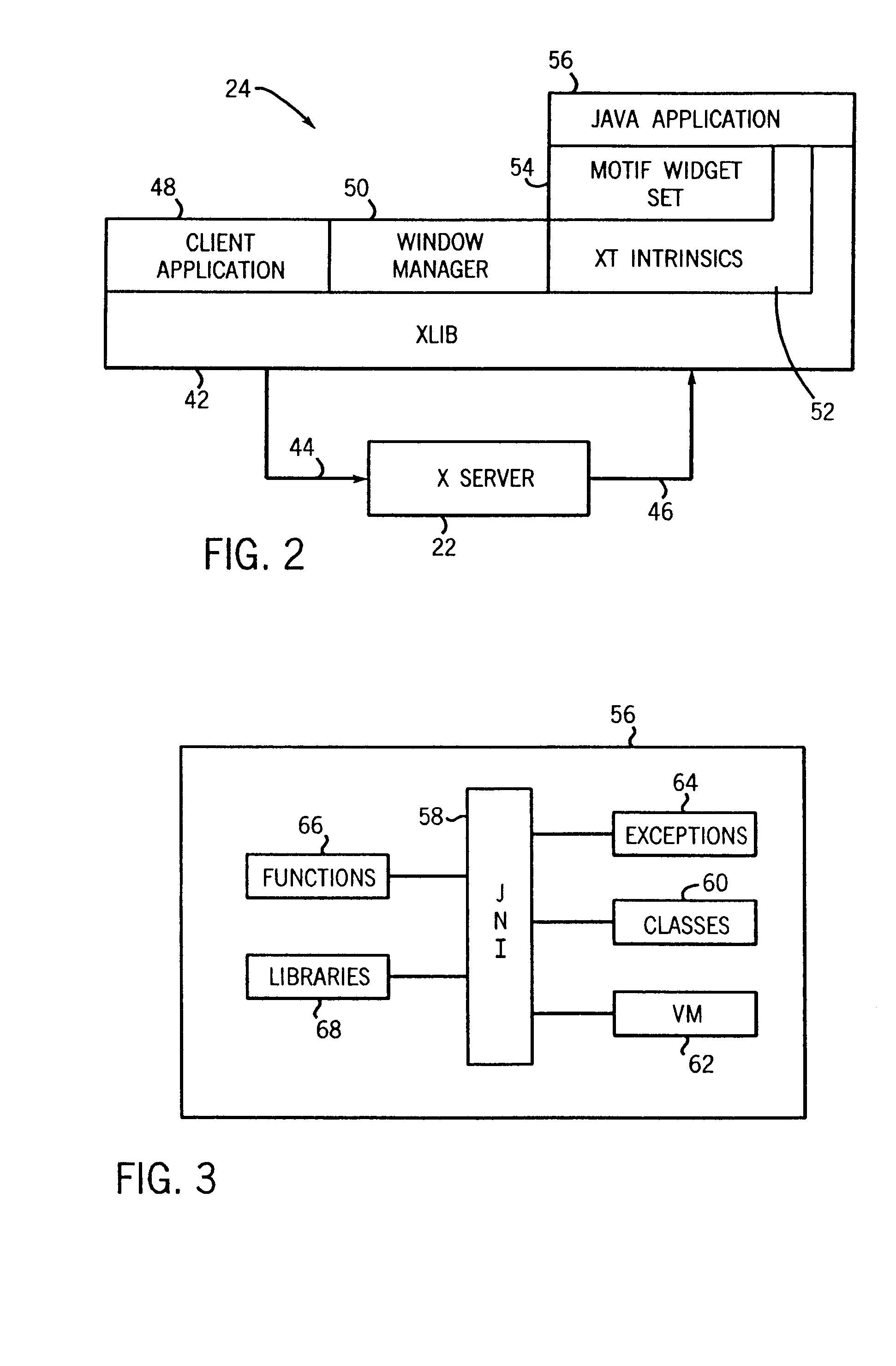
InactiveUS6918125B1Without risk of data corruptionInterprogram communicationExecution for user interfacesIntrinsicsFile descriptor
A method of integrating an Xt Intrinsics based toolkit with a JAVA application. The application includes a process thread that implements an X event loop and an application thread that suspends execution of the event loop to allow a call to be made through the JAVA Native Interface to a toolkit or a widget to cause something to be displayed. The application thread includes a write socket to communicate a token to a read socket of the event loop, and performs a blocking read suspending the thread. The event loop returns an acknowledgment token via a write socket to a read socket of the thread that unblocks its blocking read and the event loop invokes its own blocking read suspending its execution. The file descriptor function, XtAppAddInput, preferably, is used to read the token and to set the blocking read. After a toolkit call is made, a token is sent from a second write socket of the thread to a second read socket of the event loop that unblocks its blocking read resuming the event loop. JAVA multithreading support services, such as JAVA's wait and notifyAll methods, are employed in multithreaded applications to ensure that only one thread at a time can make a call. Use of a separate Intrinsics application context to service the event loop is employed, windows are managed in separate hierarchies associated with each application context, and a special JAVA Canvas manages native windows transparent to the programmer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
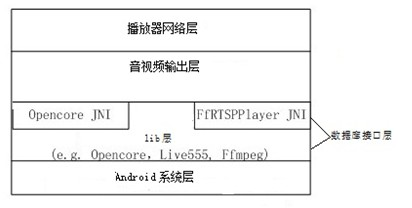
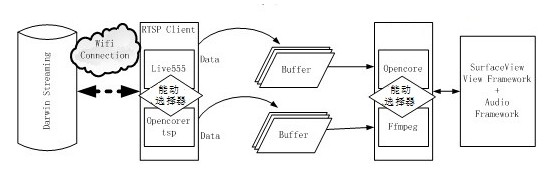
Software development kit (SDK) module for Android real time streaming protocol (RTSP) player
ActiveCN102306103ARealize optionalityRealize transmissionSpecific program execution arrangementsDatabase interfaceSoftware development process
The invention belongs to the field of the software development kit (SDK) design of an Android real time streaming protocol (RTSP) player application scheme, and in particular relates to an SDK module for an Android RTSP player. The SDK module comprises an Android system layer, a database interface layer, an audio / video output layer and a player network layer from bottom to top, wherein the database interface layer comprises a lib layer and a java native interface (JNI) layer from bottom to top; the lib layer comprises an Opencore module and an RTSPFfmpeg module; the player network layer is provided with an RTSP server and an RTSP client which are mutually connected; the RTSPFfmpeg module comprises an Ffmpeg decoding module and a Live555 transmission module and is provided with a JNI and an application programming interface (API); the RTSP client comprises an Opencorertsp client which is based on the Opencore module, and a Live555 client; and the player network layer is provided with an active selector and calls the API of the module in the lib layer through the active selector. The SDK module supports two optional modules, namely the Opencore module and the Ffmpeg module, and supports various audio / video formats.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
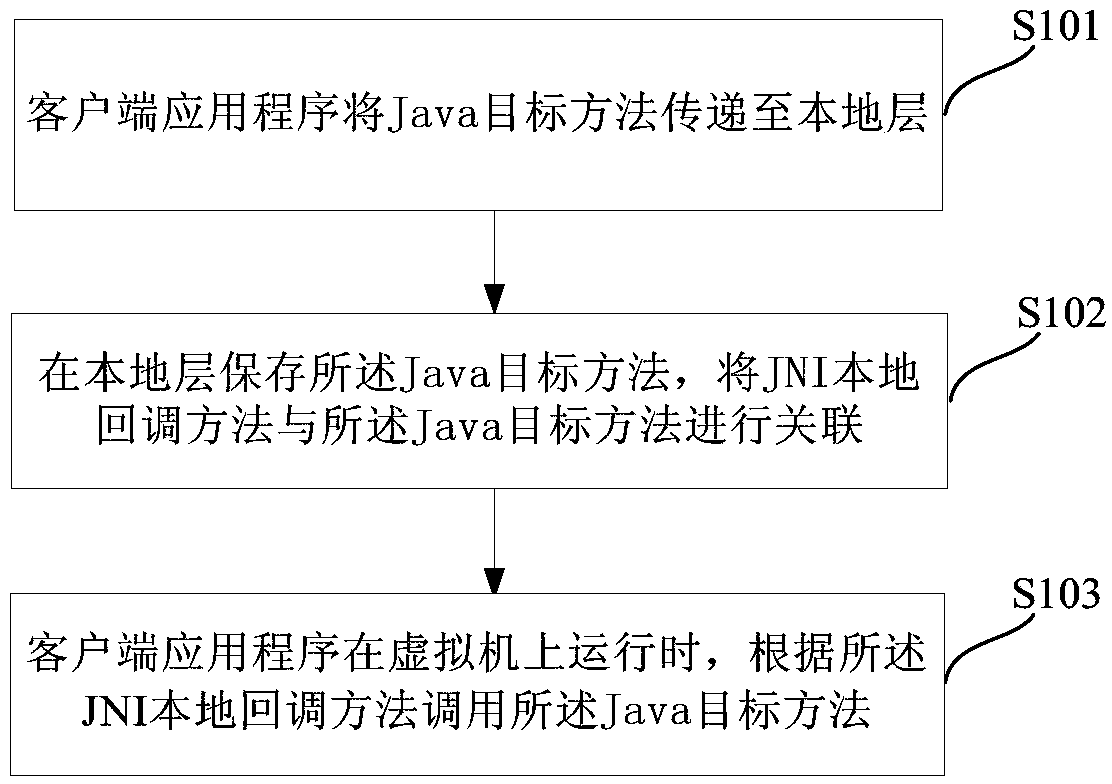
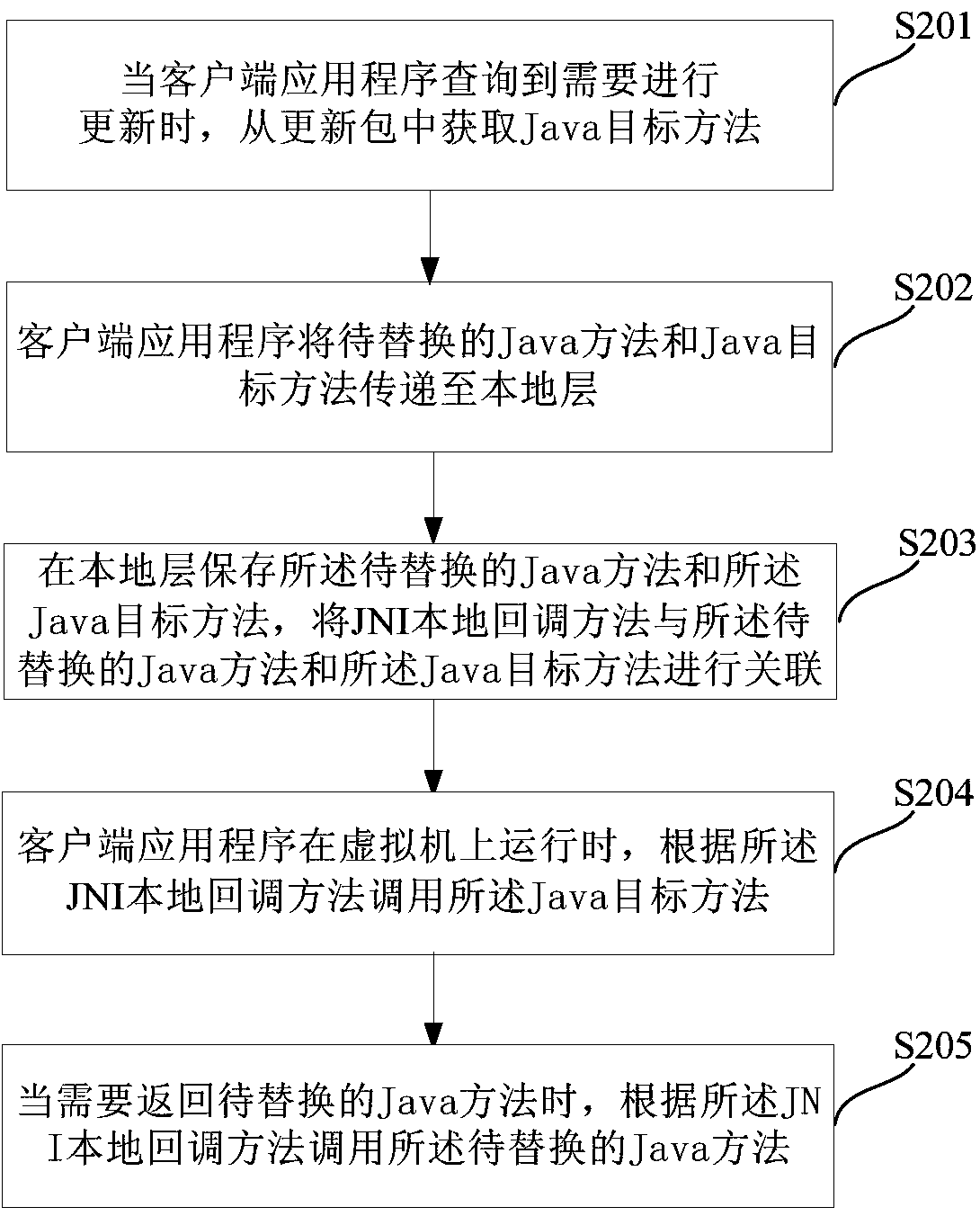
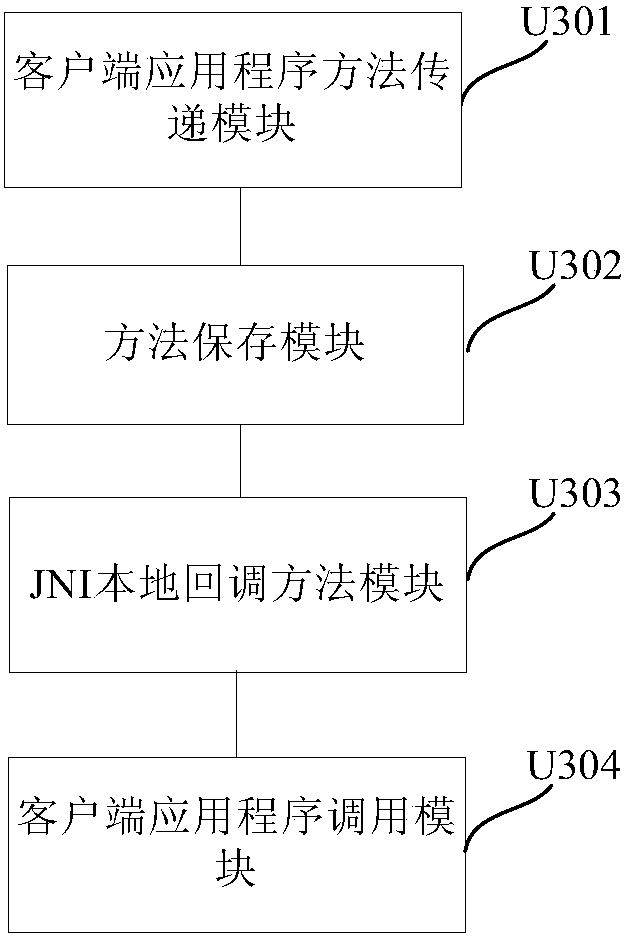
Client application partial updating method and apparatus
The embodiment of the application discloses a client application partial updating method and apparatus. Characteristics and a JNI (Java Native Interface) mechanism of an Android system framework are utilized; after acquiring a Java target method from an update pack, a client application transmits the Java target method to a local layer, stores the Java target method and associates the Java target method with a JNI local callback method; when the client application operates on a Dalvik virtual machine and needs to call a Java method to be replaced, the JNI local callback method, instead of an original Java method to be replaced, is called; and the JNI local callback method calls the Java target method according to parameters transmitted by the client application so as to complete partial updating on a code of the client application. The client application partial updating method disclosed by the application can be accurate to a Method level of a Java class.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
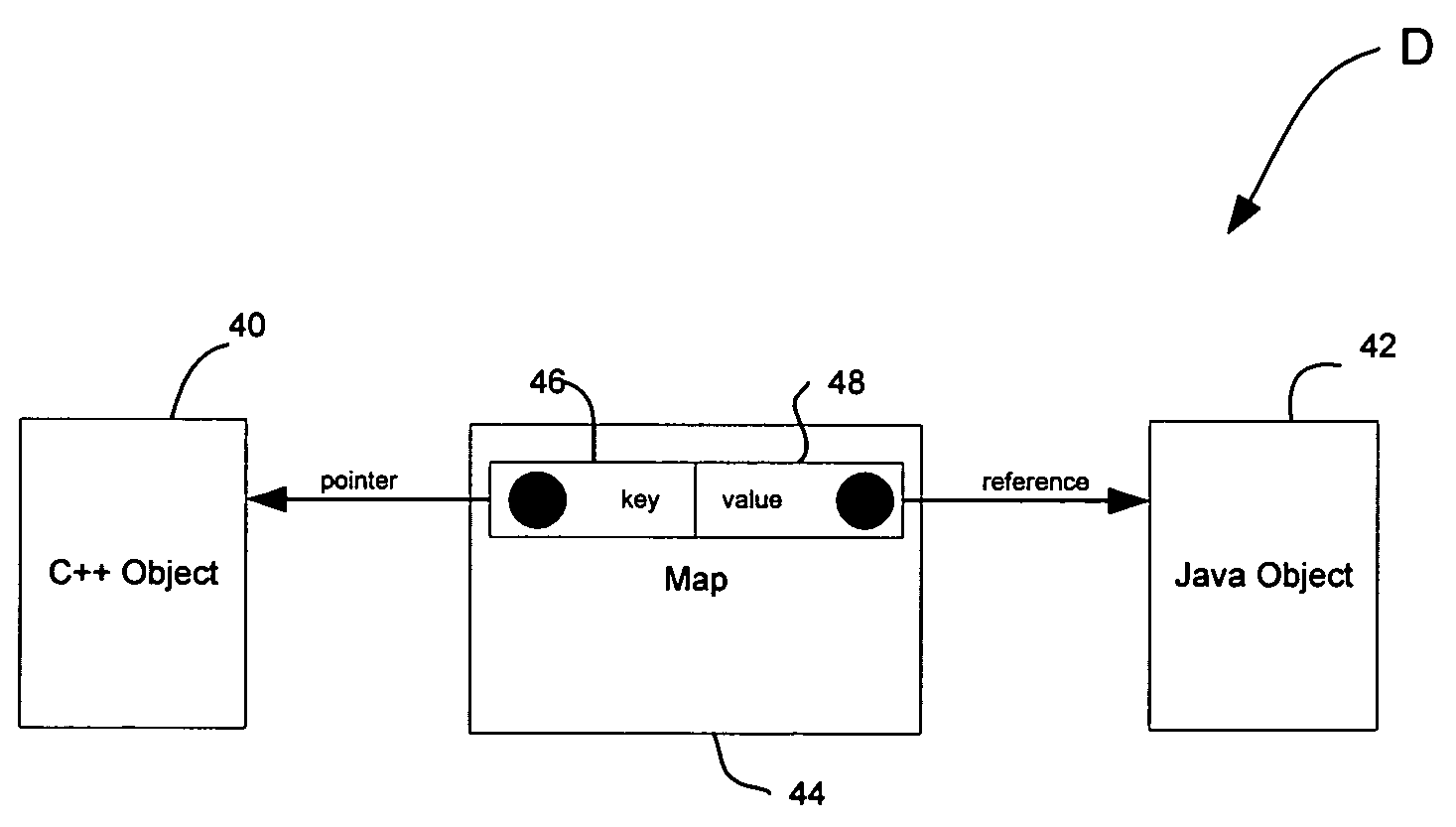
Method and apparatus for object-to-object Java Native Interface mapping
InactiveUS7350197B2Specific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsObject structureProgramming language
This invention is directed to a method and apparatus for implementing native code directly in C++ with object structure very closely resembling the object structure of JAVA. The method provides for the mapping of JAVA to C++ objects and invoking the JAVA Native Interface, mapping C++ objects to JAVA and returning a corresponding JAVA object, retrieving and returning a class factory by class name, and collecting garbage in both the C++ and JAVA environments.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
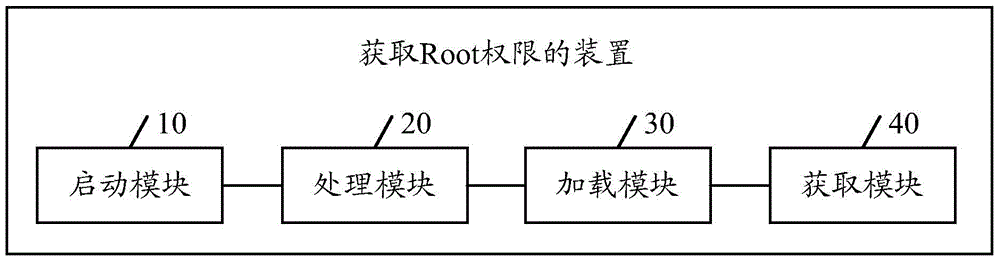
Method and device for obtaining Root permission
ActiveCN104134036AIncrease success rateImprove experienceComputer security arrangementsComputer scienceEnvironment variable
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for obtaining a Root permission. The method comprises the following steps that: a terminal opens a native process by using the identity of an SU (Switch User), and a JNI (Java Native Interface) module is started in the native process; the user identity of the native process is set as the ID (Identity) of the SU by the terminal via the JIN module, the operation permission of the SU is obtained, and the security environment variable of a system is cleared; the terminal starts a sub process through the JNI module, and a Jar packet is loaded in the sub process through the operation permission of the SU; and the terminal starts a resident service process of the Jar packet, and the Root permission is obtained through the resident service process. The embodiment of the invention also discloses a device for obtaining the Root permission. After the adoption, the method and the device disclosed by the invention have the advantages that the consumption of resources for obtaining the Root permission can be concretely reduced; the success rate of obtaining the Root permission is improved; the applicability is high; and the experience of a user obtaining the Root permission is enhanced.
Owner:ZHUHAI BAOQU TECH CO LTD
Method and system for optimizing array sizes in a JAVA virtual machine
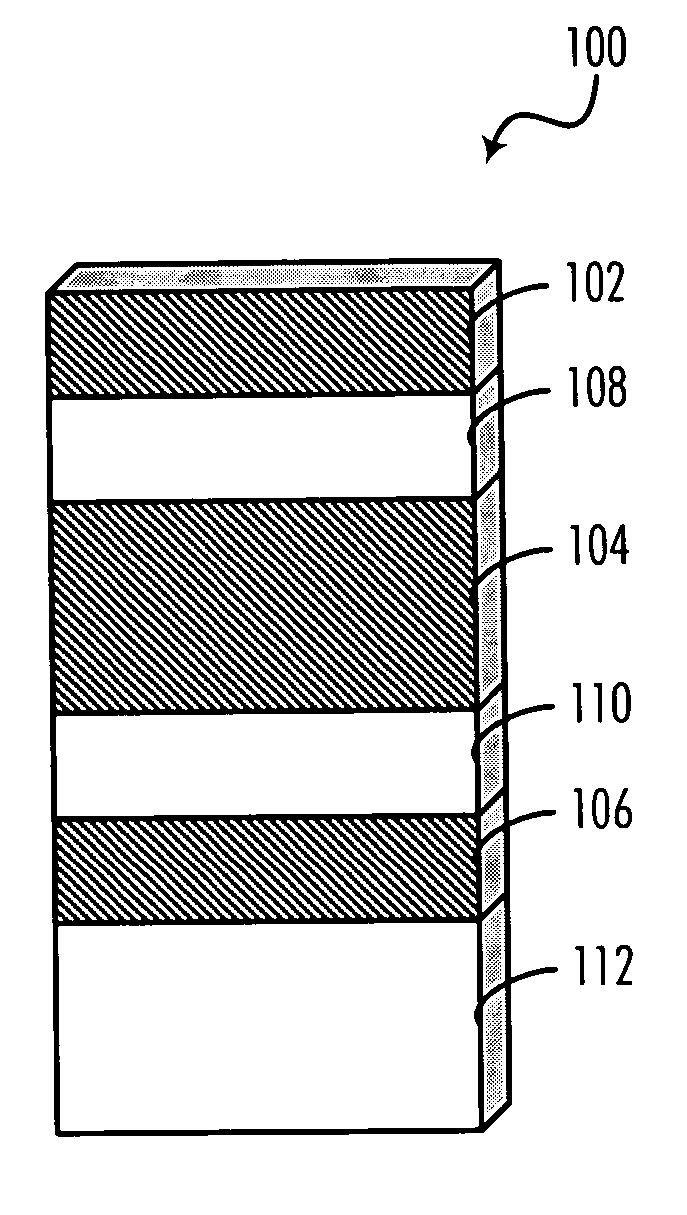
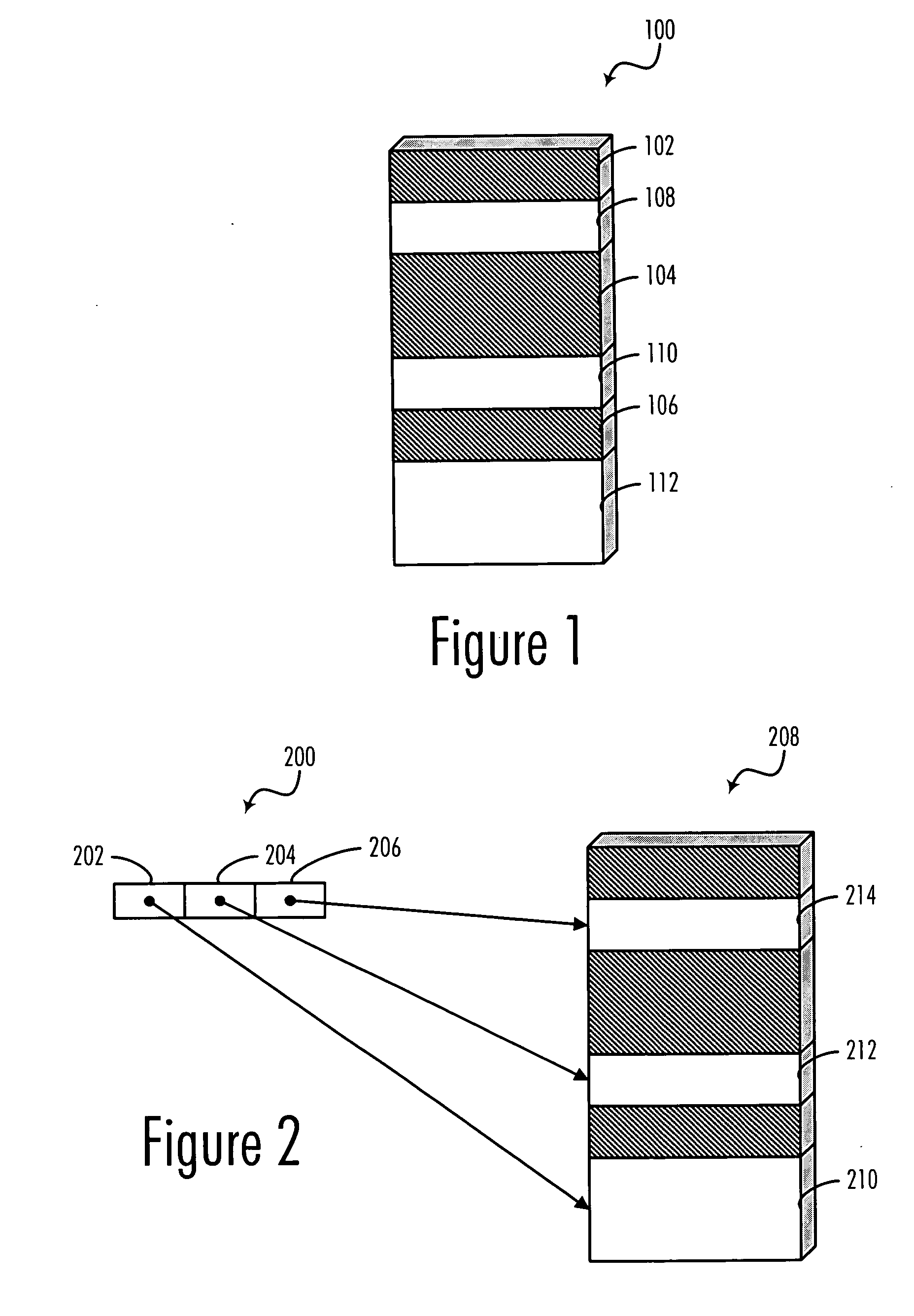
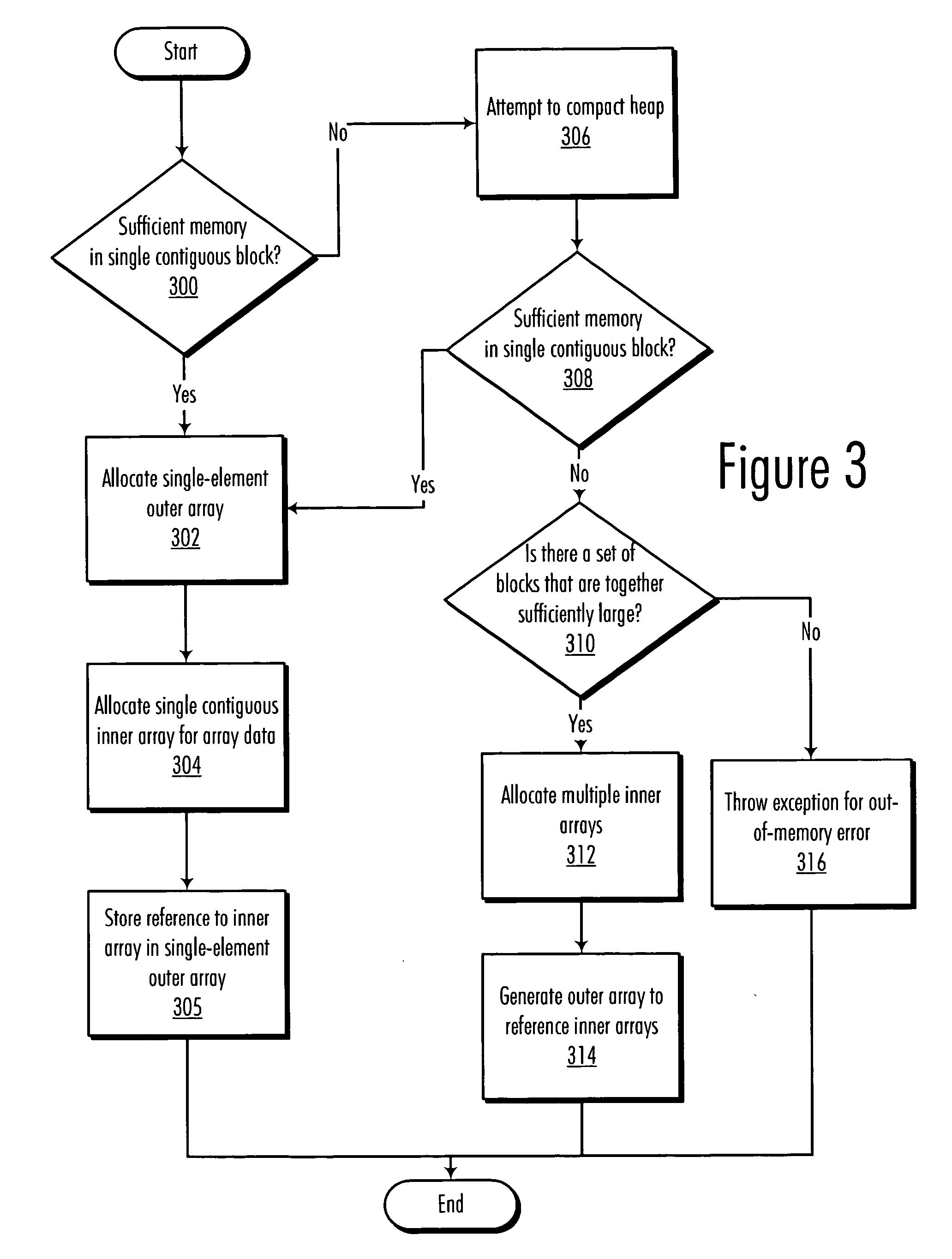
InactiveUS20060242635A1Minimize impactProgram controlMemory systemsData processing systemArray data structure
A method, computer program product, and data processing system for allocating memory for arrays in a fragmented heap is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, a JAVA virtual machine (JVM) is enhanced to organize each array as an array of arrays (or, internally, an array of pointers to arrays, since JAVA arrays are reference types). The individual “inner arrays” within the “outer array” are segments that collectively simulate a larger “virtual array.” Because all accesses and allocations of these arrays are performed by the JAVA virtual machine, the array segmentation is entirely transparent to the programmer, at least at the JAVA-language level. Support for native methods is provided by making relatively minor modifications to some of the array manipulation functions of the JAVA Native Interface (JNI), so as to minimize the impact of the segmentation scheme on native code.
Owner:IBM CORP
Android-system-based safety protection method
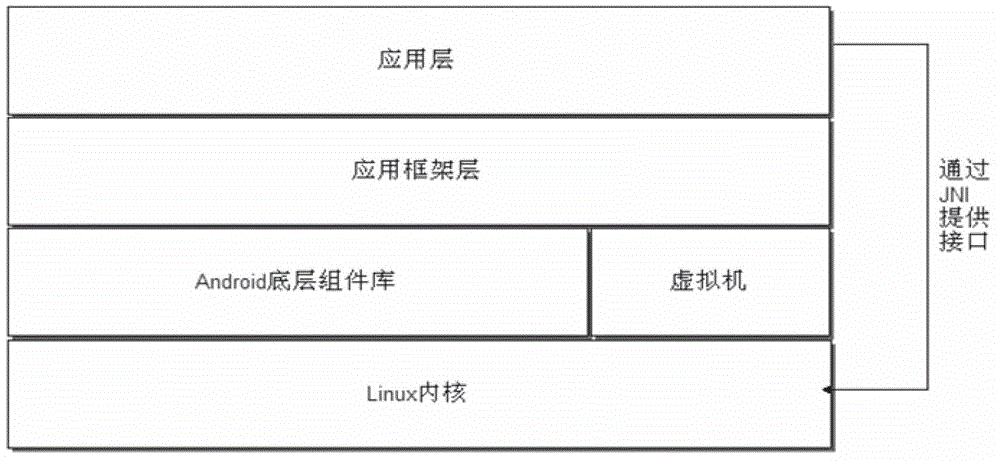
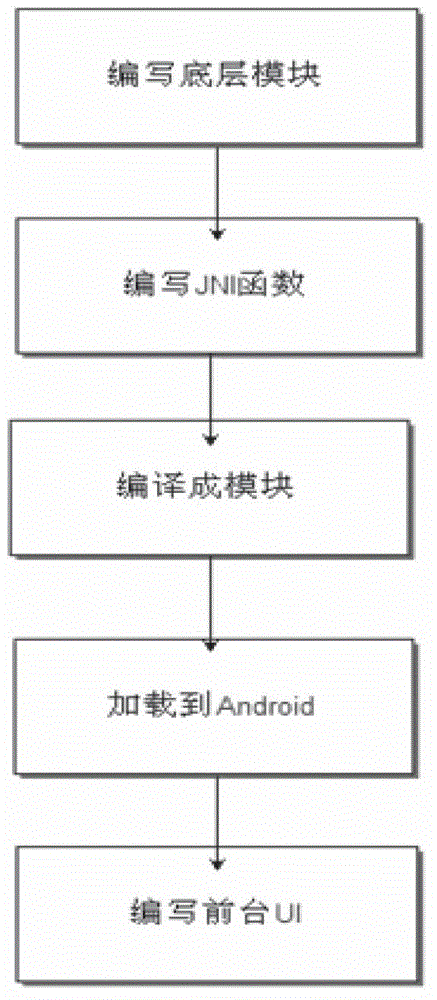
InactiveCN102867142AProtection from external network attacksImplement security mechanismsPlatform integrity maintainancePerformance functionOperational system
The invention relates to a computer operating system, and discloses an Android-system-based safety protection method. An Android-system-based mobile terminal is effectively protected from an external network attack. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: (a) writing a bottom-layer module according to a Linux2.6 core of Android, and reserving an interface for a java native interface (JNI) function to call; (b) writing the JNI function according to the specification of the JNI, calling a performance function of the bottom-layer module according to needs, and encapsulating the performance function; (c) compiling the performance function into a modular form by utilizing a compiler of the Android; (d) loading the compiled module into an Android system by using a debugging tool; and (e) writing a foreground user interface (UI) and a user processing program, and calling an interface provided by the loaded module. The method is applied to the safety protection of the Android-system-based mobile terminal.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
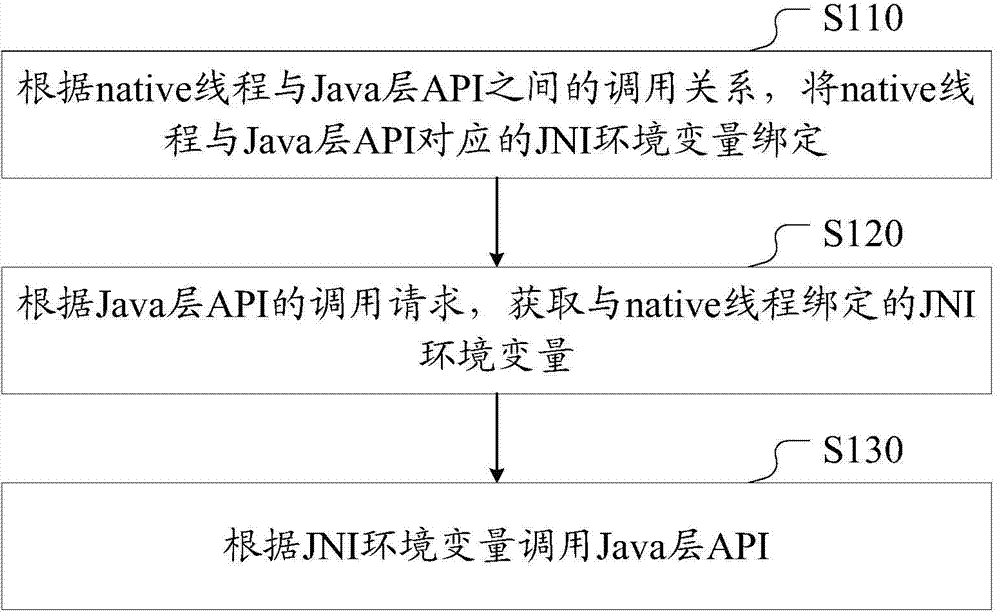
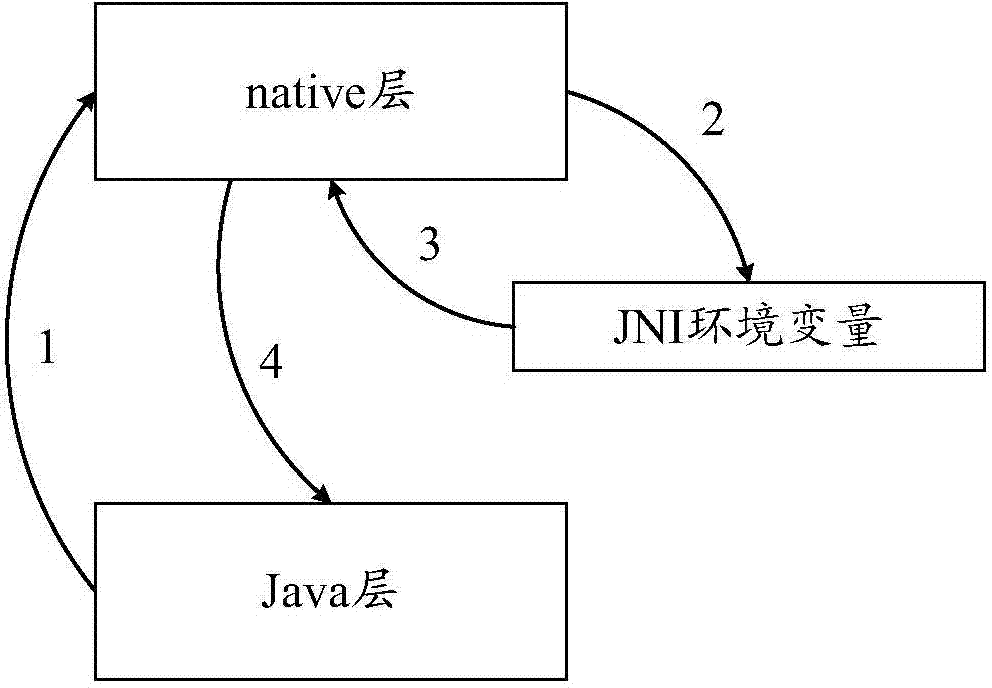
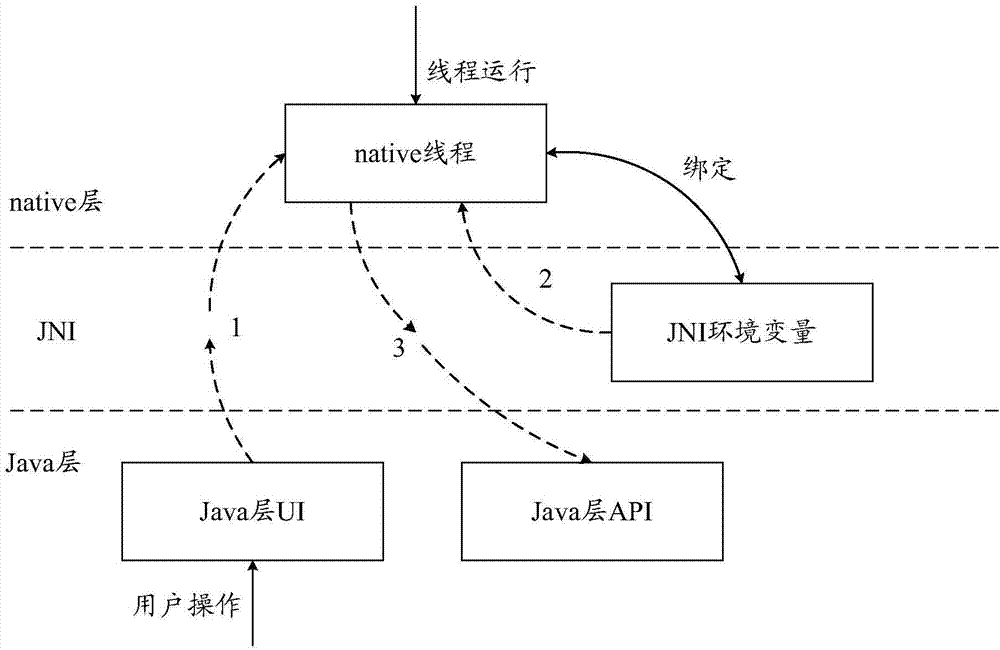
Method and device for calling Java layer API (Application Program Interface) by native layer in Android system
ActiveCN104778075AAvoid program crashesAvoid problems such as memory leaksMultiprogramming arrangementsApplication programming interfaceLayer interface
The invention discloses a method and a device for calling a Java layer API (Application Program Interface) by a native layer in an Android system. The method and the device are applied to the native layer of the Android system. The method comprises the steps of binding a native thread with a JNI (Java Native Interface) environment variable corresponding to the Java layer API according to the calling relationship between the native thread and the Java layer API; obtaining the JNI environment variable bound with the native thread according to a calling request of the Java layer API; calling the Java layer API according to the JNI environment variable. Through the scheme, in the process of calling the Java layer API by the native layer, the step of calling a native layer interface by the Java layer to set the JNI environment variable is omitted, the problems of program crash, memory leakage and the like possibly caused by frequent mutual calling between the native layer and the Java layer are avoided, and the efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIJING QIHOO TECH CO LTD
JAVA native interface array handling in a distributed JAVA virtual machine
InactiveUS20140068579A1Lower latencySoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsArray data structureParallel computing
A method for executing native code in a distributed Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is disclosed herein. The method may include receiving, in a first thread executing in a remote execution container, a first native code-generated call, such as a Java Native Interface (JNI) call, to a second thread, the first call including a first array write request. The first call may be stored in an instruction cache and bundled with a second native code-generated call and sent to the second thread. The calls are unbundled and executed in the second thread. An opaque handle to an array returned by the second call is bundled with corresponding array data and returned to the first thread. The array data of the bundle is stored in a data cache and retrieved in response to requests for the array data addressed to the second thread. A corresponding computer program product is also disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
C++ and Java communication method in Android platform and C++ and Java communication system in Android platform
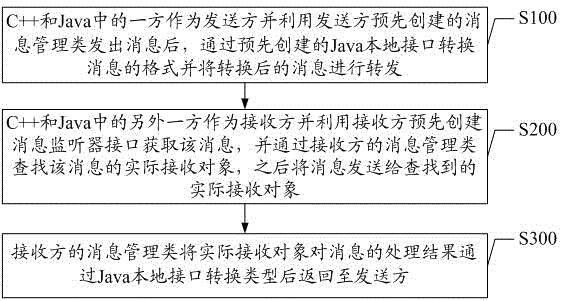
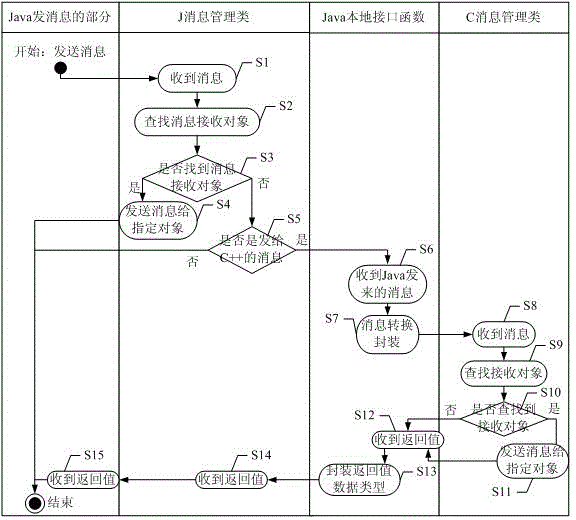
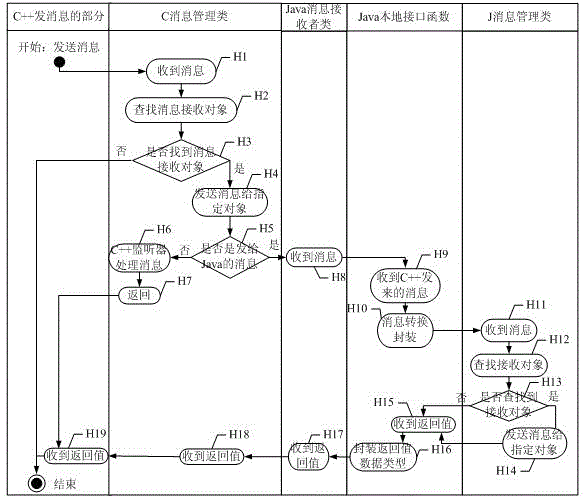
ActiveCN105279033AEasy development workReduce development difficultyInterprogram communicationCommunication interfaceCommunications system
The invention discloses a C++ and Java communication method in an Android platform and a C++ and Java communication system in the Android platform. The method comprises the following steps that: A, after either C++ or Java is used as a sender for sending out a message by utilizing a message management class of the sender, the message format is converted by a local interface of the Java, and the converted message is forwarded; B, the other one of the C++ or the Java is used as a receiver and obtains the message by utilizing a message monitor interface of the receiver, a practical receiving object is found by the message management class, and then, the message is sent to the found practical receiving object; and C, the return value of the practical received object is subjected to type conversion by the message management class of the receiver via the local interface of the Java and is returned to the sender. The method has the advantages that the complicated process for building Jni communication is omitted; a set of simple and practical C++ and Java communication interface is provided for a developer; and the development difficulty of programs involving with C++ and Java communication is reduced.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Method of integrating X Window Intrinsics based toolkits and widgets with JAVA
InactiveUS20050060724A1Without risk of data corruptionInterprogram communicationExecution for user interfacesIntrinsicsFile descriptor
A method of integrating an Xt Intrinsics based toolkit with a JAVA application. The application includes a process thread that implements an X event loop and an application thread that suspends execution of the event loop to allow a call to be made through the JAVA Native Interface to a toolkit or a widget to cause something to be displayed. The application thread includes a write socket to communicate a token to a read socket of the event loop, and performs a blocking read suspending the thread. The event loop returns an acknowledgment token via a write socket to a read socket of the thread that unblocks its blocking read and the event loop invokes its own blocking read suspending its execution. The file descriptor function, XtAppAddInput, preferably, is used to read the token and to set the blocking read. After a toolkit call is made, a token is sent from a second write socket of the thread to a second read socket of the event loop that unblocks its blocking read resuming the event loop. JAVA multithreading support services, such as JAVA's wait and notifyAll methods, are employed in multithreaded applications to ensure that only one thread at a time can make a call. Use of a separate Intrinsics application context to service the event loop is employed, windows are managed in separate hierarchies associated with each application context, and a special JAVA Canvas manages native windows transparent to the programmer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Android terminal and method for realizing TR069 network management agent
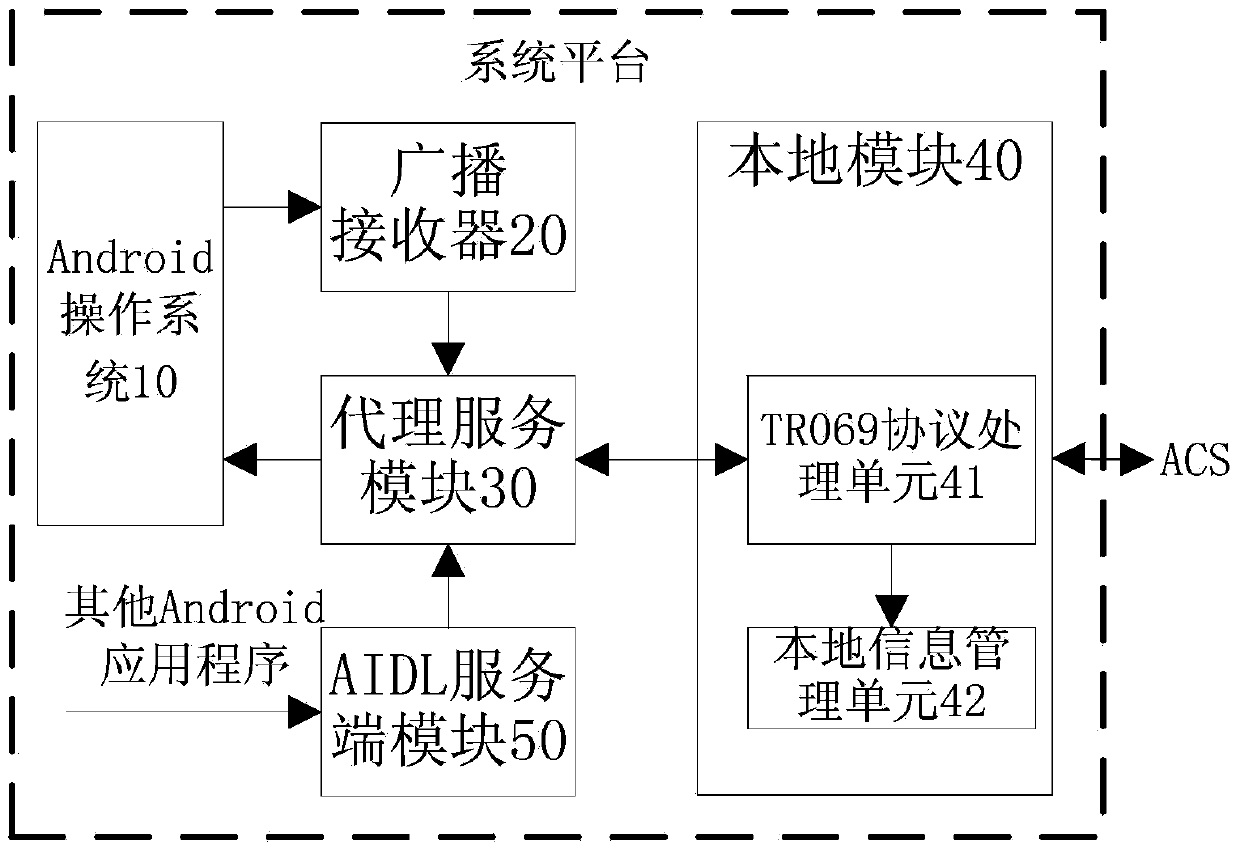
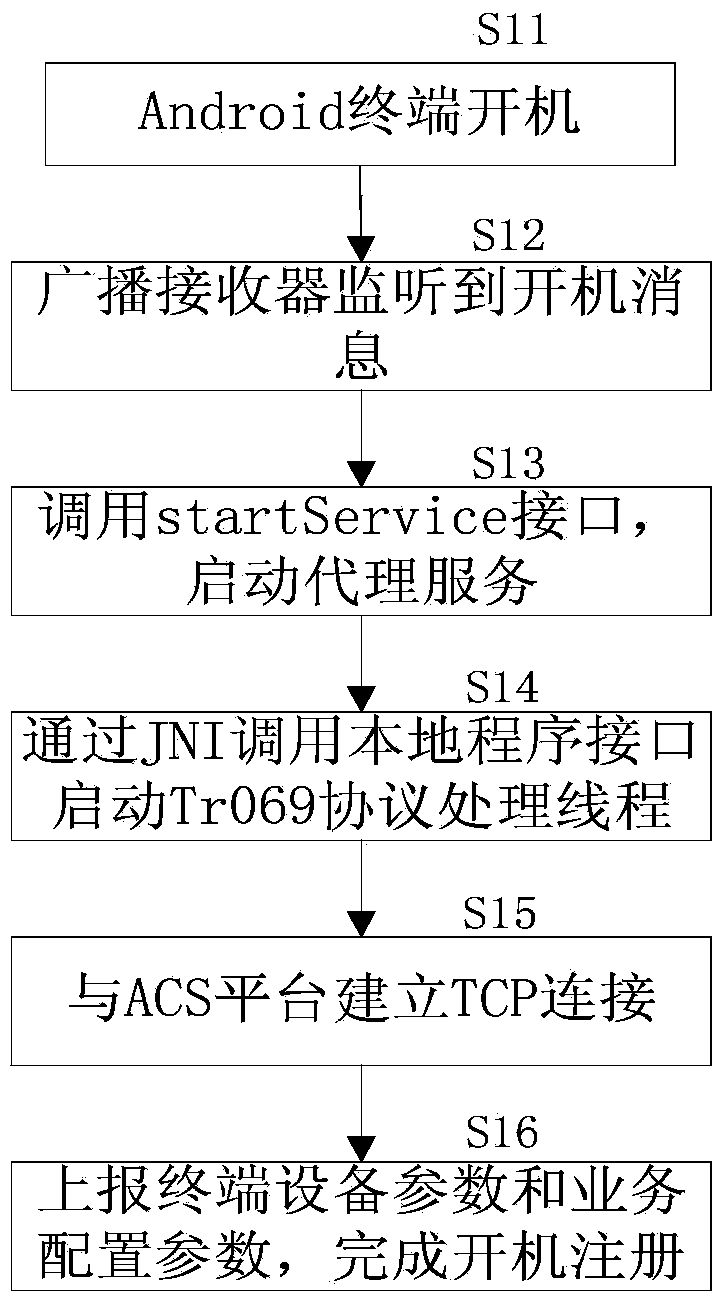
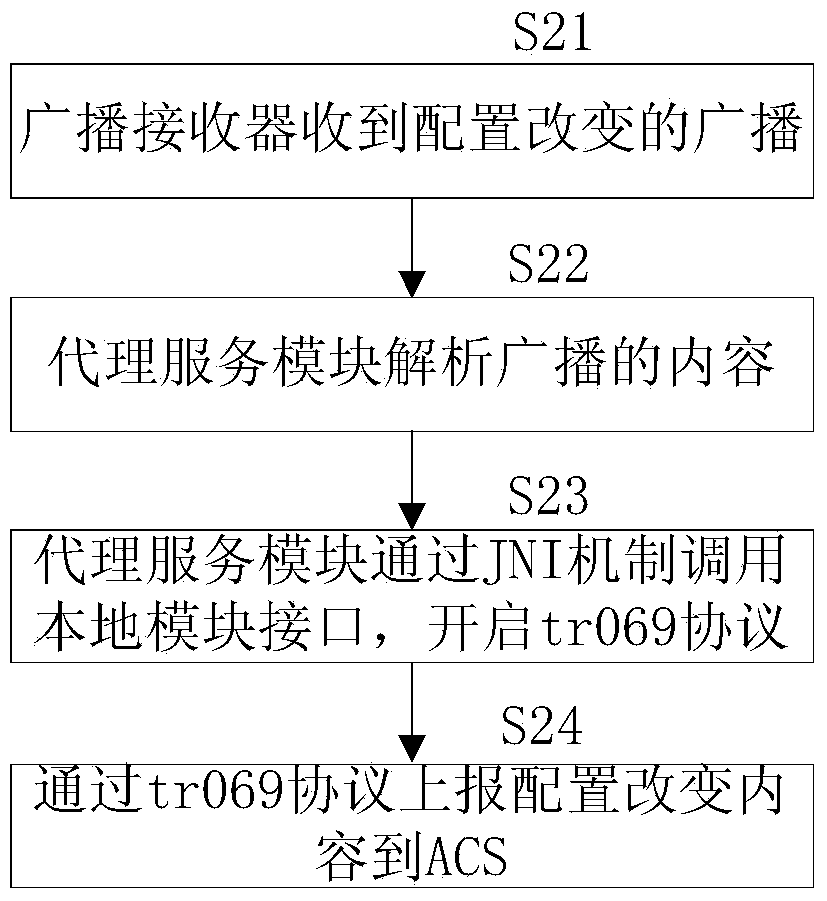
ActiveCN104184618AEffective analysis efficiencyOvercoming Fragmentation DisadvantagesData switching networksInformation repositorySystem configuration
The invention discloses an Android terminal and a method for realizing a TR069 network management agent. The method comprises the steps of continuously using an a TR069 protocol processing unit of a c-code local module on an original Linux platform to carry out interaction with a network-side network management platform, continuously using a local information management unit applicable to an Android environment on the original Linux platform to carry out maintenance on a local information base, and using an agent service module and an AIDL (Android interface definition language) service end module which correspond to an Android version prepared by using JAVA to carry out interaction with a user-side Android application program; the agent service module and the AIDL service end module mutually call the TR069 protocol processing unit through a JNI (Java native interface), thereby realizing report and registration of system configuration, updating of the system configuration and calling of related functions of Android application programs. The method disclosed by the invention makes full use of a JNI mechanism of an Android system, realizes mutual call of Java and local C-codes, and realizes the TR069 network management agent; a defect of fragmentation of the Android system is overcome; and a scheme of an existing Linux platform C can be directly transplanted.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for simulating multimedia subsystem based on IP
InactiveCN101008904AImprove scalabilityEasy to testTransmissionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationExtensibilitySimulation
This invention relates to one multi-media sub system based on IP , which comprises at least one leg simulation engine, at least one simulation machine and at least one compatible test part, wherein, the engine comprises at least one Java virtual machine, at least one agreement layer and at least one leg execution engine; the agreement layer and above leg executive engine interface is of Java local interface; the agreement layer comprises at least on dialogue initial agreement, one super text transmission agreement, one expansive label language, one simple subject visit agreement, one Diameter or Radium, one COPS and one real time transmission or real time transmission control agreement.
Owner:诺基亚西门子通信系统技术(北京)有限公司
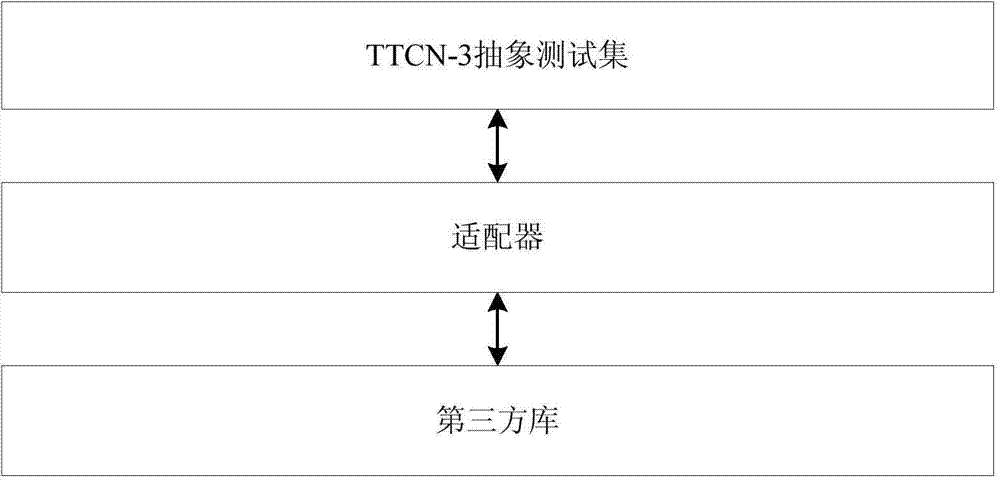
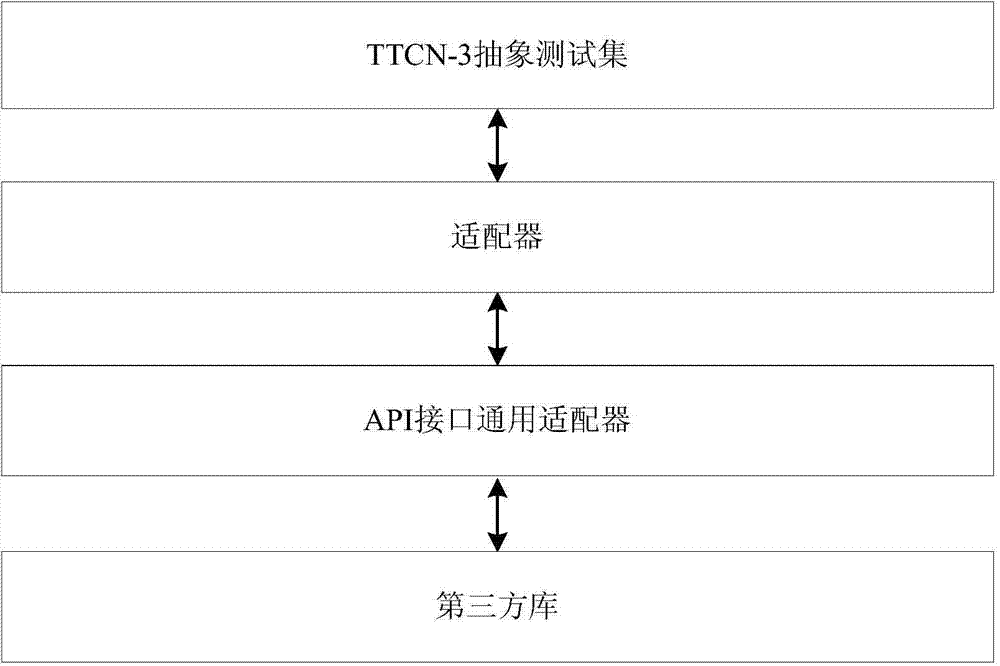
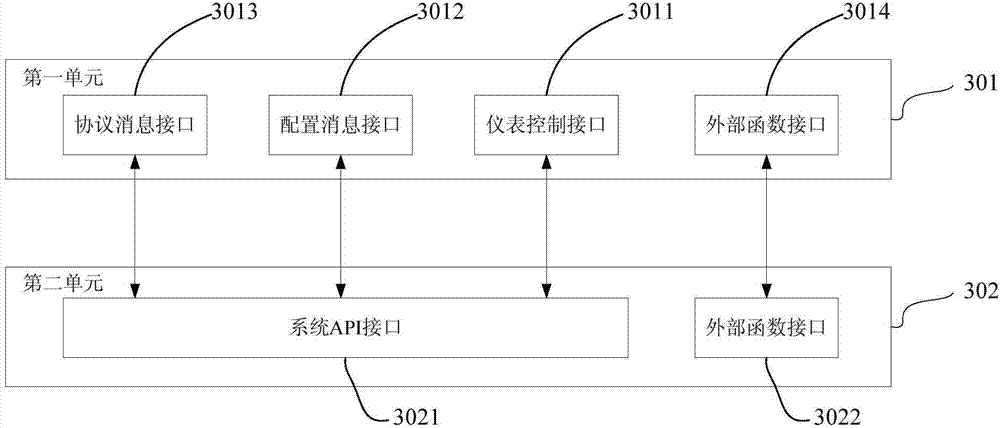
Terminal consistency testing method and API (application program interface) interface general adapter for terminal consistency testing method
ActiveCN103546342AGuaranteed uptimePortableSoftware testing/debuggingData switching networksApplication programming interfaceComputer terminal
The invention provides a terminal consistency testing method and an API (application program interface) interface general adapter for the terminal consistency testing method. The API interface general adapter comprises a first unit and a second unit. The interface of the first unit is java format and used for communicating with testing and testing control symbol 3TTCN-3 test set equipment; the interface of the second unit is C or C++ language format and used for communicating with an instrument and an external function library. The first unit calls the second unit through JNI (java native interface). The adapter performs a terminal consistency testing and is capable of mutually transforming port data format of a TTCN-3 abstracted test set and data format supported by the instrument so as to shield difference of bottom instruments, so that the testing system can be normally operated on main computers with different operating systems; the adapter is capable of supporting various external function libraries, so that the terminal testing system has good portability and expandability.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF INFORMATION & COMM
Method and device for injecting Java bit codes into target process
ActiveCN104657258AFunction increaseSoftware testing/debuggingProgram controlOperational systemProcessor register
Method and System for injecting Java bytecode into a target process of an application program are disclosed. The method includes: at a device having one or more processors and memory: during execution of the target process of the application program, detecting a call to load a predetermined code injection function; in response to the detected call to load the predetermined code injection function, loading Java bytecode referenced by the code injection function into a virtual machine; in accordance with a pre-stored Java native interface corresponding to the loaded Java bytecode, calling an entrypoint function in the Java bytecode, wherein the entrypoint function is configured to perform one or more extended tasks for the application program; and executing the entrypoint function in the virtual machine to accomplish the one or more extended tasks of the application program.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Method of integrating X Window Intrinsics based toolkits and widgets with JAVA
InactiveUS7546612B2Without risk of data corruptionProgram synchronisationInterprogram communicationIntrinsicsFile descriptor
A method of integrating an Xt Intrinsics based toolkit with a JAVA application. The application includes a process thread that implements an X event loop and an application thread that suspends execution of the event loop to allow a call to be made through the JAVA Native Interface to a toolkit or a widget to cause something to be displayed. The application thread includes a write socket to communicate a token to a read socket of the event loop, and performs a blocking read suspending the thread. The event loop returns an acknowledgment token via a write socket to a read socket of the thread that unblocks its blocking read and the event loop invokes its own blocking read suspending its execution. The file descriptor function, XtAppAddInput, preferably, is used to read the token and to set the blocking read. After a toolkit call is made, a token is sent from a second write socket of the thread to a second read socket of the event loop that unblocks its blocking read resuming the event loop. JAVA multithreading support services, such as JAVA's wait and notifyAll methods, are employed in multithreaded applications to ensure that only one thread at a time can make a call. Use of a separate Intrinsics application context to service the event loop is employed, windows are managed in separate hierarchies associated with each application context, and a special JAVA Canvas manages native windows transparent to the programmer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method of loading client certificate for Android system by OpenSSL engine
InactiveCN103065078AAchieving Security and ReliabilityDigital data authenticationTransmissionInterface layerHypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer
The invention relates to a processing method, in particular to a method of loading a client certificate for an Android system by OpenSSL engine, and belongs to the field of techniques of loading client certificates in the Android system. According to the technical scheme, the method includes the steps of a, loading the OpenSSL engine in an Android system client, and allowing the OpenSSL engine to take out the preset client certificate and a preset key from a Java local interface layer; and b, allowing an OpenSSL callback function to import the obtained client certificate and the obtained key into communication flow in a secure sockets layer between the Android system client and a HTTPS (hypertext transfer protocol secure) server so as to allow the HTTPS server to verify the client certificate for the Android system client. The method is convenient to operate and is higher in reliability of loading the client certificate.
Owner:宁波市奉化区金都机械铸造有限公司
Method for cross-platform communication of mobile terminal
InactiveCN108848154AImprove securityImprove efficiencyExecution paradigmsTransmissionAccess methodMessage type
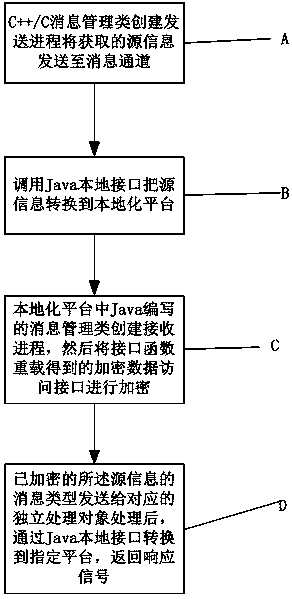
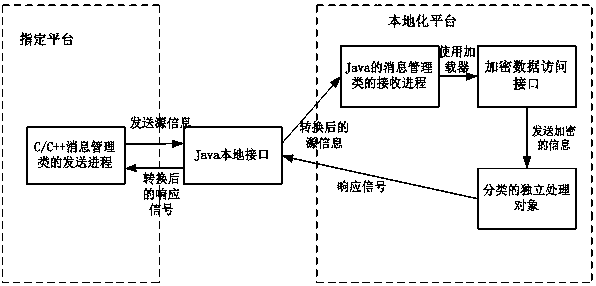
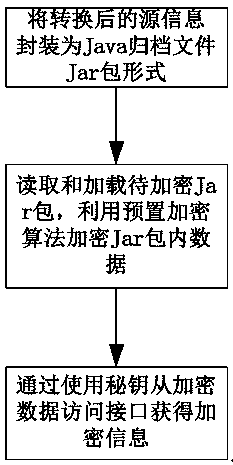
The invention relates to a method for cross-platform communication of a mobile terminal. The access method comprises the following steps: A, creating a sending process to send source information by using a C++ / C message management class written by a specified platform by the mobile terminal; B, calling a pre-created Java local interface to convert from the specified platform to the localization platform; C, creating a receiving process by the message management class written in Java in the localization platform, reloading the message listener interface pre-created in the Java part as an encrypted data access interface, and performing the encryption operation; and D, sending the message management class written by Java in the localization platform to the corresponding independent processingobject according to the message type of the encrypted source information, correspondingly converting the processing result from the localization platform to the specified platform through the Java local interface, and returning a response signal to complete communication. Compared with the prior art, the invention reduces the time for establishing communication in a weak security environment, andreduces the difficulty of cross-platform development.
Owner:AMICRO SEMICON CORP
A Big Data Processing System
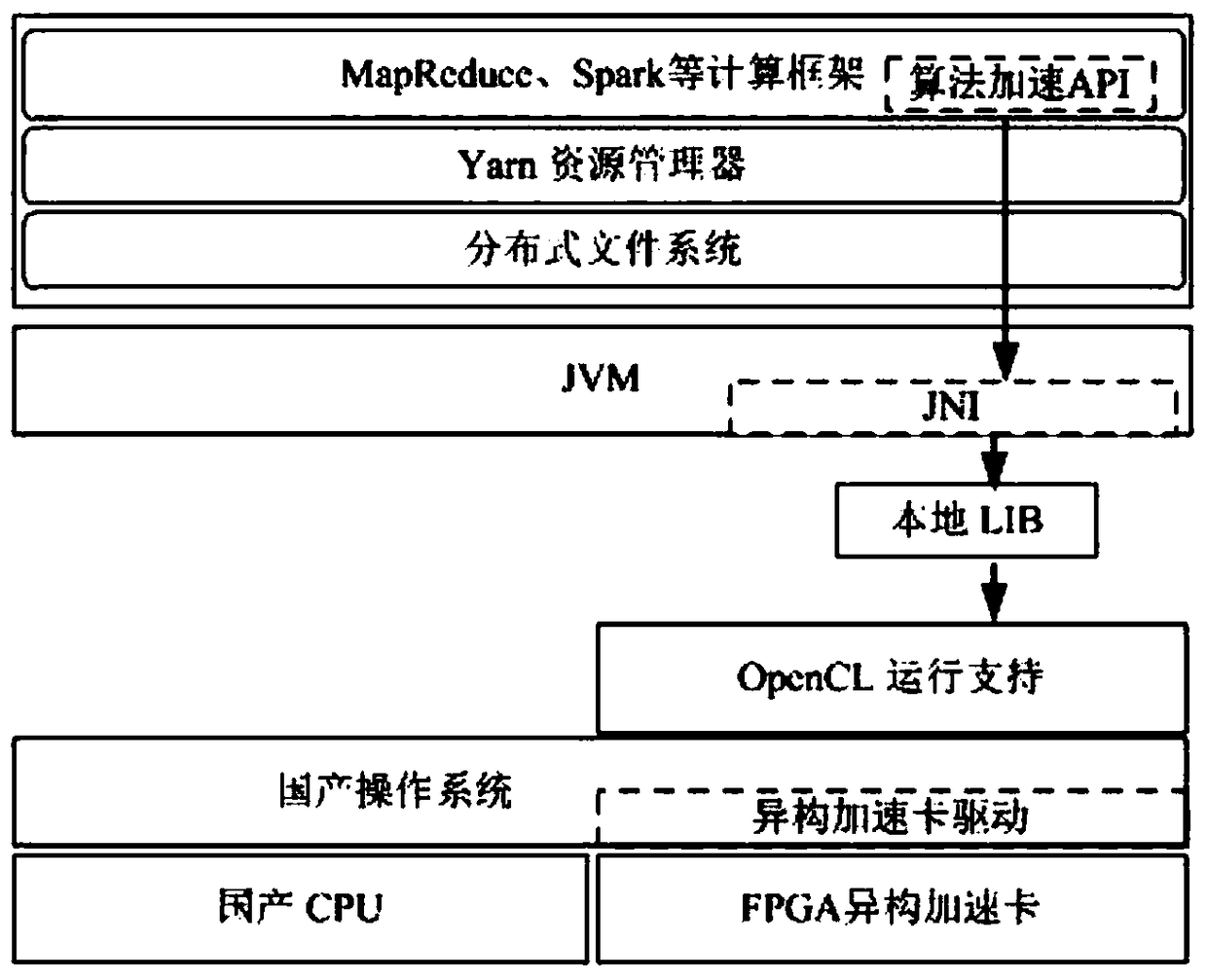
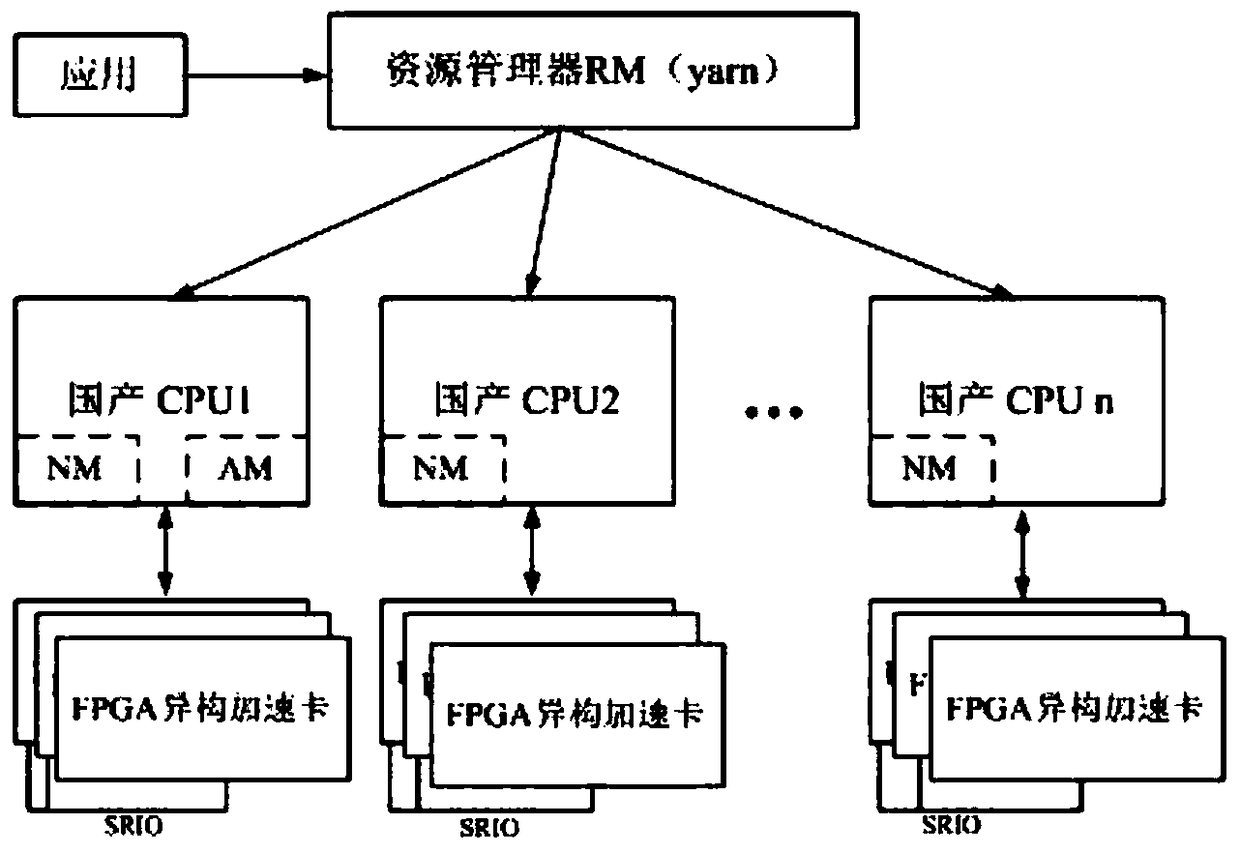
PendingCN109343896AImplement parallel processingReduce data transmission delayConcurrent instruction executionData transmissionJava Native Interface
The invention discloses a big data processing system, comprising a plurality of data nodes. Each data node comprises: a bottom hardware layer, wherein the bottom hardware layer at least comprises a CPU and an FPGA heterogeneous acceleration card. The FPGA heterogeneous acceleration card communicates with the CPU through a bus. A system drive layer load at least an FPGA heterogeneous acceleration card driver; A JVM layer provided with a Java native interface; Big data frame layer, which invokes FPGA heterogeneous acceleration card through Java local interface through JVM layer; And a running support library layer which is used for FPGA heterogeneous computing. The large data processing system of the invention can meet the real-time requirement of the task with high computational complexity,realize the pipeline parallel processing of the computational task, reduce the data transmission delay of the JVM and the FPGA, and realize the online updating function of the label.
Owner:SHANDONG CHAOYUE DATA CONTROL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
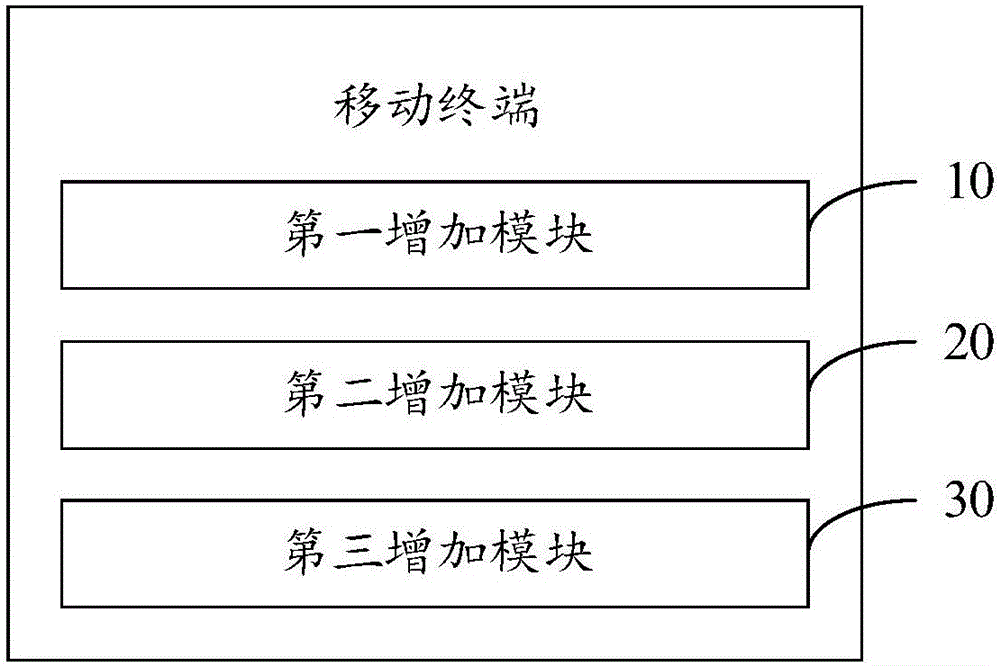
Mobile terminal and method for implementing super screenshot
InactiveCN106843689AReduce the difficulty of implementationReduce workloadCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecific program execution arrangementsComputer architectureApplication programming interface
The invention discloses a mobile terminal which comprises a first add module, a second add module and a third add module. The first add module is used for adding particular implementation of super screenshot functions to a hardware abstraction layer, so that data acquired by a fingerprint chip of a bottom layer can be abstracted and encapsulated; the second add module is used for adding callback functions for calling back the data acquired by the fingerprint chip to a JNI (java native interface) layer, so that operation interfaces can be provided for an application framework layer; the third add module is used for adding application program programming interfaces for implementing the super screenshot functions to the application framework layer, so that the application program programming interfaces can be invoked by an application layer, and the super screenshot functions can be implemented. The invention further discloses a method for implementing super screenshot. The mobile terminal and the method have the advantage that the super screenshot implementation difficulty can be lowered.
Owner:宁波珍学网教育科技有限公司
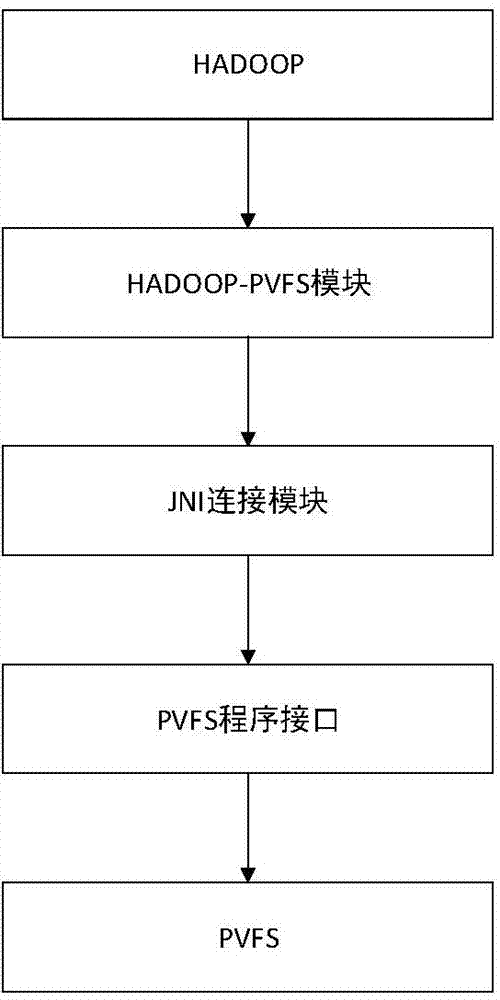
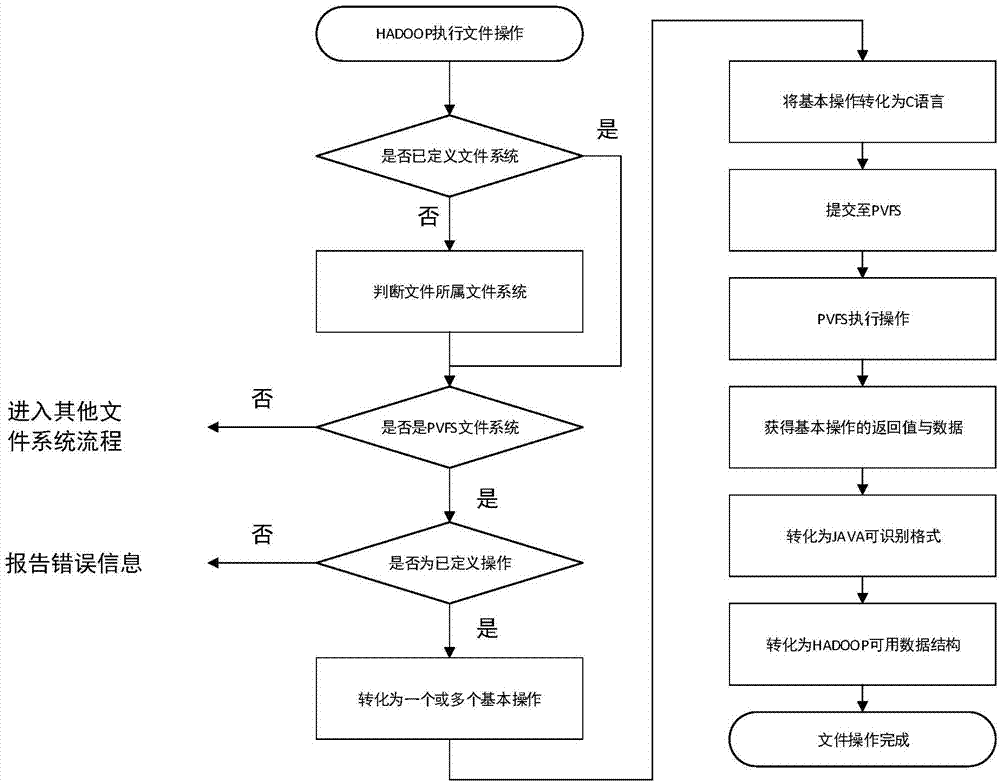
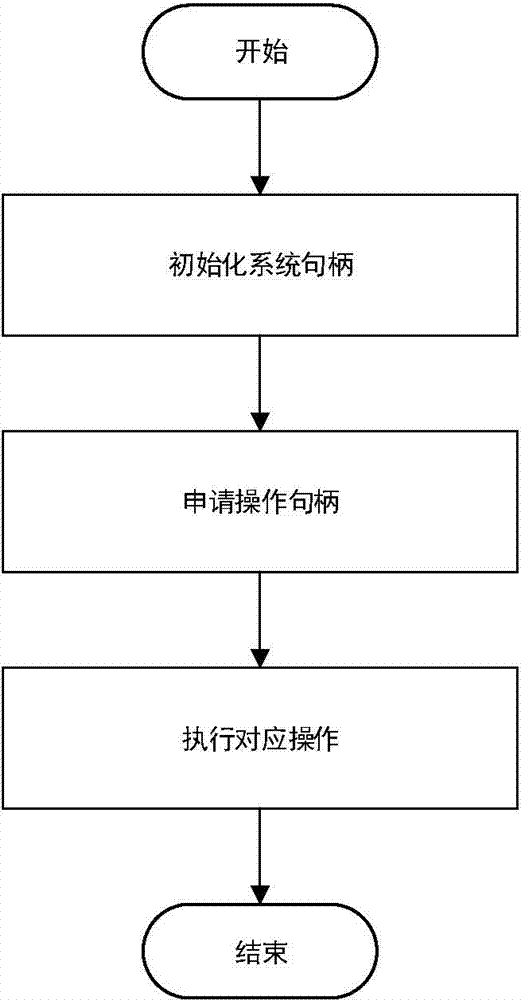
Method for replacing Hadoop storage module by using PVFS (Parallel Virtual File System)
ActiveCN104850401AImprove parallelismReduce overheadSpecific program execution arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsVirtual file systemMap reduce
A method for replacing HADOOP storage module by using a PVFS (Parallel Virtual File System) utilizes the parallel virtual file system PVFS to replace a Hadoop distributed type file system HDFS module. By virtue of the method, the connection from HADOOP to the PVFS is realized; and three modules including a PVFS program interface, a HADOOP-PVFS module and a JNI (Java Native Interface) connection module are provided. The method provided by the invention aims at selecting the more suitable distributed type file system as the storage module of the HADOOP to replace the HDFS, so that the expenditure of the HADOOP in the aspect of file operation is reduced, Map Reduce calculation of the HADOOP is improved, and particularly, the representation of data dense type calculation is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com