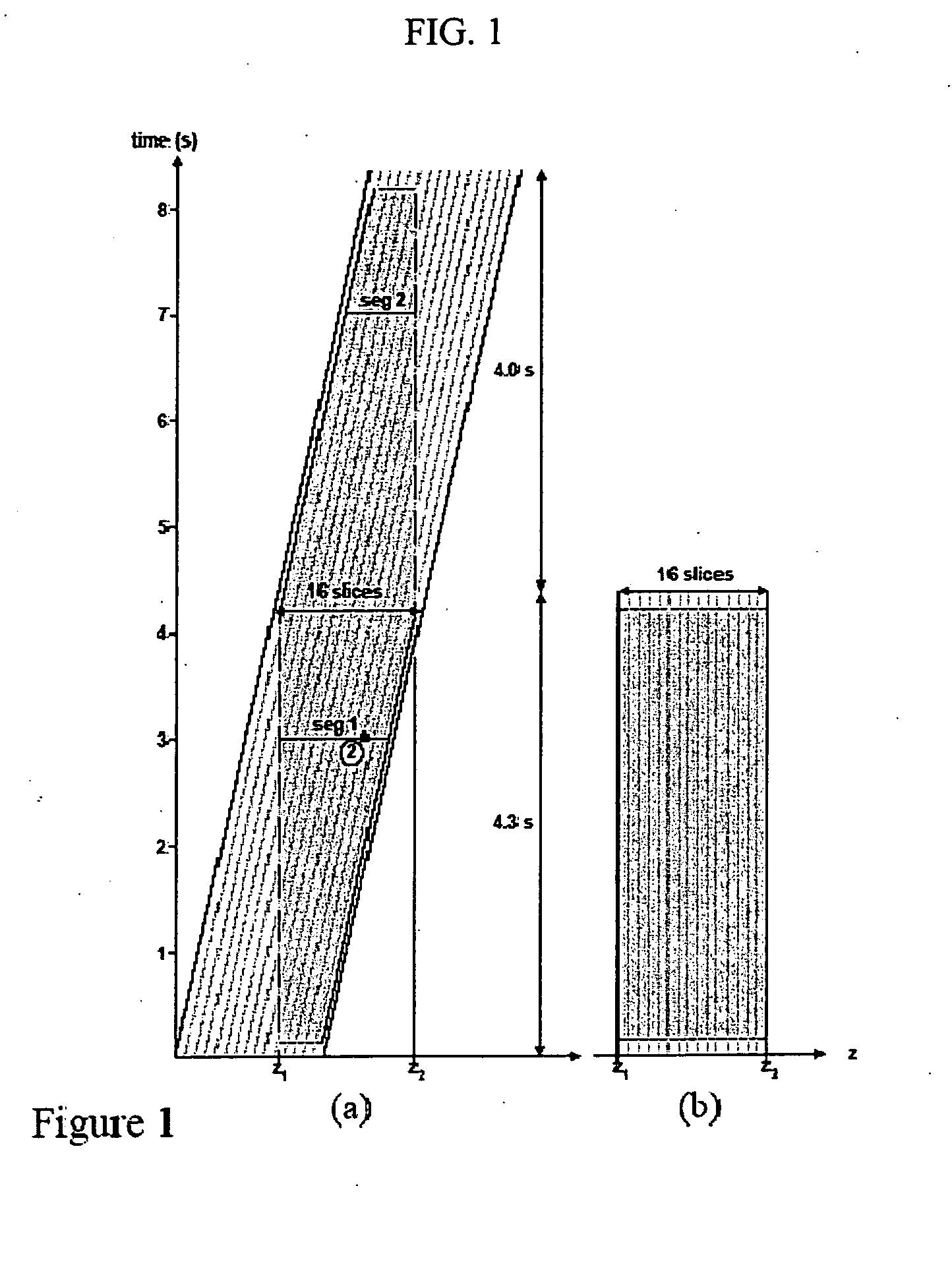
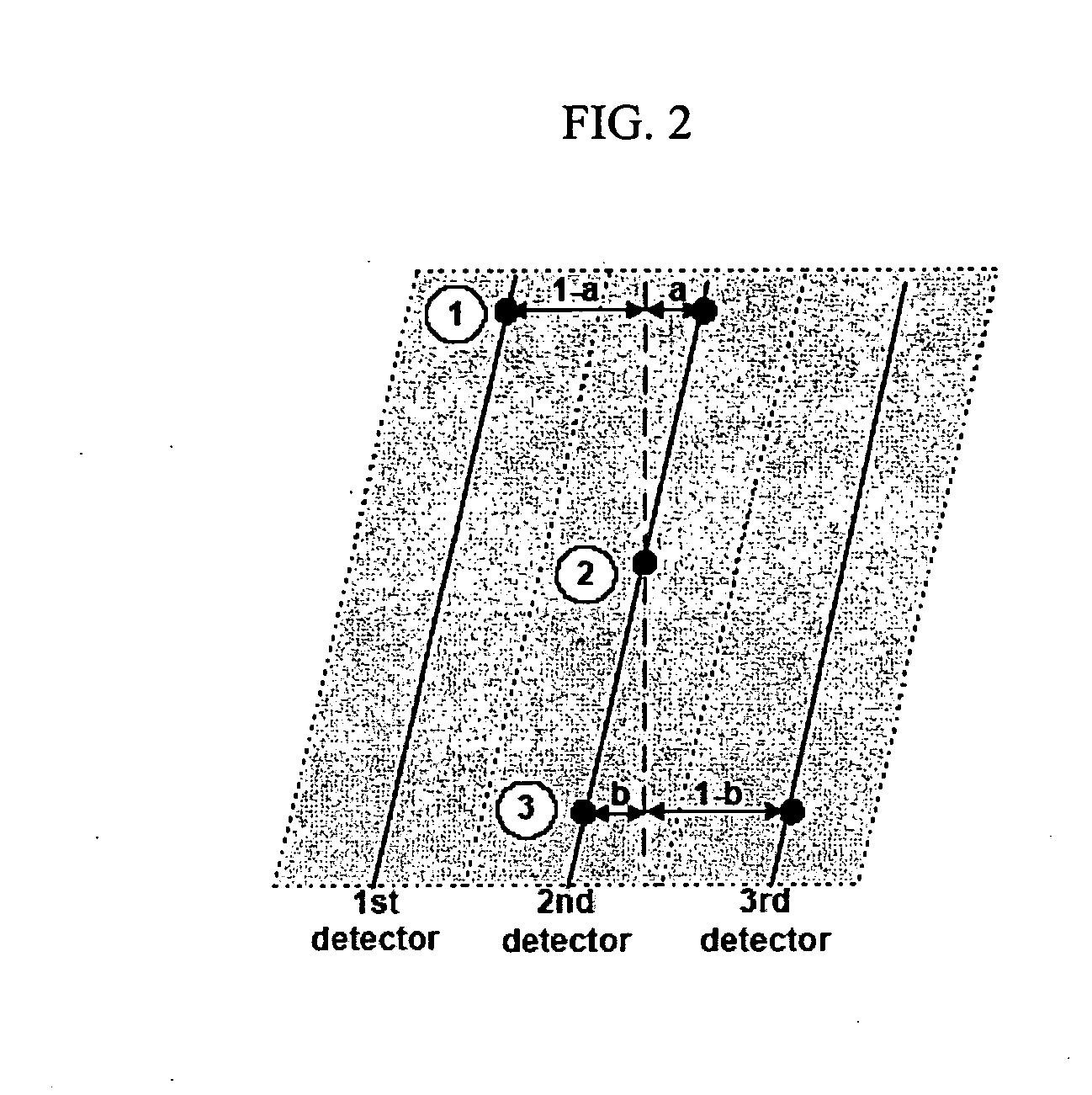
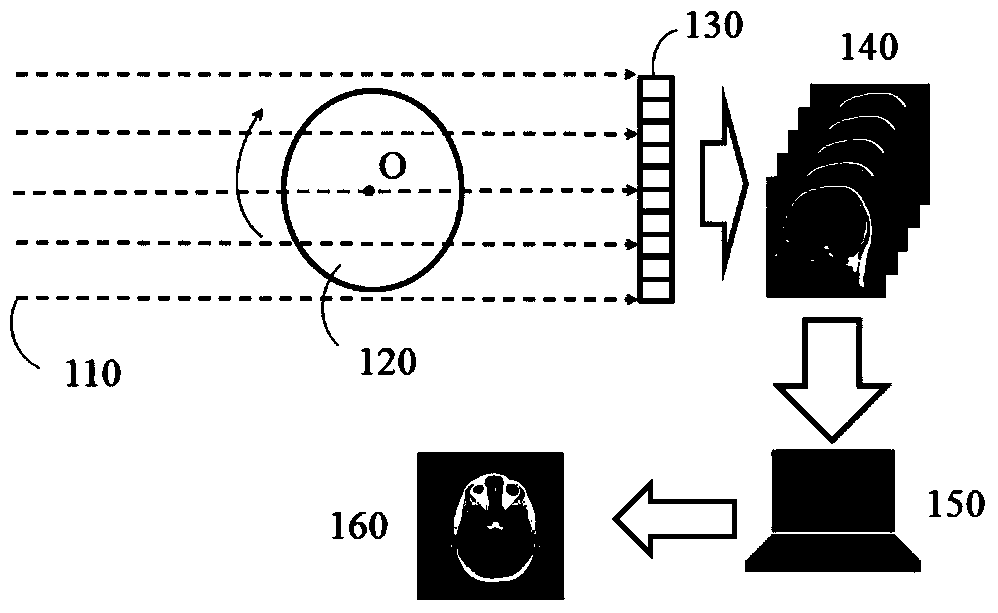
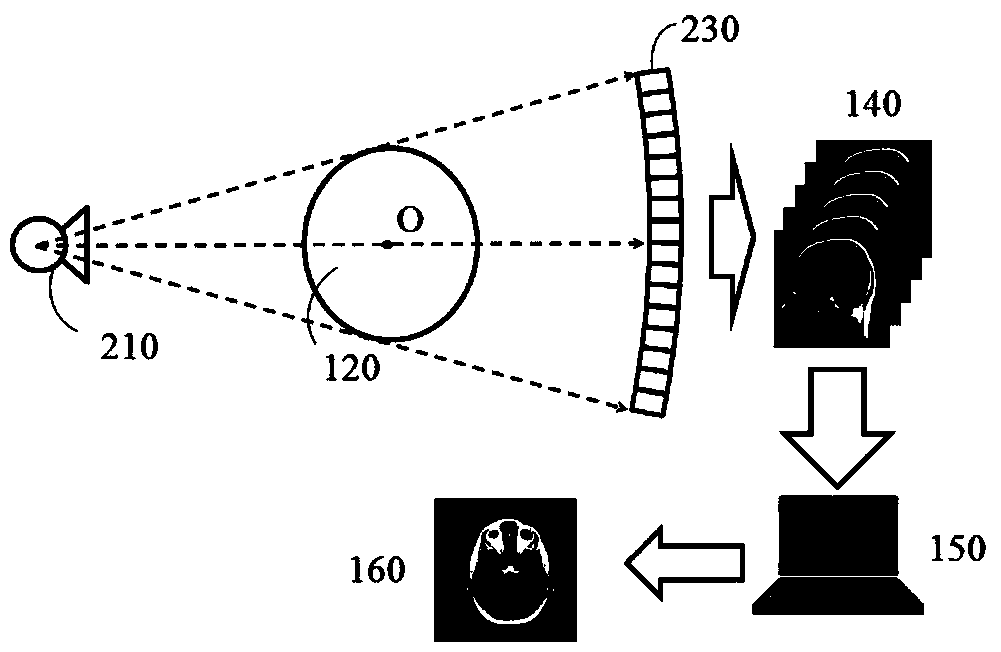
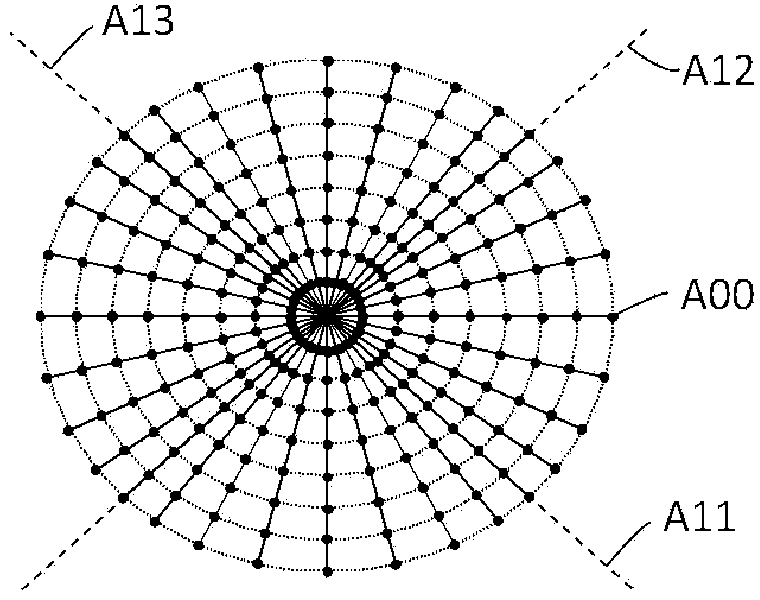
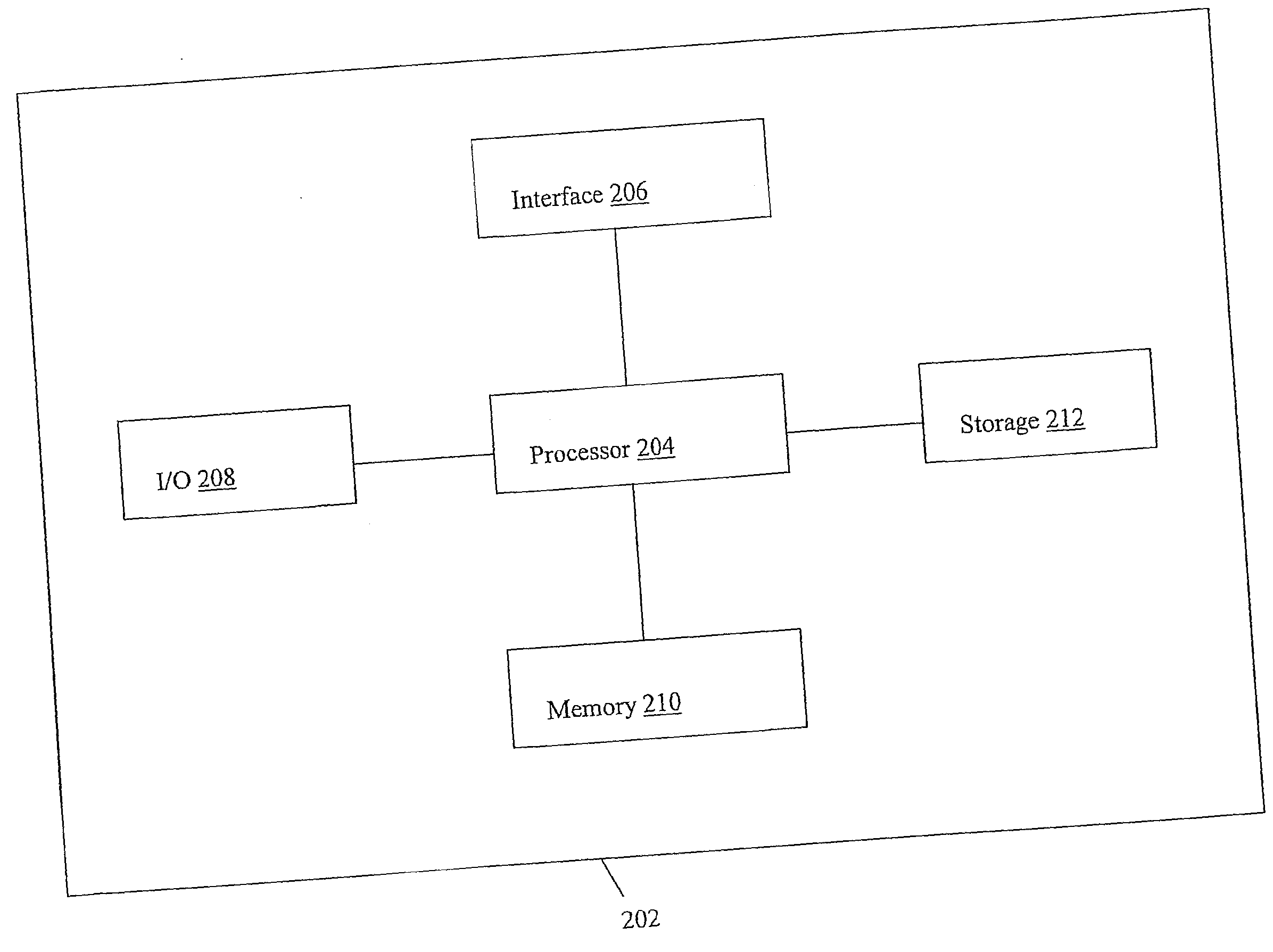
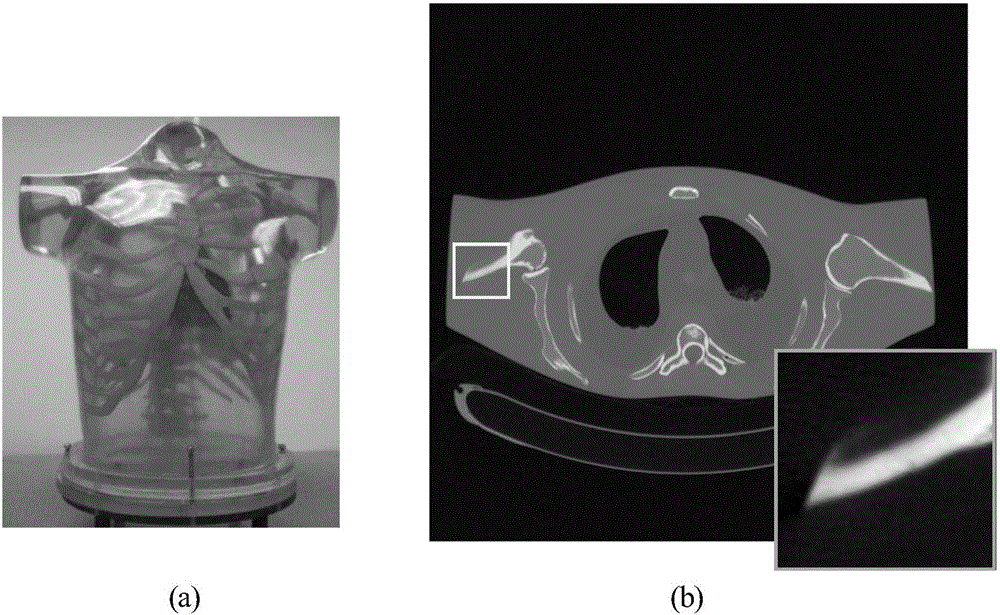
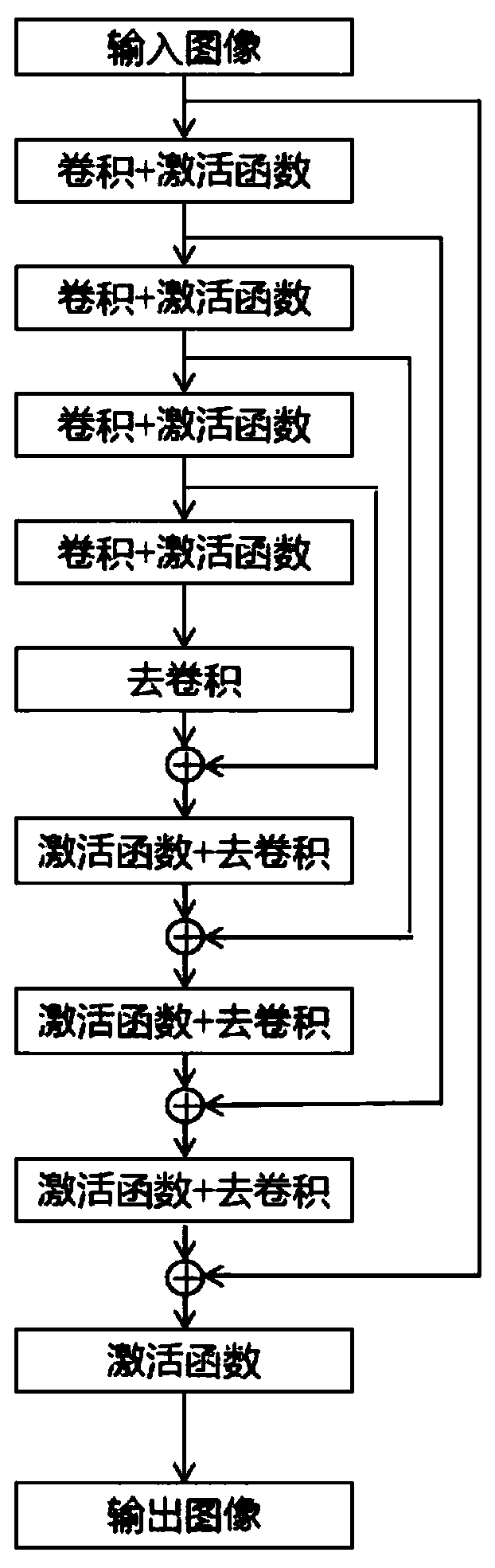
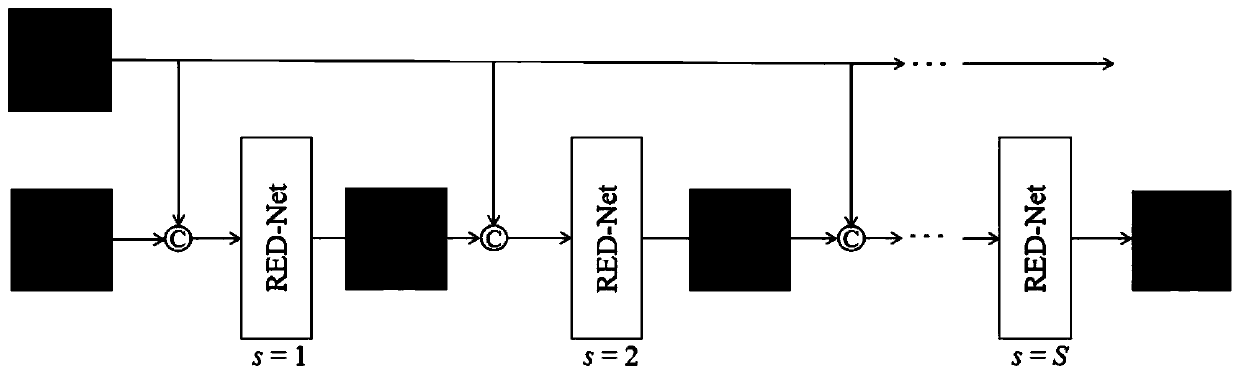
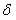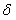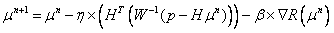Patents
Literature
63 results about "Low dose ct" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
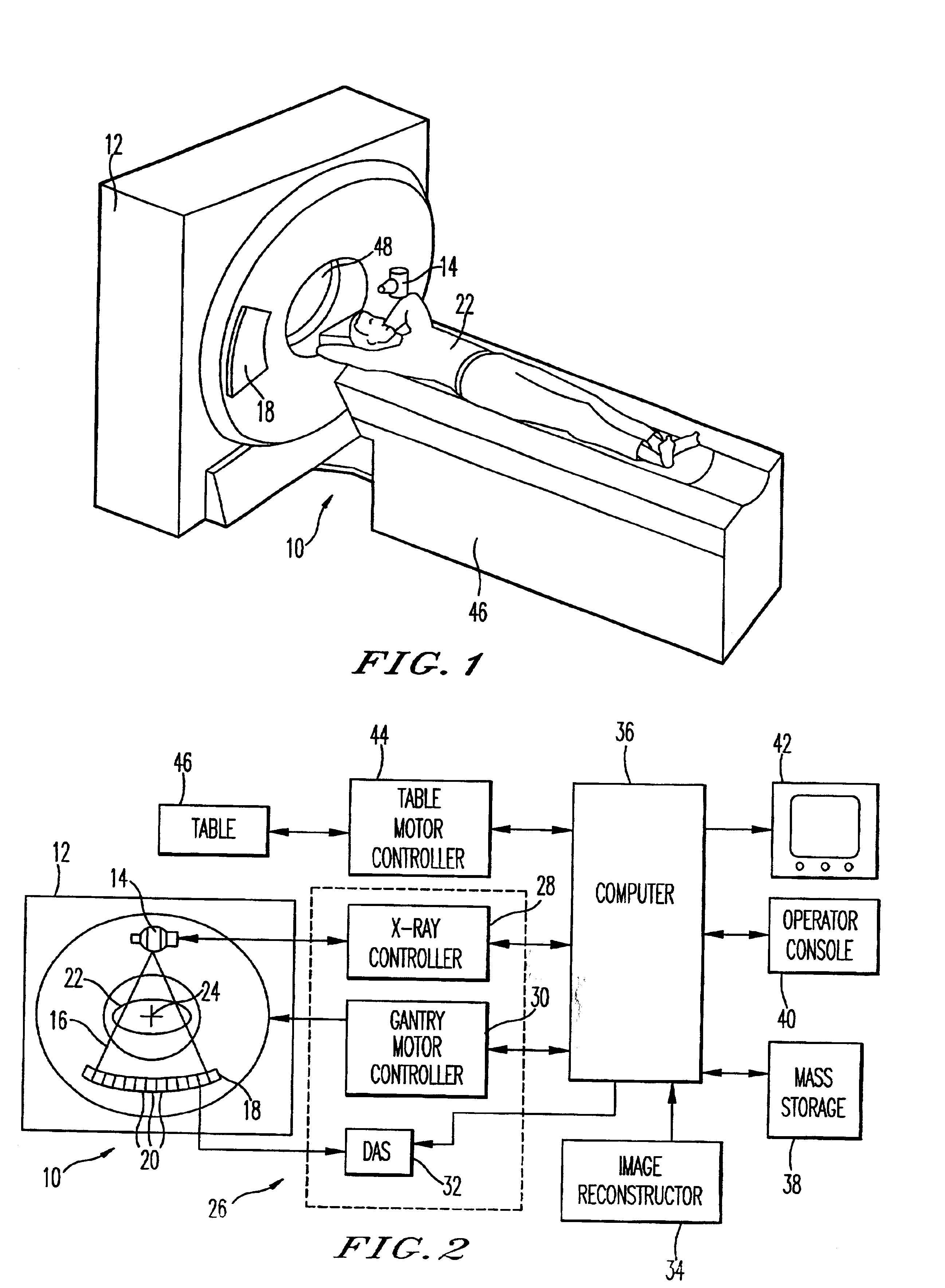
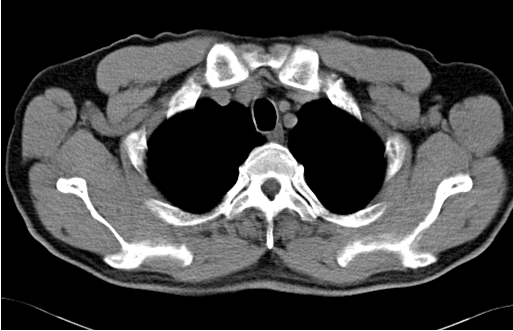
A low dose Computed Tomography (CT) scan provides an image of the inside of a patient’s body with minimal radiation. This reduces risks for the patient by limiting overall radiation exposure in association with the medical imaging study.
Computerized scheme for distinction between benign and malignant nodules in thoracic low-dose CT
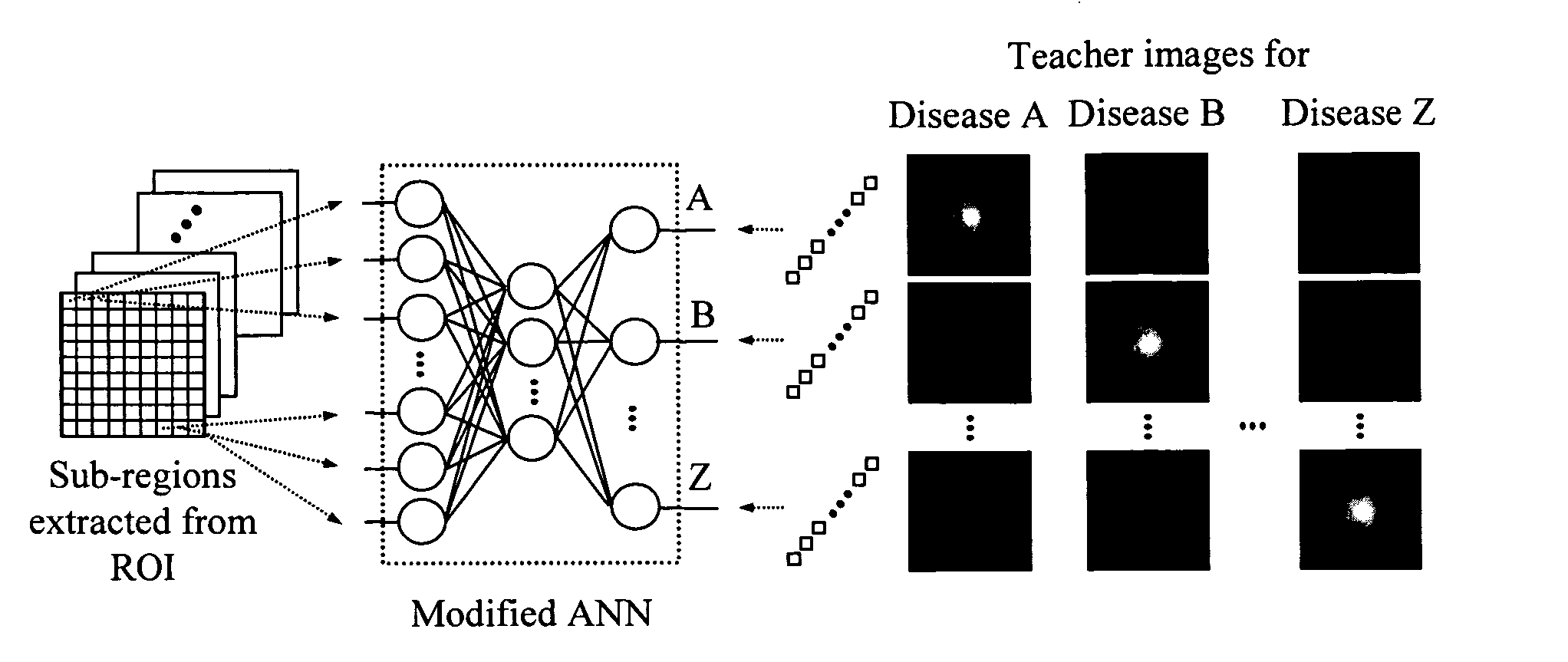
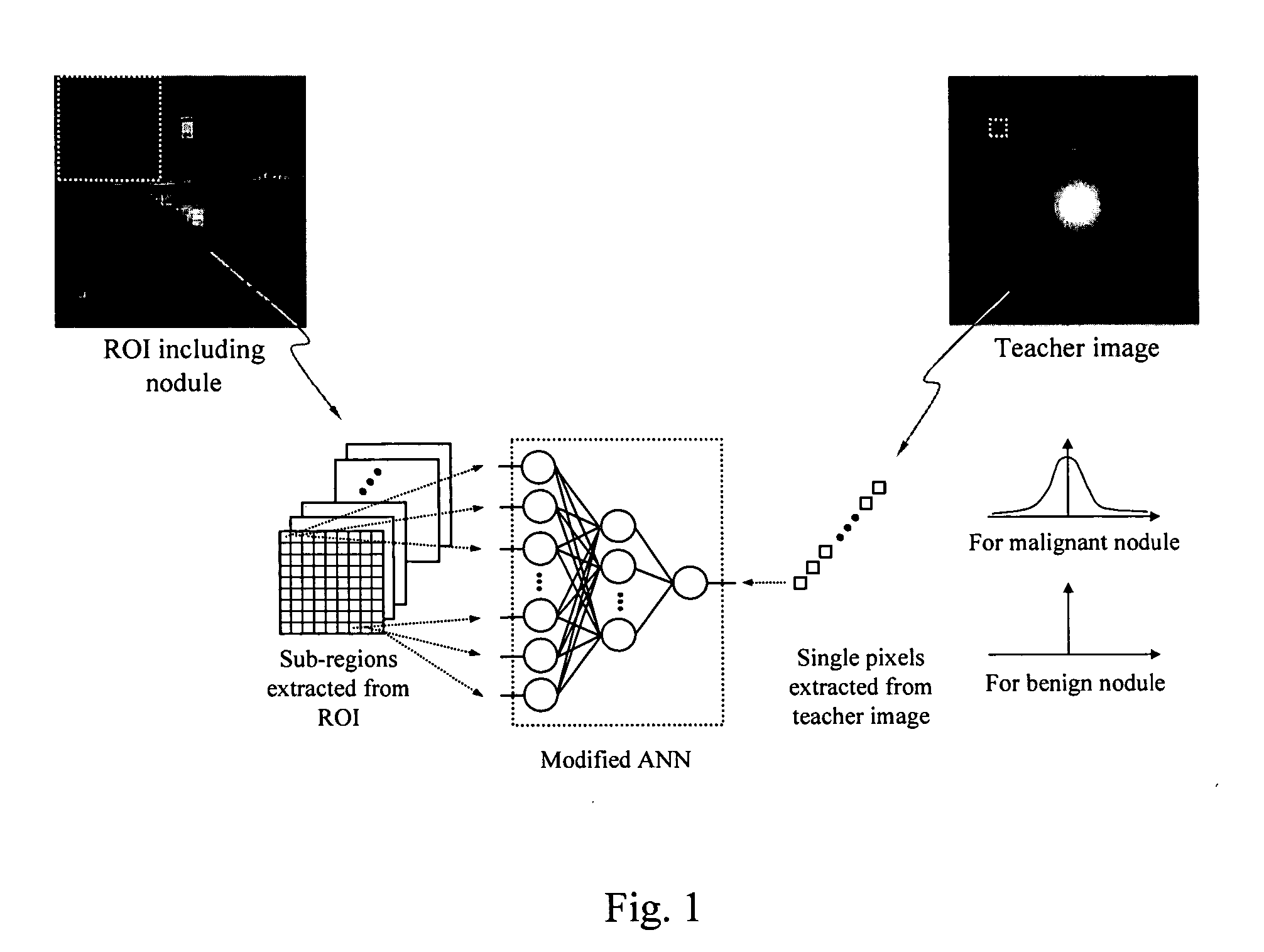
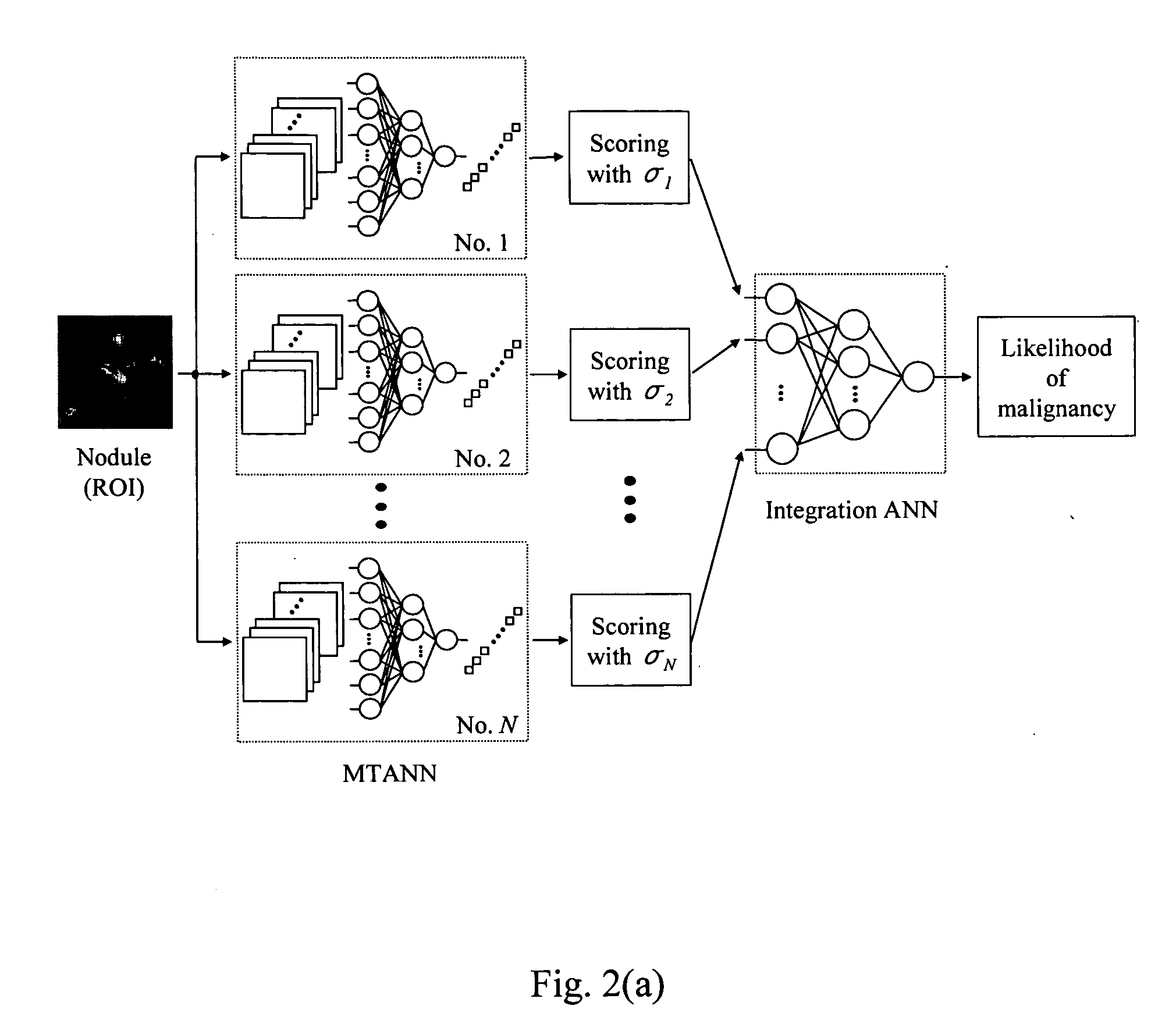
A system, method, and computer program product for classifying a target structure in an image into abnormality types. The system has a scanning mechanism that scans a local window across sub-regions of the target structure by moving the local window across the image to obtain sub-region pixel sets. A mechanism inputs the sub-region pixel sets into a classifier to provide output pixel values based on the sub-region pixel sets, each output pixel value representing a likelihood that respective image pixels have a predetermined abnormality, the output pixel values collectively determining a likelihood distribution output image map. A mechanism scores the likelihood distribution map to classify the target structure into abnormality types. The classifier can be, e.g., a single-output or multiple-output massive training artificial neural network (MTANN).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
System, program product, and methods for attenuation correction of emission data on PET/CT and SPECT/CT
ActiveUS20070081704A1Easy to quantifyImprove tumor tumor localizationImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImage resolutionLow dose ct
Embodiments of the present invention provide the use of average CT (ACT) to match the temporal resolution of CT and PET to enhance PET imaging and evaluated tumor quantification with HCT and ACT. For example, an embodiment of a method of enhanced PET imaging on a PET / CT scanner includes generating an average CT scan responsive to 4D CT emission image data to thereby correct attenuation in PET emission image data. Another embodiment of a method of attenuation correction in a PET / CT scan includes averaging a plurality of consecutive low dose CT images of approximately one breathing cycle to thereby obtain an average CT.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Sparse angle X-ray captive test (CT) imaging method
InactiveCN103136773ARemove Motion ArtifactsQuality rebuild2D-image generationRadiologyNuclear medicine
A sparse angle X-ray captive test (CT) imaging method comprises the following steps: (1) system parameters, all angle projection data scanned previously and sparse angle projection data scanned previously in different periods are obtained; (2) image reconstruction is respectively performed to the all angle projection data scanned previously and the sparse angle projection data scanned previously which are obtained in step (1) so that a previously scanned CT image and a currently reconstructed CT image are obtained; (3) weighting even filtering processing is performed to the previously scanned CT image and the currently reconstructed CT image which are obtained in the step (2) so that a prior image is obtained; (4) a sparse angle CT image reconstruction model is constructed by the prior image obtained in the step (3); and (5) a final reconstructed image is obtained through optimization solution. According to the sparse angle X-ray CT imaging method, motion artifact caused by mismatching of imaging positions between the previously scanned CT image and the currently reconstructed CT image is removed so that high quality reconstruction of a low dose CT image is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Non-partial regularization prior reconstruction method for low-dosage X-ray captive test (CT) image
The invention discloses a non-partial regularization prior reconstruction method for a low-dosage X-ray captive test (CT) image. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) acquiring a previously scanned standard dosage image of a patient by X-ray CT imaging equipment; (2) acquiring CT projection data of the patient by the X-ray CT imaging equipment under a Low-mAs scanning protocol, and simultaneously acquiring a corresponding correction parameter and a system matrix; (3) constructing a math model for image reconstruction according to statistical distribution met by the projection data acquired in the step (2); (4) constructing a non-partial regularization prior guided by the previously scanned standard dosage image in the step (1), performing model transformation by adopting a maximum posterior estimation method, and constructing a target function for image reconstruction according to the math model obtained in the step (3); and (5) calculating the target function for CT image reconstruction, which is constructed in the step (4), by adopting an iteration algorithm to finish image reconstruction. By the method, the low-dosage CT image can be reconstructed under the Low-mAs scanning protocol.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
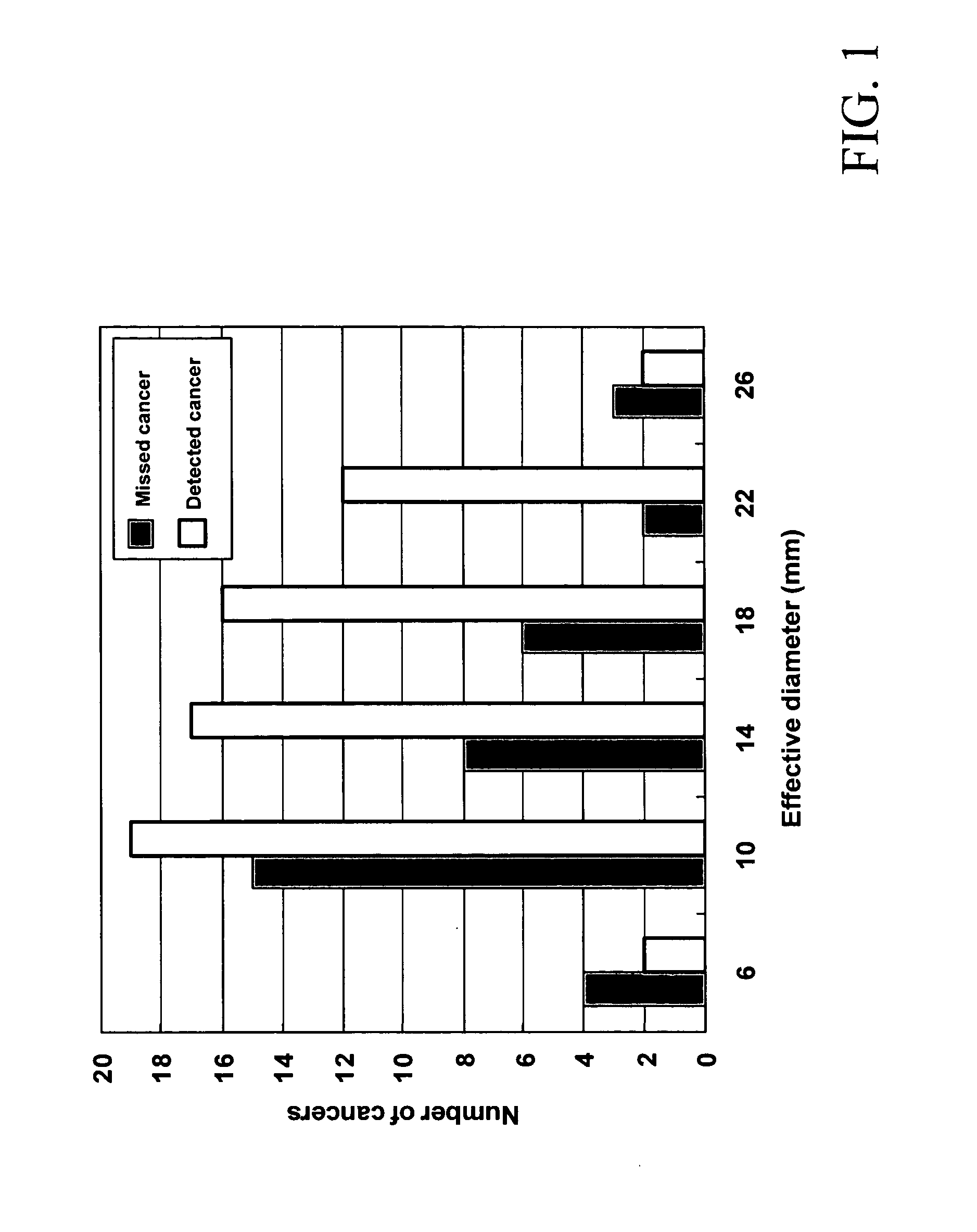
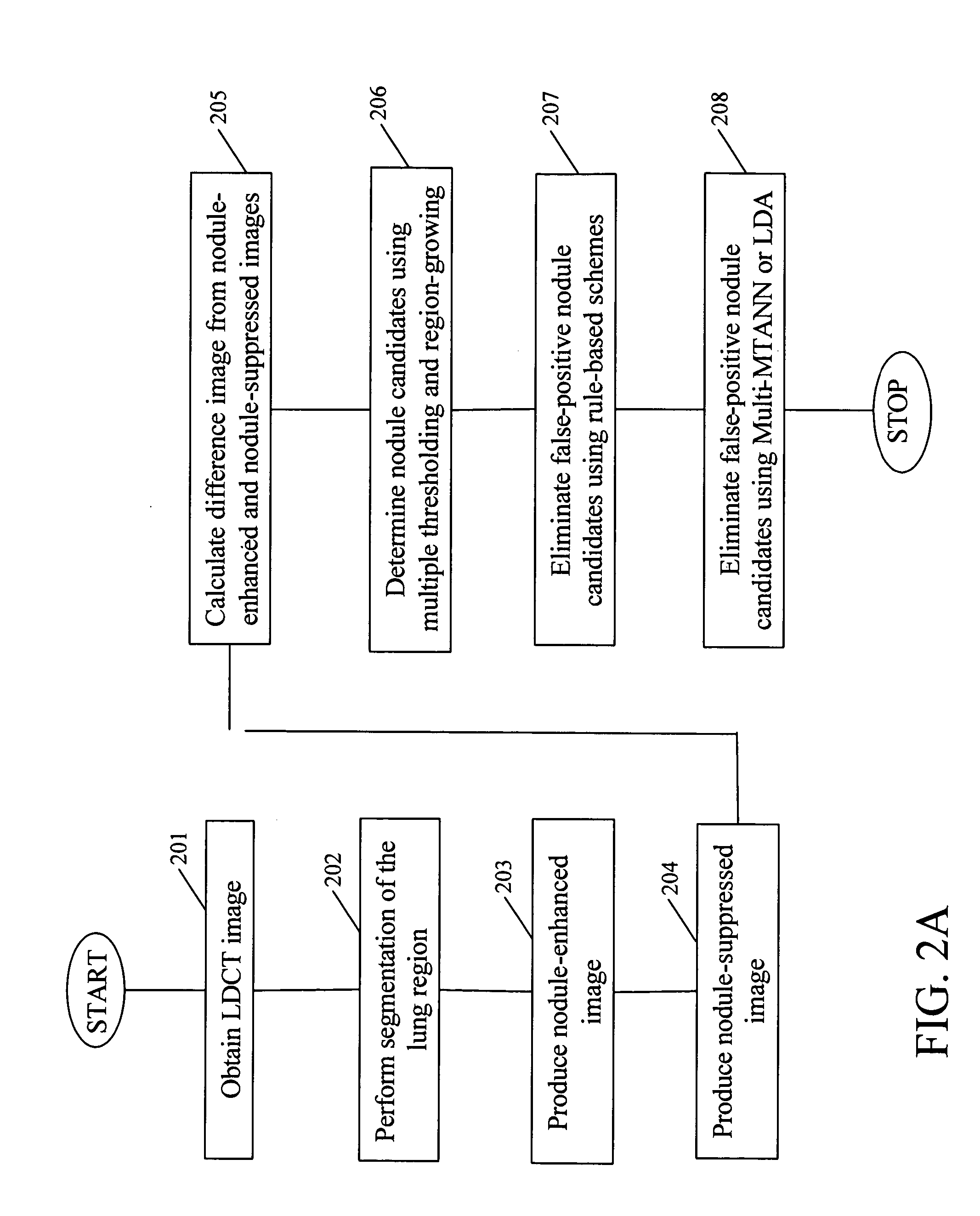
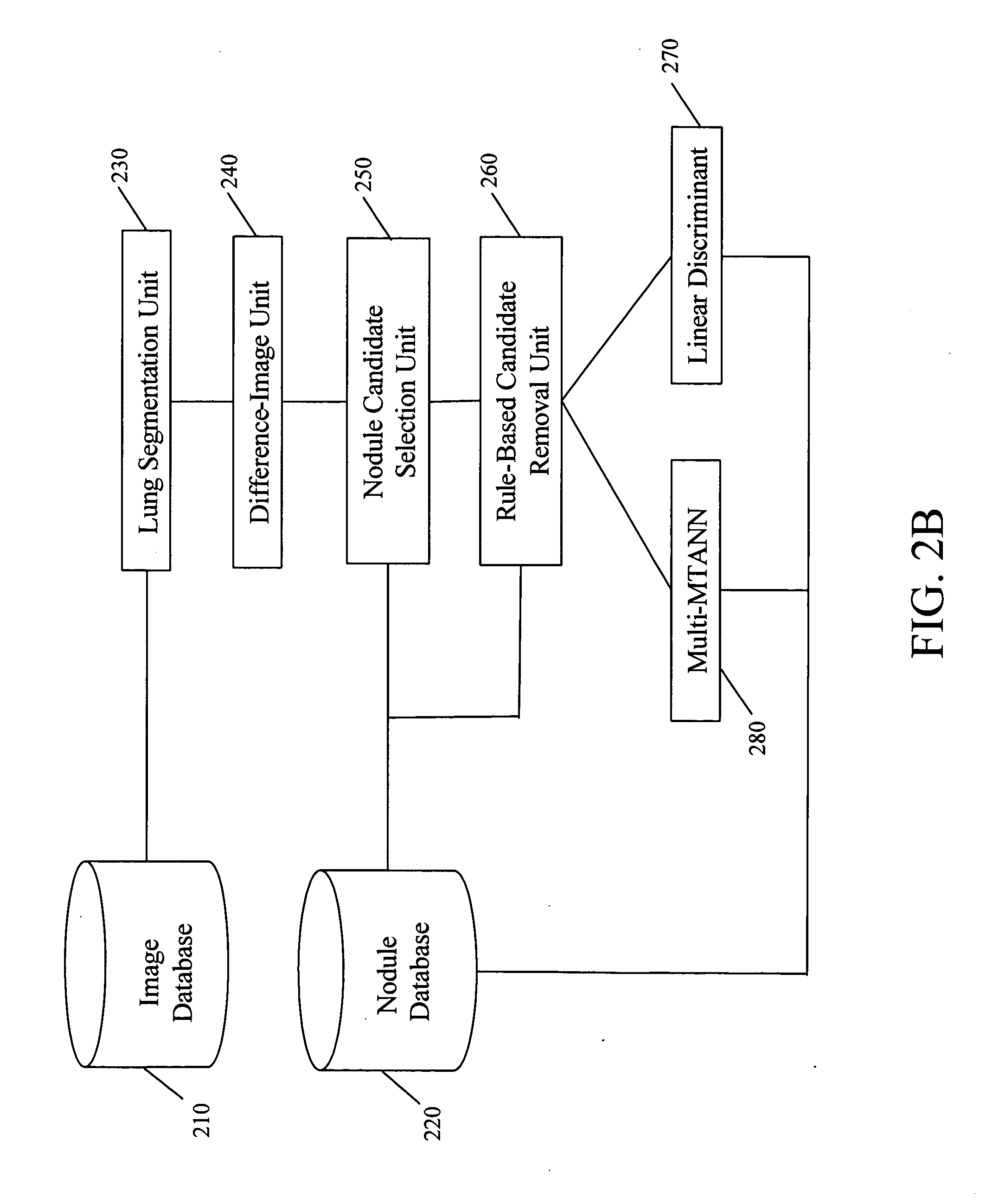
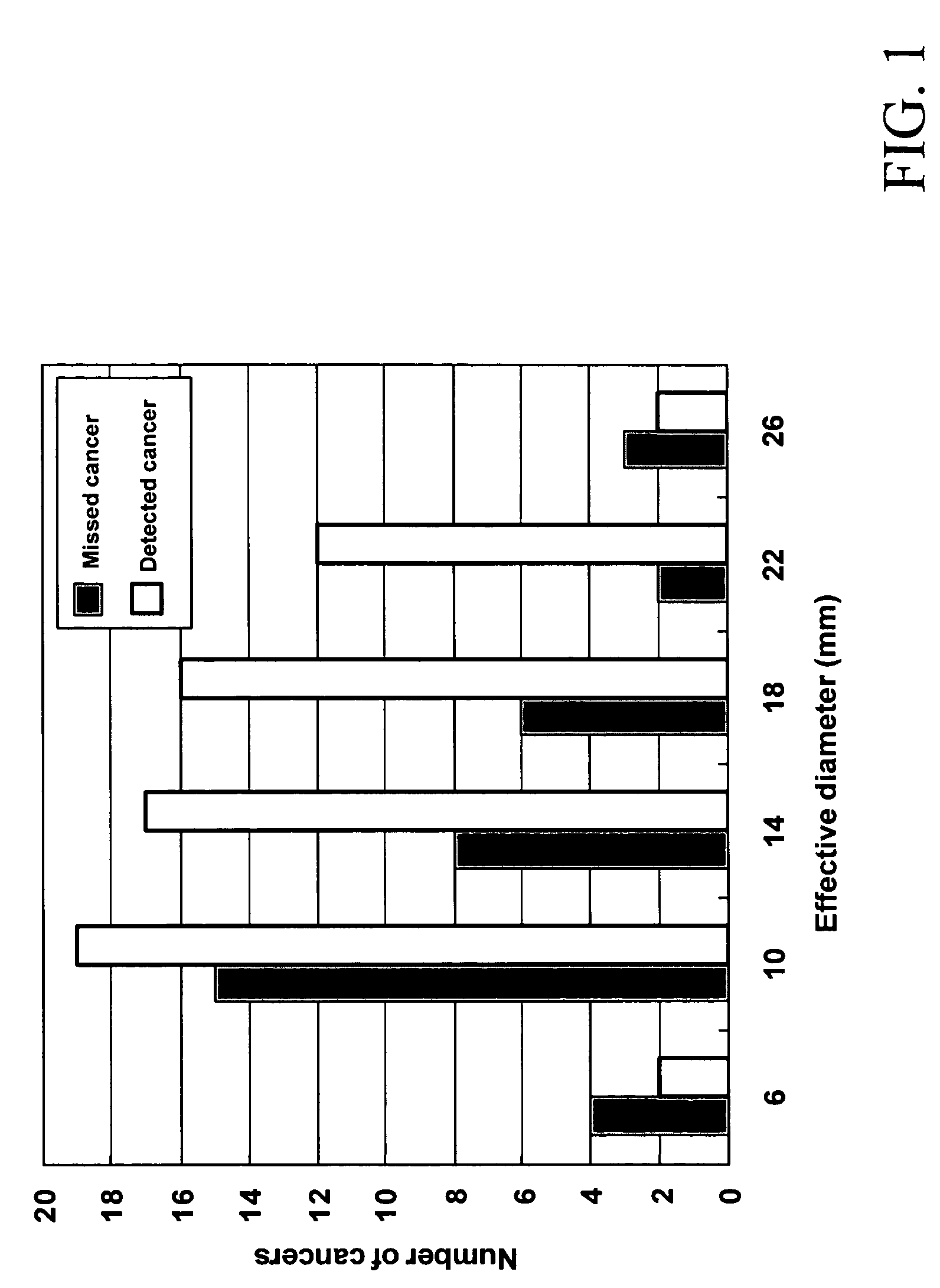
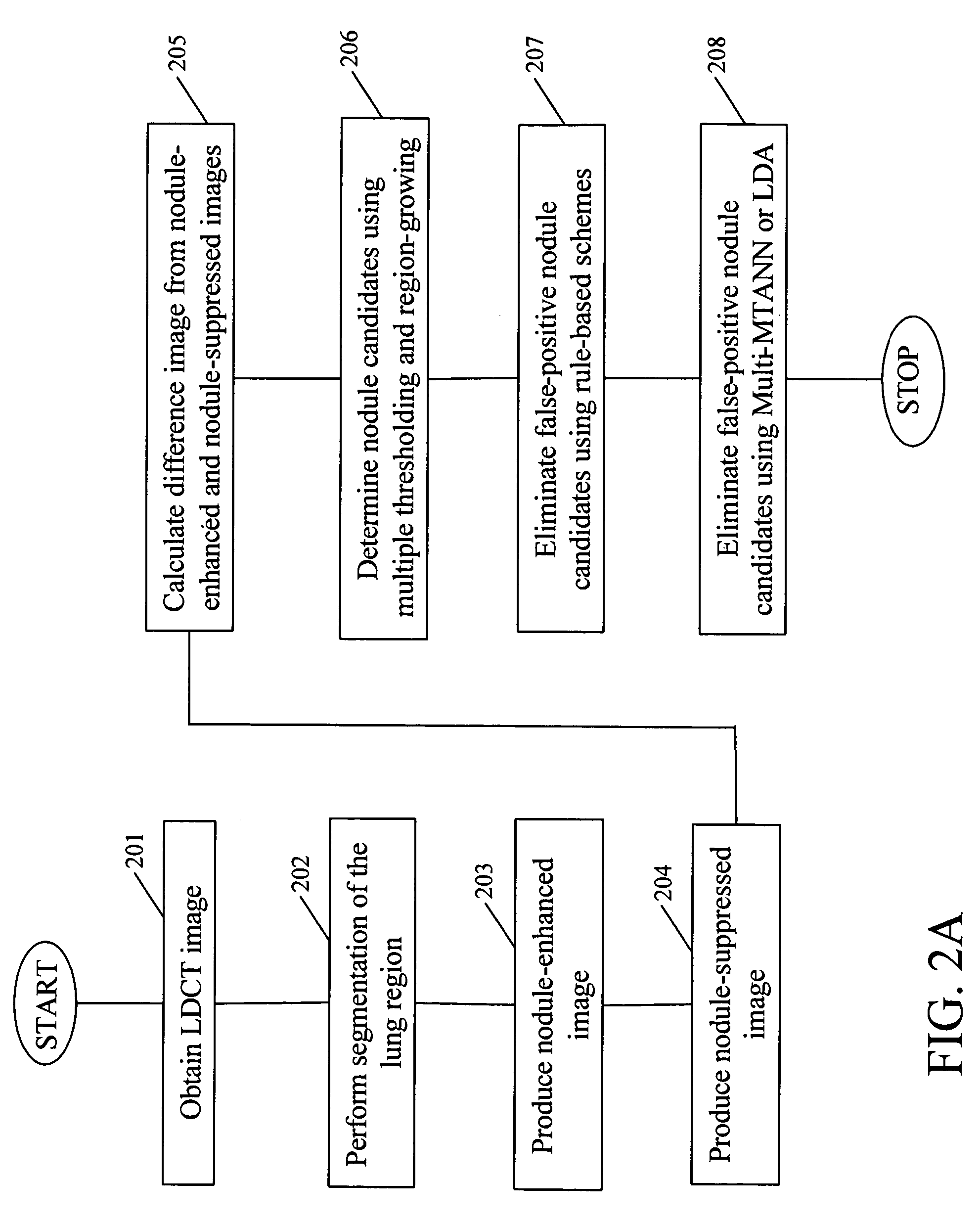
Automated method and system for the detection of lung nodules in low-dose CT image for lung-cancer screening
InactiveUS20050171409A1Image enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationLinearityLinear discriminant analysis
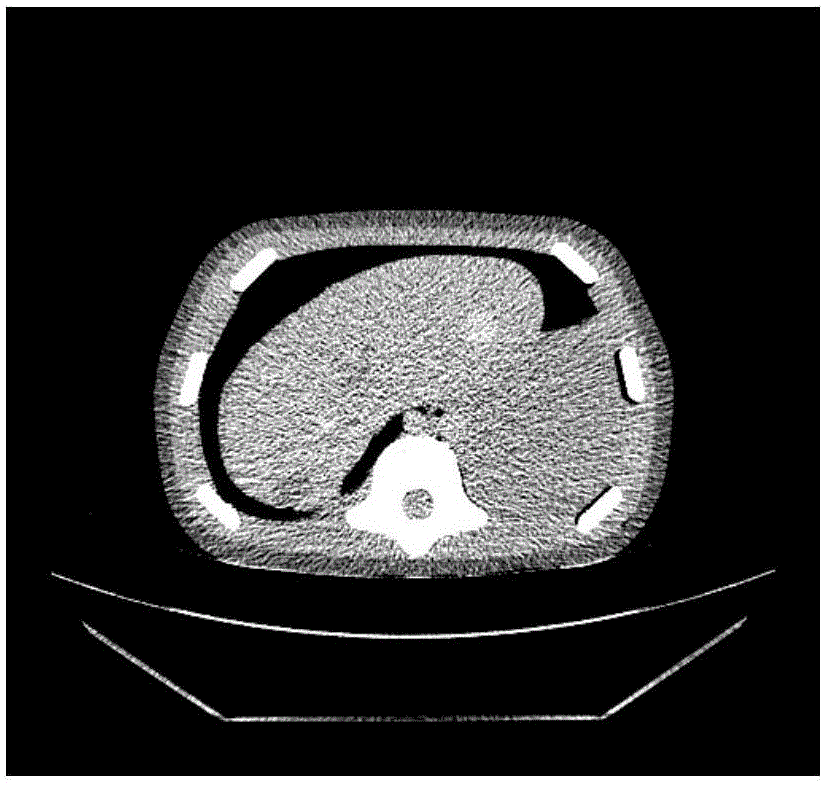
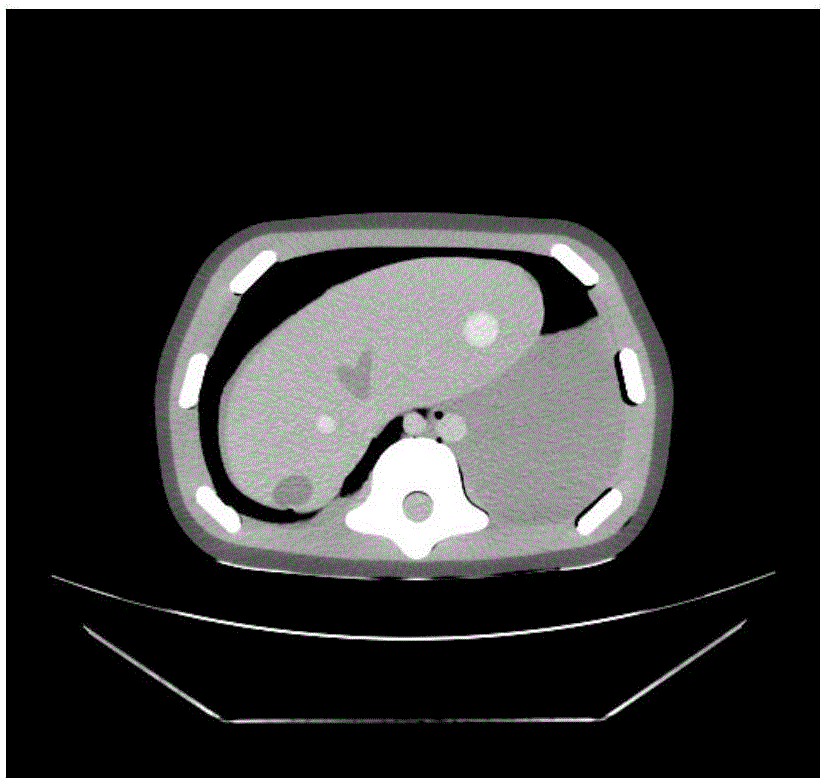
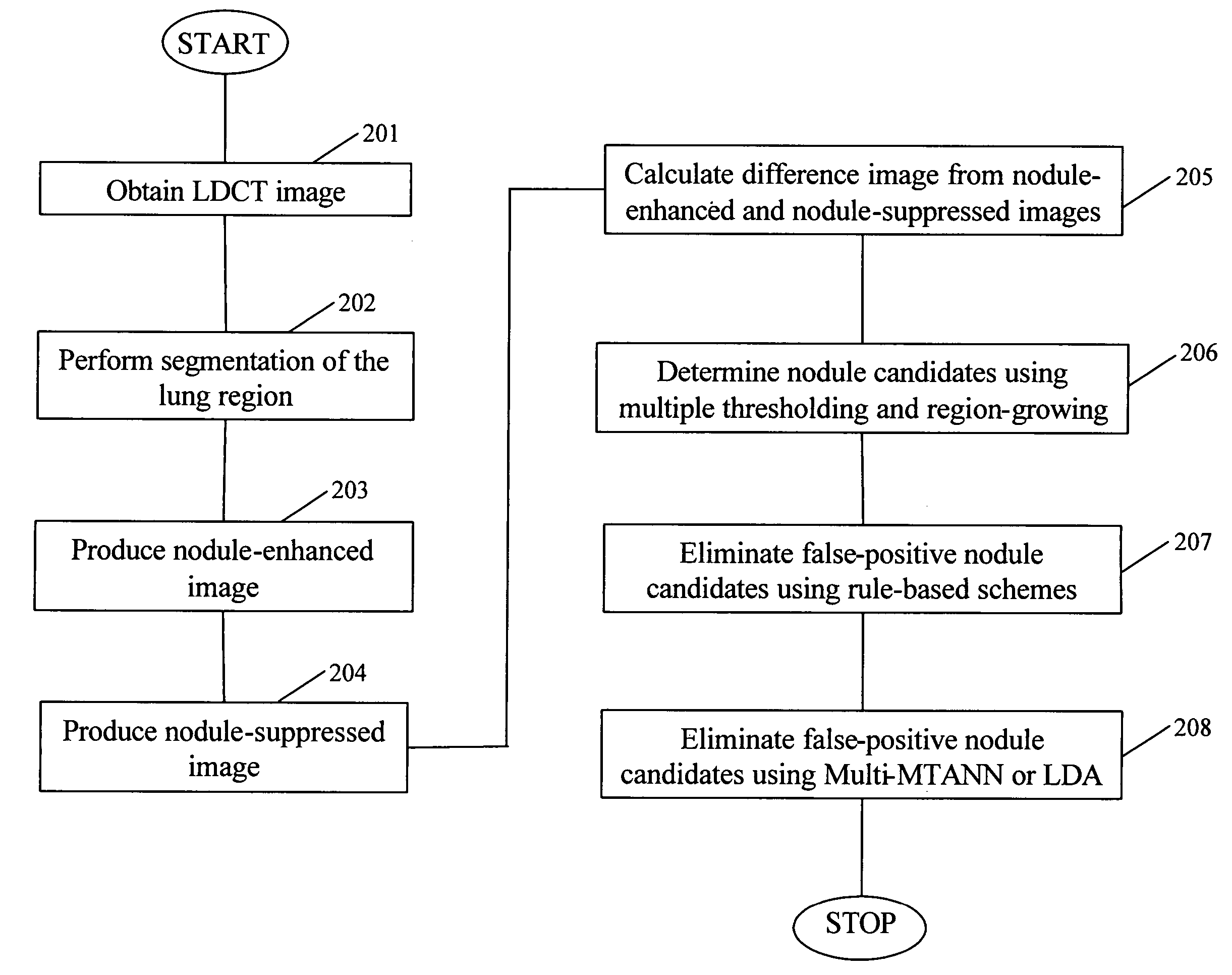
A method, system, and computer program product for detecting at least one nodule in a medical image of a subject, including identifying, in the medical image, an anatomical region corresponding to at least a portion of an organ of interest; filtering the medical image to obtain a difference image; detecting, in the difference image, a first plurality of nodule candidates within the anatomical region; calculating respective nodule feature values of the first plurality of nodule candidates based on pixel values of at least one of the medical image and the difference image; removing false positive nodule candidates from the first plurality of nodule candidates based on the respective nodule feature values to obtain a second plurality of nodule candidates; and determining the at least one nodule by classifying each of the second plurality of nodule candidates as a nodule or a non-nodule based on at least one of the pixel values and the respective nodule feature values. True-positive nodules are identified using linear discriminant analysis and / or a Multi-MTANN.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF
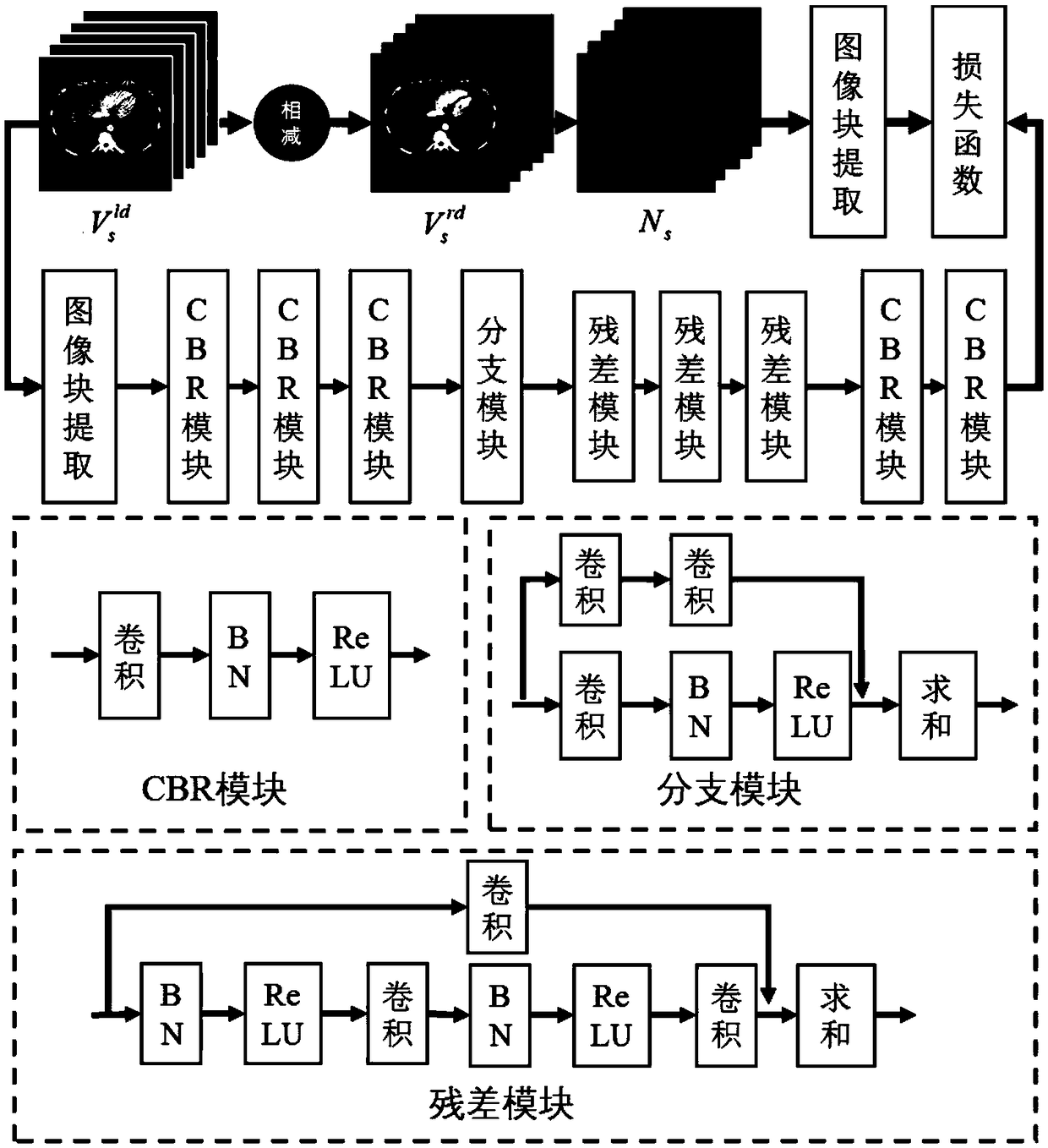
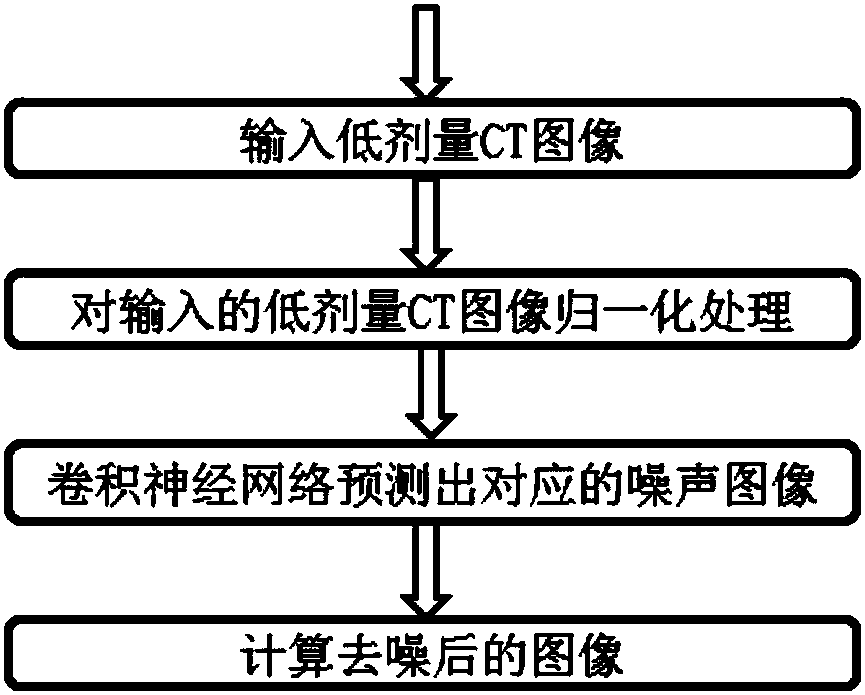
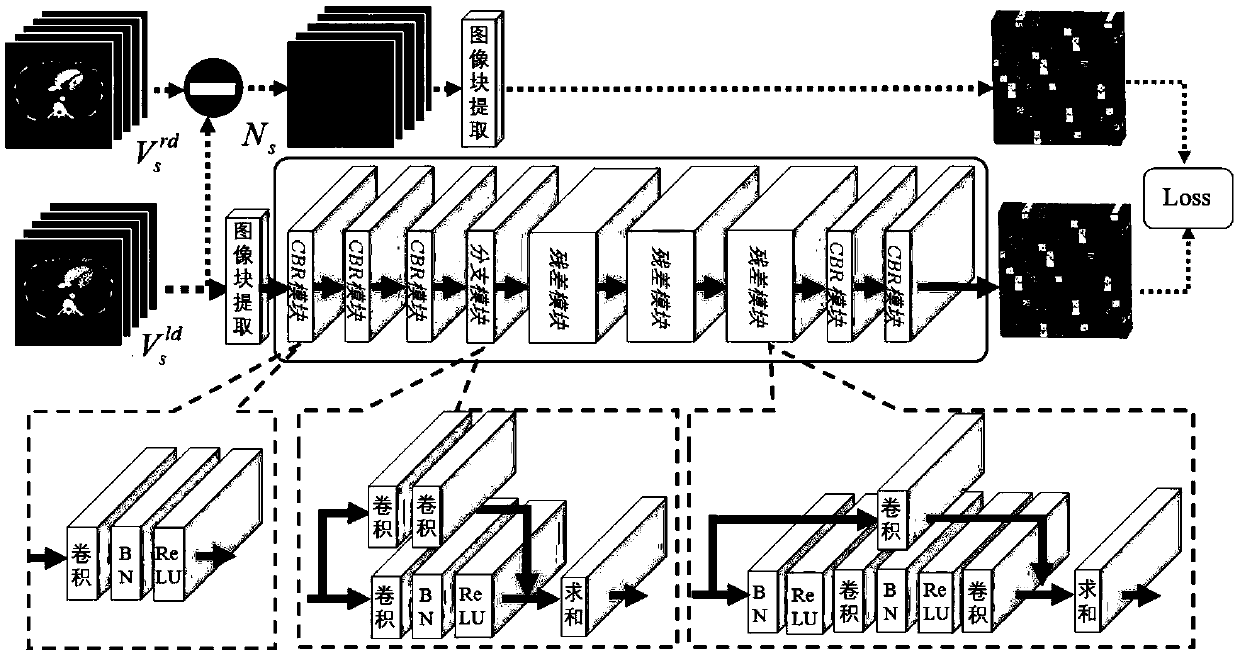
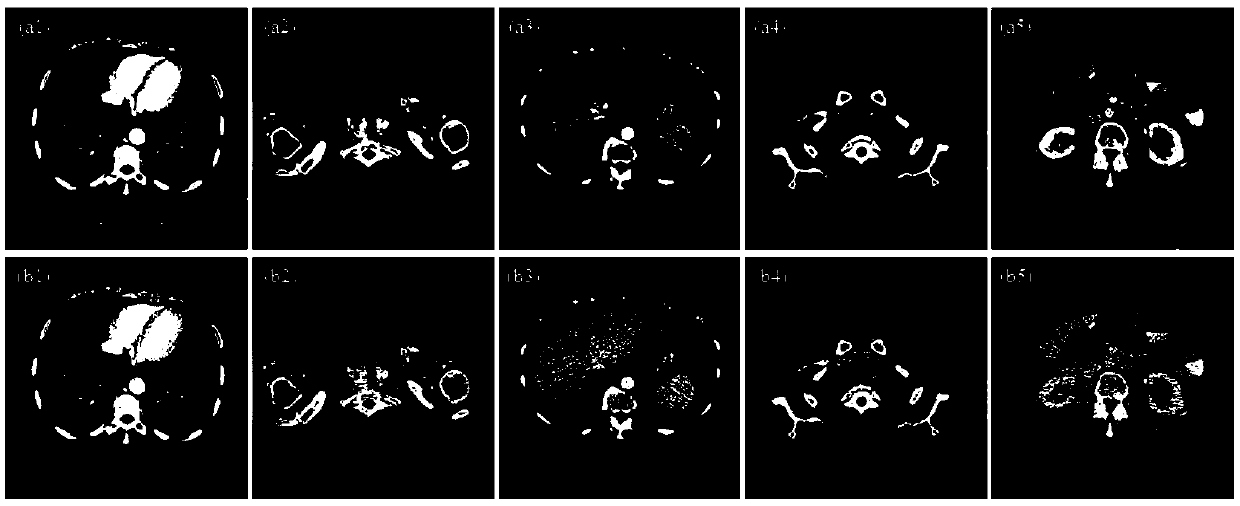
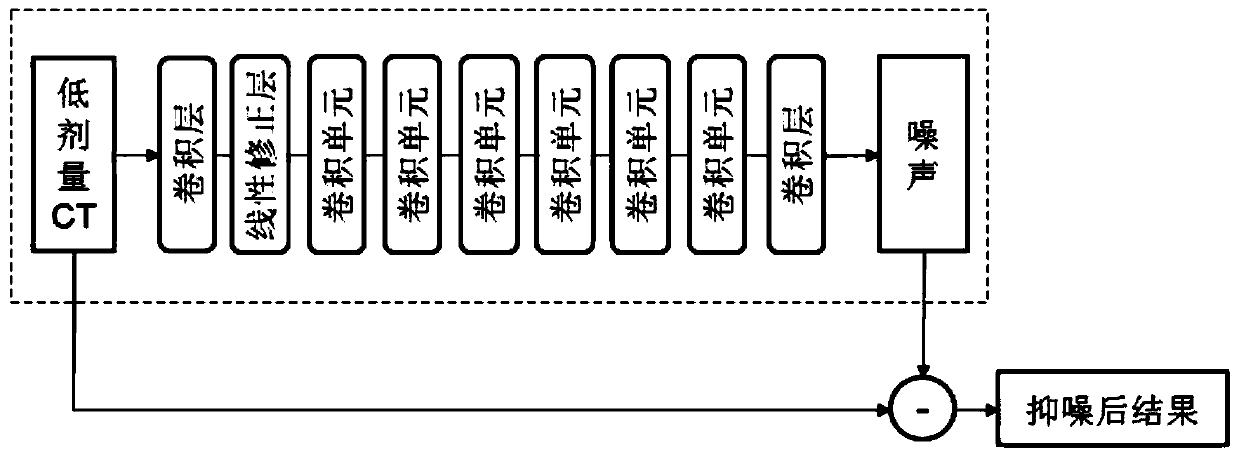
A low-dose CT image processing system based on noise artifact suppression convolutional neural network
PendingCN109166161AEasy to handleReduce radiation dose damageImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionImaging processingProcess module
The invention discloses a low-dose CT image processing system based on a noise artifact suppression convolutional neural network. The system includes: an image preprocessing module, which is used to obtain multiple sets of matched low-dose CT images V<s><ld>and conventional dose CT images V<s><rd> and to subtract V<s><ld> and V<s><ld> to obtain noise artifact image Ns; a noise artifact suppression convolutional neural network building module, which is used for using V<s><ld> as a training image and Ns as a label image to establish a mapped convolutional neural network between V<s><ld> and Ns;a network training module, configured to train a noise artifact suppression convolutional neural network by reducing a loss function of the neural network; a network processing module, which is usedfor inputting a low-dose CT image to be processed V<t><ld> to the mapping convolutional neural network for processing and obtaining a predicted noise artifact image N<t>; and a noise artifact suppression module, which is used for subtracting N<t> from V<t><ld> to obtain a noise artifact suppressed image V<t>. The present invention can effectively suppress noise in low dose CT data Acoustic artifacts, the image quality after processing can meet the clinical analysis, diagnosis and other requirements, and the image effect of low-dose CT imaging is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for reconstructing low-dose CT images based on redundant information of standard dose images
ActiveCN102063728APrecise registrationImplement Adaptive Estimation2D-image generationComputerised tomographsImage resolutionPhysical model
The invention discloses a method for reconstructing low-dose CT images based on redundant information of standard dose images, wherein the method comprises the following steps of: calculating a non-local weight matrix for reconstructing the low-dose CT images by using the redundant information of the previous standard dose images. Based on the calculating manner of the non-local weight matrix, the method of the invention is not dependent on the matching precision between the low-dose CT images and standard-dose CT images. The method performs qualitative and quantitative experimental evaluations to physical models and clinic belly images, and the result proves that the method of the invention is capable of effectively improving the precision of reconstructing the images and the resolution ratio of the reconstructed images.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Convolutional neural network-based low-dosage CT image noise inhibition method
PendingCN108564553AAvoid cumbersomePreserve image detailsImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseGray level
The invention relates to a convolutional neural network-based low-dosage CT image noise inhibition method. The convolutional neural network-based low-dosage CT image noise inhibition method comprisesthe following steps: (1) performing normalization processing on the input original low-dosage CT image L by utilizing the low-dosage CT image obtained through low tube current tube voltage scanning, evaluating the mean value and the standard deviation of the gray level of all the pixels of the low-dosage CT image, and subtracting the mean value from the L and dividing the standard deviation to obtain a CT image L0; (2) taking the acquired preprocessed low-dosage CT image L0 as input of the convolutional neural network and predicting a noise CT image D0 corresponding to a low-dosage CT image I;and (3) subtracting the predicted noise image D0 from the L0, multiplying the standard deviation of the low-dosage CT image and adding the mean value of the low-dosage CT image to acquire the denoised image H0. The low-dosage CT image is subjected to denoising processing by the convolutional neural network, so that the image is guaranteed to meet the diagnosis quality, the irradiation dosage of asubject is reduced, the detection rate of the focus is increased and the disease is diagnosed early.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Low-dosage CT image decomposition method based on three-dimensional distinctive feature representation
ActiveCN105118066AAchieve decompositionImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDecomposition
The invention discloses a low-dosage CT image decomposition method based on three-dimensional distinctive feature representation. The method comprises steps of: scanning a phantom to acquire a group of corresponding low-dosage and normal-dosage phantom CT images; selecting a feature block in the normal-dosage phantom CT image to form a feature dictionary, performing subtraction on the low-dosage and normal-dosage phantom CT images so as to obtain a low-dosage noise pseudo shadow image, and selecting a feature block in the noise pseudo shadow image to form a noise pseudo shadow dictionary; and representing a clinic low-dosage CT image by using a three-dimensional distinctive dictionary formed by the feature dictionary and the noise pseudo shadow dictionary in order to obtain a feature image represented by the feature dictionary and a noise pseudo shadow image represented by the noise pseudo shadow dictionary, thereby achieving decomposition of the low-dosage CT image. The method may effectively separate noise and strip-shaped pseudo shadow from feature structure components in the low-dosage CT image, satisfies a quality requirement of clinic analysis and diagnosis, and improves the use efficiency of the low-dosage CT image.
Owner:江苏一影医疗设备有限公司
Automated method and system for the detection of lung nodules in low-dose CT images for lung-cancer screening
InactiveUS7305111B2Image enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationLinear discriminant analysisLow dose ct
A method, system, and computer program product for detecting at least one nodule in a medical image of a subject, including identifying, in the medical image, an anatomical region corresponding to at least a portion of an organ of interest; filtering the medical image to obtain a difference image; detecting, in the difference image, a first plurality of nodule candidates within the anatomical region; calculating respective nodule feature values of the first plurality of nodule candidates based on pixel values of at least one of the medical image and the difference image; removing false positive nodule candidates from the first plurality of nodule candidates based on the respective nodule feature values to obtain a second plurality of nodule candidates; and determining the at least one nodule by classifying each of the second plurality of nodule candidates as a nodule or a non-nodule based on at least one of the pixel values and the respective nodule feature values. True-positive nodules are identified using linear discriminant analysis and / or a Multi-MTANN.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF
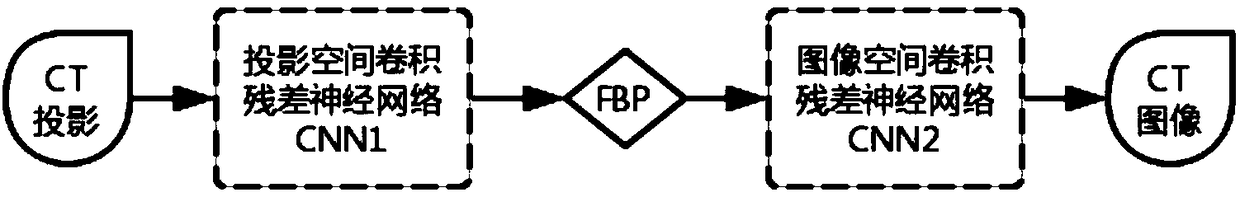
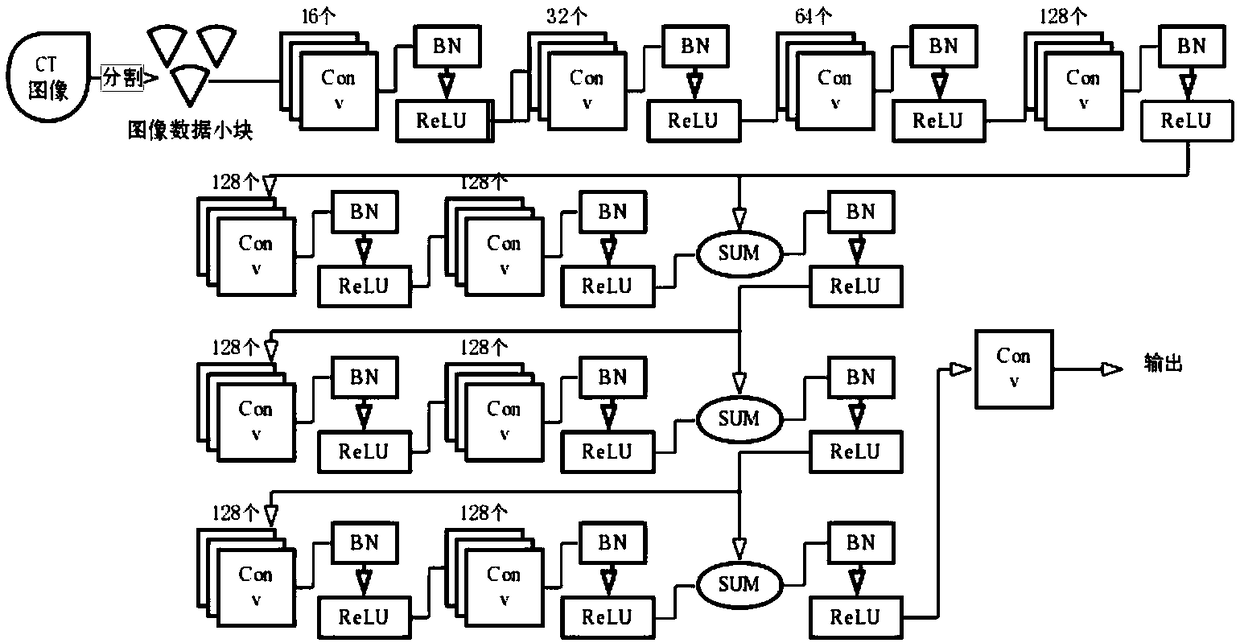
Full-network low-dose CT imaging method and apparatus based on convolution residual network
ActiveCN109102550AReduce noiseReduce artifactsImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Imaging quality
The invention discloses a full-network low-dose CT imaging method and a device based on a convolution residual network. Firstly, the method obtains a plurality of sets of corresponding CT original projection data under low-dose and normal-dose. Secondly, a convolution residual network (CNN1) is established in the projection space, which inputs low dose CT projection data and outputs processed datato reduce the noise and artifacts in low dose CT projection data and improve the signal-to-noise ratio. Then, the projection data is reconstructed into the image space by FBP based on Ramp filter kernel, and the image space is reprocessed based on convolution residual network (CNN2) to reduce the artifacts and noise in the low dose data. The invention can effectively reduce artifacts and noises in low-dose CT data, the data quality can meet the requirements of clinical analysis, diagnosis and the like, and improves the image quality of low-dose CT imaging.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Computerized method for determination of the likelihood of malignancy for pulmonary nodules on low-dose CT
An automated computerized scheme for determination of the likelihood of malignancy in pulmonary nodules. The present invention includes steps of obtaining at least one computed tomography medical image of a pulmonary nodule in determining if the pulmonary nodule is malignant based on the examination of seven patient or image features. The method can be implemented when instructions are loaded into a computer to program the computer. The significance of employing seven patient or image features is that statistically, seven features are the most practical based on the unique implementation of statistical analysis. Out of the seven features that are now analyzed to determine if a pulmonary nodule is malignant, these features are selected to optimize the accuracy of the diagnosis of a pulmonary nodule. Through a unique sampling scheme, different embodiments of the present invention utilize different combinations of features to optimize the accuracy of the method of the present invention.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF
Convolutional neural network-based low-dose CT image decomposition method
ActiveCN108961237AImprove image qualityAchieve decompositionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionAnatomical structuresSoft x ray
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
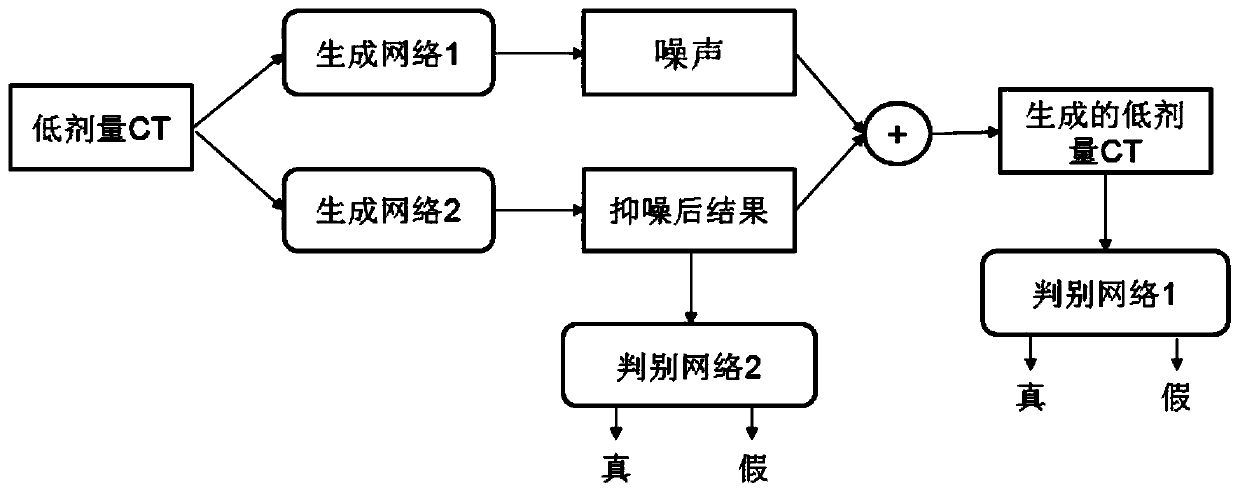
An unregistered low-dose CT denoising method based on an adversarial generative network and a computer
PendingCN109785243ASolve the noise reduction problemAchieve noise reductionImage enhancementInternal combustion piston enginesDiscriminatorData set
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical image processing, and discloses an unregistered low-dose CT denoising method based on an adversarial generative network and a computer. The method comprises; acquiring LDCT data and NDCT data; Analyzing the data, and dividing the data into a training data set and a test data set in proportion; carrying out Programming in TensorFlow to realizea network framework; reading Data in and preprocessed, and adjusting the sizes of the images to be the same; Inputting LDCT into the two generators respectively to obtain a noise result and a noise suppression result respectively, and adding the noise result and the noise suppression result to obtain a false LDCT; Using the two discriminators to respectively discriminate the result after noise suppression and the false LDCT; Calculating loss functions of the two generators and the two discriminators through the generation result and the discrimination result; Optimizing the network through anoptimization algorithm to obtain a network with trained parameters; And testing on the test set to obtain an LDCT noise suppression result. The method can be used for the noise suppression problem ofunpaired data and the noise suppression problem of paired data.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
System, program product, and methods for attenuation correction of emission data on PET/CT and SPECt/CT
ActiveUS7787675B2Improving Imaging AccuracyEasy to implementImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAbnormal tissue growthUltrasound attenuation
Embodiments of the present invention provide the use of average CT (ACT) to match the temporal resolution of CT and PET to enhance PET imaging and evaluated tumor quantification with HCT and ACT. For example, an embodiment of a method of enhanced PET imaging on a PET / CT scanner includes generating an average CT scan responsive to 4D CT emission image data to thereby correct attenuation in PET emission image data. Another embodiment of a method of attenuation correction in a PET / CT scan includes averaging a plurality of consecutive low dose CT images of approximately one breathing cycle to thereby obtain an average CT.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
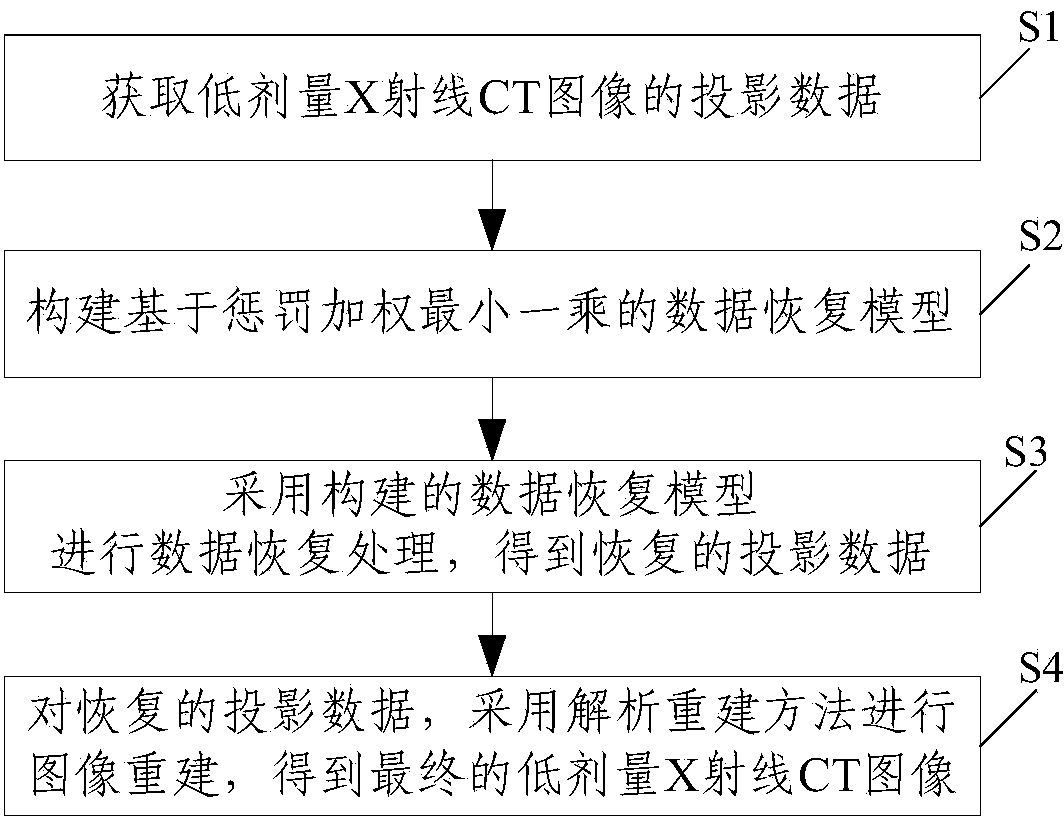
Low-dose X-ray CT projection data restoring method
ActiveCN103810734AQuality rebuildSolve the noiseImage enhancement2D-image generationX-rayComputer science
The invention discloses a low-dose X-ray CT projection data restoring method. The low-dose X-ray CT projection data restoring method includes acquiring projection data y<raw> of a low-dose X-ray CT image; setting up a data restoring model (shown in the description) based on penalized weighted least absolute for the projection data y raw, restoring the projection data y<raw> to obtain restored projection data y<restored>, wherein p is ideal projection data to be calculated, the parameter lambda is a non-negative real number, w is a weight factor (shown in the description), wherein both the parameters beta and epsilon are non-negative real numbers, and (shown in the description) is variance of the projection data y<raw>; reconstructing an image for the restored projection data y<restored> by means of an analyzing and reconstructing method to obtain the final low-dose X-ray CT image. The low-dose X-ray CT projection data restoring method is capable of restoring the low-dose CT projection data which is capable of reducing the tube current and scanning time and reconstructing the image through the analyzing and reconstructing method, the image noise is eliminated effectively, the streak artifact is inhibited, and the detail information of the image is well kept.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Low dose CT image filtering method
InactiveCN103226815ASuppresses star-streaked artifactsSuppress noiseImage enhancementComputerised tomographsDictionary learningImaging processing
The invention discloses a low dose CT (Computerized Tomography) image filtering method, and belongs to the technical field of medical image processing. The method comprises the steps that a dictionary learning method is used for filtering block noise in the original low dose CT image, and an obtained image is subjected to unsharp filtering for enhancing image border information inhibited by the dictionary learning method. The method can effectively inhibit star strip artifacts and noise in the low dose CT image, and improve the quality of the CT image.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Low-dose CT image reconstruction method
InactiveCN104050631AAchieve reconstructionHigh precisionImage enhancementTime domainReconstruction method
The invention provides a low-dose CT image reconstruction method. The low-dose CT image reconstruction method comprises the following steps that (1) projection data of equal-slope increments with different projection angles theta are obtained; (2) the projection data are corrected; (3) Fourier transform is conducted on the corrected projection data so that the corrected projection data can be converted into frequency domain spatial data in a polar coordinate system; (4) the frequency domain spatial data in the polar coordinate system are converted into frequency domain spatial data in a pseudo-polar coordinate system; (5) repeated conversion between the frequency domain space in the pseudo-polar coordinate system and the time domain space in a Cartesian coordinate system is conducted on the frequency domain spatial data obtained in the step (4) through the iteration method until the preset final condition is met; (6) a time domain image meeting the final condition is output. By the adoption of the low-dose CT image reconstruction method, the quality of a reconstructed image is guaranteed, and the radiation dose borne by a sample can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Reduction of Streak Artifacts In Low Dose CT Imaging through Multi Image Compounding
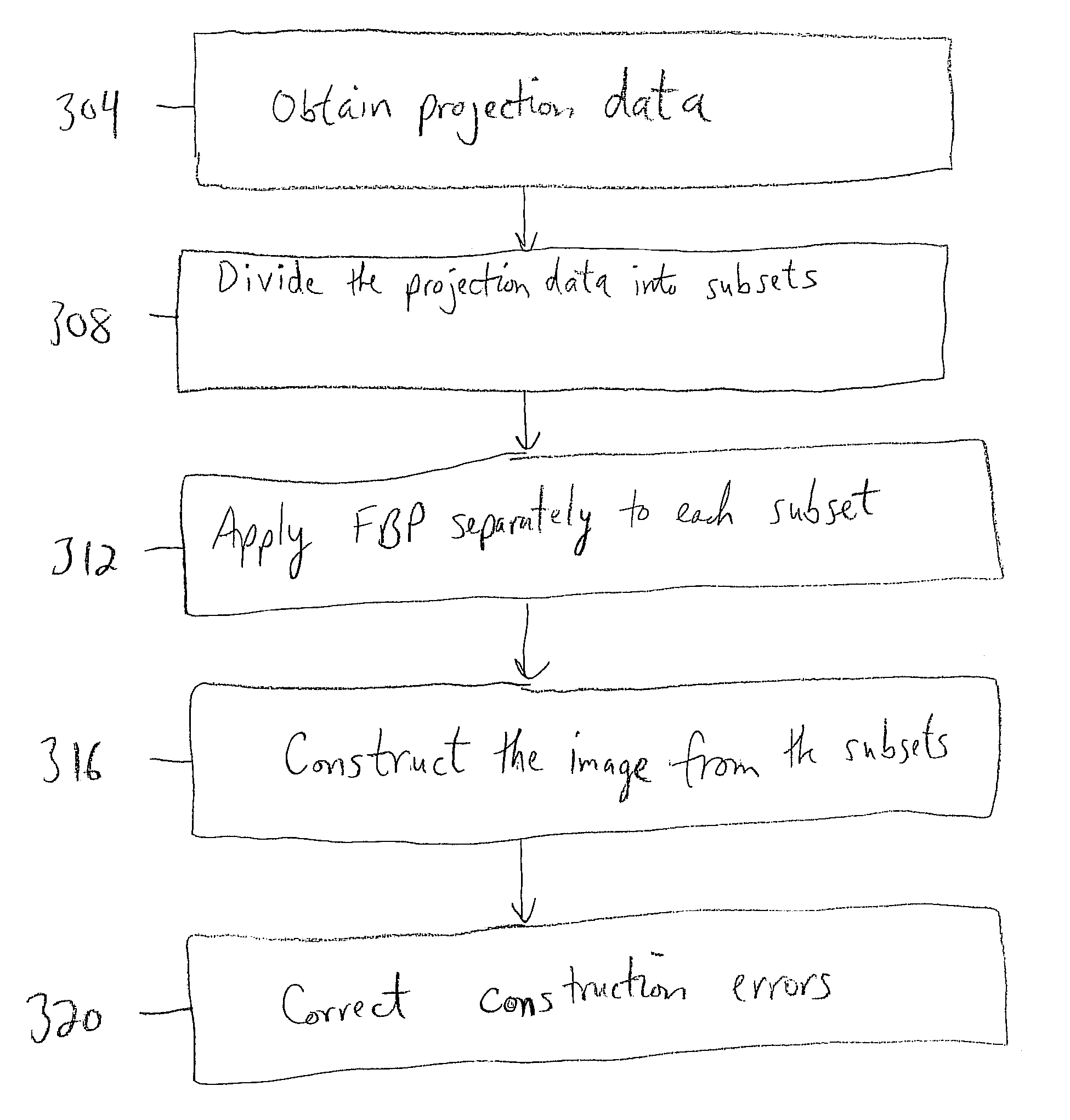
InactiveUS20070140407A1Improve reconstruction qualityImprove image qualityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMulti-imageBack projection
Disclosed is a method and system for constructing, from a computerized tomography (CT) scan, an image relating to a physical structure. Projection data associated with the image is obtained and divided into a plurality of subsets. Filtered back projection (FBP) is then applied to each subset in the plurality of subsets. The image is constructed based on the application of the FBP to each subset in the plurality of subsets.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Dictionary learning based image reconstruction
ActiveUS20170091964A1Reconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningLearning based
A computationally efficient dictionary learning-based term is employed in an iterative reconstruction framework to keep more spatial information than two-dimensional dictionary learning and require less computational cost than three-dimensional dictionary learning. In one such implementation, a non-local regularization algorithm is employed in an MBIR context (such as in a low dose CT image reconstruction context) based on dictionary learning in which dictionaries from different directions (e.g., x,y-plane, y,z-plane, x,z-plane) are employed and the sparse coefficients calculated accordingly. In this manner, spatial information from all three directions is retained and computational cost is constrained.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
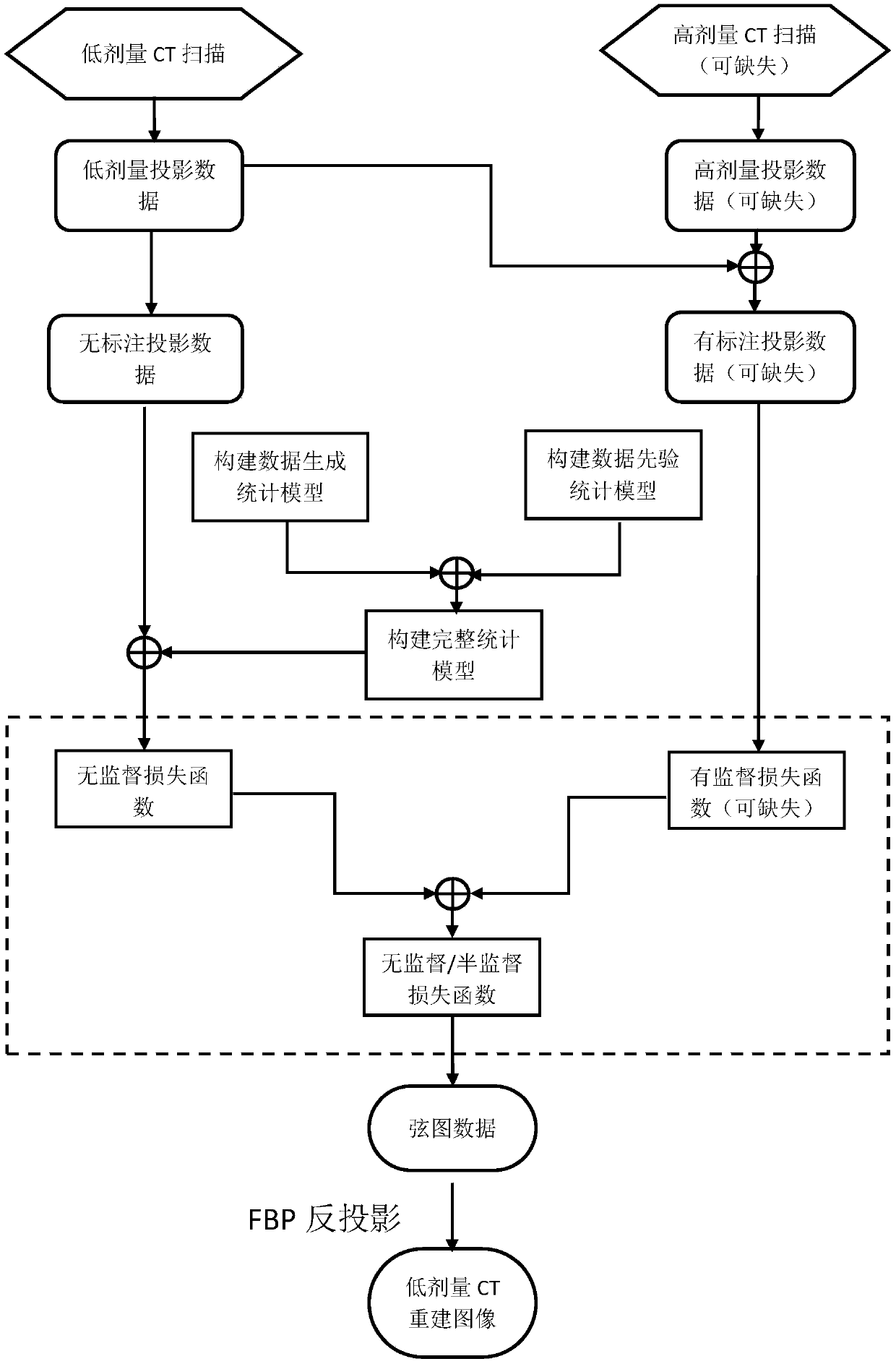
An unsupervised/semi-supervised CT image reconstruction depth network train method
ActiveCN109035169AAvoid collectingHigh speedImage enhancementImage analysisData informationHigh doses
An unsupervised / semi-supervised CT image reconstruction depth network train method is provided. Firstly, the CT chord data under the CT scanning protocol and the imaging system parameters of the CT equipment are obtained. The data include low-dose CT chord data without labeling, and a small amount of low-dose CT chord data correspond to labeled CT chord data. The labeled CT chord data refers to the clear CT chord data information of known low dose data corresponding to high dose. The loss functions of unlabeled and labeled data are constructed respectively, and the total loss functions of unsupervised / semi-supervised network are obtained by weighted summation, and the denoising network is trained by this loss function. The method achieves the effect of a CT image denoising network with higher precision and higher speed by using non-annotated data only or only a small amount of annotated data. The invention aims at establishing a method of combining a chord data restoration model and adepth learning model, thereby realizing high-quality CT image reconstruction.
Owner:广州本影医疗科技有限公司
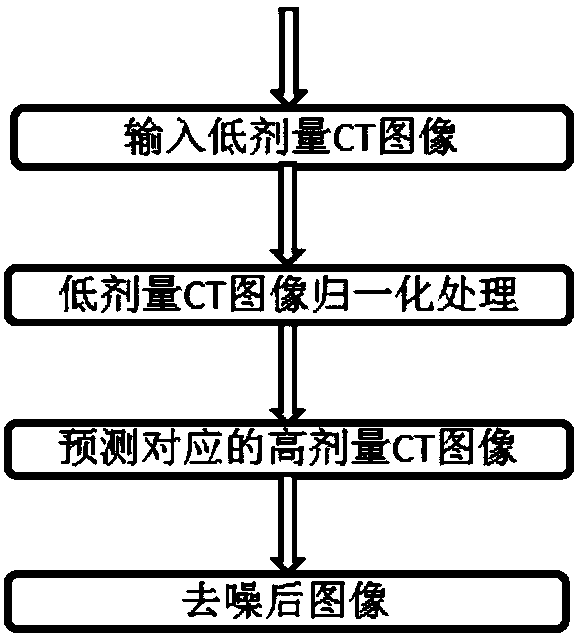
Method and system for converting multi-mode low-dose CT into high-dose CT based on GAN, and medium
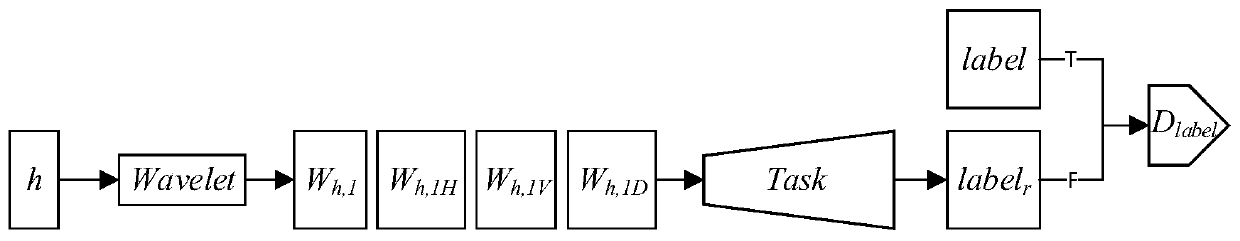
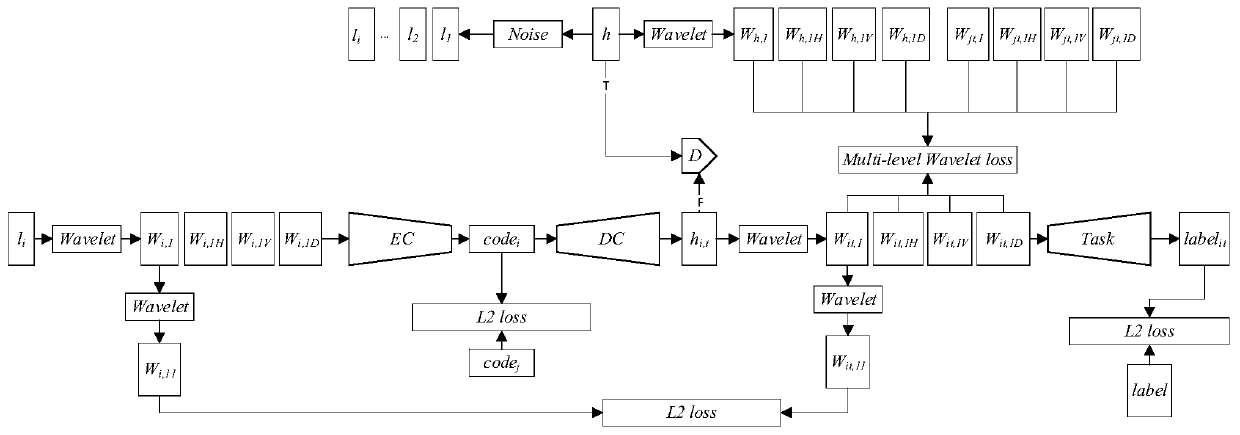
ActiveCN110559009ARealize generationRadiation diagnostic image/data processingComputerised tomographsPattern recognitionDecomposition
The invention discloses a method and system for converting multi-mode low-dose CT into high-dose CT based on a GAN, and a medium. The method comprises the steps: inputting low-dose CT in any mode; performing two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform on the low-dose CT to obtain a plurality of decomposition results; and inputting the low-dose CT and a plurality of decomposition results into a trained encoder in the GAN network, encoding, and decoding the encoding result through a decoder in the GAN network to obtain a corresponding high-dose modal image. The method is based on the wide development of GAN in multi-domain conversion and the decomposition capability of traditional wavelet transform, the low-dose CT and the wavelet transform result are inputted into the trained encoder in theGAN network together for encoding, the encoding result is decoded through the decoder in the GAN network to obtain the corresponding high-dose modal image, and low-dose CT image conversion in any modeis conveniently converted to the high-dose CT image.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
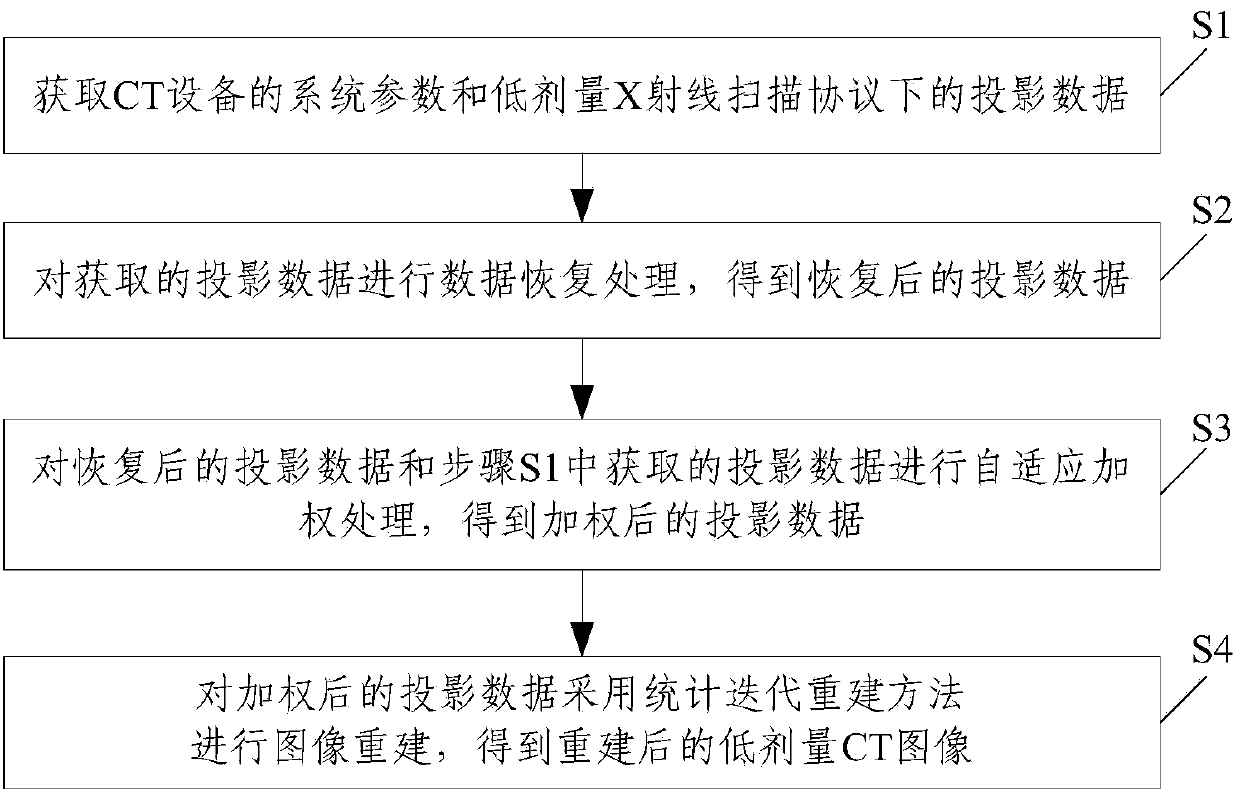
Statistical iteration reconstruction method of sparse-angle X-ray CT (electronic computer X-ray tomography technique) image
ActiveCN103810733AEffective Noise Reduction ProcessingAchieving Quality RebuildsImage enhancement2D-image generationAdaptive weightingReconstruction method
The invention discloses a statistical iteration reconstruction method of a sparse-angle X-ray CT image. The method comprises the steps of obtaining the system parameters of a CT device and the projection data yraw of sparse-angle low-dose X-ray CT scanning, and performing data restoration based on mid-value prior constraints on the projection data yraw to obtain restored projection data yrestored; performing self-adaptive weighting on the projection data yraw and the restrored projection data yrestored to obtain weighted projection data yweight; performing image reconstruction on the weighted projection data yweight through a statistical iteration reconstruction method to obtain a reconstructed low-dose CT image. According to the statistical iteration reconstruction method of the sparse-angle X-ray CT image, by means of the data restoration based on the mid-value prior constraints and the self-adaptive weighting, the collected sparse low-dose CT projection data can be effectively noise-reduced, and finally high-quality reconstruction of the sparse low-dose CT image can be achieved; the reconstructed CT image can effectively eliminate plaque effects caused by noise in the reconstructed image, and the quality of the CT image can be improved significantly.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
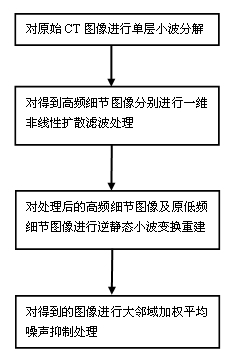
Low-dose computed tomography (CT) image processing method based on wavelet space directional filtering
InactiveCN102024267AQuality improvementSuppress noise2D-image generationImaging processingTomography
The invention discloses a low-dose computed tomography (CT) image processing method based on wavelet space directional filtering, belonging to the technical field of computerized tomography. The method is as follows: firstly, static wavelet transform is used for carrying out single-layer decomposition on the low-dose CT image to be processed, then high-frequency detailed images in the horizontal, vertical and opposite angle directions are subjected to one-dimensional nonlinear diffusion filtering in the vertical and horizontal directions respectively so as to restrain the information intensity of star-strip artifacts in high-frequency detailed images in different directions, and then inverse static wavelet transform is conducted according to the processed high-frequency detailed images in the horizontal, vertical and opposite angle directions and the original low-frequency images for rebuilding to obtain artifacts so as to obtain restrained CT images, finally, the image is further processed by using the existing large adjacent region weighted average noise suppression method. By utilizing the method, the star-strip artifacts and noise in the low-dose CT image can be effectively restrained, and the quality of the low-dose CT image can be improved, so that the low dose CT image meets the quality requirements of clinical diagnosis.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Reduction of streak artifacts in low dose CT imaging through multi image compounding
InactiveUS7672421B2Improve image qualityImprove reconstruction qualityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMulti-imageBack projection
Disclosed is a method and system for constructing, from a computerized tomography (CT) scan, an image relating to a physical structure. Projection data associated with the image is obtained and divided into a plurality of subsets. Filtered back projection (FBP) is then applied to each subset in the plurality of subsets. The image is constructed based on the application of the FBP to each subset in the plurality of subsets.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Low-dose X-ray CT image reconstruction method
ActiveCN106780641AKeep intactSufficiently Accurate Statistical ModelingImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionEstimation methodsReconstruction method
The present invention provides a low-dose X-ray CT image reconstruction method. The method comprises: obtaining imaging system parameters of a CT device and projection data in the low-dose CT scanning protocol; constructing a statistics generation model of the chordal graph data through the statistical law of the imaging process; constructing the priori statistic model of the chordal graph data; constructing a complete statistic model, and converting a model to a chordal graph data recovery model according to the maximum posterior estimation method; applying the chordal graph data recovery model, and obtaining estimated chordal graph data and other statistical variables; and performing CT image reconstruction according to the obtained chordal graph data to obtain and output a CT graph according to the obtained chordal graph data. The objective is to establish a high-quality chordal graph data recovery model and method based on the chordal graph data generation principle and the statistical prior therein so as to realize the CT image high-quality reconstruction capable of greatly reducing image noise / artifact and recovering image details.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Shallow residual encoding and decoding recursive network for low-dose CT image denoising
ActiveCN110223255AReduce complexityImprove performanceImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionImage denoisingImaging processing
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing, and particularly relates to a low-dose CT image denoising recursion algorithm based on a residual encoding and decoding network. According to the specific technical scheme, the invention discloses a shallow residual error coding and decoding recursive network for low-dose CT image denoising. The recursive shallow residual encoding and decoding network reduces the complexity of the network by reducing the number of layers and the number of convolution kernels in the residual encoding and decoding network. The network performanceis improved by using a recursion process. According to the algorithm, end-to-end mapping is trained through a network to obtain a high-quality image. At each recursion, original low-dose CT images arecascaded to the next input. The problem of distortion of the image after multiple recursions can be effectively avoided, image features can be better extracted, detail information of the image can bereserved, the complexity of the network can be reduced, the network performance can be improved, image details of the denoised image can be well reserved, and the image structure is clearer.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
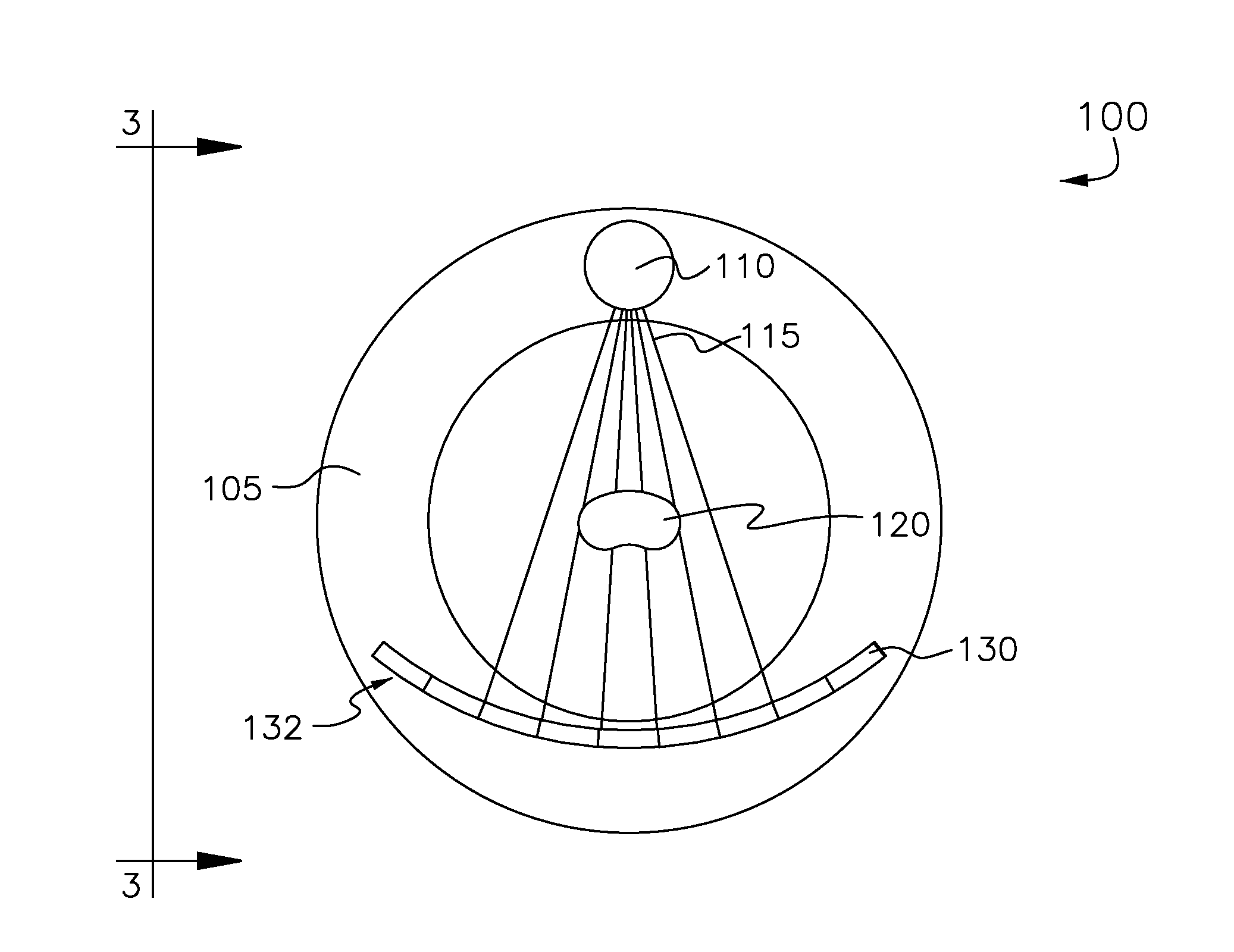
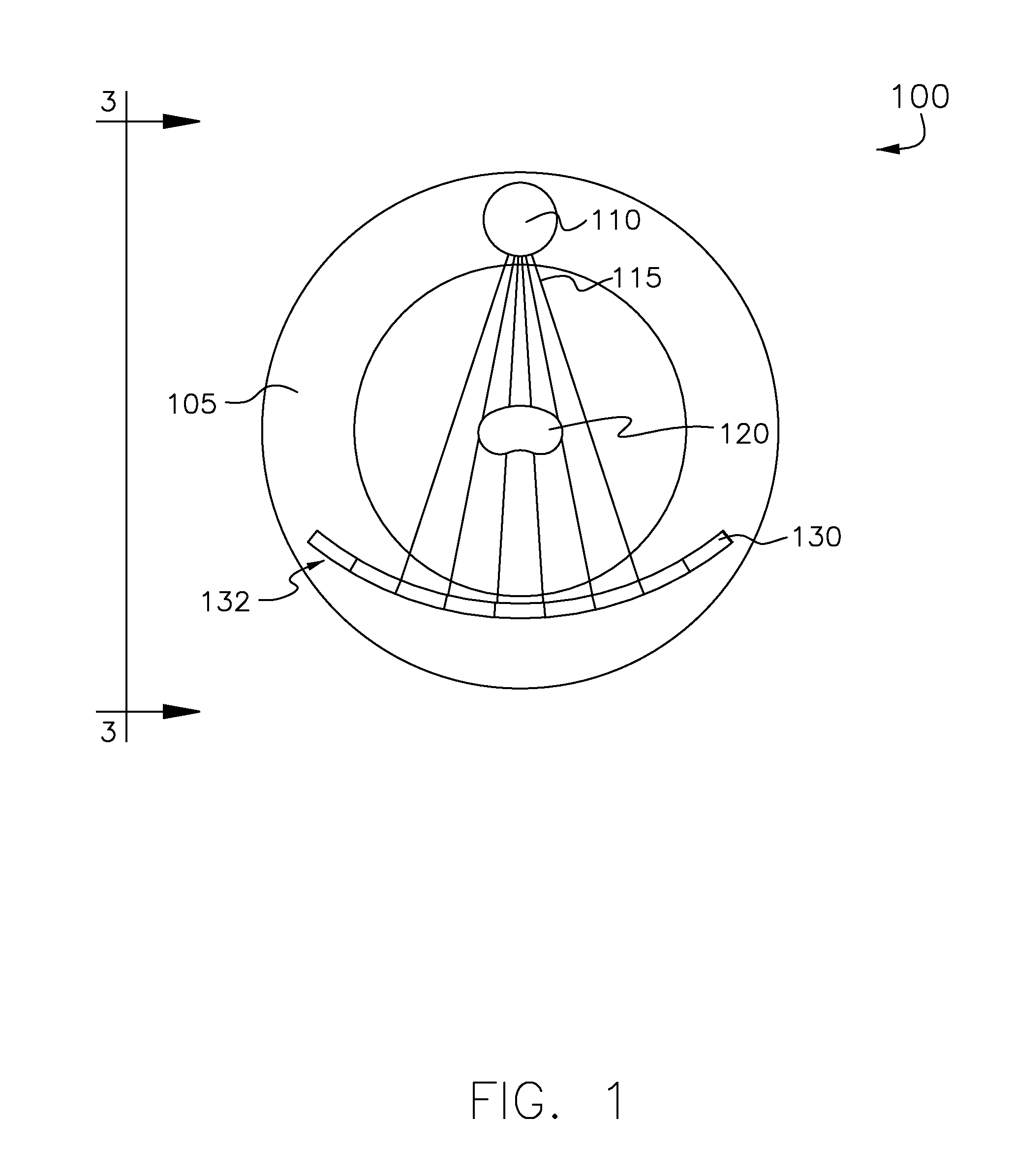
Multi-source low dose x-ray ct imaging aparatus
InactiveUS20120087464A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayElectronic communication
Some embodiments include a low-dose CT apparatus. Such an apparatus can comprise a plurality of x-ray sources disposed on a gantry and spaced apart along a z-axis. The sources may be configured to produce substantially overlapping fan beams, wherein overlap is substantially complete at a detector surface. Some embodiments also include a controller in electronic communication with the plurality of x-ray sources. The controller may be adapted to switch the plurality of x-ray sources between on and off states such that only one x-ray source is in an on state at any time. Furthermore, the controller circuit may be in electronic communication with at least one x-ray detector and may be adapted to synchronize the x-ray detector with the plurality of x-ray sources such that detected x-rays can be matched to an x-ray source.
Owner:FMI TECH
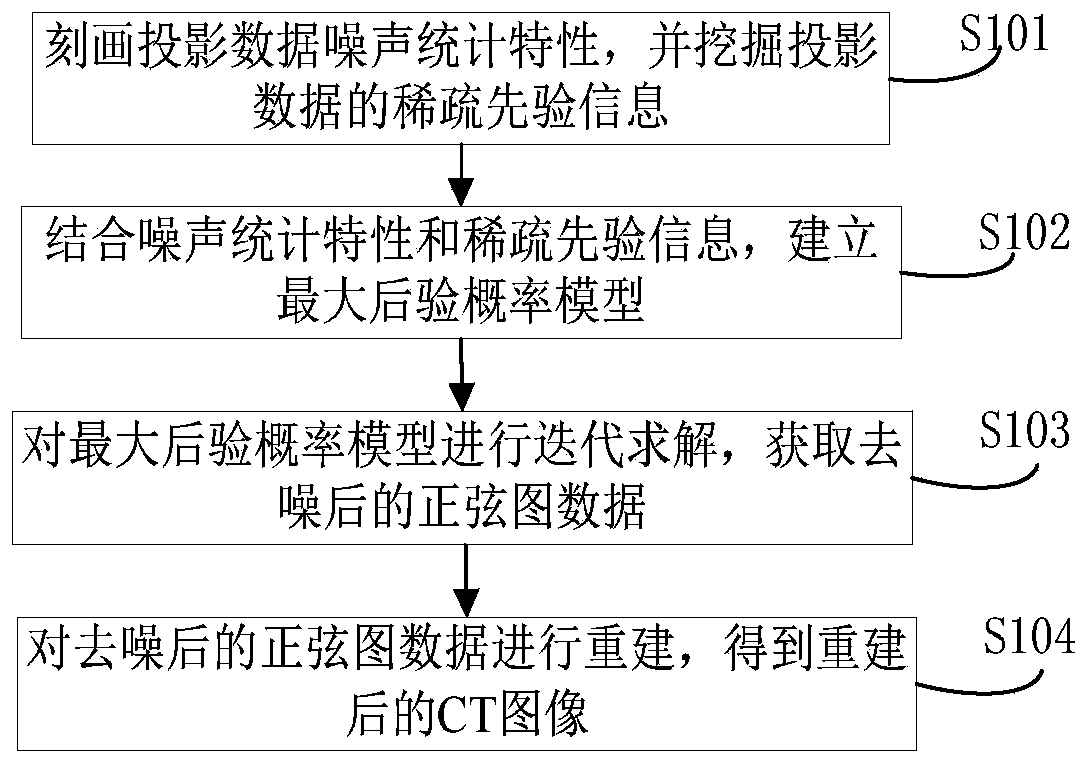
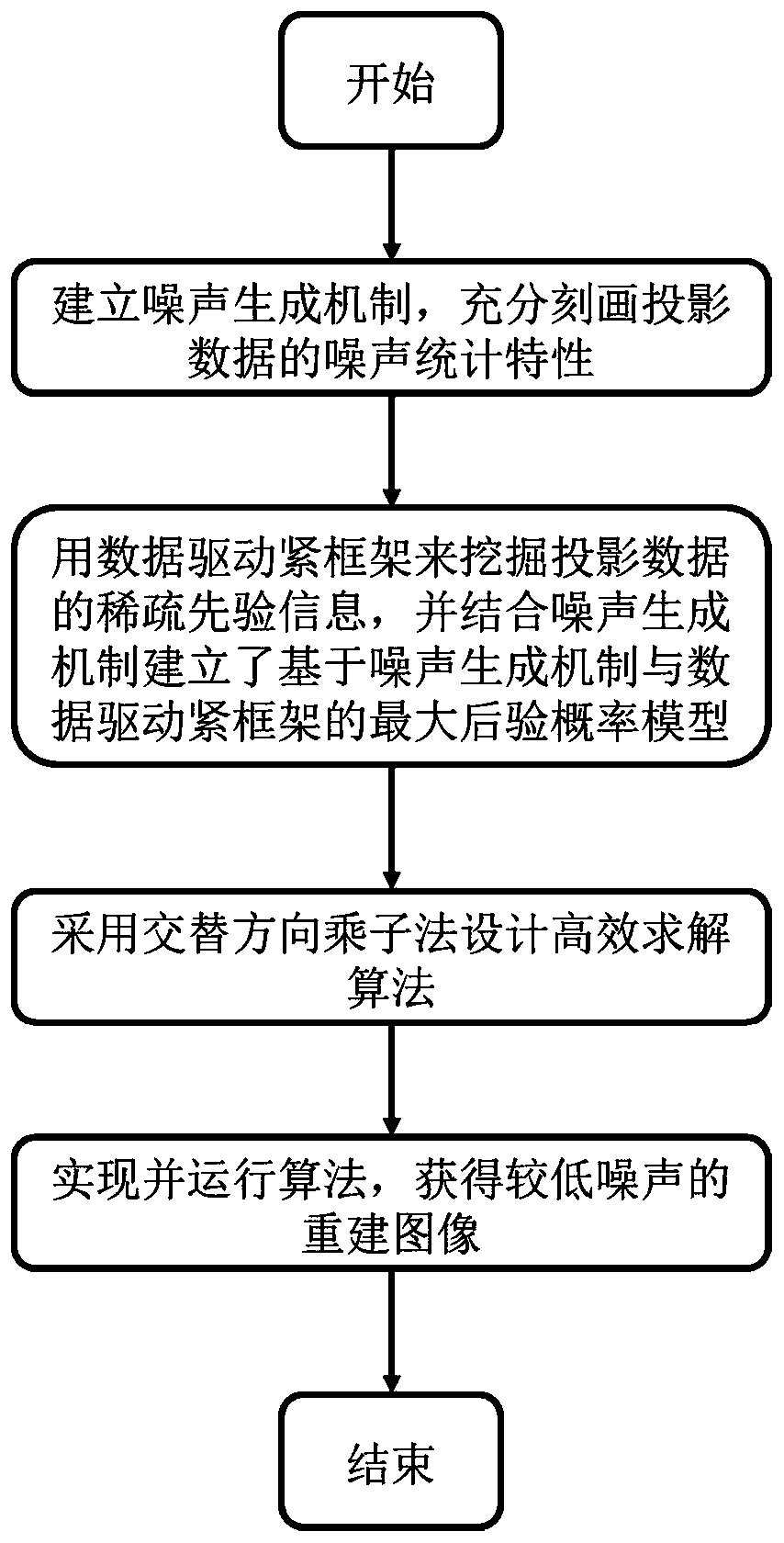
CT projection denoising reconstruction method and device based on noise generation mechanism and data driving tight frame
ActiveCN110136218AQuality improvementImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionNoise generationPrior information
The invention belongs to the technical field of CT image reconstruction, and particularly relates to a CT projection denoising reconstruction method and device based on a noise generation mechanism and a data driving tight frame, and the method comprises the steps: firstly describing the noise statistical characteristics of projection data, and mining sparse prior information of the projection data; establishing a maximum posterior probability model by combining the two data; carrying out iterative solution on the model to obtain denoised sine map data; and acquiring CT image by reconstruction. According to the method, the problem that serious noise and artifacts are easily remained in a reconstructed image due to the fact that noise of projection data is depicted in an approximation modein a traditional low-dose CT reconstruction algorithm is solved; noise can be removed while useful information of projection data is reserved as much as possible, noise and artifacts of a reconstructed image are effectively restrained, and the method has high application value in the aspect of improving the quality of a low-dose CT reconstructed image.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
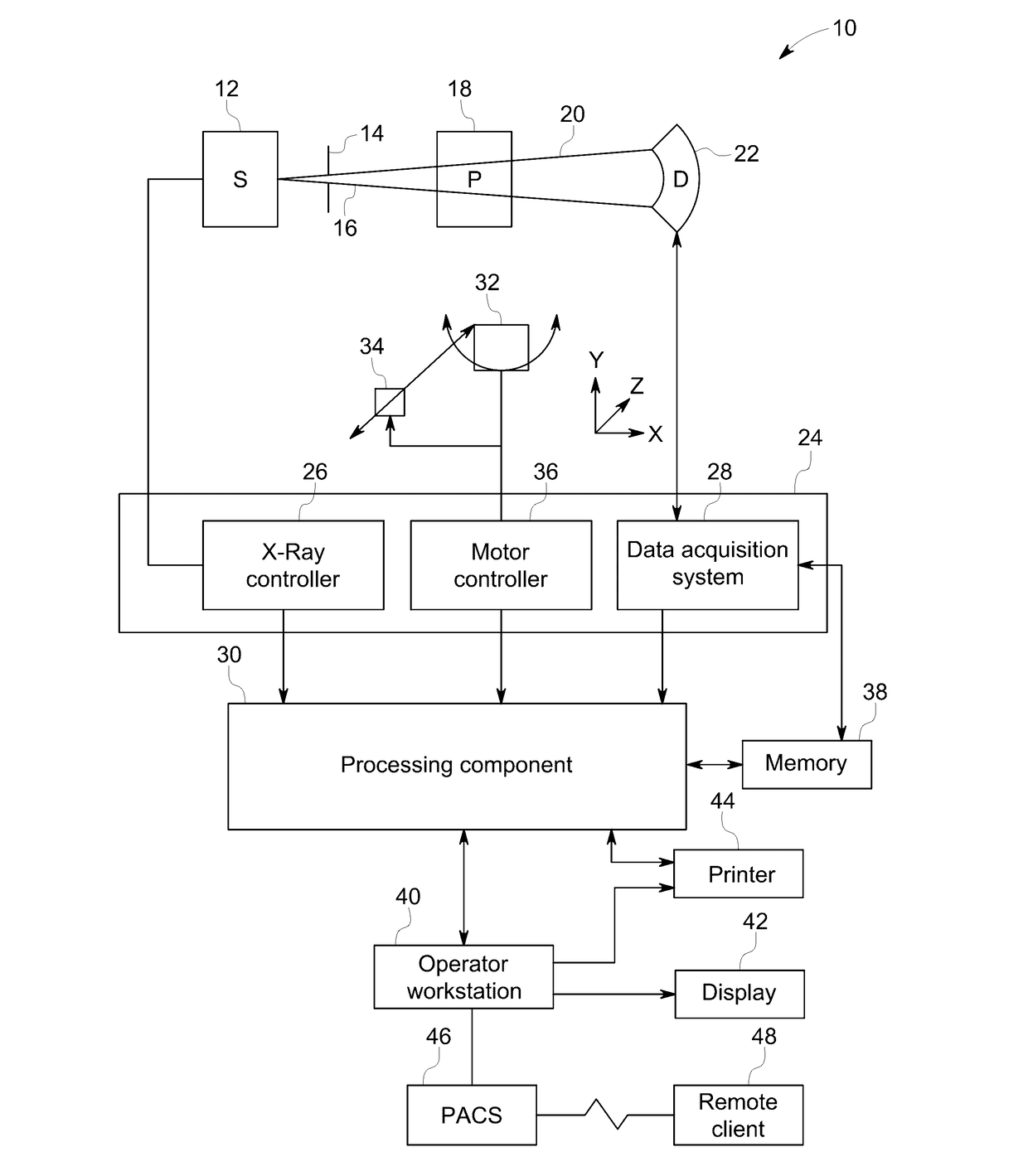
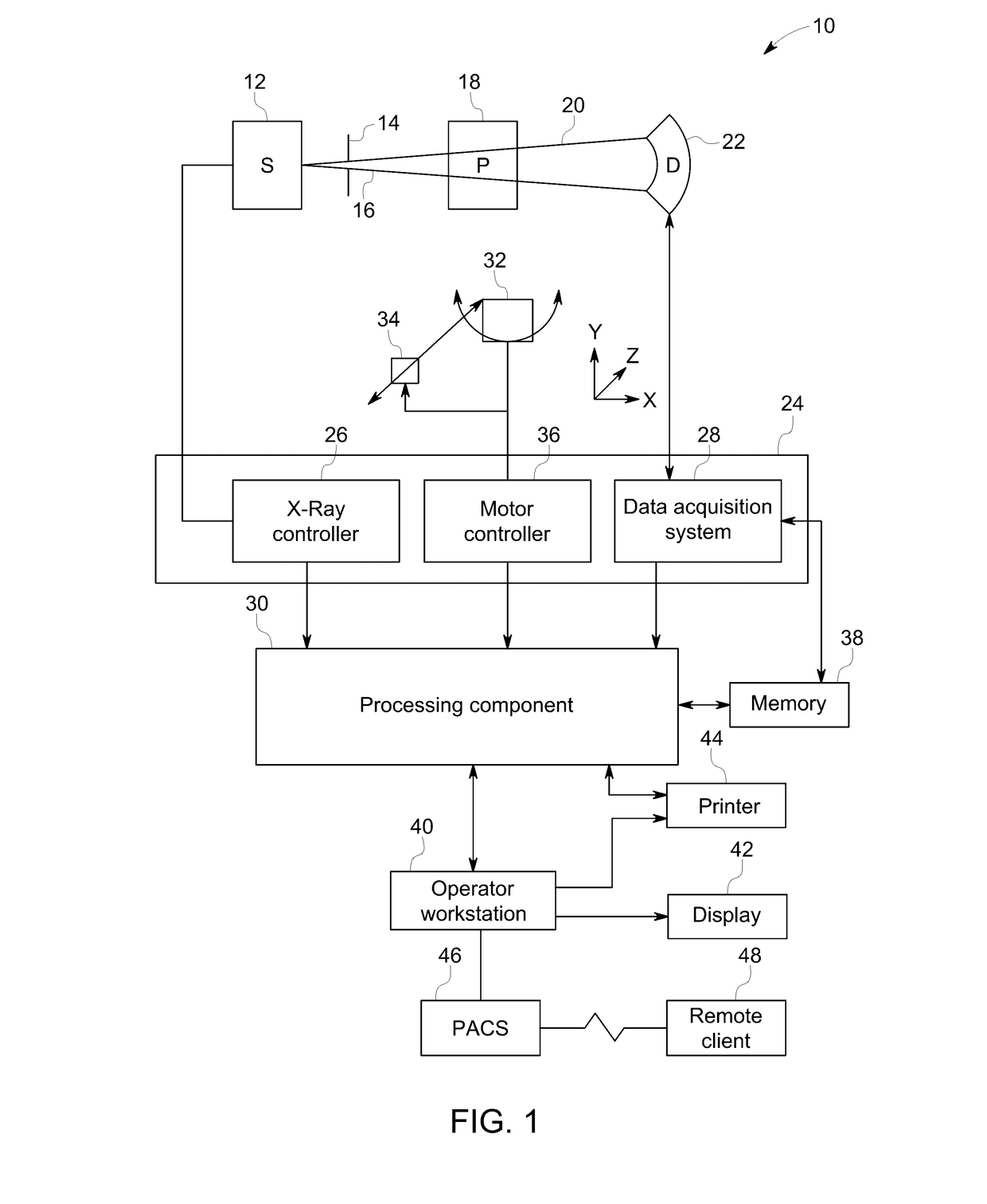
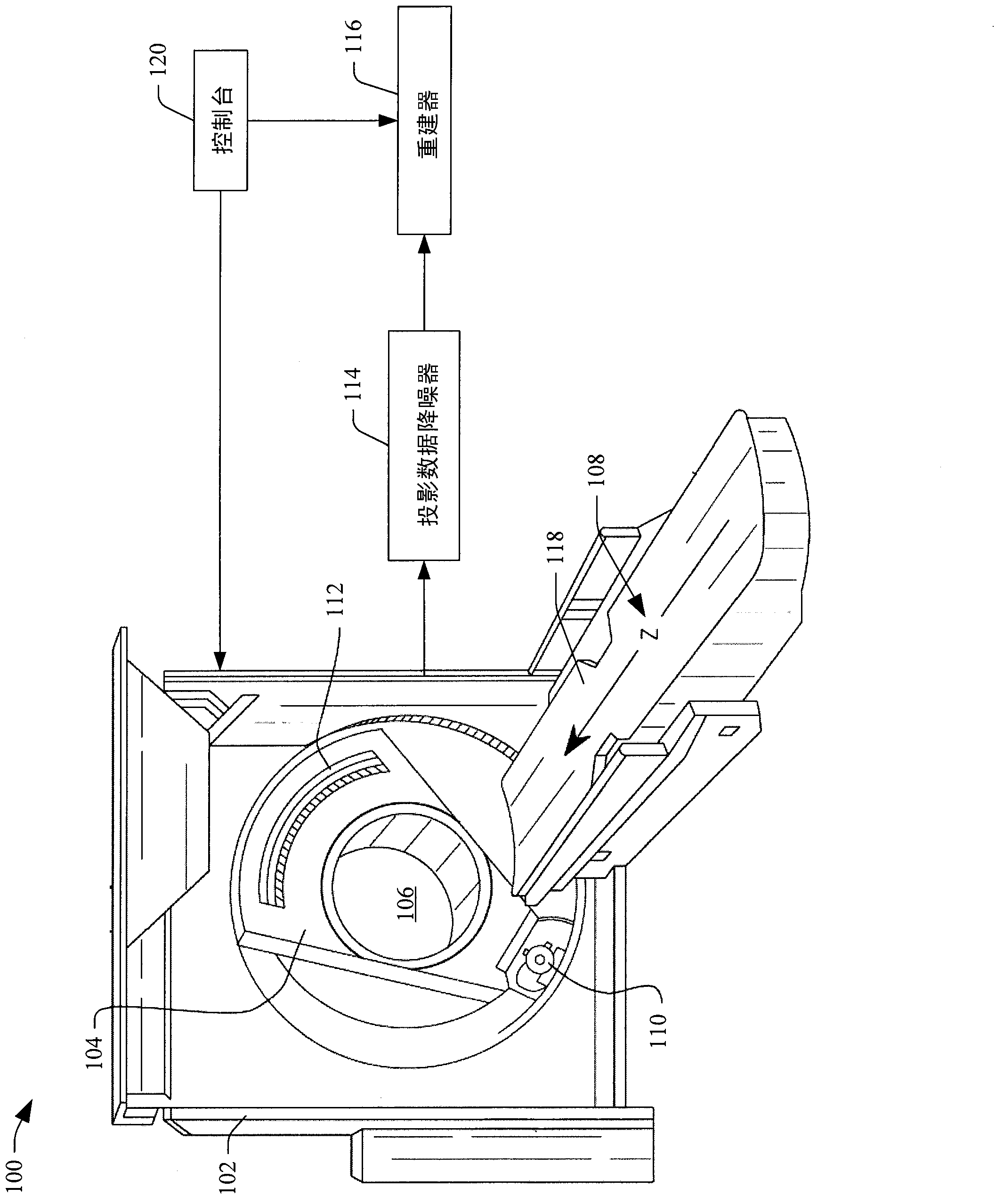
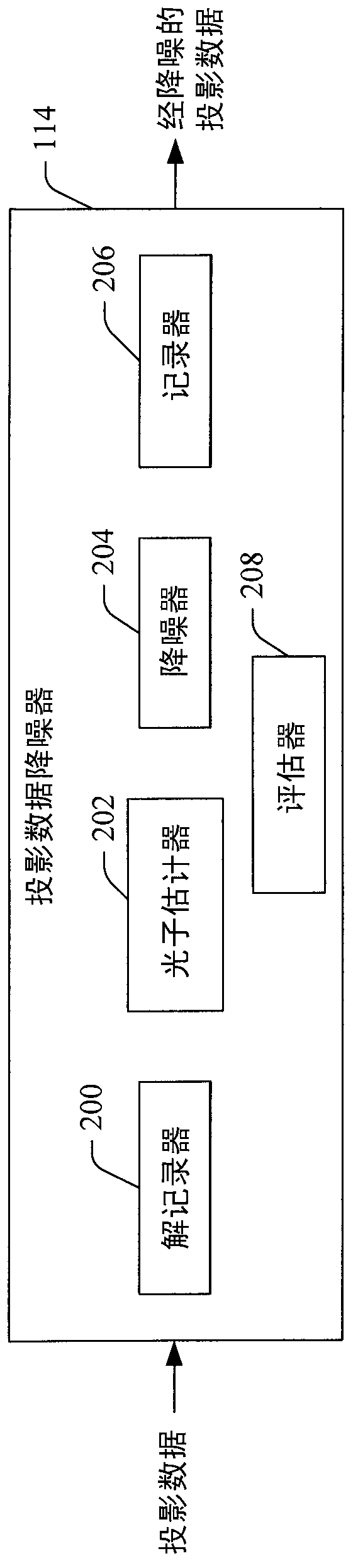
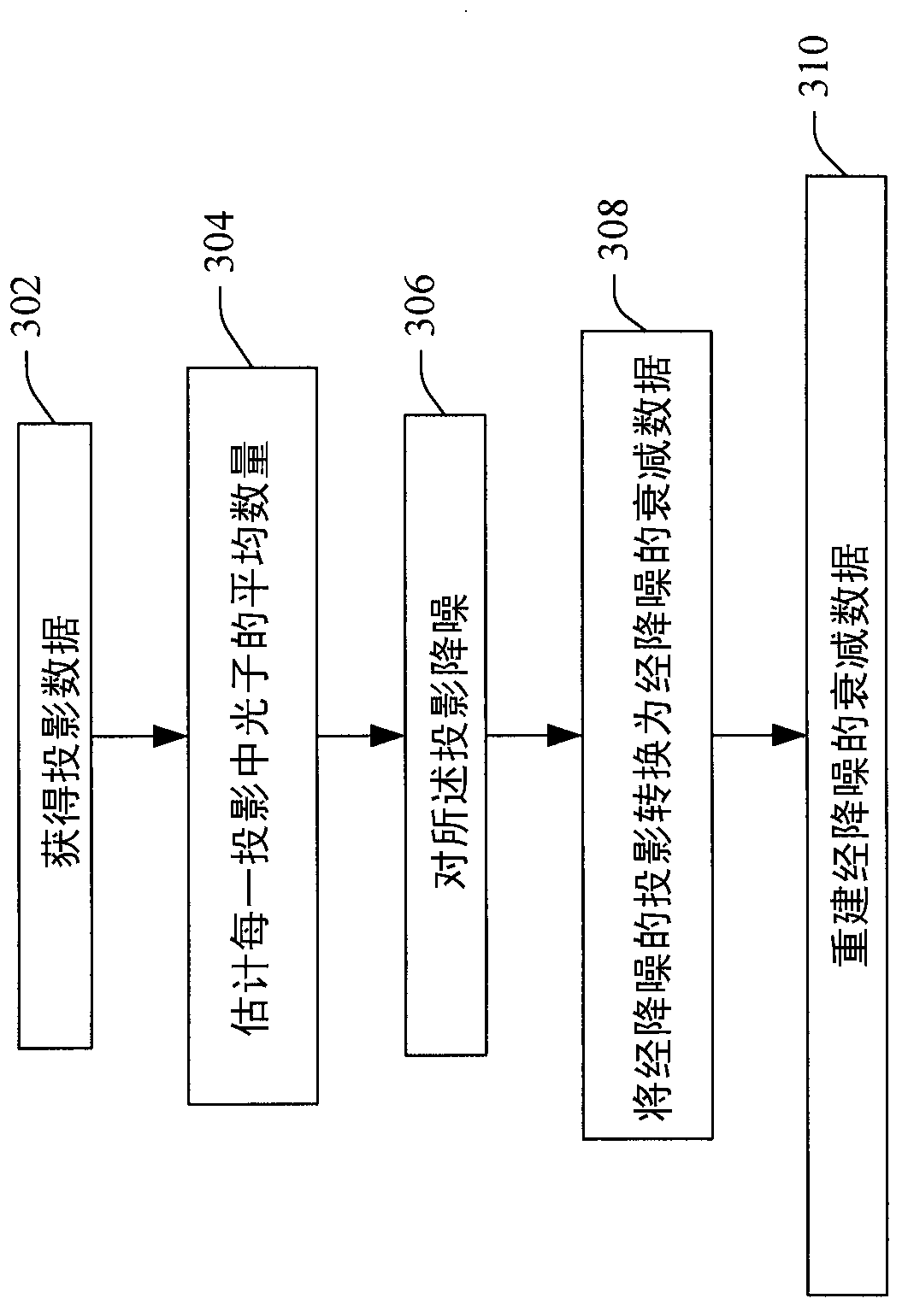
Low dose CT denoising
A system includes a source that rotates about an examination region and emits radiation that traverses the examination region, a radiation sensitive detector array that detects radiation traversing the examination region and generates projection data indicative of the detected radiation, and a projection data de-noiser that de-noises the projection data, wherein the de-noiser de-noises a projection based on a number of detected photons for the projection.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com