Patents
Literature
132 results about "Resistive switching memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
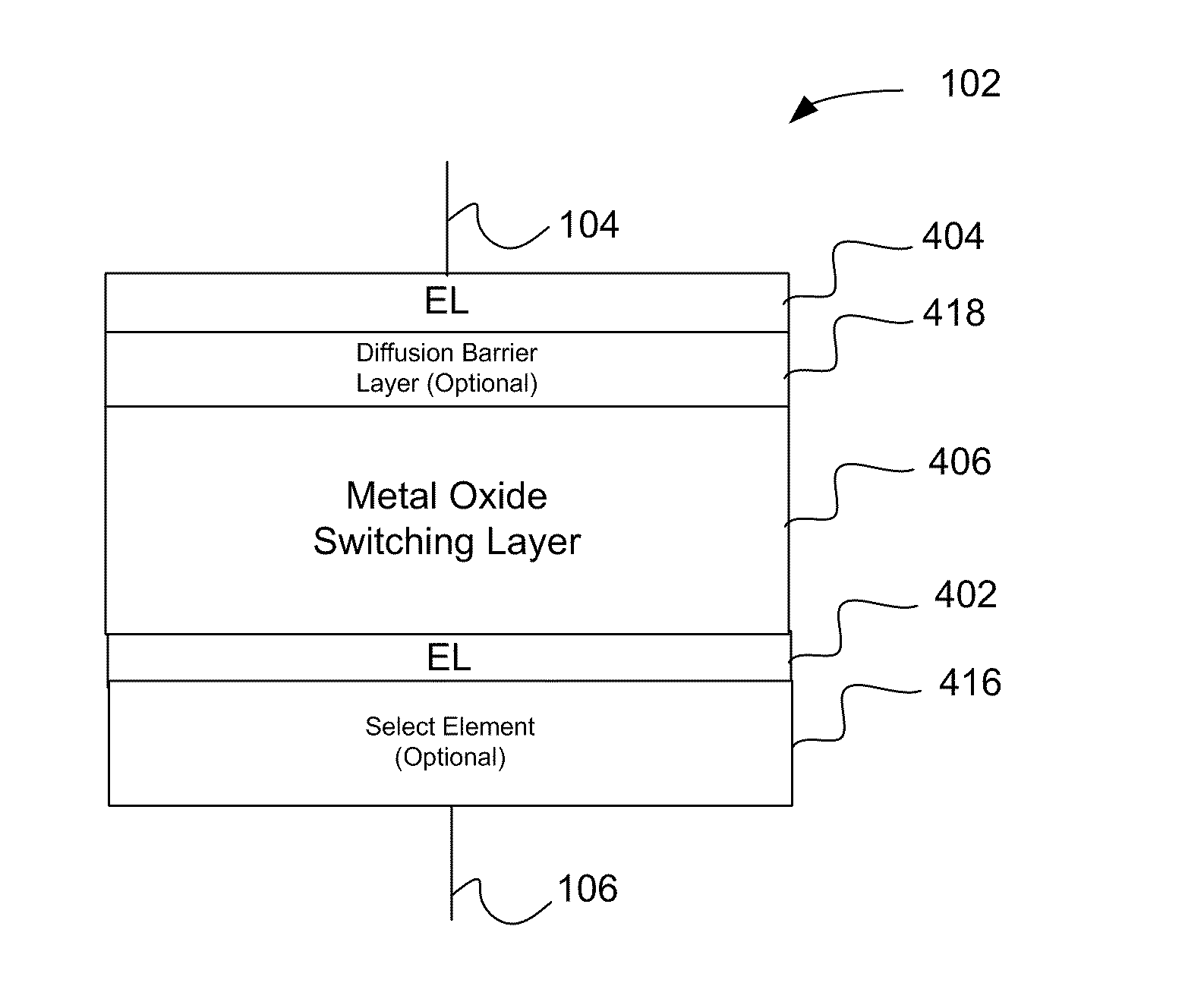
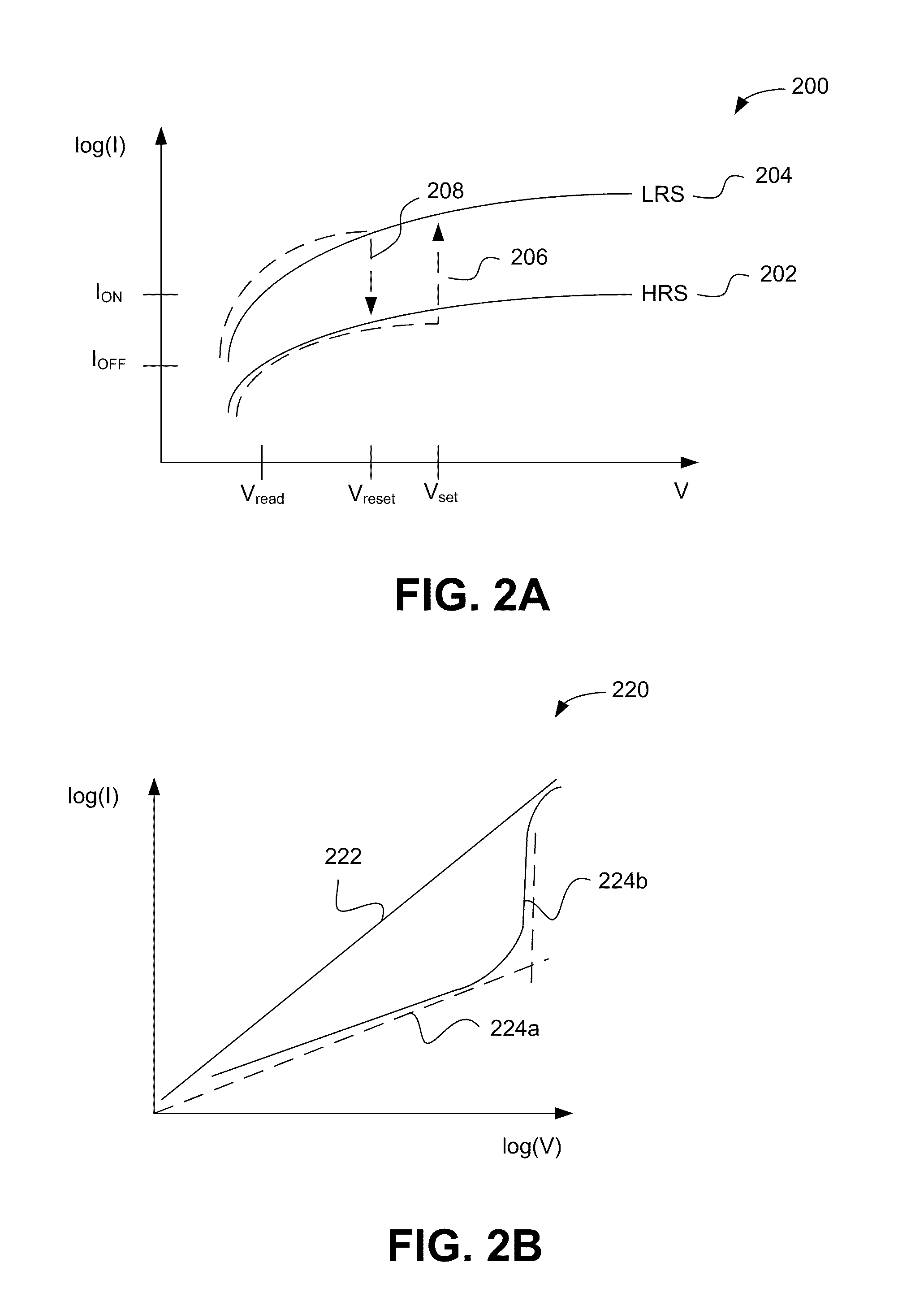
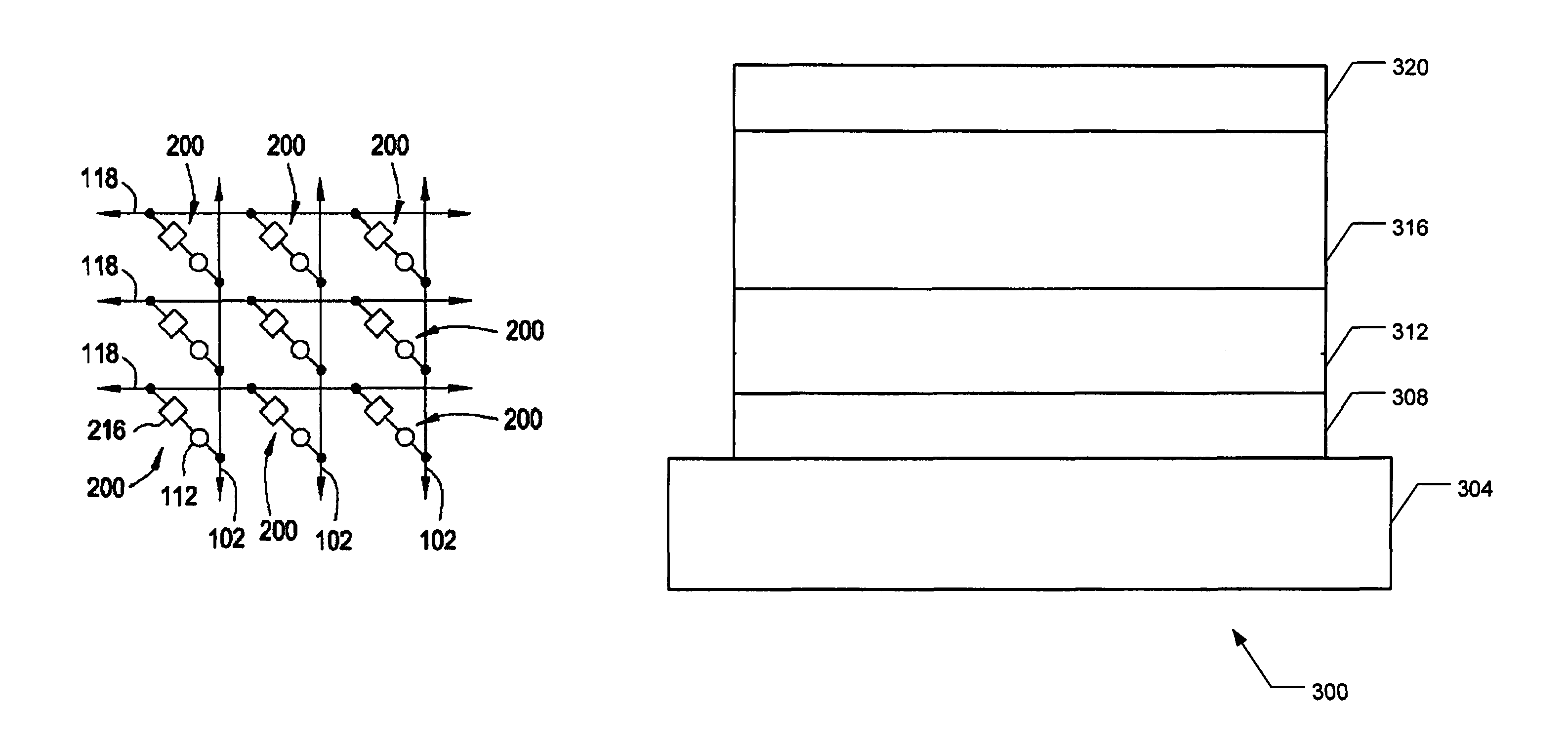
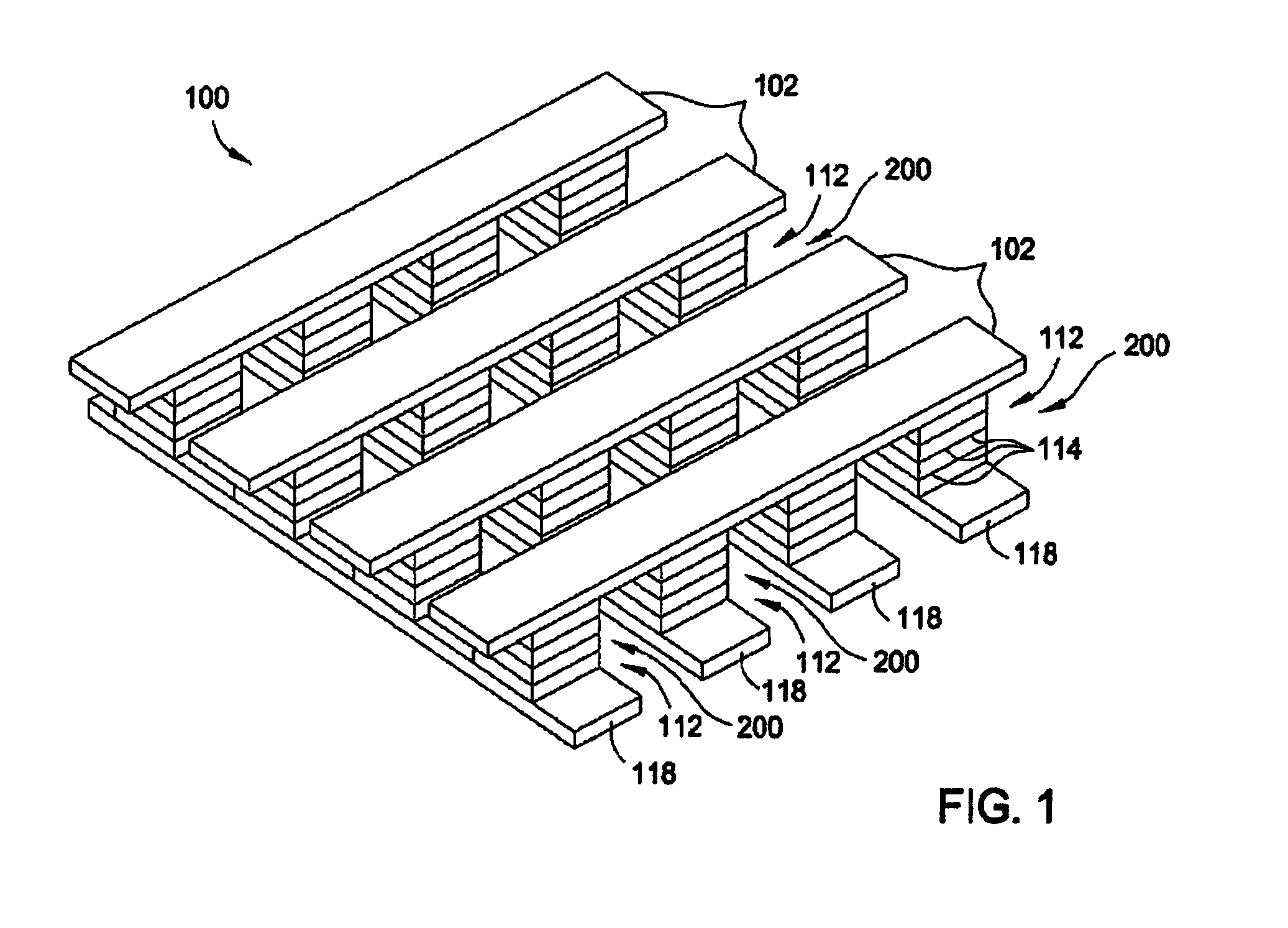
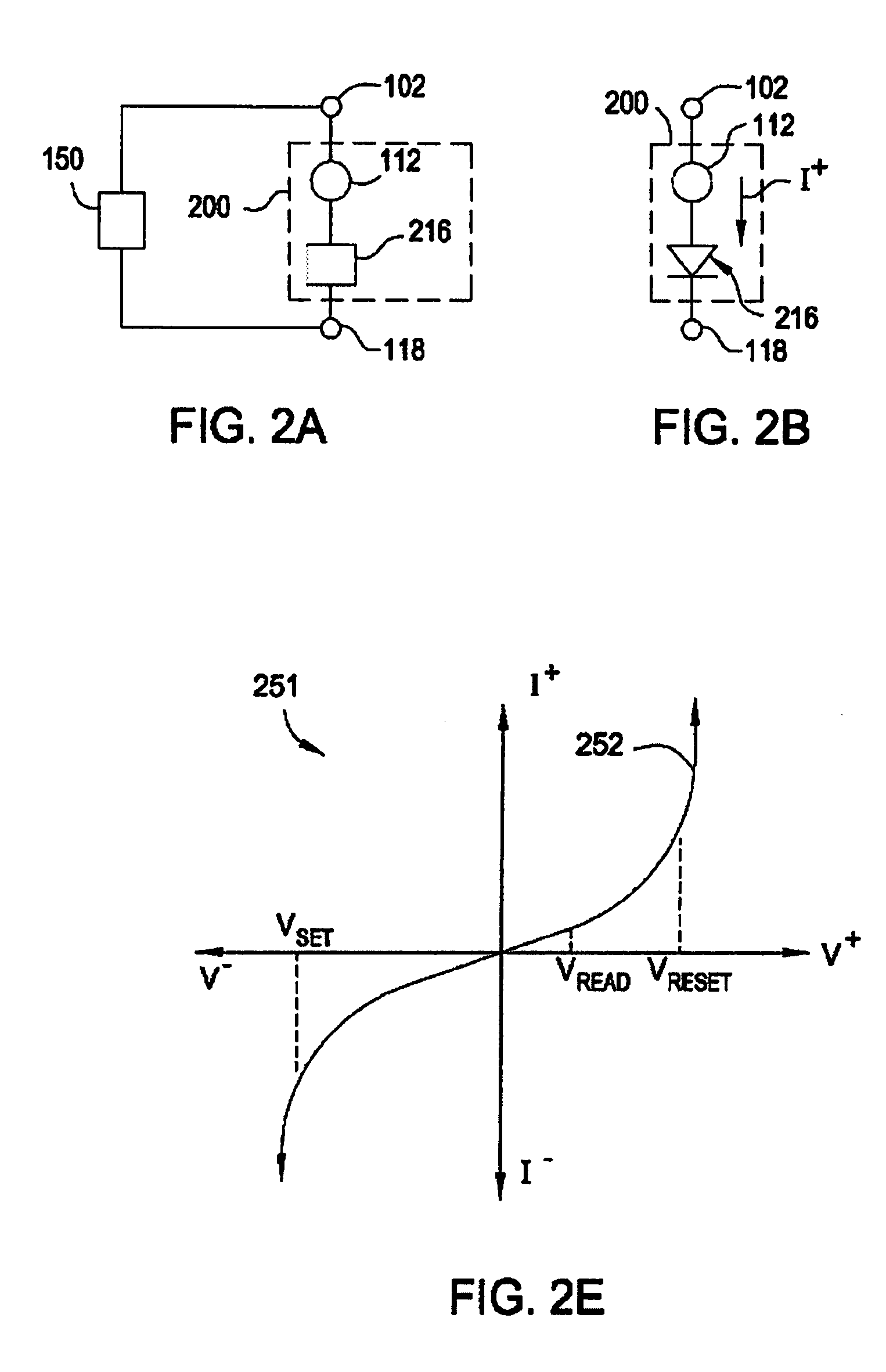
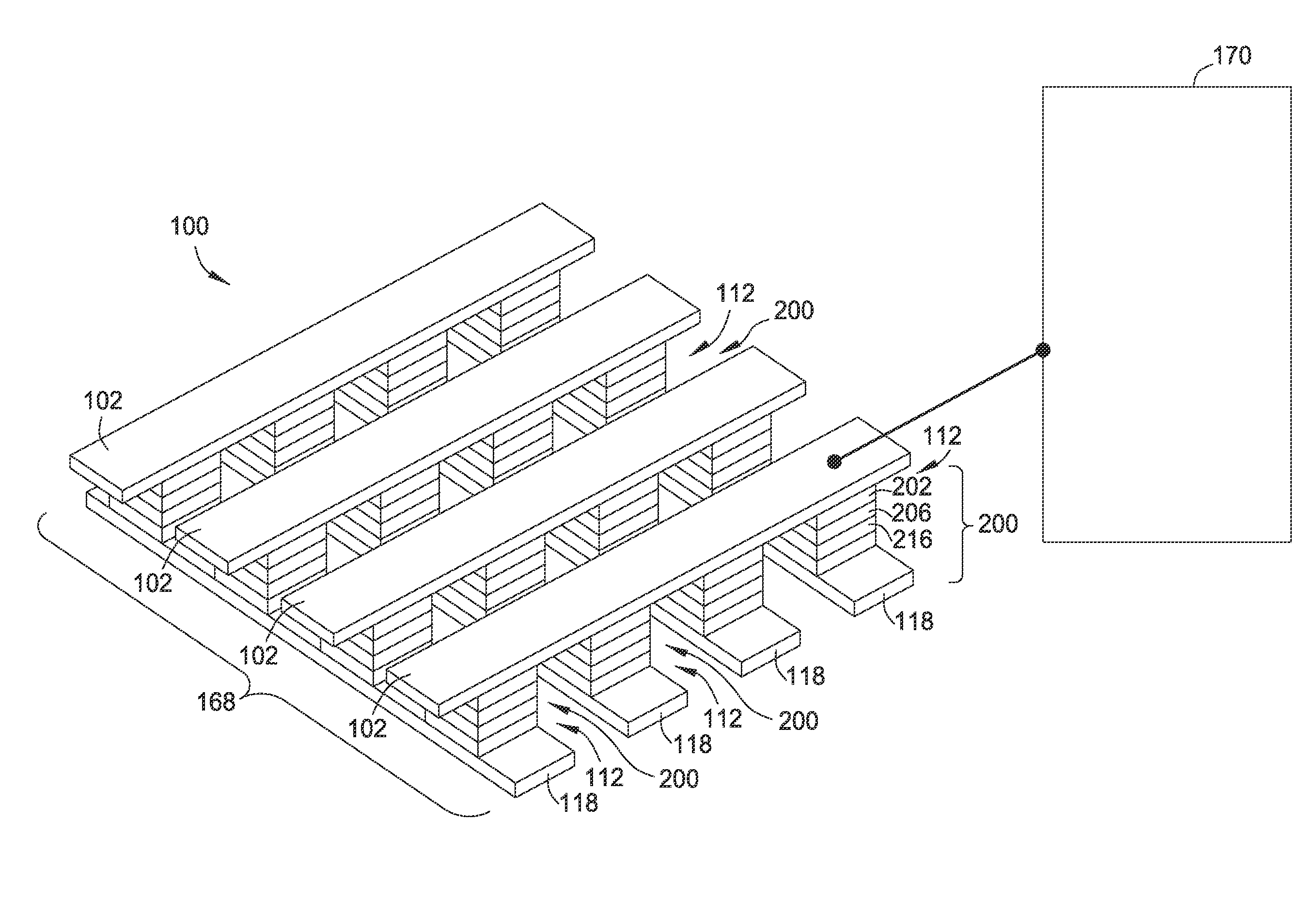
Nonvolatile memory device using a varistor as a current limiter element
ActiveUS20130214232A1Reduce voltageTotal current dropSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoftware engineeringMusic player
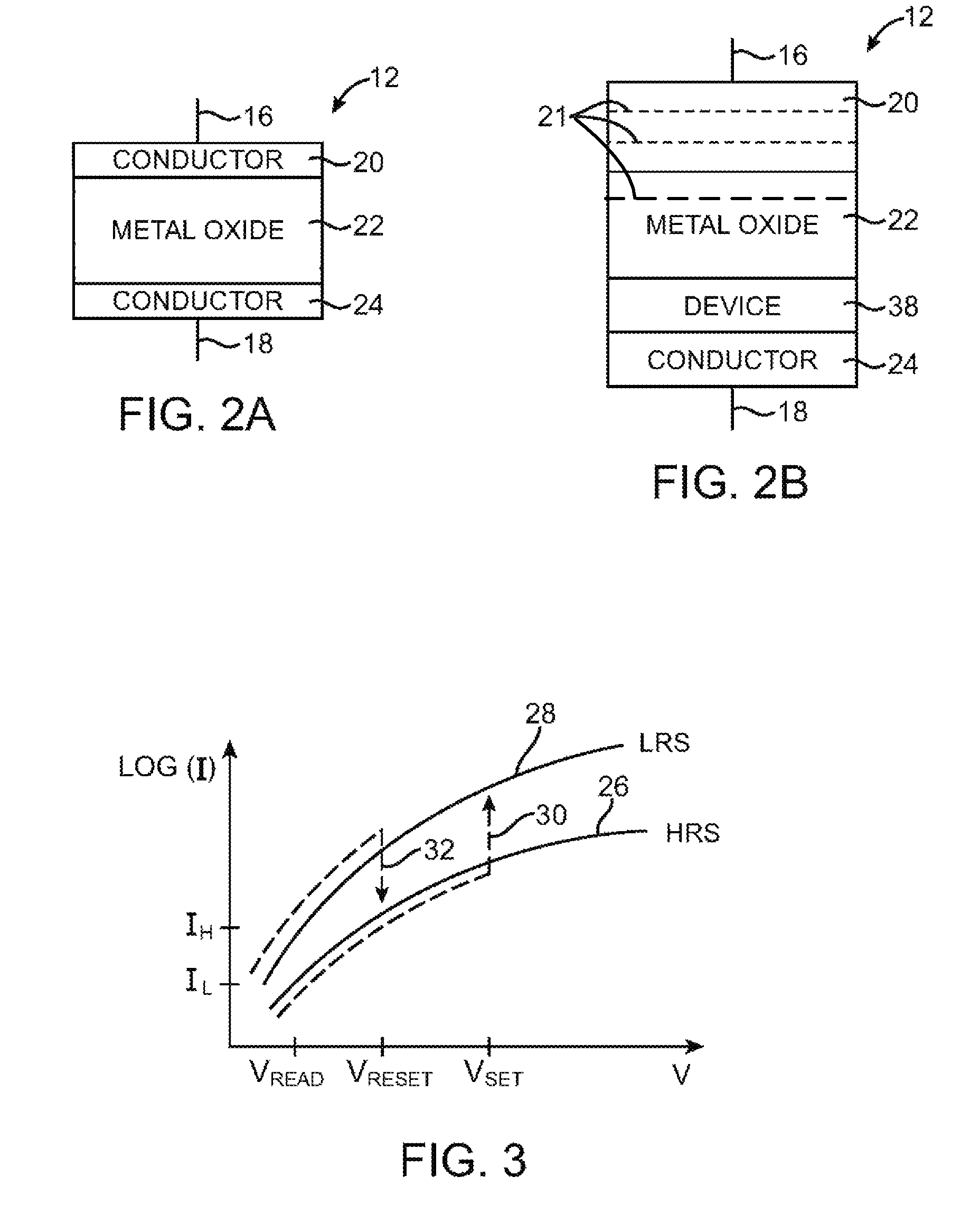
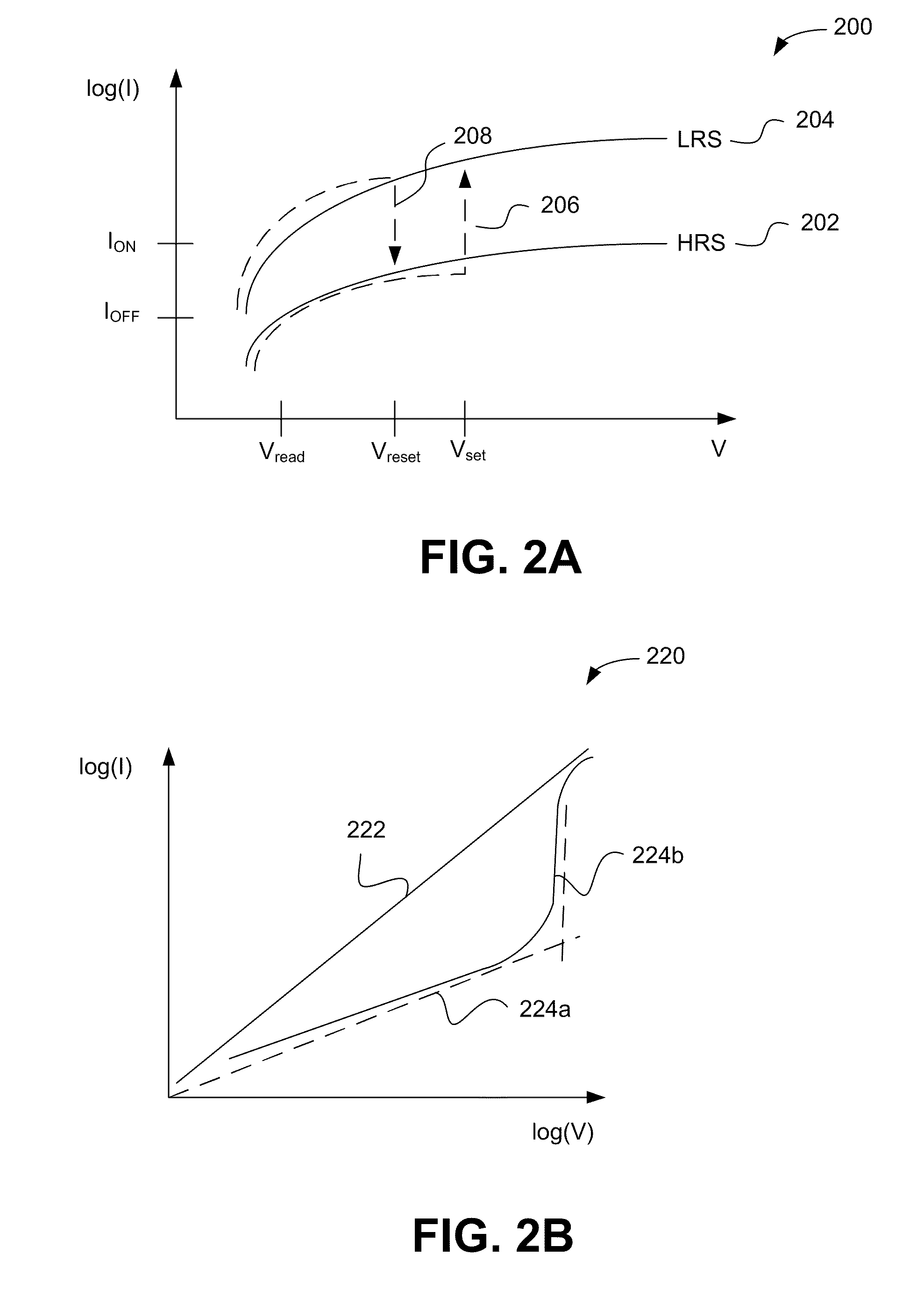
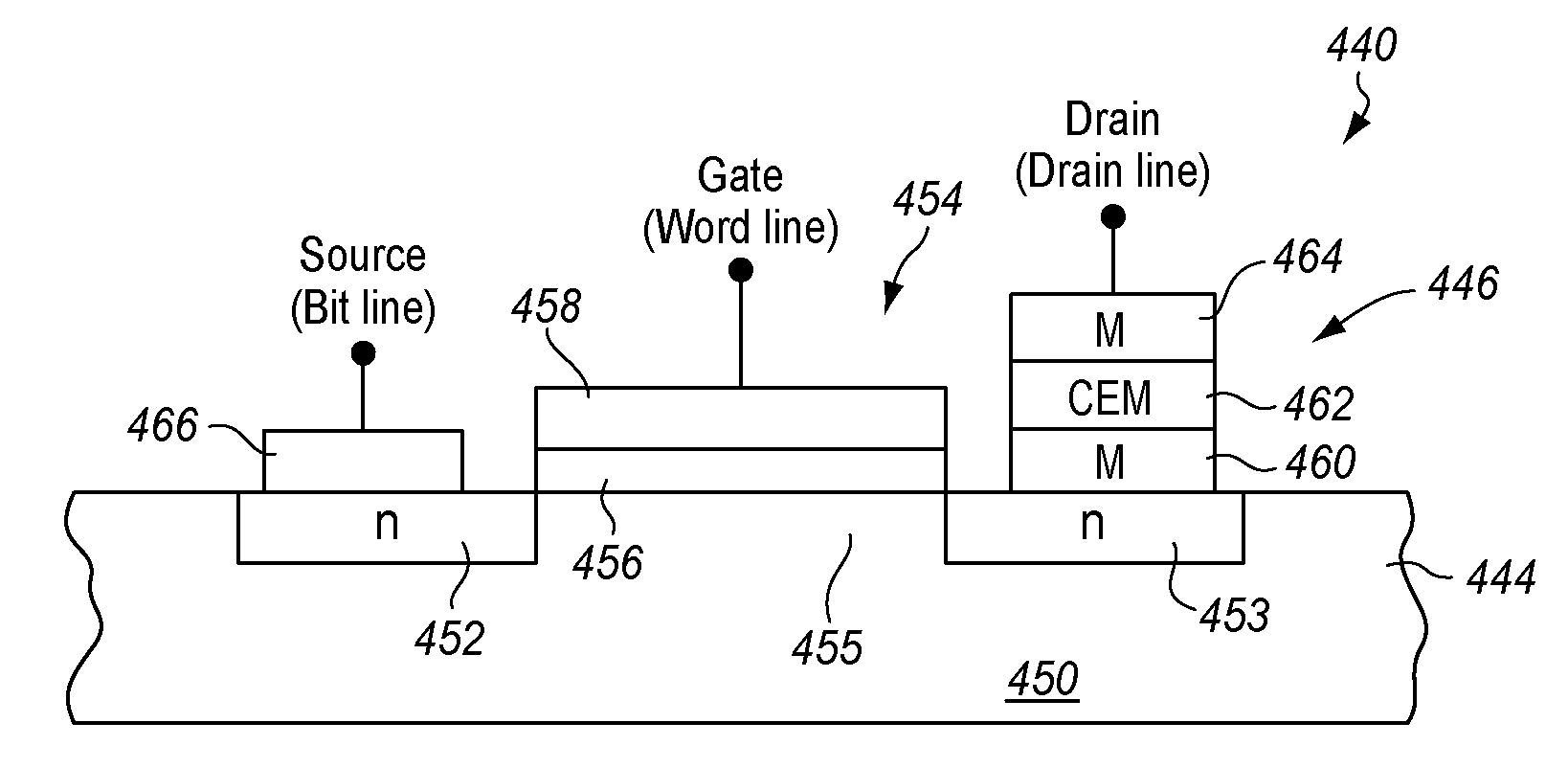
Embodiments of the invention include a method of forming a nonvolatile memory device that contains a resistive switching memory element that has improved device switching performance and lifetime, due to the addition of a current limiting component disposed therein. The electrical properties of the current limiting component are configured to lower the current flow through the variable resistance layer during the logic state programming steps by adding a fixed series resistance in the resistive switching memory element of the nonvolatile memory device. In some embodiments, the current limiting component comprises a varistor that is a current limiting material disposed within a resistive switching memory element in a nonvolatile resistive switching memory device. Typically, resistive switching memory elements may be formed as part of a high-capacity nonvolatile memory integrated circuit, which can be used in various electronic devices, such as digital cameras, mobile telephones, handheld computers, and music players.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
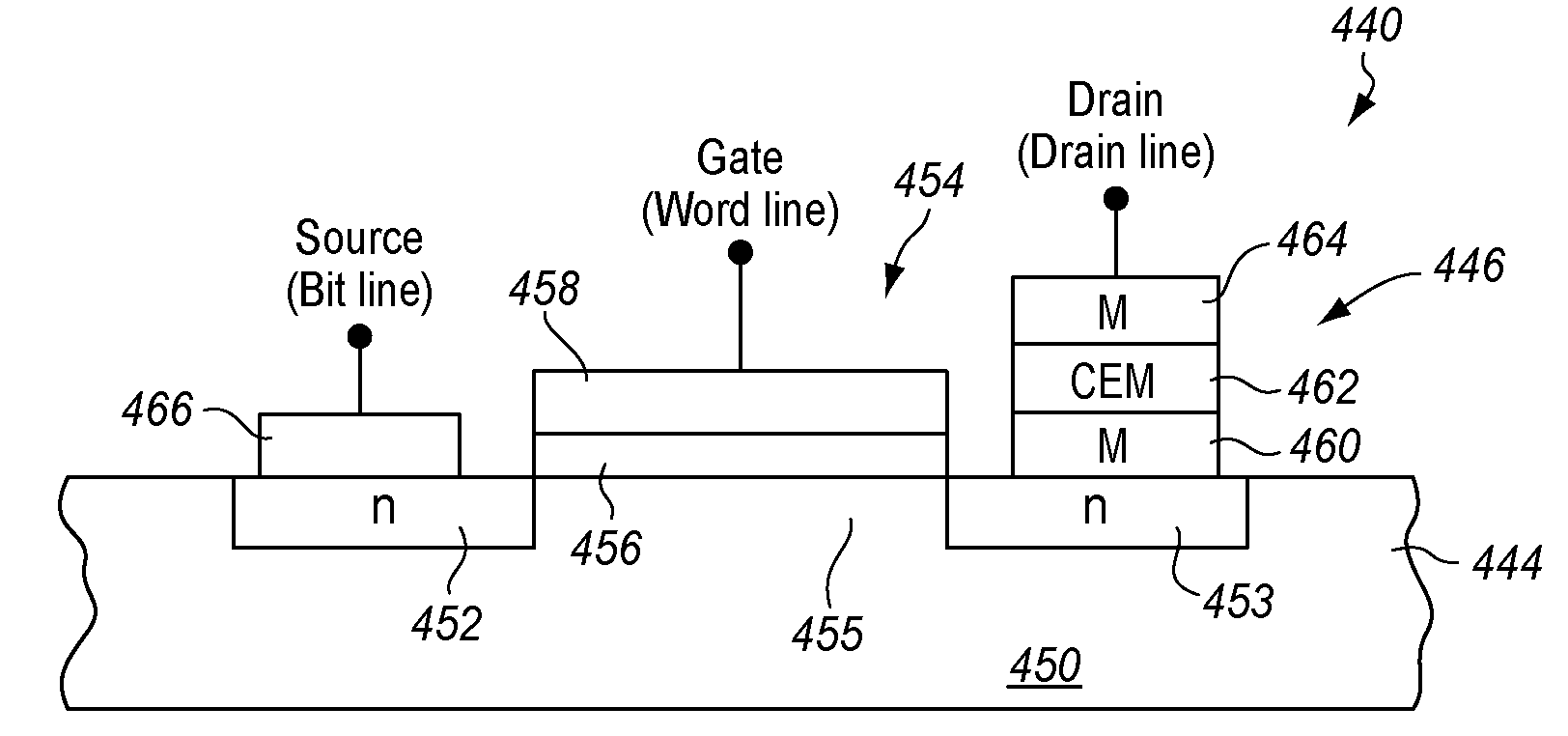
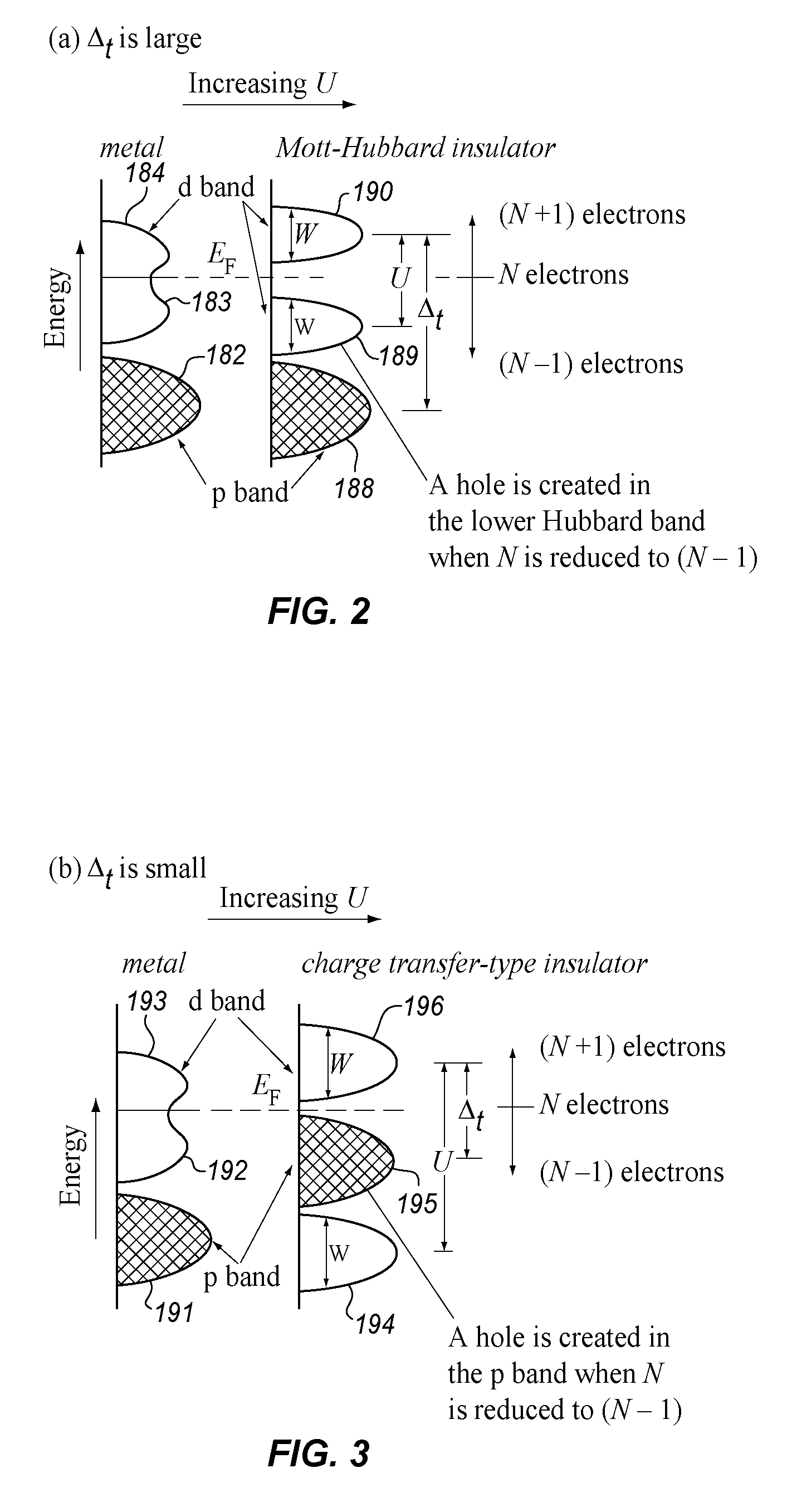
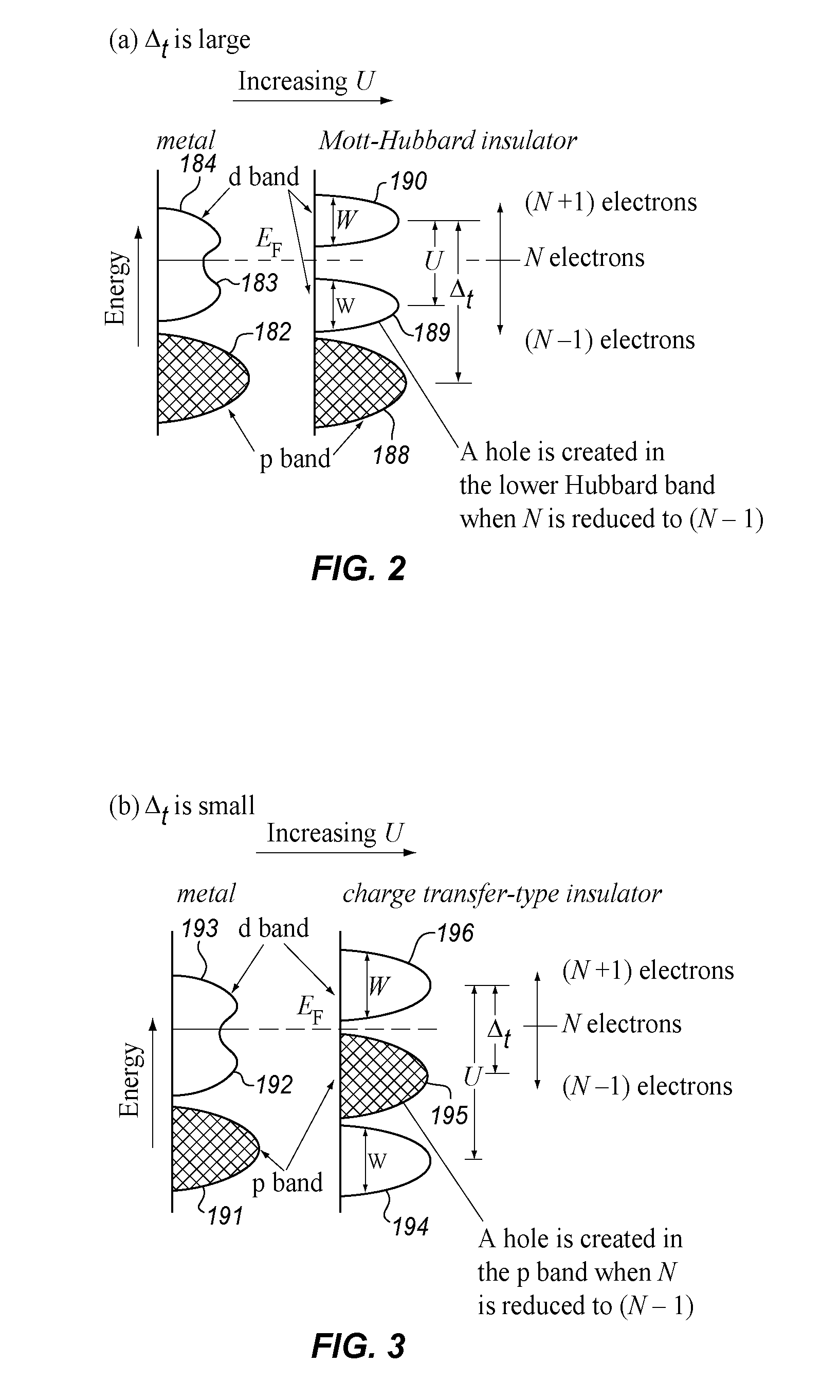
Correlated electron memory
ActiveUS20080106925A1Improve staminaFaster program and erase cyclesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMott transitionElectron
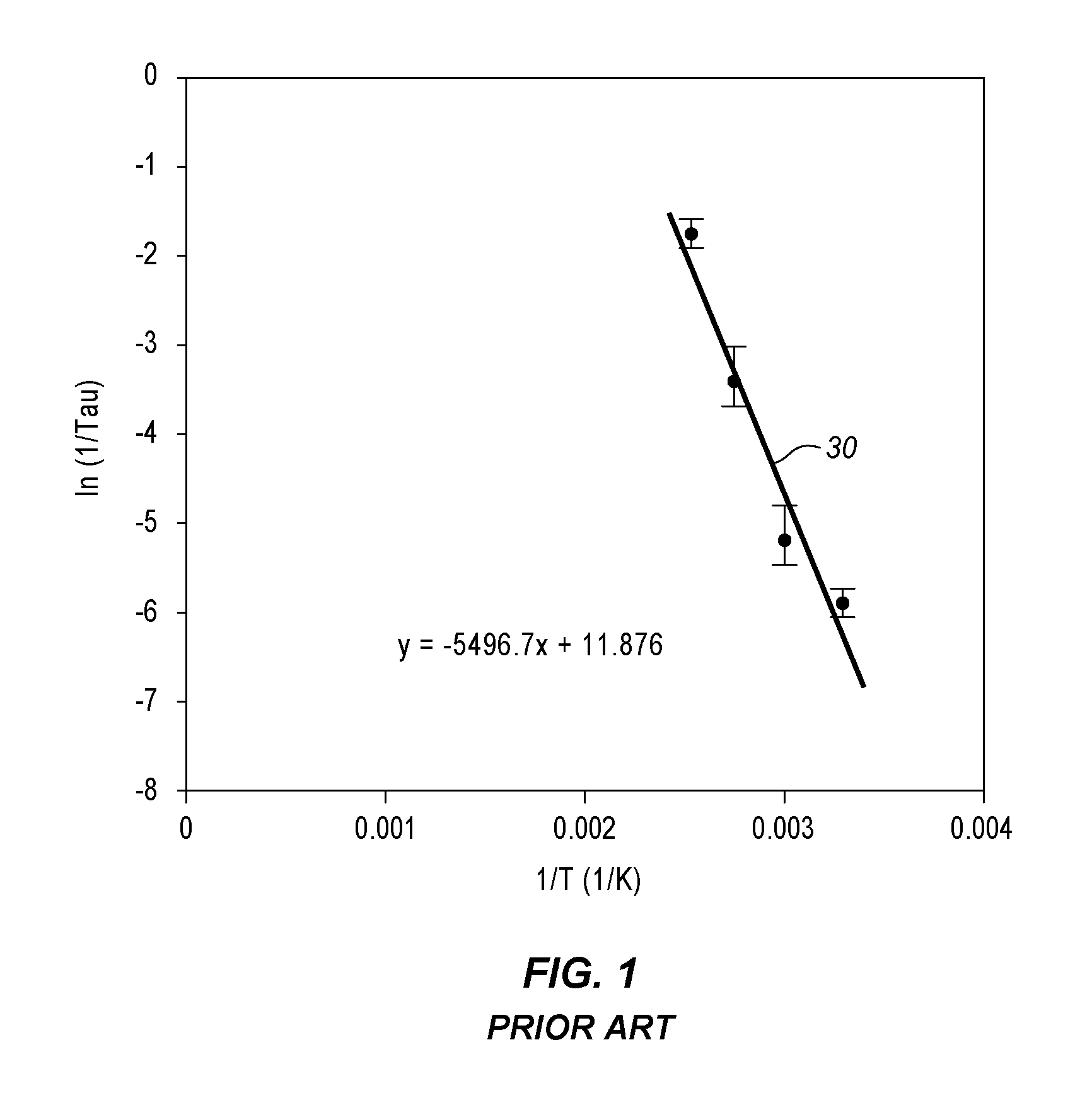
A non-volatile resistive switching memory that includes a homogeneous material which changes between the insulative and conductive states due to correlations between electrons, particularly via a Mott transition. The material is crystallized into the conductive state and does not require electroforming.
Owner:SYMETRIX MEMORY
Stabilized resistive switching memory
A non-volatile resistive switching memory that includes a material which changes between the insulative and conductive states. The material is stabilized against charge trapping by oxygen vacancies by an extrinsic ligand, such as carbon.
Owner:SYMETRIX MEMORY
Correlated electron memory
ActiveUS7872900B2Improve staminaFaster program and erase cyclesSolid-state devicesDigital storageMott transitionElectron
A non-volatile resistive switching memory that includes a homogeneous material which changes between the insulative and conductive states due to correlations between electrons, particularly via a Mott transition. The material is crystallized into the conductive state and does not require electroforming.
Owner:SYMETRIX MEMORY
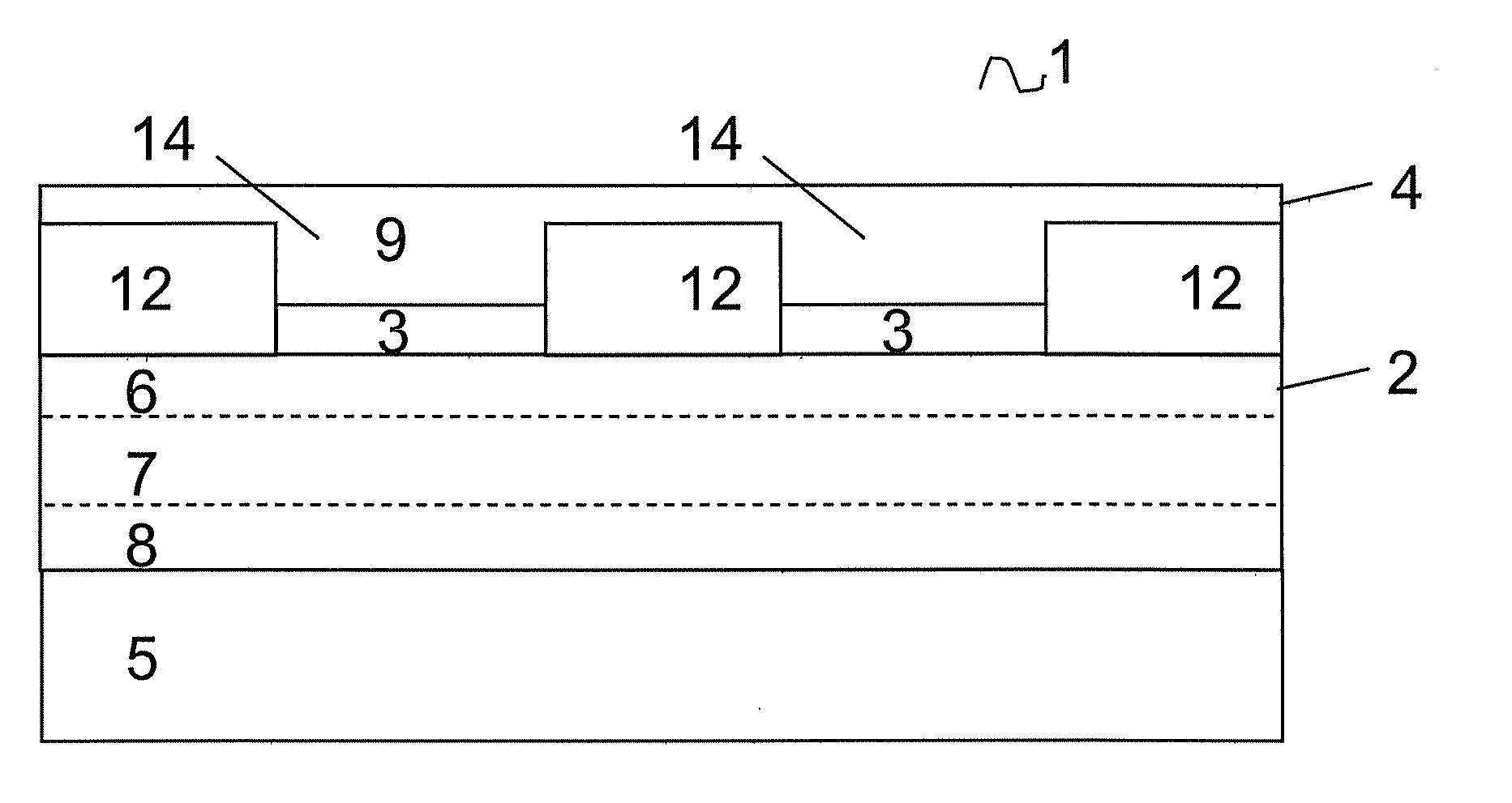
Resistive switching memory element including doped silicon electrode
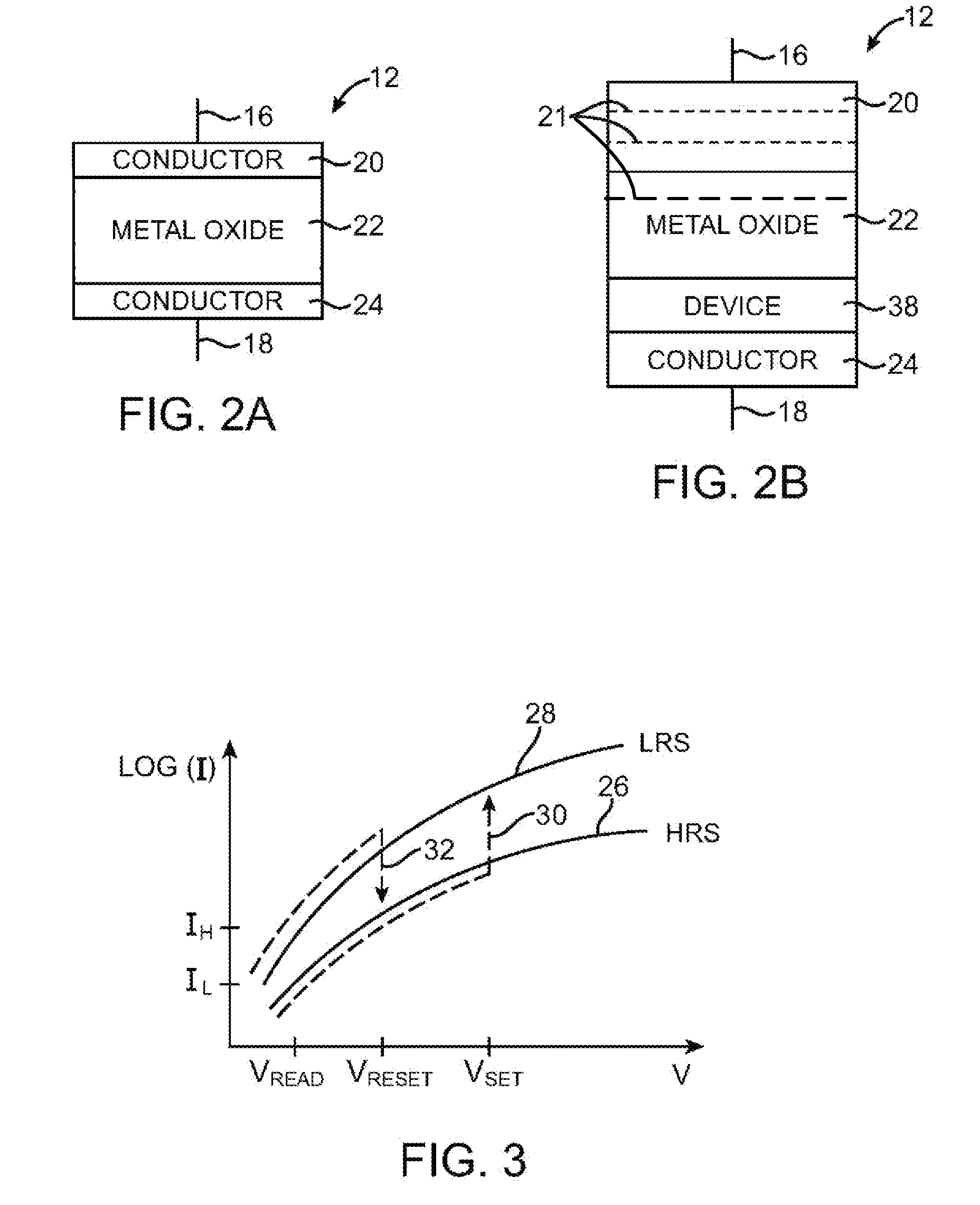
A resistive switching memory element including a doped silicon electrode is described, including a first electrode comprising doped silicon having a first work function, a second electrode having a second work function that is different from the first work function by between 0.1 and 1.0 electron volts (eV), a metal oxide layer between the first electrode and the second electrode, the metal oxide layer switches using bulk-mediated switching and has a bandgap of greater than 4 eV, and the memory element switches from a low resistance state to a high resistance state and vice versa.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Non-Volatile Resistive-Switching Memories
ActiveUS20090272959A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLeakage current densitySquare Centimeter
Non-volatile resistive-switching memories are described, including a memory element having a first electrode, a second electrode, a metal oxide between the first electrode and the second electrode. The metal oxide switches using bulk-mediated switching, has a bandgap greater than 4 electron volts (eV), has a set voltage for a set operation of at least one volt per one hundred angstroms of a thickness of the metal oxide, and has a leakage current density less than 40 amps per square centimeter (A / cm2) measured at 0.5 volts (V) per twenty angstroms of the thickness of the metal oxide.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Resistive-switching memory elements having improved switching characteristics
ActiveUS20100258782A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCouplingTitanium
Resistive-switching memory elements having improved switching characteristics are described, including a memory element having a first electrode and a second electrode, a switching layer between the first electrode and the second electrode comprising hafnium oxide and having a first thickness, and a coupling layer between the switching layer and the second electrode, the coupling layer comprising a material including metal titanium and having a second thickness that is less than 25 percent of the first thickness.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Methods for forming resistive switching memory elements by heating deposited layers
ActiveUS8143092B2Reduce process complexitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygenRapid thermal annealing
Resistive switching nonvolatile memory elements are provided. A metal-containing layer and an oxide layer for a memory element can be heated using rapid thermal annealing techniques. During heating, the oxide layer may decompose and react with the metal-containing layer. Oxygen from the decomposing oxide layer may form a metal oxide with metal from the metal-containing layer. The resulting metal oxide may exhibit resistive switching for the resistive switching memory elements.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
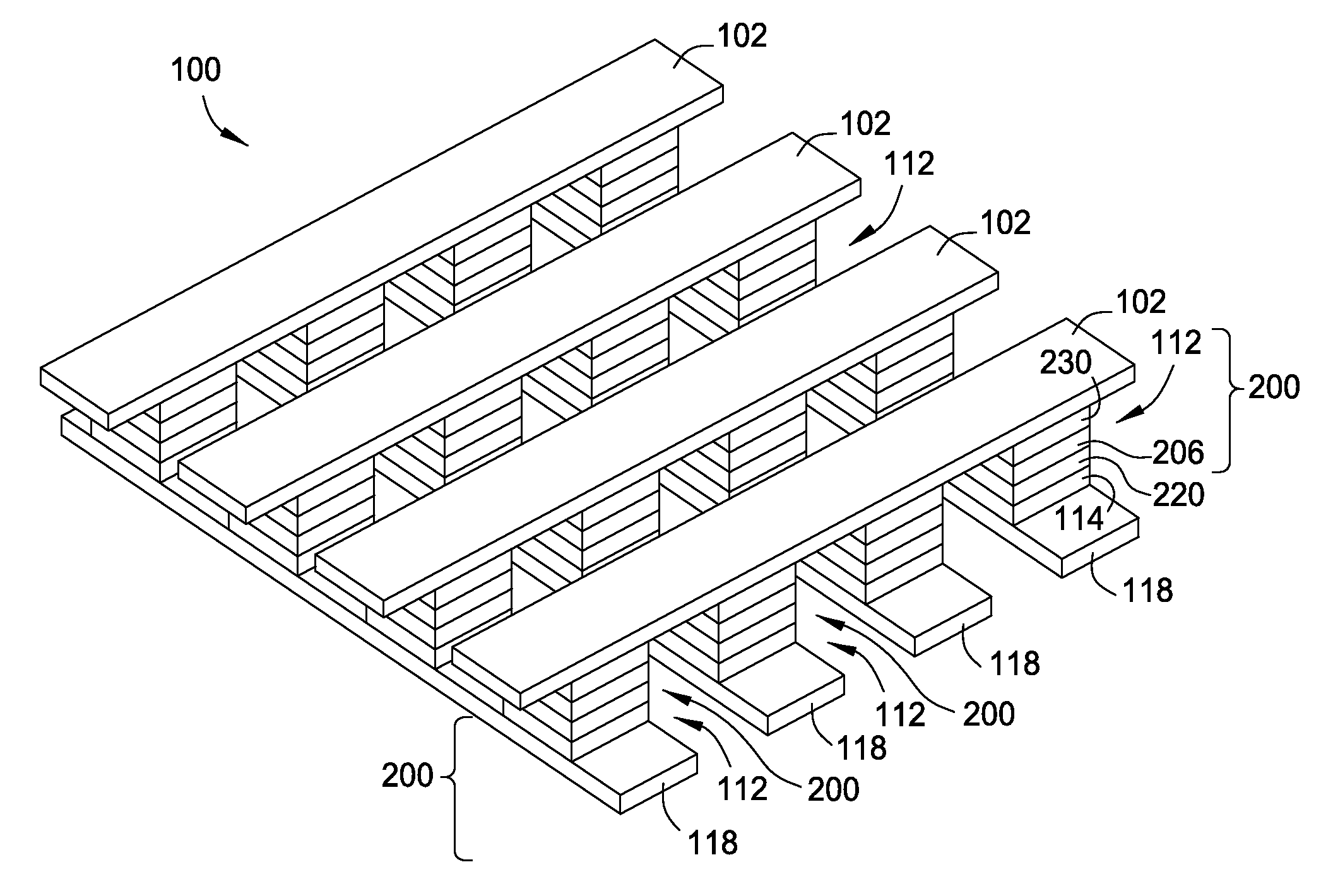
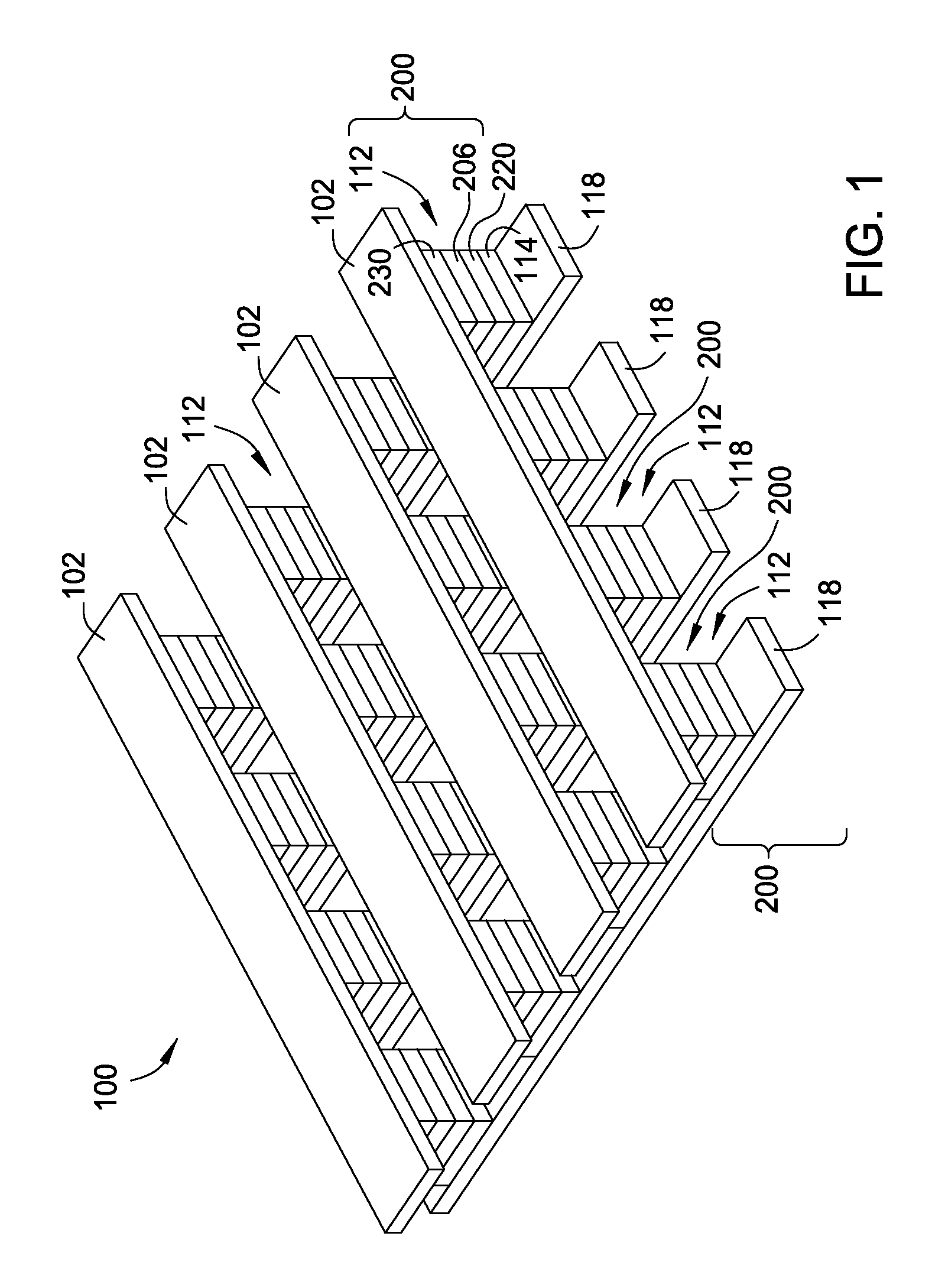
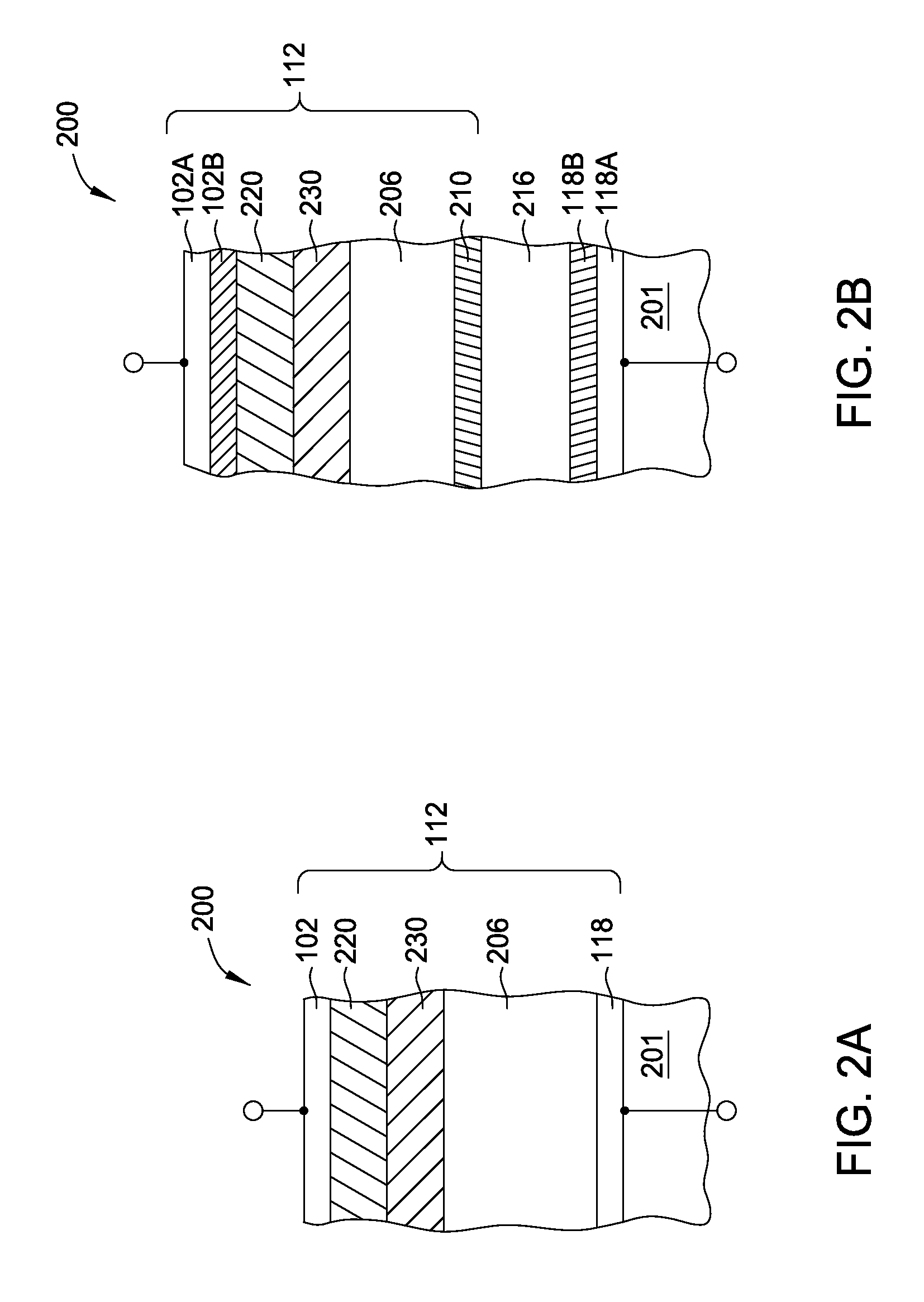
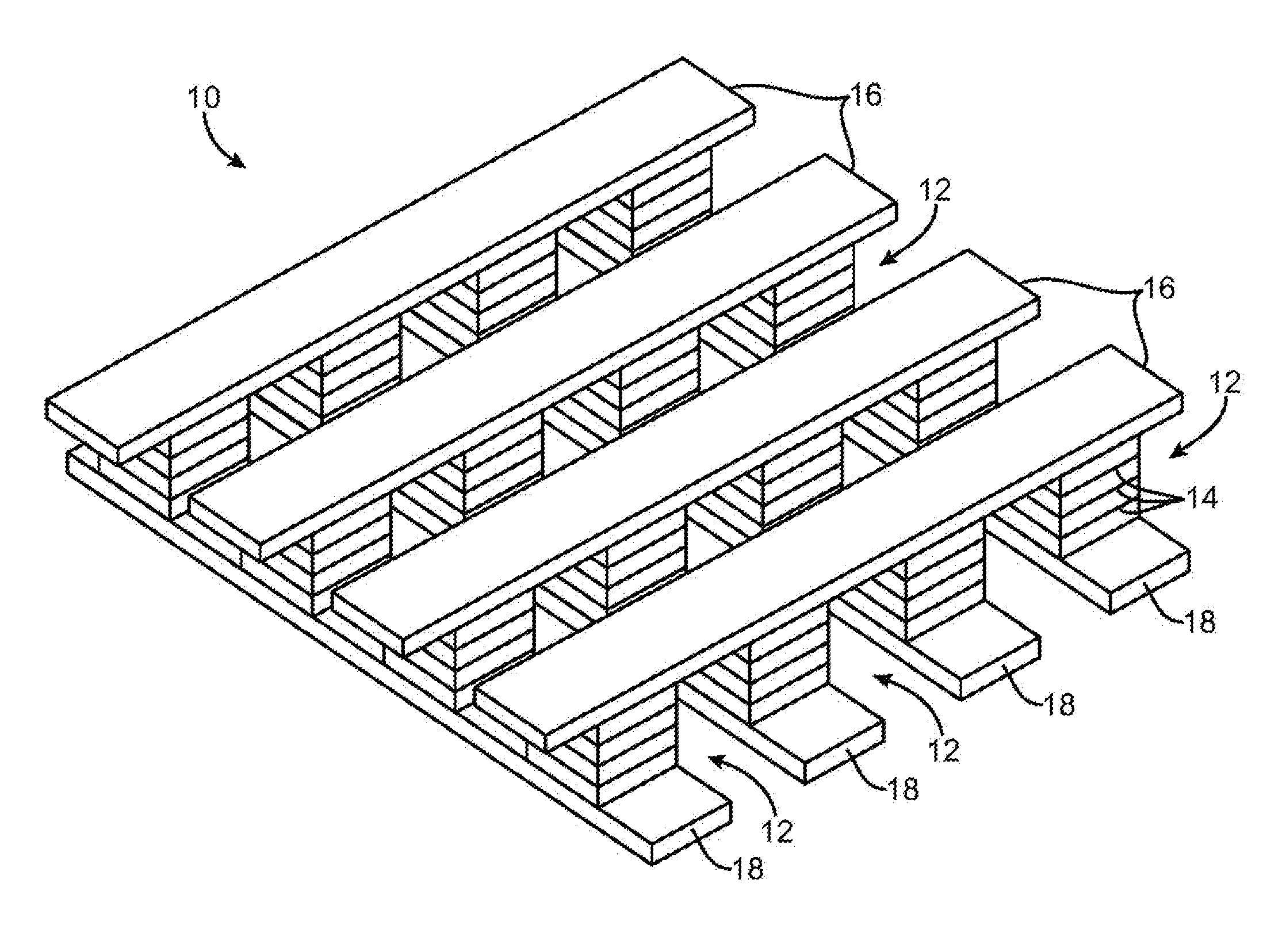
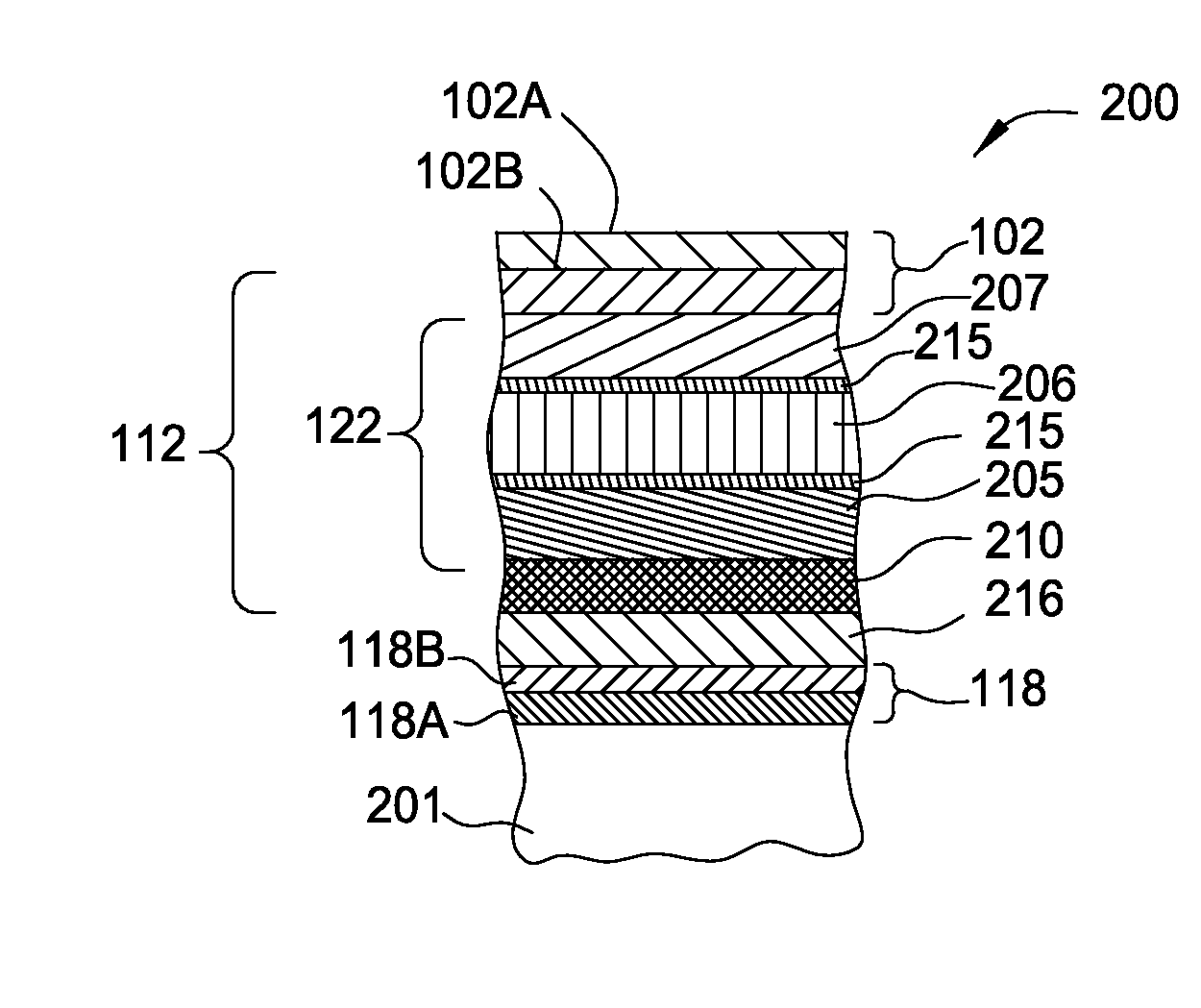
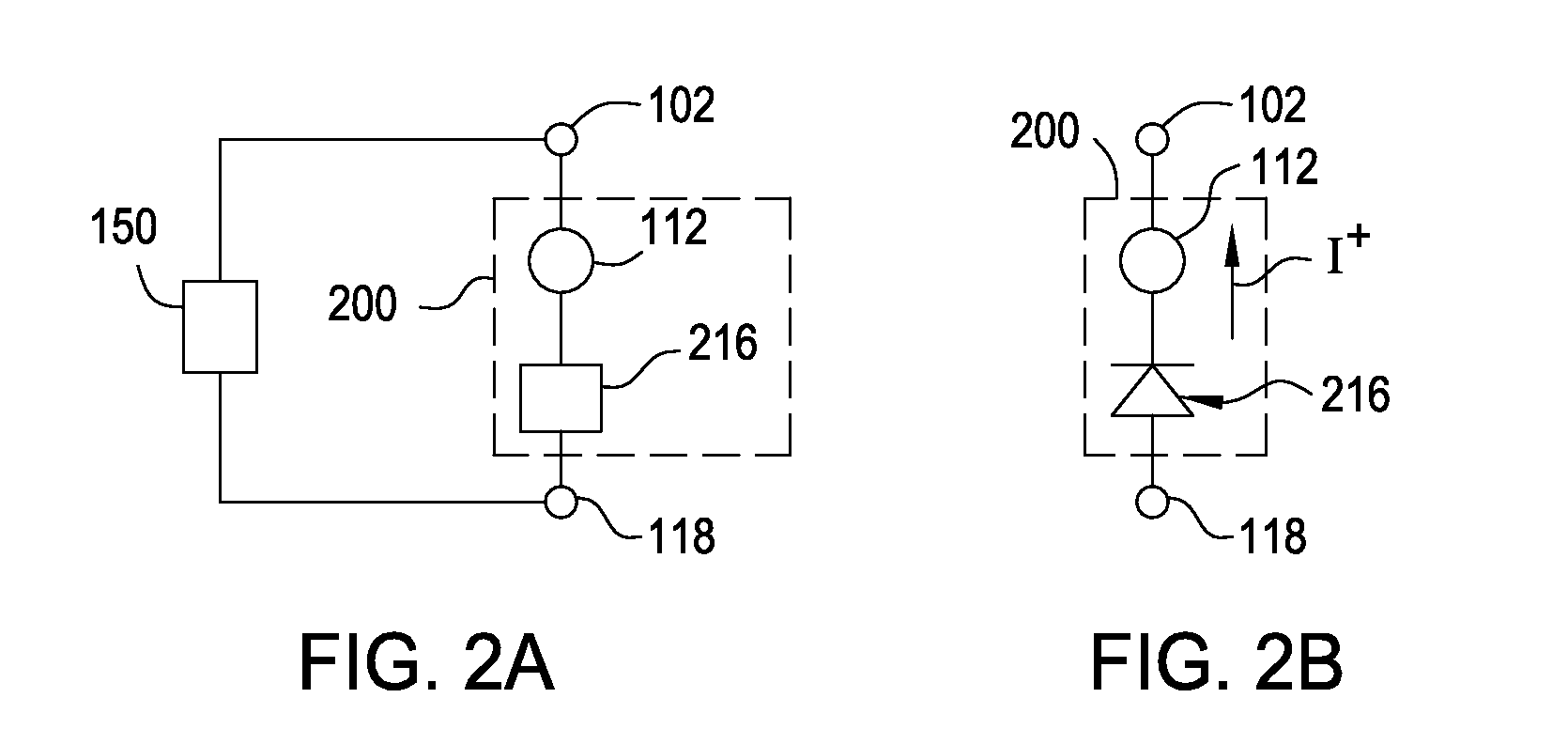
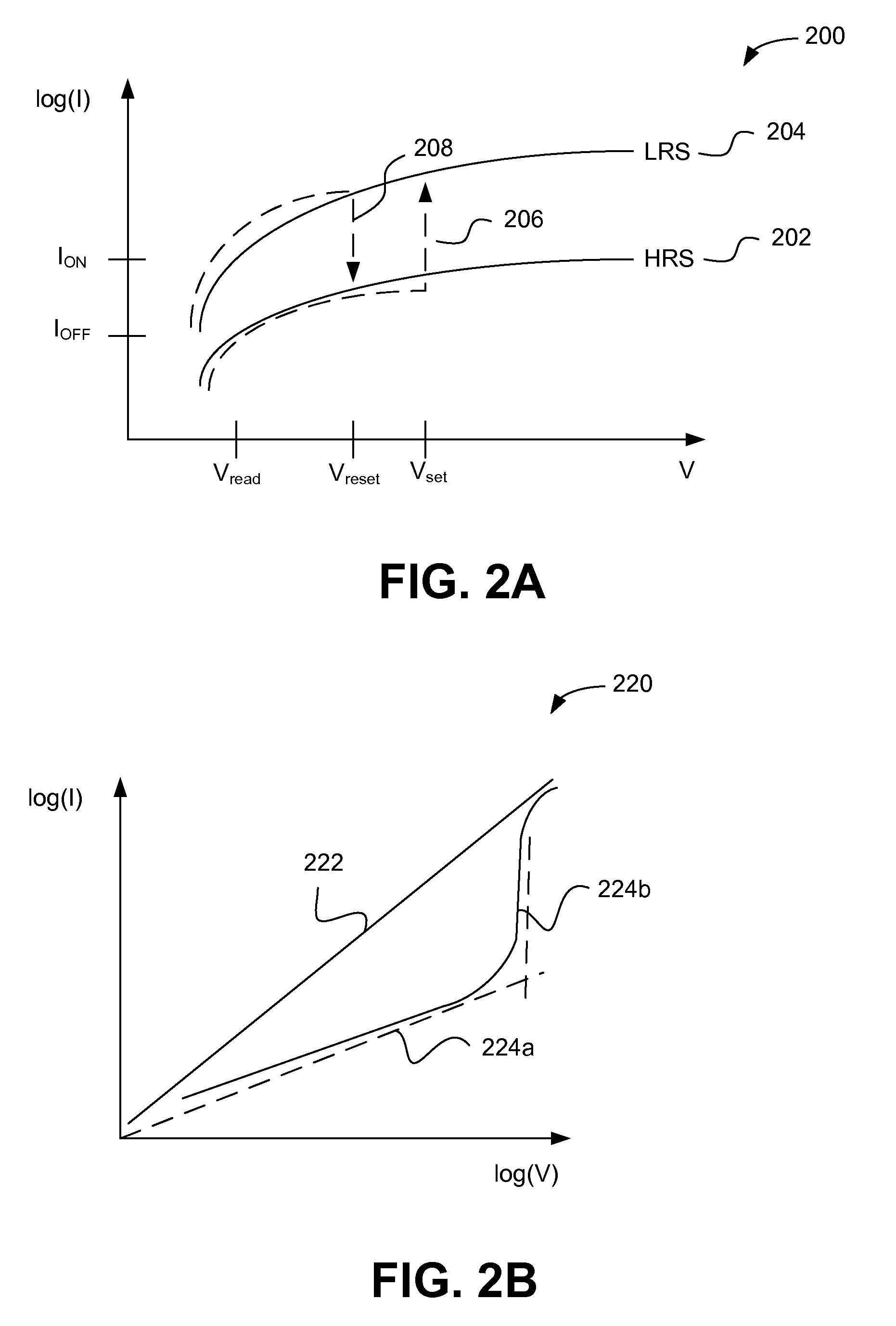
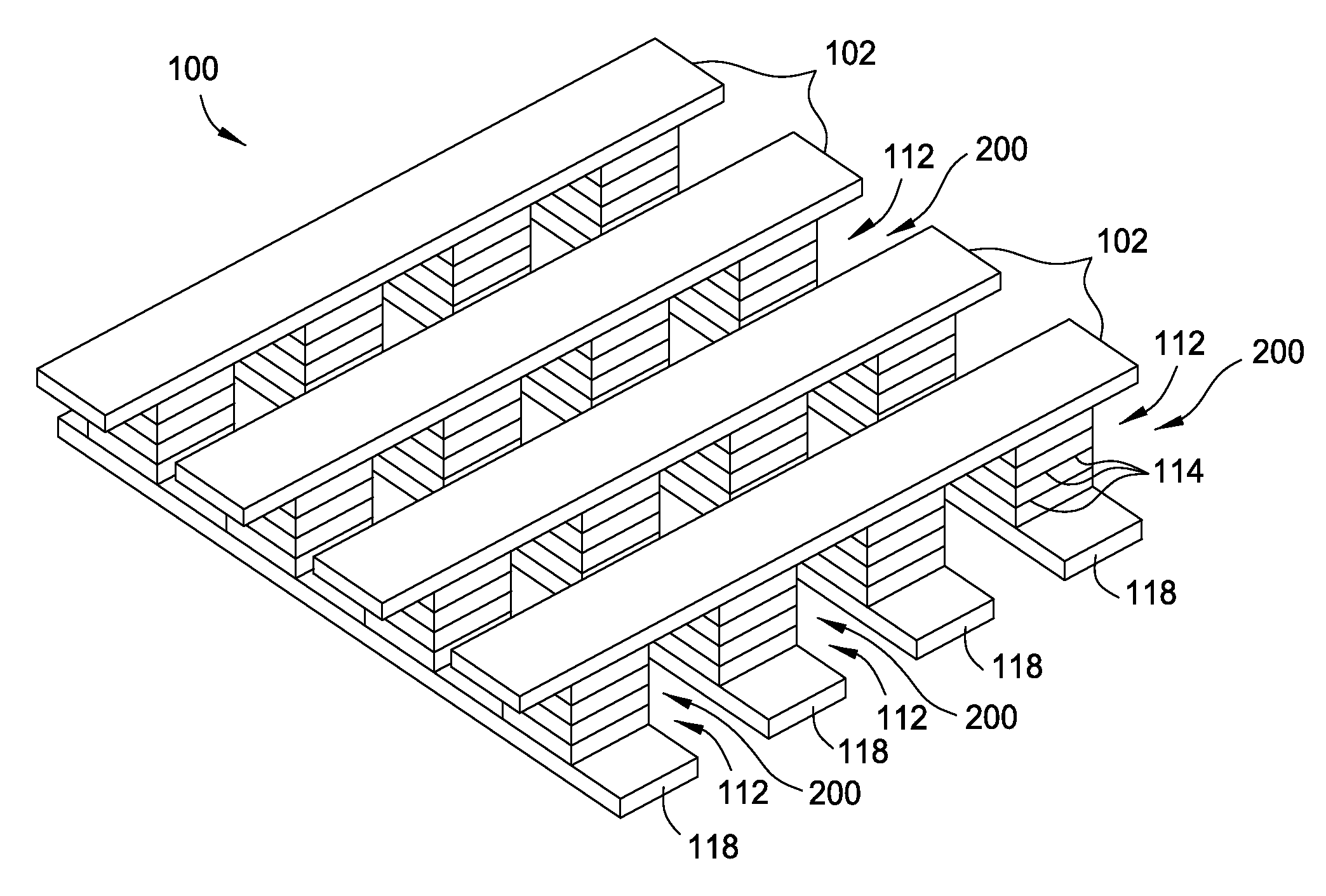
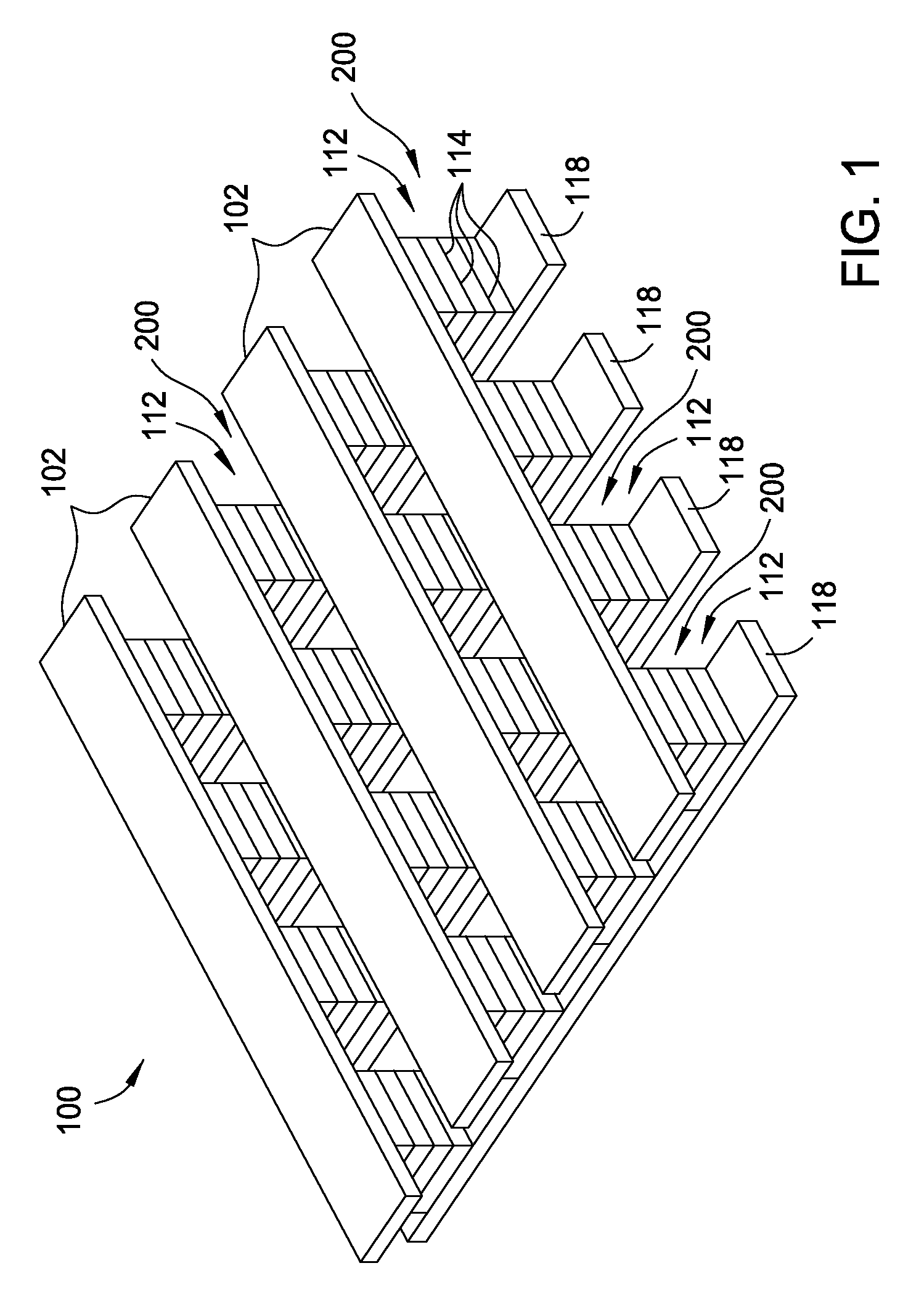
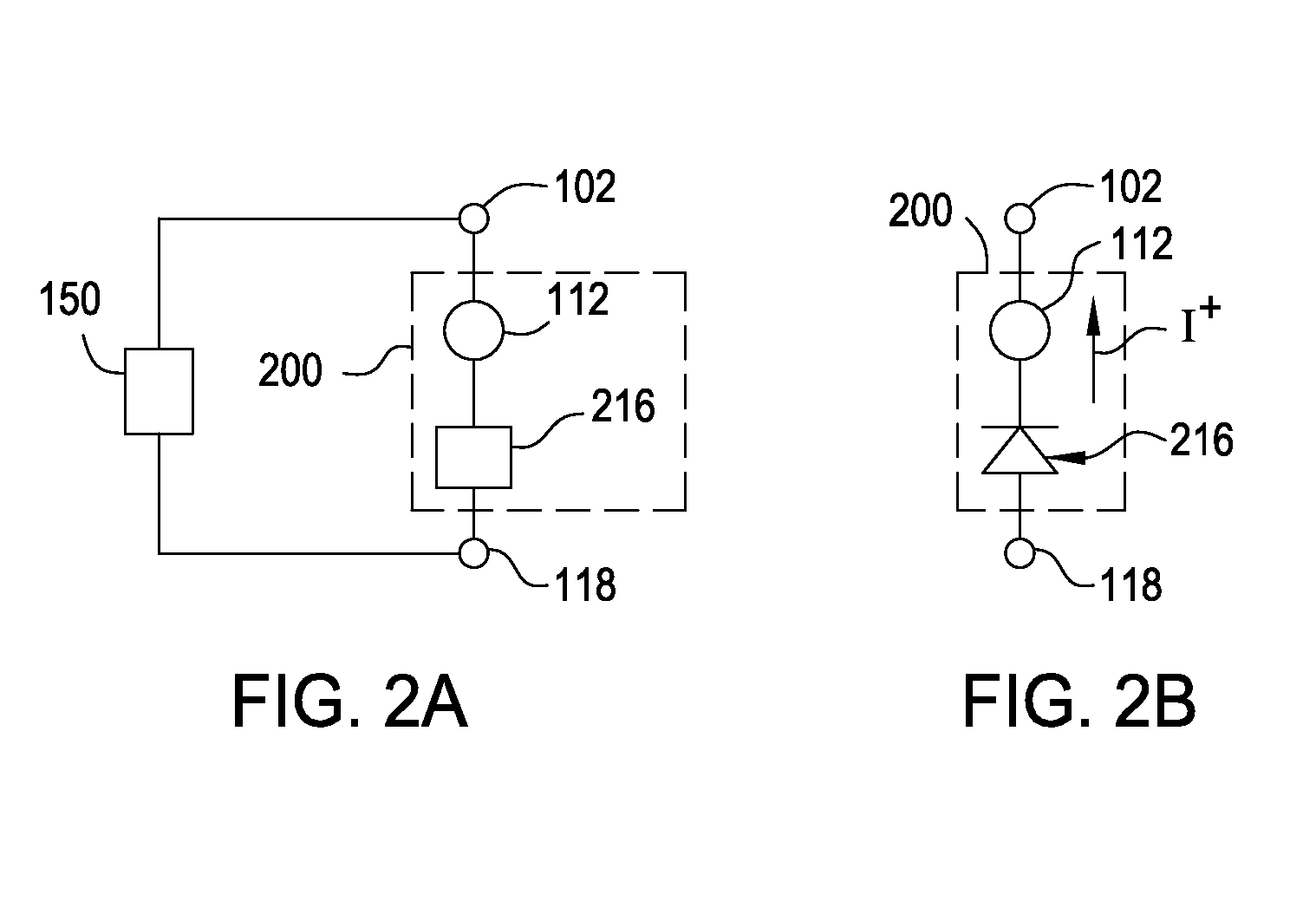
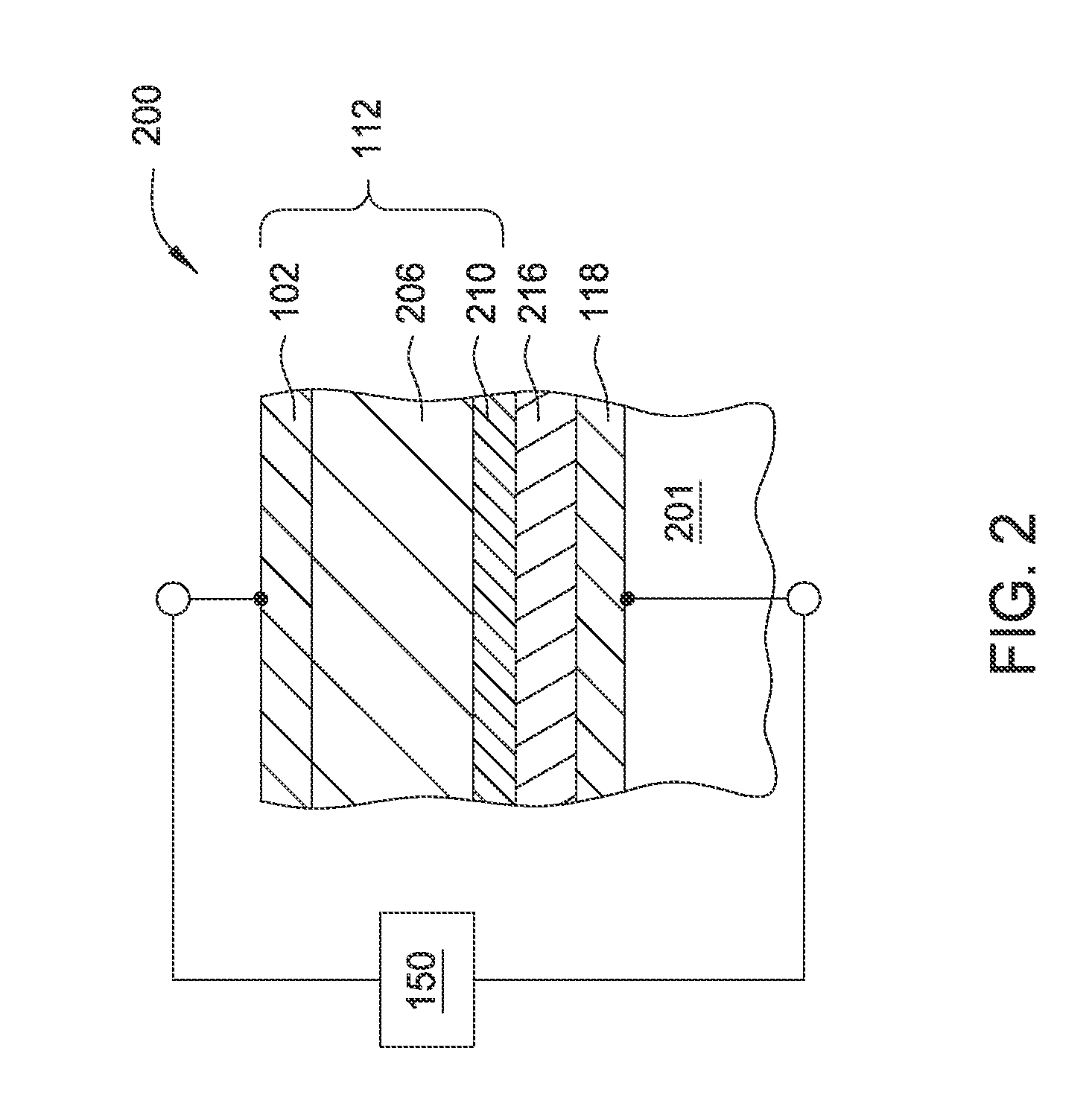
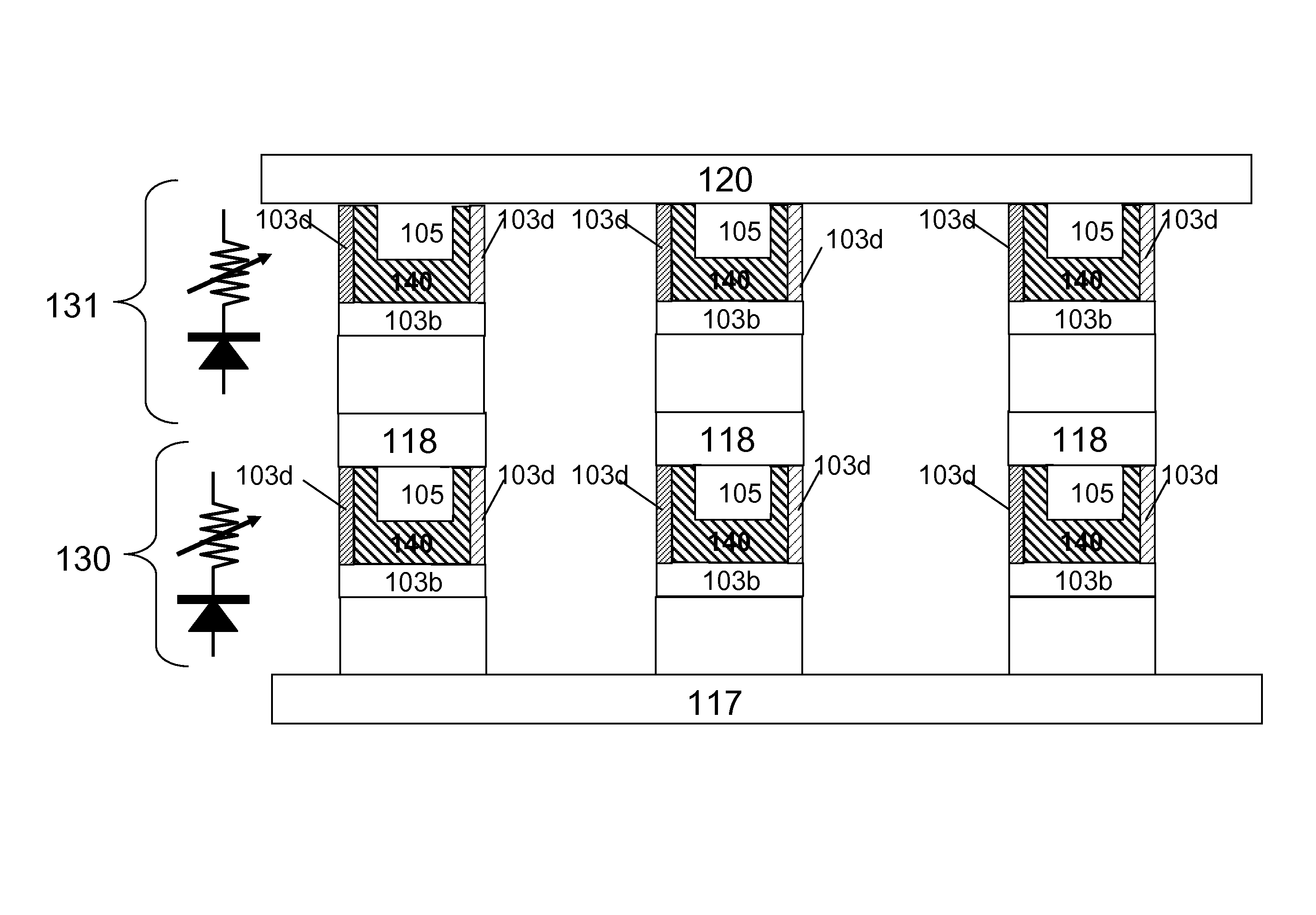
Current-limiting layer and a current-reducing layer in a memory device
ActiveUS20130026438A1Lower Level RequirementsMinimize power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceCurrent limiting
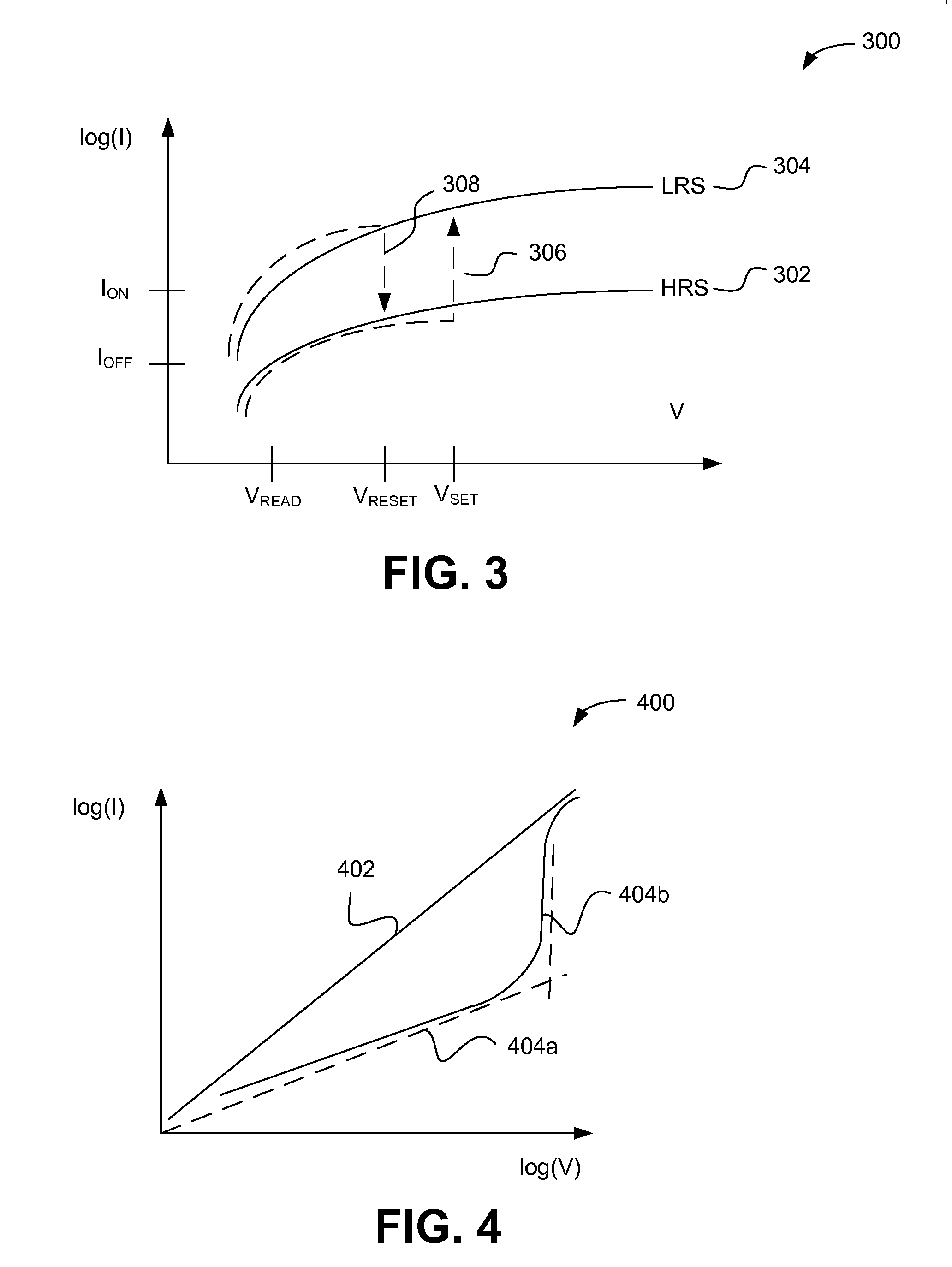
A current-limiting layer and a current-reducing layer are incorporated into a resistive switching memory device to form memory arrays. The incorporated current-limiting layer reduces the occurrence of current spikes during the programming of the resistive switching memory device and the incorporated current-reducing layer minimizes the overall current levels that can flow through the resistive switching memory device. Together, the two incorporated layers help improve device performance and lifetime.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC +1
Methods for Forming Resistive Switching Memory Elements by Heating Deposited Layers
ActiveUS20090227067A1Reduce process complexitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxideResistive switching memory
Resistive switching nonvolatile memory elements are provided. A metal-containing layer and an oxide layer for a memory element can be heated using rapid thermal annealing techniques. During heating, the oxide layer may decompose and react with the metal-containing layer. Oxygen from the decomposing oxide layer may form a metal oxide with metal from the metal-containing layer. The resulting metal oxide may exhibit resistive switching for the resistive switching memory elements.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Confinement techniques for non-volatile resistive-switching memories
ActiveUS20090278109A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricMaterials science
Confinment techniques for non-volatile resistive-switching memories are described, including a memory element having a first electrode, a second electrode, a metal oxide between the first electrode and the second electrode. A resistive switching memory element described herein includes a first electrode adjacent to an interlayer dielectric, a spacer over at least a portion of the interlayer dielectric and over a portion of the first electrode and a metal oxide layer over the spacer and the first electrode such that an interface between the metal oxide layer and the electrode is smaller than a top surface of the electrode.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
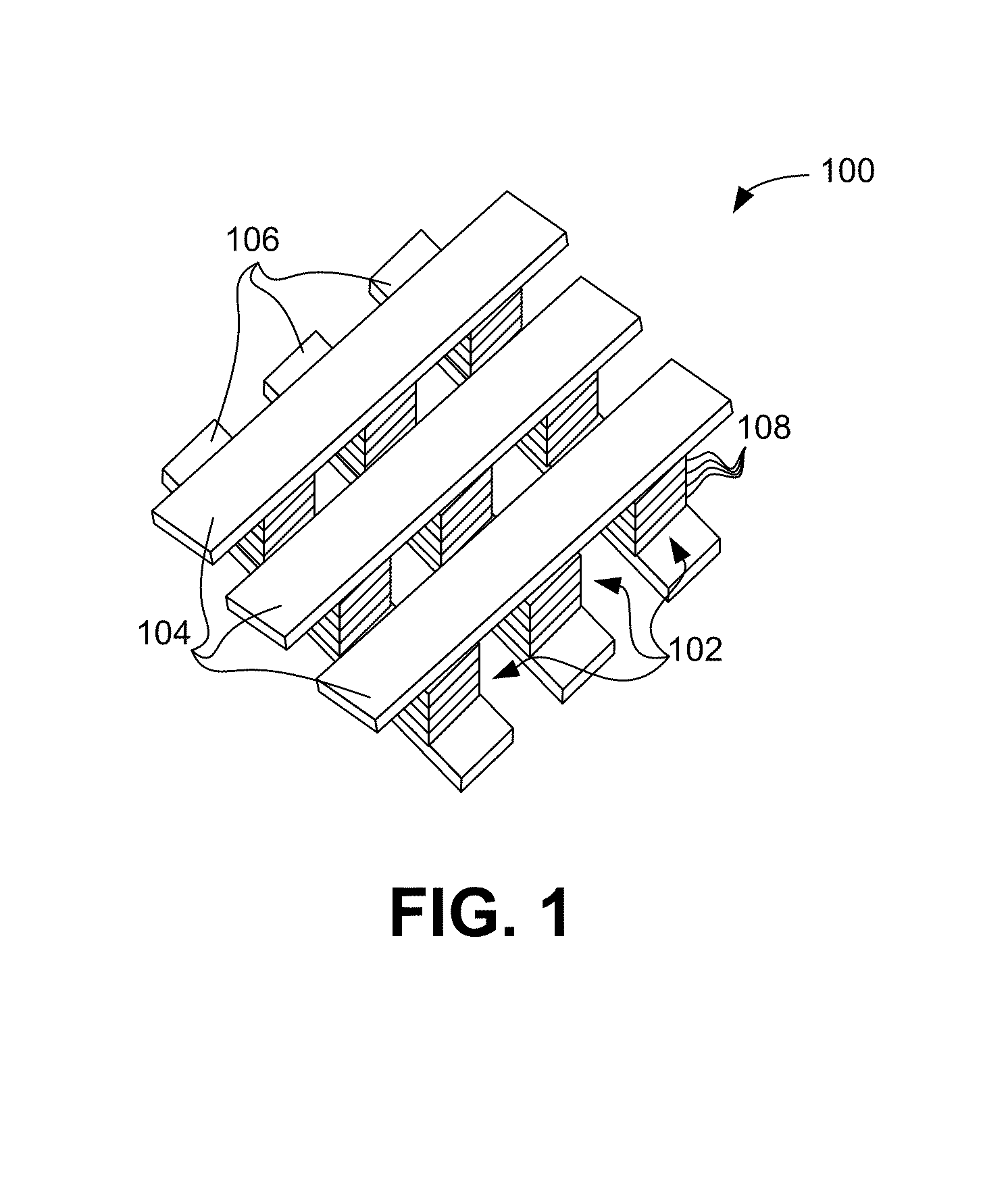
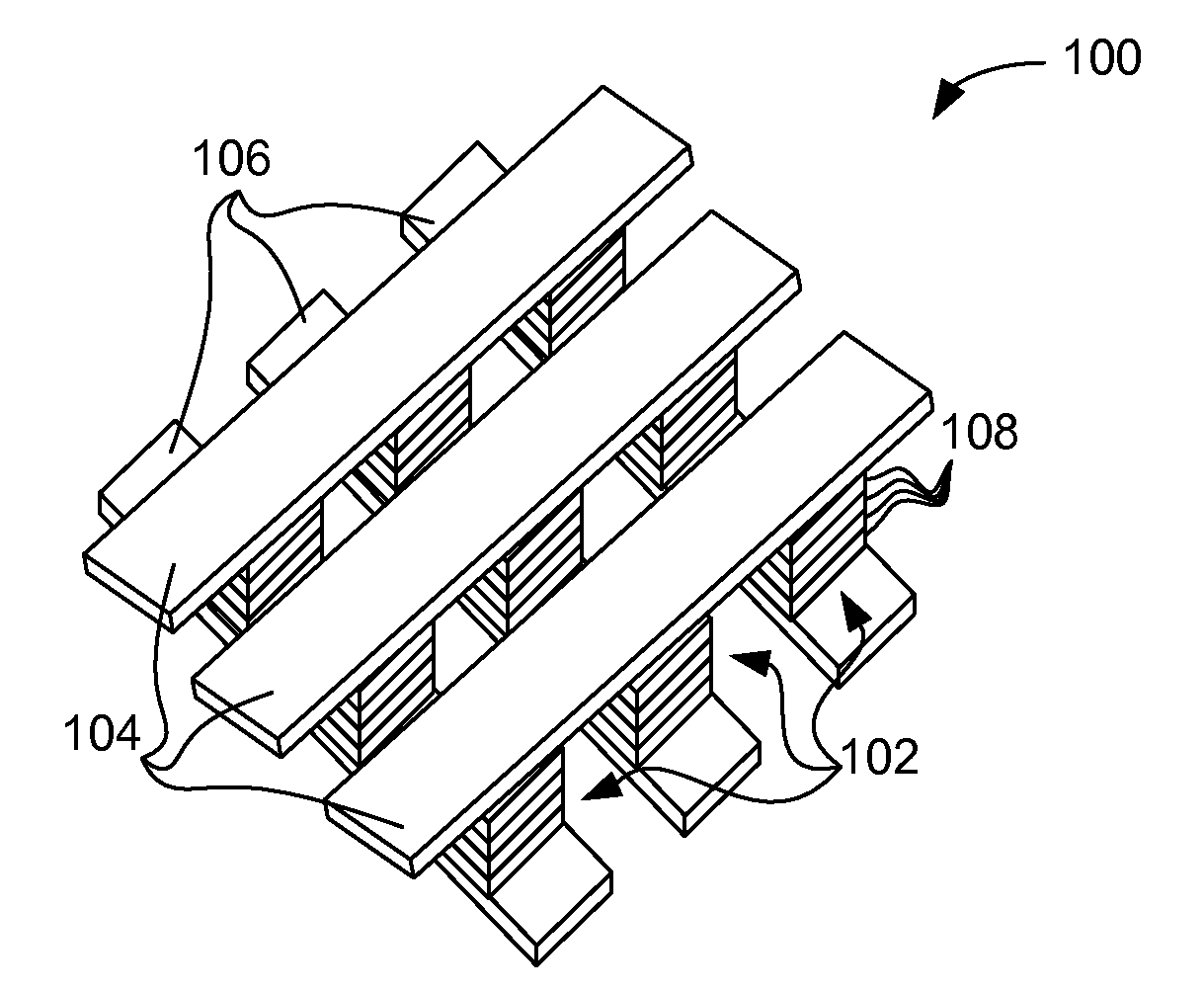
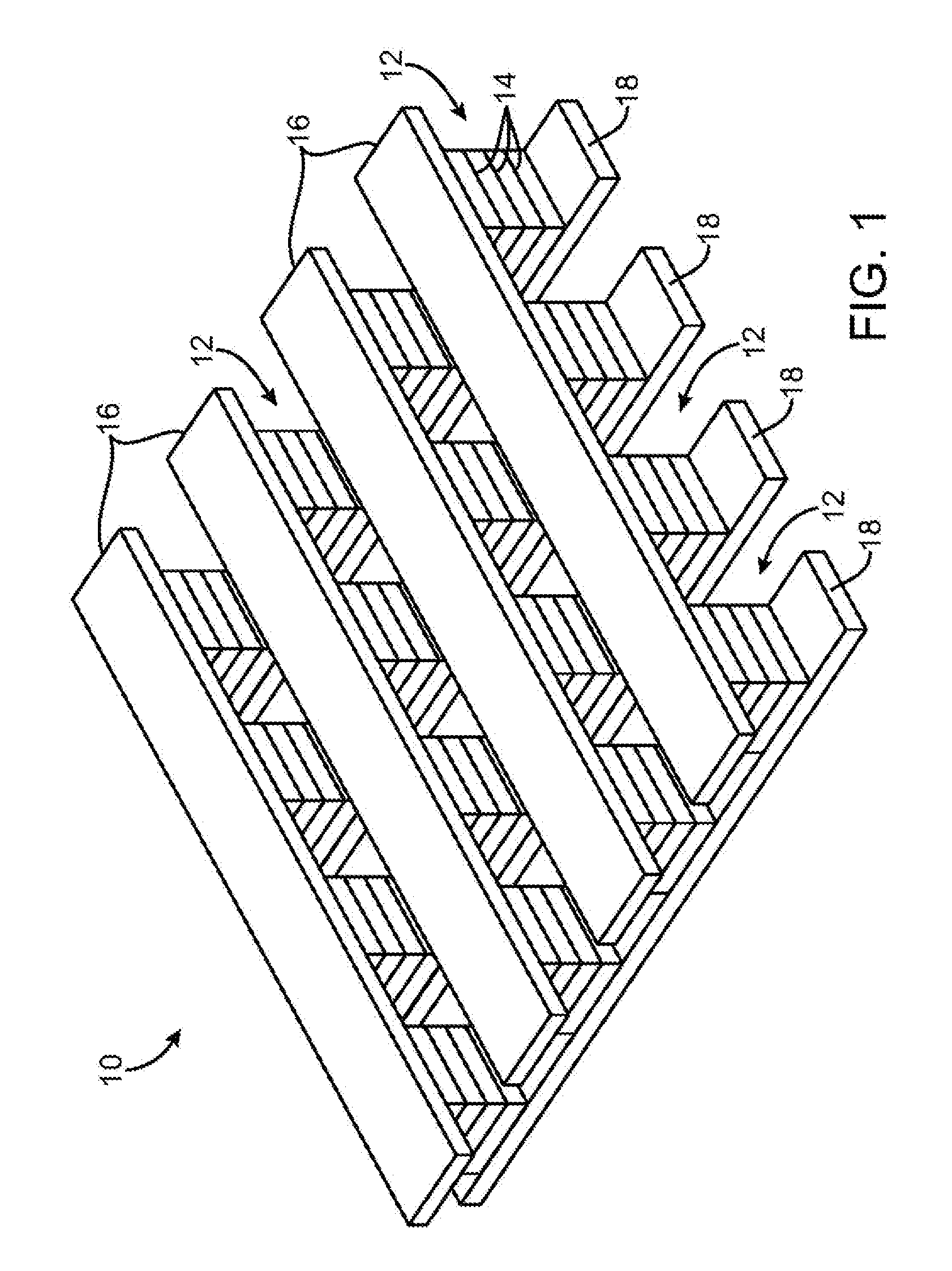
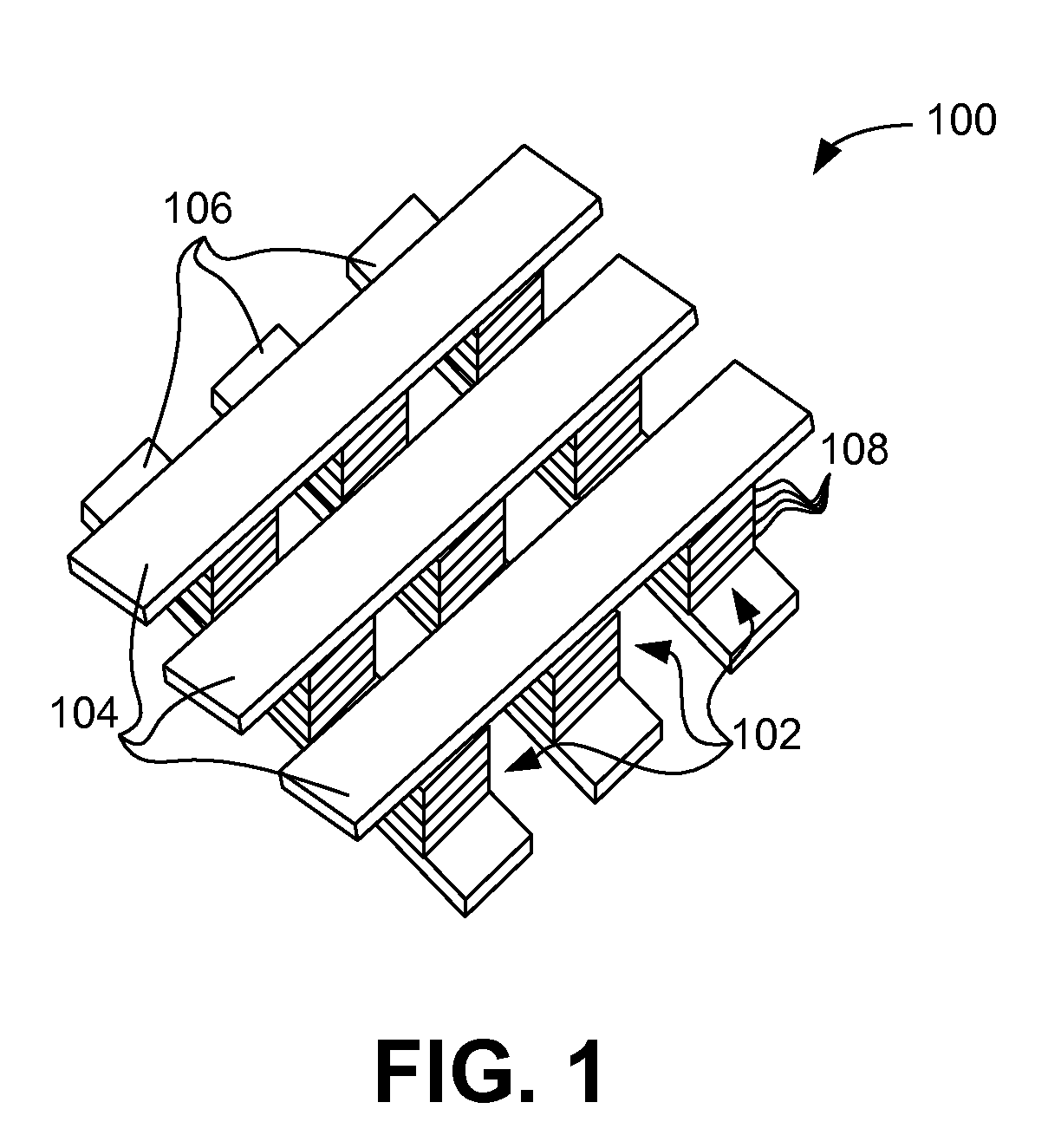
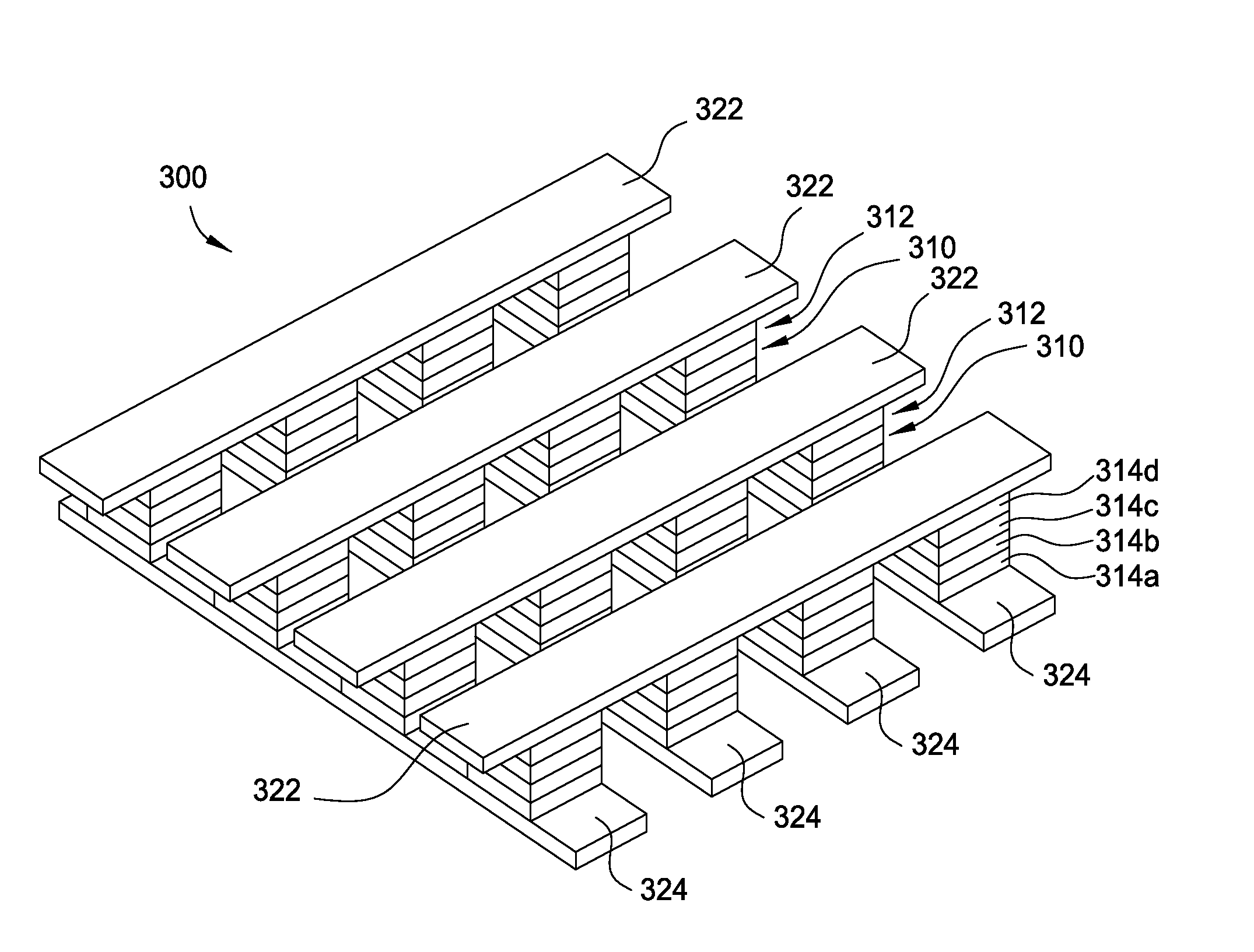
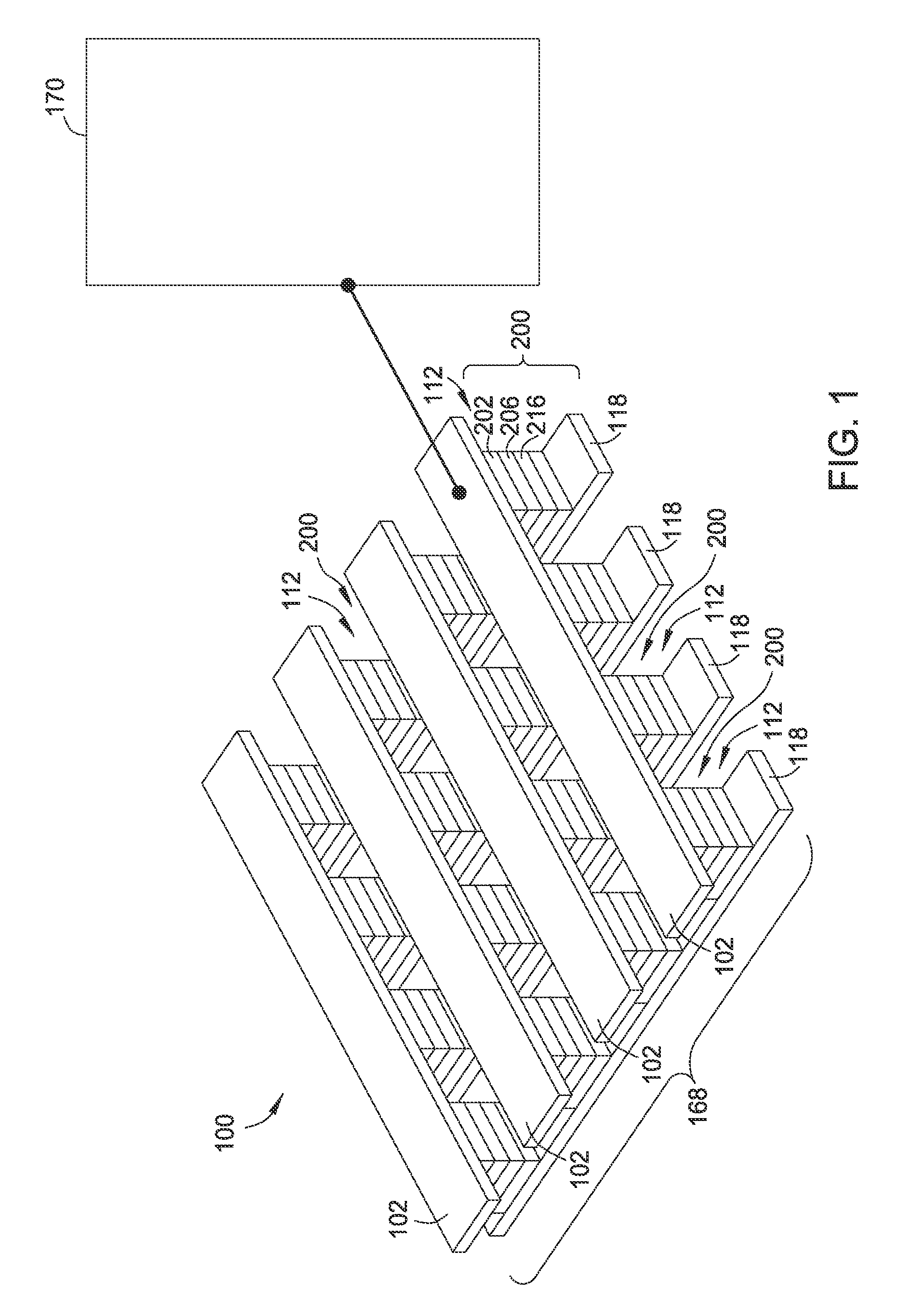
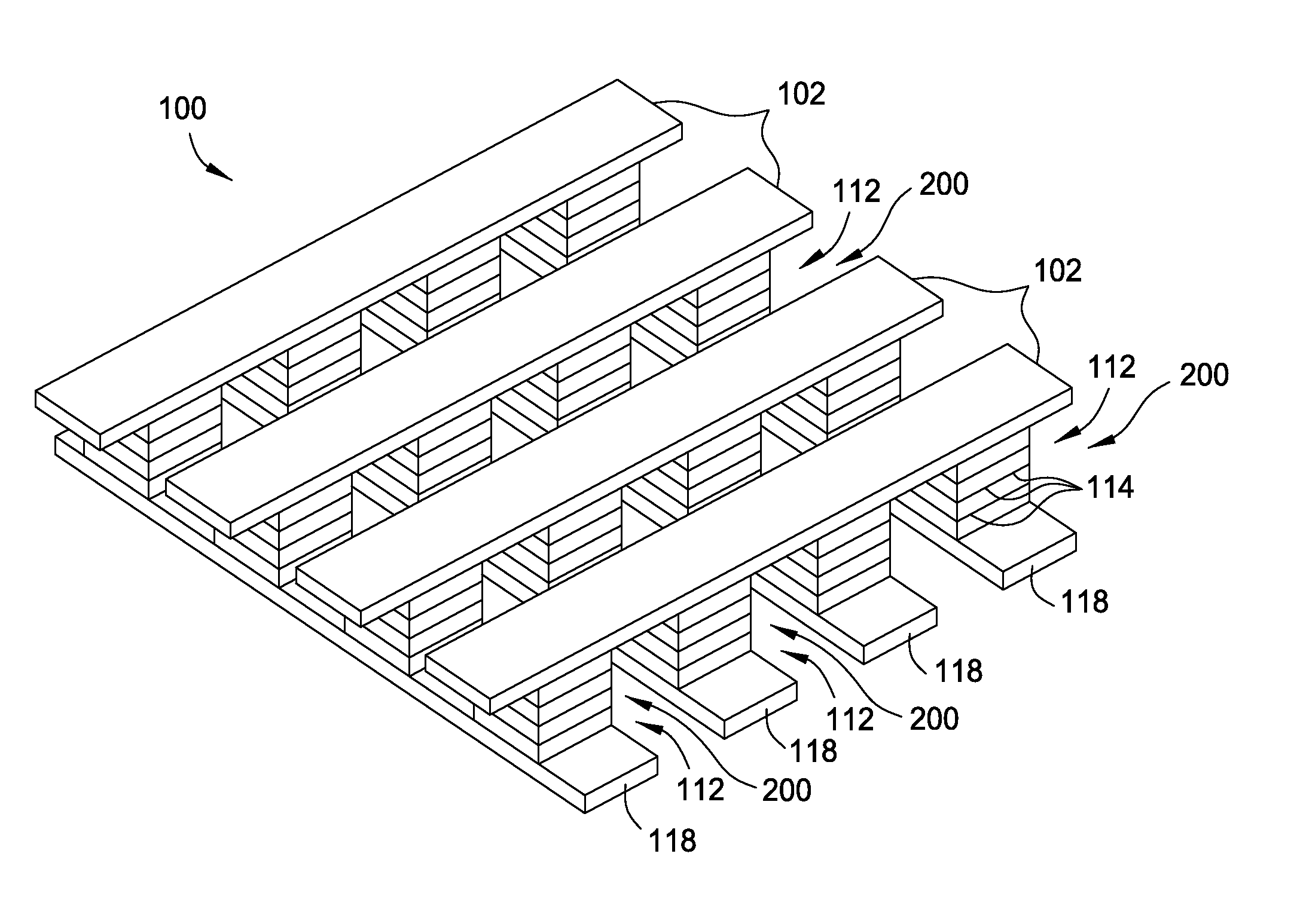
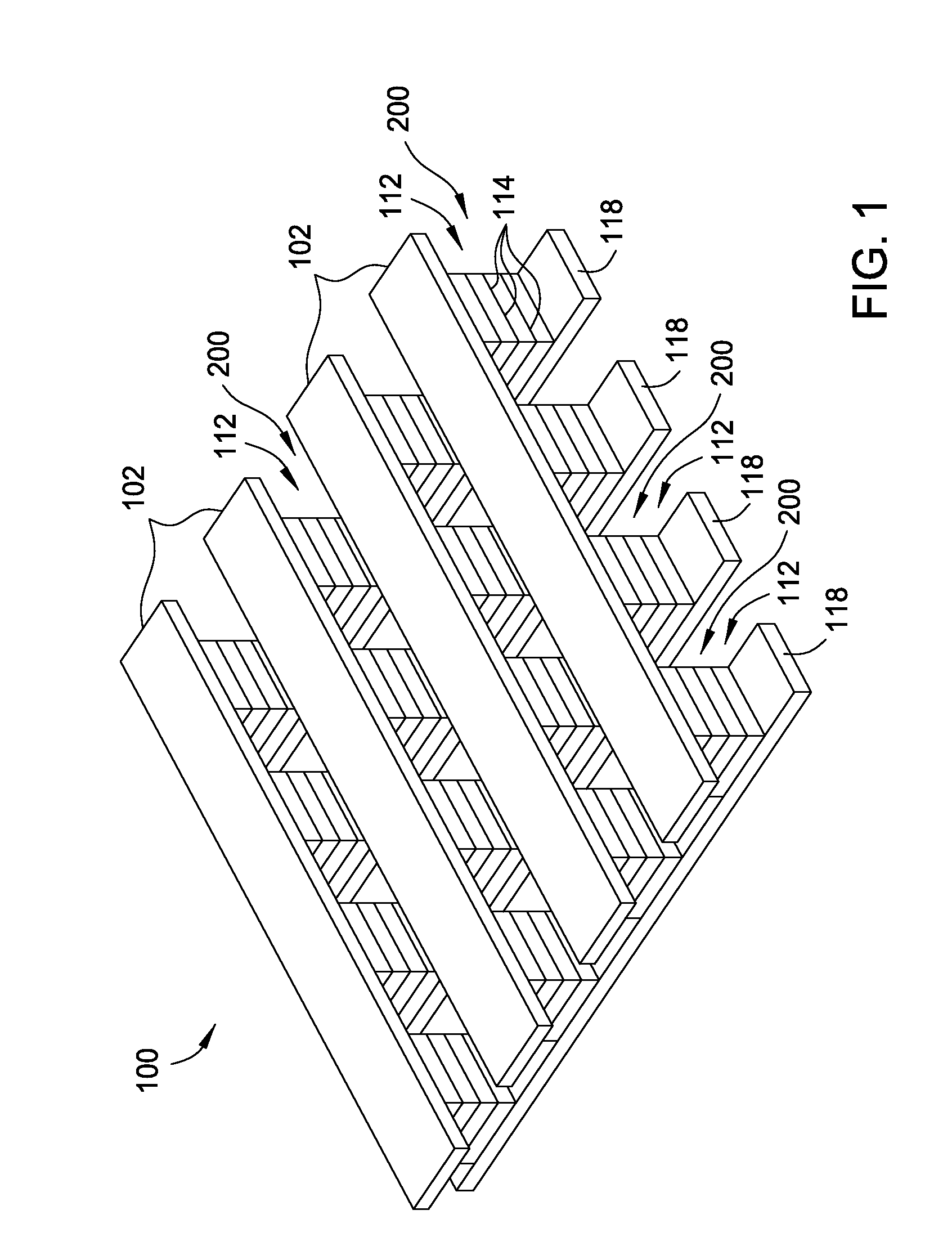
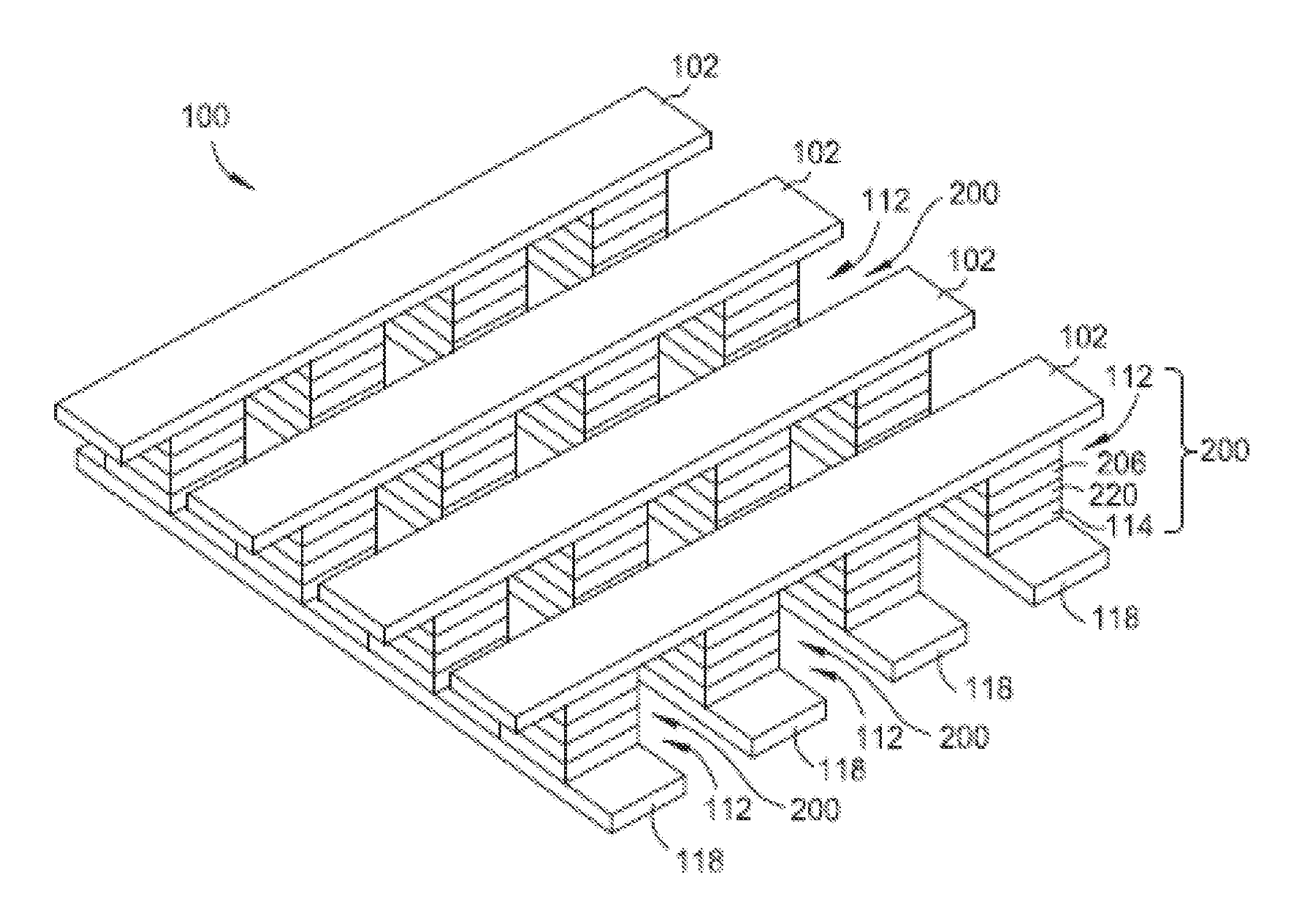
Stackable non-volatile resistive switching memory device and method
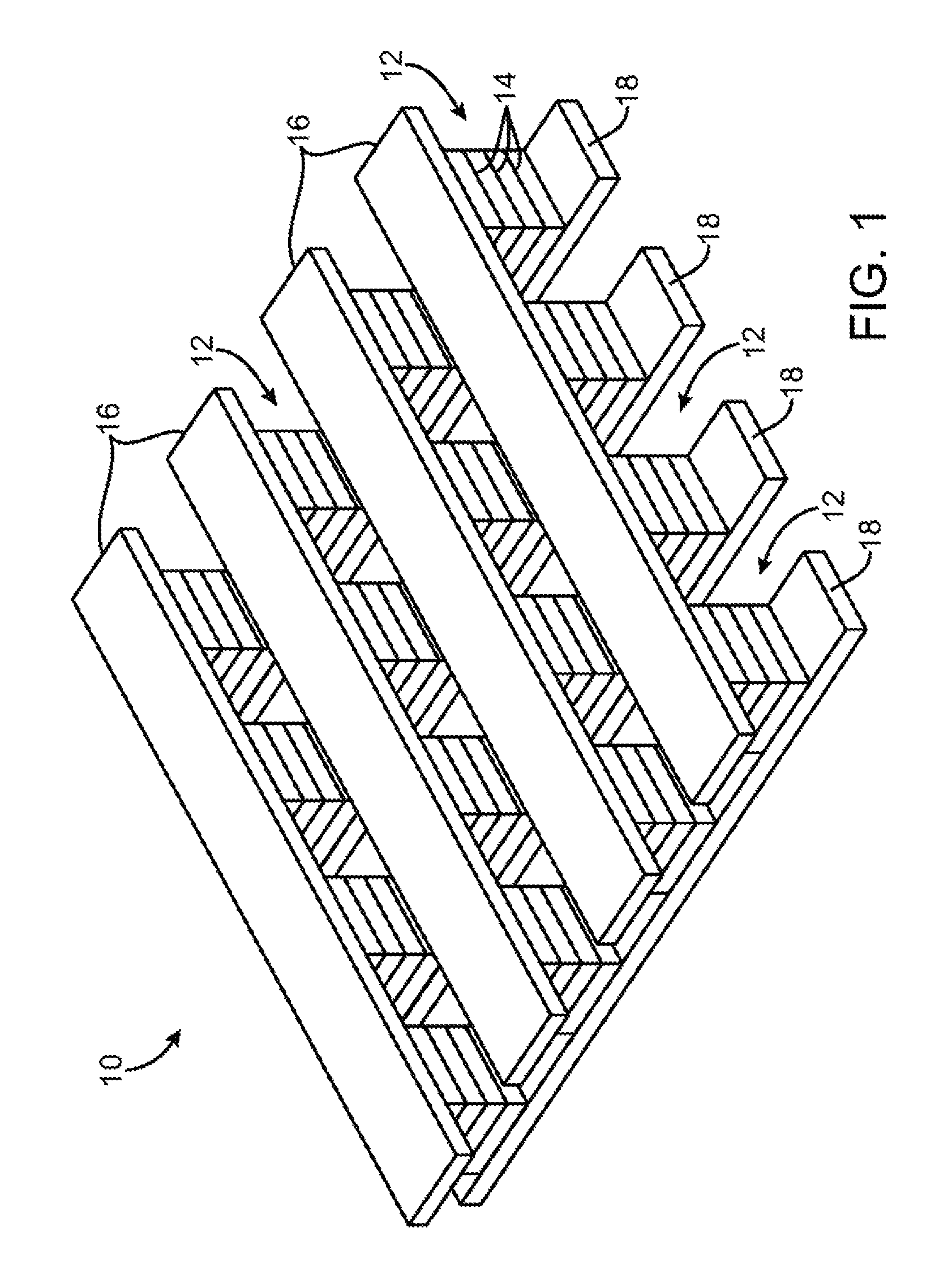
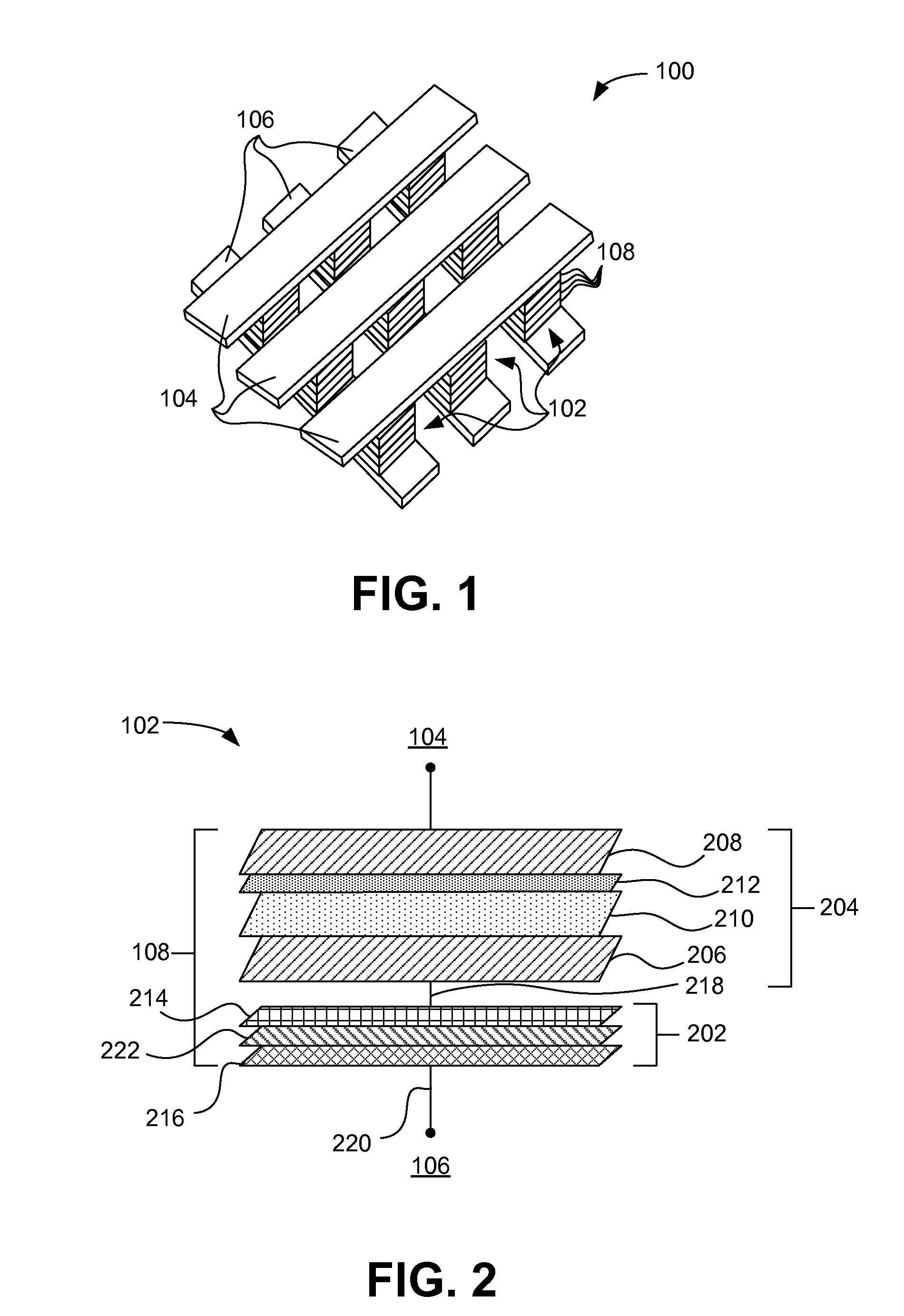
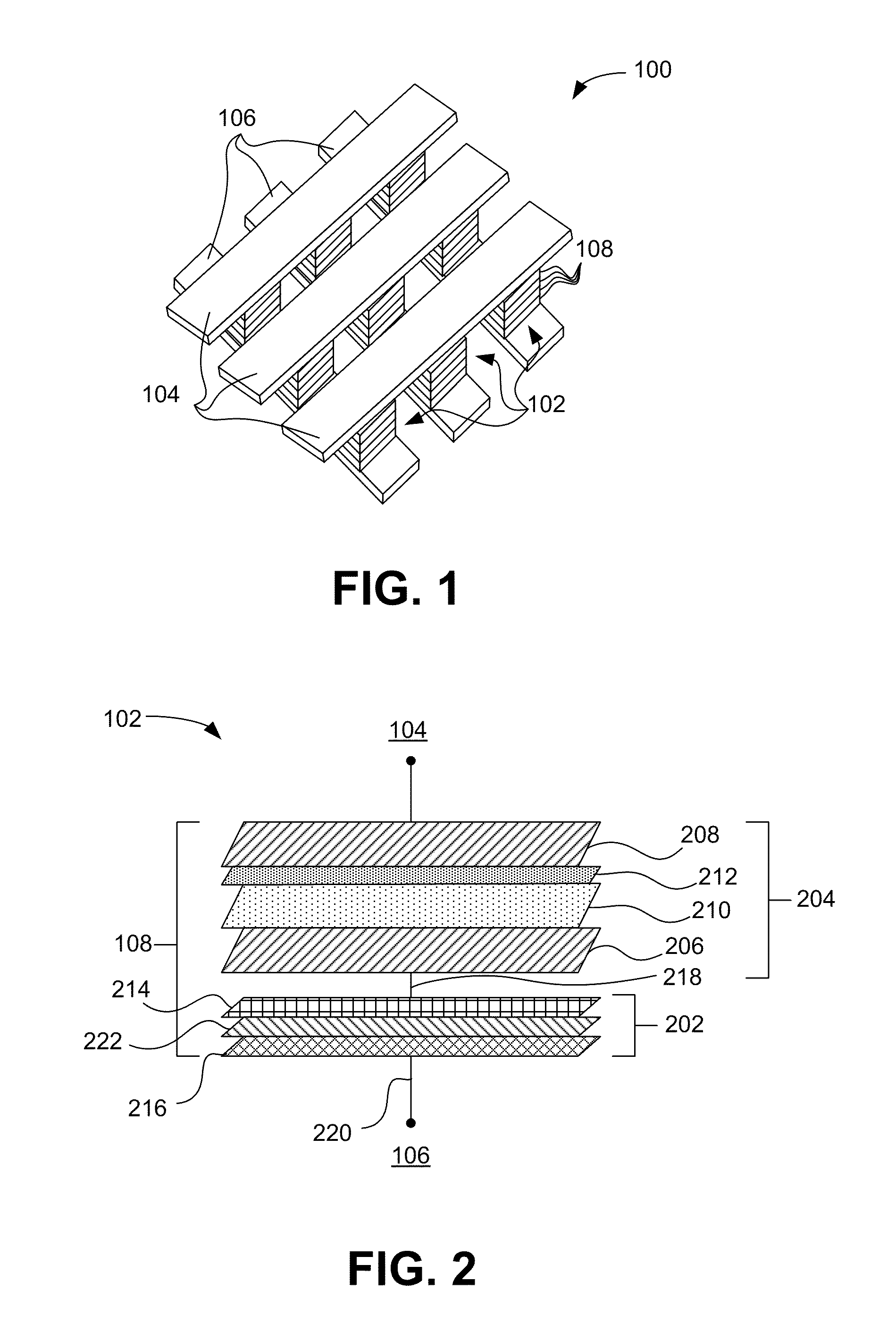
A method for forming a vertically stacked memory device. The method includes providing a semiconductor substrate having a surface region and forming a first dielectric material overlying the surface region. A first plurality of memory cells are formed overlying the first dielectric material. Each of the first plurality of memory cells includes at least a first top metal wiring structure spatially extending in a first direction, a first bottom wiring structure spatially extending in a second direction orthogonal to the first top metal wiring structure, and a first switching element sandwiched in an intersection region between the first top metal wiring structure and the first bottom metal wiring structure. In a specific embodiment, the method forms a thickness of second dielectric material overlying the first plurality of memory. A second plurality of memory cells are formed overlying the second dielectric material. Each of the second plurality of memory cells includes at least a second top metal wiring structure extending in the first direction, a second bottom wiring structure arranged spatially orthogonal to the second top metal wiring structure, and a second switching element sandwiched in an intersection region of the second top metal wiring structure and the second bottom metal wiring structure.
Owner:INNOSTAR SEMICON SHANGHAI CO LTD
Bipolar multistate nonvolatile memory
ActiveUS20130207065A1Lower requirementReduce complexitySolid-state devicesBulk negative resistance effect devicesHigh resistanceDigital data
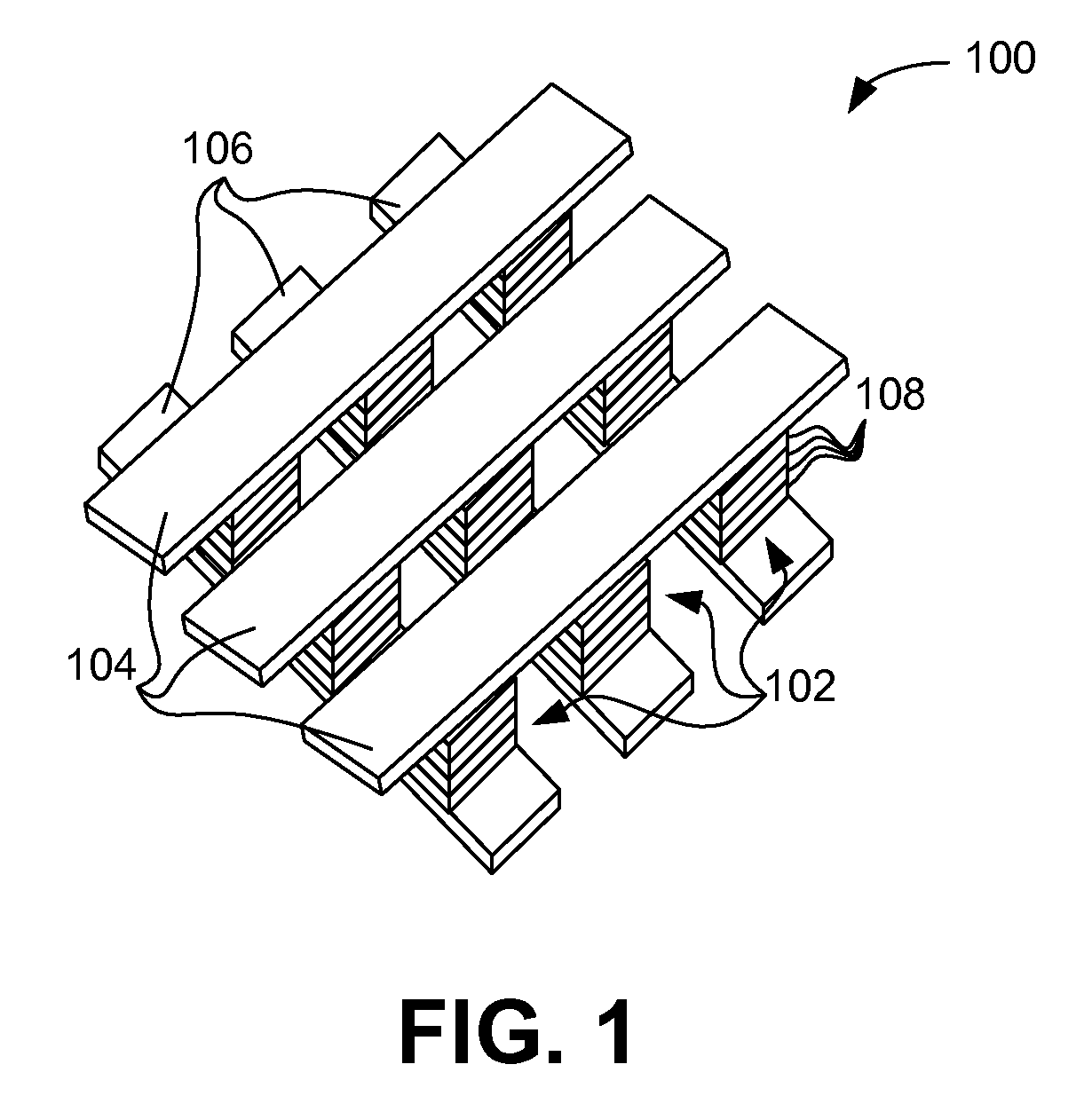
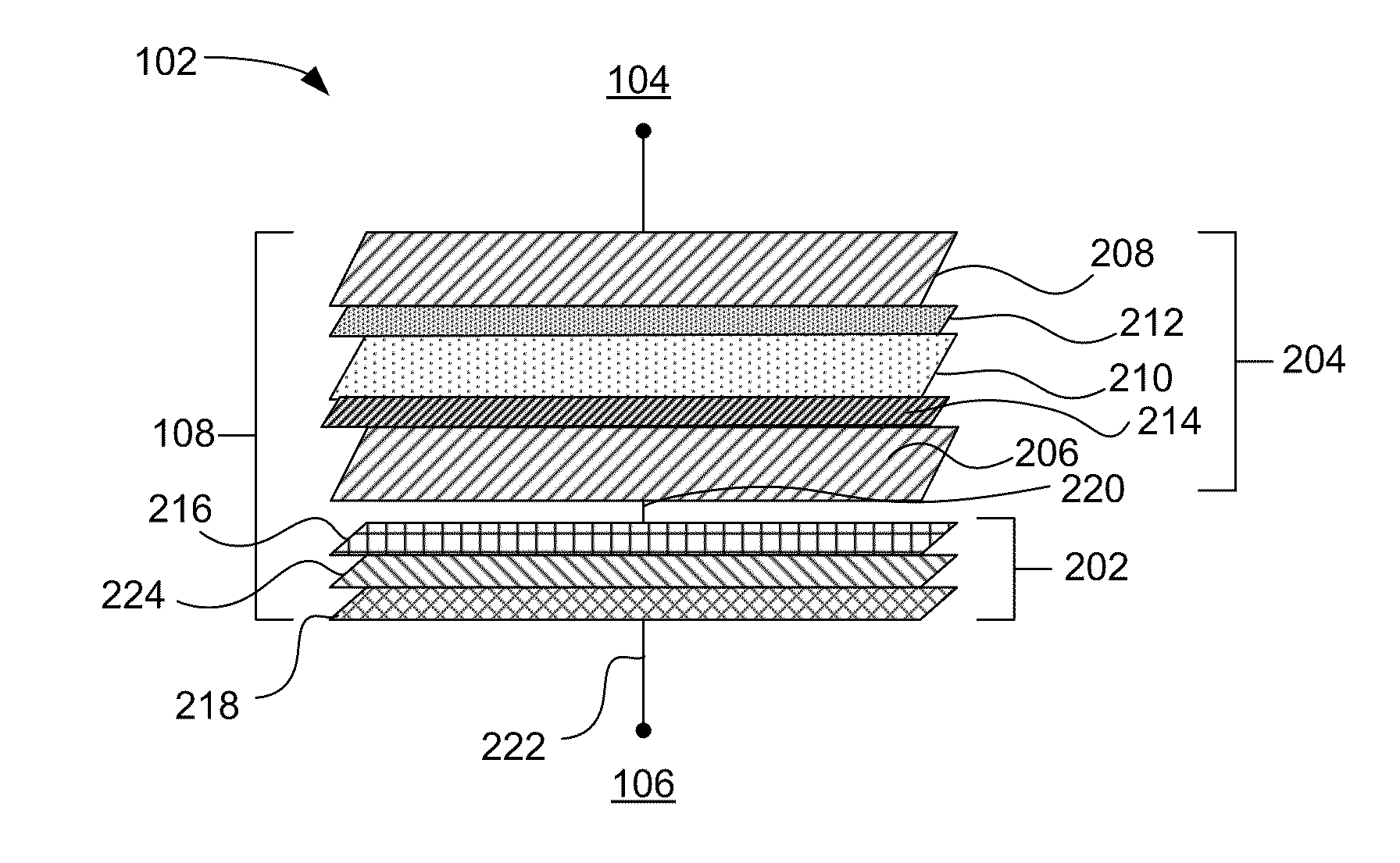
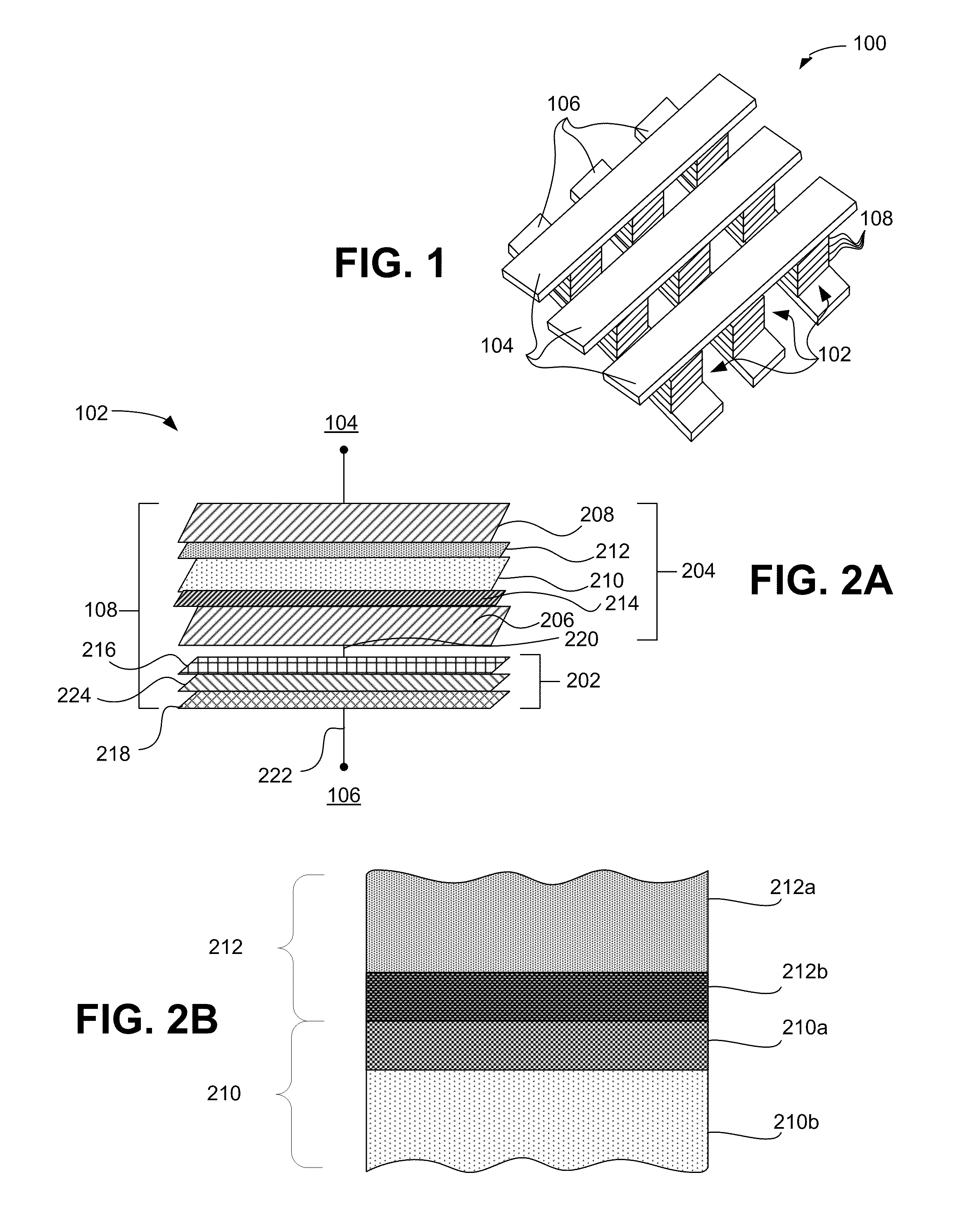
Embodiments generally include a method of forming a nonvolatile memory device that contains a resistive switching memory element that has an improved device switching capacity by using multiple layers of variable resistance layers. In one embodiment, the resistive switching element comprises at least three layers of variable resistance materials to increase the number of logic states. Each variable resistance layer may have an associated high resistance state and an associated low resistance state. As the resistance of each variable resistance layer determines the digital data bit that is stored, the multiple variable resistance layers per memory element allows for additional data storage without the need to further increase the density of nonvolatile memory devices. Typically, resistive switching memory elements may be formed as part of a high-capacity nonvolatile memory integrated circuit, which can be used in various electronic devices, such as digital cameras, mobile telephones, handheld computers, and music players.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
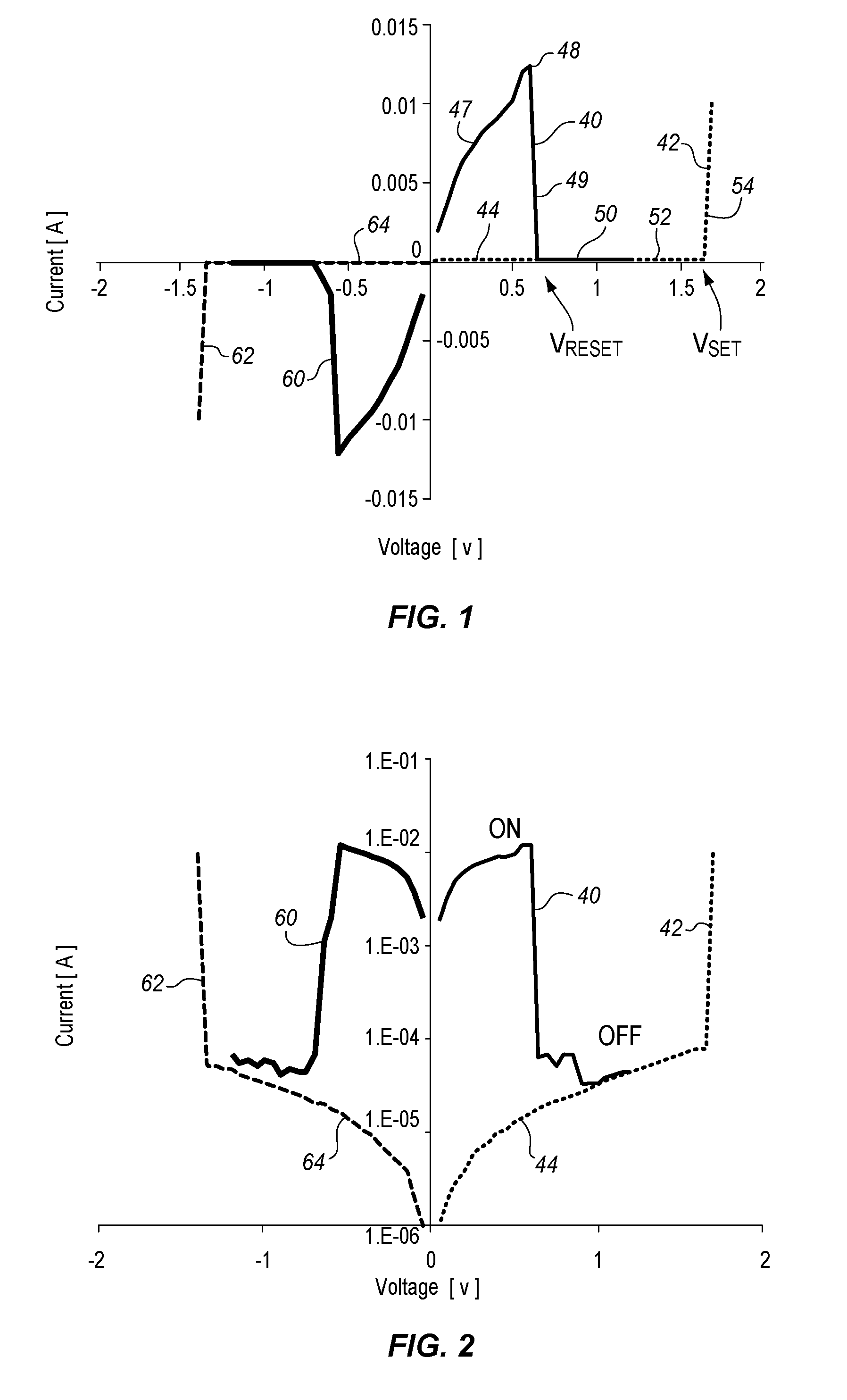
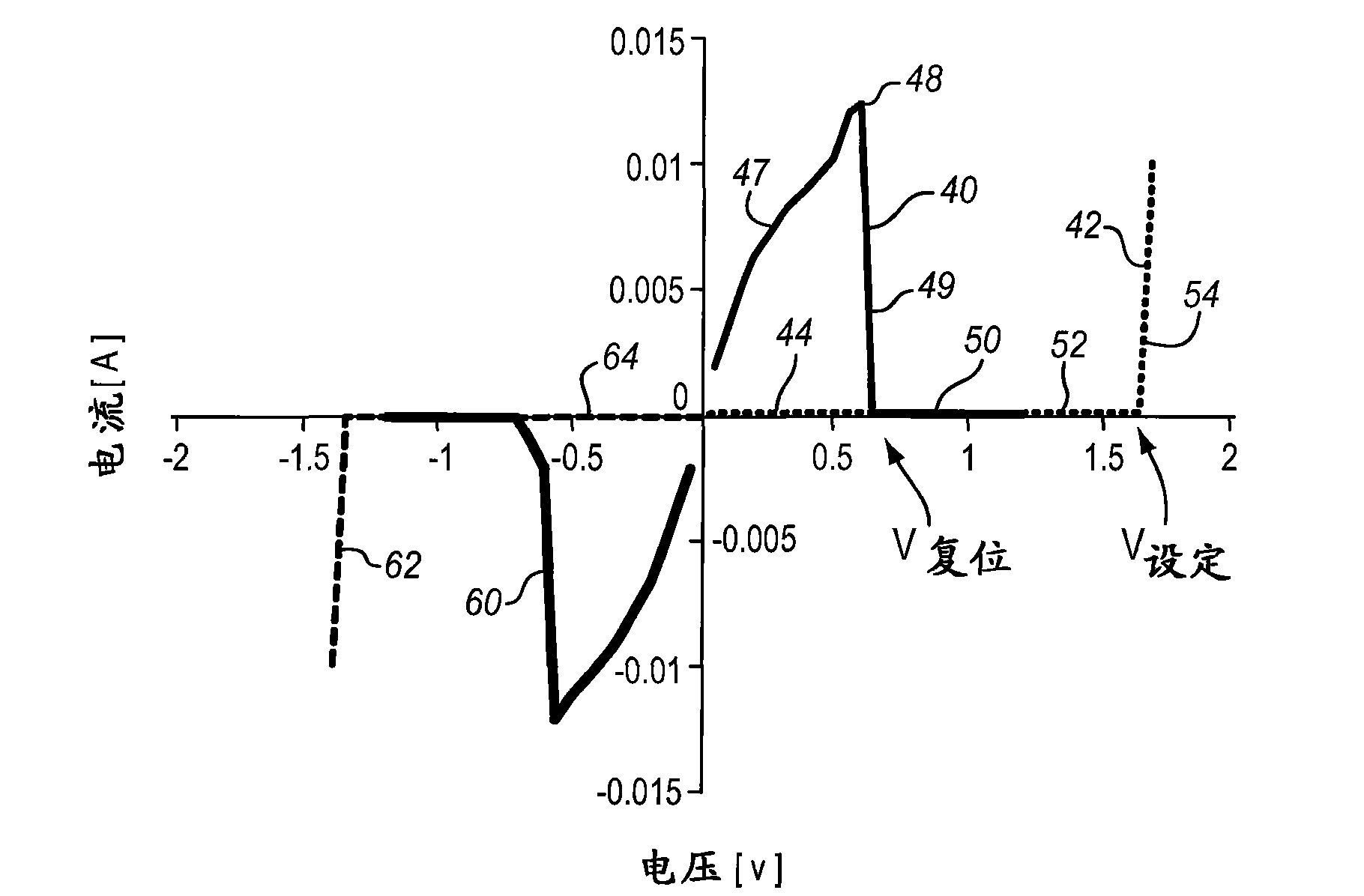
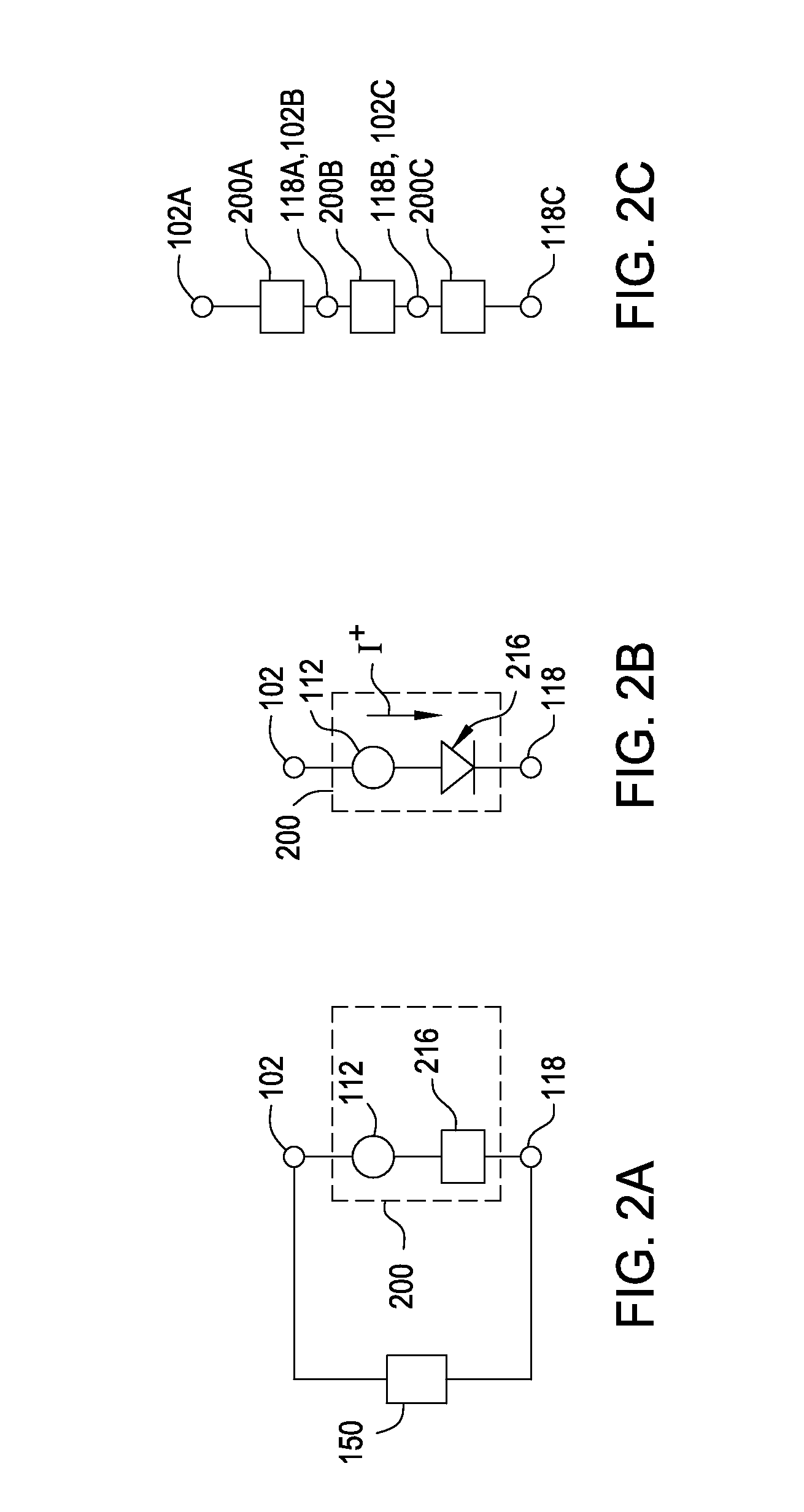
Bipolar resistive-switching memory with a single diode per memory cell
According to various embodiments, a resistive-switching memory element and memory element array that uses a bipolar switching includes a select element comprising only a single diode that is not a Zener diode. The resistive-switching memory elements described herein can switch even when a switching voltage less than the breakdown voltage of the diode is applied in the reverse-bias direction of the diode. The memory elements are able to switch during the very brief period when a transient pulse voltage is visible to the memory element, and therefore can use a single diode per memory cell.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Stabilized resistive switching memory
ActiveUS20080106927A1High resistance stateConductive materialSolid-state devicesOxygen vacancyEngineering
A non-volatile resistive switching memory that includes a material which changes between the insulative and conductive states. The material is stabilized against charge trapping by oxygen vacancies by an extrinsic ligand, such as carbon.
Owner:SYMETRIX MEMORY
Resistive switching memory element including doped silicon electrode
ActiveUS20100258781A1Solid-state devicesBulk negative resistance effect devicesHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A resistive switching memory element including a doped silicon electrode is described, including a first electrode comprising doped silicon having a first work function, a second electrode having a second work function that is different from the first work function by between 0.1 and 1.0 electron volts (eV), a metal oxide layer between the first electrode and the second electrode, the metal oxide layer switches using bulk-mediated switching and has a bandgap of greater than 4 eV, and the memory element switches from a low resistance state to a high resistance state and vice versa.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
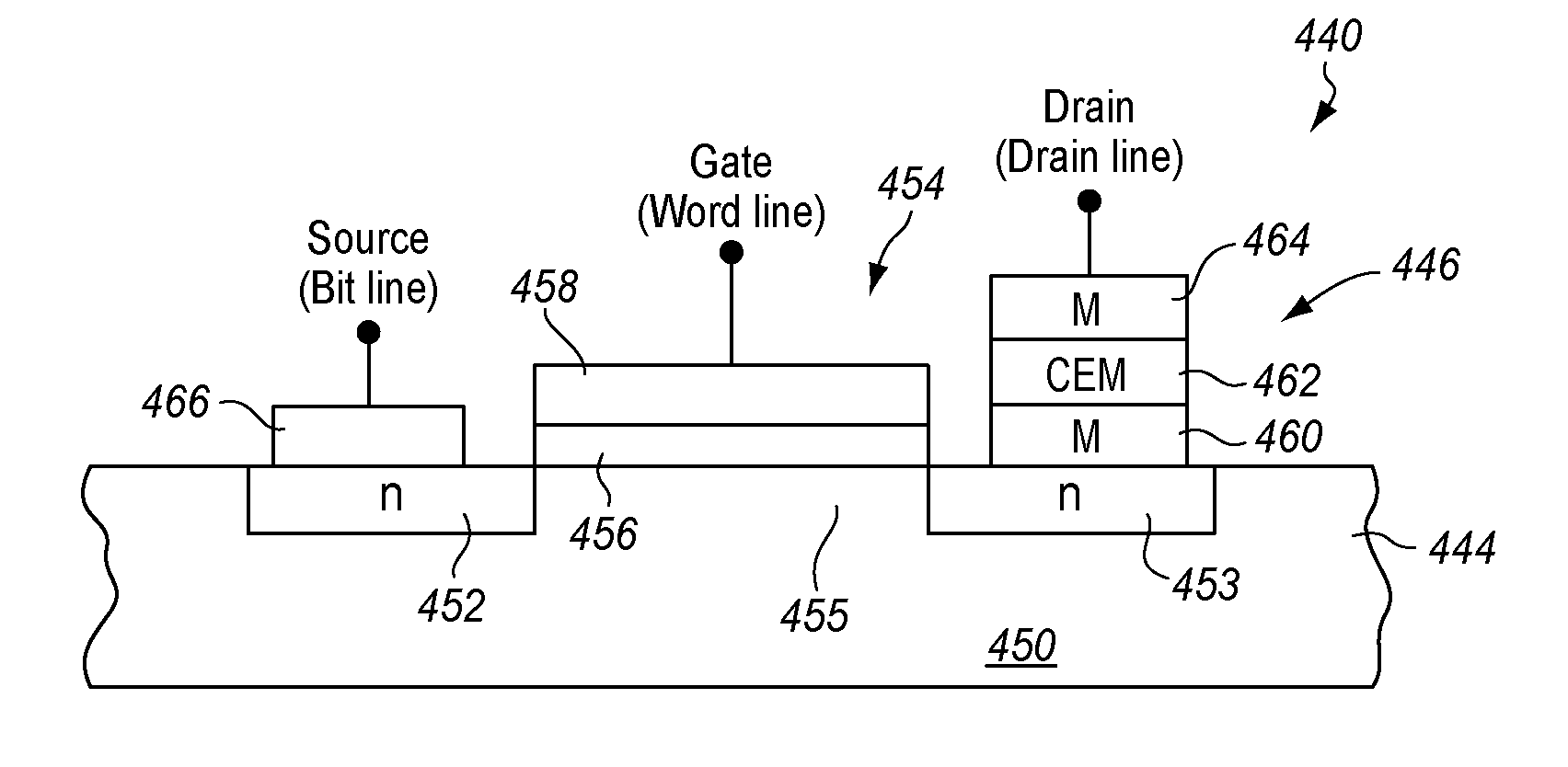
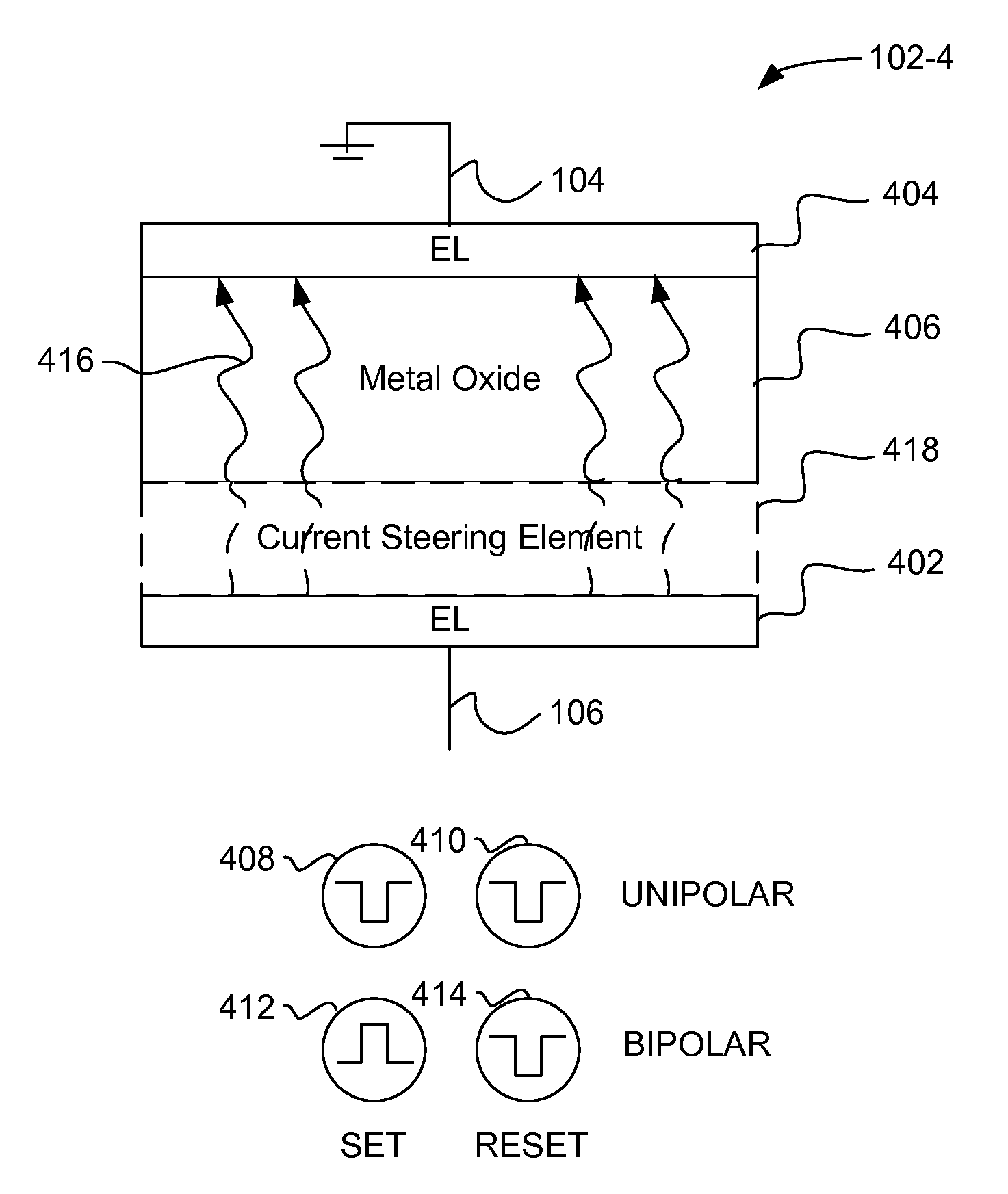
Nonvolatile memory device having a current limiting element
ActiveUS20130028003A1Total current dropForming voltage can be reducedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductancePower flow
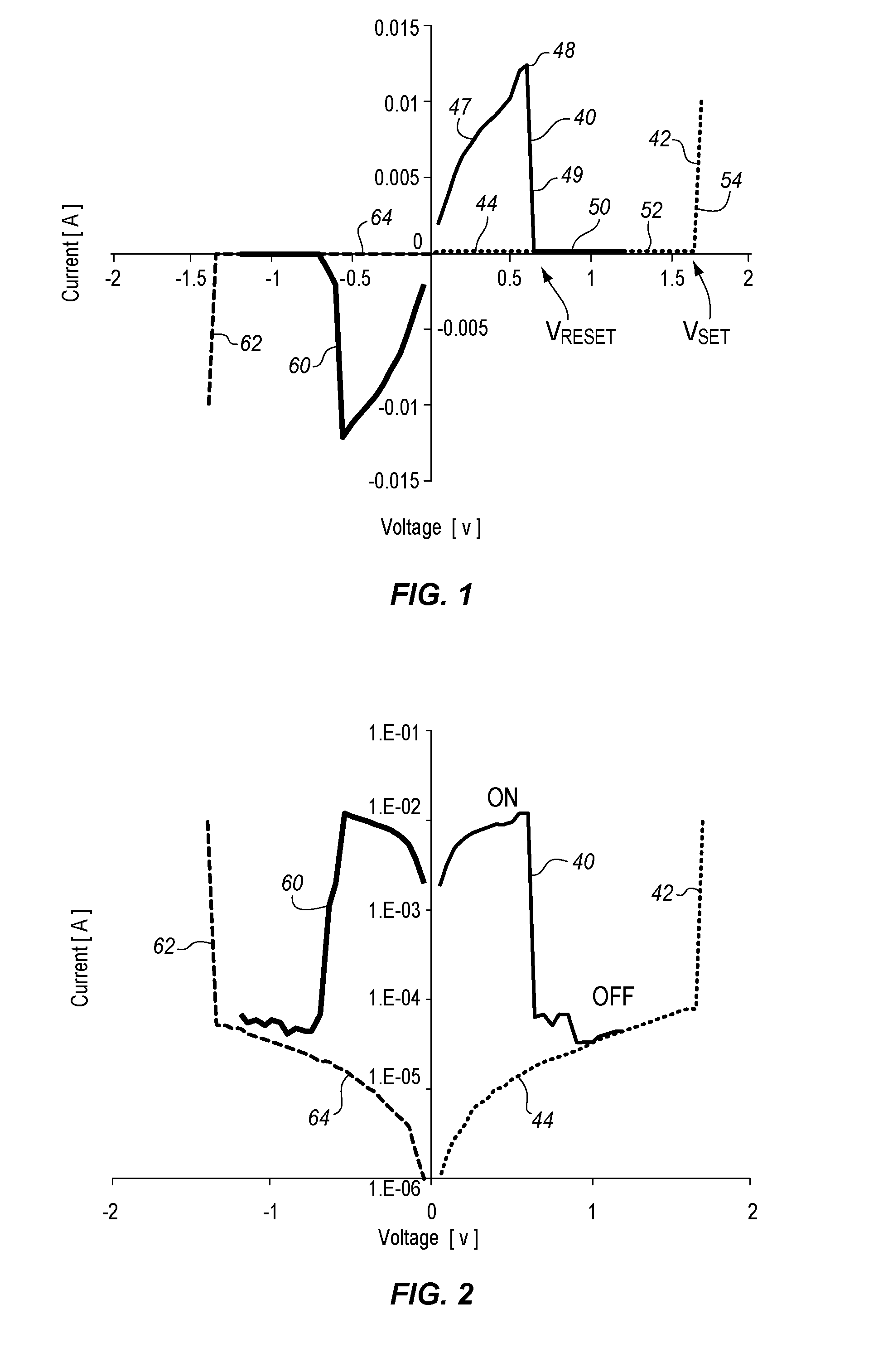
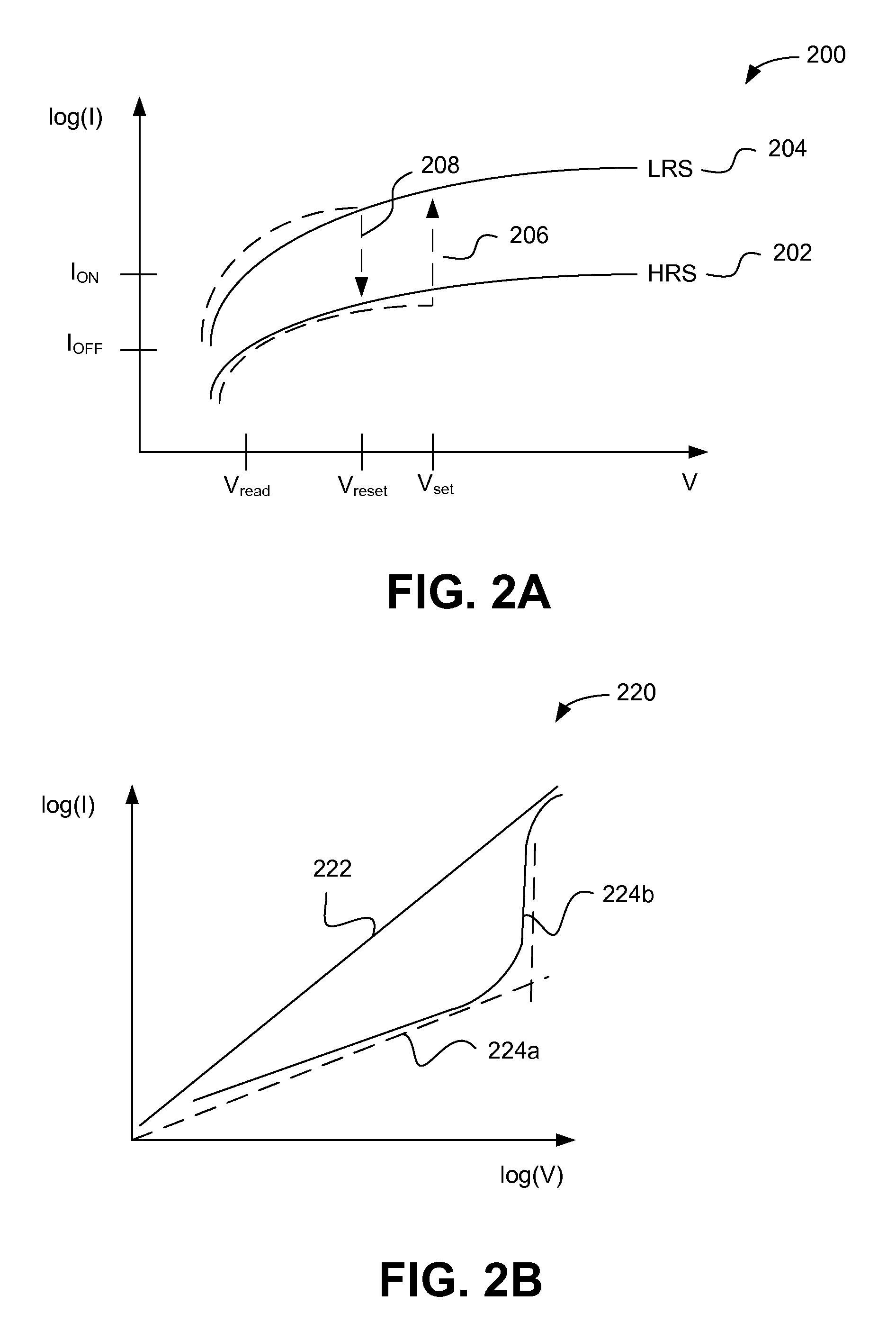
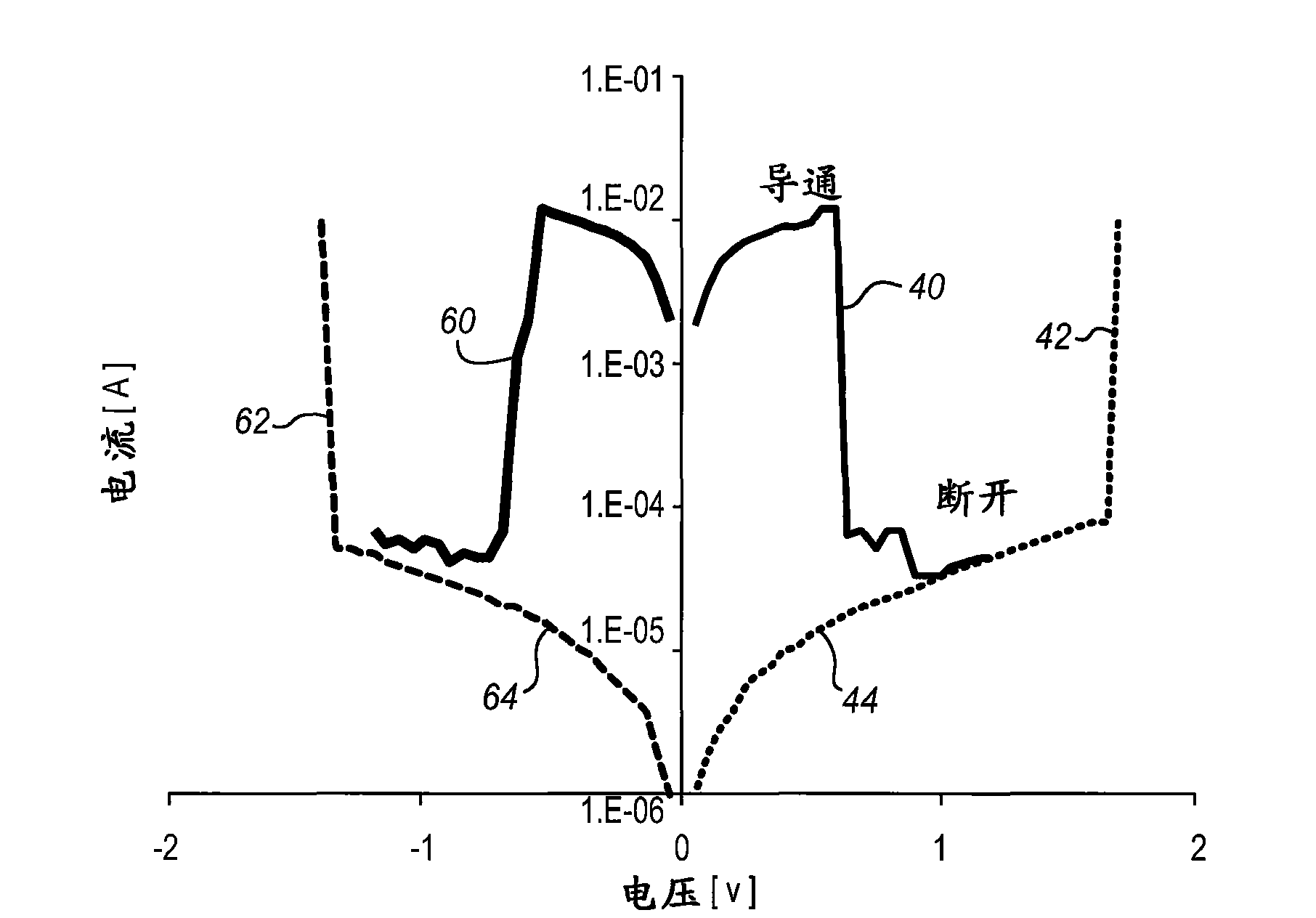
Embodiments of the invention generally include a method of forming a nonvolatile memory device that contains a resistive switching memory element that has an improved device switching performance and lifetime, due to the addition of a current limiting component disposed therein. In one embodiment, the current limiting component comprises at least one layer of resistive material that is configured to improve the switching performance and lifetime of the formed resistive switching memory element. The electrical properties of the formed current limiting layer, or resistive layer, are configured to lower the current flow through the variable resistance layer during the logic state programming steps (i.e., “set” and “reset” steps) by adding a fixed series resistance in the formed resistive switching memory element found in the nonvolatile memory device.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Correlated electron memory
ActiveCN101681911AEliminate injected dependenciesEliminate breakdownSolid-state devicesDigital storageMott transitionElectron
A non-volatile resistive switching memory that includes a material which changes between the insulative and conductive states due to correlations between electrons, particularly via a Mott transition.The material is crystallized into the conductive state and does not require electroforming.
Owner:思美存储器有限公司
Biploar resistive-switching memory with a single diode per memory cell
According to various embodiments, a resistive-switching memory element and memory element array that uses a bipolar switching includes a select element comprising only a single diode that is not a Zener diode. The resistive-switching memory elements described herein can switch even when a switching voltage less than the breakdown voltage of the diode is applied in the reverse-bias direction of the diode. The memory elements are able to switch during the very brief period when a transient pulse voltage is visible to the memory element, and therefore can use a single diode per memory cell.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
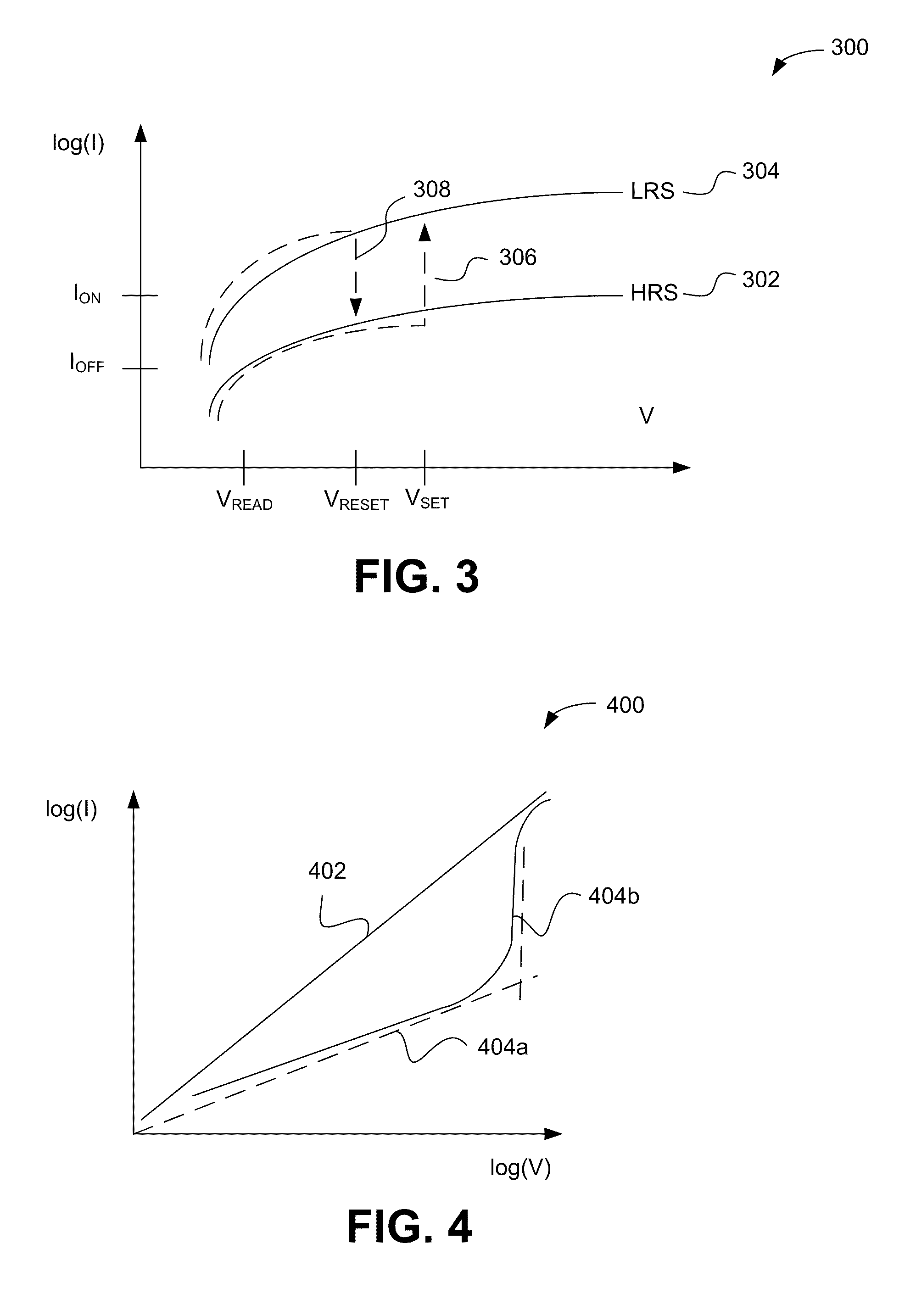
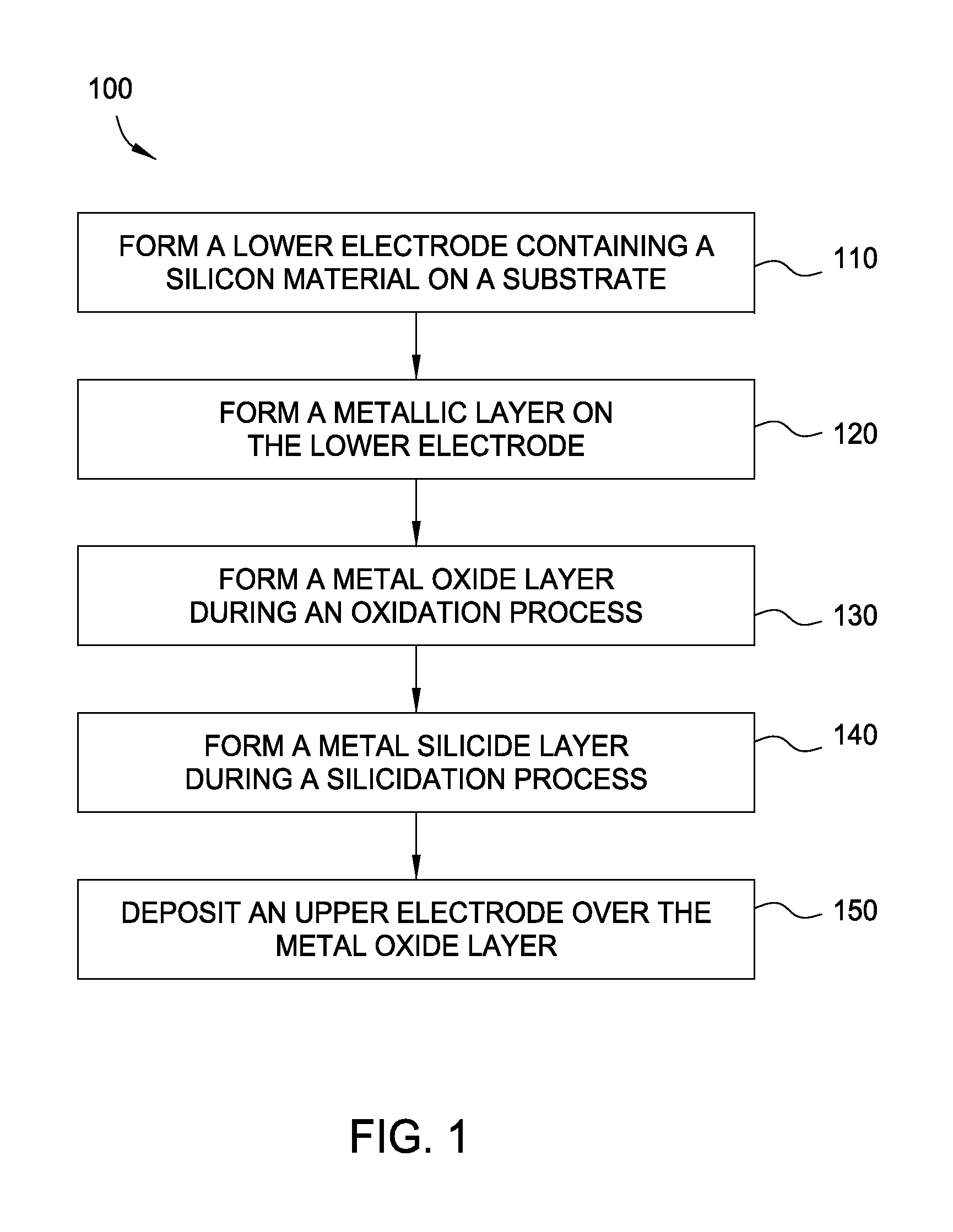
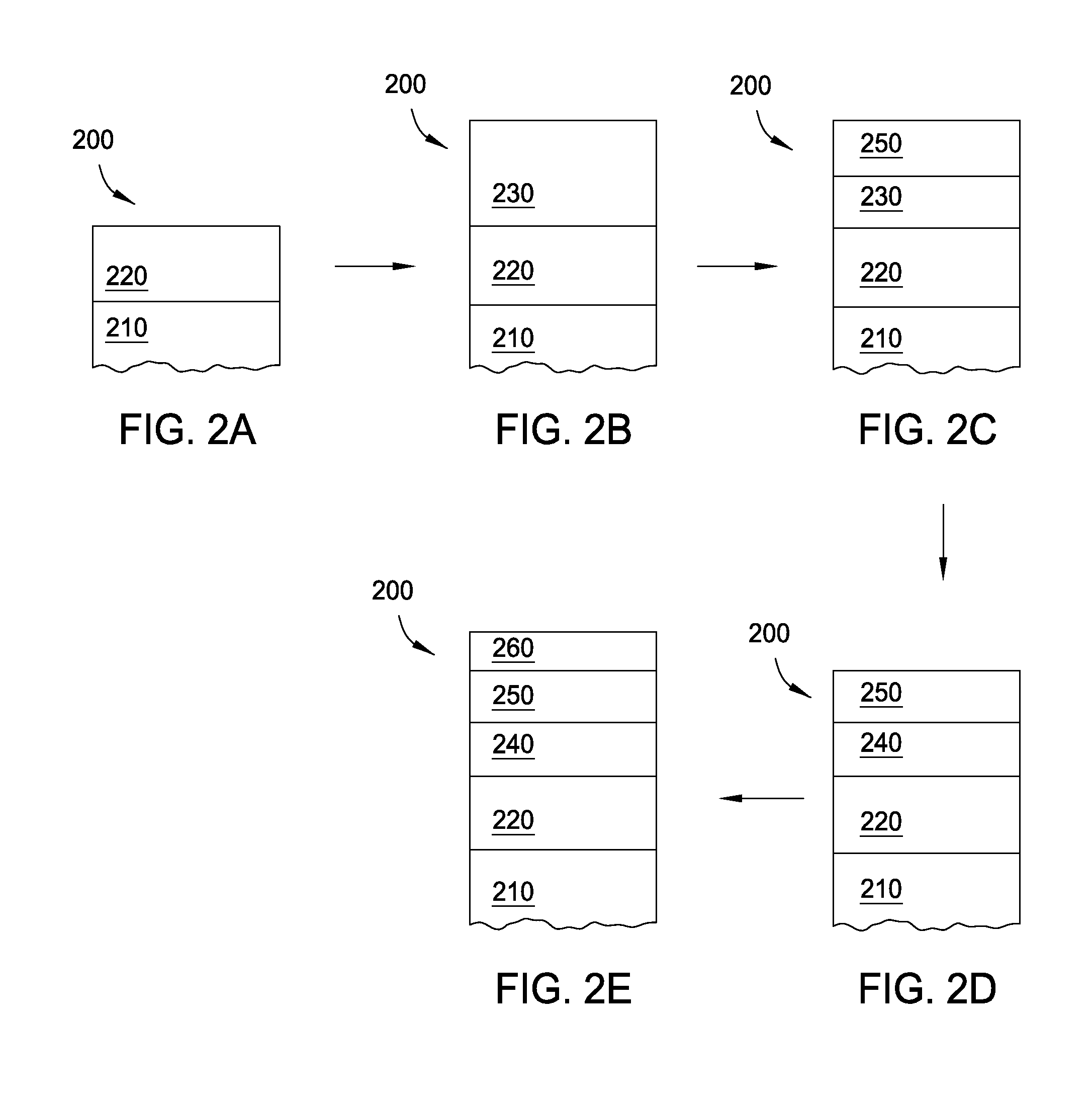
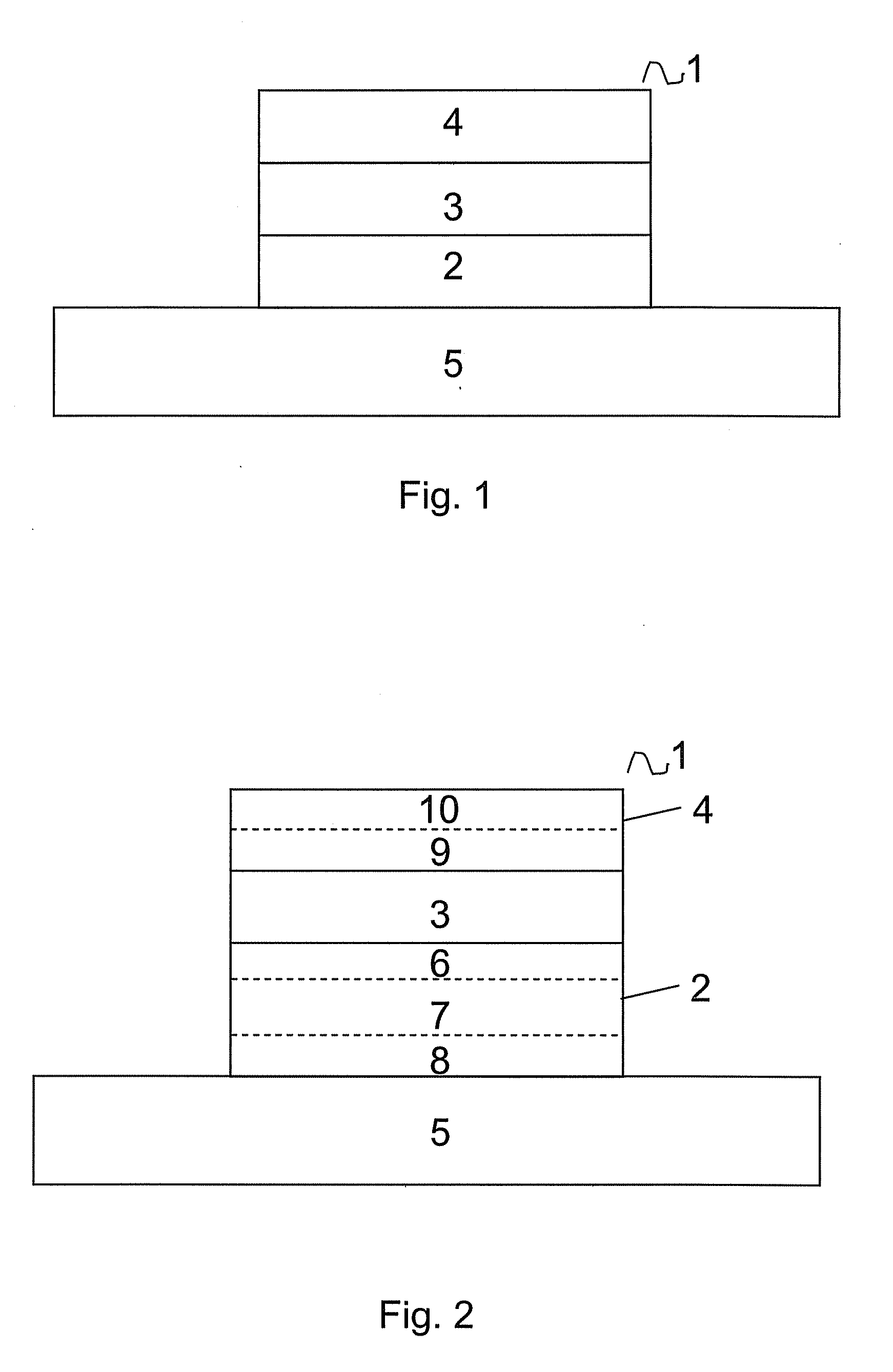
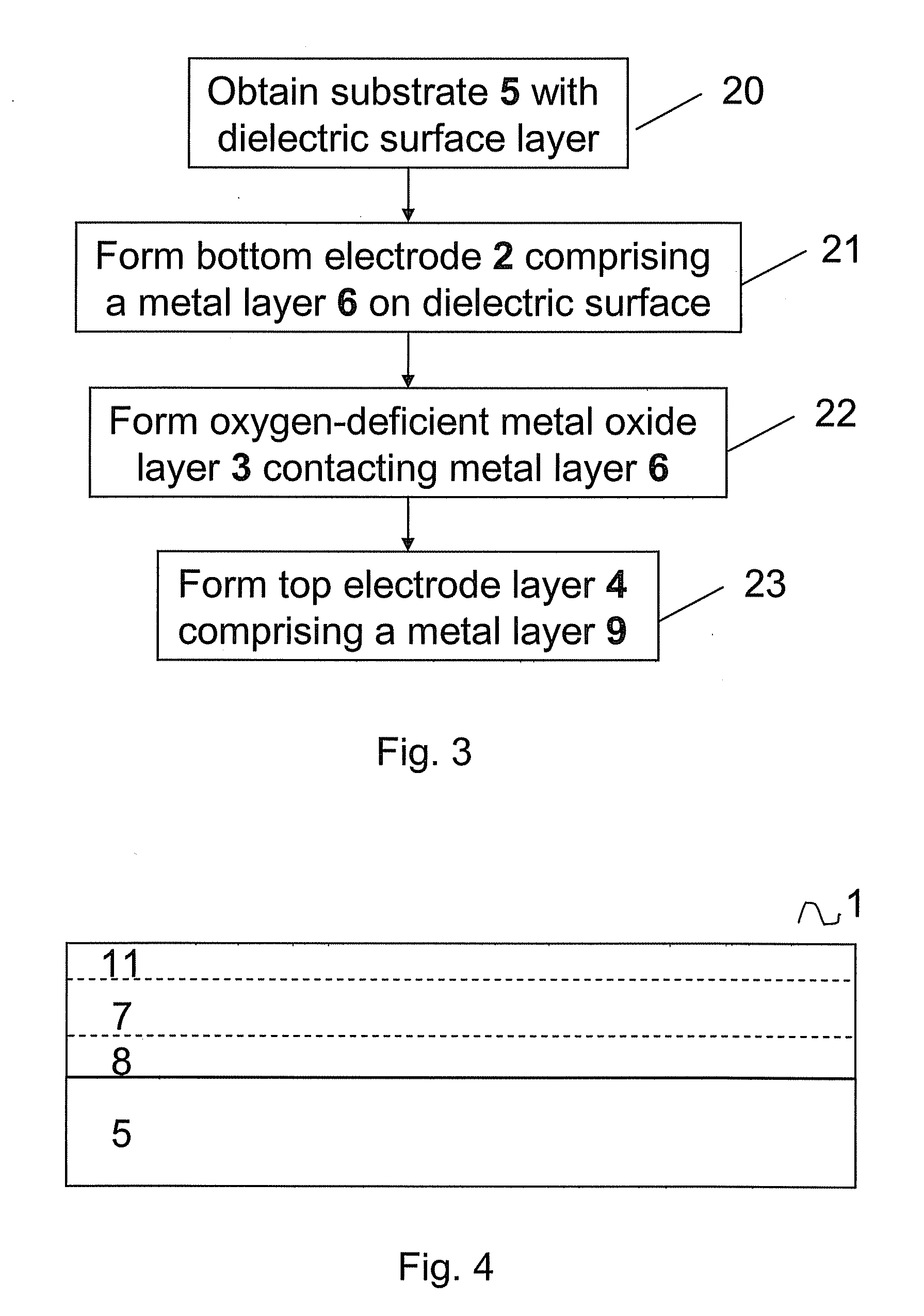
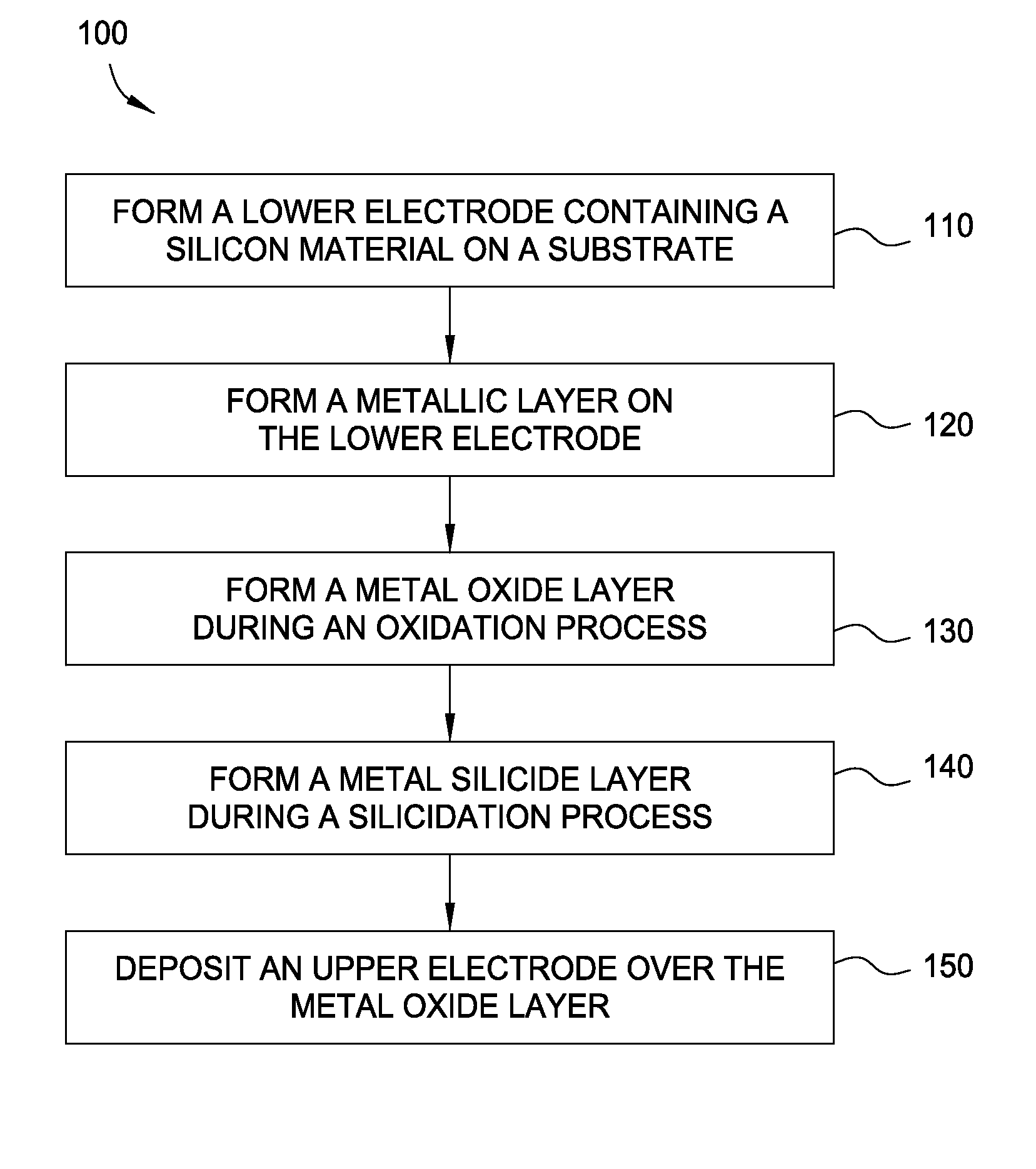
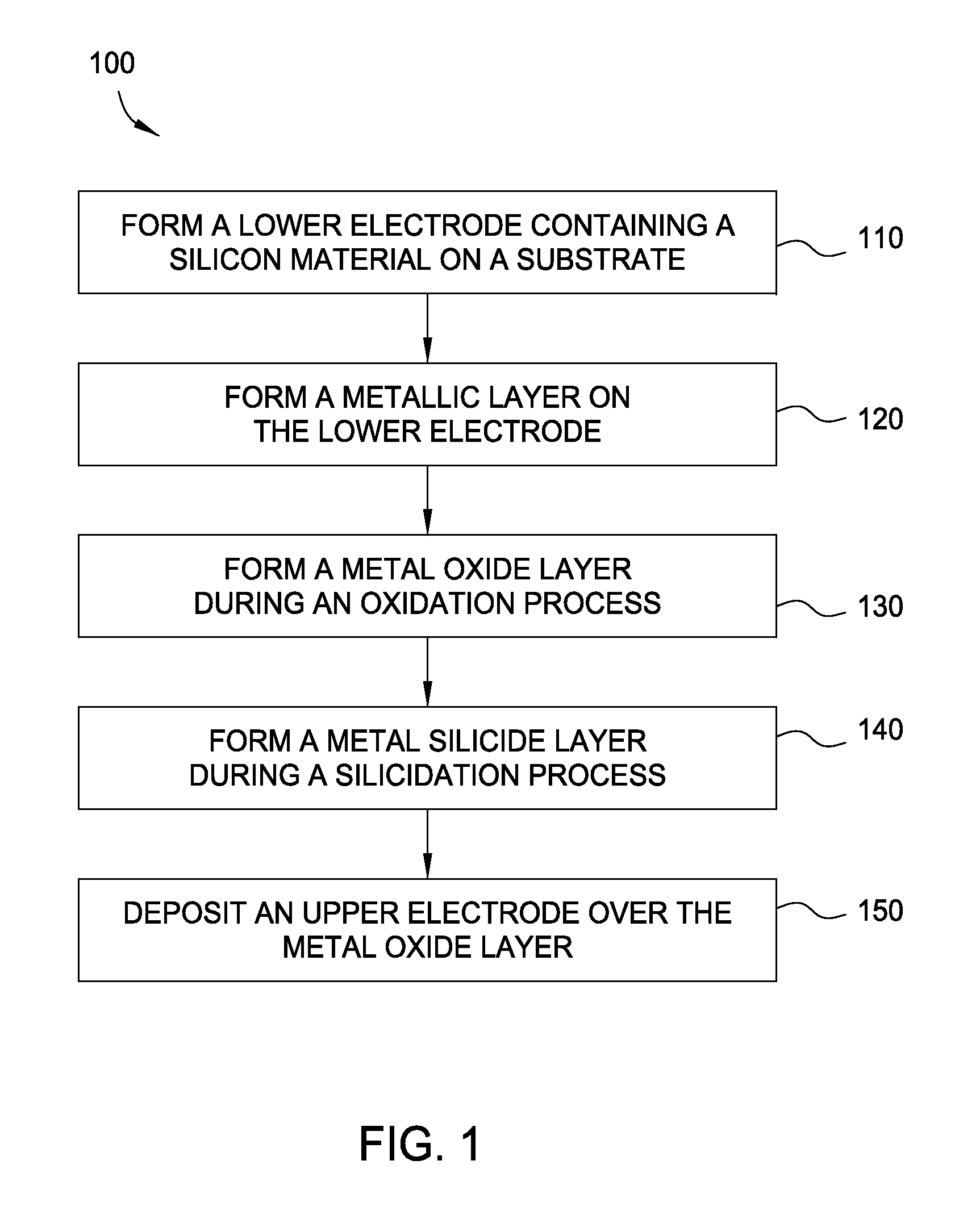
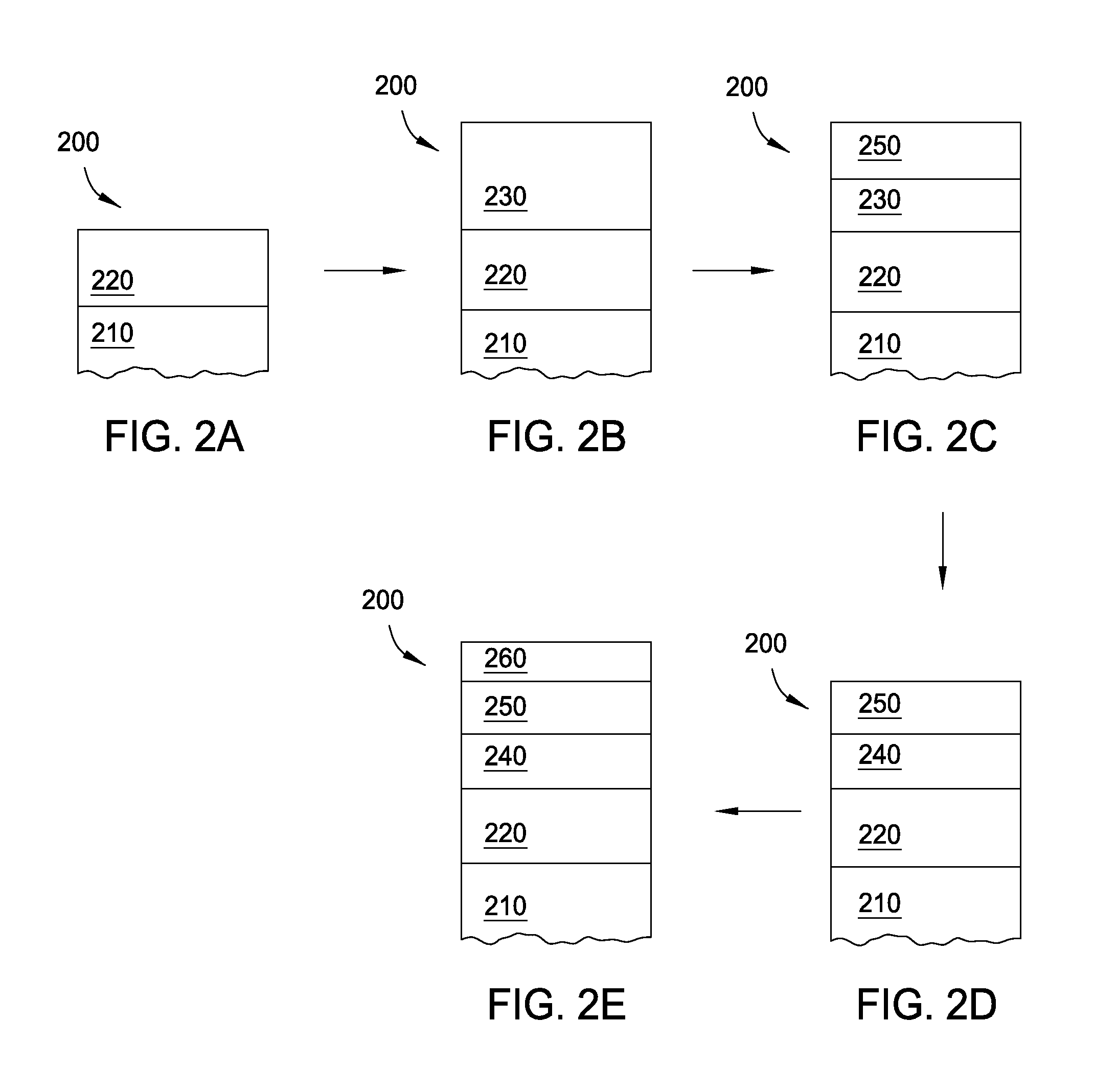
Method for forming metal oxides and silicides in a memory device
ActiveUS20130023085A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal silicideHafnium
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to memory devices and methods for fabricating such memory devices. In one embodiment, a method for fabricating a resistive switching memory device includes depositing a metallic layer on a lower electrode disposed on a substrate and exposing the metallic layer to an activated oxygen source while heating the substrate to an oxidizing temperature within a range from about 300° C. to about 600° C. and forming a metal oxide layer from an upper portion of the metallic layer during an oxidation process. The lower electrode contains a silicon material and the metallic layer contains hafnium or zirconium. Subsequent to the oxidation process, the method further includes heating the substrate to an annealing temperature within a range from greater than 600° C. to about 850° C. while forming a metal silicide layer from a lower portion of the metallic layer during a silicidation process.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR +2
ReRAM stacks preparation by using single ALD or PVD chamber
InactiveUS8846484B2Reduces exposure to air and to particulateImprove throughputSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingParticulatesCurrent limiting
Systems and methods for preparing resistive switching memory devices such as resistive random access memory (ReRAM) devices wherein both oxide and nitride layers are deposited in a single chamber are provided. Various oxide and nitride based layers in the ReRAM device such as the switching layer, current-limiting layer, and the top electrode (and optionally the bottom electrode) are deposited in the single chamber. By fabricating the ReRAM device in a single chamber, throughput is increased and cost is decreased. Moreover, processing in a single chamber reduces device exposure to air and to particulates, thereby minimizing device defects.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC +2
Multi-Level Memory Array Having Resistive Elements For Multi-Bit Data Storage
InactiveUS20140177315A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageMemory chipMultilevel memory
A resistor array for multi-bit data storage without the need to increase the size of a memory chip or scale down the feature size of a memory cell contained within the memory chip is provided. The resistor array incorporates a number of discrete resistive elements to be selectively connected, in different series combinations, to at least one memory cell or memory device. In one configuration, by connecting each memory cell or device with at least one resistor array, a resistive switching layer found in the resistive switching memory element of the connected memory device is capable of being at multiple resistance states for storing multiple bits of digital information. During device programming operations, when a desired series combination of the resistive elements within the resistor array is selected, the resistive switching layer in the connected memory device can be in a desired resistance state.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC +2
Ald processing techniques for forming non-volatile resistive-switching memories
ActiveUS20090302296A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCelsius DegreeAtomic layer deposition
ALD processing techniques for forming non-volatile resistive-switching memories are described. In one embodiment, a method includes forming a first electrode on a substrate, maintaining a pedestal temperature for an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process of less than 100° Celsius, forming at least one metal oxide layer over the first electrode, wherein the forming the at least one metal oxide layer is performed using the ALD process using a purge duration of less than 20 seconds, and forming a second electrode over the at least one metal oxide layer.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Resistive-switching memory elements having improved switching characteristics
Resistive-switching memory elements having improved switching characteristics are described, including a memory element having a first electrode and a second electrode, a switching layer between the first electrode and the second electrode comprising hafnium oxide and having a first thickness, and a coupling layer between the switching layer and the second electrode, the coupling layer comprising a material including metal titanium and having a second thickness that is less than 25 percent of the first thickness.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Defect gradient to boost nonvolatile memory performance
ActiveUS20130056700A1Reduce distanceSolid-state devicesBulk negative resistance effect devicesDigital dataEngineering
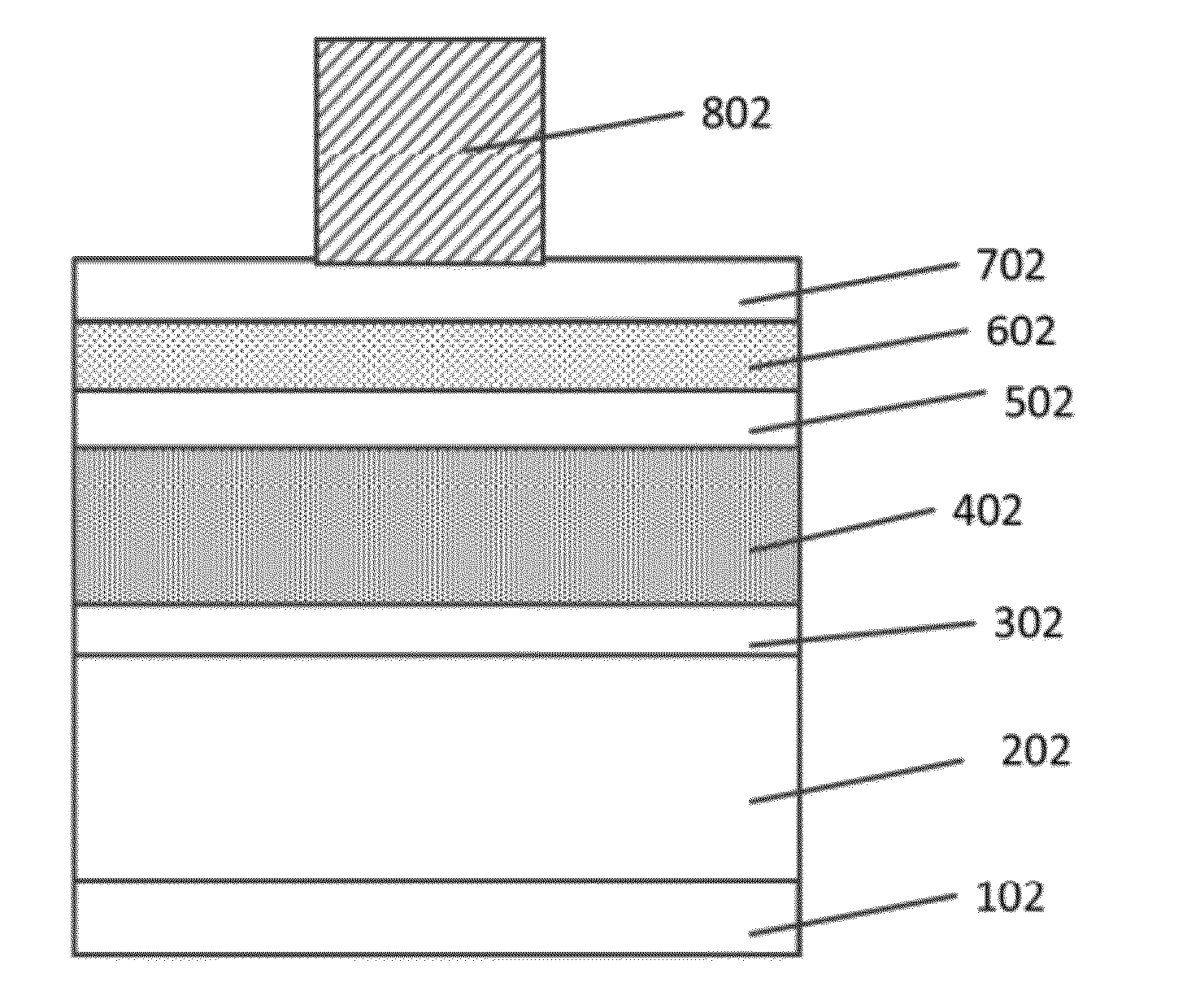
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to a resistive switching nonvolatile memory element that is formed in a resistive switching memory device that may be used in a memory array to store digital data. The memory element is generally constructed as a metal-insulator-metal stack. The resistive switching portion of the memory element includes a getter portion and / or a defect portion. In general, the getter portion is an area of the memory element that is used to help form, during the resistive switching memory device's fabrication process, a region of the resistive switching layer that has a greater number of vacancies or defects as compared to the remainder of resistive switching layer. The defect portion is an area of the memory element that has a greater number of vacancies or defects as compared to the remainder of the resistive switching layer, and is formed during the resistive switching memory device's fabrication process. The addition of the getter or defect portions in a formed memory device generally improves the reliability of the resistive switching memory device, improves the switching characteristics of the formed memory device and can eliminate or reduce the need for the time consuming additional post fabrication “burn-in” or pre-programming steps.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP +1
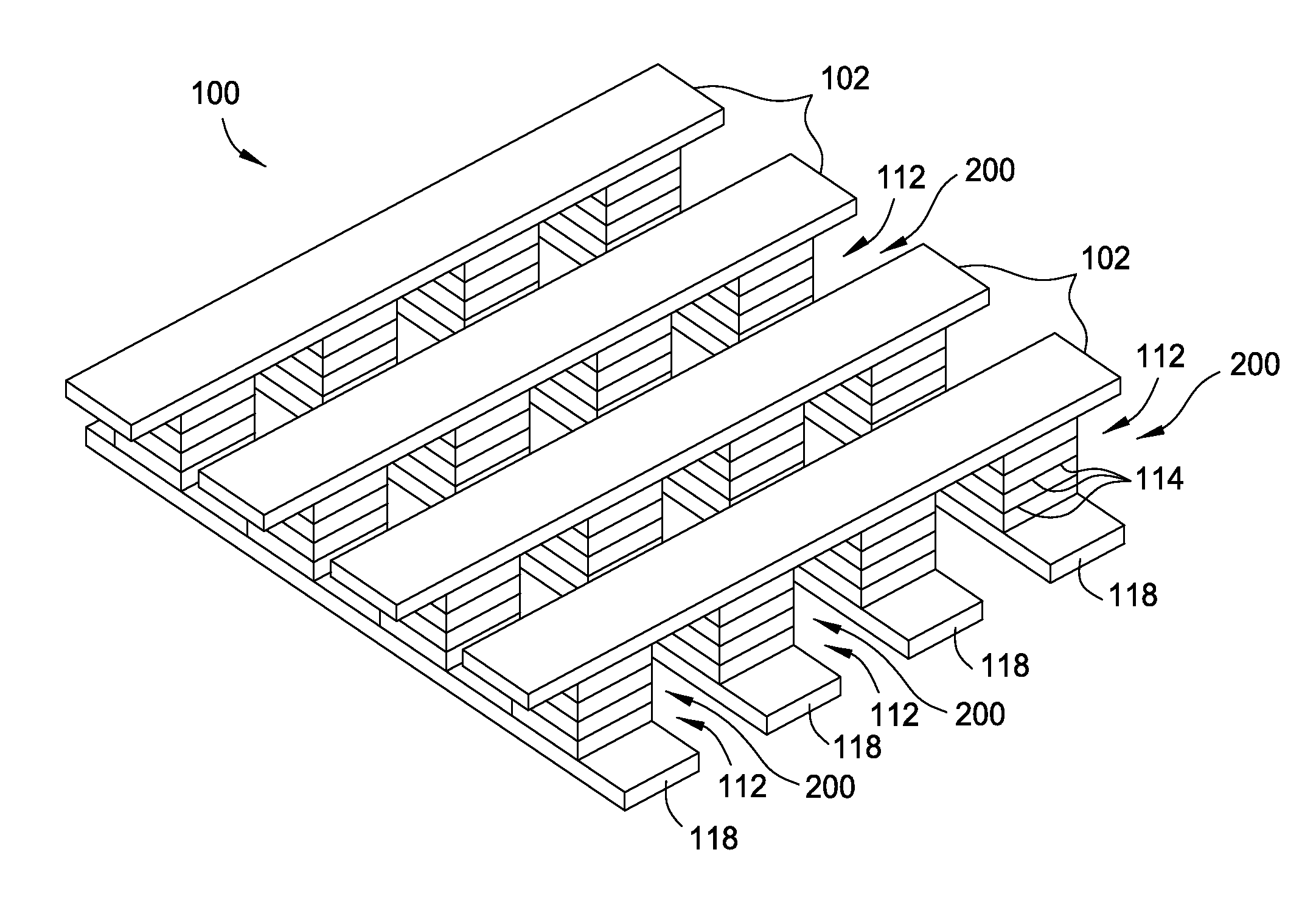
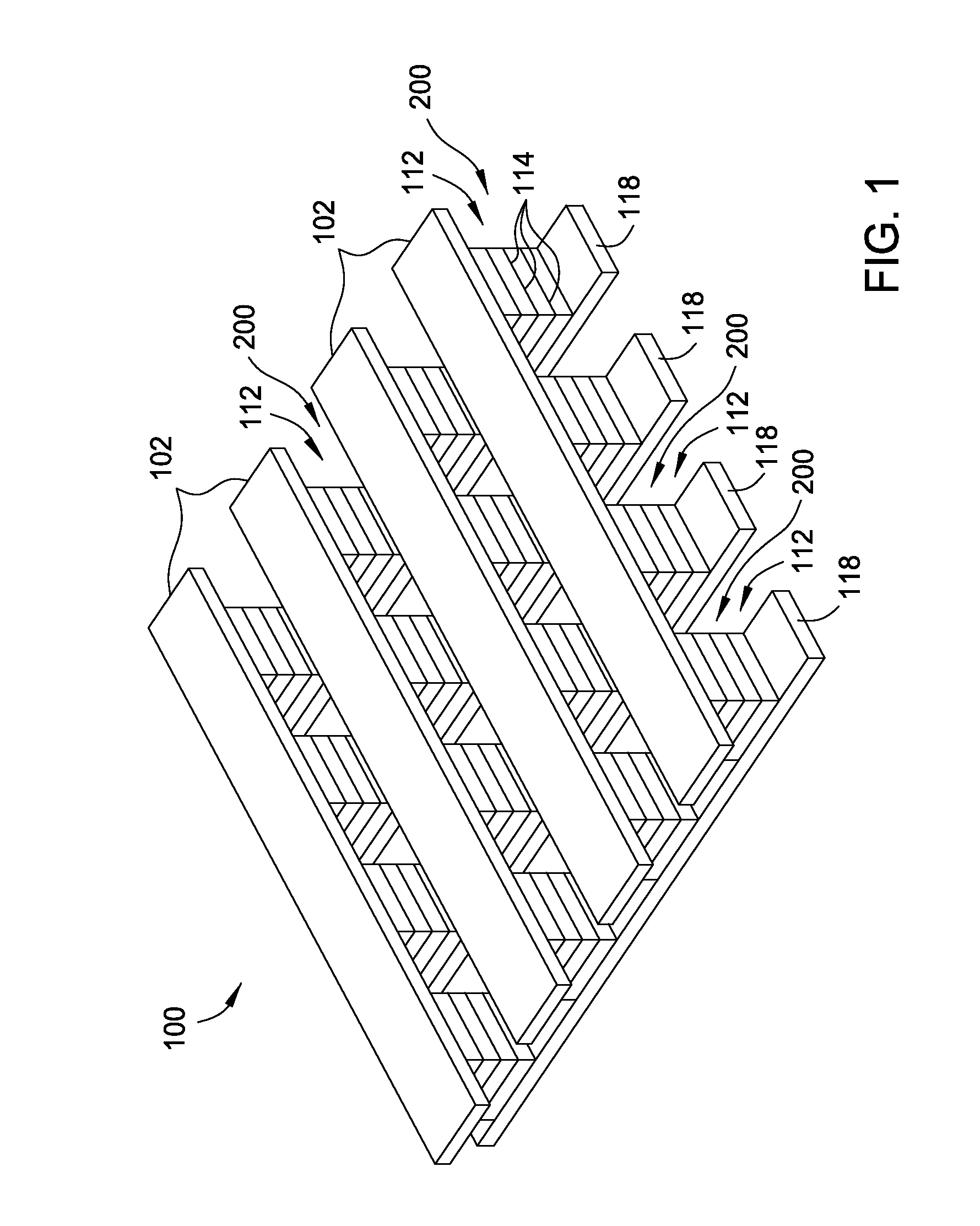
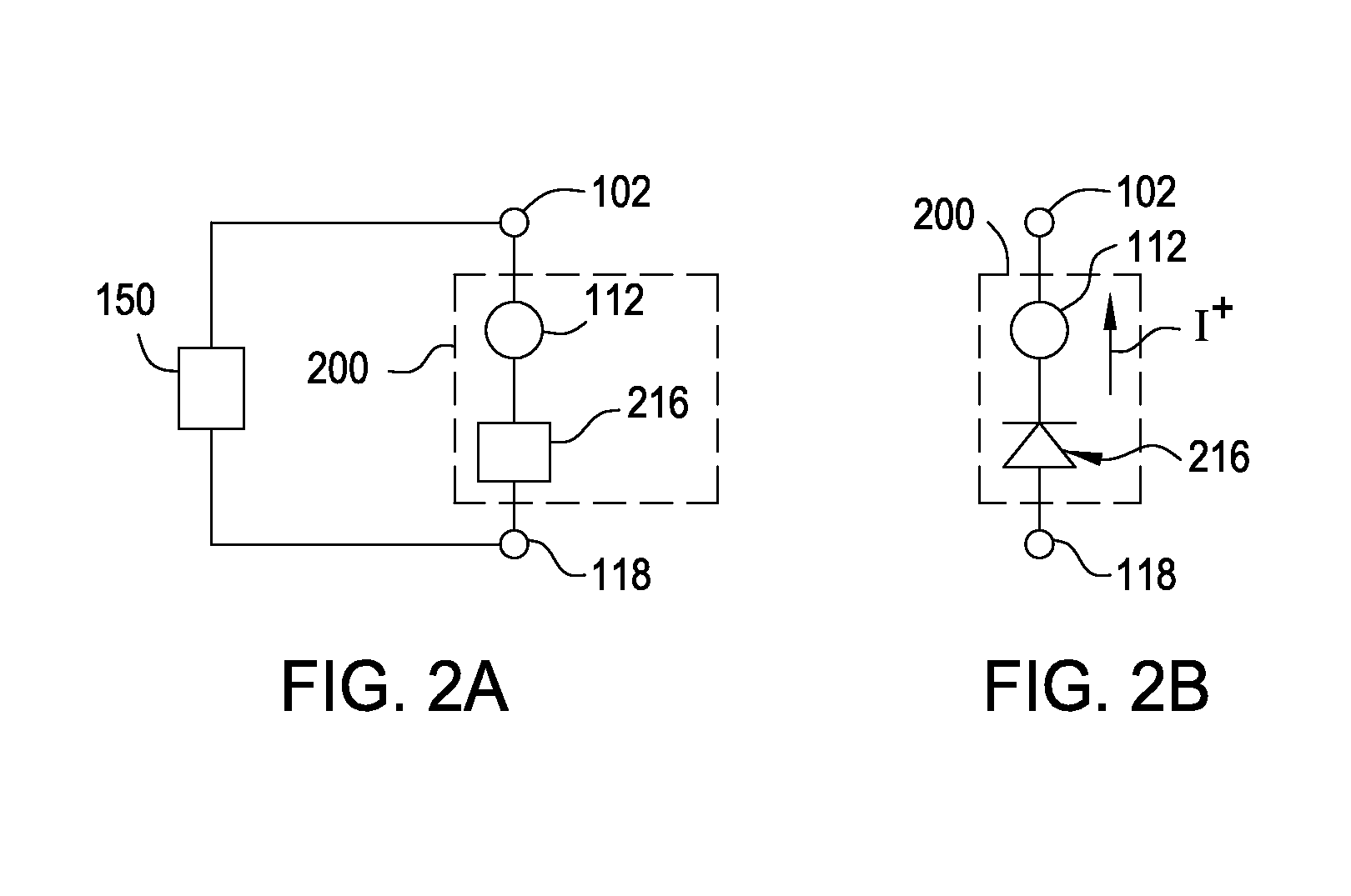
Memory Cell Having an Integrated Two-Terminal Current Limiting Resistor
ActiveUS20130221315A1Long lastingInhibit currentSolid-state devicesBulk negative resistance effect devicesEngineeringElectron
A resistor structure incorporated into a resistive switching memory cell with improved performance and lifetime is provided. The resistor structure may be a two-terminal structure designed to reduce the maximum current flowing through a memory cell. A method is also provided for making such a memory cell. The method includes depositing a resistor structure and depositing a variable resistance layer of a resistive switching memory cell of the memory cell, where the resistor structure is disposed in series with the variable resistance layer to limit the switching current of the memory cell. The incorporation of the resistor structure is very useful in obtaining desirable levels of switching currents that meet the switching specification of various types of memory cells. The memory cells may be formed as part of a high-capacity nonvolatile memory integrated circuit, which can be used in various electronic devices.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC +2
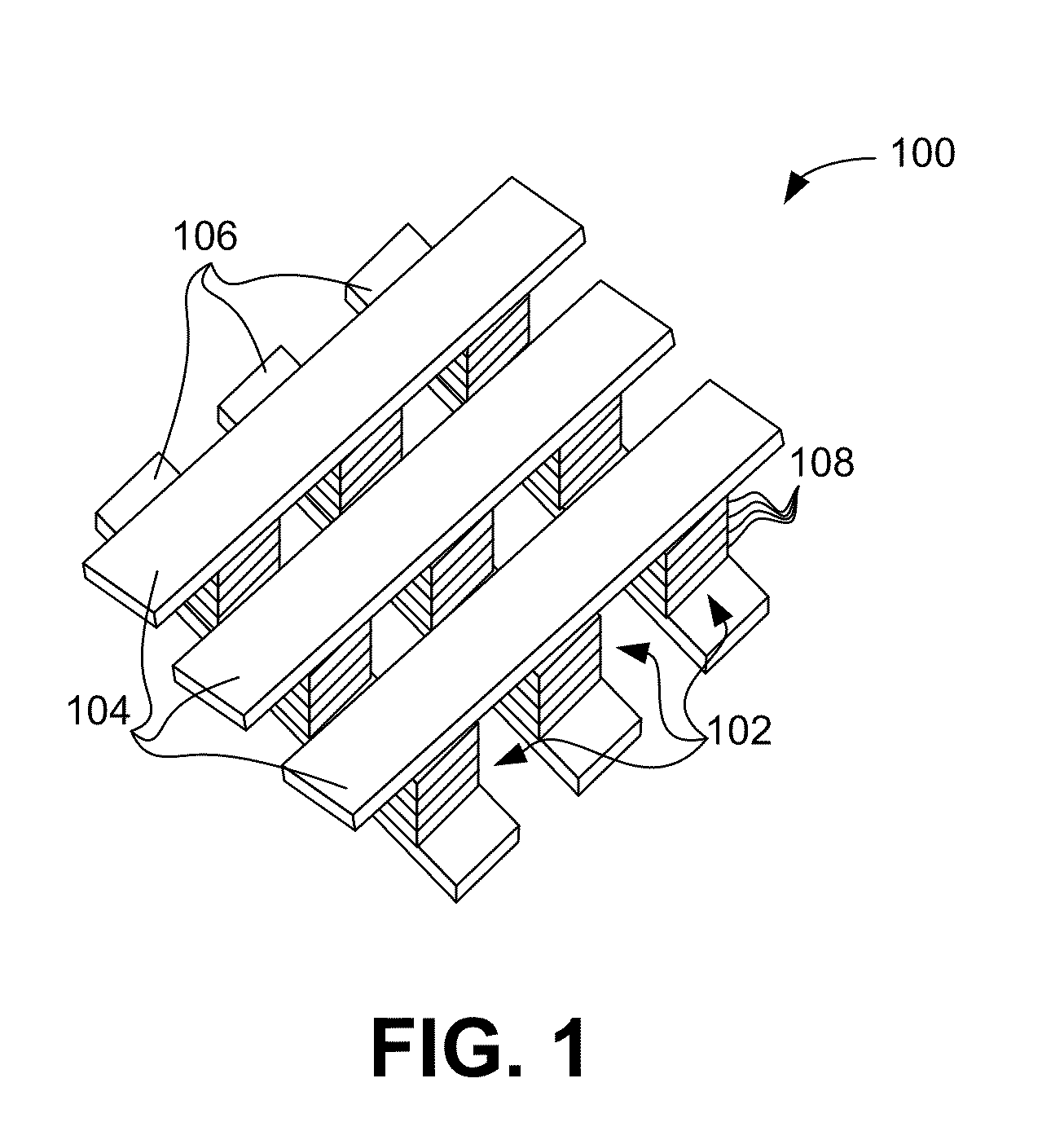
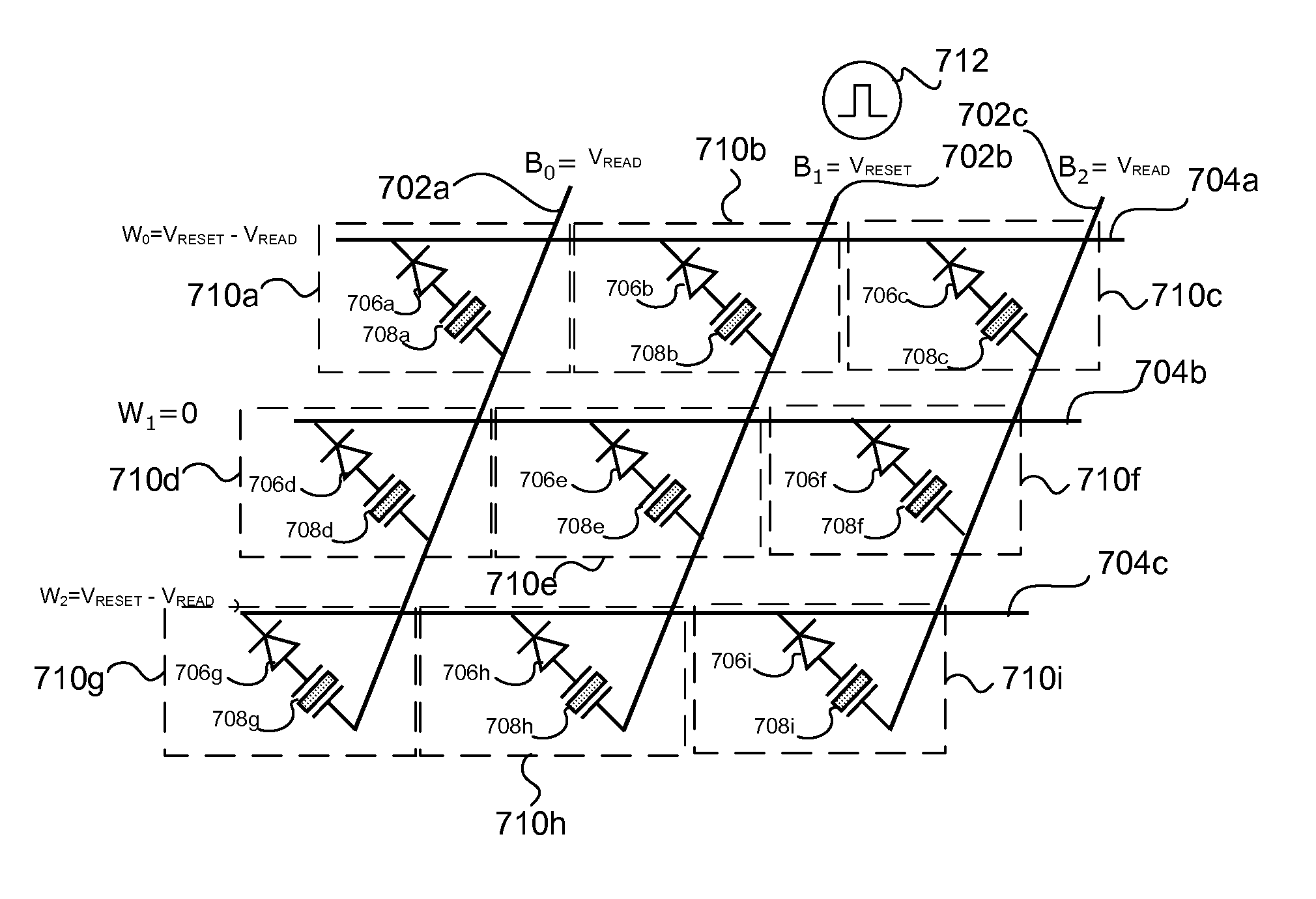
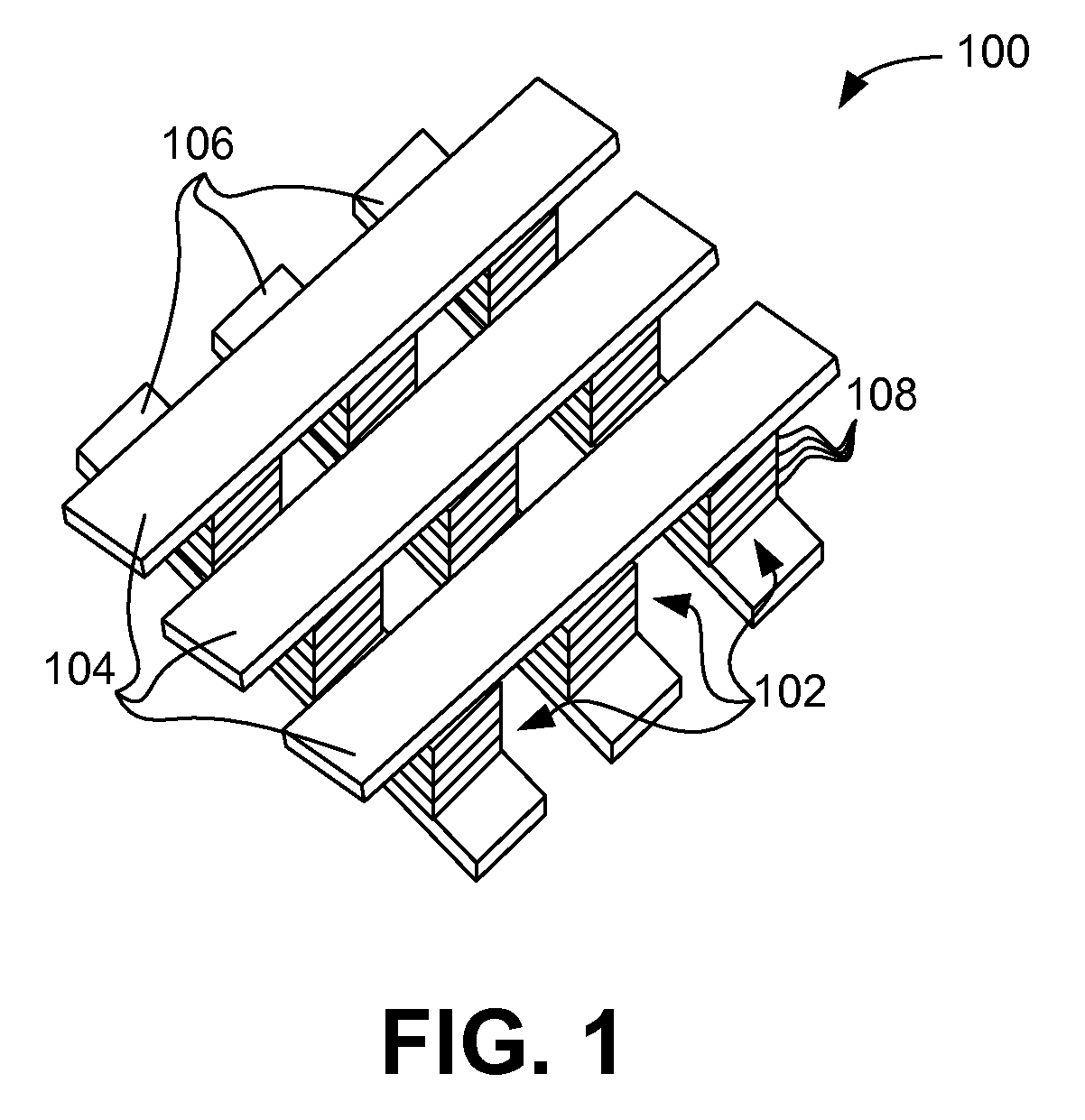
Cross point memory array devices
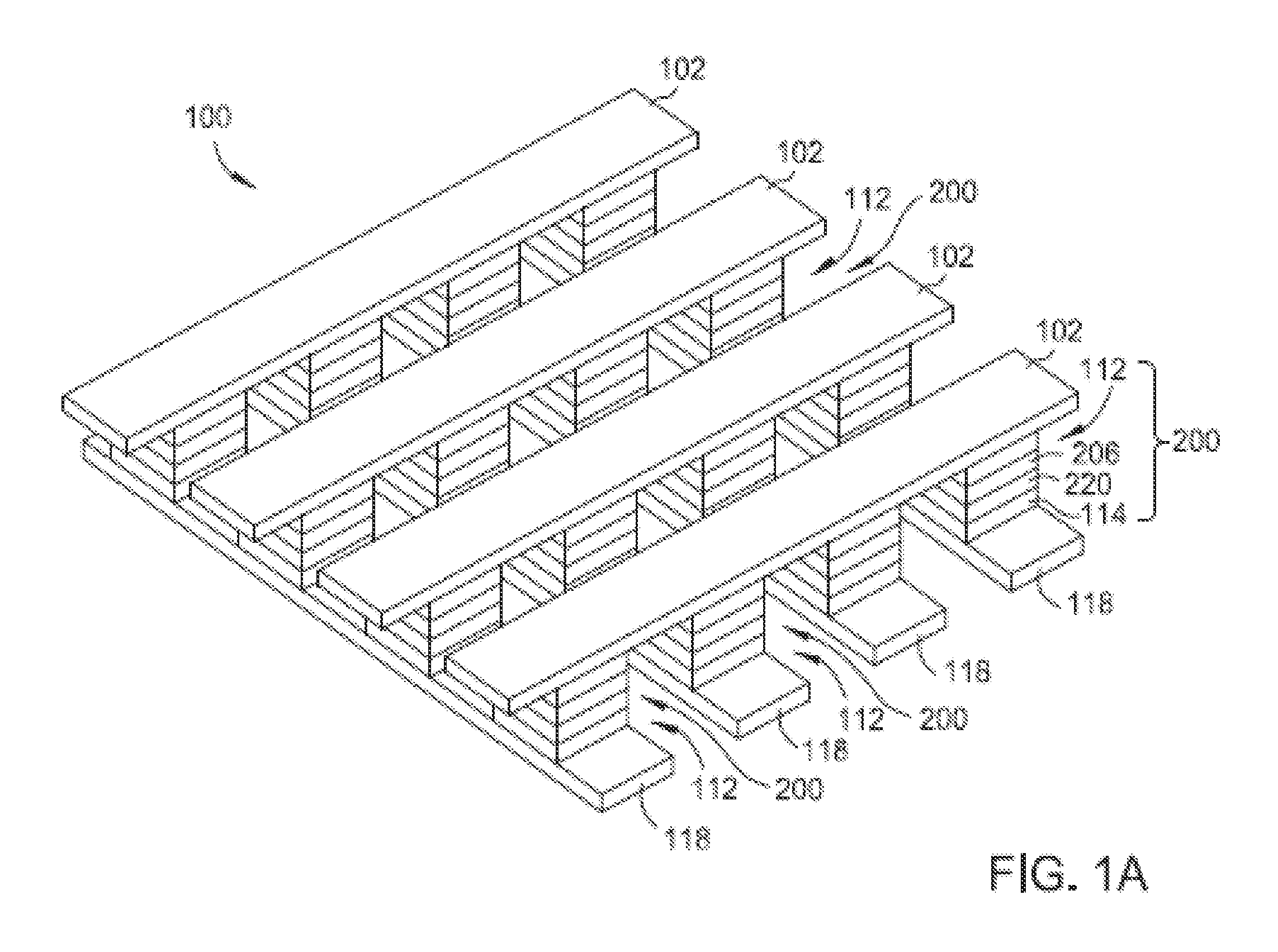
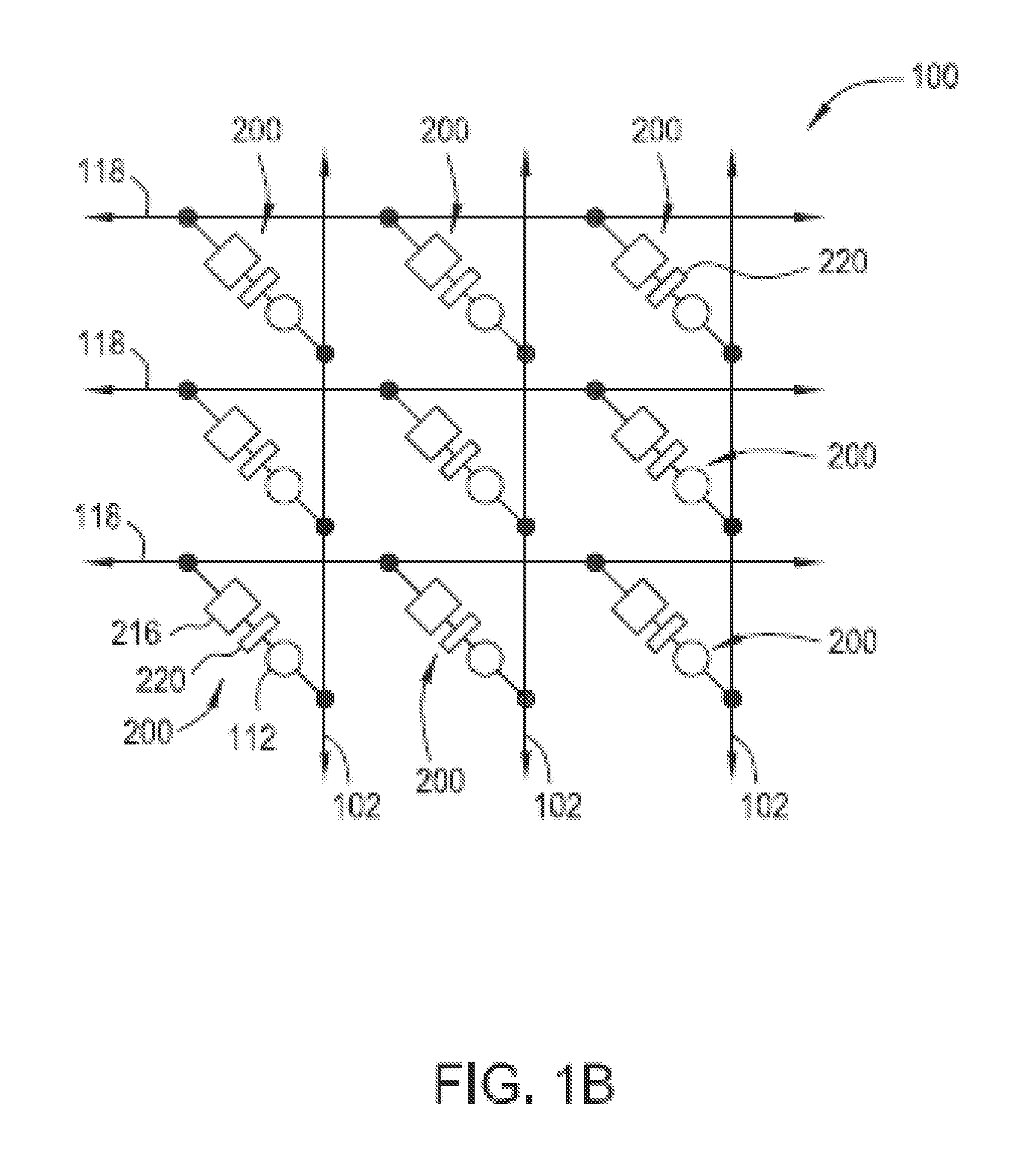
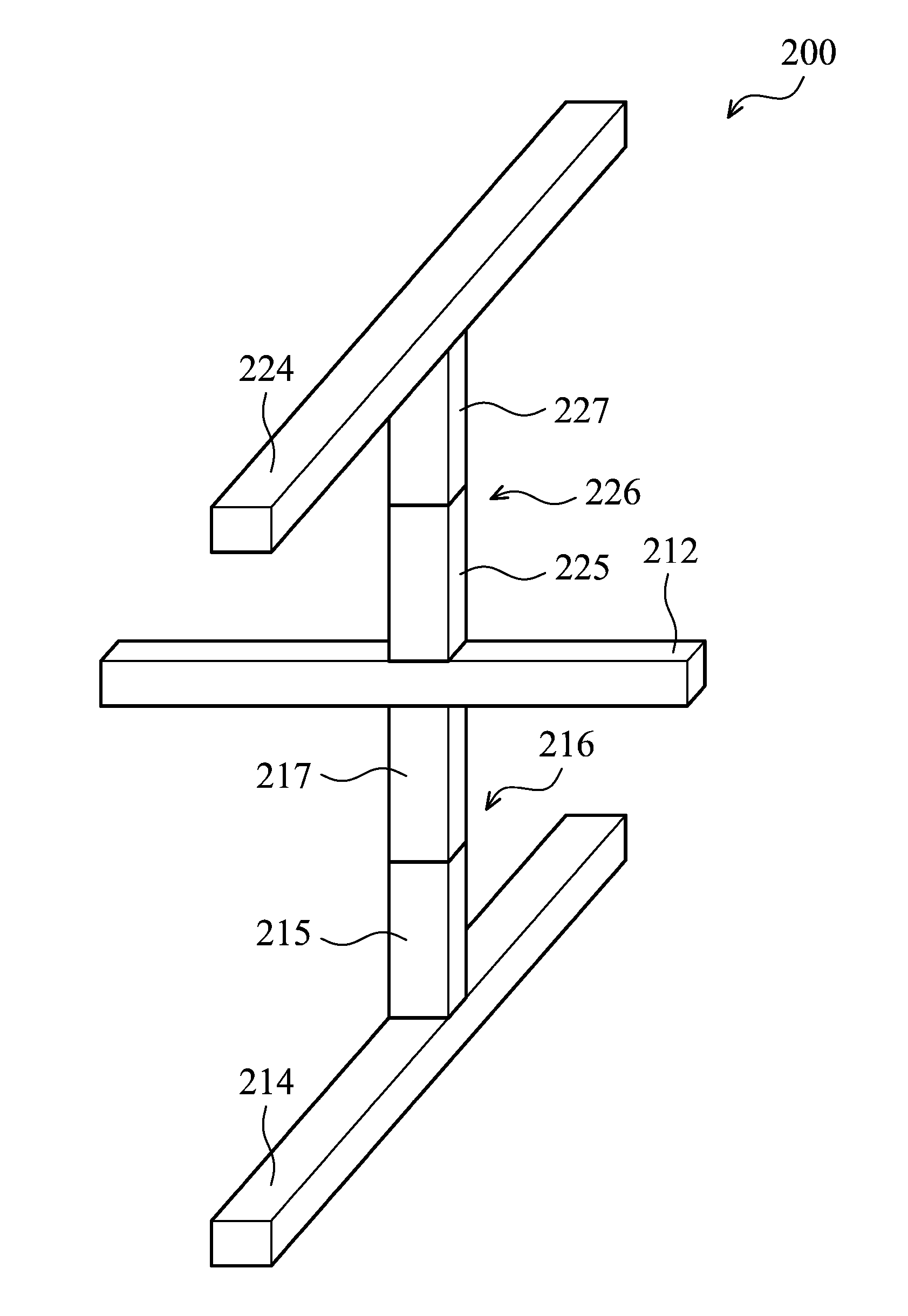
Cross point memory arrays with CBRAM and RRAM stacks are presented. A cross point memory array includes a first group of substantially parallel conductive lines and a second group of substantially parallel conductive lines, oriented substantially perpendicular to the first group of substantially parallel conductive lines. An array of memory stack is located at the intersections of the first group of substantially parallel conductive lines and the second group of substantially parallel conductive lines, wherein each memory stack comprises a conductive bridge memory element in series with a resistive-switching memory element.
Owner:NAN YA TECH
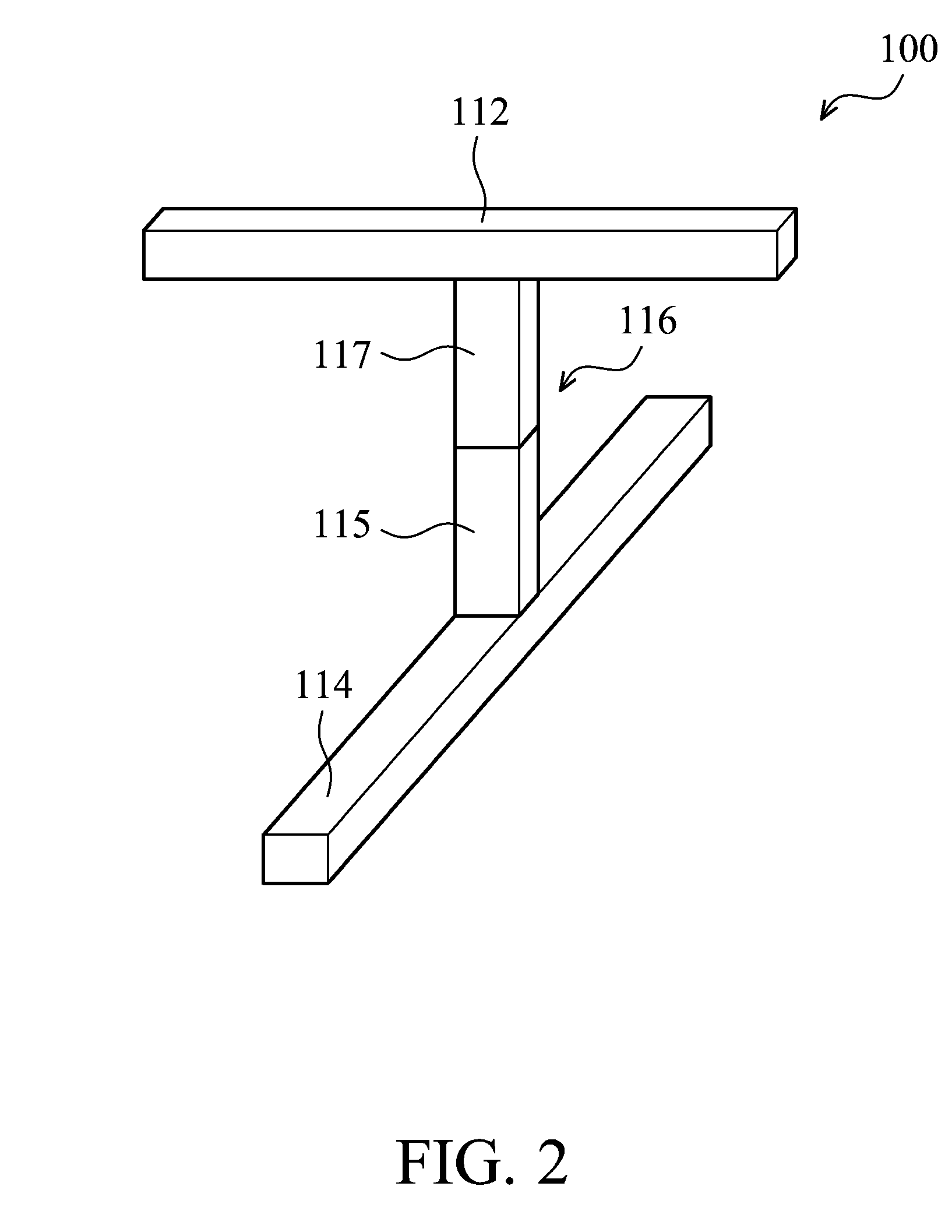
Method for manufacturing a resistive switching memory device and devices obtained thereof
ActiveUS8206995B2Easy to integrateTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Method for Manufacturing a Resistive Switching Memory Cell Comprising a Nickel Oxide Layer Operable at Low-Power and Memory Cells Obtained Thereof
ActiveUS20110044089A1Reduce voltageImprove retentionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageOxygenMetal
A resistive switching non-volatile memory element is disclosed comprising a resistive switching metal-oxide layer sandwiched between and in contact with a top electrode and a bottom electrode, the resistive switching metal oxide layer having a substantial isotropic non-stoichiometric metal-to-oxygen ratio. For example, the memory element may comprise a nickel oxide resistive switching layer sandwiched between and in contact with a nickel top electrode and a nickel bottom electrode whereby the ratio oxygen-to-nickel of the nickel oxide layer is between 0 and 0.85.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Method for forming metal oxides and silicides in a memory device
ActiveUS8466005B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicideMetal silicide
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to memory devices and methods for fabricating such memory devices. In one embodiment, a method for fabricating a resistive switching memory device includes depositing a metallic layer on a lower electrode disposed on a substrate and exposing the metallic layer to an activated oxygen source while heating the substrate to an oxidizing temperature within a range from about 300° C. to about 600° C. and forming a metal oxide layer from an upper portion of the metallic layer during an oxidation process. The lower electrode contains a silicon material and the metallic layer contains hafnium or zirconium. Subsequent to the oxidation process, the method further includes heating the substrate to an annealing temperature within a range from greater than 600° C. to about 850° C. while forming a metal silicide layer from a lower portion of the metallic layer during a silicidation process.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com