Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Minimize blurring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
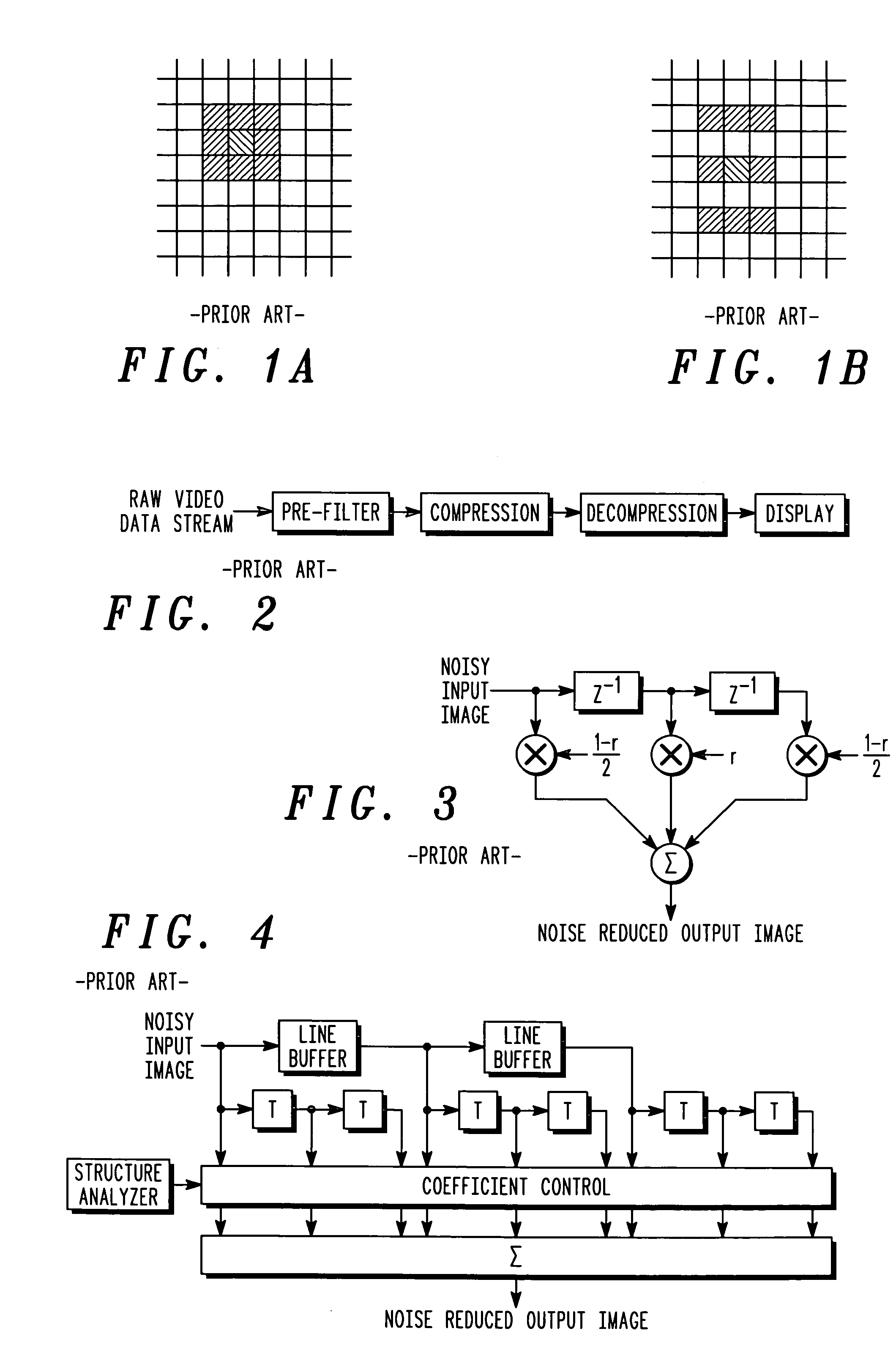
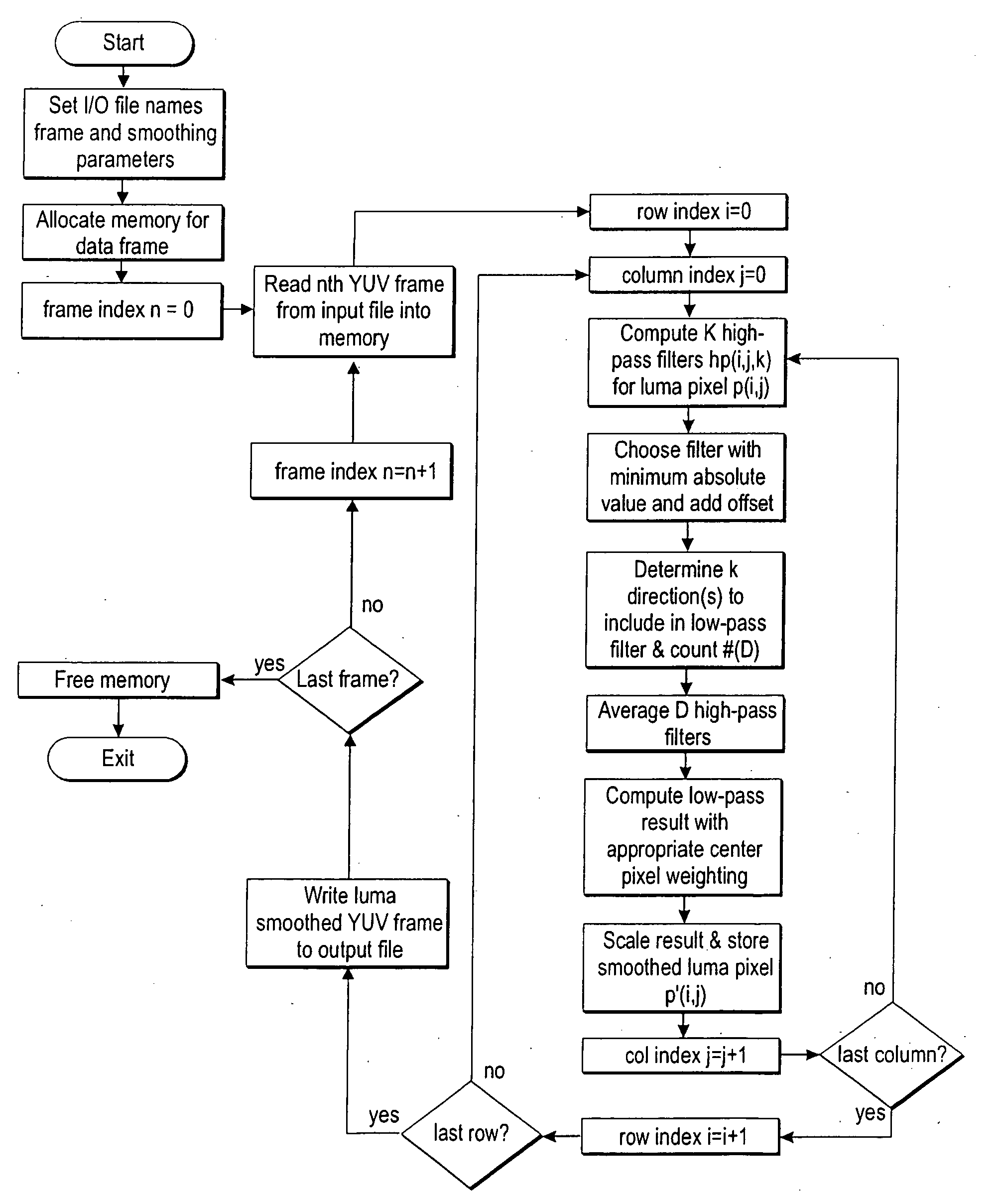
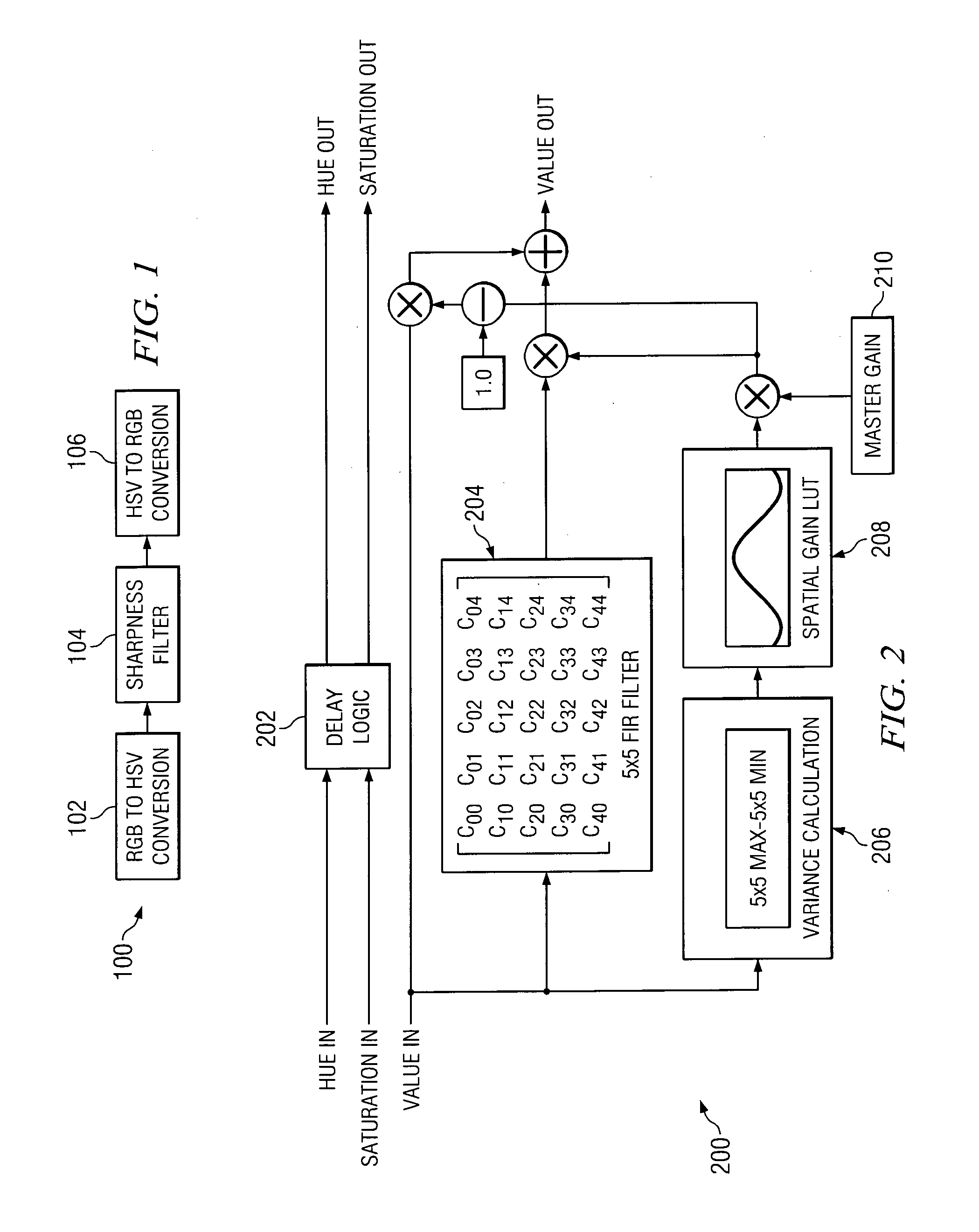
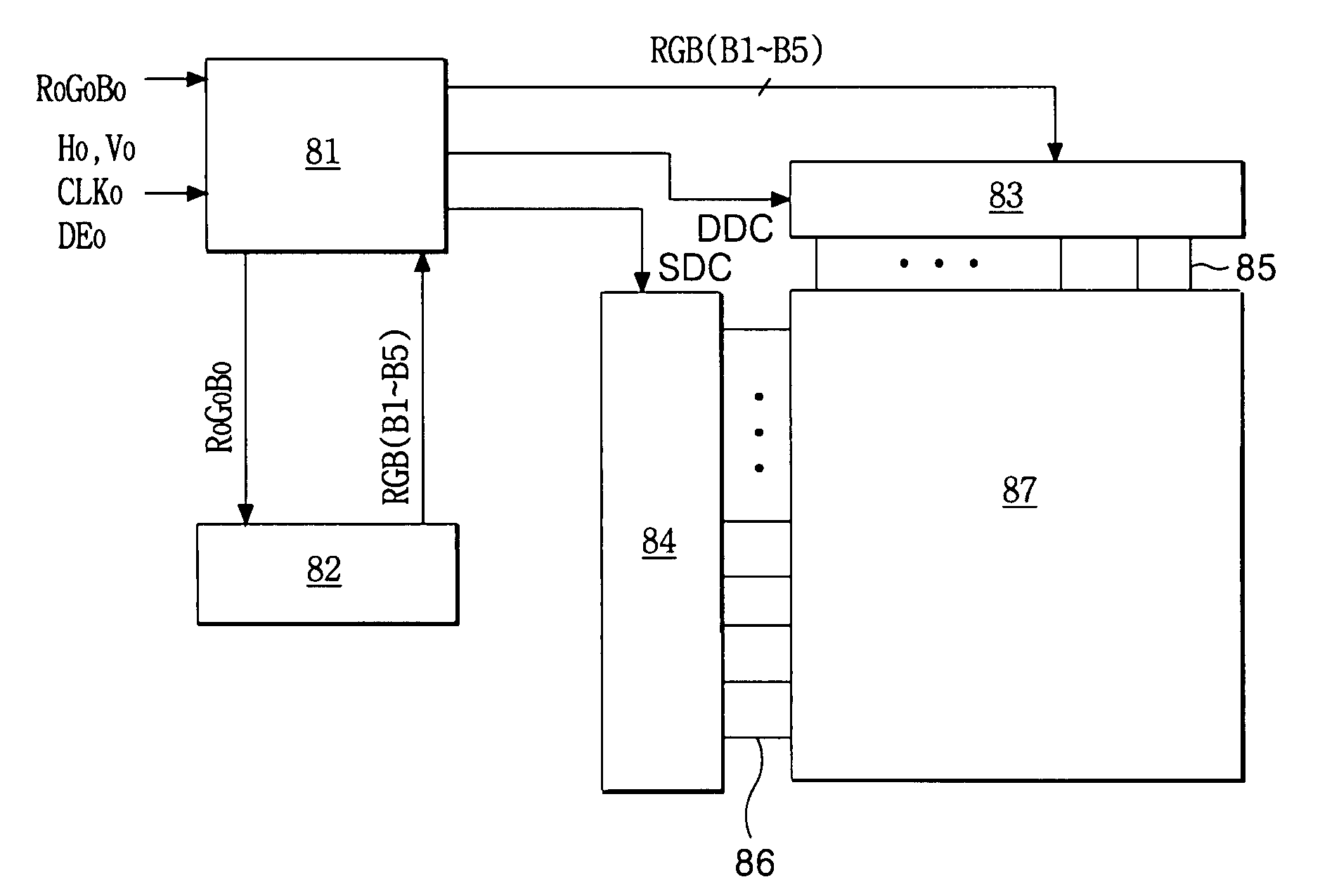
Directional spatial video noise reduction
InactiveUS20050135700A1Quality improvementLighten the computational burdenImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionSpatial noise
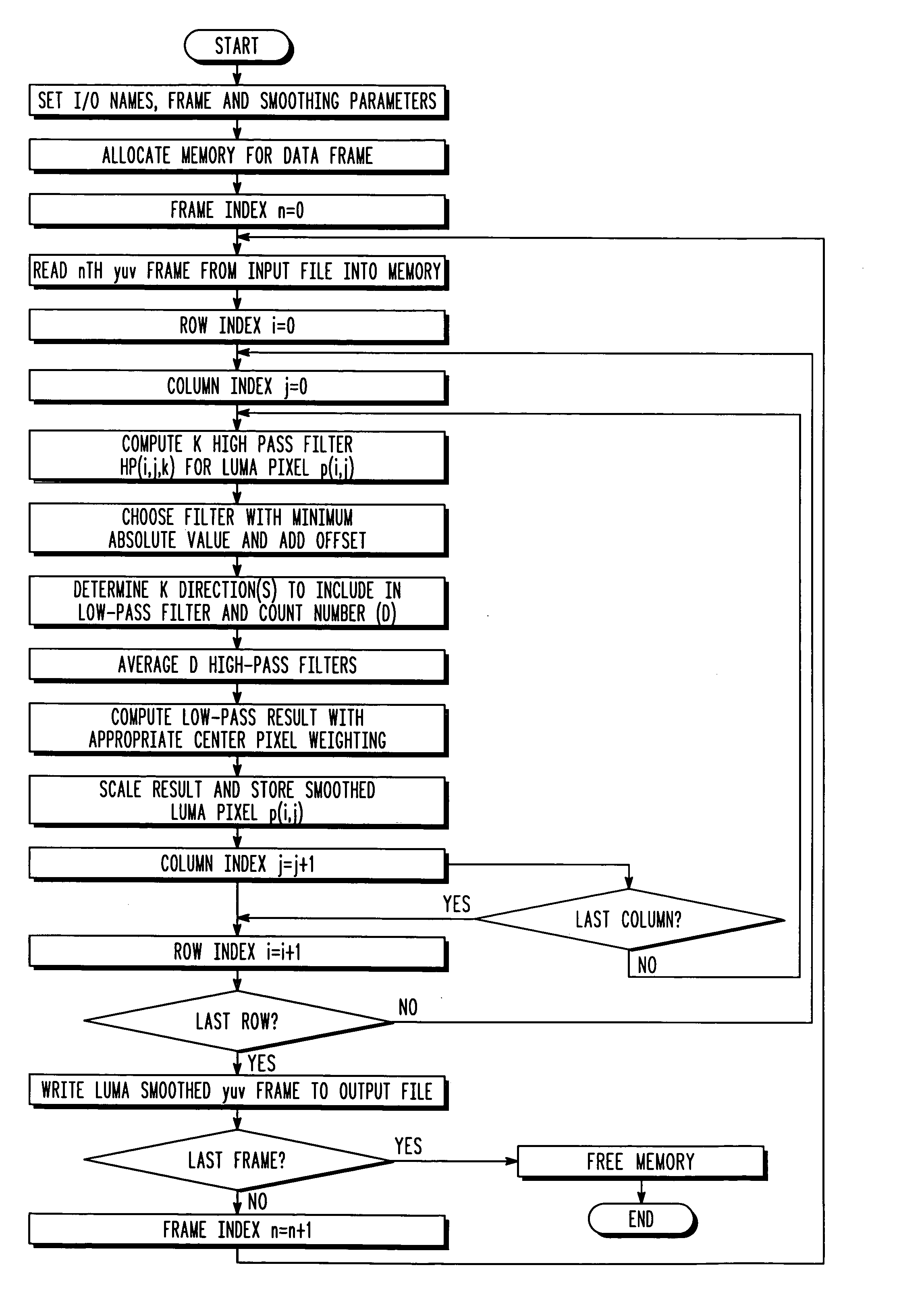
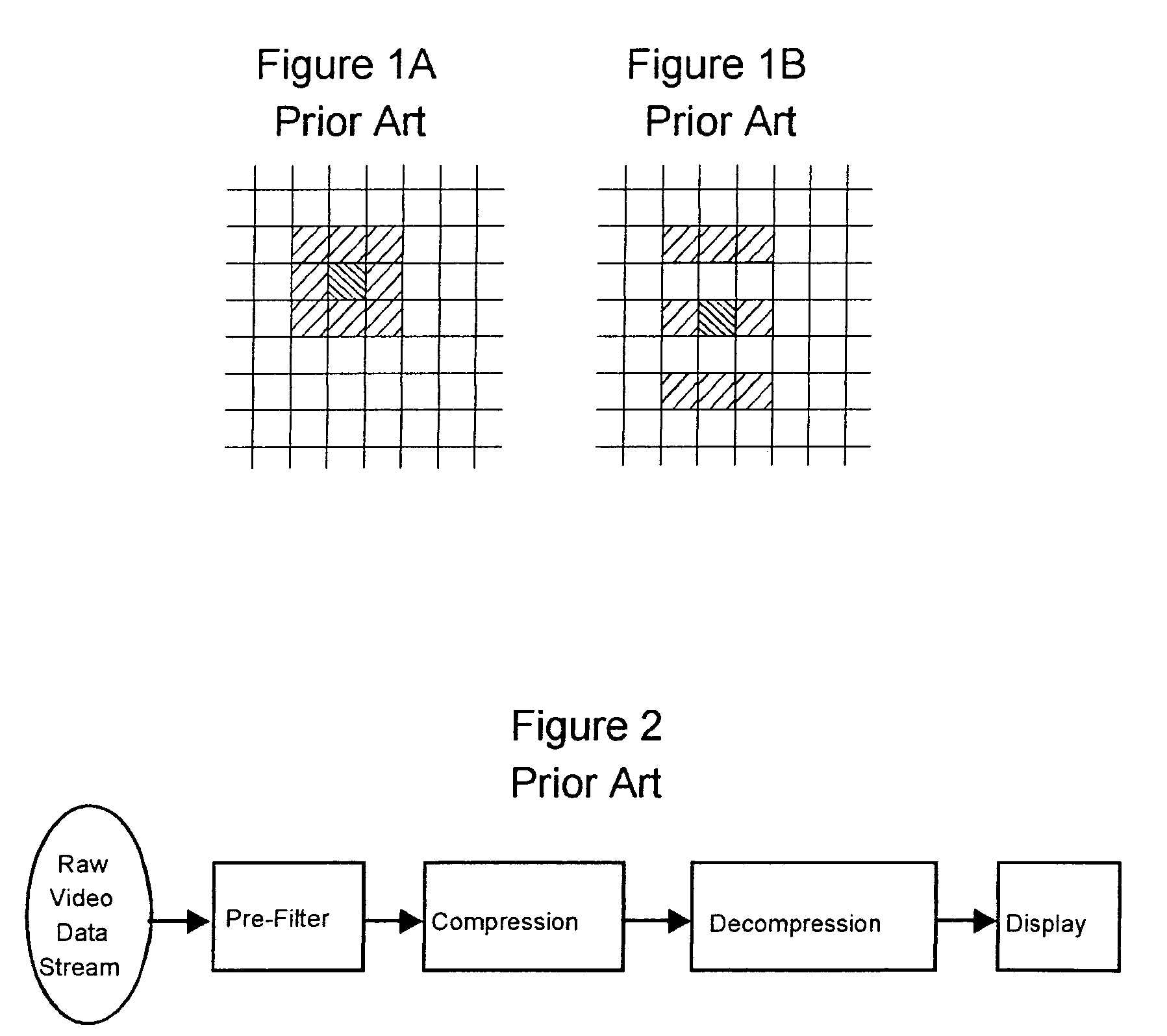
A method of reducing spatial noise in an image. Low-pass (smoothing) filters are calculated simultaneously from three successive image rows. Three blocks (m1, m2, m3) are associated with the three successive image rows, and the blocks are processed in row-major order. This implementation is applicable to both luminance and chrominance. The number of smoothing parameters is reduced to one. The technique is applicable to both luminance and chrominance. Directional mapping is used. Extension of the technique to spatial filtering using a 5×5 neighborhood (using five successive image rows) is described. Embodiments of the method using the MMX instruction set are described.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Directional spatial video noise reduction
InactiveUS7437013B2Quality improvementLighten the computational burdenImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionSpatial noise
A method of reducing spatial noise in an image. Low-pass (smoothing) filters are calculated simultaneously from three successive image rows. Three blocks (m1, m2, m3) are associated with the three successive image rows, and the blocks are processed in row-major order. This implementation is applicable to both luminance and chrominance. The number of smoothing parameters is reduced to one. The technique is applicable to both luminance and chrominance. Directional mapping is used. Extension of the technique to spatial filtering using a 5×5 neighborhood (using five successive image rows) is described. Embodiments of the method using the MMX instruction set are described.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
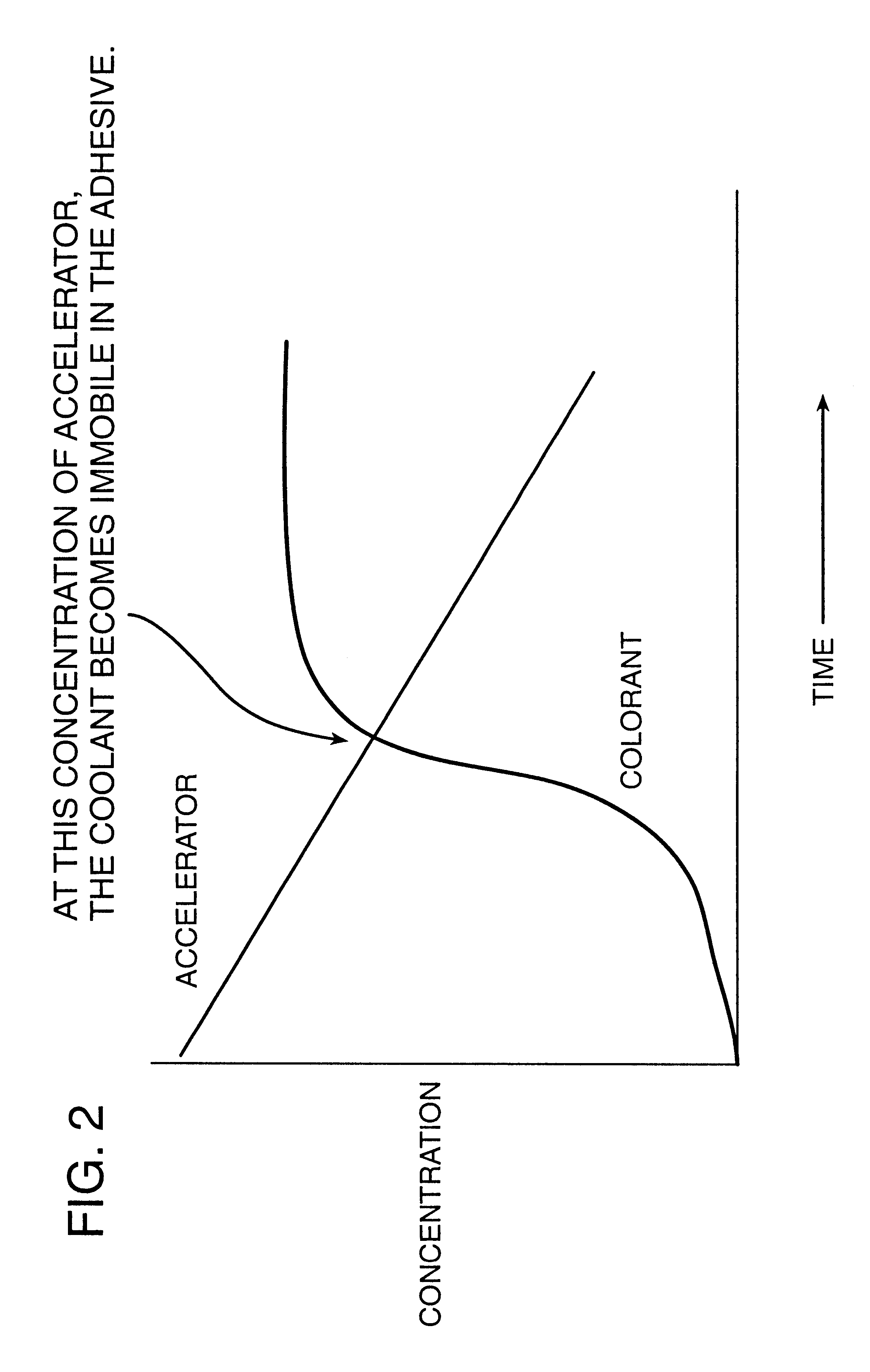
Fixating image in migrating dye indicator
InactiveUS6295252B1Minimize blurringInhibit migrationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsFrequency stabilisation mechanismChemistry
A migrating dye indicator that includes a display layer and a base substrate layer. An adhesive layer is on one surface of the display layer for adhesively attaching the display layer to the base layer. The base layer includes a migrating dye capable of migrating through the adhesive layer to the display layer when the adhesive layer is placed in contact therewith. The adhesive layer contains an accelerator for enhancing the migration of the dye through the adhesive layer. The base layer contains a means for absorbing the accelerator into the base layer.
Owner:BRADY WORLDWIDE INC
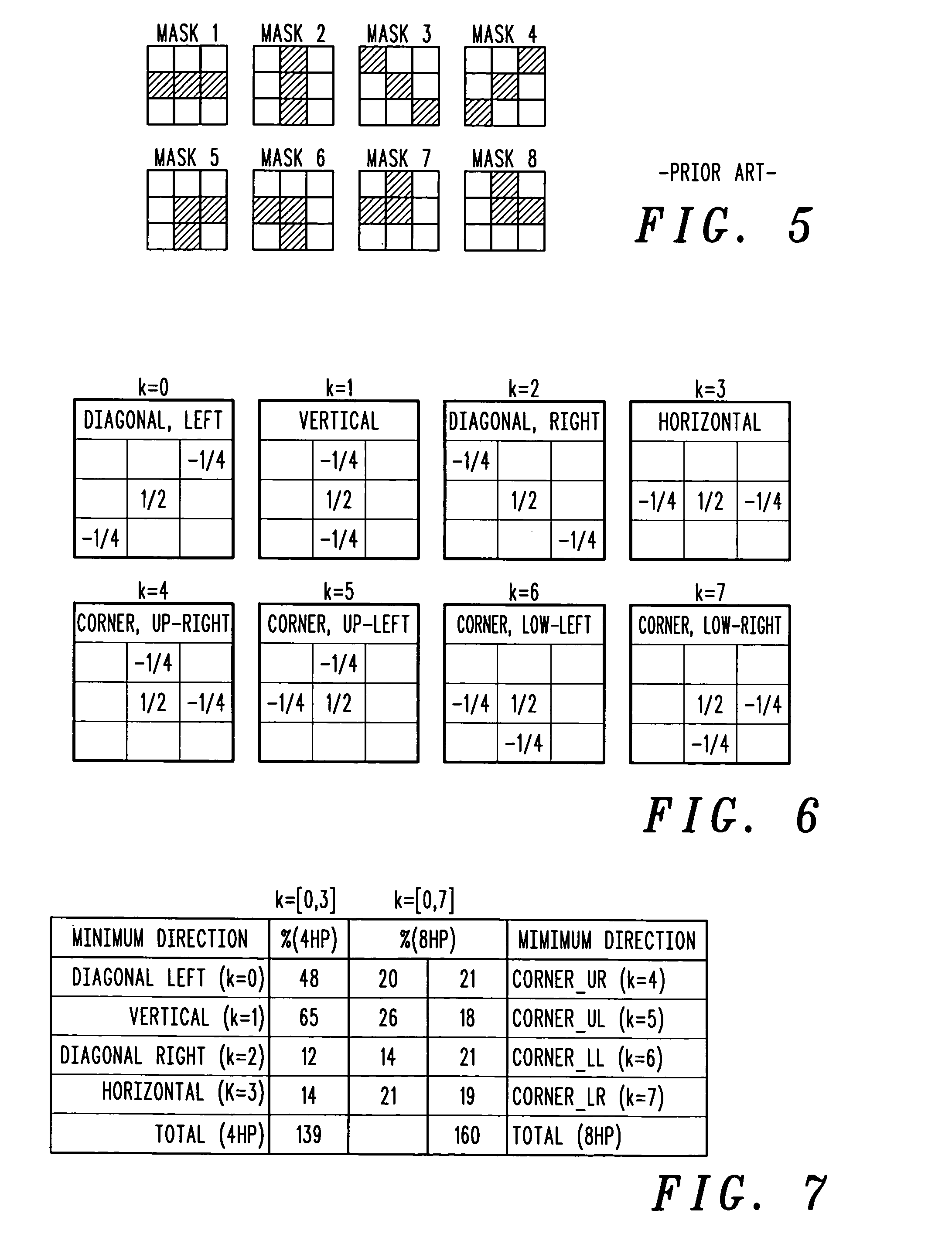
Directional video filters for locally adaptive spatial noise reduction
ActiveUS20050135699A1Improves compression qualityReduces computational burdenImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSelf adaptiveHigh-pass filter
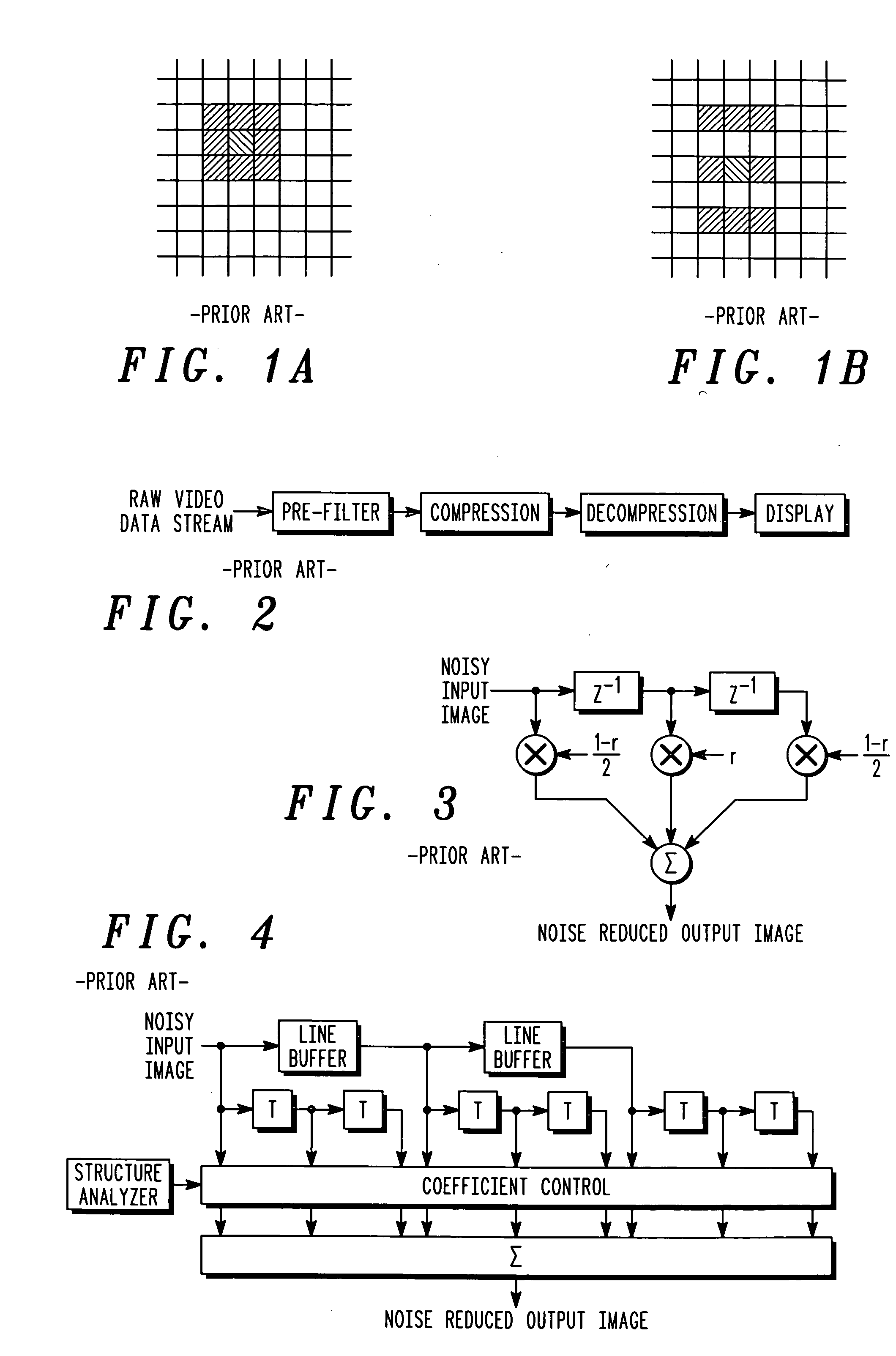
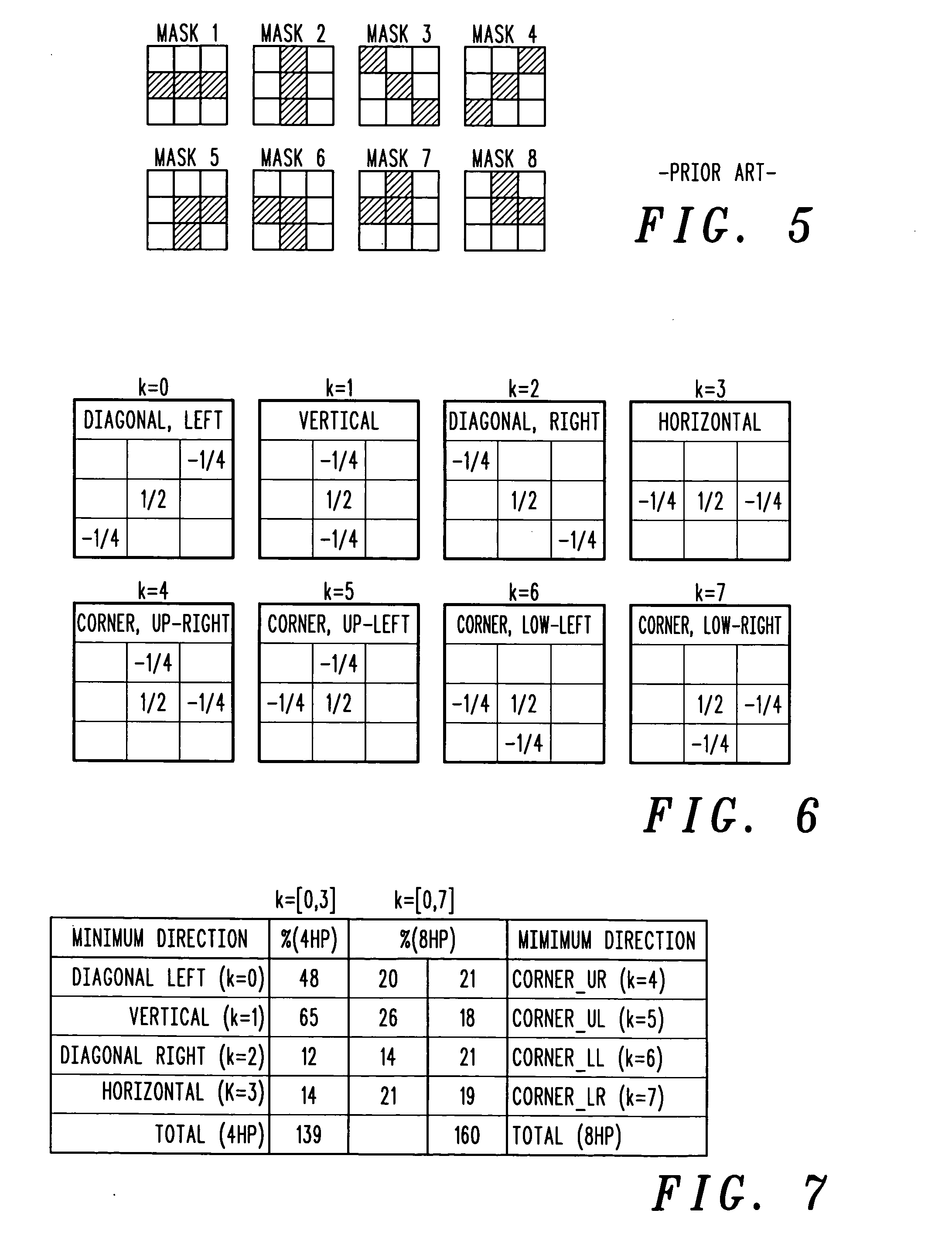
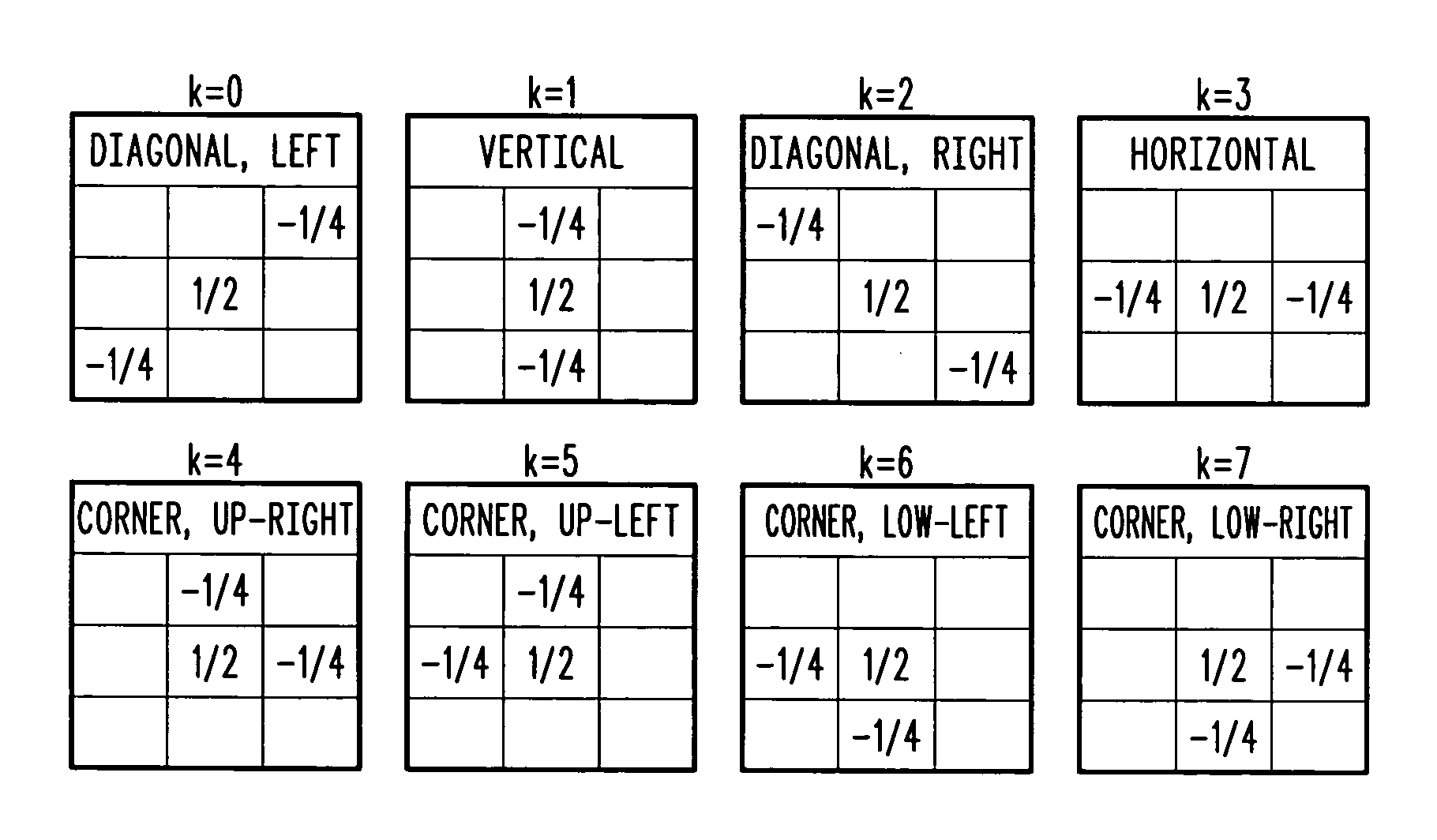
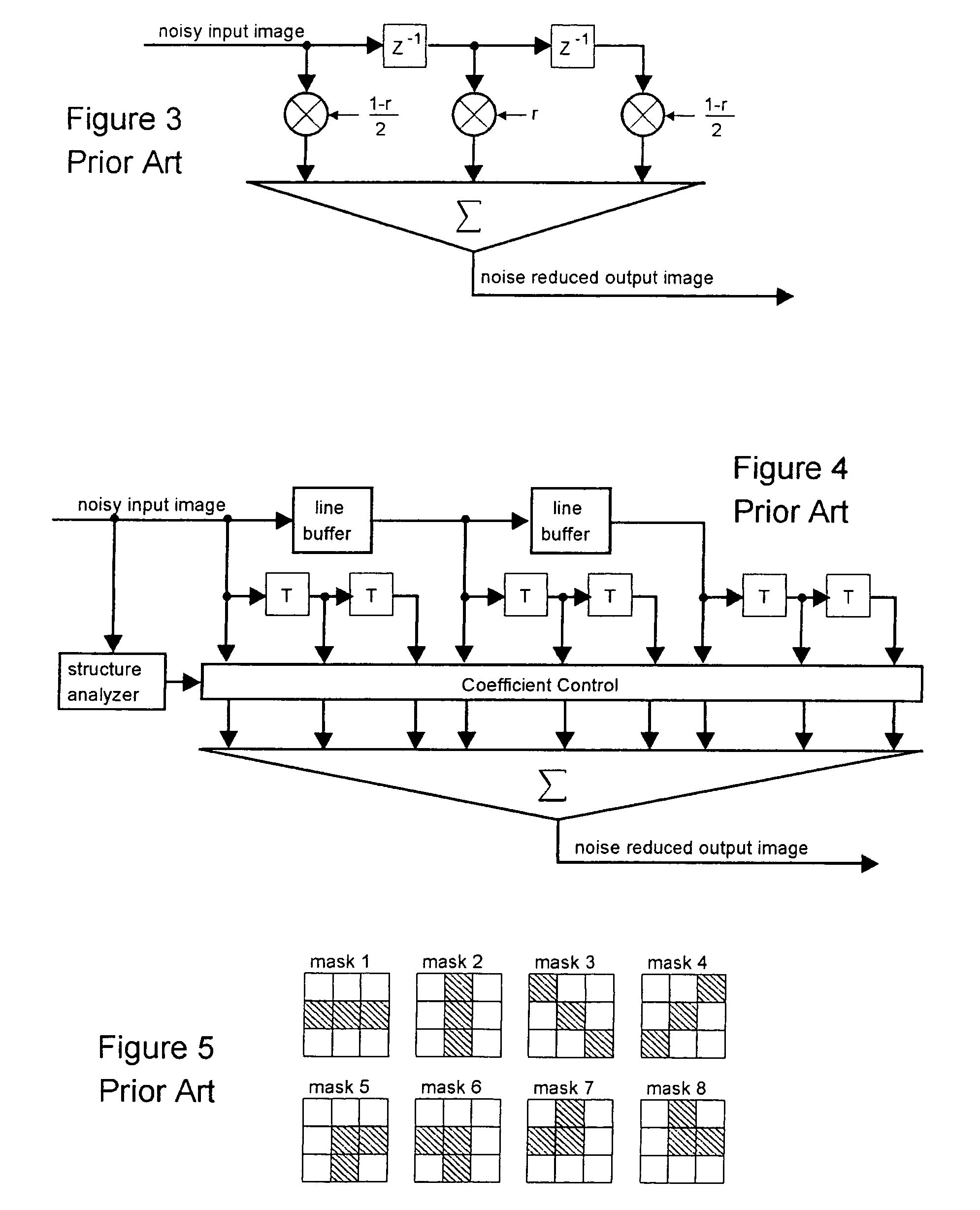
Spatial noise is reduced in an image having a plurality of pixels by detecting object boundaries and unstructured areas in the image and applying 3-tap high pass filters to each pixel in the image in at least four, but less than eight directions to determine the best direction for local low pass filtering. Low pass filtering is applied only along object boundaries and unstructured areas within the image so as to minimize the tendency to blur image edges. Using only four high pass filters to locate horizontal, vertical and diagonal image edges passing through the center of a 3×3 pixel array provides good results.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Sensor aided video stabilization
InactiveUS20130107066A1Eliminate unintentional tremorEliminate shakingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsGyroscopeImaging processing
Techniques described herein provide a method for improved image and video stabilization using inertial sensors. Gyroscopes, accelerometers and magnetometers are examples of such inertial sensors. The movement of the camera causes shifts in the image captured. Image processing techniques may be used to track the shift in the image on a frame-by-frame basis. The movement of the camera may be tracked using inertial sensors. By calculating the degree of similarity between the image shift as predicted by image processing techniques with shift of the device estimated using one or more inertial sensor, the device may estimate the portions of the image that are stationary and those that are moving. Stationary portions of the image may be used to transform and align the images. For video stabilization, the realigned images may be combined to generate the video. For image stabilization, the realigned images may be either added or averaged to generate the de-blurred image.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
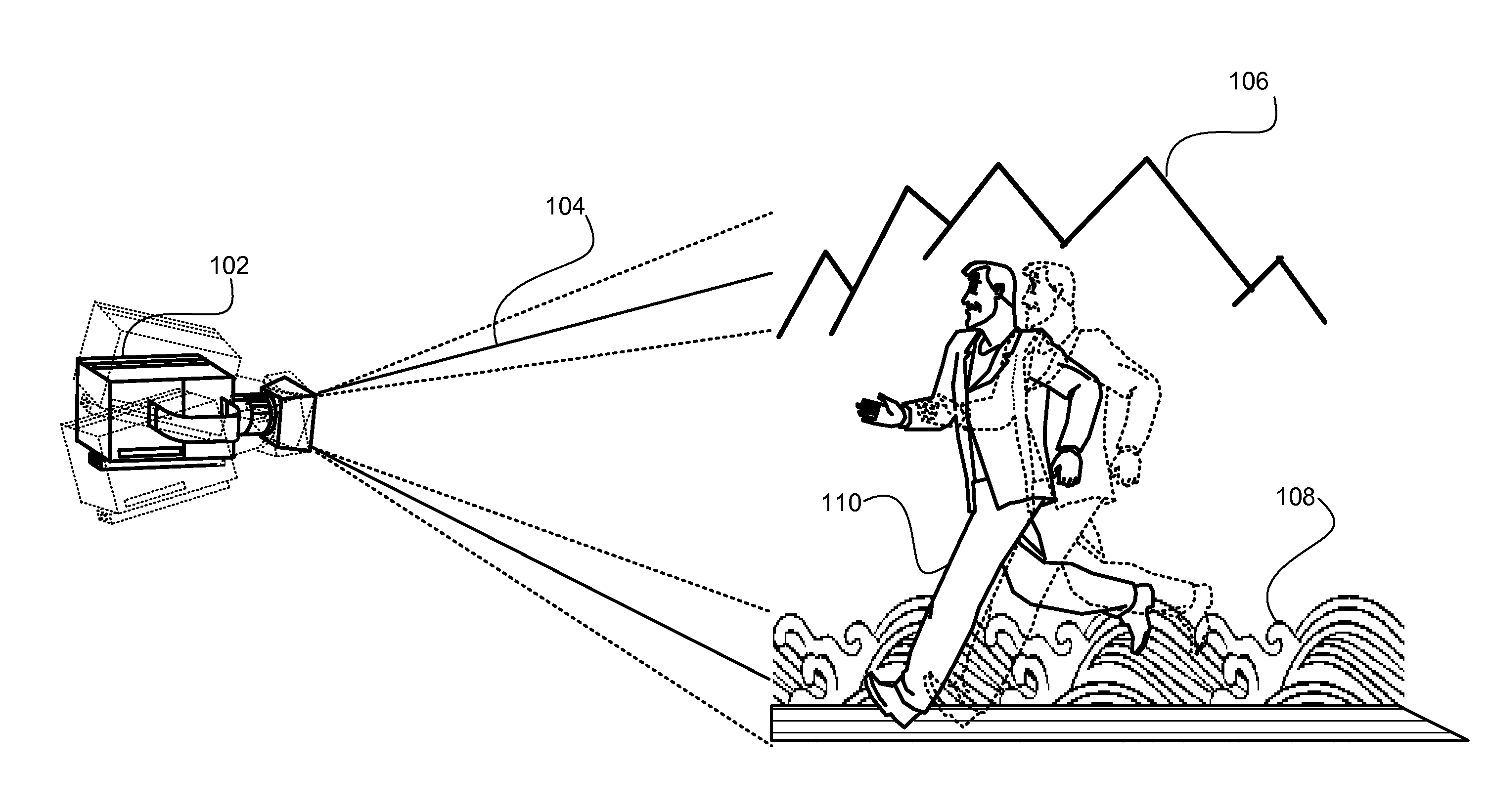
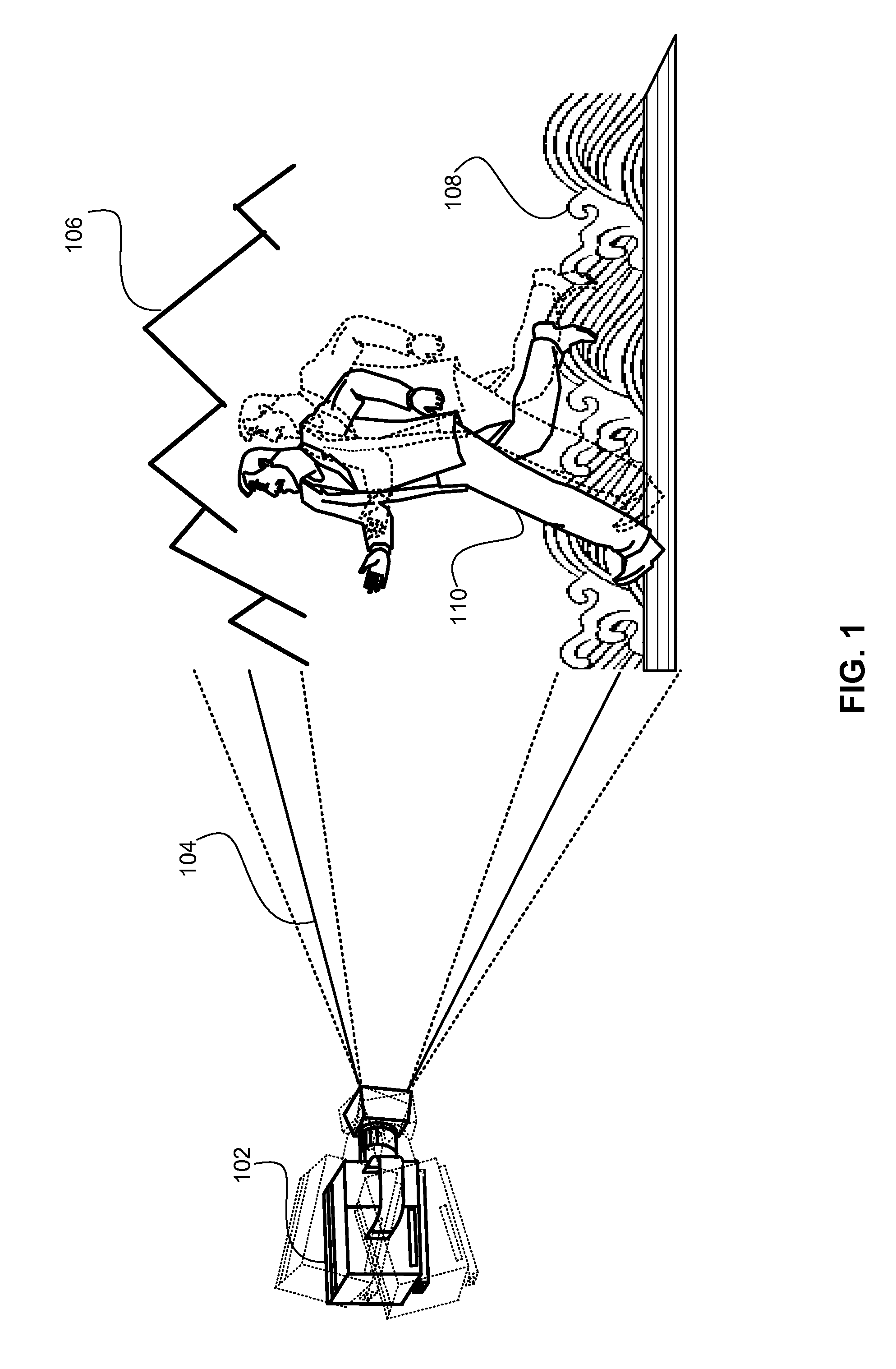
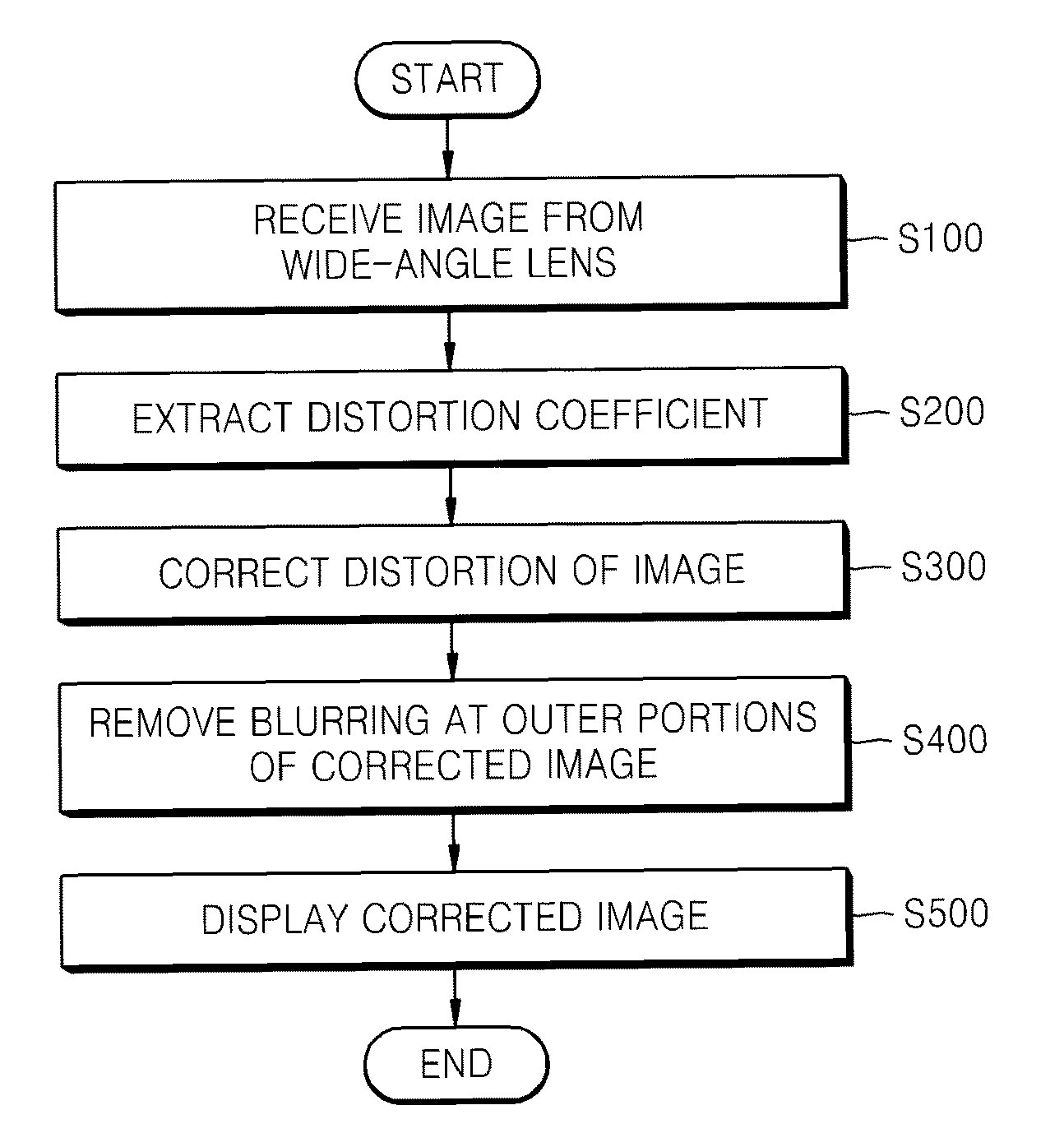
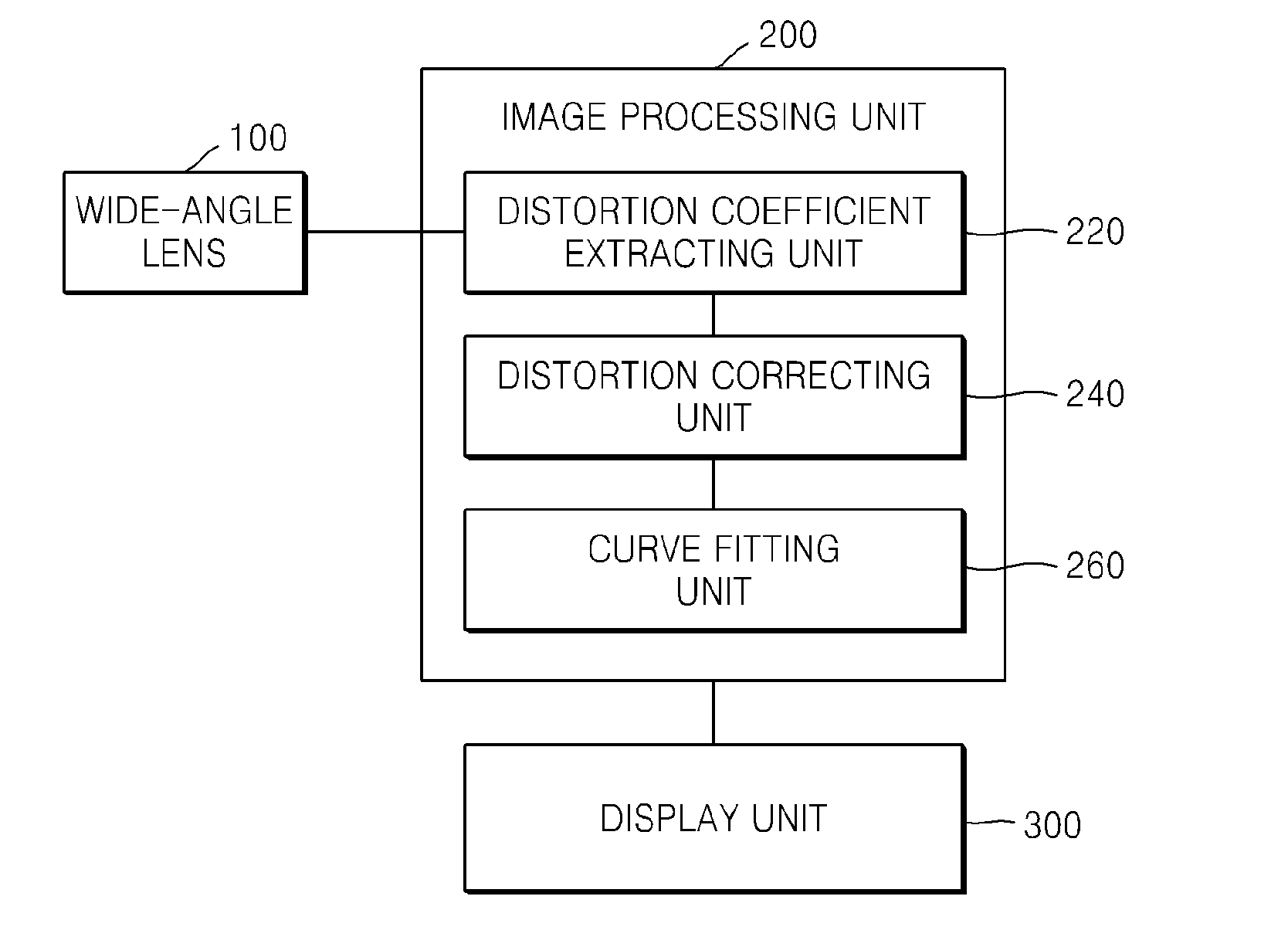
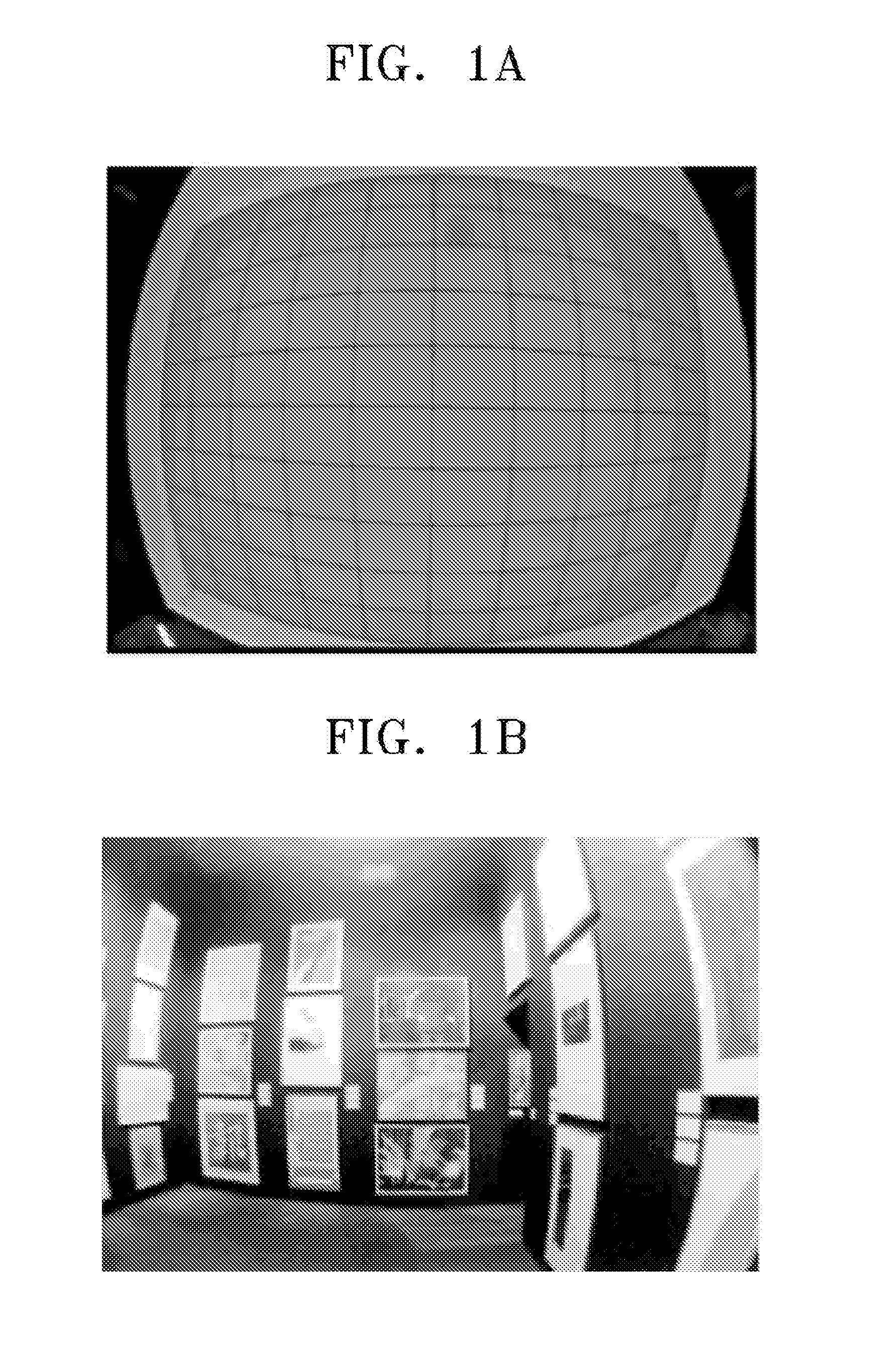
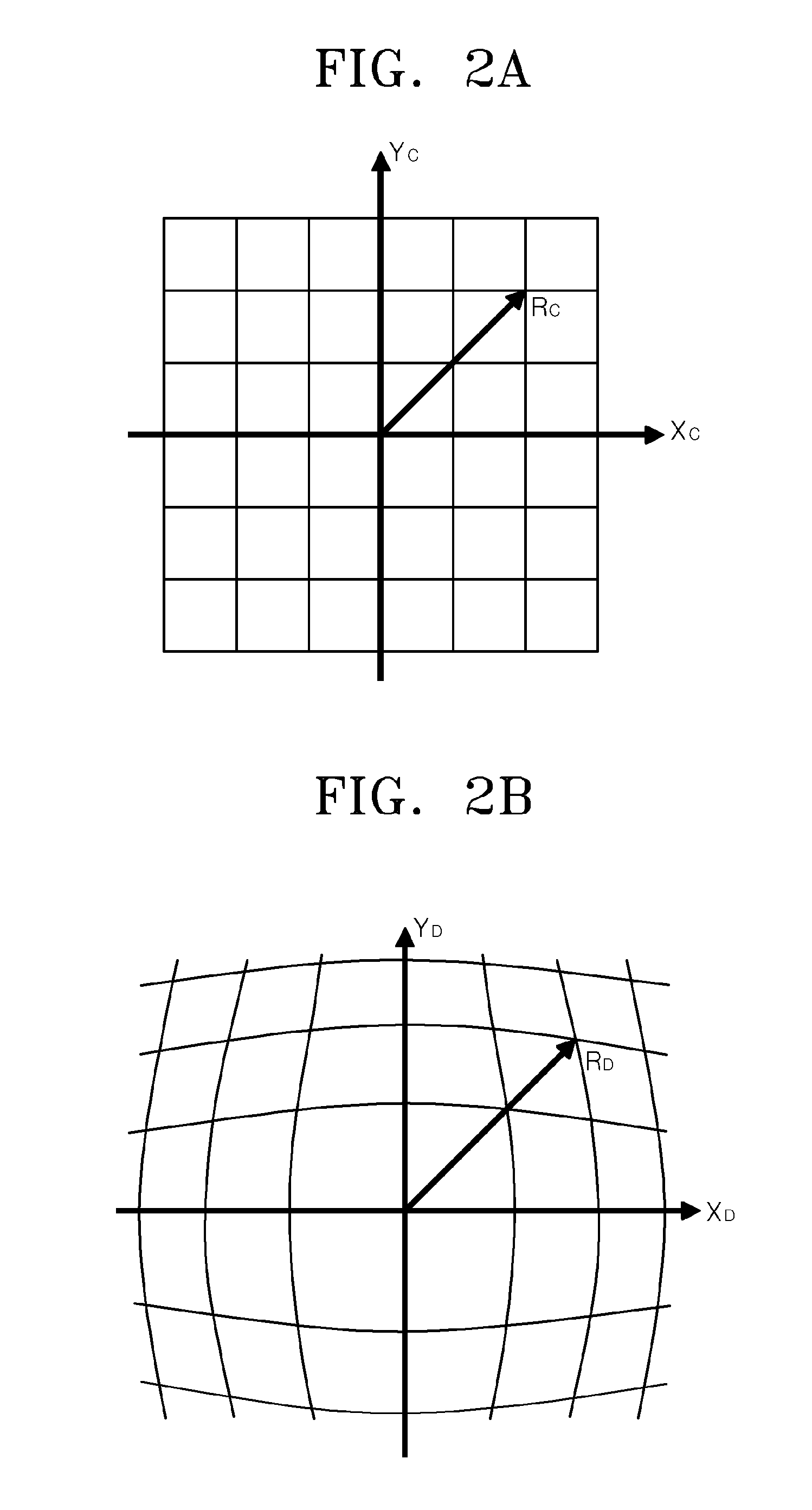
Method of correcting image distortion and apparatus for processing image using the method
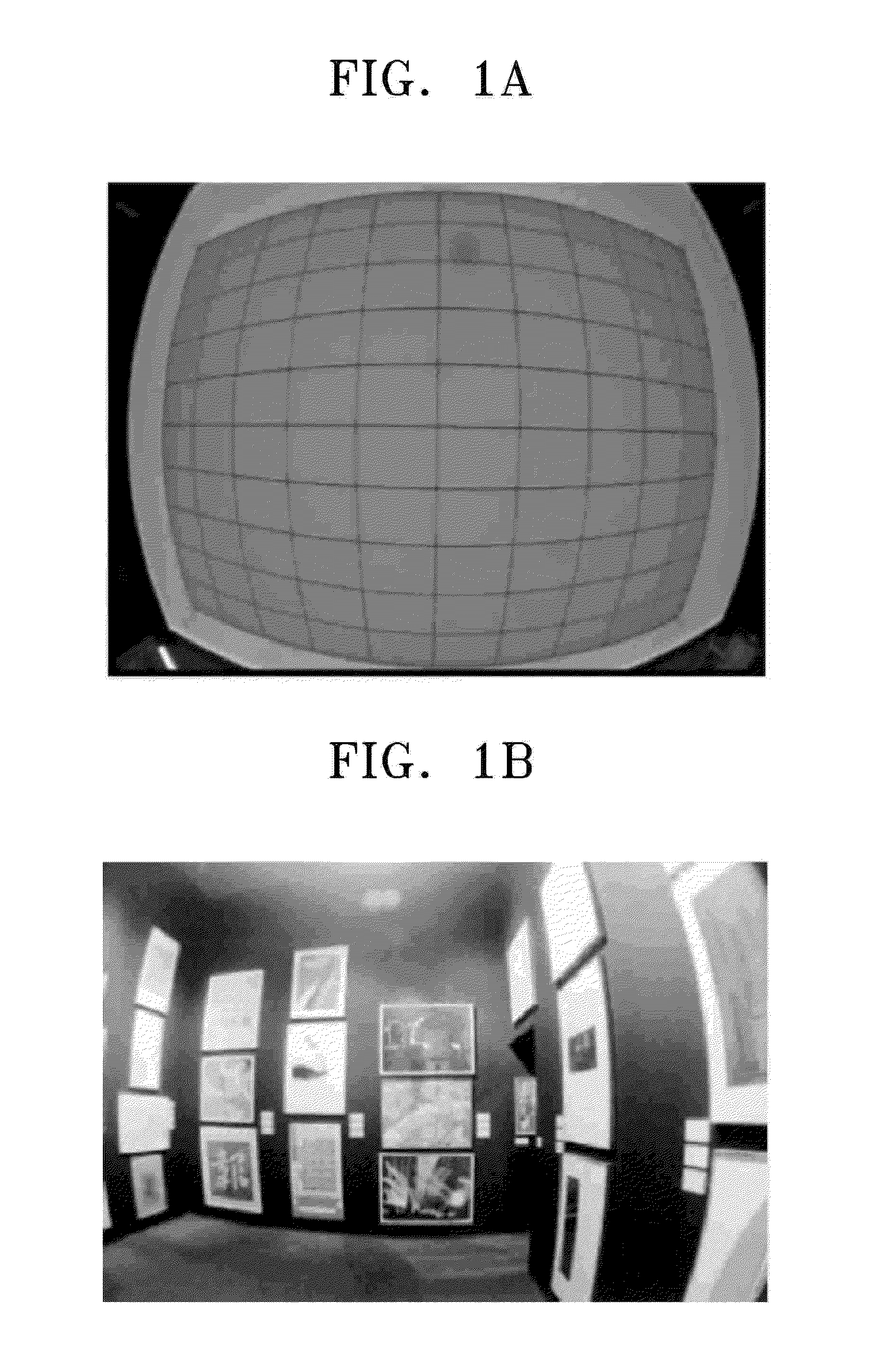
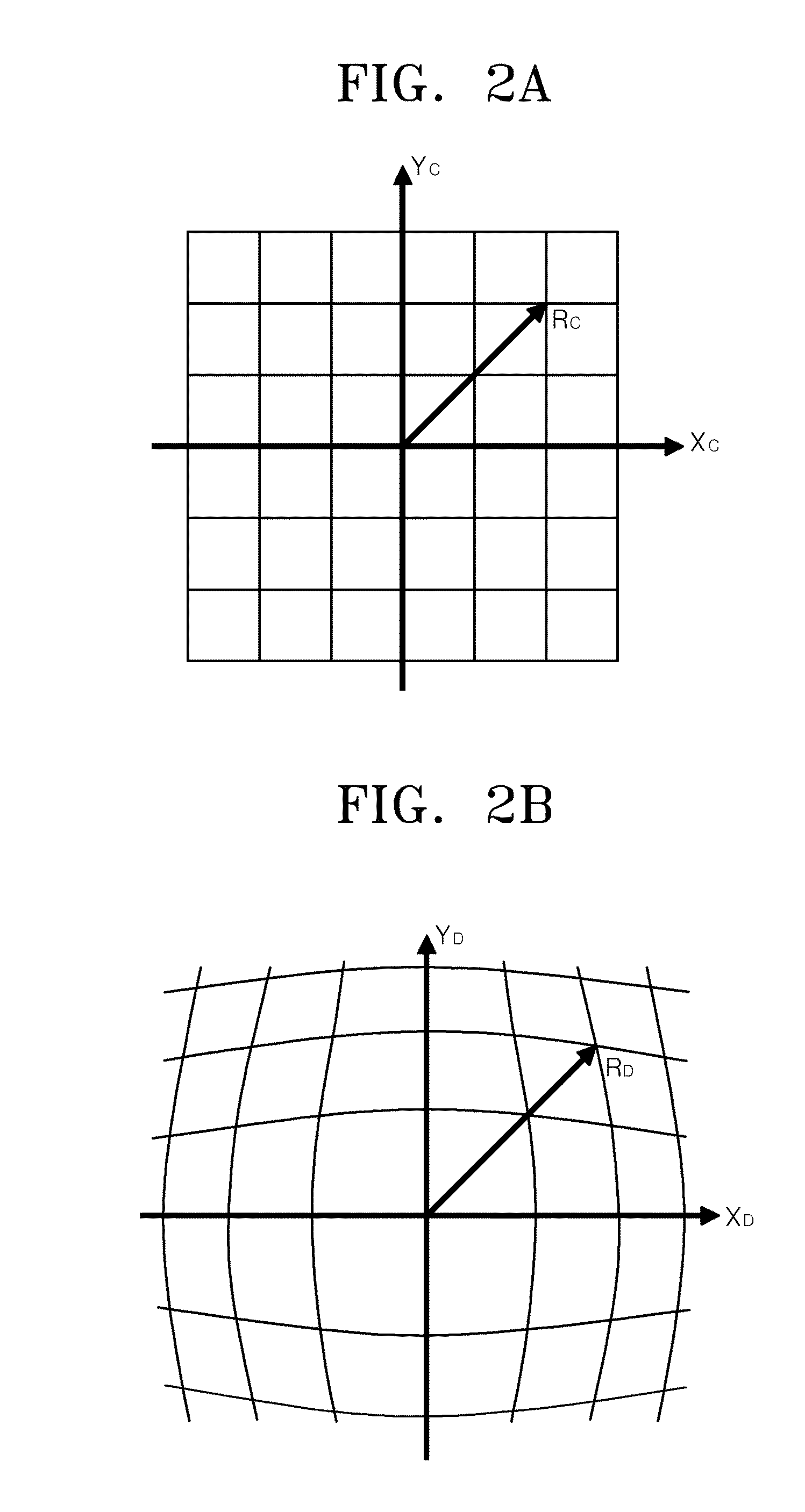
InactiveUS8000559B2Reduce image quality degradationOvercome disadvantagesTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingDistortion
A method of correcting image distortion and an apparatus for processing an image using the method are provided, where the method can overcome the disadvantages of the conventional methods of correcting lens distortion and can minimize image quality degradation at outer portions,. The method includes: receiving an image from a wide-angle lens; extracting a distortion coefficient of the distortion in the image caused by the wide-angle lens; correcting the distortion of the image by using the extracted distortion coefficient; and displaying a corrected image. The apparatus includes: a wide-angle lens for receiving an image; an image processing unit comprising a distortion coefficient extracting unit for extracting a distortion coefficient of distortion in the image caused by the wide-angle lens and a distortion correcting unit for correcting the distortion of the image using the extracted distortion coefficient; and a display unit for displaying a corrected image.
Owner:CORELOGIC
Charged particle beam column
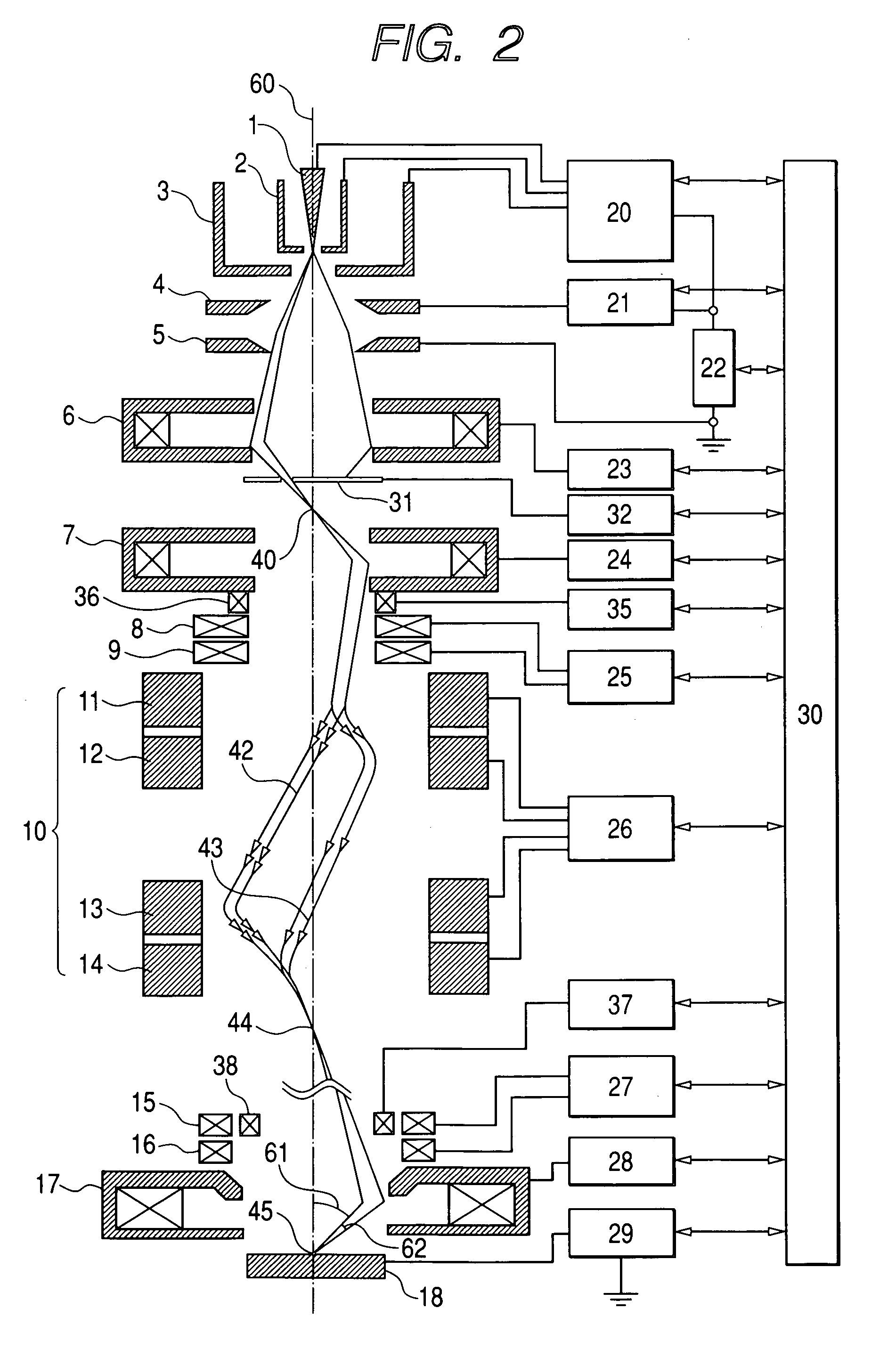
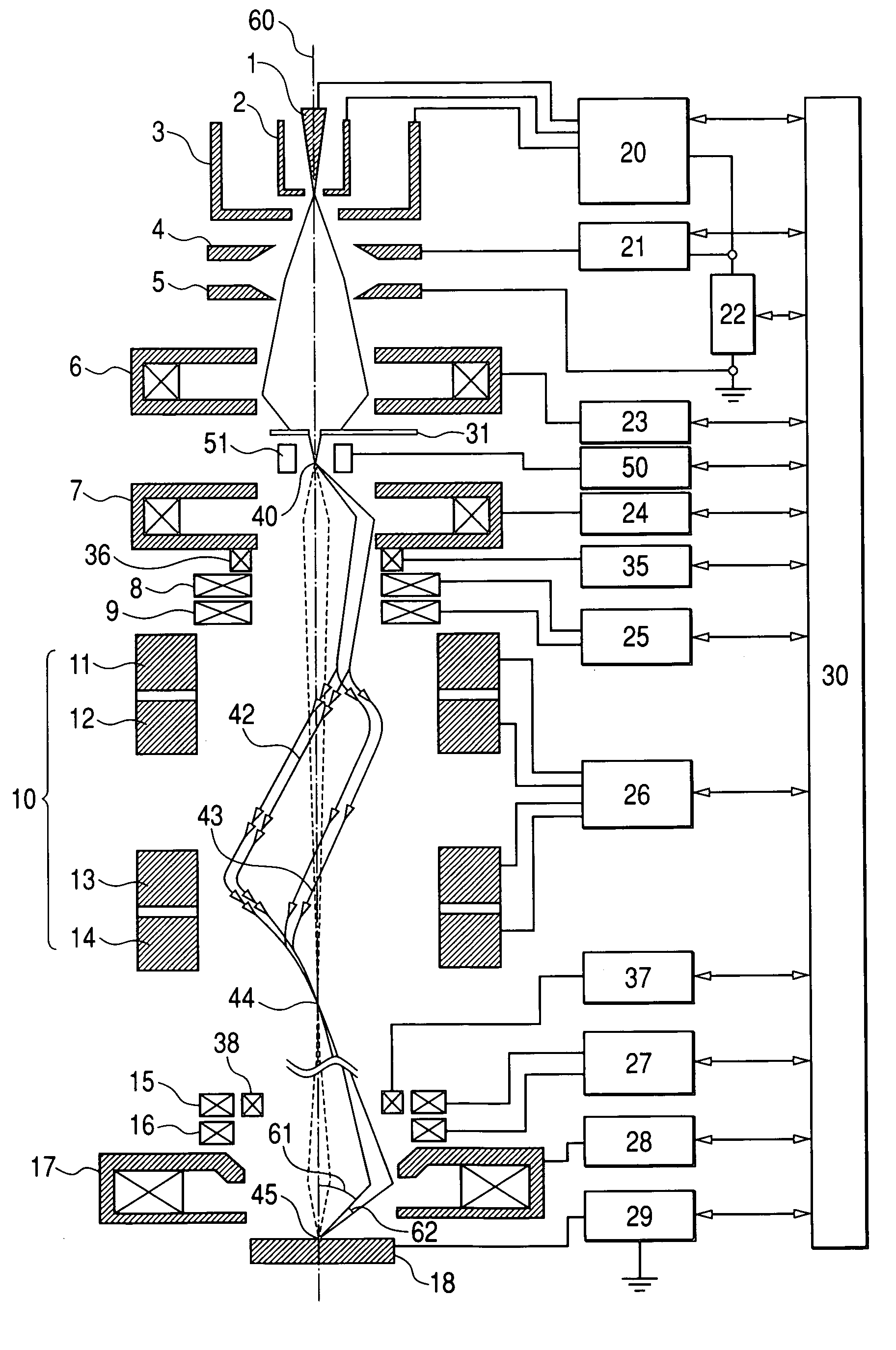
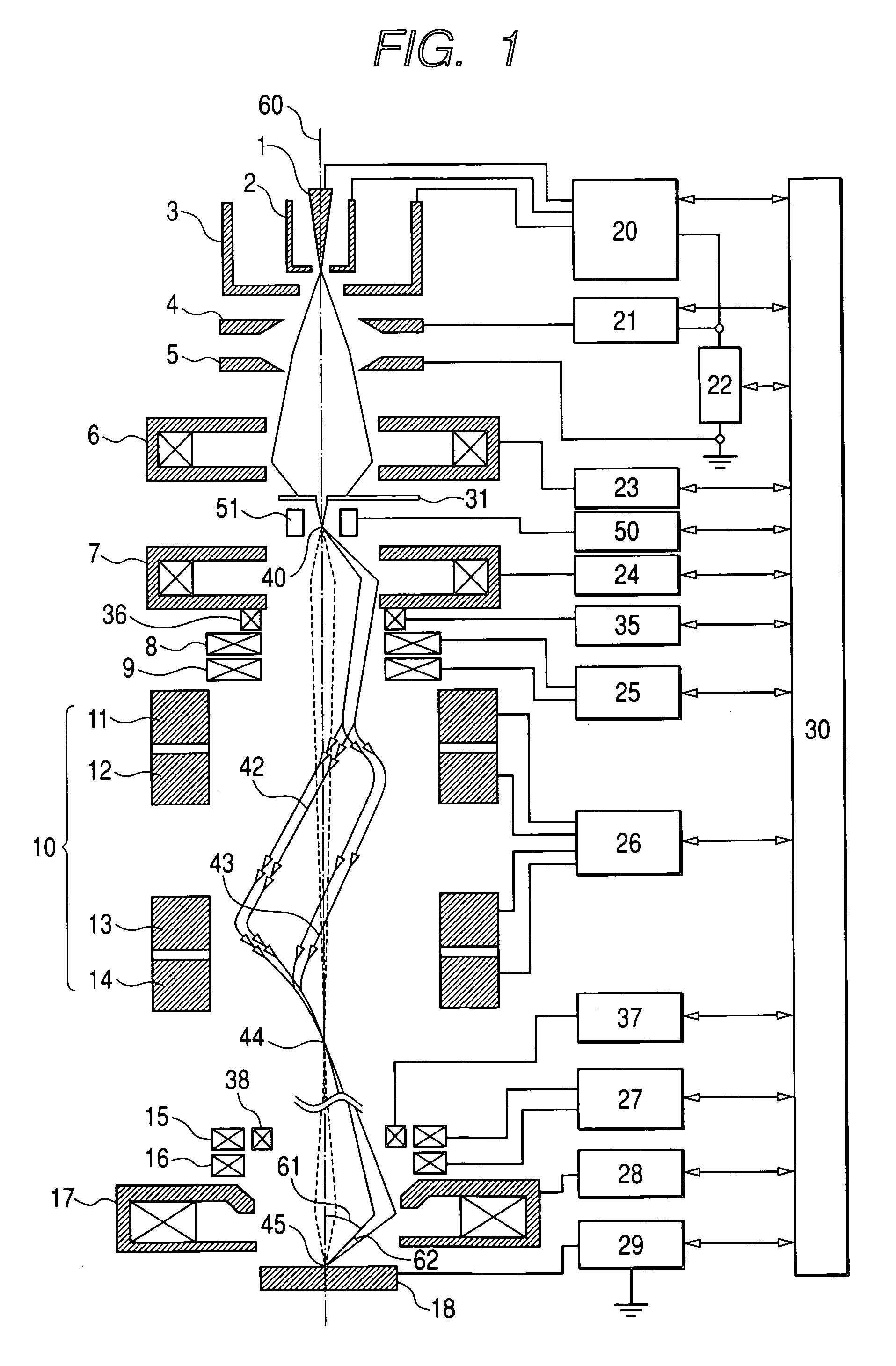
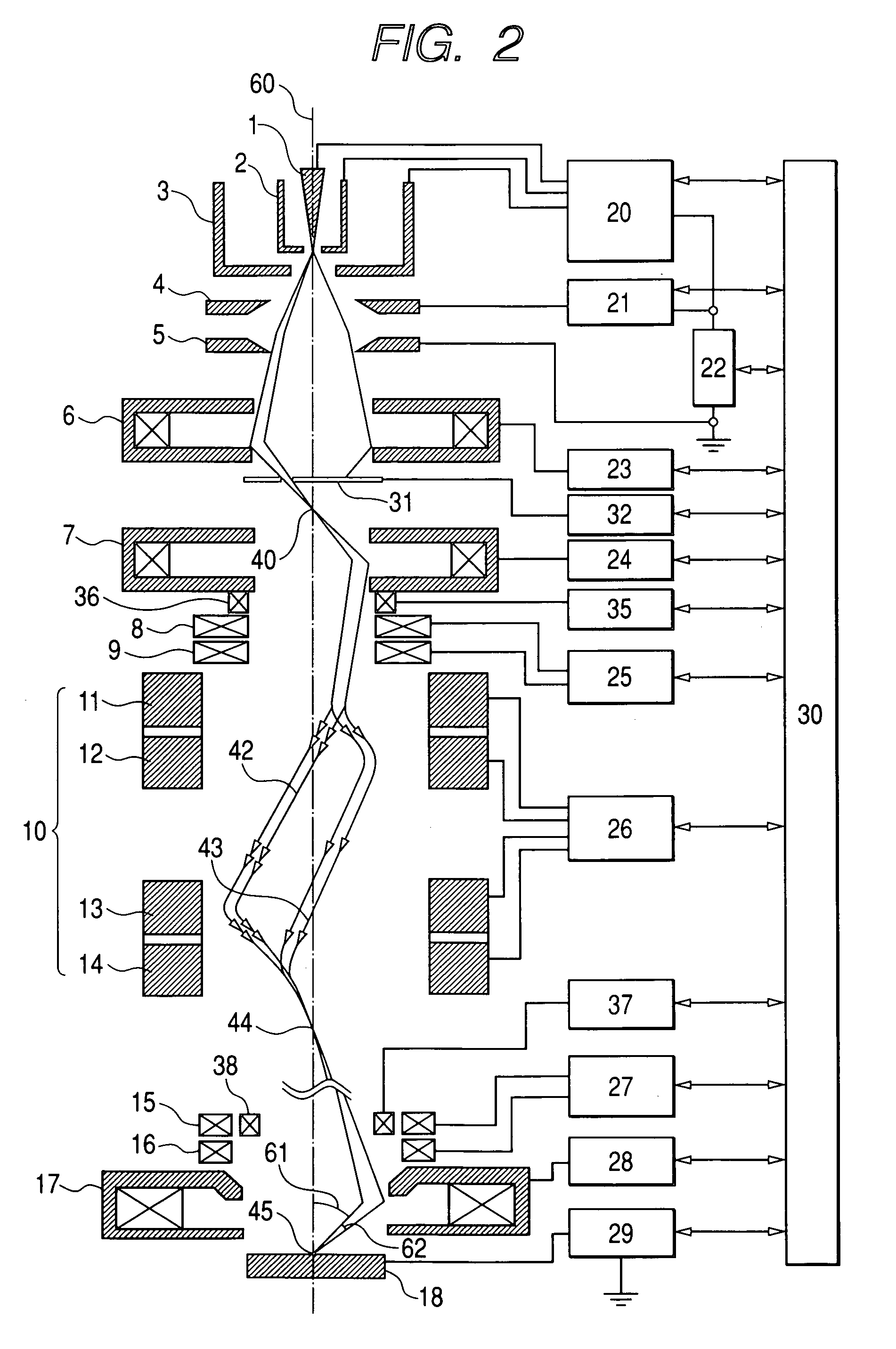
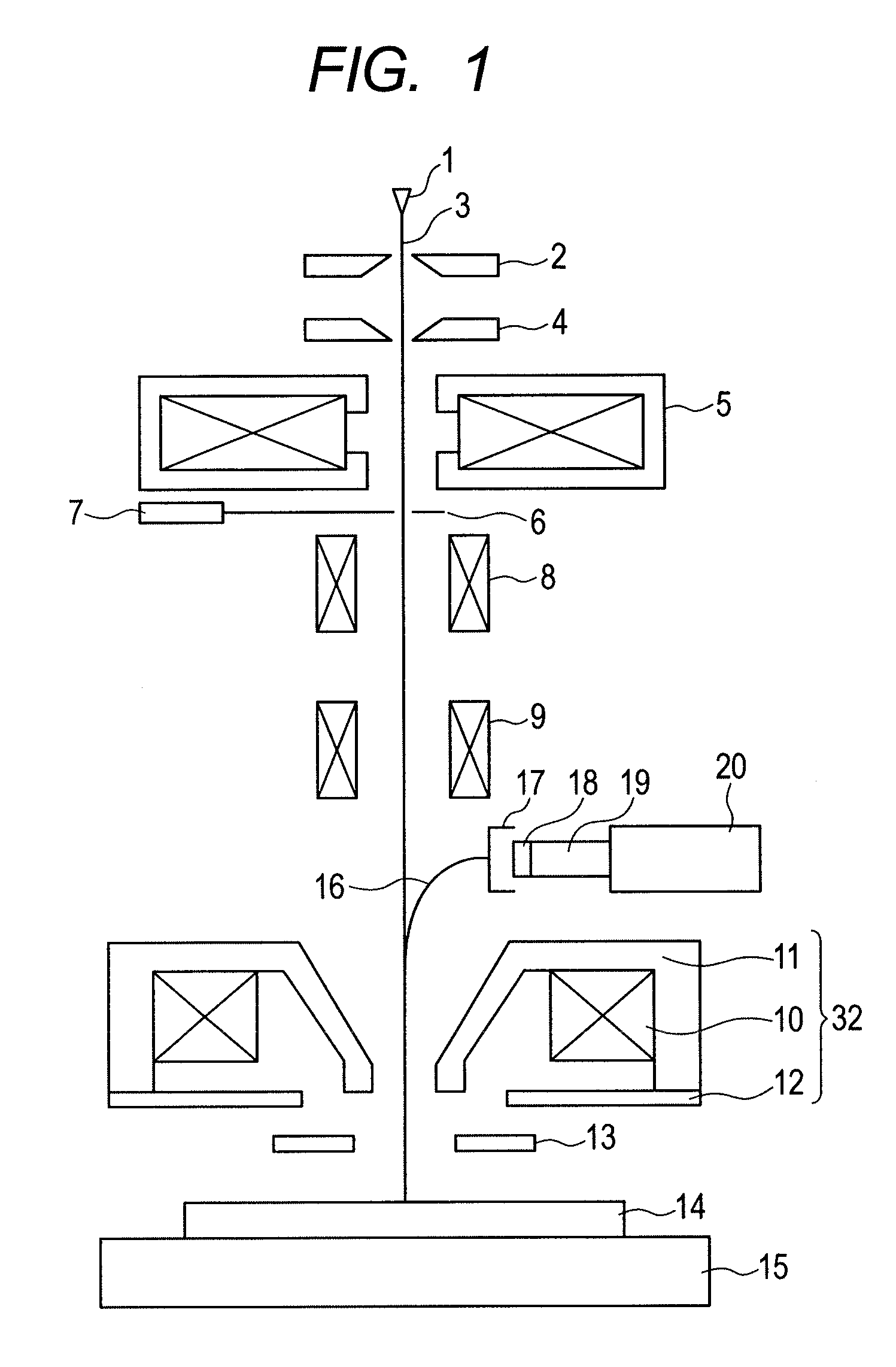
ActiveUS20060033037A1Minimize blurringPrevent degradationThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationOptical axisImage resolution
The present invention provides a charged particle beam column that does not cause displacement of an image or degradation of a resolution of images when a charged particle beam is tilted at a large angle. In the charged particle beam column including an aberration corrector, a deflector is used to control the direction of incidence of the charged particle beam on a second condenser lens but the object point of a condenser lens is not shifted. Consequently, the converging charged particle beam is tilted at a large angle with respect to the surface of a specimen without the necessity of shifting the object point of an objective lens lying on the optical axis of the charged particle beam column. At this time, the aberration corrector prevents a shift of an image or degradation of a resolution derived from the tilt of the charged particle beam.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Charged particle beam column
ActiveUS7223983B2Minimize blurringPrevent degradationThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersObject pointImage resolution
The present invention provides a charged particle beam column that does not cause displacement of an image or degradation of a resolution of images when a charged particle beam is tilted at a large angle. In the charged particle beam column including an aberration corrector, a deflector is used to control the direction of incidence of the charged particle beam on a second condenser lens but the object point of a condenser lens is not shifted. Consequently, the converging charged particle beam is tilted at a large angle with respect to the surface of a specimen without the necessity of shifting the object point of an objective lens lying on the optical axis of the charged particle beam column. At this time, the aberration corrector prevents a shift of an image or degradation of a resolution derived from the tilt of the charged particle beam.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Method of correcting image distortion and apparatus for processing image using the method
InactiveUS20090059041A1Remove jagged-edge artifactMinimize blurringTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingComputer science
A method of correcting image distortion and an apparatus for processing an image using the method are provided, where the method can overcome the disadvantages of the conventional methods of correcting lens distortion and can minimize image quality degradation at outer portions,. The method includes: receiving an image from a wide-angle lens; extracting a distortion coefficient of the distortion in the image caused by the wide-angle lens; correcting the distortion of the image by using the extracted distortion coefficient; and displaying a corrected image. The apparatus includes: a wide-angle lens for receiving an image; an image processing unit comprising a distortion coefficient extracting unit for extracting a distortion coefficient of distortion in the image caused by the wide-angle lens and a distortion correcting unit for correcting the distortion of the image using the extracted distortion coefficient; and a display unit for displaying a corrected image.
Owner:CORELOGIC
Directional video filters for locally adaptive spatial noise reduction
ActiveUS7373013B2Quality improvementReduce spatial noiseTelevision system detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionSpatial noise
Spatial noise is reduced in an image having a plurality of pixels by detecting object boundaries and unstructured areas in the image and applying 3-tap high pass filters to each pixel in the image in at least four, but less than eight directions to determine the best direction for local low pass filtering. Low pass filtering is applied only along object boundaries and unstructured areas within the image so as to minimize the tendency to blur image edges. Using only four high pass filters to locate horizontal, vertical and diagonal image edges passing through the center of a 3×3 pixel array provides good results.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Display and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20070057959A1Minimize blurringIncrease brightnessCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGray levelDisplay device
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
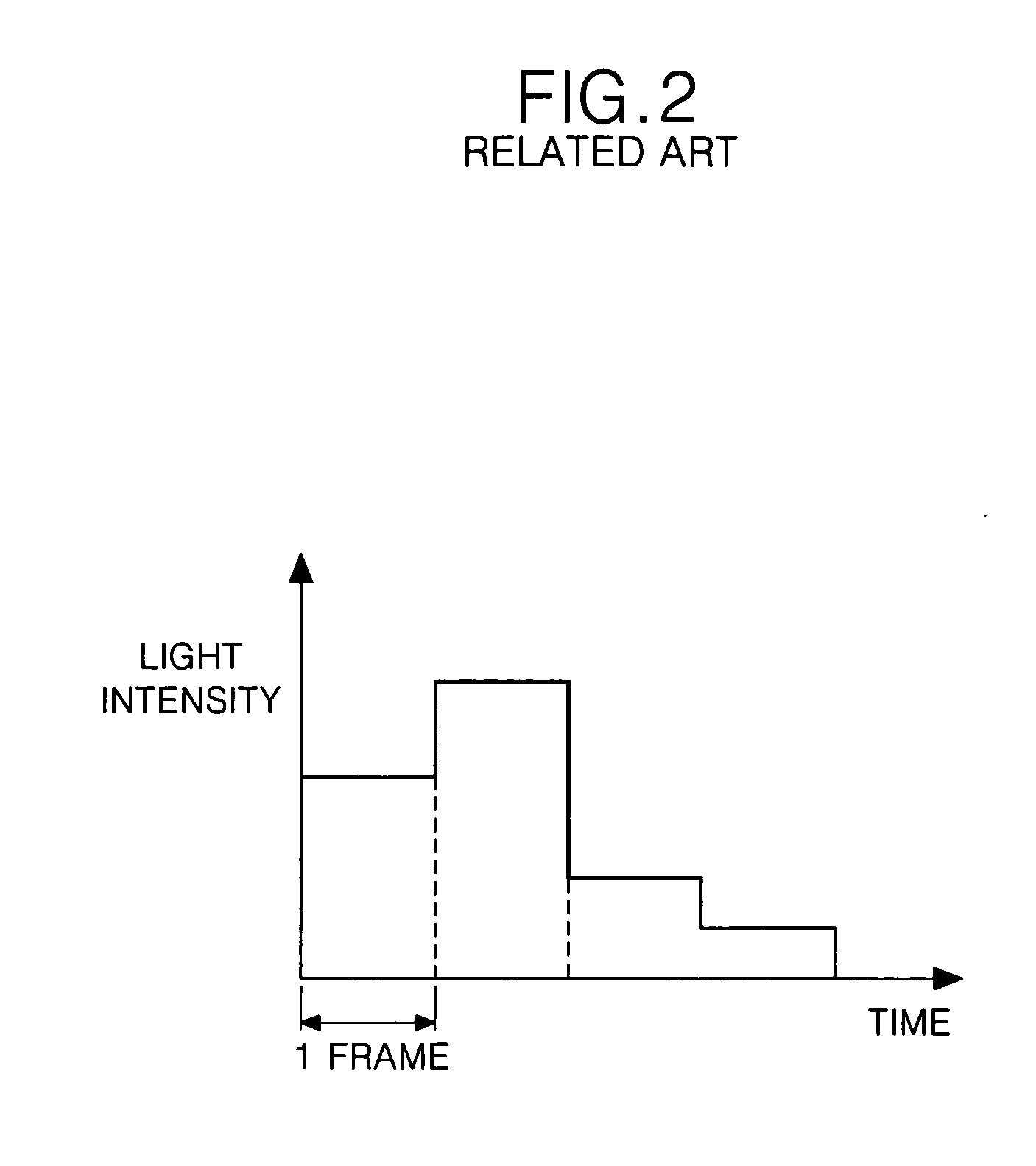
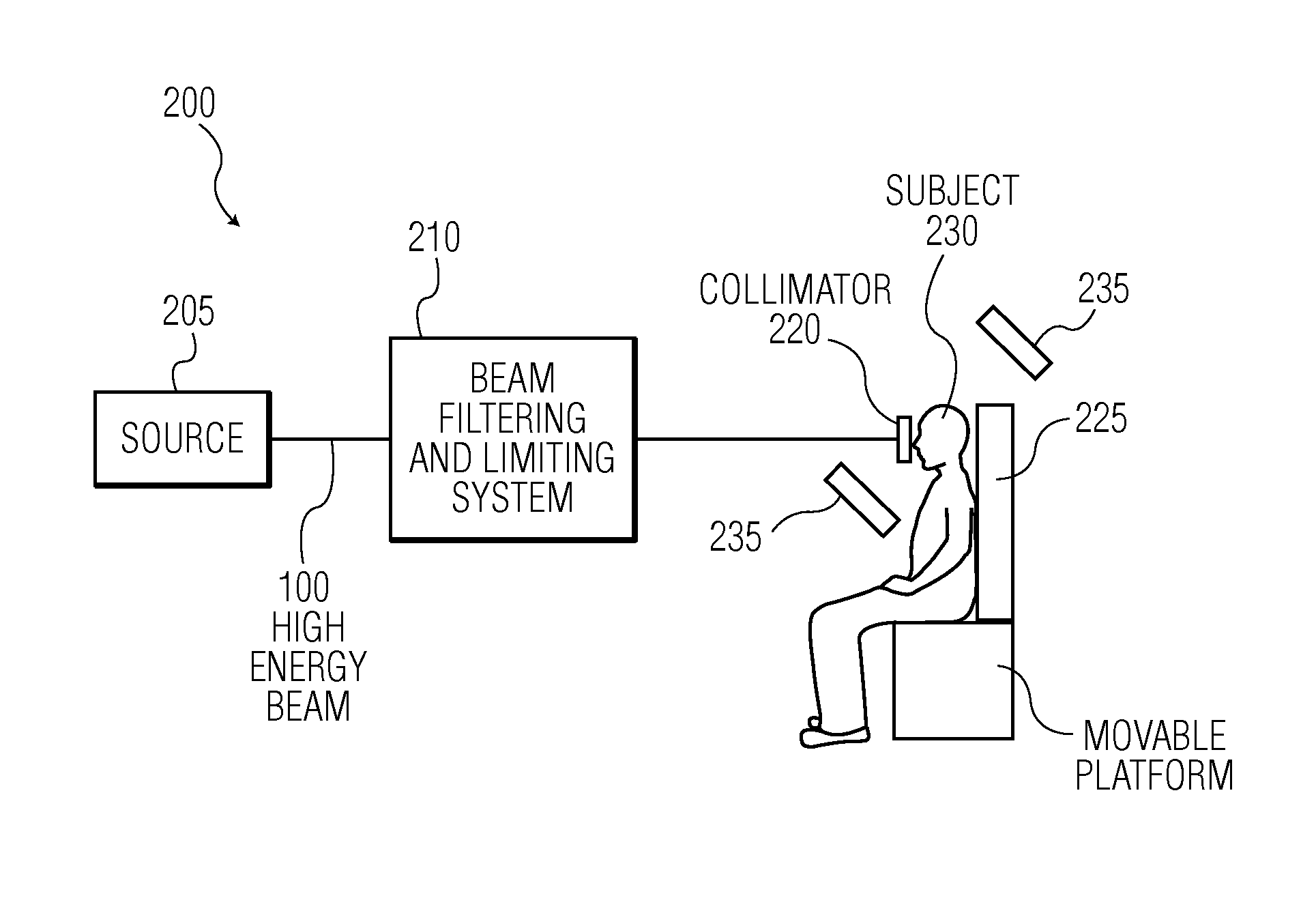
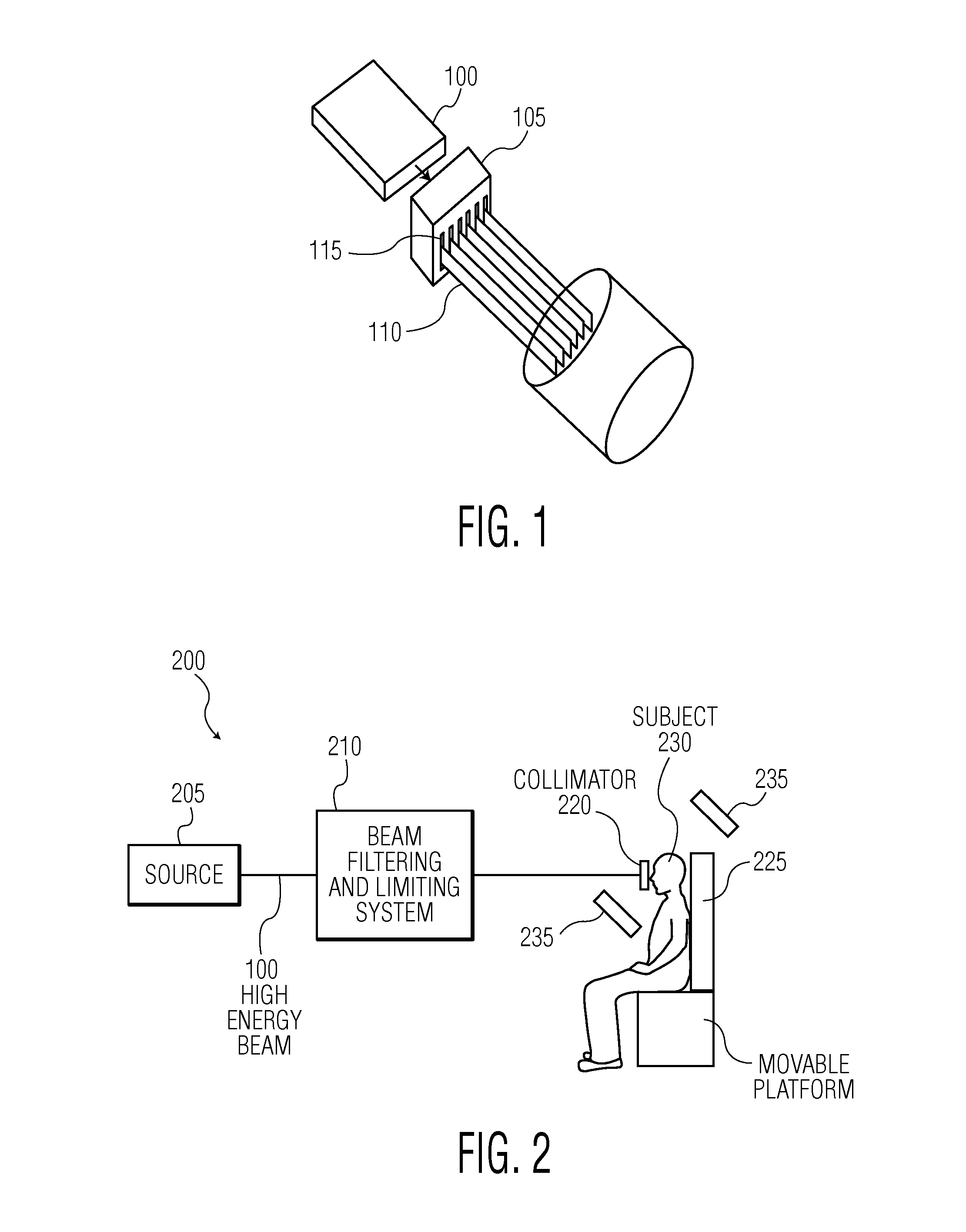
Magnetic confinement for microbeam radiation damage area
ActiveUS9233260B2Quickly yet safely treatMinimize blurringX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyHigh energyLight beam
Various embodiments relate to a method of performing microbeam radiation therapy on a subject, including: producing a high-energy radiation beam in a first direction; producing planar microbeams using the high-energy radiation beam in the first direction, wherein the microbeams have a width, wherein the planar microbeams produce scattered electrons; and applying a magnetic field in a direction lying in a plane substantially parallel to the planar microbeams, wherein the strength of the magnetic field corresponds to the width of the microbeam.
Owner:COPERNICUS DYNAMICS GRP LP
Sensor aided image stabilization
InactiveUS20130107064A1Eliminate unintentional tremorEliminate shakingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAccelerometerGyroscope
Techniques described herein provide a method for improved image and video stabilization using inertial sensors. Gyroscopes, accelerometers and magnetometers are examples of such inertial sensors. The movement of the camera causes shifts in the image captured. Image processing techniques may be used to track the shift in the image on a frame by frame basis. The movement of the camera may be tracked using inertial sensors. By calculating the degree of similarity between the image shift as predicted by image processing techniques with shift of the device estimated using one or more inertial sensor, the device may estimate the portions of the image that are stationary and those that are moving. Stationary portions of the image may be used to transform and align the images. For video stabilization, the realigned images may be combined to generate the video. For image stabilization, the realigned images may be either added or averaged to generate the de-blurred image.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
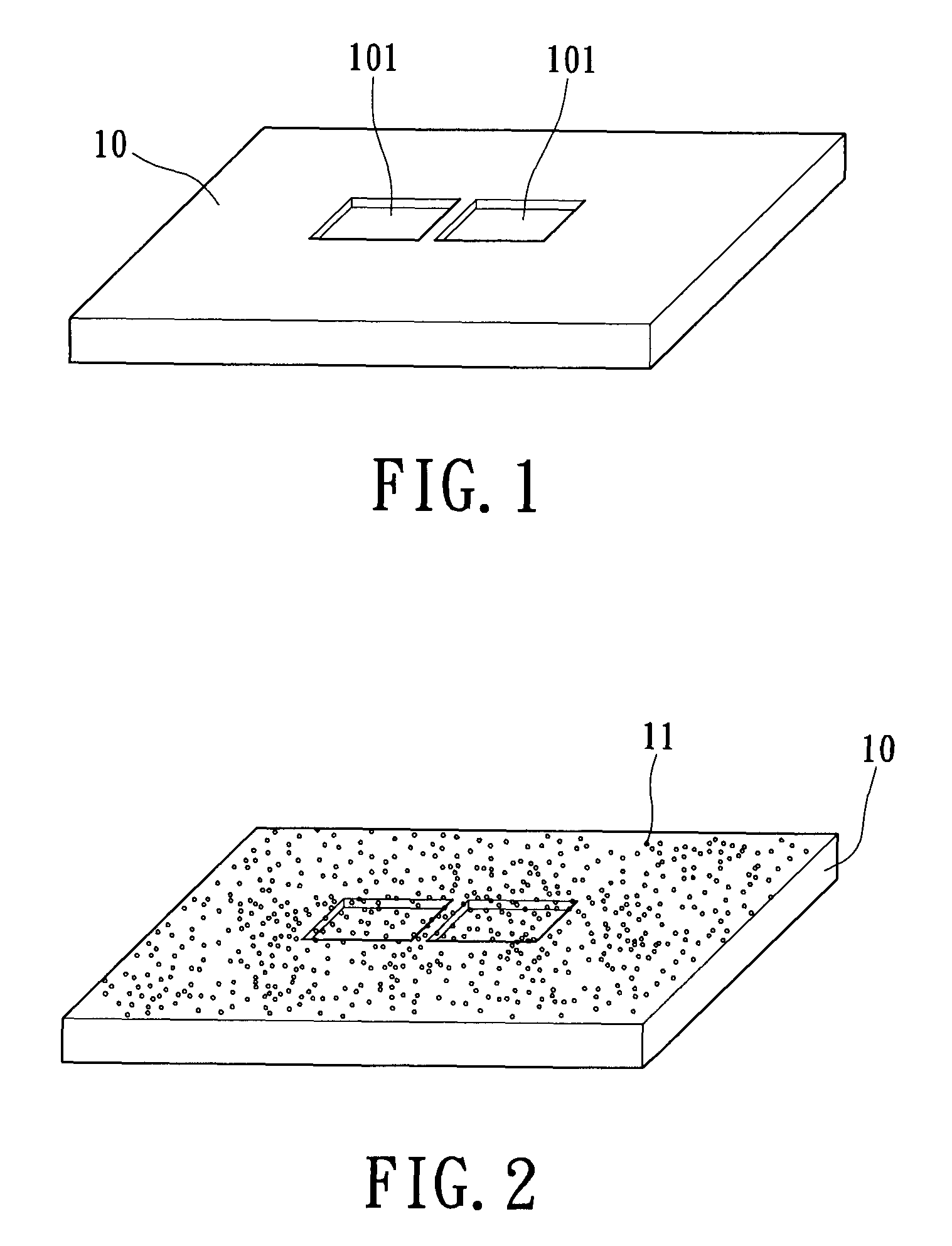
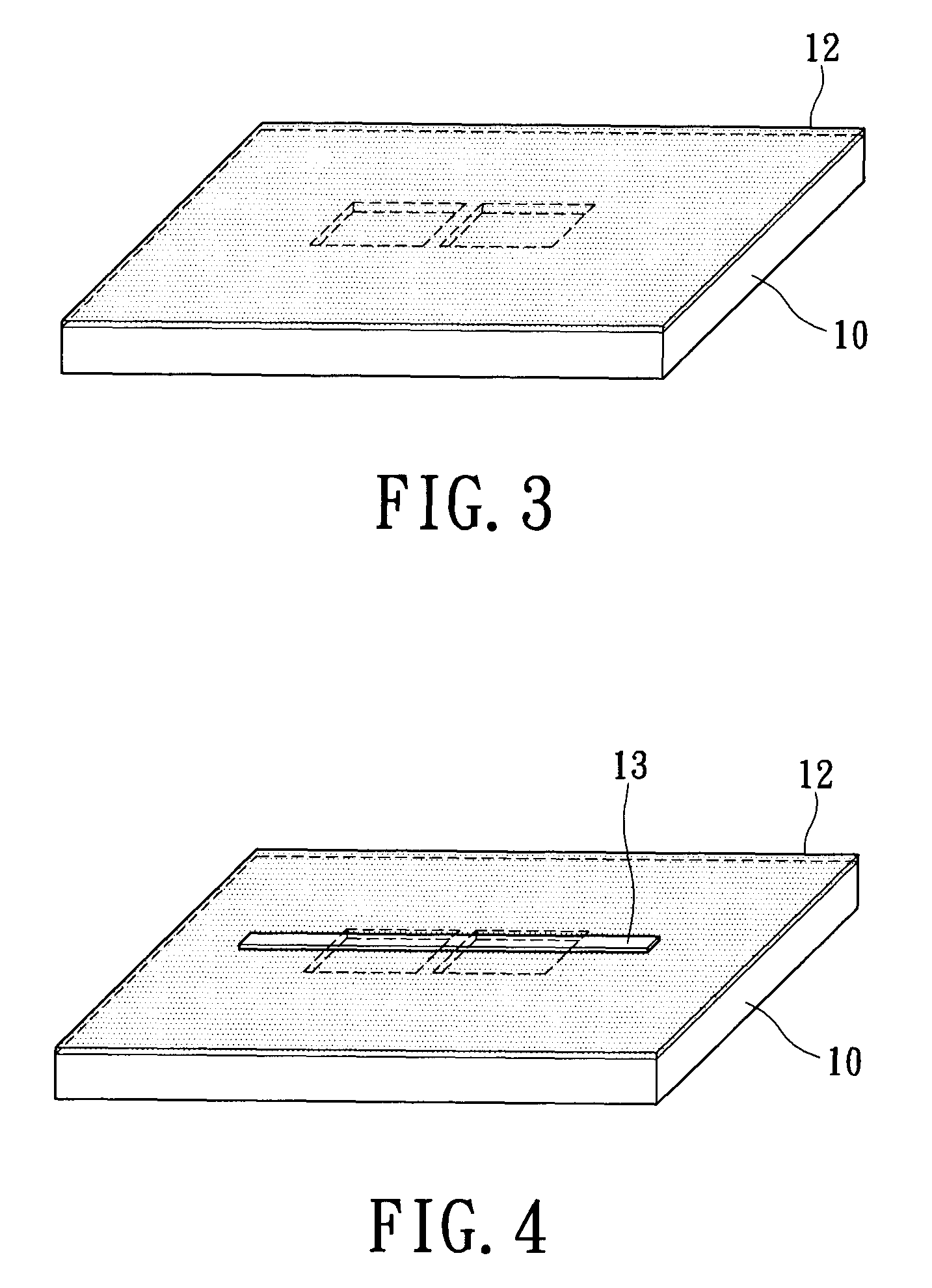
Preparation method for an electron tomography sample with embedded markers and a method for reconstructing a three-dimensional image
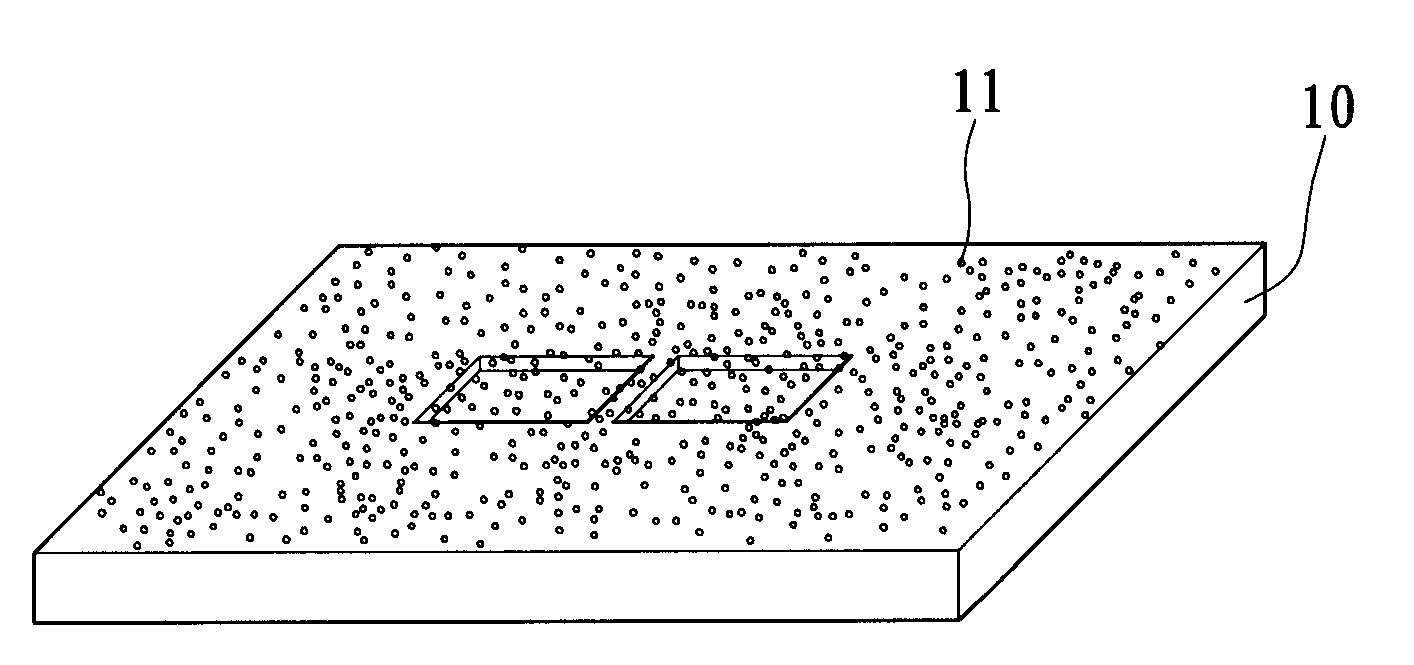
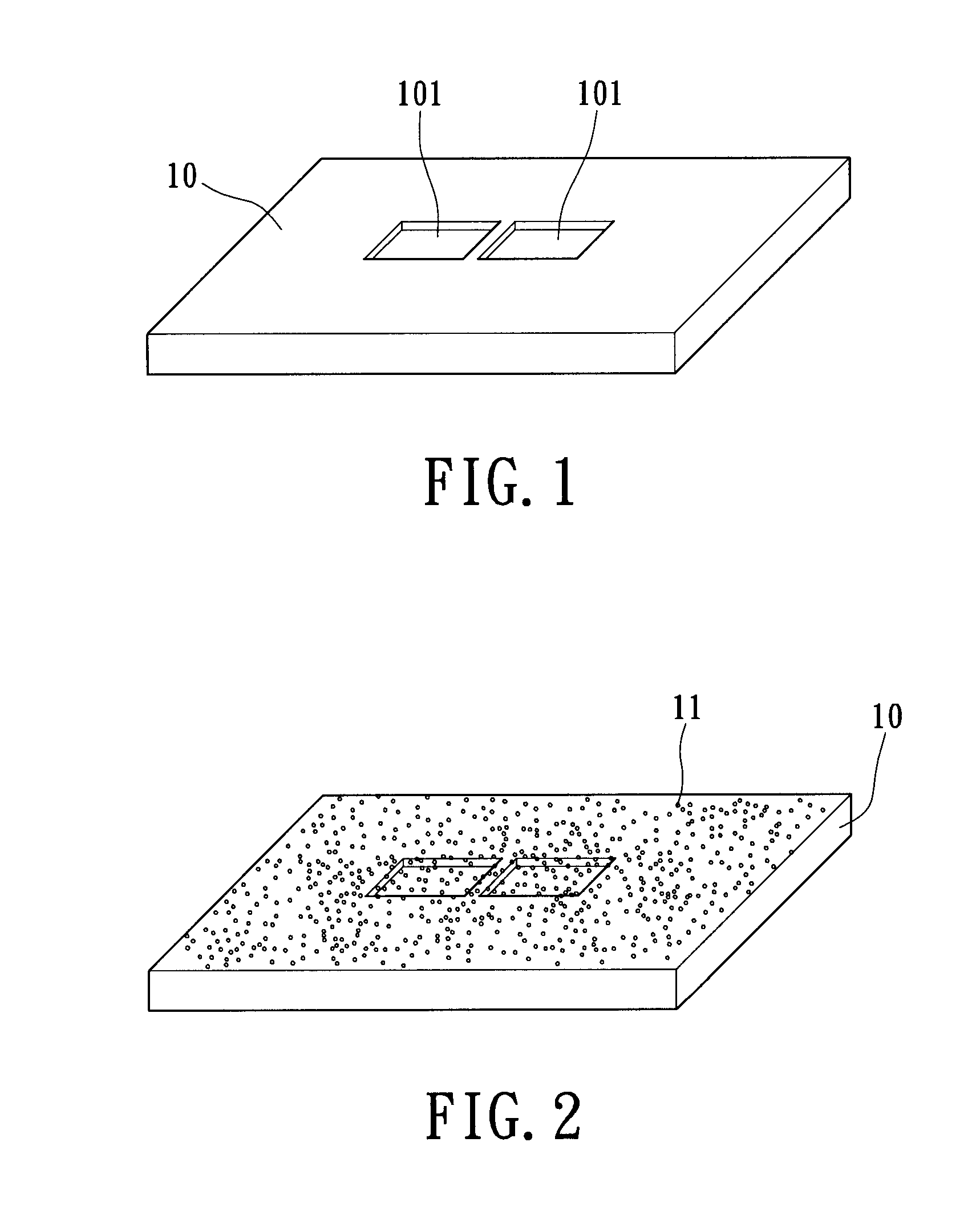
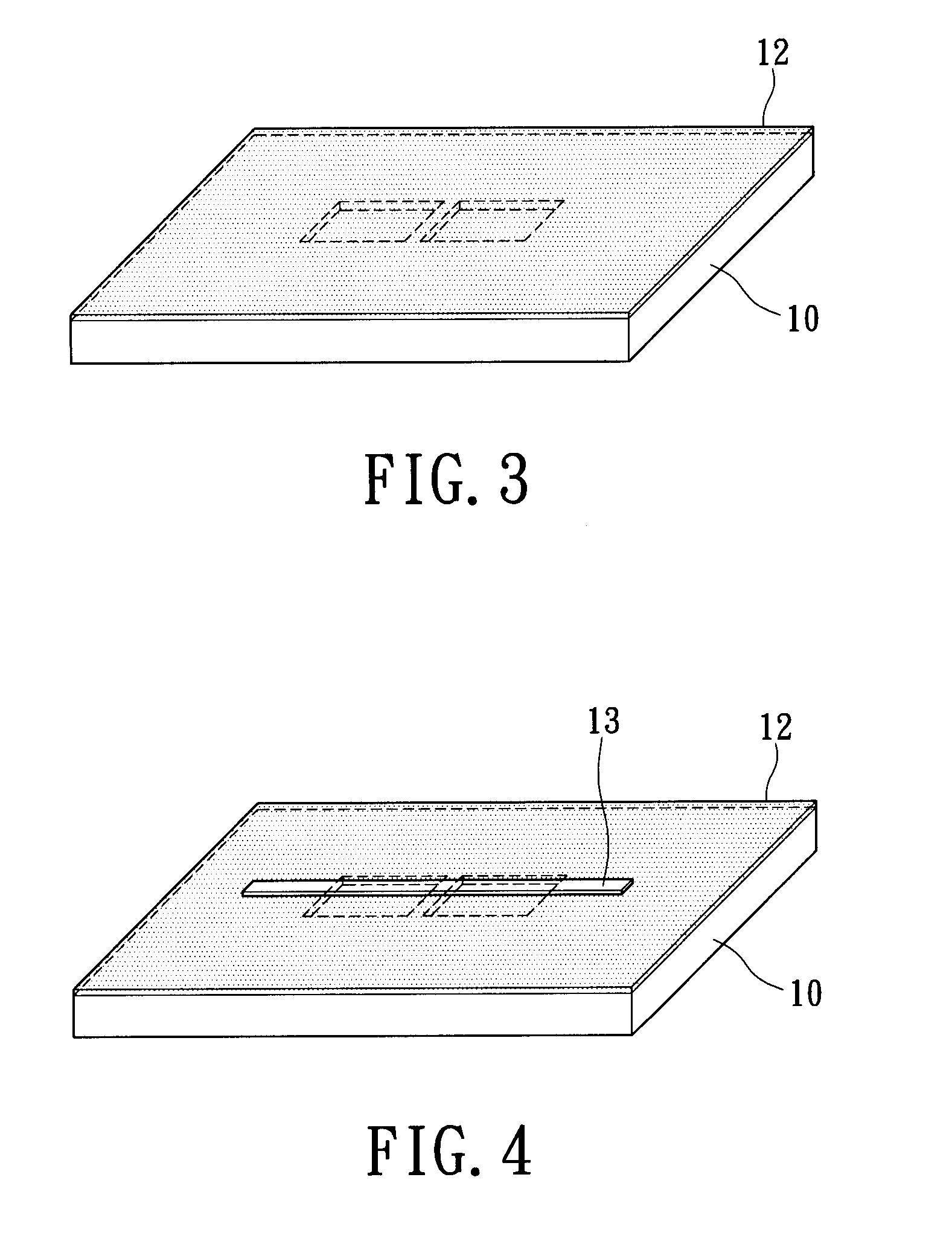
InactiveUS7939906B2Minimize blurringEasy to trackElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFeature trackingEngineering
A manufacturing method for an electron tomography specimen with embedded fiducial markers includes the following steps. A chip of wafer is provided. The chip includes at least one inspecting area. At least one trench is produced beside the inspecting area. A liquid with the markers is filled into the trenches. A first protection layer is coated on the chip, and then a second protection layer is deposited on the first protection layer. Therefore, the markers can be embedded into the electron tomography specimen. The embedded markers can improve the alignment process, due to those embedded markers are easily tracked during feature tracking procedure. In addition, our novel invention also successfully provides a modified version of the technique to deposit gold beads onto TEM pillar samples for much improved 3D reconstruction.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
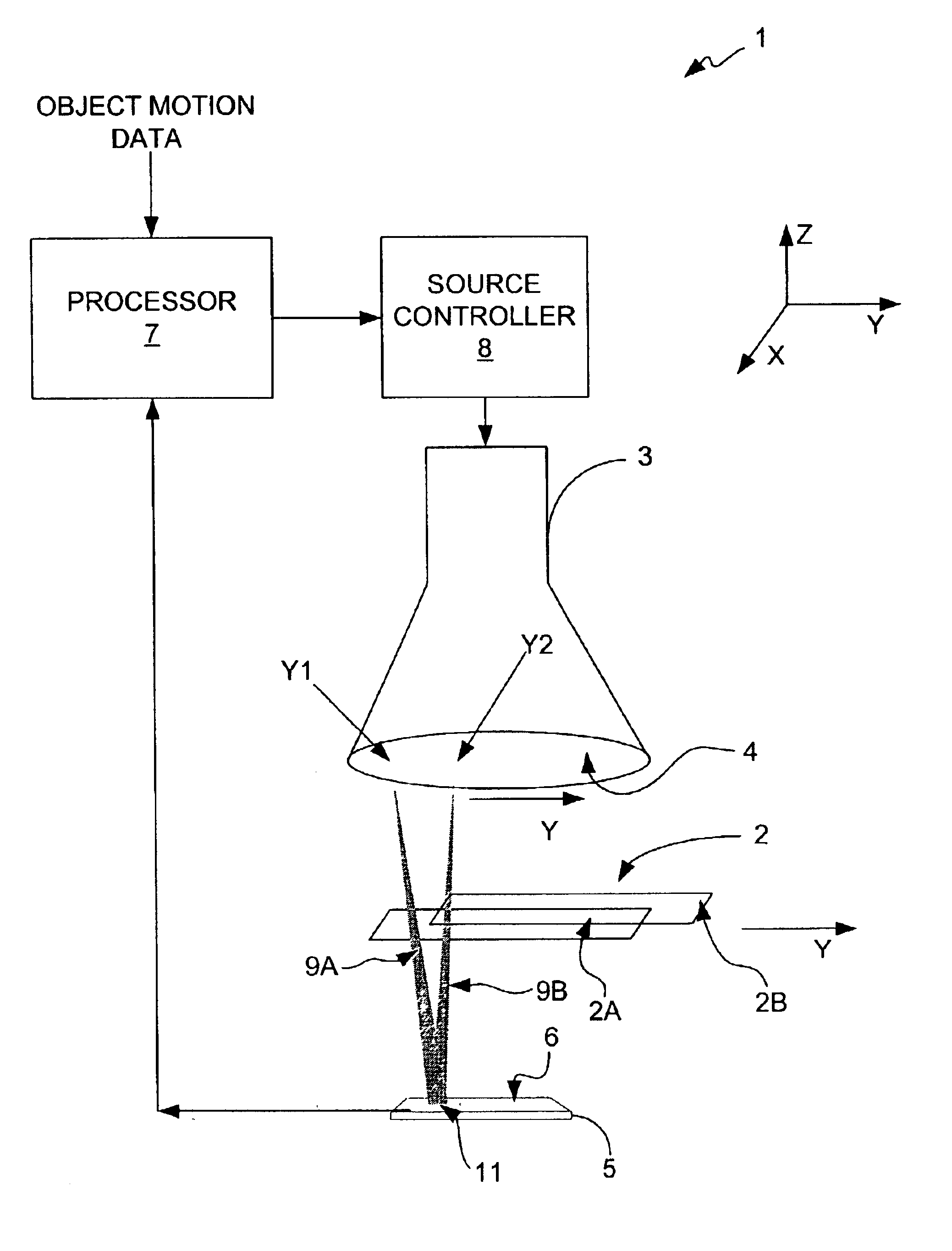
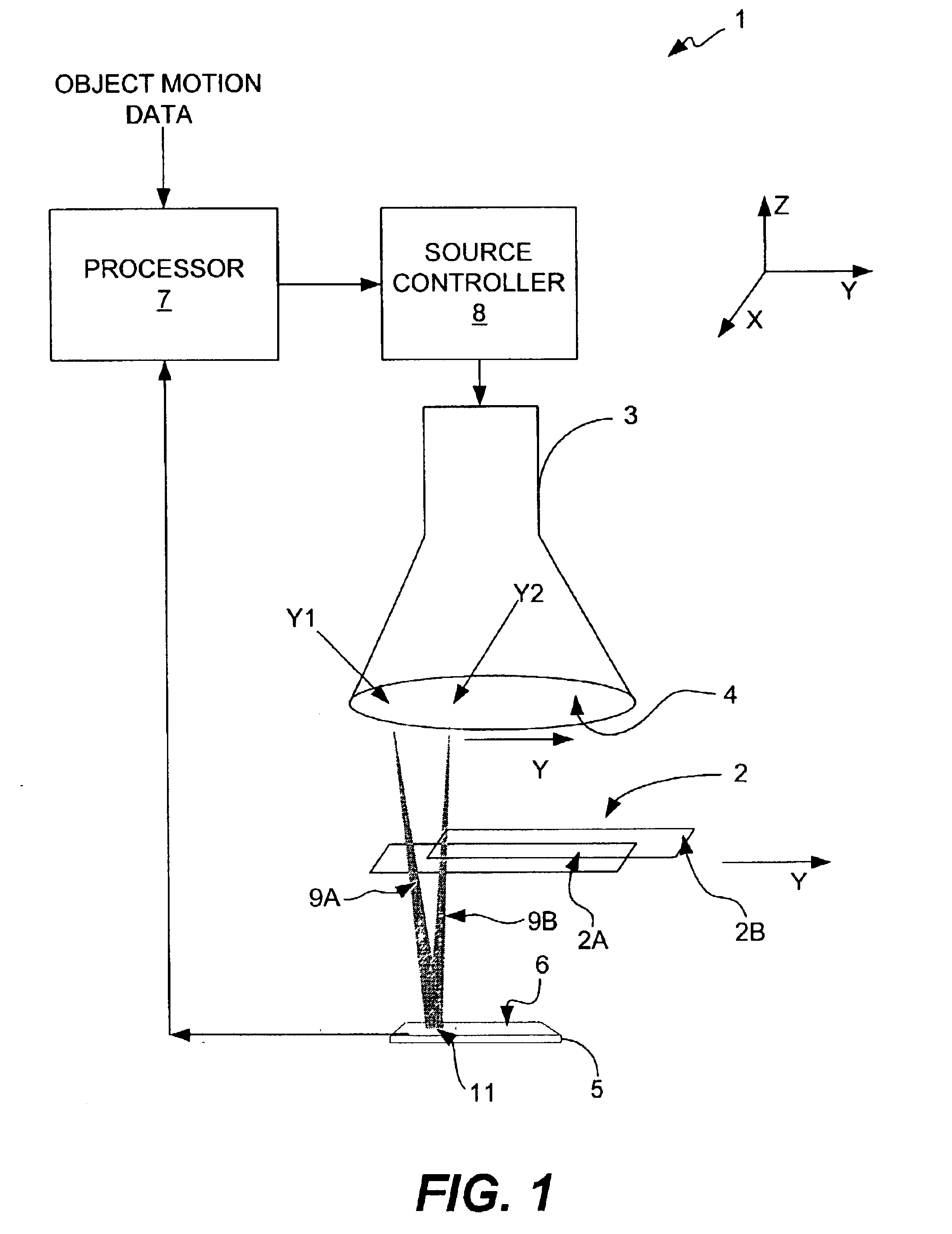
Capturing images of moving objects with a moving illumination point source
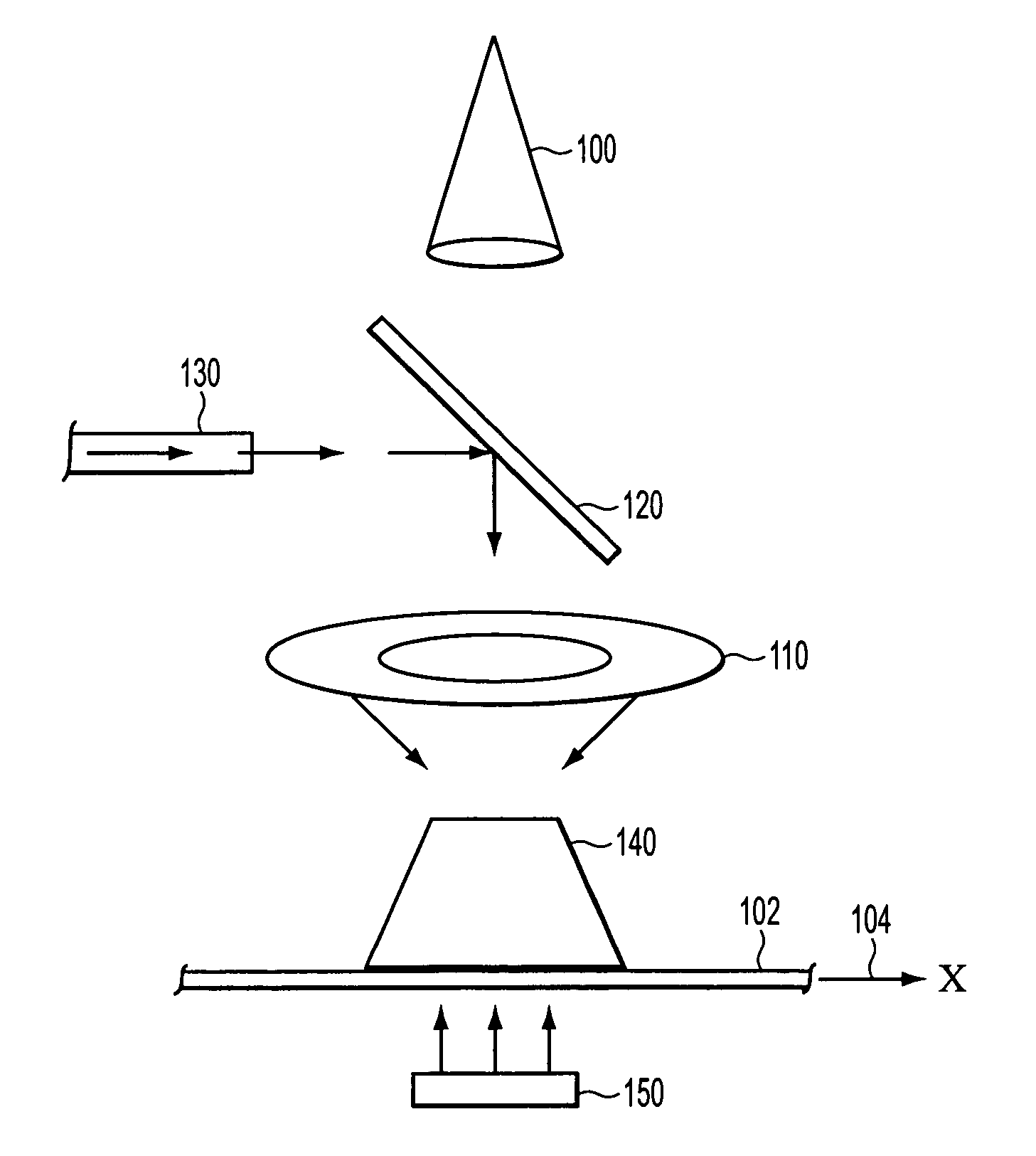
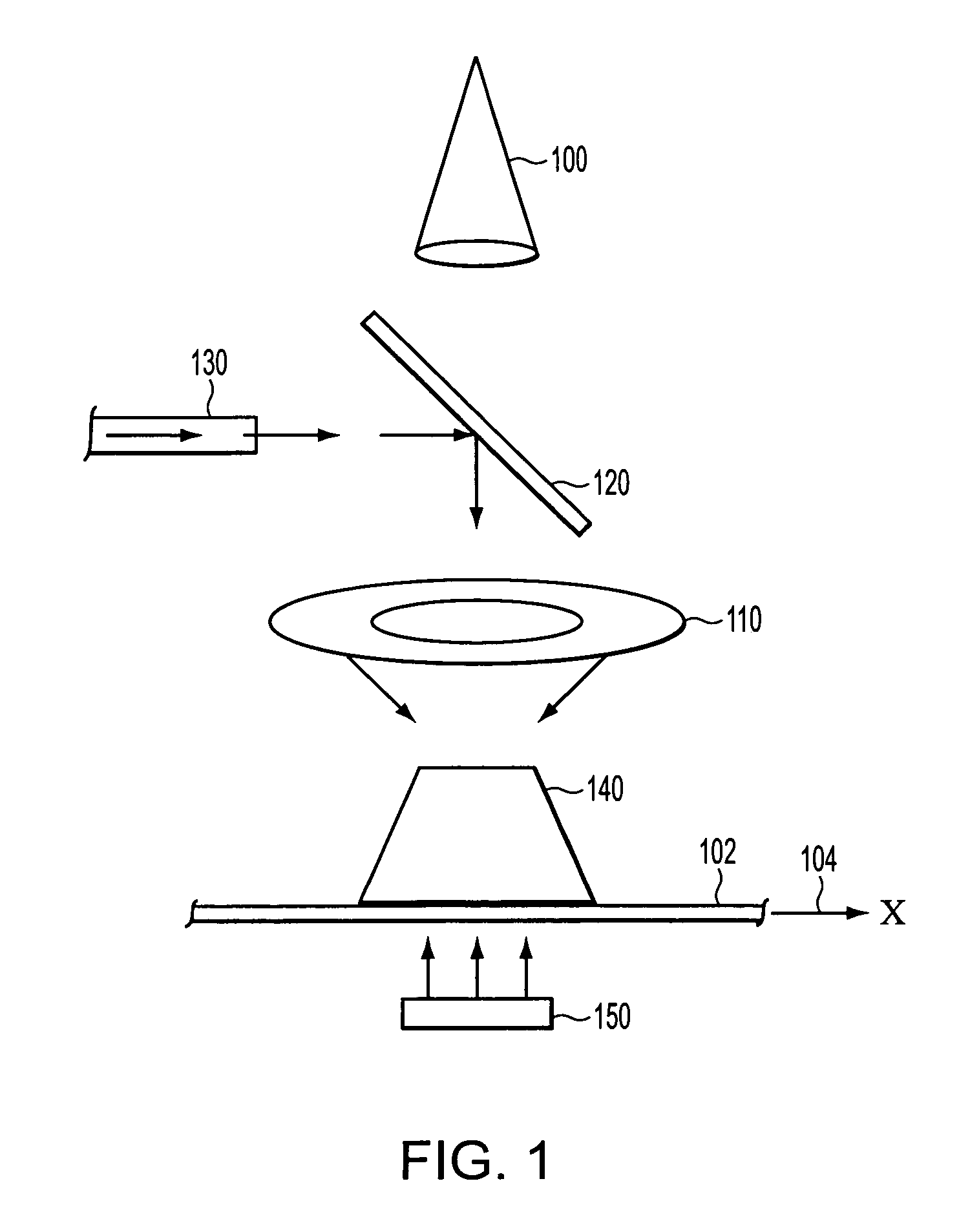
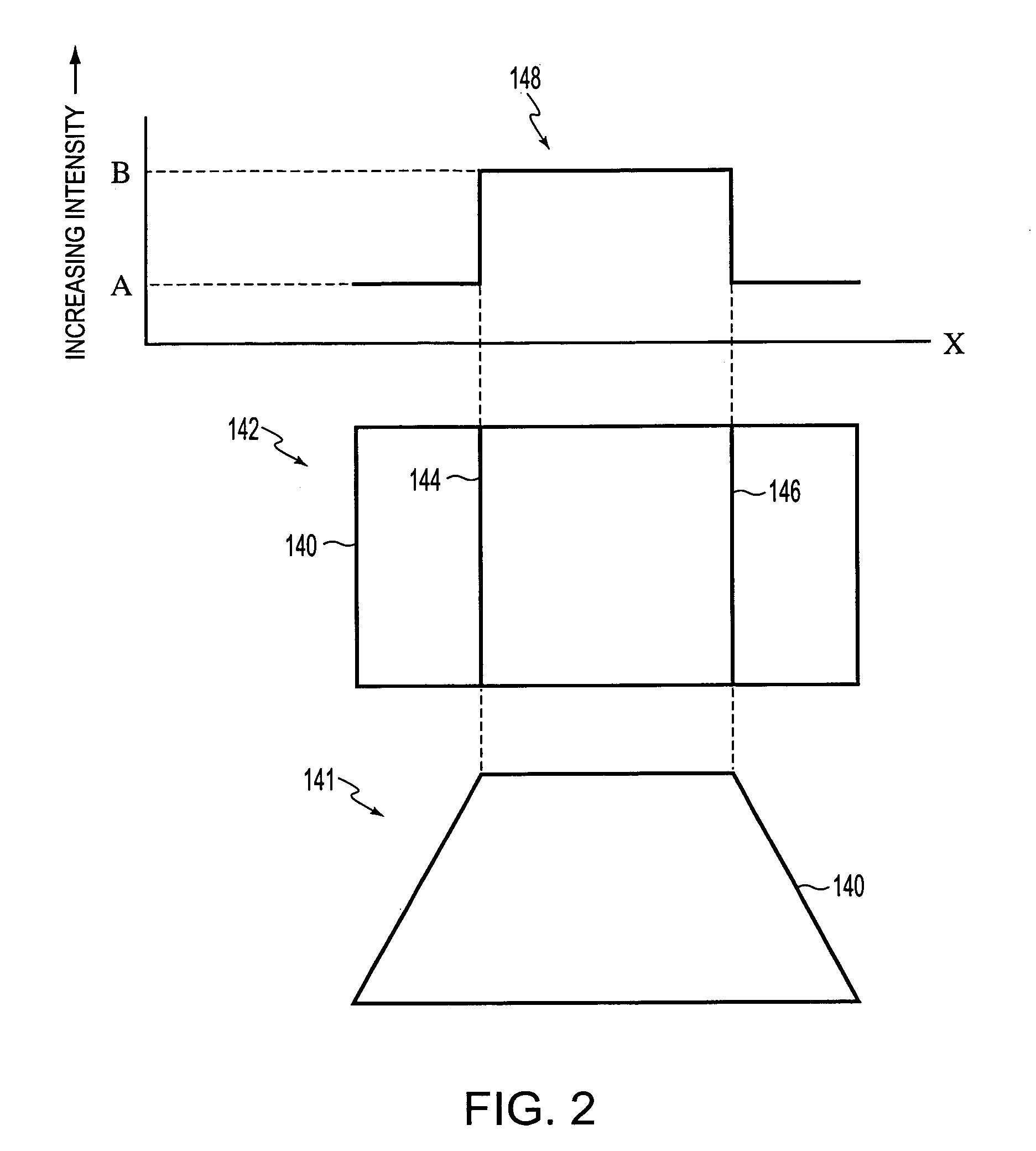
InactiveUS6907103B2Minimal blurringIncreased imaging throughputUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationPoint sourcePhysics
An imaging system that is capable of capturing images of moving objects as they are moving with minimal blurring by moving a point source of illumination such that the position from which illumination is projected is changed as the object moves to ensure that the position of the image projected onto an imaging plane remains substantially effectively stationary. The position from which illumination is projected functions as a point source of illumination. A image sensor of the imaging system is positioned in the imaging plane and receives illumination projected from the position of the illumination source that passes through the moving object. The image sensor produces electrical signals in response to the received illumination. Because the image of the moving object remains effectively stationary on the image sensor, which is located in the imaging plane, an image of at least a portion of the moving object can be constructed with minimal blurring and without having to halt the object to capture an image of it. Because it is not necessary to halt the object and allow the object to settle before capturing an image of it, the throughput of the imaging system is increased and the captured images are greatly improved.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
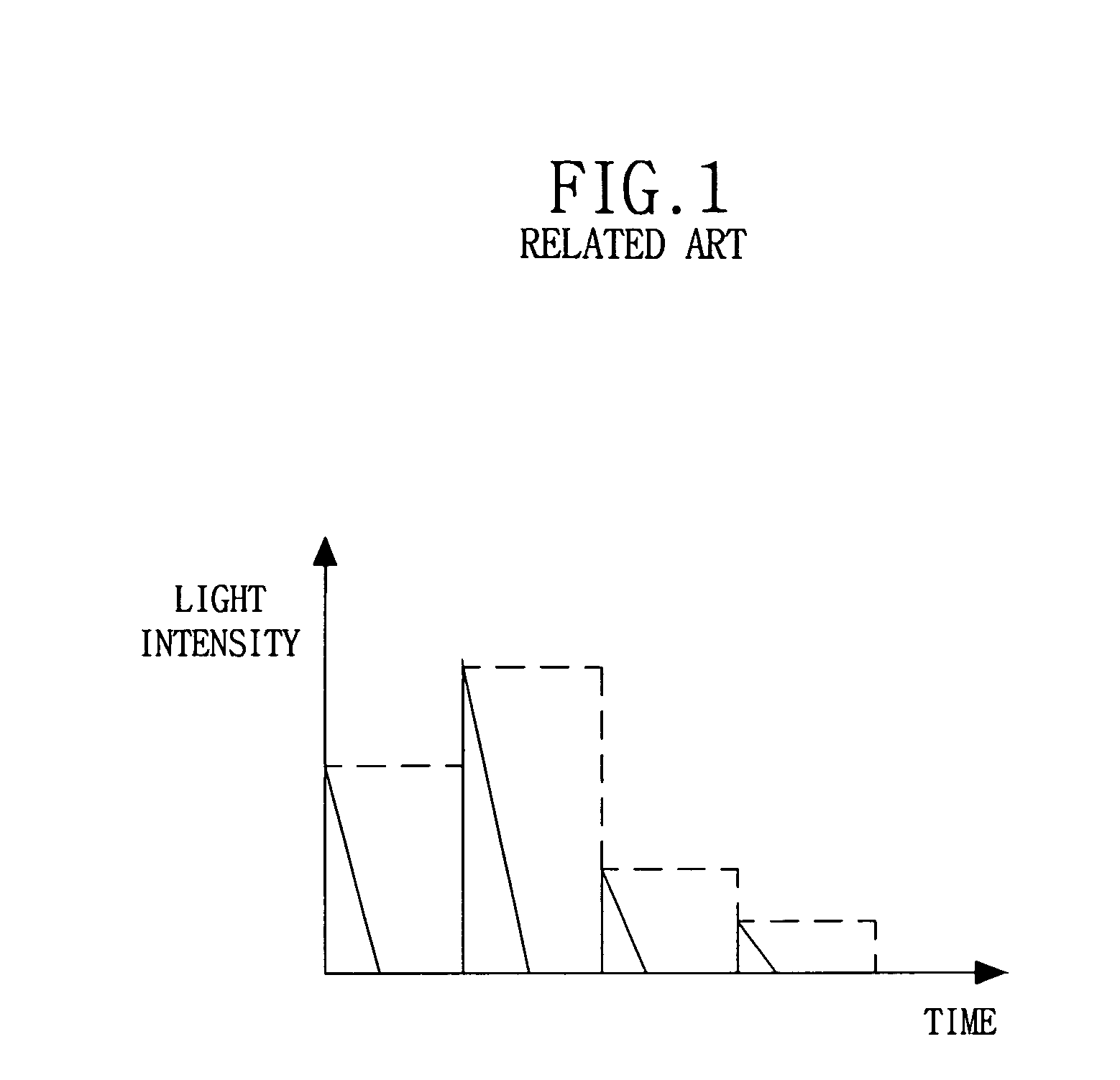
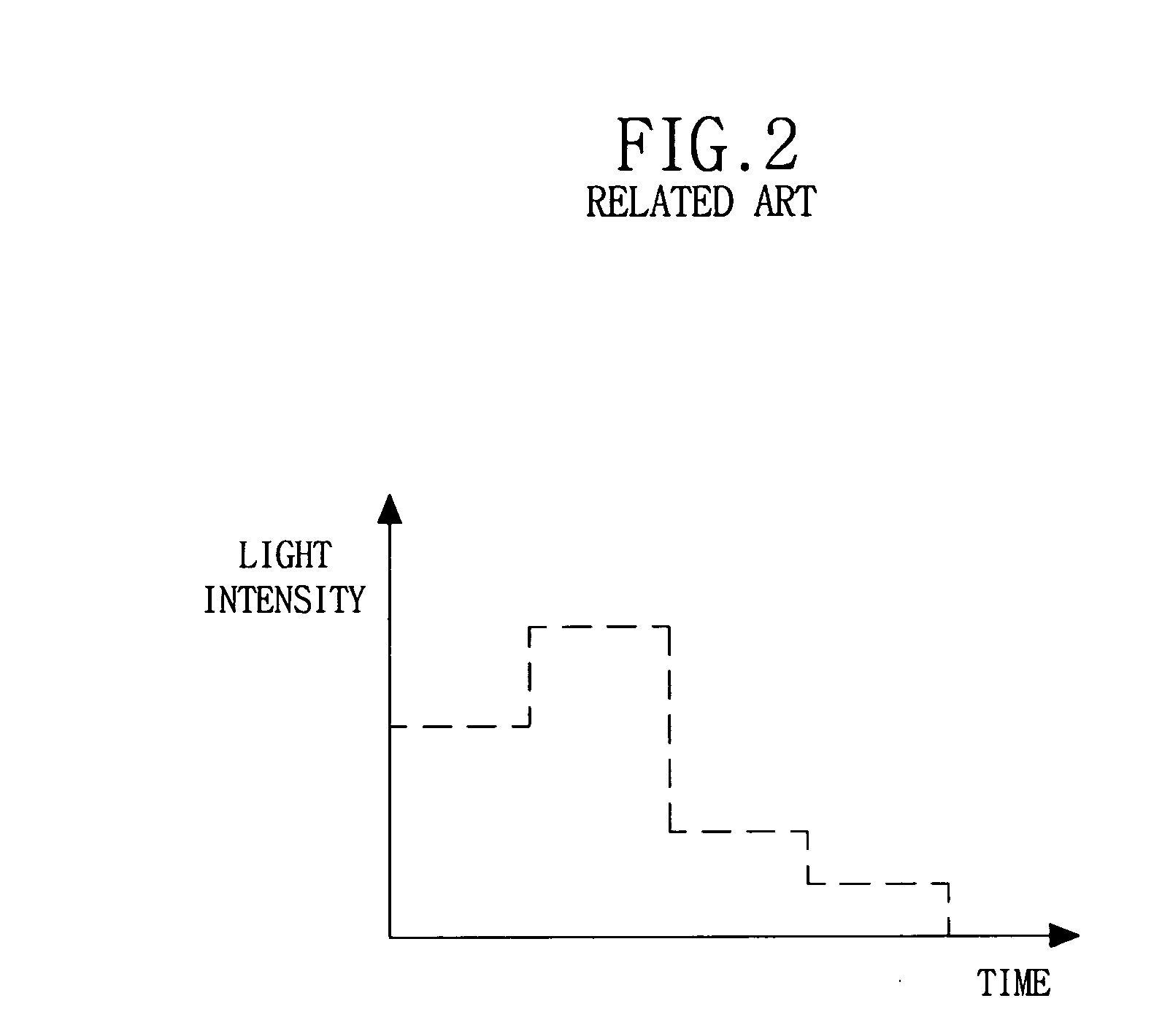
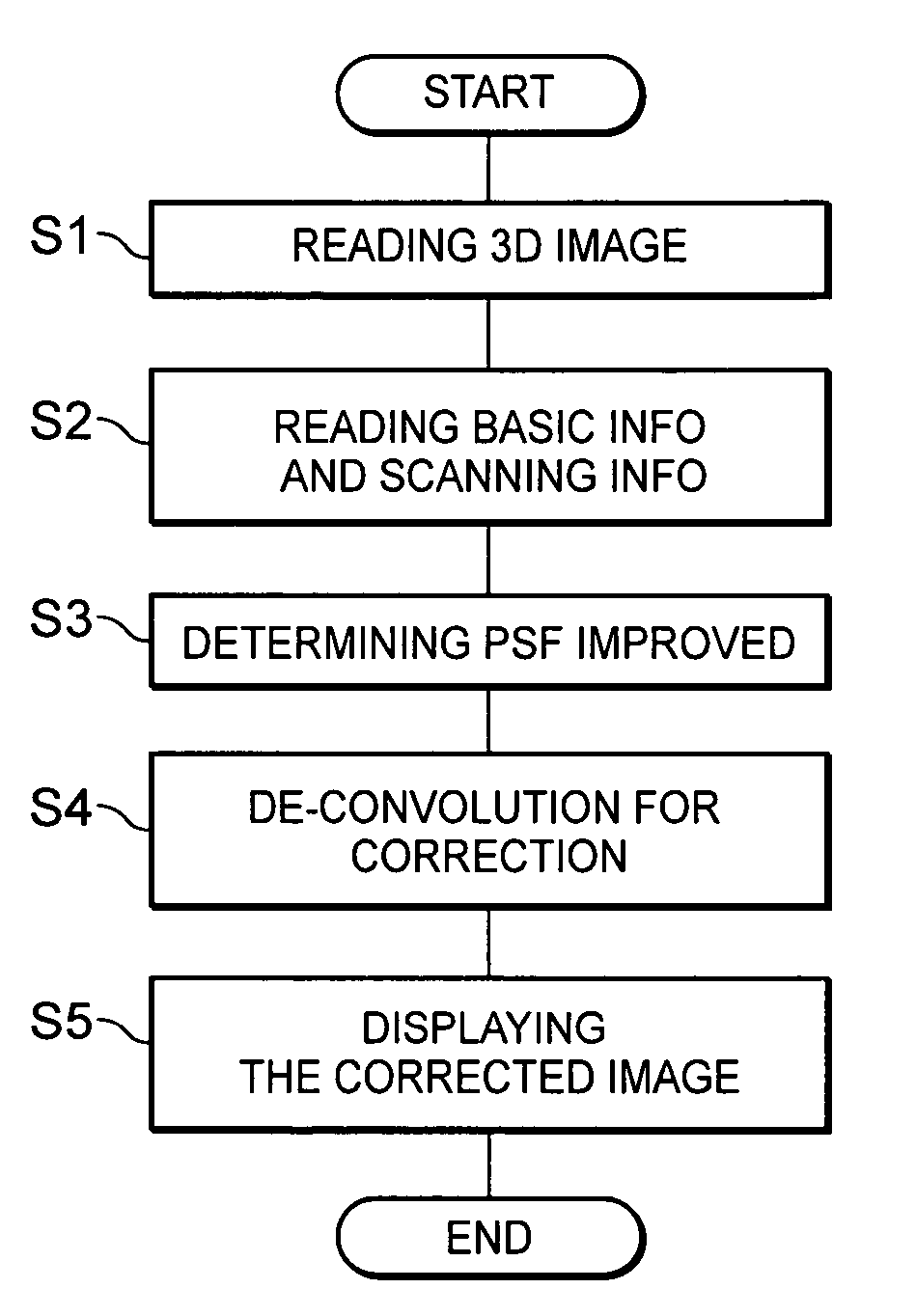
Image enhancement or correction software, method, apparatus and system for substantially minimizing blur in the scanned image
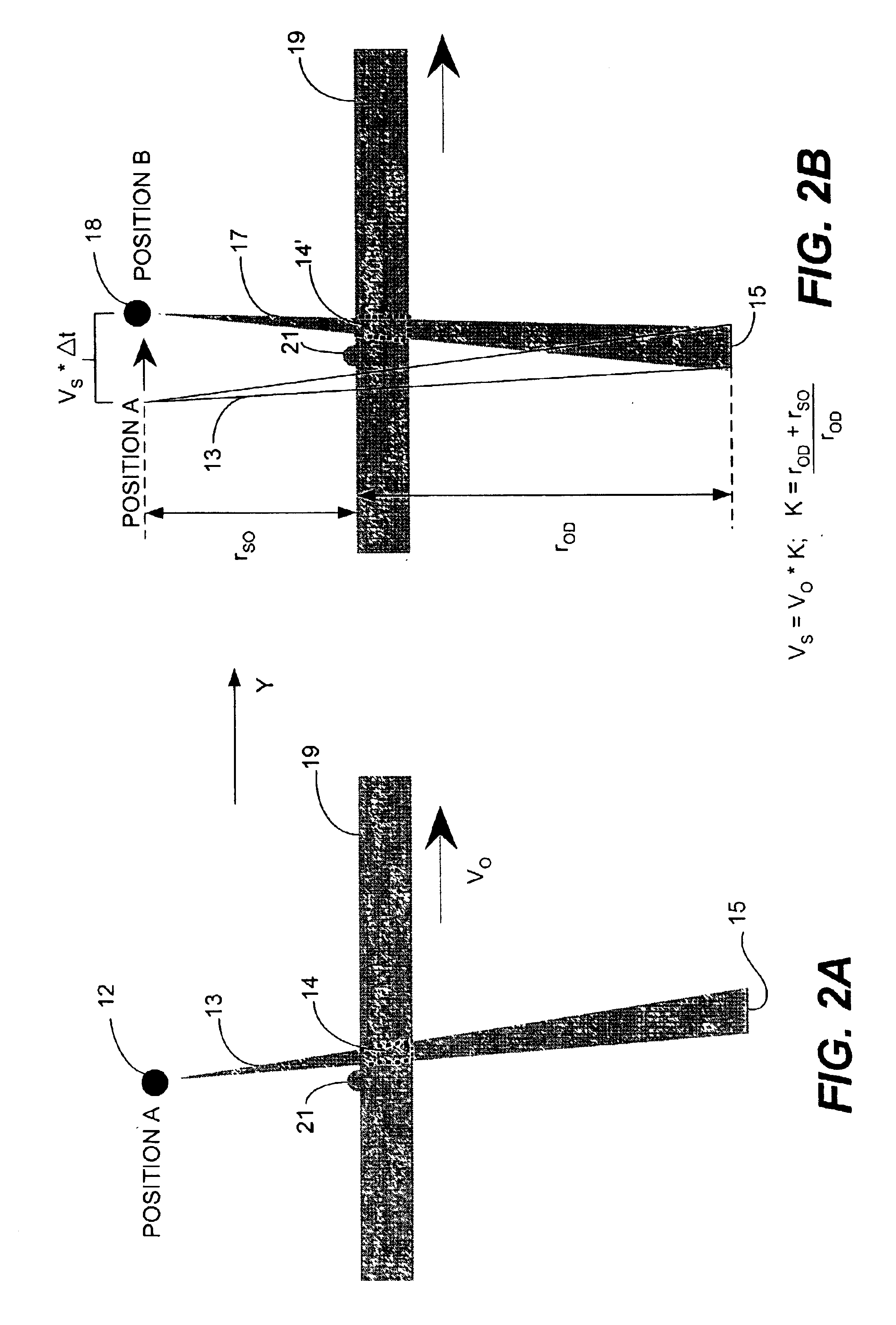
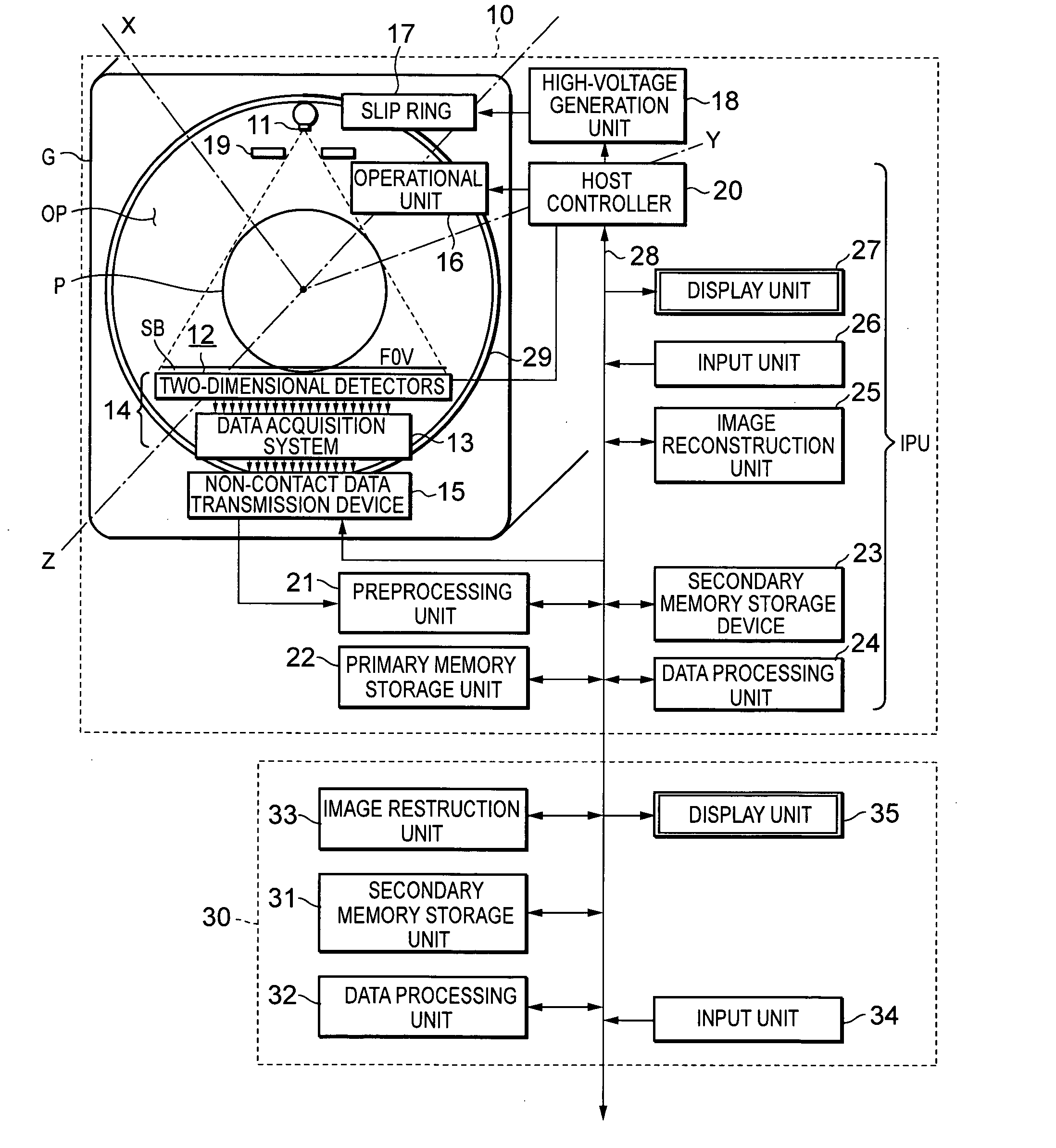
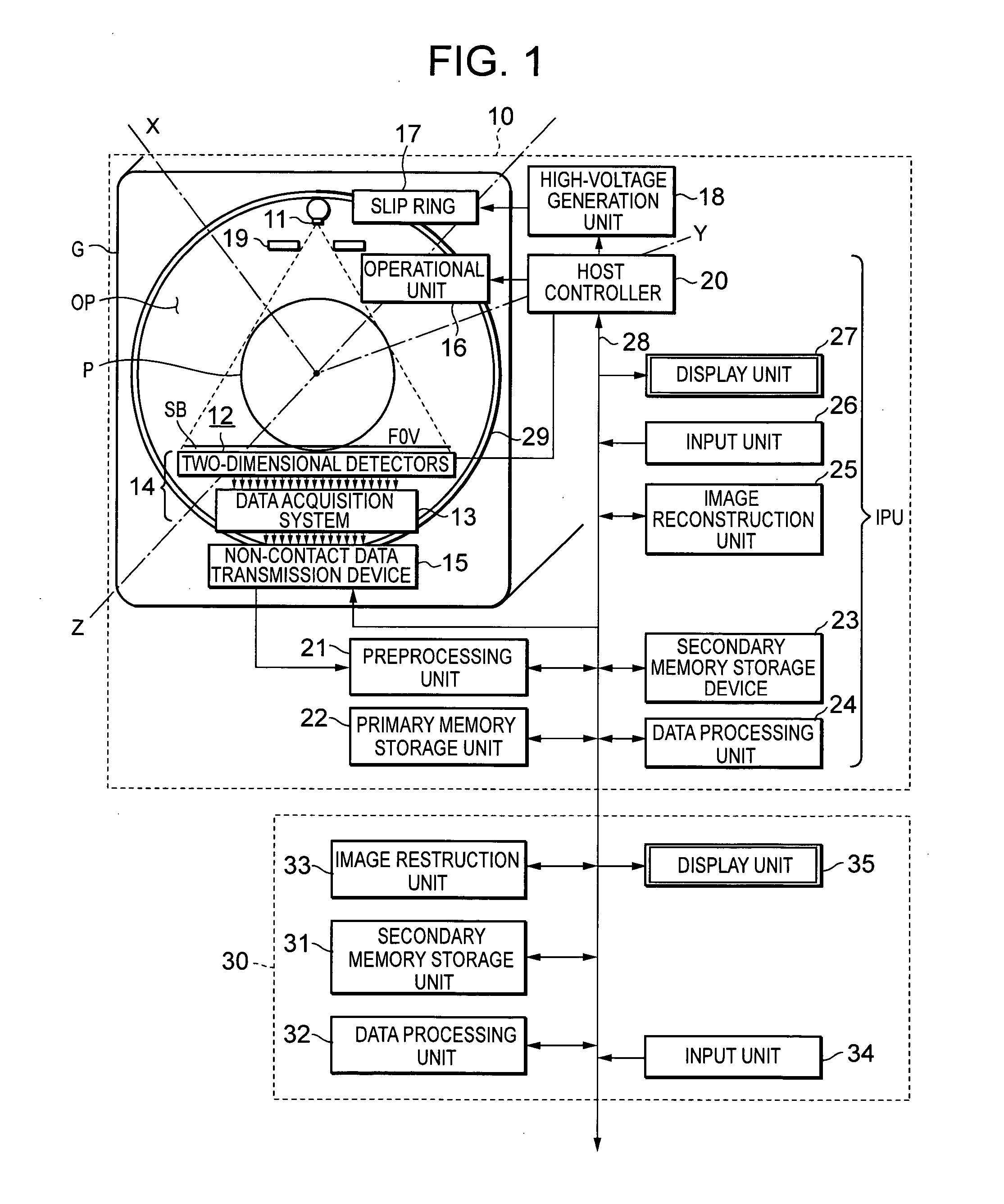
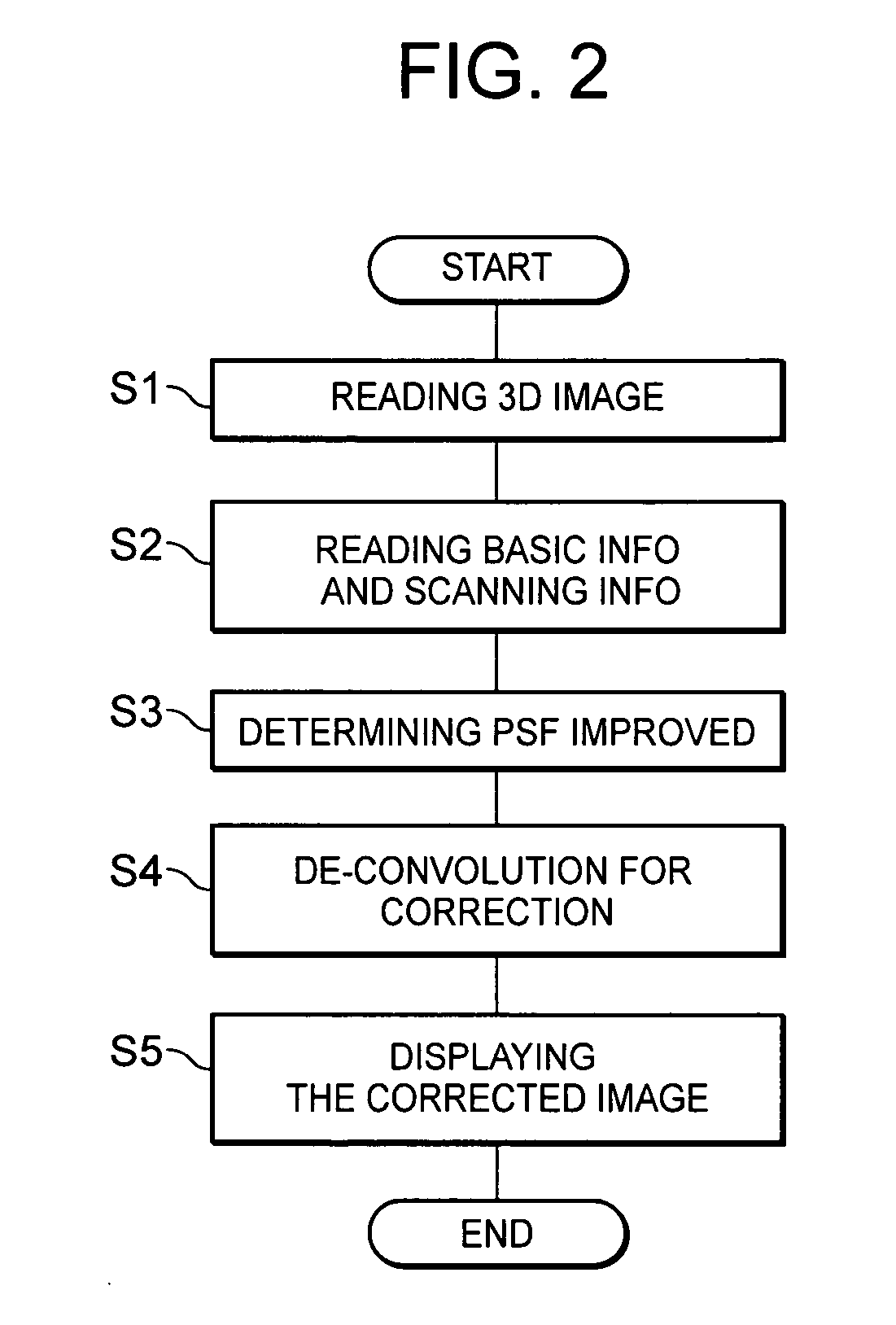
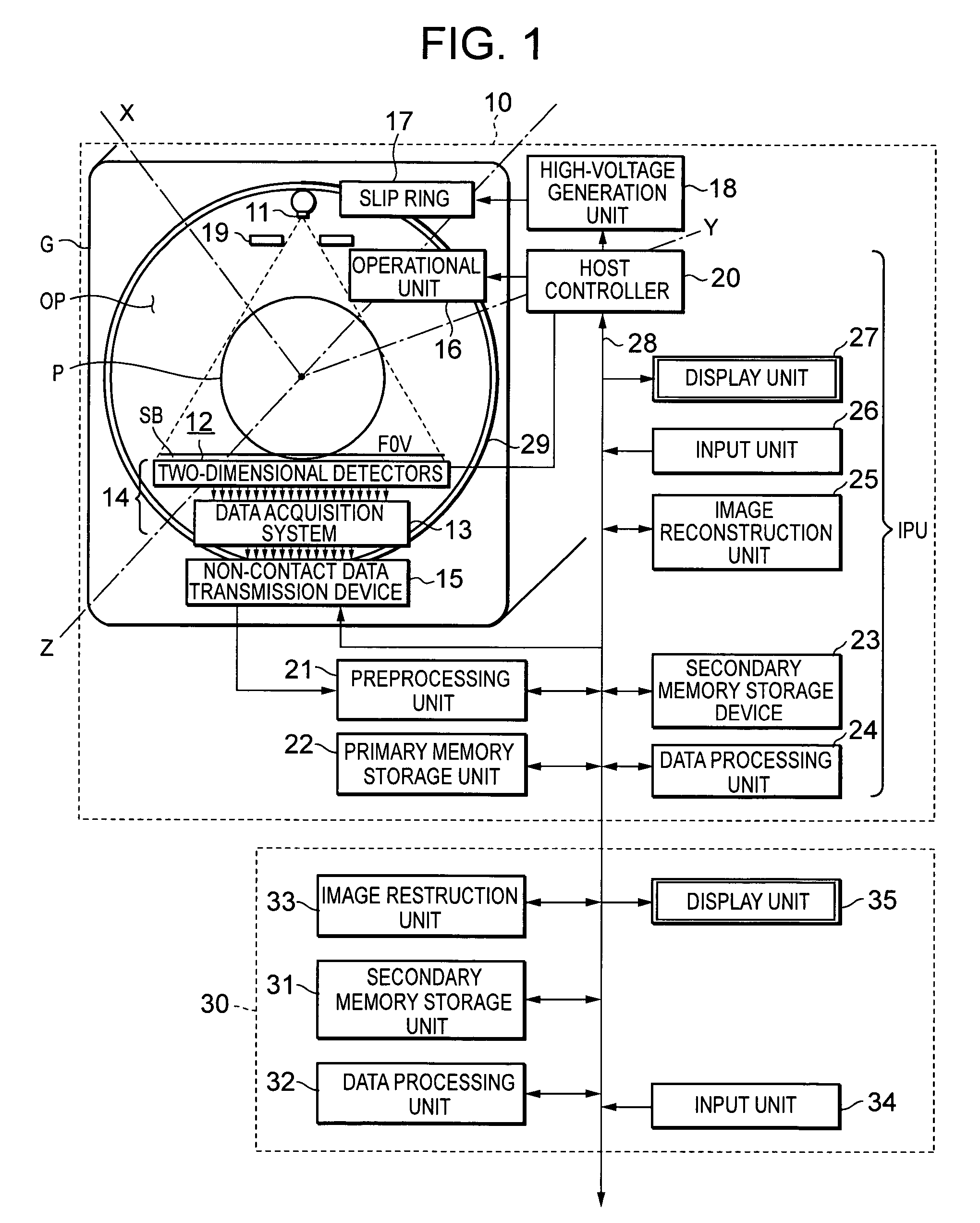
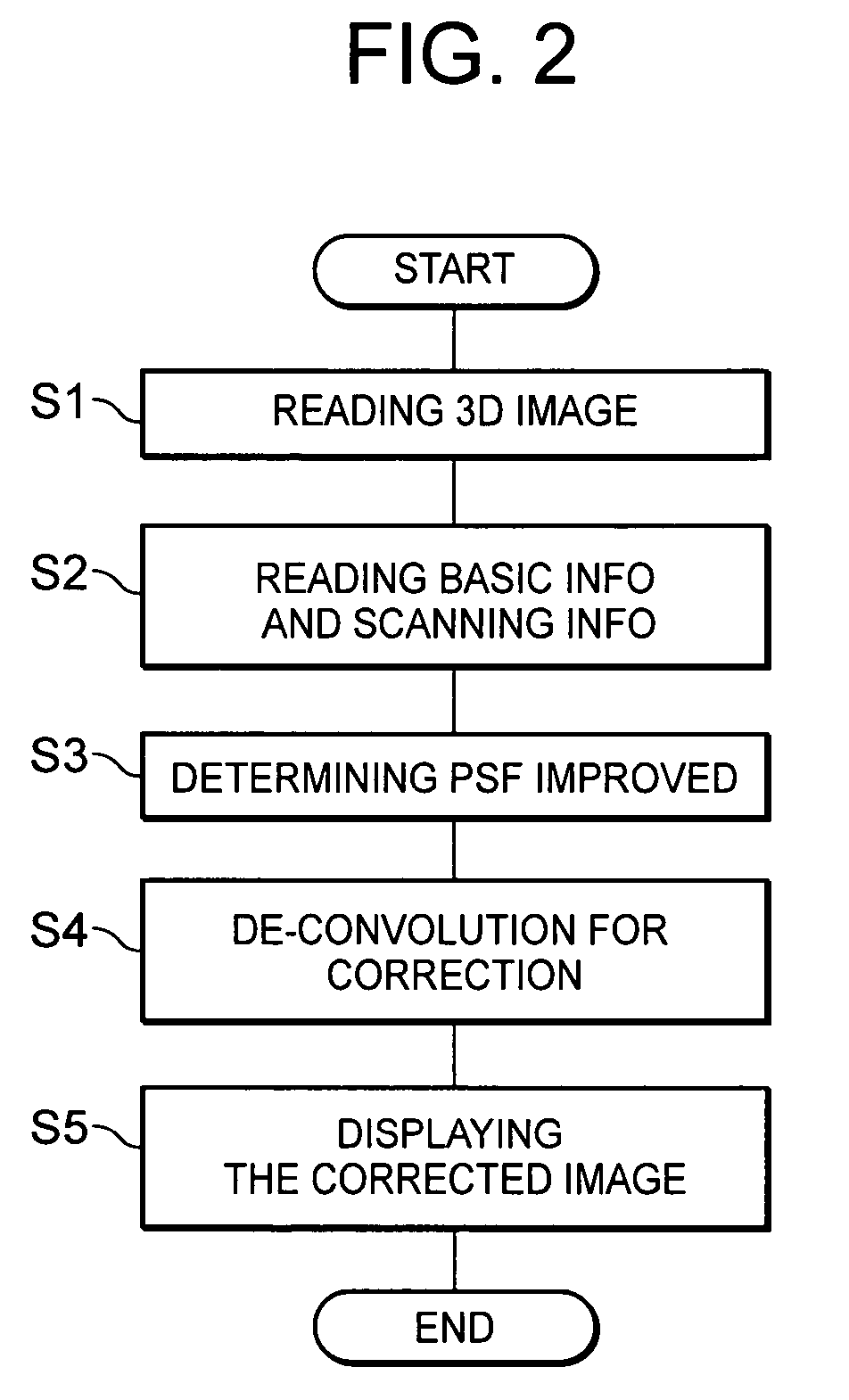
InactiveUS20050220357A1Minimize blurringMinimize in image dataImage enhancementImage analysisCt scannersX-ray
Three-dimensionally reconstructed images are not ideal due to blur or smear that is caused by various sources in an X-ray CT scanner. In order to substantially minimize the blur in the three-dimensionally reconstructed image, a known PSF is weighed according to a combination of predetermined parameters. The parameters include two types of information. One group of the parameters is related to device characteristics of the scanner device while the other is related to the scanning conditions of a particular scan. The improvement is performed in any combination of the X, Y and Z directions. The improved PSF's are used to de-convolute the three-dimensionally reconstructed CT image. As a result, the blur and smear are substantially removed from the three-dimensionally reconstructed image data for good visualization as well as accurate physical measurements in the scanned image. The improved techniques according to the current invention are applicable to two-dimensional image data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Preparation method for an electron tomography sample with embedded markers and a method for reconstructing a three-dimensional image
InactiveUS20100084555A1Minimize blurringEasy to trackMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesFeature trackingEngineering
A manufacturing method for an electron tomography specimen with embedded fiducial markers includes the following steps. A chip of wafer is provided. The chip includes at least one inspecting area. At least one trench is produced beside the inspecting area. A liquid with the markers is filled into the trenches. A first protection layer is coated on the chip, and then a second protection layer is deposited on the first protection layer. Therefore, the markers can be embedded into the electron tomography specimen. The embedded markers can improve the alignment process, due to those embedded markers are easily tracked during feature tracking procedure. In addition, our novel invention also successfully provides a modified version of the technique to deposit gold beads onto TEM pillar samples for much improved 3D reconstruction.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
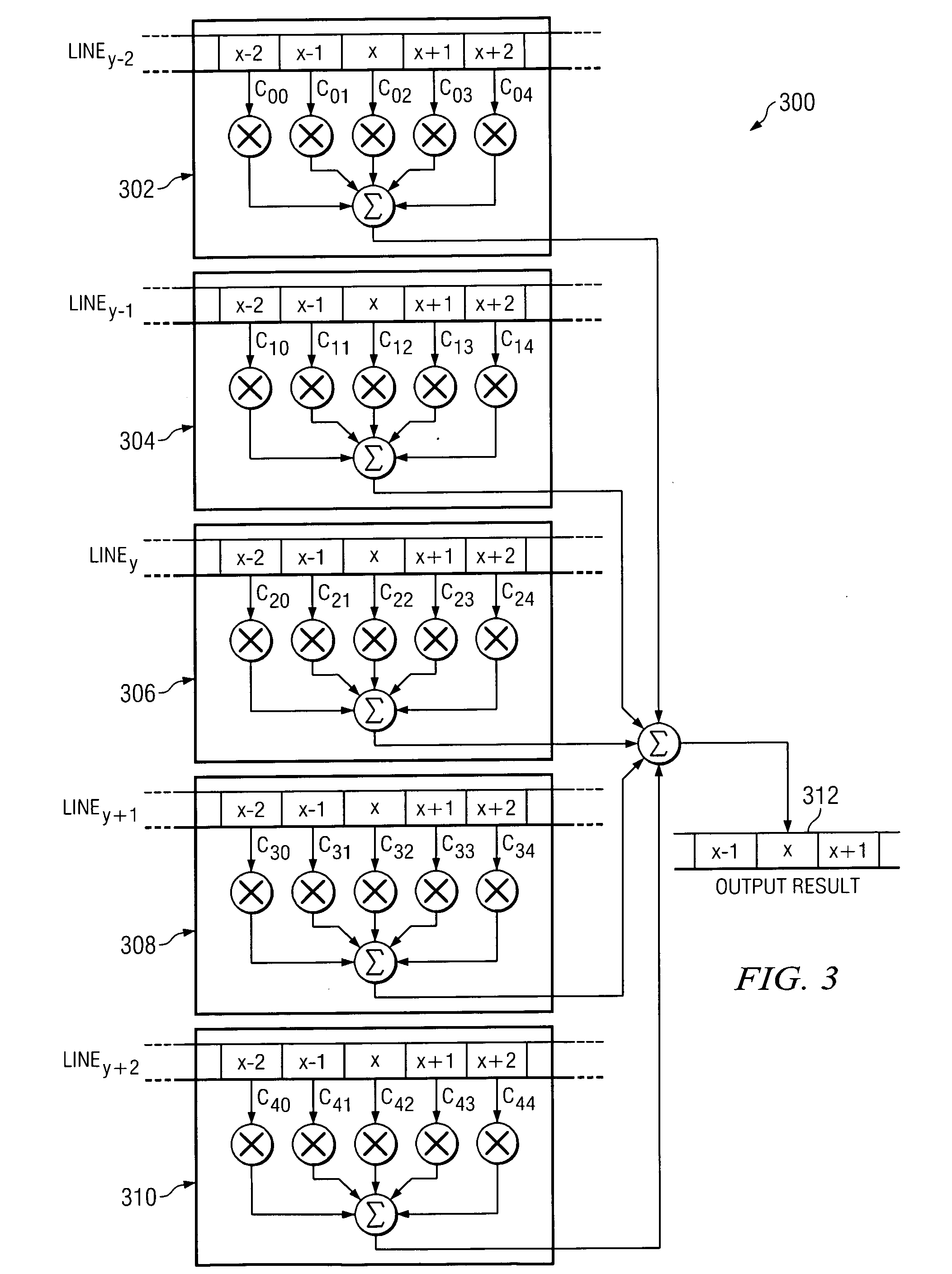
System and method for sharpness filter for picture-smoothing architectures
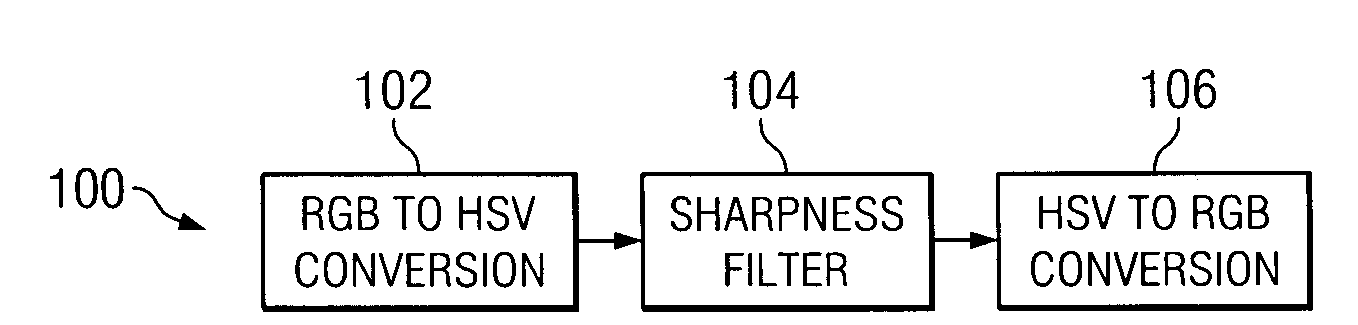
InactiveUS20060204123A1Minimize blurringIncrease sharpness of imageImage enhancementImage analysisLocal varianceImpulse response
According to teachings of the present invention, a system and method for a sharpness filter for picture-smoothing architectures are provided. In one embodiment, the method includes applying a finite impulse response filter to a brightness channel of an image prior to applying a picture-smoothing algorithm to the image, determining a local variance estimate for the image, and varying a gain of the finite impulse response filter based upon the local variance estimate, wherein the finite impulse response filter is an inverse of a filter that approximates the picture-smoothing algorithm.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Electron Microscope
ActiveUS20120217393A1Minimize blurringMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesElectron sourceImage resolution
A scanning electron microscope suppresses a beam drift by reducing charging on a sample surface while suppressing resolution degradation upon observation of an insulator sample. An electron microscope includes an electron source and an objective lens that focuses an electron beam emitted from the electron source, which provides an image using a secondary signal generated from the sample irradiated with the electron beam. A magnetic body with a continuous structure and an inside diameter larger than an inside diameter of an upper pole piece that forms the objective lens is provided between the objective lens and the sample.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Methods and apparatus for correction for 2-3 field patterns
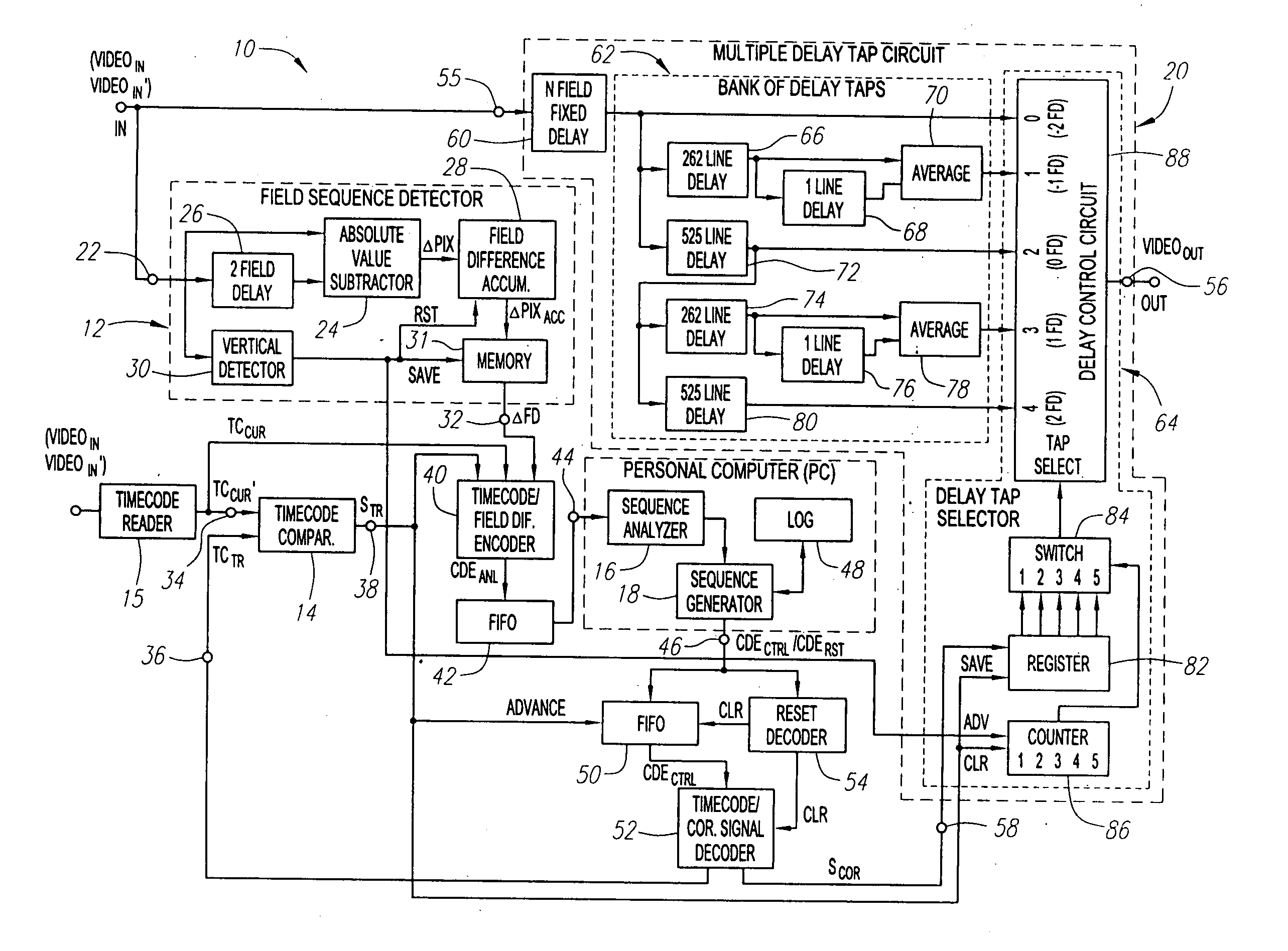
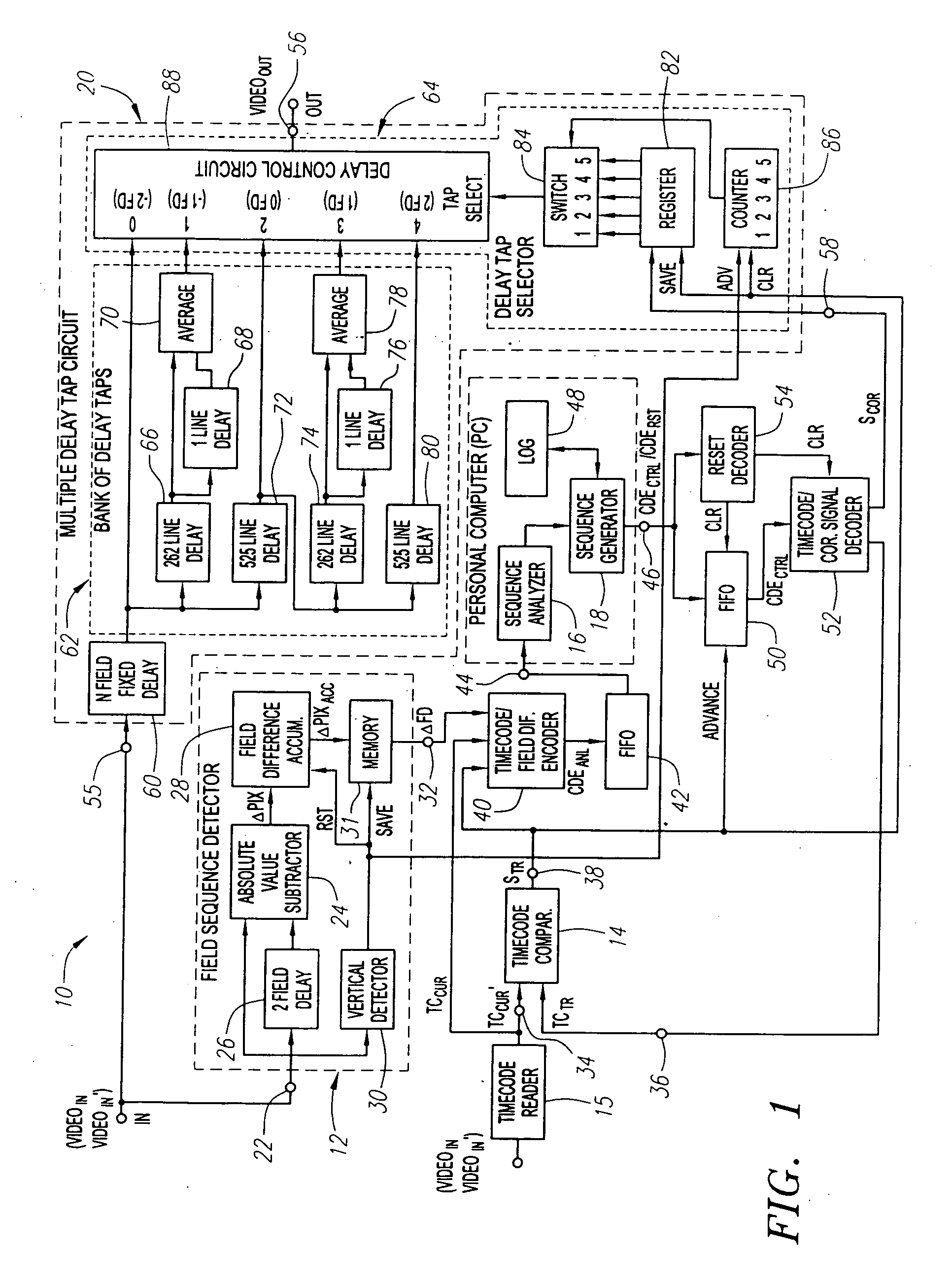
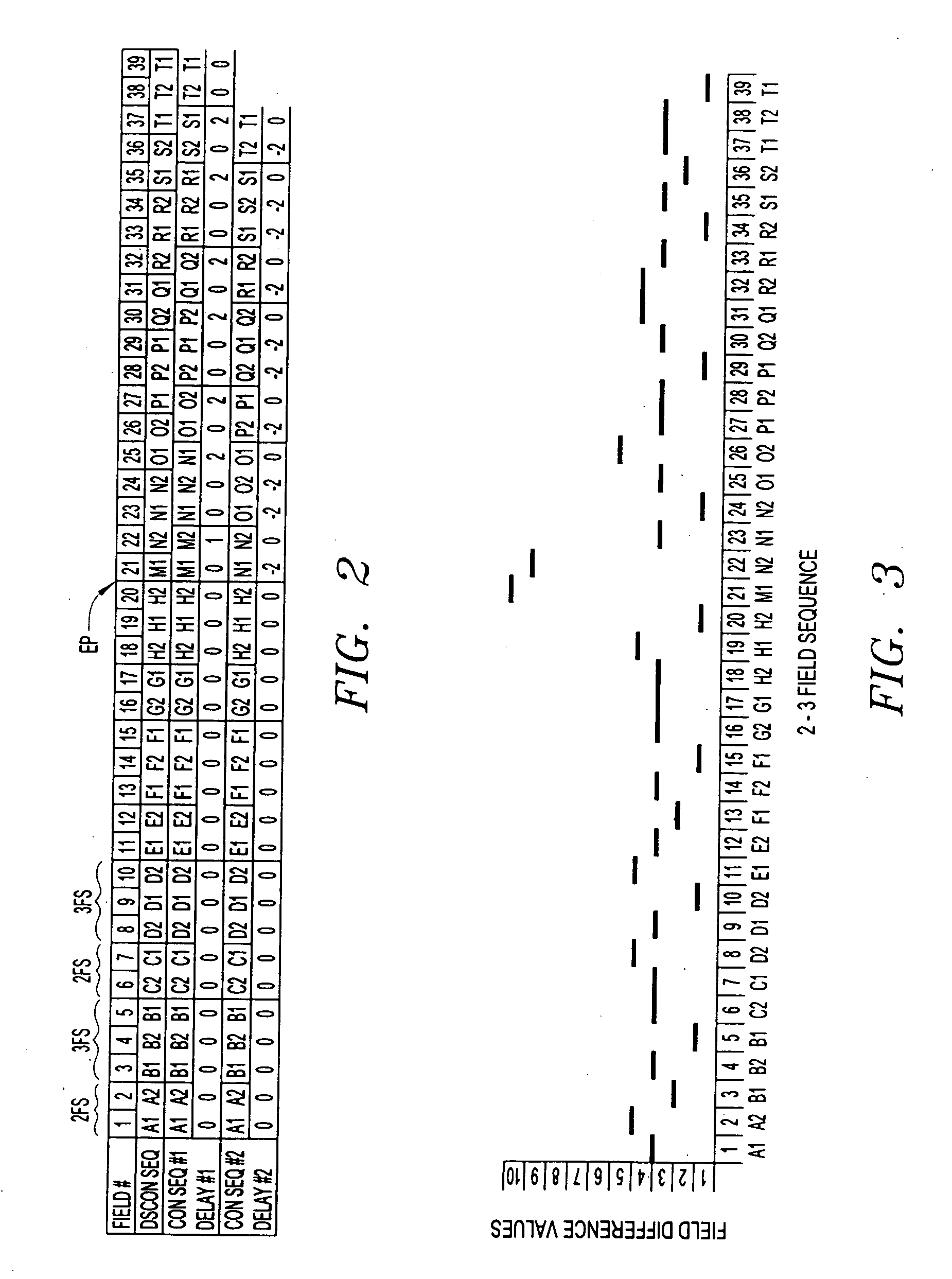
InactiveUS7139029B2Signal delayMinimize the numberTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsSequence analysisComputer science
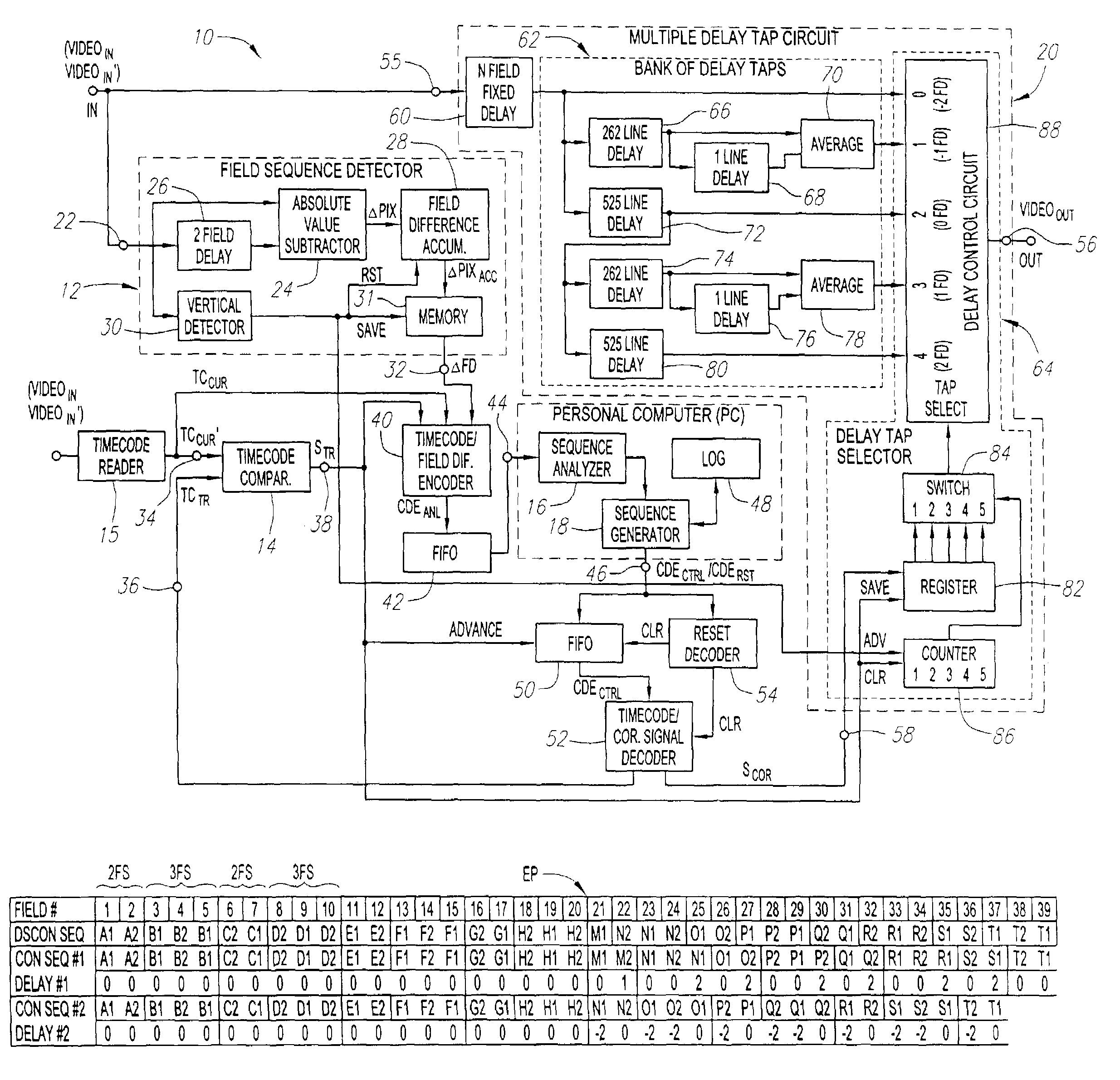
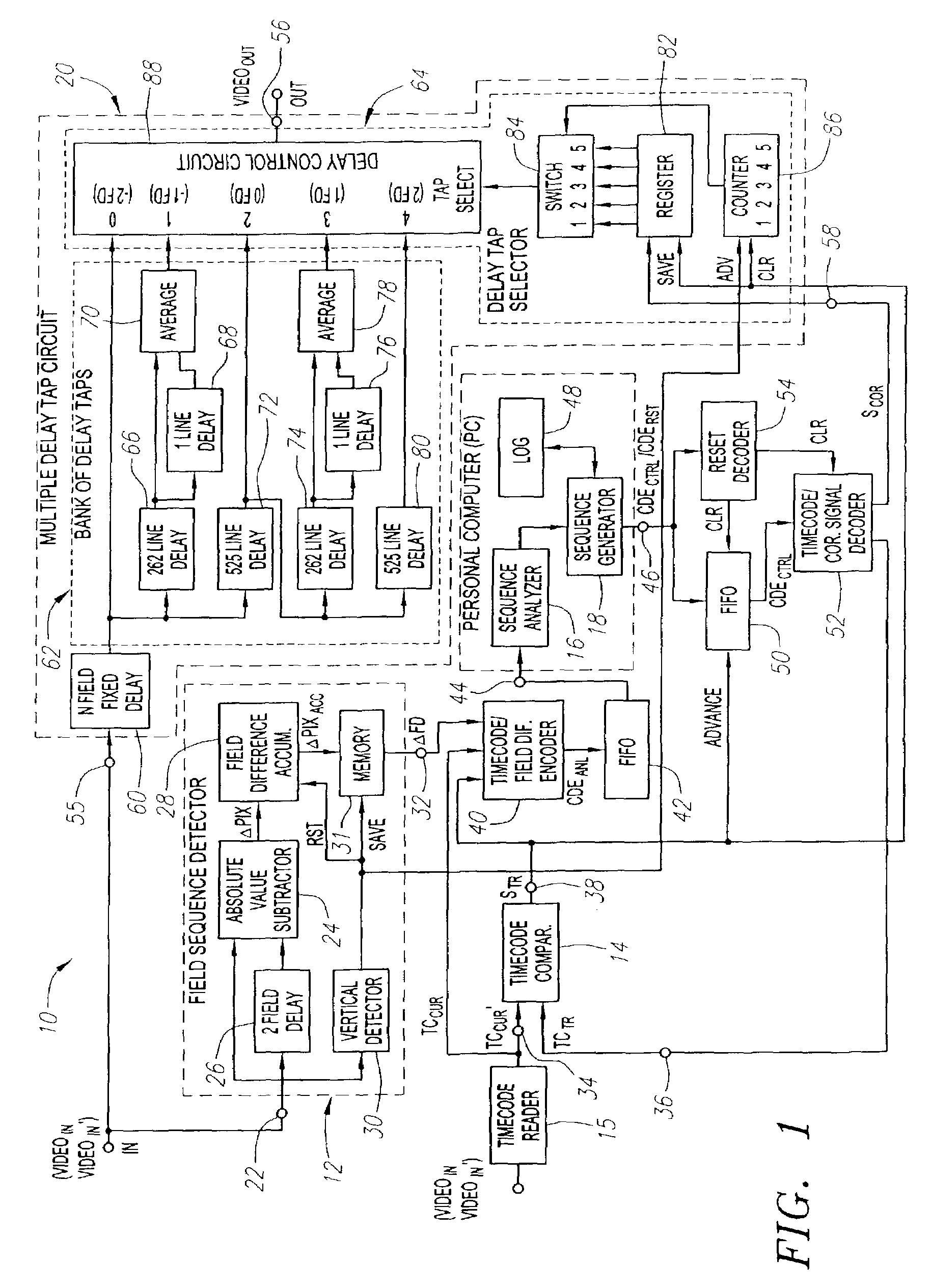
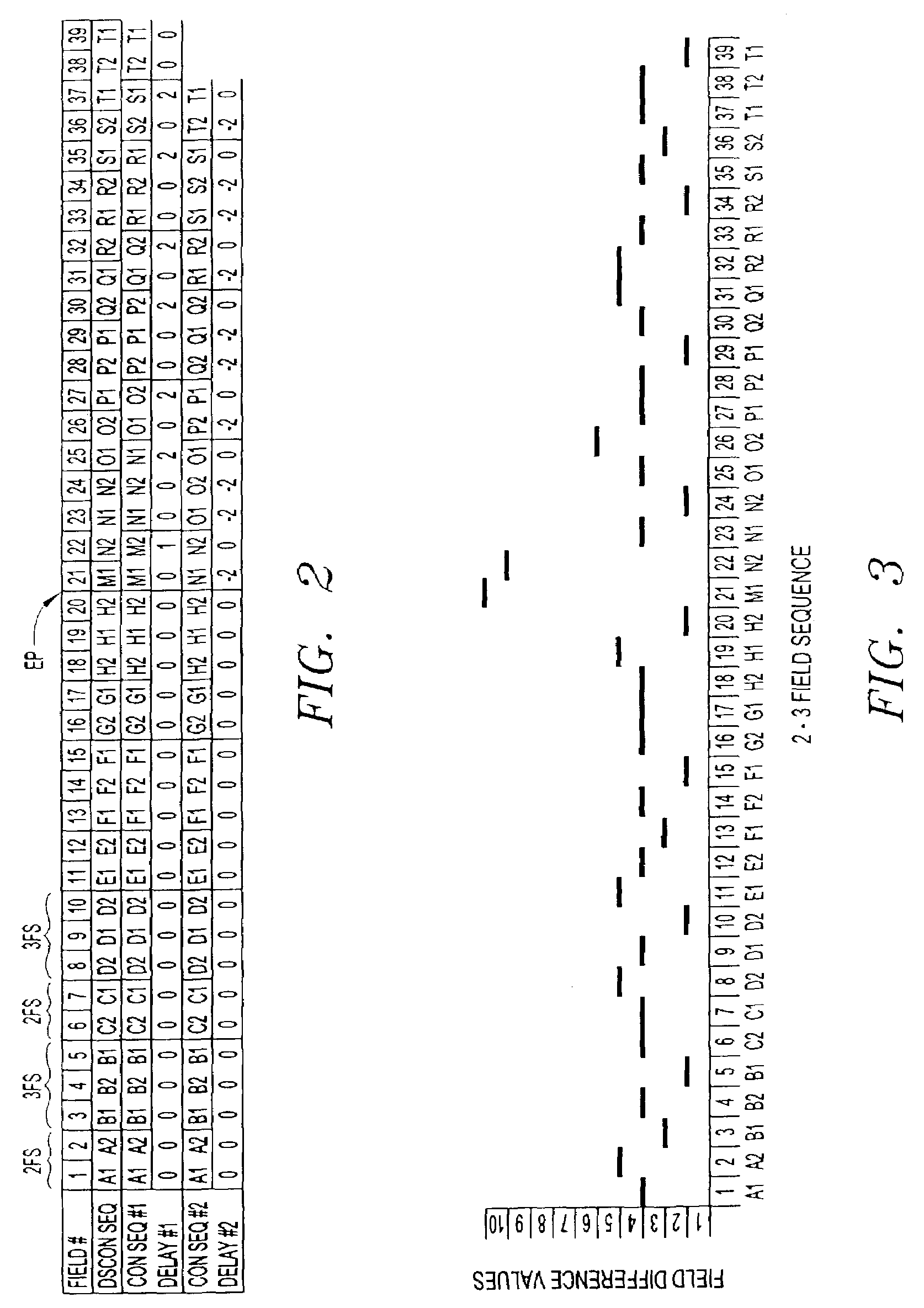
Systems and methods are provided for allowing a user to correct a discontinuous 2-3 field sequence within a disrupted video signal. A 2-3 field pattern fixer can be operated in a one-pass mode and / or a two-pass mode. In the one-pass mode, the disrupted video signal is analyzed to generate correction information, which is used to correct the disrupted video signal as it passes through the 2-3 pattern fixer, resulting in an undisrupted video signal with a continuous 2-3 field sequence. In the two-pass mode, the disrupted video signal is analyzed to generate correction information, which is then stored. This correction information is then used to correct a duplicate of the disrupted video signal, resulting in an undisrupted video signal with a continuous 2-3 field sequence. In this connection, the 2-3 field pattern fixer includes a field sequence detector, a field sequence analyzer, a field sequence generator and a multiple delay tap circuit. The field sequence detector generates field difference values in response to receiving the disrupted video signal. The field sequence analyzer analyzes these field difference values to determine one or more discontinuities within the discontinuous 2-3 field sequence. The field sequence generator generates one or more field sequence correction signals in response to this analysis. The multiple delay tap circuit applies these correction signals to a video signal to generate an undisrupted video signal having a continuous 2-3 field sequence. The 2-3 field pattern fixer can optionally includes a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) memory and a time code comparator, which can be used to store a multitude of the correction signals during the first pass of the two-pass mode, and for synchronizing the application of each of the correction signals to the duplicated disrupted video signal during the second pass of the two-pass mode.
Owner:ASCENT MEDIA GROUP
Display and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20070146384A1Minimizing brightness deteriorationMinimize blurringCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGray levelAlgorithm
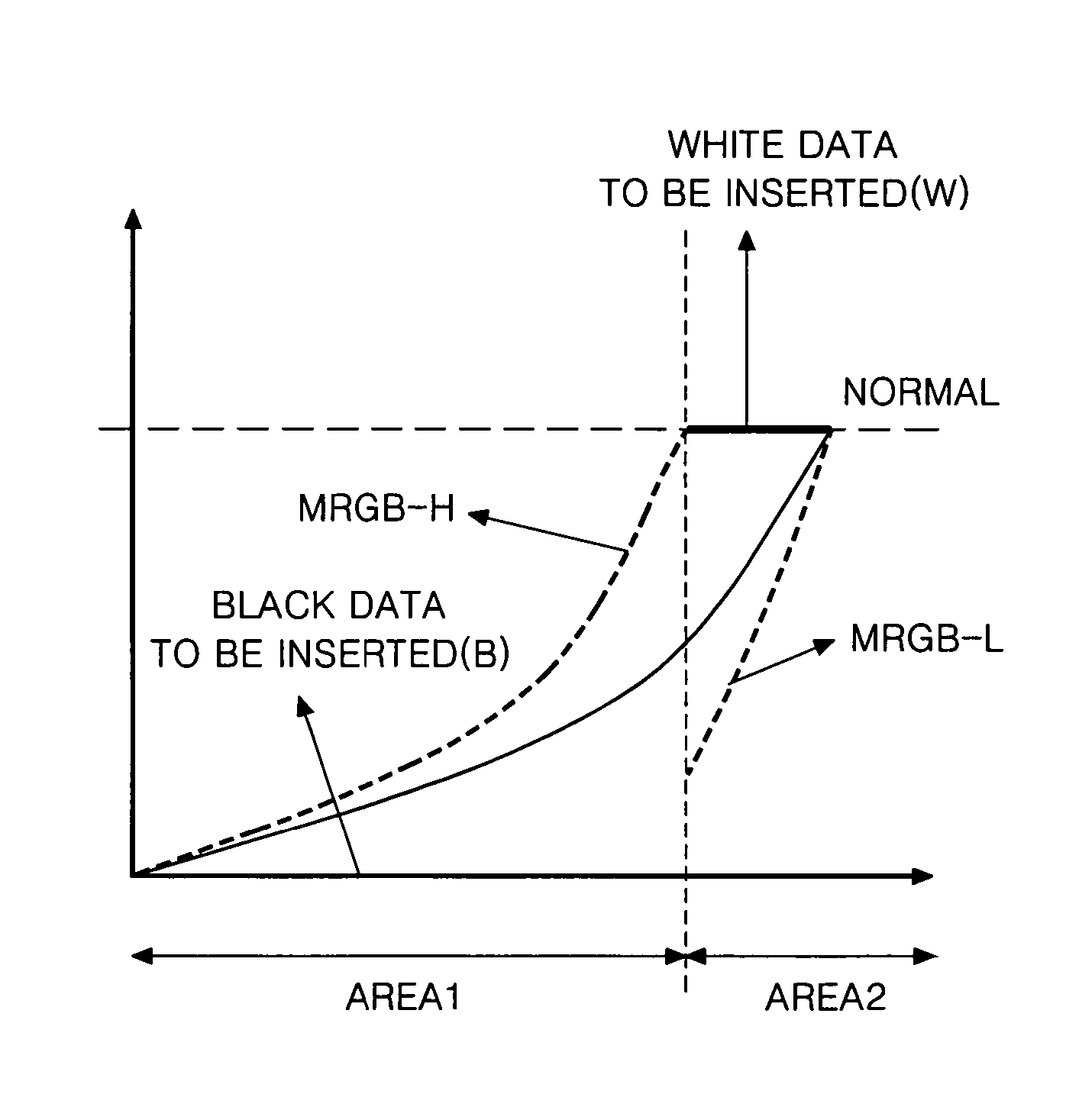
A display device adapted to minimize brightness deterioration and motion blurring in a motion picture and a driving method thereof are disclosed. The display device may include a data aligning part that analyzes a gray level of input data and inserts black data into frame data having less than a designated reference gray level; and a driver that displays the data from the data aligning part in a display panel.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Image enhancement or correction software, method, apparatus and system for substantially minimizing blur in the scanned image
InactiveUS7330594B2Minimize blurringMinimizing in image dataImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceImaging data
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Printing device
InactiveUS20110193905A1Increase delivery speedIncrease printing speedInking apparatusOther printing apparatusEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A printing device includes a plurality of heads, a movement mechanism, and a calculation unit. The heads are configured to print an image on a medium by discharging colored inks onto the medium. The heads discharge the inks at different positions in a predetermined direction. The movement mechanism is configured to move the medium and the heads in the predetermined direction relative to each other. The calculation unit is configured to determine respective discharge amounts of ink discharged from each of the heads when the image is printed. A position in the predetermined direction, in which the inks are discharged from the heads, is varied based on the discharge amounts determined by the calculation unit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Strobe illumination
ActiveUS7127159B2Minimize blurringReduce (if not eliminate) artifactsTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansDuration periodTime segment
An illumination technique is provided that adjusts the respective light intensities of each of a plurality of light sources that are strobed at desirable consistent intensities by adjusting a respective light pulse pattern for each respective light source. All the light sources are controlled to illuminate an object throughout a strobe duration period. The light pulse patterns may be micro-strobed light pulse patterns, formed by a variety of methods. The illumination technique is usable to preserve the general shape of the edge intensity profile on an object, and allow precision edge position measurements, regardless of whether the object is moving or not during image acquisition.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Display and driving method thereof
ActiveUS8054321B2Minimize blurringIncrease brightnessCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGray levelDisplay device
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Electron microscope
ActiveUS8742342B2Minimize blurringMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesElectron sourceScanning tunneling microscope
A scanning electron microscope suppresses a beam drift by reducing charging on a sample surface while suppressing resolution degradation upon observation of an insulator sample. An electron microscope includes an electron source and an objective lens that focuses an electron beam emitted from the electron source, which provides an image using a secondary signal generated from the sample irradiated with the electron beam. A magnetic body with a continuous structure and an inside diameter larger than an inside diameter of an upper pole piece that forms the objective lens is provided between the objective lens and the sample.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Electron beam exposure apparatus and method
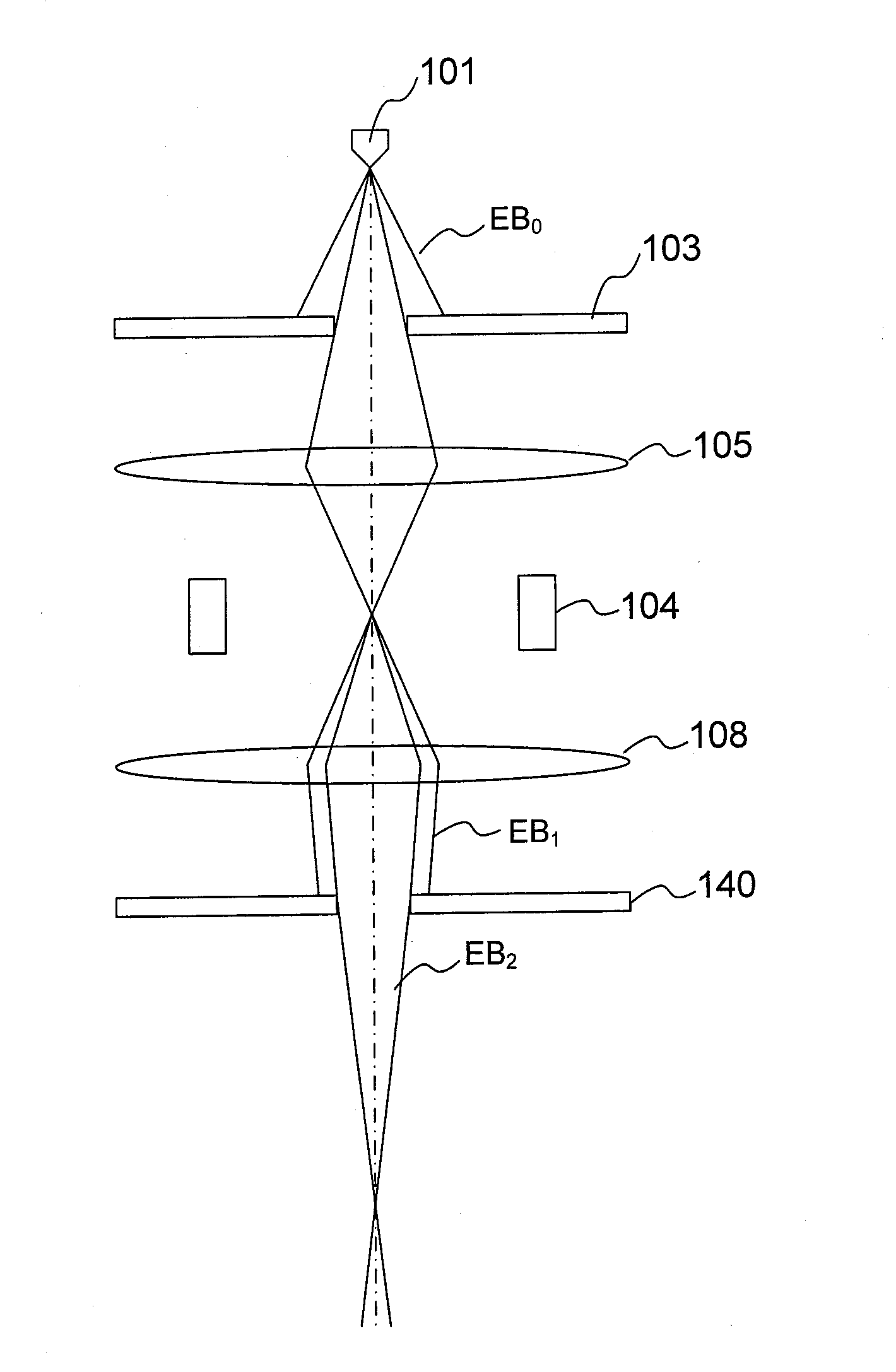
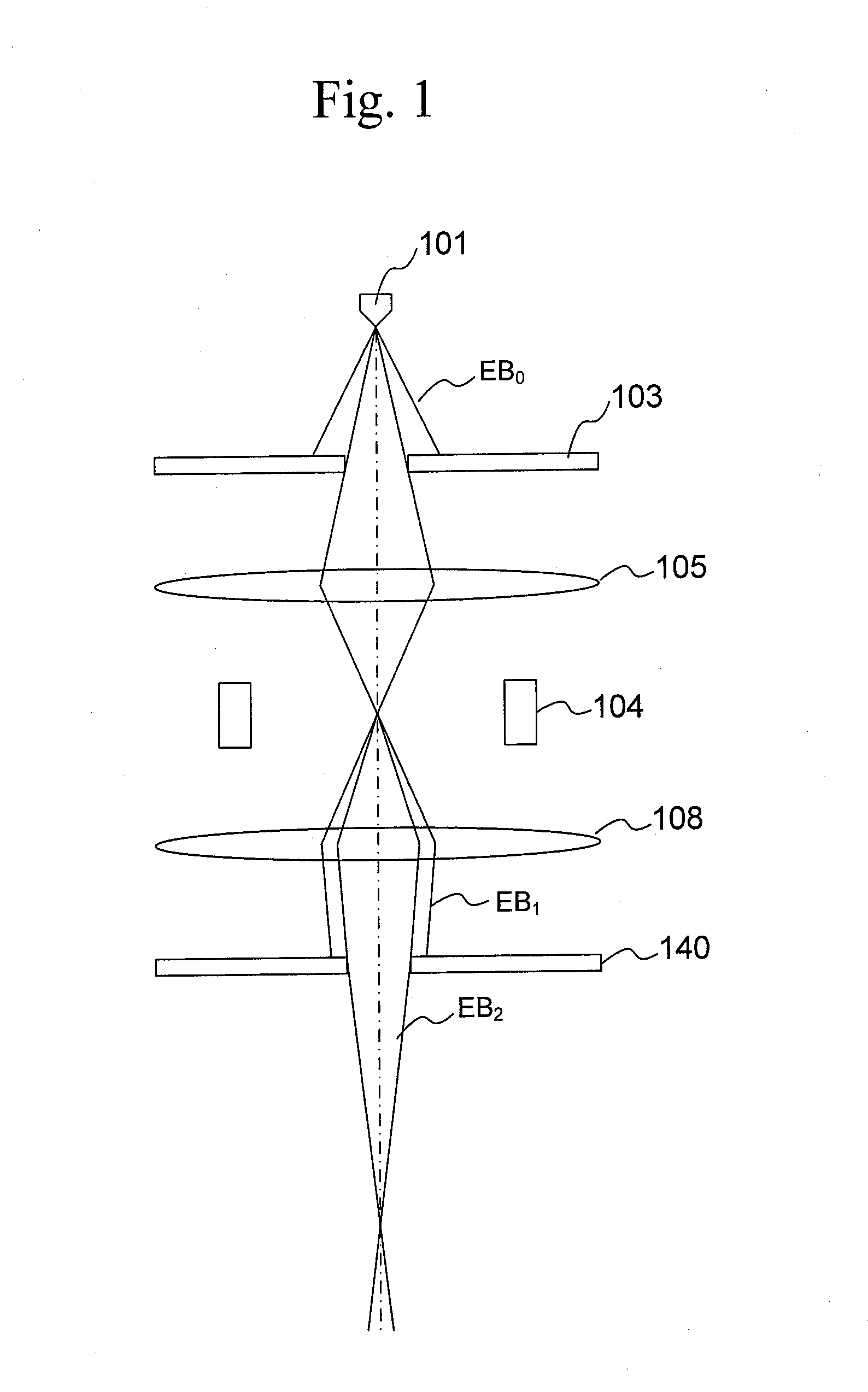
InactiveUS20140131589A1Minimize blurringIncrease currentStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsHigh current densityElectron-beam lithography
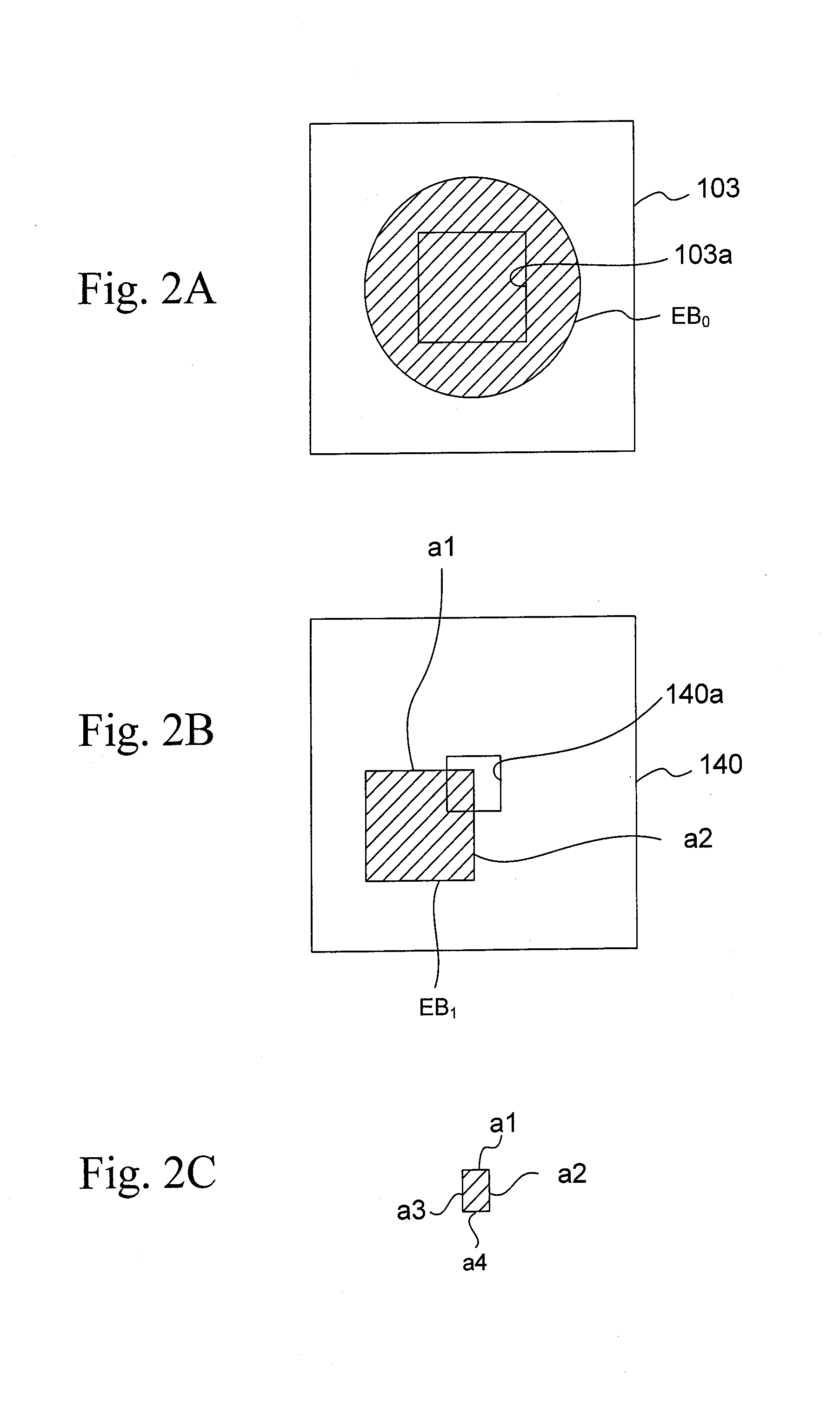
An electron beam EB0 emitted from an electron gun 101 is cut by a first aperture 103a into a rectangular electron beam DB', which is then cut by second and third apertures 140a, 150a into an electron beam EB3 so that the edge cut by the first aperture 103a is removed from the electron beam EB1. This can prevent blur due to the influence of coulomb interaction of the electron beam EB1 between the first and second apertures 103a to 140a and perform highly accurate exposure with the electron beam EB3 having high current density.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Image Capturing Device and Method
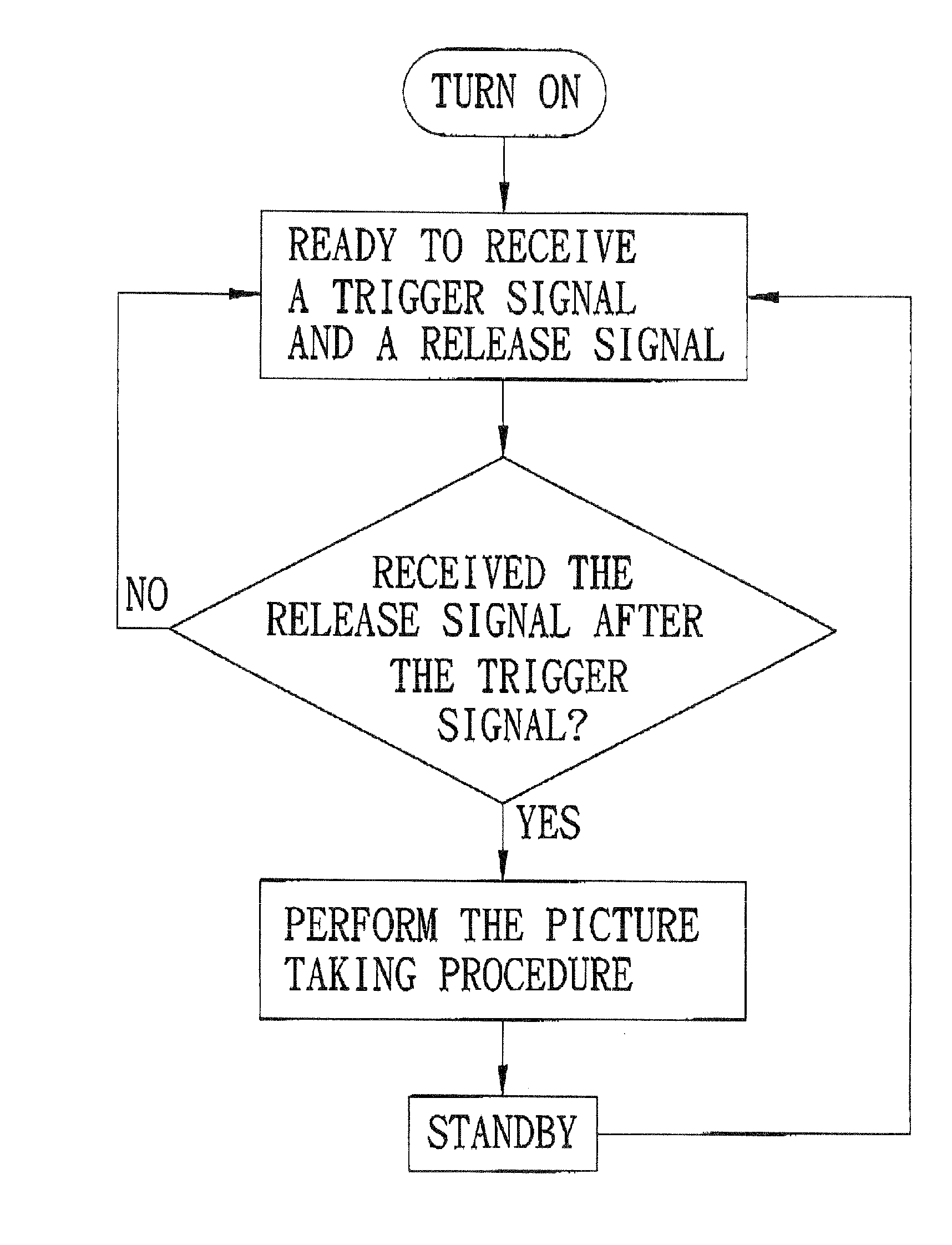
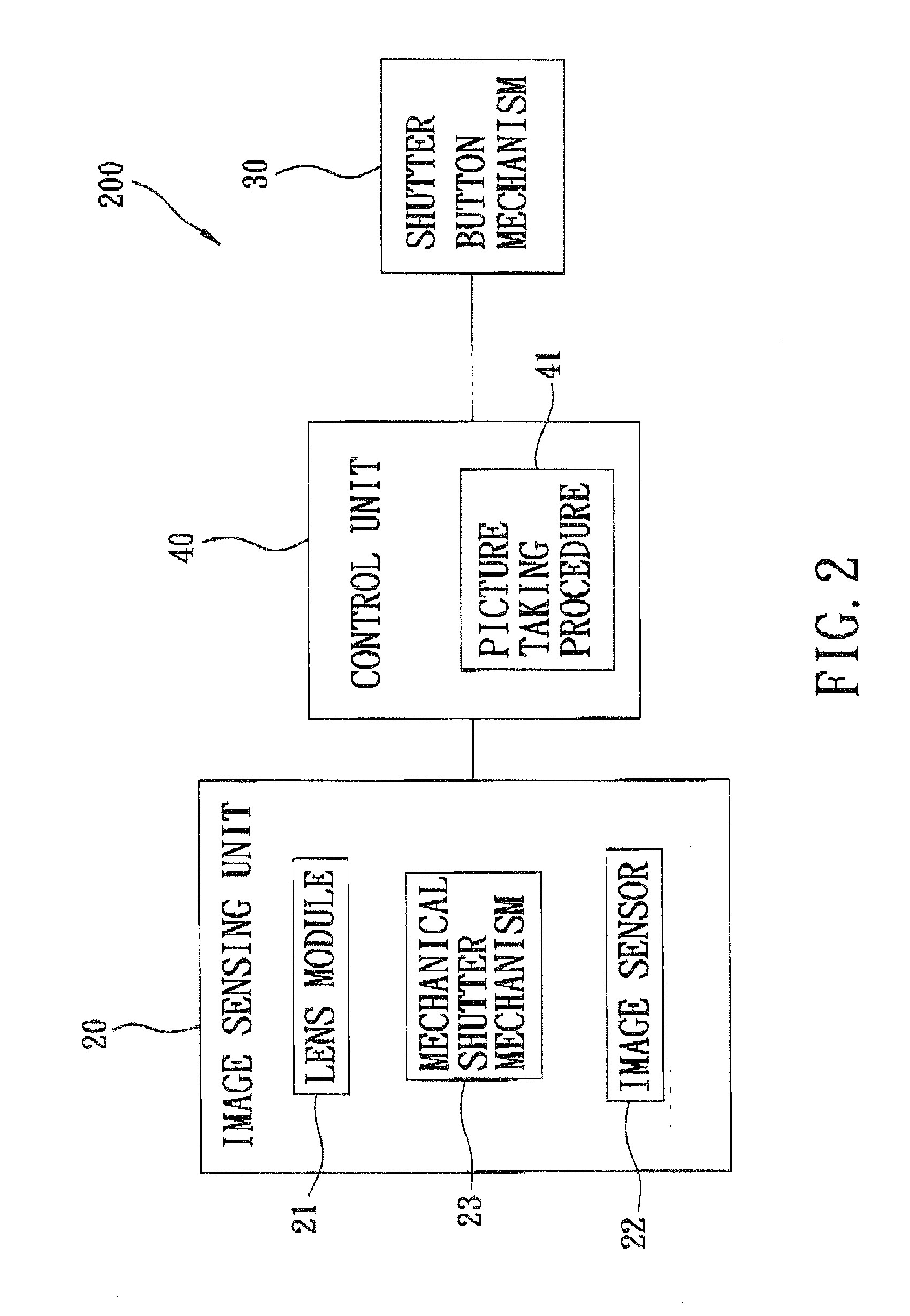
An image capturing device includes an image sensing unit, a shutter button mechanism, and a control unit. The image sensing unit includes a lens module and an image sensor. The shutter button mechanism is operable to generate a trigger signal when pressed and to generate a release signal when the shutter button mechanism is released after being pressed. The control unit is configured to perform, in response to the release signal from the shutter button mechanism, a picture taking procedure for controlling the image sensing unit to capture an image.
Owner:ASIA OPTICAL CO INC
Methods and apparatus for correction of 2-3 field patterns
InactiveUS20070064148A1Signal delayMinimize the numberPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningSequence analysisComputer science
Systems and methods are provided for allowing a user to correct a discontinuous 2-3 field sequence within a disrupted video signal. A 2-3 field pattern fixer can be operated in a one-pass mode and / or a two-pass mode. In the one-pass mode, the disrupted video signal is analyzed to generate correction information, which is used to correct the disrupted video signal as it passes through the 2-3 pattern fixer, resulting in an undisrupted video signal with a continuous 2-3 field sequence. In the two-pass mode, the disrupted video signal is analyzed to generate correction information, which is then stored. This correction information is then used to correct a duplicate of the disrupted video signal, resulting in an undisrupted video signal with a continuous 2-3 field sequence. In this connection, the 2-3 field pattern fixer includes a field sequence detector, a field sequence analyzer, a field sequence generator and a multiple delay tap circuit. The field sequence detector generates field difference values in response to receiving the disrupted video signal. The field sequence analyzer analyzes these field difference values to determine one or more discontinuities within the discontinuous 2-3 field sequence. The field sequence generator generates one or more field sequence correction signals in response to this analysis. The multiple delay tap circuit applies these correction signals to a video signal to generate an undisrupted video signal having a continuous 2-3 field sequence. The 2-3 field pattern fixer can optionally includes a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) memory and a time code comparator, which can be used to store a multitude of the correction signals during the first pass of the two-pass mode, and for synchronizing the application of each of the correction signals to the duplicated disrupted video signal during the second pass of the two-pass mode.
Owner:ASCENT MEDIA GROUP
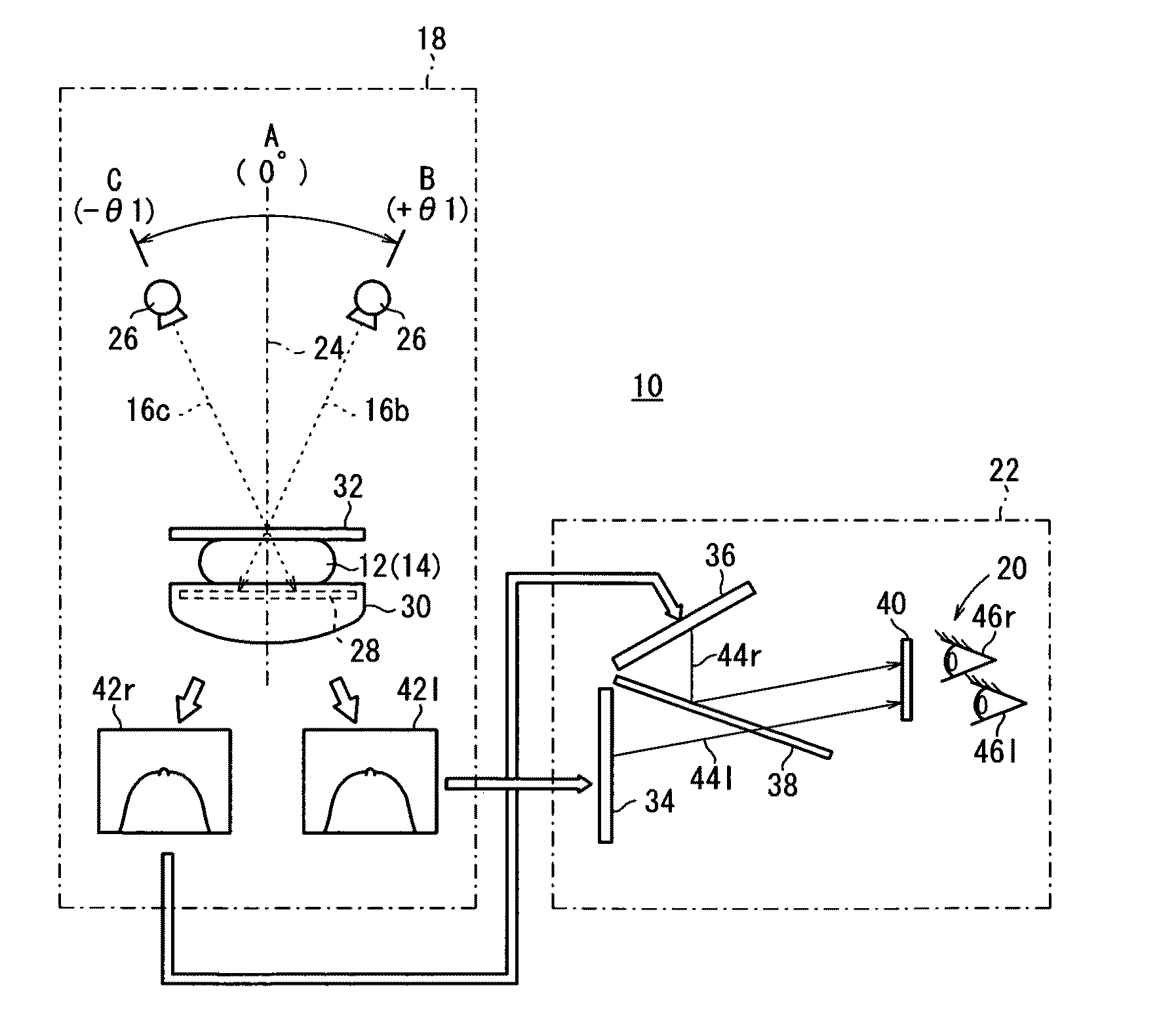
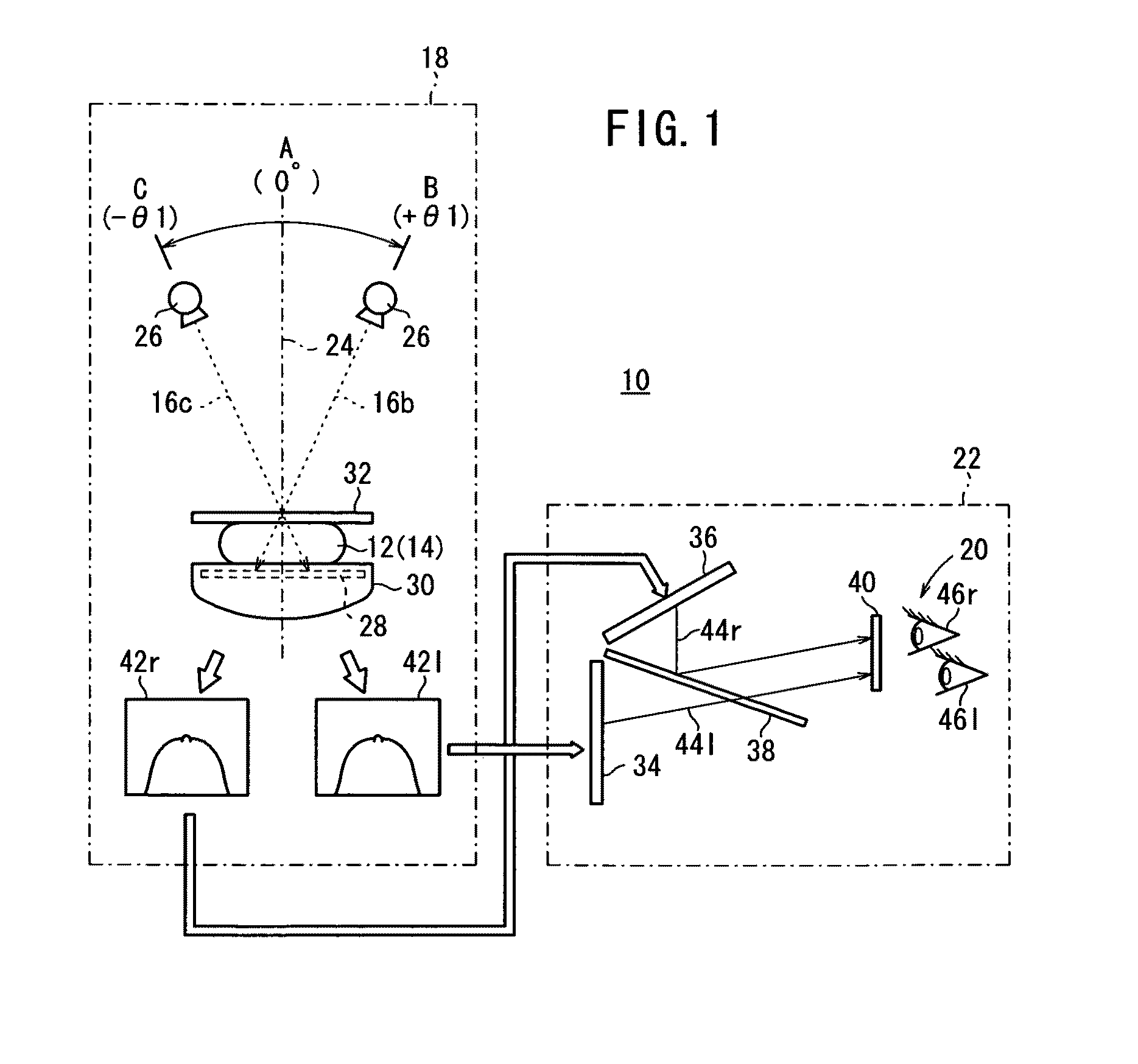
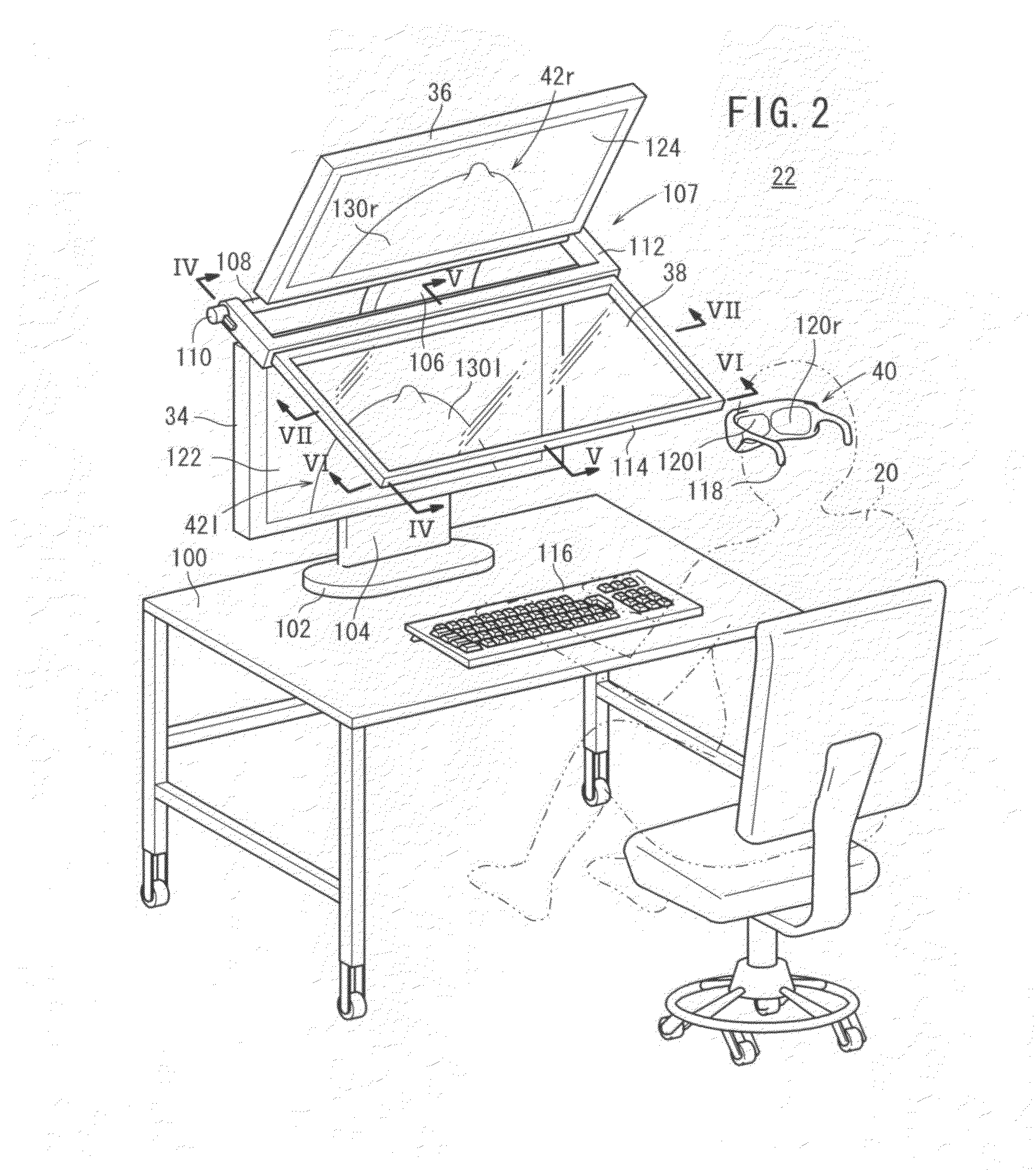
Three-dimensional image display apparatus and method of adjusting displayed image
InactiveUS20110205624A1Minimize blurringThe relative position is appropriateSteroscopic systemsOptical elementsComputer graphics (images)Left eye
A three-dimensional image display apparatus includes an image combiner which combines a grid-like right-eye image and a grid-like left-eye image, which are substantially identical to each other, into a grid-like combined image, and a position adjusting mechanism which adjusts a position of the image combiner with respect to an observer to adjust a blur in the grid-like combined image due to a positional deviation between the grid-like right-eye image and the grid-like left-eye image.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com