Patents
Literature
121results about How to "Show normaly" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
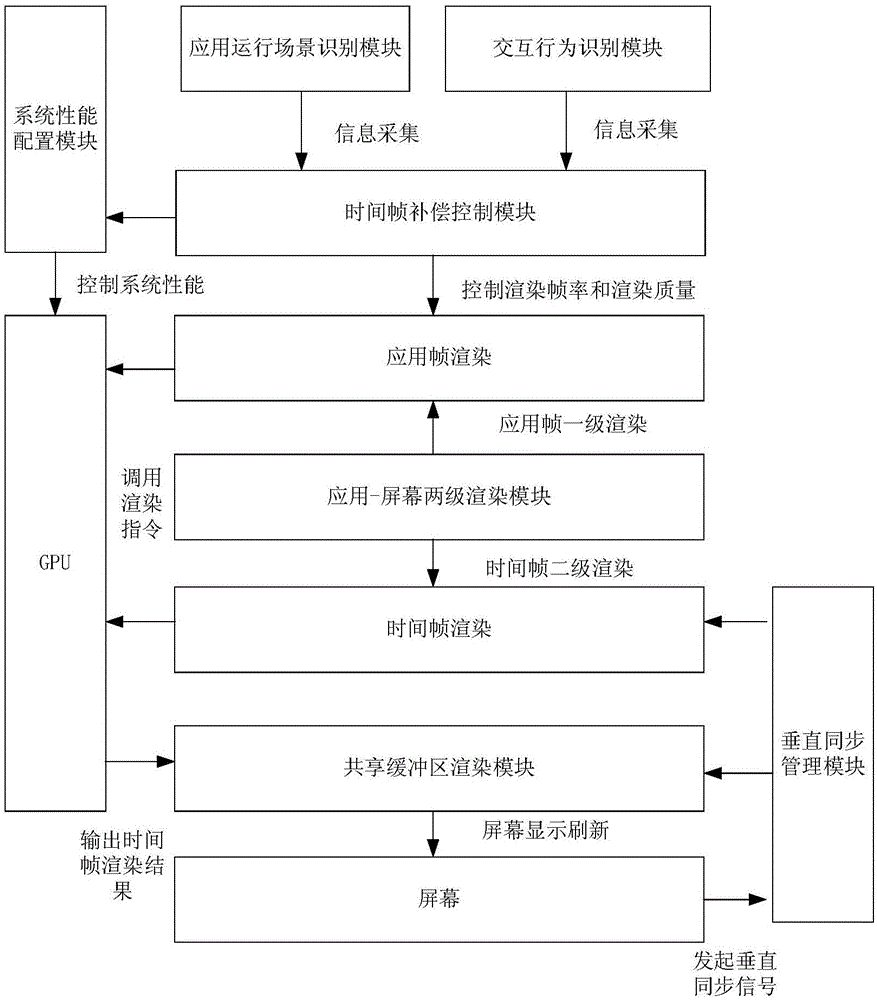
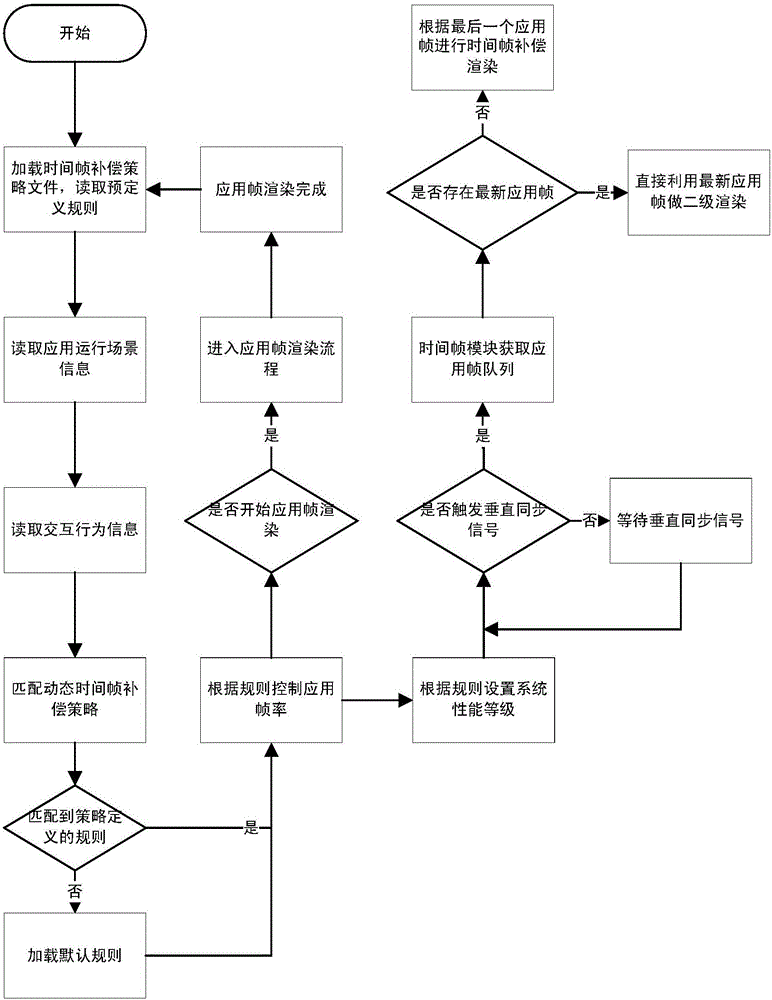
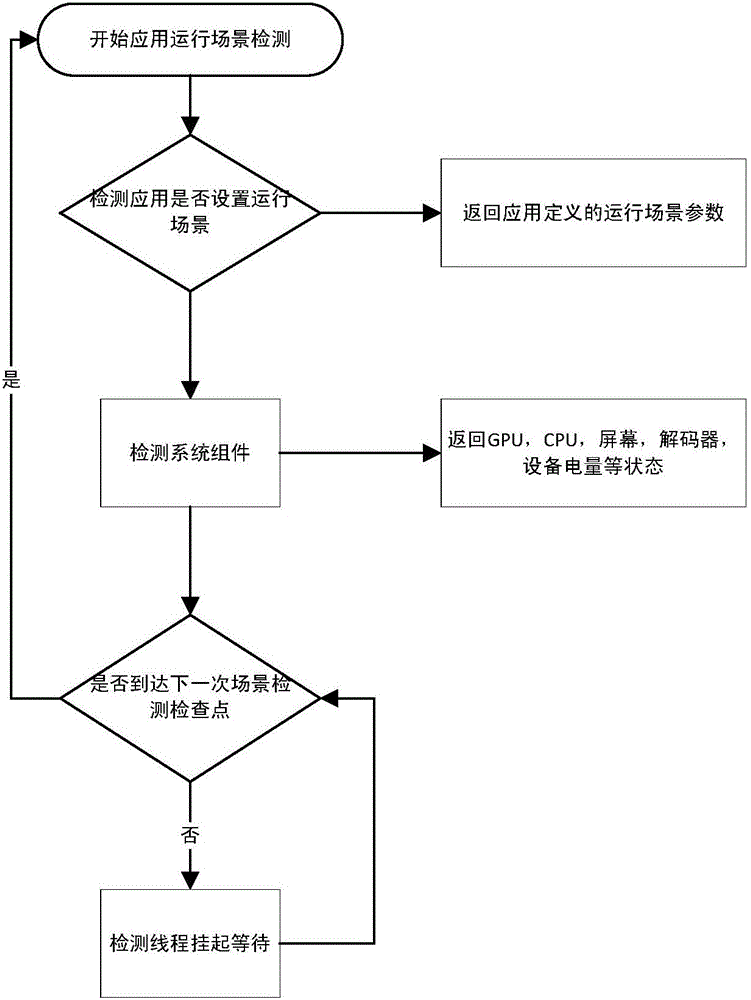
Dynamic time frame compensation rendering system and dynamic time frame compensation rendering method for virtual-reality mobile terminal
ActiveCN106296566ALower latencyControl rendering timeImage memory managementProcessor architectures/configurationSequence controlComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a dynamic time frame compensation rendering system and a dynamic time frame compensation rendering method for a virtual-reality mobile terminal. The method comprises the following steps of generating an application frame buffer sequence by use of frame rendering, extracting the up-to-date or latest application frame from the application frame buffer sequence, and performing secondary rendering, thereby obtaining a time frame; sending the time frame to a shared buffer; and under sequence control of a vertical synchronous management module, reading a time frame rendering result by use of a screen, and performing updating. By virtue of the design of the shared buffer, a GPU rendering result is directly stored in a cache updated by the screen, so that delay of multi-caching exchange is reduced; by virtue of vertical synchronous time management, the GPU rendering time is controlled, collision between GPU rendering writing and screen update reading is avoided, frames can be normally displayed with low delay, and no splitting is generated.
Owner:NANJING RUIYUE INFORMATION TECH
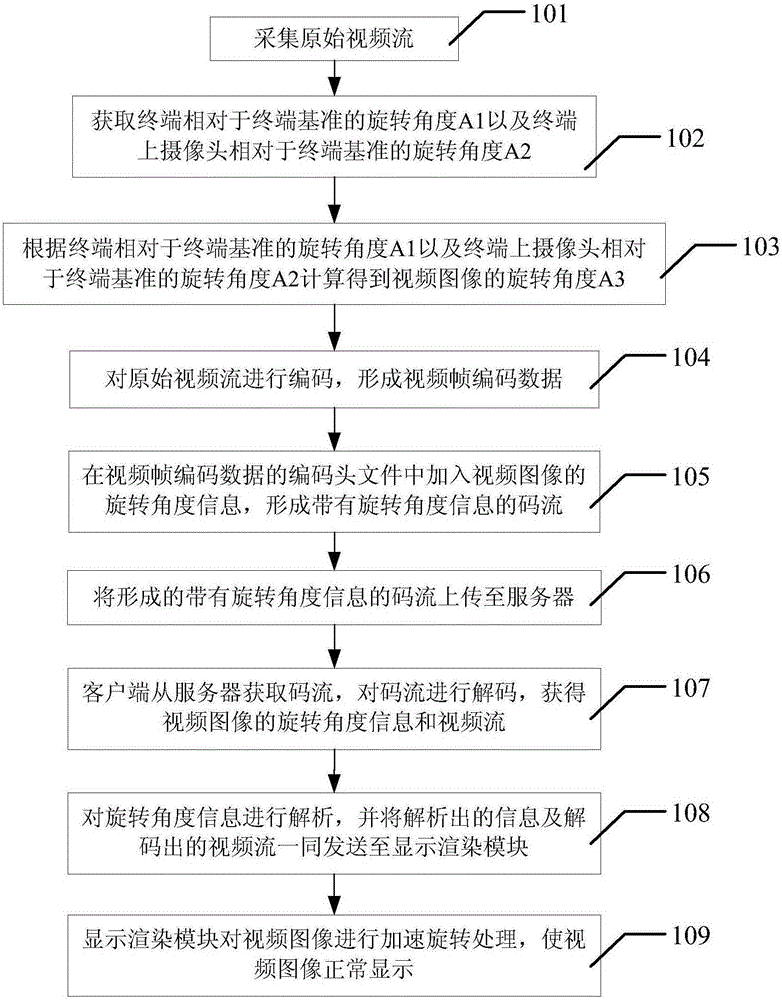
Method and system applied to terminal for collecting streaming media and automatically identifying and adjusting direction
ActiveCN105227963ASolve the problem of not displaying properlyShow normalyDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Computer module
The invention discloses a method and a system applied to a terminal for collecting streaming media and automatically identifying and adjusting direction. The method comprises the steps of: collecting an original video stream; obtaining a rotating angle A1 of the terminal relating to a terminal benchmark and a rotating angle A2 of a camera on the terminal relating to the terminal benchmark; calculating a rotating angle A3 of the video image; coding the original video stream to form video frame coded data; adding the rotating angle information of the video image into the coded header file of the video frame coded data to form a code stream with the rotating angle information; uploading the formed code stream with the rotating angle information to a server; obtaining the code stream from the server by a client to decode the code stream to obtain the rotating angle information of the video image and the video stream; parsing the rotating angle information, and sending both the parsed information and the decoded video stream to a display rendering module; acceleratedly rotating the video image by the display rendering module to allow the video image to be displayed normally.
Owner:BEIJING BAOFENG TECH
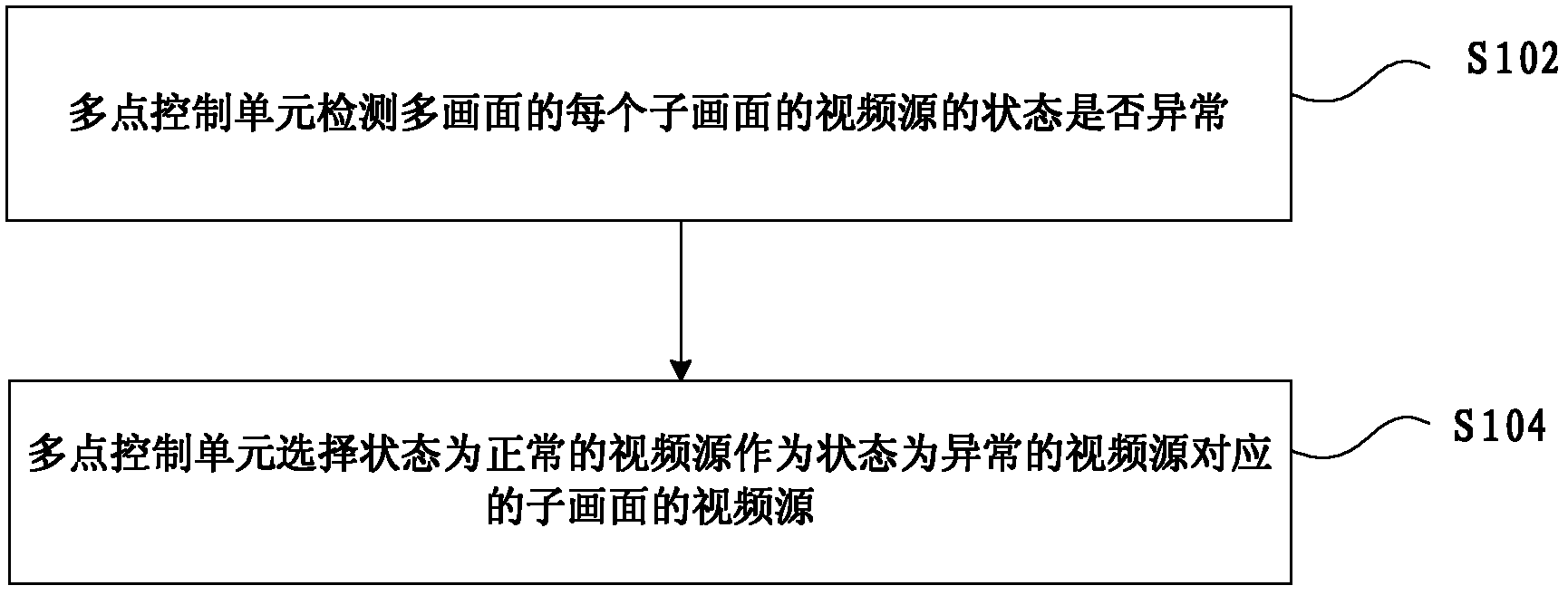
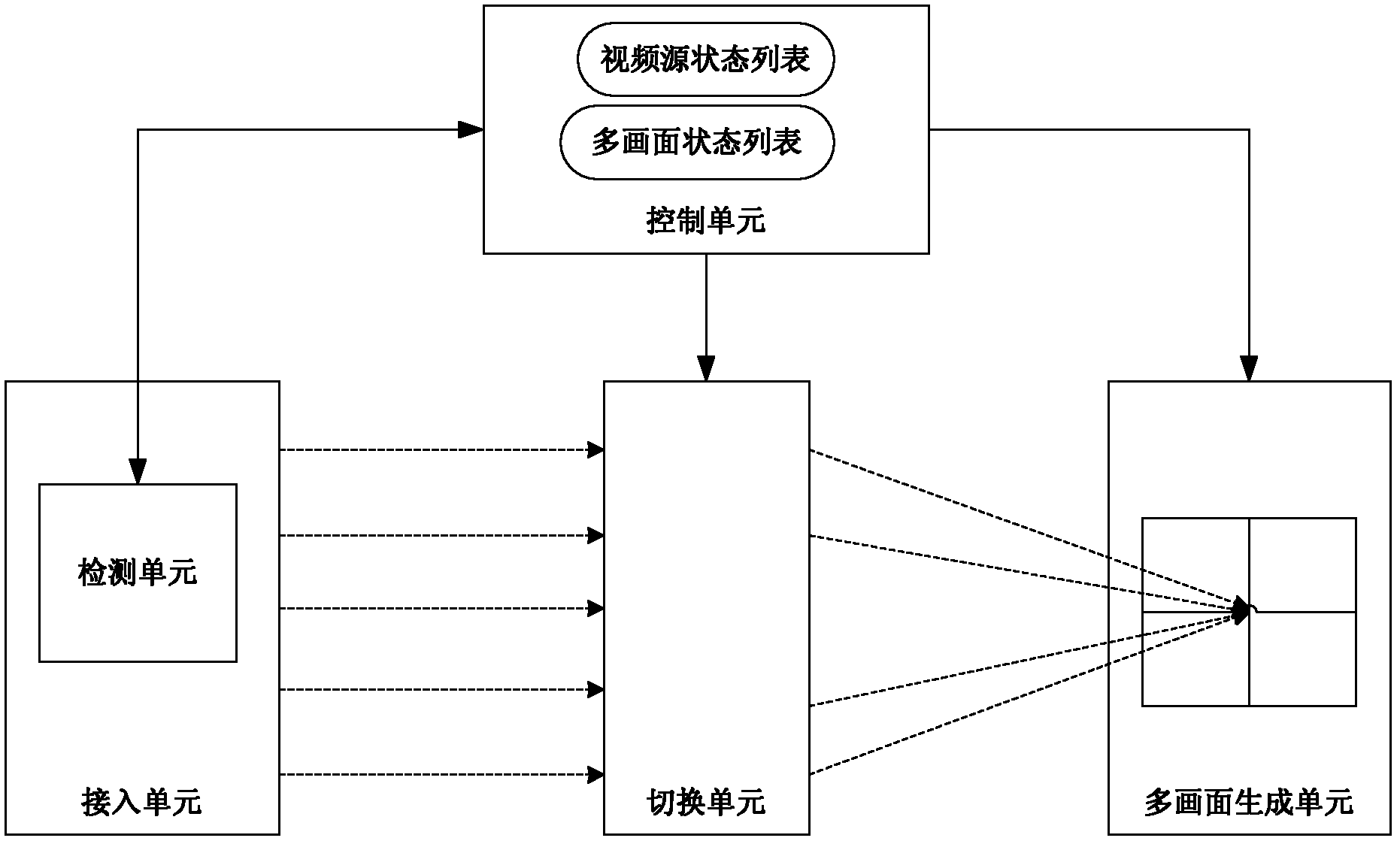
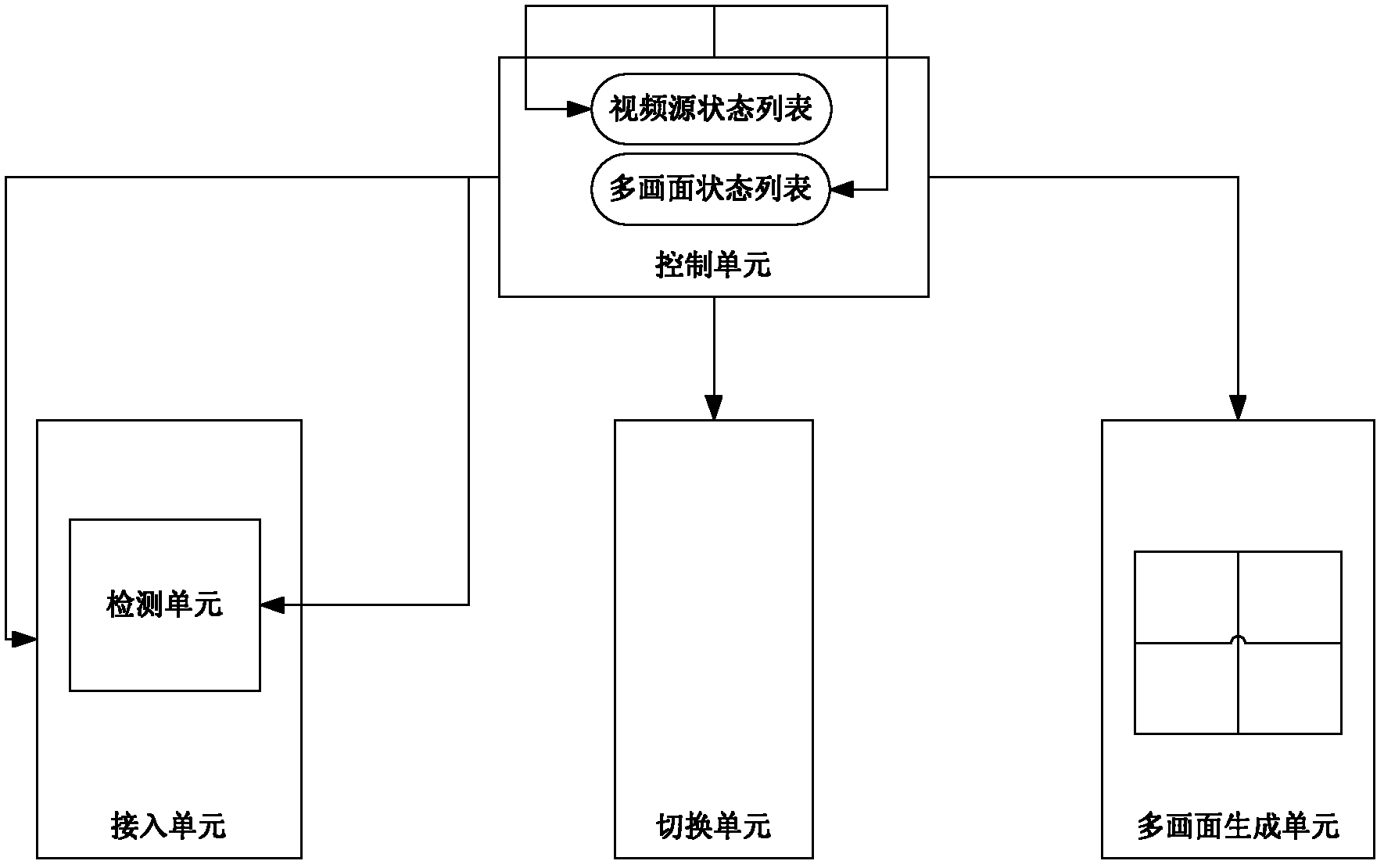
Selection method and device for video source of sub-picture of multi-picture in multimedia conference
ActiveCN102215375ASolve the problem of meeting qualityShow normalyTelevision conference systemsTwo-way working systemsSelection methodComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a selection method and device for a video source of a sub-picture of a multi-picture in a multimedia conference. The method comprises the following steps that: a multi point control unit detects if the state of the video source of each sub-picture of the multi-picture is abnormal; and the multi-point control unit selects the video source in a normal state as a video source of the sub-picture corresponding to the video source in an abnormal state. The invention solves the problem that the input fault of a terminal video or no video input affects the conference quality of the video conference in correlation techniques, and achieves the effect of normal image display for the sub-pictures of the multi-picture.
Owner:ZTE CORP
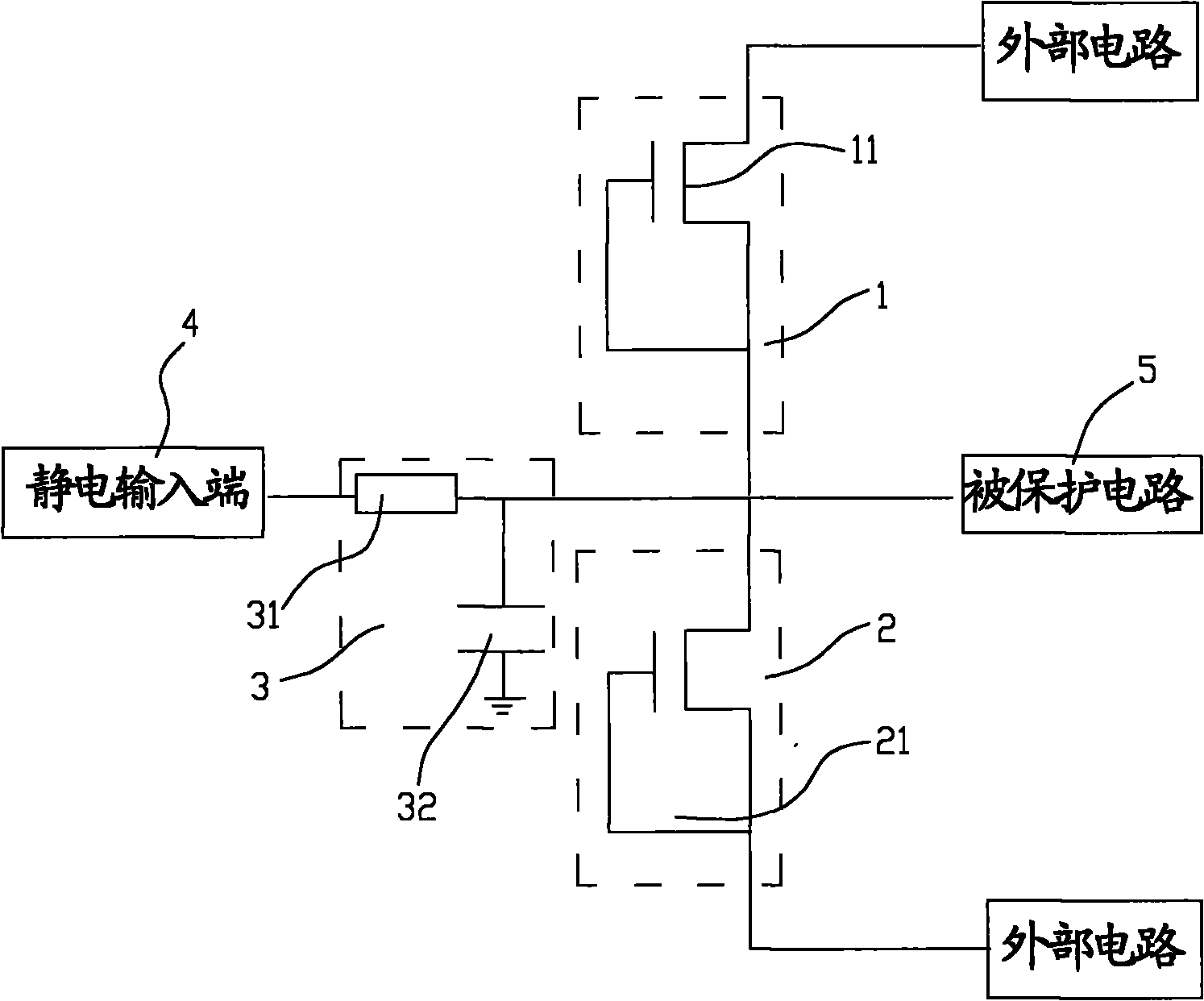
Static protection circuit, in particular static protection circuit of liquid crystal display panel and static protection circuit array of liquid crystal display panel
ActiveCN102118024AImprove the ability to resist positive and negative high voltage static electricityShow normalyStatic indicating devicesEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
The invention relates to a static protection circuit, in particular to a static protection circuit of a liquid crystal display panel and a static protection circuit array of the liquid crystal display panel. The static protection circuit comprises a discharging unit and a delay circuit, wherein the output end of the delay circuit is connected with the input end of the discharging unit; and by means of the delay circuit, a static pulse is delayed and the pulse width of the static pulse is increased to ensure that the pulse width of the static pulse is greater than the response time of the discharging unit so that static electricity is released through the discharging unit. Through the static protection circuit, the static pulse is prevented from entering a protected circuit.
Owner:BEIHAI HKC OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
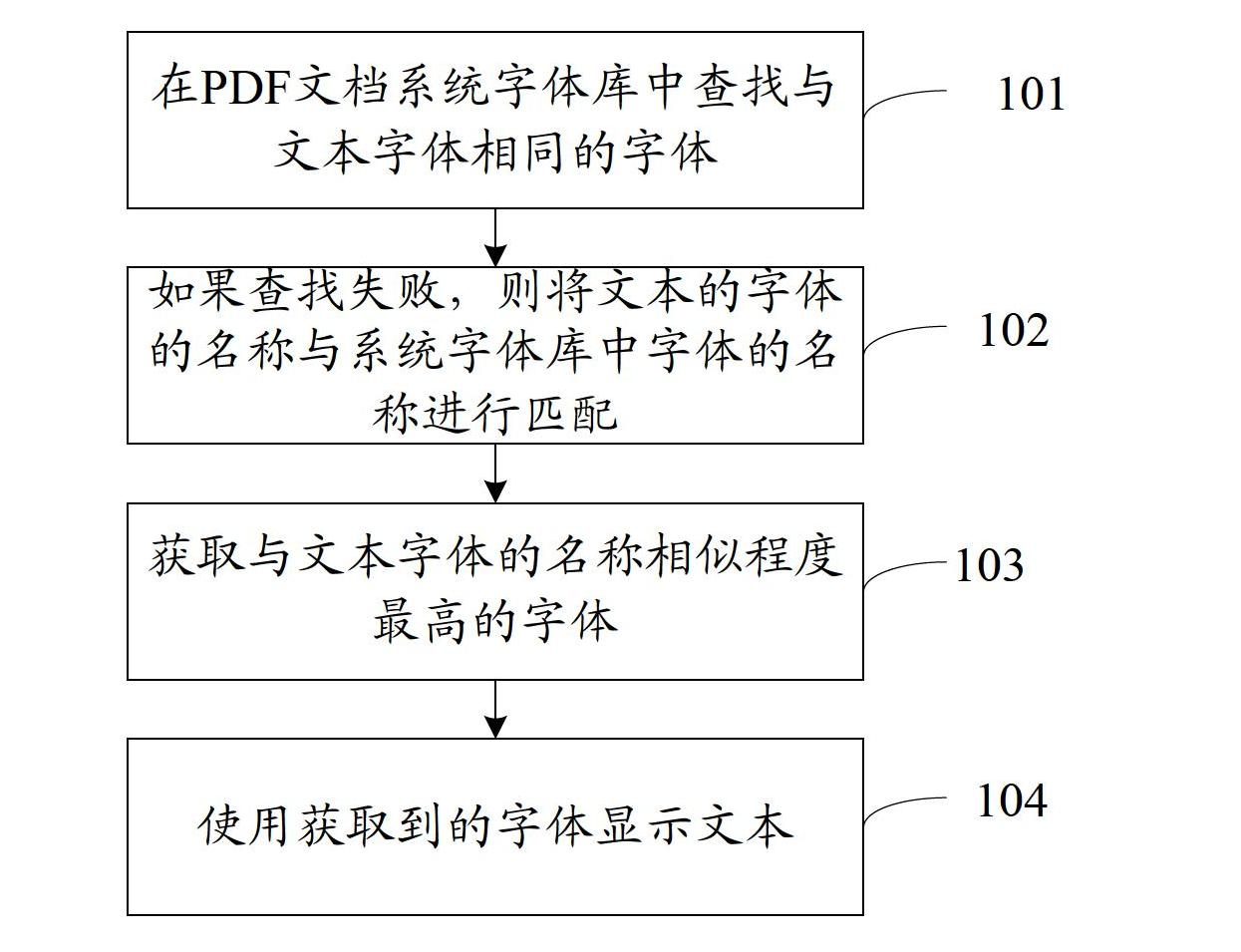
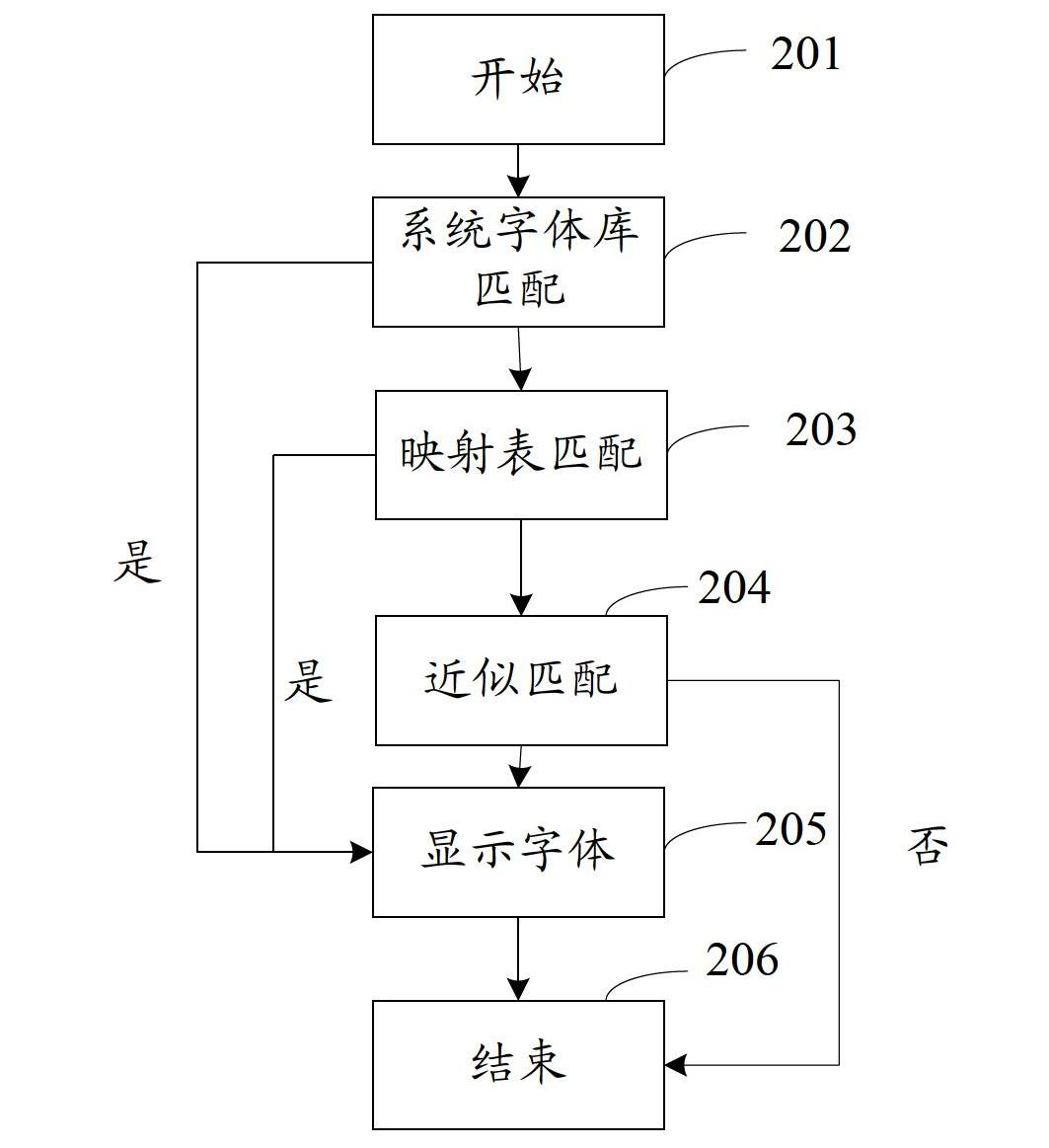
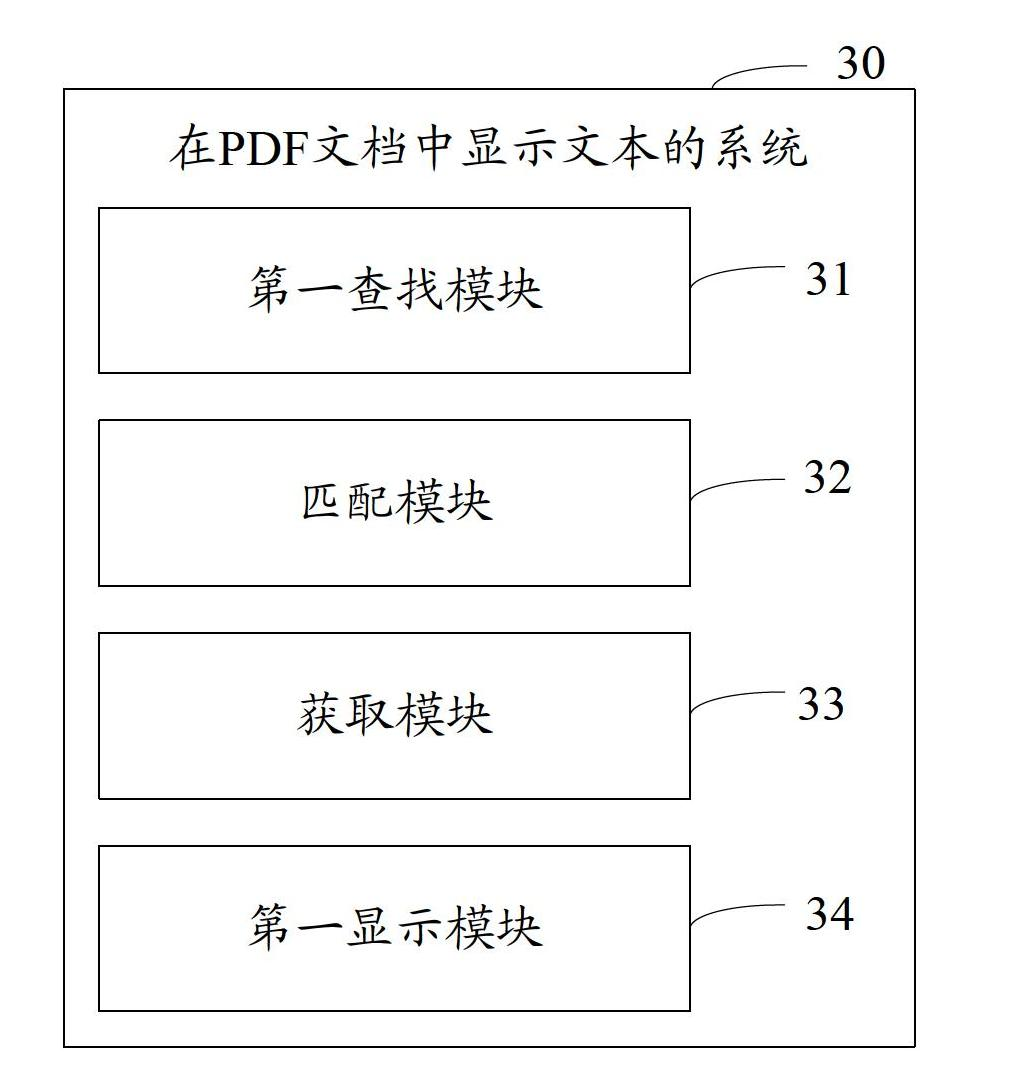
Method and system for displaying text in PDF (portable document format) document
InactiveCN102681978AEasy to useShow normalySpecial data processing applicationsPortable document formatInformation retrieval
The invention discloses a method and system for displaying a text in a PDF document, which are used for solving the problem that the system can not normally display the document when a user edits the text by a PDF document in the prior art. According to the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, a font same with a text font is looked up from a PDF document system font library; if failed, the name of the text font is matched with the name of the font in the system font library to obtain the font which has the highest similar degree with the name of the text font; and the text is displayed by the obtained font. According to the technical scheme, a purpose that the text font can be normally displayed when the user edits the text in the PDF document, thereby bringing convenience for users.
Owner:WONDERSHARE TECH CO LTD
Array substrate and display device
ActiveCN107731151AIncrease width sizeShow normalyStatic indicating devicesImage resolutionDisplay device
The invention discloses an array substrate and a display device. The array substrate comprises a display area and a non-display area, wherein the display area comprises a first sub display area and aplurality of second sub display areas; the non-display area comprises a first sub non-display area, a second sub non-display area and a plurality of third sub non-display area groups; each third sub non-display area group comprises a pair of third sub non-display areas; multiple lines of pixel driving circuits are arranged in the first sub display area; a plurality of first scanning circuits are arranged in the first sub non-display area; a plurality of second scanning circuits and third scanning circuits are arranged in the second sub non-display area; multiple lines of pixel driving circuitsare also arranged in the second sub display area; in the two third sub non-display areas of the same group of third sub non-display areas, one of the third sub non-display areas is provided with a plurality of first scanning driving circuits, and the other third sub non-display area is provided with a plurality of second scanning driving circuits. According to the array substrate and the displaydevice, the display device, which is relatively large in size and ultra-high in resolution ratio, can achieve normal display.
Owner:TRULY HUIZHOU SMART DISPLAY
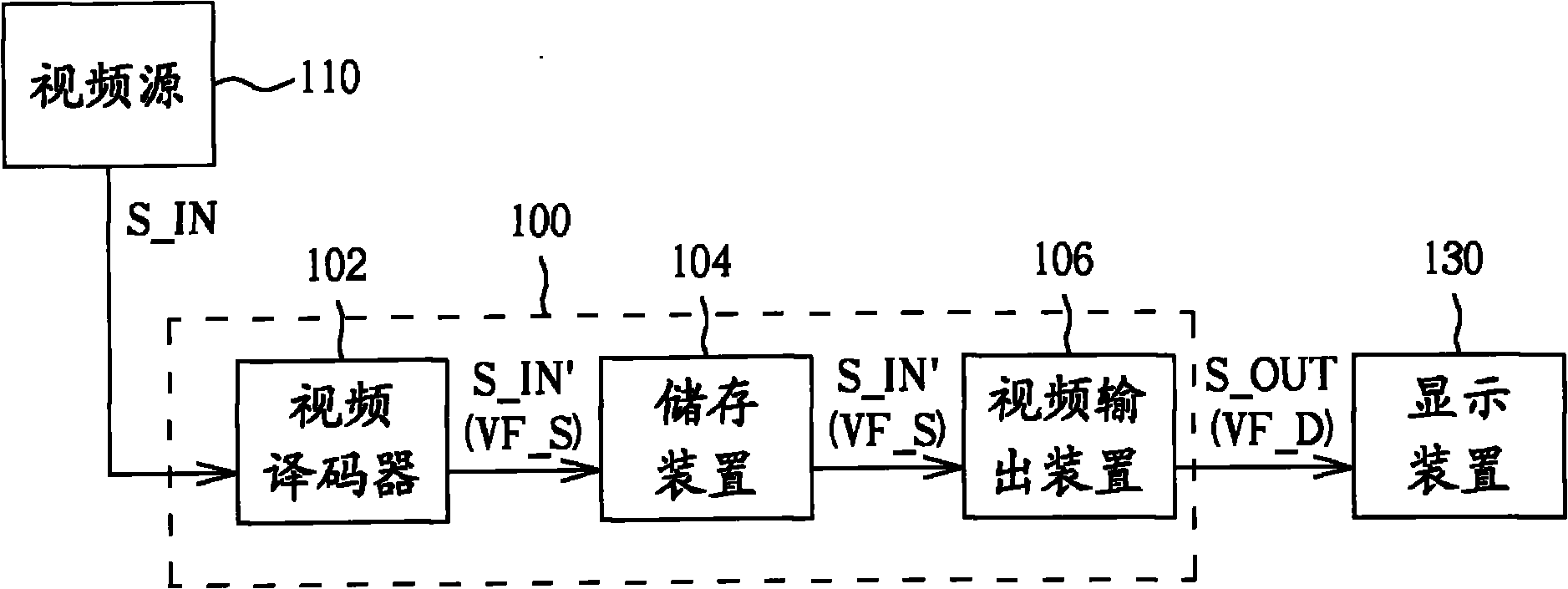
Video processing apparatus and related method thereof
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Display panel and production method thereof
ActiveCN113054133AHigh light transmittanceShow normalySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaterials sciencePhotochemistry
The embodiment of the invention discloses a display panel and a production method thereof. The display panel comprises a first display area and a second display area, the display panel further comprises a substrate and a pixel definition layer arranged on one side of the substrate, and the pixel definition layer is provided with pixel openings. A cathode suppression layer made of a light-transmitting material is arranged between every two adjacent pixel openings in the first display area; and the area of the orthographic projection of the cathode suppression layer on the substrate is smaller than or equal to 0.95 times of the area of the first display area. By arranging the cathode suppression layer, when the cathode layer is formed by adopting a whole-surface evaporation process, the cathode layer deposited on the cathode suppression layer is thinner or no cathode layer is deposited so that the light transmittance of the light-transmitting area is greatly improved, and meanwhile, the area ratio of the cathode suppression layer to the first display area is set; and the light transmittance of the first display area is improved as much as possible on the premise that normal display of the first display area is guaranteed.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
Display device
ActiveCN106847215AShow normalyImprove reliabilityStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
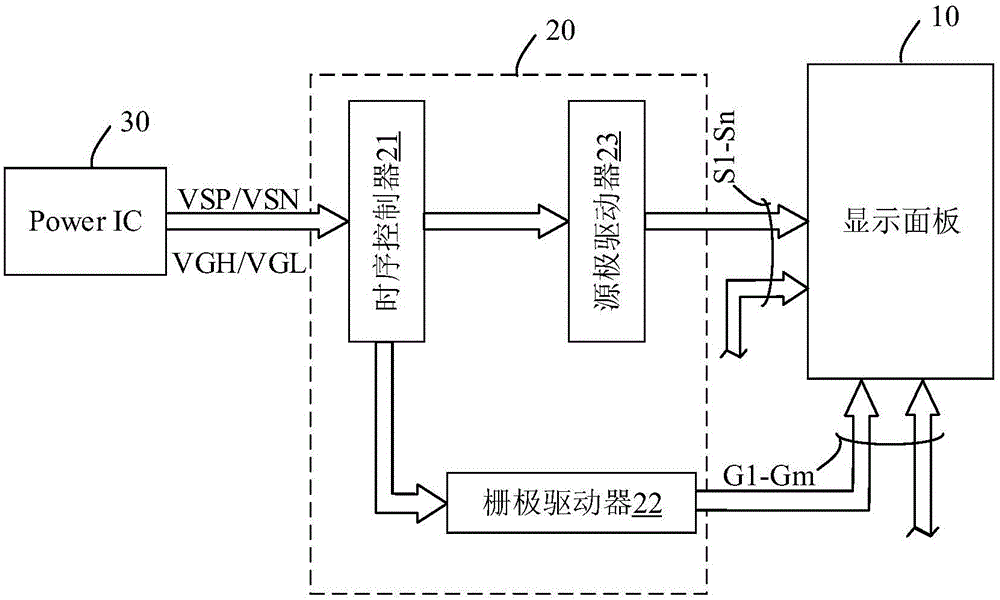
The present invention discloses a display device. The device comprises: a display panel; a power supply chip connected with the display panel and configured to provide supply voltage for the display panel to generate a first set of time series signals; a driving chip configured to generate grid selection signals and gray-scale signals according to a second set of time series signals to drive the display panel to display an image; and a first time series regulation circuit connected between the driving chip and the power supply chip and configured to convert the first set of time series signals to the second set of time series signals. The display device provided by the invention converts the first set of time series signals provided by the power supply chip to the second set of time series signals required by the driving chip through the first time series regulation circuit so as to avoid the problem that time series provided by the power supply chip is not matched with the time series required by the driving chip to cause that a liquid-crystal display device cannot normally display.
Owner:KUSN INFOVISION OPTOELECTRONICS
Image display device and image display method
InactiveCN105243966AShow normalyCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer graphics (images)Programmable logic device
The invention discloses an image display device and an image display method. The image display device comprises multiple spliced display screens, gravity sensors which are integrated on all display screens, an on-site programmable logic device which is electrically connected with all the display screens and all the gravity sensors and a storage which is electrically connected with the on-site programmable logic device. The placing direction of each display screen is determined through a corresponding gravity sensor, and the on-site programmable logic device automatically adjusts and reads the sequence of image information in the storage according to display screen placing direction results determined through the corresponding gravity sensor and outputs the read image information to the corresponding display screens, so that it is guaranteed that the image display device can normally display images no matter the display screens are placed in the positive direction or placed in the reverse direction.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Liquid crystal display device
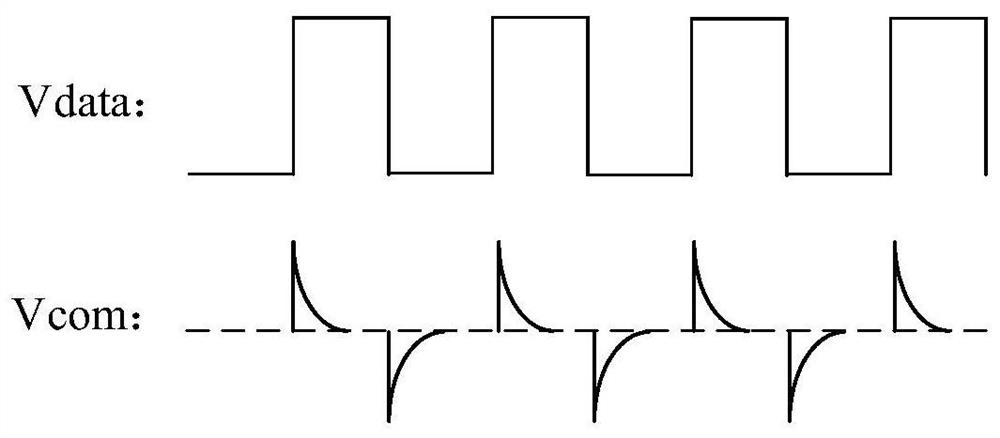
ActiveCN105044971AEliminate undesirable problems such as afterimagesLow costStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsPeriodic alternatingControl signal
A liquid crystal display device comprises a colored-film substrate, an array substrate and a liquid crystal layer. The colored-film substrate comprises a first substrate, a color-blocking layer, a block matrix and a shielding layer, wherein the color-blocking layer, the block matrix and the shielding layer are arranged on the first substrate. The array substrate is opposite to the colored-film substrate and comprises a second substrate, a pixel electrode, a public electrode and an insulation layer located between the pixel electrode and the public electrode, wherein the pixel electrode and the public electrode are arranged on the second substrate. A control signal for driving foreign ions in the liquid crystal layer to be detained is loaded on the shielding layer and is a periodic alternating-current voltage signal, the frequency of the signal is higher than or equal to the refresh rate of the liquid crystal display device, and the control signal is synchronous with the refresh of the liquid crystal display device. The control signal is loaded on the shielding layer of the colored-film substrate of the liquid crystal display device and produces an electric field in the liquid crystal display device, so that the probability that foreign ions in the liquid crystal layer are absorbed on the array substrate is reduced. Accordingly, the liquid crystal display device can perform normal display and is low in cost and short in consumed time.
Owner:KUSN INFOVISION OPTOELECTRONICS
Display device and driving module thereof, voltage control circuit and method
ActiveCN103123779ATimely compensationShow normalyStatic indicating devicesVoltage referenceGenerating unit
The present invention relates to a display device and a driving module thereof, a voltage control circuit and method. The voltage control circuit can control an operation voltage of a grid driver array of the display device, and comprises a grid driving pulse generating unit and a controller. The grid driving pulse generating unit generates a grid driving pulse, receives a scanning signal and a reference voltage outputted by the grid driver array, and controls the length of the grid driving pulse according to the level relation of the scanning signal and the reference voltage. The controller is coupled with the grid driving pulse generating unit to receive a grid driving pulse, and controls the level of the operation voltage according to the length of the grid driving pulse.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Liquid crystal display panel and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN108121106AShow normalyEliminate technical problems of leaking colored lightNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayColor film
The invention provides a liquid crystal display panel and a manufacturing method thereof. The display panel comprising a display area and a non-display area is characterized in that the non-display area surrounds the display area; the display panel comprises an array substrate, a liquid crystal layer and a color film substrate, wherein the color film substrate comprises a color resistance layer; the color resistance layer comprises a first color resistance area and a second color resistance layer, wherein the first color resistance layer corresponds to the display area, and the second color resistance layer corresponds to the non-display area; the second color resistance area comprises a first color resistance and a second color resistance, wherein the second color resistance is formed onthe first color resistance. The liquid crystal display panel has the advantages of eliminating the technical problem of having leaked colored light in a peripheral BM (black matrix) trenching area through the superposition of two color resistance blocks of two different colors, and enabling the liquid crystal display panel to display normally.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
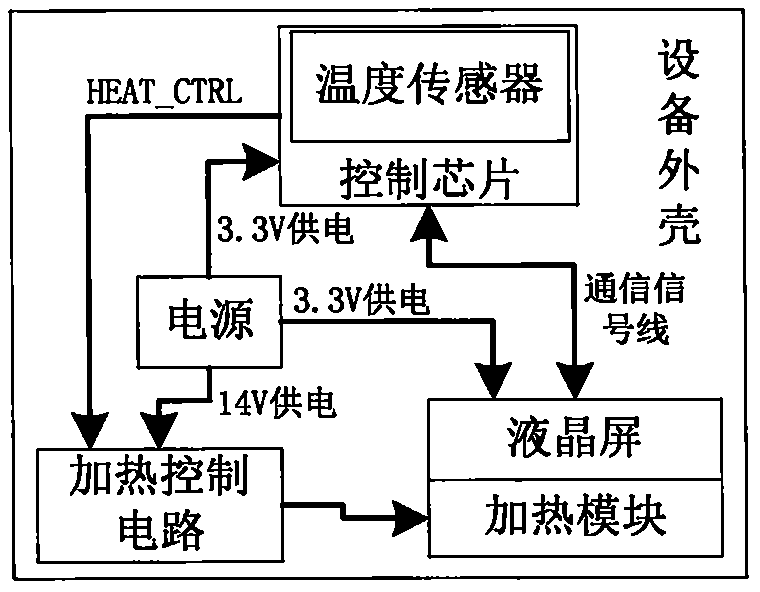
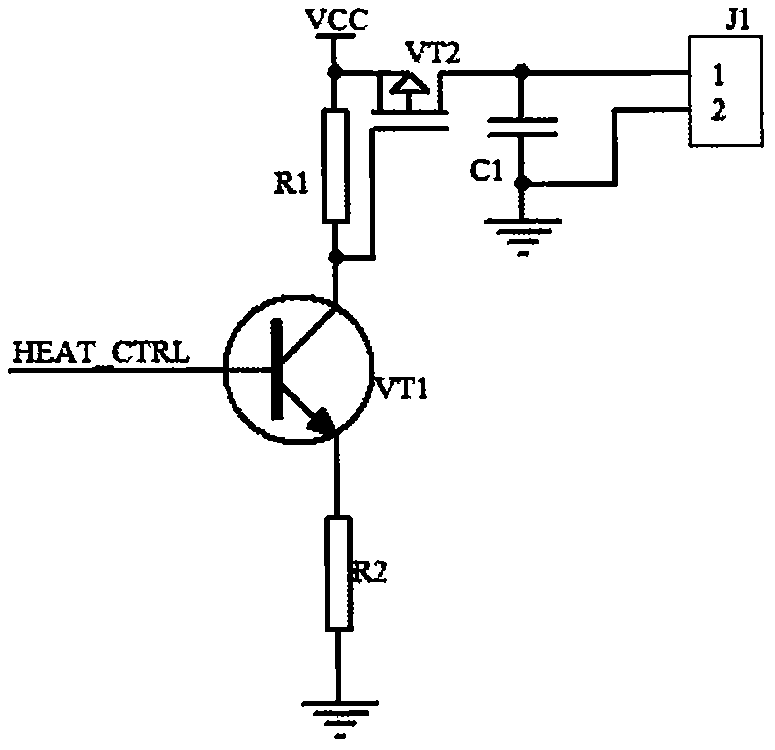
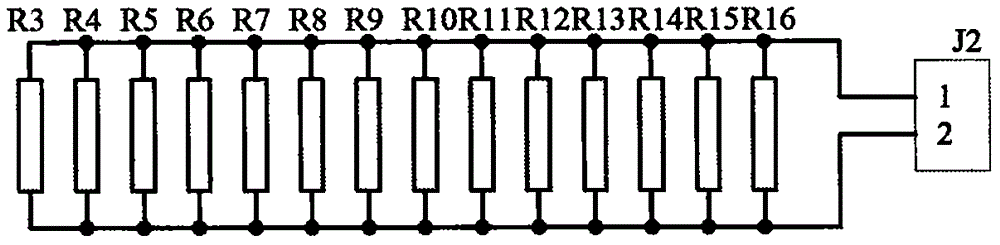
Control method for automatically heating liquid crystal screen in low-temperature environment
InactiveCN106094304AEasy to detectRealize the heating effectNon-linear opticsTemperature controlControl signal
The invention discloses a liquid crystal screen heating module used for automatically heating a liquid crystal screen in low-temperature environment and a temperature control method. The module comprises a liquid crystal screen module body, a liquid crystal screen heating module body, a temperature detection circuit and a main control module body; the liquid crystal screen module body is provided with an interface communicating with the main control module body, a temperature collecting sensor is arranged in the main control module body, and the heating control signal output pins are arranged on the main control module body; a liquid crystal screen heating circuit is connected with the heating control signal output pins, and heating ends of the liquid crystal screen heating circuit are distributed on the back face of a liquid crystal screen in the form of heating resistors distributed uniformly. The temperature sensor and the heating control pins arranged in a control chip cooperate with the heating circuit on the periphery to detect the low-temperature of the liquid crystal screen and heat the liquid crystal screen, the problem that the liquid crystal screen does not work normally in the low-temperature environment is solved, namely the liquid crystal screen heating module can work normally even in the environment at minus 50 DEG C.
Owner:QINGDAO TOPSCOMM COMM
Common voltage compensation method and liquid crystal display device
ActiveCN113284470AShow normalyAvoid crosstalkStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
The invention provides a common voltage compensation method and a liquid crystal display device, and relates to the technical field of display, and the common voltage compensation method comprises the following steps: when the driving mode of a display picture is dot inversion, column 2-dot inversion or row 2-dot inversion, determining whether the display picture belongs to a first type of display pictures; when the display picture does not belong to the first type of display pictures, determining the number of first target sub-pixels and the number of second target sub-pixels in each row of sub-pixels; and when the number of the first target sub-pixels is not equal to the number of the second target sub-pixels, determining a corresponding common voltage compensation value according to the data voltages of the plurality of first target sub-pixels and the data voltages of the plurality of second target sub-pixels, and outputting the common voltage compensation value. Whether the number of the positive and negative polarity sub-pixels needs to be determined or not is judged by determining the driving mode and type of the display picture, and then the corresponding common voltage compensation value is determined through the data voltage of the positive and negative polarity sub-pixels and is compensated, so the compensated display picture can be normally displayed.
Owner:HKC CORP LTD
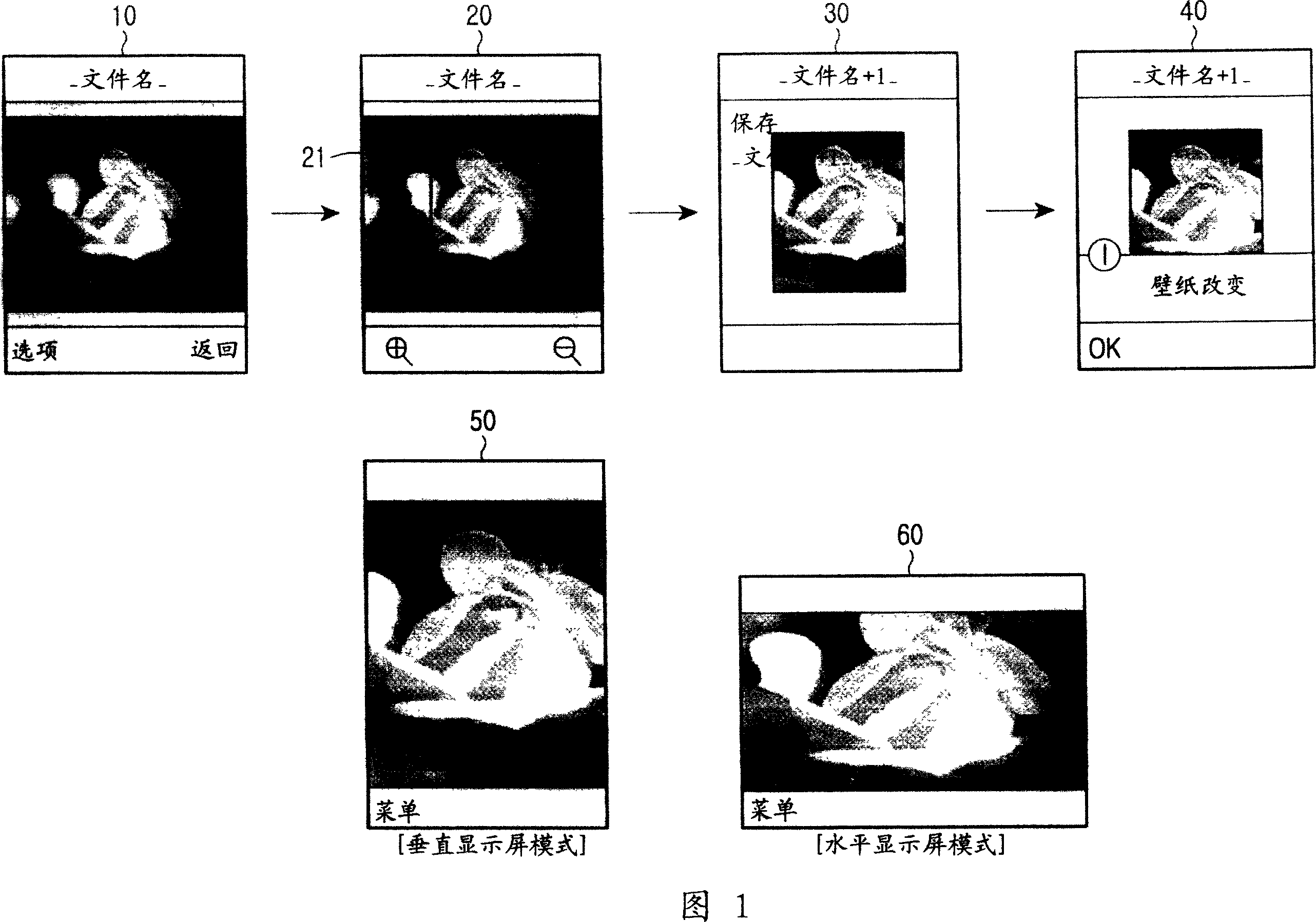
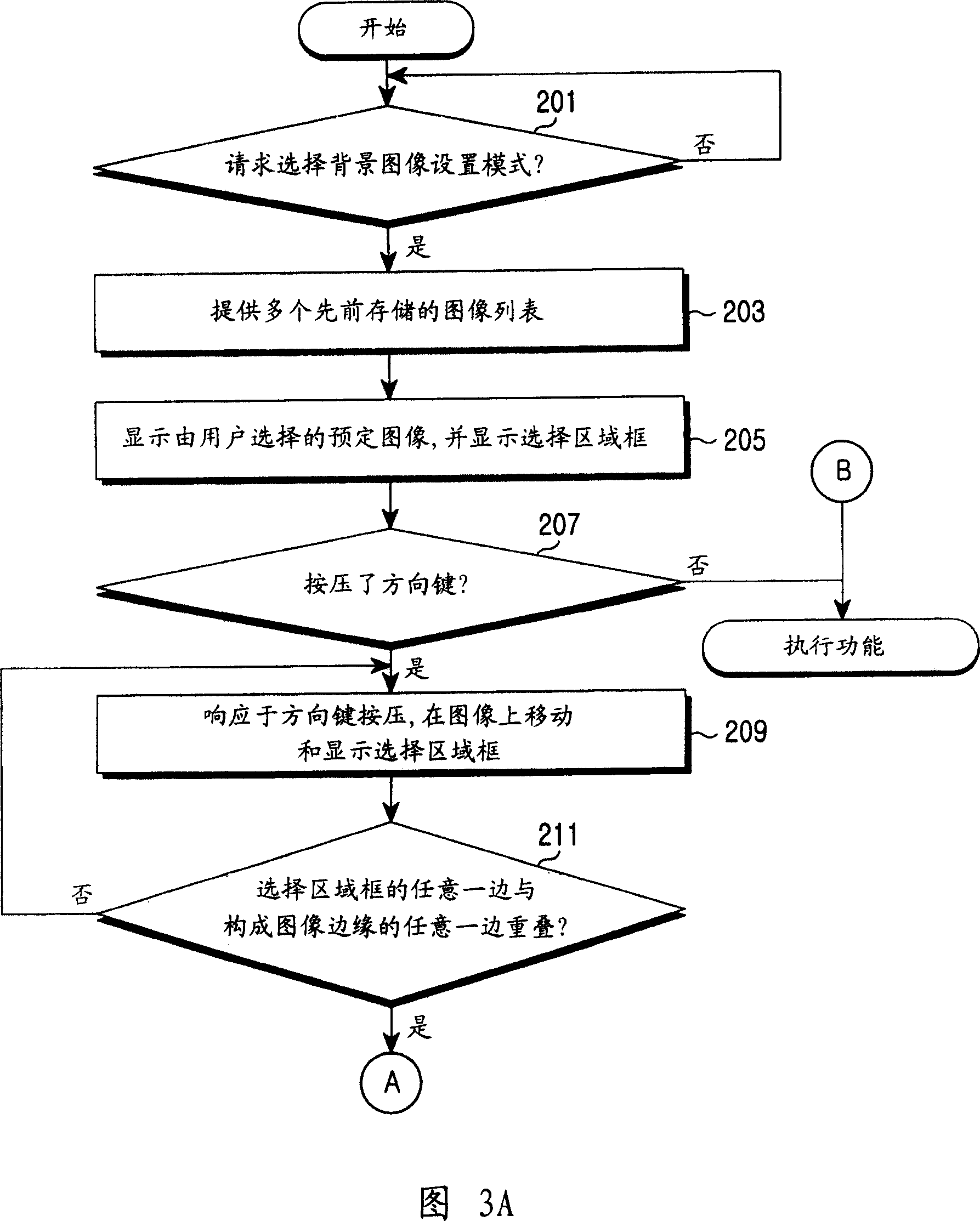
Method for displaying background image in mobile communication terminal
InactiveCN101009881AShow normalyCathode-ray tube indicatorsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsComputer graphics (images)Computer terminal
Provided is a method for displaying a background image in a mobile communication terminal. The method includes storing a predetermined image as background image depending on user's selection, storing position information of vertical screen frame and horizontal screen frame on the background image, and setting the background image; displaying an image of a region associated with the vertical screen frame among the background image, as background image, in response to a request for displaying a display screen of the mobile communication terminal in vertical direction; and displaying an image of a region associated with the horizontal screen frame among the background image, as background image, in response to a request for displaying the display screen of the mobile communication terminal in horizontal direction.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
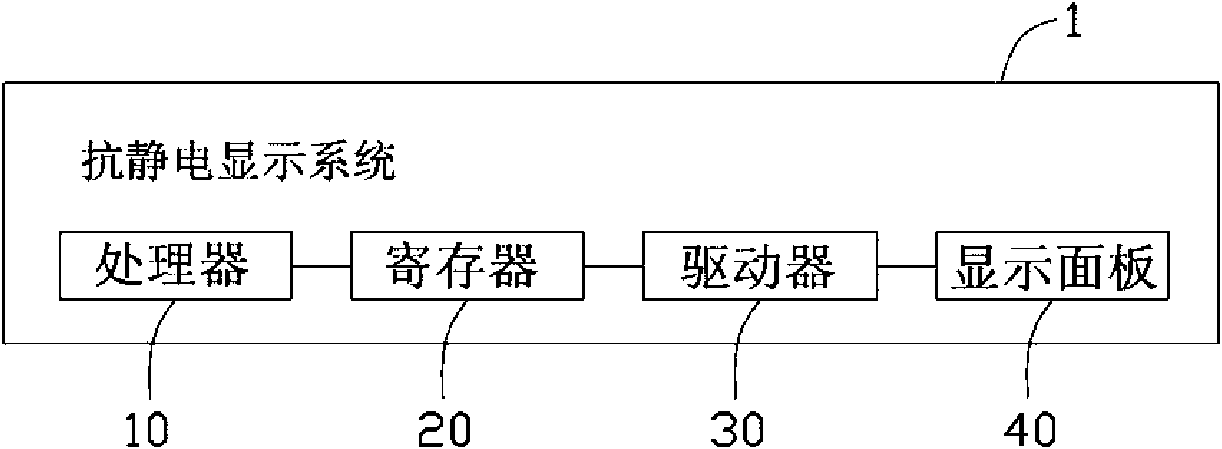
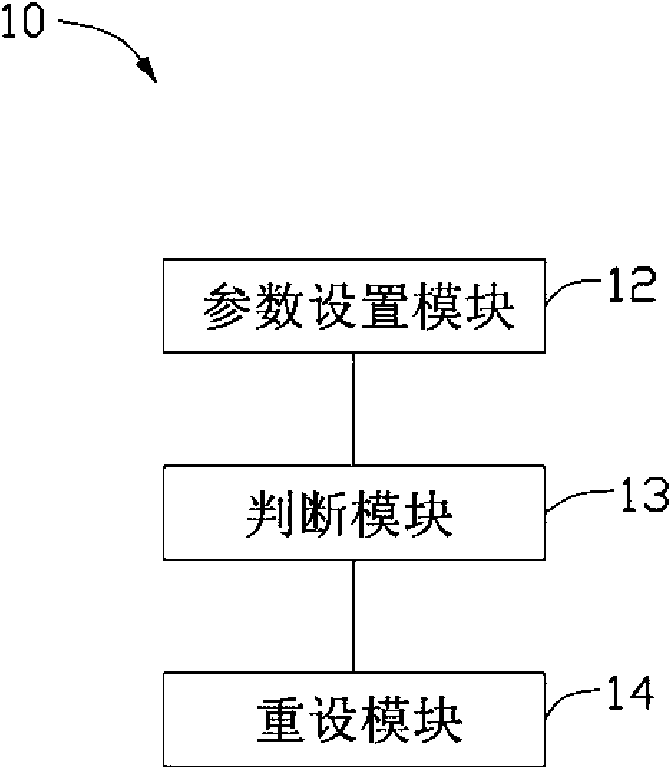
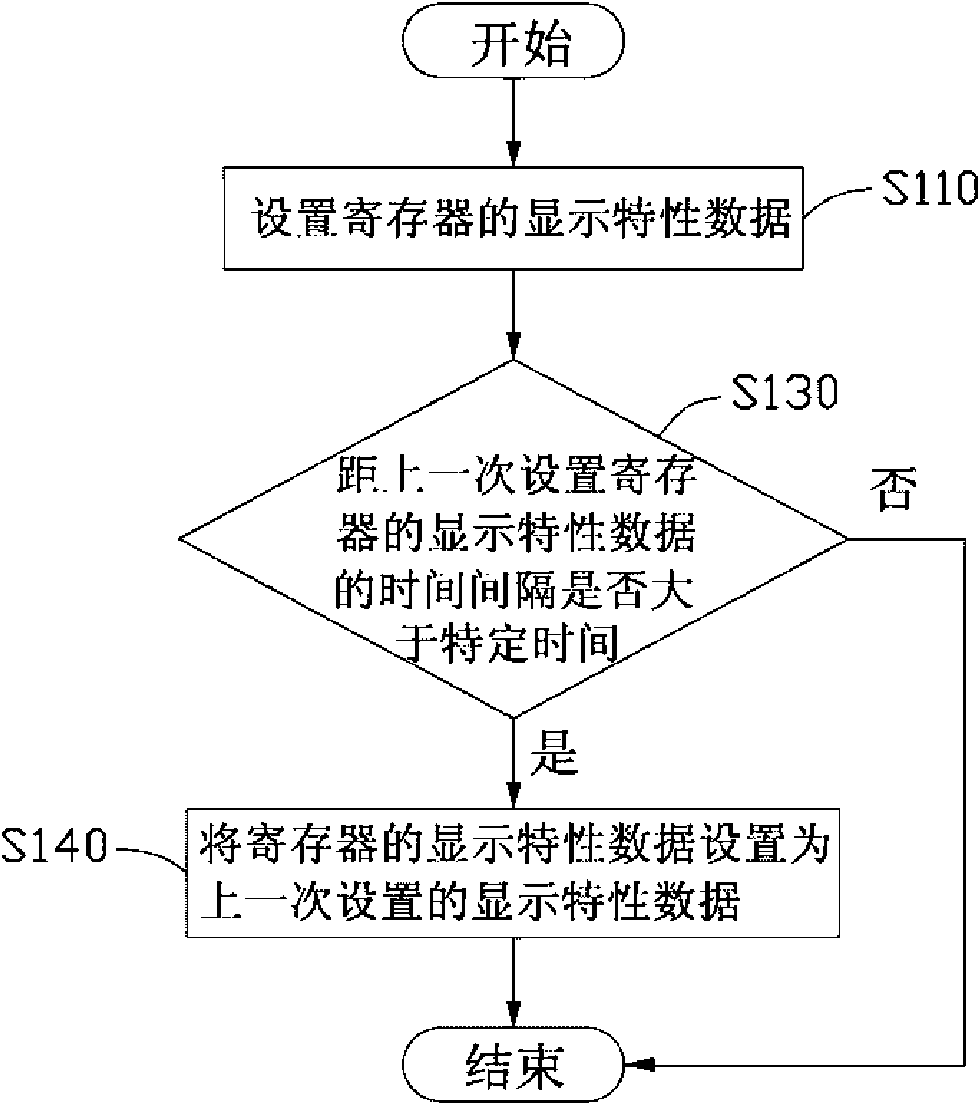
Antistatic display system and method
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Imaging system and imaging method for realizing camera direction unlimited setting
ActiveCN107197157AShow normalyNo imaging abnormalitiesTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer terminalDirection detection
The invention relates to an imaging system and an imaging method for realizing camera direction unlimited setting. The imaging method comprises the following steps: S1, a program burning module burns to form a corresponding image rotation program aiming at each setting direction of a camera; S2, each image rotation program formed by burning is stored in a program storage module; S3, a direction detection module detects and judges a camera setting direction on an intelligent mobile terminal; and S4, a program calling module calls the corresponding image rotation program according to the setting direction of the camera when the intelligent mobile terminal starts a shooting function, thereby adjusting the imaged image direction. By using the imaging method disclosed by the invention, a design position of a hardware FPC is unnecessary to adjust, the imaging abnormality is avoided, the shot image can be normally displayed for the camera adopting any direction setting.
Owner:SHANGHAI TRANSSION CO LTD
Photograph control device and method for high brightness shot object
InactiveCN1801897ANarrow downShow normalyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVideokymographyVideo image
Said invention refers to photograph controller and method for high brilliance object. When part area in shot object existing high brilliant light source, said invention can detects and control any area of light source, in order to prevent the reducing of aperture open and can normally display the main object in other areas of video image. Said invention can greatly raises monitoring function.
Owner:LEJIN GUANGDIAN ELECTRONIC CO LTD SHANGHAI
Intelligent watch and arc liquid crystal screen
InactiveCN104730910AImprove comfortImprove visual effectsVisual indicationsNon-linear opticsLight guideEngineering
The invention relates to an intelligent watch and an arc liquid crystal screen. An arc watch head of the intelligent watch comprises a shell and the arc liquid crystal screen in the shell, and the liquid crystal screen comprises an arc liquid crystal panel and a backlight module. The backlight module comprises a light guide plate, a reflection piece and an annular sleeve, wherein a plurality of light emitting elements are arranged on the inner surface of the annular sleeve, a plurality of grooves are formed in the outer peripheral surface of the light guide plate, the upper surface of the light guide plate is a convex surface, and the lower surface of the light guide plate is a flat surface. The backlight module in the intelligent watch can provide sufficient light for the arc liquid crystal panel so that the arc liquid crystal screen can be used normally.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD +1
Active array base board for plane display and its repair method
ActiveCN101101917AReduce loadReduce capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
The invention is concerned with the initiative array plaque of the plane monitor and its repair method. It includes the plaque with the display section, several of the first and the second electric guiding wires, and several of the first and the second repairing wires set on the plaque separately, the first and the second electric guiding wires are interleaving one with another but without connection, the first and the second repairing wires are interleaving with the second electric guiding wires separately, but connecting the two opposite sides outside the display section with electricity, and also several of the third repairing wires outside the display section and connecting the first and the second repairing wires electrically. The class of second electric guiding wires can form several of the second electric guiding wires group classes and they are opposite any one of the third repairing wires.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
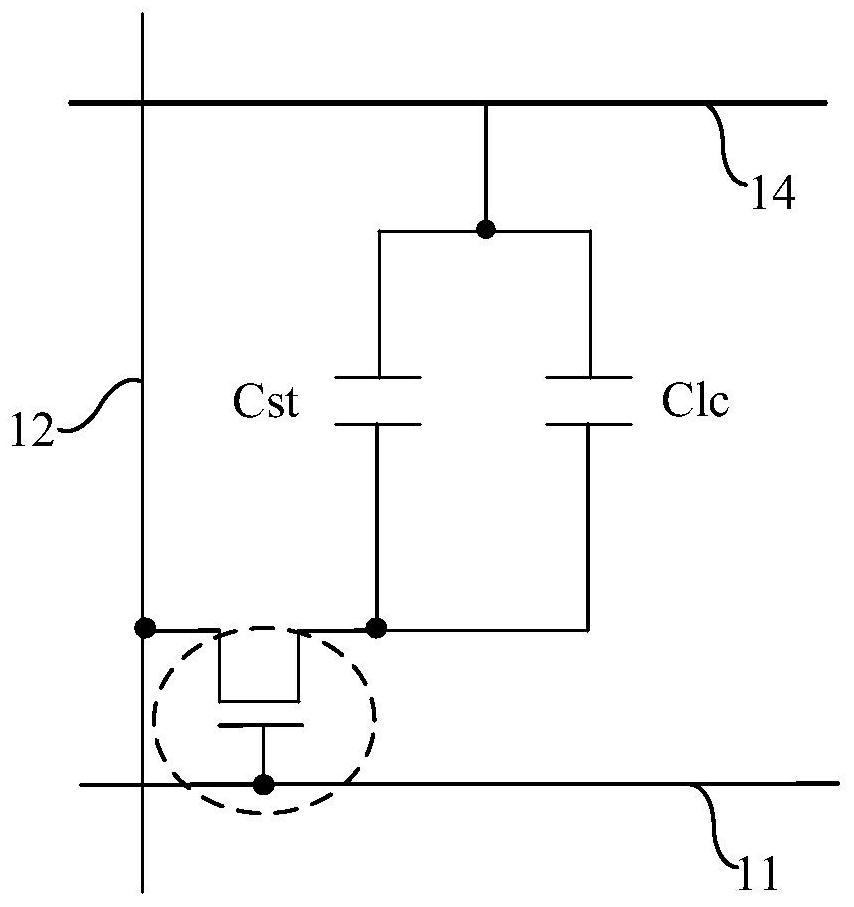
Pixel structure
InactiveCN101655626AShow normalyNo metamorphosisStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsCapacitanceMean square
The invention discloses a pixel structure, comprising a substrate, an insulation layer, a protective layer, a pixel electrode, a common voltage connecting line and a selecting line, wherein the insulation layer is formed on the substrate, the protective layer is arranged on the insulation layer, and the pixel electrode is arranged on the protective layer, the common voltage connecting line and theselecting line are arranged between the substrate and the insulation layer, the common voltage connecting lien and the pixel electrode form a storage capacitor, the selecting line and the pixel electrode form a coupling capacitor. Because of that a liquid crystal capacitor obtains a pulse signal from the coupling capacitor, the mean square root of the pixel voltage is higher than a threshold voltage, the white-state voltage can be closer to the threshold voltage, therefore the light transmittance of liquid crystal at white picture is improved.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
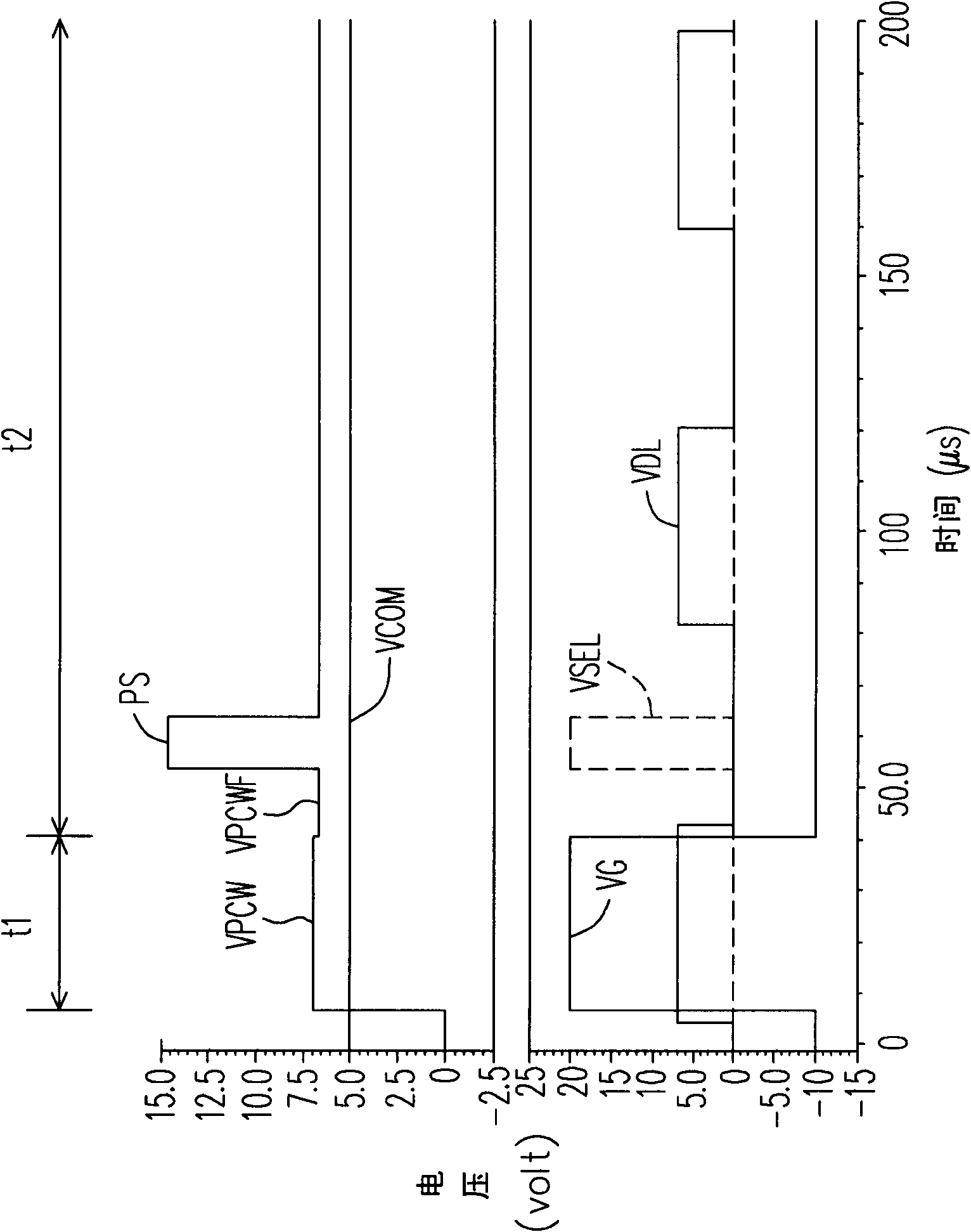
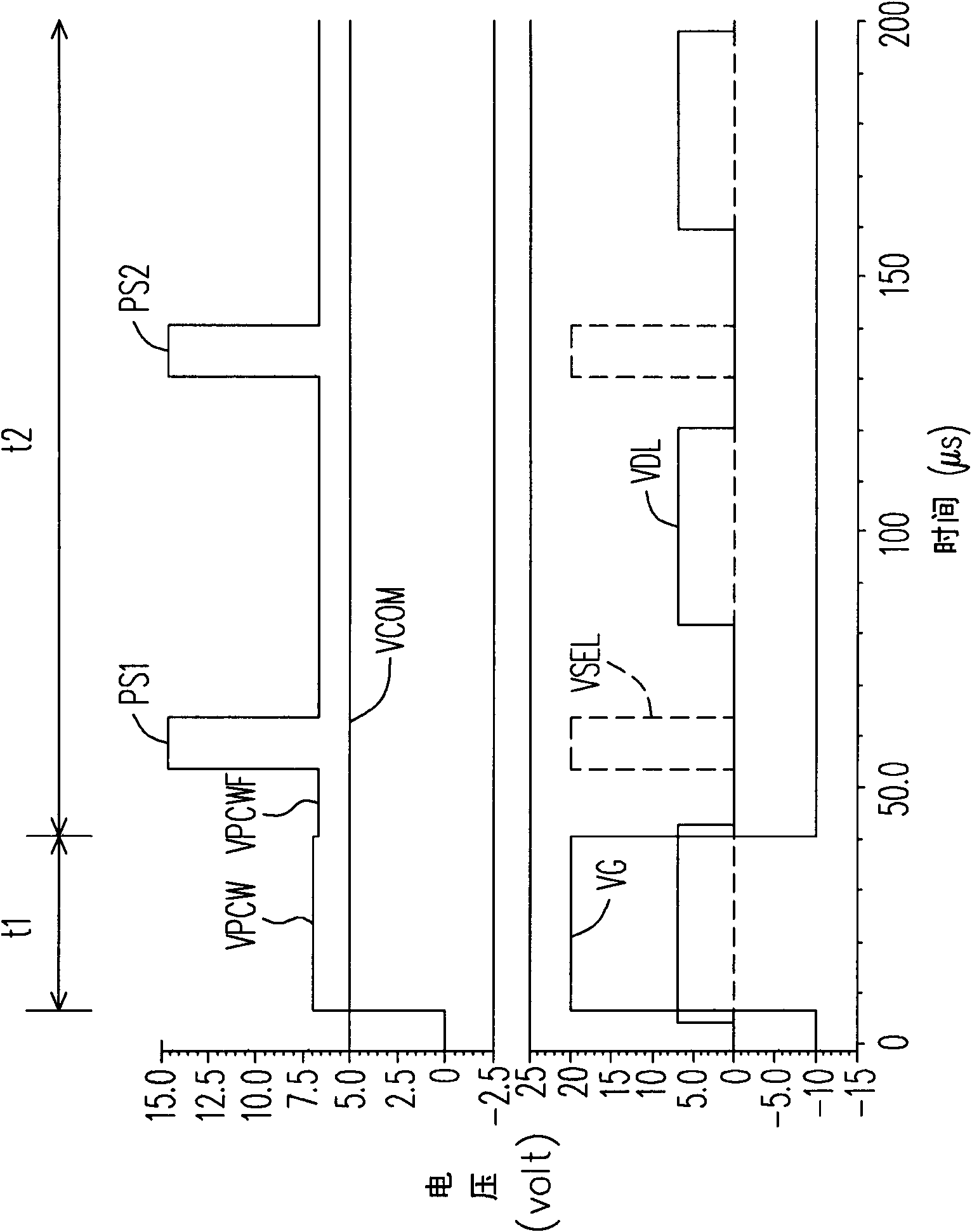
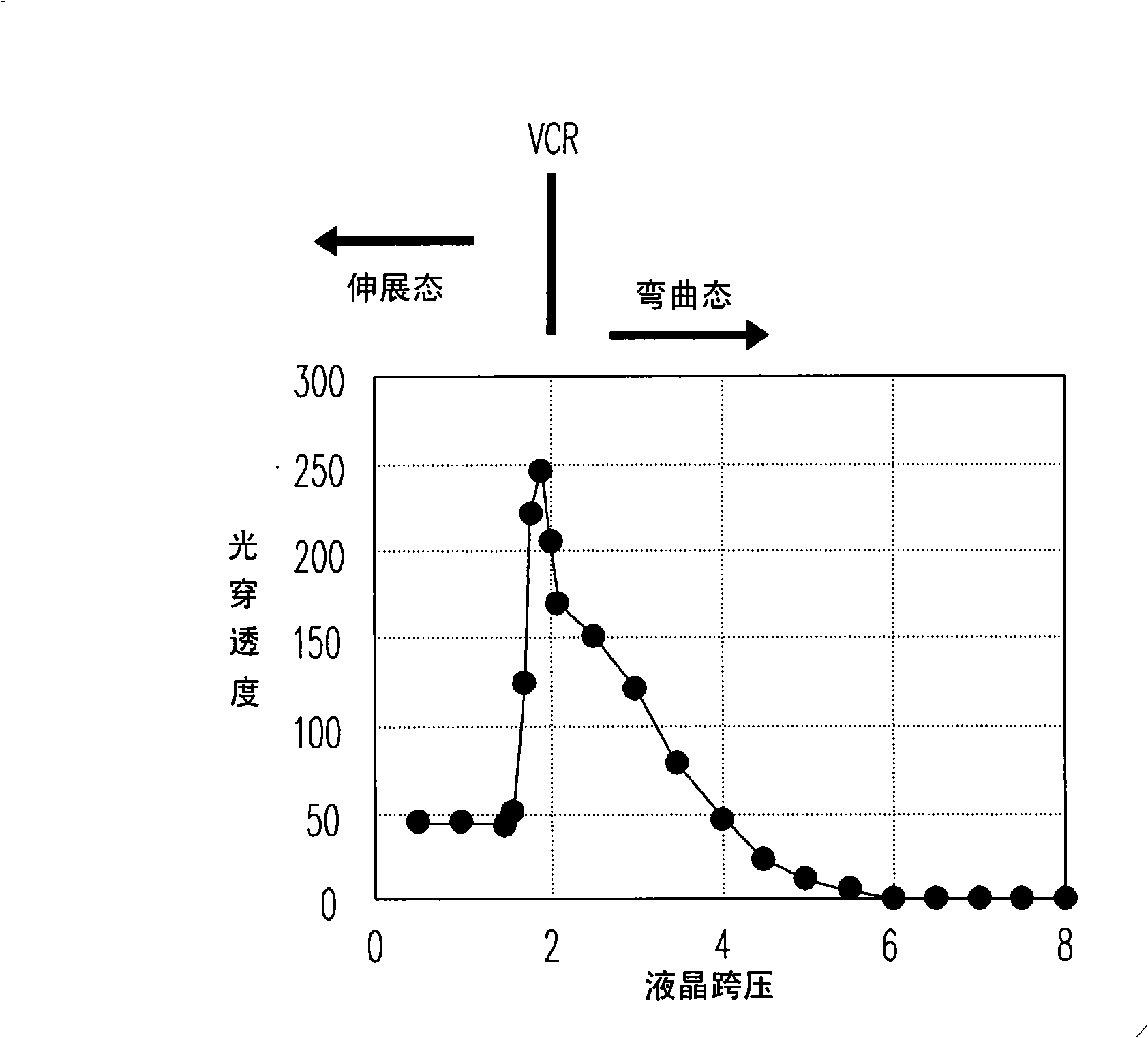
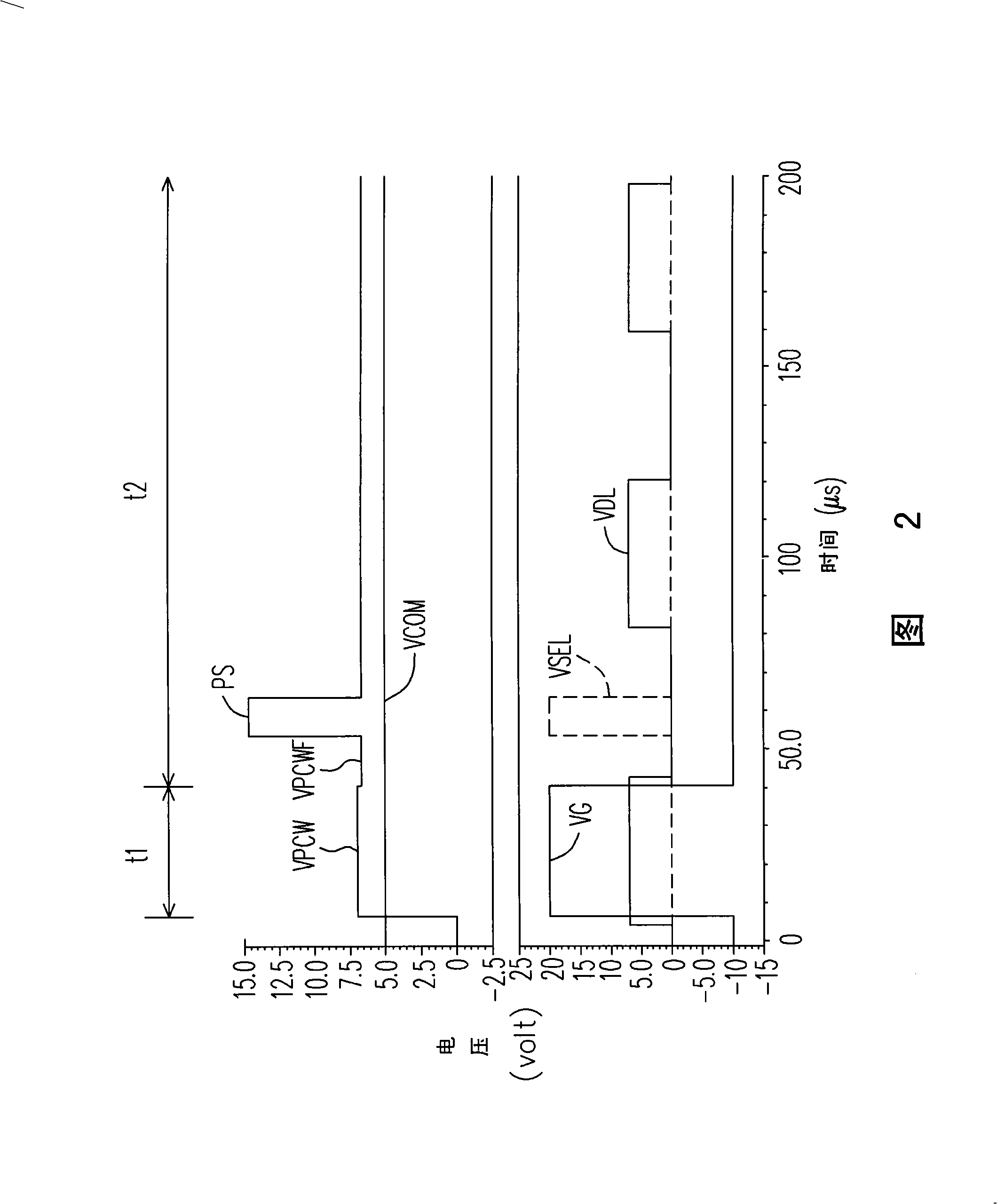
Optical compensation bending mode liquid crystal display pixel and its drive method
InactiveCN101308298AShow normalyNo metamorphosisStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsCapacitanceLiquid-crystal display
The invention discloses a pixel, comprising a transistor, a liquid crystal capacitor, a storage capacitor and a coupling capacitor. The first end of the transistor is coupled to a data line; the liquid crystal capacitor and the storage capacitor are coupled between the second end of the transistor and a common voltage; the coupling capacitor is coupled between the second end of the transistor and a selection line. When the data line inputs a drive voltage into the liquid crystal capacitor and the storage capacitor, the selection line enables a pulse signal to be coupled to the liquid crystal capacitor through the coupling capacitor. The pulse signal can enhance the liquid crystal drive capacity of an electric field, so that even if the minimum cross-pressure of the liquid crystal is insufficient, the liquid crystal can remain at bending state and can normally display the image.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
Liquid crystal display panel and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN108121107AShow normalyEliminate technical problems of leaking colored lightNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayColor film
The invention provides a liquid crystal display panel and a manufacturing method thereof. The display panel comprising a display area and a non-display area is characterized in that the non-display area surrounds the display area; the display panel comprises an array substrate, a liquid crystal layer and a color film substrate, wherein the color film substrate comprises a color resistance layer; the color resistance layer comprises a first color resistance area and a second color resistance layer, wherein the first color resistance layer corresponds to the display area, and the second color resistance layer corresponds to the non-display area. The liquid crystal display panel has the advantages of eliminating the technical problem of having leaked colored light in a peripheral BM (black matrix) trenching area with a second black matrix arranged on a color resistance block of the second color resistance area, and enabling the liquid crystal display panel to display normally.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
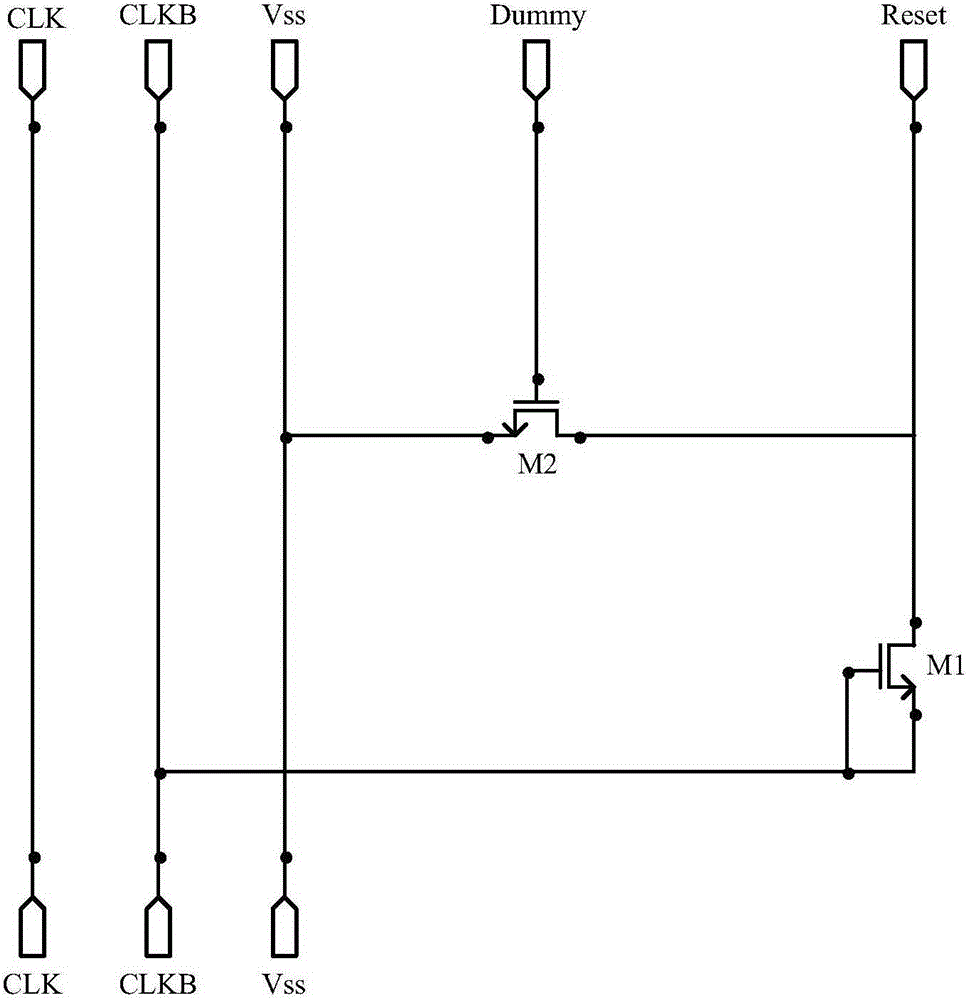
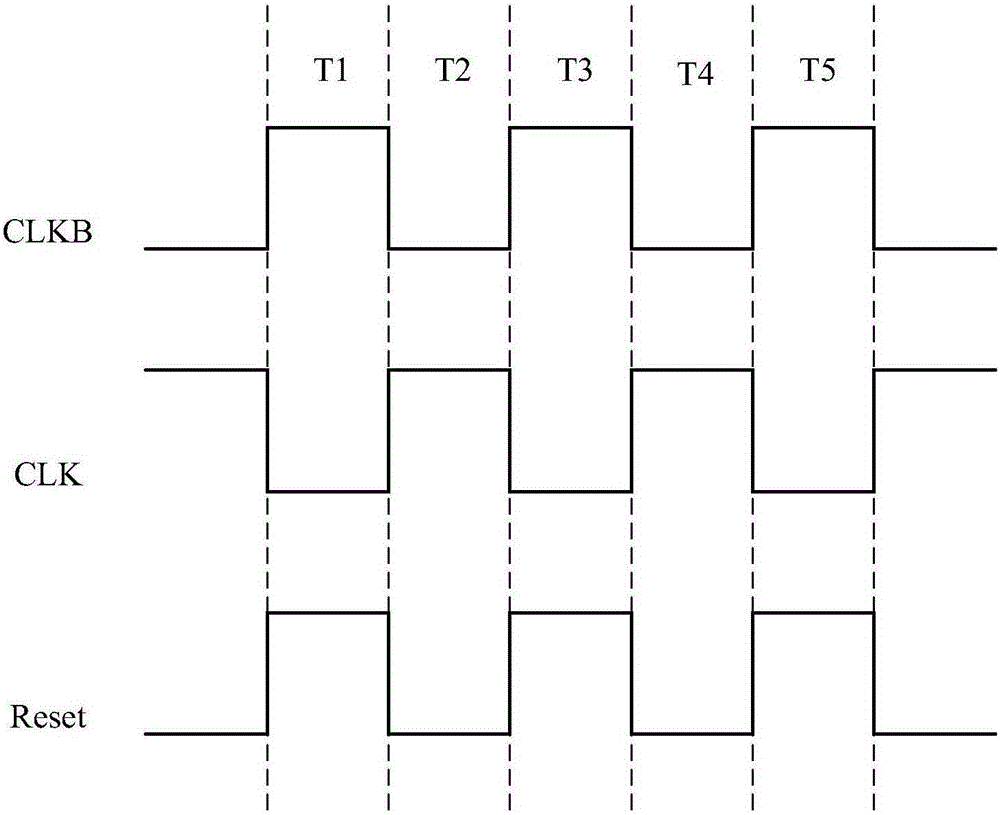
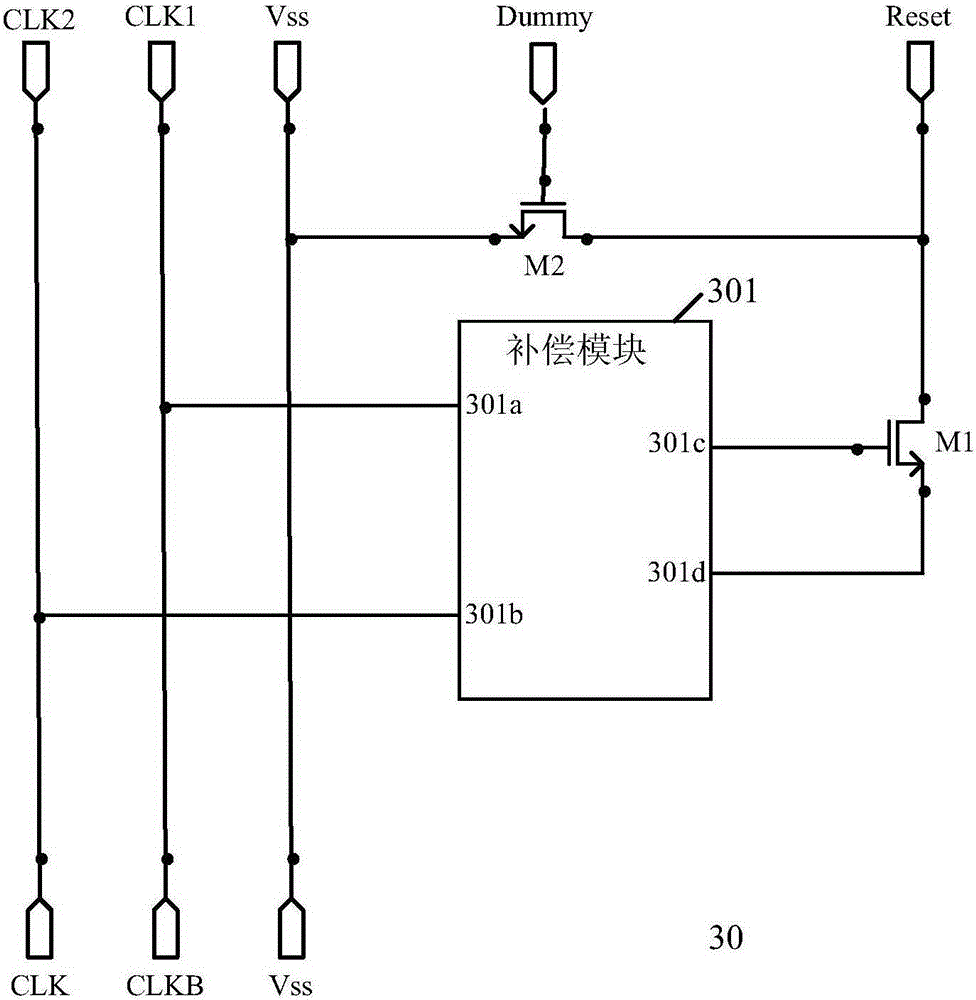
Reset device
ActiveCN105206235AEliminate the effects ofShow normalyStatic indicating devicesDriver circuitThreshold voltage
The embodiment of the invention provides a reset device, an array substrate grid electrode driver and a liquid crystal device. The reset device comprises a first thin film transistor, a second thin film transistor and a compensation module. The first thin film transistor is used for outputting reset signals from a drain electrode. A grid electrode of the second thin film transistor is used for receiving output signals from the grid electrode driver, a drain electrode of the second thin film transistor is connected with the drain electrode of the first thin film transistor, and a source electrode of the second thin film transistor is grounded. The compensation module is used for compensating for threshold voltage of the first thin film transistor and is provided with a first input end, a second input end, a first output end and a second output end. The first input end receives first clock signals, the second input end receives second cloth signals, the first output end is connected with a grid electrode of the first thin film transistor, and the second output end is connected with a source electrode of the first thin film transistor. The first clock signals and the second clock signals have the difference of a half cycle, and the lasting time of a high level is shorter than that of a lower level.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
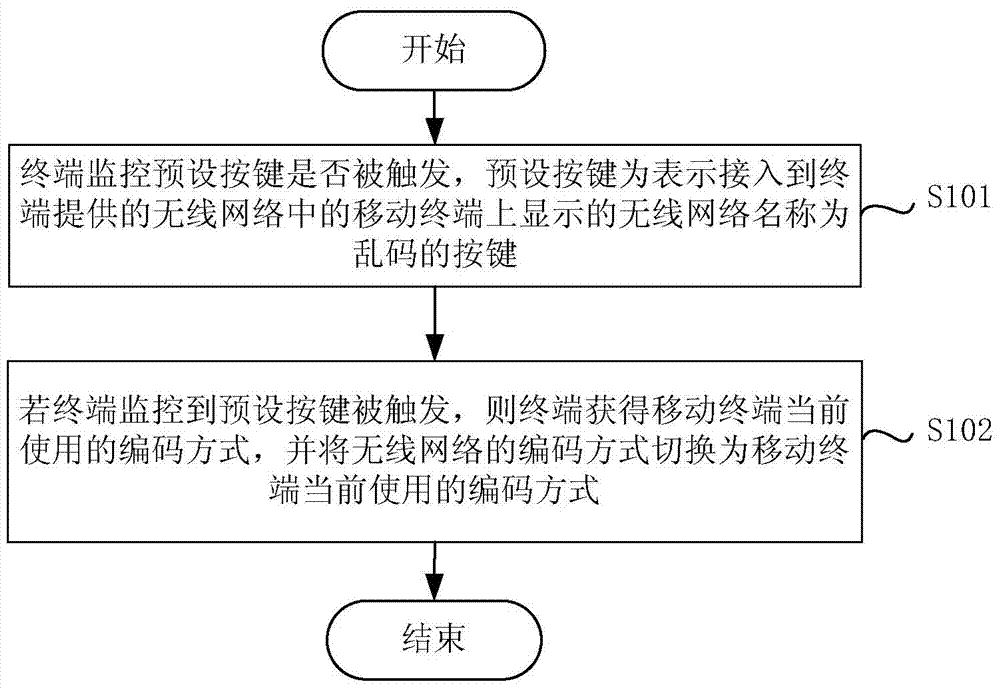
Wireless network name repairing method and device
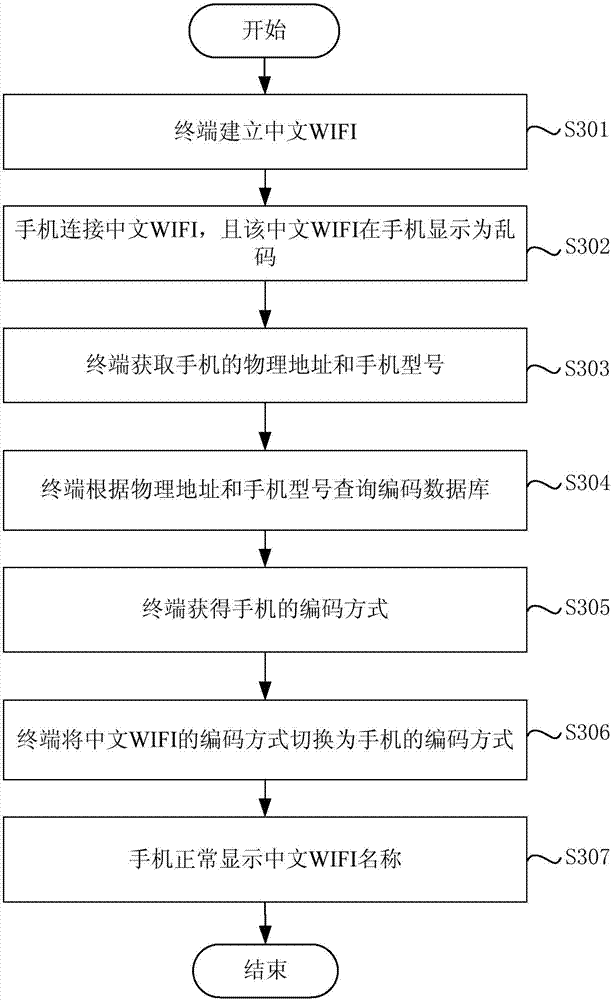
ActiveCN104125336AFix the problem that the wireless network name is displayed as garbled charactersShow normalySubstation equipmentTelecommunicationsWireless mesh network
The invention discloses a wireless network name repairing method and device. The wireless network name repairing method comprises the following steps: monitoring the triggering of a preset key through a terminal, wherein the preset key is the key that shows that the wireless network name displayed in a mobile terminal connected to the wireless network supplied by the terminal is a messy code; obtaining the currently used coding mode of the mobile terminal through the terminal as that the preset key is triggered is monitored by the terminal; switching the coding mode of the wireless network into the currently used coding mode of the mobile terminal. According to the wireless network name repairing method and device, the coding mode of the wireless network supplied by the terminal is switched into the currently used coding mode of the mobile terminal by triggering the preset key, and thereby the problem that the wireless network name displayed in the mobile terminal is the messy code is removed, the mobile terminal is able to normally display the wireless network name, and a user can connect with the wireless network conveniently.
Owner:ZHUHAI BAOQU TECH CO LTD
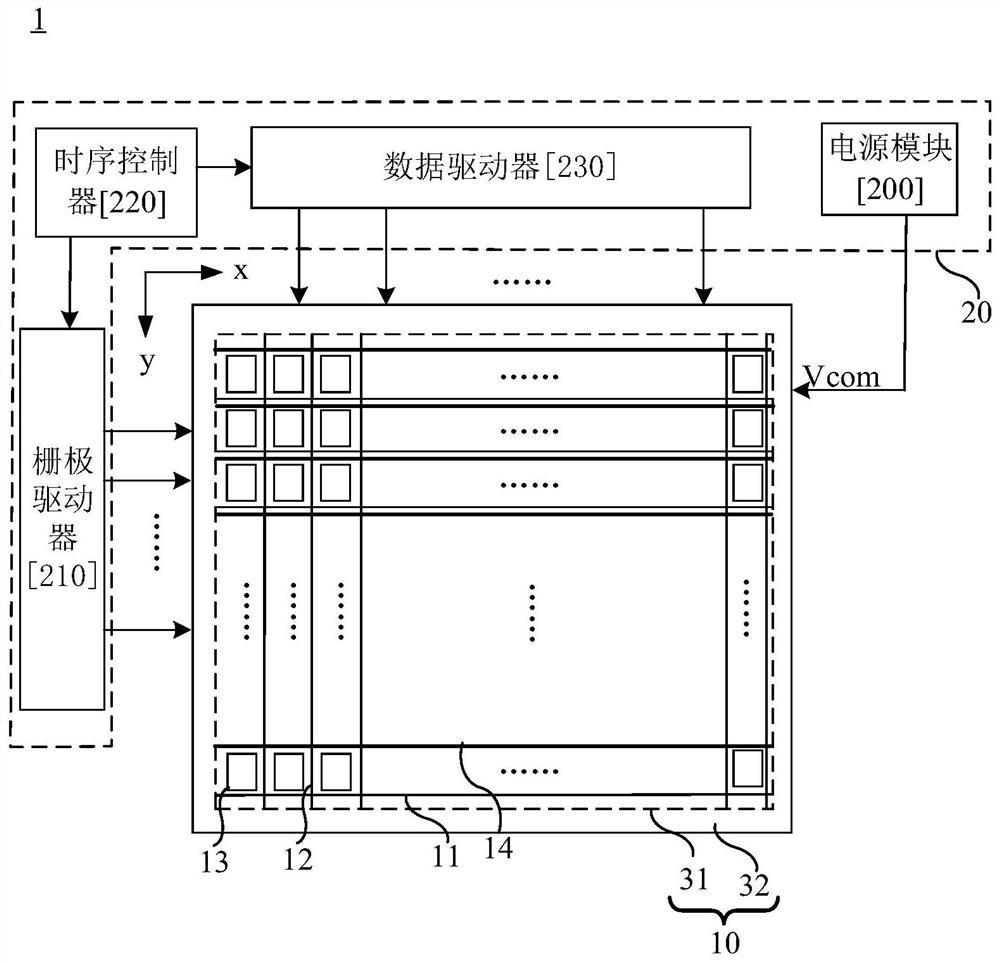
Shift register unit, gate driving circuit, and display device
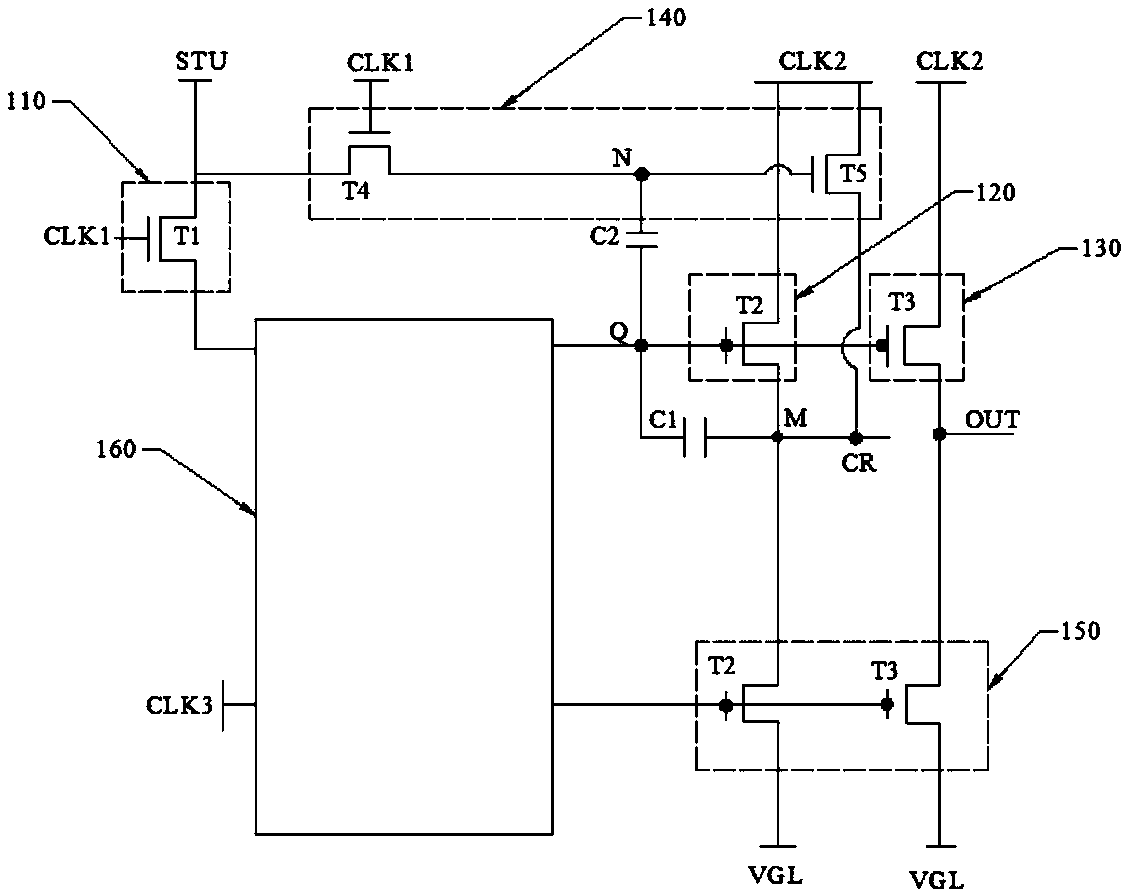
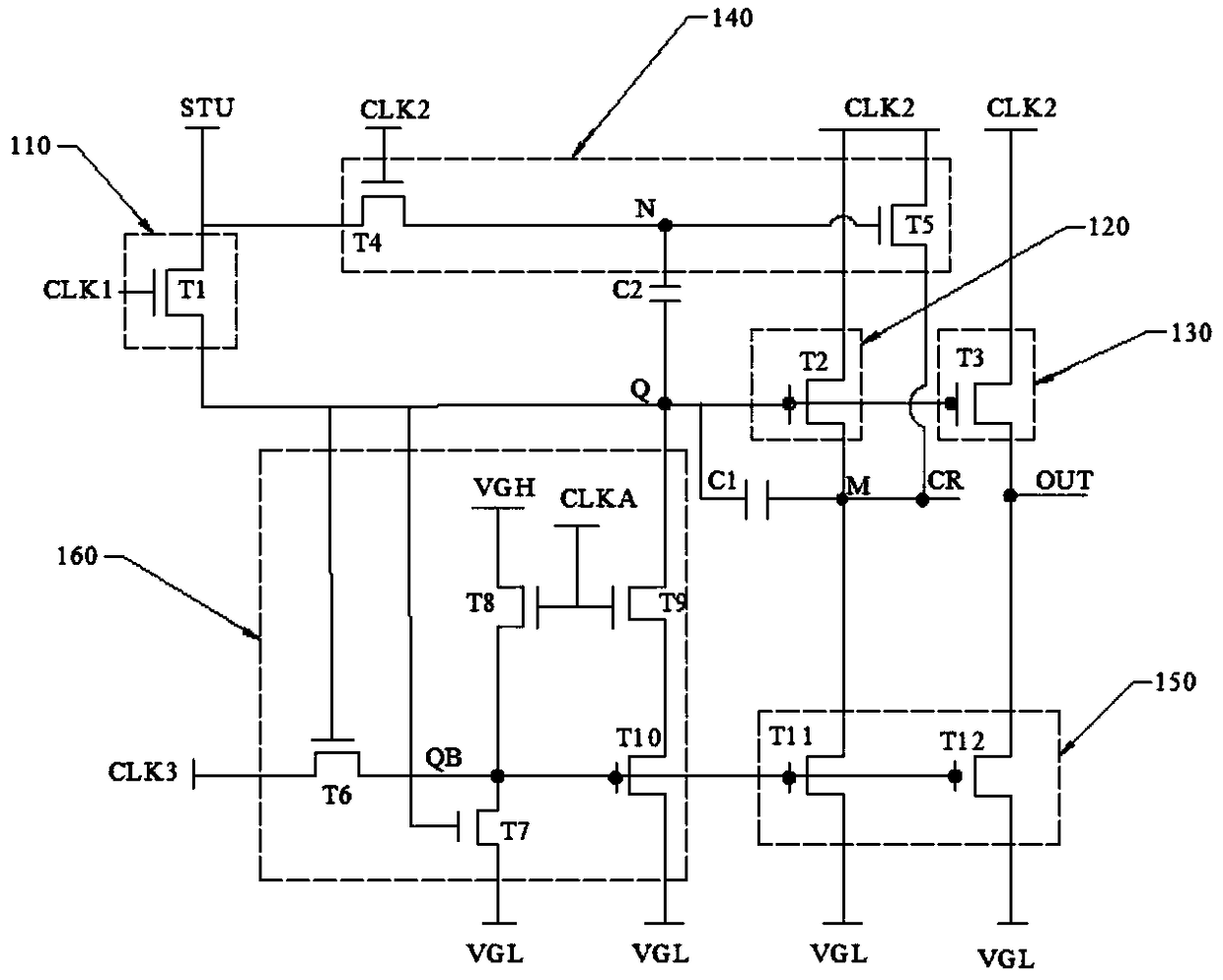
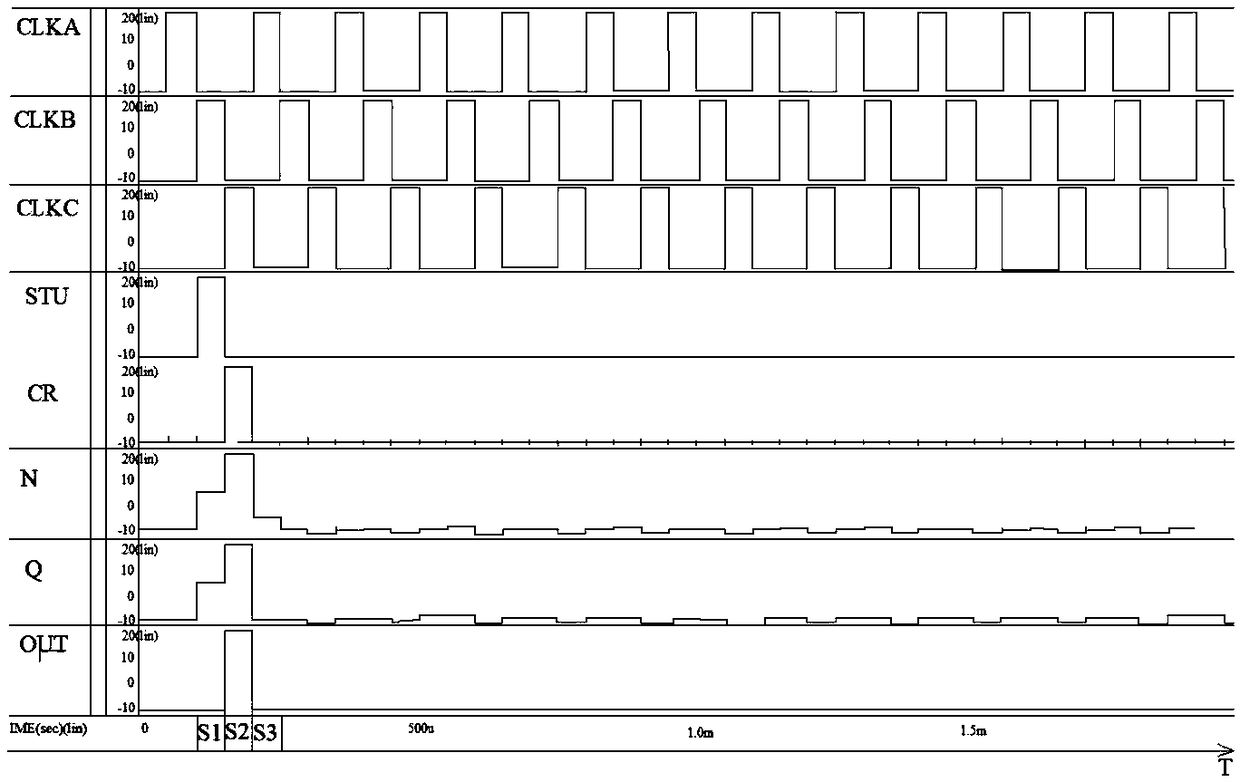
The invention relates to the technical field of display and provides a shift register unit. The shift register unit comprises an input module, a pull-up module, an output module, an auxiliary module,a pull-down module, a first storage capacitor and a second storage capacitor. The auxiliary module is connected with a first clock signal terminal, a second clock signal terminal, an input terminal and a first output terminal. A second storage capacitor is connected between the first node and the pull-up node; when the first storage capacitor and one or more elements in the pull-up module fail tofunction properly during actual production or when the shift register unit is operated, the second storage capacitor and the auxiliary module cooperate to enable the normal operation of the shift register unit, thereby enabling the display panel to be displayed normally. The second storage capacitor and the auxiliary module cooperate to enable the shift register unit to function normally.
Owner:HEFEI BOE OPTOELECTRONICS TECH +1
Display method and electronic equipment
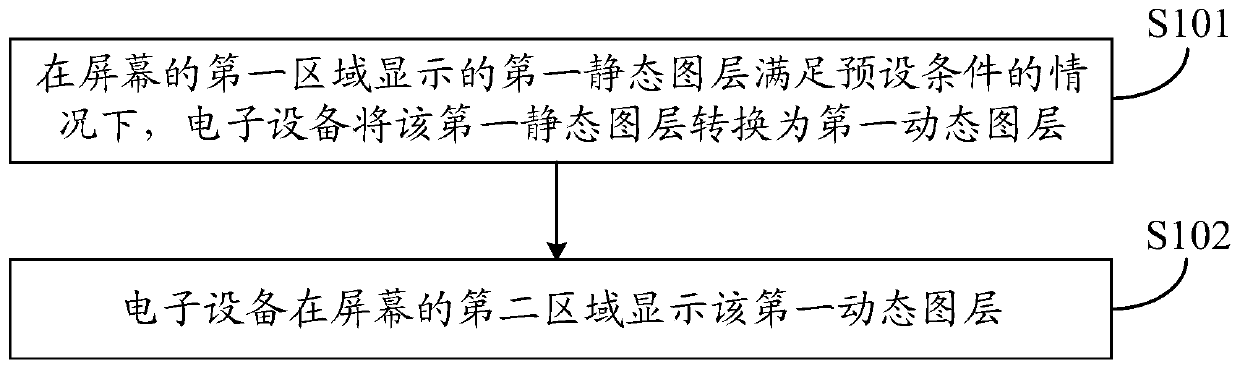
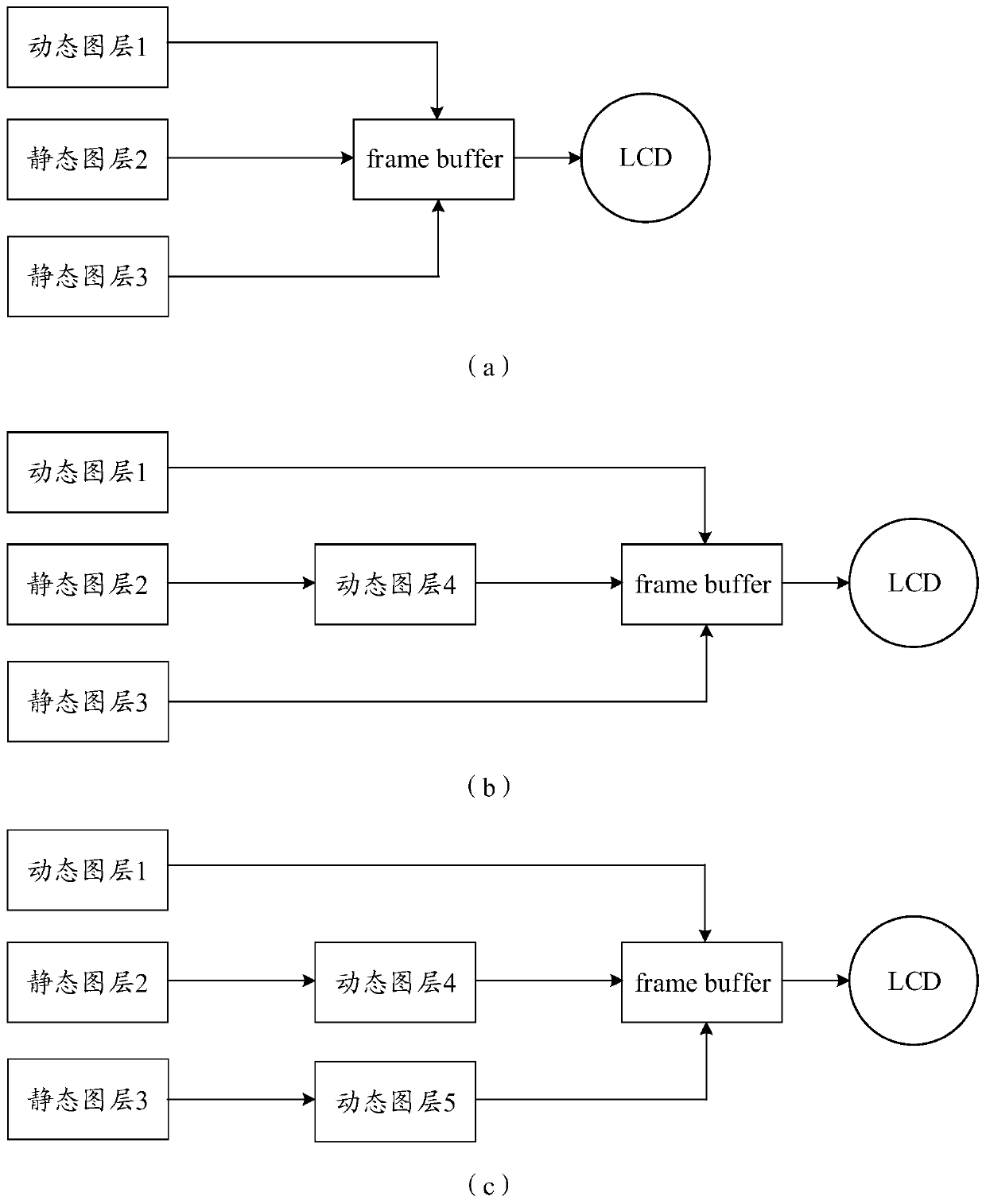
PendingCN111309429AShow normalyQuality improvementExecution for user interfacesDigital output to display deviceComputer hardwareImaging quality
The embodiment of the invention discloses a display method and electronic equipment, relates to the technical field of communication, and aims to solve the problem that the image quality is reduced because a static image layer and a display screen cannot be compatible. The method comprises the steps of converting a first static layer into a first dynamic layer under the condition that the first static layer displayed in a first area of a screen meets a preset condition; displaying the first dynamic layer in a second area of the screen; wherein the preset condition comprises any one of the following items: the first static layer cannot be normally displayed in the first area, and a first input of a user to the first static layer in the first area is received.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
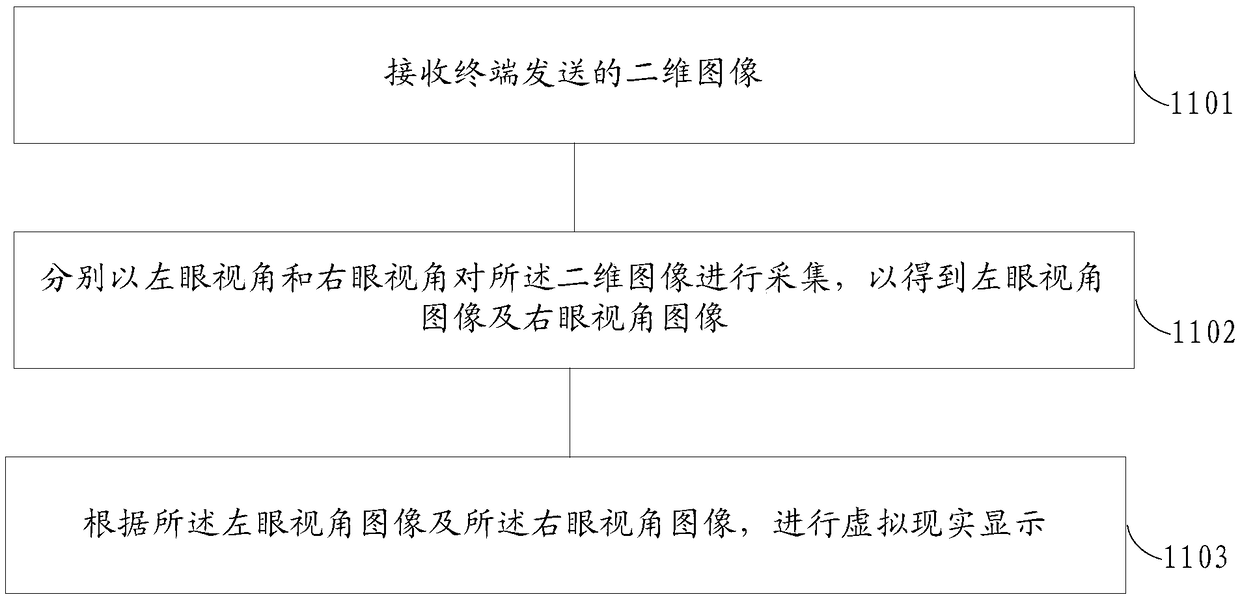
Image display method, apparatus, apparatus, and storage medium for virtual reality device
The embodiment of the invention provides an image display method, a device, a device and a storage medium of a virtual reality device, which relate to the technical field of computer application. Themethod comprises the following steps: receiving a two-dimensional image sent by a terminal; collecting the two-dimensional images from the left-eye perspective and the right-eye perspective respectively to obtain the left-eye perspective images and the right-eye perspective images; performing a virtual reality display according to the left-eye view angle image and the right-eye view angle image. The technical schemel provided by the embodiment of the invention can normally display two-dimensional images in a VR device.
Owner:GOERTEK OPTICAL TECH CO LTD
Display panel manufacturing process and baking device for display panel
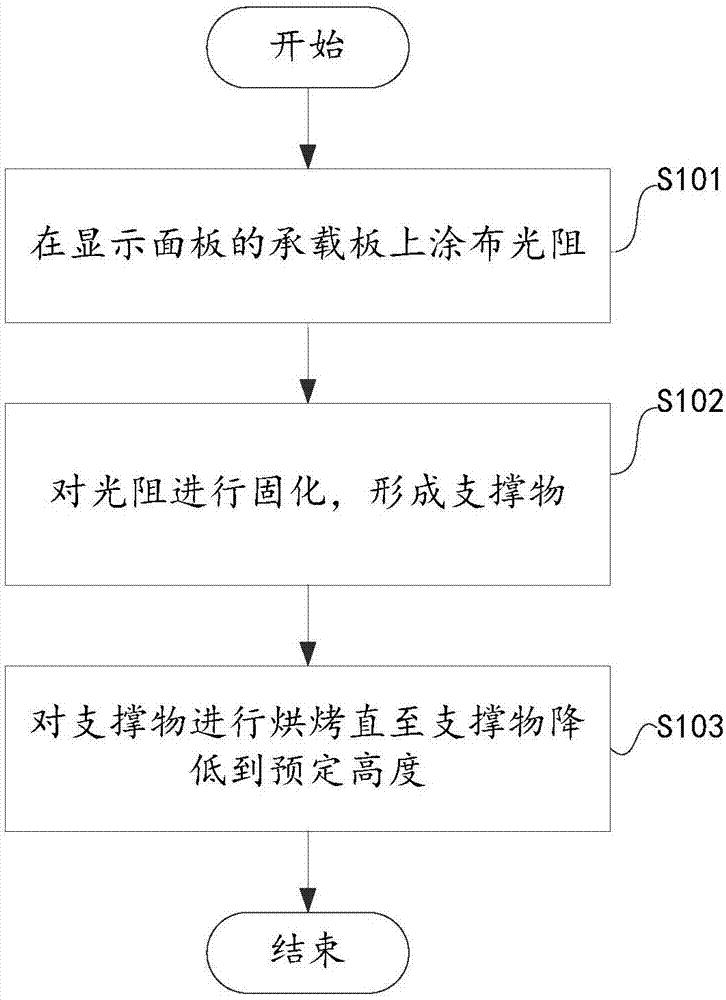
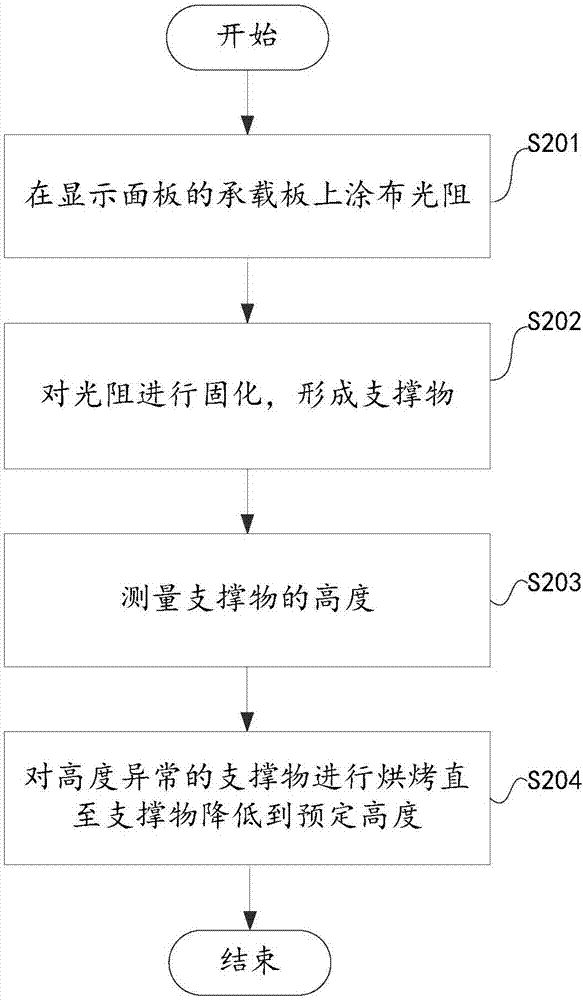
InactiveCN107045215AShow normalyLower the altitudeNon-linear opticsEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a display panel manufacturing process and a baking device for a display panel. The display panel manufacturing process includes the following steps: coating a transmitting substrate of the display panel with a light resistor; performing patterning and solidifying on the light resistor to form a supporting body; and baking the supporting body till the supporting body descends to a preset height. Micro adjustment and repairing of the supporting body can be achieved by baking the support body, local high structures of the supporting body can be avoided, the bad phenomenon that the display panel is white and uneven can be prevented, and the display panel can achieve normal display. The supporting body is locally baked, the baking intensity and the baking time is easy to control during baking, the supporting body can be controlled accurately, and an optimal shrinkage of the supporting body can be achieved.
Owner:HKC CORP LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com