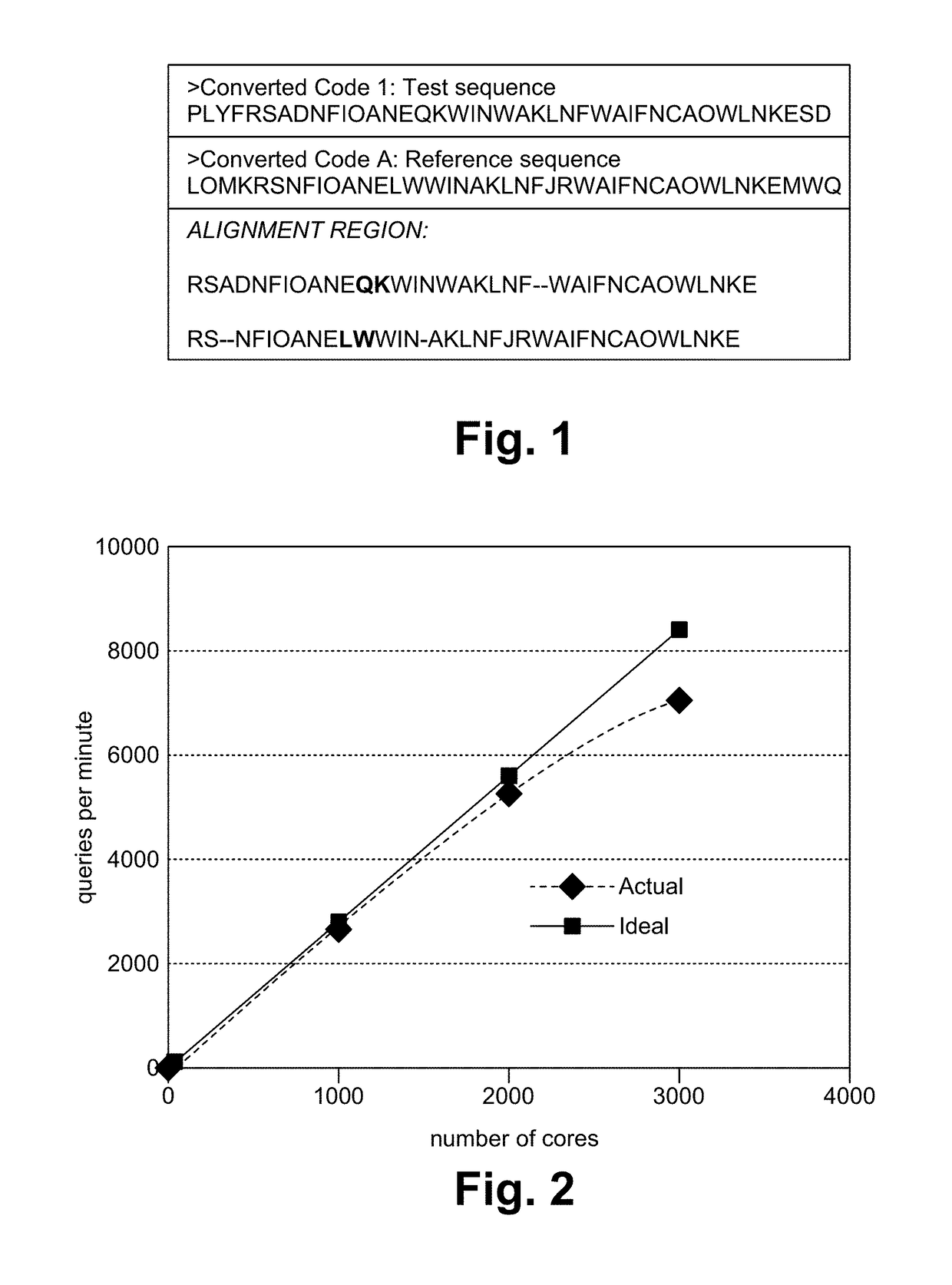
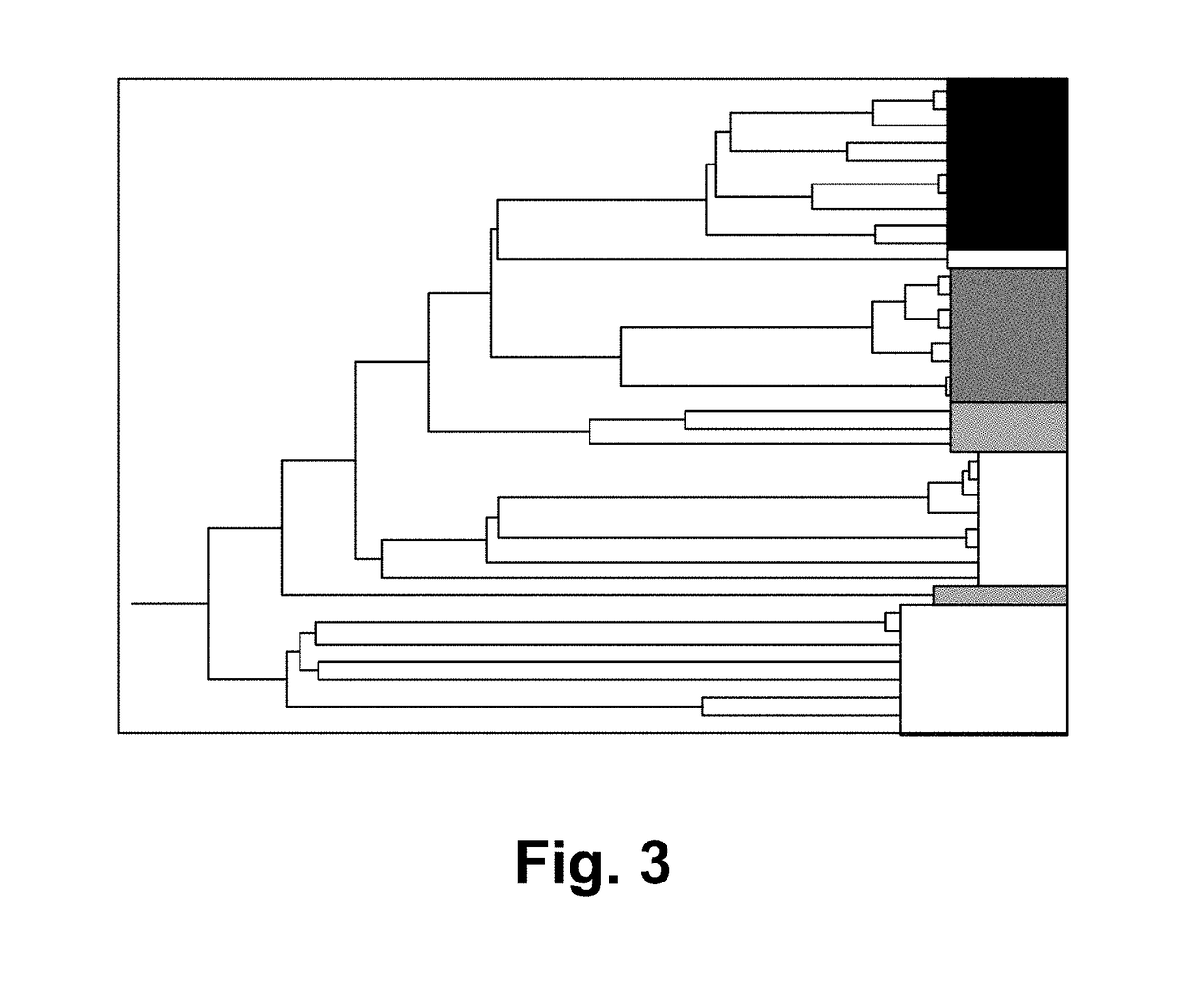
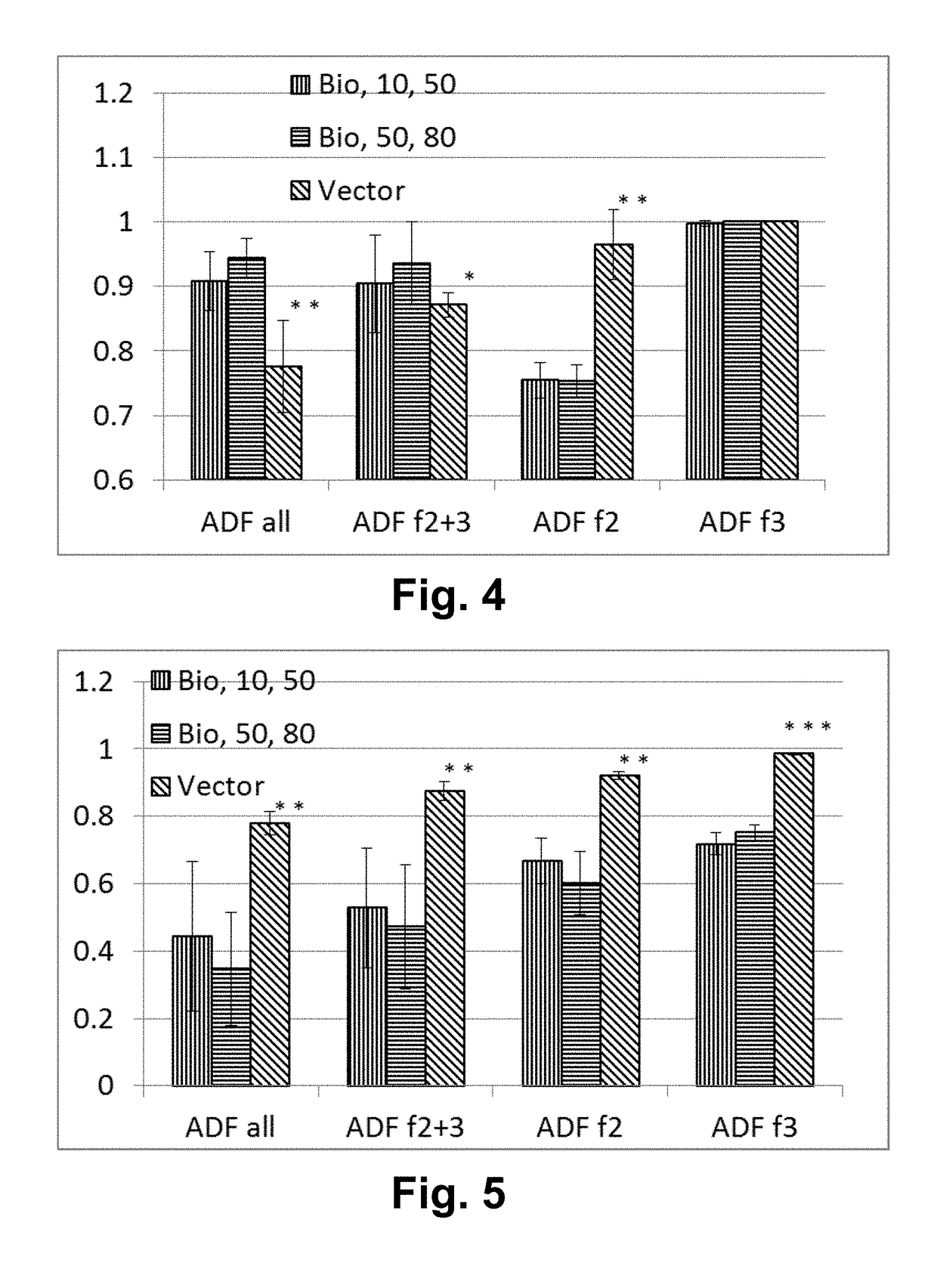
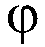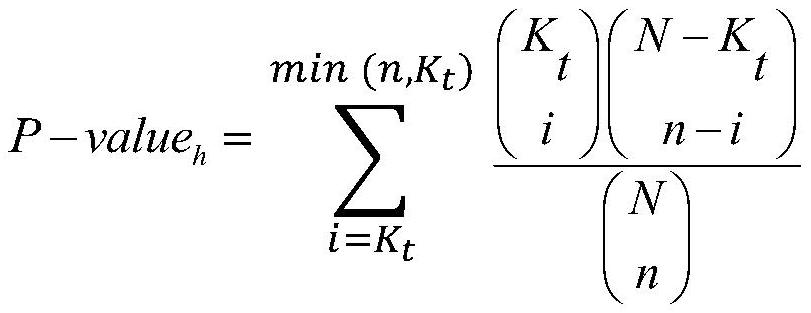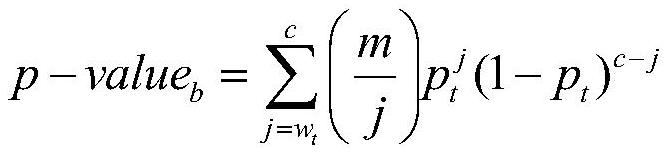Patents
Literature
39 results about "Biosequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
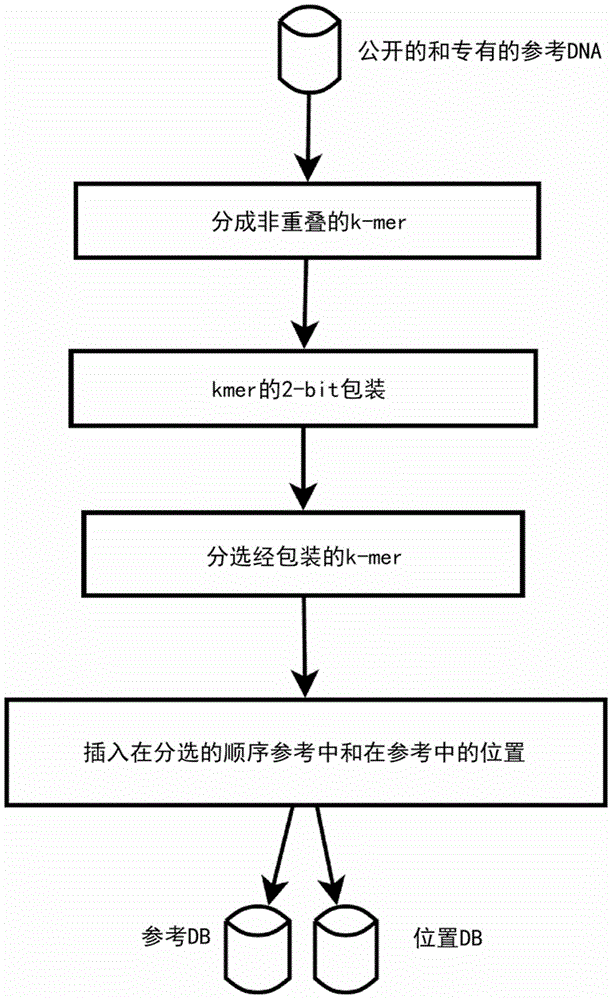
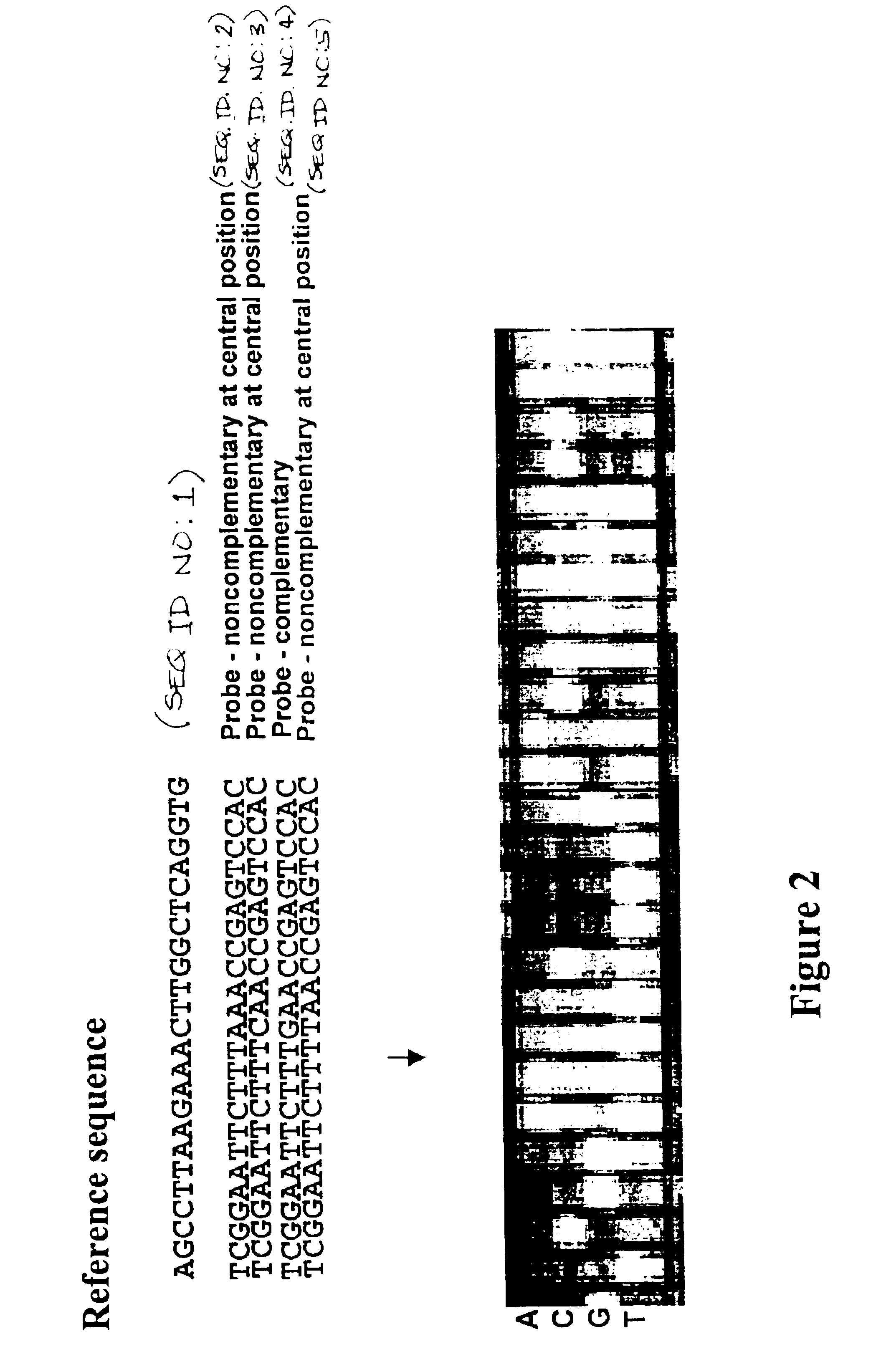
A BioSequence is an object representation of a DNA, RNA, or protein sequence. It can be represented by a Clone, Gene, or the sequence. (caMAGE)
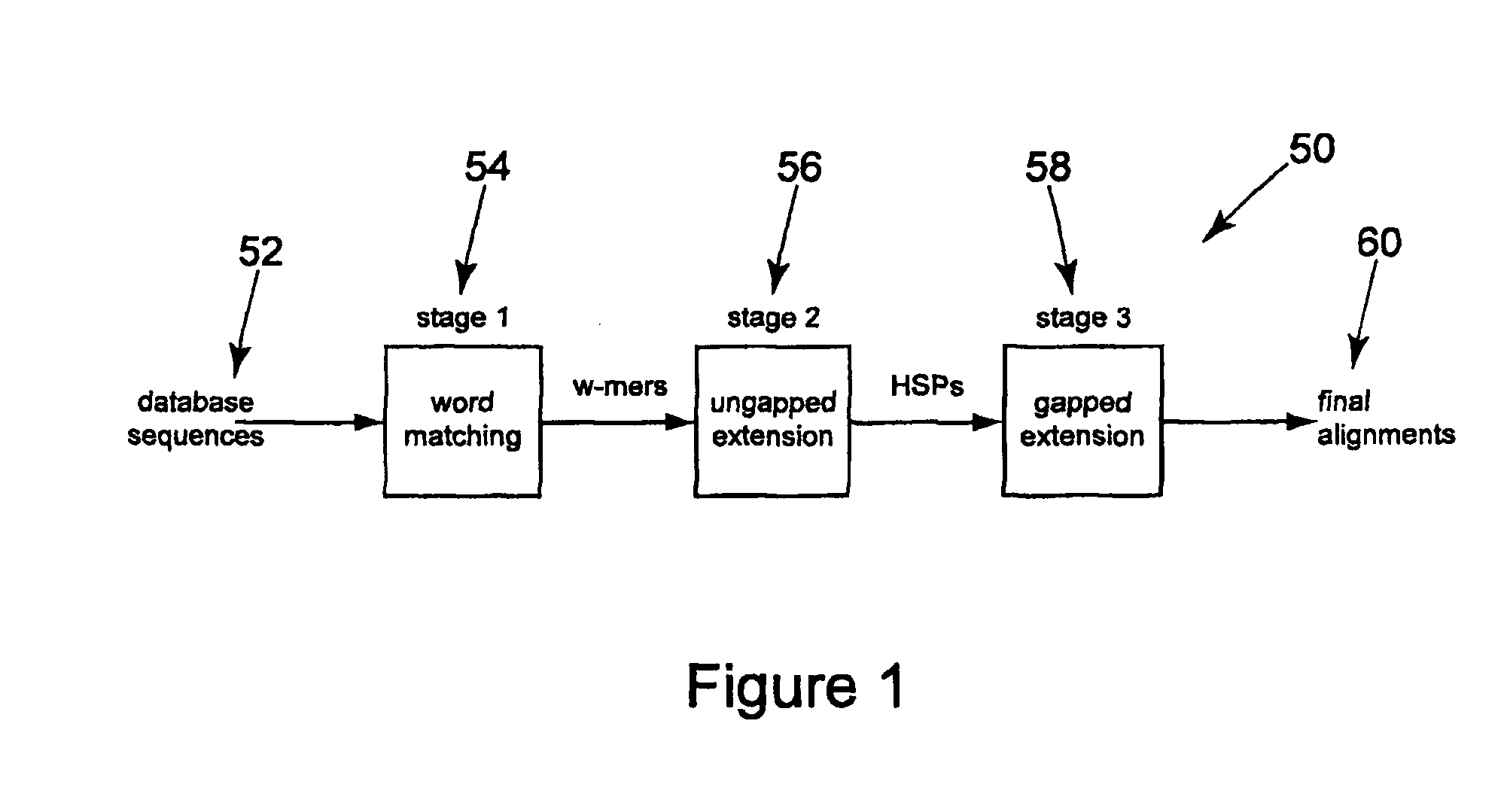
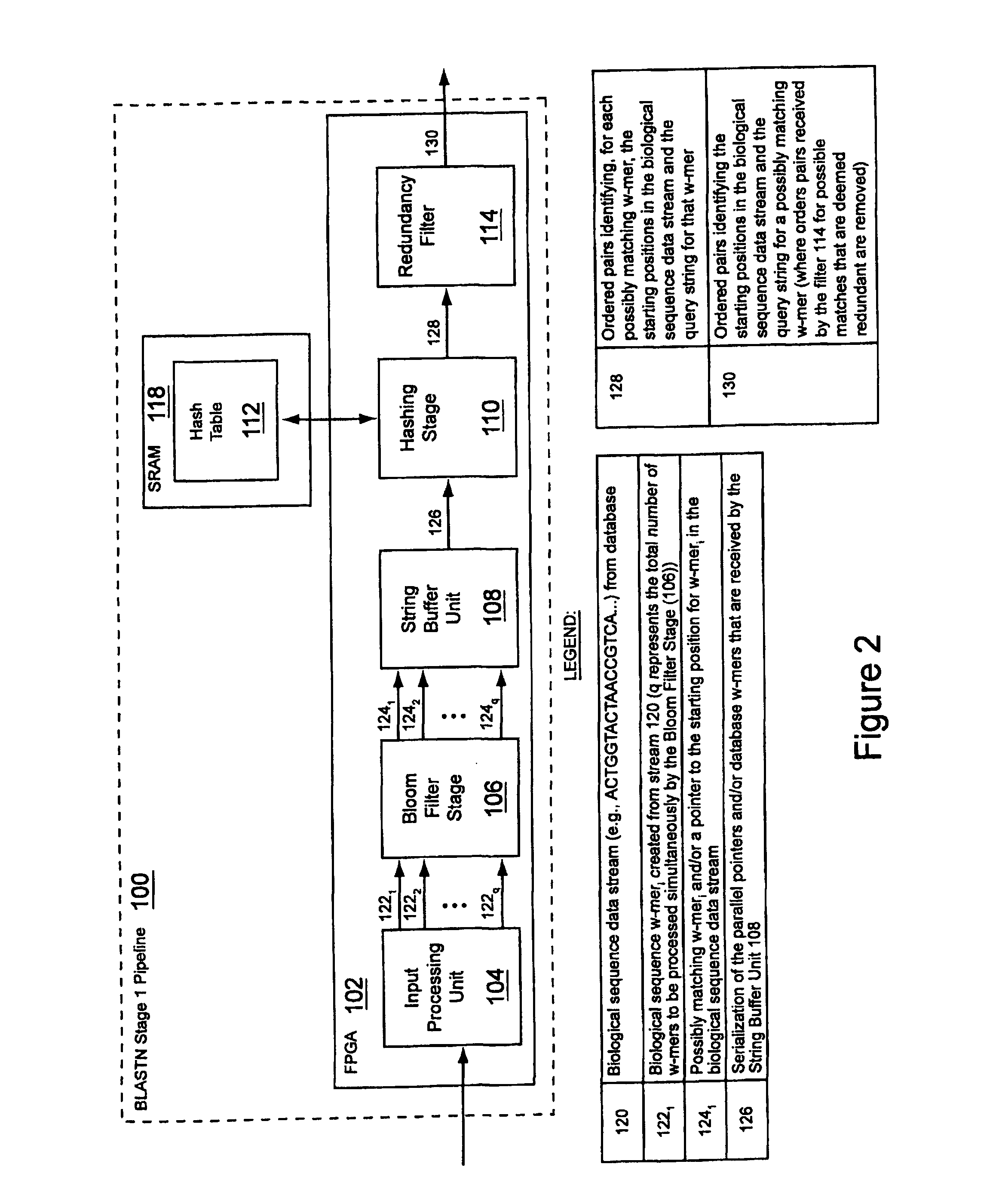
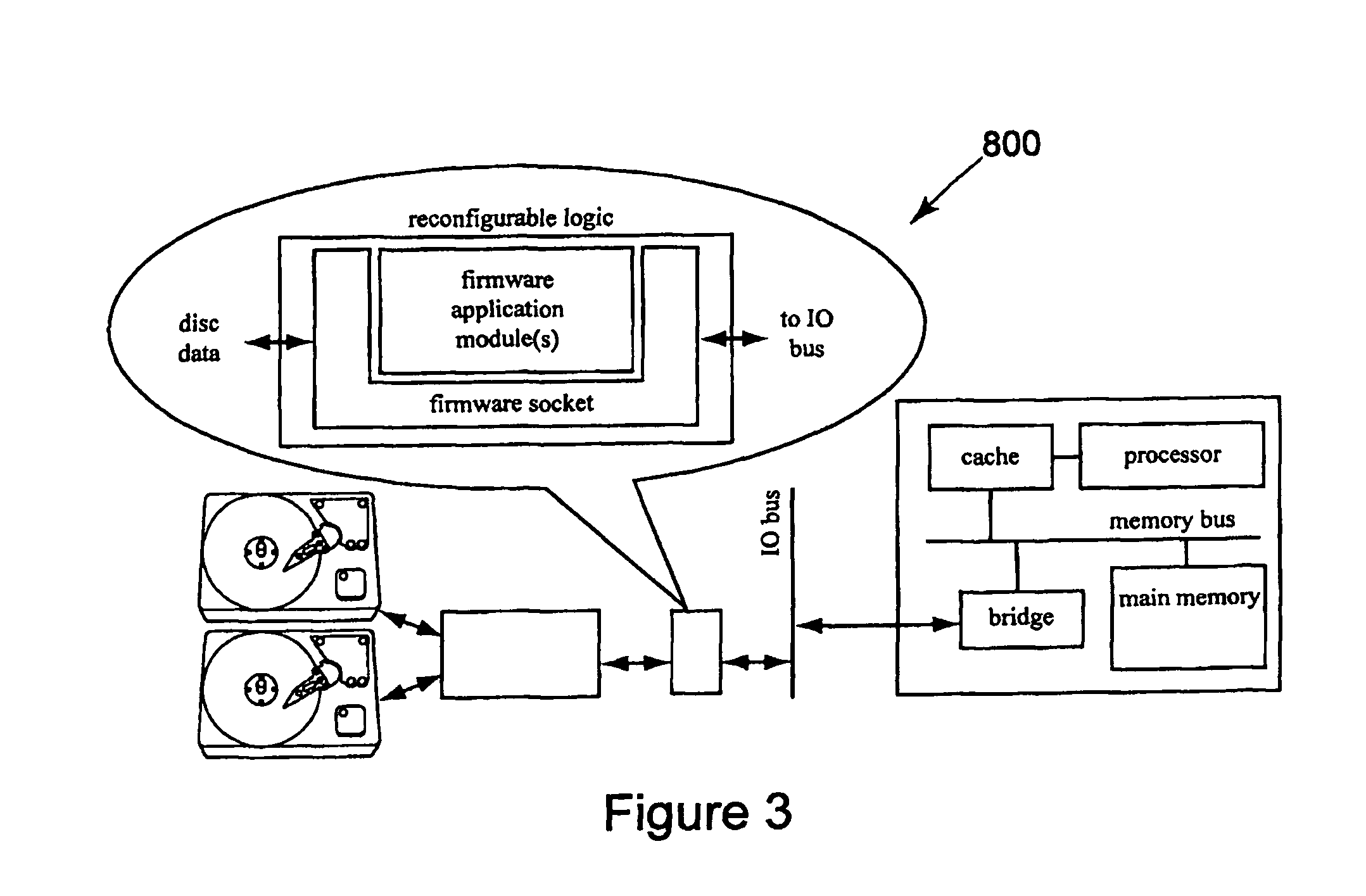
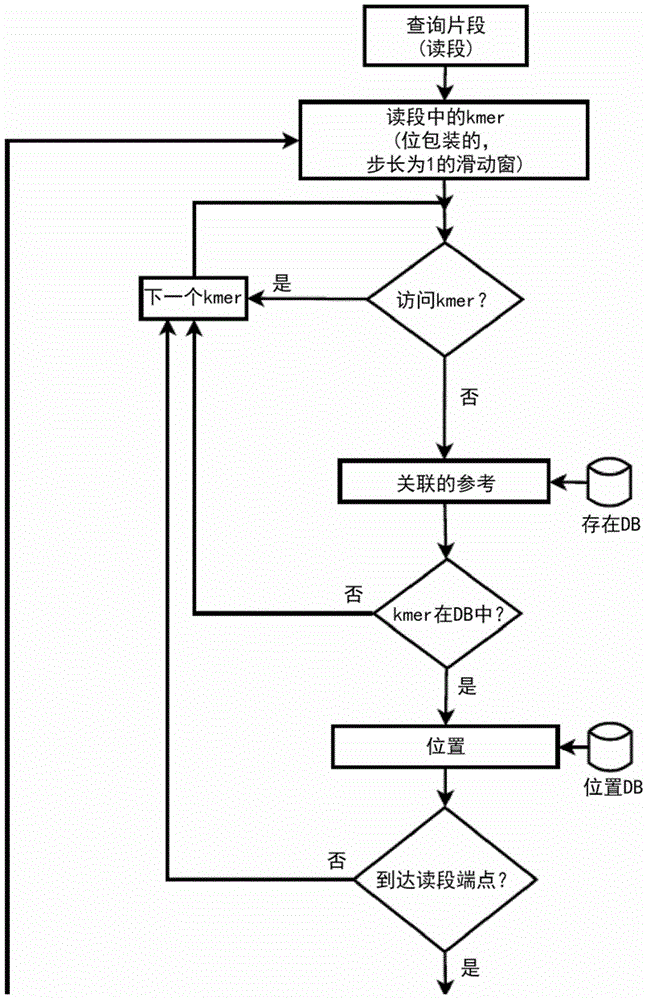
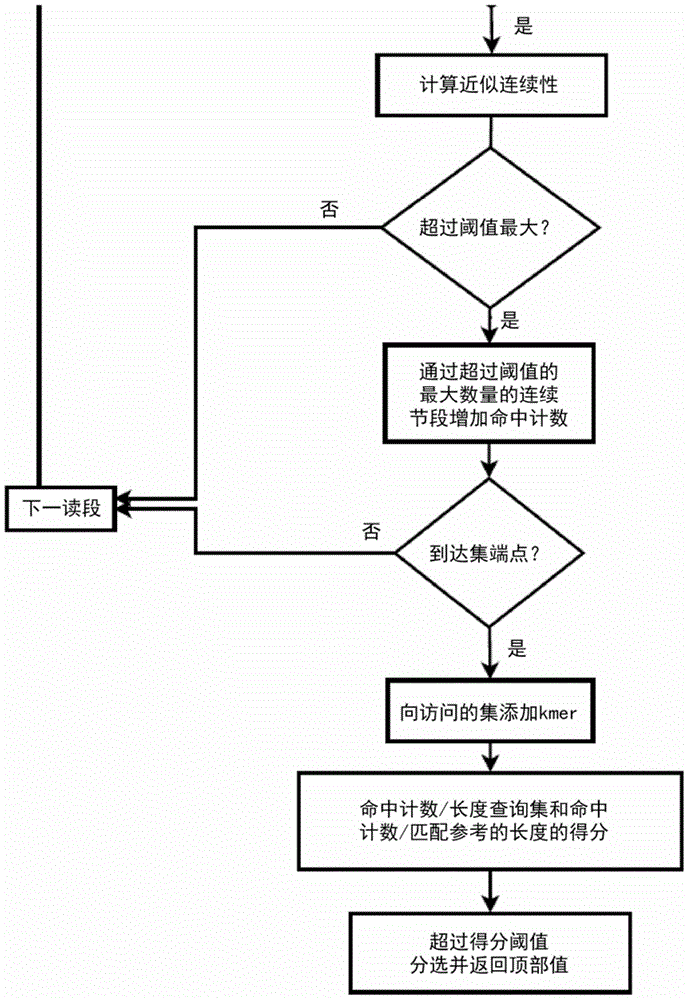
Method and apparatus for performing biosequence similarity searching
A system and method for performing biological sequence similarity searching is disclosed. This includes a programmable logic device configured to include a pipeline that comprises a matching stage, the matching stage being configured to receive a data stream comprising a plurality of possible matches between a plurality of biological sequence data strings and a plurality of substrings of a query string. The pipeline may further include a ungapped extension prefilter stage located downstream from the matching stage, the prefilter stage being configured to shift through pattern matches between the biological sequence data strings and the plurality of substrings of a query string and provide a score so that only pattern matches that exceed a user defined score will pass downstream from the prefilter stage. The matching stage may include at least one Bloom filter.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
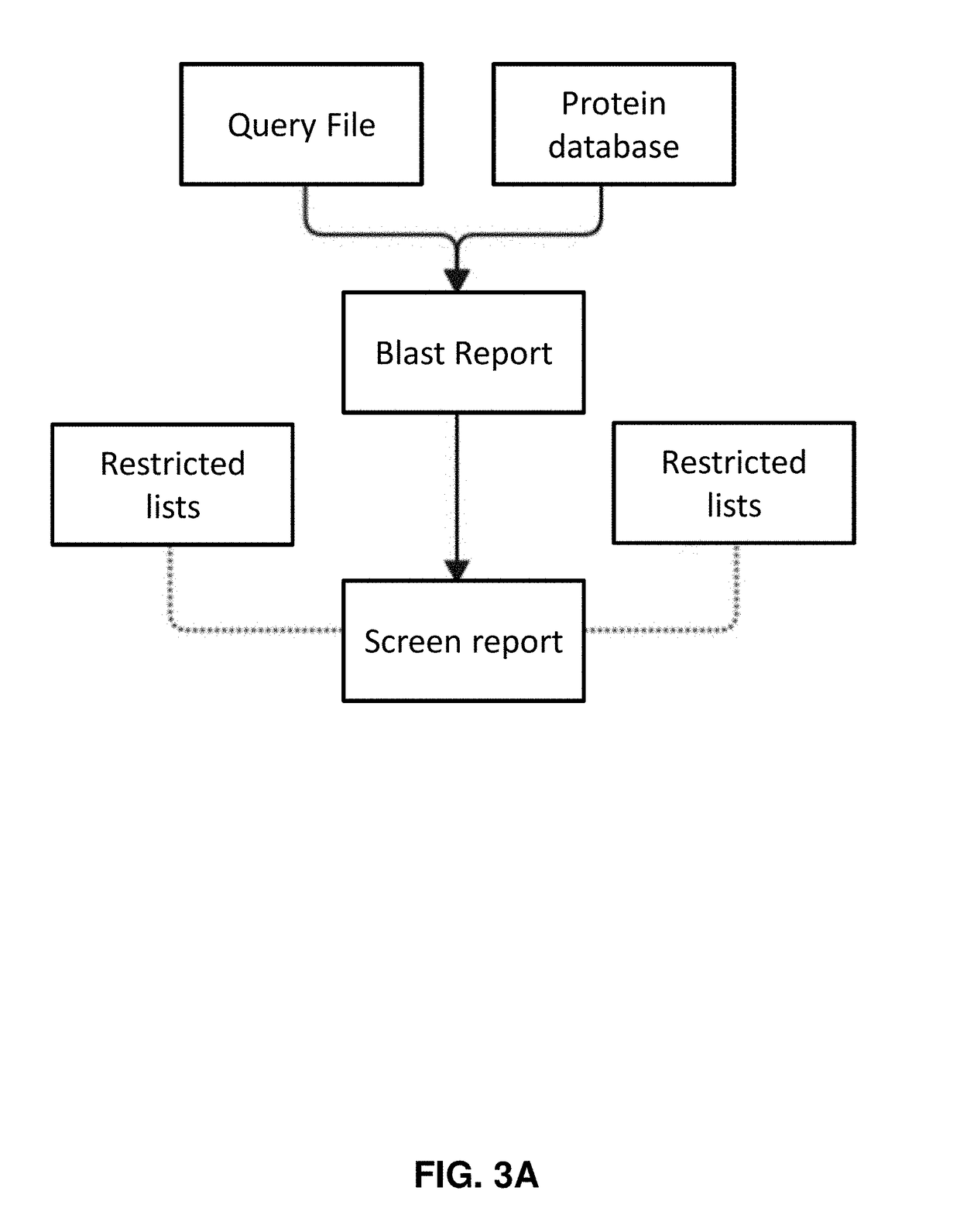
Systems and methods for automated annotation and screening of biological sequences
PendingUS20170357752A1Enhanced polynucleotide synthesisComputer controlSequence analysisKnowledge levelBiological organism
The present disclosure describes software tools for effective biosecurity based on community knowledge and participation. Annotation tools described herein provide assistance to the synthetic biology community to track emerging science on the link between individual proteins and negative outcomes. Screening tools described herein enables the community to broaden both interest and effective practice of biosecurity so that practitioners and biological sequence or construct providers are empowered to evaluate the safety of order requests rather than waiting until synthesis or even expression. In addition, screening tools described herein provide for screening of polynucleotides across the same or multiple orders for sequences associated with harmful biological sequences from a reference database.
Owner:TWIST BIOSCI
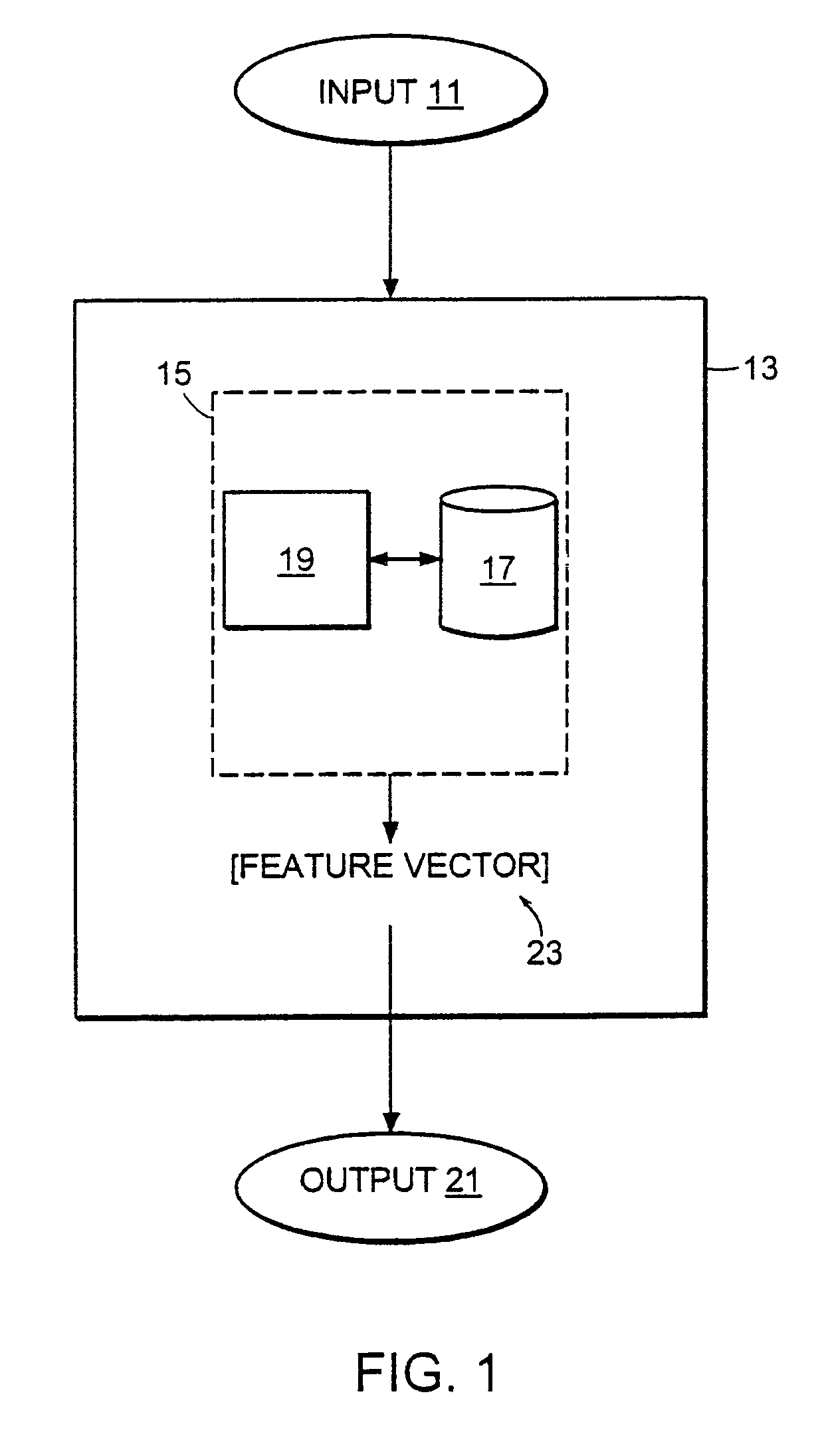
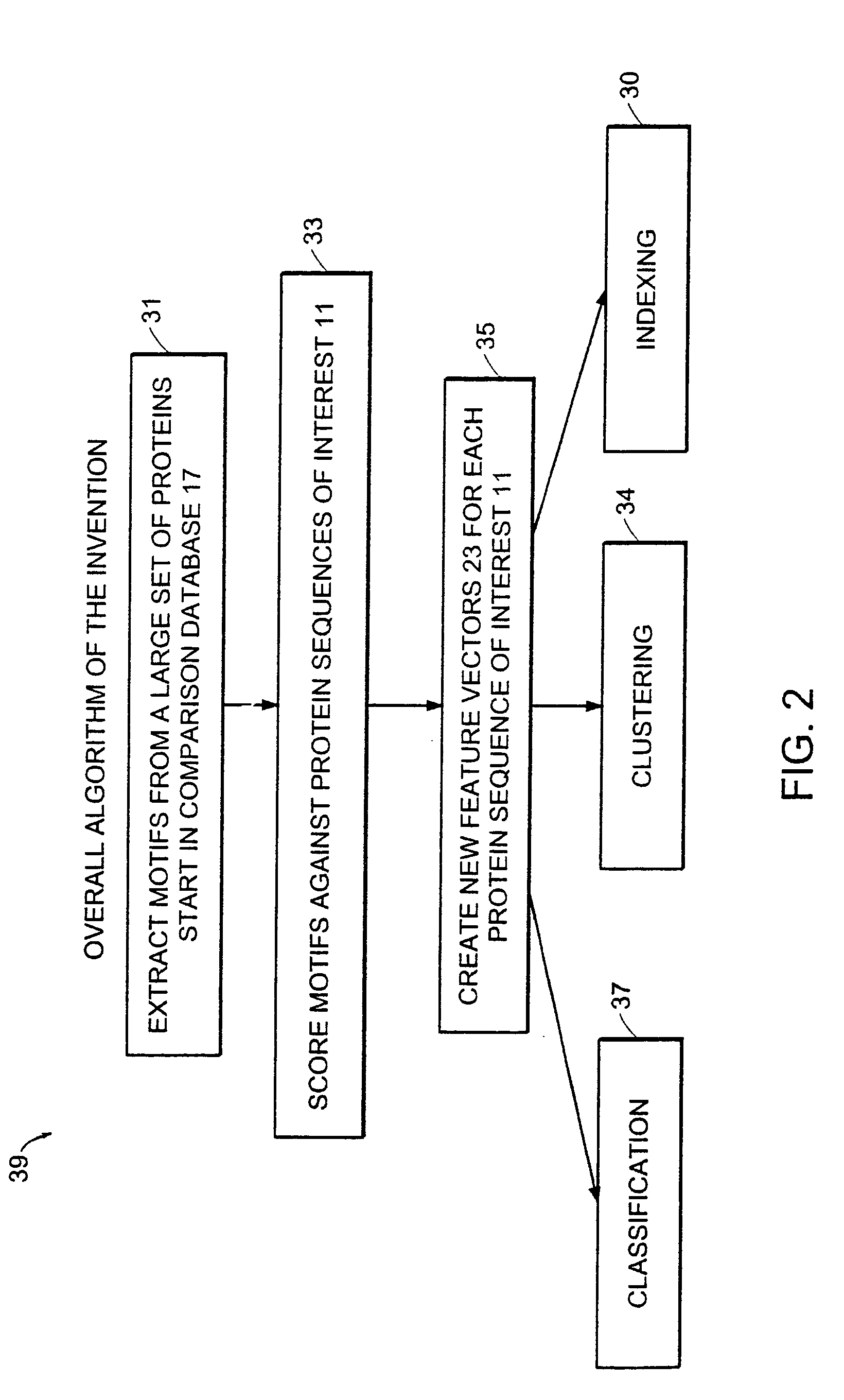
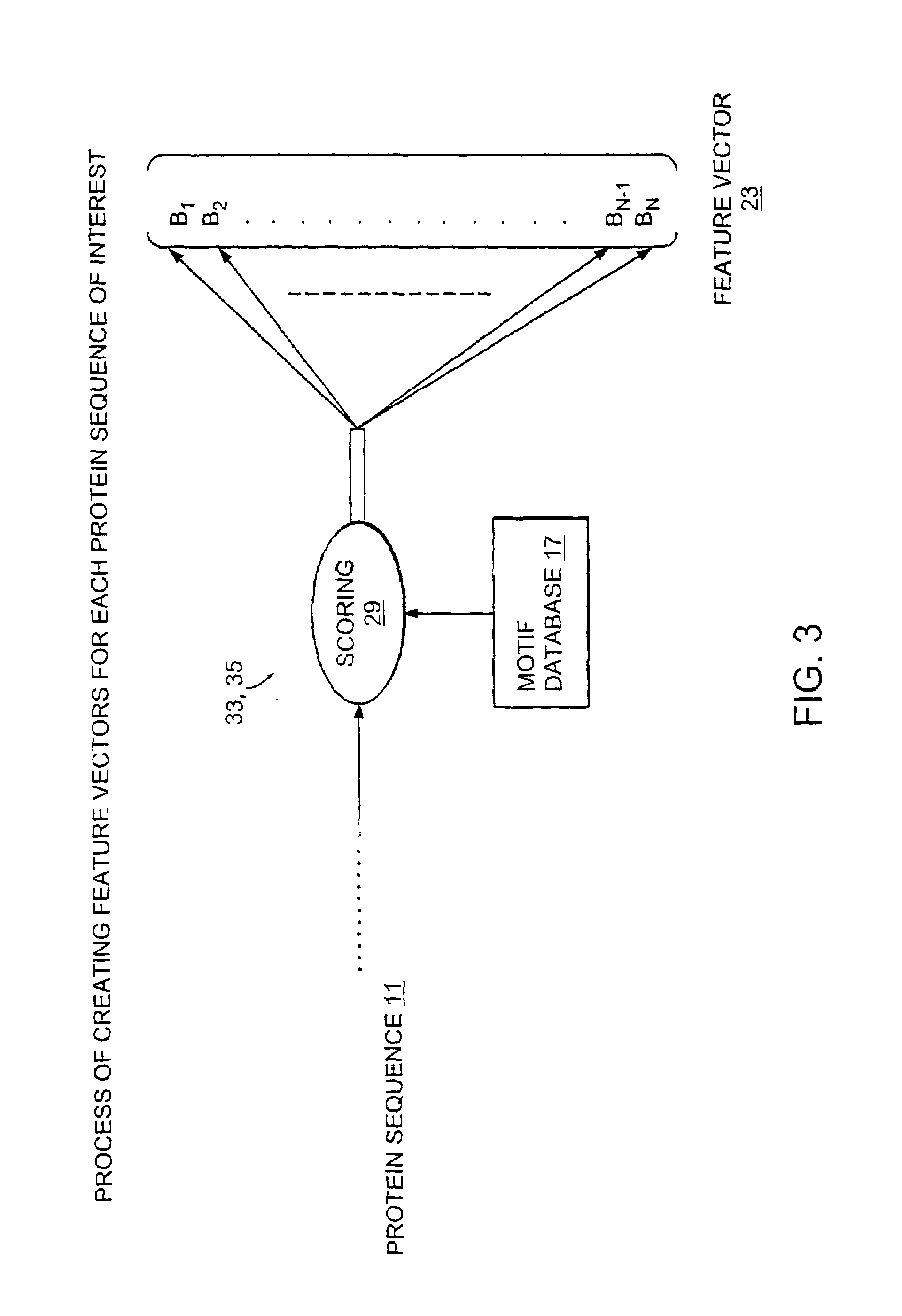
Computer method and apparatus for uniform representation of genome sequences
InactiveUS7047137B1Data processing applicationsSugar derivativesUniform representationVector element
A method and apparatus transforms typically differing length text string representations (i.e., sequences) of biological fragments into uniform length representations. A comparison database stores a predefined number of known biological sequences. A comparison routine compares and scores a subject sequence against each known sequence in the database. Each individual score (one for each known sequence in the database) serves as a vector element forming a fixed length vector representation of the subject sequence. Vector length equals the predefined number of known biological sequences in the database. Scoring is a probability or an occurrence count of the known biological sequence in the subject sequence.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
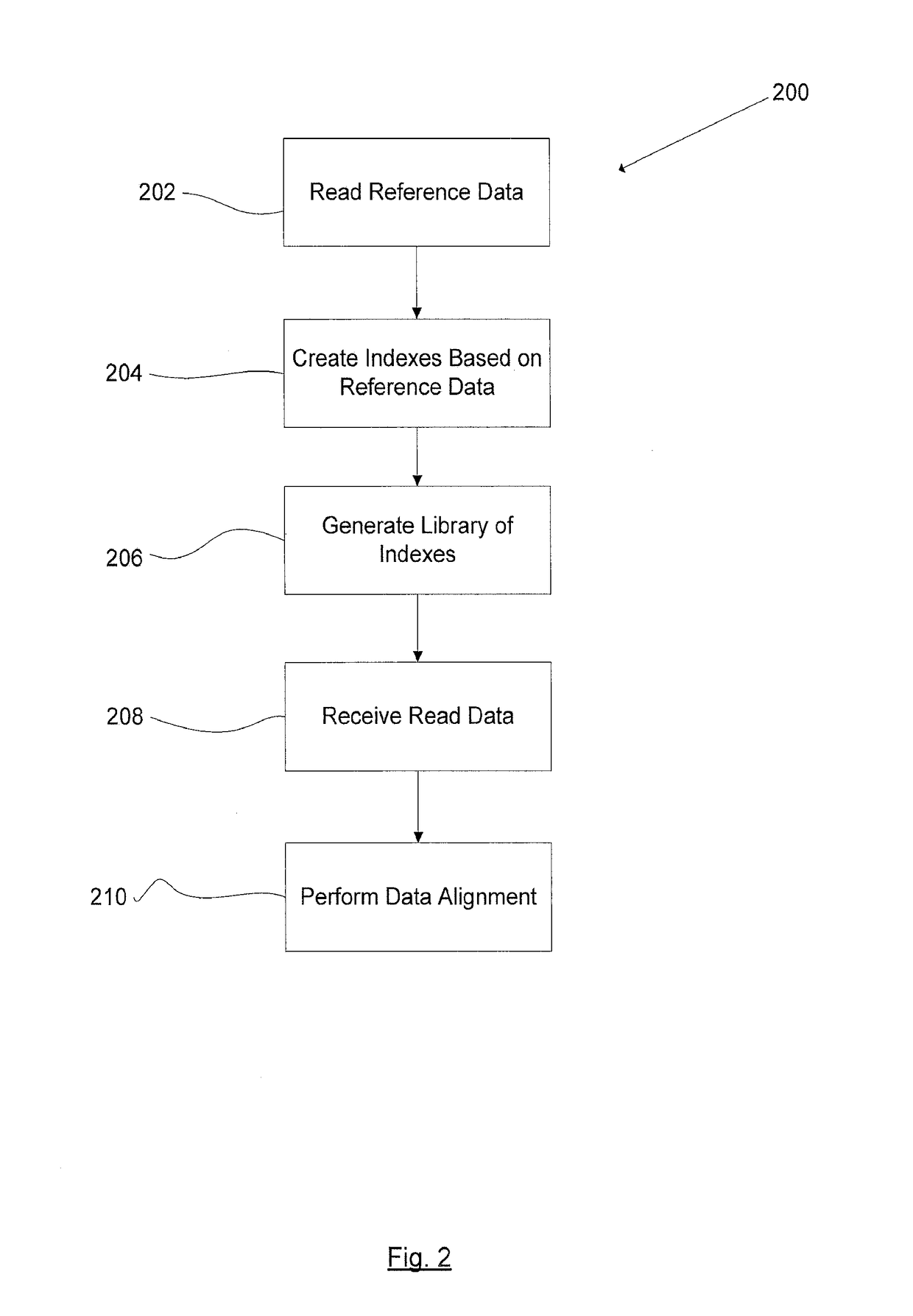
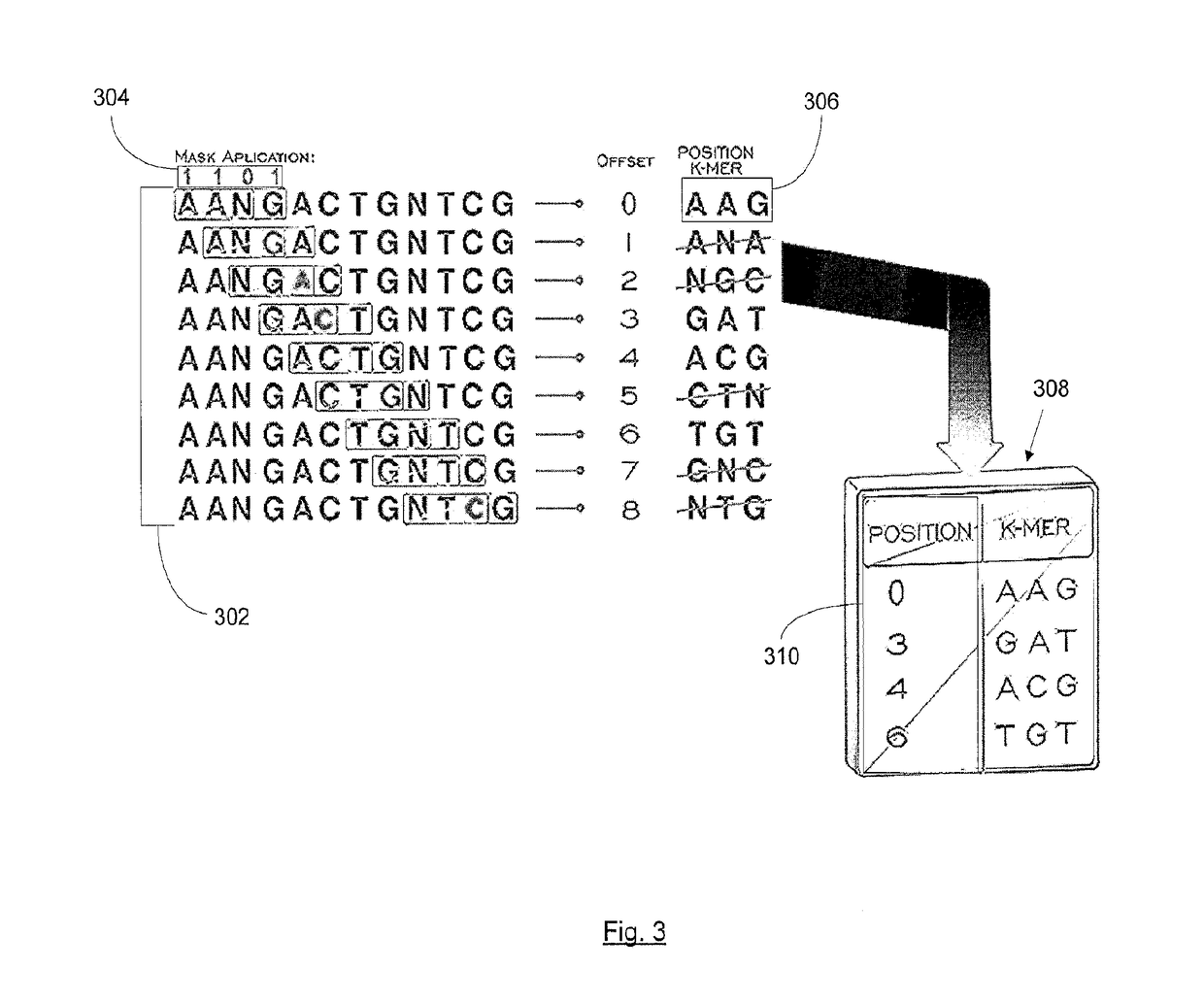
Methods and systems for biological sequence alignment
InactiveUS20170068776A1Overcomes drawbackSequence analysisSystems biologyAssociative arrayComputer science
A method for transforming a plurality of random biological sequence data to an ordered biological data sequence, the method comprises reading a reference biological data sequence; generating a plurality of indexes based on the reference biological data sequence; generating a library, the library including the plurality of indexes; organizing the library into an associative array; reading the plurality of random biological sequence data; encoding the plurality of random biological sequence data; comparing the encoded plurality of random biological sequence data to the reference biological sequence; and aligning the encoded plurality of random biological sequence data to the reference biological sequence using an alignment algorithm to generate a plurality of alignment data.
Owner:ARC BIO LLC
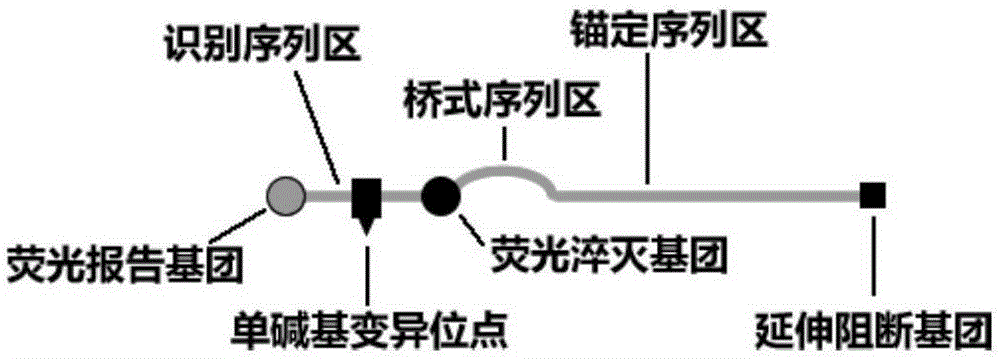
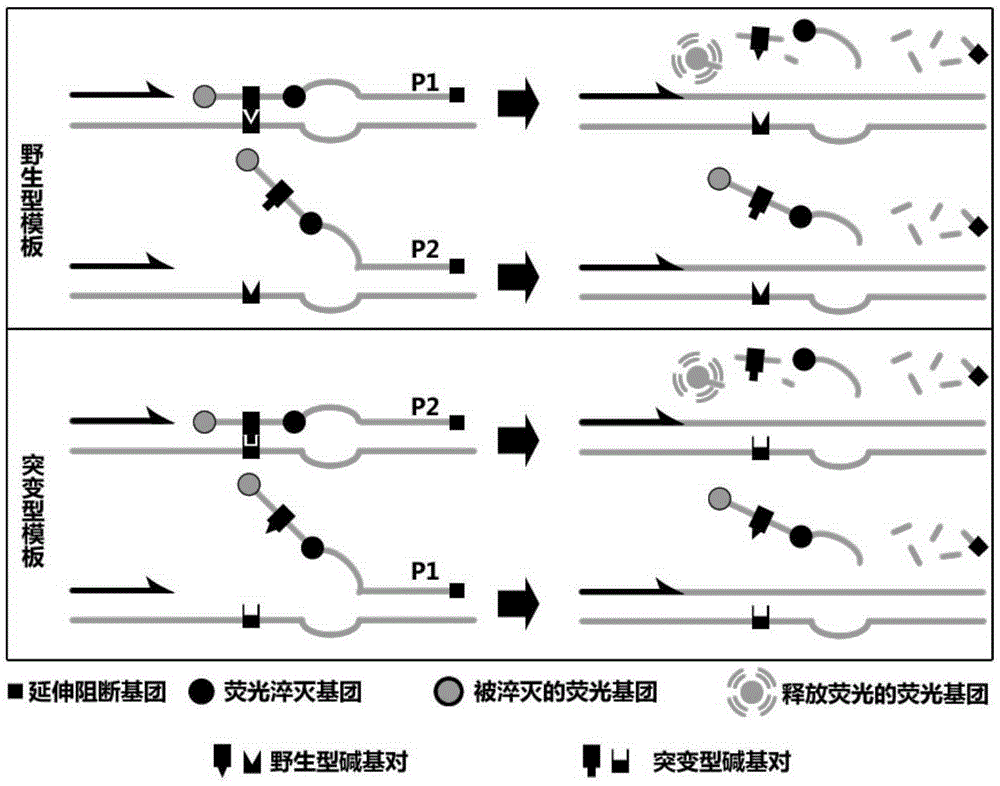
Bridge type fluorescent probe with bridge type sequence zone doping into mismatched bases and application and method
InactiveCN105274096ASimple designHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceBridge type
The present invention discloses a bridge type fluorescent probe with a bridge type sequence zone doping into mismatched bases and application and a method, the bridge type fluorescent probe 5'-end to 3'-end nucleic acid sequence successively comprises a recognition sequence zone complementary to a nucleic acid sequence of a to-be-tested mutant gene, the bridge type sequence zone, and an anchor sequence zone, wherein the anchor sequence zone is complementary to the outer side sequence zone of 3'-end of the to-be-tested mutant gene, the 3'-end of the anchor sequence is connected with an extension blocking group ; the bridge type sequence zone is a nucleotide derivative sequence containing at least one mismatched bases, an interactiveness fluorescent marking system is marked between the recognition sequence zone and the bridge type sequence zone, the bridge type fluorescent probe is simple in design, can specifically recognizes the gene, is high in sensitivity, and can be used to detect single base mutation and identify highly homologous species and subtypes.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA +1
Method and apparatus for object based biological information, manipulation and management
InactiveUS20050015207A1Encourage creativityQuick testBiological testingBioinformaticsObject basedData file
A biological data manipulation system, and a programming language and system, and a method of use thereof, are disclosed. The system, apparatus, and method include a first data file receiver for receiving a first data file having data indicative of a first data file type and data indicative of at least one biological data object, a first classifier that applies a plurality of rules to the first data file to parse the first data file into a first data file type and into a plurality of string classes, a second classifier that differentiates a master class for ones of the plurality of string classes, wherein the master class is differentiated against at least one selected from the group consisting of a single biosequence master and a multiple biosequence master, and a third classifier that classifies an at least one biological data object of the first data file, wherein the at least one biological data object is multiple inherited to the master class in accordance with at least one of the plurality of rules, and in accordance with at least a partial sequence of stored biodata compared by the third classifier against at least a partial sequence of at least one of the plurality of string classes.
Owner:HELIX GENOMICS PVT LTD IN INDIA
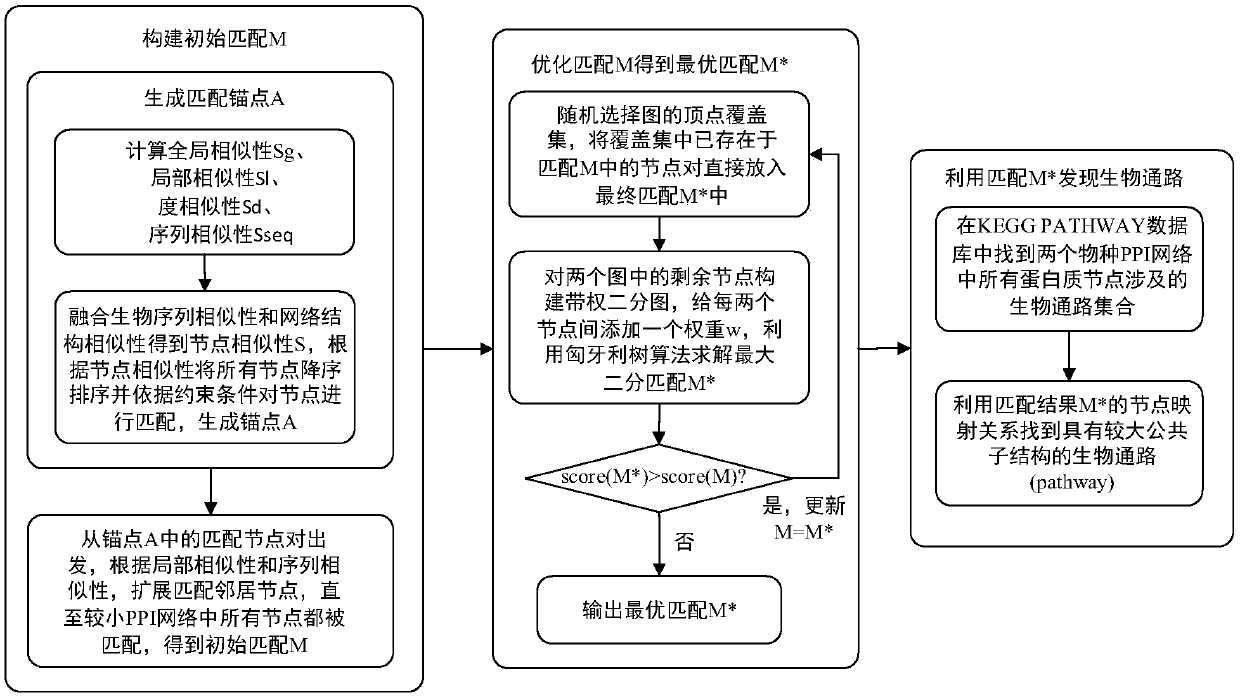
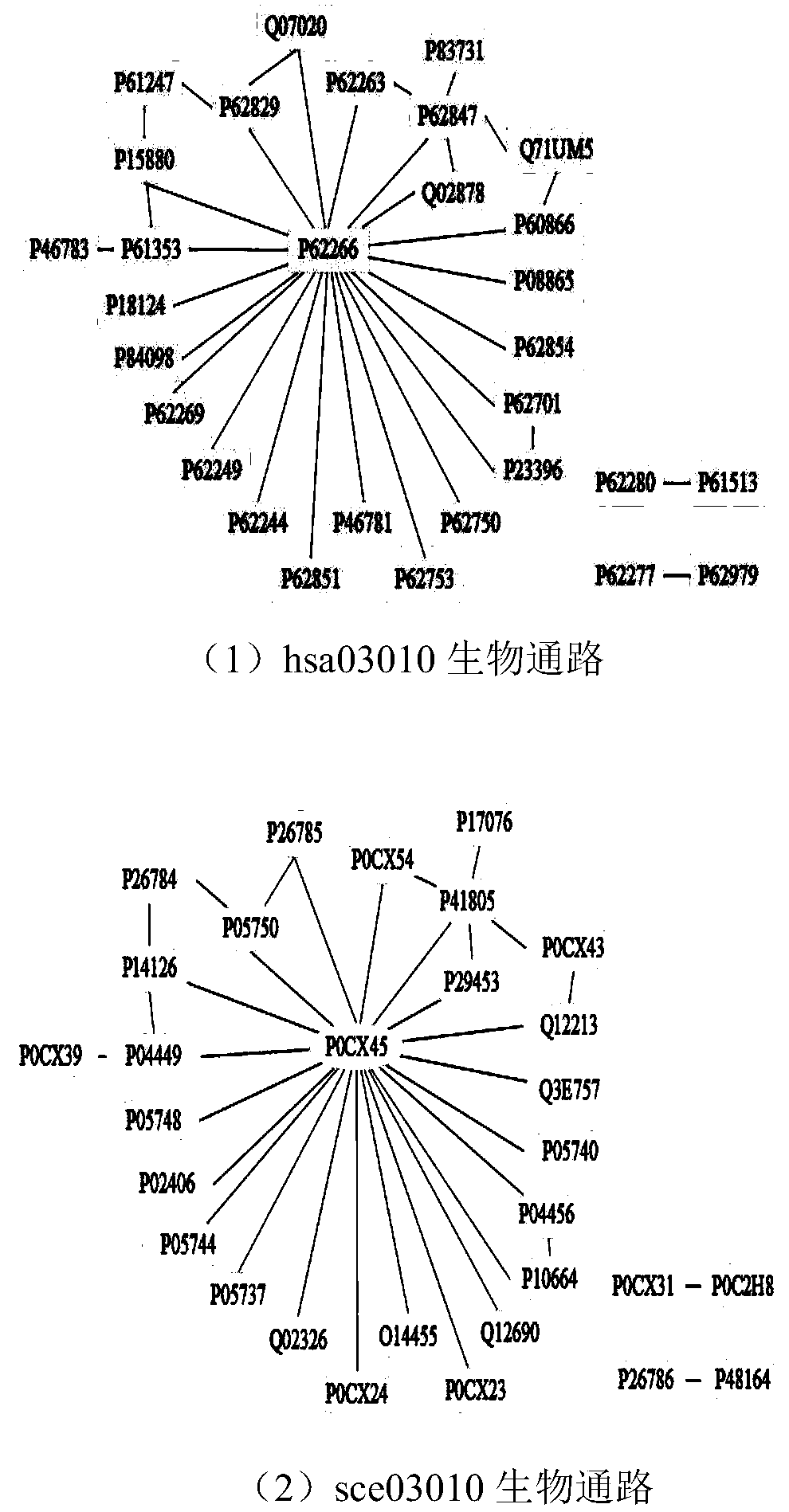
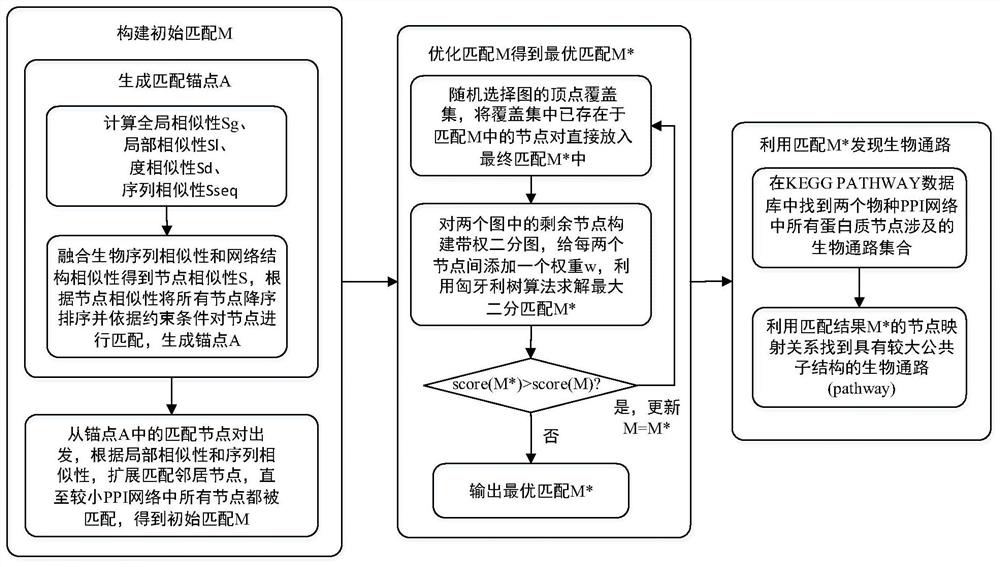
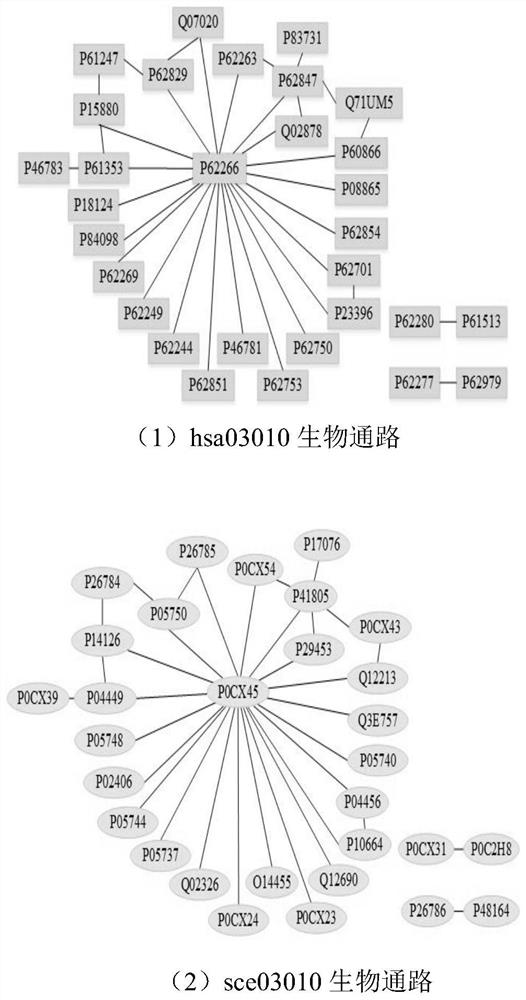
Graph matching based cross-species biological access discovery method
ActiveCN107832583AEasy to integrateProteomicsGenomicsProtein Interaction NetworksMethod of undetermined coefficients
The invention discloses a graph matching based cross-species biological access discovery method, which can solve the problem that the conventional biochemistry experiment methods are low in biologicalaccess discovery efficiency, and the problem that the conventional graph matching methods cannot integrate the biological sequence similarity and the protein interaction network structure similaritytogether. In the method, the biological sequence similarity and the protein interaction network structure similarity can be integrated together, coexisting larger sub structures in protein interactionnetworks of different species can be discovered, biological accesses having the similar functions in the different species can be effectively discovered, and the method has guiding significance for research on relation between different species in biology.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
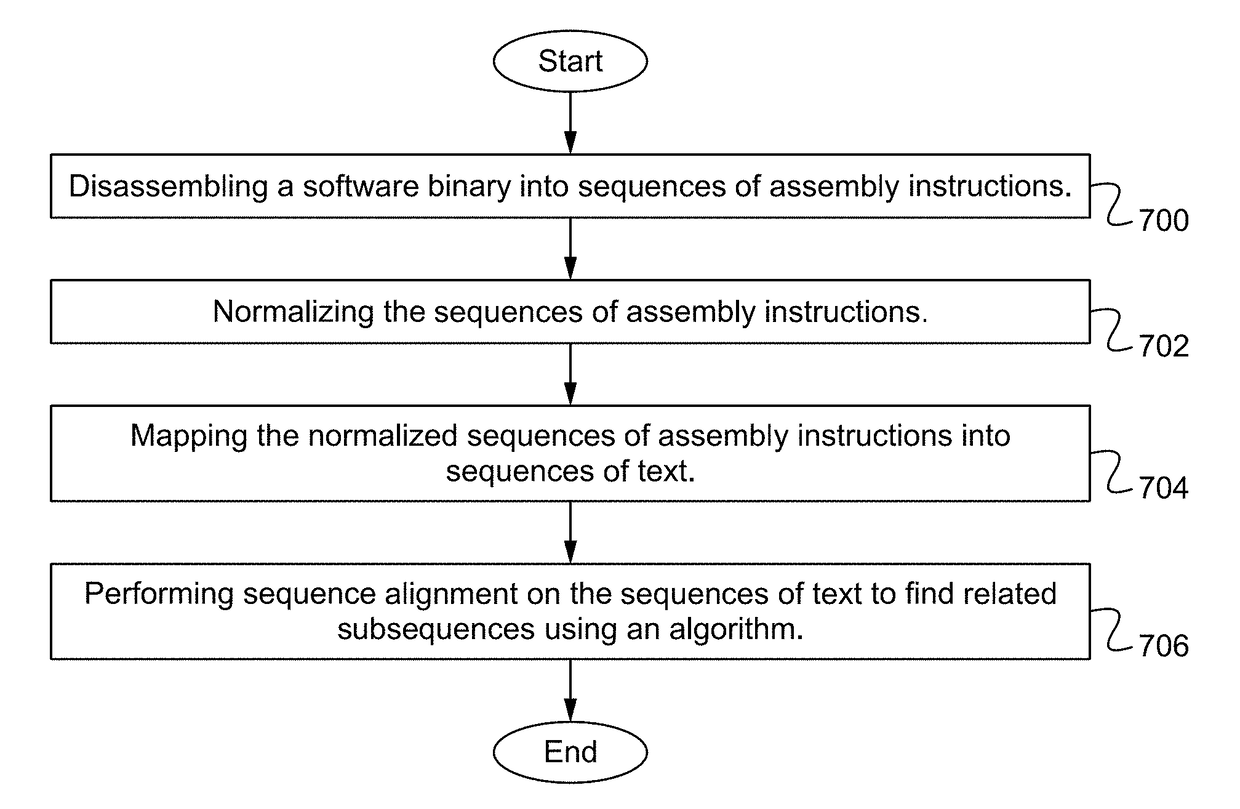
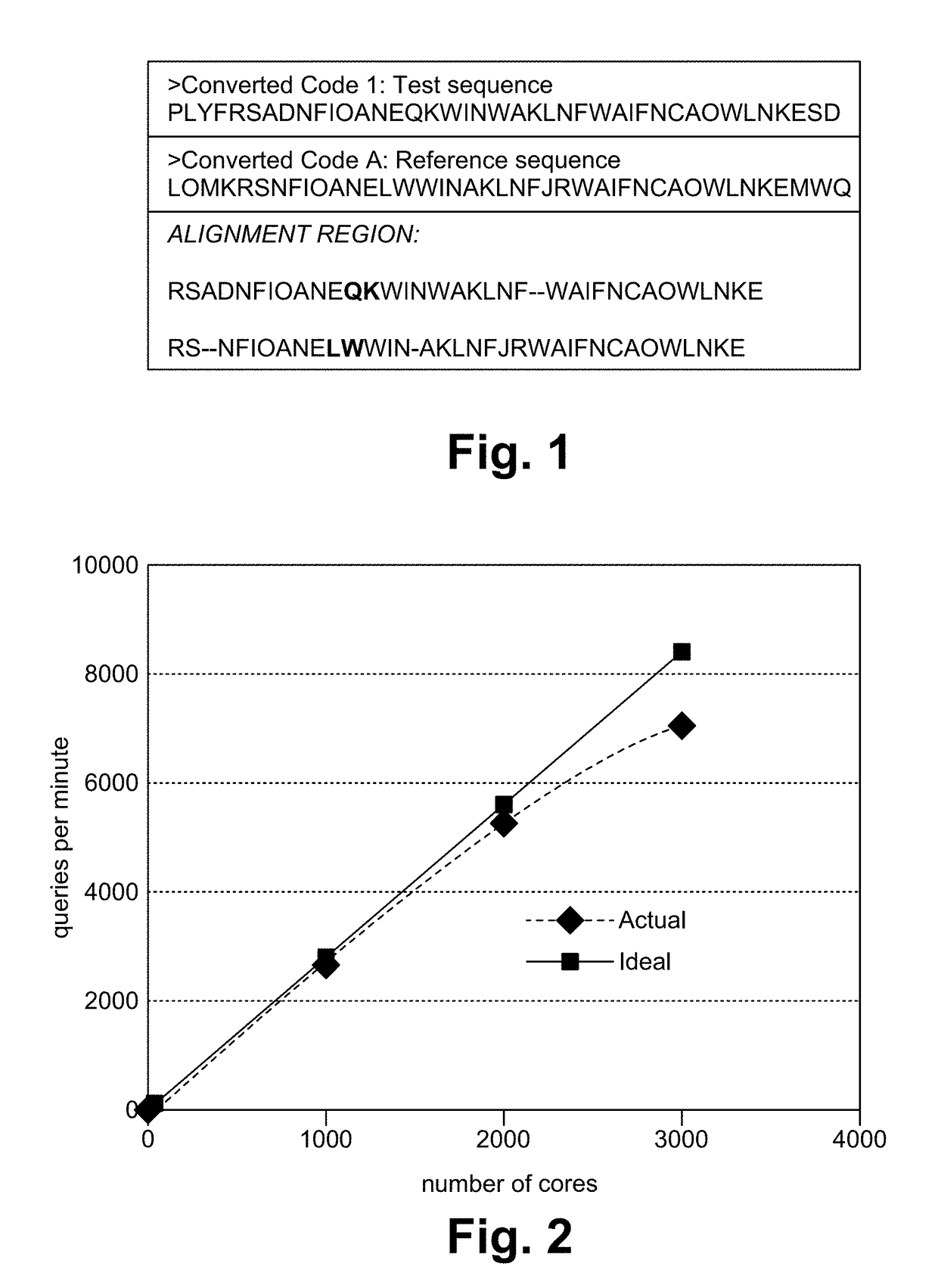
Biosequence-based approach to analyzing binaries
ActiveUS20170344352A1Decompilation/disassemblyDigital data protectionMulti user environmentTheoretical computer science
In a dynamic computing environment, it is a nontrivial task to verify code running in the environment because most approaches to software similarity require extensive and time-consuming analysis of a binary, or the approaches fail to recognize executables that are similar but nonidentical. A biosequence-based method for quantifying similarity of executable binaries is used to identify allowed codes in a real-world multi-user environment.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Biological sequence analysis method based on gap spectrum
InactiveCN101497924AHigh speedHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsSequence analysisAnalysis method
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Database-driven primary analysis of raw sequencing data
InactiveCN104919466ASequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsSequence databaseFood safety
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
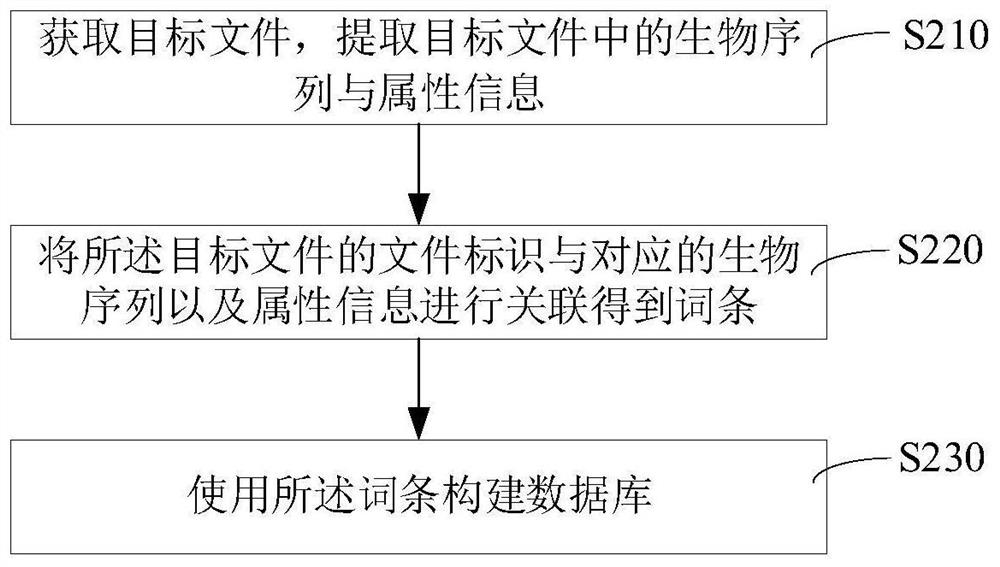
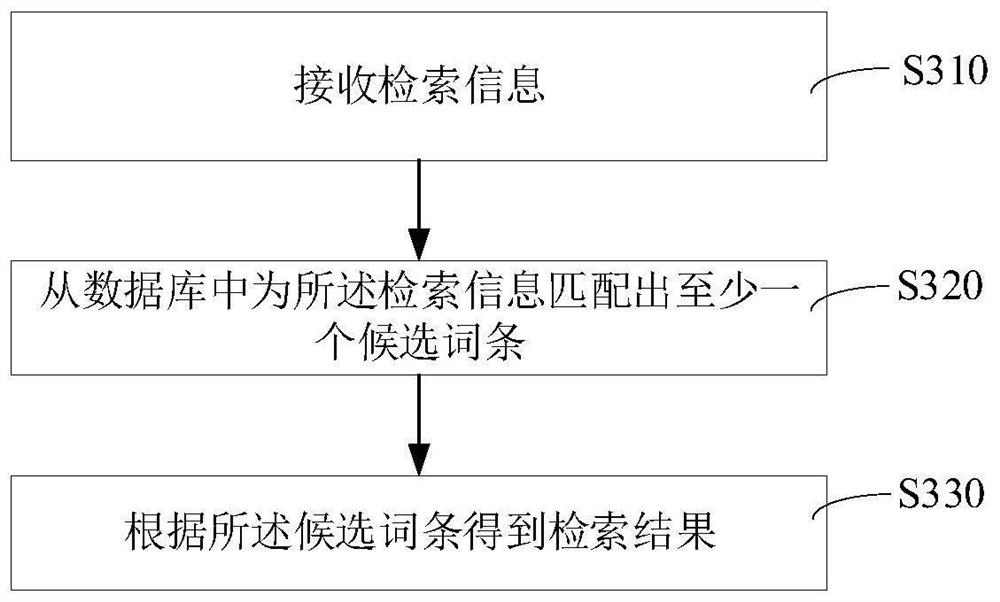
Database construction method and device and file retrieval method and device
The invention relates to a database construction method and device, gene sequence association degree labeling and device, a file retrieval method and device, computer equipment and a computer readablestorage medium. According to the scheme, biological sequences and attribute information are extracted from a target file, and entries in a database are constructed based on the extracted biological sequences and attribute information; when a user performs retrieval based on the database, the server can match entries for the user through the biological sequences, the attribute information or the combination of the biological sequences and the attribute information in the entries, so that when the database is applied to a retrieval platform, various retrieval supports such as biological sequence retrieval, biological sequence attribute retrieval and comprehensive biological sequence and biological sequence attributes can be provided for users.
Owner:PATSNAP CN SUZHOU LTD
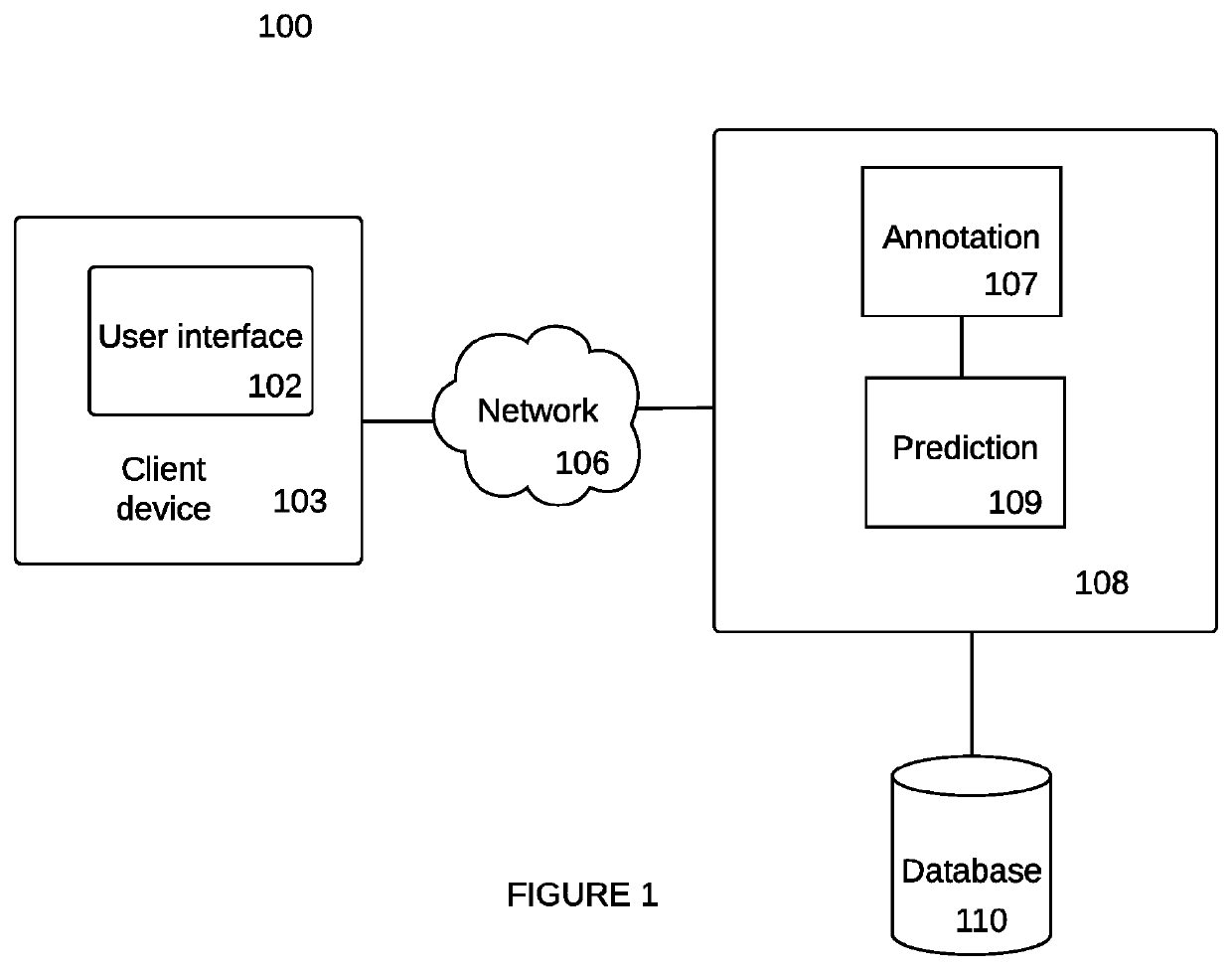
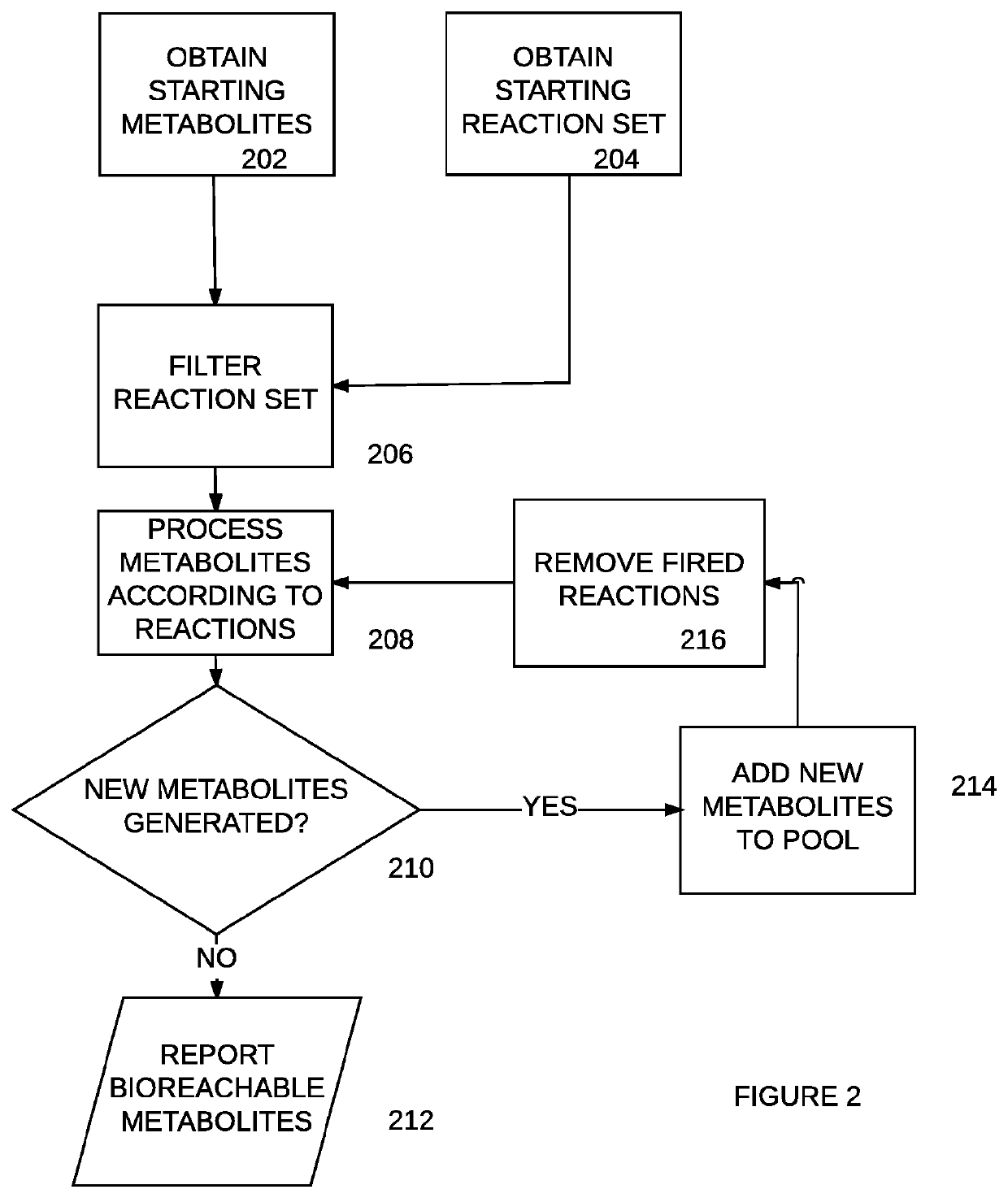
Bio-reachable prediction tool with biological sequence selection
Owner:ZYMERGEN INC
Bioreachable prediction tool with biological sequence selection
PendingUS20210225455A1Increase productionOvercome disadvantagesBiostatisticsProteomicsEnzymeBioinformatics
Systems, methods and non-transitory computer-readable media identify a candidate biological sequence for enabling a function in a host cell. Embodiments access a predictive model that associates a plurality of biological sequences, such as enzymes, with one or more functions, such as reaction catalysis; predict, using the predictive model, that one or more candidate sequences of the plurality of biological sequences enable a desired function; and classify using a processor, candidate sequences that satisfy a confidence threshold as filtered candidate sequences.
Owner:ZYMERGEN INC
Methods for obtaining and correcting biological sequence information
A method for sequencing a biological molecule, such as a nucleic acid molecule, and a method for detecting and / or correcting sequencing error(s) in the sequencing results are provided. Kits and systems based on the above methods are also provided.
Owner:CYGNUS BIOSCI BEIJING CO LTD
Biosequence-based approach to analyzing binaries
ActiveUS10191726B2Decompilation/disassemblyDigital data protectionMulti user environmentTheoretical computer science
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
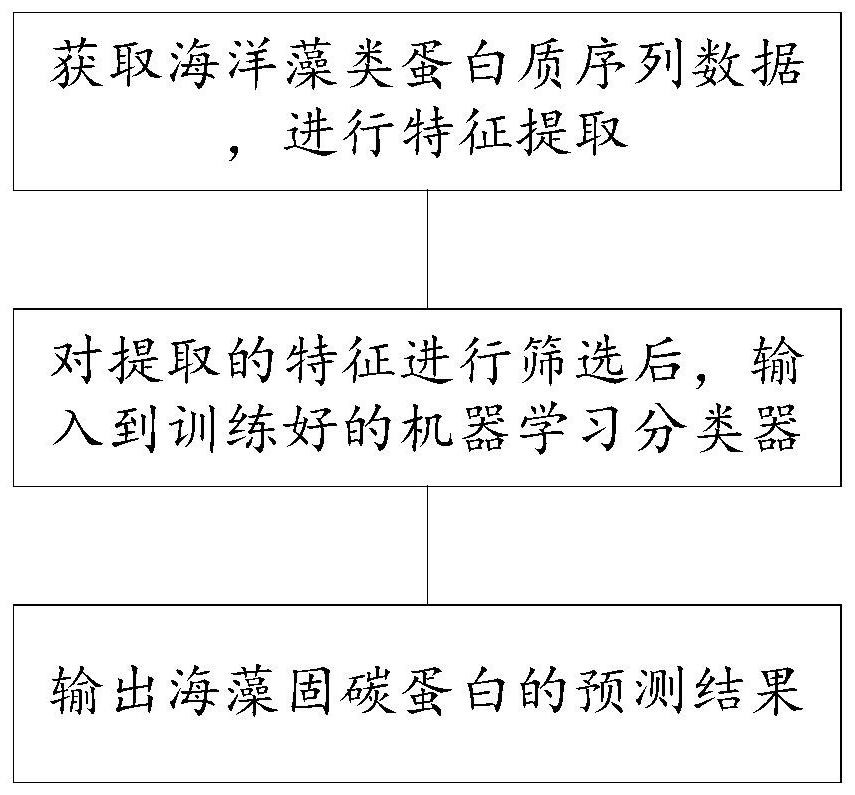
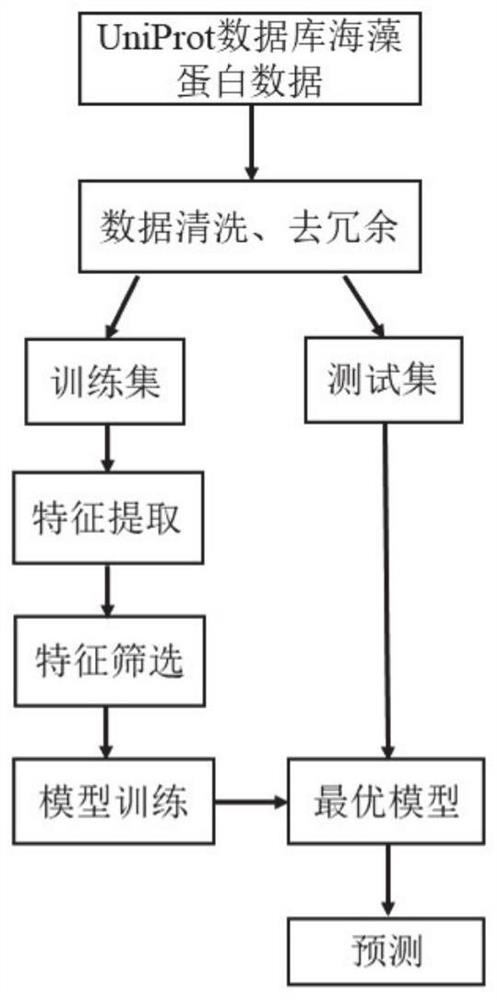
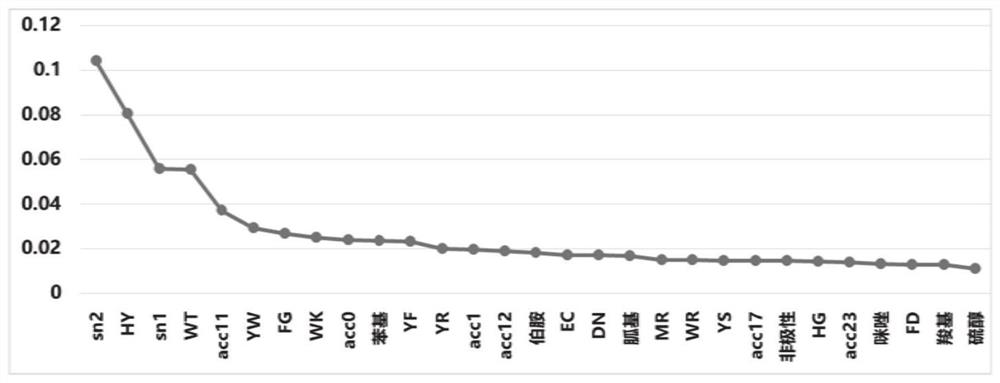
Seaweed carbon sequestration protein prediction method and system based on machine learning
ActiveCN112309495AAvoid interferenceSave manpower and material resourcesBiostatisticsProteomicsFeature extractionComputer science
The invention discloses a seaweed carbon sequestration protein prediction method and system based on machine learning. The method comprises the steps: acquiring marine algae protein sequence data, andcarrying out the feature extraction of the data; screening the extracted features, and inputting the screened features into a trained machine learning classifier; and outputting a prediction result of the seaweed carbon sequestration protein. According to the method, a machine learning algorithm is adopted to predict whether the protein has the carbon sequestration function or not, compared witha mode of analyzing a large number of biological sequences based on a traditional biochemical experiment, manpower and material resources can be effectively saved, introduction of personal errors to interfere with a result or cause interference is avoided, and the method has higher prediction efficiency and accuracy.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
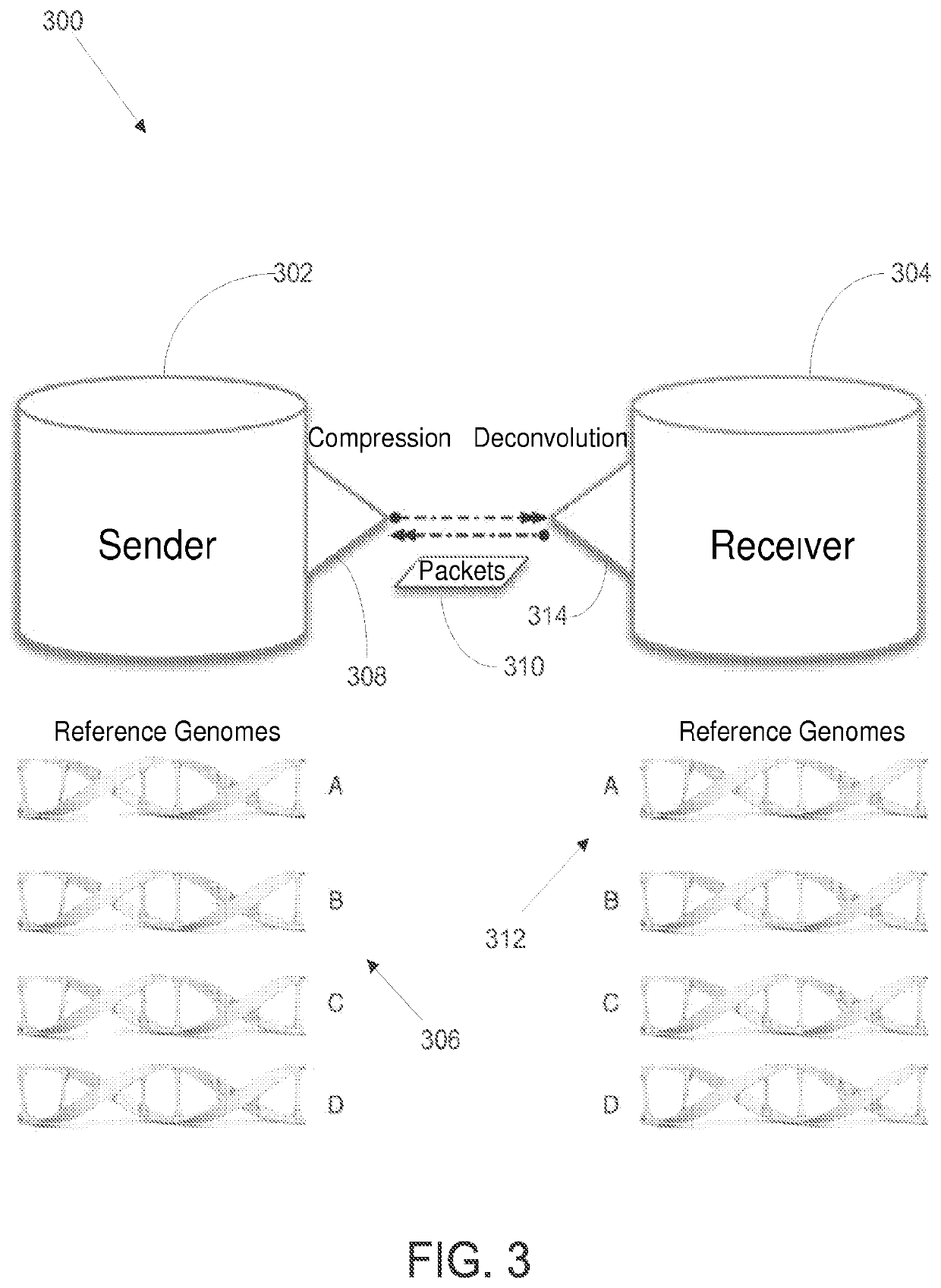
Methods and systems for biological sequence compression transfer and encryption
ActiveUS20200228507A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer hardwareTelecommunications link
A device for compressing subject data. the device comprises a communication link, the communication link capable of receiving a set of subject data; a compression module, the compression module configured to apply a compression algorithm to the set of subject data, the compression algorithm compressing the set of subject data using a reference string of subject data; and a transmission module, the transmission module configured to transmit the compressed subject data. The device further comprising an encryption module for encrypting the subject data.
Owner:ARC BIO LLC
Methods and systems for biological sequence compression transfer and encryption
ActiveUS10630812B2Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer hardwareTelecommunications link
A device for compressing subject data, the device comprises a communication link, the communication link capable of receiving a set of subject data; a compression module, the compression module configured to apply a compression algorithm to the set of subject data, the compression algorithm compressing the set of subject data using a reference string of subject data; and a transmission module, the transmission module configured to transmit the compressed subject data. The device further comprising an encryption module for encrypting the subject data.
Owner:ARC BIO LLC
A similarity analysis method, implementation system and medium based on negative sequence patterns of biological sequences
ActiveCN112182497BEfficient expressionEfficient analysisData visualisationBiostatisticsData setDegree of similarity
Owner:山东元竞信息科技有限公司
Microbial metagenomic analysis system and method for aerobic composting of kitchen waste
ActiveCN109166602BSolve the low efficiency of analysisImprove analysis efficiencyData visualisationBiostatisticsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
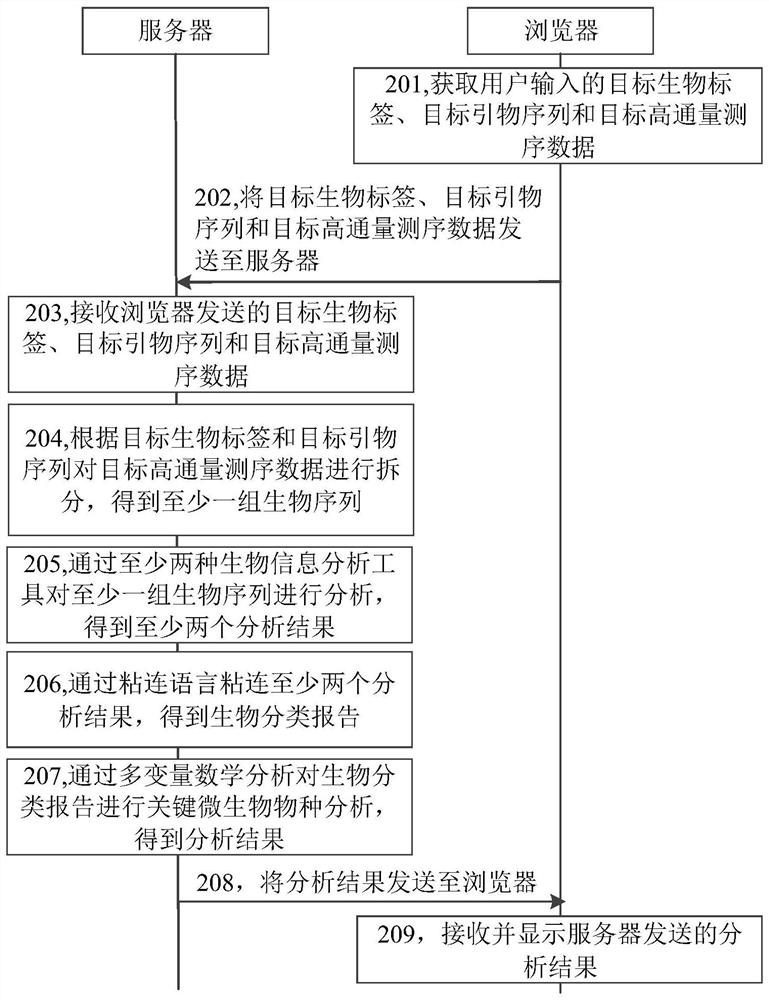
This application relates to a microbial metagenomic analysis system and method for aerobic composting of kitchen waste, which belongs to the technical field of bioinformatics. The system includes: a browser to obtain target biological tags, target primer sequences and target high-throughput sequencing data; The server splits the target high-throughput sequencing data according to the target biological tags and target primer sequences to obtain at least one set of biological sequences; at least two sets of biological sequences are analyzed by at least two biological information analysis tools to obtain at least two Analysis results; glue at least two analysis results through the glue program to obtain the biological taxonomy report; analyze the key microbial species on the biological taxonomy report through multivariate mathematical analysis to obtain the analysis results; send the analysis results to the browser for display; can improve the microbial macro Increase the efficiency of gene analysis and reduce the difficulty of analysis.
Owner:苏州微宏生物科技有限公司
Biological sequence information handling
A repository of fingerprint data strings for a biological sequence database such that each fingerprint data string represents a characteristic biological subsequence made up of sequence units. Each characteristic biological subsequence has in the biological sequence database a combinatory number which is lower than the total number of different sequence units available thereto. The combinatory number of a biological subsequence is defined as the number of different sequence units that appear in the biological sequence database as a consecutive sequence unit of the biological subsequence.
Owner:BIOKEY BV
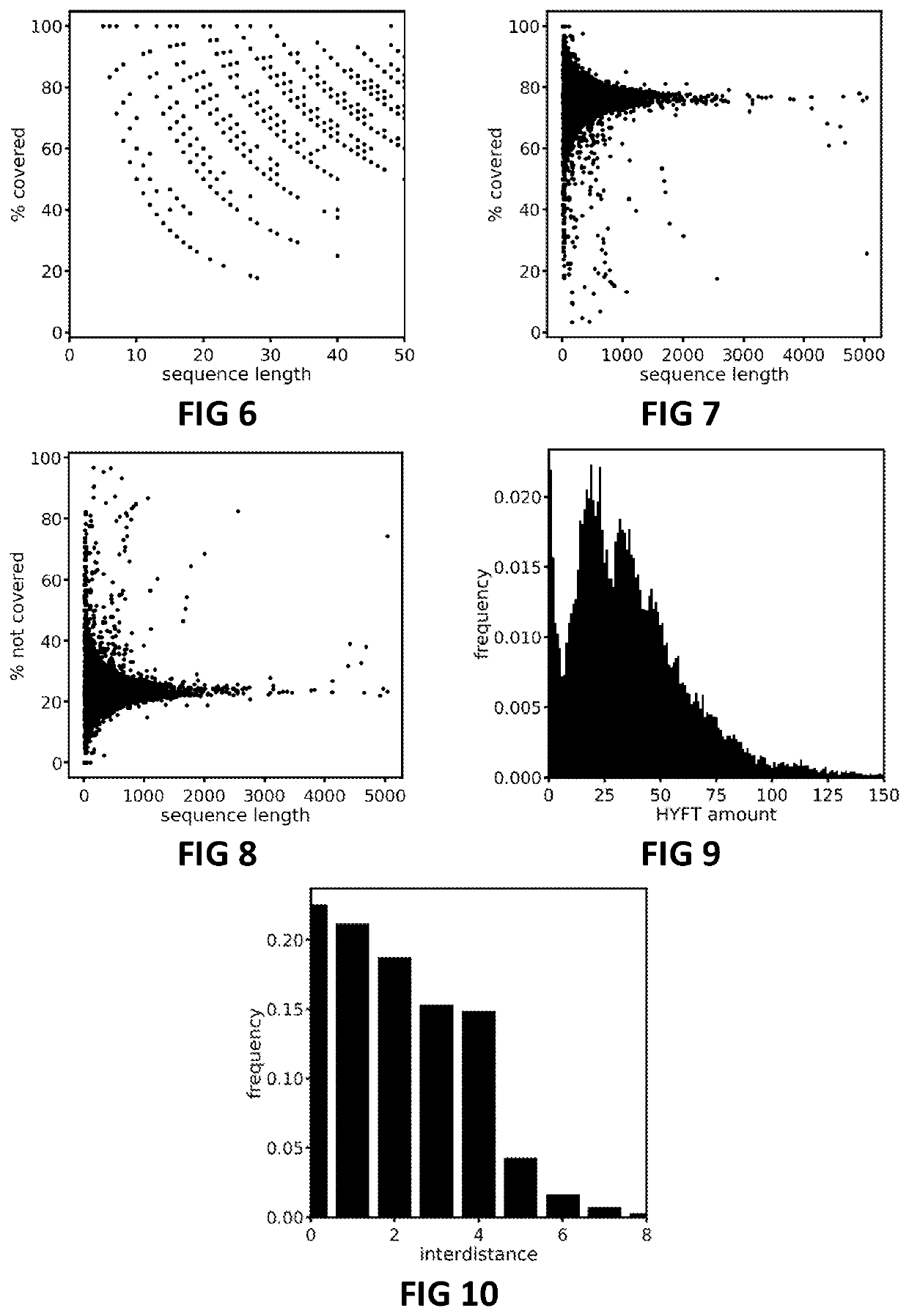
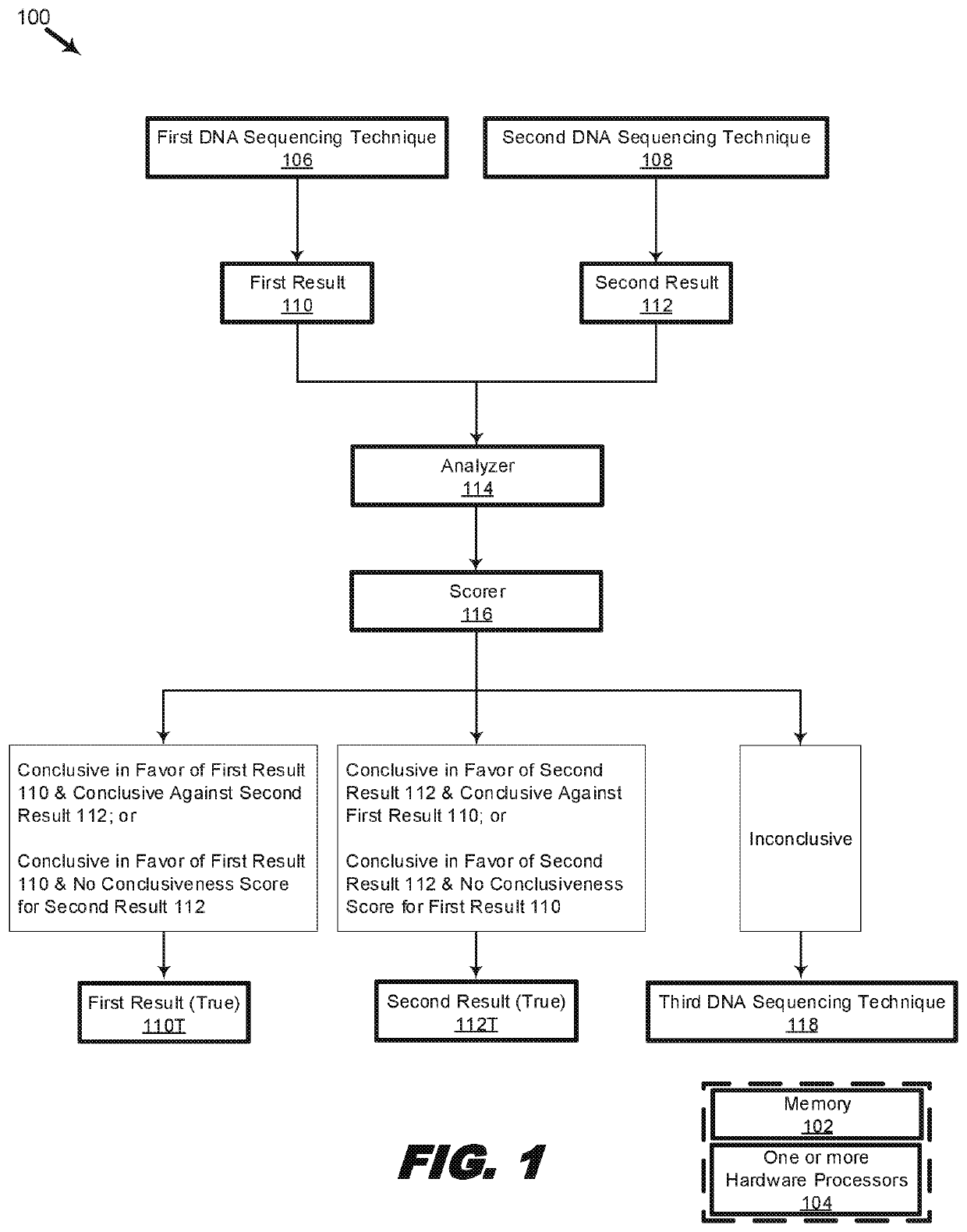
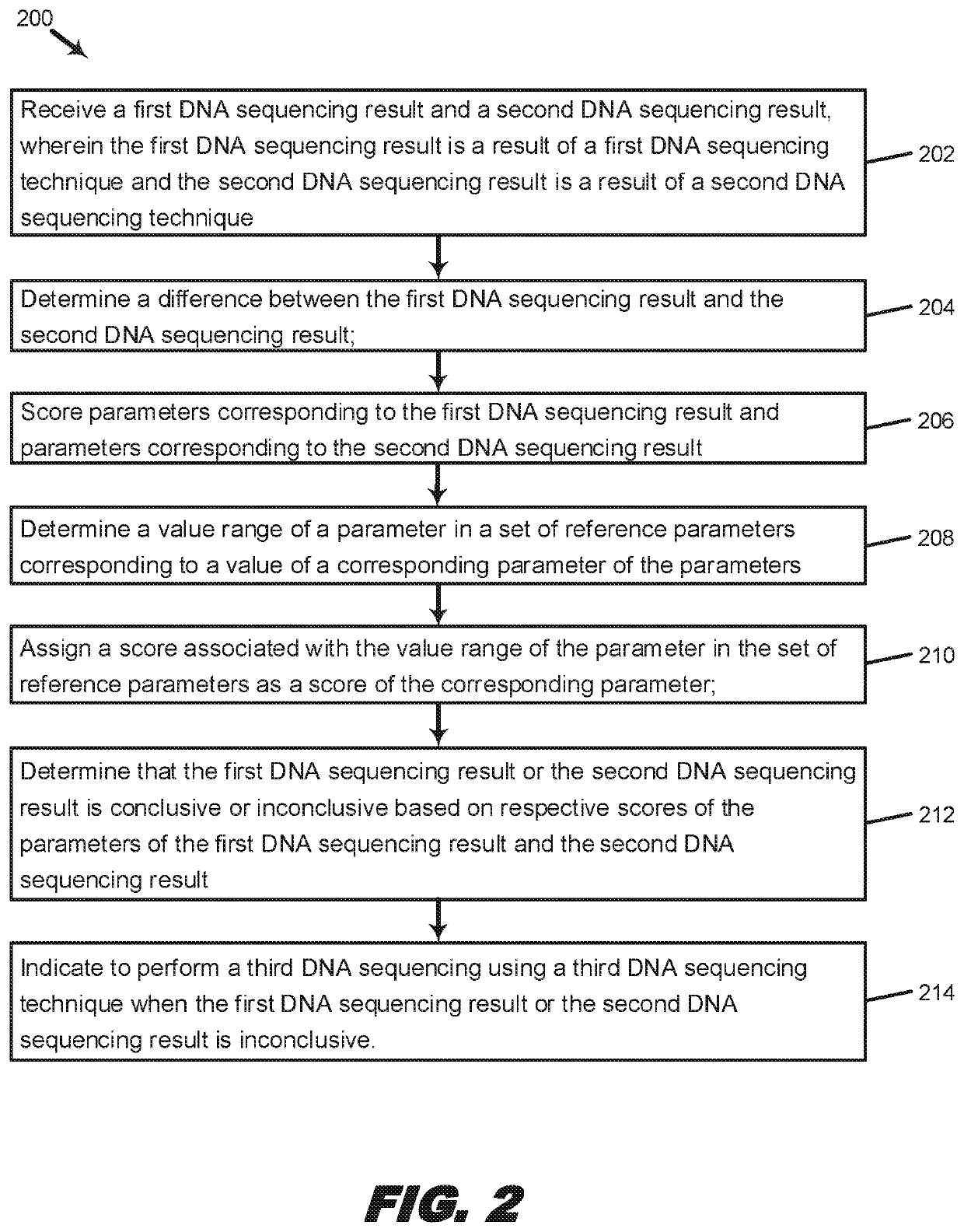
Systems and methods for scoring results of identification processes used to identify a biological sequence
Systems, methods, and machine-readable instructions stored on machine-readable media are disclosed for receiving a first DNA sequencing result and a second DNA sequencing result, wherein the first DNA sequencing result is a result of a first DNA sequencing technique and the second DNA sequencing result is a result of a second DNA sequencing technique. A difference is determined between the first DNA sequencing result and the second DNA sequencing result. Parameters are scored corresponding to the first DNA sequencing result and to the second DNA sequencing result, wherein the scoring includes: determining a value range of a parameter in a set of reference parameters corresponding to a value of a corresponding parameter of the parameters; and assigning a score associated with the value range of the parameter in the set of reference parameters as a score of the corresponding parameter. A determination is made that the first DNA sequencing result or the second DNA sequencing result is conclusive or inconclusive based on respective scores of the parameters of the first DNA sequencing result and the second DNA sequencing result. An indication is made to perform a third DNA sequencing using a third DNA sequencing technique when the first DNA sequencing result or the second DNA sequencing result is inconclusive.
Owner:ADVANCED MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS LLC
A cross-species biological pathway discovery method based on graph matching
The invention discloses a cross-species biological pathway discovery method based on graph matching. The invention aims to solve the problem of low efficiency in discovering biological pathways by using traditional biochemical experimental methods, and cannot well combine biological sequence similarity with existing graph matching algorithms. and protein interaction network structural similarity problem. Through the present invention, the similarity of biological sequences and the similarity of network structures can be well integrated, and larger substructures coexisting in the protein interaction network of different species can be found, so as to more effectively find biological species with similar functions existing in different species Pathways have guiding significance for biological research on the connection between different species.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Methods for identifying the evolutionarily conserved sequences
InactiveUS6963805B2Improve identityCommonly can be doneMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingConserved sequenceNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides methods for determining sequence similarity (conserved sequences) between nucleic acids from a first organism and nucleic acids from a second, different organism without having to know a priori the nucleic acid sequence from the second, different organism. The first nucleic acid can be from any organism where the sequence of the nucleic acid is known and the second nucleic acid can be from any organism. The method involves determining which bases from the second nucleic acid are identical to the first nucleic acid, and allows one to determine the sequence of portions of the second nucleic acid. The invention is useful for identifying putative functional regions or putative organism-sequences in a genome.
Owner:PERLEGEN SCIENCES INC
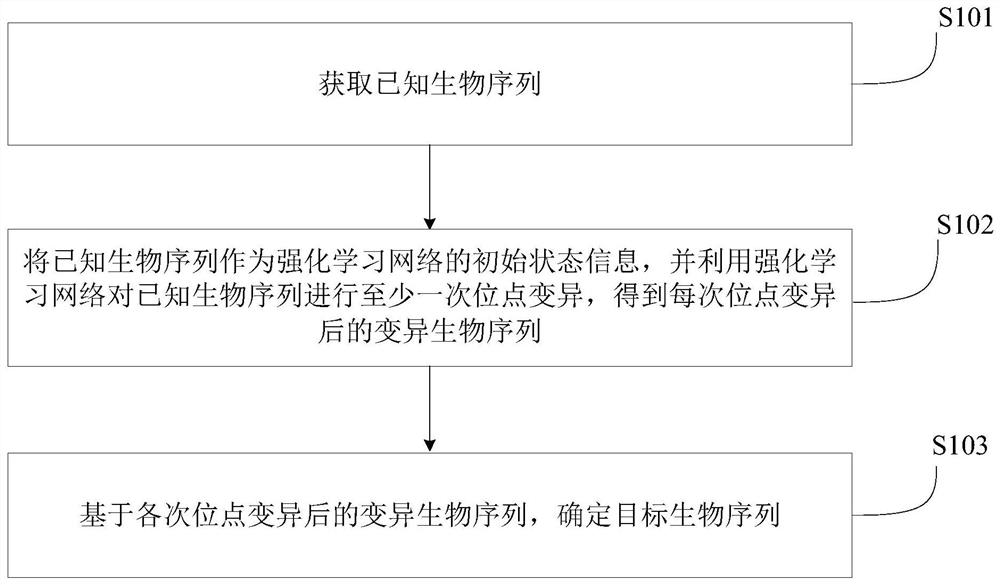
Biological sequence retrieval method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
The invention provides a biological sequence retrieval method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a known biological sequence; taking the known biological sequence as initial state information of a reinforcement learning network, and performing at least one time of site variation on the known biological sequence by using the reinforcement learning network to obtain a variation biological sequence after each time of site variation; and determining a target biological sequence based on the variation biological sequence after each time of site variation. According to the method, the characteristics of the selected variant biological sequence are better by increasing the number of reinforcement learning training times, so that the generated target biological sequence can better meet the requirements of the biological field.
Owner:SHANGHAI SENSETIME INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Biological information handling
PendingCN113454726AImproved sequencingImproved biopolymer fragmentsProteomicsGenomicsInformation processingSequence database
Owner:生物海滩公司
Method and system for analyzing biological sequence with known sequence
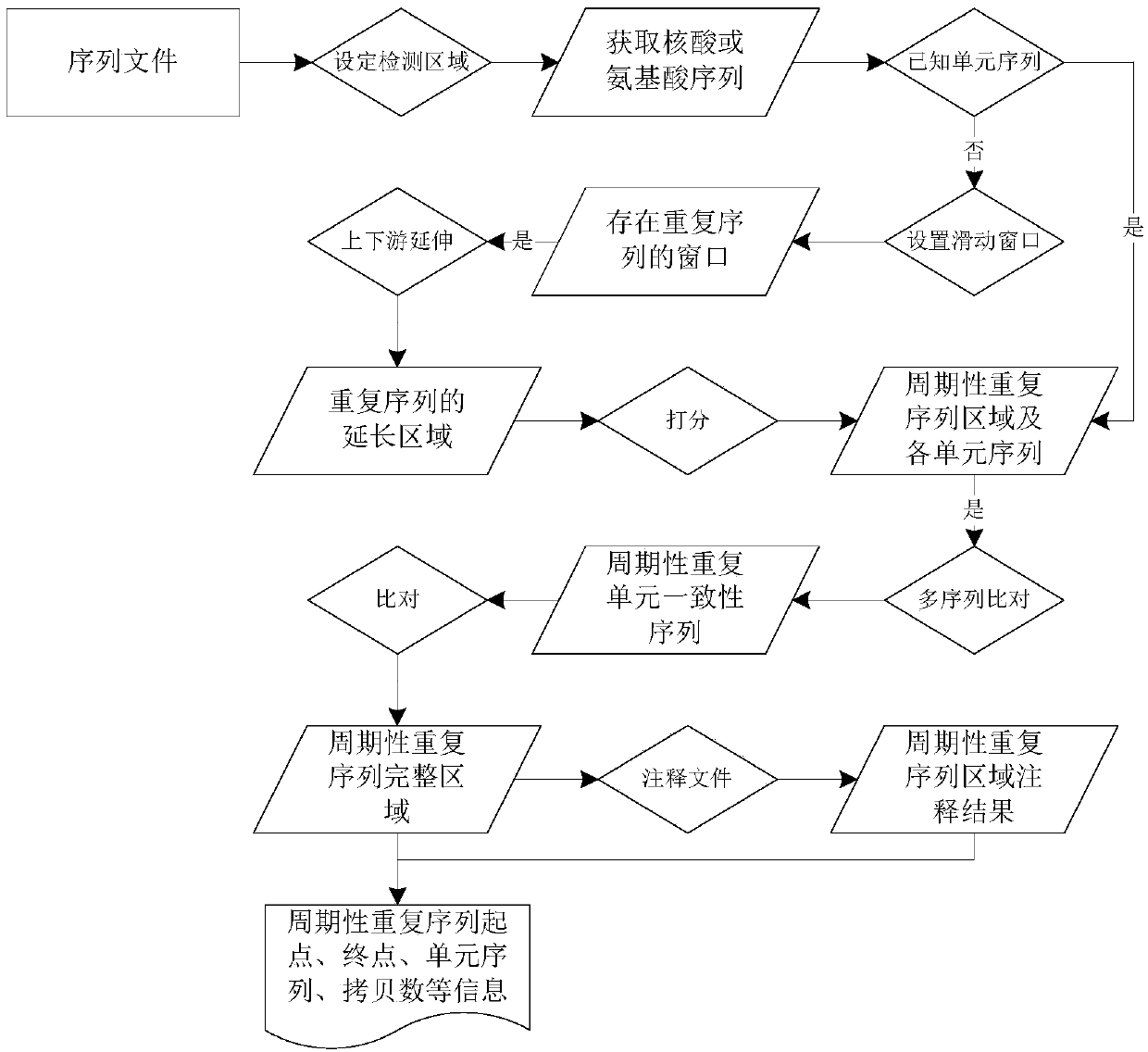
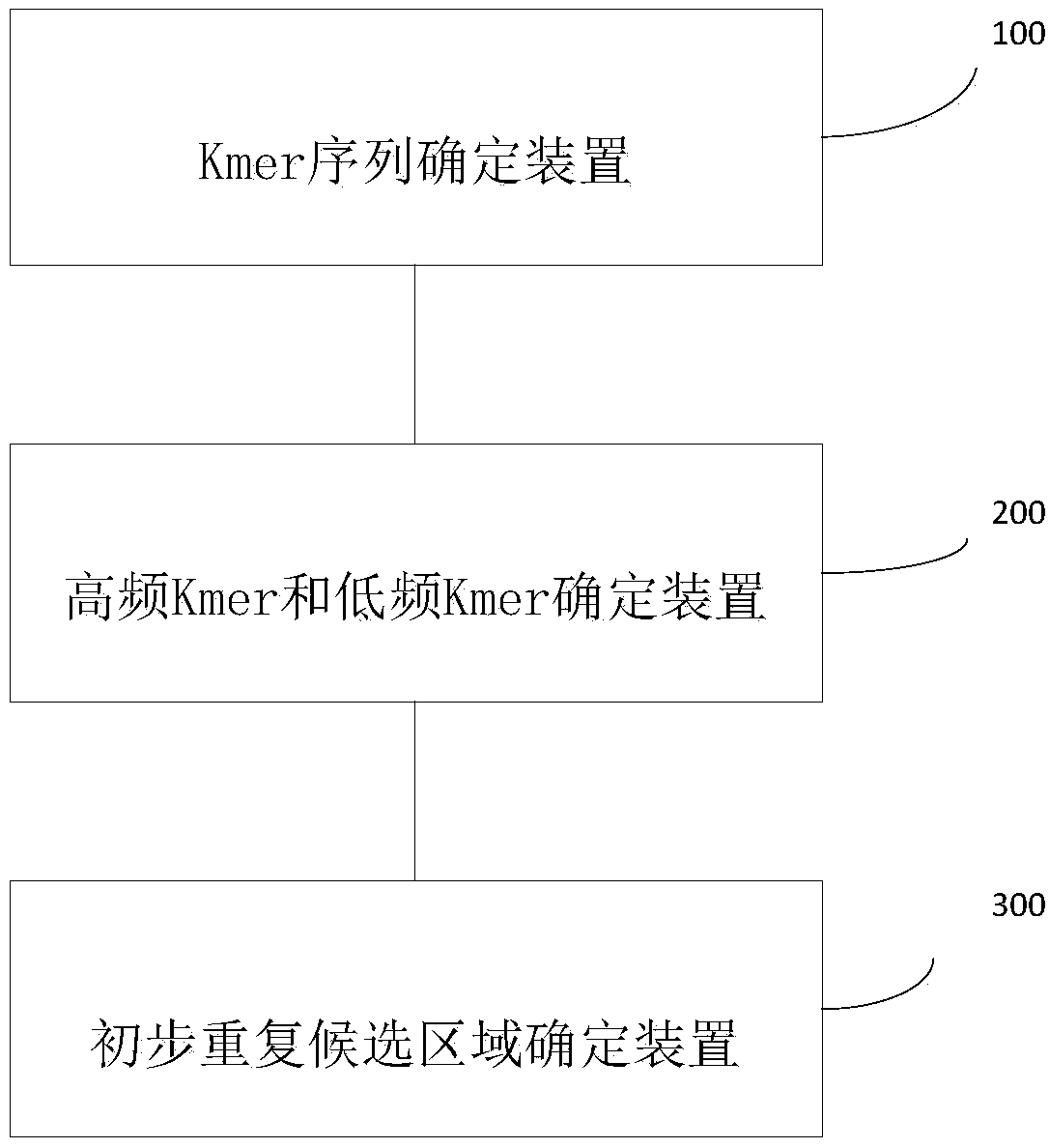
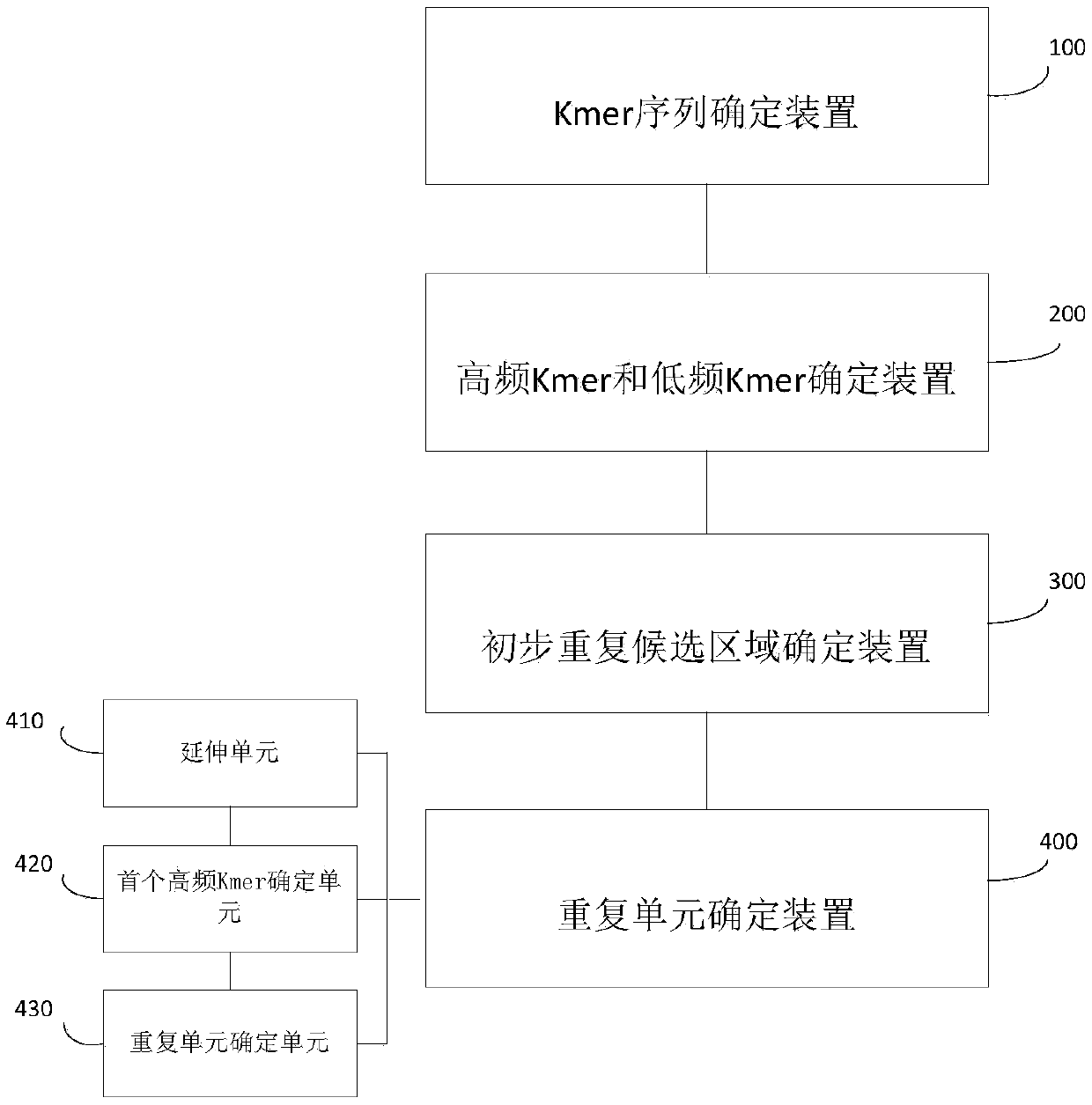
The invention provides a method for analyzing a biological sequence with a known sequence. The method comprises the following steps: (a) determining all Kmer sequences of a biological sequence on thebasis of the biological sequence, wherein the biological sequence is obtained by windowing a large-fragment amino acid sequence or nucleotide sequence; (b) determining the frequency number of each ofall the Kmer sequences, and determining at least one high-frequency Kmer and at least one low-frequency Kmer based on the frequency number; and (c) determining a preliminary repetition candidate region based on the one high-frequency Kmer, and determining whether to integrate the low-frequency Kmer into the preliminary repetition candidate region based on the distance between the low-frequency Kmer and the adjacent high-frequency Kmer.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
An Integrative Method for Multi-Class Biological Sequence Annotation
ActiveCN110223732BIncrease profitExcellent quantitative abilitySequence analysisInstrumentsSequence annotationComputer science
The invention discloses a method for integrating annotations of multiple types of biological sequences, comprising: selecting one biological sequencing data from biological sequencing data as a main biological sequence set, and the rest as auxiliary biological sequence sets; establishing a sequence-gene association mapping set; According to the gene transcription start point, the basic association region and the extended association region of the gene are obtained; for the sequence of the main biological sequence set, the extended association region of the gene is traversed, and if the region where the sequence is located overlaps with the extended association region of a gene, then the Sequence-gene association mapping of genes and sequences; the hypergeometric test and binomial test are used to calculate the significance of the results of reference data applied to the biological sequence annotations in the sequence-gene association mapping set; the annotations obtained by the two methods are sorted separately, and Add up the sequence numbers of the same annotations and then sort them again as the annotation results of various biological sequence data. The invention realizes the annotation of various features, and has application value in the medical field.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
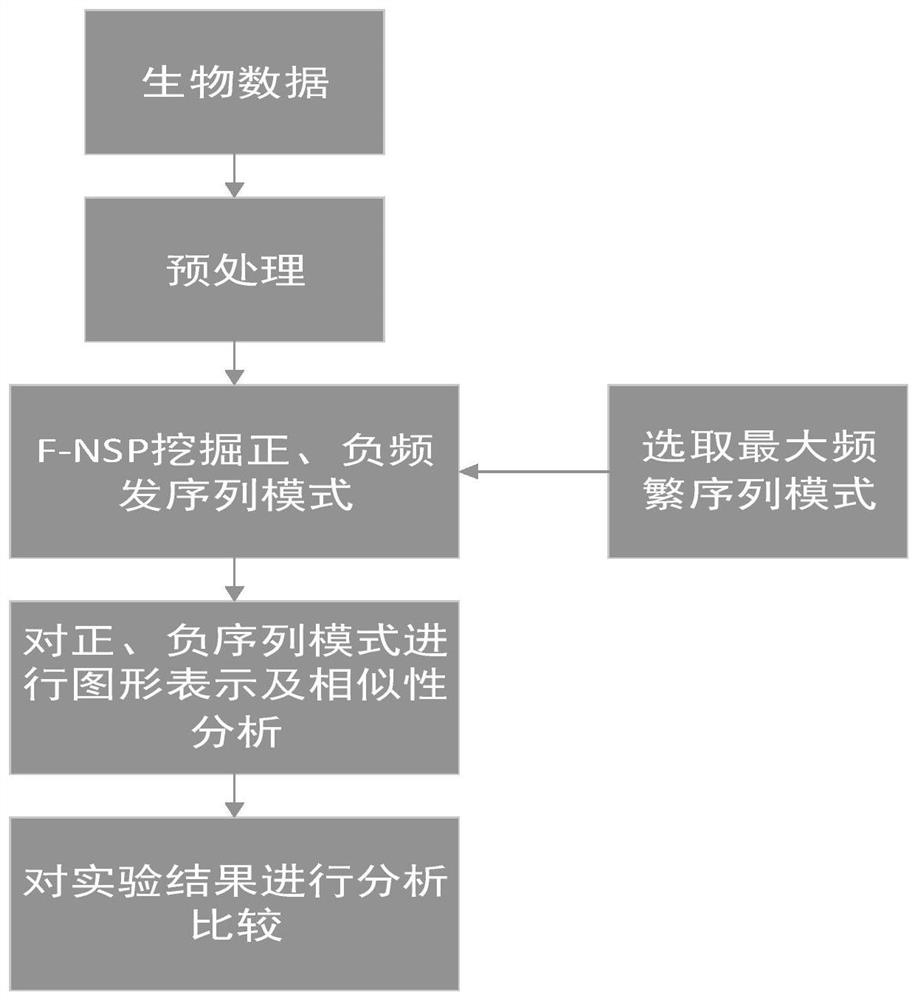
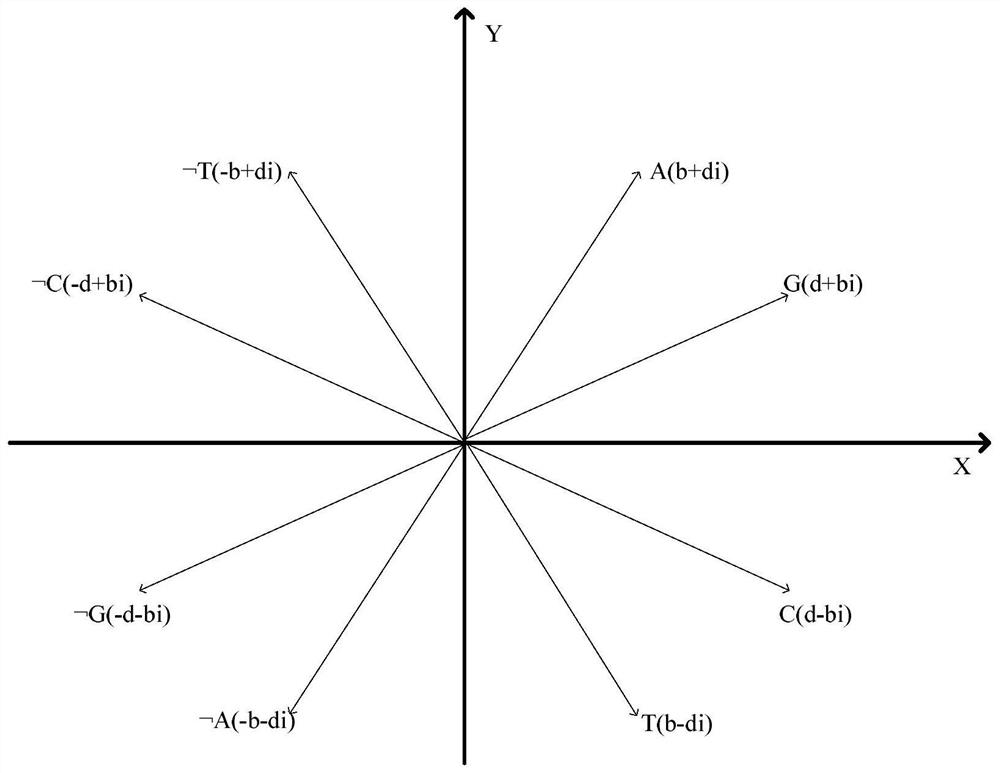
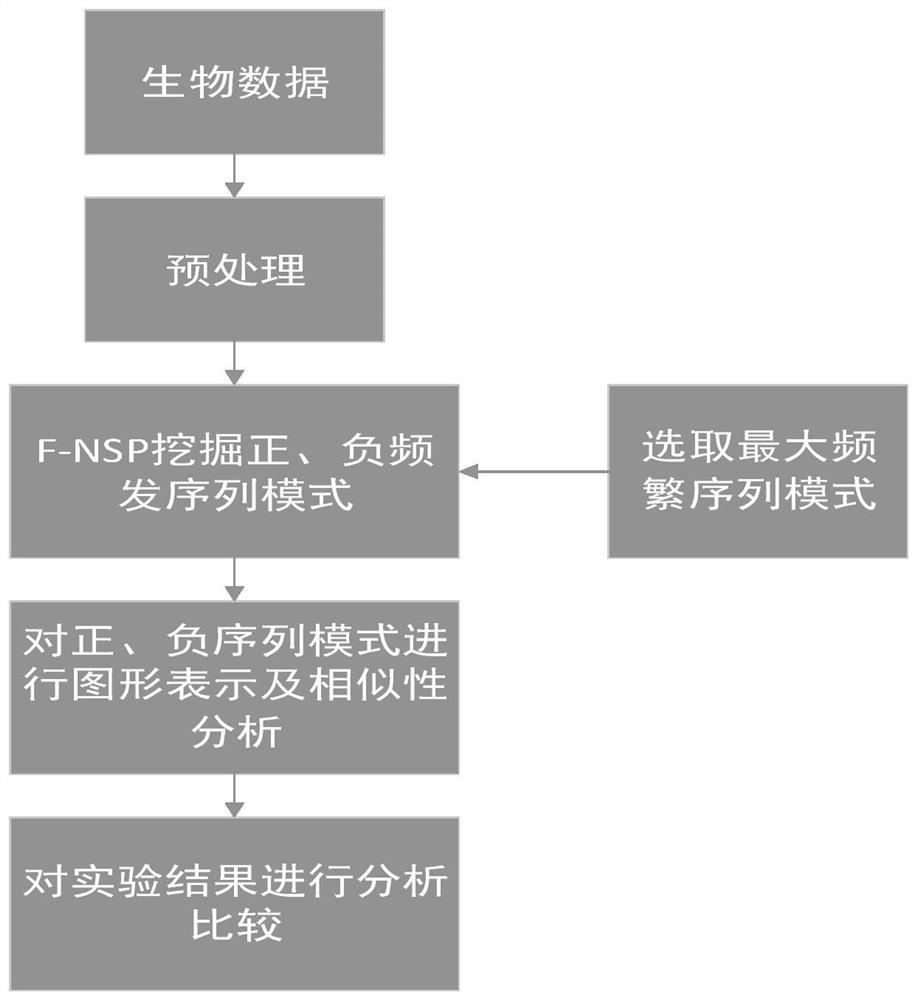
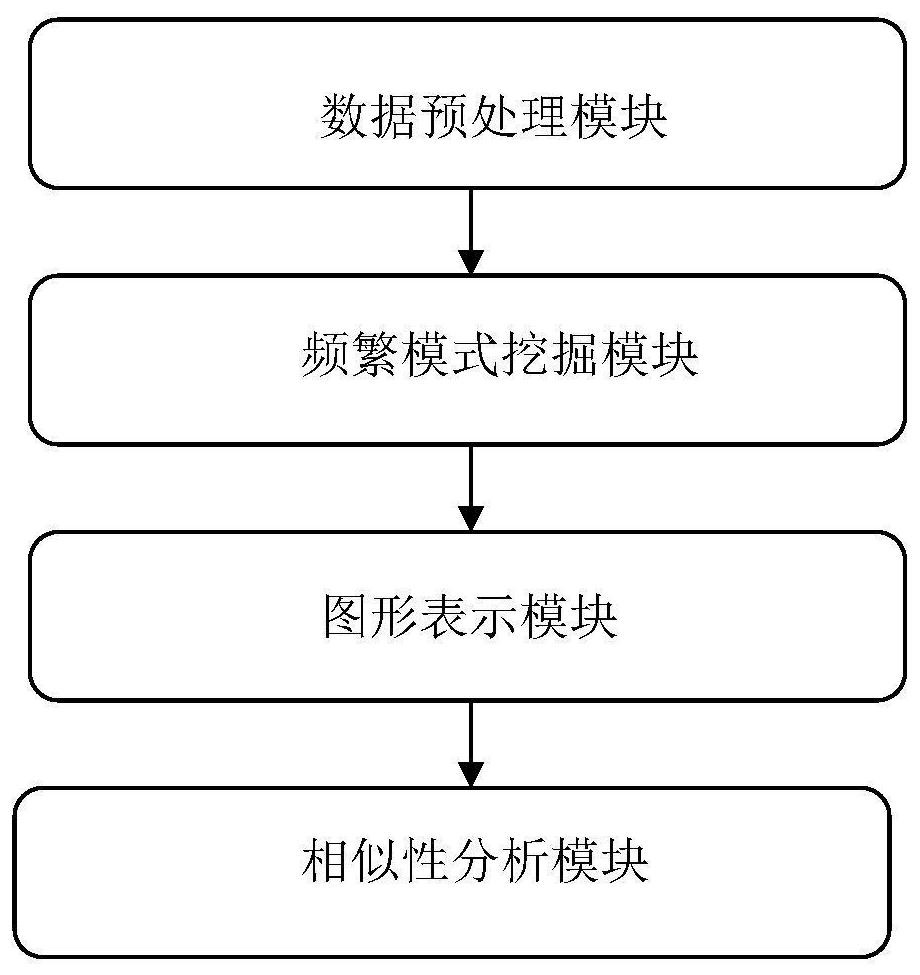
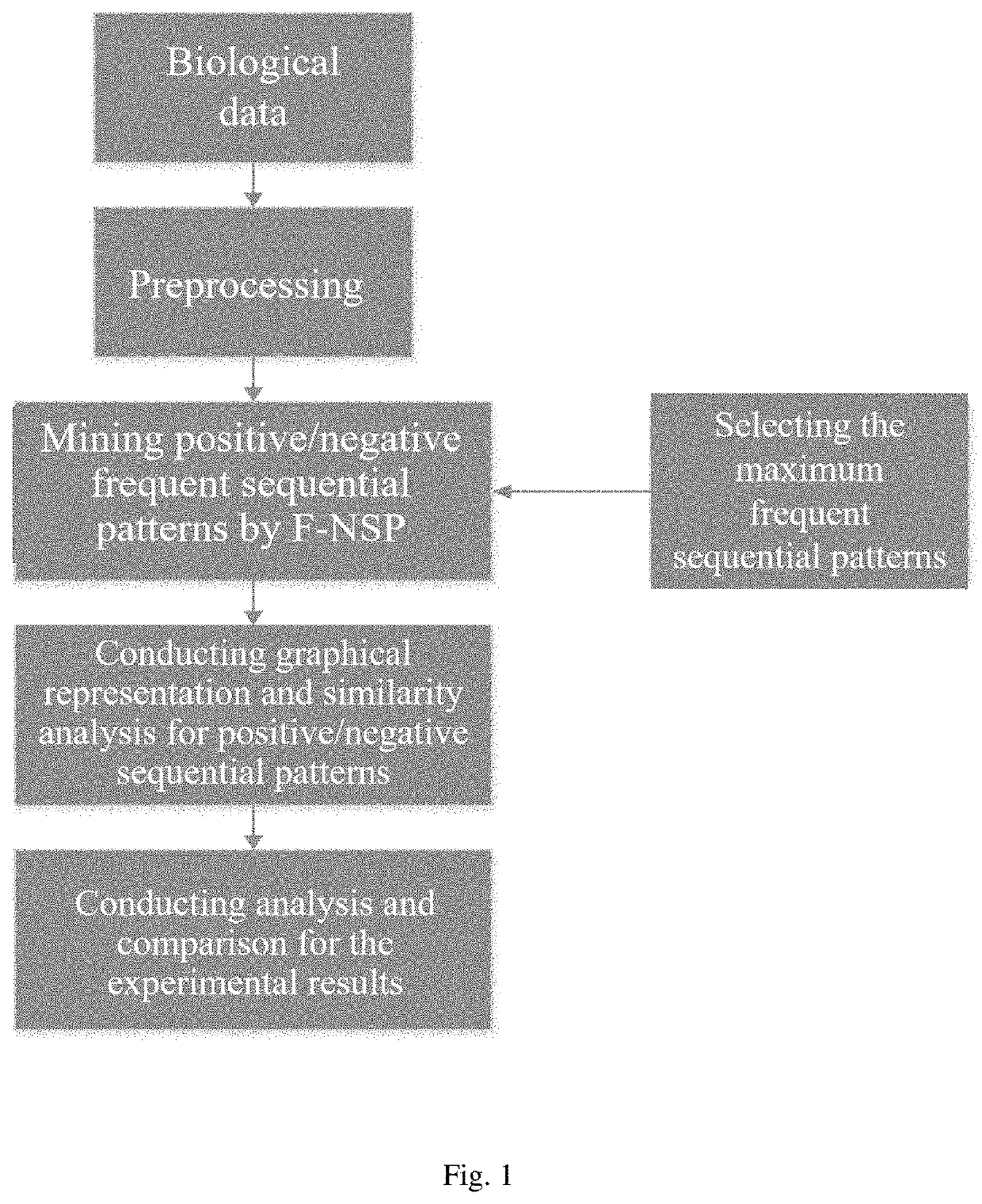
Similarity analysis method of negative sequence mode based on biological sequence, implementation system and medium
ActiveCN112182497AEfficient expressionEfficient analysisData visualisationBiostatisticsData setA-DNA
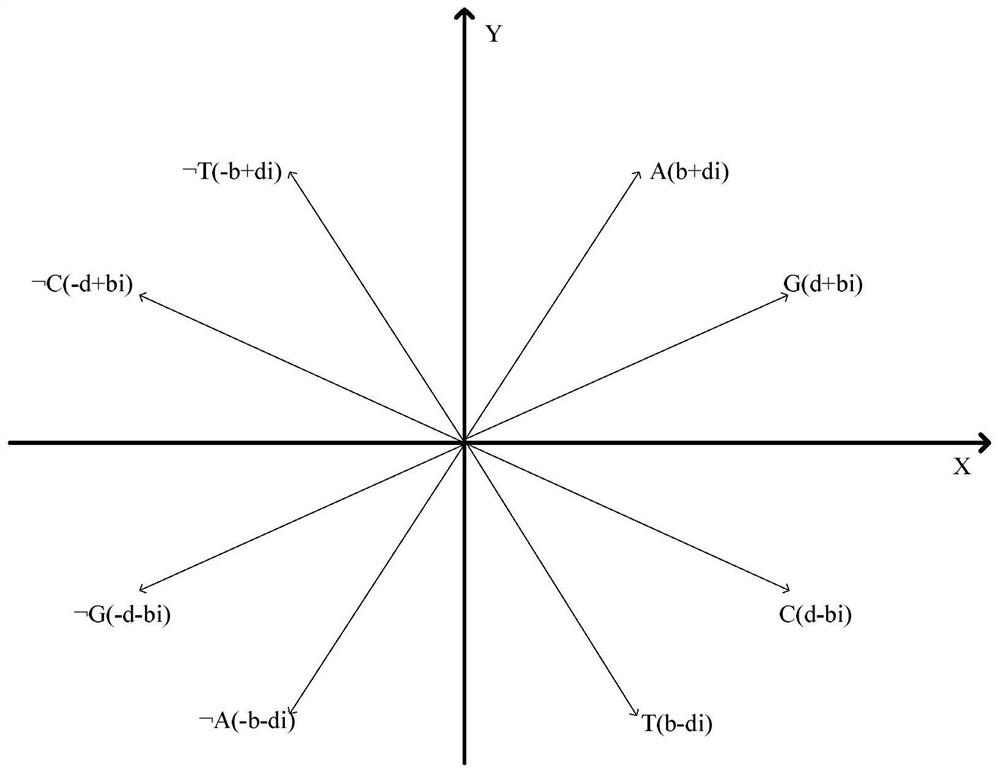
The invention relates to a similarity analysis method of a biological sequence based on a negative sequence mode, an implementation system and a medium. The similarity analysis method comprises the following steps: (1) data preprocessing: representing letters in a DNA sequence with numbers; dividing the data into a plurality of blocks, and taking the obtained blocks as a data set for frequent pattern mining; (2) frequent pattern mining: using an fNSP algorithm to mine a data set; (3) performing graphic representation on the maximum frequent positive and negative sequence modes; converting themaximum frequent positive and negative sequence modes into a digital sequence; (4) similarity analysis of the DNA sequences: solving the similarity of different DNA sequences, and selecting the DNA sequence corresponding to the minimum similarity as the DNA sequence to be researched. According to the method, the negative sequence can be effectively expressed and analyzed, and different analysis results can be obtained by selecting different maximum frequent pattern combinations, and therefore the memory and time consumption of a computer are greatly reduced.
Owner:山东元竞信息科技有限公司
Similarity analysis method of negative sequential patterns based on biological sequences and its implementation system and medium
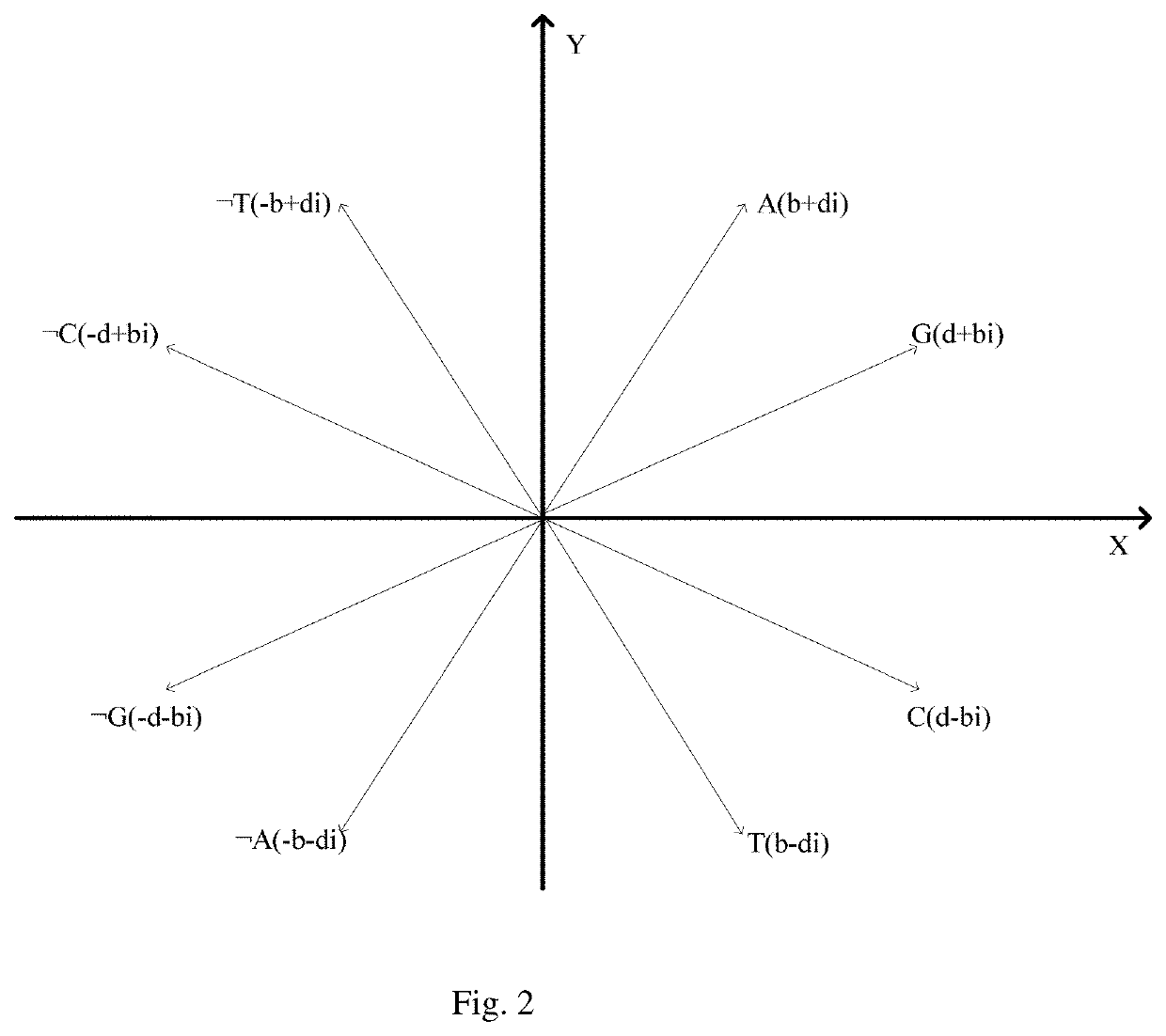
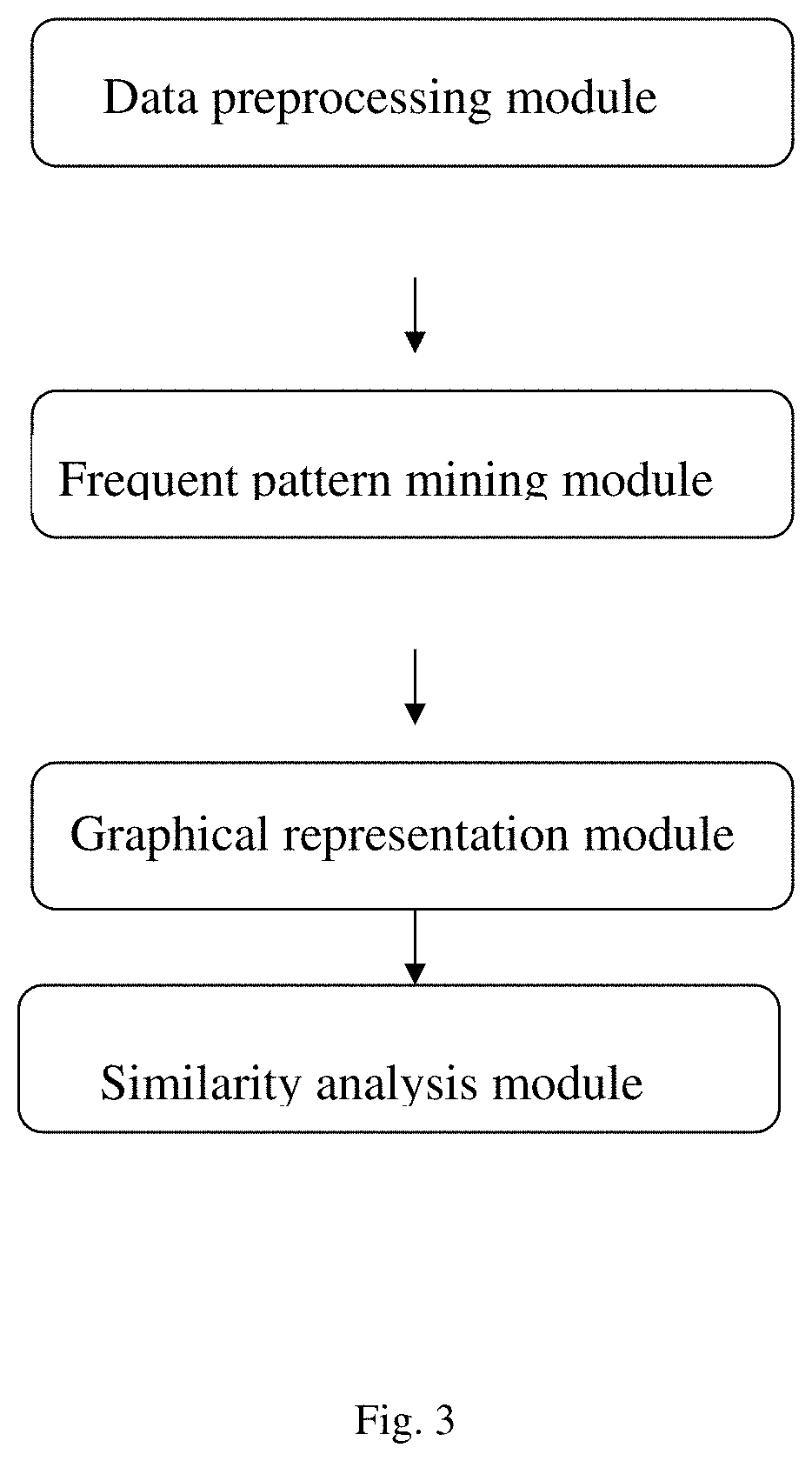
InactiveUS20220101949A1Add supportReduce in quantityData visualisationBiostatisticsData setData pre-processing
A similarity analysis method of negative sequential patterns based on biological sequences and its implementation system and medium comprises: (1) Data preprocessing: represent the letters in the DNA sequence with numbers; divide the sequence represented by numbers into several blocks as datasets for frequent pattern mining; (2) Frequent pattern mining: utilize the f-NSP algorithm to mine the data sets; (3) Represent the maximum frequent positive and negative sequential patterns graphically; convert the maximum frequent positive and negative sequential patterns into number sequences; (4) Similarity analysis of DNA sequence: calculate the similarity of different DNA sequences; select the DNA sequence corresponding to the minimum similarity as the sequence to be studied.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com