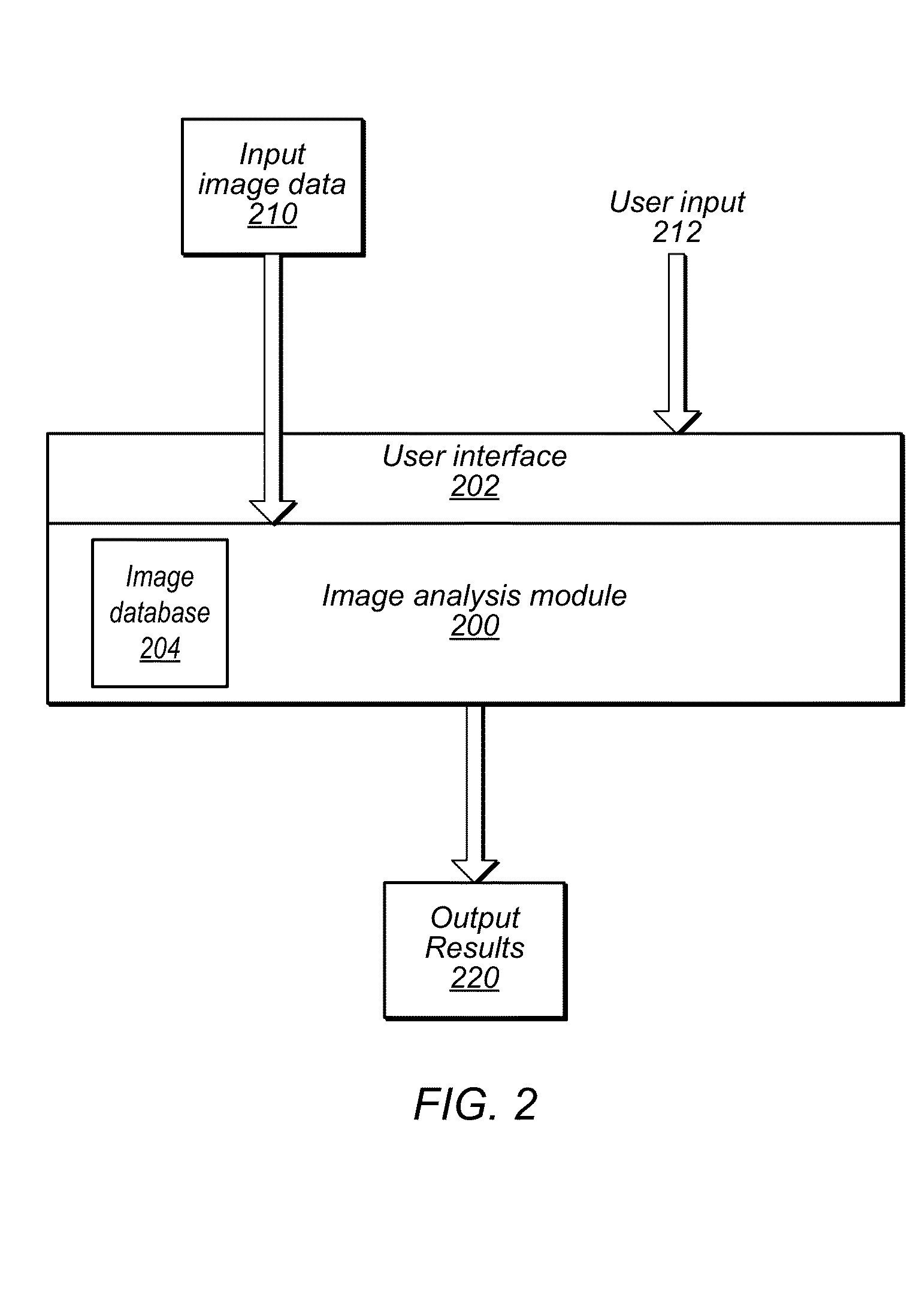
Patents
Literature
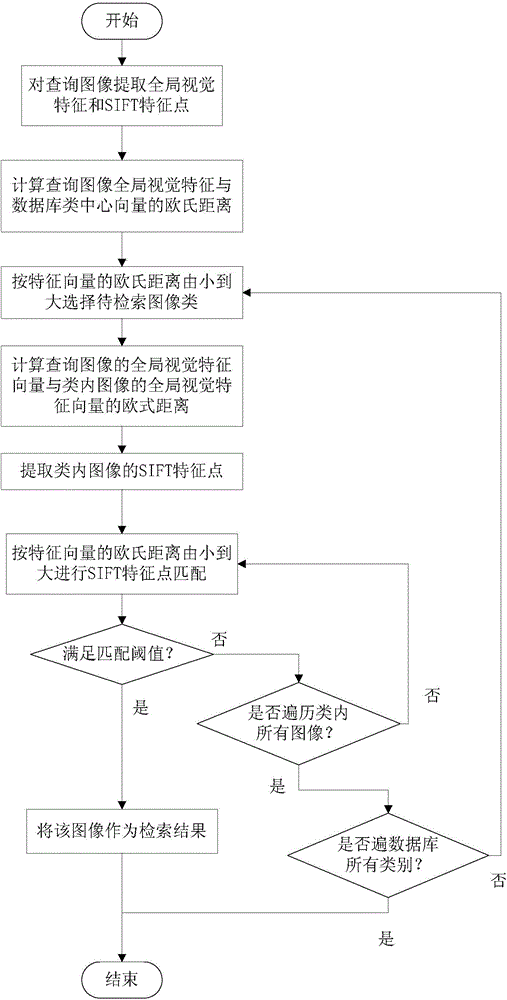
193 results about "Database image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and apparatus for locating multi-region objects in an image or video database
InactiveUS6691126B1Robust methodDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsIts regionData mining
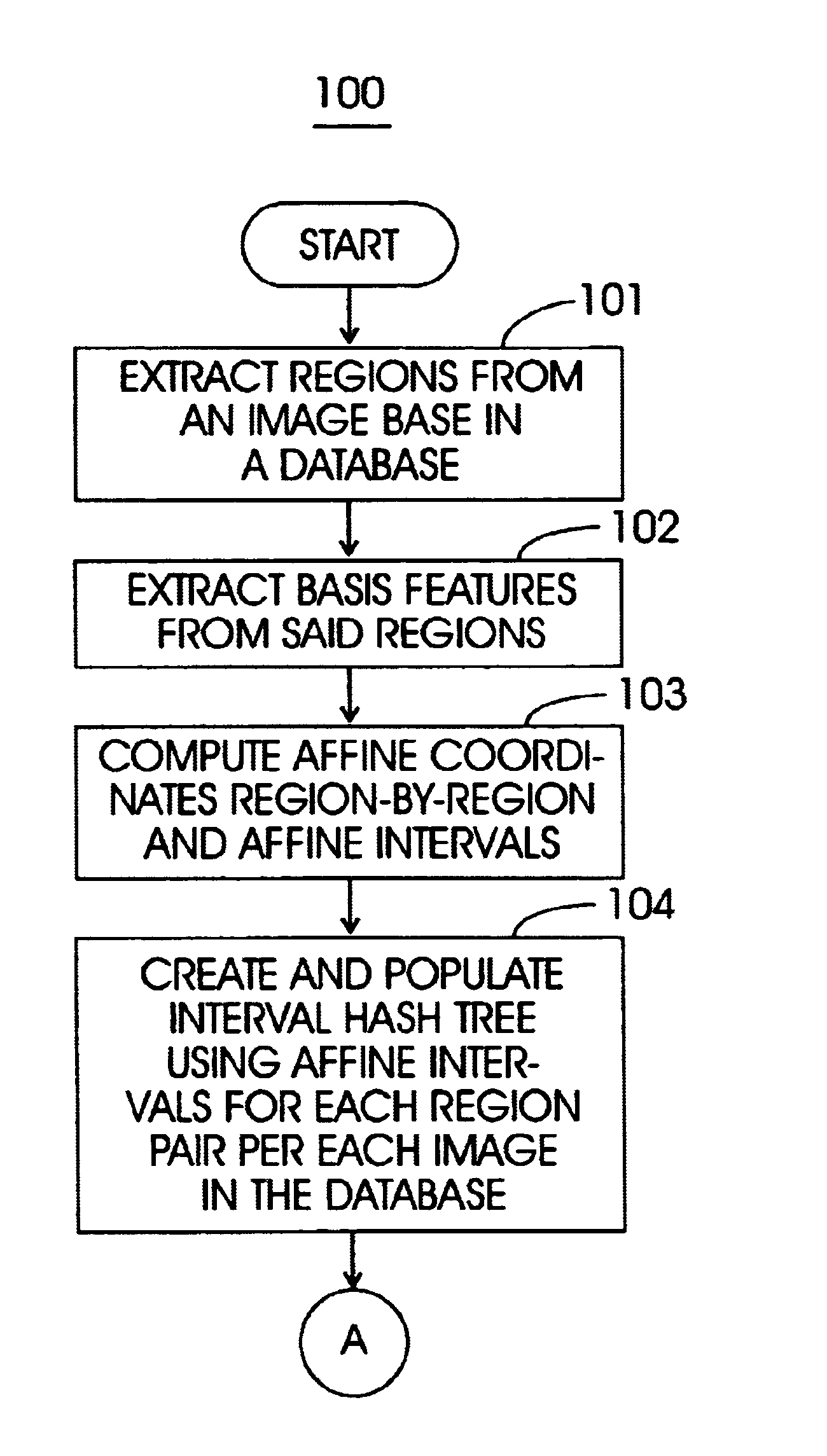
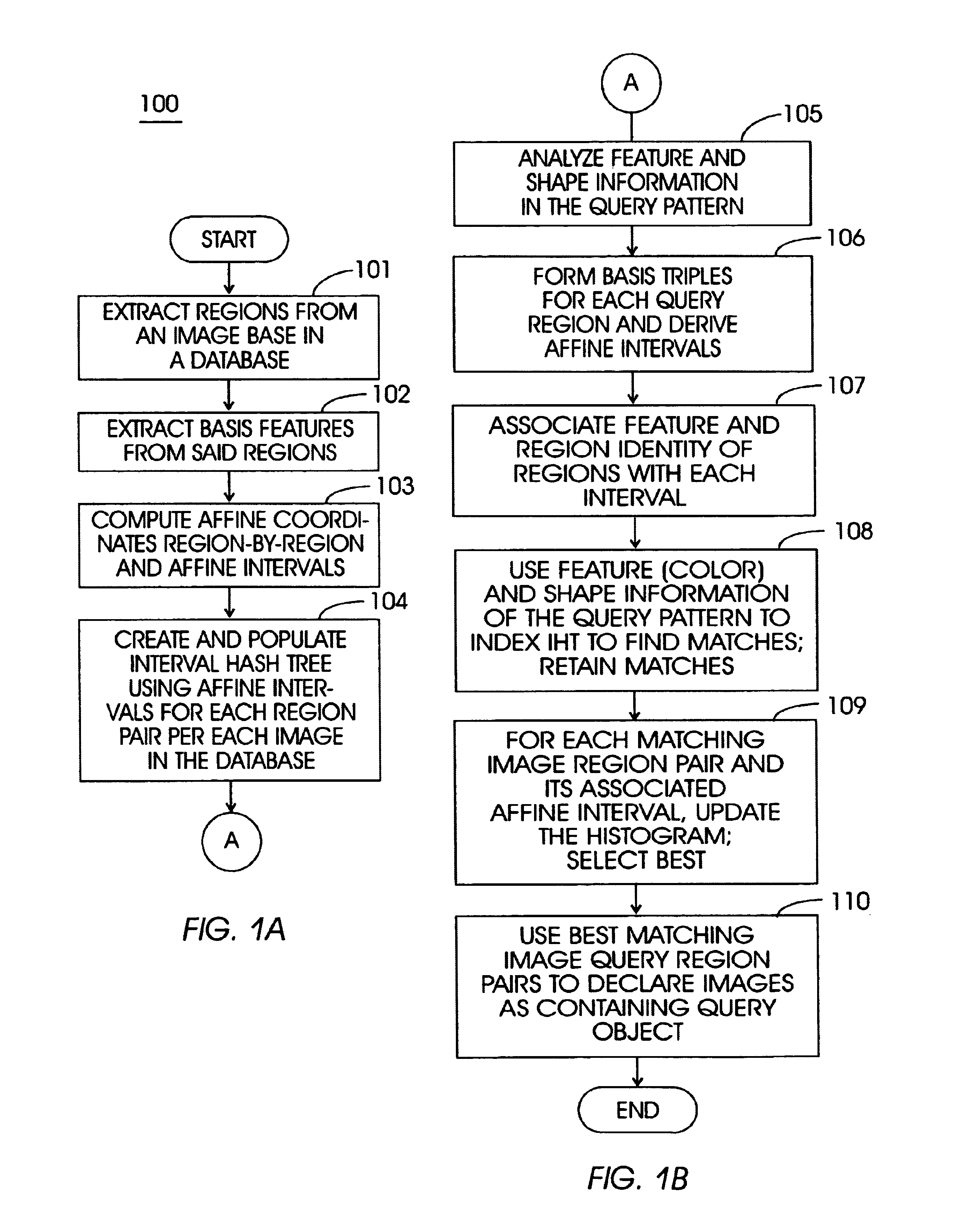
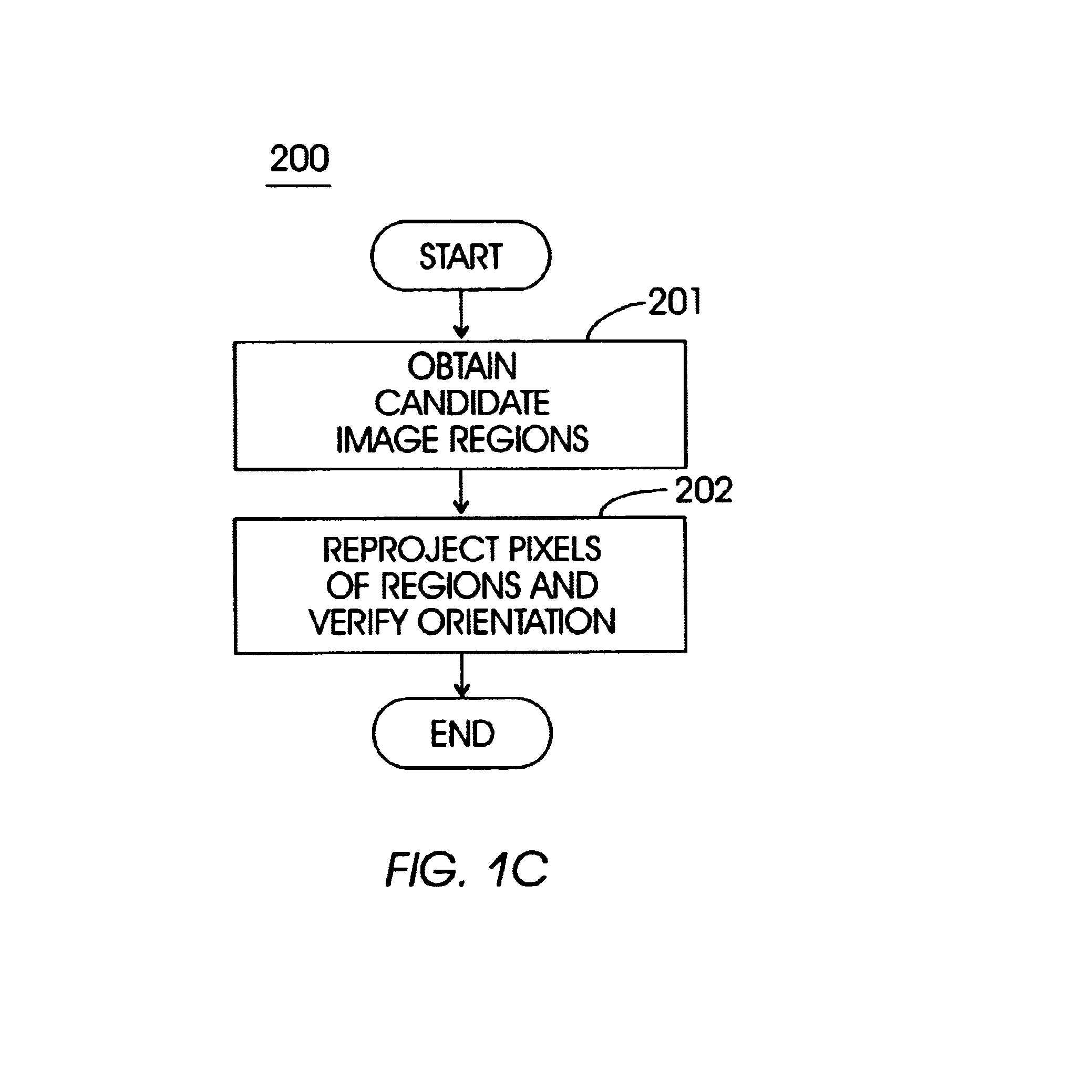
A method (and system) for specifying the region layout of objects in an affine invariant manner as a set of affine intervals between pairs of regions, includes representing database and query regions using affine intervals along with their region identity, matching query region layout to layout of database image regions using an index structure, and retrieving relevant images of the database by hashing for dominant hit regions in the index structure.
Owner:IBM CORP
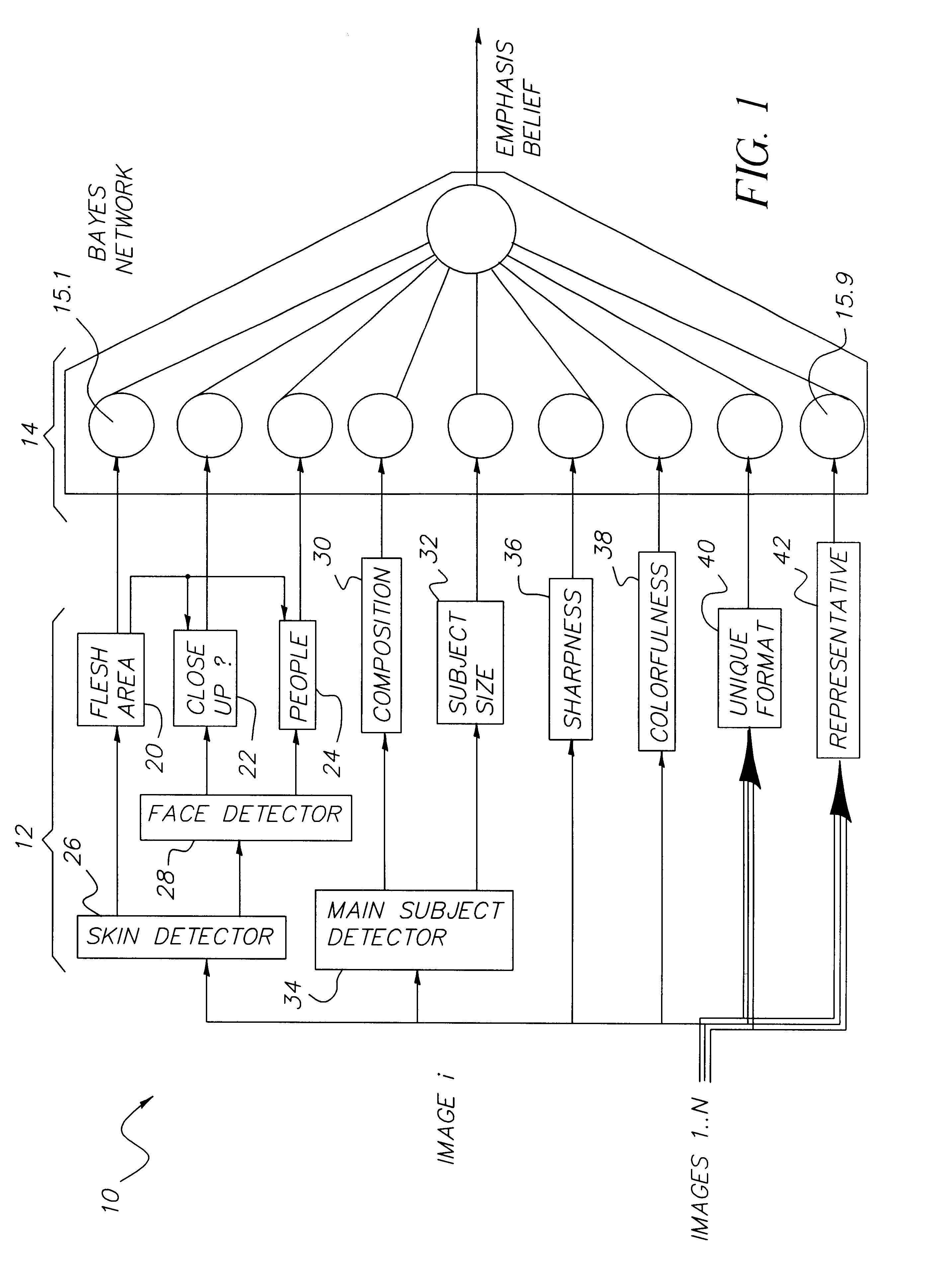
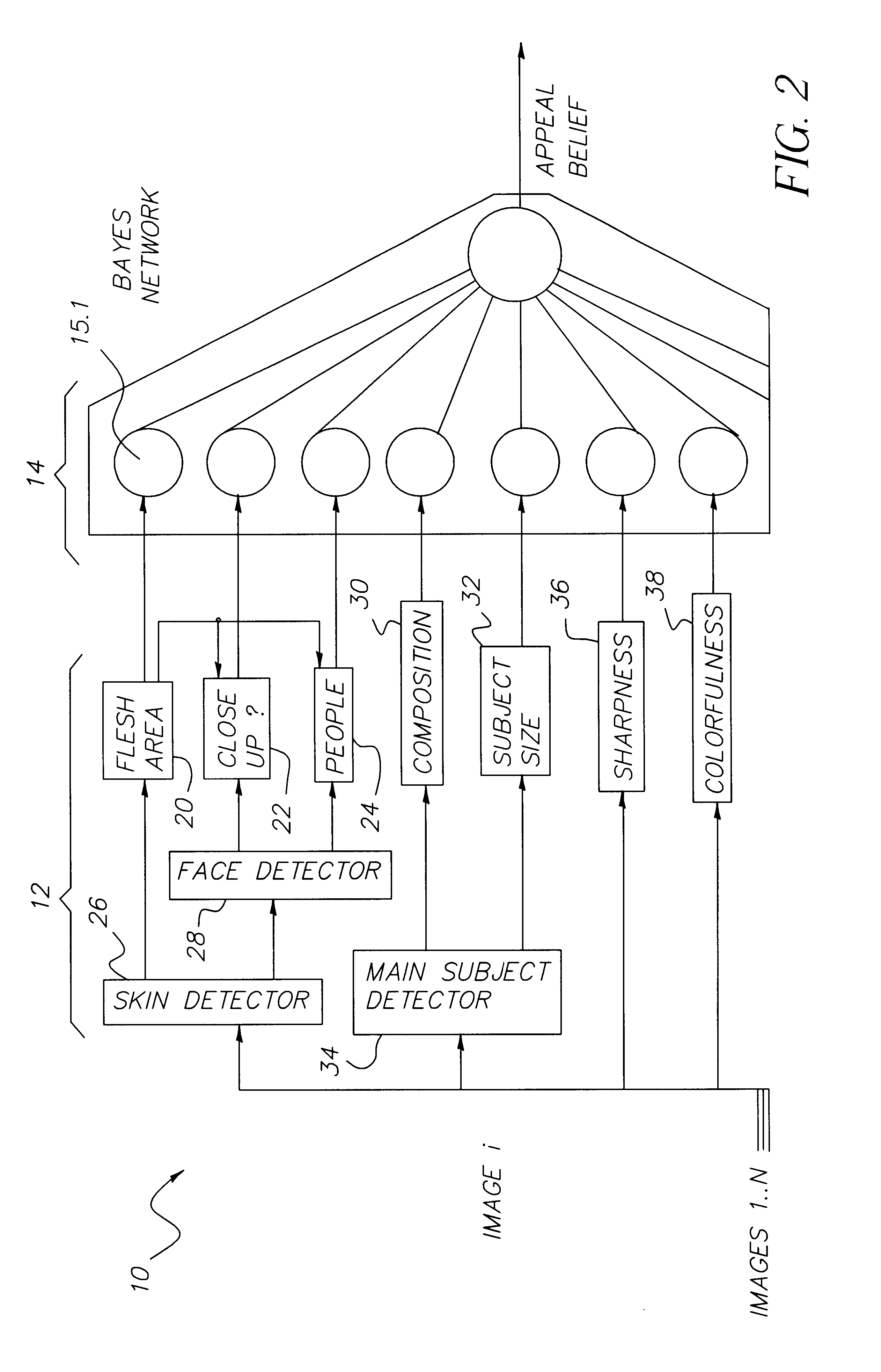
Retrieval and browsing of database images based on image emphasis and appeal
InactiveUS6847733B2Efficiently processed and treatedDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionReasoning algorithmSubject matter
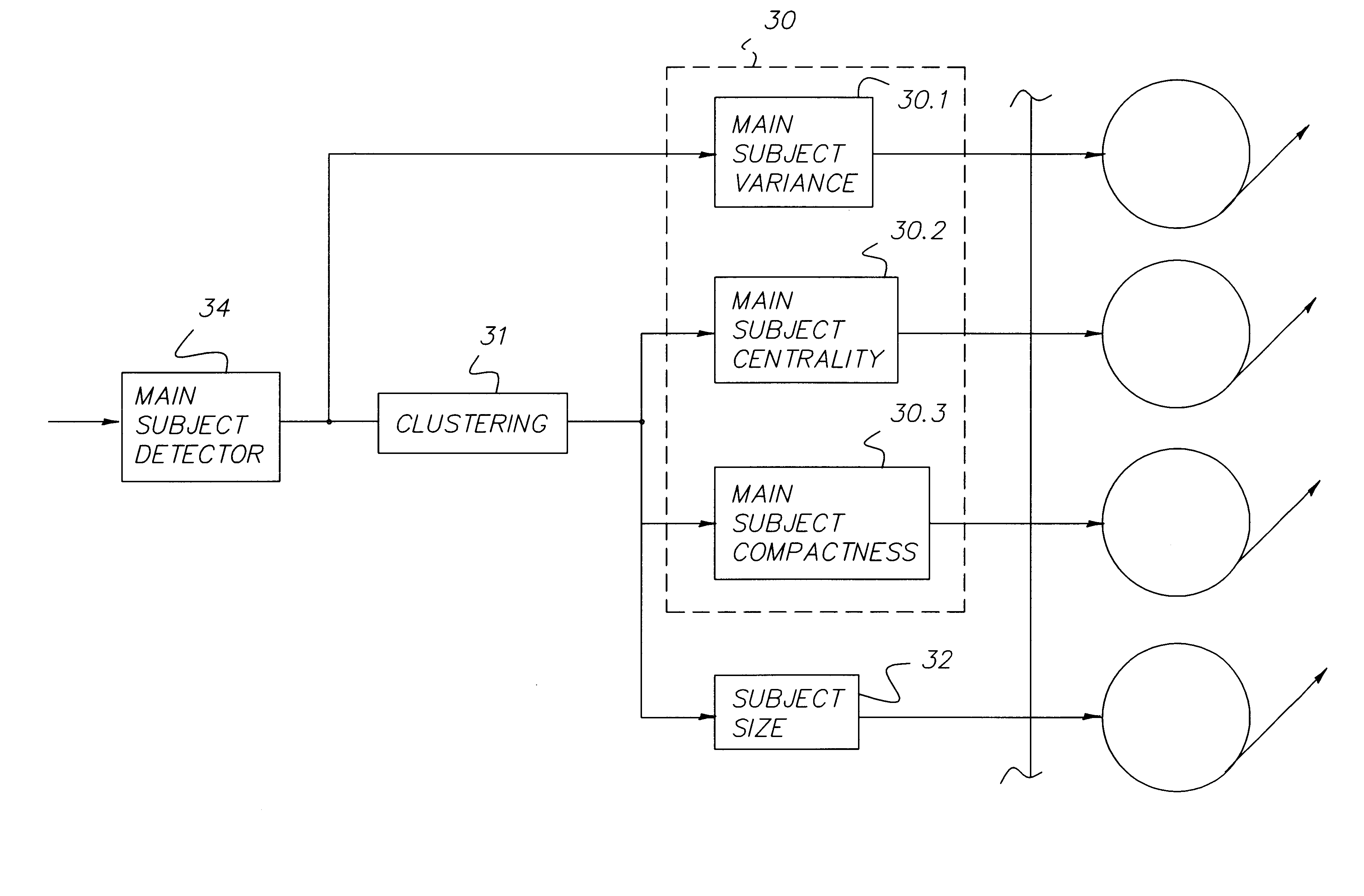
An image is automatically assessed with respect to certain features, wherein the assessment is a determination of the degree of importance, interest or attractiveness of the image. First, a digital image is obtained corresponding to the image. Then one or more quantities are computed that are related to one or more features in the digital image, including one or more features pertaining to the content of the digital image. The quantities are processed with a reasoning algorithm that is trained on the opinions of one or more human observers, and an output is obtained from the reasoning algorithm that assesses the image. More specifically, the reasoning algorithm is a Bayesian network that provides a score which, when done for a group of images, selects one image as the emphasis image or the appeal image. The features pertaining to the content of the digital image include people-related features and / or subject-related features. Moreover, additional quantities may be computed that relate to objective measures of the digital image, such as colorfulness and / or sharpness.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
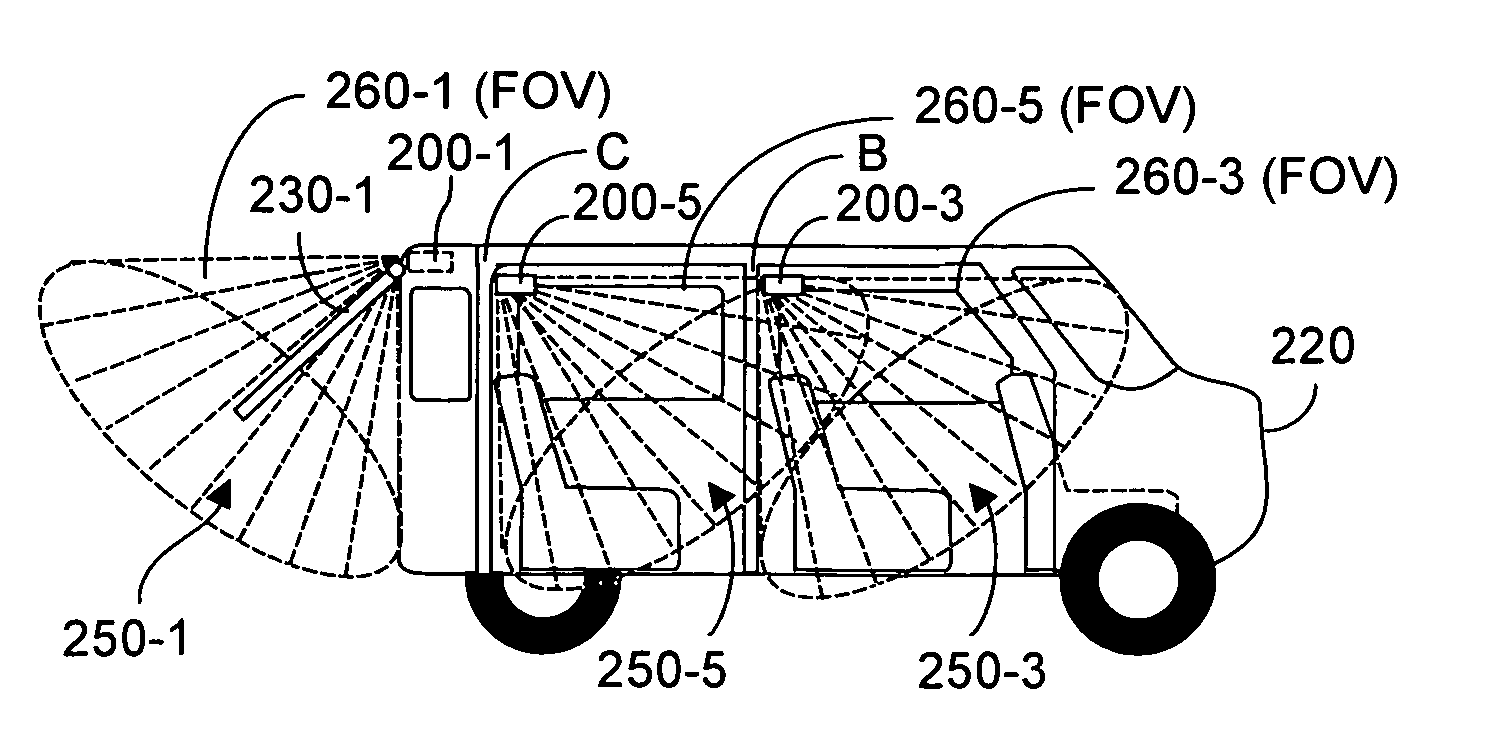
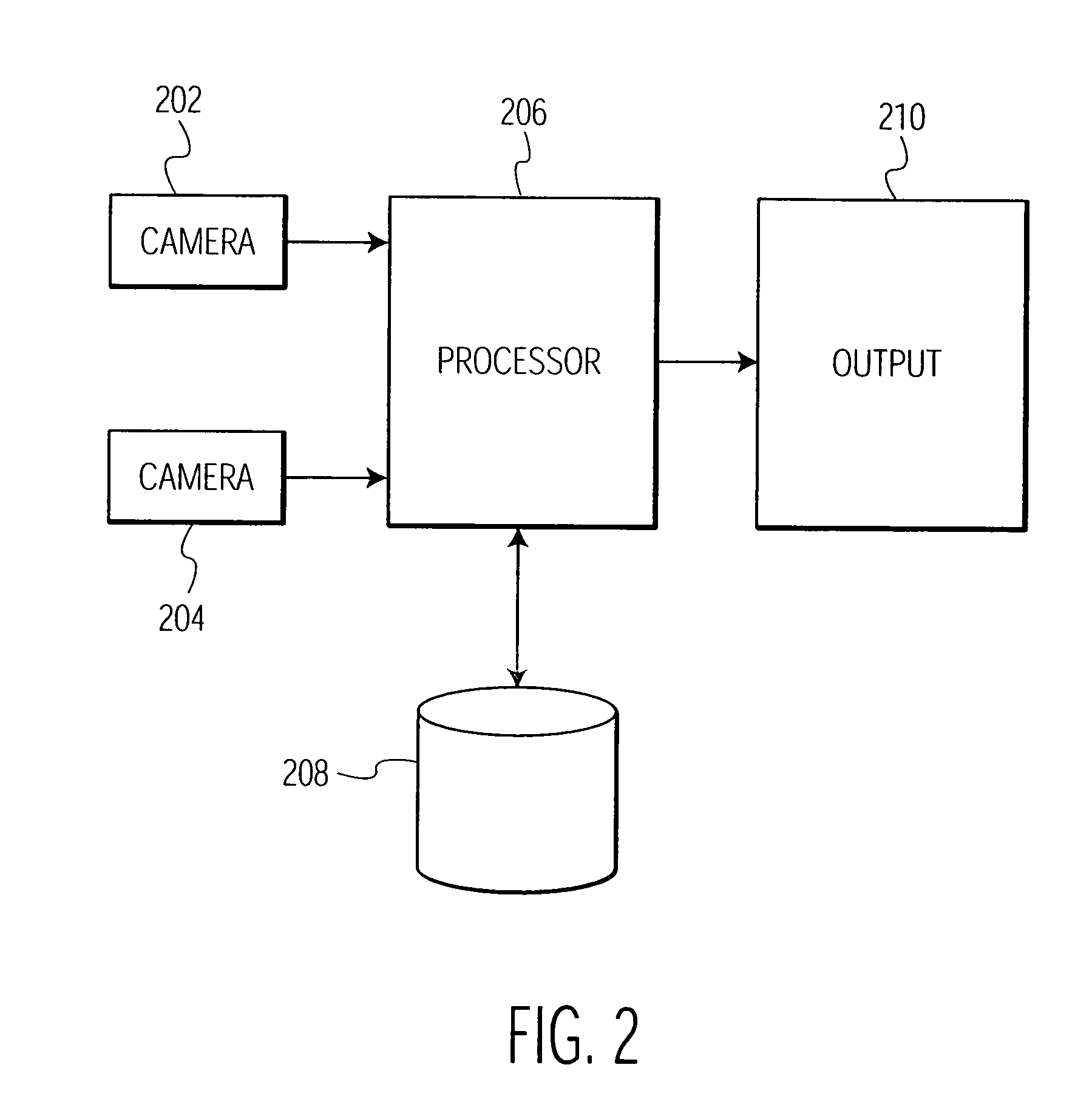
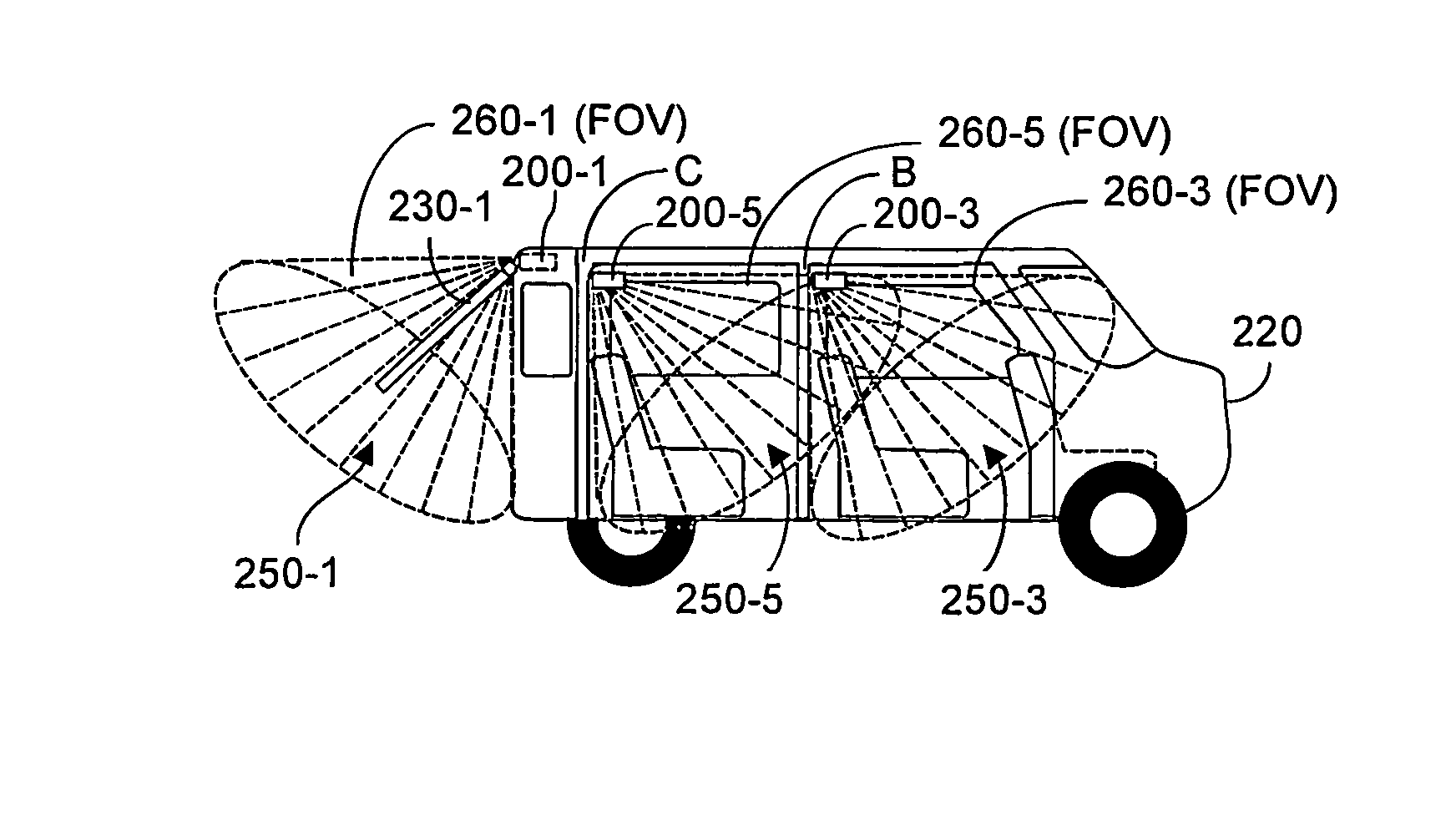
Contactless obstacle detection for power doors and the like
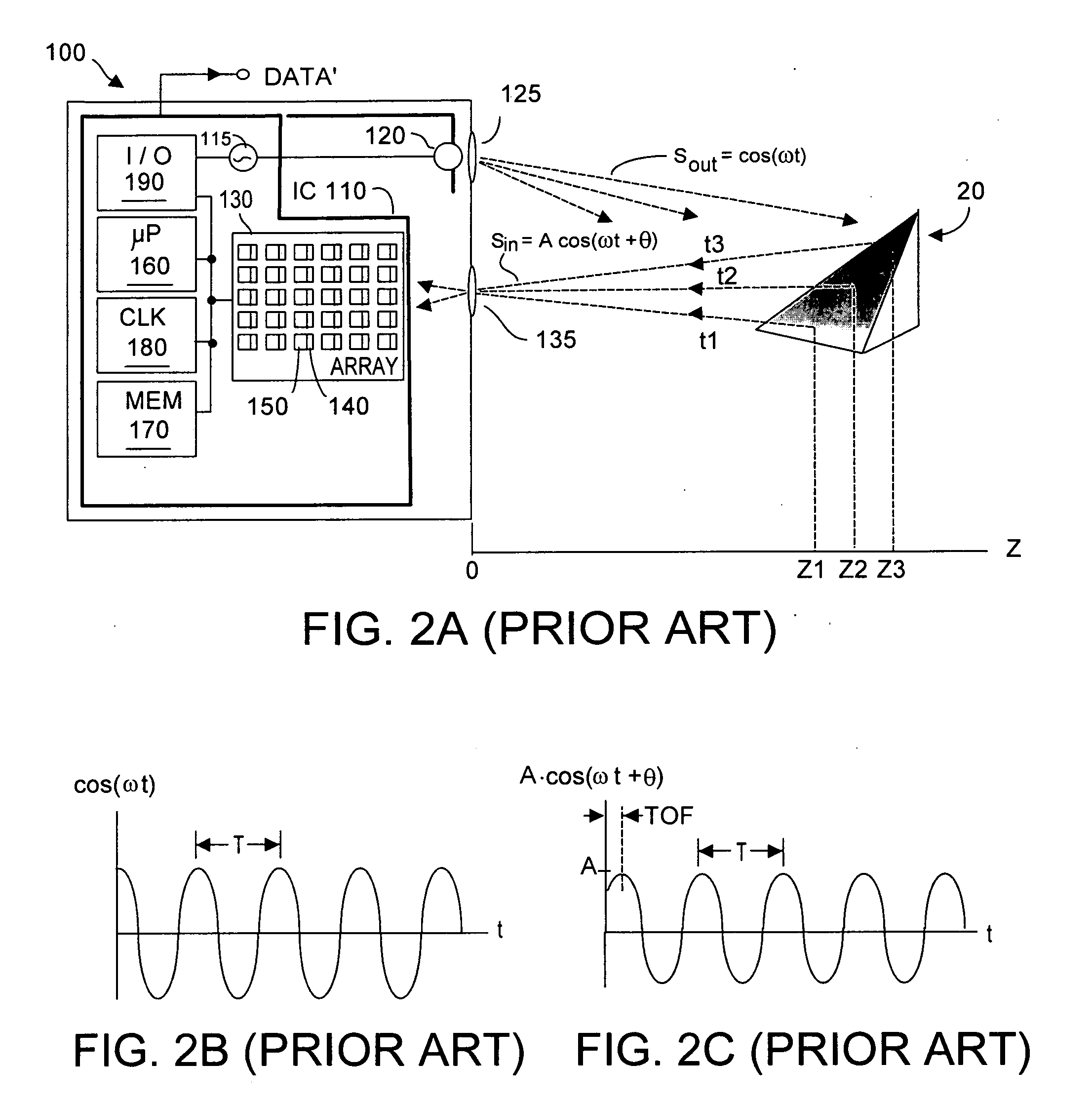
InactiveUS20110295469A1Quick fixImage enhancementDC motor speed/torque controlVehicle frameControl signal
Time-of-flight (TOF) three-dimensional sensing systems are deployed on or in a motor vehicle to image contact zones associated with potential contact between an avoidable object and the vehicle or vehicle frame and / or remotely controllable motorized moving door or liftgate. An algorithm processes depth data acquired by each TOF system to determine whether an avoidable object is in the associated contact zone. If present, a control signal issues to halt or reverse the mechanism moving the door. A stored database preferably includes a depth image of the contact zone absent any object, an image of the door, and volume of the door. Database images are compared to newly acquired depth images to identify pixel sensors whose depth values are statistically unlikely to represent background or the door. Pixels within the contact zone so identified are an object, and the control signal is issued.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods and Apparatus for Visual Search
ActiveUS20130121600A1Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionBag of features
Each image of a set of images is characterized with a set of sparse feature descriptors and a set of dense feature descriptors. In some embodiments, both the set of sparse feature descriptors and the set of dense feature descriptors are calculated based on a fixed rotation for computing texture descriptors, while color descriptors are rotation invariant. In some embodiments, the descriptors of both sparse and dense features are then quantized into visual words. Each database image is represented by a feature index including the visual words computed from both sparse and dense features. A query image is characterized with the visual words computed from both sparse and dense features of the query image. A rotated local Bag-of-Features (BoF) operation is performed upon a set of rotated query images against the set of database images. Each of the set of images is ranked based on the rotated local Bag-of-Features operation.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
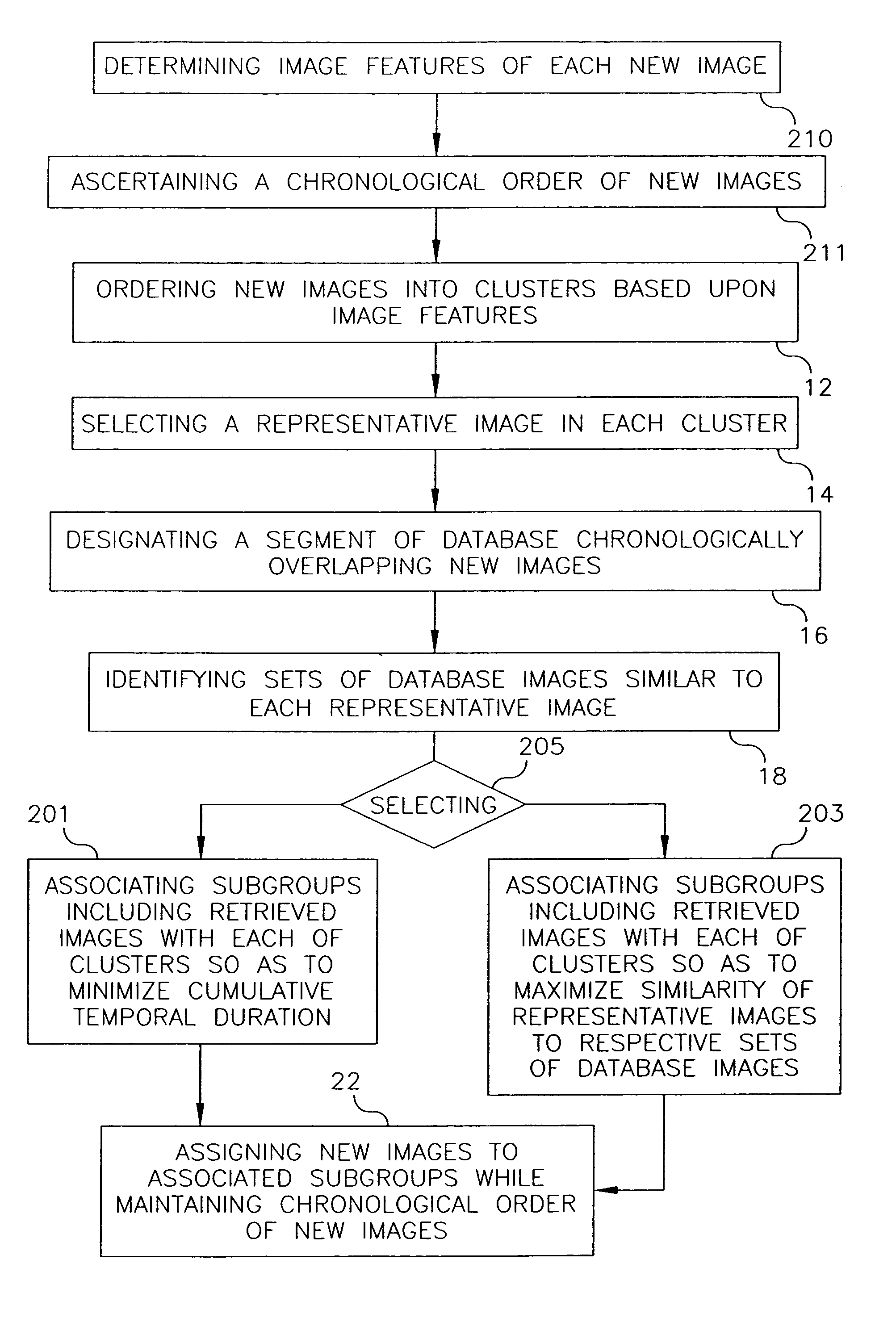
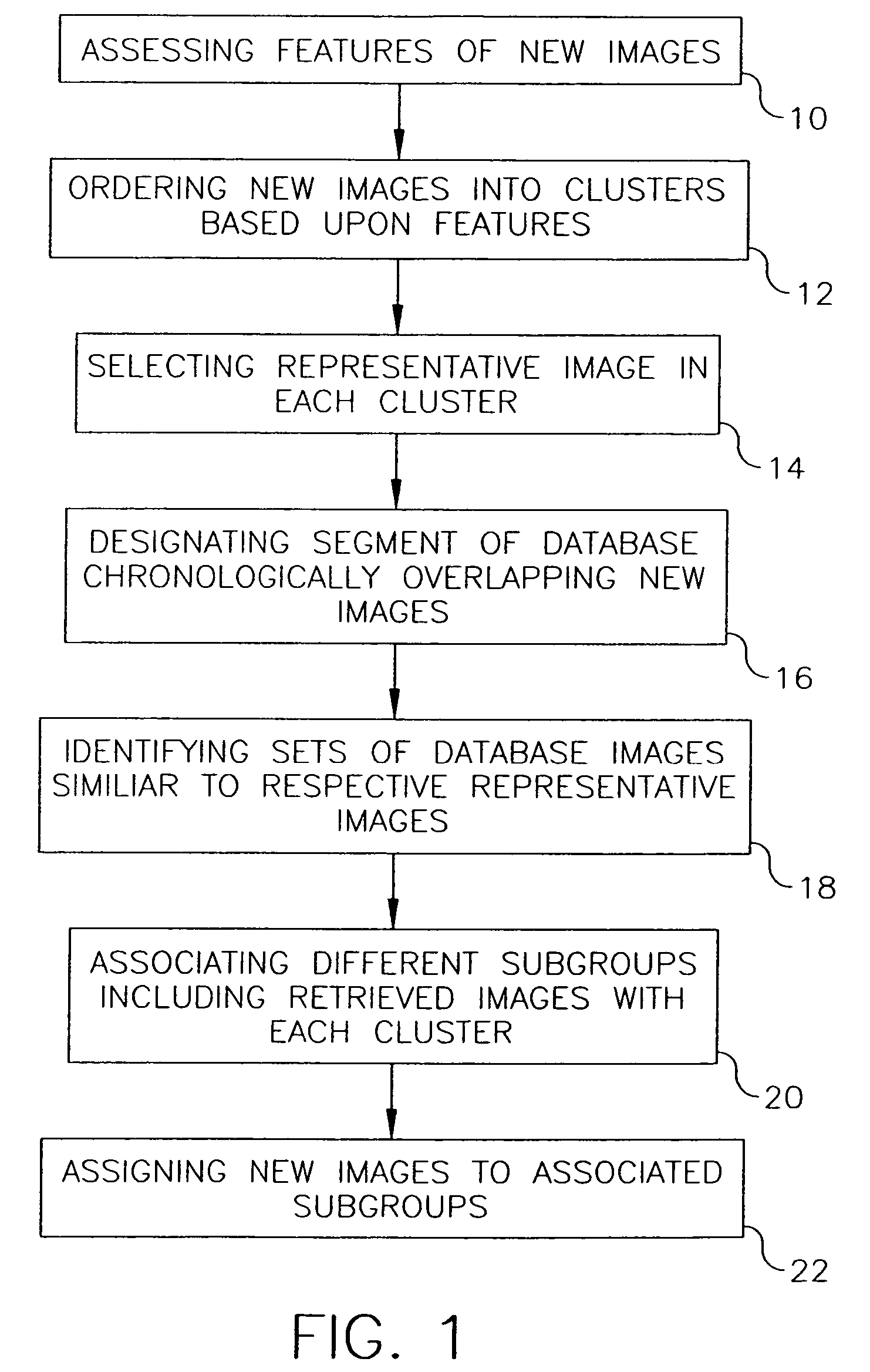
Additive clustering of images lacking individualized date-time information
InactiveUS20060200475A1Digital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionTemporal informationPersonalization
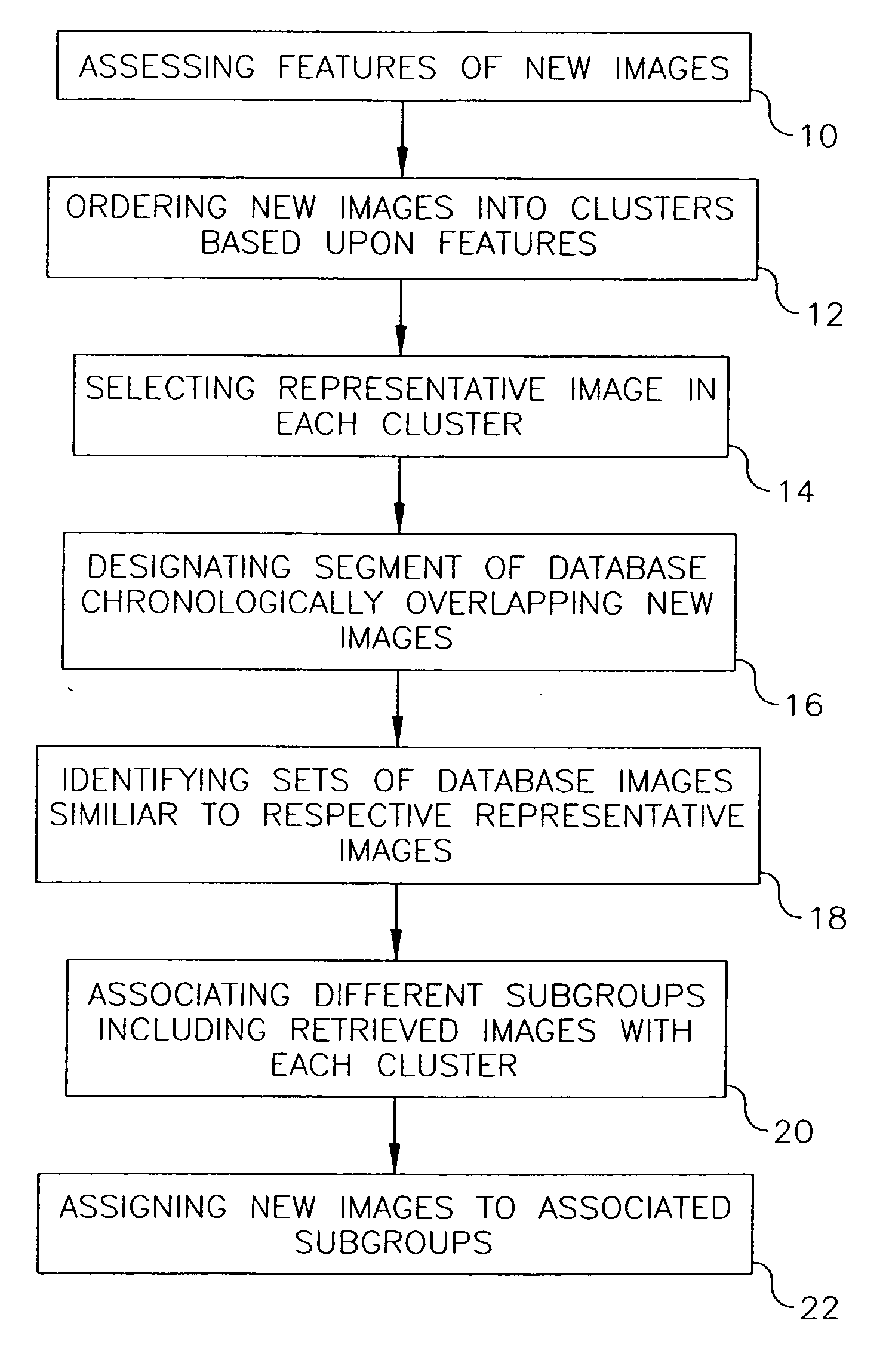
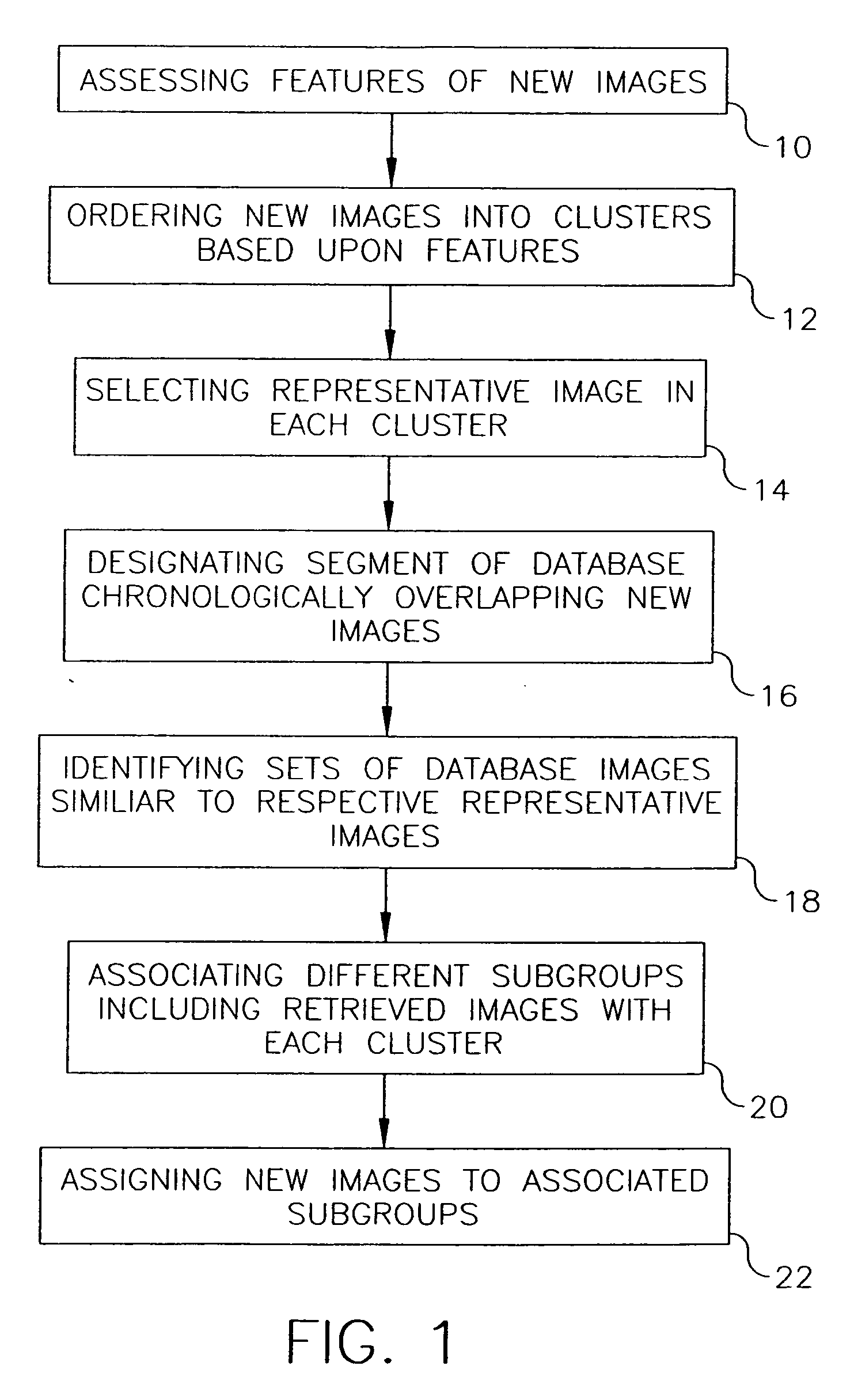
A database has chronologically ordered images classified into event groups based upon a time difference threshold, and into subgroups based upon a similarity measure. In a method and system for combining new images into such a database, new image are ordered into clusters based upon assessed image features. A representative image is selected in each cluster. A database segment chronologically overlapping the new images is designated and a set of database images similar to each representative image are identified in the segment. Different subgroups including one or more retrieved images are associated with each of cluster to provide matched subgroups. The new images are assigned to matched subgroups associated with respective clusters.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Digital media recognition apparatus and methods
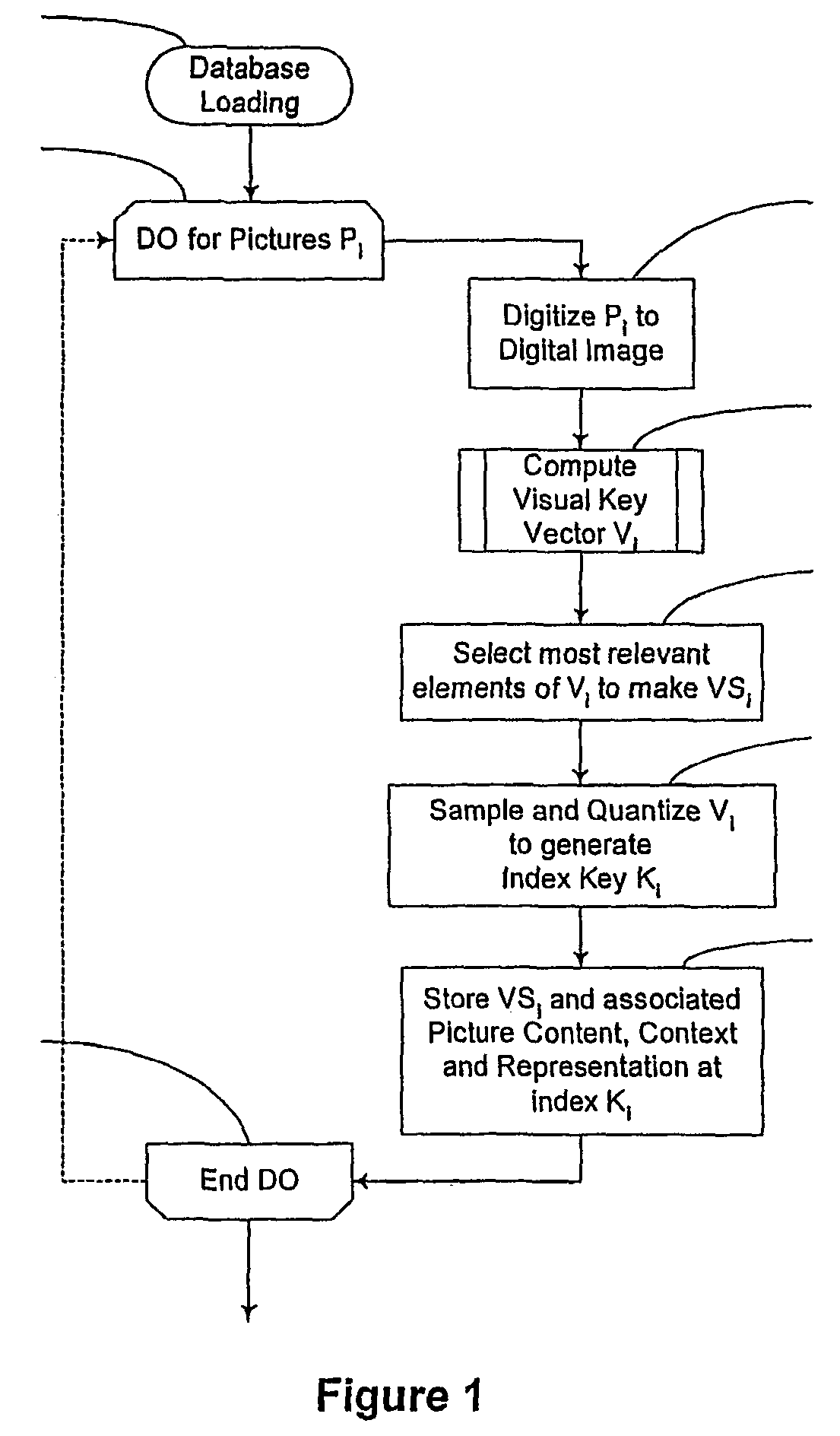
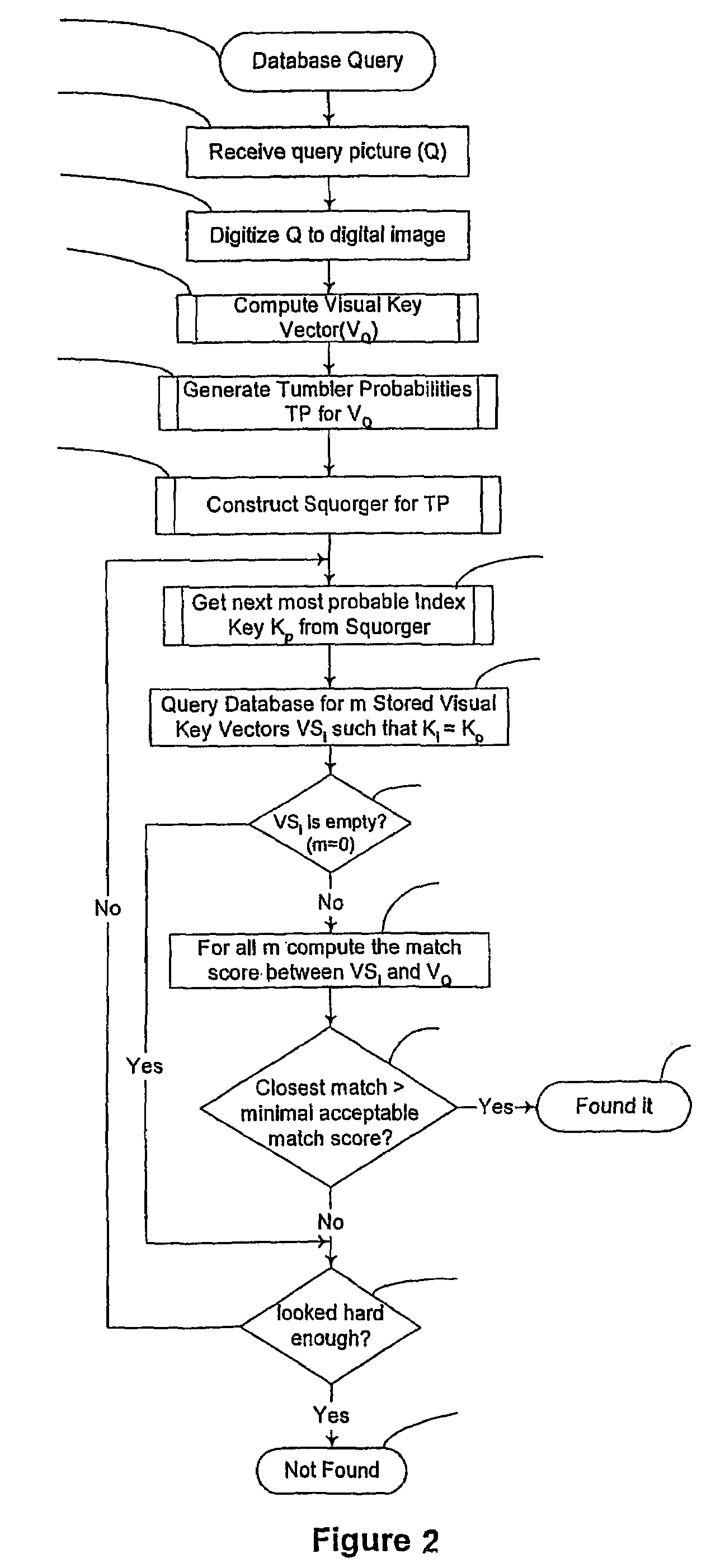
ActiveUS7474759B2Improve uniformityEvenly distributedDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionStatistical criterionDatabase image
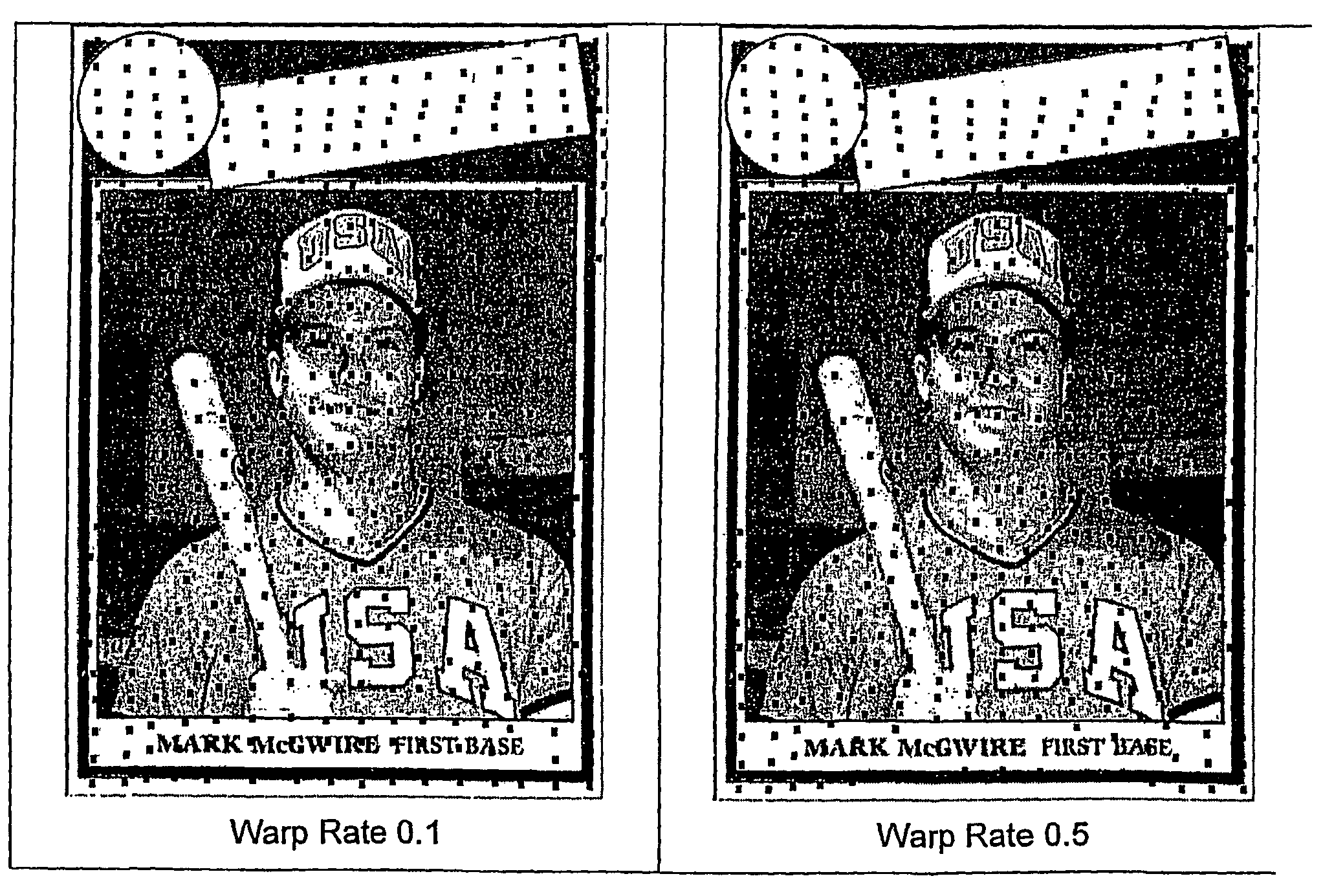
Physical objects, including still and moving images, sound / audio and text are transformed into more compact forms for identification and other purposes using a method unrelated to existing image-matching systems which rely on feature extraction. An auxiliary construct, preferably a warp grid, is associated with an object, and a series of transformations are imposed to generate a unique visual key for identification, comparisons, and other operations. Search methods are also disclosed for matching an unknown image to one previously represented in a visual key database. Broadly, a preferred search method sequentially examines candidate database images for their closeness of match in a sequential order determined by their a priori match probability. Thus, the most likely match candidate is examined first, the next most likely second, and so forth. With respect to the recognition of video sequences and other information streams, inventive holotropic stream recognition principles are deployed, wherein the statistics of the spatial distribution of warp grid points is used to generate index keys. The invention is applicable to various fields of endeavor, including governmental, scientific, industrial, commercial, and recreational object identification and information retrieval. Extensions of the technology are also disclosed to achieve a uniform distribution of objects over the database search, a consideration which is central to scalability. In particular, a generalized method has been developed based on reticle projection, which greatly enhances the uniformity of object distributions in the collected data Thus, whereas statistical criteria are used with respect to particular embodiments in transforming a construct associated with an image, audio, text or other representation, a reticle projection may alternatively be used in attribute transformation according to alternative embodiments of the invention.
Owner:SYTE VISUAL CONCEPTION LTD
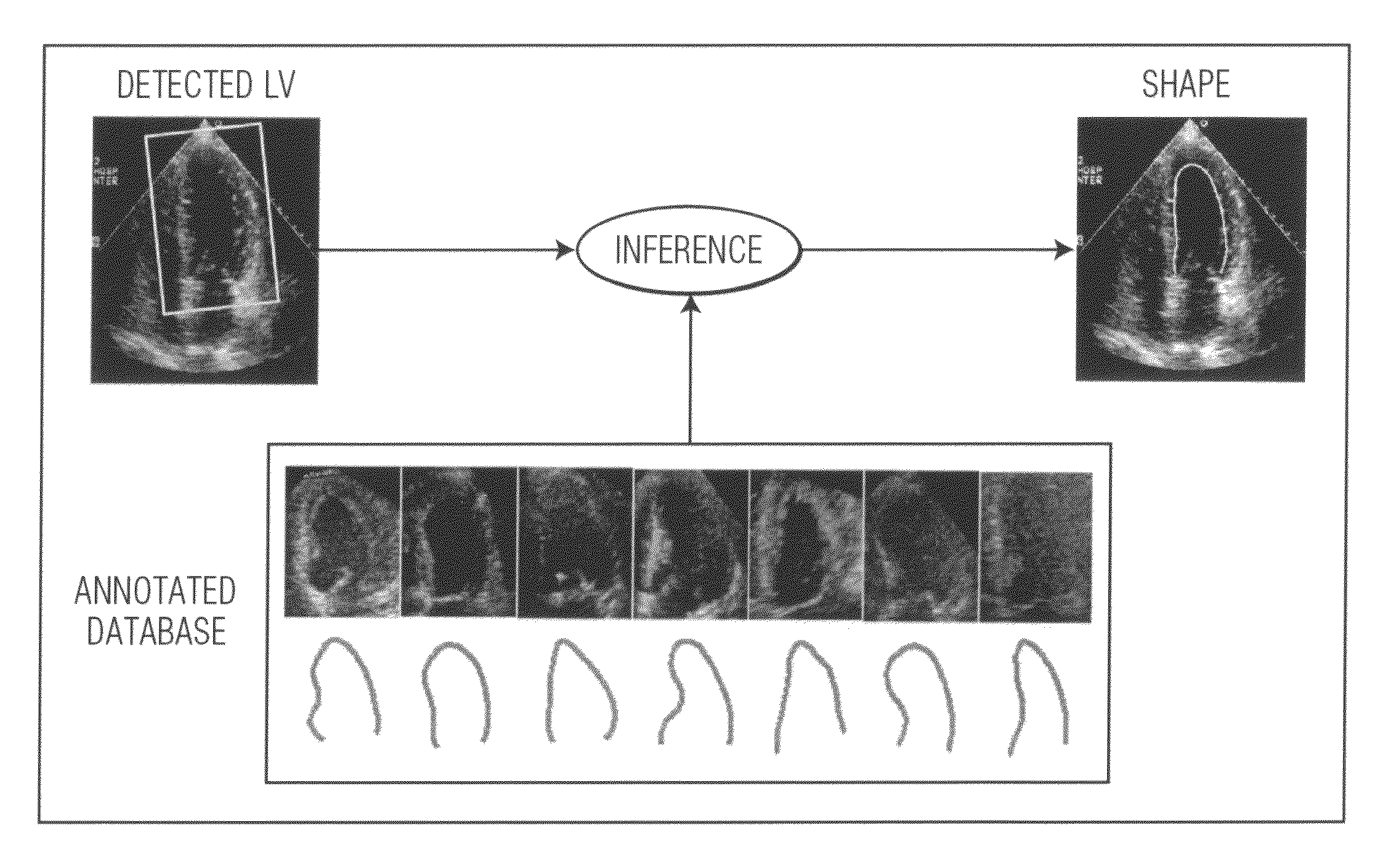
Method of database-guided segmentation of anatomical structures having complex appearances
A method for segmenting an anatomical structure of interest within an image is disclosed. The anatomical structure of interest is compared to a database of images of like anatomical structures. Those database images of like anatomical structures that are similar to the anatomical structure of interest are identified. The identified database images are used to detect the anatomical structure of interest in the image. The identified database images are also used to determine the shape of the anatomical structure of interest. The anatomical structure of interest is segmented from the image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
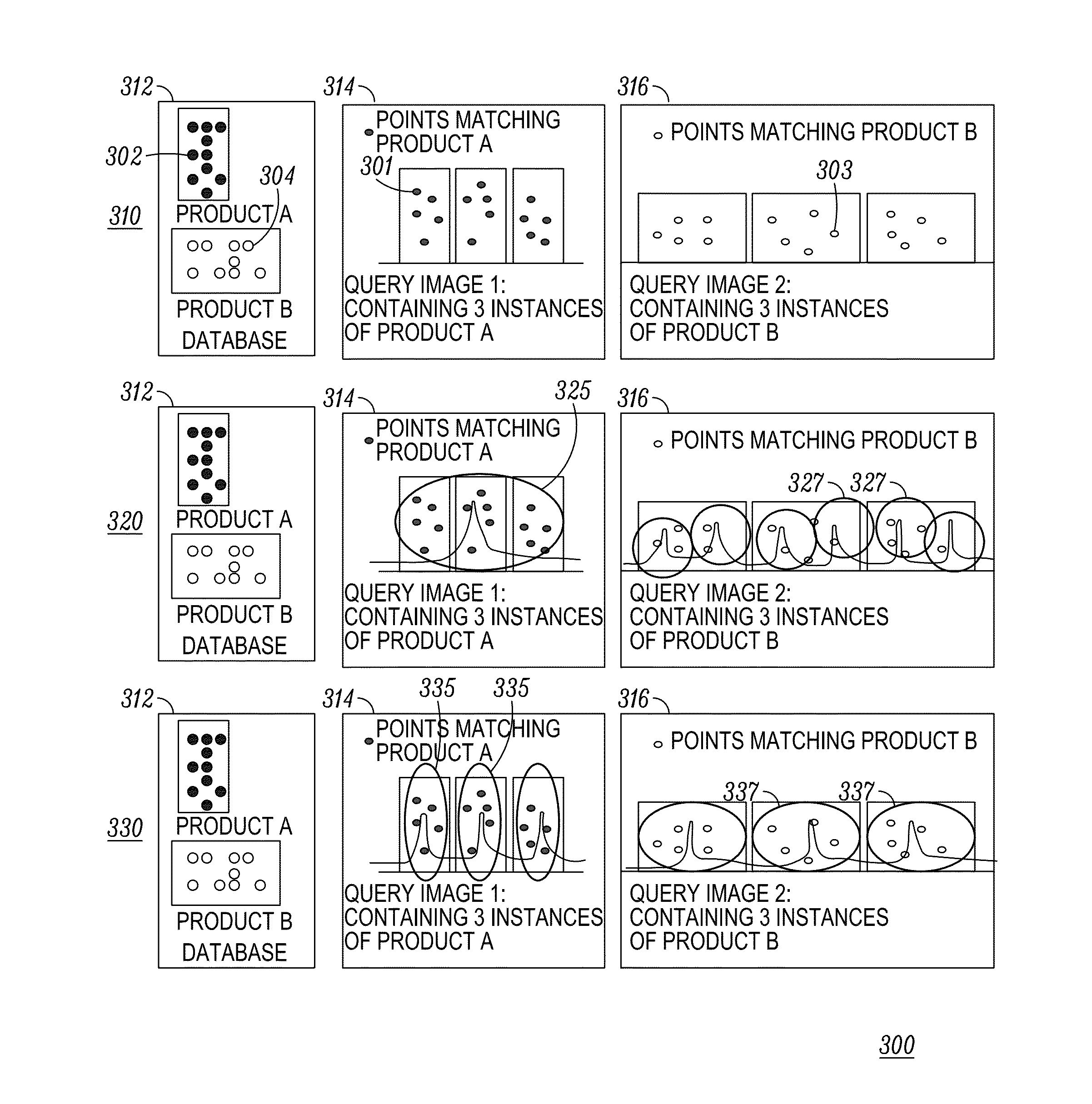
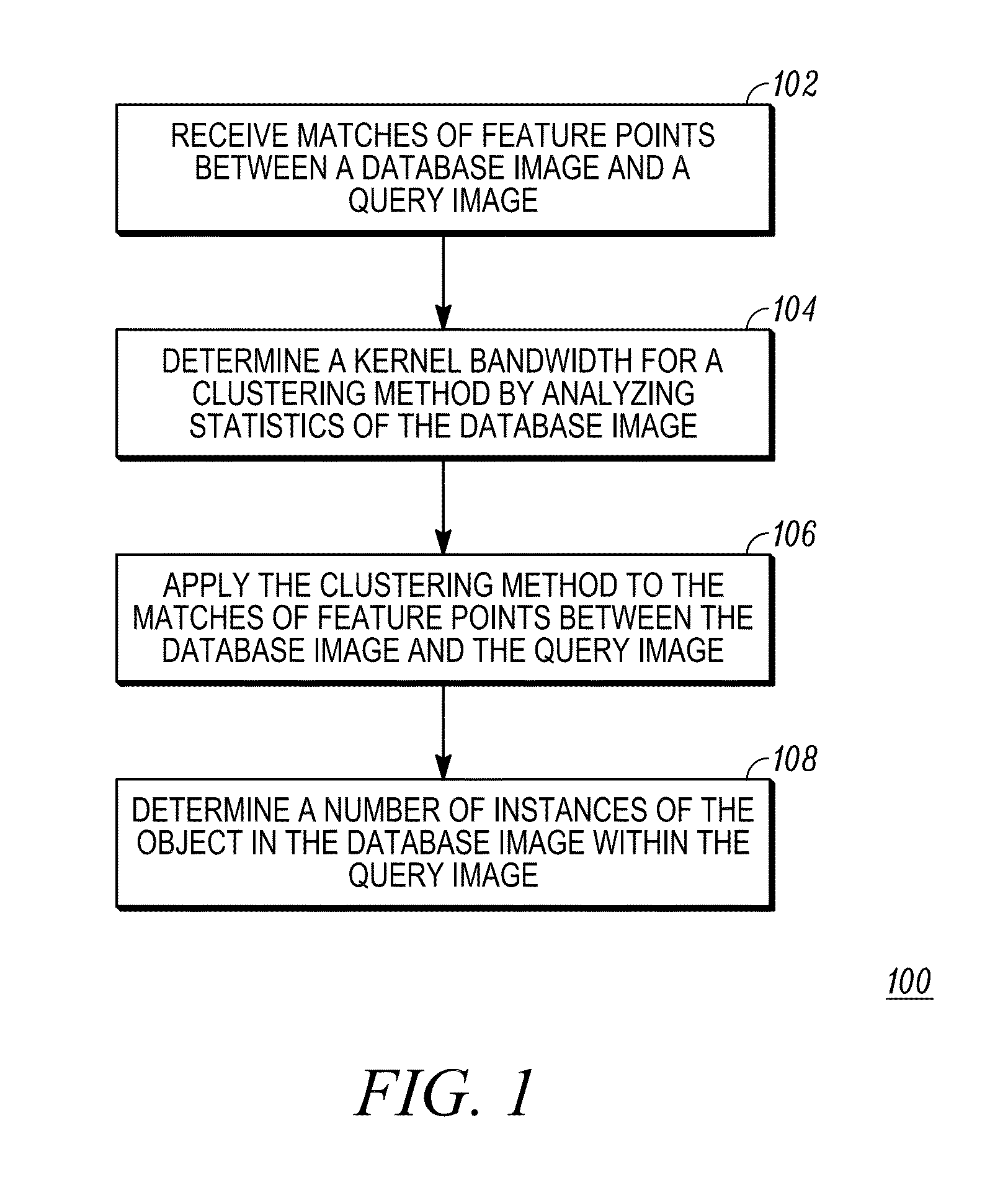
Method for detecting a plurality of instances of an object
ActiveUS20140369607A1Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionSingle imageFeature point matching
An improved object recognition method is provided that enables the recognition of many objects in a single image. Multiple instances of an object in an image can now be detected with high accuracy. The method receives a plurality of matches of feature points between a database image and a query image and determines a kernel bandwidth based on statistics of the database image. The kernel bandwidth is used in clustering the matches. The clustered matches are then analyzed to determine the number of instances of the object within each cluster. A recursive geometric fitting can be applied to each cluster to further improve accuracy.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Contactless obstacle detection for power doors and the like
Time-of-flight (TOF) three-dimensional sensing systems are deployed on or in a motor vehicle to image contact zones associated with potential contact between an avoidable object and the vehicle or vehicle frame and / or remotely controllable motorized moving door or liftgate. An algorithm processes depth data acquired by each TOF system to determine whether an avoidable object is in the associated contact zone. If present, a control signal issues to halt or reverse the mechanism moving the door. A stored database preferably includes a depth image of the contact zone absent any object, an image of the door, and volume of the door. Database images are compared to newly acquired depth images to identify pixel sensors whose depth values are statistically unlikely to represent background or the door. Pixels within the contact zone so identified are an object, and the control signal is issued.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method of database-guided segmentation of anatomical structures having complex appearances
A method for segmenting an anatomical structure of interest within an image is disclosed. The anatomical structure of interest is compared to a database of images of like anatomical structures. Those database images of like anatomical structures that are similar to the anatomical structure of interest are identified. The identified database images are used to detect the anatomical structure of interest in the image. The identified database images are also used to determine the shape of the anatomical structure of interest. The anatomical structure of interest is segmented from the image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
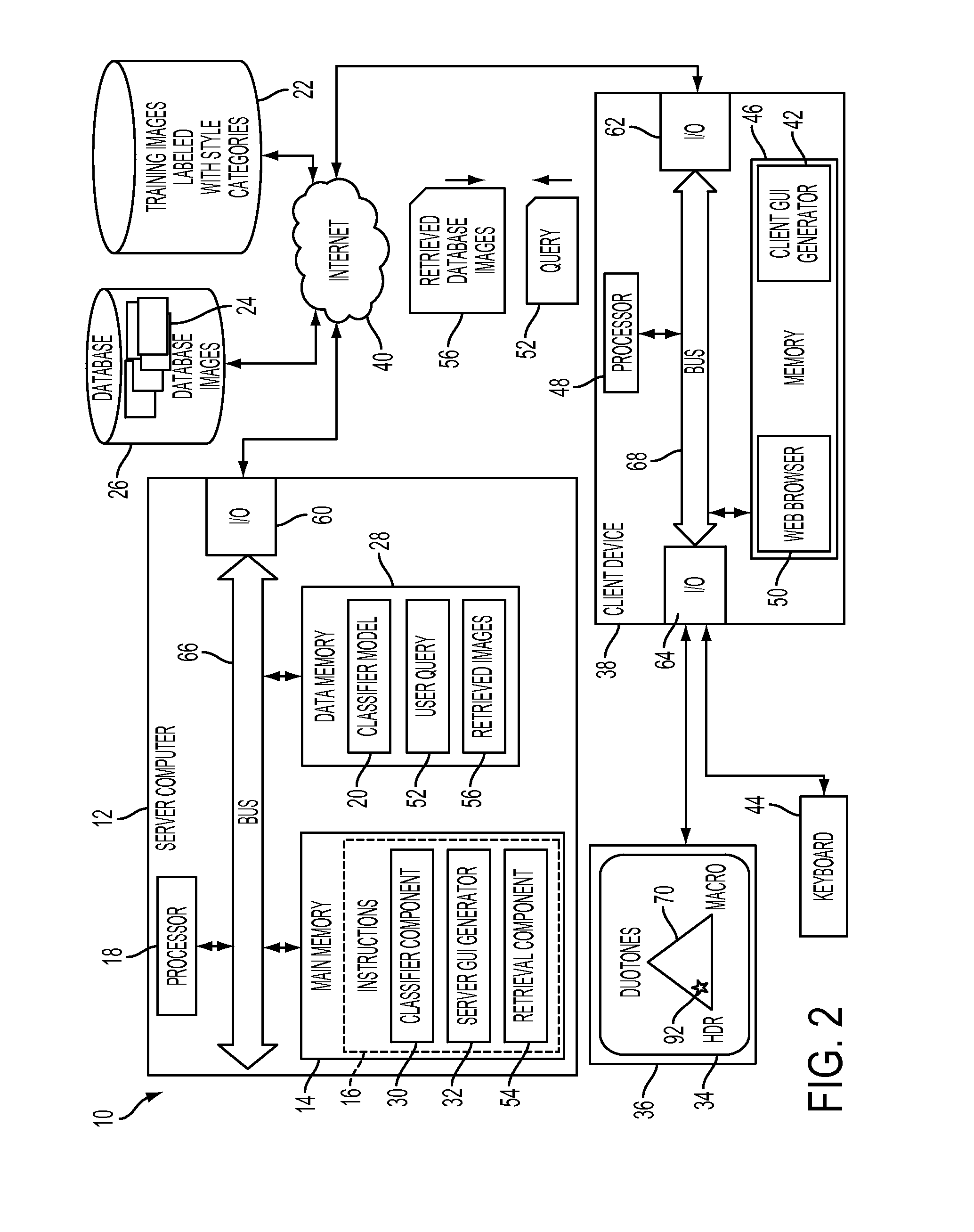
Image selection based on photographic style
ActiveUS20130315477A1Character and pattern recognitionMetadata still image retrievalPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A system and method are disclosed for image selection based on photographic style in which photographic style annotations are learned using a data-driven approach. The method includes assigning a style value for each of a set of photographic style categories to each of a set of database images with a trained classifier of a computing device. A user's selection of a subset of the photographic style categories, such as three style categories, is received. A user interface is generated for assigning values to each of the selected photographic style categories. A set of database images is identified, based on the assigned values for each of the selected photographic style categories and the style values for each of the selected photographic style categories of the database images.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Addition of new images to an image database by clustering according to date/time and image content and representative image comparison
InactiveUS7831599B2Character and pattern recognitionMetadata still image retrievalImaging FeatureChronological time
A database has chronologically ordered images classified into event groups based upon a time difference threshold, and into subgroups based upon a similarity measure. In a method and system for combining new images into such a database, new images are ordered into clusters based upon assessed image features. A representative image is selected in each cluster. A database segment chronologically overlapping the new images is designated and a set of database images similar to each representative image are identified in the segment. Different subgroups including one or more retrieved images are associated with each cluster to provide matched subgroups. The new images are assigned to matched subgroups associated with respective clusters.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Wildcard color searching
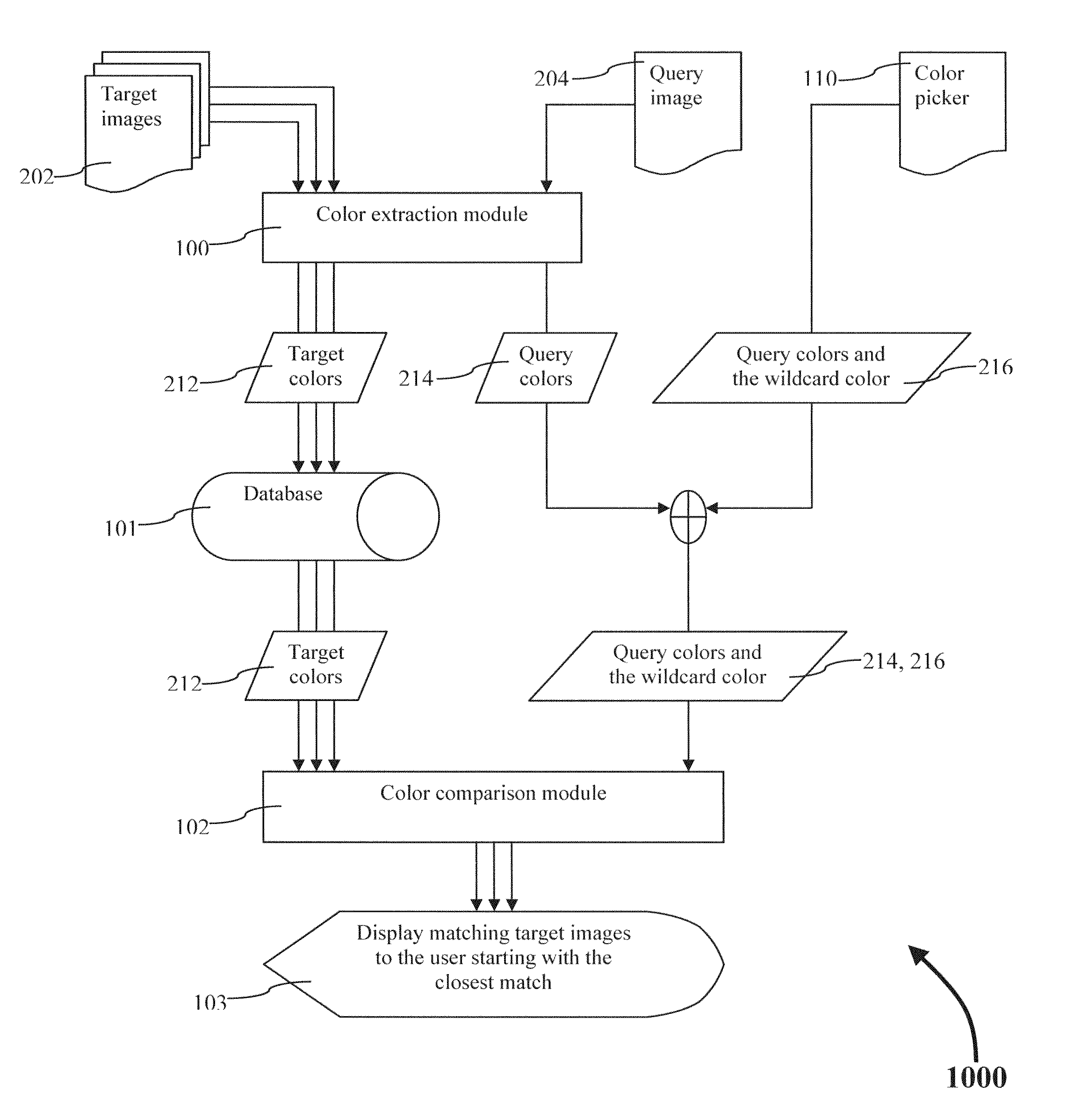
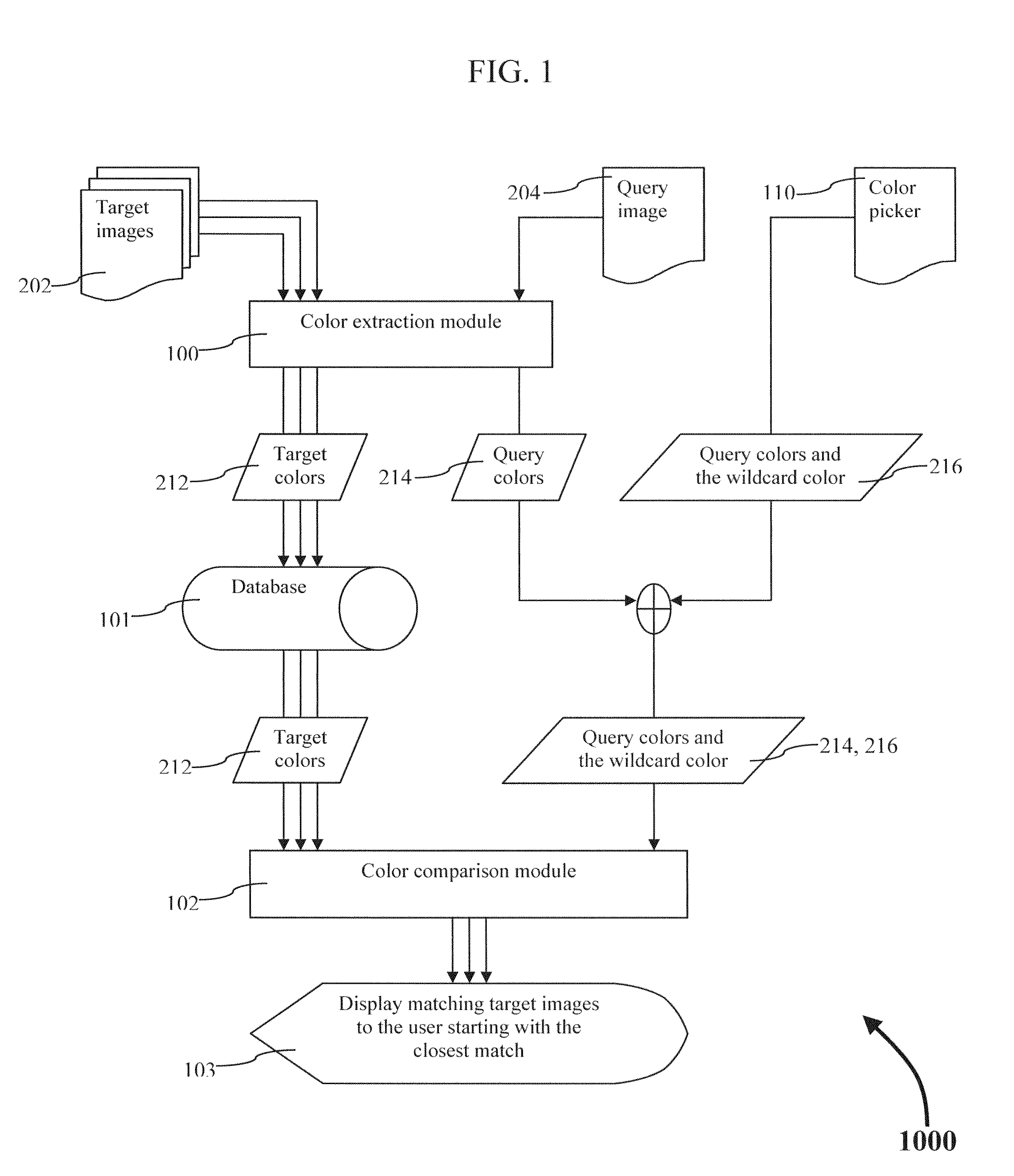
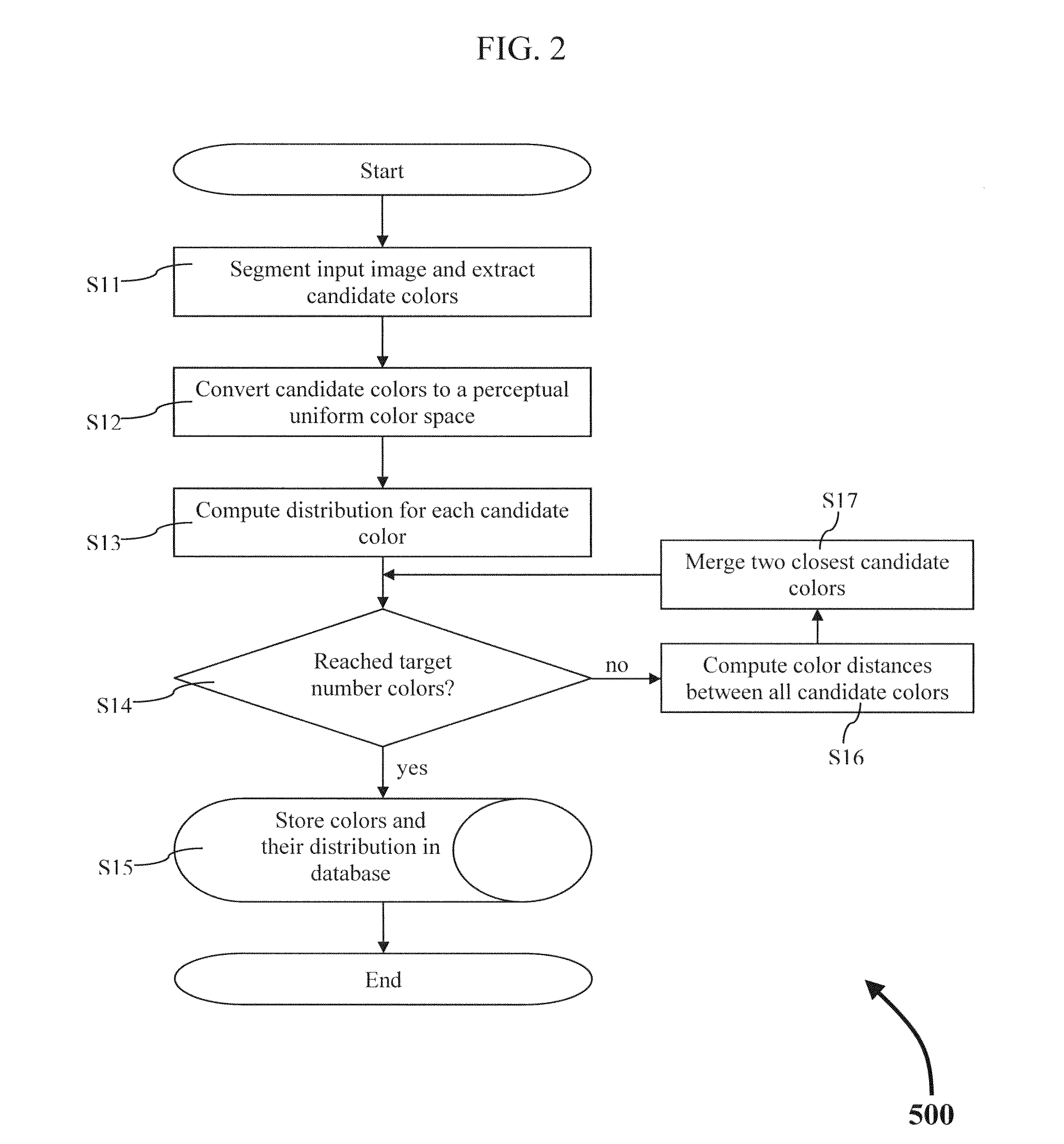
ActiveUS20140334722A1Method is fastEasy to useImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionWildcard character
A method of extracting the dominant colors from a set of target images and storing those colors in a database is described. A method of comparing colors stored in a database with a set of colors extracted from a query image. Also, a method of comparing colors stored in the database with a set of colors defined by a user using a color picker. The user defined colors may or may not include a wildcard color. The list of matching database images may or may no be filtered using metadata.
Owner:IDEE
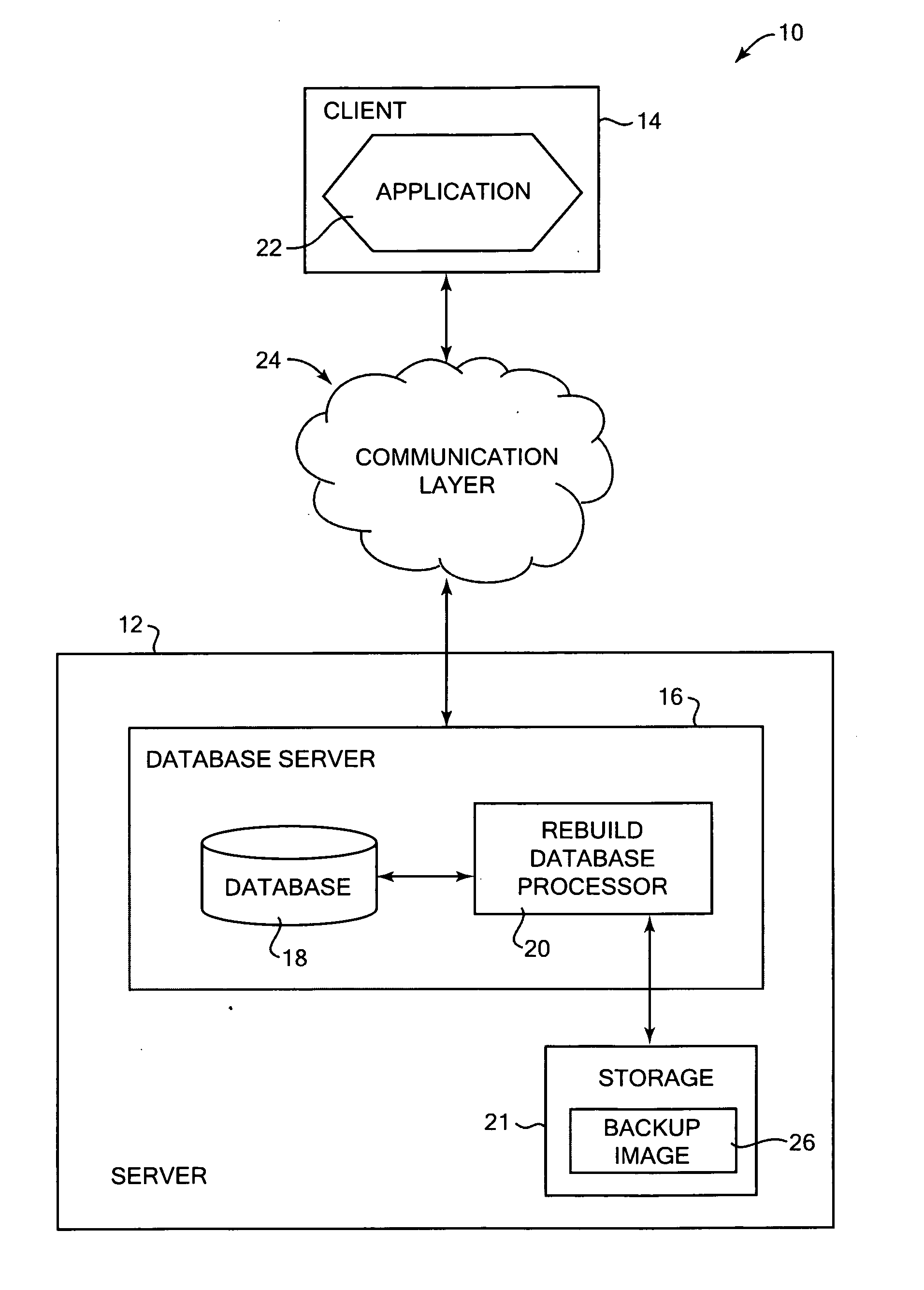
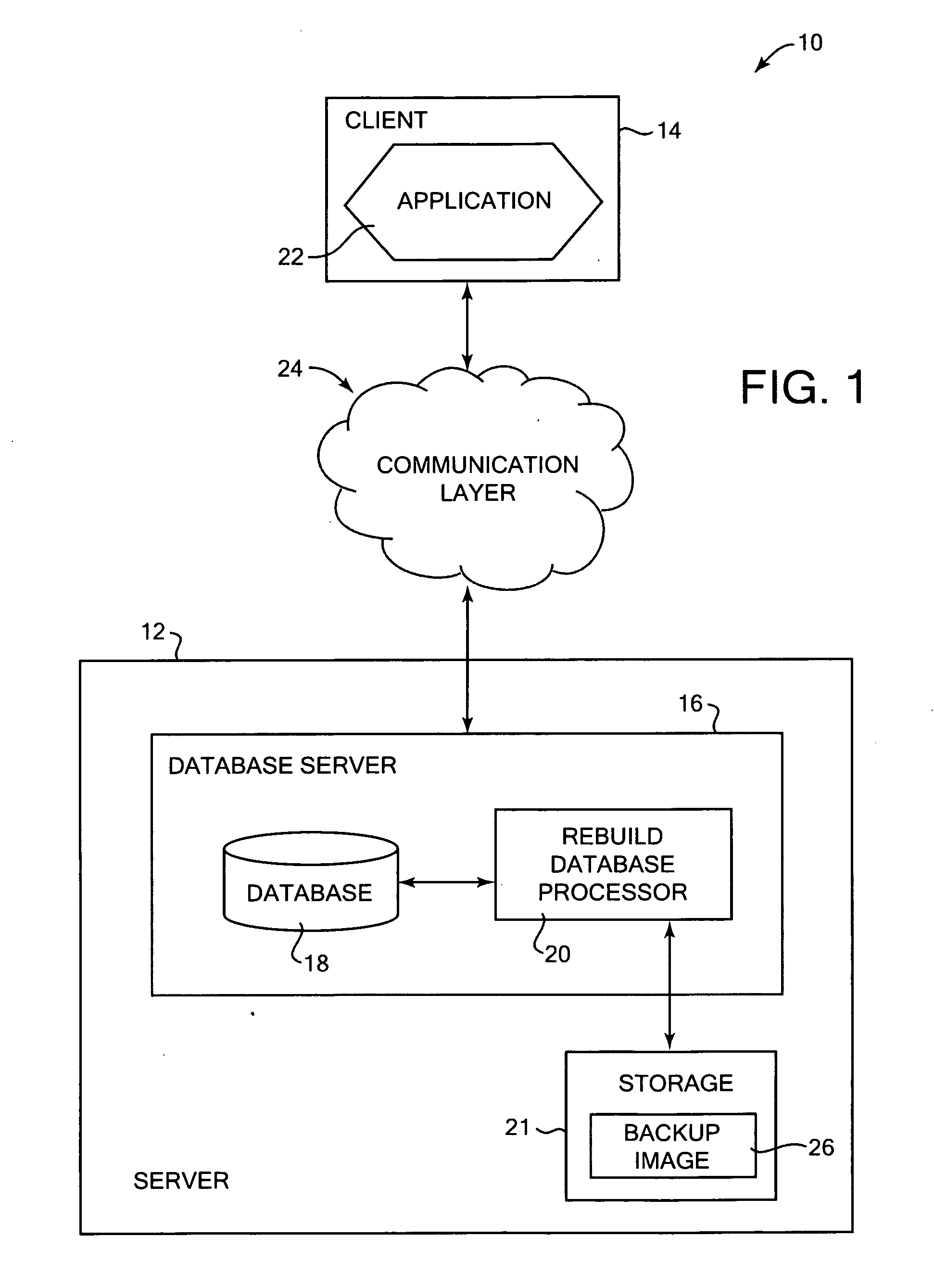
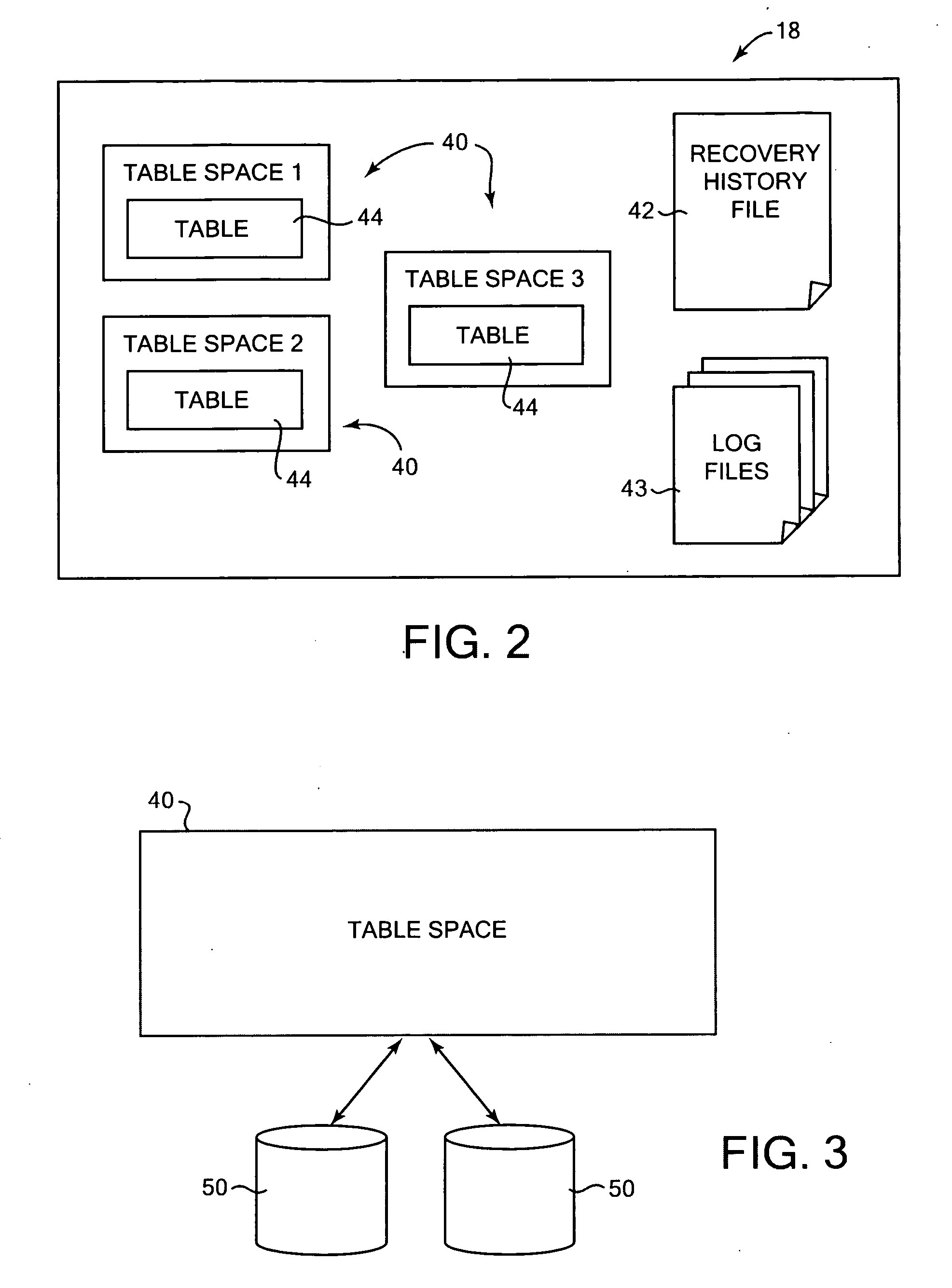
Method and system for building a database from backup data images
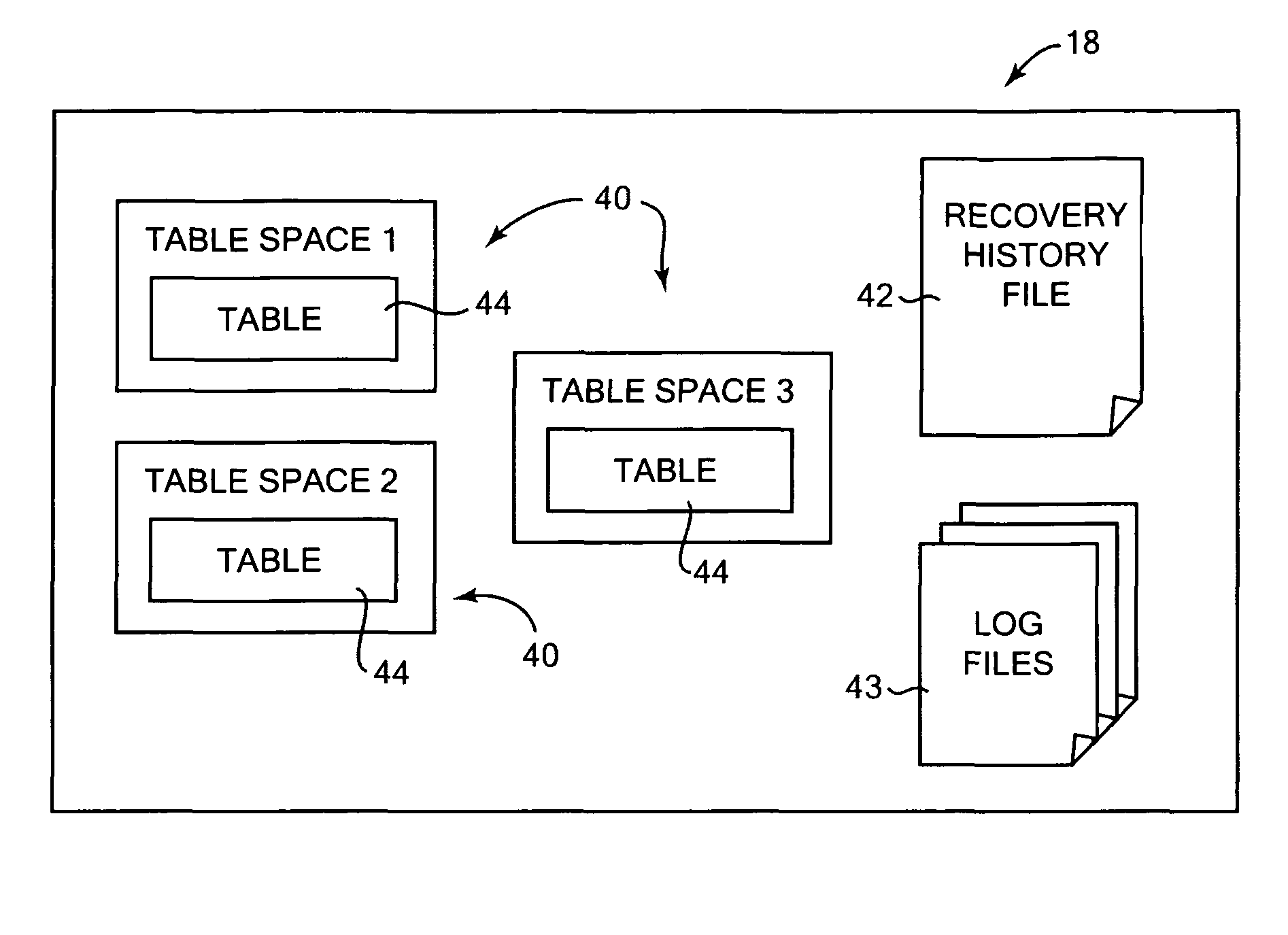
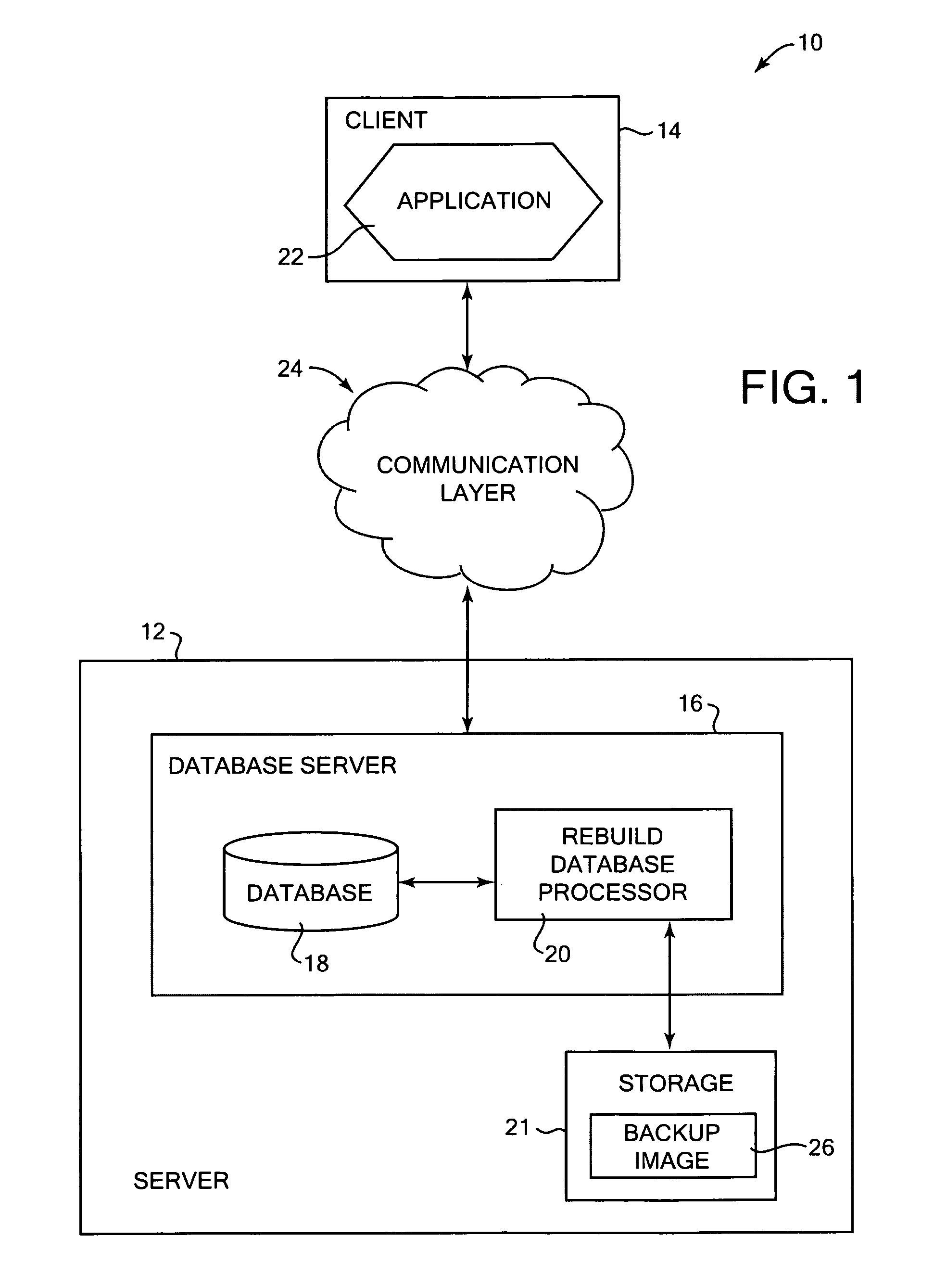
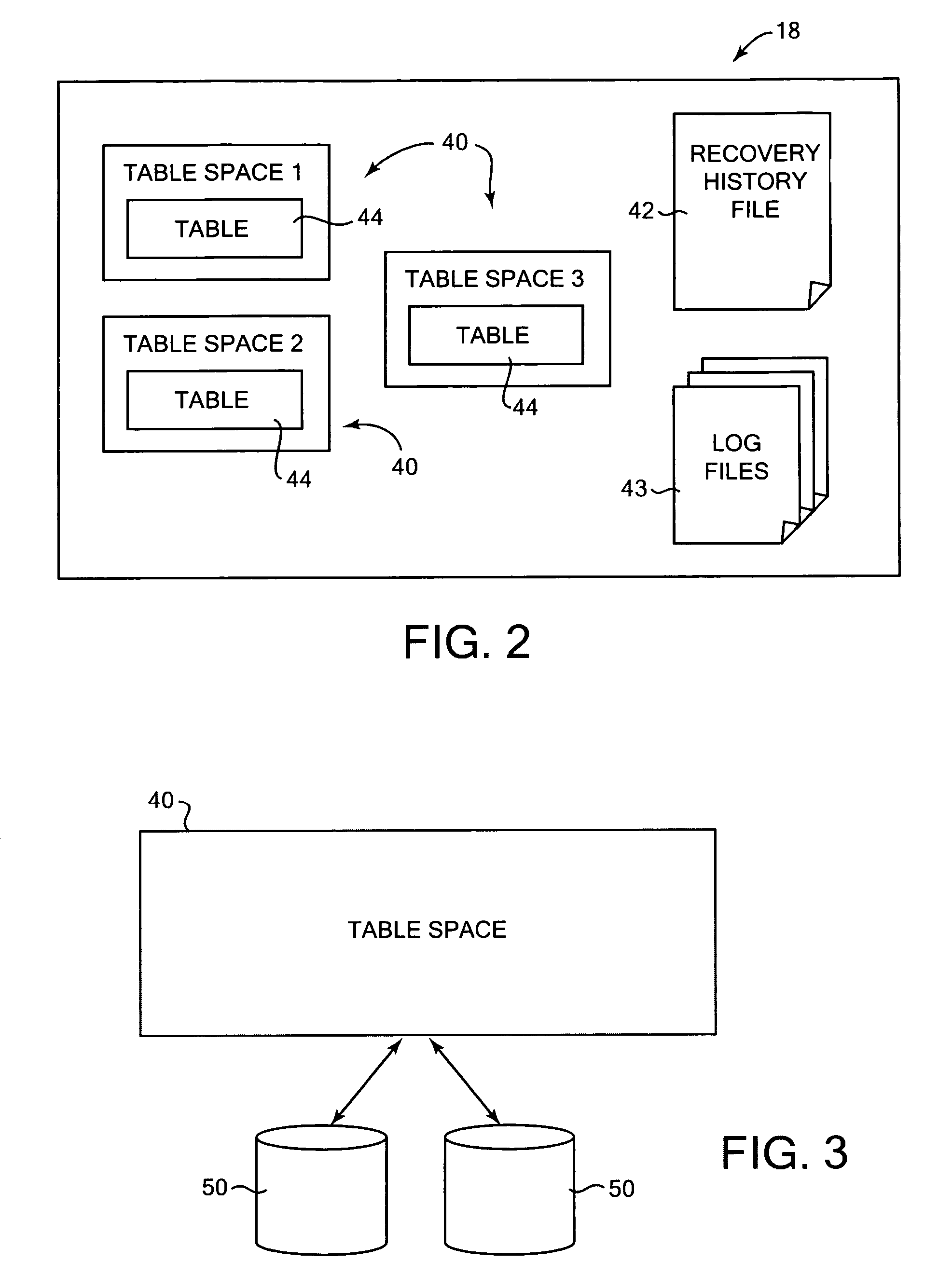
InactiveUS20070174325A1Less table spacePromote recoveryDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionDatabaseDatabase image
Building a database from stored backup data images. In one aspect, an identification of a target image is received, the target image including a copy of a logical storage unit of data from a previous database and description information that describes the previous database. The target image holds a copy of a subset of the data of the previous database. A received list has at least one desired logical storage unit of data from the previous database to be included in a built database. The desired logical storage unit is restored from at least one stored data image to the built database using the description information in the target image. Other aspects include the target image being a database image, and the desired logical storage units of data being a subset of database data.
Owner:IBM CORP
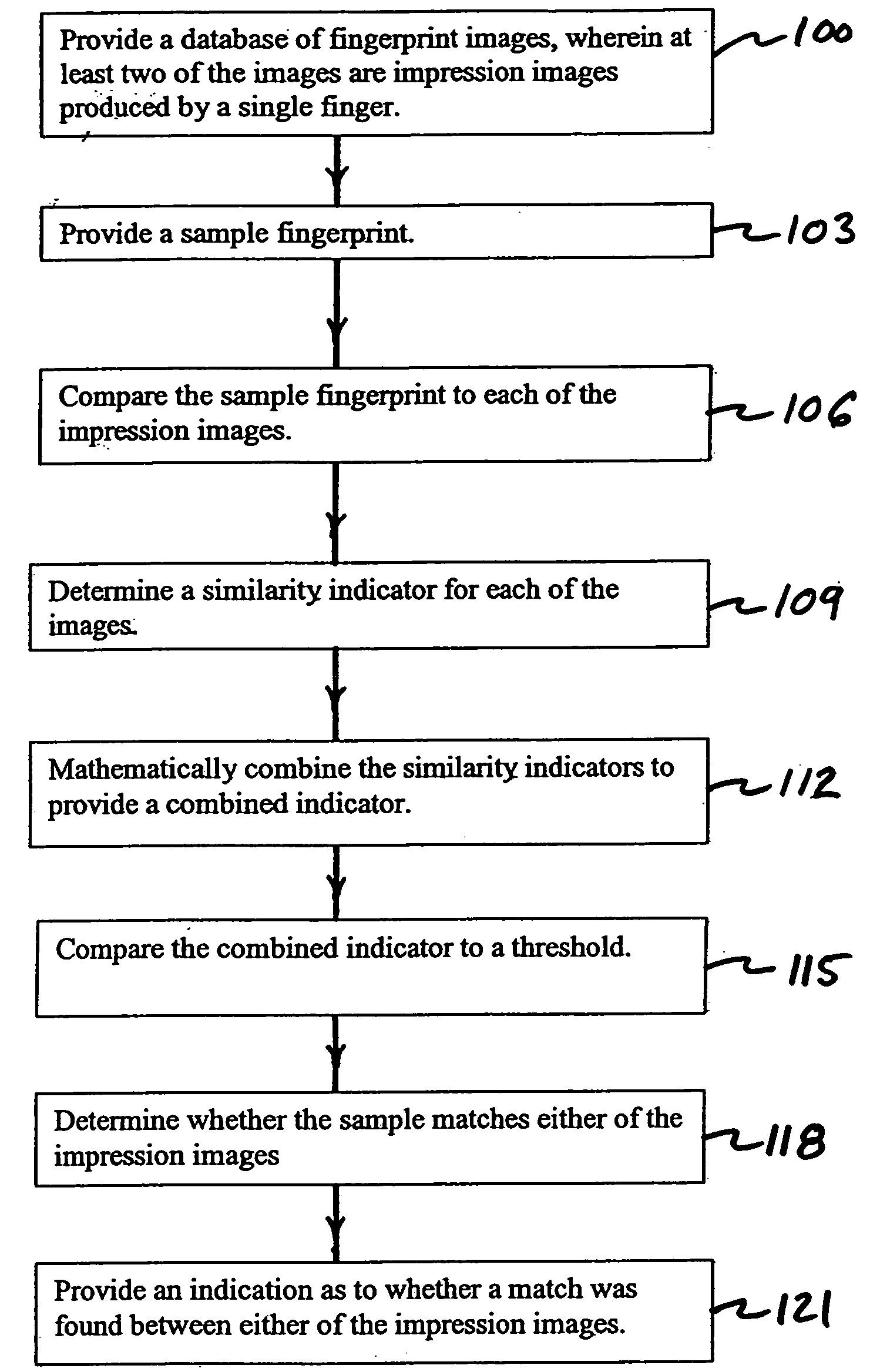
Fingerprint image database and method of matching fingerprint sample to fingerprint images
A database of fingerprint images and methods of using such a database are disclosed. The database may have at least two fingerprint images that are impression images produced by a single finger. Each impression image shows a different portion of the friction ridge surface of the finger. Methods using the database may be focused on determining whether a match exists between a fingerprint sample and the database images.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
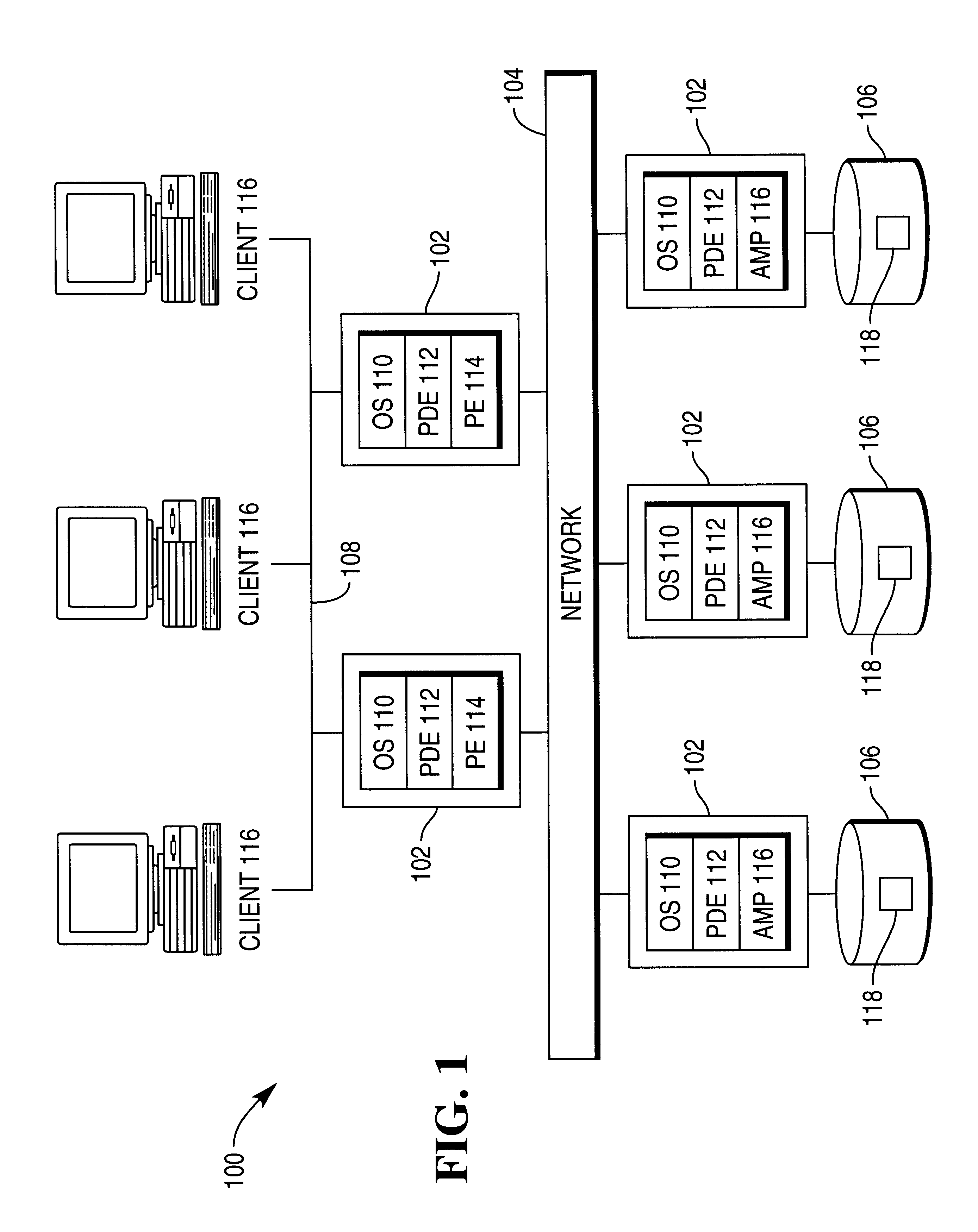
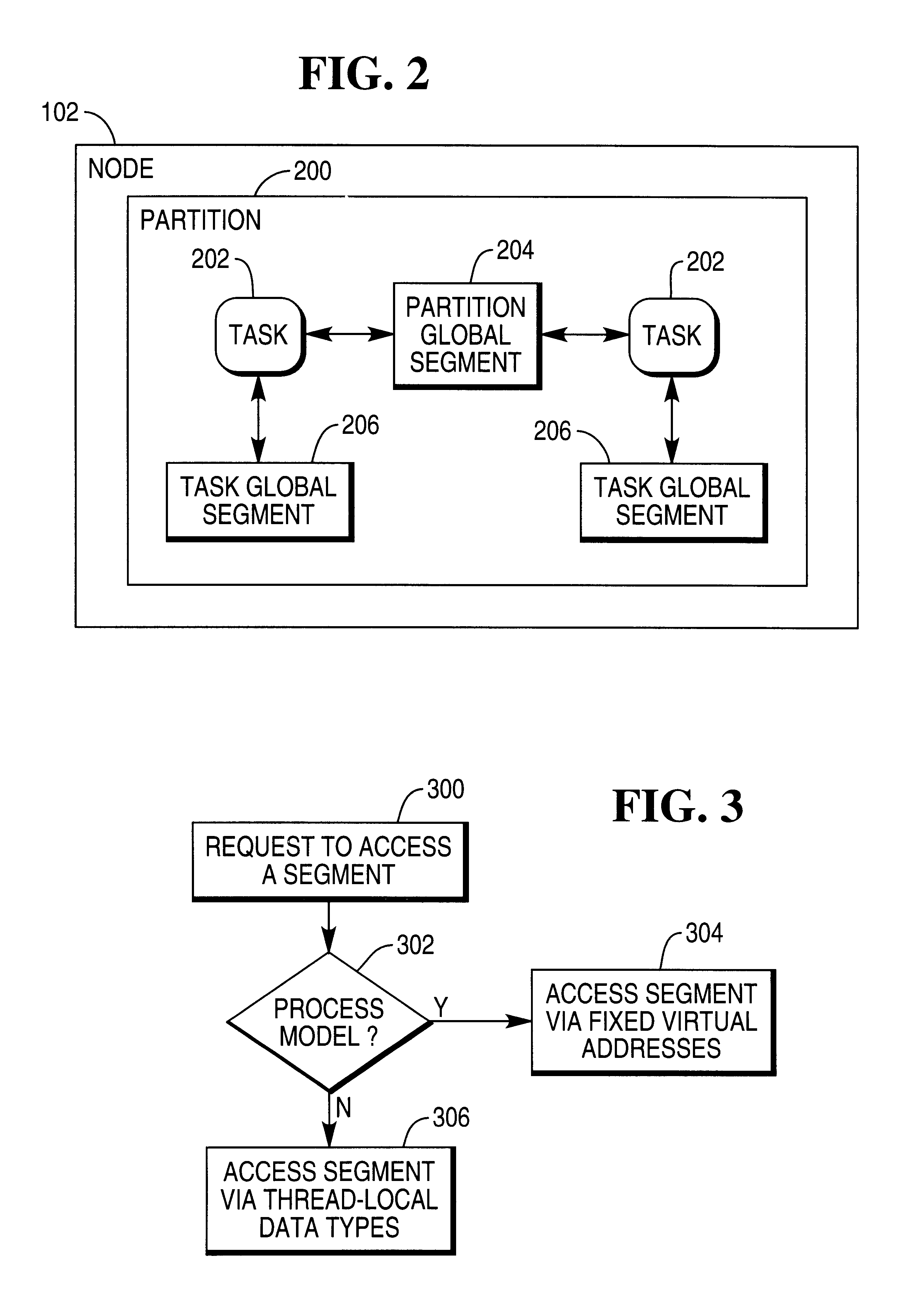
Multi-threading, multi-tasking architecture for a relational database management system
InactiveUS6351749B1Data processing applicationsRelational databasesOperational systemRelational database management system
A parallel processing architecture for a relational database management system (RDBMS) that supports both a process model operating system and a thread model operating system. The RDBMS is implemented as a shared nothing, single database image utilizing Parallel Database Extensions (PDEs) that insulate the RDBMS from the specifics of the operating system and that provide the necessary techniques for accessing common memory segments.
Owner:TERADATA US
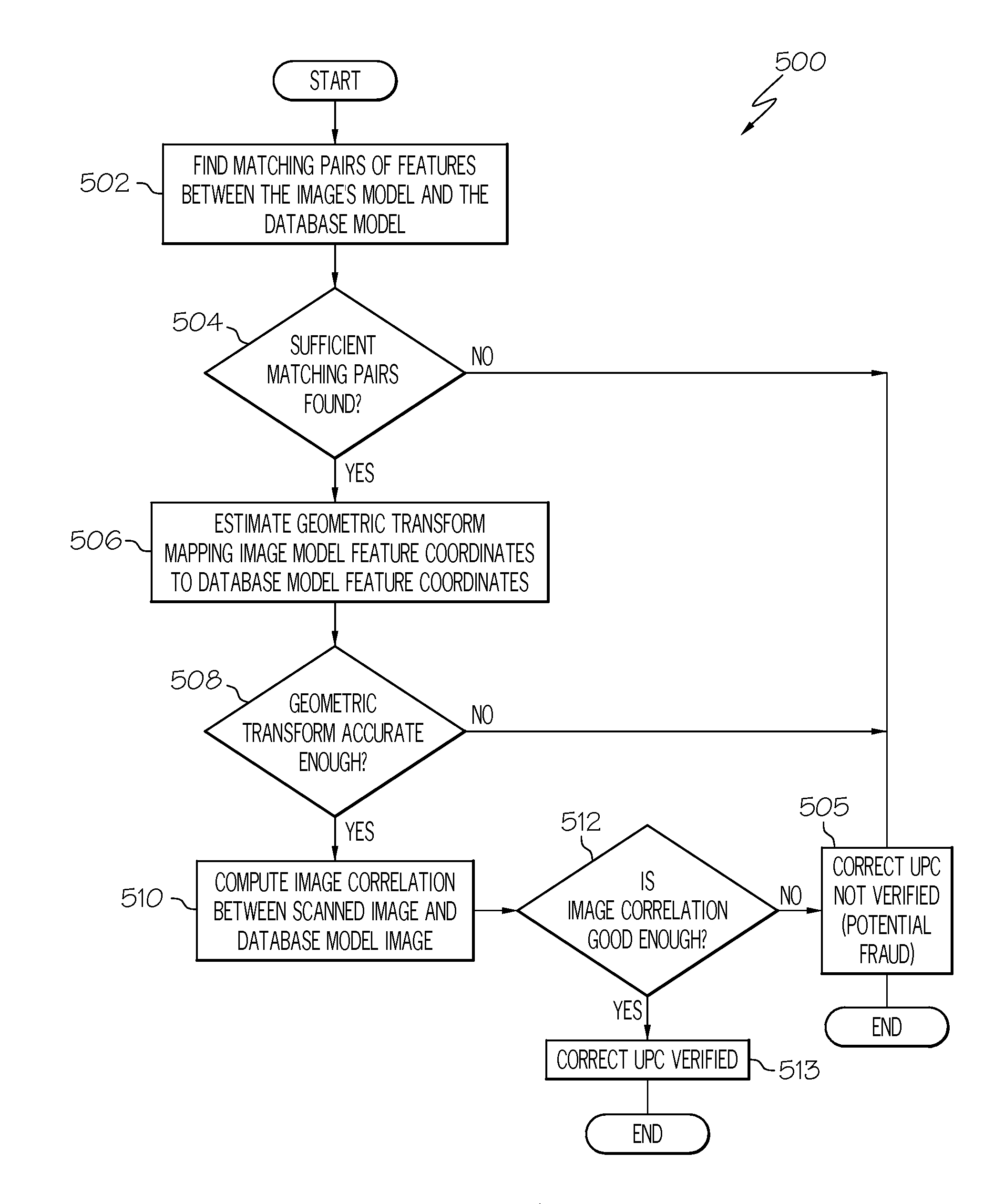
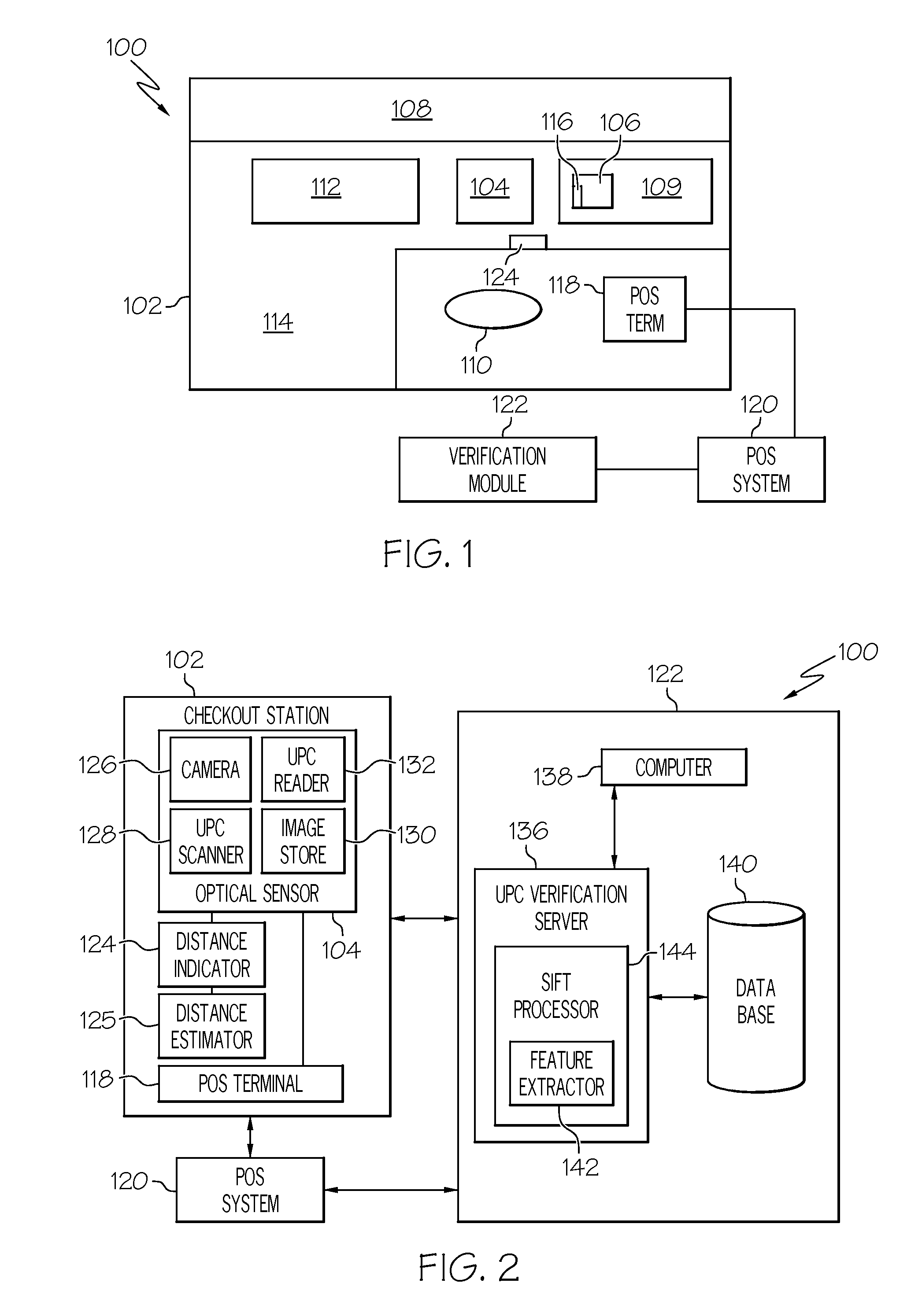
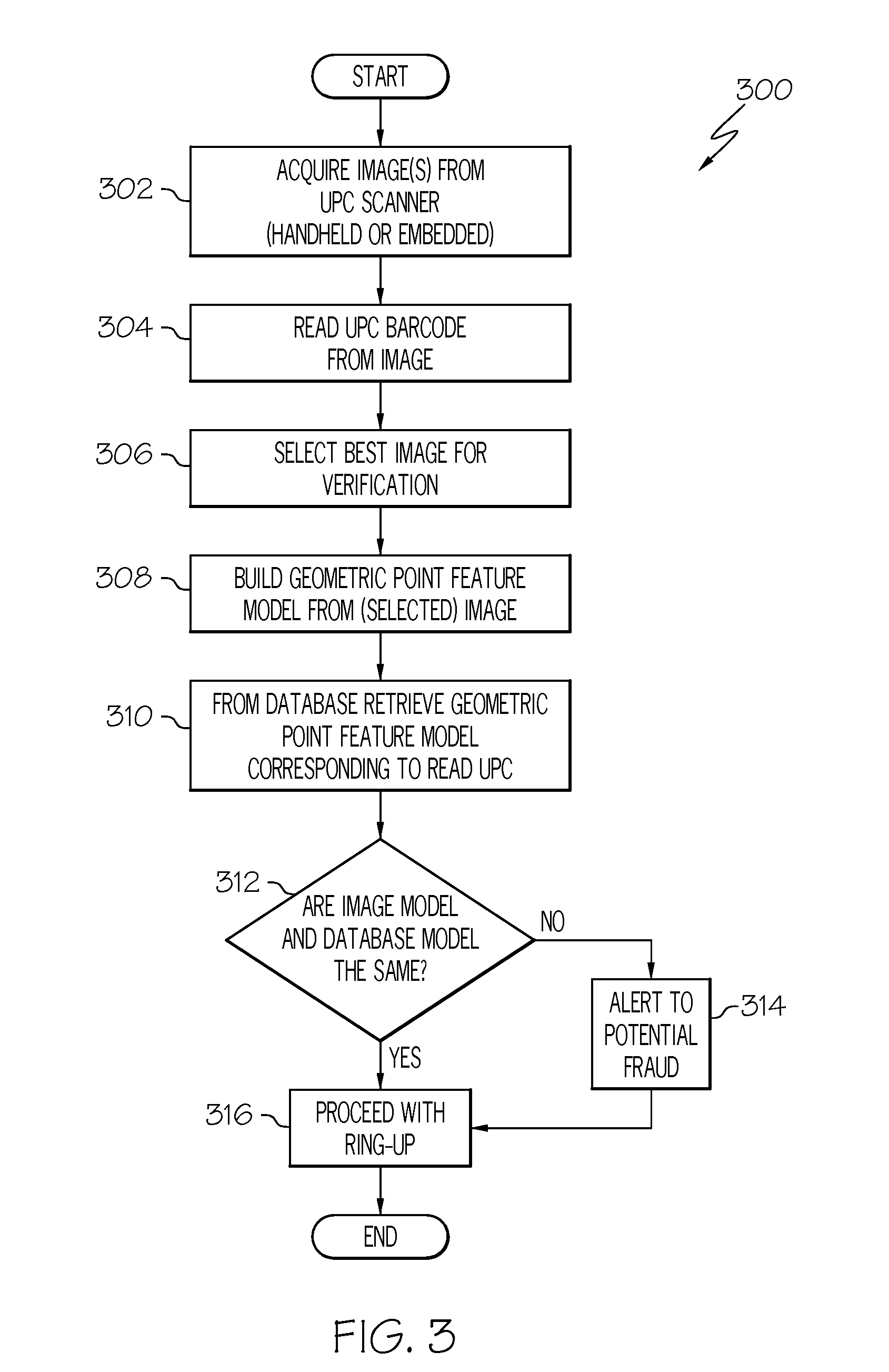
UPC substitution fraud prevention
A system and method for detecting fraudulent identification tags, such as Universal Product Codes (UPC) applied to goods to be purchased is disclosed. Images of the goods to be purchased and corresponding feature models are stored in a database. When a customer desires to purchase an item containing a UPC, a scanned image of the item about to be purchased may be acquired and a feature model of the scanned image may be created. The system may retrieve from the database the image and feature model previously stored for the item associated with the just-scanned UPC. A variety of image processing techniques may be used to compare the scanned and database images and / or the scanned and database feature models. In one embodiment, these image processing techniques may include determining a geometric transformation that maps the features of the scanned image onto the features of a database model.
Owner:DATALOGIC ADC
Image retrieval method based on interest target
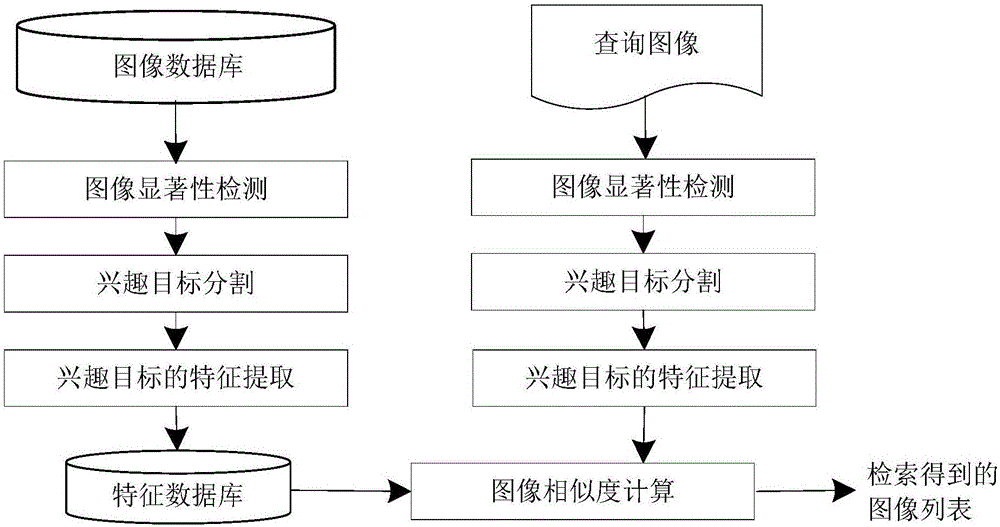
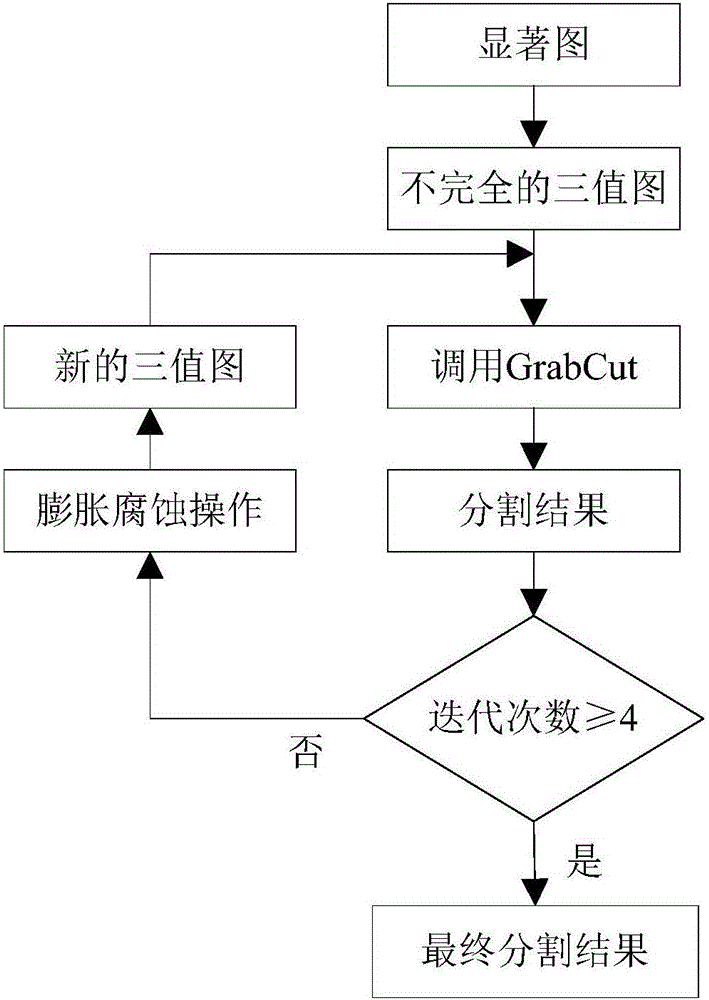
ActiveCN106649487AInhibition effectImprove recallCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSemantic featureRetrieval result
The invention relates to an image retrieval method based on an interest target. The method comprises the first step of analyzing the interest target of a user according to an HS saliency detecting algorithm, and combining a SaliencyCut algorithm to segment the interest target; the second step of extracting an HSV color feature, an SIFT local feature and a CNN semantic feature from the interest target of the user; the third step of conducting feature similarity matching between the extracted features of the interest target and a database image, and obtaining a retrieval result based on the interest target according to the rank of similarity. By extracting the features merely in the regions of the interest target, an influence of a background on the retrieval result can be effectively inhibited, and the recall ratio and the precision ratio of the retrieval can be increased.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Systems and Methods for Localized Bag-of-Features Retrieval
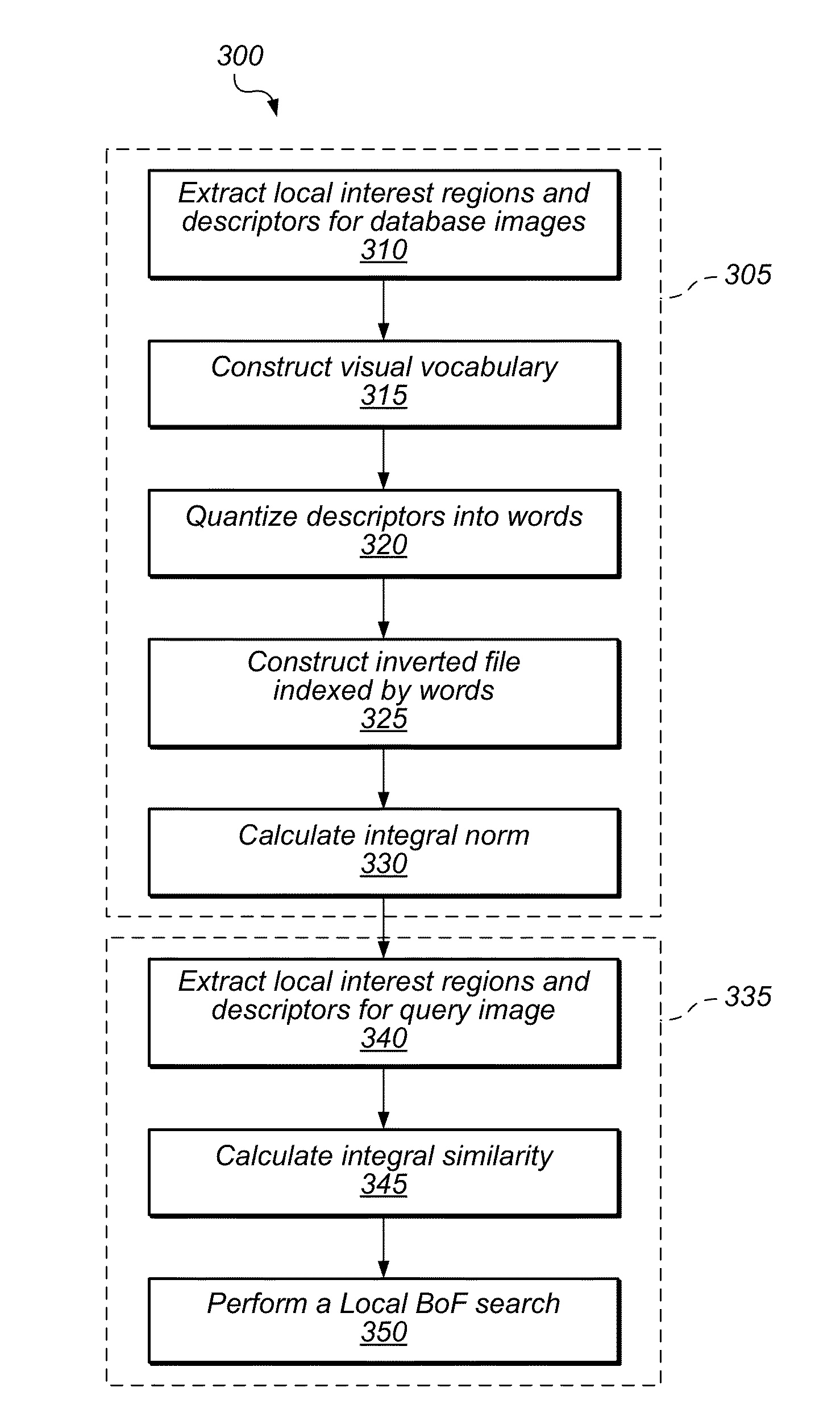
InactiveUS20130132377A1Reduce computational overheadLocalized similarities to be computed very efficientlyDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsPattern recognitionViewpoints
Methods and systems for performing fast, large-scale, localized Bag-of-Features (Local BoF) retrieval are disclosed. In some embodiments, a method may include receiving a query image and ranking each image of a large set of database images as a function of its similarity to the query image with a Local BoF operation. A Local BoF operation may be configured to localize, for each ranked image, a region that has a highest similarity to the query image. As such, the systems and methods described herein may be suitable for use in large-scale image search and retrieval or categorization operations that may identify objects of interest with arbitrary rotations, significantly different viewpoints, in the presence of clutter. In some embodiments, systems and methods described herein may be used as building blocks of various computer vision and image processing applications including, for example, object recognition and categorization, 3D modeling, mapping, navigation, gesture interfaces, etc.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Method and system for building a database from backup data images
InactiveUS7840539B2Less table spacePromote recoveryError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsData storeStorage cell
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
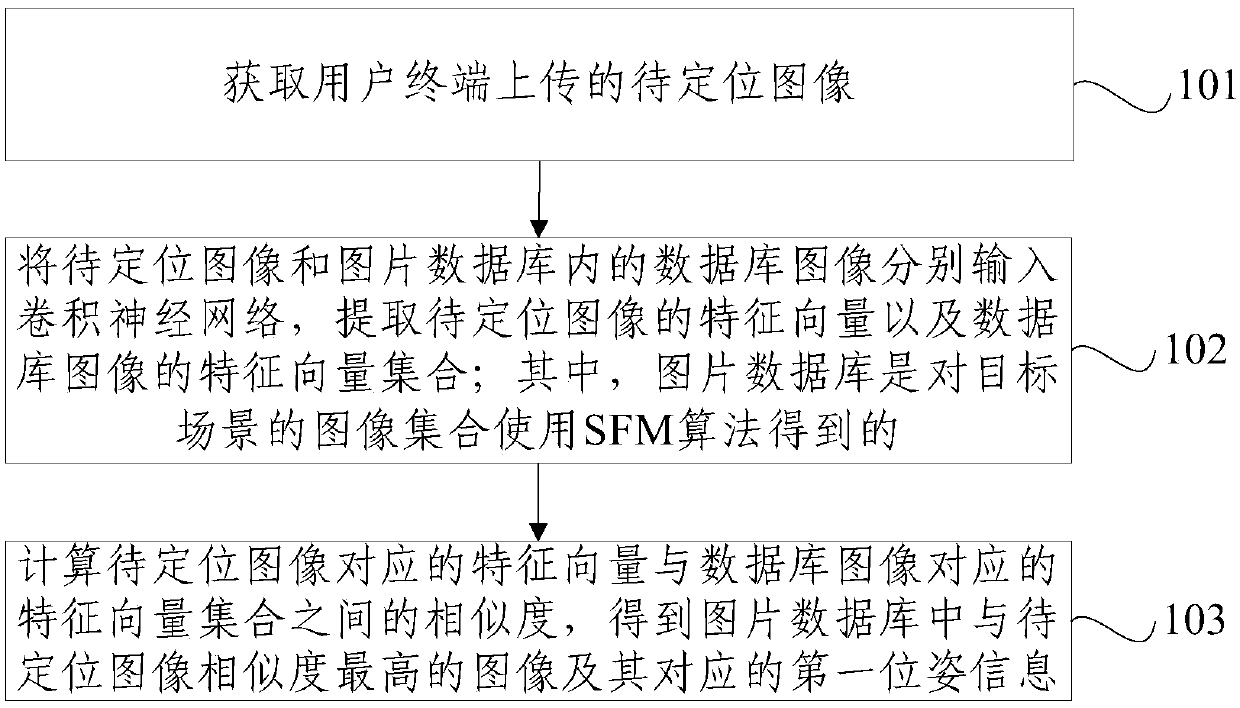
An indoor positioning method and device based on SLAM
InactiveCN109671119AImprove recognition accuracyAccurate acquisitionImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorNeural network learning
The embodiment of the invention provides an indoor positioning method and device based on SLAM. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a to-be-positioned image uploaded by a user terminal, constructing a picture database with pose information rapidly through an SFM algorithm; extracting a feature vector of a to-be-positioned image and a feature vector set of a database image through a convolutional neural network; calculating the similarity between the feature vectors of the to-be-positioned image and the database image, completing loopback detection, and obtaining the image with the highest similarity with the to-be-positioned image in the image database and the first pose information corresponding to the image, thereby obtaining the accurate position and pose information of the userterminal. Compared with a traditional visual SLAM algorithm which adopts a word bag model and is weak in recognition capability, the deep features of the image are learned through the neural network,the higher recognition accuracy can be achieved, and the accuracy of loop detection is improved.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ultrasound acquisition feedback guidance to a target view
Guidance in acquiring ultrasound imaging of a subject to achieve a target view, such as a standard view, entails emitting ultrasound to the subject and receiving, in response, a current ultrasound view (502);matching the received image to a pre-existing image, such as a three-dimensional reference image (503); and, for user assistance, generating, based on the matching, feedback (514-528) for the guidance. The reference image may be a statistical atlas or it may be derived from patient-specific CT or MR scans. The pre-existing image may instead stead be a database image corresponding to a state in a state space. The feedback can be an image derived from the reference image;a graphic indication (508) of a plane of the target view; the received view fused (512) to an image derived from the reference image; or the received view and an image derived from said reference image, the derived image appearing concurrently and enhanced to spatially indicate where the received view registers to the reference image. The target view (510) may be a view of a body organ, or vessel,of the subject. Both the atlas and database can be specialized for imaging of an organ,or vessel, and its surrounding tissue.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Binocular visual indoor positioning method based on logo
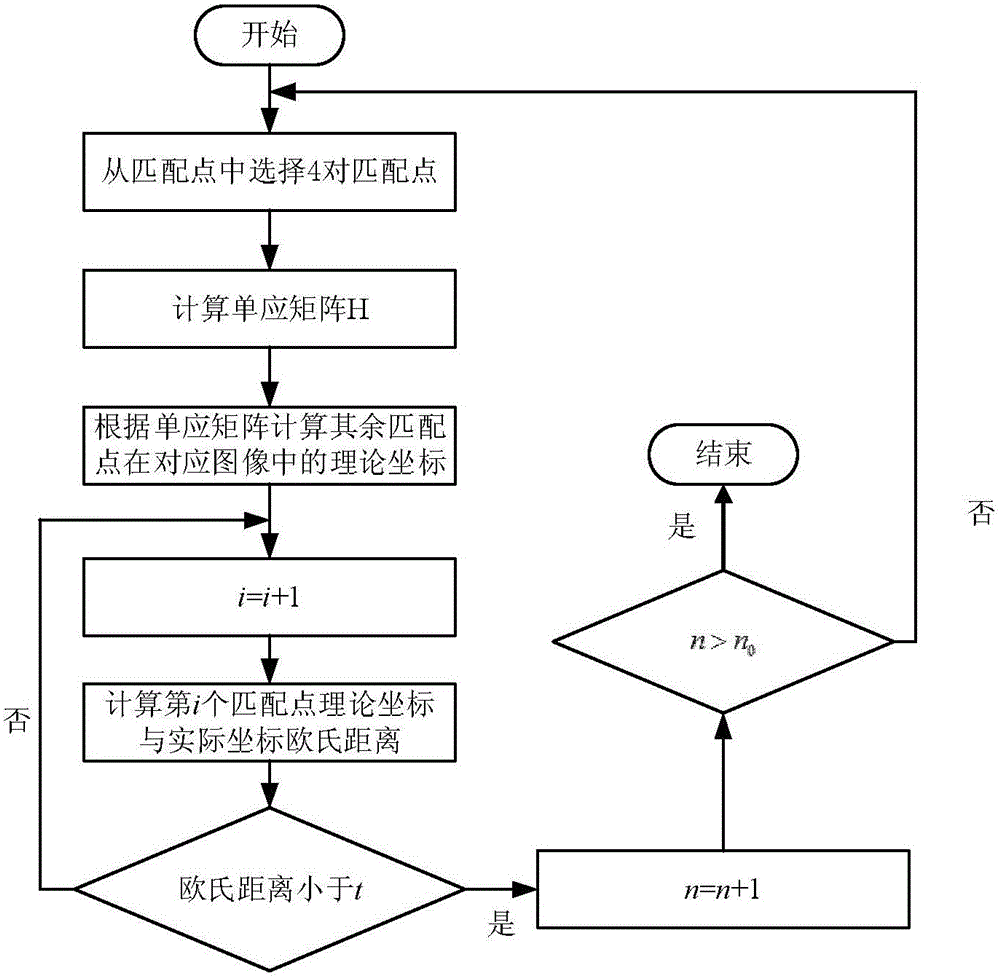
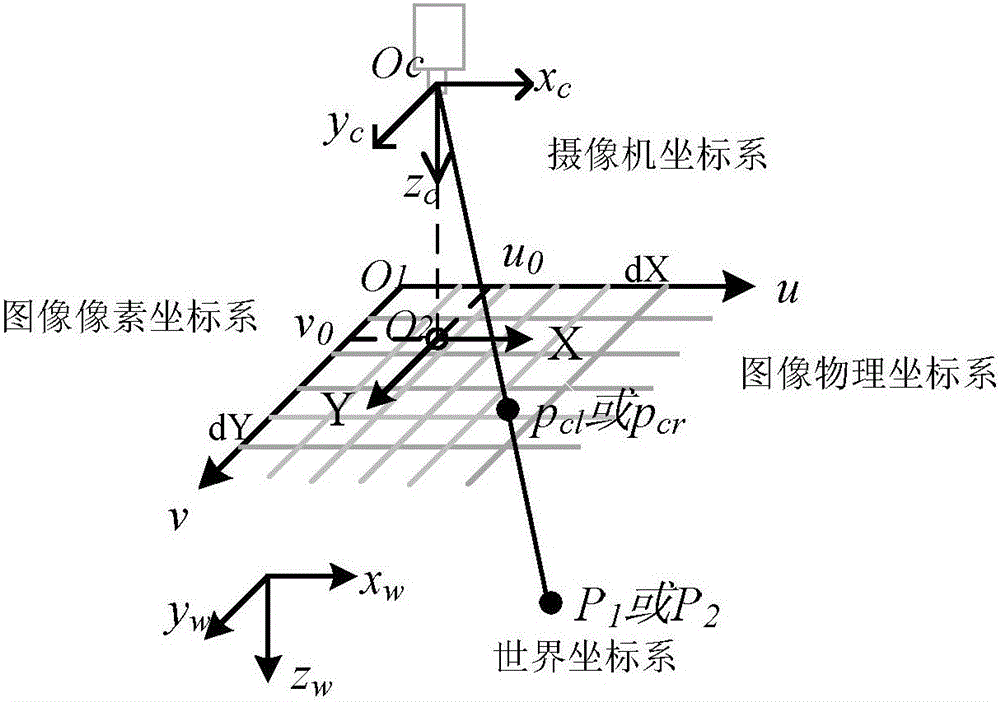
The invention provides a binocular visual indoor positioning method based on logo, and relates to the binocular visual indoor positioning method. The binocular visual indoor positioning method based on logo aims at the problems in the prior art that target three-dimensional information is not easily extracted through a monocular manner. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a visual map database through logo image acquisition is established; secondly, the internal parameters and the external parameters of a left video camera and a right video camera are solved; thirdly, logo images are photographed by using a binocular video camera, and logo image visual information characteristics are matched with Visual Map database image visual information characteristics; matching points are reserved and mismatching points are eliminated; fourthly, the three-dimensional coordinates of vertexes P1 and P2 are calculated; and fifthly, the coordinates of the left video camera under a world coordinate system are solved. The binocular visual indoor positioning method based on logo is applied to the field of the binocular visual indoor positioning method.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED MEDICAL DEVICES SHENZHEN
Relational Compressed Database Images (for Accelerated Querying of Databases)
InactiveUS20080133573A1Answered efficientlyEfficient storageDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsData setData mining
The invention relates to a data bank interrogation system, wherein two or more data bank tables are linked by means of a common key or several keys which are respectively common to at least two data bank tables. In an analysis query and a selection of data sets in the first data bank, a selection of data sets is determined in the second data bank corresponding to the selection according to the common key and the analysis query is answered using the thus selected data sets in the second data bank.
Owner:PANORATIO DATABASE IMAGES
A compact Hash code learning method based on semantic protection
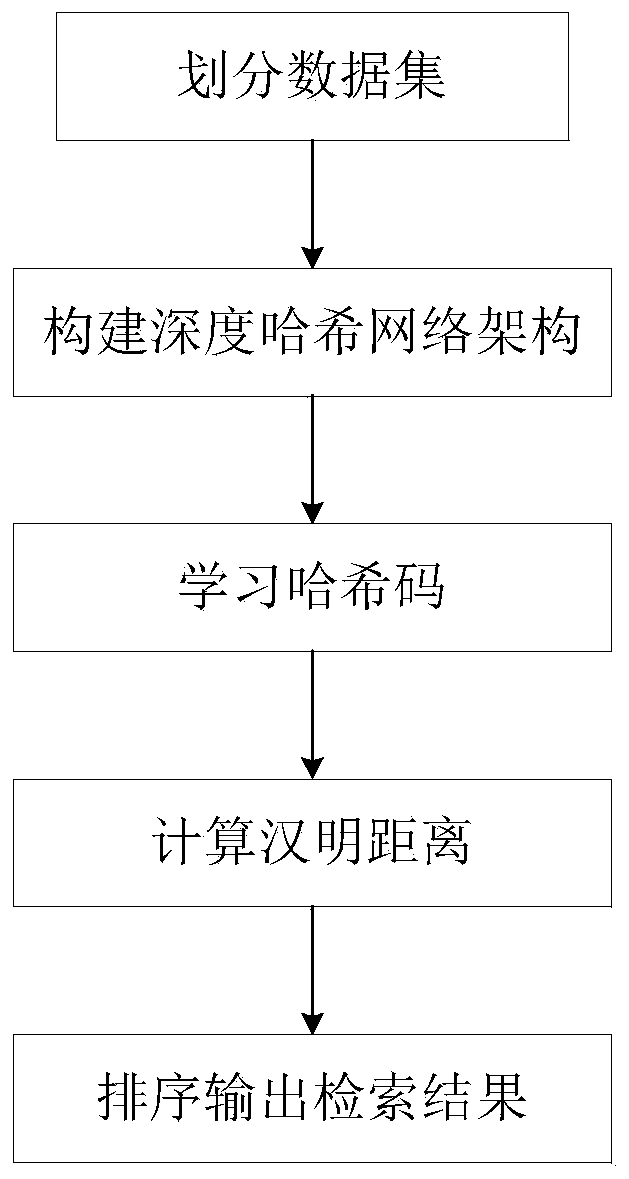
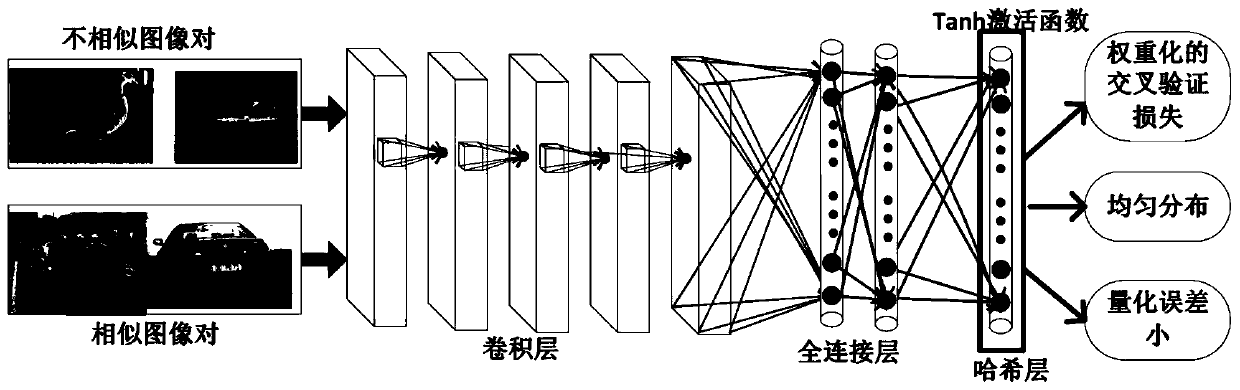
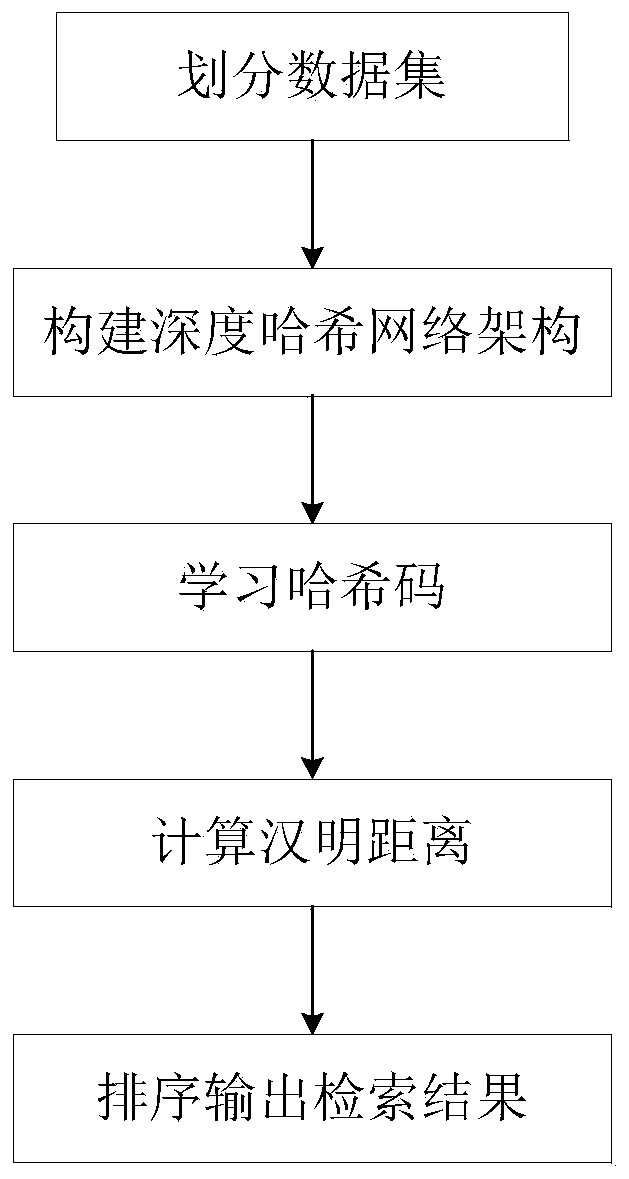
InactiveCN109918528APreserving Semantic SimilarityGreat Hamming distanceStill image data indexingNeural architecturesHidden layerData set
The invention provides a compact Hash code learning method based on semantic protection, and the method comprises the steps: dividing a data set, and obtaining a test sample set, a training sample set, and an image library; then constructing a deep Hash network model; adding a hidden layer (Hash layer) to the last full connection layer of a common convolutional neural network model, the number ofneurons of the hidden layer is the length of Hash codes, an activation function is a panh function, designing a constraint function, protecting the semantic similarity of images, and meanwhile it is guaranteed that the learned Hash codes are evenly distributed and the quantization error is small; extracting Hash codes of the query image and the database image through the trained model, and calculating Hamming distances between the Hash codes of the image and the Hash codes of all the images in the database; and finally, sorting the Hash codes in the database according to a sequence of distances from small to large, and sequentially outputting the original images corresponding to the Hash codes to obtain a similar image retrieval result. According to the method, retrieval of large-scale images is more accurate and effective.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Video indexing and image retrieval system
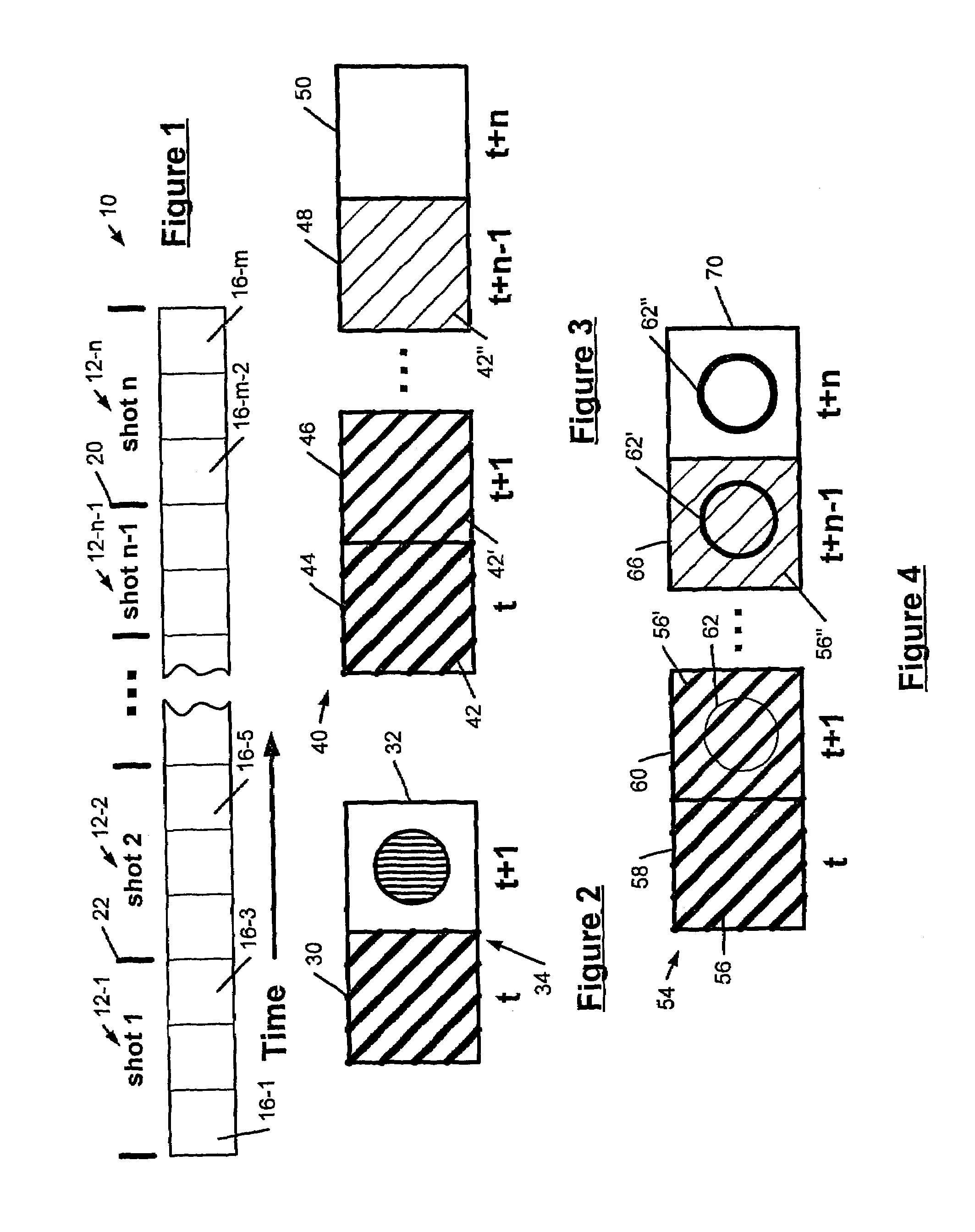
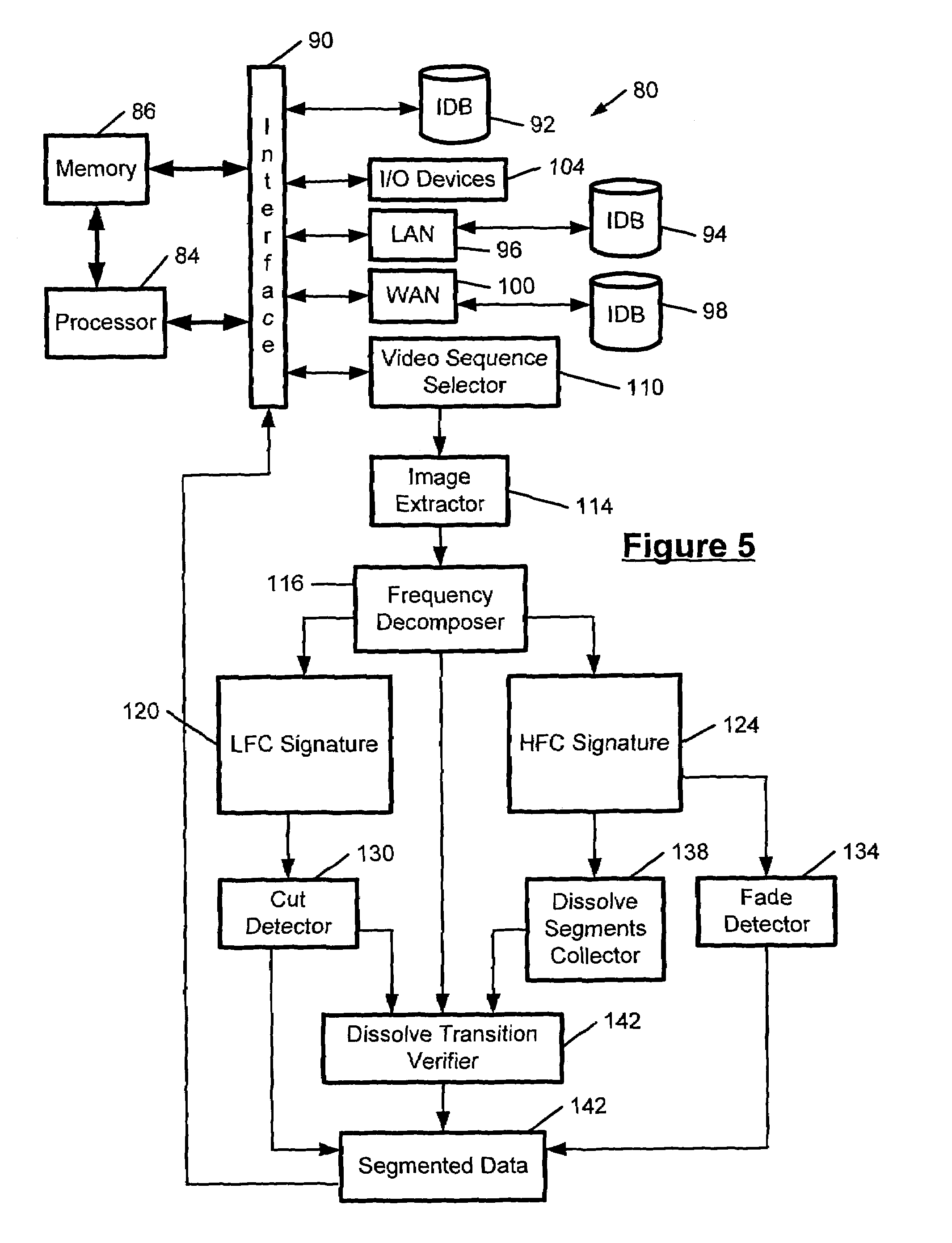
InactiveUS7042525B1Increase available bandwidthIncrease storage capacityTelevision system detailsImage analysisVideo retrievalDecomposition
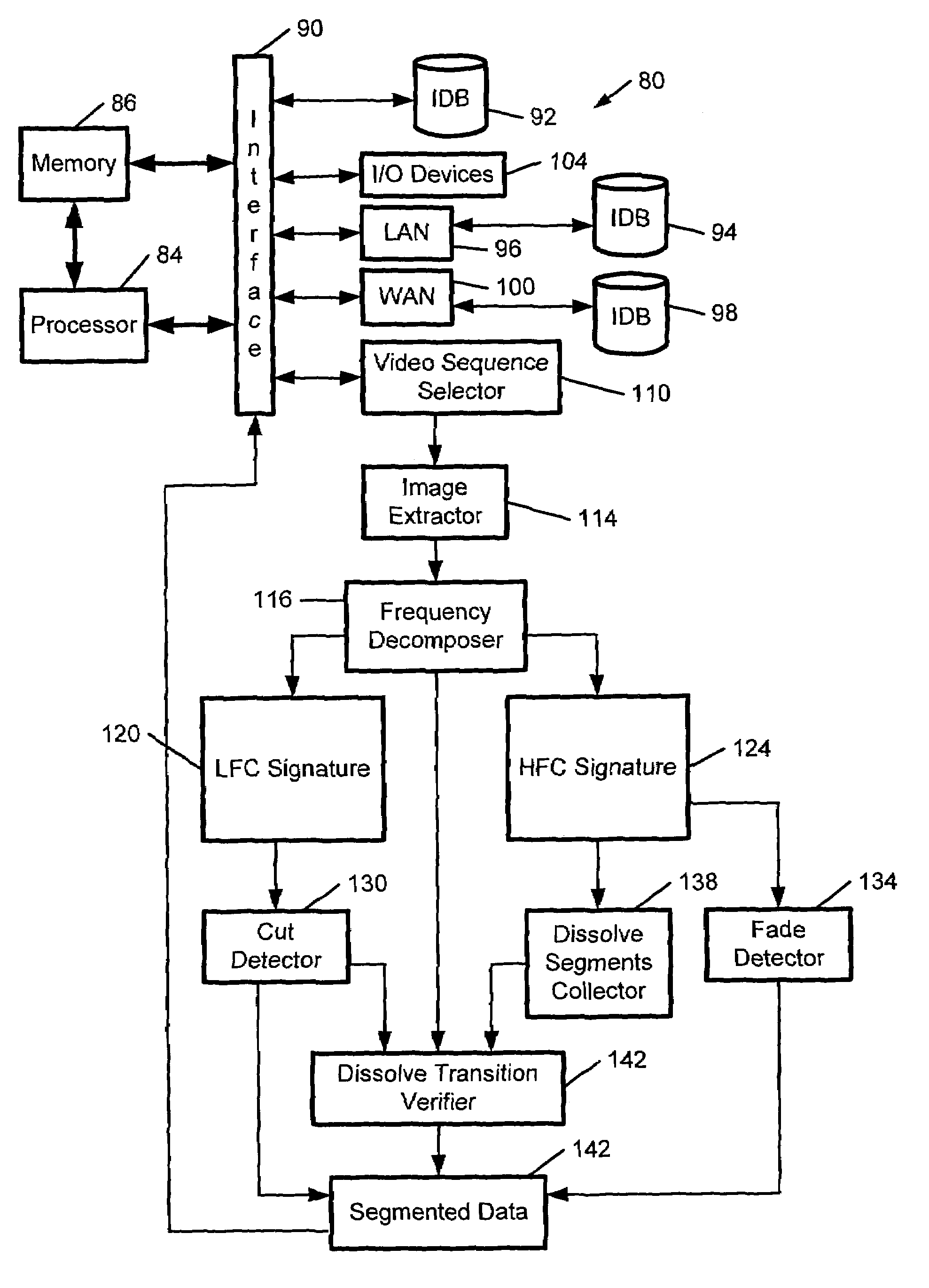
A video segmentation system generates an S-distance measurement that is a representation of the similarity between adjacent frames of a video sequence. The video segmentation system employs frequency decomposition of a direct current (DC) luminance signal of a compressed video sequence. High and low frequency component signatures are generated from a frequency-decomposed signal using wavelet transformation. A cut detector identifies cut transitions from the low frequency component signature. A fade detector identifies fade transitions the high frequency component signature. A dissolve transition detector employs a double frame differencing algorithm to identify dissolve transitions. A video retrieval system likewise generates an S-distance between a query image and a database image. The video retrieval system employs the low and high frequency component signature to generate the S-distance measurement of the similarity between the query image and the database image. The results of the S-distance measurement allow browsing and searching of the similar database images.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Image classification and searching method based on geographic position characteristics and overall situation vision characteristics
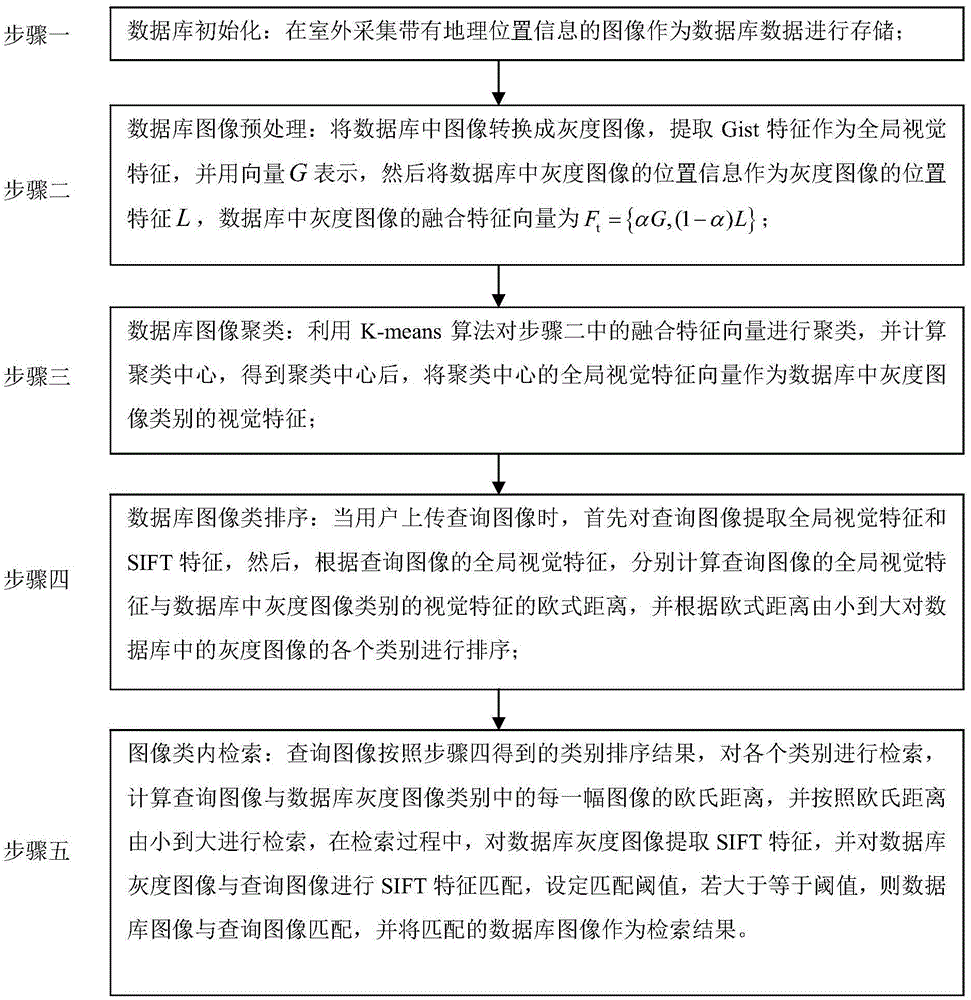
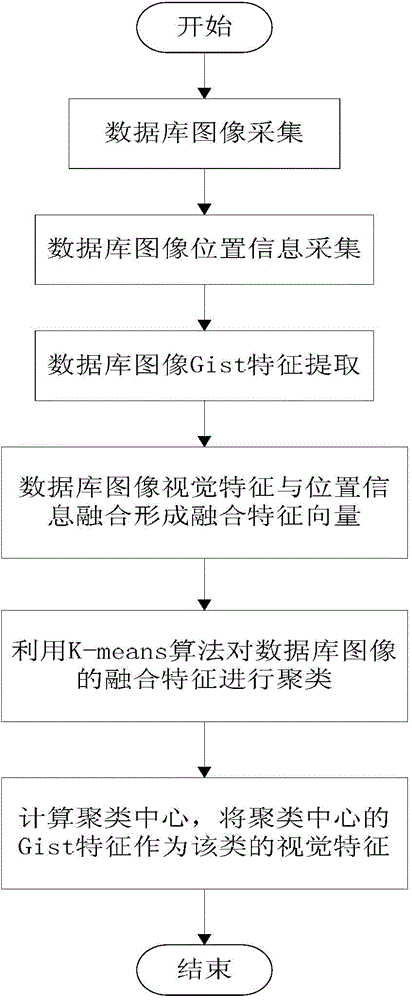
ActiveCN104820718AImprove classification accuracyHigh precisionStill image data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsGeographic siteGeolocation
The invention relates to an image classification and searching method and provides the image classification and searching method based on geographic position characteristics and overall situation vision characteristics. The image classification and searching method aims at solving the problems that the precision is low when an existing outdoor image is subjected to scene classification by vision characteristics and a lot of time for an image searching process is spent along the gradual enlarging of a database scale, the instantaneity of a navigation positioning algorithm is influenced, and the position service requirements of a user cannot be guaranteed. The image classification and searching method is realized through the following technical scheme: step 1, initializing a database; step 2, pre-processing a database image; step 3, gathering the database image; step 4, sorting a database image type; and step 5, searching in the image type. The image classification and searching method is applied to the field of computer vision and image processing in an information technology.
Owner:严格集团股份有限公司
Fingerprint identification method combining point with line
InactiveCN101329727AImprove reliabilityReduce the impactCharacter and pattern recognitionLength weightImage matching
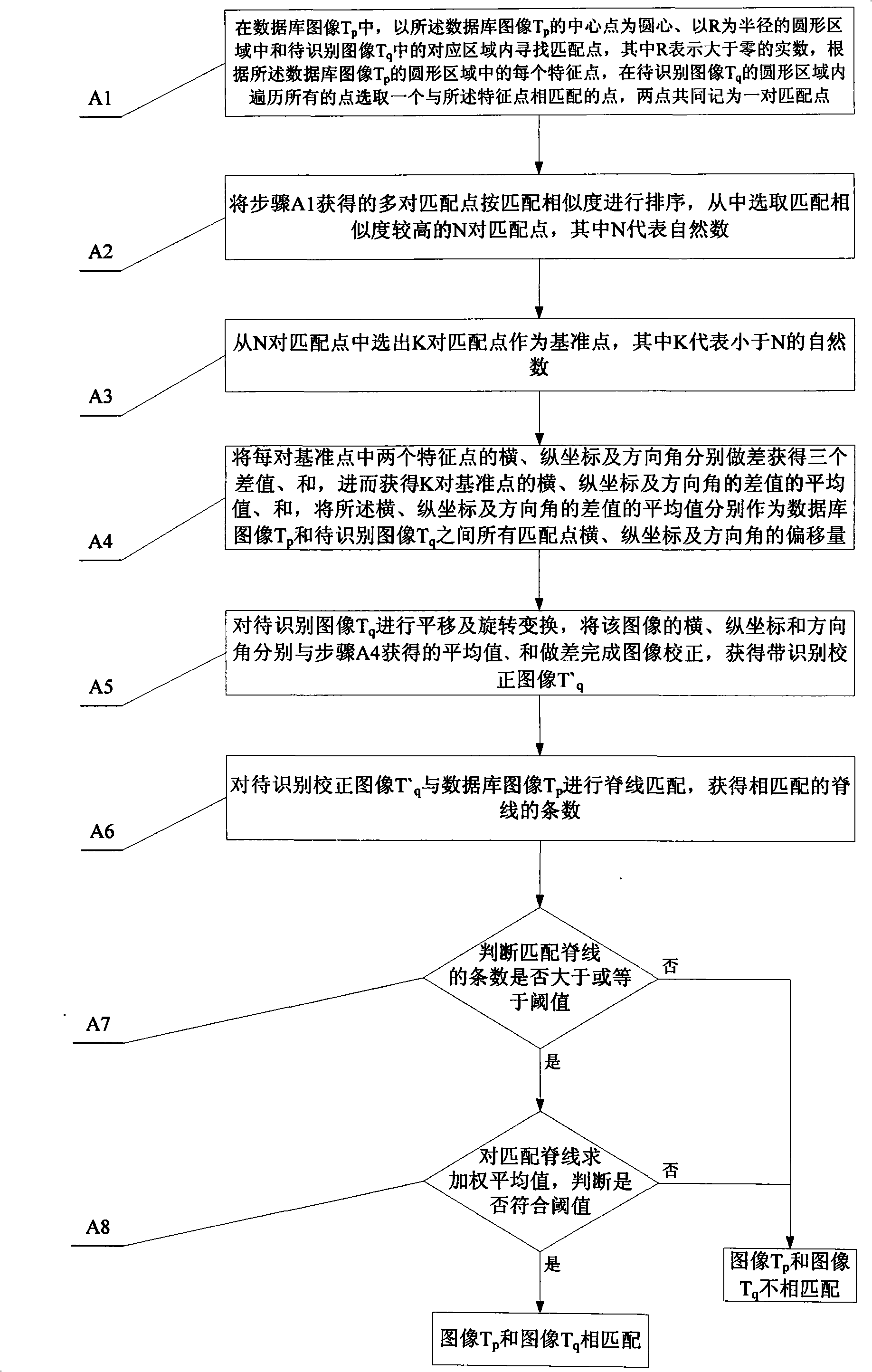
The invention discloses a fingerprint identification method by using the joint of lines and points, which relates to a fingerprint identification method by using the joint of lines and points so as to solve the problems that the existing fingerprint identification method using dot matching easily leads to wrong identification, is greatly affected by fake characteristic points and has relatively poor noise immunity, and the fingerprint identification method using line matching has relatively large calculation work and low identification speed. All matching points in a database image Tp and an image Tq to be identified are selected; sorting is carried out to a plurality of obtained matched points according to matching similarity, and N pairs of matching points with the highest matching similarity are selected; K pairs of matched points are selected from the N pairs of matched points to serve as reference points; the difference between the X-axis and Y-axis and a direction angle is obtained to serve as the offset of two images; translation and rotation transformation are carried out to the image Tq; after correction, the ridge lines of the image Tq and the image Tp mutually match; the matched number is recorded; if the length weighted average value of all matched ridge lines meets a threshold value, the image Tp is identified to match with the image Tq; otherwise, the image Tp is identified not to match with the image Tq.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
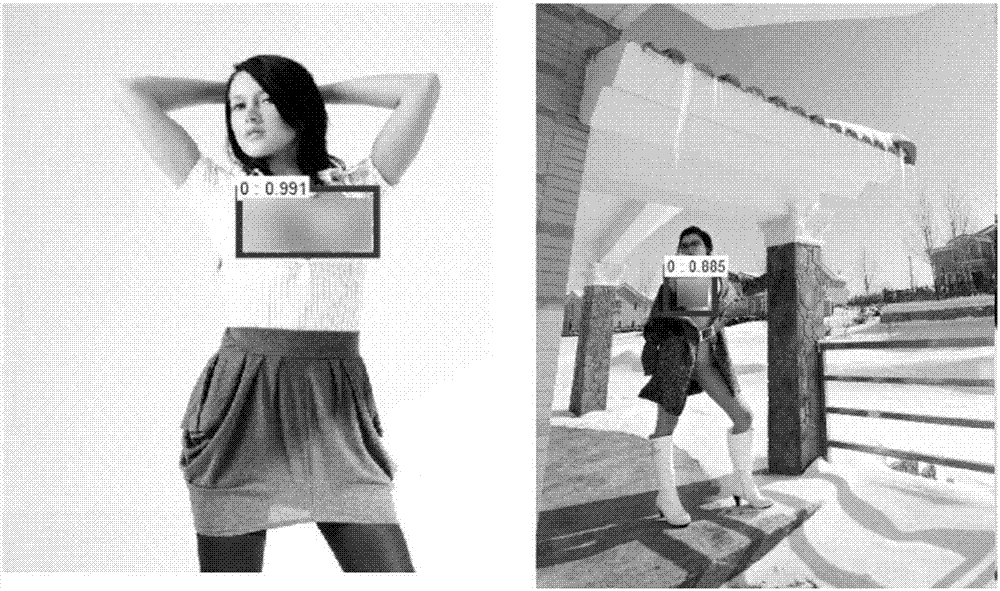
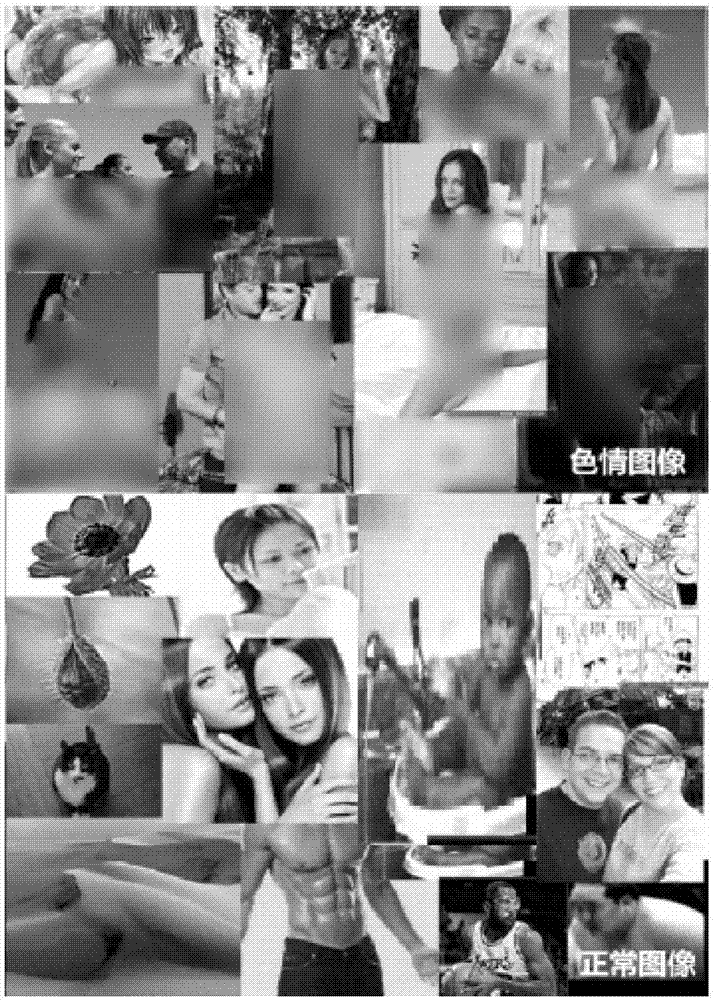
Pornographic image identification method based on multi-step identification and fusion key portion detection
InactiveCN107330453AGood for classification performanceConsistent Intraclass FeaturesCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsVisual technologyImaging processing
The present invention provides a pornographic image identification method based on multi-step identification and fusion key portion detection, belonging to the design image processing and computer vision technology field. The method comprises: employing a network spider technology and a data augmentation method to construct a pornographic image database; employing a database to perform fine regulation of a GoogLeNet network, and obtaining an image cartoon / non-carton dichotomy model; employing a residual network to perform fine regulation on a selected training set, and obtaining the normal / pornographic dichotomy model of a carton-type image and the normal / pornographic dichotomy model of a non-cartoon image; and finally performing marking of a naked chest for the database image, employing a target detection network Faster RCNN to perform training and obtaining of a chest detection model, and performing secondary identification of the detected chest through cascading of a classification network after the Faster RCNN so as to ensure the accuracy of the chest detection and allow a pornographic image having the naked chest and a small skin color area not to be undetected.
Owner:COMMUNICATION UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
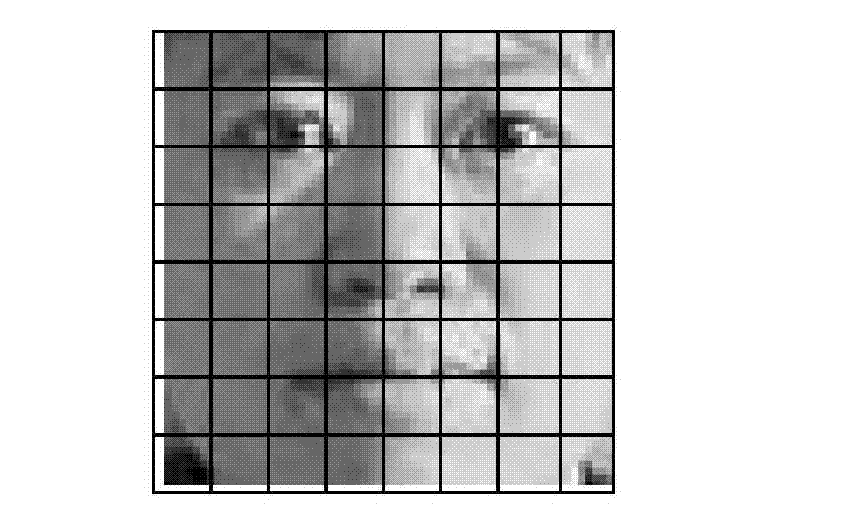
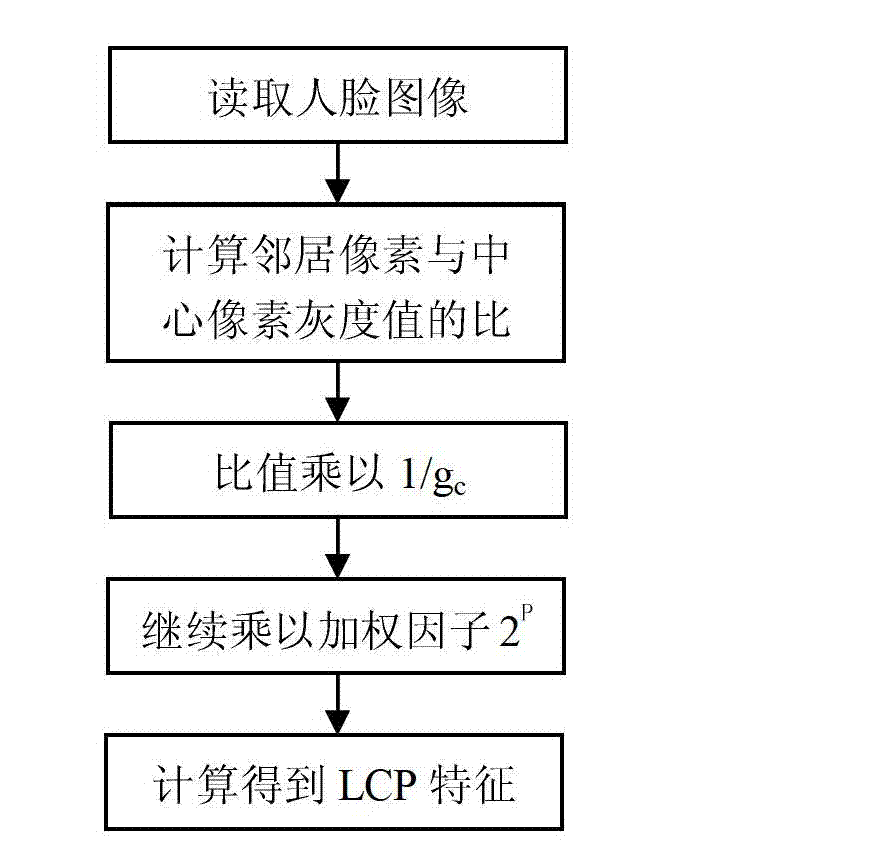
Human-face identification method based on local contrast pattern
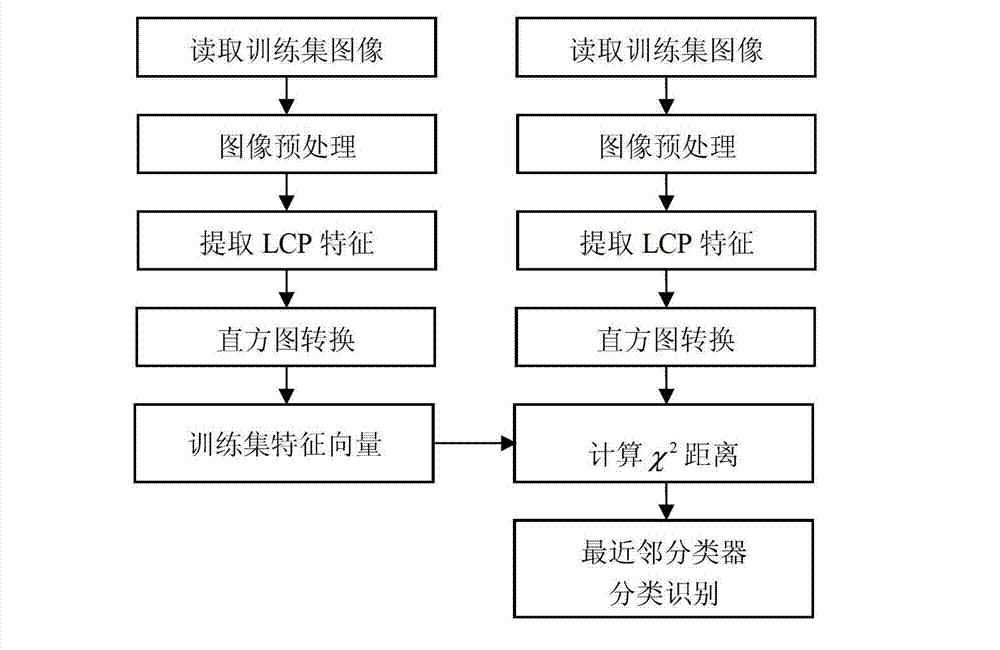
InactiveCN102779273AImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionNearest neighbor classifierTest set
The invention relates to a human-face identification method based on a local contrast pattern (LCP) and belongs to the technical field of pattern identification. The human-face identification method based on the LCP includes that human-face database images are preprocessed firstly so as to weaken influences of illumination on feature extraction; calculation of LCP feature matrixes is performed on training set images and testing set images respectively; the obtained LCP feature matrixes are converted into a column diagram; calculation of feature similarity of testing samples and training samples is performed on the column diagram by adopting a chi-square (X<2>) distance function; and the testing samples are classified and identified by using a nearest neighbor classifier. The human-face identification method based on the LCP has high human-face identification accuracy.
Owner:北京梅龙德科技发展有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com