Patents
Literature
43 results about "FGF Receptor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
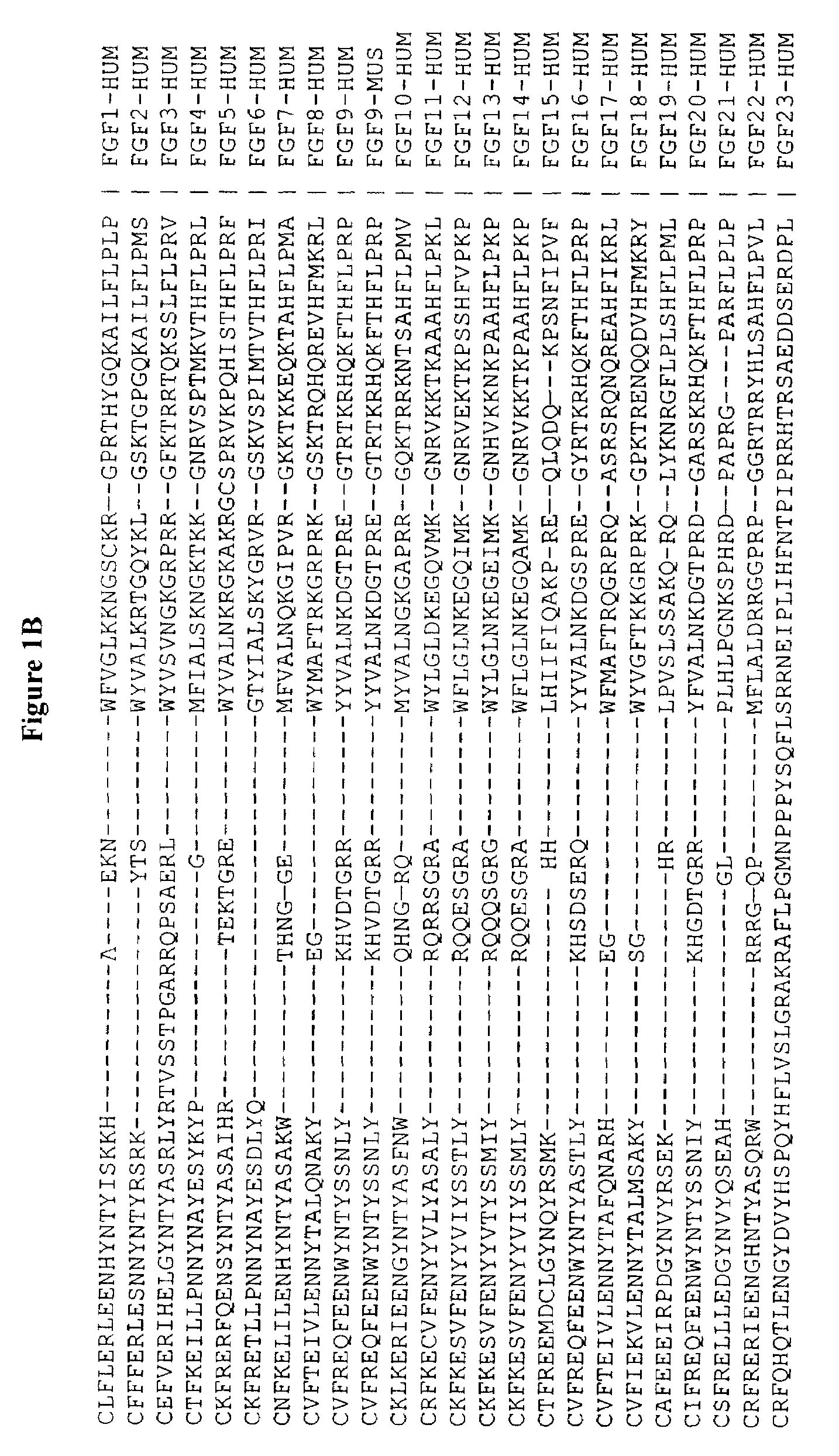
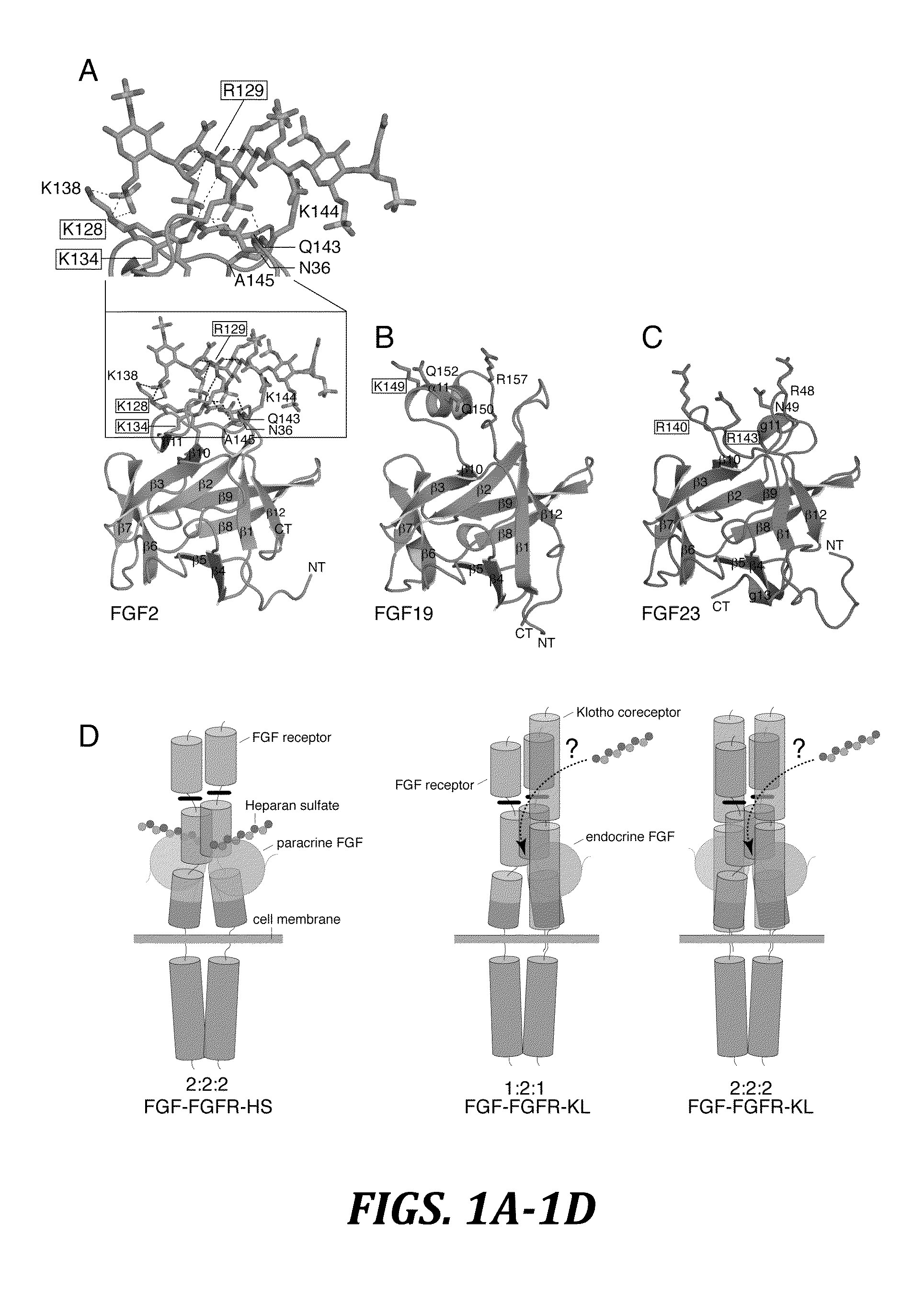
Active variants of FGF with improved specificity
InactiveUS7288406B2Enhanced receptor specificityImprove in vivo activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseReceptor subtype
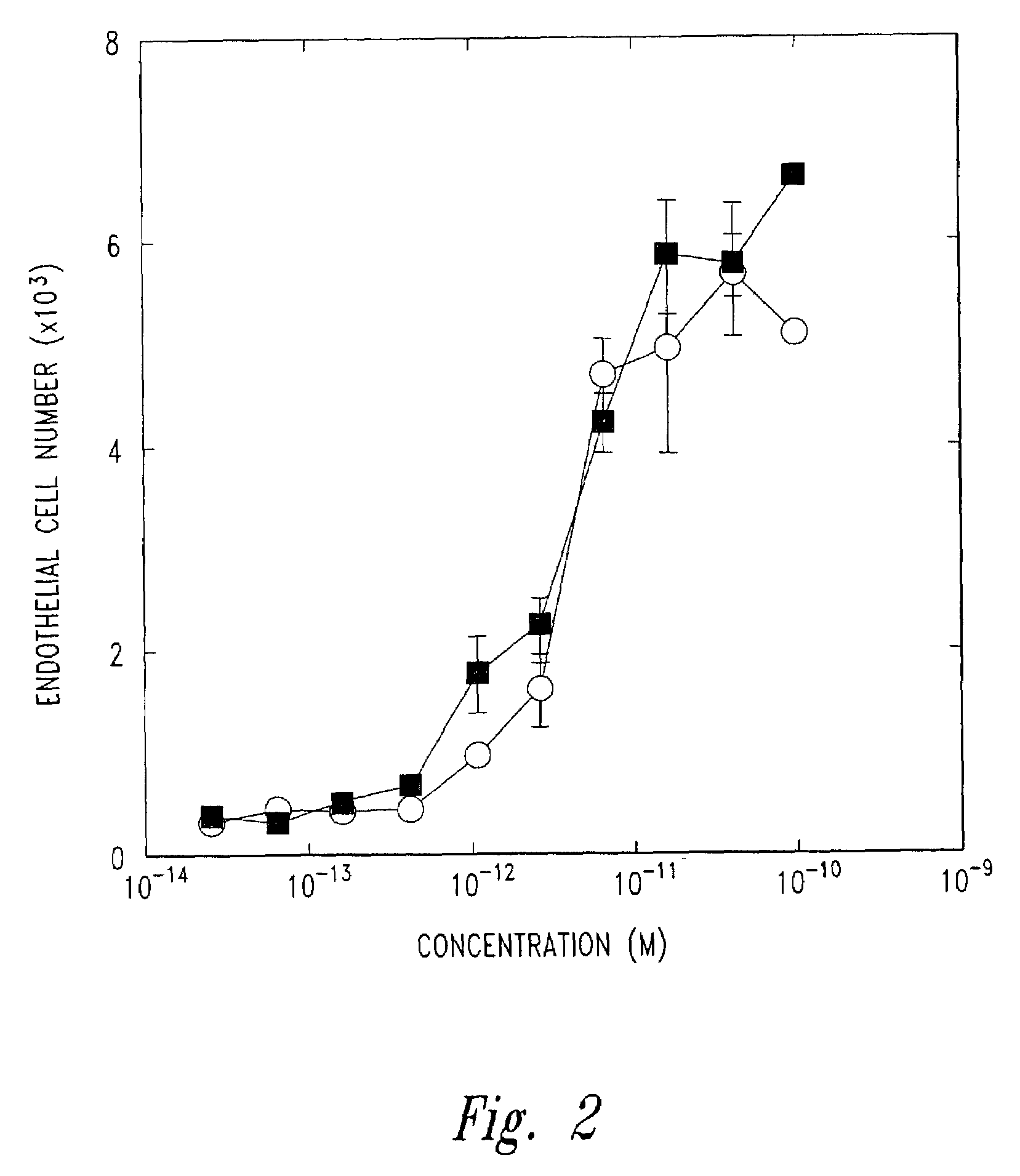
The present invention provides active fibroblast growth factor variants demonstrating enhanced receptor subtype specificity. The preferred novel variants retain binding to FGF Receptor Type 3 (FGFR3) triggering intracellular downstream mechanisms leading to activation of a biological response. Methods of utilizing preferred FGF mutants in preparation of medicaments for the treatment of malignancies and skeletal disorders including osteoporosis and enhancing fracture healing and wound healing processes are provided.
Owner:PROCHON BIOTECH
Method for activating receptor by cofactor and method for utilizing ligand activity
InactiveUS20100184665A1Increase and inhibits activityExcellent screening systemCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsCell systemBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
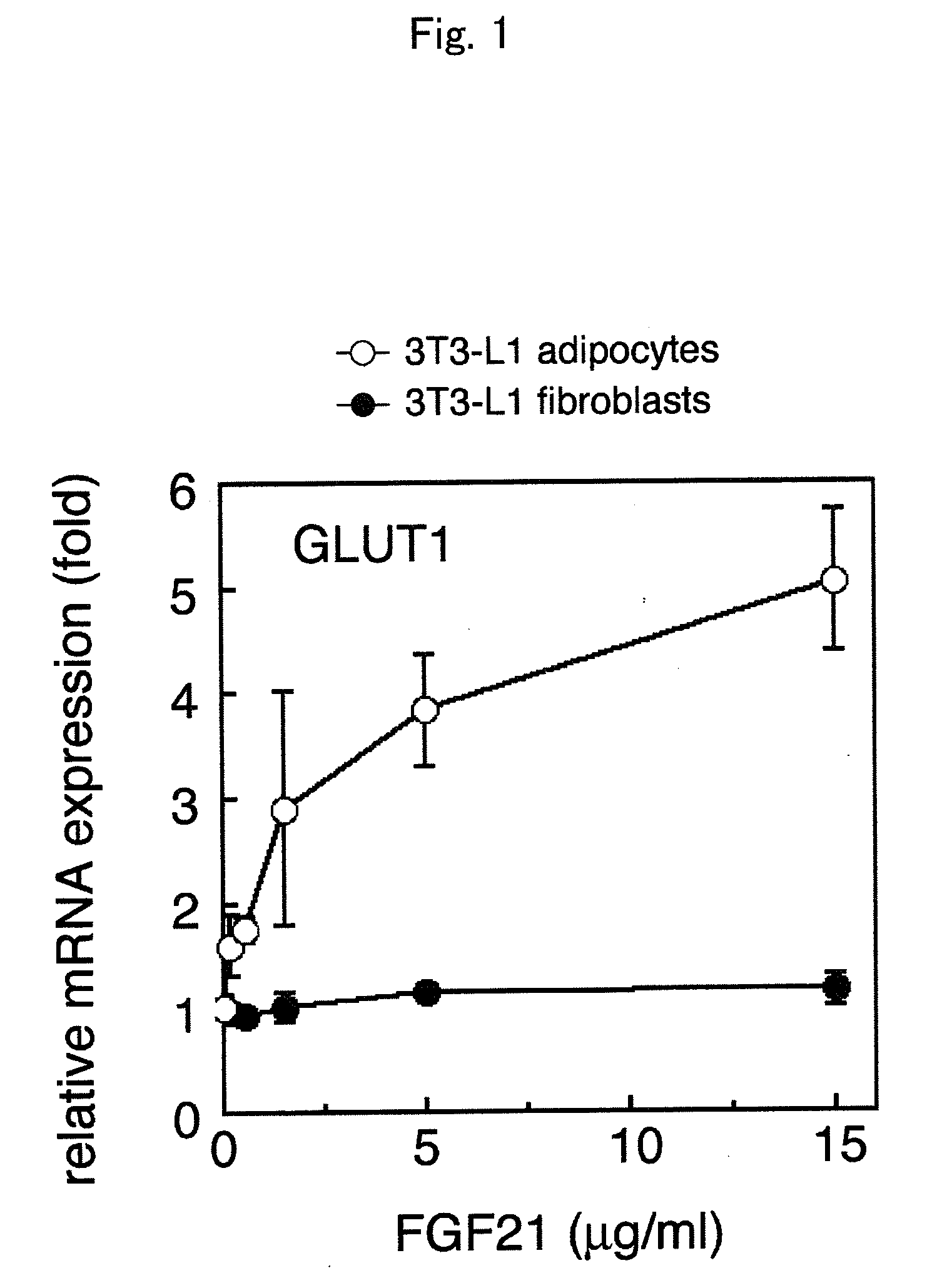
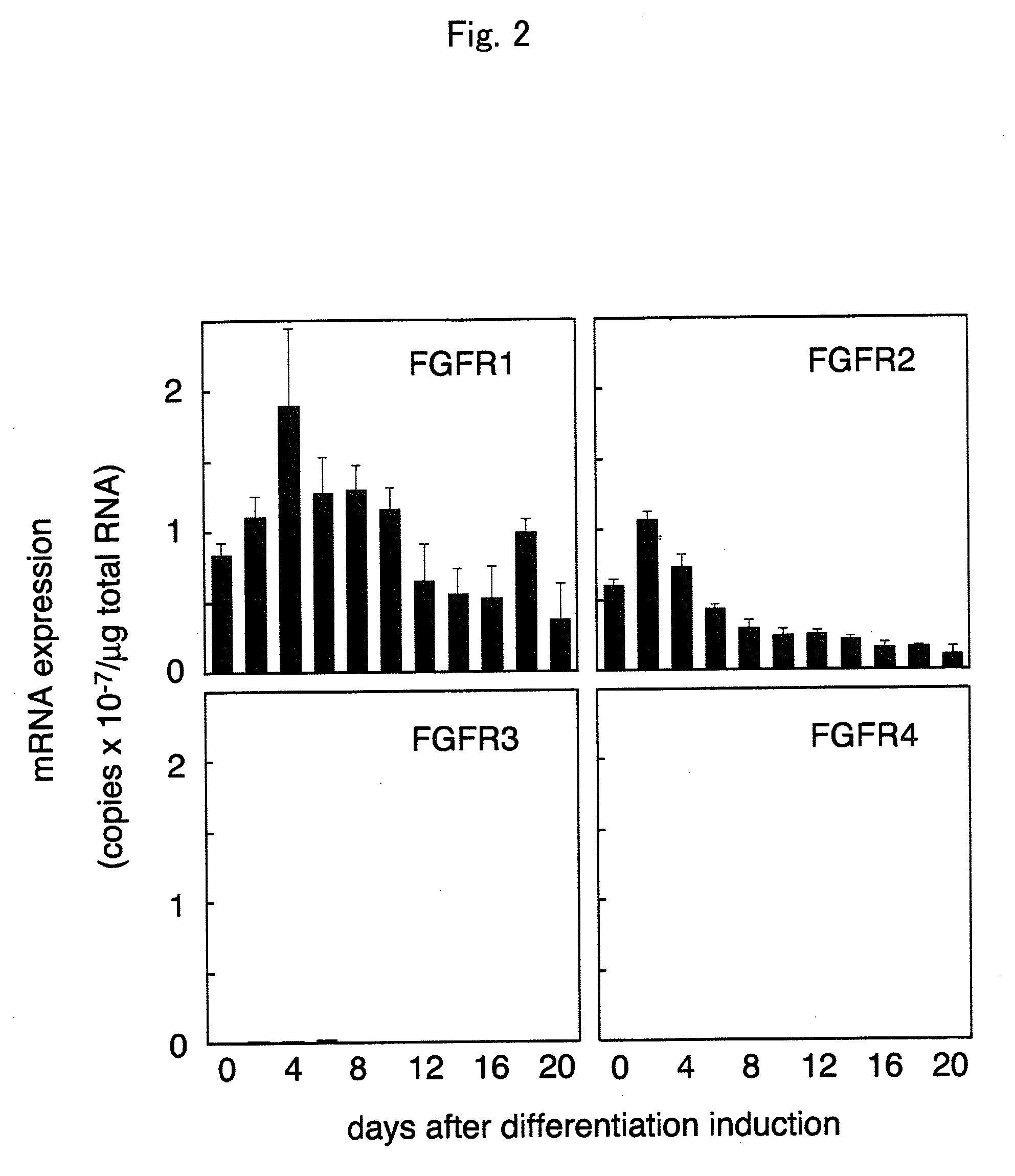
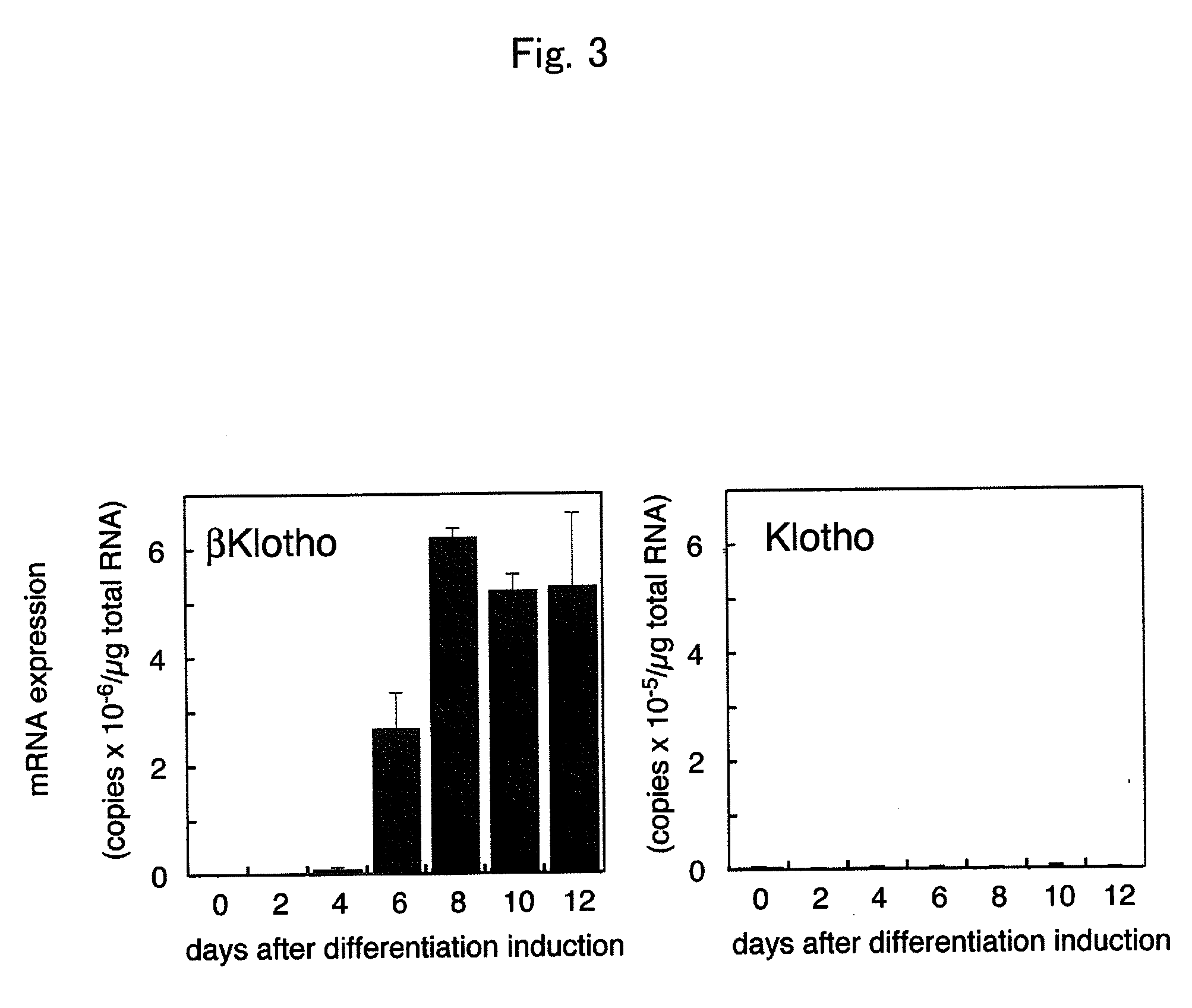
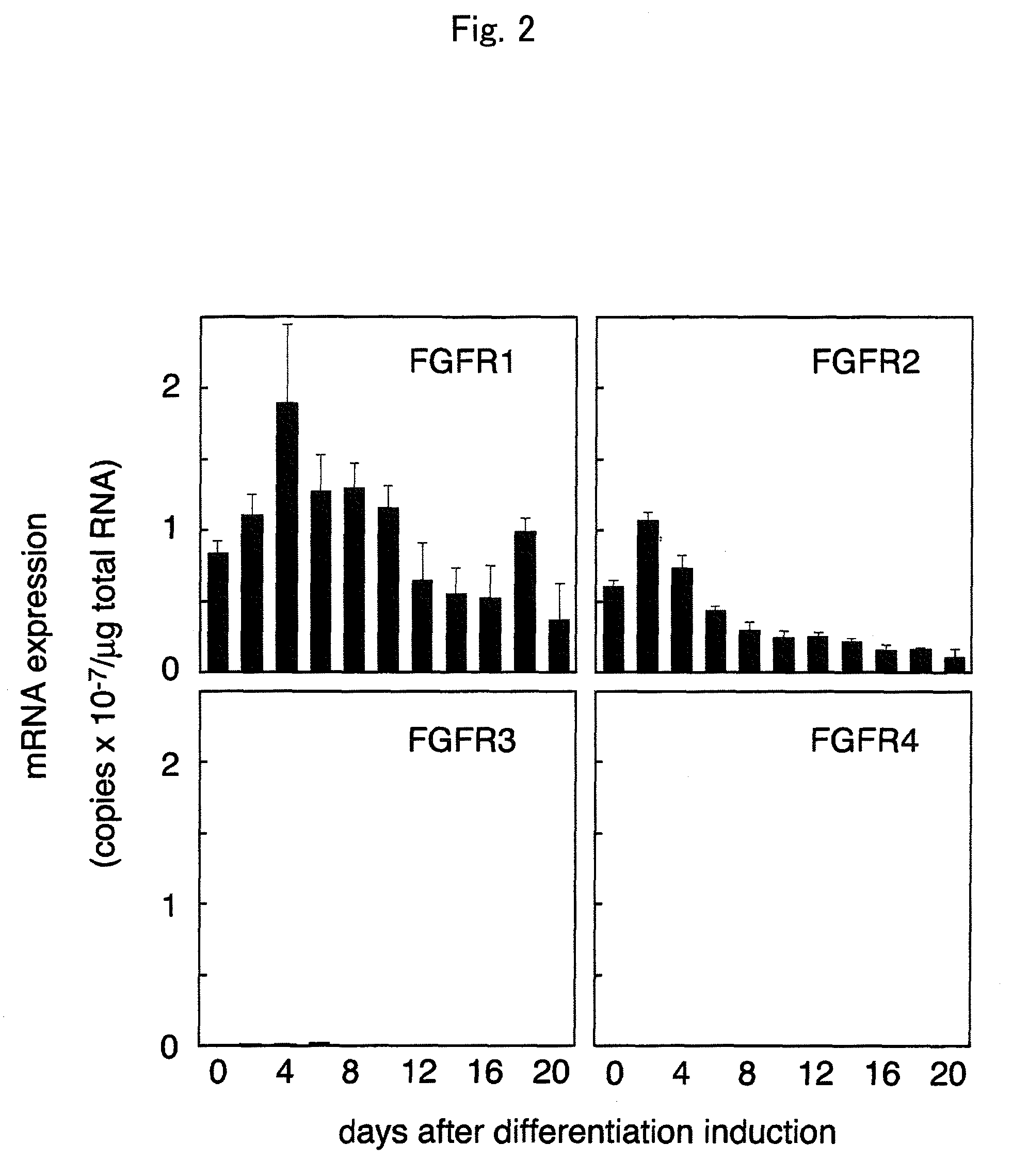
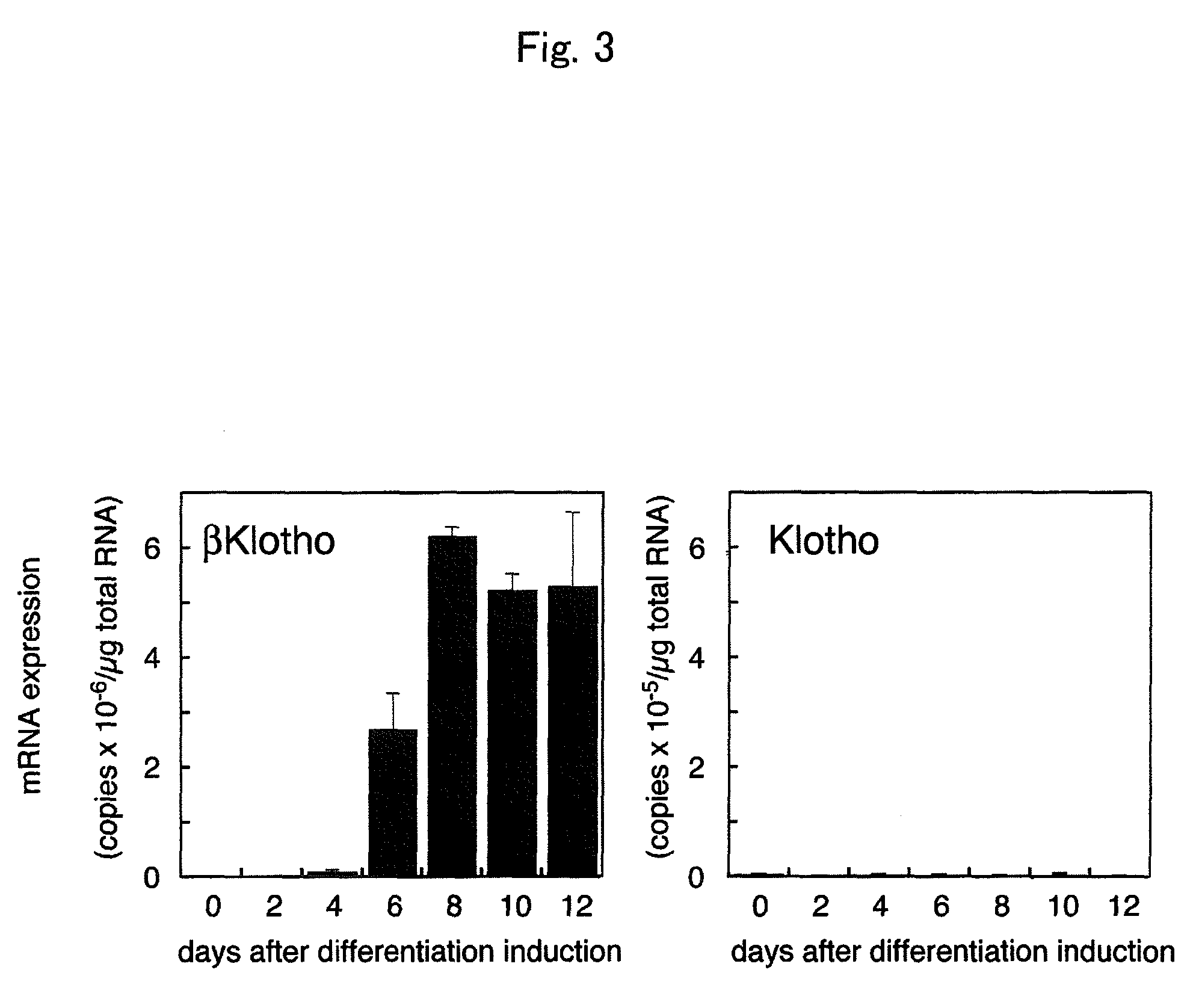
Using betaKlotho or a substance that increases or inhibits betaKlotho activity as an agent for controlling the activity of FGF21 mediated by an FGF receptor, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising such betaKlotho or such substance as an active ingredient, particularly, a pharmaceutical composition for anti-metabolic syndrome, and further particularly, a pharmaceutical composition for therapeutic or preventive use associated with the control of blood glucose level. In addition, the present invention provides a screening system for each of a substance that enhances or suppresses betaKlotho activity, an FGF21-like active substance, and a betaKlotho-like active substance, which uses a cell system that has expressed an FGF receptor and / or betaKlotho on the surface thereof.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
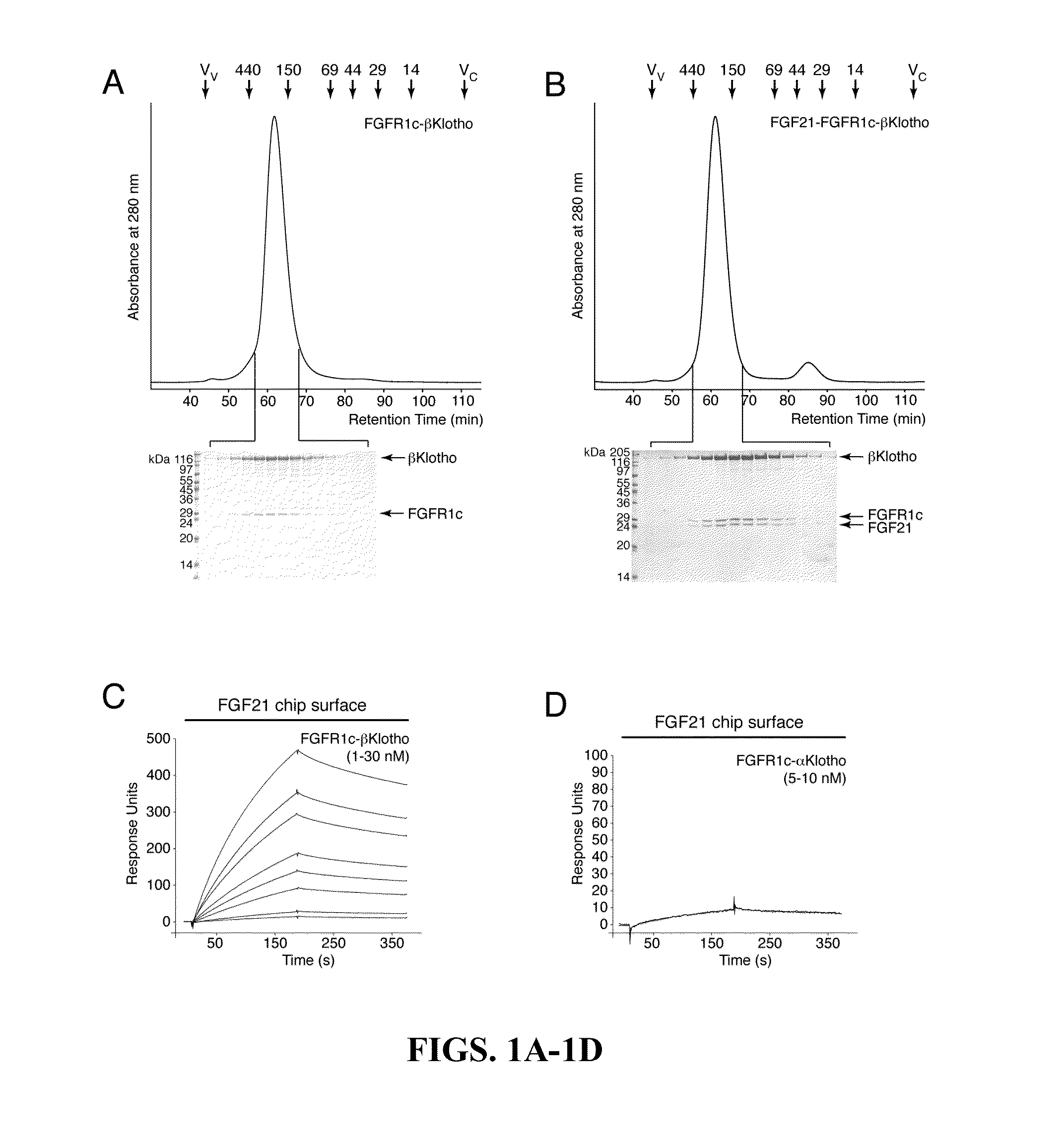
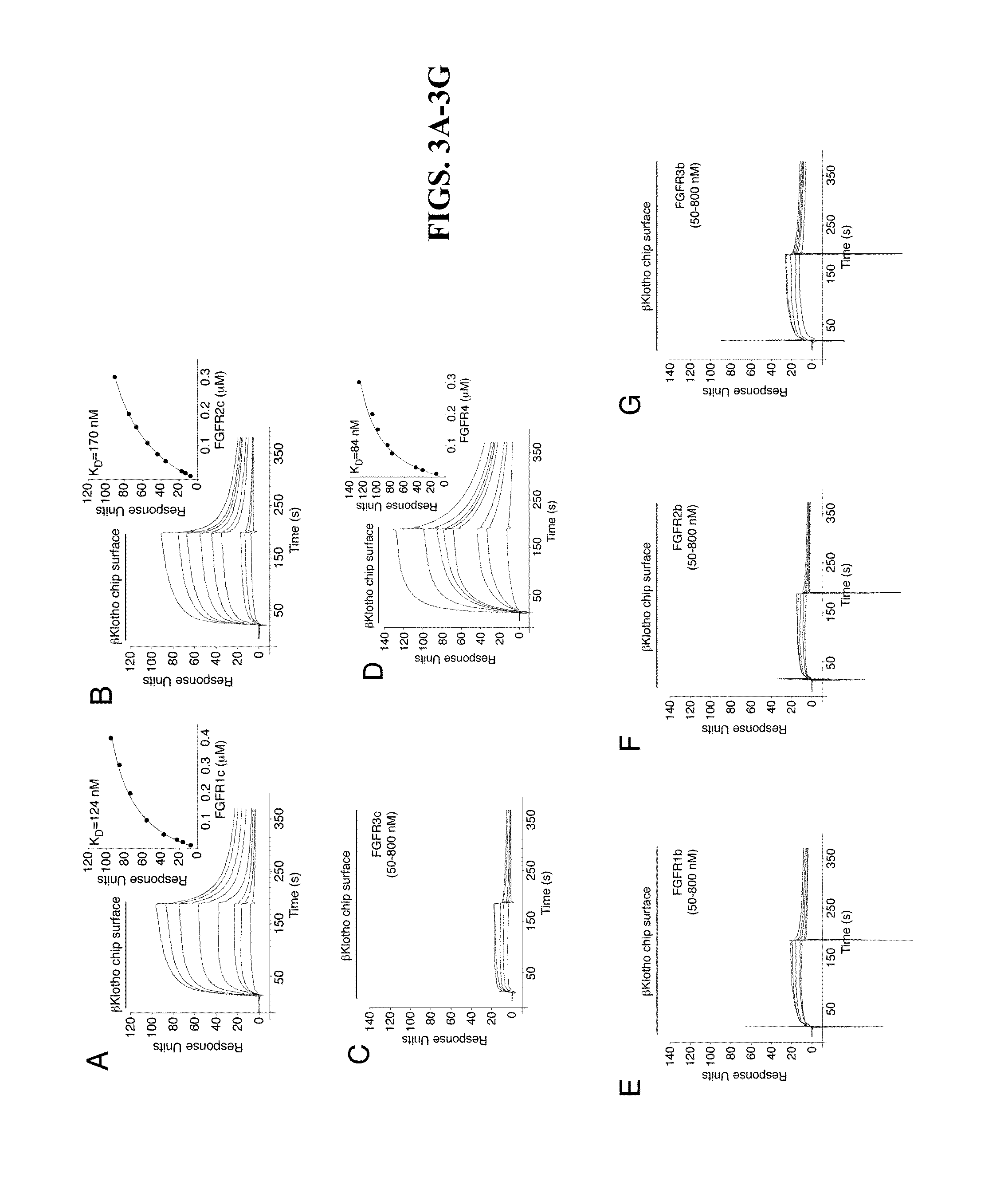
Chimeric fgf21 proteins with enhanced binding affinity for beta-klotho for the treatment of type ii diabetes, obesity, and related metabolic disorders
The present invention relates to chimeric proteins that include an N-terminus coupled to a C-terminus, where the N-terminus includes an N-terminal portion of fibroblast growth factor 21 (“FGF21”) and the C-terminus includes a C-terminal portion of fibroblast growth factor 19 (“FGF19”). The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions including chimeric proteins according to the present invention, as well as methods for treating a subject suffering from diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome, methods of treating a subject in need of increased FGF21-βKlotho-FGF receptor complex formation, methods of causing increased FGF21 receptor agonist-βKlotho-FGF receptor complex formation, and methods of screening for compounds with enhanced binding affinity for the βKlotho-FGF receptor complex involving the use of chimeric proteins of the present invention.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
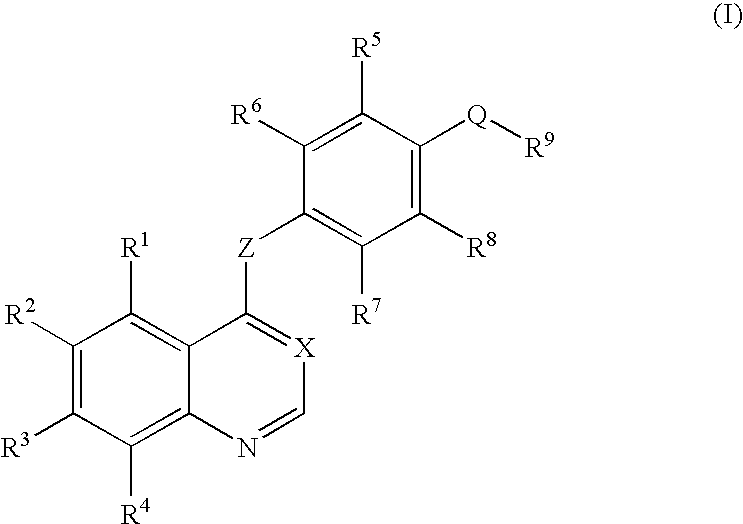
Quinoline or quinazoline derivatives inhibiting auto-phosphorylation of fibroblast growth factor receptors
InactiveUS20050049264A1Antitumor activityGrowth inhibitionBiocideOrganic chemistryCancer cellHalogen
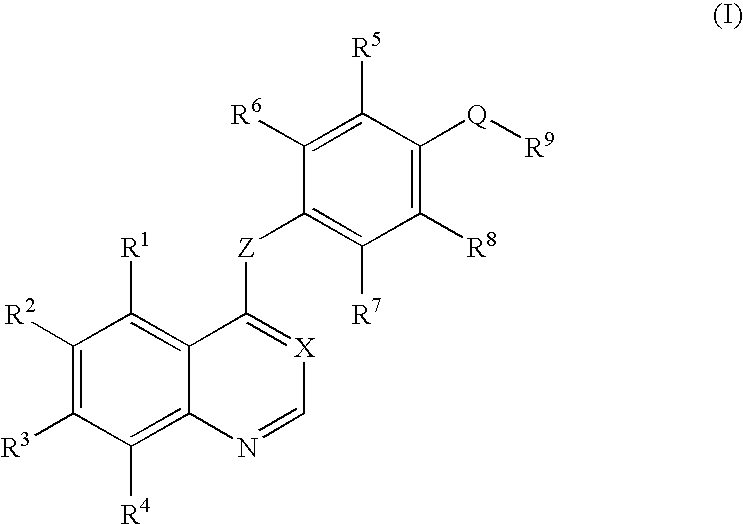
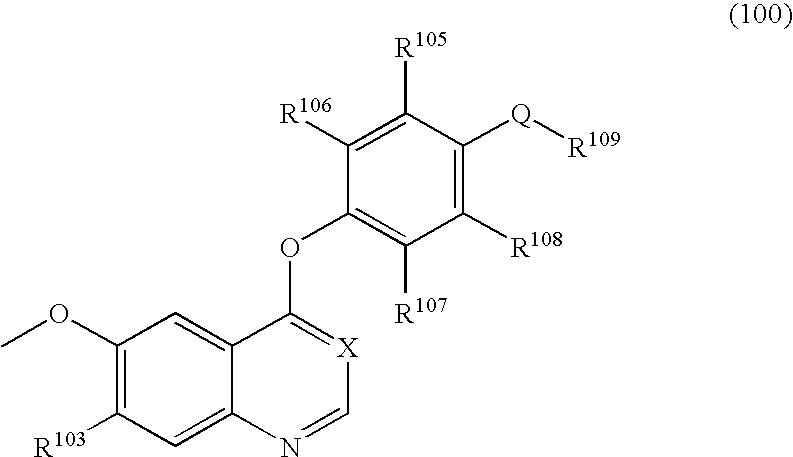
An objective of the present invention is to provide novel compounds which have inhibitory activity against autophosphorylation of an FGF receptor family and, when orally or intraveneously administered, can suppress the growth of cancer cells. The compounds of the present invention are represented by formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof: wherein X represents CH or N; Z represents O or S; Q represents NR10, CR11R2, carbonyl, O, S(═O)m, wherein m is 0 to 2, or urea; R1 to R3 each independently represent H, OH, halogen, nitro, amino, alkyl, alkoxy or the like in which the alkyl and alkoxy groups are optionally substituted; R4 represents H; R5 to R8 each independently represent H, halogen, alkyl, or alkoxy; and R9 represents an optionally substituted carbocyclic or heterocyclic group.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
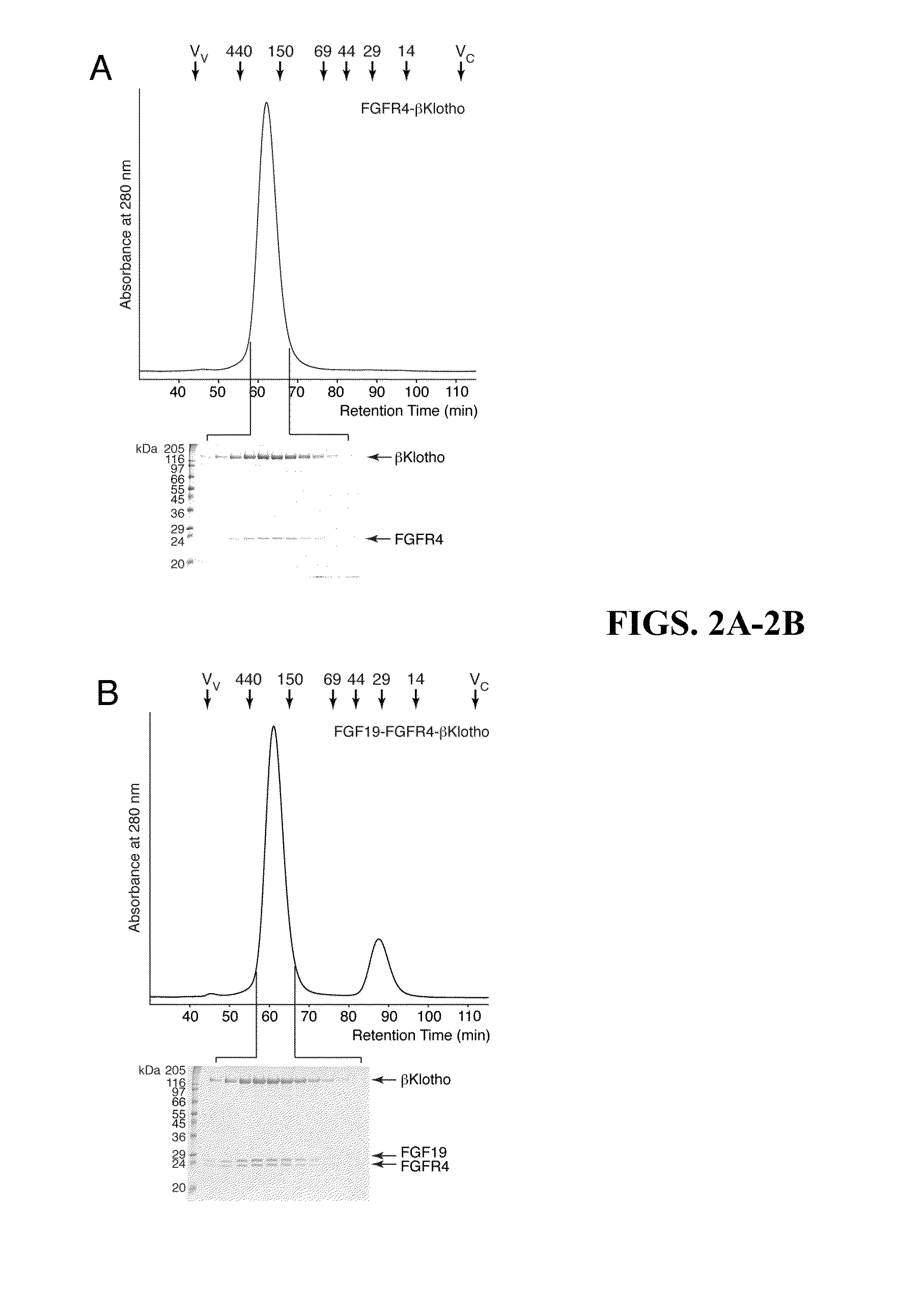
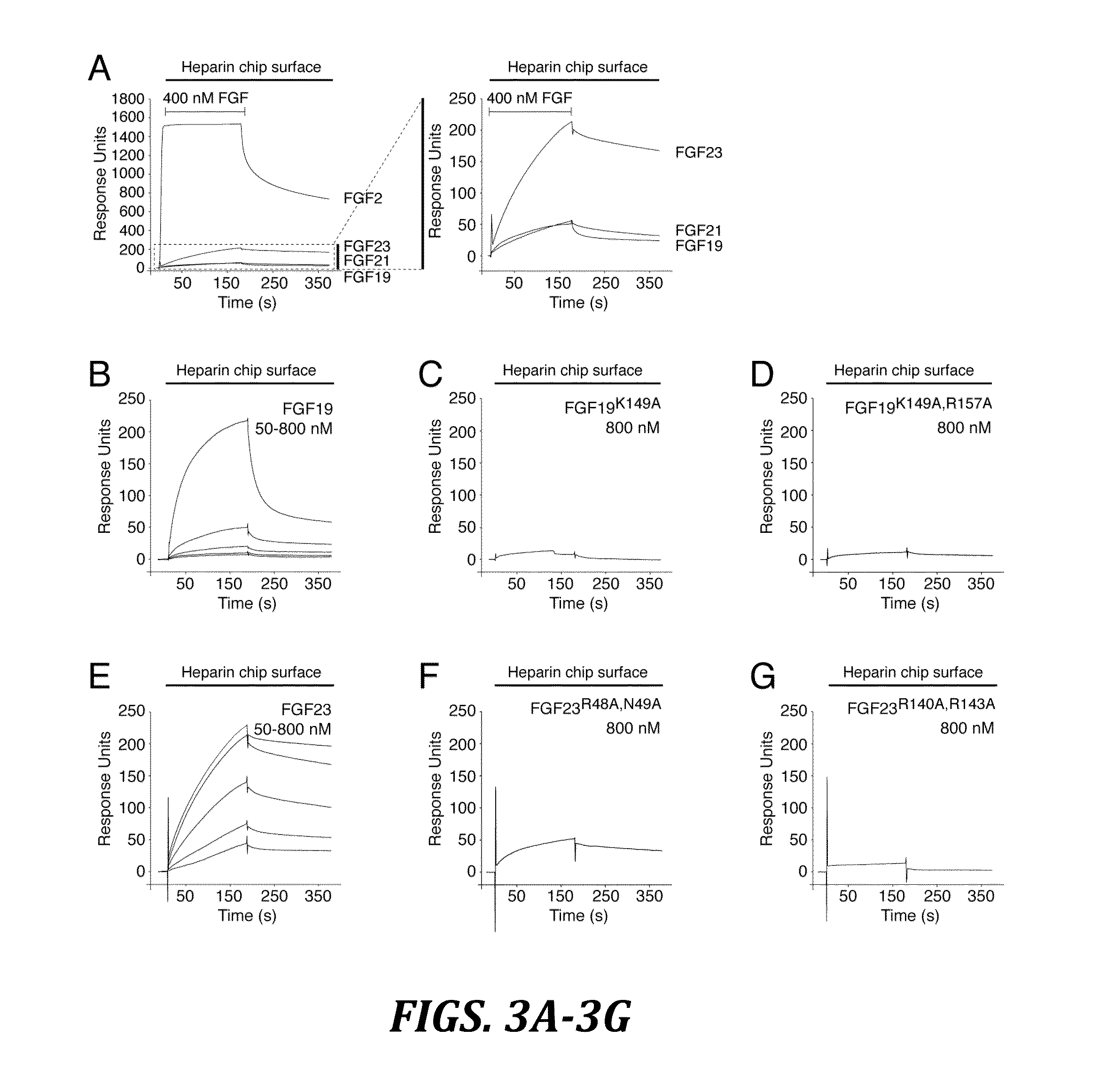
Chimeric fibroblast growth factor 19 proteins and methods of use
ActiveUS20130331317A1Enhanced endocrine activityLow affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsKlothoHeparin-DHE
The present invention relates to a chimeric protein that includes an N-terminus coupled to a C-terminus, where the N-terminus includes a portion of a paracrine fibroblast growth factor (“FGF”) and the C-terminus includes a C-terminal portion of an FGF19 molecule. The portion of the paracrine FGF is modified to decrease binding affinity for heparin and / or heparan sulfate compared to the portion without the modification. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions including chimeric proteins according to the present invention, methods for treating a subject suffering from diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome, and methods of screening for compounds with enhanced binding affinity for the βKlotho-FGF receptor complex involving the use of chimeric proteins of the present invention.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES +2
Structure-based design and synthesis of FGF inhibitors and FGF modulator compounds
InactiveUS20050187150A1Promotes dimerizationTreat and ameliorate disorderCompound screeningApoptosis detectionTernary complexFGF Receptor
The present invention provides methods and compositions for modulating FGF-signaling and activities associated therewith, such as mitogenesis and angiogenesis. In particular, the invention provides crystal structure coordinates for a ternary complex of an FGF receptor, and FGF ligand, and a third compound, sucrose octasulfate, that binds to the FGF receptor and ligand to promote formation and dimerization of the ternary complex. Screening methods are provided by which novel agonists and antagonist for FGF-mediating signaling and activities may be identified using these crystal structure coordinates. Exemplary compounds are also provided that have novel utilities as agonists or antagonists of FGF-mediated signaling and activites.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
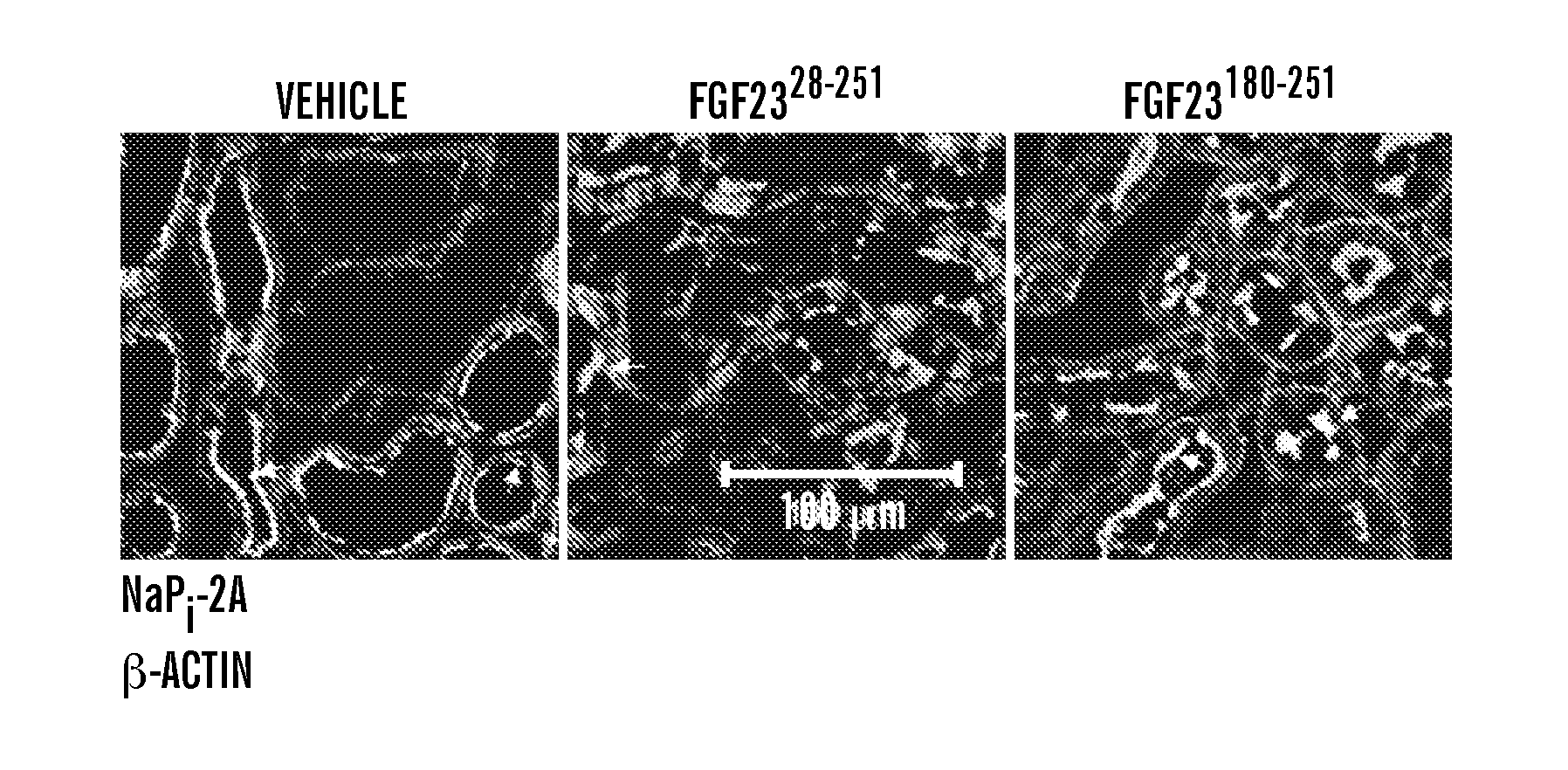
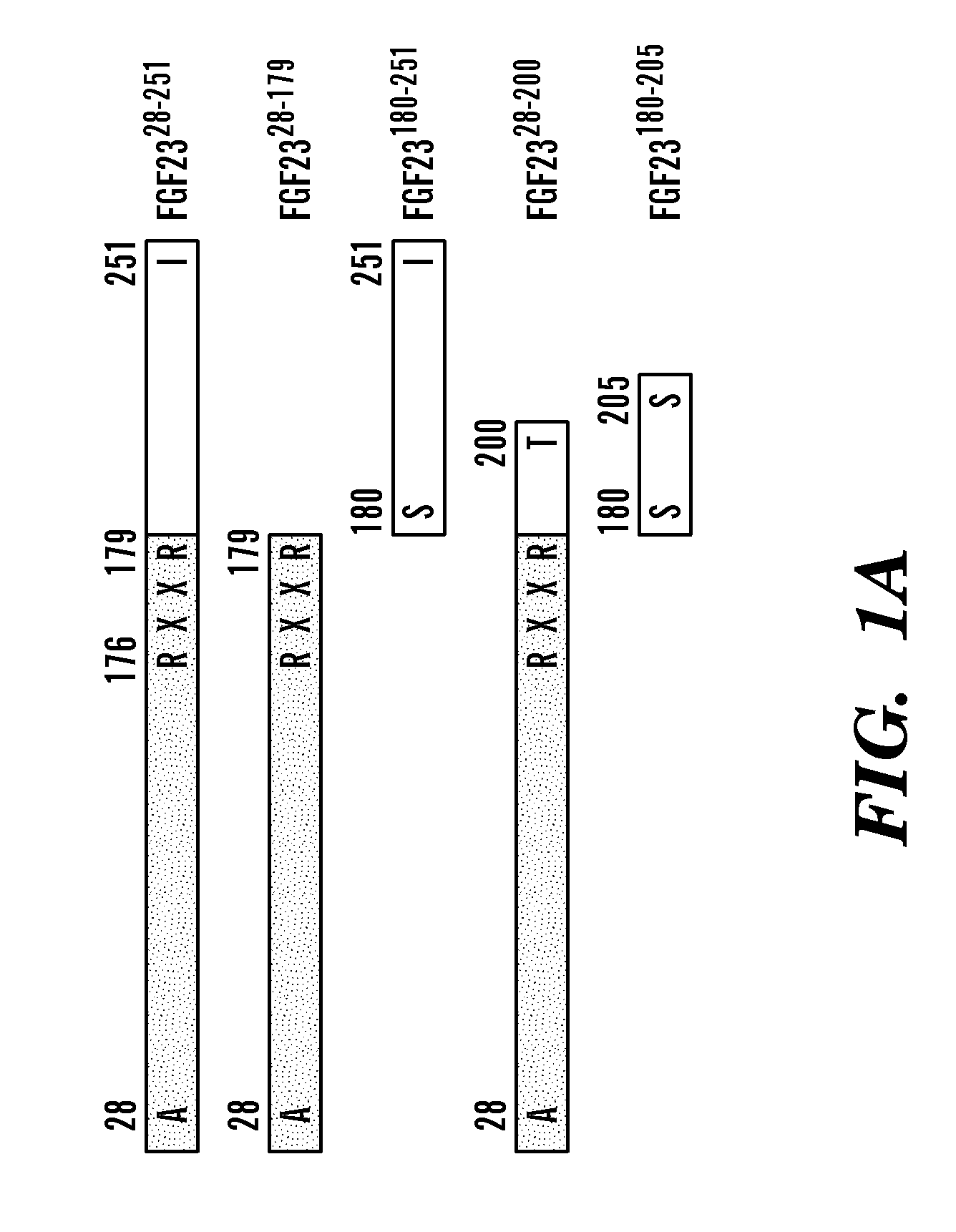
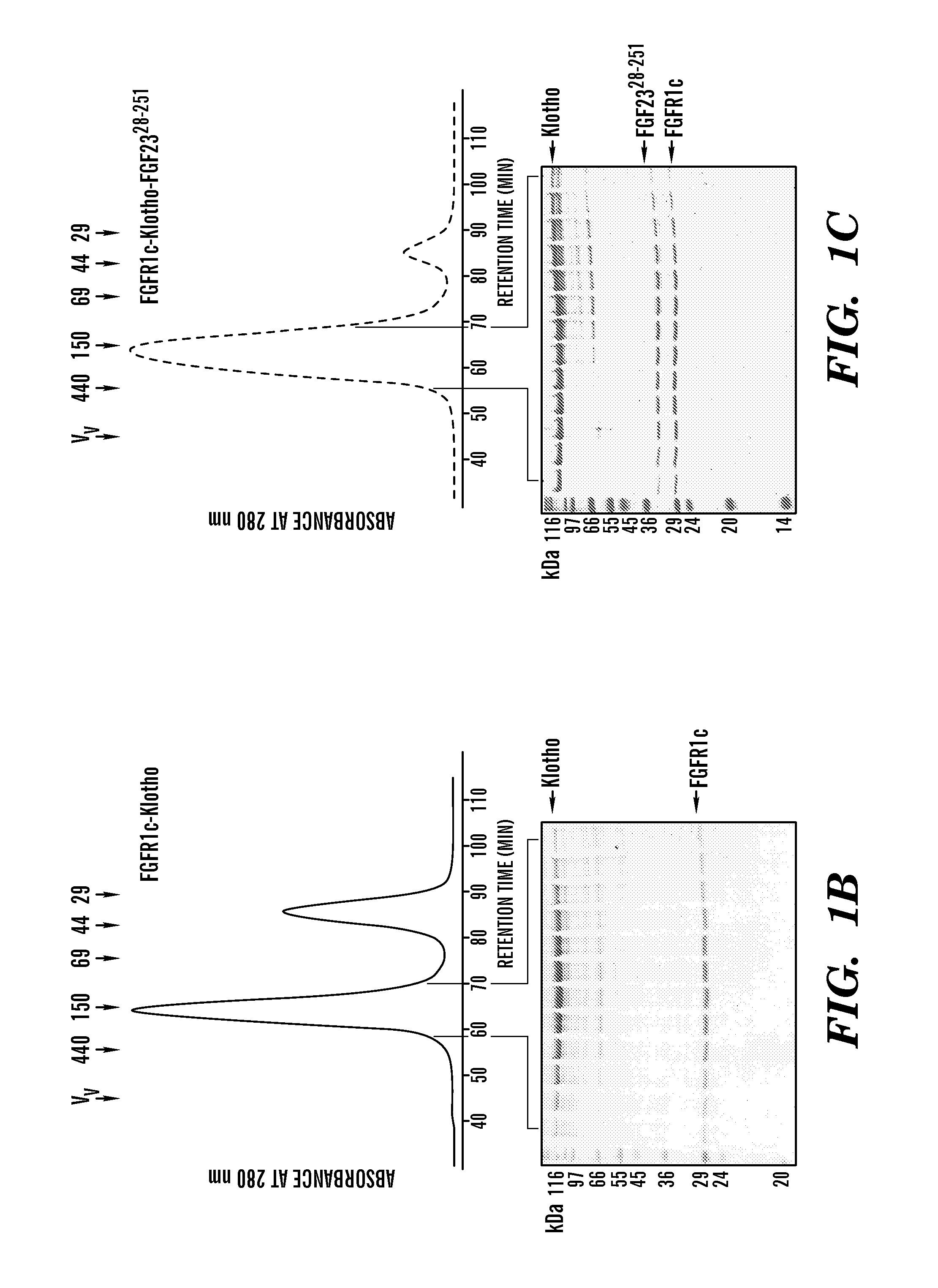
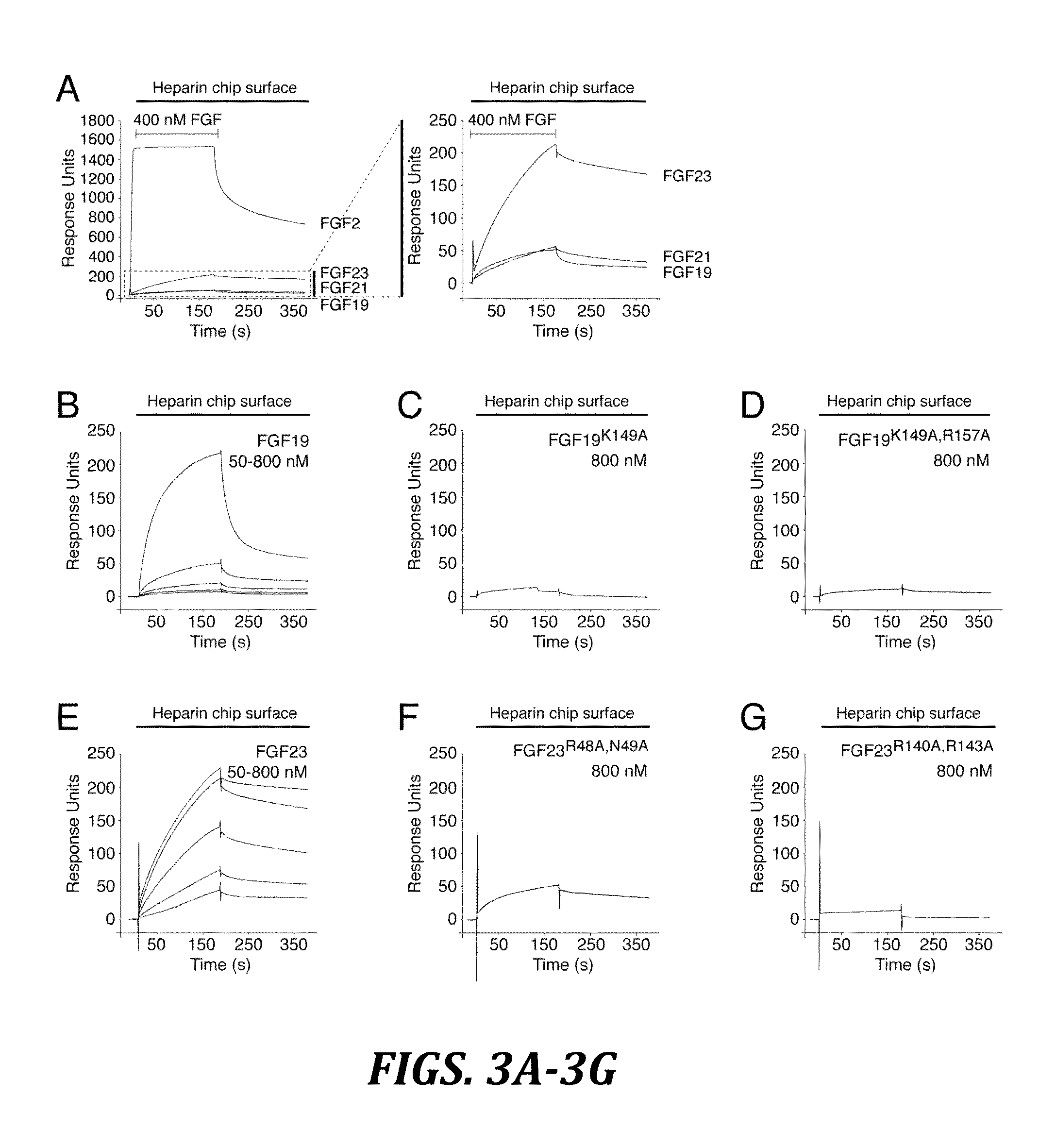
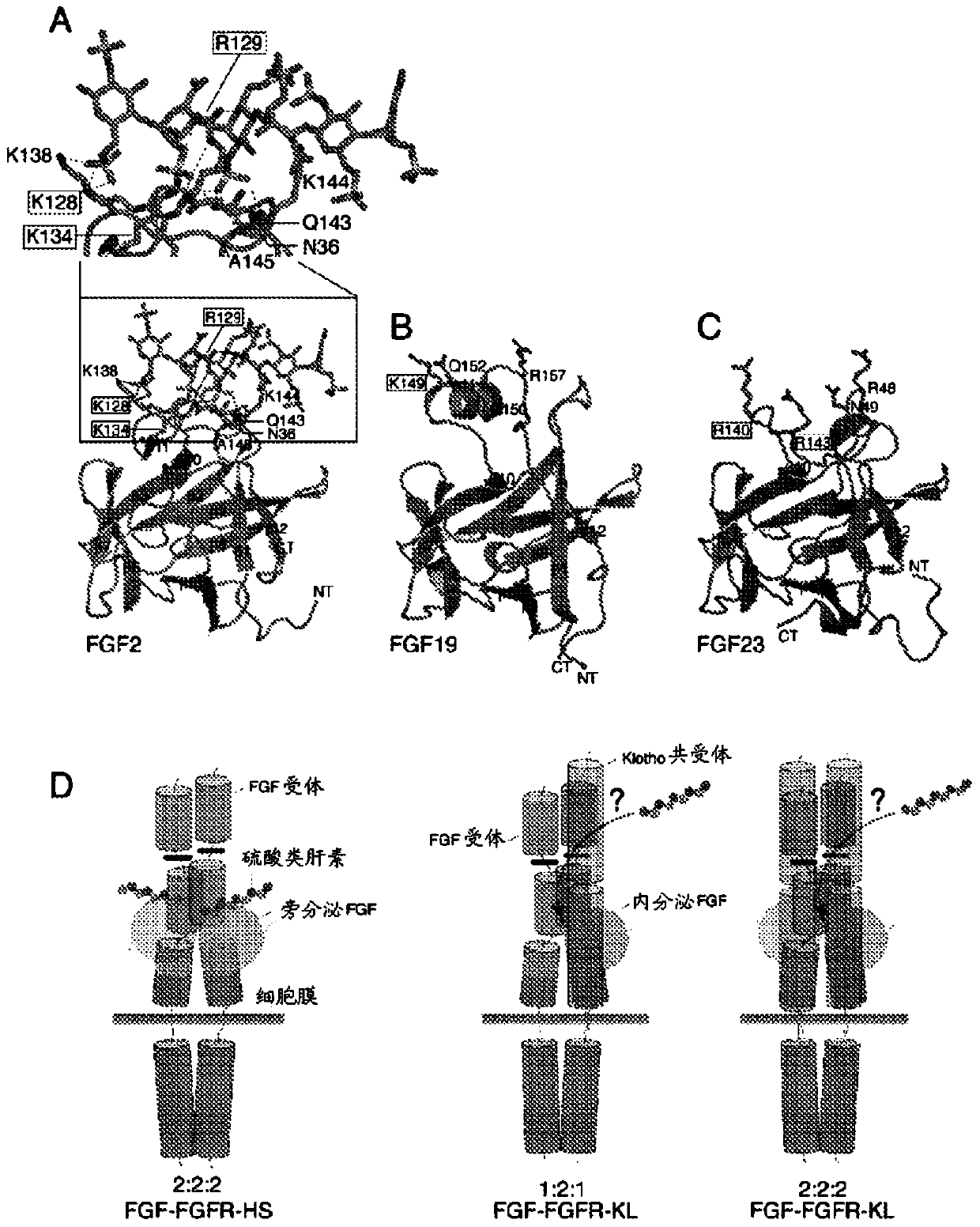
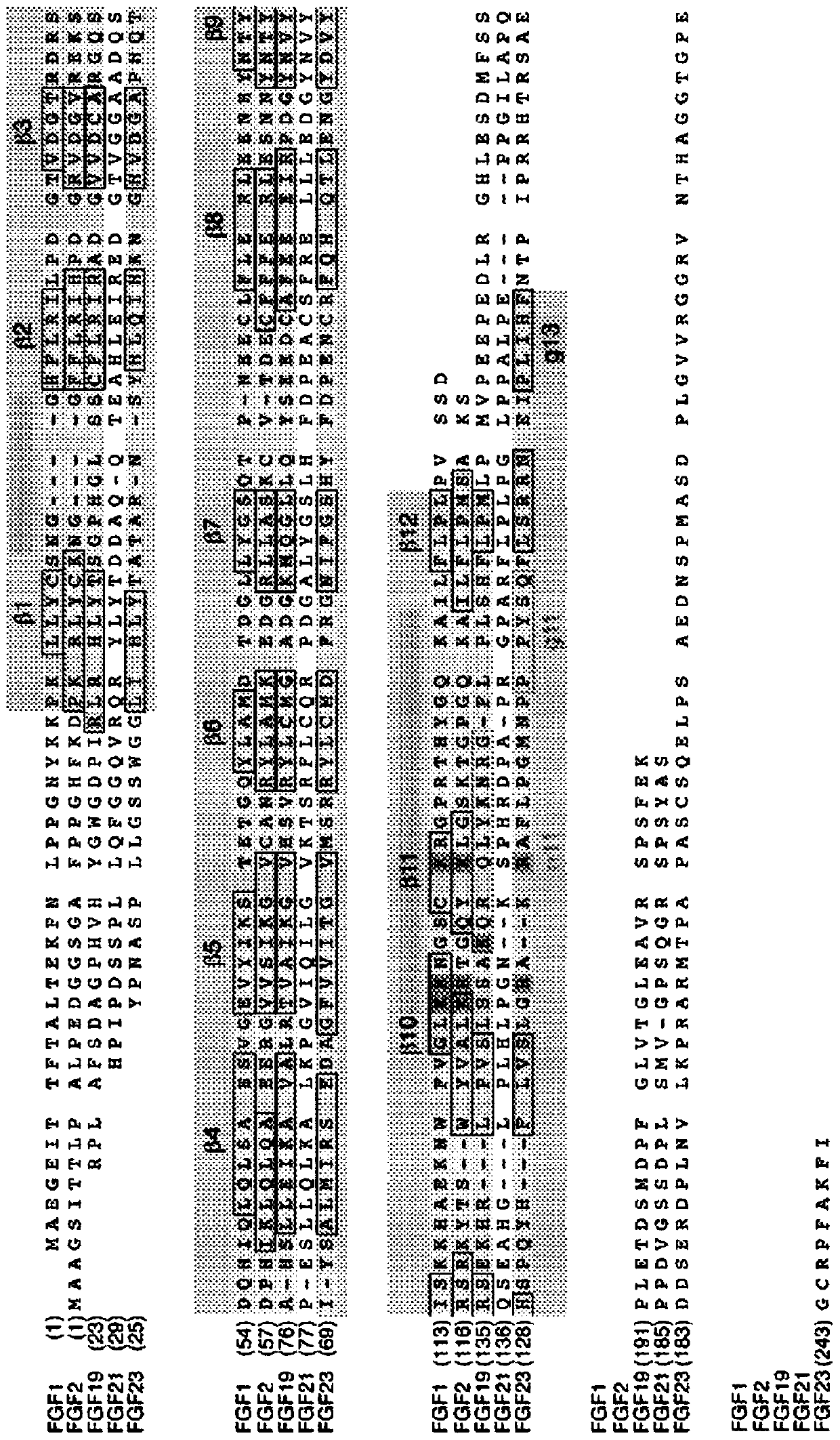
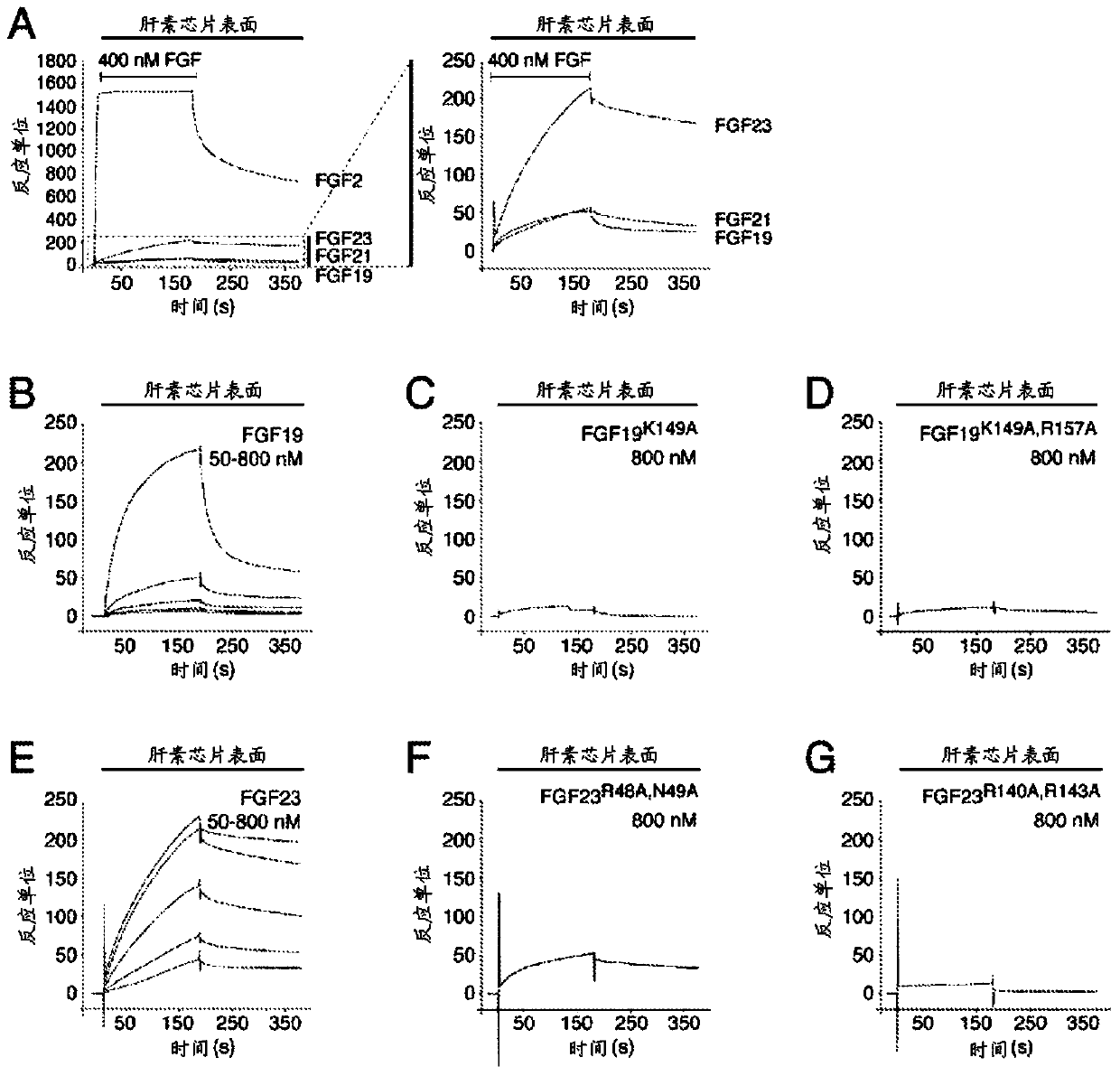
Inhibiting binding of fgf23 to the binary fgfr-klotho complex for the treatment of hypophosphatemia
ActiveUS20110190207A1Inhibit FGF2 signalingOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCompound specificTernary complex
The present invention is directed to a method of treating hypophosphatemia in a subject. This method involves selecting a subject with hypophosphatemia associated with elevated or normal FGF23 and administering to the selected subject an inhibitor of FGF23-Klotho-FGF receptor complex formation under conditions effective to treat the hypophosphatemia. The present invention is also directed to a method of screening for compounds suitable for treatment of hypophosphatemia associated with elevated or normal FGF23. This method involves providing FGF23, FGFR-Klotho complex, and one or more candidate compounds. The FGF23, the FGFR-Klotho complex, and the candidate compounds are combined under conditions effective for the FGF23 and the binary FGFR-Klotho complex to form a ternary complex if present by themselves. This method also involves identifying the candidate compounds, which prevent formation of the complex as being potentially suitable in treating hypophosphatemic conditions associated with elevated or normal FGF23. A method of screening the specificity of compounds which prevent formation of the FGF23-Klotho-FGFR complex is also disclosed.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
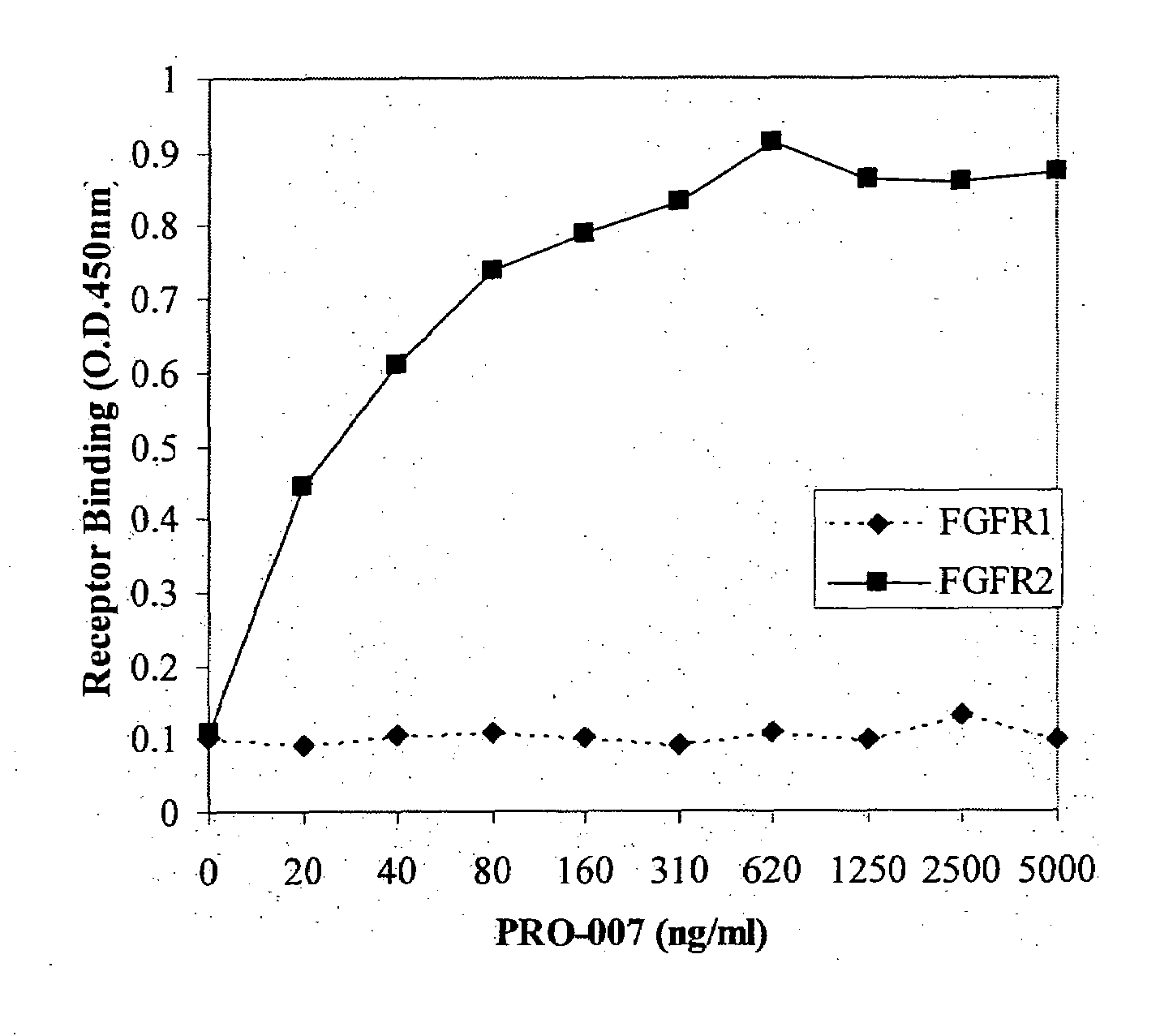
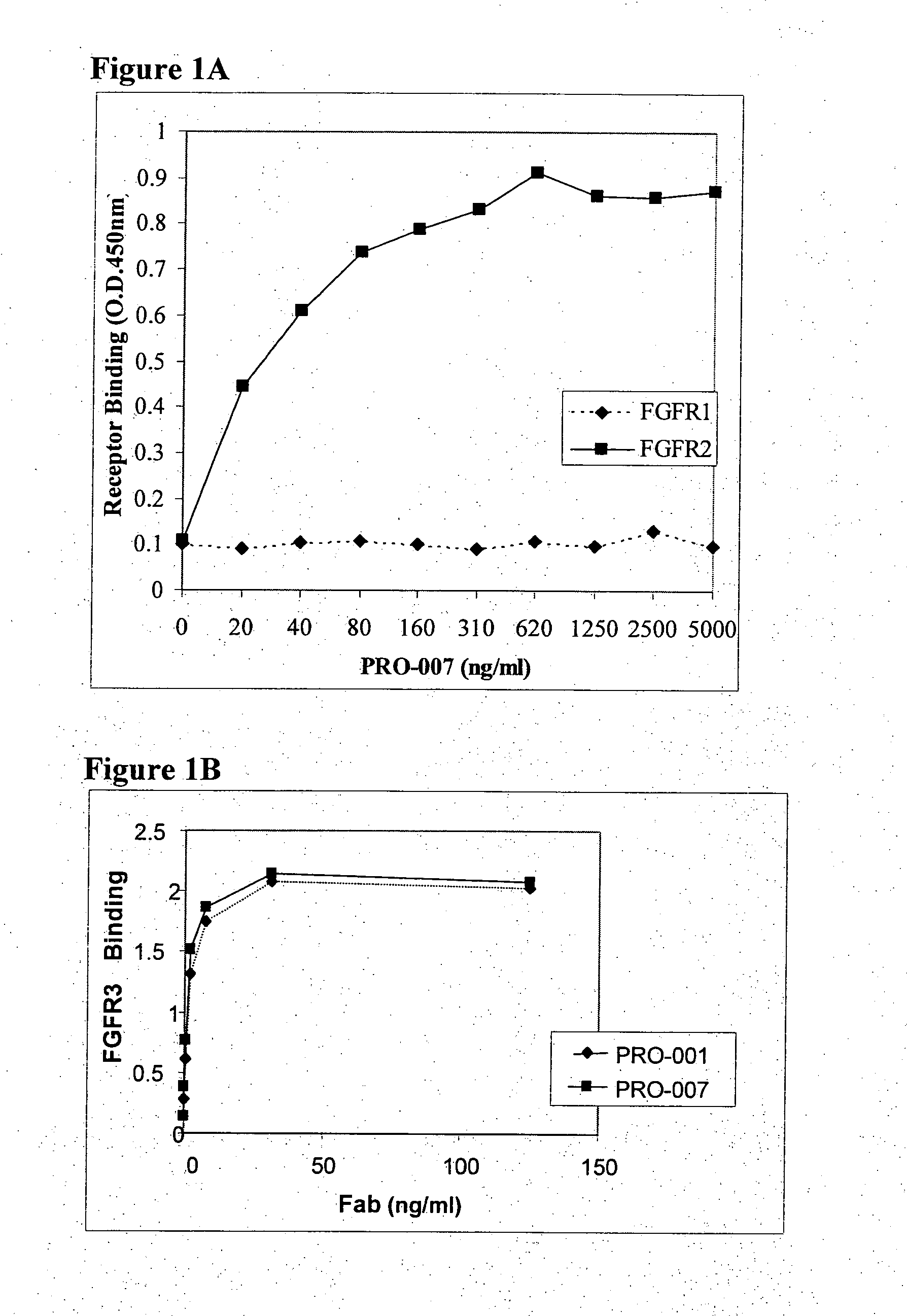
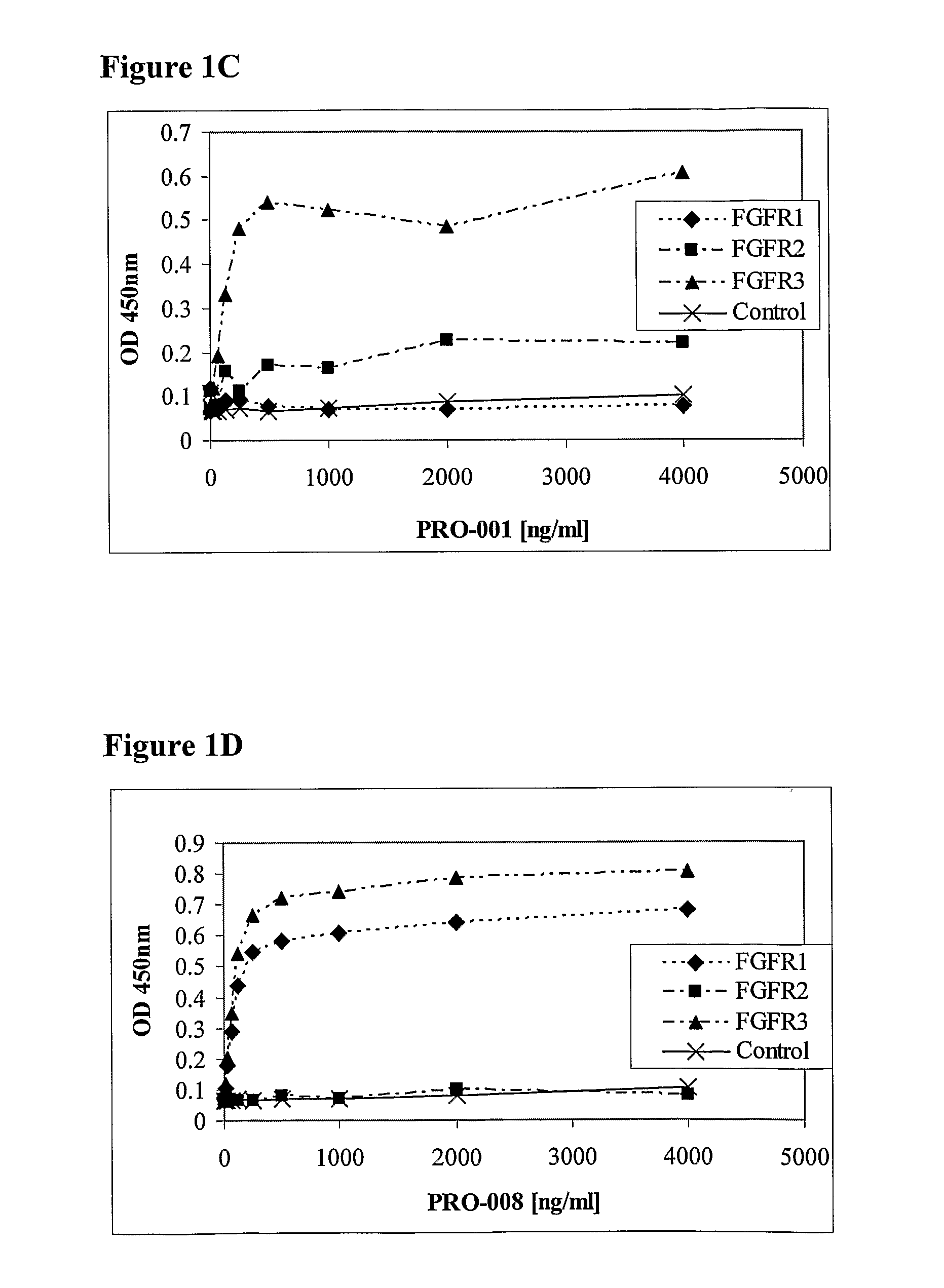
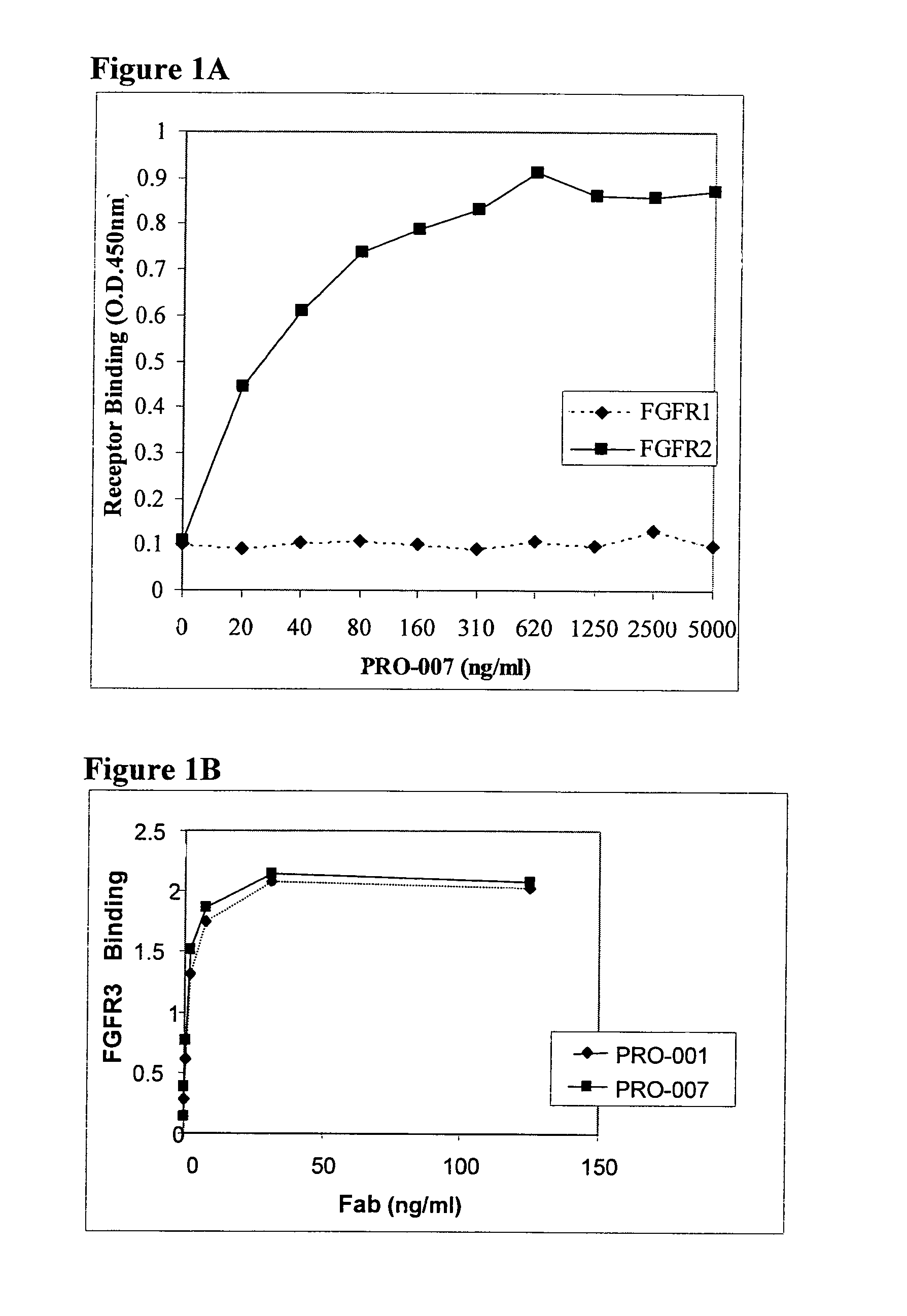
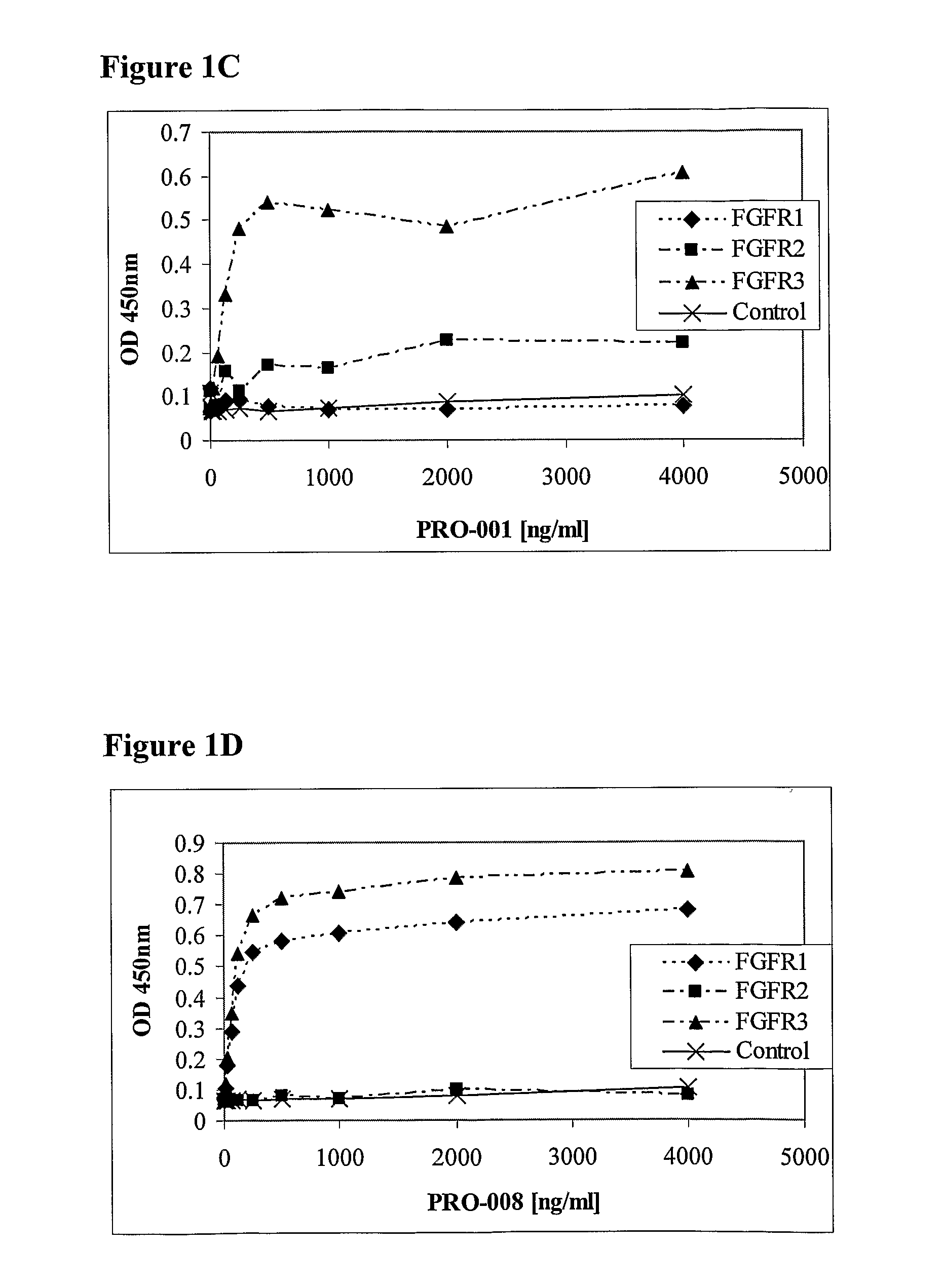
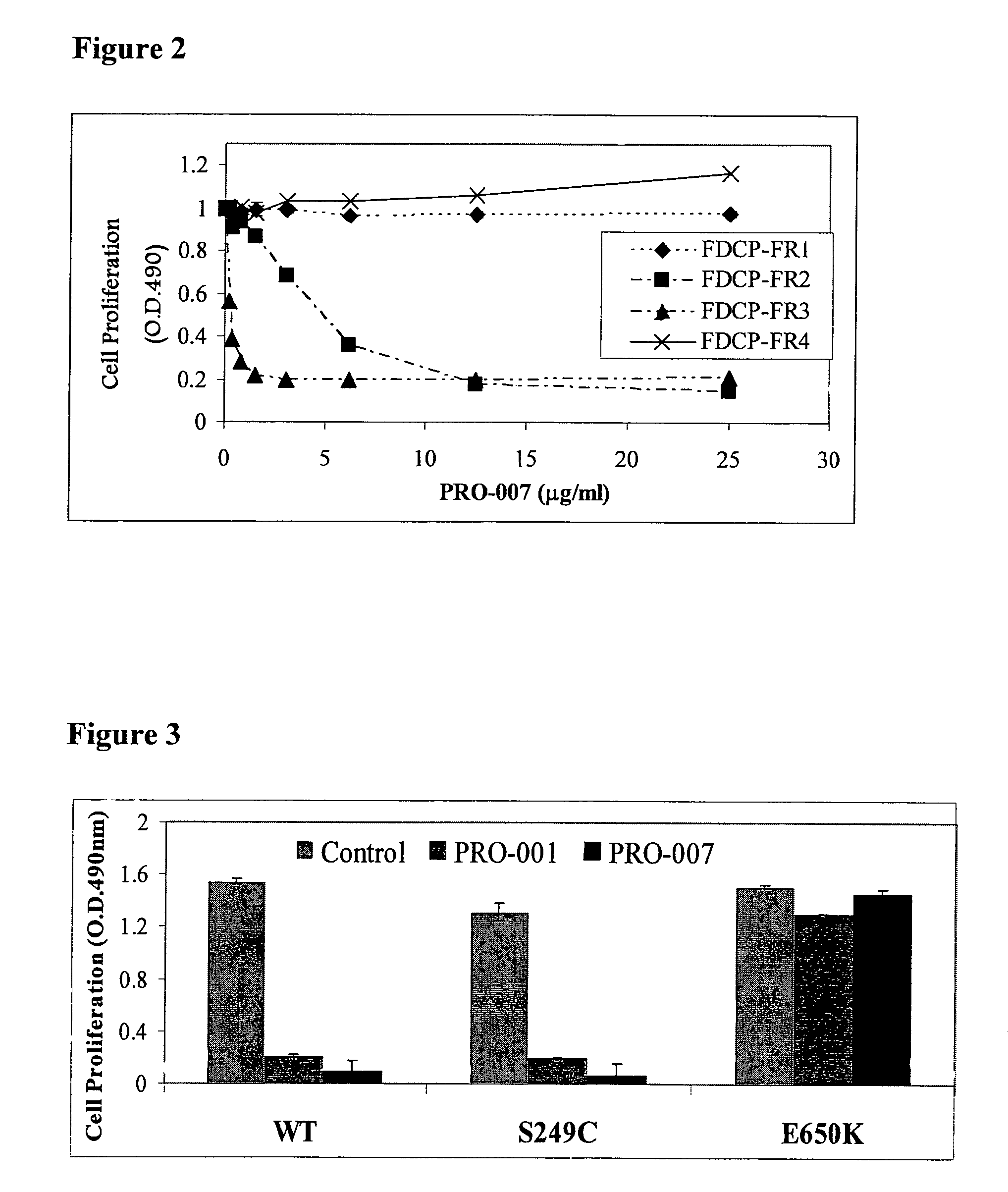
Antibodies blocking fibroblast growth factor receptor activation and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20100047251A1Strong specificityHigh affinityImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAntibody ingredientsFGF ReceptorReceptor activation
The present invention is related to antibodies with binding affinity to fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) optionally with binding affinity to other FGF receptors, which block both ligand-dependent and constitutive ligand independent receptor activation. Specifically, the present invention relates to antibodies with high affinity to more than one FGF receptor subtype, and fragments thereof, useful in treating disorders including cell proliferative diseases.
Owner:FIBRON
Pluripotent cells from rat and other species
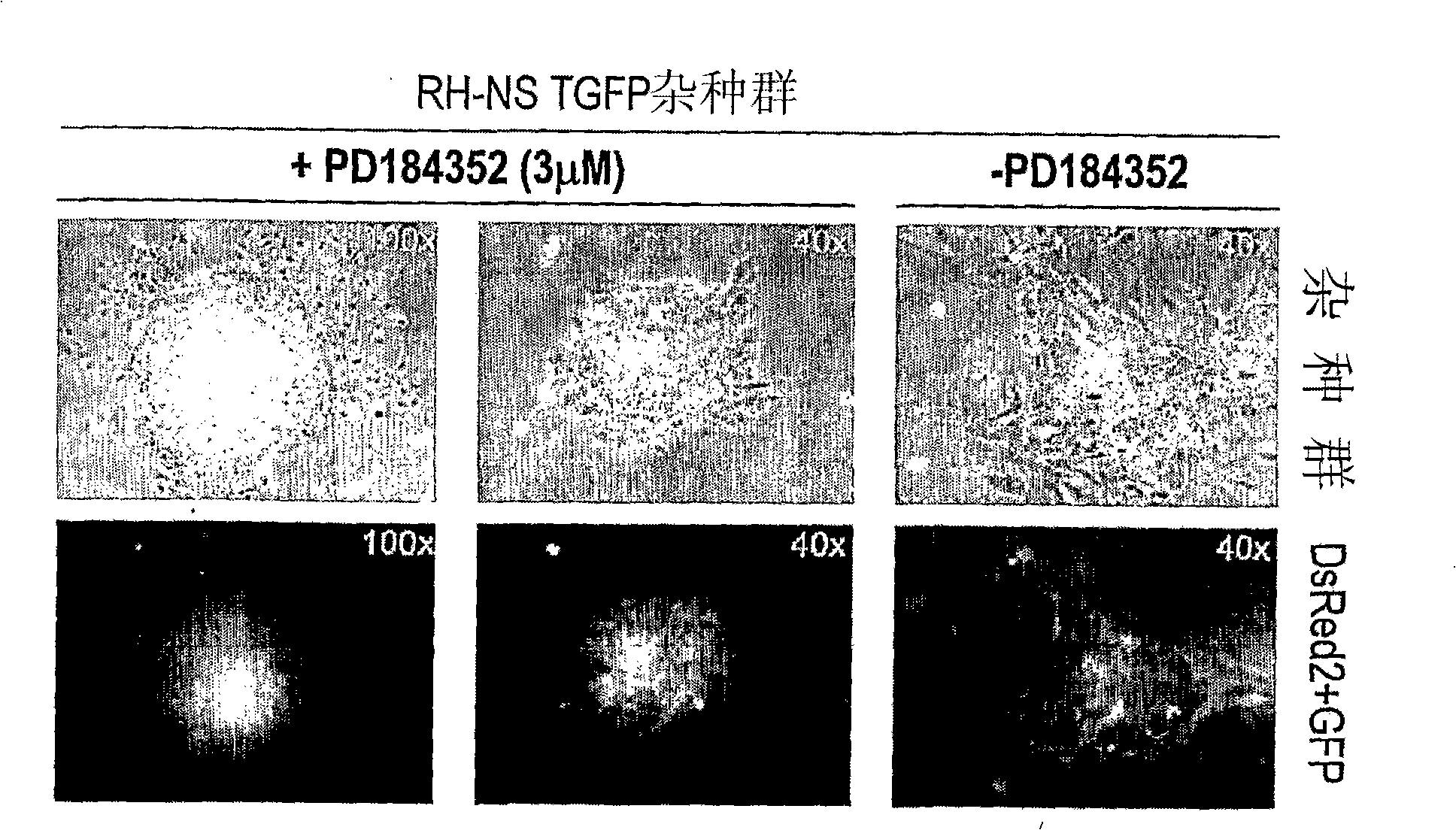
InactiveCN101657535ALow costStable storageCompounds screening/testingCell culture active agentsSerum igeMEK inhibitor
Pluripotent cells are derived and maintained in a self-renewing state in serum-free culture medium comprising a MEK inhibitor, a GSK3 inhibitor and an antagonist of an FGF receptor.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF EDINBURGH
Chimeric fibroblast growth factor 19 proteins and methods of use
The present invention relates to a chimeric protein that includes an N-terminus coupled to a C-terminus, where the N-terminus includes a portion of a paracrine fibroblast growth factor (“FGF”) and the C-terminus includes a C-terminal portion of an FGF19 molecule. The portion of the paracrine FGF is modified to decrease binding affinity for heparin and / or heparan sulfate compared to the portion without the modification. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions including chimeric proteins according to the present invention, methods for treating a subject suffering from diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome, and methods of screening for compounds with enhanced binding affinity for the βKlotho-FGF receptor complex involving the use of chimeric proteins of the present invention.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Antibodies blocking fibroblast growth factor receptor activation and methods of use thereof
The present invention is related to antibodies with binding affinity to fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) optionally with binding affinity to other FGF receptors, which block both ligand-dependent and constitutive ligand independent receptor activation. Specifically, the present invention relates to antibodies with high affinity to more than one FGF receptor subtype, and fragments thereof, useful in treating disorders including cell proliferative diseases.
Owner:FIBRON
Blood vessel target liposome carrier mediated by fiber forming growth factor receptor and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101361712ADecreased body clearanceImprove distributionOrganic active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsCarrier mediatedCholesterol
The invention belongs to the biology medicine field, and relates to a fiber growth factor receptor (FGFR)-mediated vascular targeted liposome carrier, a preparation method thereof and an application thereof. The invention aims at solving the technical problem of proving a cationic liposome with high transfection efficiency and tumor vascular targeting. The targeted liposome is prepared by using the components with the following mixture ratios: the mixture ration of DOTAP, cholesterol and tb FGF polypeptide is: the mol ratio of the DOTAP to the cholesterol equals to 2:1-2, and the weight of the tb FGF polypeptide is 10-80 percent of the total weight of the DOTAP and the cholesterol. The liposome can be combined with the FGF receptor (FGFR) on the surface of tumor new-generated vascular cells particularly, and can realize the preparation method thereof and the application of tumor vascular targeting therapy by wrapping up various micromolecule anti-tumor drugs, therapy genes and adenoviral vectors carrying therapy genes.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
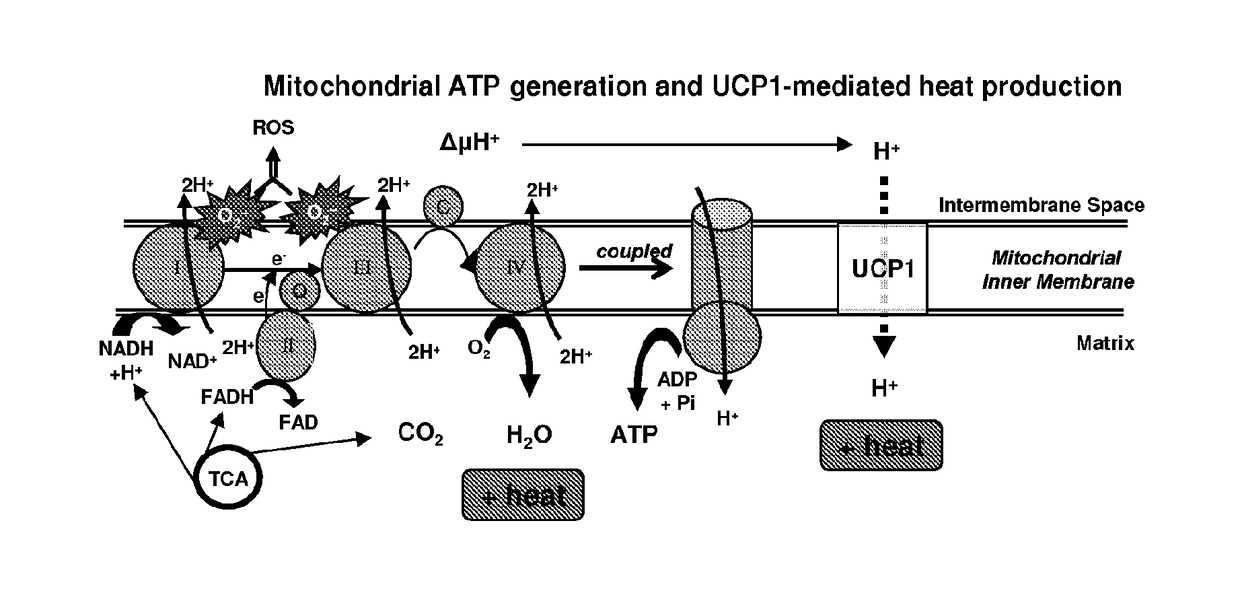
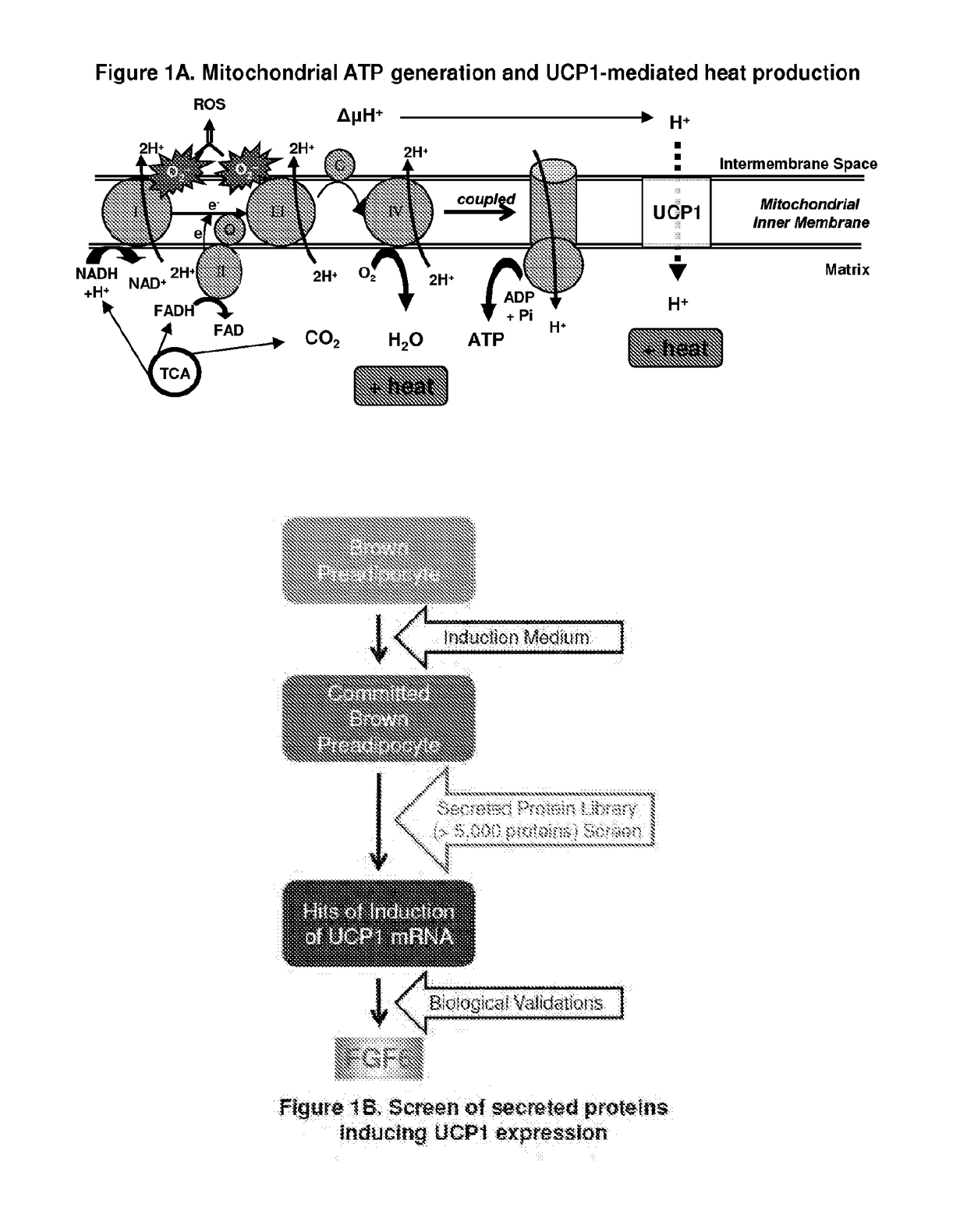
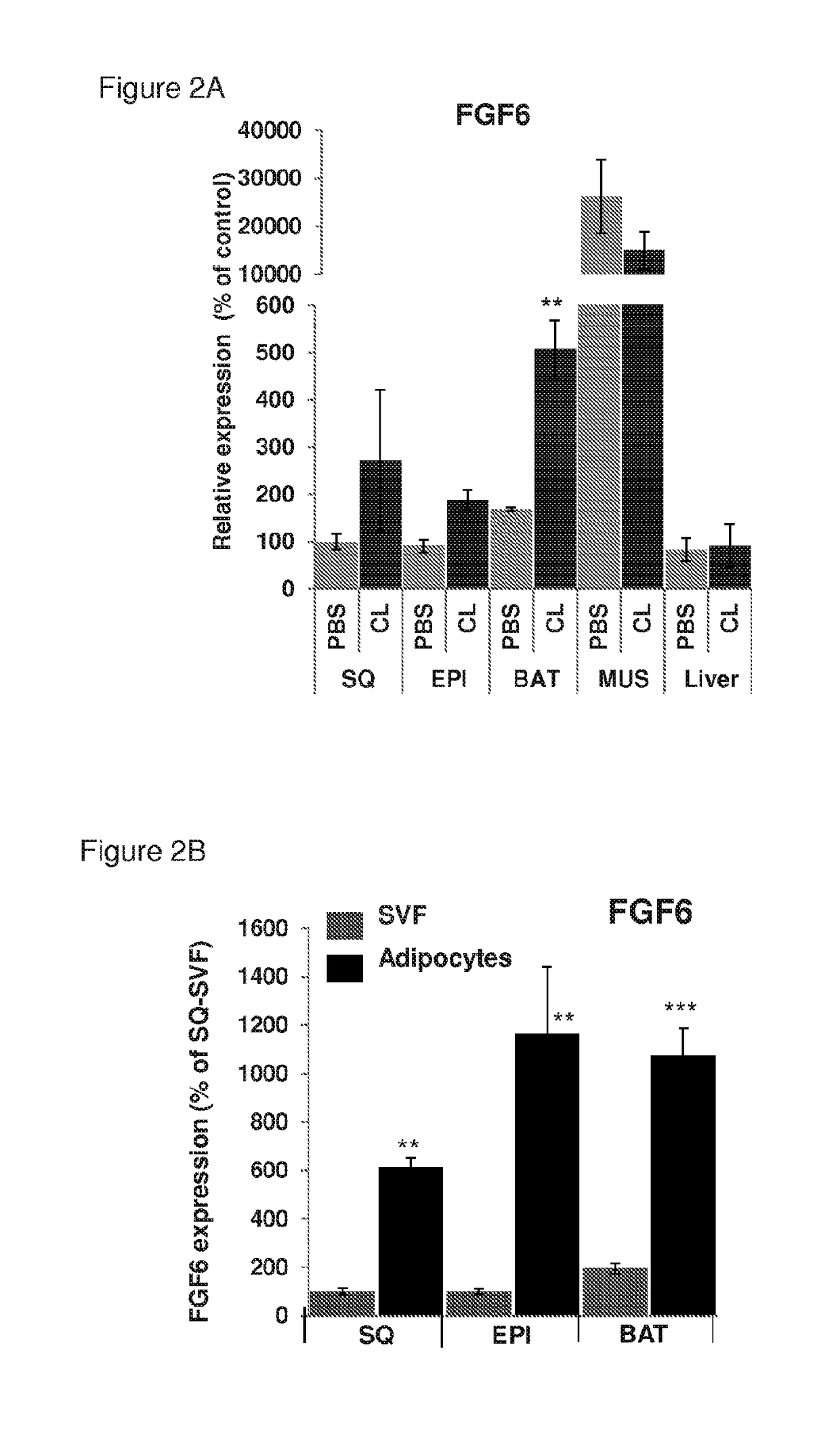
Methods and compositions for induction of ucp1 expression
PendingUS20170173114A1Reduce weightPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsAntigenAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the induction of expression of UCP1 independent of lipid accumulation. The invention, in particular, features methods for converting FGF receptive cells, e.g., preadipocyte cells, into energy consuming cells through FGF-mediated UCP1 expression. The invention further provides methods and compositions for treating metabolic disorders with an FGF receptor agonist, (e.g., an FGF protein, or fragment thereof, a nucleic acid encoding an FGF protein, an FGF mimetic, an anti-FGF receptor agonist antibody, or antigen binding fragment thereof), or a cell contacted with an FGF receptor agonist, including FGF6.
Owner:JOSLIN D ABETES CENTER INC
Recombinant soluble human FGFR2 extracellular fragment and production method and application thereof
The present invention discloses a recombinant soluble FGFR2 extracellular domain and the production method as well s the application of the extracellular domain. The present invention is based on the high-efficient expression FGFR2 of escherichia coli. Qualitative and quantitative researches have done concerning a plurality of factors that affect the renaturing efficiency. A proper method for recombinant soluble FGFR2 extracellular domain is determined. The renaturing efficiency can be of 10 percent to 20 percent. The present invention is of low cost and short cycle. The present invention is suitable for mass production. And the present invention takes advantage of the combination of dissociative extracellular domain of FGFRs with the FGFs in the tumor tissue to reduce the amount of dissociative FGFs, competitively leading to the repressive FGFs signals and the restraining proliferation and transfer of tumor as well as the depressed formation of blood vessels. S252W+P253R extracellular domain and double-mutant FGFR2 extracellular domain are of the best efficiency.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Chimeric fgf21 proteins with enhanced binding affinity for beta-klotho for the treatment of type ii diabetes, obesity, and related metabolic disorders
ActiveUS20170096462A1Improve stabilityHigh affinityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionFGF19C-terminus
The present invention relates to chimeric proteins that include an N-terminus coupled to a C-terminus, where the N-terminus includes an N-terminal portion of fibroblast growth factor 21 (“FGF21”) and the C-terminus includes a C-terminal portion of fibroblast growth factor 19 (“FGF19”). The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions including chimeric proteins according to the present invention, as well as methods for treating a subject suffering from diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome, methods of treating a subject in need of increased FGF21-βKlotho-FGF receptor complex formation, methods of causing increased FGF21 receptor agonist-βKlotho-FGF receptor complex formation, and methods of screening for compounds with enhanced binding affinity for the βKlotho-FGF receptor complex involving the use of chimeric proteins of the present invention.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Culture medium containing kinase inhibitors, and uses thereof
Pluripotent cells are maintained in a self-renewing state in serum-free culture medium comprising a MEK inhibitor, a GSK3 inhibitor and, optionally, an antagonist of an FGF receptor. Pluripotent cells are also maintained in a self-renewing state in serum-free culture medium comprising a MEK inhibitor and an antagonist of an FGF receptor.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF EDINBURGH
Methods for targeting cells that express fibroblast growth receptor-3 or -2
Fibroblast growth factor-18 (FGF-18) binds with FGF receptors-2 and -3. Compositions comprising an FGF-18 component can be used to target cells that express these receptors. Suitable targets include tumor cells that express constitutively activated forms of FGF receptors-2 and -3. For example, conjugates of FGF-18 and saporin can be used to target tumor cells that express FGF receptors-2 or -3, and to inhibit the proliferation of these cells.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Chimeric fibroblast growth factor 21 proteins and methods of use
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
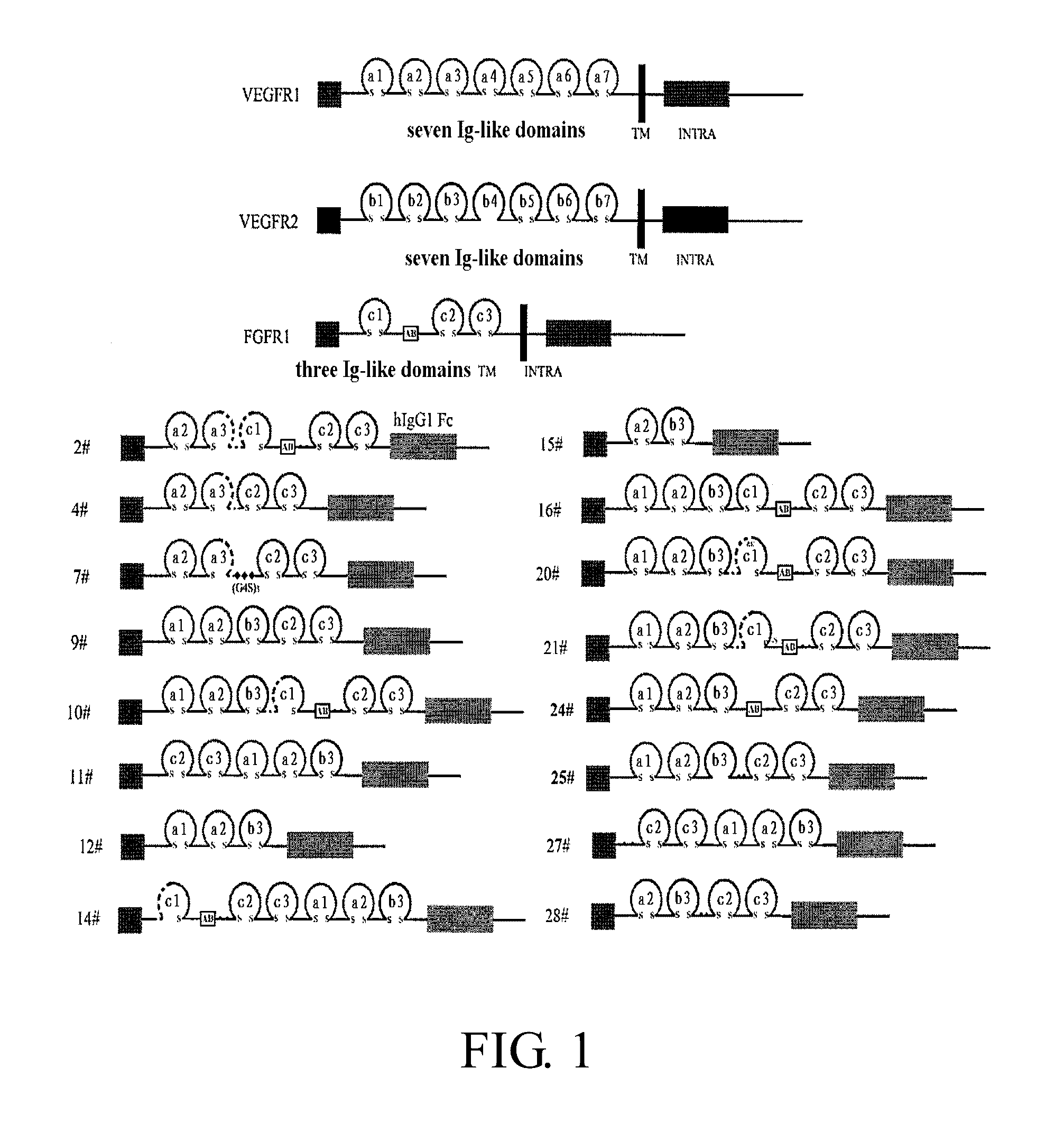
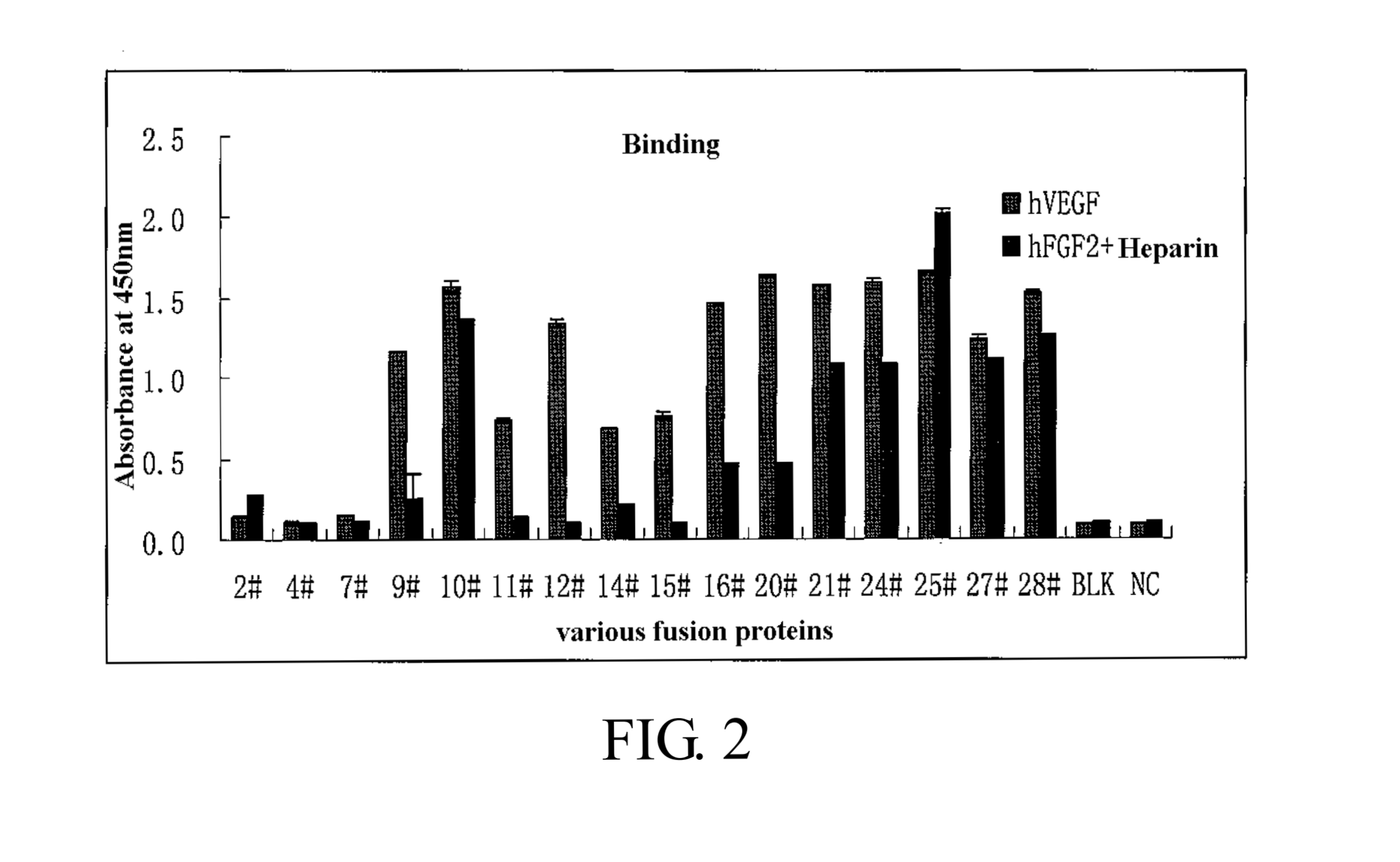
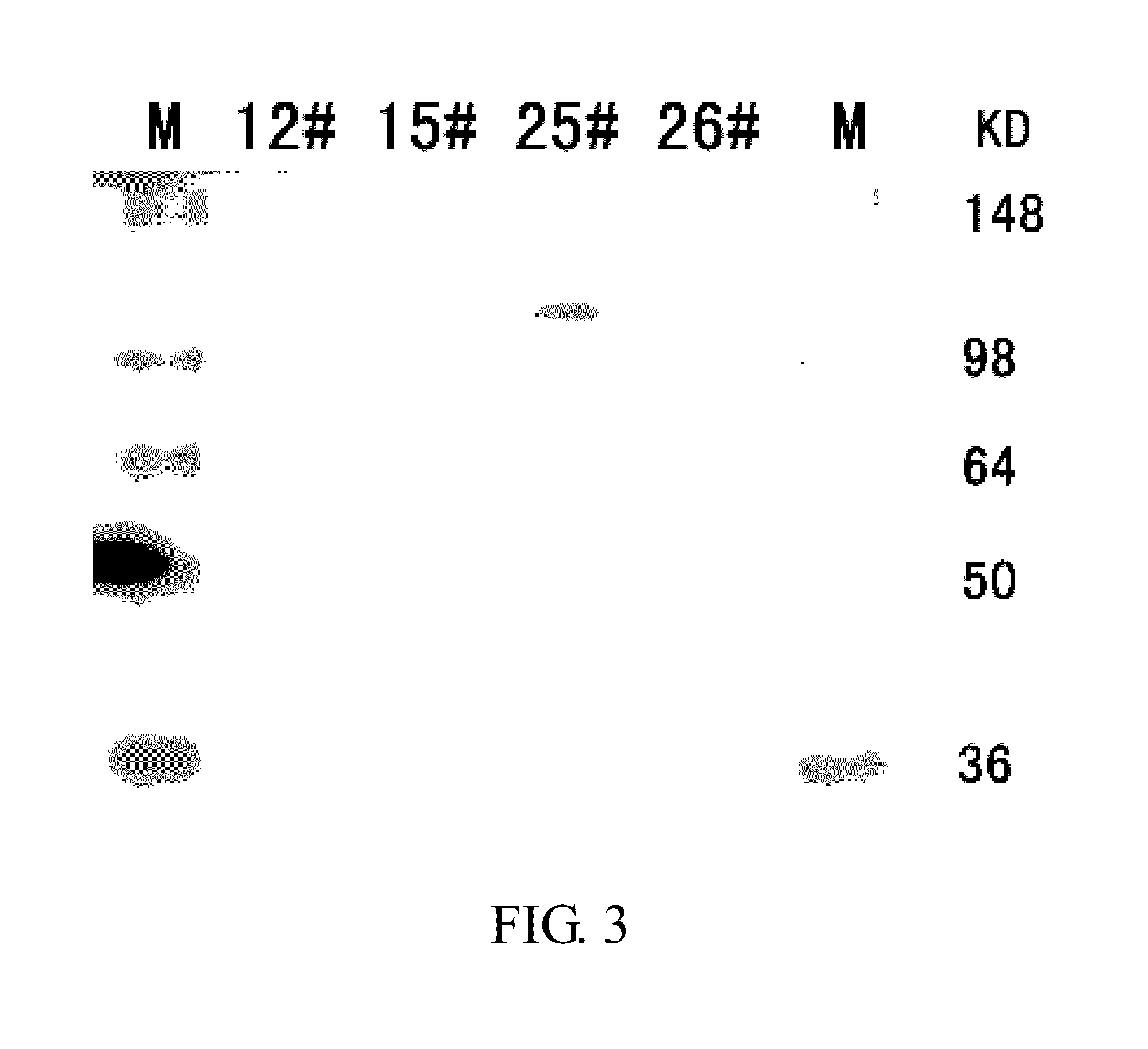
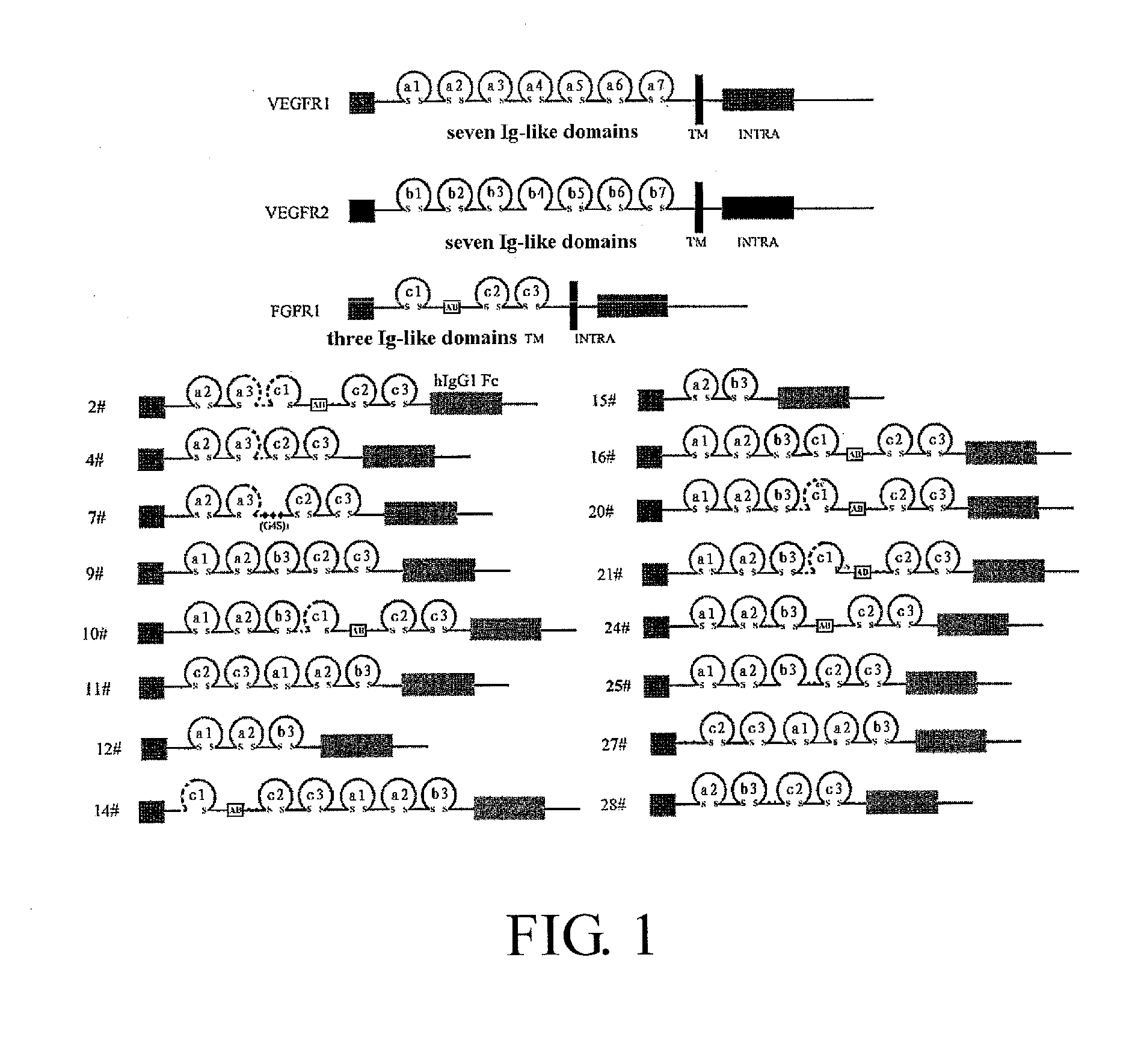
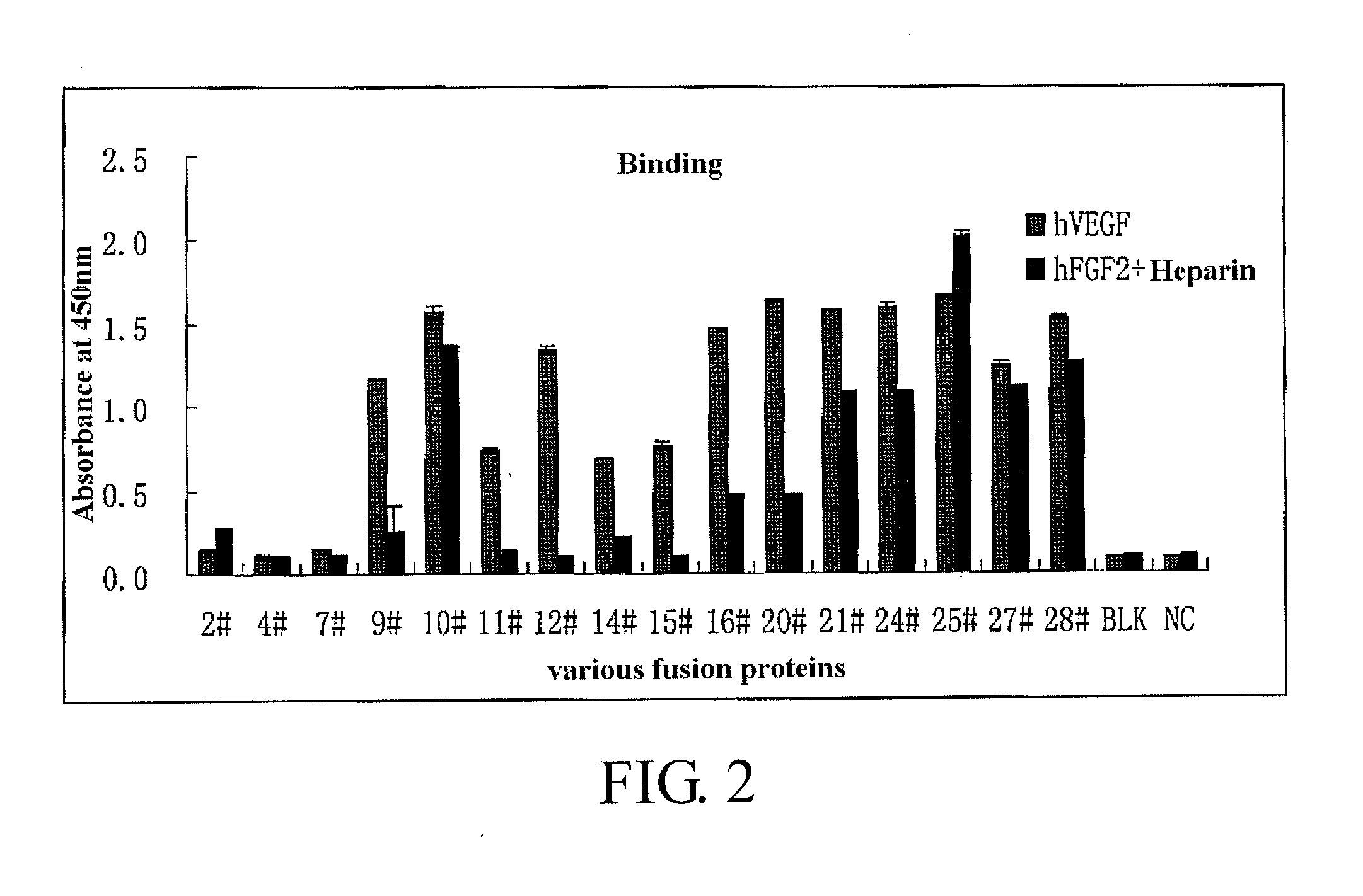
Fusion protein for antagonizing angiogenesis inducible factors and uses thereof
The present invention relates to angiogenesis-inhibitory fusion proteins and use thereof. Particularly, the present invention provides fusion proteins inhibiting a plurality of angiogenic factors. More particularly, the present invention relates to the fusion proteins of VEGF receptor and FGF receptor and their applications in the treatment of angiogenesis related diseases.
Owner:REMEGEN CO LTD
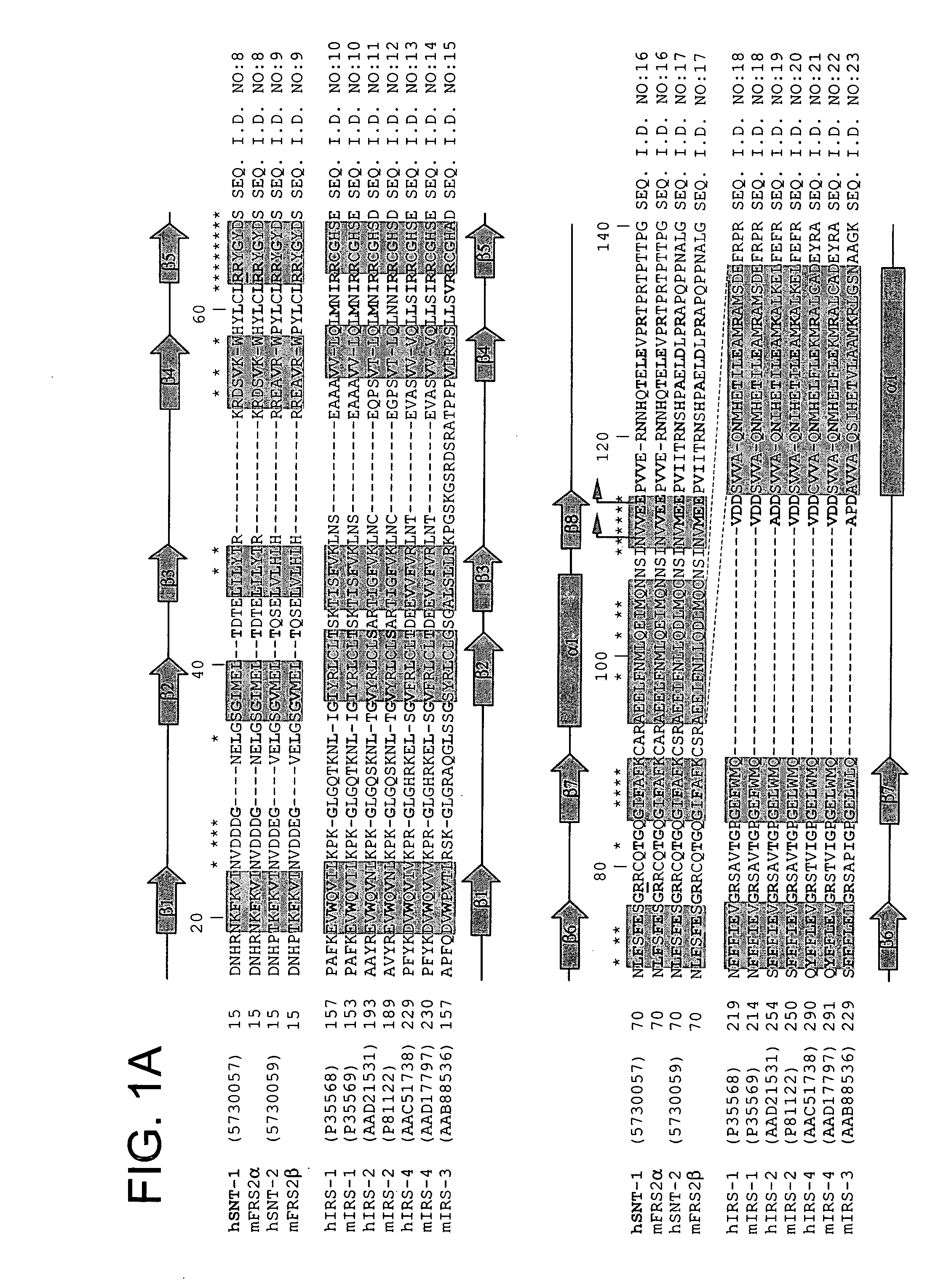
Methods of indentifying modulators of the FGF receptor
InactiveUS20060019296A1Modulate bindingStability of complexAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTissue cultureFGF ReceptorSpectroscopy
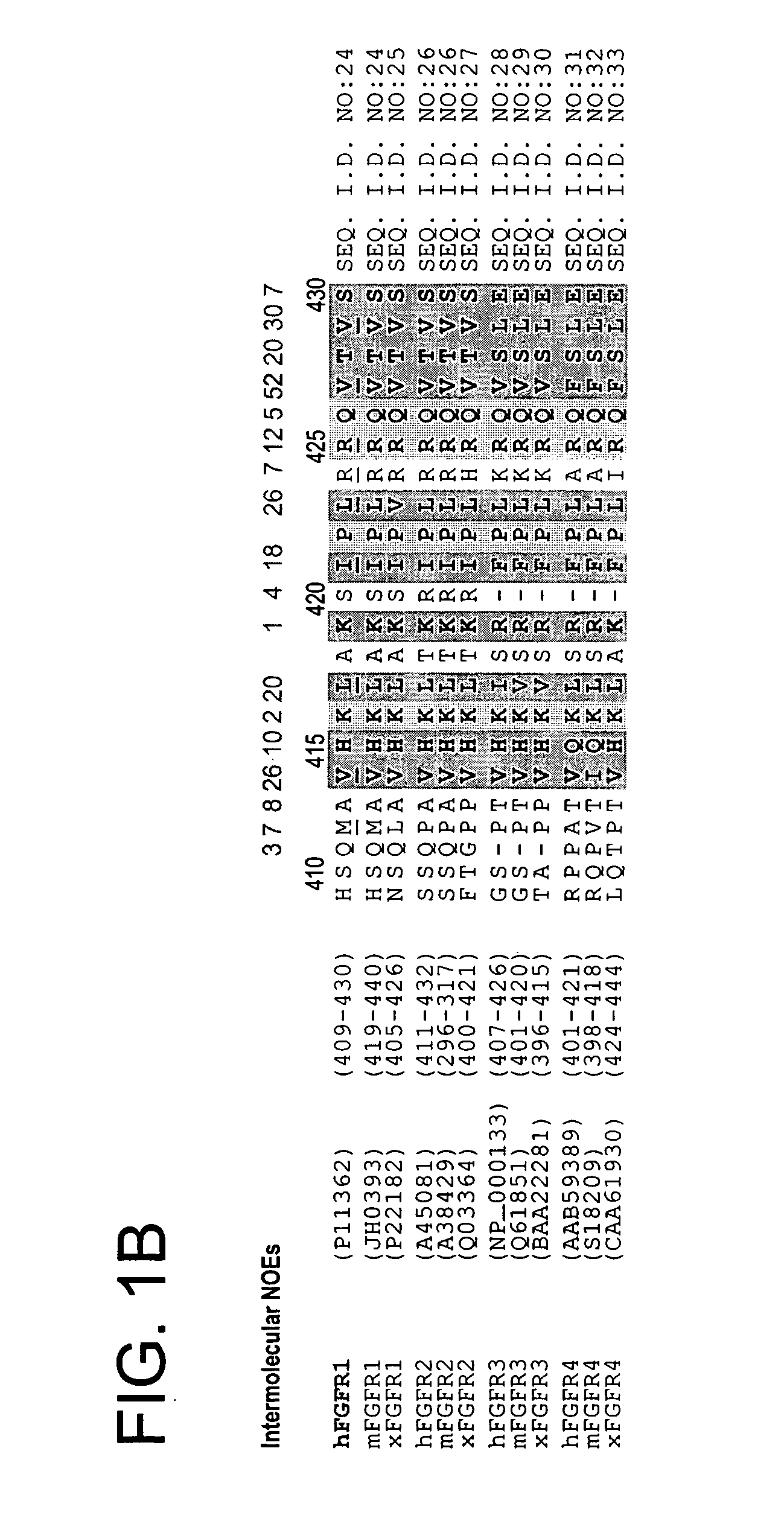
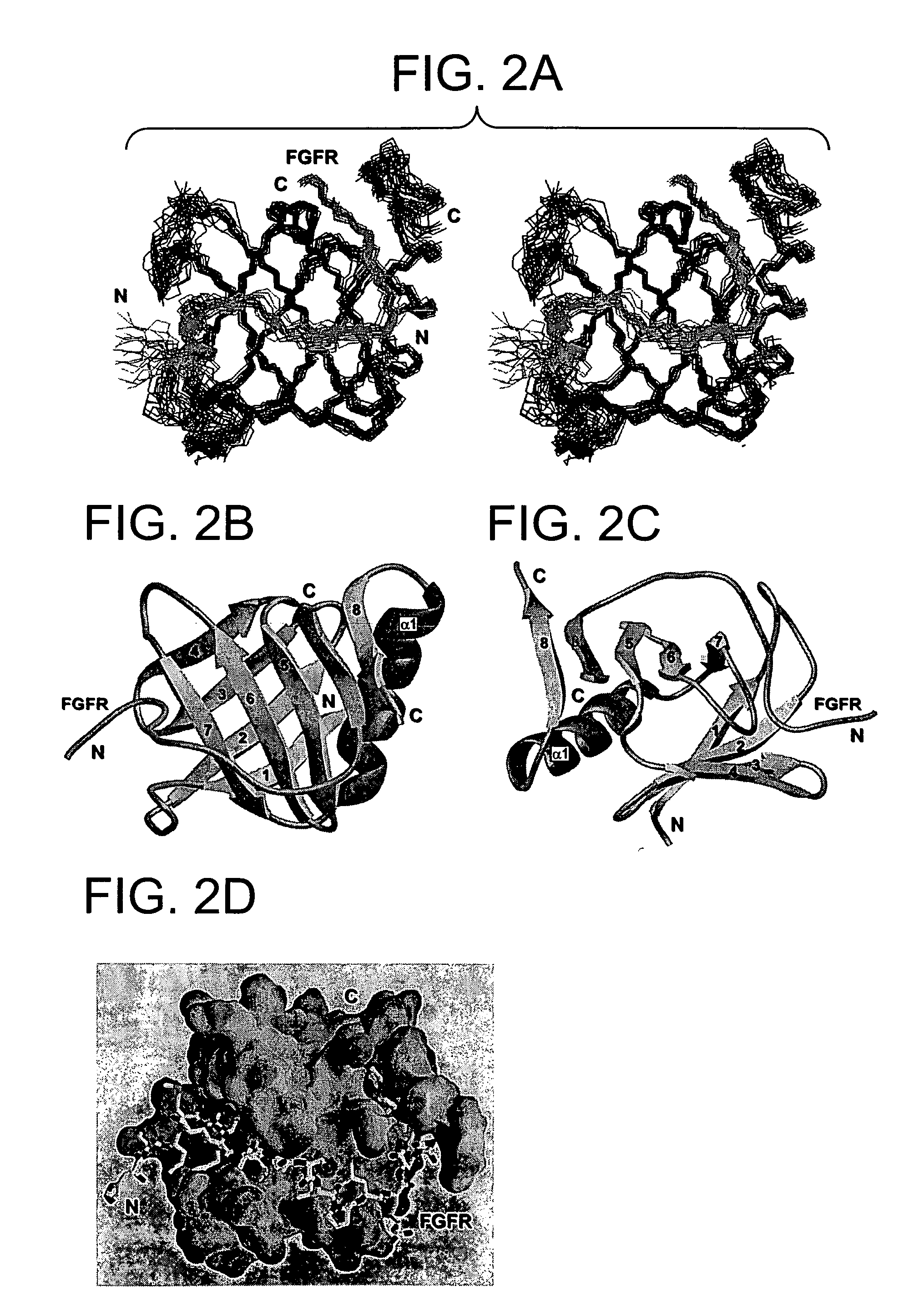
The present invention provides fragments of SNT and FGFR which can form a binding complex that is amenable to structural determinations by NMR spectroscopy. The three-dimensional structural data is also included as part of the invention. In addition, the present invention provides methodology for related structure based rational drug design using the three-dimensional data. Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the fragments are also provided.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Bridged bispecific fusion protein
The invention relates to a bridged bispecific fusion protein, specifically, relates to an improved fusion protein for antagonizing an angiogenesis inducible factor and a use thereof, more specifically, relates to the fusion protein of a VEGF receptor and an FGF receptor and the use thereof in treatment of angiogenesis-related diseases.
Owner:REMEGEN CO LTD
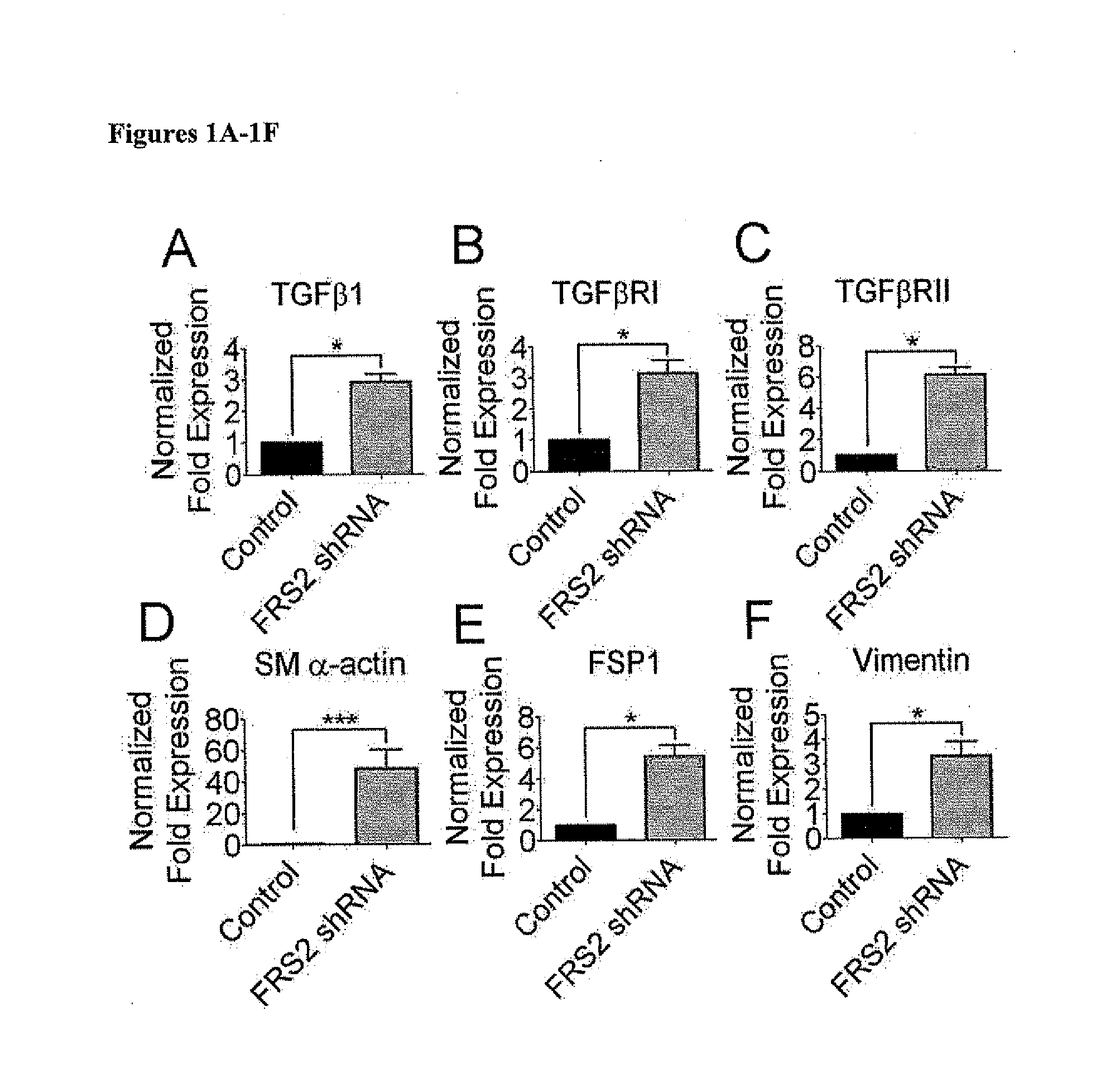
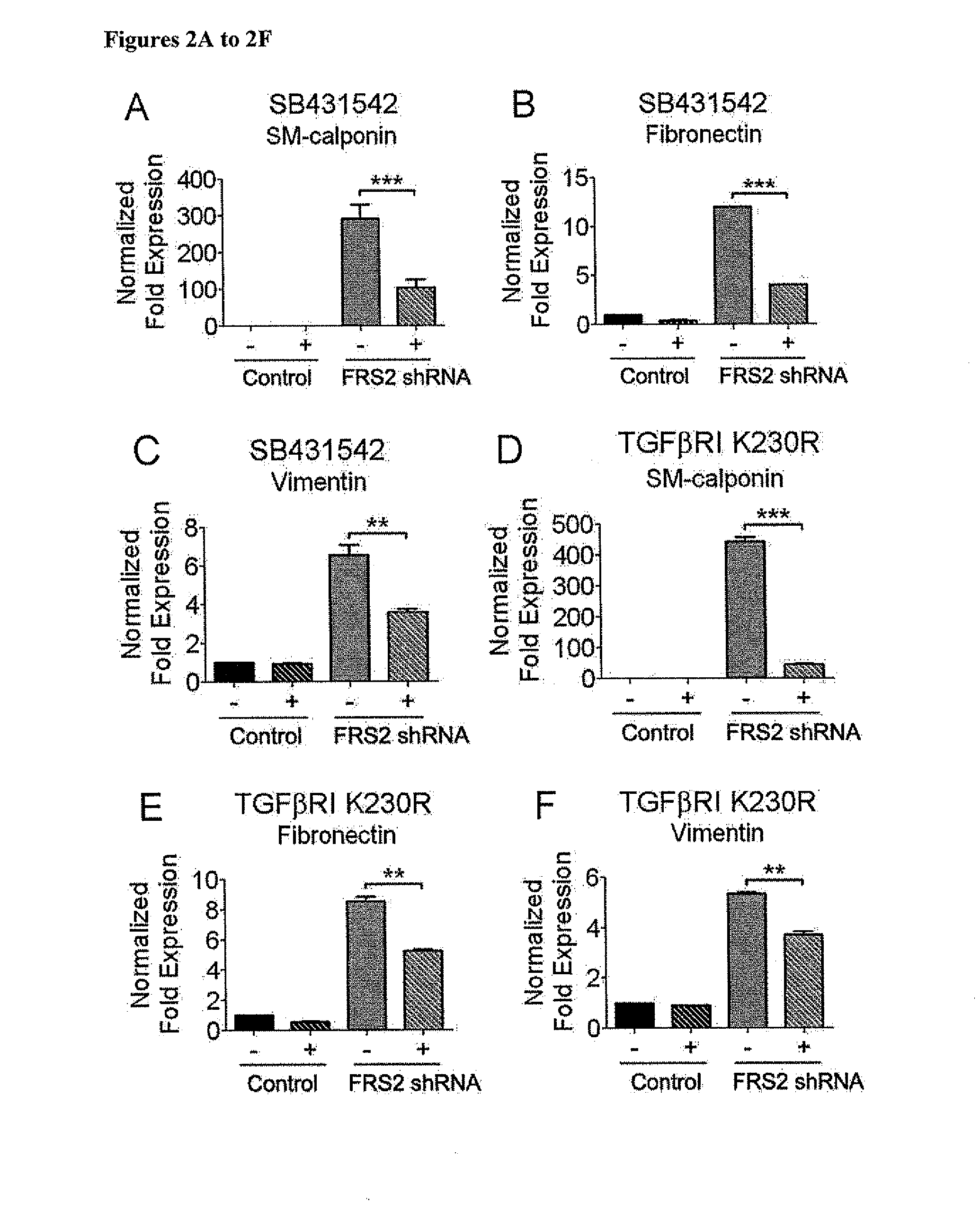
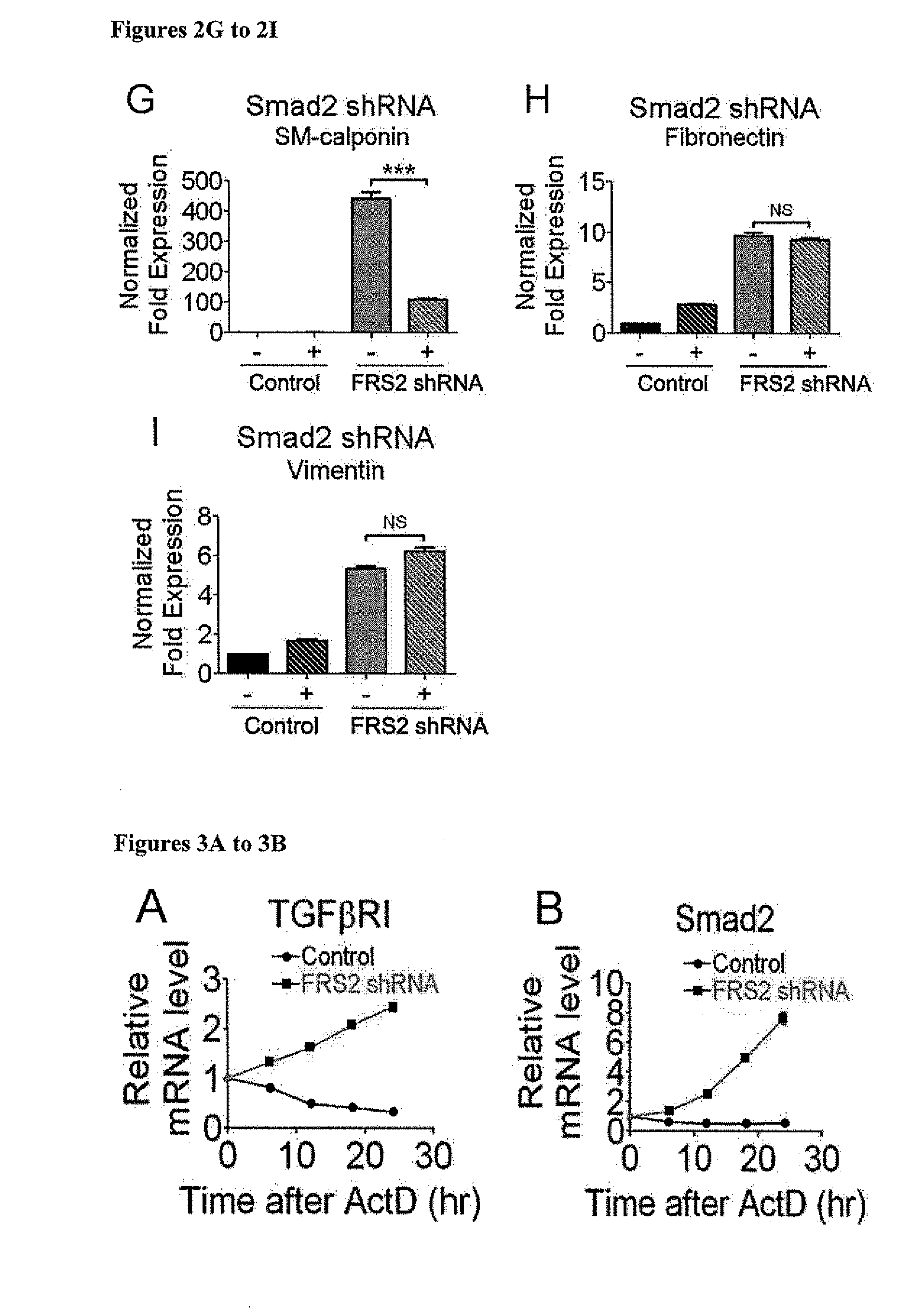
Compositions and Methods for Treating and Preventing Neointimal Stenosis
ActiveUS20140348889A1Convenient and smoothGreater off-the-shelf availabilityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell freeNeointima
Methods for treating or preventing neointima stenosis are disclosed. The methods generally involve the use of a TGFβ inhibitor, a SMAD2 inhibitor, an FGF Receptor agonist, a Let-7 agonist, or a combination thereof, to inhibit endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (Endo-MT) of vascular endothelial cells into smooth muscle cells (SMC) at sites of endothelial damage. The disclosed methods can therefore be used to prevent or inhibit neointimal stenosis or restenosis, e.g., after angioplasty, vascular graft, or stent. Also disclosed are methods for increasing the patency of biodegradable, synthetic vascular grafts using a composition that inhibits Endo-MT. A cell-free tissue engineered vascular graft (TEVG) produced by this method is also disclosed.
Owner:YALE UNIV
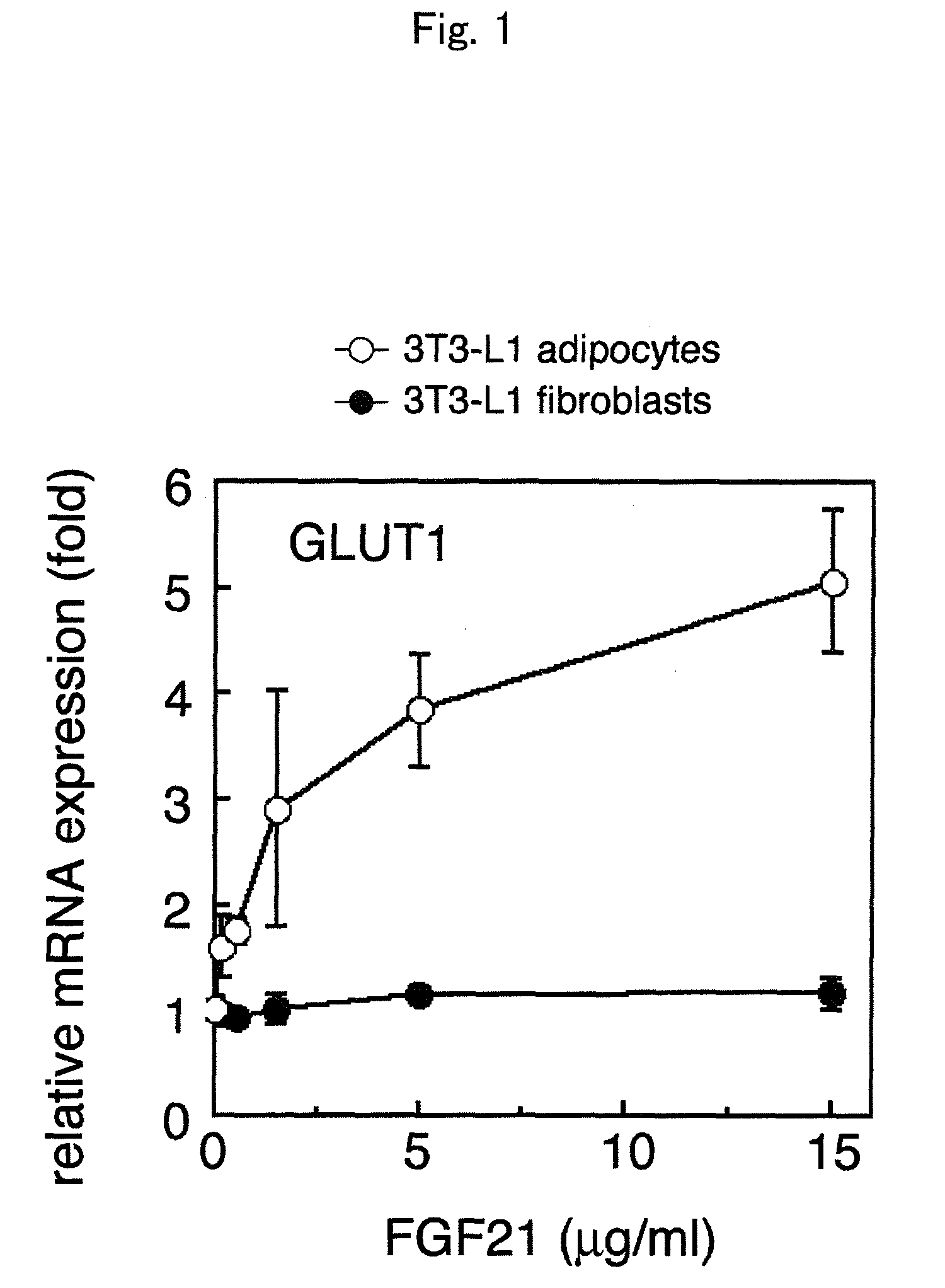
Method for screening a test substance for activating a receptor associated with FGF 21 activity
InactiveUS8697369B2Effective factorReduced activityCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsCell systemBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Using betaKlotho or a substance that increases or inhibits betaKlotho activity as an agent for controlling the activity of FGF21 mediated by an FGF receptor, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising such betaKlotho or such substance as an active ingredient, particularly, a pharmaceutical composition for anti-metabolic syndrome, and further particularly, a pharmaceutical composition for therapeutic or preventive use associated with the control of blood glucose level. In addition, the present invention provides a screening system for each of a substance that enhances or suppresses betaKlotho activity, an FGF21-like active substance, and a betaKlotho-like active substance, which uses a cell system that has expressed an FGF receptor and / or betaKlotho on the surface thereof.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Devices containing DNA encoding neurotrophic agents and related compositions and methods
InactiveUS20080152689A1Efficient transferPromotes neuronal survivalPowder deliveryVirusesNervous systemAnti fibrotic
Devices useful in the delivery of DNA encoding neurotrophic agents, anti-fibrotic agents, and related compositions are disclosed herein for use in the treatment of central and / or peripheral nervous system injury. Methods of making and using the disclosed devices and DNA are also described. In various embodiments, the invention also discloses compositions and devices that may further include a targeting agent, such as a polypeptide that is reactive with an FGF receptor (e.g., bFGF), or another ligand that binds to cell surface receptors on neuronal cells, or a support cell. The invention also discloses methods of promoting neuronal survival and regeneration via transfection of an axon as it grows through a device or composition of the present invention, or via transfection of a repair cell.
Owner:TISSUE REPAIR CO +2
Compositions containing nucleic acids and ligands for therapeutic treatment
InactiveUS7138381B2Increase flexibilityVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityTherapeutic treatment
Preparations of conjugates of a receptor-binding internalized ligand and a cytocide-encoding agent and compositions containing such preparations are provided. The conjugates contain a polypeptide that is reactive with an FGF receptor, such as bFGF, or another heparin-binding growth factor, cytokine, or growth factor coupled to a nucleic acid binding domain. One or more linkers may be used in the conjugation. The linker is selected to increase the specificity, toxicity, solubility, serum stability, or intracellular availability, and promote nucleic acid condensation of the targeted moiety. The conjugates are complexed with a cytocide-encoding agent, such as DNA encoding saporin. Conjugates of a receptor-binding internalized ligand to a nucleic acid molecule are also provided.
Owner:CARDIUM BIOLOGICS
Neural stem cells
ActiveCN103146649ARestore neural circuitsRestore brain functionNervous disorderMicroorganism based processesFGF ReceptorSignalling pathways
A homogenous, symmetrically dividing population of adherent neural stem cells is obtained from ES cells or foetal or adult brain isolates, using an activator of a signalling pathway downstream of a receptor of the EGF receptor family, optionally in combination with an activator of a signalling pathway downstream of an FGF receptor. The neural stem cell population is highly pure and retains the ability to differentiate into neurons after in excess of 100 passages.
Owner:THE UNIV OF EDINBURGH
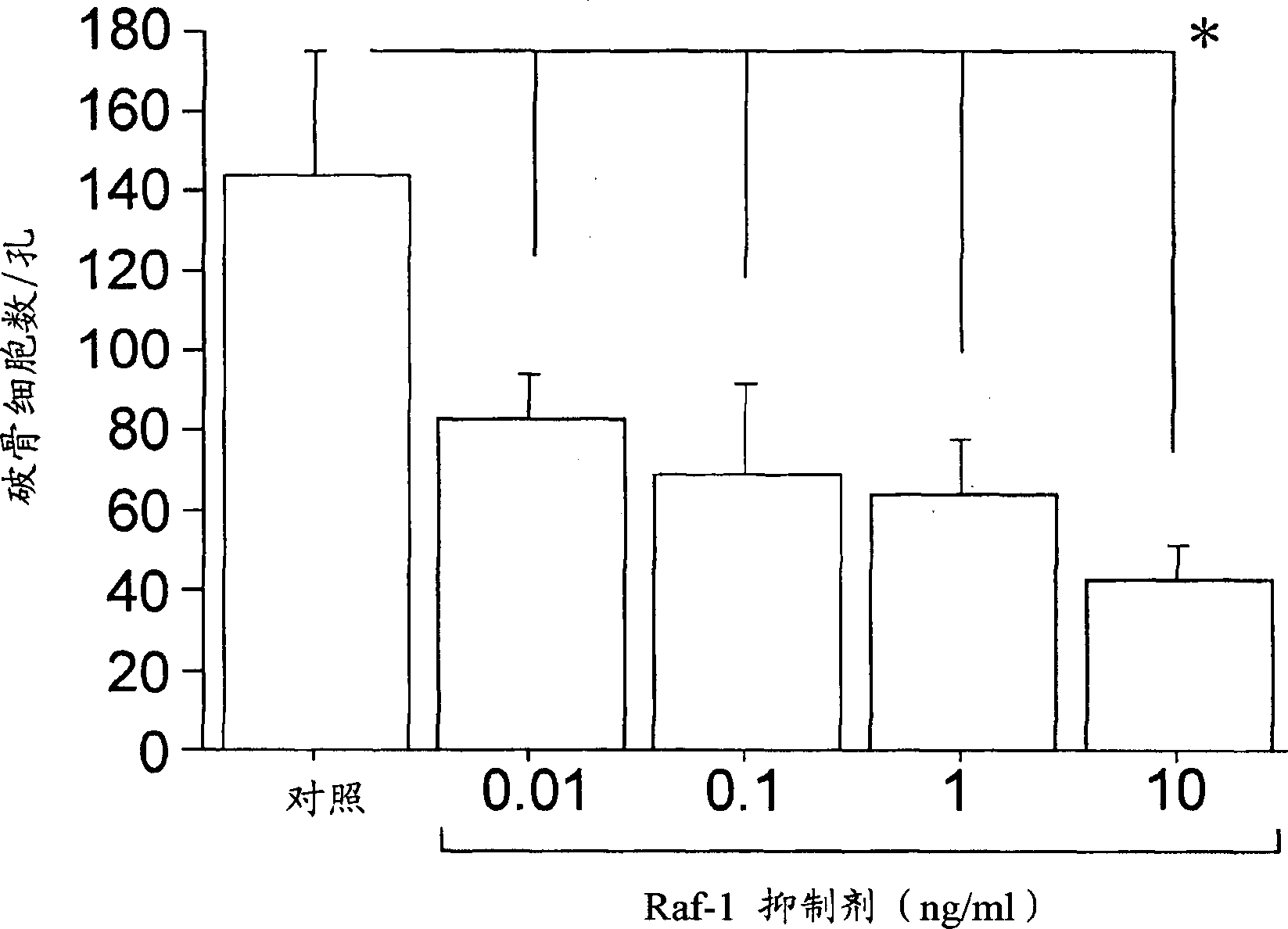
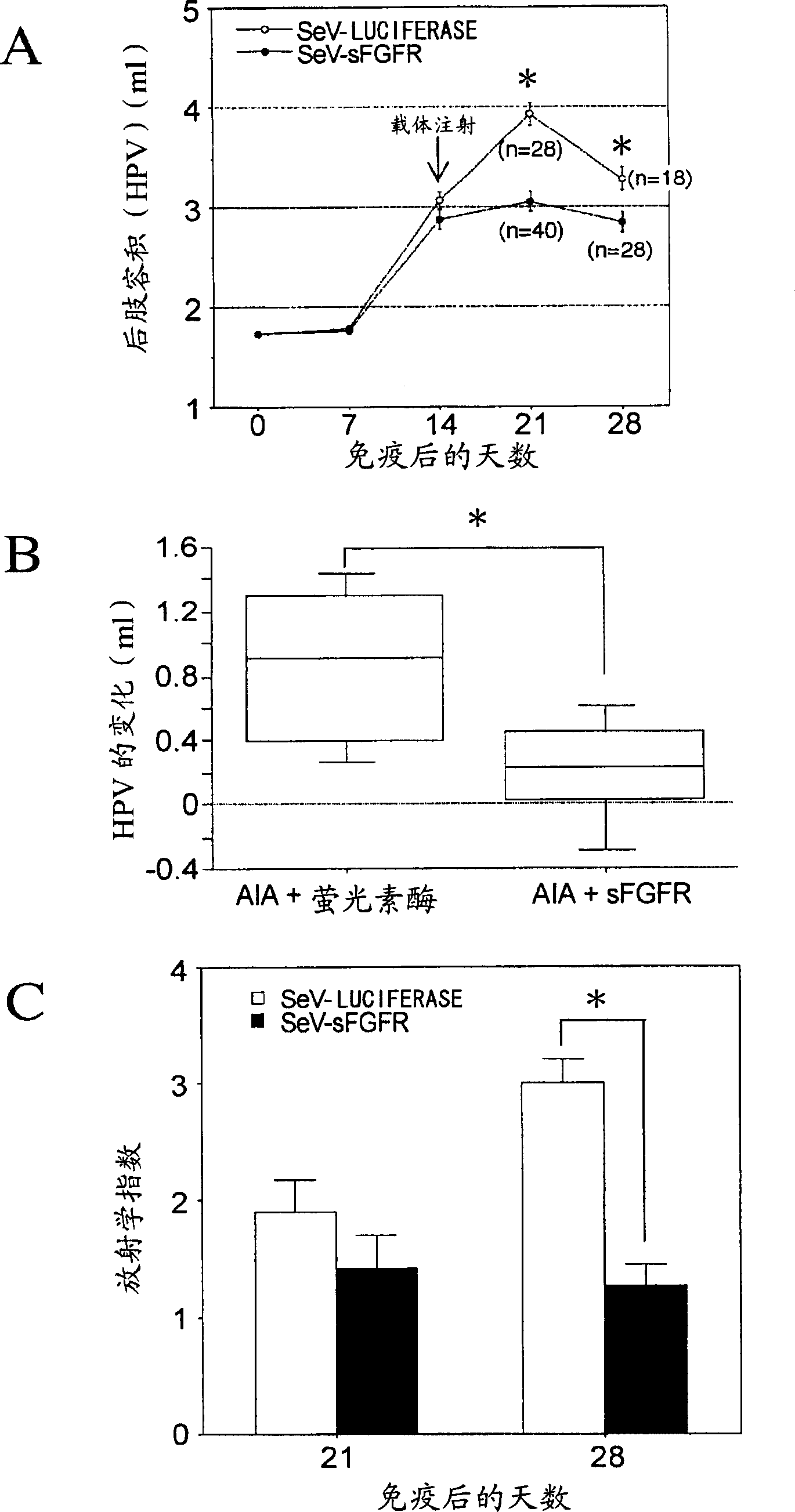
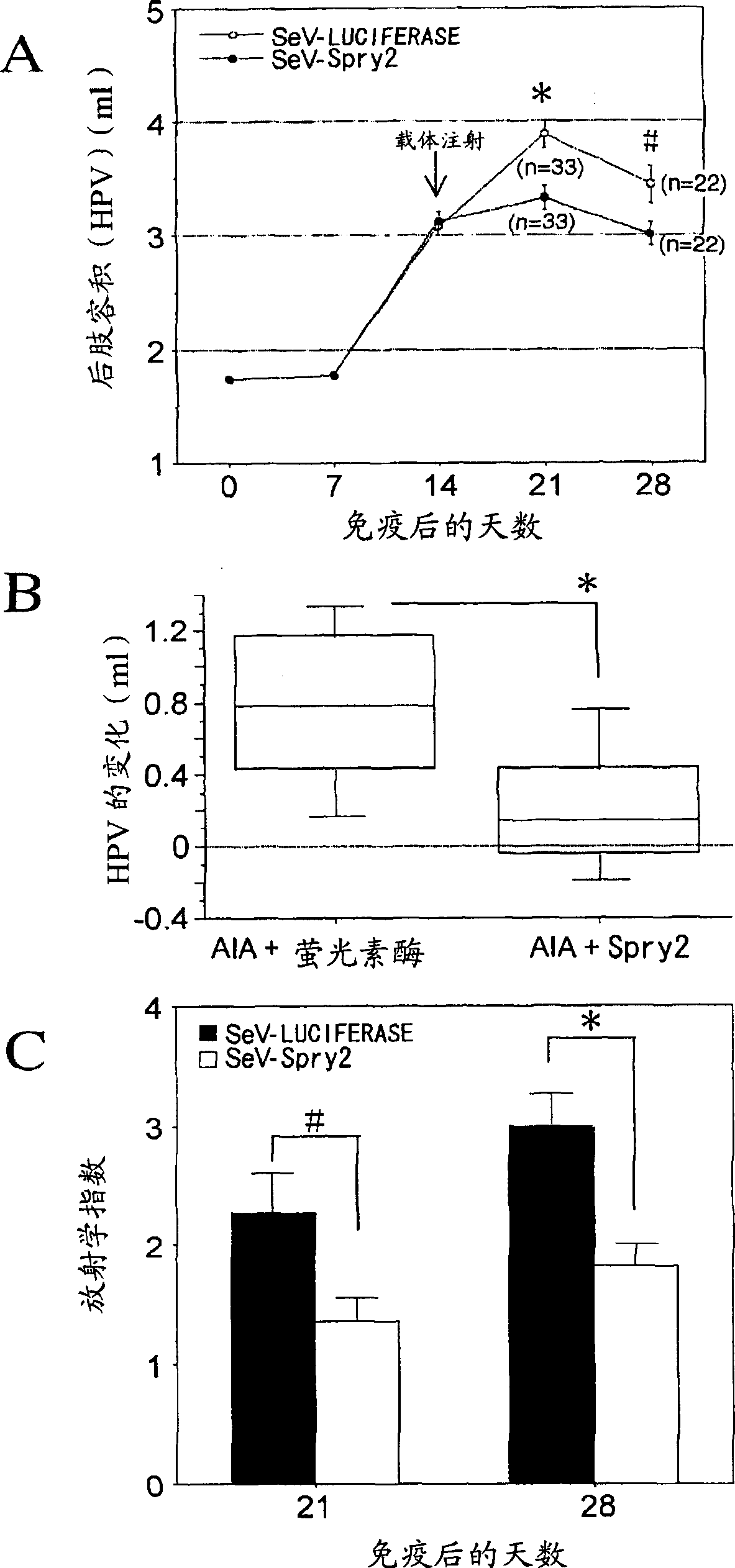
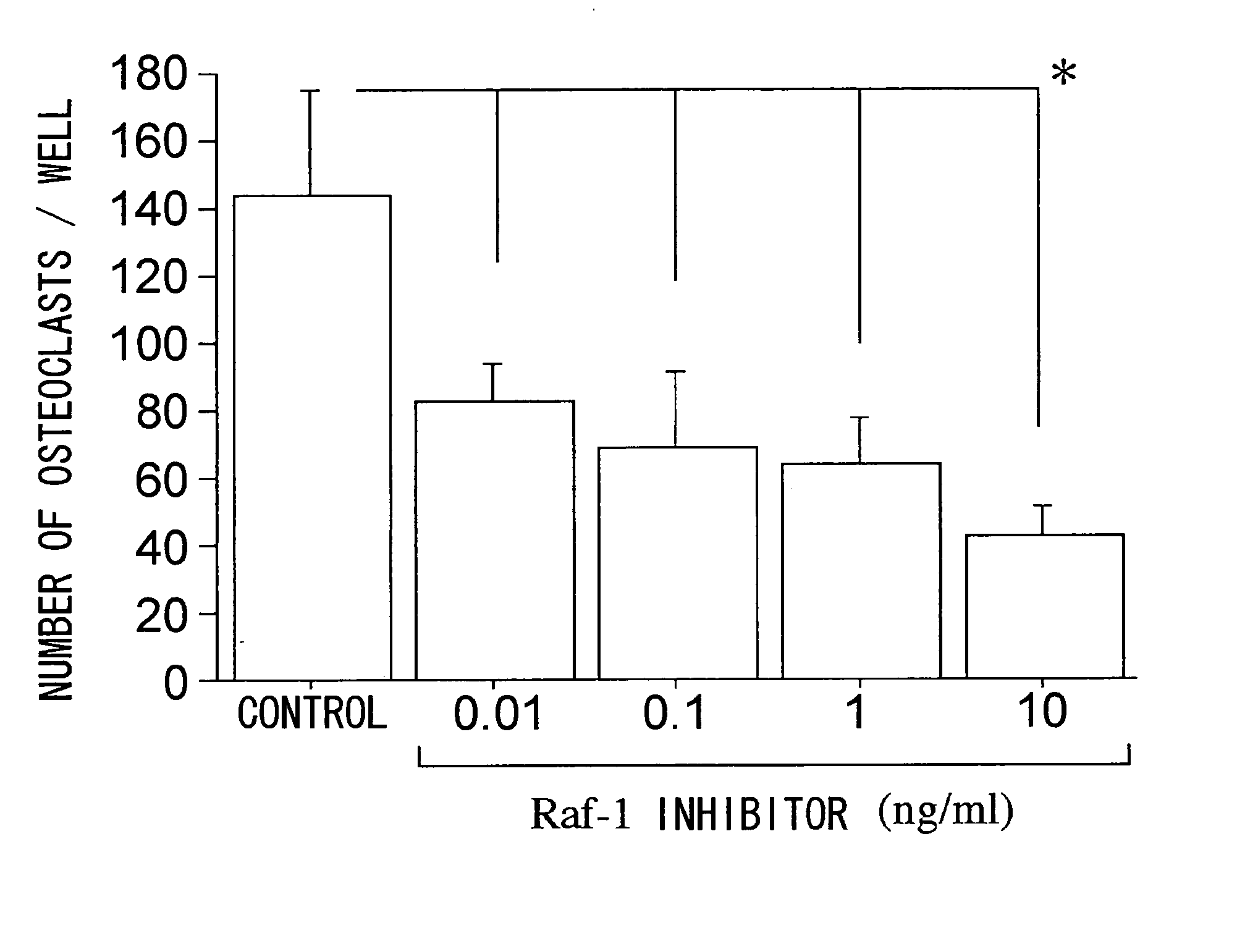
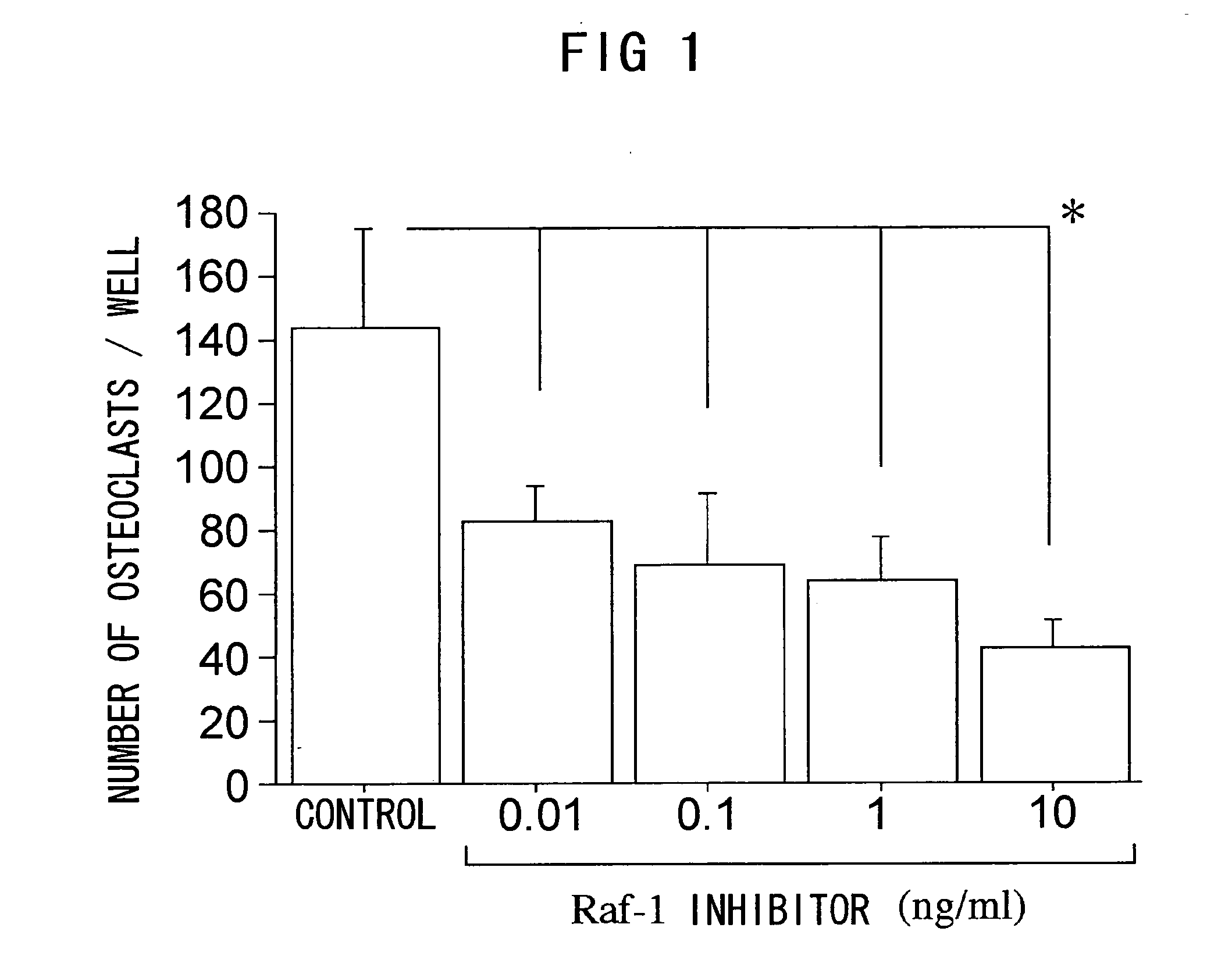
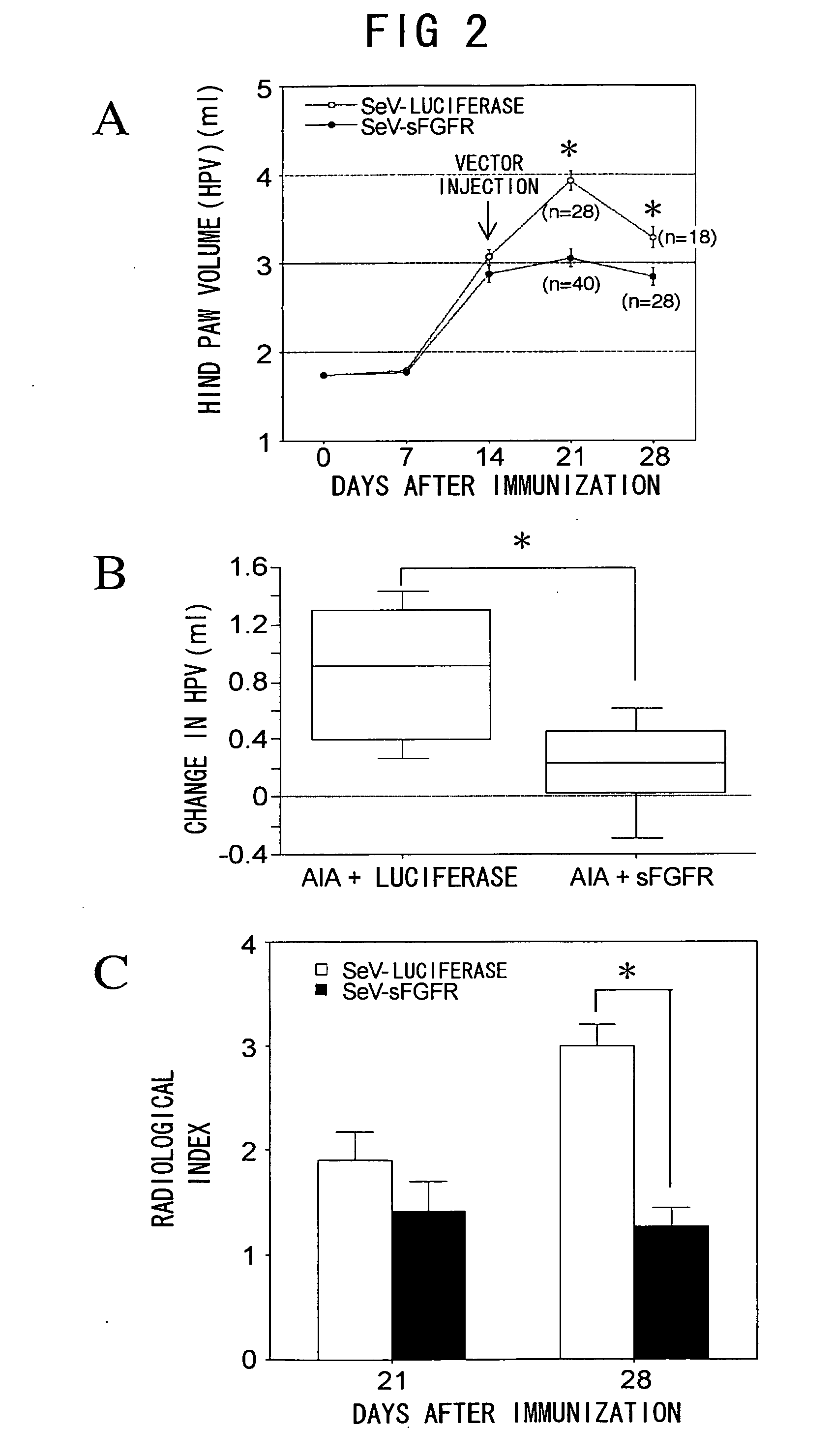
Methods of treating inflammatory diseases associated with bone destruction
InactiveUS20070173466A1Joint inflammation was significantly suppressedBone mass reduction was easedOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsFGF ReceptorKinase
The present invention relates to methods for treating inflammatory diseases accompanied by bone destruction, comprising the step of administering a viral vector comprising a gene which inhibits signal transduction mediated by fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF2)-FGF receptor 1-Ras-Raf-MAP kinase to a diseased region. Furthermore, the present invention relates to therapeutic compositions for inflammatory diseases accompanied by bone destruction, which comprise these vectors. By inhibiting FGF2 signal transduction through local administration of viral vectors, both inflammation and bone destruction in inflammatory bone destruction were simultaneously suppressed. The present invention provides disease-specific and effective therapeutic methods, and therapeutic compositions for inflammatory diseases such as osteoarthritis, for which therapy has so far been difficult.
Owner:DNAVEC RES
Fusion protein for antagonizing angiogenesis inducible factors and uses thereof
The present invention relates to angiogenesis-inhibitory fusion proteins and use thereof. Particularly, the present invention provides fusion proteins inhibiting a plurality of angiogenic factors. More particularly, the present invention relates to the fusion proteins of VEGF receptor and FGF receptor and their applications in the treatment of angiogenesis related diseases.
Owner:REMEGEN CO LTD
4,6-dimethyl-oxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-5,7(4H,6H)-dione derivative acting on FGF receptor
The invention discloses a 4,6-dimethyl-oxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-5,7(4H,6H)-dione derivative acting on a fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor. A target compound is prepared by implementing nitrosation on 1,3-dimethyl pyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione which serves as a starting material through NaNO2, reducing the material through Na2S2O4, implementing a Schiff alkali reaction with aromatic aldehyde, and finally cyclizing through SOCl2. The 4,6-dimethyl-oxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-5,7(4H,6H)-dione derivative disclosed by the invention has a certain inhibiting function on experimental cells and shows a certain antitumor activity. For an H460 cell, IC50 values of compounds N5a, N5g and N5k are less than that of a positive control drug; for a B16F10 cell, IC50 values of compounds N5f, N5h and N5i are less than IC50 value of the positive control drug; for an A549 cell, IC50 value of the positive control is relatively high, and IC50 values of compounds N5f, N5g, N5h and N5l are less than IC50 value of the positive control drug.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Method of treating inflammtory disease associated with bone destruction
The present invention relates to a method for treating inflammatory diseases accompanied by bone destruction, comprising administering to the diseased site a viral vector containing inhibitory fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF2)-FGF receptor 1-Ras-Raf-MAP kinase Genes that mediate signaling. The present invention also relates to a therapeutic composition for the treatment of inflammatory diseases accompanied by bone destruction, comprising the above-mentioned carrier. Inhibition of FGF2 signaling by topical administration of viral vectors can simultaneously inhibit both inflammation and bone destruction in inflammatory bone destruction. The invention provides an effective treatment method and a treatment composition specifically for inflammatory diseases such as osteoarthritis which are currently difficult to treat.
Owner:DNAVEC RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com






![4,6-dimethyl-oxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-5,7(4H,6H)-dione derivative acting on FGF receptor 4,6-dimethyl-oxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-5,7(4H,6H)-dione derivative acting on FGF receptor](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/bbc25202-a55e-4ba2-937a-acb1451160f4/HDA0000468144480000011.PNG)
![4,6-dimethyl-oxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-5,7(4H,6H)-dione derivative acting on FGF receptor 4,6-dimethyl-oxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-5,7(4H,6H)-dione derivative acting on FGF receptor](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/bbc25202-a55e-4ba2-937a-acb1451160f4/HDA0000468144480000021.PNG)
![4,6-dimethyl-oxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-5,7(4H,6H)-dione derivative acting on FGF receptor 4,6-dimethyl-oxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-5,7(4H,6H)-dione derivative acting on FGF receptor](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/bbc25202-a55e-4ba2-937a-acb1451160f4/HDA0000468144480000031.PNG)