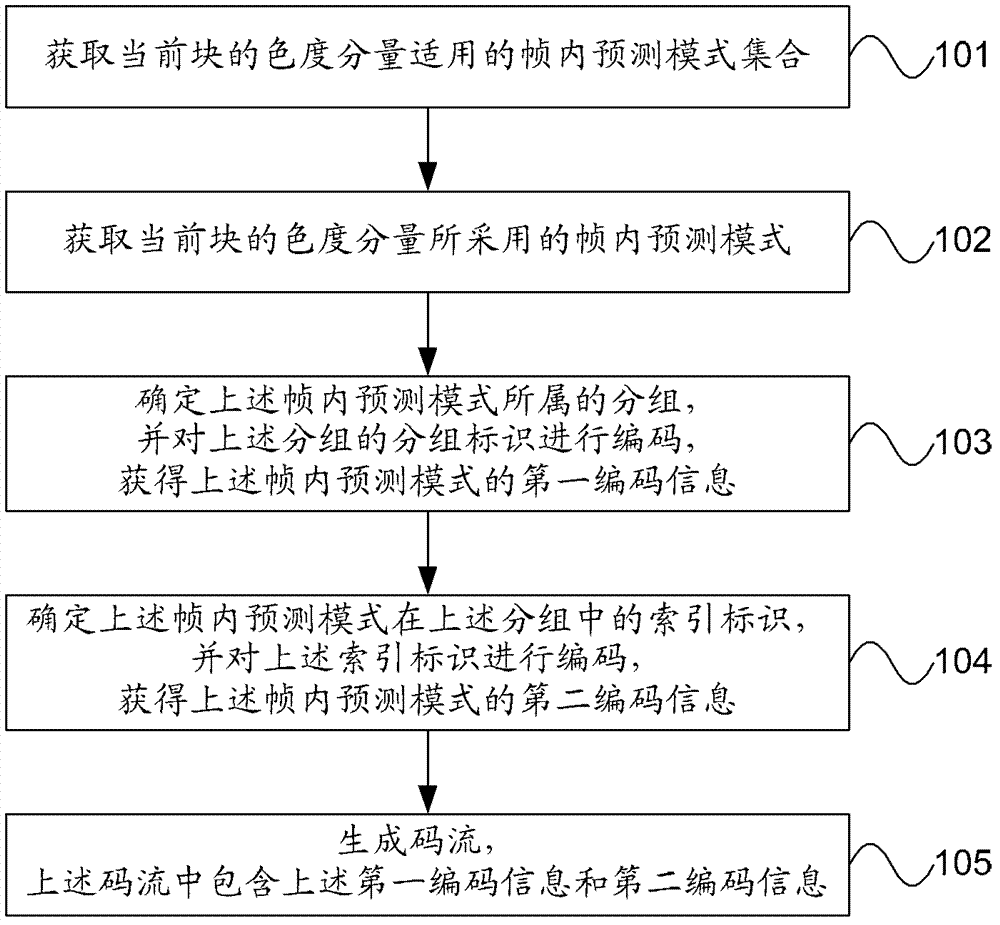
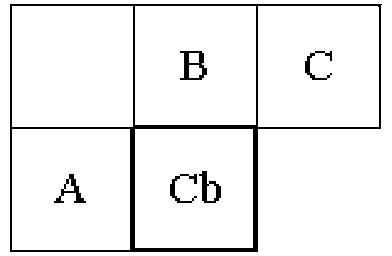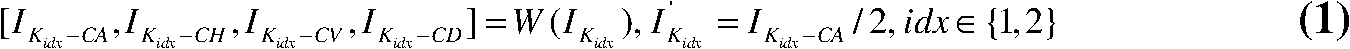Patents
Literature
122 results about "Spiht coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
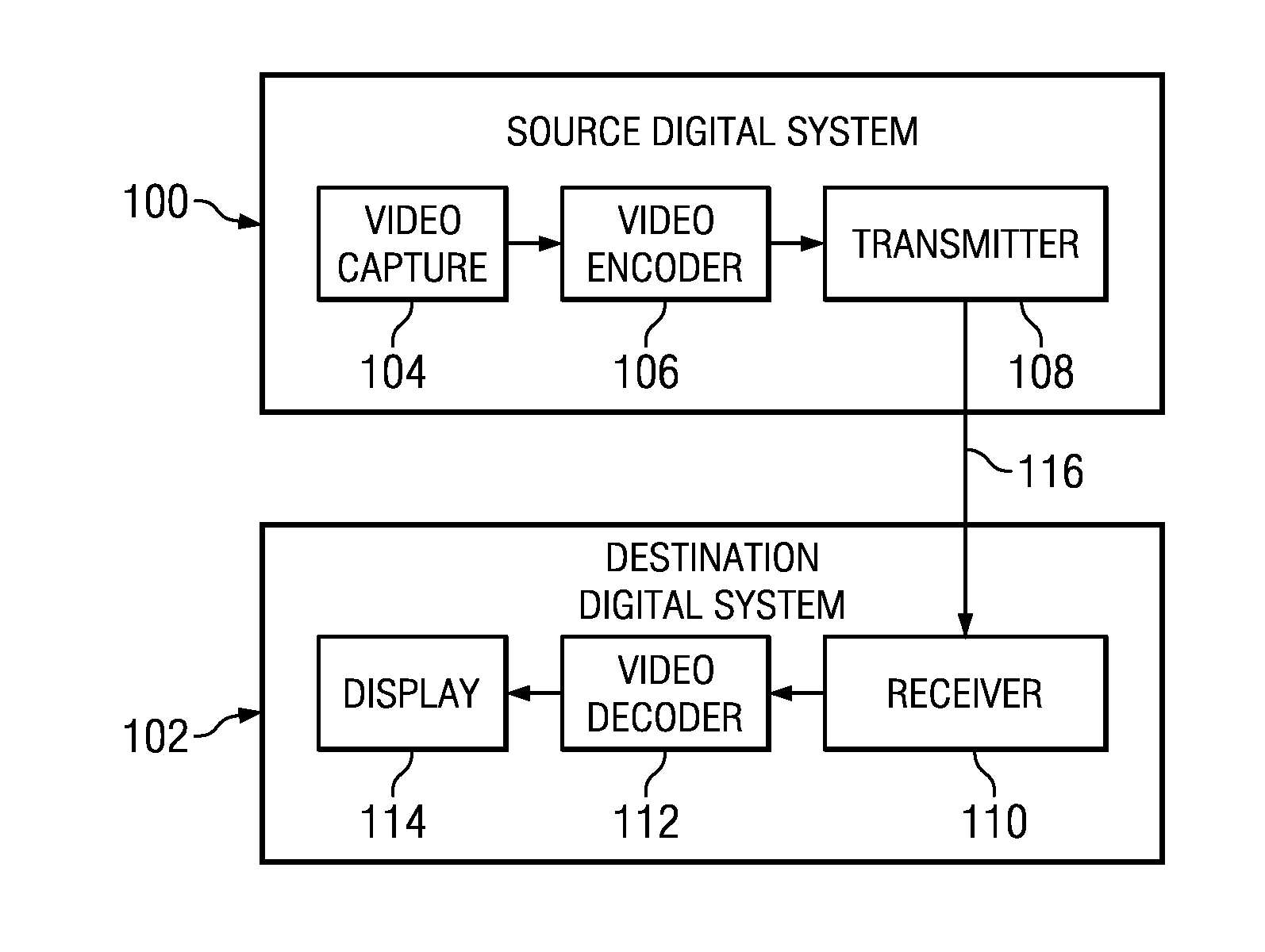
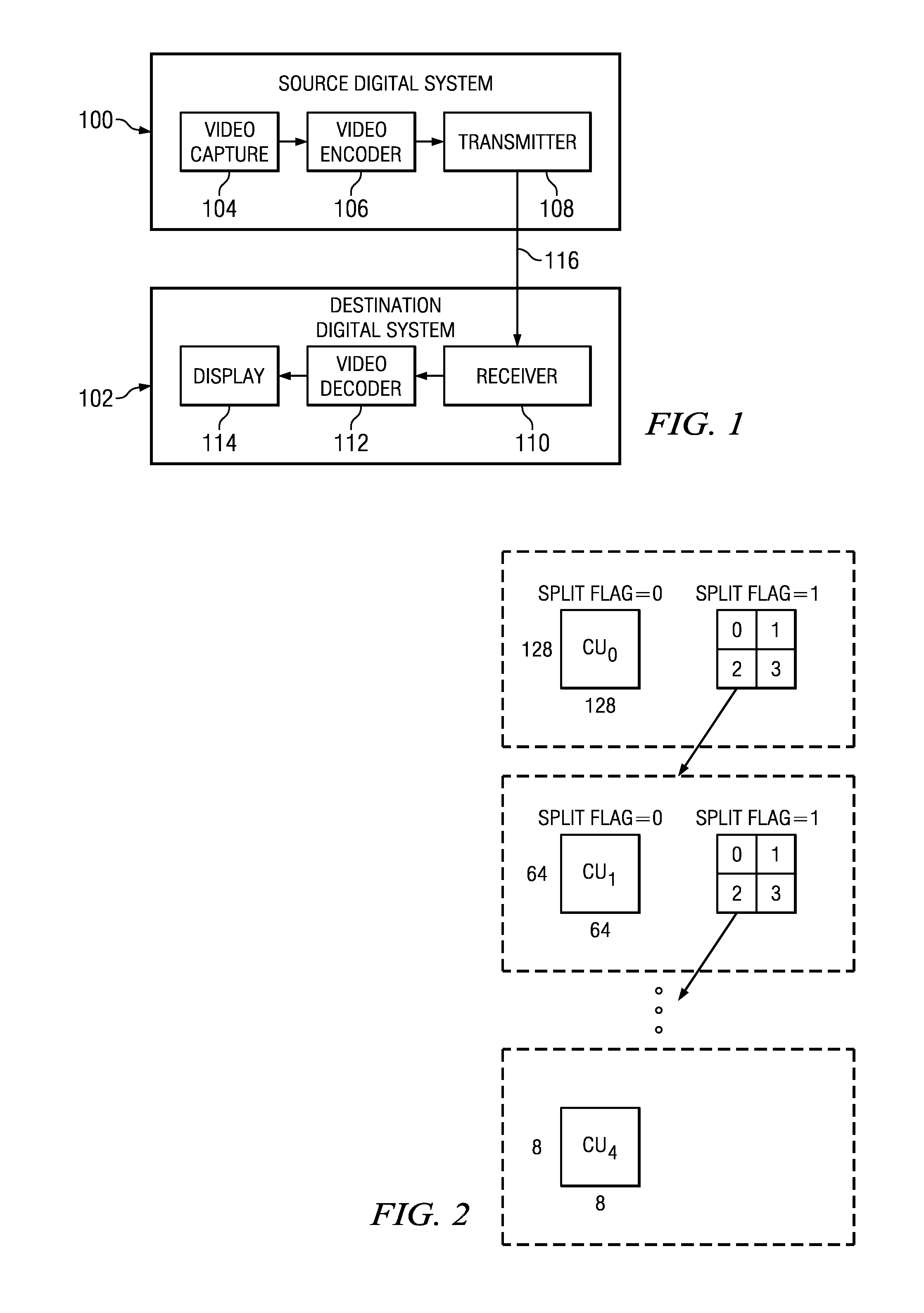
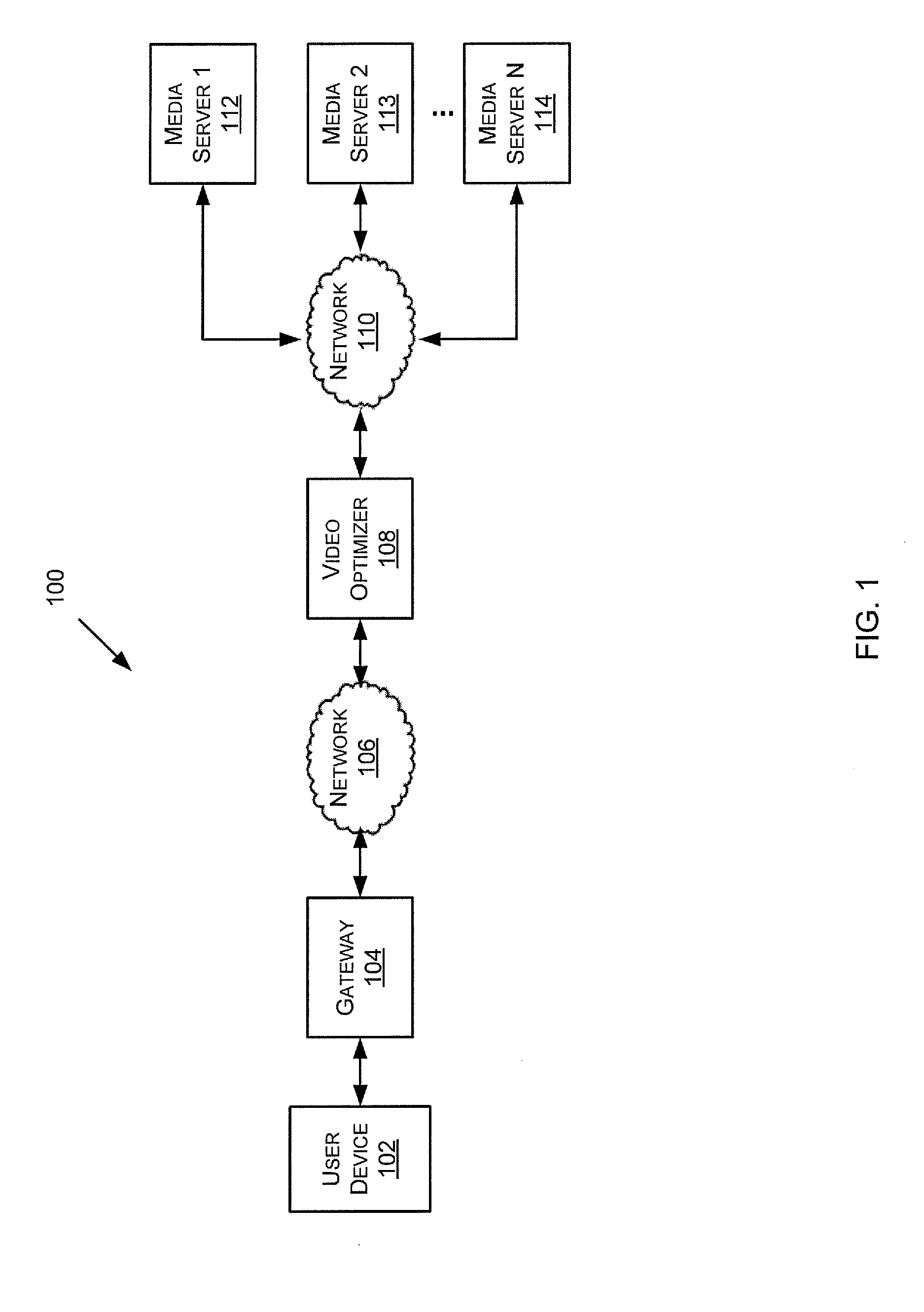
Coding Unit Quantization Parameters in Video Coding
InactiveUS20110274162A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureVideo encoding
A method is provided that includes receiving a coded largest coding unit in a video decoder, wherein the coded largest coding unit includes a coded coding unit structure and a plurality of coded quantization parameters, and decoding the coded largest coding unit based on the coded coding unit structure and the plurality of coded quantization parameters.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
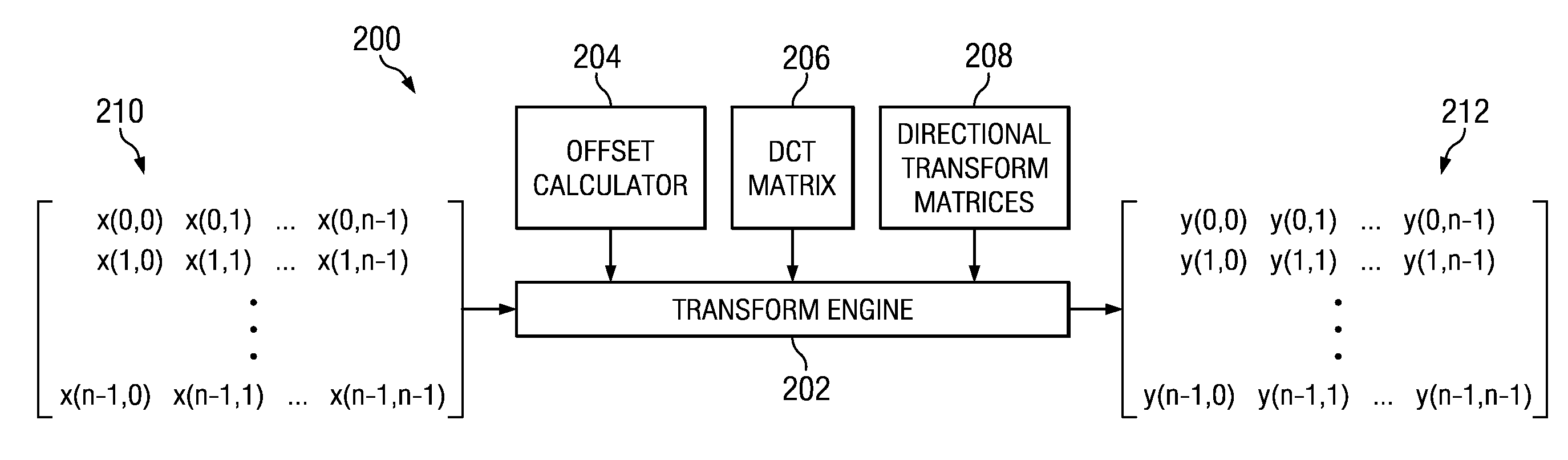
Transform and Quantization Architecture for Video Coding and Decoding
ActiveUS20120082212A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer graphics (images)Video encoding
A method of encoding a video stream in a video encoder is provided that includes computing an offset into a transform matrix based on a transform block size, wherein a size of the transform matrix is larger than the transform block size, and wherein the transform matrix is one selected from a group consisting of a DCT transform matrix and an IDCT transform matrix, and transforming a residual block to generate a DCT coefficient block, wherein the offset is used to select elements of rows and columns of a DCT submatrix of the transform block size from the transform matrix.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Video encoding and decoding using transforms
ActiveUS20140056362A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionOn columnComputer graphics (images)
Video encoding or decoding utilising a spatial transform operating on rows and columns of a block, with a set of transform skip modes including: transform on rows and columns; transform on rows only; transform on columns only; no transform. An indication of the selected mode is provided to the decoder. Coefficients are scaled by a factor dependent upon the norm of the transform vector of the skipped transform to bring the untransformed image values to the same level as transformed coefficients.
Owner:BRITISH BROADCASTING CORP
Method and apparatus of motion and disparity vector derivation for 3D video coding and HEVC
ActiveCN103907346AReduce precisionReduce offsetDigital video signal modificationSteroscopic systemsParallaxComputer graphics (images)
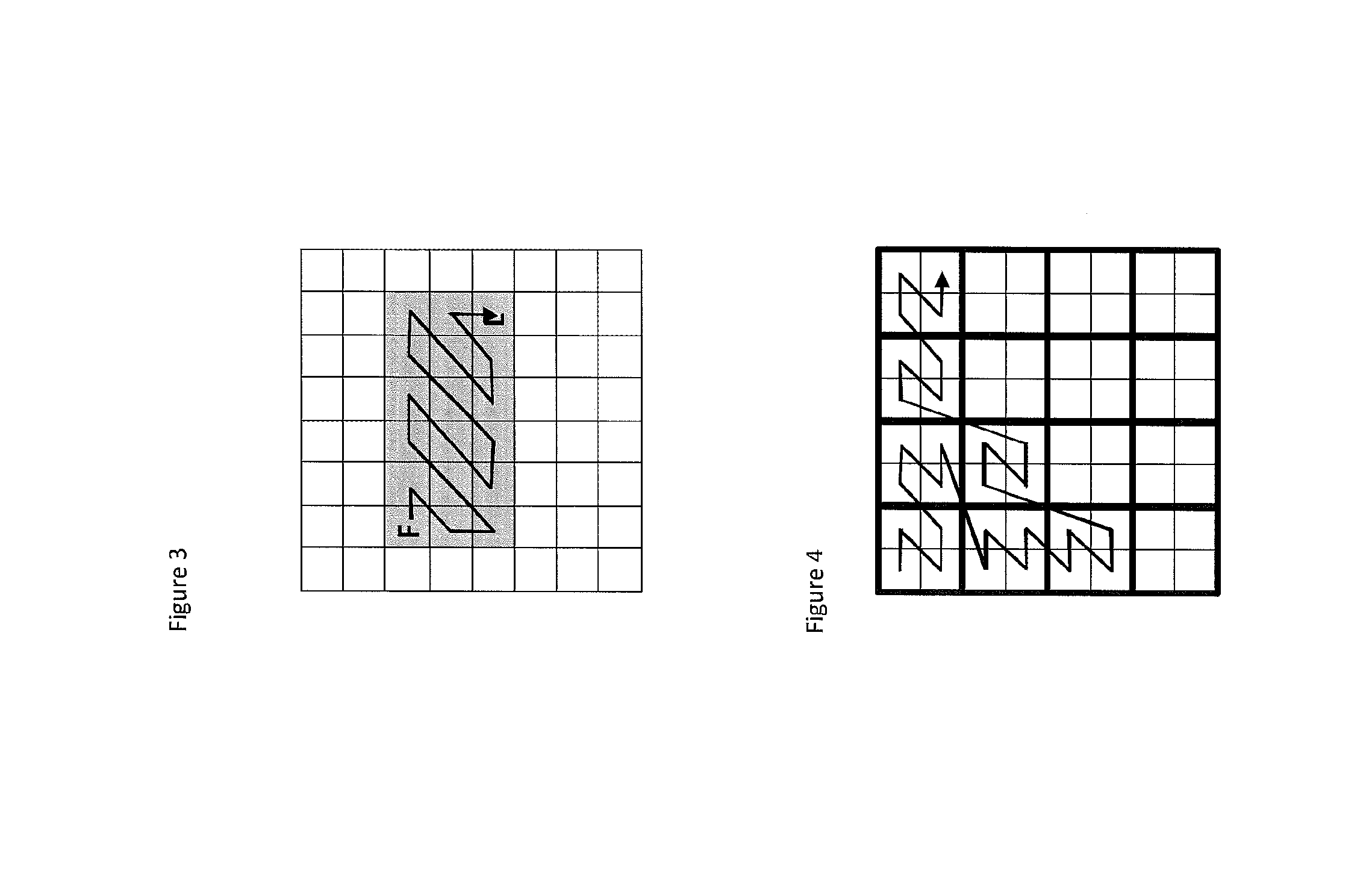
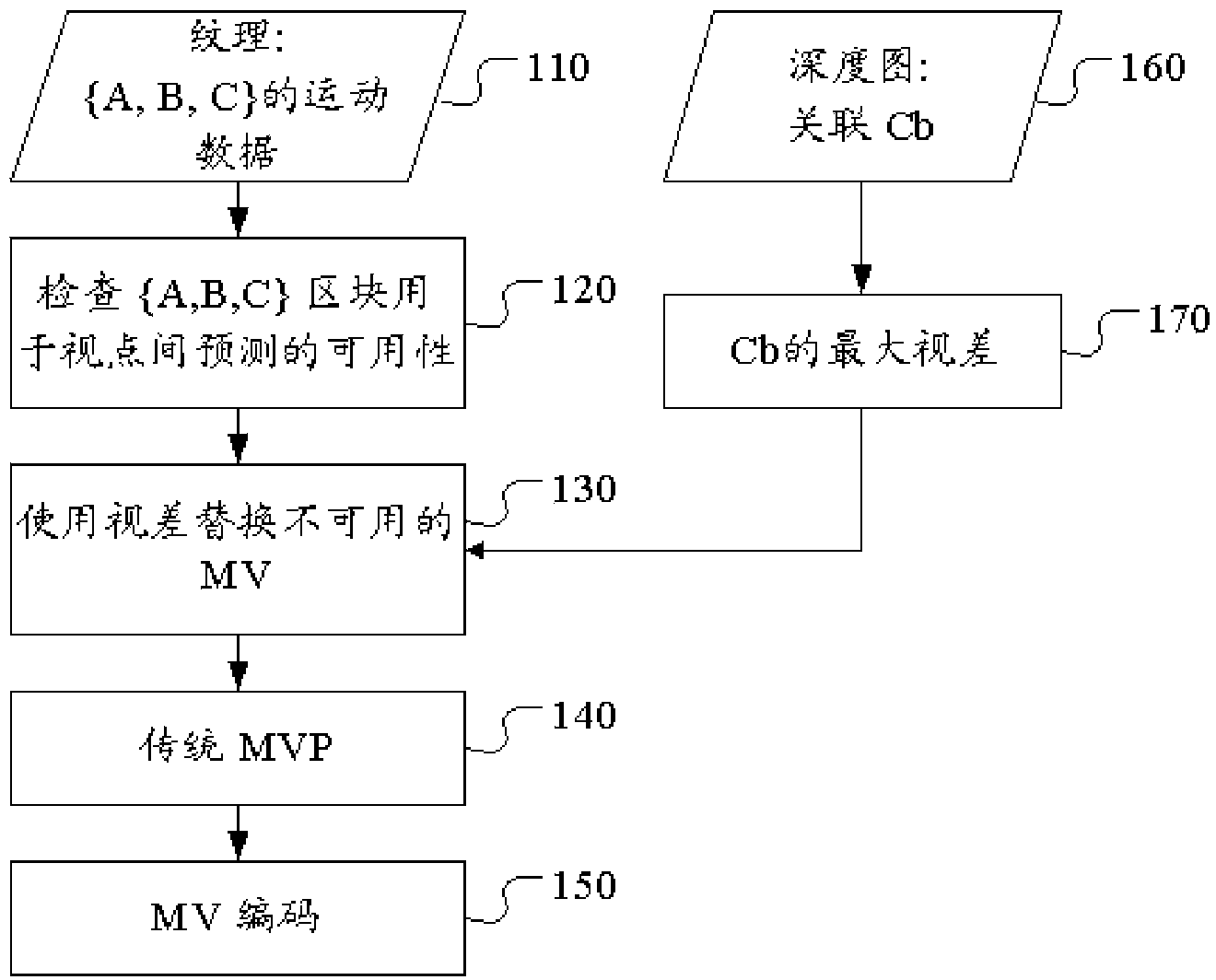
A method and apparatus for deriving MVP (motion vector predictor) for a block for three-dimensional video coding or multi-view video coding are disclosed. Embodiments according to the present invention replace an unavailable inter-view MV of one neighboring block with a disparity vector derived from depth data of a subset of a depth block corresponding to one neighboring block. A method and apparatus for generating additional candidates for motion vector prediction associated with Merge mode or AMVP (Inter) mode for a block are disclosed. Embodiments according to the present invention generate one or more additional MVP candidates to add to the MVP list if the MVP list size is less than a given list size. The additional MVP candidates are generated either by reducing precision of an available MVP in the MVP list or by adding an offset to the available MVP in the MVP list.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
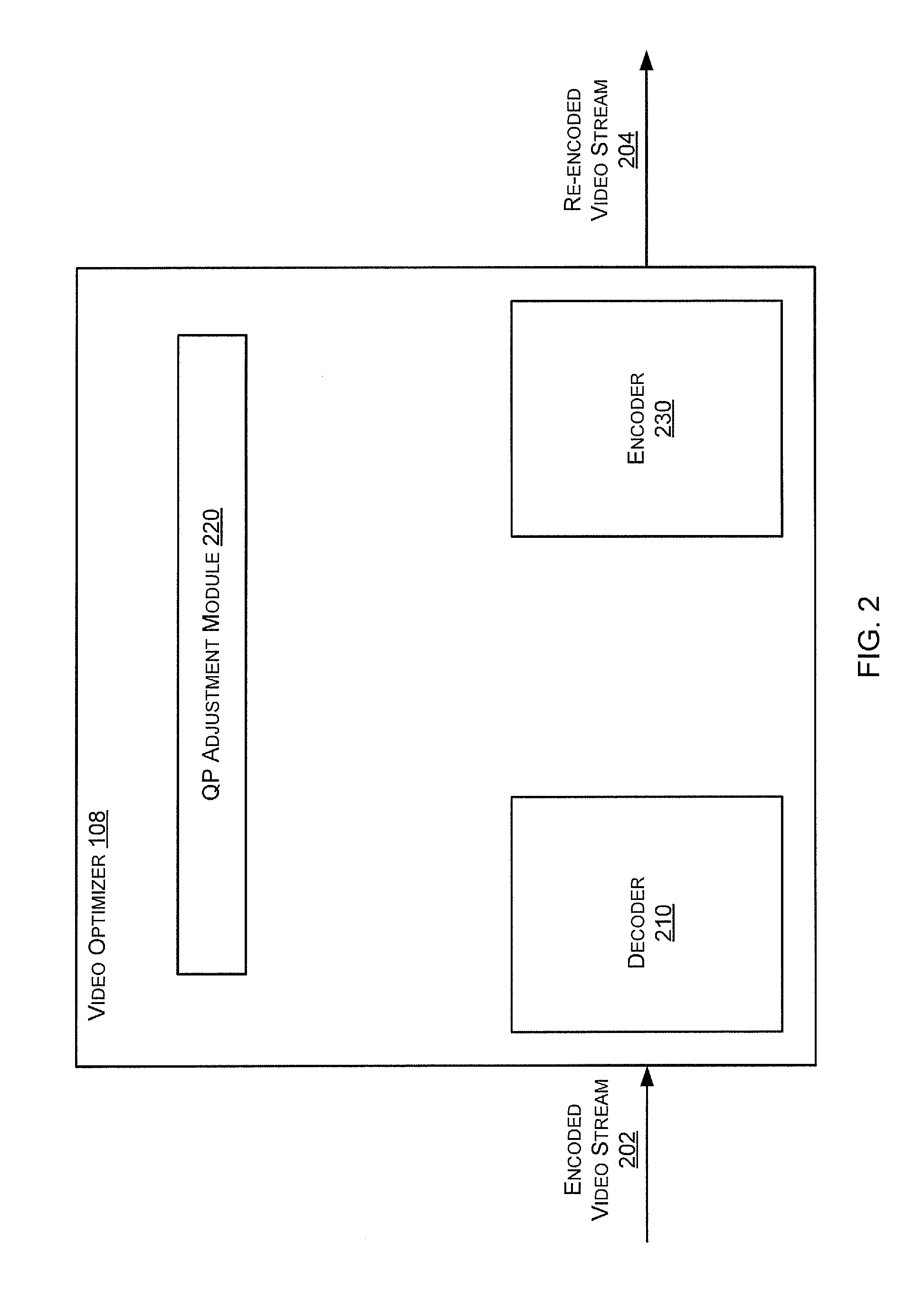
Macroblock-Level Adaptive Quantization in Quality-Aware Video Optimization
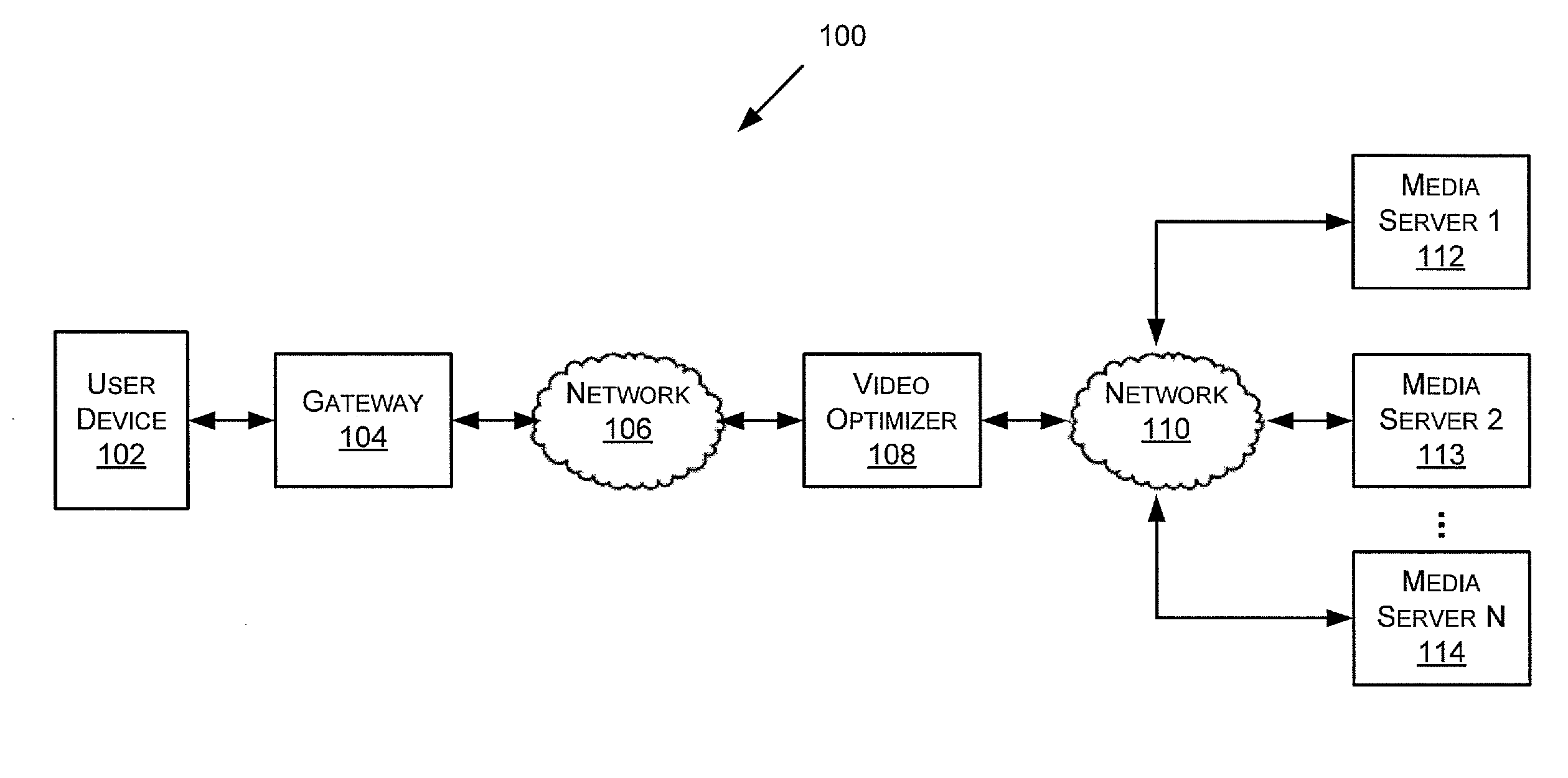
ActiveUS20120314764A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo optimizationPattern recognition
A method of optimizing an encoded video stream comprising one or more video frames, each video frame comprising a plurality of macroblocks, each macroblock comprising a plurality of pixels. The method includes receiving an encoded macroblock, decoding the encoded macroblock, and extracting a first quantization parameter. The first quantization parameter corresponds to quantization settings originally used for compressing the encoded macroblock. The method also includes computing a second quantization parameter based at least in part on the first quantization parameter, re-encoding the decoded macroblock based on the second quantization parameter, and providing the re-encoded macroblock.
Owner:BYTEMOBILE INNOVATIONS LLC
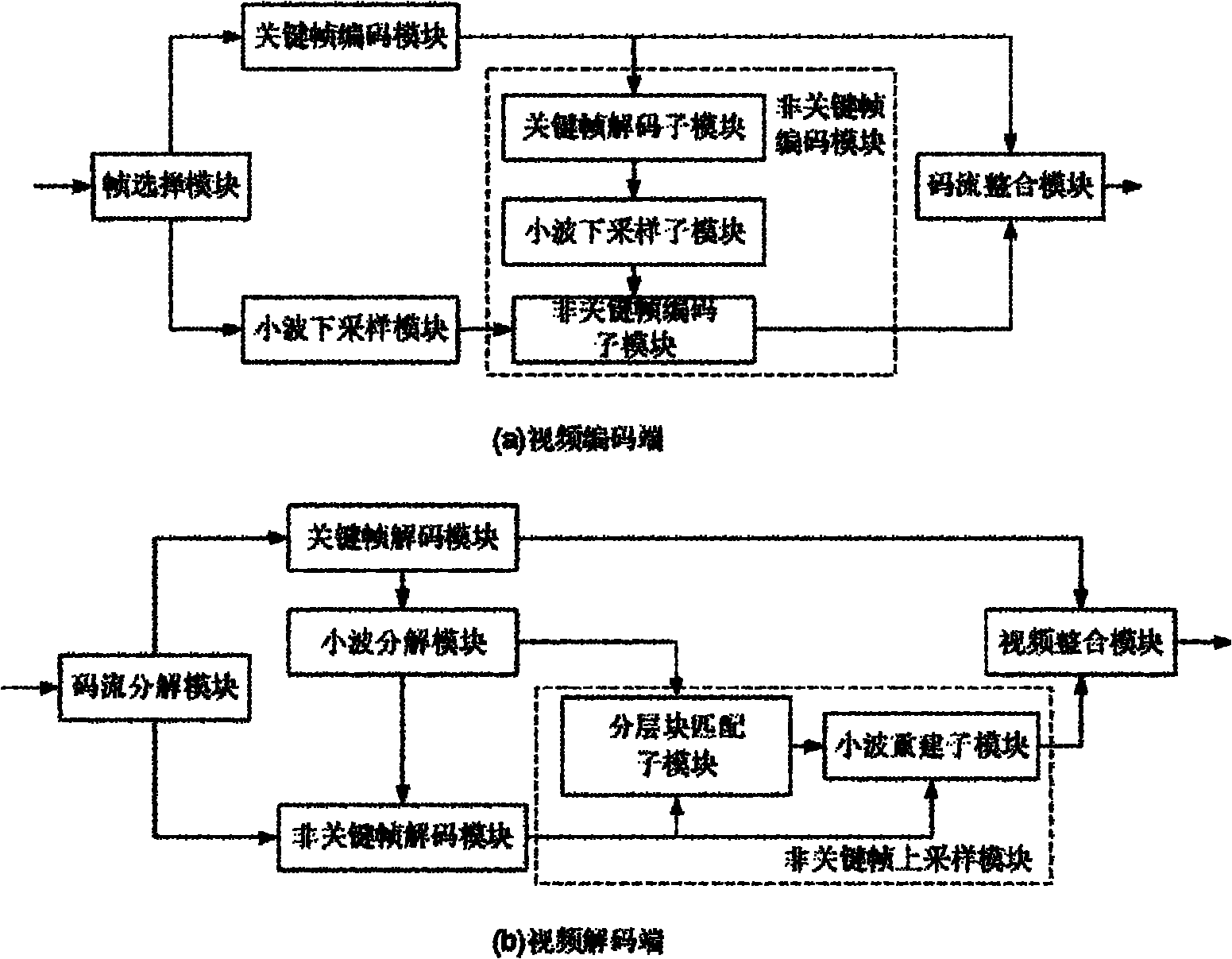
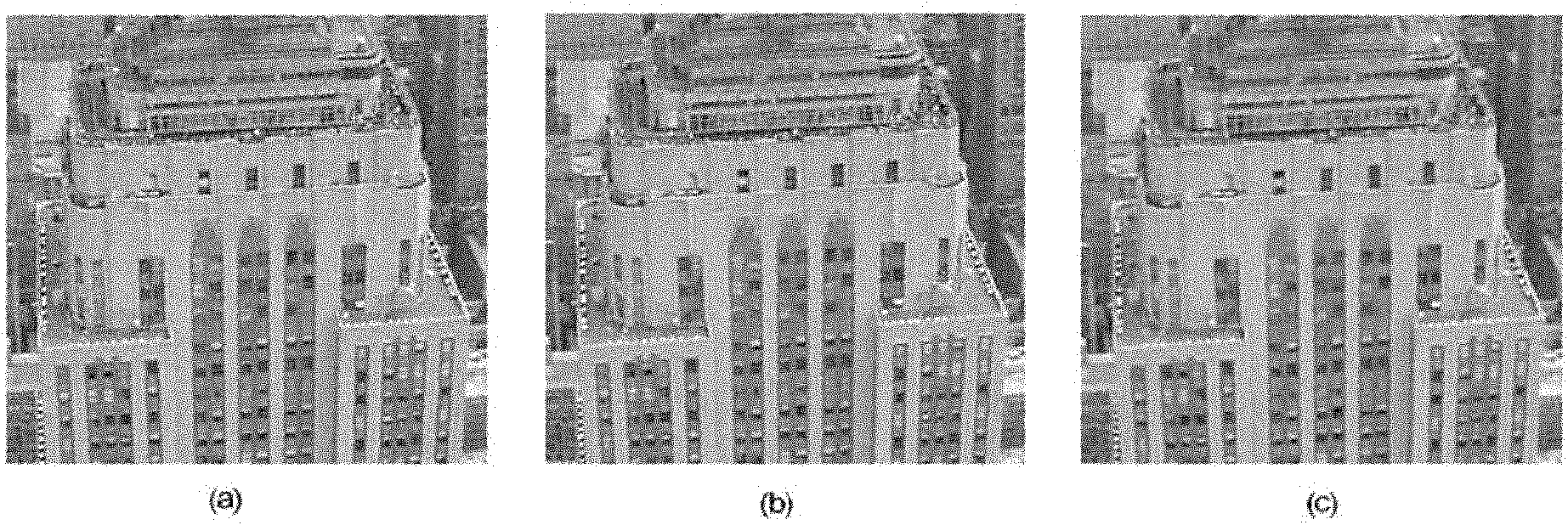
Video coding and decoding system based on keyframe super-resolution reconstruction
InactiveCN101938656AQuality is not affectedReduce bit rateTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationCode moduleWavelet decomposition
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Hybrid skip mode used for depth map encoding and decoding
ActiveCN102752595ATelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionDepth map coding
The invention provides a hybrid skip mode used for depth map encoding and decoding. Compared with a texture view, the differences are that a depth map image has a smooth area and has no complex texture at the edge of an object or rapid change of a pixel value. Although the conventional interframe predicting skip mode is very effective for encoding the texture view, no intra-frame predicting capabilities are included, and the intra-frame prediction is very effective for encoding the smooth area. The hybrid predicting skip mode provided by the invention comprises an interframe predicting skip mode which is coupled with various intra-frame predicting modes; and the predicting mode is selected through calculating the side matching distortion (SMD) of the predicting mode. As no additional indicator bit is required and the bit stream syntax is not changed, high encoding efficiency is kept; and moreover, the encoding program provided by the invention and used for encoding the depth map can be used as the extension of the existing standard and can be realized more easily.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
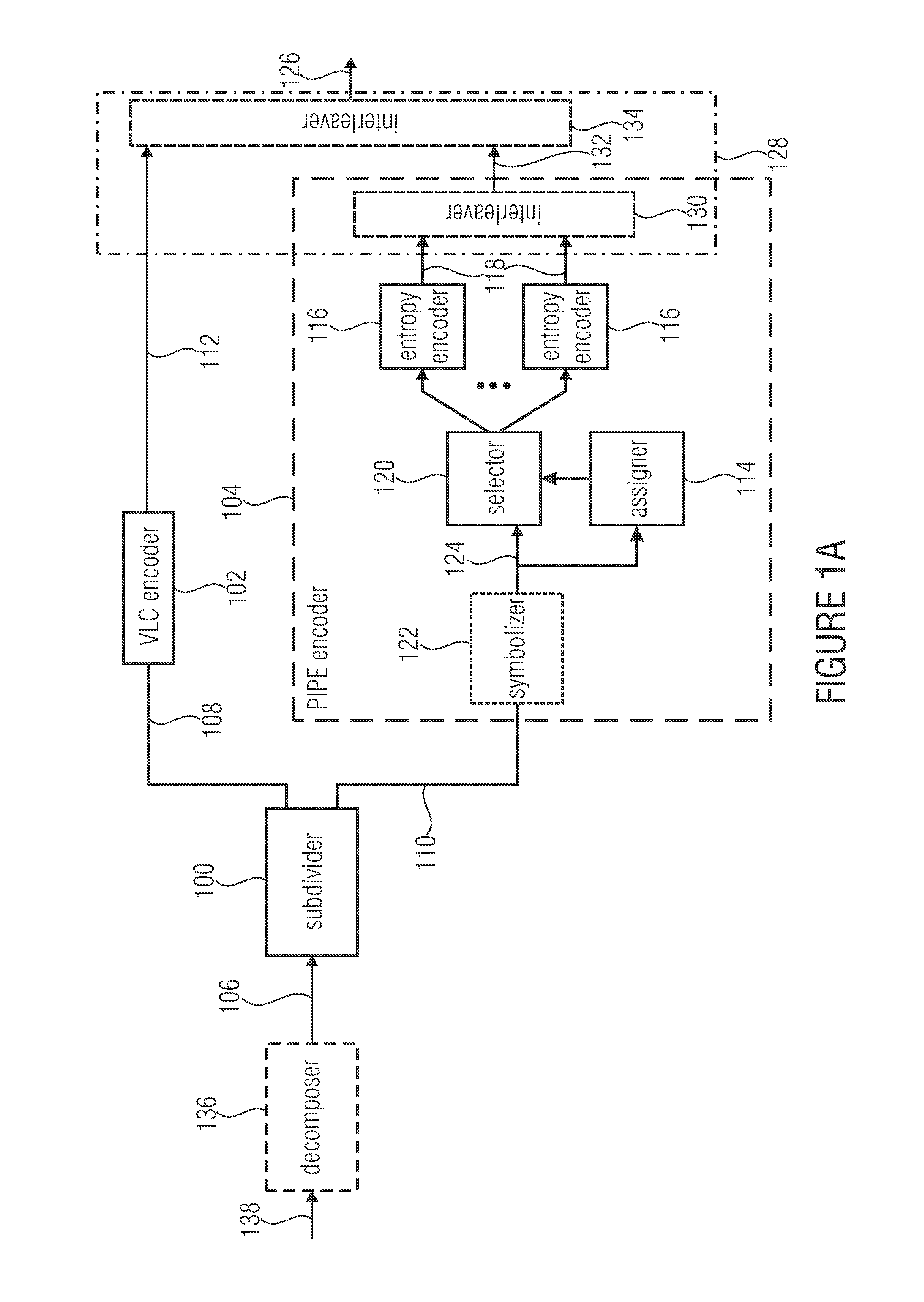
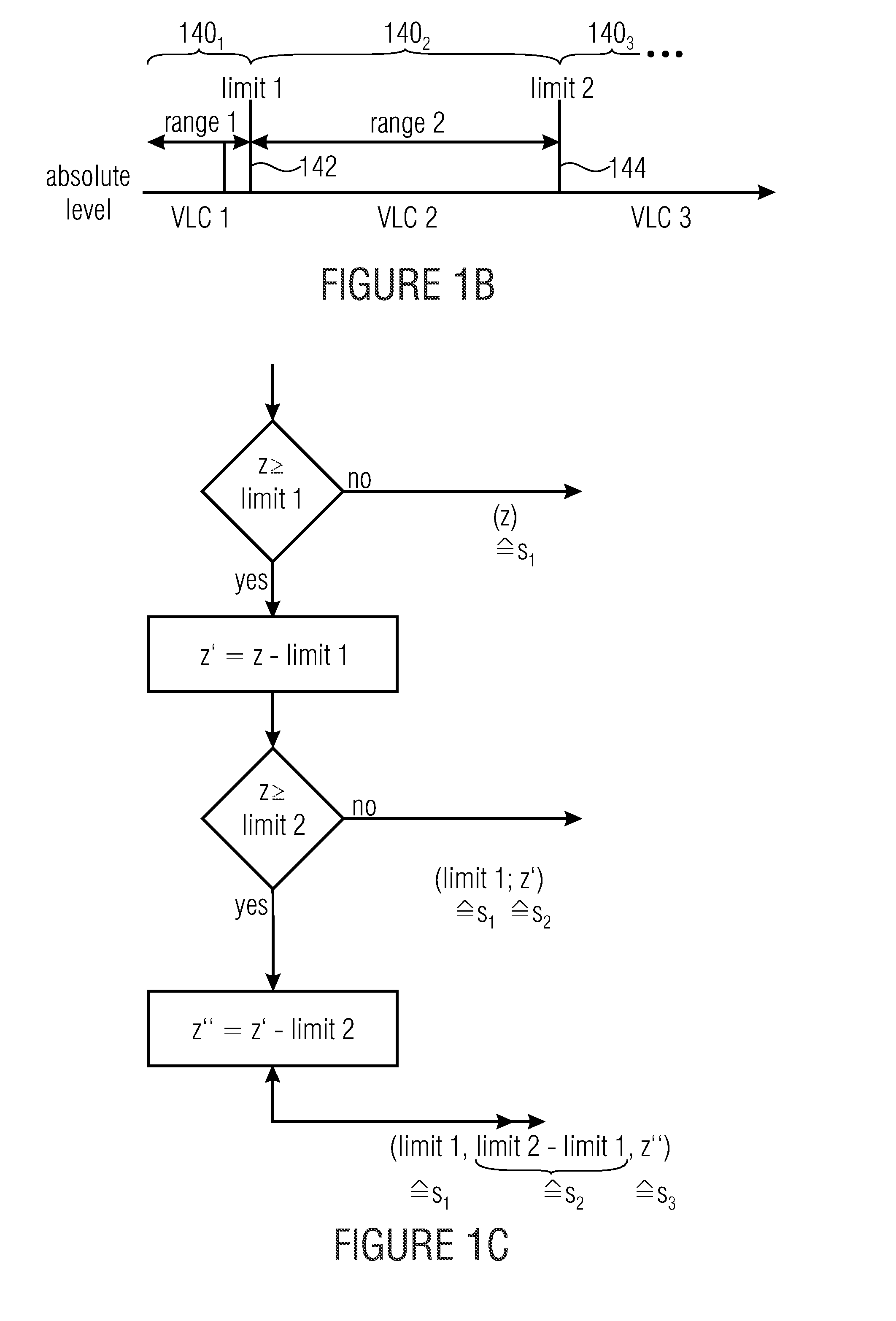
Entropy encoding and decoding scheme using VLC coding and pipe or entropy coding for high compression efficiency
ActiveUS9083374B2Improve compression efficiencyModerate codingCode conversionDigital video signal modificationSyntaxComputer science
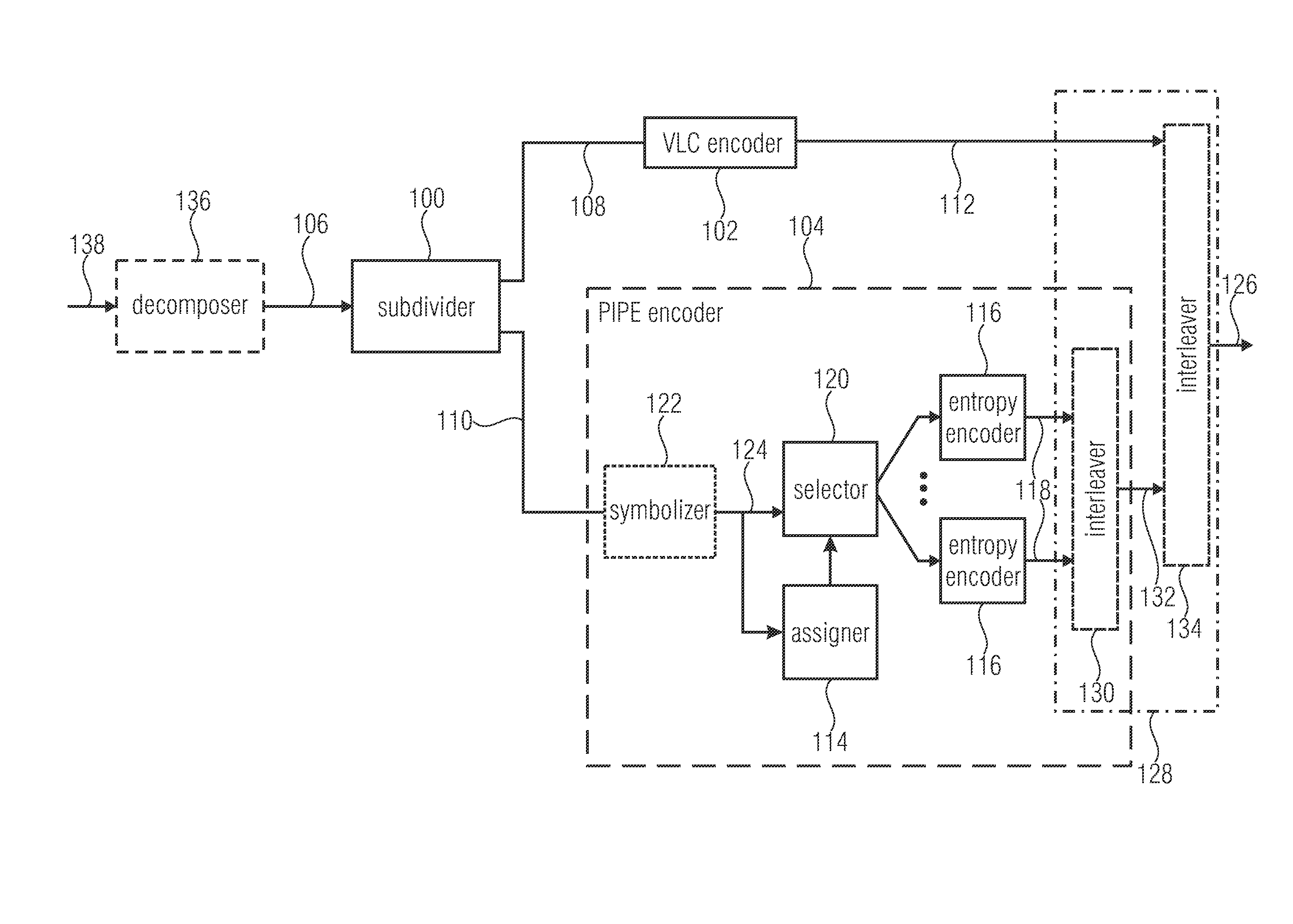
Decomposing a value range of the respective syntax elements into a sequence of n partitions with coding the components of z laying within the respective partitions separately with at least one by VLC coding and with at least one by PIPE or entropy coding is used to greatly increase the compression efficiency at a moderate coding overhead since the coding scheme used may be better adapted to the syntax element statistics. Accordingly, syntax elements are decomposed into a respective number n of source symbols si with i=1 . . . n, the respective number n of source symbols depending on as to which of a sequence of n partitions into which a value range of the respective syntax elements is sub-divided, a value z of the respective syntax elements falls into, so that a sum of values of the respective number of source symbols si yields z, and, if n>1, for all i=1 . . . n−1, the value of si corresponds to a range of the ith partition.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
Video encoding and decoding
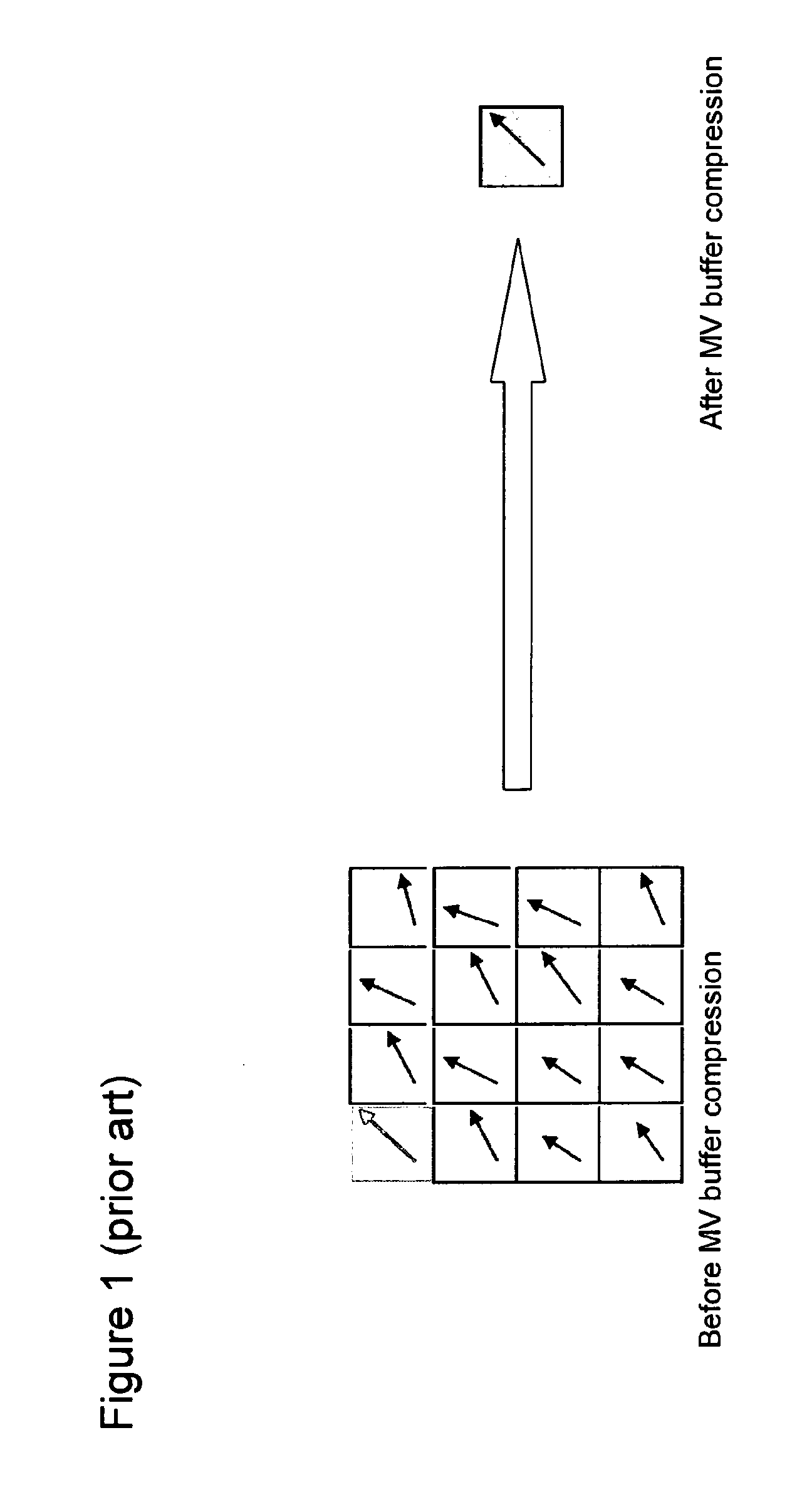
ActiveUS20140064372A1Improve coding efficiencyReduce lossesColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorVideo encoding
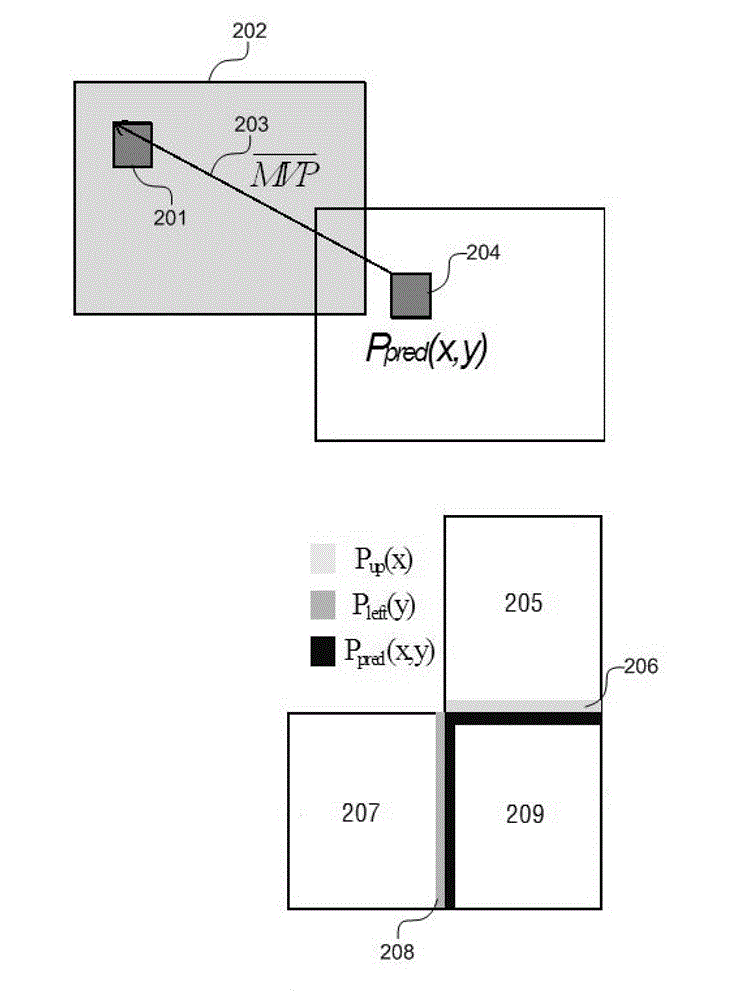
A temporal motion vector predictor is includable, together with one or more spatial motion vector predictors, in a set of motion vector predictors for a block to encode of a current frame. A method of determining the temporal motion vector predictor comprises selecting as the temporal predictor one motion vector from among motion vectors in a reference block of a reference frame different from the current frame. The reference block is a block of the reference frame collocated with the block to encode or a block of the reference frame neighboring the collocated block. The selection is based on a diversity criterion for achieving diversity among the predictors of the set.This can reduce the motion vector memory requirements with no or no significant additional coding efficiency penalty. Alternatively, even if the motion vector memory is not reduced in size, coding efficiency improvements can be achieved.
Owner:CANON KK
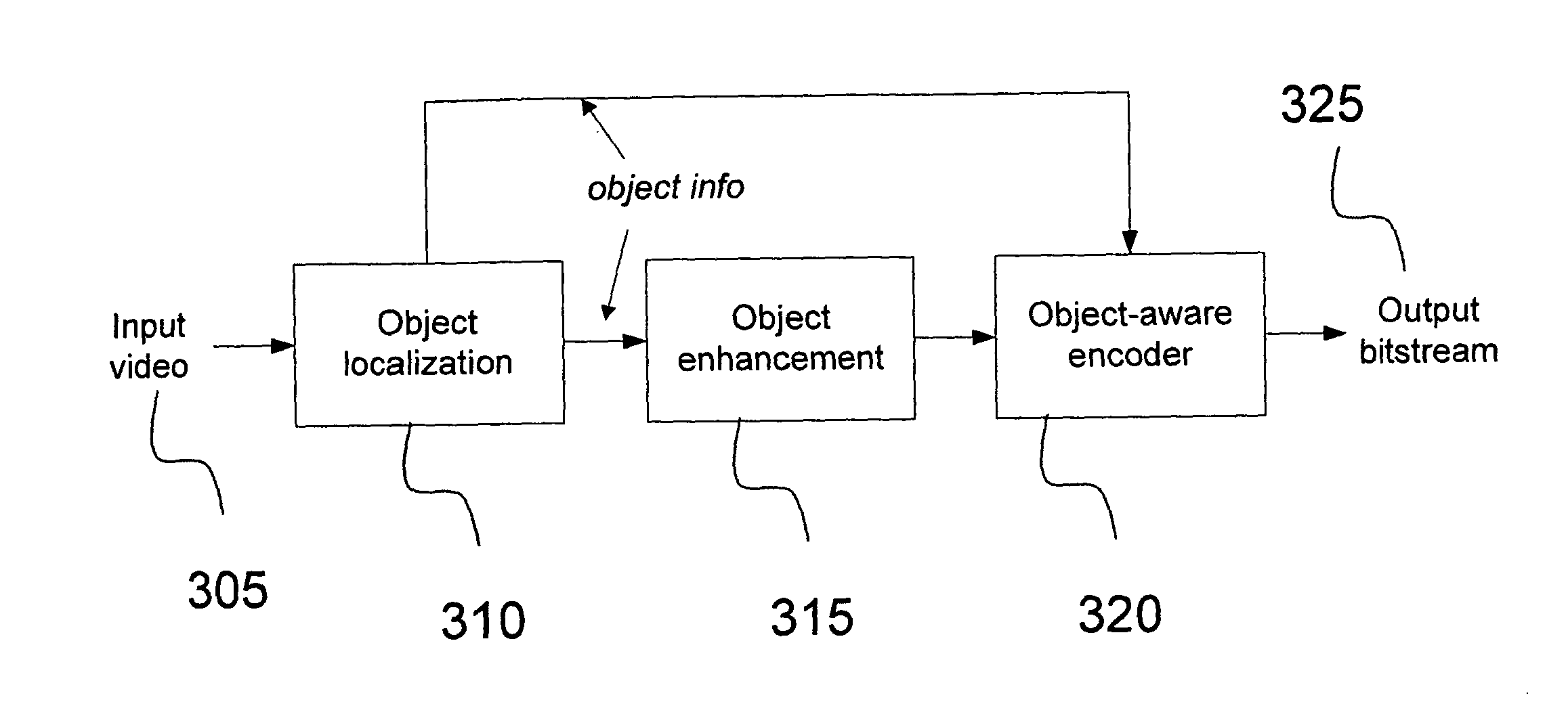
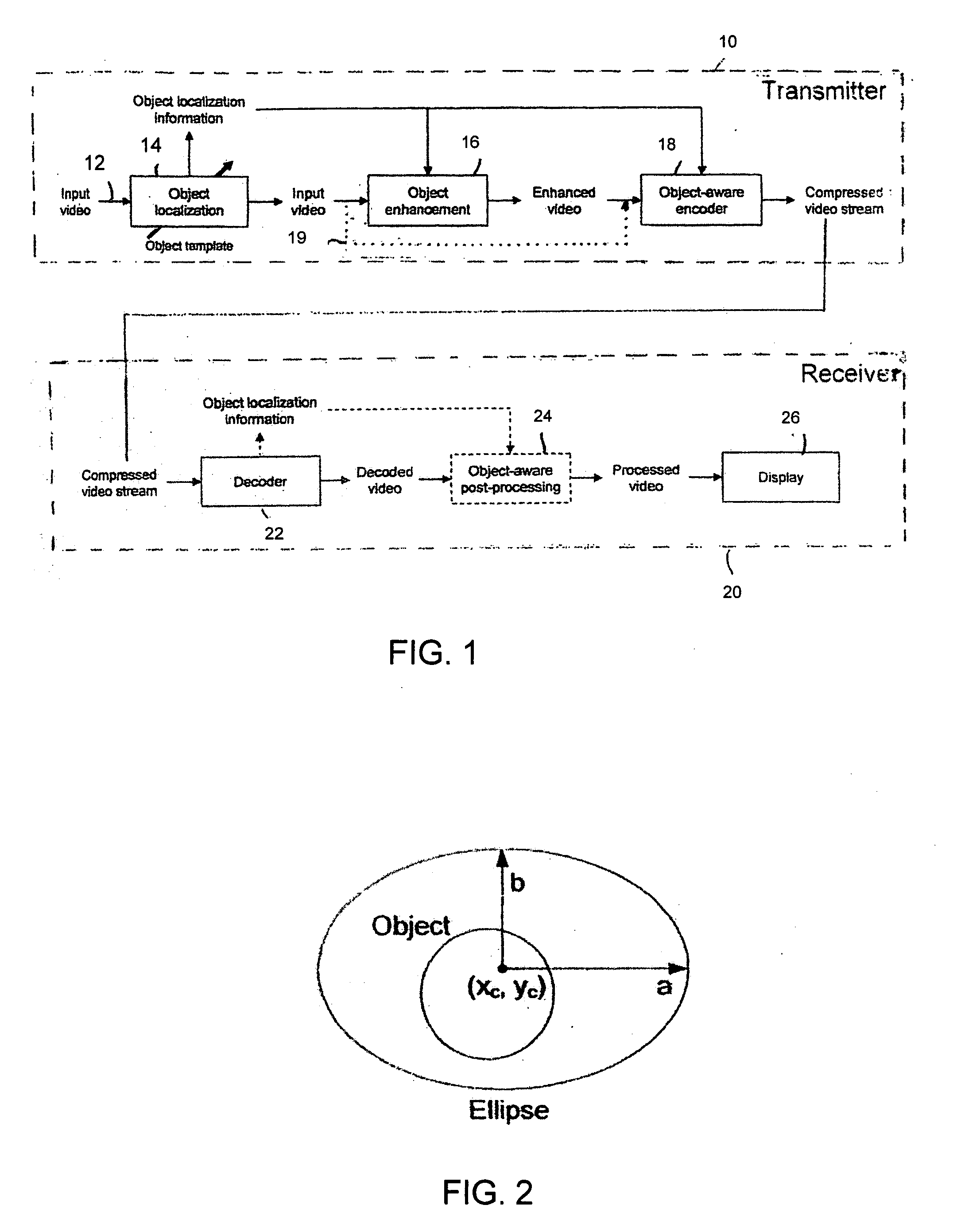
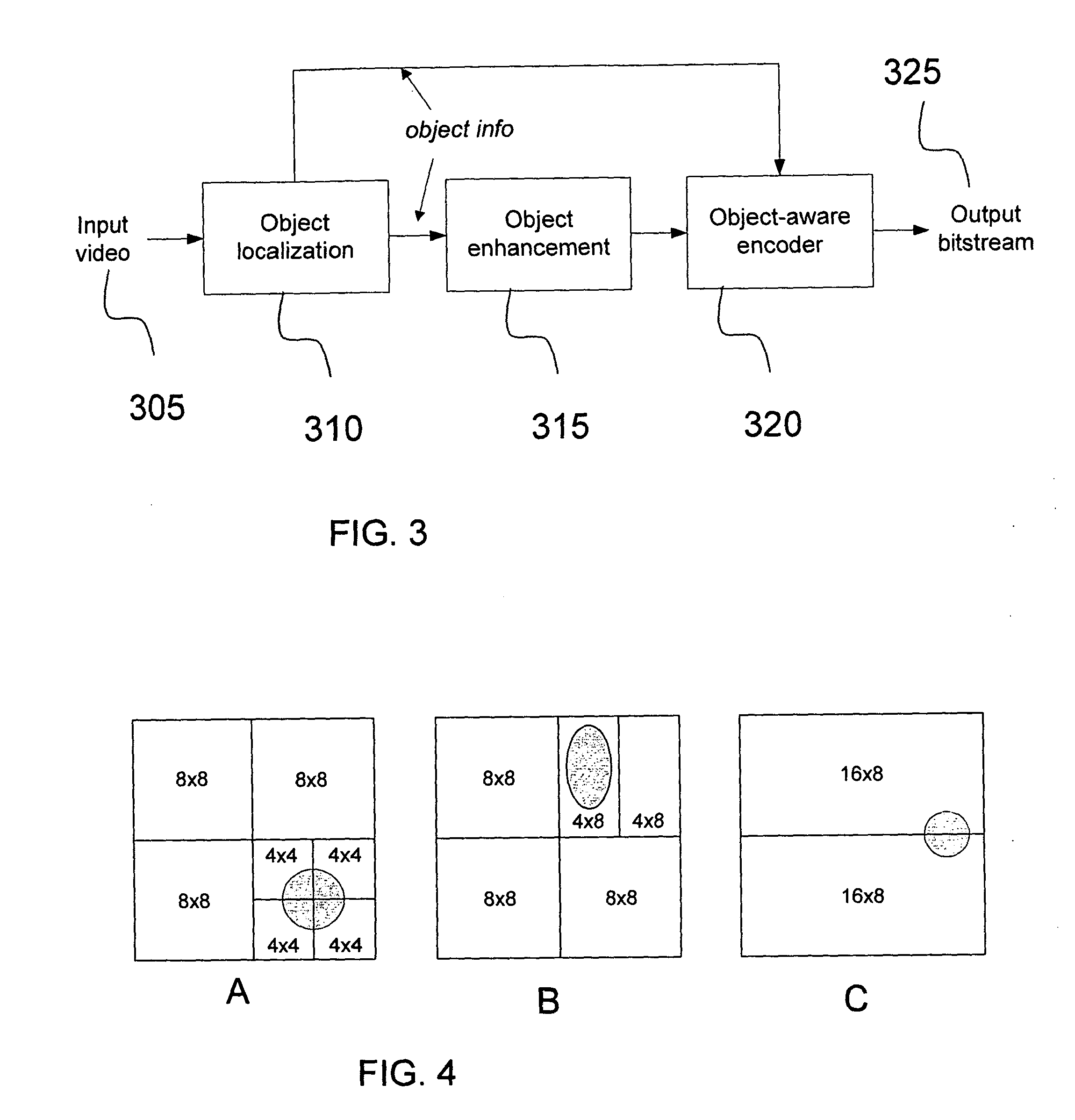
Object-aware video encoding strategies
InactiveUS20120224629A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionVideo encoding
A method of object-aware video coding is provided that comprises the steps of: receiving a video sequence having a plurality of frames; selecting at least two frames; determing total area of at least one object of interest in each of the at least two frames; comparing the total area to a threshold area; classifying each of the at least two frames as being a low object weighted frame or a high object weighted frame, low object weighted frames being frames having the total area exceeding the threshold area and high object weighted frames being frame having the total area not exceeding the threshold area; and encoding each low object weighted frame according to one encoding mode and encoding each high object weighted frame according to a different encoding mode.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Method and apparatus for intra mode derivation and coding in scalable video coding
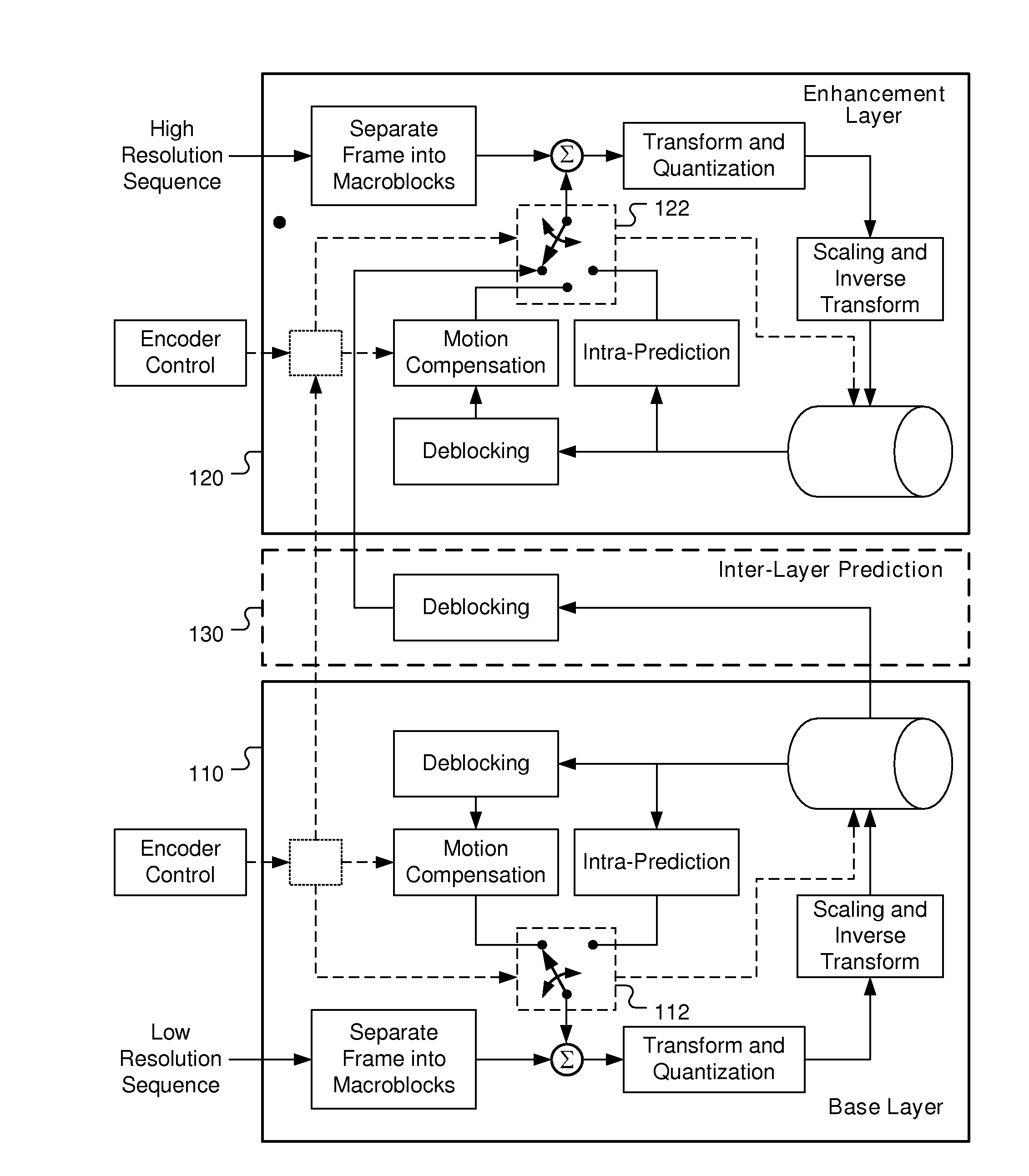
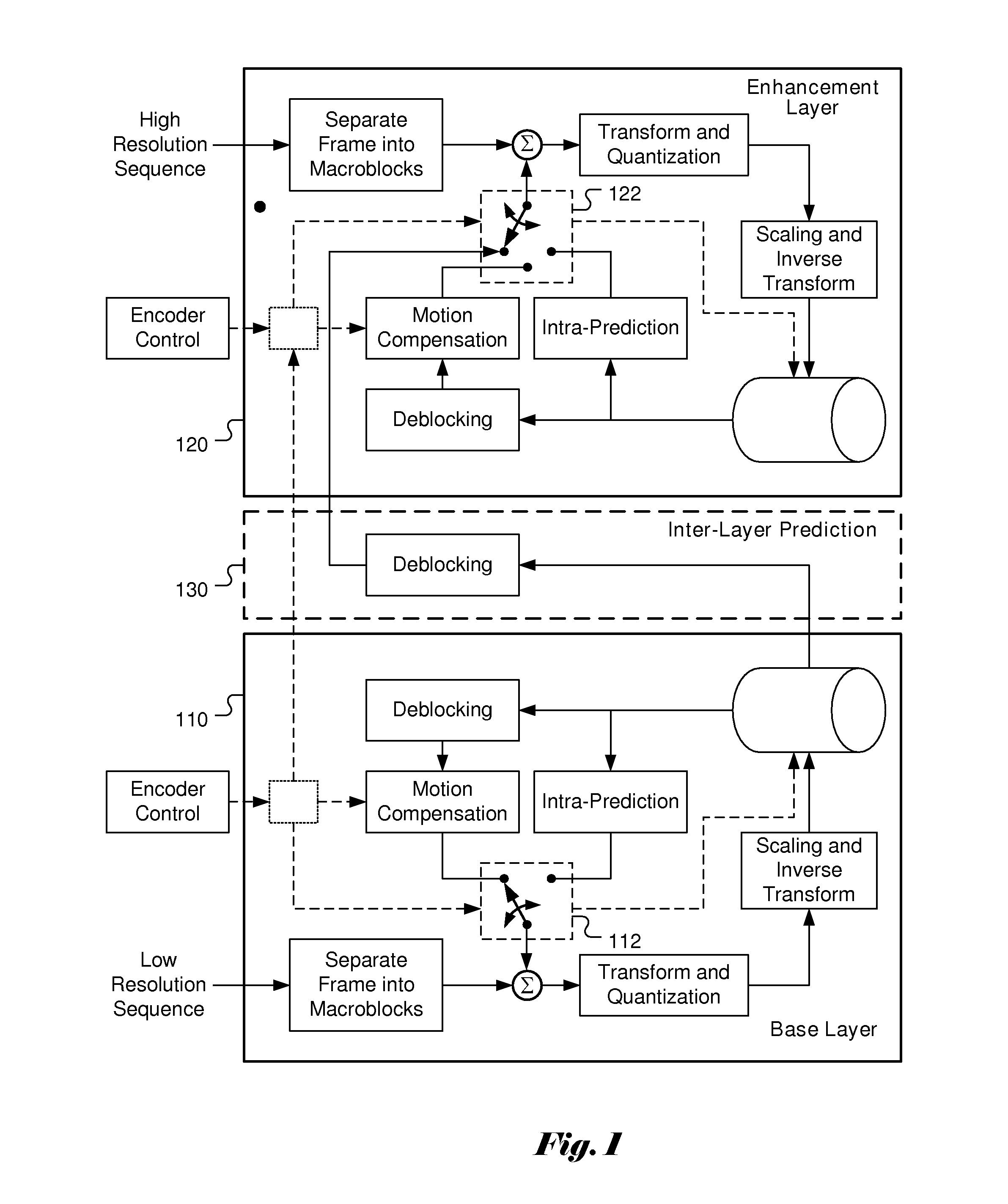
ActiveUS20150304670A1Improve spatial resolutionImprove video qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionCoding blockComputer architecture
A method and apparatus of Intra mode coding for a scalable video coding system are disclosed. For a current Intra-coded block in the enhancement layer (EL), predictive coding is applied to the current Intra mode based on the base layer (BL) coding mode associated with the co-located block in the BL and neighboring coding modes associated with neighboring blocks of the current block in the EL. The neighboring blocks of the current block in the EL comprise a left block adjacent to a left side of the current block and a top block adjacent to a top side of the current block. One or more most probable modes (MPMs) can be derived from the neighboring coding modes and the BL coding mode, and the MPMs is then used for predictive coding of the current Intra mode.
Owner:MEDIATEK SINGAPORE PTE LTD SINGAPORE
Compressive perceptual coding and decoding method and system in video sensor network
InactiveCN102630011AKeep properlyIncrease diversityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsPattern recognition
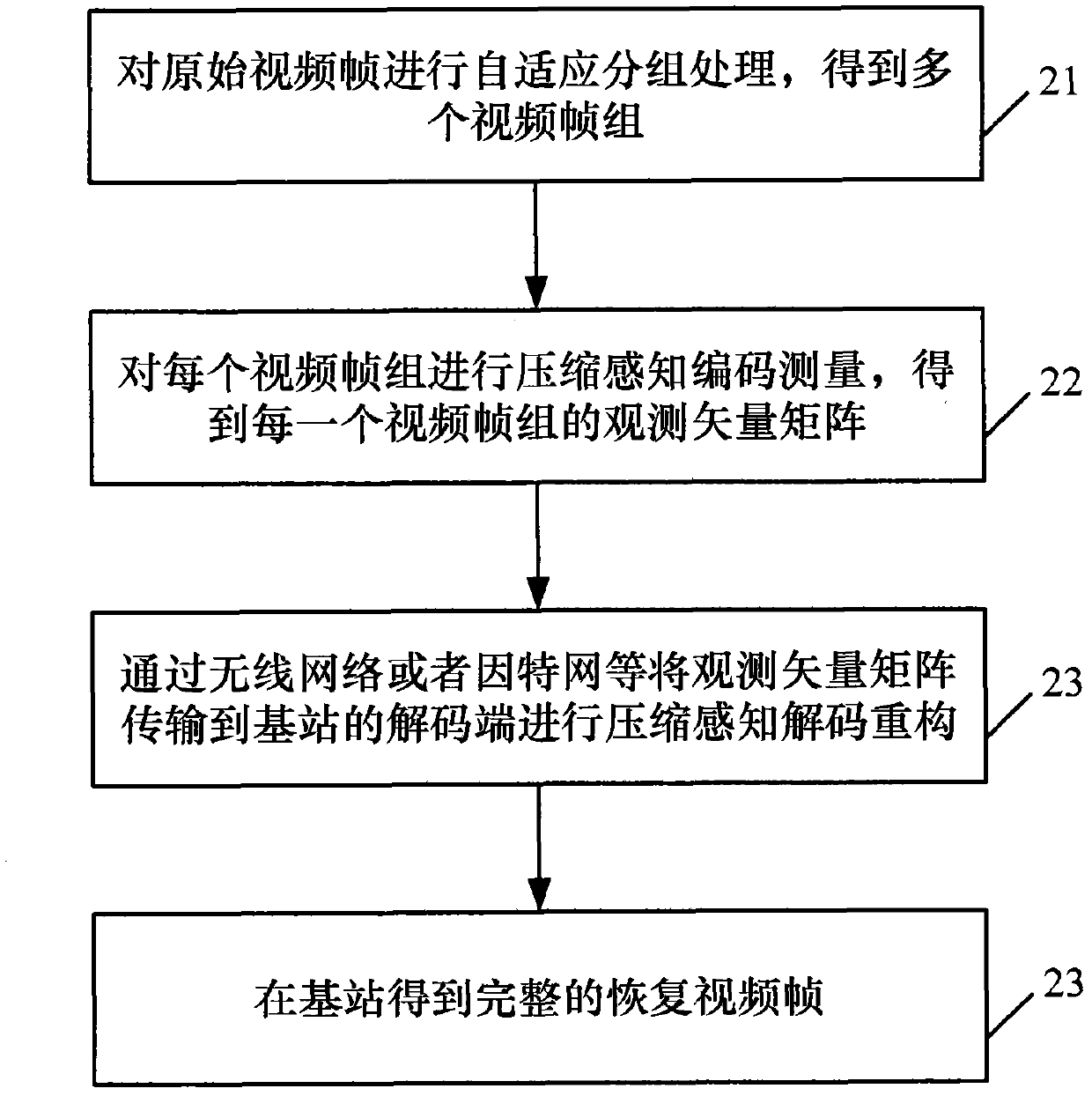
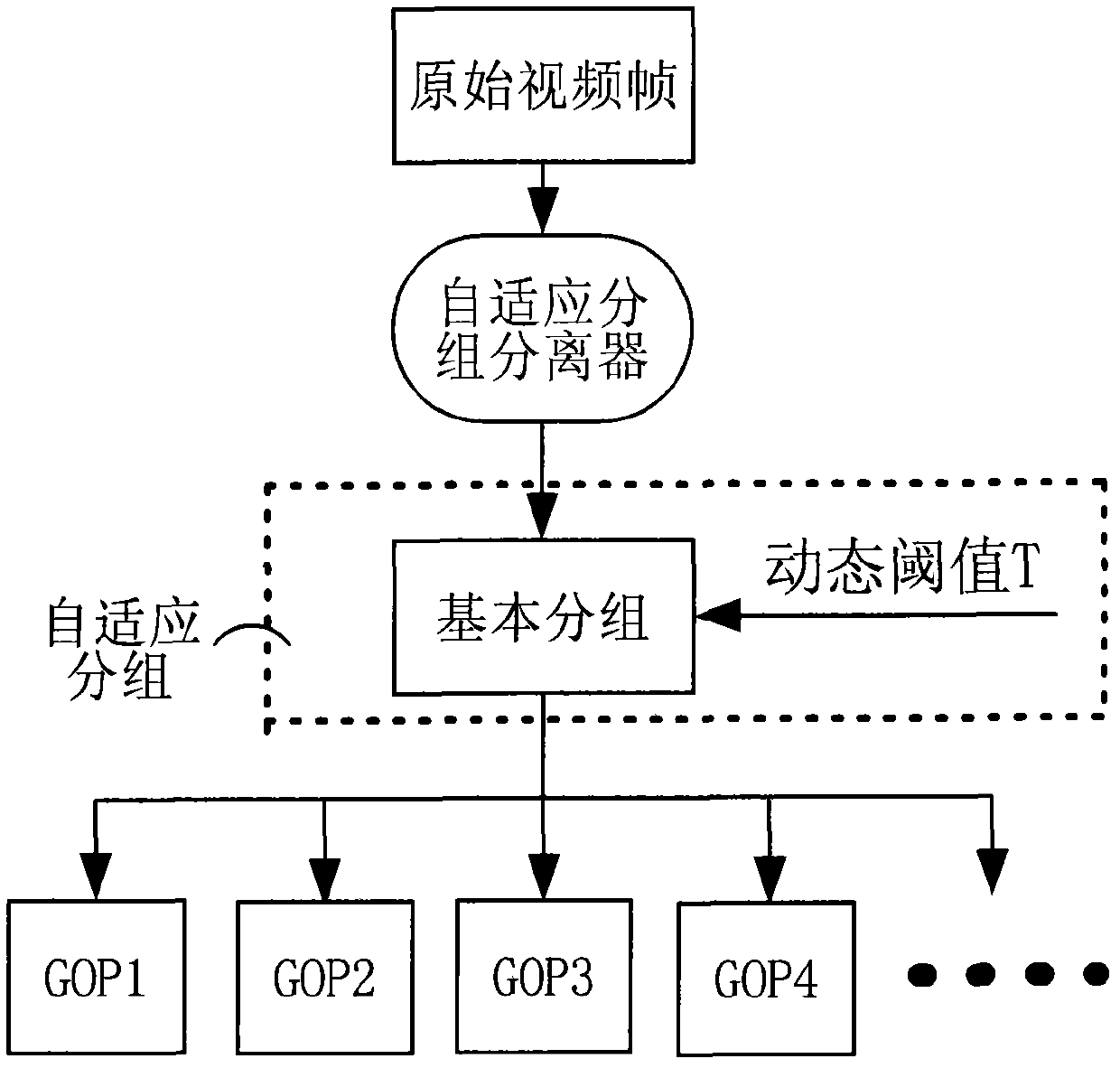
The invention discloses a compressive perceptual coding and decoding method and a system in a video sensor network, which can achieve high compression ratio and have a good reconstruction effect simultaneously. The method comprises the steps of performing a self-adaptation grouping for original video frames, performing compression perceptual coding measuring for the video frames acquired through the grouping, obtaining an observation vector matrix of each of video frame groups, and performing compressive perceptual decoding reconstruction for the observation vector matrix. Combining a compressive perceptual technique, the method and the system perform measuring, so that reconstruction performance is improved greatly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Hybrid distributed video encoding method based on intra-frame intra-frame mode decision
InactiveCN101335892AJoint Quantitative FacilityImprove rate-distortion performanceTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationSide informationKey frame
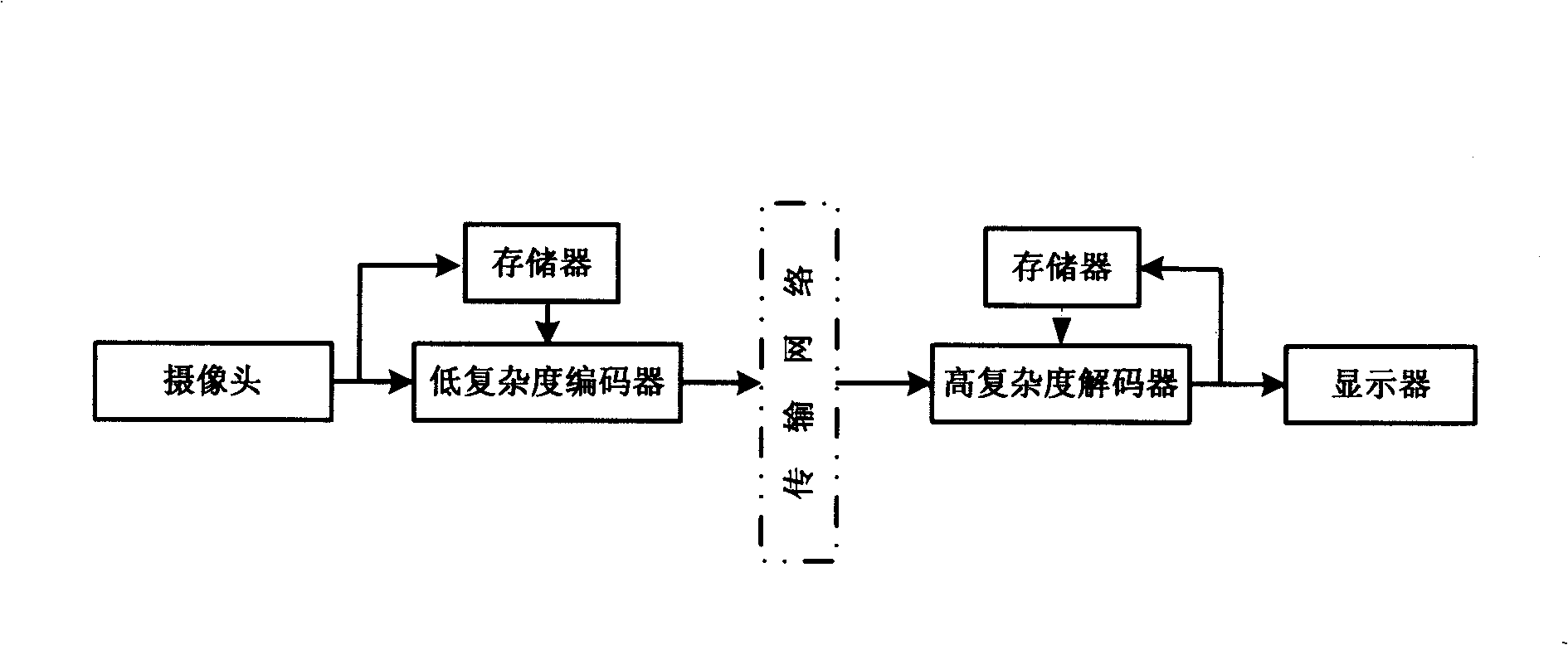
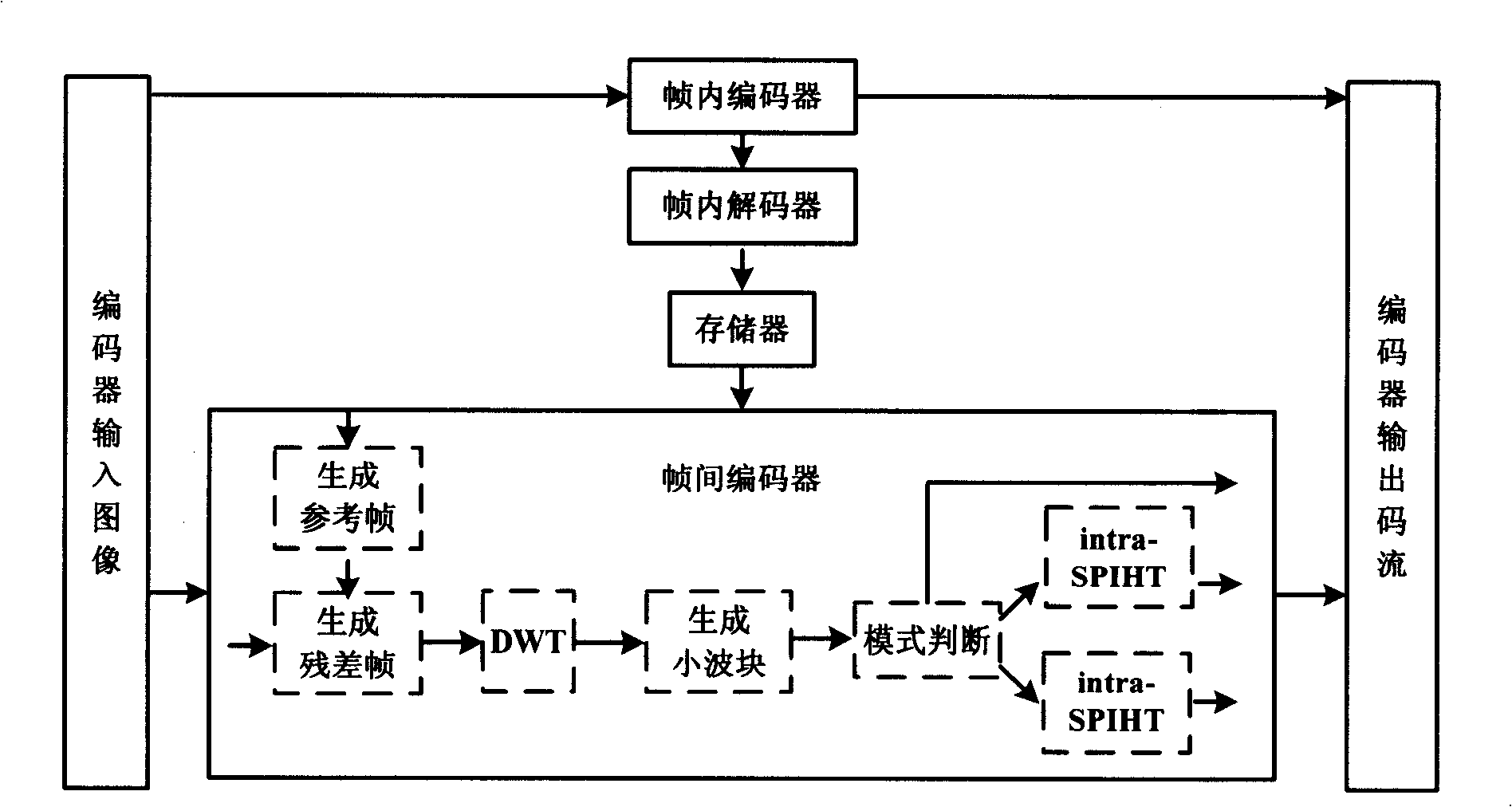
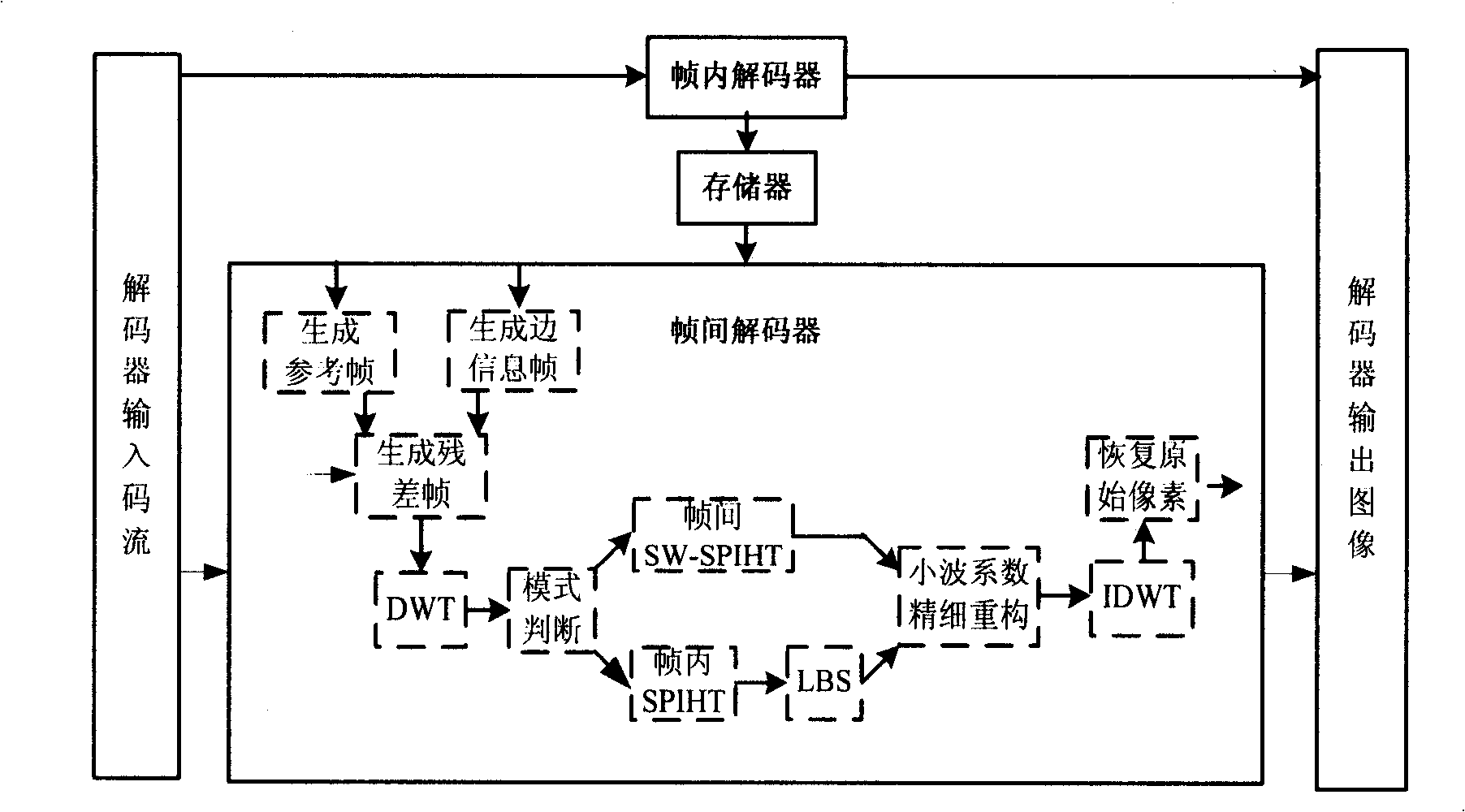
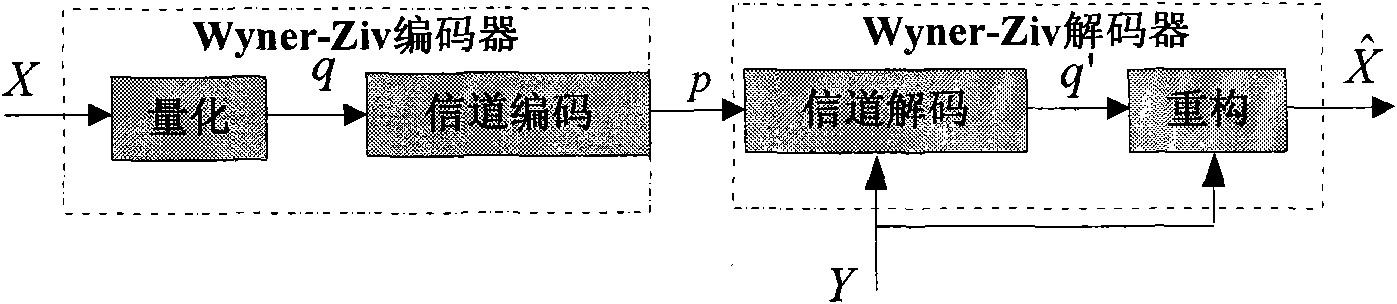
A hybrid distributed video encoding method based on wavelet domain intra-frame mode decision capable of improving rate aberration performance, is characterized by the following steps: (1) a low complexity encoding, including the following steps: using traditional intra-frame encoder to code key frames, generating the reference frame of Wyner-Ziv frame by weighted average interpolation, generating a residual frame by a subtraction arithmetic, performing discrete wavelet switch DWT to the residual frame, generating a wavelet block, intra-frame mode decision of the wavelet block, entropy coding of the mode information, and inter-frame SW-SPIHT coding or intra-frame SPIHT coding of the wavelet block; (2) a high-complexity decoding, including the following: using traditional intra-frame decoding algorithm to decode key frames, adopting a motion estimation interpolation to produce side information frame of the Wyner-Ziv, generating the reference frame of the decoding terminal by weighting average interpolation, generating a residual frame of the decoding terminal by a subtraction arithmetic, performing DWT to the residual frame, entropy decoding of the mode information, adopting LBS to perform motion estimation to generate more accurate side information, fine reconstruction of wavelet coefficients, and recovering the original pixels by inverse discrete wavelet transform (IDWT) and addition operations.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Image lossless compression and decompression method based on lifting wavelet transform
InactiveCN101984666AAchieve lossless compressionImprove the problem of excessive calculationTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationImage compressionLossless compression
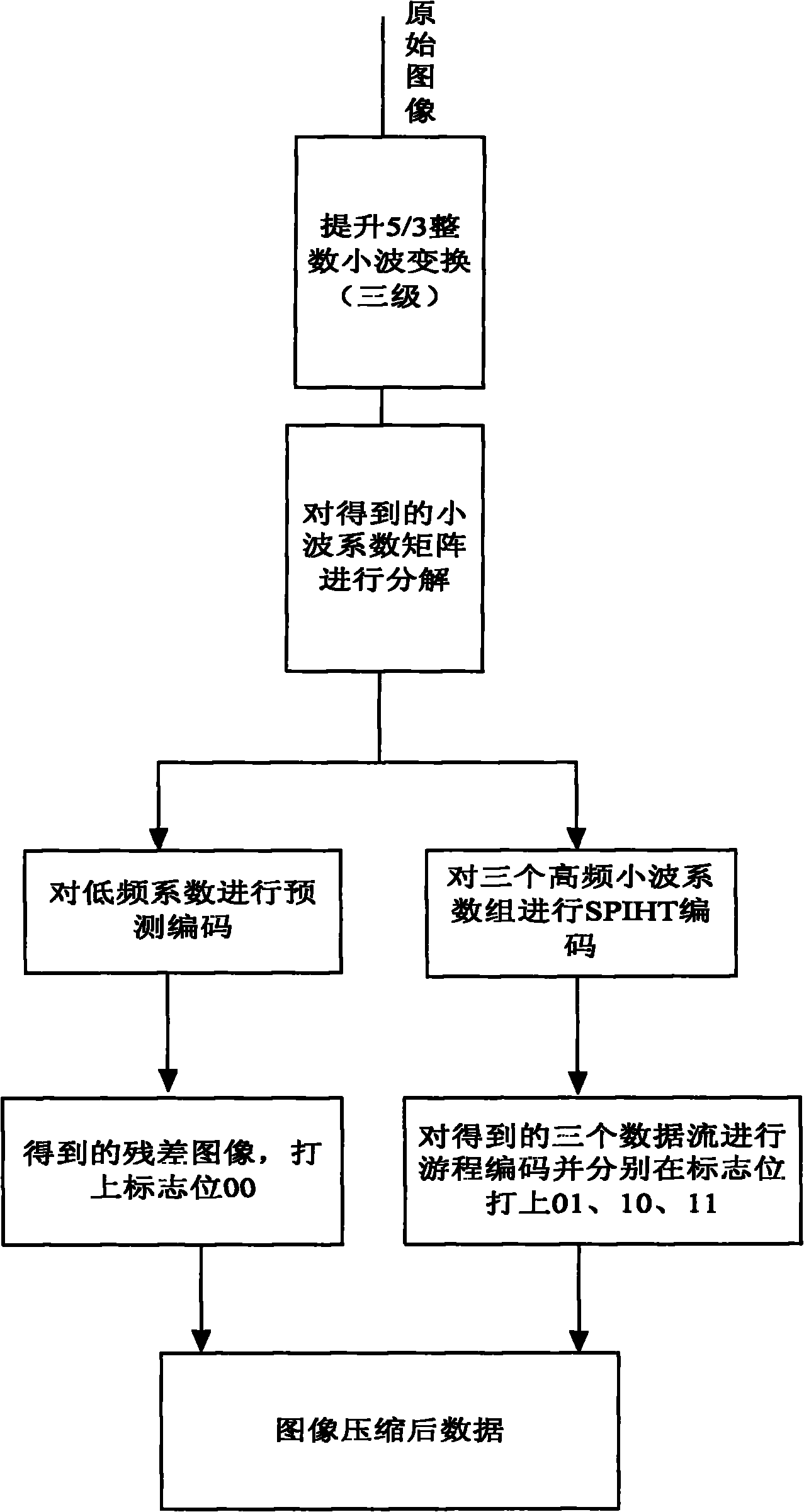
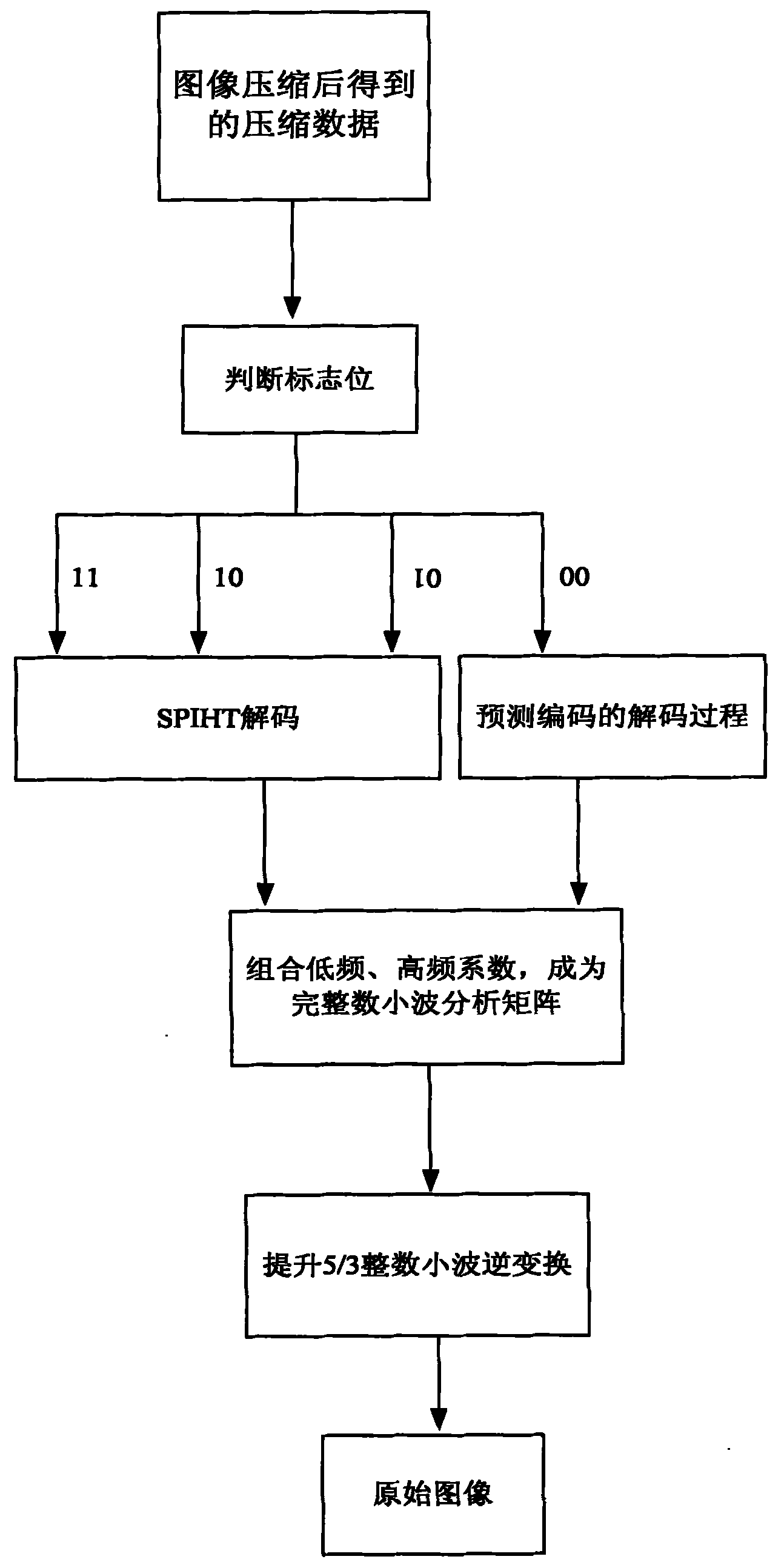
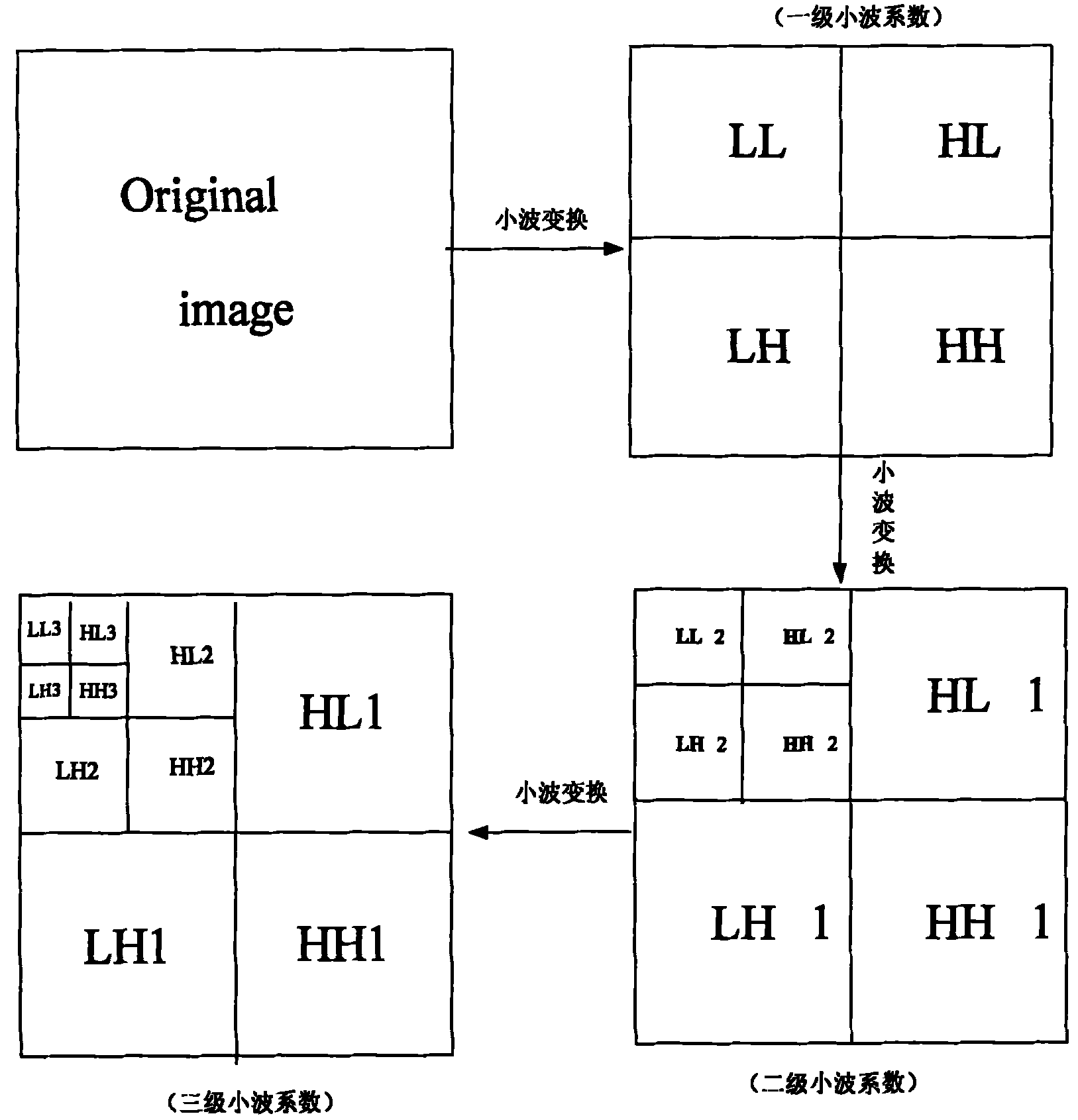
The invention relates to an image lossless compression and decompression method based on lifting wavelet transform, belonging to the image compression field. The method comprises the following steps: the lifting scheme is utilized to obtain lifting wavelet, lifting wavelet transform is performed to an original natural image, the matrix transform of integer domain is completed to obtain restorable a wavelet coefficient which is an integer; and the wavelet coefficient is decomposed according to the characteristic of the wavelet coefficient to obtain low frequency coefficients and high frequency coefficients, and the obtained low frequency coefficients and high frequency coefficients are coded respectively so as to effectively increase the coding efficiency, wherein predictive coding is adopted for the low frequency coefficients and the SPIHT coding is adopted for the tree structure formed by the high frequency coefficients, thus the aim of lossless compression can be achieved and repeated comparisons in the SPIHT algorithm can be reduced. The method of the invention can increase the compression ratio and compression efficiency of the image as far as possible under the premise of ensuring that the image is undistorted.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Digital image compression by resolution-adaptive macroblock coding
InactiveUS20110002391A1Save bandwidthPrediction is simpleColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionRate distortion
Disclosed is an image encoder that divides a digital image into a set of “macroblocks.” If appropriate, a macroblock is “downsampled” to a lower resolution. The lower-resolution macroblock is then encoded by applying spatial (and possibly temporal) prediction. The “residual” of the macroblock is calculated as the difference between the predicted and actual contents of the macroblock. The low-resolution residual is then either transmitted to an image decoder or stored for later use. In some embodiments, the encoder calculates the rate-distortion costs of encoding the original-resolution macroblock and the lower-resolution macroblock and then only encodes the lower-resolution macroblock if its cost is lower. When a decoder receives a lower-resolution residual, it recovers the lower-resolution macroblock using standard prediction techniques. Then, the macroblock is “upsampled” to its original resolution by interpolating the values left out by the encoder. The macroblocks are then joined to form the original digital image.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC +1
Novel chaos-based image lossless compression encryption joint algorithm
ActiveCN105704500AEnsure safetyLarge key spaceTelevision systemsSecuring communication by chaotic signalsLossless compression algorithmData compression ratio
The invention discloses an image lossless compression encryption joint algorithm based on multiple kinds of chaos, which belongs to the technical field of multimedia information safety. In view of high safety requirements of the image lossless compression algorithm SPIHT, an image lossless compression encryption joint algorithm based on multiple kinds of chaos is designed. The algorithm is designed to generate an encryption pseudo random sequence which is safer and is not easy to be broken, a wavelet transform coefficient matrix is encrypted in a mode of design local diffusion and overall scrambling, and during an SPIHT coding process, and multiple turns of encryption are carried out on a sorting scanning part. Theoretical analysis and experimental results show that the algorithm of the invention has the advantages that the encryption speed is quick; the safety is high; influences on a compression ratio are few; an image file can be kept to be lossless; and the application prospect and the practical value are wide.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
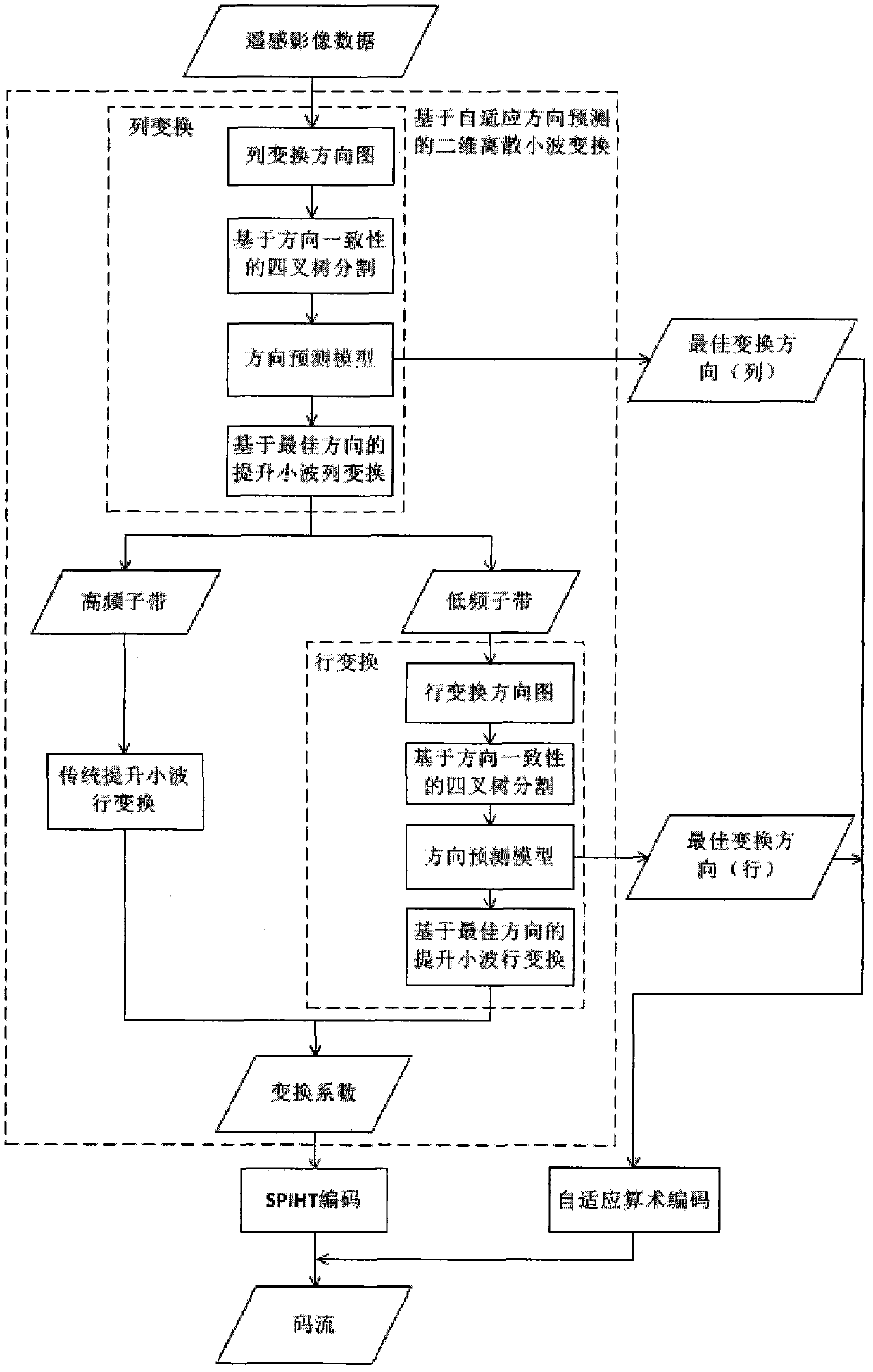
Remote-sensing image compression method for discrete wavelet transform based on self-adaptation direction prediction
ActiveCN103347187AImprove subjective qualityImprove signal-to-noise ratioImage codingTelevision systemsAviationComputation complexity
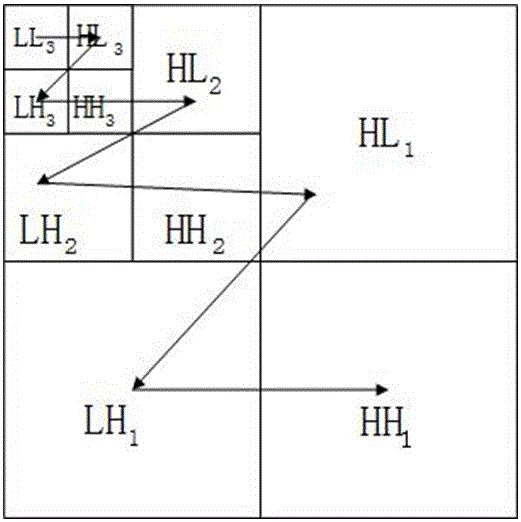
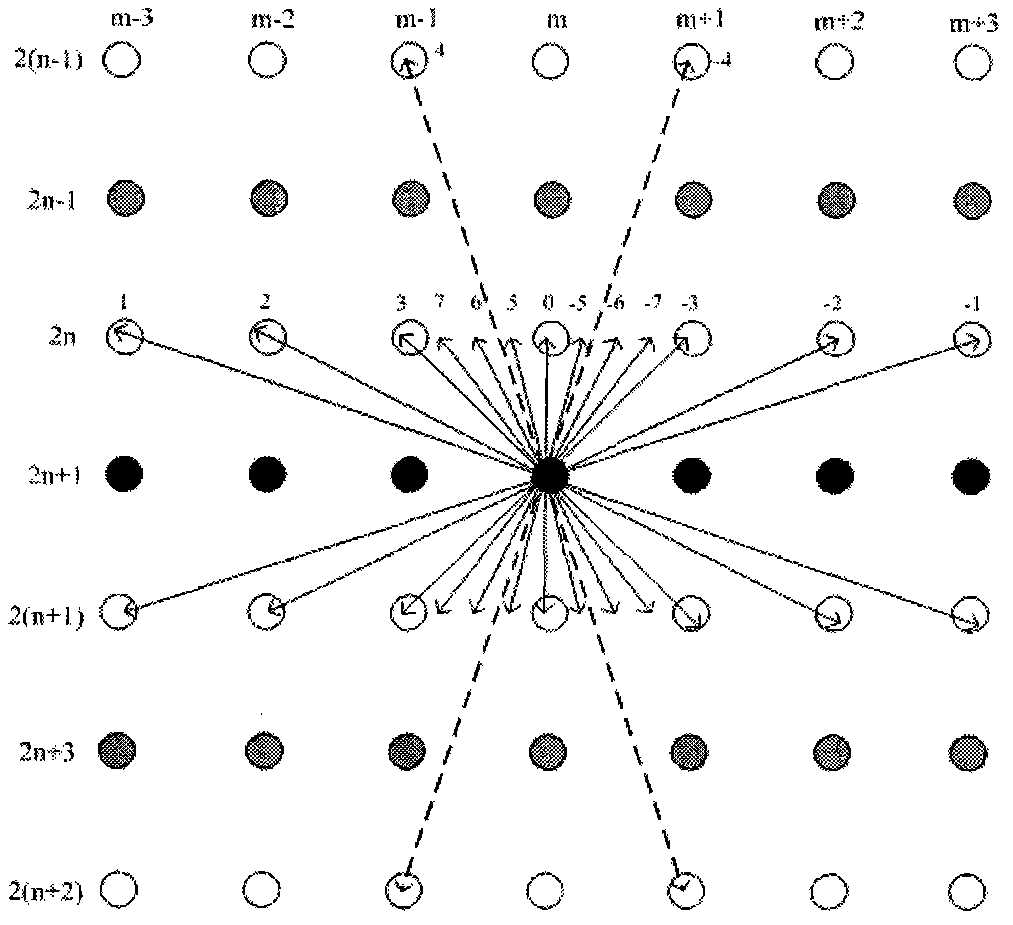
The invention discloses a remote-sensing image compression method for discrete wavelet transform based on self-adaptation direction prediction and belongs to the technical field of remote-sensing image processing. The method comprises the steps that 1) 15 directions which are formed by close-end integer and fraction pixels and far-end integer pixels are considered in a combined mode, a direction graph is established; 2) remote-sensing images are subjected to two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform based on self-adaptation direction prediction, namely quadtree division based on direction consistency is used for dividing the remote-sensing images to a plurality of image blocks which are not overlapped, a new direction prediction model is used for obtaining the best transformation direction of each image block, lifting wavelet transform is completed in the direction; 3) a transformed image coefficient is subjected to SPIHT coding, direction information is subjected to self-adaptation arithmetic coding, and a final code stream is obtained. According to the method, visual quality and peak signal-to-noise ratio of the remote-sensing images are effectively improved, computing complexity of direction wavelet transform is lowered, and the method can be widely used for efficient coding compression of the aviation and satellite remote-sensing images.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Encoding and decoding methods and encoding and decoding device of range image
ActiveCN103067715AImprove codec processing efficiencyTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationIntra-frameComputer science
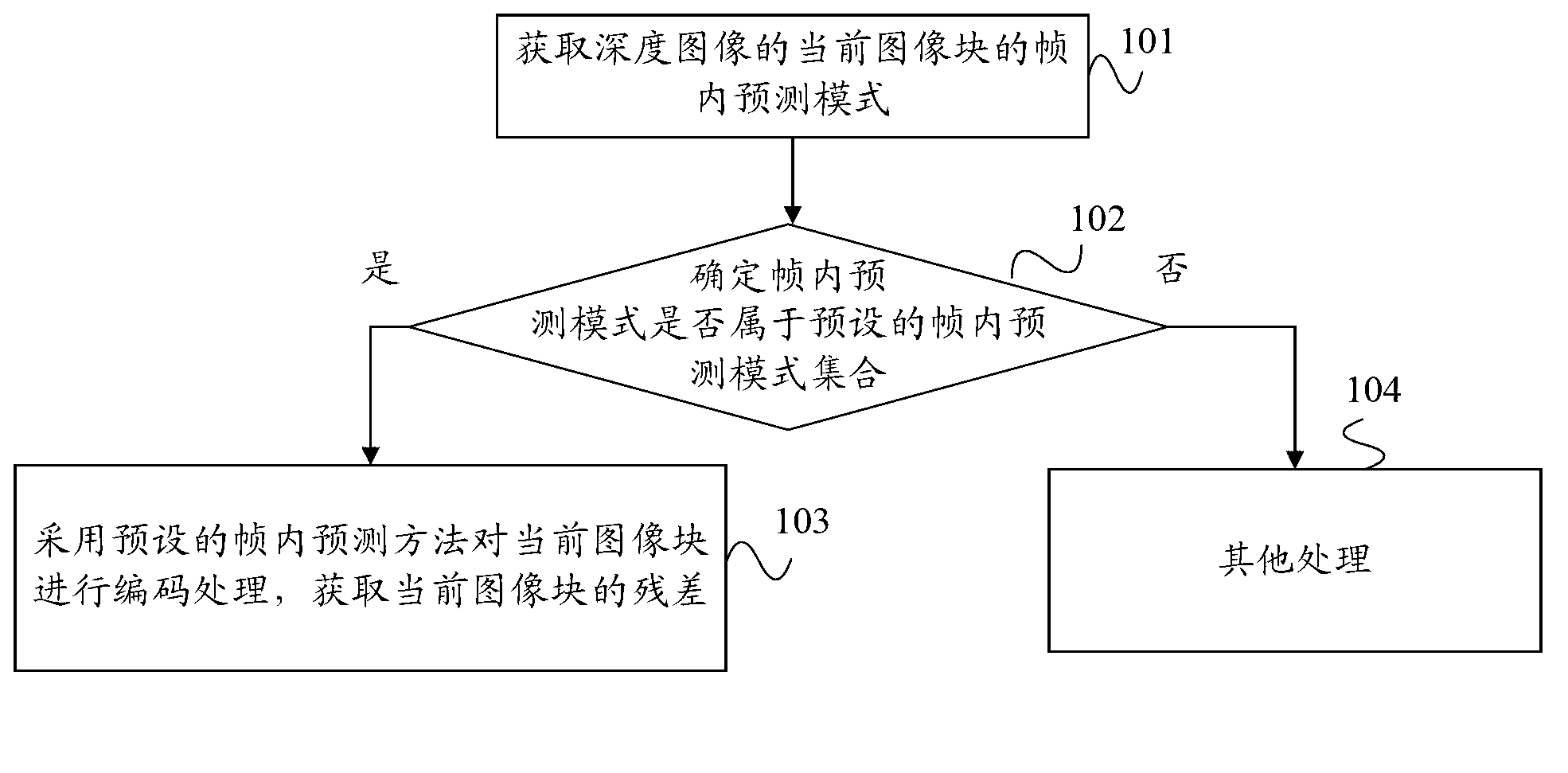
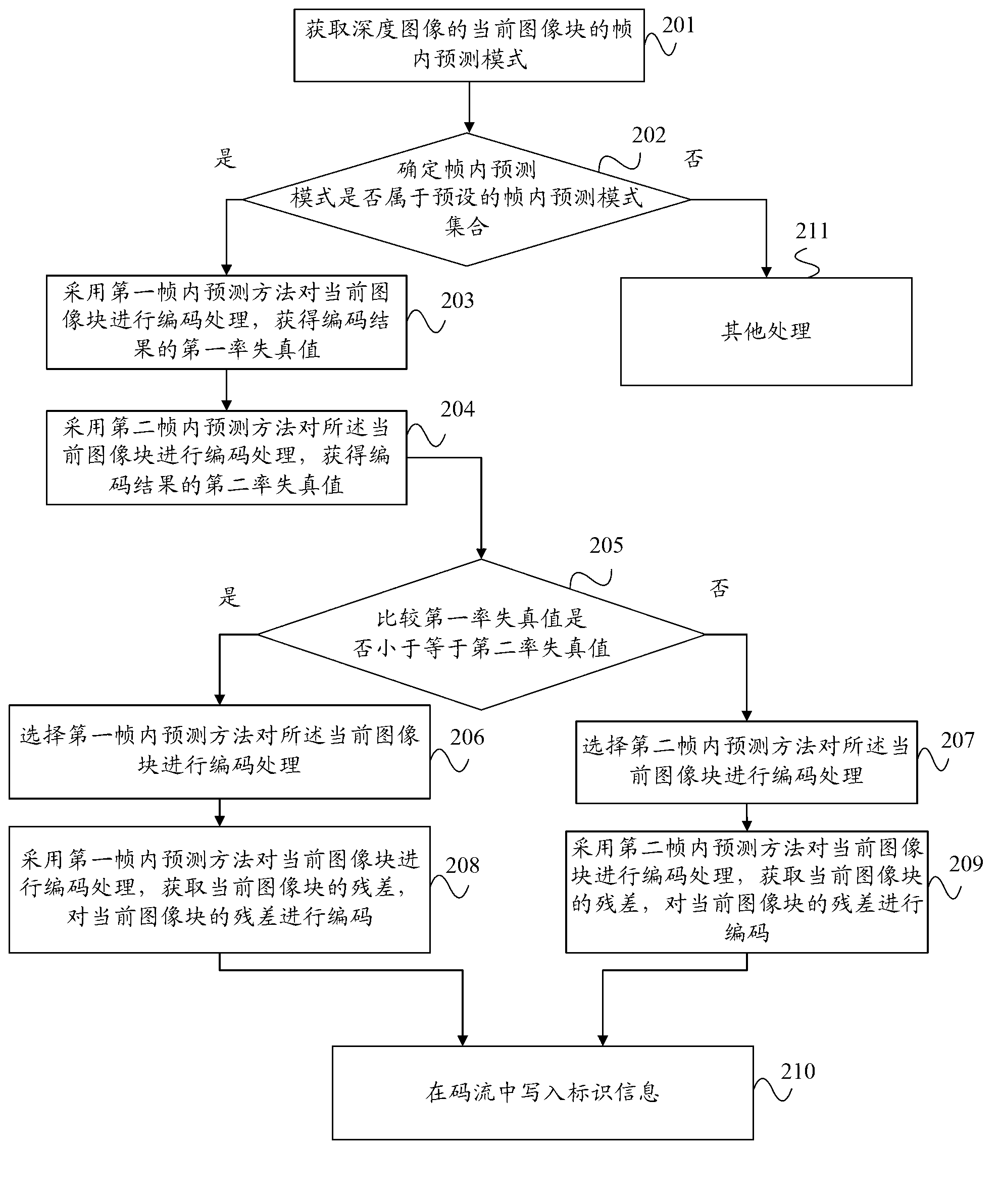
The invention provides encoding and decoding methods and an encoding and decoding device of a range image. The encoding method comprises: an intra-frame prediction mode of a current image block of the range image is got; whether the intra-frame prediction mode belongs to the presupposed intra-frame prediction mode assembly or not is confirmed; and if the intra-frame prediction mode belongs to the presupposed intra-frame prediction mode assembly, a presupposed intra-frame prediction method is adopted to encode the current image block to get a residual error of the current image block. The presupposed intra-frame prediction method comprises a first intra-frame prediction method, the difference of a pixel mean value of the current image block and a pixel mean value of predicted data is calculated to get the residual error of the current image block. Consequently, by the adoption of the presupposed intra-frame prediction method for encoding the current image block, only one residual error is needed to be encoded, accordingly, a decoding end only needs to decode the residual error, and so that the efficiency of encoding and decoding can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
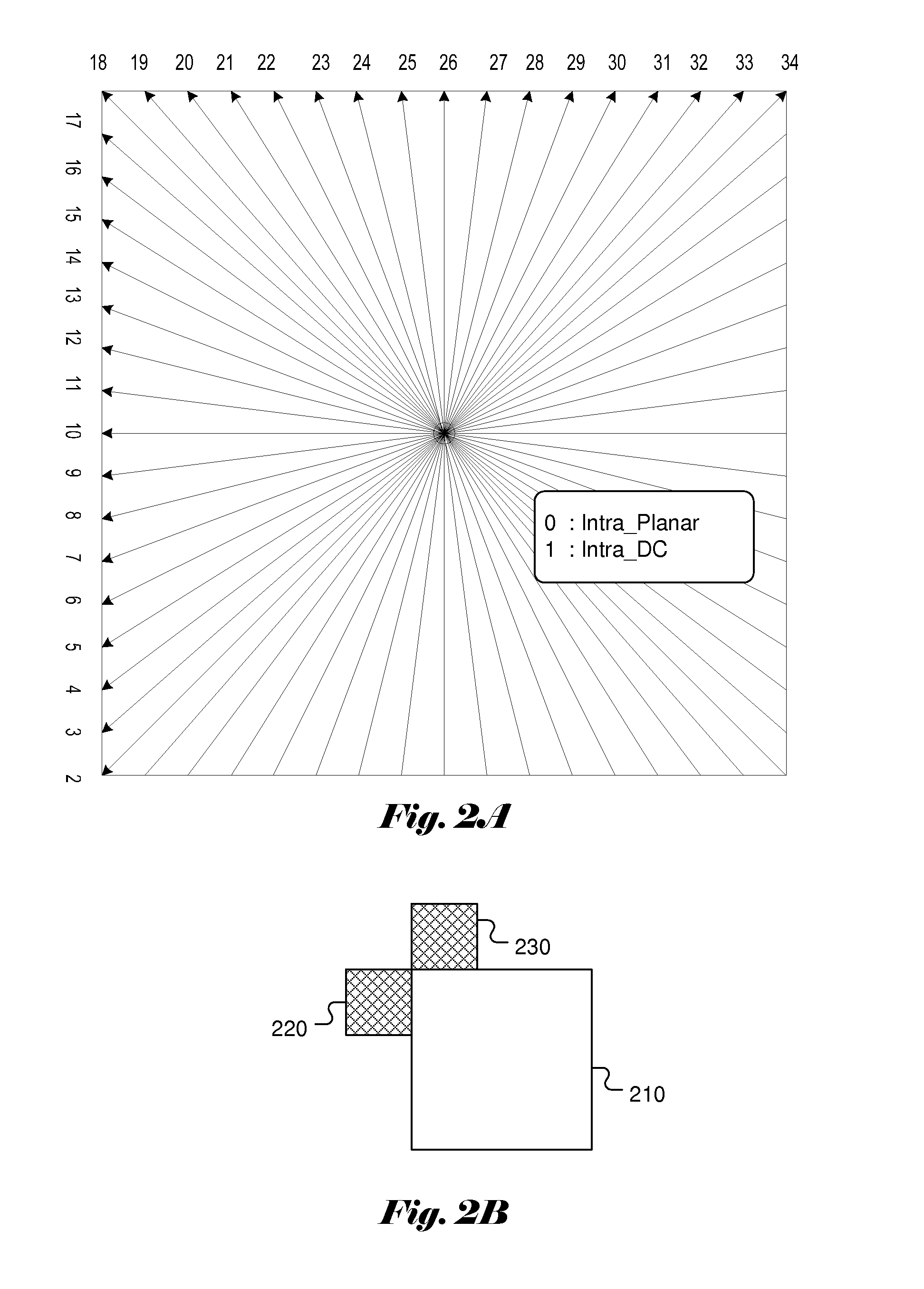
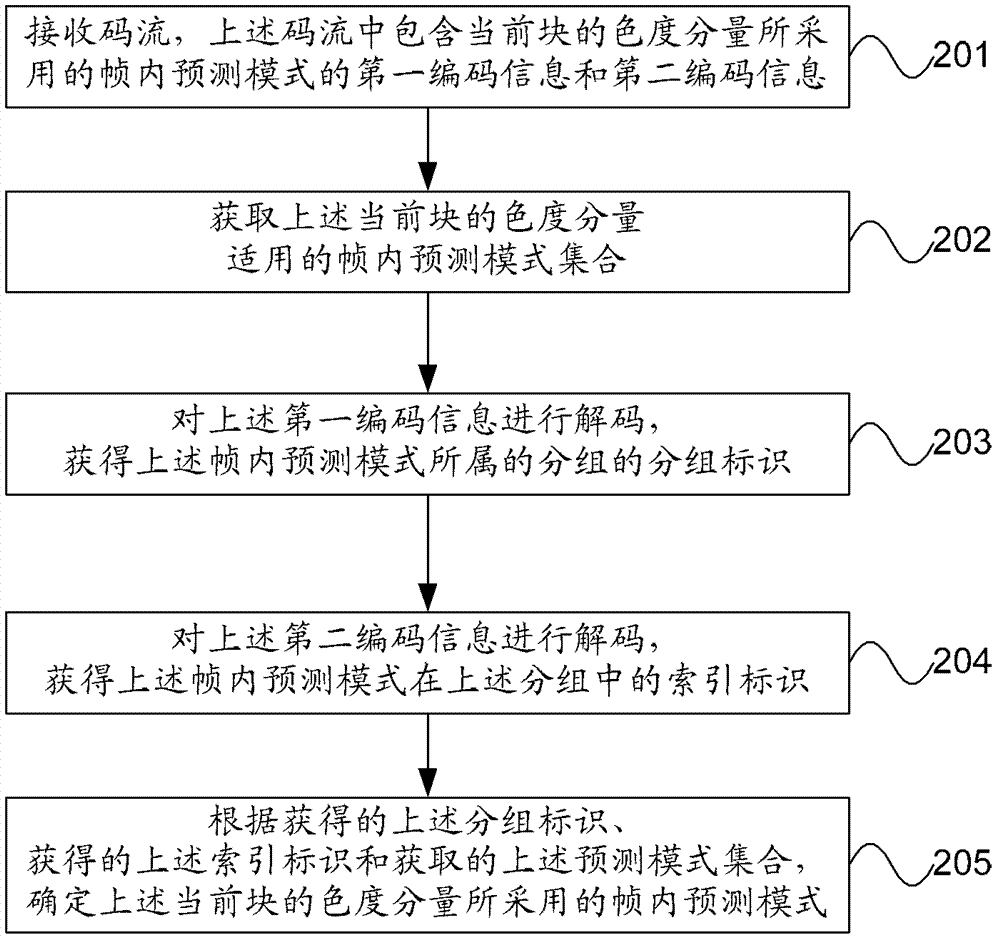
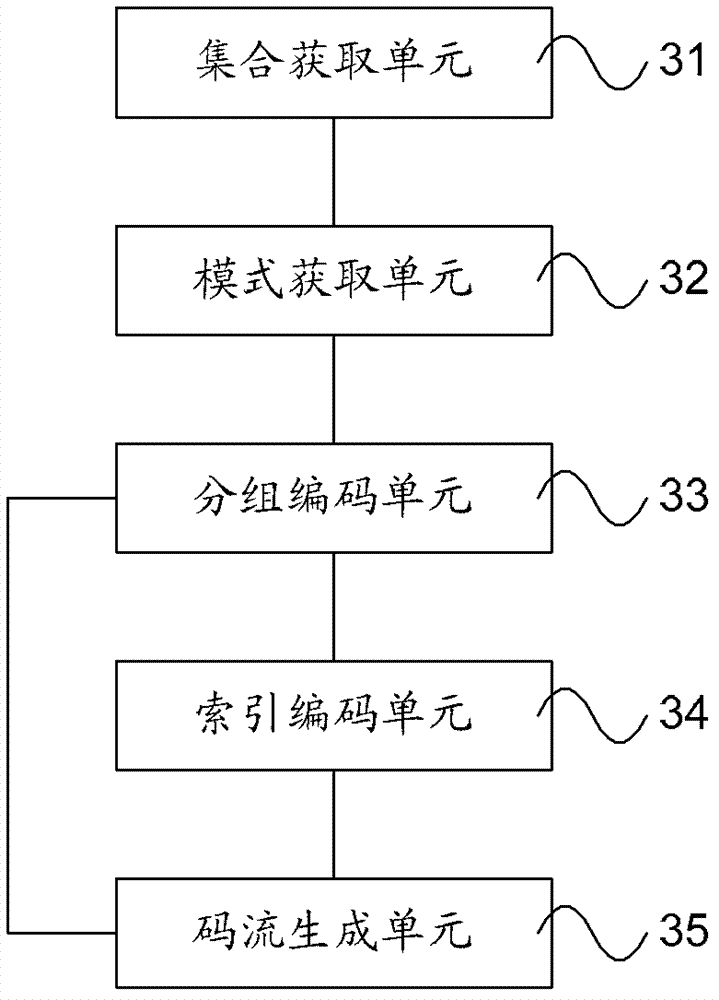
Coding and decoding methods, equipment and system of intra-frame chroma prediction modes
The invention provides coding and decoding methods, equipment and a system of intra-frame chroma prediction modes. According to the invention, intra-frame prediction modes of an intra-frame prediction mode set which is suitable for the chroma of a current block are divided into a first subgroup and a second subgroup, the amount of the intra-frame predication modes in correspondence with the first subgroup is at least two, and the amount of the intra-frame predication modes in correspondence with the second subgroup is 2<N>, wherein N is a positive integer. Due to the fact that the most required coded bit number is lower than that in the prior art, decoding throughput can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
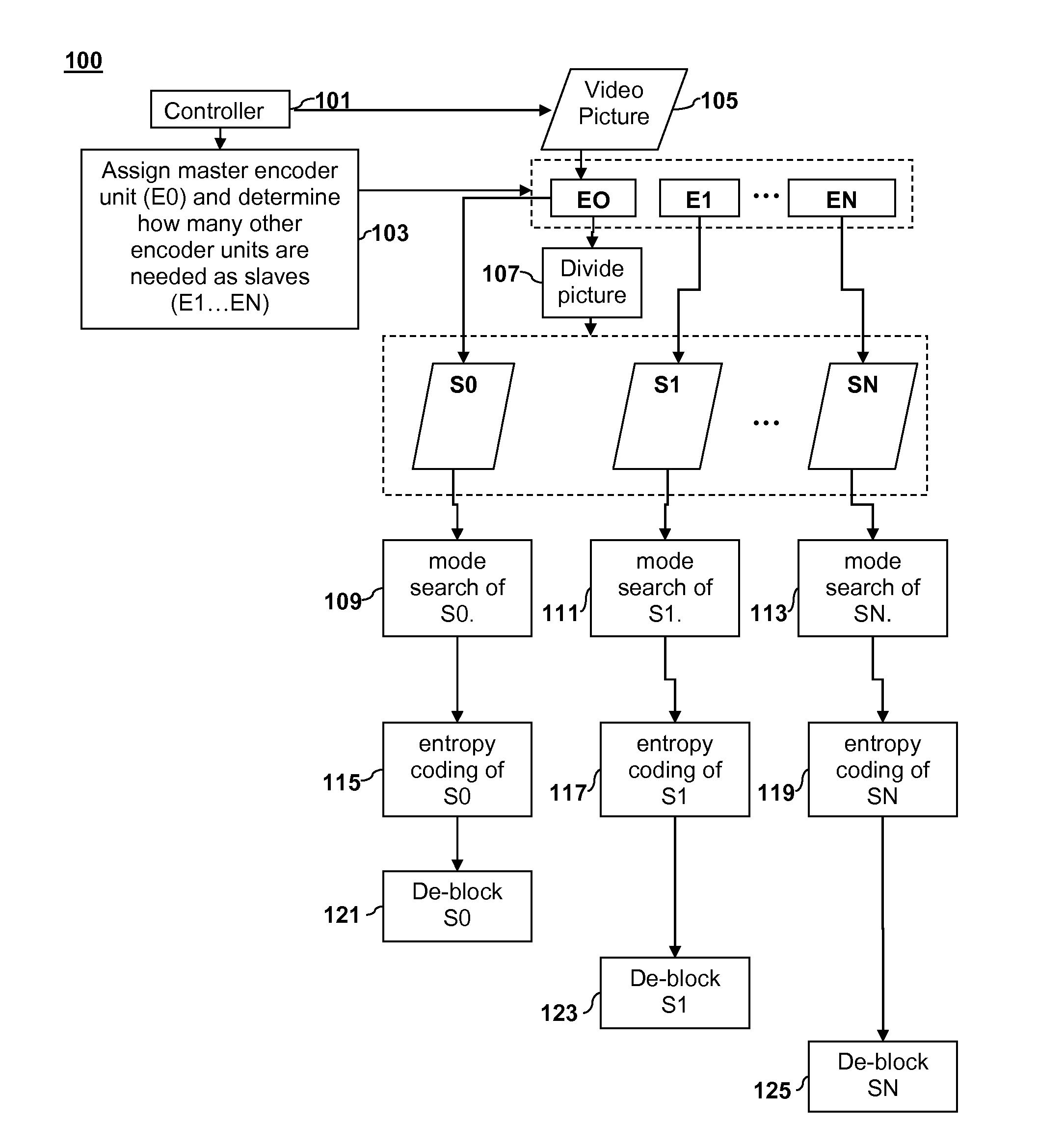
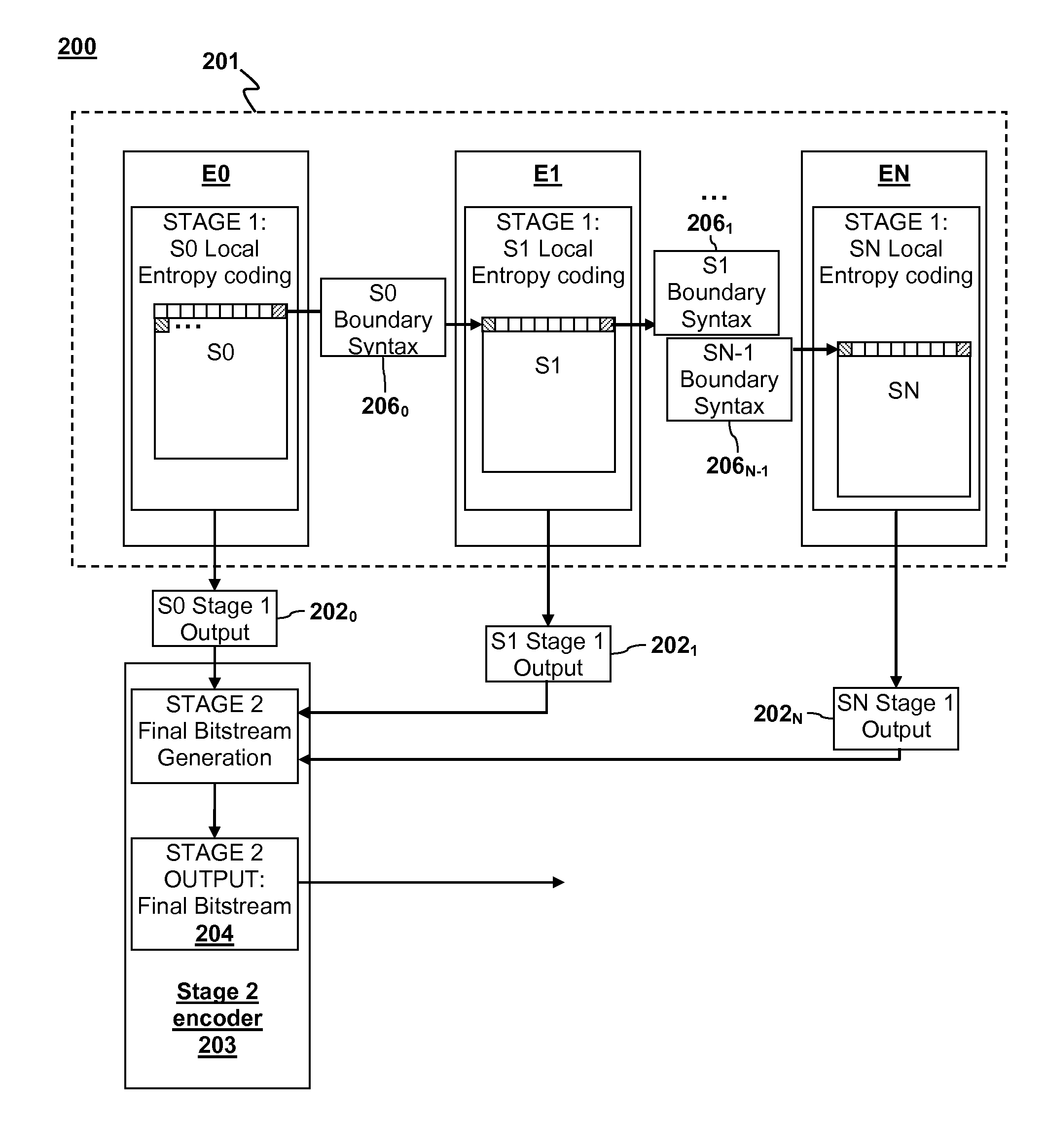
Parallel entropy coding
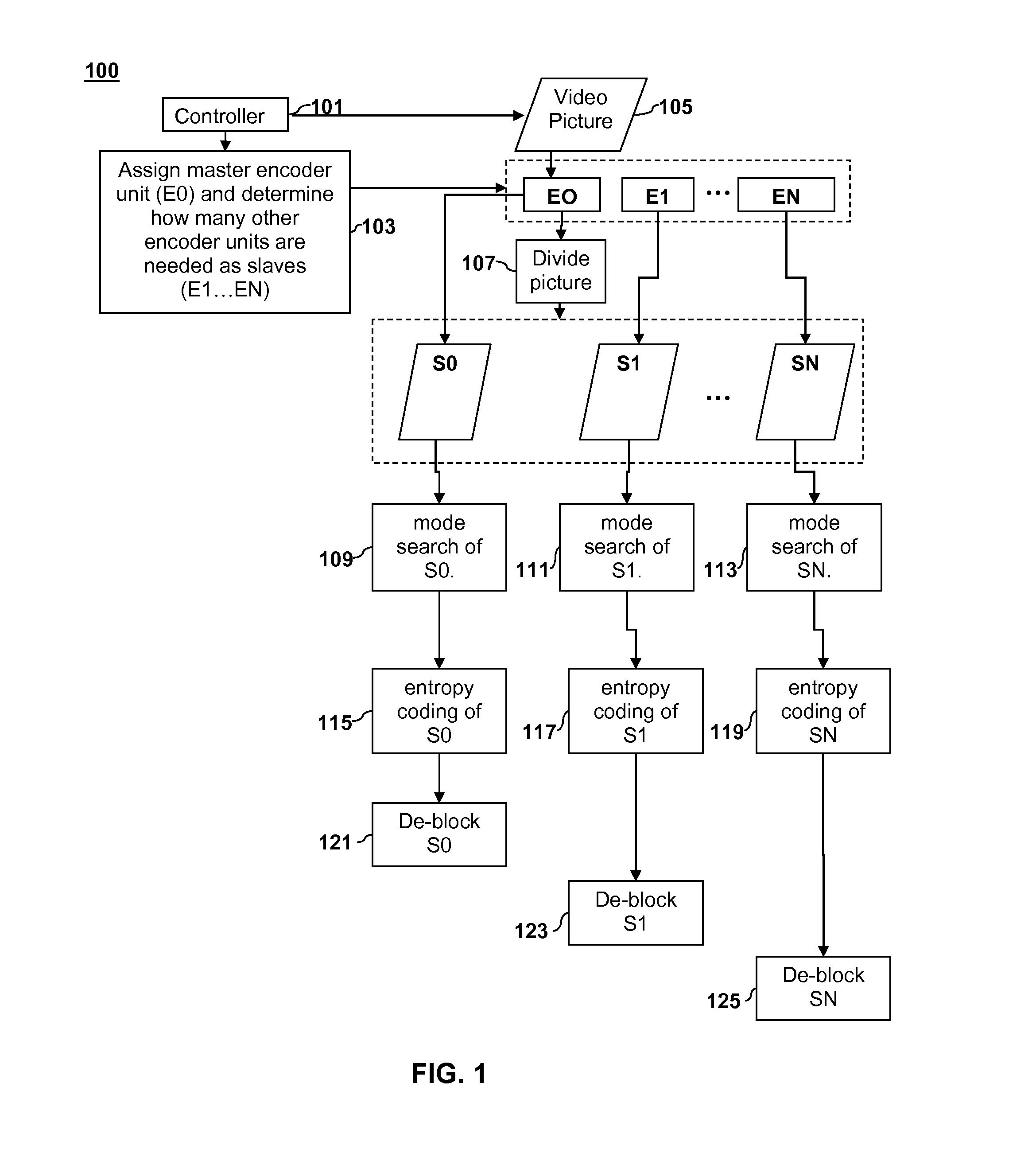
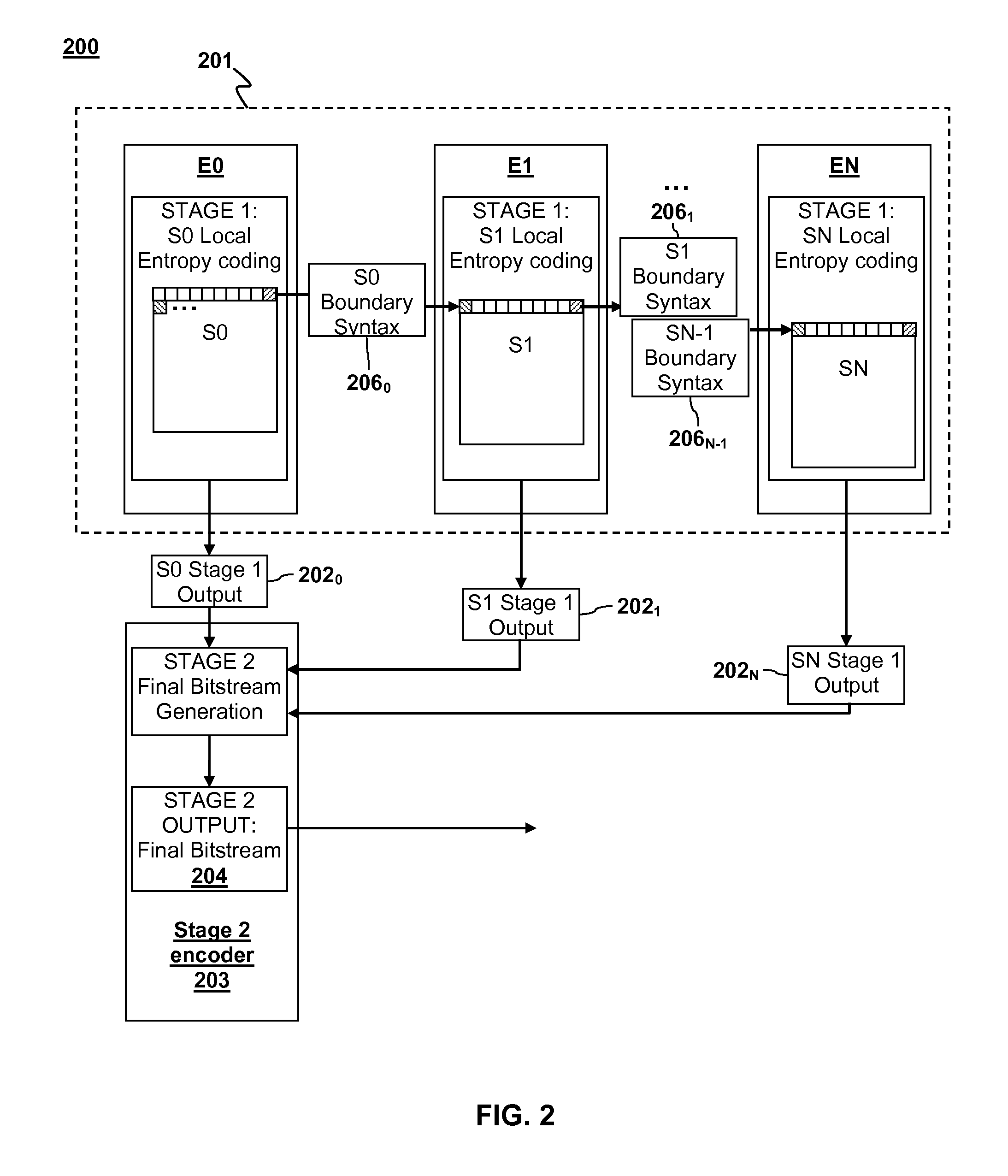
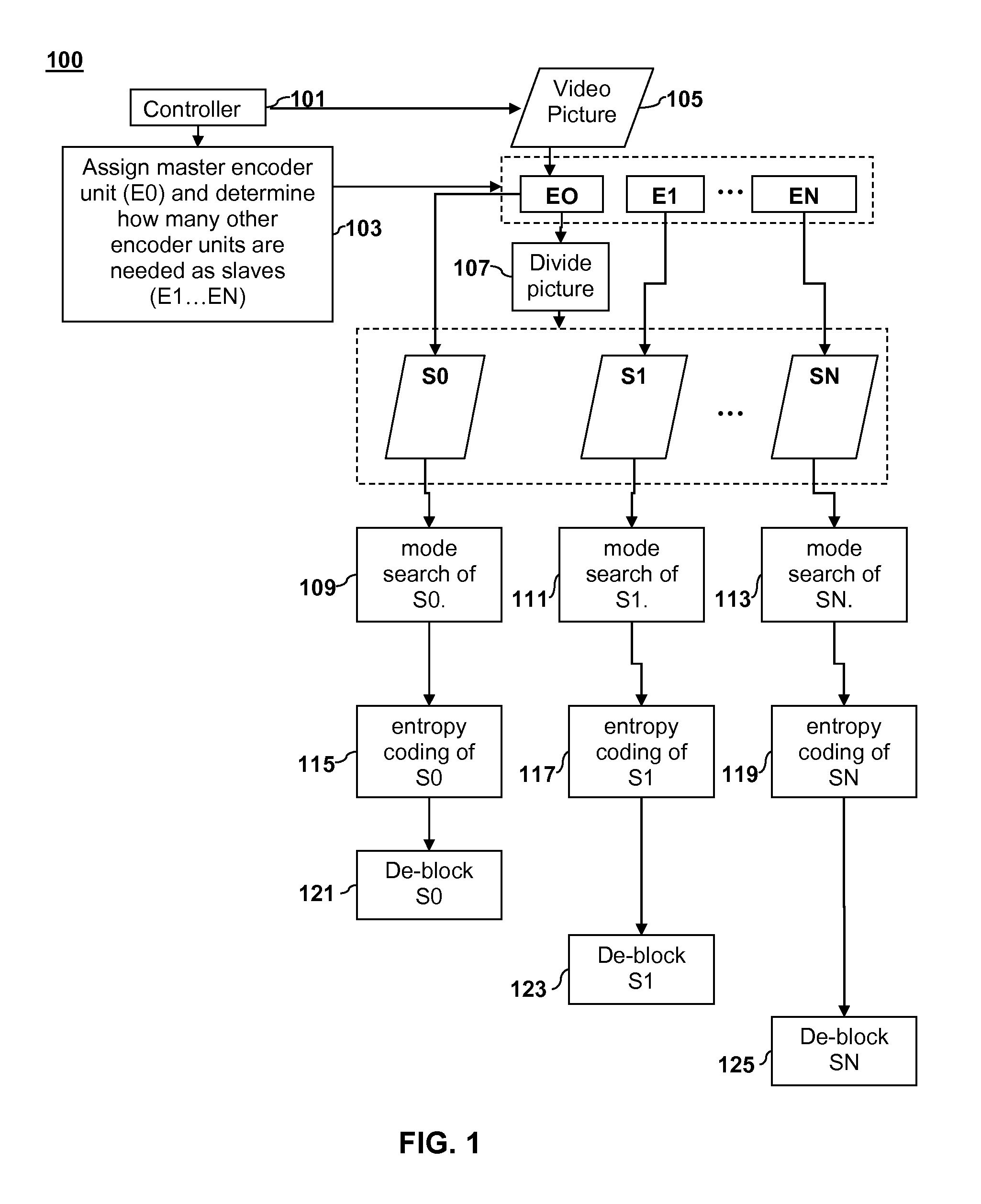
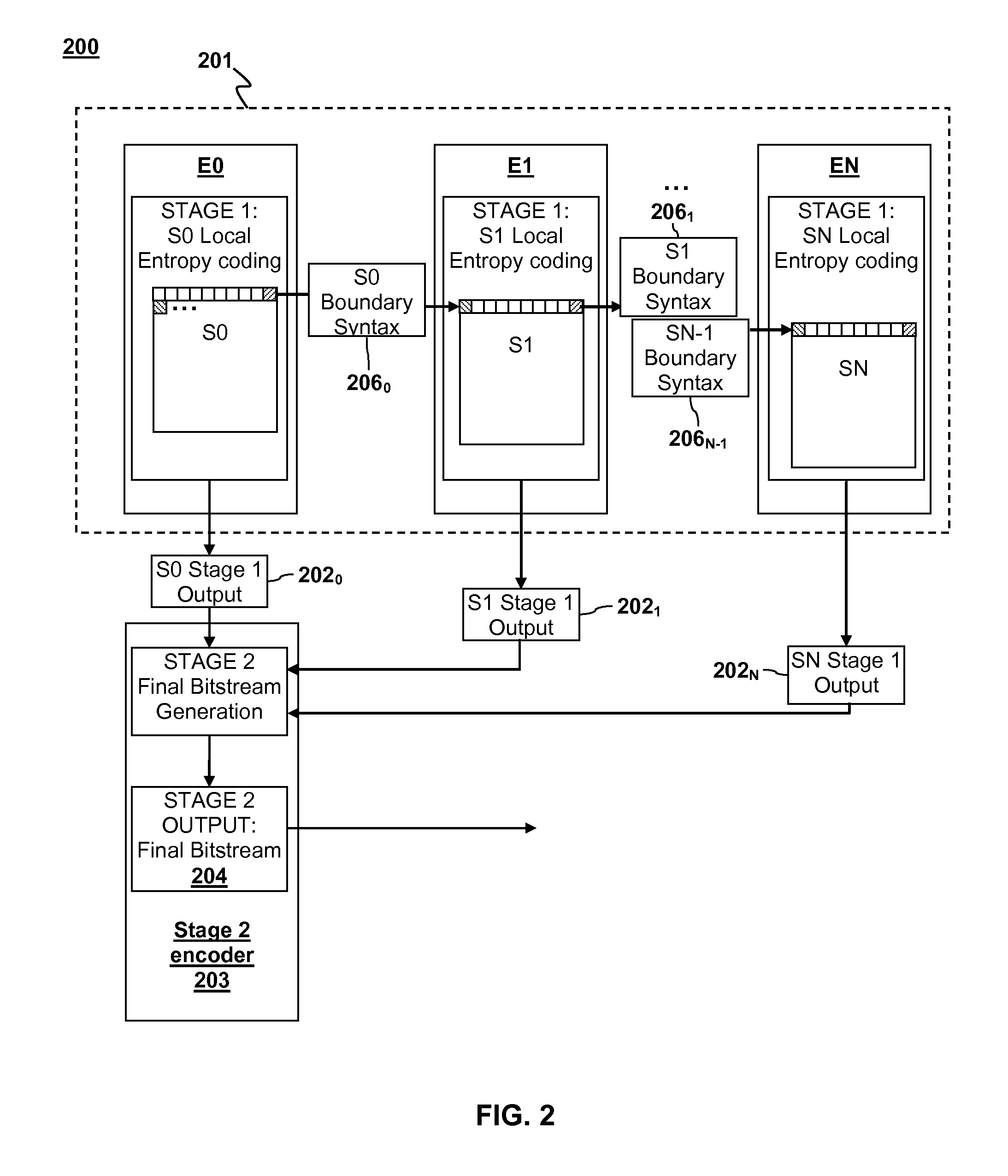
ActiveUS20110235699A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallel encodingDigital image
Parallel coding of digital pictures is described. A digital picture is divided into two or more vertical sections. Two or more corresponding Stage 1 encoder units can perform a first stage of entropy coding on the two or more vertical sections on a row-by-row basis. The entropy coding of the vertical sections can be performed in parallel such that each Stage 1 encoder unit performs entropy coding on its respective vertical section and returns a partially coded Stage 1 output to a Stage 2 encoder unit. Each partially coded Stage 1 output includes a representation of data for a corresponding vertical section that has been compressed by a compression factor greater than 1. The Stage 2 encoder unit can generate a final coded bitstream from the partially encoded Stage 1 output as a Stage 2 output.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Method and device for encoding and decoding by using parallel intra-rediction by a coding unit
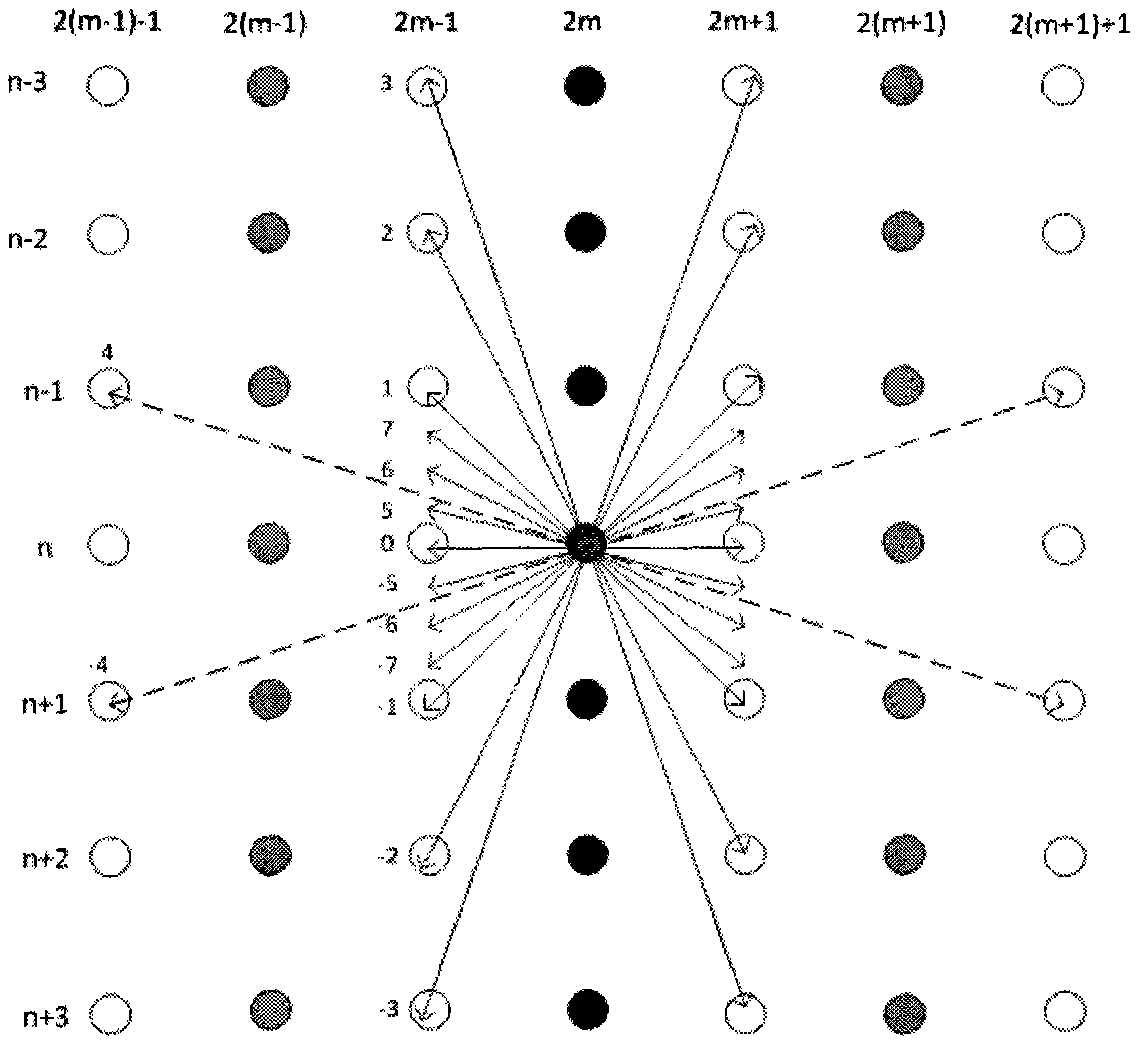
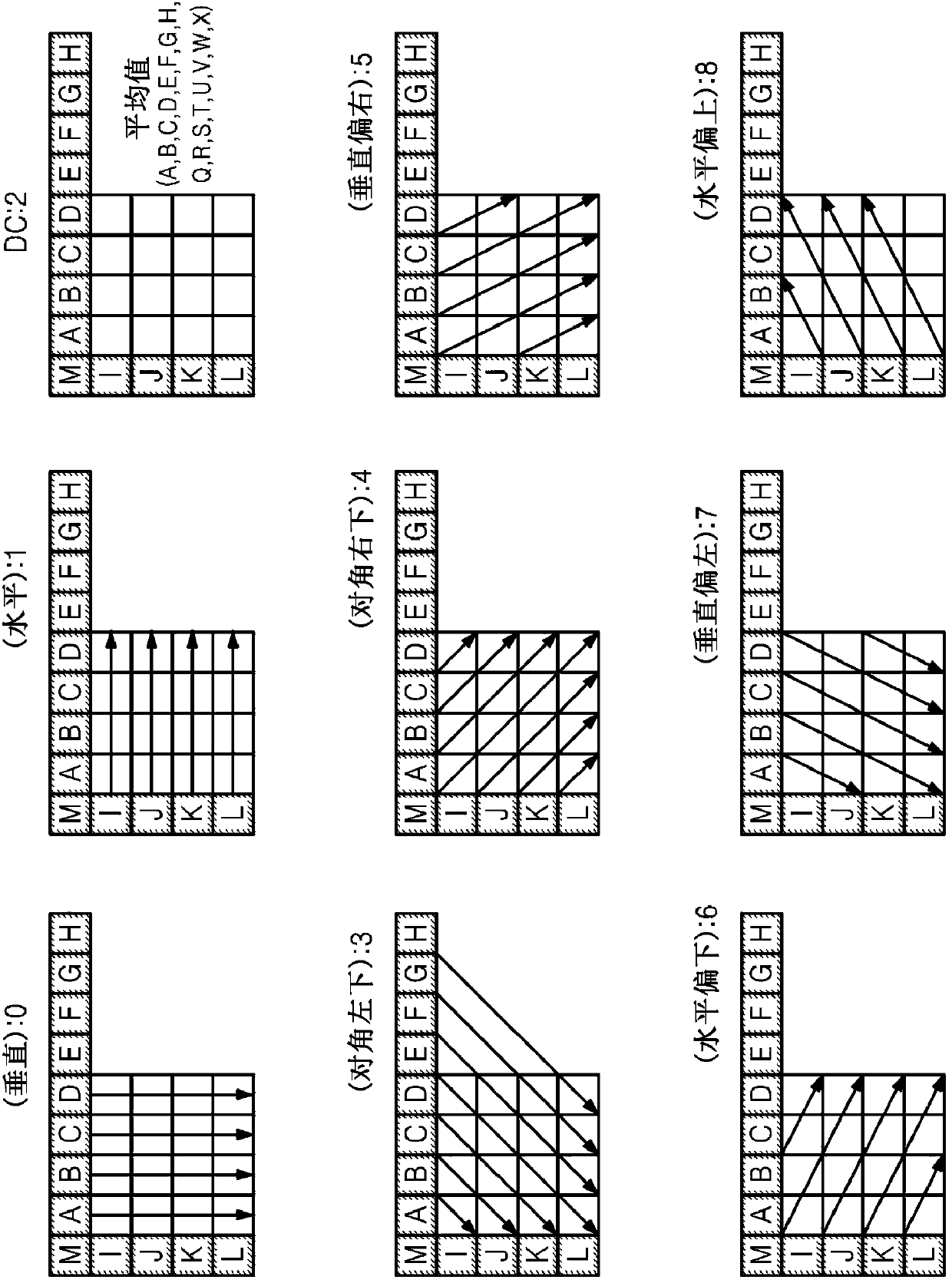
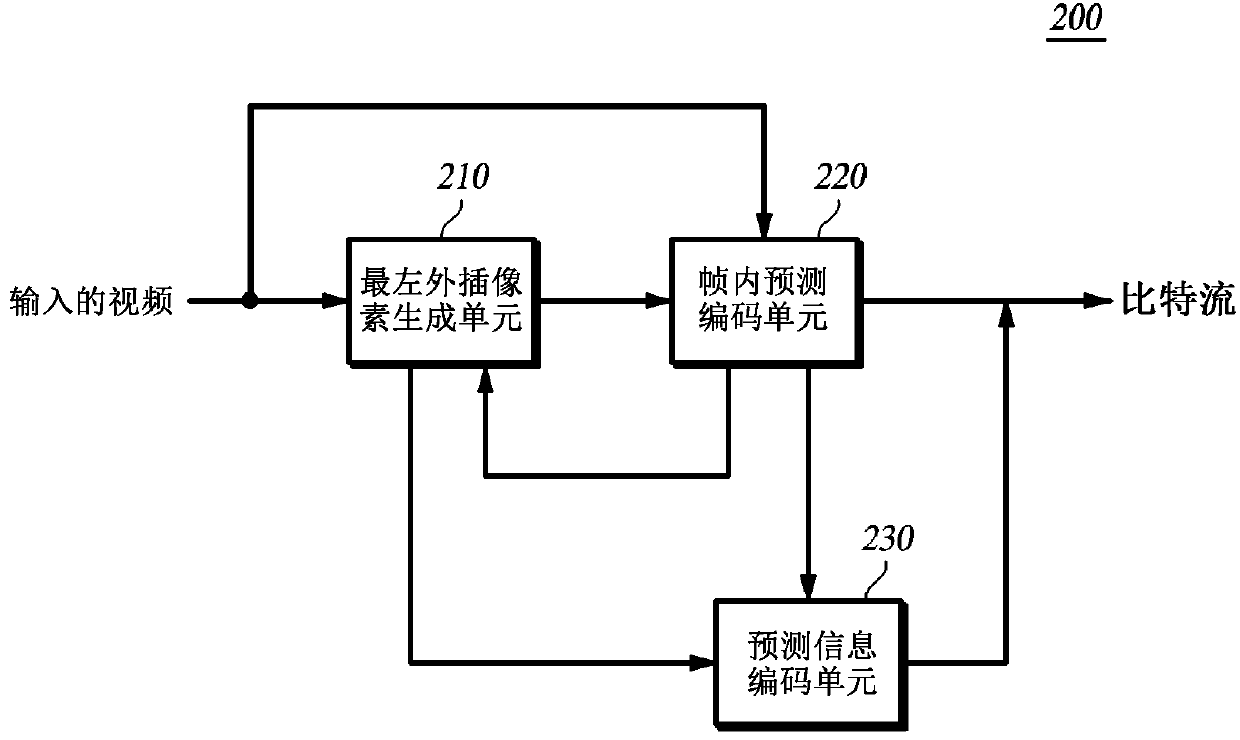
ActiveCN103283238AOmit the original left pixelTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationSpiht codingBitstream
The embodiment of the present invention relates to a method and device for encoding and decoding by using a parallel intra-prediction by a coding unit. More particularly, an embodiment of the present invention relates to a device and method for encoding / decoding images, the method comprising the steps of: generating a left extrapolation pixel of the coding unit by using the leftmost original pixel value of the coding unit or a left top block pixel value of the coding unit according to the direction of an intra-prediction mode with respect to a coding unit; generating a prediction block by intra-predicting the coding unit using an adjacent pixel which includes the left extrapolation pixel; encoding the coding unit, and encoding prediction information which includes a prediction mode performing the intra-prediction; and decoding an encoded bitstream.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
Hard decision iterative decoding method for packet Markov superposition coding
ActiveCN106992841AGood error correction performanceThe method steps are simpleError correction/detection using convolutional codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsSuperposition codingBinary information
The invention discloses a hard decision iterative decoding method for packet Markov superposition coding, and belongs to the fields of digital communication and digital storage. The hard decision iterative decoding method is used for recovering superposition-coded L groups of binary information sequences (as shown in the original PDF) with kB lengths from (L+m) hard decision vectors (as shown in the original PDF) with nB lengths corresponding to packet Markov superposition coding with a memory of m, which is constructed by a binary component code coder with a k-length input and an n-length output and for a hard decision iterative decoding method with a decoding delay as d, only {0, 1, e} is used as iterative information, wherein the e represents a state ''delete'', and a receiving end receives groups (as shown in the original PDF) of hard decision vectors and then starts decoding, so that estimation (as shown in the original PDF) of transmission information (as shown in the original PDF) is acquired. The invention further provides processing methods for each node processor in the hard decision iterative decoding method. The hard decision iterative decoding method for the packet Markov superposition coding, provided by the invention, has excellent performances, low complexity and simpleness in implementation, and can be applied to communication systems, such as optical fiber communication and the like, with the low bit error rate and low decoding time delay requirements.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
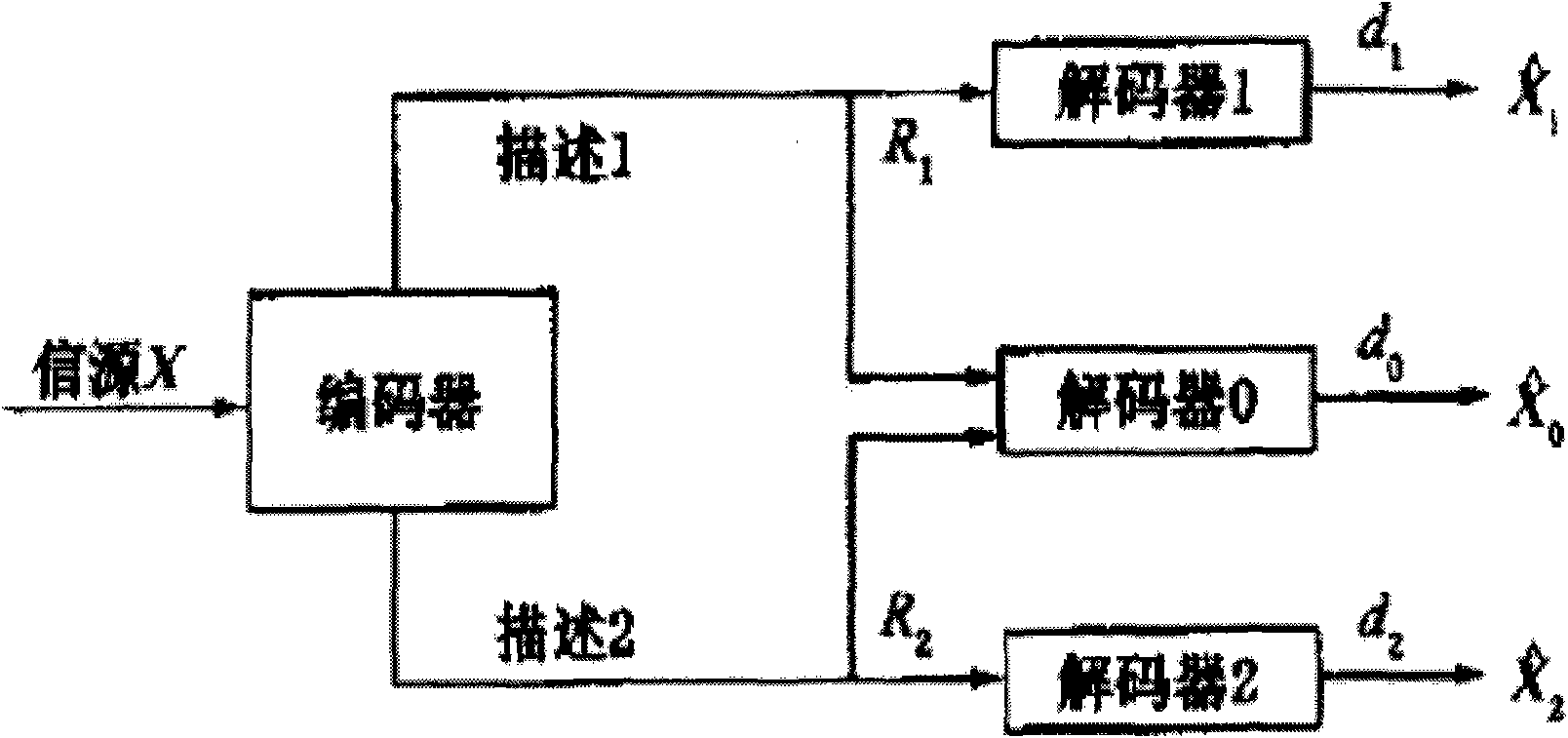
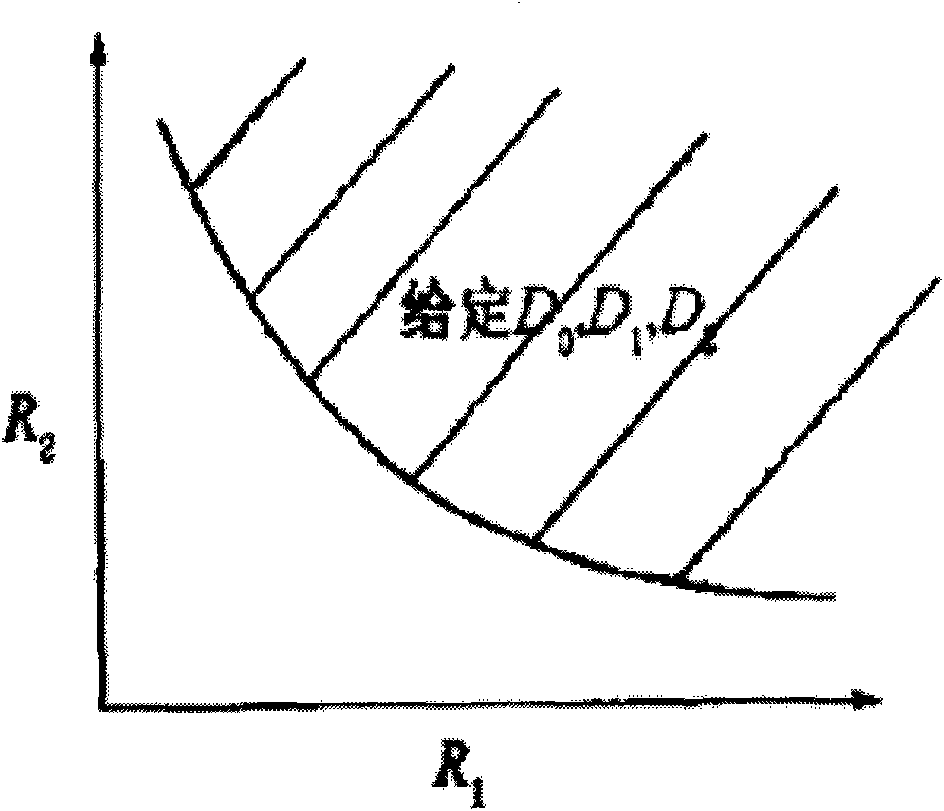
Two-description video coding method based on Wyner-Ziv principle
InactiveCN101621690AReduce coding complexityImprove robustnessTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationComputer architectureVideo transmission
The invention relates to a two-description video coding method based on Wyner-Ziv principle. The method comprises the following steps: 1) low-complexity coding, i.e., even and odd frame separation; zero-motion H.264 coding to generate a first part of description; residual SW-SPIHT coding to generate a second part of description; and redundant optimization; 2) high-complexity coding, i.e., decoding by using a central decoder when the two descriptions are received; and performing zero-motion H.264 coding to the first part if only the description 1 is received, and then generating a reference frame Wre2 and side information Y2 by using an interpolation formula as well as a difference value (D1y is equal to Y2-Wre2); and then performing SW-SPIHT decoding to restructure a difference value D'1 to obtain a formula (W''2 is equal to D'1 + Wre2), and finally, merging W'1 and W''2 to obtain a restored complete video sequence V'1. The invention adopts a video coding framework both provided with low coding complexity and good robust performance, and when a description is lost, the method has better compressive performance, also retains the low-complexity coding and also can meet the network video transmission requirement of a device with low energy consumption.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Encoding/decoding storage system with scalable input bit width
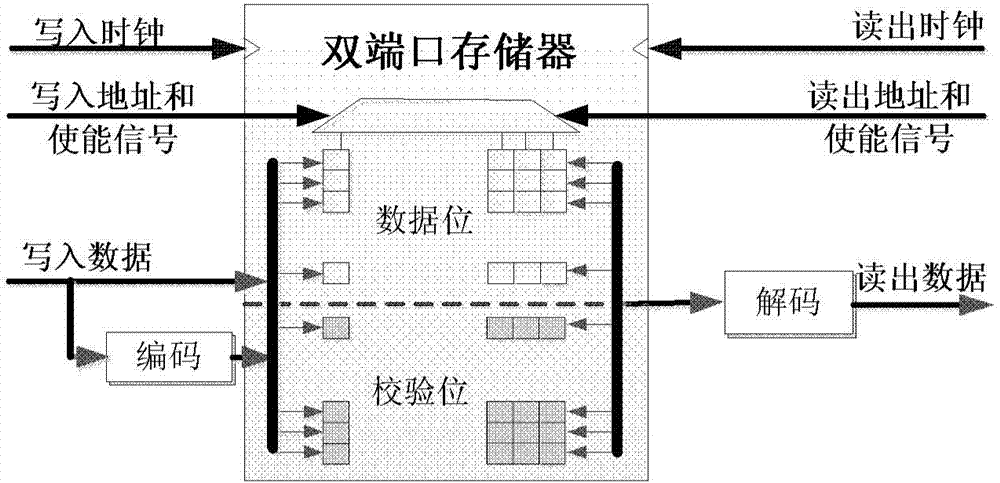
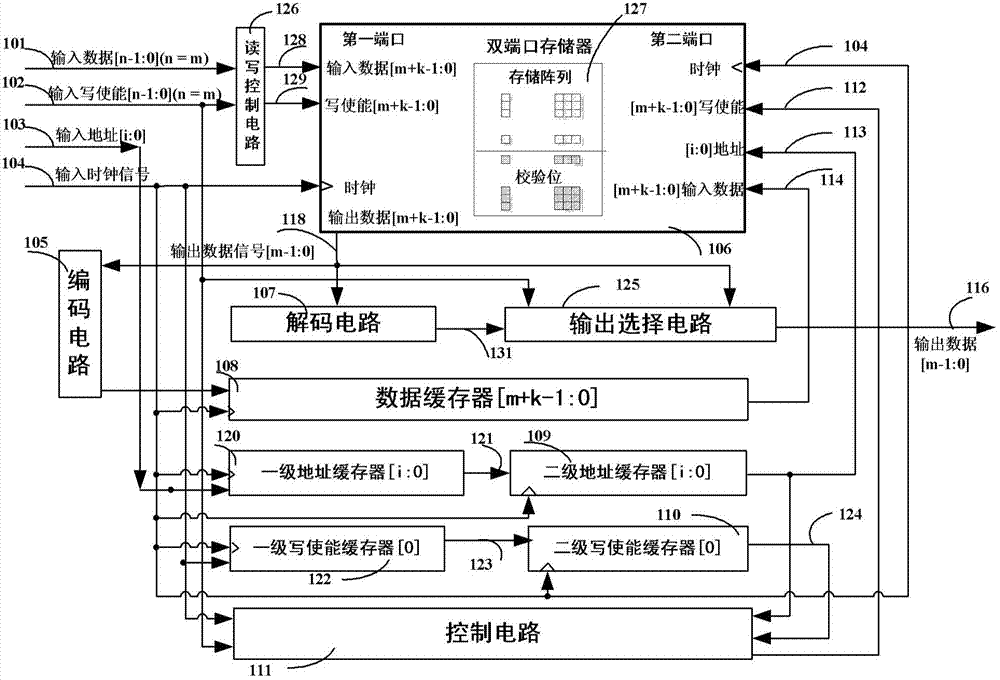
ActiveCN103886916ARealize interactive storageThe codec is correctStatic storageControl circuitSpiht coding
The invention provides an encoding / decoding storage system with scalable input bit width. The encoding / decoding storage system comprises a read and write control circuit, a memorizer, an encoding circuit, a data cache device, a first-level address buffer, a second-level address buffer, first-level write enable buffer, a second-level write enable buffer and a control circuit, wherein the first-level address buffer is cascaded with the second-level address buffer; the first-level write enable buffer is cascaded with the second-level write enable buffer. According to the encoding / decoding storage system, a cache encoding / decoding mechanism is adopted, so that interactive storage between storage array and the buffers can be realized; when the bit width of the data which needs to be written in and externally provided can not meet the requirement on the memorizer, namely, part of coded data comes from the external input, and the other part of the coded data comes from the storage array, accurate encoding and decoding can be realized; furthermore, the error correcting capabilities are consistent under the condition of different bit widths, so that normal write-in and read-out operation can be carried out on the storage array.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chroma quantization in video coding
Owner:APPLE INC
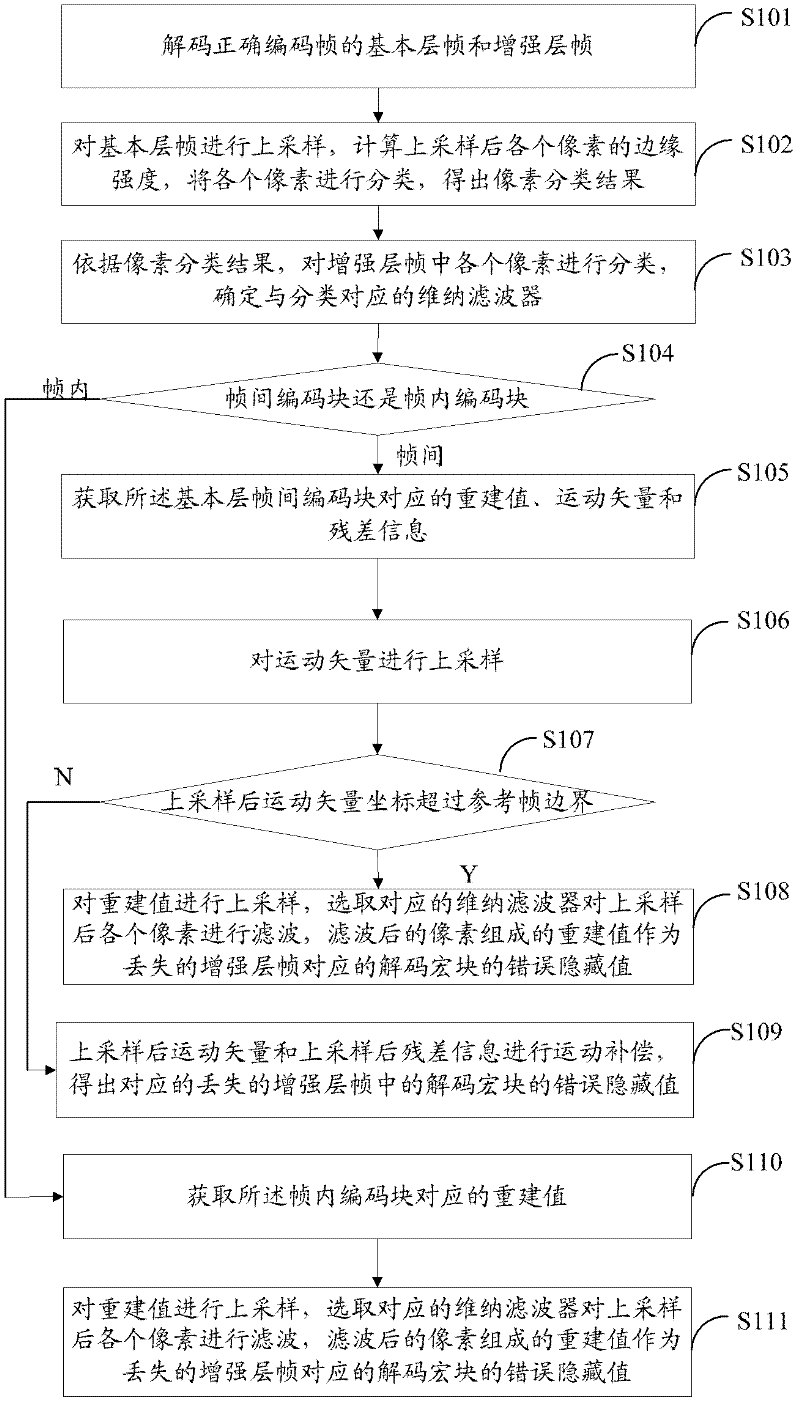
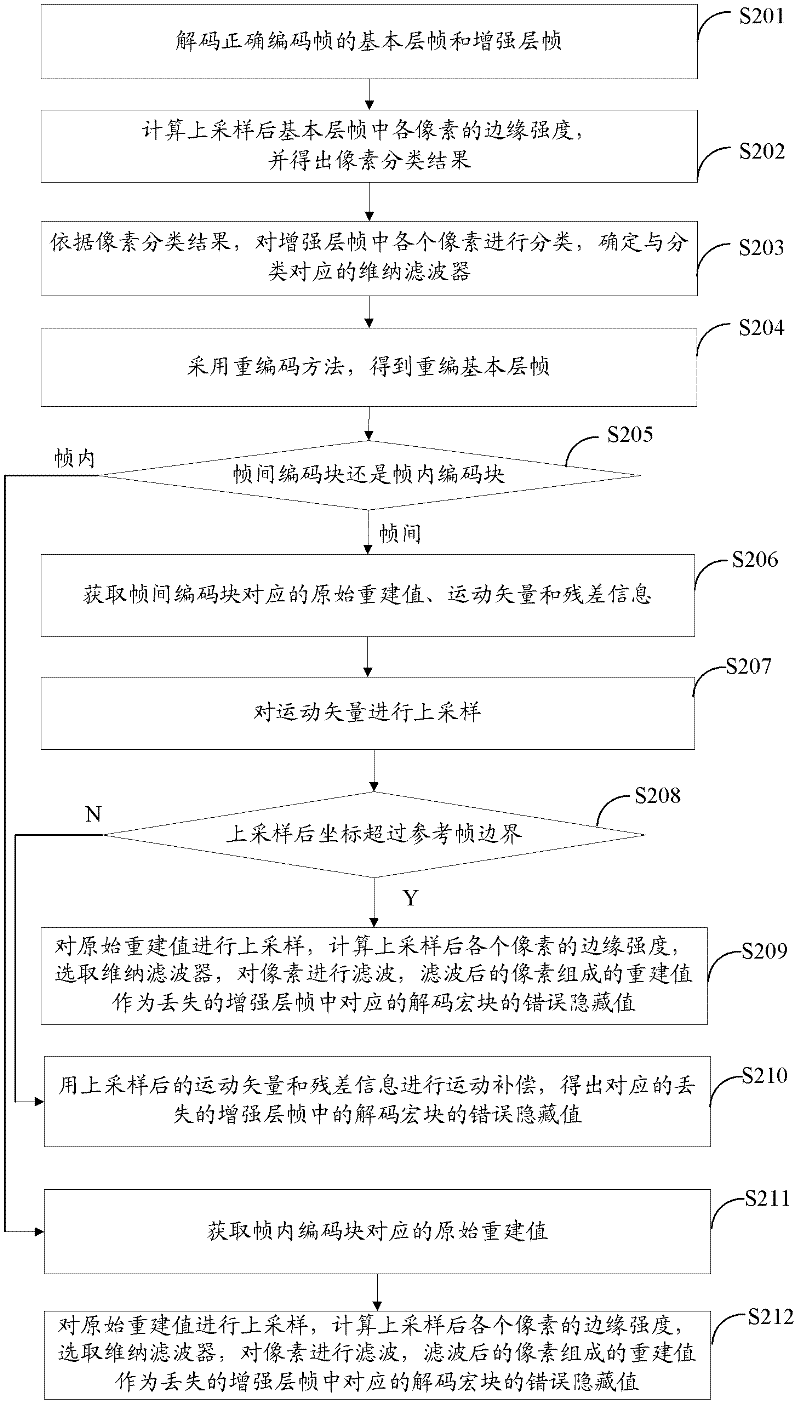
Extensible video coding error hiding method, decoder and system
ActiveCN102547282AQuality improvementImprove clarityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationCoding blockComputer hardware
The invention discloses an extensible video coding error hiding method, a decoder and a system. The extensible video coding error hiding method comprises the steps of carrying out different processing when a decoding macroblock in an interframe coding frame is an interframe coding block or an intra-frame coding block under the conditions that a basic layer frame corresponding to a lost enhancement layer frame serves as the interframe coding frame and frame losing times do not exceed a preset times, and obtaining an error hiding value of a reconstructed enhancement layer frame; and under the conditions that the basic layer frame corresponding to the lost enhancement layer frame serves as the interframe coding frame and the frame losing times exceed the preset times or the basic layer frame corresponding to the lost enhancement layer frame serves as an intra-frame coding frame, adopting a recoding method to obtain a recoding base layer frame, carrying out different processing when a decoding macroblock in the recoding base layer frame is an interframe coding block or an intra-frame coding block, and obtaining an error hiding value of a reconstructed enhancement layer frame. Compared with the prior art, quality of the reconstructed enhancement layer frame is improved, thereby improving video definition and avoiding video drawing.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Gradual updating using transform coefficients for encoding and decoding
ActiveCN107409212AEasy to codeImprove efficiencyDigital video signal modificationSpiht codingMacroblock
Innovations are provided for encoding and / or decoding video and / or image content using transform coefficient level gradual updating. Transform coefficient level gradual updating can be applied by encoding (or decoding) different subsets of the transform coefficients for the blocks, macroblocks, or other coding unit for each of a sequence of pictures. For example, a first subset of the transform coefficients of the blocks of a first picture can be encoded with the first picture, a second subset of the transform coefficients of the blocks of a second picture can be encoded with the second picture, and so on. A decoder can reconstruct pictures with increasing quality by receiving additional subsets of the transform coefficients.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Parallel entropy coding
ActiveUS8660177B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallel encodingDigital image
Parallel coding of digital pictures is described. A digital picture is divided into two or more vertical sections. Two or more corresponding Stage 1 encoder units can perform a first stage of entropy coding on the two or more vertical sections on a row-by-row basis. The entropy coding of the vertical sections can be performed in parallel such that each Stage 1 encoder unit performs entropy coding on its respective vertical section and returns a partially coded Stage 1 output to a Stage 2 encoder unit. Each partially coded Stage 1 output includes a representation of data for a corresponding vertical section that has been compressed by a compression factor greater than 1. The Stage 2 encoder unit can generate a final coded bitstream from the partially encoded Stage 1 output as a Stage 2 output.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Fast HEVC interframe coding method
ActiveCN106534849AReduce lossesShorten the timeDigital video signal modificationInterframe codingSoftware engineering
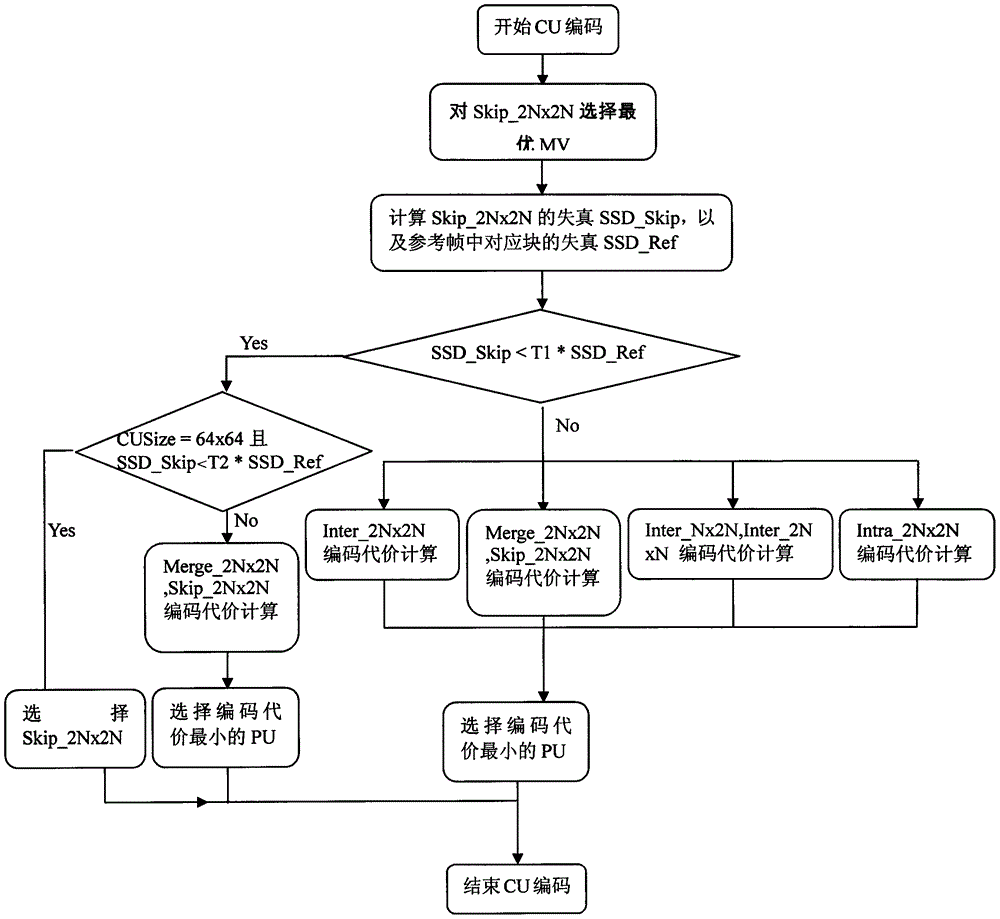
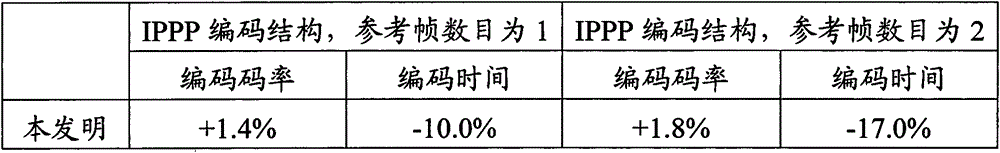
The invention discloses a fast HEVC interframe coding method, which can be applied to various scenarios, and the calculation of Inter-2Nx2N, Inter-Nx2N, Inter-2NxN and Intra-2Nx2N prediction units can be quickly and accurately jumped, thereby greatly reducing the coding time, and meanwhile reducing the loss of the coding quality as much as possible.
Owner:HANGZHOU ARCVIDEO TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Multistage LDPC encoding
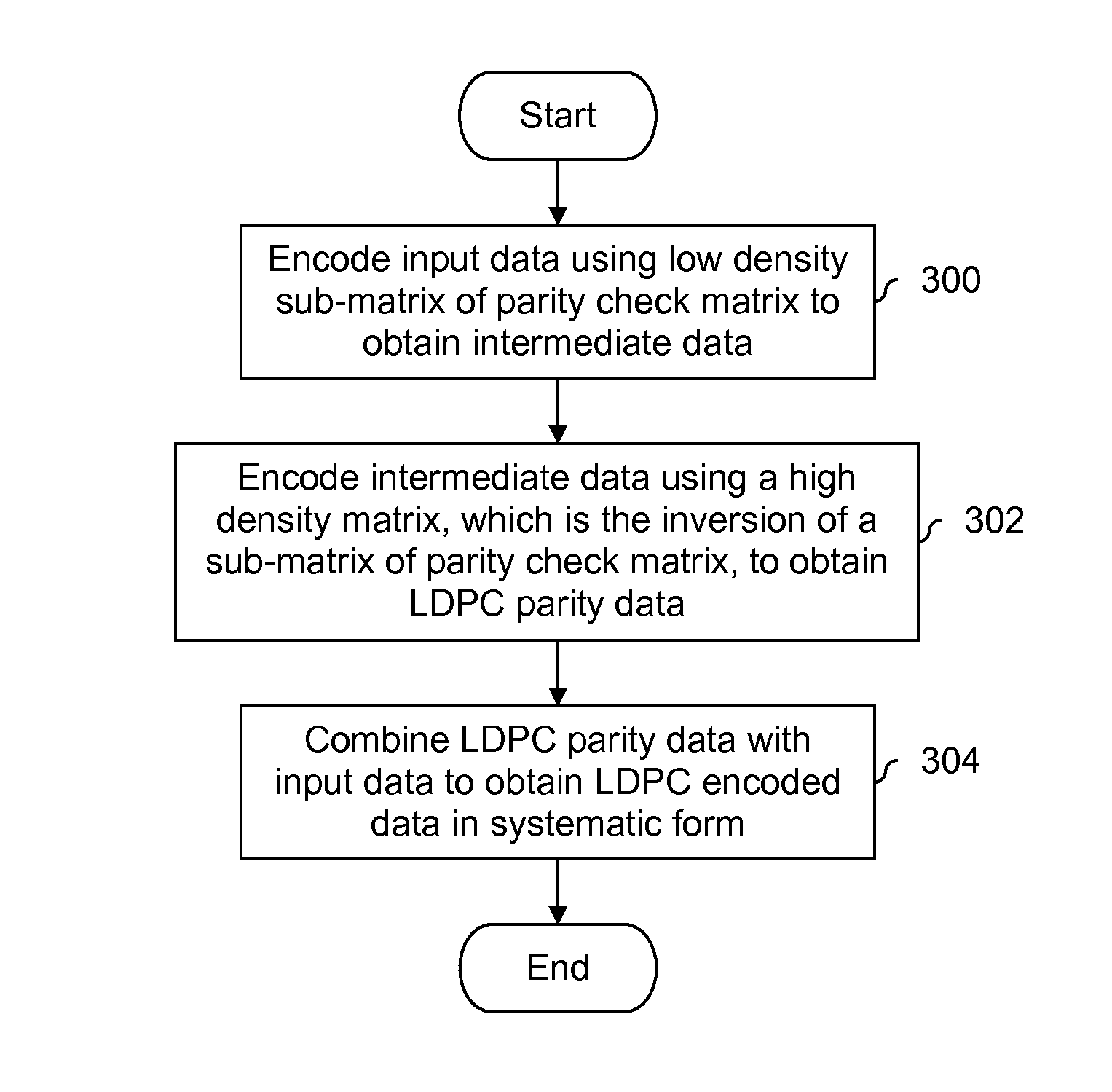
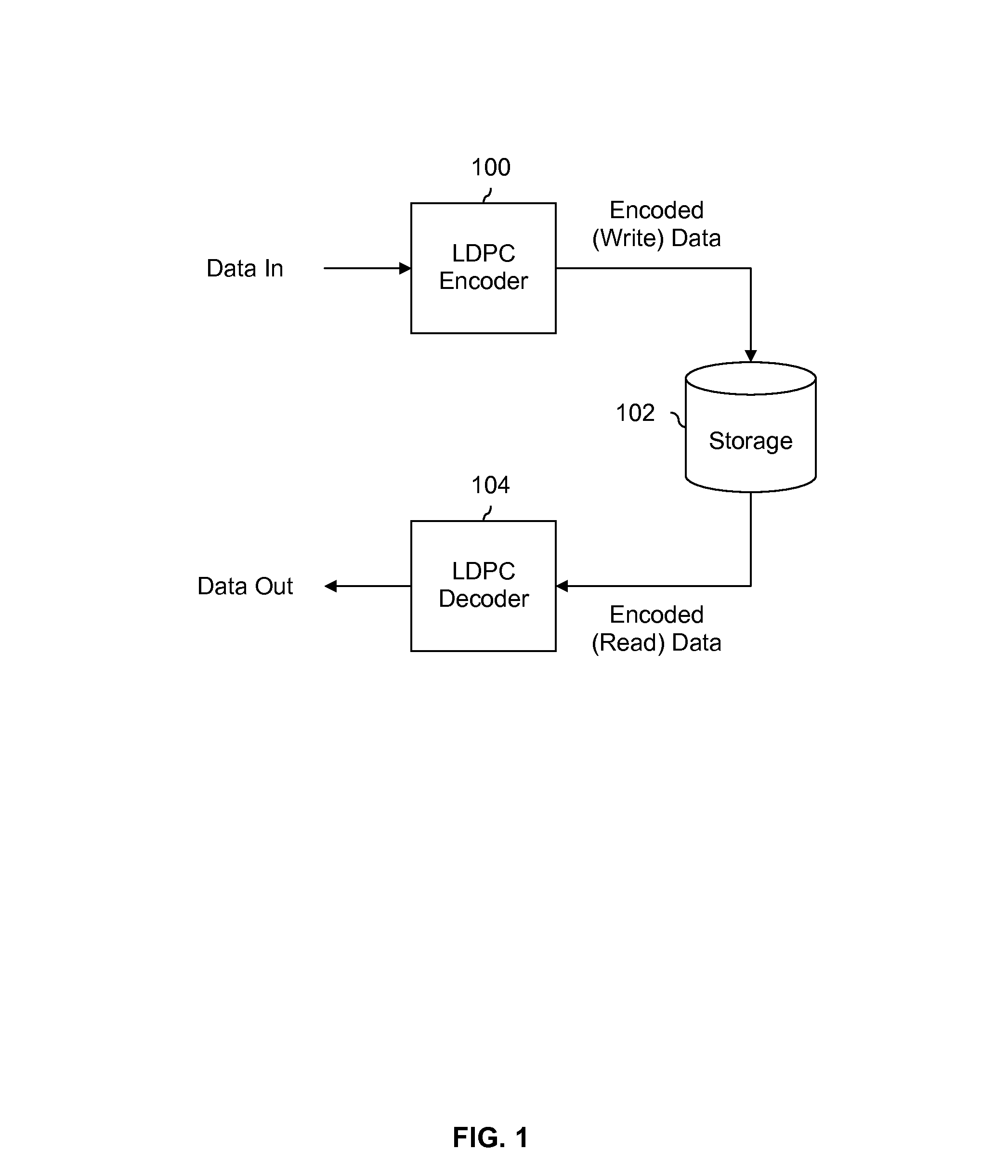
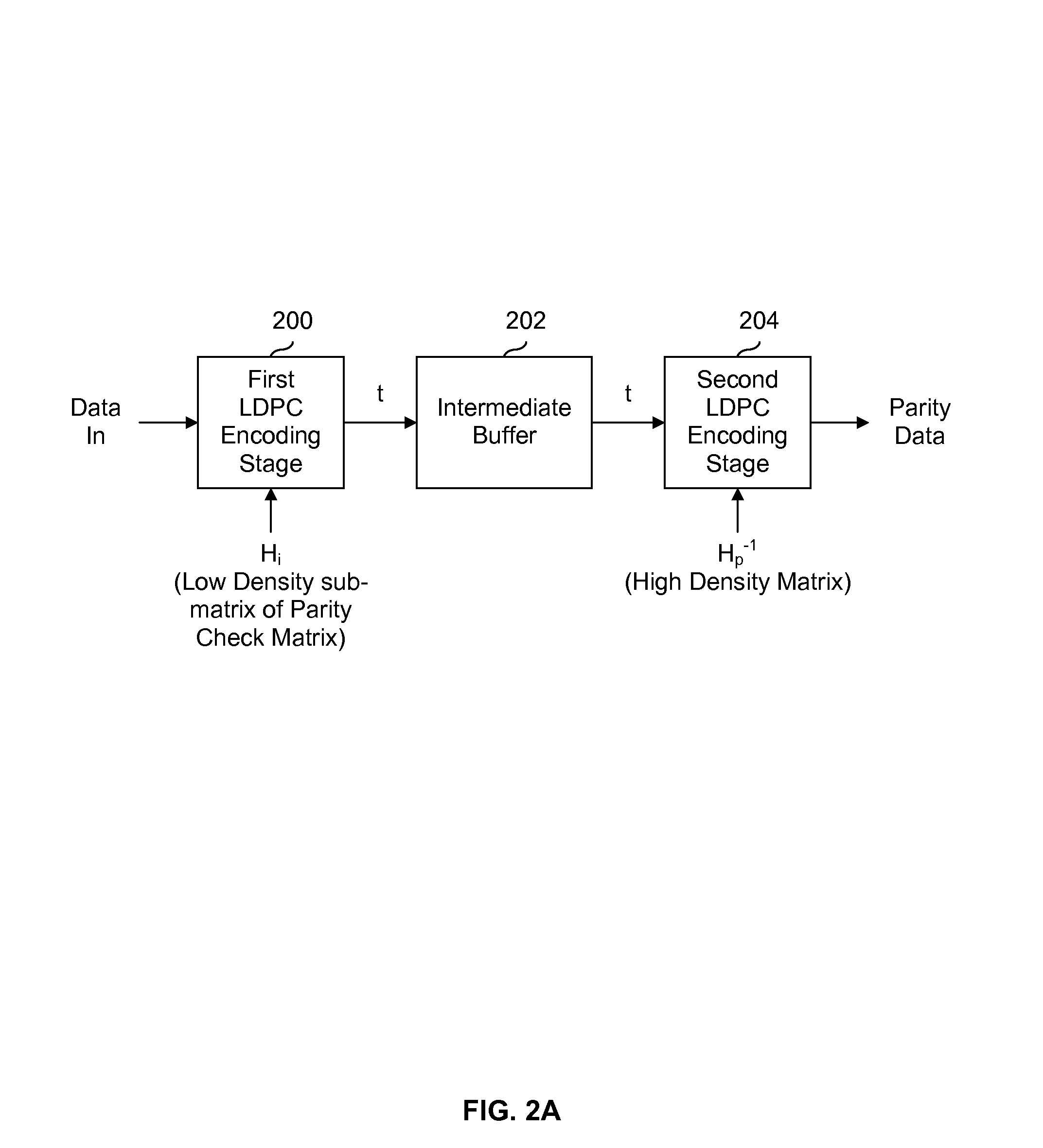
ActiveUS8448041B1Error detection/correctionCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
Low-density parity-check (LDPC) encoding is performed by encoding input data using a first sub-matrix of a parity check matrix to obtain intermediate data. The parity check matrix includes the first sub-matrix and a second sub-matrix having a matrix inversion. The intermediate data is encoded using the matrix inversion of the second sub-matrix of the parity check matrix.
Owner:SK HYNIX MEMORY SOLUTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com