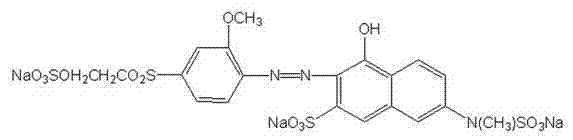
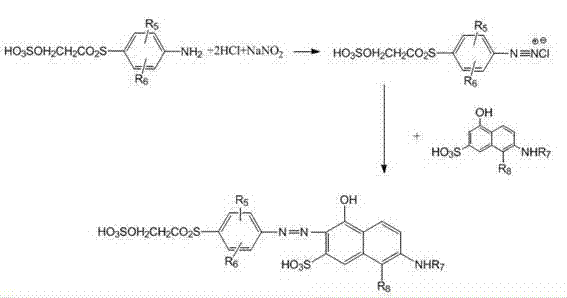
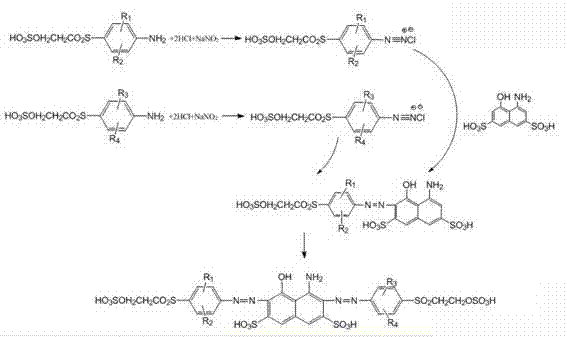
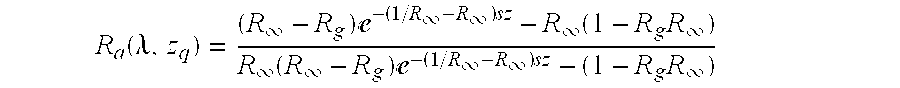Patents
Literature
53 results about "Subtractive color" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
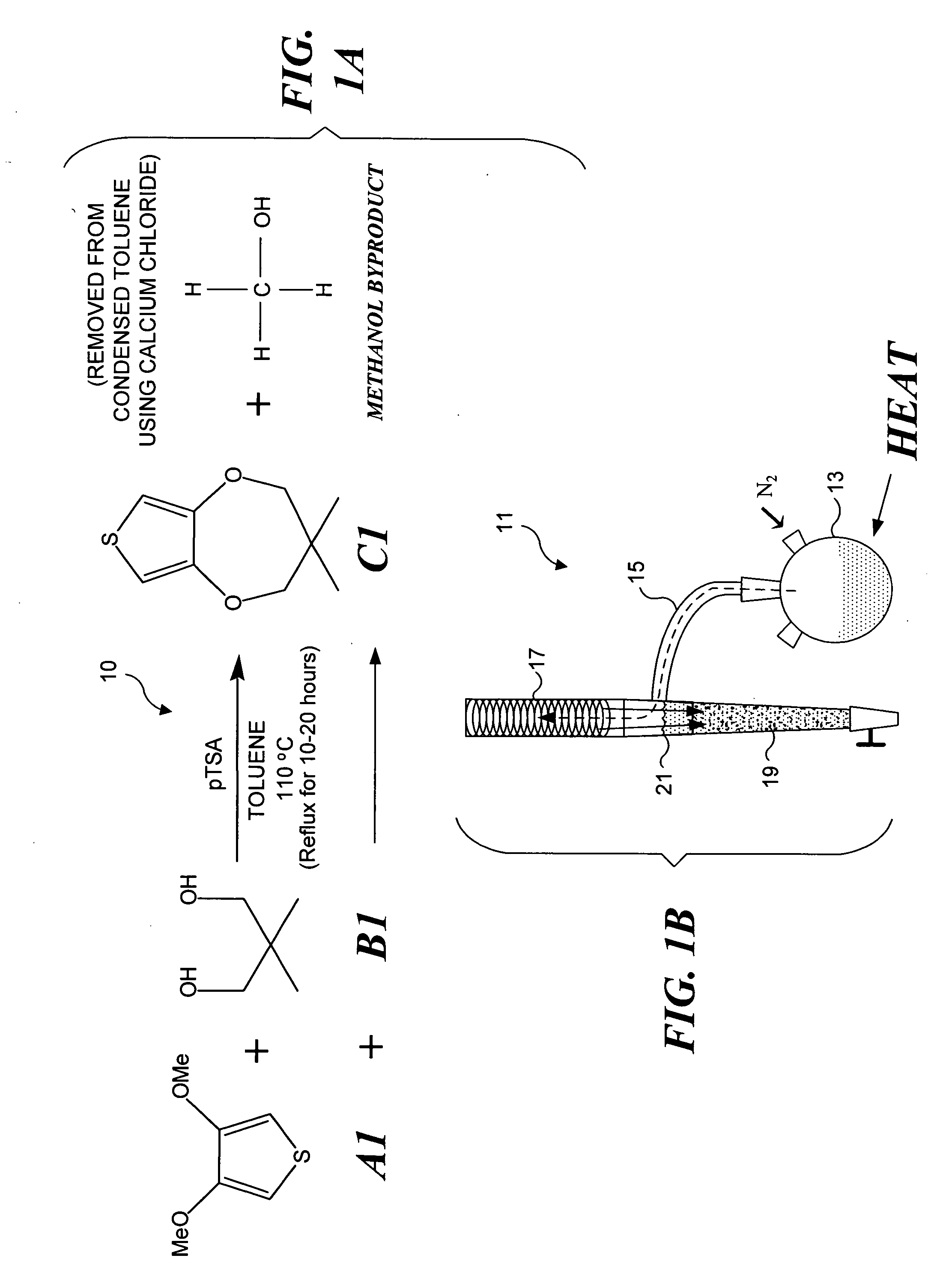
Subtractive color, or "subtractive color mixing", predicts the spectral power distribution of light after it passes through successive layers of partially absorbing media. This idealized model is the essential principle of how dyes and inks are used in color printing and photography where the perception of color is elicited after white light passes through microscopic "stacks" of partially absorbing media allowing some wavelengths of light to reach the eye and not others.
Switchable window based on electrochromic polymers
InactiveUS7256923B2Easy transitionOrganic chemistryTenebresent compositionsPolymer scienceSubtractive color
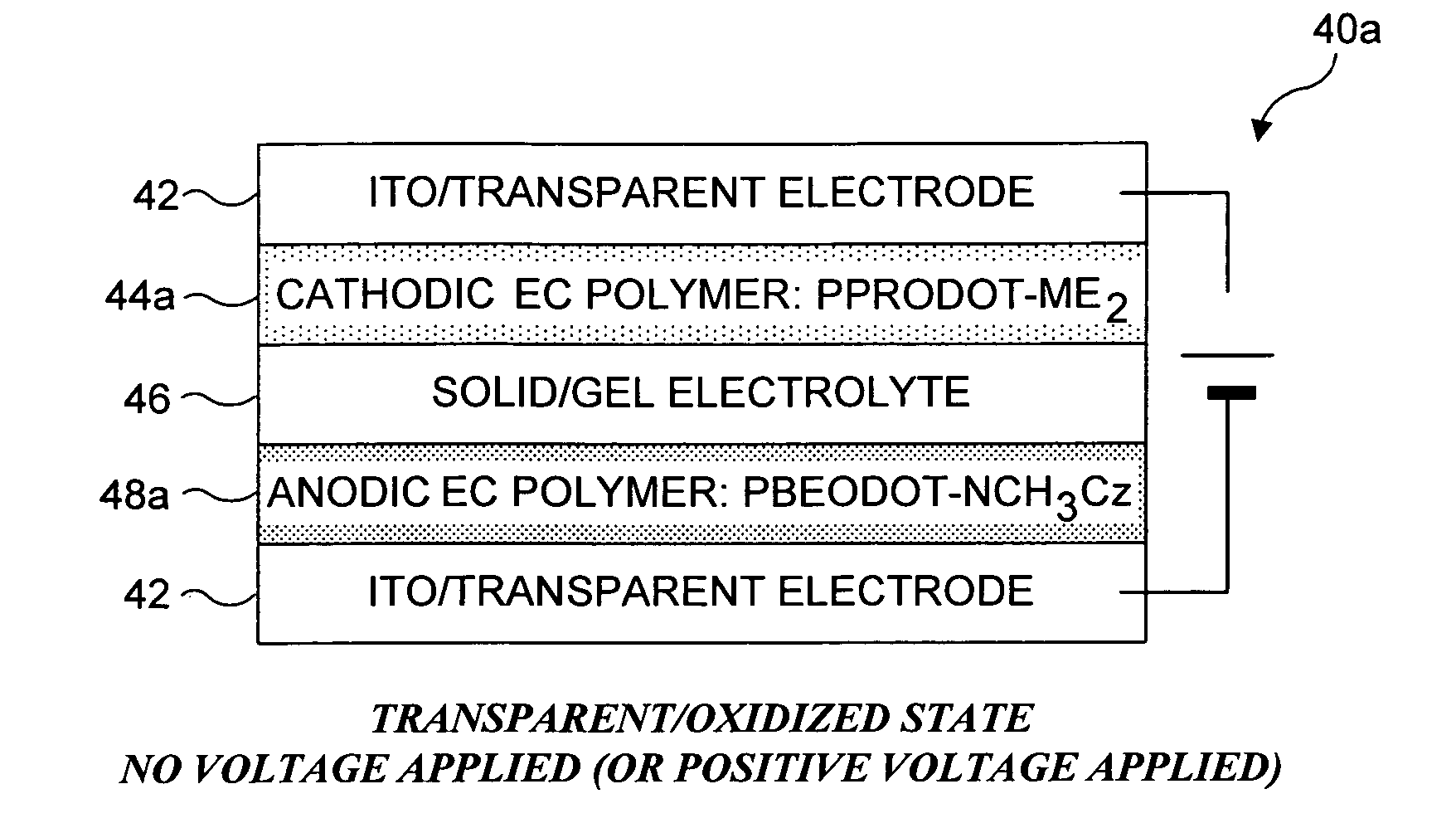
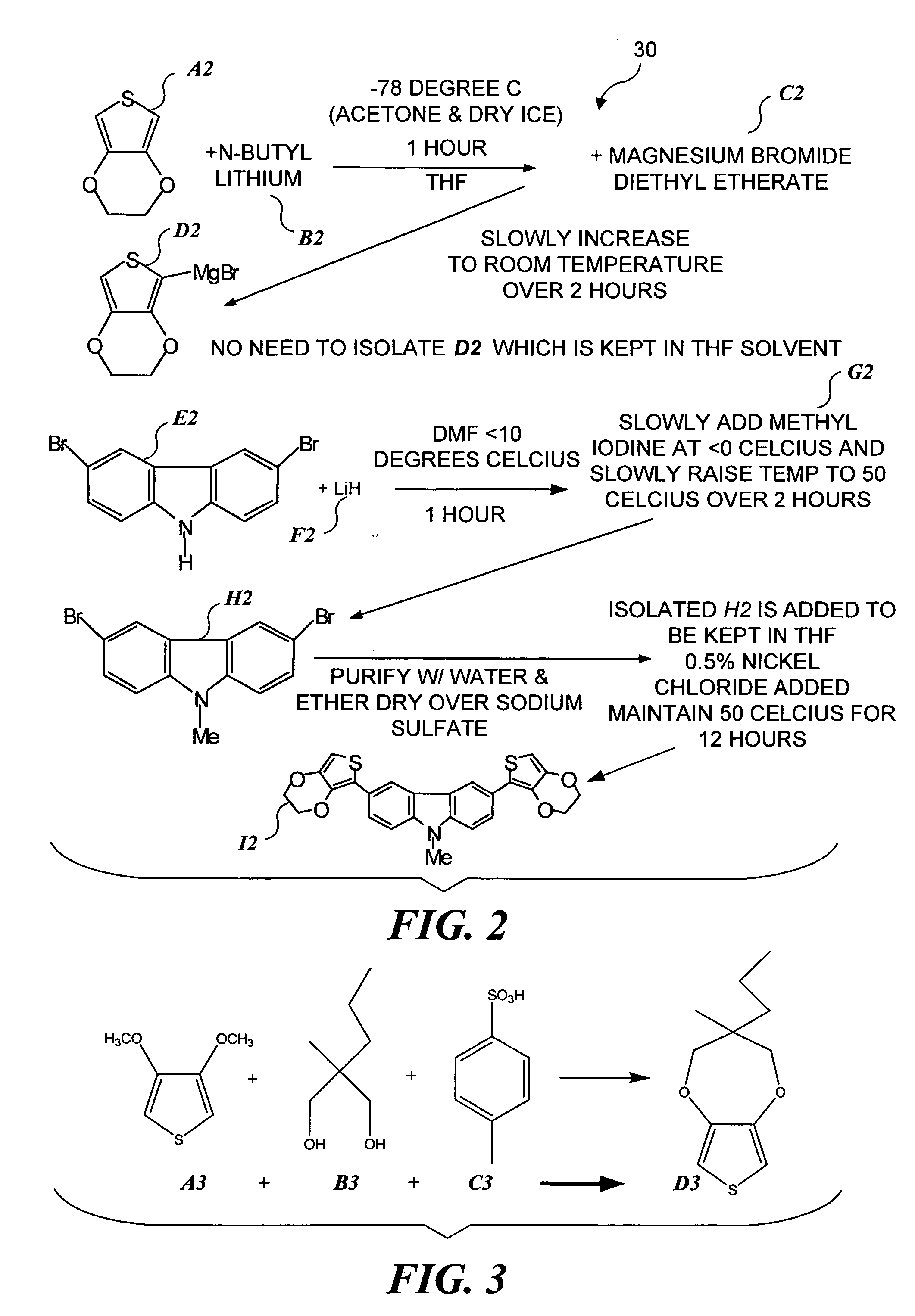
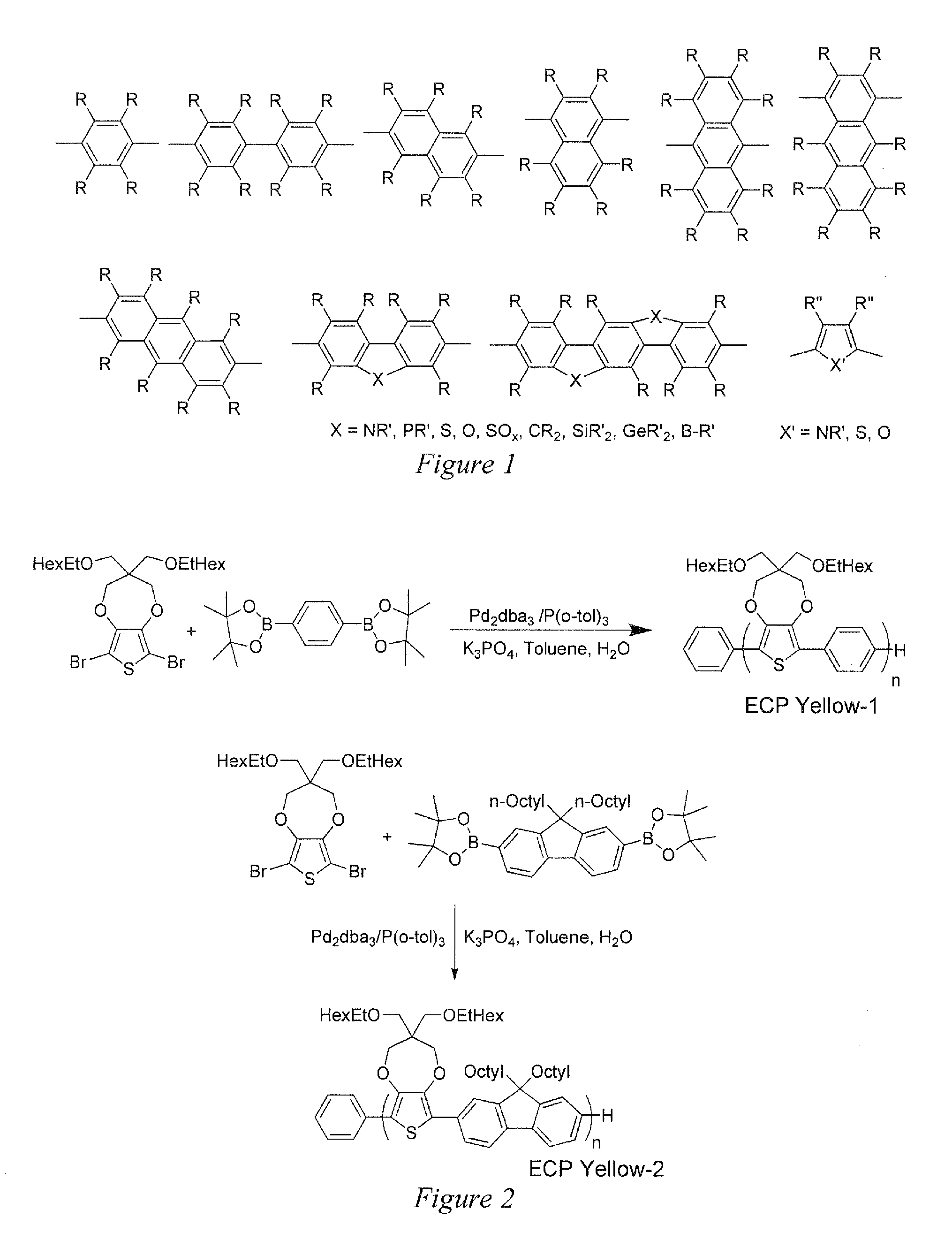
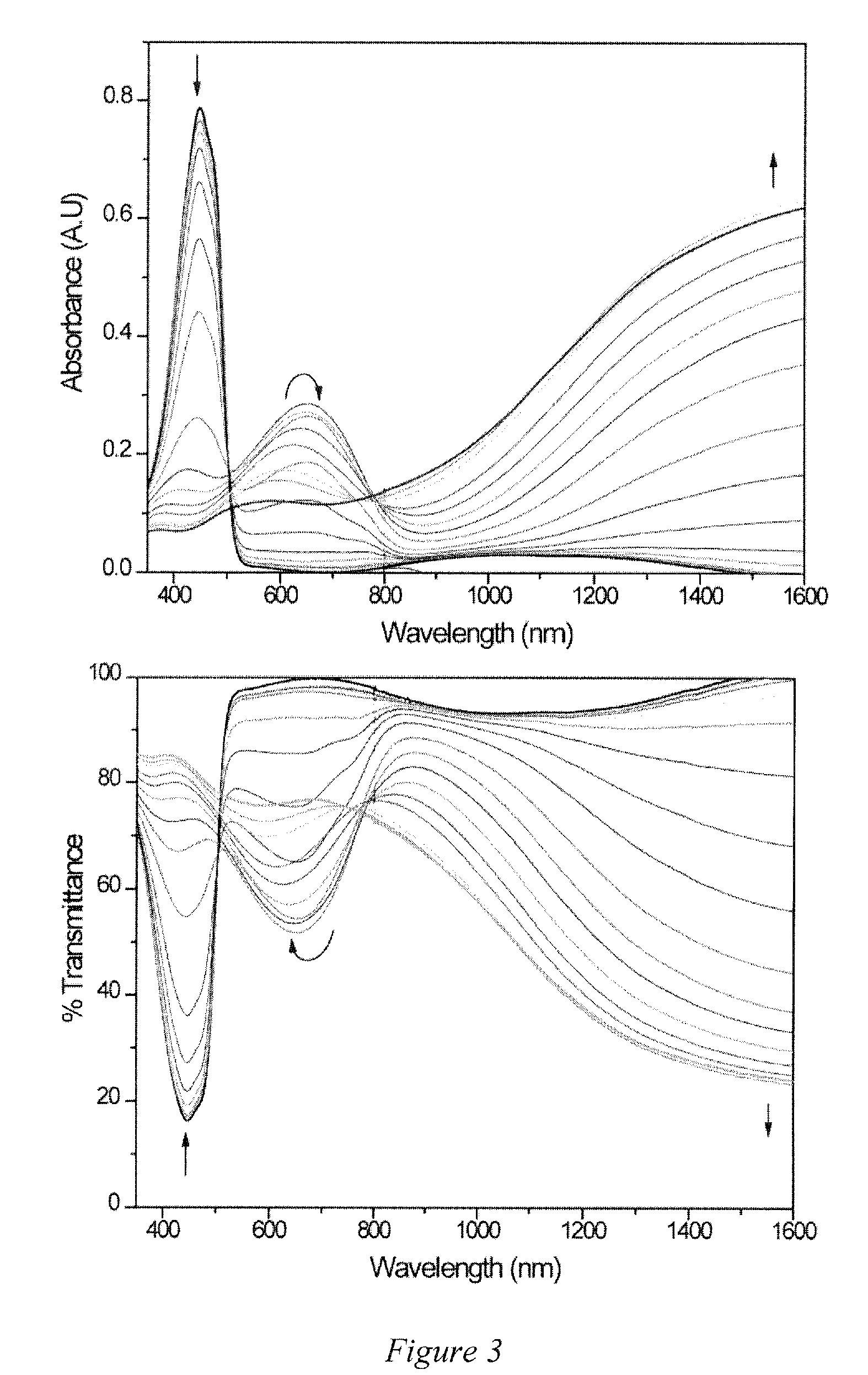
Syntheses of a new blue EC monomer (ProDOT-MePro), and a new red EC monomer (ProDOP-Et2) are described. Two additional new types of EC monomers based on 3,4-alkylenedioxythiophene include fluorinated EC monomers and an EC monomer including silicon. EC polymer devices having more than one different color EC polymer to enable additional colors to be provided using subtractive color mixing are also described, as well as EC polymer devices incorporating a logo, image, or text, are generally obscured when the device is colored, but become visible when the device is not colored. Also described are EC polymer devices that include a cathodic EC polymer layer, a gel electrolyte, a counter electrode, and a reference electrode. Working prototypes of such devices exhibit significant increases in the speed of transition of the EC device from a colored state to a transparent state.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Switchable window based on electrochromic polymers
InactiveUS20050200935A1Easy transitionOrganic chemistryTenebresent compositionsPolymer scienceSubtractive color
Syntheses of a new blue EC monomer (ProDOT-MePro), and a new red EC monomer (ProDOP-Et2) are described. Two additional new types of EC monomers based on 3,4-alkylenedioxythiophene include fluorinated EC monomers and an EC monomer including silicon. EC polymer devices having more than one different color EC polymer to enable additional colors to be provided using subtractive color mixing are also described, as well as EC polymer devices incorporating a logo, image, or text, are generally obscured when the device is colored, but become visible when the device is not colored. Also described are EC polymer devices that include a cathodic EC polymer layer, a gel electrolyte, a counter electrode, and a reference electrode. Working prototypes of such devices exhibit significant increases in the speed of transition of the EC device from a colored state to a transparent state.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
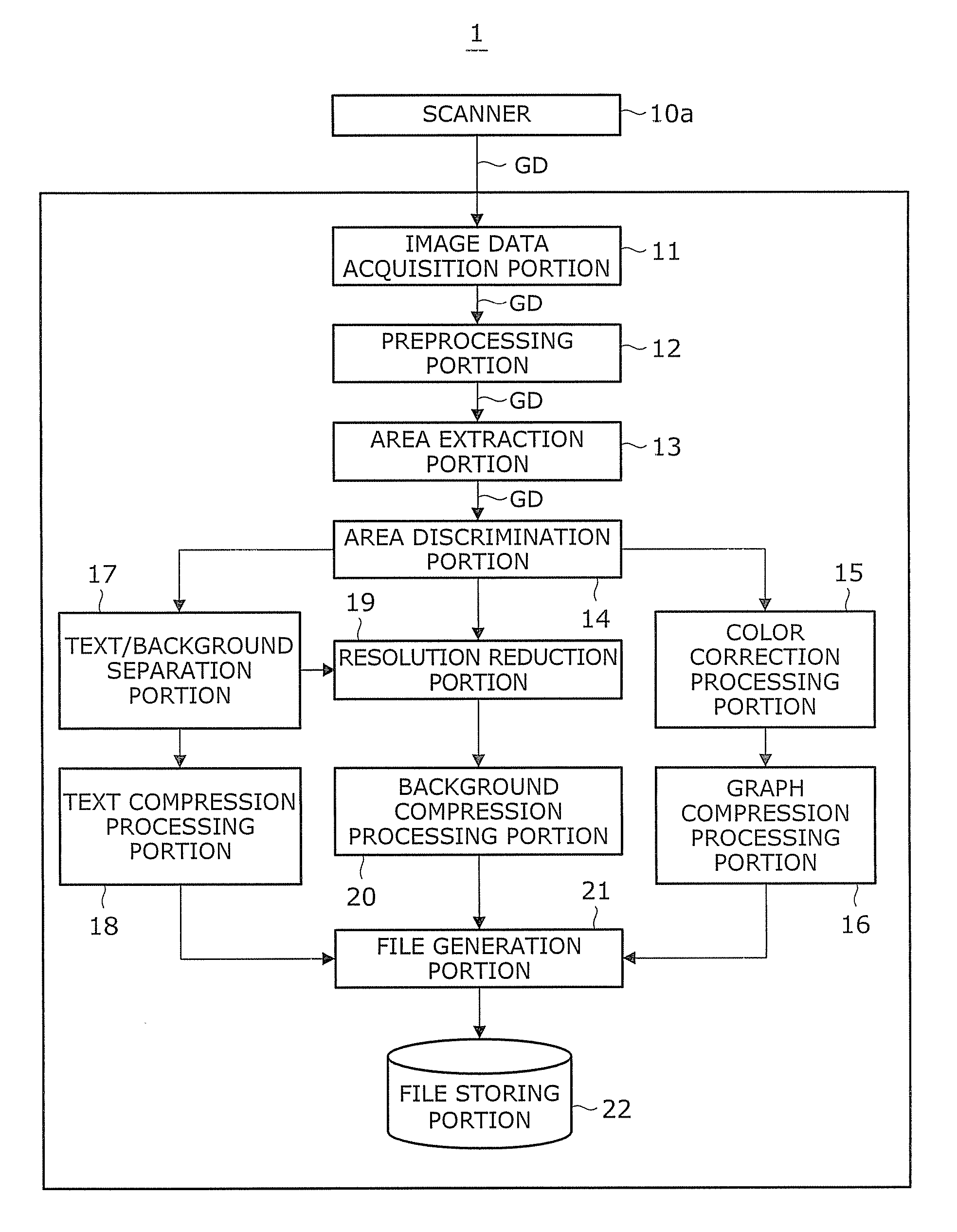
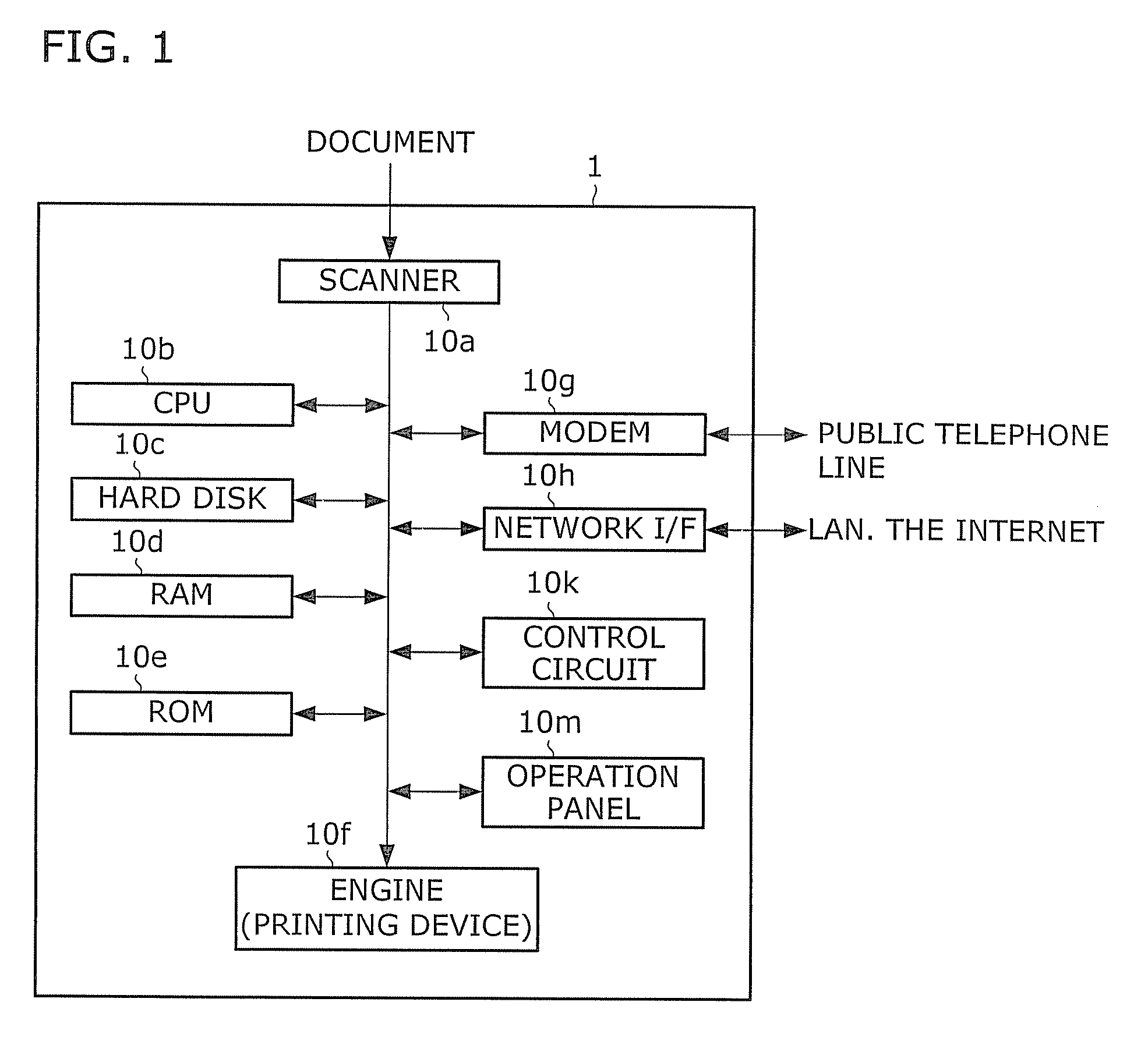
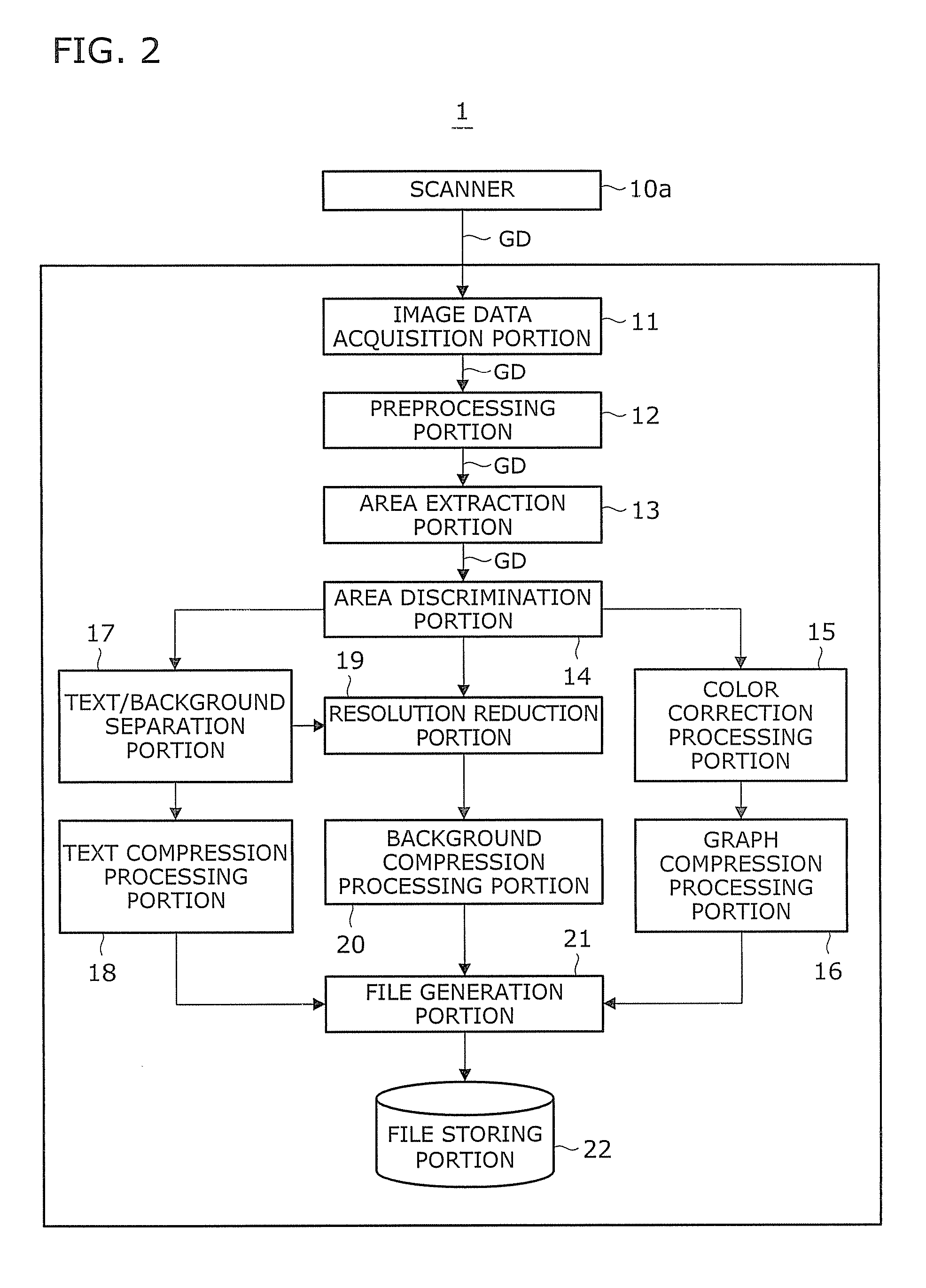
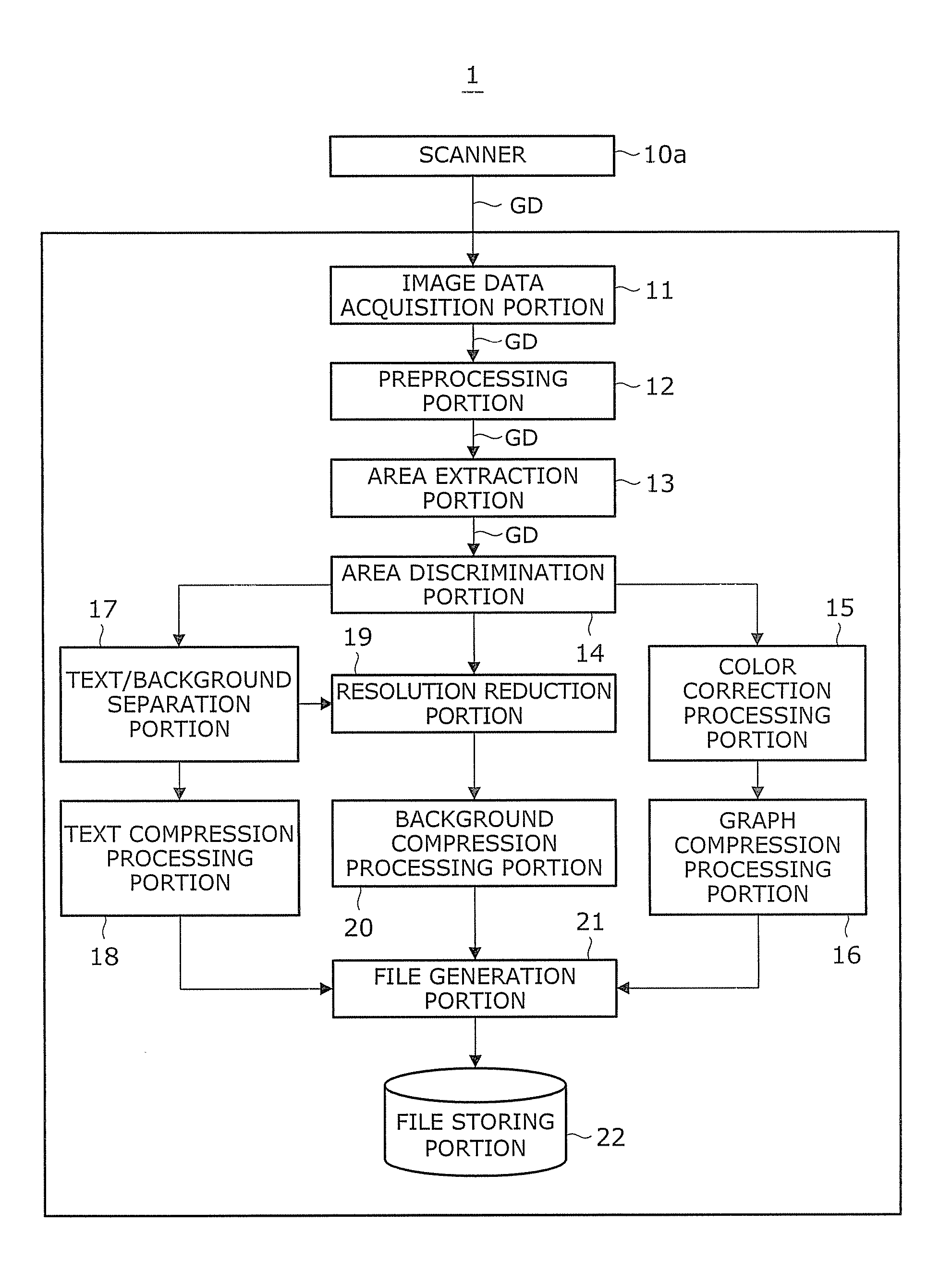
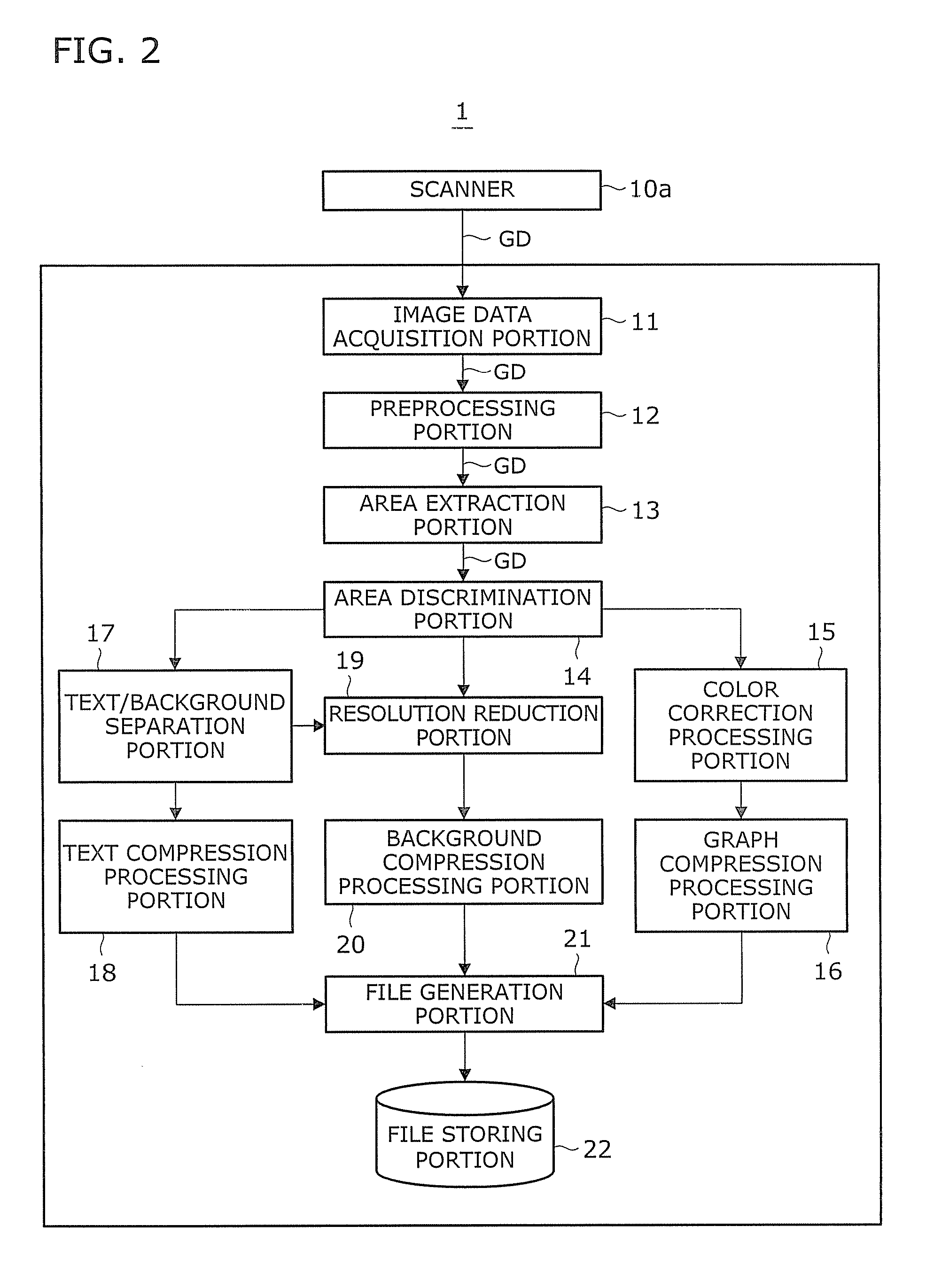
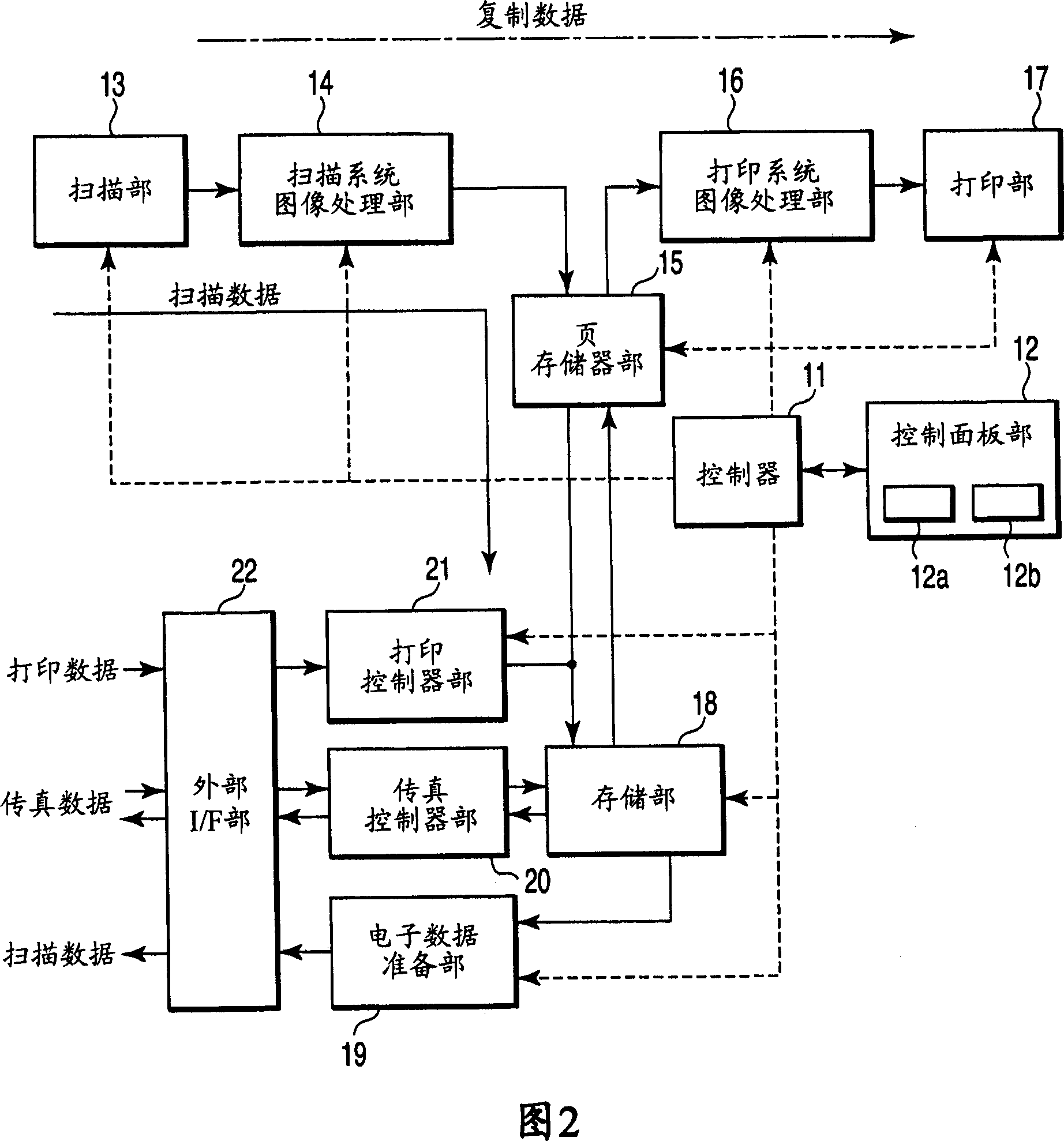
Image processing device and recording medium
InactiveUS6873436B1Improve image qualitySame resolutionImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersImaging processingImage resolution
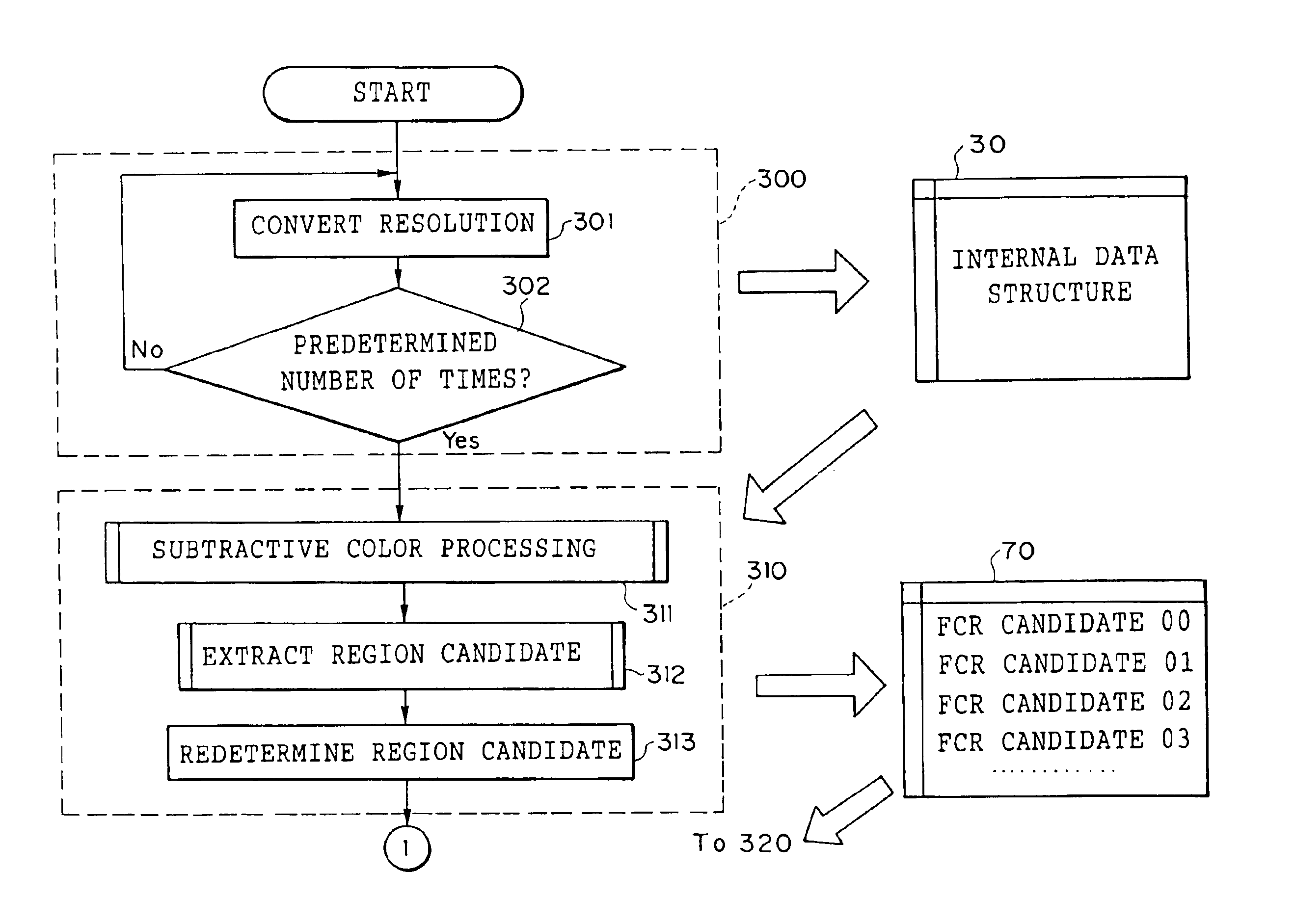
An image processing apparatus and a recording medium which can improve the quality of a color document image are provided. An input image is converted into an image having low resolution. A subtractive color image is generated using the converted image having low resolution. From the subtractive color image, adjacent pixels which are allocated to the same representative color are unified so as to extract an FCR (Flat Color Region) candidate region. A region candidate is redetermined using an image having resolution which is higher than the subtractive color image. Next, a boundary of the FCR is detected and an ultimate FCR is determined. Selection of a representative color of the determined FCR is carried out, and a specific color processing which replaces a color which is close to a pure color with the pure color is effected. Finally, image regeneration is carried out by overwriting and drawing (synthesizing) the FCR on the input image.
Owner:GTX CORP +1
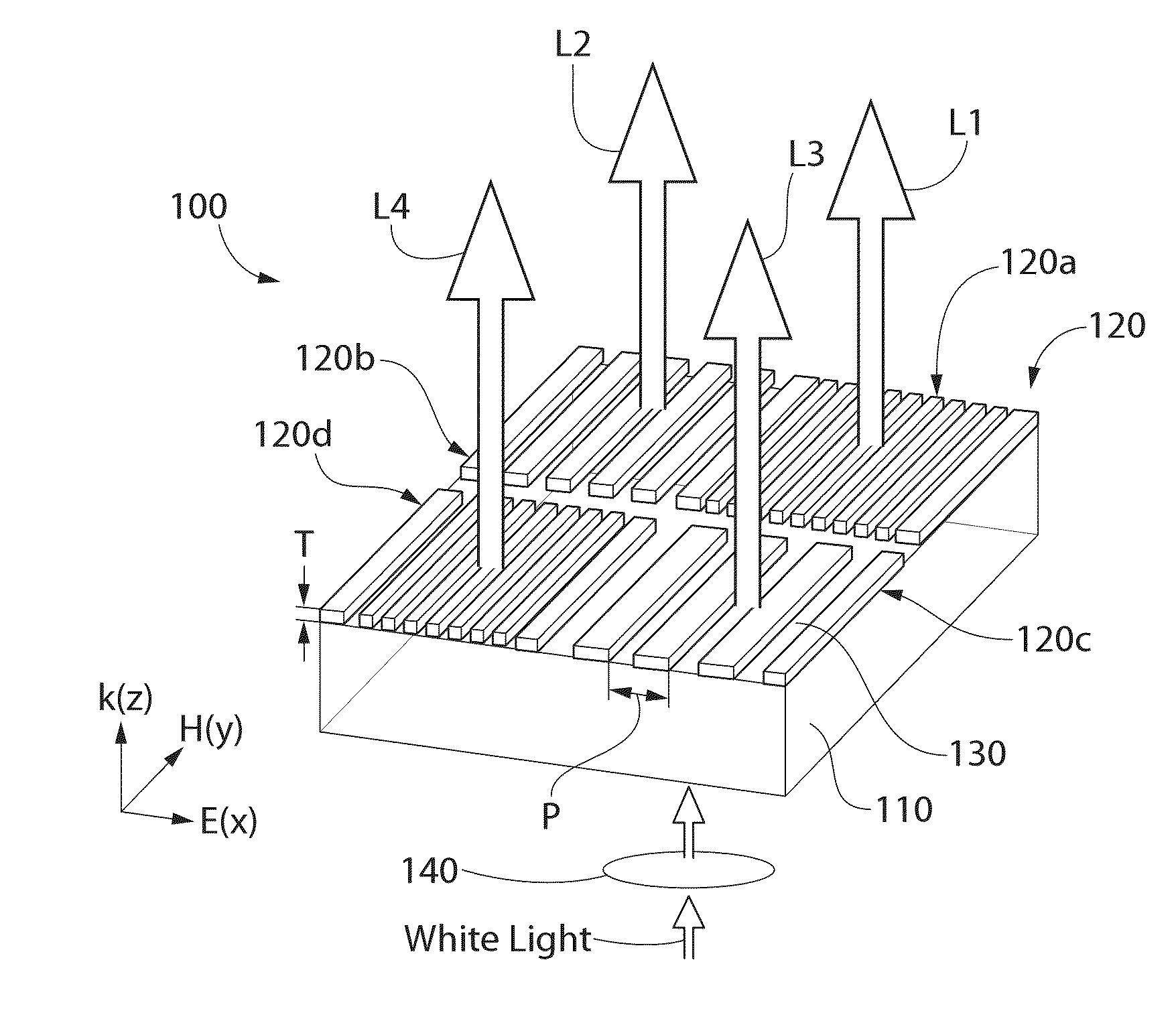
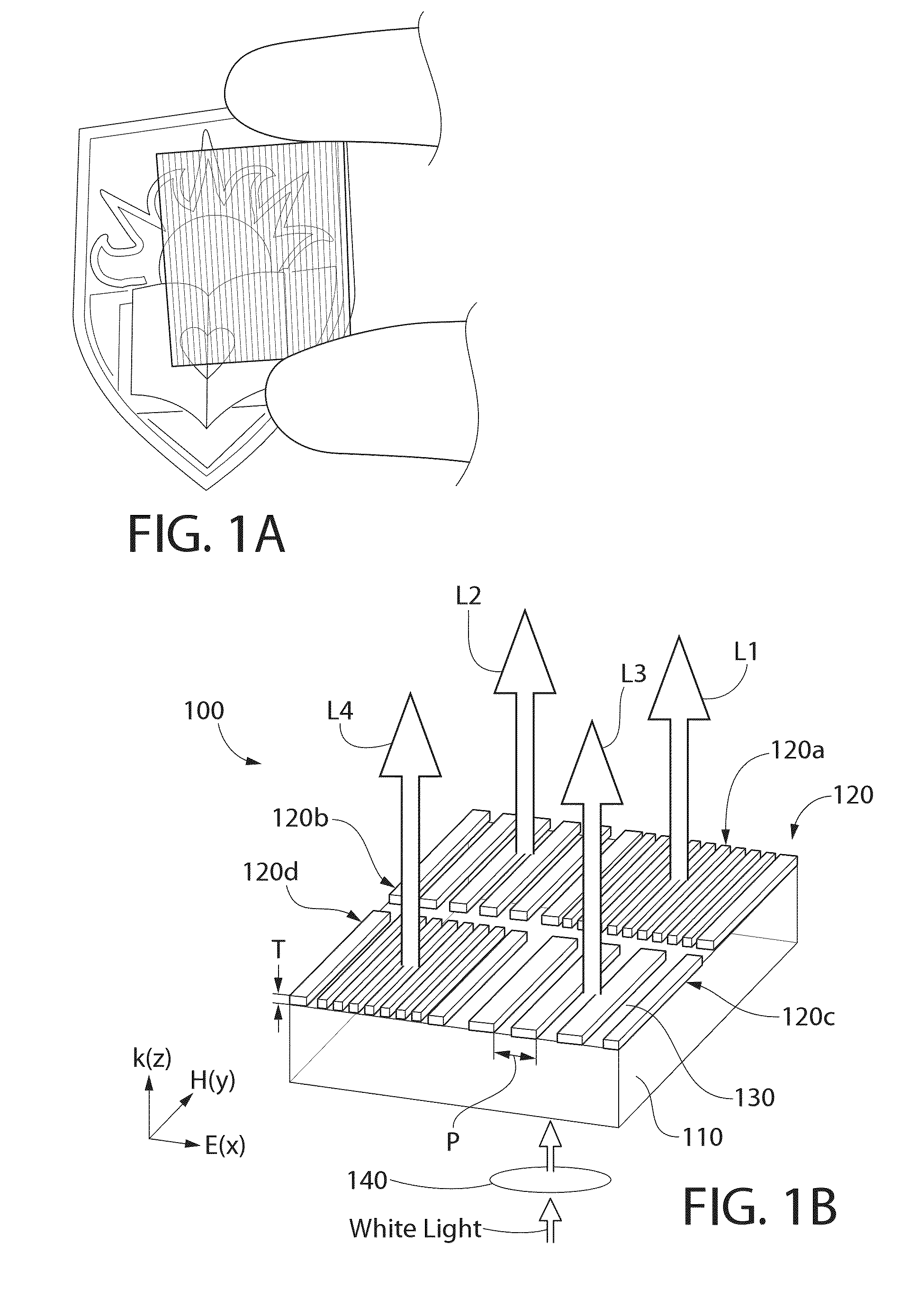
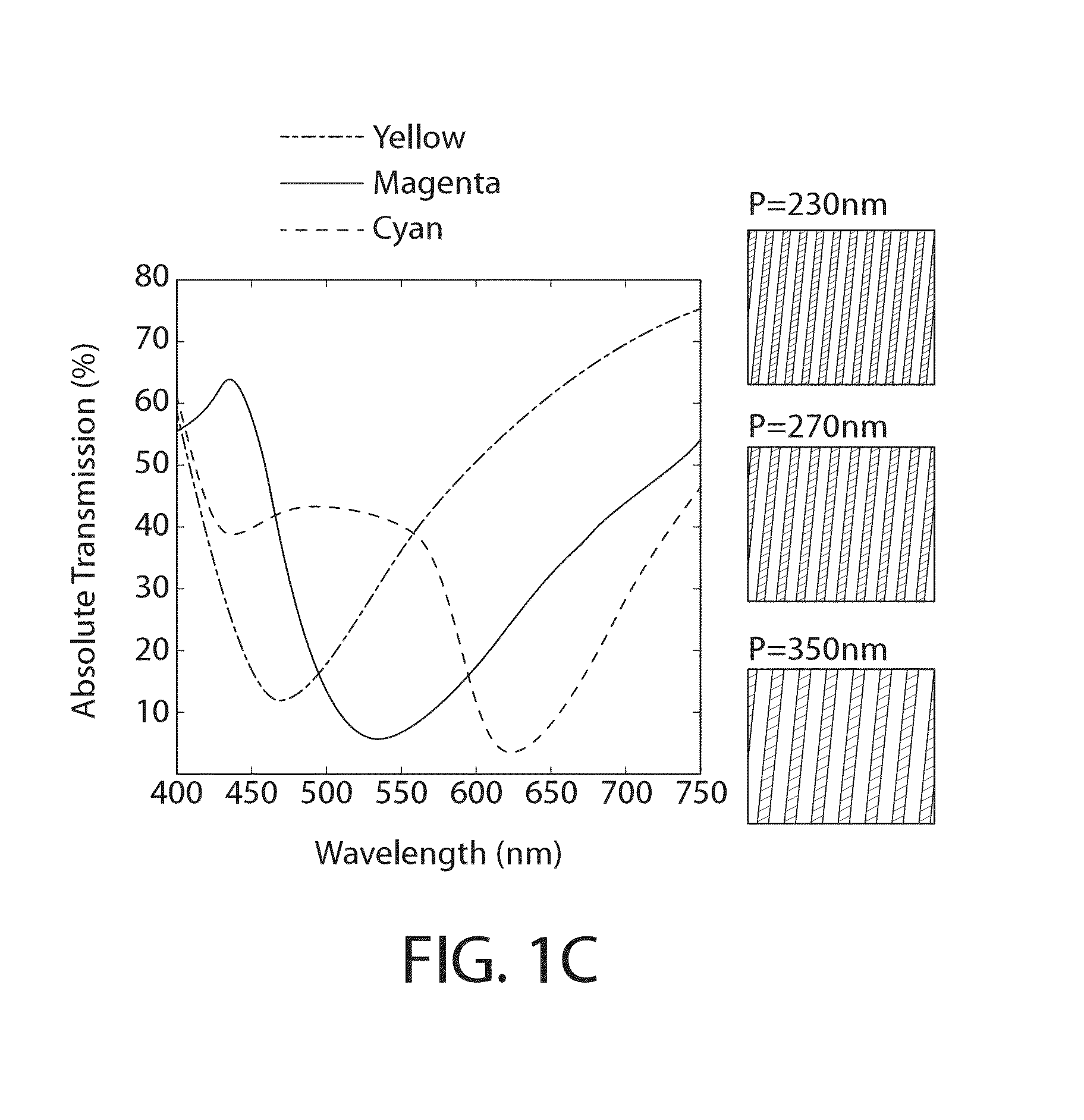
Ultrathin nanostructured metals for highly transmissive plasmonic subtractive color filters
An ultrathin plasmonic subtractive color filter in one embodiment includes a transparent substrate and an ultrathin nano-patterned film formed on the substrate. A plurality of elongated parallel nanoslits is formed through the film defining a nanograting. The nanoslits may be spaced apart at a pitch selected to transmit a wavelength of light. The film is formed of a material having a thickness selected, such that when illuminated by incident light, surface plasmon resonances are excited at top and bottom surfaces of the film which interact and couple to form hybrid plasmon modes. The film changes between colored and transparent states when alternatingly illuminated with TM-polarized light or TE-polarized light, respectively. In one configuration, an array of nanogratings may be disposed on the substrate to form a transparent display system.
Owner:LEHIGH UNIVERSITY
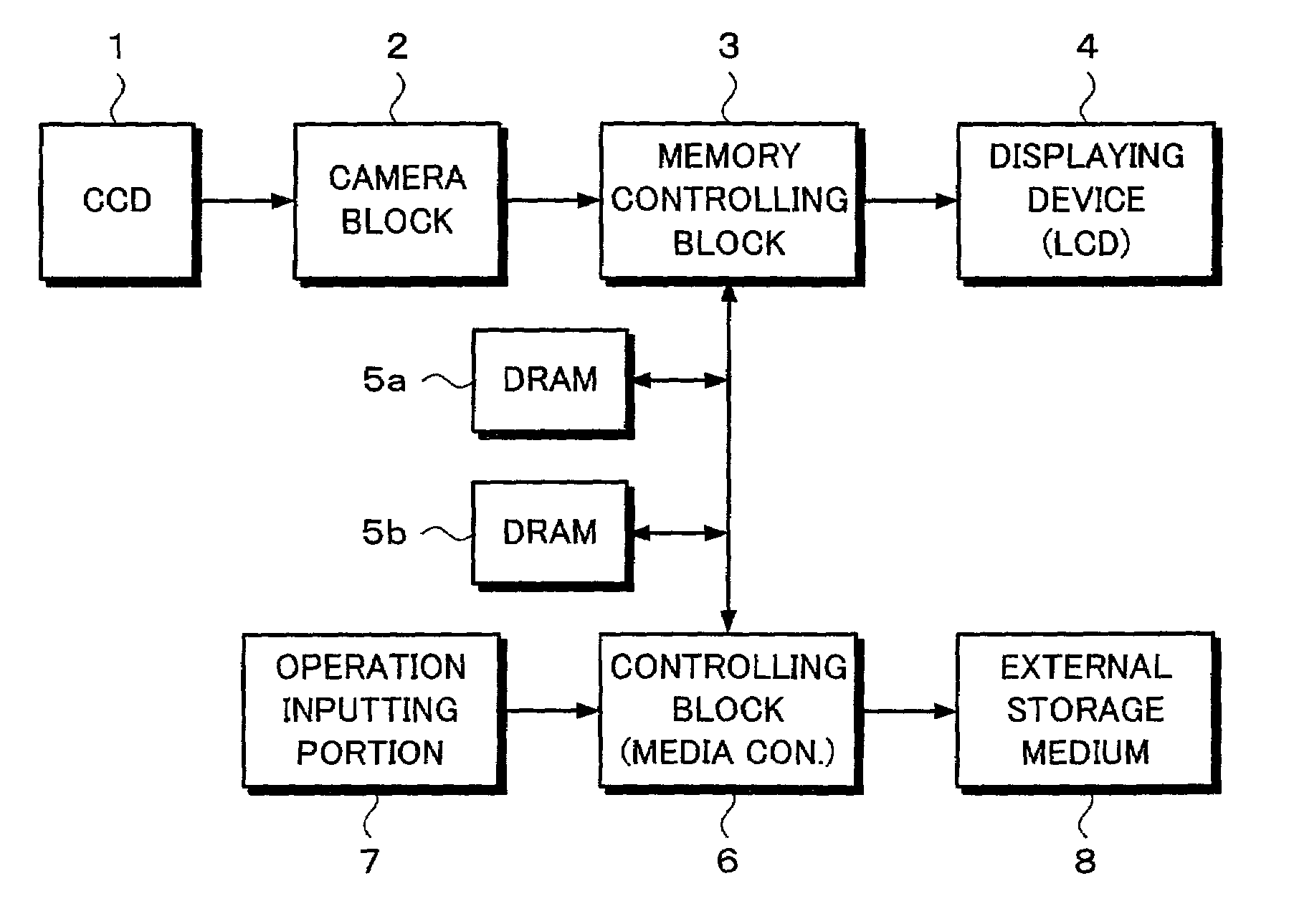
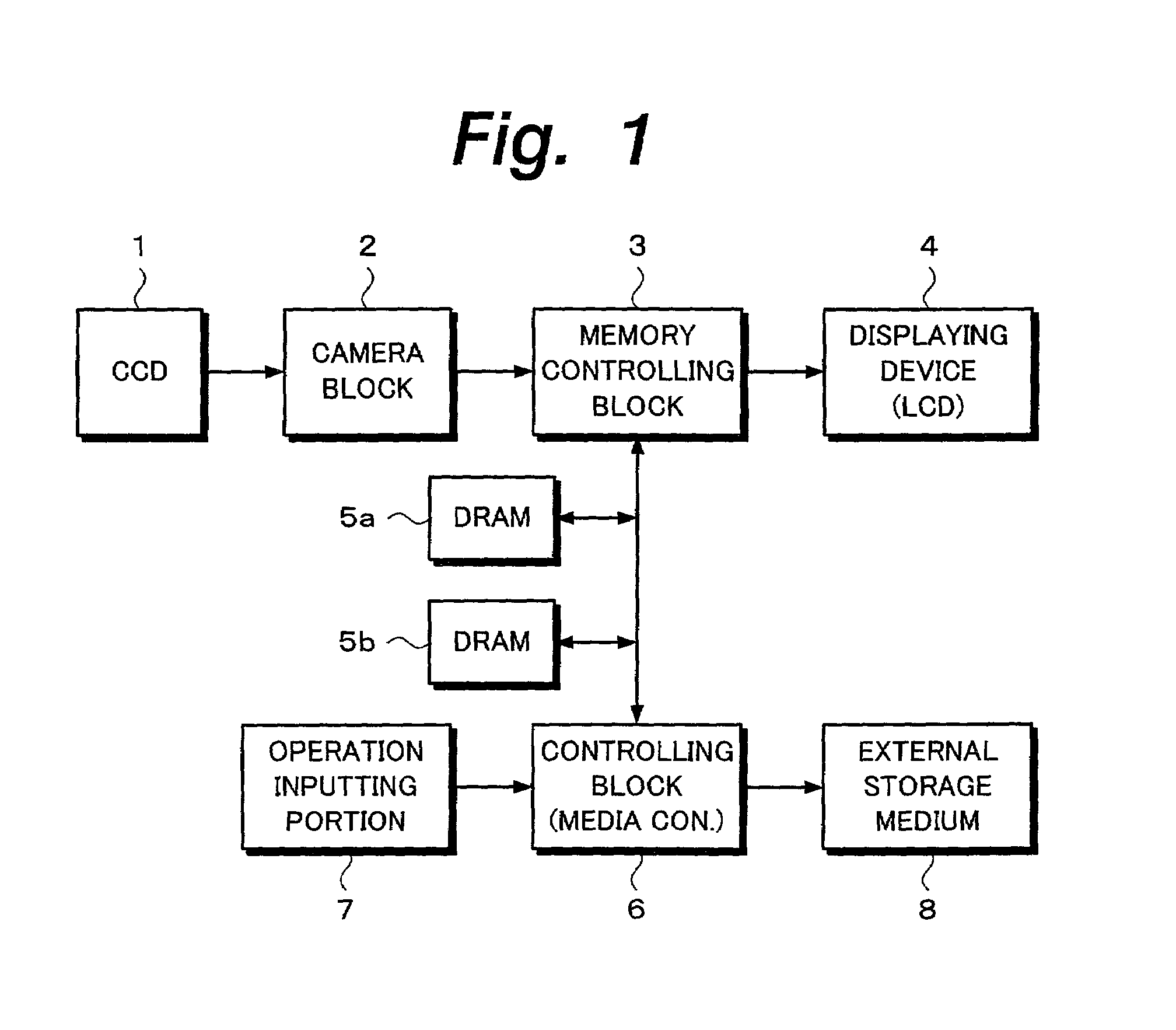
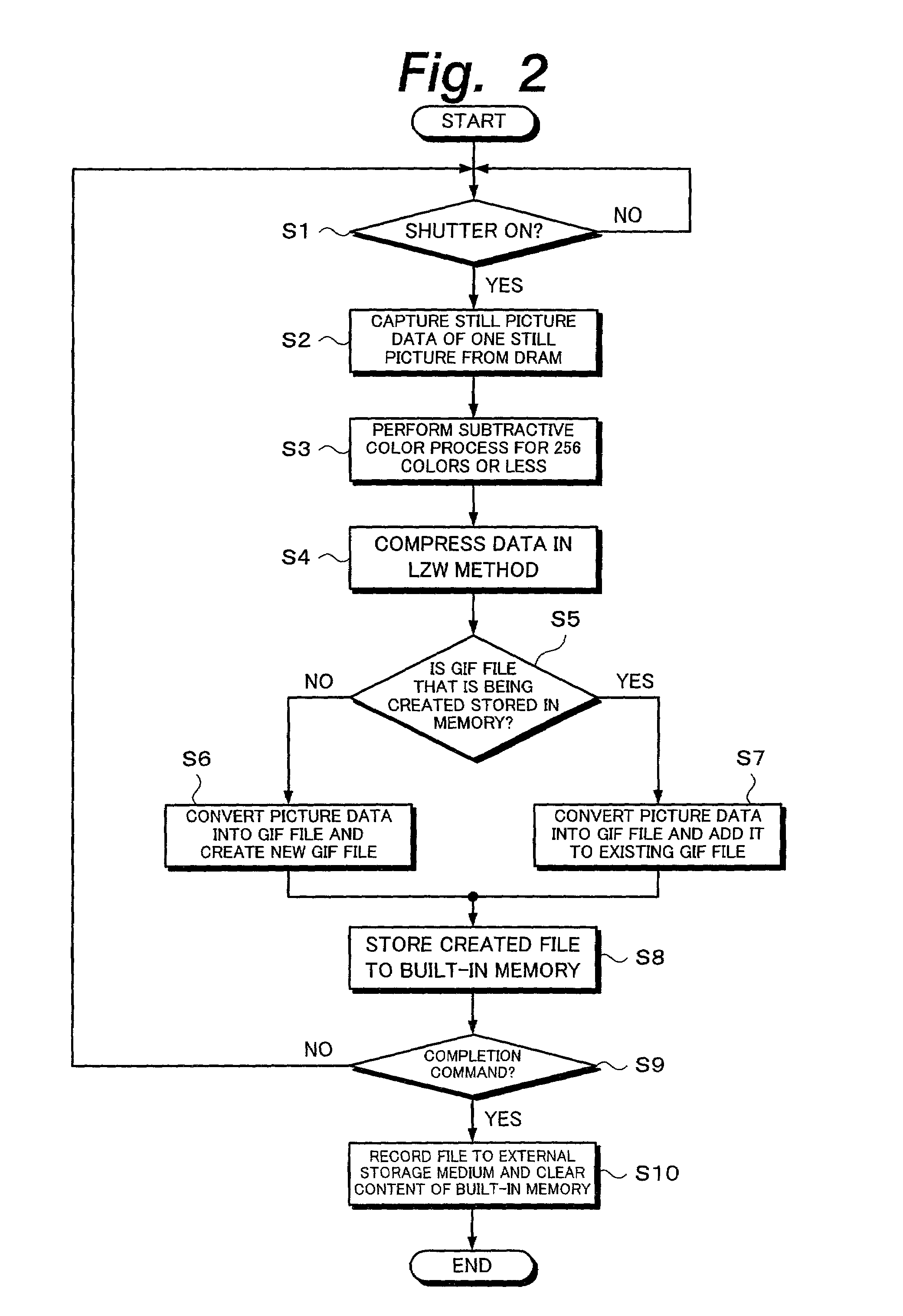
Photographing apparatus and signal processing method that allow data of still pictures to be converted into a moving picture file
When an animation mode is designated, still picture data that has been photographed or discretely read from a record medium is compressed in a subtractive color process and a data compressing process corresponding to the LZW method. The compressed data is converted into an animation GIF file of which still picture data is combined in the time sequence and it is correlatively displayed on the time base. When an animation mode completion command is input or the size of the GIF file becomes a recordable size of the external storage medium 8, the GIF file data is written to the external storage medium 8. In addition, after a photographed still picture is recorded to the external storage medium 8, an animation can be created. In addition, an animation GIF file can be created using a plurality of still pictures recorded in the external storage medium 8. In addition, an animation GIF file that has been created can be edited.
Owner:SONY CORP
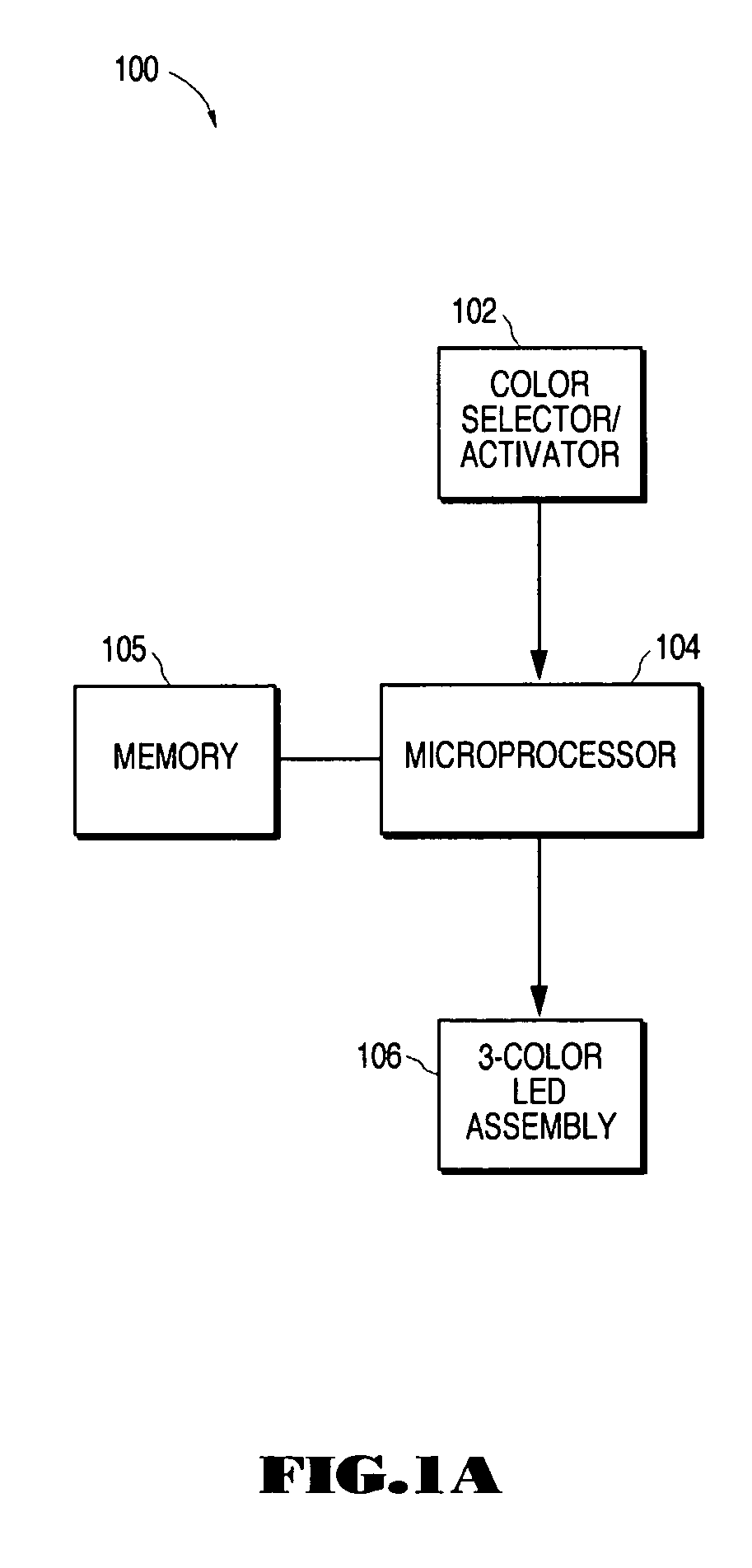
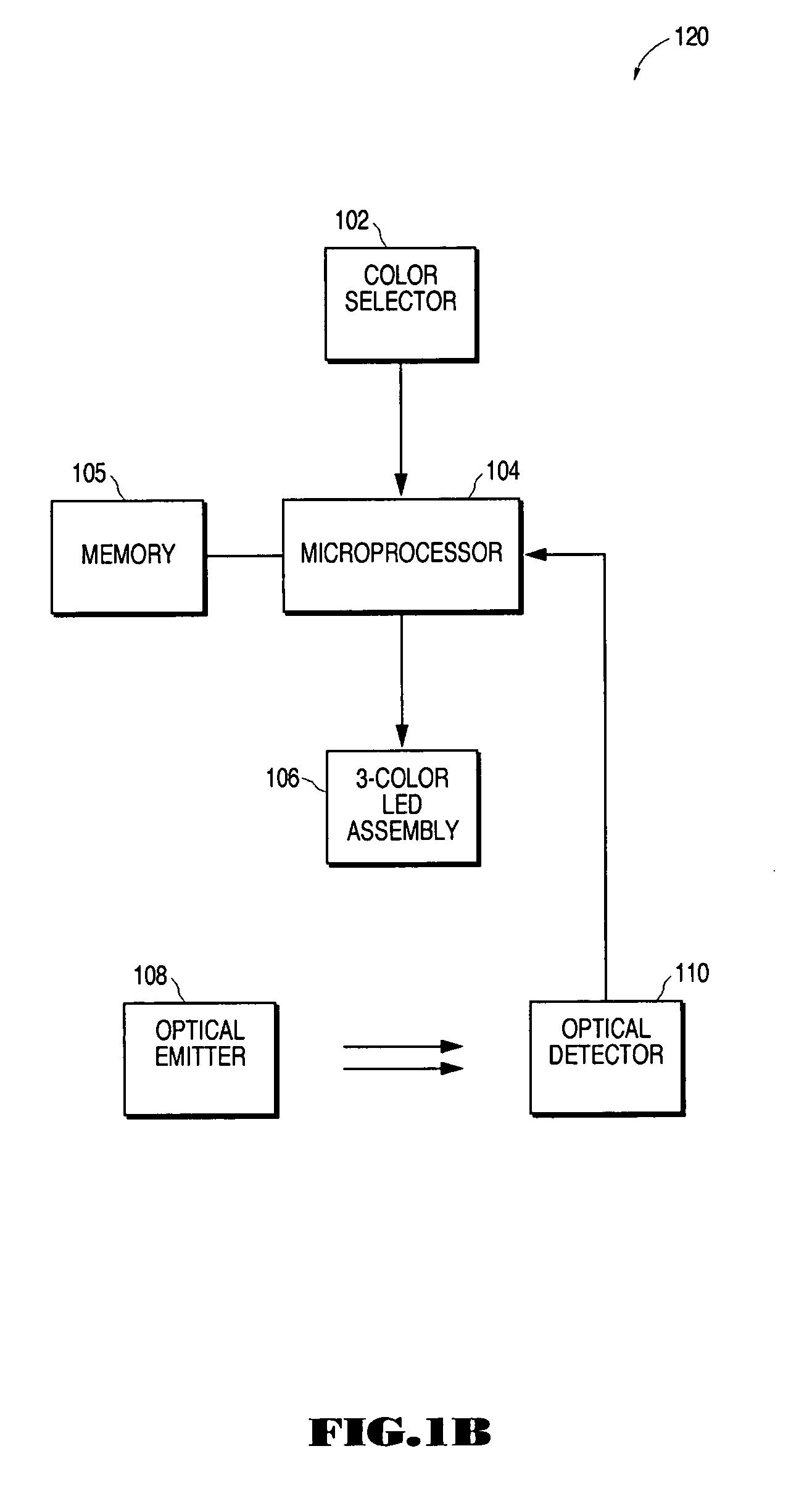
Control interface for converting subtractive color input to additive primary color output
InactiveUS20060187236A1Broaden applicationWide rangeElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesFrequency spectrumSubtractive color
A control interface for producing a composite color through the mixing of primary colors selected from a first color spectrum including red, yellow, and blue, resulting in the display of said composite color through a light array containing lights of a second primary color spectrum is disclosed. The user selects a color or colors from the first primary color spectrum, and a circuit and control algorithm controls the relative intensities of the colors comprising the second primary color spectrum, rendering the selected color or a mix of previously selected colors through the light array. Through the selection and graduated combination of the primary colors of the first spectrum, the creation of a wide range of colors in the visual spectrum is obtained for lighted color applications. When the first spectrum comprises the primary colors of red, yellow, and blue, the user is able to use the familiar three-primary, three-secondary color wheel, used in art education and taught in elementary school, for their color combination reference. The color selections from the first spectrum are coded to produce corresponding electrical signals to control the output of the light array to establish the proper mix of colors that displays the selected color.
Owner:CREATIVITY
Bead picture based on image data and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20100178448A1Beautiful picturePicture framesDecorative surface effectsColor imageFrame based
An image data of an original is recorded on a pixel unit to a computer and the recorded image data of the computer is applied with image processing to form a subtractive color image data of predetermined number of color of beads based on the size of a bead picture to be prepared and the size of a bead sphere to be used. The substractive color image data is digitalized to the color number on an image pixel unit, and the color number of the digitalized subtractive color image data is indicated on a color number arrangement table of a predetermined size corresponded to the original. A plurality of beads corresponding to the respective color numbers are arranged and supported in a picture frame based on the arrangement of the indicated color numbers thereby completing a bead picture. A transparent resin solution that cures at a normal temperature or at an elevated temperature is cast into the gap between bead groups arranged in the picture frame and the transparent resin in the gap between the beads is integrally cured with the inner surface of the front and rear transparent plates to be formed into a bead supporting and receiving portion.
Owner:NAC
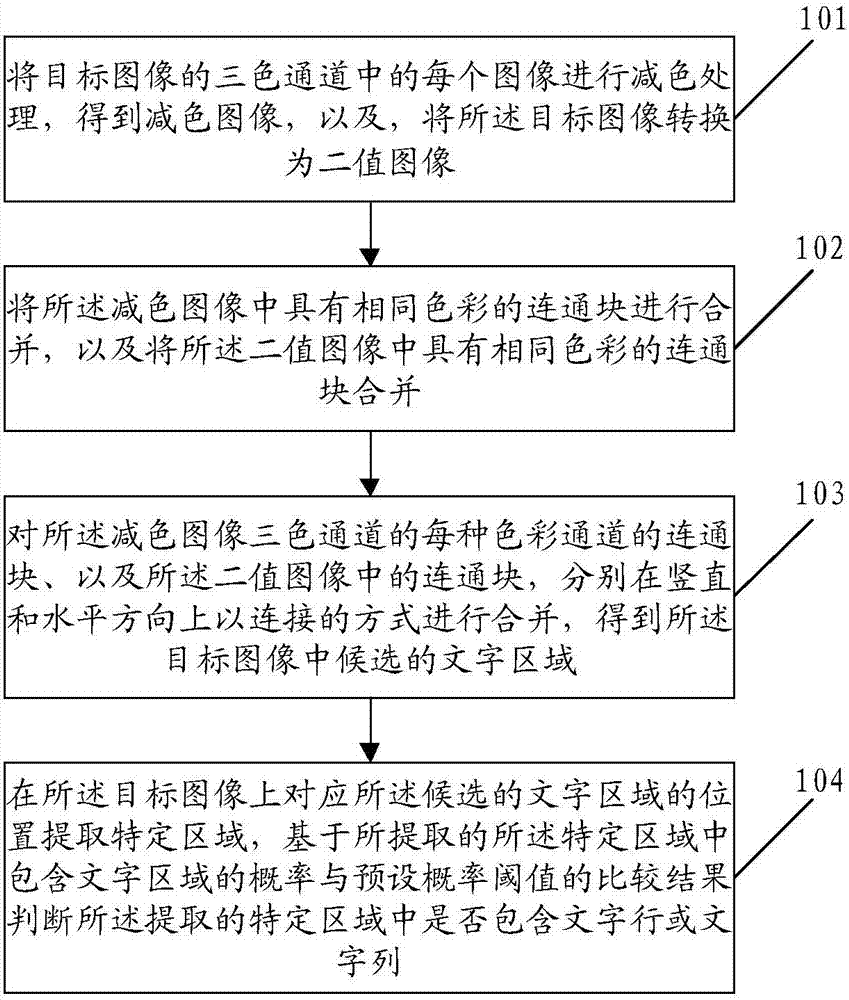
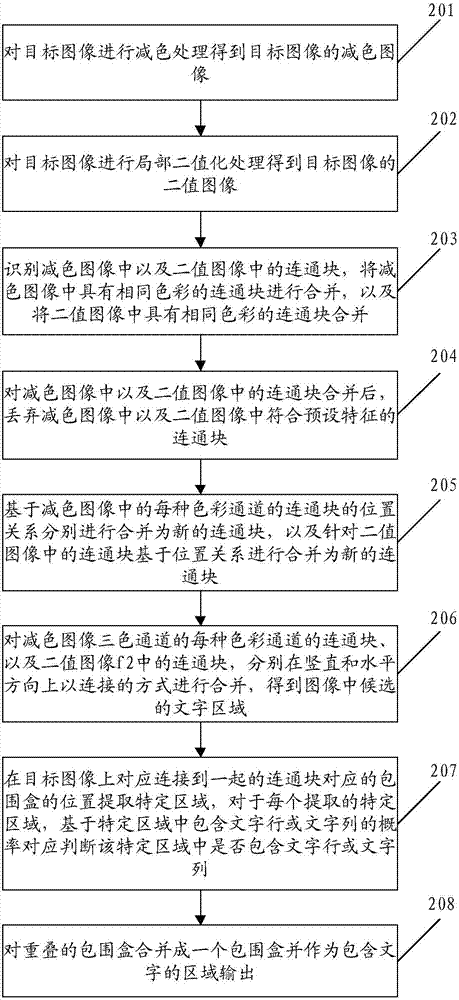
Character detection method and system
ActiveCN107093172AAccurate detectionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionSubtractive color
The invention discloses a character detection method and system. The method comprises the following steps that: carrying out subtractive color processing on each image in the three-color channel of a target image to obtain a subtractive color image, and converting the target image into a binary image; combining connected blocks with the same color in the subtractive color image, and combining the connected blocks with the same color in the binary image; independently combining the connected block of each type of color channel of the three-color channel of the subtractive color image and the connected blocks in the binary image in vertical and horizontal directions in a connection way to obtain a candidate character area in the target image; and on a position which corresponds to the candidate character area in the target image, extracting a specific area, and judging whether the extracted specific area contains a character line or character row according to a comparison result of a character area containing probability in the specific area and a preset probability threshold value. When the method is implemented, texts in the image can be accurately detected.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
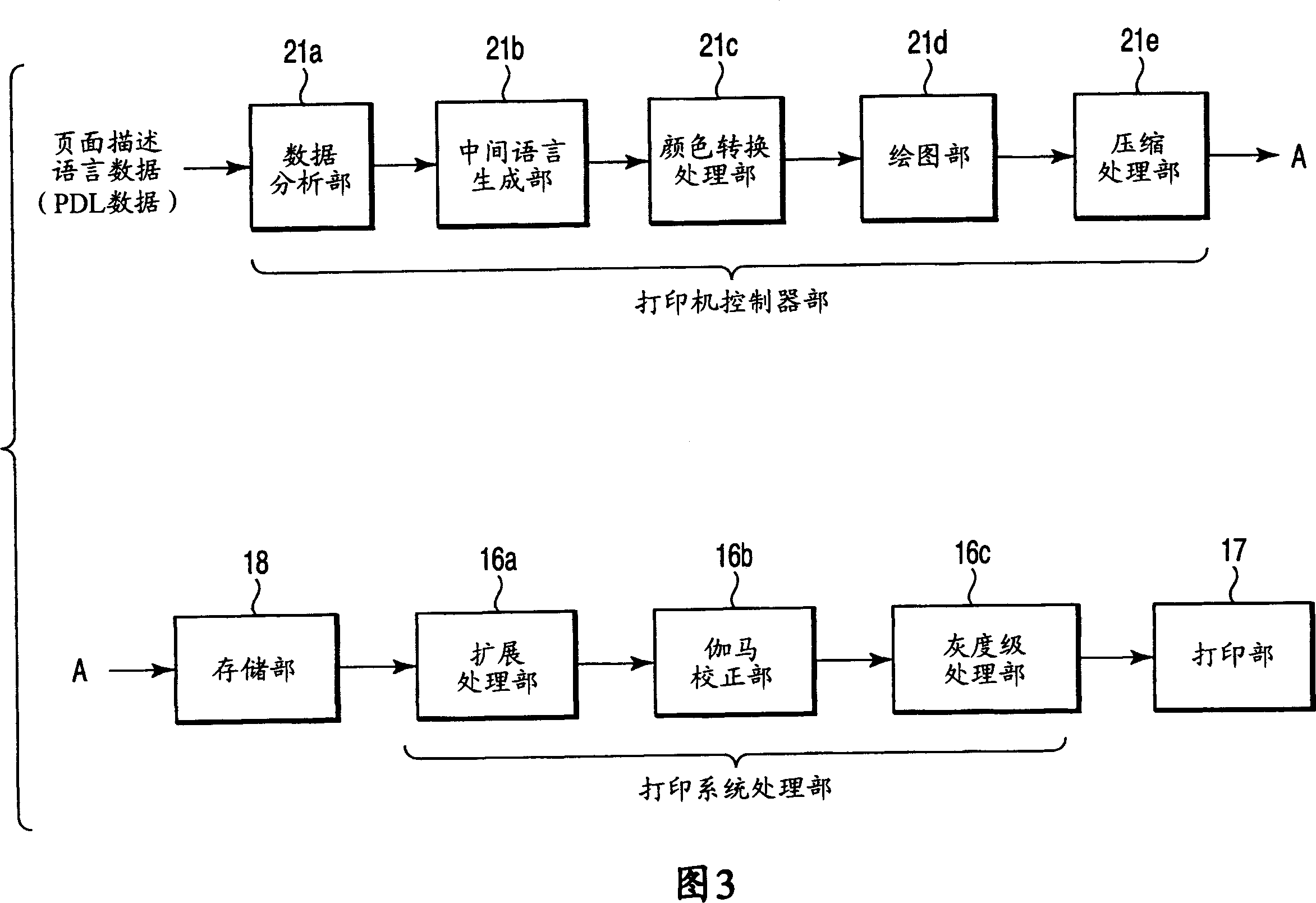
Subtractive color method, subtractive color processing apparatus, image forming apparatus, and computer-readable storage medium for computer program
ActiveUS20090303505A1Easy to operateDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsSubtractive colorImage formation
A most used color that is a most popularly used color is obtained in an image. Pixel groups formed of continued pixels having an identical color other than the most used color in the image is extracted as first pixel groups. Pixel groups having a color of which a color difference with respect to the most used color is smaller than a predetermined threshold and having a size thereof that is smaller than a predetermined size is extracted as third pixel groups among the first pixel groups thus extracted. The first pixel groups other than the third pixel groups are taken as second pixel groups. An image is generated by replacing colors of portions, which correspond to the second pixel groups in an image having an area identical with that of an image to be processed and filled with the most used color, with the corresponding second pixel groups, respectively.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
Full-color dynamic three-layer electronic paper
The invention discloses full-color dynamic three-layer electronic paper. The electronic paper comprises a substrate, a controller, a first electrowetting display layer, a second electrowetting display layer and a third electrowetting display layer. The first electrowetting display layer, the second electrowetting display layer and the third electrowetting display layer are formed by transparent upper pole plates, insulated hydrophobic layers, pixel walls, color printing ink, colorless liquids, transparent lower pole plates, packaging glues and driving chips. The driving chips are connected to the transparent upper pole plates and the transparent lower pole plates respectively. The transparent lower pole plate of the third electrowetting display layer is located above the substrate. The color printing ink filled in the first electrowetting display layer, the second electrowetting display layer and the third electrowetting display layer is cyan printing ink, carmine printing ink and yellow printing ink respectively. The controller controls voltage waveforms of the three driving chips to realize full-color display according to a subtractive mixing principle of three primary color printing. The electronic paper possesses advantages of comprehensiveness and a wide application scope and can be widely used in the electronic paper field.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY +2
Recording agent, image forming device, and image forming method
ActiveUS7285158B2Extended range of color reproductionIncrease brightnessMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsPattern recognitionSubtractive color
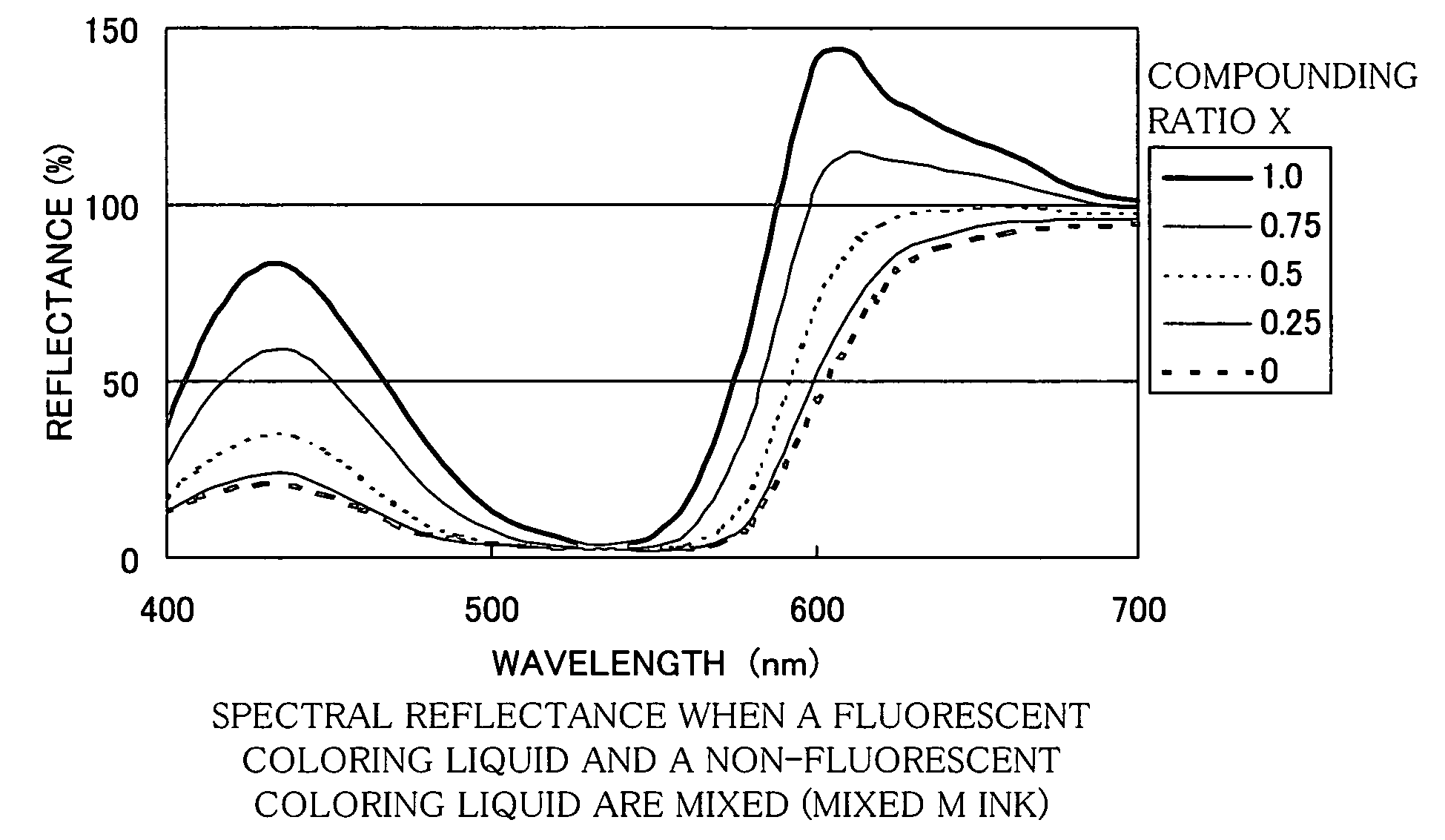
An image forming method, device and a recording agent for forming an image through subtractive color mixing by using ink of plural color components different in hue. The ink is created by mixing a first coloring agent expressing one of the color components and a second coloring agent identical in hue to the first coloring agent. The ink has a higher spectral reflectance than a spectral reflectance of the first coloring agent.
Owner:SHARP KK
Dye-doped liquid crystal microcapsule material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109293821APlay a protective effectColorful and changeableMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationCrystallographySubtractive color
The invention discloses a preparation method of a dye-doped liquid crystal microcapsule, and belongs to the technical fields of fine chemical engineering and material science. The dye-doped liquid crystal prepared by the method has a multilayer structure, and the outer dye-doped liquid crystal and a polymer shell layer which are used as a chromogenic layer and the core dye-doped liquid crystal microcapsule undergo subtractive color matching, and the chromogenic layer is also used as a protection layer to protect the inner dye-doped liquid crystal from being polluted by an external environment.The liquid crystal microcapsule prepared by the method has the advantages of bright and variable color, low driving voltage, good resistance to solvents and water, keeping of the original color performance after processing treatment, meeting of the customized and diverse chromogenic demands of liquid crystals in intelligent textiles, and broad application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Display apparatus and display panel driver
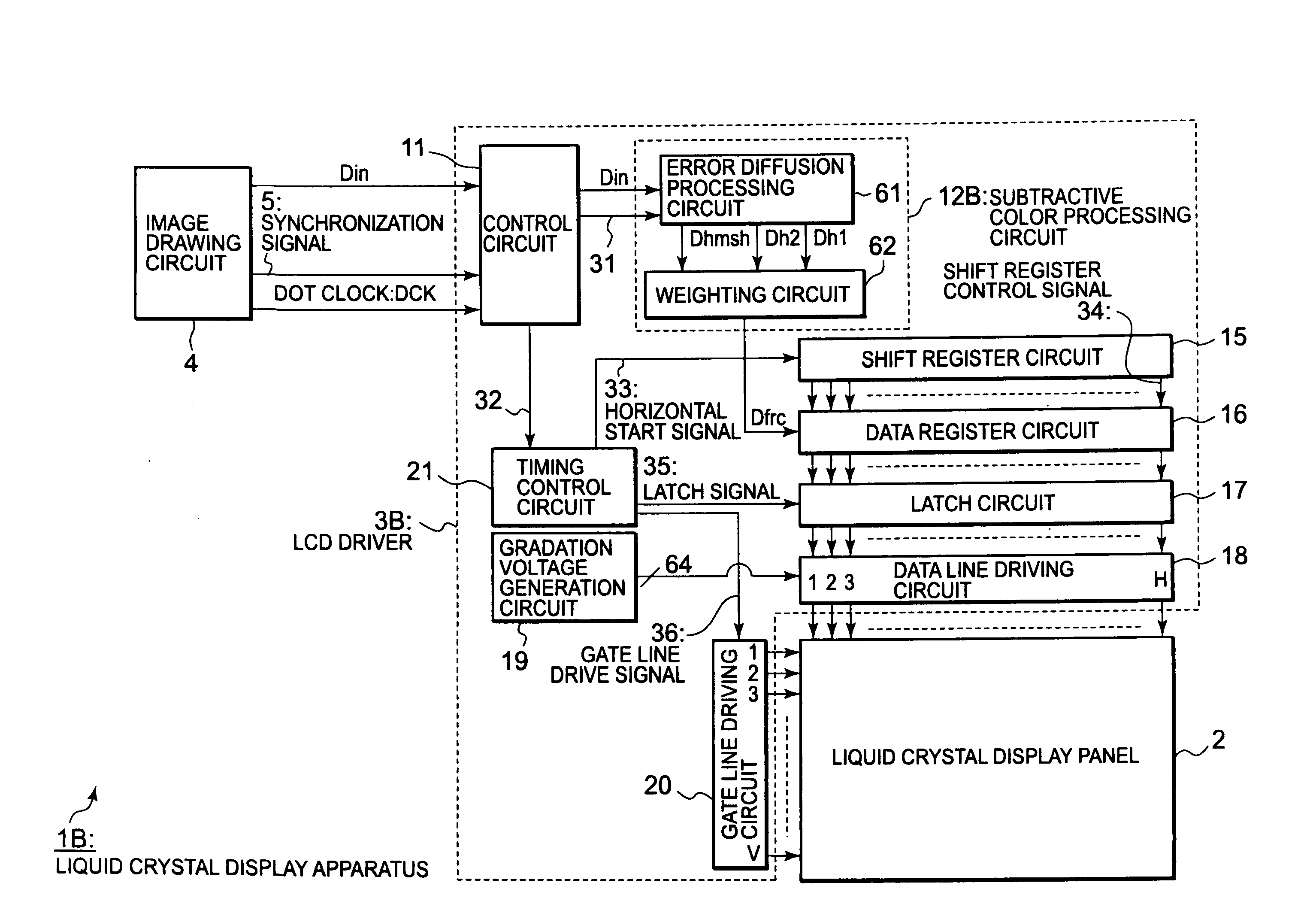
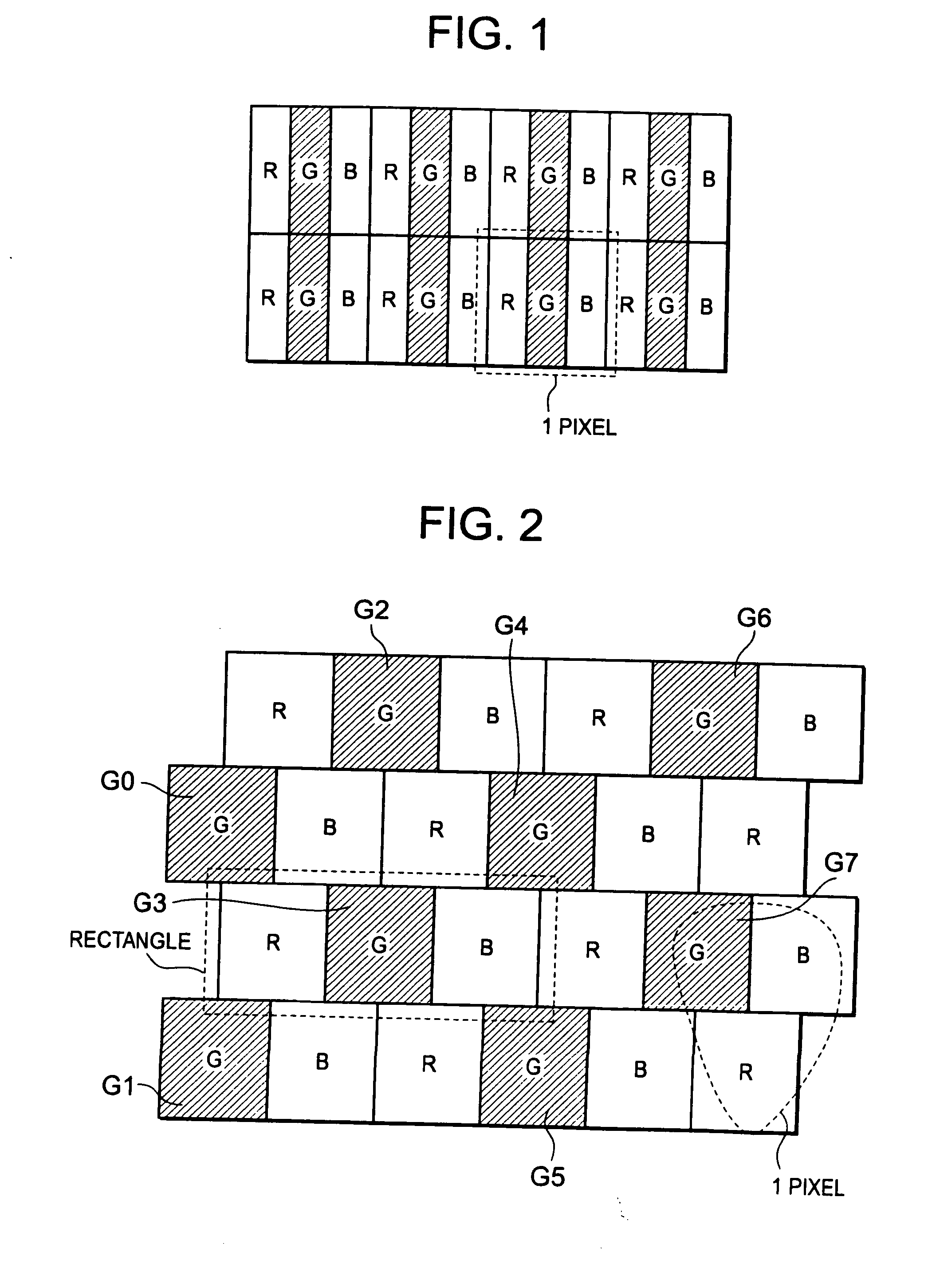
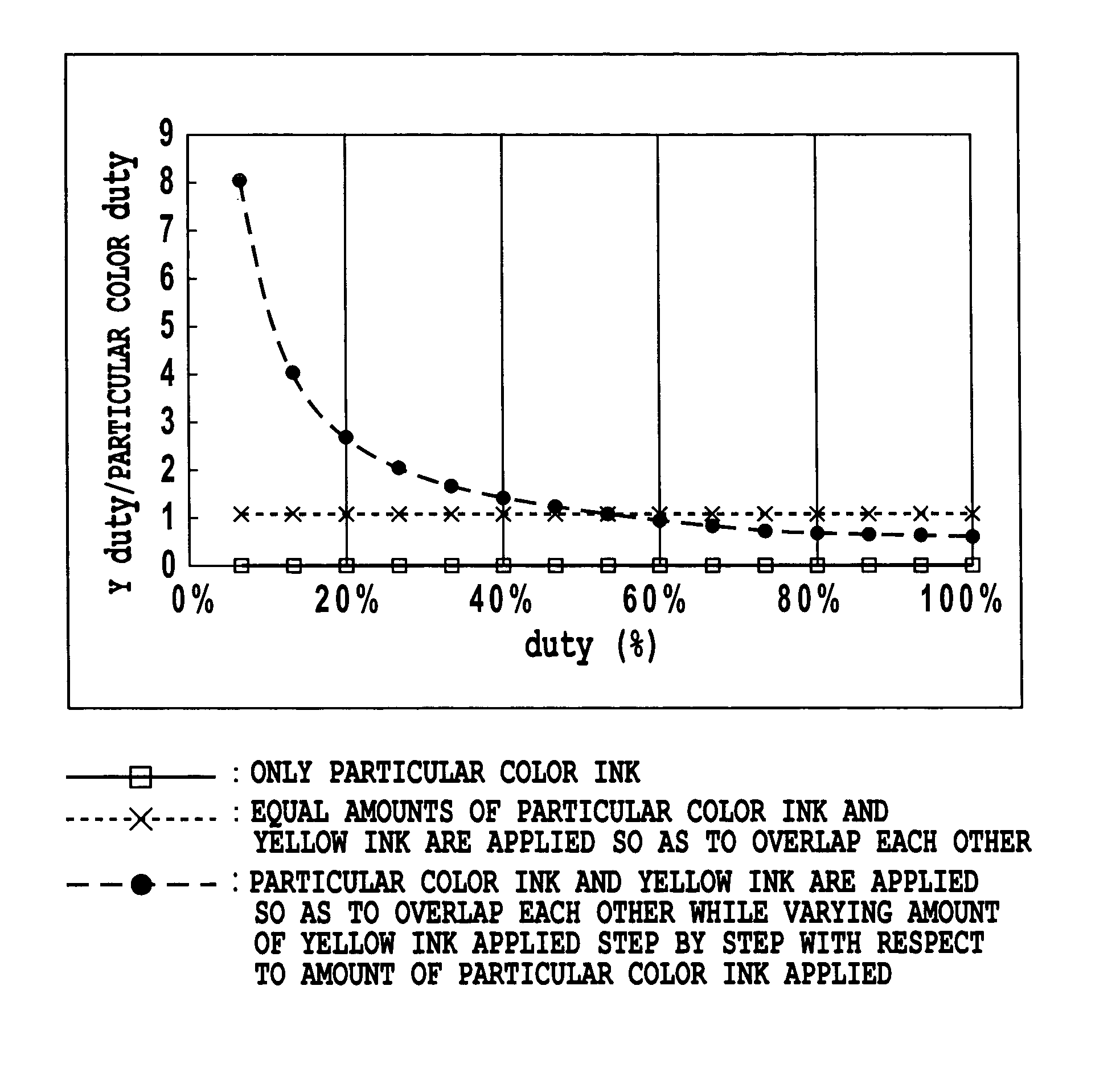
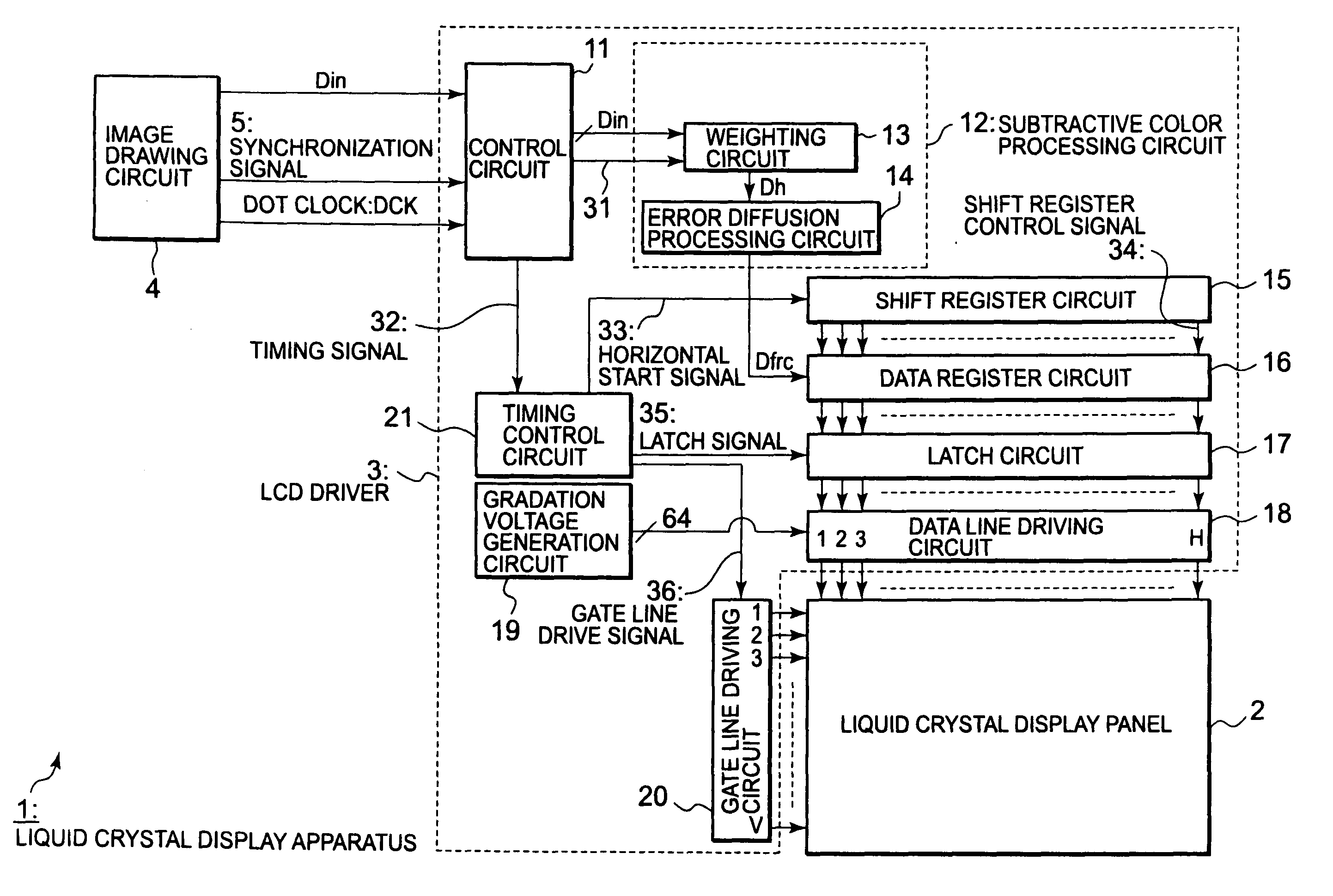
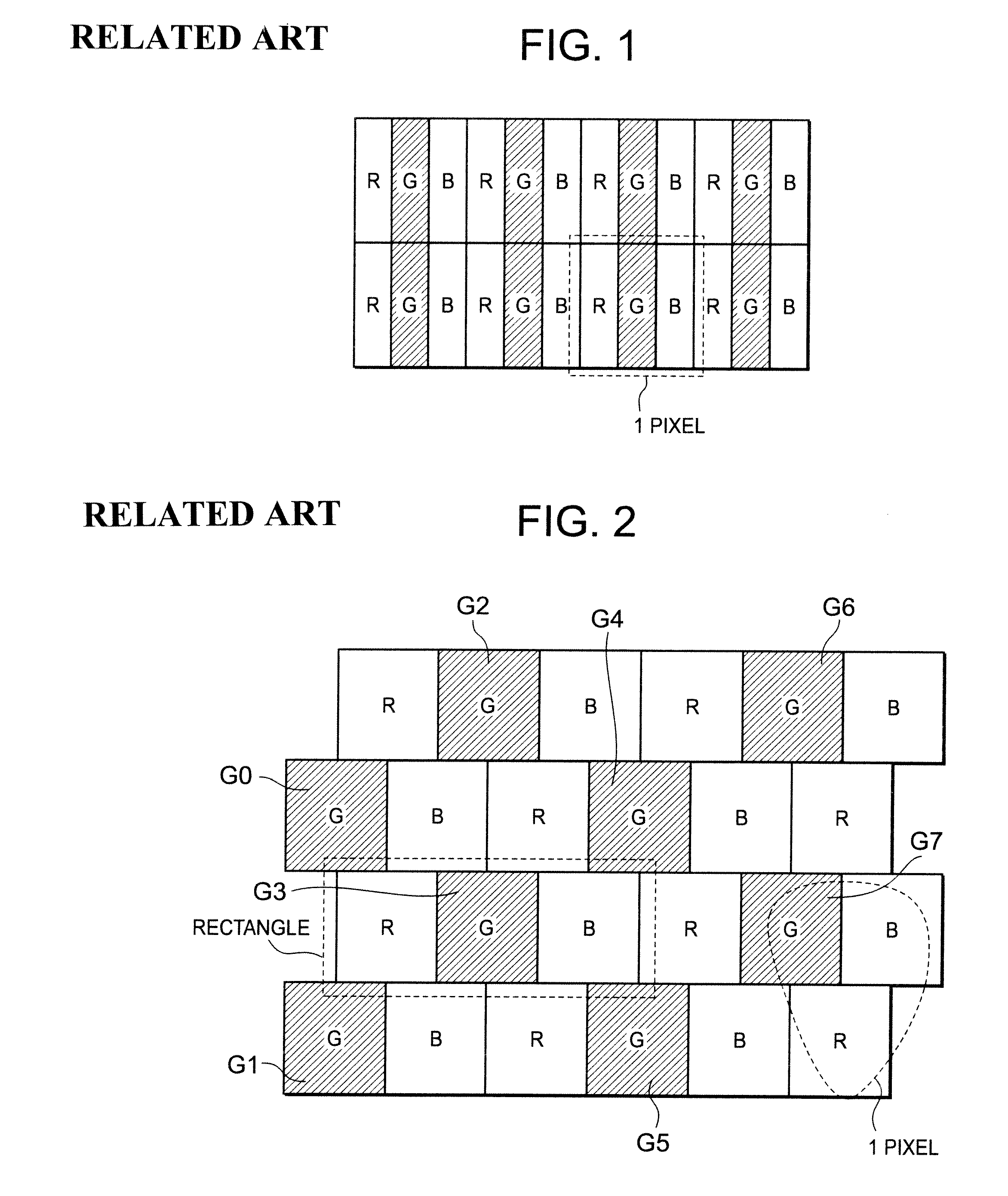
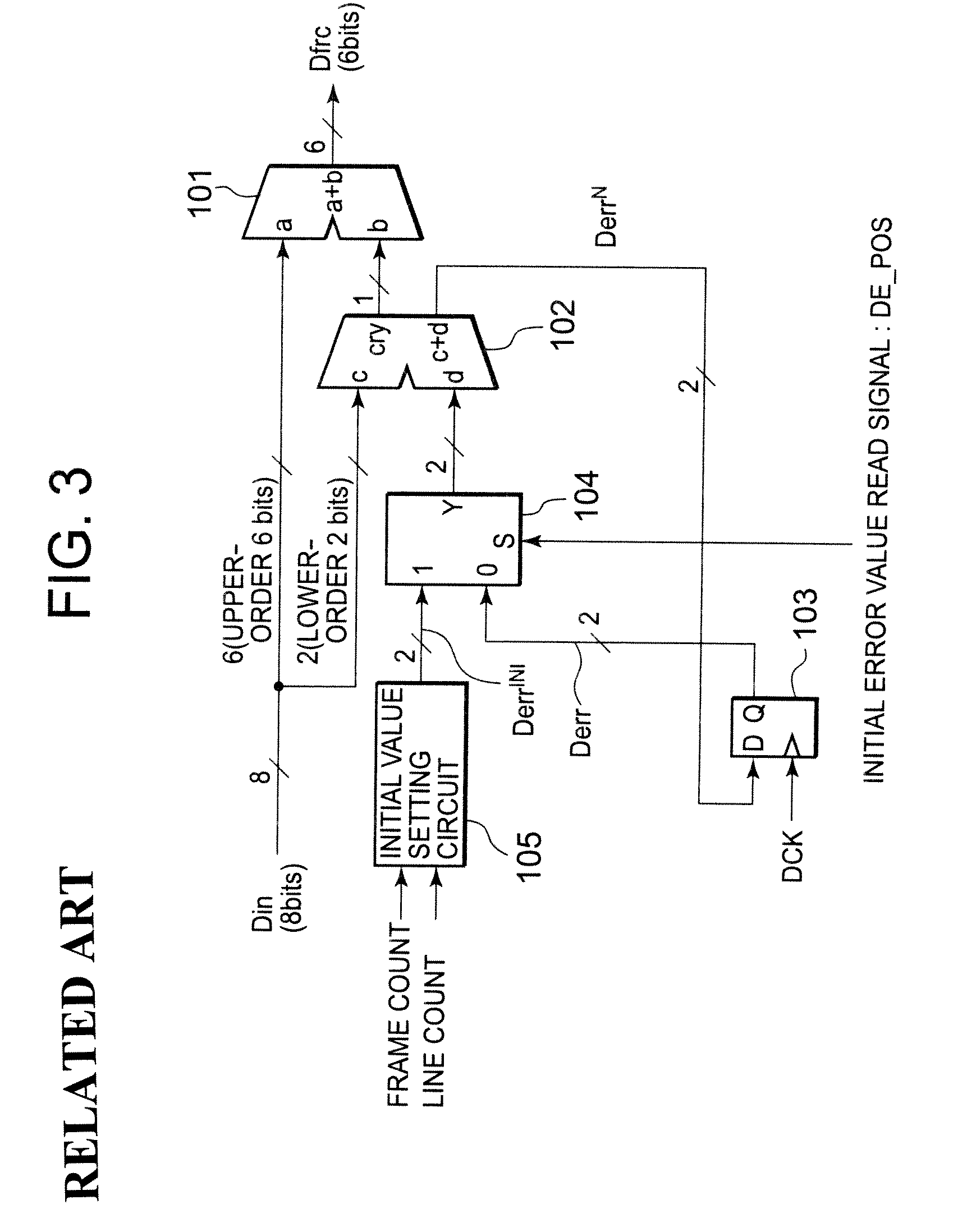
InactiveUS20080278522A1Optimal subtractive color processingImprove image qualityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLiquid-crystal displaySubtractive color
Disclosed herewith a liquid crystal display apparatus, which includes a liquid crystal display panel that employs the delta arrangement; a subtractive color processing circuit that carries out a subtractive color processing for input image data, thereby generating subtractive color image data; and data line driving circuit that drives the liquid crystal display panel in response to the subtractive color image data. The subtractive color processing circuit carries out a weighting processing that increases or decreases the subtractive color image data according to a line that includes a sub-pixel to be subjected to a subtractive color processing, then carries out an error diffusion processing for the result of the weighting processing, thereby generating subtractive color image data. The subtractive color processing circuit carries out the weighting processing so as to increase the subtractive color image data corresponding to a line and decrease the subtractive color image data corresponding to another line.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Apparatus and method for processing image data supplied to image display apparatus
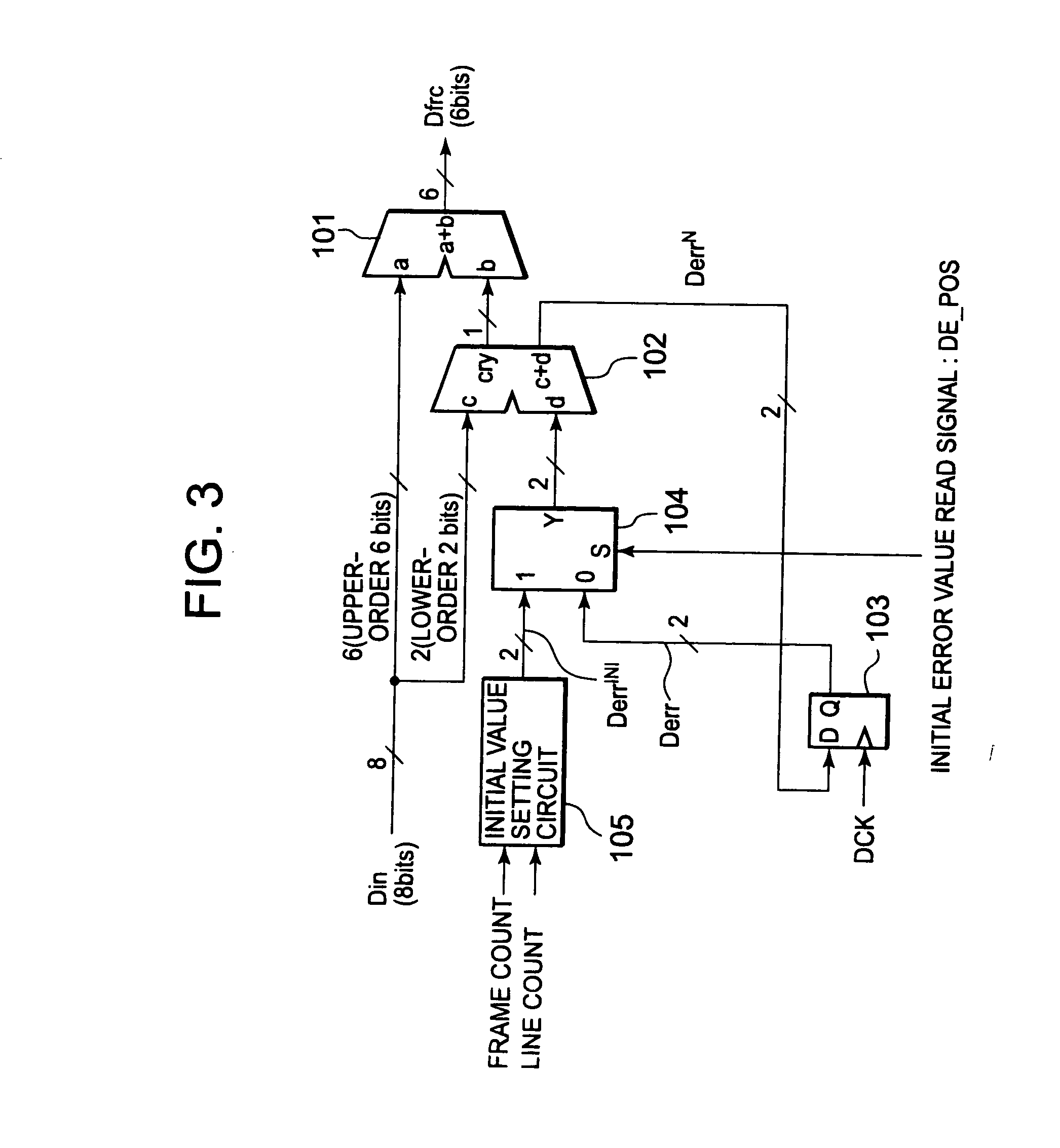
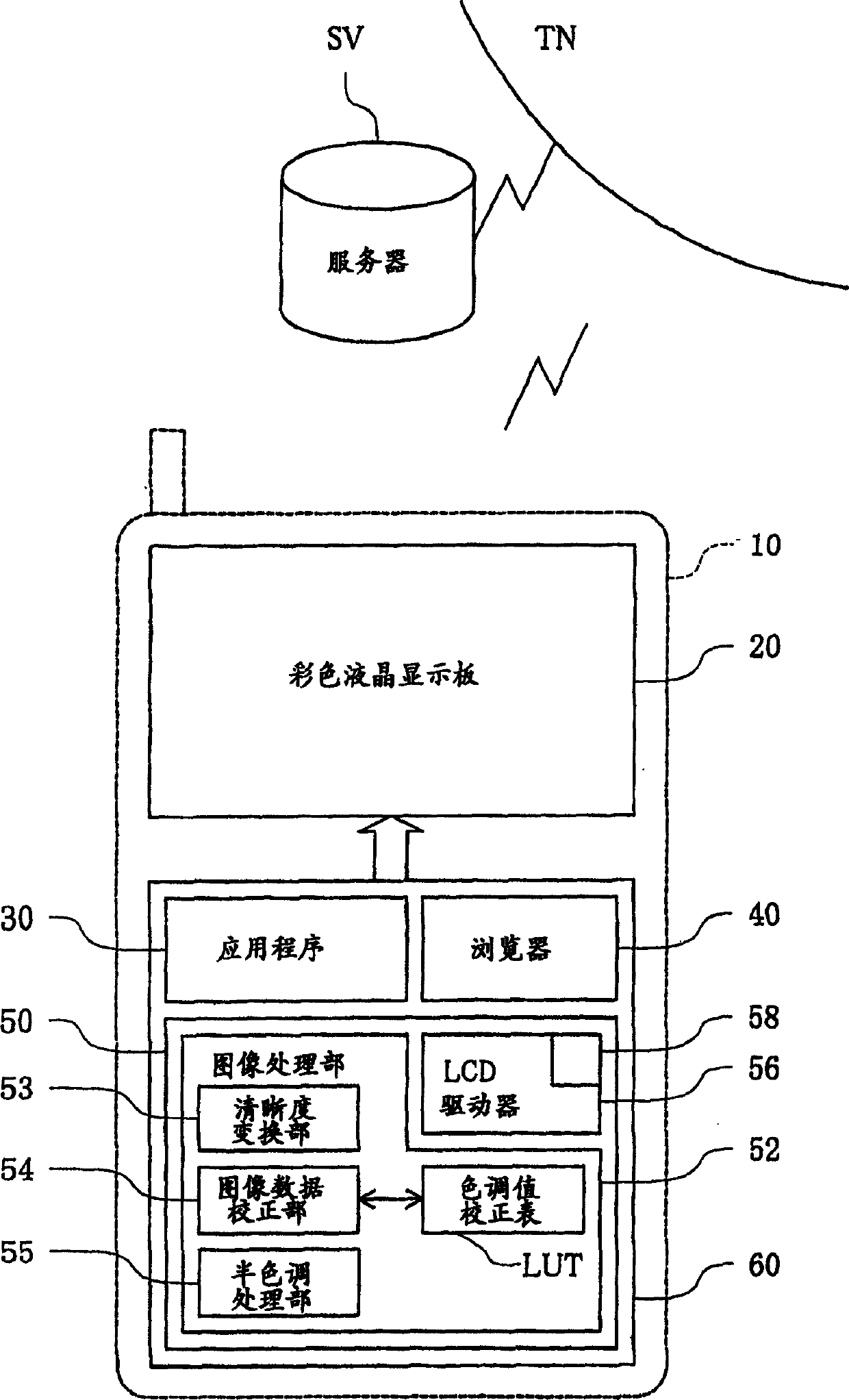
InactiveCN1619637AColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
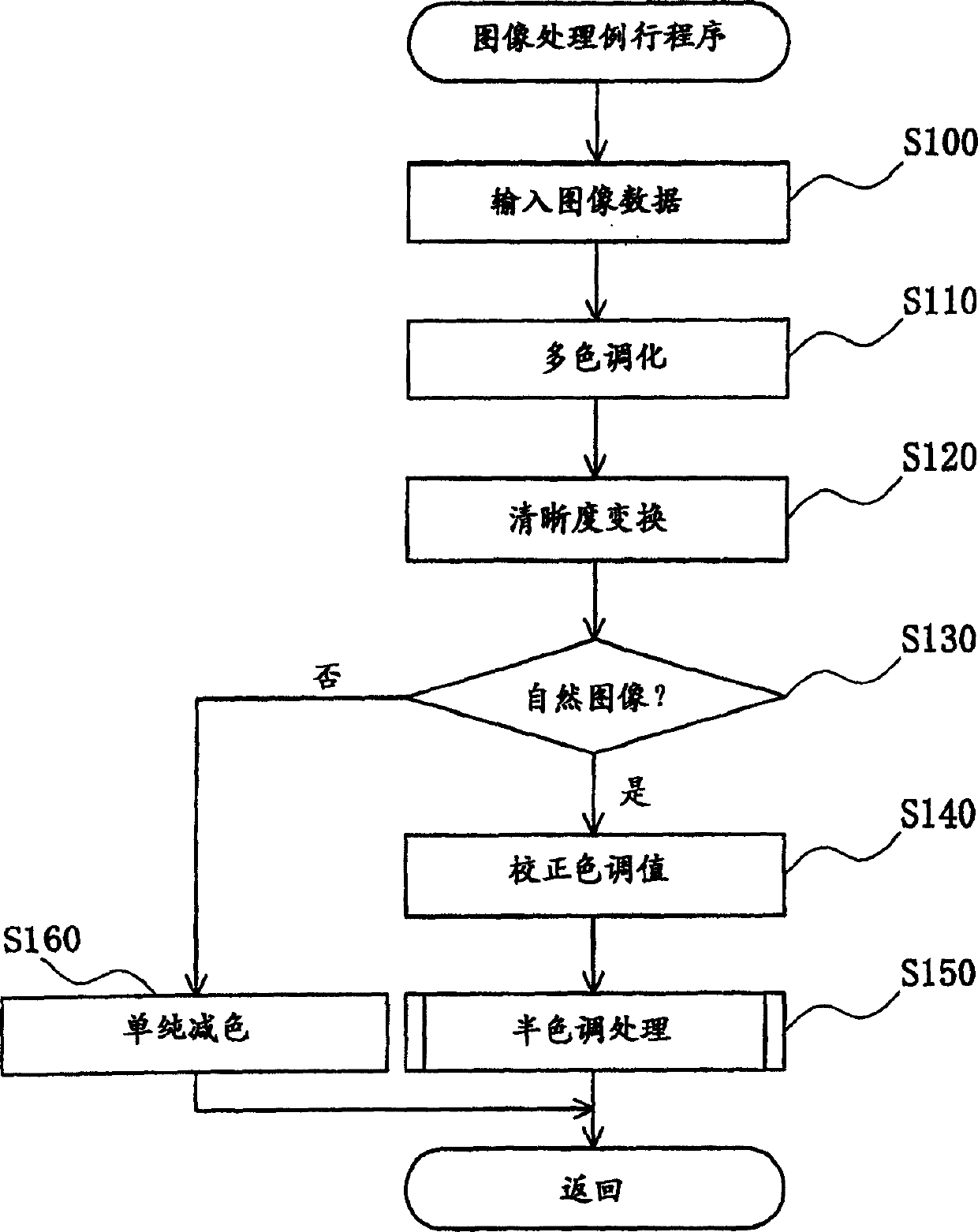
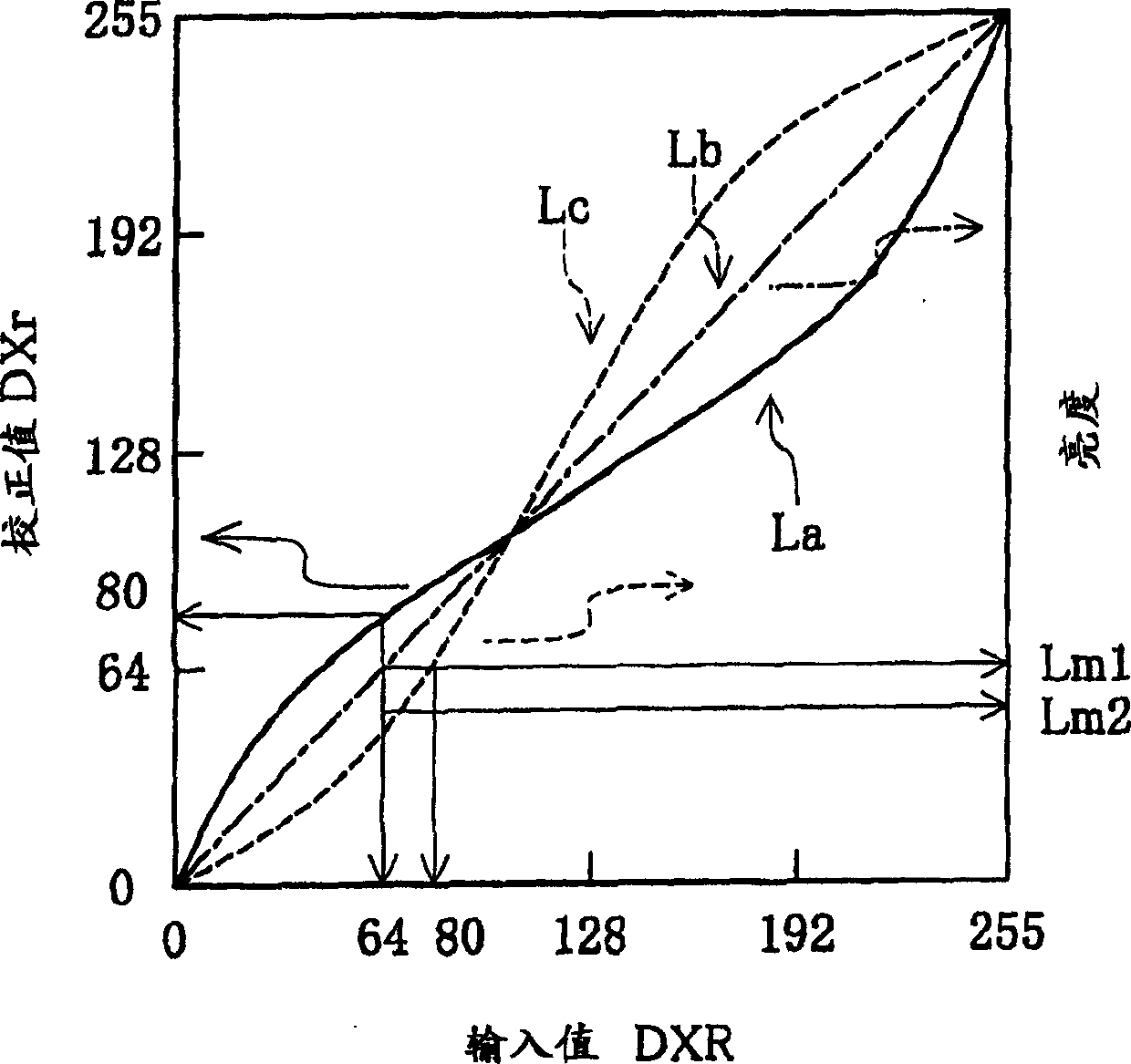
An image processing device that performs predetermined image processing on image data to be displayed on an image display device to generate display data to be supplied to the image display device, the image display device being a device capable of displaying The number of display tones on the display is less than the number of tones of the image data, and the output brightness for the display tonal value of the display data is graded, and at the same time, it has wide and narrow nonlinear display characteristics at intervals; it is characterized in that, The image processing device includes a color reduction processing unit that divides the tone range of the tone value of the image data into wide and narrow intervals corresponding to the display characteristics, according to the rule of simple color reduction processing or the rule of halftone processing. In either case, color reduction processing is performed by assigning the tone value in the interval to the display tone value.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Techniques for predicting colorimetric measurements of mixed subtractive colors
ActiveUS7738148B2Good colorEliminate the effects ofDigitally marking record carriersMulticolor photographic processingPattern recognitionSubtractive color
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
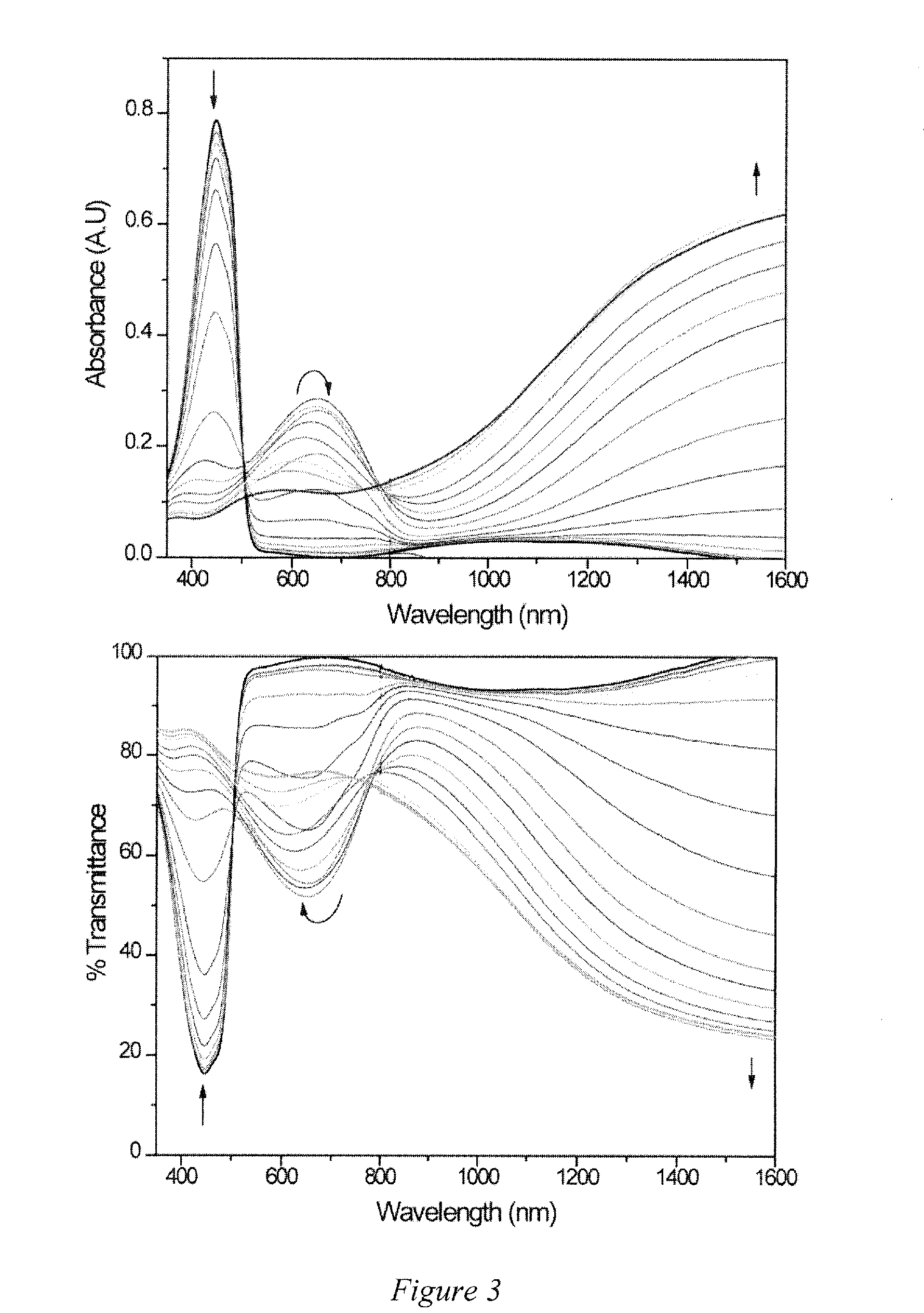
Cathodically coloring yellow soluble electrochromic and light emitting polymers
Embodiments of the invention are directed to yellow-to-transmissive conjugated polymers, a method to prepare the yellow conjugated polymers, the use of the yellow conjugated polymers in an electrochromic and / or electroluminescent device comprising neutral state primary subtractive colored conjugated polymers, and a method to prepare the device comprising the yellow conjugated polymer. The yellow conjugated polymers comprise a sequence of dioxythiophene units alternating with aromatic units, thiophene units, furan units, and / or pyrrole units. The yellow conjugated polymers are prepared by cross-condensation reactions. The yellow conjugated polymers can be soluble and preparation of the device involves deposition of the yellow conjugated polymer from solution onto a surface.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Additive and subtractive compound manufacturing equipment
PendingCN110026776AReduce temperature riseExtended service lifeAdditive manufacturing apparatusArc welding apparatusSubtractive colorSpray nozzle
The invention relates to additive and subtractive compound manufacturing equipment. In the equipment, additive and subtractive processes are finished independently, and a subtractive tool and an additive forming assembly are not switched by using a tool switching device on a machining center, so that the production efficiency is improved greatly. The equipment comprises the machining center, the additive forming assembly and a cooling nozzle. The additive forming assembly comprises a connecting plate, a motor, a rectilinear motion linear module and an energy depositing metal additive forming device. The rectilinear motion linear module is fixed to a spindle box of the machining center and is slidably connected to the connecting plate. The energy depositing metal additive forming device isfixedly mounted on the connecting plate. The motor provides power to the rectilinear motion linear module, so that the connecting plate drives the energy depositing metal additive forming device to move up and down. The cooling nozzle is fixed to the spindle box of the machining center, and an air outlet faces a working table-board of the machining center.
Owner:BEIJING WANWEI ADDITIVE MFG TECH CO LTD
Subtractive color method, subtractive color processing apparatus, image forming apparatus, and computer-readable storage medium for computer program
ActiveUS8395813B2Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsSubtractive colorImage formation
A most used color that is a most popularly used color is obtained in an image. Pixel groups formed of continued pixels having an identical color other than the most used color in the image is extracted as first pixel groups. Pixel groups having a color of which a color difference with respect to the most used color is smaller than a predetermined threshold and having a size thereof that is smaller than a predetermined size is extracted as third pixel groups among the first pixel groups thus extracted. The first pixel groups other than the third pixel groups are taken as second pixel groups. An image is generated by replacing colors of portions, which correspond to the second pixel groups in an image having an area identical with that of an image to be processed and filled with the most used color, with the corresponding second pixel groups, respectively.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
Method of forming image, image forming apparatus, and program for carrying out the method
ActiveUS7436545B2Appropriately reproducedGood colorDigitally marking record carriersMeasurement apparatus componentsSubtractive colorImage formation
Owner:CANON KK
Display apparatus and display panel driver including subtractive color processing circuit for error diffusion processing and weighting processing
InactiveUS8373727B2Increase brightnessDecrease in luminanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLiquid-crystal displaySubtractive color
Disclosed herewith a liquid crystal display apparatus, which includes a liquid crystal display panel that employs the delta arrangement; a subtractive color processing circuit that carries out a subtractive color processing for input image data, thereby generating subtractive color image data; and data line driving circuit that drives the liquid crystal display panel in response to the subtractive color image data. The subtractive color processing circuit carries out a weighting processing that increases or decreases the subtractive color image data according to a line that includes a sub-pixel to be subjected to a subtractive color processing, then carries out an error diffusion processing for the result of the weighting processing, thereby generating subtractive color image data. The subtractive color processing circuit carries out the weighting processing so as to increase the subtractive color image data corresponding to a line and decrease the subtractive color image data corresponding to another line.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Cathodically coloring yellow soluble electrochromic and light emitting polymers
Embodiments of the invention are directed to yellow-to-transmissive conjugated polymers, a method to prepare the yellow conjugated polymers, the use of the yellow conjugated polymers in an electrochromic and / or electroluminescent device comprising neutral state primary subtractive colored conjugated polymers, and a method to prepare the device comprising the yellow conjugated polymer. The yellow conjugated polymers comprise a sequence of dioxythiophene units alternating with aromatic units, thiophene units, furan units, and / or pyrrole units. The yellow conjugated polymers are prepared by cross-condensation reactions. The yellow conjugated polymers can be soluble and preparation of the device involves deposition of the yellow conjugated polymer from solution onto a surface.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Device for obtaining stereoscopic images from a conventional endoscope with single lens camera
Owner:SOOD SANDEEP +1
Subtractive color mixture electrophoretype type display device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105785686AReduce concentrationAchieve high brightness color displayNon-linear opticsSubtractive colorDisplay device
The invention discloses a subtractive color mixture electrophoretype type display device and a manufacturing method thereof. The display device comprises a pixel array, a first base plate, a second base plate, at least three public electrodes and a display electrode array, wherein the pixel array is provided with a plurality of pixel units; the first base plate and the second base plate are in opposite arrangement; the at least three public electrodes are formed on the lower surface of the first base plate; the display electrode array is formed on the upper surface of the second base plate; each display electrode and the at least three public electrodes correspondingly form a driving electrode of each pixel unit; each pixel unit comprises a micro cup layer arranged between the display electrode and the public electrode; the micro cup layer comprises at least one micro cup structure; when a plurality of micro cup structures are used, the plurality of micro cup structures are formed by micro cup walls; a display medium is arranged in the micro cup structure, and comprises electrophoretic ink and charged particles dispersed in the electrophoretic ink. The high-brightness color display of various colors can be realized; the refreshing efficiency is improved; the display stability and the high-brightness color reoccurrence are ensured.
Owner:DALIAN DKE LCD CO LTD
Password entry method and system
ActiveUS20160247000A1Improve password entry securityImprove securityTexturing/coloringDigital data protectionSubtractive colorPassword
Disclosed are a password entry method and system. In the present invention, an intelligent display terminal receives a password entry instruction of a user, and randomly generates image data of a soft keyboard; the intelligent display terminal decomposes the image data of the soft keyboard into image data of a first soft keyboard and image data of a second soft keyboard by using a subtractive color process; the intelligent display terminal displays an image of the first soft keyboard according to the image data of the first soft keyboard, and sends the image data of the second soft keyboard to a portable display terminal; and the portable display terminal combines the image data of the first soft keyboard and the image data of the second soft keyboard by using an additive color process to restore an image of the soft keyboard, and displays the image of the soft keyboard.
Owner:SHENZHEN TCL NEW TECH CO LTD
Image forming apparatus
InactiveCN1940740AElectrographic process apparatusPictoral communicationSubtractive colorColor printing
An image forming apparatus includes a color print section configured to make a color printing and a changing section configured to, when color data is printed by the color printer section, allow changing to a subtractive color printing or not according to attribute information.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Techniques for predicting colorimetric measurements of mixed subtractive colors
ActiveUS20060262364A1Improve color modelingGood colorDigitally marking record carriersMulticolor photographic processingPattern recognitionSubtractive color
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Apparatus and method for processing image data supplied to image display apparatus
InactiveCN1619636AColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An image processing apparatus for performing predetermined image processing on image data to be displayed on an image display apparatus to generate data to be supplied to the image display apparatus, characterized in that the image processing apparatus includes: a storage unit for The tone values of the image display device are stored in advance in a relationship set according to the display characteristics of the image display device; an image data correction unit performs tone correction of the image data according to the relationship; and a color subtraction processing unit converts the corrected image data Subtractive color is the number of tones that can be displayed in the image display device.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Reactive black dye mixture
ActiveCN102433029AHigh color yieldGood level dyeingOrganic dyesDyeing processReactive orangeVinyl sulfone
The invention relates to a reactive black dye mixture. The reactive black dye mixture comprises 65 to 50 percent of reactive black dye, 35 to 20 percent of reactive orange dye and 20 to 10 percent of aid. From the molecular structure angle, the reactive black dye mixture is obtained by mixing and complexing specific reactive black and orange dyes which contain vinyl sulfone reactive groups respectively in a certain proportion according to compatibility and similitude and subtractive color mixing principles; and through experiment, the fiber of the dye mixture is high in color yield, and the part, which is not colored, of the fiber is very easy to clean, so the dye mixture is good in levelling property and high in dying repeatability, and color fastness to washing, light, acid and base, and rubbing, and the like, and can adapt to requirements of various dyeing processes.
Owner:吴江桃源染料有限公司
Image formation method, personal authentication medium using the same, and determination apparatus
InactiveUS20090029124A1Superior in forgery/alteration preventing performanceFacilitate authenticity determinationInk ribbonsPaper-money testing devicesSubtractive colorImage formation
A personal authentication medium includes a substrate, and a pearl pigment ink image layer formed on the substrate by using heat transfer fusion inks containing pearl pigments. The distance between the centers of dots or lines forming the pearl pigment ink image layer is 0.5 to 100 times the largest one of the average grain sizes of the pearl pigments used. Each heat transfer fusion ink contains a pearl pigment having an interference light color corresponding to one of the three additive primary colors or one of the three subtractive primary colors.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
A dimming glass based on subtractive color mixing method
ActiveCN106526932BHigh absorption strengthImprove transmittanceLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsCrystallographySubtractive color
The invention discloses a dimming glass based on a subtractive color mixing method, which comprises two light-transmitting substrates arranged oppositely, and an adjustment area is formed between the two light-transmission substrates. The adjustment area is filled with a liquid crystal mixture, and the liquid crystal mixture includes a Photopolymerized liquid crystal monomers, dichroic dyes, ordinary dyes, photoinitiators and negative liquid crystals. When no voltage is applied, the negative liquid crystals are arranged in a single domain perpendicular to the light-transmitting substrate, and the dichroic dye molecules are also Perpendicular to the light-transmitting substrate, the dichroic dye absorbs the weakest light and presents a colorless state, at which time the light transmittance reaches the highest; when a voltage is applied, the negative liquid crystal turns to a direction parallel to the light-transmitting substrate, turning During the process, the dichroic dye is driven to rotate. Because of the irregular distribution of the polymer network, the negative liquid crystal turns into a multi-domain arrangement parallel to the light-transmitting substrate, which makes the switchable glass change from the light-transmitting state to the light-scattering state. According to the method of subtractive color mixing, the glass presents a colored fuzzy state.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com