Patents
Literature
577results about "Heat measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
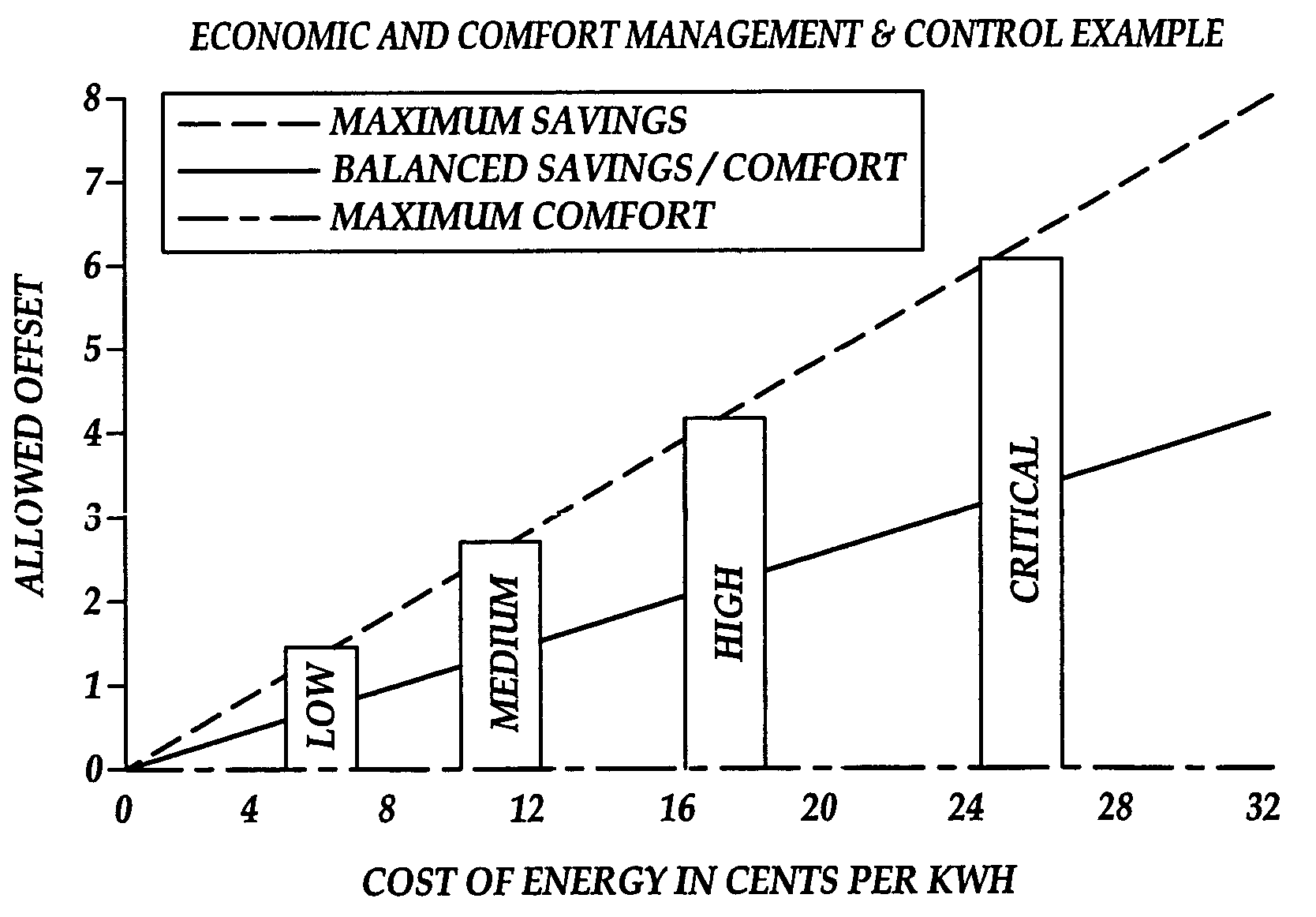
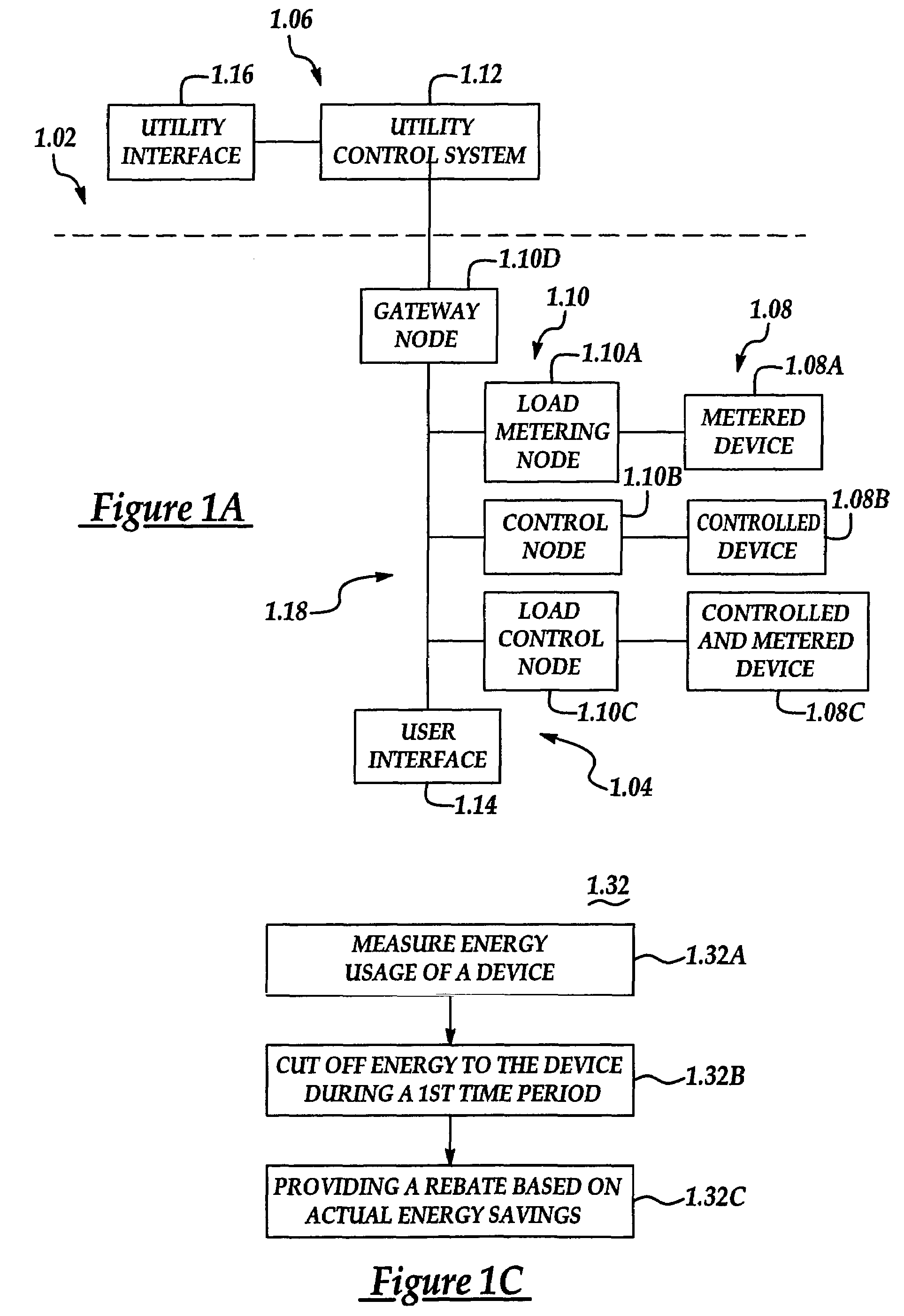
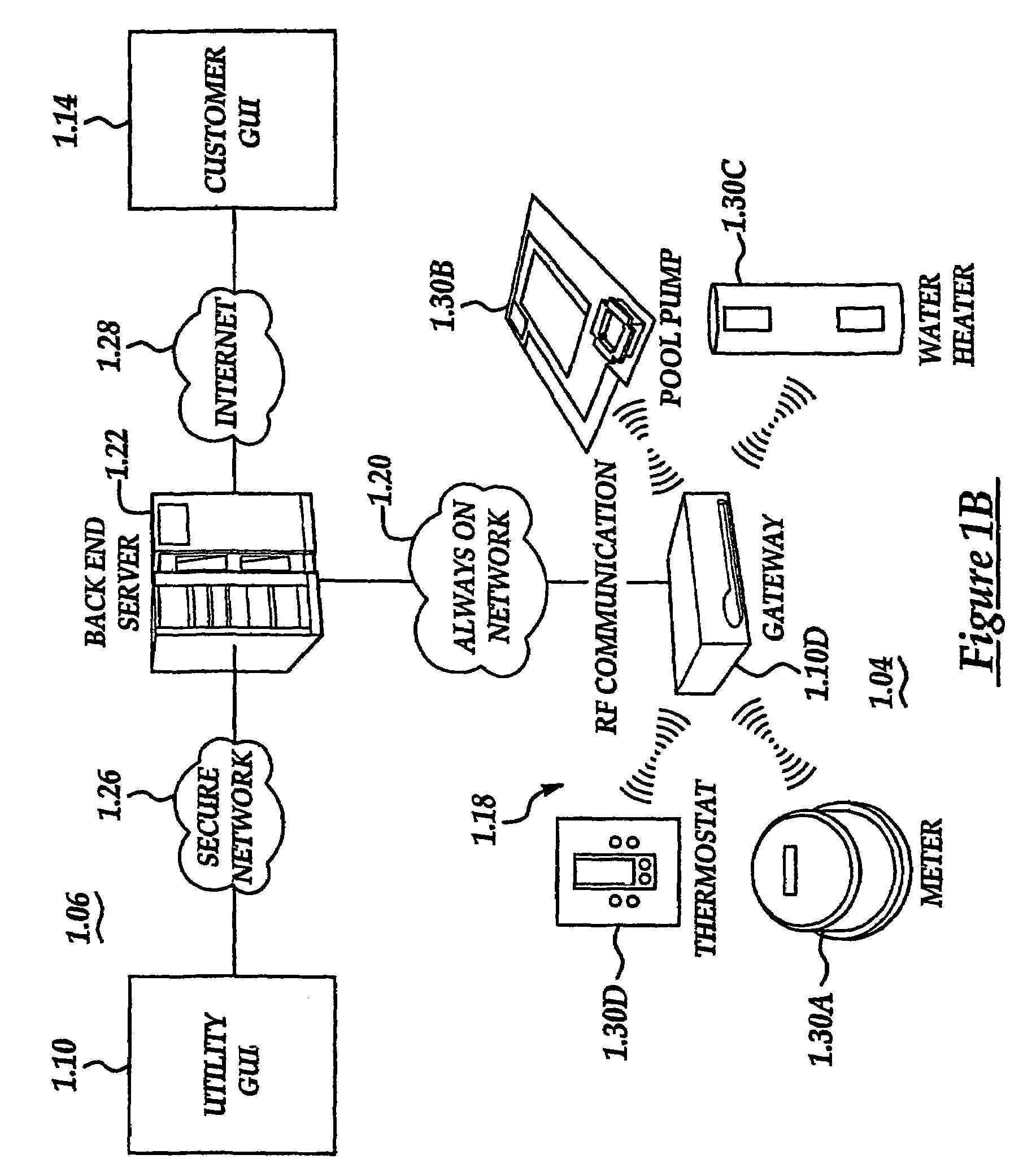
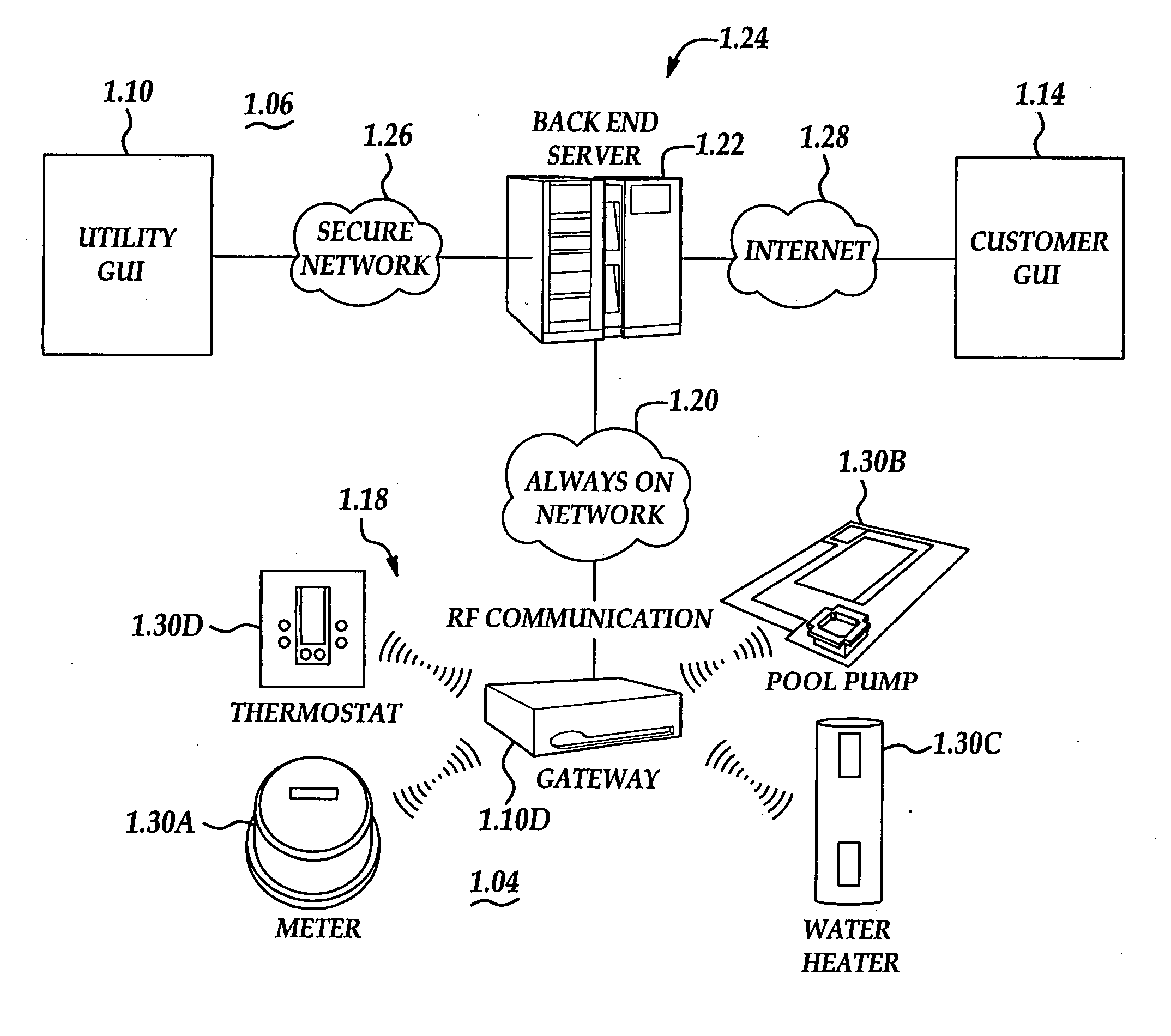
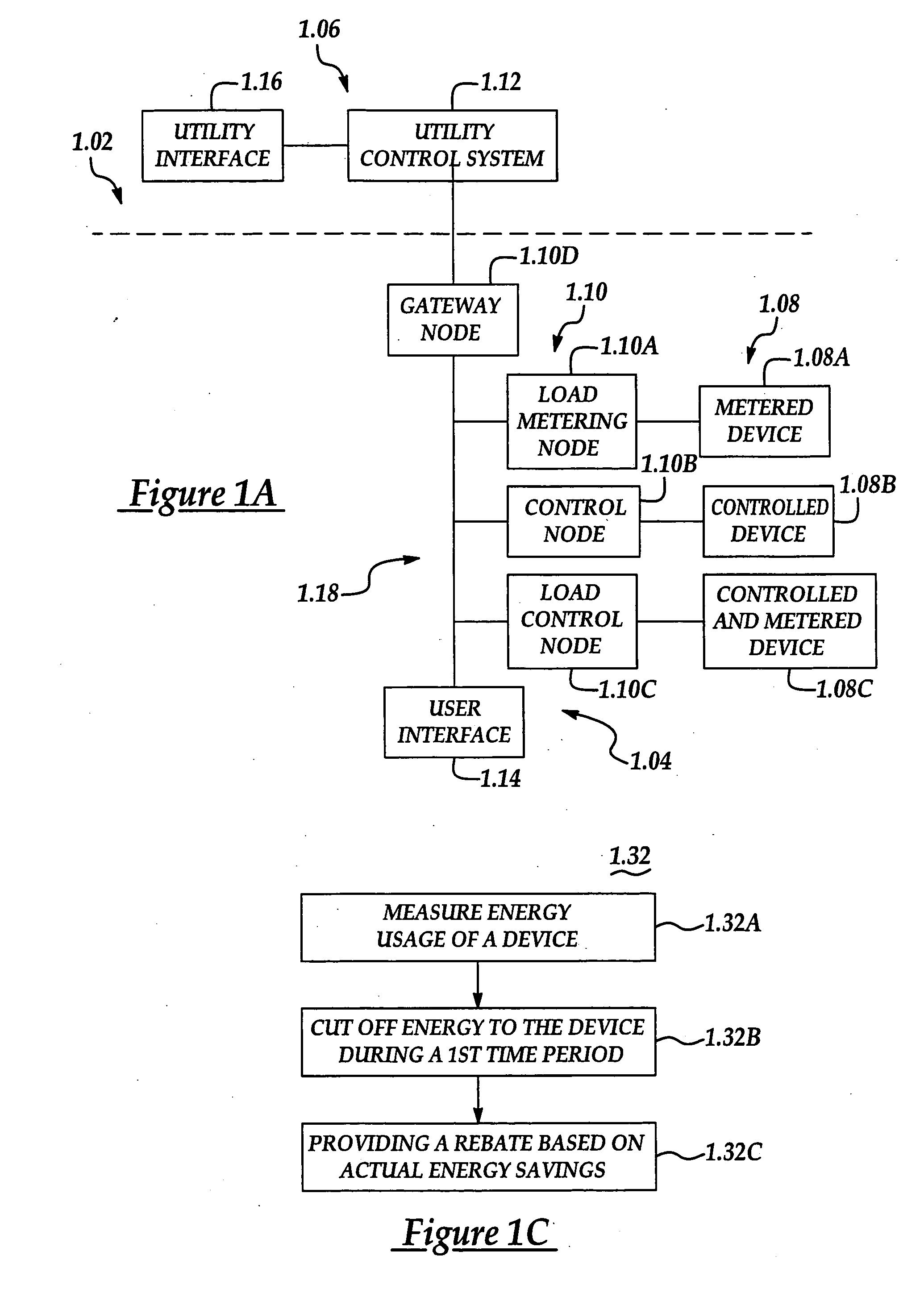
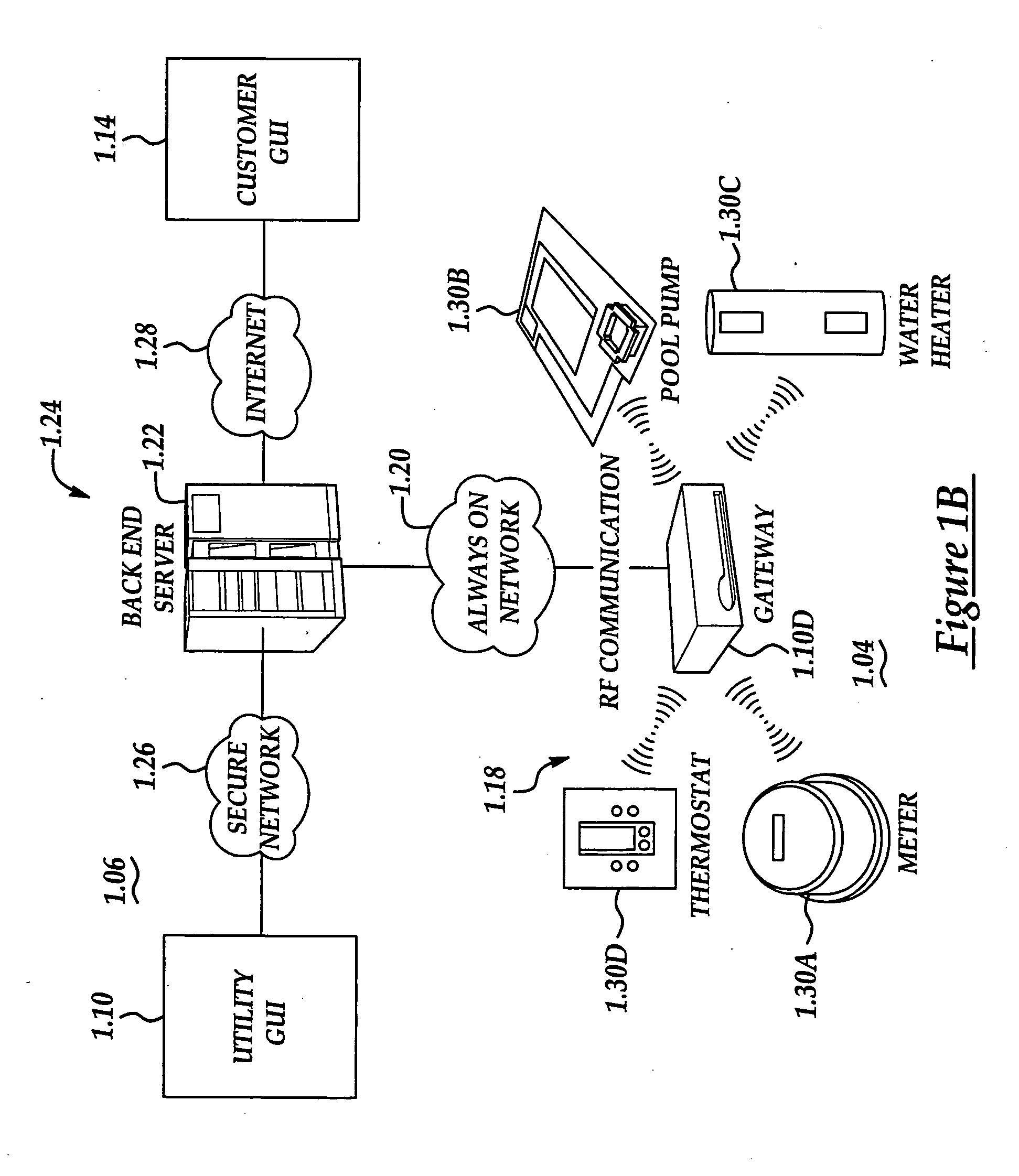
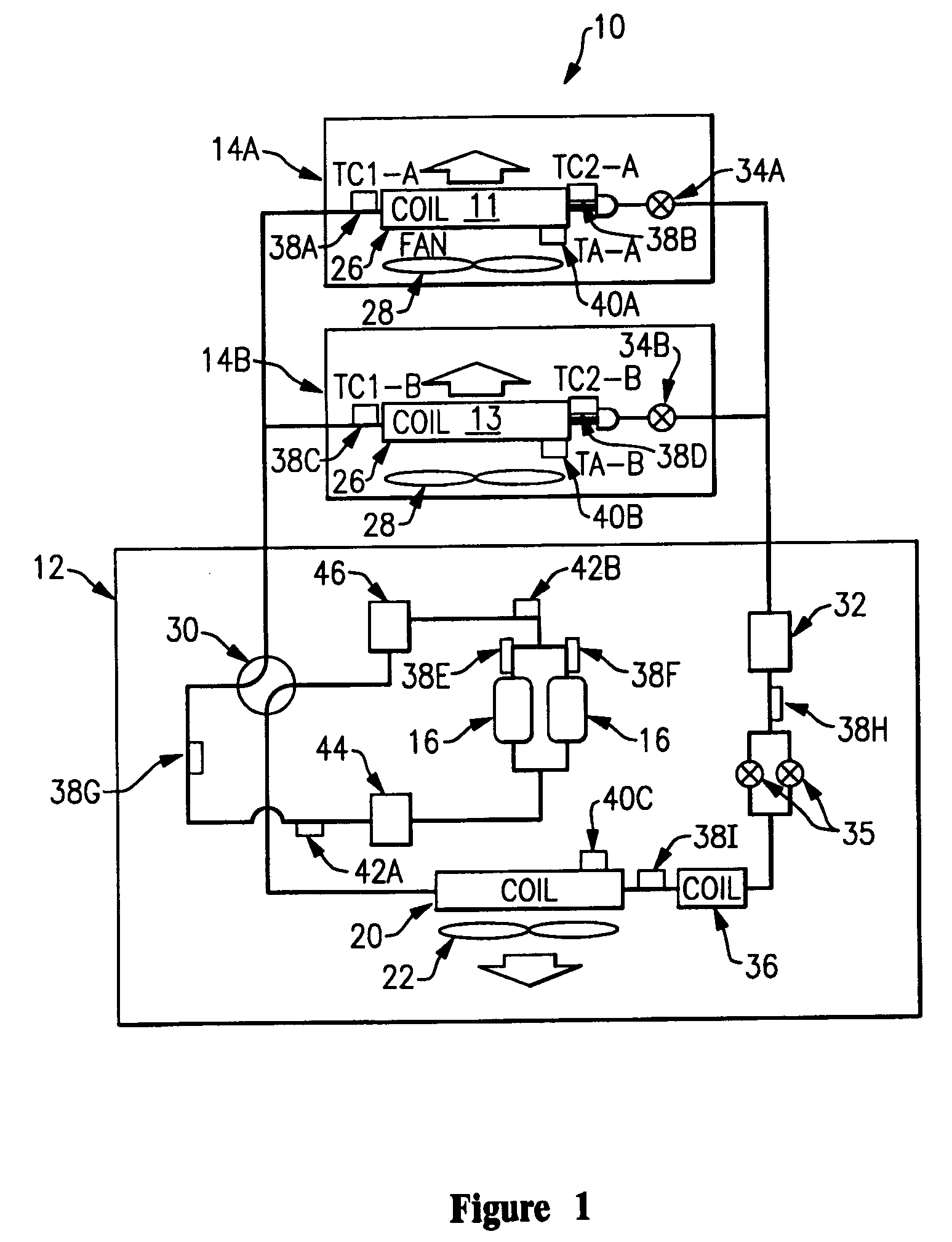
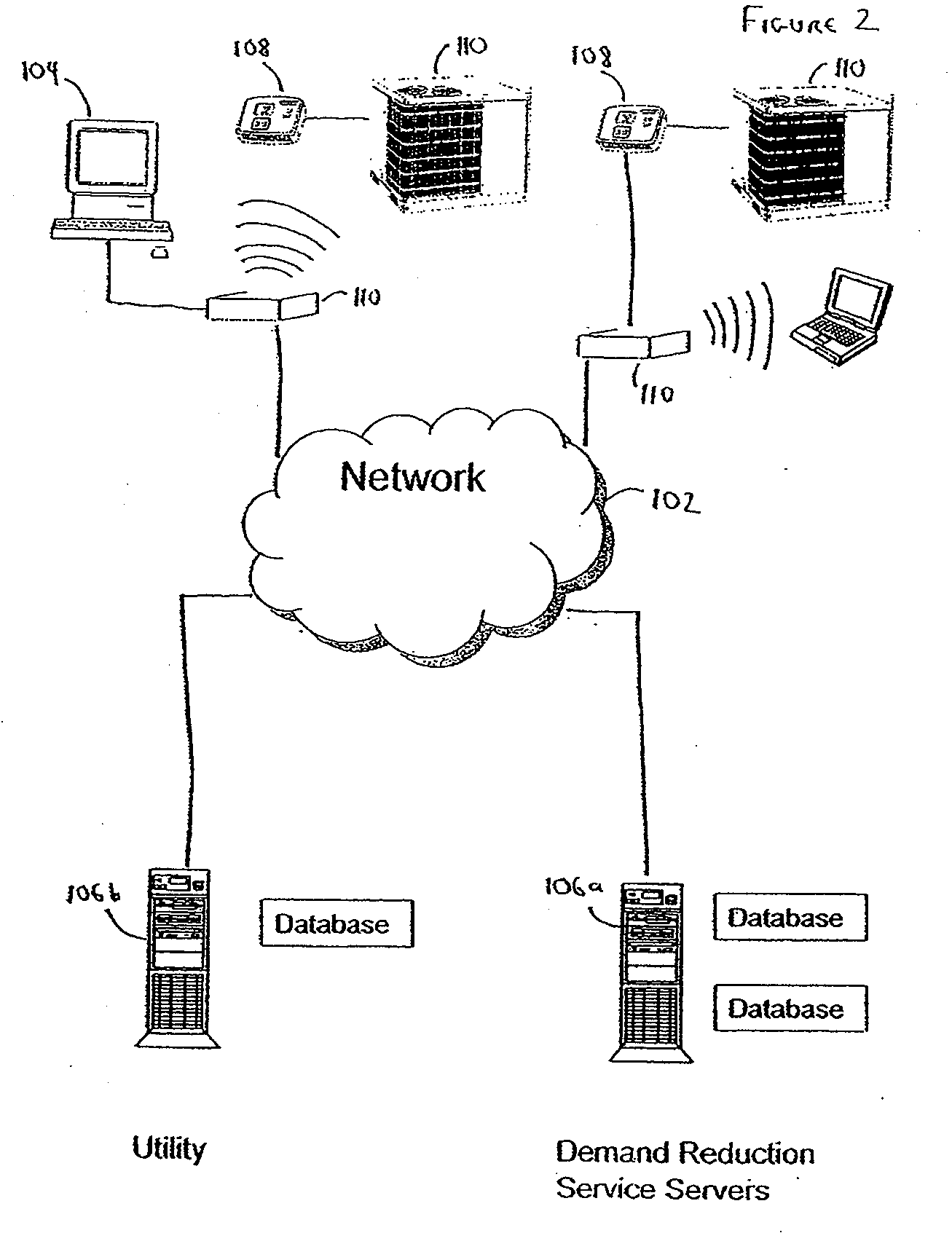
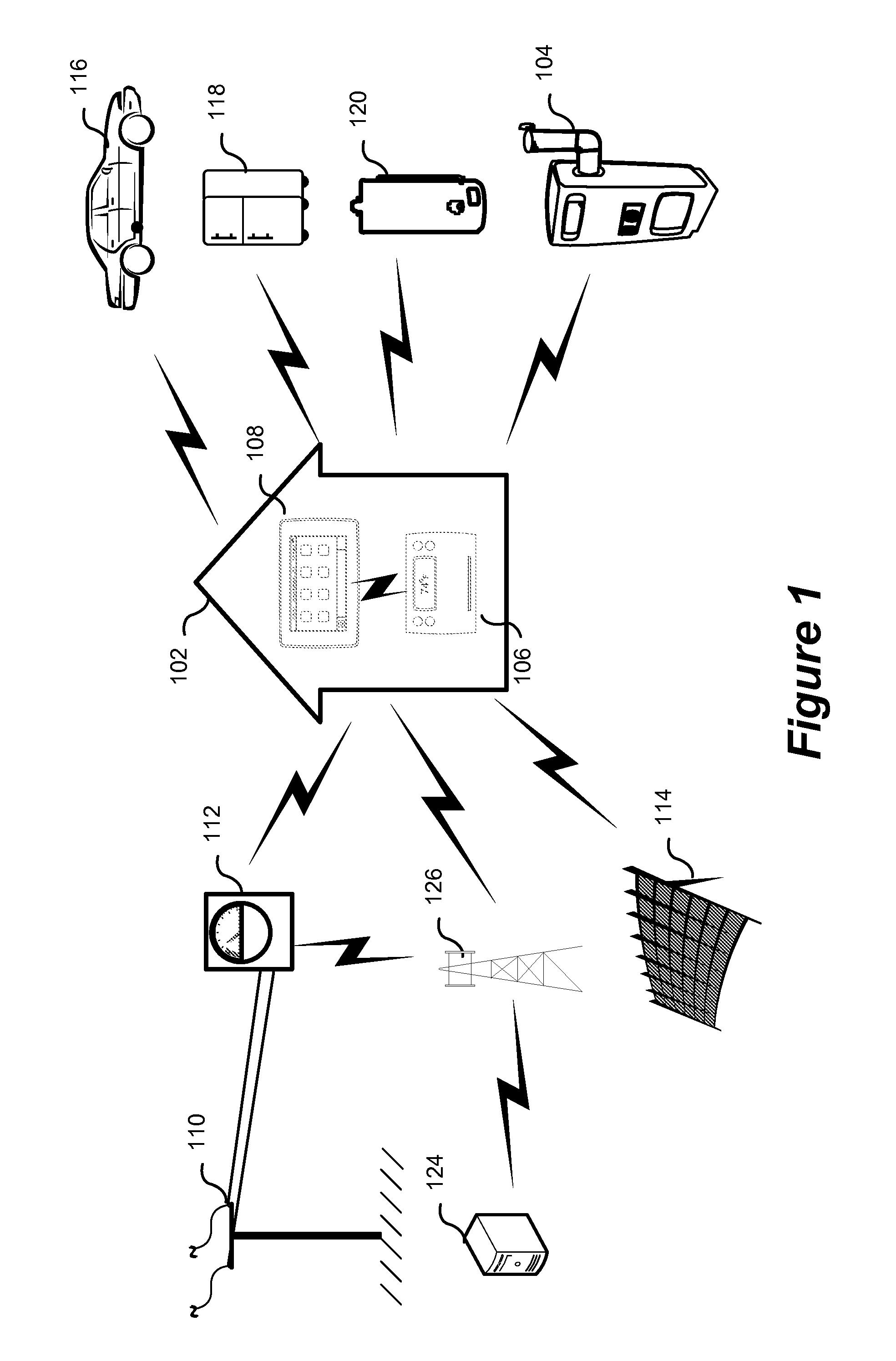
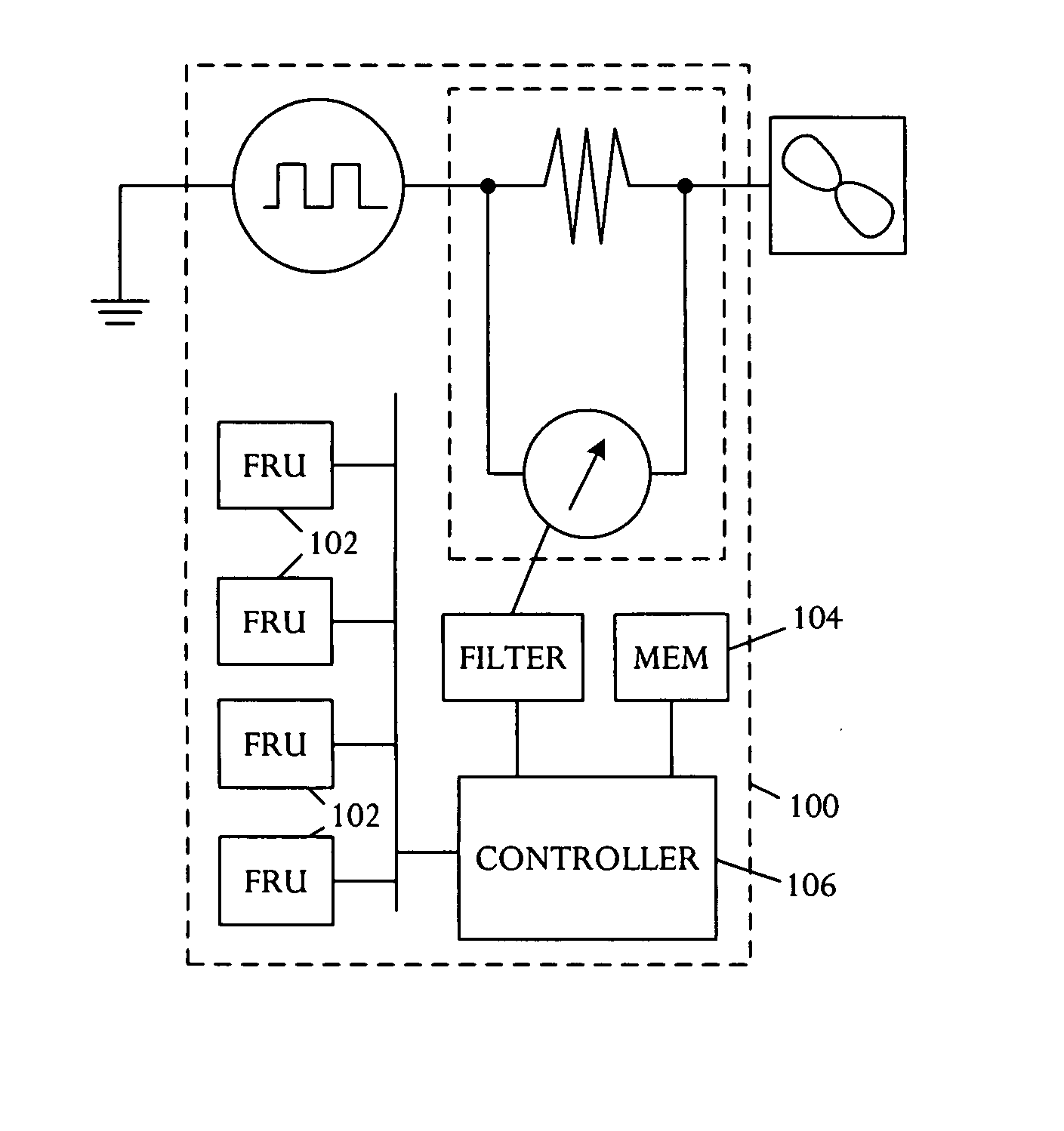
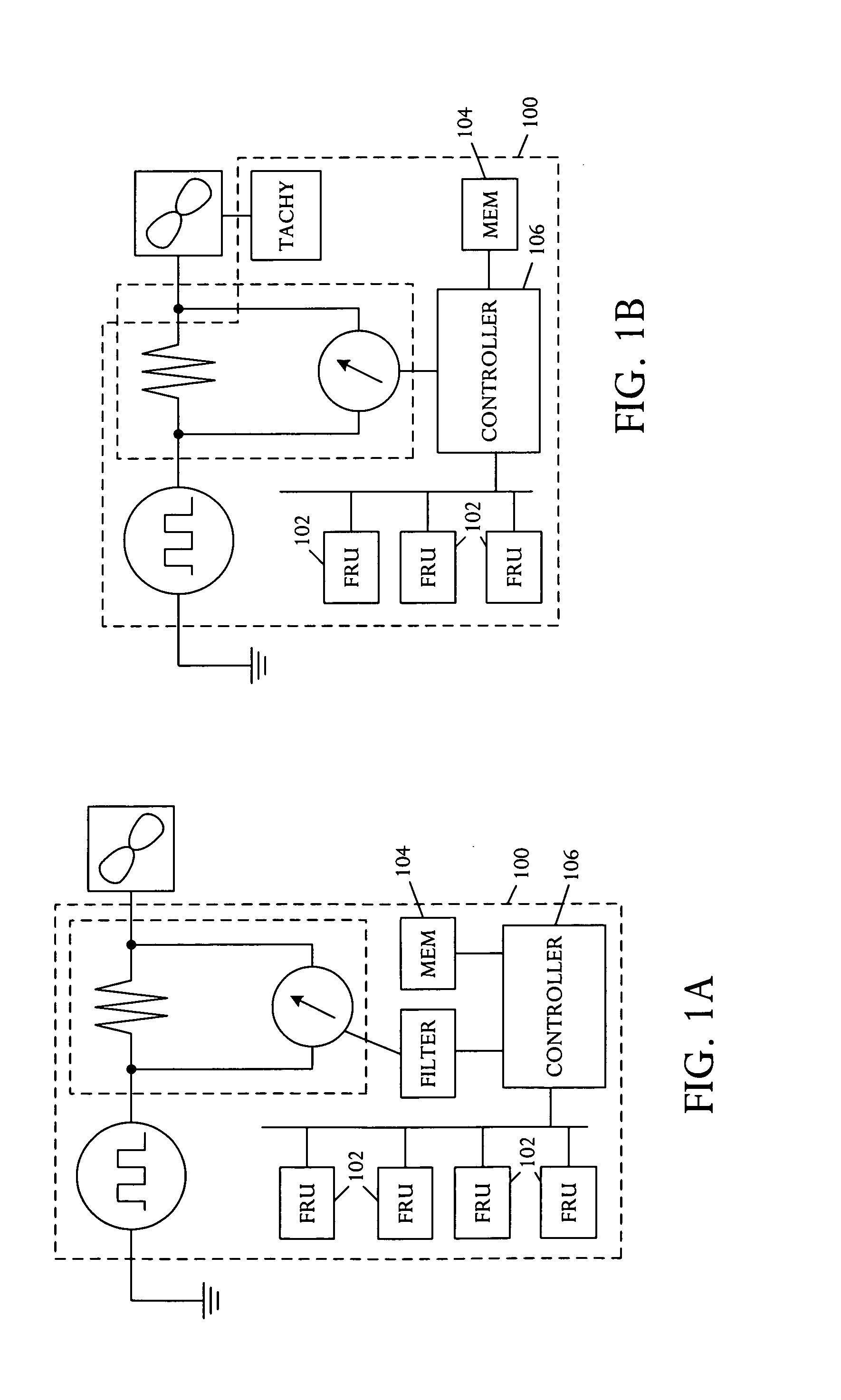
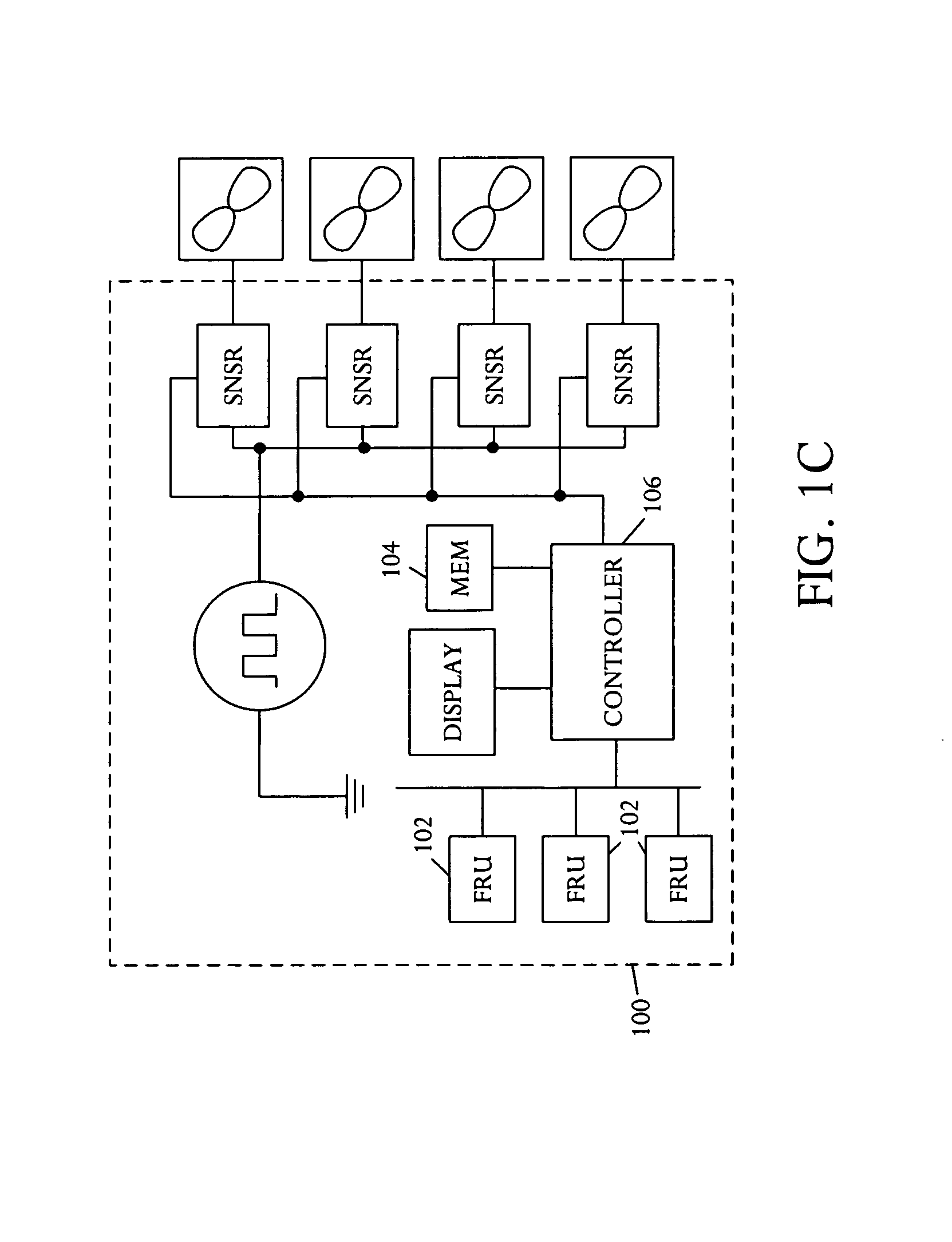
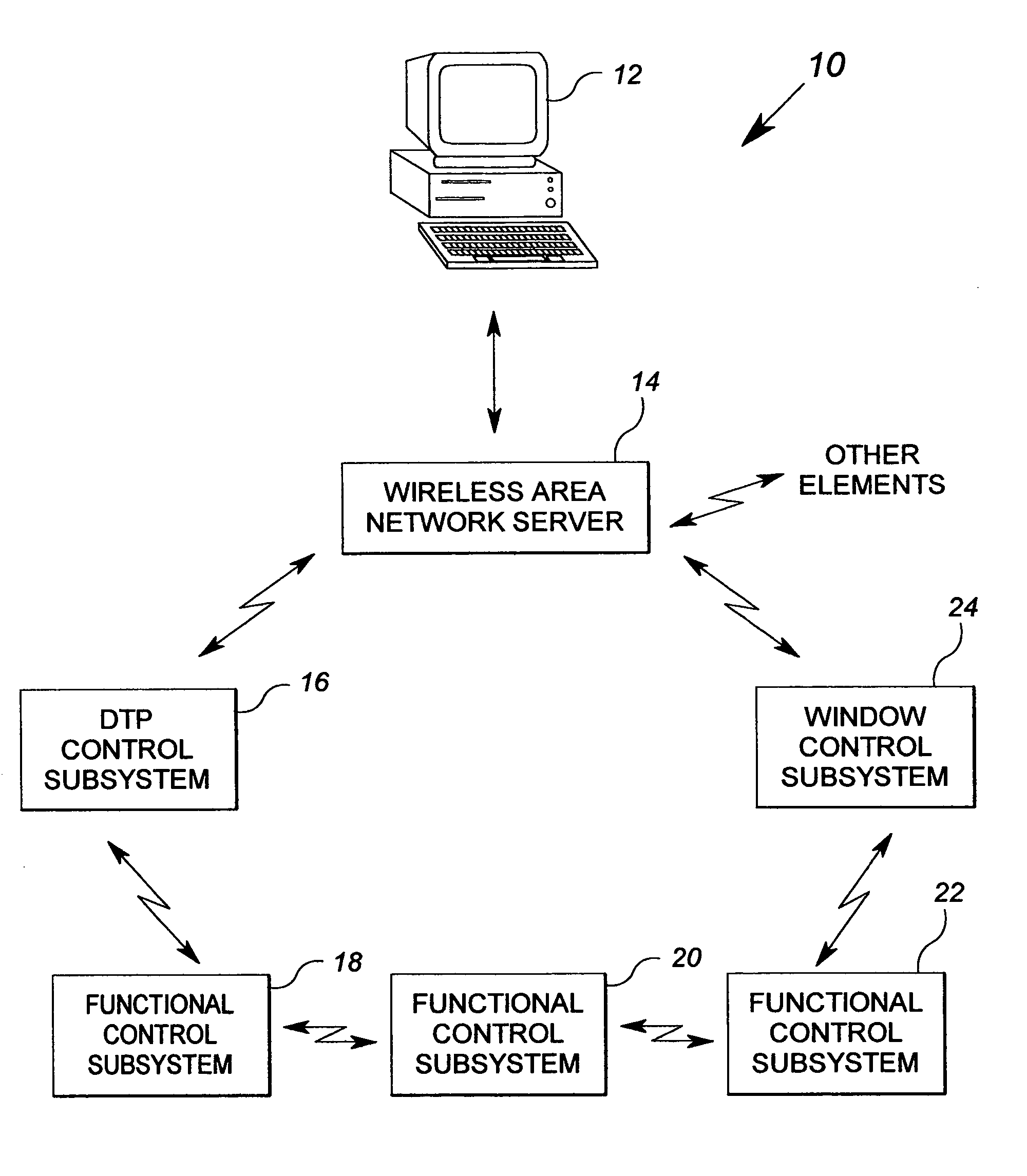
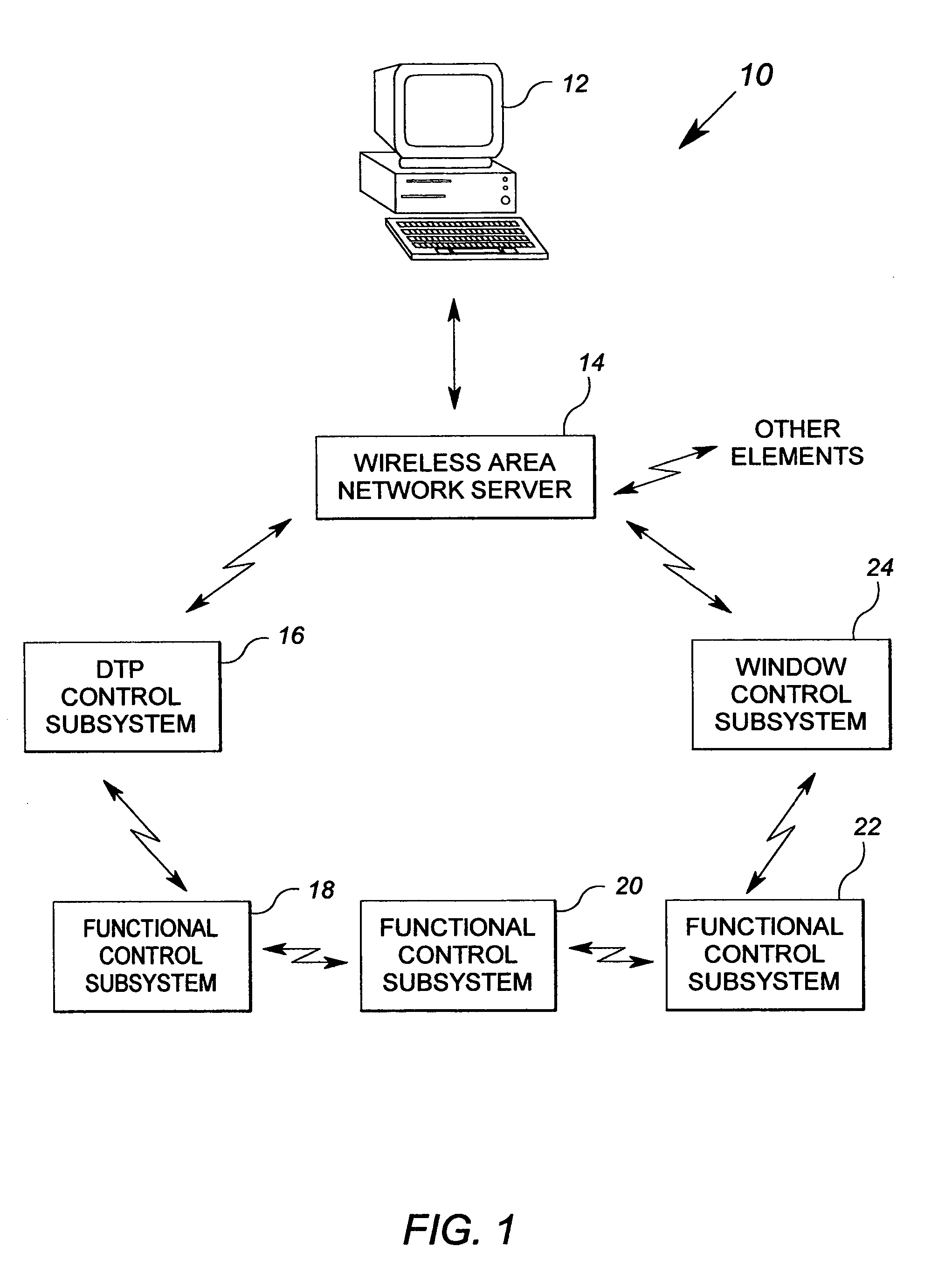
System and method of controlling an HVAC system
A system and method manage delivery of energy from a distribution network to one or more sites. Each site has at least one device coupled to the distribution network. The at least one device controllably consumes energy. The system includes a node and a control system. The node is coupled to the at least one device for sensing and controlling energy delivered to the device. A control system is coupled to the node and distribution network for delivery to the node at least one characteristic of the distribution network. The node controls the supply of energy to the device as a function of the at least one characteristic.
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
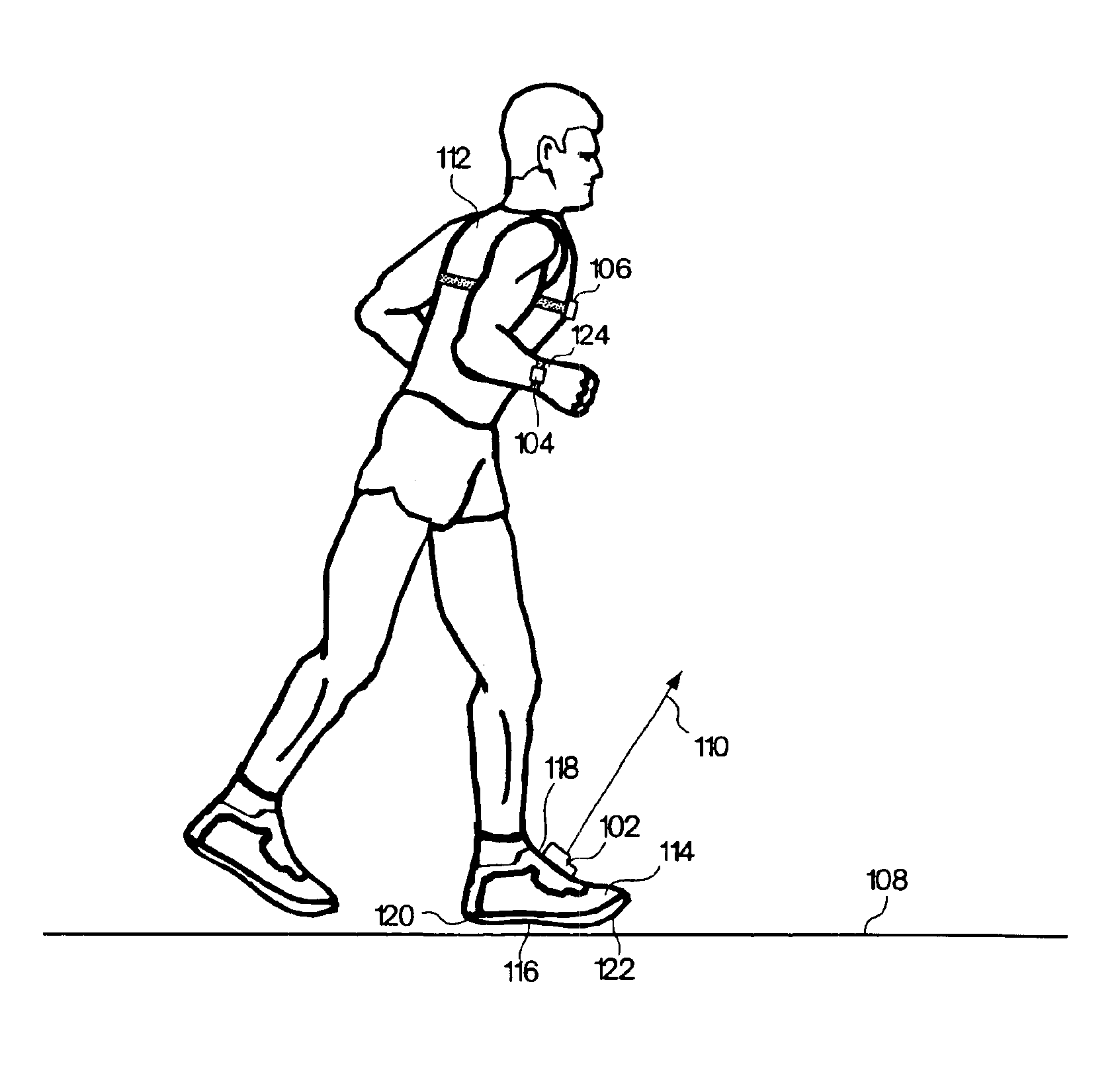
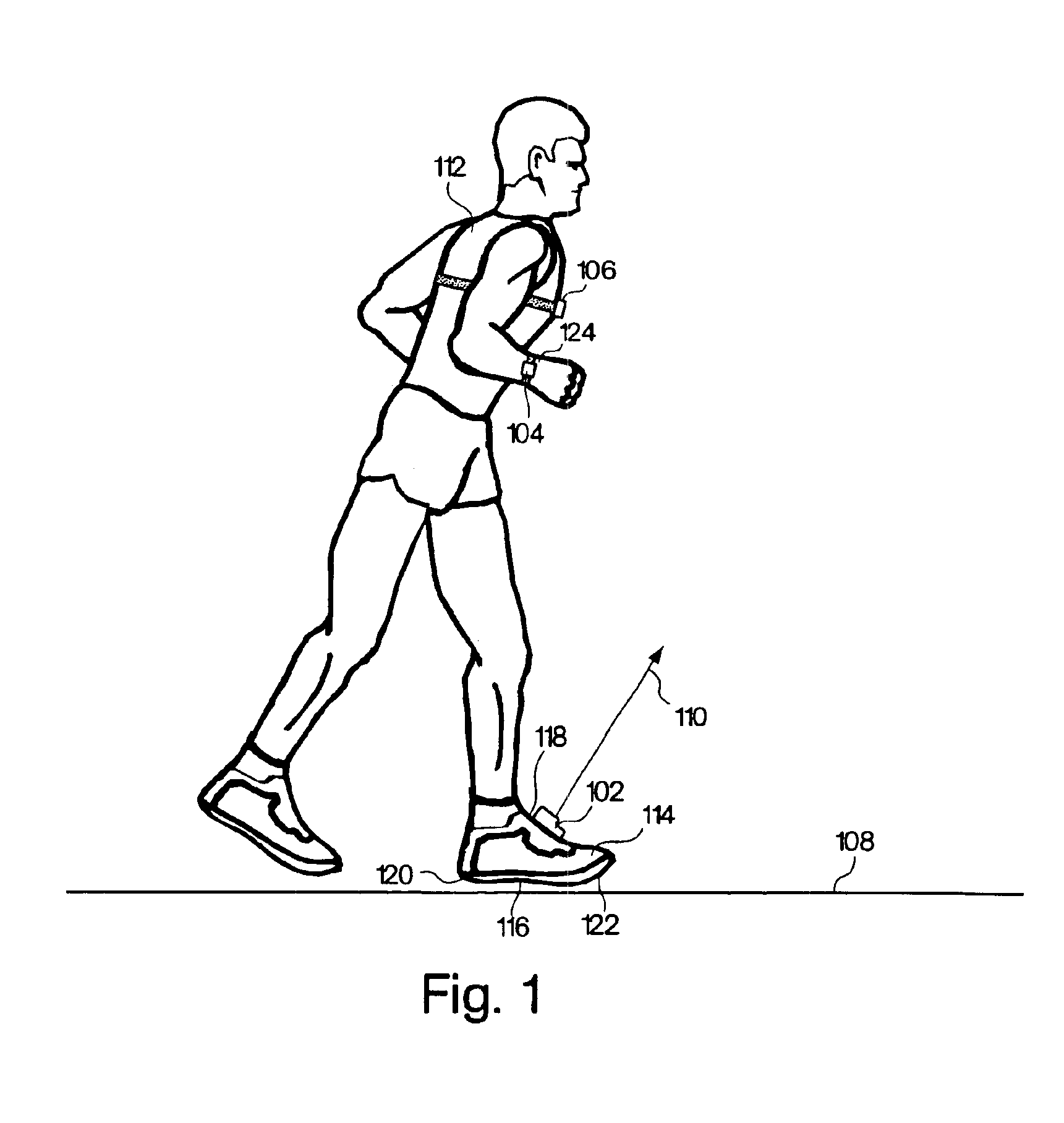
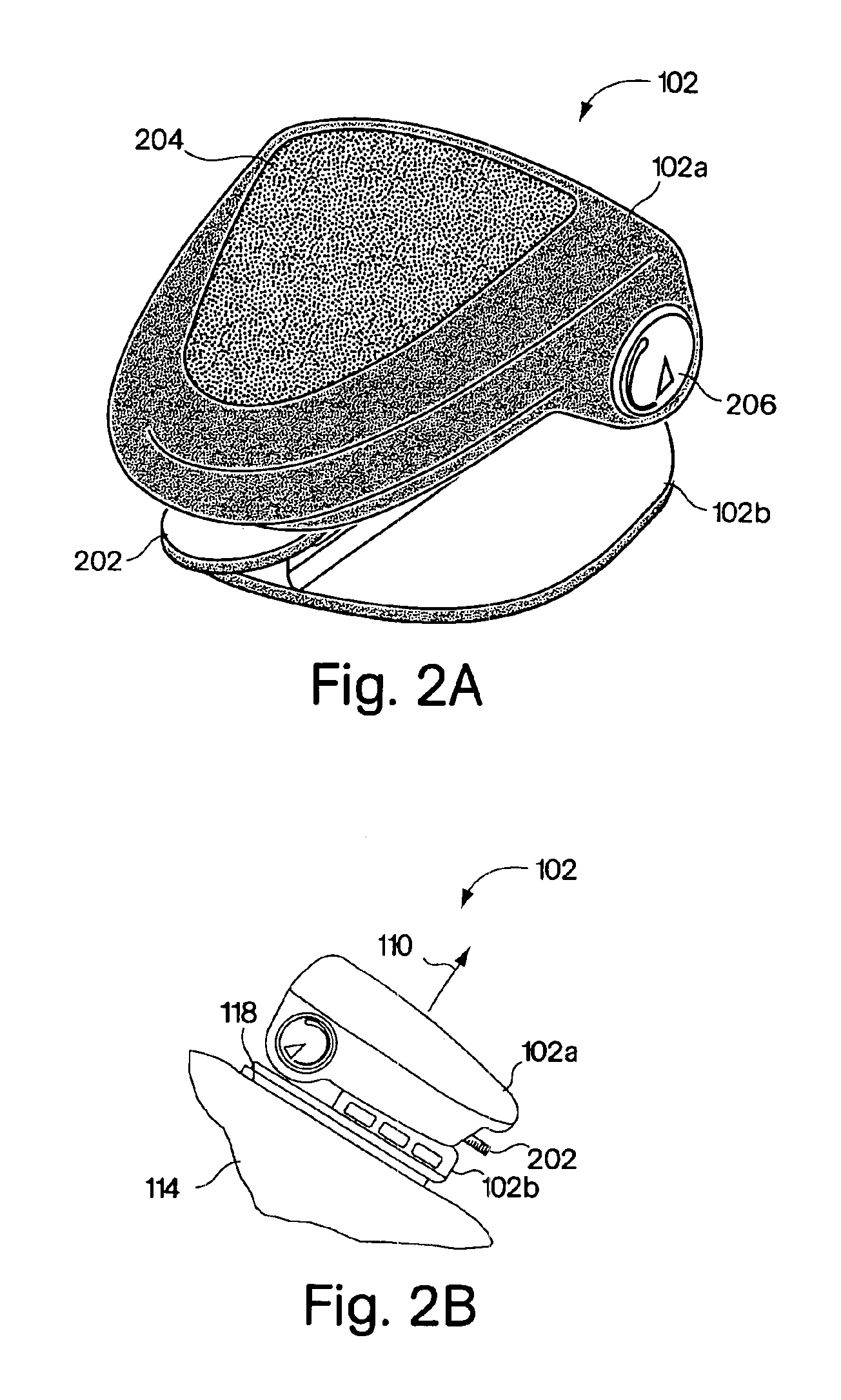
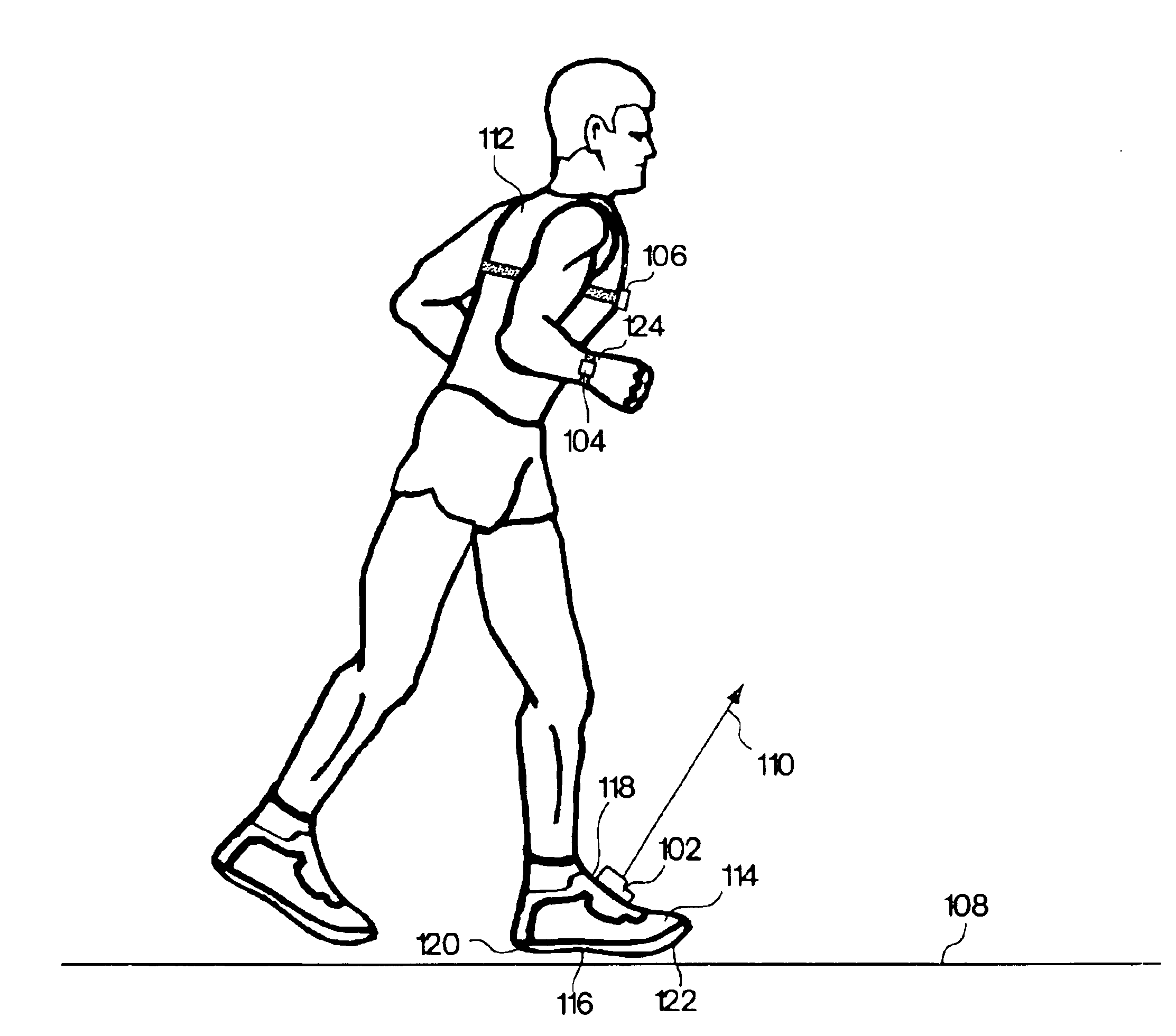
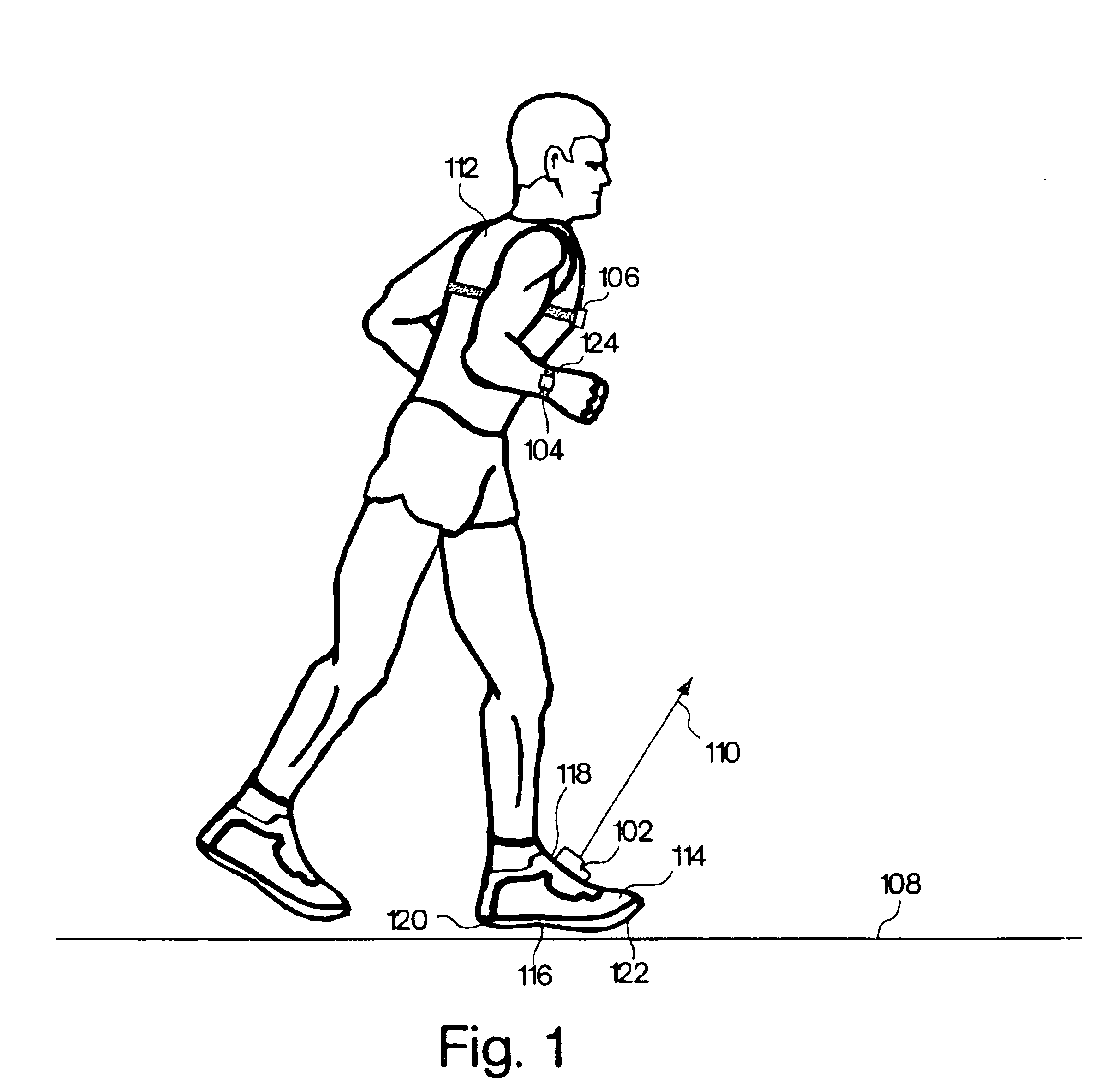
Monitoring activity of a user in locomotion on foot
InactiveUS6876947B1Physical therapies and activitiesTime indicationPacePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
In one embodiment, a method includes steps of: (a) identifying an average foot contact time of a user during a first outing; (b) identifying an average pace of the user during the first outing; (c) defining a relationship between foot contact times of the user and corresponding paces of the user, wherein the relationship is based upon the average foot contact time and the average pace identified during the first outing, and wherein no other average foot contact times and no other average paces identified during any different outings by the user are used to define the relationship; and (d) calibrating at least one device that monitors activity of the user in locomotion on foot based upon the defined relationship between foot contact times of the user and corresponding paces of the user. In another embodiment, a method includes steps of: (a) determining a single user-specific calibration constant that defines a relationship between foot contact times of a user and corresponding paces of the user, wherein no other user-specific calibration constants are used to define the relationship; and (b) calibrating at least one device that monitors activity of the user in locomotion on foot based upon the relationship between foot contact times of the user and corresponding paces of the user that is defined by the single user-specific calibration constant.
Owner:NIKE INC +1
Monitoring activity of a user in locomotion on foot
InactiveUS6898550B1Physical therapies and activitiesTime indicationPhysical medicine and rehabilitationSimulation
Owner:NIKE INC +1
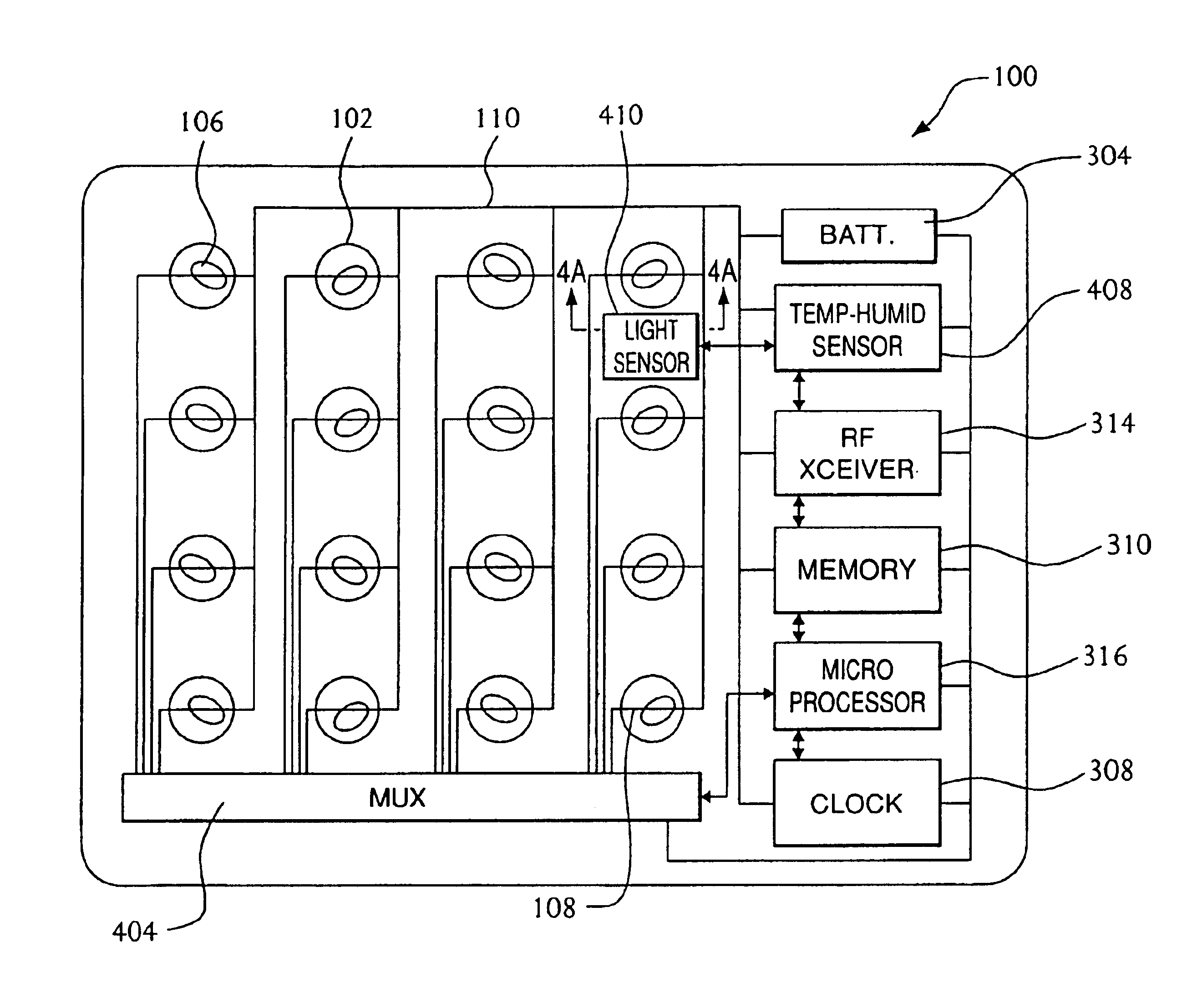
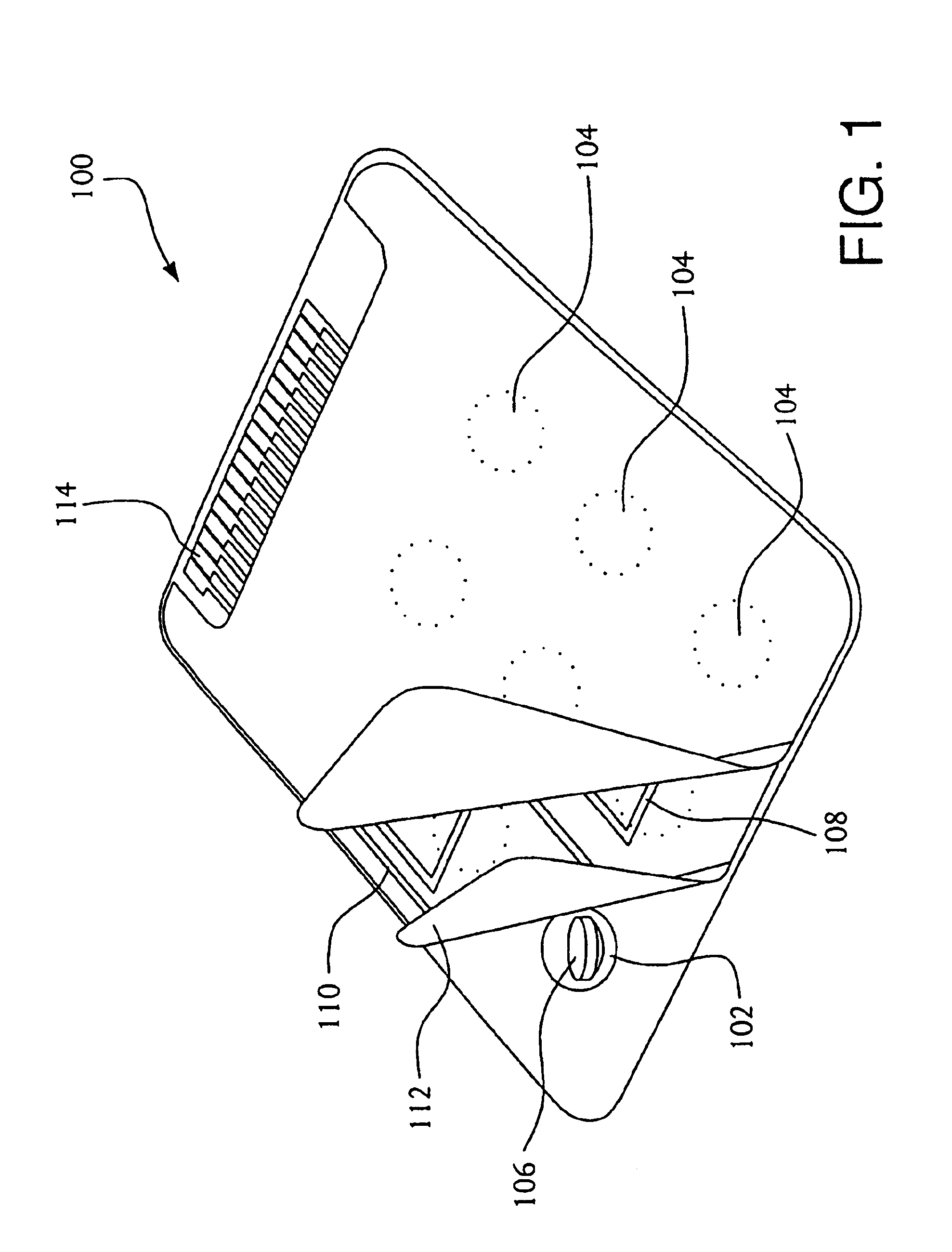
Diagnostic radio frequency identification sensors and applications thereof
ActiveUS20060290496A1Low costDevices with bluetooth interfacesBurglar alarm mechanical actuationPower sensorPoint of care
An integrated passive wireless chip diagnostic sensor system is described that can be interrogated remotely with a wireless device such as a modified cell phone incorporating multi-protocol RFID reader capabilities (such as the emerging Gen-2 standard) or Bluetooth, providing universal easy to use, low cost and immediate quantitative analyses, geolocation and sensor networking capabilities to users of the technology. The present invention can be integrated into various diagnostic platforms and is applicable for use with low power sensors such as thin films, MEMS, electrochemical, thermal, resistive, nano or microfluidic sensor technologies. Applications of the present invention include on-the-spot medical and self-diagnostics on smart skin patches, Point of Care (POC) analyses, food diagnostics, pathogen detection, disease-specific wireless biomarker detection, remote structural stresses detection and sensor networks for industrial or Homeland Security using low cost wireless devices such as modified cell phones.
Owner:ALTIVERA
System and method of controlling an HVAC system
A system and method manage delivery of energy from a distribution network to one or more sites. Each site has at least one device coupled to the distribution network. The at least one device controllably consumes energy. The system includes a node and a control system. The node is coupled to the at least one device for sensing and controlling energy delivered to the device. A control system is coupled to the node and distribution network for delivery to the node at least one characteristic of the distribution network. The node for controls the supply of energy to the device as a function of the at least one characteristic.
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
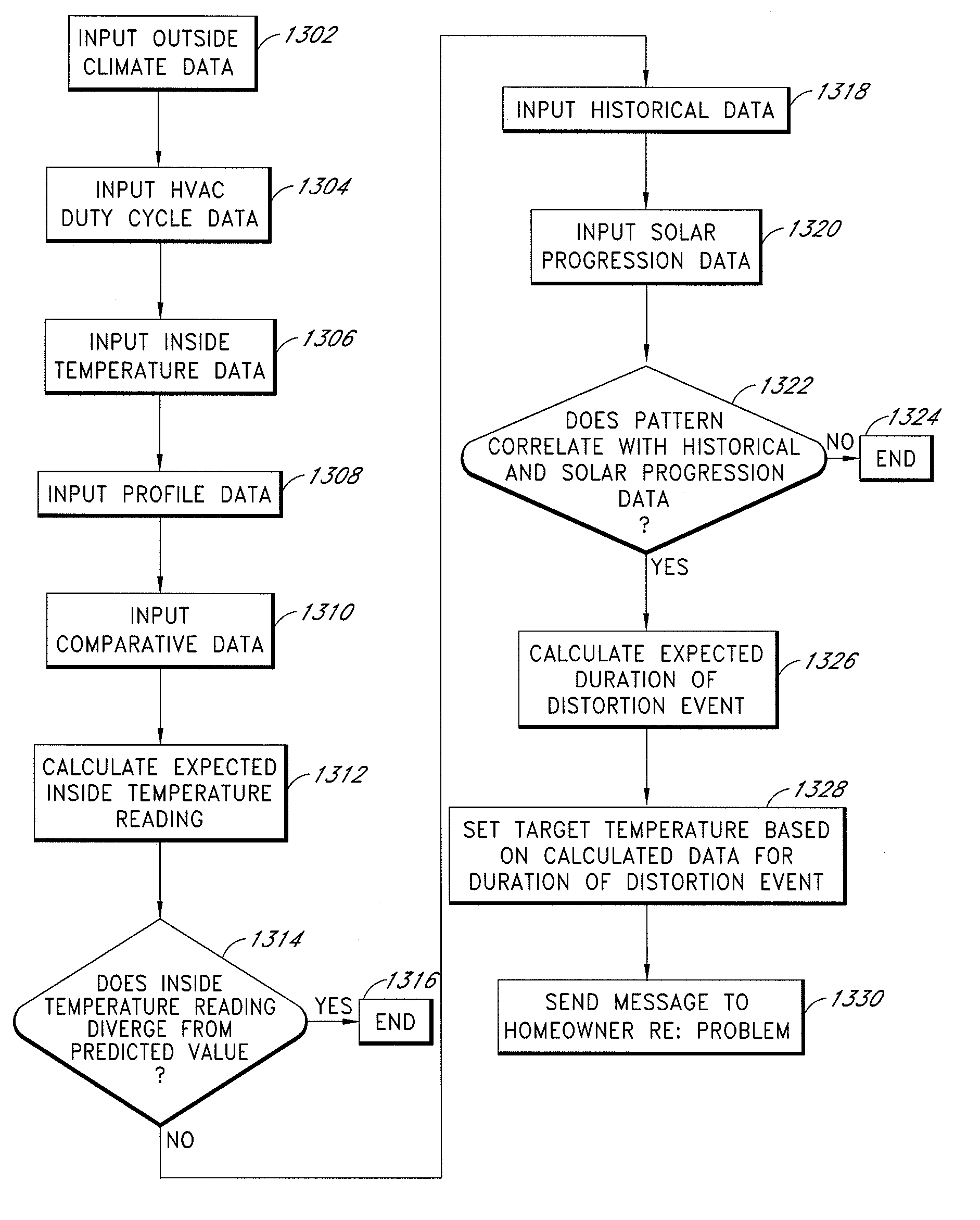
System and method for evaluating changes in the efficiency of an HVAC system
ActiveUS8019567B2Improve comfortReduce energy useTime indicationSpace heating and ventilationControl systemEngineering
The invention comprises systems and methods for evaluating changes in the operational efficiency of an HVAC system over time. The climate control system obtains temperature measurements from at least a first location conditioned by the climate system, and status of said HVAC system. One or more processors receives measurements of outside temperatures from at least one source other than said HVAC system and compares said temperature measurements from said first location with expected temperature measurements. The expected temperature measurements are based at least in part upon past temperature measurements.
Owner:ECOFACTOR
Product integrity systems and associated methods
InactiveUS7174277B2Soften contactAvoid breakingForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesLinear/angular speed measurementAccelerometerData shipping
System determines integrity of a product through shipment and has: (a) plurality of identical smart sensors for direct attachment to different locations on the product and (b) interrogating device, the identical smart sensors monitoring like environmental condition of the product during shipment and wirelessly communicating data about the environmental condition to the interrogating device during or after shipment, the interrogating device communicating the environmental condition over a network, wherein the identical smart sensors comprise an accelerometer and the environmental condition comprises acceleration. Method establishes product integrity after shipment from first location to second location by: attaching plurality of identical smart sensors directly to product at first location; monitoring environmental condition of product via the identical smart sensors during shipment; wirelessly communicating the environmental condition from the identical smart sensors to receiver at the second location; and communicating the environmental condition from the receiver to a third location.
Owner:TVIPR
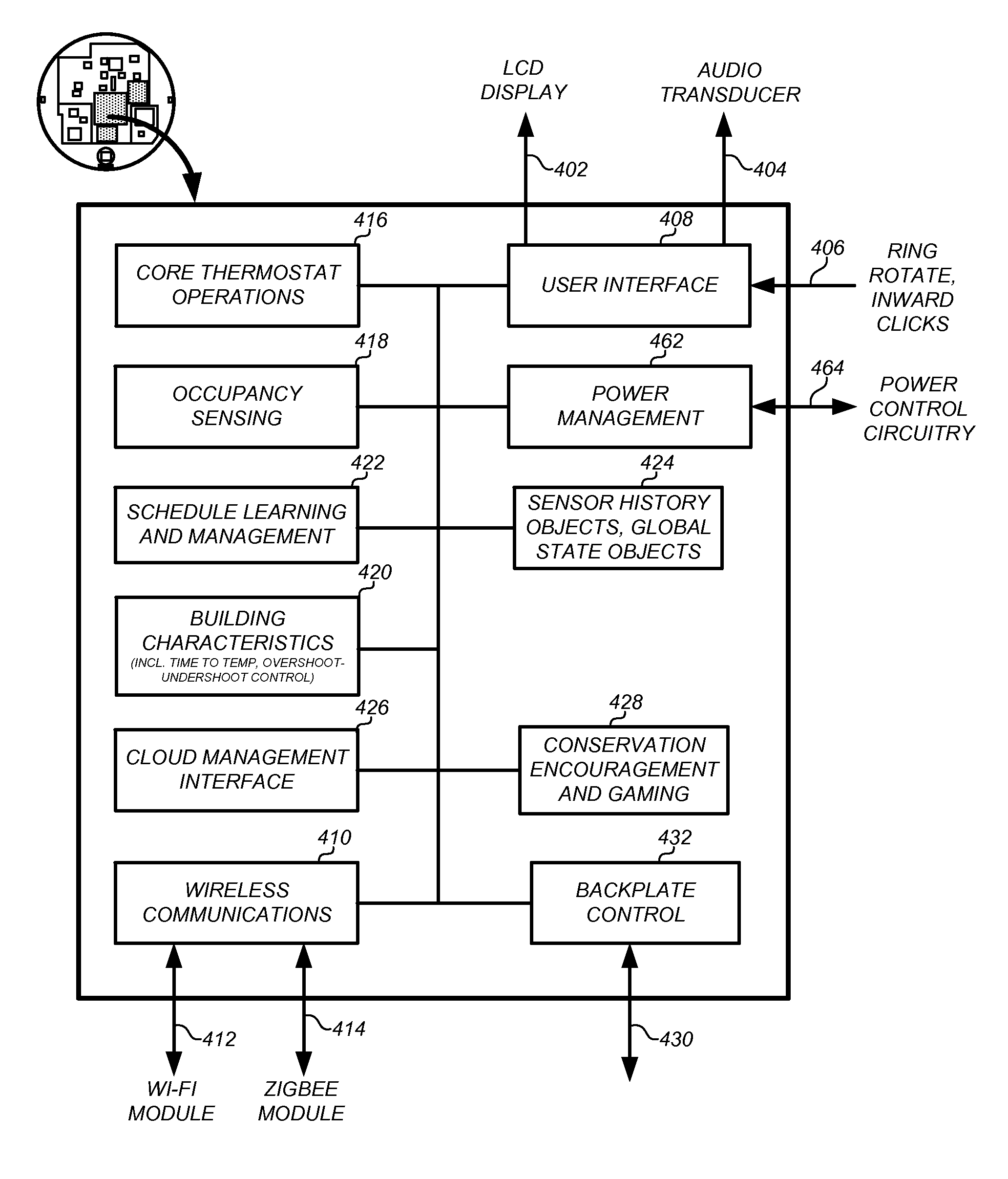
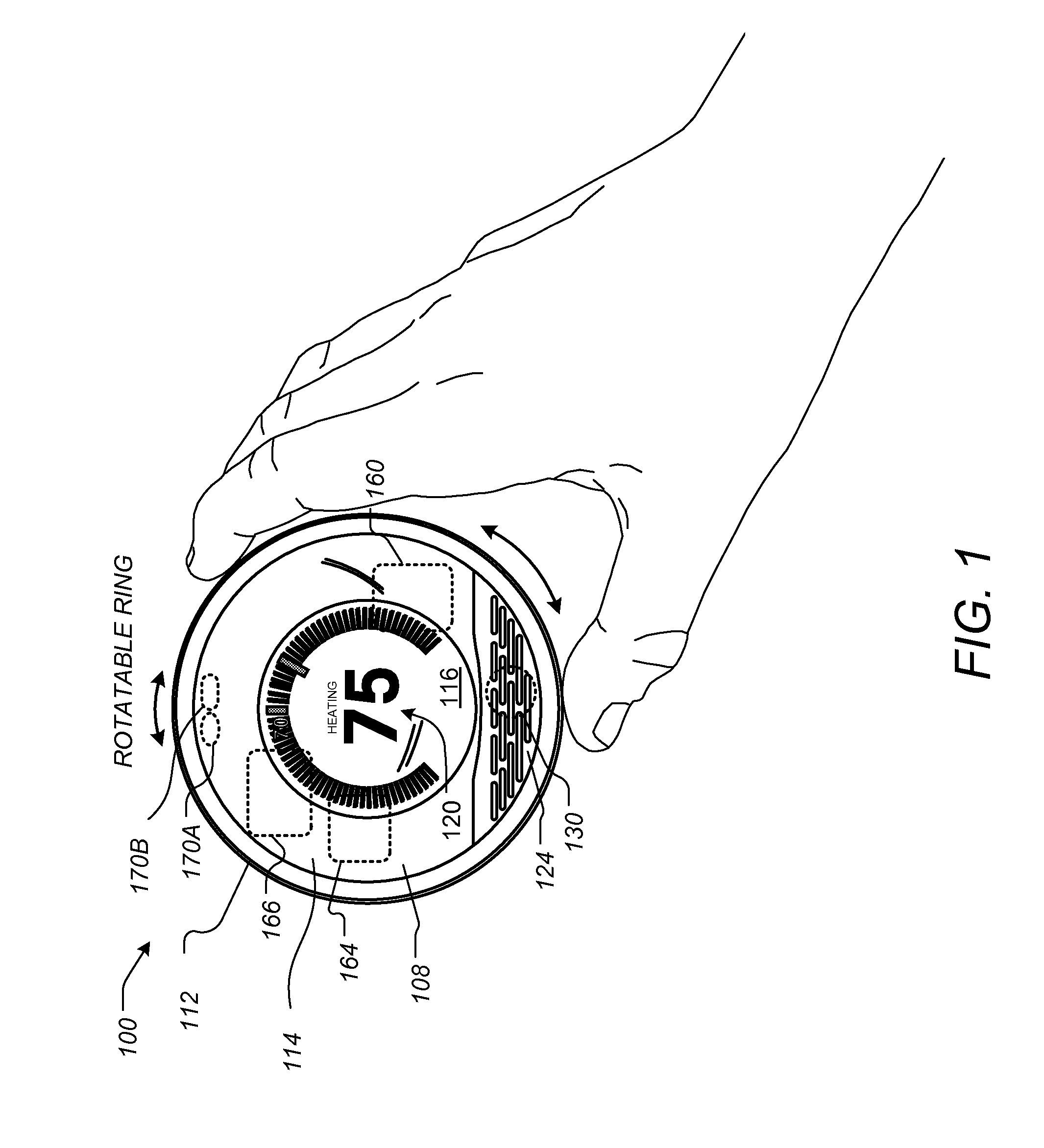
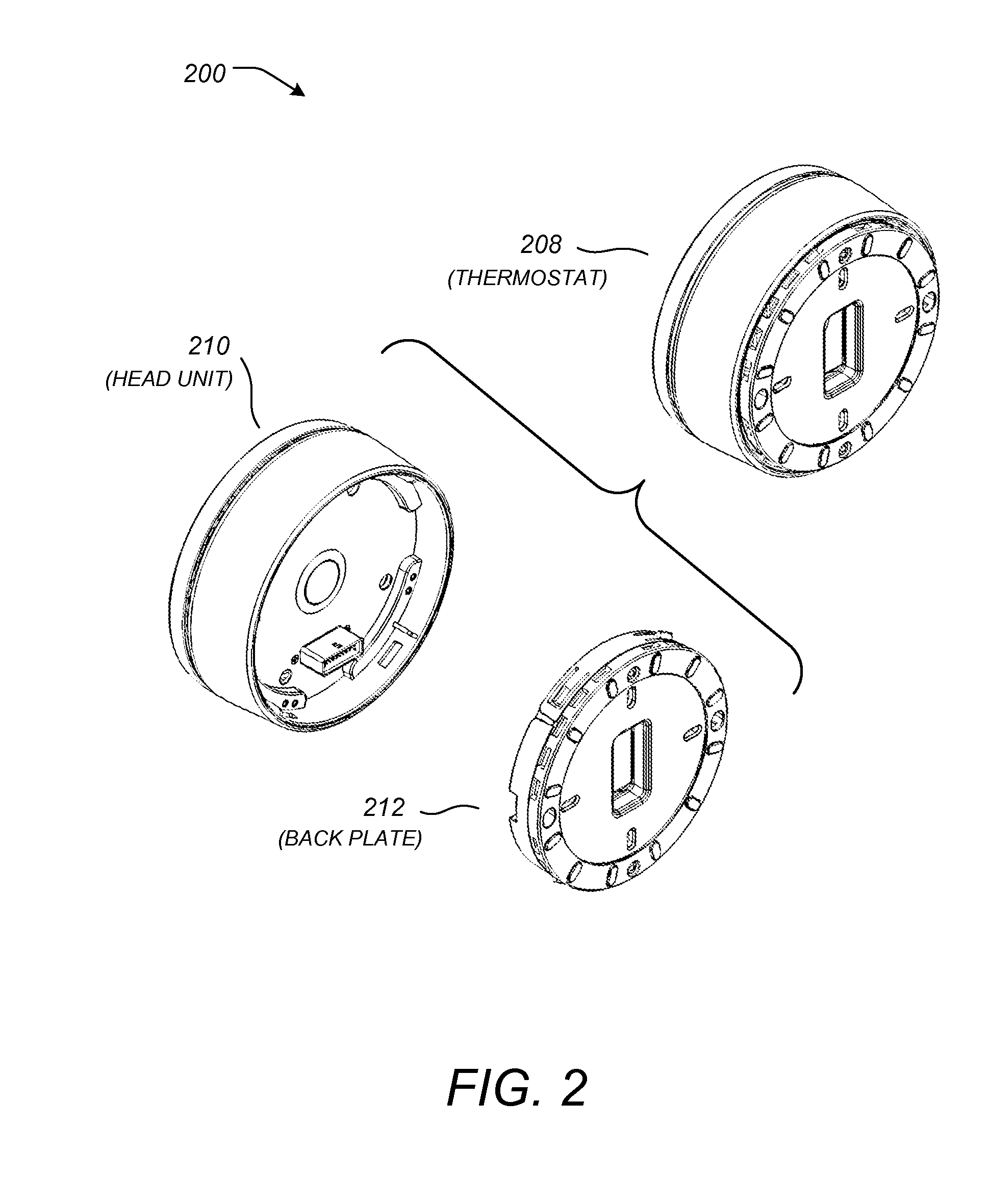
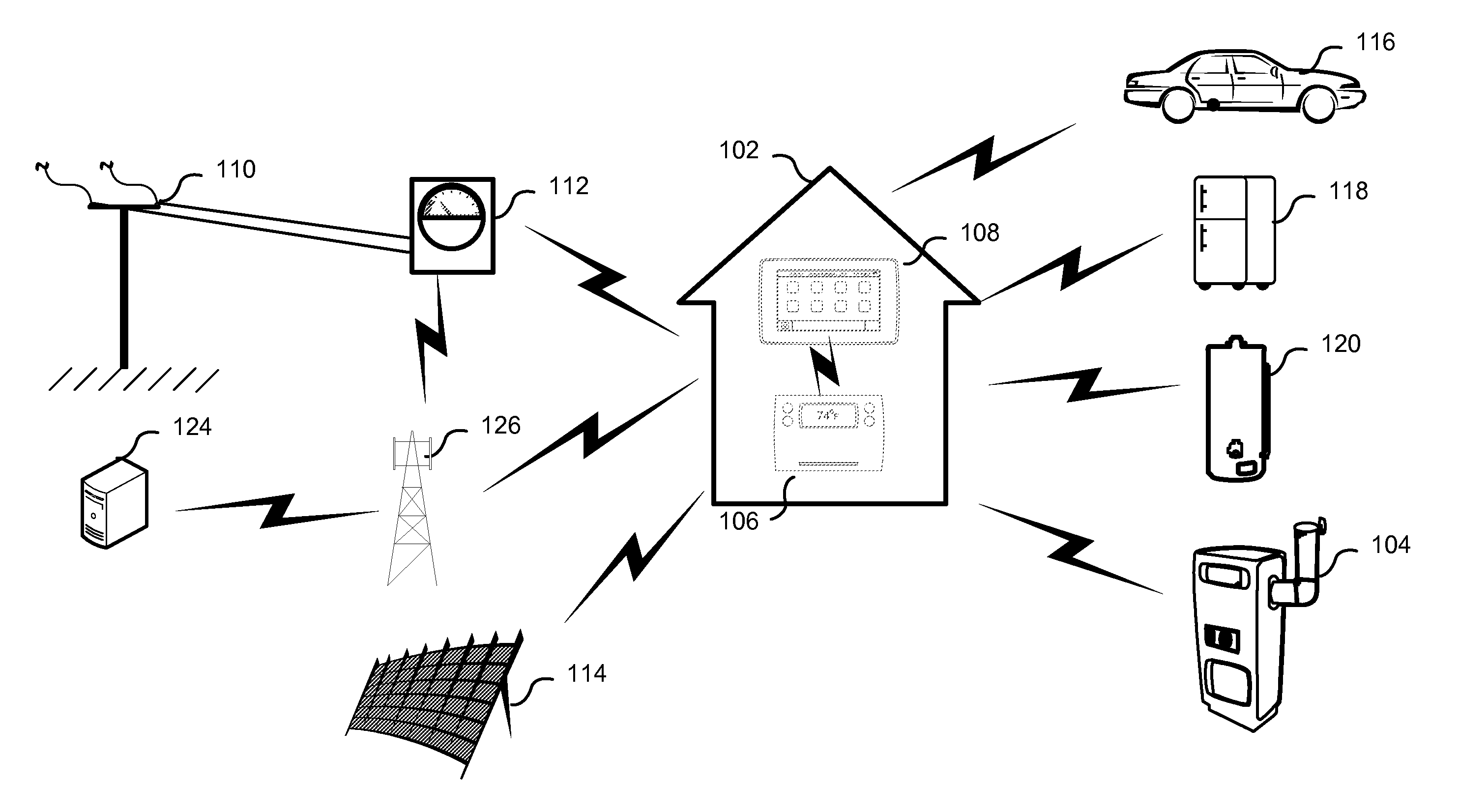
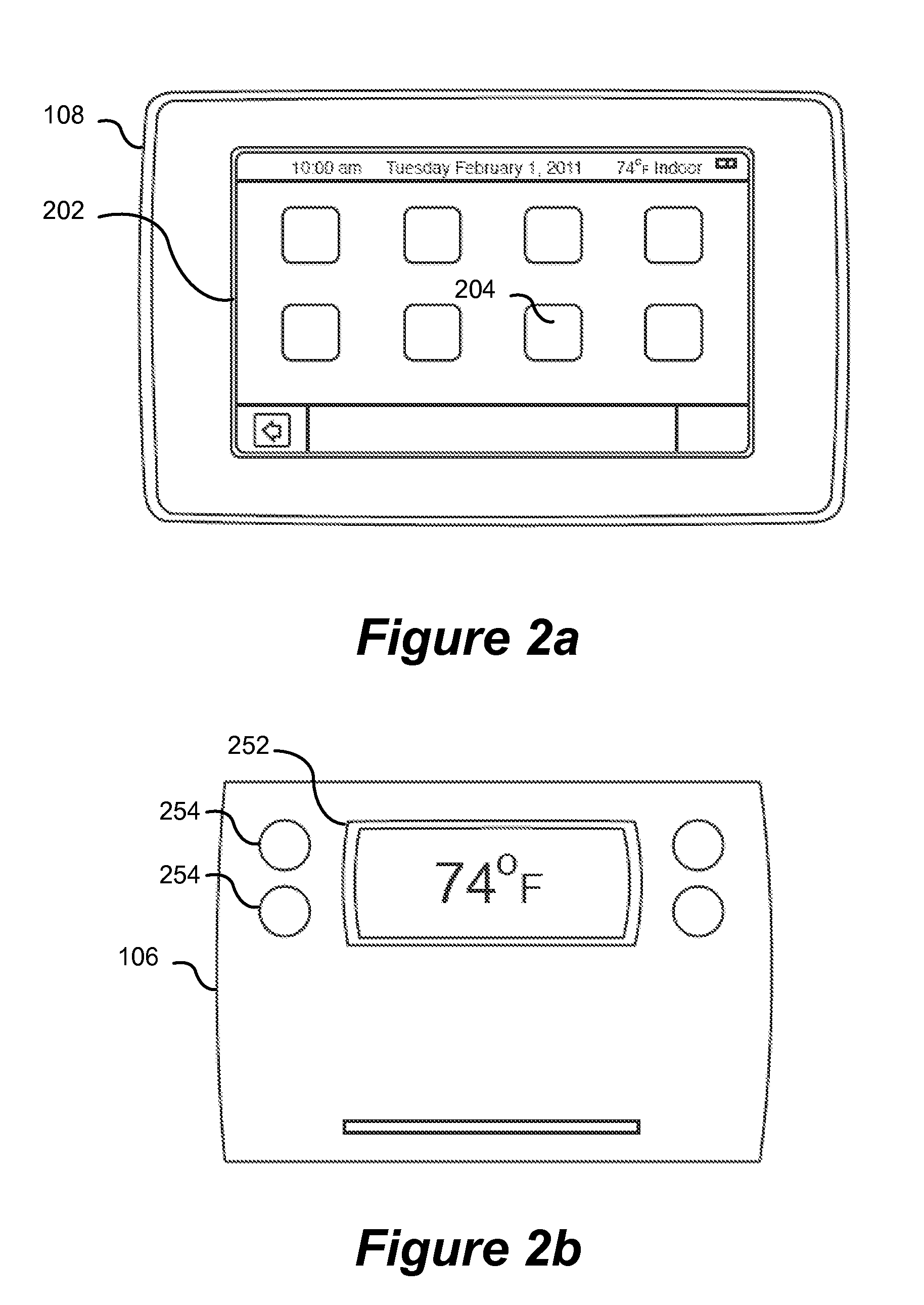
User-friendly, network connected learning thermostat and related systems and methods
ActiveUS20130173064A1Improve energy efficiencyLarge energy expenseOptical radiation measurementSpace heating and ventilationMicrocontrollerDisplay device
A user-friendly, network-connected learning thermostat is described. The thermostat is made up of (1) a wall-mountable backplate that includes a low-power consuming microcontroller used for activities such as polling sensors and switching on and off the HVAC functions, and (2) separable head unit that includes a higher-power consuming microprocessor, color LCD backlit display, user input devices, and wireless communications modules. The thermostat also includes a rechargeable battery and power-stealing circuitry adapted to harvest power from HVAC triggering circuits. By maintaining the microprocessor in a “sleep” state often compared to the lower-power microcontroller, high-power consuming activities, such as learning computations, wireless network communications and interfacing with a user, can be temporarily performed by the microprocessor even though the activities use energy at a greater rate than is available from the power stealing circuitry.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
System and method for calculating the thermal mass of a building
ActiveUS7848900B2Improve comfortReduce energy useSpace heating and ventilationTemperatue controlControl systemHVAC control system
Owner:ECOFACTOR
Fault diagnostics and prognostics based on distance fault classifiers
InactiveUS7188482B2Easy to interpret, calibrate and implementMaximize distanceAir-treating devicesSpace heating and ventilationOnline algorithmAir filter
The present invention is directed to a mathematical approach to detect faults by reconciling known data driven techniques with a physical understanding of the HVAC system and providing a direct linkage between model parameters and physical system quantities to arrive at classification rules that are easy to interpret, calibrate and implement. The fault modes of interest are low system refrigerant charge and air filter plugging. System data from standard sensors is analyzed under no-fault and full-fault conditions. The data is screened to uncover patterns though which the faults of interest manifest in sensor data and the patterns are analyzed and combined with available physical system information to develop an underlying principle that links failures to measured sensor responses. These principles are then translated into online algorithms for failure detection.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
System and method for calculating the thermal mass of a building
ActiveUS20100070084A1Improve comfortReduce energy useSpace heating and ventilationTemperatue controlControl systemEngineering
The invention comprises a system for calculating a value for the effective thermal mass of a building. The climate control system obtains temperature measurements from at least a first location conditioned by the climate system. One or more processors receive measurements of outside temperatures from at least one source other than the control system and compare the temperature measurements from the first location with expected temperature measurements. The expected temperature measurements are based at least in part upon past temperature measurements obtained by said HVAC control system and said outside temperature measurements. The processors then calculate one or more rates of change in temperature at said first location.
Owner:ECOFACTOR
Method and apparatus for graphical display of a condition in a building system with a mobile display unit
ActiveUS7548833B2Inflated body pressure measurementFrequency-division multiplex detailsGraphicsControl system
A method and apparatus uses a stored model of a building system to render an image showing a condition sensed of the building control system on a mobile display unit. The mobile display unit may be wirelessly integrated into the building control system. The mobile display unit may operate based upon voice commands and / or eye tracking.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
Adjusting proximity thresholds for activating a device user interface
ActiveUS20130103207A1Optical radiation measurementSpace heating and ventilationThermostatHuman–computer interaction
A thermostat includes a user interface that is configured to operate in at least two different modes including a first mode and a second mode. The user interface may require more power when operating in the first mode than in the second mode. The thermostat also includes a plurality of sensors, including at least one sensor configured to detect a presence of a user within a proximity of the thermostat. The thermostat additionally includes a first processing function that is configured to determine a proximity profile and to cause the user interface to be in the first mode one or more sensors provides responses that match the proximity profile. The proximity profile may be computed using a history of responses from the sensors that are likely to coincide with times where users intend to view the user interface.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and apparatus for generating a building system model
ActiveUS20050278047A1Readily apparentSpace heating and ventilationTemperatue controlControl systemComputer science
A system and method for providing data to a model of a building system includes a building control system with a communications network, a control subsystem for generating module deployment data and transmitting the module deployment data over the communications network, a memory for storing a three dimensional model of at least a portion of a building and a computer. A computer program executed by the computer includes computer instructions for associating module deployment data received from the communications network with the three dimensional model and modifying the three dimensional model based upon the module deployment data.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
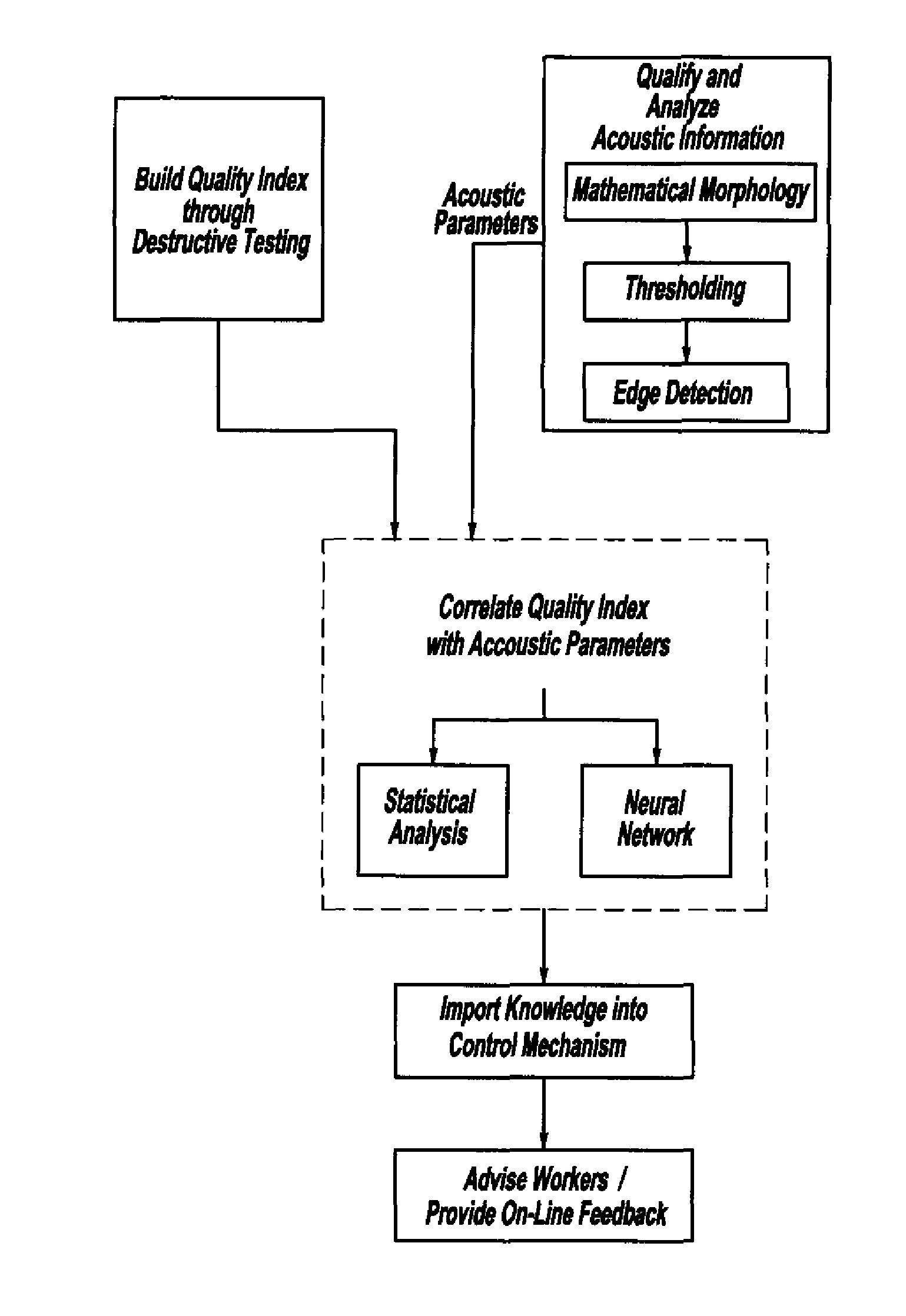
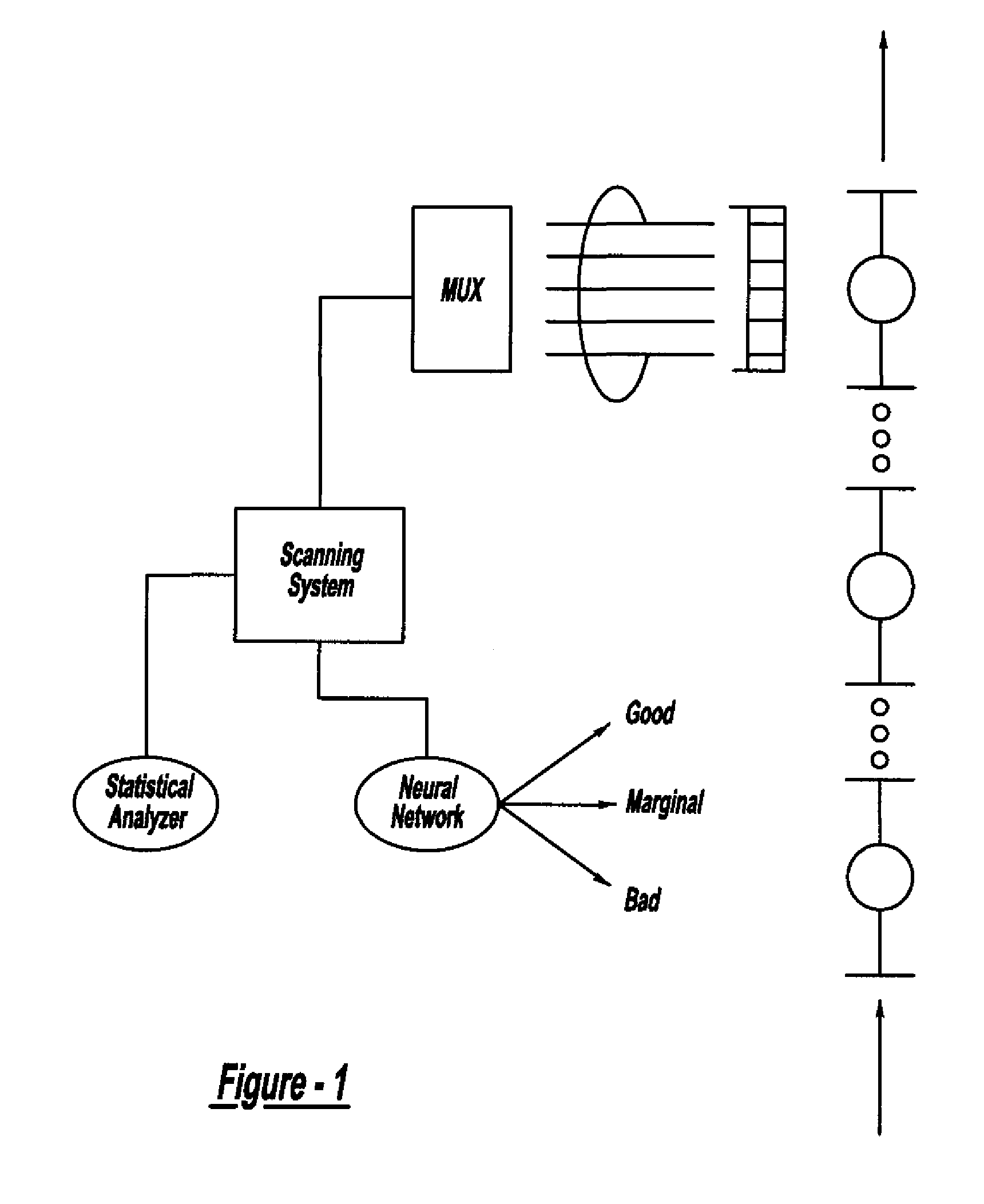
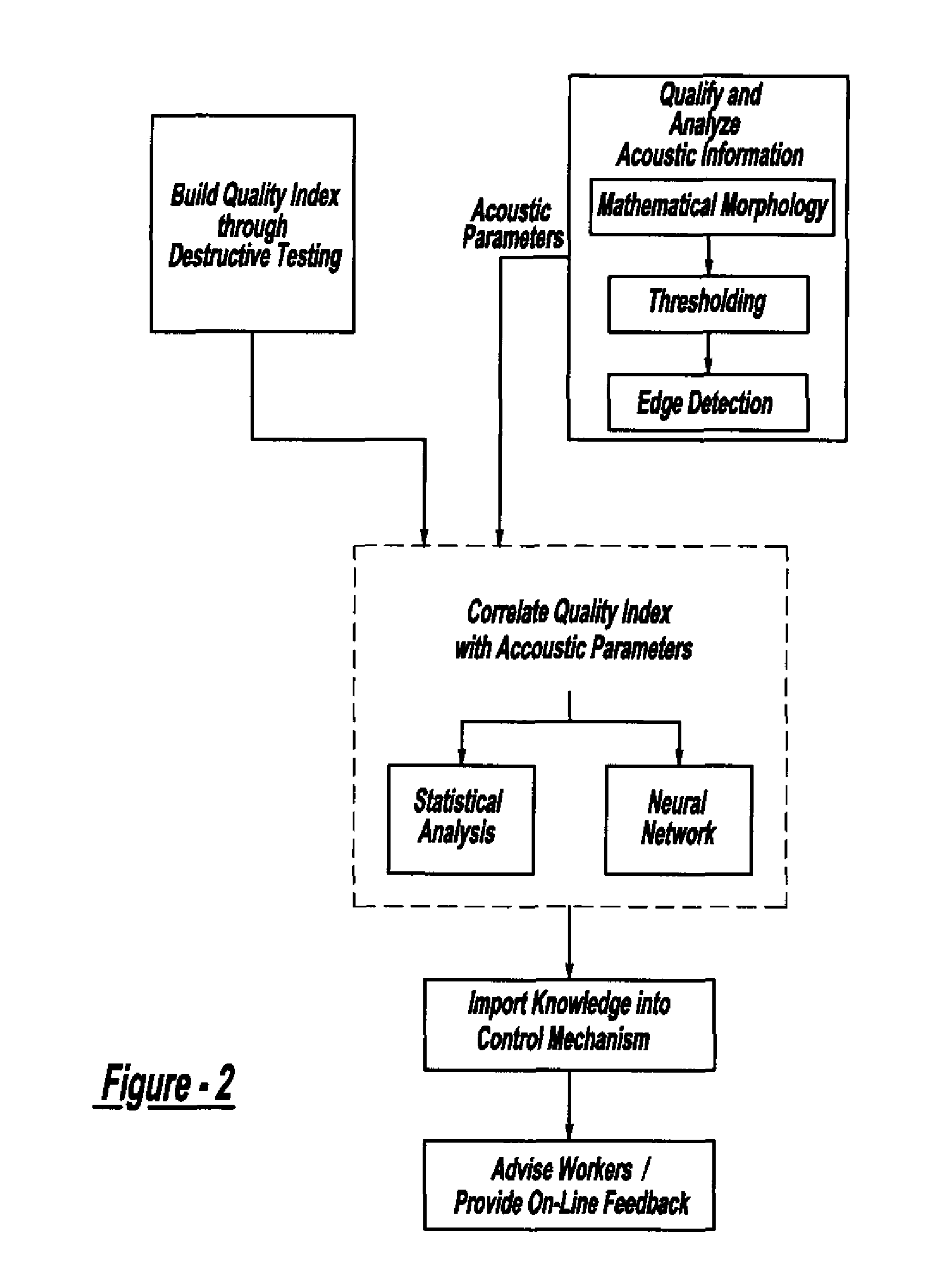
Method And System For Assessing Quality Of Spot Welds
InactiveUS20070038400A1Reduce in quantityReduce manufacturing costMultiple-port networksMagnetic property measurementsDigital dataSonification
A system and method for assessing the quality of spot weld joints between pieces of metal includes an ultrasound transducer probing a spot weld joint. The ultrasound transducer transmits ultrasonic radiation into the spot weld joint, receives corresponding echoes, and transforms the echoes into electrical signals. An image reconstructor connected to the ultrasound transducer transforms the electrical signals into numerical data representing an ultrasound image. A neural network connected to the image reconstructor analyzes the numerical data and an output system presents information representing the quality of the spot weld joint. The system is trained to assess the quality of spot weld joints by scanning a spot weld joint with an ultrasound transducer to produce the data set representing the joint; then physically deconstructing the joint to assess the joint quality.
Owner:FCA US
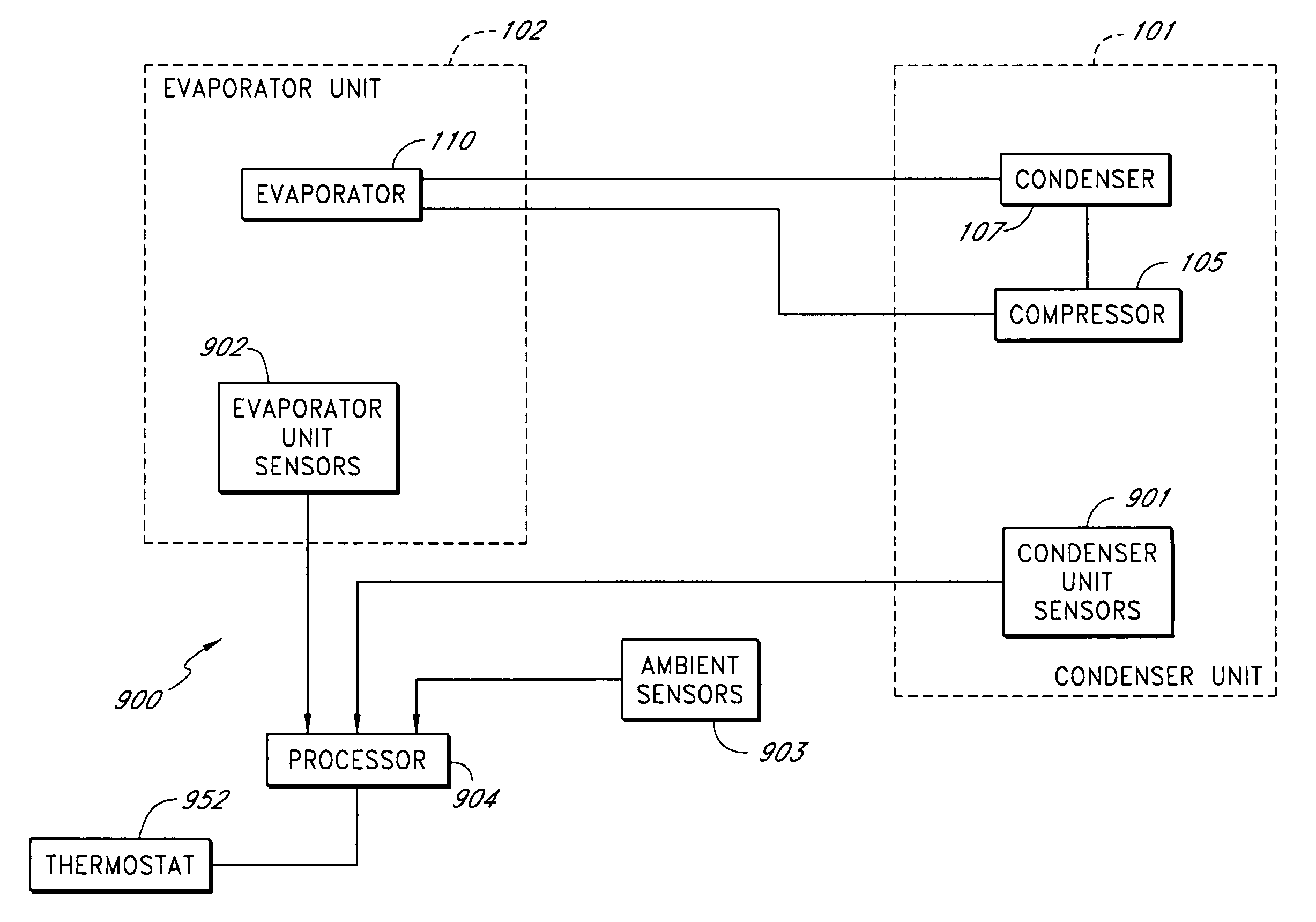
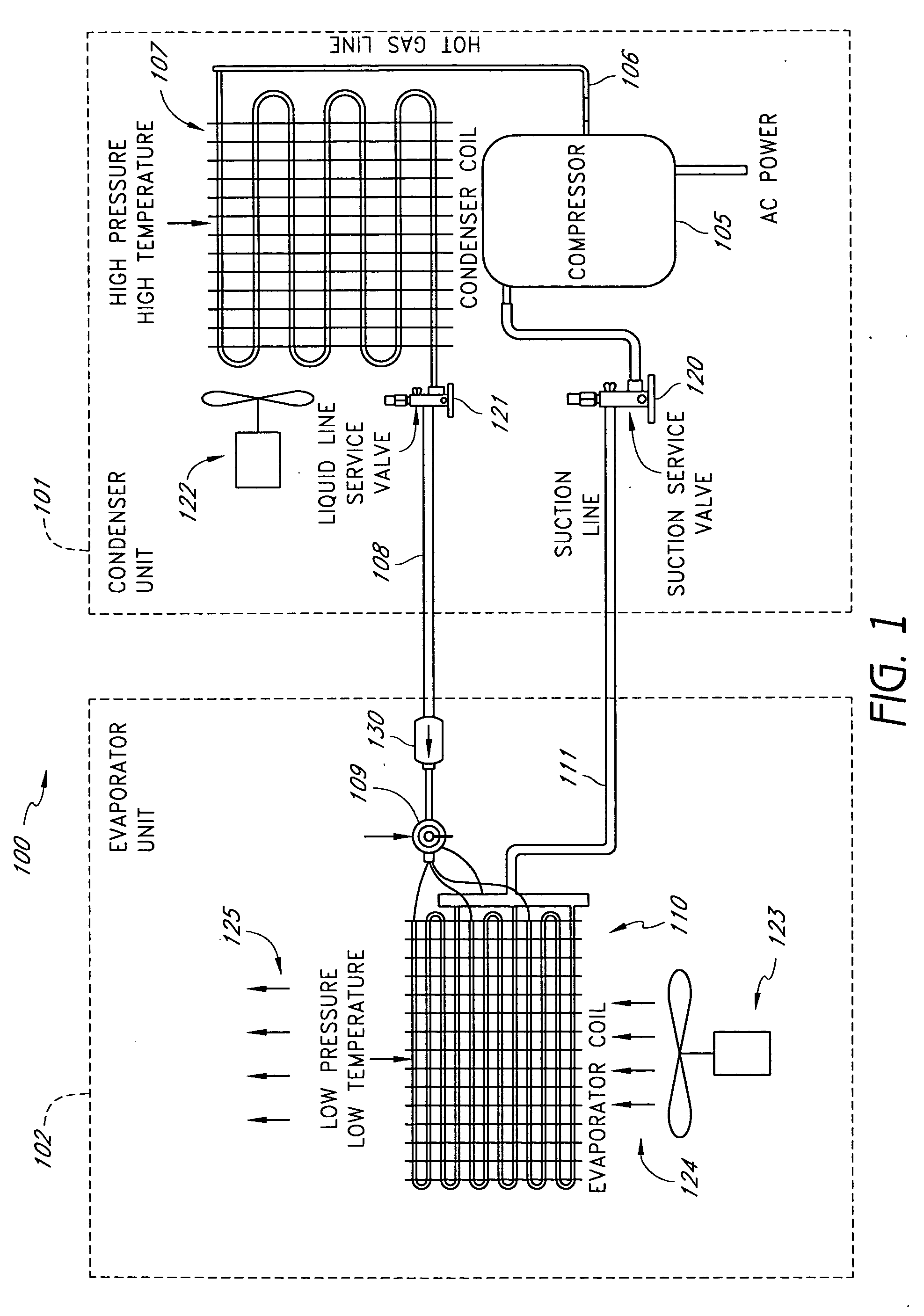
Air filter monitoring system
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:EMERSON CLIMATE TECH INC
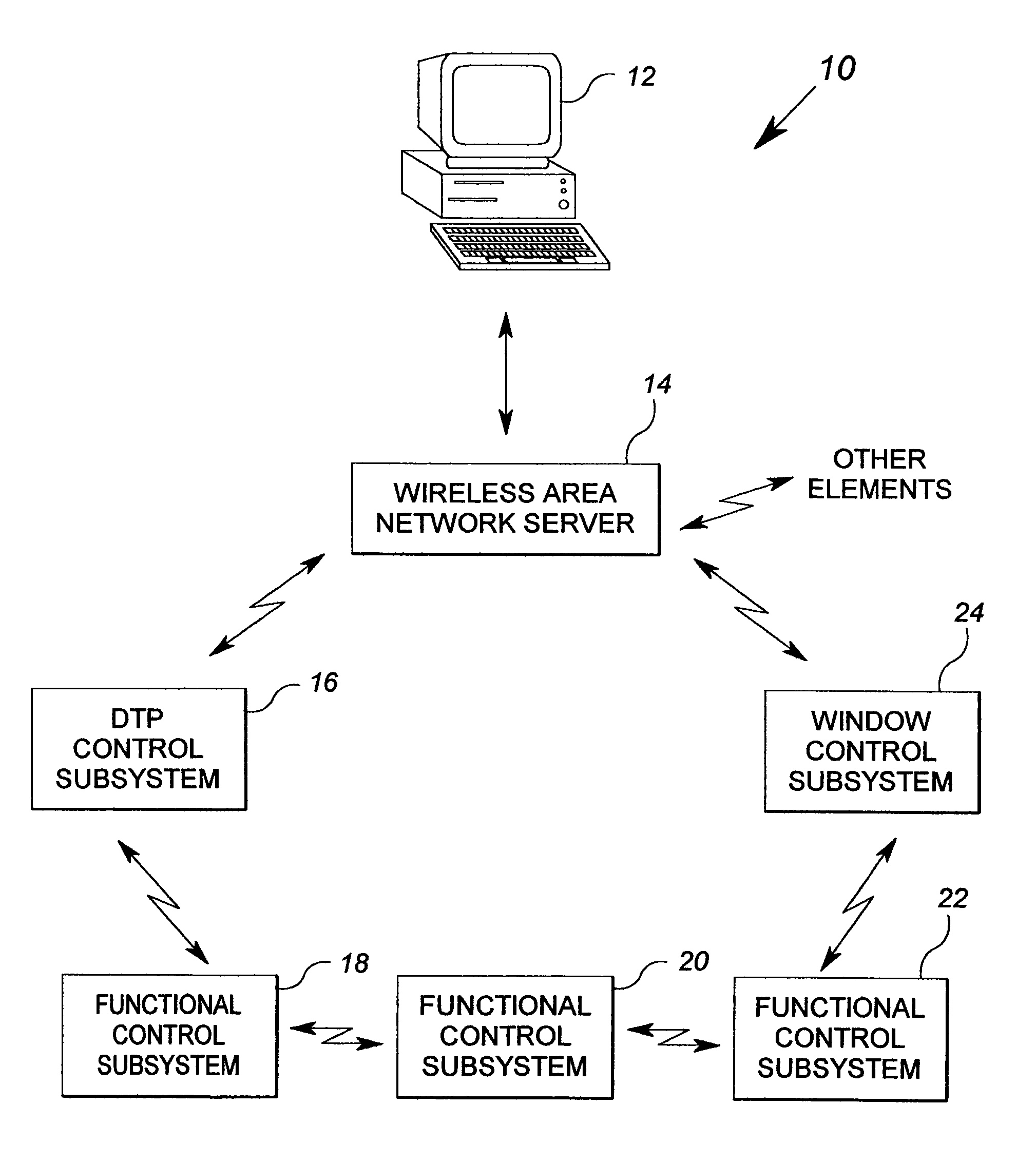
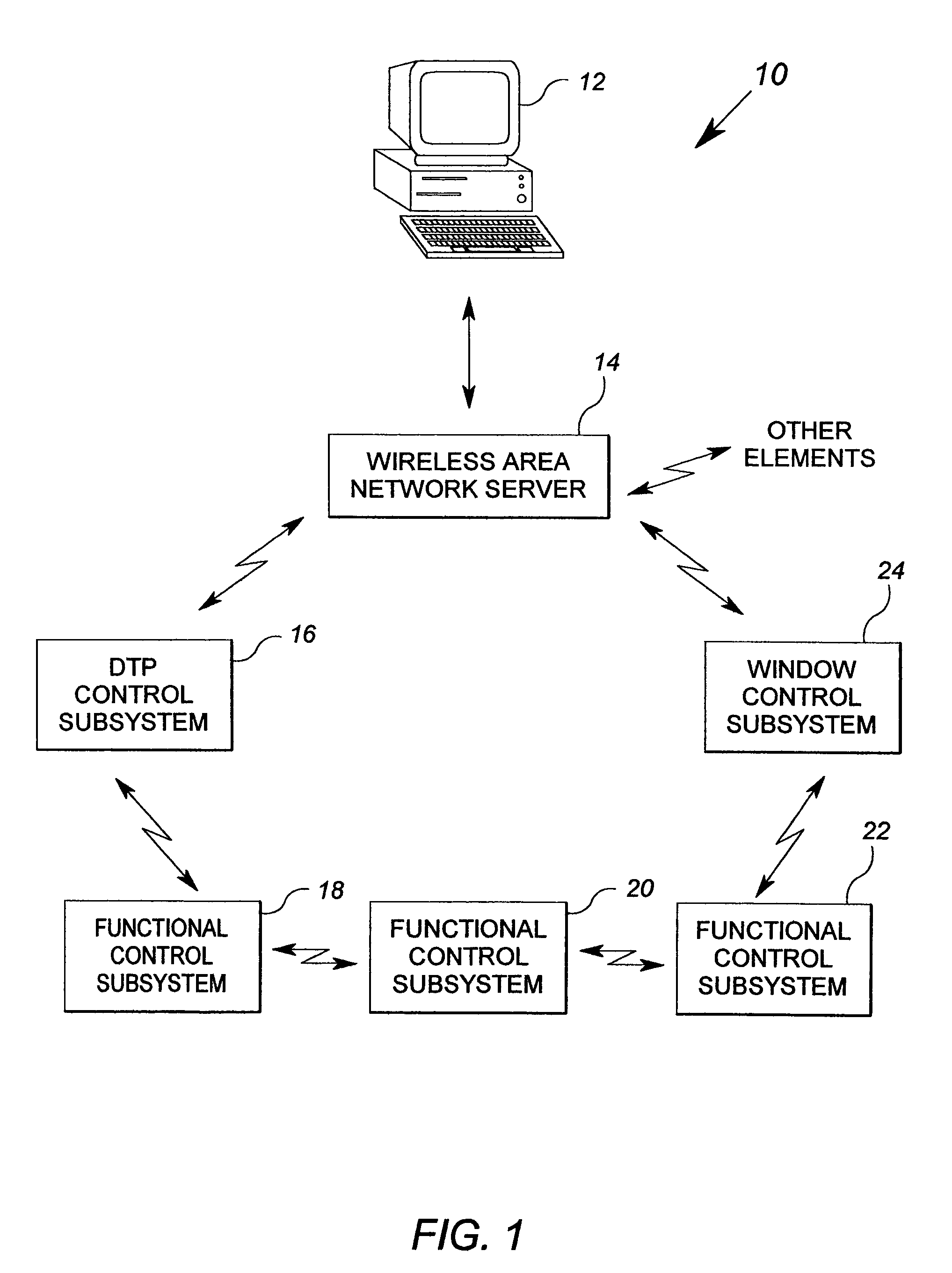
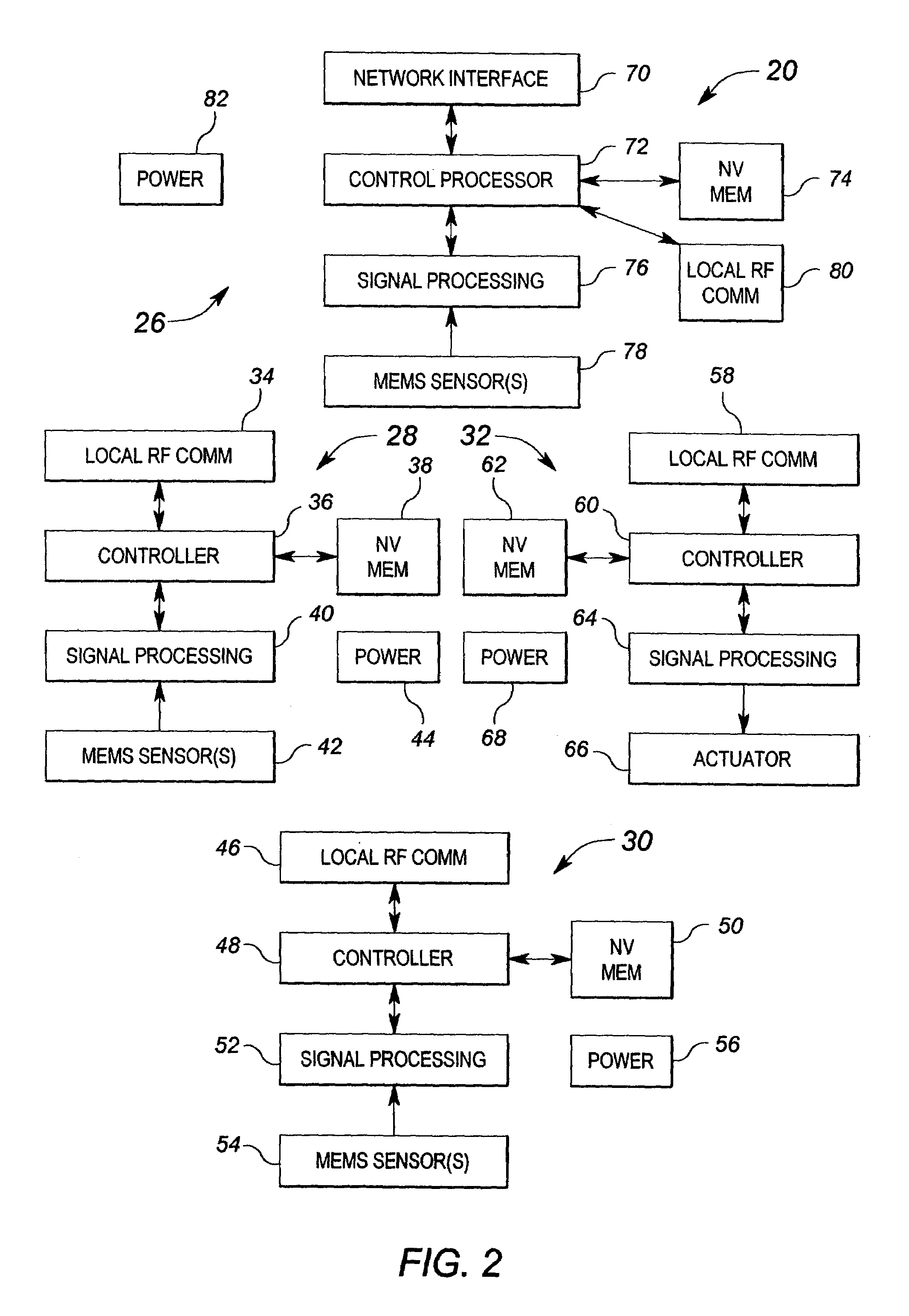
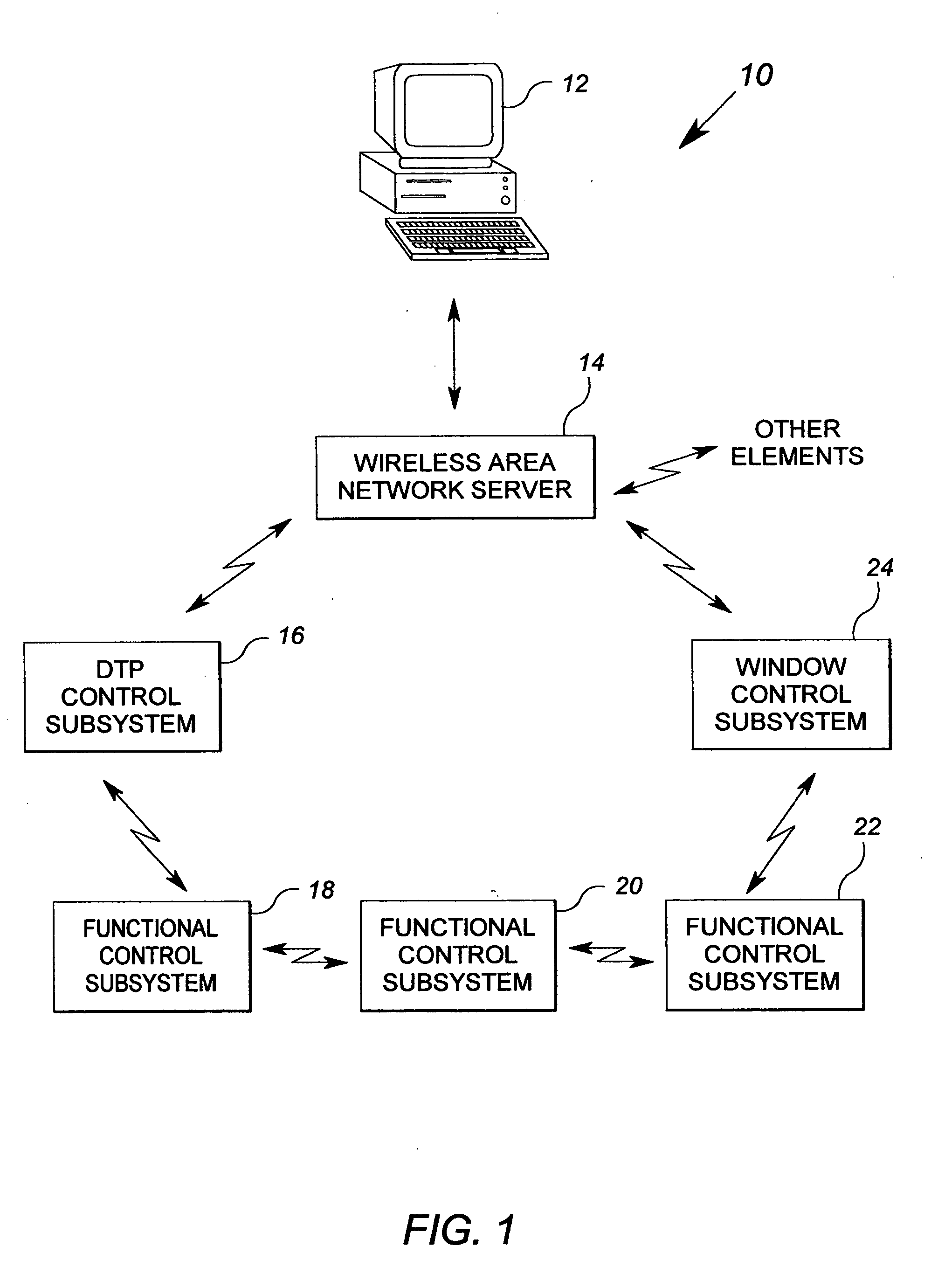
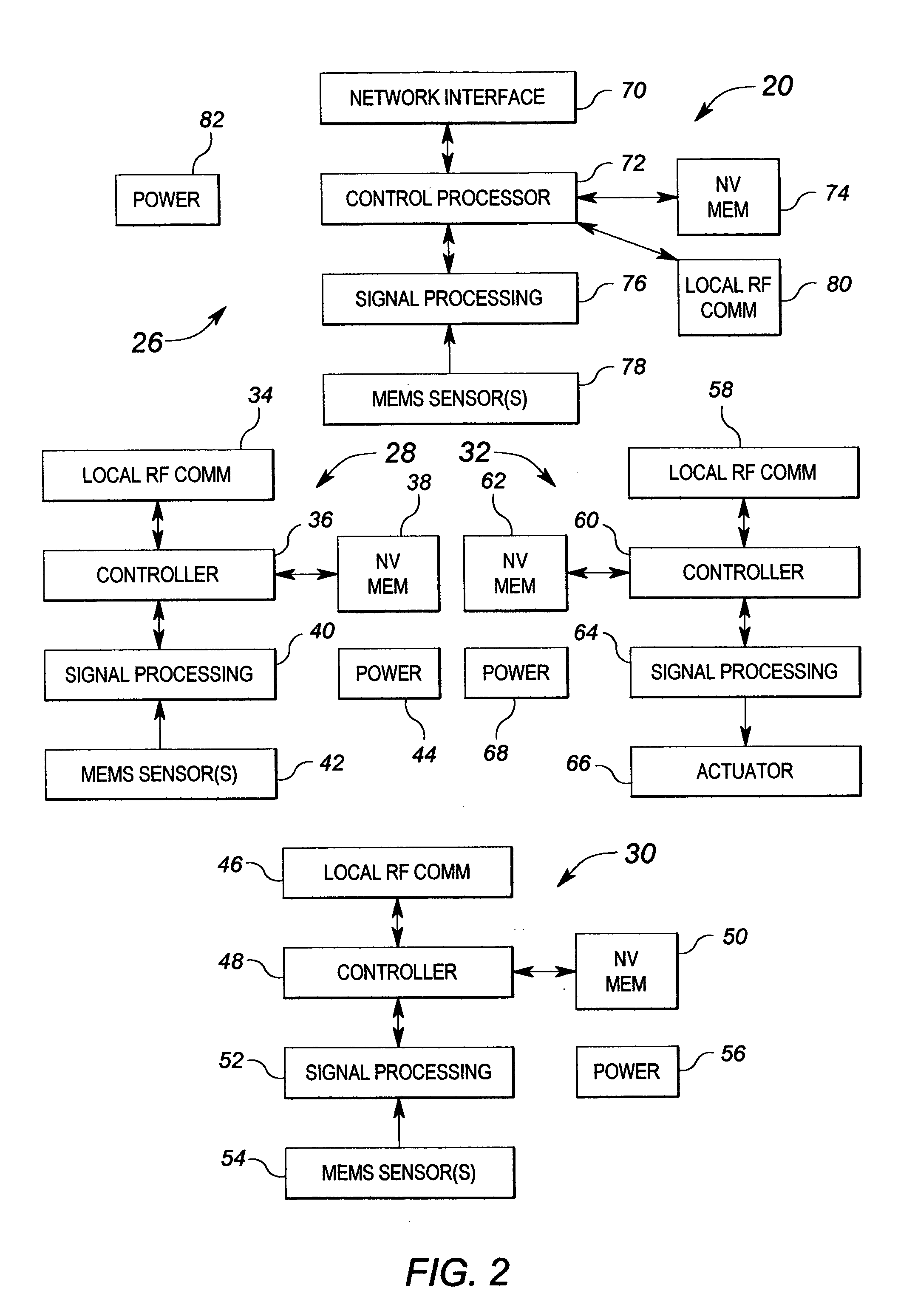
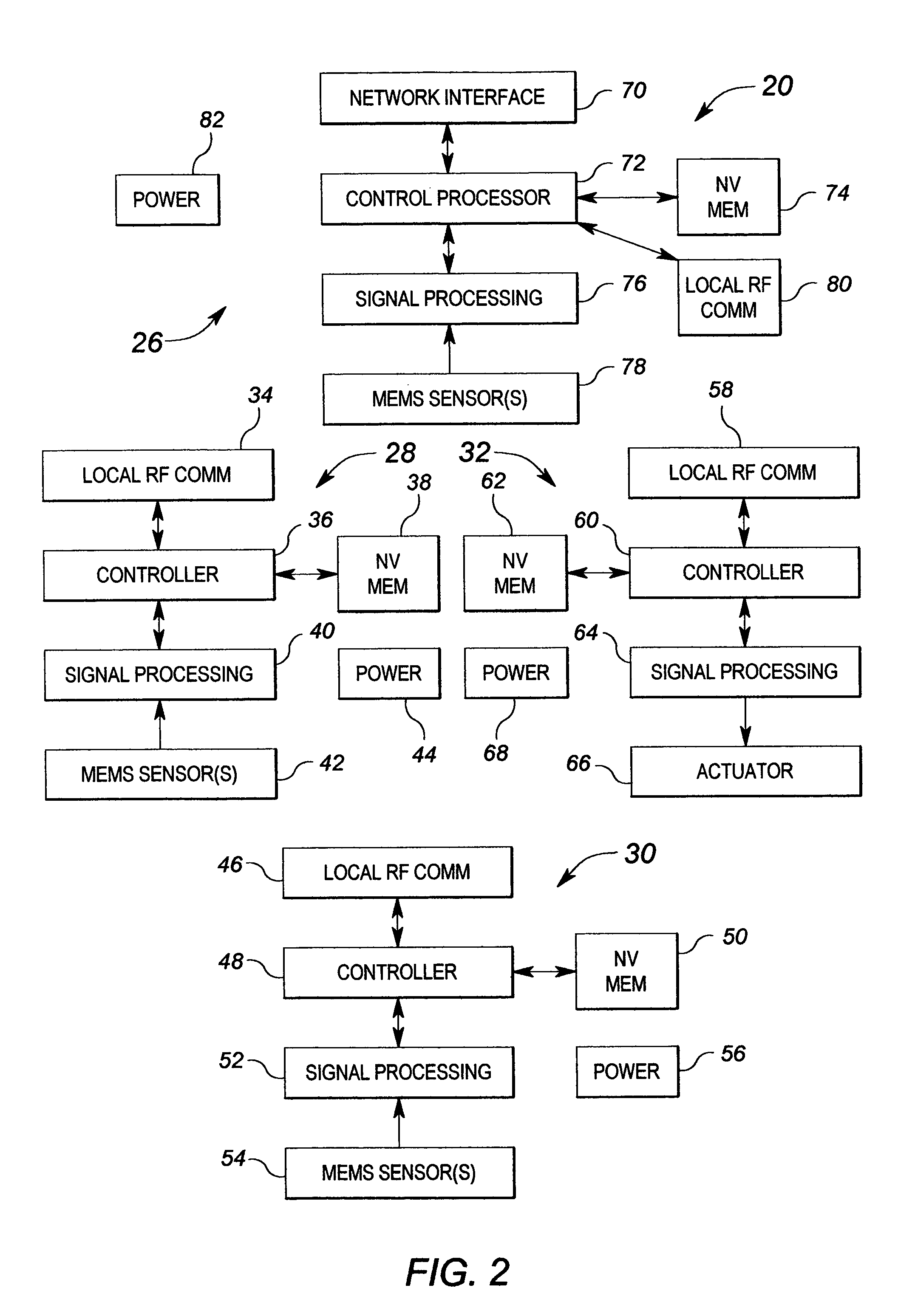
Method and apparatus for controlling building component characteristics
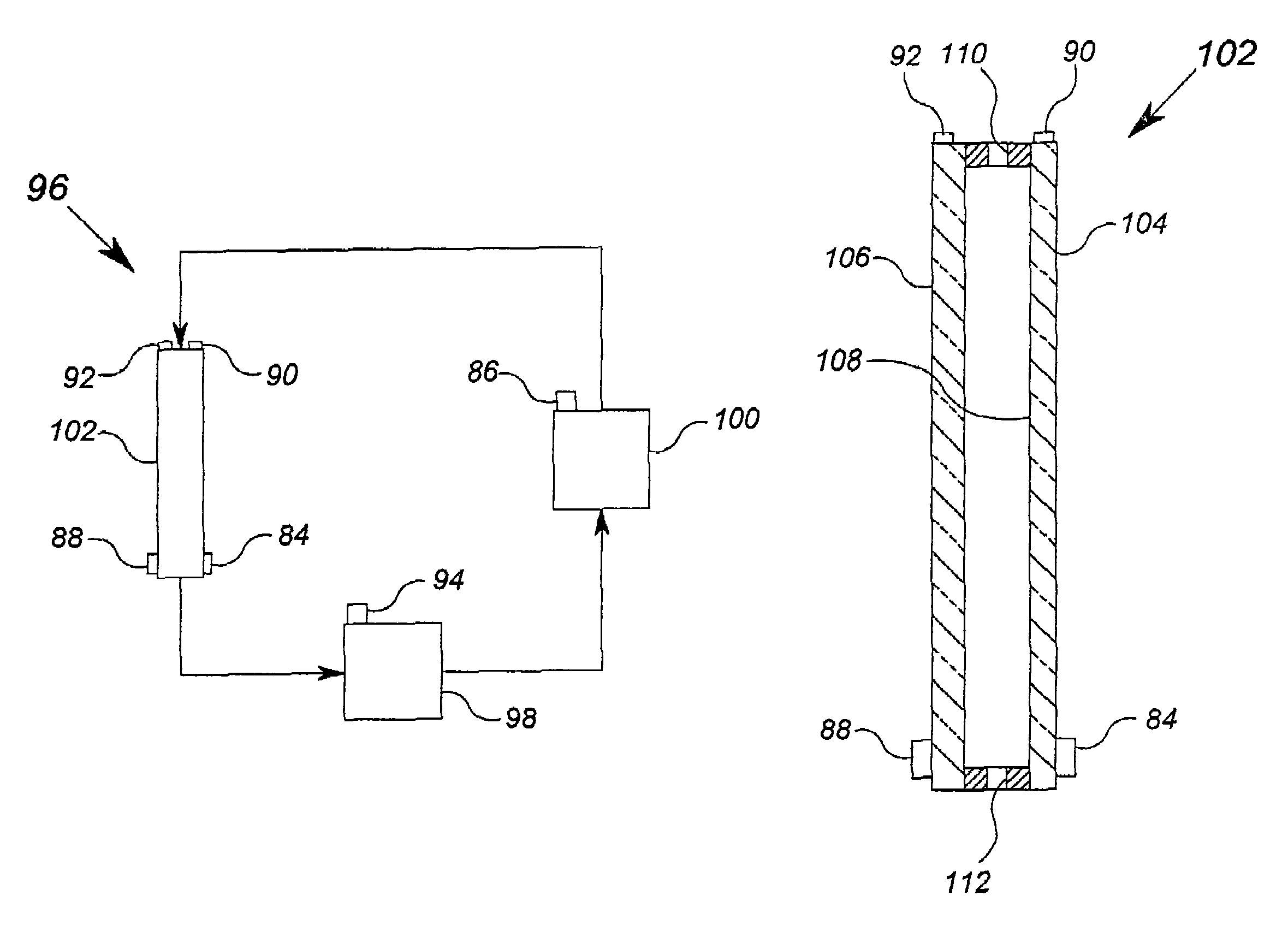
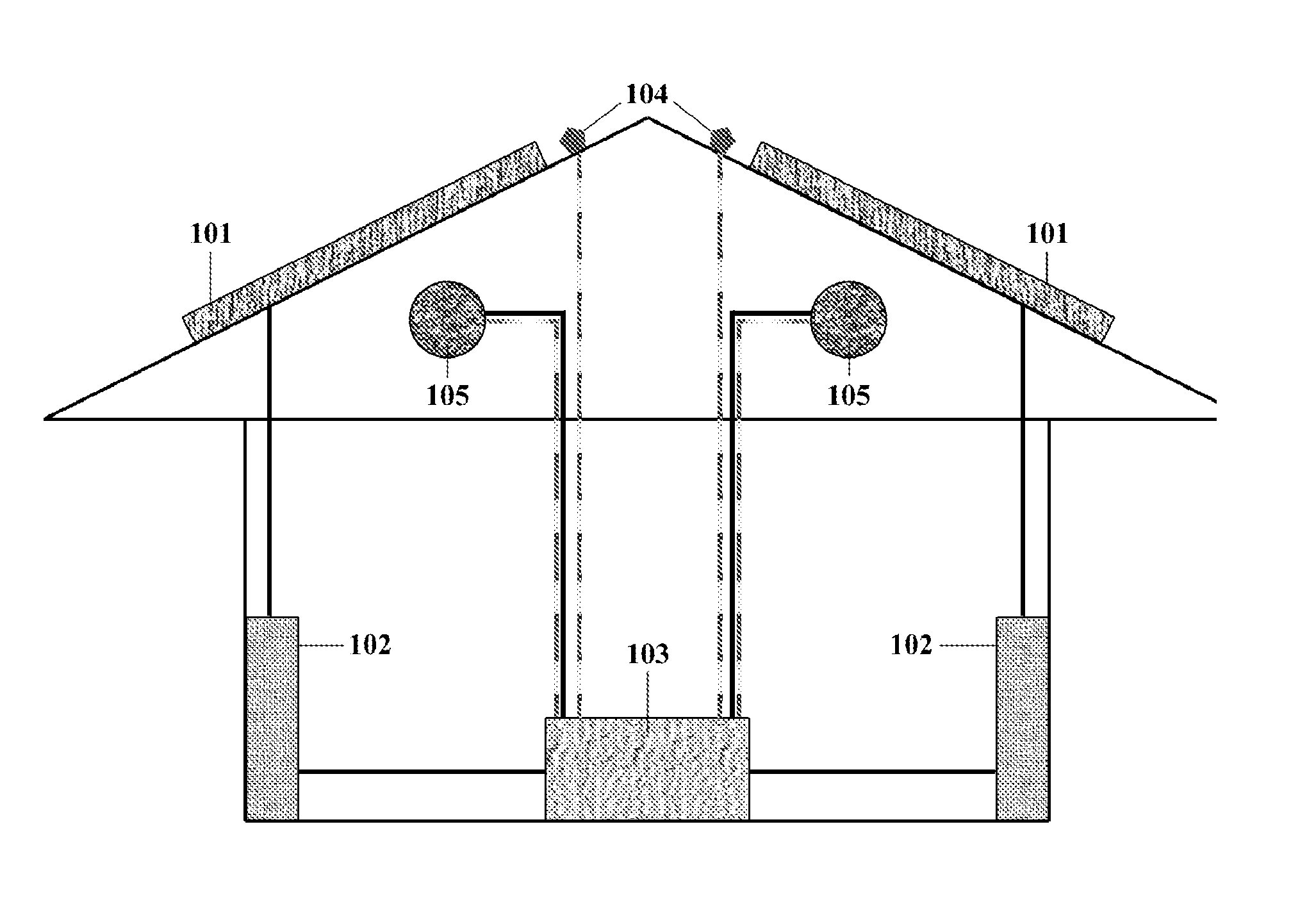
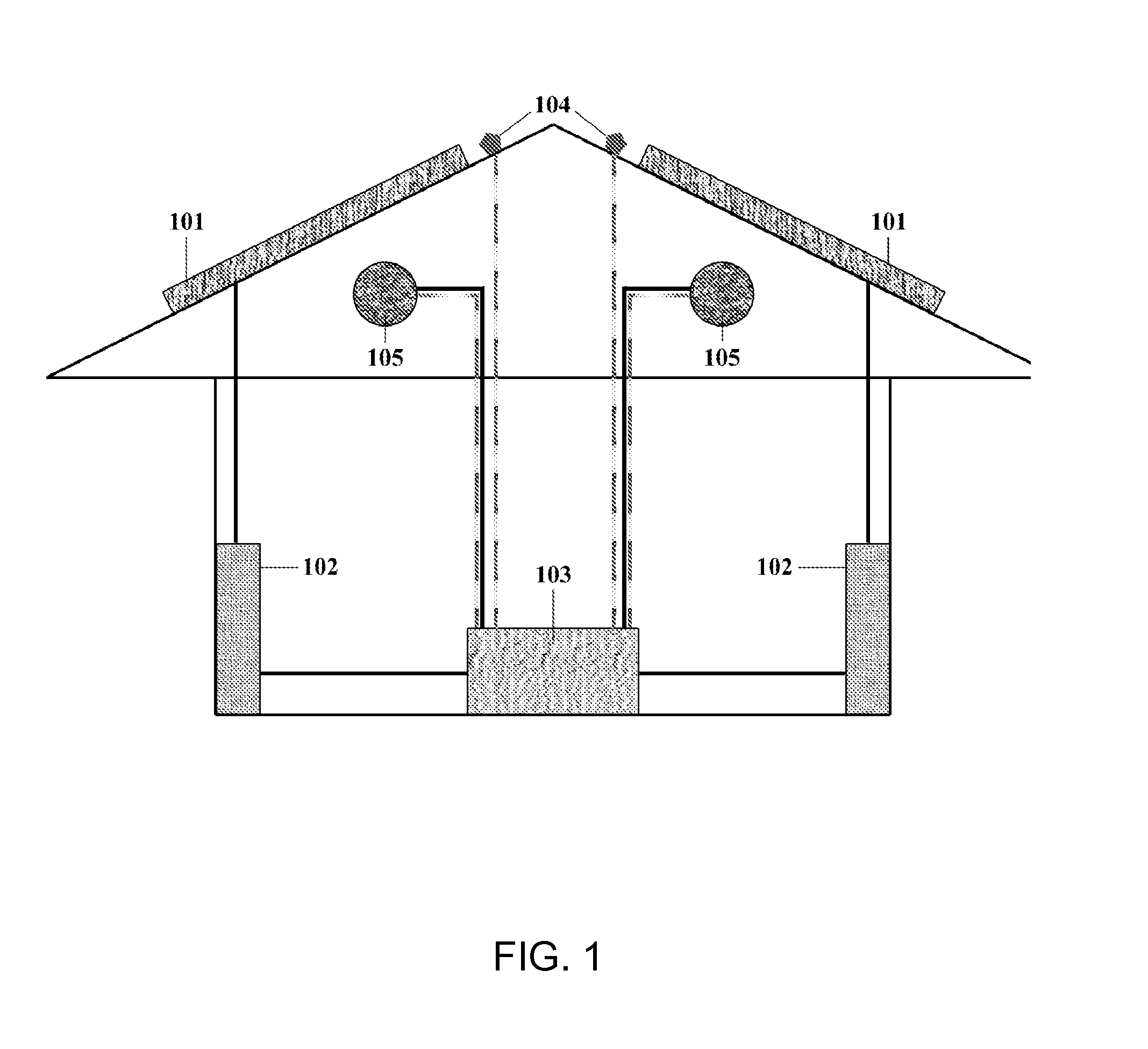
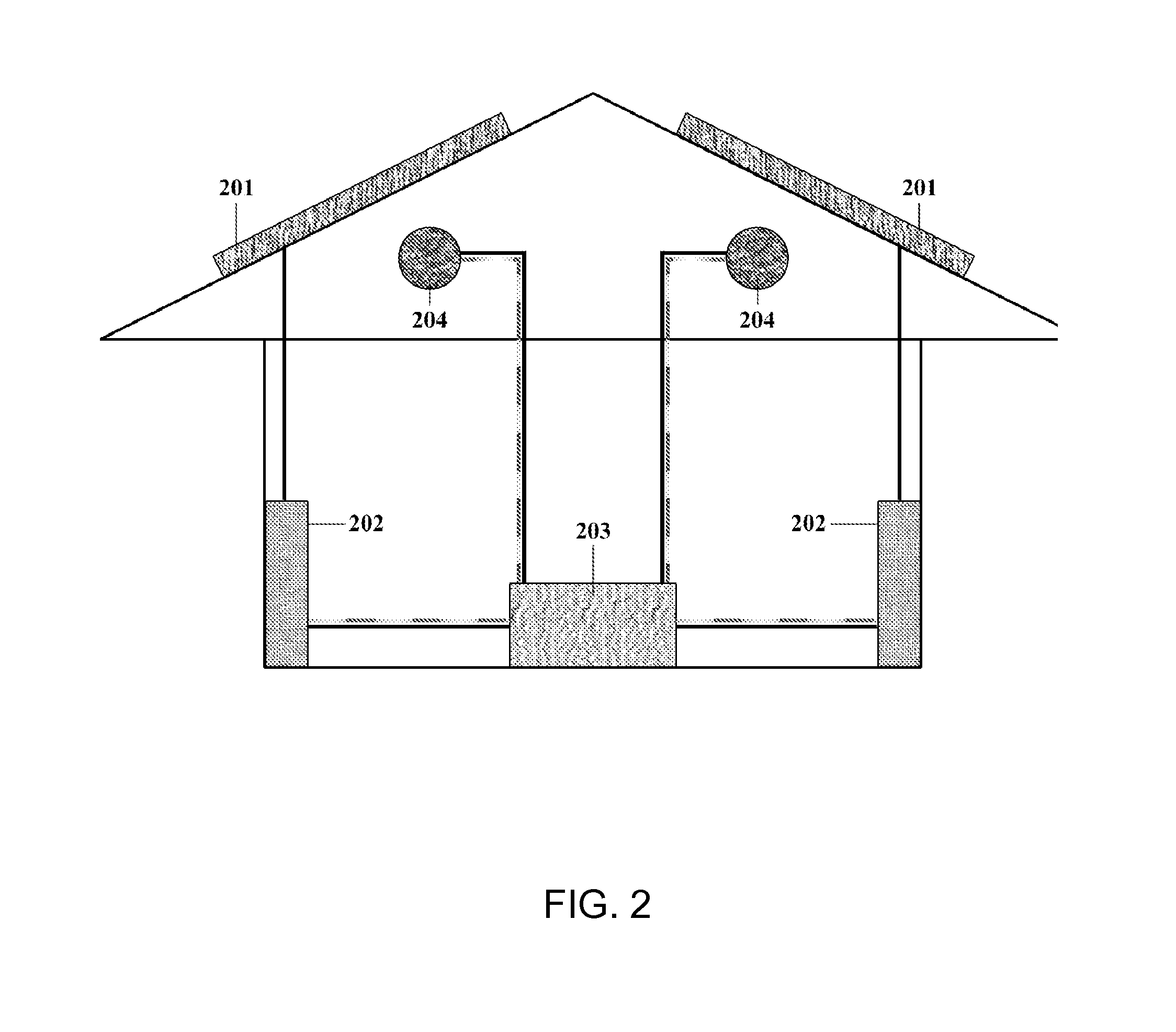
A building component system includes a building component that is controllable between a first state and a second state in response to a sensed condition. The system may include a sensor on a first side of the building component and a sensor on the second side of the building component. The building component may be a window that is controllable between an opaque state and a clear state by a micro electromechanical system (MEMS) network that senses the conditions on both sides of the window.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
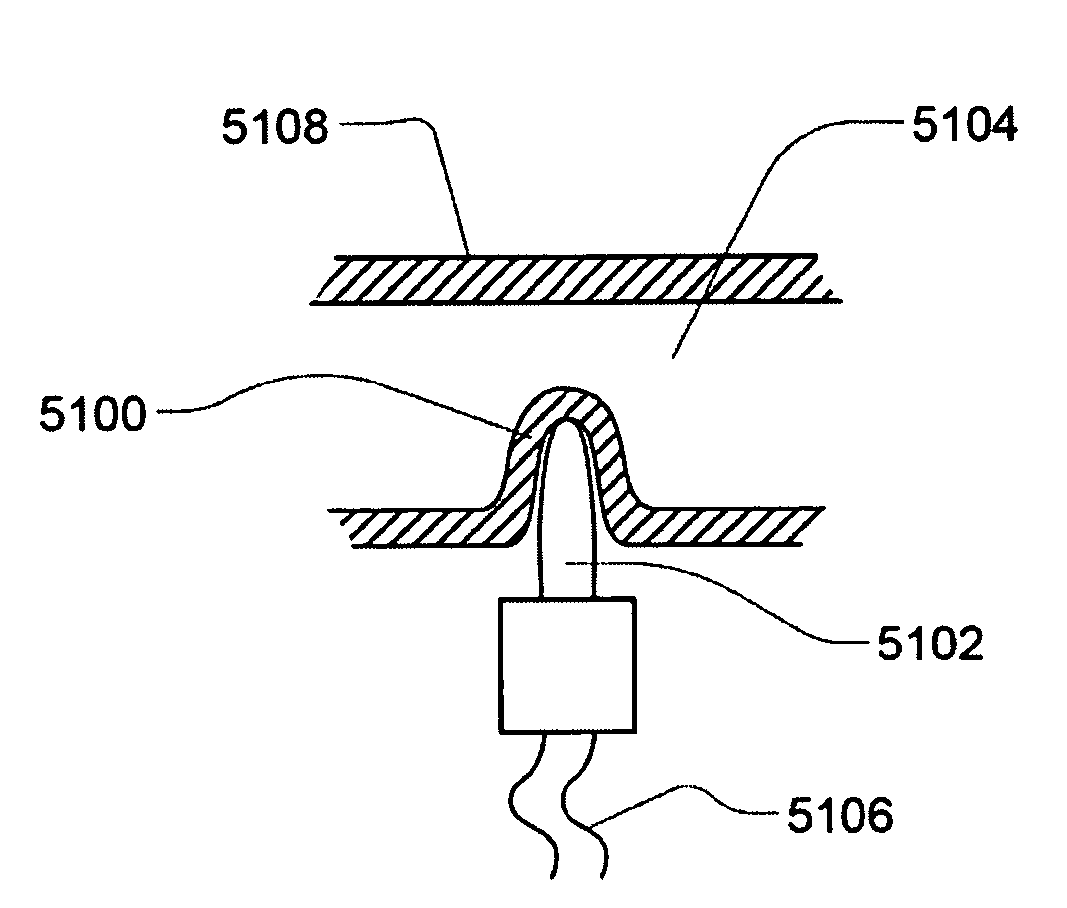
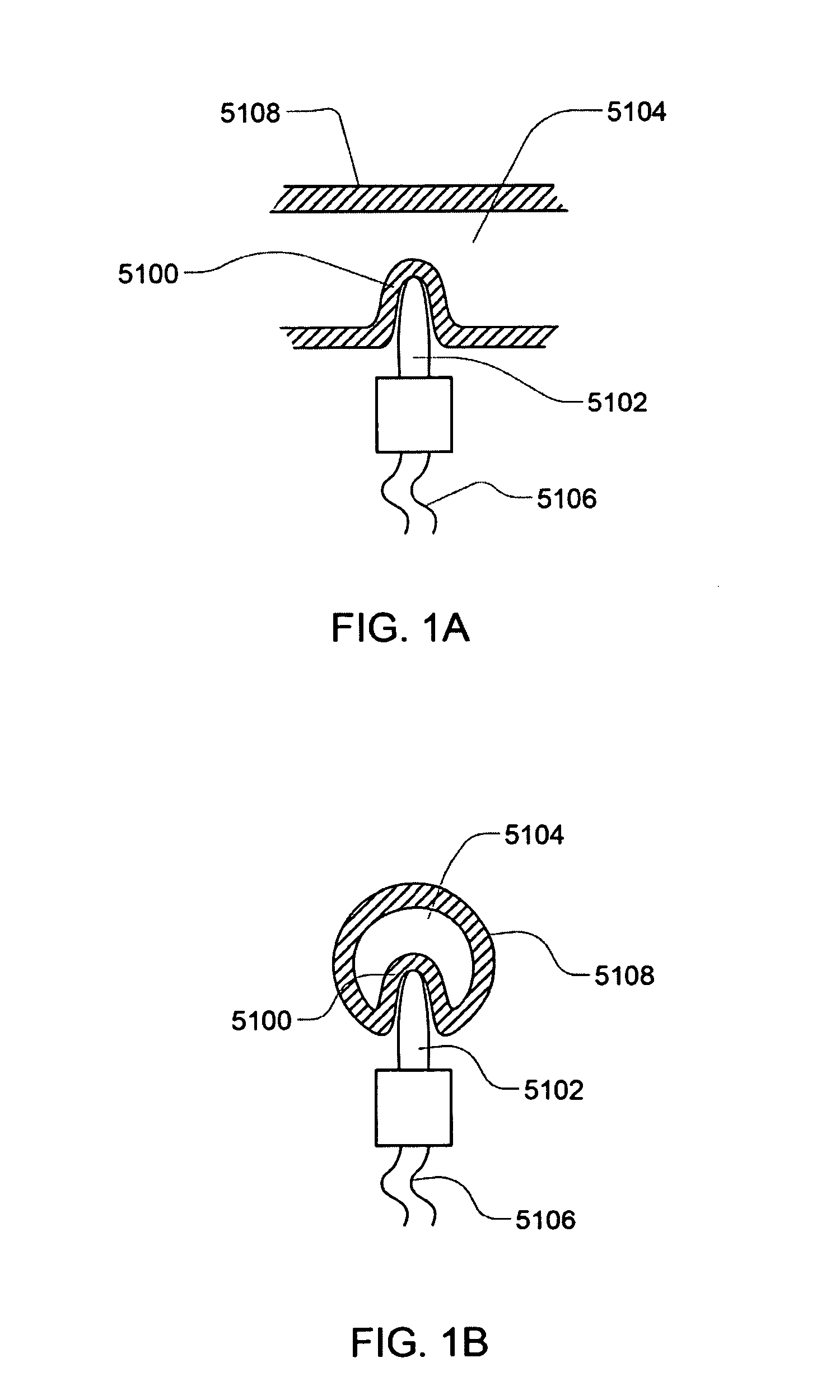
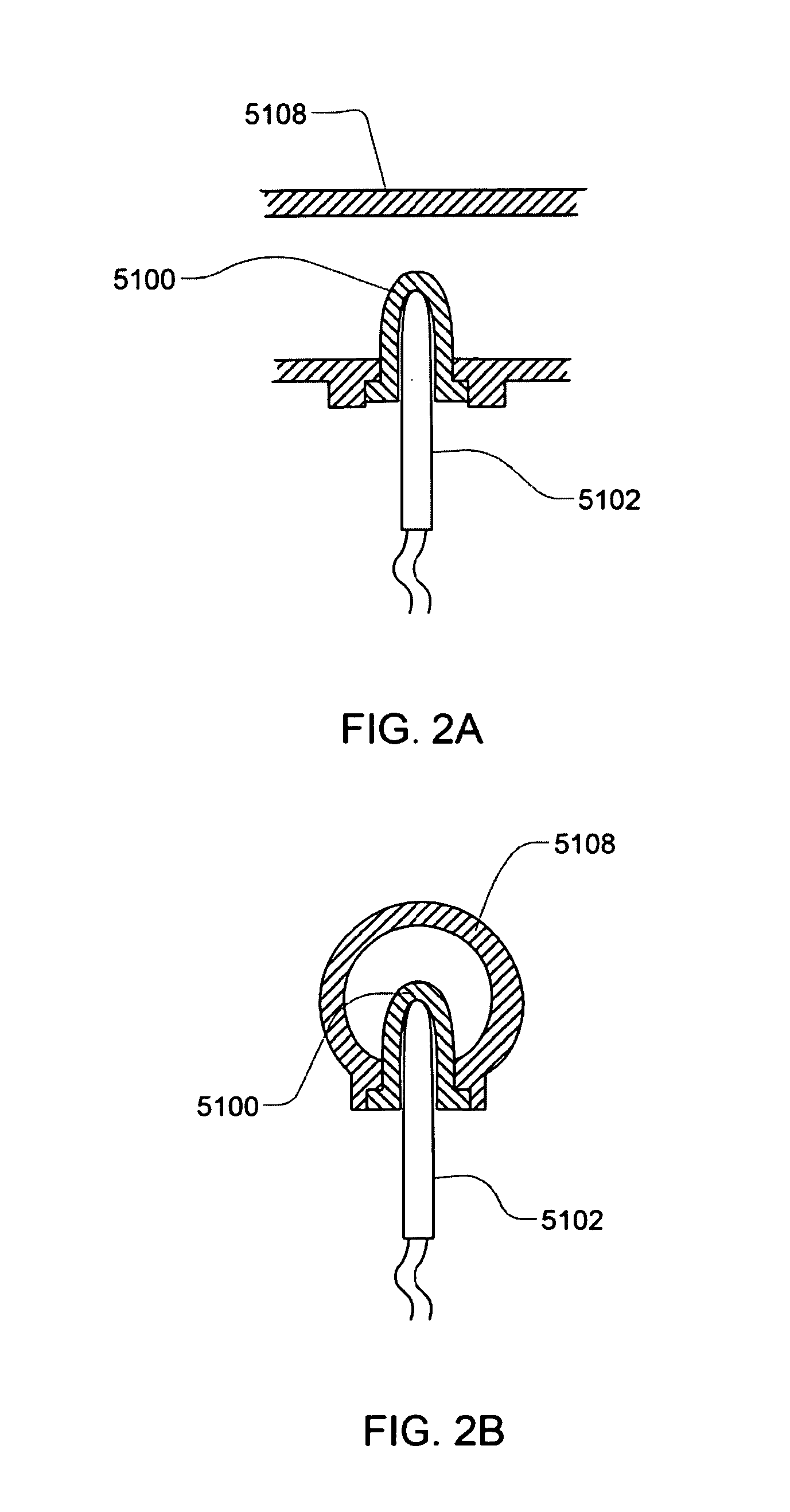
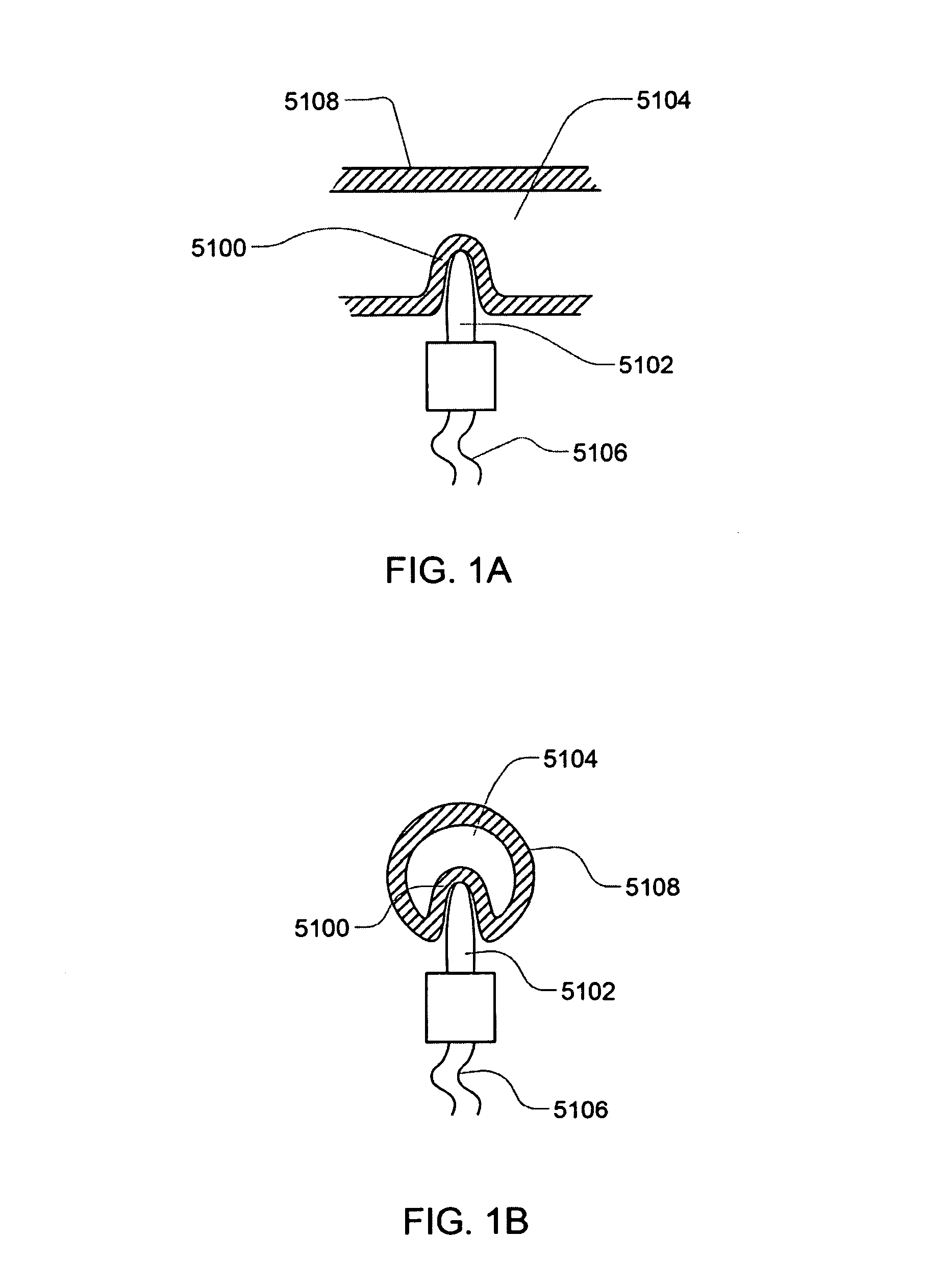
Sensor Apparatus Systems, Devices and Methods
ActiveUS20080253427A1Provide flexibilitySolvent extractionFlexible member pumpsCombined useConductive materials
A sensor apparatus and sensor apparatus system for use in conjunction with a cassette, including a disposable or replaceable cassette. In some embodiments, the cassette includes a thermal well for permitting the sensing of various properties of a subject media. The thermal well includes a hollow housing of a thermally conductive material. In other embodiments, the cassette includes sensor leads for sensing of various properties of a subject media. The thermal well has an inner surface shaped so as to form a mating relationship with a sensing probe. The mating thermally couples the inner surface with a sensing probe. In some embodiments, the thermal well is located on a disposable portion and the sensing probe on a reusable portion.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Drug delivery management system
A system for managing delivery of pharmaceutical drugs is formed of a blister package that includes a plurality of cells arranged in a grid. Each of the cells is sealed by a breakable wall and holds a unit-dose of medication. A user gains access to the medication in a given cell by puncturing the breakable wall associated with the given cell. A severable conductor is positioned proximate to each breakable wall. The severable conductor associated with a given cell ruptures upon puncturing of the breakable wall associated with the given cell. A computer chip is electrically connected to the severable conductors. The computer chip senses the puncturing of each cell in the grid by monitoring the rupturing of each of the severable conductors. An RF transmitter is coupled to the computer chip. The RF transmitter sends information corresponding to usage of each of medications stored in the blister package to a remote information transceiver.
Owner:DDMS HLDG
Method and apparatus for comprehensive energy measurement and analysis of a building
InactiveUS20100211222A1Low costReduce heat lossLevel controlSpace heating and ventilationEnergy transferElectricity
An energy monitoring and analysis system for a building includes a logging unit, a processing unit, temperature sensors that read the temperatures inside and outside the building, electric current sensors that read electric currents in all independent electric connections at the main connection panel of the building, and other types of sensors such as those related to natural gas flow. The logging unit periodically collects the data from all the sensors and transmits the data to the processing unit. The processing unit analyzes the data using highly sophisticated algorithms, extracts various parameters, profiles the electric energy usage, identifies potential problems with energy transfer and use, and lists recommendations for corrective actions. The processing unit analyzes data of the building, an HVAC system associated with the building, and consuming devices associated with the building.
Owner:GHOSN MICHEL
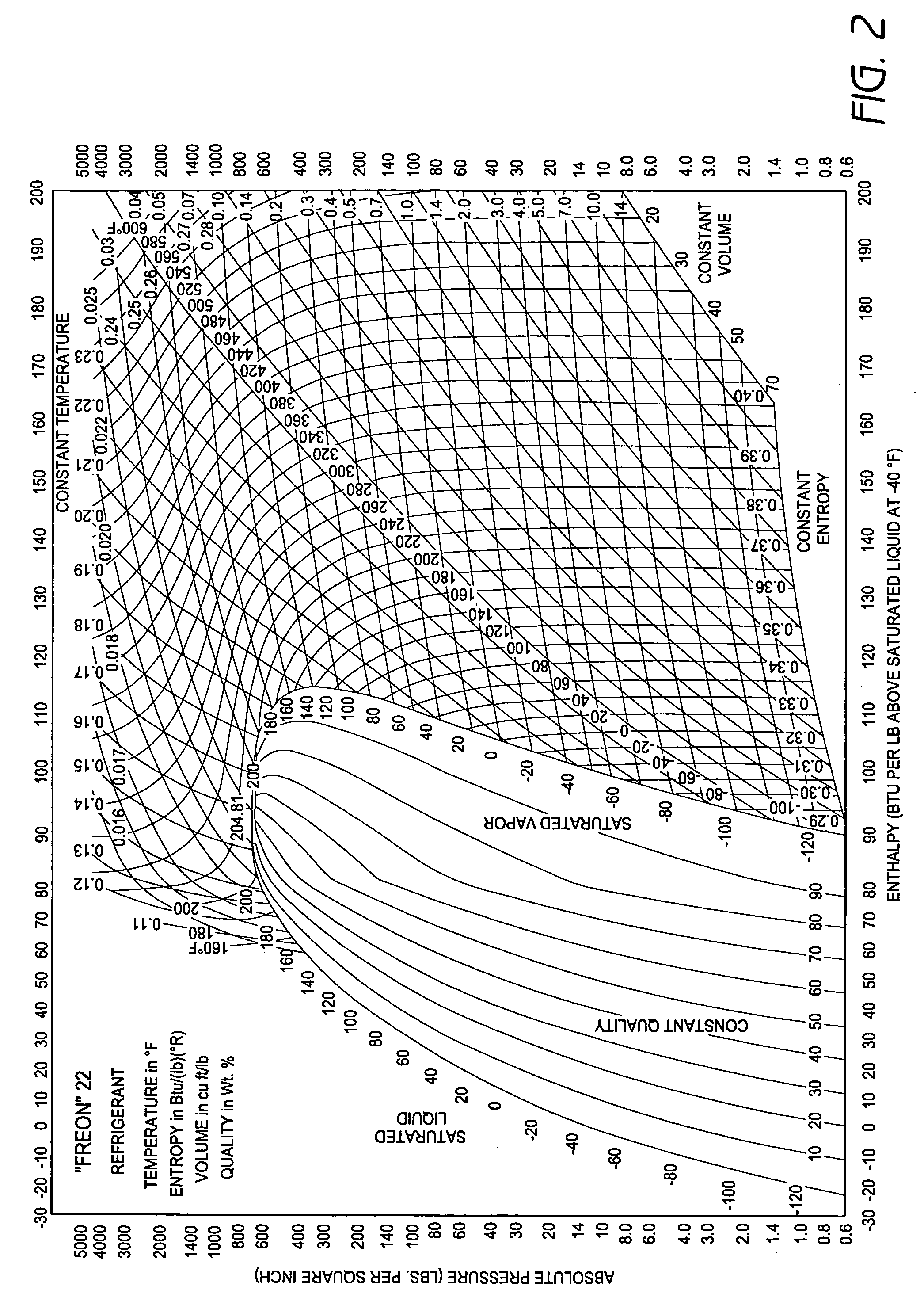
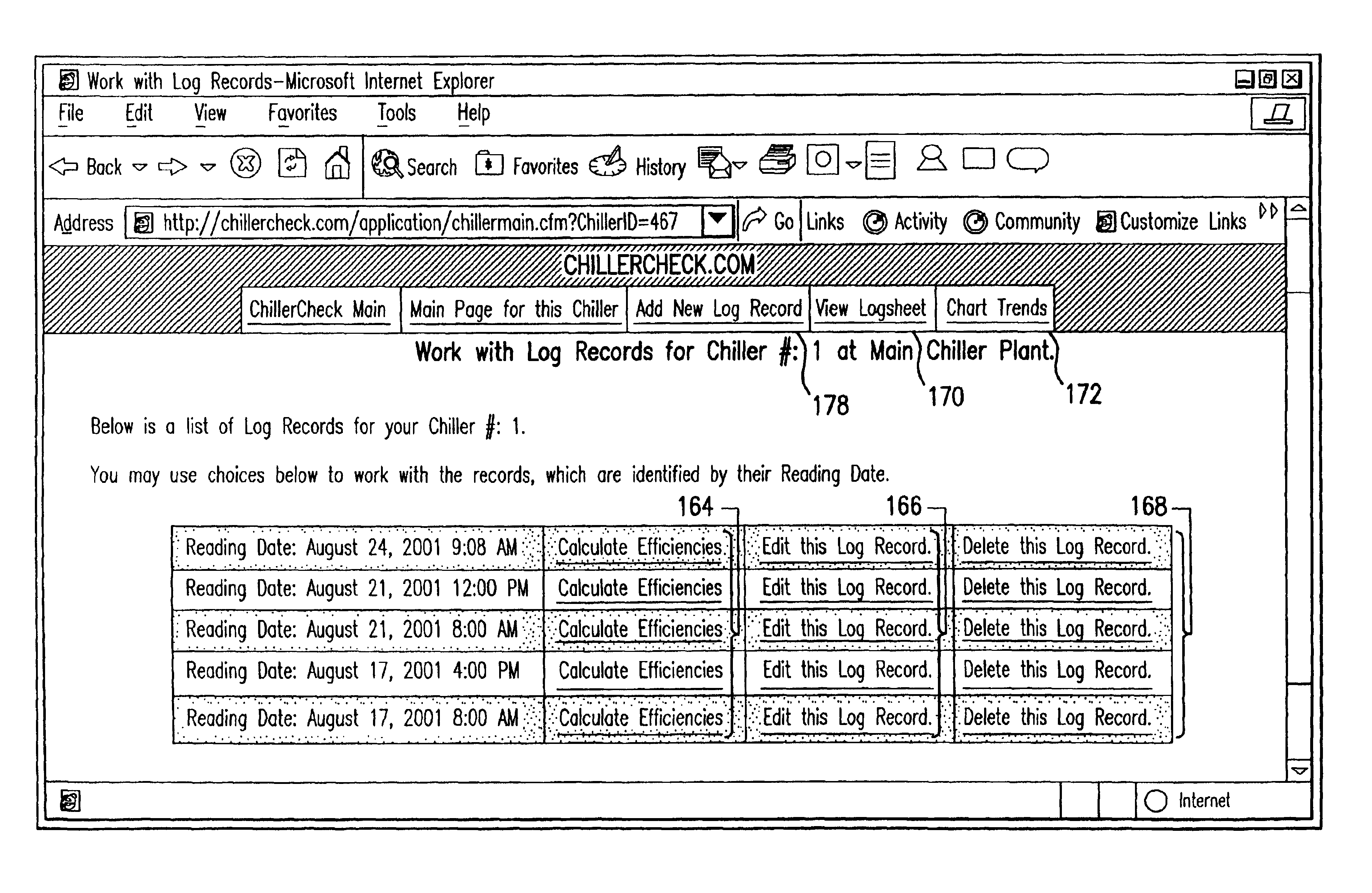
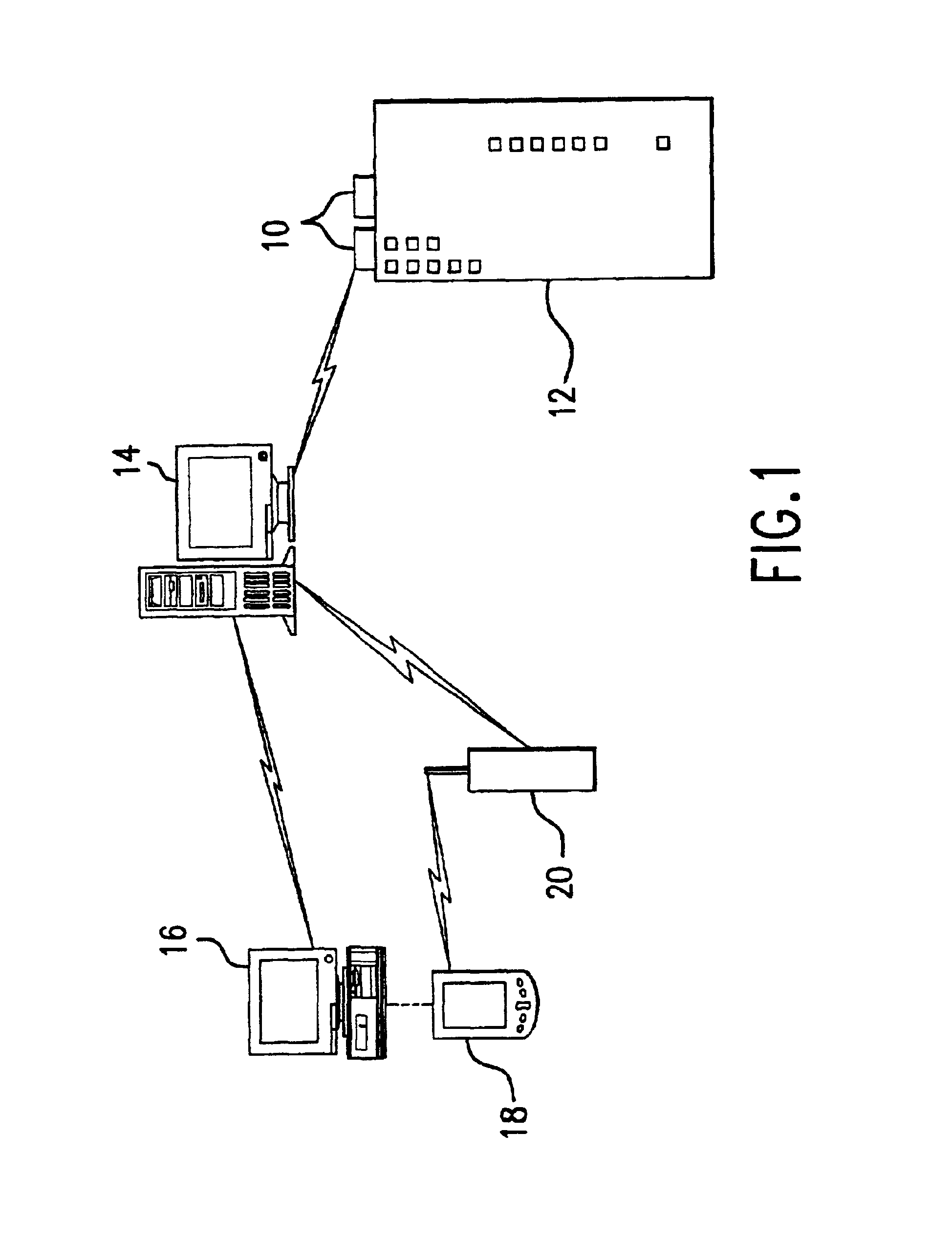
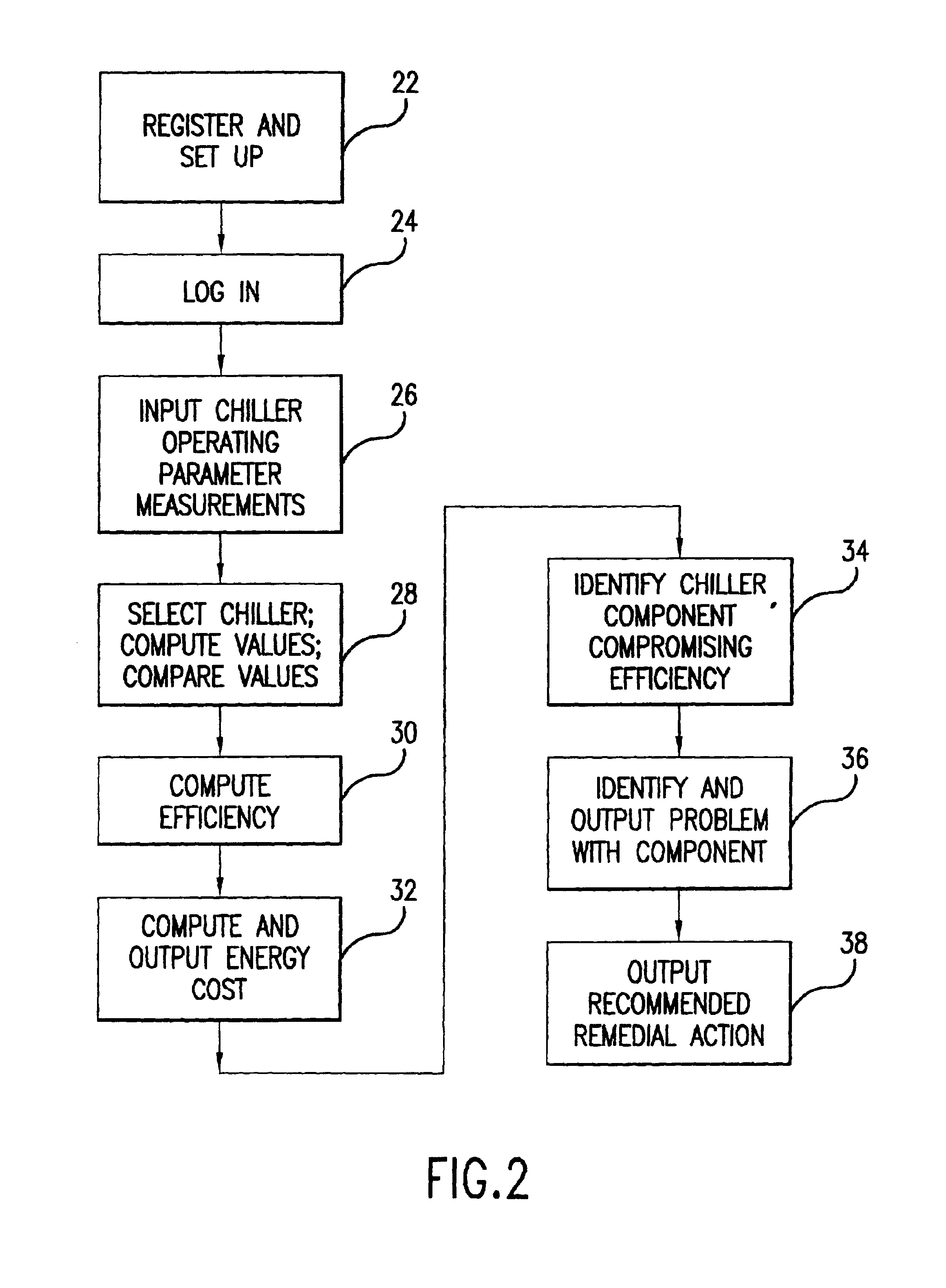
Method and system for evaluating the efficiency of an air conditioning apparatus
InactiveUS6973410B2Computing chiller efficiencySpace heating and ventilationTemperatue controlCurrent loadSimulation
Air conditioning chiller operating efficiency is evaluated in response to chiller operating parameters input to a computing device which calculates separately the efficiencies of the condenser and evaporator components of the chiller. Additional efficiency calculations are performed to identify specific causes of inefficiency in the condenser and evaporator. The computing device also adjusts the efficiency calculations as appropriate to account for actual compressor current load conditions. The device determines whether chiller efficiency is being compromised by poor performance of one or more chiller components, calculates inefficiency values, estimates the cost of the inefficiency, identifies specific causes of the inefficiency, and suggests appropriate remedial actions to restore maximum efficiency of the chiller.
Owner:CHILLERGY SYST
Portable information display dockable to a base thermostat
InactiveUS20120061480A1Batteries circuit arrangementsSpace heating and ventilationControl systemOperating energy
A thermostat system is provided that comprises a base thermostat for providing basic thermostat control and a portable information display (PID) unit, or dockable display, that provides an improved user interface. The PID unit can be docked to the base thermostat by being releasably mounted on top of a front portion of the base thermostat. The base thermostat provides control of an environmental control system, allowing the regulation of the temperature in a building. The PID unit may be used when it is mounted to the base thermostat or un-mounted from the base thermostat. The PID unit provides an improved user interface and experience over the base thermostat.
Owner:ENERGATE
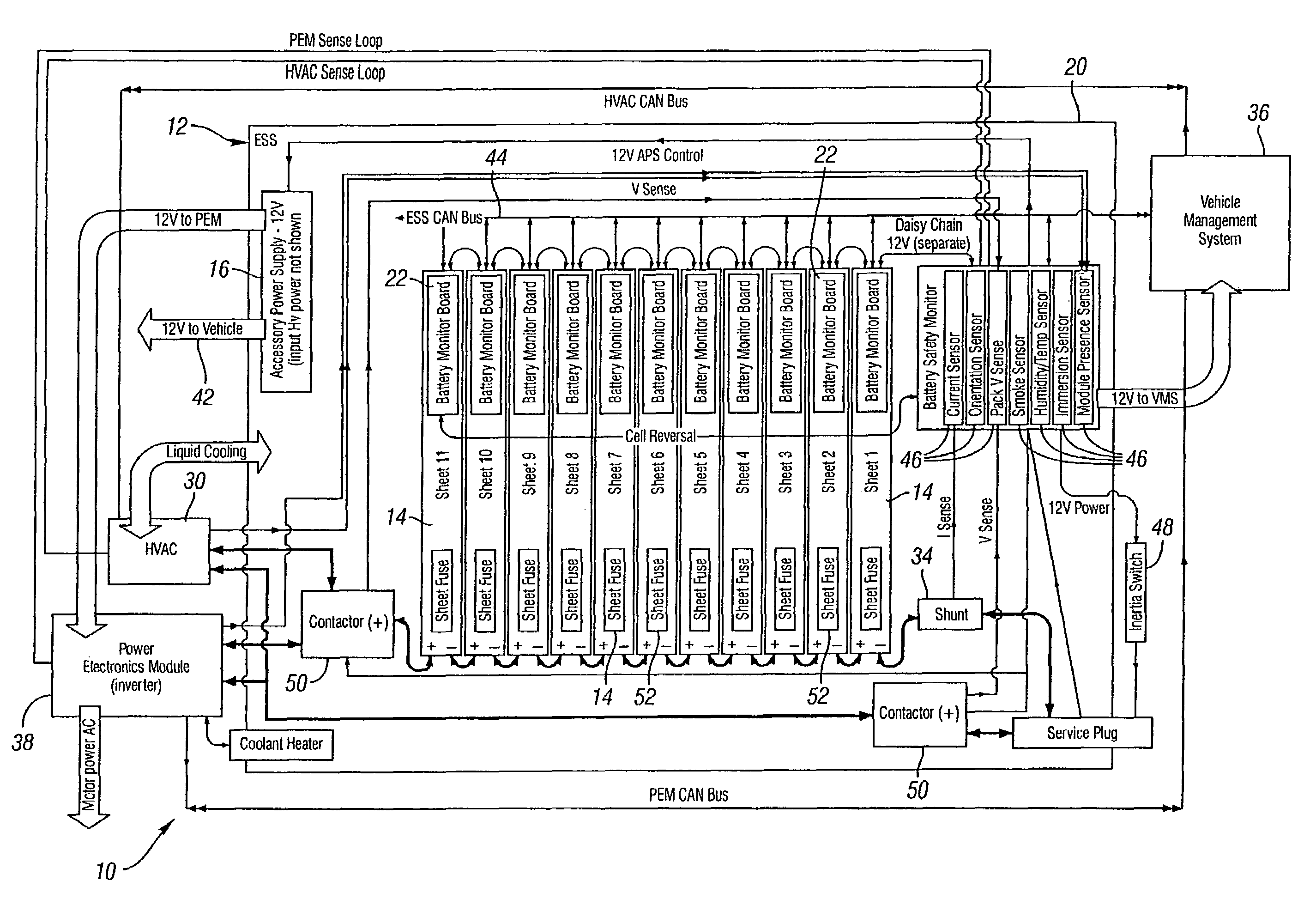
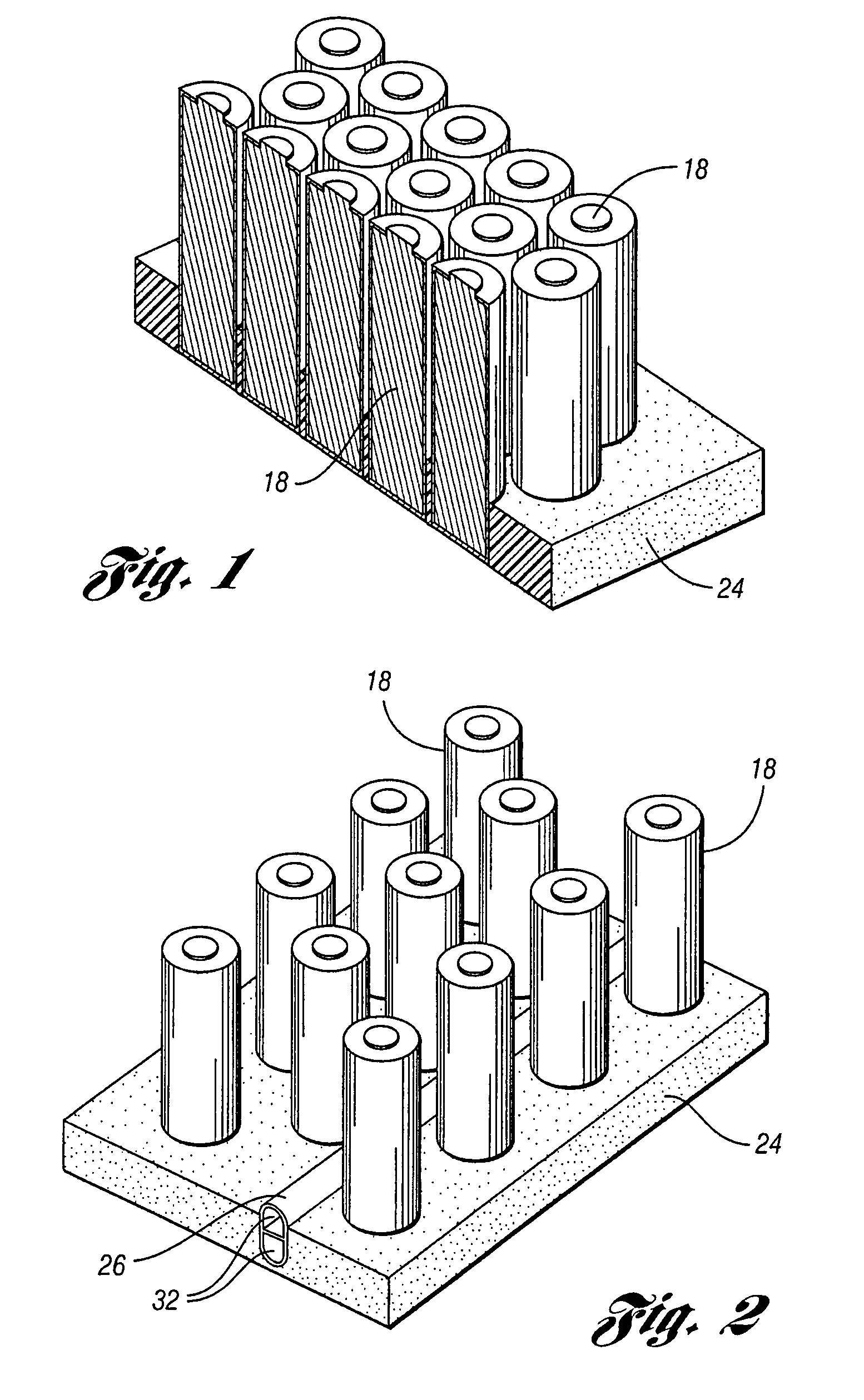
Mitigation of propagation of thermal runaway in a multi-cell battery pack
ActiveUS7433794B1Reduce temperature riseIncrease rangeElectrical testingVehicular energy storageEnergy storageBattery pack
A method of mitigating propagation of a thermal event in an energy storage system having a plurality of cells is disclosed. The method includes the steps of identifying the heat sources within the energy storage system and plurality of cells. The method then controls a temperature of the energy storage system and plurality of cells and also detects predetermined conditions within the energy storage system. The method then performs a predetermined action based on when one of the predetermined conditions is detected. A plurality of sensors and switches along with associated hardware or software will be used to control the temperature of the energy storage system upon detection of predetermined conditions involving overheating, over current, over voltage of the like.
Owner:TESLA INC
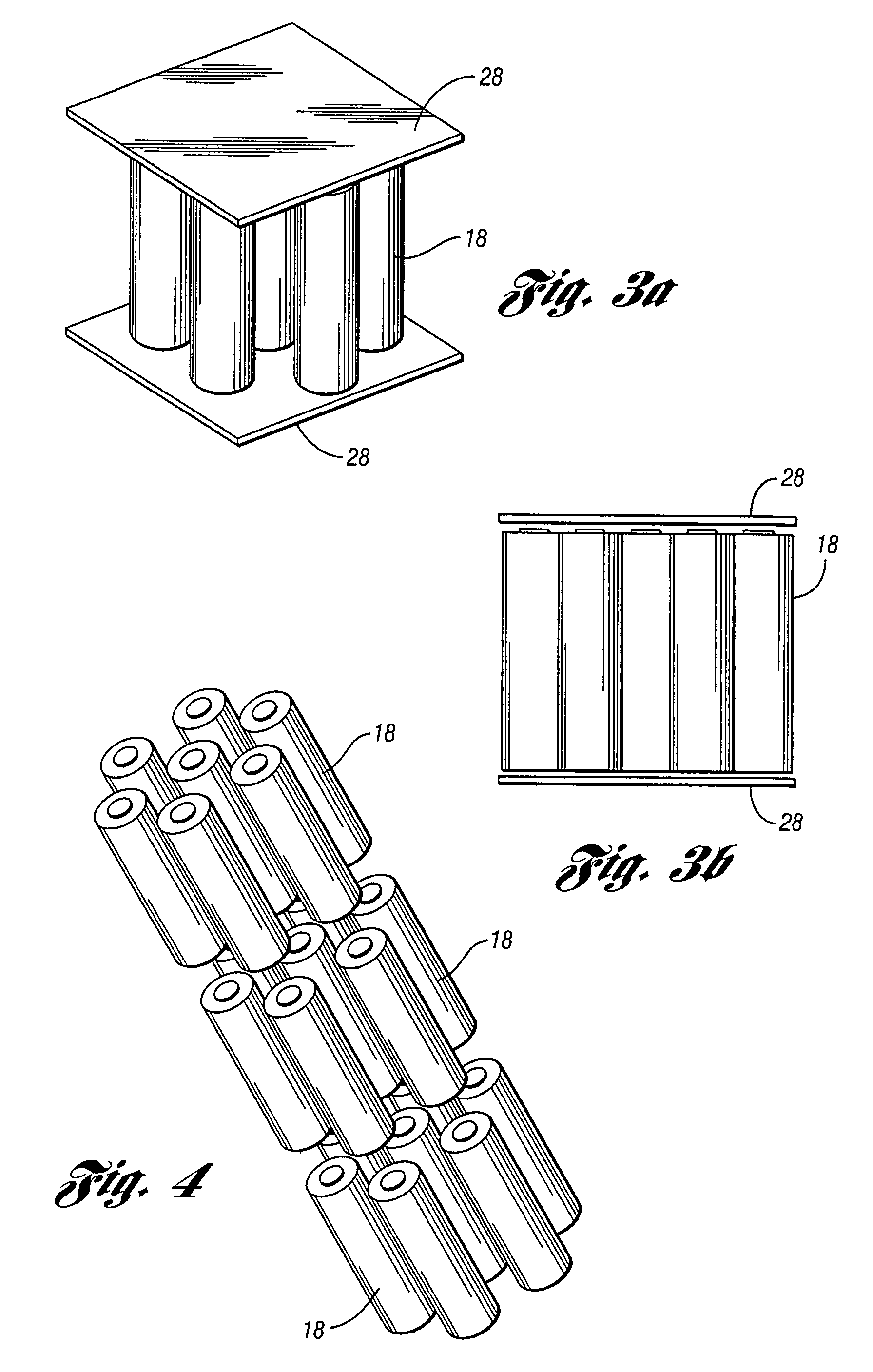
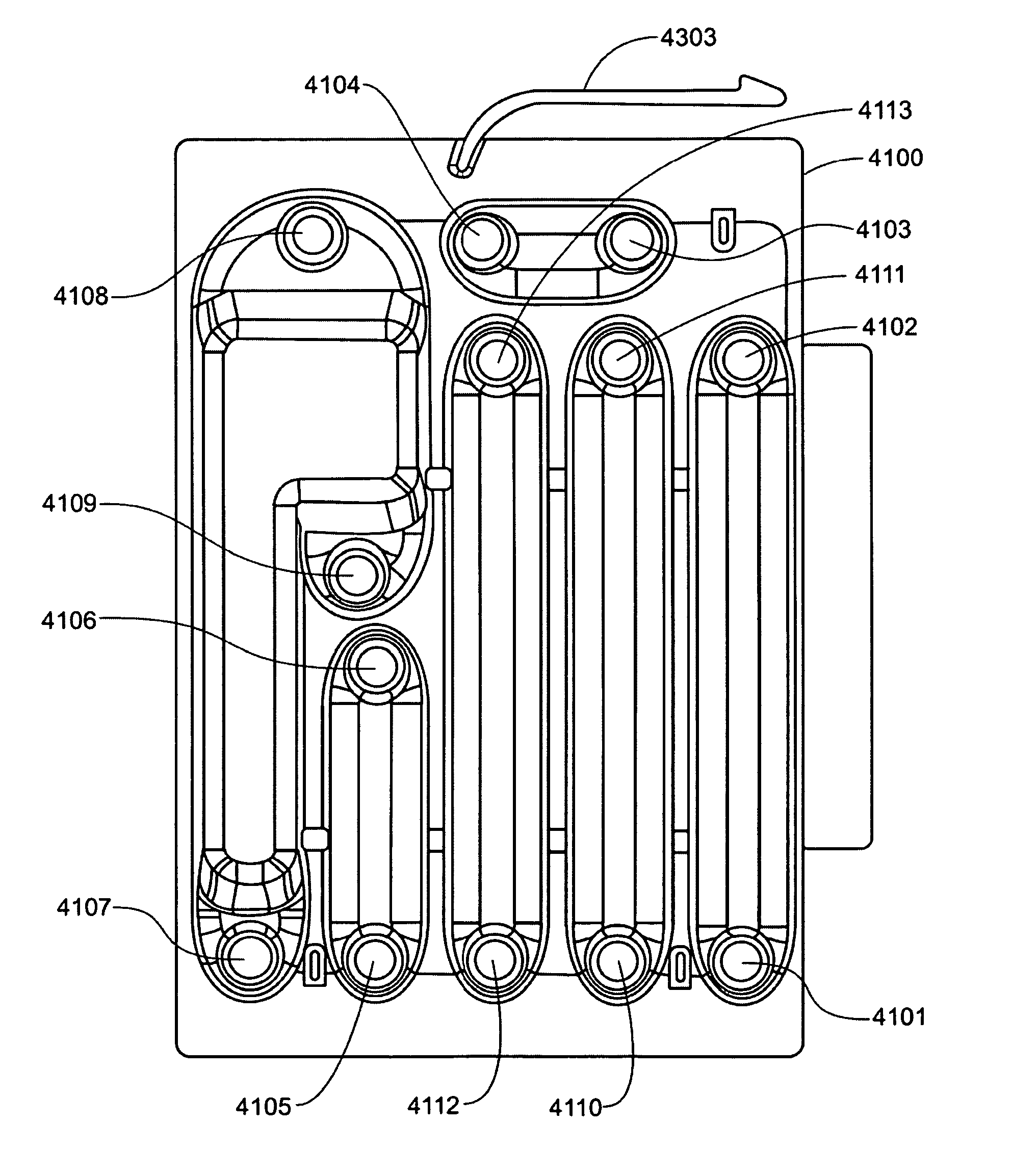
Thermal management using stored field replaceable unit thermal information
A method of managing conditions in a data center comprises storing information relating to field replaceable unit thermal properties in at least one field replaceable unit non-volatile memory and generating information for real-time dynamic temperature mapping of the data center based on the field replaceable unit thermal property information.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Sensor apparatus systems, devices and methods
A sensor apparatus and sensor apparatus system for use in conjunction with a cassette, including a disposable or replaceable cassette. In some embodiments, the cassette includes a thermal well for permitting the sensing of various properties of a subject media. The thermal well includes a hollow housing of a thermally conductive material. In other embodiments, the cassette includes sensor leads for sensing of various properties of a subject media. The thermal well has an inner surface shaped so as to form a mating relationship with a sensing probe. The mating thermally couples the inner surface with a sensing probe. In some embodiments, the thermal well is located on a disposable portion and the sensing probe on a reusable portion.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
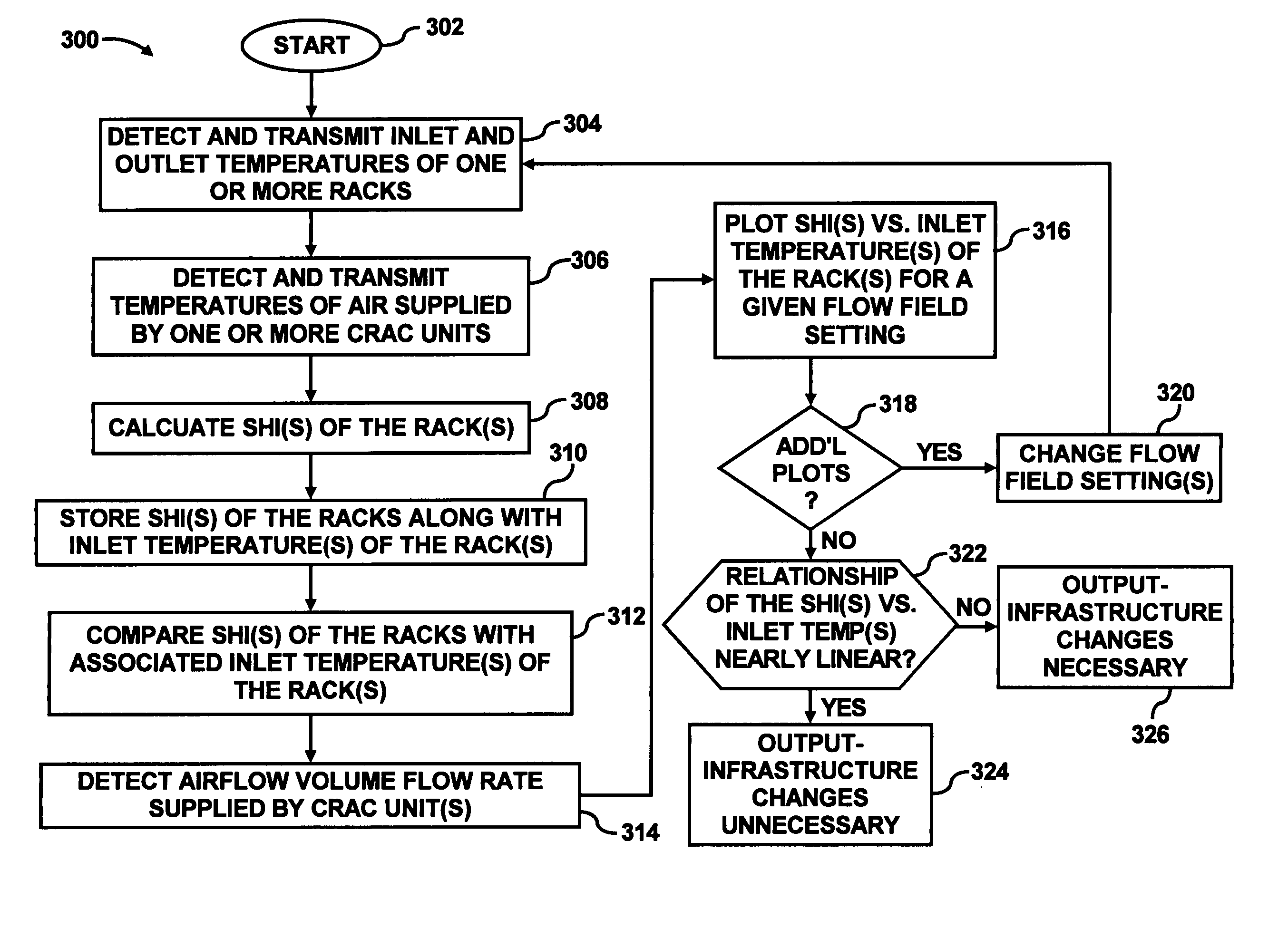
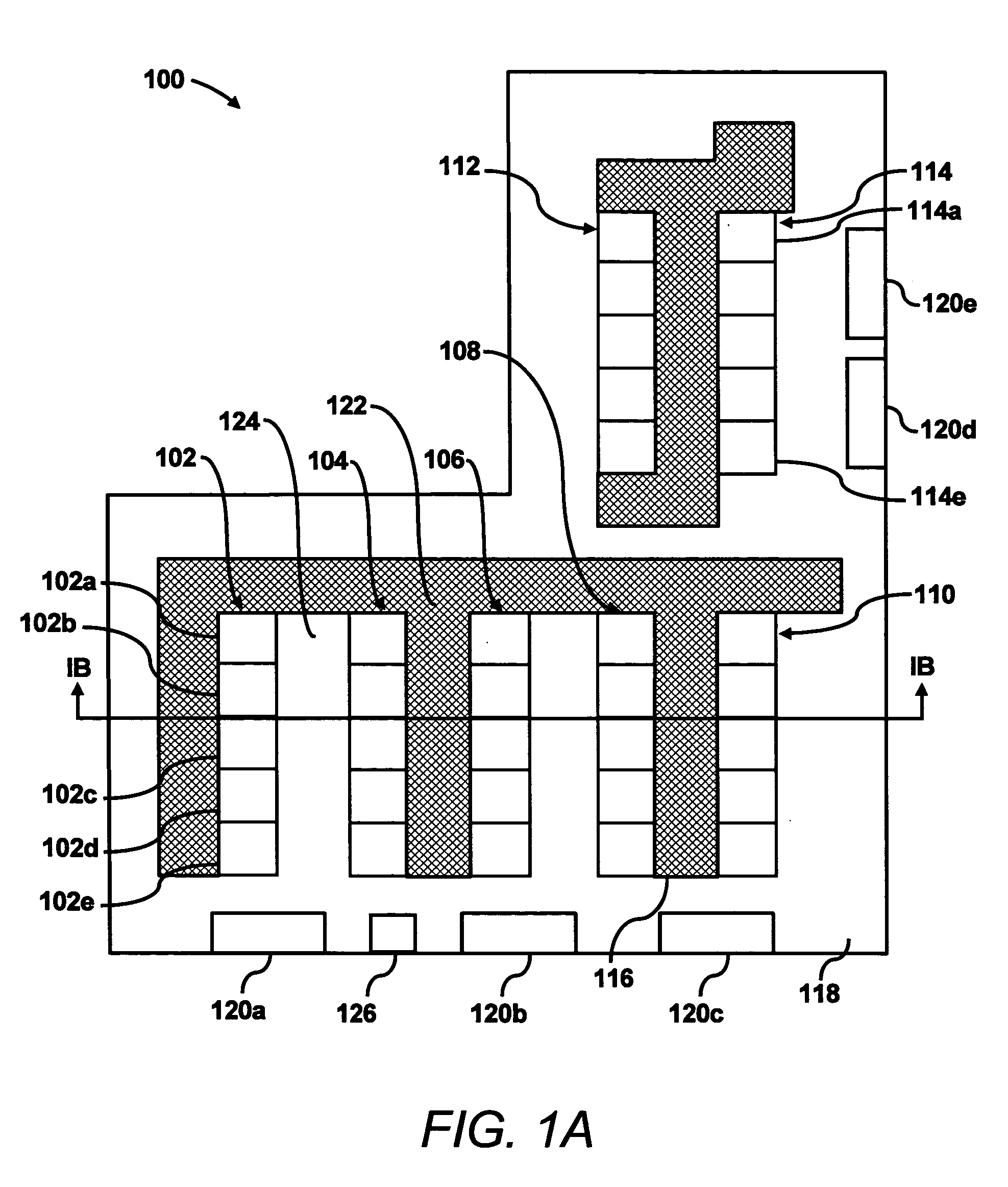
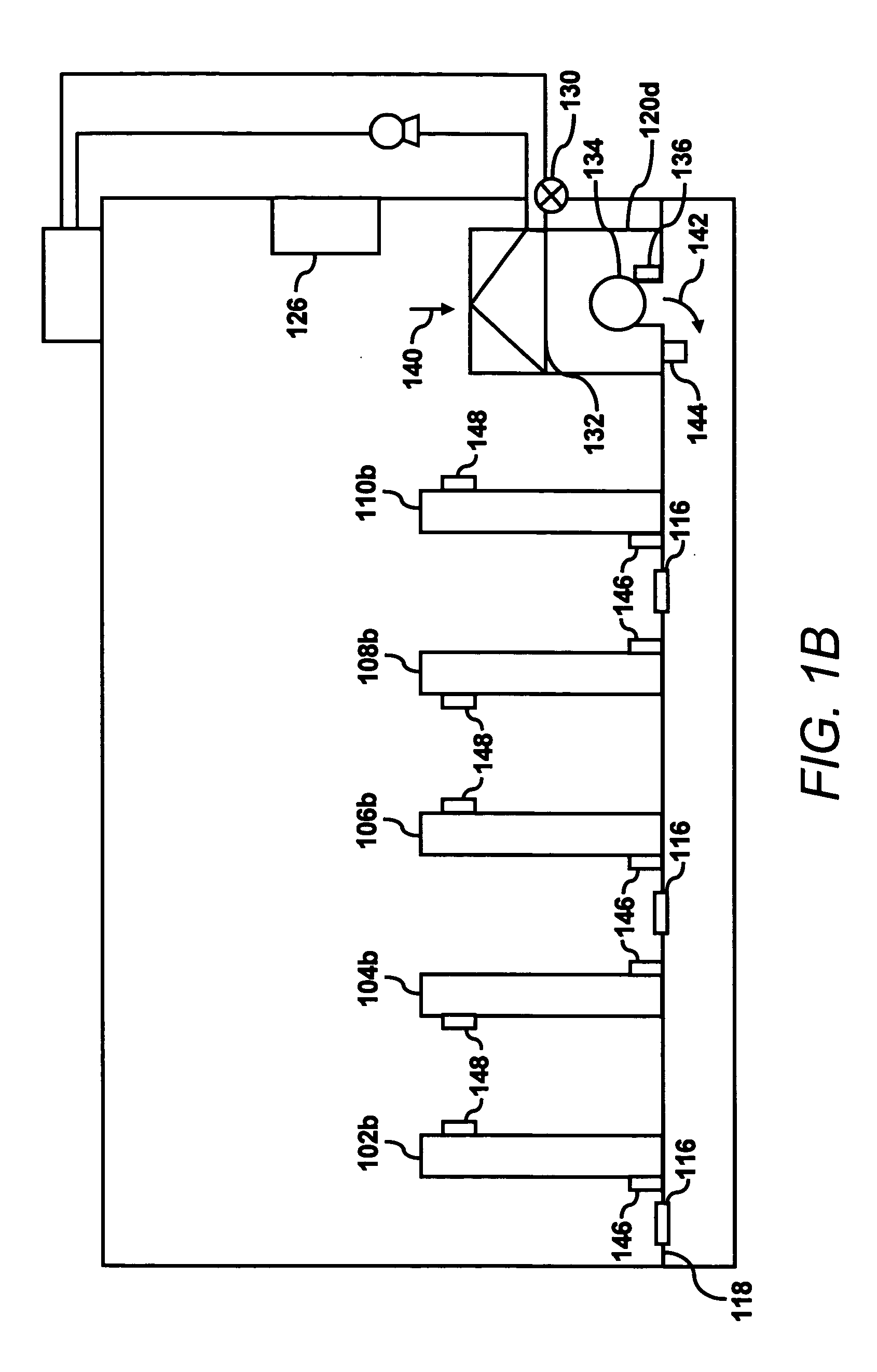
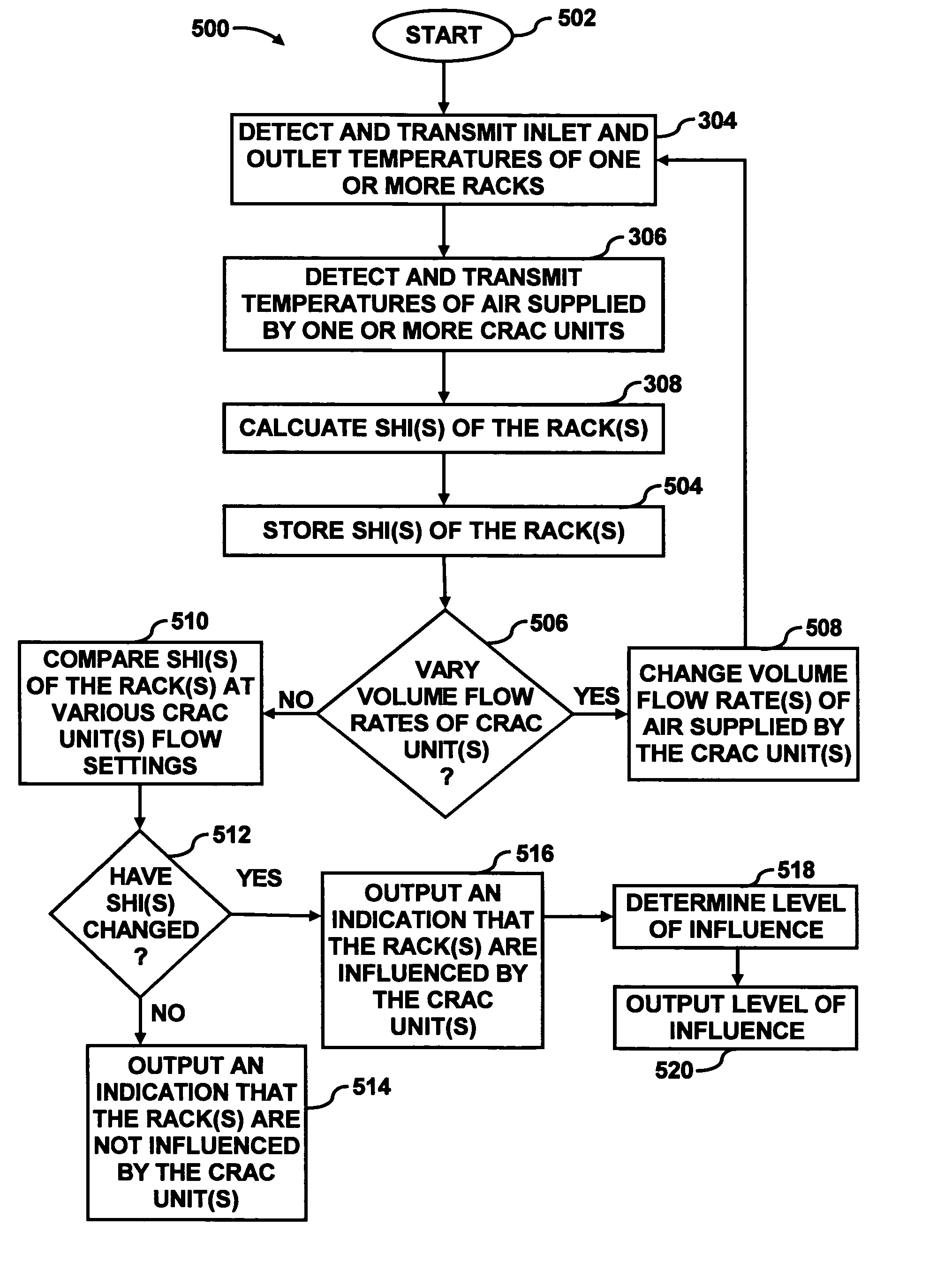
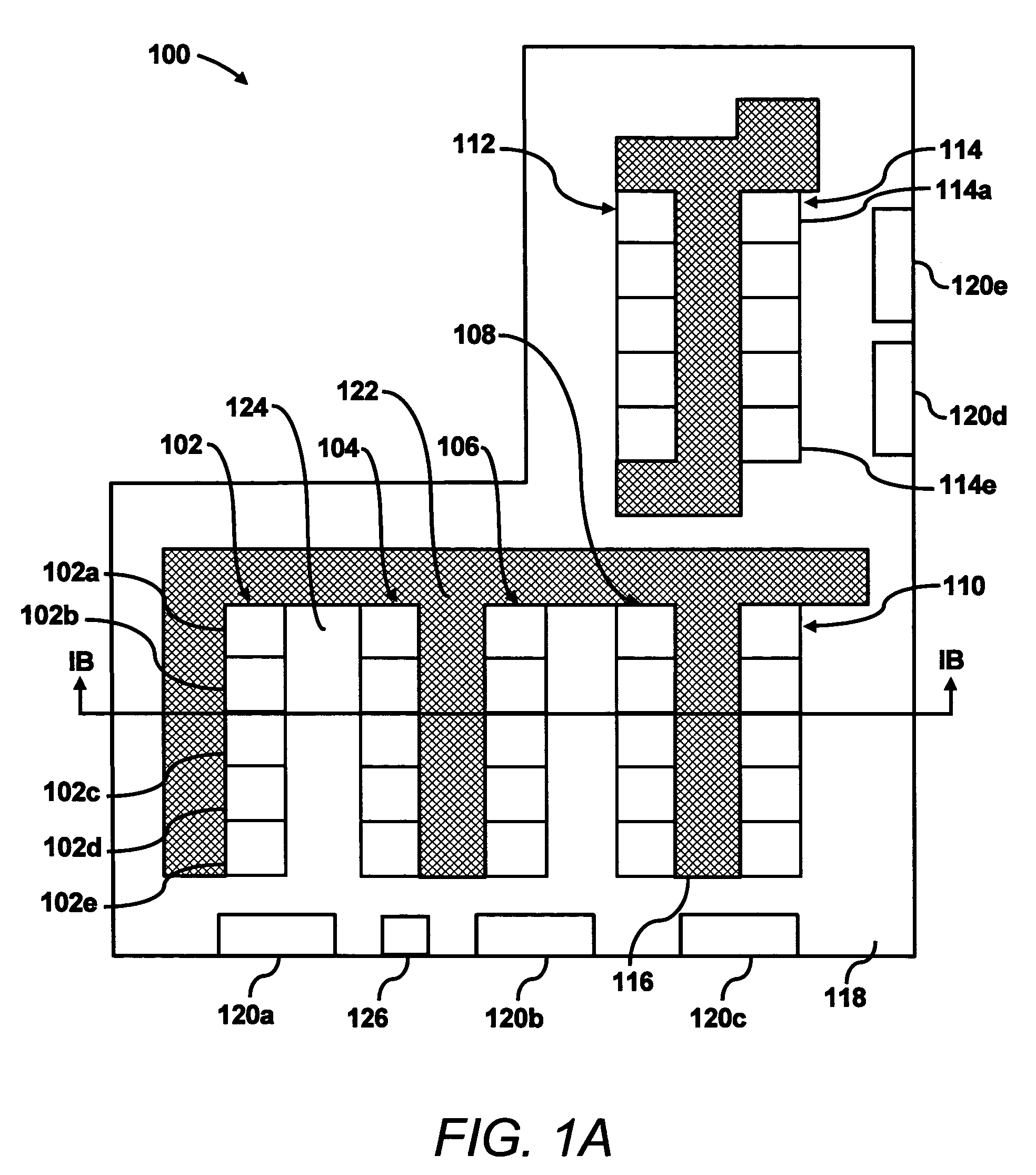
Data center evaluation using an air re-circulation index
In a method for evaluating one or more components in a data center, inlet and outlet temperatures of one or more heat dissipating devices are detected. In addition, the temperatures of air supplied by one or more computer room air conditioning (CRAC) units are also detected. Indices of air re-circulation for the one or more heat dissipating devices are calculated based upon the detected inlet temperatures, outlet temperatures and supplied air temperatures. The indices of air re-circulation are determined at various flow field settings of air delivered to the one or more heat dissipating devices and the one or more components are evaluated based upon changes in the indices of air re-circulation for the one or more heat dissipating devices at the various flow field settings.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Data center evaluation using an air re-circulation index
ActiveUS7031870B2Sampled-variable control systemsSpace heating and ventilationData centerProcess engineering
In a method for evaluating one or more components in a data center, inlet and outlet temperatures of one or more heat dissipating devices are detected. In addition, the temperatures of air supplied by one or more computer room air conditioning (CRAC) units are also detected. Indices of air re-circulation for the one or more heat dissipating devices are calculated based upon the detected inlet temperatures, outlet temperatures and supplied air temperatures. The indices of air re-circulation are determined at various flow field settings of air delivered to the one or more heat dissipating devices and the one or more components are evaluated based upon changes in the indices of air re-circulation for the one or more heat dissipating devices at the various flow field settings.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
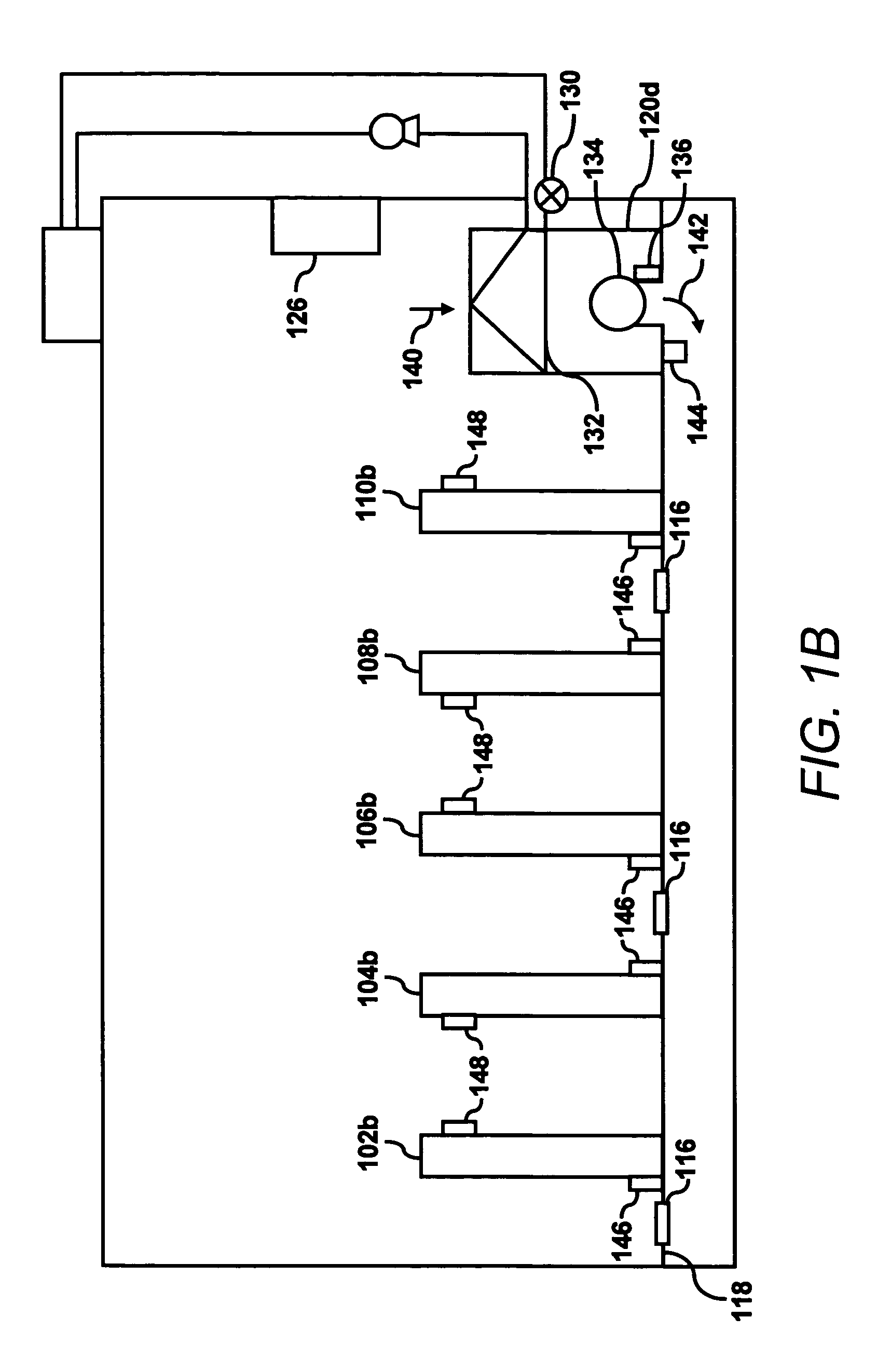
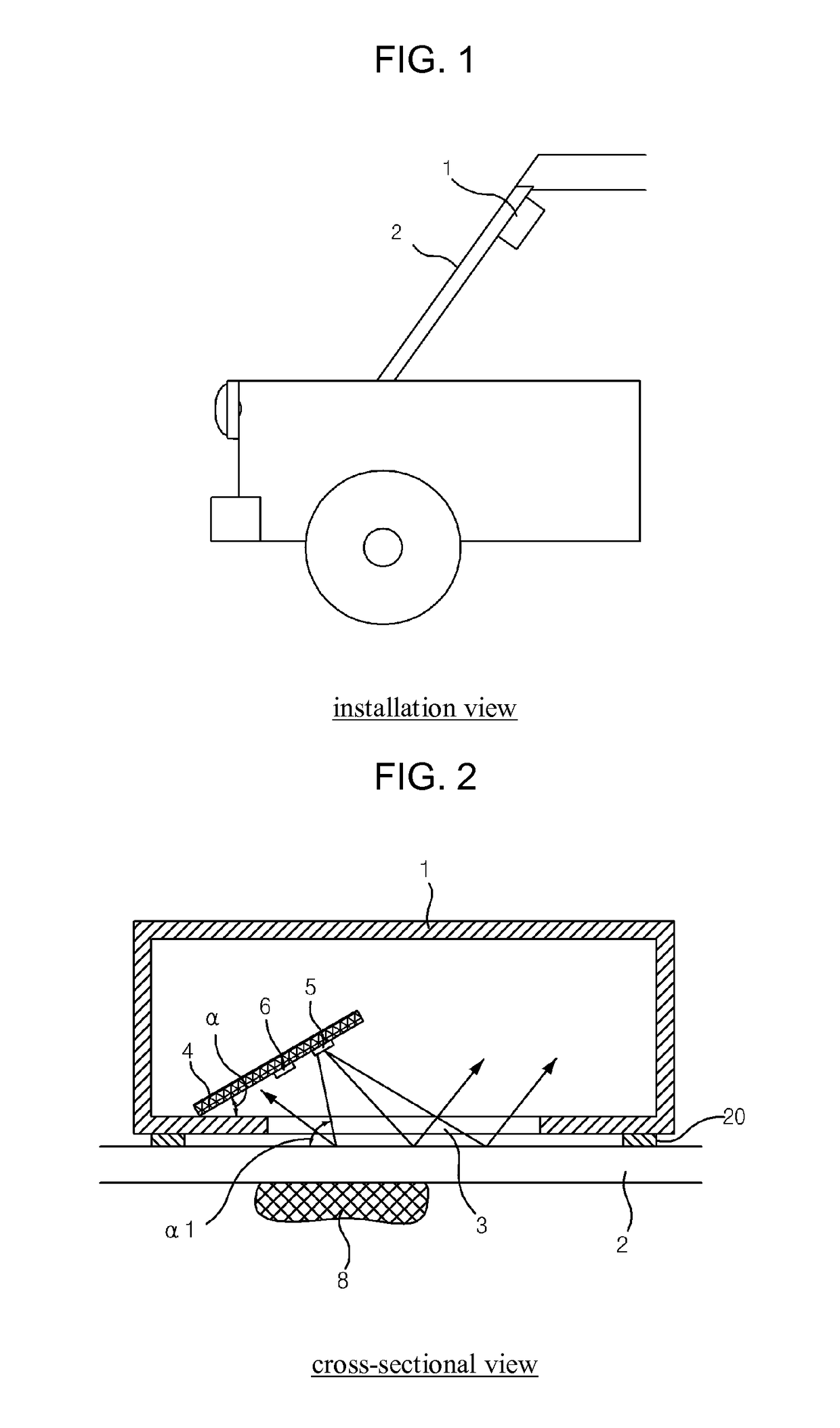
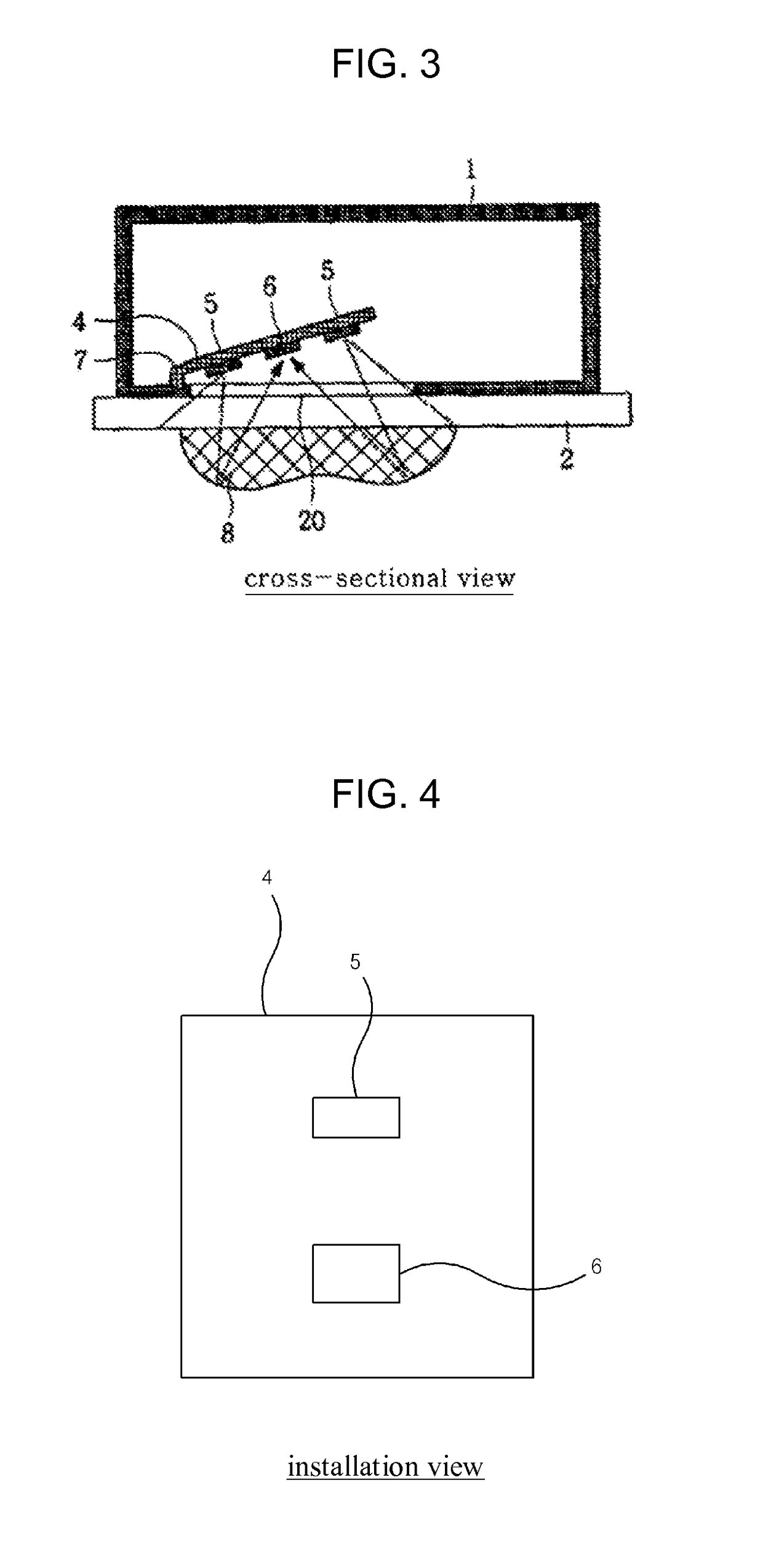
Rain sensor
ActiveUS8471513B2Low failure ratePrevent degradationOptical radiation measurementDC motor speed/torque controlOptoelectronicsRain sensor
During rain, including a light source (5) for radiating light such that the light is transmitted through a vehicle window (2), a light receiving element (6) for sensing an optical signal when the light radiated from the light source (5) is reflected from the raindrop fallen on the vehicle window (2) and performing a photoelectric transduction, and a receiver (9) for receiving the photoelectrically transduced signal from the light receiving element (6) and judging the level of rainfall. The light source (5) and the light receiving element (6) are inclined with respect to the surface of the vehicle window (2) such that the light of the light source (5) directly reflected from the vehicle window (2) exits to the outside of the light receiving element (6) and the light reflected from a raindrop (8) on the vehicle window (2) is received by the light receiving element (6) to operate a vehicle wiper.
Owner:HAN SEA YEOUN
Building integrated photovoltaic devices as smart sensors for intelligent building energy management systems
ActiveUS20140330538A1Increase flexibilityImprove usabilityOptical radiation measurementSolar heating energyBuilding energyEngineering
Building-integrated photovoltaic devices can be provided, which function as sensors, wherein the output parameters from the device are used to provide information about light intensity and ambient temperature, in addition to providing power, to an intelligent building energy management system.
Owner:SOLARWINDOW TECH
Method and apparatus for generating a building system model
A system and method for providing data to a model of a building system includes a building control system with a communications network, a control subsystem for generating module deployment data and transmitting the module deployment data over the communications network, a memory for storing a three dimensional model of at least a portion of a building and a computer. A computer program executed by the computer includes computer instructions for associating module deployment data received from the communications network with the three dimensional model and modifying the three dimensional model based upon the module deployment data.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com