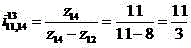Patents
Literature
32results about How to "High output stiffness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
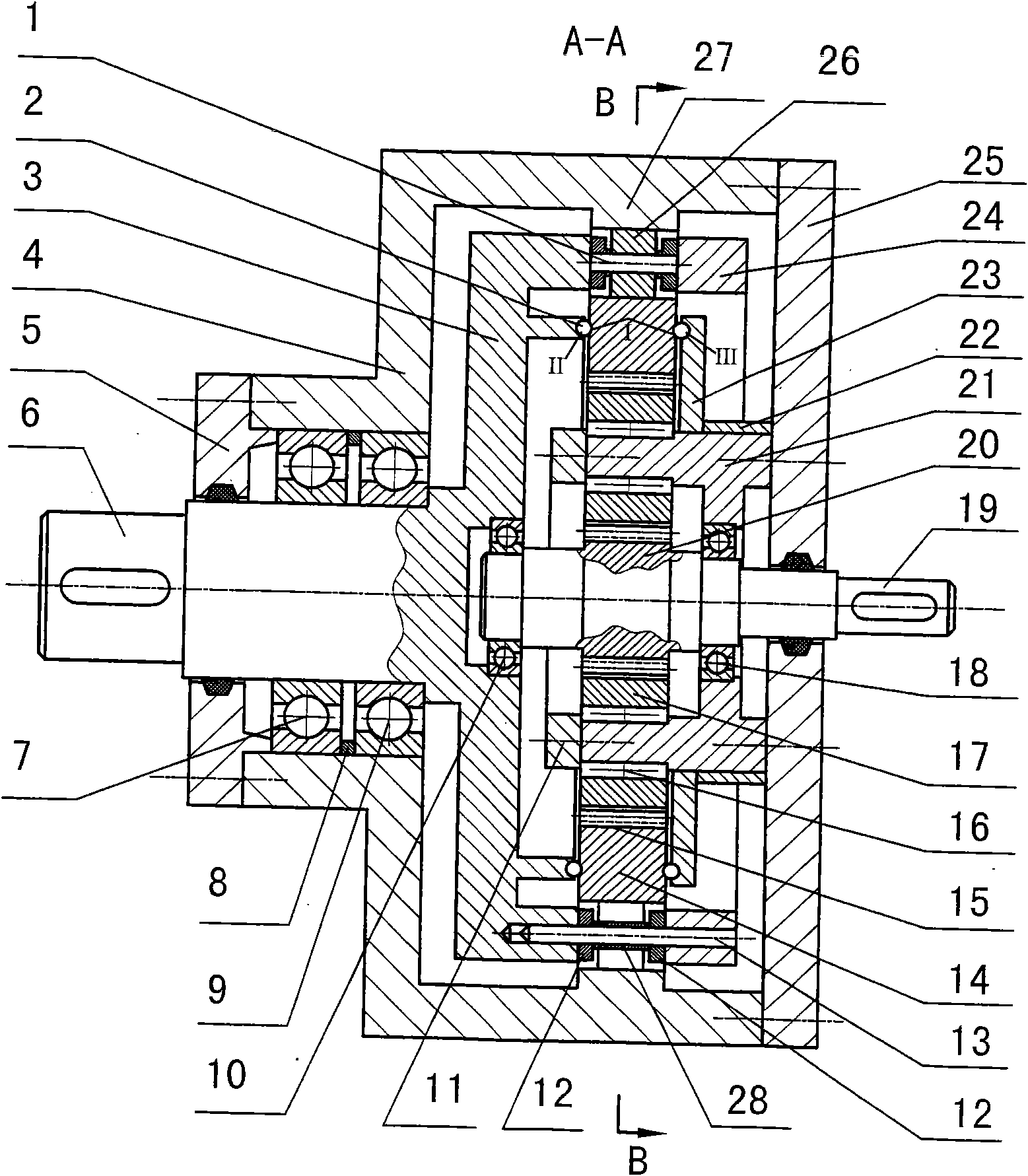
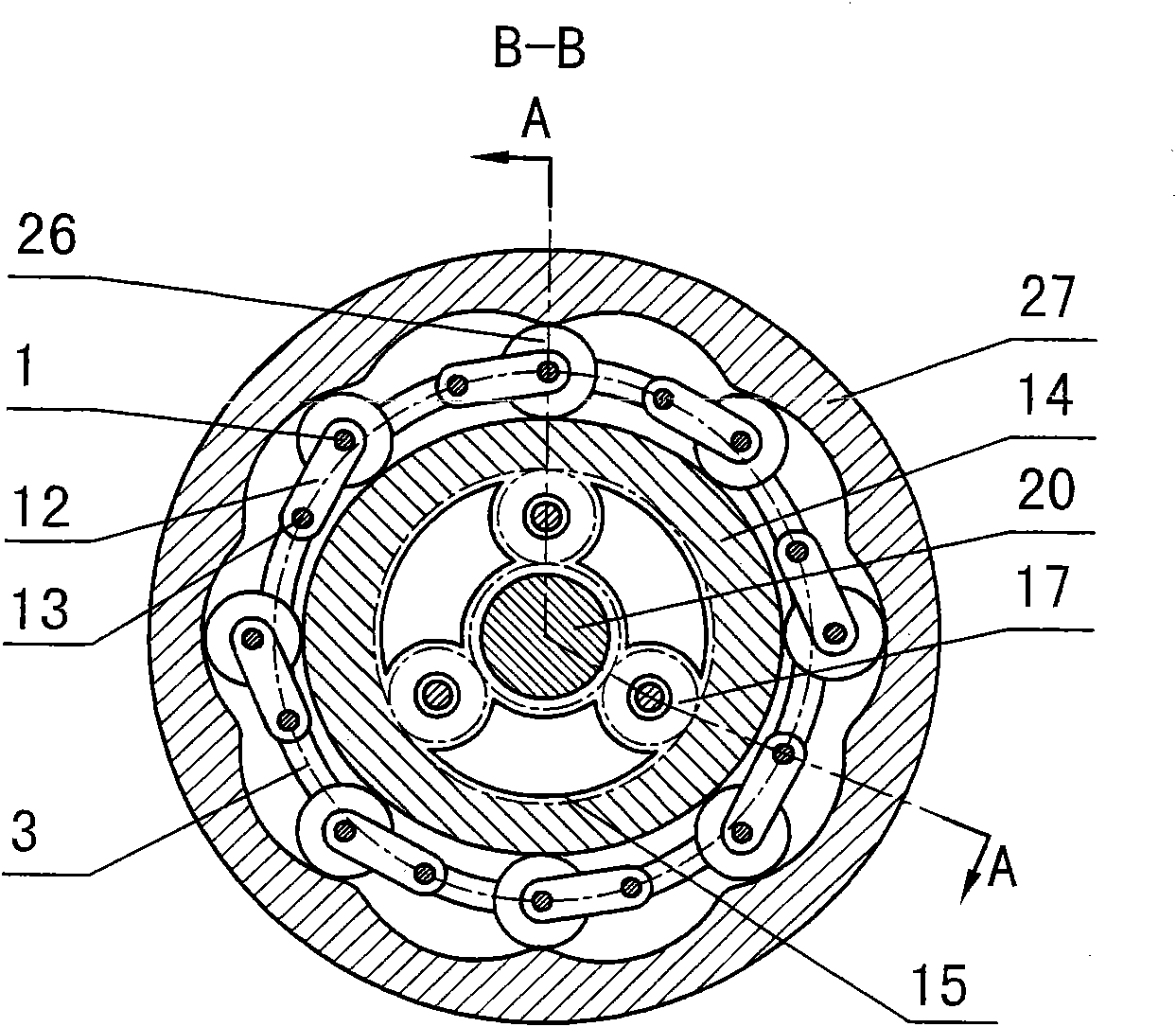
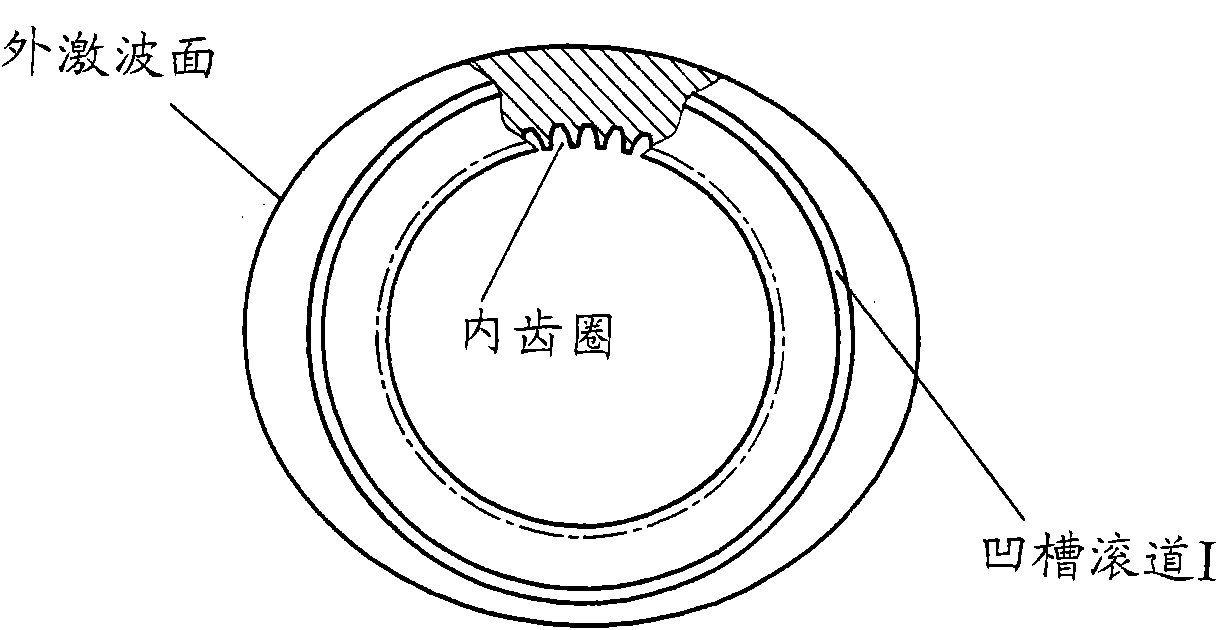
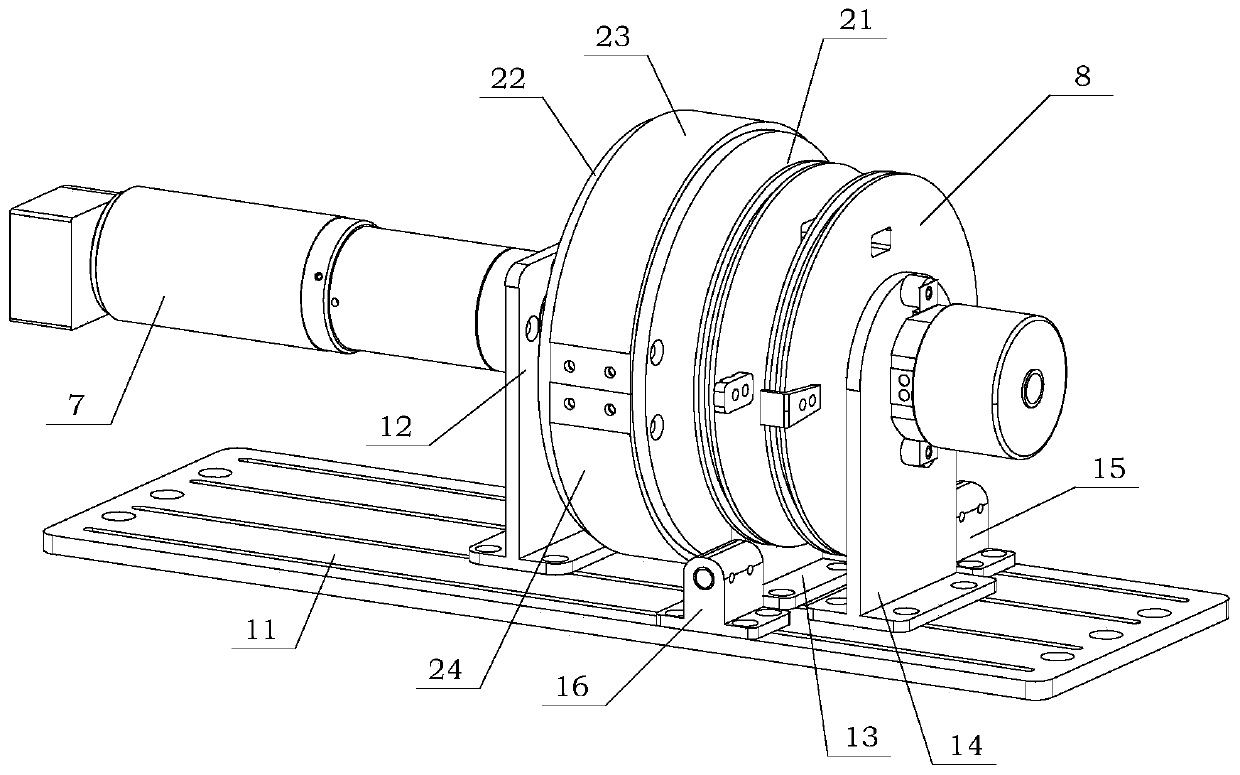
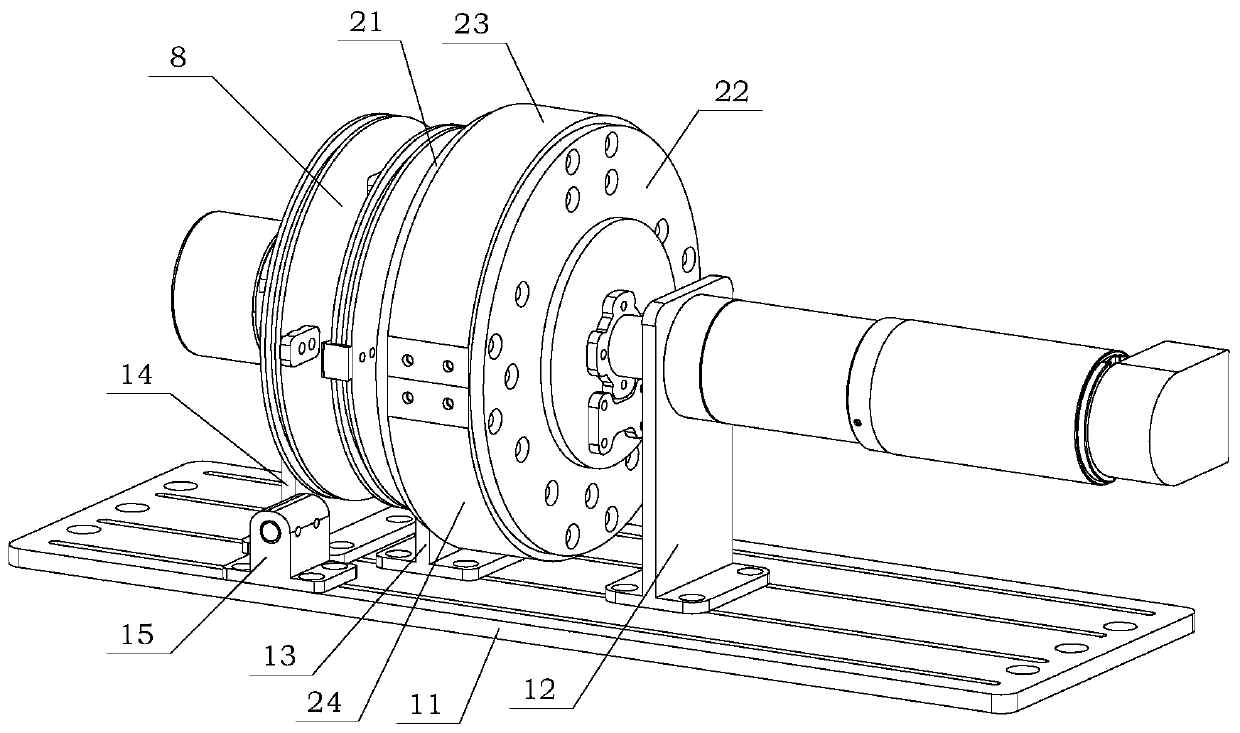
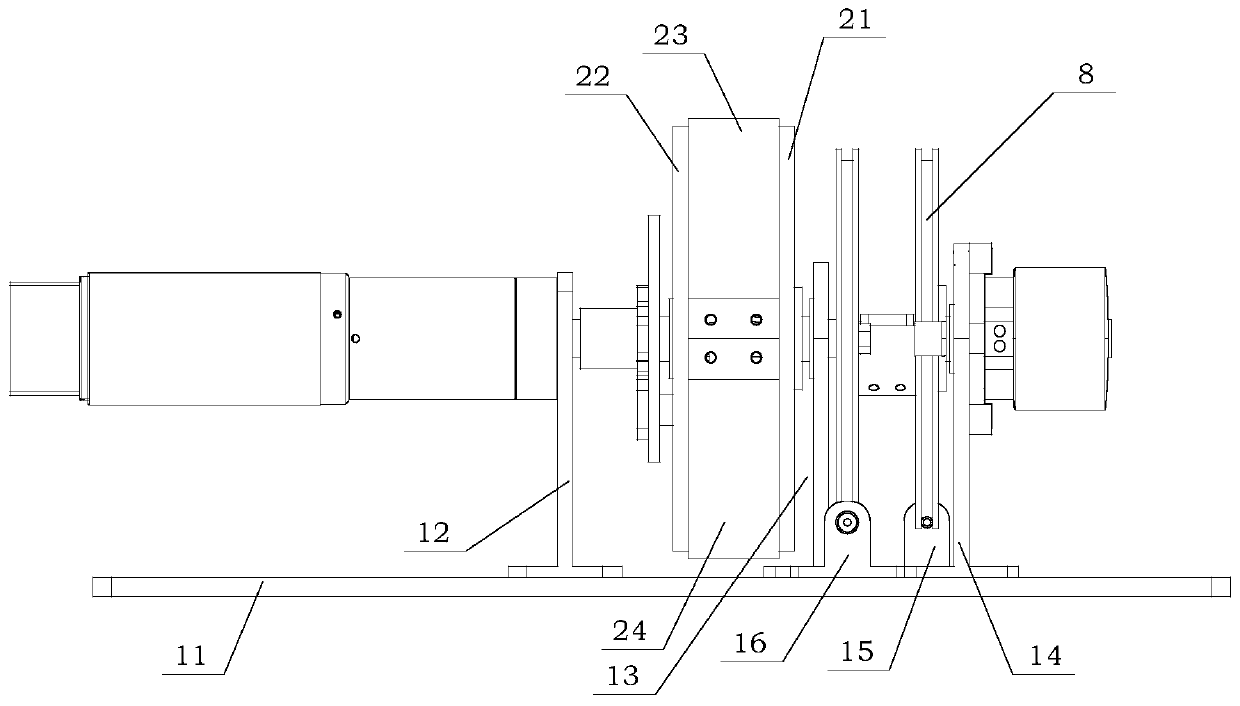
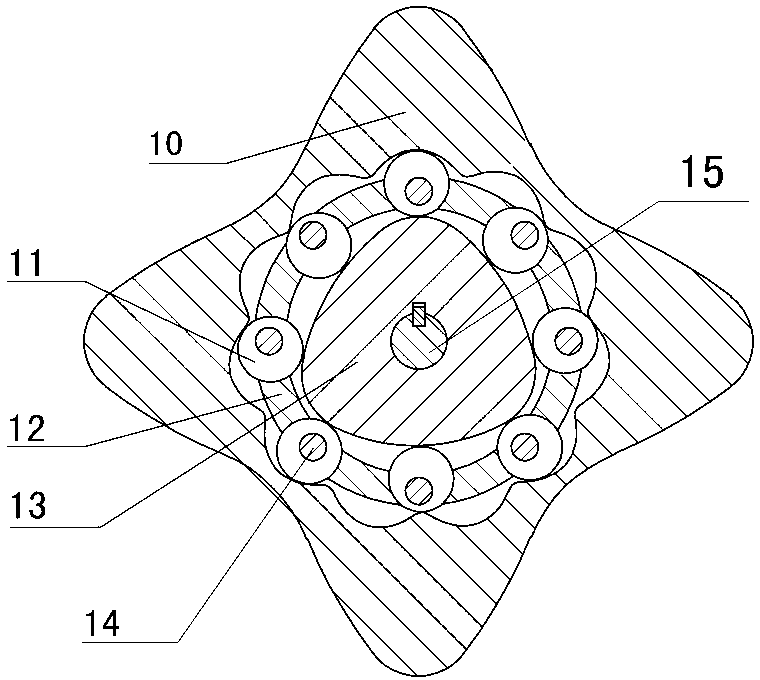
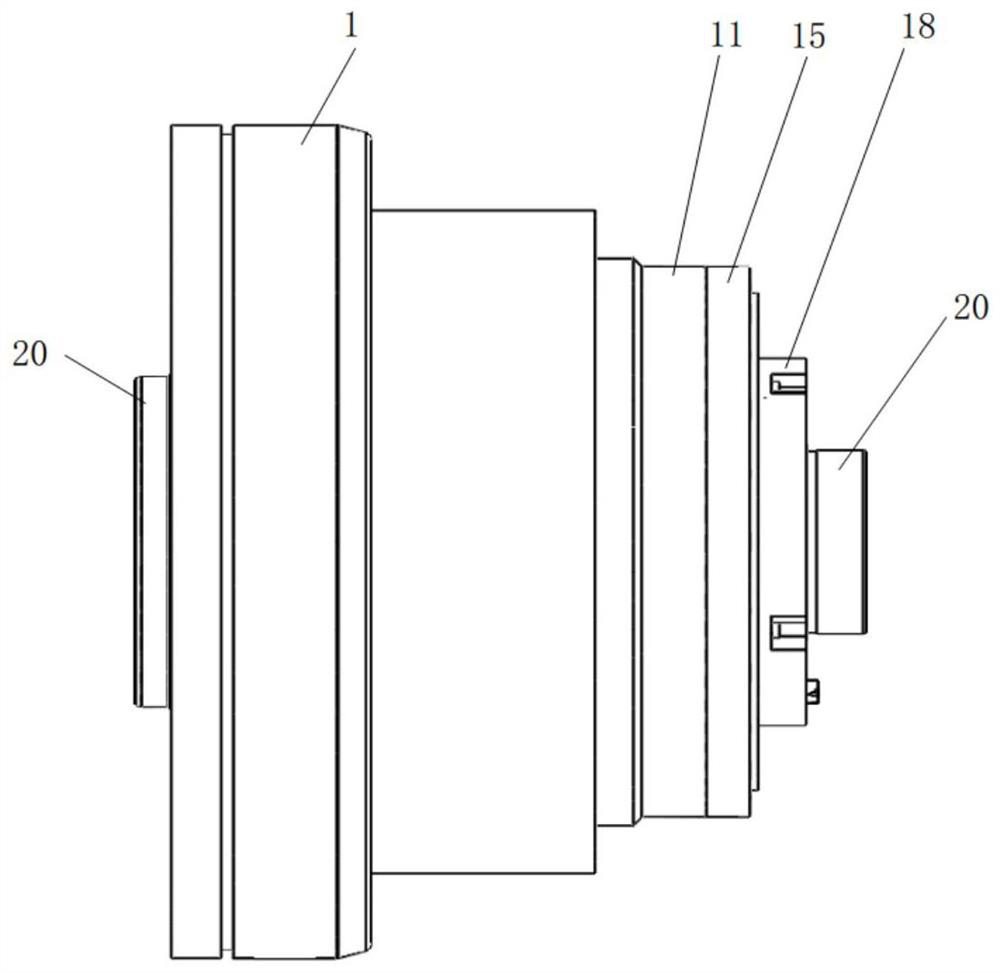
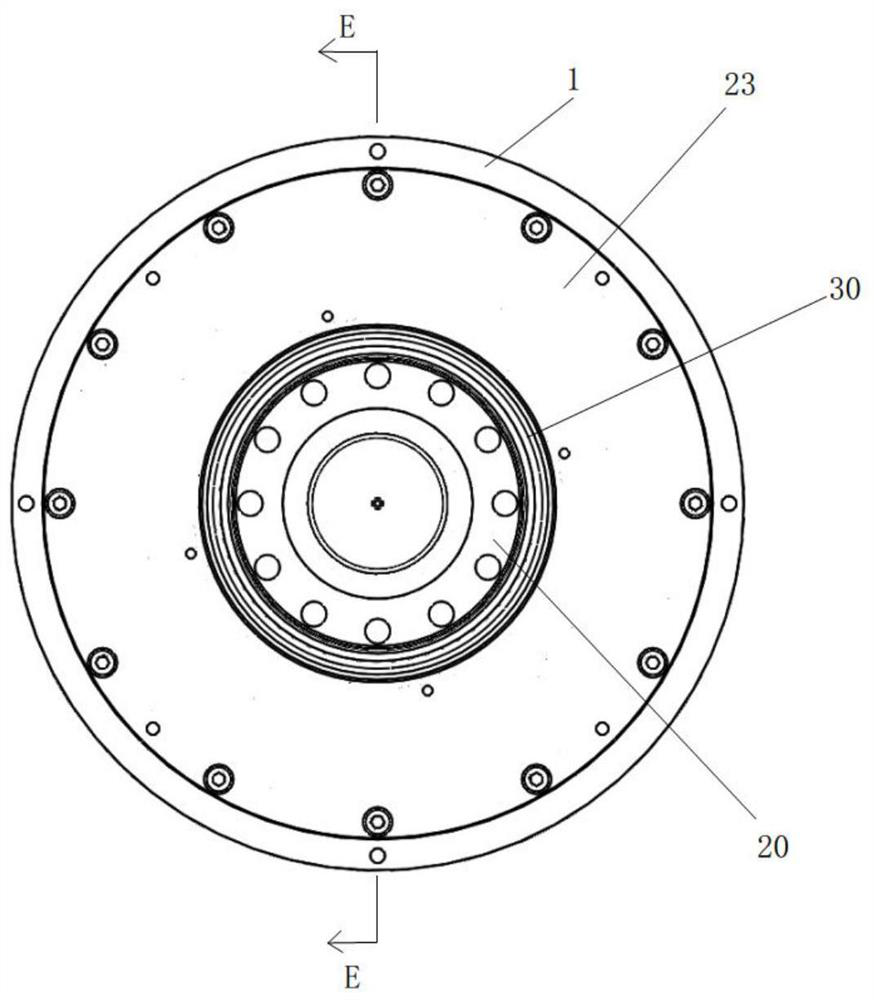
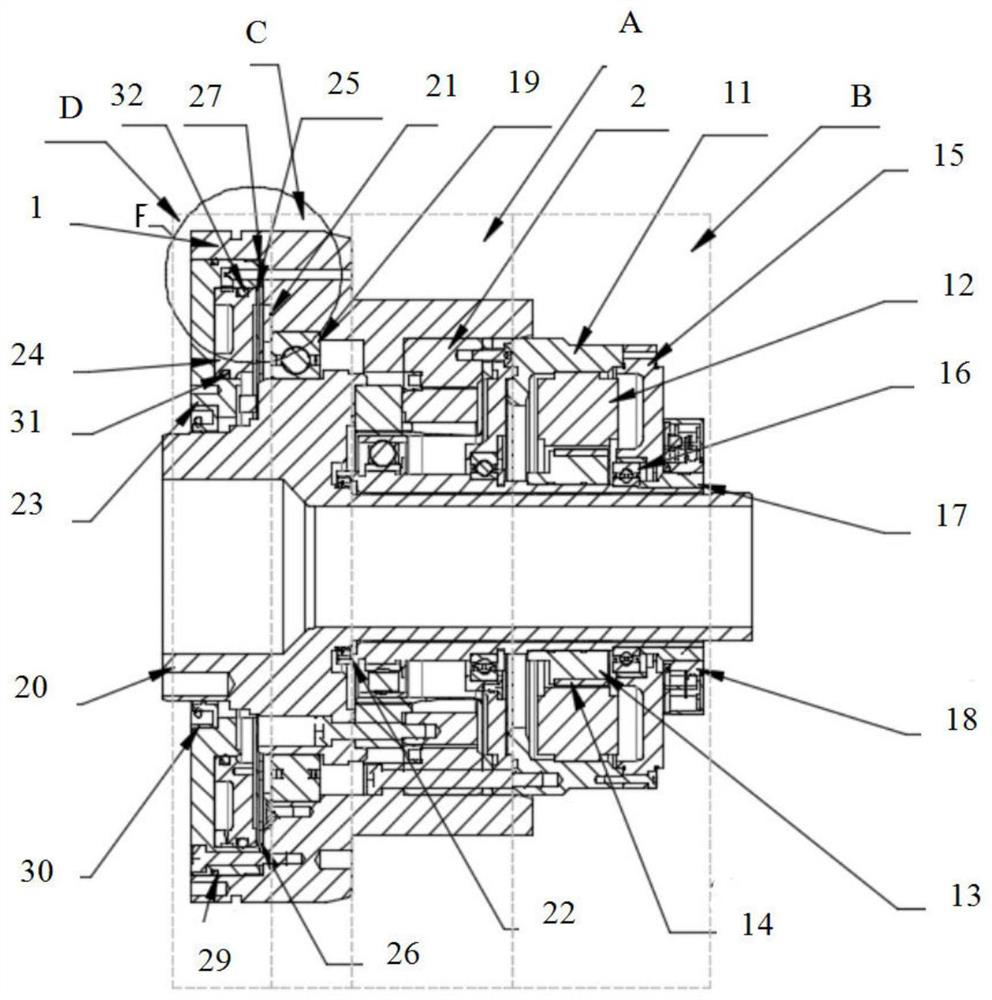
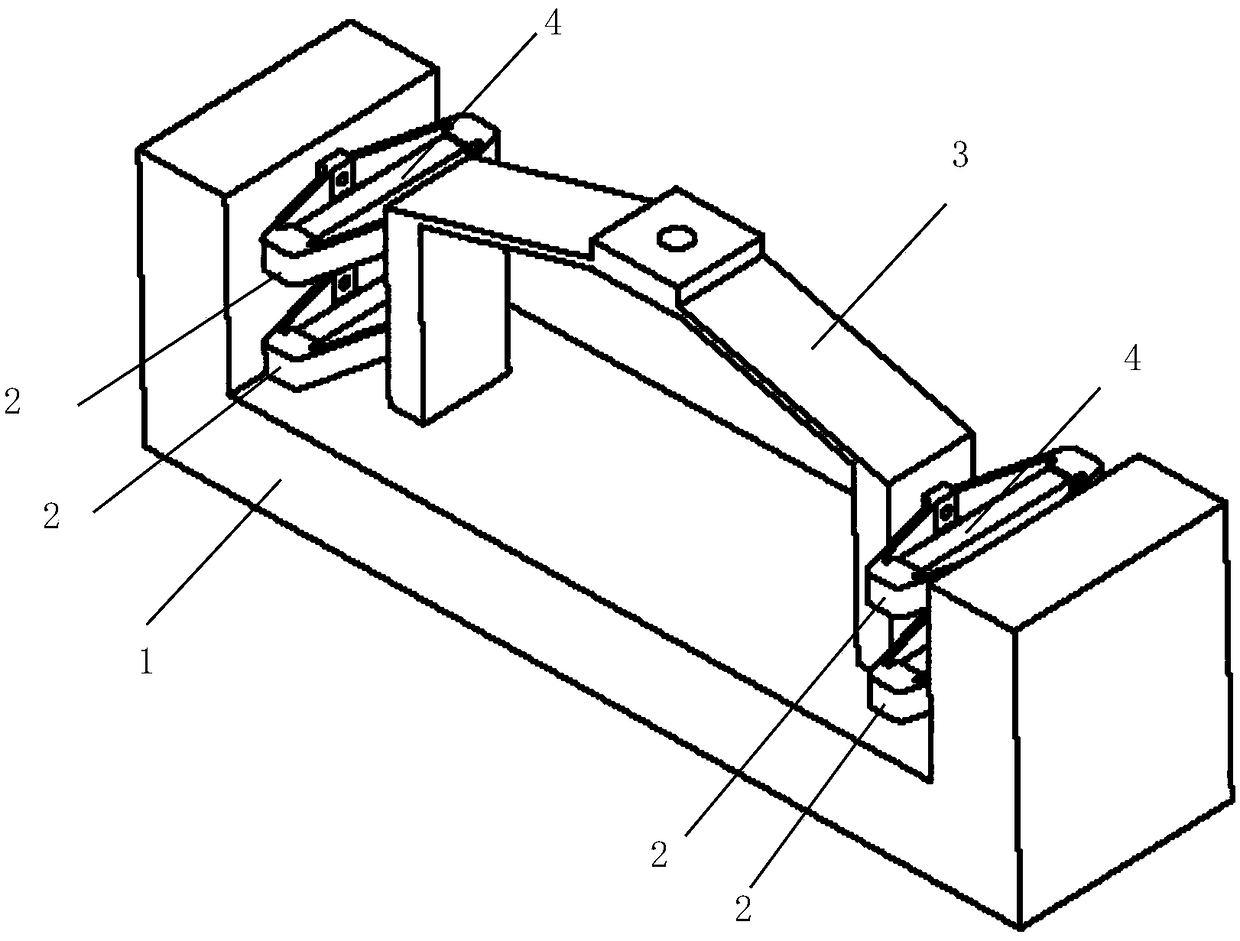
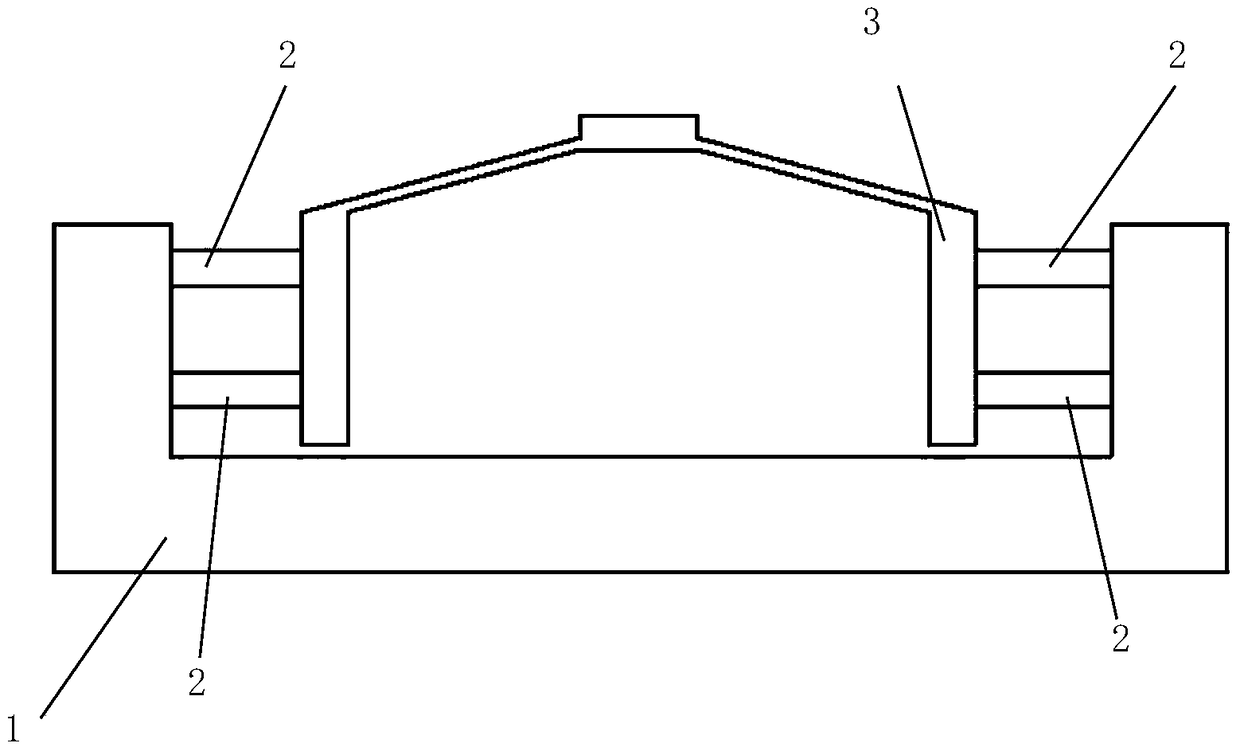
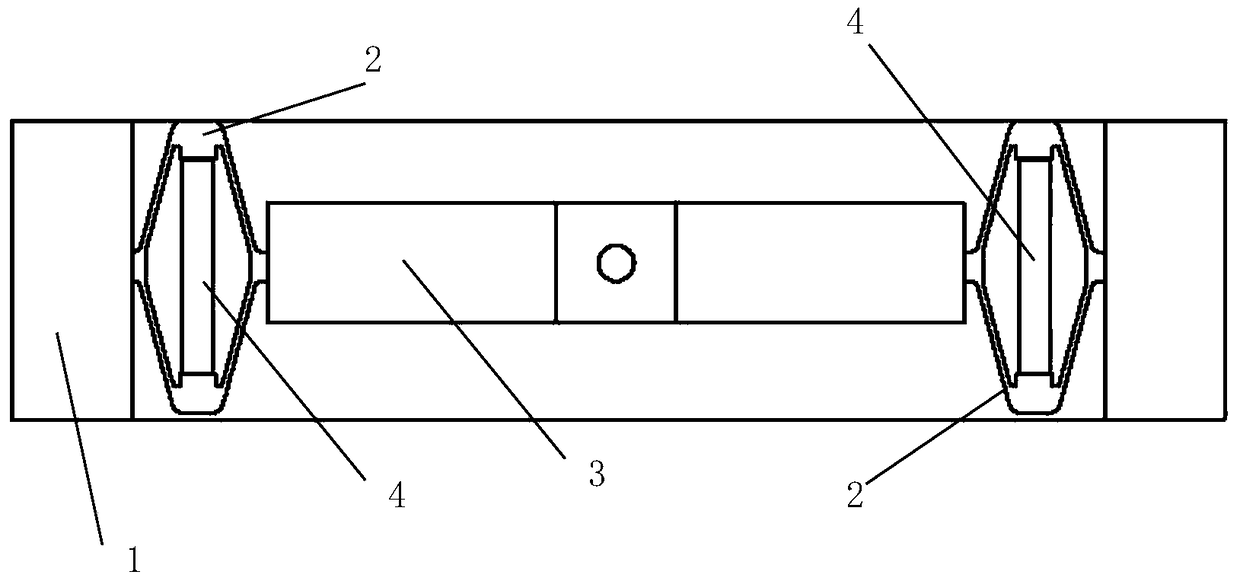
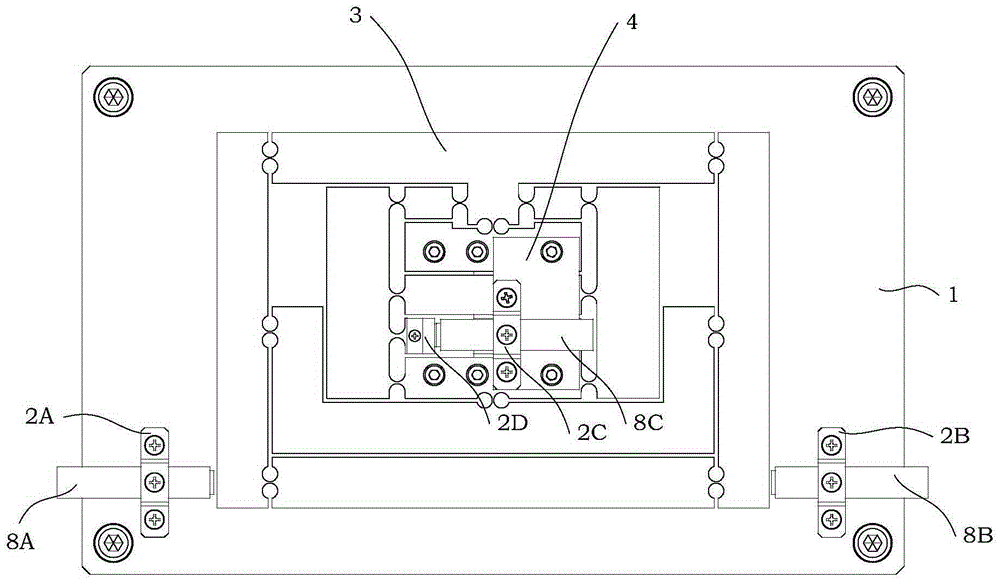
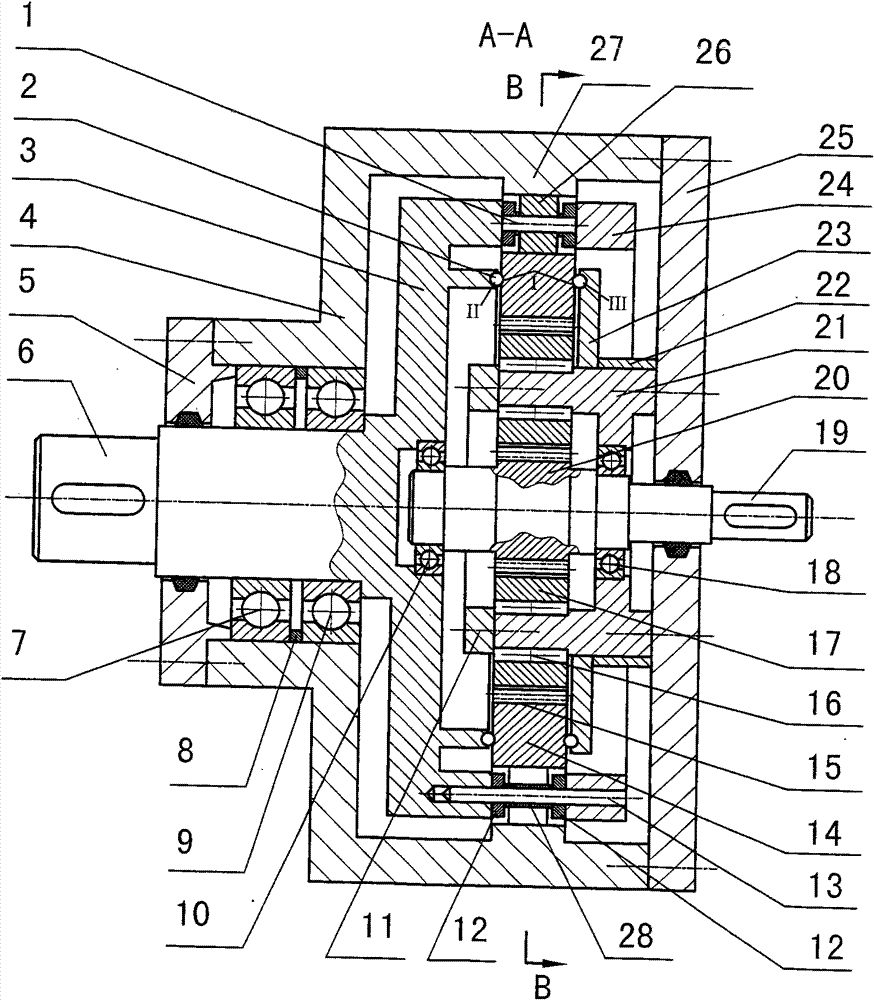
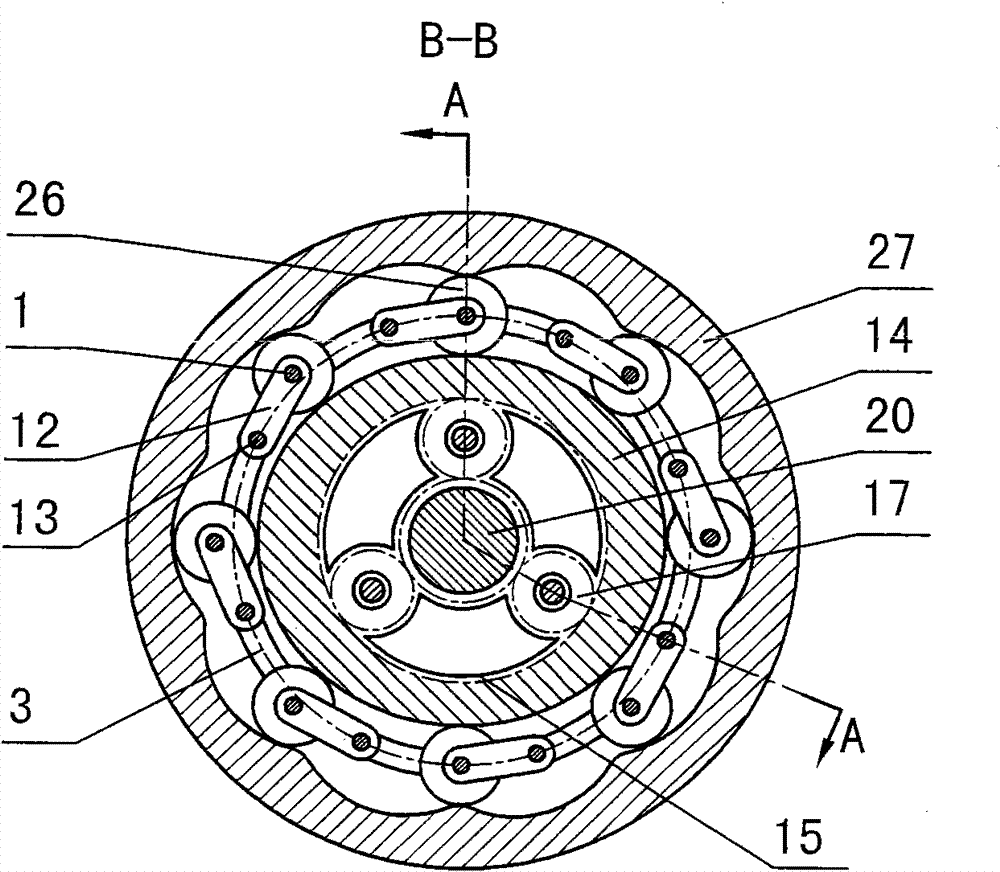
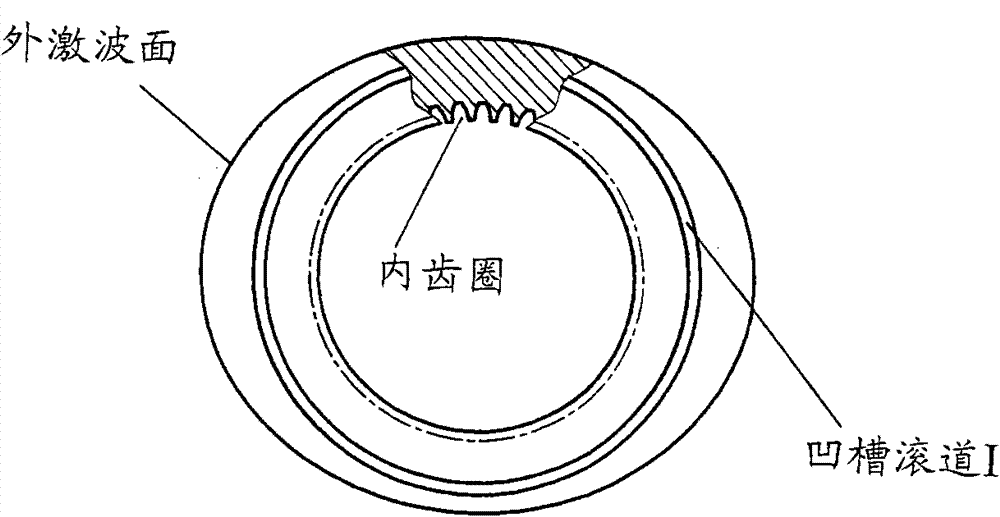
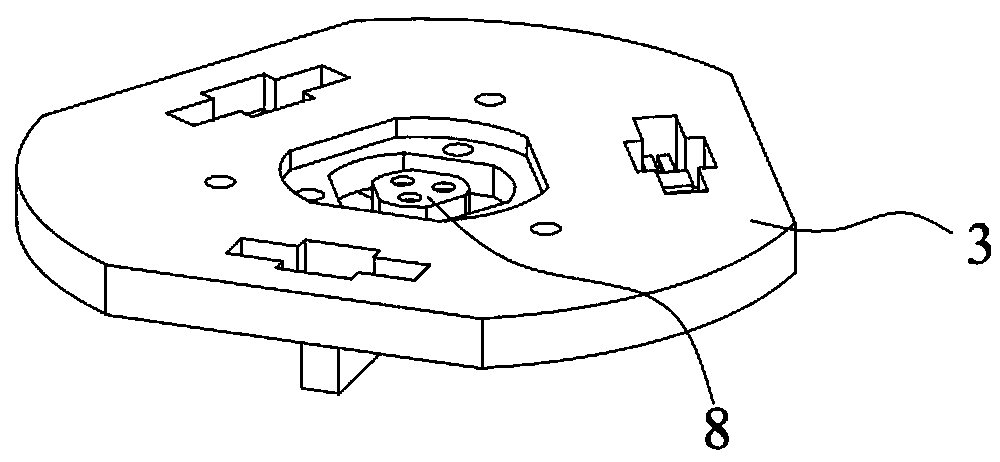
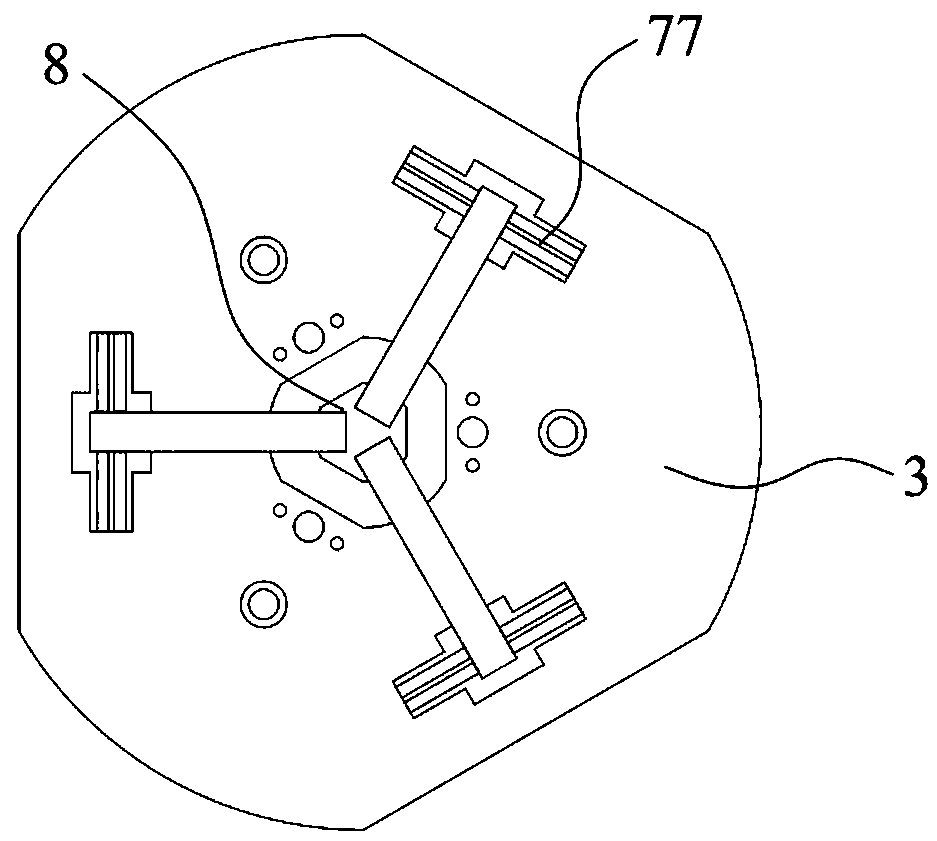
Two-phase shock wave swing link movable-teeth compound transmission speed reducer
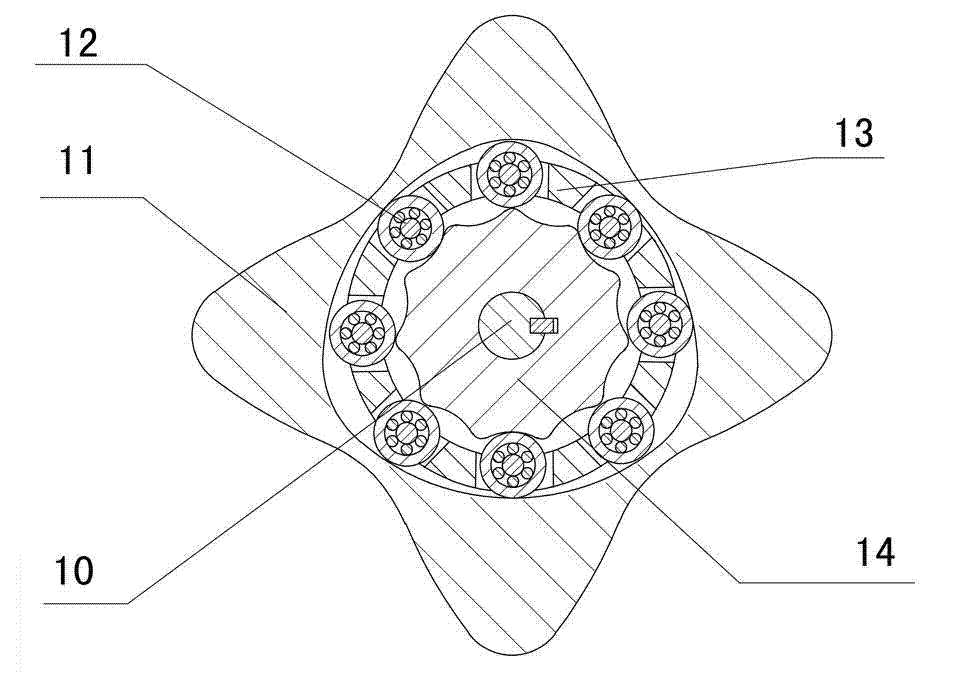
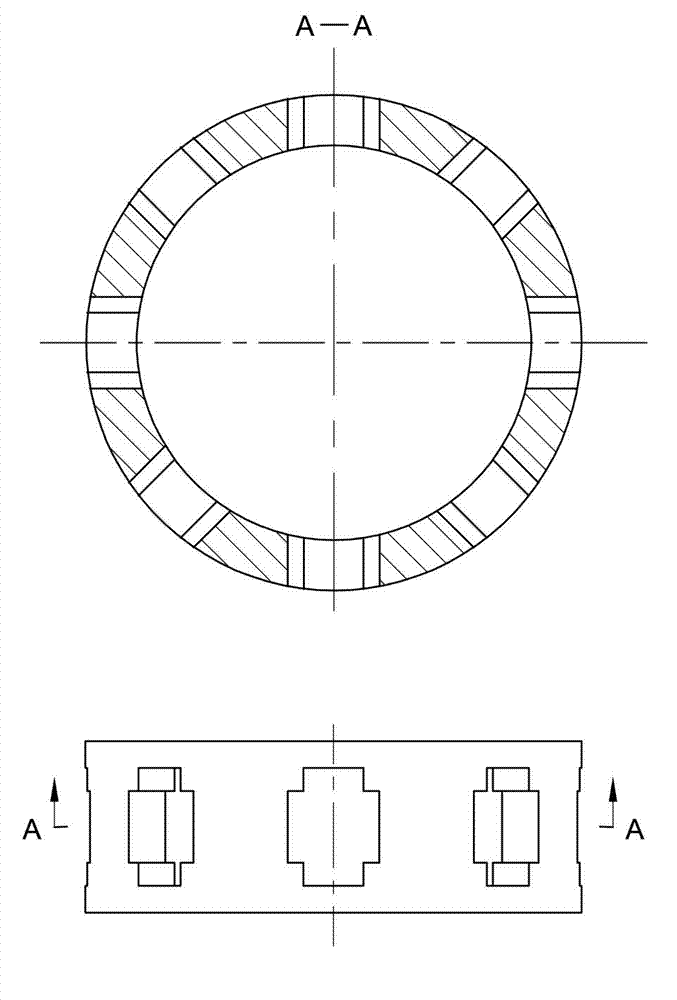
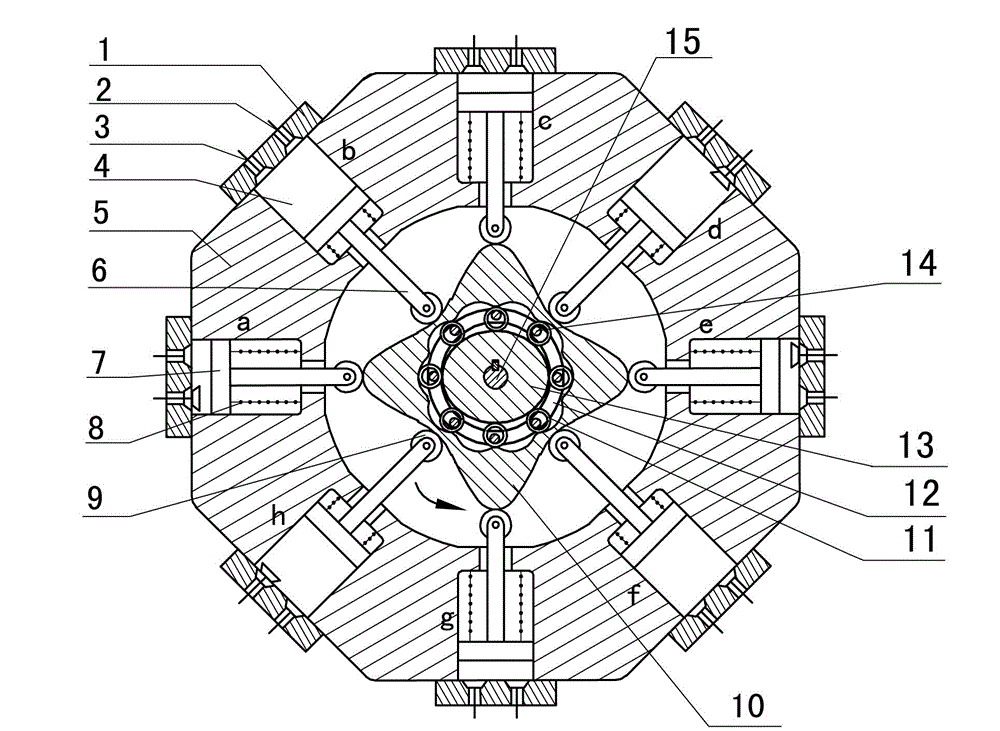
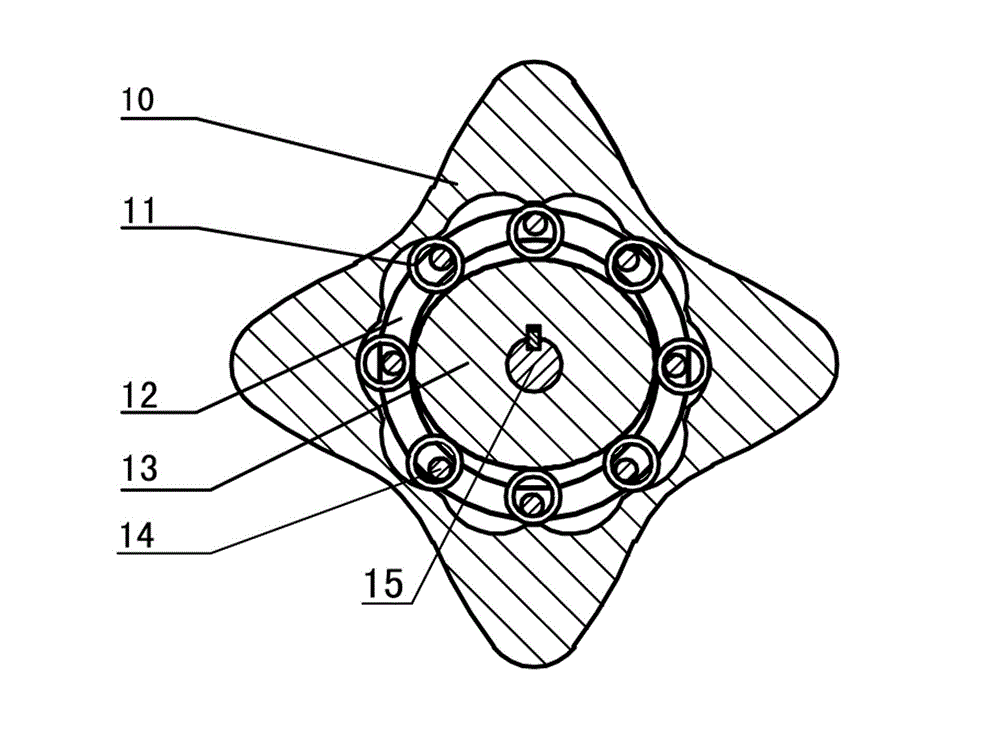
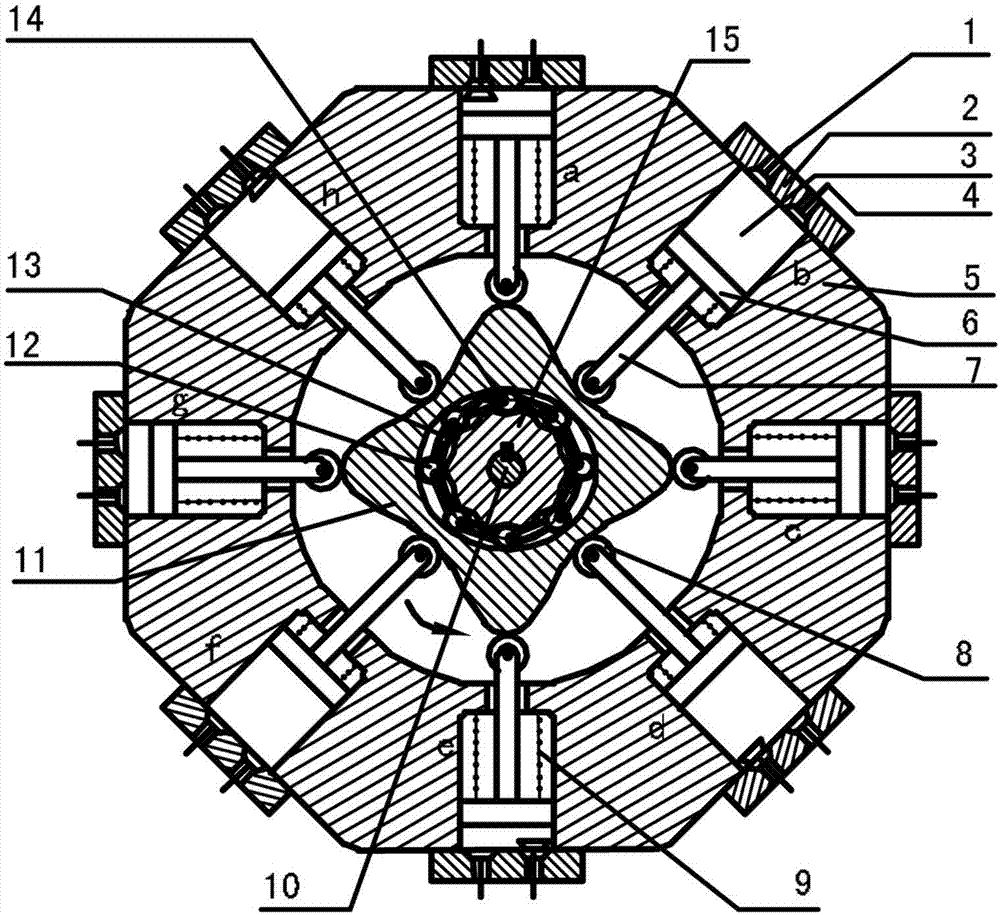
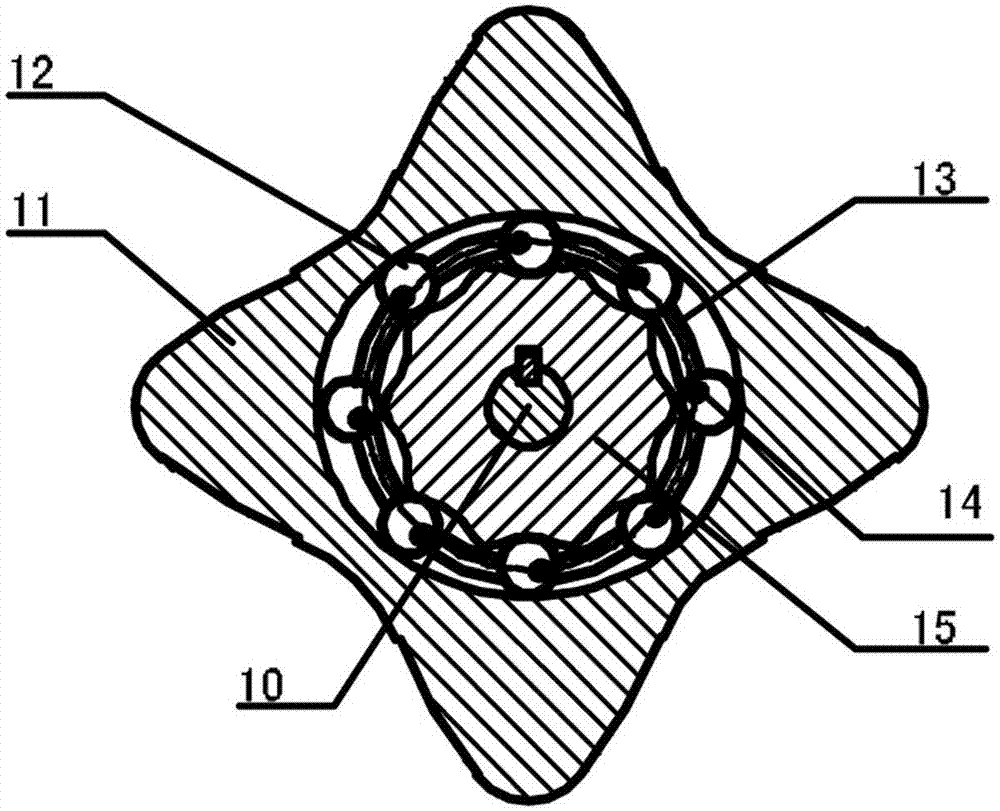
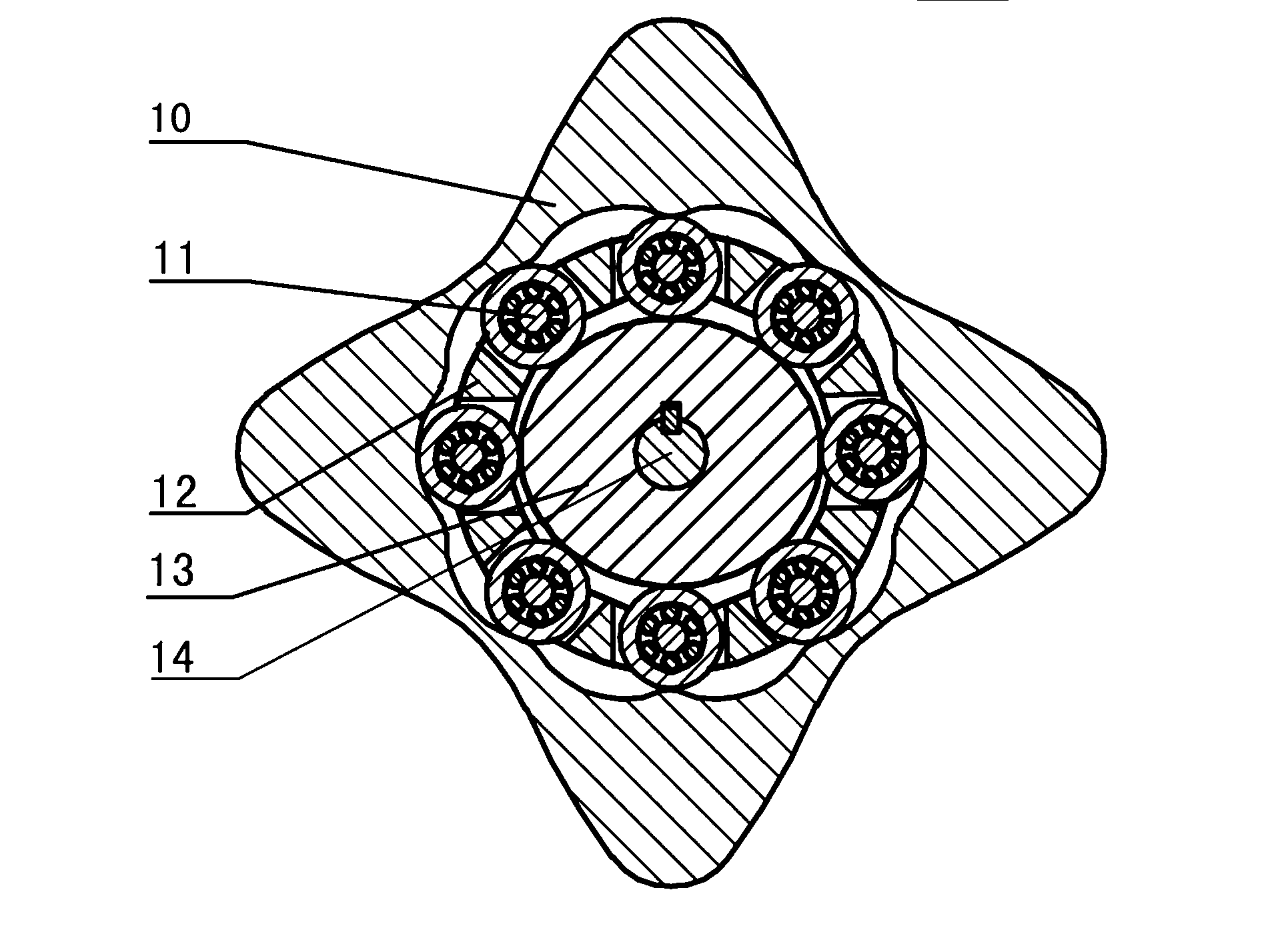
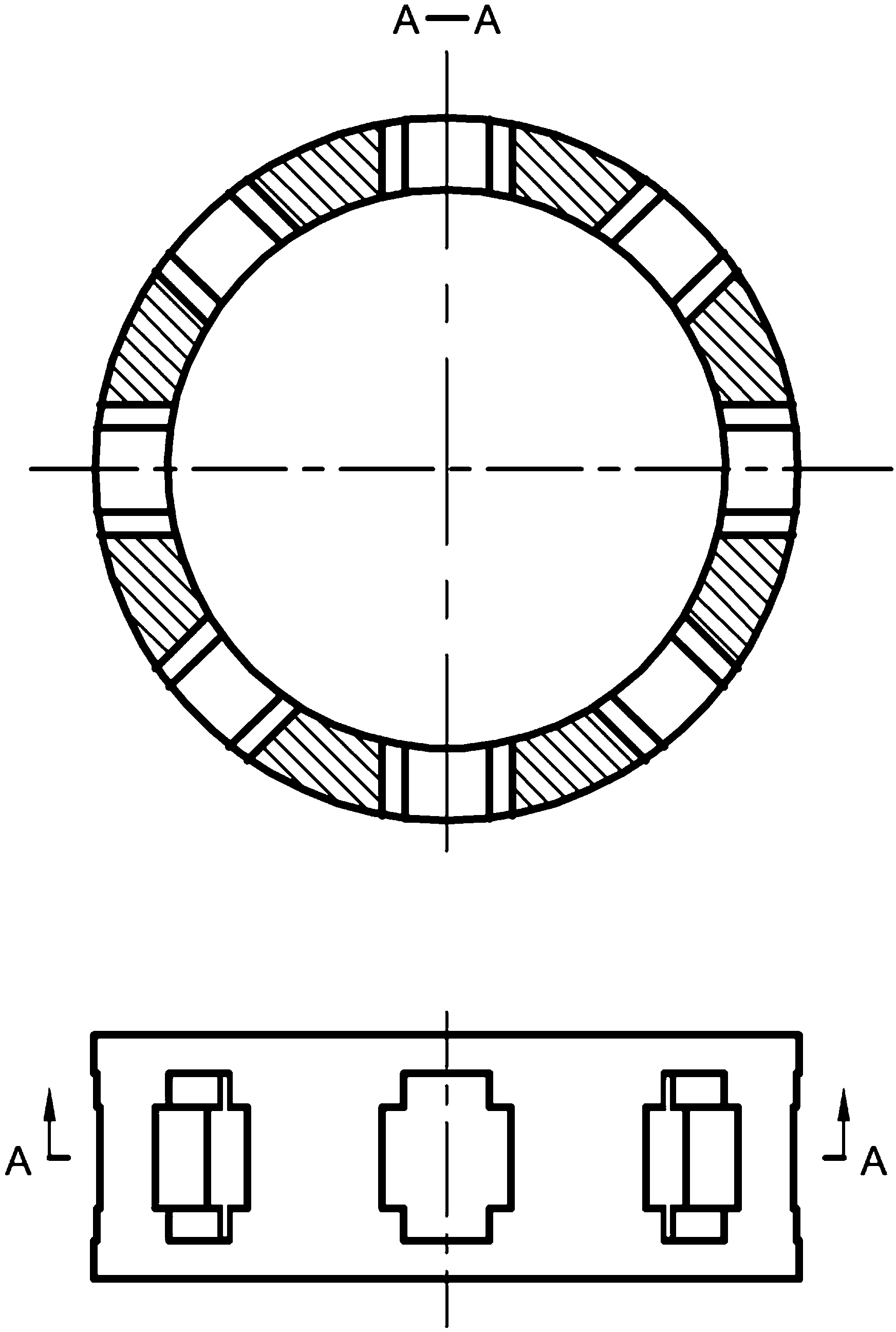
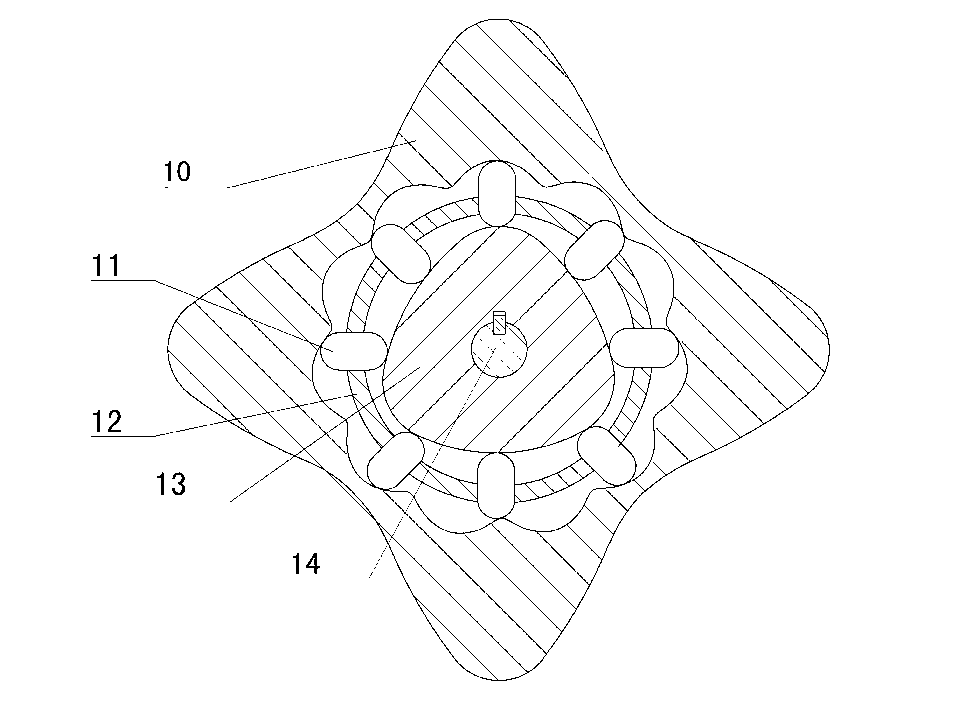
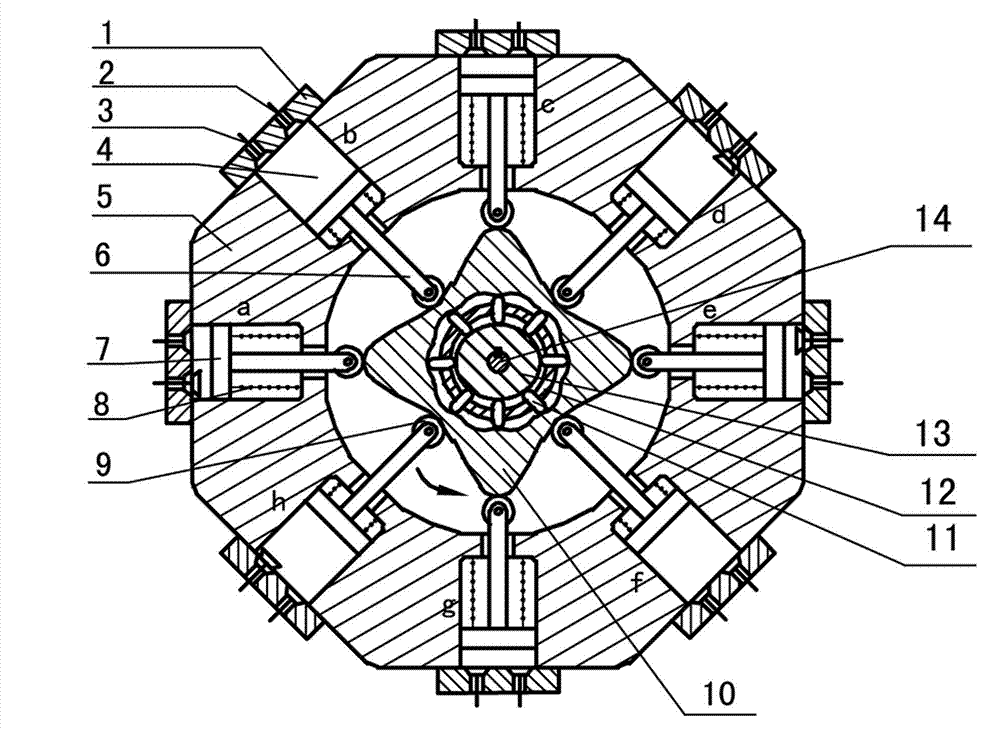
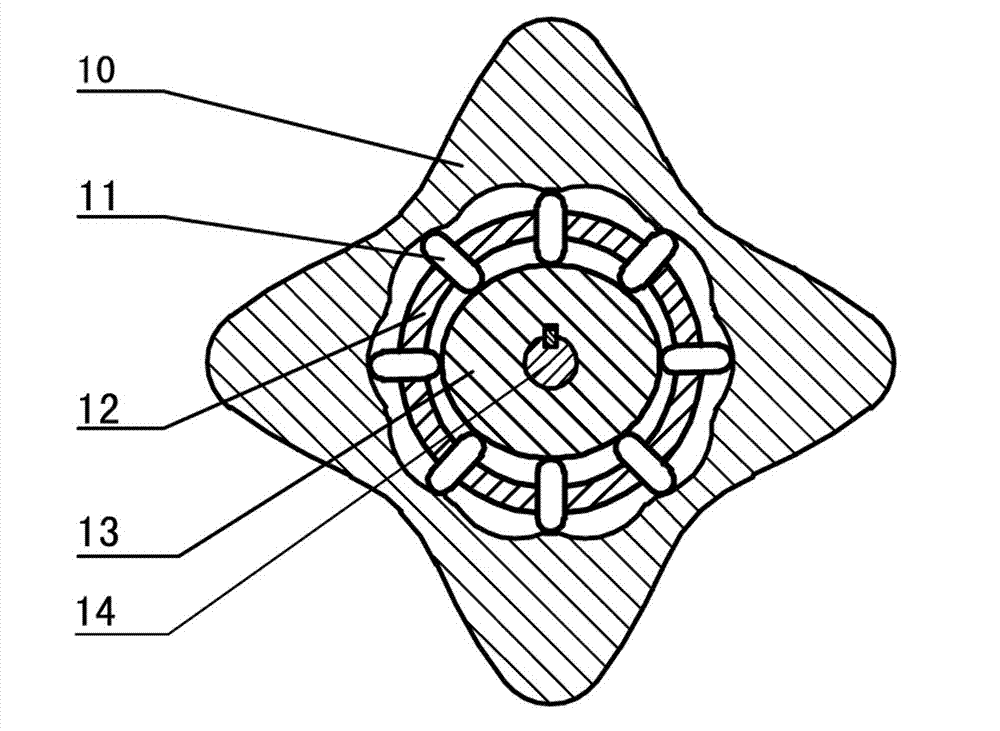
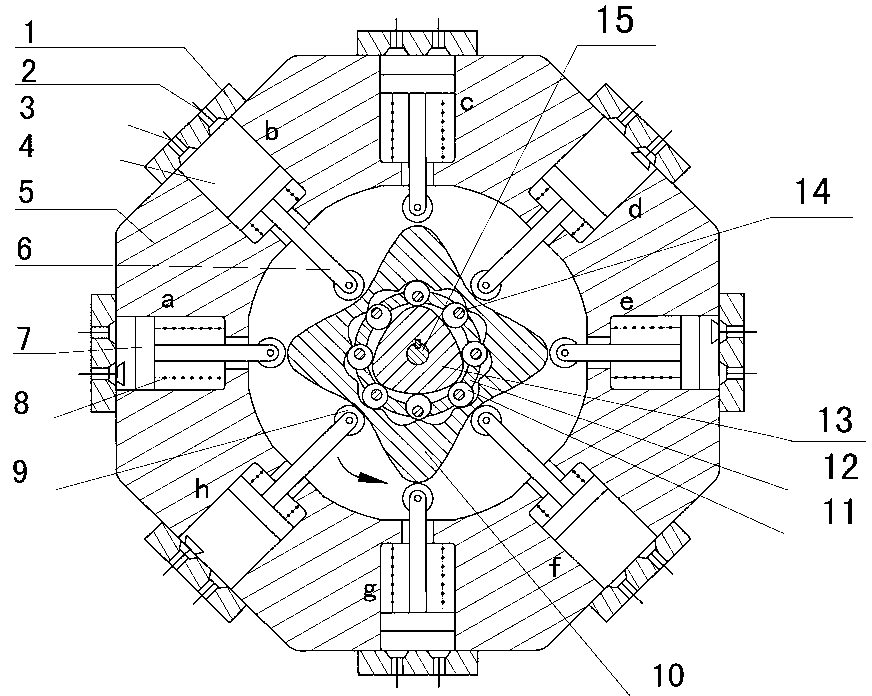
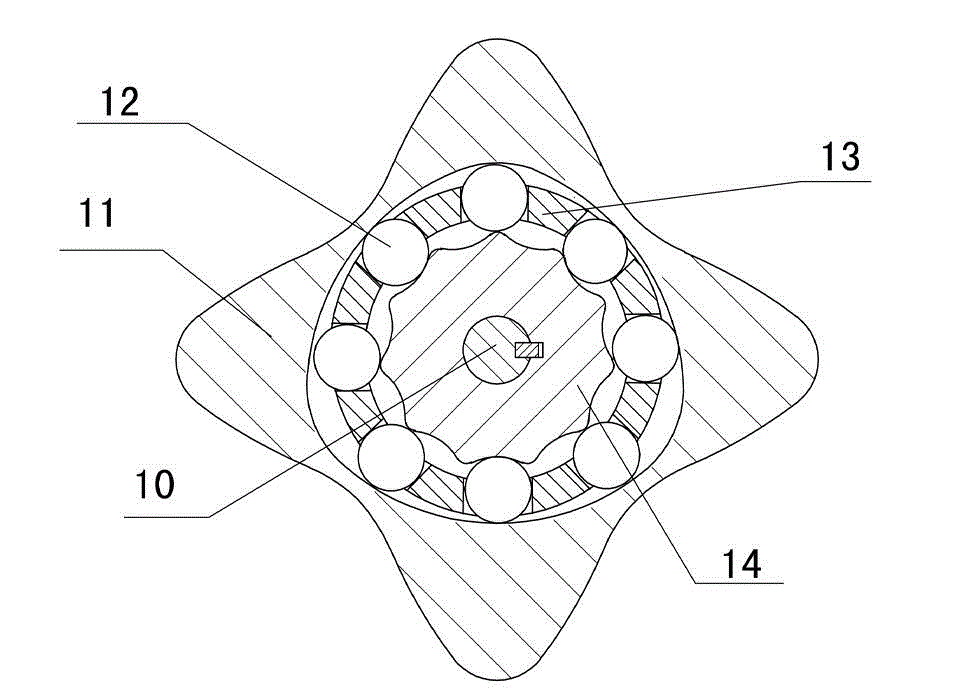
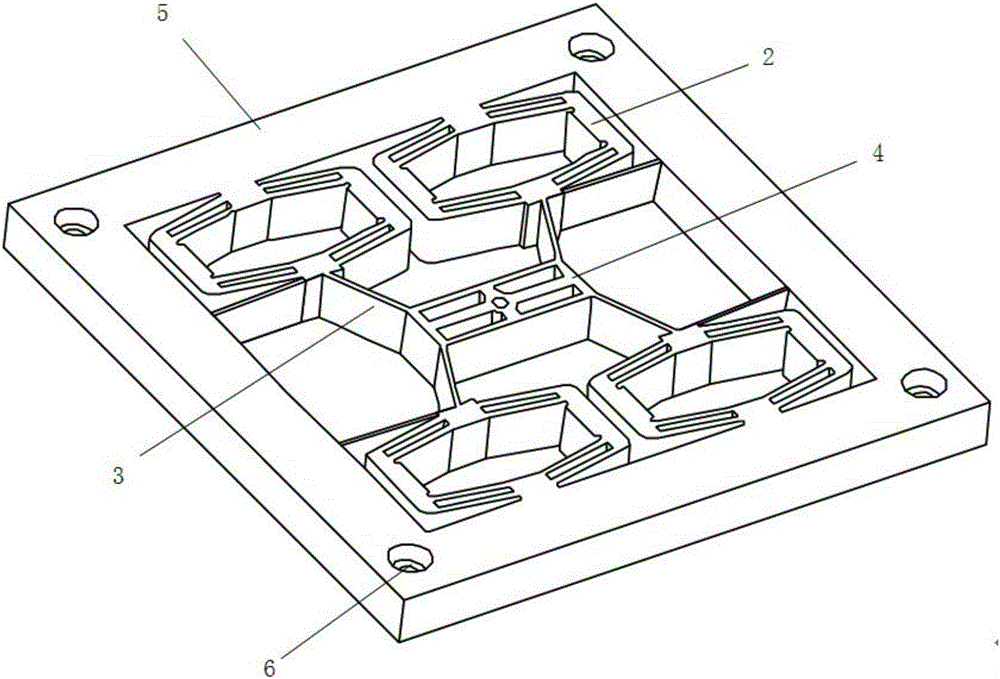
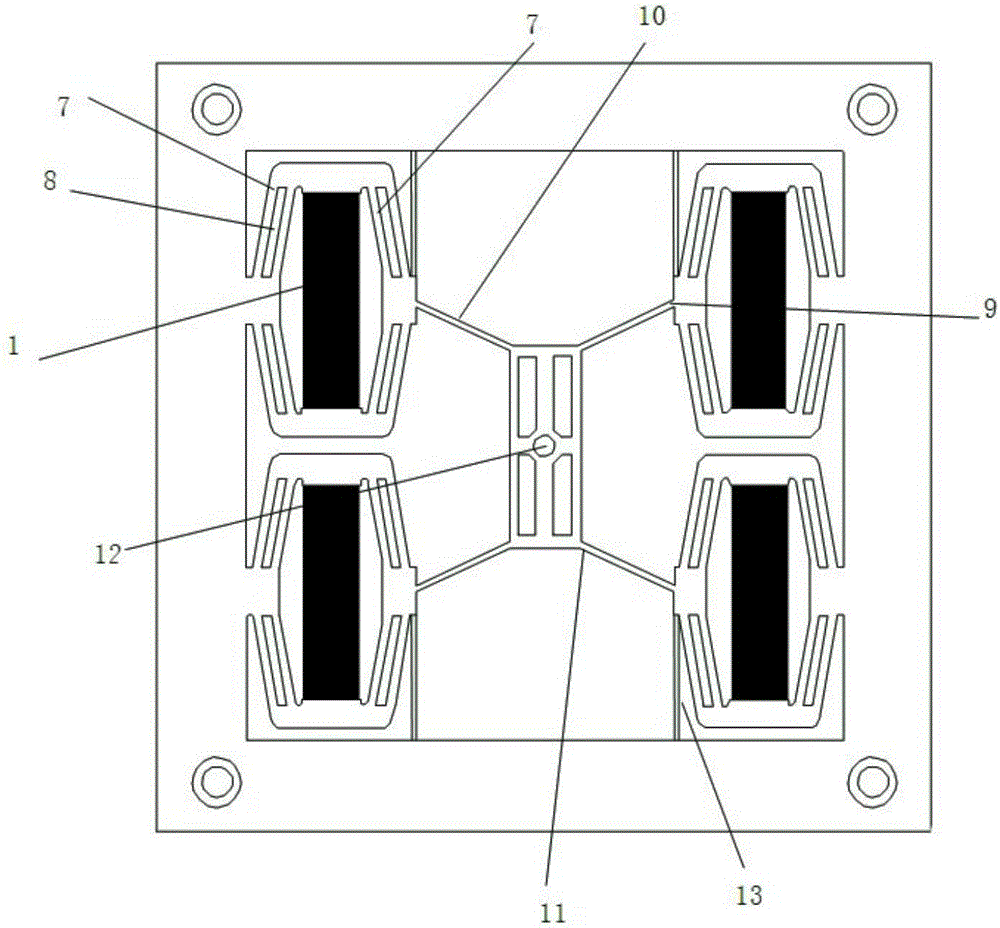
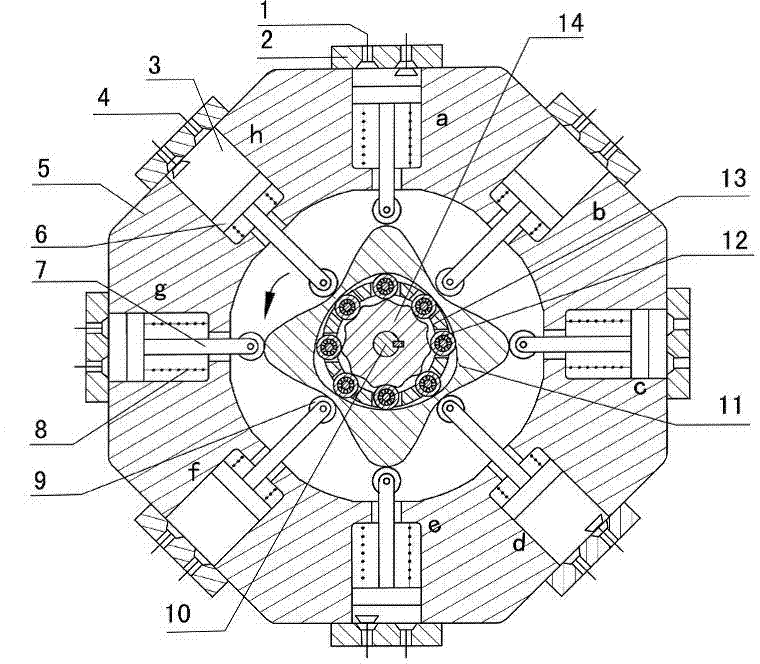
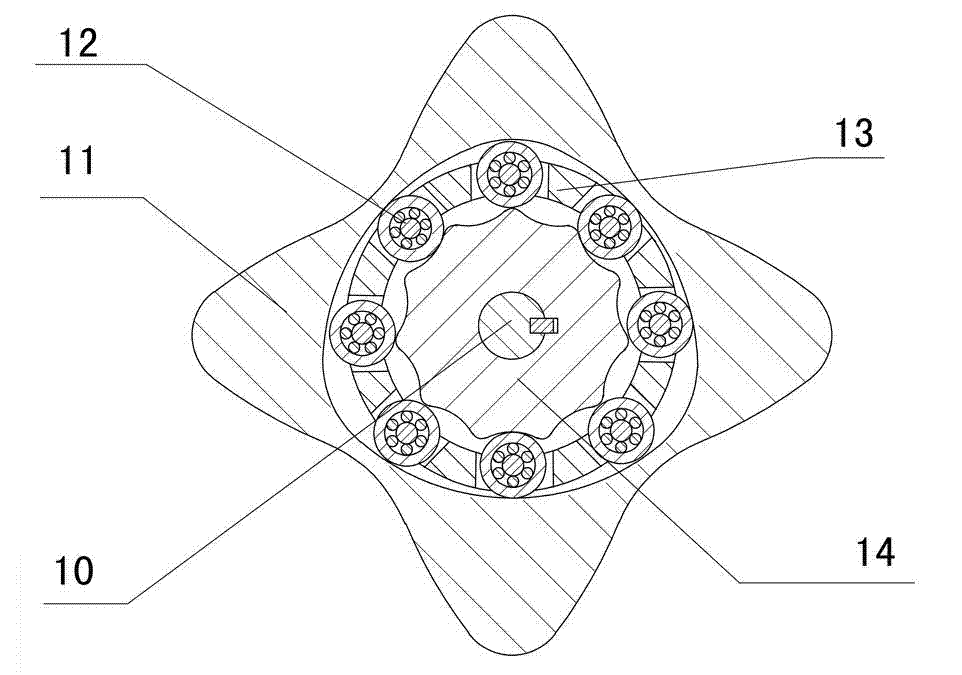
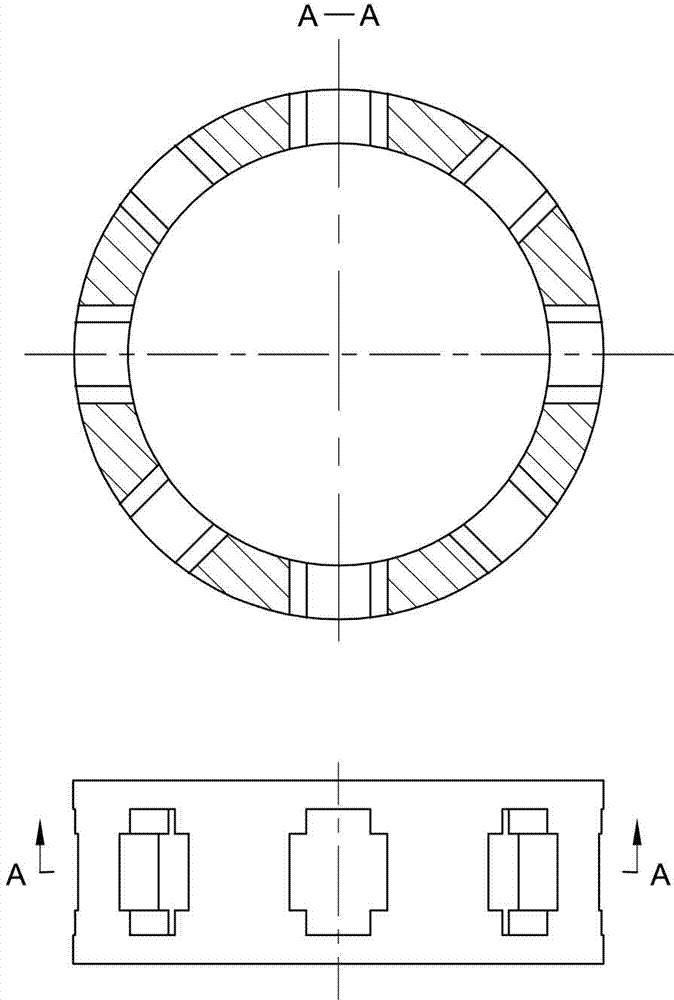
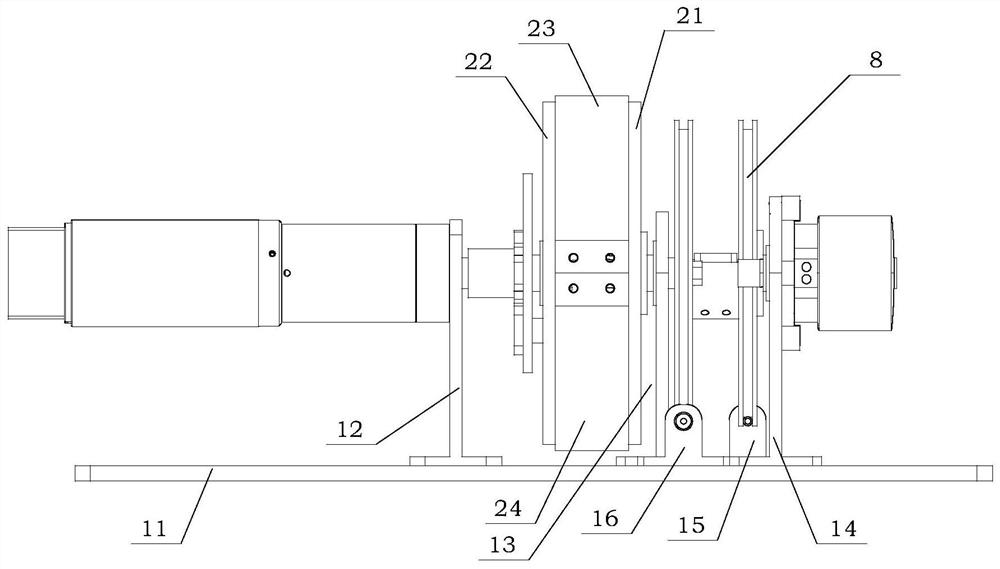
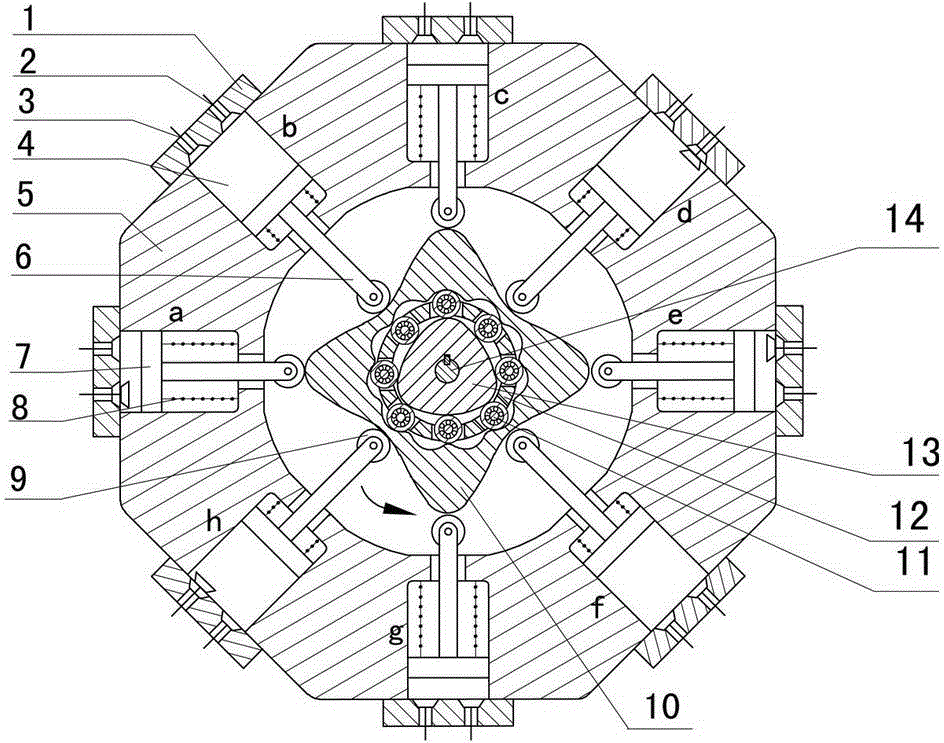
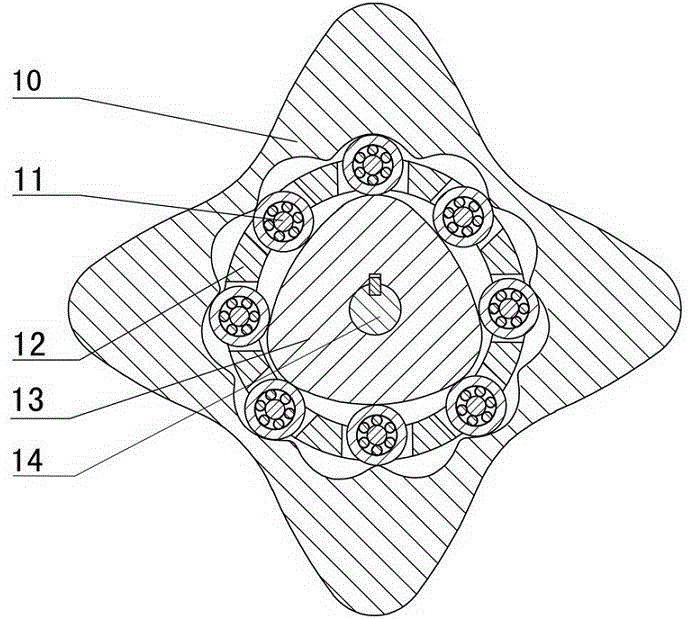
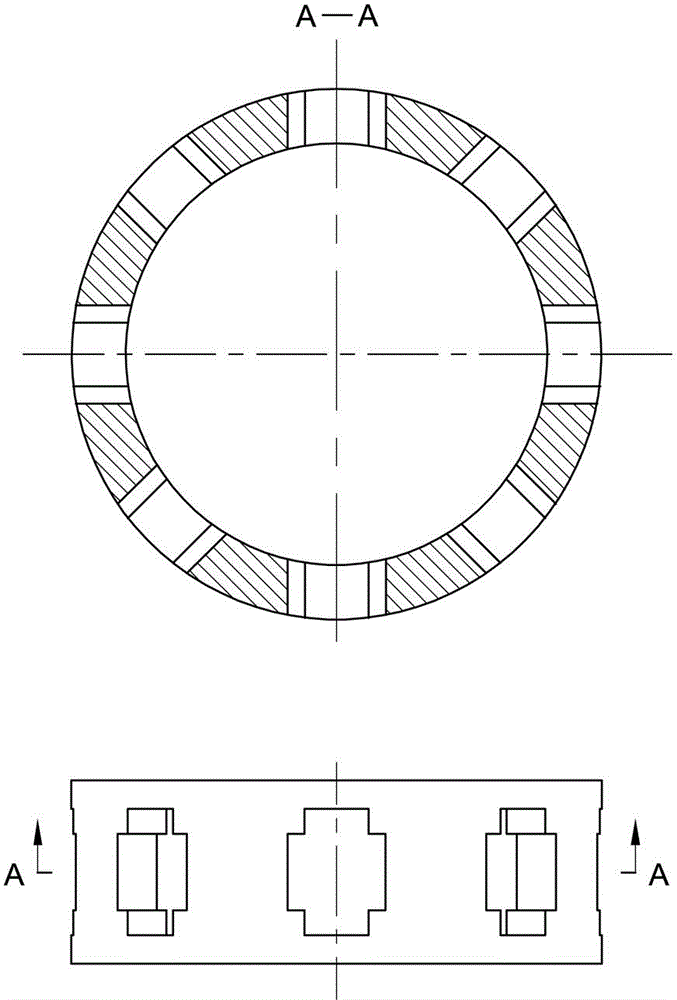
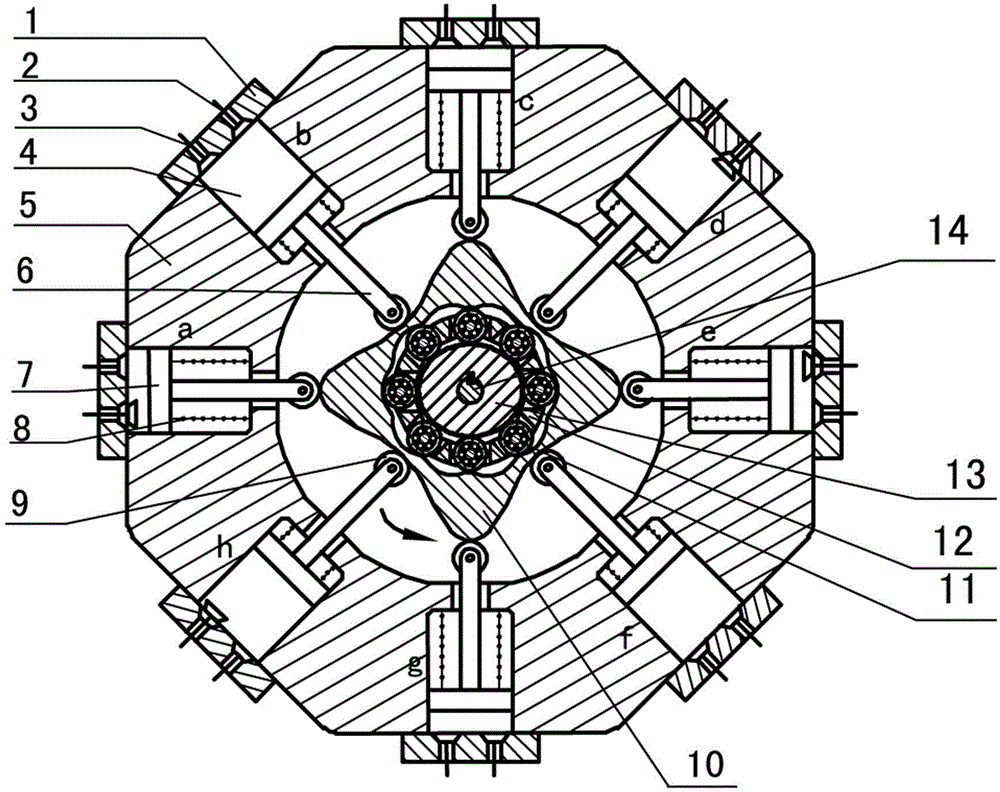
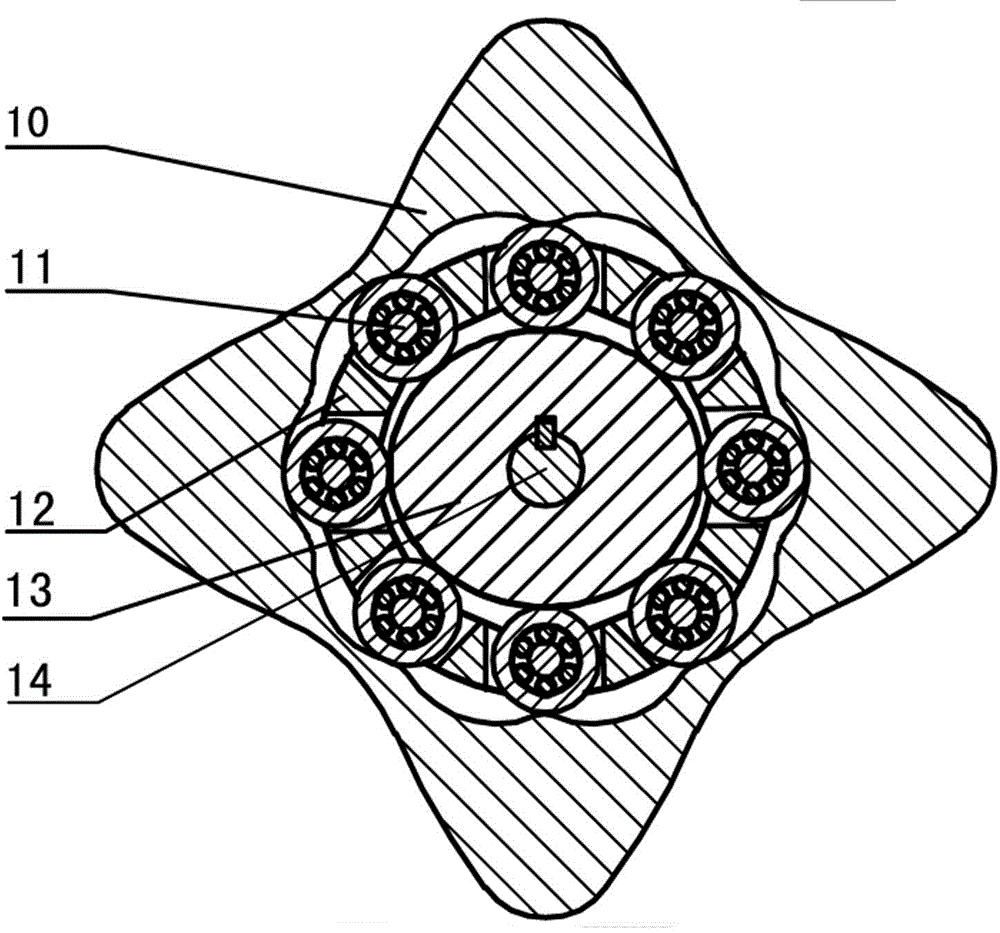
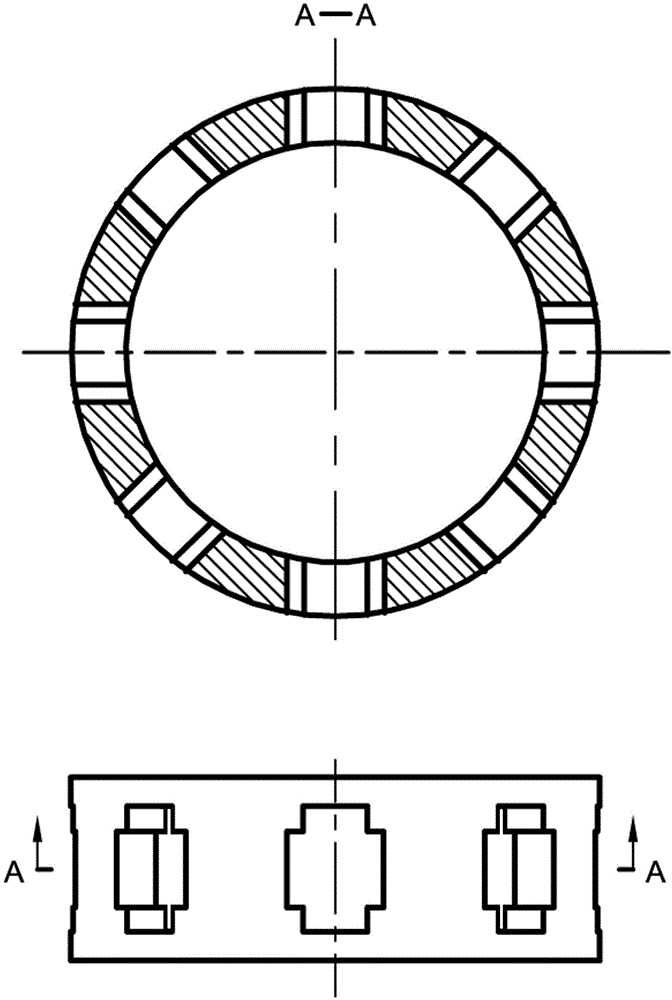
The invention discloses a two-phase shock wave swing link movable-teeth compound transmission speed reducer and relates to the technical field of mechanical transmission. The compound transmission speed reducer mainly comprises a two-phase shock wave device, movable teeth, a swing link, a pin shaft, a movable-teeth frame, a central wheel and a fixed axis gear train which is embedded into the shock wave device. The exterior of the shock wave device has a cam profile and the interior of the shock wave device has an inner gear ring profile; an input gear is engaged with a pinion and the pinion is engaged with the inner gear ring so as to form the fixed axis gear train; the input gear and an input shaft are integrated; the rotation of the input gear is decelerated through the fixed axis gear train and drives the shock wave device to rotate; the shock wave device and the movable teeth are in rolling contact engagement, so that the movable teeth swing along with the swing link and moves along the tooth profile of the central wheel simultaneously; and the shock wave device and the central wheel coact to make the movable teeth drive the movable-teeth frame to rotate and output power through the swing link. By setting pre-deceleration in swing link movable-teeth transmission, the transmission ratio is increased, and the problem of over-high temperature rise of movable-teeth transmission is also solved; and the speed reducer has the advantages of novel and compact structure, high bearing capacity, self-balancing stress and the like, and is suitable for decelerating transmission between two coaxial shafts.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
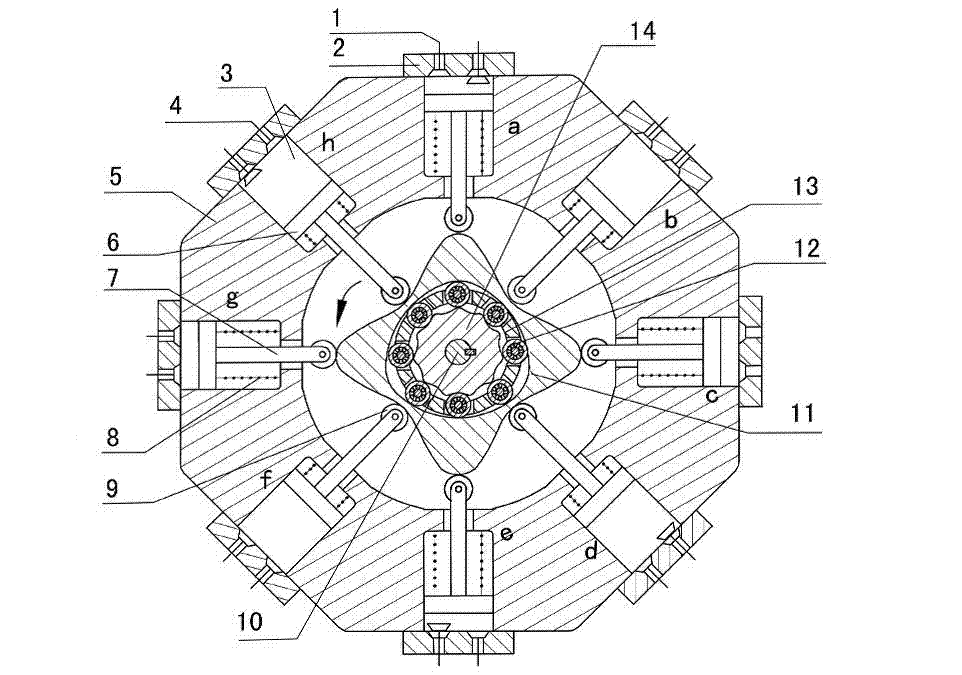
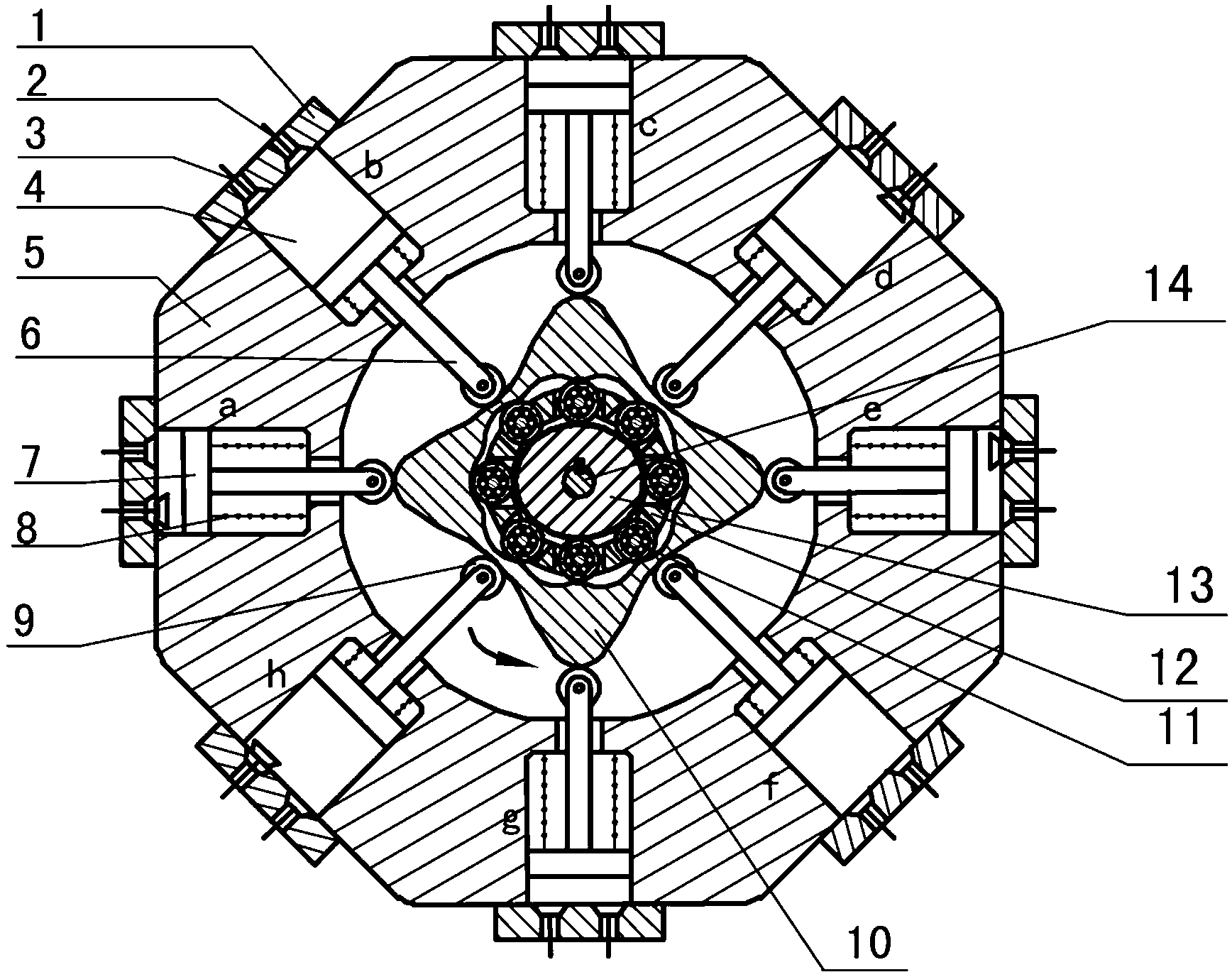
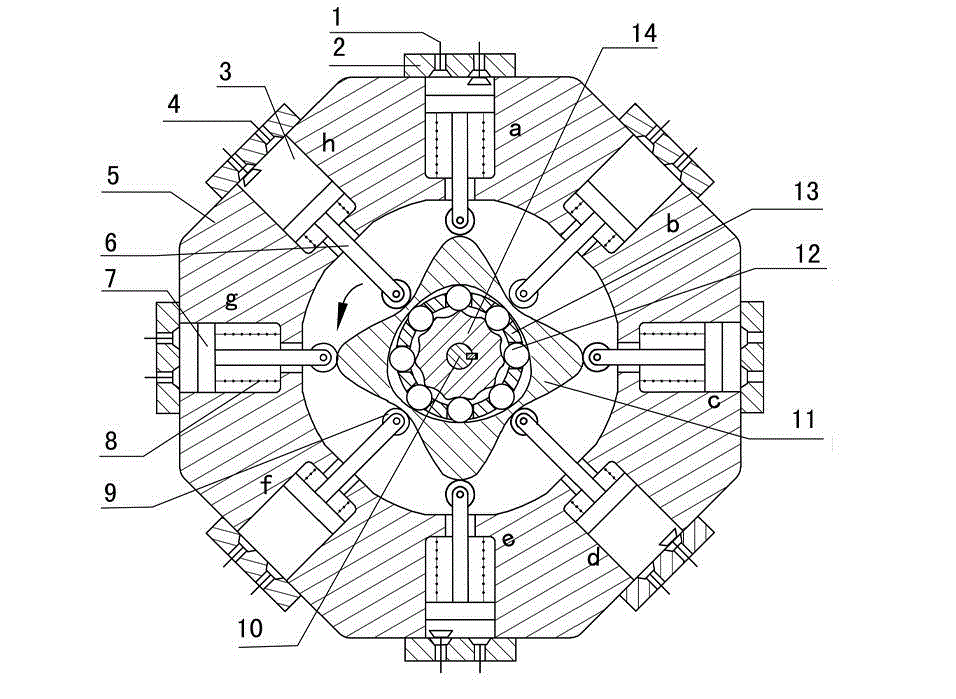
Outer convex inner arbitrary gear difference cam rolling moving transmission internal-combustion engine
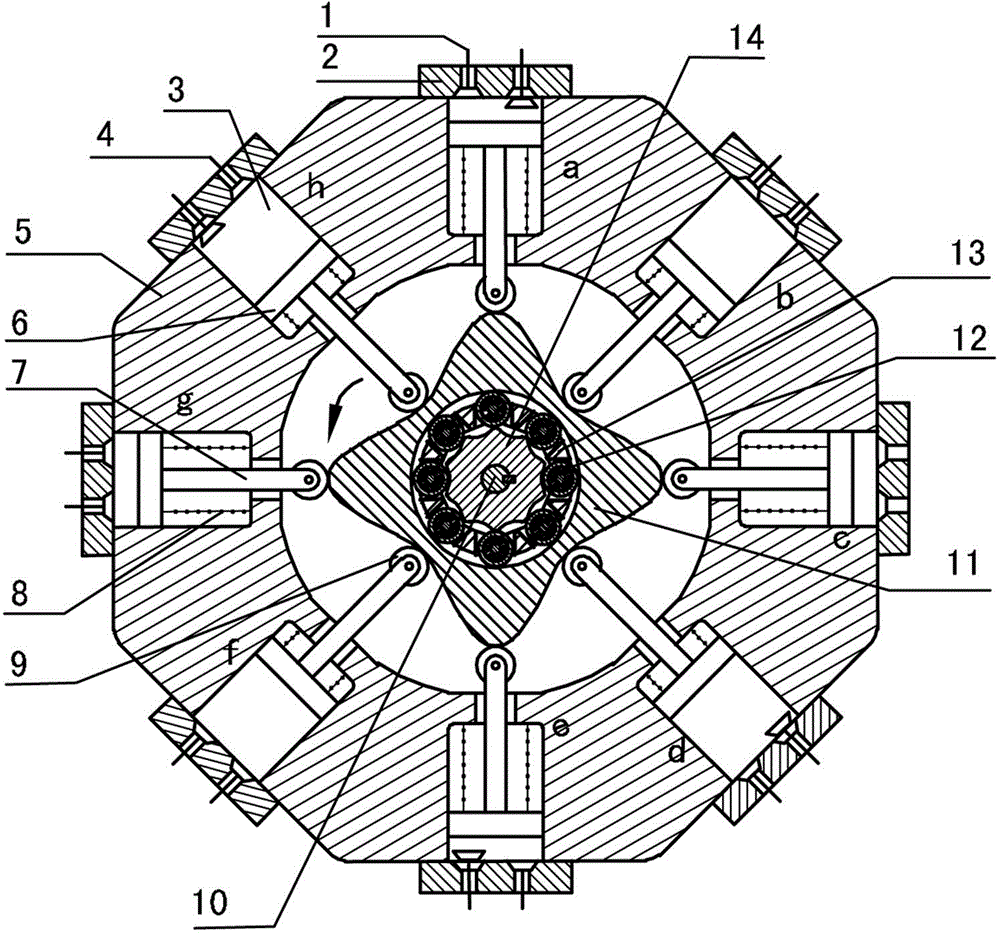
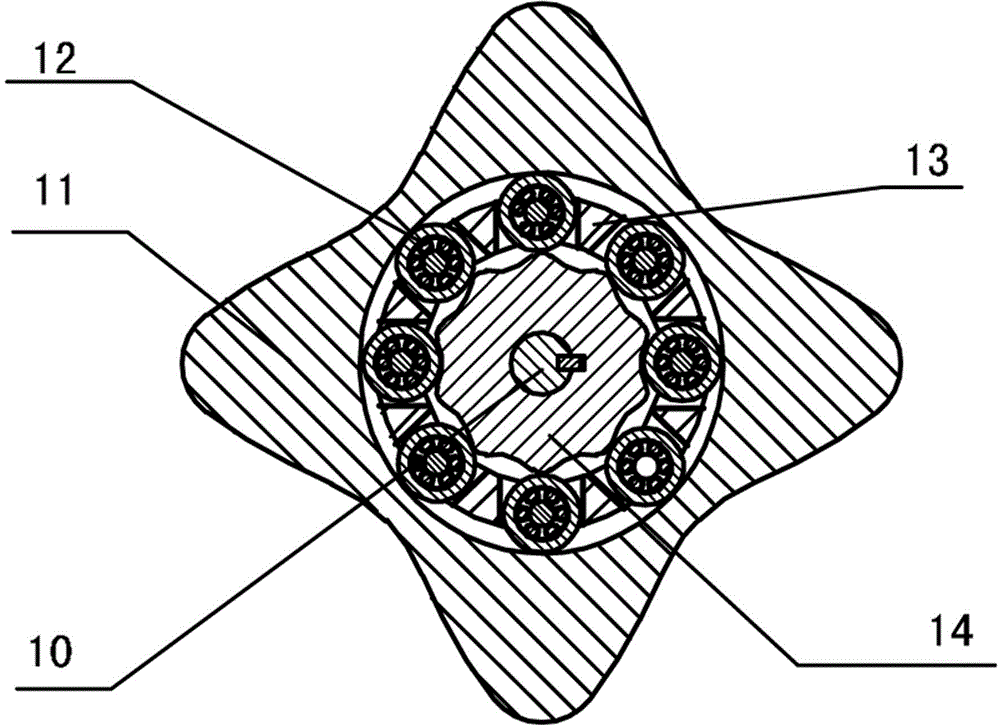
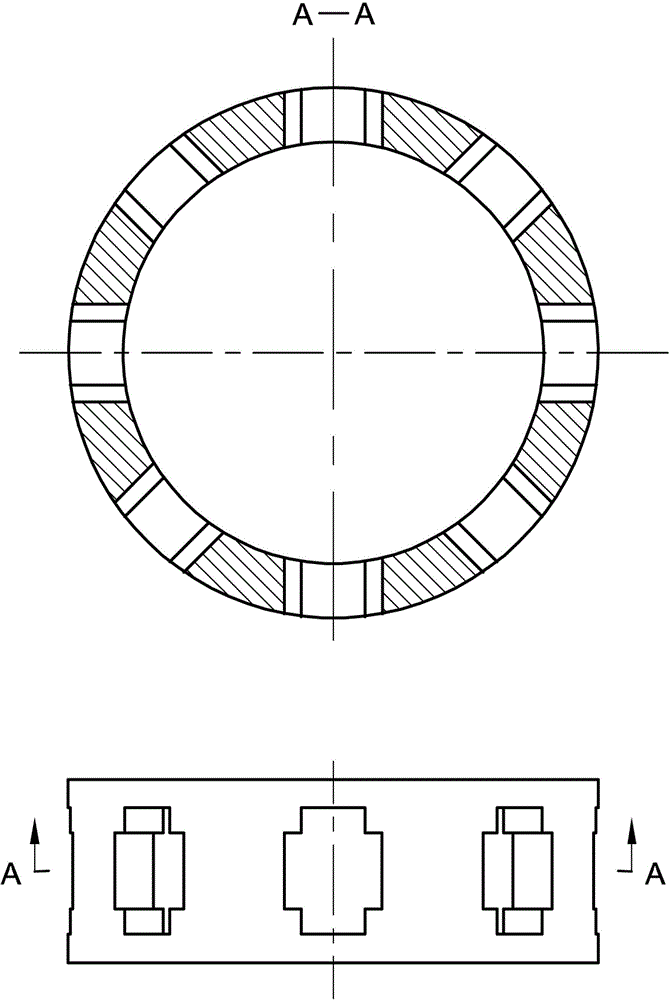
The invention discloses an outer convex inner arbitrary gear difference cam rolling moving transmission internal-combustion engine, relating to the field of fuel gas power and belonging to a multi-cylinder internal-combustion engine. The invention provides a novel internal-combustion engine; eight cylinders are distributed on the periphery of an outer convex inner multiphase inner cam symmetrically in a ring shape, so that a resultant force of the outer convex inner multiphase inner cam is zero; each cylinder piston directly acts on the outer convex inner multiphase inner cam through a push rod; and power is transmitted to an output shaft connected with a central wheel key by the outer convex inner multiphase inner cam through arbitrary gear difference inner cam rolling moving movable gear transmission. With the adoption of the internal-combustion engine, a connecting rod and a crank shaft in the traditional internal-combustion engine are saved; an outer convex multiphase inner cam rolling moving transmission mechanism has the characteristics of having no eccentric mass, and having an inertia force and working load self-balancing; the rotating speed of the output shaft depends on transmission ratio of movable gear transmission; when a movable gear frame is fixed, output by a central wheel is in low speed and large torque; and the internal-combustion engine can be widely applied to the fields of high-power engineering machinery and military and the like, such as excavators and armored cars. The internal-combustion engine is simple and compact in structure, small in axial size, self-balancing in stress, and stable in rotating.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Two-phase outer cam sleeve type high-rotational-speed internal-combustion engine
InactiveCN102877942AHigh speed outputReduce axial sizeGearingMachines/enginesEngineeringInternal combustion engine
The invention discloses a two-phase outer cam sleeve type high-rotational-speed internal-combustion engine, and relates to the field of power of fuel gas. The invention provides a novel internal-combustion engine. Eight cylinders are annularly, symmetrically and uniformly distributed around an outwards convex inner gear ring, so that resultant force from which the outwards convex inner gear ring is suffered is zero; pistons of the cylinders directly act on the outwards convex inner gear ring through push rods; and power is transferred to an output shaft connected with a symmetric two-phase cam through a key by the outwards convex inner gear ring through the drive of a two-phase outer cam type sleeve oscillating tooth. By using the internal-combustion engine, a connecting rod and a crankshaft in a conventional internal-combustion engine are omitted; a two-phase outer cam sleeve driving mechanism of the outwards convex inner gear ring of the internal-combustion engine does not have an eccentric mass; the internal-combustion engine has the characteristic of the self balancing of inertia force and a working load; the rotational speed of the output shaft depends on the drive ratio of the drive of the oscillating tooth; if a dowel pin frame is fixedly arranged, the symmetric two-phase cam carries out output at a high speed; the internal-combustion engine can be widely applied to the field of high rotational speeds, such as engines of helicopters, and miniature engines; and when an output rotational speed is constant, the emission of harmful gas can be reduced. The internal-combustion engine is simple and compact in structure, small in axial dimension and self-balancing in stress, and is stable to run.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
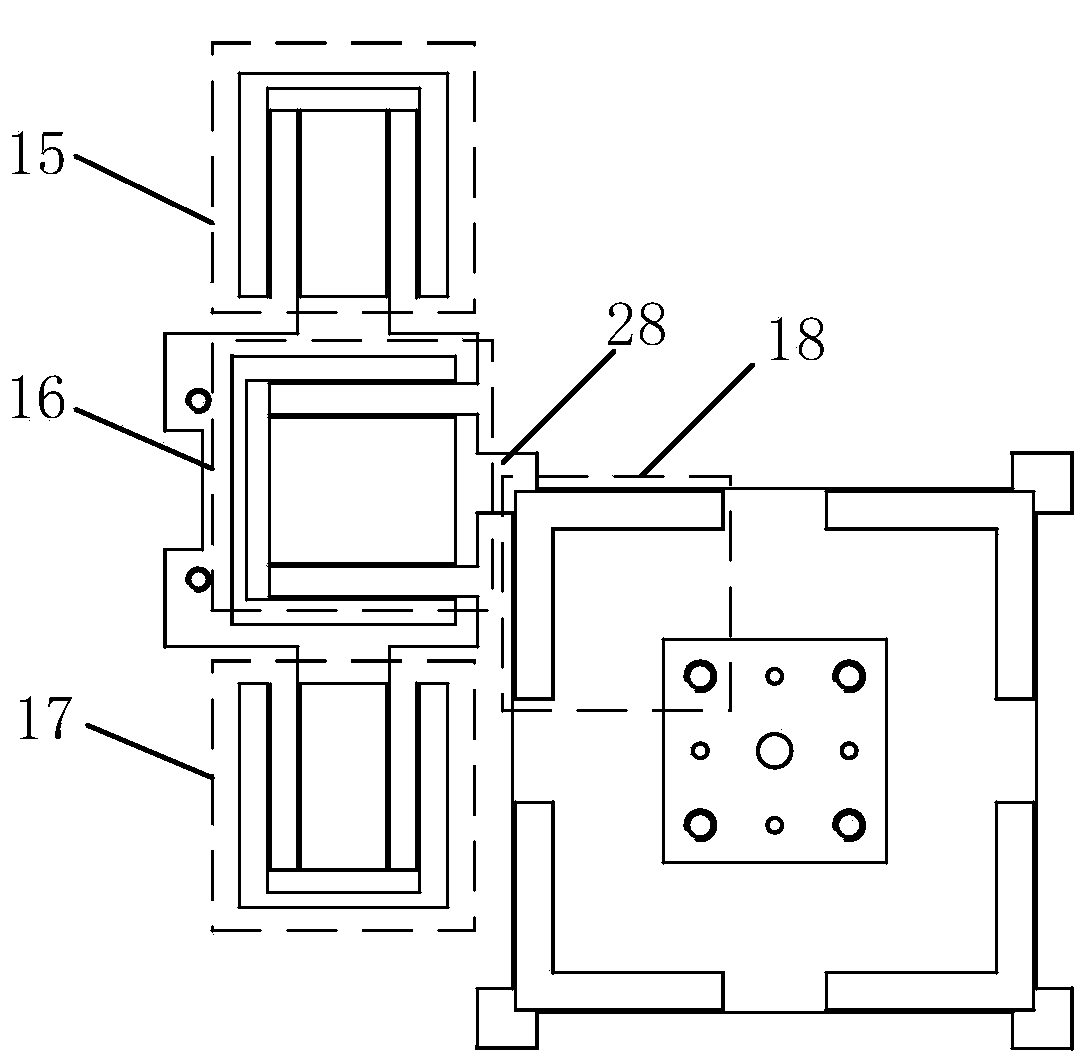
Parallel alignment platform based on flexible parallelogram mechanism and provided with remote rotating center
ActiveCN104626111AHigh rotational positioning resolutionCompact structureProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectricityEngineering
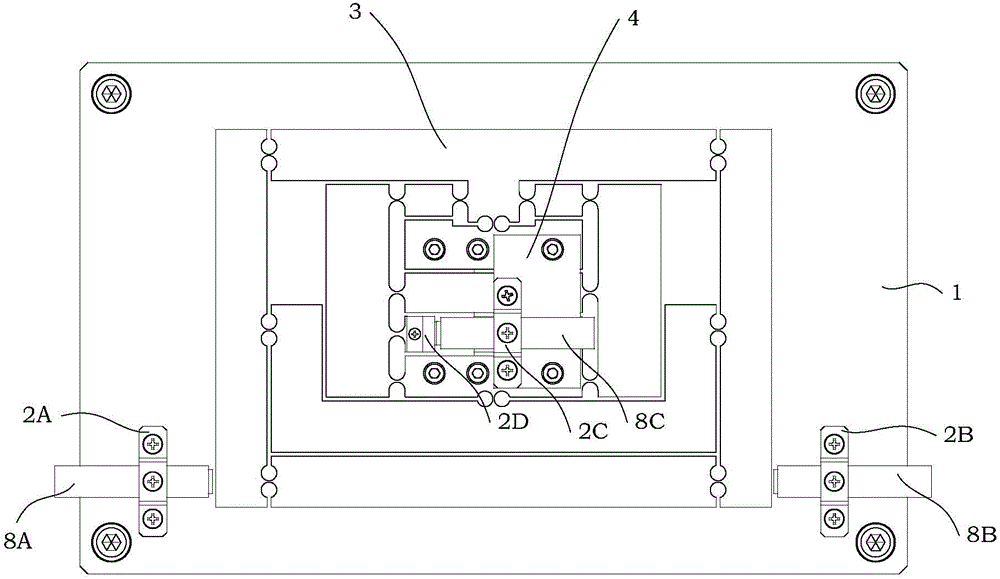
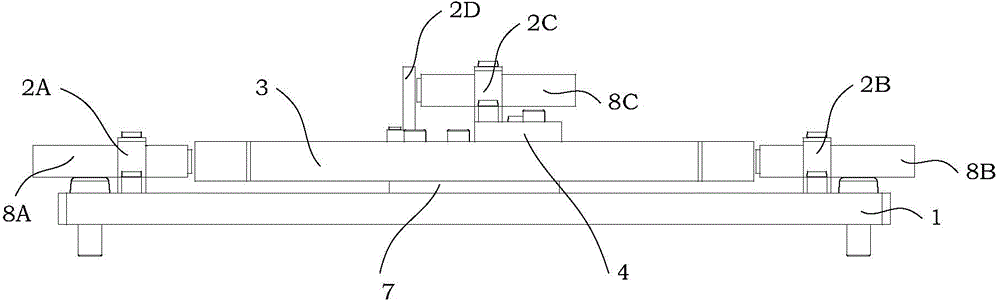
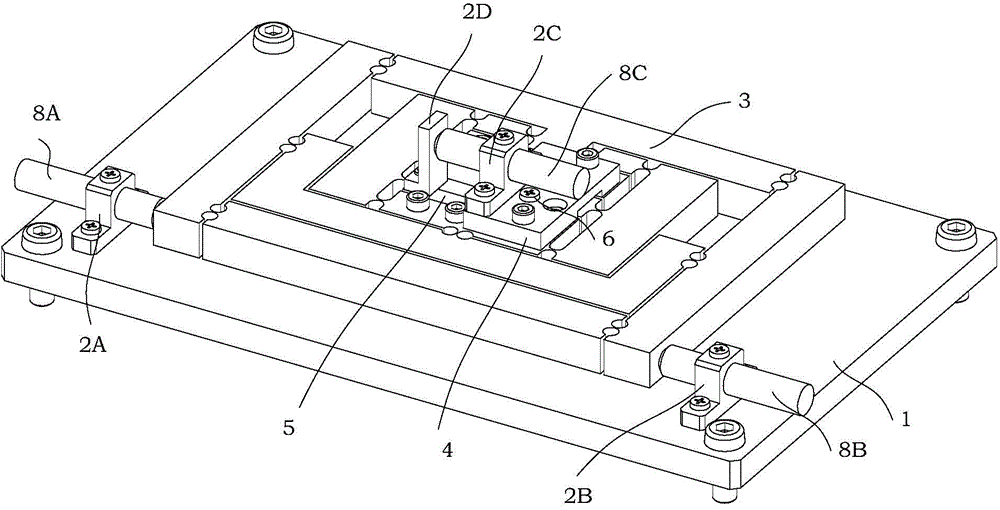
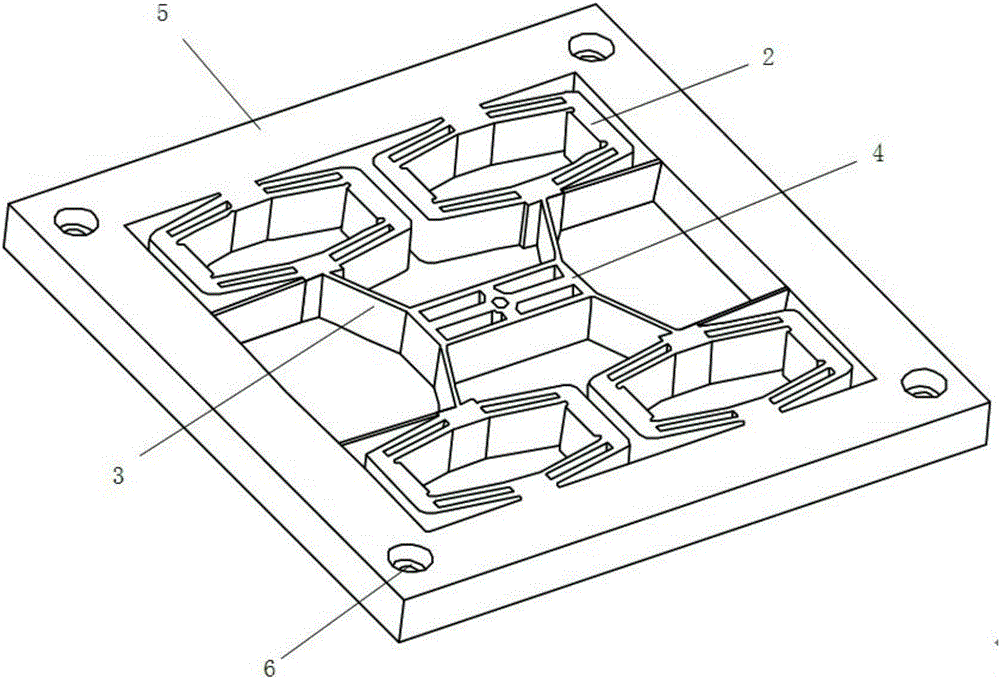
The invention discloses a parallel alignment platform based on a flexible parallelogram mechanism and provided with a remote rotating center. The parallel alignment platform comprises a base, a pre-tightening screw, a capacitive sensor, a sensor support, a cover plate, a platform base plate, a movement transmission mechanism, a piezoelectric ceramic driver and a gasket. The cover plate, the movement transmission mechanism, the platform base plate and the base are arranged in the thickness direction. The base and the movement transmission mechanism are fixedly installed through a screw. The pre-tightening screw is installed on the cover plate and makes contact with the gasket. The piezoelectric ceramic driver and the gasket are installed between the movement transmission mechanism and the platform base plate. According to the designed parallel alignment platform, through a dual-lever amplifying mechanism and a dual-parallelogram guide mechanism in the movement transmission mechanism, the parallel alignment function of rotation around a remote center can be achieved.
Owner:电科北方数字科技(山东)有限公司
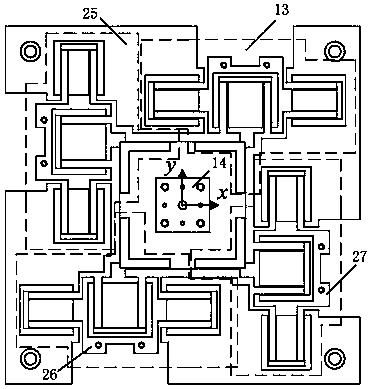
X, Y and theta plane three-freedom-degree precision positioning platform
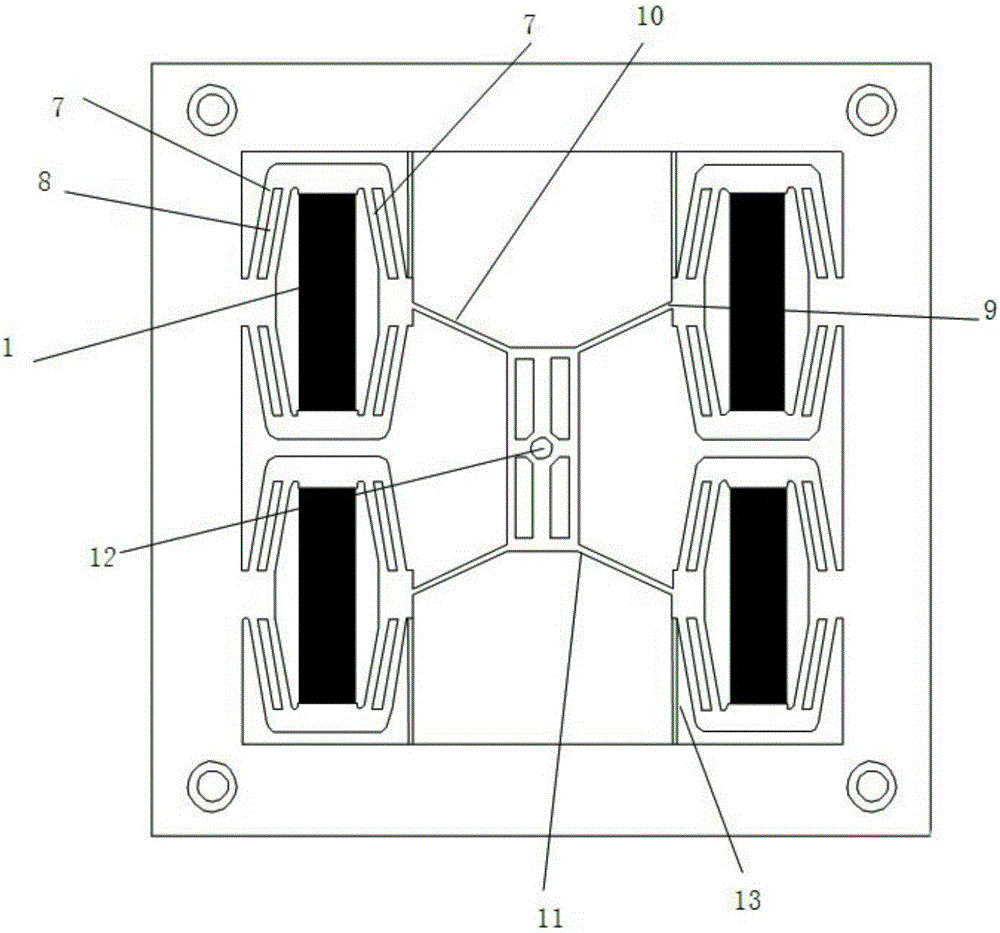
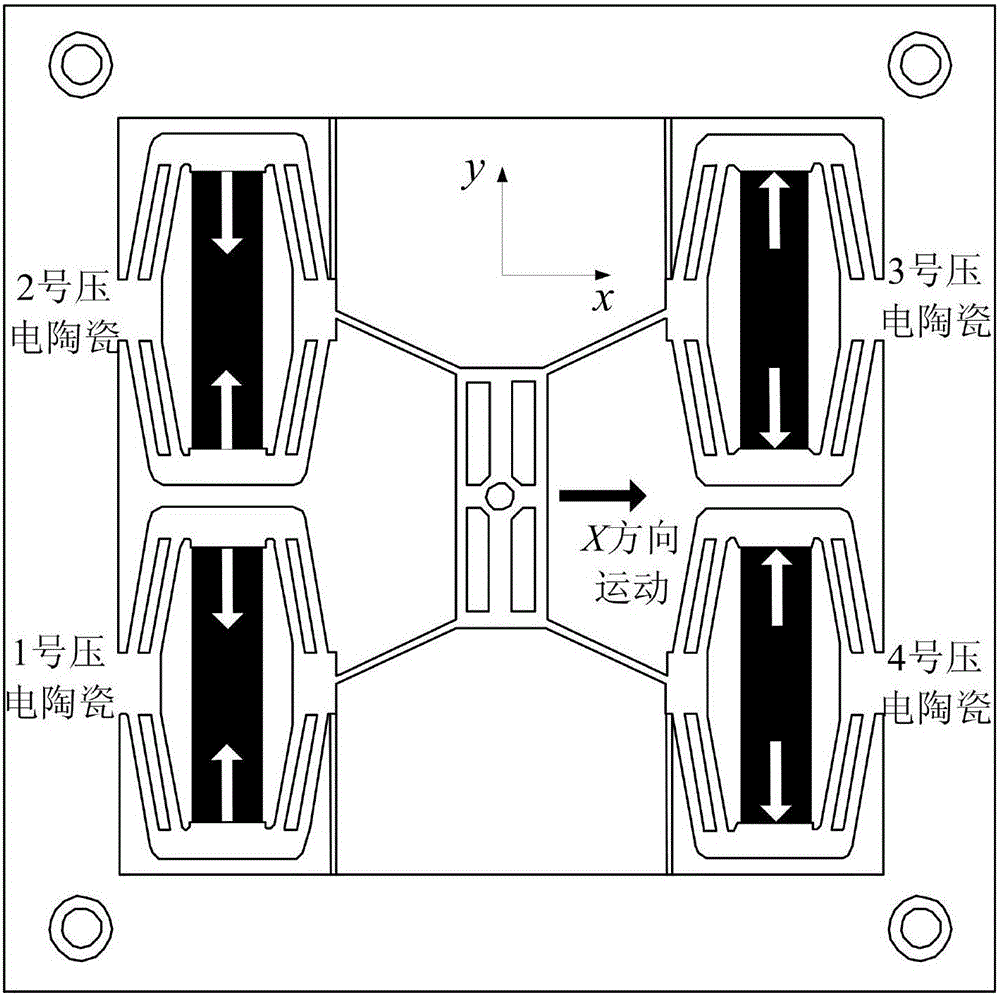
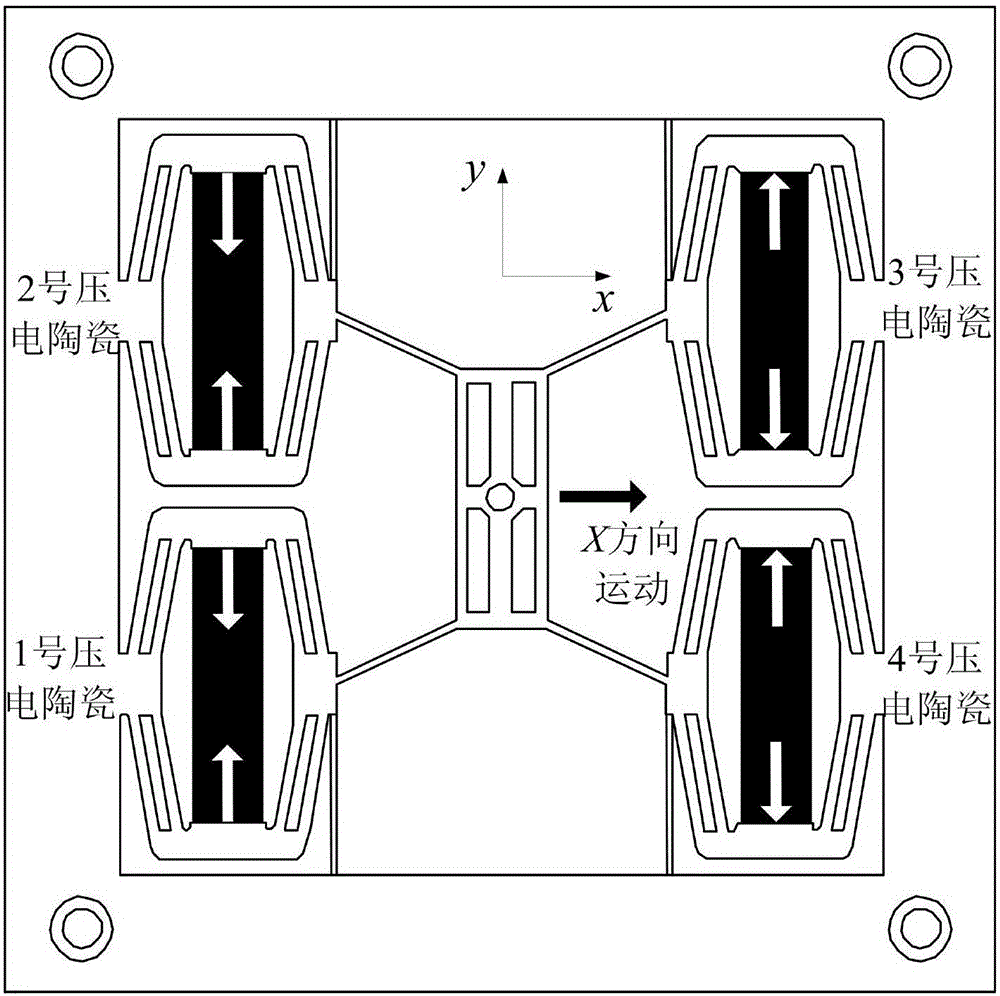
ActiveCN106195556ARaise the natural frequencyHigh output stiffnessStands/trestlesBridge typeFixed frame
The invention discloses an X, Y and theta plane three-freedom-degree precision positioning platform. The X, Y and theta plane three-freedom-degree precision positioning platform comprises piezoelectric ceramic, composite rhombus displacement amplification mechanisms, bridge type displacement amplification mechanisms, a motion platform and a fixing frame. The piezoelectric ceramic is installed in the composite rhombus displacement amplification mechanisms, and the four composite rhombus displacement amplification mechanisms are arranged in parallel and located at the four corners of the fixing frame; and the motion platform is located at the center of the fixing frame, and the two side faces of the motion platform are connected with the composite rhombus displacement amplification mechanisms located on the two sides of the motion platform through the two bridge type displacement amplification mechanisms. Through the combination of the four composite rhombus displacement amplification mechanisms and the two bridge type displacement amplification mechanisms, the X, Y and theta plane three-freedom-degree precision positioning platform has two transverse motion freedom degrees and one rotation freedom degree; and through combination of two-stage displacement amplification and different drives, three-plane-freedom-degree motion is achieved, the structure of the platform is simple and compact, and the output displacement is large.
Owner:GENERAL ENG RES INST CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Two-phase inner cam type swinging transmission internal combustion engine
InactiveCN102828824AForce self-balancingLarge transmission ratioGearingMachines/enginesLow speedEngineering
The invention provides a two-phase inner cam type swinging transmission internal combustion engine, which relates to the field of gas motive power and belongs to a multi-cylinder internal combustion engine. The invention provides a novel internal combustion engine, eight air cylinders are annularly, symmetrically and uniformly distributed around an outer convex inner two-phase inner cam, the resultant force of the outer convex inner two-phase inner cam is zero, an air cylinder piston directly acts on the outer convex inner two-phase inner cam through a push rod, and the motive power is transferred to an output shaft connected with a center wheel key through a two-phase inner cam type swinging movable tooth via the outer convex inner two-phase inner cam. The internal combustion engine has the characteristics that a connecting rod and a crankshaft in the traditional internal combustion engine are omitted, and an outer convex inner two-phase inner cam type swinging transmission mechanism does not have the eccentric mass, and has the inertia force and work load self balance characteristic. The rotating speed of the output shaft depends on the transmission ratio of the movable tooth transmission, when the movable tooth frame is fixed, a center wheel realizes low-speed and large-torque output, and the internal combustion engine can be widely applied to engineering machinery, armored car and the like with high-powder requirements. The internal combustion engine has the advantages that the structure is simple and compact, the axial dimension is small, the self balance of the stress is realized, and the operation is stable.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Smooth variable-stiffness driver for lower limb exoskeleton
ActiveCN110253621AConforms to joint stiffness propertiesHigh output stiffnessProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsVariable stiffnessKnee Joint
The invention discloses a smooth variable-stiffness driver for a lower limb exoskeleton. The driver comprises a support assembly, an outer shell assembly, a spring assembly, a driving assembly and a roller assembly, wherein the outer shell assembly and the roller assembly keep synchronous movement. According to the driver, a linear spring is compressed in a non-linear manner by using a pair of gear structures, so that the smooth variable stiffness characteristic of the output torque is realized. The driver can be applied to hip joints and knee joints of the lower limb exoskeleton.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Two-phase outer cam shock wave rolling transmission internal combustion engine
InactiveCN102937048AReduce axial sizeCompact structureValve drivesMachines/enginesShock waveExternal combustion engine
The invention provides a two-phase outer cam shock wave rolling transmission internal combustion engine and relates to the field of gas power. According to the novel internal combustion engine, eight cylinders are annularly symmetrically evenly distributed around a convex inner tooth ring, the resultant force which the convex inner tooth ring is subjected to is zero, and a cylinder piston directly acts on the convex inner tooth ring through a push rod, power is transmitted to an output shaft connected with a two-phase outer cam key by two-phase outer cam shock wave rolling oscillating tooth transmission through the convex inner tooth ring. According to the internal combustion engine, a connecting rod and a crankshaft in a traditional internal combustion engine are not required, a convex inner two-phase shock wave rolling transmission mechanism does not have eccentric mass and has the advantages of self balancing of inertia force and working load, and the rotating speed of the output shaft depends on the transmission ratio of oscillating tooth transmission. If an oscillating tooth brace is fixed, a two-phase outer cam performs high-speed output and can be widely applied to the fields requiring for high rotating speeds, such as helicopter engines and small generators, and discharge of harmful gas can be reduced when the output rotating speed is fixed. The internal combustion engine is simple and compact in structure, small in axial dimensions self-balancing in stress and runs stably.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
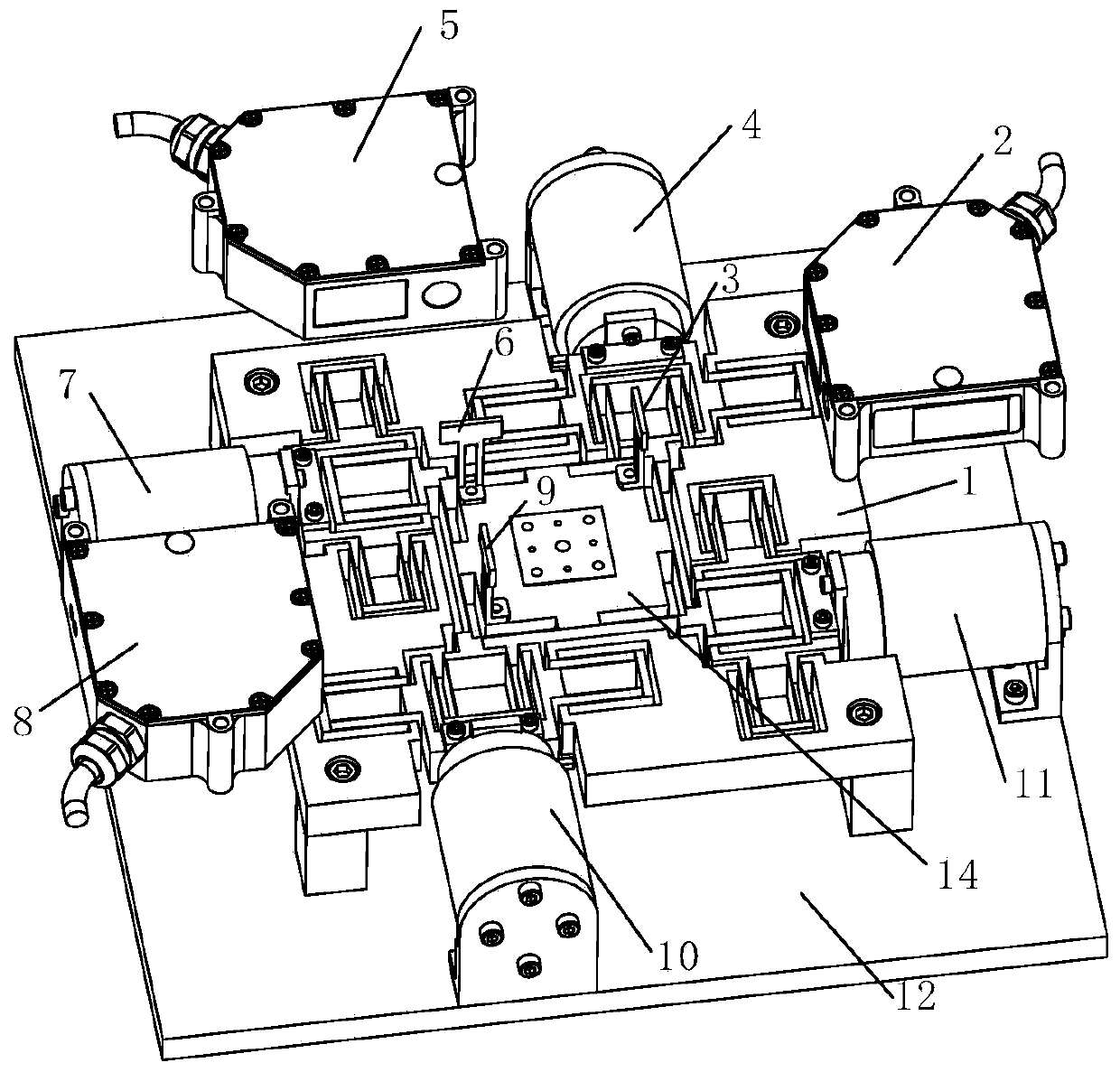
Large-displacement high-frequency-response three-degree-of-freedom piezoelectric driving precise locating platform
ActiveCN106229012AHigh output stiffnessRaise the natural frequencyInstrumental componentsHigh bandwidthThree degrees of freedom
Disclosed is a large-displacement high-frequency-response three-degree-of-freedom piezoelectric driving precise locating platform. The locating platform comprises a rigid base. The two sides of the rigid base are connected with one first rigid output end of a rhombus displacement amplifying mechanism. The other first rigid output end of the rhombus displacement amplifying mechanism is connected with one second rigid input end of a bridge-shaped displacement amplifying mechanism. Piezoelectric ceramics are connected to two first rigid input ends of the rhombus displacement amplifying mechanism. The rhombus displacement amplifying mechanism forms a flexible mechanism based on the triangulation principle through connection of a flexible arm, the two first rigid input ends and the two first rigid output ends. The bridge-shaped displacement amplifying mechanism is an arch-bridge-shaped flexible mechanism composed of two flexible beams, two second rigid input ends and a first second rigid output end. The two symmetrical flexible beams form bevel edges of the bridge-shaped displacement amplifying mechanism. Through the locating platform, large-stroke high-bandwidth high-precision displacement output can be achieved, and the structure is simple and compact.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Multi-degree-of-freedom nanometer positioning platform based on flexible parallel mechanism
ActiveCN109502542AHigh precisionHigh output stiffnessMicrostructural devicesPosition/direction controlMicro nanoHigh bandwidth
The invention relates to the technical field of micro-nano machining and manufacturing devices, in particular to a multi-degree-of-freedom nanometer positioning platform based on a flexible parallel mechanism. Branch movement chains include a first branch movement chain and a second branch movement chain; one end of the first branch movement chain is connected with a first fixed base, and the other end of the first branch movement chain is connected with an end executor; and one end of the second branch movement chain is connected with the first fixed base, a supporting point is provided by asecond fixed base, and the other end of the second branch movement chain is connected with the end executor. The end executor can realize single-degree-of-freedom output through the multi-axis secondbranch movement chain in a vertical direction; through redundant driving with the nanoscale precision, high output rigidity, high acting force, large load capacity, high bandwidth and high precision in the vertical direction can be realized; and the platform can be used as a main shaft in the fields of micro-nano machining and manufacturing, and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Any-tooth-difference movable type high rotation speed internal combustion engine
InactiveCN103047008ACompact structureReduce axial sizeGearingMachines/enginesThrough transmissionElectric generator
The invention provides an any-tooth-difference movable type high rotation speed internal combustion engine and relates to the field of combustion gas power. Eight cylinder are annularly and evenly distributed around an outward-protruding inner gear to enable the outward-protruding inner gear to be subjected to zero stress, cylinder pistons directly act on the outward-protruding inner gear through pushing rods, and power is transferred to an output shaft connected with a multiple-phase shock wave cam key through transmission of the outward-protruding inner gear and a multiple-phase cam type moving oscillating teeth. A connecting rod and a crankshaft in a traditional internal combustion engine are omitted, an outward-protruding inner multiple-phase cam type moving transmission mechanism has the advantages of being free of eccentric mass and having inertia force and working load self balance, the rotating speed of the output shaft depends on the transmission ratio of the oscillating teeth, if an oscillating tooth frame is fixed, a multiple-phase shock wave cam performs high-speed output, and the high rotation speed internal combustion engine can be widely applied to the field of machines needing high rotation speed, such as a helicopter engine, a small power generator and the like. When the output rotation speed is fixed, emission of harmful gas can be reduced. The any-tooth-difference movable type high rotation speed internal combustion engine is simple and compact in structure, small in axial size, self-balancing in stress and stable in operation.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Two-phase shock wave movable type high-rotation speed internal combustion engine
InactiveCN102900524AReduce axial sizeCompact structureMachines/enginesExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
The invention discloses a two-phase shock wave movable type high-rotation speed internal combustion engine, relates to the field of fuel gas power and provides a novel internal combustion engine. According to the internal combustion engine, eight cylinders are symmetrically arranged at the periphery of an externally raised inner gear ring uniformly, so that resultant force applied to the externally raised inner gear ring is zero; pistons of the cylinders directly act on the externally raised inner gear ring through push rods; and power is transmitted by the externally raised inner gear ring through a two-phase shock wave movable teeth transmission mechanism to an output shaft which is in keyed connection with a two-phase shock wave device. By the internal combustion engine, connection rods and crank shafts in the conventional internal combustion engine are eliminated, so that an externally raised inner two-phase shock wave movable transmission mechanism does not have eccentric mass, and the internal combustion engine has the characteristics that inertia force and working load are self-balanced; the rotation speed of the output shaft depends on a movable teeth transmission ratio; if movable teeth frames are fixed, the two-phase shock wave device outputs power at high speed; the internal combustion engine can be widely applied to field such as helicopter engines and small engines in which high rotation speed is required; when the output rotation speed is fixed, emission of harmful gas can be reduced; and besides, the internal combustion engine is simple and compact in structure, has a small axial size and stably runs, and stress is self-balanced.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Optional tooth difference swing type high-rotation-speed internal-combustion engine
An optional tooth difference swing type high-rotation-speed internal-combustion engine relates to the field of gas power. The tooth difference swing type high-rotation-speed internal-combustion engine is characterized in that eight air cylinders are annularly evenly distributed on the periphery of a protruding inner gear ring to allow resultant force borne by the inner gear ring to be zero. An air cylinder piston directly acts on the protruding inner gear ring through a push rod. Power is transmitted by protruding inner gear ring to an output shaft connected with a multi-phase shock wave wheel key through transmission of a multi-phase cam swing movable tooth. A connecting rod and a crankshaft in traditional internal-combustion engines are omitted, and the protruding inner multi-phase cam swing transmission mechanism has no eccentric weight, and has the advantages that self-balancing of inertia force and work load. Rotation speed of the output shafts depends on transmission ratio of movable tooth transmission. If a movable tooth frame is fixed, high-speed output of the multi-phase shock wave wheel is achieved. The internal-combustion engine is widely applicable to fields, which need high rotation speed, such as helicopter engines and small power generators. When rotation speed is fixed, emission of harmful gas can be reduced. The internal-combustion engine is simple and compact in structure, low in axial size, self-balancing in stress, and stable in operation.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Plane three-degree-of-freedom precision positioning platform, and using method and control method thereof
ActiveCN110905909ADeformation constraintsNo deformationInstrumental componentsStands/trestlesThree degrees of freedomControl engineering
The invention provides a plane three-degree-of-freedom precision positioning platform, and a using method and a control method thereof. The positioning platform comprises a base, a movable platform and a transmission mechanism positioned on the base, and four voice coil motors; the transmission mechanism comprises four flexible branched chains, and each flexible branched chain comprises three flexible P units and one flexible R unit, through the structural design of the flexible P units, the connection design of each flexible P unit, the structural design of the flexible R units and the connection design with the flexible P units, translation along the X axis and the Y axis and rotation around the Z axis are realized. Compared with the prior art, the plane three-degree-of-freedom precisionpositioning platform solves the contradiction between the motion range, the motion rigidity and the motion precision of the transmission mechanism, and the positioning platform has large motion range, high output rigidity and high motion precision; meanwhile, the problem of insufficient thrust of the voice coil motors can be effectively solved, and the requirement on the driving force peak valueof the voice coil motors is reduced due to the addition of redundant driving branch chains.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Hollow hydraulic braking third harmonic speed reduction all-in-one machine
PendingCN112953109ACompact structureLayout innovationAxially engaging brakesGearingReduction driveElectric machinery
The invention discloses a hollow hydraulic braking third harmonic speed reduction all-in-one machine, and the machine comprises a harmonic speed reduction part, wherein the harmonic speed reduction part comprises a fixed shell, a third harmonic speed reducer and an input shaft, the third harmonic speed reducer is arranged on the fixed shell, and the input shaft is arranged on the third harmonic speed reducer; a power supply part which comprises a motor shell, a stator and a rotor, wherein the motor shell is arranged on the fixed shell, the stator is arranged on the motor shell, and the rotor is arranged on the input shaft; an output supporting part which comprises a first bearing and an output shaft, wherein the first bearing is arranged on the fixing shell, the output shaft is arranged on the first bearing, and the output shaft is connected with the third harmonic reducer; and a hydraulic brake part which can brake the output shaft. The machine has the advantages of compact structure, innovative layout, high integration level, small volume, light weight, convenience in installation, high output rigidity, high output precision, large output torque, good braking effect, extremely small reverse back clearance and long precision retention time.
Owner:江苏开璇智能科技有限公司
Outer convex cam roller transmission internal combustion engine with any inner tooth difference
InactiveCN103147856ACompact structureReduce axial sizeValve drivesMachines/enginesLow speedExternal combustion engine
The invention discloses an outer convex cam roller transmission internal combustion engine with any inner tooth difference, relates to the field of gas power and belongs to a multi-cylinder engine. The invention provides a novel internal combustion engine; eight cylinders are annularly and symmetrically distributed at the periphery of an outer convex multiphase inner cam evenly, so that the force of the outer convex multiphase inner cam is zero; pistons of the cylinders directly act on the outer convex multiphase inner cam by push rods; and power is transmitted to an output shaft which is connected with a center wheel in a key way by the outer convex multiphase inner cam through cam roller oscillating teeth with any inner tooth-difference. The internal combustion engine omits connecting rods and crankshafts of the traditional internal combustion engine; and an outer convex multiphase inner cam roller transmission mechanism does not have eccentric mass and has the advantages of inertia force and working load self-balancing. The rotating speed of the output shaft depends on the transmission ratio of oscillating tooth transmission; if an oscillating tooth carrier is fixed, the center wheel is output in large torque and at the lower speed; and the outer convex cam roller transmission internal combustion engine with any inner tooth difference can be widely used for the fields of engineering and military in need of the high power, such as engineering machinery, armored cars and the like. The internal combustion engine has the advantages of simplicity and compactness in structure, small axial dimension, self-balancing in stress and stability in operation.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
A three-degree-of-freedom precision positioning platform in xyθ plane
ActiveCN106195556BRaise the natural frequencyHigh output stiffnessStands/trestlesBridge typeThree degrees of freedom
The invention discloses an X, Y and theta plane three-freedom-degree precision positioning platform. The X, Y and theta plane three-freedom-degree precision positioning platform comprises piezoelectric ceramic, composite rhombus displacement amplification mechanisms, bridge type displacement amplification mechanisms, a motion platform and a fixing frame. The piezoelectric ceramic is installed in the composite rhombus displacement amplification mechanisms, and the four composite rhombus displacement amplification mechanisms are arranged in parallel and located at the four corners of the fixing frame; and the motion platform is located at the center of the fixing frame, and the two side faces of the motion platform are connected with the composite rhombus displacement amplification mechanisms located on the two sides of the motion platform through the two bridge type displacement amplification mechanisms. Through the combination of the four composite rhombus displacement amplification mechanisms and the two bridge type displacement amplification mechanisms, the X, Y and theta plane three-freedom-degree precision positioning platform has two transverse motion freedom degrees and one rotation freedom degree; and through combination of two-stage displacement amplification and different drives, three-plane-freedom-degree motion is achieved, the structure of the platform is simple and compact, and the output displacement is large.
Owner:GENERAL ENG RES INST CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Curved-surface thin-wall part vibration control device based on permanent magnet driving
ActiveCN110332277ACompact structureHigh output stiffnessNon-rotating vibration suppressionGearingVibration controlReciprocating motion
The invention provides a curved-surface thin-wall part vibration control device based on permanent magnet driving. The device comprises an electromagnetic permanent magnet driving mechanism, a drivenmechanism, a movement conversing mechanism and a self-adaptive jacking mechanism; the electromagnetic permanent magnet driving mechanism is arranged on the base, and the electromagnetic permanent magnet driving mechanism is connected with the driven mechanism and provides a power source for the driven mechanism; the driven mechanism is connected with the movement conversing mechanism, the movementconversing mechanism converts the reciprocating movement of the driven mechanism into vertical movement; and the movement conversing mechanism is also arranged on the base, the movement conversing mechanism is connected with the self-adaptive jacking mechanism, and the self-adaptive jacking mechanism can move up and down under driving of the movement conversing mechanism. According to the curved-surface thin-wall part vibration control device, the movement output of a plurality of positions can be realized by one driving source, so that the driving sources are saved, and the overall structureof a system is more compact, and in addition, the power source is generated by utilizing an electromagnetic permanent magnet mode, so that compared with a linear motor and a voice coil motor with thesame size, the output rigidity of the electromagnetic permanent magnet driving mechanism is larger.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Cam rolling transmission internal combustion engine with external convex internal arbitrary tooth difference
The invention discloses an outer convex inner arbitrary gear difference cam rolling moving transmission internal-combustion engine, relating to the field of fuel gas power and belonging to a multi-cylinder internal-combustion engine. The invention provides a novel internal-combustion engine; eight cylinders are distributed on the periphery of an outer convex inner multiphase inner cam symmetrically in a ring shape, so that a resultant force of the outer convex inner multiphase inner cam is zero; each cylinder piston directly acts on the outer convex inner multiphase inner cam through a push rod; and power is transmitted to an output shaft connected with a central wheel key by the outer convex inner multiphase inner cam through arbitrary gear difference inner cam rolling moving movable gear transmission. With the adoption of the internal-combustion engine, a connecting rod and a crank shaft in the traditional internal-combustion engine are saved; an outer convex multiphase inner cam rolling moving transmission mechanism has the characteristics of having no eccentric mass, and having an inertia force and working load self-balancing; the rotating speed of the output shaft depends on transmission ratio of movable gear transmission; when a movable gear frame is fixed, output by a central wheel is in low speed and large torque; and the internal-combustion engine can be widely applied to the fields of high-power engineering machinery and military and the like, such as excavators and armored cars. The internal-combustion engine is simple and compact in structure, small in axial size, self-balancing in stress, and stable in rotating.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
A Variable Stiffness Joint Based on Torsion Spring Characteristics
The invention relates to a variable-rigidity joint, in particular to a variable-rigidity joint based on characteristics of torsional springs. The variable-rigidity joint aims at solving the defects that in the prior art, energy saved by an existing rigid joint is not enough, variable-rigidity performance cannot be ensured easily and the variable-rigidity range is small, and aims at solving the problems that in the rigidity regulation manner that the position of a fulcrum is moved based on the lever principle, energy consumption generated when the fulcrum conducts sliding friction in a groove is large, the number of required parts is large and the structural design is not reasonable. The variable-rigidity joint comprises the set of torsional springs, a slide block, a slide rail, a first output plate, a second output plate, an input plate, an input plate rotating shaft, two rollers, a set of torsional spring supports and two connection pieces. The set of torsional springs include the first torsional spring and the second torsional spring. The set of torsional spring supports include the first torsional spring support and the second torsional spring support. The first output plate, the second output plate and the input plate are all disks. The variable-rigidity joint is used for the field of robot joints.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
A compliant variable stiffness actuator for lower extremity exoskeleton
ActiveCN110253621BConforms to joint stiffness propertiesHigh output stiffnessProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsVariable stiffnessGear wheel
The invention discloses a smooth variable-stiffness driver for a lower limb exoskeleton. The driver comprises a support assembly, an outer shell assembly, a spring assembly, a driving assembly and a roller assembly, wherein the outer shell assembly and the roller assembly keep synchronous movement. According to the driver, a linear spring is compressed in a non-linear manner by using a pair of gear structures, so that the smooth variable stiffness characteristic of the output torque is realized. The driver can be applied to hip joints and knee joints of the lower limb exoskeleton.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Convex inner two-phase cam rolling shifting transmission internal-combustion engine
InactiveCN102926862BReduce axial sizeCompact structureValve drivesMachines/enginesLow speedEngineering
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
A three-degree-of-freedom piezoelectric-driven precision positioning platform with large displacement and high frequency response
ActiveCN106229012BHigh output stiffnessRaise the natural frequencyInstrumental componentsHigh bandwidthThree degrees of freedom
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
A Parallel Alignment Platform with a Remote Center of Rotation Based on a Flexible Parallelogram Mechanism
ActiveCN104626111BHigh rotational positioning resolutionCompact structureProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringMotion transfer
The invention discloses a parallel alignment platform based on a flexible parallelogram mechanism and provided with a remote rotating center. The parallel alignment platform comprises a base, a pre-tightening screw, a capacitive sensor, a sensor support, a cover plate, a platform base plate, a movement transmission mechanism, a piezoelectric ceramic driver and a gasket. The cover plate, the movement transmission mechanism, the platform base plate and the base are arranged in the thickness direction. The base and the movement transmission mechanism are fixedly installed through a screw. The pre-tightening screw is installed on the cover plate and makes contact with the gasket. The piezoelectric ceramic driver and the gasket are installed between the movement transmission mechanism and the platform base plate. According to the designed parallel alignment platform, through a dual-lever amplifying mechanism and a dual-parallelogram guide mechanism in the movement transmission mechanism, the parallel alignment function of rotation around a remote center can be achieved.
Owner:电科北方数字科技(山东)有限公司
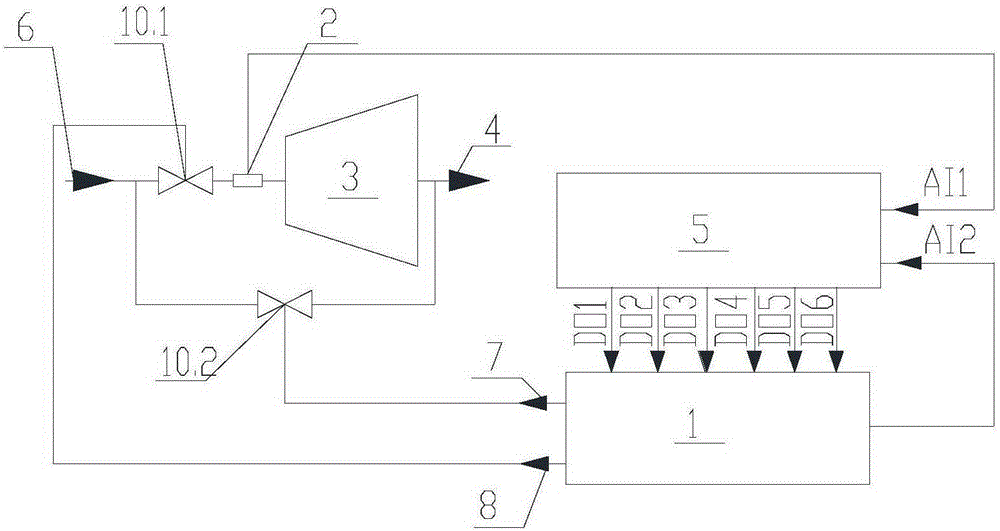
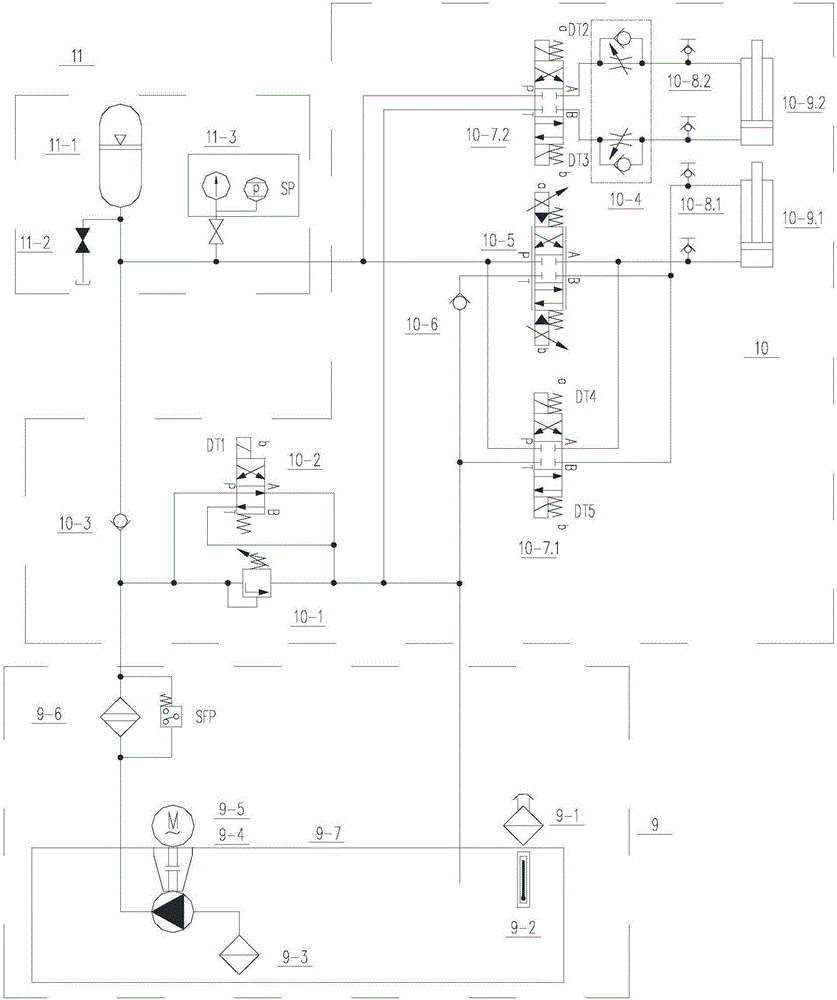
Self-contained steam turbine speed protection and adjustment device
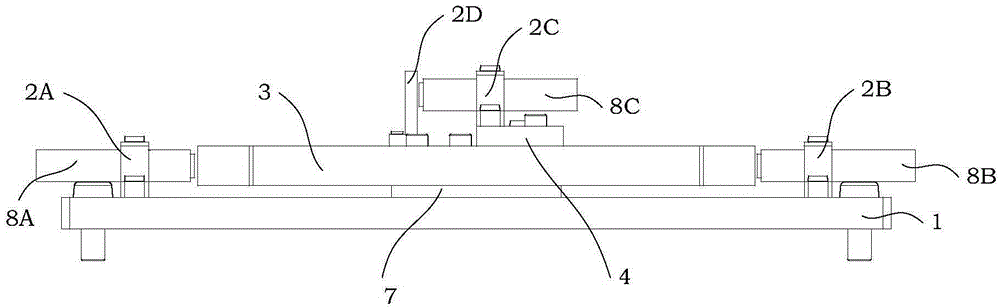
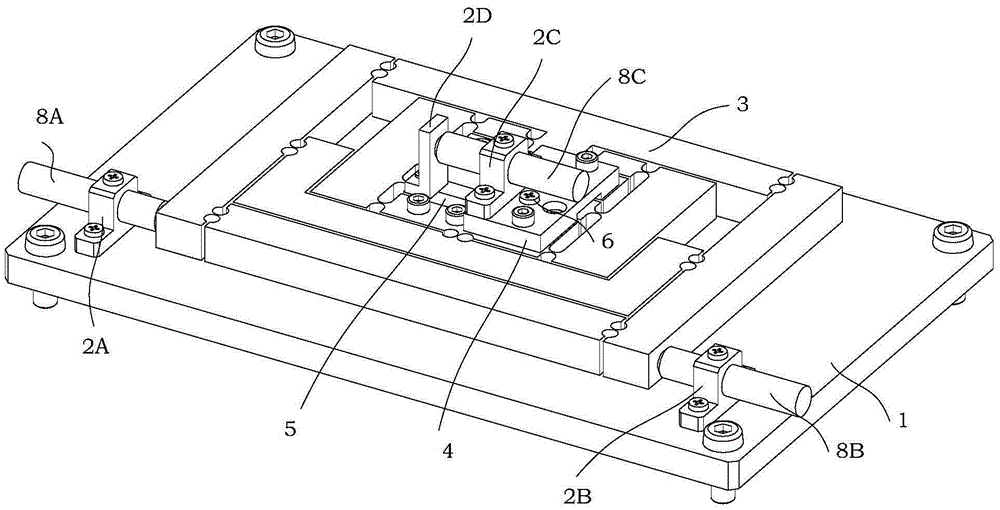
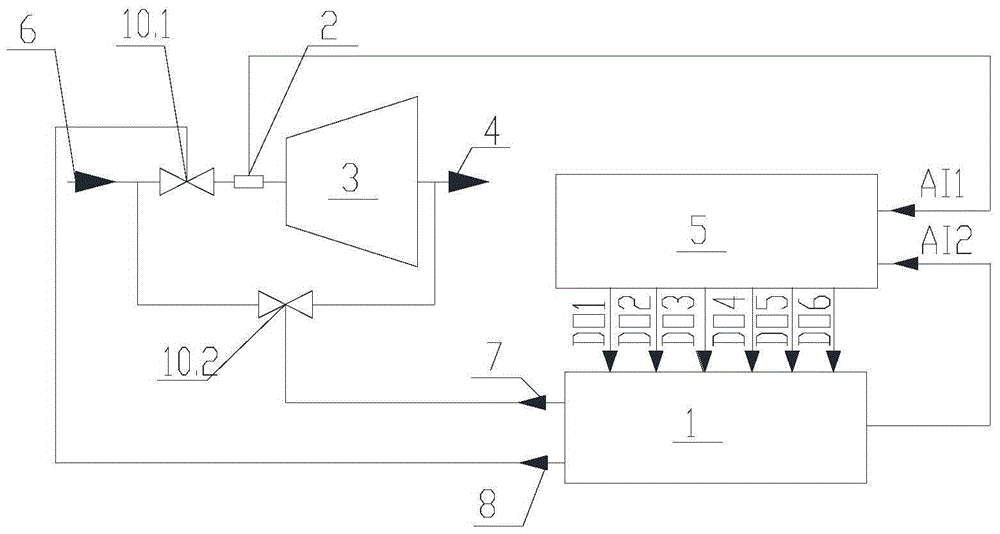
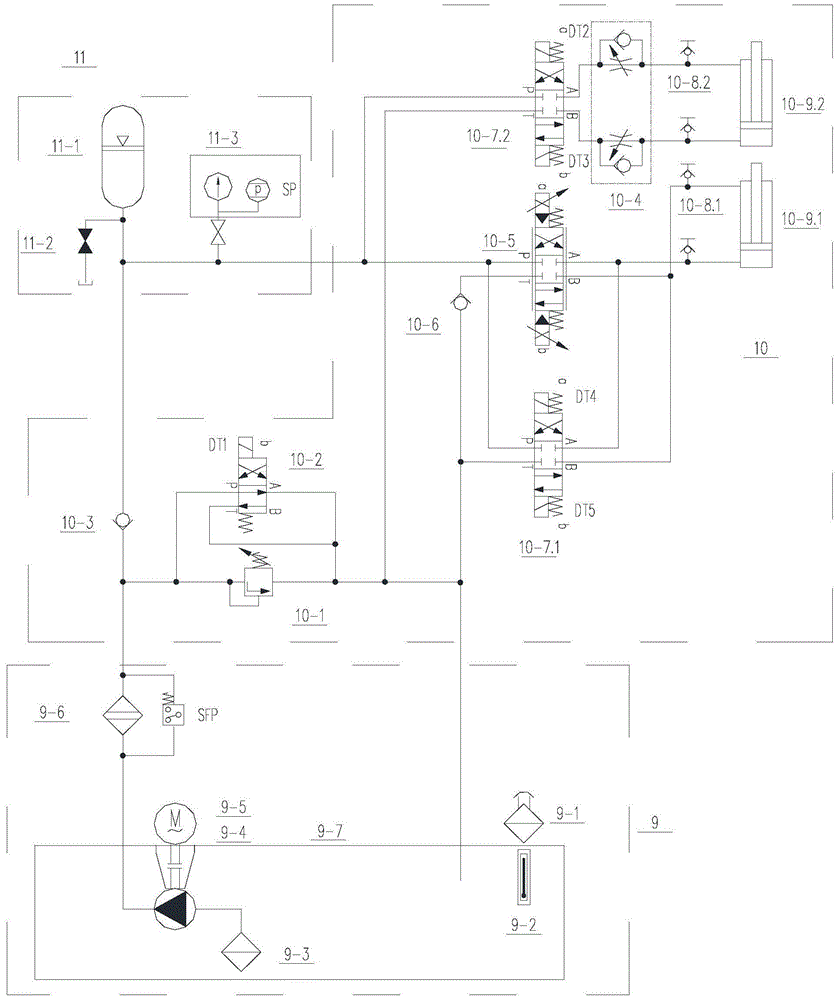
InactiveCN105179025BNo toxicityNo degradationMachines/enginesSafety/regulatory devicesInterference resistanceControl signal
The invention relates to a rotation speed protection adjustment device of a self-contained steam turbine, and belongs to the technical field of rotation speed protection adjustment of steam turbines. The device comprises an integrated electro-hydraulic actuator, a speed measurement device, a controller, a steam adjustment valve, a steam bypass valve, and an oil pipeline, wherein a sensor of the speed measurement device is mounted on a gear on the bottom of the steam turbine; the controller is connected with the electro-hydraulic actuator by a control signal line; the integrated electro-hydraulic actuator is connected with the steam bypass valve by a soft oil pipe and connected with the steam adjustment valve by the soft oil pipe; the steam adjustment valve is connected with the steam inlet side of the steam turbine, the steam turbine is bypassed with the steam adjustment valve by the steam bypass valve, and two ends of the steam bypass valve are connected with the steam inlet and the steam outlet respectively. The device has features of simple and compact structure, strong interference resistance, fast dynamic response, high output rigidity and high positioning accuracy, and such as installation and debugging are easy to standardize and the complexity degree of the related work is high.
Owner:北京市可持续发展促进会
Arbitrary-tooth difference rolling transmission internal combustion engine
InactiveCN102979619BIncrease powerSmooth transmissionGearingMachines/enginesShock waveExternal combustion engine
The invention discloses an arbitrary-tooth difference rolling transmission internal combustion engine, and relates to the field of gas power. According to a novel internal combustion engine, eight cylinders are annularly, symmetrically and uniformly distributed around an outer cam inner gear ring, so that resultant force on the outer cam inner gear ring is zero; and pistons of the cylinders directly act on the outer cam inner gear ring through pushrods, and power is transmitted to an output shaft in key connection with a multi-phase outer cam in a multi-phase outer cam impact wave rolling oscillating tooth transmission way through the outer cam inner gear ring. According to the internal combustion engine, a connecting rod and a crankshaft in the conventional internal combustion engine are eliminated, a multi-phase outer cam impact wave rolling transmission mechanism has the characteristics of no eccentric mass and self-balance of inertia force and a working load, the rotating speed of the output shaft is determined by the transmission ratio of oscillating teeth, and if an oscillating tooth rack is fixed, the output of the multi-phase outer cam is realized at high speed. The internal combustion engine can be widely applied to fields with requirements on high rotating speed, such as a helicopter engine and a miniature generator, and when the output rotating speed is fixed, the emissions of harmful gases can be reduced. The internal combustion engine is simple and compact in structure and small in axial size, has a force self-balancing function, and can run stably.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Two-phase outer cam shock wave rolling transmission internal combustion engine
InactiveCN102937048BTransmission ratio is smallIncrease powerValve drivesMachines/enginesShock waveExternal combustion engine
The invention provides a two-phase outer cam shock wave rolling transmission internal combustion engine and relates to the field of gas power. According to the novel internal combustion engine, eight cylinders are annularly symmetrically evenly distributed around a convex inner tooth ring, the resultant force which the convex inner tooth ring is subjected to is zero, and a cylinder piston directly acts on the convex inner tooth ring through a push rod, power is transmitted to an output shaft connected with a two-phase outer cam key by two-phase outer cam shock wave rolling oscillating tooth transmission through the convex inner tooth ring. According to the internal combustion engine, a connecting rod and a crankshaft in a traditional internal combustion engine are not required, a convex inner two-phase shock wave rolling transmission mechanism does not have eccentric mass and has the advantages of self balancing of inertia force and working load, and the rotating speed of the output shaft depends on the transmission ratio of oscillating tooth transmission. If an oscillating tooth brace is fixed, a two-phase outer cam performs high-speed output and can be widely applied to the fields requiring for high rotating speeds, such as helicopter engines and small generators, and discharge of harmful gas can be reduced when the output rotating speed is fixed. The internal combustion engine is simple and compact in structure, small in axial dimensions self-balancing in stress and runs stably.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Rotation speed protection adjustment device of self-contained steam turbine
InactiveCN105179025ANo toxicityNo degradationMachines/enginesSafety/regulatory devicesInterference resistanceControl signal
The invention relates to a rotation speed protection adjustment device of a self-contained steam turbine, and belongs to the technical field of rotation speed protection adjustment of steam turbines. The device comprises an integrated electro-hydraulic actuator, a speed measurement device, a controller, a steam adjustment valve, a steam bypass valve, and an oil pipeline, wherein a sensor of the speed measurement device is mounted on a gear on the bottom of the steam turbine; the controller is connected with the electro-hydraulic actuator by a control signal line; the integrated electro-hydraulic actuator is connected with the steam bypass valve by a soft oil pipe and connected with the steam adjustment valve by the soft oil pipe; the steam adjustment valve is connected with the steam inlet side of the steam turbine, the steam turbine is bypassed with the steam adjustment valve by the steam bypass valve, and two ends of the steam bypass valve are connected with the steam inlet and the steam outlet respectively. The device has features of simple and compact structure, strong interference resistance, fast dynamic response, high output rigidity and high positioning accuracy, and such as installation and debugging are easy to standardize and the complexity degree of the related work is high.
Owner:北京市可持续发展促进会
Two-phase shock wave swing link movable-teeth compound transmission speed reducer
The invention discloses a two-phase shock wave swing link movable-teeth compound transmission speed reducer and relates to the technical field of mechanical transmission. The compound transmission speed reducer mainly comprises a two-phase shock wave device, movable teeth, a swing link, a pin shaft, a movable-teeth frame, a central wheel and a fixed axis gear train which is embedded into the shock wave device. The exterior of the shock wave device has a cam profile and the interior of the shock wave device has an inner gear ring profile; an input gear is engaged with a pinion and the pinion is engaged with the inner gear ring so as to form the fixed axis gear train; the input gear and an input shaft are integrated; the rotation of the input gear is decelerated through the fixed axis gear train and drives the shock wave device to rotate; the shock wave device and the movable teeth are in rolling contact engagement, so that the movable teeth swing along with the swing link and moves along the tooth profile of the central wheel simultaneously; and the shock wave device and the central wheel coact to make the movable teeth drive the movable-teeth frame to rotate and output power through the swing link. By setting pre-deceleration in swing link movable-teeth transmission, the transmission ratio is increased, and the problem of over-high temperature rise of movable-teeth transmission is also solved; and the speed reducer has the advantages of novel and compact structure, high bearing capacity, self-balancing stress and the like, and is suitable for decelerating transmission between two coaxial shafts.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
A multi-degree-of-freedom nanopositioning platform based on a compliant parallel mechanism
ActiveCN109502542BHigh precisionHigh output stiffnessMicrostructural devicesPosition/direction controlHigh bandwidthEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of micro-nano machining and manufacturing devices, in particular to a multi-degree-of-freedom nanometer positioning platform based on a flexible parallel mechanism. Branch movement chains include a first branch movement chain and a second branch movement chain; one end of the first branch movement chain is connected with a first fixed base, and the other end of the first branch movement chain is connected with an end executor; and one end of the second branch movement chain is connected with the first fixed base, a supporting point is provided by asecond fixed base, and the other end of the second branch movement chain is connected with the end executor. The end executor can realize single-degree-of-freedom output through the multi-axis secondbranch movement chain in a vertical direction; through redundant driving with the nanoscale precision, high output rigidity, high acting force, large load capacity, high bandwidth and high precision in the vertical direction can be realized; and the platform can be used as a main shaft in the fields of micro-nano machining and manufacturing, and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com