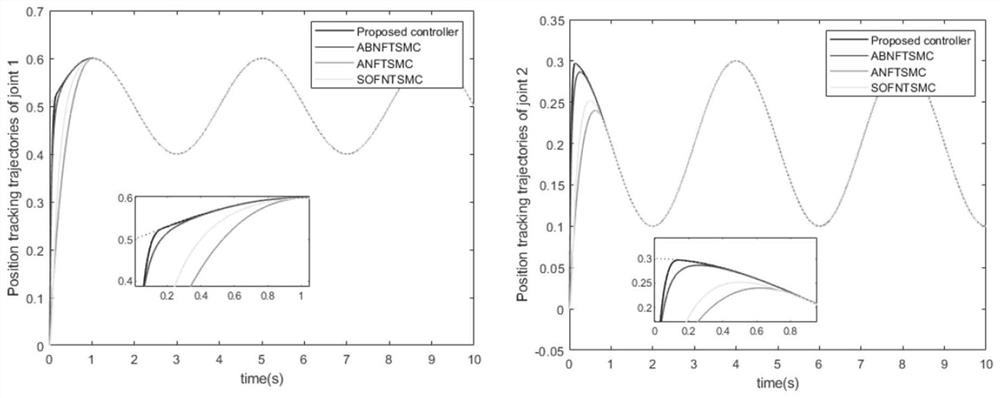
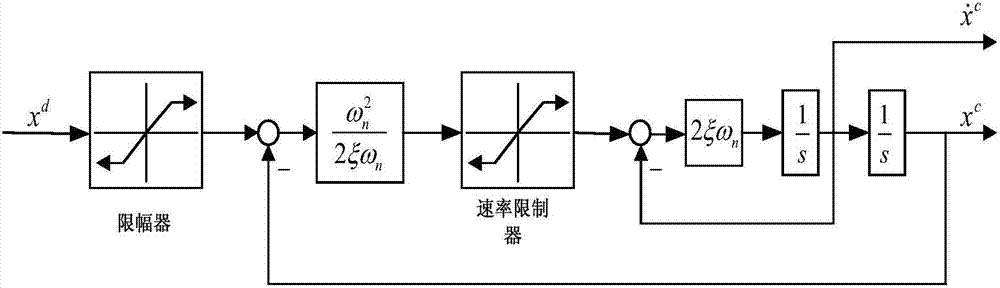
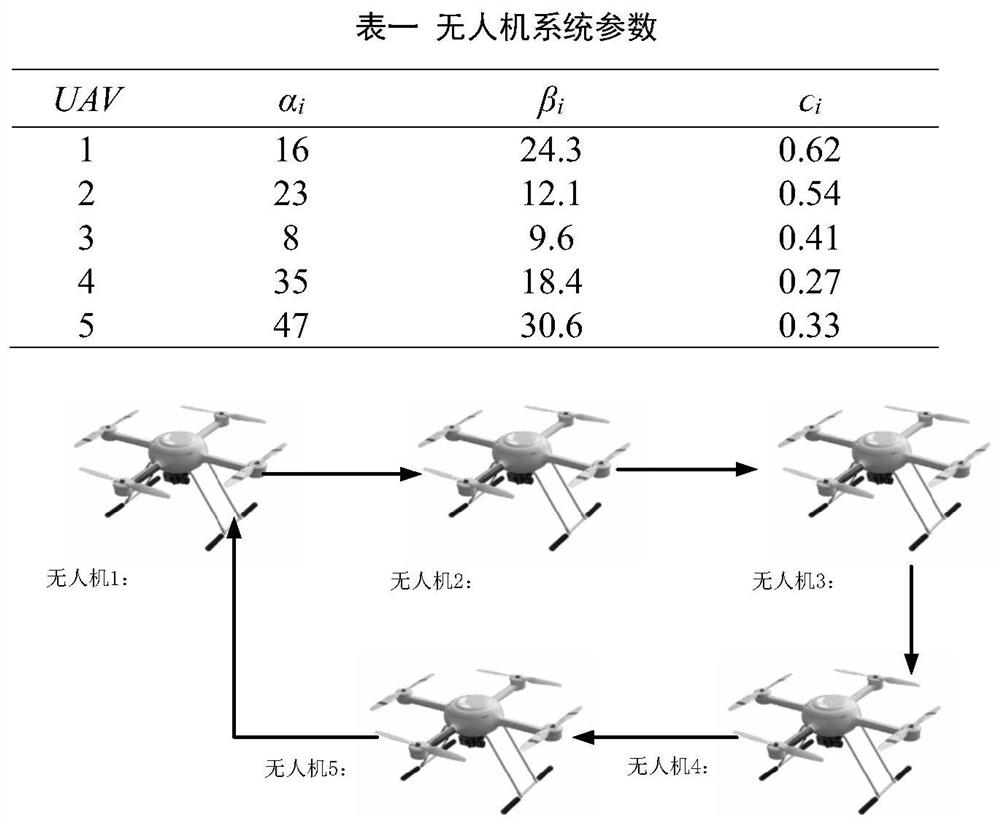
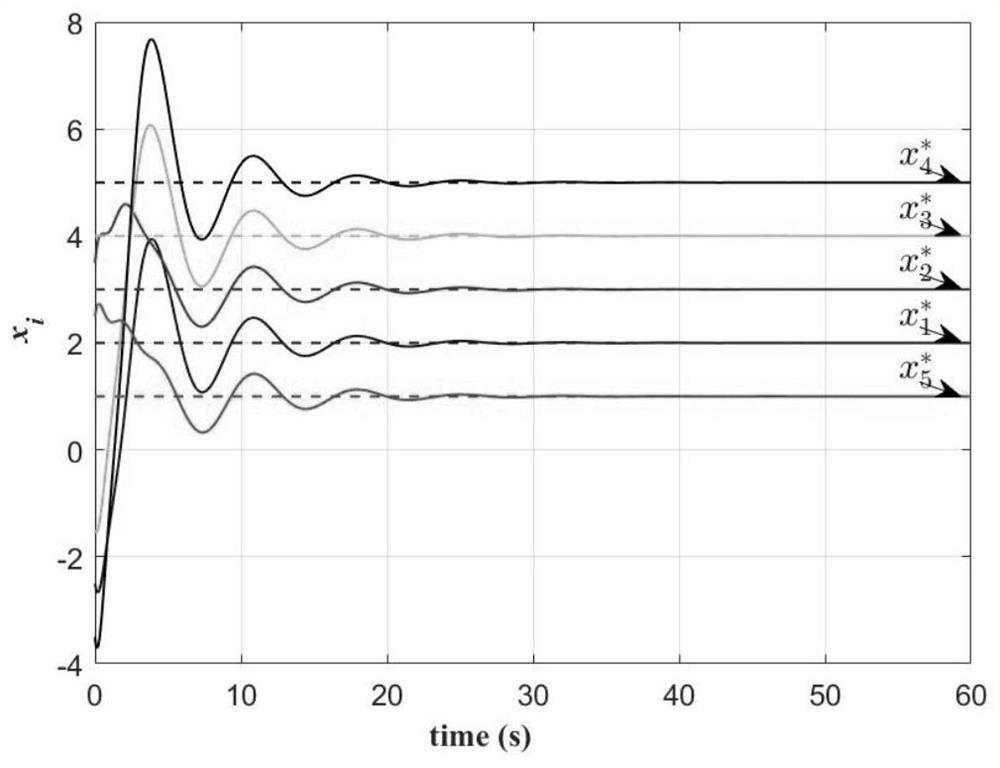
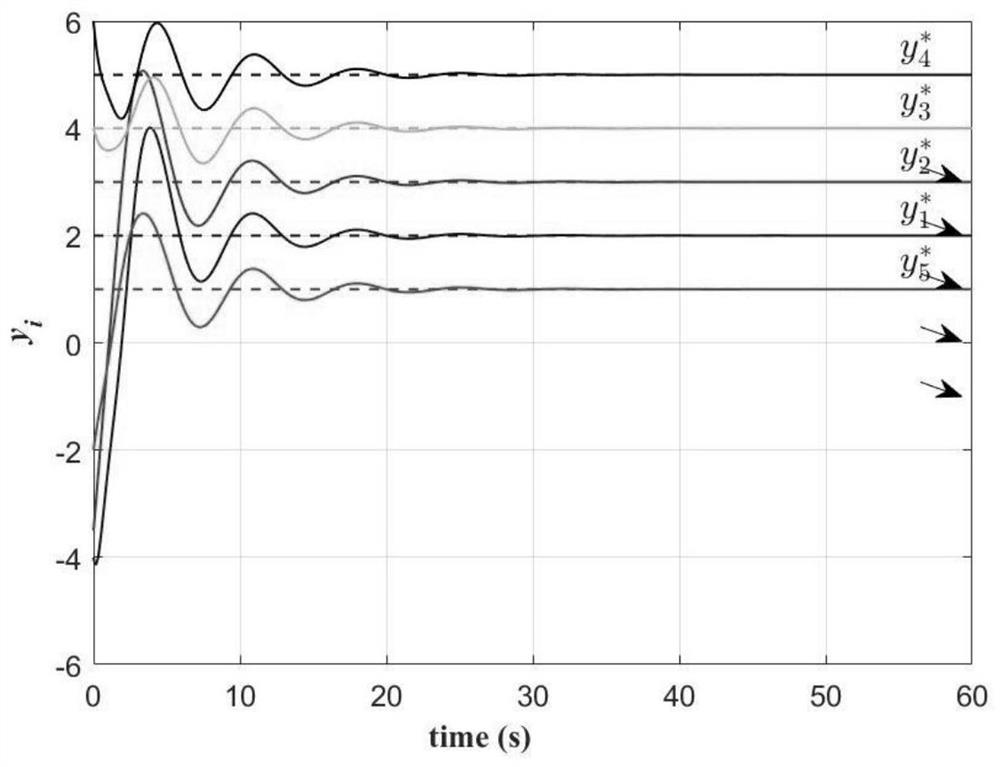
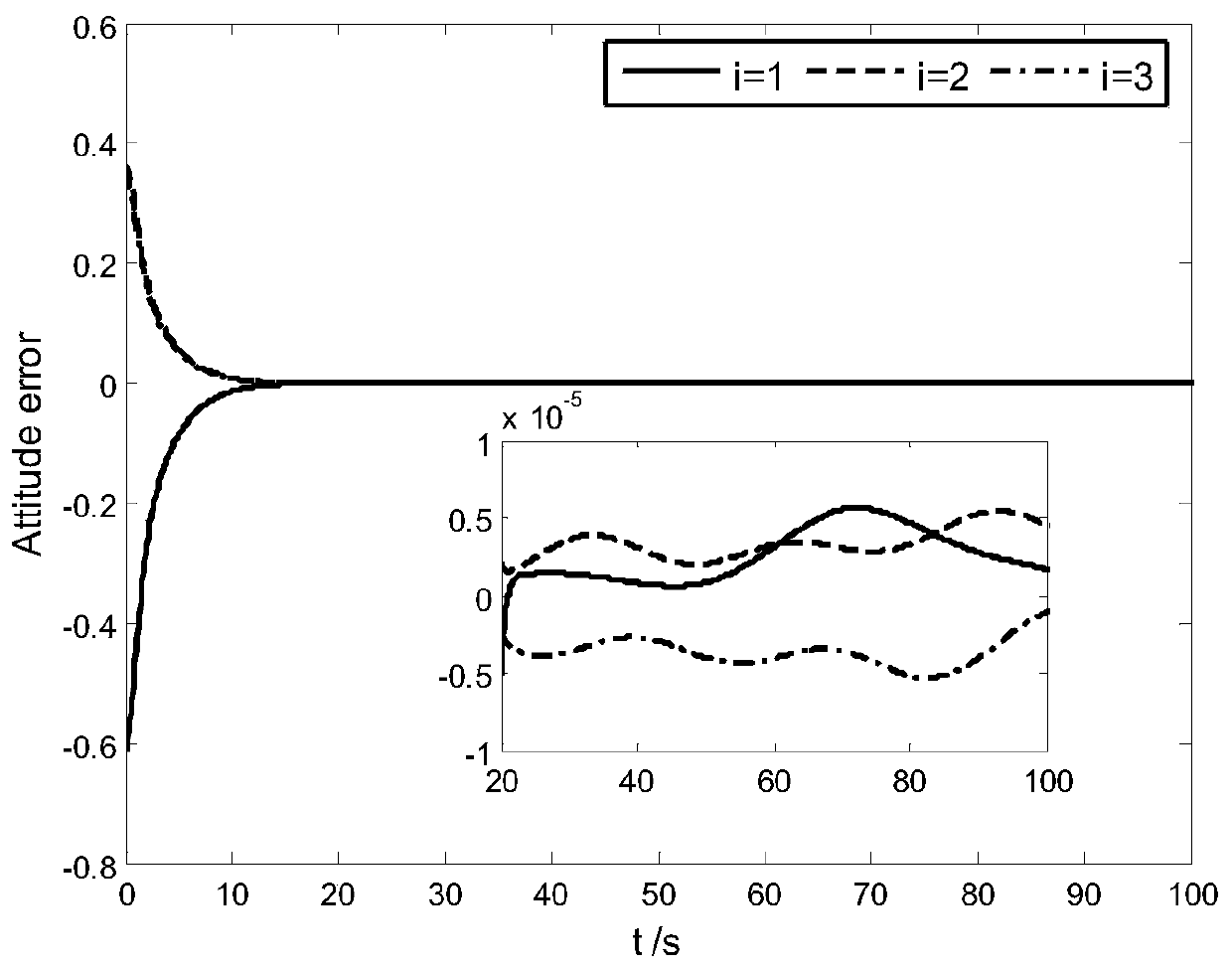
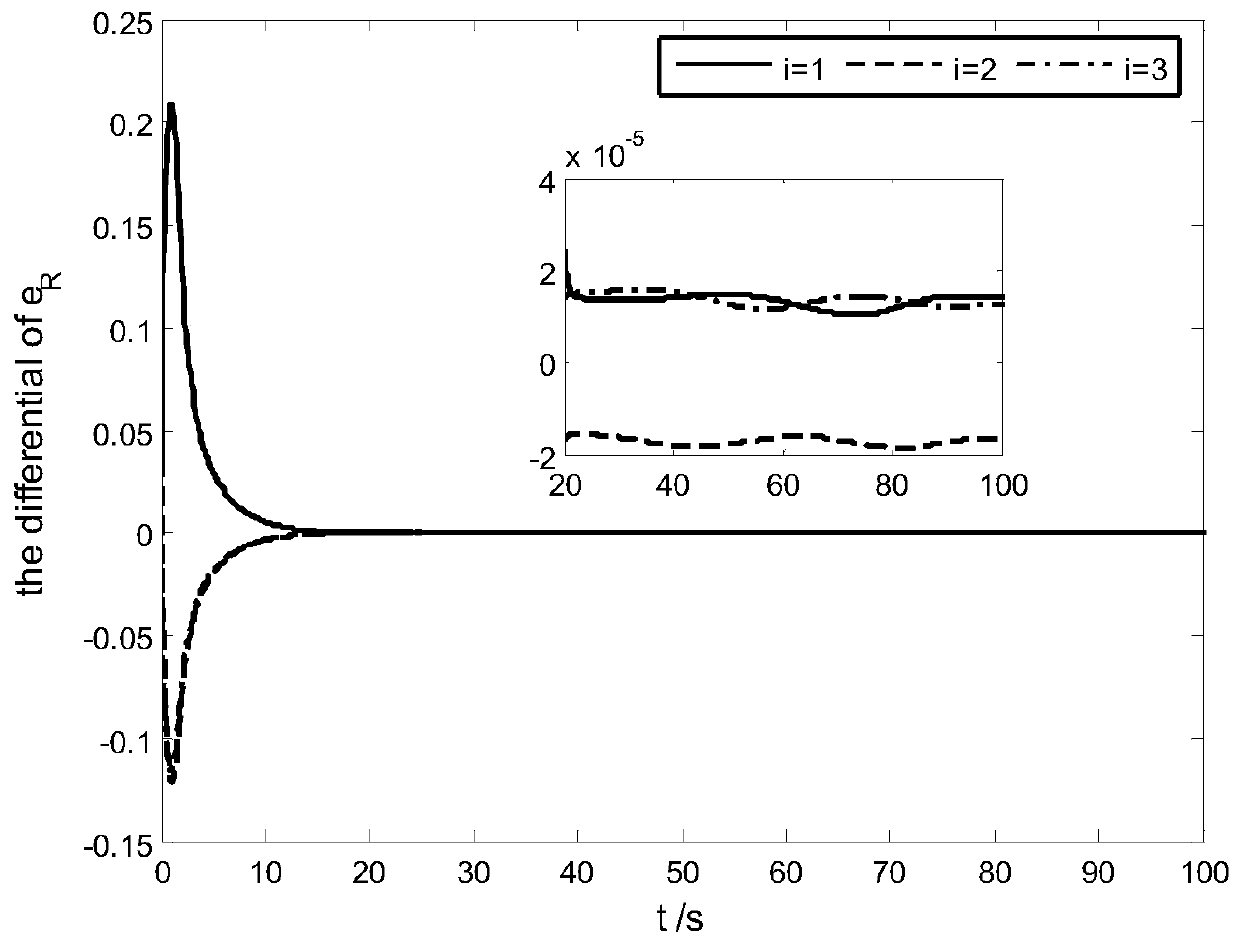
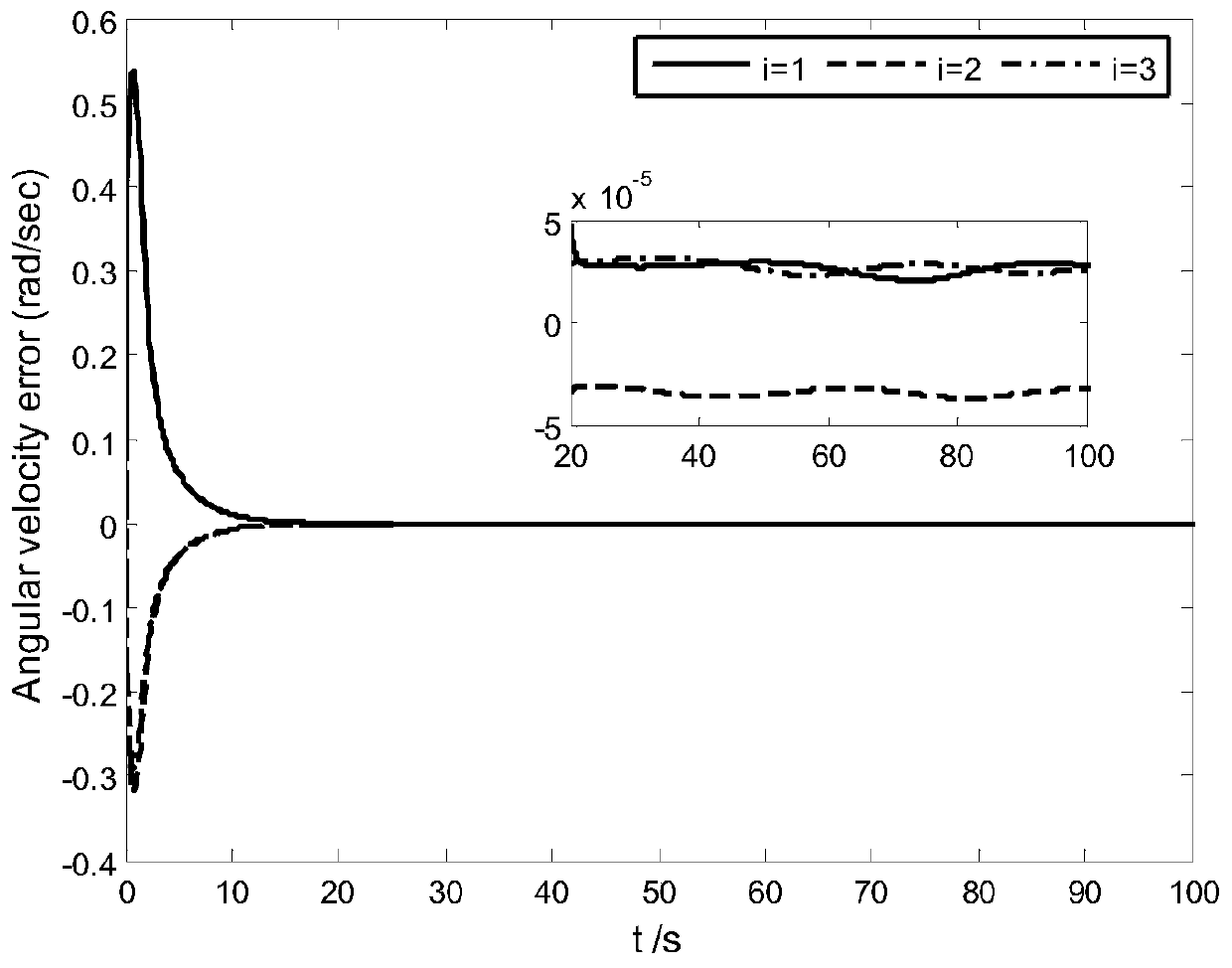
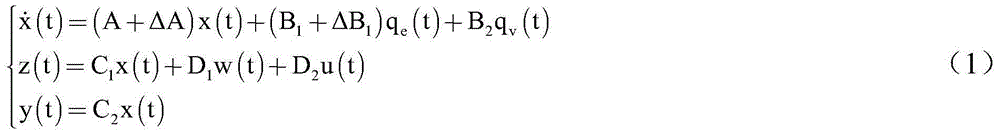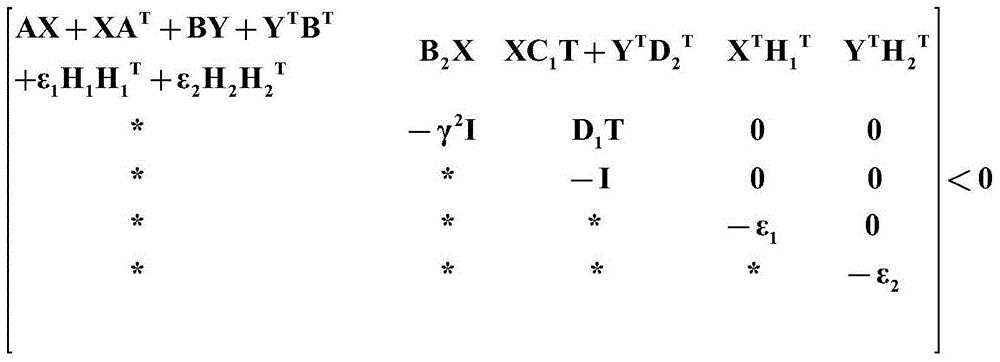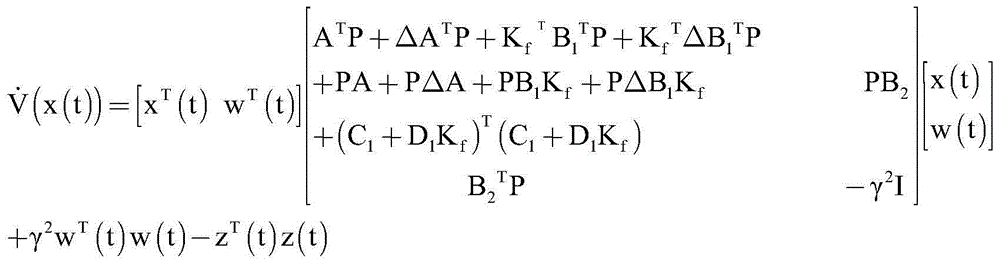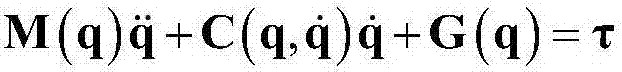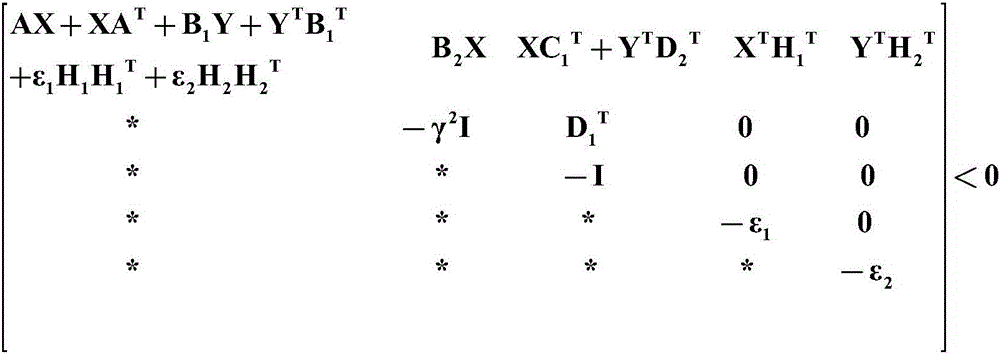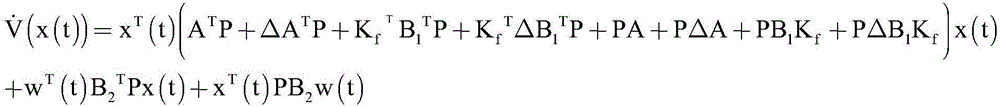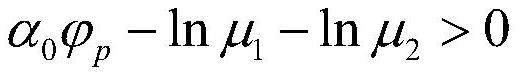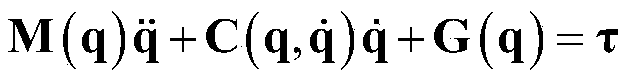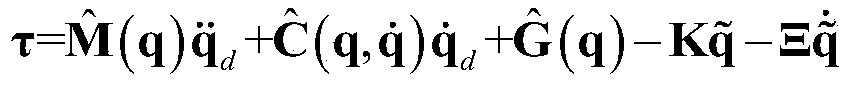Patents
Literature
30 results about "Lyapunov theorem" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lyapunov theorem. Lyapunov's theorem in probability theory is a theorem that establishes very general sufficient conditions for the convergence of the distributions of sums of independent random variables to the normal distribution.
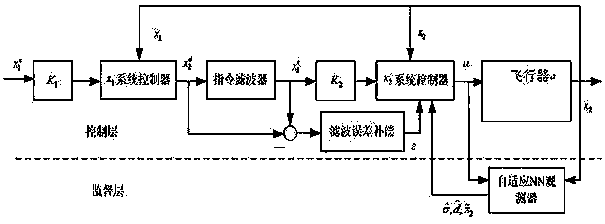
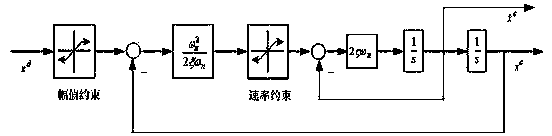
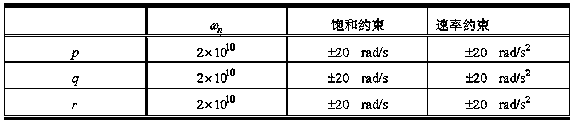
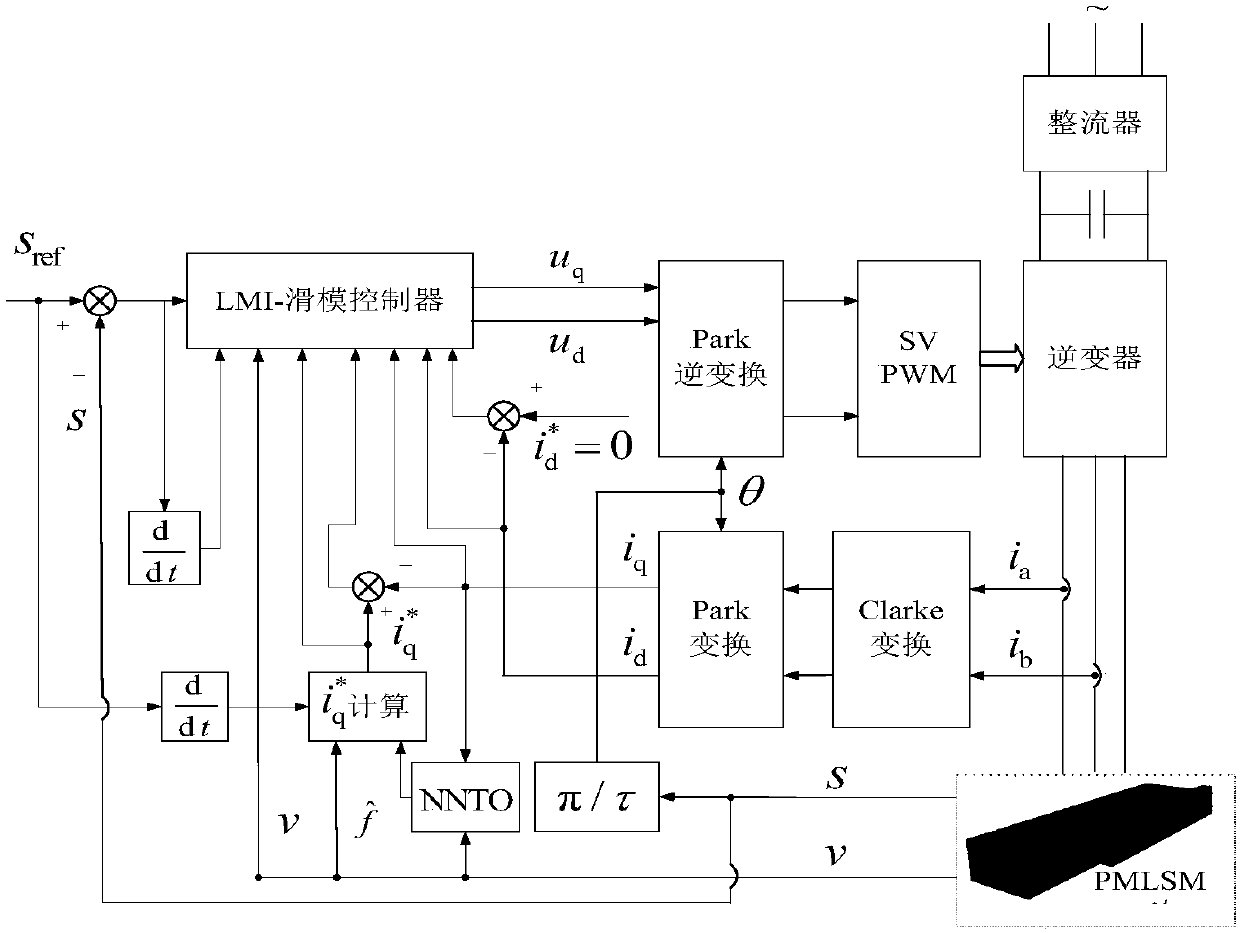
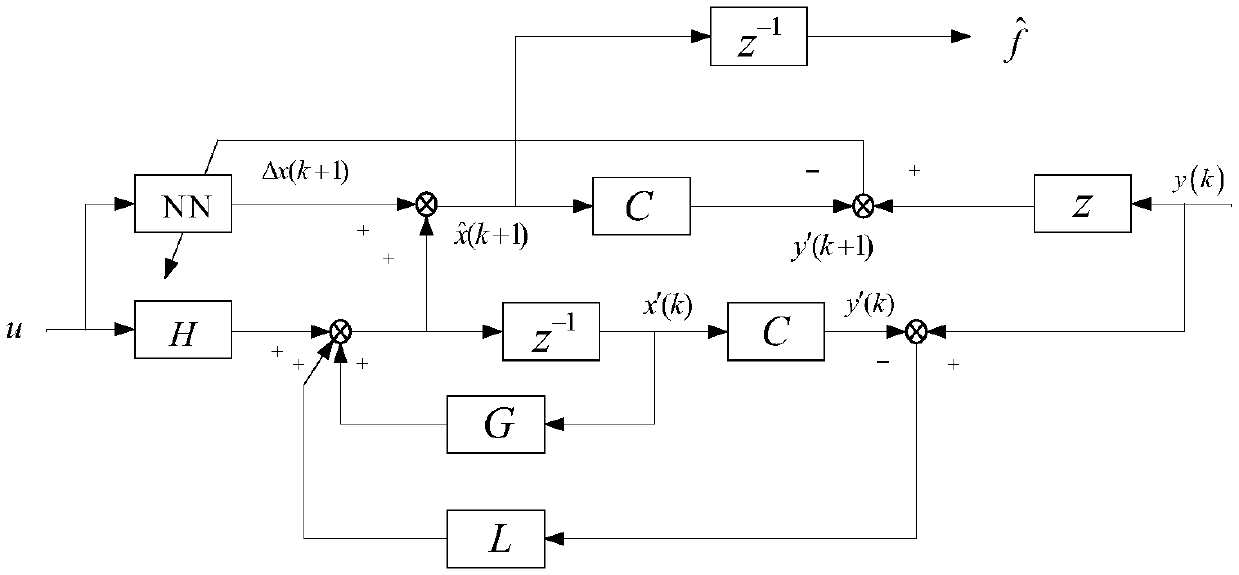
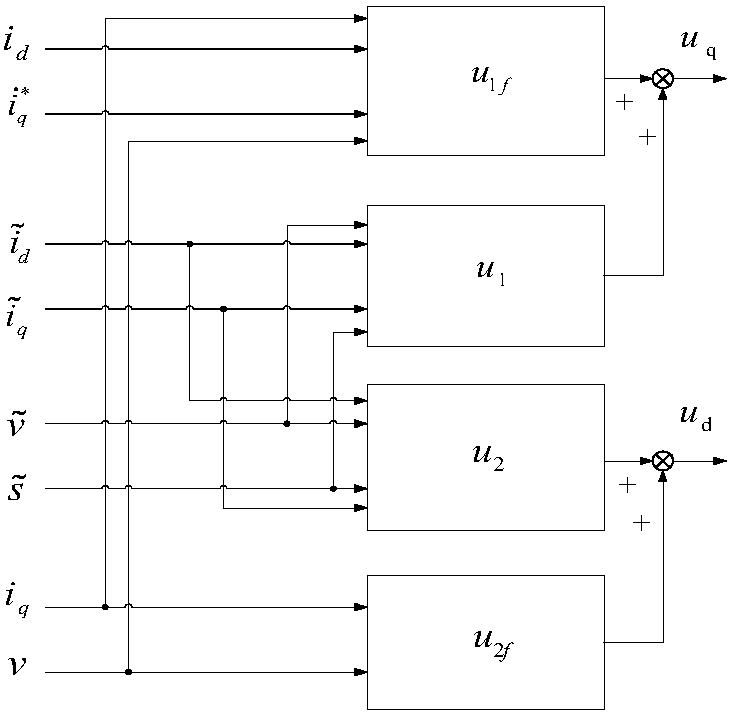
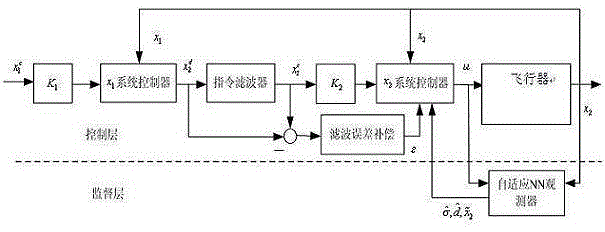
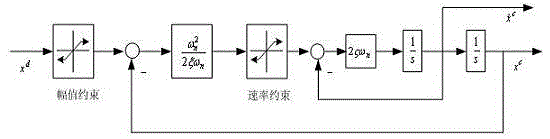
Unmanned air vehicle attitude robust fault tolerance control method based on neural network observer
Based on a neural network technology and an instruction filtering inversion method, the invention discloses a robust fault tolerance control system design structure based on instruction filtering inversion. Firstly, a mathematical model of an NSV attitude control system is given out, uncertainties and external disturbance caused by modeling errors are considered based on the mathematical model, a state equation of the NSV attitude control system under the fault of a control surface is also considered. The method mainly includes the two design parts including design of an auxiliary system and design of a controller based on the auxiliary system. The auxiliary system is introduced into the neural network to ensure robustness of the auxiliary system, and stability of a closed-loop system is strictly proved through Lyapunov theorem. Meanwhile, simulation is carried out on an attitude control system of a corresponding air vehicle, and a result shows that the method enables the uncertain flight control system with the external disturbance to have the ideal fault tolerance tracking performance under damage to the control surface.
Owner:南京晓飞智能科技有限公司
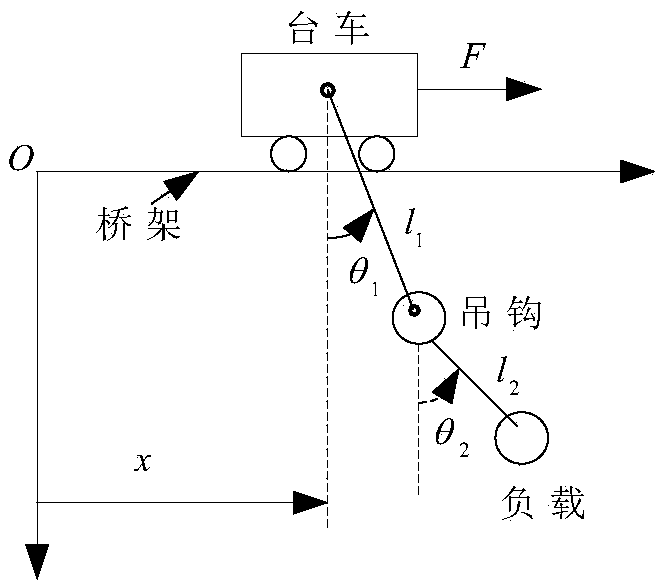
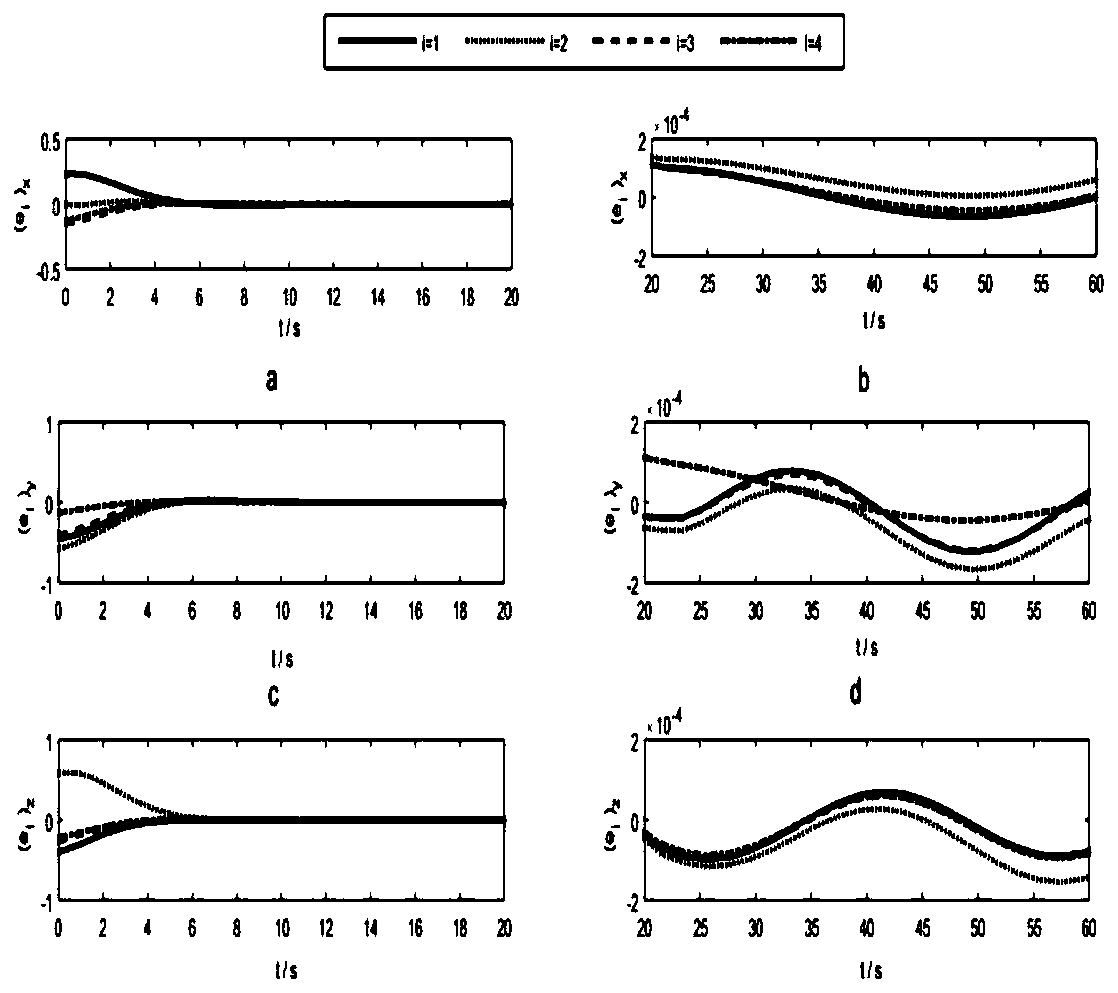
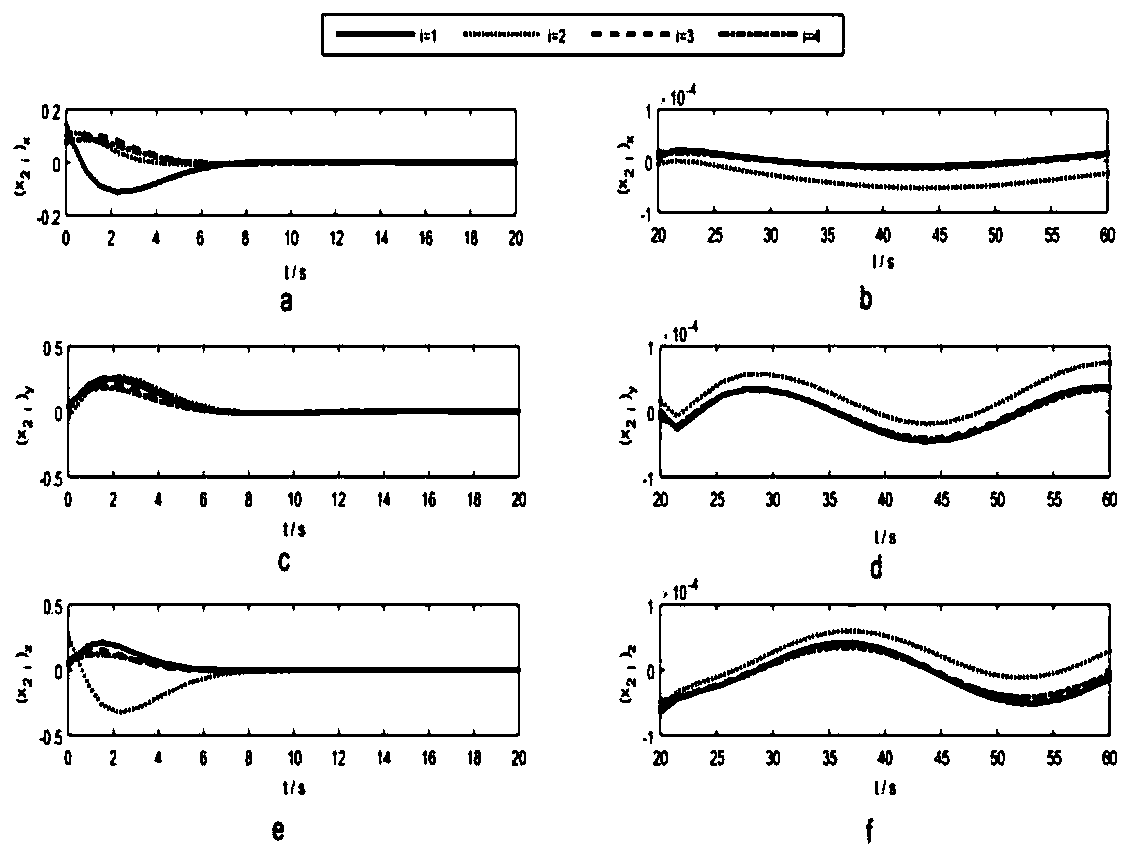
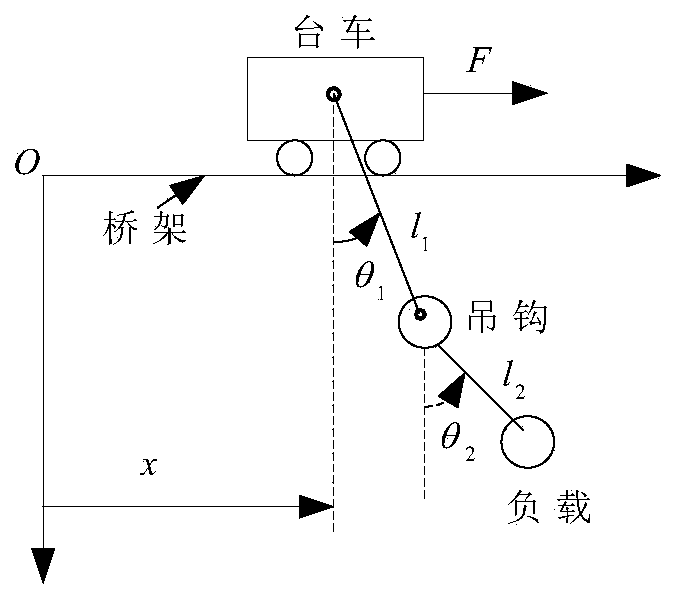
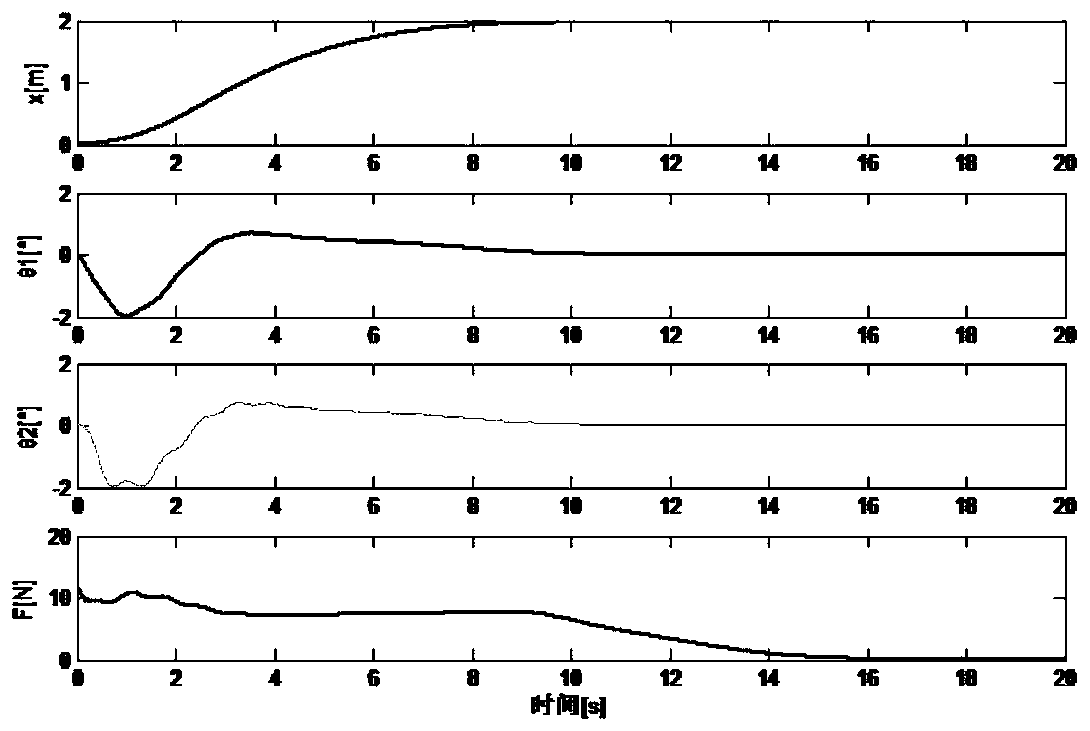
Coupling enhancing non-linear PD-type sliding mode controller for bridge crane system, and method
ActiveCN108557664AStrengthen the coupling relationshipImprove transient control performanceCranesTransient stateCoupling
The invention provides a coupling enhancing non-linear PD-type sliding mode controller for a bridge crane system, and a method. The designed controller is composed of a PD control part and an SMC control part. The SMC control part is used for constructing a frame of the controller. Quite high robustness is achieved aiming at an indeterminate model, different and indeterminate system parameters andexternal disturbance of a system. The PD control part is used for stably controlling the system. In addition, a generalized function is introduced, the coupling relation among trolley movement, lifting hook swinging and load swinging is enhanced, and thus the transient control property of the system is improved. By utilizing the Lyapunov theorem and Schur complement, it is proved that the asymptotic stability and convergence of the system can still be ensured through the provided control method even if the model and the system parameters are indeterminate and external disturbance exists. Thesimulation result shows the correctness of the provided control method and the excellent control property.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Adaptive inversion integral nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode controller design method
ActiveCN112241124ASimulation running statusHigh control precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorAdaptive controlBacksteppingState observer
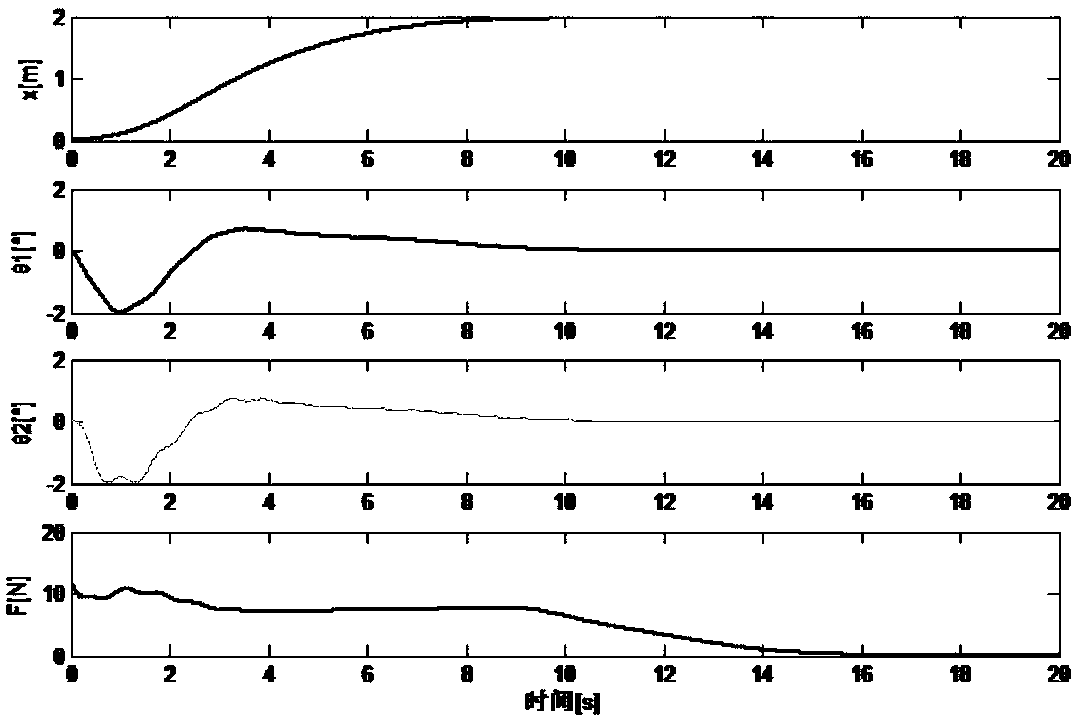
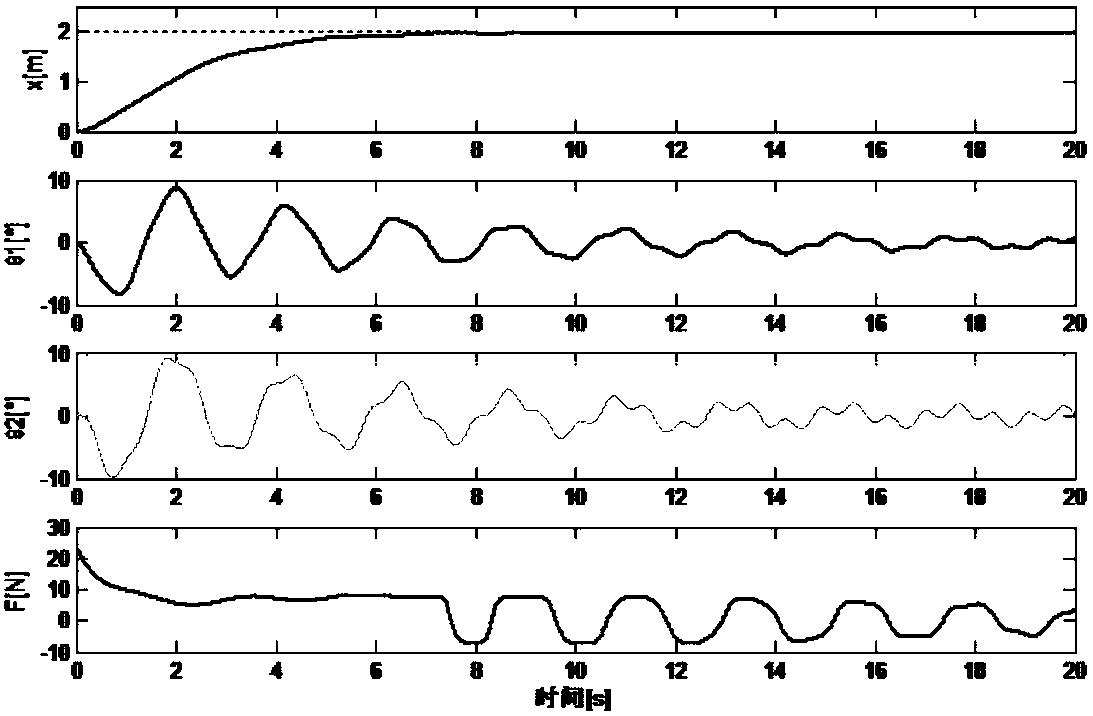
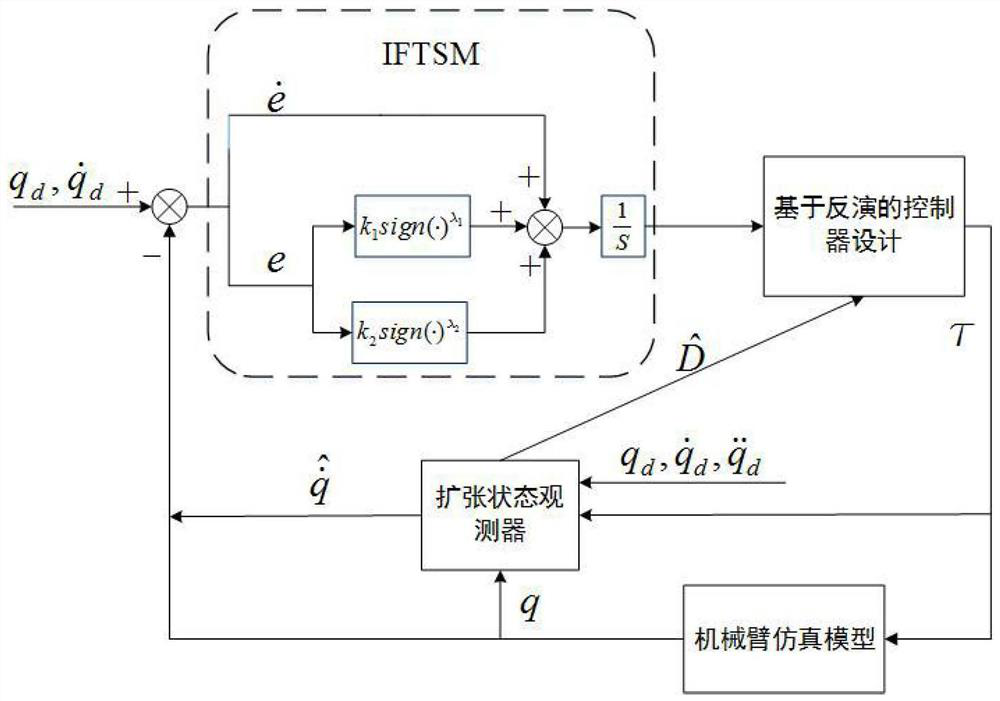
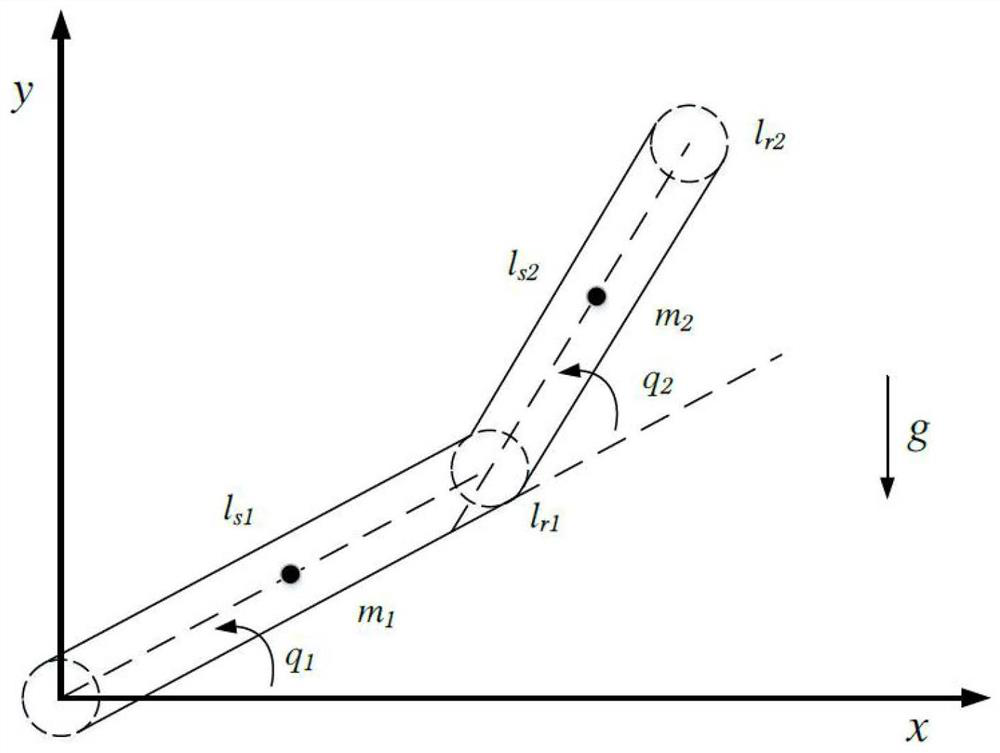
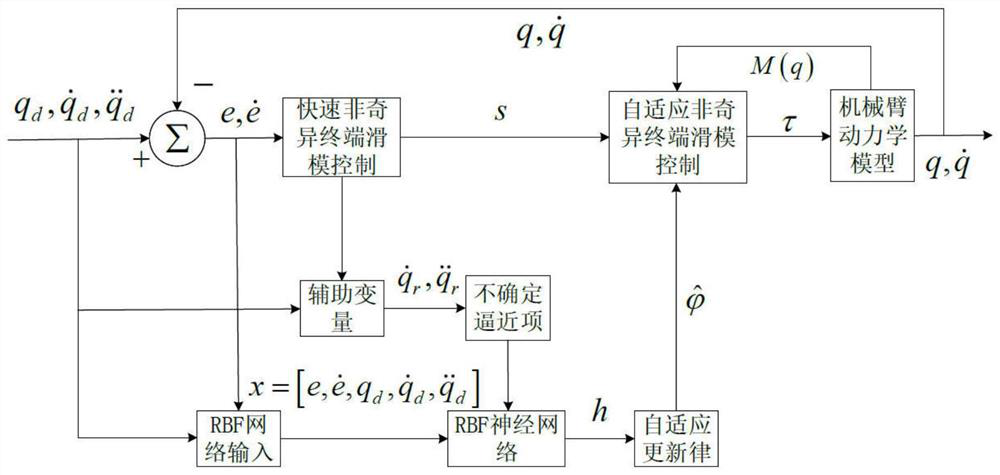
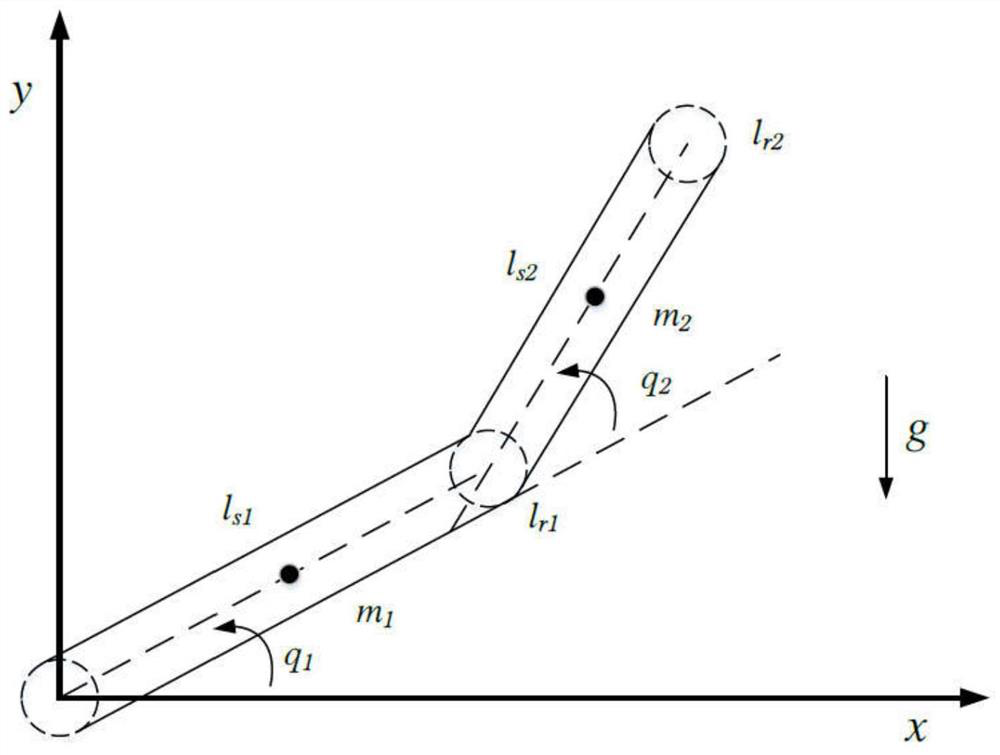
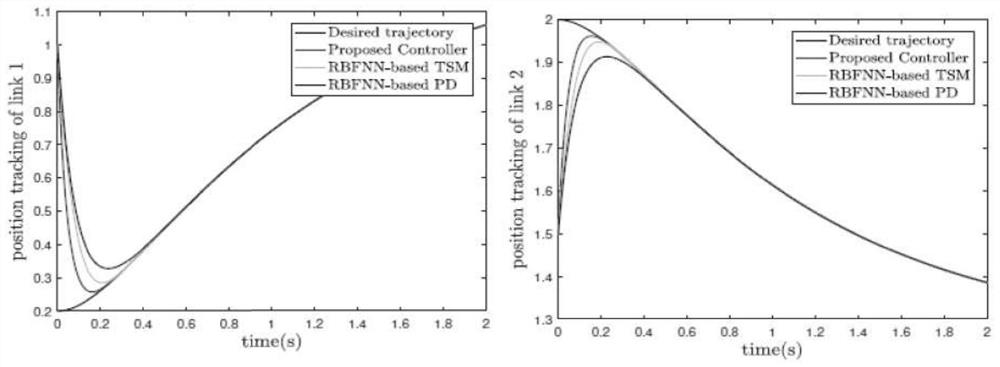
The invention discloses an adaptive inversion integral nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode controller design method based on an extended state observer for mechanical arm trajectory tracking control. Firstly, in order to better reflect the state of the mechanical arm in actual work and improve the control precision, a LuGre friction force model is combined with a mechanical arm kinetic model. And a novel integral fast terminal sliding mode surface is designed on the basis, so that the convergence speed and the tracking precision can be greatly improved, and a reasonable saturation functionis designed for a singular item to avoid singularity. Due to the fact that external disturbance and system uncertainty are unknown, an extended state observer is adopted to estimate and compensate theexternal disturbance and the system uncertainty, and meanwhile buffeting can be effectively eliminated. The speed information of the mechanical arm joint can be obtained through the expansion observer, and therefore people only need to measure the position information of the joint through the encoder. And finally, a control moment is designed by using a backstepping method to realize global asymptotic stability based on the Lyapunov theorem.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Formation flying spacecraft back-stepping sliding-mode control method
ActiveCN107577145AControlling time-varying external disturbancesReduce communication burdenAttitude controlAdaptive controlClosed loopEngineering
The invention relates to a formation flying spacecraft back-stepping sliding-mode control method, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft posture adjustment. By the back-stepping sliding-modemethod, two distributed robust consistency tracking controllers are designed. The first robust controller can compensate known bounded external interface, is continuous and free from buffeting. In order to meet the use requirements of self-adaptive control, the second robust finite time controller does not need the upper bound of the known external interface. As the two controllers are designed based on a rotation matrix, attitude represented by the rotation matrix has global unique attribute, and the shortcoming of system unwinding can be overcome. By the aid of Lyapunov theorem, a whole closed-loop system is stable in finite time, simulation experiments prove that absolute attitude can be tracked, and formation member attitude consistency can be kept.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Model-free quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory tracking controller based on RPD-SMC and RISE, and method
ActiveCN108445766ASimple structureHigh precisionAdaptive controlLyapunov stabilityControl parameters
The invention discloses a model-free quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory tracking controller based on RPD-SMC and RISE, and a method, and a RPD-SMC controller is designed. The controller combines advantages of a proportional differential-sliding mode controller (PD-SMC) and online estimation capability of a radial basis function neural network (RBFNN) on arbitrary function. Through introducing self-adaptive RBFNN feedforward, disturbance and unknown dynamic conditions are estimated and compensated, so that selection of control parameters of the PD-SMC is more rational, to achieve objectives of reducing controlling quantity and saving electric energy. Aimed at an inner-loop control system, an error symbol integral (RISE) controller based on robustness is designed. The RISE controller can ensure rapid convergence of a posture angle and has strong robustness on disturbance. Beneficial effects are that the lyapunov theorem of stability proves stability of the inner-loop and outer-loop systems, and simulation experiment results prove that the controller has validity.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
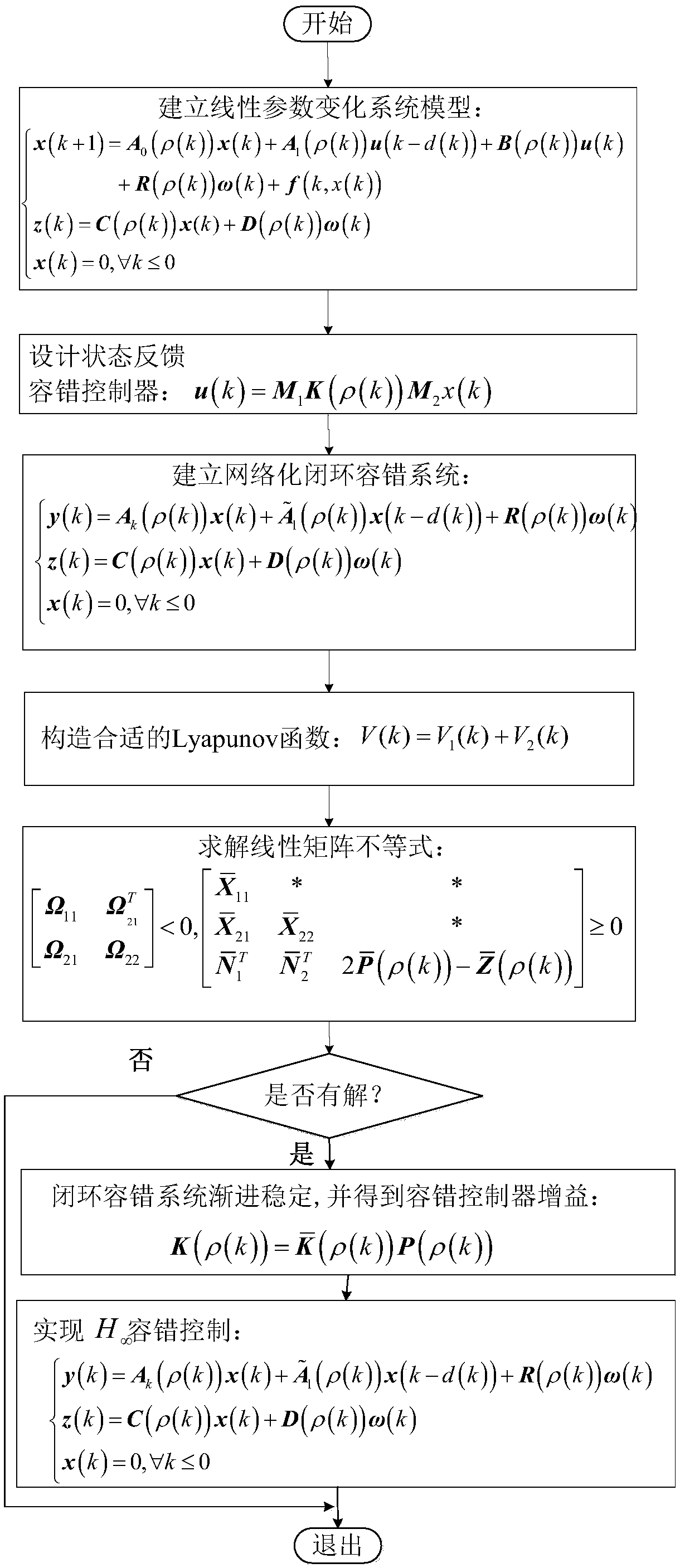
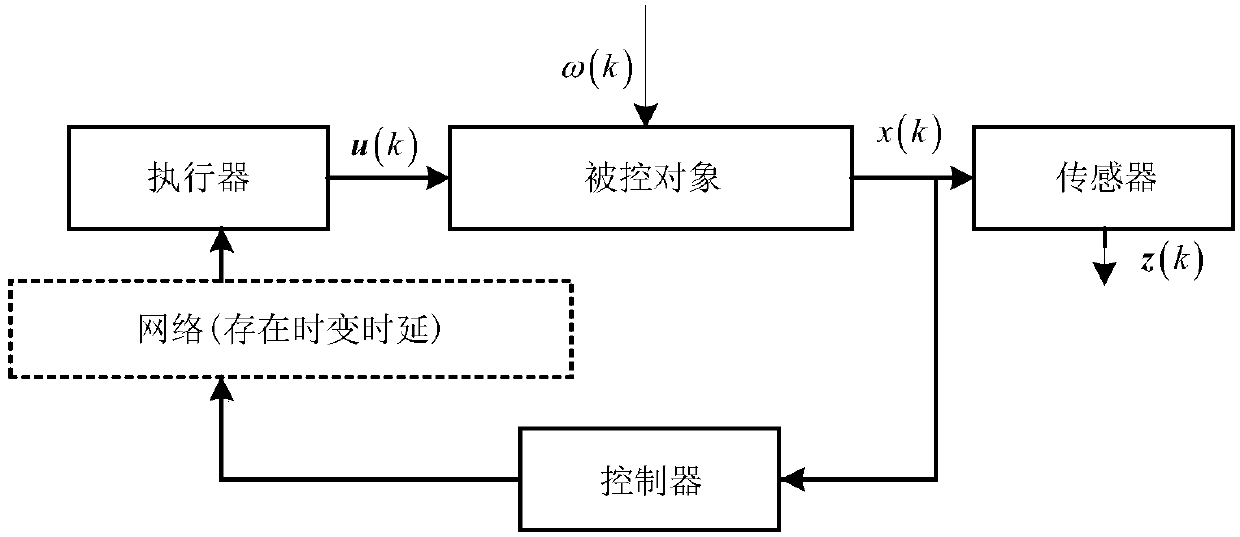
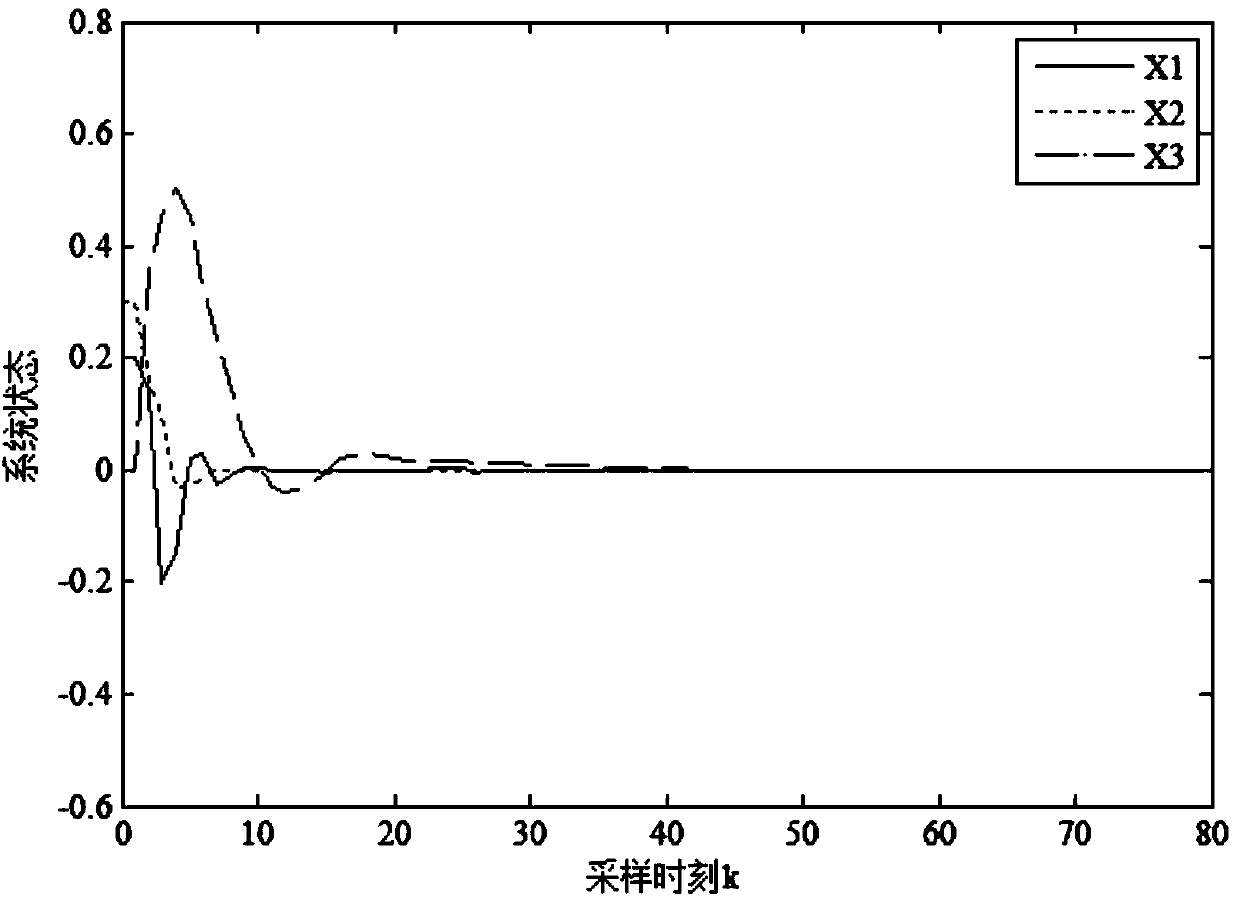
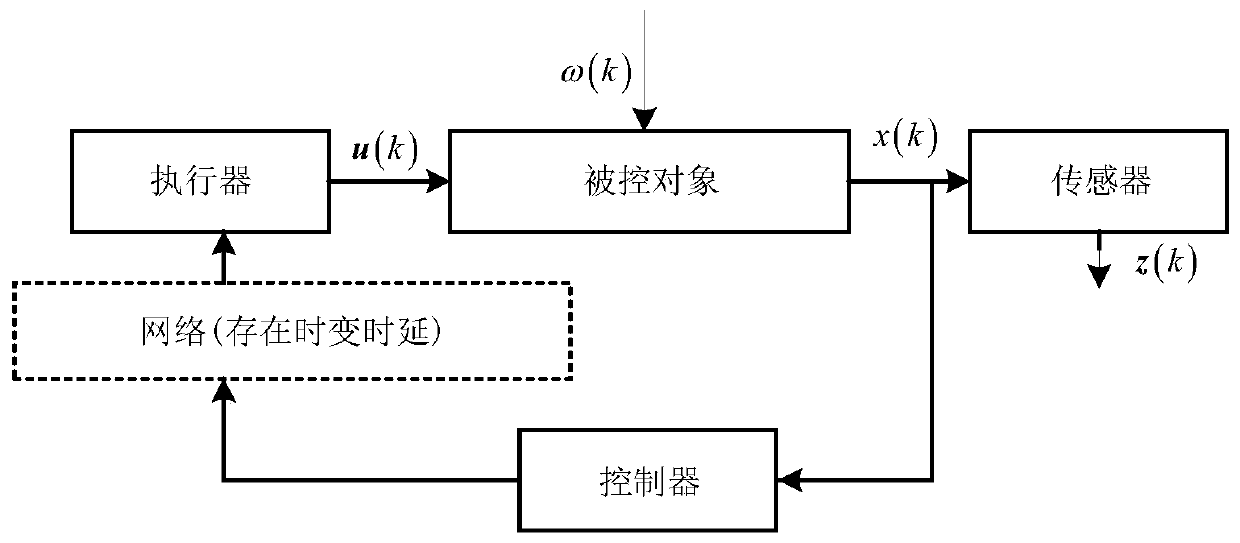
H8 fault tolerance control method for networked linear parameter variation system with time variation and time delay
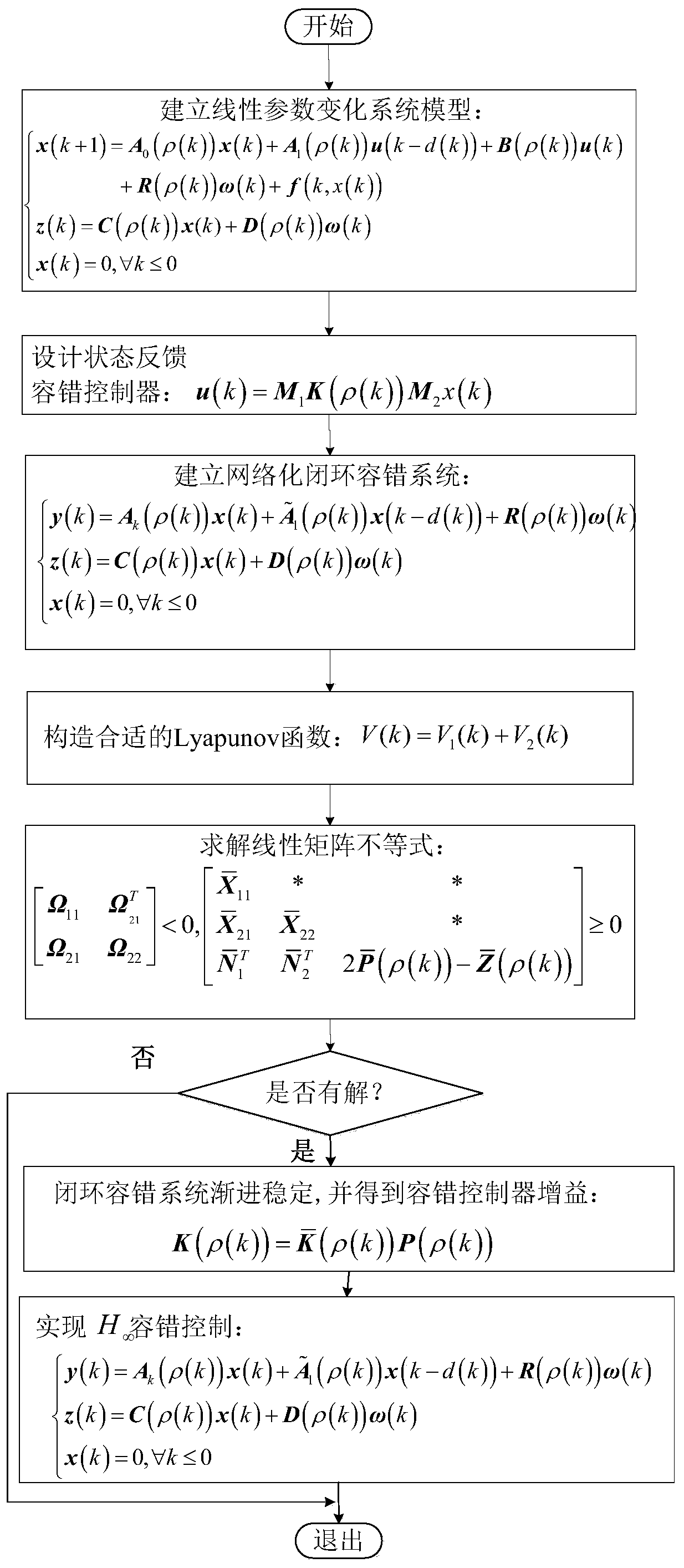
The invention provides an H8 fault tolerance control method for a networked linear parameter variation system with time variation and time delay, and belongs to the field of networked linear parametervariation system control. The method takes the situations that a linear parameter variation system has network time variation and time delay and a sensor and an executor break down simultaneously inaccount, firstly a method of free-weighting matrix is used to establish a Lyapunov function for processing the time variation and time delay to obtain sufficient conditions of closed-loop fault tolerance control system stability, then a Lyapunov theorem of stability and a linear matrix inequality analysis method are used to obtain sufficient conditions of H8 fault tolerance controller existence, lastly an approximate primary function and a gridding technology are used to approximate a solving problem of an infinite dimensional linear matrix inequality system with a solving problem of a finitedimensional linear matrix inequality system, a Matlab LMI toolkit is used for solution, and a gain matrix of an H8 fault tolerance controller is provided. The H8 fault tolerance control method for thenetworked linear parameter variation system with the time variation and the time delay reduces the conservatism of the H8 fault tolerance controller.
Owner:龙岩荣创信息科技有限公司
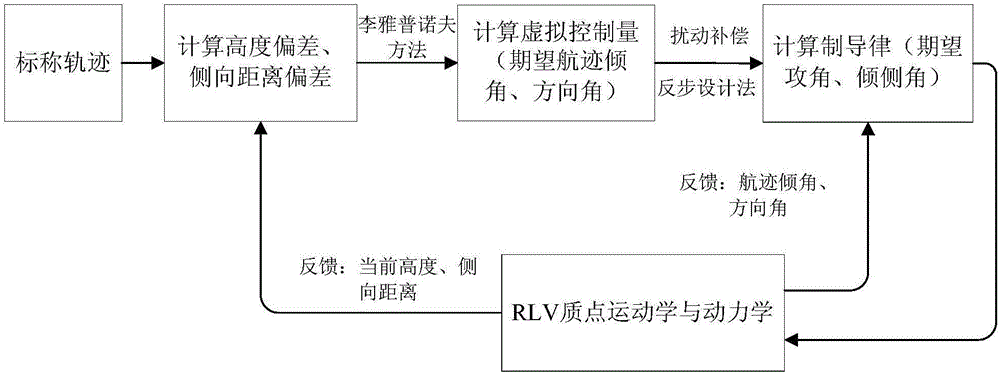
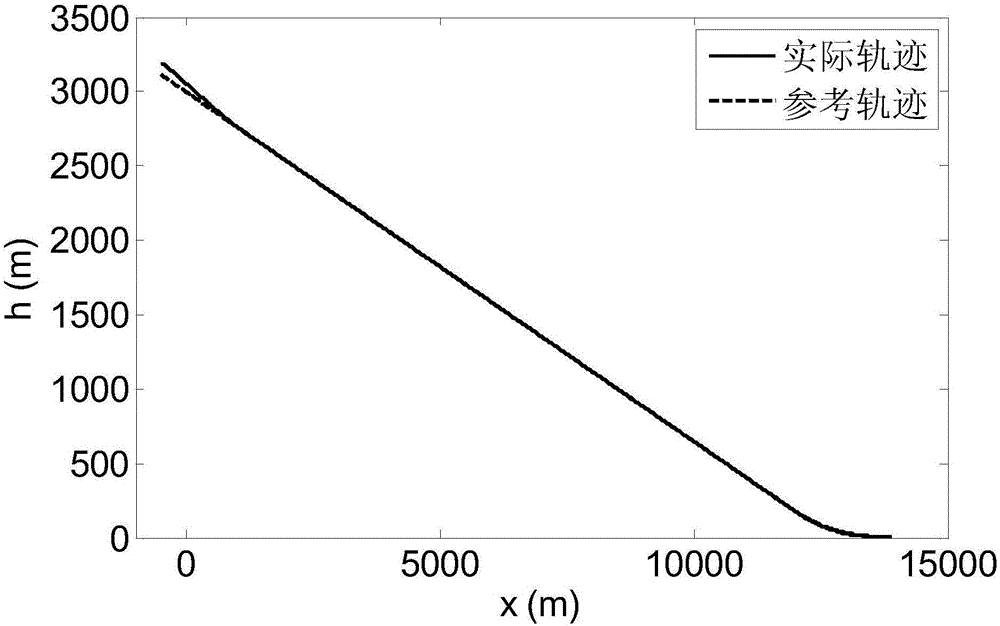
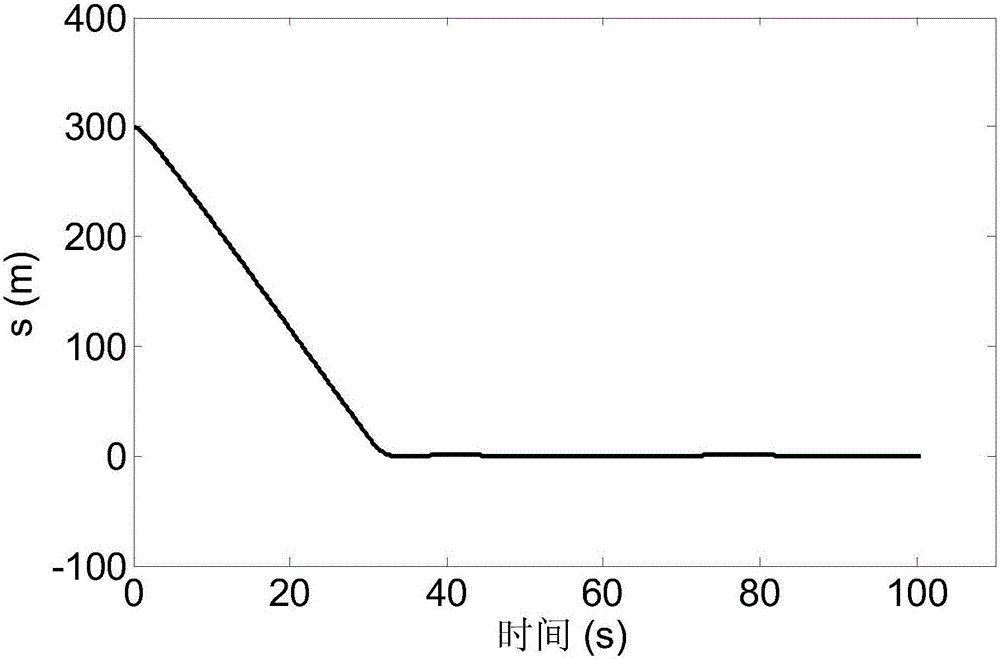
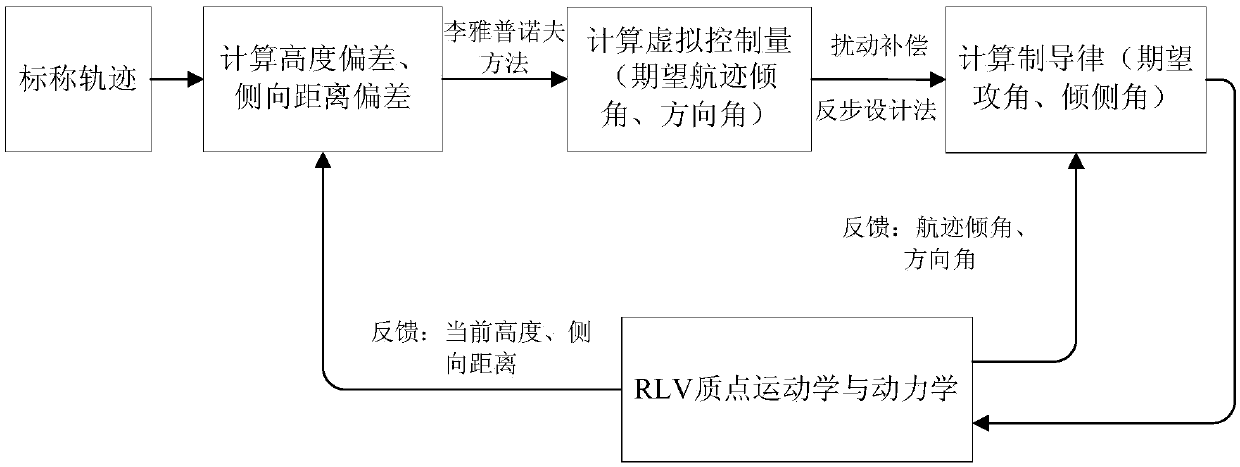
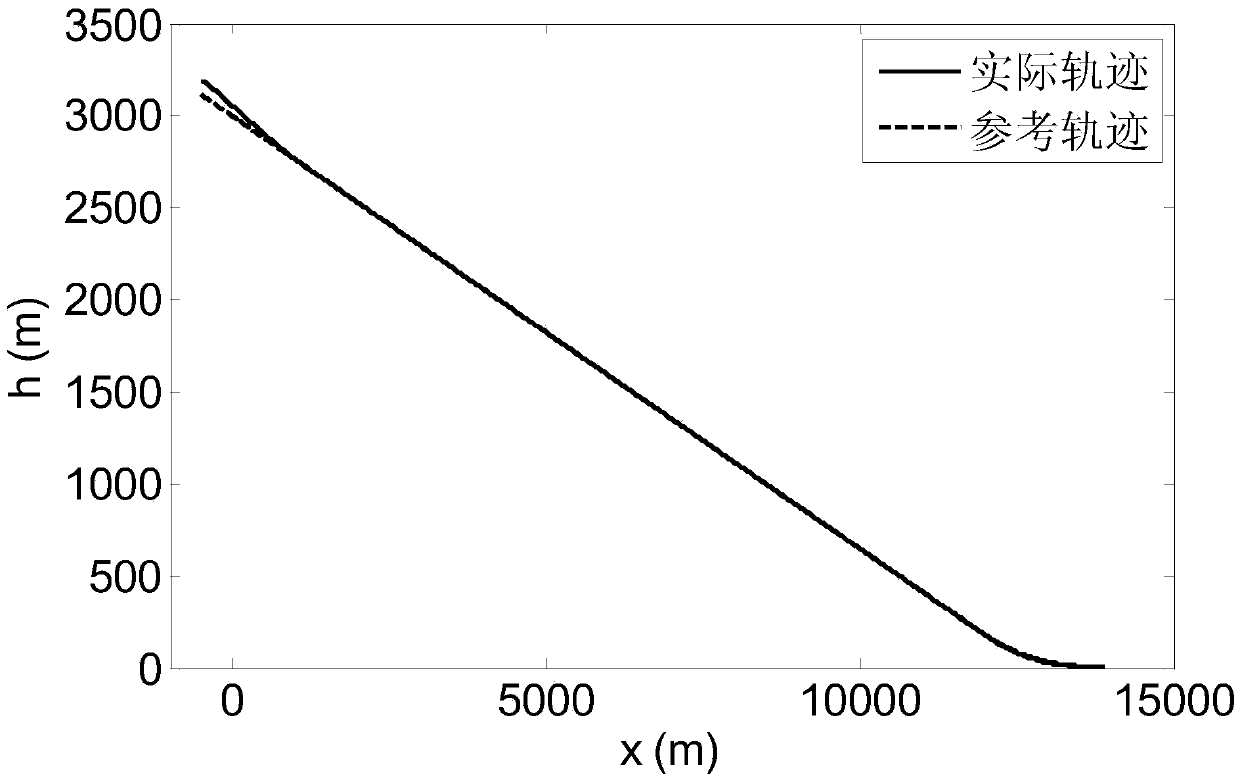
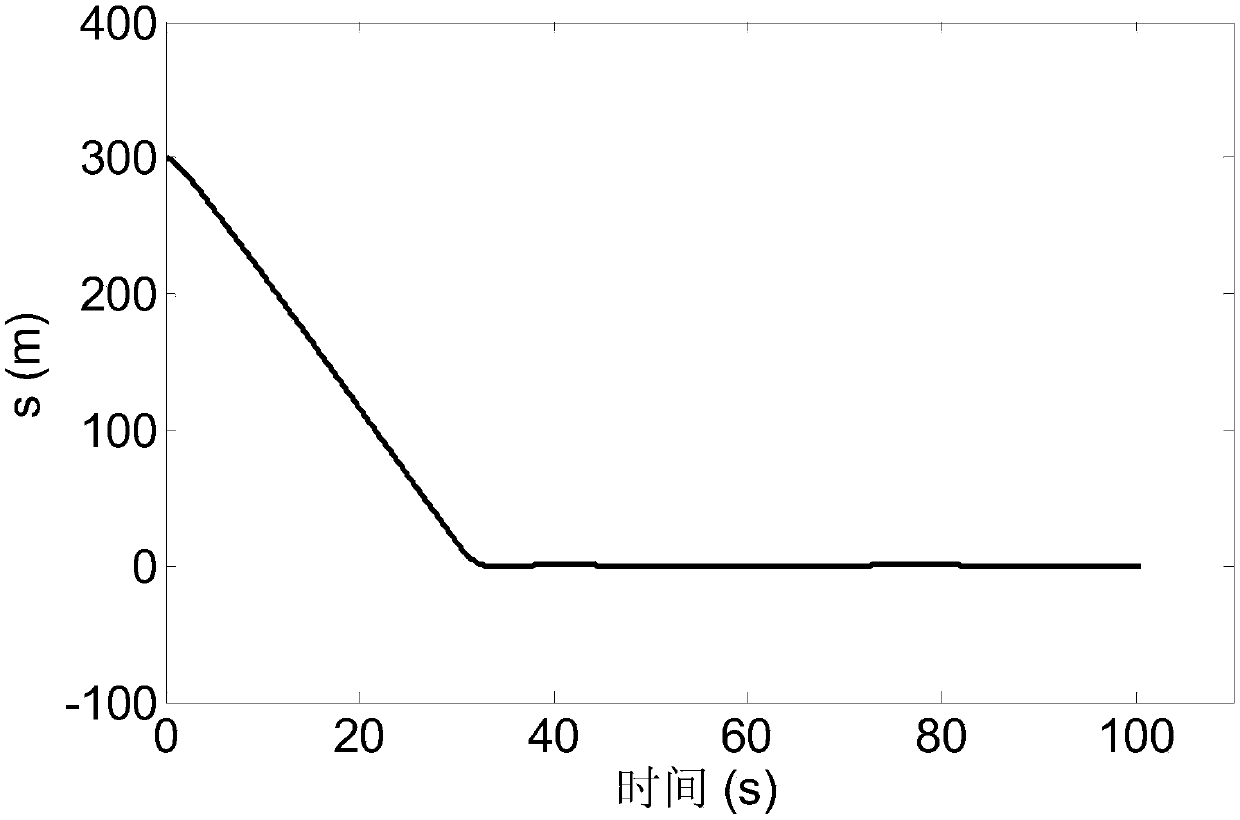
Disturbance compensation based RLV (reusable launch vehicle) approach landing guidance law acquisition method
ActiveCN106292701AGuaranteed stabilityAvoid the problem of not converging to zeroAdaptive controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsGuidance systemBackstepping
A disturbance compensation based RLV (reusable launch vehicle) approach landing guidance law acquisition method includes: firstly, calculating a height deviation and a lateral distance deviation according to an RLV approach landing nominal trajectory; secondly, using the Lyapunov theorem to obtain an anticipated flight path angle and a direction angle, namely virtual control laws according to a tracking deviation of the nominal trajectory; finally, adopting a backstepping design method to provide a guidance acquisition method capable of guaranteeing stability of a guidance loop. In a design process, an uncertainty upper bound of the guidance loop is obtained by analysis of aerodynamic data and inhibited by introduction of a compensation term, and consequently a guiding system has asymptotic stability in uncertainty of disturbance and the like. By adoption of the disturbance compensation based RLV approach landing guidance law acquisition method, influences of uncertainty on the RLV guiding system can be effectively overcome, and accordingly guiding precision is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
LMIs state feedback system control method based on uncertain model
ActiveCN104407515AImprove certaintyImprove robustnessSpecial data processing applicationsAdaptive controlRobustificationComponent Object Model
The invention discloses a LMIs state feedback system control method based on an uncertain model. The LMIs state feedback system control method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: establishing a controlled object model containing uncertain parameters at first, introducing a system state feedback controller, constructing a function of a closed-loop system, and designing a nonlinear system control law in the event of satisfying a Lyapunov theorem. The control method disclosed by the invention considers the control problems including influence caused by modelling error, model parameter variation, system noise and the like, of a system having uncertainty in a certain degree; the control method disclosed by the invention has good adaptive capacity to the uncertain factors of the system; in addition, compared with general conventional methods, the method disclosed by the invention is more rapid in response speed and higher in stability and robustness.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Linear servo position tracking control based on linear matrix inequality and sliding mode control
ActiveCN108123648AGuaranteed real-timeGood robust tracking performanceElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlLinear matrixEngineering
The invention relates to linear servo position tracking control based on a linear matrix inequality and sliding mode control. Control designing is performed through using a mechanical subsystem and anelectrical subsystem as a whole member. A complicated problem which is hard to solve is converted to a relatively easy linear matrix inequality (LMI) problem. An Lyapunov theory is used for proving system stability. An MATLAB-LMI toolset is used for calculating a result. Offline studying is performed on periodical linear factors such as end effect and friction by means of a neural network thrustobserver for ensuring system real-time performance, and then the factors are applied to the system for observing load disturbance. Finally the invention realizes a purpose of realizing high robust tracking performance of the system.
Owner:东能(沈阳)能源工程技术有限公司
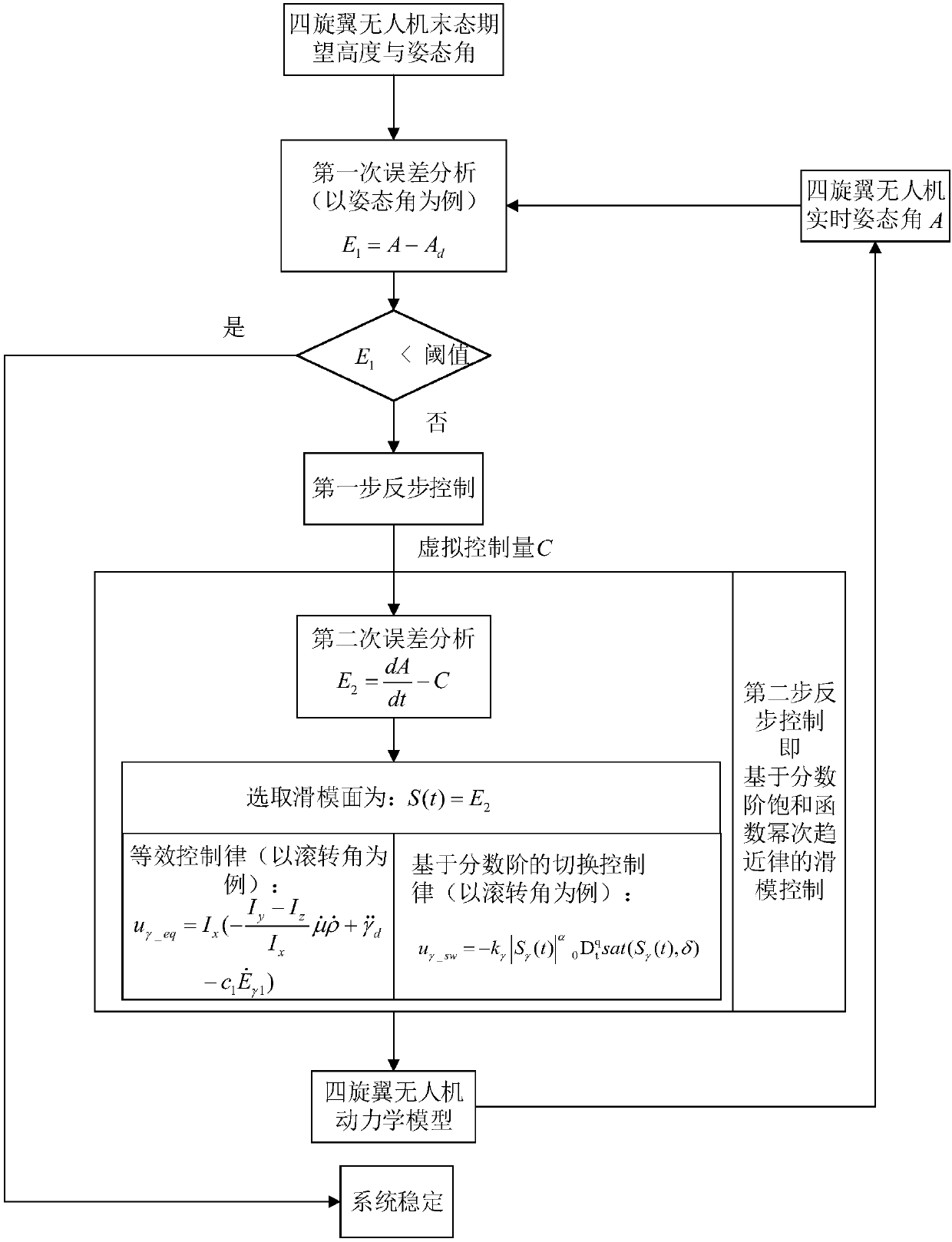
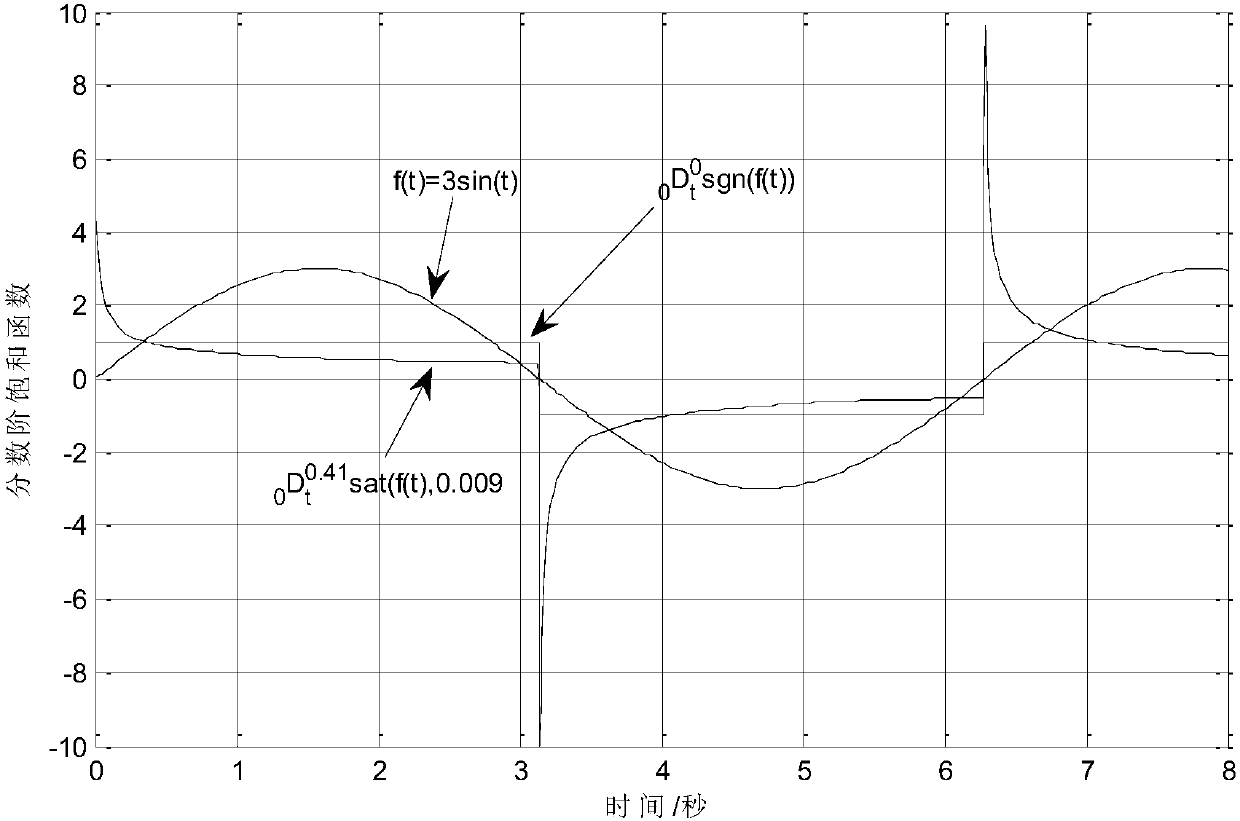
Four-rotor flight control method based on fractional order saturation function power switching law
ActiveCN108549398AFast convergenceGuaranteed functionalityAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsRobustificationBackstepping
The invention discloses a four-rotor flight control method based on the fractional order saturation function power switching law. A system is split into two subsystems through utilizing the backstepping control method, the traditional backstepping control method and the sliding mode control method are utilized to design sub-control laws satisfying the Lyapunov theorem for the two subsystems, specifically, the backstepping control method is to inherit integrity and unity, and the sliding mode control method is to improve robustness and the anti-interference ability. When the sliding mode control method is utilized, the fractional order saturation function power switching law is introduced to improve performance of a controller, trembling is suppressed, fast response of the flight control ofa four-rotor drone is guaranteed, through adjusting saturation function parameters, nonlinear characteristics of the controller can be further improved, trembling in controller output is filtered, and smoothness of the controller is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
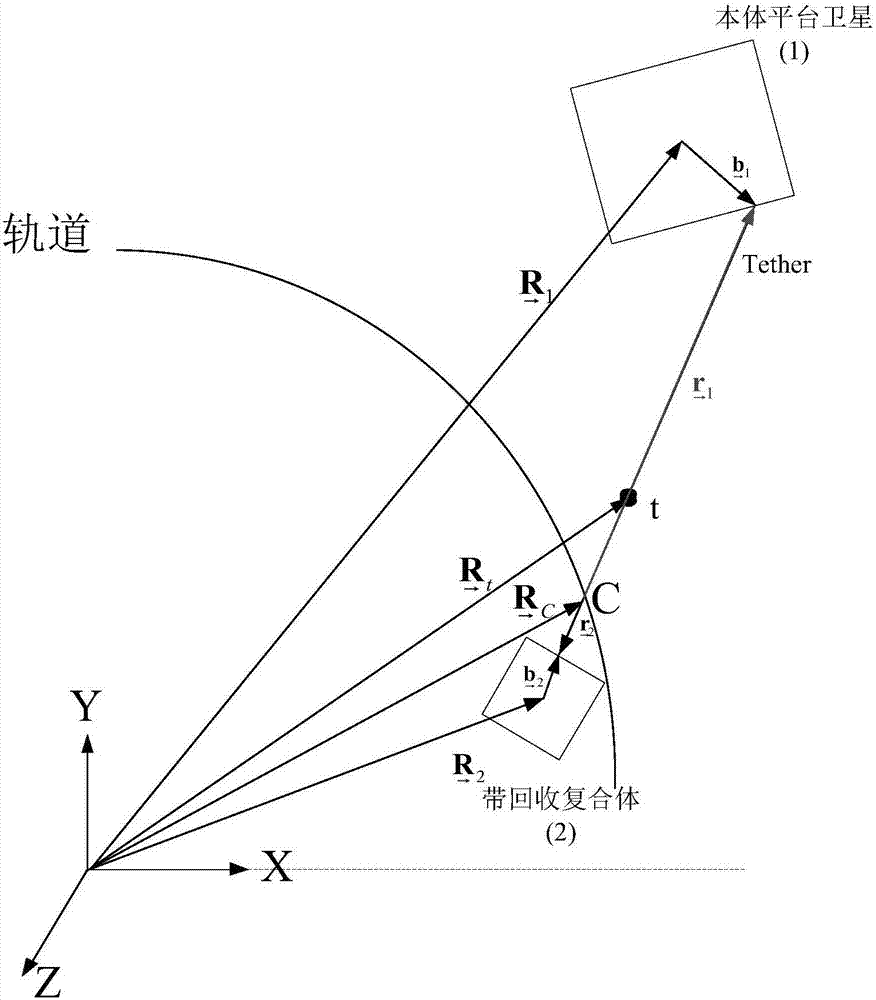
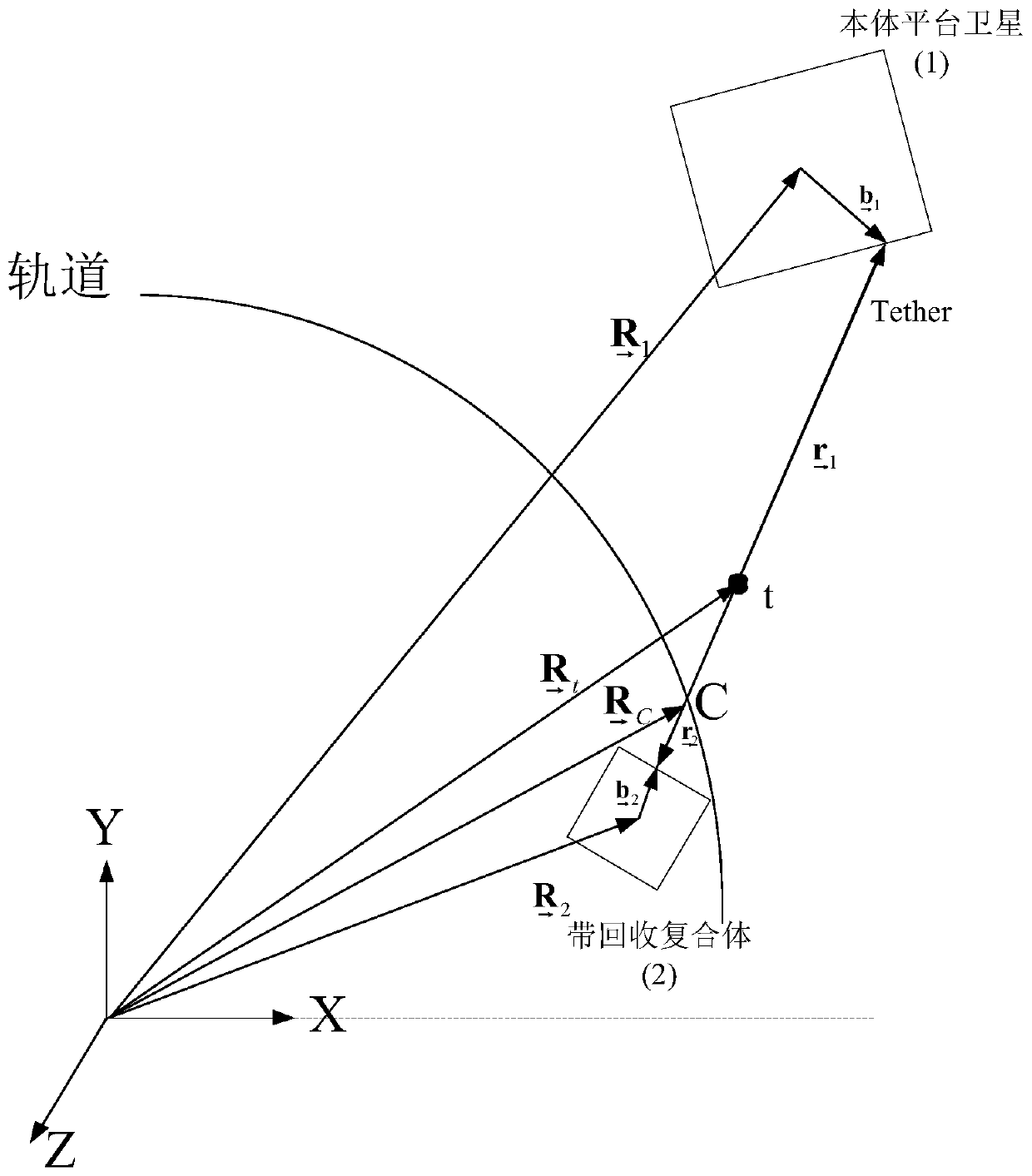
Adaptive control method for target recycling of space tethered robot after close-range capture
The invention relates to an adaptive control method for target recycling of a space tethered robot after close-range capture. The adaptive control method comprises the steps of firstly deriving a compound body formed by the tethered robot and a captured target satellite, building a dynamic equation of the system in the recycling process, then designing the control force / moment in the recycling process according to a Lyapunov theorem, and designing a dynamic parameter identification law for the compound body, thereby achieving stable recycling of the compound body. According to the adaptive control method, the dynamic parameter identification law is put forwards for the first time, the whole recycling process can be enabled to be more accurate in calculation for control variables, and thus the recycling is more stable. The adaptive control method enables the compound body formed by the space tethered robot after capturing a non-cooperative target to be recycled stably and quickly through tether tension. The adaptive control method can overcome the natural instability in a problem of tether recycling on the basis of dynamic parameters of the compound body, and the compound body is recycled stably.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
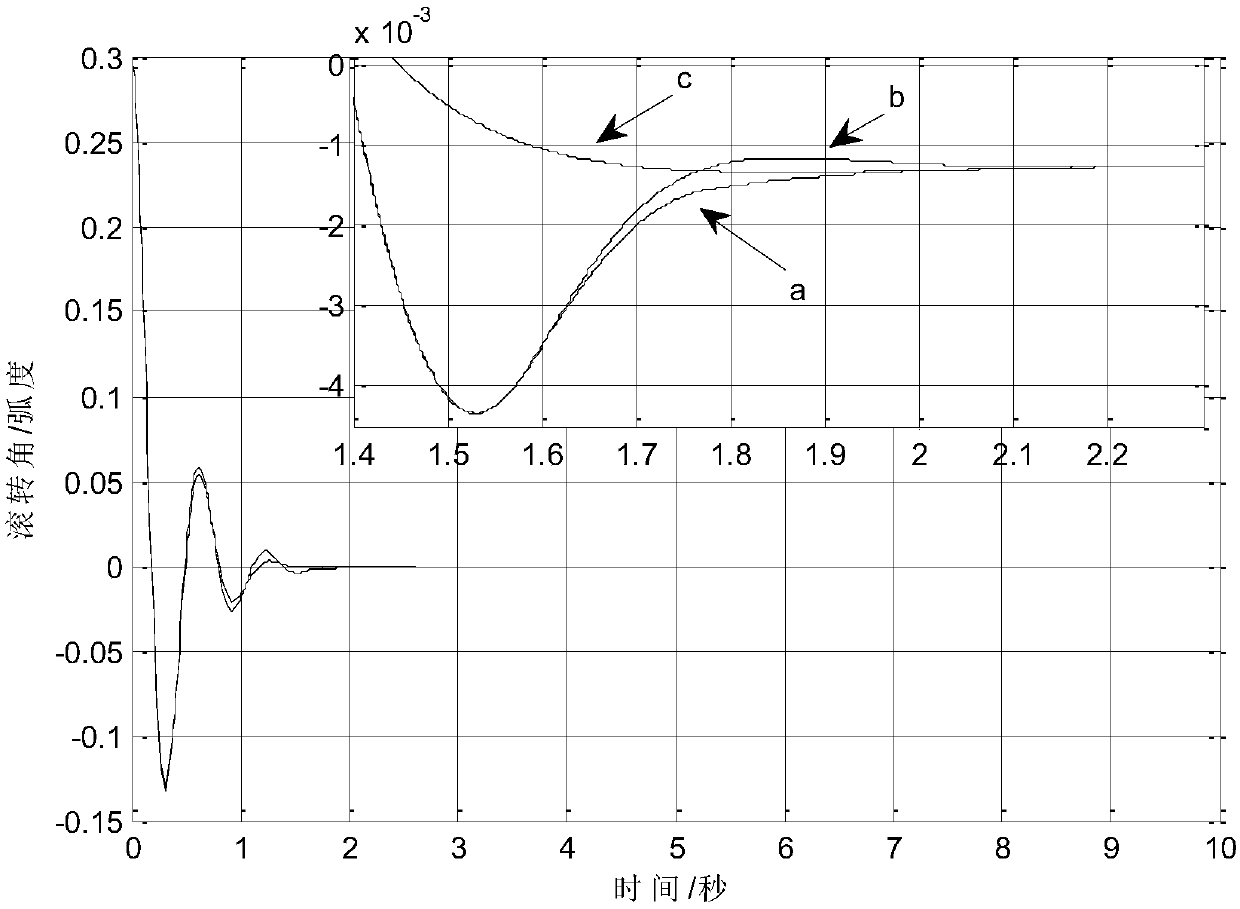
Sliding mode control method of input saturated spacecraft attitude terminal
The invention relates to a sliding mode control method of an input saturated spacecraft attitude terminal, belonging to the technical field of spacecraft attitude adjustment. According to the method,two non-unwinding robust finite-time control methods are designed for a spacecraft and are a compensation known bounded method and a hyperbola tangent function and auxiliary system control method. According to the compensation known bounded method, known bounded external disturbances can be compensated, and external disturbance and input saturation problems can be solved by using the hyperbola tangent function and auxiliary system control method. The Lyapunov theorem is used to prove the finite-time stability and asymptotic stability of an entire closed-loop system. A simulation result shows that a controller can make the spacecraft to track a time-varying reference attitude signal within a limited time.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
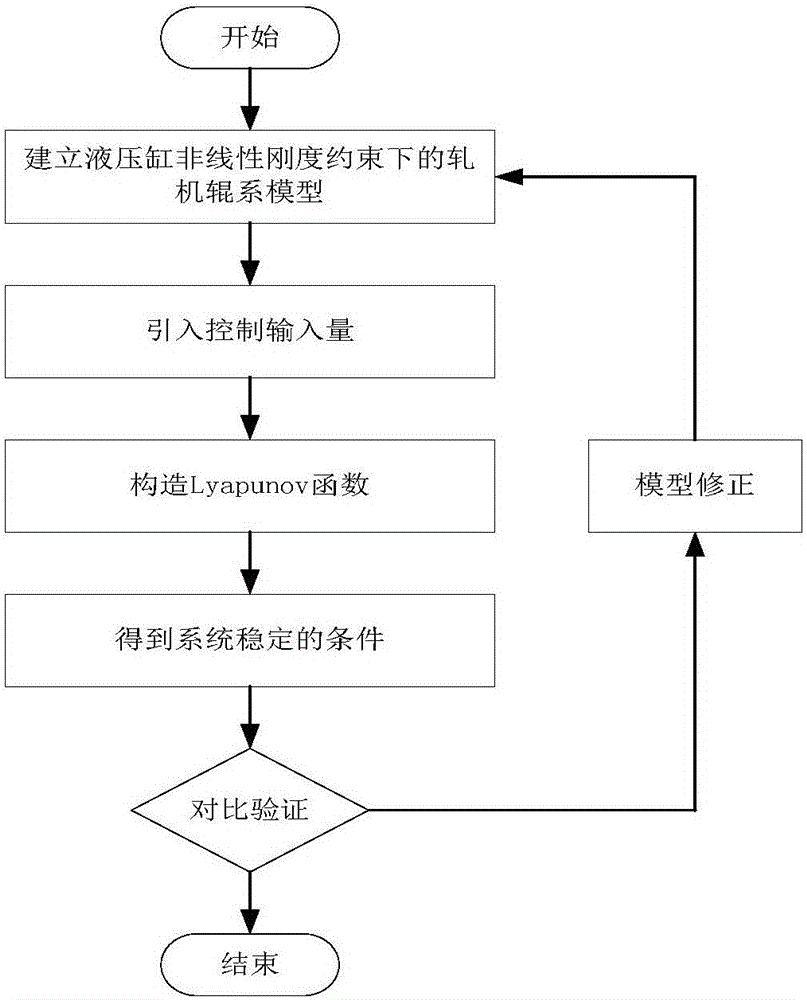
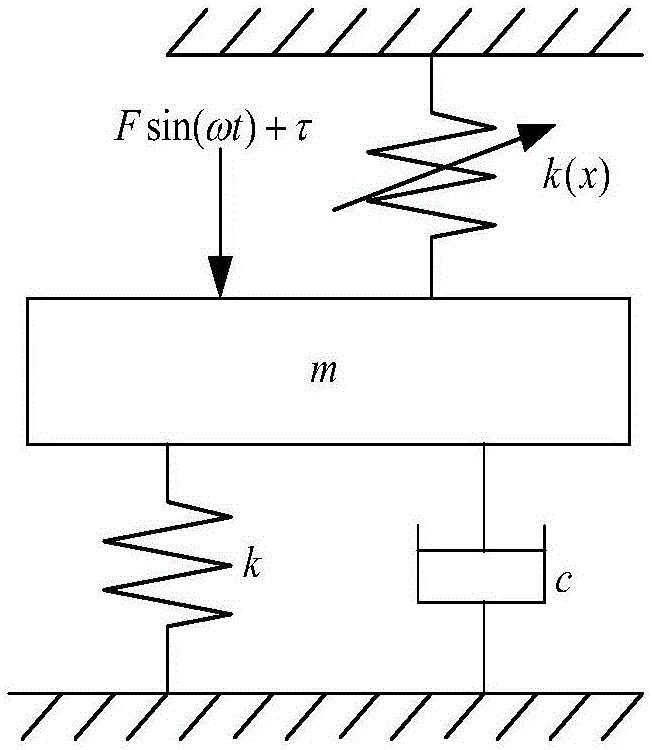
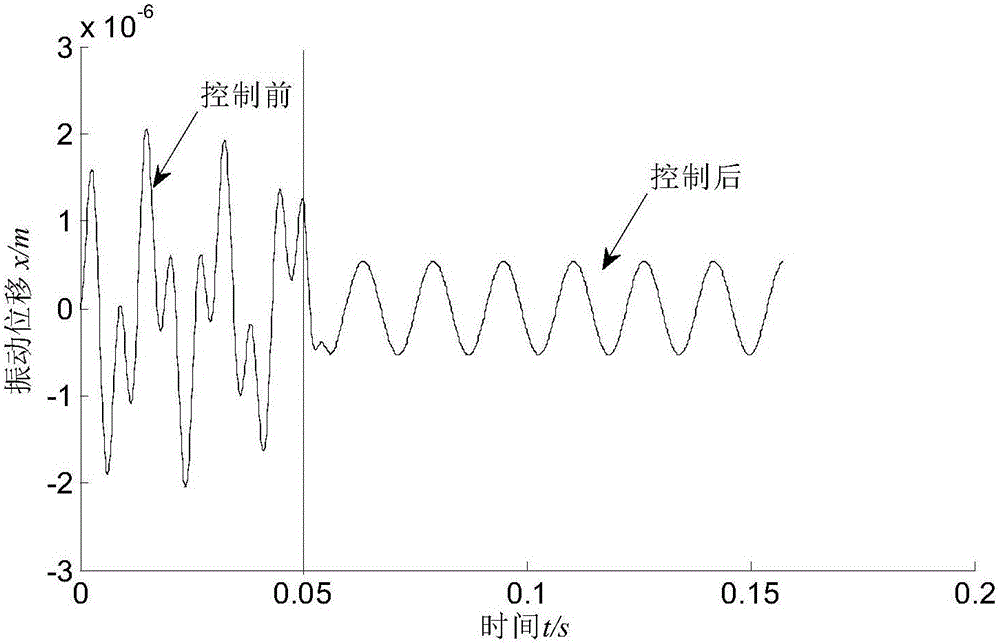
Stability control method of mill roll system under nonlinear stiffness constraint of hydraulic cylinder
ActiveCN105855296ASimple methodReasonable designRoll mill control devicesMetal rolling arrangementsHydraulic cylinderStable state
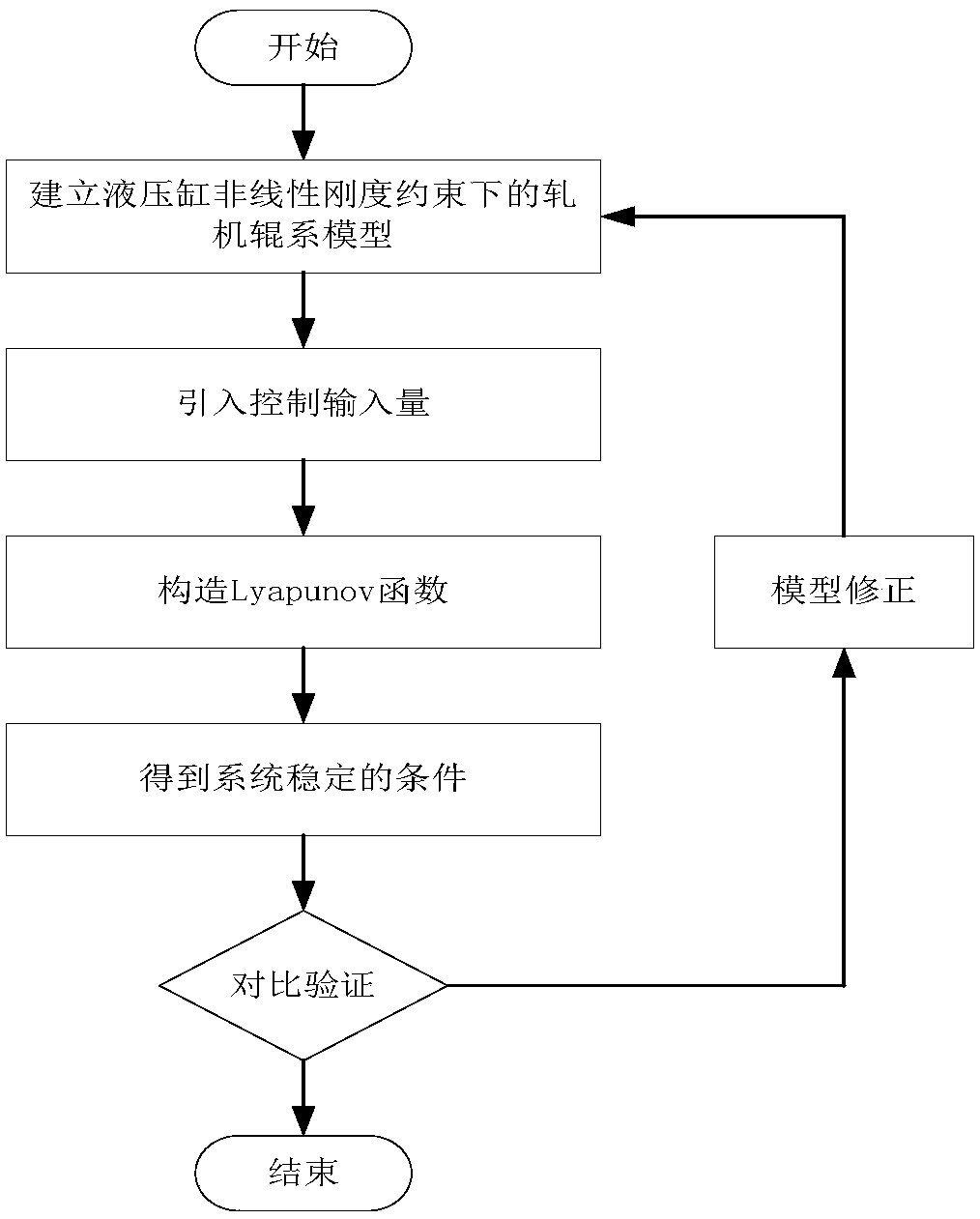
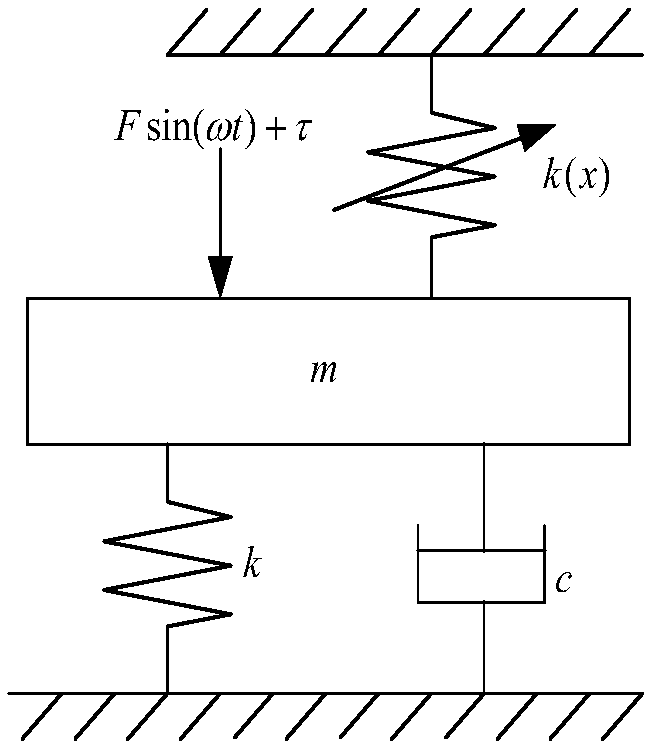
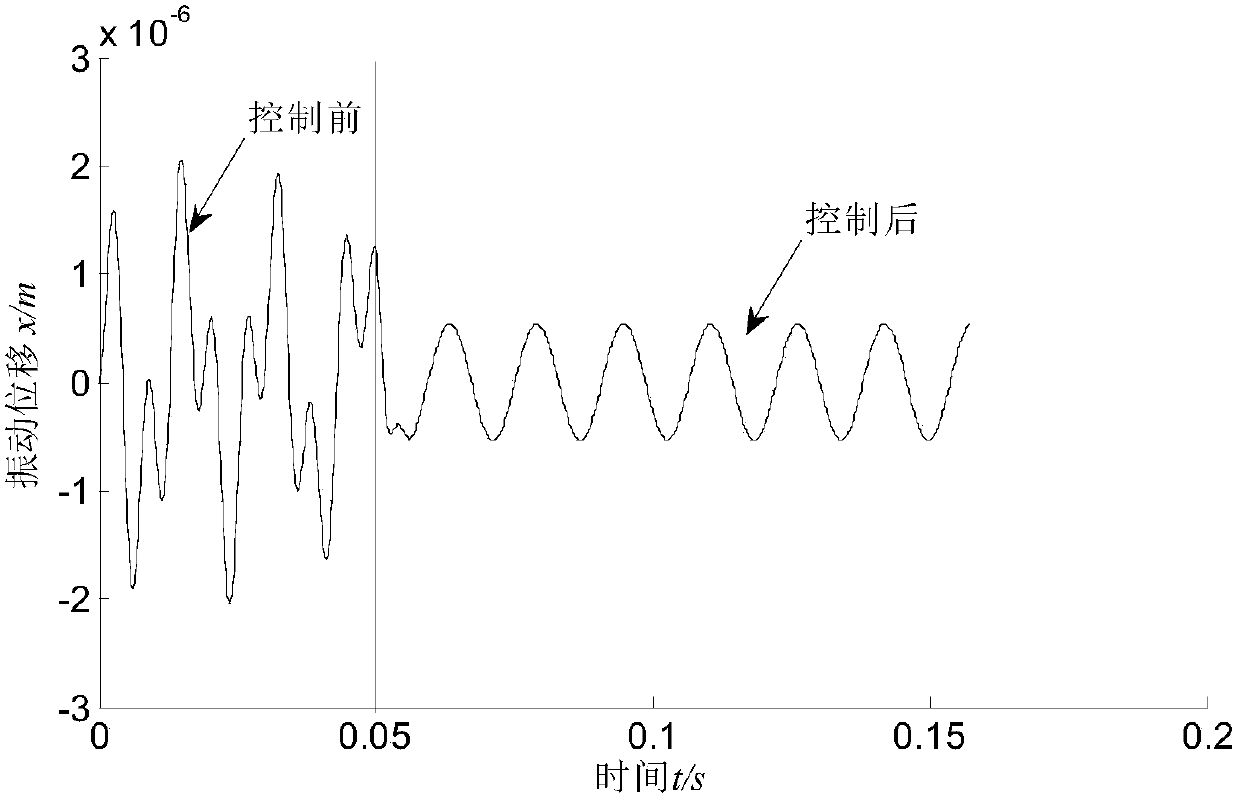
The invention relates to a stability control method of a mill roll system under a nonlinear stiffness constraint of a hydraulic cylinder. The method mainly comprises the following steps: establishing a vibrating model of the mill roll system under the nonlinear stiffness constraint of the hydraulic cylinder, and listing a dynamic equilibrium equation of the system according to a generalized dissipation Lagrange principle; introducing a controlled input quantity based on the dynamic equilibrium equation; simplifying the dynamic equilibrium equation with the controlled input quantity and constructing a Lyapunov function; giving a stability condition of the system through a Lyapunov theorem; properly adjusting the sizes of gains kd and kp, and controlling the mill roll system to reach a stable state; and comparing the stability of the uncontrolled system and the controlled system and correcting the model. The control method provided by the invention can effectively inhibit vibration of the mill roll system and improve the stability of the system, thereby providing a novel solution for controlling the stability of the mill roll system.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
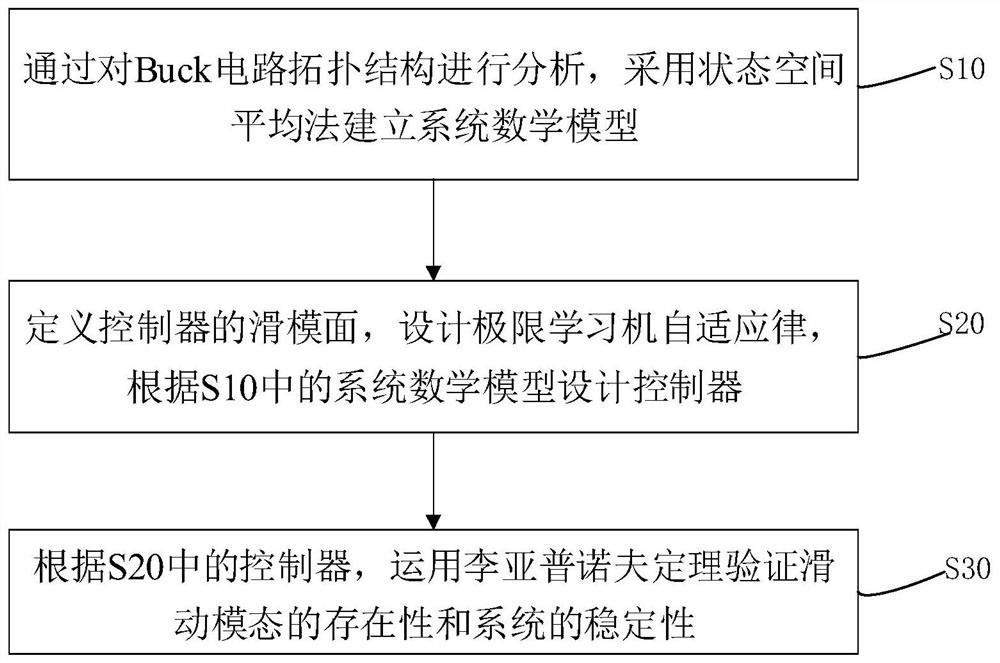
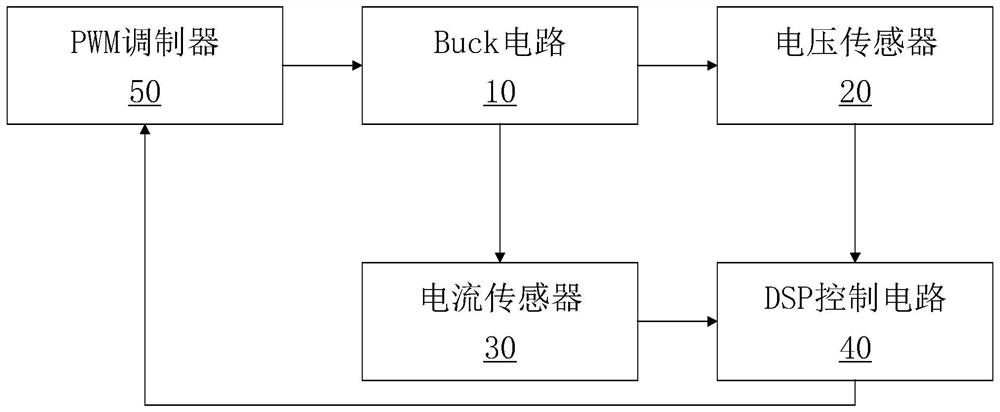
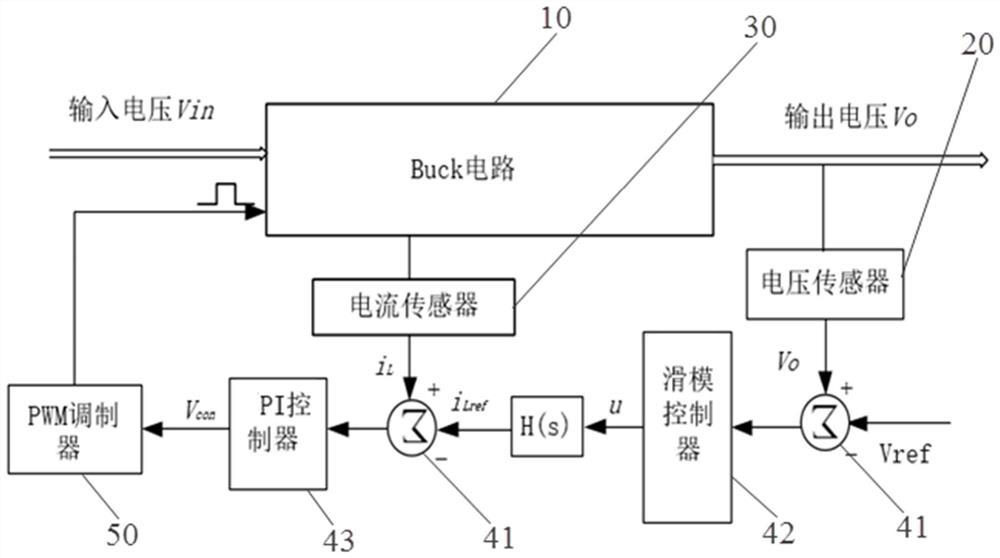
Buck circuit control method of sliding mode variable structure based on extreme learning machine
ActiveCN113410987AAccurate calibrationImprove tracking accuracyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLearning machineMathematical model
The invention discloses a sliding mode variable structure Buck circuit control method based on an extreme learning machine, and the method comprises the following steps: S10, carrying out the analysis of a Buck circuit topological structure, and building a system mathematical model through a state space averaging method; S20, defining a sliding mode surface of a controller, designing an extreme learning machine adaptive law, and designing the controller according to the system mathematical model in the S10; S30, verifying the existence of the sliding mode and the stability of the system by using the Lyapunov theorem according to the controller in the S20. Voltage and current signal changes of the circuit are monitored at the same time, and duty ratio signals output by a system are corrected in real time; the system can rapidly reach the sliding mode surface from any initial state, loads are switched when the circuit is in a steady state, the system can be stabilized to a steady-state output voltage value in a short time, the robustness of a controller is guaranteed, and system buffeting is weakened.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
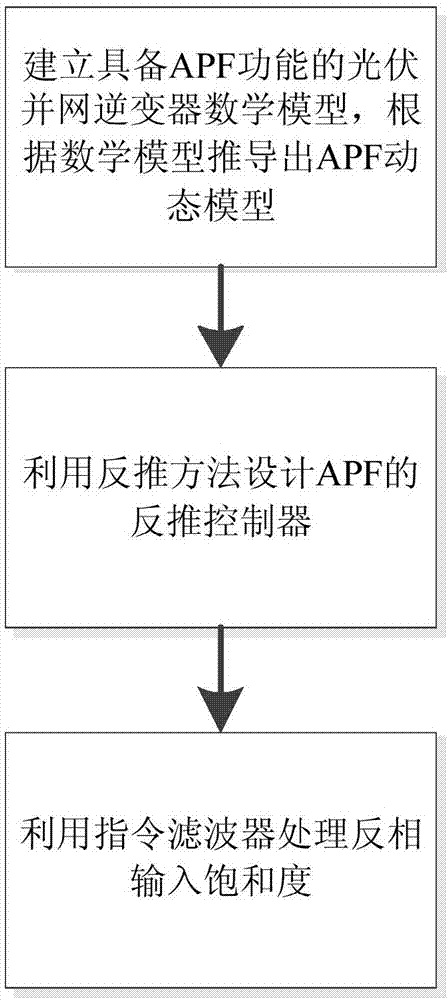
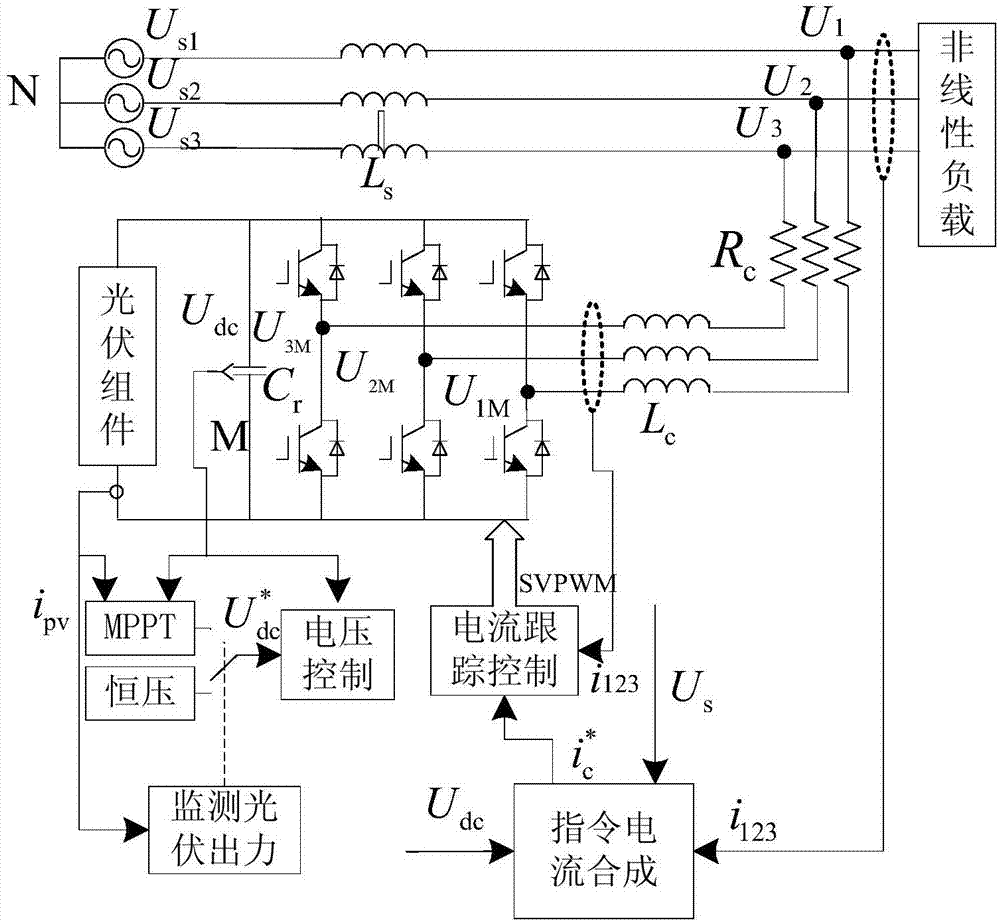
Current control method of photovoltaic grid-connected inverter with APF function
InactiveCN107482938AReduce adverse effectsImproved current trackingActive power filteringReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationGrid connected inverterControl system
The invention discloses a current control method of a photovoltaic grid-connected inverter with the APF function. An inverse method is applied to a design of a current tracking control system; an instruction filter is introduced to deal with a problem of inverting input saturation; an instruction filter compensation signal is designed to reduce adverse effects caused by the instruction filter; and the stability and onvergence of the whole system are proved by the asymptotically stable Lyapunov theorem. Compared with the traditional APF, the control method enables the current tracking to be improved and the energy quality to be improved. Compared with the traditional PI algorithm, the method disclosed by the invention has the good dynamic performance and high robustness.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
Internal model anti-interference control method of quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle system
PendingCN112764426AImprove robustnessConvergent stabilityAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsVehicle dynamicsGraph theoretic
The invention provides an unmanned aerial vehicle anti-interference control method based on an internal model control principle. A physical system of an unmanned aerial vehicle is considered. The intelligent control method comprises the steps of establishing an unmanned aerial vehicle dynamics model with external disturbance, building an external disturbance system, designing an unmanned aerial vehicle distributed control algorithm with external disturbance based on theoretical knowledge such as graph theory and convex analysis, further designing a Lyapunov function. The convergence of the designed algorithm is proved through the Lyapunov theorem, it is guaranteed that the state variables of the unmanned aerial vehicle converge to the target, finally the effectiveness and feasibility of the method are verified again through a numerical simulation example, and dynamic tracking of the unmanned aerial vehicle and formation of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be well achieved under the disturbance condition. The control precision of the unmanned aerial vehicle system is improved, and the method has certain practical value in both civil and military aspects.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Sliding mode controller design method based on multi-parameter self-adaptive neural network
PendingCN113589689ASimplify Control DesignImplementing Adaptive Neural Network ControlAdaptive controlDynamic modelsRobot dynamic
The invention discloses a sliding mode controller design method based on a multi-parameter self-adaptive neural network. The sliding mode controller design method comprises the steps: 1, establishing an n-degree-of-freedom rotary joint rigid mechanical arm dynamic model; 2, converting the model system in the step 1 into a second-order state equation based on a joint position, and designing a fast terminal sliding mode surface for the second-order state equation; 3, approaching unknown dynamic parameters of the system by using an RBF neural network; and 4, designing a self-adaptive nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode controller, and realizing model-free control of a mechanical arm based on the dynamic parameter approximation result in the step 3. The method is suitable for trajectory tracking control of the mechanical arm influenced by model uncertainty and external interference, the number of self-adaptive design parameters given in a control design program is reduced, and an unknown nonlinear function of robot dynamics is approximated on the basis of RBFNN; and in addition, the convergence speed and tracking precision of errors are improved, and global asymptotic stability based on the lyapunov theorem is achieved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
A Control Method of lmis State Feedback System Based on Uncertain Model
ActiveCN104407515BImprove certaintyImprove robustnessSpecial data processing applicationsAdaptive controlRobustificationFeedback controller
The invention discloses a LMIs state feedback system control method based on an uncertain model. The LMIs state feedback system control method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: establishing a controlled object model containing uncertain parameters at first, introducing a system state feedback controller, constructing a function of a closed-loop system, and designing a nonlinear system control law in the event of satisfying a Lyapunov theorem. The control method disclosed by the invention considers the control problems including influence caused by modelling error, model parameter variation, system noise and the like, of a system having uncertainty in a certain degree; the control method disclosed by the invention has good adaptive capacity to the uncertain factors of the system; in addition, compared with general conventional methods, the method disclosed by the invention is more rapid in response speed and higher in stability and robustness.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Robust Fault Tolerant Control Method of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Attitude Based on Neural Network Observer
Based on neural network (Neural Network: Neural Network) technology and command filter inversion method, this application proposes a robust fault-tolerant control system design architecture based on command filter inversion. Firstly, the mathematical model of the NSV attitude control system is given, and on this basis, the uncertainty caused by modeling errors and external disturbances, and the state equation of the NSV attitude control system under control surface failures are considered. Its main design involves two units: one is the design of the auxiliary system, and the other is the design of the controller based on the auxiliary system. The auxiliary system introduces the neural network to ensure the robustness of the auxiliary system, and strictly proves the stability of the closed-loop system through the Lyapunov theorem. And the simulation is carried out on the attitude control system of the corresponding aircraft. The results show that the method proposed in this application can make the uncertain flight control system with external interference have ideal fault-tolerant tracking performance under the damage of the control surface.
Owner:南京晓飞智能科技有限公司
Model-free quadrotor UAV trajectory tracking controller and method based on rpd-smc and rise
The invention discloses a model-free quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory tracking controller based on RPD-SMC and RISE, and a method, and a RPD-SMC controller is designed. The controller combines advantages of a proportional differential-sliding mode controller (PD-SMC) and online estimation capability of a radial basis function neural network (RBFNN) on arbitrary function. Through introducing self-adaptive RBFNN feedforward, disturbance and unknown dynamic conditions are estimated and compensated, so that selection of control parameters of the PD-SMC is more rational, to achieve objectives of reducing controlling quantity and saving electric energy. Aimed at an inner-loop control system, an error symbol integral (RISE) controller based on robustness is designed. The RISE controller can ensure rapid convergence of a posture angle and has strong robustness on disturbance. Beneficial effects are that the lyapunov theorem of stability proves stability of the inner-loop and outer-loop systems, and simulation experiment results prove that the controller has validity.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
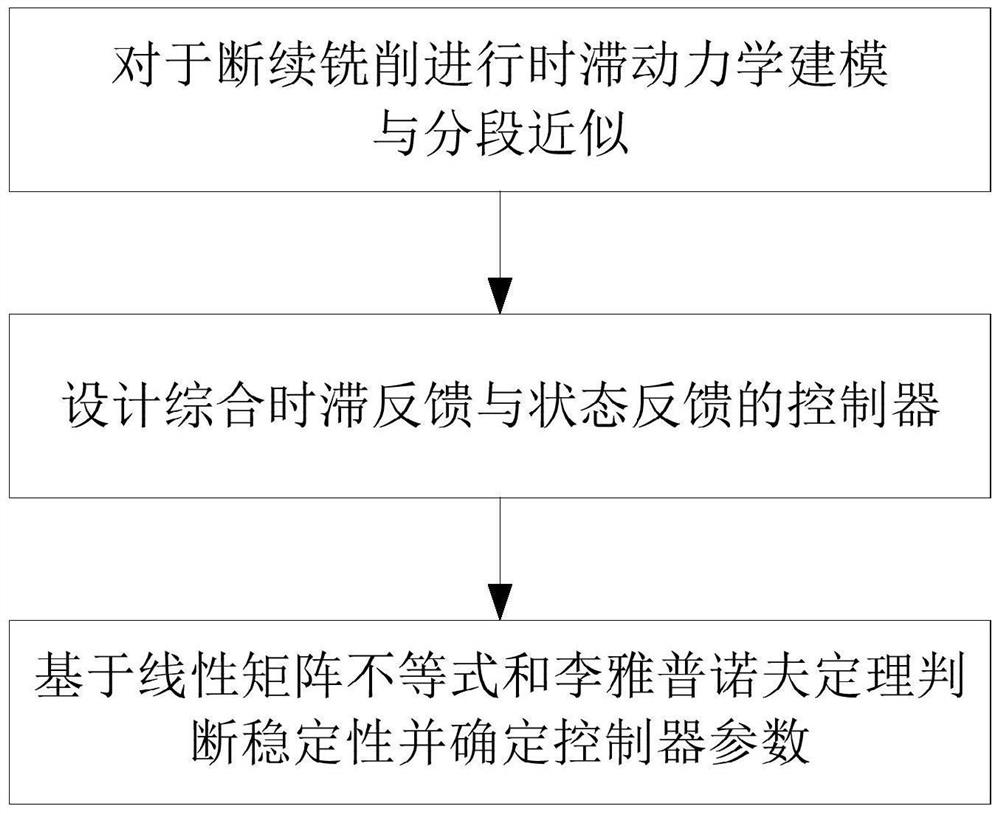
Intermittent milling vibration subsection control method
ActiveCN111722586AReduce gainHigh stability discrimination accuracyNumerical controlMilling cutterControl engineering
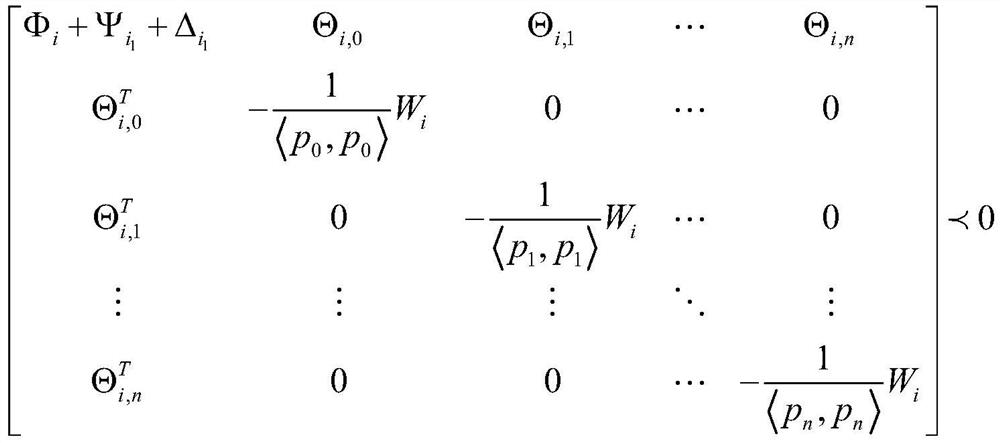
The invention provides an intermittent milling vibration subsection control method, which comprises the steps of analyzing the cut-in and cut-out process of an intermittent milling cutter, wherein thenon-cutting process is a free vibration state, and the cutting process is a forced vibration state, and carrying out time-lag dynamics modeling and subsection approximation on intermittent milling; designing a controller integrating time lag feedback and state feedback, and allowing an unstable phenomenon to occur in a forced vibration stage by taking the stability of the whole system as a target; and judging the stability based on the linear matrix inequality and the Lyapunov theorem, and determining controller parameters. The method provided by the invention has relatively small controllergain and relatively high stability discrimination precision.
Owner:HUST WUXI RES INST +1
Backstepping sliding mode control method for formation flying spacecraft
ActiveCN107577145BControlling time-varying external disturbancesReduce communication burdenAttitude controlAdaptive controlMode controlRobust control
The invention relates to a formation flying spacecraft back-stepping sliding-mode control method, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft posture adjustment. By the back-stepping sliding-modemethod, two distributed robust consistency tracking controllers are designed. The first robust controller can compensate known bounded external interface, is continuous and free from buffeting. In order to meet the use requirements of self-adaptive control, the second robust finite time controller does not need the upper bound of the known external interface. As the two controllers are designed based on a rotation matrix, attitude represented by the rotation matrix has global unique attribute, and the shortcoming of system unwinding can be overcome. By the aid of Lyapunov theorem, a whole closed-loop system is stable in finite time, simulation experiments prove that absolute attitude can be tracked, and formation member attitude consistency can be kept.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Enhanced coupling nonlinear pd sliding mode controller and method for bridge crane system
ActiveCN108557664BStrengthen the coupling relationshipImprove transient control performanceCranesTransient stateCoupling
The invention provides a coupling enhancing non-linear PD-type sliding mode controller for a bridge crane system, and a method. The designed controller is composed of a PD control part and an SMC control part. The SMC control part is used for constructing a frame of the controller. Quite high robustness is achieved aiming at an indeterminate model, different and indeterminate system parameters andexternal disturbance of a system. The PD control part is used for stably controlling the system. In addition, a generalized function is introduced, the coupling relation among trolley movement, lifting hook swinging and load swinging is enhanced, and thus the transient control property of the system is improved. By utilizing the Lyapunov theorem and Schur complement, it is proved that the asymptotic stability and convergence of the system can still be ensured through the provided control method even if the model and the system parameters are indeterminate and external disturbance exists. Thesimulation result shows the correctness of the provided control method and the excellent control property.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Linear Servo Position Tracking Control Based on Linear Matrix Inequality and Sliding Mode Control
ActiveCN108123648BGuaranteed real-timeGood robust tracking performanceElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlControl engineeringSystem stability
The linear servo position tracking control based on linear matrix inequality and sliding mode control, the mechanical subsystem and the electrical subsystem are designed as a whole to control the design, and the complex problem that is difficult to solve is transformed into a relatively simple linear matrix inequality (LMI) problem, using The Lyapunov theorem proves the stability of the system, and then uses the MATLAB‑LMI toolbox to solve the result. Utilize the neural network thrust observer to conduct off-line learning of periodic nonlinear factors such as end effect and friction to ensure the real-time performance of the system, and then apply it to the system to observe the load disturbance, and finally achieve the purpose of the present invention, that is, to achieve a good robustness of the system Great track performance.
Owner:东能(沈阳)能源工程技术有限公司
A method for controlling the stability of rolling mill roll system under the constraint of nonlinear stiffness of hydraulic cylinder
ActiveCN105855296BSimple methodReasonable designRoll mill control devicesMetal rolling arrangementsHydraulic cylinderStable state
The invention relates to a stability control method of a mill roll system under a nonlinear stiffness constraint of a hydraulic cylinder. The method mainly comprises the following steps: establishing a vibrating model of the mill roll system under the nonlinear stiffness constraint of the hydraulic cylinder, and listing a dynamic equilibrium equation of the system according to a generalized dissipation Lagrange principle; introducing a controlled input quantity based on the dynamic equilibrium equation; simplifying the dynamic equilibrium equation with the controlled input quantity and constructing a Lyapunov function; giving a stability condition of the system through a Lyapunov theorem; properly adjusting the sizes of gains kd and kp, and controlling the mill roll system to reach a stable state; and comparing the stability of the uncontrolled system and the controlled system and correcting the model. The control method provided by the invention can effectively inhibit vibration of the mill roll system and improve the stability of the system, thereby providing a novel solution for controlling the stability of the mill roll system.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
An h∞ fault-tolerant control method for a class of networked linear parameter-varying systems with time-varying delays
The invention provides an H8 fault tolerance control method for a networked linear parameter variation system with time variation and time delay, and belongs to the field of networked linear parametervariation system control. The method takes the situations that a linear parameter variation system has network time variation and time delay and a sensor and an executor break down simultaneously inaccount, firstly a method of free-weighting matrix is used to establish a Lyapunov function for processing the time variation and time delay to obtain sufficient conditions of closed-loop fault tolerance control system stability, then a Lyapunov theorem of stability and a linear matrix inequality analysis method are used to obtain sufficient conditions of H8 fault tolerance controller existence, lastly an approximate primary function and a gridding technology are used to approximate a solving problem of an infinite dimensional linear matrix inequality system with a solving problem of a finitedimensional linear matrix inequality system, a Matlab LMI toolkit is used for solution, and a gain matrix of an H8 fault tolerance controller is provided. The H8 fault tolerance control method for thenetworked linear parameter variation system with the time variation and the time delay reduces the conservatism of the H8 fault tolerance controller.
Owner:龙岩荣创信息科技有限公司
Adaptive control method for space tethered robot to recover target after close-range capture
The invention relates to an adaptive control method for target recycling of a space tethered robot after close-range capture. The adaptive control method comprises the steps of firstly deriving a compound body formed by the tethered robot and a captured target satellite, building a dynamic equation of the system in the recycling process, then designing the control force / moment in the recycling process according to a Lyapunov theorem, and designing a dynamic parameter identification law for the compound body, thereby achieving stable recycling of the compound body. According to the adaptive control method, the dynamic parameter identification law is put forwards for the first time, the whole recycling process can be enabled to be more accurate in calculation for control variables, and thus the recycling is more stable. The adaptive control method enables the compound body formed by the space tethered robot after capturing a non-cooperative target to be recycled stably and quickly through tether tension. The adaptive control method can overcome the natural instability in a problem of tether recycling on the basis of dynamic parameters of the compound body, and the compound body is recycled stably.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Input Saturated Spacecraft Attitude Terminal Sliding Mode Tracking Control Method
The invention relates to a sliding mode control method of an input saturated spacecraft attitude terminal, belonging to the technical field of spacecraft attitude adjustment. According to the method,two non-unwinding robust finite-time control methods are designed for a spacecraft and are a compensation known bounded method and a hyperbola tangent function and auxiliary system control method. According to the compensation known bounded method, known bounded external disturbances can be compensated, and external disturbance and input saturation problems can be solved by using the hyperbola tangent function and auxiliary system control method. The Lyapunov theorem is used to prove the finite-time stability and asymptotic stability of an entire closed-loop system. A simulation result shows that a controller can make the spacecraft to track a time-varying reference attitude signal within a limited time.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Image orthogonal moment numerical stability analyzing method
InactiveCN106504224ASolving the problem of numerical instability of orthogonal momentsImage analysisNumerical stabilityDecomposition
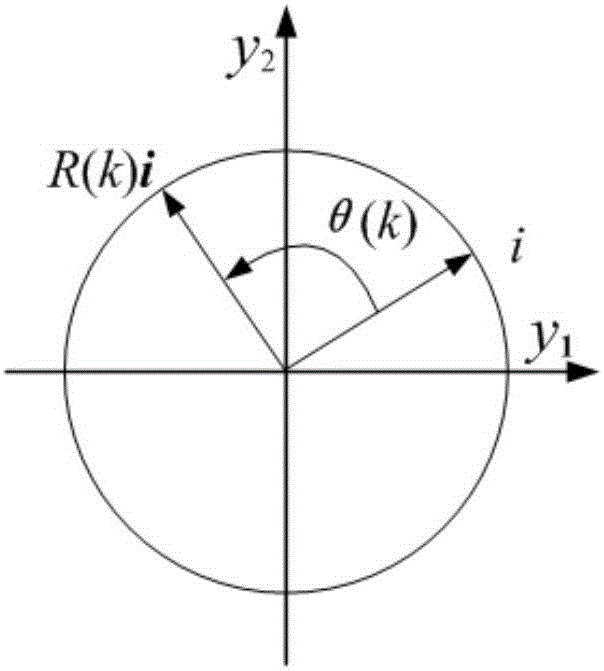
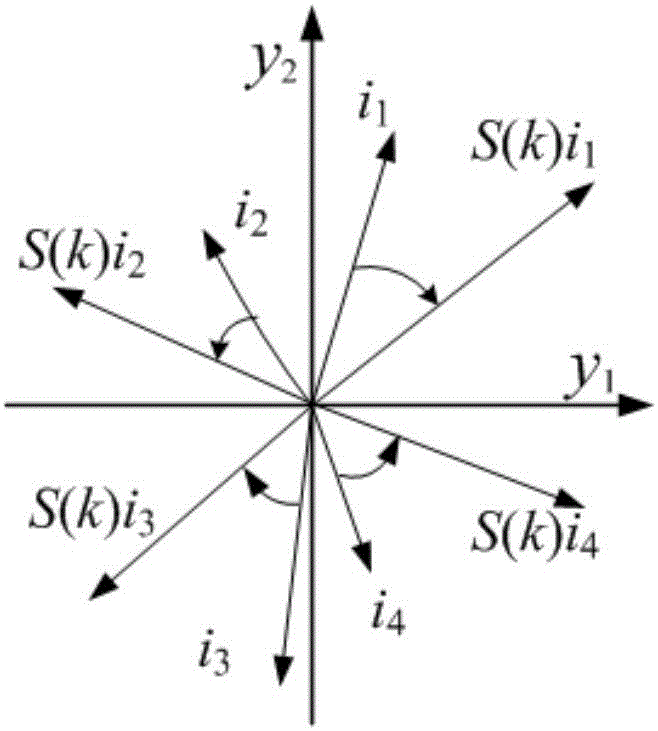
The invention discloses an image orthogonal moment numerical stability analyzing method, which belongs to the image processing and mode recognizing field. Based on the discrete control theory, the three recursive formulas of an orthogonal polynomial are transformed into the variable coefficient differential equations for the order k, that is, the zero input response of a discrete linear time-varying system is discussed; and through the use of the SVD decomposition of a matrix, the original state equation is transformed as an equivalent state equation constructed by a rotation matrix and a diagonal matrix. Based on the Lyapunov theorem, two new instabilities are derived. With the method, the problem with the instability of the orthogonal moments caused by the divergence of the orthogonal polynomials is solved in the calculation process of the orthogonal moments of three recursive formulas; and the root causes of the recursive computational instability of the classical Tchebichef and Krawtchouk polynomials are found so as to provide reference for future research.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
A Method of Acquiring the Guidance Law of Rlv Approach and Landing Based on the Idea of Disturbance Compensation
ActiveCN106292701BGuaranteed stabilityAvoid the problem of not converging to zeroAdaptive controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsGuidance systemBackstepping
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com