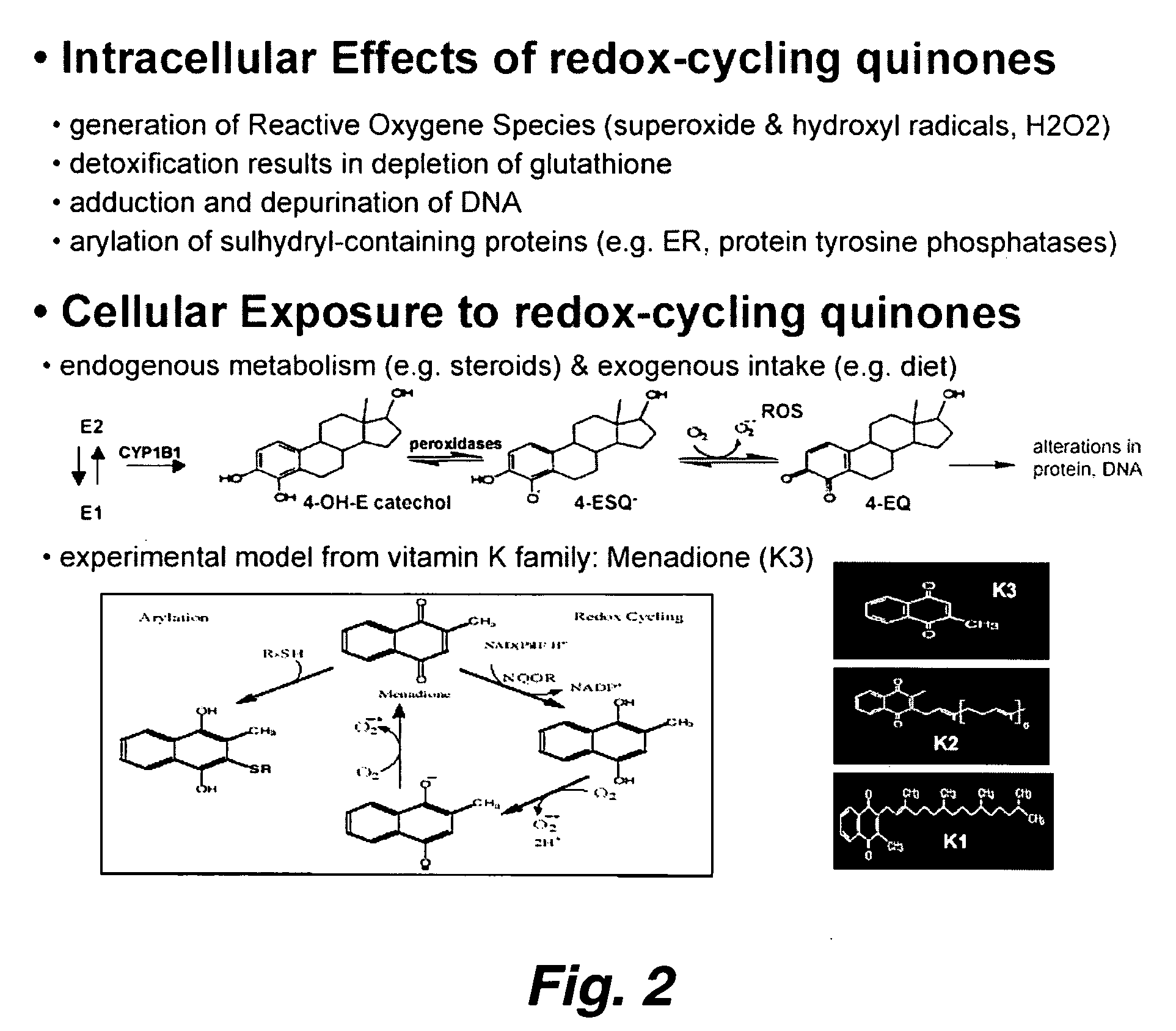
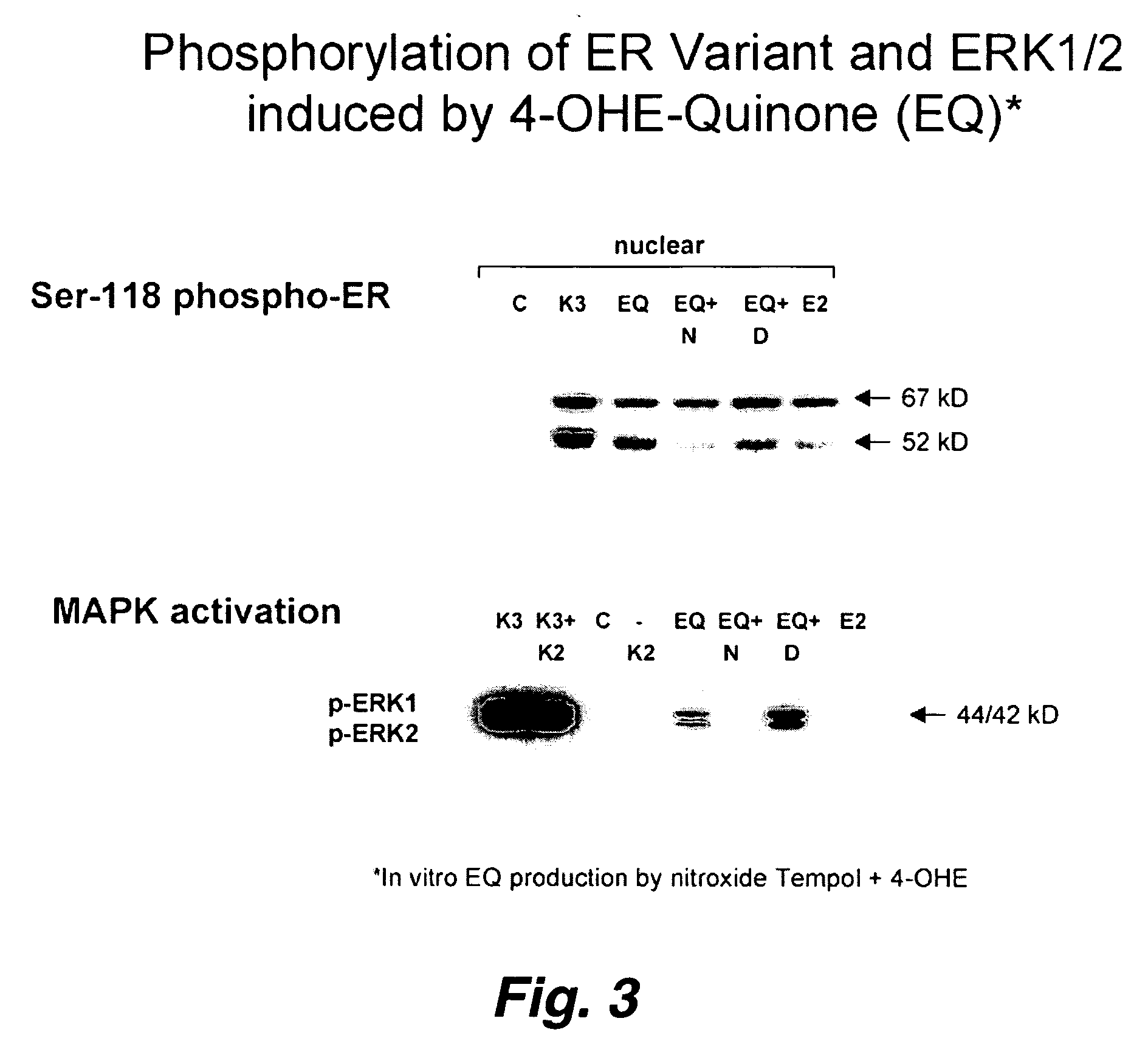
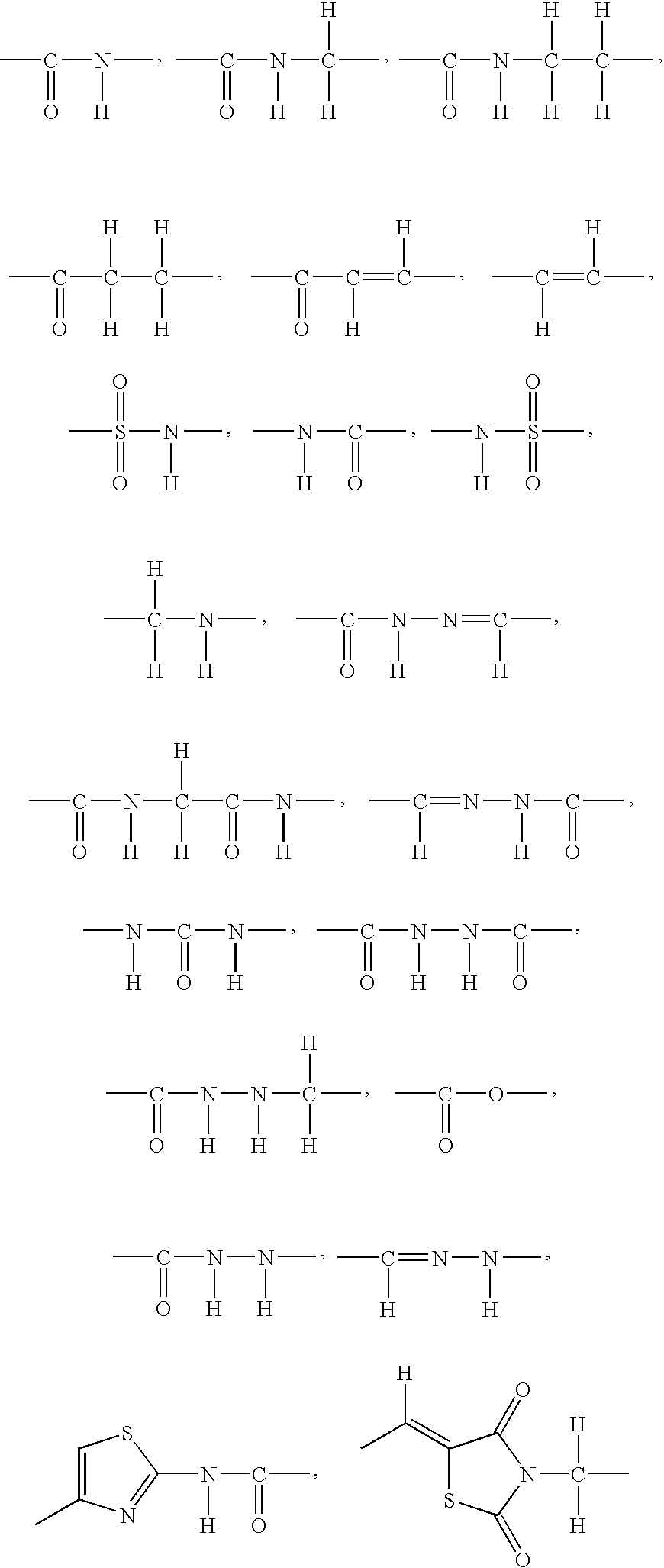
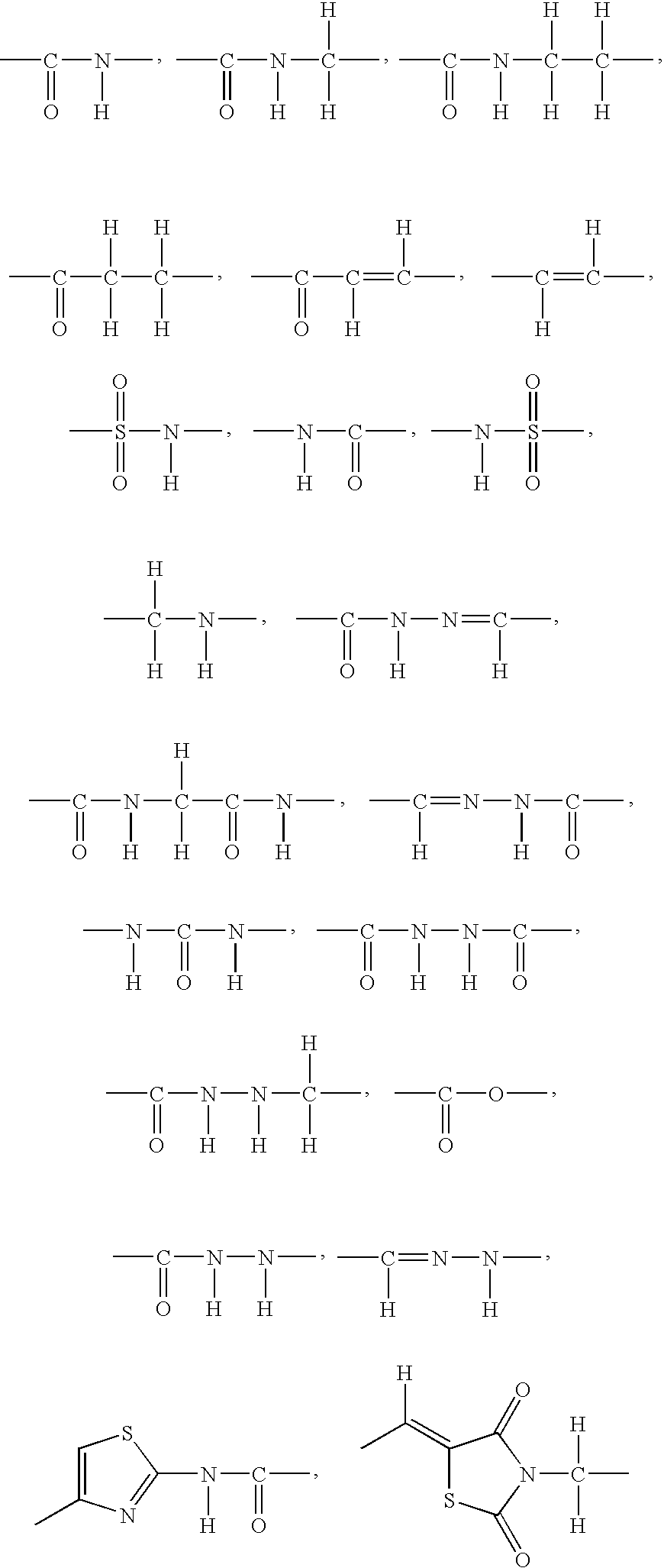
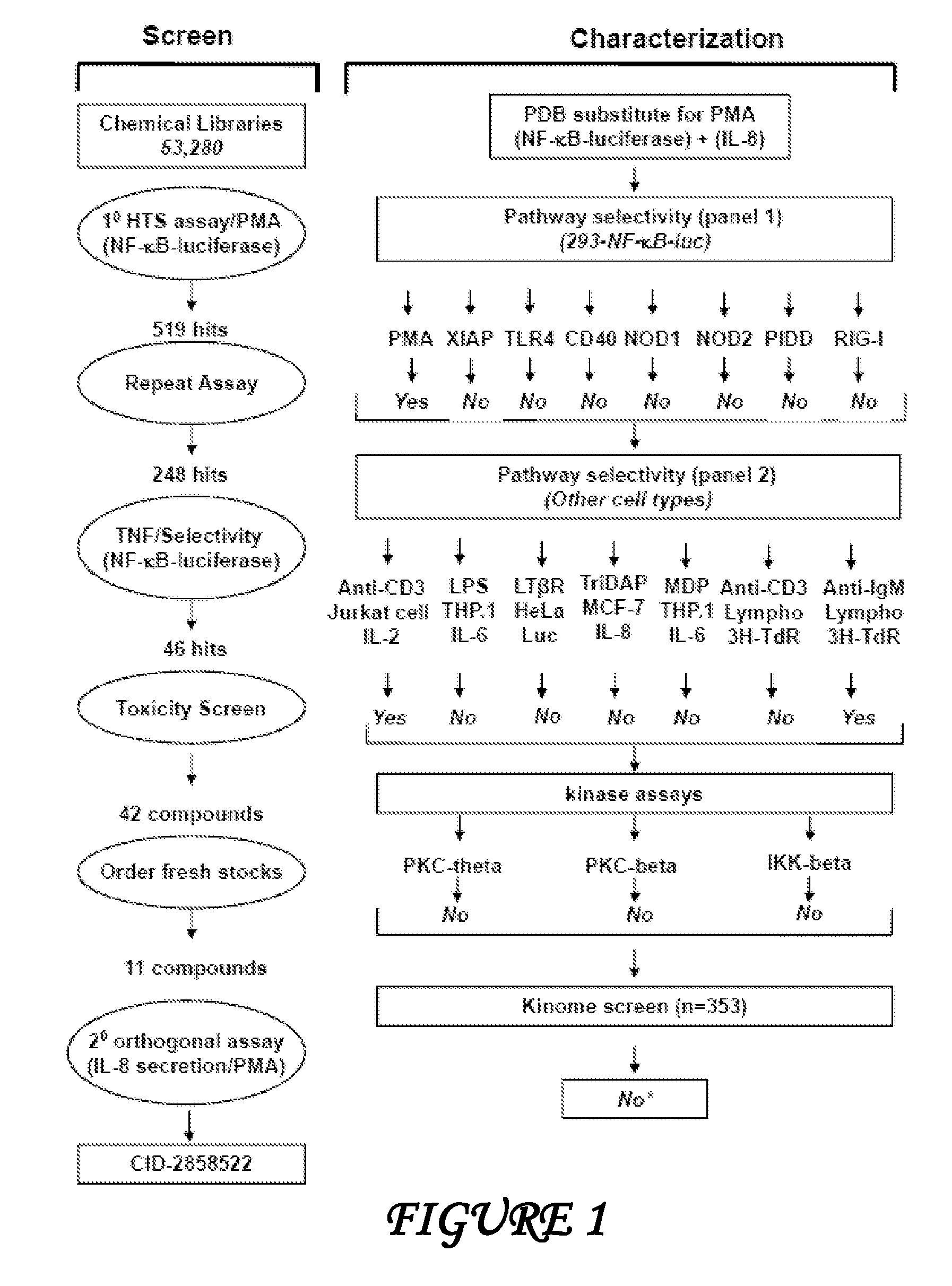
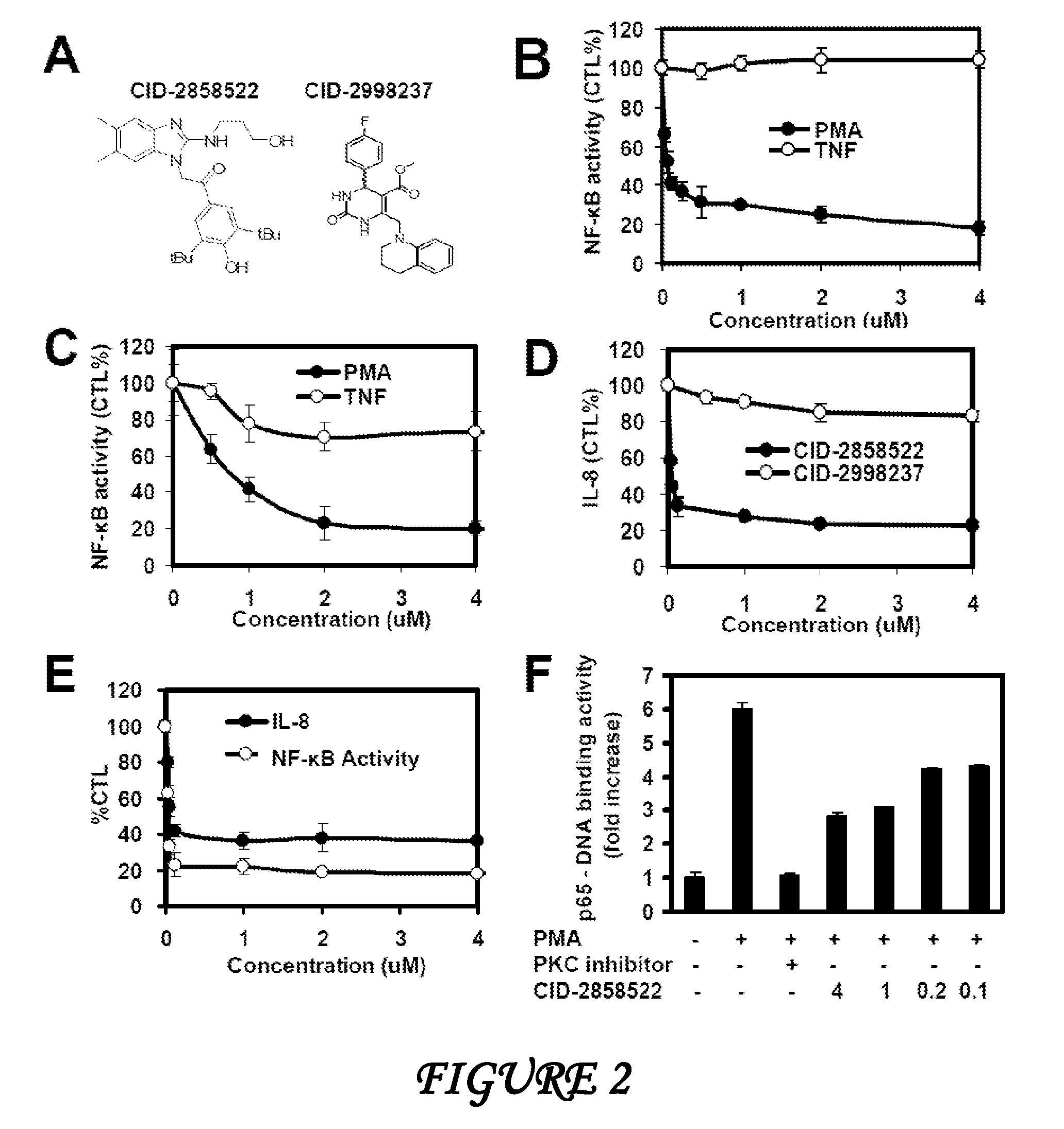
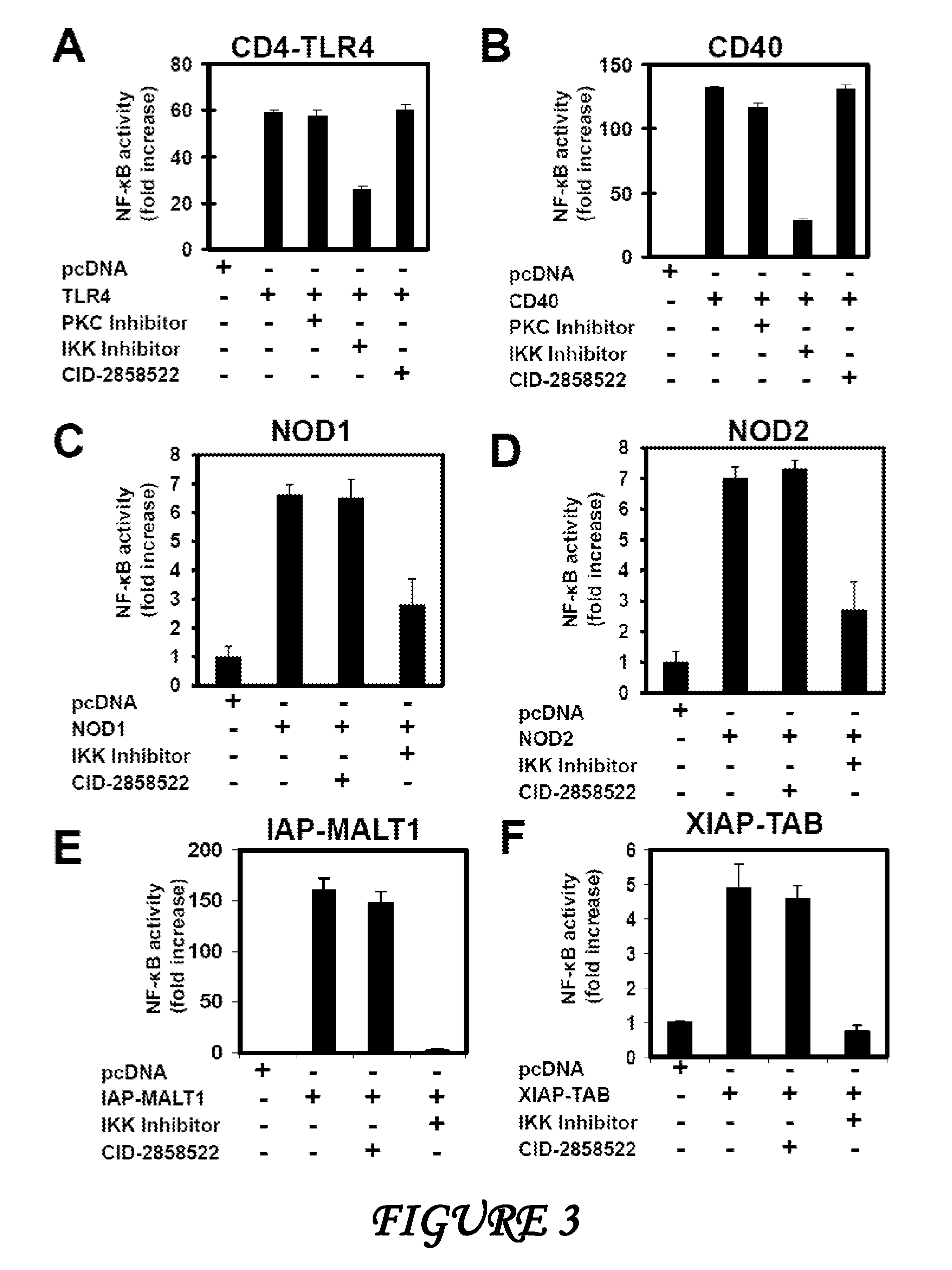
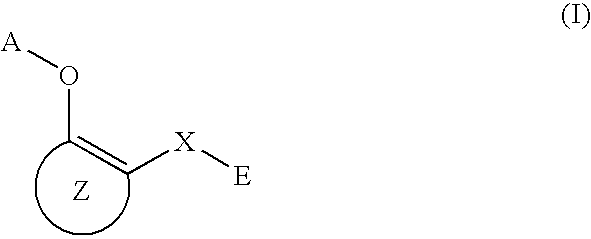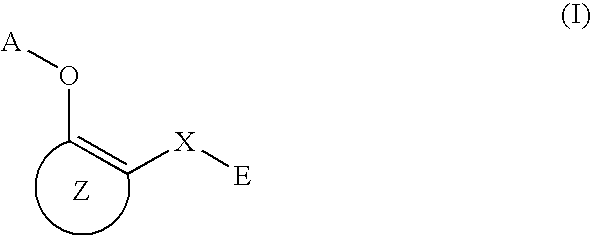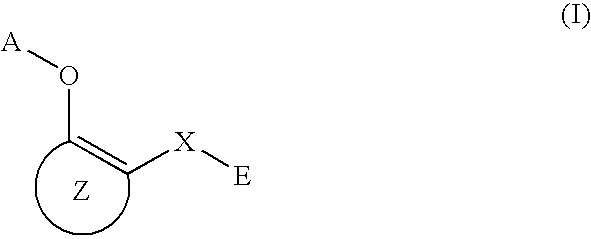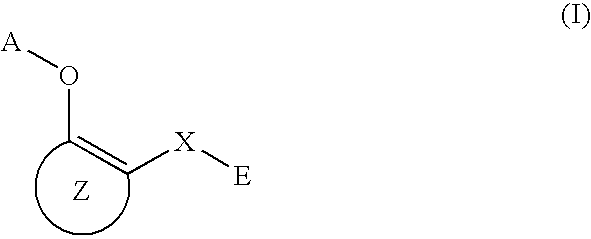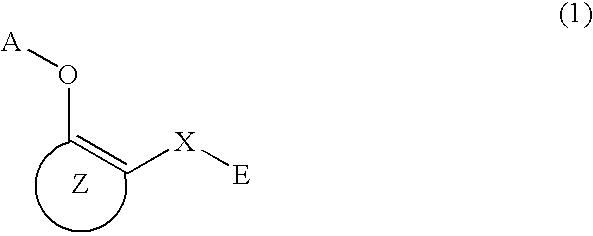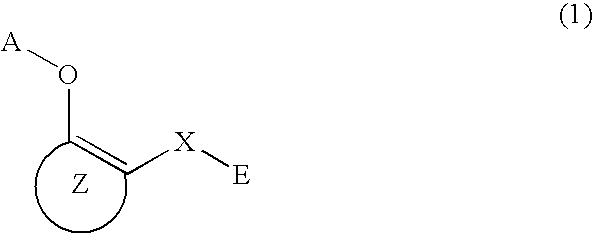Patents
Literature
37 results about "Nf κb activation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
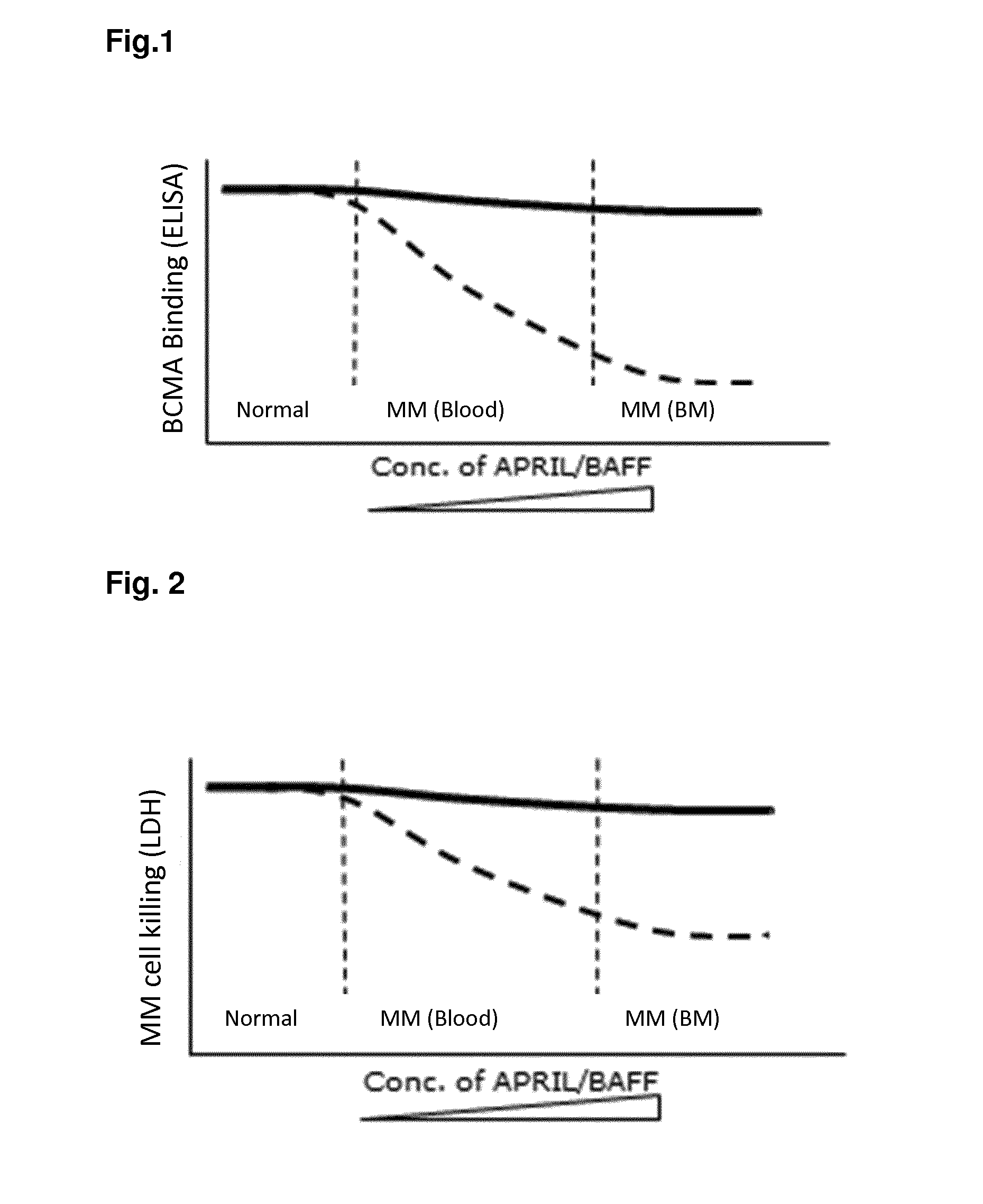
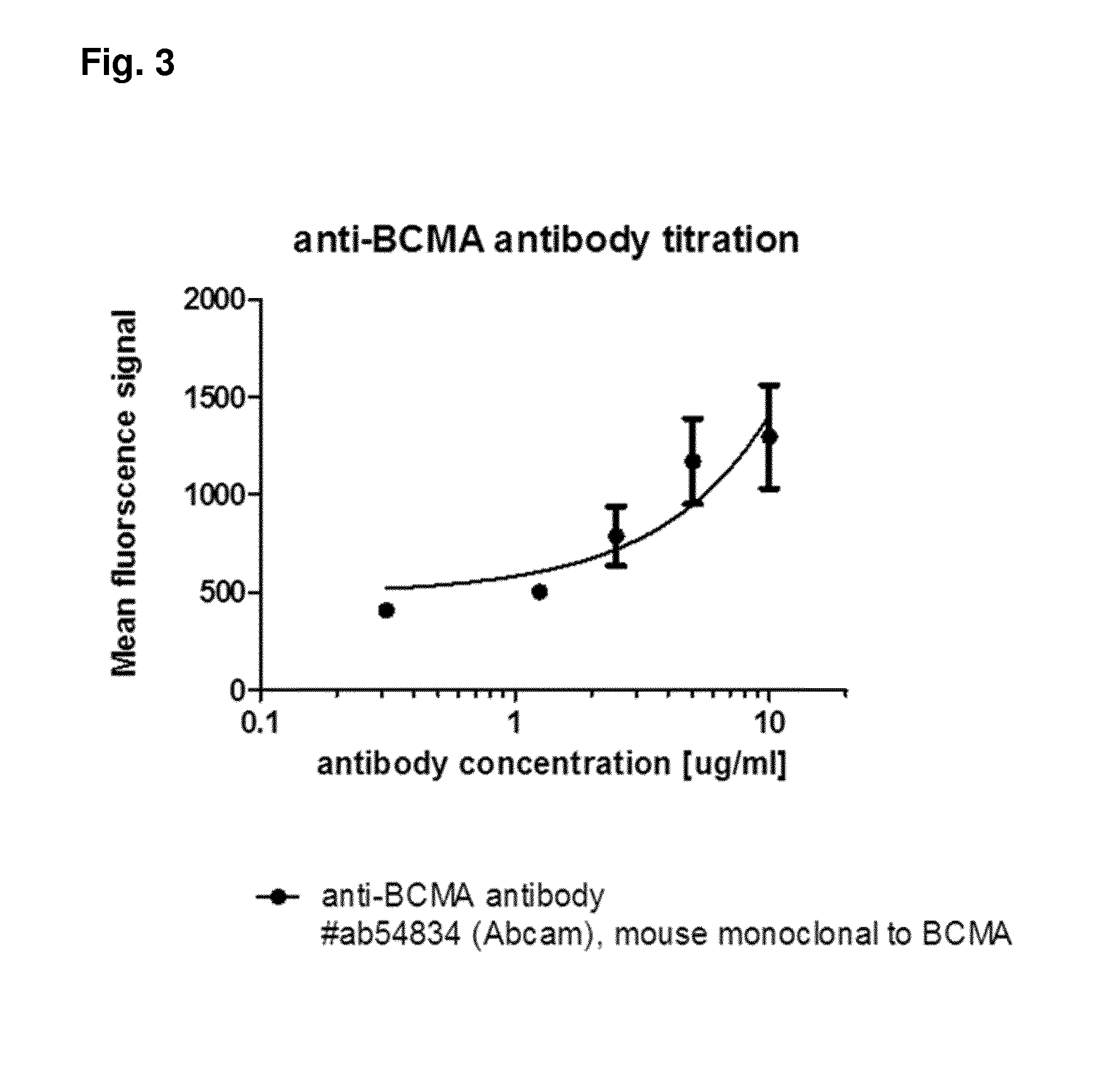
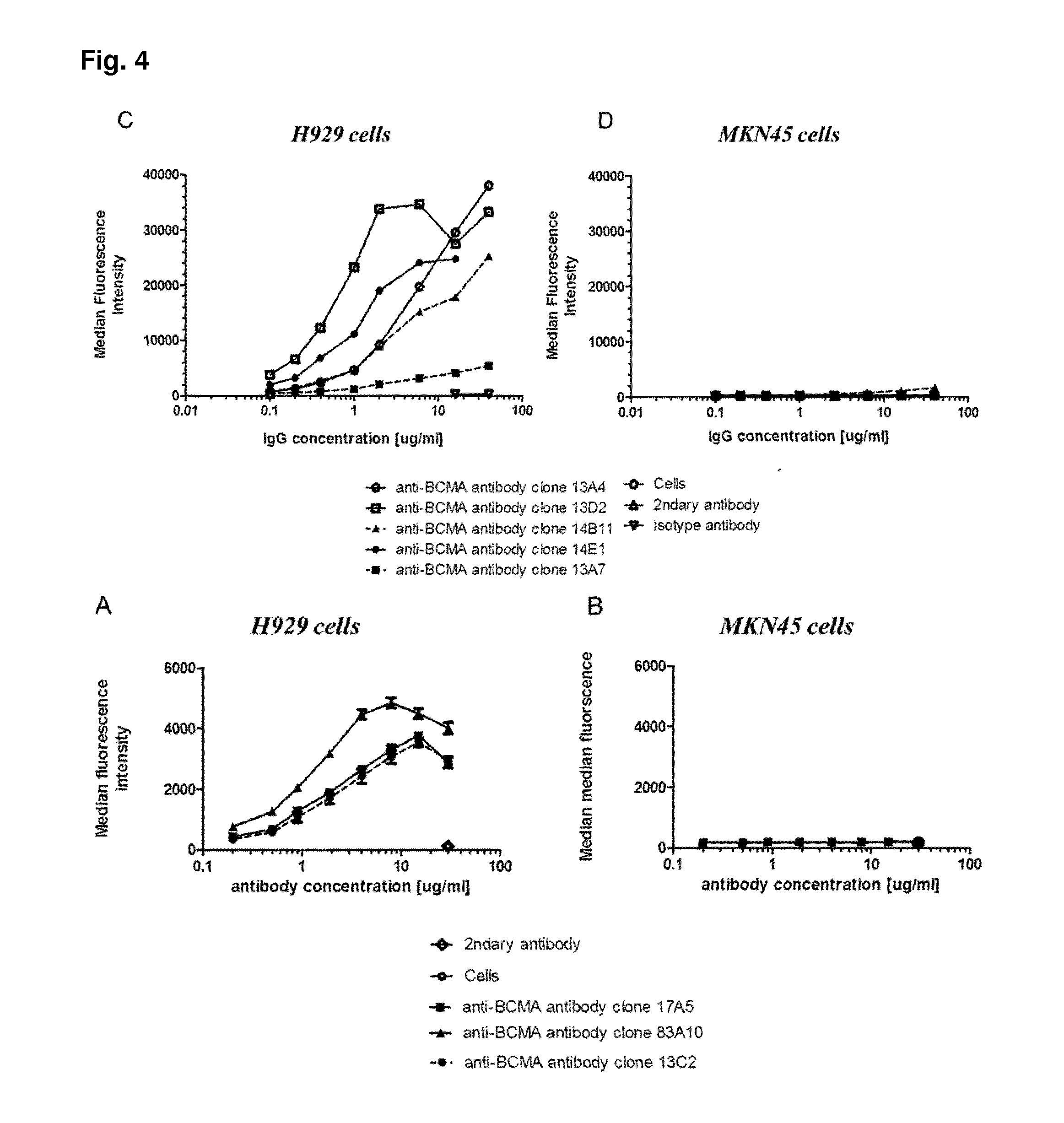
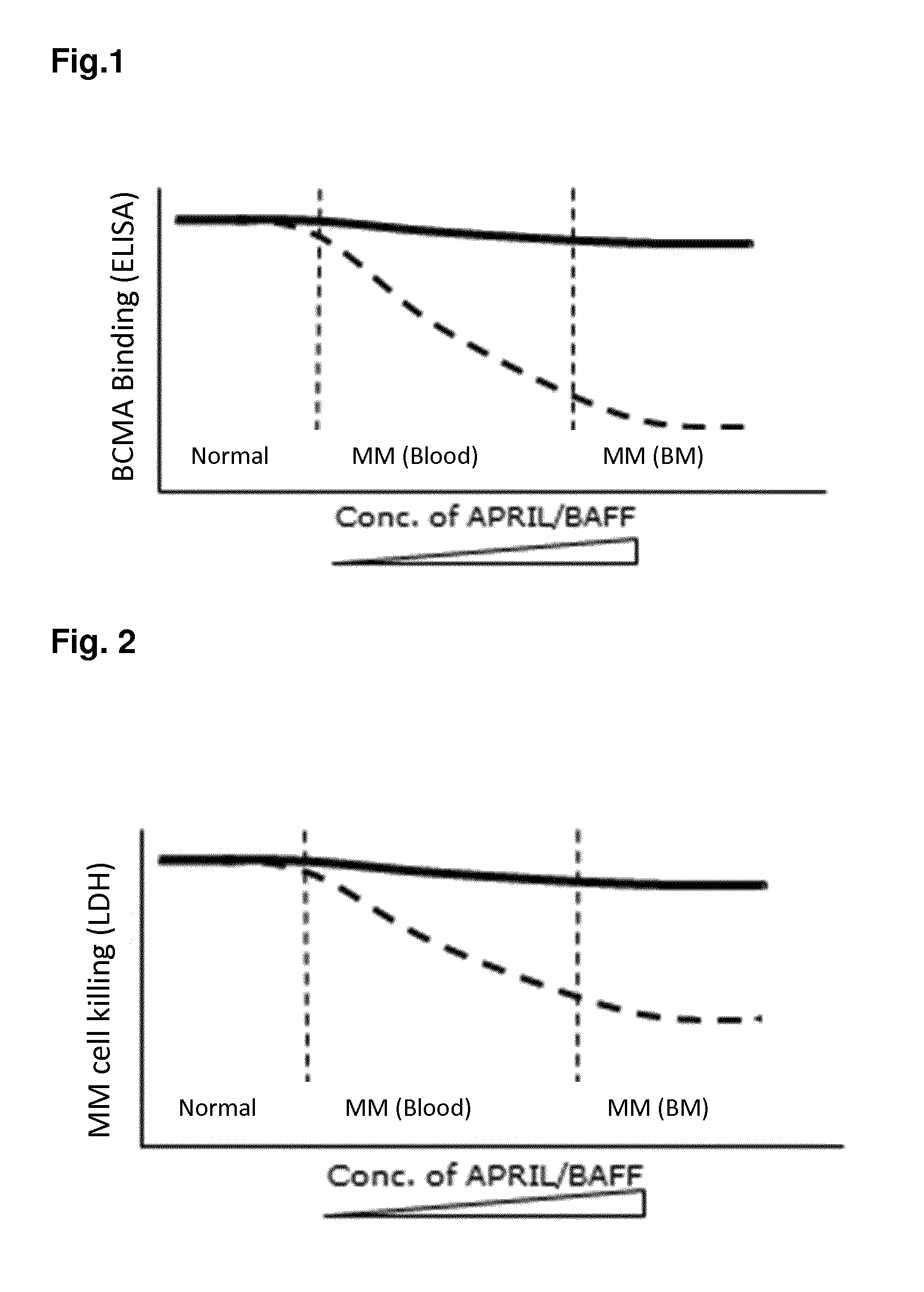
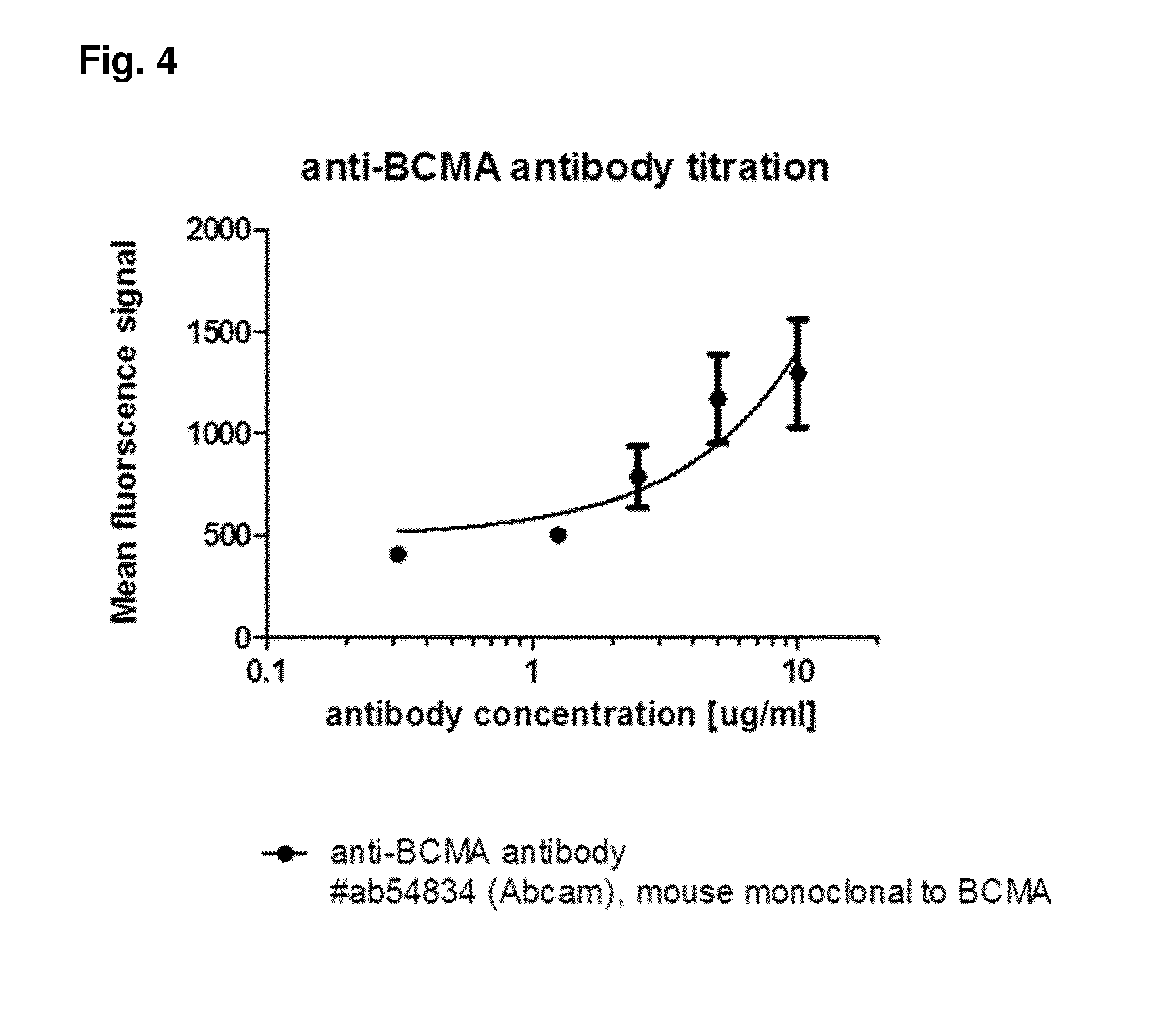
Method for the selection of antibodies against bcma
ActiveUS20150368351A1High cytotoxic activityHigh activityAnimal cellsCompound screeningNf κb activationAntibody
An antibody specifically binding to human BCMA, characterized in that the binding of said antibody is not reduced by APRIL and not reduced by BAFF, said antibody does not alter APRIL-dependent NF-κB activation, BAFF-dependent NF-κB activation, and does not alter NF-κB activation without BAFF and APRIL is useful as a therapeutic agent.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
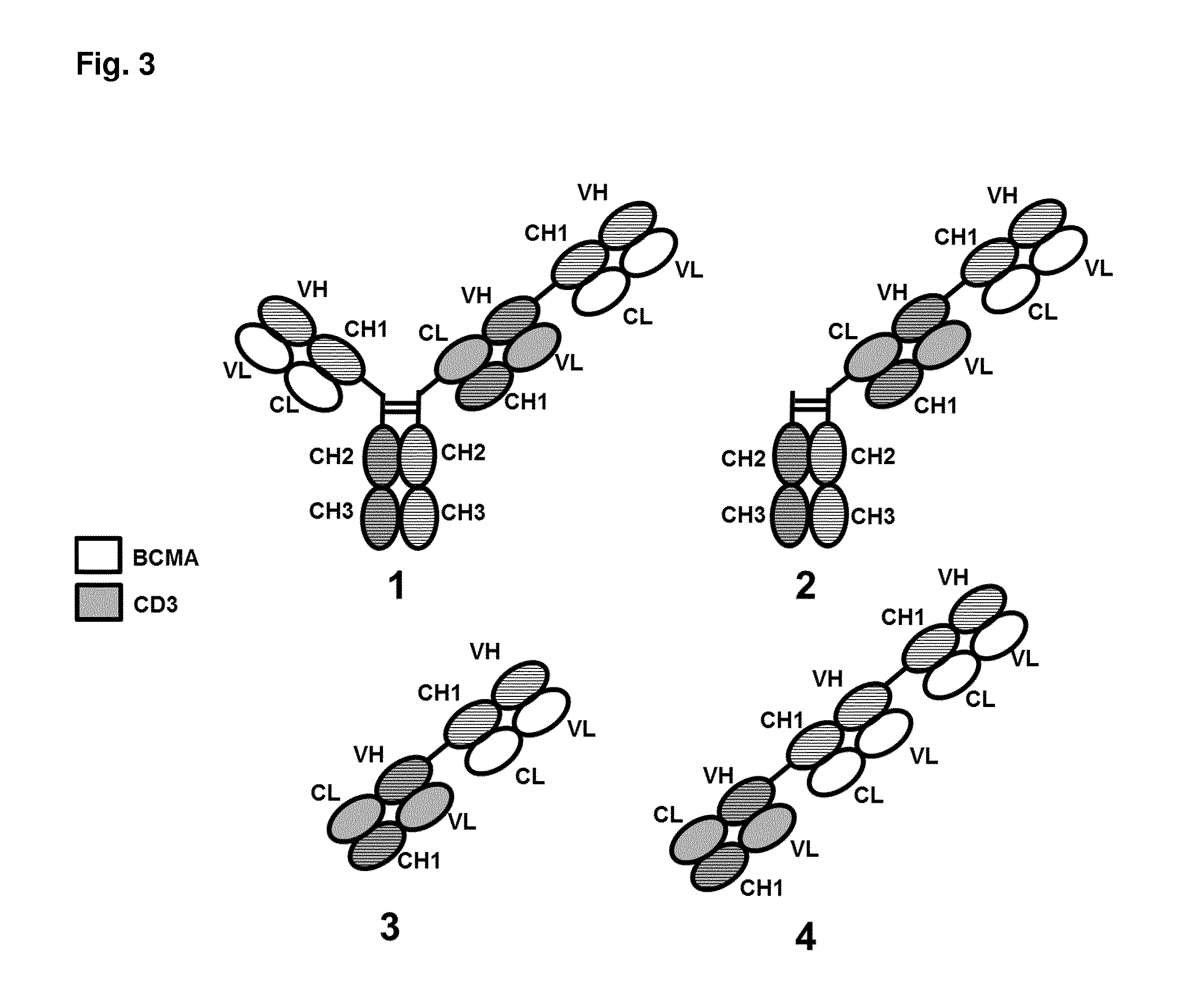
Bispecific antibodies against cd3 and bcma
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
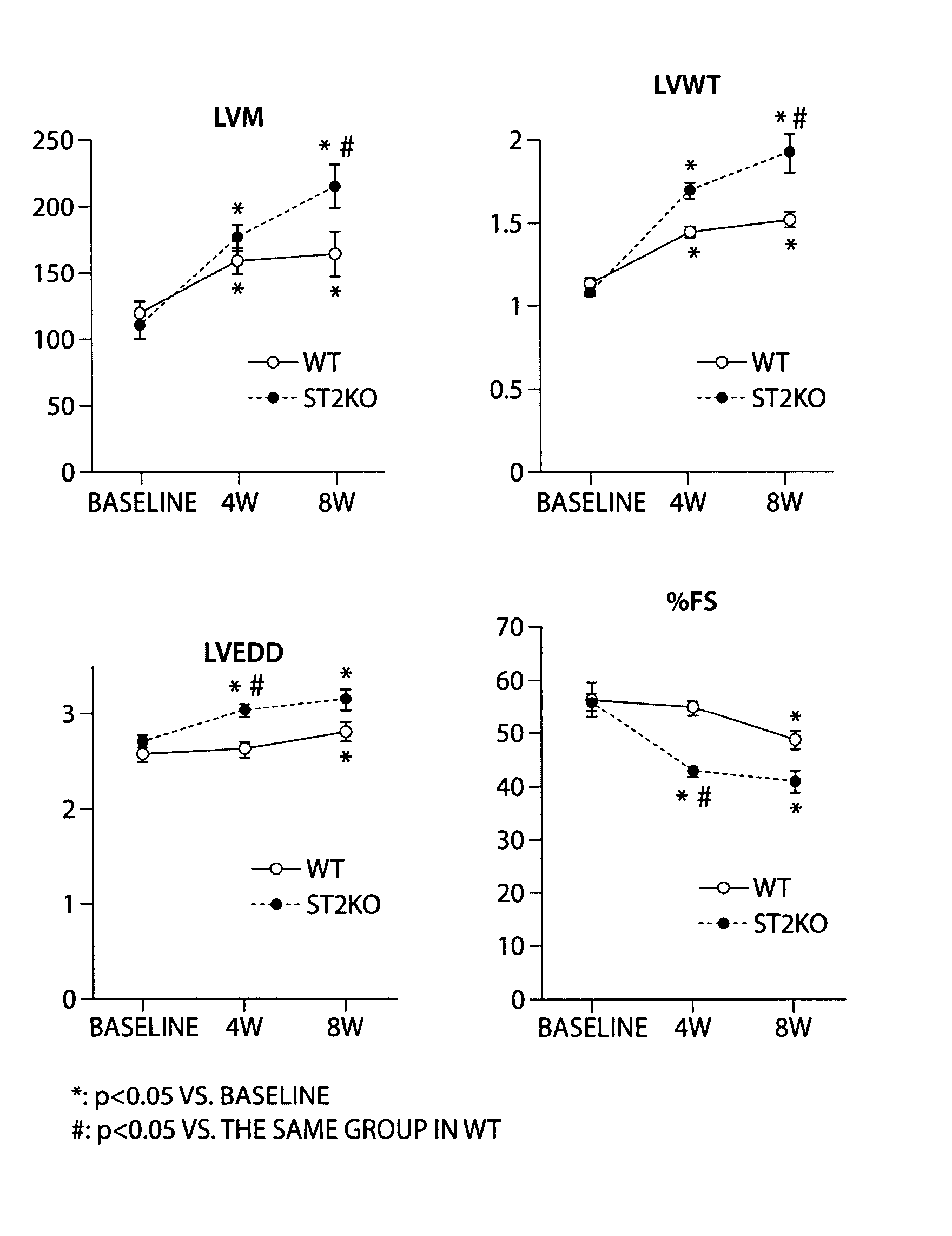
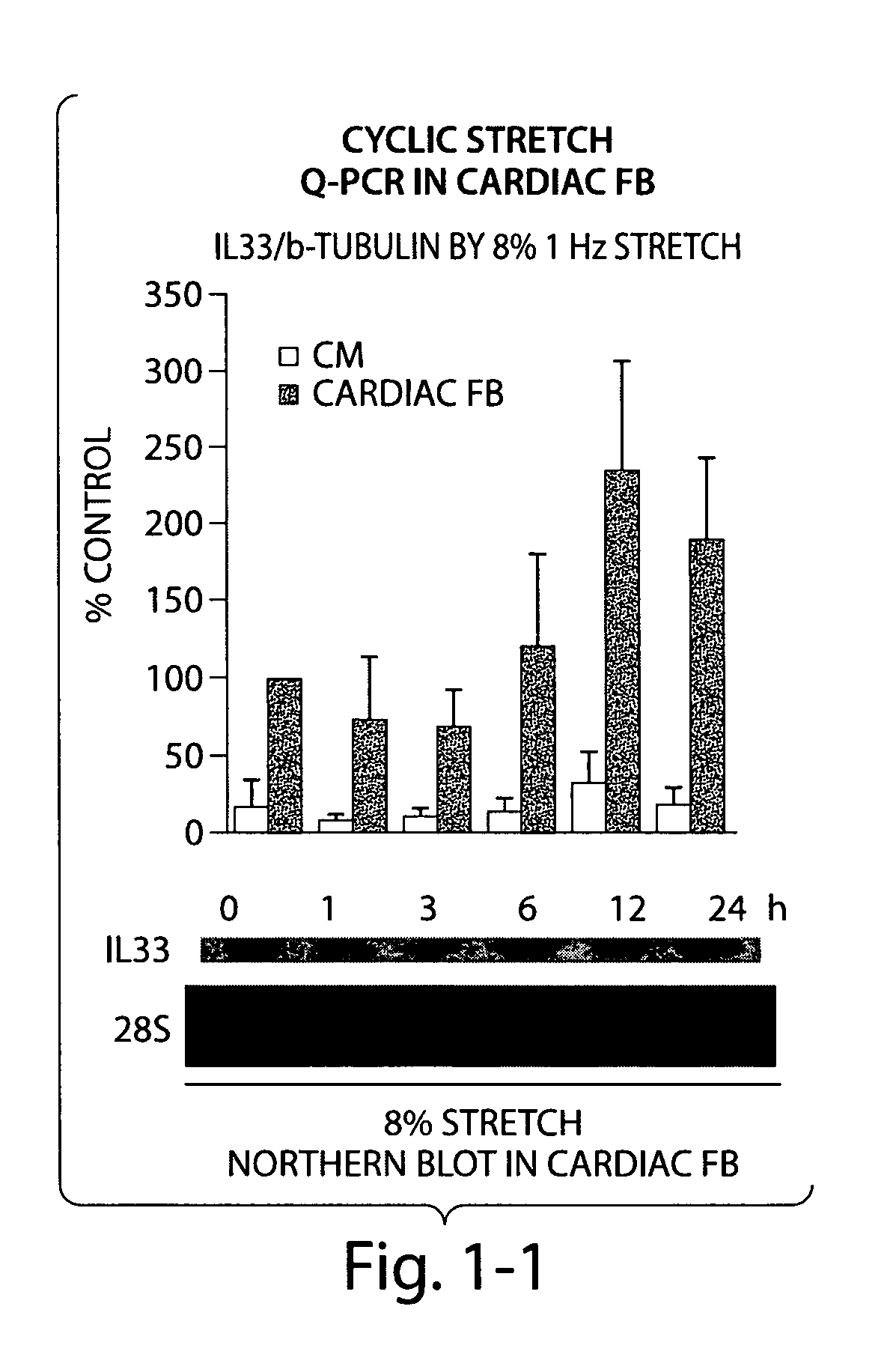
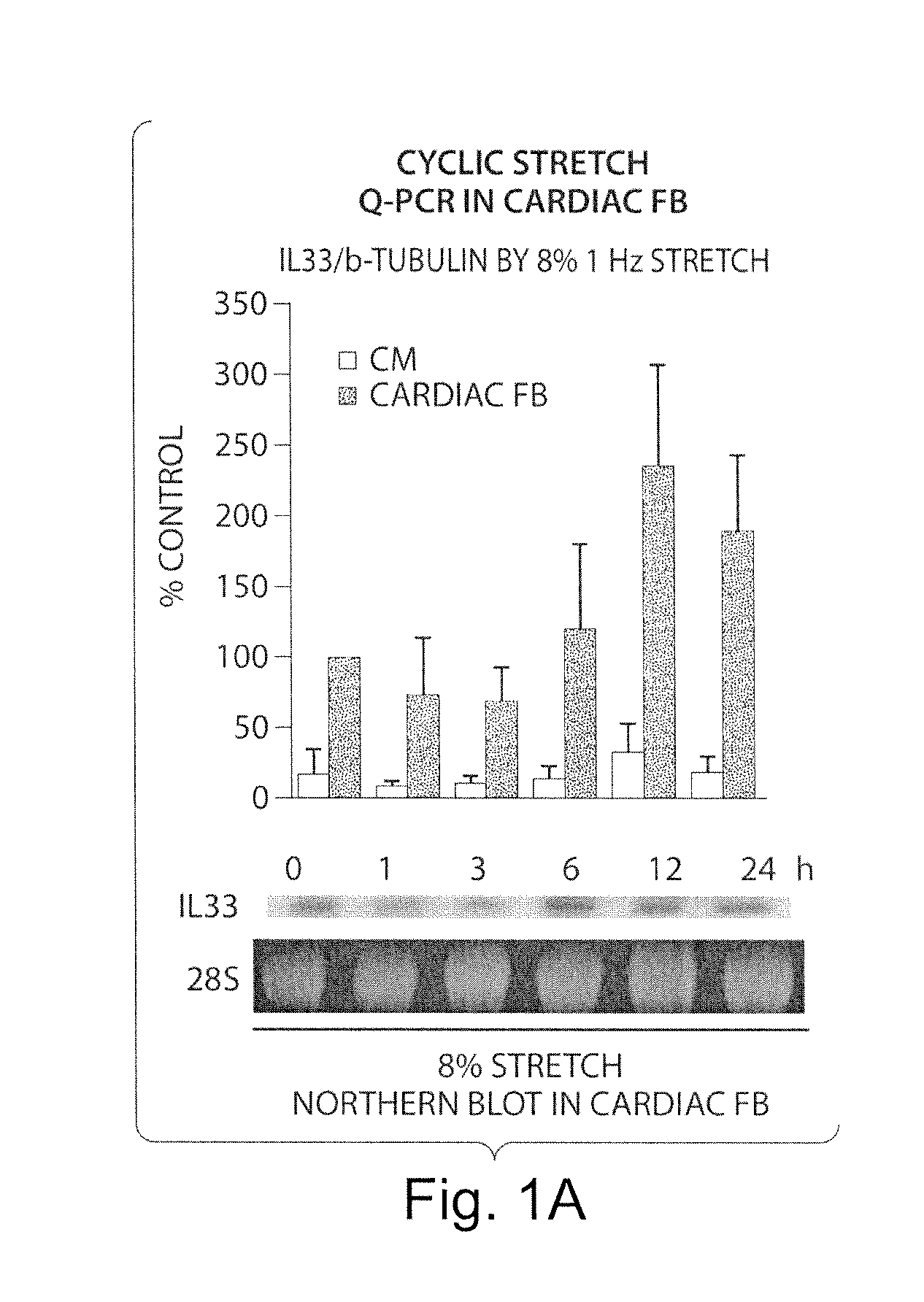
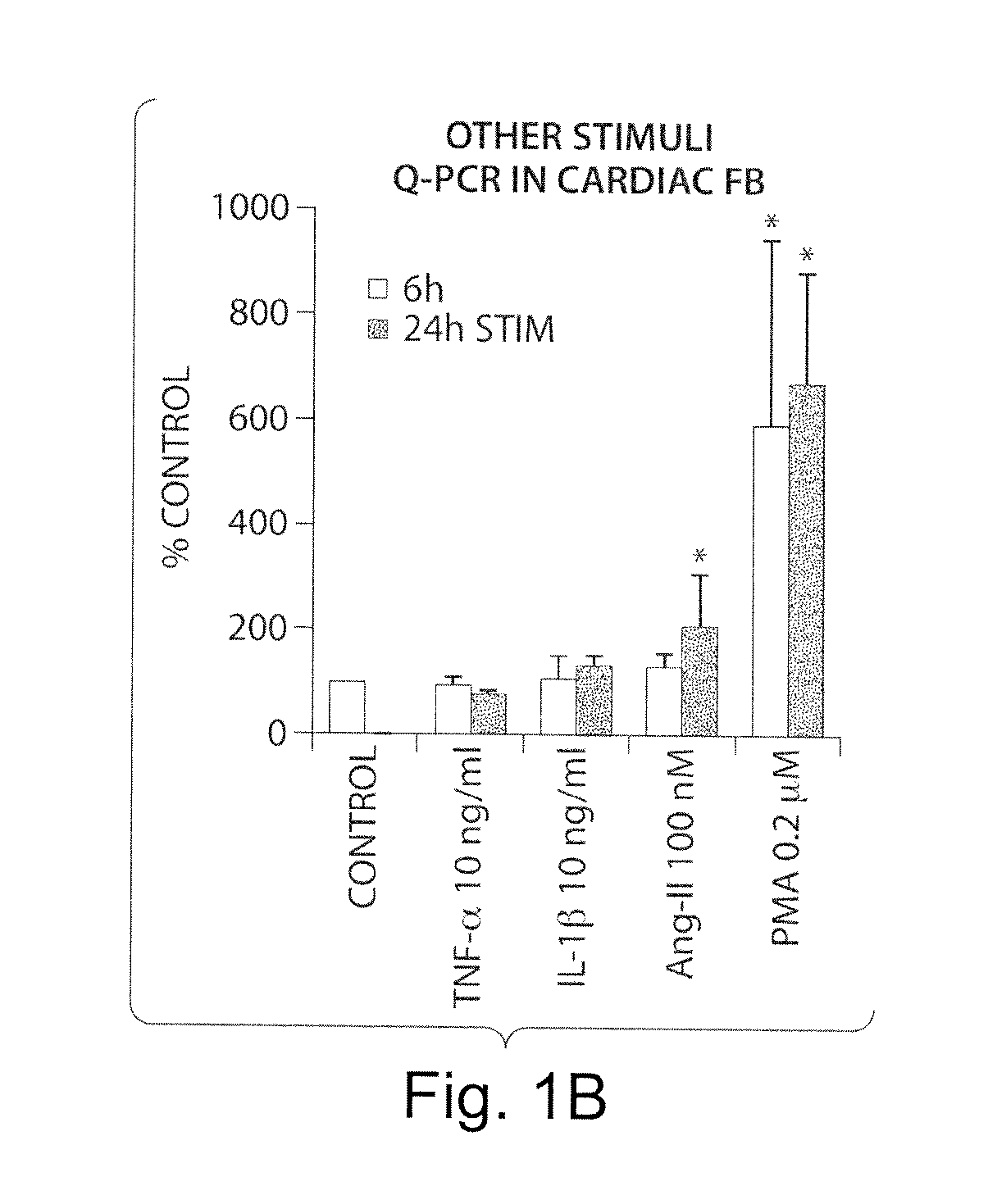
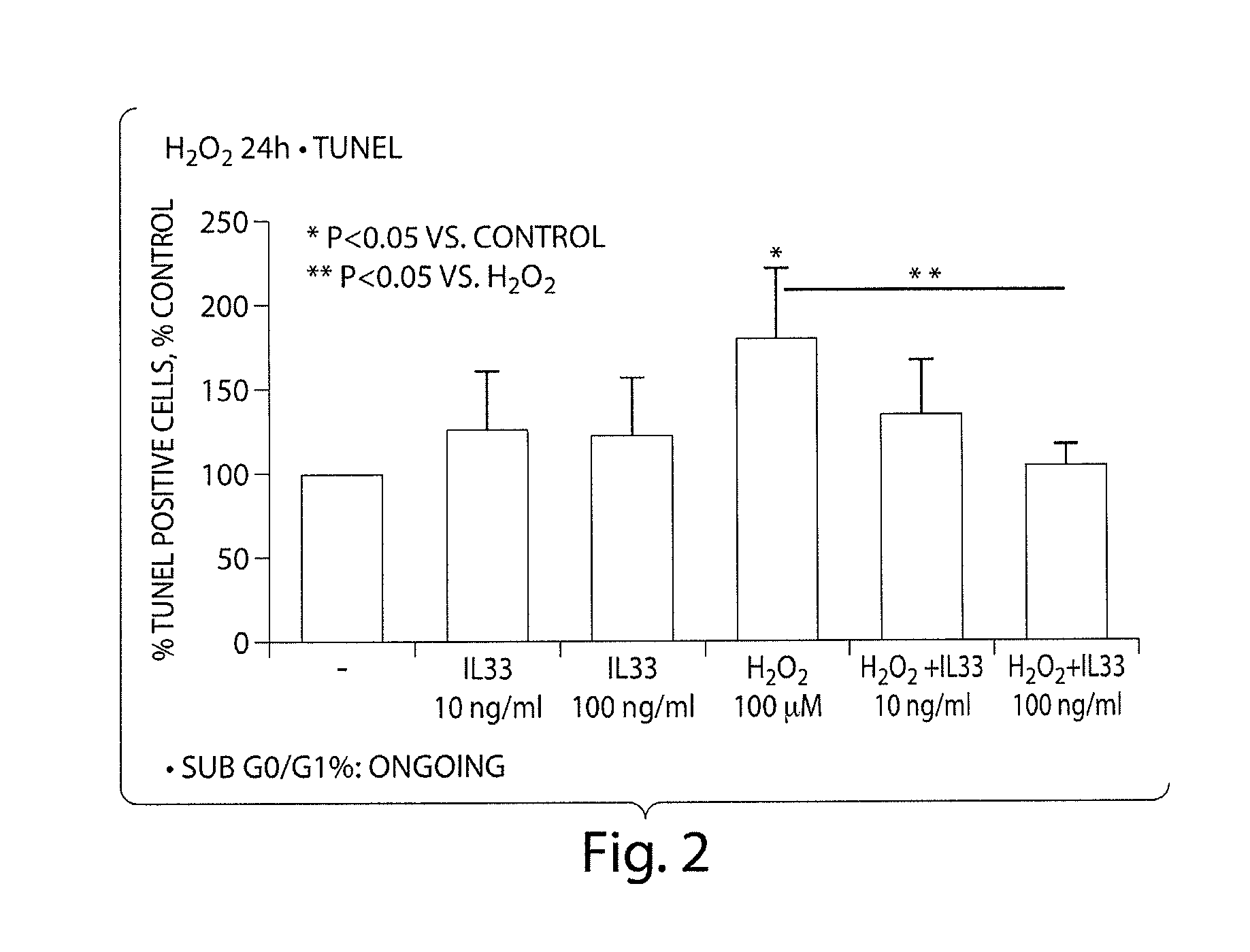
IL-33 in the treatment and diagnosis of diseases and disorders
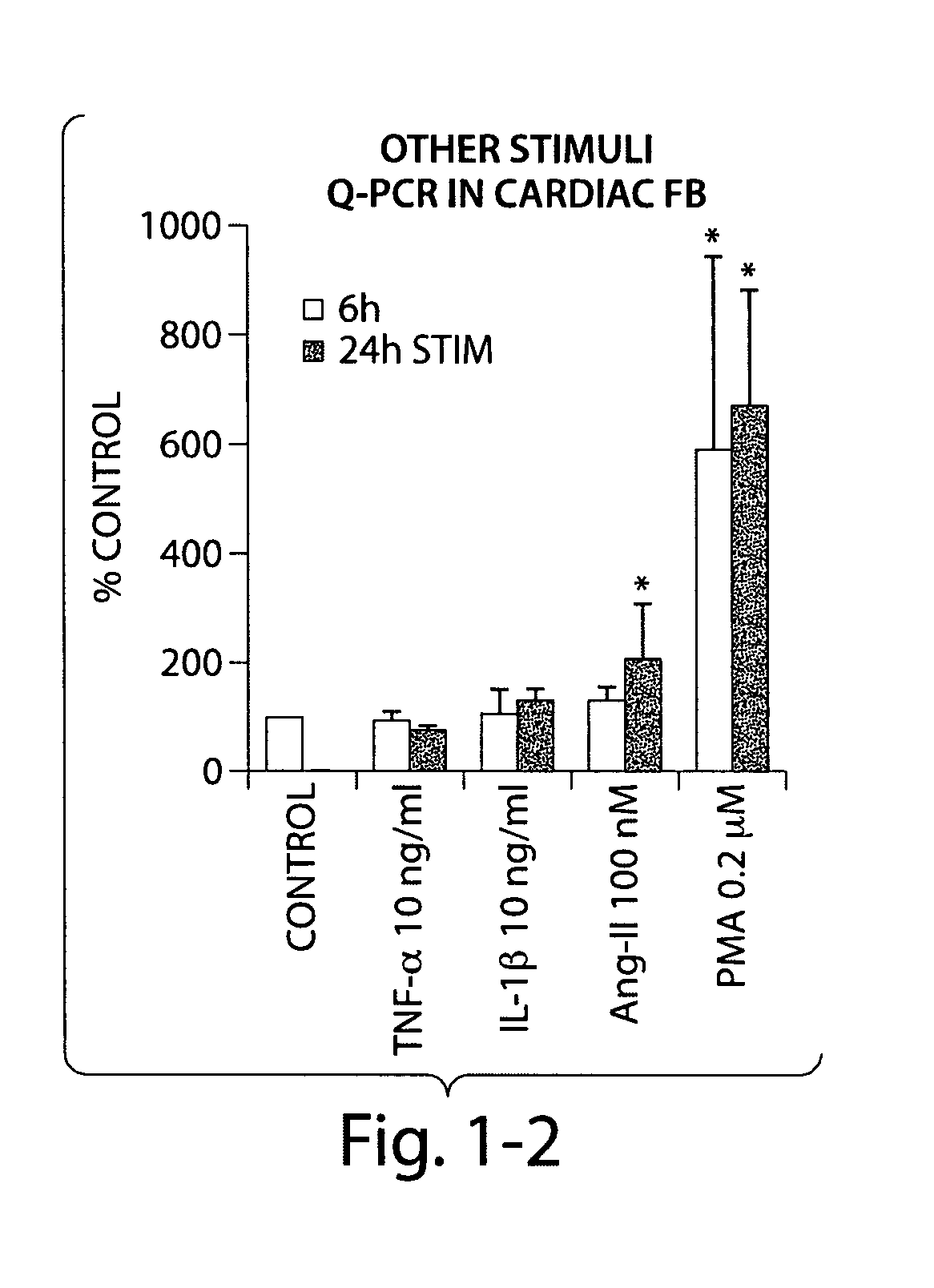
This invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment and diagnosis of cardiac diseases and disorders, such as cardiac hypertrophy, myocardial infarction, stroke, arteriosclerosis and heart failure. The invention also relates to methods and compositions for the treatment of fibrosis-related diseases as well as methods and compositions for reducing apoptosis, increasing ST2L signaling, decreasing NF-κB activation, decreasing IκBα phosphorylation, decreasing P38MAPK phosphorylation, decreasing JNK phosphorylation, decreasing reactive oxygen species generation, decreasing macrophage infiltration and / or decreasing the expression of hypertrophic genes. More specifically, the invention relates to IL-33 and / or soluble ST2 inhibiting agents for use in the methods and compositions provided.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
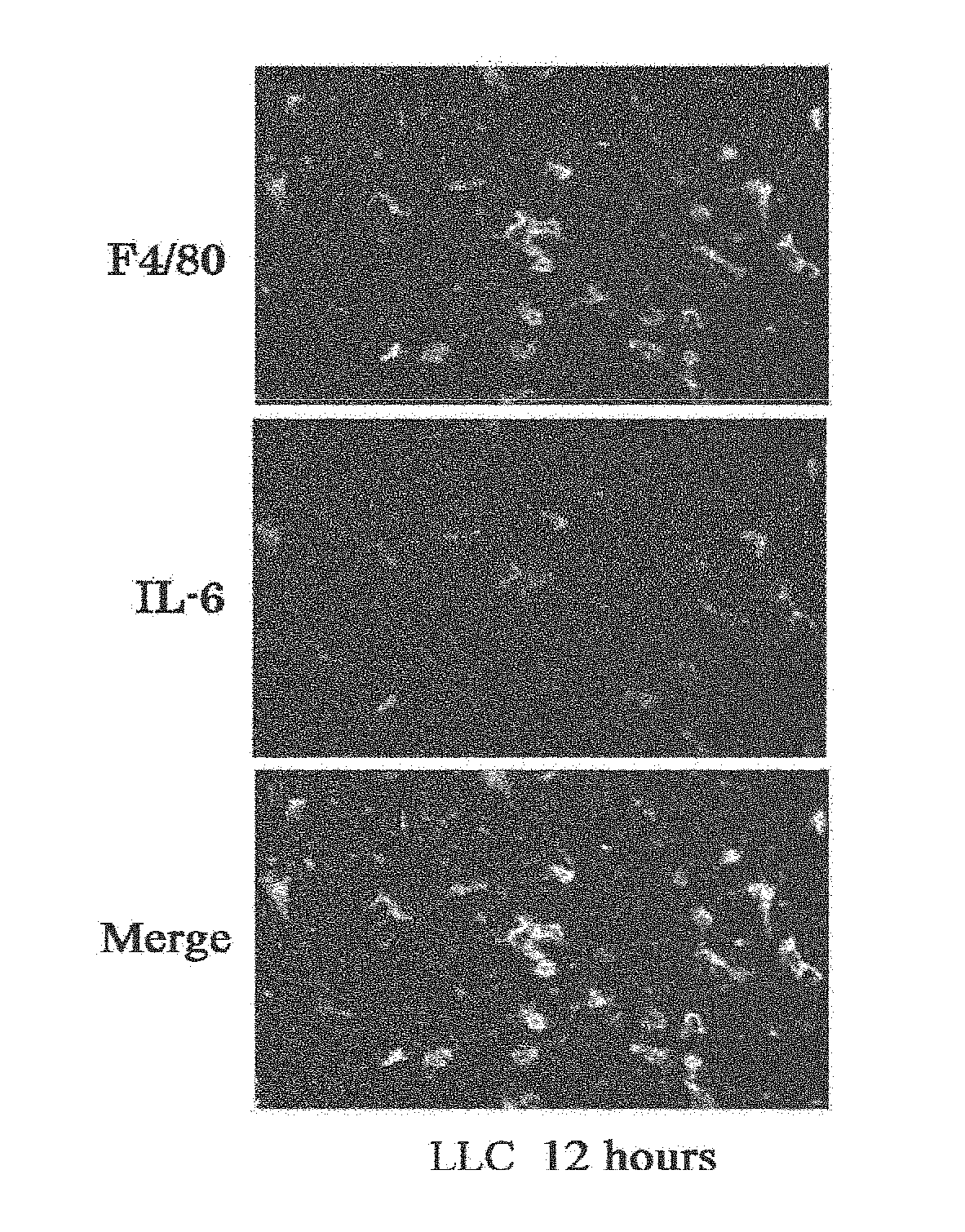
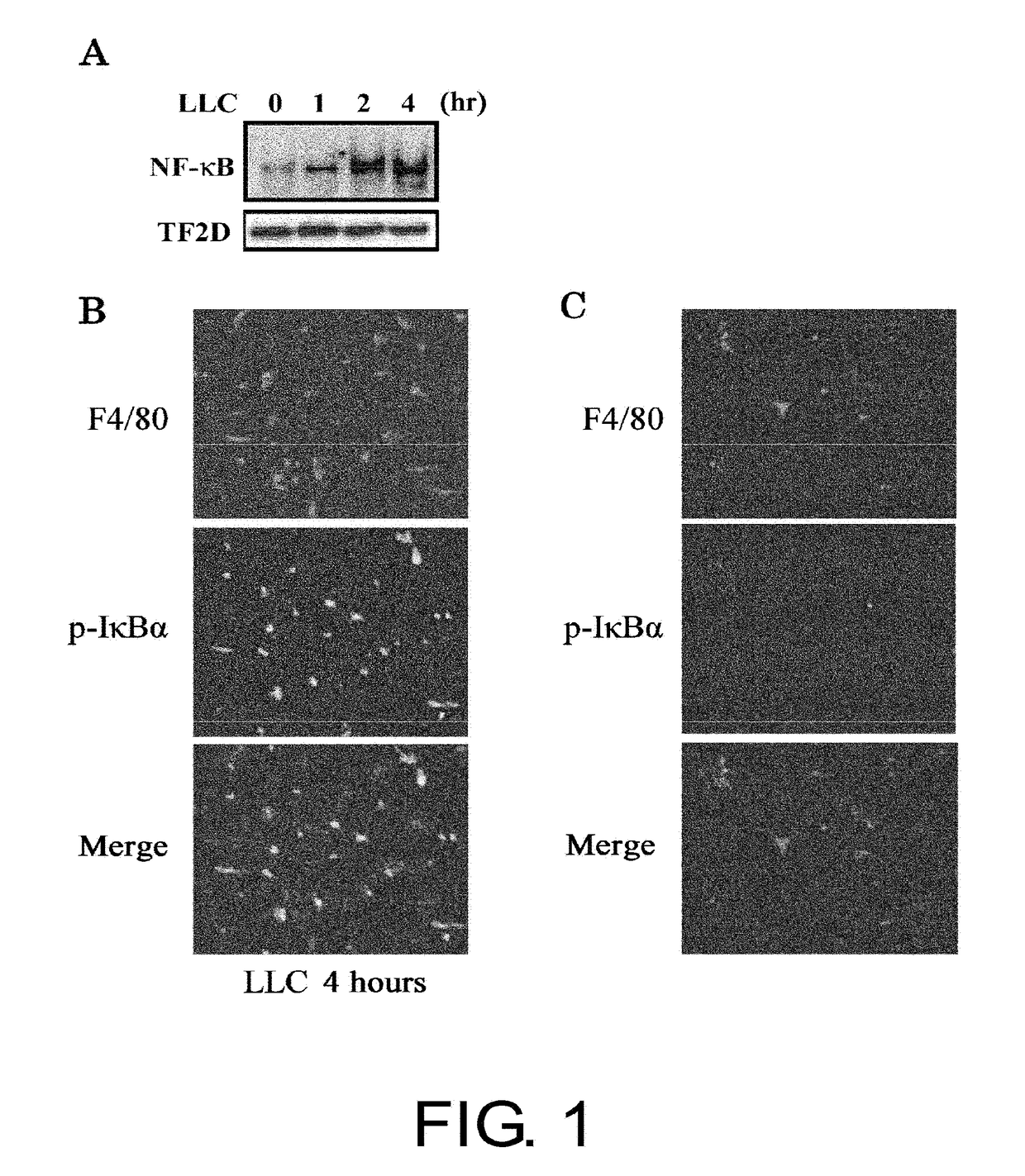
Cancer Metastasis Inhibitor
InactiveUS20120183539A1Promoted angiogenesisPromoted tumor growthImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsHematopoietic cellLymphatic Spread
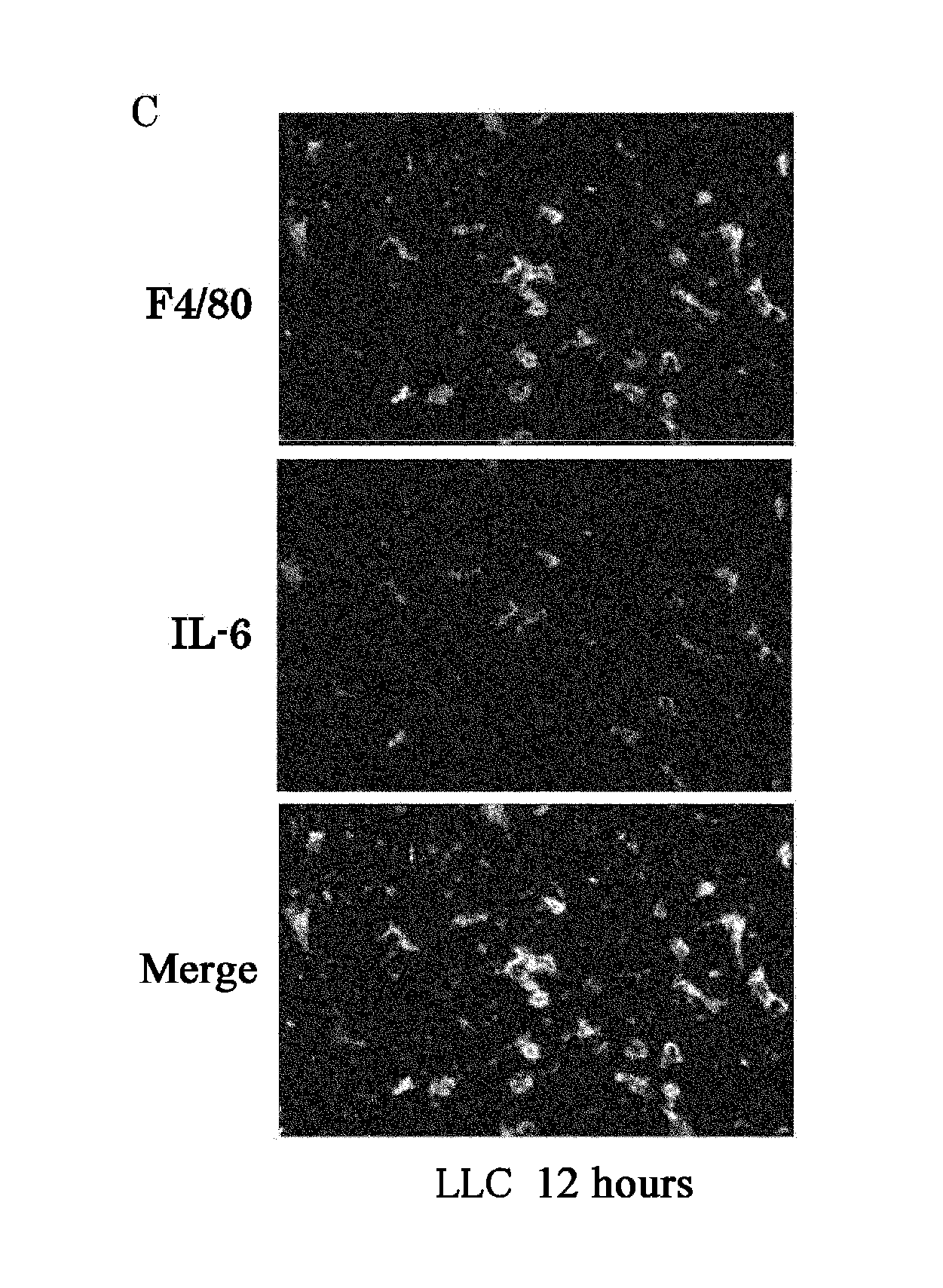
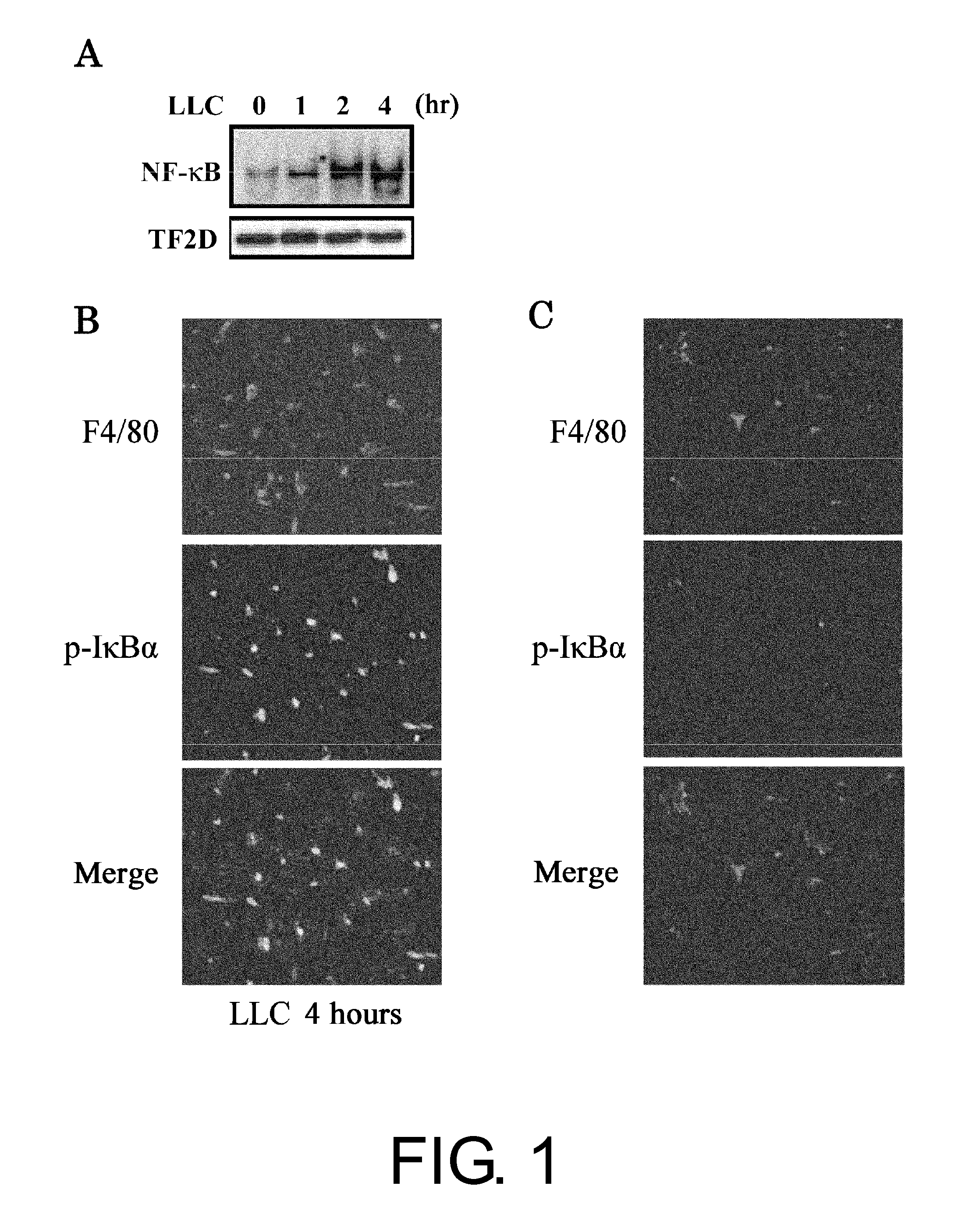
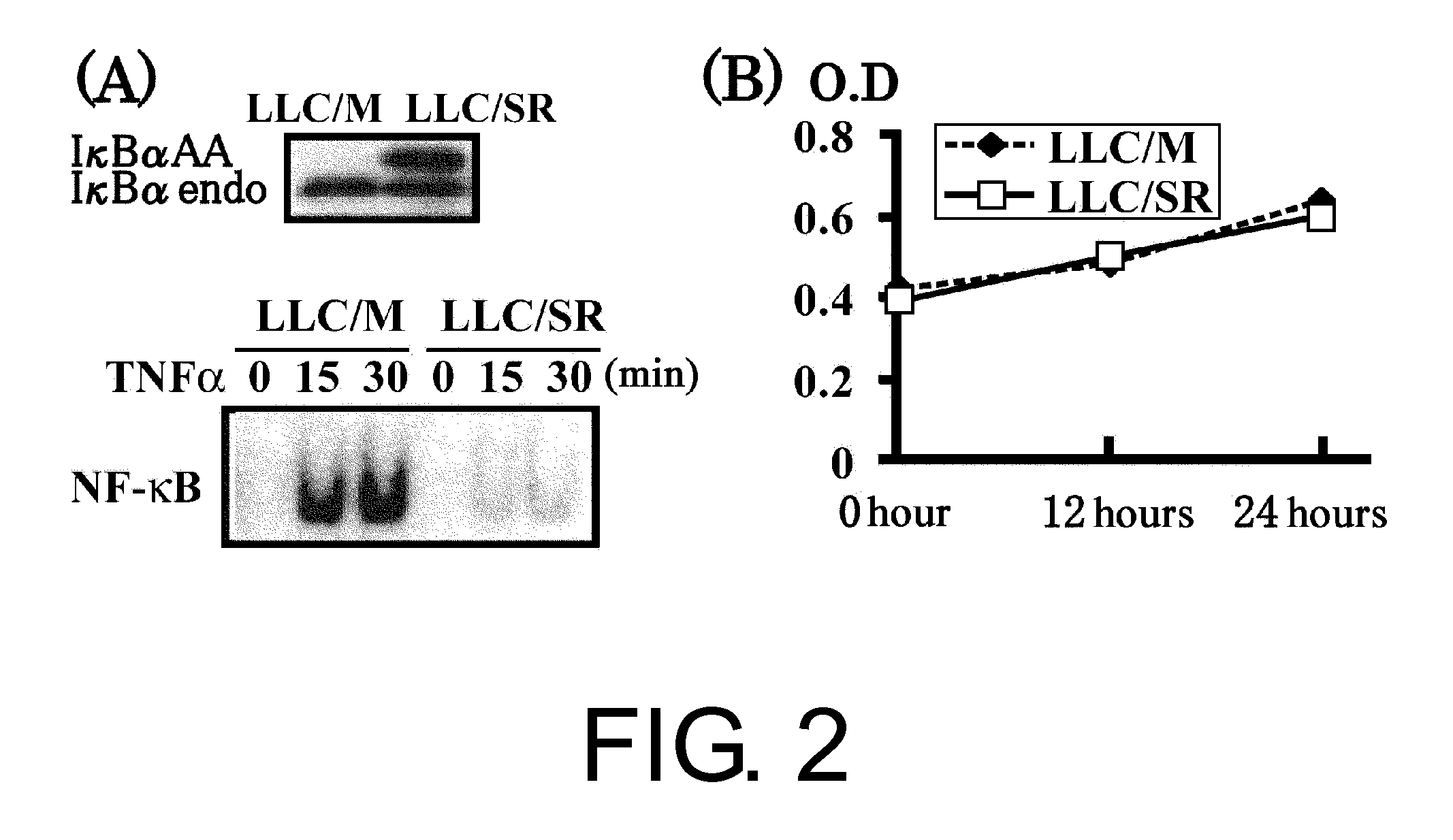
The present inventors used a model of intrasplenically induced liver metastasis to determine whether or not NF-κB activation in the liver is involved in the onset of metastatic tumors. When IKKβ was deleted from both liver cells and hematopoietically-derived cells, the onset of tumors was reduced remarkably. Tumor cells activated neighboring bone marrow cells (Kupffer cells) and produced mitogens such as interleukin (IL)-6, and this promoted angiogenesis and growth of tumors. The mitogen production depended on NF-κB in hematopoietically-derived Kupffer cells. Furthermore, treatment with an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody decreased the degree of metastatic tumor development. That is, the present inventors showed that tumor metastasis depends on inflammation, and proinflammatory intervention that targets Kupffer cells is useful for chemical prevention of metastatic tumors. Furthermore, it was shown that inhibition of the IKKβ / NF-κB signal transduction pathway, in particular IL-6 inhibition, can be utilized for anti-metastasis agents.
Owner:MAEDA CORPORATION
Methods for treating pancreatitis with curcumin compounds and inhibitors of reactive oxygen species
Disclosed are methods of treating, preventing, modulating, attenuating, or inhibiting a disease or a disorder associated with inflammation related to NF-κB activation in a subject which comprises administering to the subject at least one curcumin compound. Also disclosed are combination therapies comprising the administration of at least one curcumin compound and at least one ROS inhibitor. Pharmaceutical compositions and kits are also disclosed.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
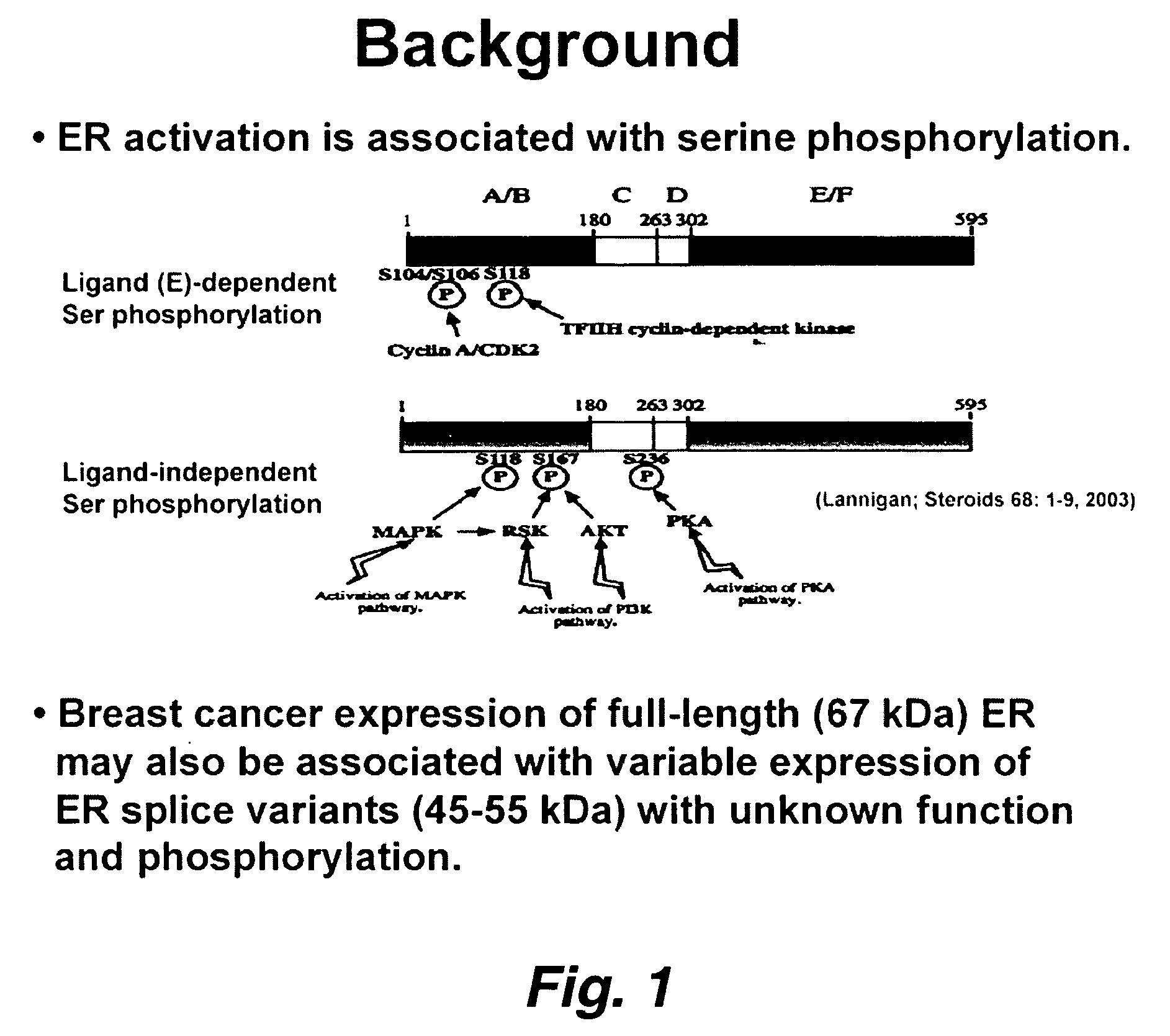
Novel pathways in the etiology of cancer
This invention pertains to the identification of two novel epithelial signaling pathways in ER-positive breast cancer s and the discovery that the cellular biology and (likely also the clinical outcome) of ER-positive breast cancer cells is unexpectedly altered when these signaling pathways are activated. The first pathway pertains to the discovery that NF-κB activation and / or DNA binding is implicated in the etiology of ER-positive breast (and other) cancers. The second pathway involves ligand-independent quinine-mediated ER activation by posphorylation (e.g. on SER-118 and SER-167 residues of ER) and nuclear translocation of full-length (67 kDA) ER as well as the phorphorylating activation of a truncated and nuclear-localized ER variant (˜52 kDa).
Owner:THE BUCK INST FOR RES ON AGING
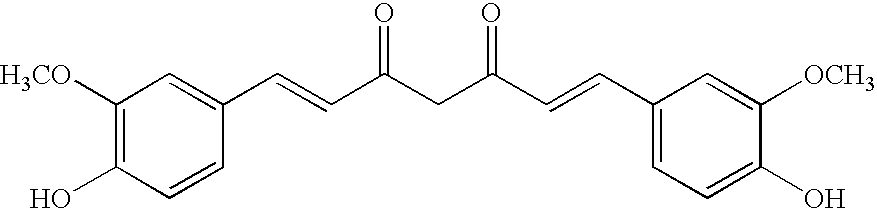
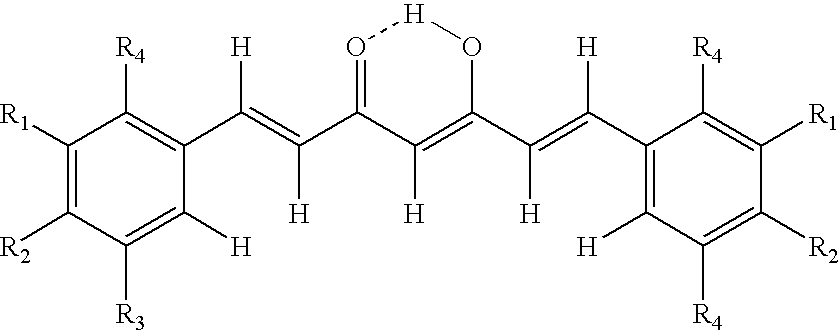
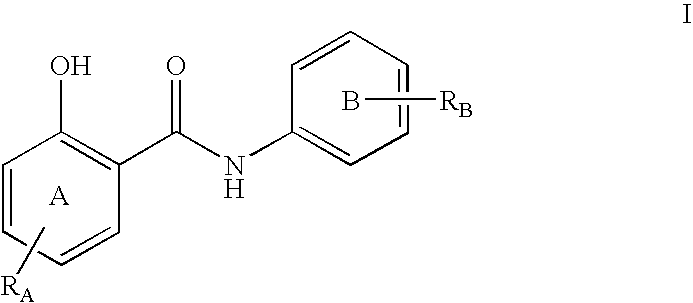
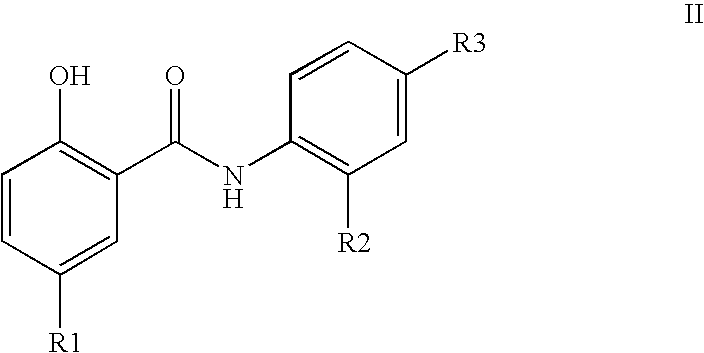
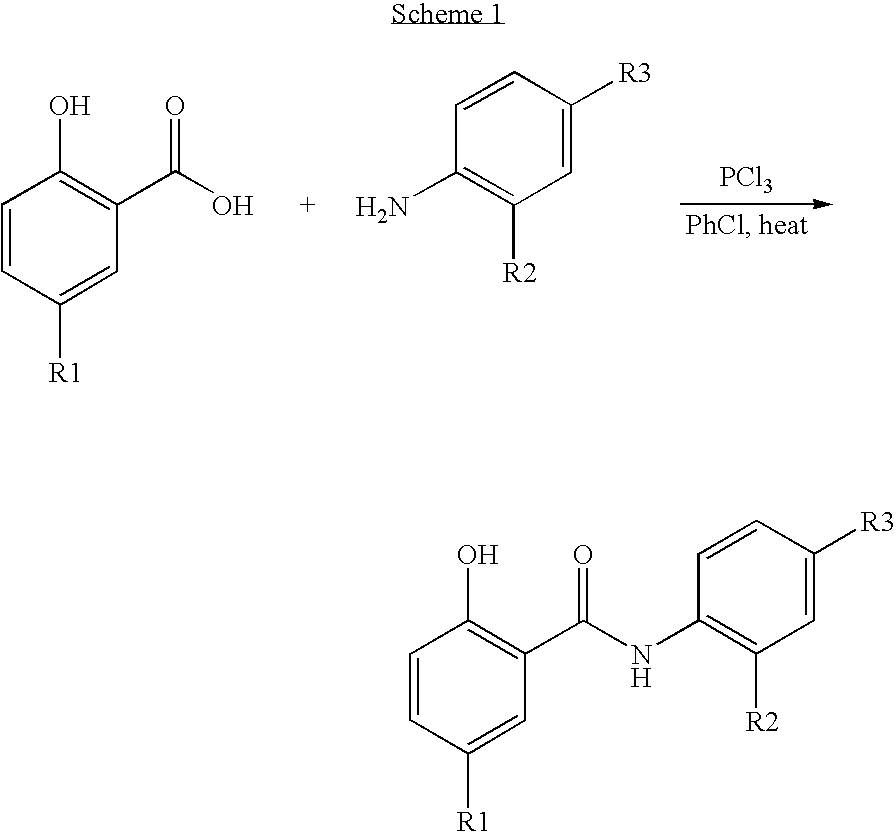
O-substituted hydroxyaryl derivatives
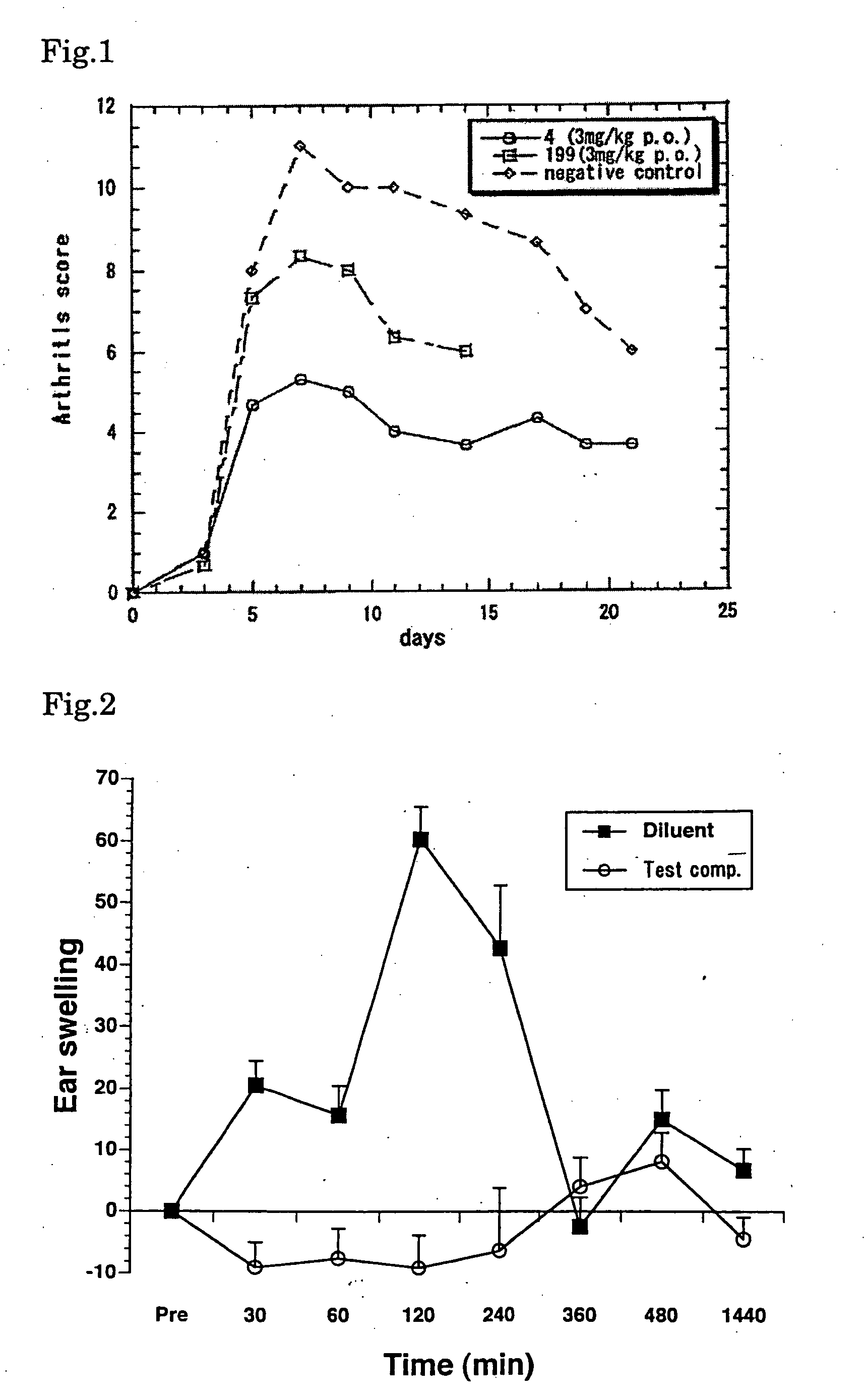
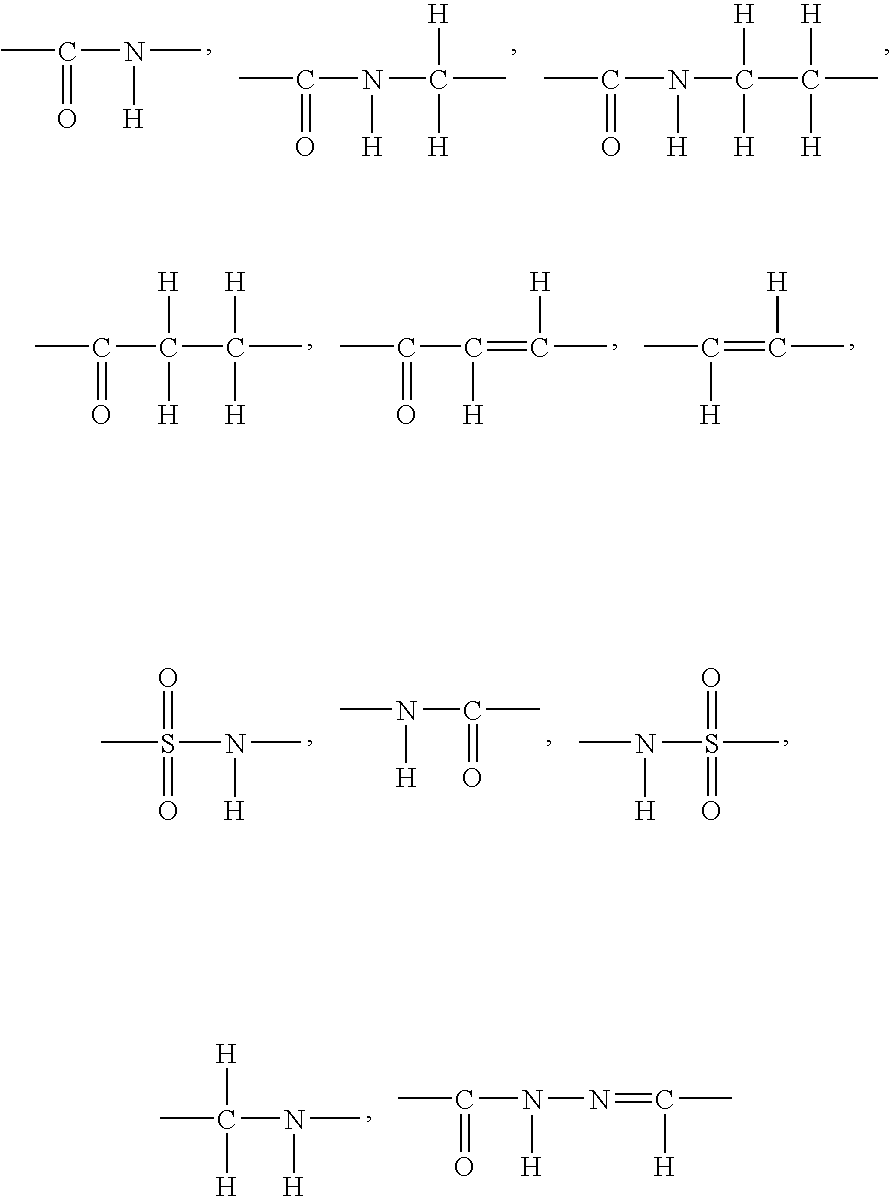
A medicament having inhibitory activity against NF-κB activation which comprises as an active ingredient a substance selected from the group consisting of a compound represented by the following general formula (I) and a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof, and a hydrate thereof and a solvate thereof:wherein X represents a connecting group whose number of atoms in a main chain is 2 to 5 (said connecting group may be substituted),“A” represents an acyl group which may be substituted, (provided that unsubstituted acetyl group and unsubstituted acryloyl group are excluded,) or a C1 to C6 alkyl group which may be substituted, or A may bind to connecting group X to form a cyclic structure which may be substituted,“E” represents an aryl group which may be substituted or a heteroaryl group which may be substituted,ring Z represents an arene which may have one or more substituents in addition to the group represented by formula —O-A wherein A has the same meaning as that defined above and the group represented by formula —X-E wherein each of X and E has the same meaning as that defined above, or a heteroarene which may have one or more substituents in addition to the group represented by formula —O-A wherein A has the same meaning as that defined above and the group represented by formula —X-E wherein each of X and E has the same meaning as that defined above.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL MOLECULAR DESIGN
O-substituted hydroxyaryl derivatives
A medicament having inhibitory activity against NF-κB activation which comprises as an active ingredient a substance selected from the group consisting of a compound represented by the following general formula (I) and a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof, and a hydrate thereof and a solvate thereof: wherein X represents a connecting group whose number of atoms in a main chain is 2 to 5 (said connecting group may be substituted), “A” represents an acyl group which may be substituted, (provided that unsubstituted acetyl group and unsubstituted acryloyl group are excluded,) or a C1 to C6 alkyl group which may be substituted, or A may bind to connecting group X to form a cyclic structure which may be substituted, “E” represents an aryl group which may be substituted or a heteroaryl group which may be substituted, ring Z represents an arene which may have one or more substituents in addition to the group represented by formula —O-A wherein A has the same meaning as that defined above and the group represented by formula —X-E wherein each of X and E has the same meaning as that defined above, or a heteroarene which may have one or more substituents in addition to the group represented by formula —O-A wherein A has the same meaning as that defined above and the group represented by formula —X-E wherein each of X and E has the same meaning as that defined above.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL MOLECULAR DESIGN
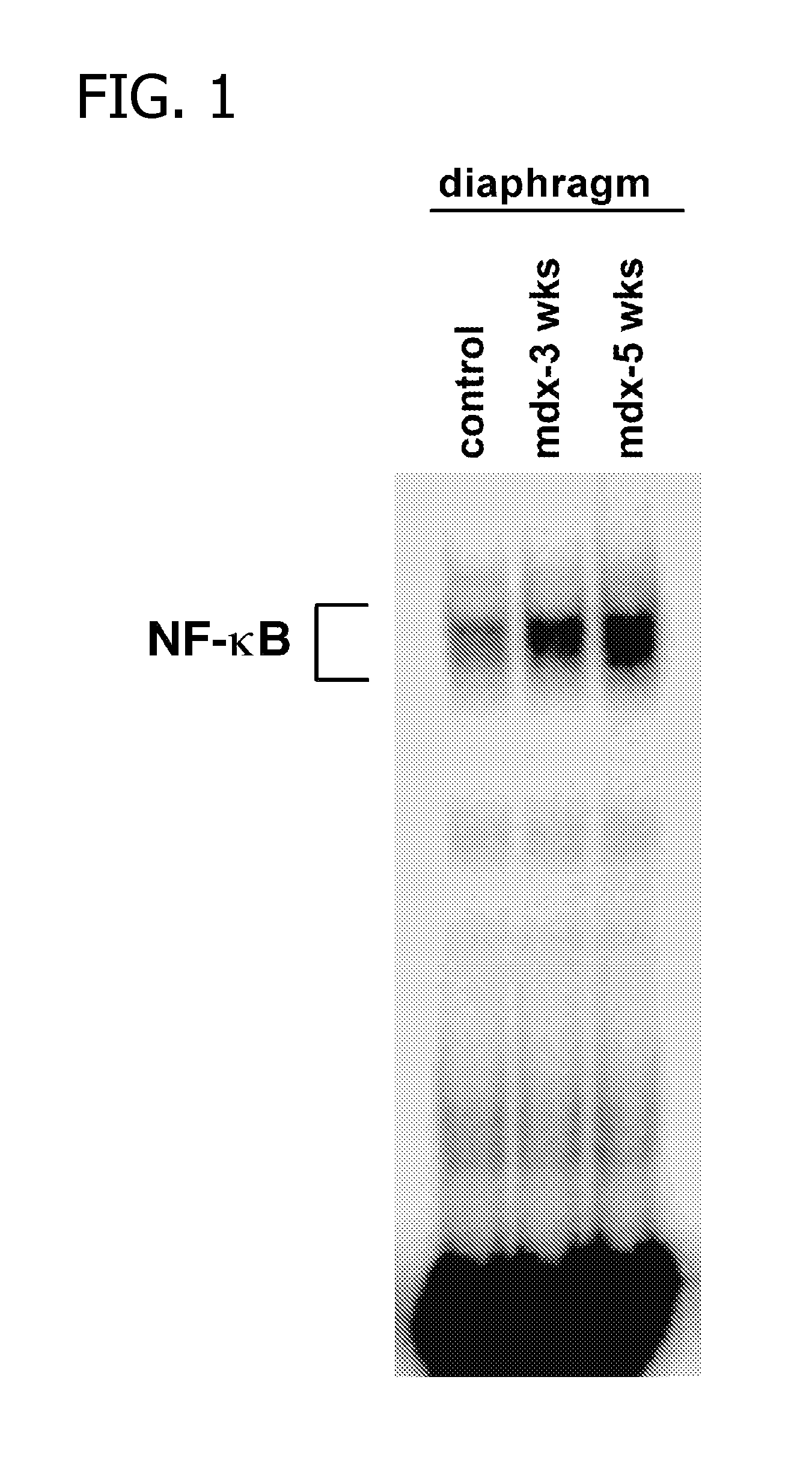
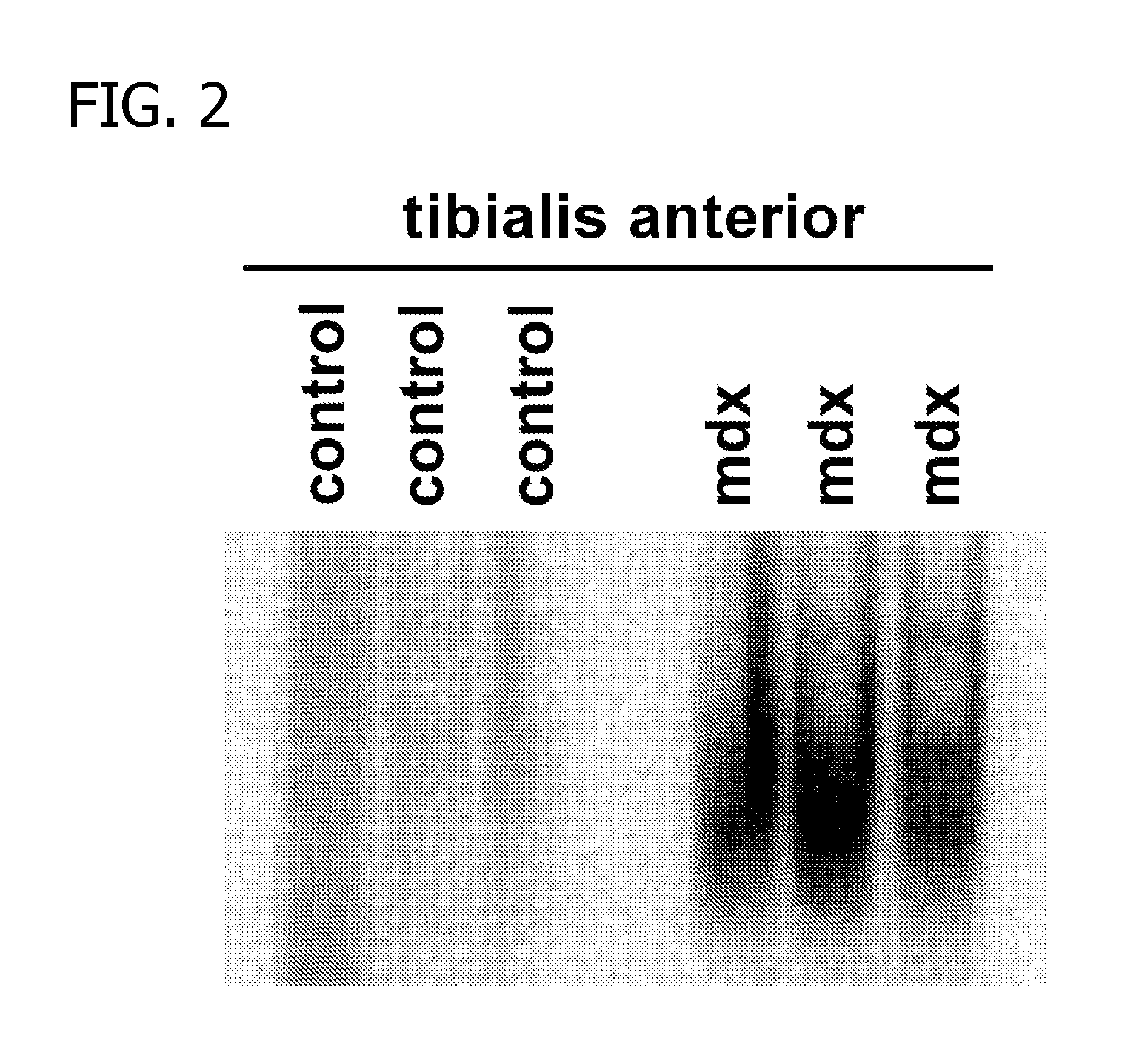
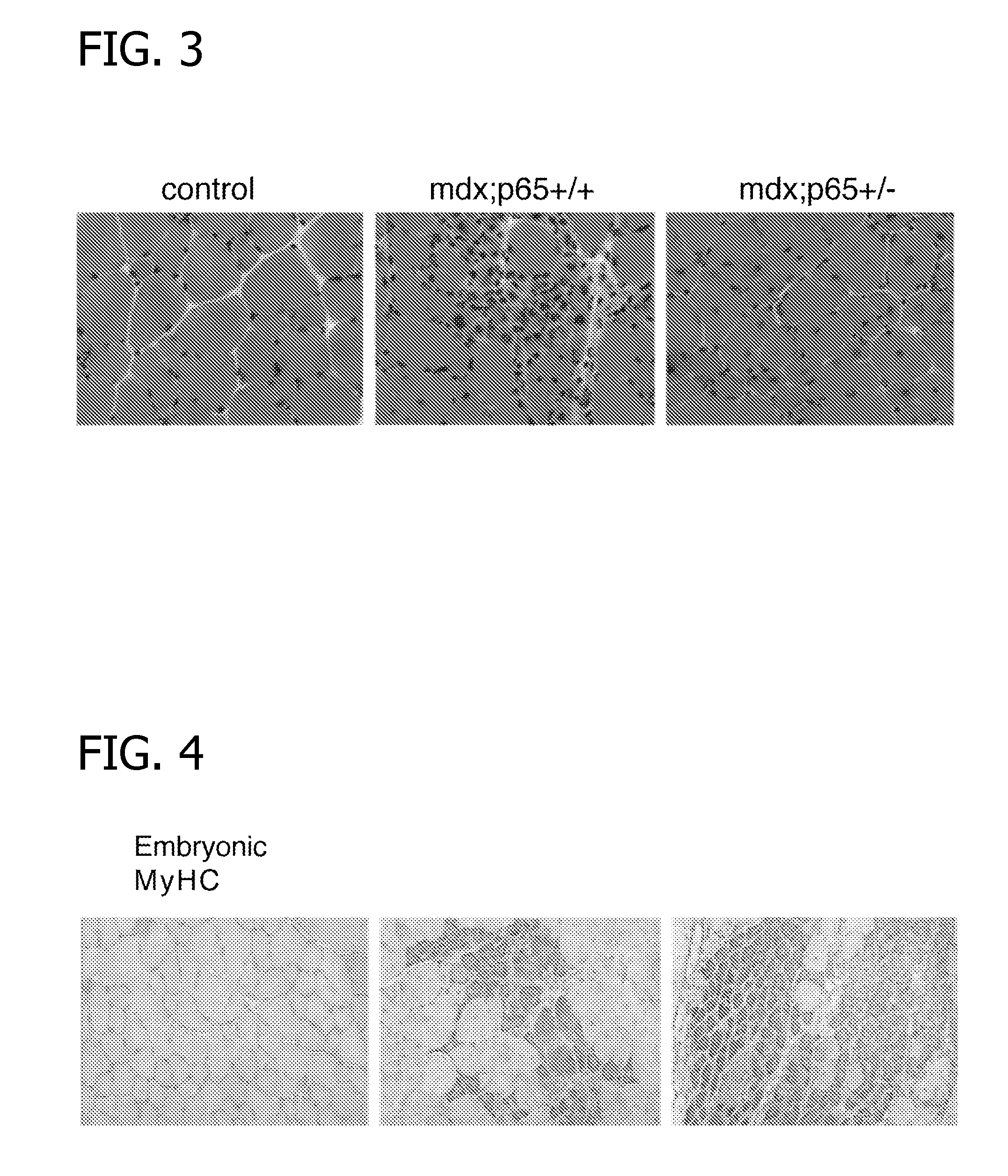
Methods of Treating Muscular Wasting Diseases Using NF-kB Activation Inhibitors
ActiveUS20070225315A1Inhibiting muscular wasting diseaseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiological activationDuchenne's Muscular Dystrophy
Methods for treating muscular wasting diseases such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy are disclosed. Specifically, the methods include administering to a subject in need of treatment for a muscular wasting disease, an NF-κB activation inhibitor capable of blocking the activation of NF-κB.
Owner:THERALOGICS
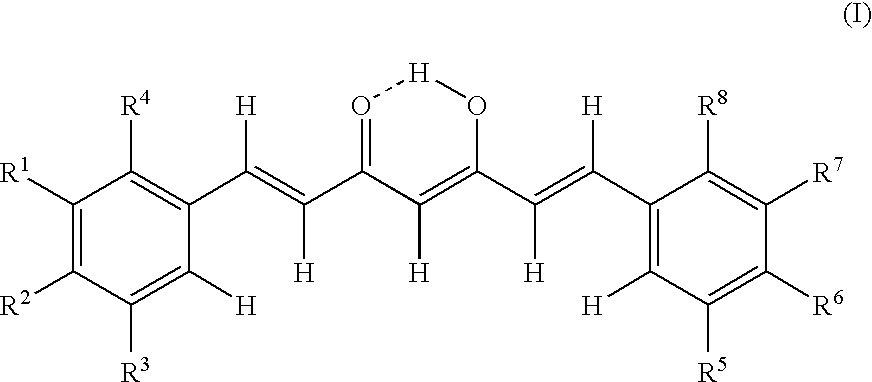
Inhibitors against activation of NF-kappaB
A method of inhibiting NF-κB activation in a mammal including a human, which comprises the step of administering an effective dose of a substance selected from the group consisting of a compound represented by the following general formula (I) and a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof, and a hydrate thereof and a solvate thereof:
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL MOLECULAR DESIGN
Inflammatory cytokine release inhibitor
InactiveUS20080318956A1Avoid side effectsInhibitory activity against NF-κB activationBiocideSenses disorderArylHydrogen atom
A medicament having inhibitory activity against NF-κB activation, which comprises a compound represented by the following general formula (I) or a pharmacologically acceptable salt as an active ingredient:wherein X represents a connecting group, A represents hydrogen atom or acetyl group, E represents an aryl group or a heteroaryl group, and ring X represents an arene or a heteroarene.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL MOLECULAR DESIGN
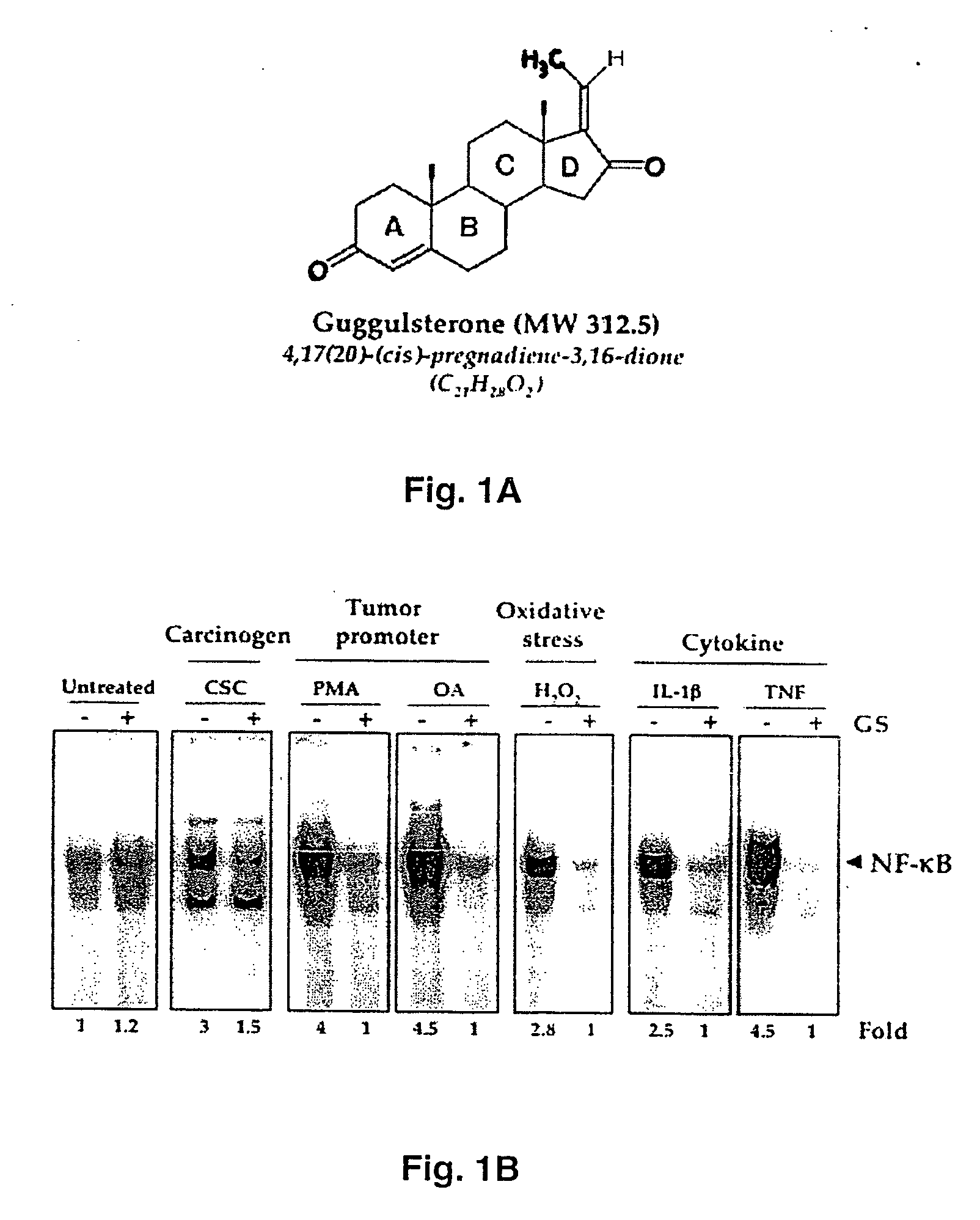
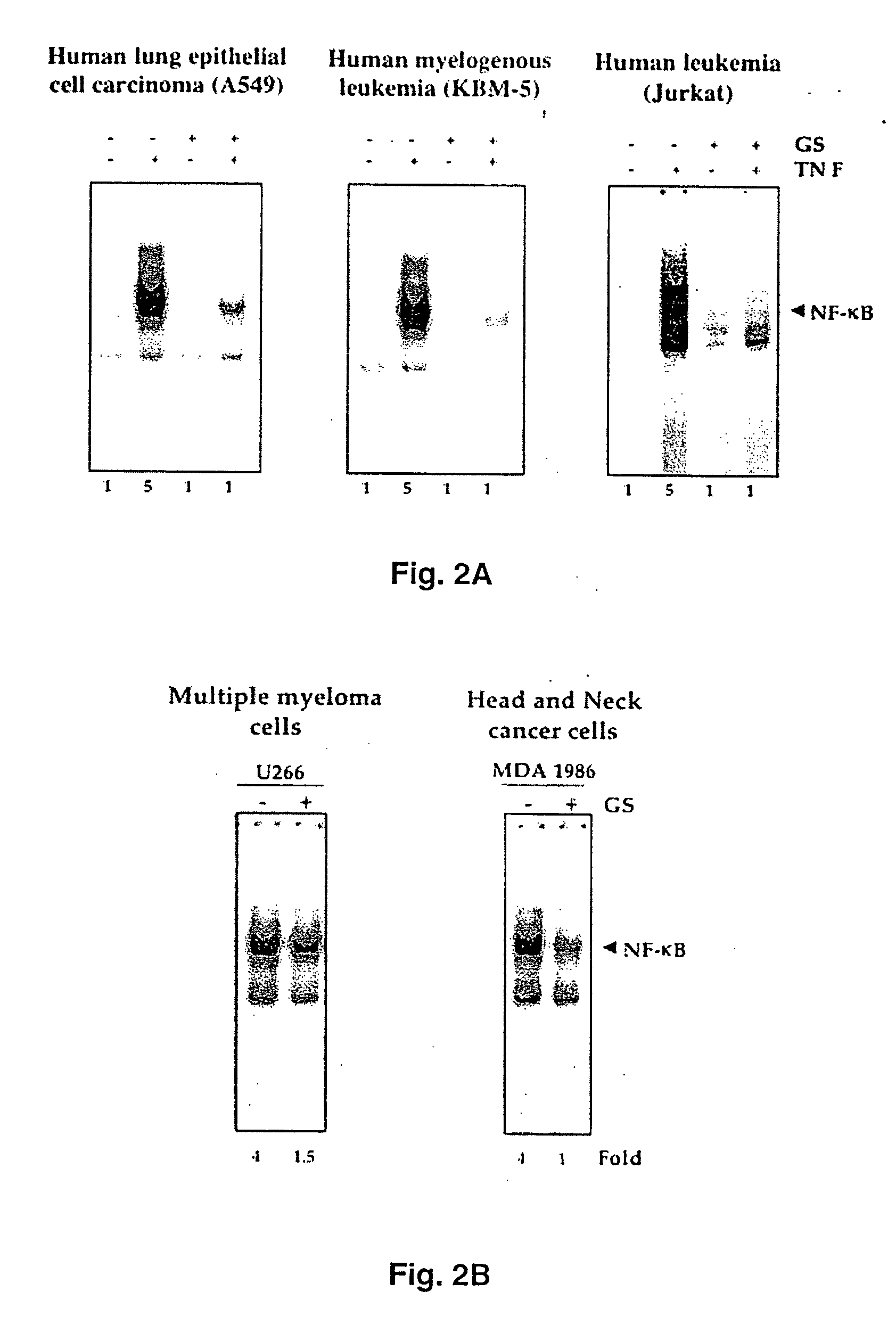
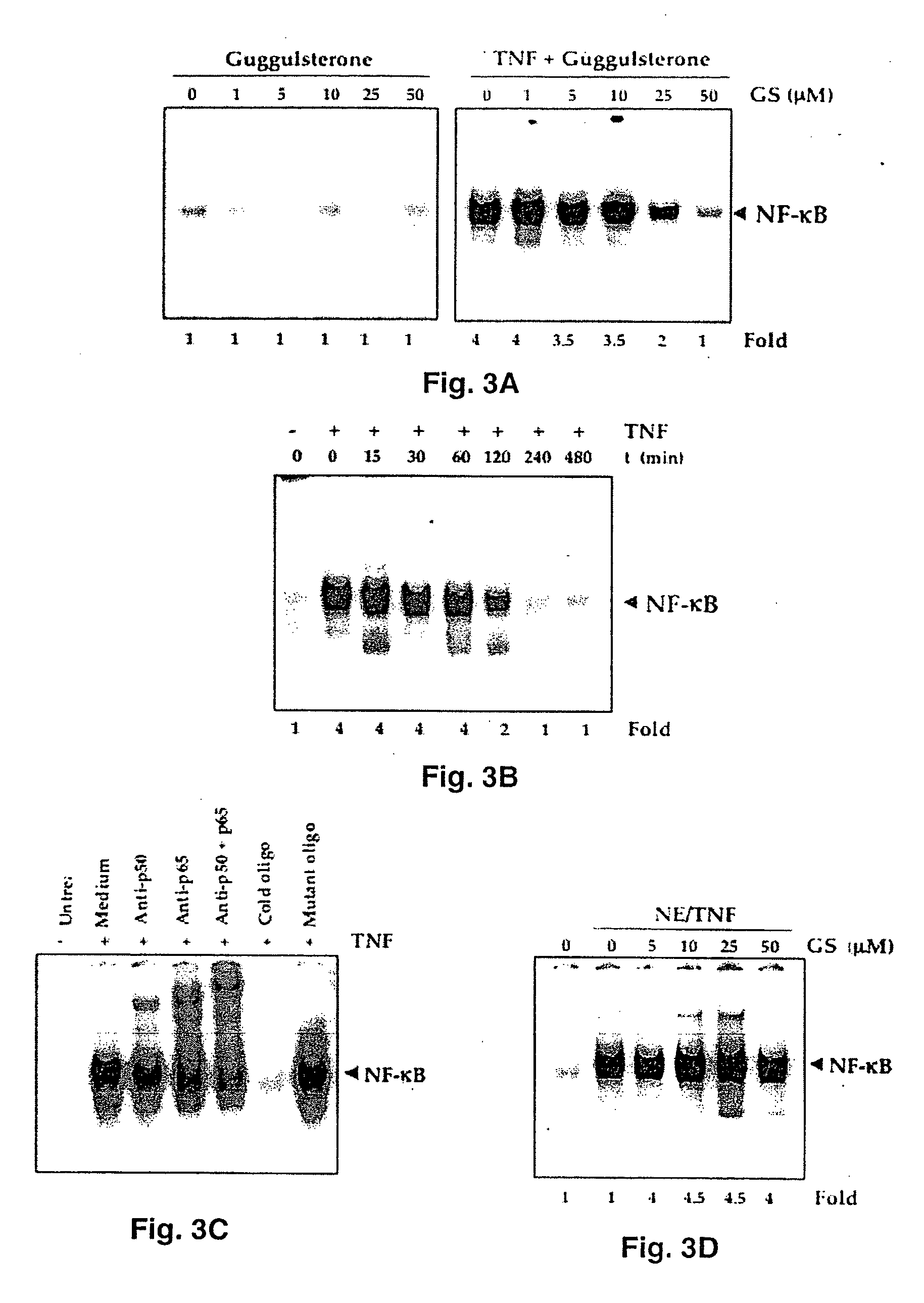
Guggulsterone: an inhibitor of nuclear factor - kappaB and IkappaBalpha kinase activation and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060019907A1Good effectHigh activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLymphatic SpreadCyclin D1
The present invention provides an inhibitor of NF-κB, guggulsterone and its analogs. Guggulsterone suppresses NF-κB activation induced by TNF, phorbol ester, okadaic acid, cigarette smoke, H2O2 and IL-1β, as well as constitutive NF-κB activation expressed in most tumor cells. One mechanism by which guggulsterone inhibits activation of NF-κB is through suppression of IκBα phosphorylation and IκBα degradation. NF-κB-dependent gene transcription is modulated by guggulsterone and its analogs. In particular, induction by TNF, TNFR1, TRADD, TRAF2, NIK and IKK, is modulated by guggulsterone and its analogs. In addition, guggulsterone decreased the expression of genes involved in anti-apoptosis (IAP1, XIAP, Bfl-1 / A1, bcl-2, cFLIP, survivin), proliferation (cyclin D1, c-myc) and metastasis (MMP-9, COX2 and VEGF).
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
IL-33 in the treatment and diagnosis of diseases and disorders
This invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment and diagnosis of cardiac diseases and disorders, such as cardiac hypertrophy, myocardial infarction, stroke, arteriosclerosis and heart failure. The invention also relates to methods and compositions for the treatment of fibrosis-related diseases as well as methods and compositions for reducing apoptosis, increasing ST2L signaling, decreasing NF-κB activation, decreasing IκBα phosphorylation, decreasing P38MAPK phosphorylation, decreasing JNK phosphorylation, decreasing reactive oxygen species generation, decreasing macrophage infiltration and / or decreasing the expression of hypertrophic genes. More specifically, the invention relates to IL-33 and / or soluble ST2 inhibiting agents for use in the methods and compositions provided.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
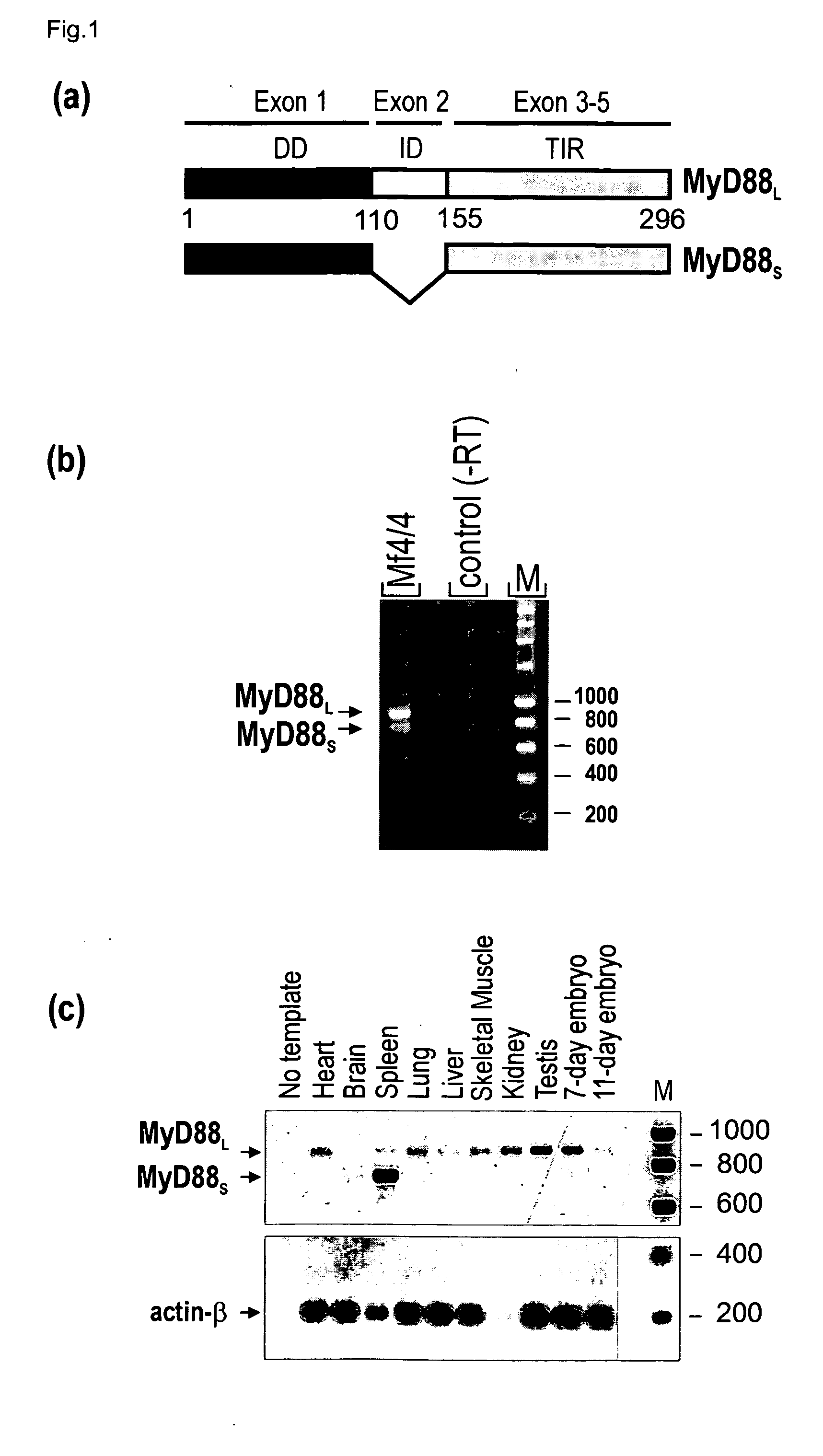
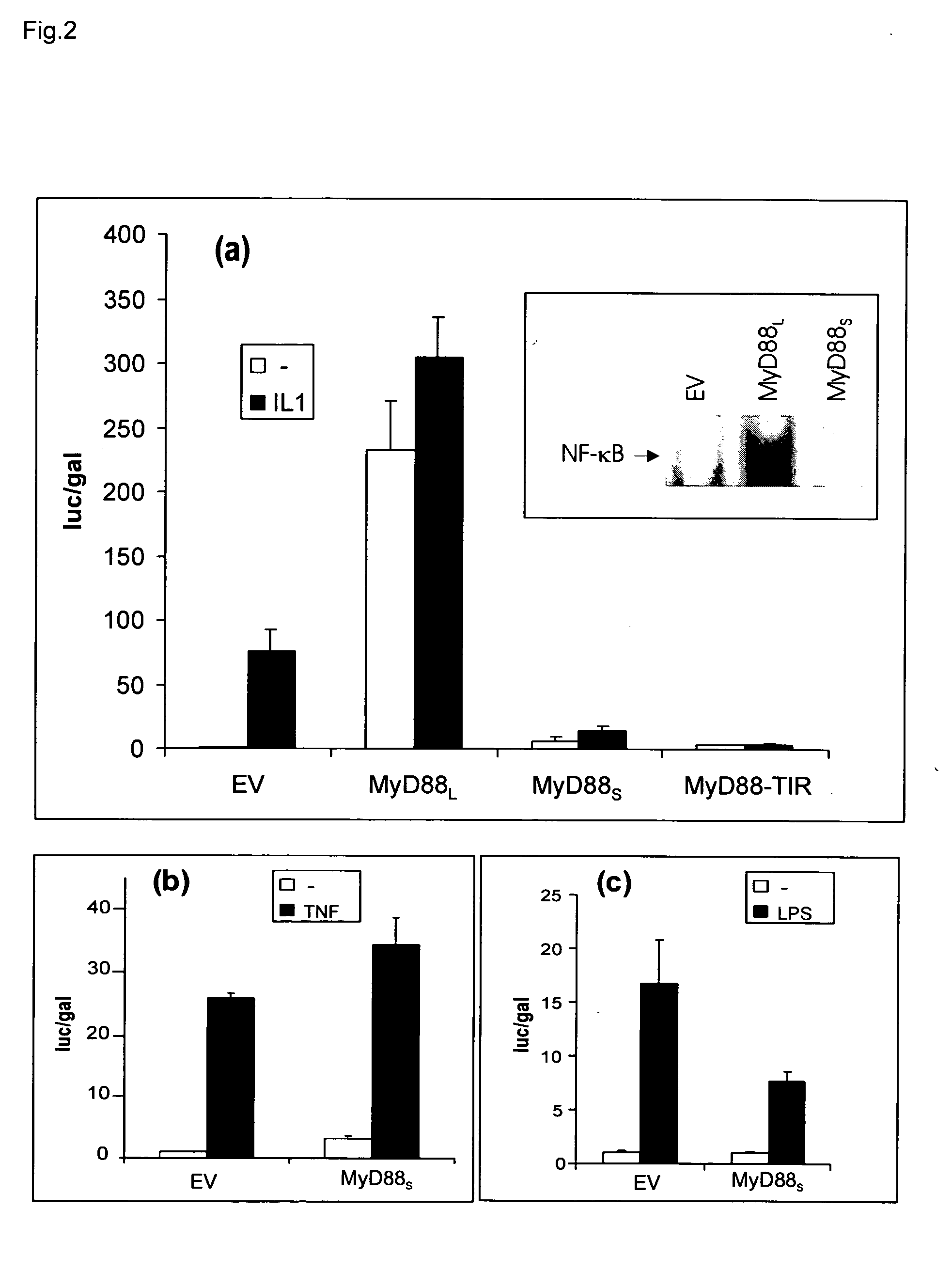
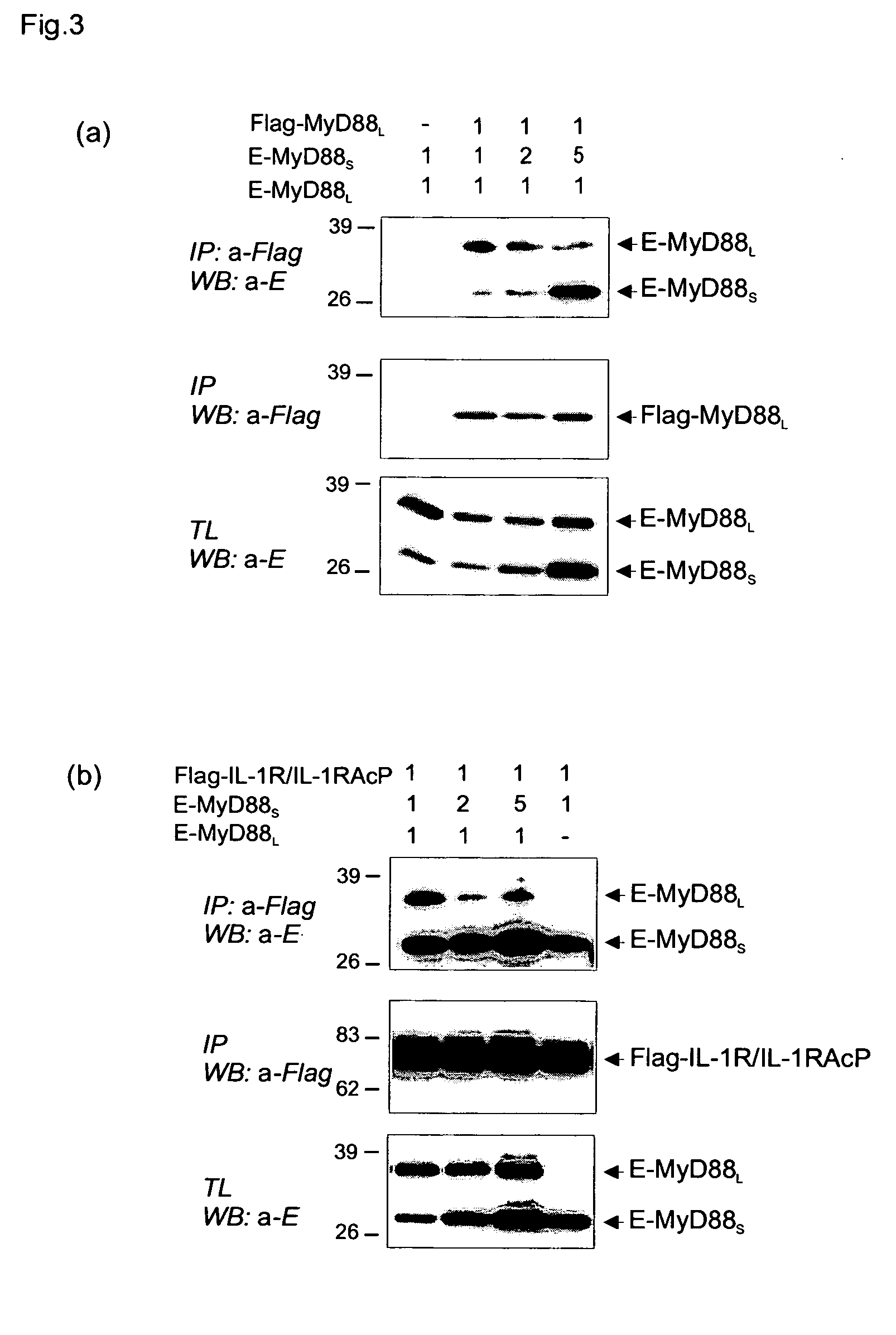
Novel splice variant of MyD88 and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050181476A1Enhance cell viabilityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesBiological activationToxin
The present invention relates to the field of infection and inflammation and, more specifically, to the field of pathogen-induced nuclear factor kappa B activation. More specifically, a novel splice variant of MyD88, (MyD88S), which has been identified encoding a protein that inhibits LPS-induced NF-κB activation. MyD88S is a target to inhibit the phenomenon of endotoxin-tolerance that occurs in sepsis.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
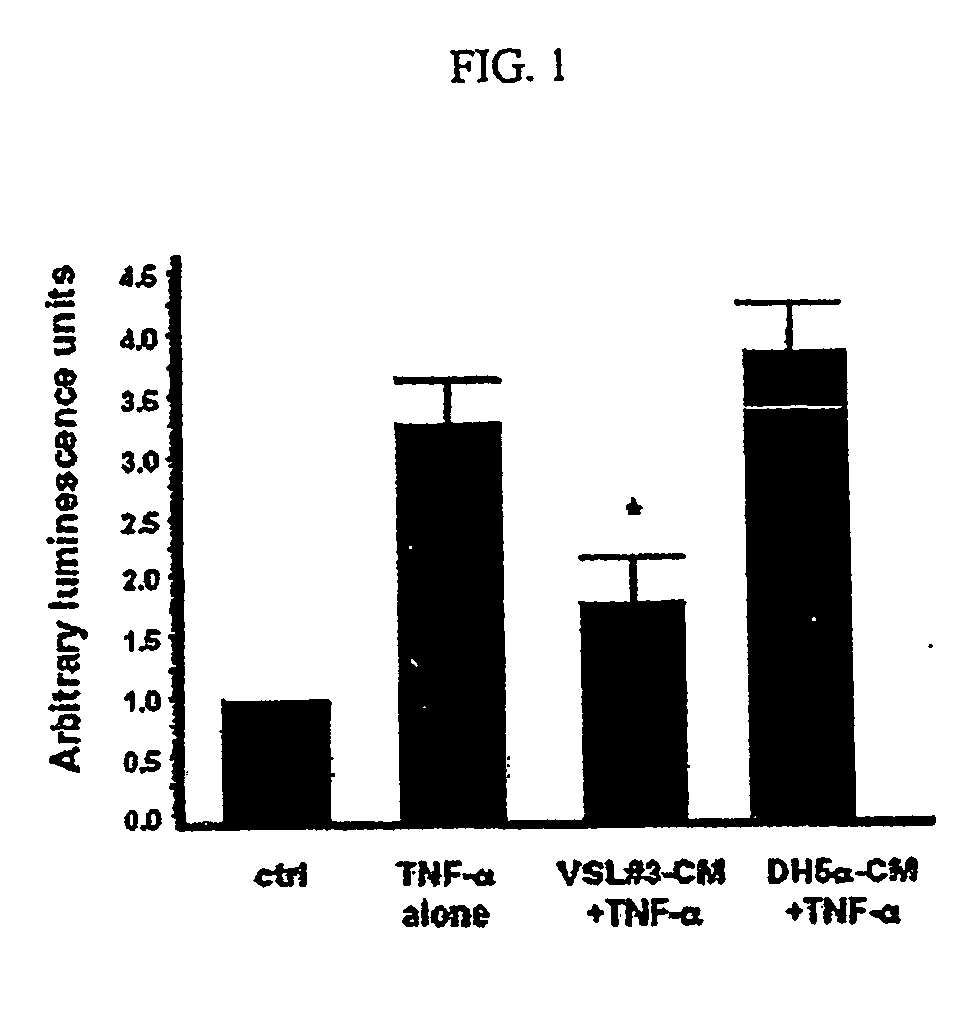
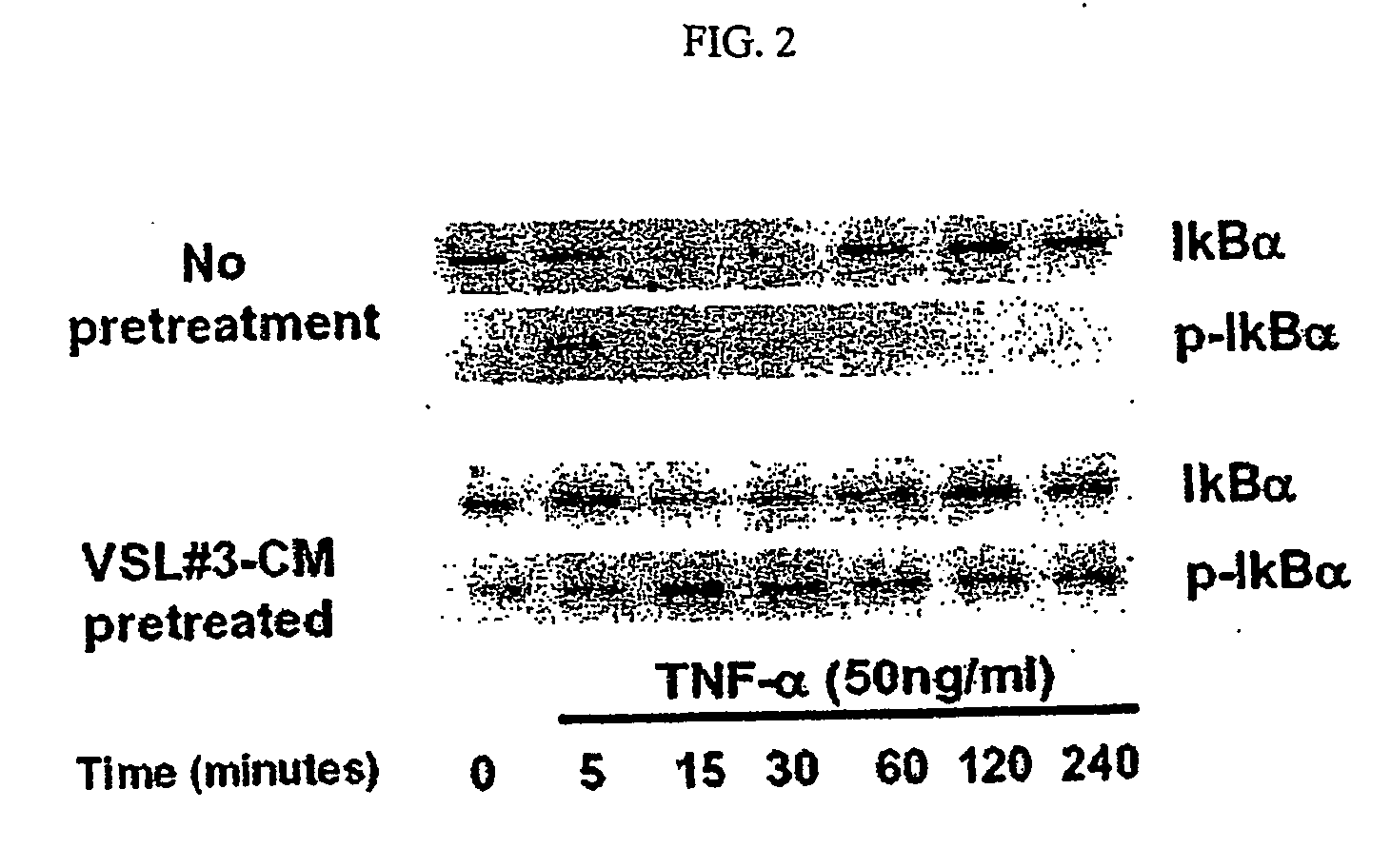
Anti-inflammatory, cytoprotective factor derivable from a probiotic organism
InactiveUS20070128303A1Inhibiting proteasome activityHigh expressionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsInflammatory Bowel DiseasesOrganism
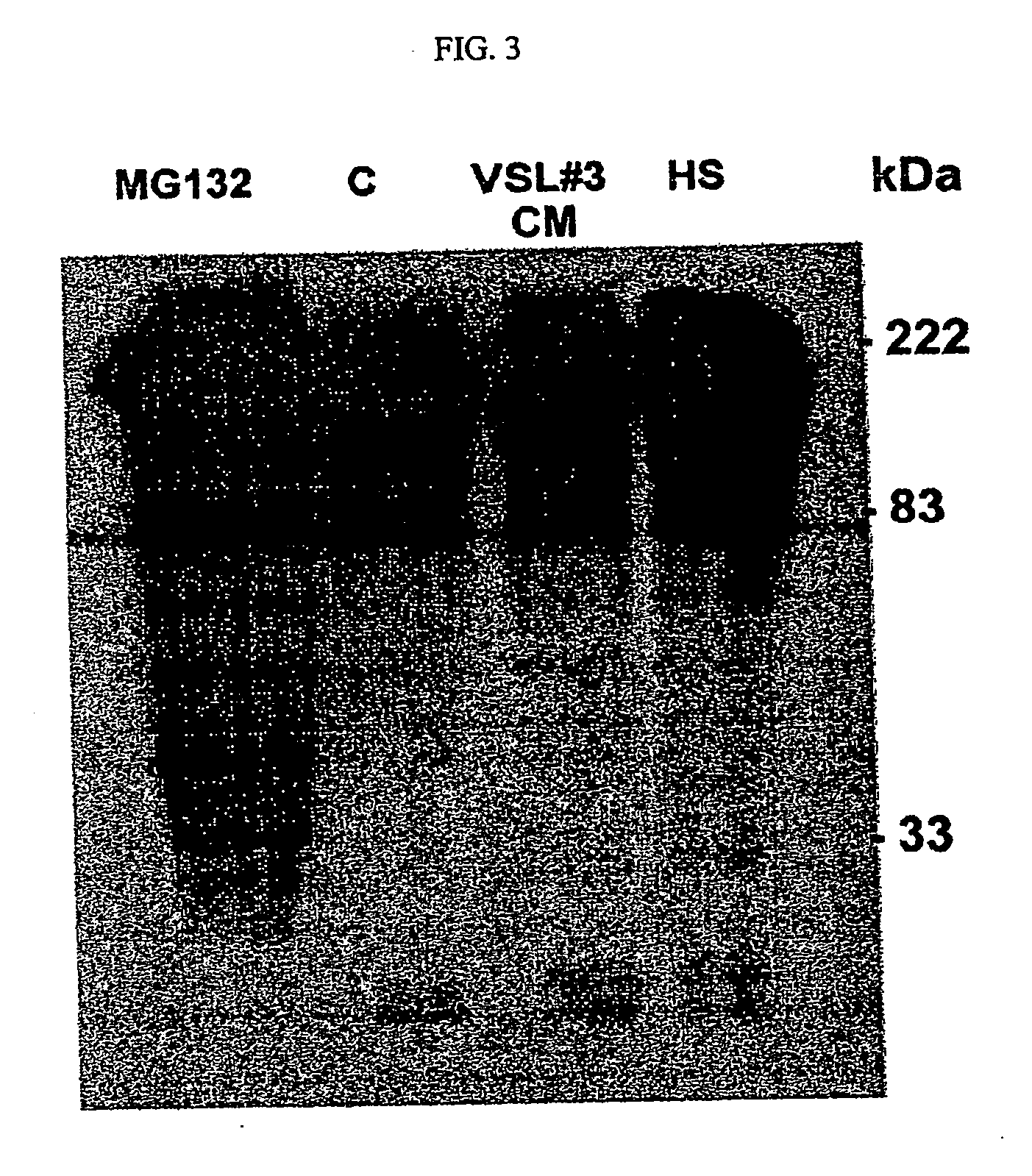
The invention provides an isolated, anti-inflammatory, cytoprotective compound that is soluble in aqueous fluid, is derivable from the conditioned medium of a probiotic culture, such as VSL#3, induces heat shock protein expression, and has shown the capacity to inhibit NF-κB activation. The compound is amenable to formulation in a pharmaceutical composition and to packaging in a kit form with instructions for use in methods according to the invention, which include methods of preventing, treating, or ameliorating a symptom of an inflammatory disorder, such as an inflammatory epithelial disease, e.g., inflammatory bowel disease, characterized by inflammation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
NF-kappaB activating gene
Provided are proteins having NF-κB activity, which are used for diagnosing, treating or preventing diseases associated with the excessive activation or inhibition of NF-κB. Using plasmid pNFκB-Luc, cDNA encoding a protein capable of activating NF-κB has been cloned from a cDNA library constructed from human lung fibroblasts, and the DNA sequence and the deduced amino acid sequence determined. The protein, the DNA encoding the protein, a recombinant vector containing the DNA, and a transformant containing the recombinant vector are useful for screening a substance inhibiting or promoting NF-κB activation.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI PHARMA
Inhibitors of transcription factor NF-kappaB
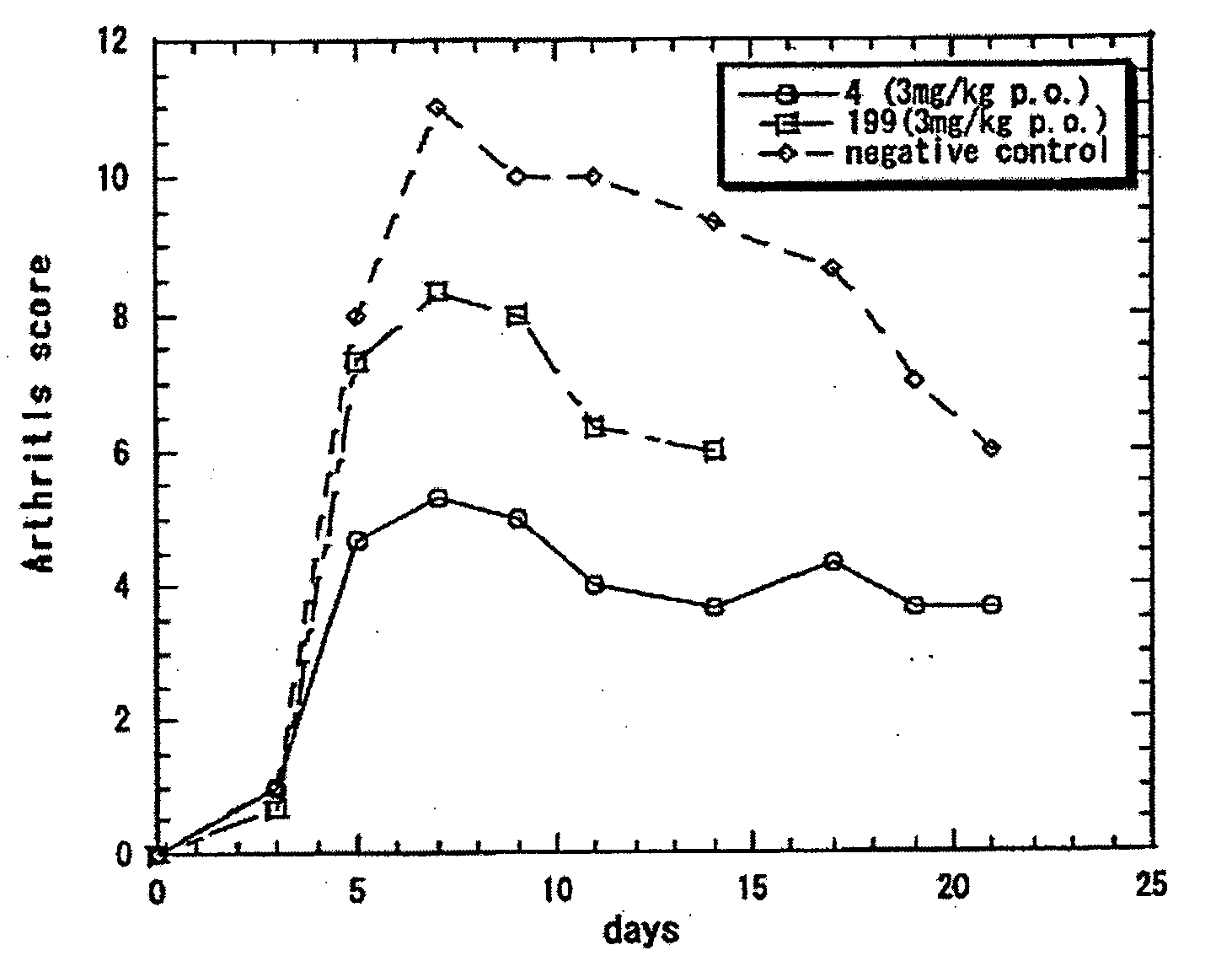
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions of salicylanilide inhibitors of transcription factor NF-κB, and methods for treating diseases in which activation of NF-κB is implicated. More specifically, the present invention provides methods of treatment of a variety of diseases associated with NF-κB activation including inflammatory disorders; particularly rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and asthma; dermatosis, including psoriasis and atopic dermatitis; autoimmune diseases; tissue and organ rejection; Alzheimer's disease; stroke; atherosclerosis; restenosis; cancer, including Hodgkin's disease; certain viral infections, including AIDS; osteoarthritis; osteoporosis; and Ataxia Telangiestasia by administering to a patient in need thereof a compound of the present invention.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
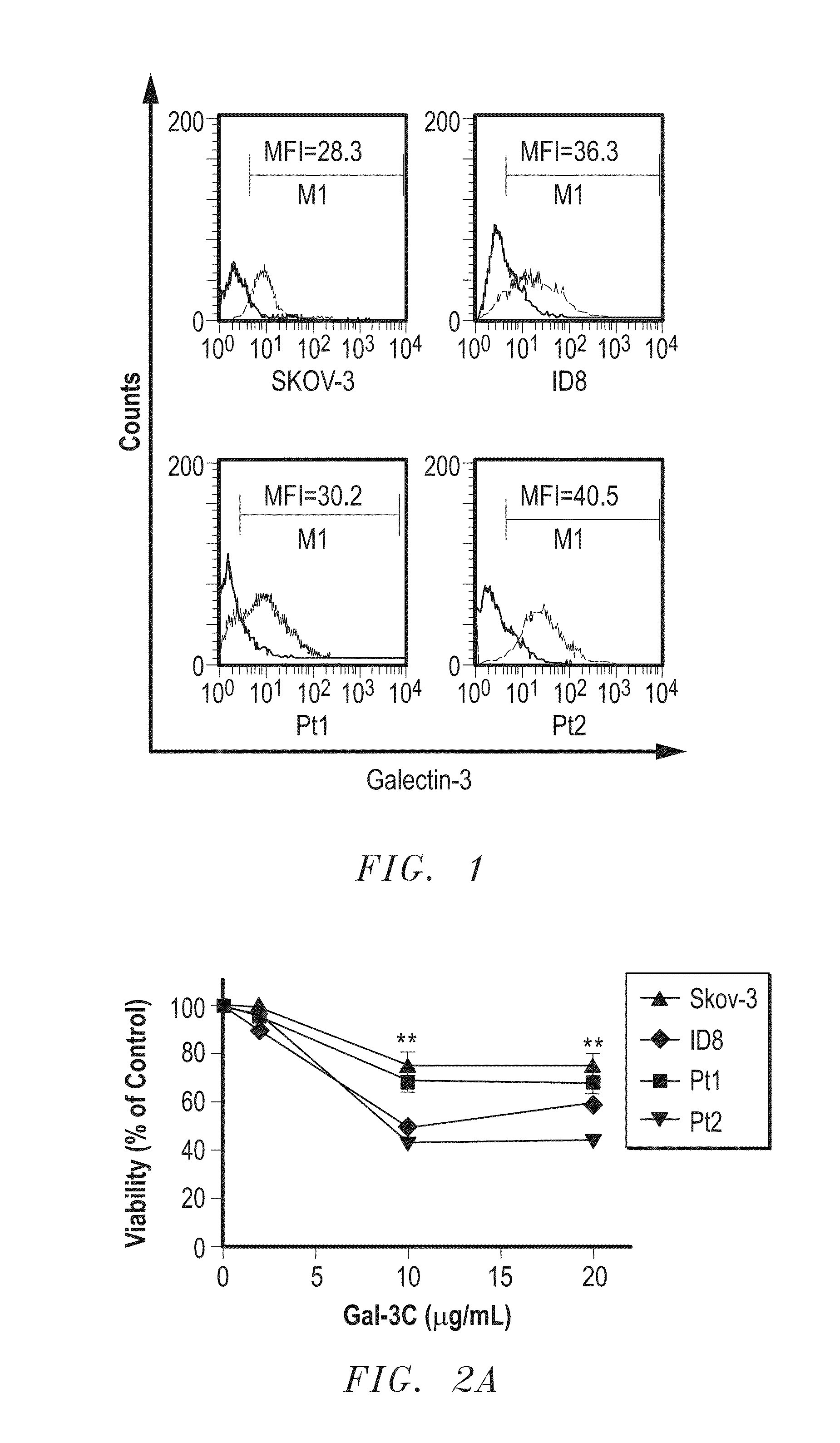
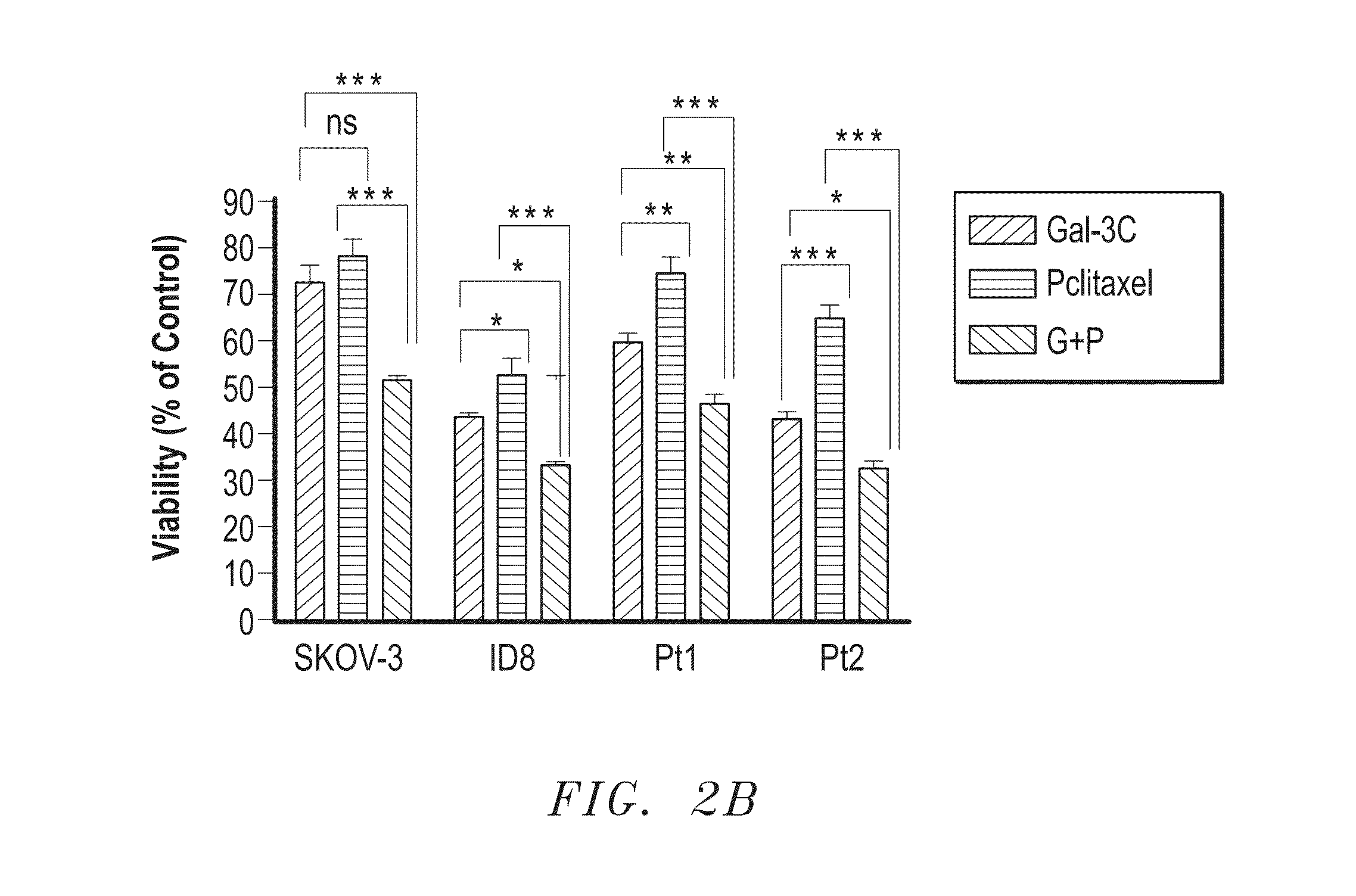
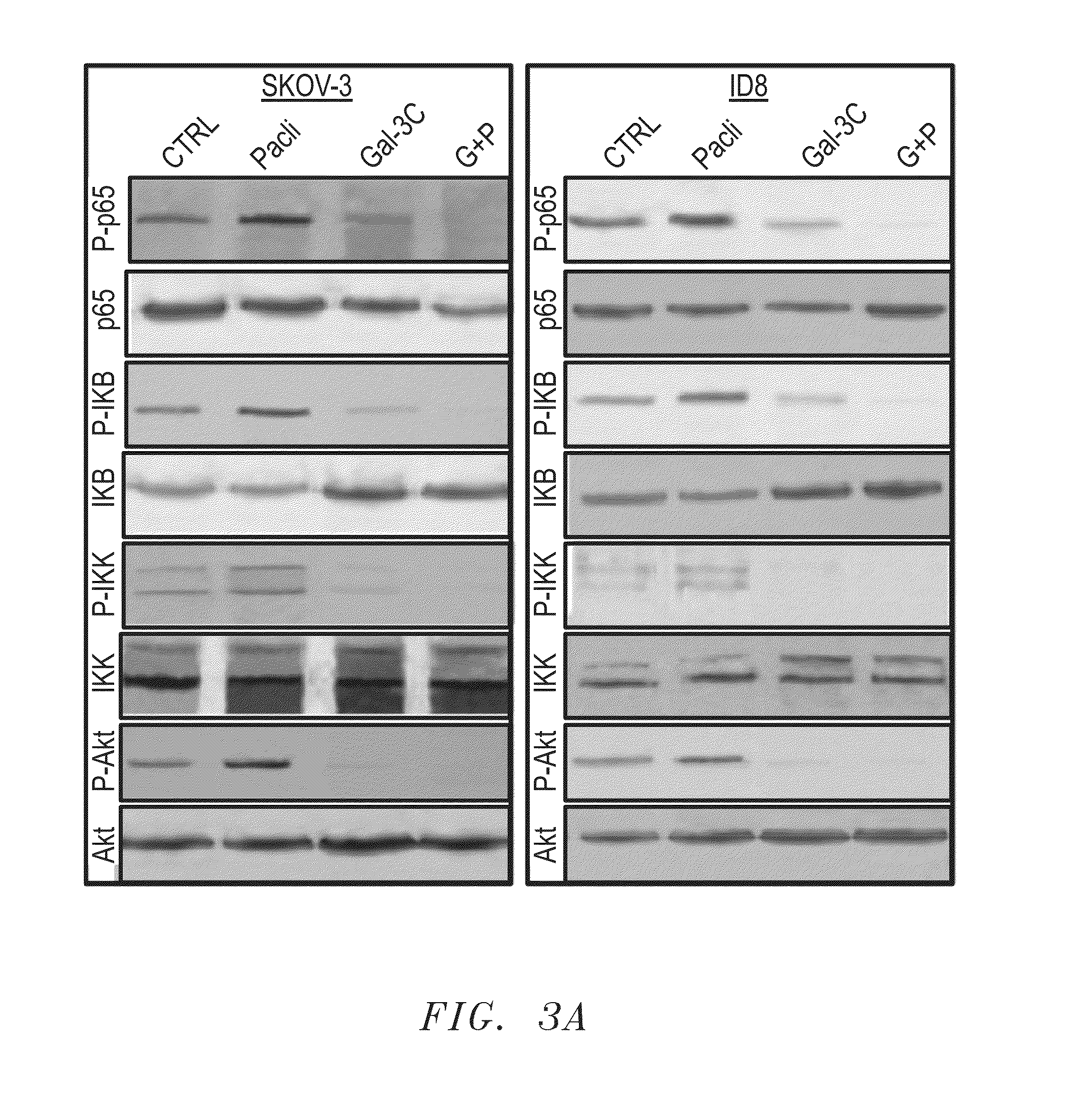
Galectin-3 to Treat Ovarian Cancer
InactiveUS20150157691A1Reduce eliminateReduce or eliminate the ovarian cancerCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsGynecologyMotility
The present invention includes a method for the treatment of an advanced ovarian cancer, comprising: identifying a patient with advanced ovarian cancer; and administering to the patient an effective amount of truncated, dominant negative form of Galectin-3 sufficient to reduce the advanced ovarian cancer. In certain aspects, the truncated, dominant negative form of Galectin-3 is provided in an amount sufficient to reduce at least one of growth, motility, invasion, angiogenesis, or prevents Akt / NF-κB activation of the ovarian cancer.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST
Cancer metastasis inhibitor
InactiveUS20180222986A1Degree of reductionOnset of tumors was decreasedImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthHematopoietic cell
Owner:MAEDA CORPORATION
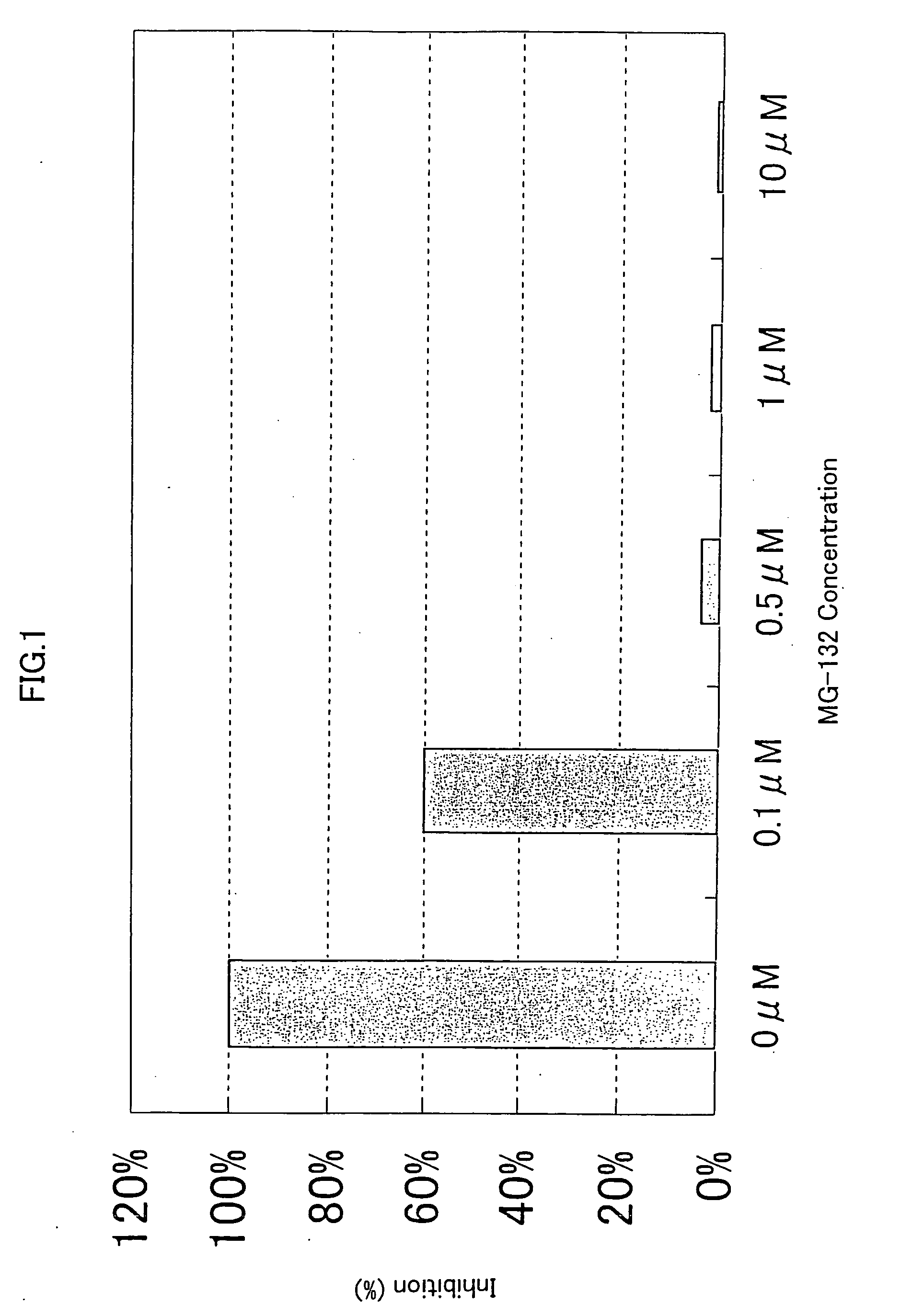
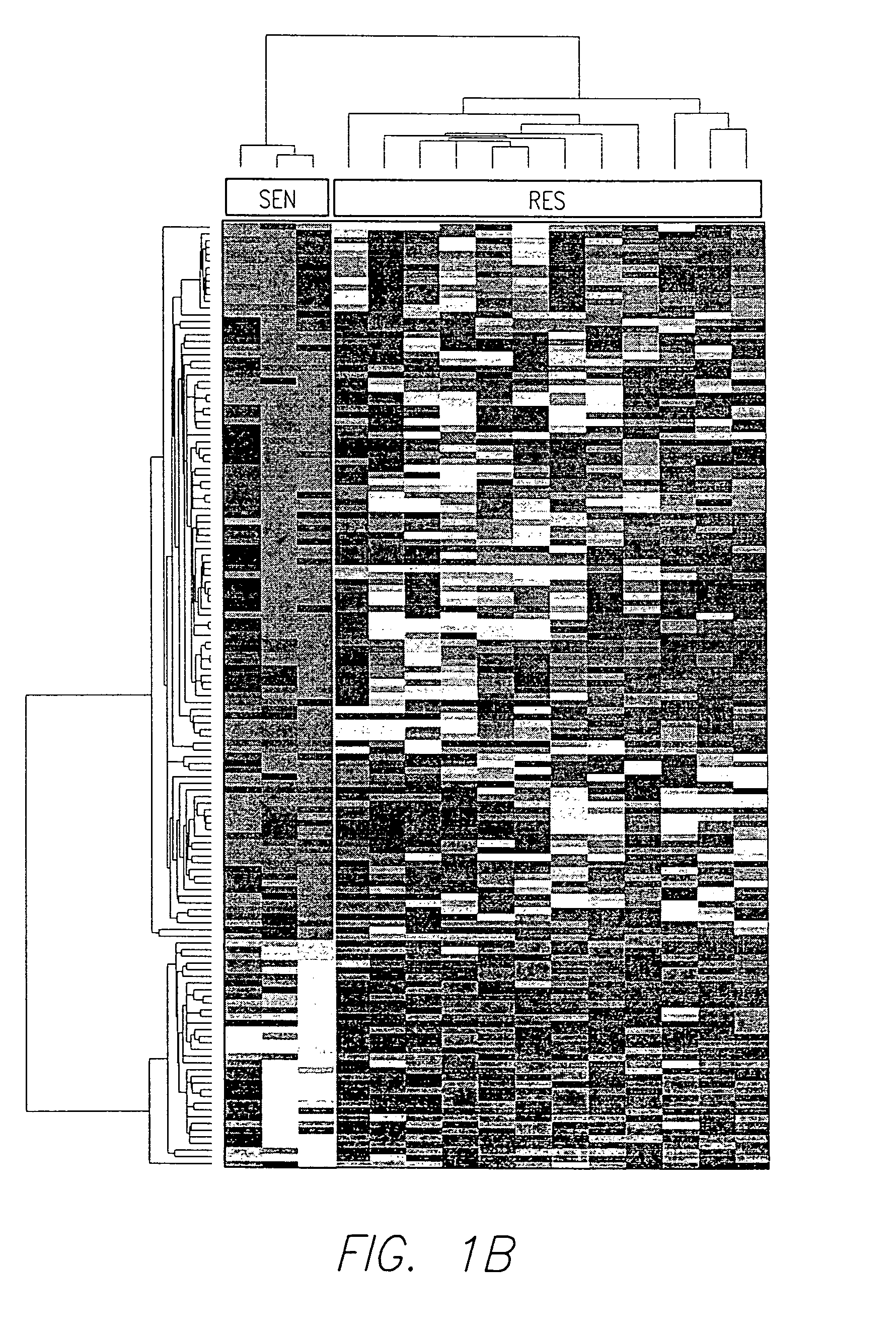
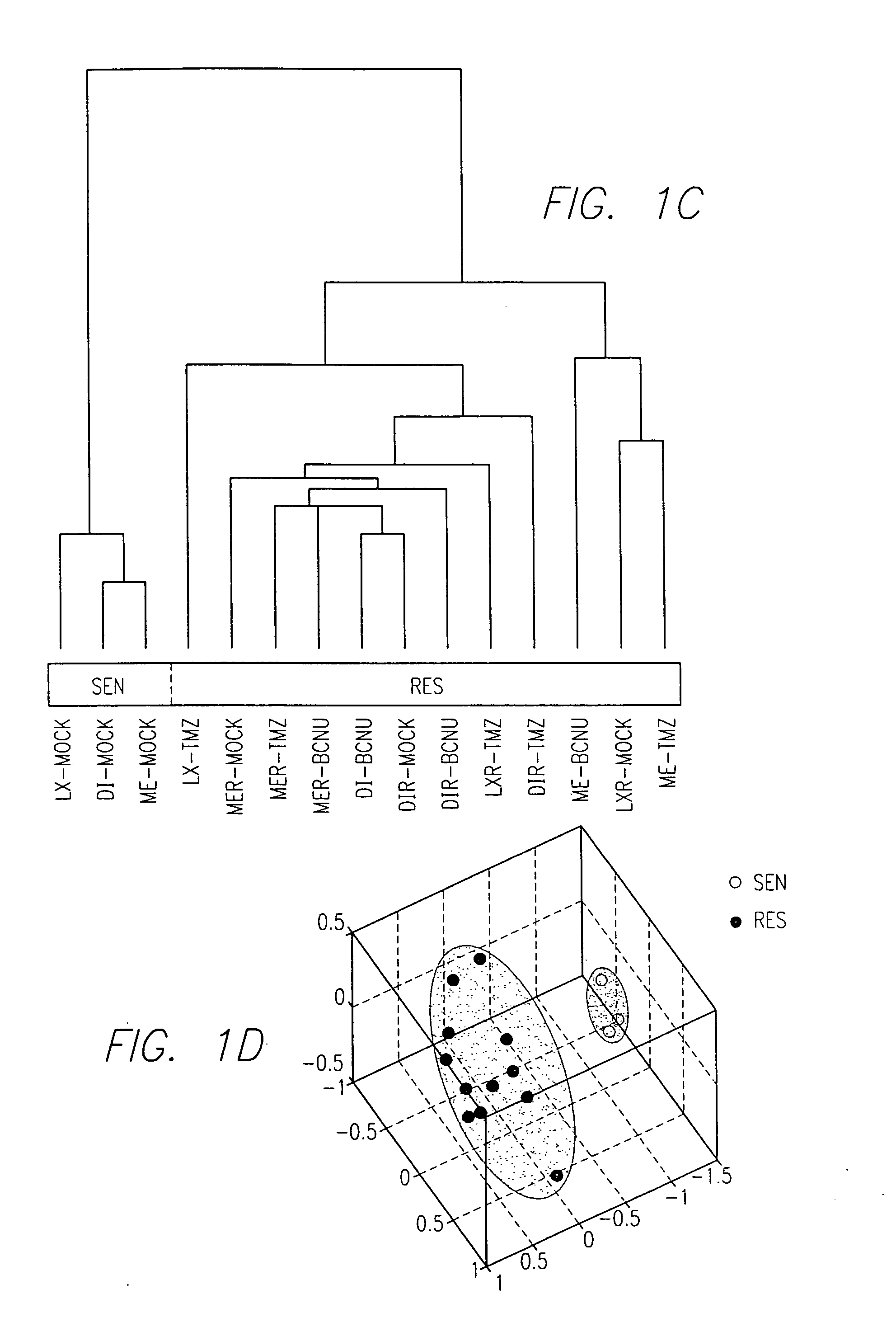
Protein modulators of resistance to alkylating agents
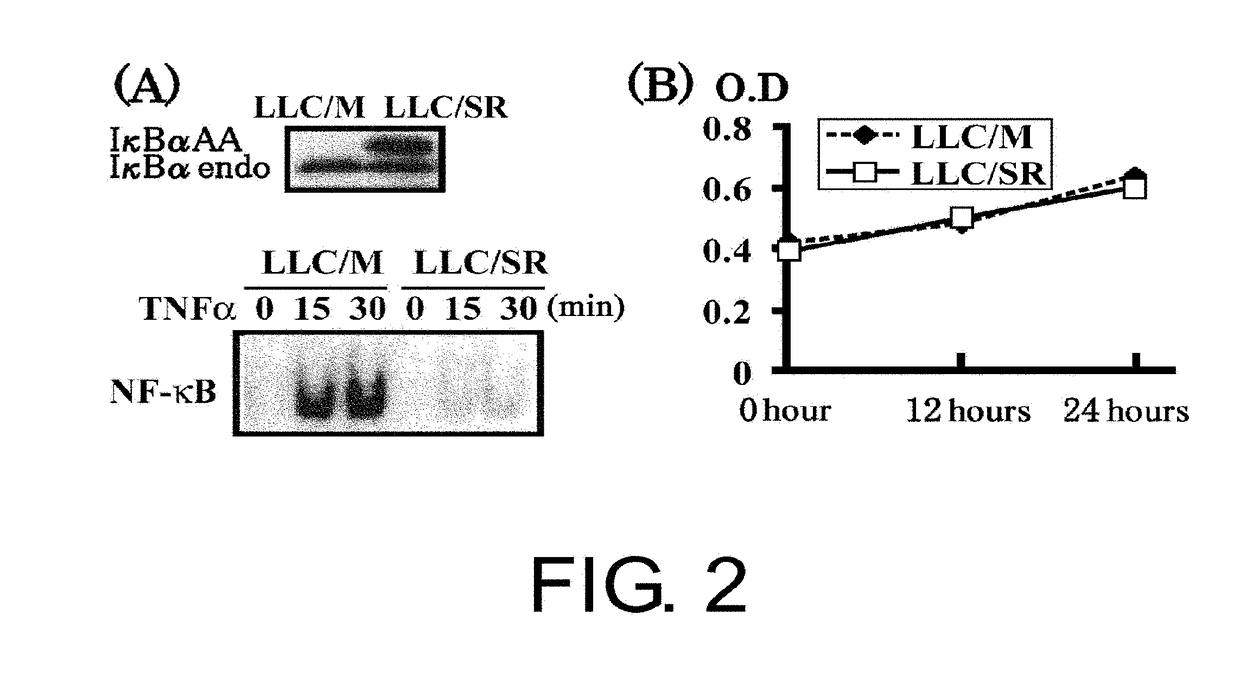
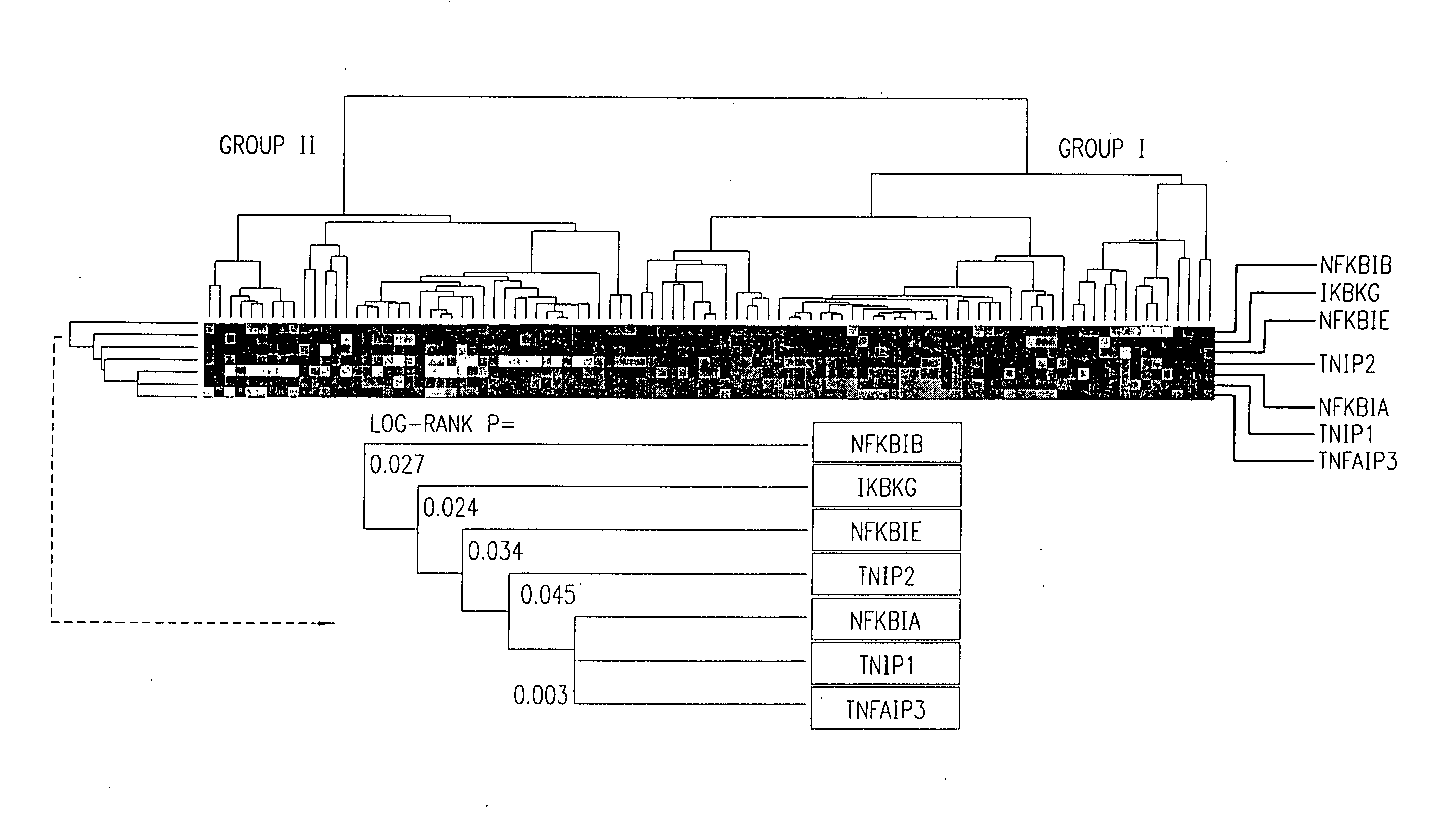
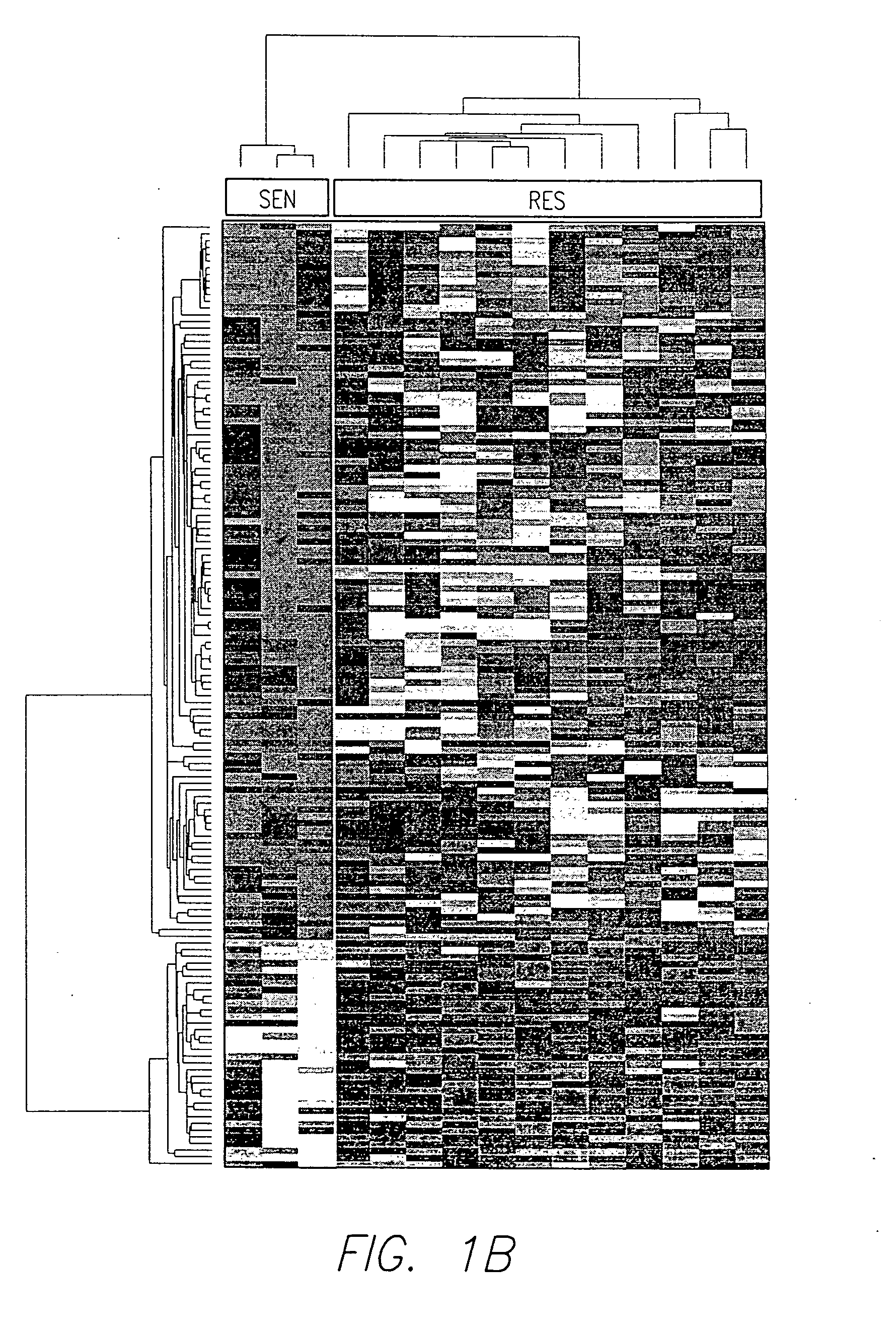
There is disclosed a method for identifying a therapeutically responsive phenotype, as distinguished, e.g. from an alkylating agent resistant phenotype in a cell, which method may be used to evaluate the likelihood of successful outcome of treating a tumor cell with an alkylating agent. The method is directed to the NF-κB activation in response to DNA damage caused by alkylating agents. It comprises the step of measuring a level of expression of a protein, which participates in the NF-κB pathway. Preferably it comprises measuring the expression of TNFAIP3 in the cell, wherein a resistant phenotype has less expression of TNFAIP3 than a sensitive phenotype. Another particularly significant gene, which predicts survival, is NFKBIA. Other genes whose altered expression level is associated with resistance or prognosis are TNIP1, TNIP2, RIP, NFKBIB, Beta4GalNAc-T4, NFKBIE, C8orf4, LIF, CD44, FBXO32, and SDC1, and these are also measured in certain embodiments.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
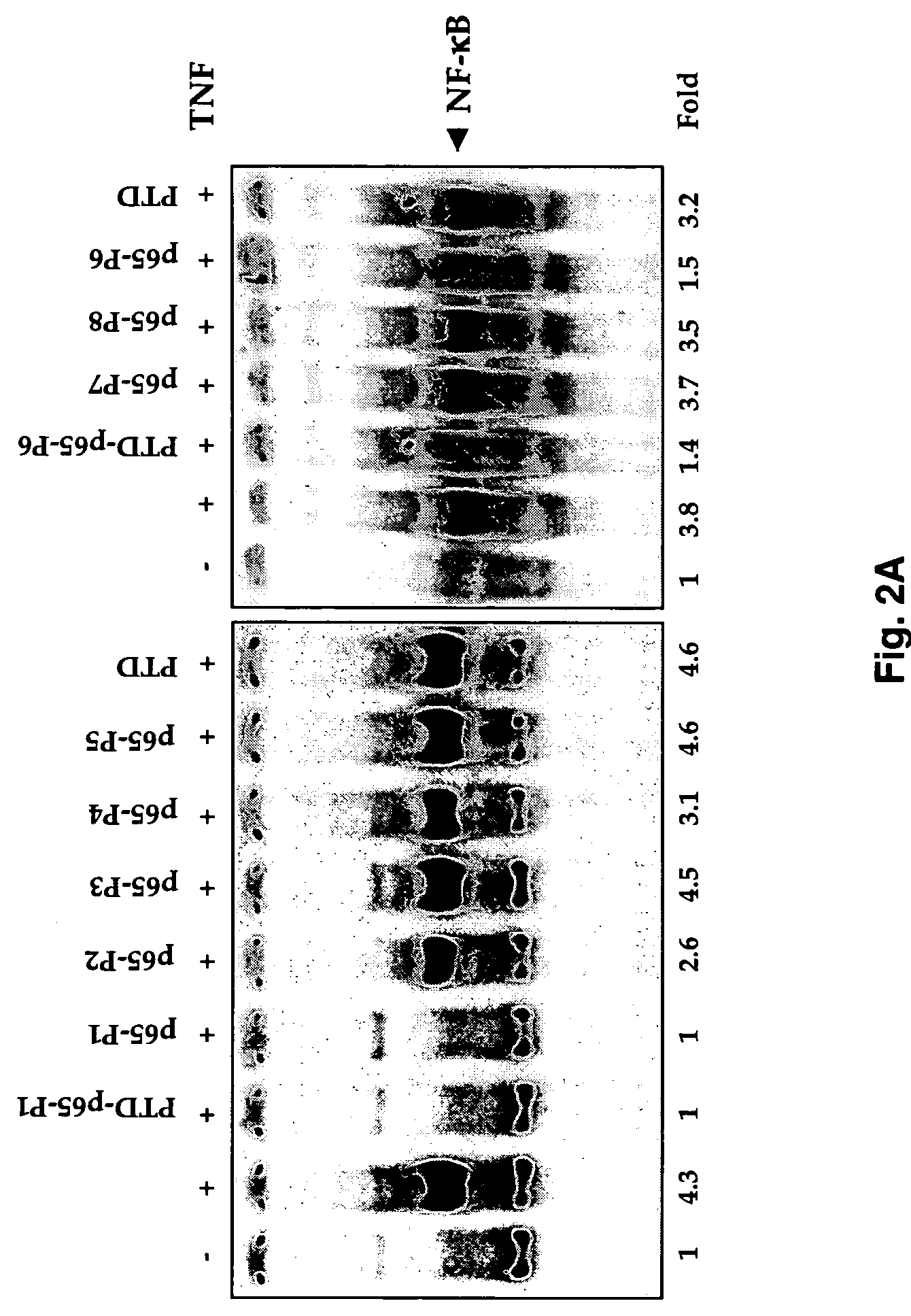
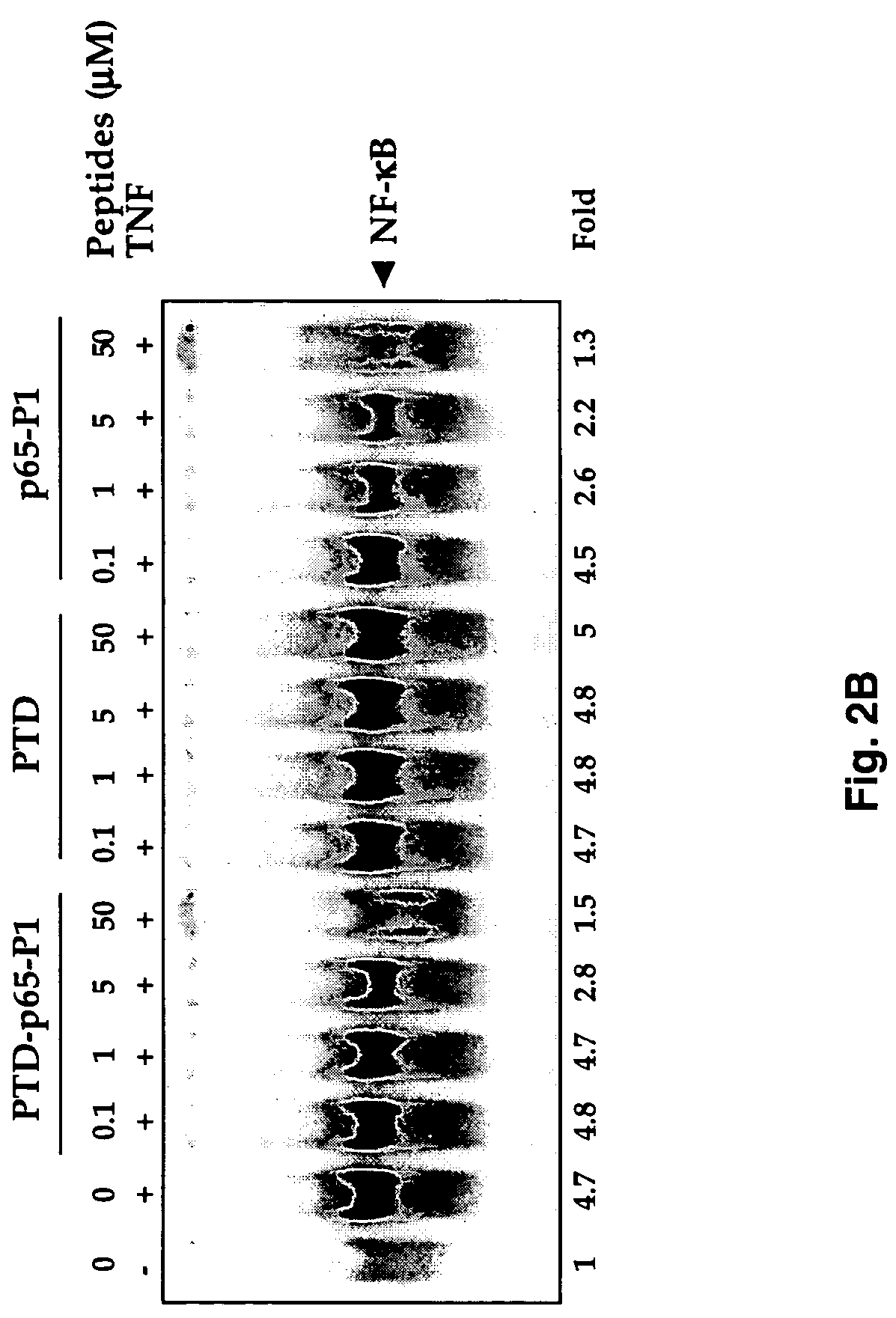
Selective inhibitors of nuclear factor-kappaB activation and uses thereof
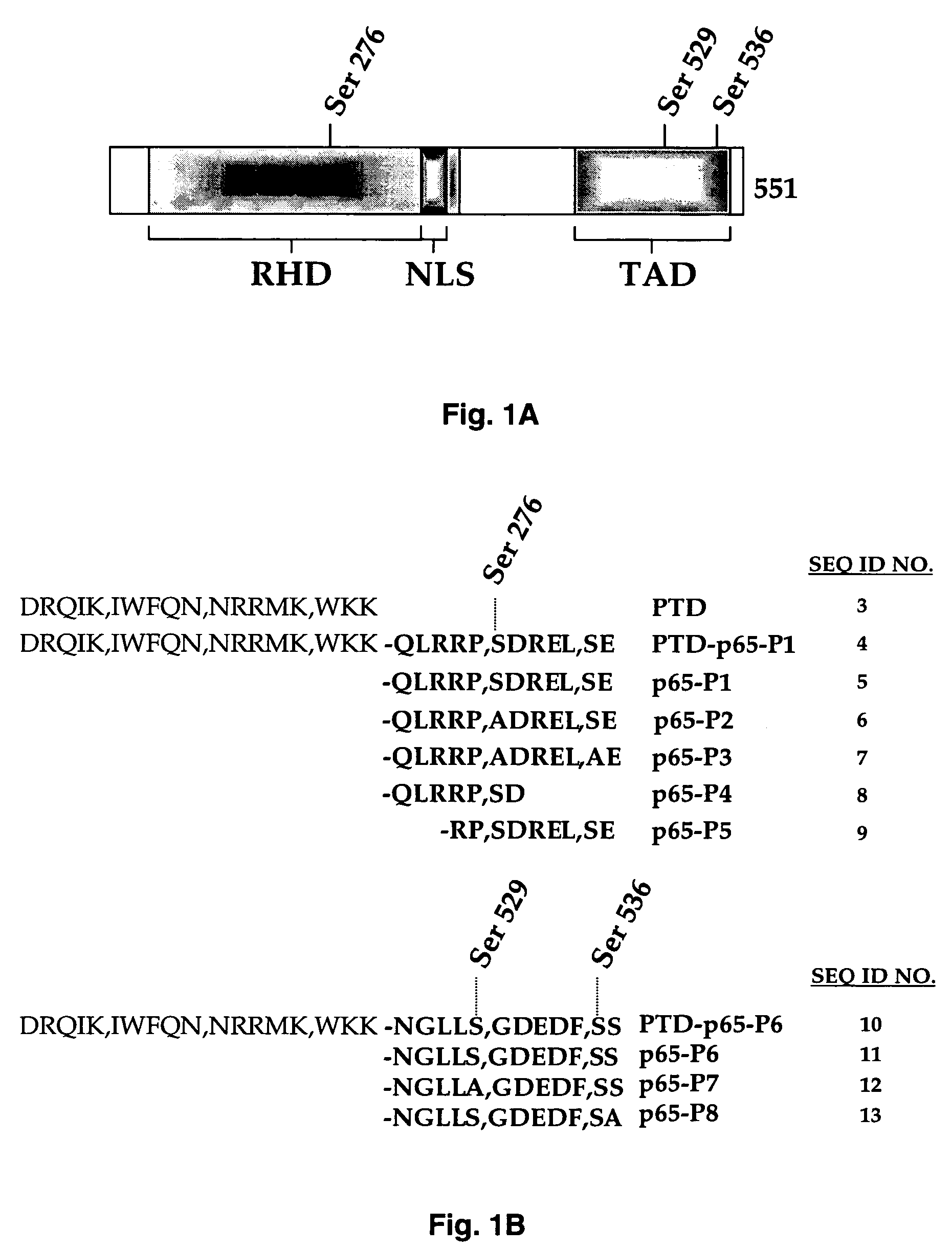
The present invention provides cell permeable NF-κB inhibitors consist of a polypeptide derived from the p65 subunit of NF-κB and a protein transduction domain derived from antennapedia third helix sequence. The inhibitor suppressed NF-κB activation induced by TNF, LPS, IL-1, okadaic acid, PMA, H2O2 and cigarette smoke condensate. NF-κB-regulated reporter gene expression induced by TNF, TNFR1, TRADD, TRAF2, NIK, IKK and p65 was suppressed by the inhibitor. The inhibitor enhanced TNF- and chemotherapeutic agent-induced apoptosis. Overall these results demonstrate a NF-κB inhibitor that can selectively inhibit NF-κB activation induced by various inflammatory stimuli, downregulate NF-κB mediated gene expression and upregulate apoptosis.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
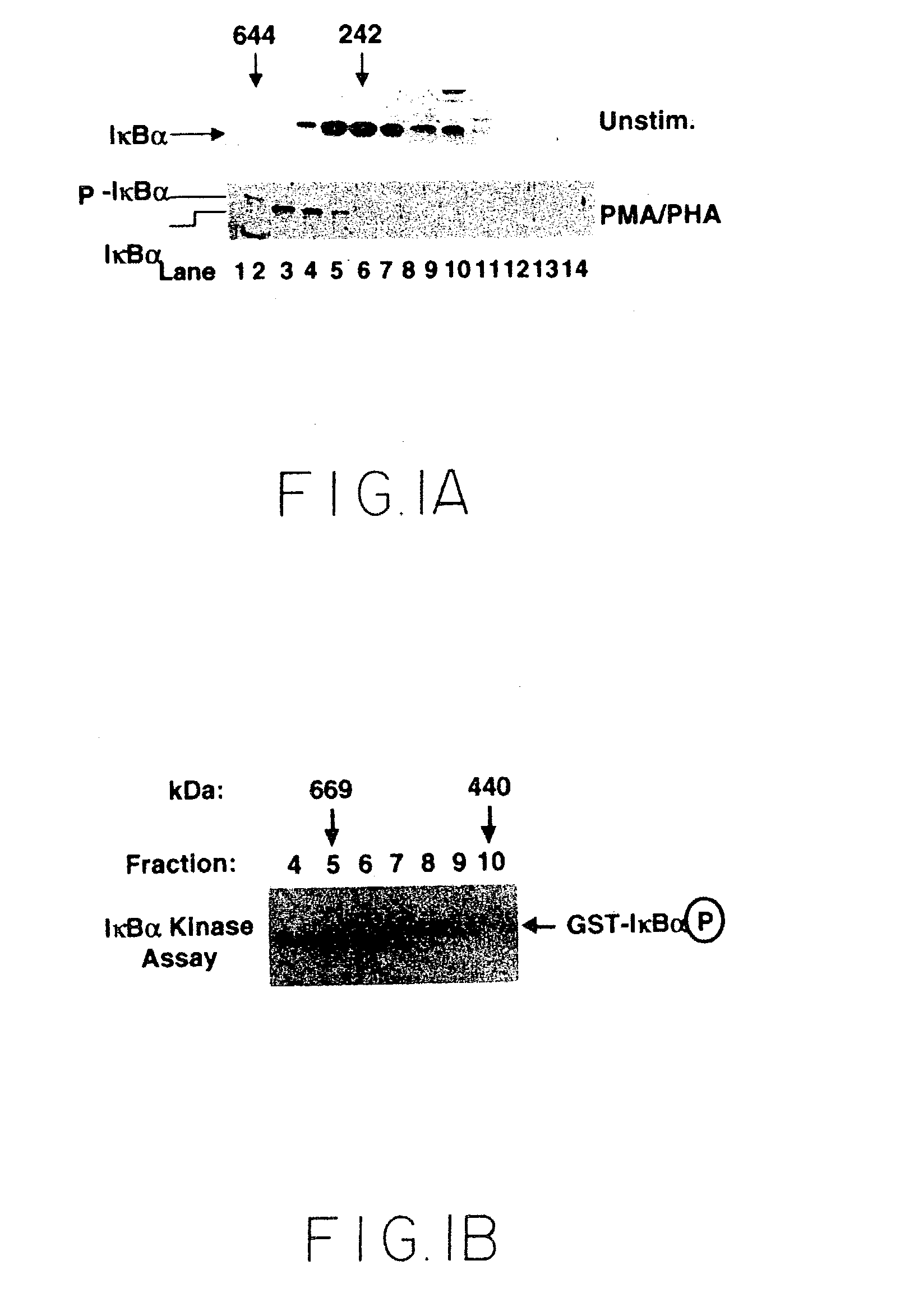
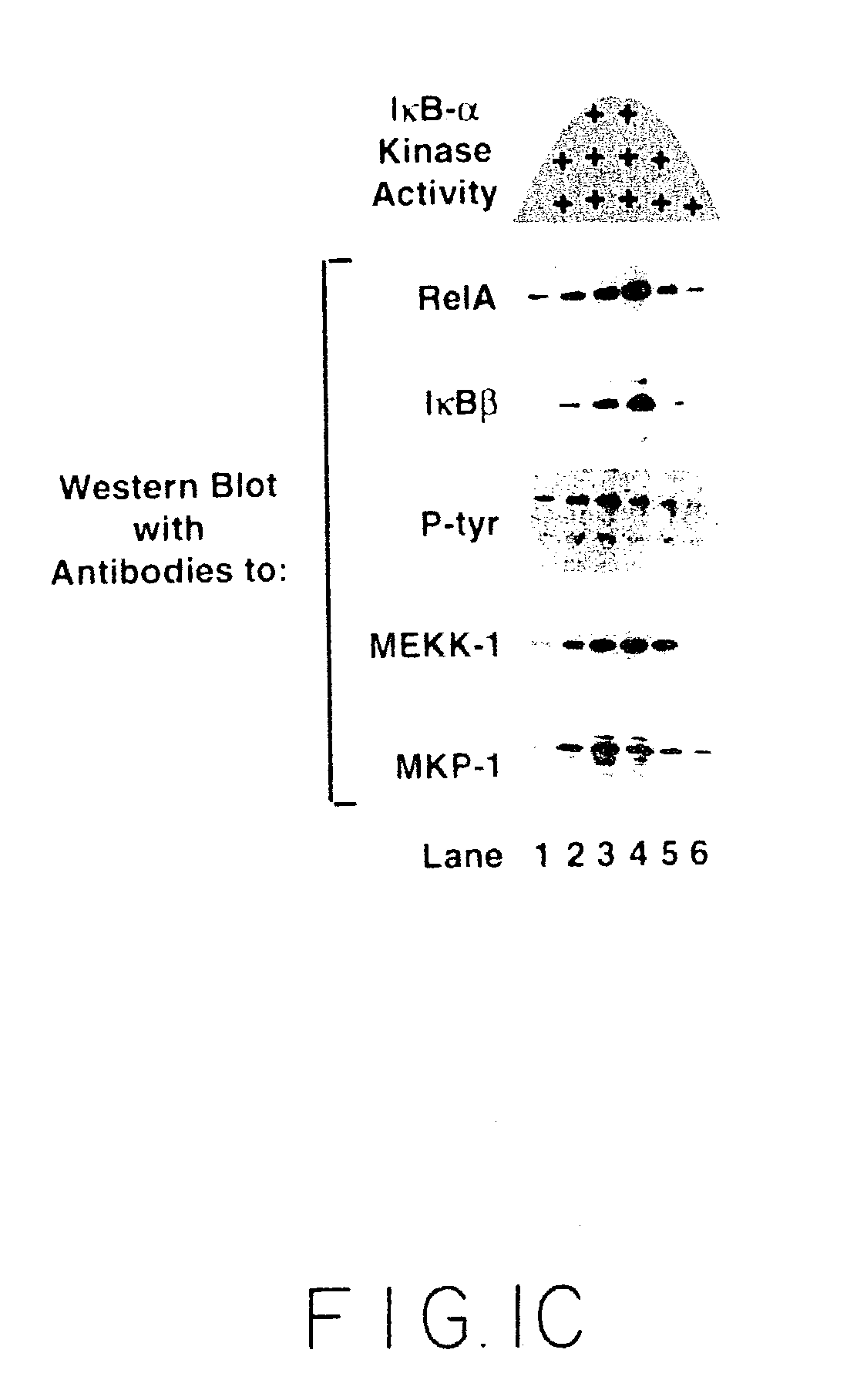
Stimulus-inducible protein kinase complex and methods of use therefor
Compositions and methods are provided for treating NF-κB-related conditions. In particular, the invention provides a stimulus-inducible IKK signalsome, and components and variants thereof. An IKK signalsome or component thereof may be used, for example, to identify antibodies and other modulating agents that inhibit or activate signal transduction via the NF-κB cascade. IKK signalsome, components thereof and / or modulating agents may also be used for the treatment of diseases associated with NF-κB activation.
Owner:SIGNAL PHARMA LLC
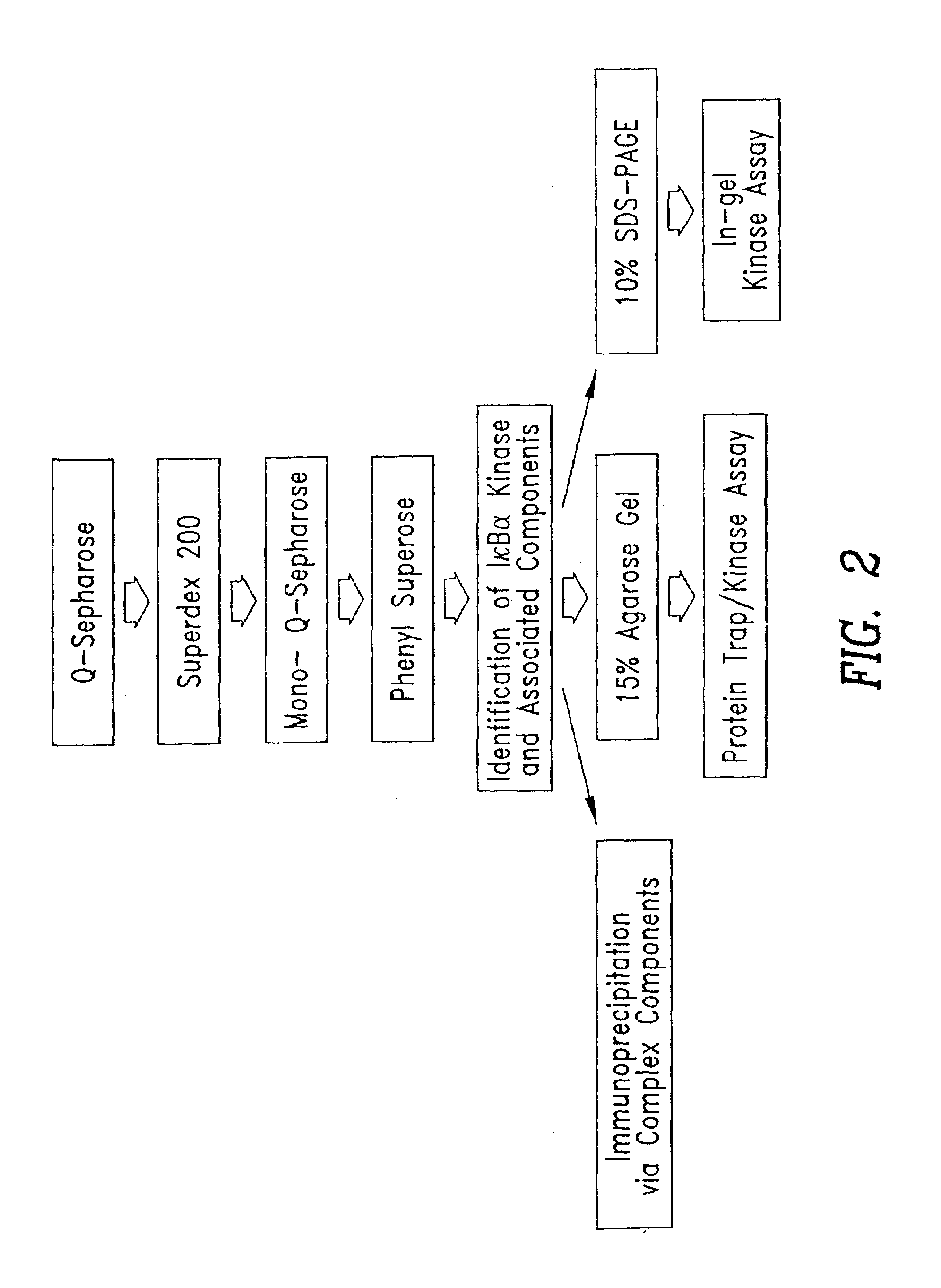
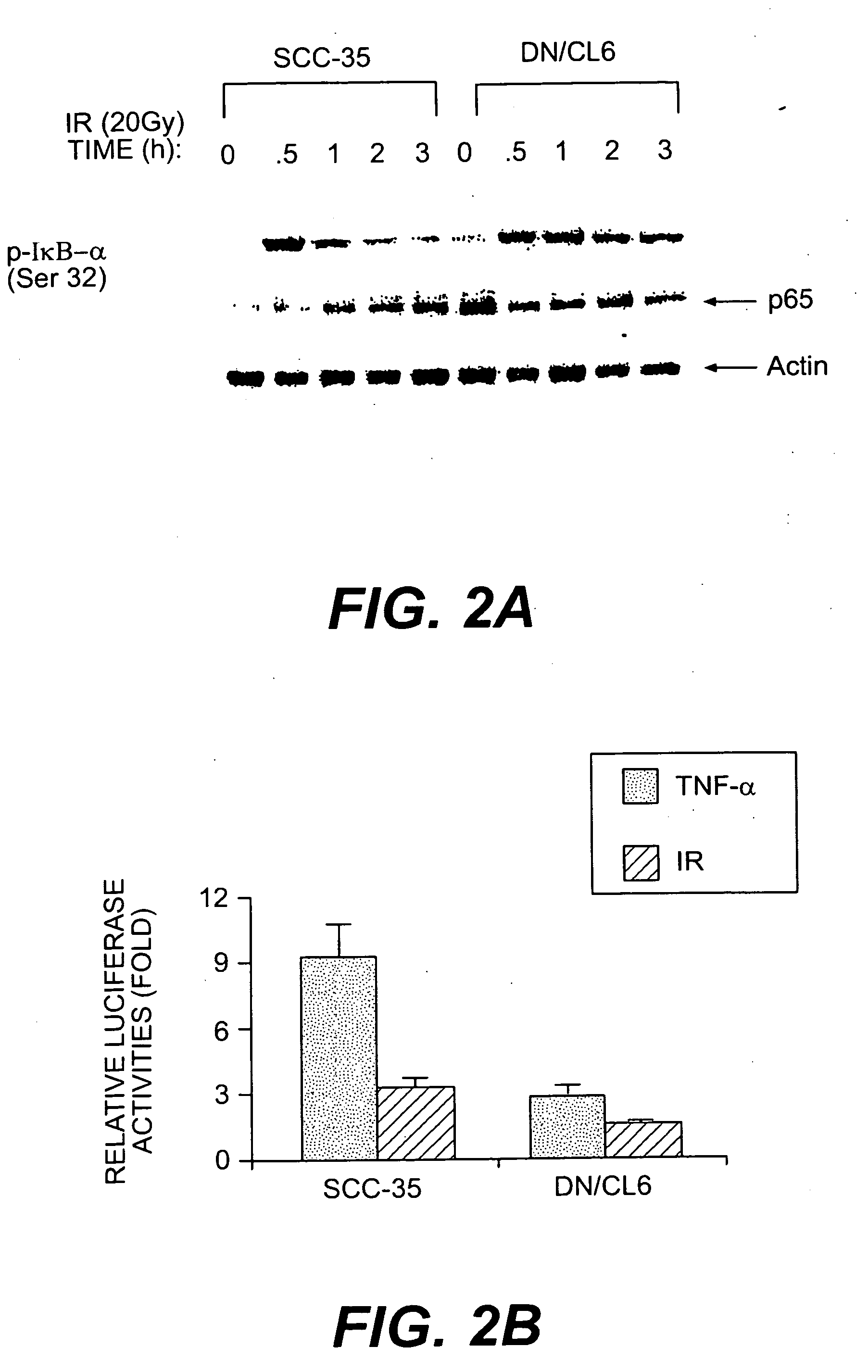
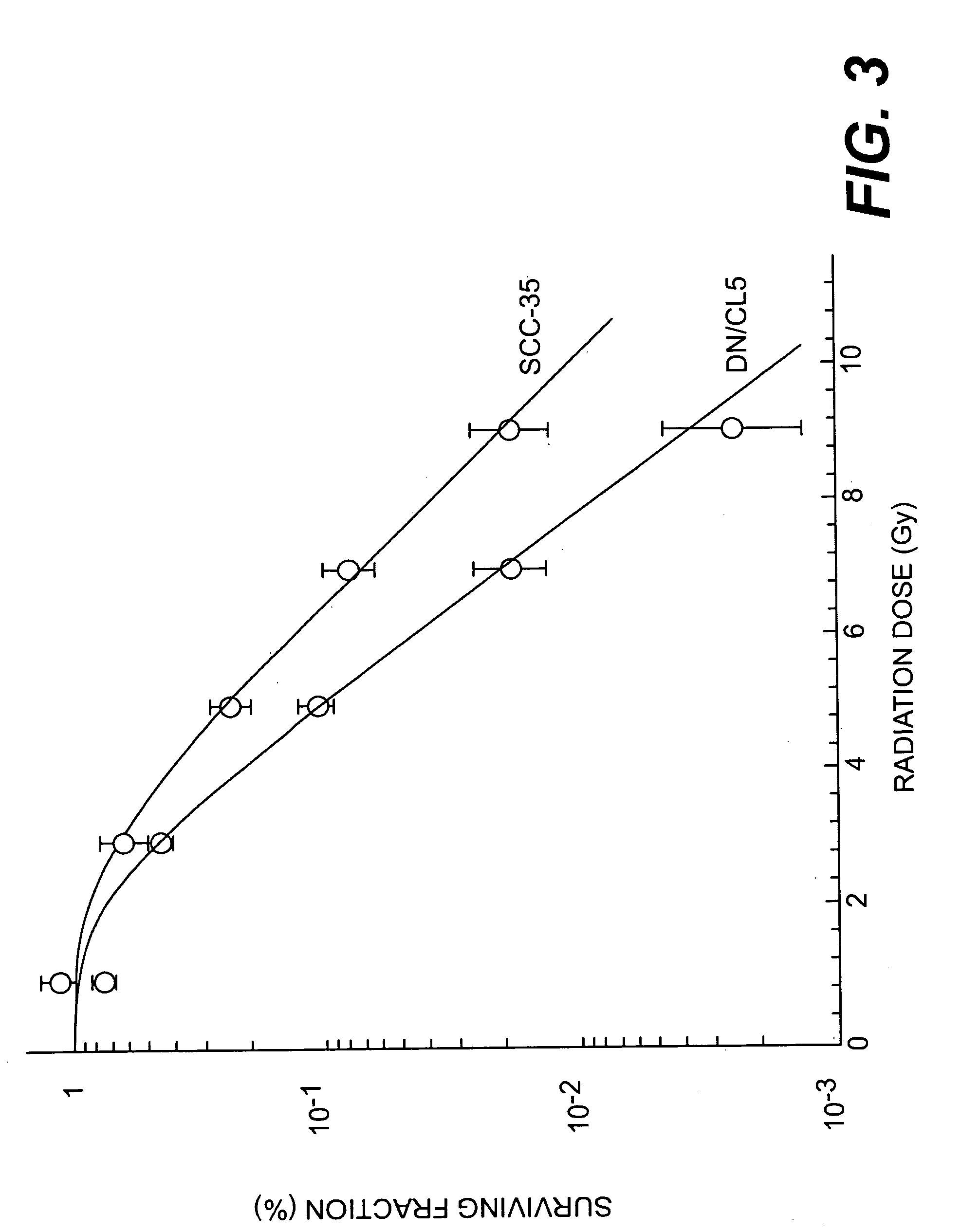
The p65 subunit of nf-kb for the radiosensitization of cells
InactiveUS20050287158A1Reduce activationReduced gene expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticAbnormal tissue growthRadiation induced apoptosis
The transcription factor NF-κB is activated in response to various stimuli including ionizing radiation. Disruption of NFκB activation by mutant forms of the NF-κB inhibitor IκB-α or by proteasome inhibitors enhances both sensitivity to radiation and radiation-induced apoptasis. The present invention shows that expression of a dominant negative fragment of human p65 (p65DN) leads to down-regulation of both endogenous p65 protein and its mRNA. The dominant negative protein also inhibits radiation-induced NF-κB activation by preventing the proteolysis of IκB-α, resulting in enhancement of cellular radiosensitivity and radiation-induced apoptosis. The region of p65 in the dominant negative fragment is thus a molecular target for disruption of NF-κB activation and sensitization of tumors to radiotherapy.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
NF-kappa B activating gene
Provided are proteins having NF-κB activity, which are used for diagnosing, treating or preventing diseases associated with the excessive activation or inhibition of NF-κB. Using plasmid pNFκB-Luc, cDNA encoding a protein capable of activating NF-κB has been cloned from a cDNA library constructed from human lung fibroblasts, and the DNA sequence and the deduced amino acid sequence determined. The protein, the DNA encoding the protein, a recombinant vector containing the DNA, and a transforrnant containing the recombinant vector are useful for screening a substance inhibiting or promoting NF-κB activation.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI PHARMA
Use of nibp polypeptides
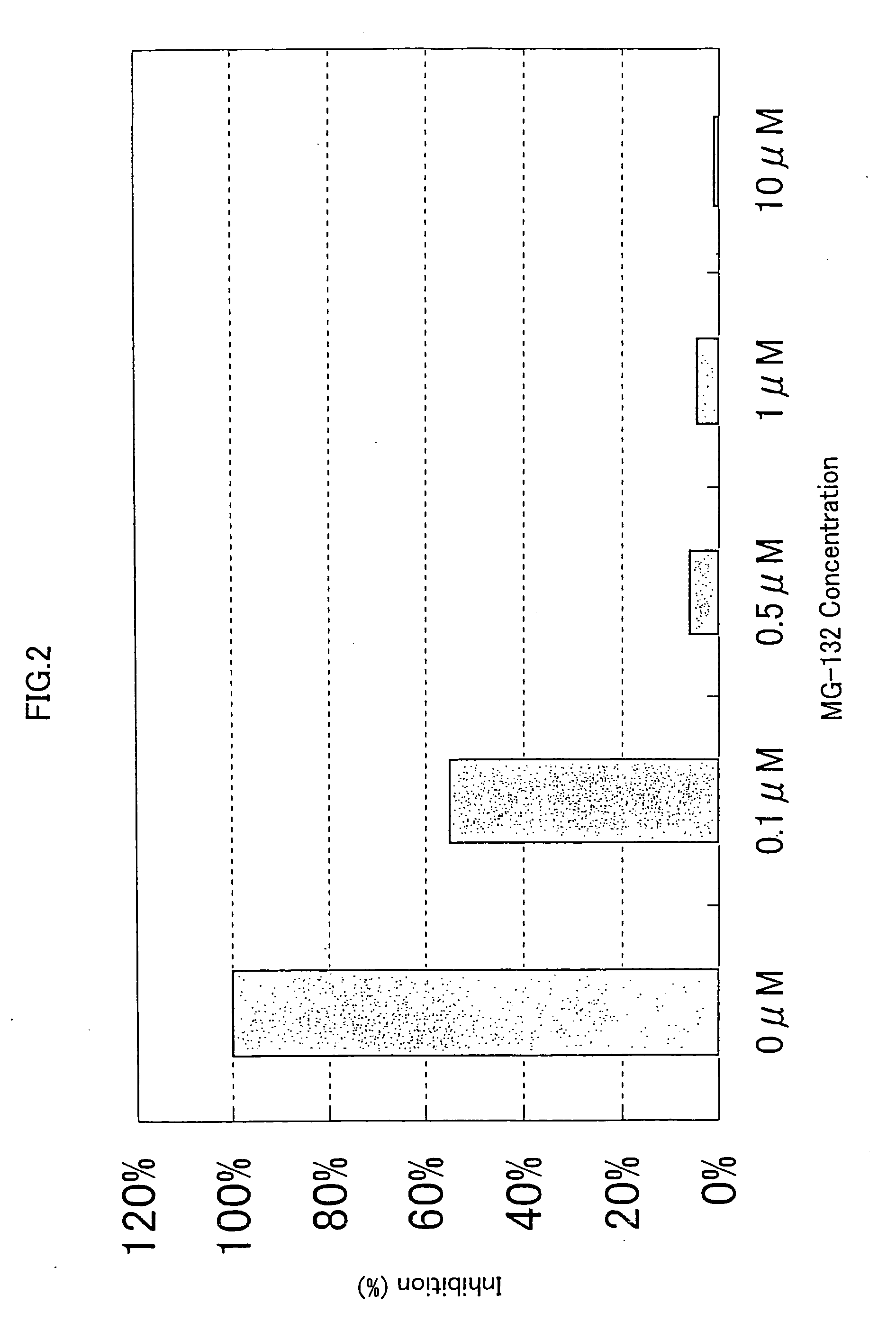
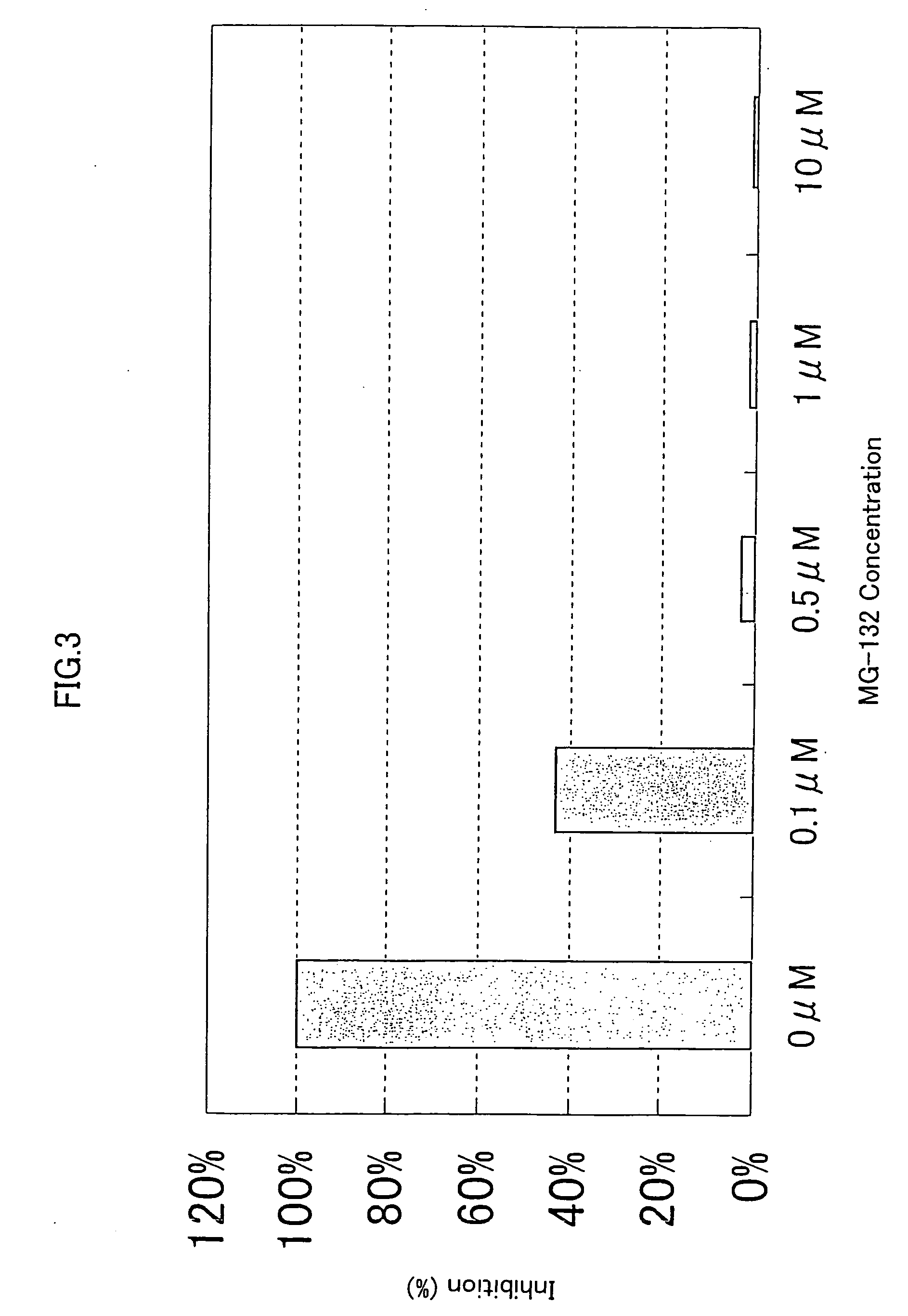
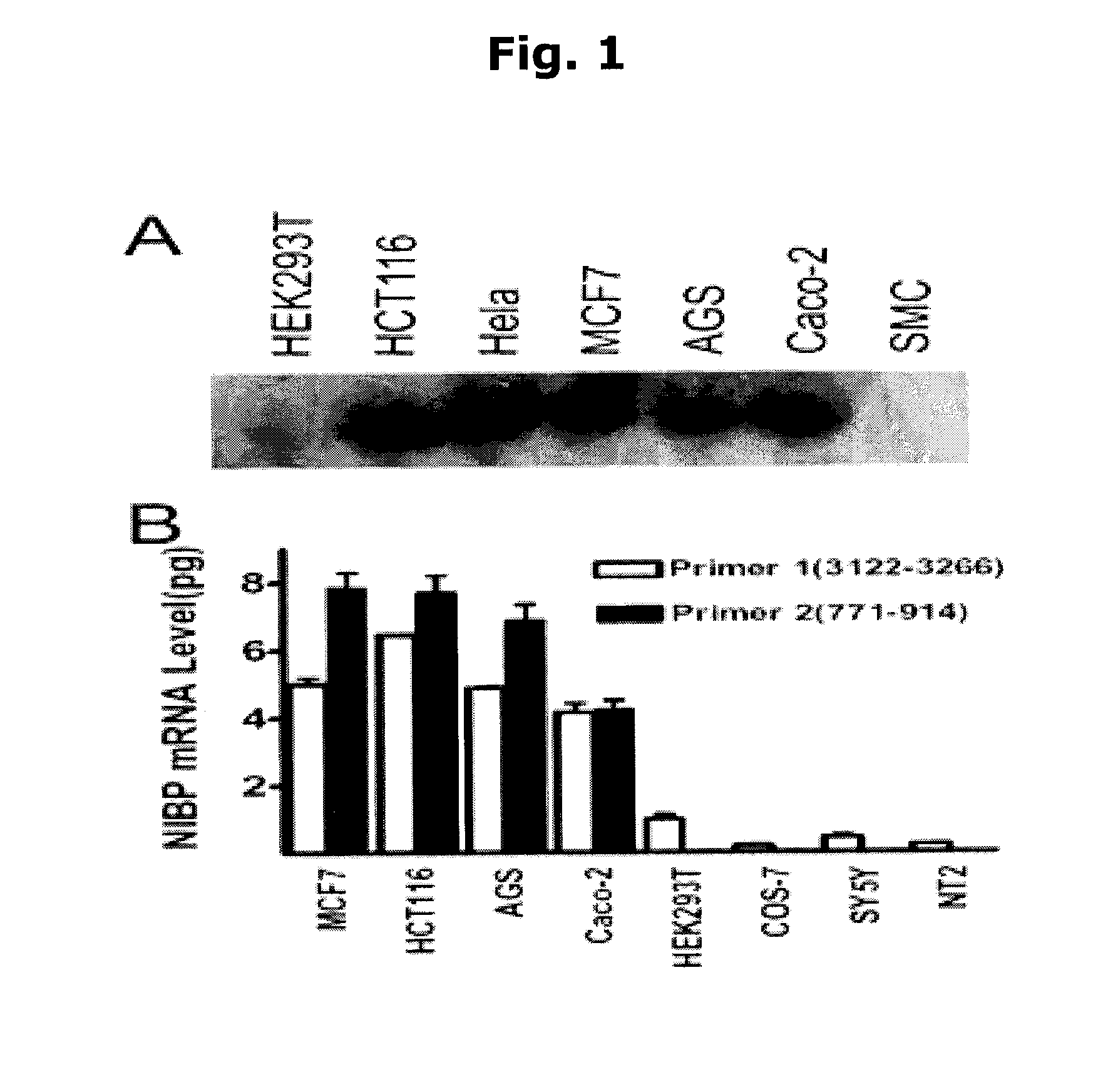
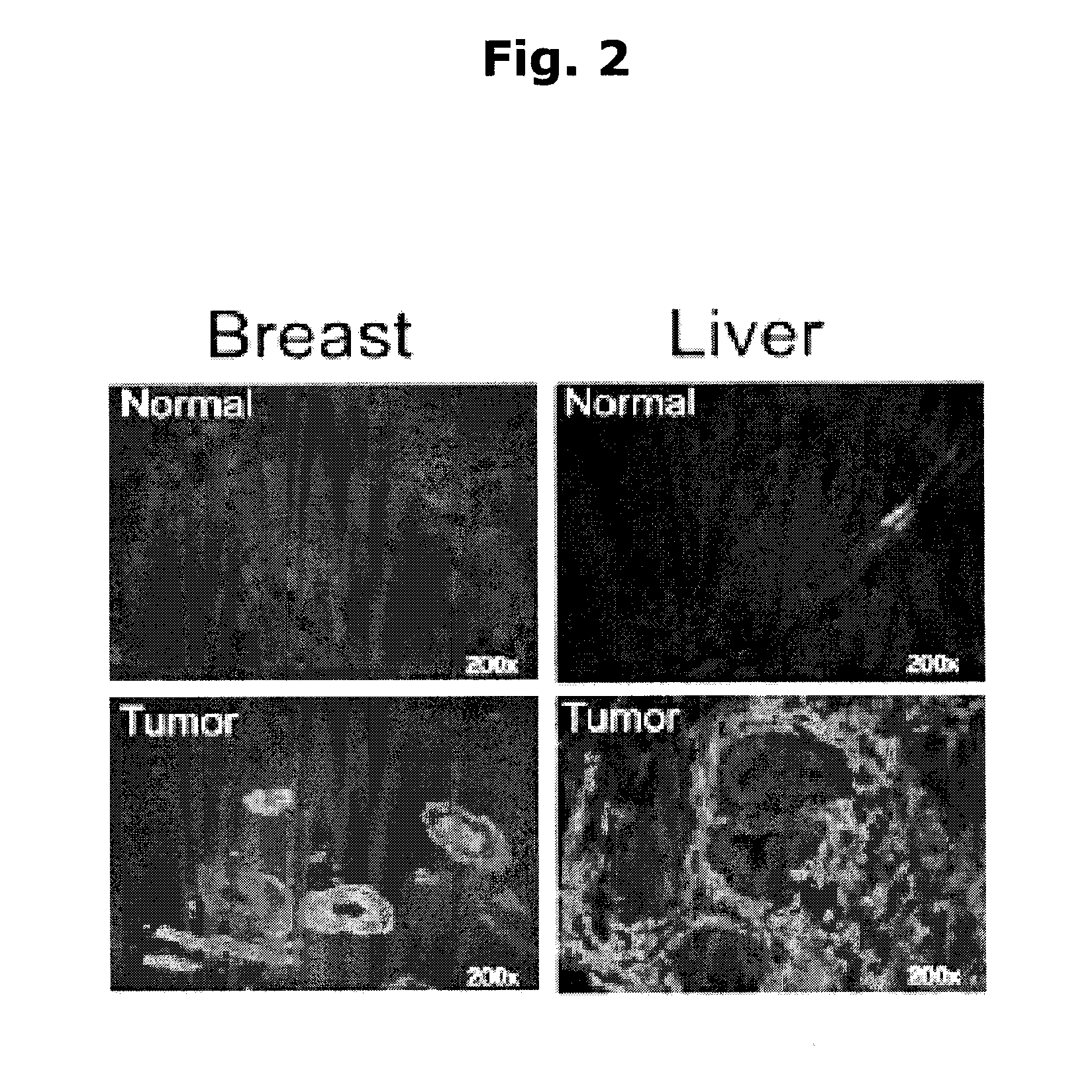
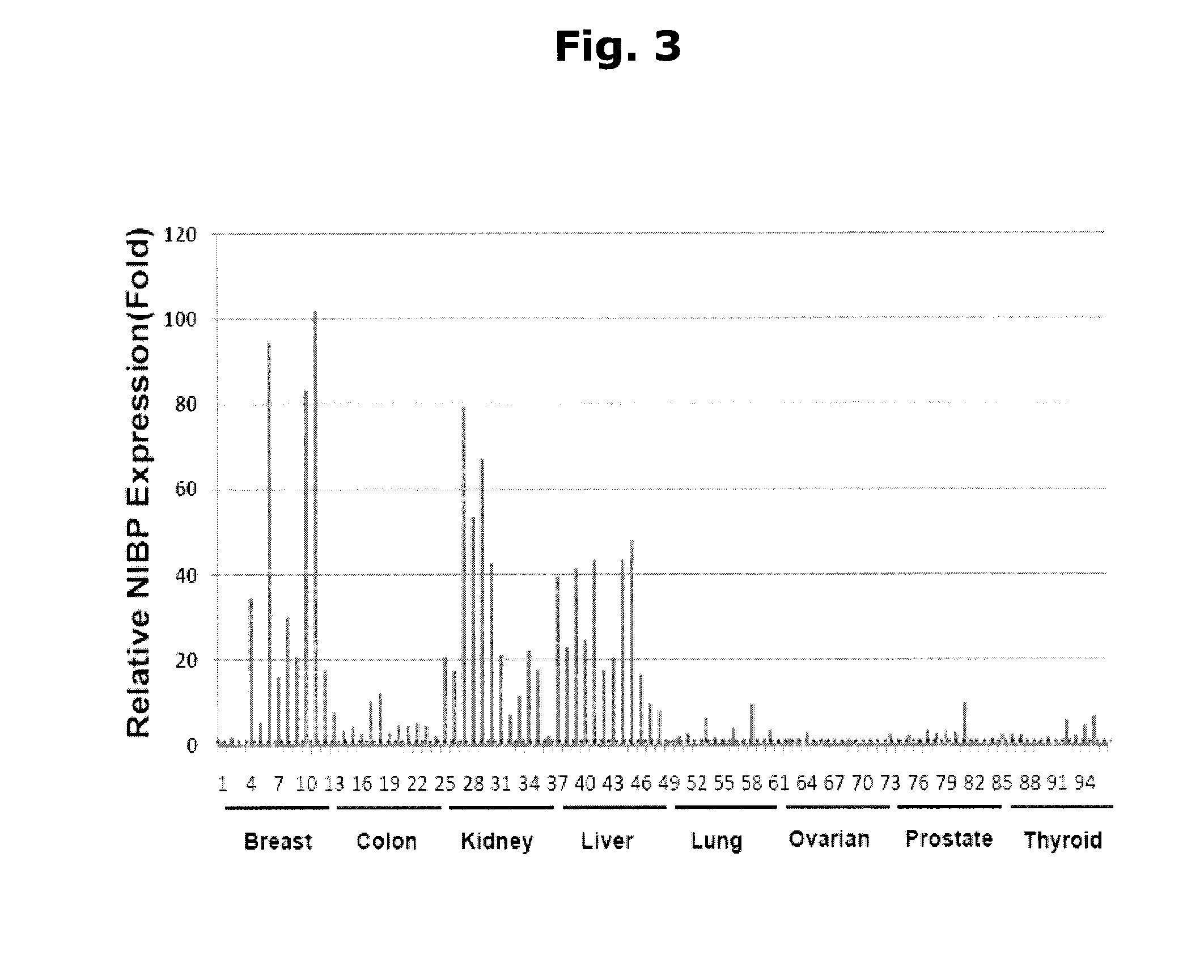
InactiveUS20120258539A1Inhibition of activationPromote cell deathPeptidesFermentationCancer cellNF-kappaB activation
Methods for regulating NF-κB activation in cells comprising introducing into the cell a vector comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding a NIK and IKK2 Binding Protein (NIBP) polypeptide, wherein the NIBP polypeptide is expressed in the cell, are provided. Also provided are methods for reversing the cancerous phenotype of a cancer cell and for modulating neuronal differentiation.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
Abin-mediated hepatitis protection
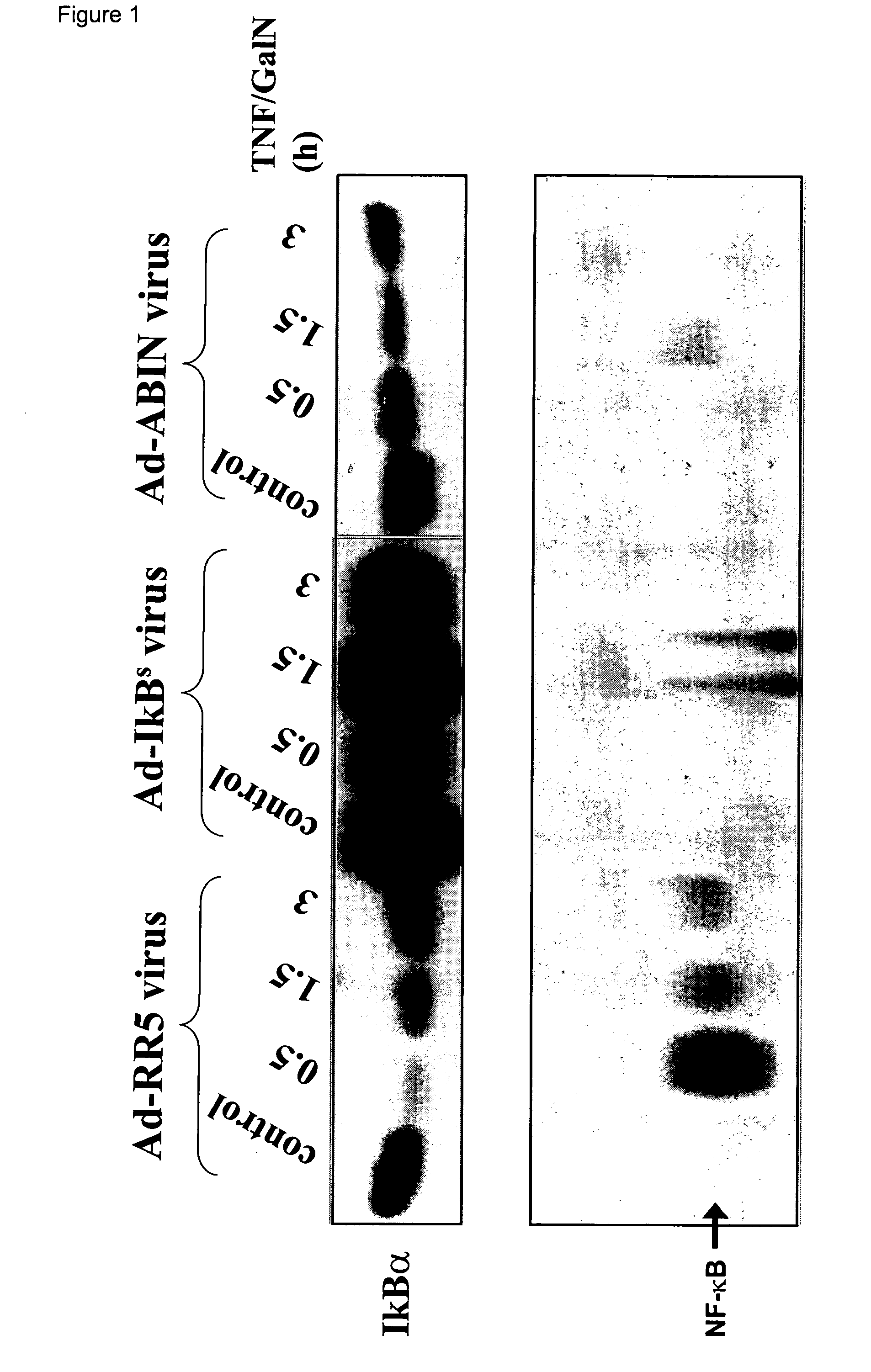
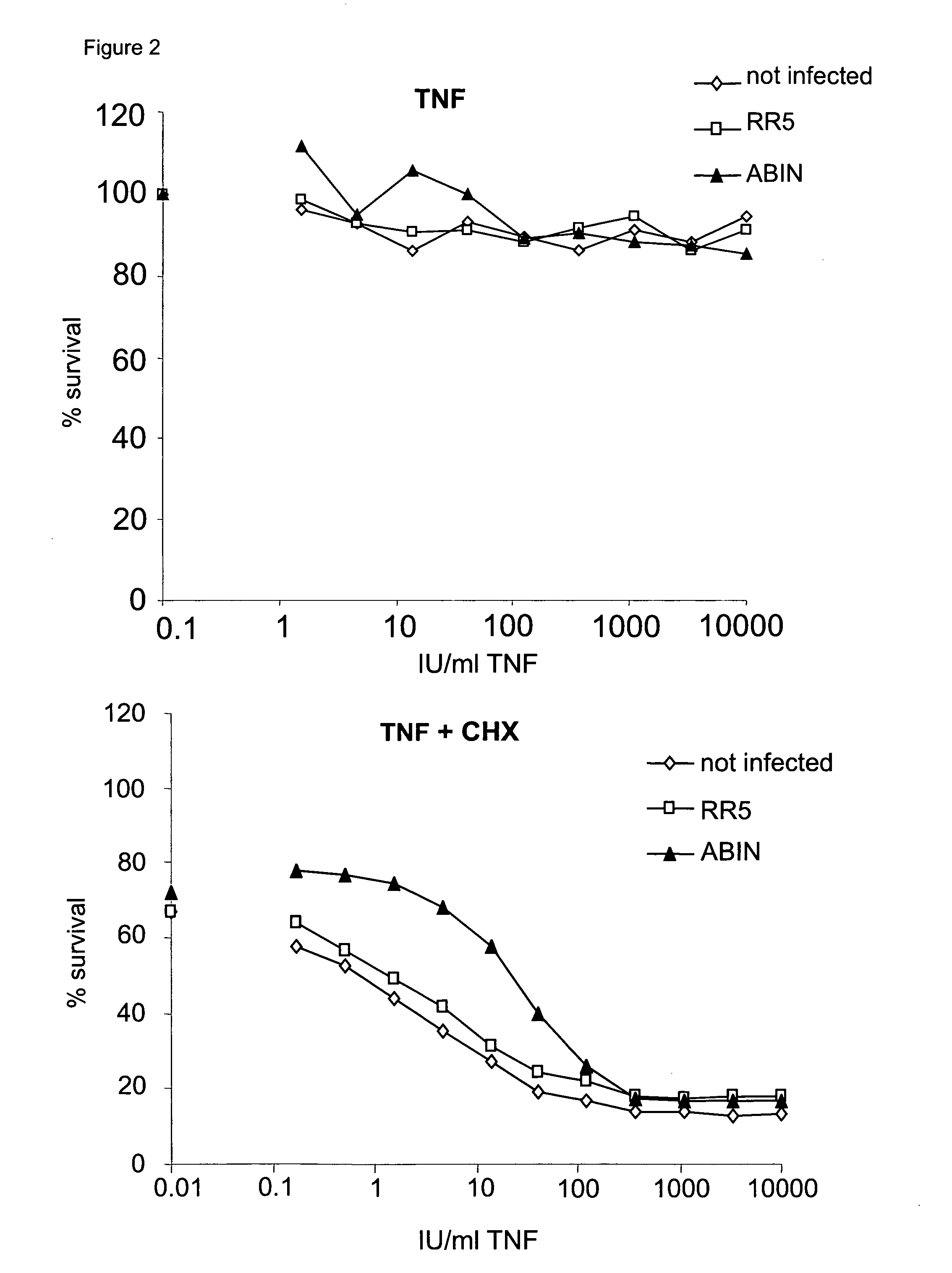
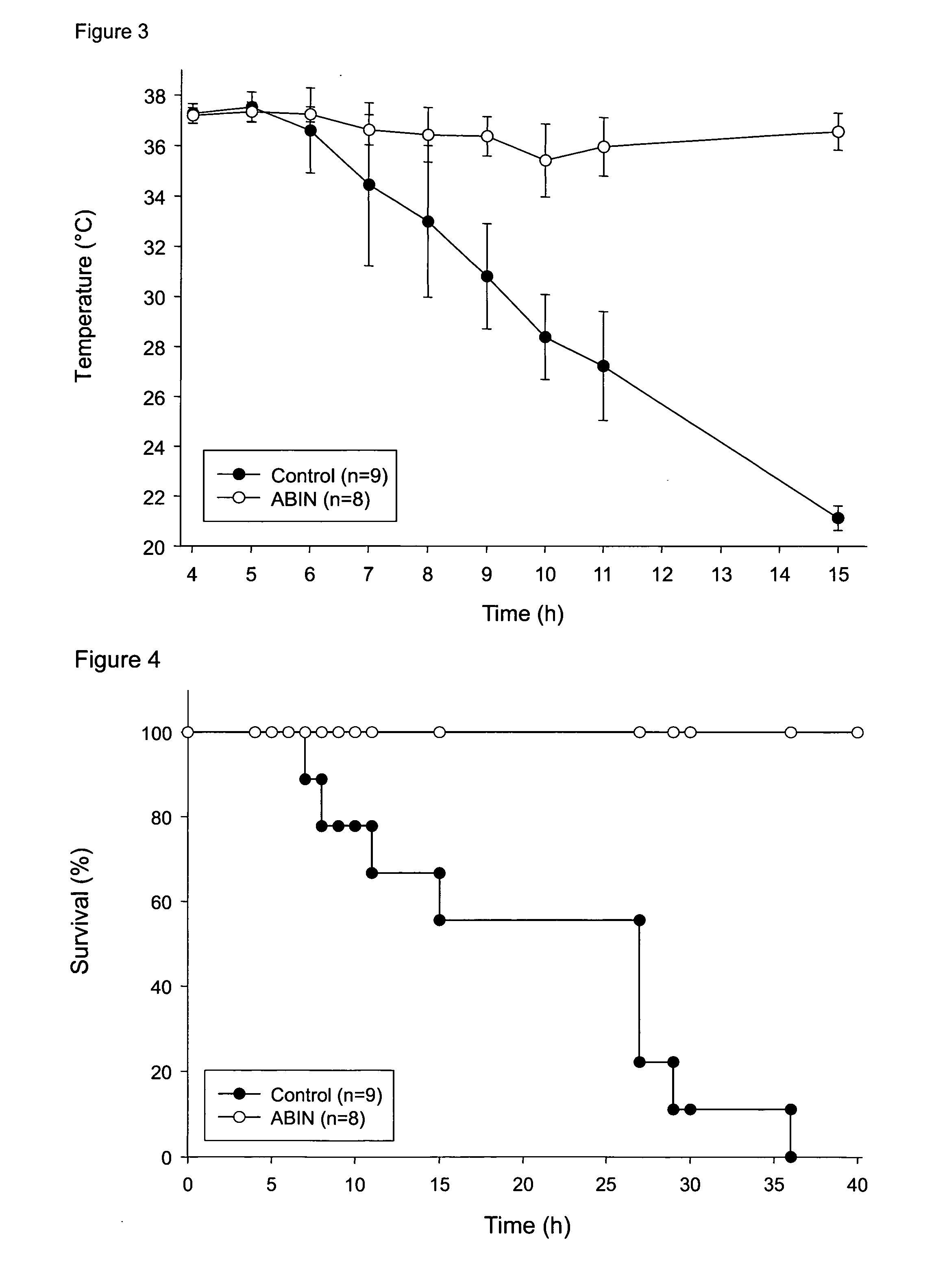
InactiveUS7094756B2Prevents TNF-induced lethal hepatitisBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseLiver function
The present invention relates to the use of the A20-binding inhibitor of NF-κB activation (ABIN), or a functional fragment or variant thereof to protect against TNF-induced liver failure, such as viral hepatitis and alcoholic liver disease. More particularly, it relates to the prevention of the toxic effects of said diseases, including lethality, by overexpressing ABIN.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW
Protein modulators of resistance to alkylating agents
There is disclosed a method for identifying a therapeutically responsive phenotype, as distinguished, e.g. from an alkylating agent resistant phenotype in a cell, which method may be used to evaluate the likelihood of successful outcome of treating a tumor cell with an alkylating agent. The method is directed to the NF-κB activation in response to DNA damage caused by alkylating agents. It comprises the step of measuring a level of expression of a protein, which participates in the NF-κB pathway. Preferably it comprises measuring the expression of TNFAIP3 in the cell, wherein a resistant phenotype has less expression of TNFAIP3 than a sensitive phenotype. Another particularly significant gene, which predicts survival, is NFKBIA. Other genes whose altered expression level is associated with resistance or prognosis are TNIP1, TNIP2, RIP, NFKBIB, Beta4GalNAc-T4, NFKBIE, C8orf4, LIF, CD44, FBXO32, and SDC1, and these are also measured in certain embodiments.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods for inhibiting osteoclastogenesis
InactiveUS20070167510A1Inhibit osteoclastogenesisInhibition is effectiveBiocideMuscular disorderMedicineCOX-2 inhibitor
Methods for the treatment of osteolytic bone disease and for the inhibition of osteoclastogenesis are disclosed. The methods utilize COX-2 inhibitors and / or inhibitors of NF-κB activation, administered to patients in an amount effective to inhibit osteoclastogenesis. Also disclosed are methods to modulate the expression of MIP-1α in a subject.
Owner:LENTZSCH SUZANNE
Methods for identifying inhibitors of neuronal degeneration
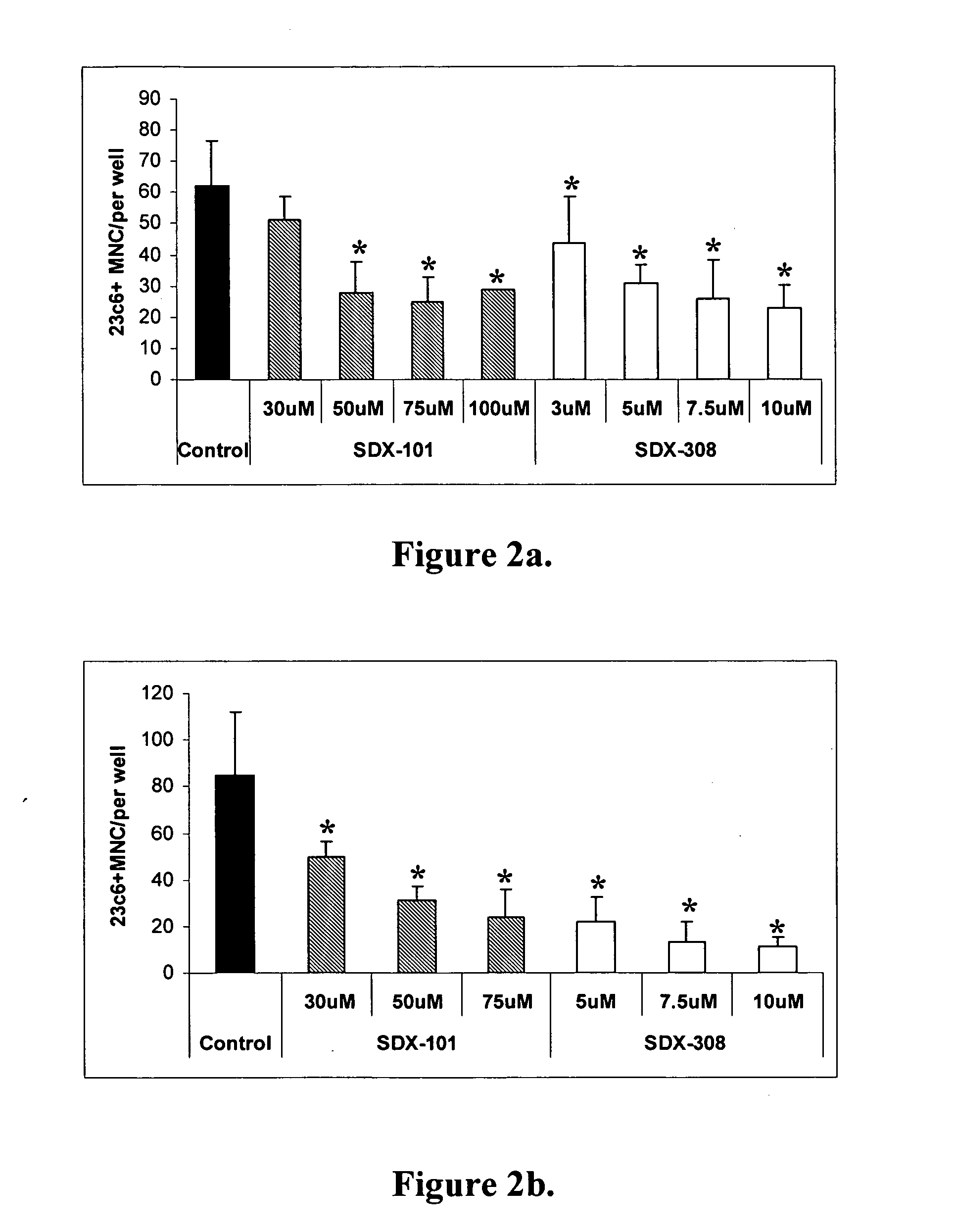
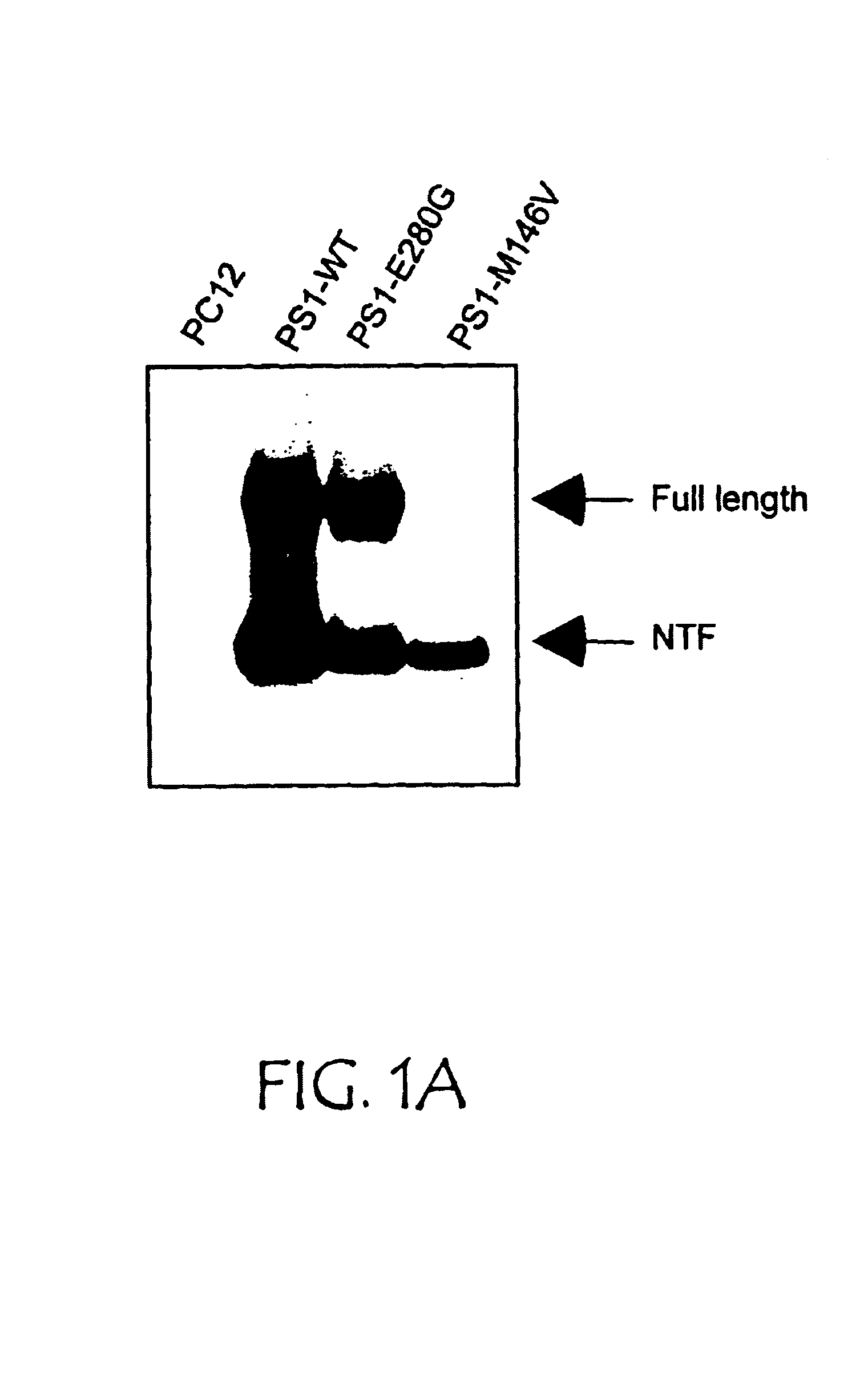
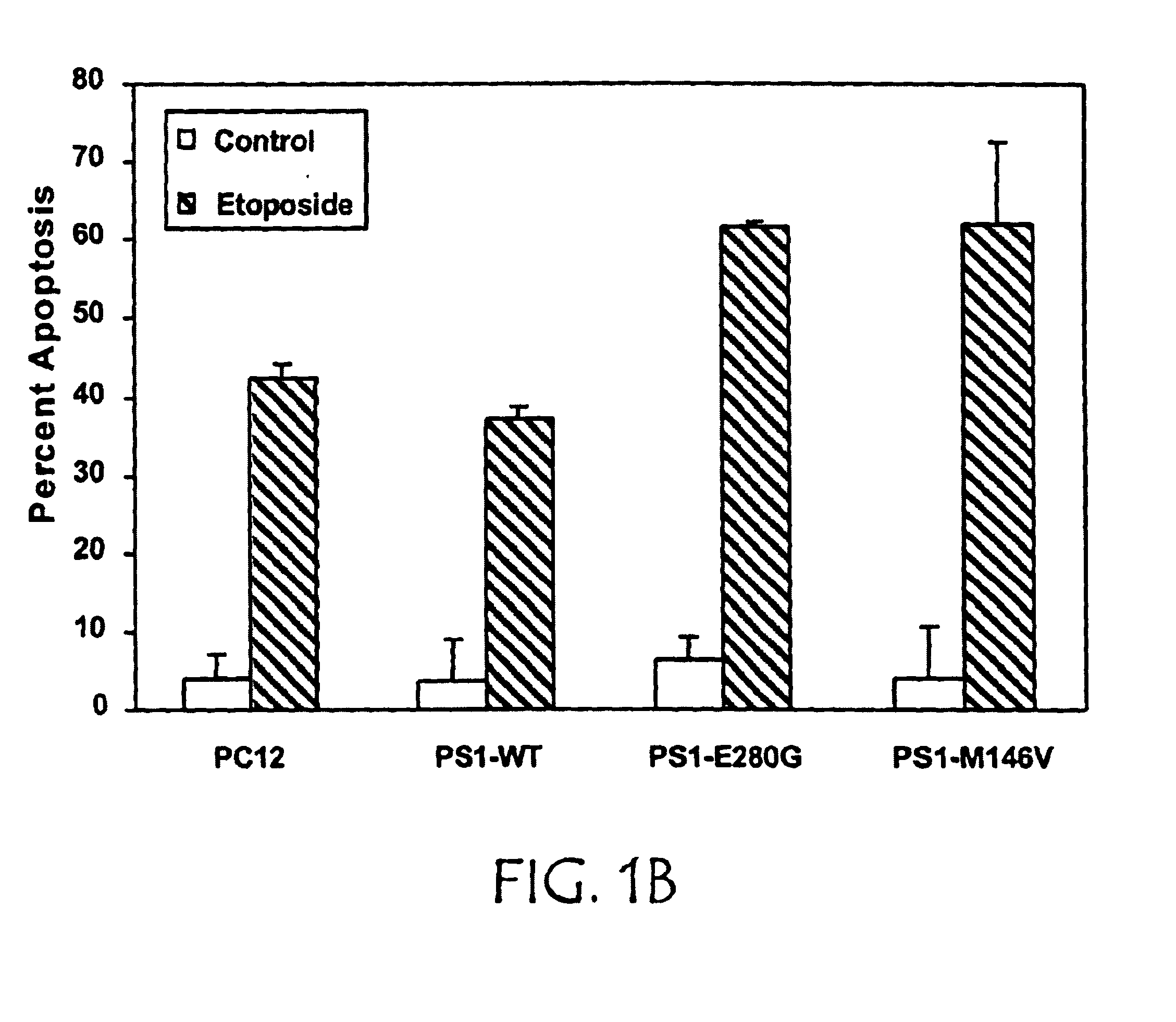
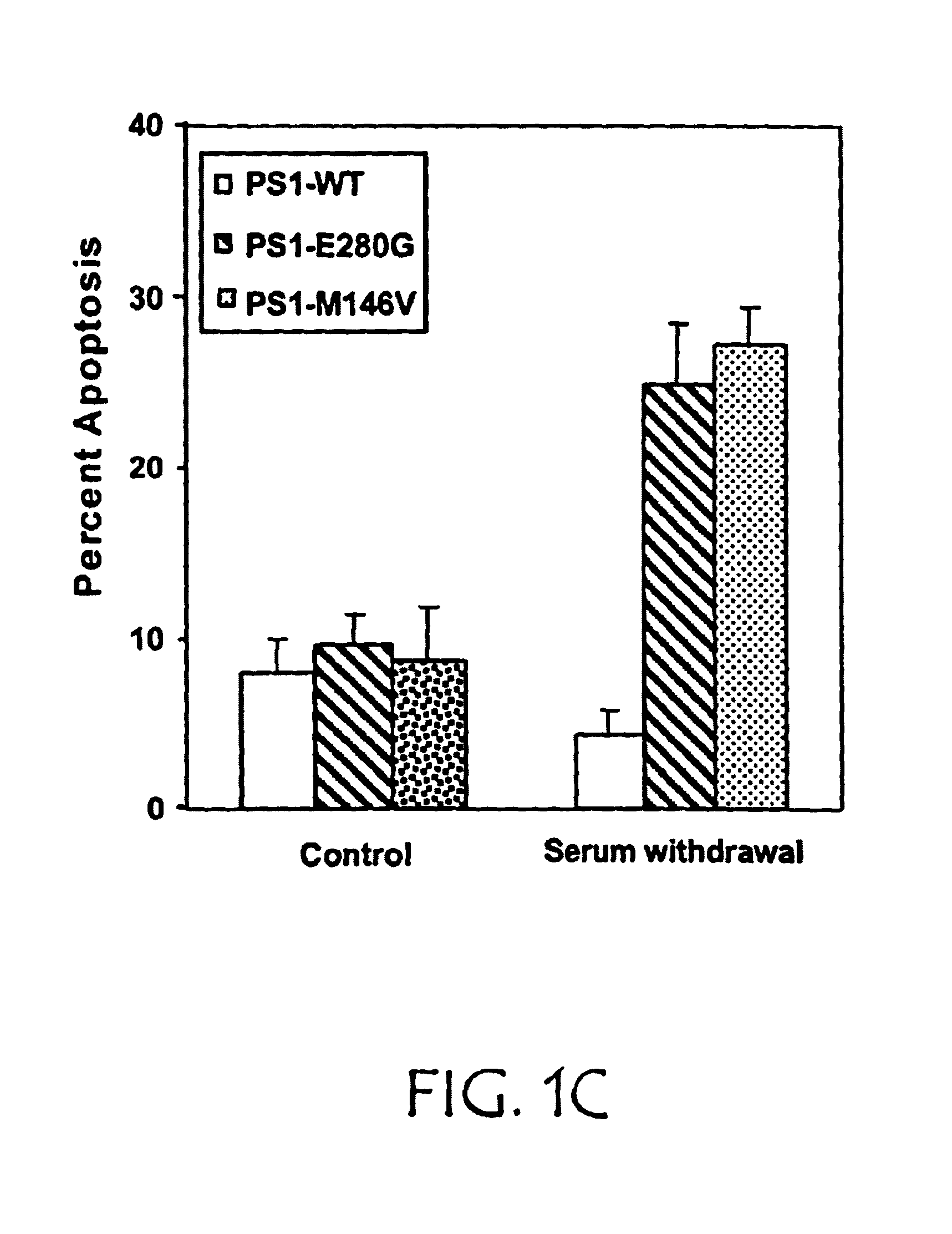
InactiveUS6979537B2Inhibiting neuronal degenerationInhibitory activityMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureNeuronal degenerationNf κb activation
The present invention concerns methods and means for identifying inhibitors of neuronal degeneration, and their use in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. In particular the invention concerns methods and means for identifying inhibitors of neuronal degeneration or cell death by taking advantage of the involvement of presenilin (PS) and Par-4 in NF-κB activation.
Owner:SCIOS
INHIBITORS OF ANTIGEN RECEPTOR-INDUCED NF-kappa B ACTIVATION
InactiveUS20090247520A1Decreased cellular responseOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAntigen receptorBiological activation
Owner:BURNHAM INST FOR MEDICAL RES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com