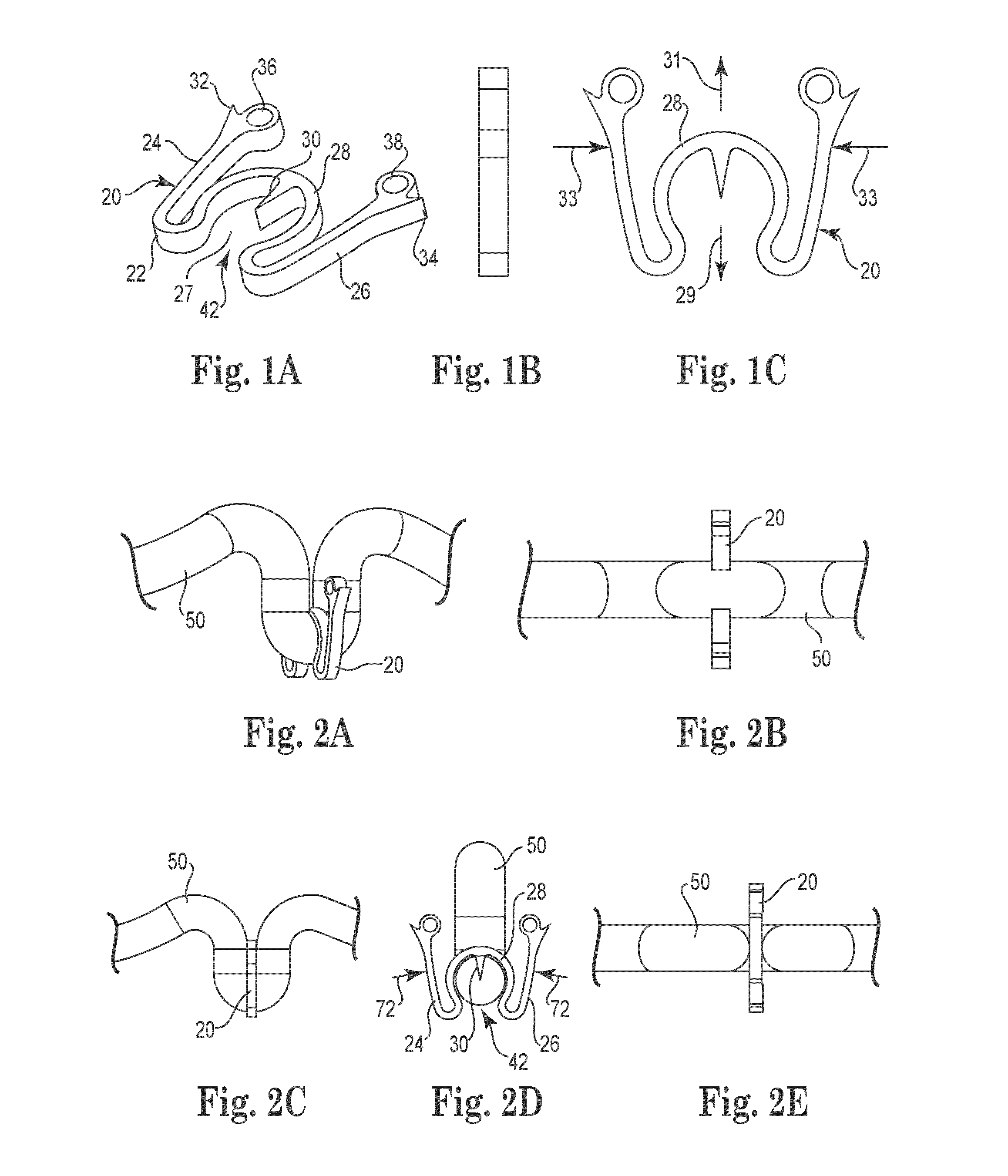
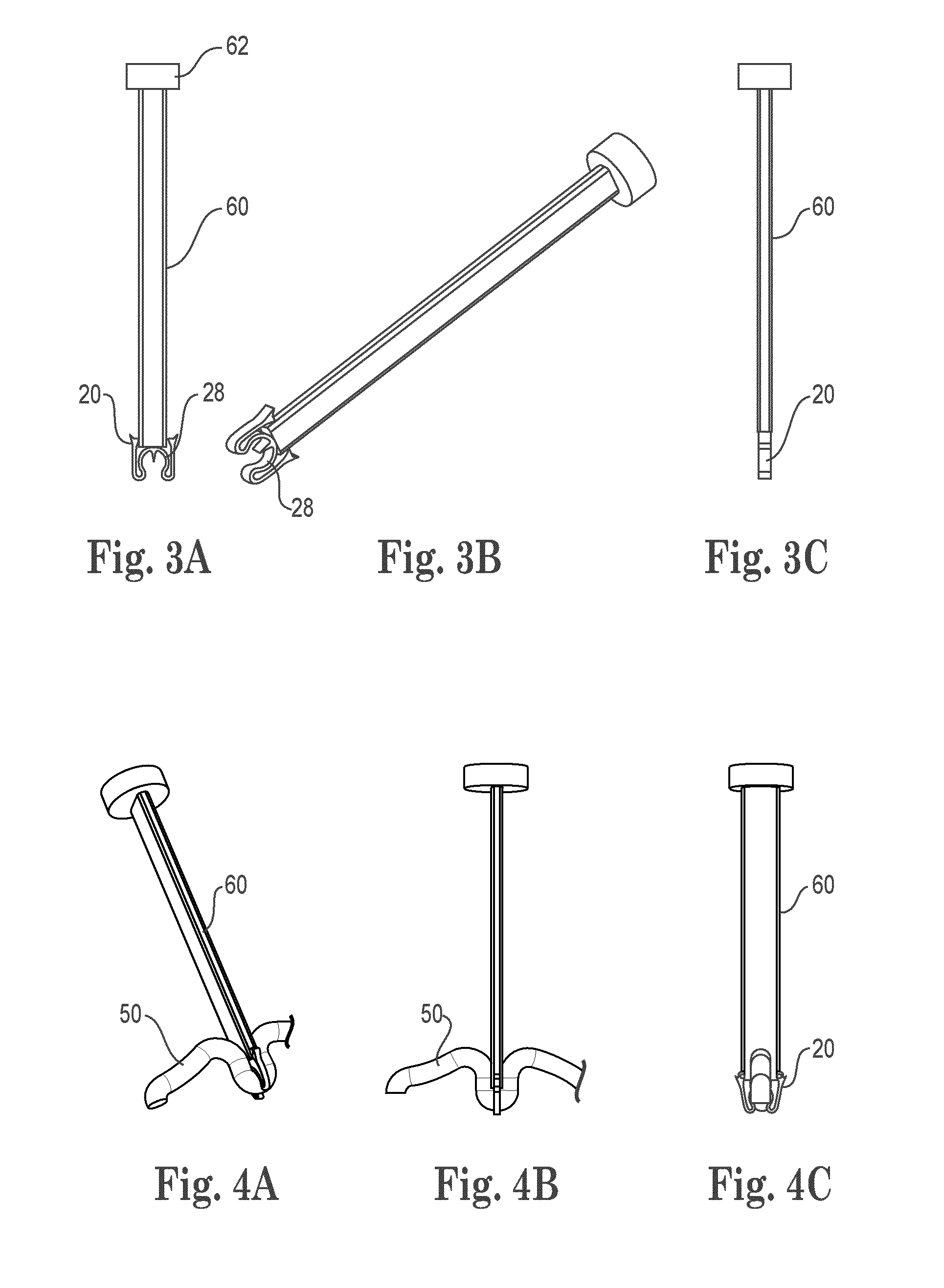
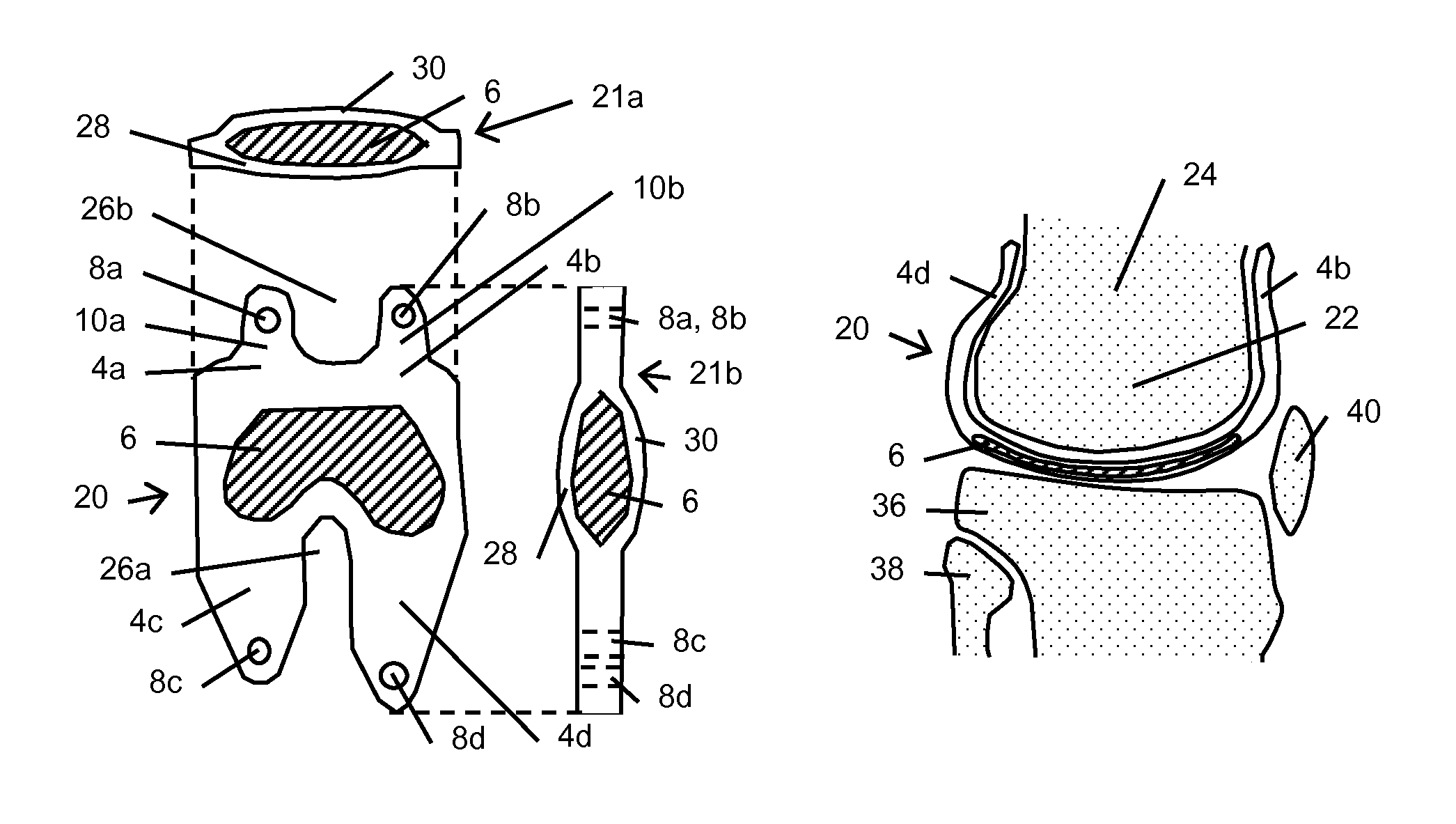
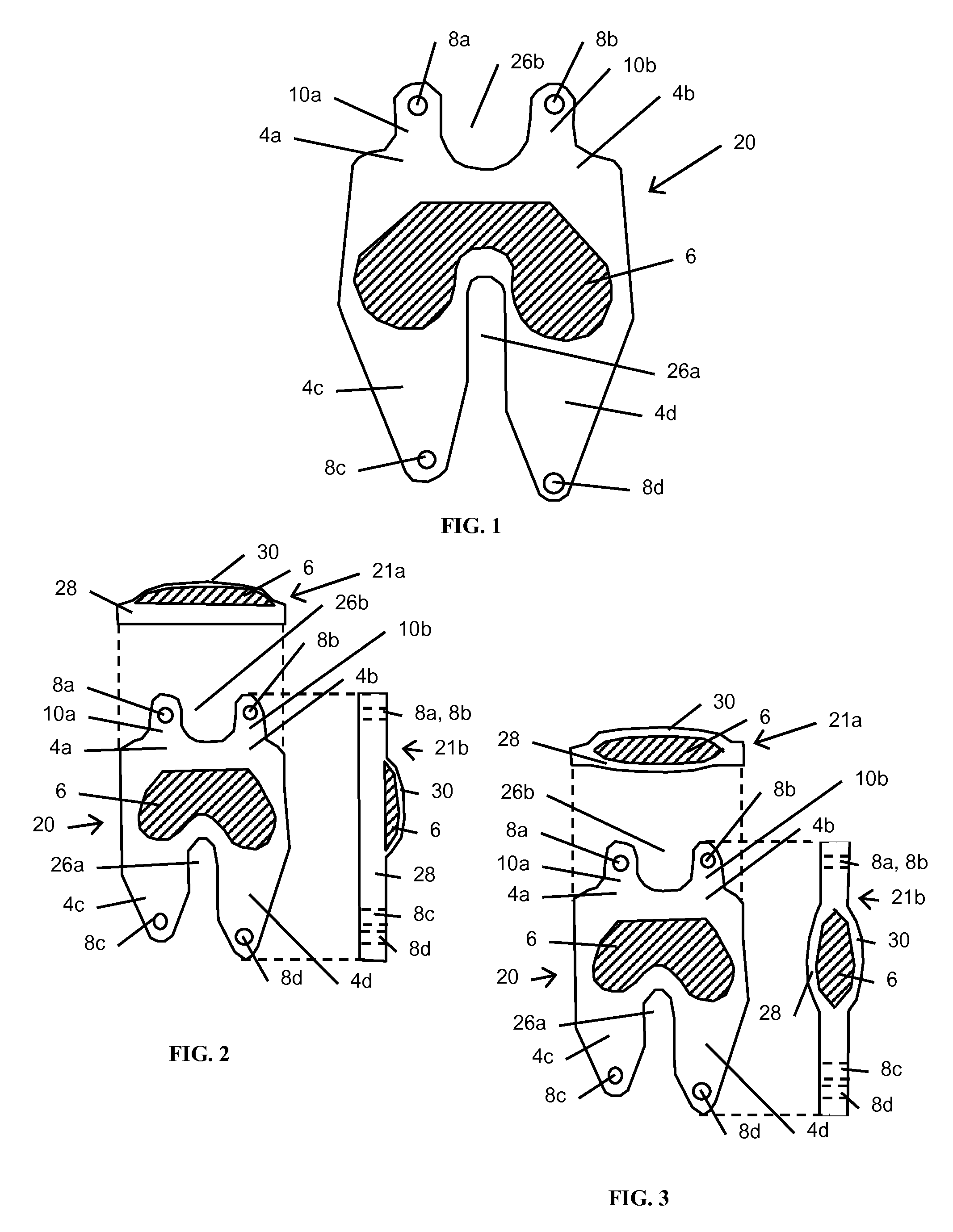
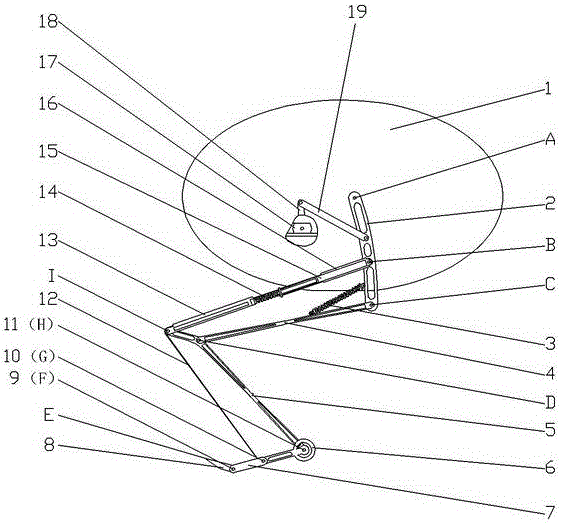
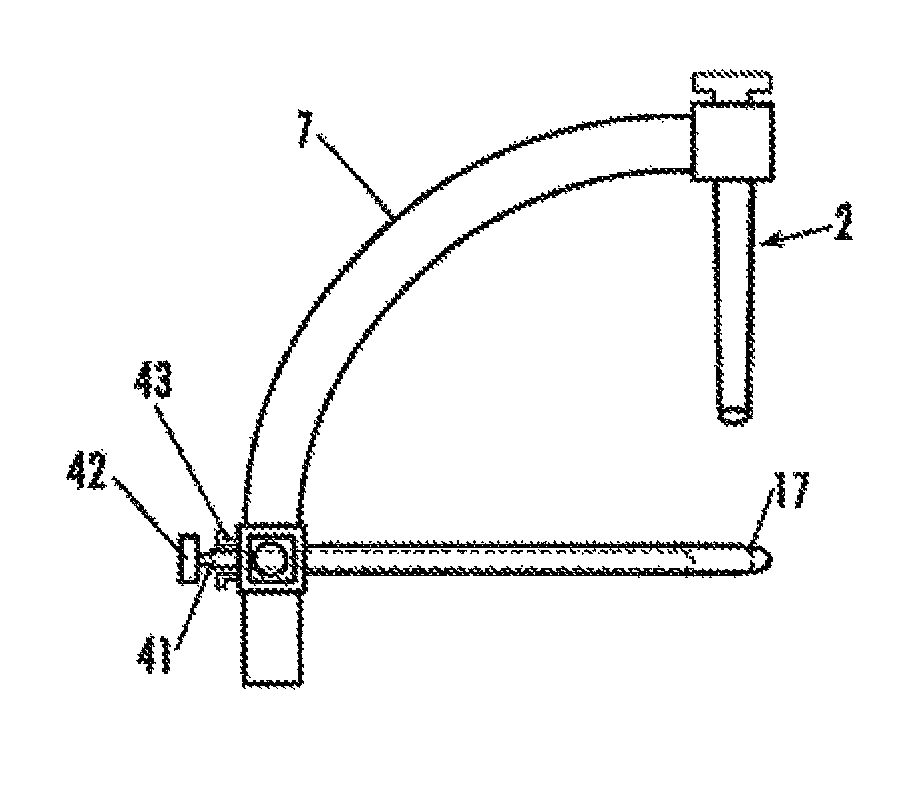
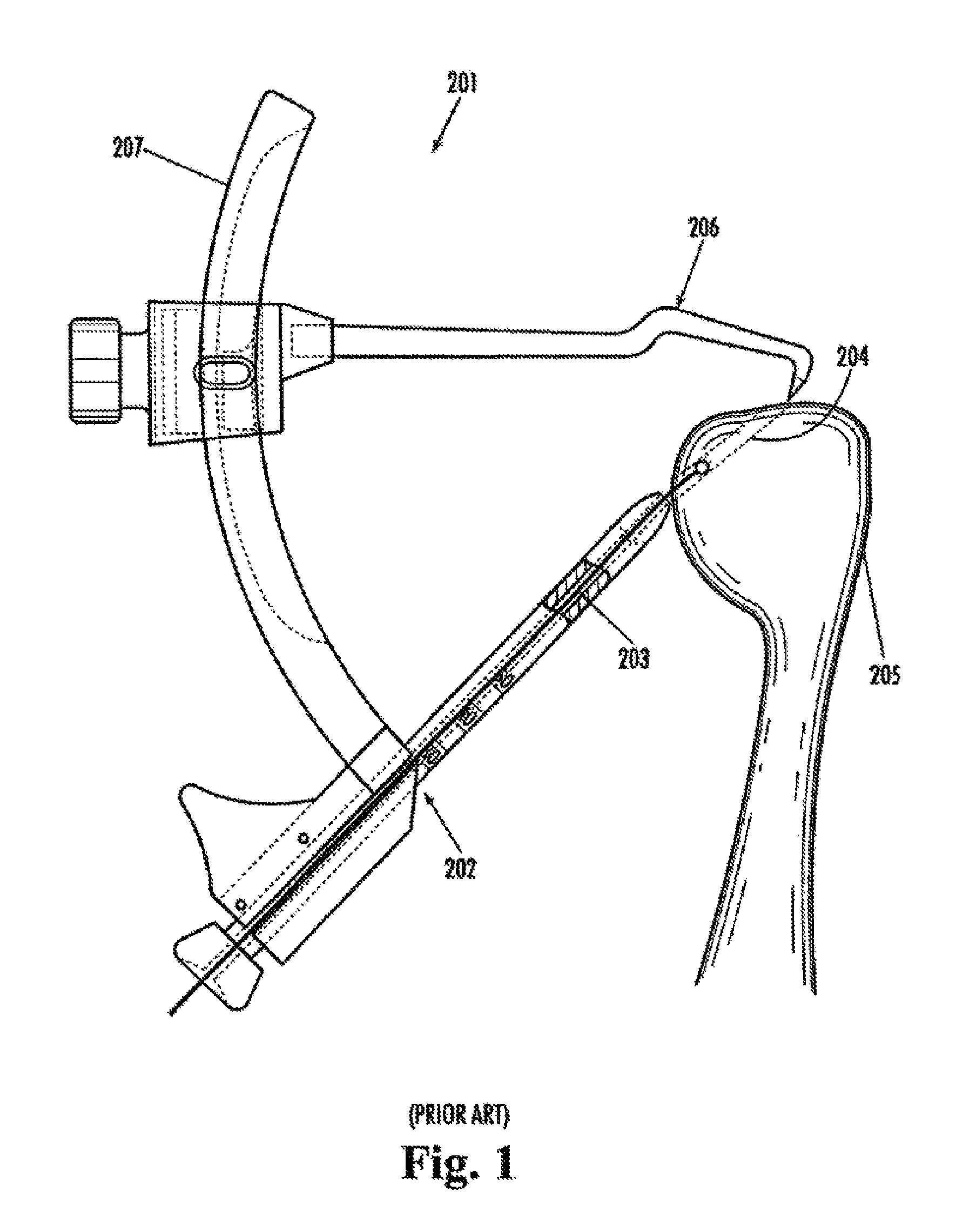
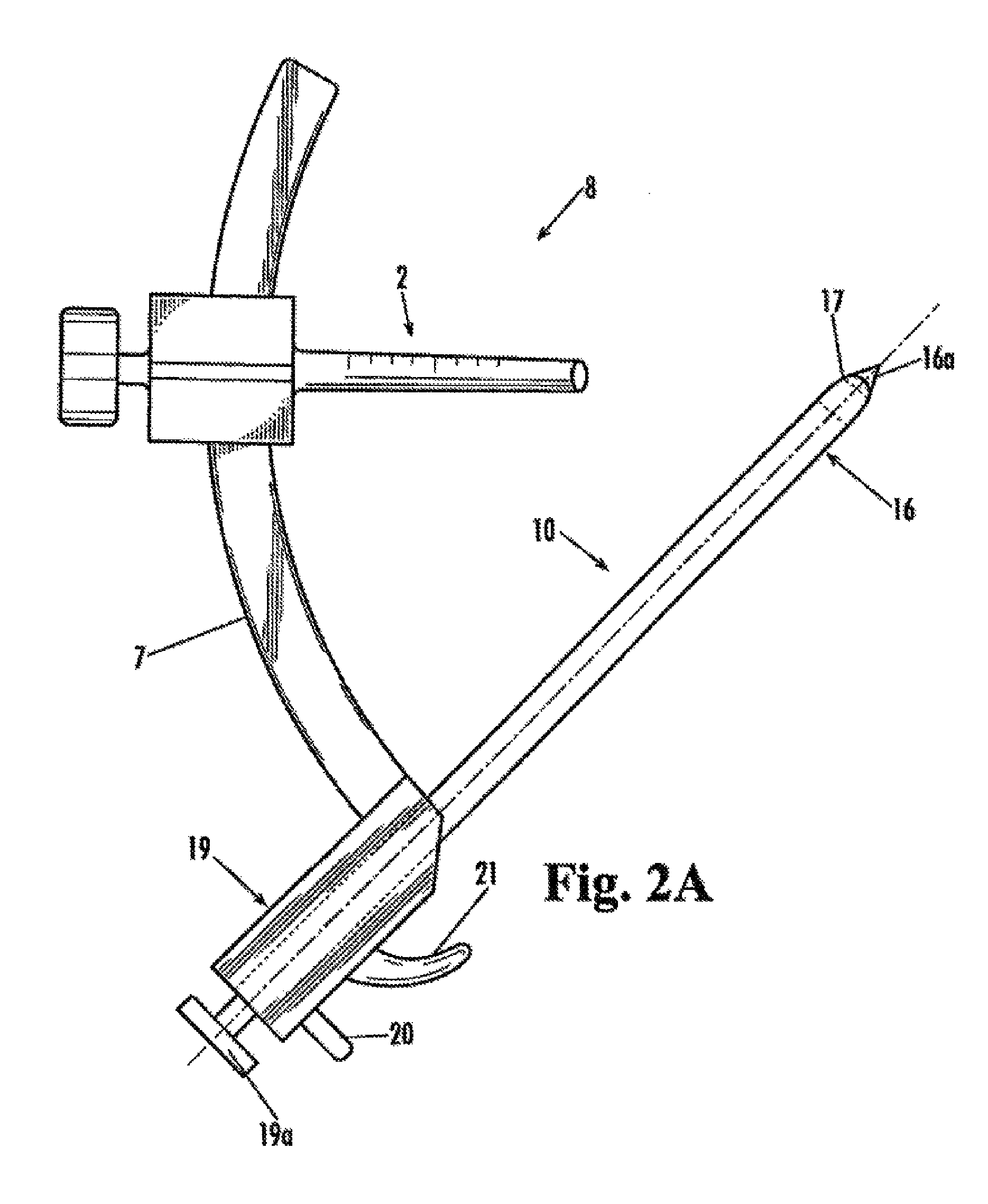
Patents
Literature
294 results about "Plantaris tendon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
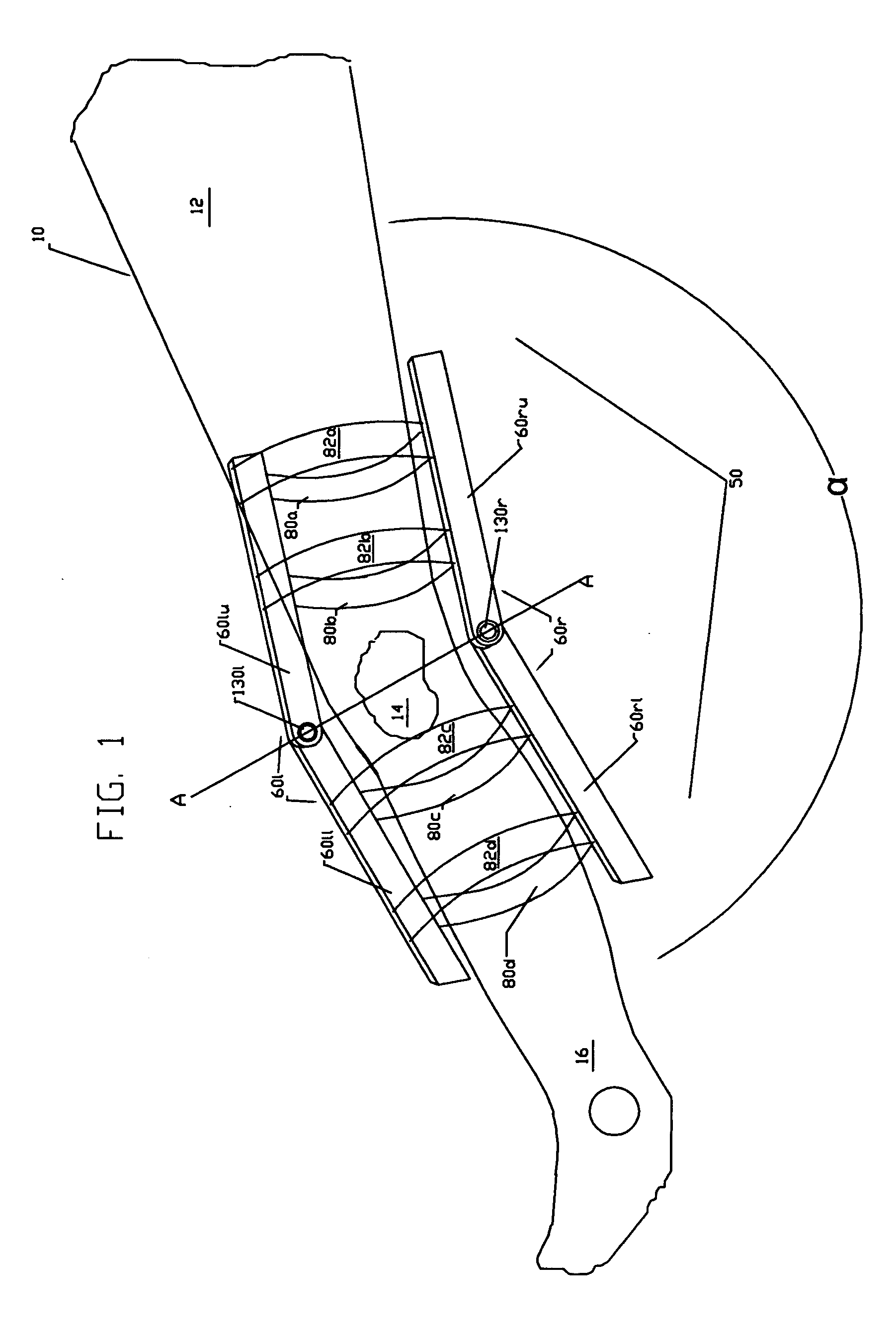
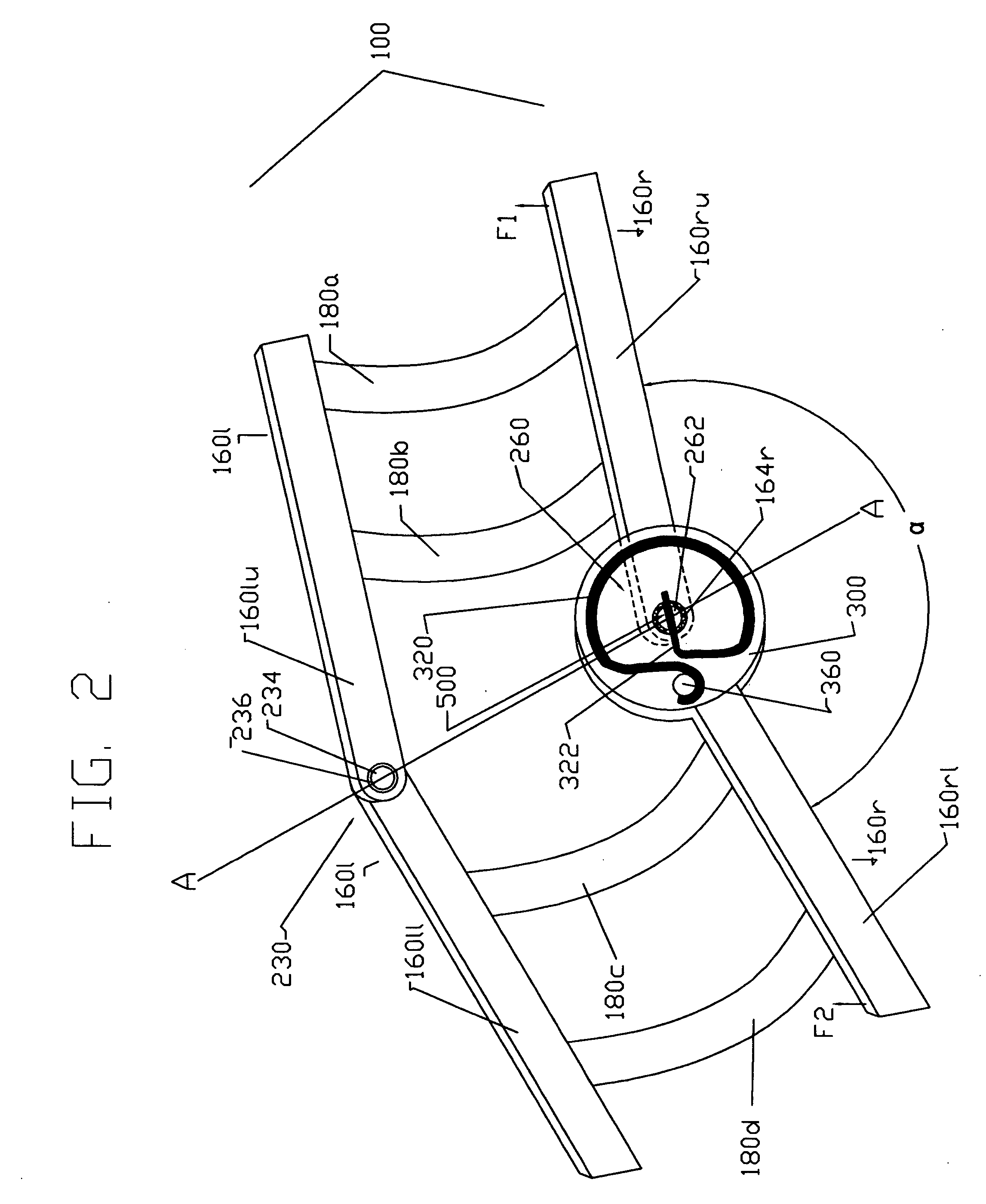
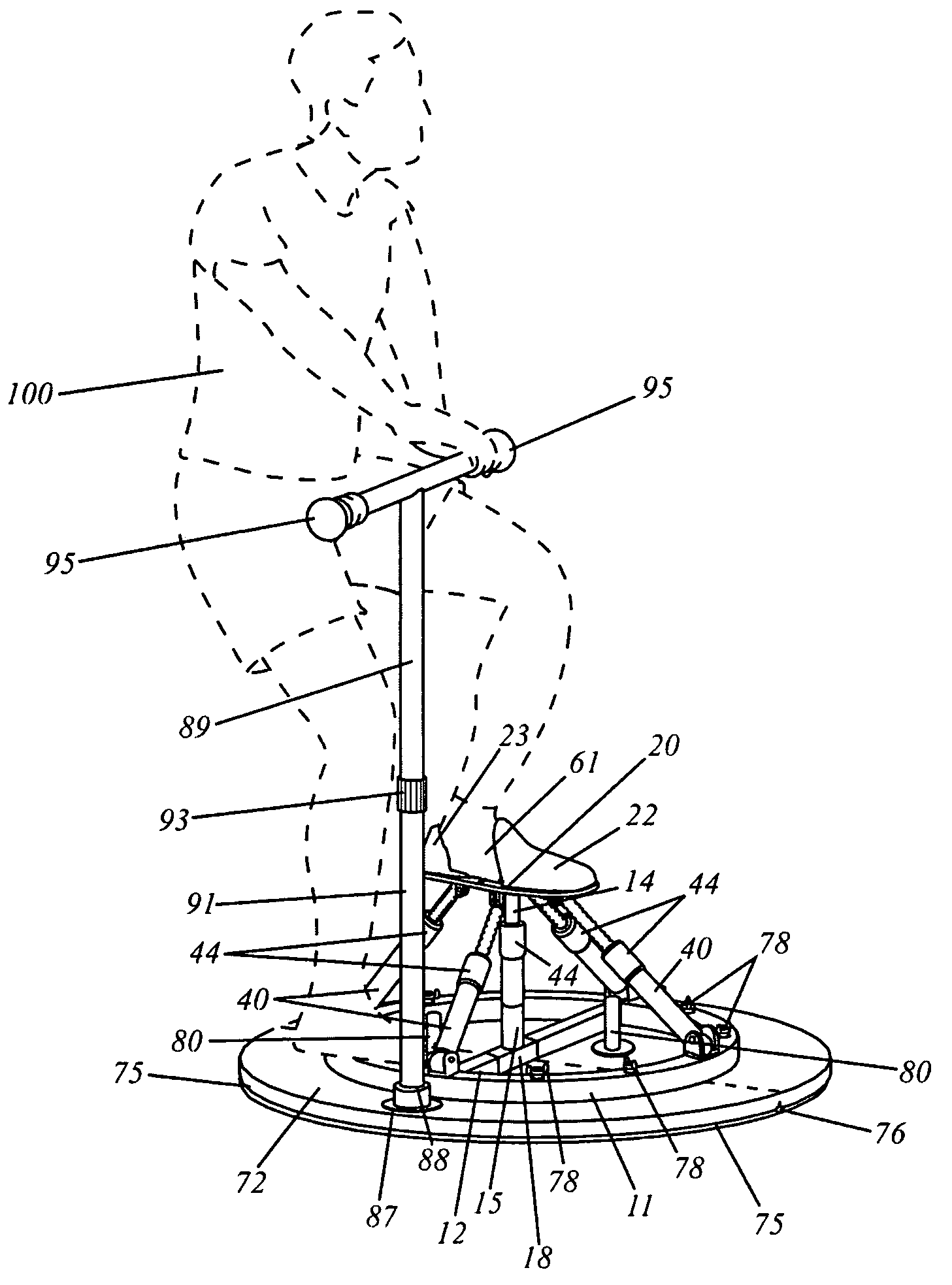
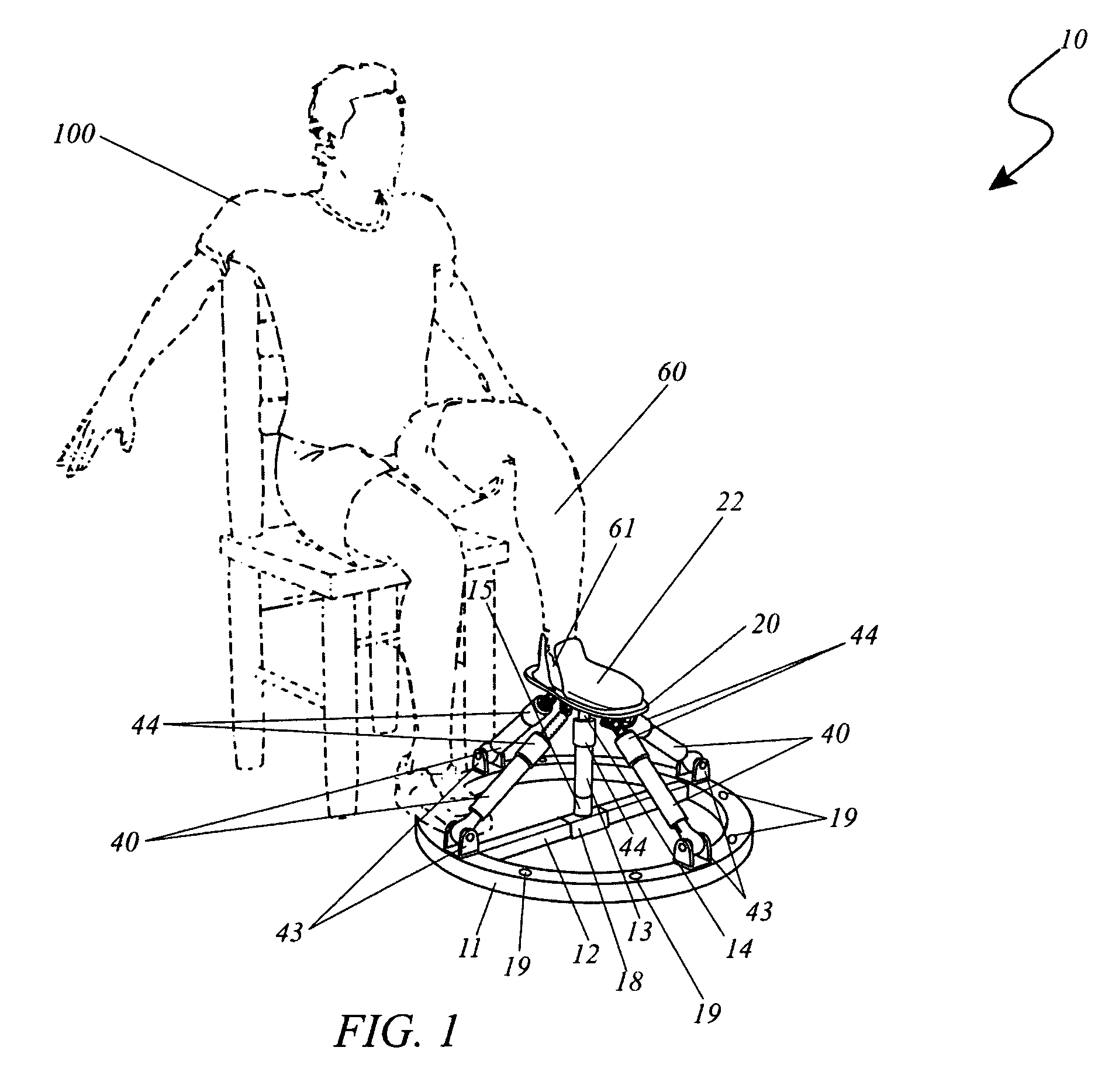
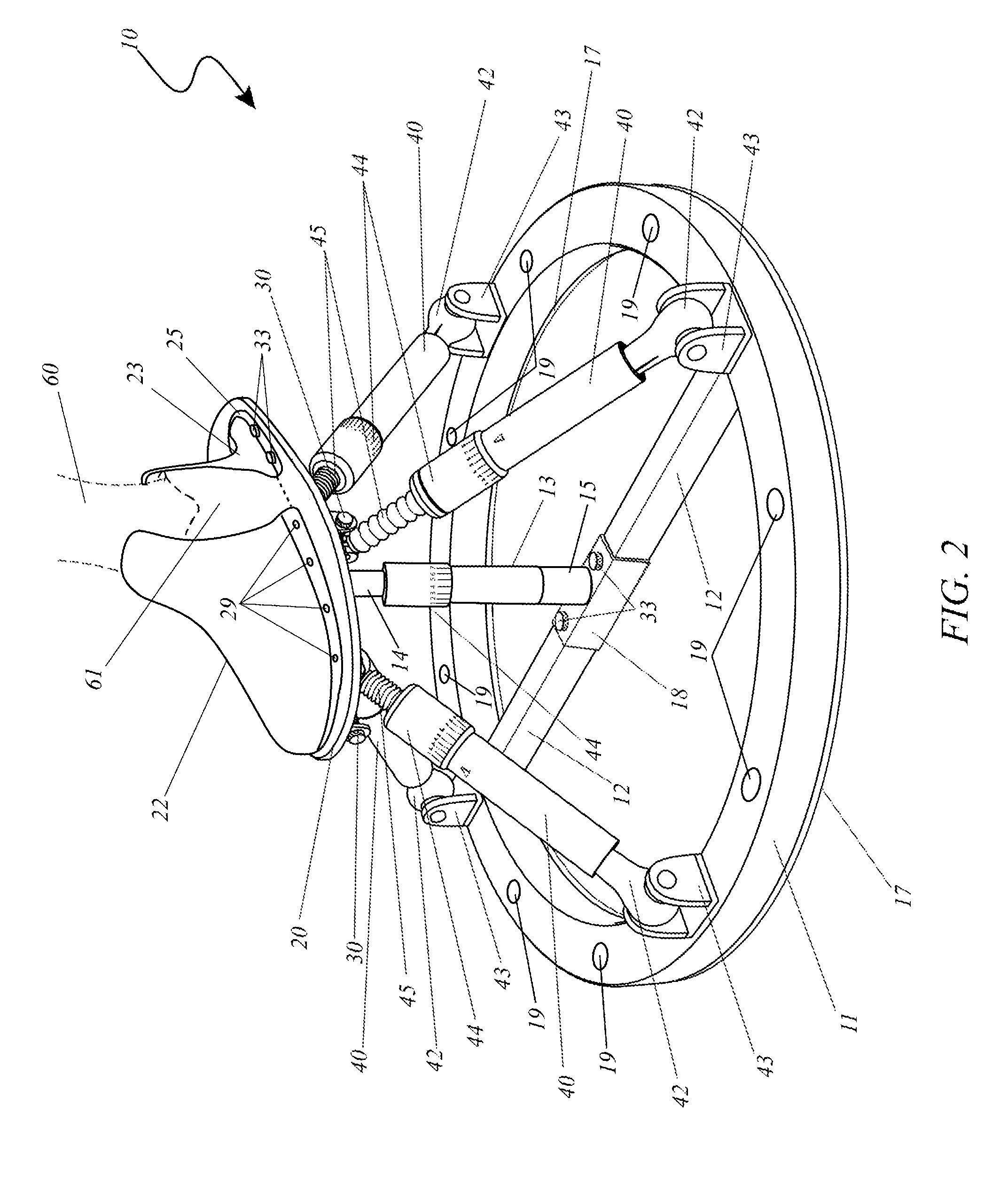
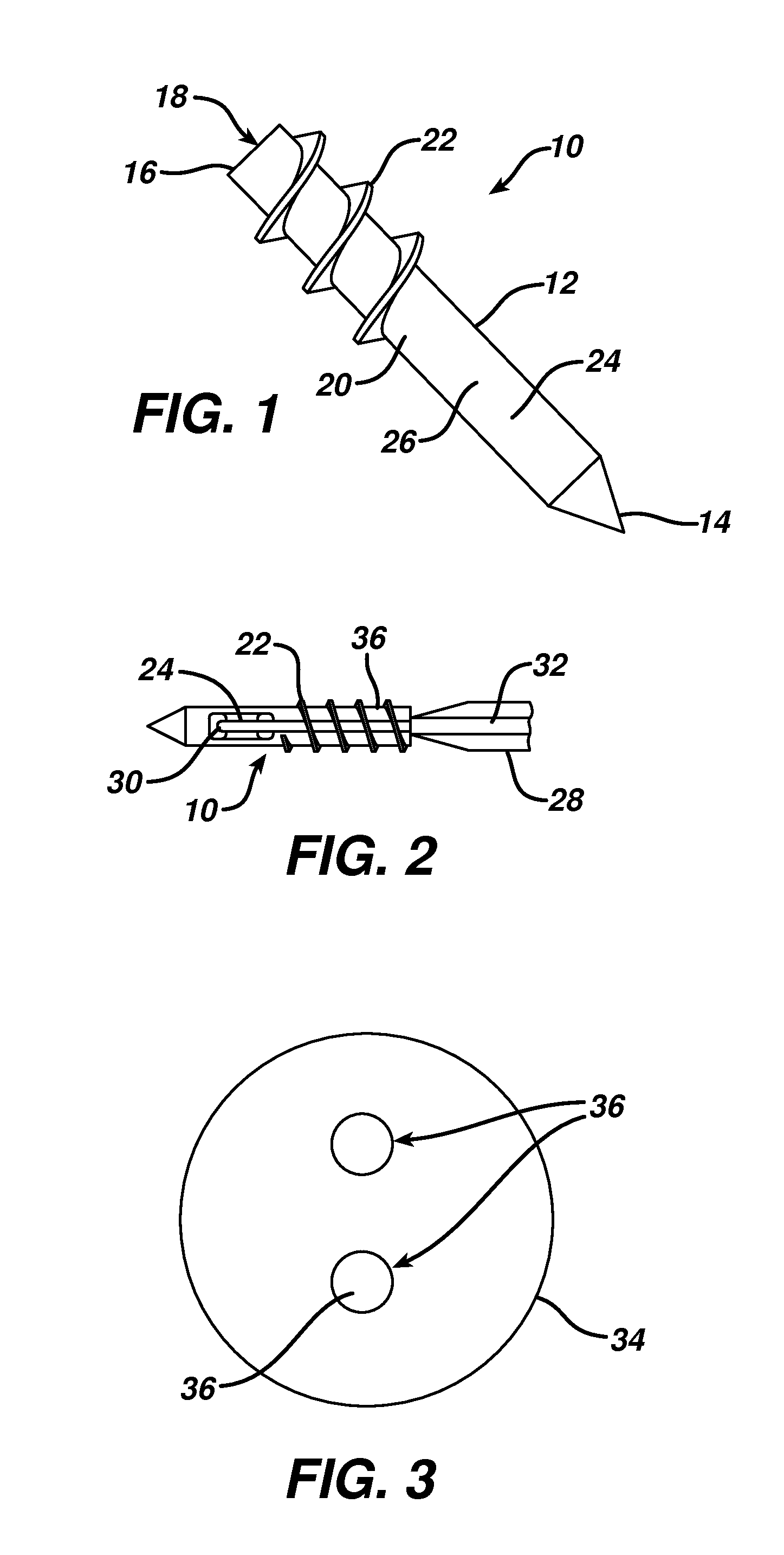
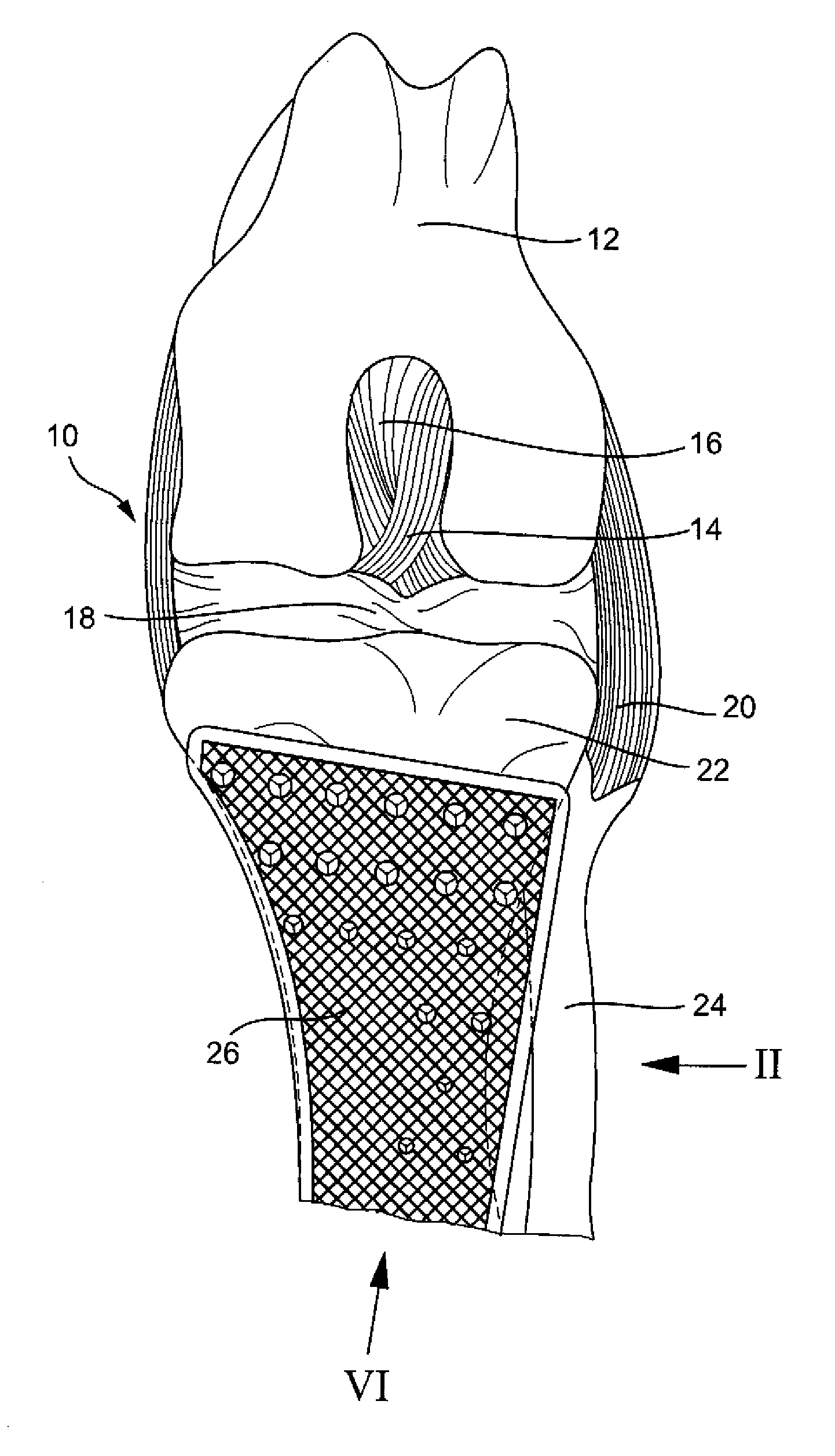
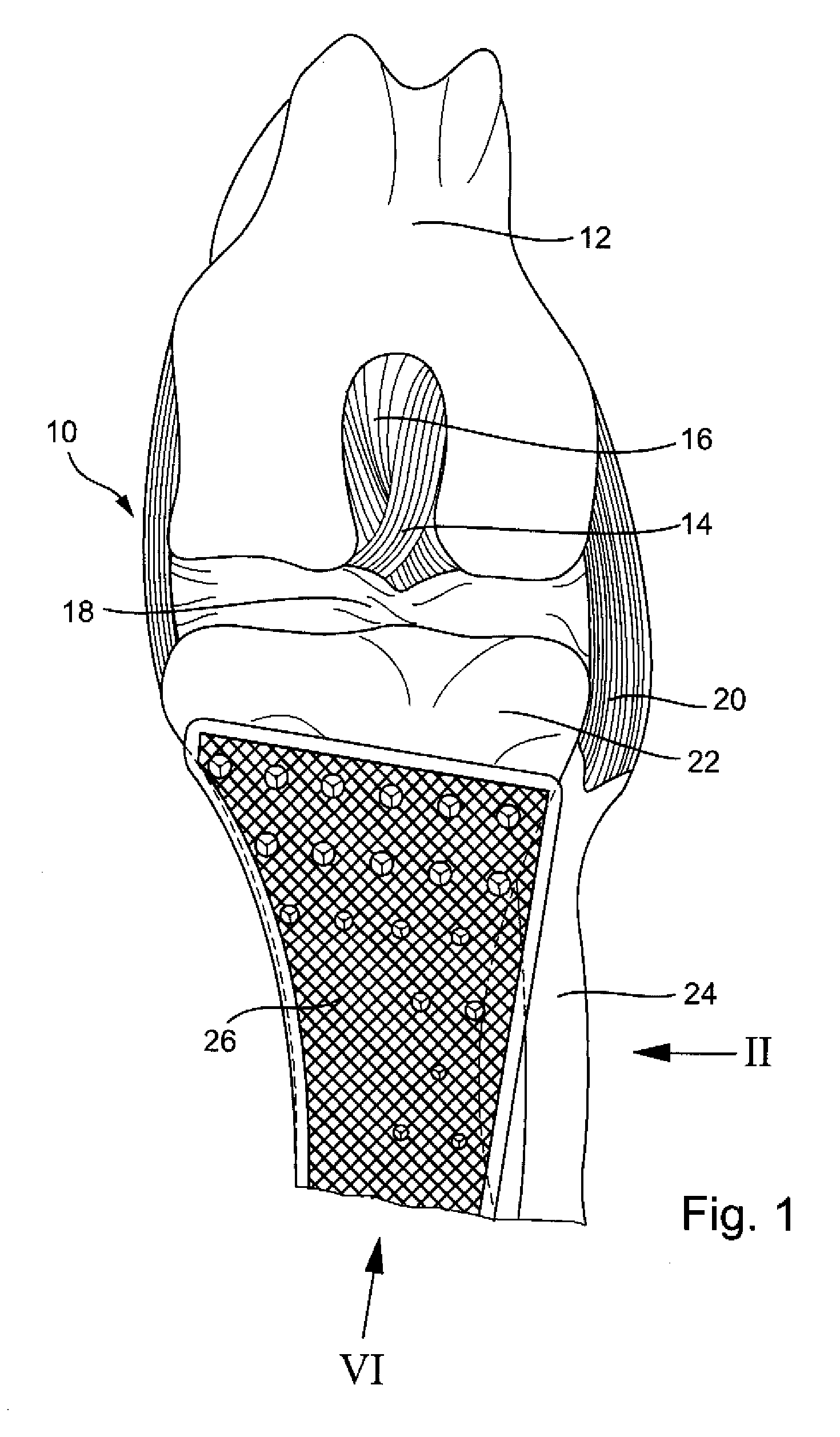
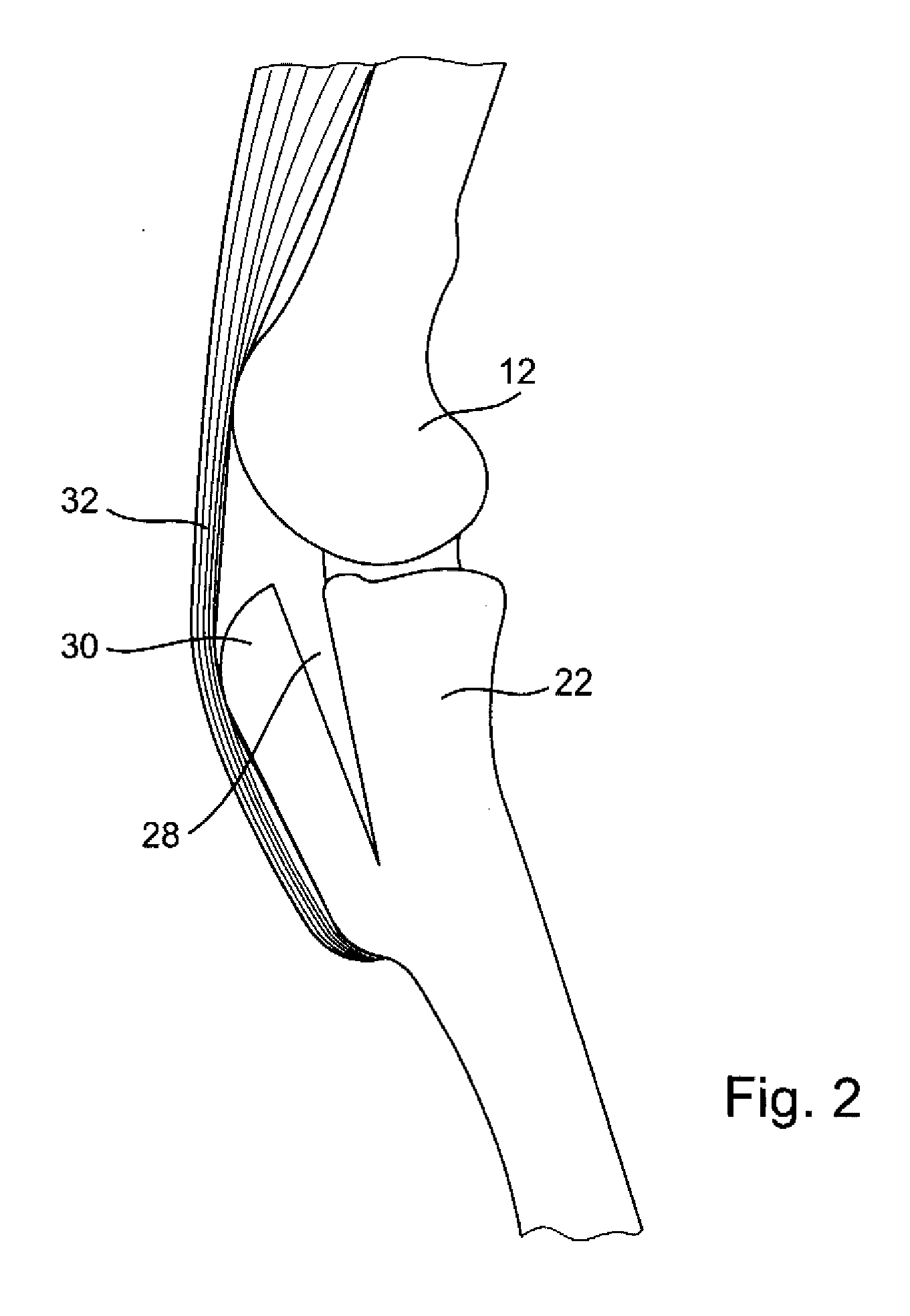
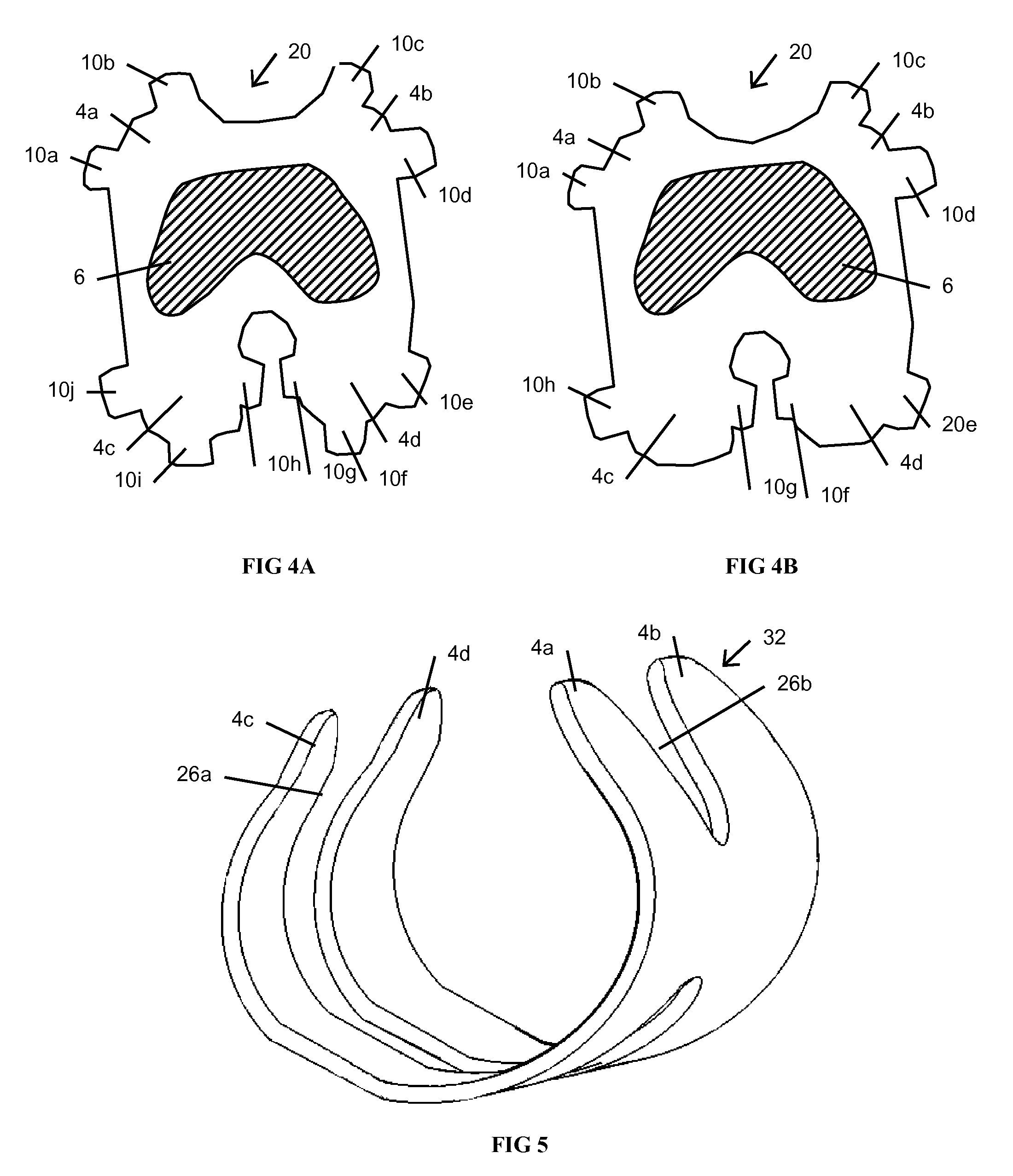
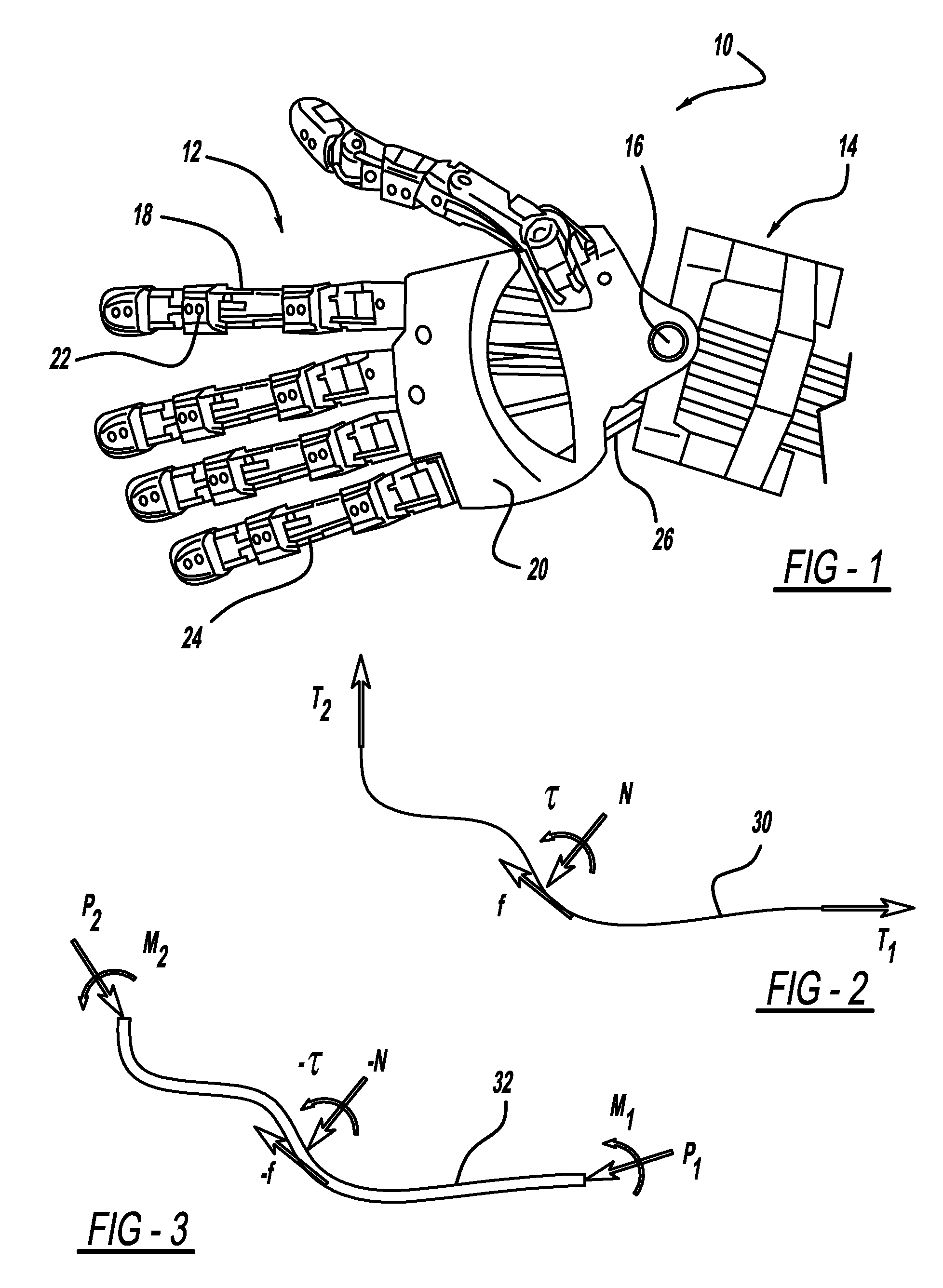
Adjustable artificial chordeae tendineae with suture loops
ActiveUS8790394B2Easy to implantGuaranteed functionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesDistal portionPlantaris tendon
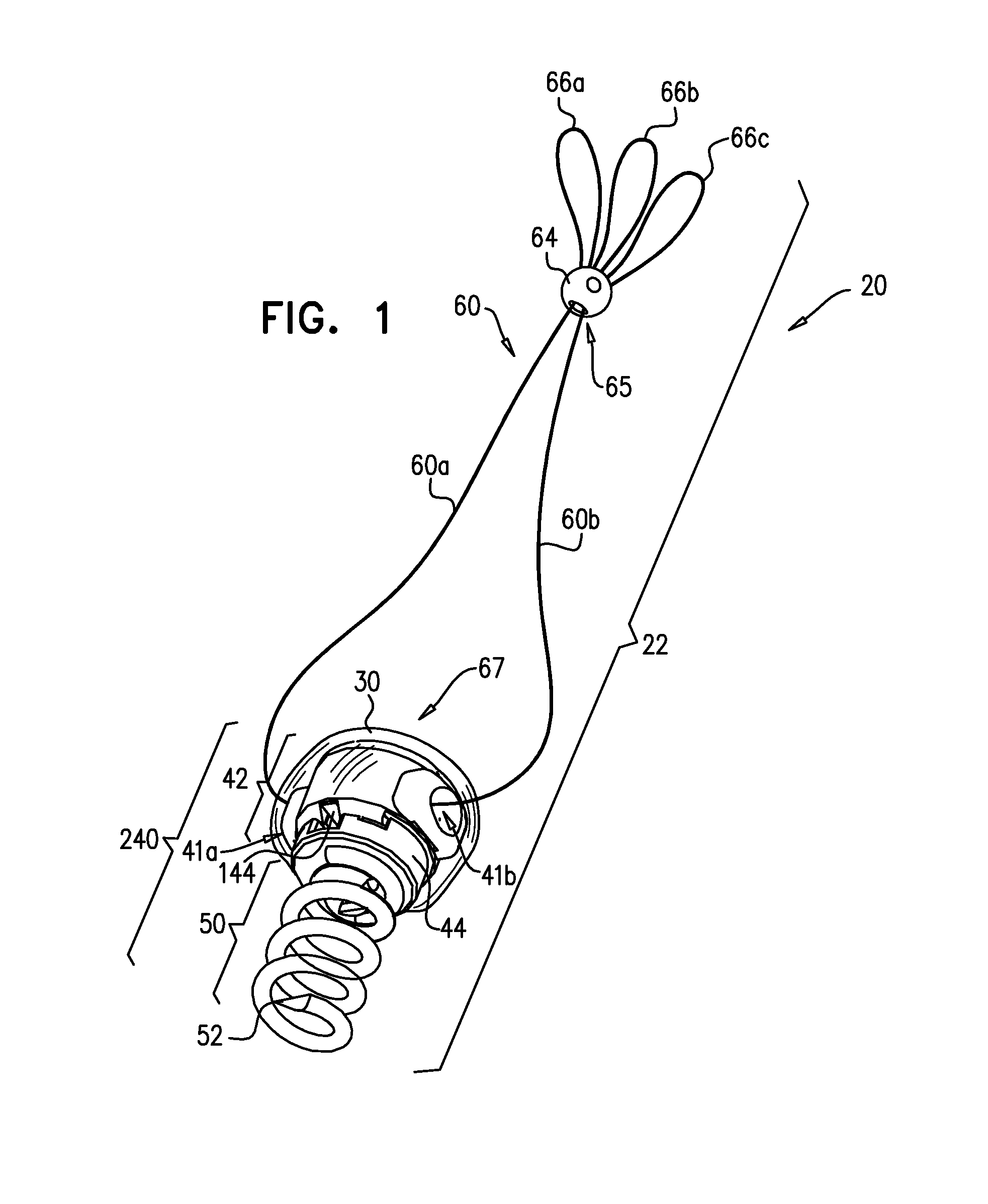
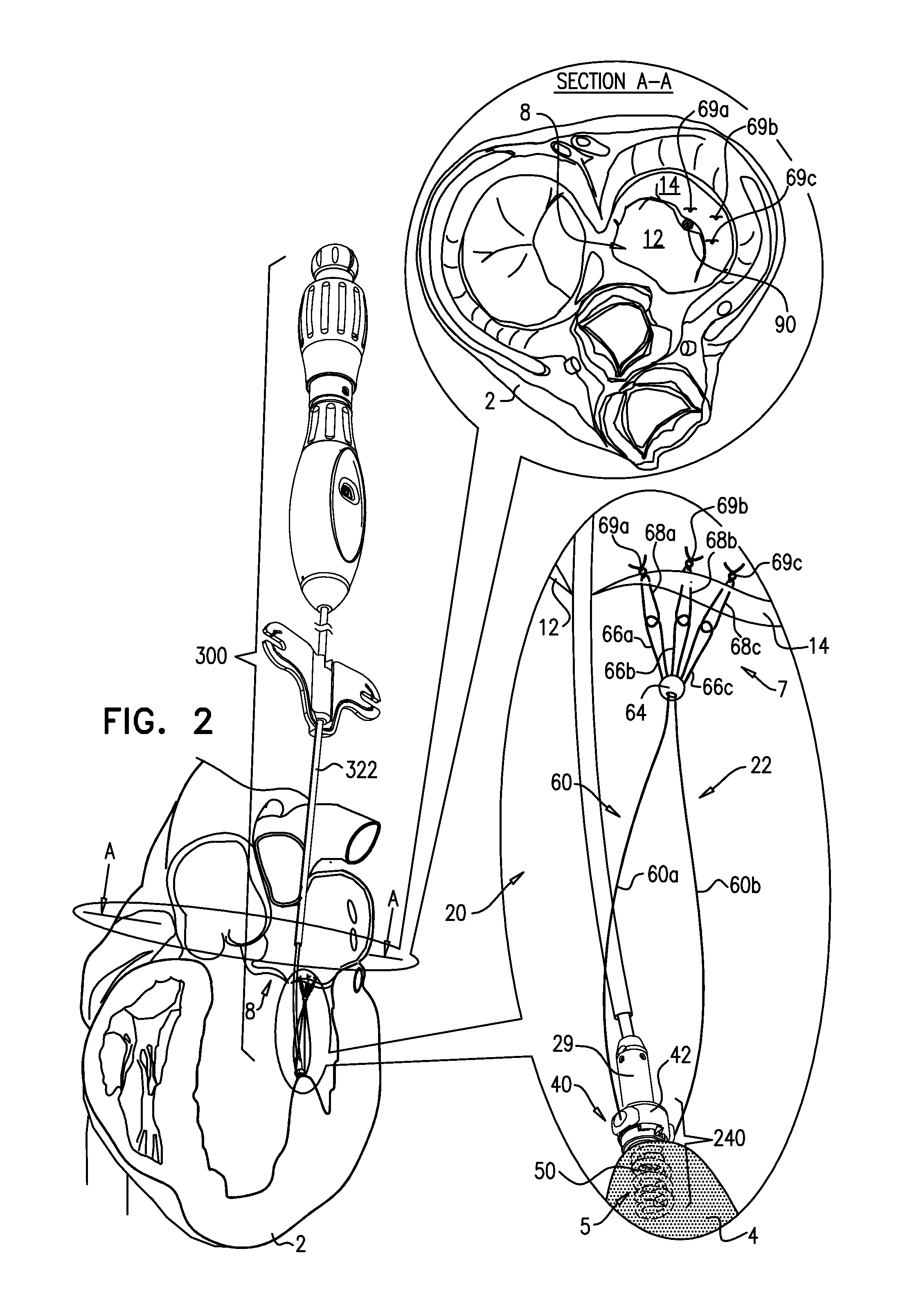
Apparatus is provided, including an artificial-chordeae-tendineae-adjustment mechanism and at least one primary artificial chordea tendinea coupled at a distal portion thereof to the artificial-chordeae-tendineae-adjustment mechanism. A degree of tension of the at least one primary artificial chordea tendinea is adjustable by the artificial-chordeae-tendineae-adjustment mechanism. One or more loops are coupled at a proximal portion of the at least one primary artificial chordea tendinea. The one or more loops are configured to facilitate suturing of the one or more loops to respective portions of a leaflet of an atrioventricular valve of a patient. Other applications are also described.
Owner:VALTECH CARDIO LTD
Tendon repair implant and method of arthroscopic implantation
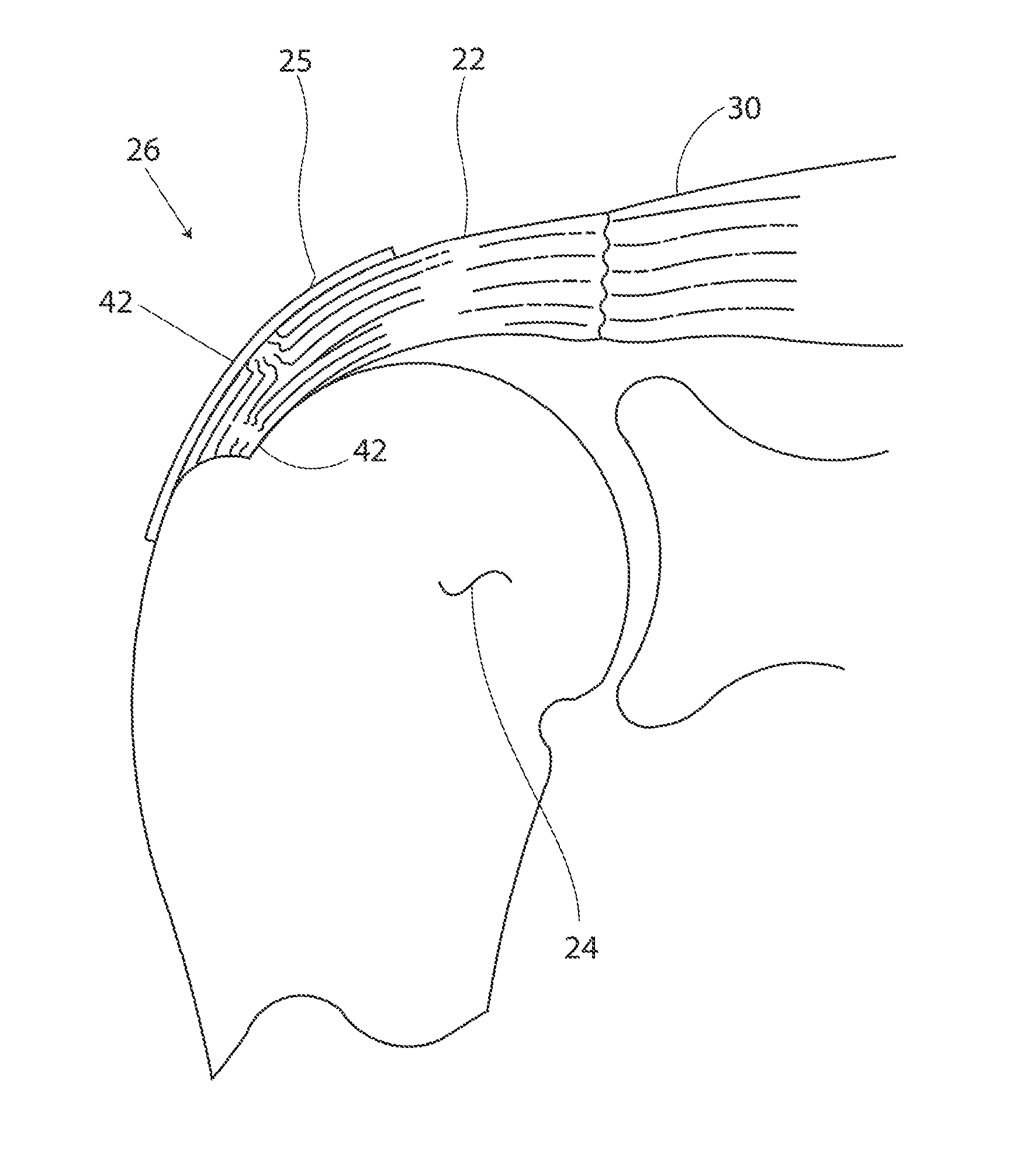
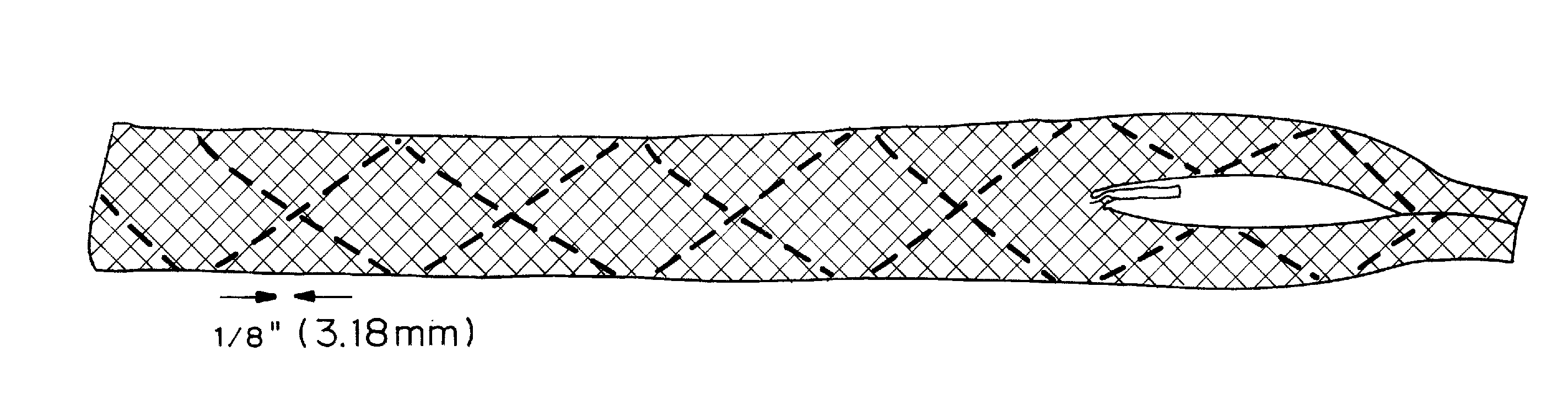
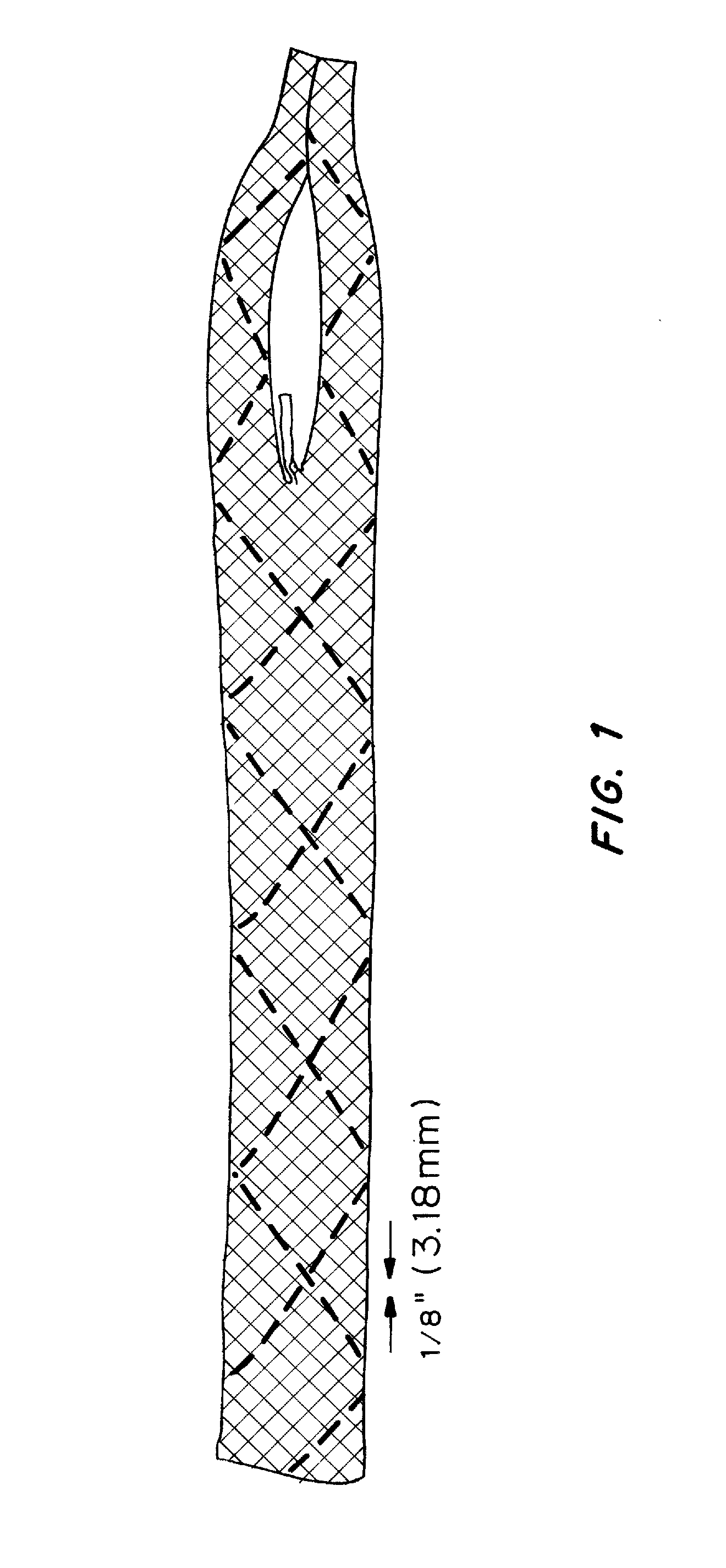
A tendon repair implant for treatment of a partial thickness tear in the supraspinatus tendon of the shoulder is provided. The implant may incorporate features of rapid deployment and fixation by arthroscopic means that compliment current procedures; tensile properties that result in desired sharing of anatomical load between the implant and native tendon during rehabilitation; selected porosity and longitudinal pathways for tissue in-growth; sufficient cyclic straining of the implant in the longitudinal direction to promote remodeling of new tissue to tendon-like tissue; and, may include a bioresorbable construction to provide transfer of additional load to new tendon-like tissue and native tendon over time.
Owner:ROTATION MEDICAL
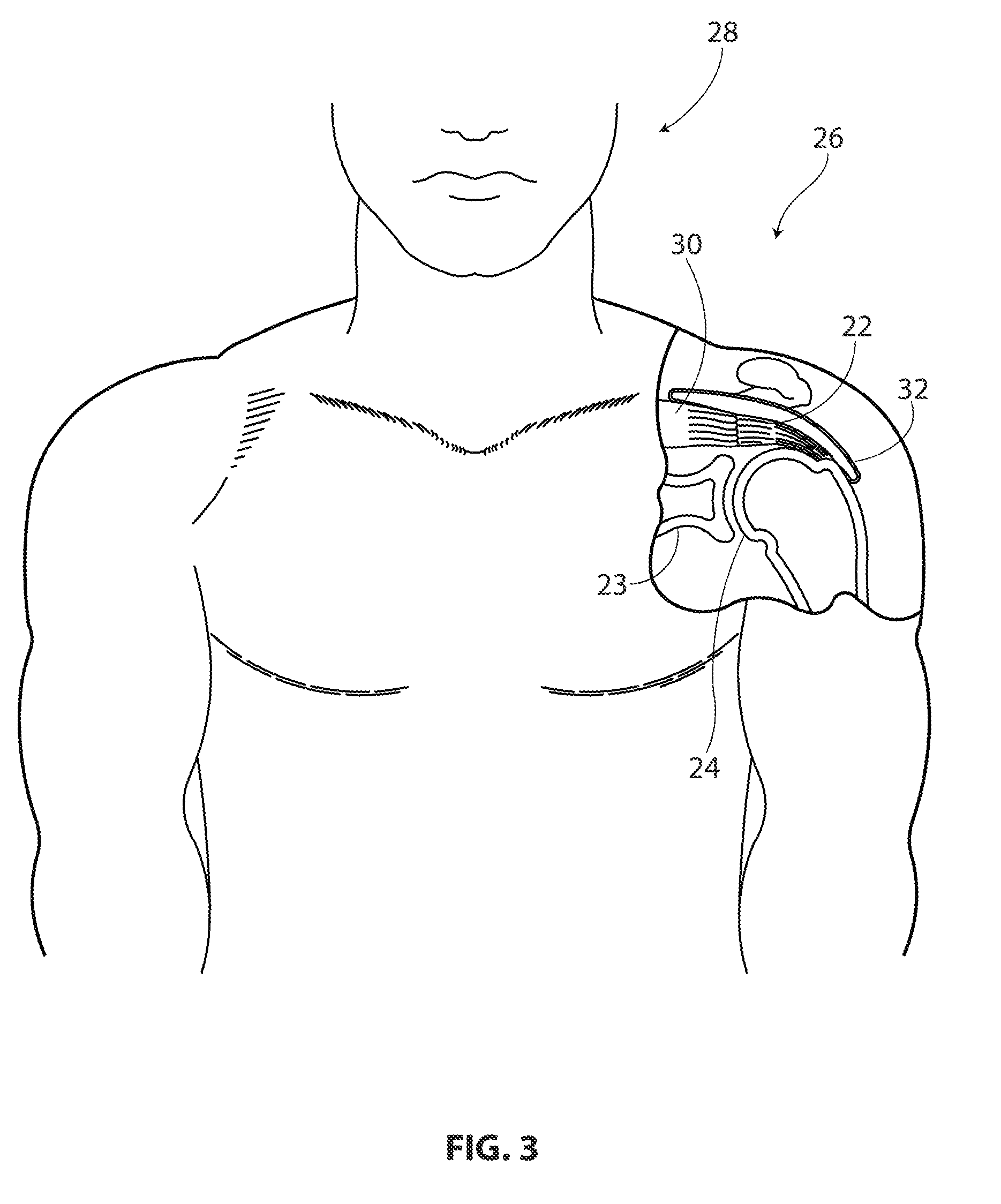
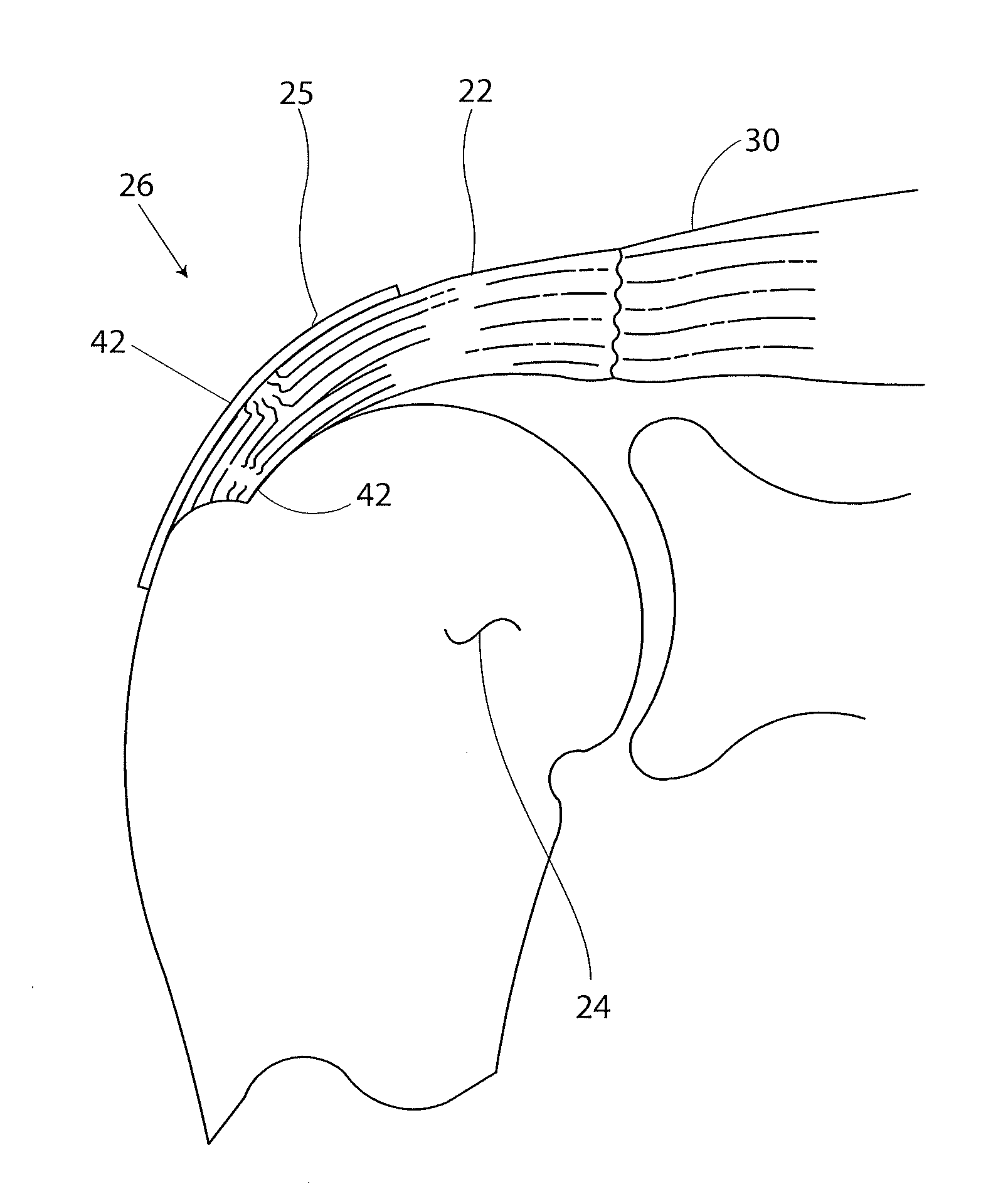
Mechanically Competent Scaffold for Rotator Cuff and Tendon Augmentation
A device has been developed to augment the rotator cuff tendon tissue as it proceeds in healing. The device has two purposes: to provide initial stability to the rotator cuff repair site to allow early mobilization of the upper extremity of the patient, and to allow for reinforcement of rotator cuff tendon repairs to increase the likelihood of successful rotator cuff tendon repairs. The device consists of an inter-connected, open pore structure that enables even and random distribution and in-growth of tendon cells. The braided structure allows for distribution of mechanical forces over a larger area of tissue at the fixation point(s).
Owner:BIOREZ INC
Tendon repair implant and method of arthroscopic implantation
A tendon repair implant for treatment of a partial thickness tear in the supraspinatus tendon of the shoulder is provided. The implant may incorporate features of rapid deployment and fixation by arthroscopic means that compliment current procedures; tensile properties that result in desired sharing of anatomical load between the implant and native tendon during rehabilitation; selected porosity and longitudinal pathways for tissue in-growth; sufficient cyclic straining of the implant in the longitudinal direction to promote remodeling of new tissue to tendon-like tissue; and, may include a bioresorbable construction to provide transfer of additional load to new tendon-like tissue and native tendon over time.
Owner:ROTATION MEDICAL
Method for double row fixation of tendon to bone
A system and method for soft tissue to bone repair employing at least one suture anchor combined with at least one knotless fixation device. The method for soft tissue to bone fixation includes: (i) providing a first medial row constructed with a first plurality of fixation devices, at least one of the first plurality of fixation devices is an anchor; and (ii) providing a second lateral row constructed with a second plurality of fixation devices, at least one of the second plurality of fixation devices is a knotless fixation device, and suture or tape or allograft / biological component extending over the soft tissue and secured in place by the anchors in the first and second medial rows.
Owner:ARTHREX
Biocompatible scaffold for ligament or tendon repair
Owner:DEPUY MITEK INC
Active assist for the ankle, knee and other human joints
InactiveUS20060142680A1Reduce the risk of injuryLower requirementNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSports activityKnee Joint
A human joint assist device that applies a torque at the joint to assist physiological exertion forces, that is the load carrying task of the joint and surrounding muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The application of this device reduces the physiological exertion force requirement, and may be adjusted with respect to assist level, to suit the issue associated with joint motion and is useful for joint rehabilitation and sports activities. Among other things, this results in a reduction of physiological exertion force in a fashion that makes it easier to extend the levers (long bones) associated with extension against a given resistance. For example, standing from a squatted position with the assist of this device reduces the stress on physiological members associated with joint articulation.
Owner:IAROCCI MICHAEL ANTHONY
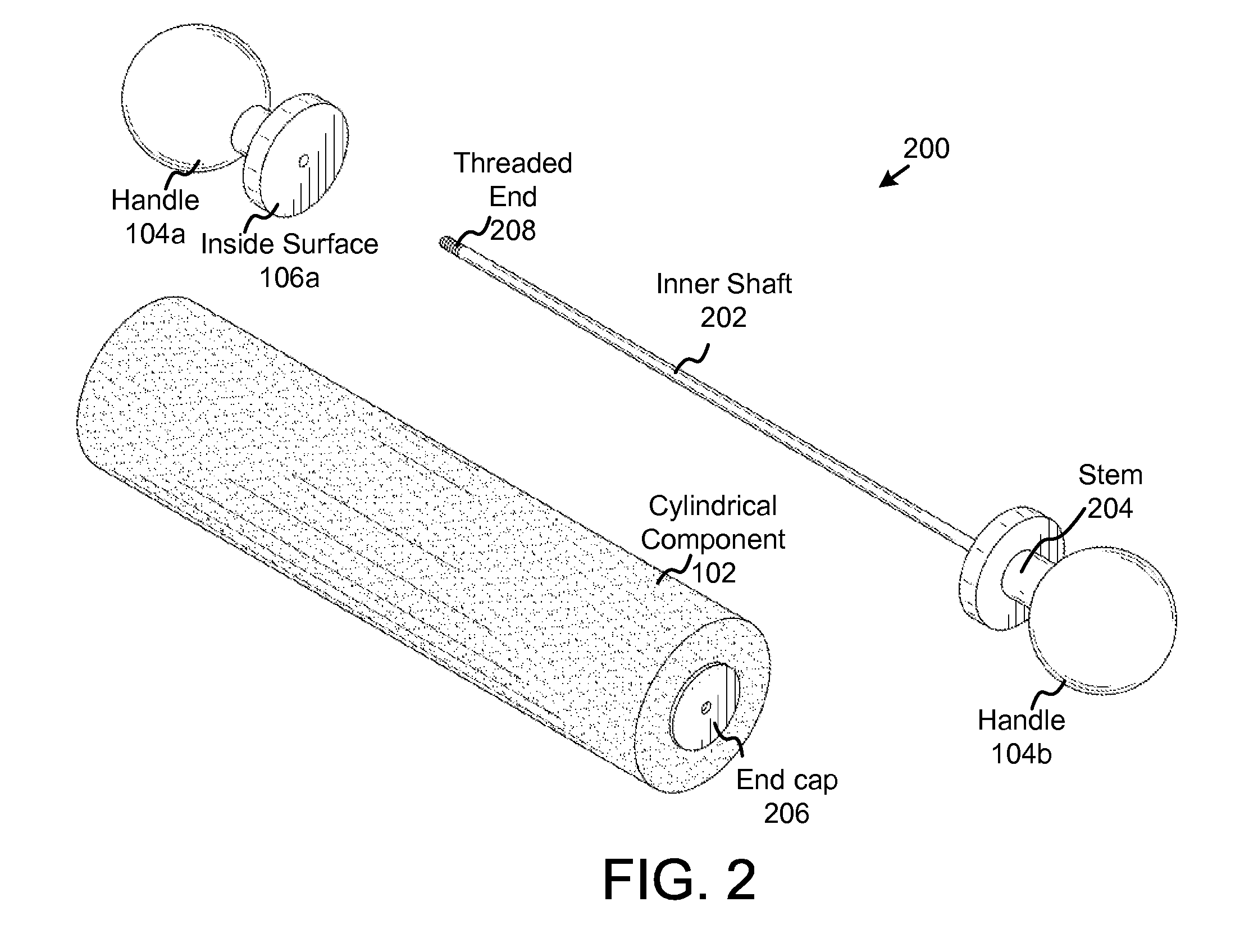
Cylindrical roller massage tool
InactiveUS20120310125A1Reduced usabilityApply pressure to largeDevices for pressing relfex pointsVibration massagePlantaris tendonScroll wheel
A manually operated cylindrical roller is disclosed which facilitates the even application of pressure to the body tissue of a client during massage therapy, including tendons, ligaments, and muscles (e.g. the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, sartorius, plantaris, and the like). Variations of the disclosed tool comprise inflatable and non-inflatable components, as well as foam components. The disclosed invention relieves sore and achy muscles, helps blood circulation, relieving muscle cramps, loosening tight and knotted muscles, and relieving pressure from the massage therapist's hands.
Owner:HALL WENDELL +3
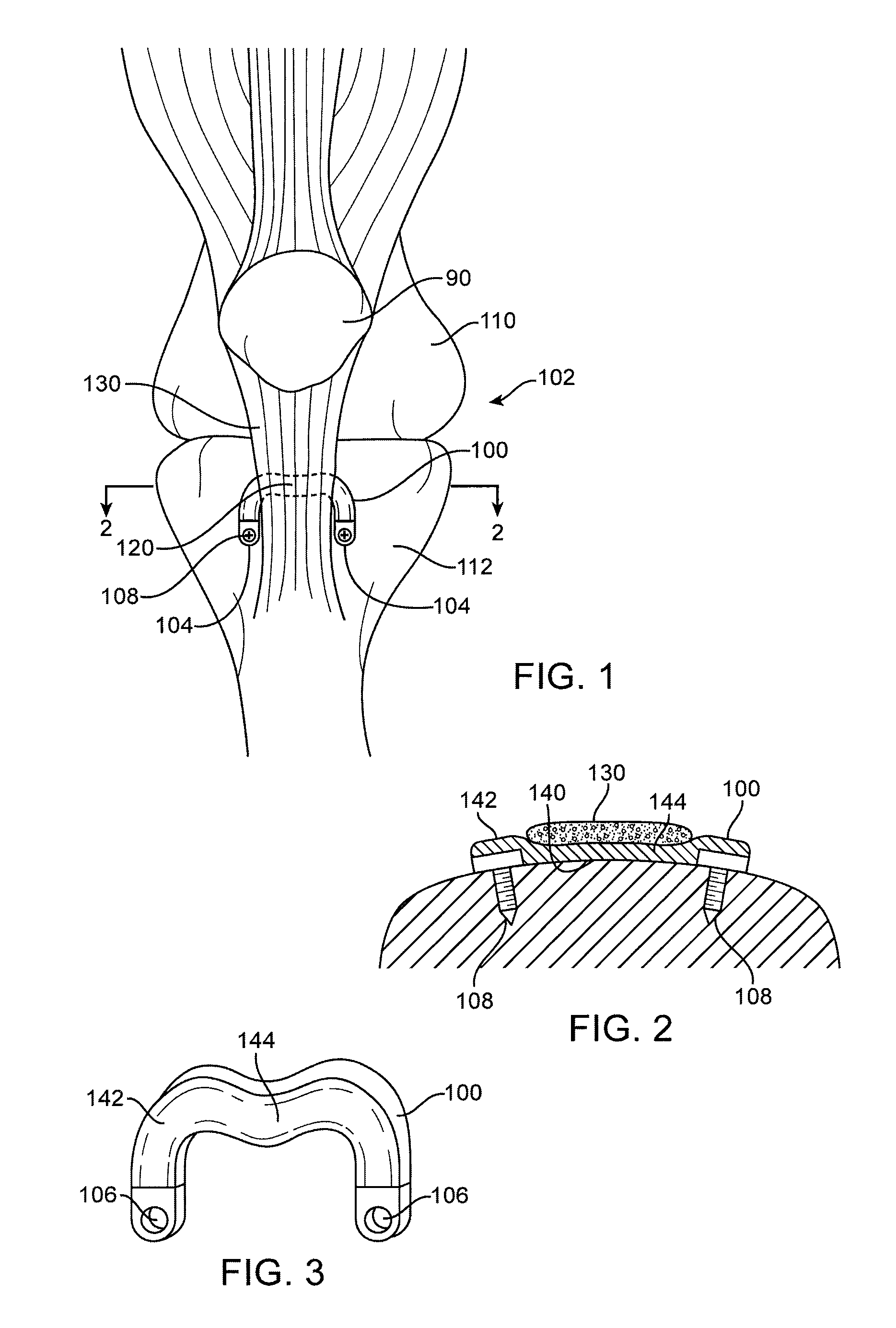
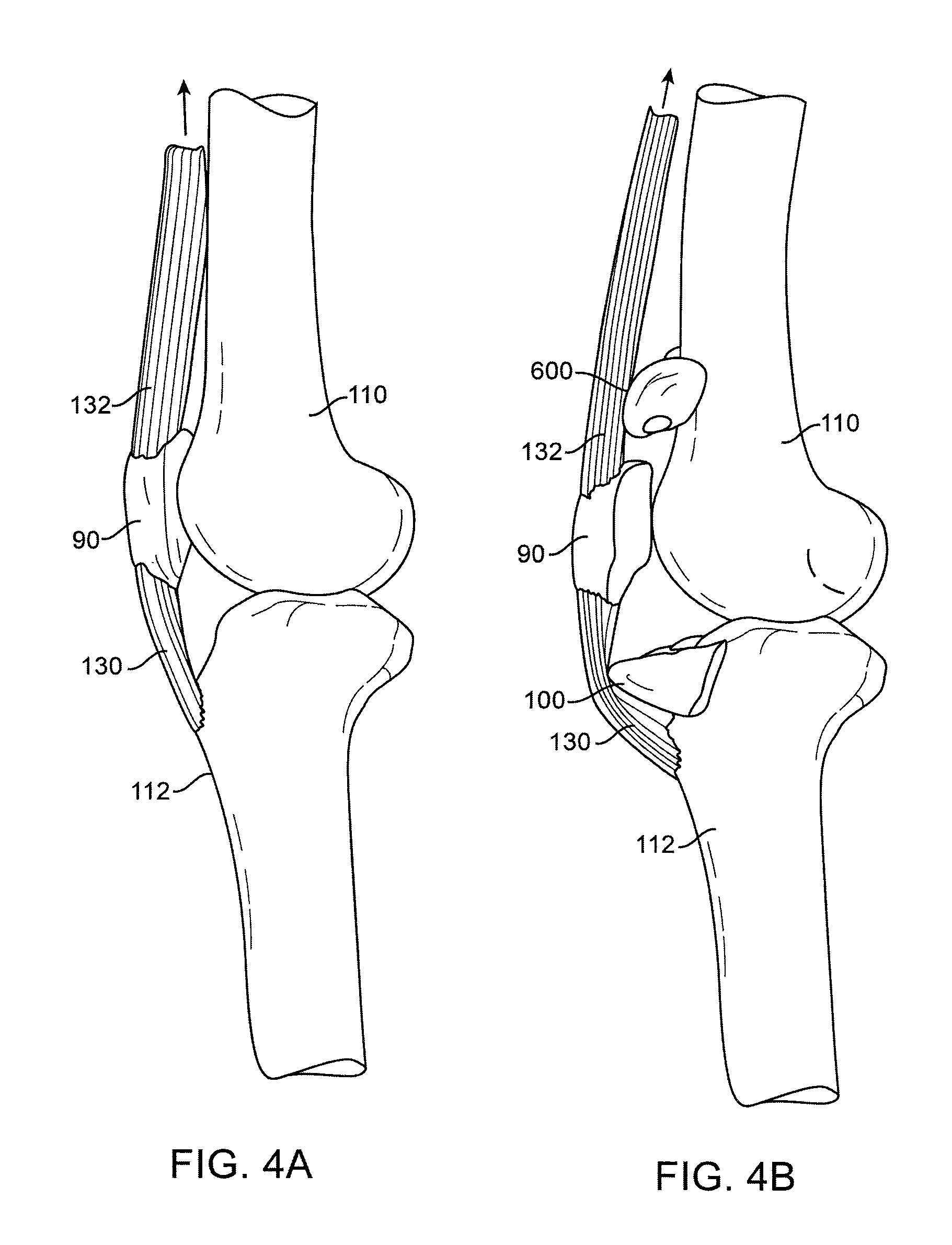
Spacers for Redistributing Forces for the Patella
Implant apparatus and methods directed toward treating conditions involving the knee joint and the patella specifically are disclosed. Full range of motion of the knee joint and tissue integrity are maintained in treatment approaches involving implanting a joint surface load reducing implant proximate the joint to change the direction of the tendons or muscles exerting forces on the joints.
Owner:MOXIMED INC
Shock absorber ankle exercise device
InactiveUS7892154B1Easy to storeEase of transportationSpace saving gamesMuscle exercising devicesMotion resistancePlantaris tendon
An apparatus and method designed to strengthen, develop, and rehabilitate the anatomy of the human ankle is herein disclosed, comprising a large stable floor base and a plurality of resistant shock absorber-like members extending therefrom a foot securing platform. A user's foot is placed thereon and connected thereto the foot platform by toe and heel cuffs. Each motion resistant cylinder has adjustment means for reducing or adding resistance. In use, the attached lower leg and foot is restrained in all planar and vertical axes; however, the user is able to move their foot in a vertical and orbital manner against the resistance of the cylinders resulting in rehabilitation and / or strengthening of the muscles, tendons and ligaments surrounding the ankle. Improving ankle strength and mobility using this apparatus would have athletic, fitness, and therapeutic benefits.
Owner:ALEXA AUSTEN
Cannula system and method for partial thickness rotator cuff repair
ActiveUS20120123473A1Expand accessIncrease surface areaSuture equipmentsLigamentsSuture anchorsDistal portion
A trans-soft tissue anchor implantation system in one embodiment includes a positioning wire having a tissue penetrating distal tip, a cannula for passage through the soft tissue and a suture anchor. The cannula has an axial lumen therethrough sized to accommodate at least the positioning wire, a thin-walled distal portion and a tissue engaging feature, such as an arcuate groove, on at least a portion of an outer surface of the cannula proximal of and adjacent to the distal portion. Tissue, such as a tendon, expands into the groove allowing a surgeon to manipulate the tissue with the cannula.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Method of tendon repair with amnion and chorion constructs
It is described a construct for use in surgical repair of tendon. The construct contains at least one layer of human amnion and chorion tissues and is generally cylindrical with a C-shaped cross-section to allow for ease of implantation over the tendon. Methods for preparing the construct is described. In addition, an improved method for surgical repair of a damaged or diseased tendon using the construct is also described. The improved method reduces adhesions, scar formation, inflammation and risk of post-operative infection.
Owner:LIVENTA BIOSCI
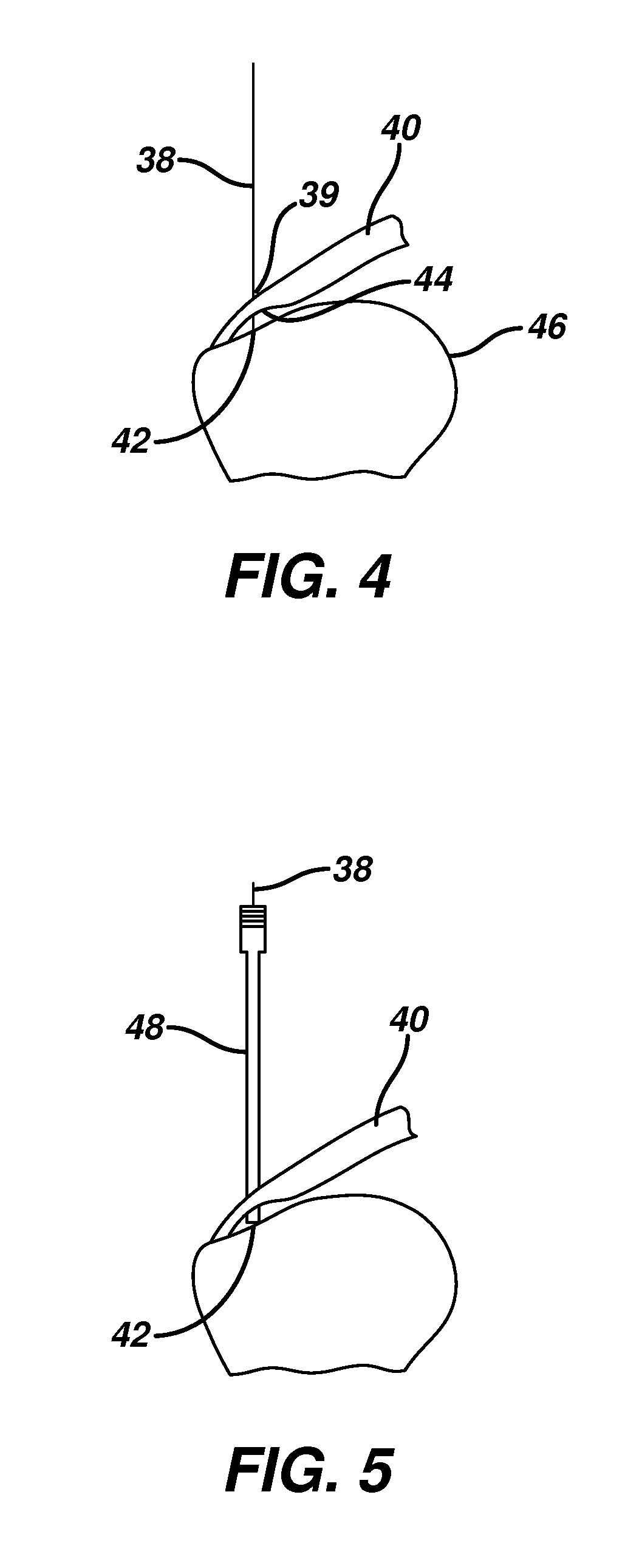
Method of loading tendons into the knee
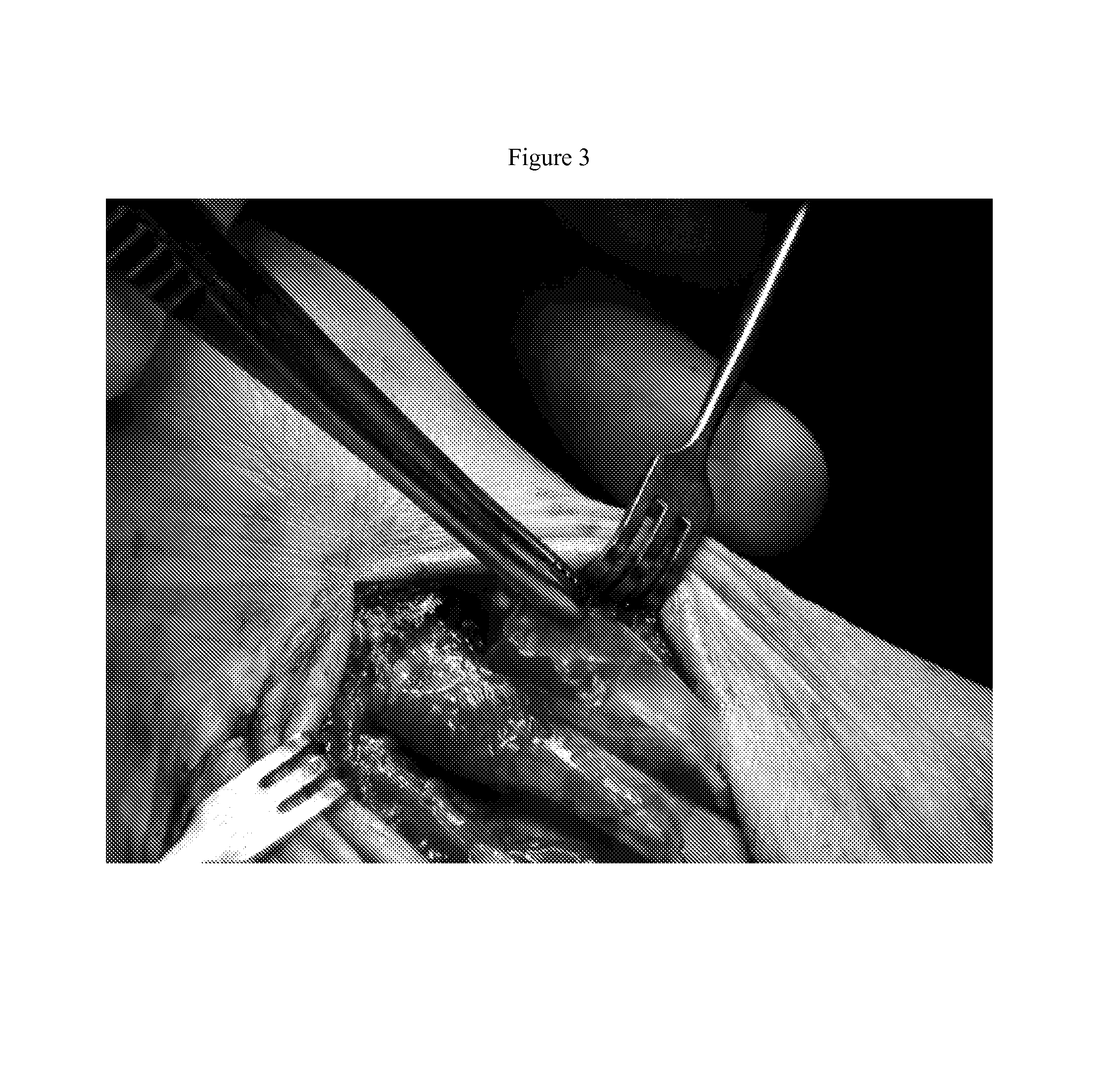
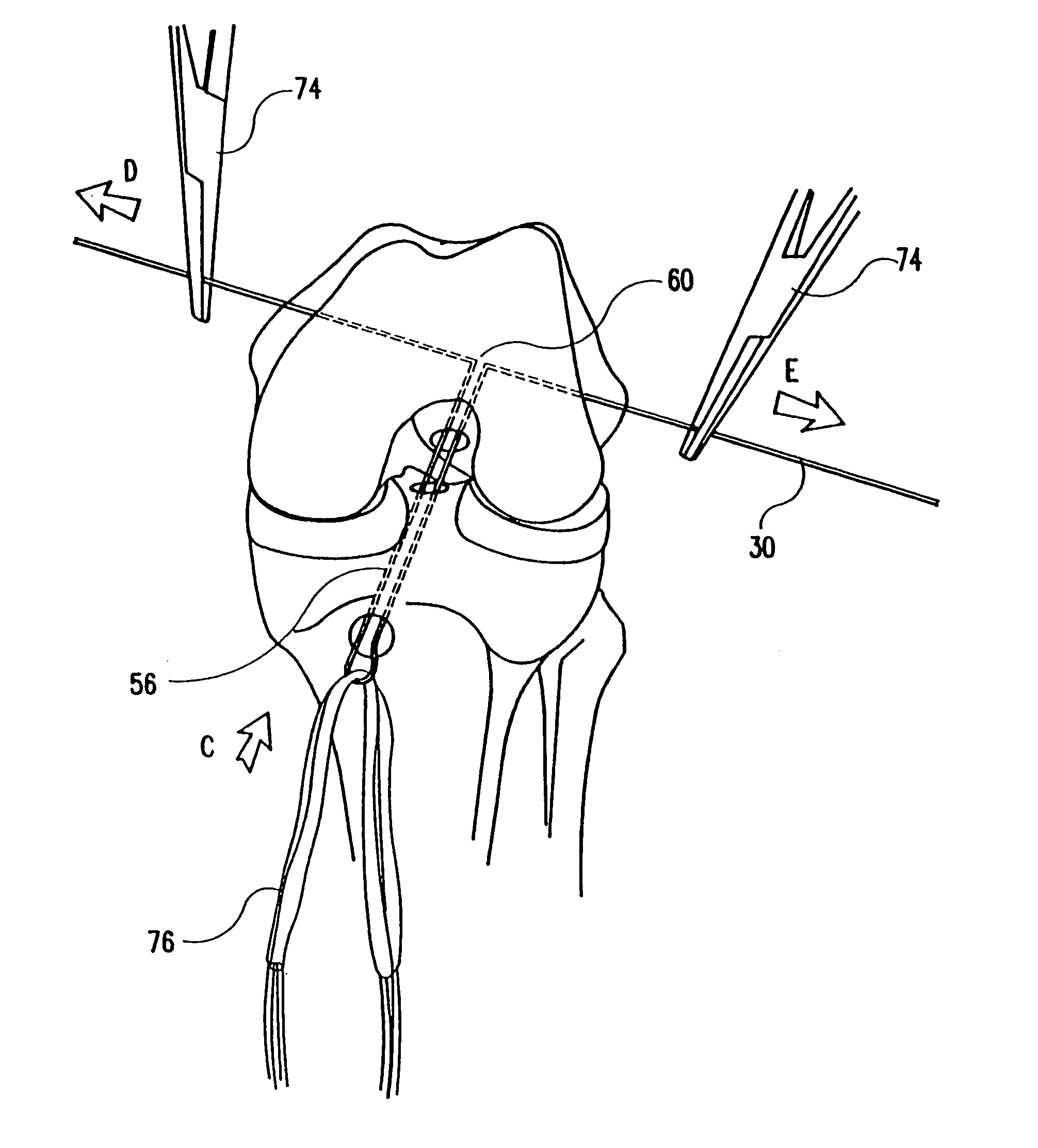
InactiveUS20060116684A1Overcome problemsSuture equipmentsNail extractorsLigament structurePlantaris tendon
A surgical method for loading ligament grafts into a joint. A longitudinal socket formed in a bone is intersected by a transverse pin. A flexible strand is drawn with the pin through the bone. A looped portion of the strand is diverted so as to protrude out of the entrance to the longitudinal socket. The ends of the strand remaining accessible on either side of the bone. The ligament graft is captured within the strand loop protruding from the entrance to the socket. The strand is retracted into the socket, drawing the graft into the socket by pulling on the accessible ends of the flexible strand. The graft is fixed in the socket using a transverse implant.
Owner:ARTHREX
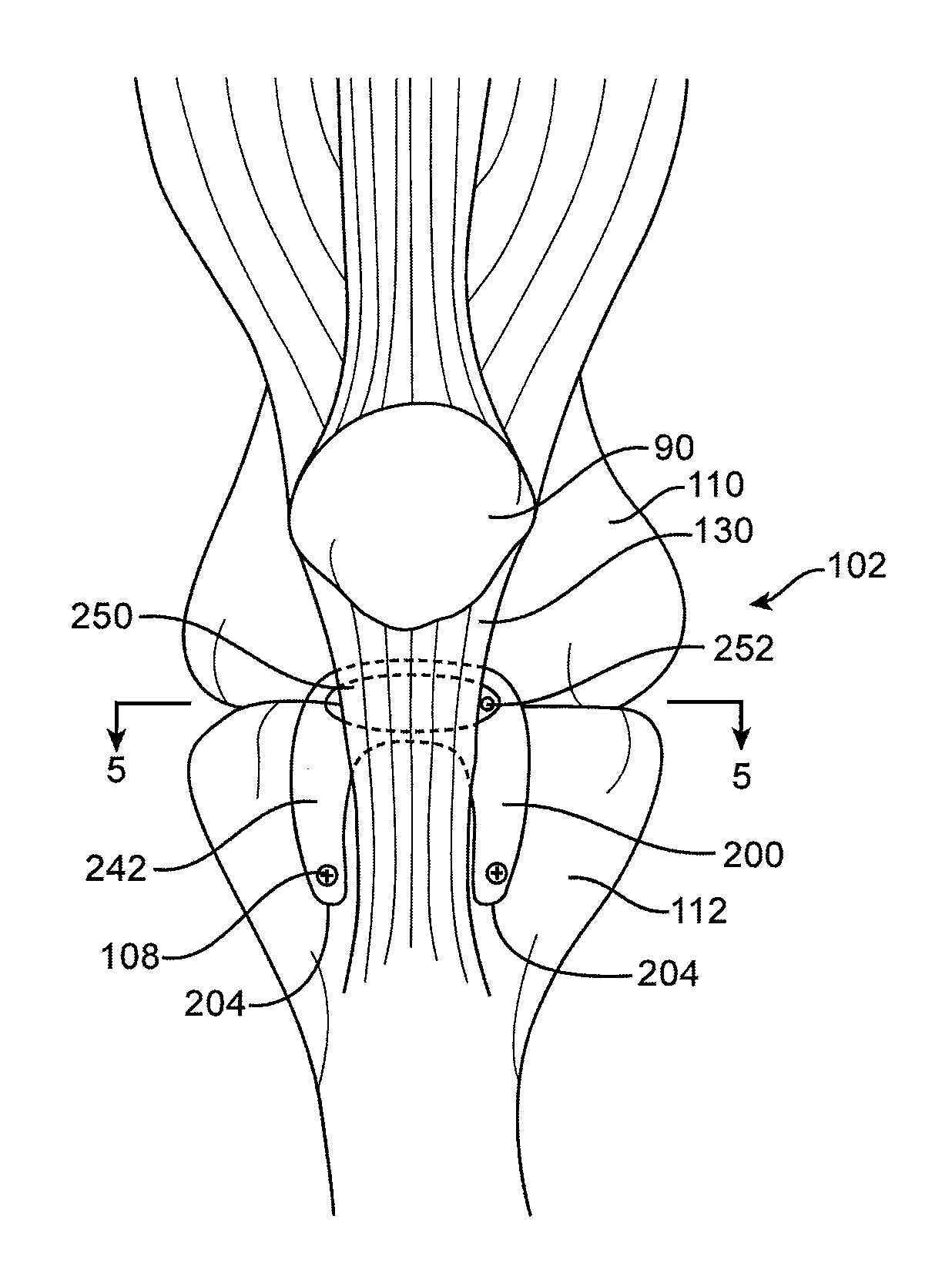
Tibia implant for tightening the patella tendons
ActiveUS20130030540A1Prevent movementRapid manufacturing methodJoint implantsSkullTibiaPlantaris tendon
A tibia implant for tightening the patella tendons, has a vertical cross section which in mounted position tapers downward, an essentially vertically arranged base plate which carries a sponge structure, wherein the sponge structure on both sides rests against a respective vertical cut surface of a vertical knee proximal incision of the tibia.
Owner:RITA LEIBINGER
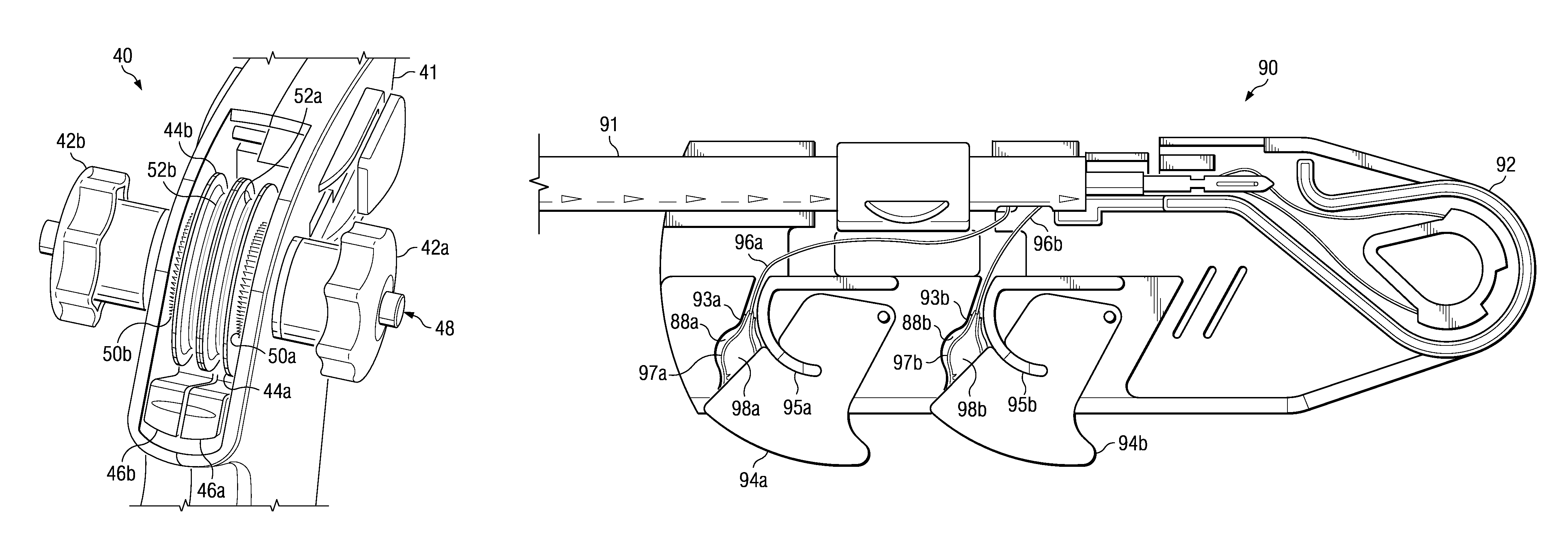
Independent suture tensioning and snaring apparatus
ActiveUS8105343B2Reduce tensionPrevent rotationSuture equipmentsOsteosynthesis devicesPlantaris tendonRotator cuff
In repairing soft tissue with a bone anchoring instrument (such as reattaching a tendon of a torn rotator cuff), the bone anchoring instrument may be used to anchor the soft tissue to a region of bone. The anchors inserted into the underlying bone may have one or more lengths of suture or wire attached thereto which may be tensioned independently of one another to affix the soft tissue to the bone by having a selector mechanism selectively engage and disengage ratcheted tensioning wheels from one another. Suture loading mechanisms may be employed for passing suture lengths into and / or through the anchors prior to deployment into the bone where such mechanisms may employ suture snares which are configured to reconfigure from an expanded shape through which suture lengths may be easily passed to a low-profile shape which secures the suture lengths within the snare.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Resilient medically inflatable interpositional arthroplasty device
InactiveUS20120316645A1Preserve joint motionFree from painAnkle jointsSurgeryArticular surfacesAnatomical structures
This disclosure is directed to a resilient interpositional arthroplasty implant for application into joints to pad cartilage defects, cushion joints, and replace or restore the articular surface, which may preserve joint integrity, reduce pain and improve function. The implant may endure variable joint compressive and shear forces and cyclic loads. The implant may repair, reconstruct, and regenerate joint anatomy, and thereby improve upon joint replacement alternatives. Rather than using periosteal harvesting for cell containment in joint resurfacing, the walls of this invention may capture, distribute and hold living cells until aggregation and hyaline cartilage regrowth occurs. The implant may be deployed into debrided joint spaces, molding and conforming to surrounding structures with sufficient stability to avoid extrusion or dislocation. Appendages of the implant may repair or reconstruct tendons or ligaments, and an interior of the implant that is inflatable may accommodate motions which mimic or approximate normal joint motion.
Owner:GROTZ R THOMAS
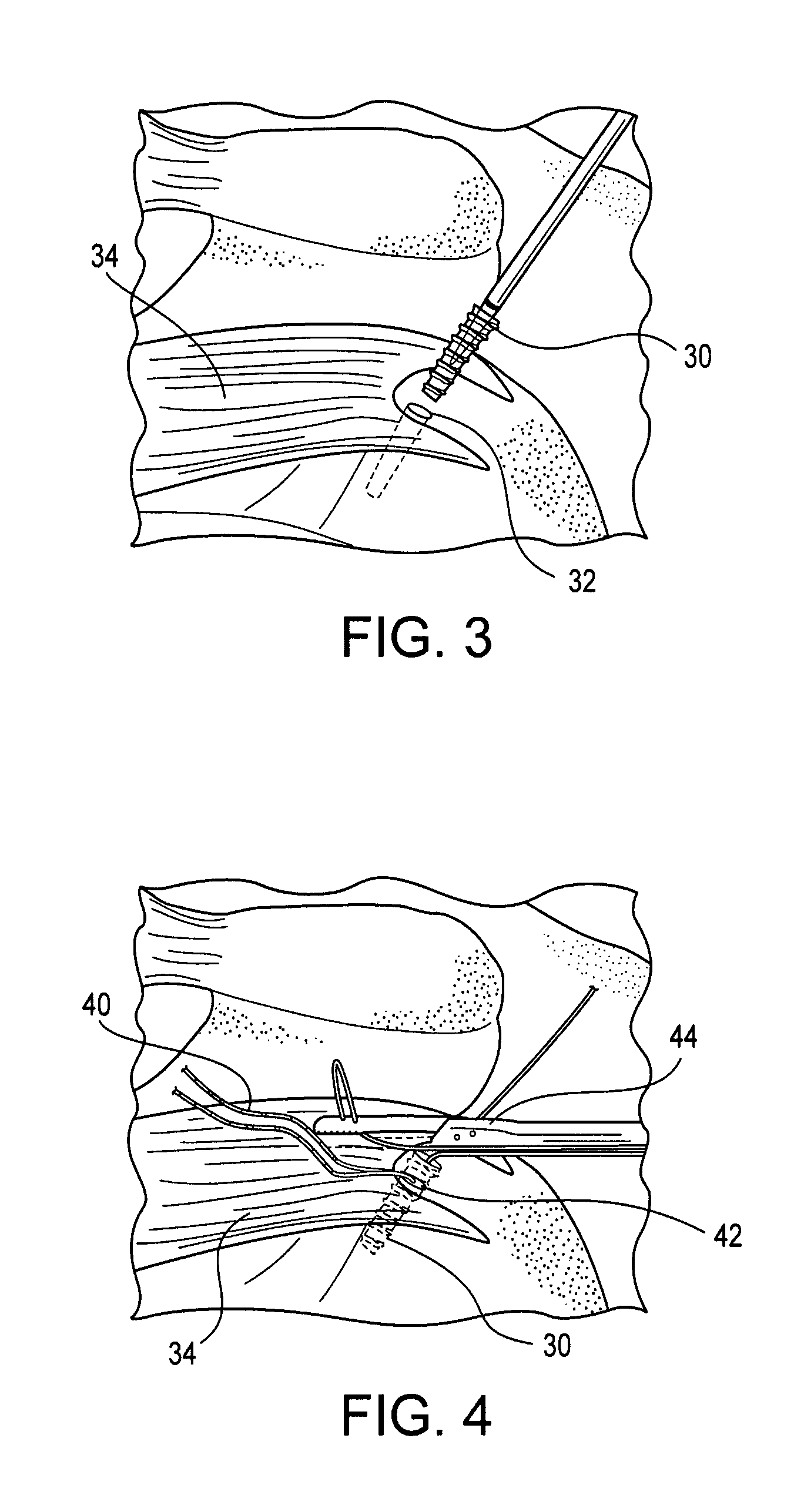
Method for minimally invasive tendon sheath release using device with hemi-cannula
ActiveUS8771303B1Minimal dissectionPrecision releaseDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTendon sheathPlantaris tendon
A method for minimally invasive tendon sheath release is presented herein. The method enables a surgeon to cut (“open”) a pulley that is obstructing a nodule and keeping a tendon from sliding smoothly. A guide probe of the device is inserted through a small incision and is used to find the edge of the pulley. Once found, the probe is guided to an end of the pulley. Proper placement of the device may be confirmed through the use of ultrasound. After proper position is assured, a hemi-cannula is moved over the guide probe to isolate the pulley from the surrounding tissue. A cutting blade is then used to sever the pulley. A dilation device may be inserted prior to the insertion of the spherical tipped guide probe to dilate the area.
Owner:SONICSURG INNOVATIONS
Tissue fixation system with single component anchor
InactiveUS20110112558A1Easy to grab and moveEasy to participateSuture equipmentsLigamentsBone tunnelBiceps tendon
A method and apparatus for biceps tenodesis or attachment of other tendon, or other soft tissue to bone. The tissue fixation system incorporates a single component anchor fabricated from a unitary piece or thin wafers bonded into a single component. The anchors incorporate features to engage a tendon or other soft tissue and maintain that engagement as the anchor and tendon are positioned into a bone tunnel or channel. The anchor secures to bone ensuring the tendon or other soft tissue are engaged within the bone tunnel or channel to produce the required fixation.
Owner:OC2
Resilient knee implant and methods
ActiveUS8771363B2Preserve joint motionsRemoving dysfunctionJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesAnatomical structures
This disclosure is directed to a resilient interpositional arthroplasty implant for application into a knee joint to pad cartilage defects, cushion a joint, and replace or restore the articular surface, which may preserve joint integrity, reduce pain and improve function. The implant may endure variable joint compressive and shear forces and cyclic loads. The implant may repair, reconstruct, and regenerate joint anatomy, and thereby improve upon joint replacement alternatives. Rather than using periosteal harvesting for cell containment in joint resurfacing, the walls of this invention may capture, distribute and hold living cells until aggregation and hyaline cartilage regrowth occurs. The implant may be deployed into debrided joint spaces, molding and conforming to surrounding structures with sufficient stability to avoid extrusion or dislocation. Appendages of the implant may repair or reconstruct tendons or ligaments, and an interior of the implant that is inflatable may accommodate motions which mimic or approximate normal joint motion.
Owner:IORTHOPEDICS INC
Method for minimally invasive tendon sheath release
A device and method for minimally invasive tendon sheath release. The device and method that enables a surgeon to cut (“open”) a pulley that is obstructing a nodule and keeping a tendon from sliding smoothly. A ball tipped guide probe goes through a small incision and is used to find the edge of the pulley. Once found, the probe is guided to an end of the pulley. After proper position is assured, a cutting blade is deployed by pushing and holding a blade deployment switch. This deploys the sharp end of a retractable cutting shaft beyond the sheath. The entire device is then pushed or pulled using the device handle along the pulley until the pulley is completely released or where resistance is no longer felt. In an alternate embodiment, the cutting blade is static.
Owner:SONICSURG INNOVATIONS
Device and method for assisting in flexor tendon repair and rehabilitation
ActiveUS20090048616A1Smoothly glide intoSmooth outSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsRepair siteSurgical repair
A surgical device and method used to assist in the surgical repair and rehabilitation of damaged and / or severed tendons. In one embodiment of the present invention, the device is comprised of a hollow member, preferably shaped as a partial funnel and / or cone, having an inner and outer surface, a flared mouth, a shaft, and an apical end. In another embodiment, the device is comprised of a hollow member, preferably shaped as funnel or barrel cut in half along its longitudinal axis, having an inner and outer surface, two flared mouths, and a shaft. The device may further include a thin, elongated handle for ease of manipulation, and can be implantable or non-implantable. The present invention further discloses a method of passing a severed flexor tendon and / or repair site through the edge of a pulley in the flexor tendon sheath, wherein the hollow member of the device disclosed in the present invention is introduced into the edge of a flexor tendon sheath's pulley and a severed tendon end and / or repair site is passed through the flared mouth of the device and is gently compressed through the shaft and apical end of the device so that the tendon end or repair site can be simultaneously squeezed into the pulley in a smooth and non-damaging manner.
Owner:TOBY ORTHOPAEDICS
Method and apparatus for repairing a tendon or ligament
The invention comprises methods and apparatus for reattaching anatomical members, such as tendons, ligaments, or bone, during preparing and healing of the member using a surgical repair device that can be securely attached to the member and then safely guided through tortuous anatomy for reattachment and repair. The repair device further includes structural means to secure opposed ends of the member against separation during healing. Devices for aiding in the positioning of the surgical repair device also are provided, such as a crimp connector holder tool for holding the crimp connector during threading therethrough of two sutures attached to two tendon stumps for bringing the two stumps into abutment and crimping them in place.
Owner:CORE ESSENCE ORTHOPAEDICS
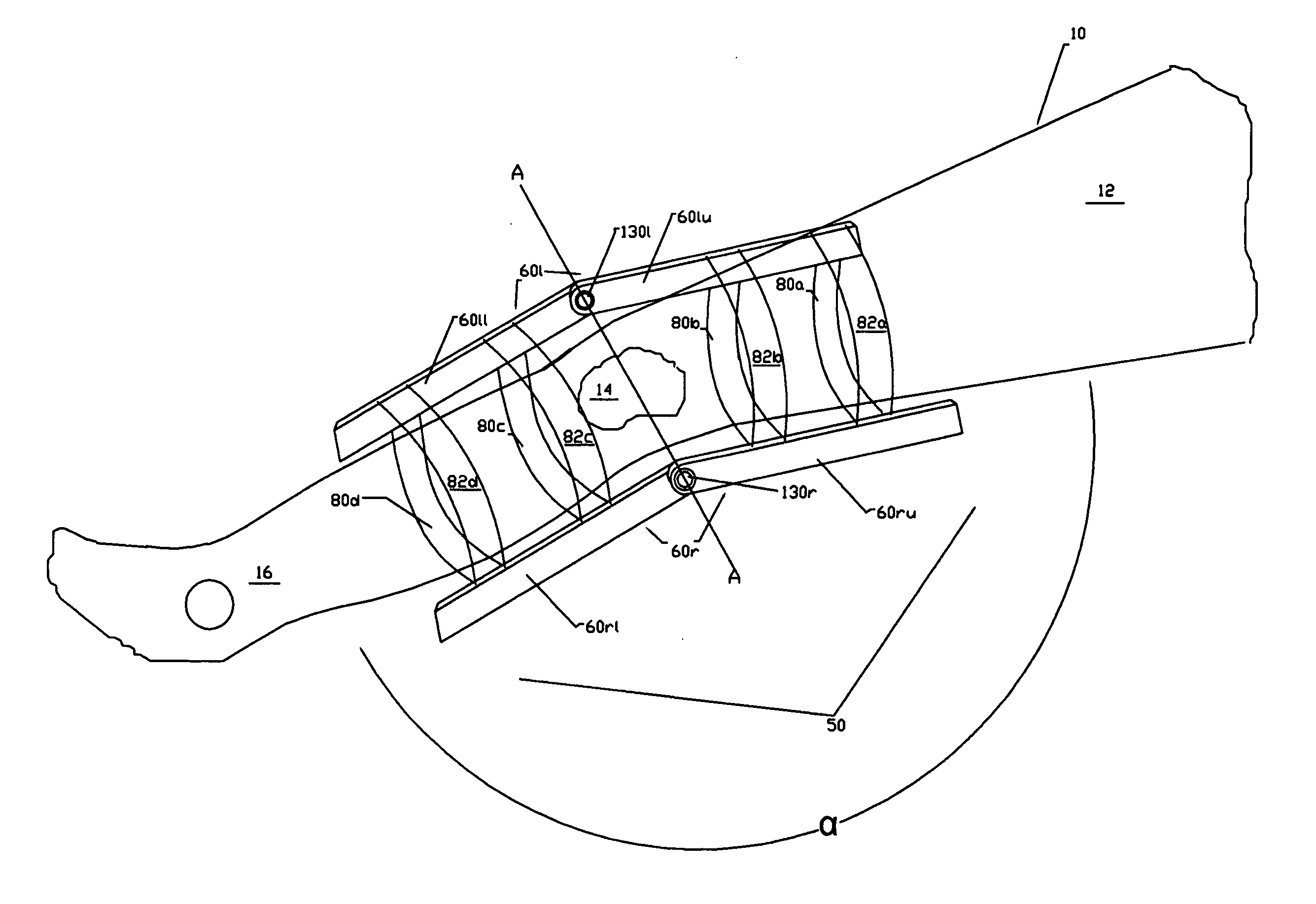
Artificial ligaments and tendons comprising multifilaments and nanofibers and methods for making
ActiveUS20090306775A1Good biocompatibilityImprove mechanical characteristicsMonocomponent polyurethanes artificial filamentElectric discharge heatingBiomedical engineeringNanofiber
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Tendon repair implant and method of implantation
A tendon repair implant for treatment of a complete or partial thickness tear in the supraspinatus tendon of the shoulder is provided. The implant may incorporate features of rapid deployment and fixation by arthroscopic means that compliment current procedures; tensile properties that result in desired sharing of anatomical load between the implant and native tendon during rehabilitation; selected porosity and longitudinal pathways for tissue in-growth; sufficient cyclic straining of the implant in the longitudinal direction to promote remodeling of new tissue to tendon-like tissue; and, may include a bioresorbable construction to provide transfer of additional load to new tendon-like tissue and native tendon over time.
Owner:ROTATION MEDICAL
Devices and methods for tendon repair
ActiveUS20130274879A1Strengthen tendon repairProvide strengthSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesPlantaris tendonUltimate tensile strength
Disclosed is a device and method for repairing a partially or totally ruptured tendon. The device comprises an implant placed inside or outside of the tendon on either side of the rupture in order to strengthen the ruptured area during repair. Once positioned inside the tendon, the tendon is held in place so it can heal either by sewing or stapling through the tendon and implant, or by any other suitable method that utilizes the implant to provide strength to the ruptured area. In this manner the tendon can heal with less chance of rupturing again prior to healing.
Owner:EXSOMED CORP
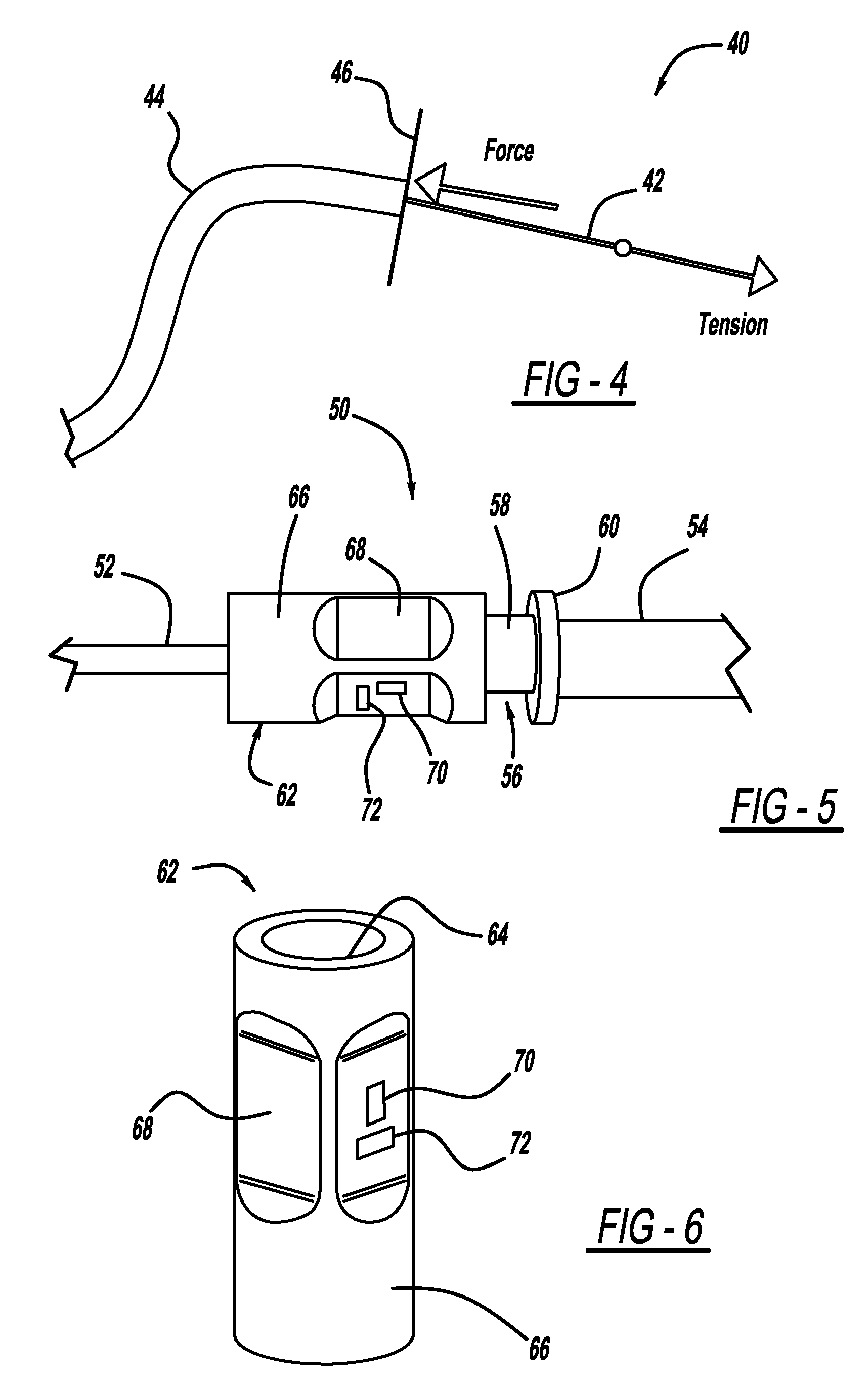
Sensing the tendon tension through the conduit reaction forces
A technique that determines the tension in a tendon using a conduit reaction force applied to an end of a conduit through which the tendon is threaded. Any suitable tendon tension sensor can be employed that uses the conduit reaction force for this purpose. In one non-limiting embodiment, the tendon tension sensor includes a cylindrical strain gauge element and a force member mounted to an end of the conduit. The force member includes a cylindrical portion having a bore and a plate portion, where the cylindrical portion is inserted into a bore in the strain gauge element. The tendon is threaded through the strain gauge element and the force member. A strain gauge is mounted to the strain gauge element and measures the reaction force when tension on the tendon causes the strain gauge element to be pushed against the force member.
Owner:NASA +1
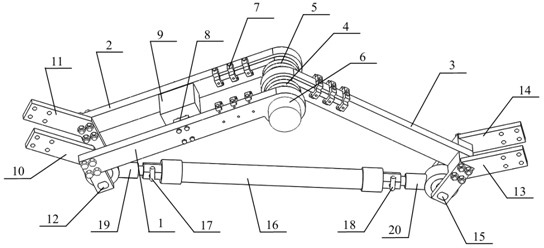
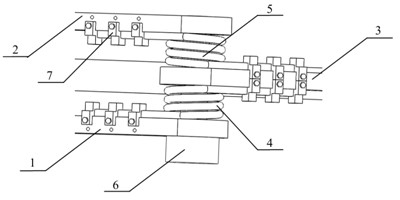
Mechanical leg imitating ostrich hind limb
The invention discloses a bionic mechanical leg imitating the motion function characteristic of an ostrich hind limb. The mechanical leg comprises a body, a hip joint motion mechanism, a knee joint motion mechanism and an ankle joint motion mechanism. The hip joint motion mechanism is composed of a motor and a crank-rocker mechanism, wherein the crank-rocker mechanism comprises a crank, a femur and a connecting rod. The knee joint motion mechanism comprises the femur, a first spring, a tibia, a metatarsus, a brake cable, a lower fibula, a second spring, an air cylinder and an upper fibula. The ankle joint motion mechanism comprises the metatarsus, a first apotelus bone, a second apotelus bone, a third apotelus bone, a third torsional spring, a second torsional spring and a first torsional spring. The ostrich hind limb capable of efficiently moving serves as the bionic prototype, through combination of testing on hind limb motion parameters during running of an ostrich and biological anatomic analysis, the mechanical leg imitating the ostrich hind limb is obtained through optimization design according to the tendon-bone and muscle-tendon interaction mechanism of the ostrich, and the mechanical leg is simple in structure, safe, reliable, low in vibration, and capable of efficiently saving energy.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for drilling enlarged sections of angled osteal tunnels
ActiveUS8361079B2Facilitating the accurate drilling of an angledDifferent sizeSuture equipmentsProsthesisPlantaris tendonReamer
Methods for drilling enlarged osteal tunnels using osteal guides capable of drilling an angled osteal tunnel, namely, an osteal tunnel having an angle or turn within the bone and for drawing a muscle, tendon or ligament in need of repair into the enlarged osteal tunnel such that the bone can mend about, around, over and / or within the muscle, tendon or ligament. A reamer and guide wire can be used to create the enlarged osteal tunnel to accommodate a portion of the muscle, tendon or ligament in need of repair. The device allows for the blind intraosseous preparation of osteal tunnels and the blind intraosseous retrieval of sutures from such osteal tunnels.
Owner:PANDYA RAJIV D
Bionic elastic spine mechanism of quadruped robots
The invention relates to a bionic elastic spine mechanism of quadruped robots. Two left and right symmetrical torsion springs are mounted on spinal rotation joints, accordingly, the rotation of the spinal joints and the bending of the torsion springs are restrained together, the torsion springs deforms along with the bending of the spinal joints to produce reverse direction torque and store elastic potential energy. A pneumatic muscle tendon is connected to two ends of the spine, the rotation of the spinal joints is controlled by the active expansion of the pneumatic muscle tendon, elastic coefficients of the whole elastic spine can be changed by regulating the expansion speed of the pneumatic muscle tendon, and simultaneously, the elasticity of the pneumatic muscle tendon can also assist in storing energy and restraining the moving range of the spinal joints. The bionic elastic spine mechanism can effectively improve the moving capacity of quadruped robots, and enhance utilization efficiency of energy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com