Patents
Literature
79 results about "Annulus of Zinn" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
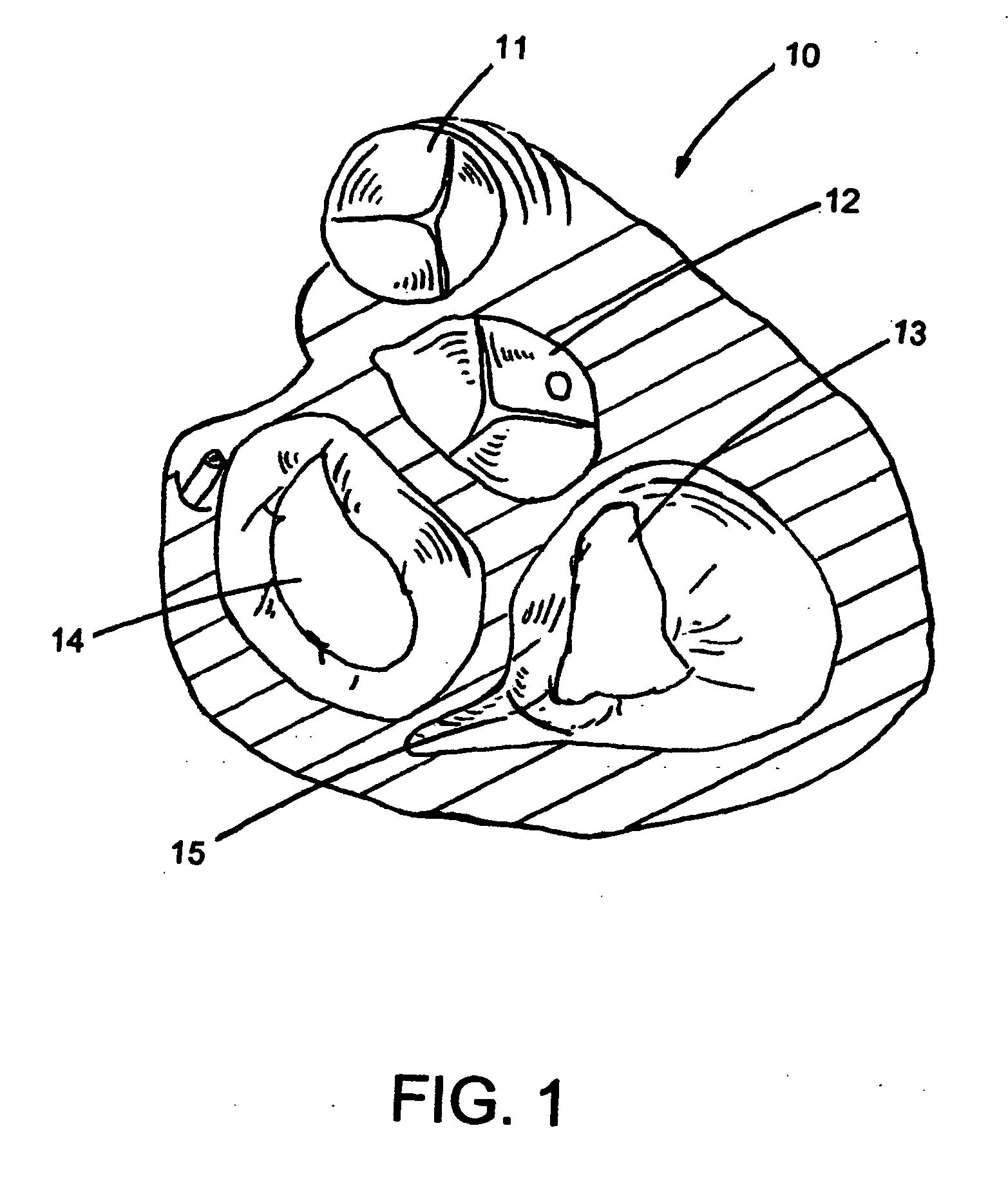
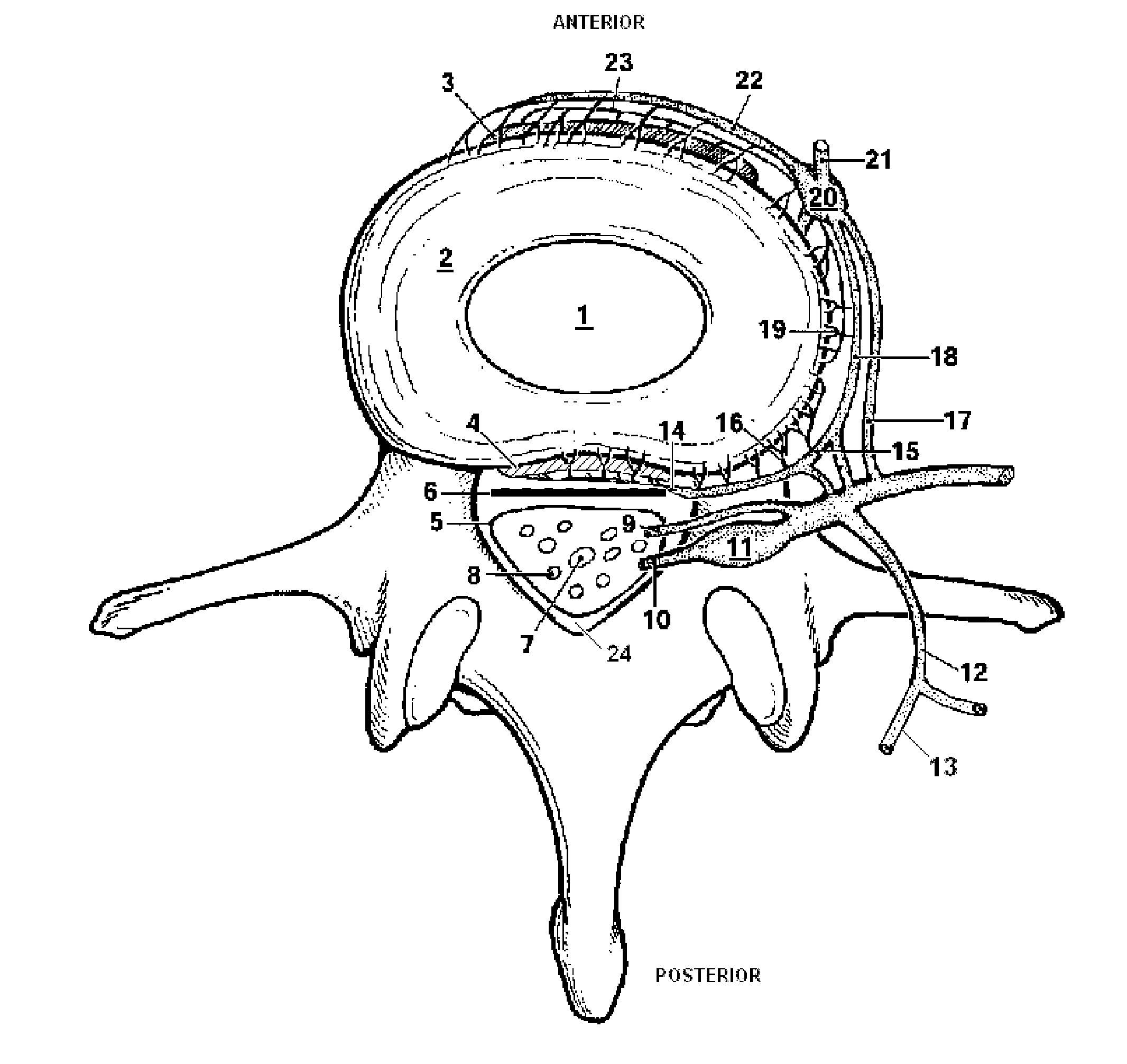
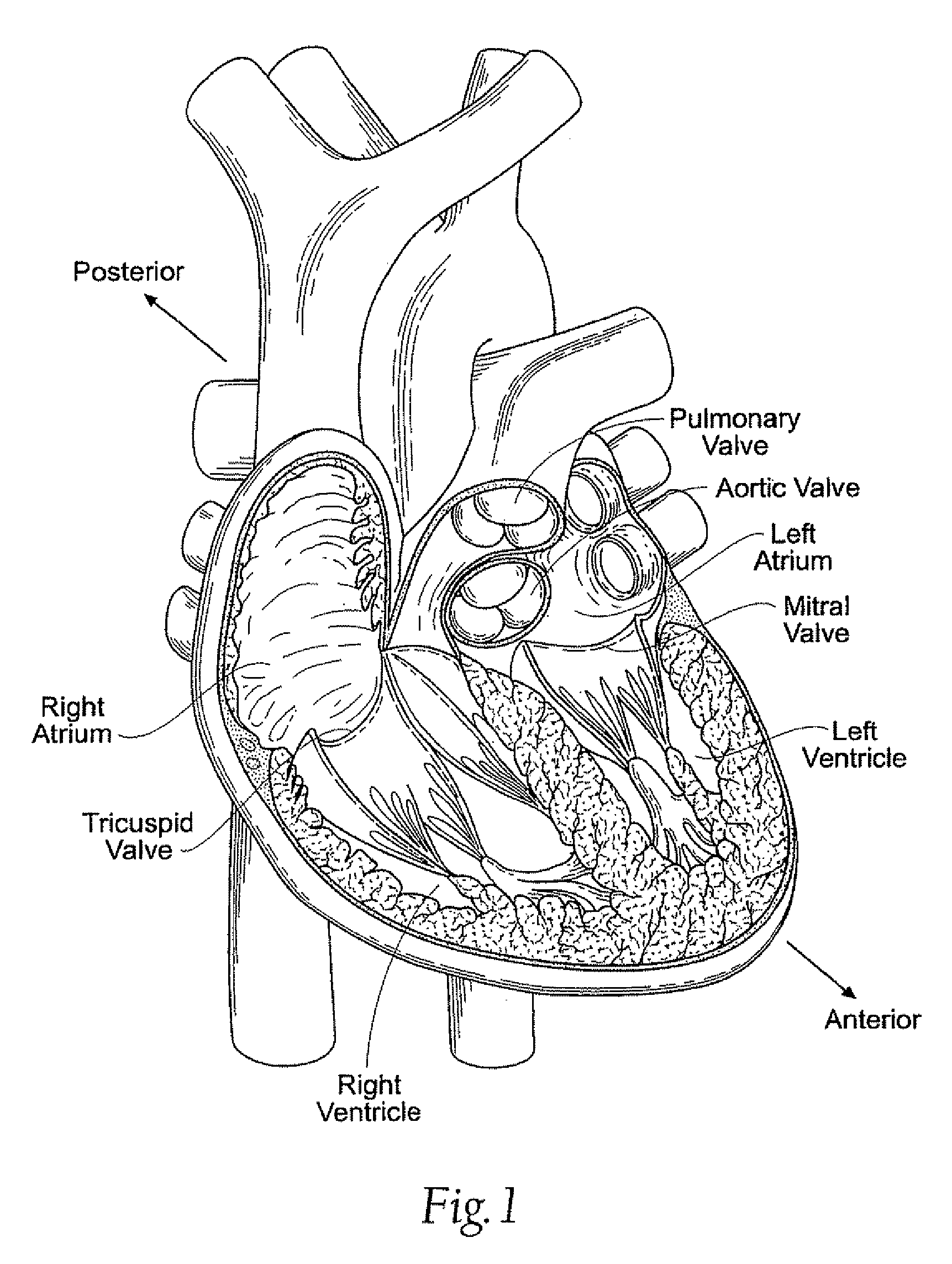
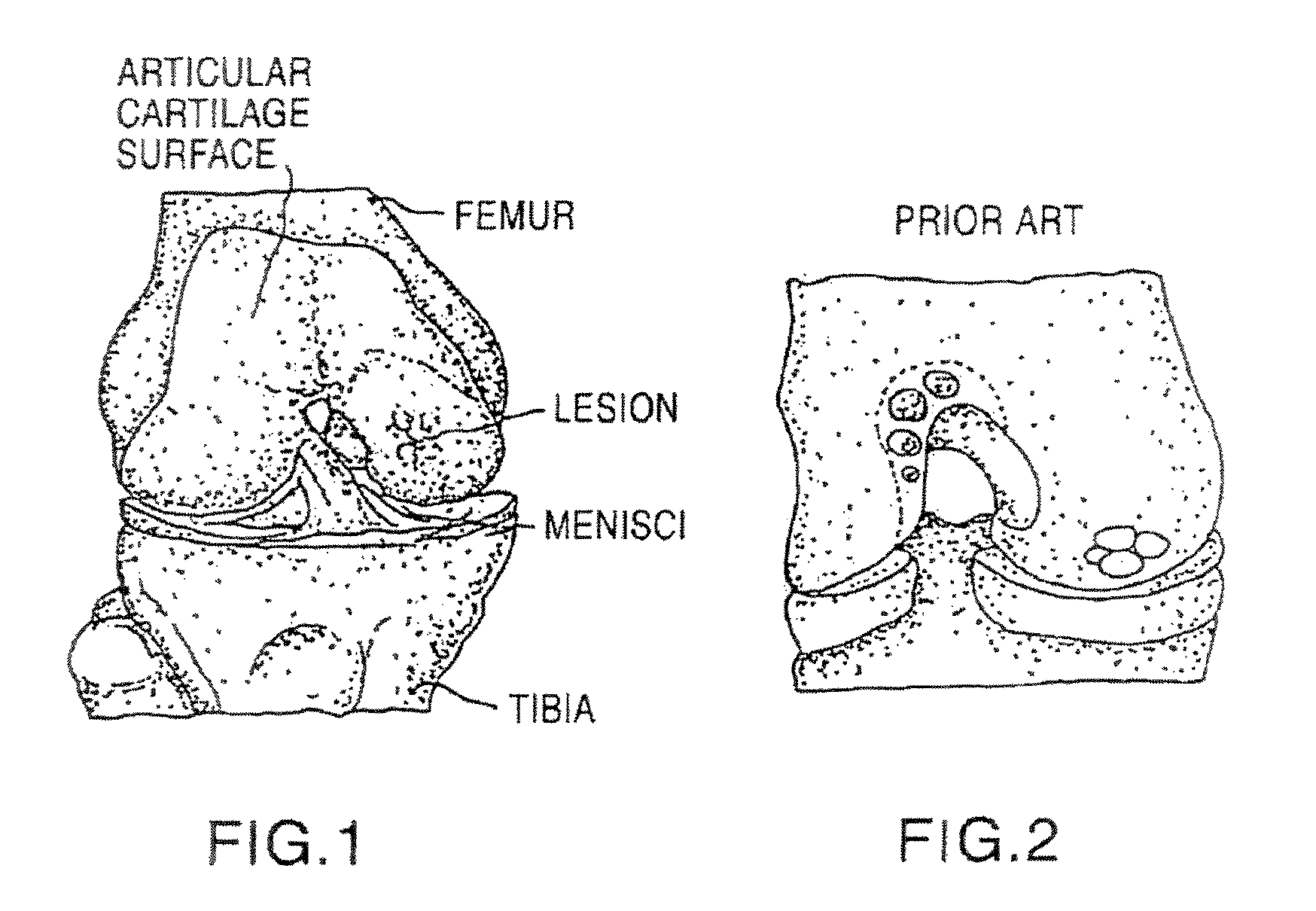
The annulus of Zinn, also known as the annular tendon or common tendinous ring, is a ring of fibrous tissue surrounding the optic nerve at its entrance at the apex of the orbit. It is the common origin of the four rectus muscles (extraocular muscles).
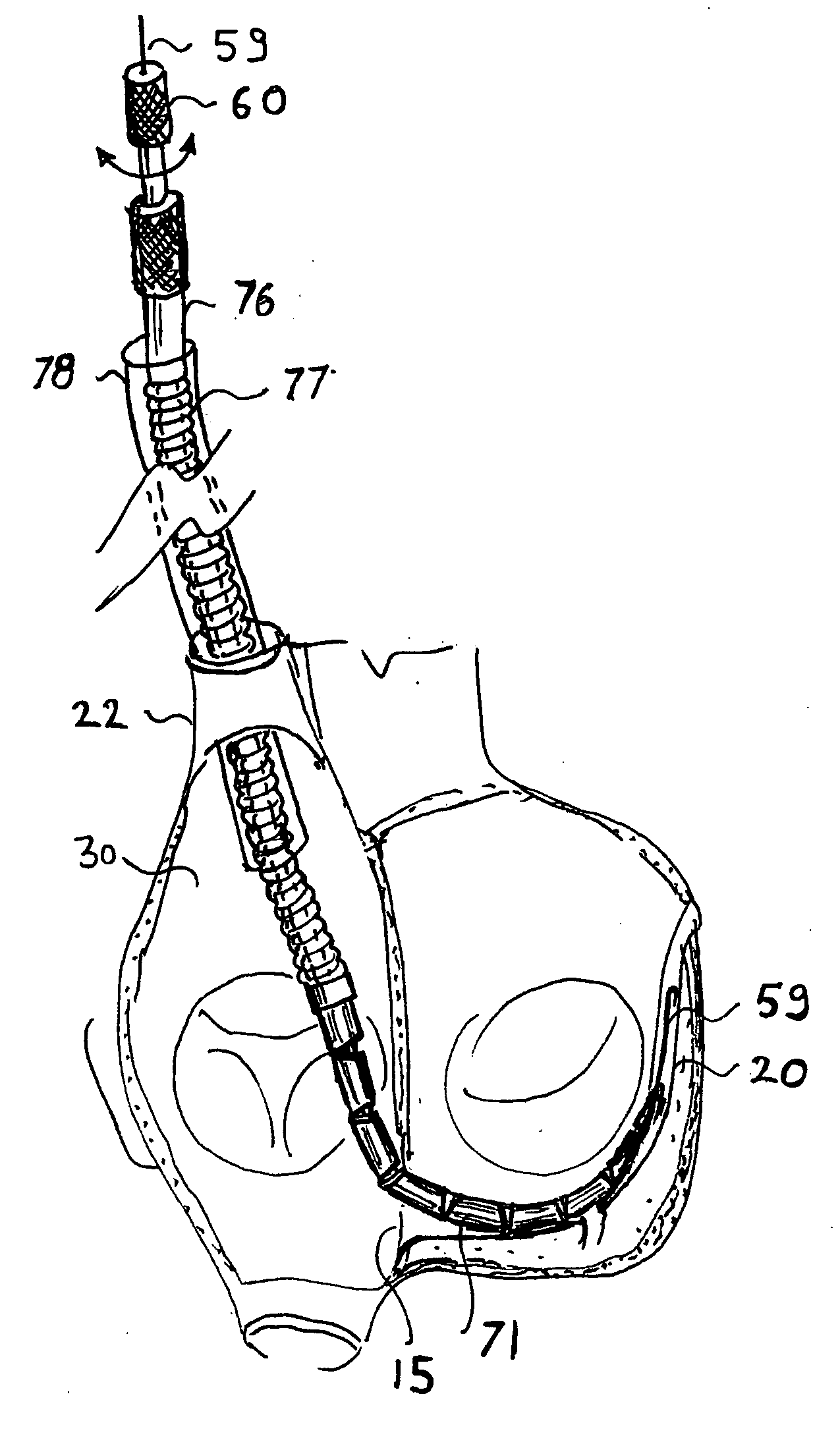
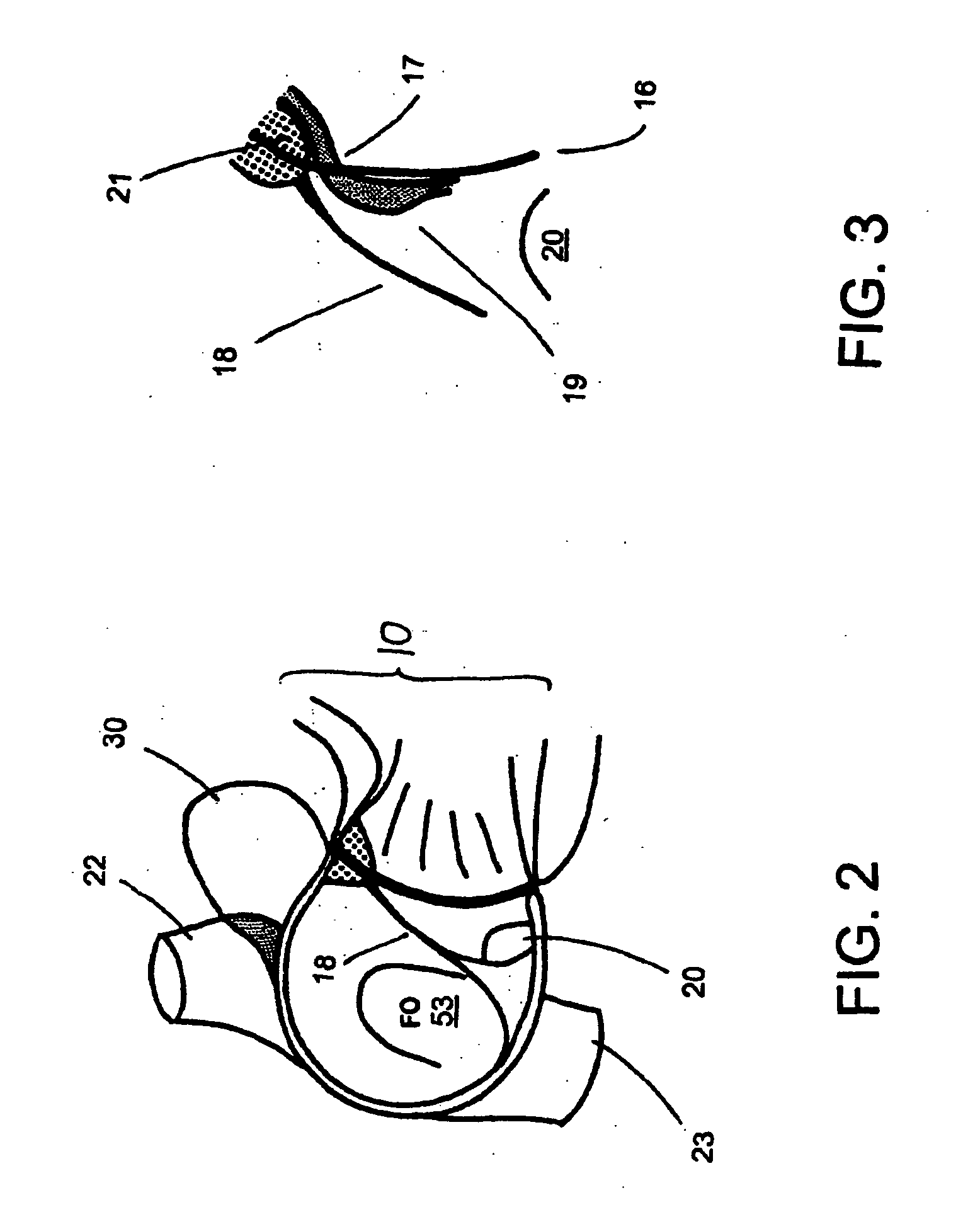
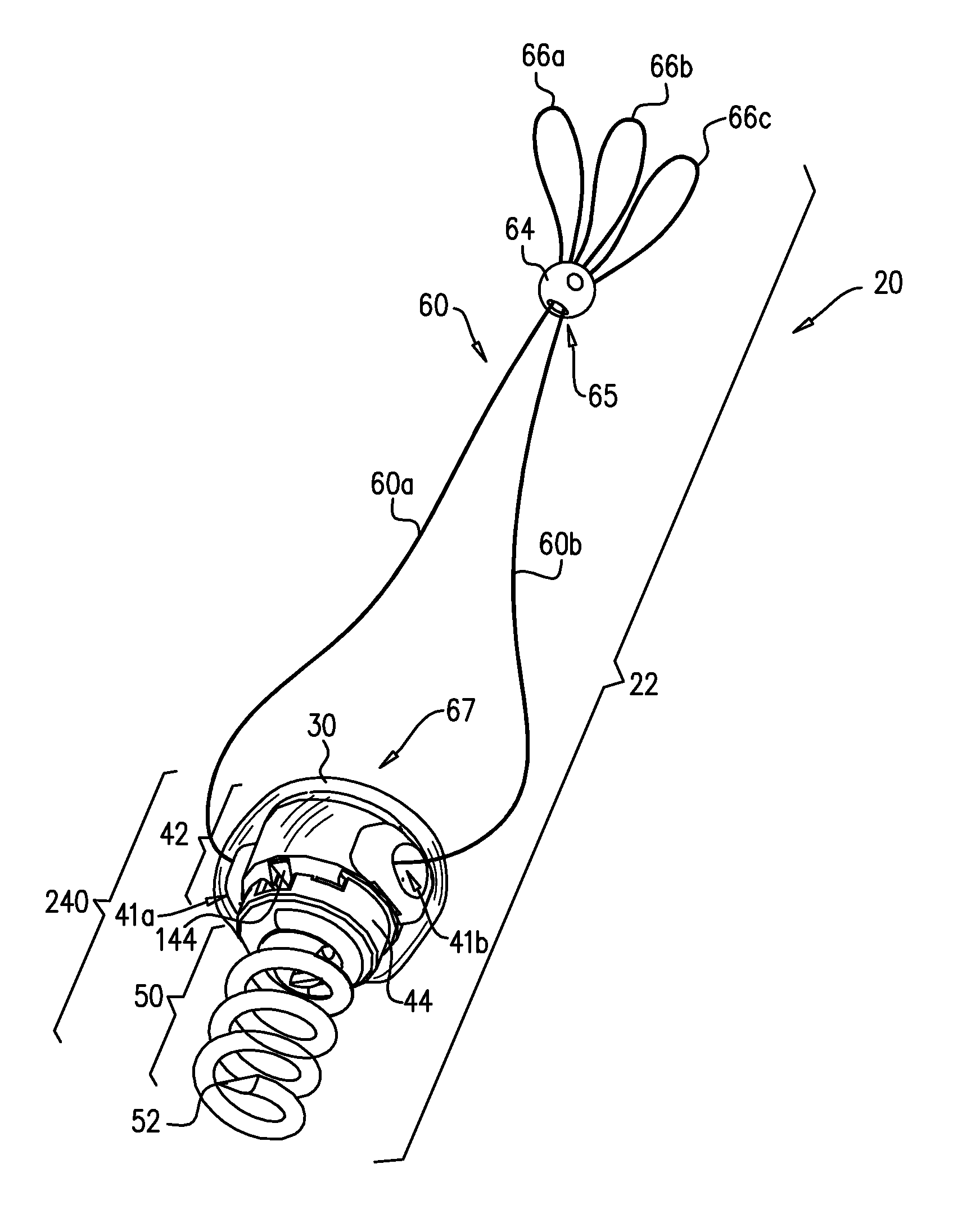
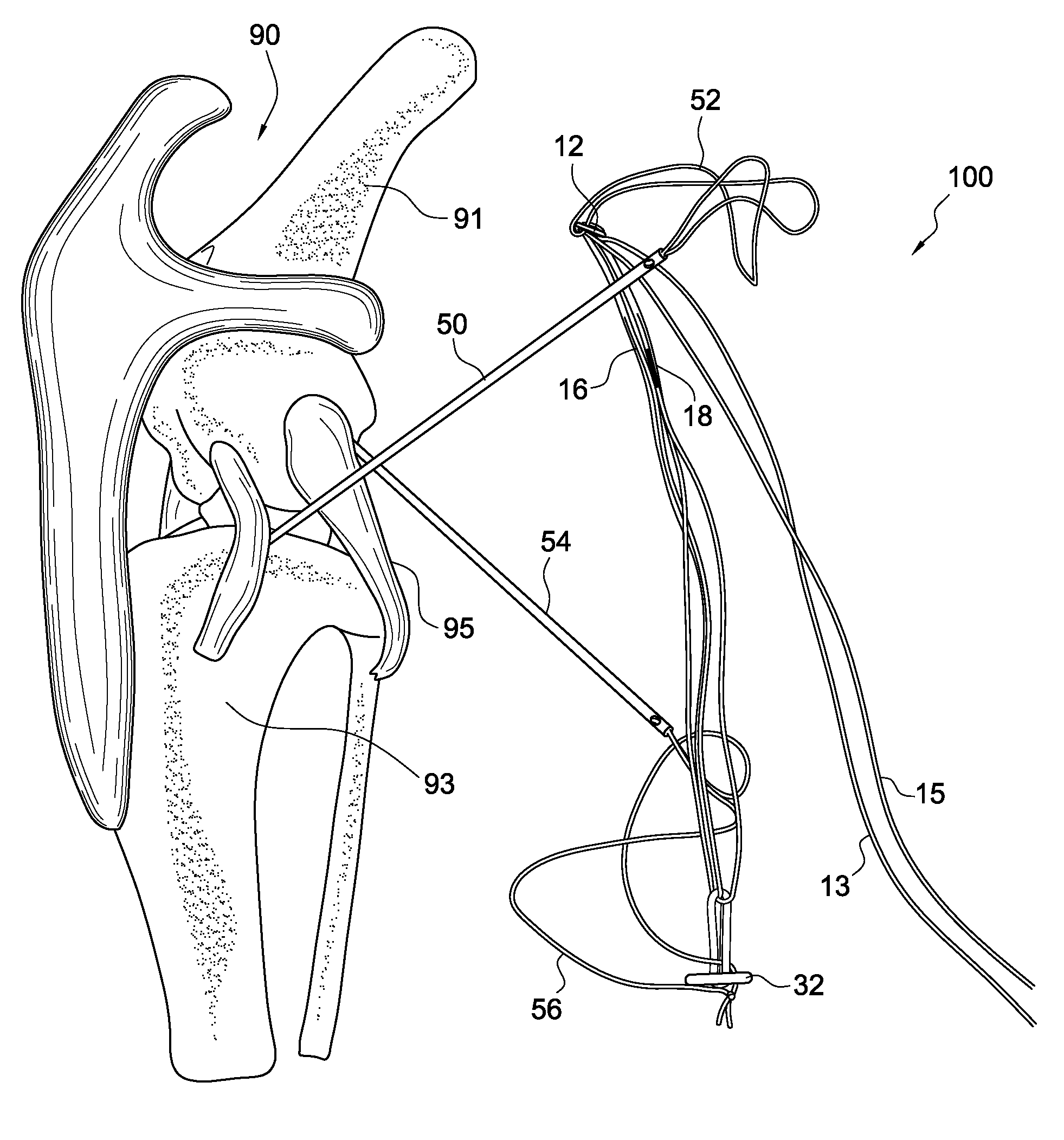
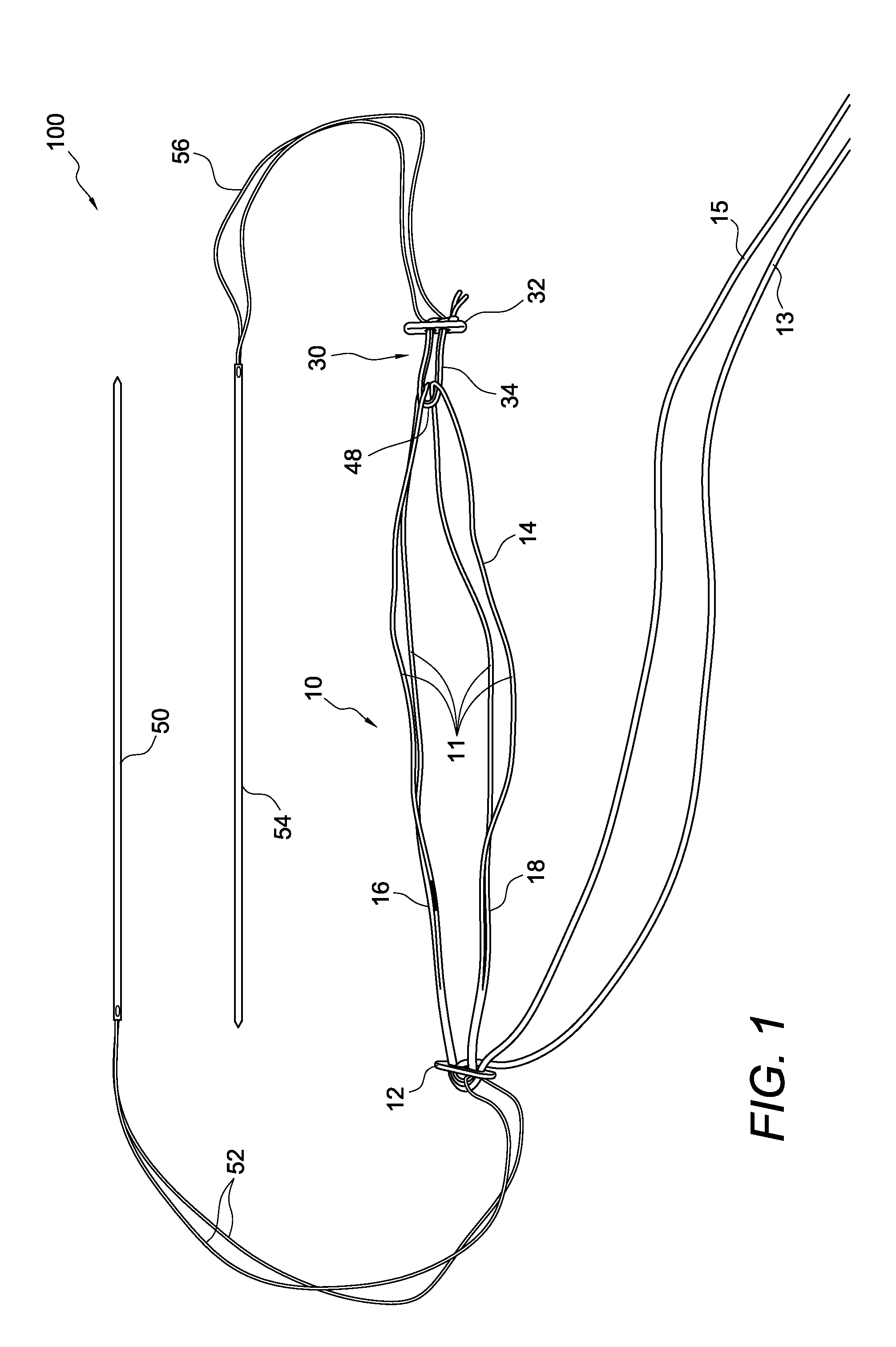
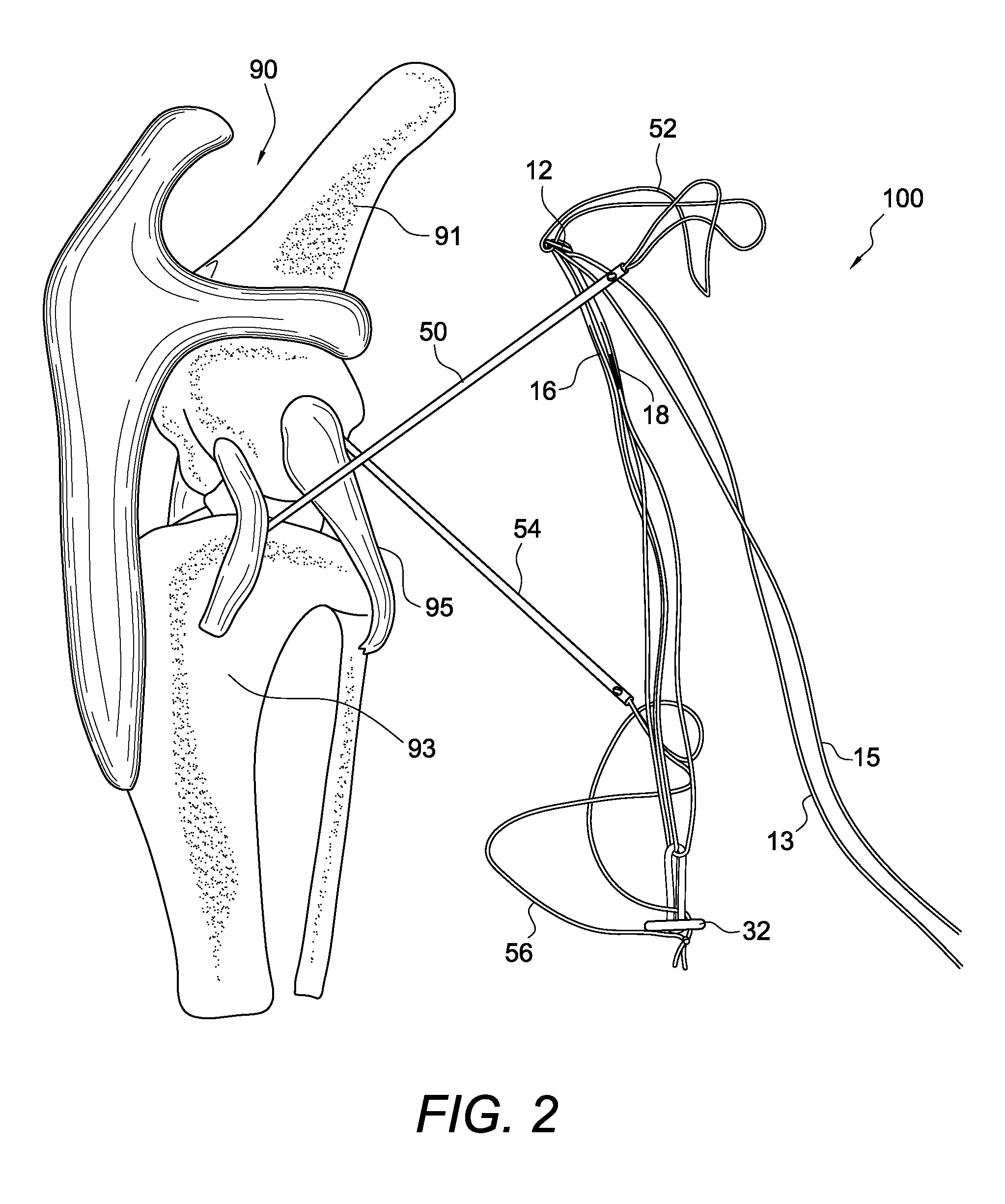
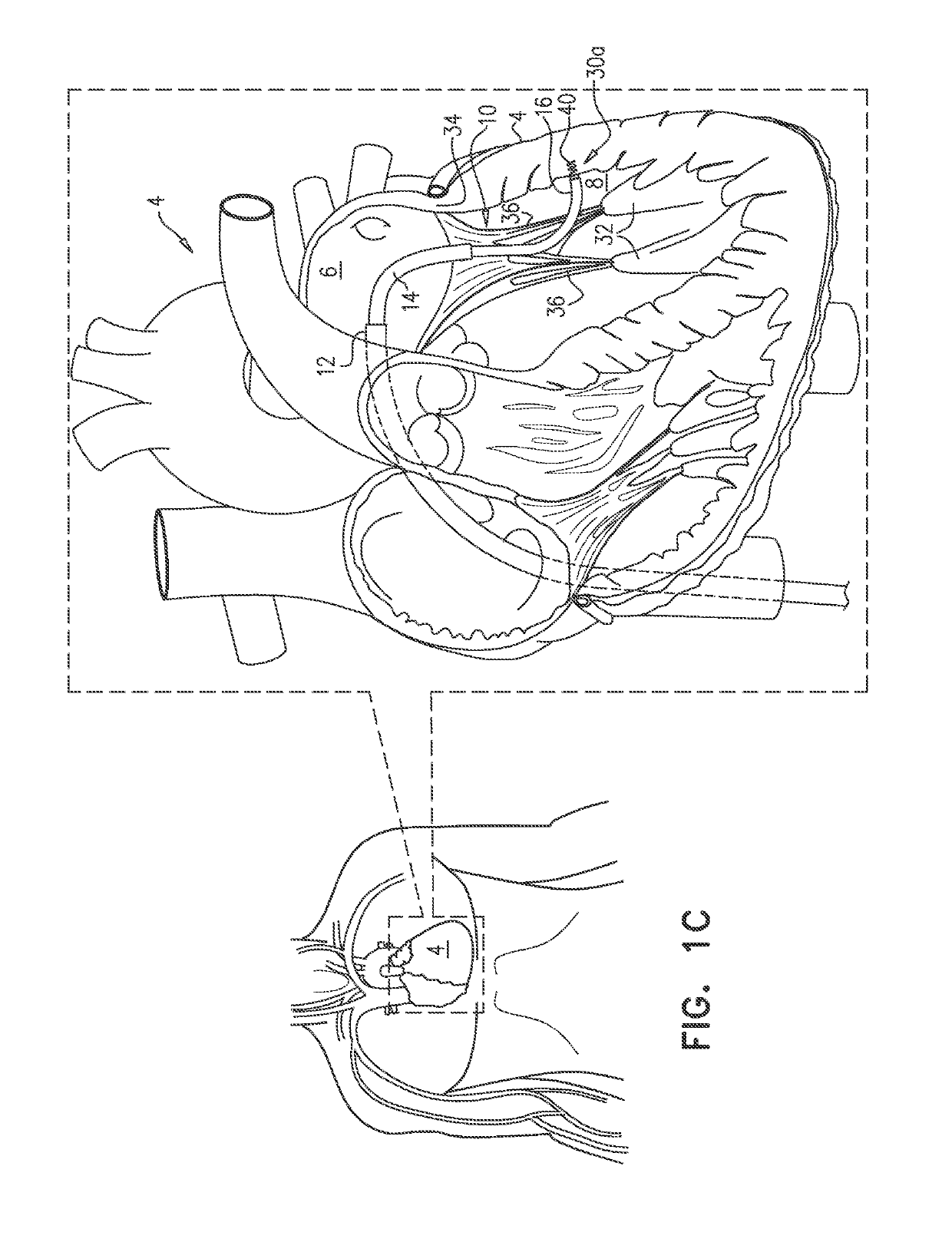
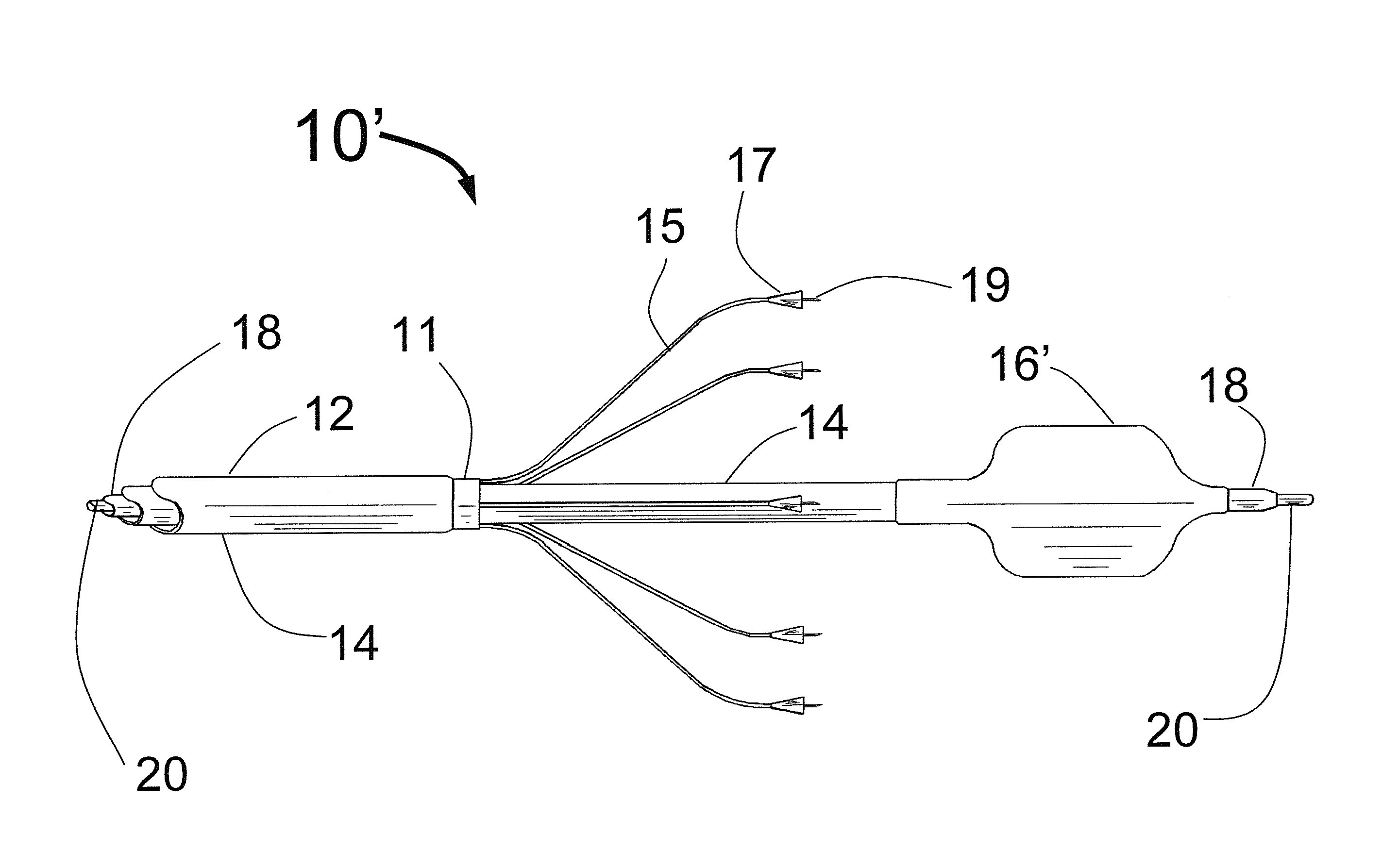
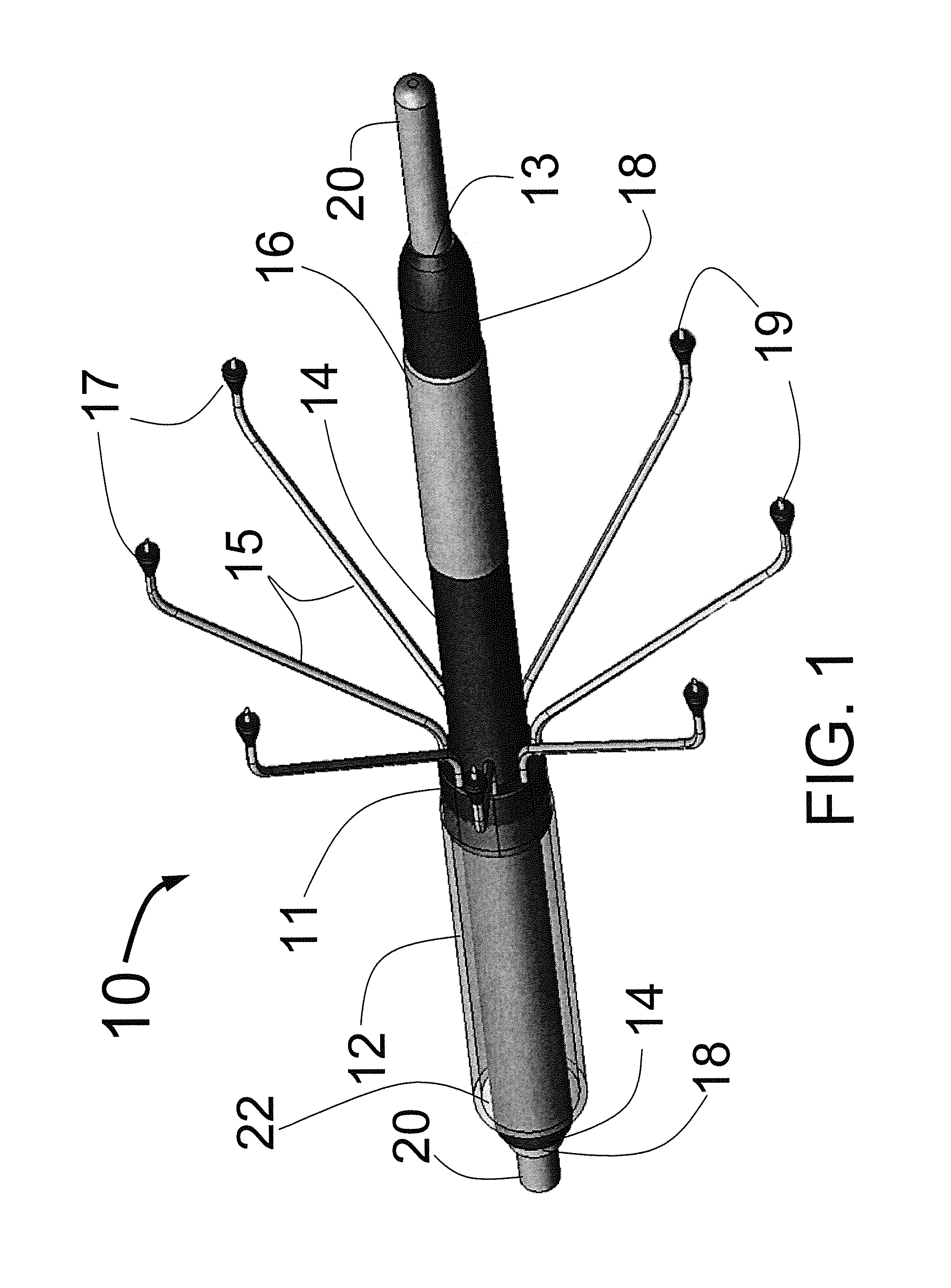
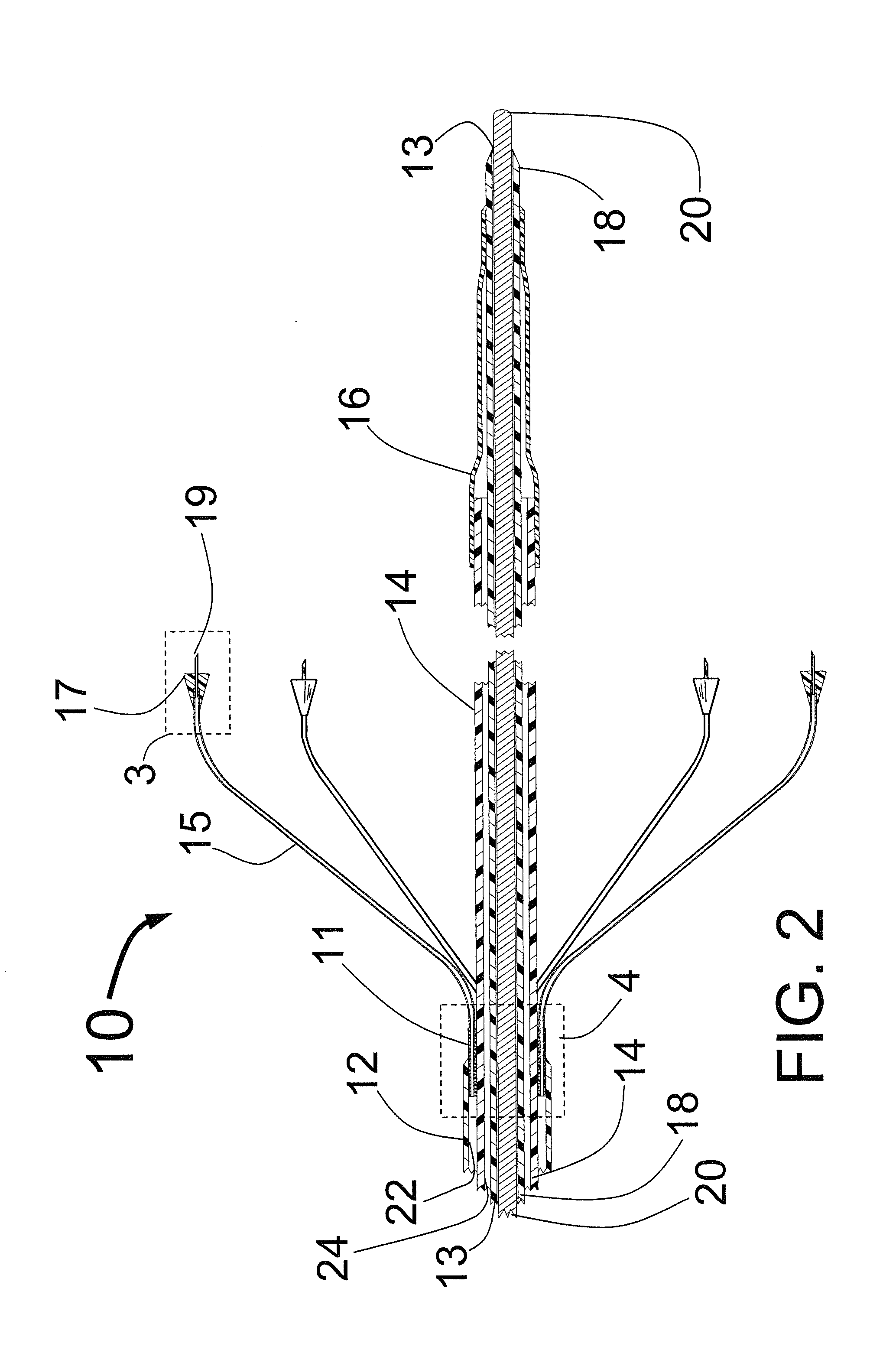
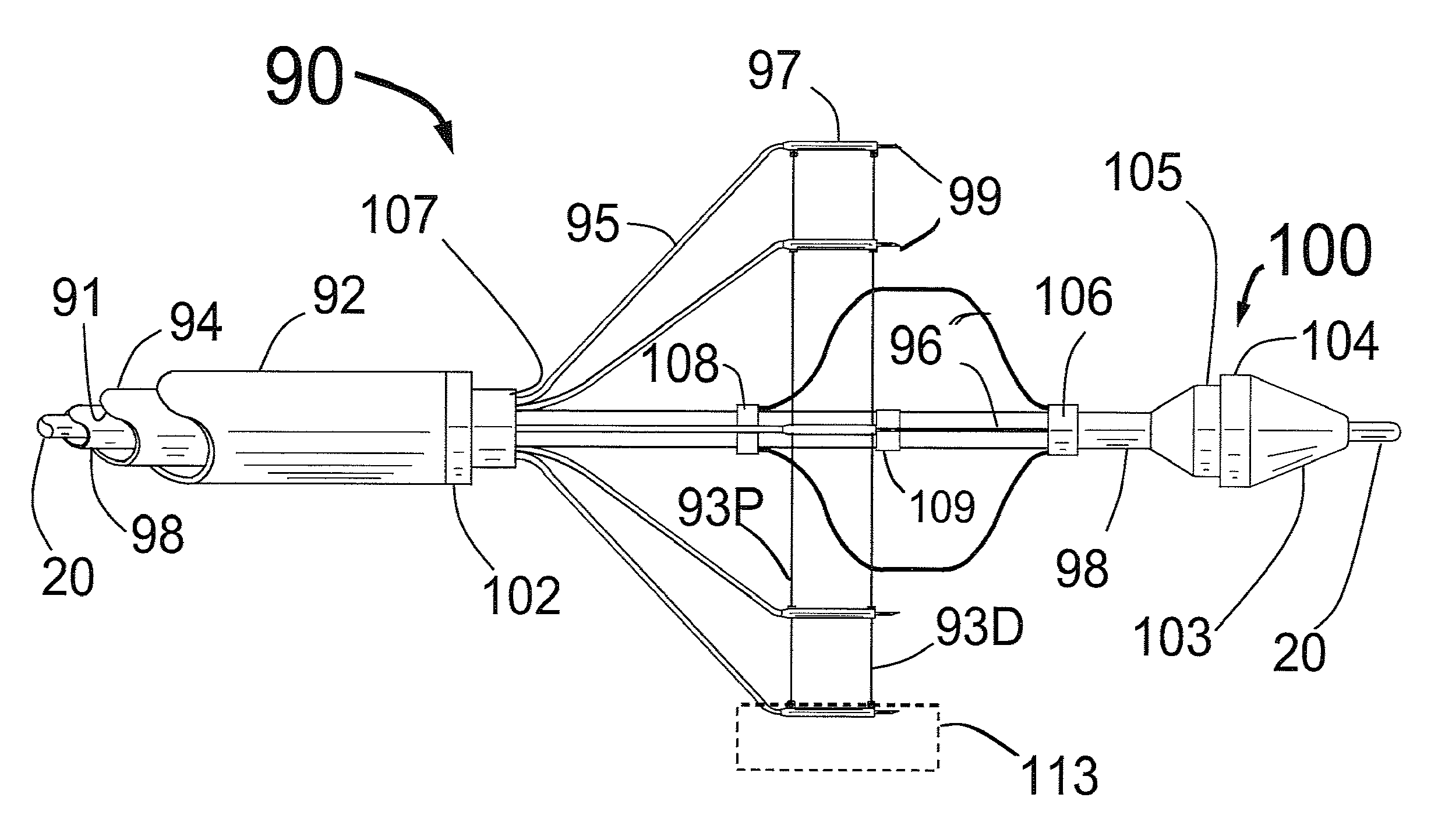
Method and apparatus for percutaneous reduction of anterior-posterior diameter of mitral valve
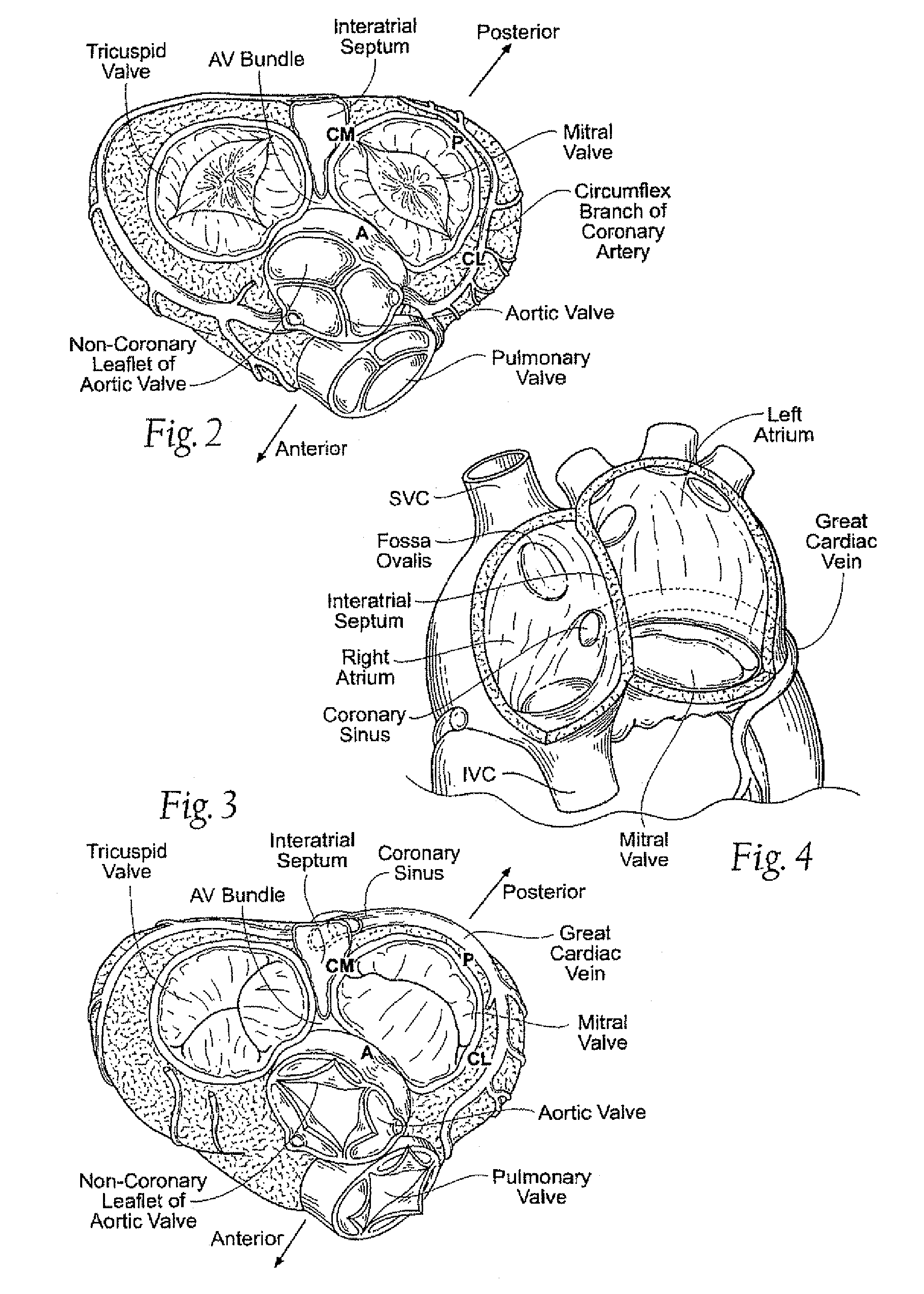
A method and apparatus for treating mitral regurgitation by approximating the septal and lateral (clinically referred to as anterior and posterior) annulus of the mitral valve. The distal end of the device is inserted into the coronary sinus of the heart and the proximal end of the device rests within the right atrium along the tendon of Todaro and extends to at least the membranous septum of the tricuspid valve. Because the coronary sinus approximates the lateral (posterior) annulus of the mitral valve and the tendon of Todaro approximates the septal (anterior) annulus of the mitral valve, the device encircles approximately one half of the mitral valve annulus. The apparatus is then adapted to deform the underlying structures i.e. the septal annulus and lateral annulus of the mitral valve in order to move the posterior leaflet anteriorly and the anterior leaflet posteriorly and thereby improve leaflet coaptation and eliminate mitral regurgitation.
Owner:KARDIUM
Adjustable artificial chordeae tendineae with suture loops
ActiveUS8790394B2Easy to implantGuaranteed functionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesDistal portionPlantaris tendon
Apparatus is provided, including an artificial-chordeae-tendineae-adjustment mechanism and at least one primary artificial chordea tendinea coupled at a distal portion thereof to the artificial-chordeae-tendineae-adjustment mechanism. A degree of tension of the at least one primary artificial chordea tendinea is adjustable by the artificial-chordeae-tendineae-adjustment mechanism. One or more loops are coupled at a proximal portion of the at least one primary artificial chordea tendinea. The one or more loops are configured to facilitate suturing of the one or more loops to respective portions of a leaflet of an atrioventricular valve of a patient. Other applications are also described.
Owner:VALTECH CARDIO LTD
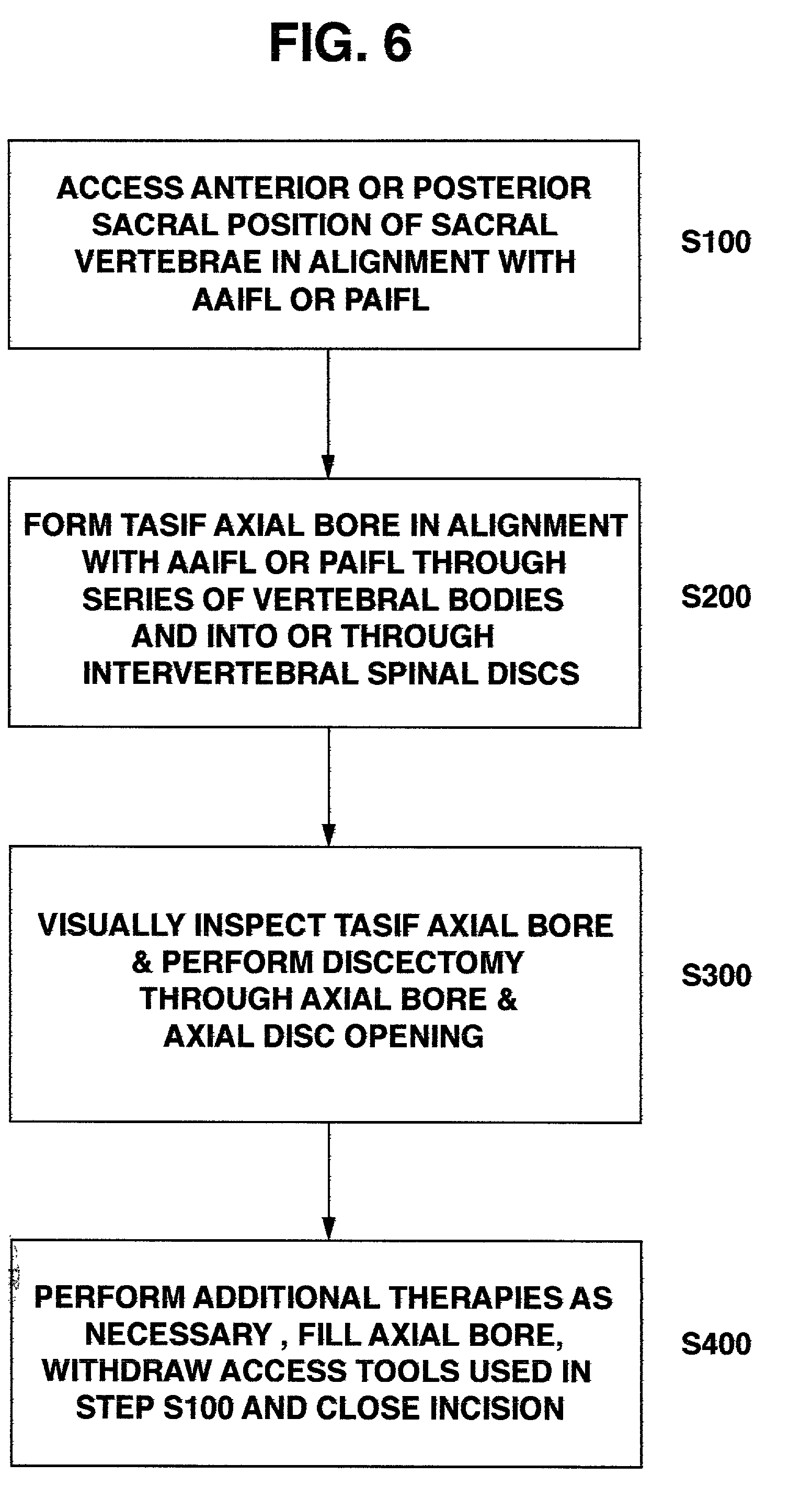
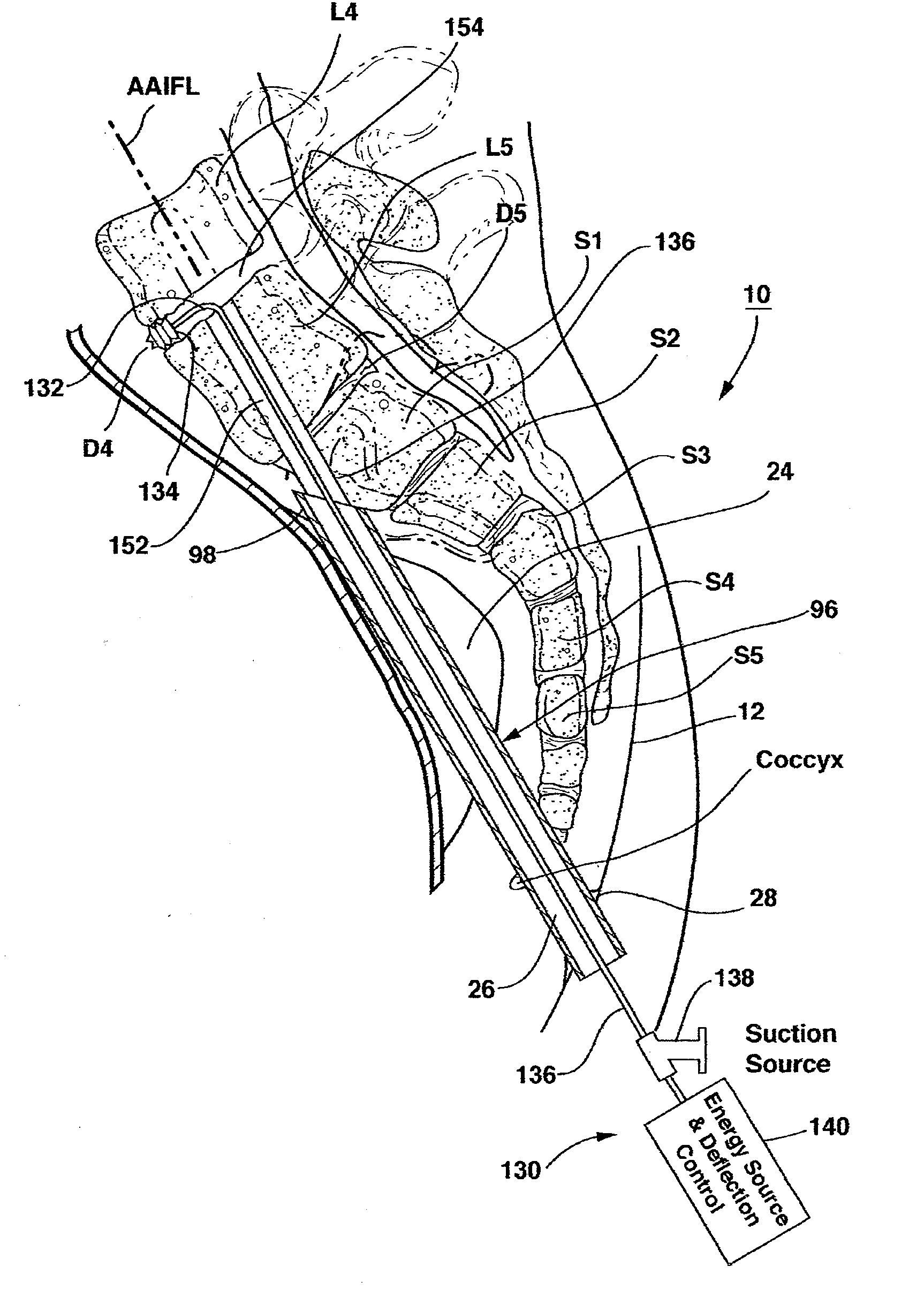
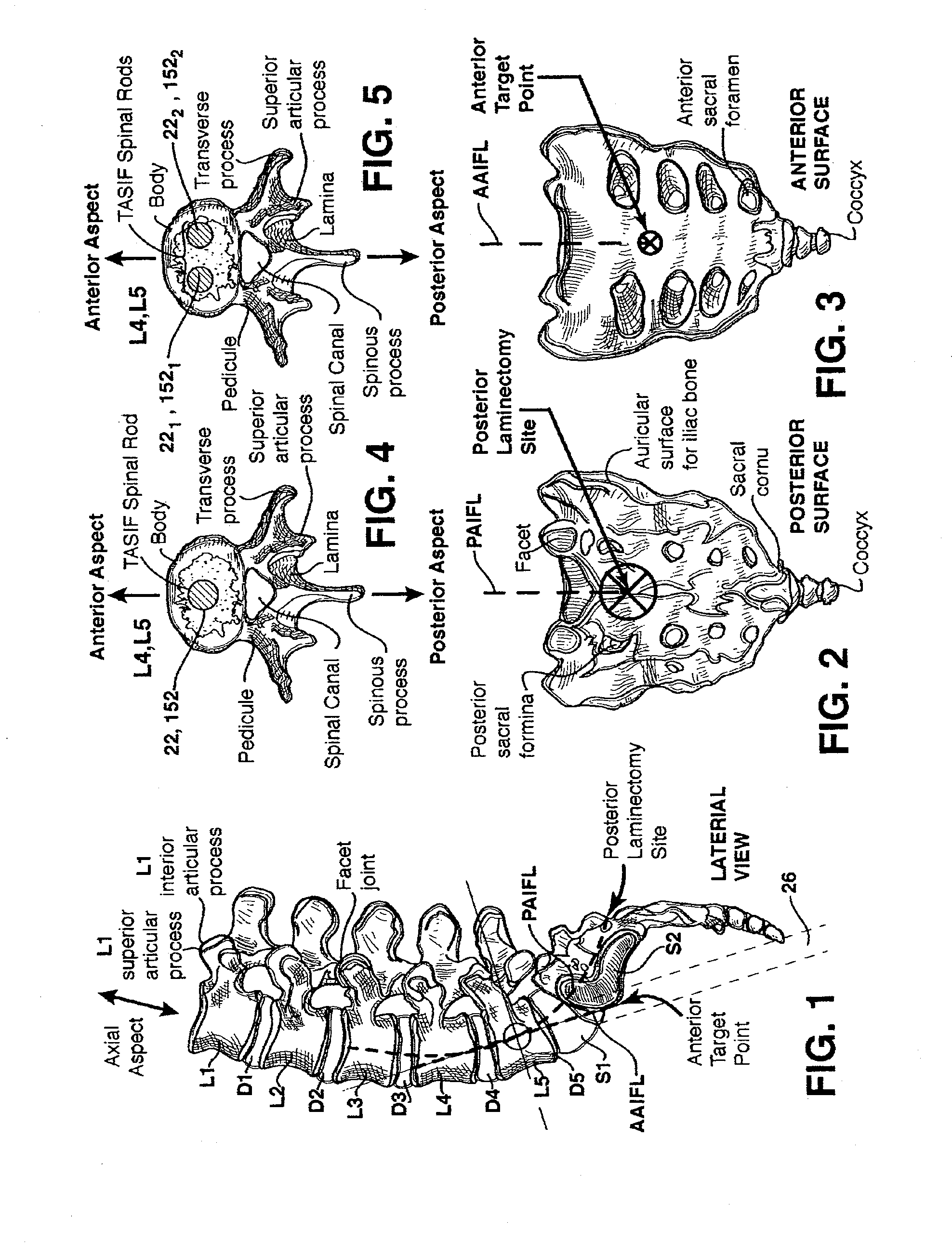
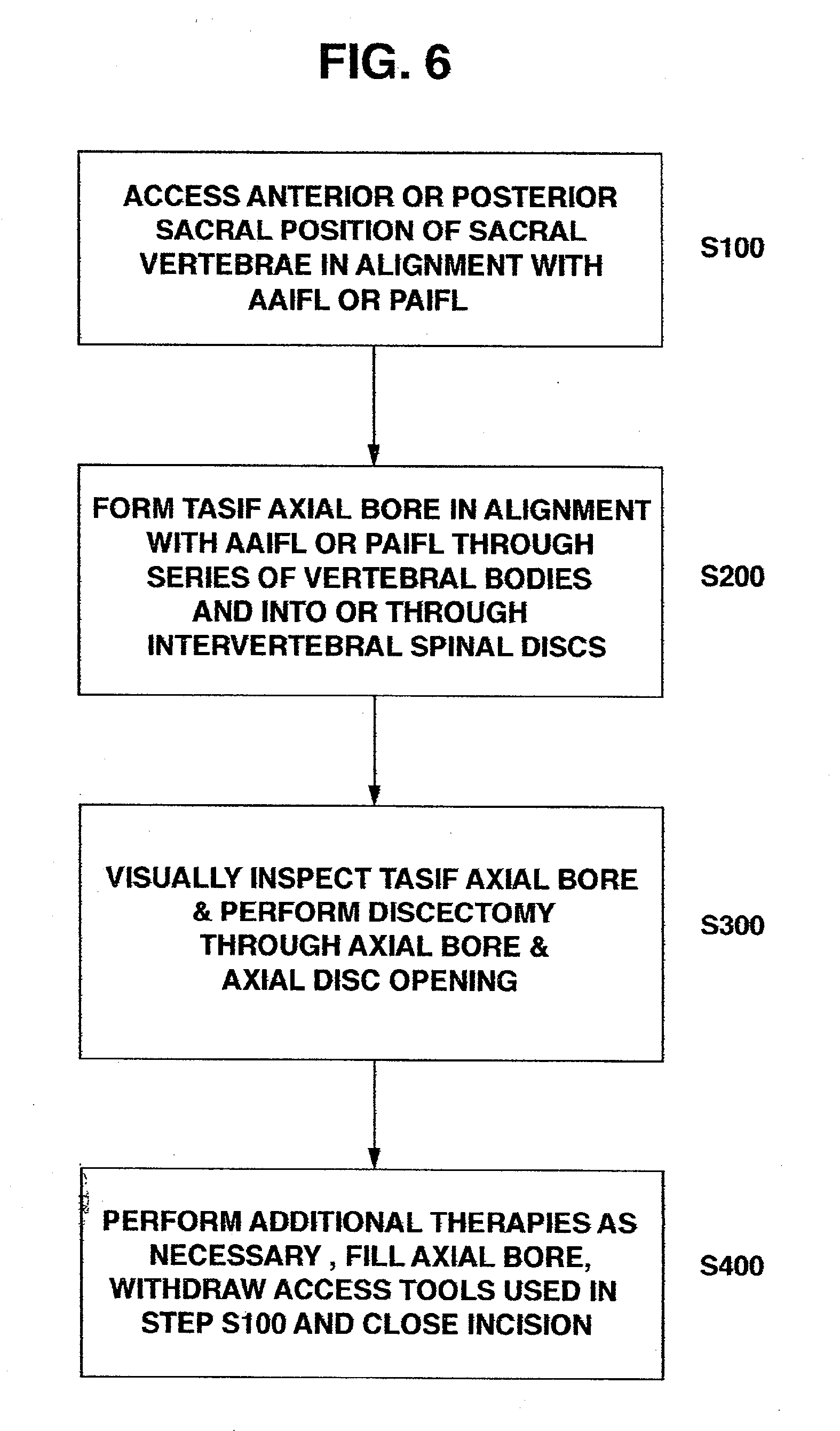
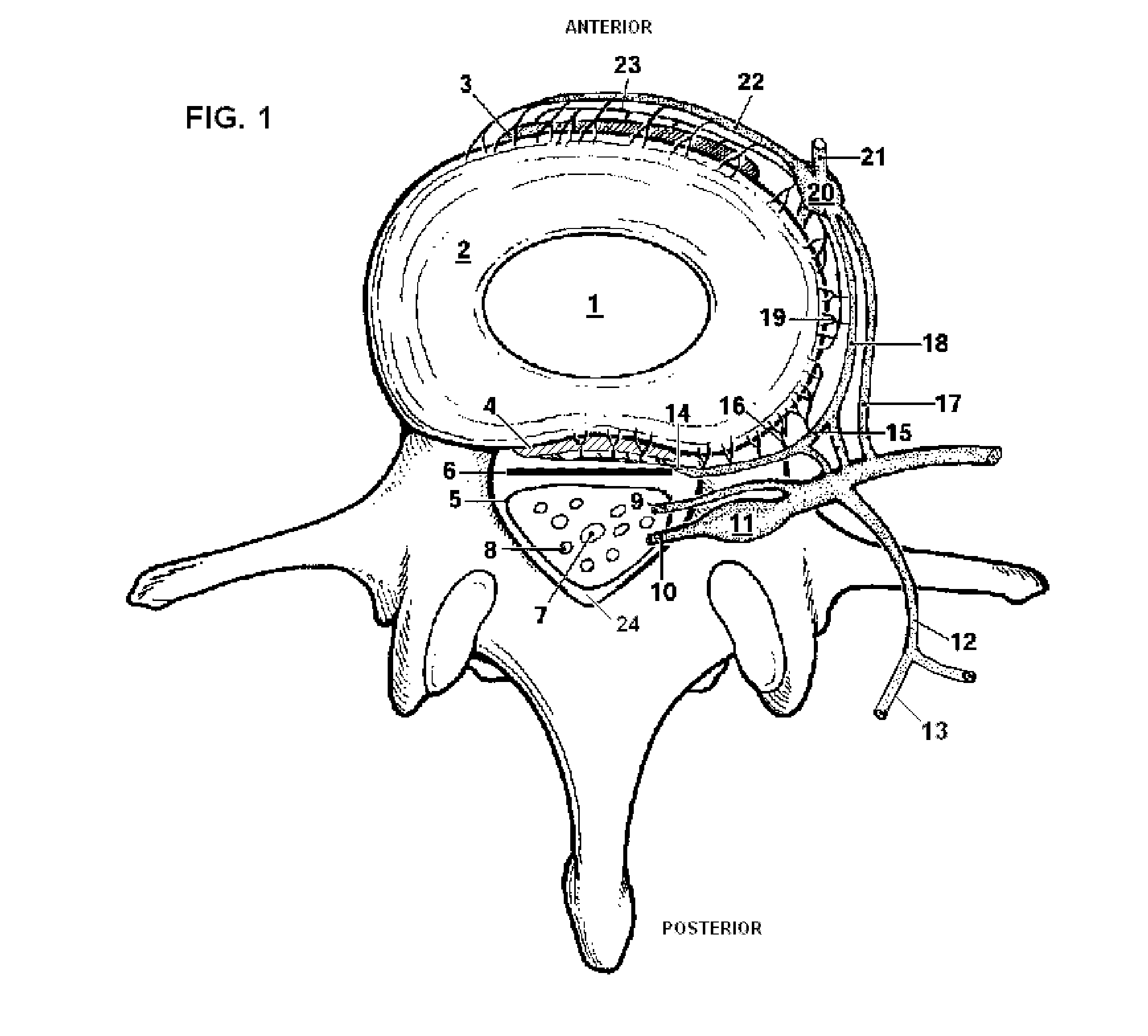
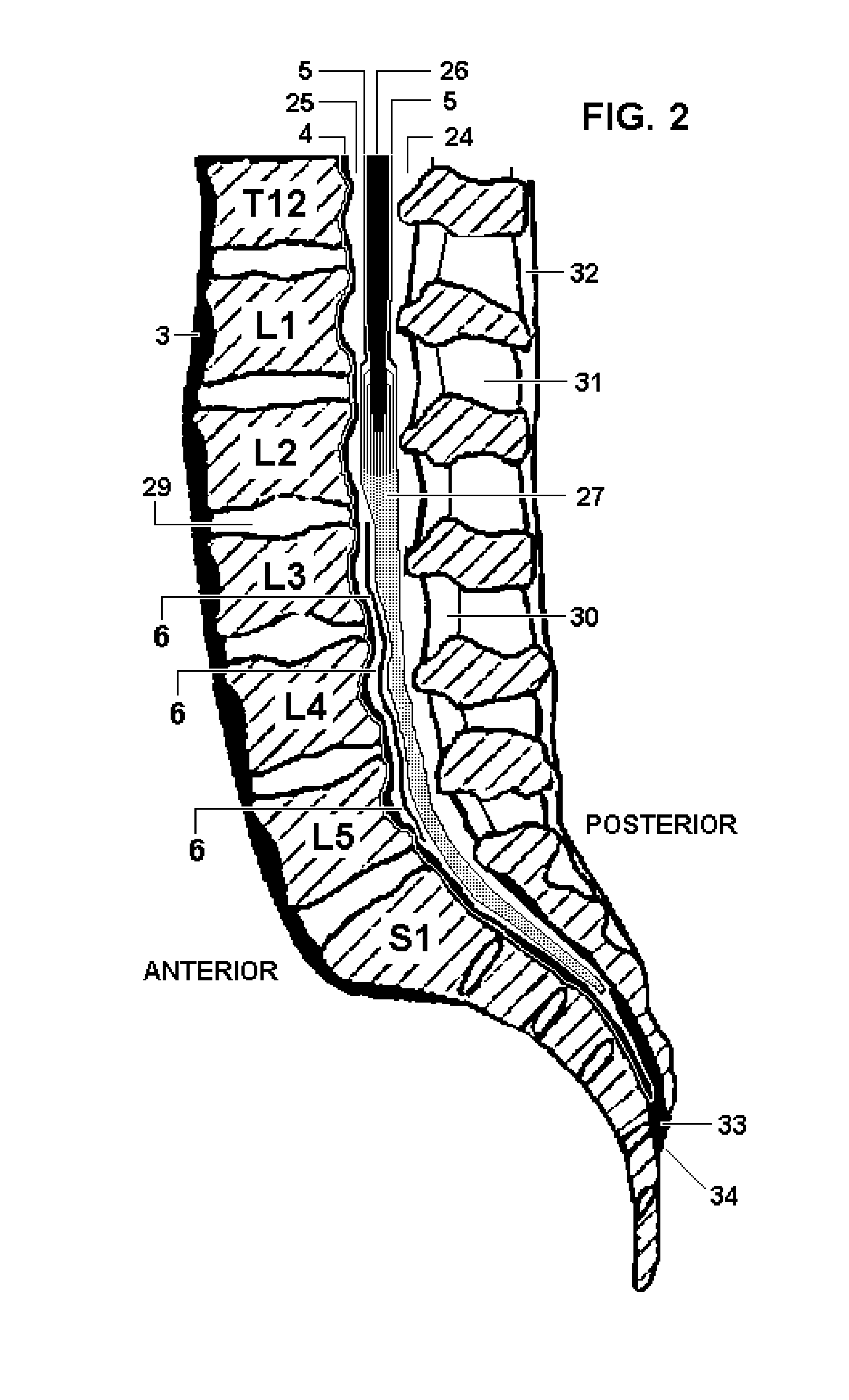
Apparatus for performing a discectomy through a trans-sacral axial bore within the vertebrae of the spine
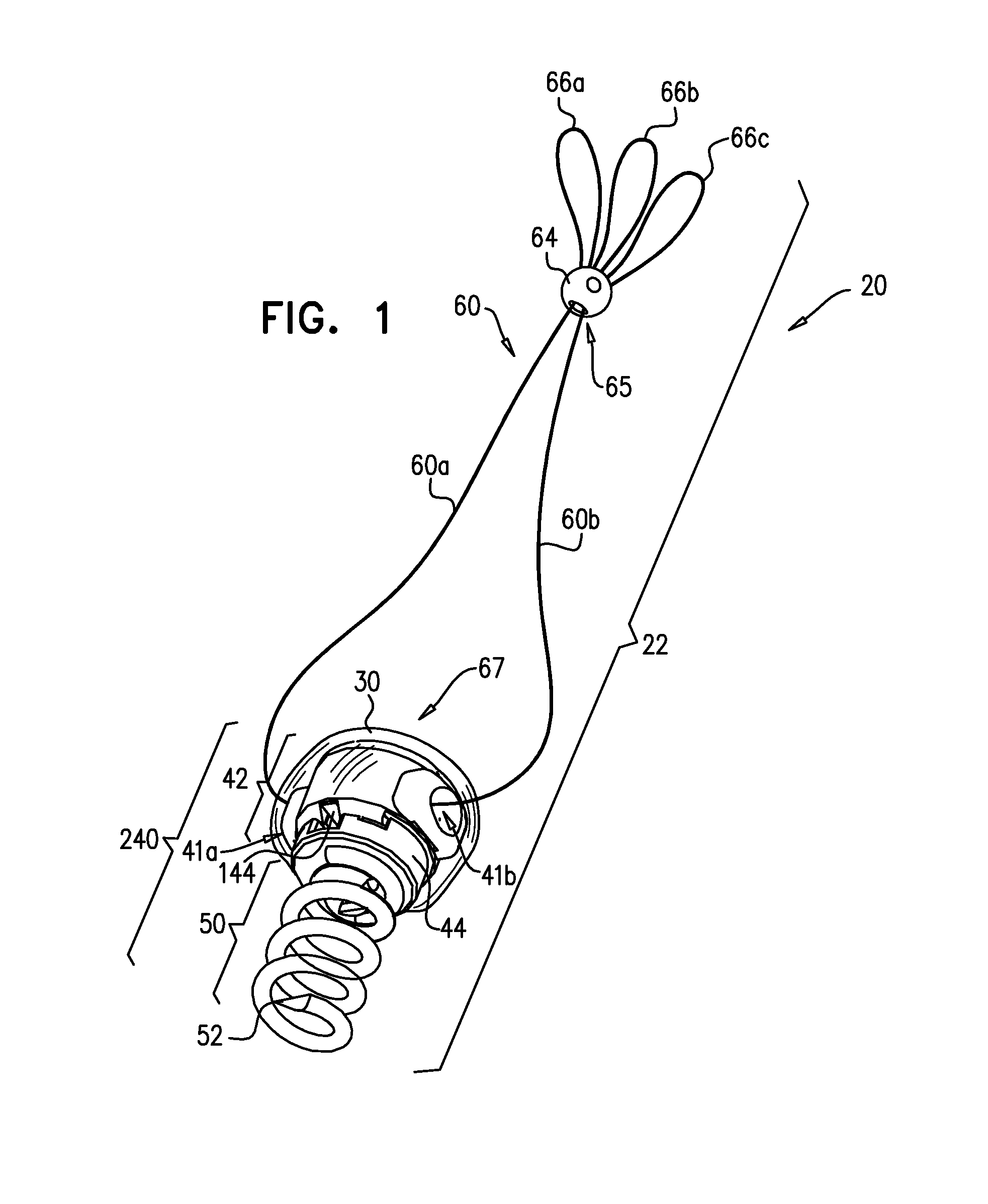
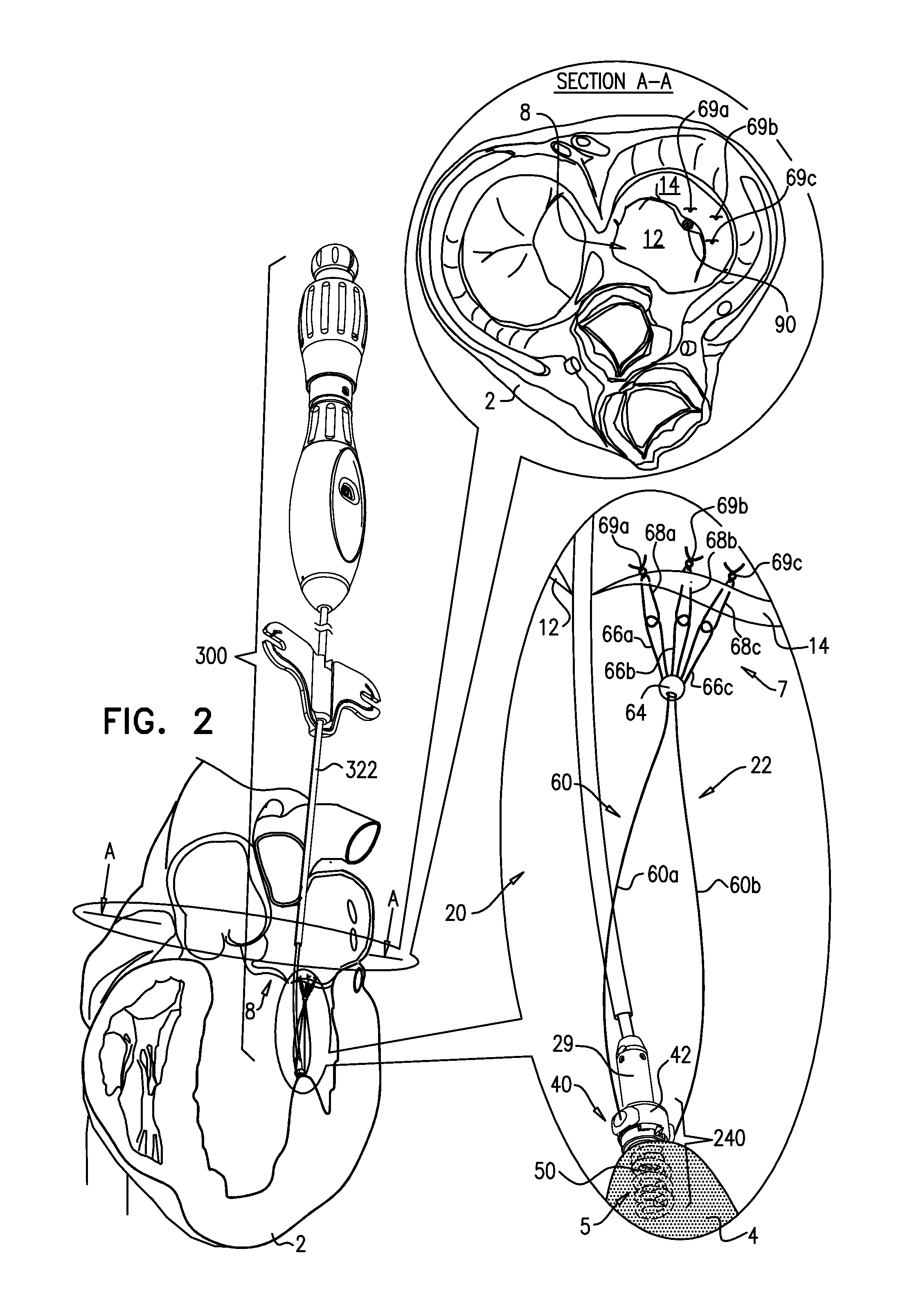
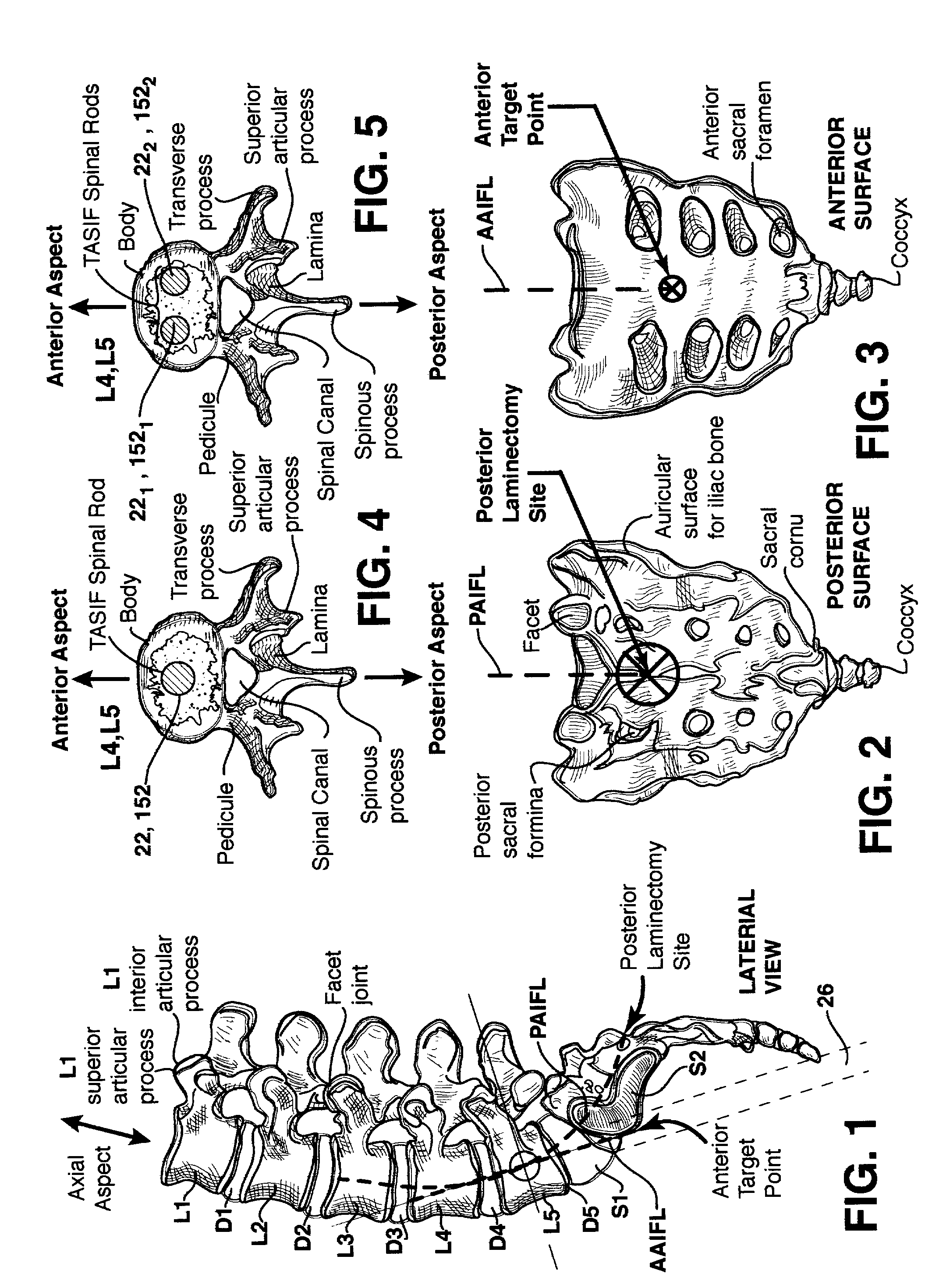
Methods and apparatus for and performing a partial or complete discectomy of an intervertebral spinal disc accessed by one or more trans-sacral axial spinal instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore formed through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) line. A discectomy instrument is introduced through the axial bore, the axial disc opening, and into the nucleus to locate a discectomy instrument cutting head at the distal end of the discectomy instrument shaft within the nucleus. The cutting head is operated by operating means coupled to the instrument body proximal end for extending the cutting head laterally away from the disc opening within the nucleus of the intervertebral spinal disc and for operating the cutting head to form a disc cavity within the annulus extending laterally and away from the disc opening or a disc space wherein the disc cavity extends through at least a portion of the annulus. A discectomy sheath that is first introduced to extend from the skin incision through the axial bore and into the axial disc opening having a discectomy sheath lumen that the discectomy instrument is introduced through. The discectomy sheath is preferably employed for irrigation and aspiration of the disc cavity or just aspiration if irrigation fluids are introduced through a discectomy instrument shaft lumen. The cutting head of the discectomy tool is deflected from the sheath lumen laterally and radially toward the annulus using a deflecting catheter or pull wire.
Owner:TRANSI
Artificial Disc Replacement Using Posterior Approach
Methods and devices are provided for replacing a spinal disc. In an exemplary embodiment, artificial disc replacements and methods are provided wherein at least a portion of a disc replacement can be implanted using a posterolateral approach. With a posterolateral approach, the spine is accessed more from the side of the spinal canal through an incision formed in the patient's back. A pathway is created from the incision to the disc space between adjacent vertebrae. Portions of the posterolateral annulus, and posterior lip of the vertebral body may be removed to access the disc space, leaving the remaining annulus and the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments in tact. The disc implant can be at least partially introduced using a posterolateral approach, yet it has a size that is sufficient to restore height to the adjacent vertebrae, and that is sufficient to maximize contact with the endplates of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Apparatus for performing a discectomy through a trans-sacral axial bore within the vertebrae of the spine
Methods and apparatus for and performing a partial or complete discectomy of an intervertebral spinal disc accessed by one or more trans-sacral axial spinal instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore formed through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) line. A discectomy instrument is introduced through the axial bore, the axial disc opening, and into the nucleus to locate a discectomy instrument cutting head at the distal end of the discectomy instrument shaft within the nucleus. The cutting head is operated by operating means coupled to the instrument body proximal end for extending the cutting head laterally away from the disc opening within the nucleus of the intervertebral spinal disc and for operating the cutting head to form a disc cavity within the annulus extending laterally and away from the disc opening or a disc space wherein the disc cavity extends through at least a portion of the annulus. A discectomy sheath that is first introduced to extend from the skin incision through the axial bore and into the axial disc opening having a discectomy sheath lumen that the discectomy instrument is introduced through. The discectomy sheath is preferably employed for irrigation and aspiration of the disc cavity or just aspiration if irrigation fluids are introduced through a discectomy instrument shaft lumen. The cutting head of the discectomy tool is deflected from the sheath lumen laterally and radially toward the annulus using a deflecting catheter or pull wire.
Owner:BAXANO SURGICAL
System and Method for Electrical Stimulation of the Lumbar Vertebral Column
ActiveUS20120215218A1Inhibit migrationPrevent rotationSpinal electrodesSurgical instruments for heatingElectrical impulseElectrical stimulations
Disclosed methods and devices treat chronic lower back pain from degenerated or injured intervertebral discs. Electrodes connected to a pulse generator deliver electrical impulses to nerves located within the posterior longitudinal ligament and annulus fibrosus of lumbar intervertebral discs. The stimulation reduces back pain reversibly, adjustably, and with almost complete coverage of the pain-generating region. A temporary percutaneous lead and a permanent paddle lead are used. The percutaneous lead, designed to prevent inappropriate stimulation of the thecal sac, is inserted using a specially-designed introducer cannula and lead blank. The paddle lead is configured individually for implantation in the anterior epidural space of each patient. Electrical stimulation parameters may also be selected so as to ablate the nerves, using non-thermal irreversible electroporation, or using joule heating wherein a thermal insulator covers substantially all of the thecal sac, thereby shielding the thecal sac from potential heat damage.
Owner:LIPANI JOHN D
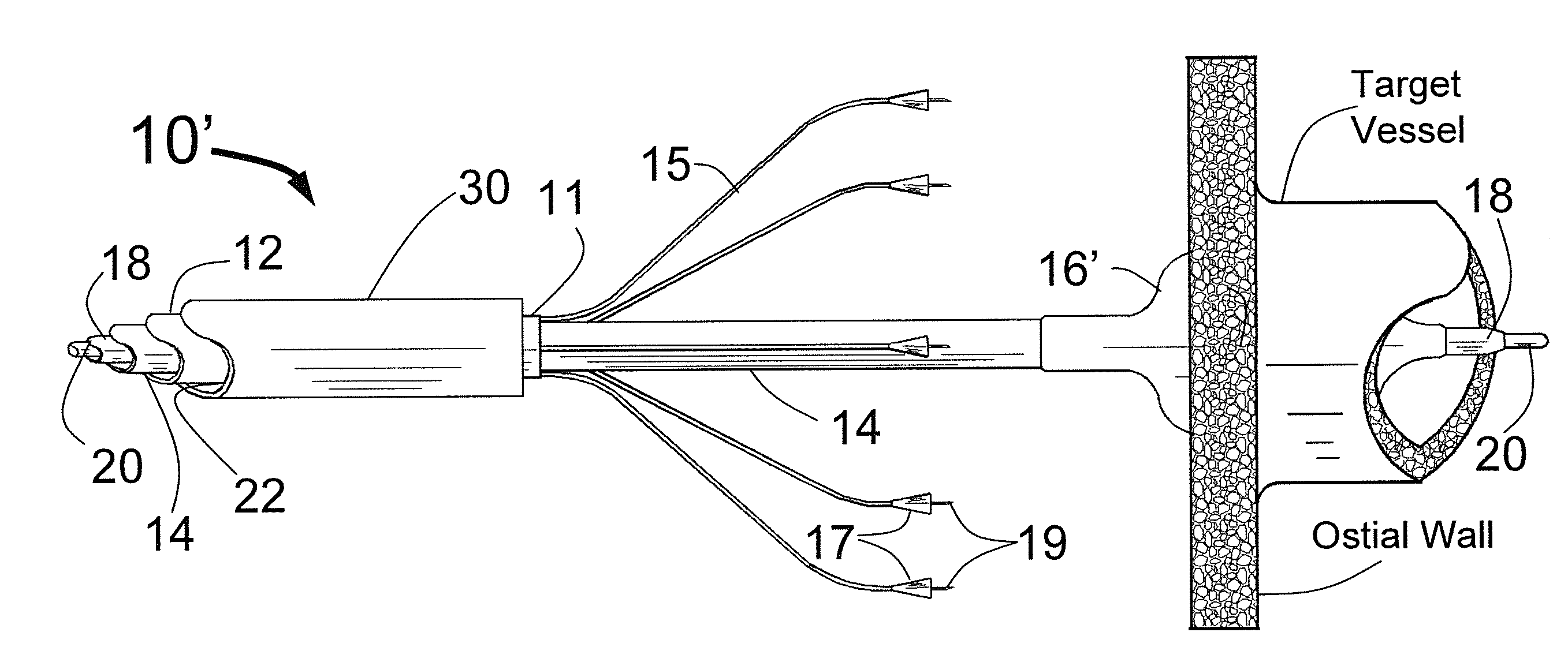
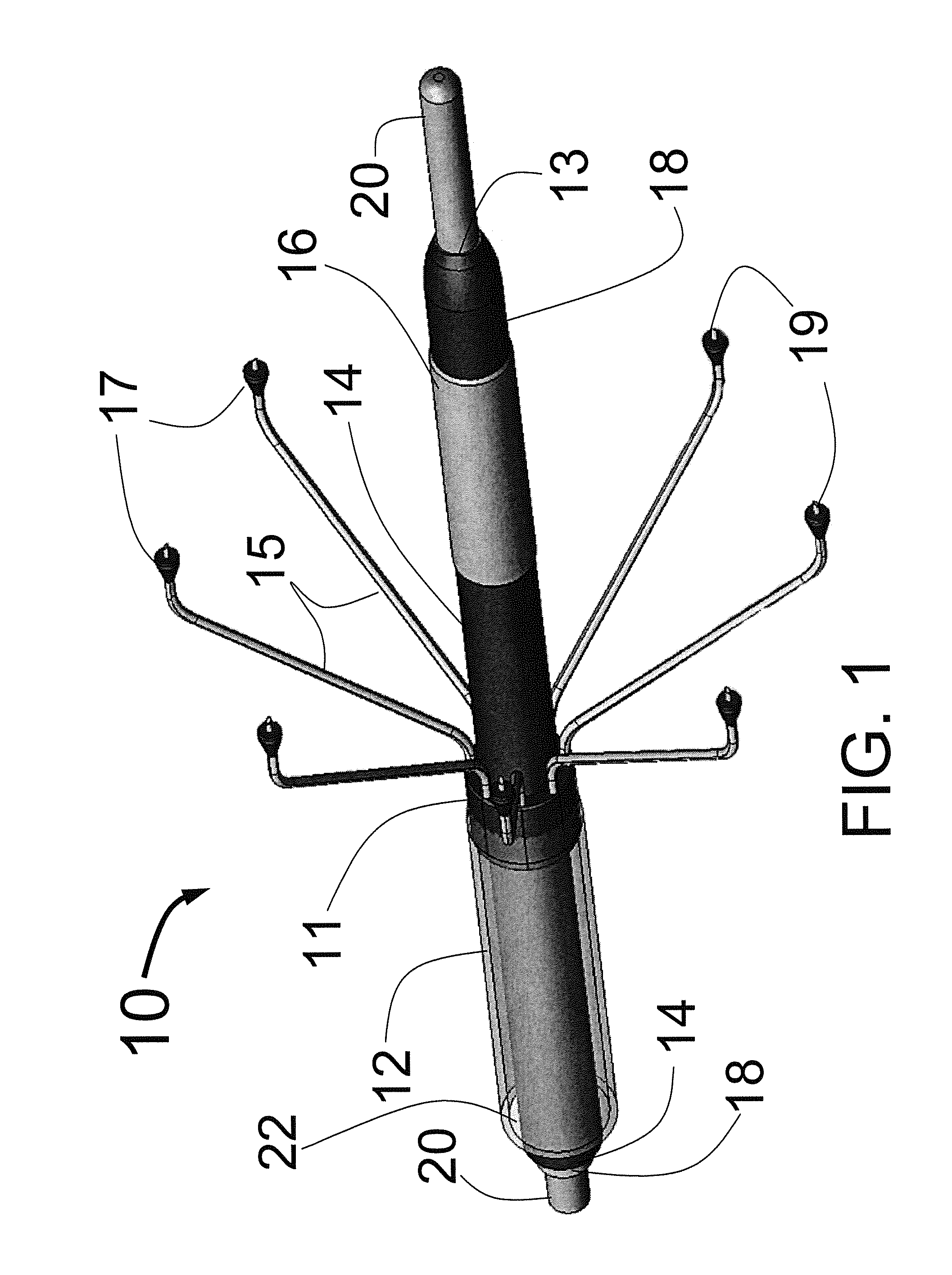
Expandable catheter system for peri-ostial injection and muscle and nerve fiber ablation
ActiveUS20120271301A1Improve control and treatmentTime efficient and safeIntravenous devicesSurgical instruments for heatingCapital equipmentLeft atrium
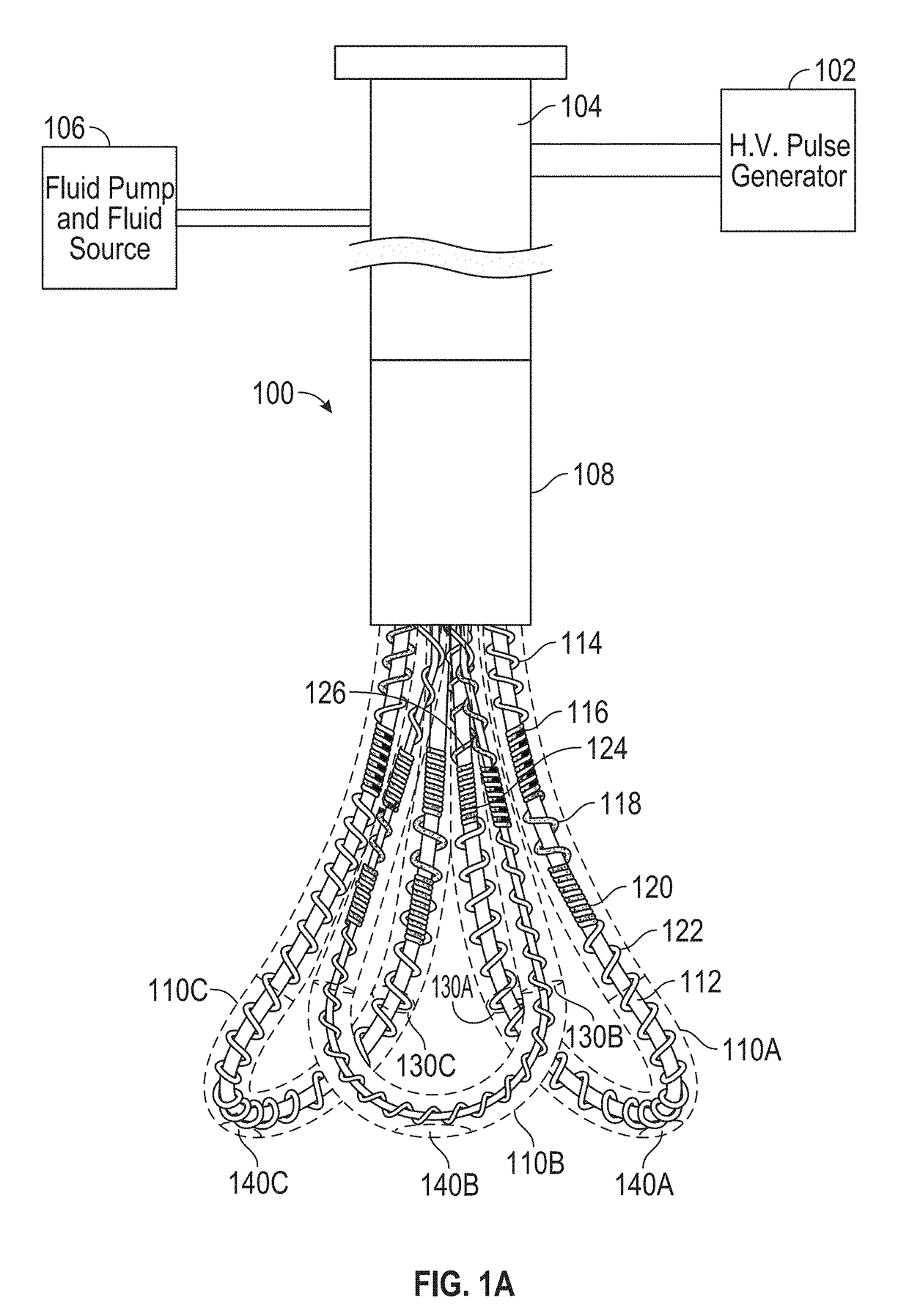
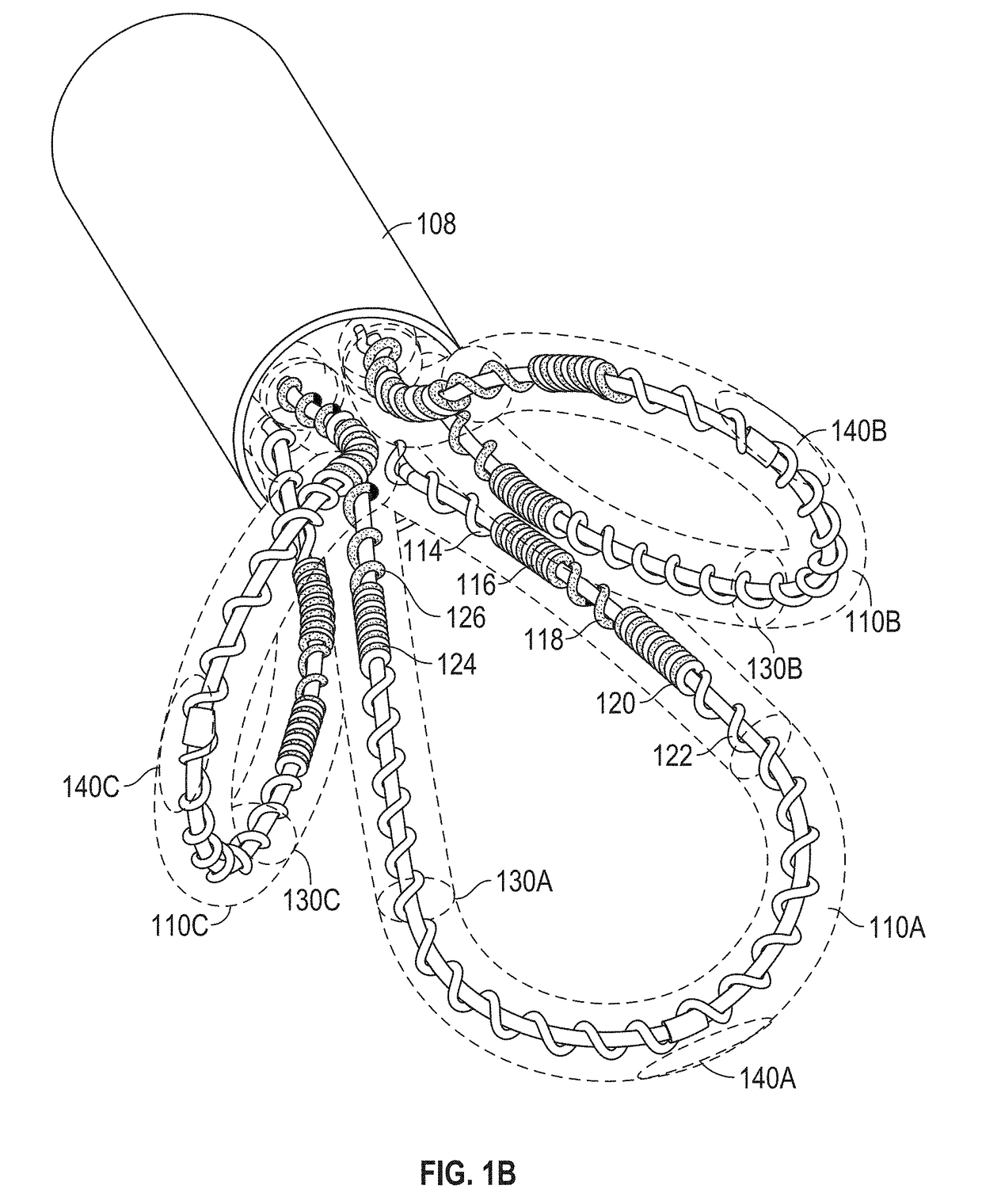
At the present time, physicians often treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) using radiofrequency (RF) catheter systems to ablate conducting tissue in the wall of the Left Atrium of the heart around the ostium of the pulmonary veins. These systems are expensive and take time consuming to use. The present invention circular ablation system CAS includes a multiplicity of expandable needles that can be expanded around a central axis and positioned to inject a fluid like ethanol to ablate conductive tissue in a ring around the ostium of a pulmonary vein quickly and without the need for expensive capital equipment. The expansion of the needles is accomplished by self-expanding or balloon expandable structures. The invention includes centering means so that the needles will be situated in a pattern surrounding the outside of the ostium of a vein. Also included are members that limit the distance of penetration of the needles into the wall of the left atrium. The present invention also has application to ablating tissue around the ostium of a renal artery for the treatment of hypertension.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Artificial Disc Replacement Using Posterior Approach
Methods and devices are provided for replacing a spinal disc. In an exemplary embodiment, artificial disc replacements and methods are provided wherein at least a portion of a disc replacement can be implanted using a posterolateral approach. With a posterolateral approach, the spine is accessed more from the side of the spinal canal through an incision formed in the patient's back. A pathway is created from the incision to the disc space between adjacent vertebrae. Portions of the posterolateral annulus, and posterior lip of the vertebral body may be removed to access the disc space, leaving the remaining annulus and the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments in tact. The disc implant can be at least partially introduced using a posterolateral approach, yet it has a size that is sufficient to restore height to the adjacent vertebrae, and that is sufficient to maximize contact with the endplates of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
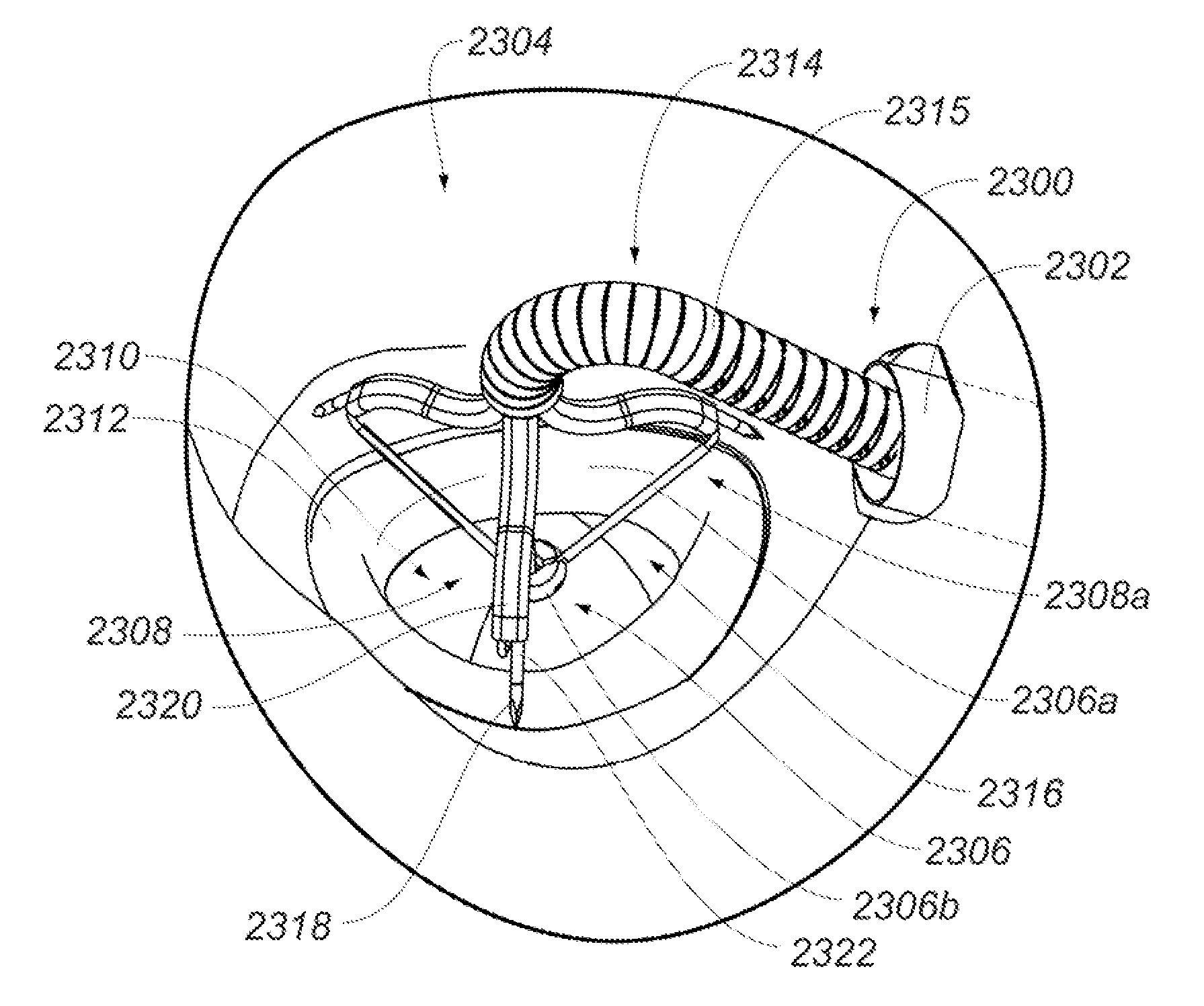
Medical device, kit and method for constricting tissue or a bodily orifice, for example, a mitral valve
ActiveUS20130345797A1Prevent retreatSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsPosterior leafletAnnuloplasty rings
A device, kit and method may employ an implantable device (e.g., annuloplasty implant) and a tool to implant such. The implantable device is positionable in a cavity of a bodily organ (e.g., a heart) and operable to constrict a bodily orifice (e.g., a mitral valve). Tissue anchors are guided into precise position by an intravascularly deployed anchor guide frame and embedded in an annulus. Constriction of the orifice may be accomplished via a variety of structures, for example by cinching a flexible cable or anchored annuloplasty ring, the cable or ring attached to the tissue anchors. The annuloplasty ring may be delivered in a generally elongated configuration, and implanted in an anchored generally arch, arcuate or annular configuration. Such may move a posterior leaflet anteriorly and an anterior leaflet posteriorly, improving leaflet coaptation to eliminate mitral regurgitation.
Owner:KARDIUM
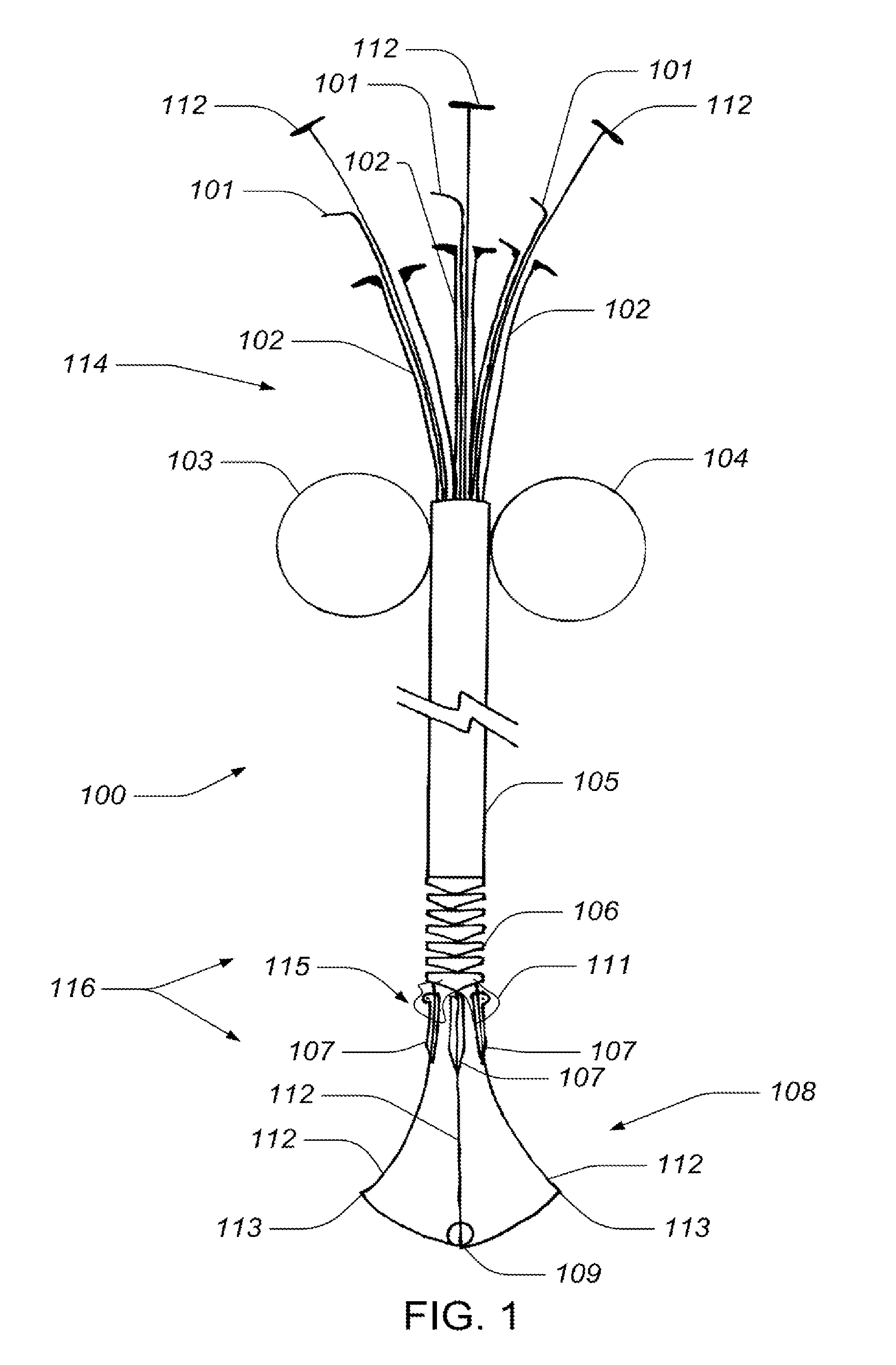
Adjustable suture-button construct for knotless stabilization of cranial cruciate deficient ligament stifle
An adjustable, knotless button / loop / needle construct for fixation of cranial cruciate ligament deficient stifle. The adjustable, knotless construct includes two fixation devices (for example, two buttons), at least one flexible, adjustable loop attached to at least one of the fixation devices (e.g., the buttons), and two needles (each needle being attached to one fixation device, e.g., the buttons). The adjustable, knotless construct has an adjustable loop length and allows adjustment in one direction while preventing or locking the construct from loosening in the opposite direction, due to applied tensile forces. The construct and technique of the present invention provides an improved knotless system for cruciate ligament repair.
Owner:ARTHREX
Cinching of dilated heart muscle
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for treating a heart are provided. Methods can include obtaining and using an implant. One or more catheters can be used to properly position and attach the implant in a desired location in a chamber of the heart, for example, on a ventricular wall of the left ventricle between one or more papillary muscles of the left ventricle and the annulus. Then a distance along the implant or a region of the heart, for example, between the papillary muscle and the annulus, can be reduced by contracting the implant along its longitudinal axis by applying tension to a contraction member of the implant. Other embodiments are described.
Owner:VALTECH CARDIO LTD
Methods of treating atrial fibrillation
ActiveUS20140046298A1Improve control and treatmentTime efficient and safeMedical devicesIntravenous devicesCapital equipmentLeft atrium
At the present time, physicians often treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) using radiofrequency (RF) catheter systems to ablate conducting tissue in the wall of the Left Atrium of the heart around the ostium of the pulmonary veins. These systems are expensive and take time consuming to use. The present invention circular ablation system CAS includes a multiplicity of expandable needles that can be expanded around a central axis and positioned to inject a fluid like ethanol to ablate conductive tissue in a ring around the ostium of a pulmonary vein quickly and without the need for expensive capital equipment. The expansion of the needles is accomplished by self-expanding or balloon expandable structures. The invention includes centering means so that the needles will be situated in a pattern surrounding the outside of the ostium of a vein. Also included are members that limit the distance of penetration of the needles into the wall of the left atrium. The present invention also has application to ablating tissue around the ostium of a renal artery for the treatment of hypertension.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Expandable catheter system for peri-ostial injection and muscle and nerve fiber ablation
ActiveUS9237925B2Improve control and treatmentTime efficient and safeElectrocardiographySurgical needlesFiberCapital equipment
At the present time, physicians often treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) using radiofrequency (RF) catheter systems to ablate conducting tissue in the wall of the Left Atrium of the heart around the ostium of the pulmonary veins. These systems are expensive and take time consuming to use. The present invention circular ablation system CAS includes a multiplicity of expandable needles that can be expanded around a central axis and positioned to inject a fluid like ethanol to ablate conductive tissue in a ring around the ostium of a pulmonary vein quickly and without the need for expensive capital equipment. The expansion of the needles is accomplished by self-expanding or balloon expandable structures. The invention includes centering means so that the needles will be situated in a pattern surrounding the outside of the ostium of a vein. Also included are members that limit the distance of penetration of the needles into the wall of the left atrium, or the aortic wall. The present invention also has an important application to ablate tissue around the ostium of one or both renal arteries, for the ablation of the sympathetic nerve fibers and / or other afferent or efferent nerves going to or from each kidney in order to treat hypertension.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Adjustable vertebral spacer for artificial vertebrae
InactiveUS20090164019A1Improve positional stabilityEasy to adjustBone implantSpinal implantsEngineeringVertebral bone
An adjustable vertebral spacer includes a spacer body, a movable member coupled to the spacer body, an adjustment ring mounted on the spacer body and rotatable to move the movable member and to further adjust the combined height of the spacer body and the movable member, a lock ring mounted on the spacer body for locking the movable member to the adjustment ring, and a top endplate coupled to the movable member at the top and tiltable to fit the angle of the adjacent upper vertebral body during surgery operation.
Owner:CHAO CHING KONG +3
Artificial disc replacement using posterior approach
Methods and devices are provided for replacing a spinal disc. In an exemplary embodiment, artificial disc replacements and methods are provided wherein at least a portion of a disc replacement can be implanted using a posterolateral approach. With a posterolateral approach, the spine is accessed more from the side of the spinal canal through an incision formed in the patient's back. A pathway is created from the incision to the disc space between adjacent vertebrae. Portions of the posterolateral annulus, and posterior lip of the vertebral body may be removed to access the disc space, leaving the remaining annulus and the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments in tact. The disc implant can be at least partially introduced using a posterolateral approach, yet it has a size that is sufficient to restore height to the adjacent vertebrae, and that is sufficient to maximize contact with the endplates of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Flower catheter for mapping and ablating veinous and other tubular locations
InactiveCN103315806AGuaranteed contactCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringDistal portionBiomedical engineering
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Aortic leaflet repair using shock wave applicators
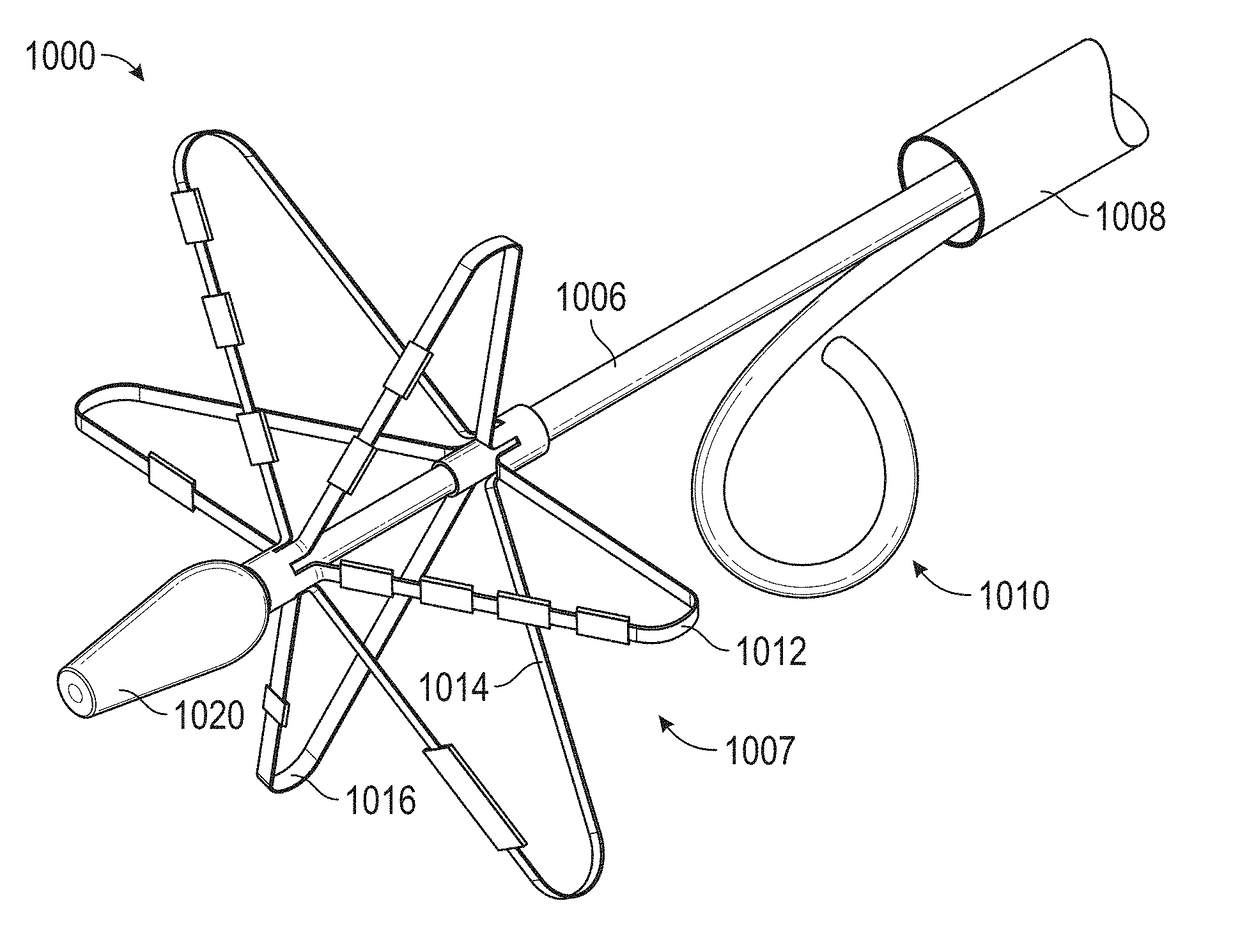
Described herein are shock wave devices and methods for the treatment of calcified heart valves. One variation of a shock wave device may comprise an elongated flexible tube carried by a sheath. The tube may have a fluid input end, which may be located near a proximal end of the sheath. The tube may include a loop portion. The loop portion may be configured to be at least partially accommodated within a cusp of the heart valve. The tube may be fillable with a conductive fluid. In some variations, the shock wave device may include an array of electrode pairs associated with a plurality of wires positioned within the loop portion of a tube. The electrode pairs may be electrically connectable to a voltage source and configured to generate shock waves in the conductive fluid in response to voltage pulses.
Owner:SHOCKWAVE MEDICAL
Transverse fixation technique for ACL reconstruction using bone-tendon-bone graft
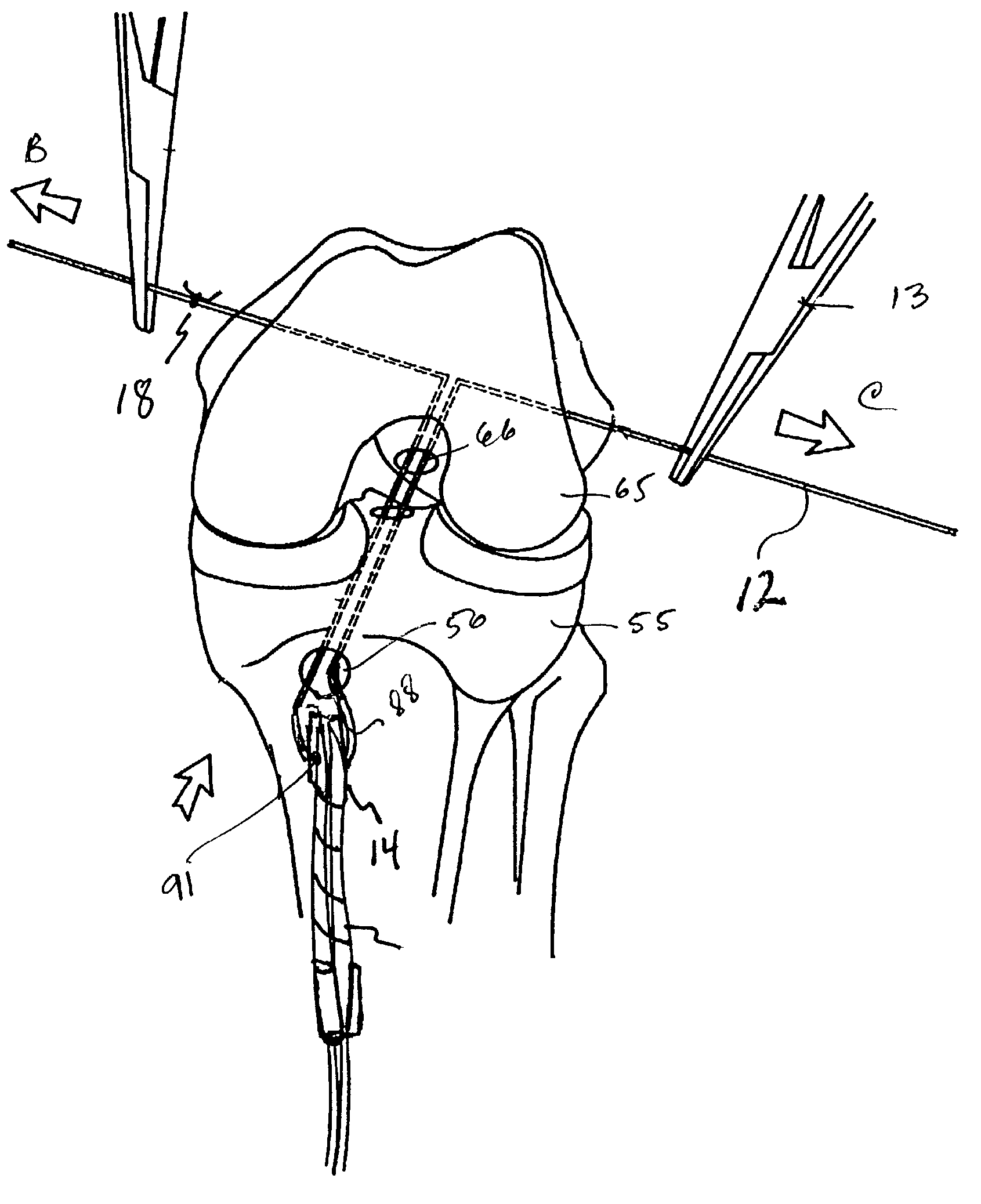
A surgical method for transosseous fixation of a BTB graft into a joint is disclosed. A longitudinal tunnel formed in a bone is intersected by a transverse pin. A flexible strand is drawn with the pin through the bone. A looped portion of the strand is diverted so as to protrude out of the entrance to the longitudinal tunnel. The loop is severed so that one end of the strand is passed through a hole in the bone block of the BTB graft. The free ends of the loop are subsequently reattached using a knot to form a reformed loop. The strand with the reformed loop is retracted into the tunnel, drawing the attached BTB graft into the tunnel. The BTB graft is fixed in the tunnel using a transverse implant.
Owner:ARTHREX
Intraocular lens rings
InactiveUS20130184816A1Suitable and consistent visual acuityLong lasting fitIntraocular lensAqueous humorEquator
The invention is directed to a lens that comprises an optic and at least two haptic rings, one positioned to rest against the posterior capsule distally outward from the optic zone, the other to rest on the anterior capsule some distance from the equator. The haptic rings of the lens are connected by segments of haptic material that may be arched or straight, and sections of open space to provide for ample circulation of the aqueous humor. The optic is suspended between the two haptic rings such that the distance between the optic and the anterior ring is constant while the distance between the optic and the posterior ring may vary according to the overall capsular dimensions of the eye of the patient.
Owner:ANEW IOL TECH
Capsular opacification blocking lens
The invention is directed to a lens that comprises an optic and two haptic rings, one positioned to rest against the posterior capsule distally outward from the optic zone, the other to rest on the anterior capsule some distance from the equator. The haptic rings of the lens are connected by segments of haptic material that may be arched or straight, and sections of open space to provide for ample circulation of the aqueous humor. The optic is positioned against the posterior capsule as close as possible to the nodal zone of the eye.
Owner:ANEW IOL TECH
Cancellous construct with support ring for repair of osteochondral defects
InactiveUS20080220044A1Facilitating bone healingPromote repairPeptide/protein ingredientsBone implantCancellous boneBiomedical engineering
The invention is directed toward an osteochondral repair assembly comprising a shaped allograft construct comprising an unbalanced barbell-shaped cylindrical cancellous bone primary member formed with a mineralized cylindrical base section having a smaller diameter cylindrical stem leading to a second cylindrical section which is demineralized. A mineralized ring-shaped support member is forced over the compressed demineralized second demineralized the aperture of the ring-shaped member to fit around the stem with one ring surface being adjacent the bottom surface to the second cylindrical section and the opposite ring surface being adjacent the upper surface of the mineralized cylindrical base section.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
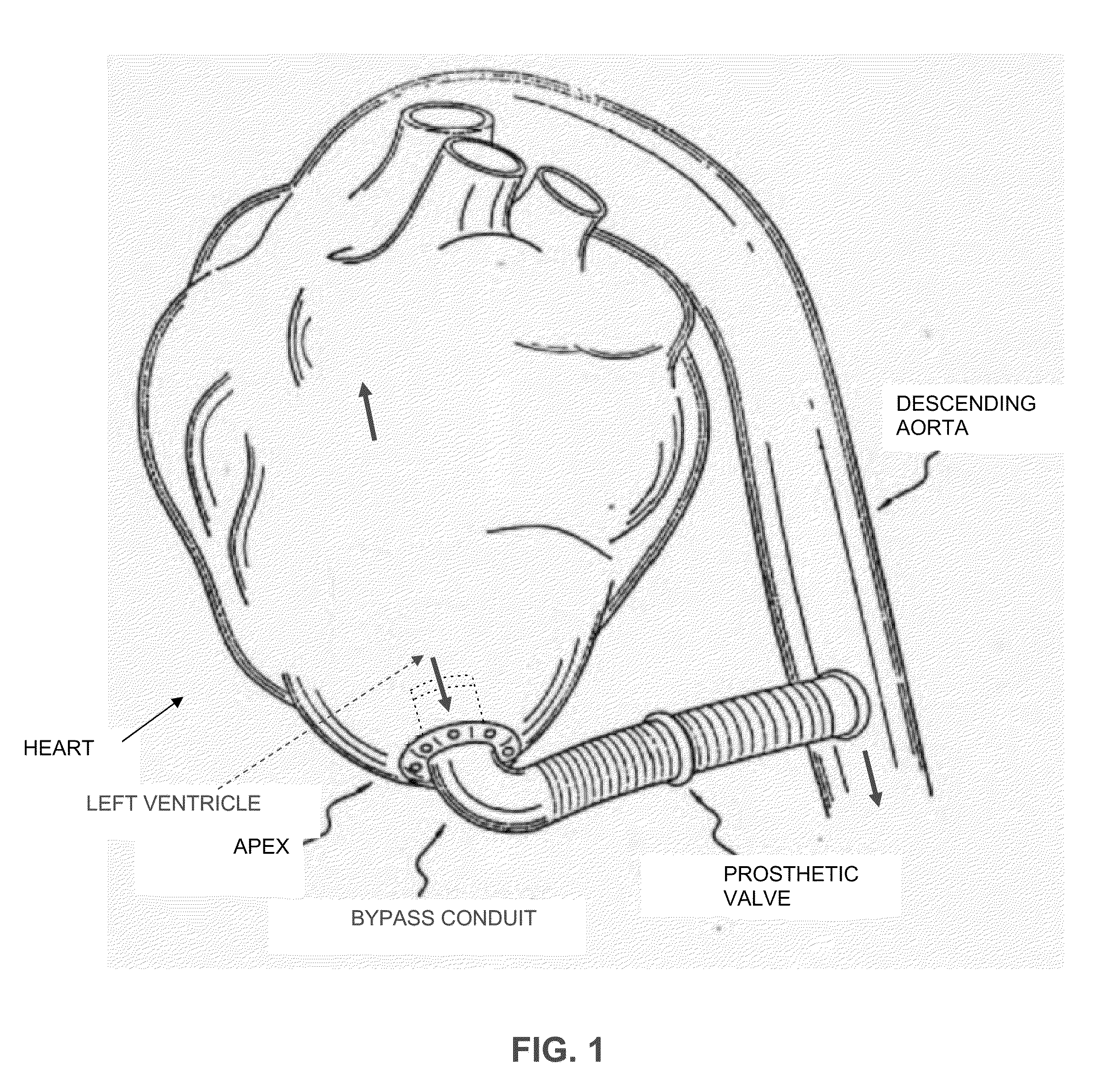
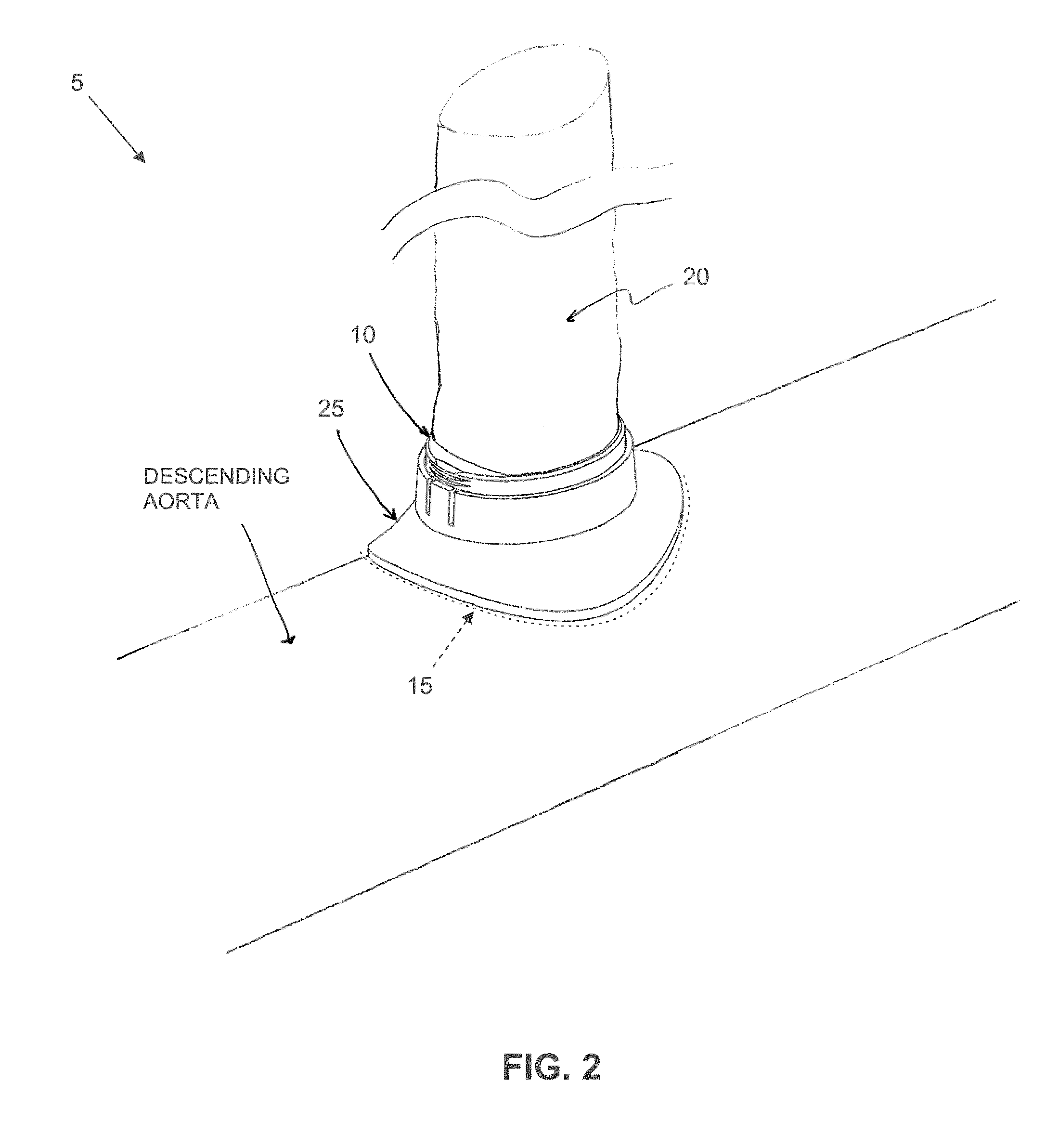
Method and apparatus for effecting a minimally invasive distal anastomosis for an aortic valve bypass
Owner:CORREX
Puborectalis-simulated type dual-ring artificial anal sphincter prosthesis
The invention provides a puborectalis-simulated type dual-ring artificial anal sphincter prosthesis which comprises an upper fixing ring, a lower fixing ring, a connecting support, a power unit, a speed reduction gear box and a movable semi-ring, wherein the upper fixing ring and the lower fixing ring are arranged in parallel, implanted into the periphery of the intestinal tract of a patient to be fixed and arranged at the two ends of the connecting support respectively, the middle of the connecting support is connected with the movable semi-ring, the power unit and the speed reduction gear box are both integrated with the connecting support, and the power unit controls the movable semi-ring through the speed reduction gear box, so that the movable semi-ring moves towards a center hole of the upper fixing ring and a center hole of the lower fixing ring or in the circumferential direction of the upper fixing ring and the lower fixing ring. The puborectalis-simulated type dual-ring artificial anal sphincter prosthesis is small in size, light in weight and capable of increasing the success rate of prosthesis implantation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
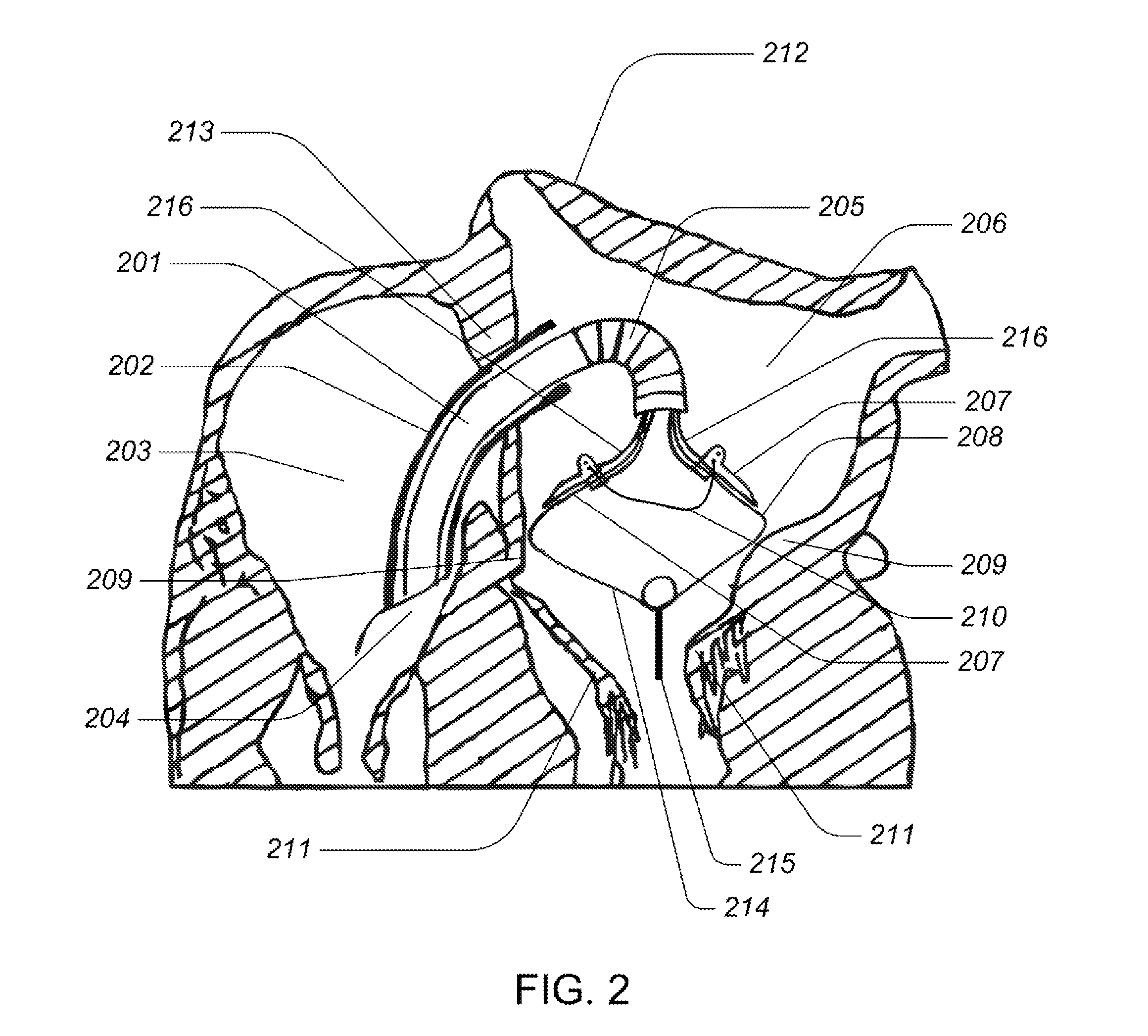
Prosthetic device for heart valve reinforcement and remodeling procedures
A prosthetic heart valve reinforcement ring is disclosed. The prosthetic includes an outer ring sized and dimensioned to fit around an annulus of a heart valve and an inner ring configured and arranged to couple to the outer ring. The inner ring and the outer ring have complimentary mating formations configured and arranged to grip sutures therebetween. A method of reinforcing heart valve is also disclosed. Sutures are provided around an annulus of a heart valve. The sutures are corralled within an outer sizing ring. The outer sizing ring is placed around the annulus of the heart valve. An inner sizing ring is inserted within the outer ring, locking the sutures. The sutures are adjusted and the heart valve is tested for a proper fit. The outer sizing ring is removed and a prosthetic ring is placed over the inner sizing ring, locking the sutures. The sutures are tied.
Owner:NIKOLA DOBRILOVIC LLC
Inwardly-bowed tricuspid annuloplasty ring
A prosthetic tricuspid remodeling annuloplasty ring having two free ends and at least one inward bow to help reduce chordal tethering. The ring may have segments corresponding to the anterior, posterior and septal leaflets, with inward bows located adjacent one, two or all leaflets. Convex corners separate the concave inward bows, with inflection points therebetween. The ring has a semi-rigid inner body covered by fabric or a suture interface such as silicone and fabric.
Owner:ALFIERI OTTAVIO
Position limitation protection type ani sphincter prosthesis
A position limitation protection type ani sphincter prosthesis comprises an upper fixed ring arranged on an upper ring sleeve in a sleeving mode, a movable middle ring arranged on a middle ring sleeve in a sleeving mode and a lower fixed ring arranged on a motor sleeve in a sleeving mode, wherein the upper fixed ring, the movable middle ring and the lower fixed ring are sequentially connected, the upper ring sleeve is axially connected with the middle ring sleeve, a reduction gearbox connected with a motor is arranged between the middle ring sleeve and the upper ring sleeve, the movable middle ring is connected with a reduction gear train in the reduction gearbox through an inner gear ring arranged on a gear ring sleeve in a sleeving mode, a Hall element is arranged on an upper cover plate of the reduction gearbox, and two magnets matched with the Hall element are arranged at the opposite ends of the gear ring sleeve and the upper cover plate of the reduction gearbox in a spaced mode. It can be effectively avoided that intestines are damaged due to the too large swing amplitude of a swing arm of the middle ring, a mechanical is stuck due to the overturning of the motor, and the motor is burnt down due to the too large current; the opening and closing amplitude of the prosthesis can be adjusted by a mechanism according to the feeling of human intestines; the whole device is simple in structure, small in size, light in weight and beneficial for increasing the transplanting success rate.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Adaptive middle swing arm structure and puborectalis muscle-like double-ring praeternaturalis anus sphincter prosthesis thereof
The invention discloses an adaptive middle swing arm structure and a puborectalis muscle-like double-ring praeternaturalis anus sphincter prosthesis thereof. The puborectalis muscle-like double-ring praeternaturalis anus sphincter prosthesis comprises the adaptive middle swing arm structure, an upper fixed ring, a lower fixed ring, a connection bracket, a minitype motor and a gear reduction gearbox, wherein the upper fixed ring and the lower fixed ring are arranged in parallel and are implanted into the periphery of an intestinal tract to be fixed and are respectively arranged on two ends of the connection bracket; a swing arm body, the minitype motor and the gear reduction gearbox are all in integrated arrangement with the connection bracket; the minitype motor is meshed with a gear transmission device by the gear reduction gearbox. The adaptive middle swing arm structure has the advantages of small size and light weight, damage to tissues around the intestinal tract by an actuator is further lightened, and a prosthesis implantation success rate can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Device for wound suturing and hemostasis in the thoracic and the abdominal wall mainly in endoscopic operations
InactiveUS8545522B2Reduce probabilityDiminishing traumatizing effectSuture equipmentsCannulasSplit ringDevice form
A device for use with a trocar in suturing trocar wounds with flexible needles. The device includes a ring encompassing the trocar positionable adjacent to a body wall. The ring, often a split ring, has a pair of guide channels passing through it, each channel including an entry hole and an exit hole. These guide holes are disposed symmetrically on the ring such that the two entry holes and the two exit holes form lines passing through the longitudinal axis of the trocar. The channels are curved near their respective entry holes. The guide channels are angled in the region of the exit holes so that when the needles exit the channels into the body wall and then the body cavity they are at a predetermined distance from the nearest point on the trocar. The above described device forms a suturing system with the trocar.
Owner:SHPAICHLER VLADIMIR +1
Cancellous construct with support ring for repair of osteochondral defects
InactiveUS8435551B2Guaranteed functionEasily placed in defect areaPeptide/protein ingredientsBone implantCancellous boneBiomedical engineering
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
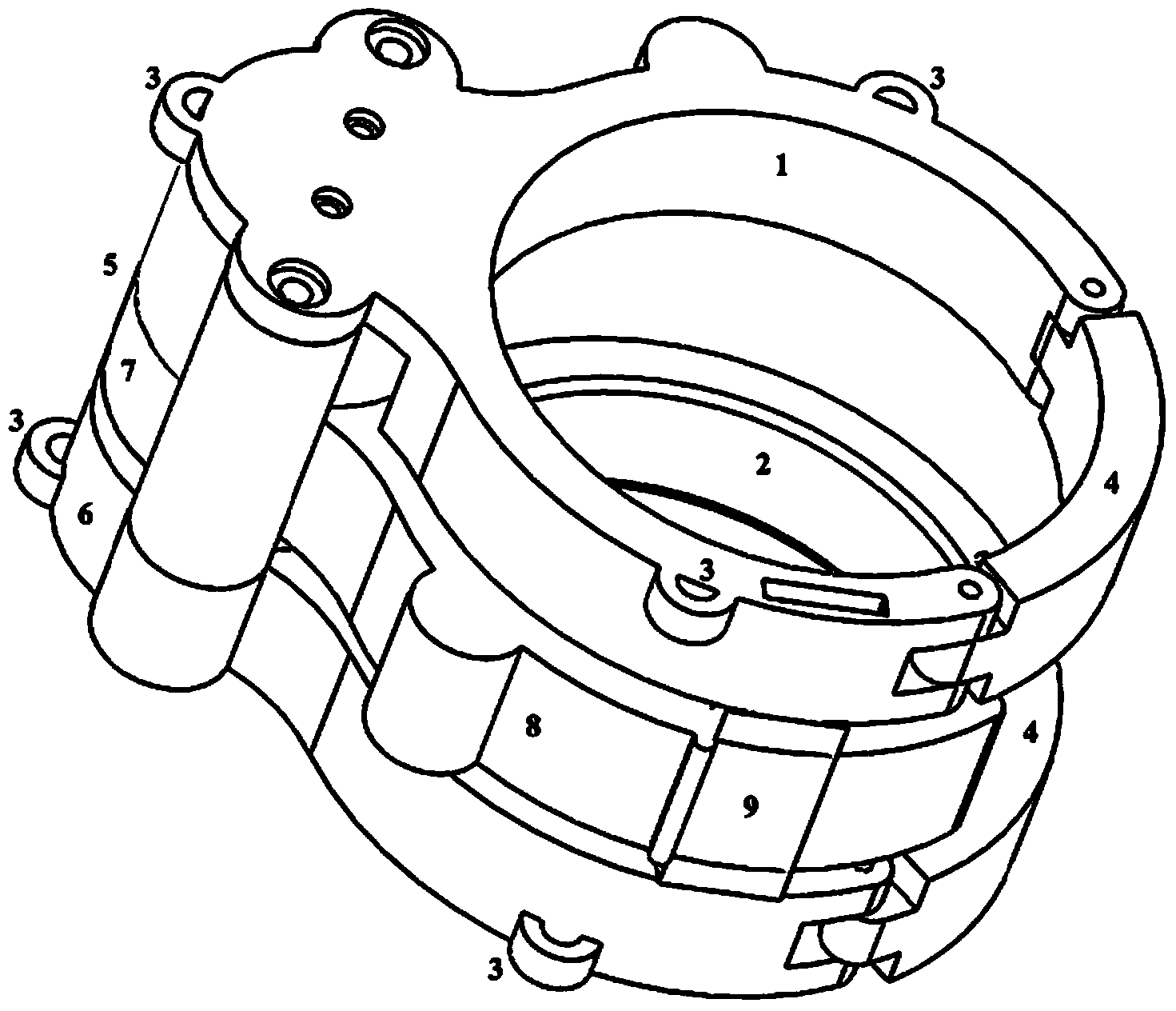
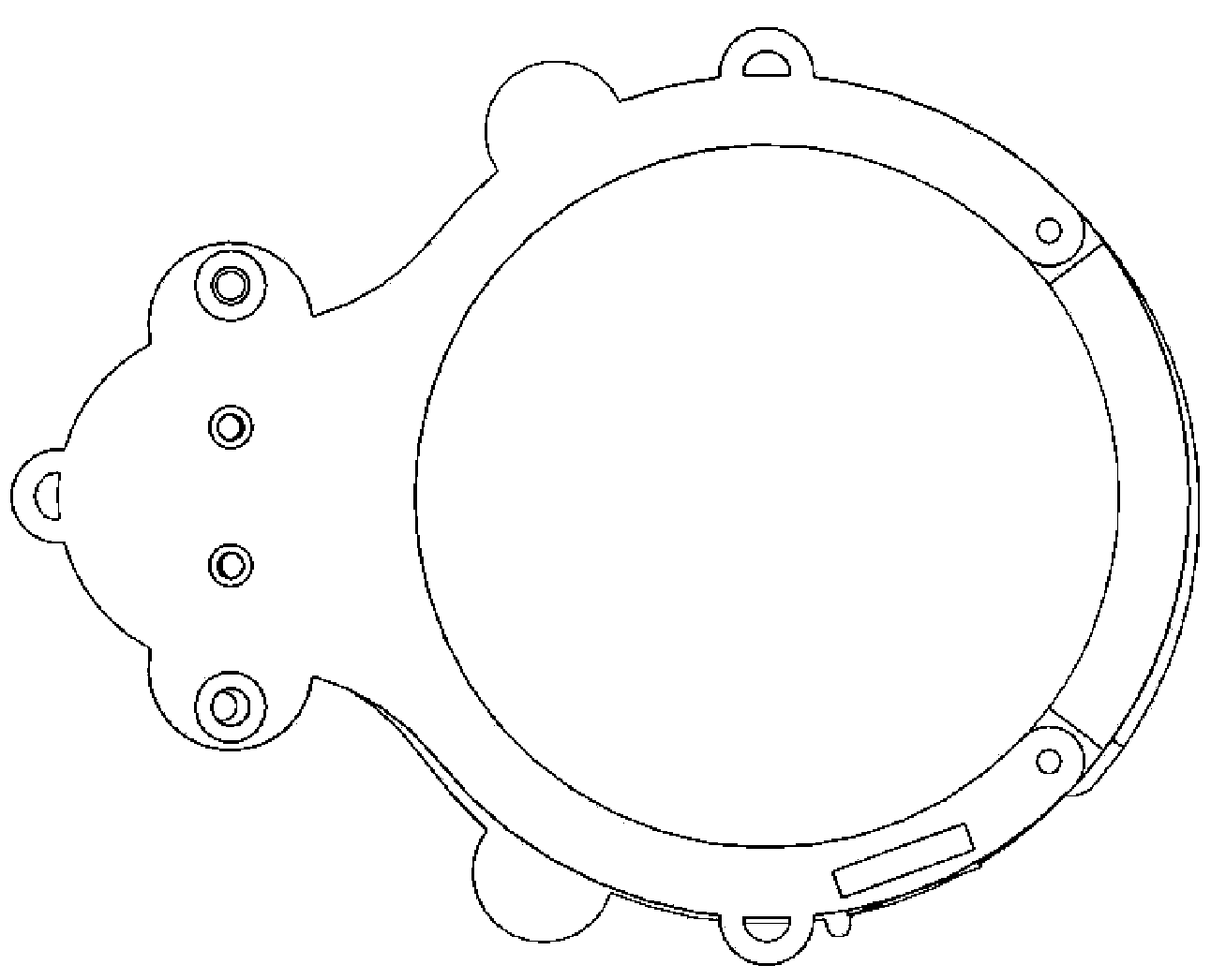
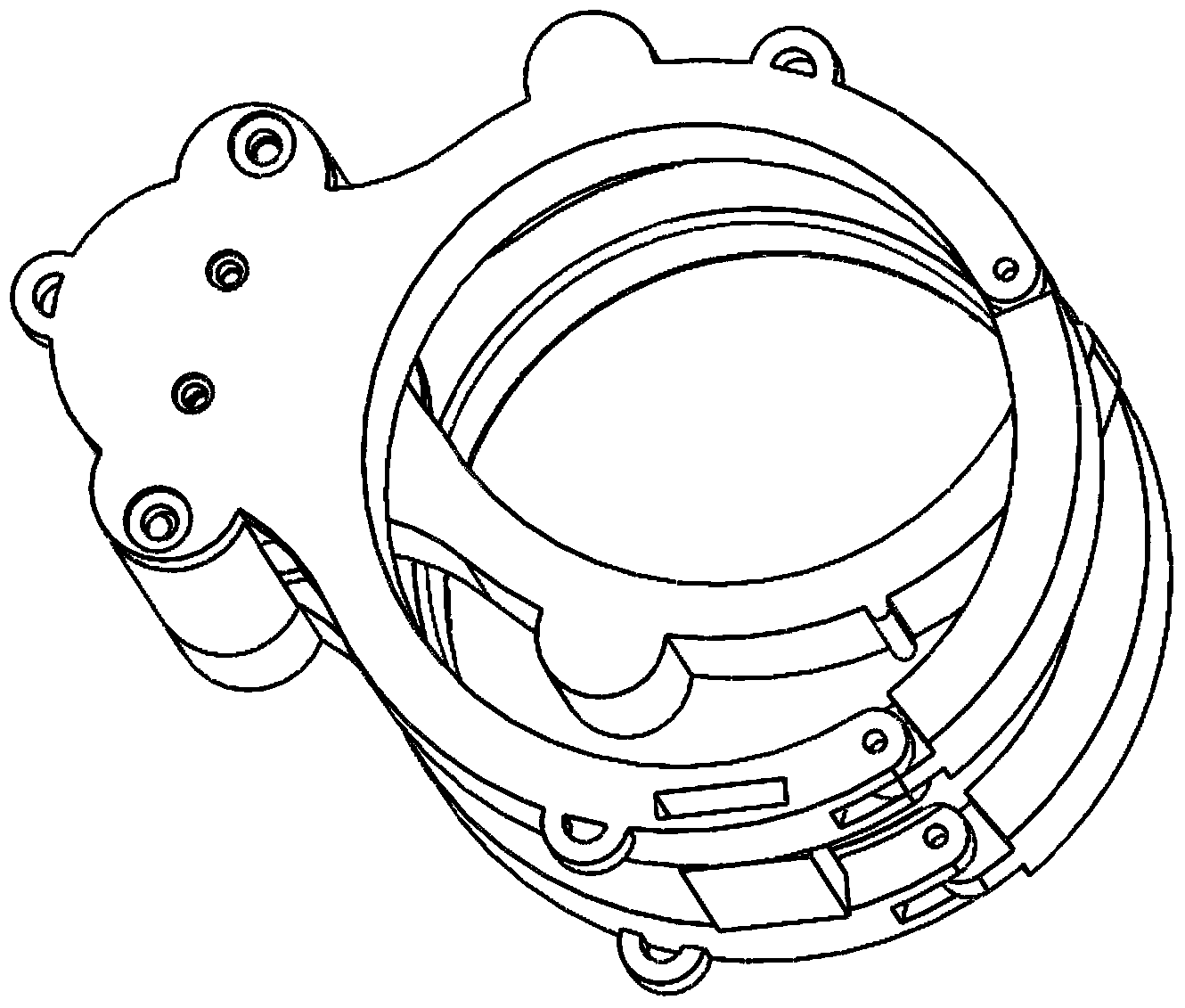
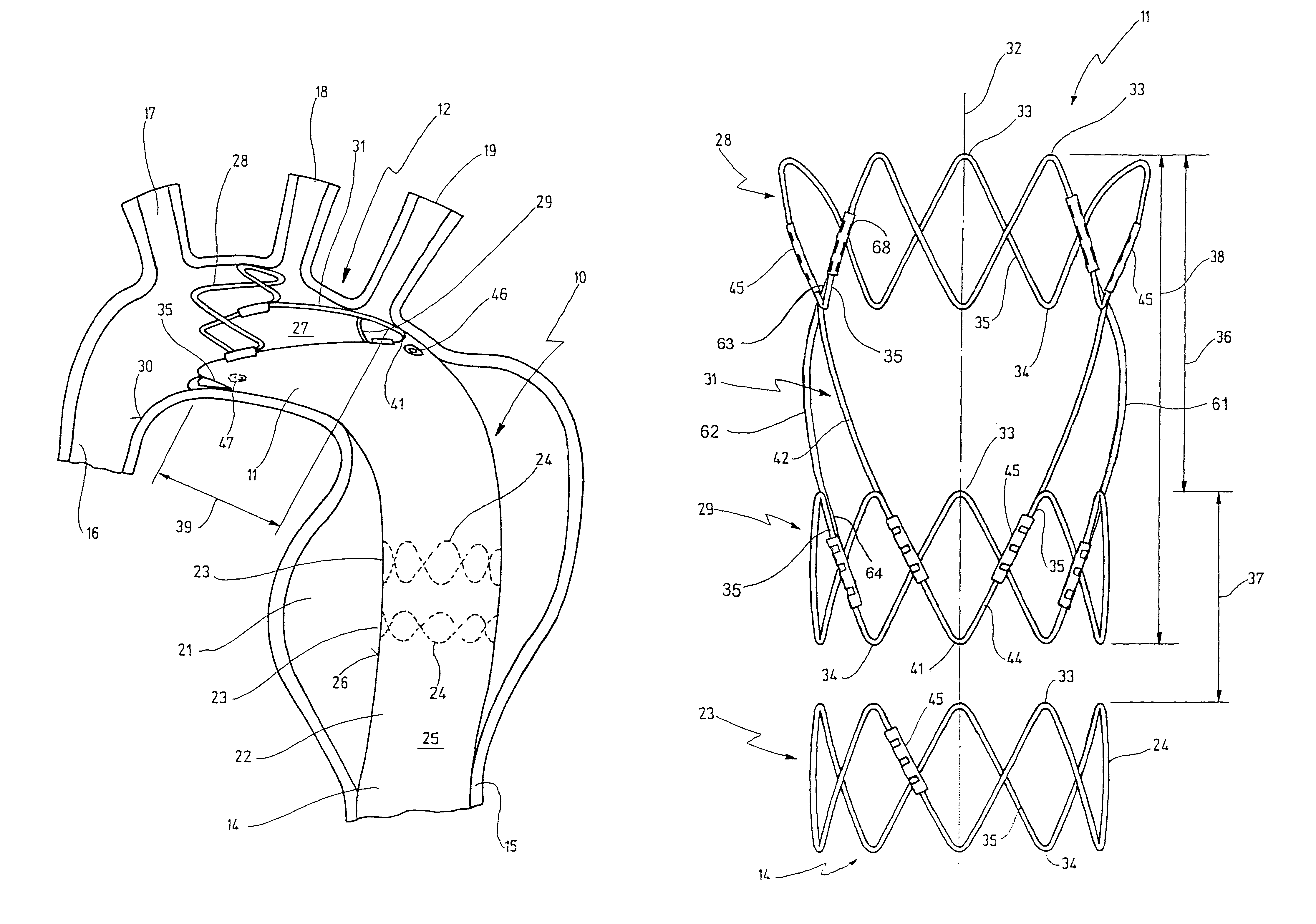
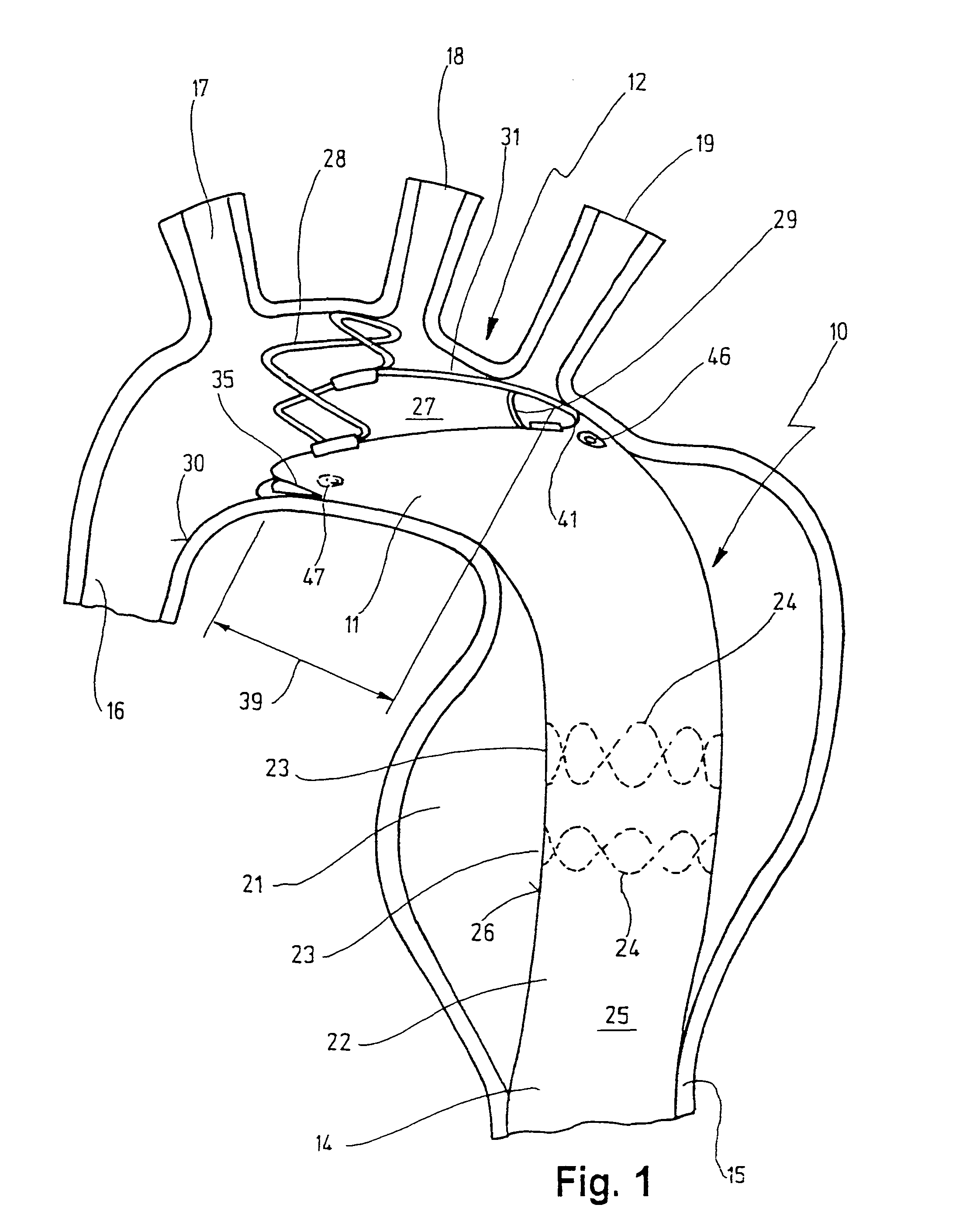
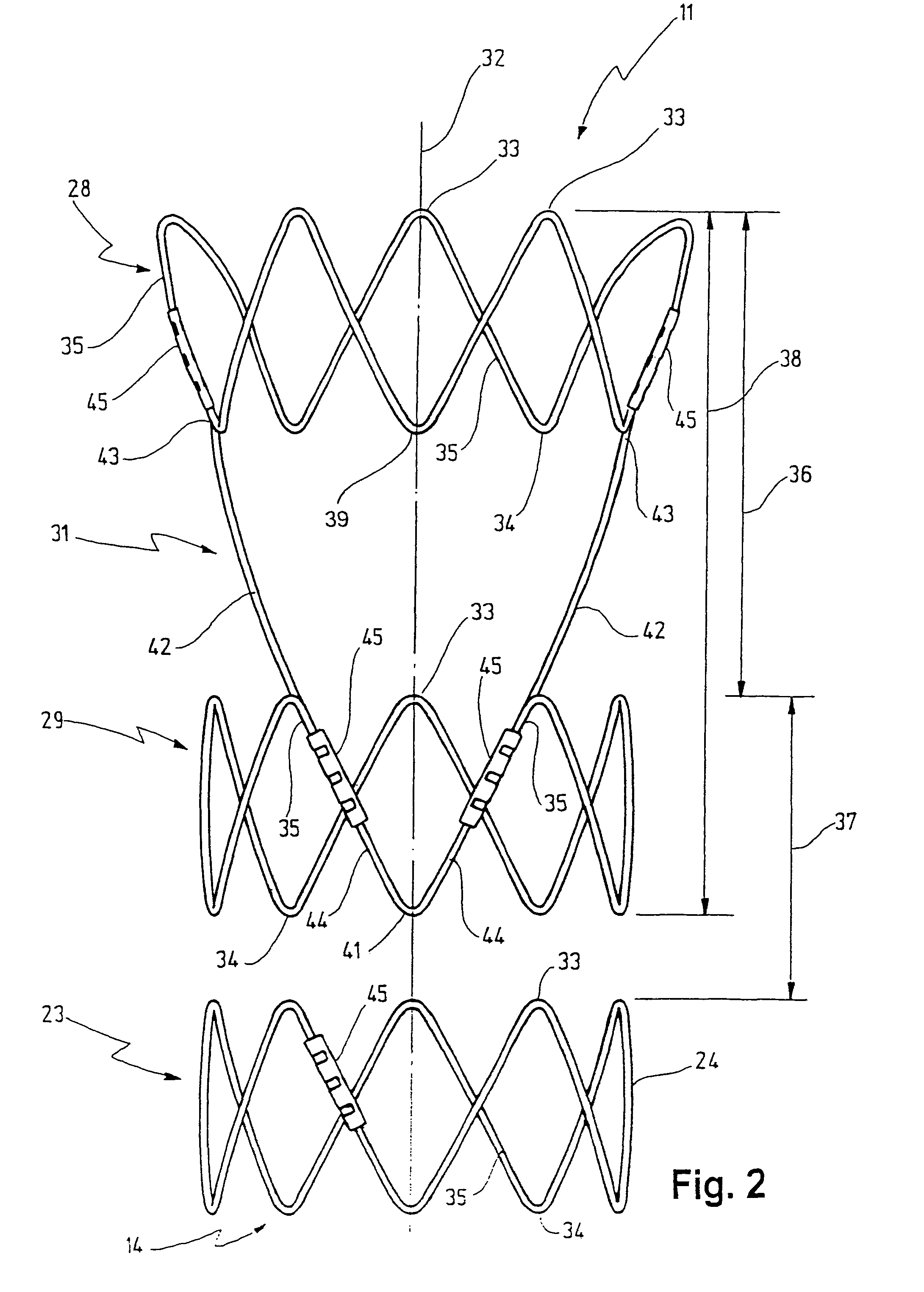
Stent for implantation in a blood vessel, especially in the region of the aortic arch
ActiveUS8668729B2Easy to produceRapid and inexpensive but reliable productionStentsBlood vesselsInsertion stentProsthesis
A stent for implantation in a blood vessel is disclosed, especially in the region of the aortic arch. The stent is comprising rings which are disposed successively in the stent's longitudinal direction and which are made up of meandering circumferential supports. The stent further comprises a prosthesis material which is fixed to the rings and which connects them, thereby forming a hollow cylindrical body with a jacket which is substantially closed on the circumference thereof. At least one connecting support is provided between the last ring and the penultimate ring at the proximal end of the stent and connects these two rings to one another.
Owner:JOTEC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com