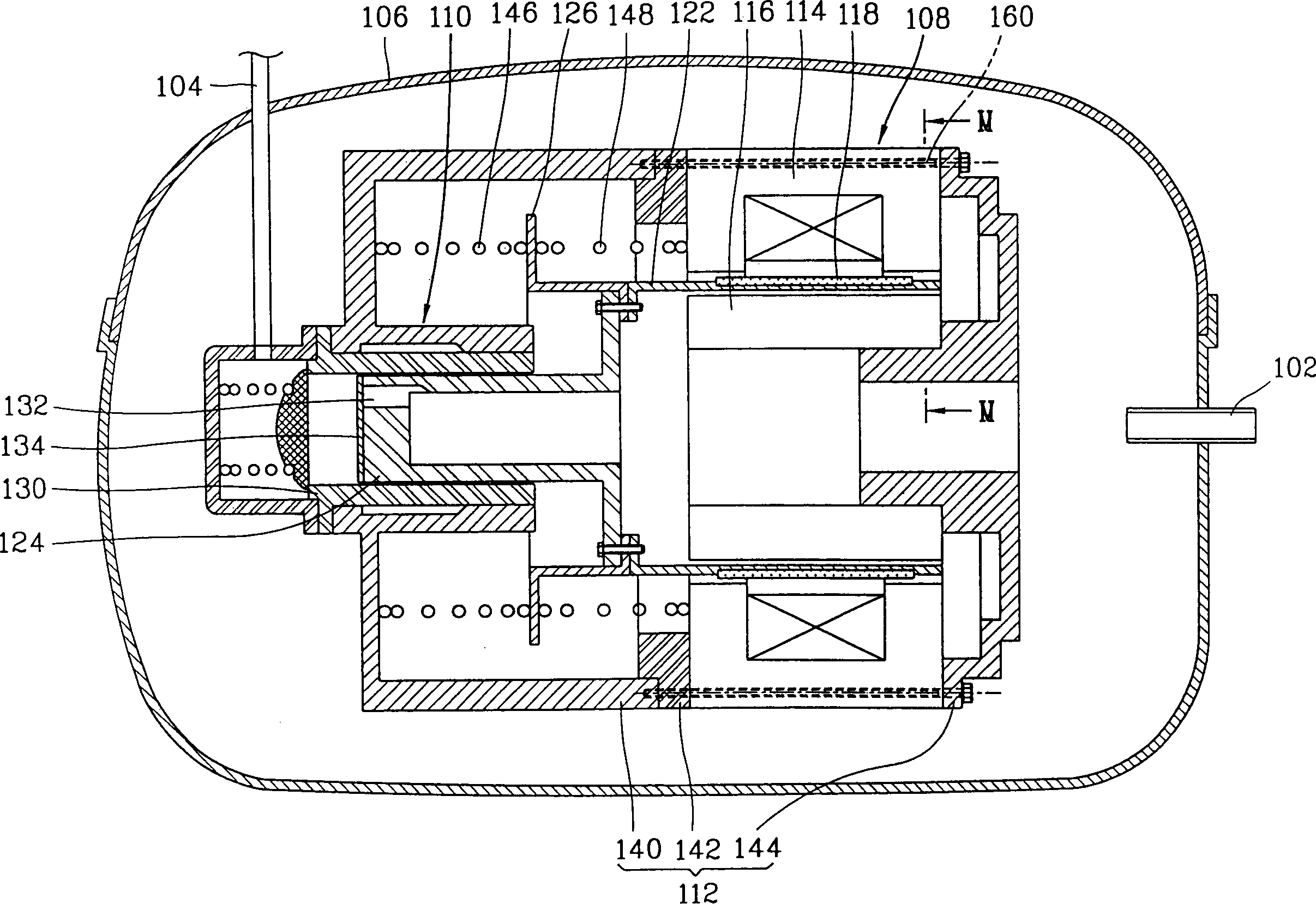
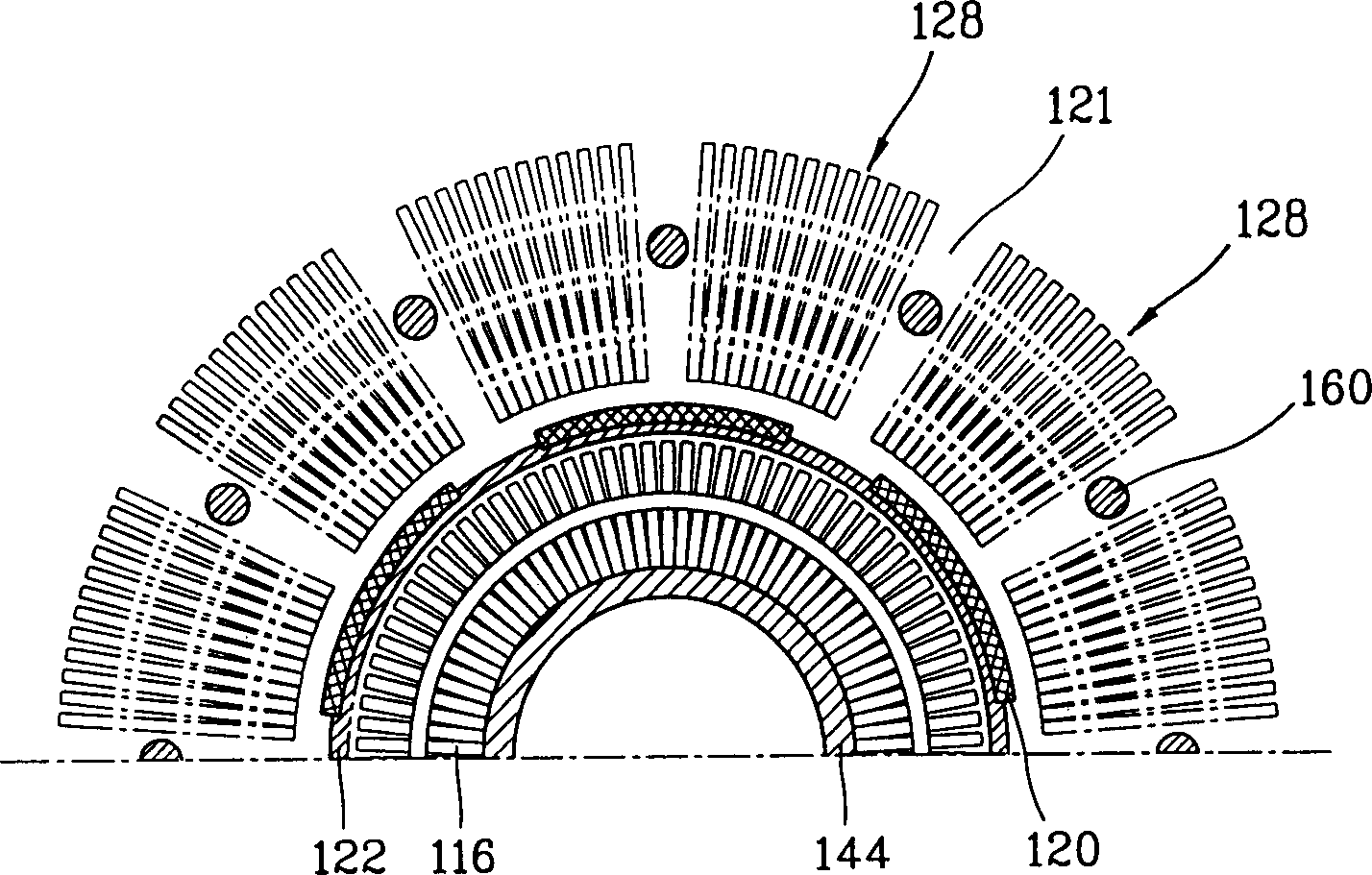
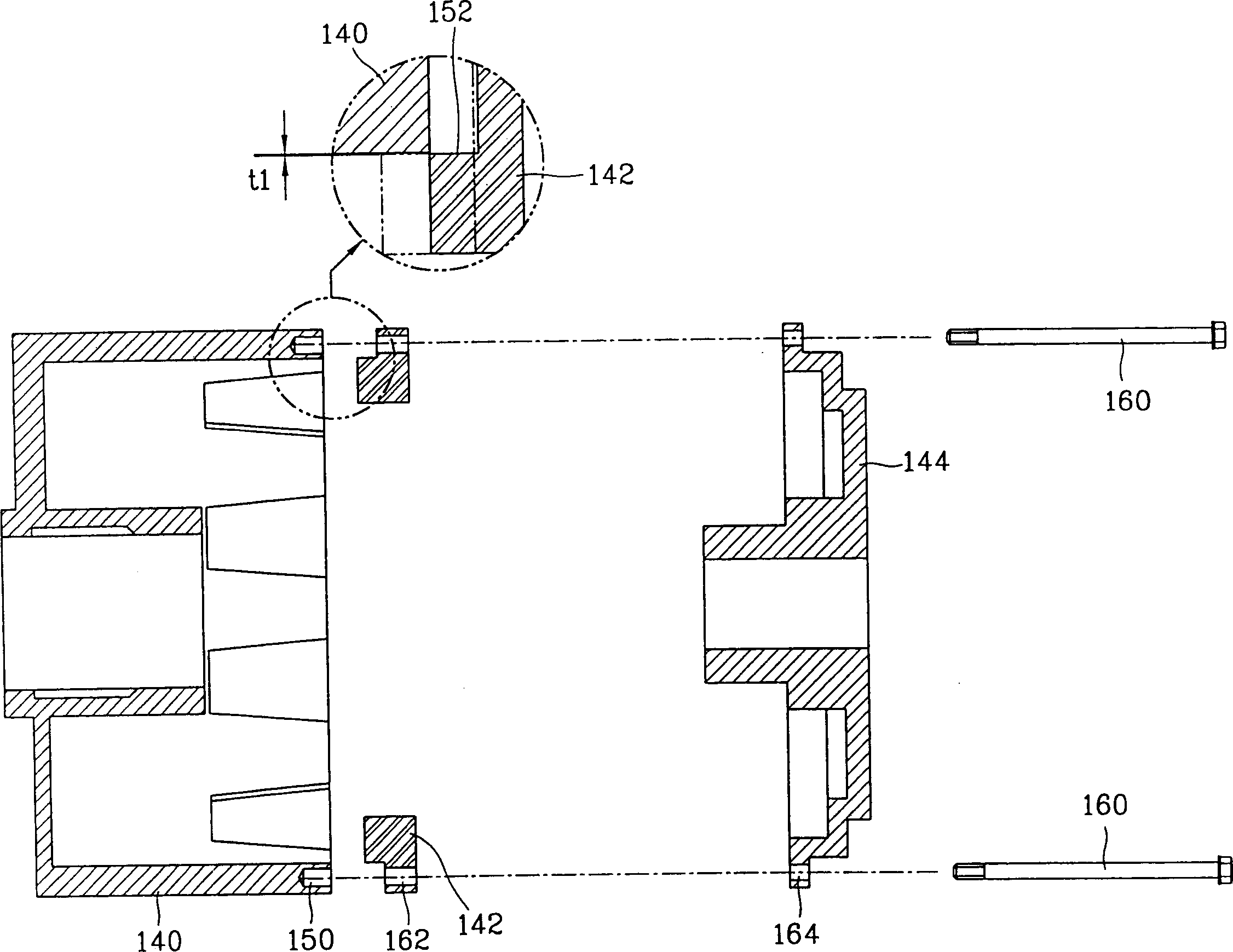
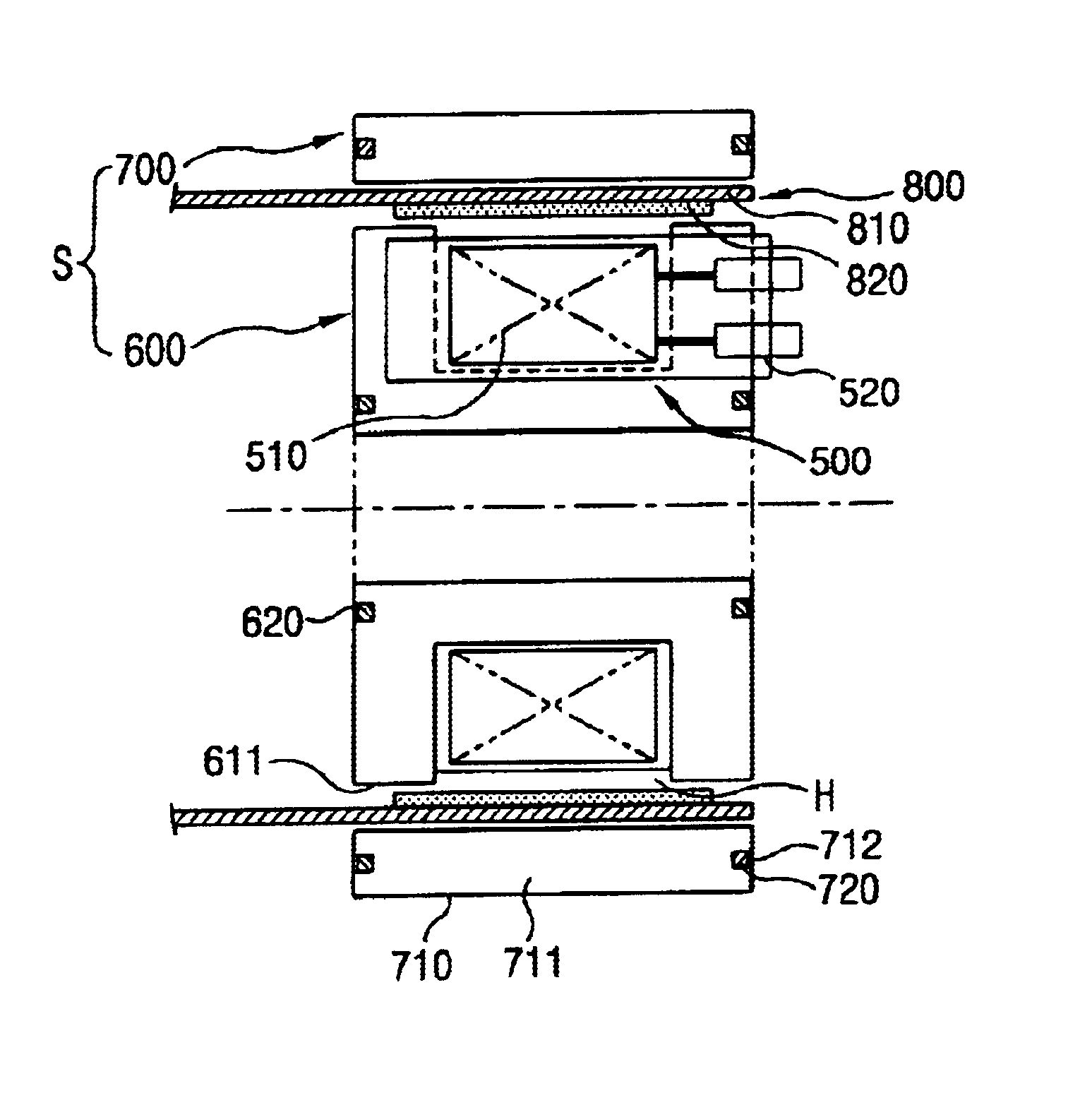
Patents
Literature
73 results about "Reciprocating electric motor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
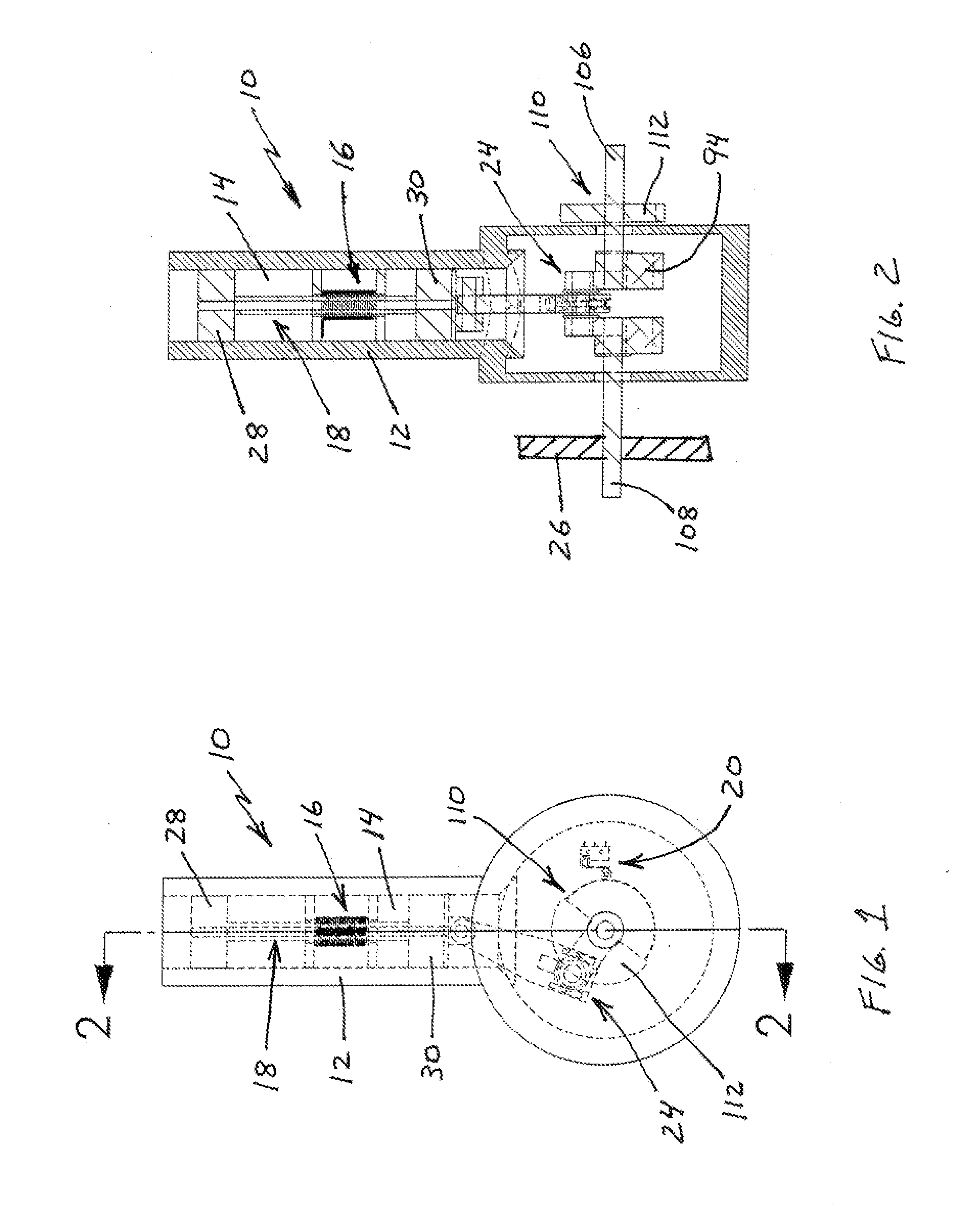
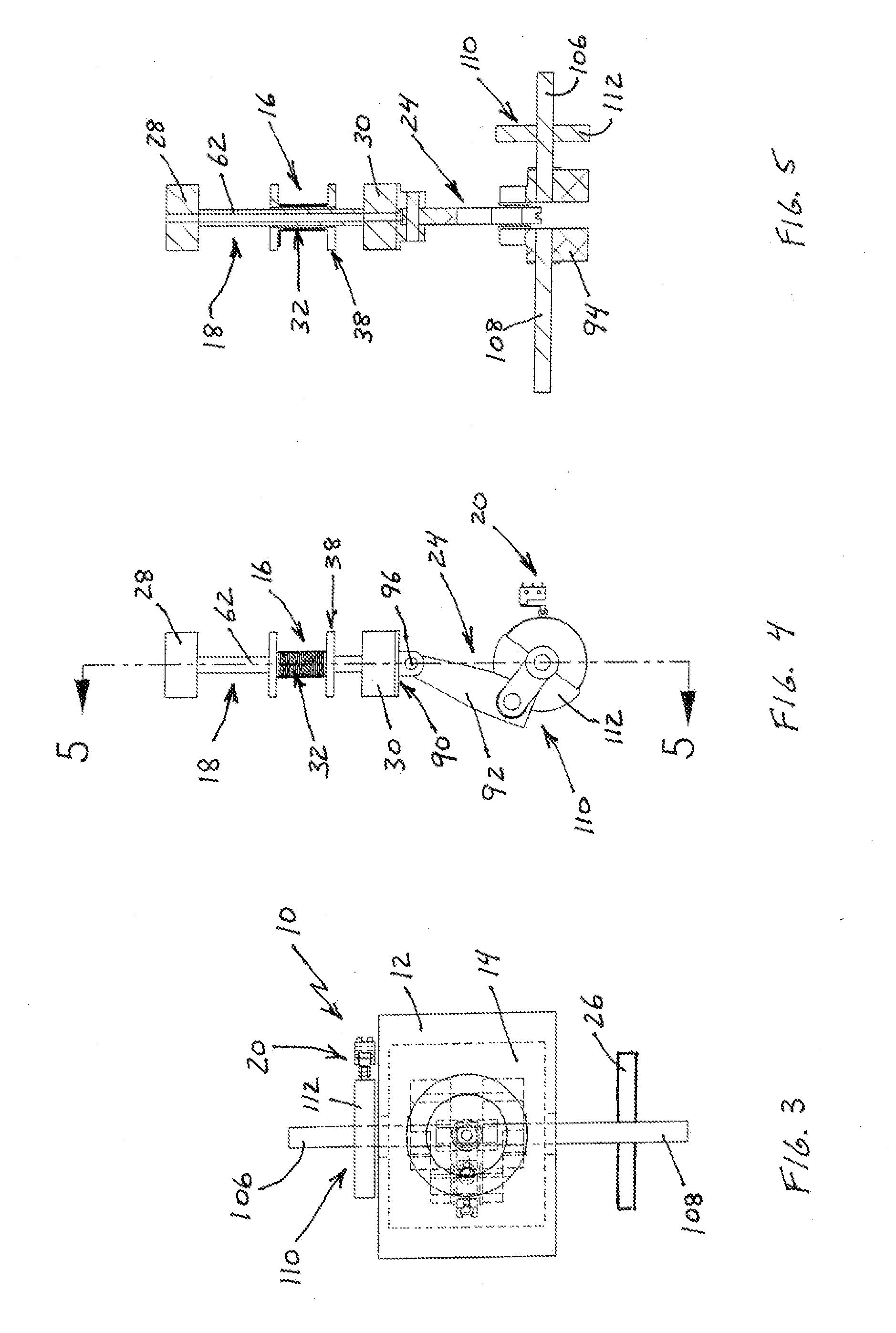
A reciprocating electric motor is a motor in which the armature moves back and forth rather than circularly. Early electric motors were sometimes of the reciprocating type, such as those made by Daniel Davis in the 1840s. Today, reciprocating electric motors are rare but they do have some niche applications, e.g. in linear compressors for cryogenics and as educational toys.
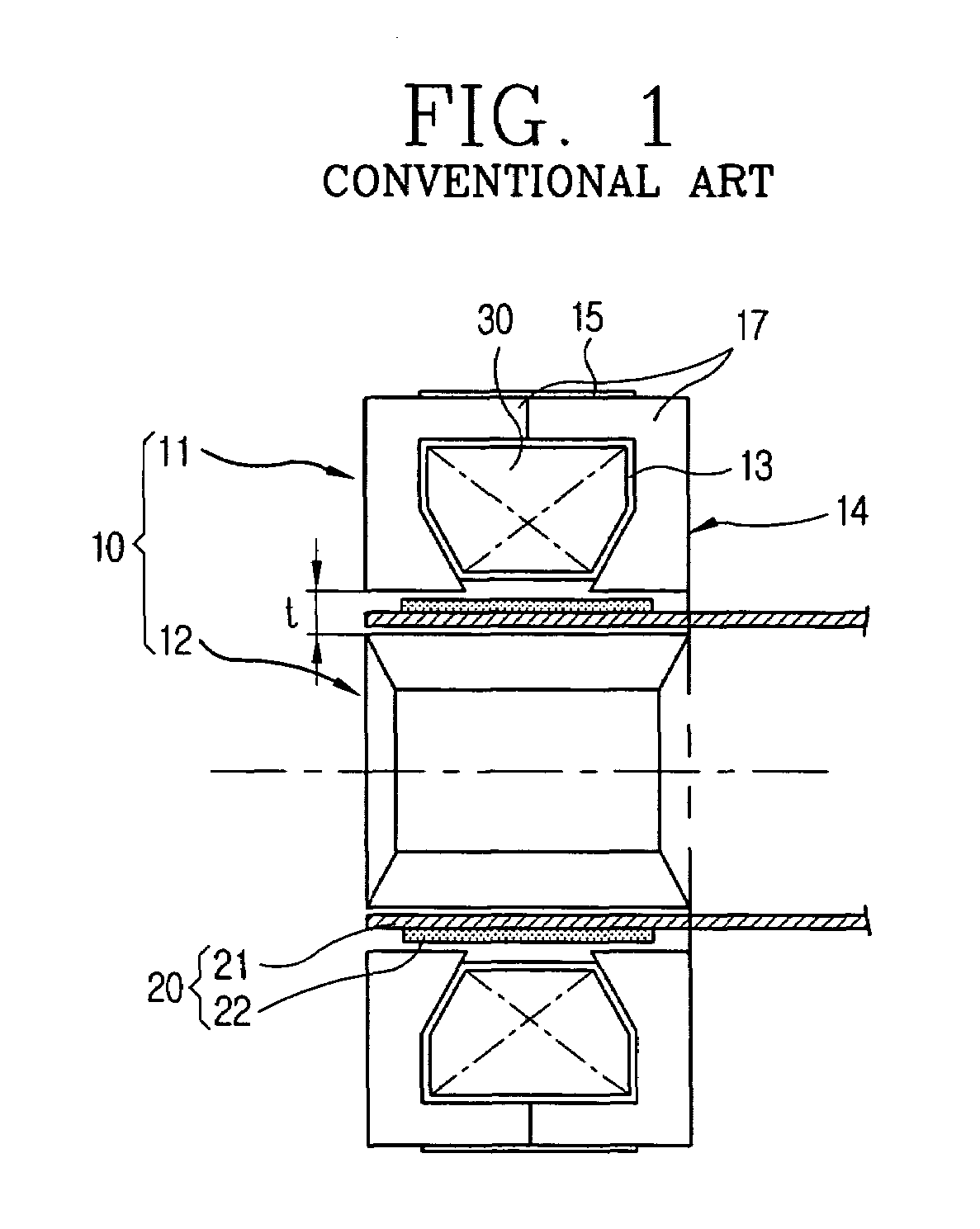
Apparatus for preventing abrasion in reciprocal compressor
InactiveUS20050142007A1Avoid scratchesPositive displacement pump componentsPlungersInterior spaceRelative motion
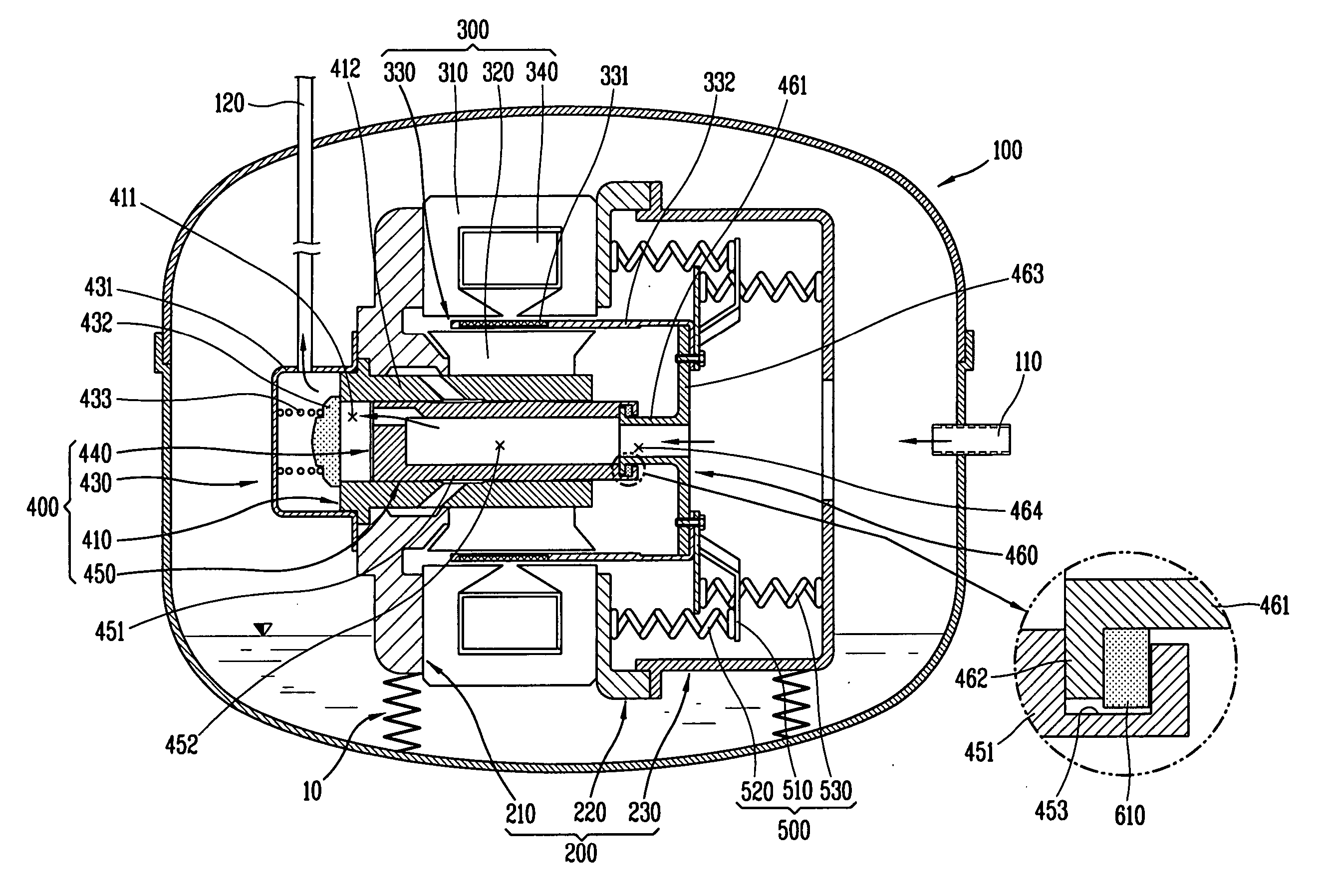
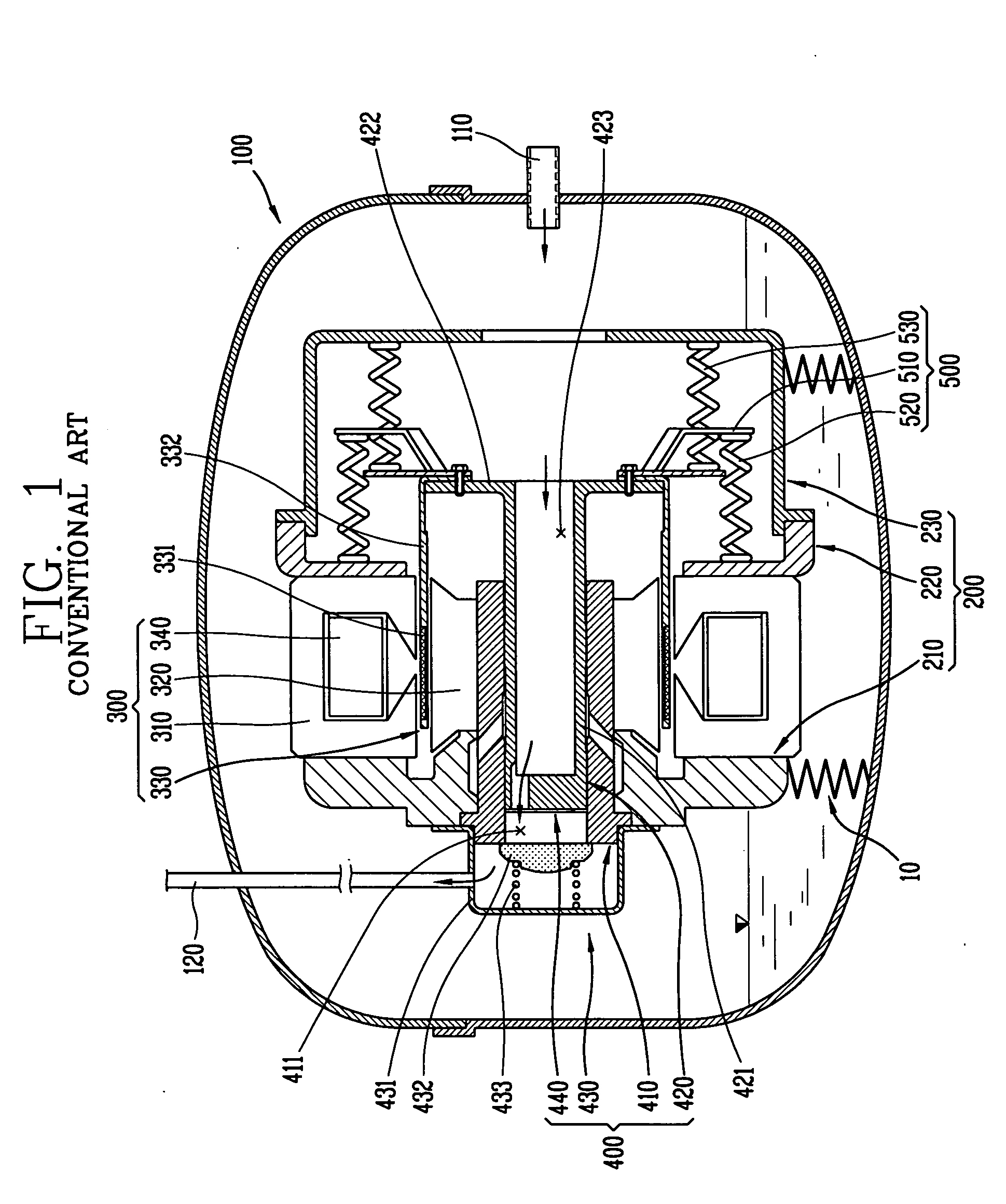
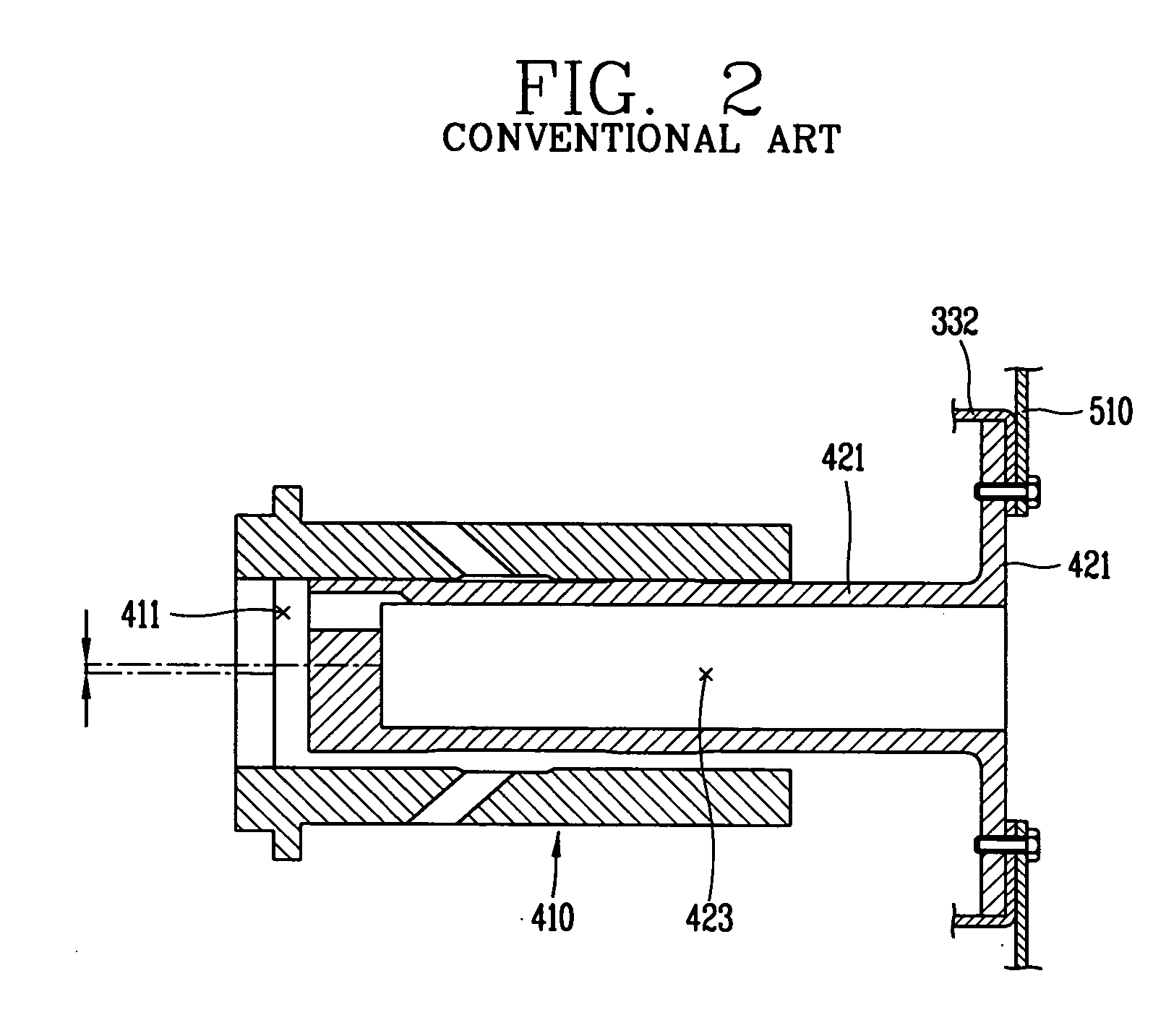
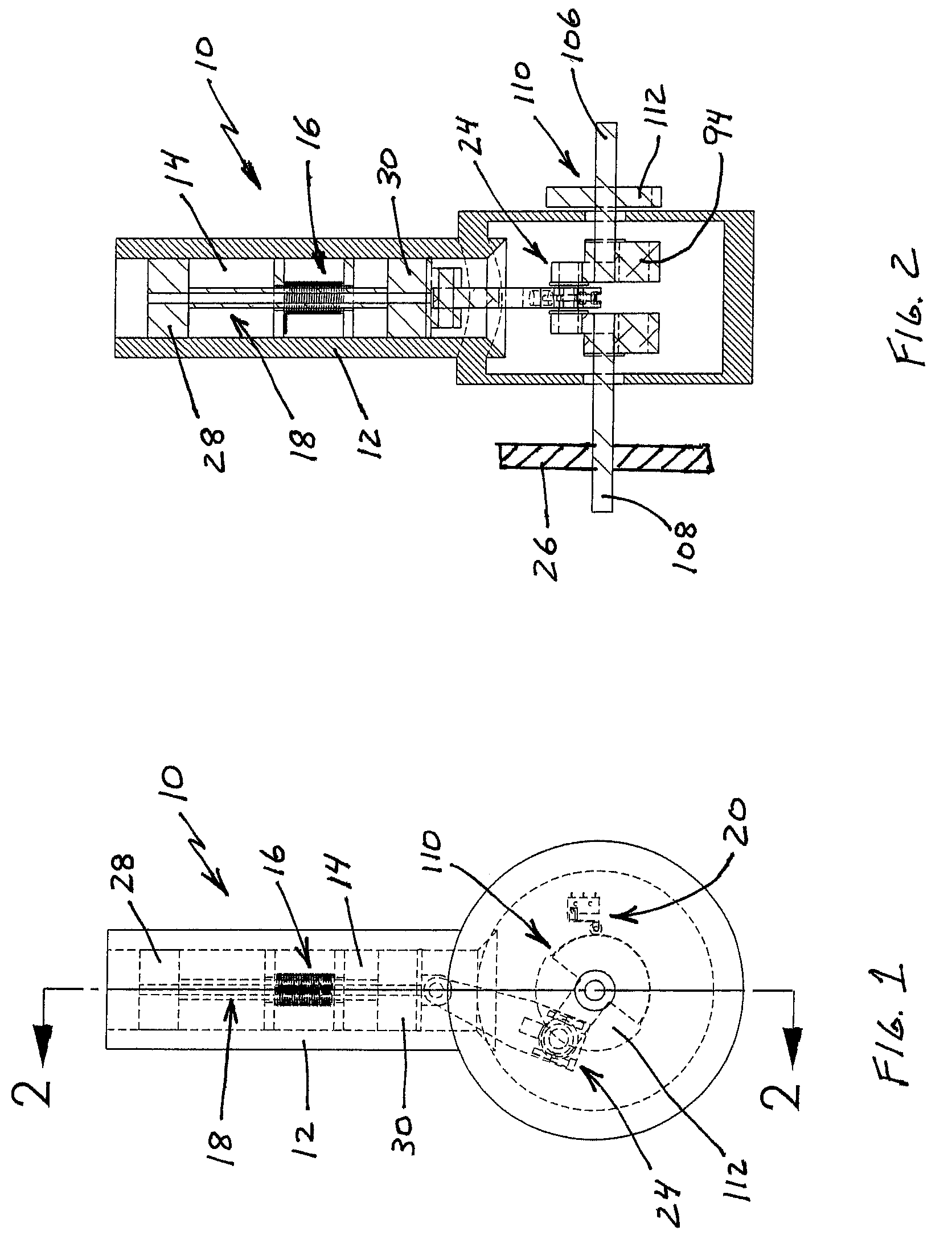
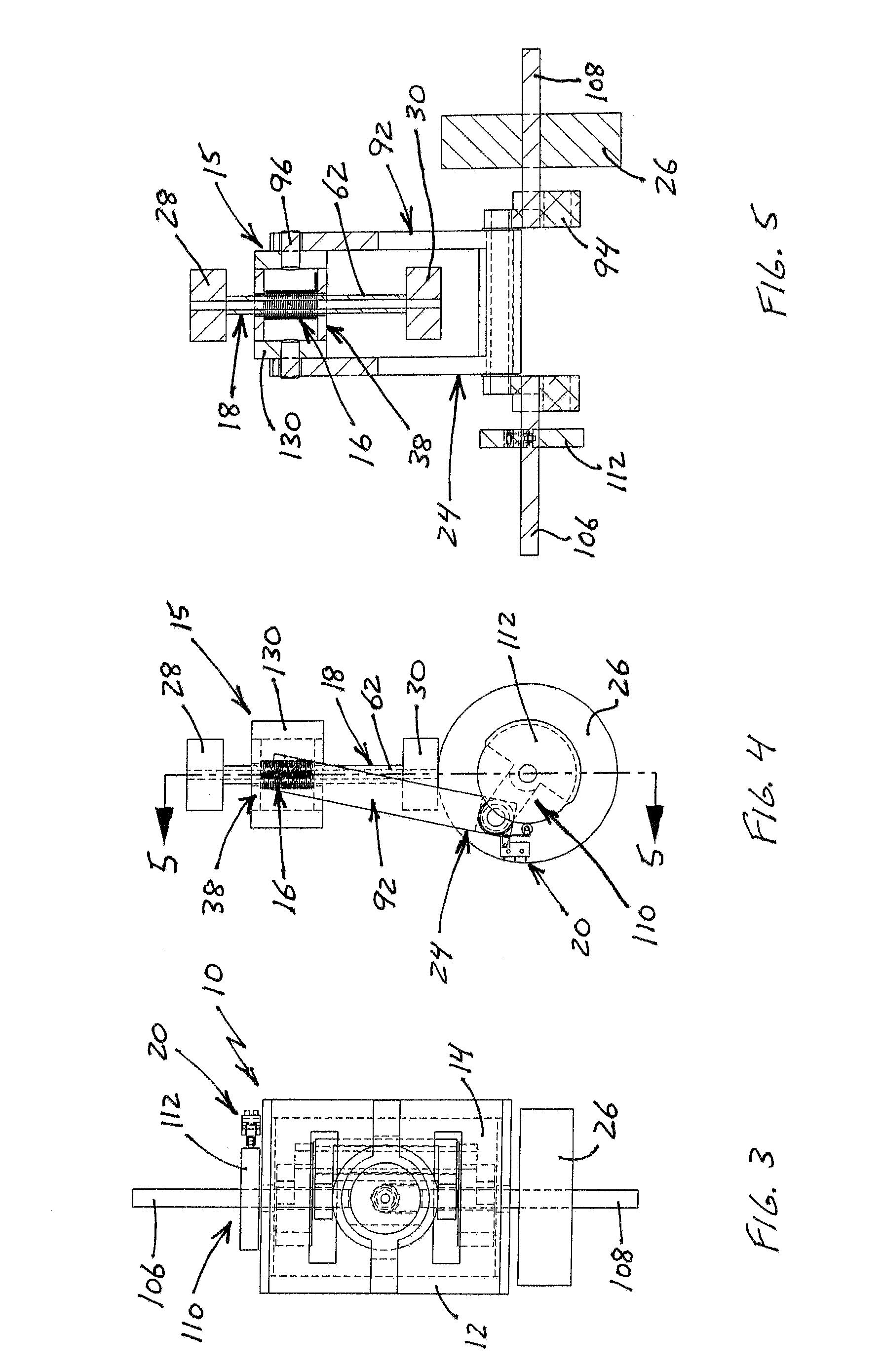
The present invention discloses an apparatus for preventing abrasion in a reciprocal compressor, including a cylinder, a reciprocal motor having a stator and a mover, and generating a linear reciprocation driving force, a piston inserted into an inside space of the cylinder to be linearly movable, a piston rod coupled to the piston to be movable in the radial direction of the piston, and coupled to the mover of the reciprocal motor, for transmitting the linear reciprocation driving force of the reciprocal motor to the piston, and a concentricity control means coupled to a junction between the piston and the piston rod, for fixing the piston and the piston rod in the axial direction, and allowing a relative motion thereof in the radial direction. The apparatus for preventing abrasion in the reciprocal compressor prevents abrasion from being generated between the cylinder and the piston due to processing errors and assembly errors of components of the reciprocal compressor.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Toroidal-coil linear stepping motor, toroidal-coil linear reciprocating motor, cylinder compressor and cylinder pump using these motors
InactiveUS7242118B2High positioning accuracyReduce loadPropulsion systemsElectric machineEngineering
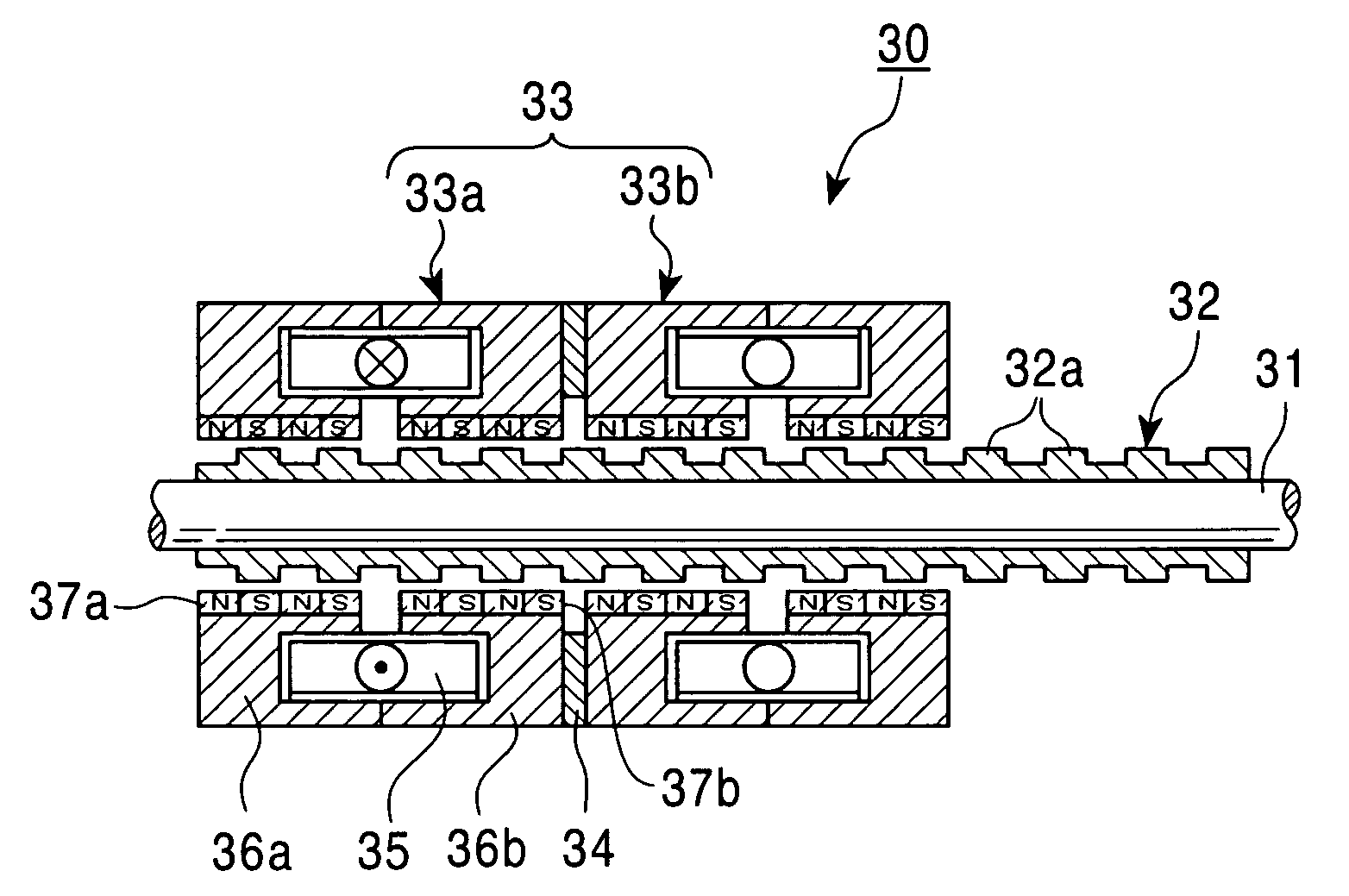
A toroidal-coil multi-phase linear stepping motor includes a cylindrical housing, an axis coaxially arranged inside the housing, a cylindrical element supported by the axis and an armature fixed to the housing around the cylindrical element through an air gap in the radial direction. The axis is fixed to the housing and the cylindrical element linearly moves along the axis. The cylindrical element has toroidal permanent magnets that are alternately magnetized in N pole and S pole in the axial direction. The armature consists of armature units arranged around the axis. Each armature unit has a toroidal coil and a pair of armature yokes that hold the toroidal coil. Each armature yoke has toroidal magnetic teeth on its inner surface. The invention also includes a toroidal-coil single-phase linear reciprocating motor and a cylinder compressor and a cylinder pump using these motors.
Owner:JAPAN SERVO CO LTD
Interchangeable blade cordless electric knife
InactiveUS6434836B1Improve securityAvoid disadvantagesPortable power-driven toolsMetal working apparatusHeavy dutyKnife blades
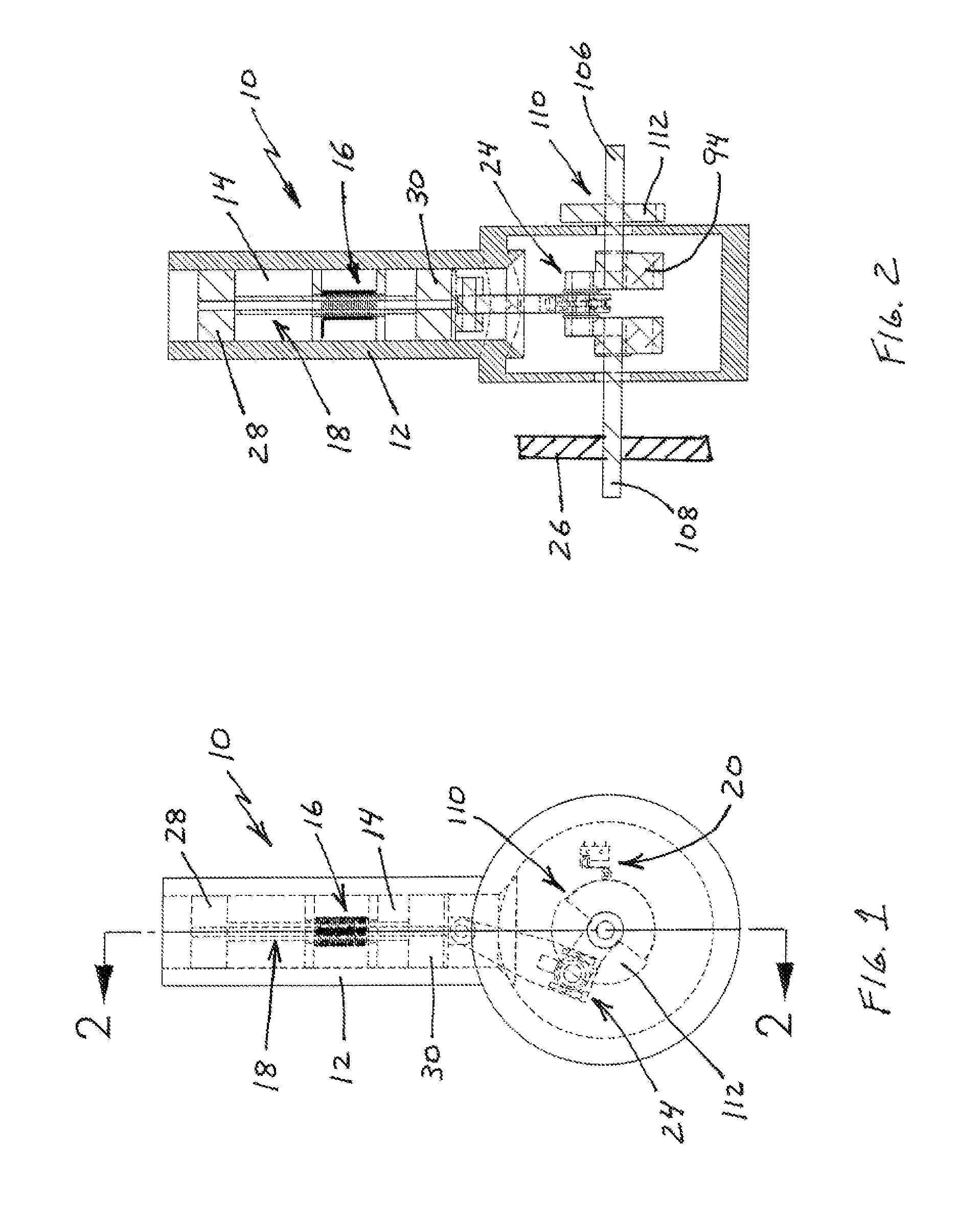
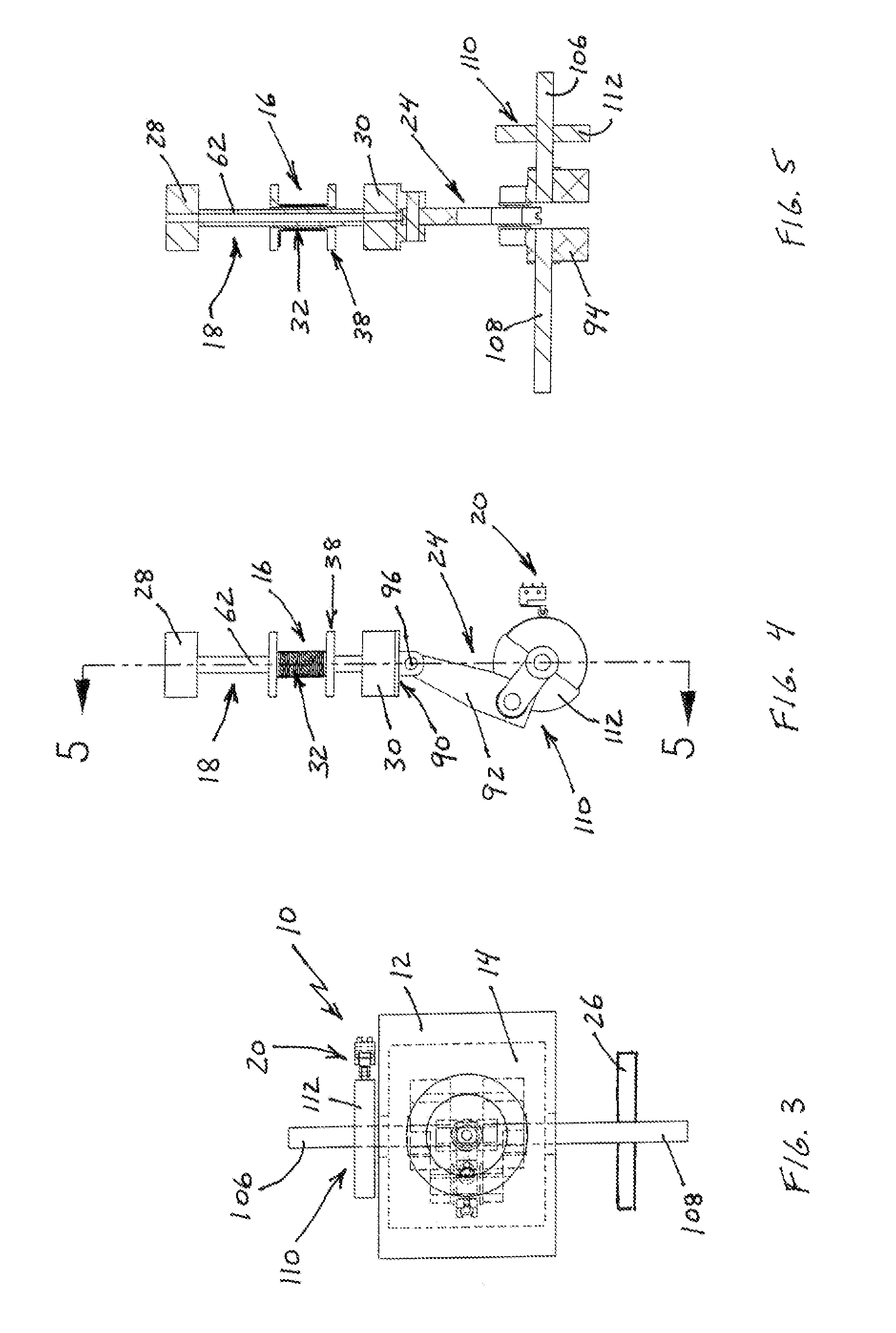
The invention is an electric knife that runs on a battery or by use of a corded power converter. The handle housing has an electric reciprocating motor activated by a power button located on the handle of the knife. Different sizes and shapes of knife blades, dependent on the task, can be inserted into a locking slot in the front of the motorized head, and only released by a heavy-duty lock knife release button. The motorized head is powered directly by an electric motor located directly behind it in the handle.
Owner:OLIVARES HECTOR
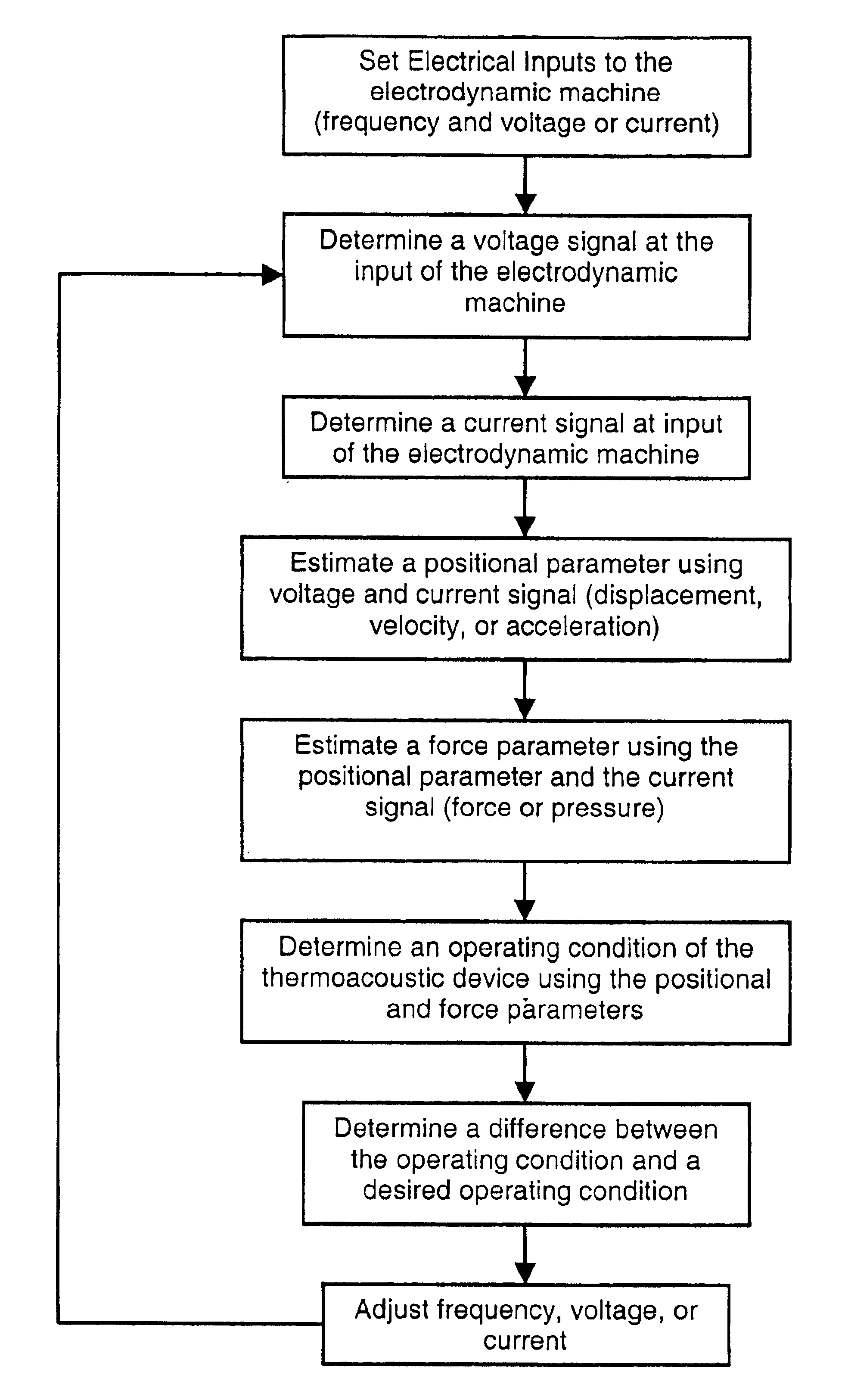
Sensorless control of a harmonically driven electrodynamic machine for a thermoacoustic device or variable load
ActiveUS6883333B2Reduce the differenceMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlHarmonicLinear machine
The present invention provides a method of sensorless control of a linear reciprocating electrodynamic machine used for driving a thermoacoustic device, and / or a similar frequency dependent load. Sensorless control is accomplished by estimating the state of predetermined performance parameters at the linear machine through the use of a system model. Thereafter, the method comprises providing a control means operative to obtain the estimated performance parameters and cause manipulation of at least one input parameter to the linear machine such that desired performance parameters are obtained in view of the estimated performance parameters.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
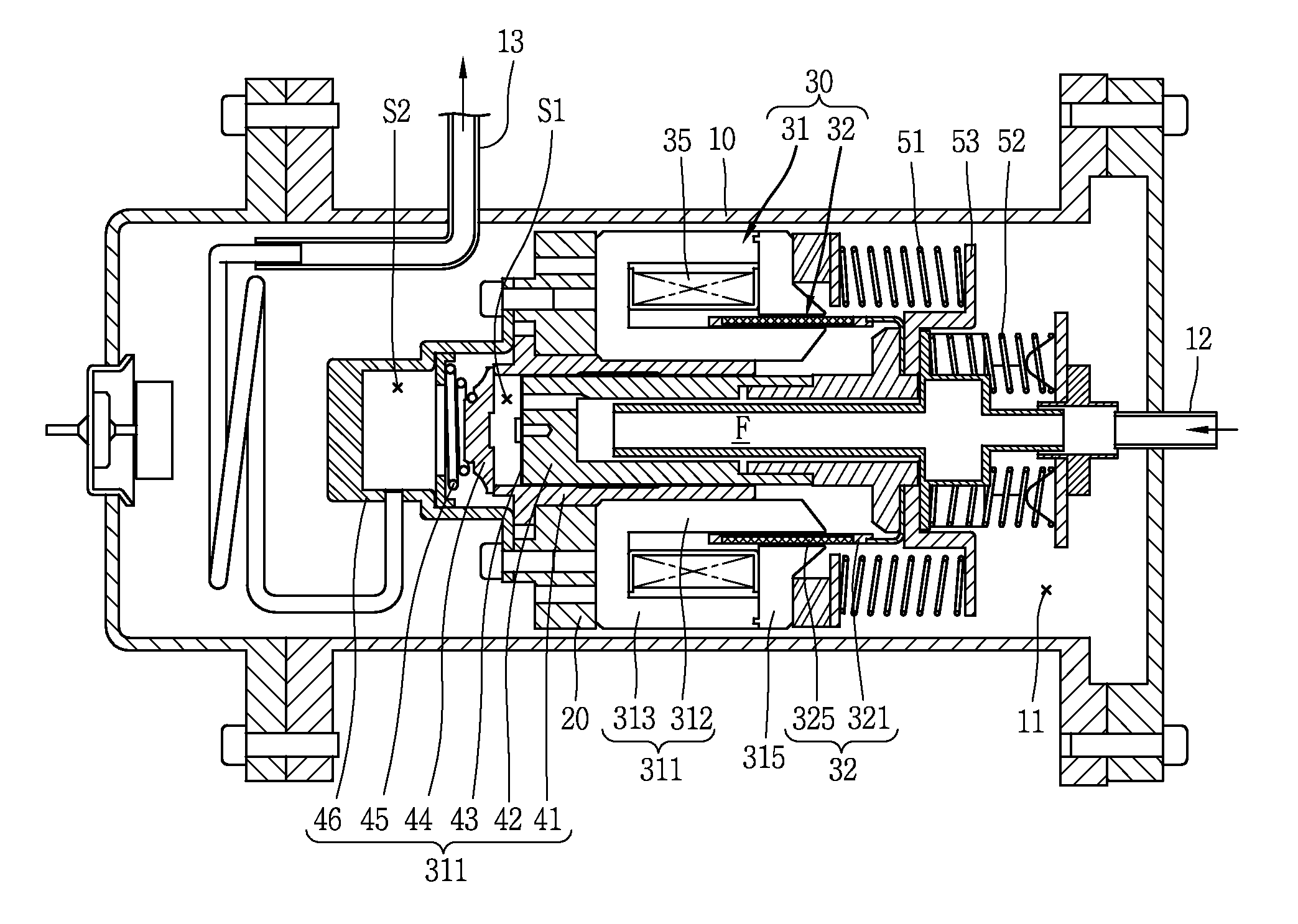
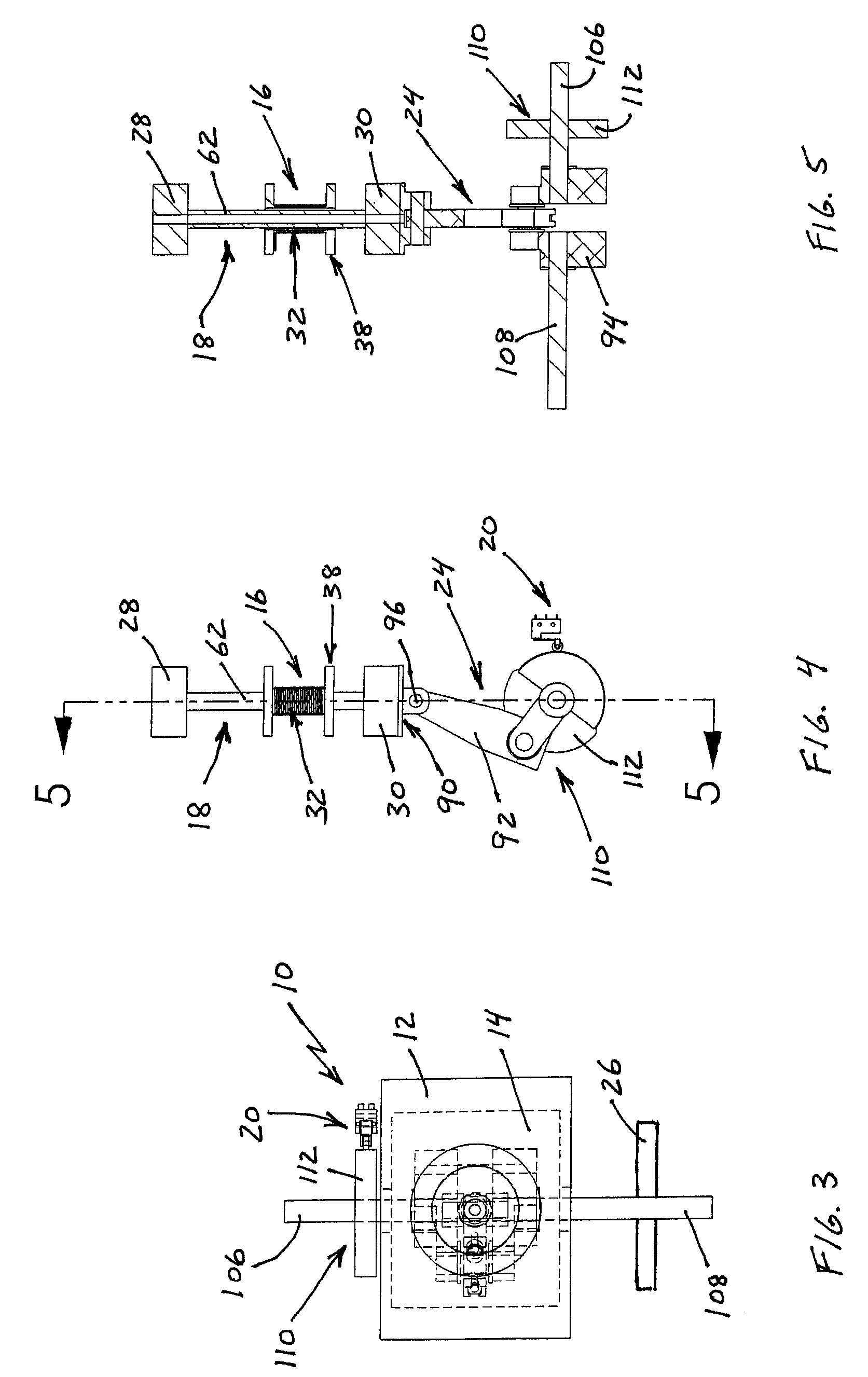
Reciprocating motor and reciprocating compressor having the same
ActiveUS20130058811A1Reduce manufacturing costEasy to manufactureMotor parameterPiston pumpsManufacturing cost reductionEngineering
A reciprocating motor and a reciprocating compressor having the same make the manufacture of a stator easier and therefore reduce manufacturing costs by configuring the stator such that an inner stator positioned inside the mover and an outer stator positioned outside the mover are integrally formed, or by making the inner and outer circumferential surfaces of the stator have the same curvature. Also, no gap is generated between the inner stator and the outer stator, and this prevents magnetic leakage, thereby improving the performance of the motor. Also, the use of magnets can be reduced by omitting magnets between stator blocks, and therefore manufacturing costs can be reduced, when compared to the efficiency of the motor.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
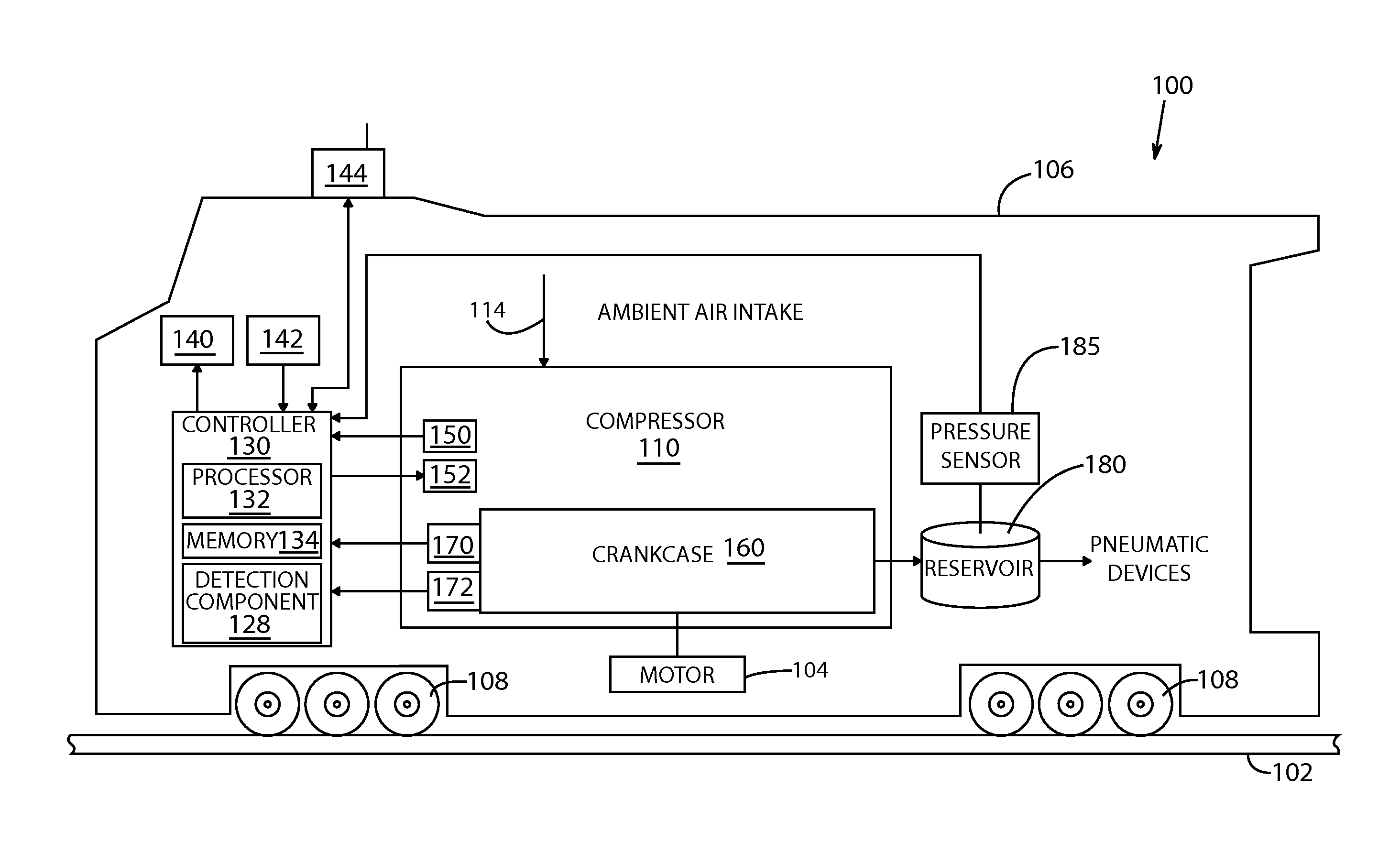
Method and system for reciprocating compressor starting
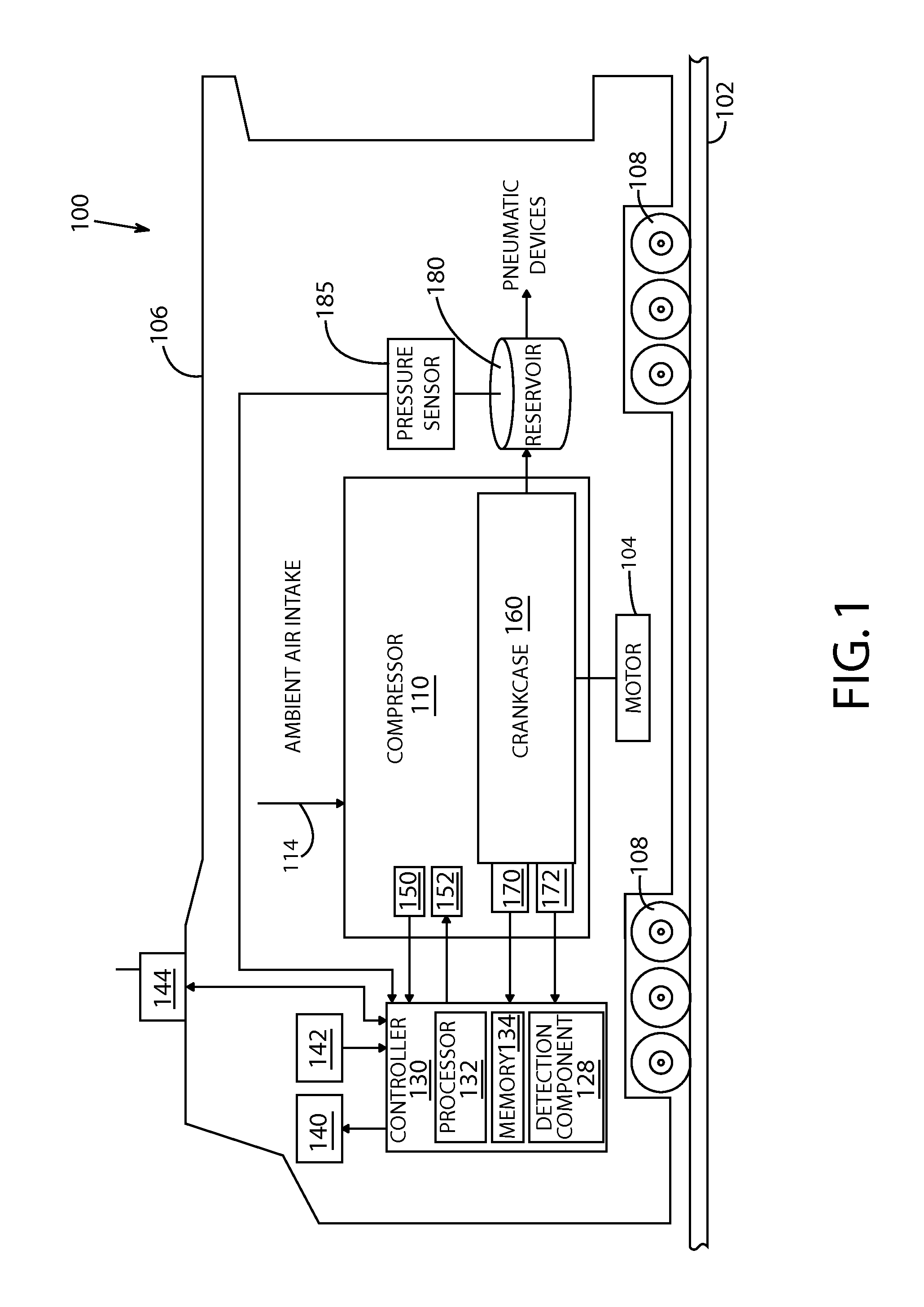
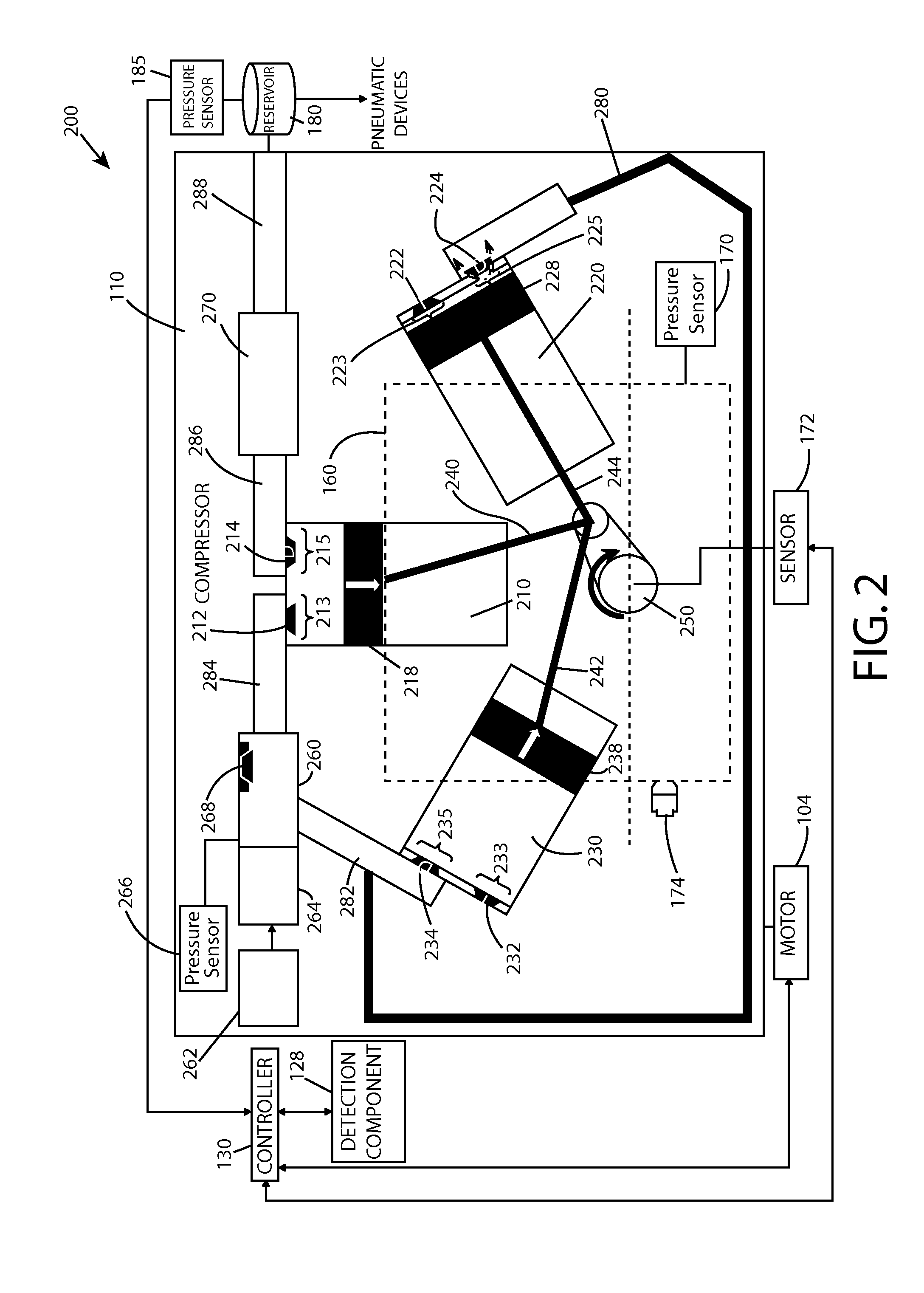
Systems and methods of the invention may overcome a higher than normal starting torque for in a reciprocating, electric motor driven air compressor for a vehicle. A detection component can be configured to detect a stall condition for a reciprocating compressor based on a force from compressed air being compressed into a reservoir of the reciprocating compressor. Based upon the detected stall condition, a controller can reverse direction or increase torque to alleviate the stall condition. In the reverse direction mode, the controller component can change a direction of a piston rotation. In the torque increase mode, the controller increases a number of poles for the motor, a line voltage, or a volt / hertz.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
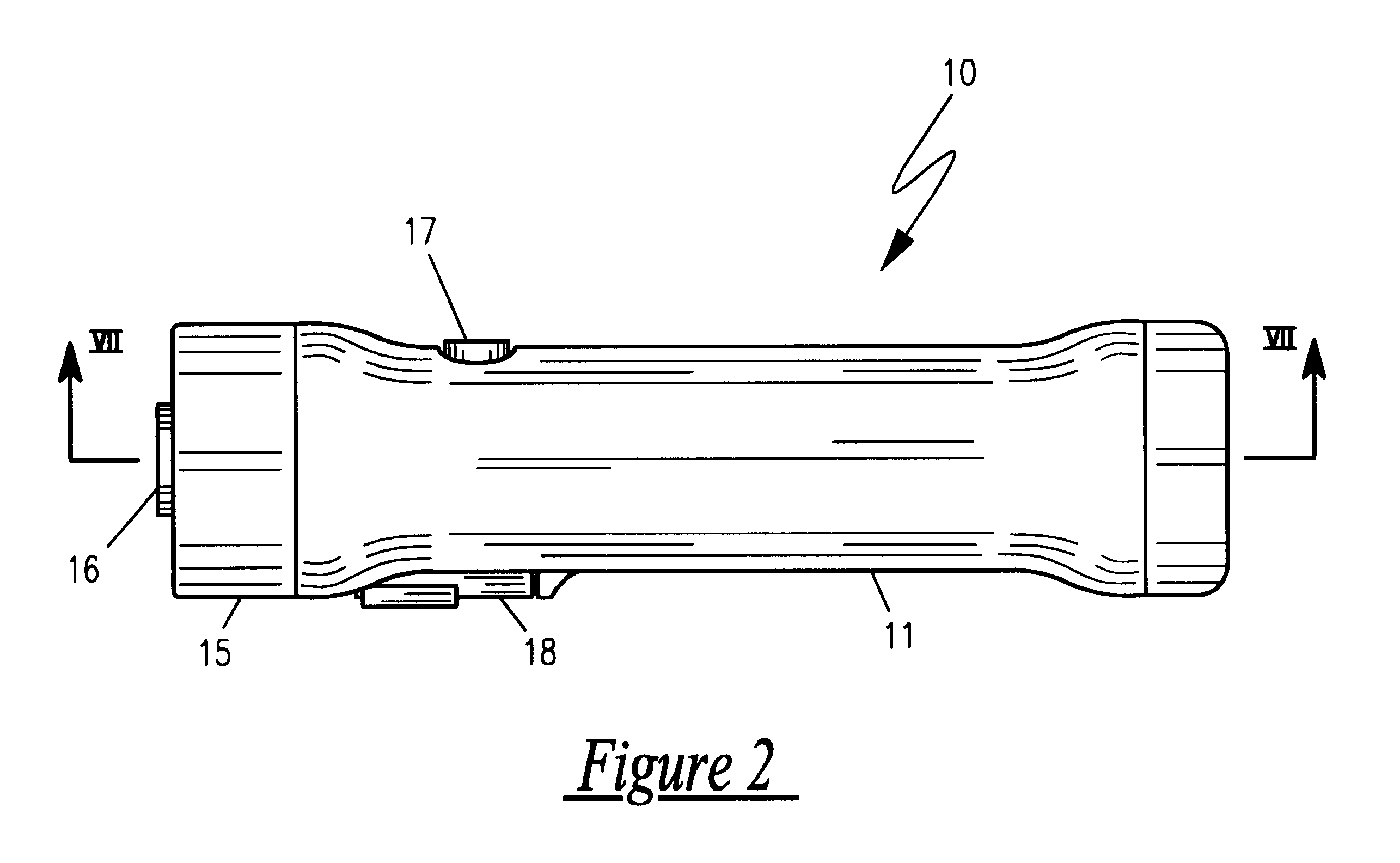
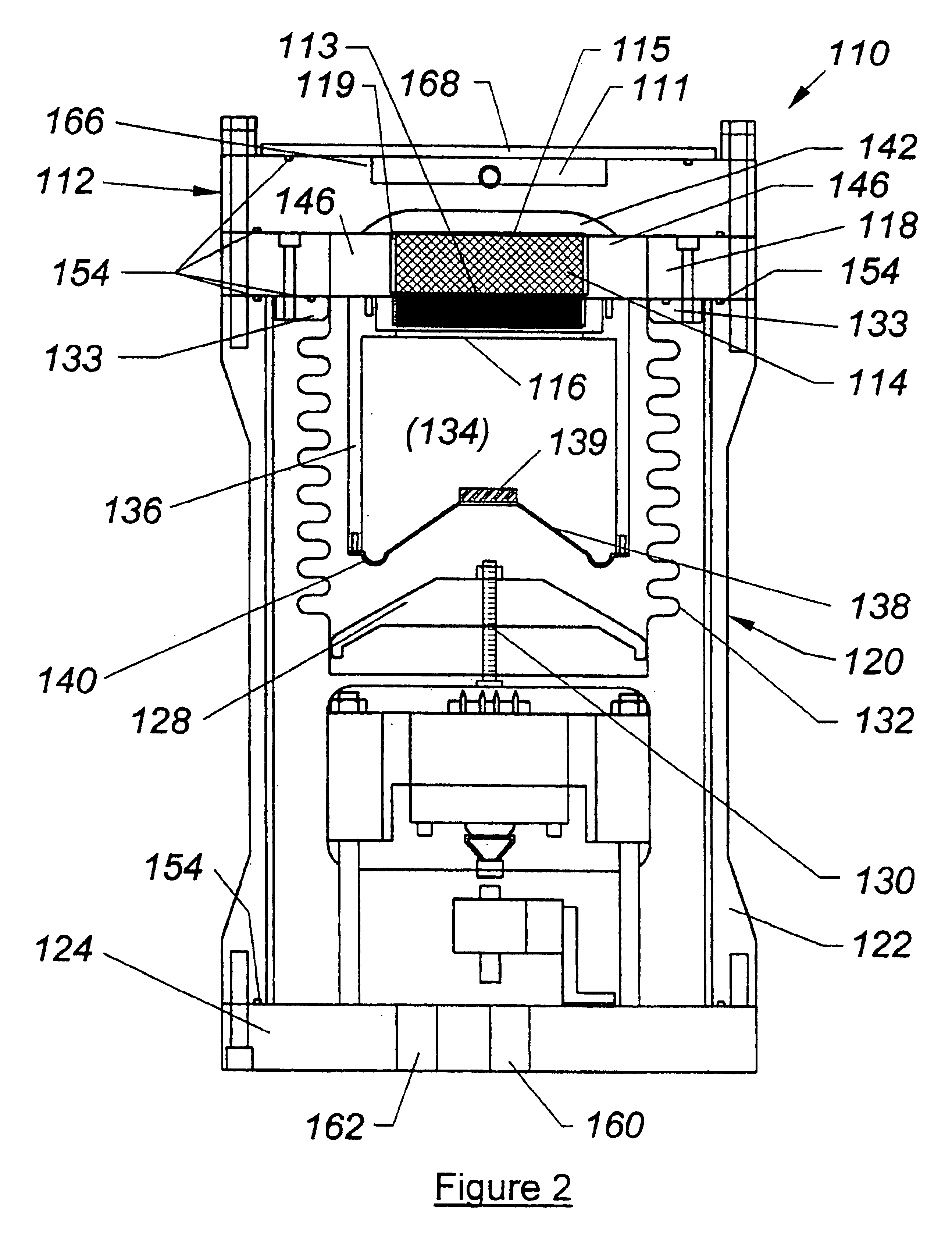
Compact Low Frequency Audio Transducer
ActiveUS20140140559A1Overcome problemsFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsTransducerEngineering
A rotary reciprocating acoustic transducer for producing sound in response to an applied electrical signal has a ported tubular housing having a generally cylindrical chamber with an interior lumen which is generally symmetrical about a central axis and opposing first and second linear reciprocating electrodynamic motors mounted over the tubular housing member's first and second open end, with a reciprocating rotatable transducer vane assembly with first and second rotating vanes projecting radially away from a central, axially aligned shaft driven by the first and second linear reciprocating motors.
Owner:GRAHAM DOUG
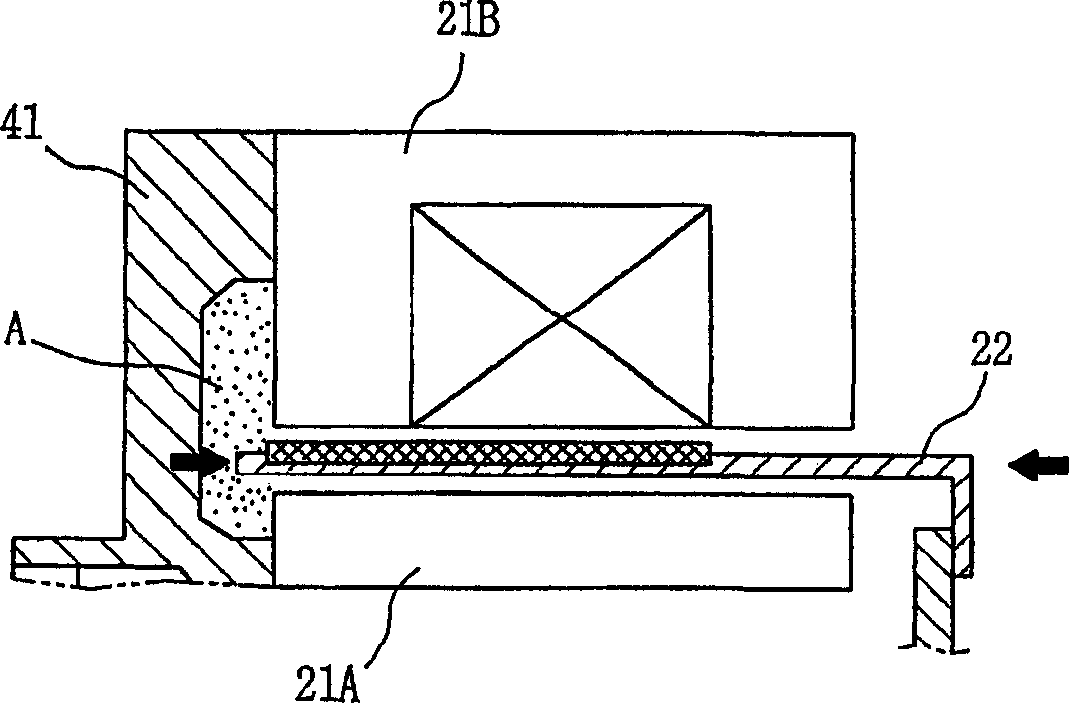
Structure for stator of reciprocating motor
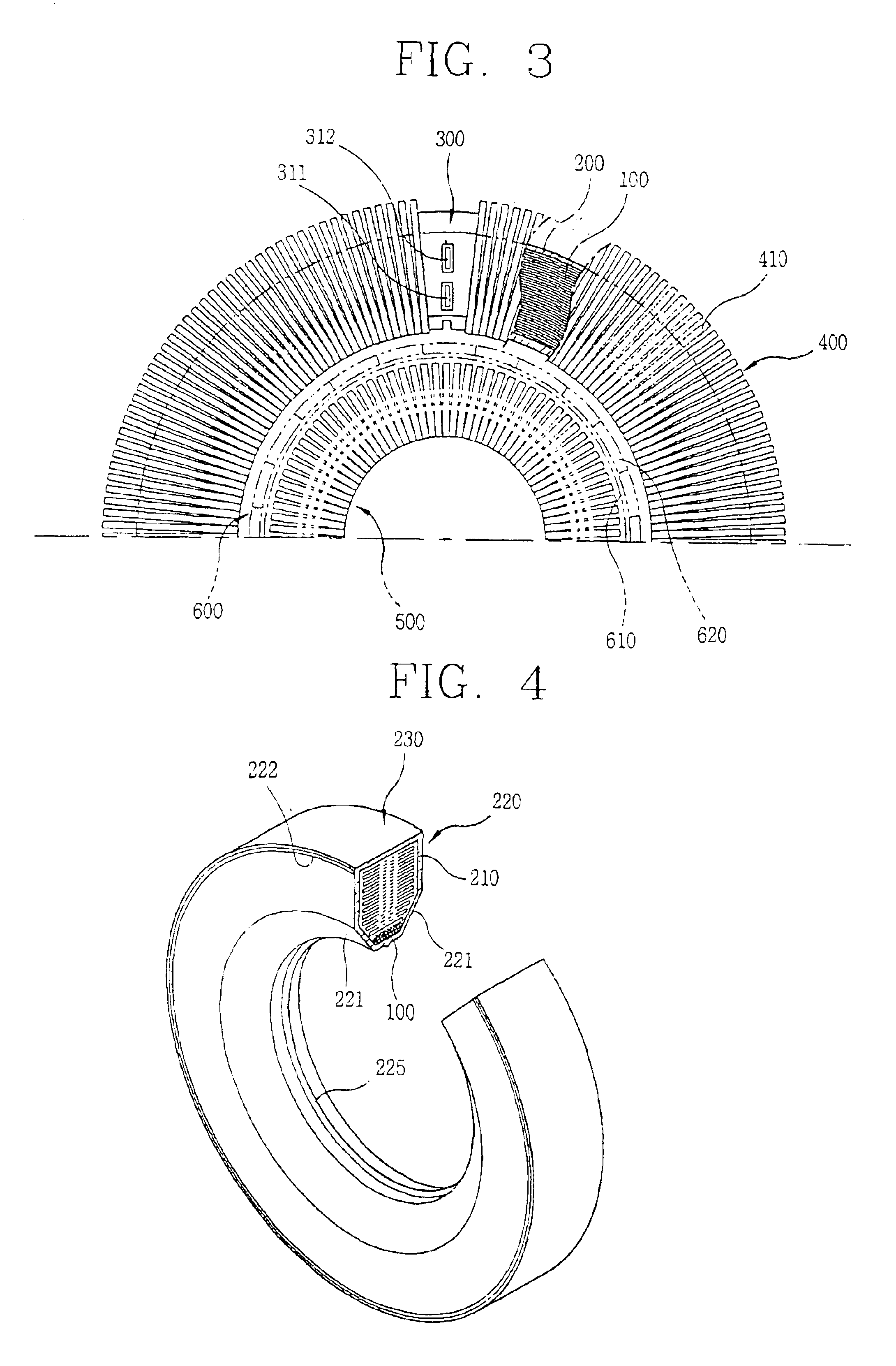
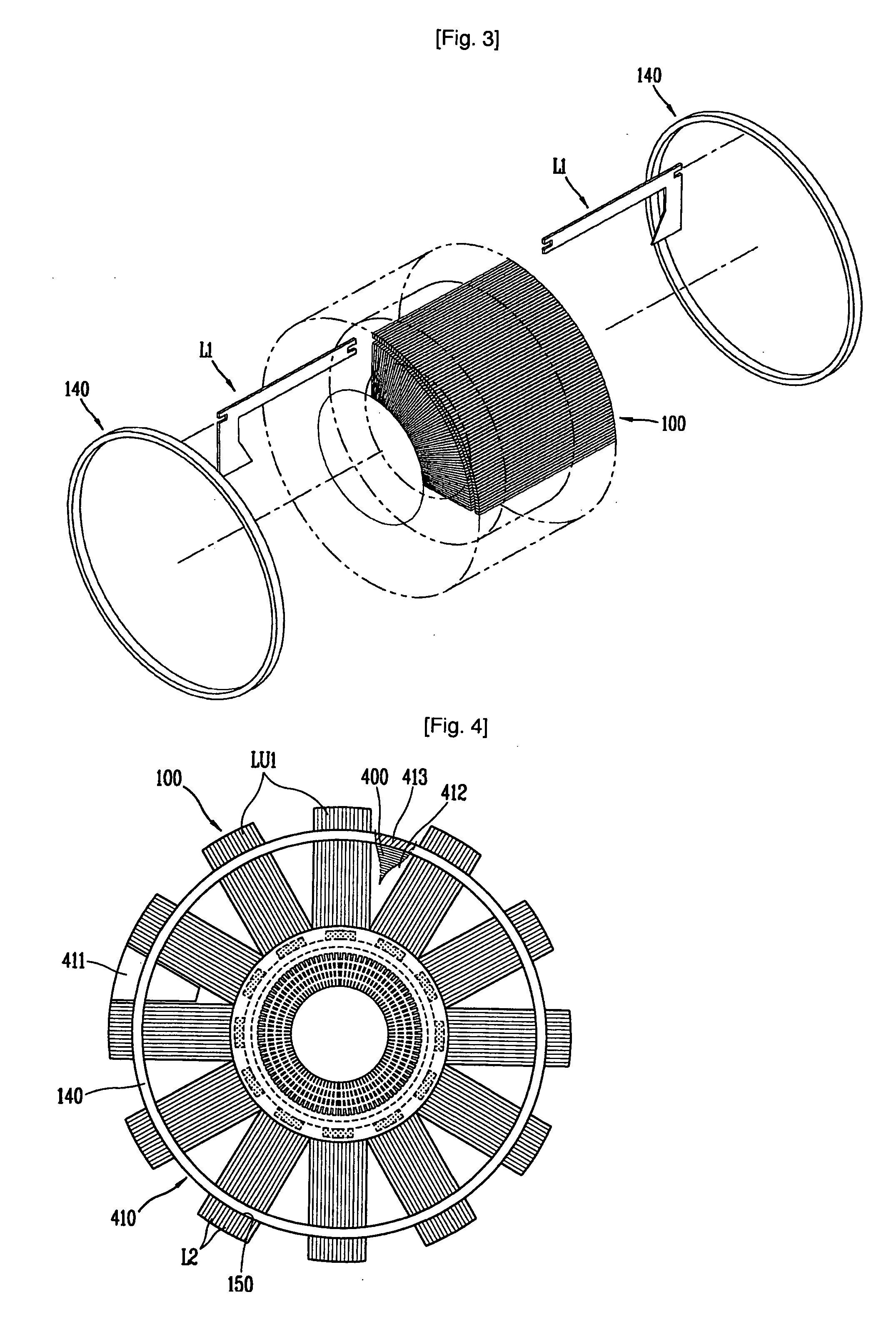
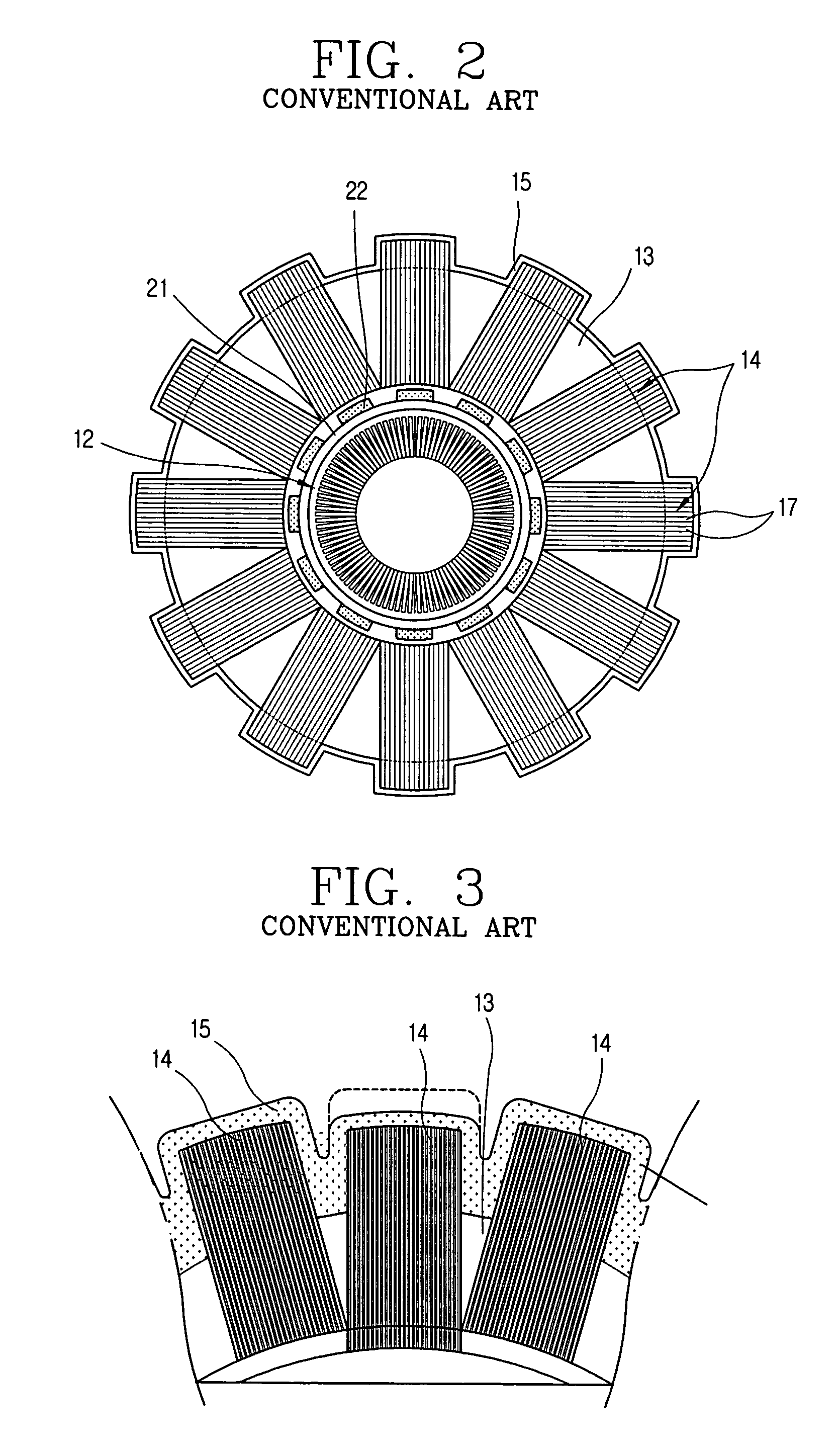
InactiveUS20020135264A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityMagnetic circuit stationary partsMechanical energy handlingOuter coreReciprocating electric motor
A structure for a stator of a reciprocating motor is capable of heightening an efficiency and a reliability of a motor by maximizing the area of a magnetic path at which a flux flows without increasing the whole volume of a reciprocating motor so that the flux, which is to be increased as an overload works on the motor, flows smoothly to thereby restrain generation of a core saturation. The stator structure includes a stator having a hollow cylindrical outer core and an inner core inserted into the outer core and formed as a plurality of mutually coupled hollow cylindrical stacked bodies and a winding coil connected into the outer core and an armature having a permanent magnet attached at one side thereof and movably inserted between the outer core and the inner core.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
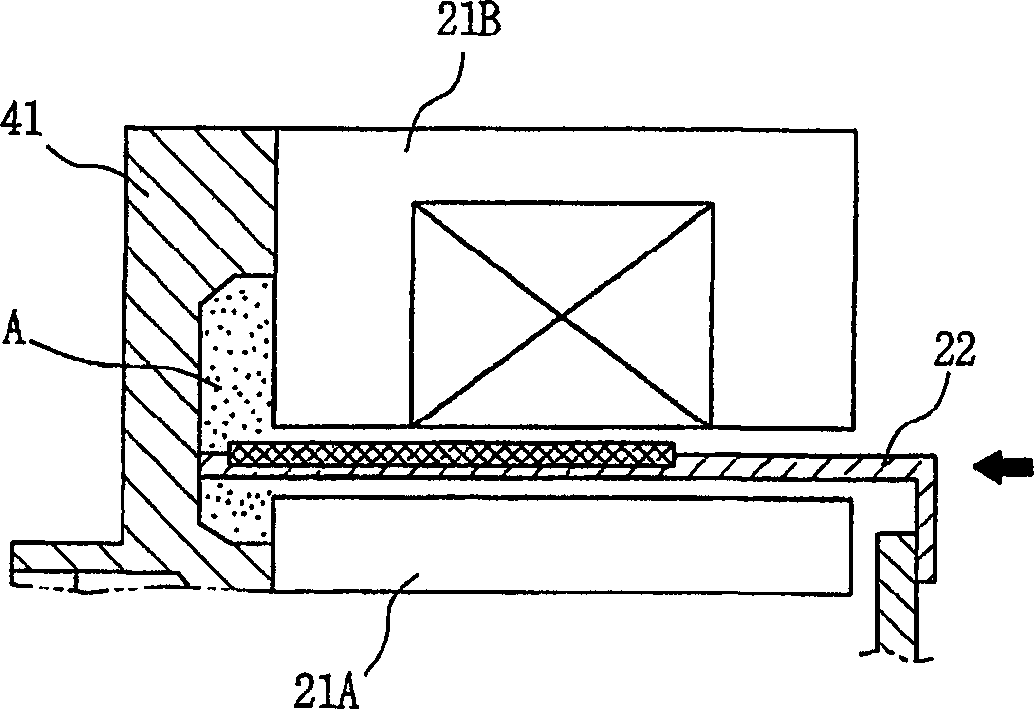
Structure for stator of reciprocating motor
InactiveUS6628018B2Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityMagnetic circuit stationary partsMechanical energy handlingOuter coreConductor Coil
A structure for a stator of a reciprocating motor is capable of heightening an efficiency and a reliability of a motor by maximizing the area of a magnetic path at which a flux flows without increasing the whole volume of a reciprocating motor so that the flux, which is to be increased as an overload works on the motor, flows smoothly to thereby restrain generation of a core saturation. The stator structure includes a stator having a hollow cylindrical outer core and an inner core inserted into the outer core and formed as a plurality of mutually coupled hollow cylindrical stacked bodies and a winding coil connected into the outer core and an armature having a permanent magnet attached at one side thereof and movably inserted between the outer core and the inner core.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Stator for reciprocating motor
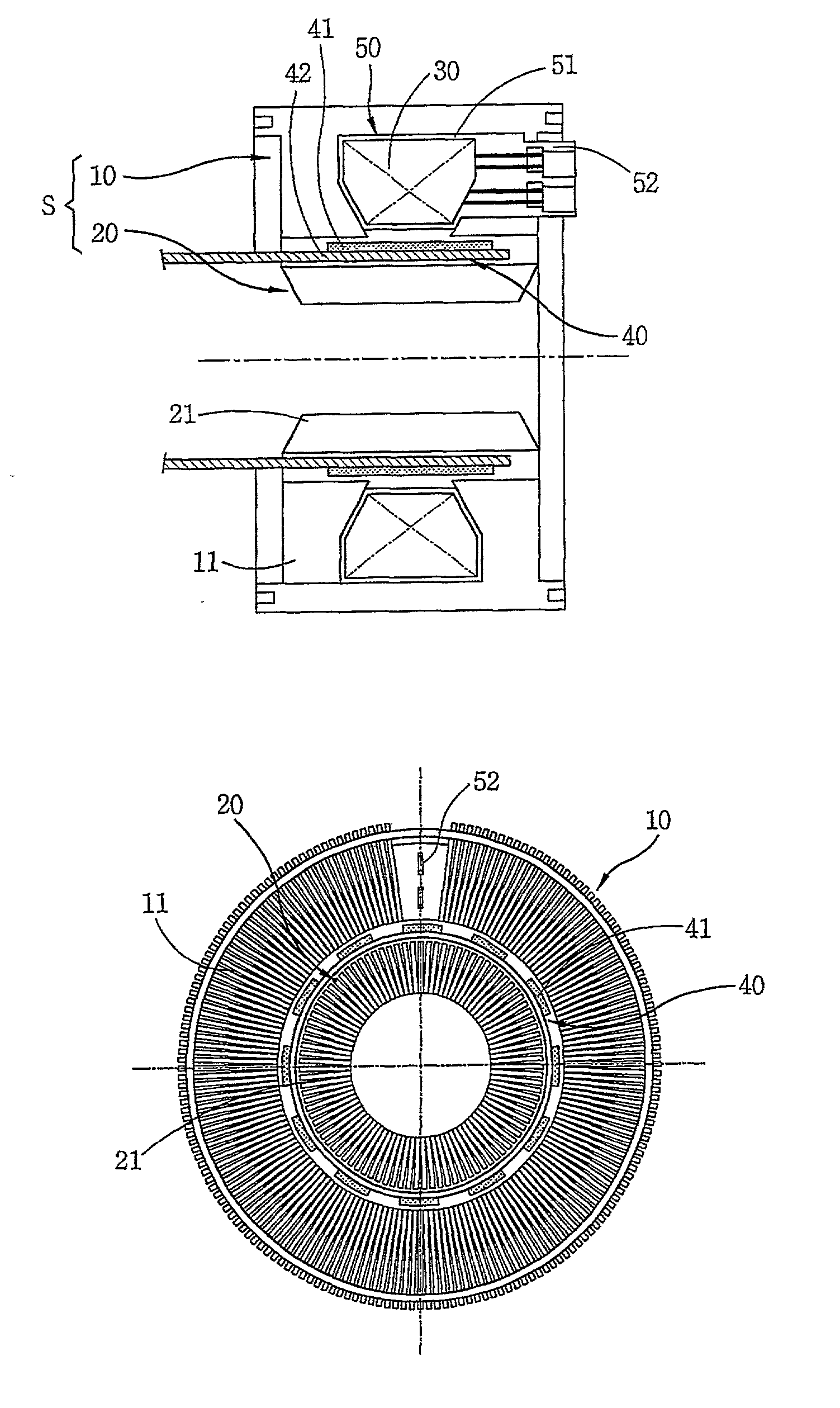
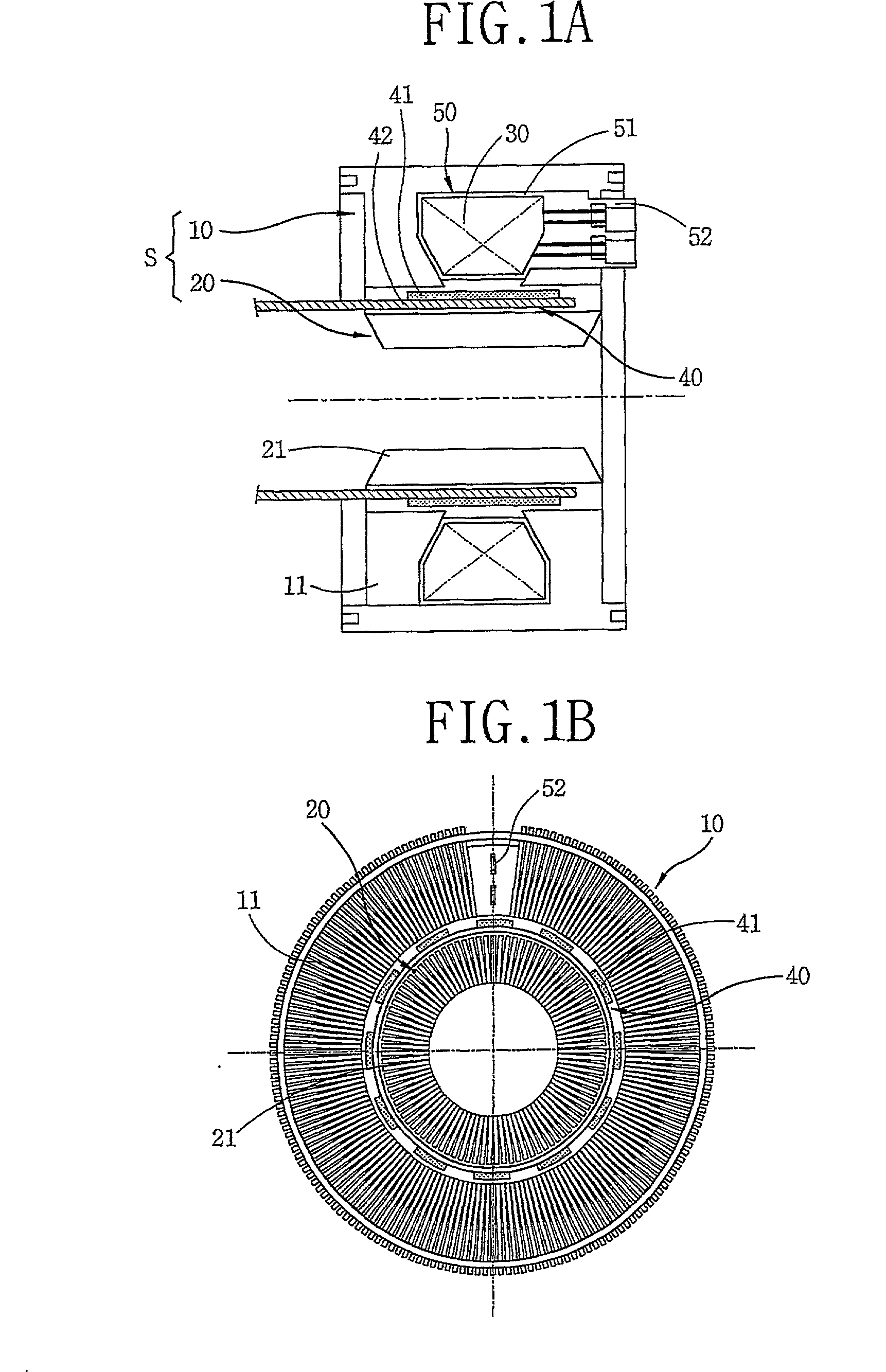
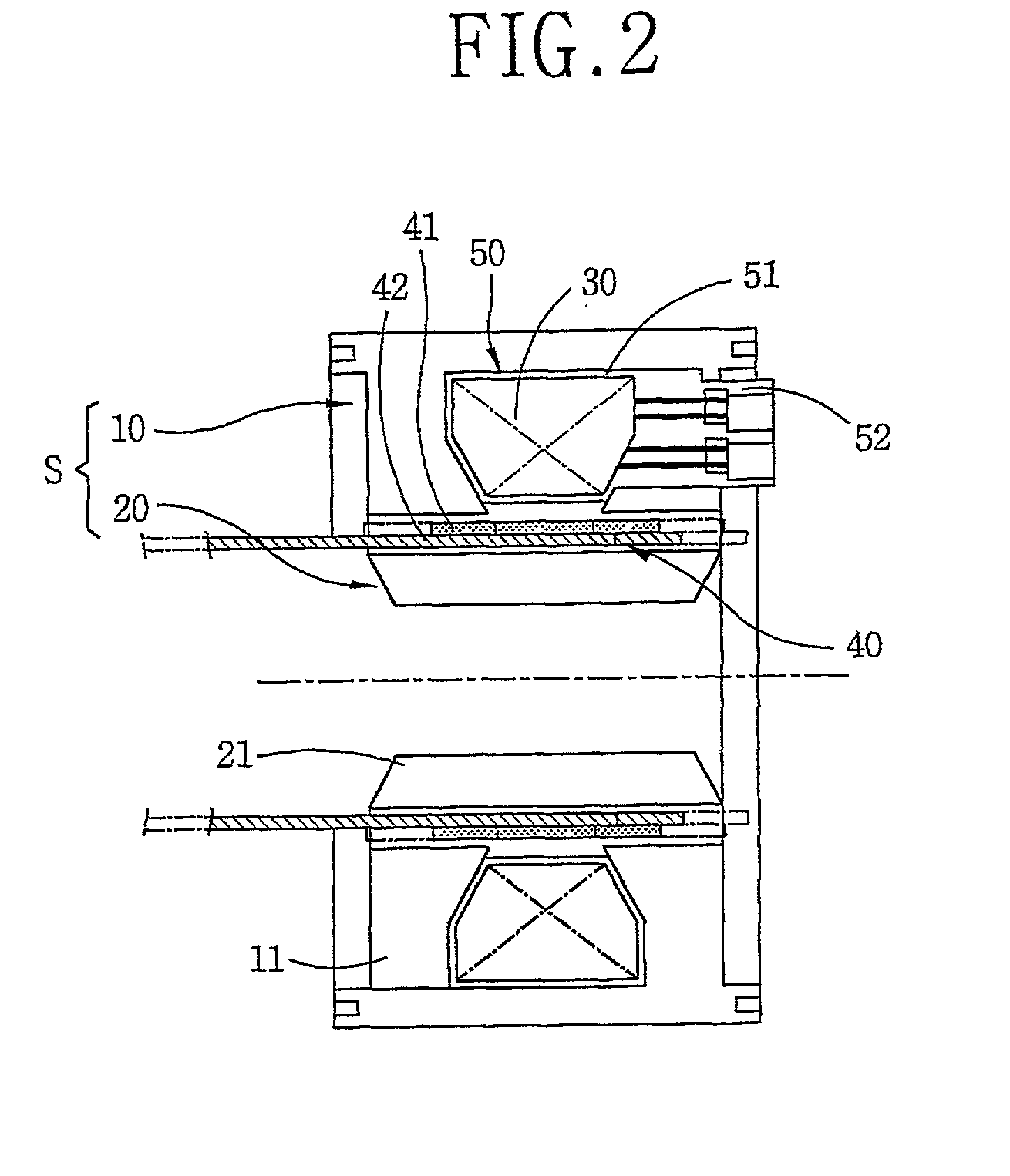
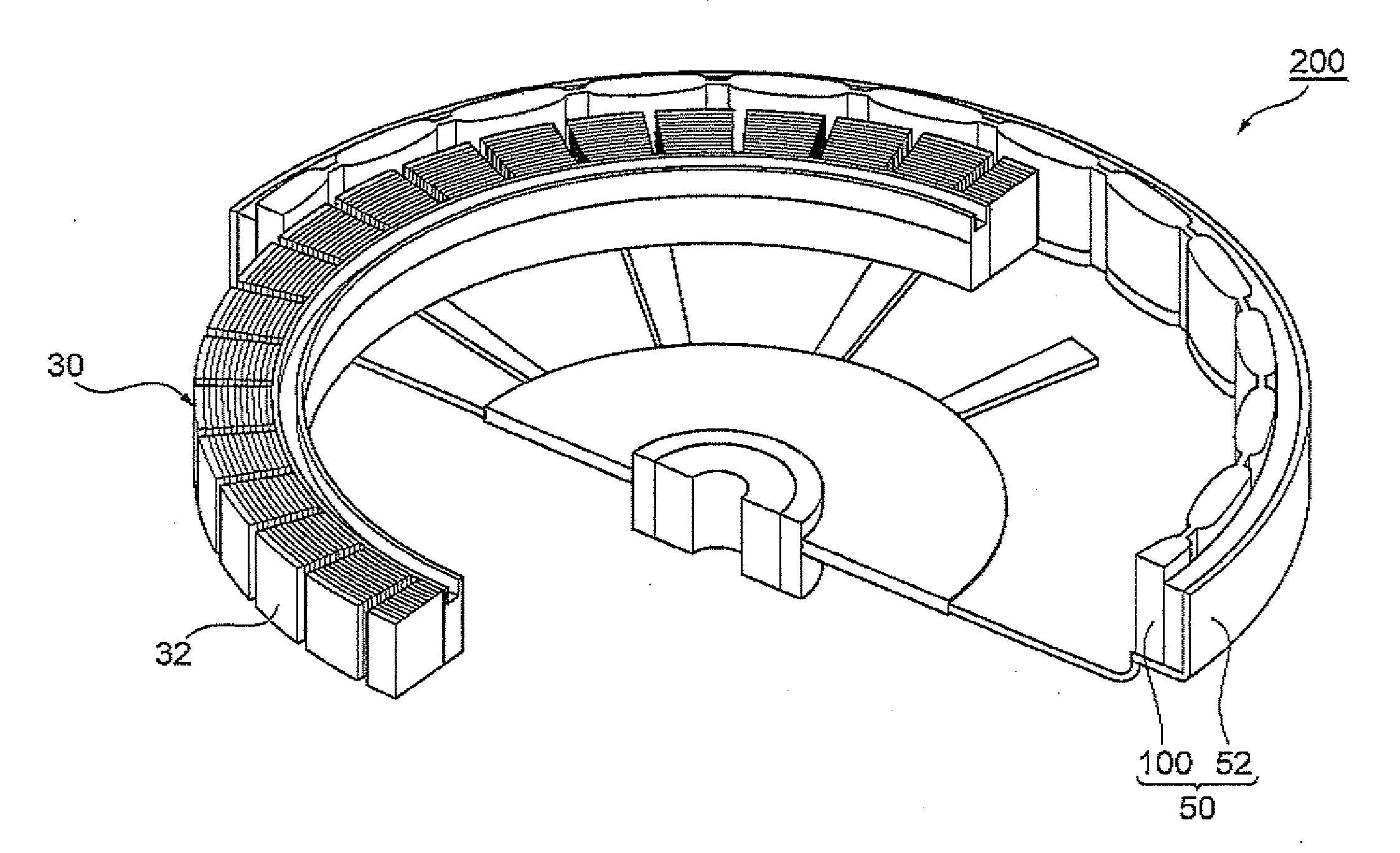
A stator for a reciprocating motor includes a bobbin made of an insulating material in which a winding coil is located; a terminal unit forming a single body with the bobbin and connecting the winding coil electrically with an outer power source; and a core unit stacked radially along with the bobbin started from one side of the terminal unit. Therefore, the winding coil and the bobbin can be coupled in simple way, and the core unit can be stacked simply and precisely, so the mass productivity of the motor is able to be increased. Also, the size of the core unit is able to be managed simply and precisely, and then, the contact and impact with other components constructing the motor is prevented, whereby the reliability of the motor can be improved.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Motorized pyrotechnic system
One aspect of the invention provides a firing apparatus that provides an arcuate visual effect. The firing apparatus includes a motor, an enclosure housing the motor and an arm connected to a shaft of the motor for moving a pyrotechnic device such as a gerb. Another aspect of the invention provides a pyrotechnic system that includes a firing apparatus including a reciprocal motor, a firing arm having a first end connected to a shaft of the reciprocal motor and a second end adapted to emit an arcuate pyrotechnic effect, a control unit in communication with the firing apparatus for controlling operation of the reciprocal motor and an ignition unit in communication with the firing apparatus for initiating the pyrotechnic effect.
Owner:STRICTLY FX LLC
Magnetically actuated reciprocating motor and process using reverse magnetic switching
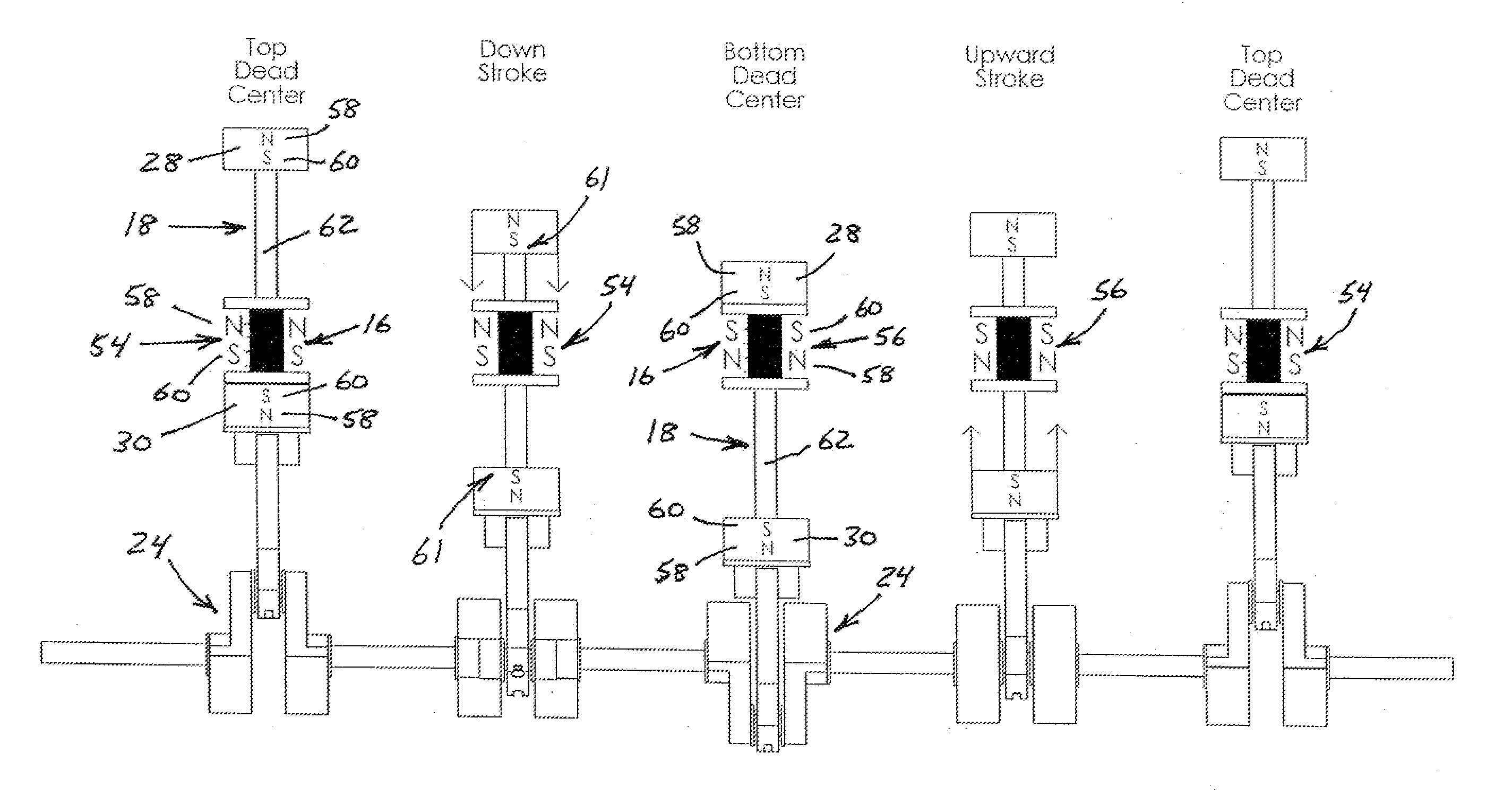
InactiveUS8344560B2Easy to operateReduce manufacturing costMechanical energy handlingPropulsion systemsStored energyElectrical polarity
A magnetically actuated reciprocating motor utilizes the stored energy of rare earth magnets and an electromagnetic field provided by a solenoid to reciprocally drive a solenoid assembly. A converting mechanism, such as a connecting rod and crankshaft, converts the reciprocating motion of the solenoid assembly to power a work object. The solenoid assembly comprises a solenoid having a nonferromagnetic spool with a tubular center section and a coil of wire wrapped around the center section. A magnetic actuator has a permanent magnet at each end of an elongated shaft that is received through the center section of the spool. A switching mechanism switches magnetic polarity at the ends of the solenoid so the solenoid assembly is alternatively repelled and attracted by the permanent magnets. A controlling mechanism interconnecting an output shaft and the switching mechanism provides the timing to switch the polarity of the solenoid and reciprocate the solenoid assembly.
Owner:GOSVENER KENDALL C
Compact low frequency audio transducer
A rotary reciprocating acoustic transducer for producing sound in response to an applied electrical signal has a ported tubular housing having a generally cylindrical chamber with an interior lumen which is generally symmetrical about a central axis and opposing first and second linear reciprocating electrodynamic motors mounted over the tubular housing member's first and second open end, with a reciprocating rotatable transducer vane assembly with first and second rotating vanes projecting radially away from a central, axially aligned shaft driven by the first and second linear reciprocating motors.
Owner:GRAHAM DOUG
Magnetically actuated reciprocating motor and process using reverse magnetic switching
InactiveUS8324763B2Easy to operateReduce manufacturing costMechanical energy handlingPropulsion systemsMagnetic tension forceStored energy
A magnetically actuated reciprocating motor utilizes the stored energy of magnets, particularly rare earth magnets, and an electromagnetic field to reciprocally drive a magnetic actuator. A converting mechanism, such as a connecting rod and crankshaft, converts the reciprocating motion of the magnetic actuator to rotary motion for powering a work object. A solenoid, comprising a nonferromagnetic spool having a tubular center section with a coil of wire wrapped around the center section, is connected to a source of power and a switching mechanism. The switching mechanism switches the magnetic polarity at the ends of the solenoid to alternatively repel and attract permanent magnets at the ends of the magnetic actuator. A shaft interconnecting the magnets is received through the center section of the solenoid. A controlling mechanism interconnecting an output shaft and the switching mechanism provides the timing to switch the polarity of the solenoid to drive the magnetic actuator.
Owner:GOSVENER KENDALL C
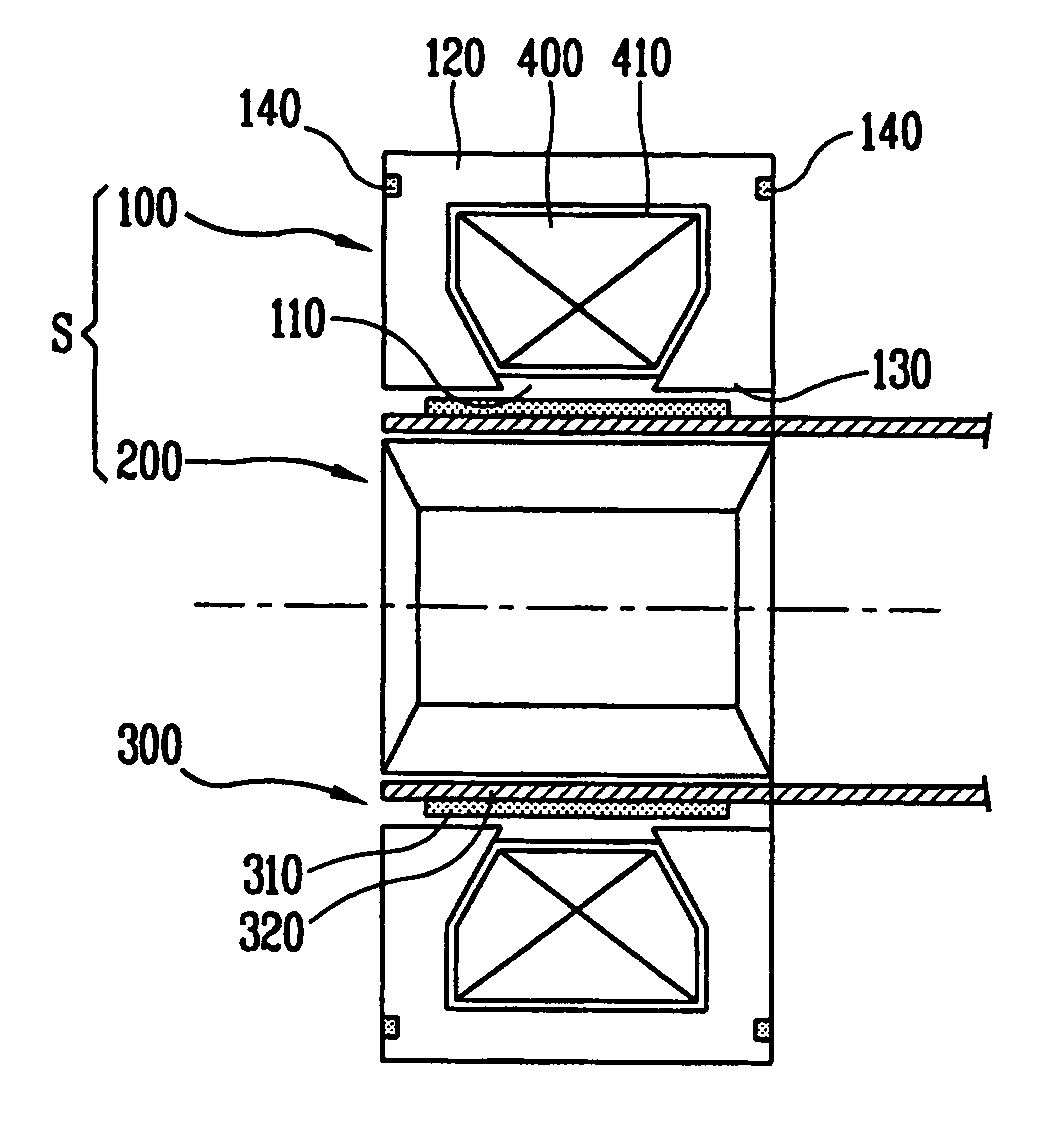
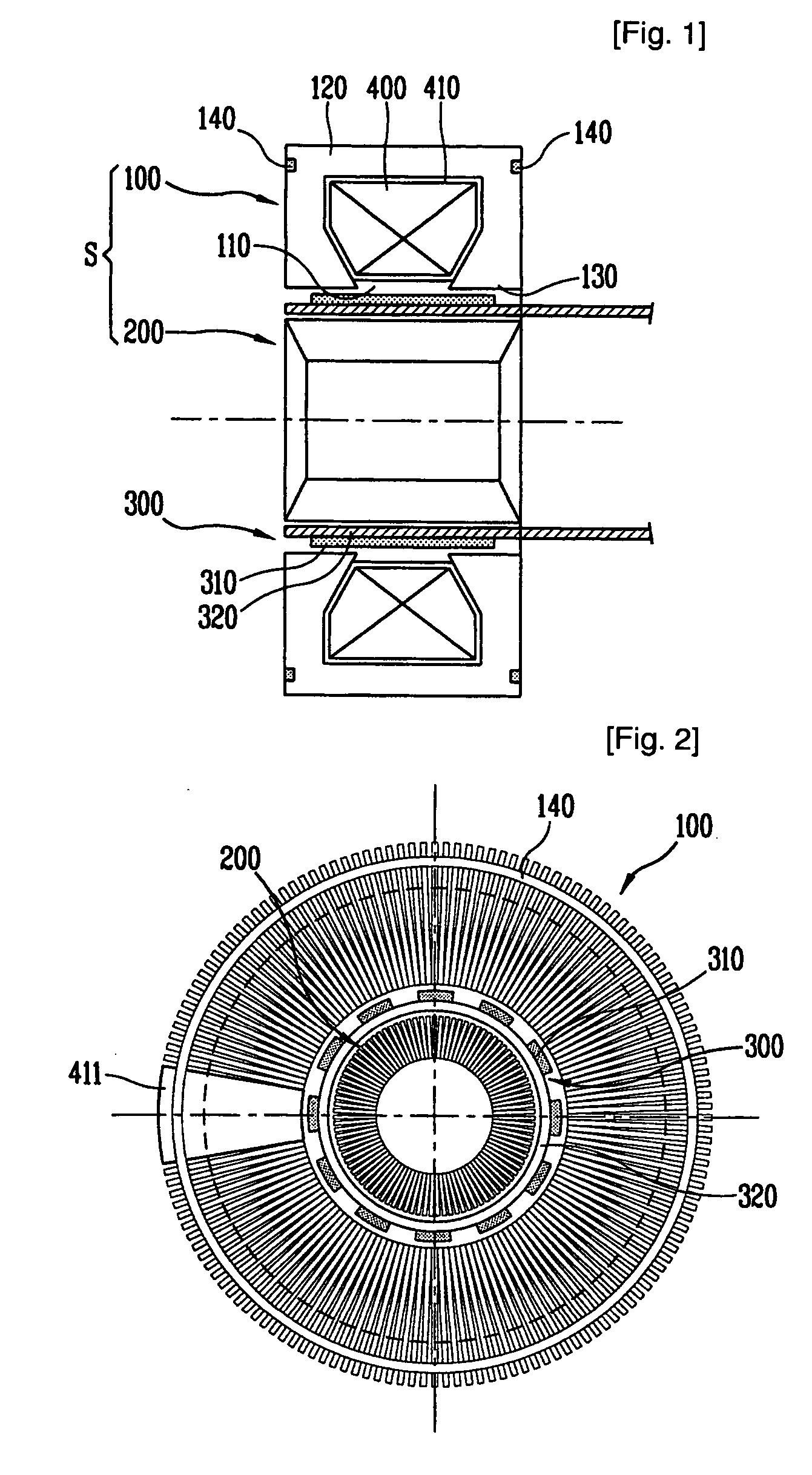
Rare-earth sintered magnet, rotator, and reciprocating motor
ActiveUS20110227424A1Excellent magnetic propertiesImprove corrosion resistancePermanent magnetsMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementSintered magnets
The present invention relates to a rare-earth sintered magnet 100 containing an R-T-B-based alloy and a nitride of a transition element, while the nitride is distributed preferentially to a surface part. (R, T, and B indicate a rare-earth element, at least one of iron and cobalt, and boron, respectively.)
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetically Actuated Reciprocating Motor and Process Using Reverse Magnetic Switching
InactiveUS20120007448A1Easy to operateReduce manufacturing costMechanical energy handlingPropulsion systemsStored energyElectrical polarity
A magnetically actuated reciprocating motor utilizes the stored energy of rare earth magnets and an electromagnetic field provided by a solenoid to reciprocally drive a solenoid assembly. A converting mechanism, such as a connecting rod and crankshaft, converts the reciprocating motion of the solenoid assembly to power a work object. The solenoid assembly comprises a solenoid having a nonferromagnetic spool with a tubular center section and a coil of wire wrapped around the center section. A magnetic actuator has a permanent magnet at each end of an elongated shaft that is received through the center section of the spool. A switching mechanism switches magnetic polarity at the ends of the solenoid so the solenoid assembly is alternatively repelled and attracted by the permanent magnets. A controlling mechanism interconnecting an output shaft and the switching mechanism provides the timing to switch the polarity of the solenoid and reciprocate the solenoid assembly.
Owner:GOSVENER KENDALL C
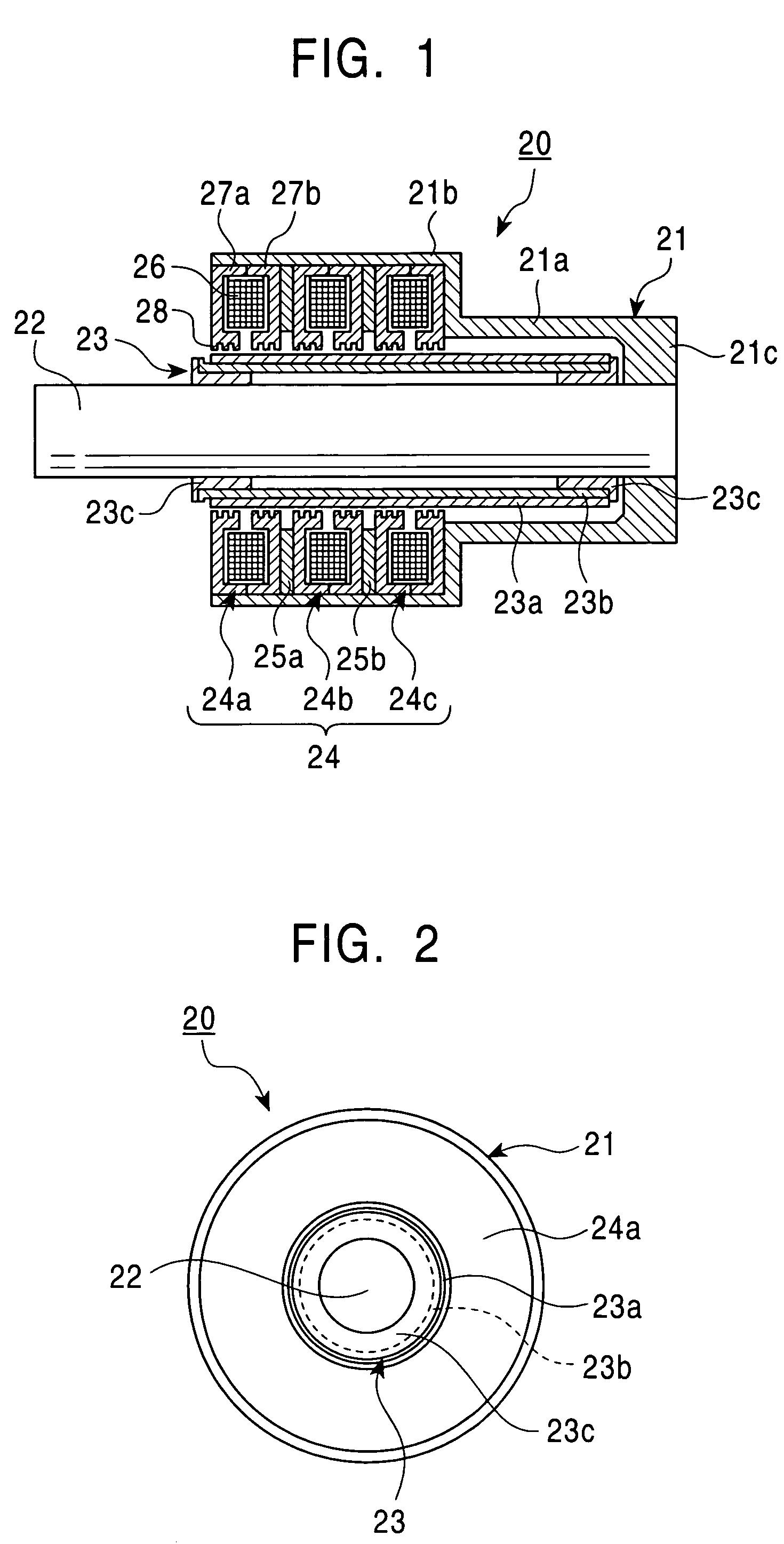
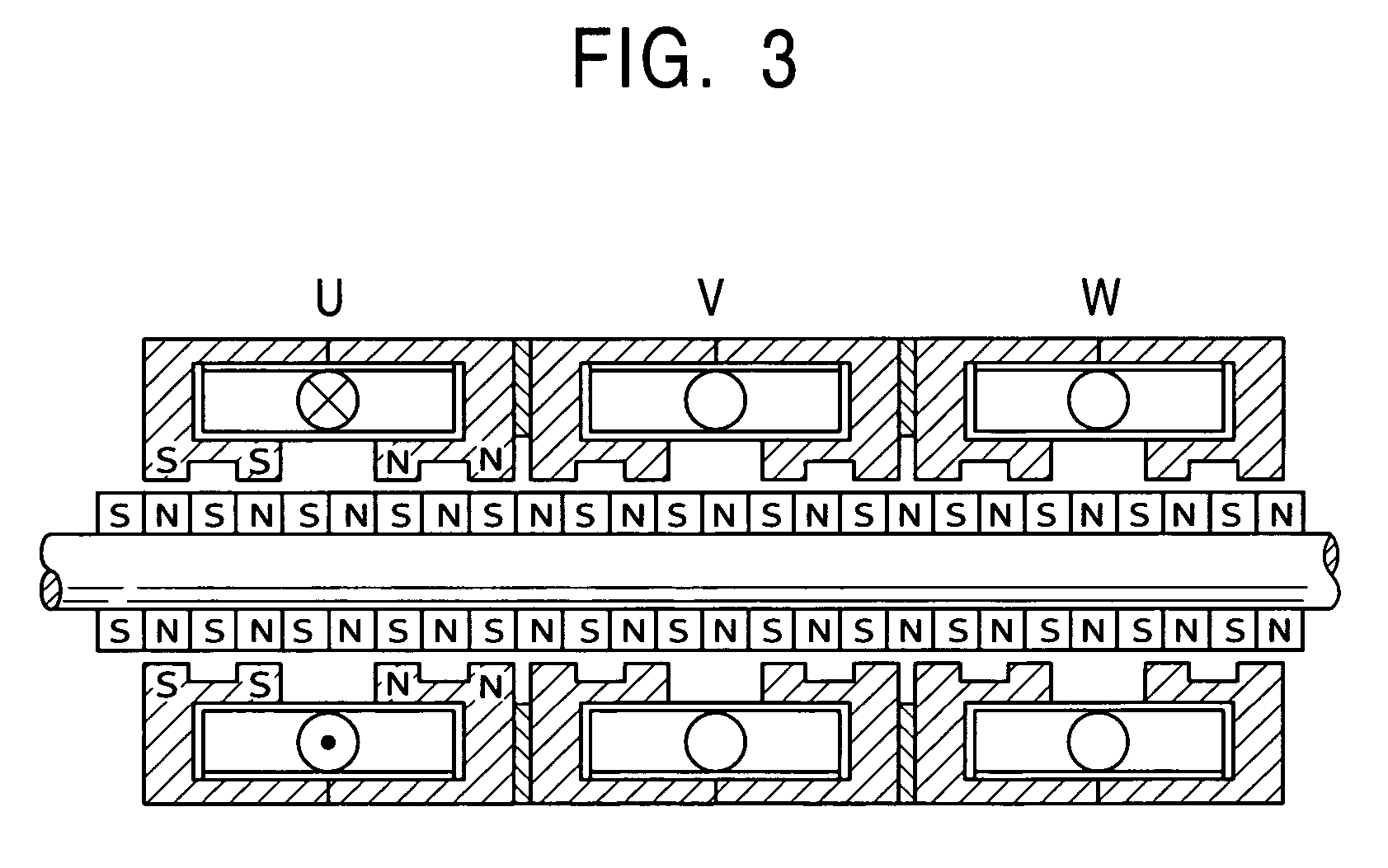
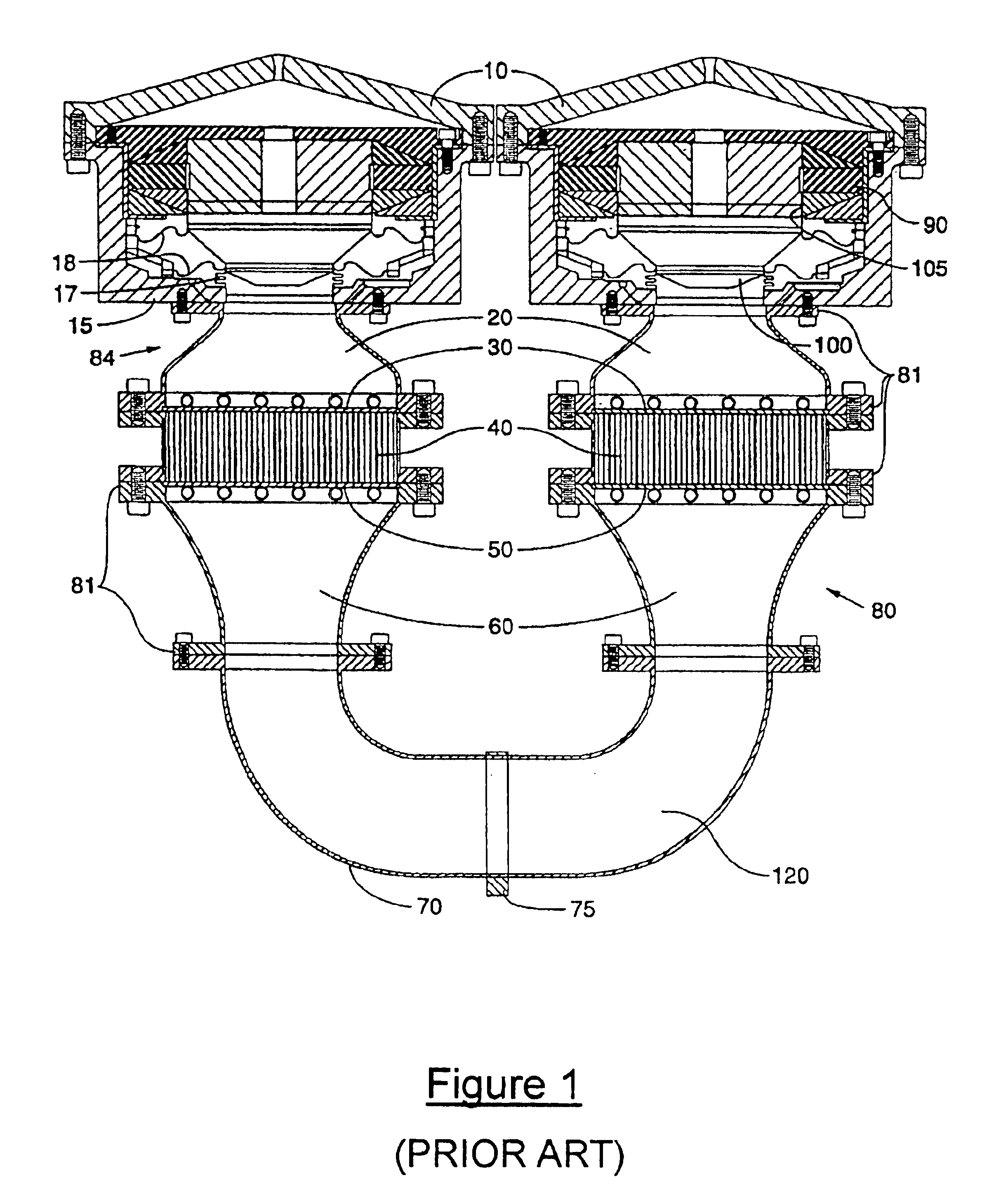
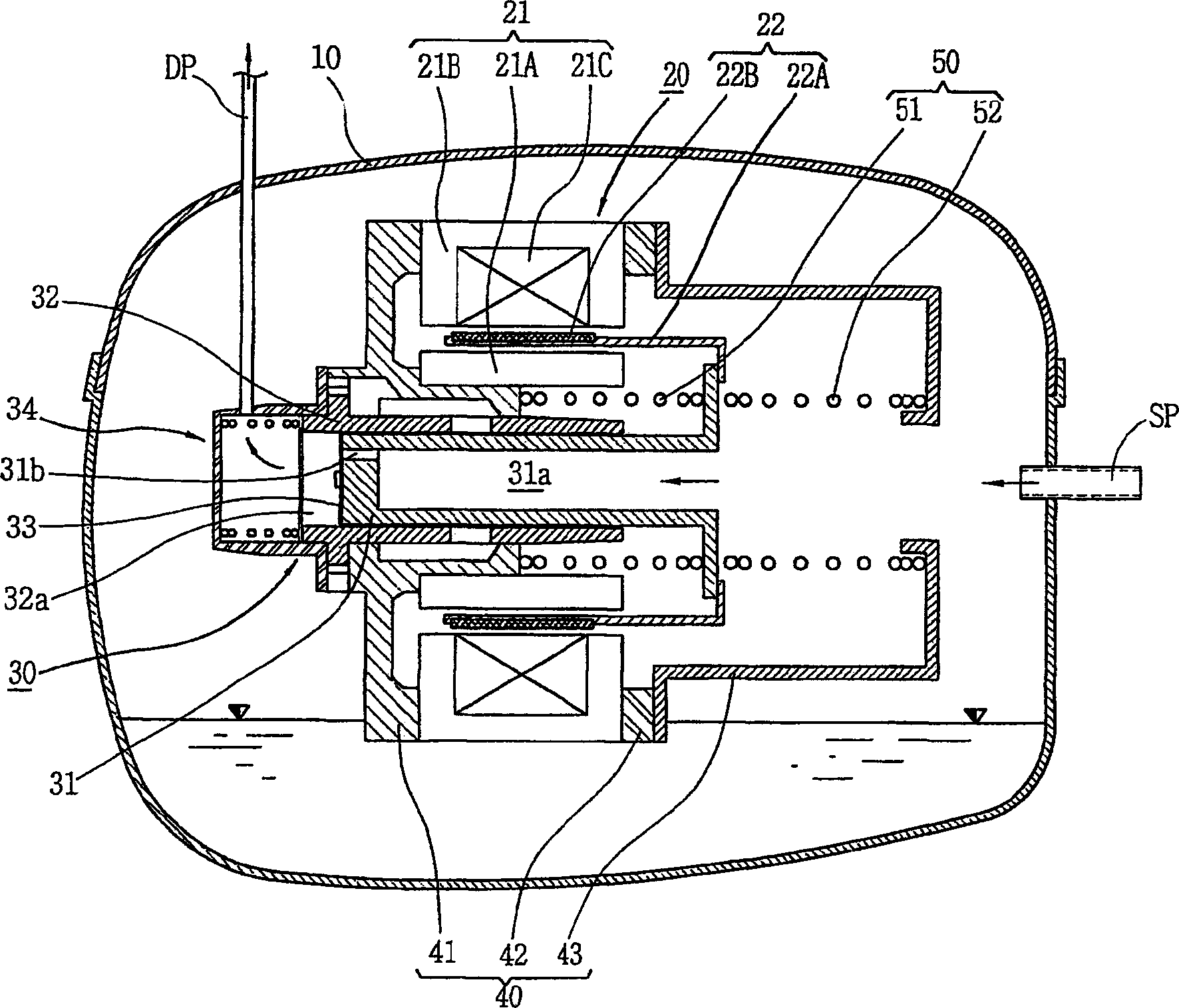
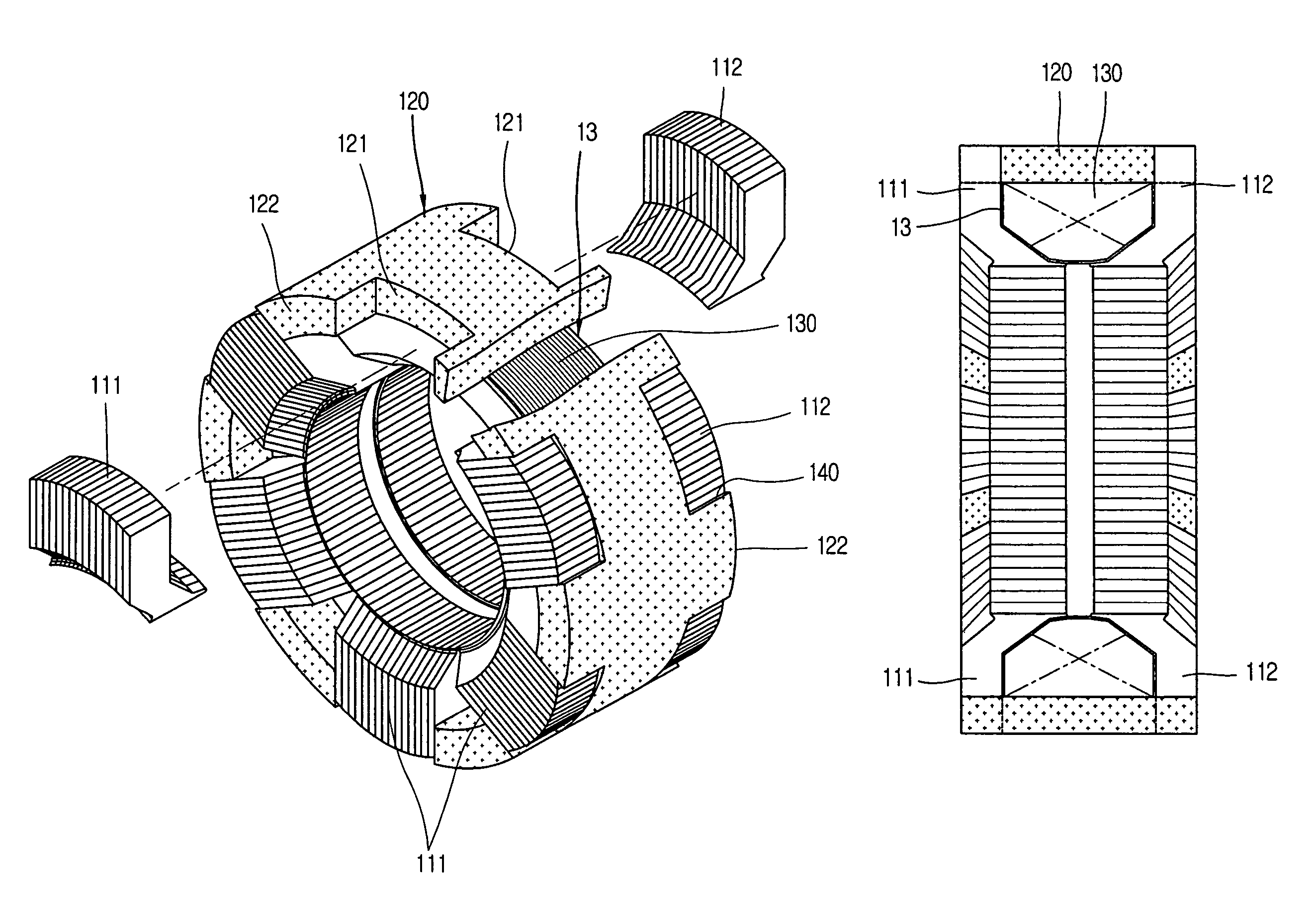
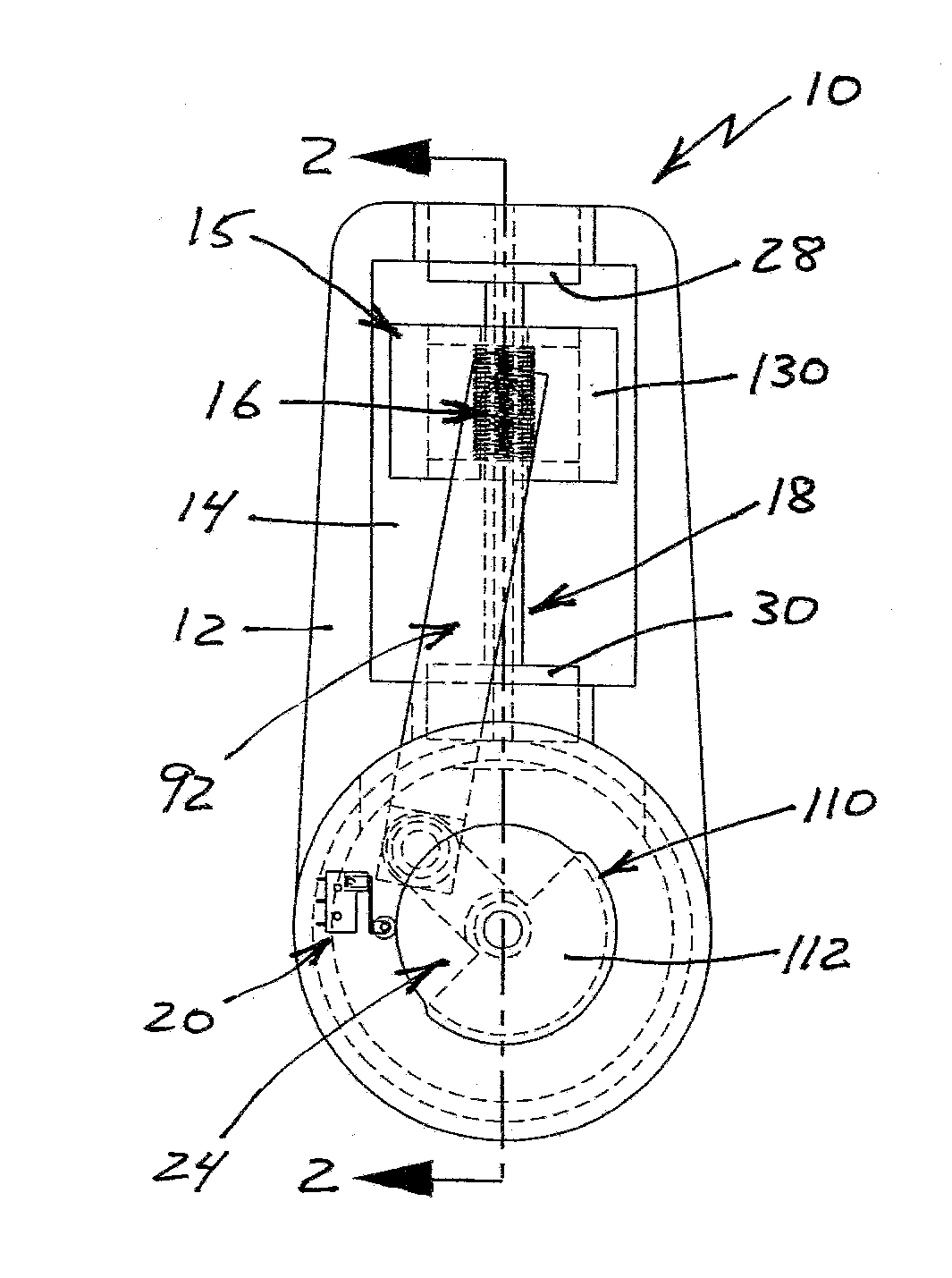
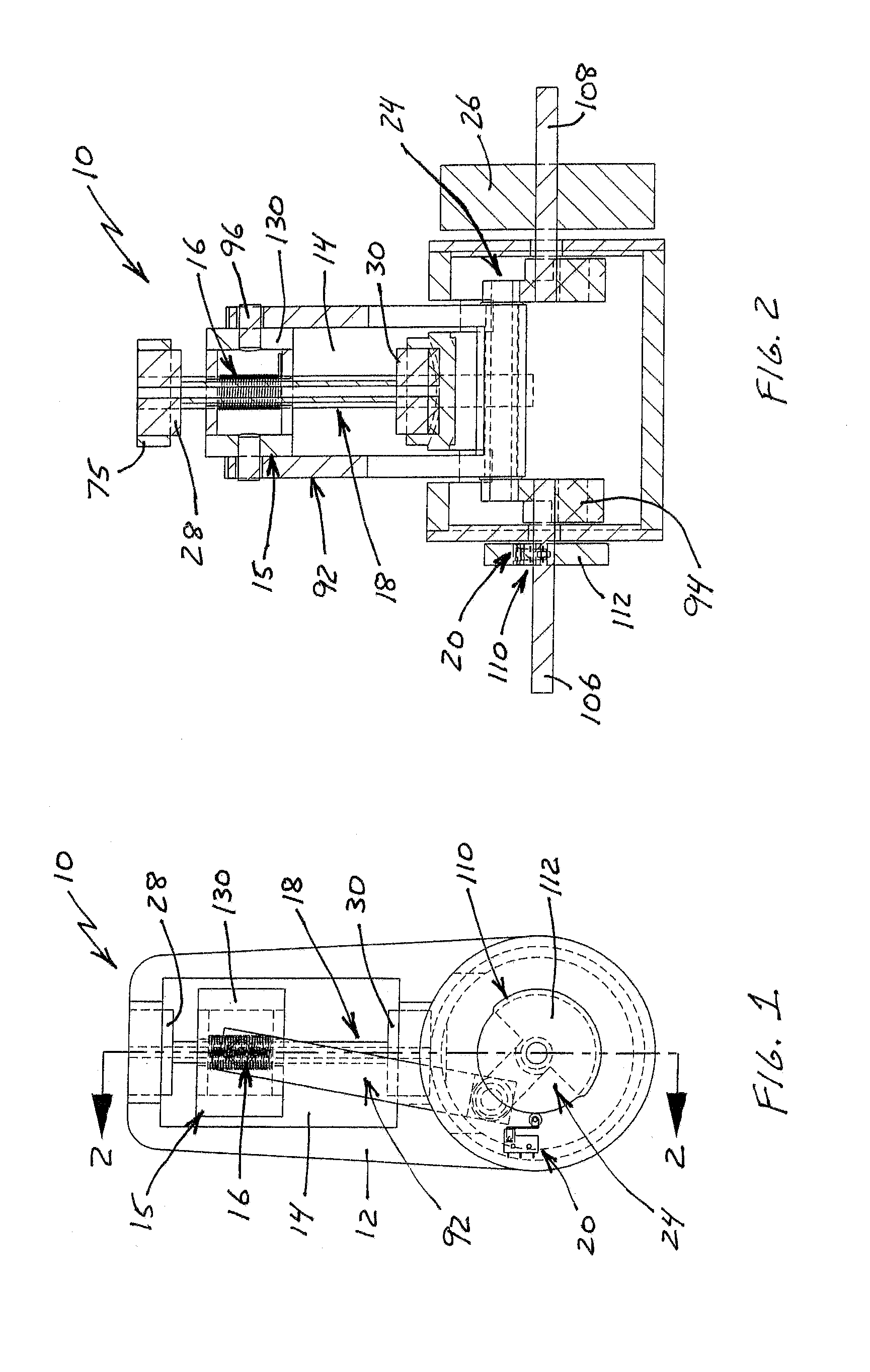
Reciprocating compressor
InactiveCN1439077ASmall flow resistanceSmall sizePositive displacement pump componentsPiston pumpsReciprocating electric motorMagnet
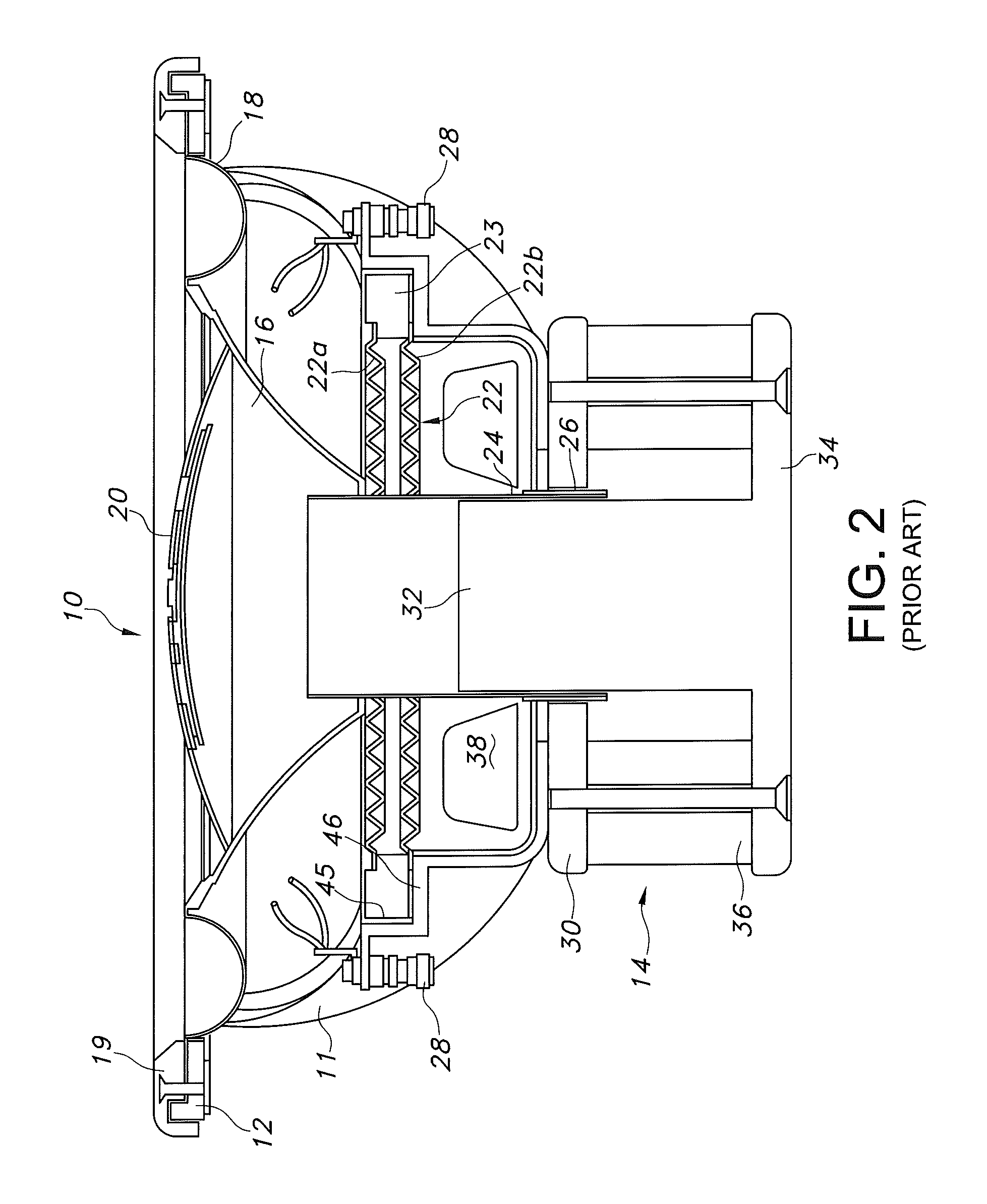
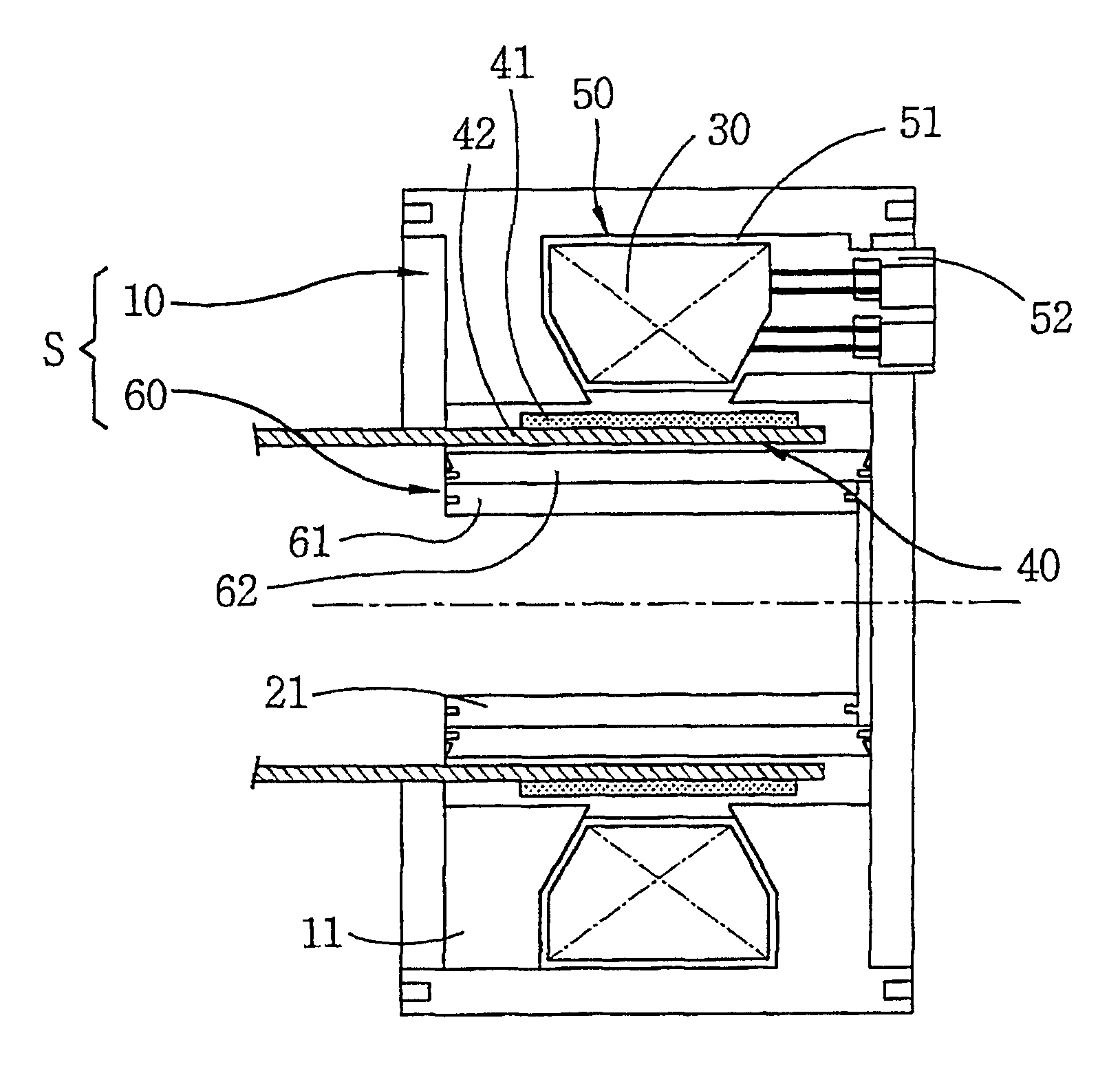
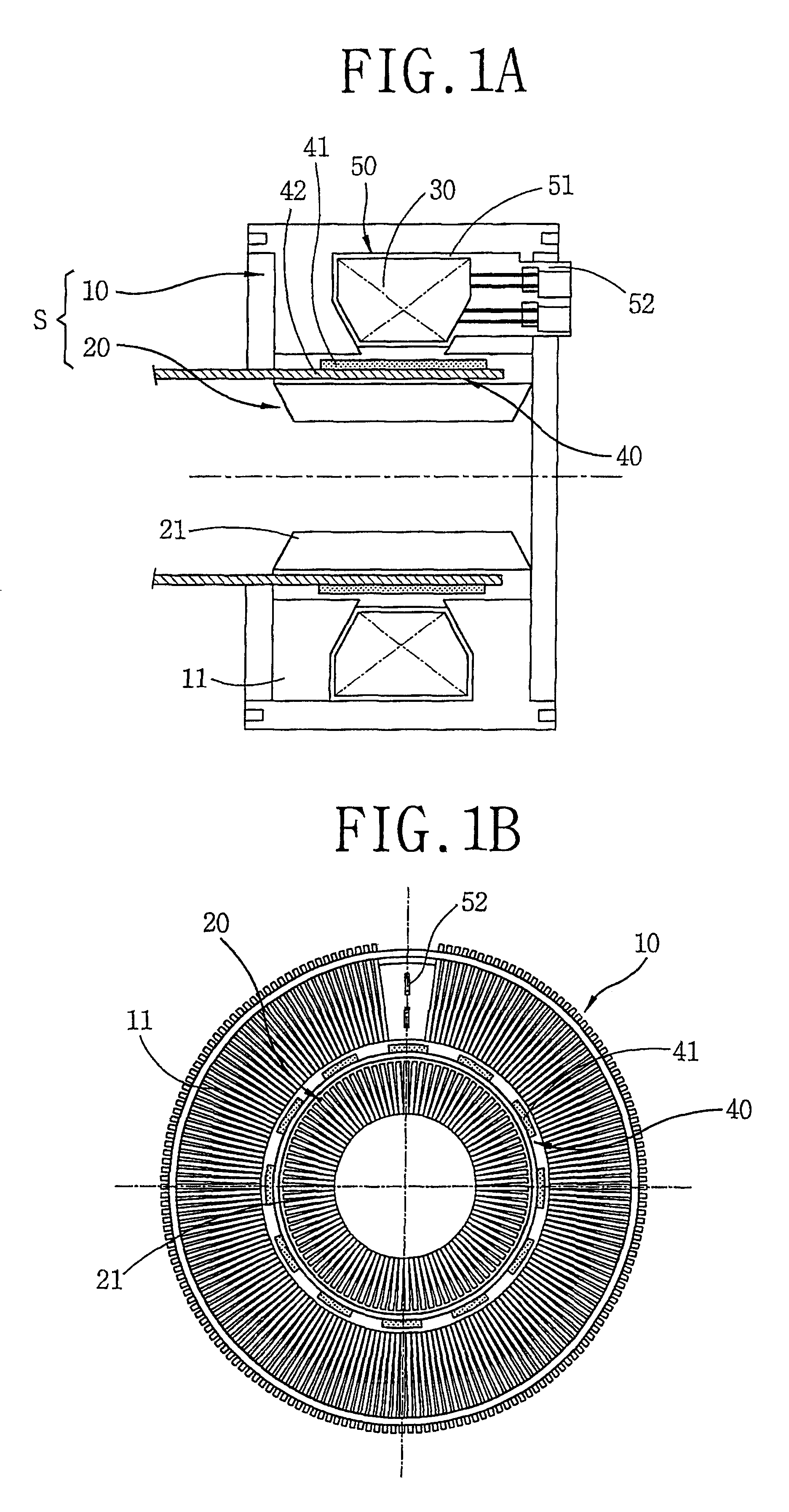
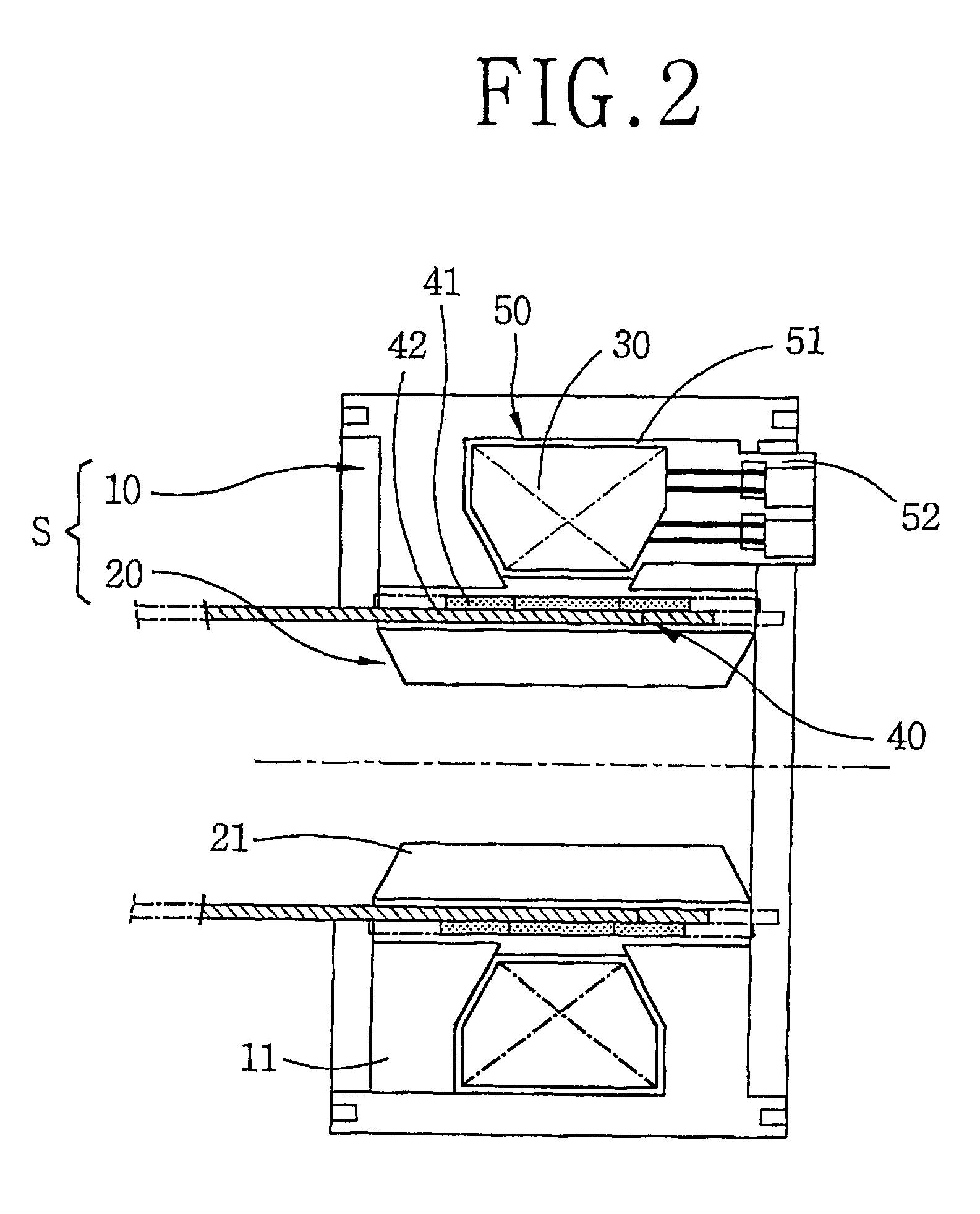
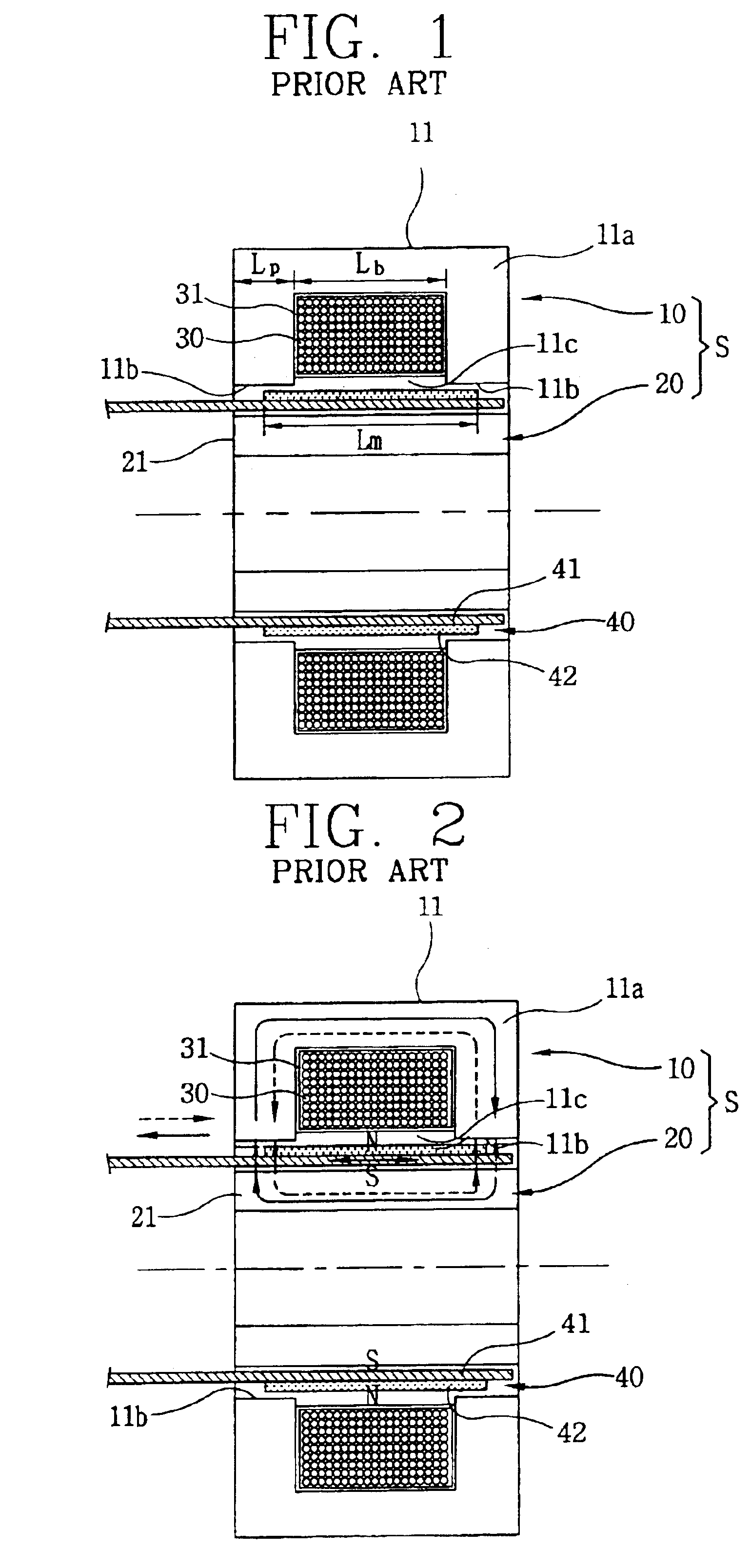
A reciprocating compressor including: a closed container (10); a reciprocating motor (20) having stators and an armature (22) disposed in the air gap between the stators (21) and making a reciprocal movement; a compression unit (30) having a piston (31) combined with the armature (22) of the reciprocating motor and a cylinder fixed inside the closed container (10); a spring unit (50) elastically supporting the armature (22) of the reciprocating motor (20) in a movement direction; and a frame unit (100) supporting the reciprocating motor (20) and the compression unit (30) having a gas hole (111) at a suitable portion thereof. Accordingly, when the armature (22) of the reciprocating motor (20) makes a reciprocal movement, the gas is compressed at the end of the armature (22), so that an increase of a flow resistance is prevented. In addition, in occurrence of an over-stroke of the armature, as the step portion (112) makes a space to prevent the magnet from releasing or damaging, the reliability of the compressor is improved.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Magnetically actuated reciprocating motor and process using reverse magnetic switching
InactiveUS8786143B2Easy to operateReduce manufacturing costMechanical energy handlingPropulsion systemsMagnetic tension forceStored energy
A magnetically actuated reciprocating motor utilizes the stored energy of permanent magnets and an electromagnetic field to reciprocally drive a magnetic actuator. A converting mechanism converts the reciprocating motion of the magnetic actuator to rotary motion for powering a work object. A solenoid, comprising a nonferromagnetic spool having a tubular center section with a coil of wire wrapped around the center section, is connected to a source of power and a switching mechanism. The magnetic actuator has permanent magnets disposed inside a tubular shaft at each end thereof. The switching mechanism switches the magnetic polarity at the ends of the solenoid to alternatively repel and attract the permanent magnets. The shaft is reciprocatively received through the center section of the solenoid. A controlling mechanism interconnects an output shaft, rotatably powered by the magnetic actuator, and the switching mechanism to switch the polarity of the solenoid to drive the magnetic actuator.
Owner:GOSVENER KENDALL C
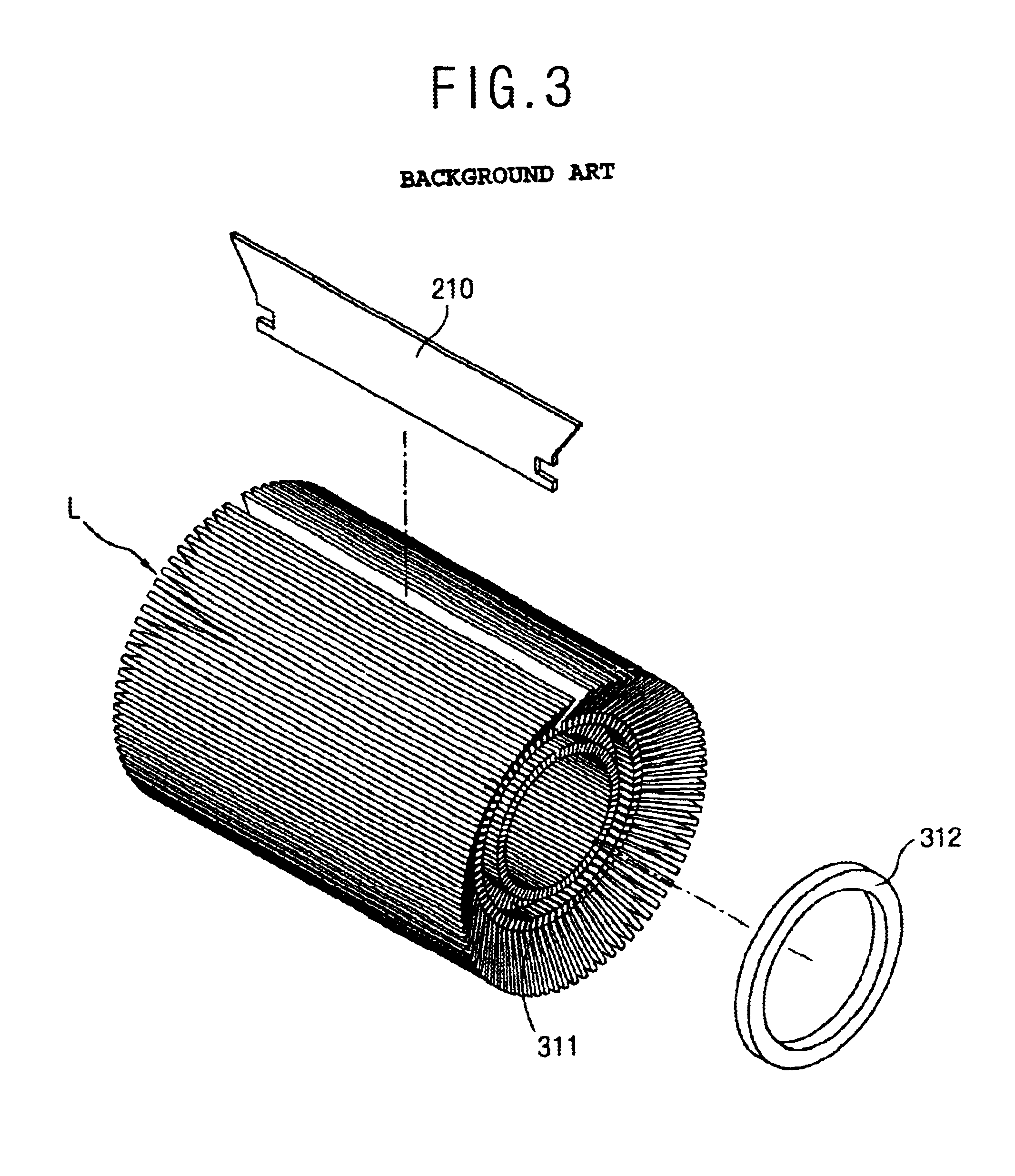
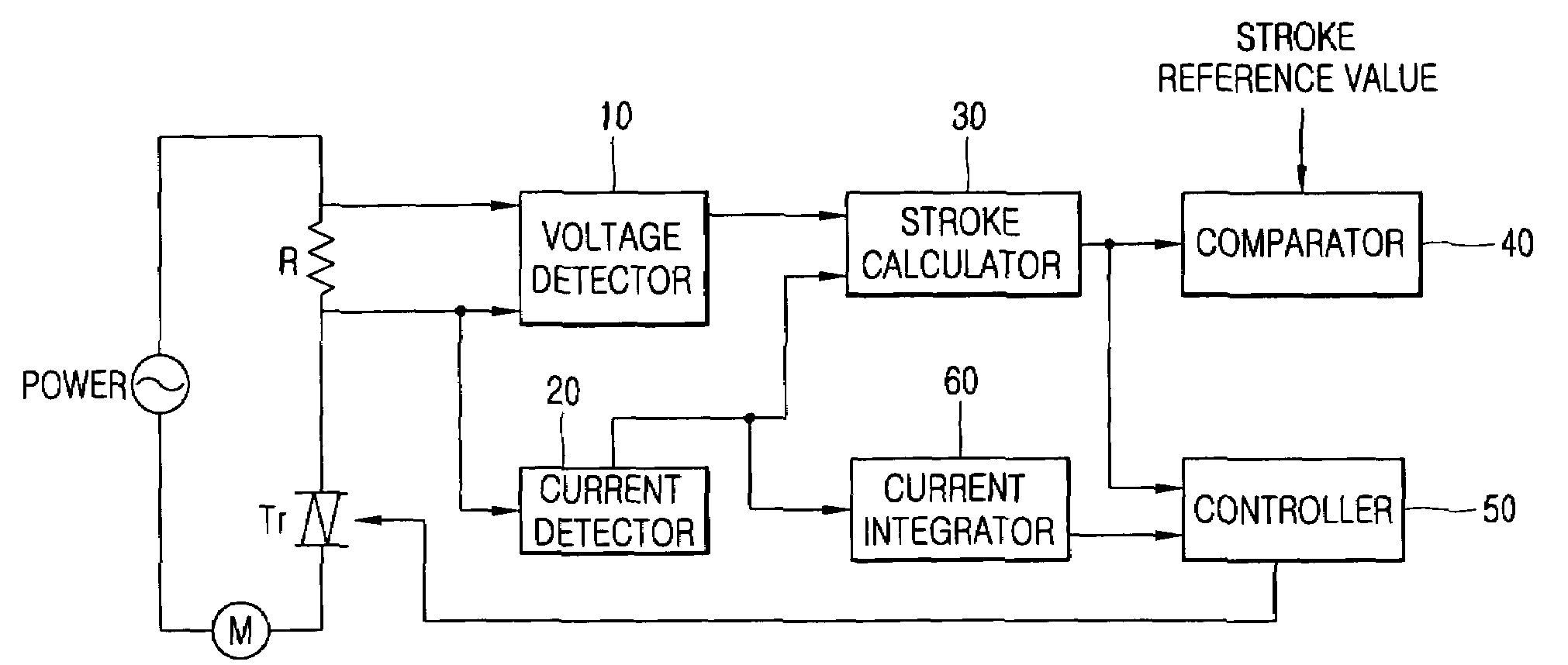
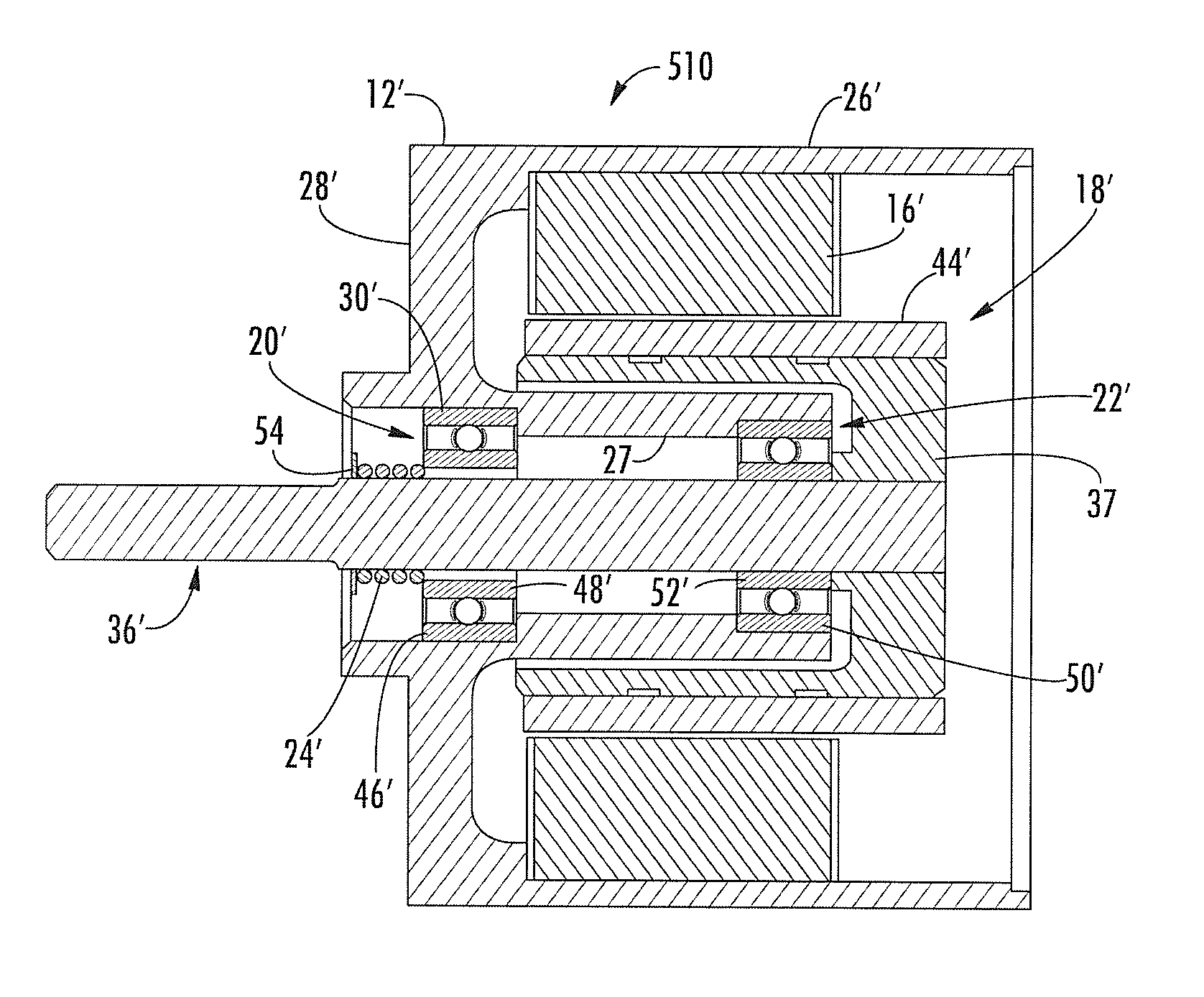
Stator of reciprocating motor
ActiveUS20060192441A1Reduce component countSmall size errorMagnetic circuit stationary partsPiston pumpsBobbinEngineering
A stator of a reciprocating motor includes a ring-shaped bobbin including a winding coil 400 therein; a plurality of unit laminated assemblies each constructed of a plurality of lamination sheets and coupled to the bobblin in a circumferential direction; a fixing means integrally formed with the bobbin and for fixing the unit laminated assemblies to the bobbin; and an inner core inserted in an outer core at a certain interval between itself and a round inner circumferential surface formed by inner surface of the unit laminated assemblies, so that components can be easily assembled, the number of assembling processes and the number of components can be reduced.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Reciprocating motor
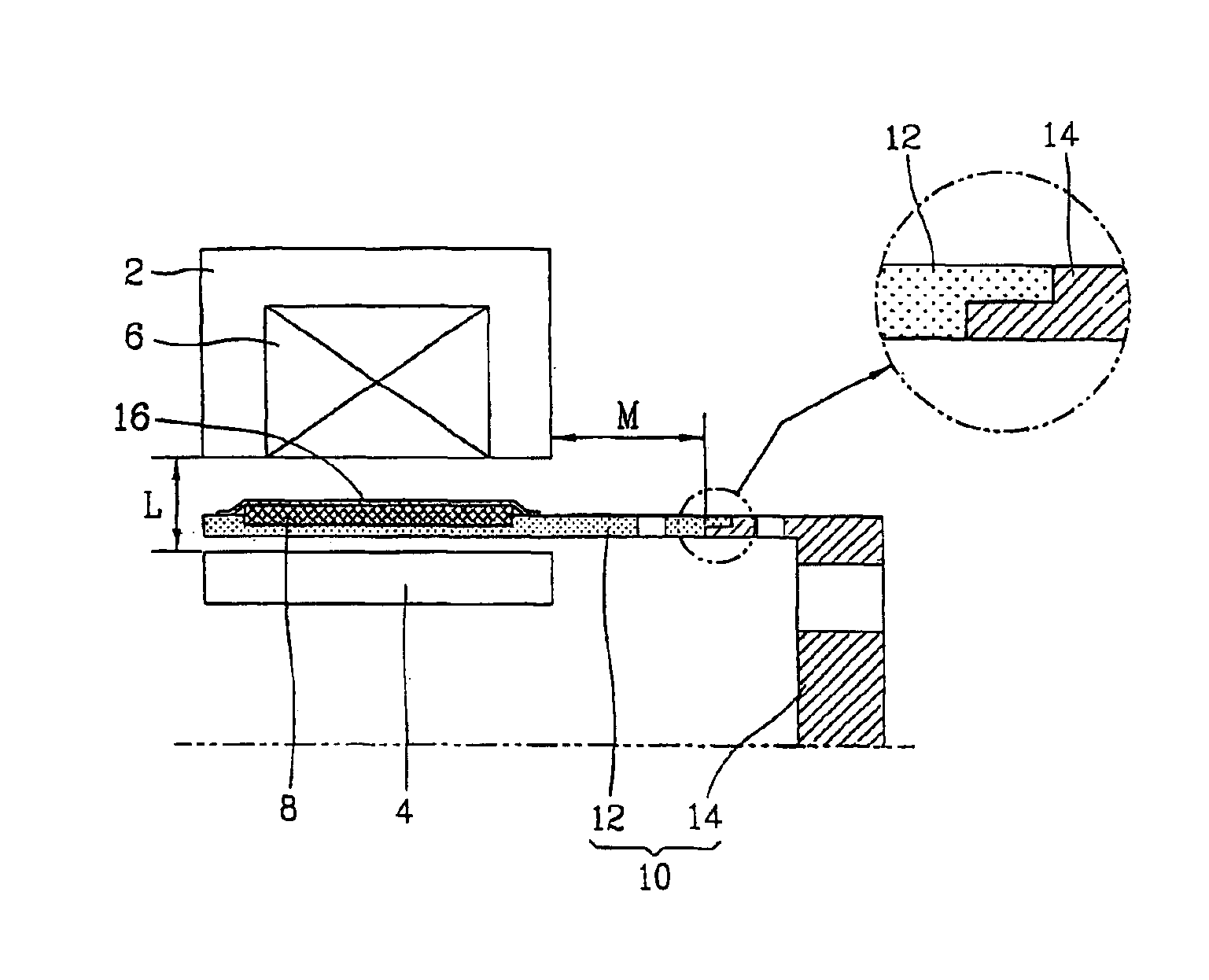
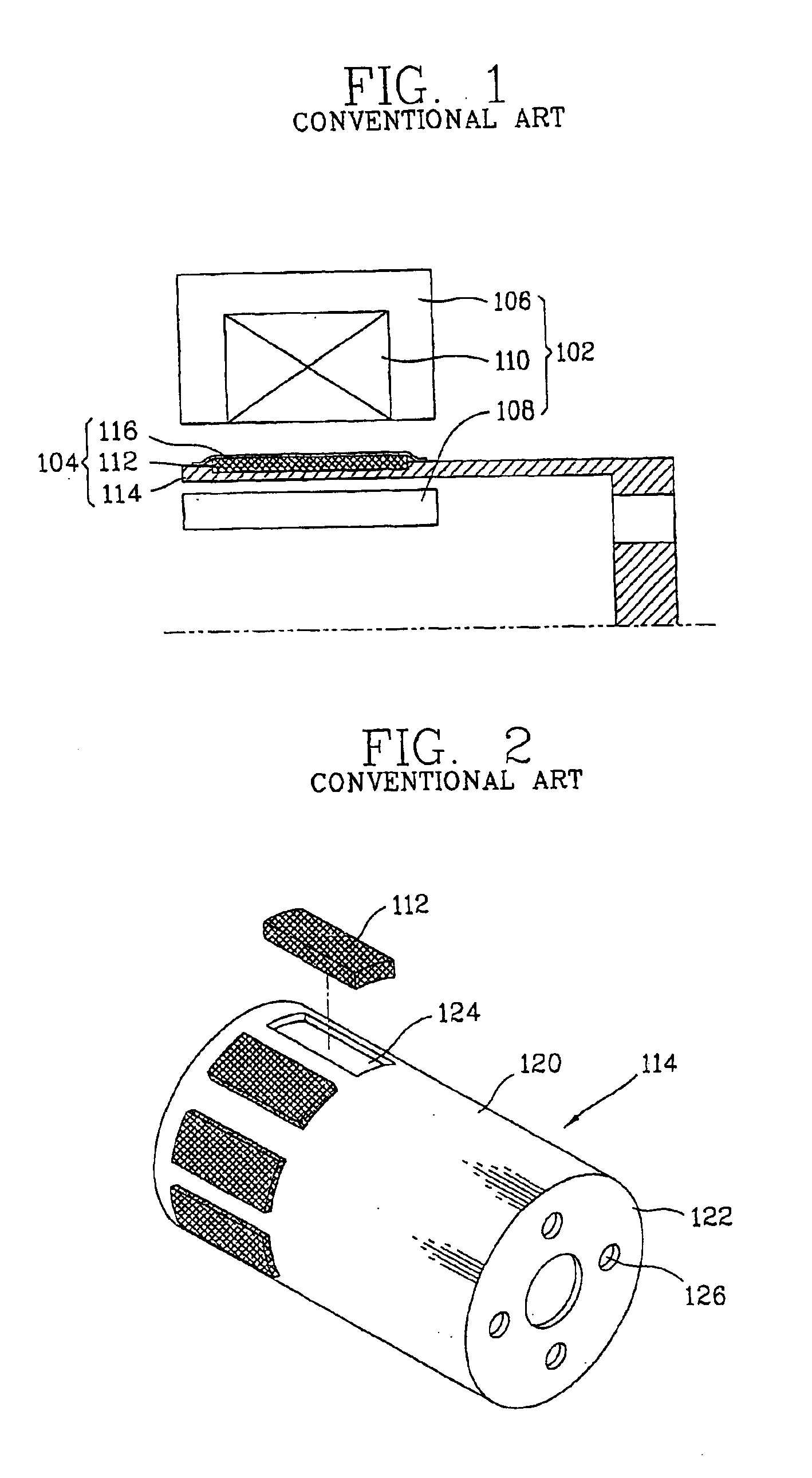
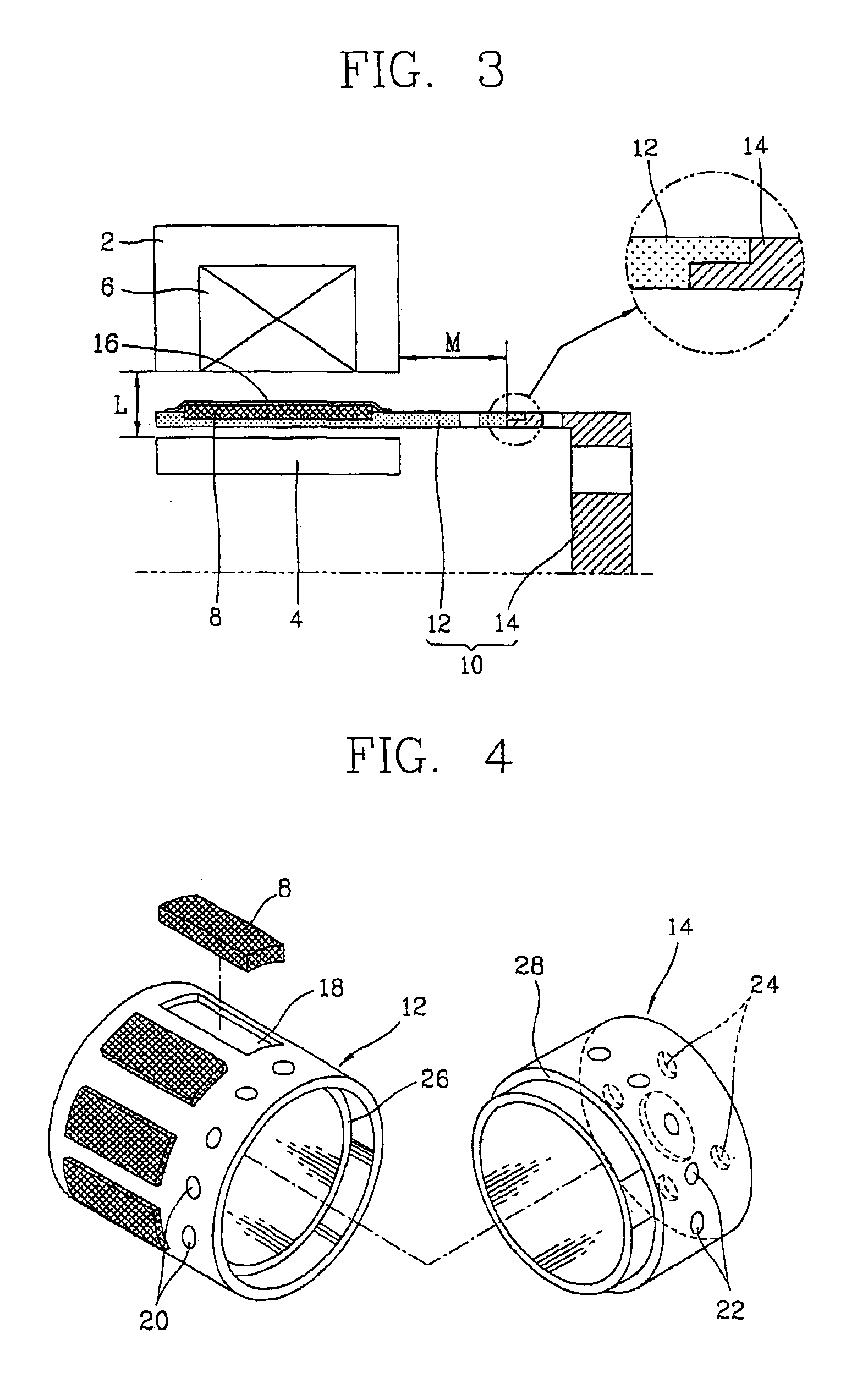
InactiveUS6894407B2Avoid efficiencyReduce lossesReciprocating/oscillating/vibrating magnetic circuit partsMagnetic circuit rotating partsMetallic materialsEngineering
A reciprocating motor is disclosed having a magnet frame (10) connected between a magnet (8) and an element to be reciprocally moved to transmit a reciprocal movement of the magnet (8) to the element, the magnet consisting of a first mounting unit (12) at which the magnet (8) is fixed and a second mounting unit (14) made of a different material with the first mounting unit (12), being connected to the first mounting (12), and with which the element is engaged. A portion of the magnet frame (10) where the magnet is fixed is made of a nonmetallic material to minimize a loss of flux generated from a winding coil (6).
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
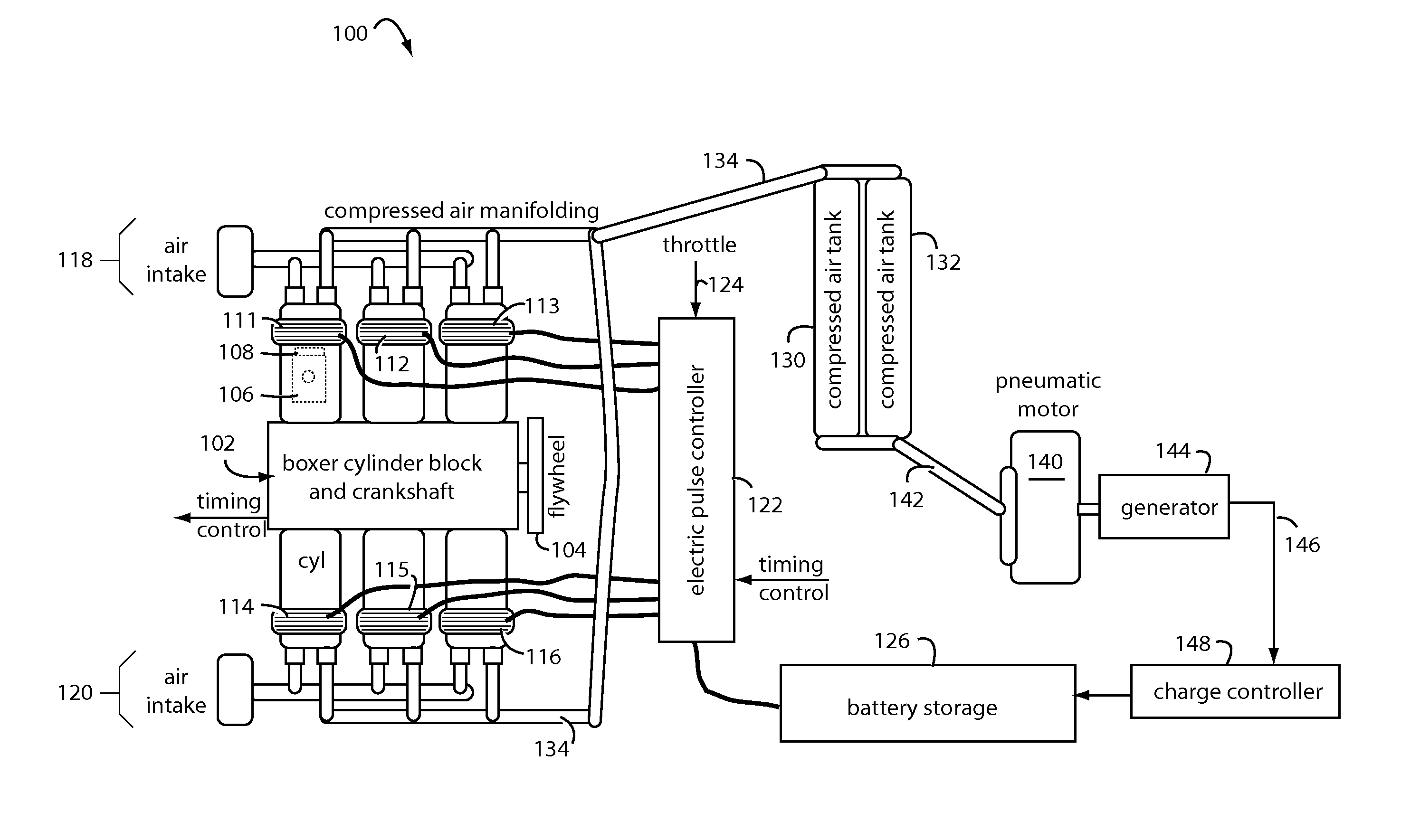
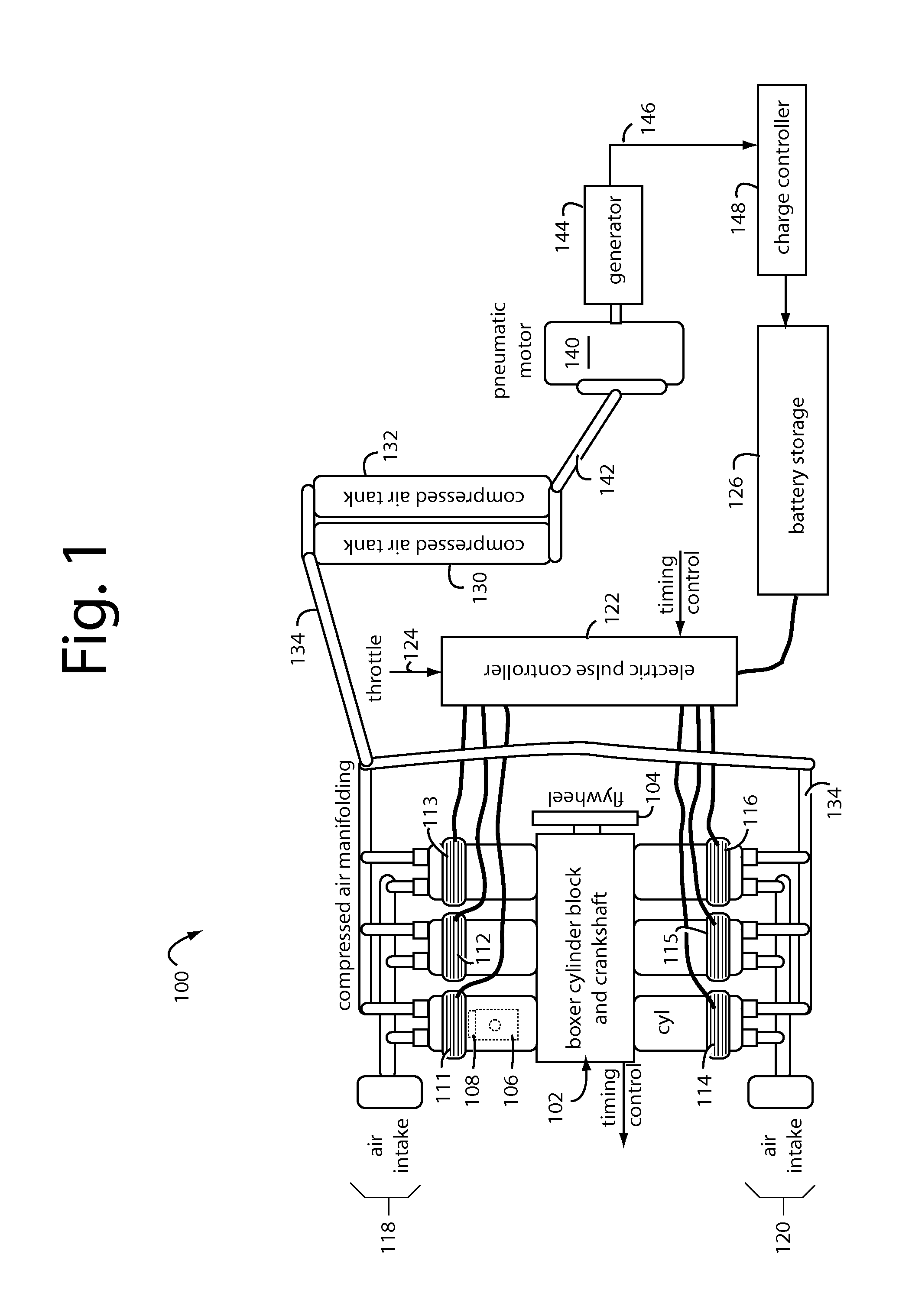
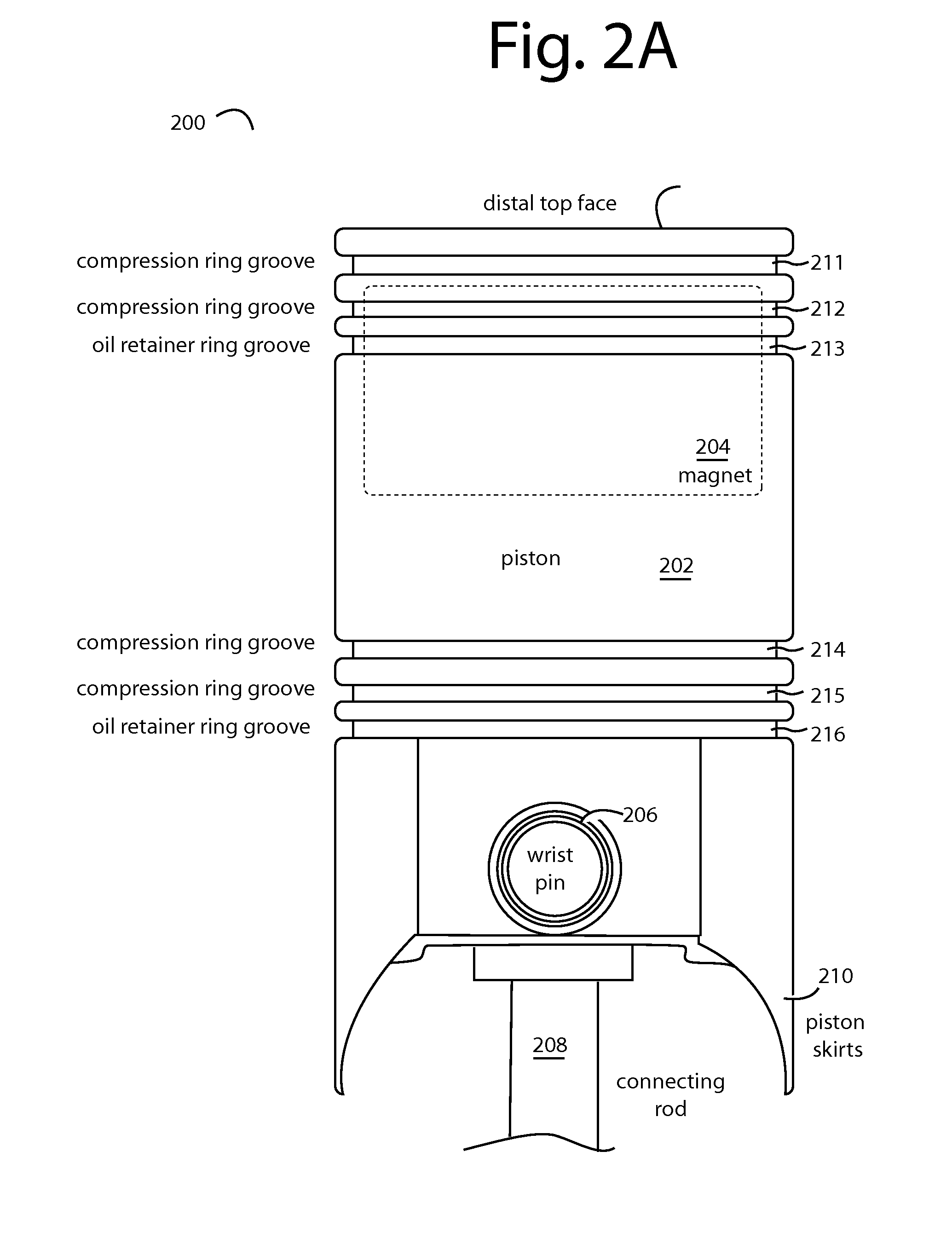
Zero emissions pneumatic-electric engine
InactiveUS20130302181A1Positive displacement pump componentsFlexible member pumpsOn boardEngineering
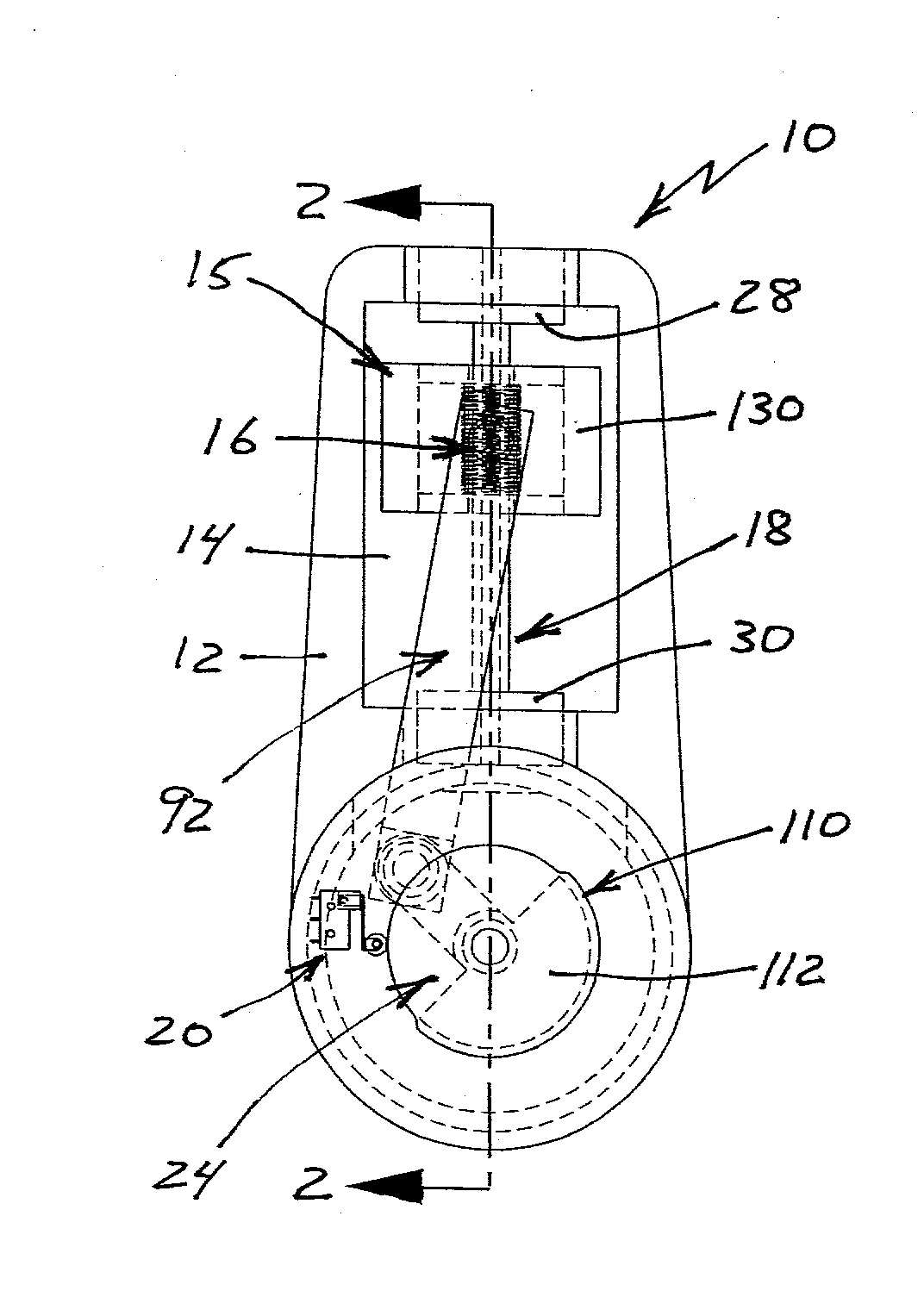
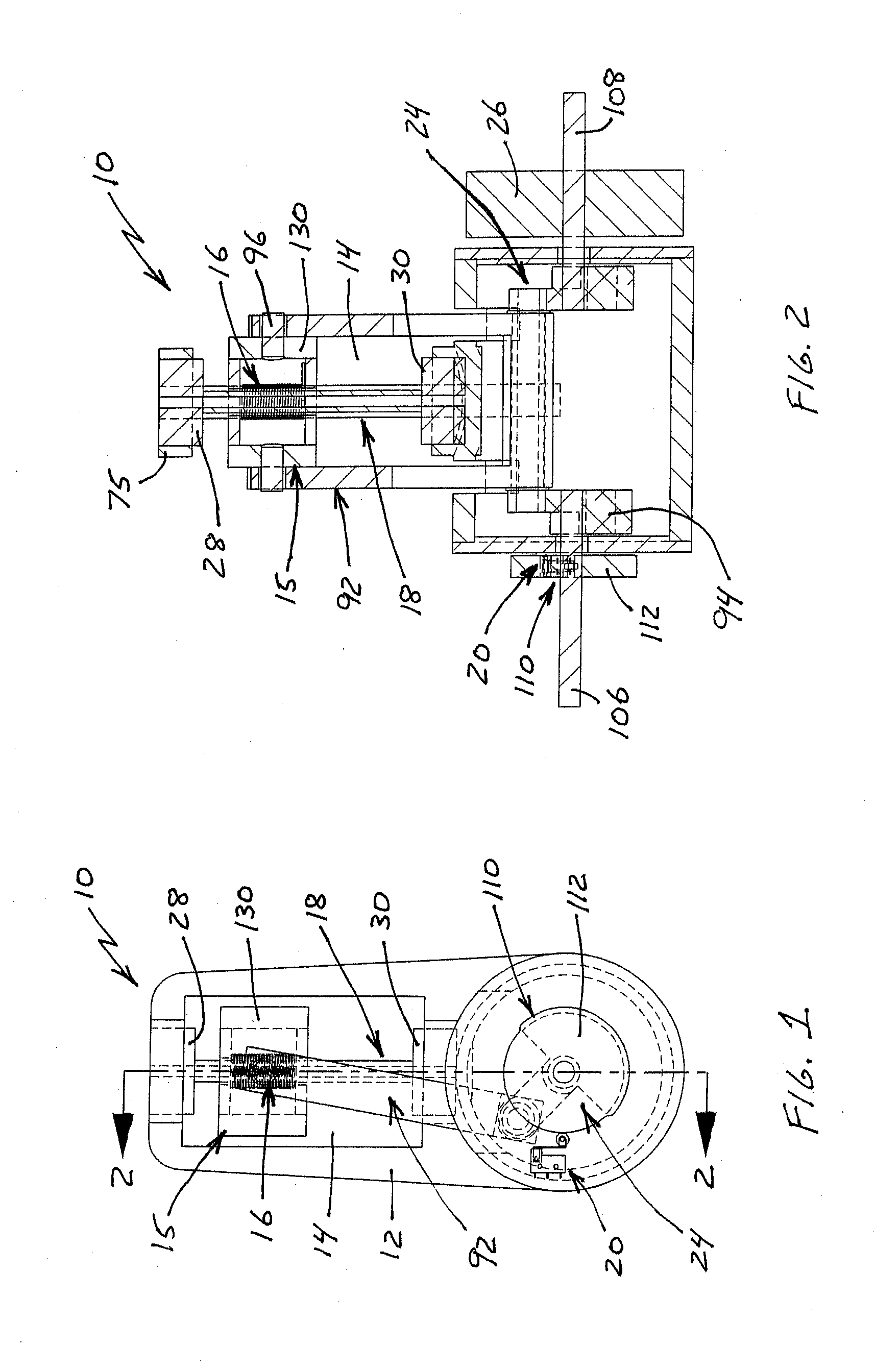
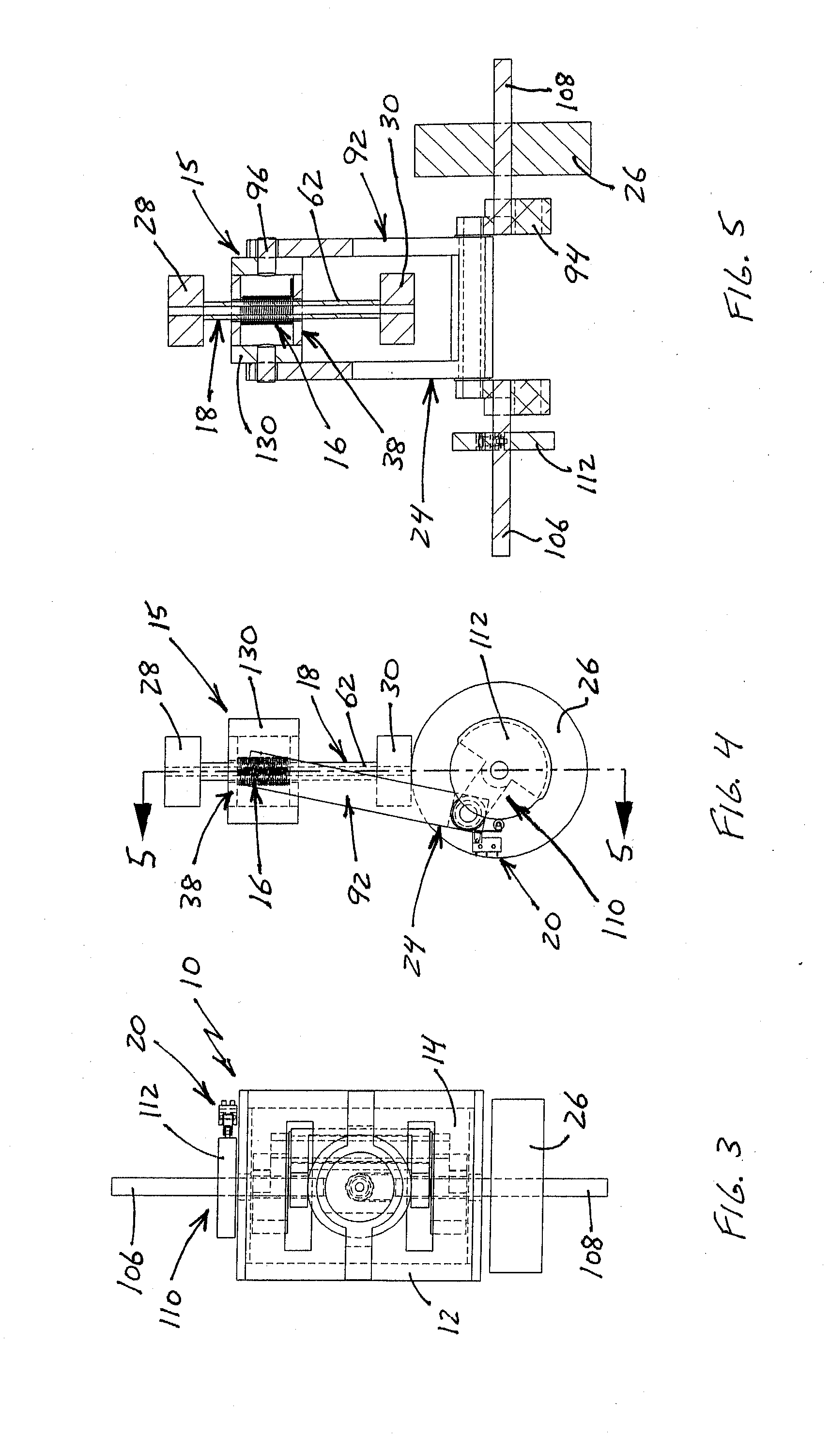
A reciprocating engine has several piston assemblies fitted with embedded magnets in positions that can be alternately repelled and attracted by electromagnetic coils within each of the piston cylinders. The magnetic piston assemblies are connected by rods to a crankshaft with a flywheel. The electromagnetic coils are vented to allow air intake and exhaust to flow through to the piston chambers. Valves and valve timing are controlled relative to the crankshaft rotation such that compressed air can be generated and stored in tanks. The compressed air is used to power air motors to turn electric generators for on-board battery charging. The reciprocating electric engine is configured to idle at a speed that overcomes friction.
Owner:CHARITY III HERMAN TYRONE
Outer stator for reciprocating motor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7323800B2Avoid deformationReduce motor sizePositive displacement pump componentsMagnetic circuit stationary partsBobbinEngineering
An outer stator of a reciprocating compressor comprises: a bobbin formed as a ring shape and provided with a winding coil therein; an outer stator frame coupled to an outer circumferential surface of the bobbin and formed of a magnetic body in which a flux flows; a plurality of first core blocks coupled to the outer stator frame and positioned radially at one side of the bobbin; and a plurality of second core blocks coupled to the outer stator frame, facing the first core blocks, and positioned at the other side of the bobbin. Accordingly, deformation which may occur during manufacturing can be prevented, and a size of a motor can be minimized.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Magnetically Actuated Reciprocating Motor and Process Using Reverse Magnetic Switching
InactiveUS20140111035A1Easy to operateReduce manufacturing costMechanical energy handlingStored energyEngineering
A magnetically actuated reciprocating motor utilizes the stored energy of rare earth magnets and an electromagnetic field provided by a solenoid to reciprocally drive a solenoid assembly. A converting mechanism, such as a connecting rod and crankshaft, converts the reciprocating motion of the solenoid assembly to power a work object. The solenoid assembly comprises a solenoid having a nonferromagnetic spool with a tubular center section and a coil of wire wrapped around the center section. The center section of the spool reciprocates over a fixed magnetic actuator having a permanent magnet at each end of an elongated tubular shaft. The two permanent magnets have extension members disposed in the shaft with inward ends that are in spaced apart relation to form a gap therebetween. A switching mechanism switches magnetic polarity at the ends of the solenoid so the solenoid assembly is alternatively repelled and attracted by the permanent magnets.
Owner:GOSVENER KENDALL C
Transport system for test sample carrier
A transport system is provided for a sample testing machine. The transport system includes a carrier holding a set of test sample devices and a drive subsystem for moving the carrier through the sample testing machine. The drive subsystem includes a reciprocating motor-driven block engaging the carrier and moving the carrier back and forth in a predetermined longitudinal path extending along a longitudinal axis from an entrance station to a plurality of processing stations in the sample testing machine. The processing stations are accessed as the carrier is moved along the path. The carrier includes features in the form of slots or voids that are detected by strategically placed optical interrupt sensors. As the carrier moves, the slots are detected by the sensors to thereby continuously track the position of the carrier and the test devices as they are moved through the instrument.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX INC
Reciprocating compressor
InactiveCN1427151AReduce manufacturing costSimplify the installation processPositive displacement pump componentsPiston pumpsManufacturing cost reductionEngineering
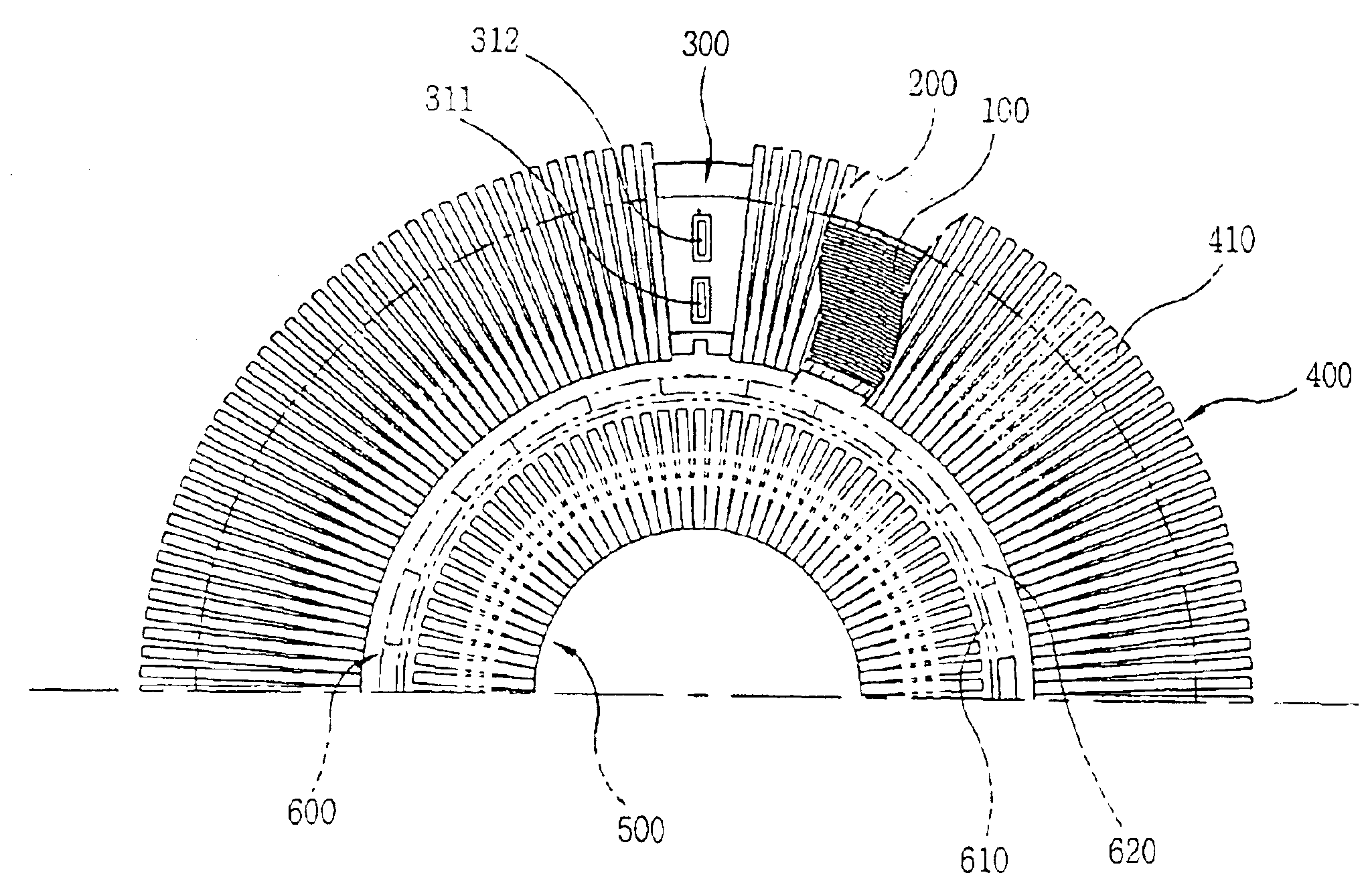
In a reciprocating compressor including a first frame for supporting a cylinder of a compressing unit, a second frame for supporting a side of an outer stator of a motor unit and a third frame for supporting the other side of the outer stator and an inner stator of the motor unit, wherein the motor unit is arranged between the second and third frames, they are combined with each other, and the assembly is combined with the first frame. Accordingly, a reciprocating compressor is capable of reducing a fabrication cost by eliminating precise processing of construction parts and simplifying an assembly process by constructing a reciprocating motor as one assembly and combining it with a compressing unit.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
Stator for reciprocating motor
InactiveUS6741008B2Improve propertiesMagnetic circuit stationary partsPropulsion systemsProduction rateBobbin
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
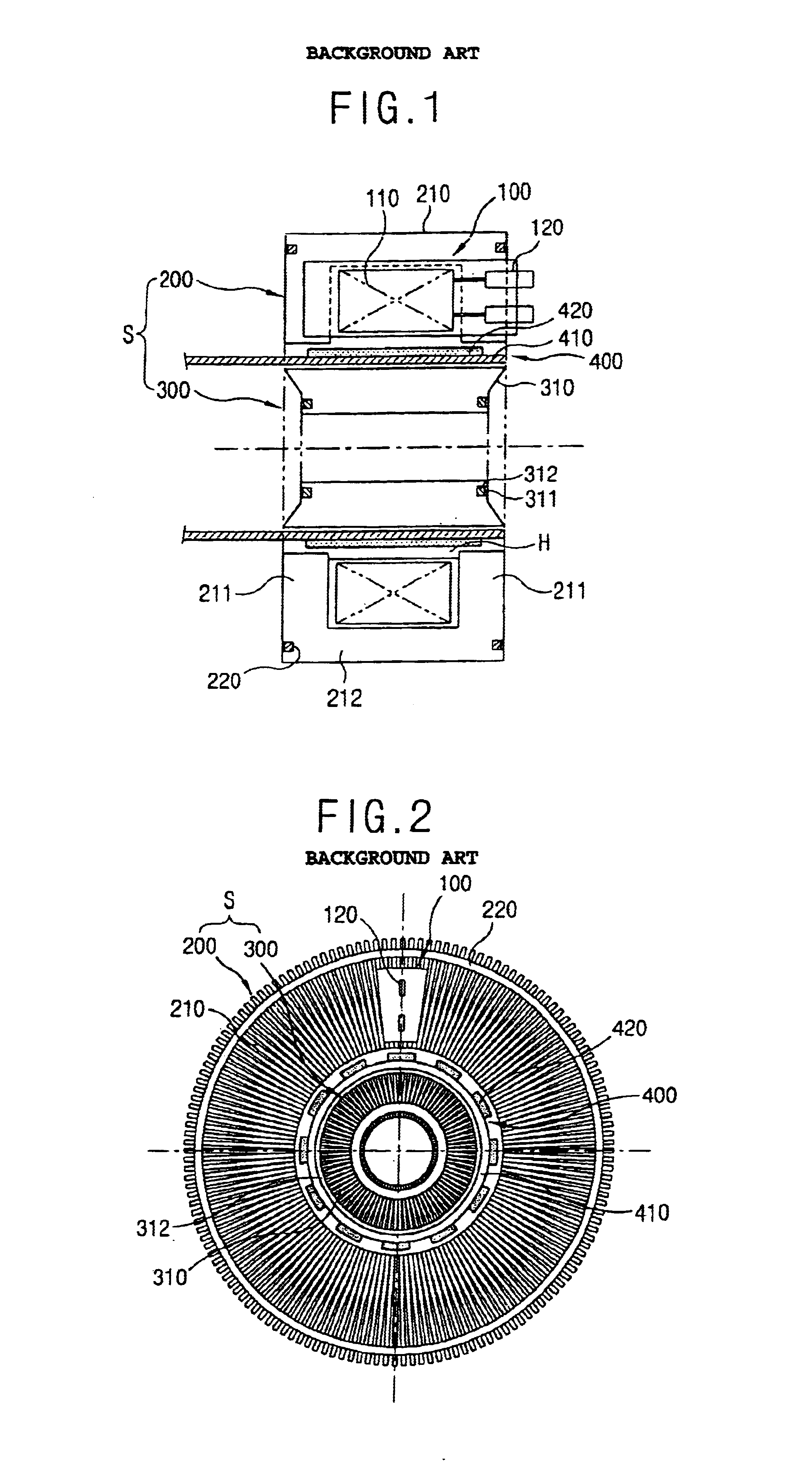
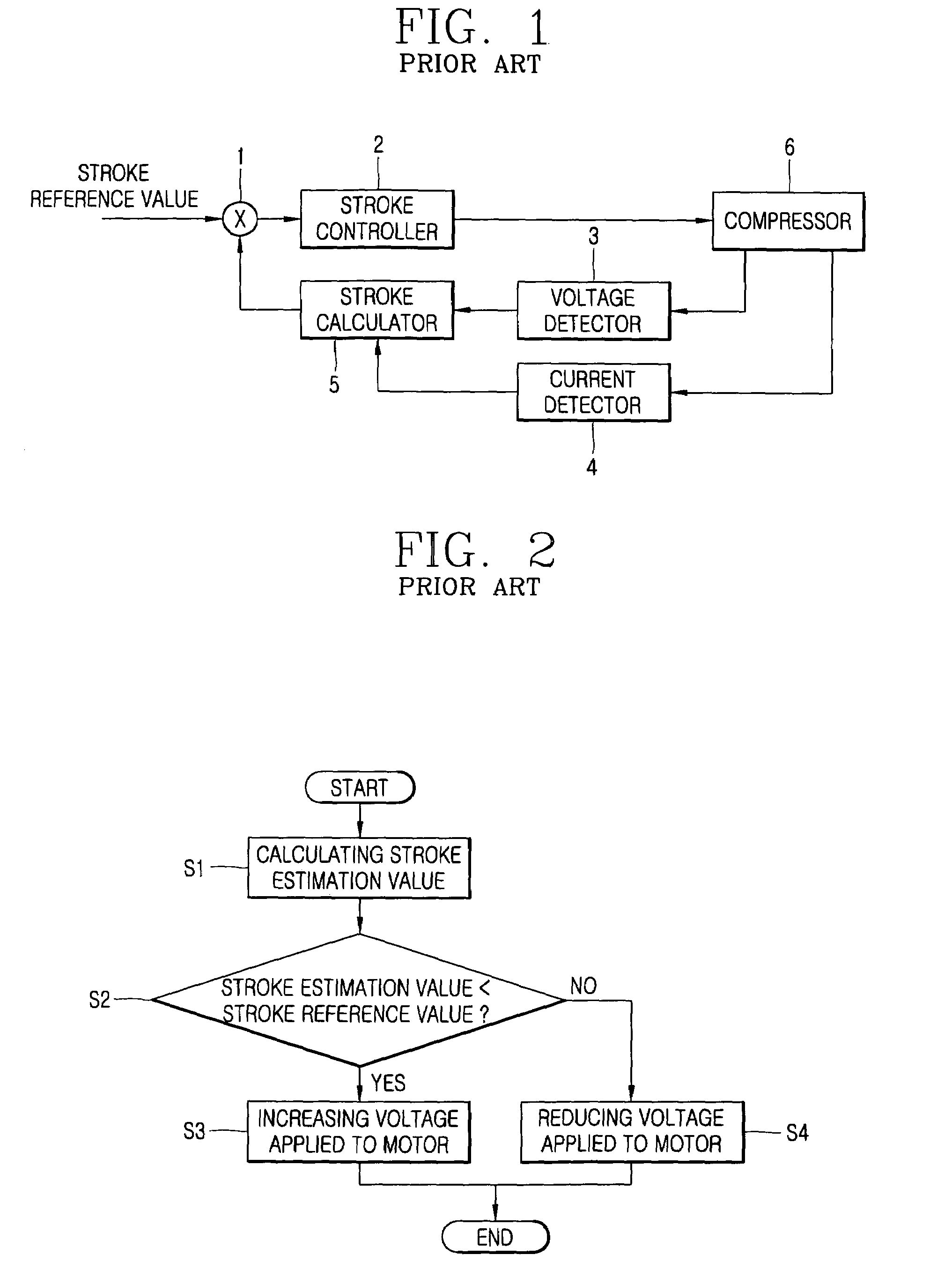
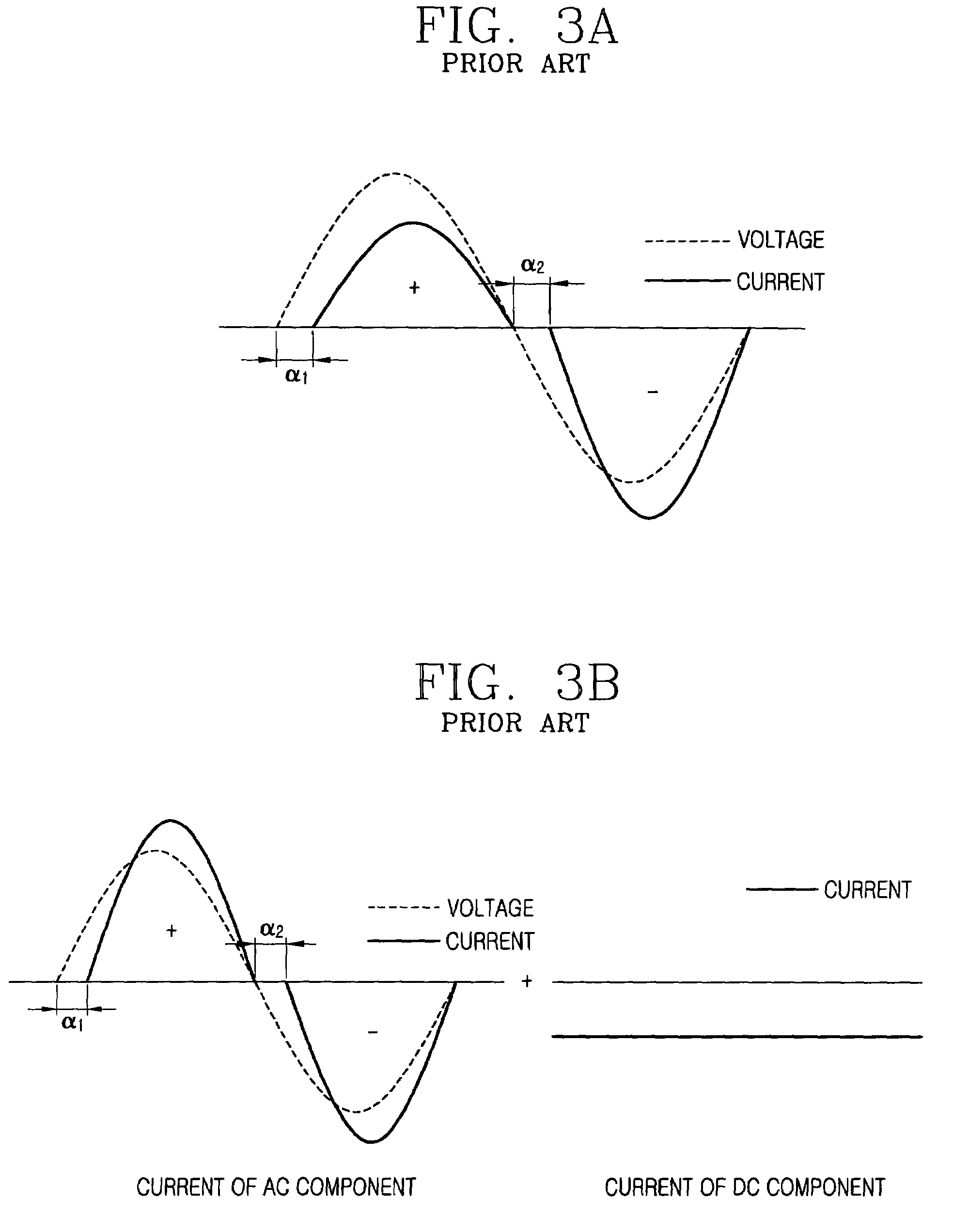
Apparatus and method for controlling operation of reciprocating motor compressor
InactiveUS7402977B2Reduce lossesElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlIntegratorNegative phase
An apparatus for controlling an operation of a reciprocating motor compressor includes a current integrator for integrating an alternating current applied to a motor of the compressor during each one cycle thereof; and a controller for differently controlling a firing angle of a triac during the positive phase and the firing angle of the triac during the negative phase of the AC voltage applied to the motor based on the integrated value of the current. A loss in the motor can be reduced by avoiding presence of a DC component in the current applied to the motor of the compressor.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Stator for reciprocating motor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7157814B2Simplify the assembly processShorten assembly timeReciprocating/oscillating/vibrating magnetic circuit partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsEngineeringReciprocating electric motor
Disclosed are a stator for a reciprocating motor and a manufacturing method thereof which are able to simplify assembling processes, to reduce assembling time, and thereby to improve productivity by laminating an inner stator to be a straight line shape and bending to be a cylindrical shape. The stator is fabricated by laminating lamination sheets as a straight line and bending it to be a cylindrical shape, and a mounting band is fixed on inner circumferential surface of the lamination sheets so as to maintain the lamination sheets connected when the lamination sheets are bent to be the cylindrical shape.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Magnetically Actuated Reciprocating Motor and Process Using Reverse Magnetic Switching
InactiveUS20120007447A1Easy to operateReduce manufacturing costMechanical energy handlingPropulsion systemsStored energyActuator
A magnetically actuated reciprocating motor utilizes the stored energy of magnets, particularly rare earth magnets, and an electromagnetic field to reciprocally drive a magnetic actuator. A converting mechanism, such as a connecting rod and crankshaft, converts the reciprocating motion of the magnetic actuator to rotary motion for powering a work object. A solenoid, comprising a nonferromagnetic spool having a tubular center section with a coil of wire wrapped around the center section, is connected to a source of power and a switching mechanism. The switching mechanism switches the magnetic polarity at the ends of the solenoid to alternatively repel and attract permanent magnets at the ends of the magnetic actuator. A shaft interconnecting the magnets is received through the center section of the solenoid. A controlling mechanism interconnecting an output shaft and the switching mechanism provides the timing to switch the polarity of the solenoid to drive the magnetic actuator.
Owner:GOSVENER KENDALL C
Method of assembling a pump motor with bearing preload
Owner:HARGRAVES TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com