Patents
Literature
159results about "Acyclic motors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
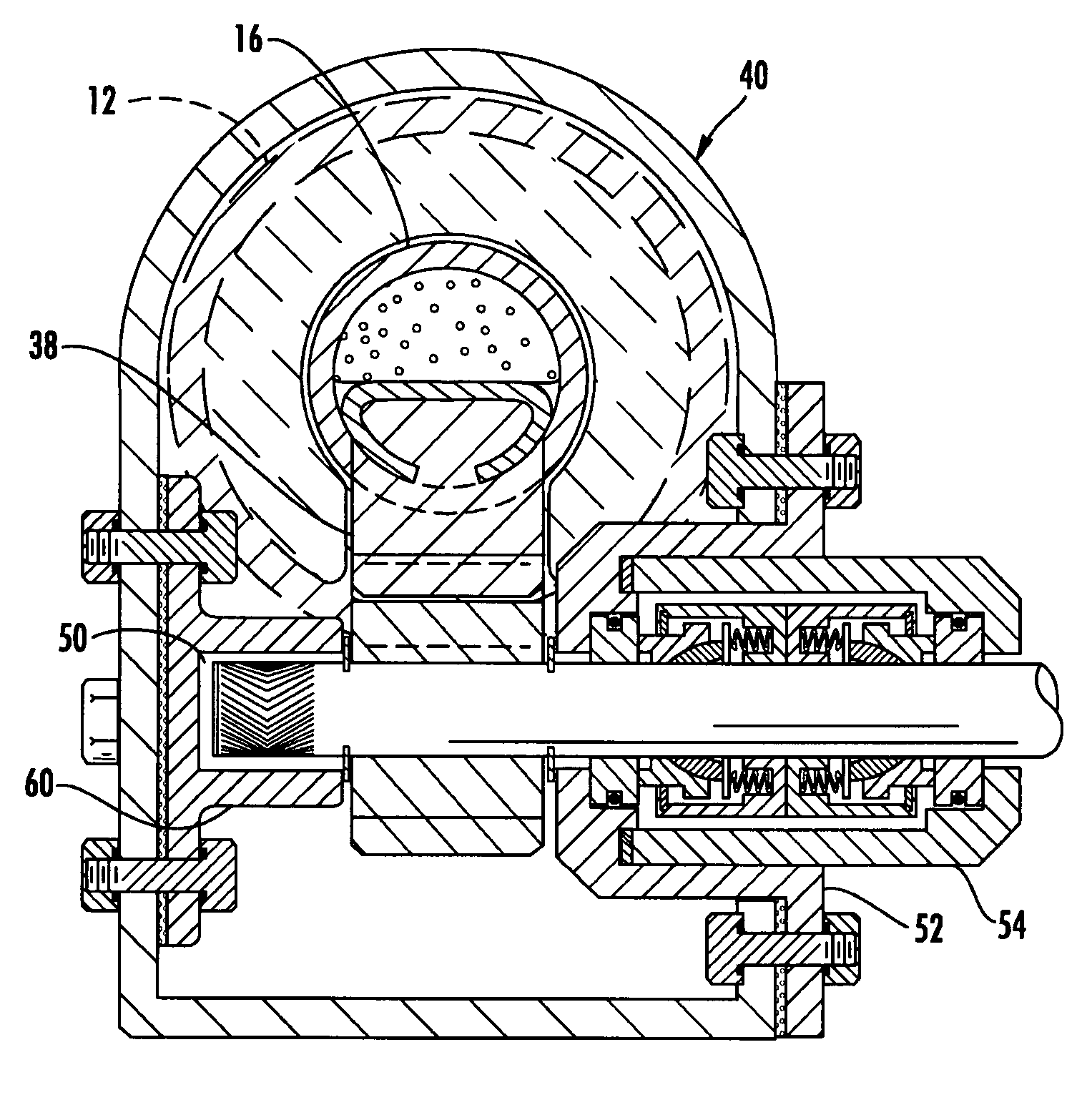
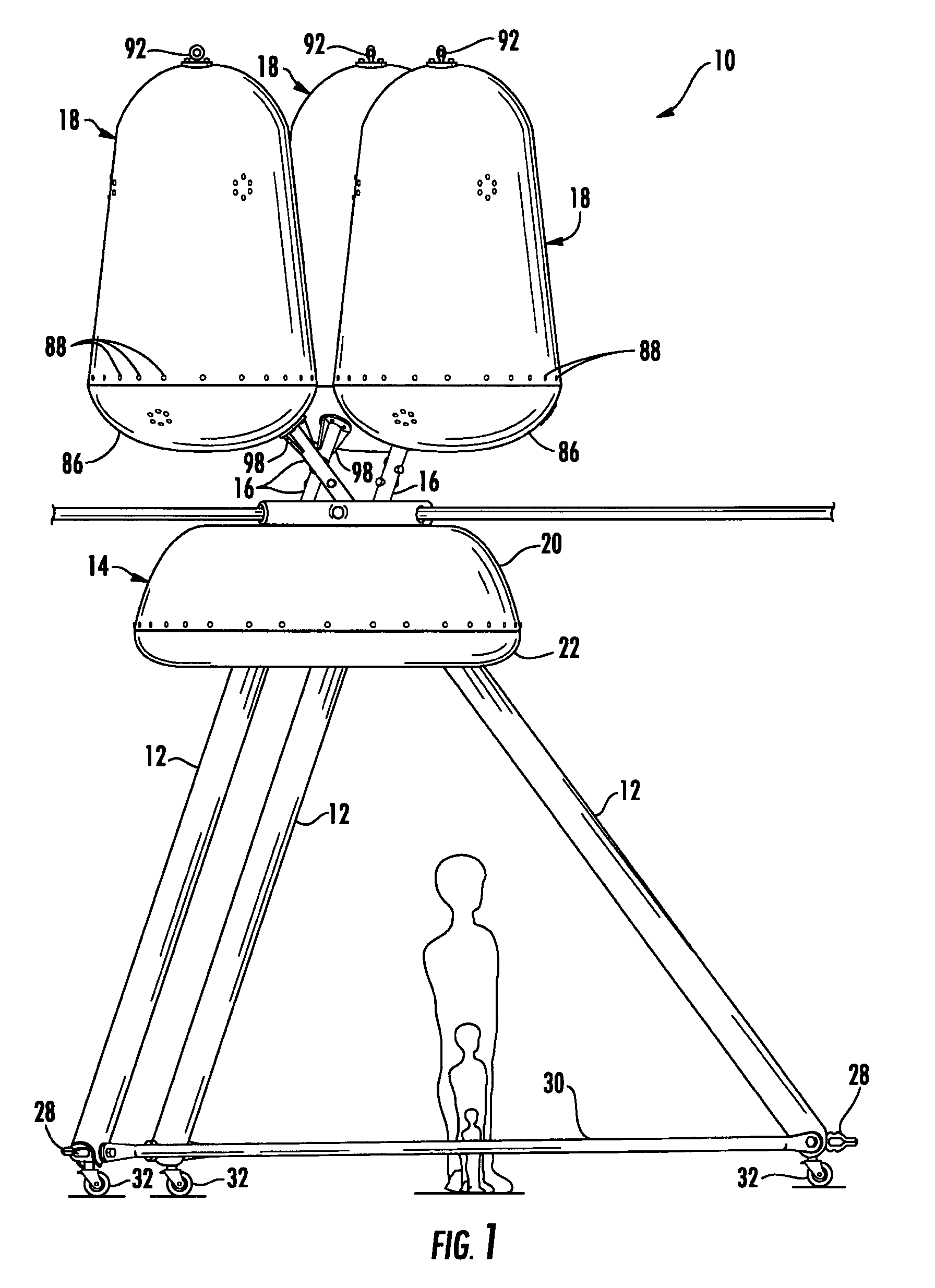
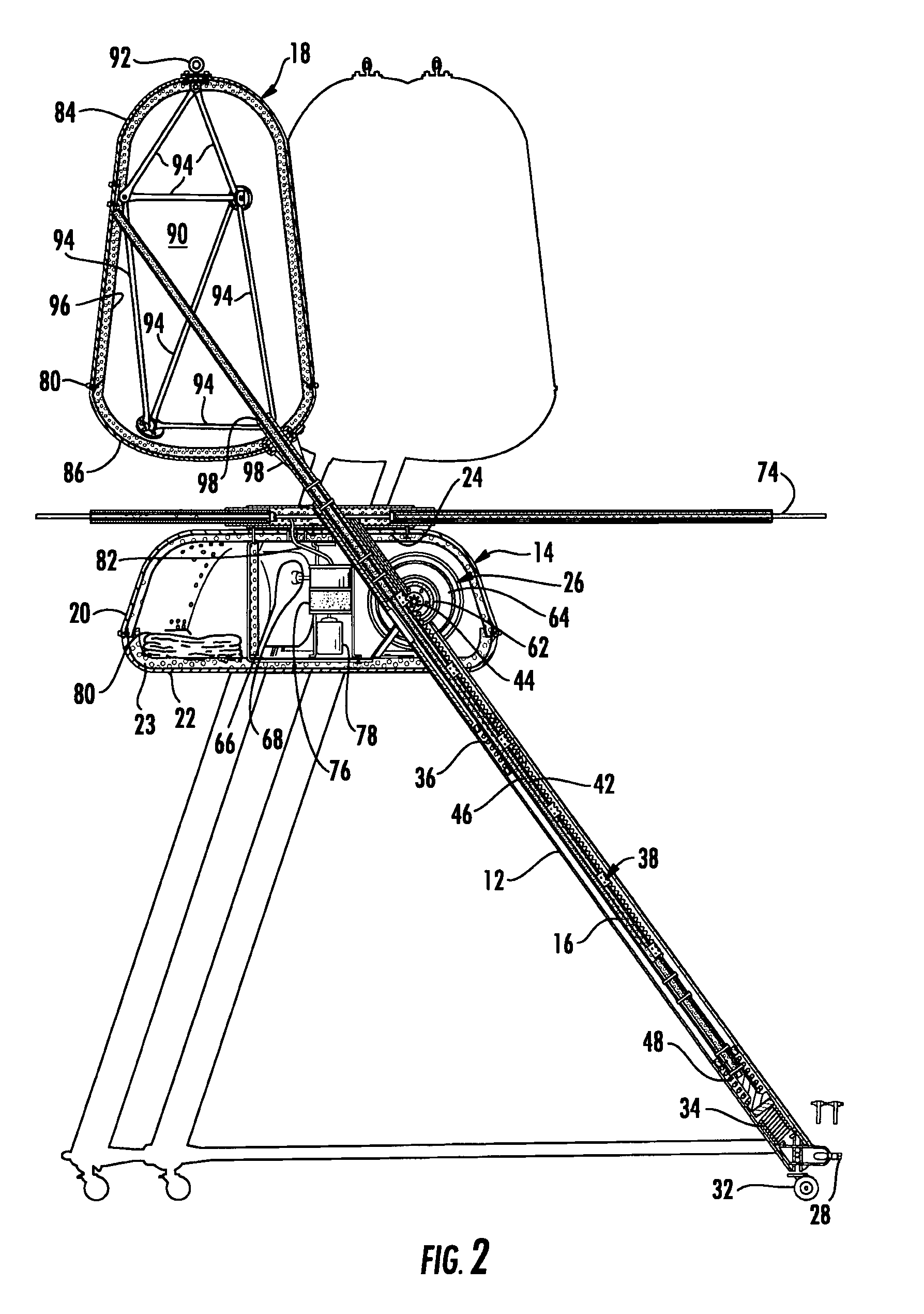
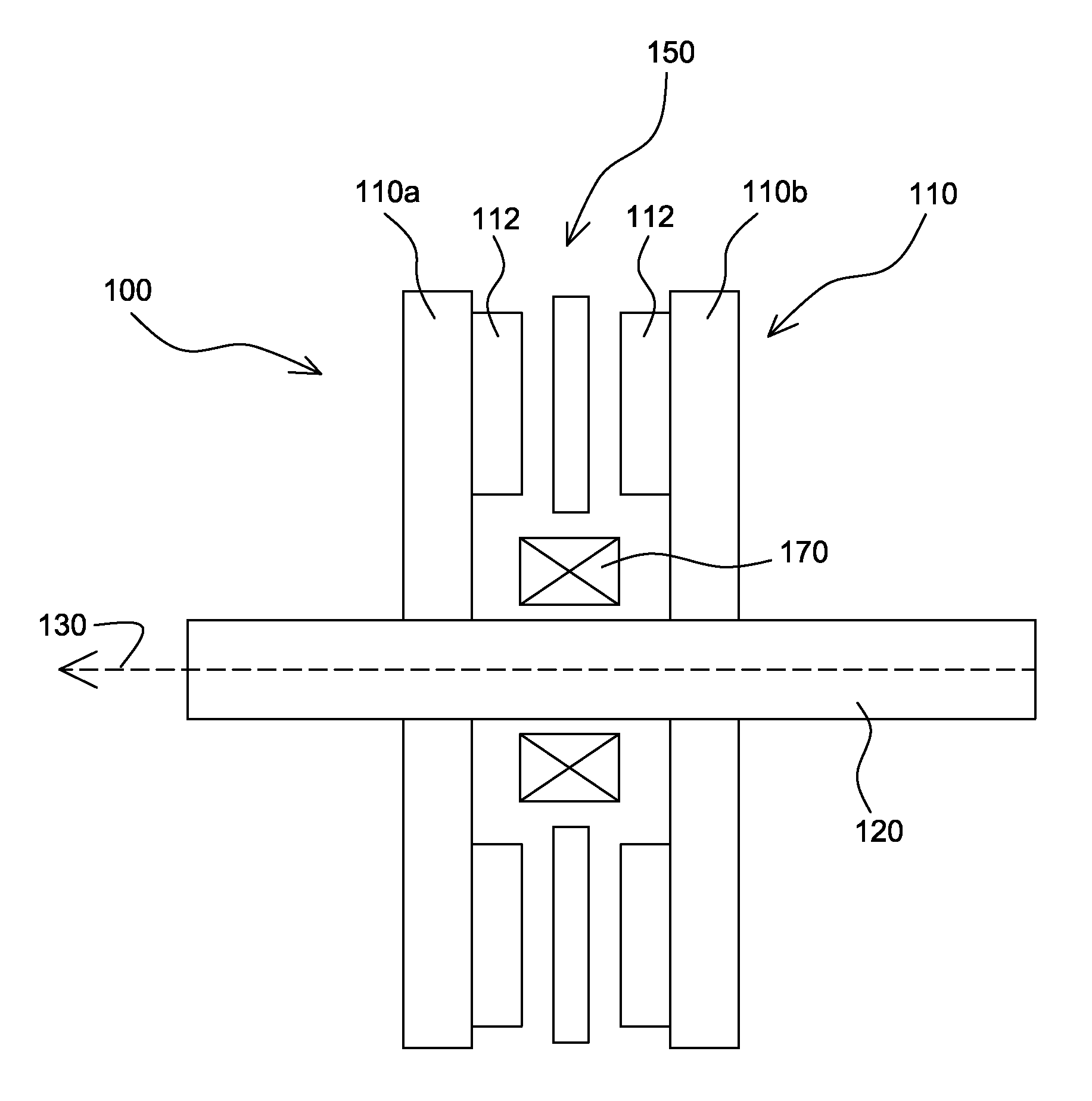
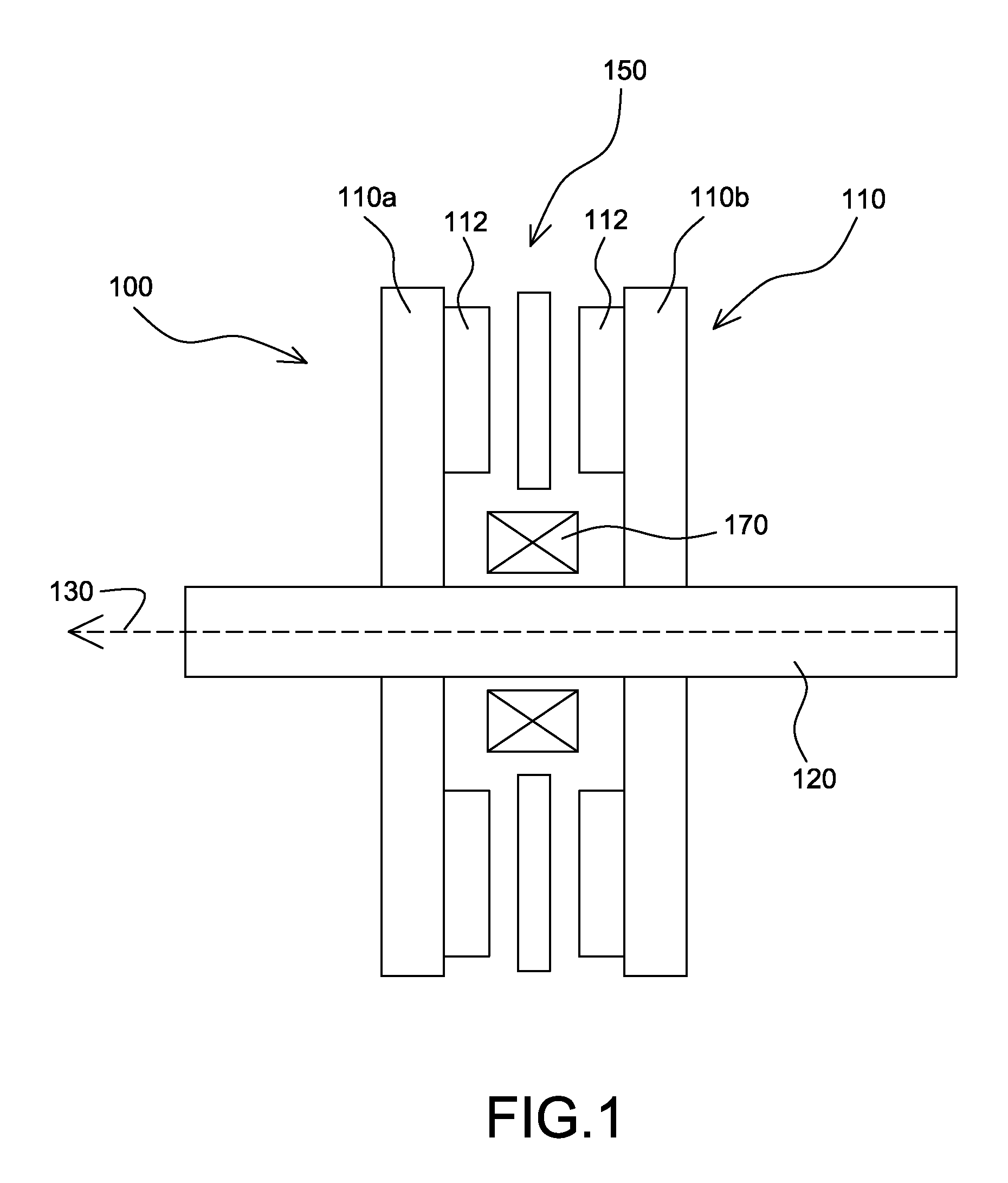
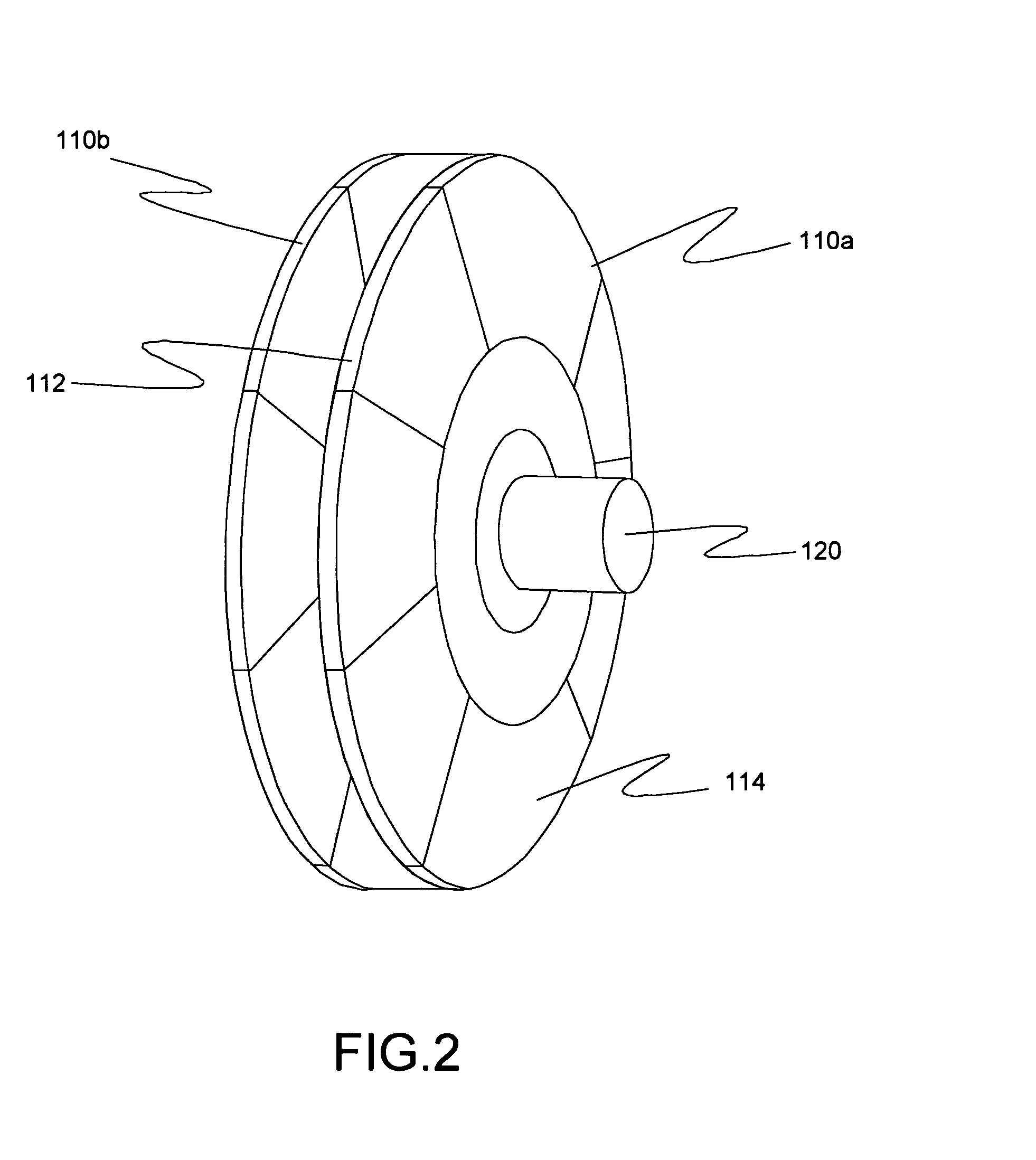
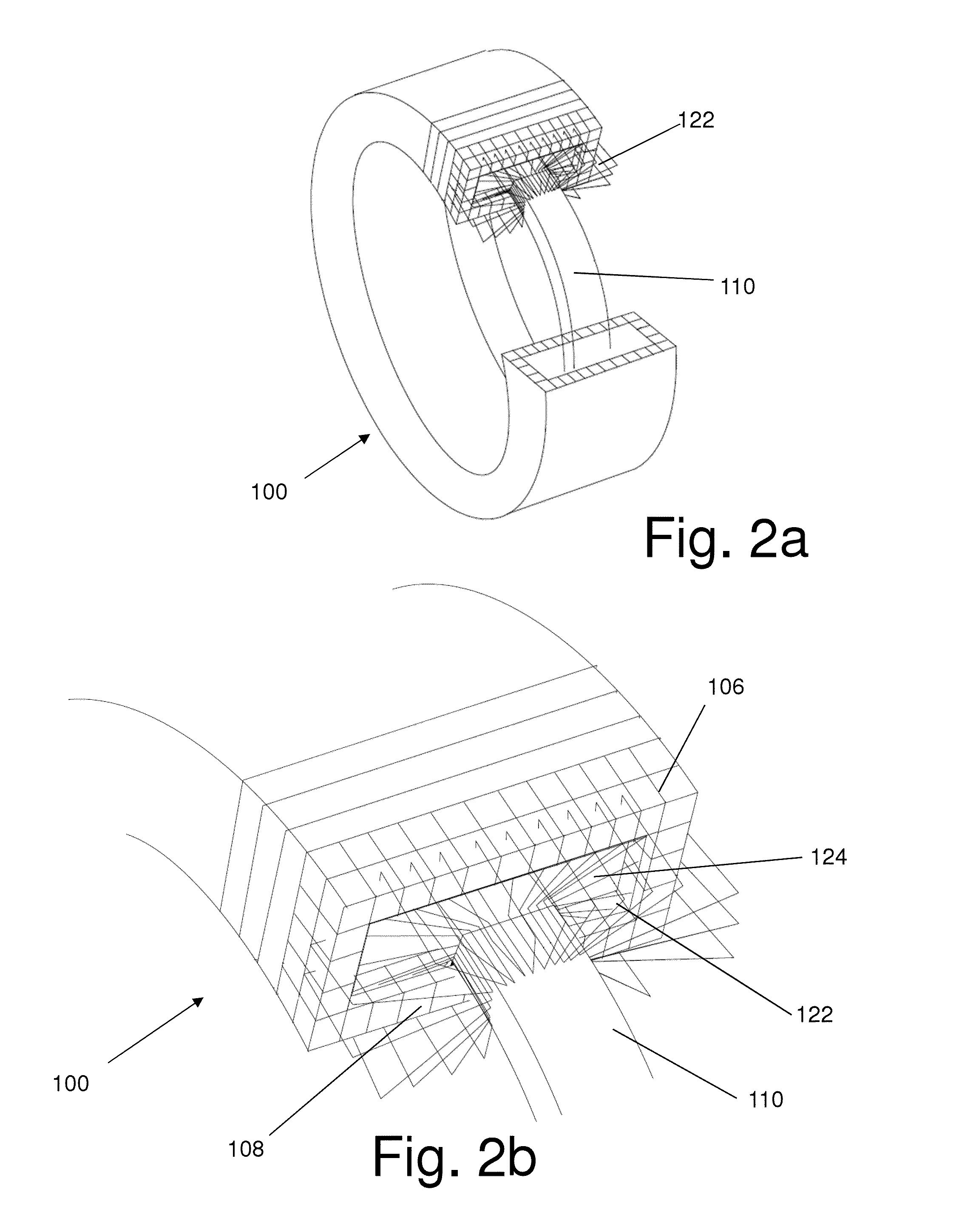
Ocean wave energy converter having an improved generator and ballast control
ActiveUS7352073B2Maximizes upstroke power generationMaximize productionMachines/enginesEngine componentsElectricityGear drive
Owner:AMES P FOERD
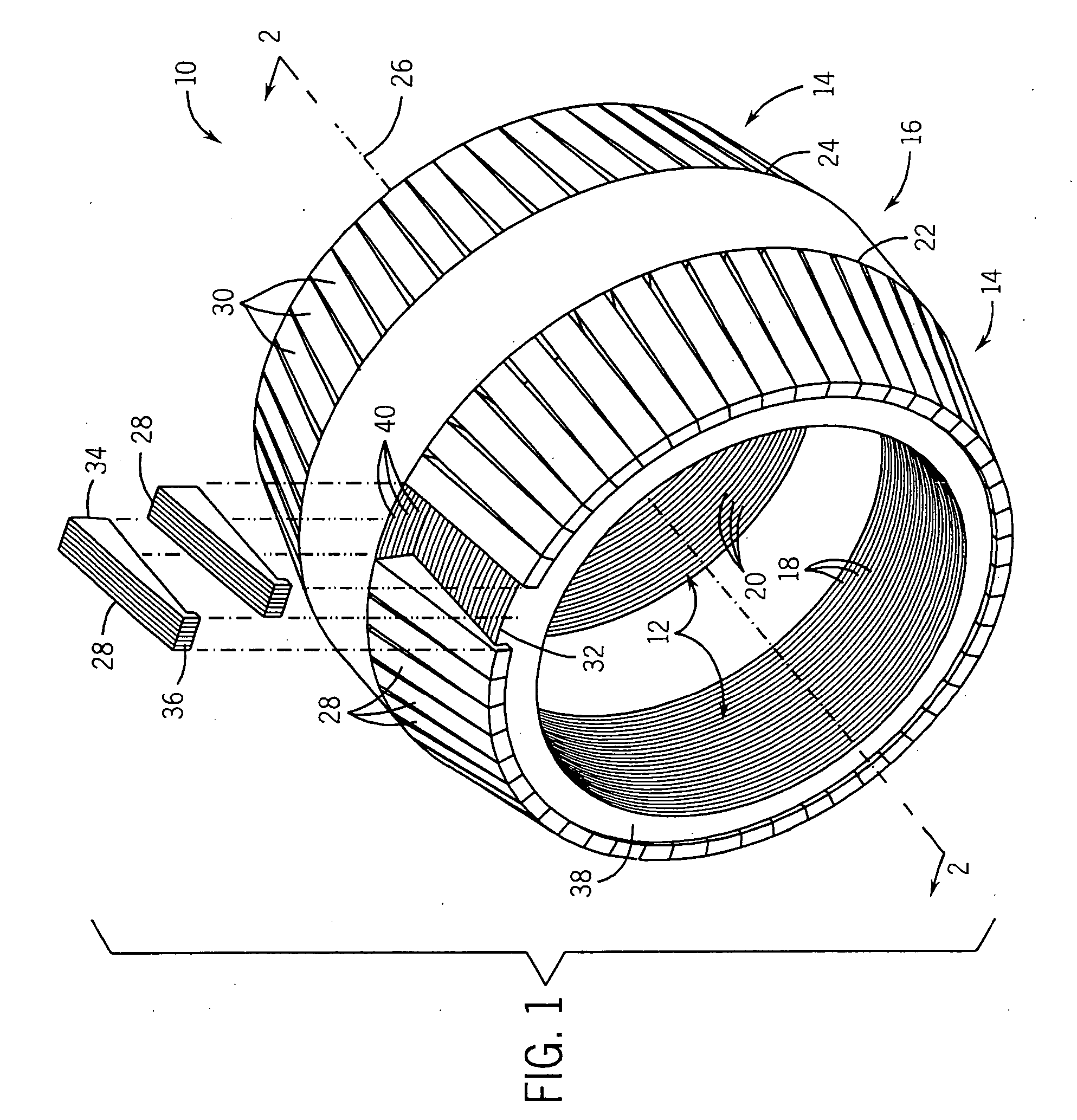
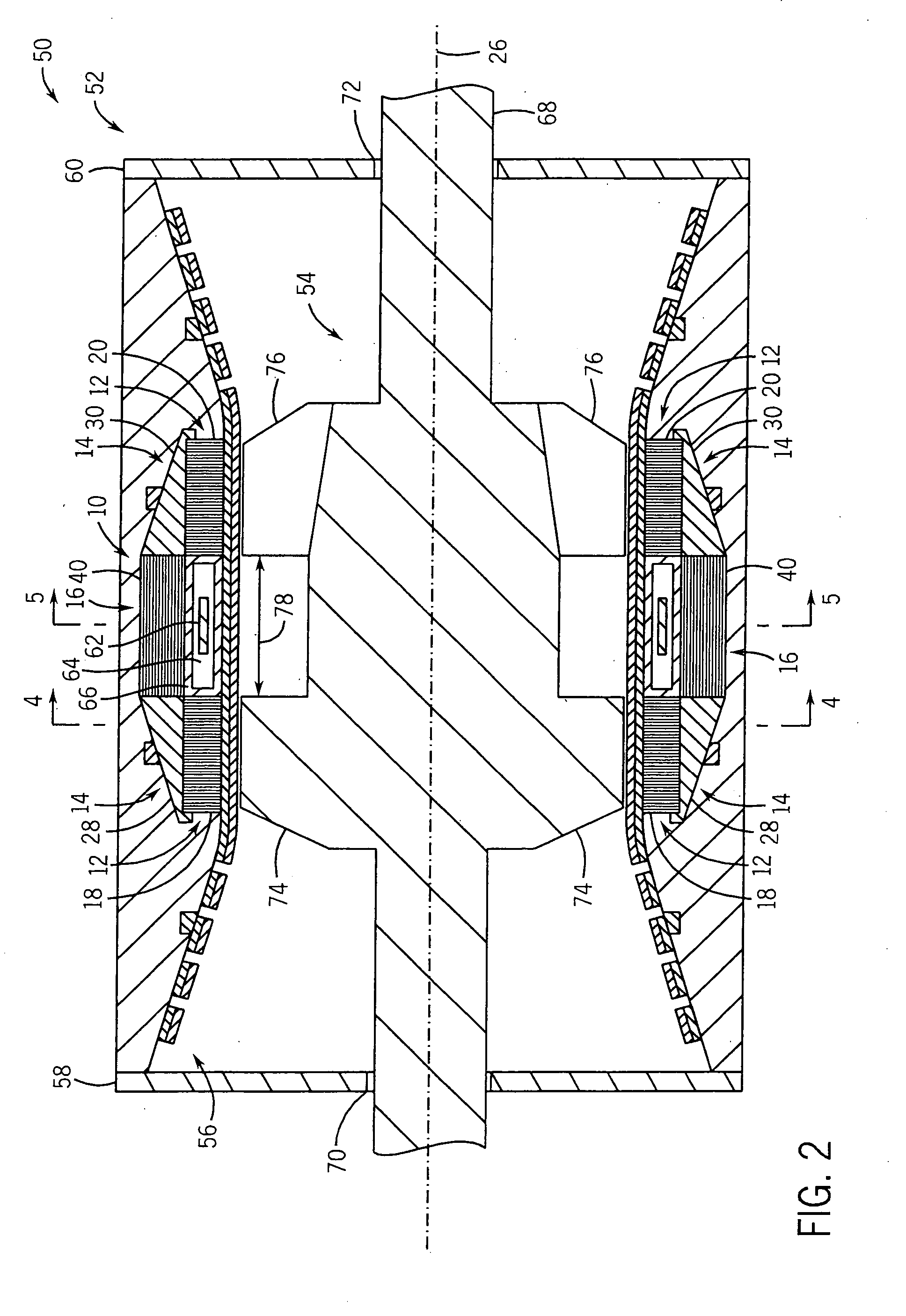
Homopolar machine with shaft axial thrust compensation for reduced thrust bearing wear and noise
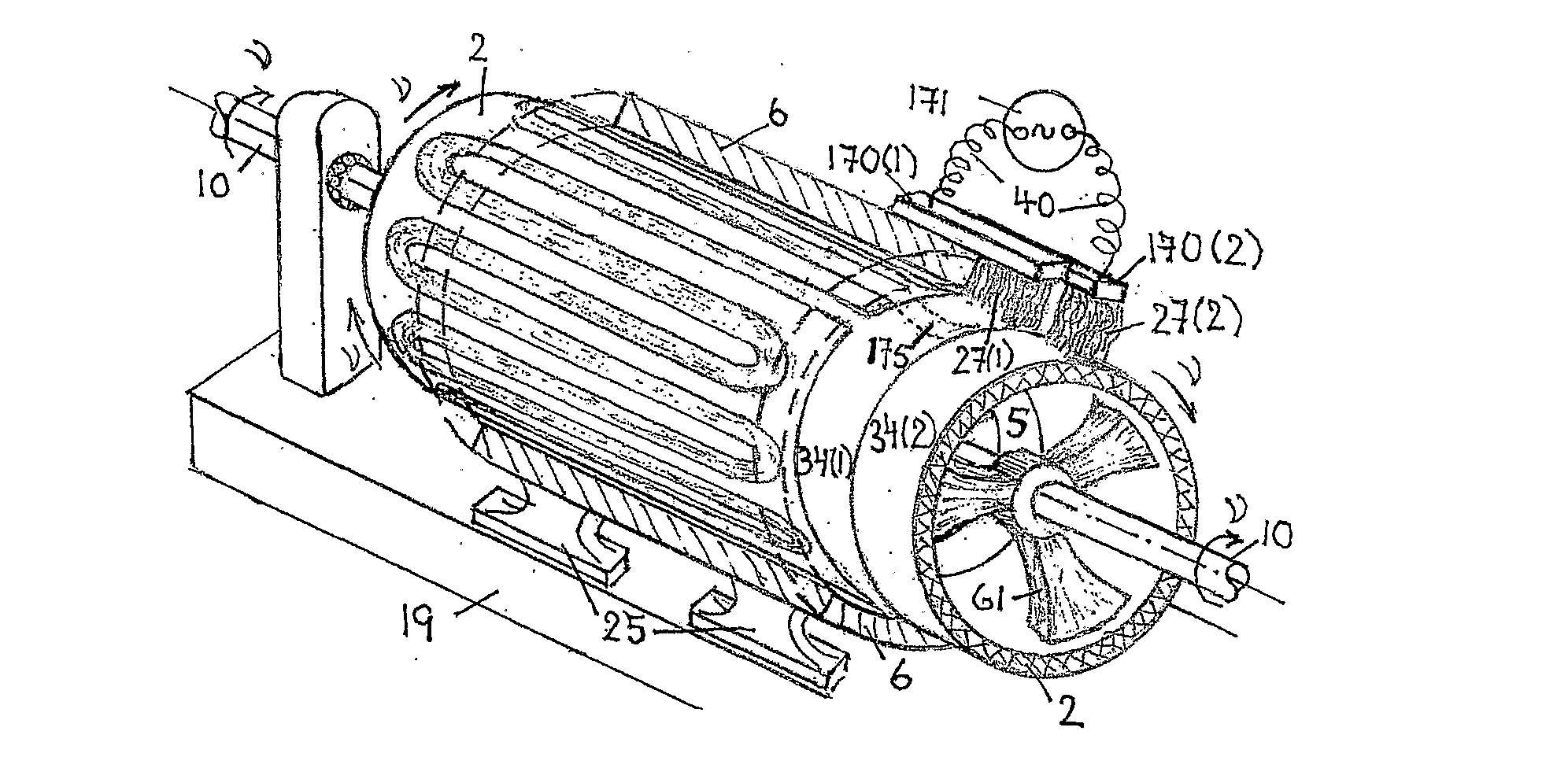
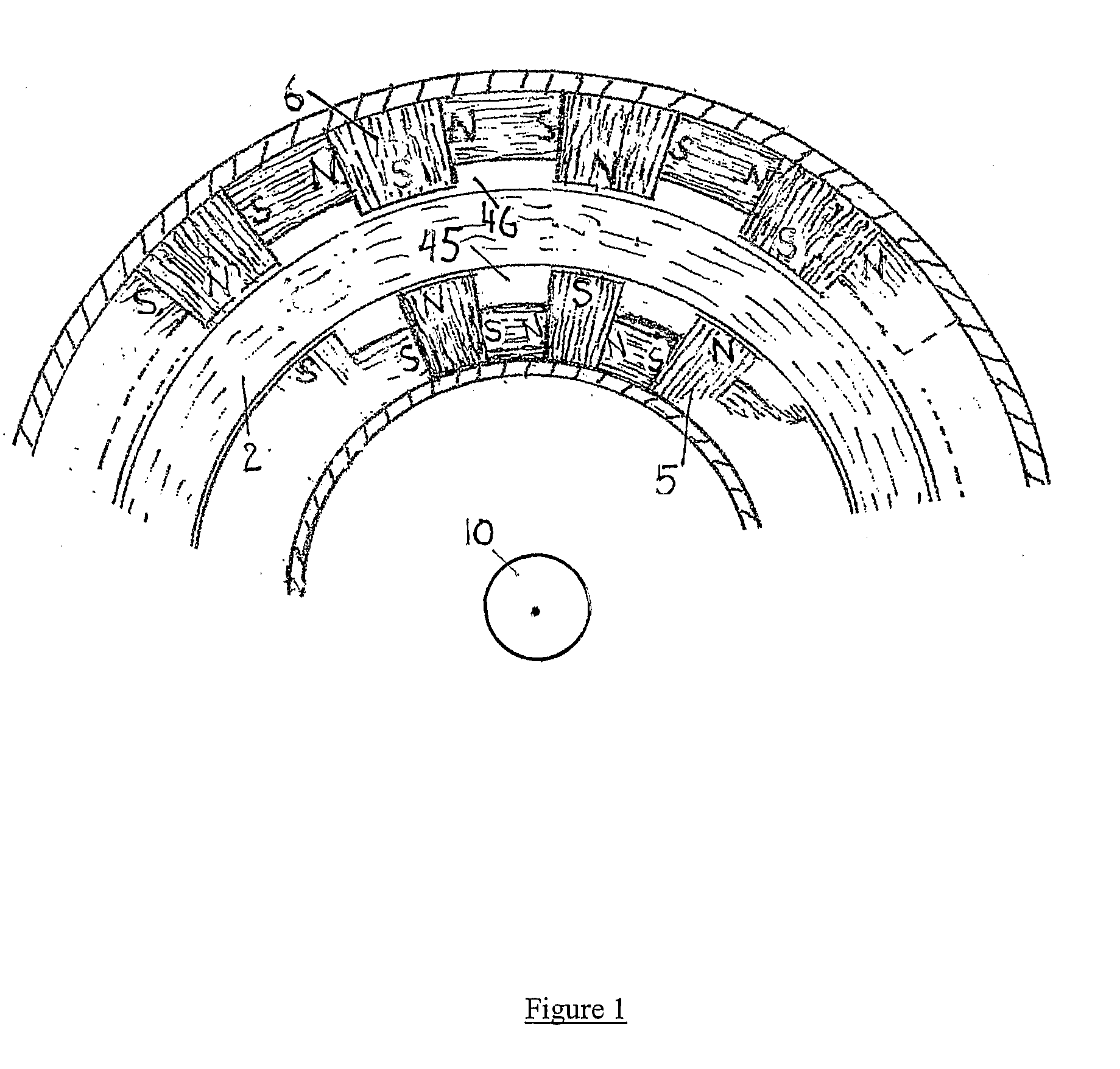
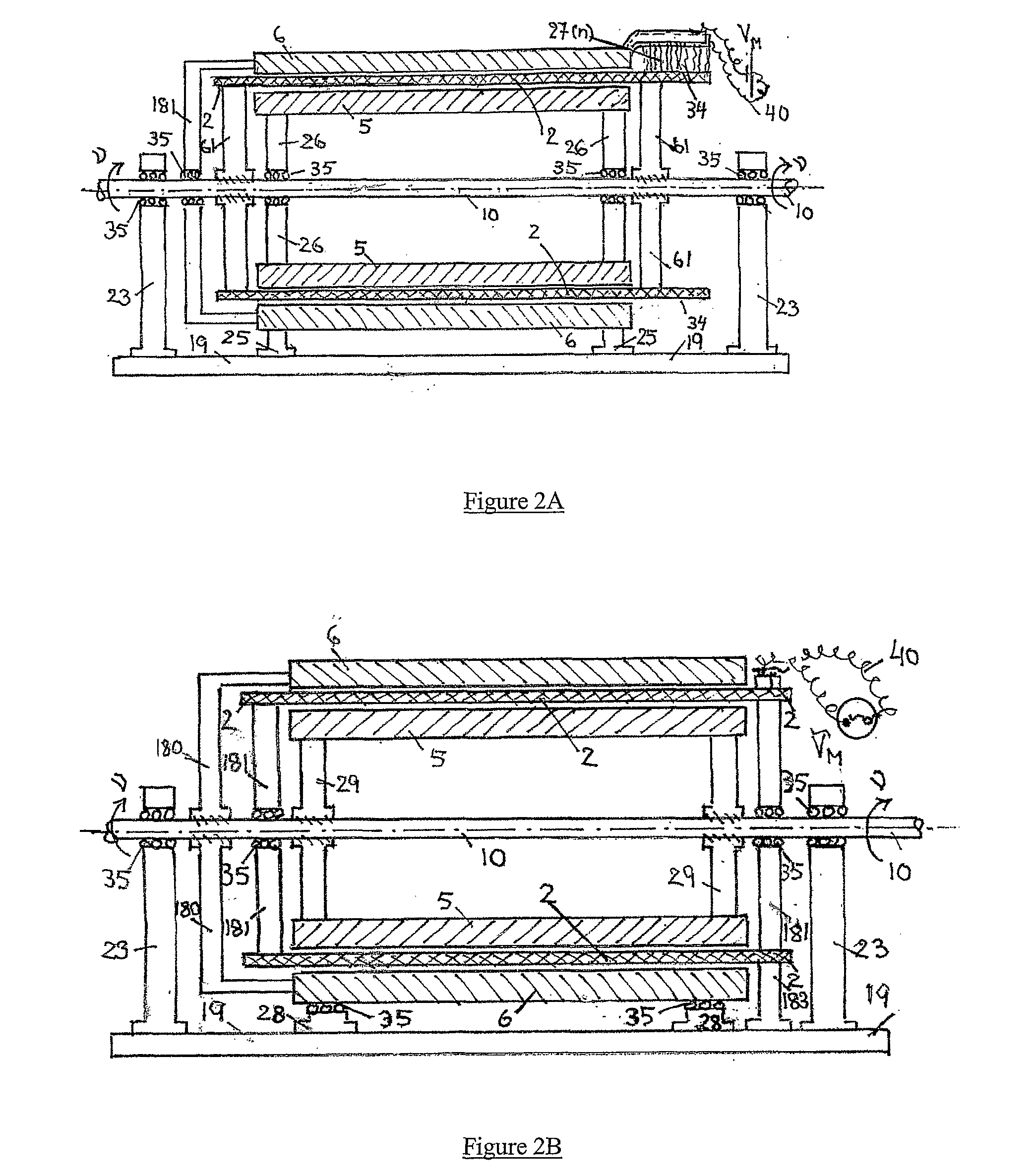
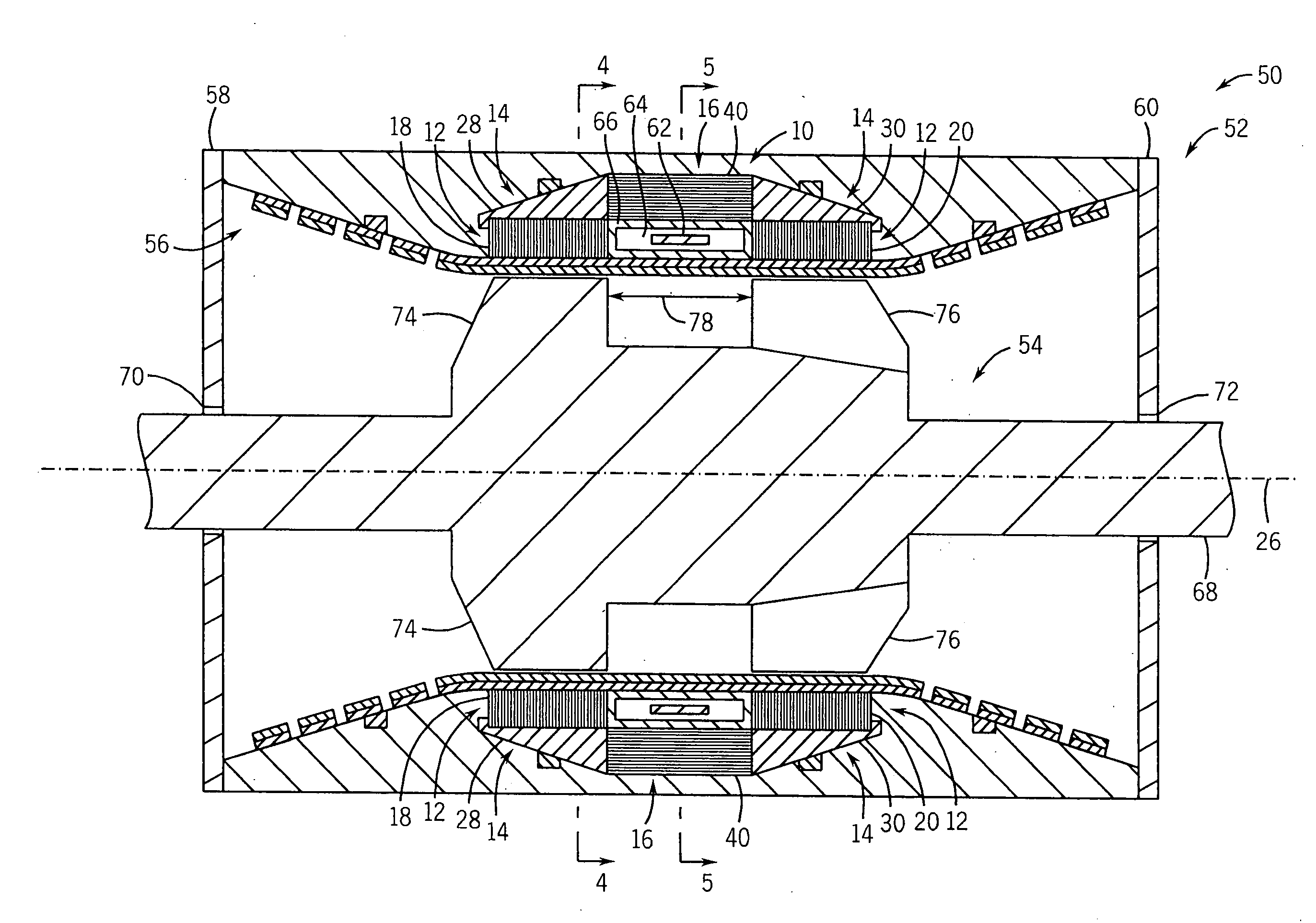
InactiveUS6856062B2Reduce induced magnetic forceConstant contact pressureRotary current collectorMagnetic bodiesFiberContact pressure
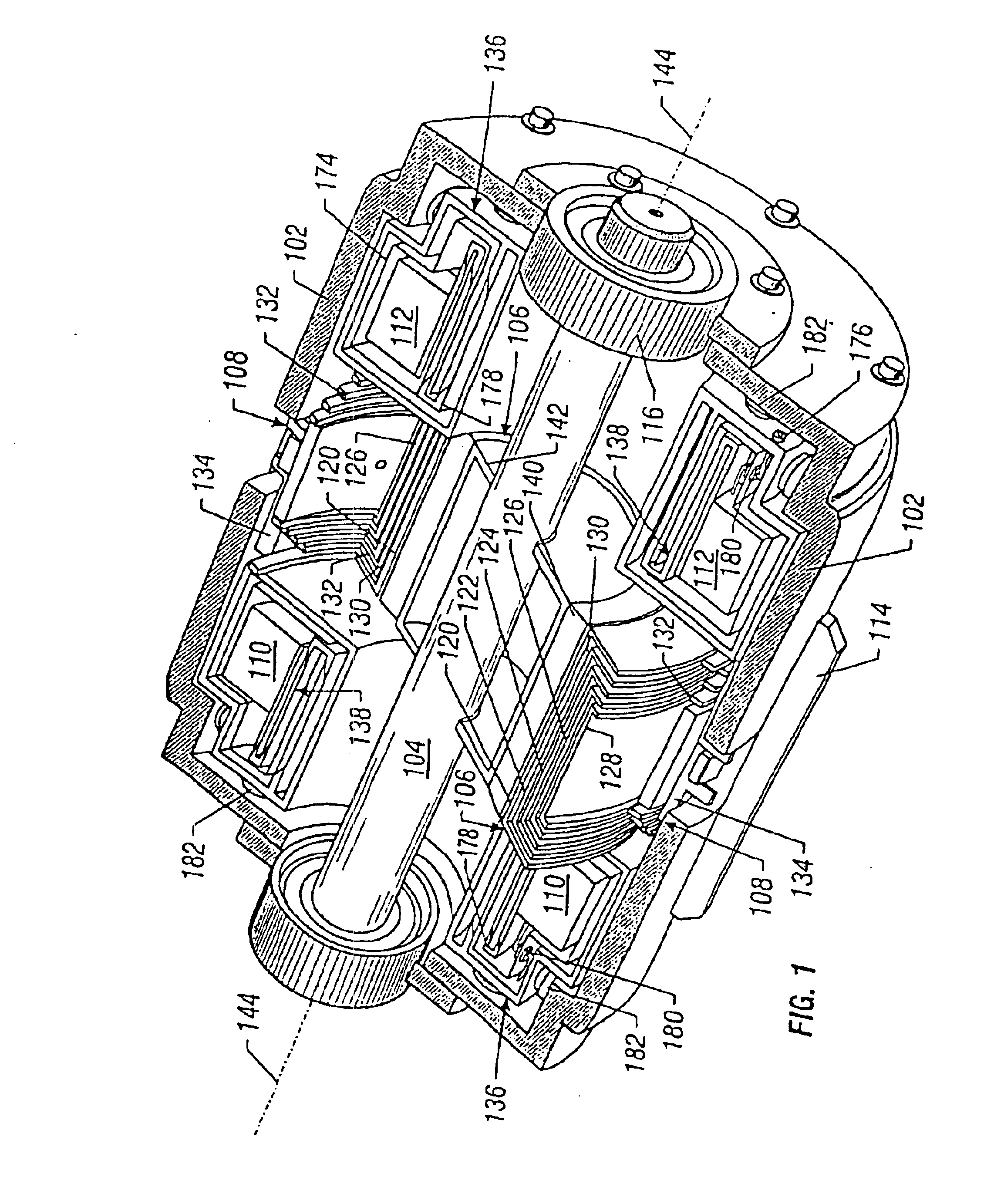
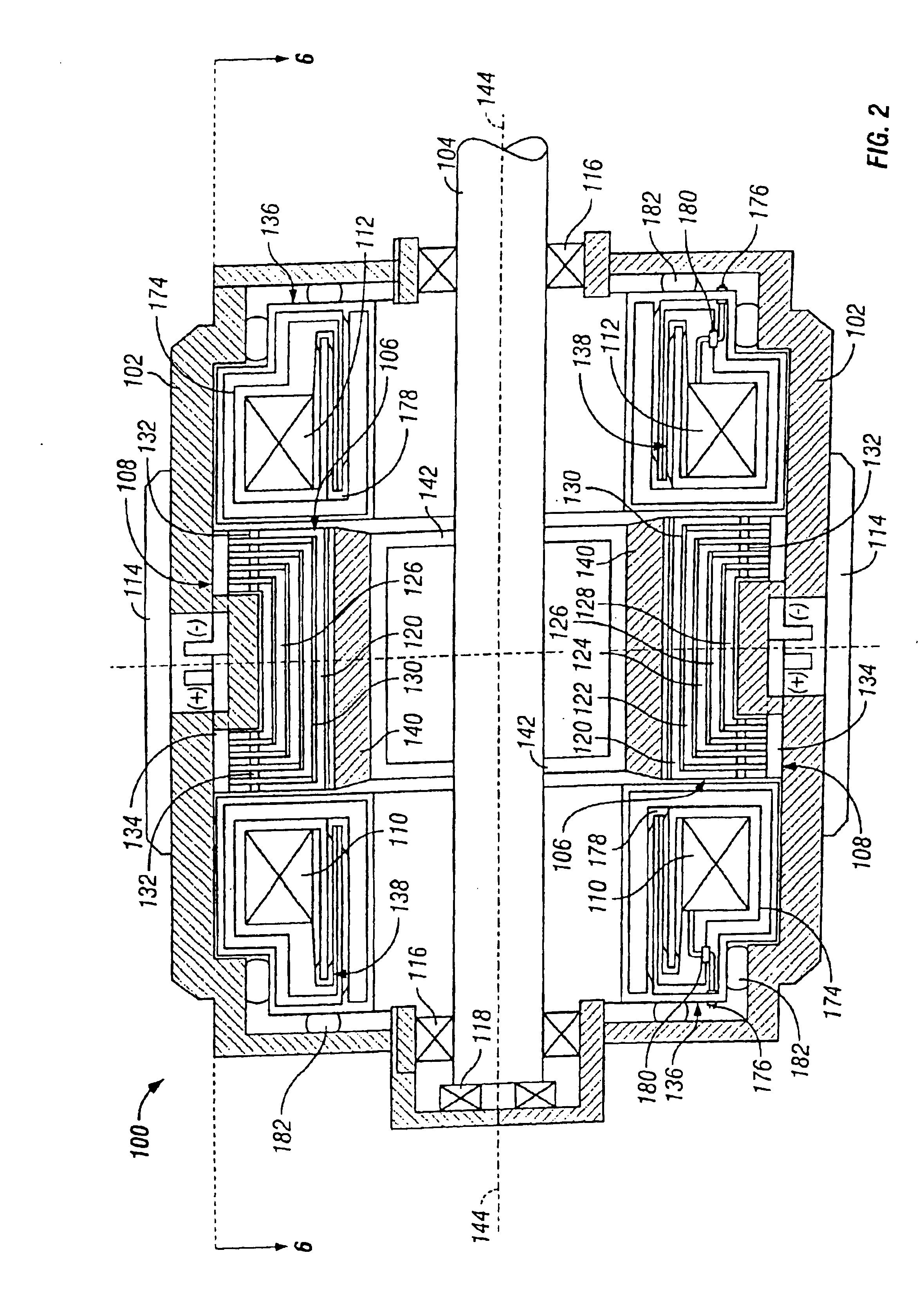
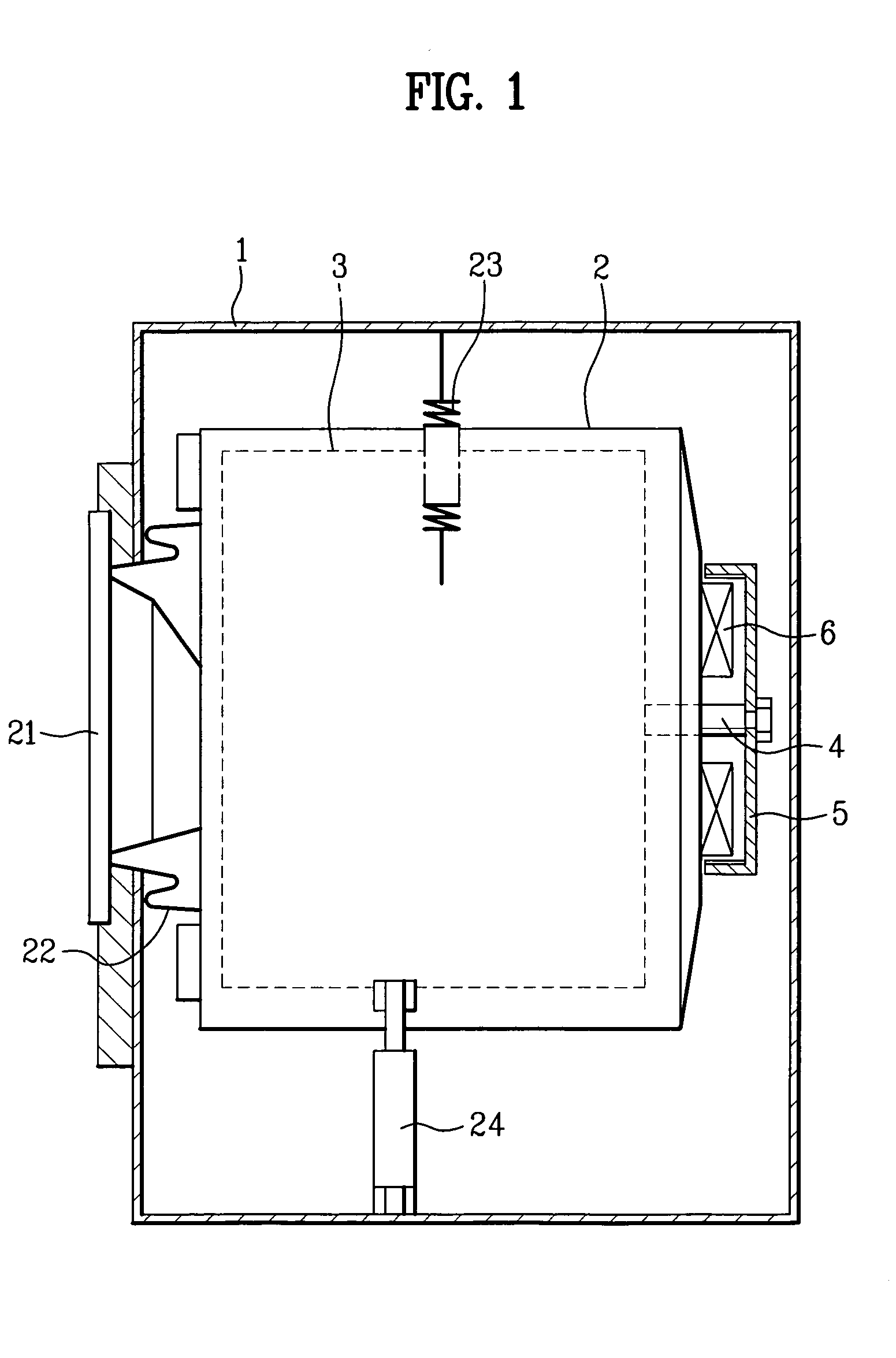
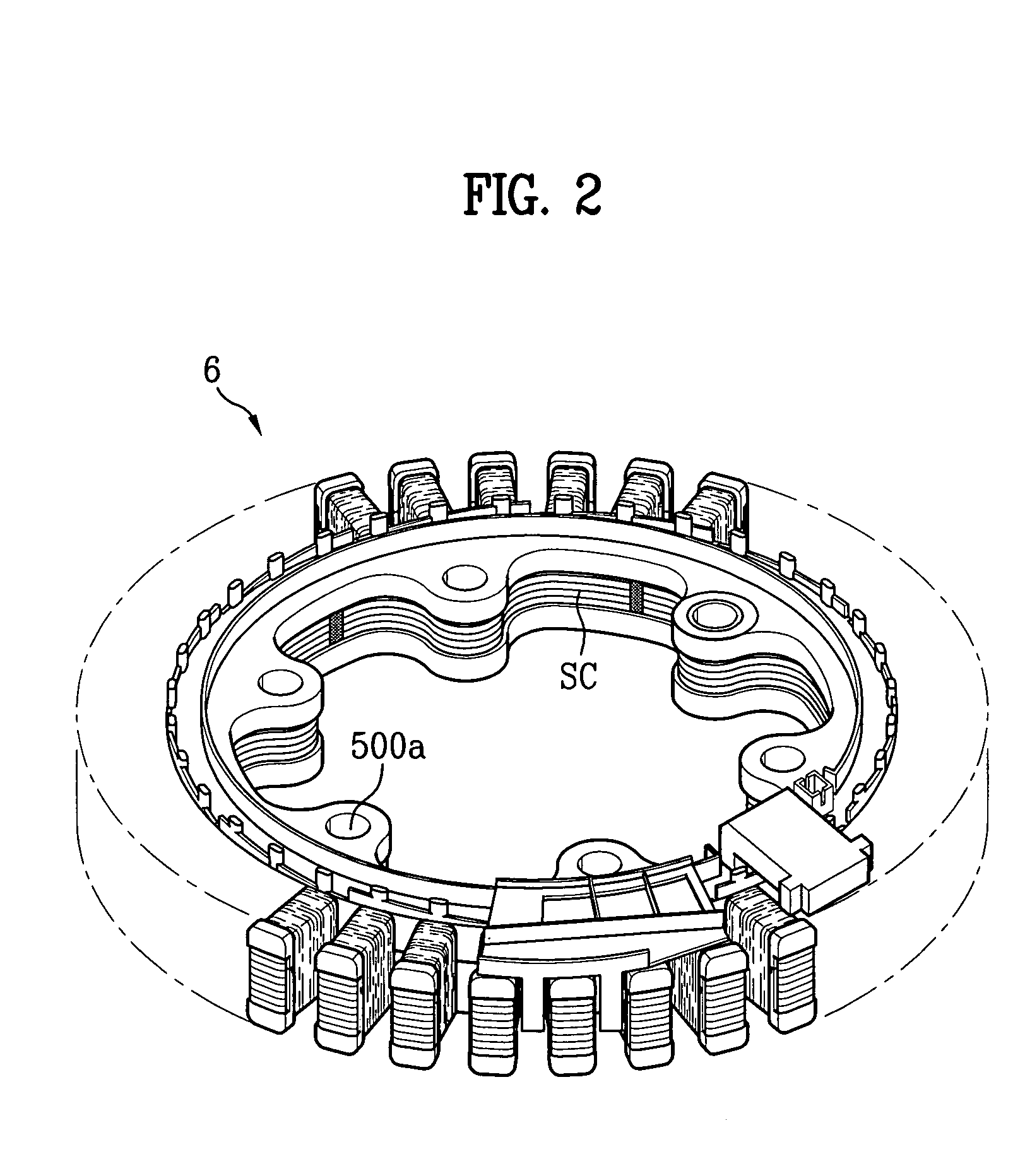
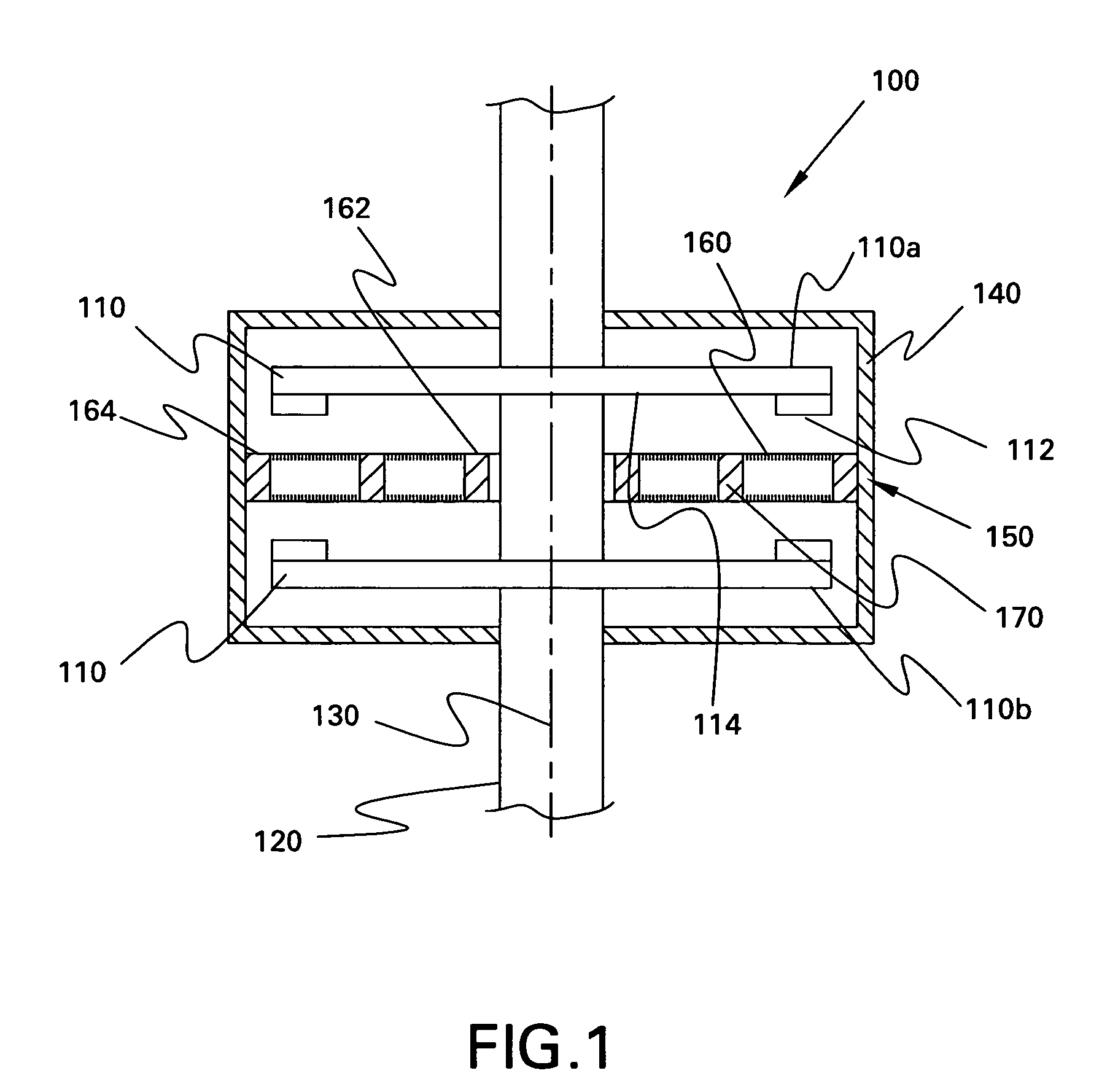
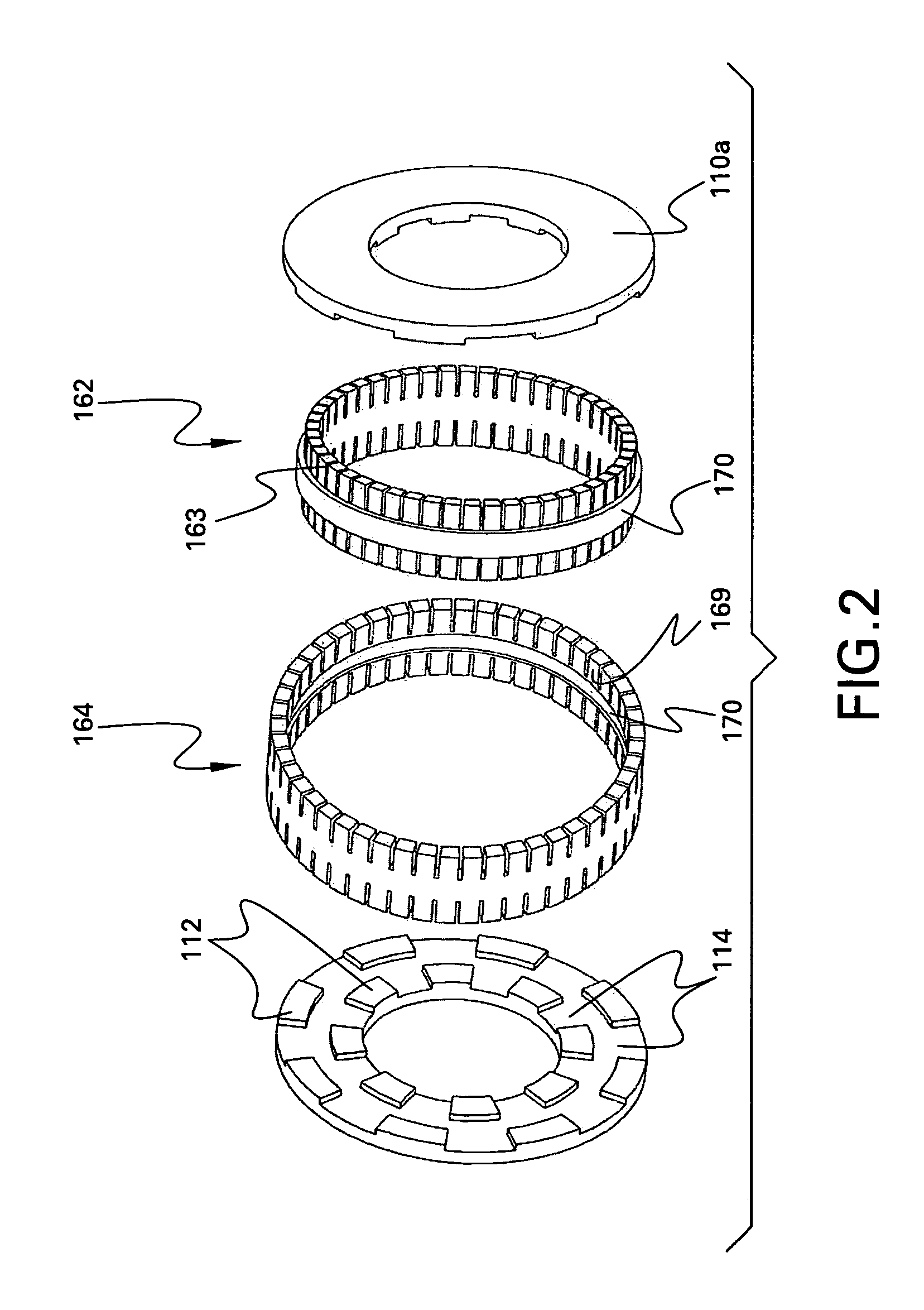
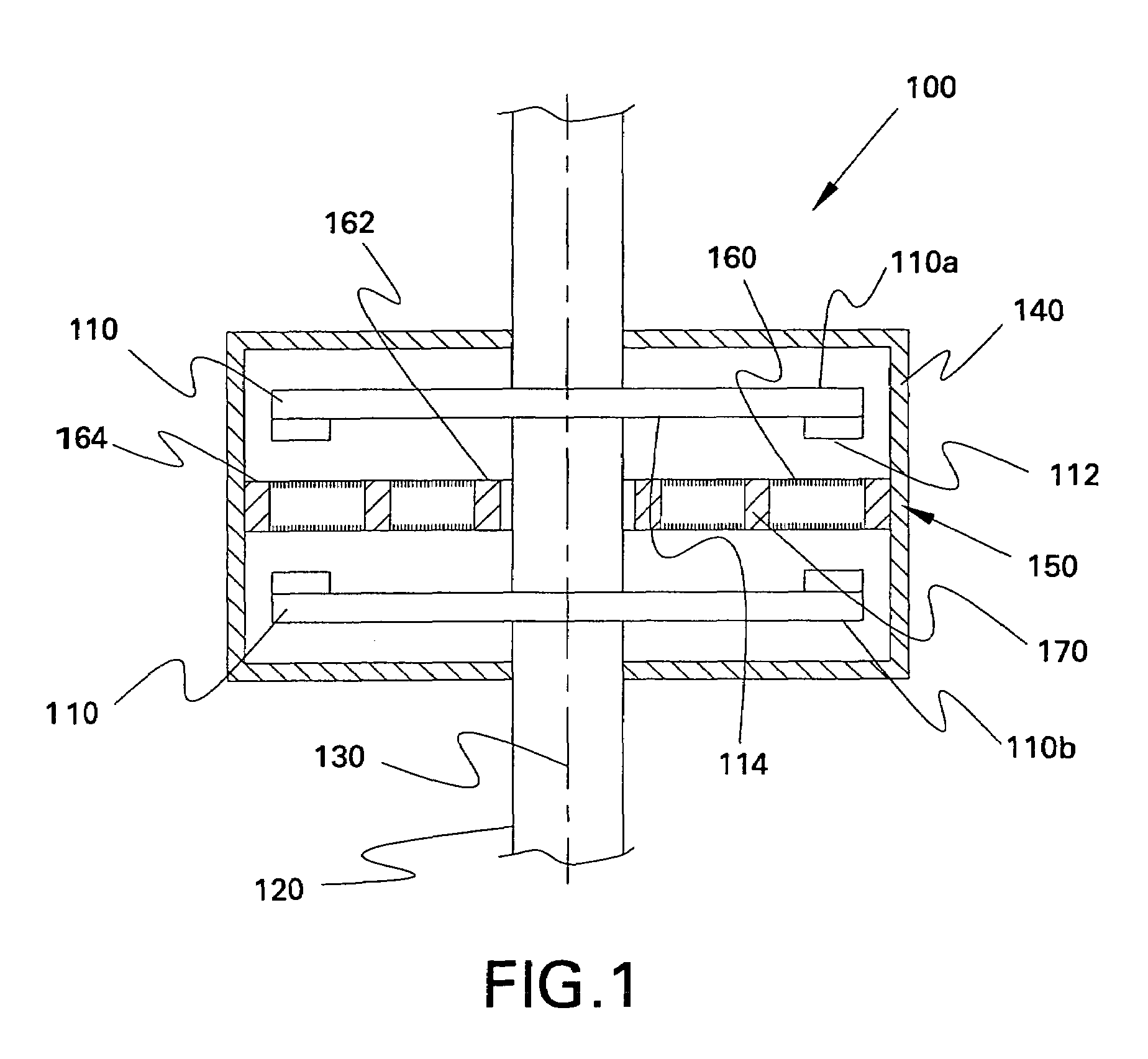
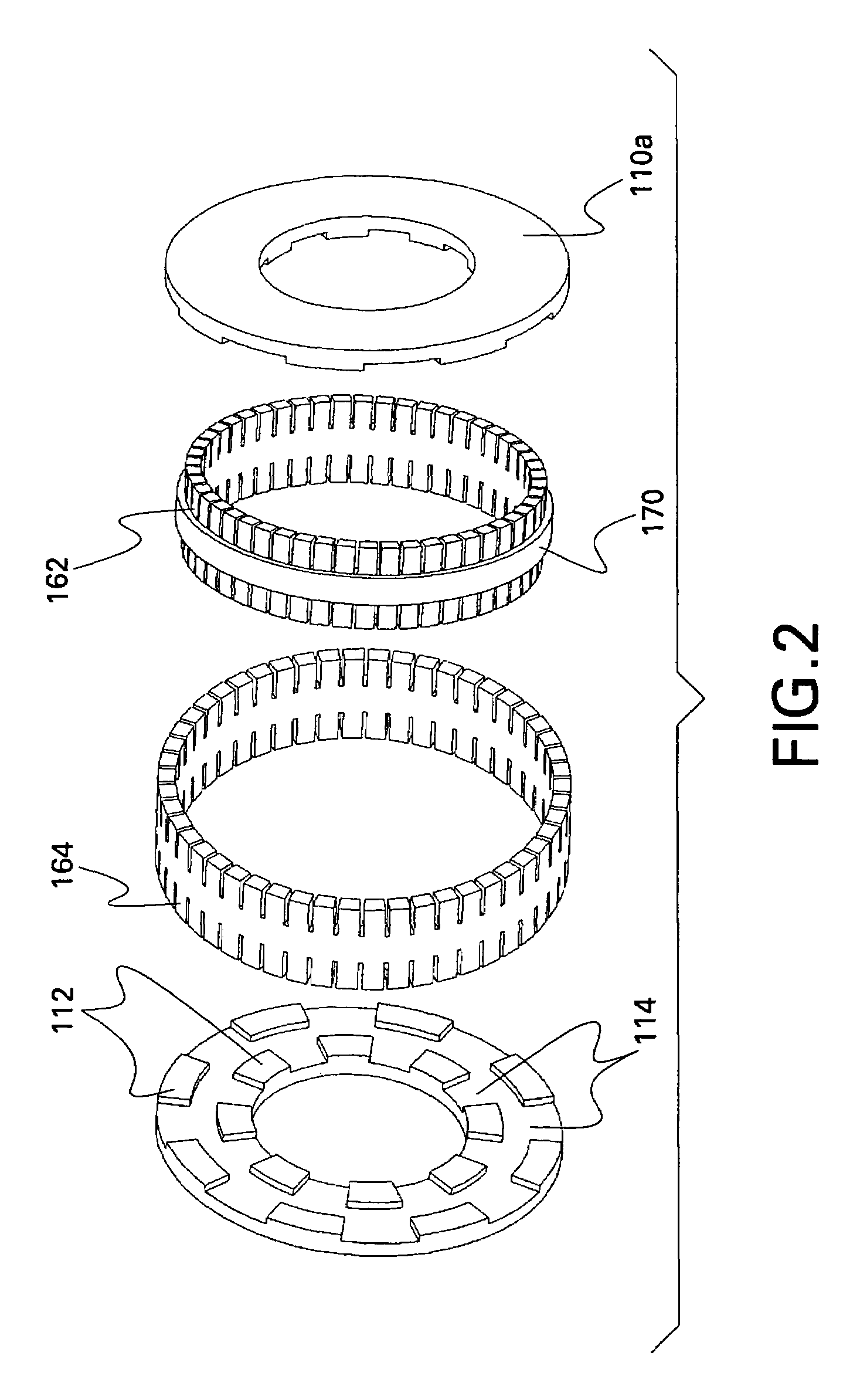
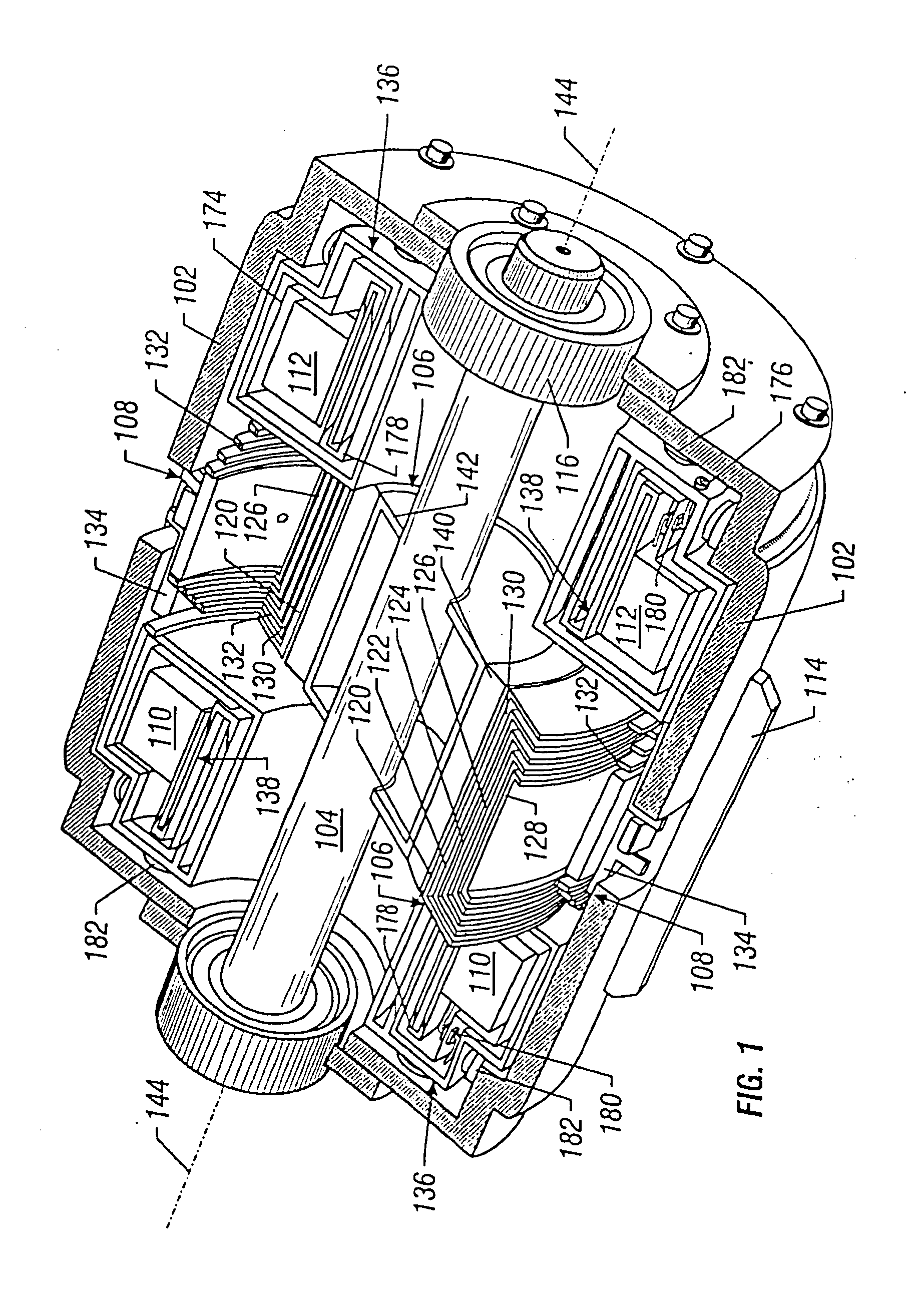
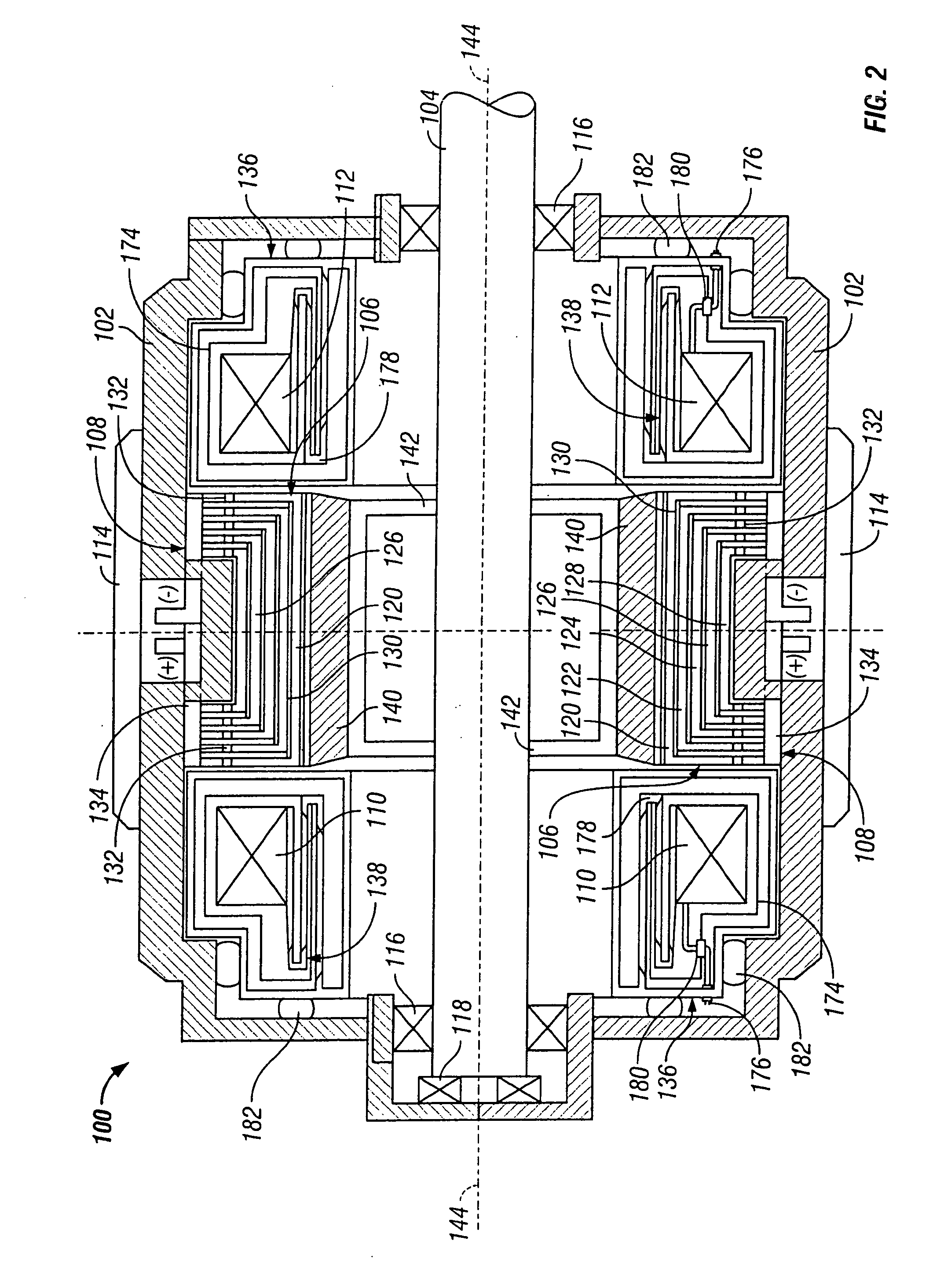
A homopolar machine produces an axial counter force on the rotating shaft to compensate for the load on the shaft's thrust bearing to reduce wear and noise and prolong bearing life. The counter force is produced through magnetic interaction between the shaft and the machine's field coils and is created by changing the current excitation of the field coils, which results in a magnetic flux asymmetry in an inner flux return coupled to the shaft. The homopolar machine may also have a configuration that uses current collectors that maintain substantially constant contact pressure in the presence of high magnetic fields to improve current collector performance. The current collectors are flexible and may be made from either electrically conductive fibers or stacked strips such that they bear up against the armature so that the pressure is maintained by the spring constant of the current collector material. The homopolar machine may also have a configuration where the brushes are oriented so that the current is aligned as much as is practical with the local magnetic field lines so as to reduce the lateral electromagnetic forces on the brushes.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Brushless DC motor system and method of controlling the same
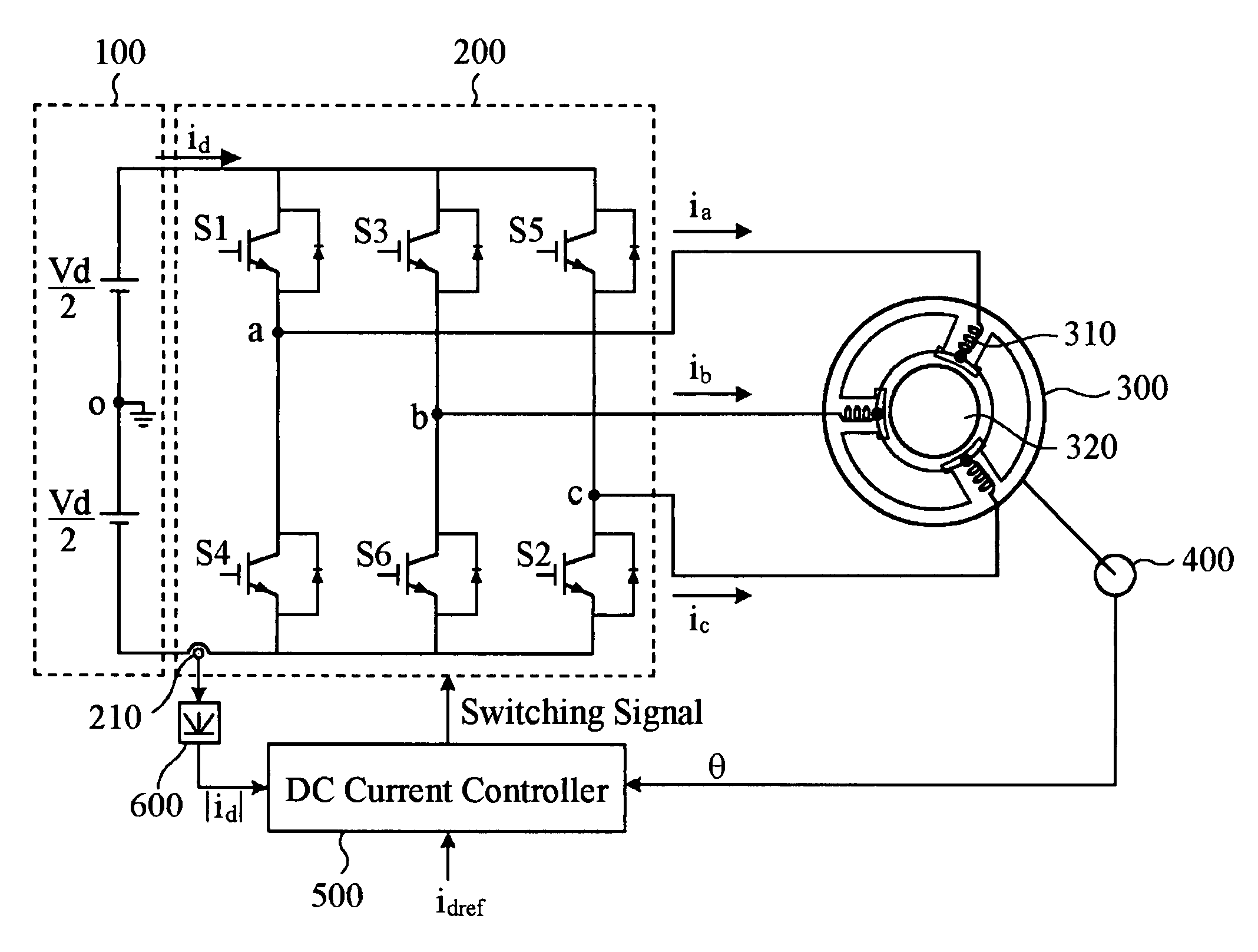
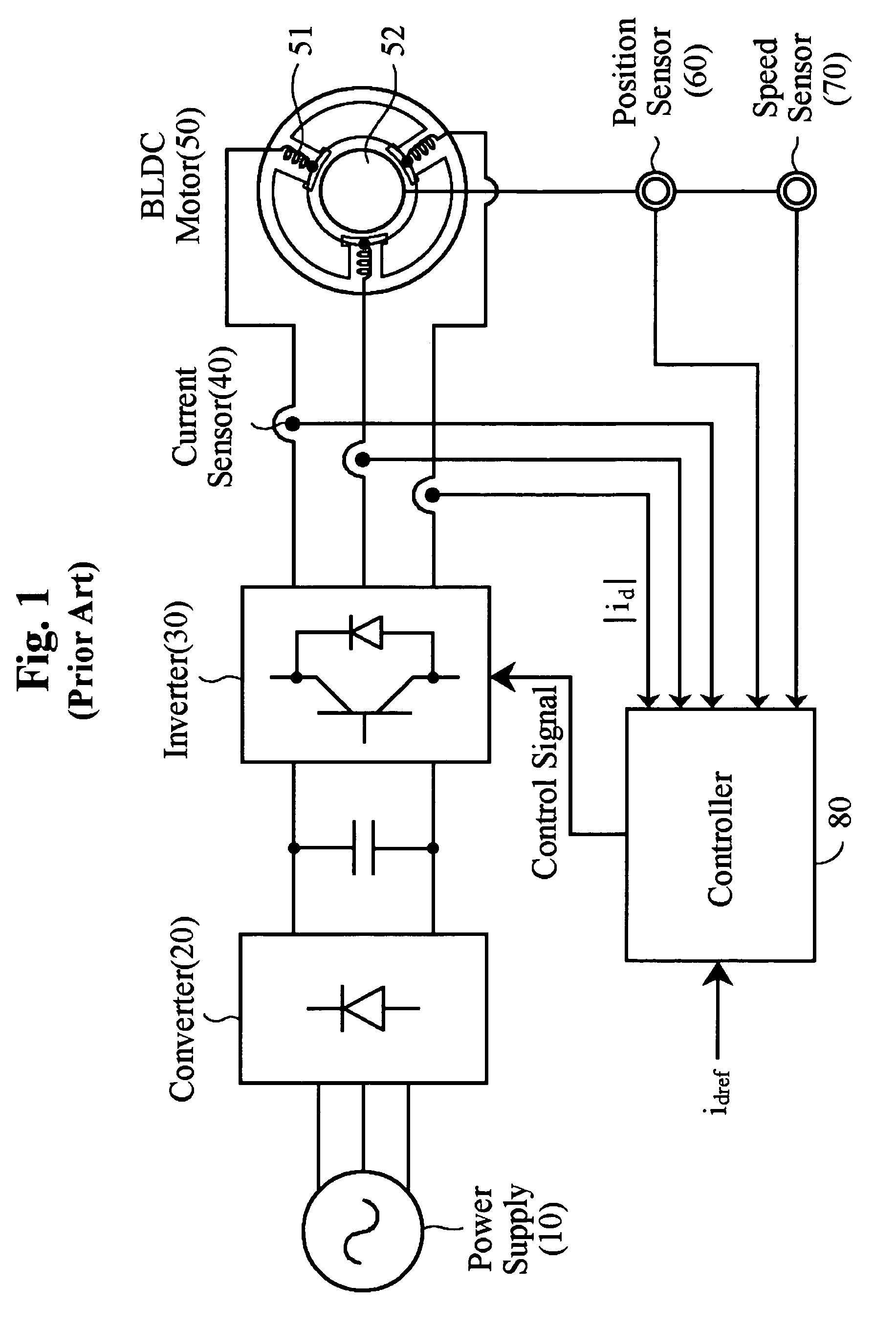
InactiveUS7141943B2Reduce a torque rippleDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlReference currentDc current
A brushless DC (BLDC) motor system and a method of controlling the same are provided. The BLDC motor system comprises a BLDC motor including a rotator and a stator, a plurality of switches, a DC current sensor, a position detector and a controller. The stator has a plurality of coils to which currents having different phase are applied. The switches are driven with switching pulses for switching the currents applied to the coils. The position detector detects a position change of the rotator to thereby generate a counter-electromotive force and the DC current sensor senses currents when the currents are applied from the switches to the coils. Based on a magnitude of the counter electromotive force, the controller generates a compensation voltage in order to control the switches during the commutation interval. Further, a duty ratio of the switching pulse is controlled based on the differences between the currents applied to the coils and a reference current.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Light-weight high-power electrical machine
InactiveUS6891302B1High energyMotor/generator magnetic lossHybrid vehiclesWindingsAlternatorElectrical polarity
A brushless electrical machine, usable as a motor, generator, or alternator, has a rotor that is comprised of a rim portion and a substantially open center portion. The rim portion has a partially hollow core in which a stationary field coil is supported. Current to the field coil generates magnetic flux that circulates in a poloidal flux path in the rim, crossing a single magnetic air gap formed by the rim. Protrusions in the rim located around the circumference form poles all having the same polarity. As the rotor rotates, the flux exiting the poles passes through multiple stationary armature windings around the circumference that are located in the single air gap. An AC voltage is induced in the armature windings from rotation.
Owner:REVOLUTION ELECTRIC MOTOR
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Stator of outer rotor type motor for drum type washing machine
ActiveUS20050189837A1Reduce materialReduce weightSynchronous generatorsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionElectric machineMechanical engineering
The present invention provides an outer rotor type motor for a drum type washing machine to reduce material and weight for fabrication, simplify fabrication process, provide stable assembly of a stator to a fixing side, such as a tub or a bearing housing, prevent unwinding of stacked steel plates in assembling a helical core, and reduce stress on the steel plates of the core. The present invention includes a helical core having multiple layers formed by winding steel plates in a helix starting from a bottom layer to a top layer, the steel plate having a base portion with teeth projected from the base portion, an upper insulator of an electric insulating material covered on an upper side of the helical core in a shape complementary to a shape of the helical core, a lower insulator of an electric insulating material covered on a lower side of the helical core at the time of assembly with the upper insulator having a shape complementary to a shape of a helical core, and a fastening means for at least two steel plates wound in a helix to prevent unwinding of any two adjacently stacked steel plates and prevent gaps between any two adjacent layers of the stacked steel plates.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
DC electric motor/generator with enhanced permanent magnet flux densities
ActiveUS20130249343A1Reduces and eliminates undesired effect and lossMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machinesMagnetic tension forceEngineering
This disclosure relates in general to a new and improved electric motor / generator, and in particular to an improved system and method for producing rotary motion from a electro-magnetic motor or generating electrical power from a rotary motion input by concentrating magnetic forces due to electromagnetism or geometric configurations.
Owner:LINEAR LABS
Disk alternator
InactiveUS20070024144A1Total current dropReduce maintenance costsMagnetic circuit rotating partsAsynchronous induction motorsElectrical conductorAlternator
A power disk alternator includes a rotor of circular cross-section arranged to rotate about an axis having at least two disks facing each other and defining at least one gap therebetween, and a shaft connected to an external source for driving the shaft in rotation about the axis. Each disk has a circular array of arcuately-spaced magnetized elements located adjacent to its periphery, each of the magnetized elements having surfaces of opposite polarity and being disposed side-by-side in a like polarity configuration. Magnetized elements of one disk face magnetized elements of the other disk of opposite polarity, creating magnetic fields between the opposite polarities in the gap between the two disks. The alternator also includes a stator comprising at least one fixed nonmetallic disk having a conductor path comprising at least one uninterrupted conductor on at least one surface thereof, each stator being located in one of the at least one air gap. A connector is provided for connecting the conductor path to a load. When the external source drives the shaft in rotation, the rotor rotates, and the resulting rotating magnetic field induces a current in the conductor path.
Owner:TECOBIM
Brushless Electric Motor/Generator
ActiveUS20160020652A1Increase flux densityAC motor controlElectric motor controlElectric generatorMagnet
Disclosed are various embodiments for a motor / generator comprising: a rotor adapted to rotate about a longitudinal axis, the rotor comprising a first partial toroidal magnetic cylinder defining a semi-circular tunnel, wherein the plurality of magnets forming the first partial toroidal magnetic cylinder have substantially all like poles facing inward toward the semi-circular tunnel, the semi-circular tunnel having an entrance and an exit forming an open throat defined by a space between the entrance and the exit, and a stator positioned about the longitudinal axis within a rotational path of the rotor.
Owner:LINEAR LABS
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils
A machine includes a rotatable rotor assembly having a number of salient poles. The machine further includes a stationary stator assembly having concentric inner and outer stators, at least one stationary superconducting field coil and at least one stator coil. The stationary superconducting field coil is disposed between the inner and outer stators and is mounted on at least one of the inner and outer stators. The stationary superconducting field coil and the salient poles are configured relative to each other, such that when the rotor assembly is rotated relative to the stator assembly around a predetermined axis, a rotating magnetic field is produced with an airgap flux direction substantially along the predetermined axis. The interaction between the stationary superconducting field coil and the rotating poles provides the only source of a time varying magnetic flux supplied to the stator coil.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Semiconducting oxide nanostructures
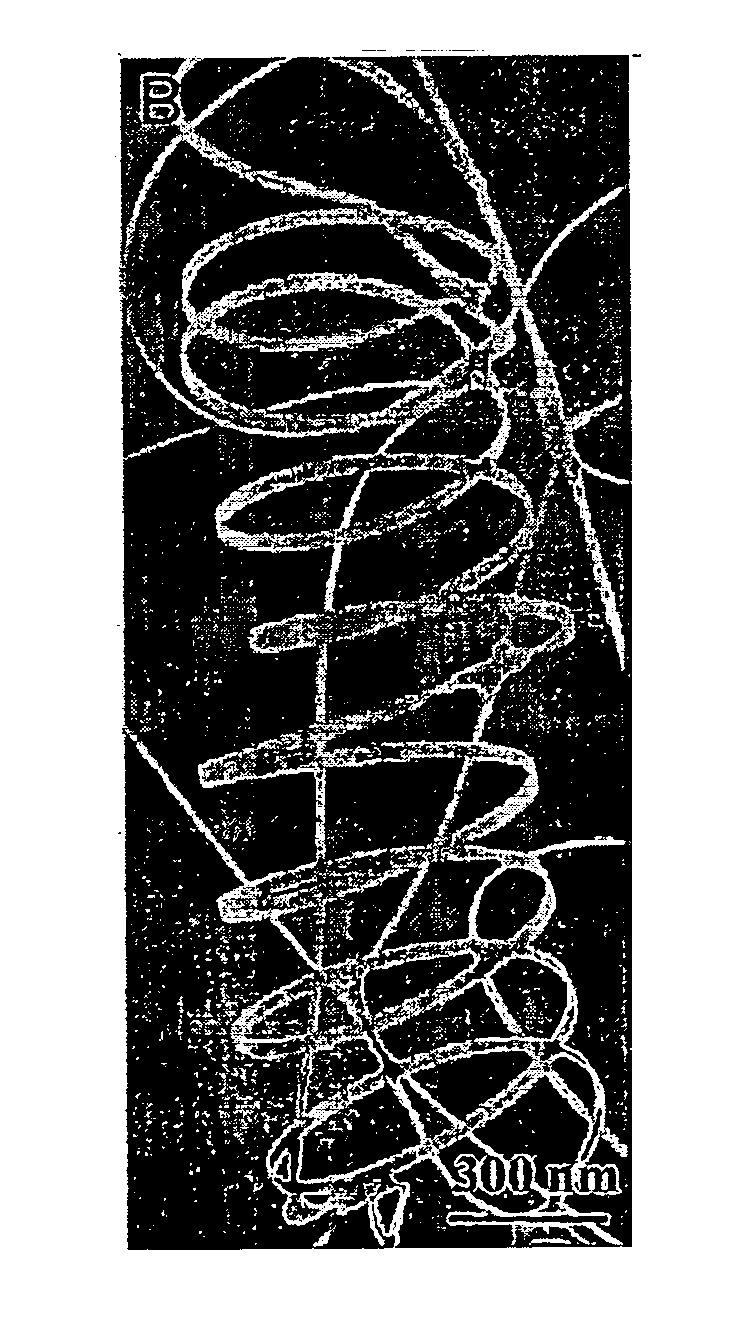
Briefly described, new types of nanostructures and methods of fabrication thereof are disclosed. A representative nanostructure includes a free-standing, helical semiconductor oxide nanostructure. The free-standing, helical semiconductor oxide nanostructure includes a nanobelt having a substantially rectangular cross-section. The the nanobelt is about 5 nanometers to about 200 nanometers in width and about 3 nanometers to about 50 nanometers in height, and the radius of the helical semiconductor oxide nanostructure is about 200 to 5000 nanometers.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils
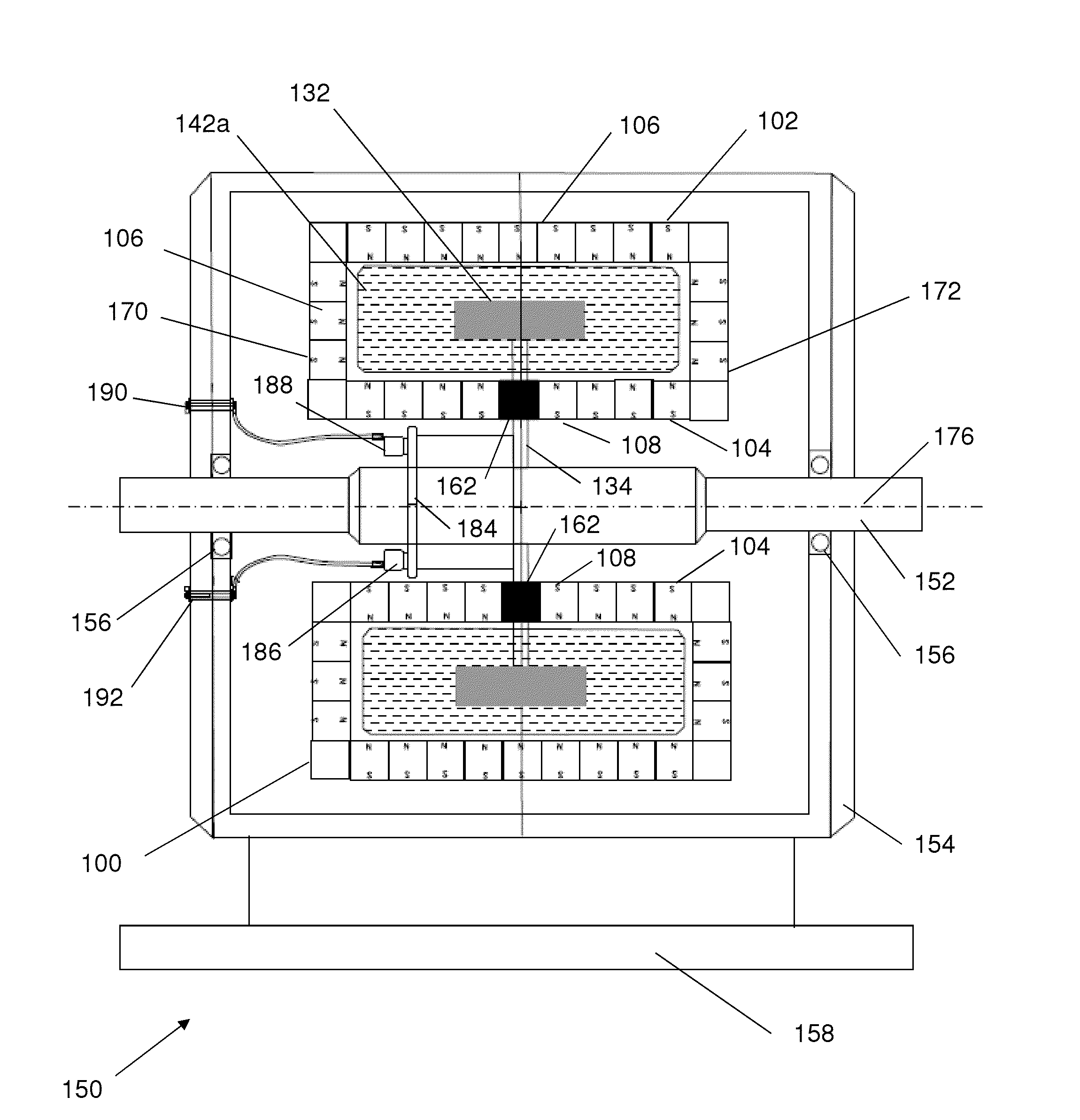
A machine includes a stator assembly that includes a stator yoke, a pair of armature coils mechanically coupled to the stator yoke, and a stationary superconducting field coil. The stator yoke comprises a magnetic material. The machine further includes a shaft rotatably mounted in the stator yoke, the shaft comprising a non-magnetic material. The machine further includes a rotor assembly rotationally engaged with the shaft. The rotor assembly includes a rotor disk extending between the armature coils, the rotor disk having an inner portion and an outer portion. The outer portion of the rotor disk includes a number of circumferentially-spaced, magnetic poles. The rotor disk is coupled to the shaft for rotation about the shaft and generation of a rotating permeance wave. The stationary superconducting field coil is disposed between the stator yoke and the rotor disk, and the stationary superconducting field coil is configured as a stationary magneto-motive force (MMF) source for the rotating permeance wave produced by the rotor assembly to produce a rotating magnetic field.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Vehicular steering system
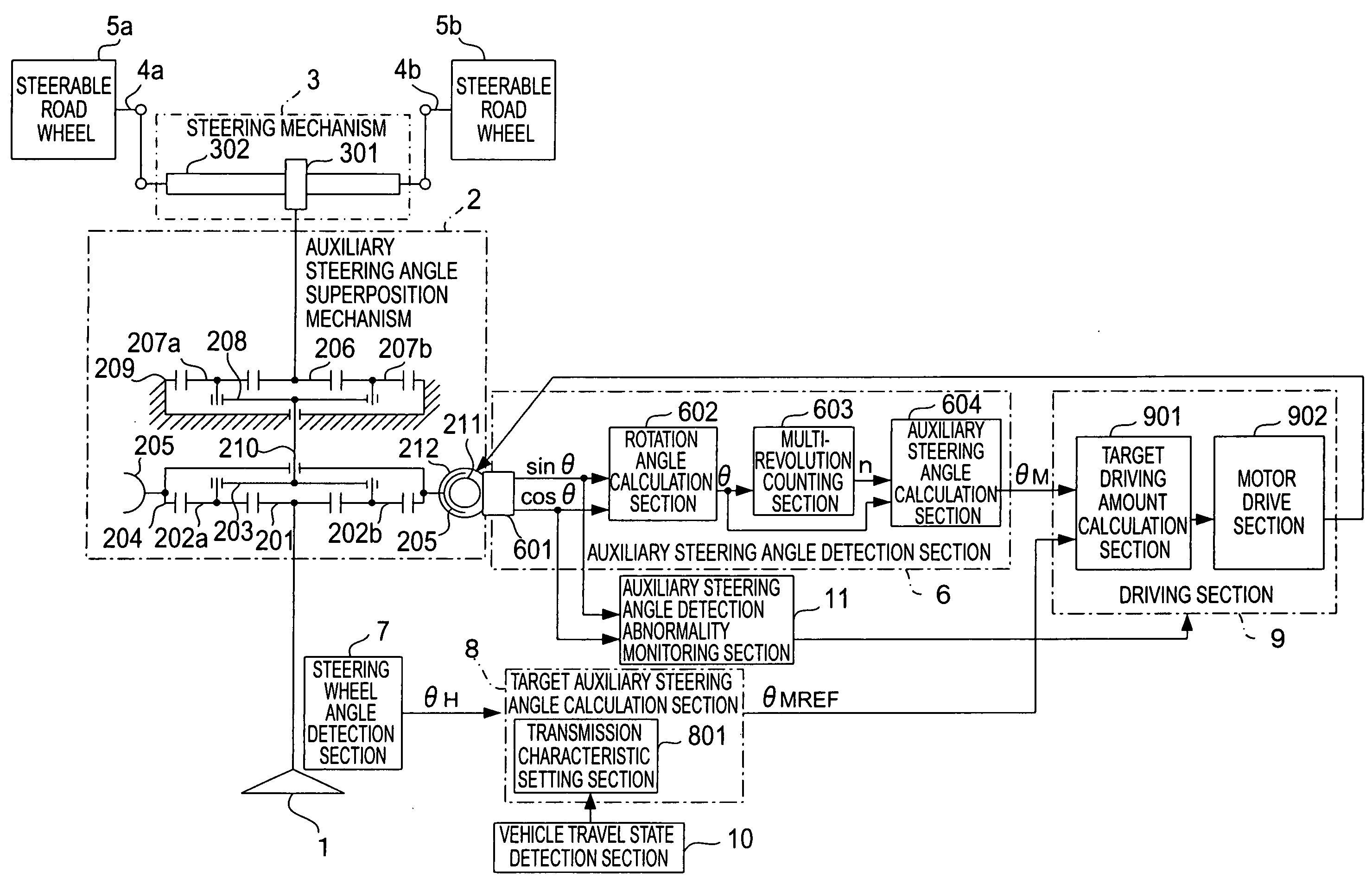
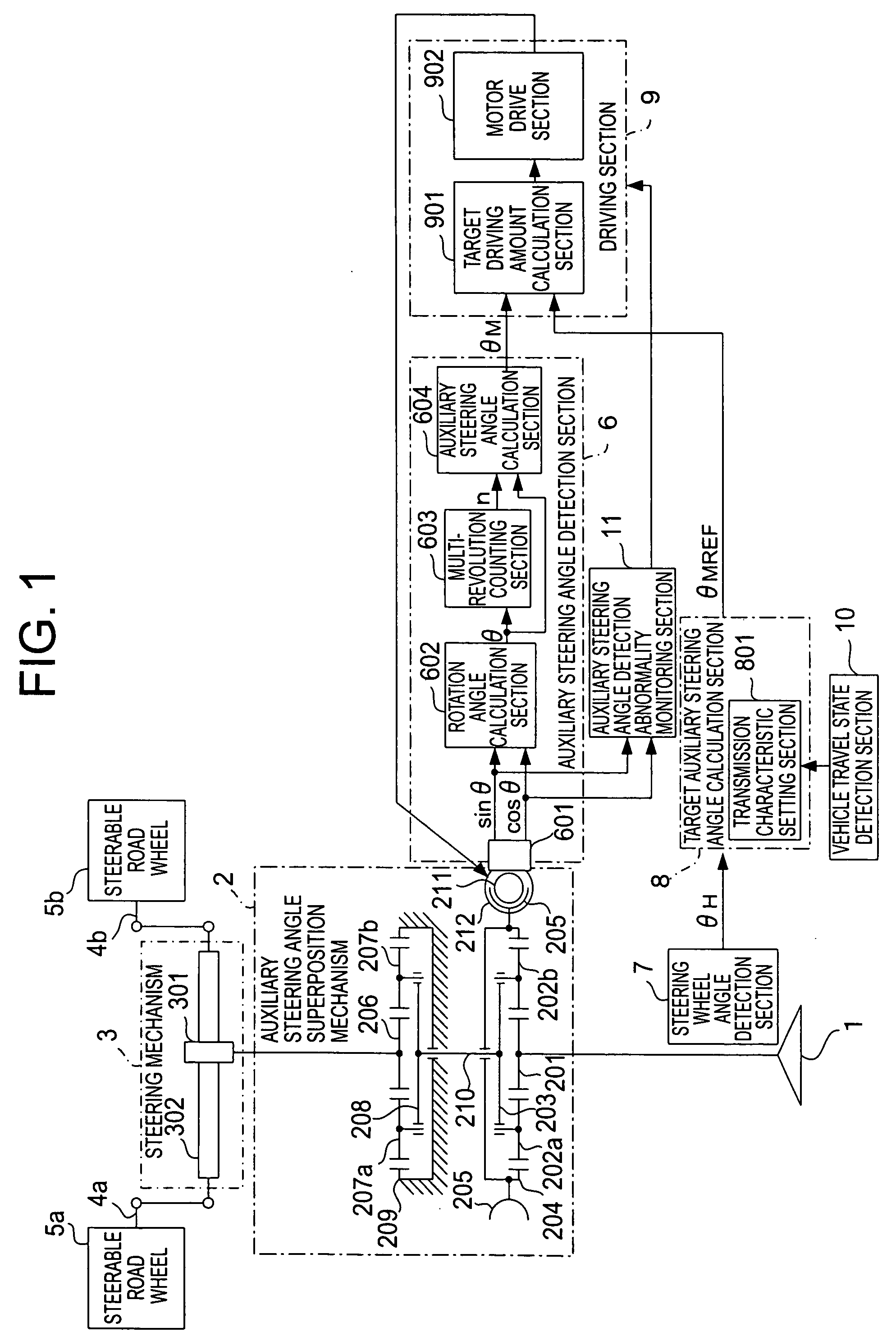
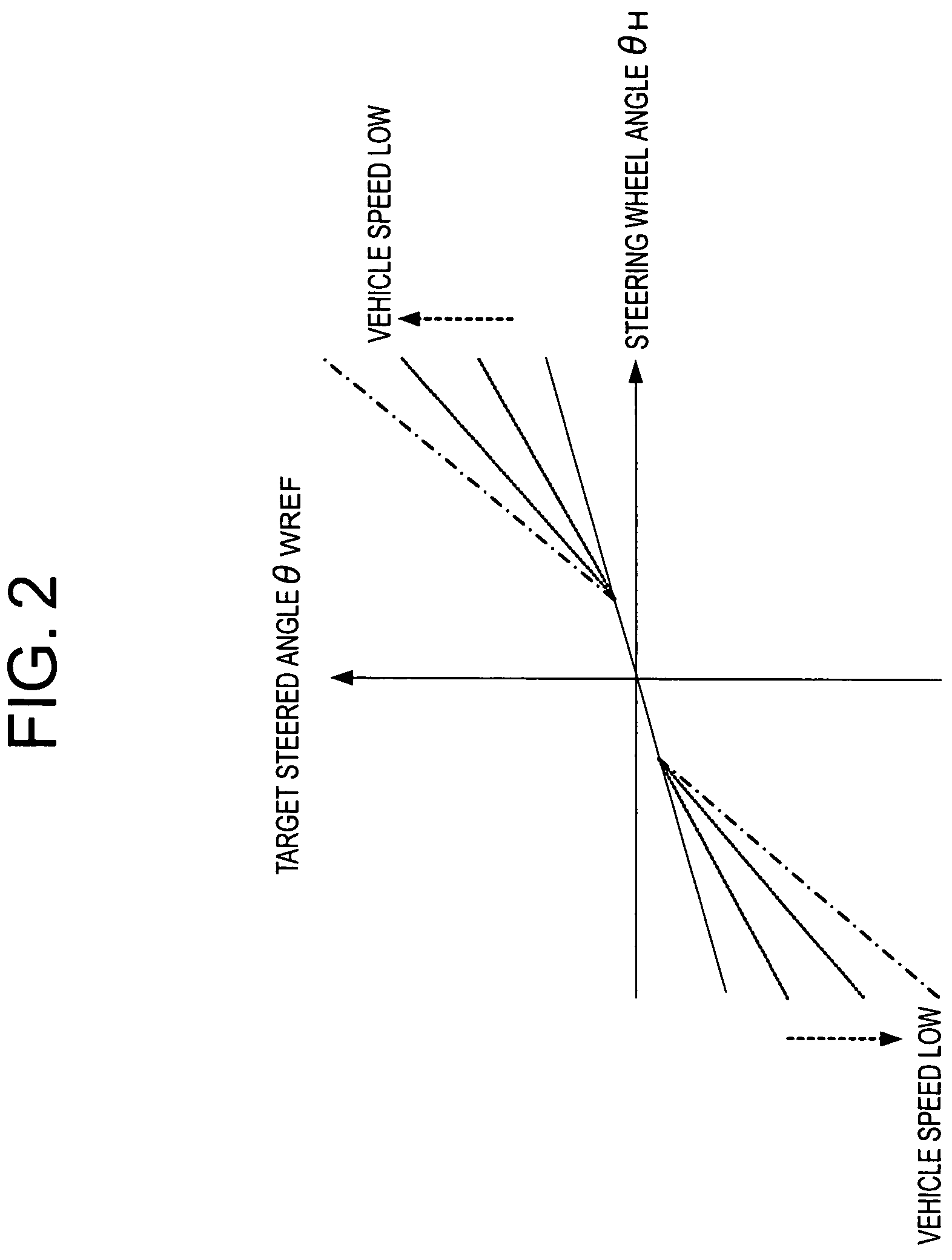
InactiveUS20080040001A1Suppression problemSuppress the steerable road wheelsDC motor speed/torque controlDigital data processing detailsSteering wheelSteering angle
A vehicular steering system can suppress steering of steerable road wheels in a direction not intended by a driver. A steering mechanism steers the steerable road wheels in accordance with a steering wheel and an auxiliary steering angle superposition mechanism. A calculation section calculates a target auxiliary steering angle corresponding to a steering wheel angle of the steering wheel. A detection section accurately detects the auxiliary steering angle based on detection signals of a rotation angle sensor that detects a rotation angle of a rotational member. A driving section controls the auxiliary steering angle superposition mechanism so as to make the auxiliary steering angle coincide with the target auxiliary steering angle. An auxiliary steering angle detection abnormality monitoring section detects abnormality of the auxiliary steering angle detection section. The auxiliary steering angle detection section includes a counting section that counts the number of revolutions per minute of the rotational member.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils and axial airgap flux
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
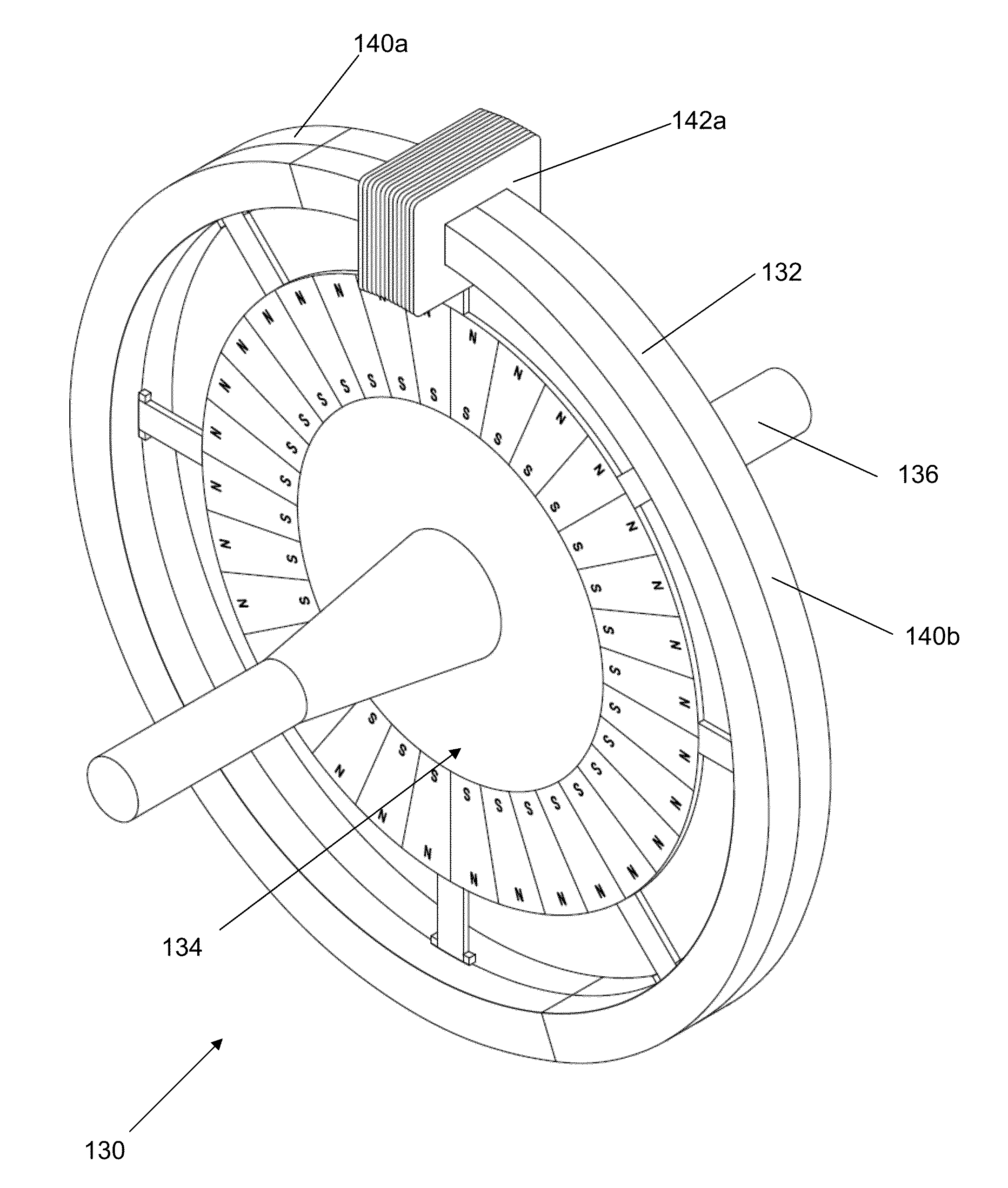
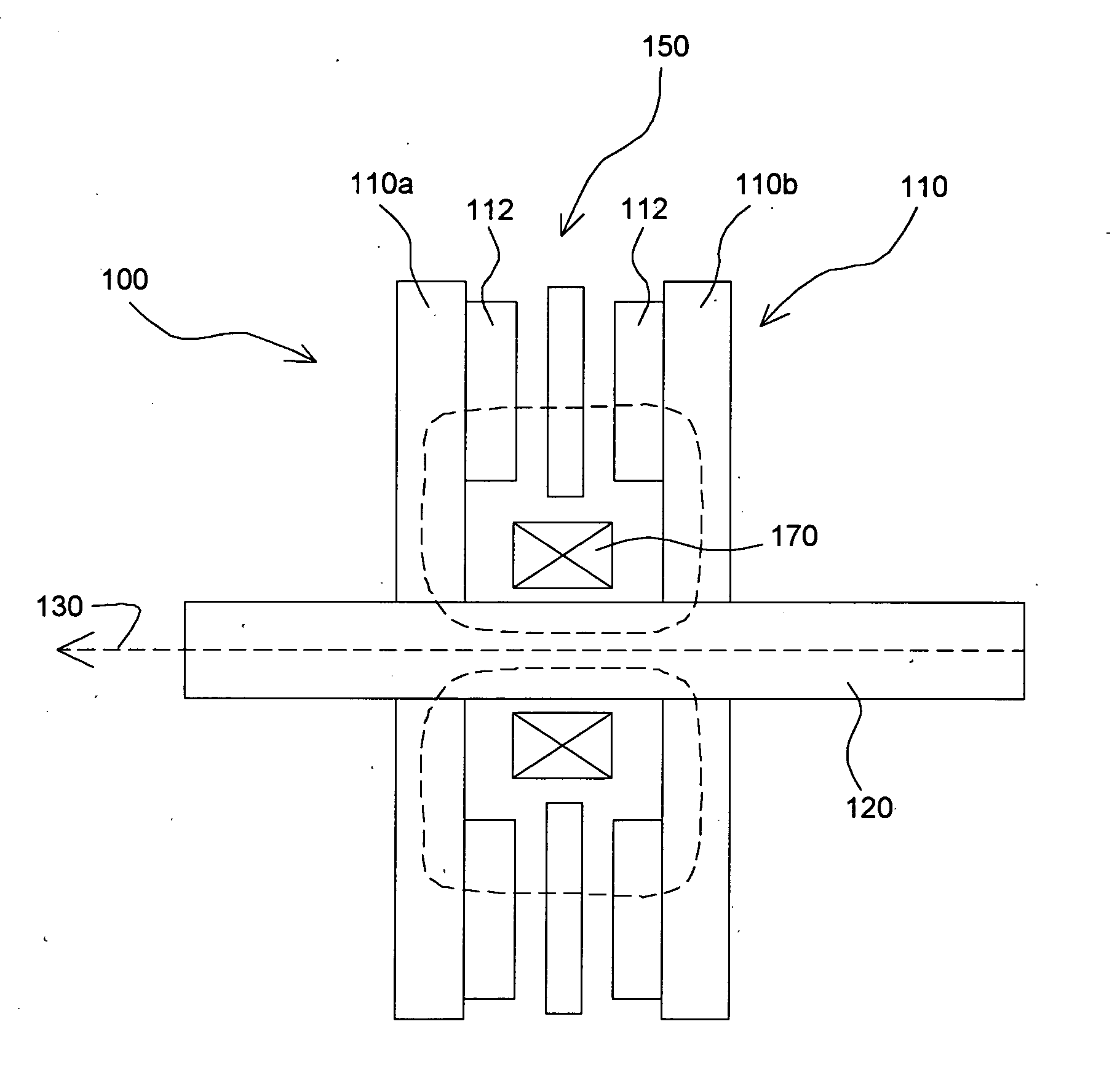
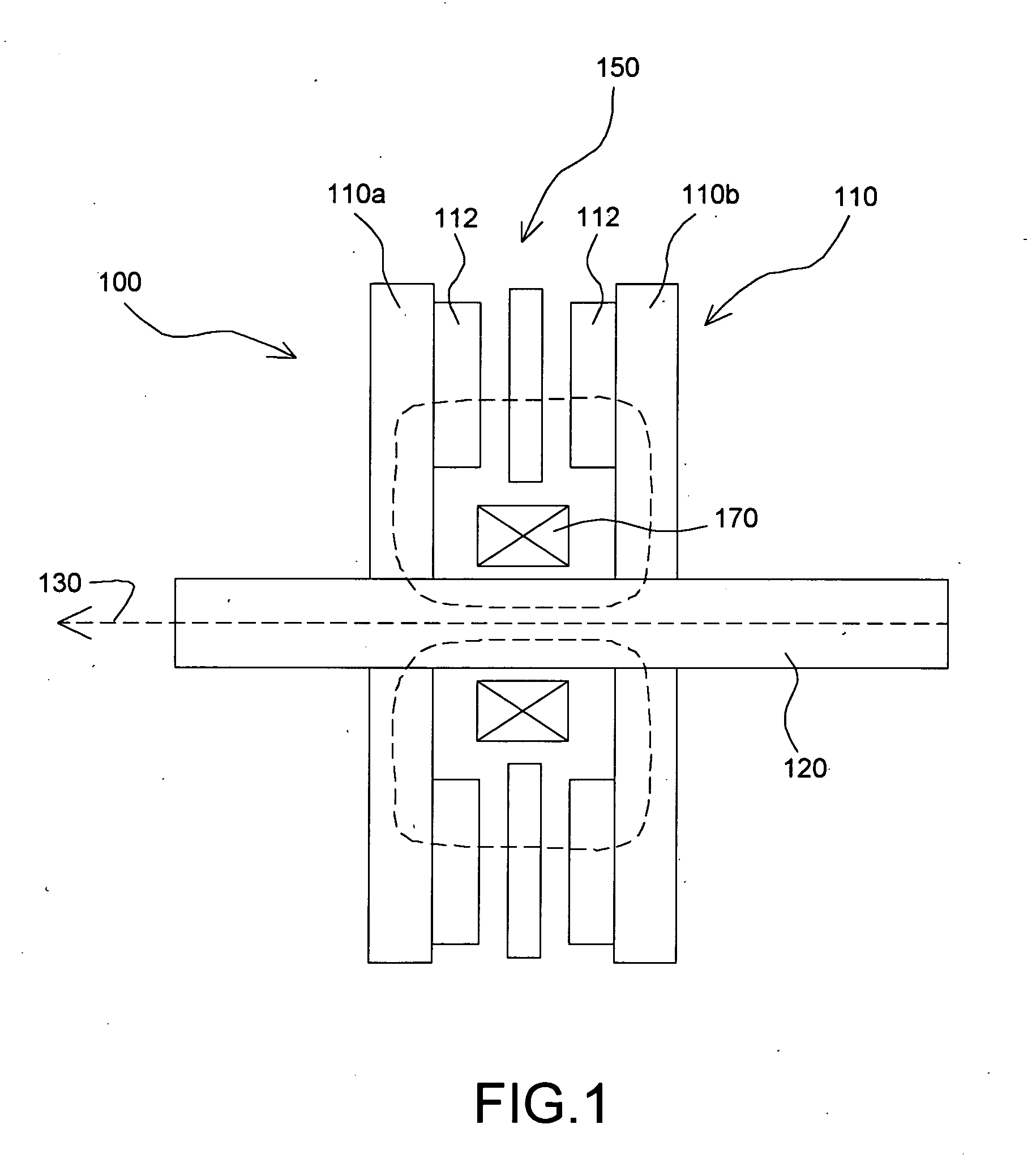
Multivariable generator and method of using the same
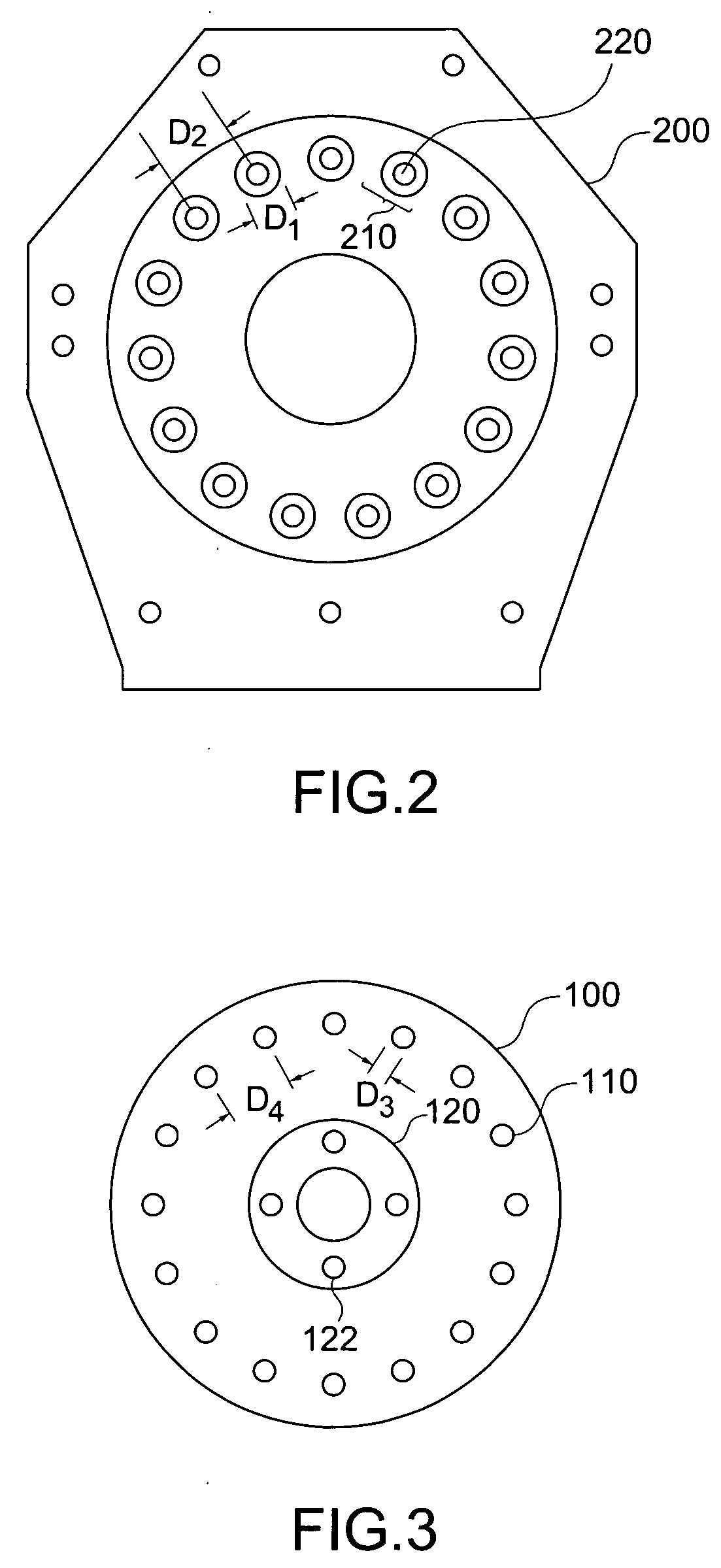
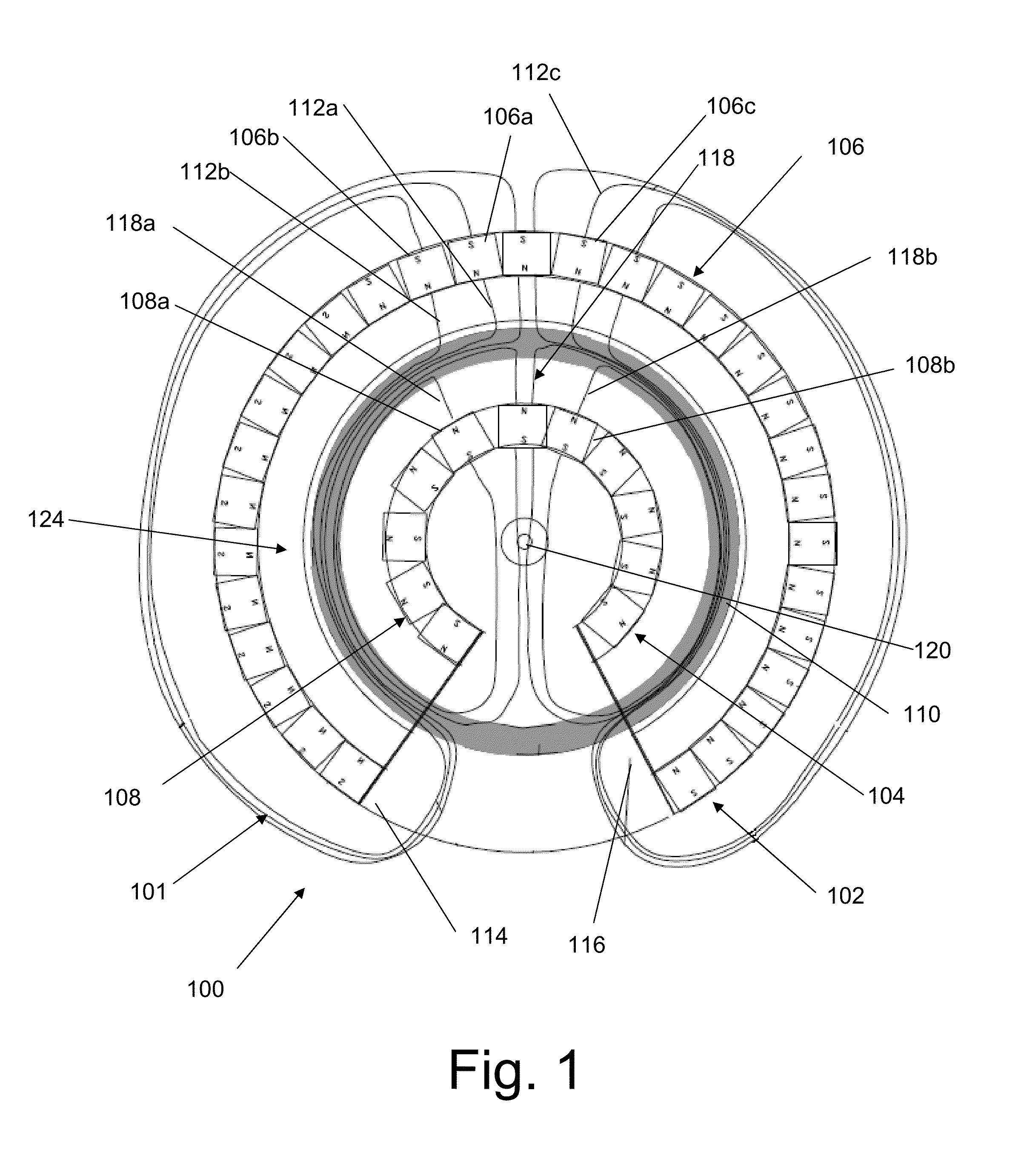
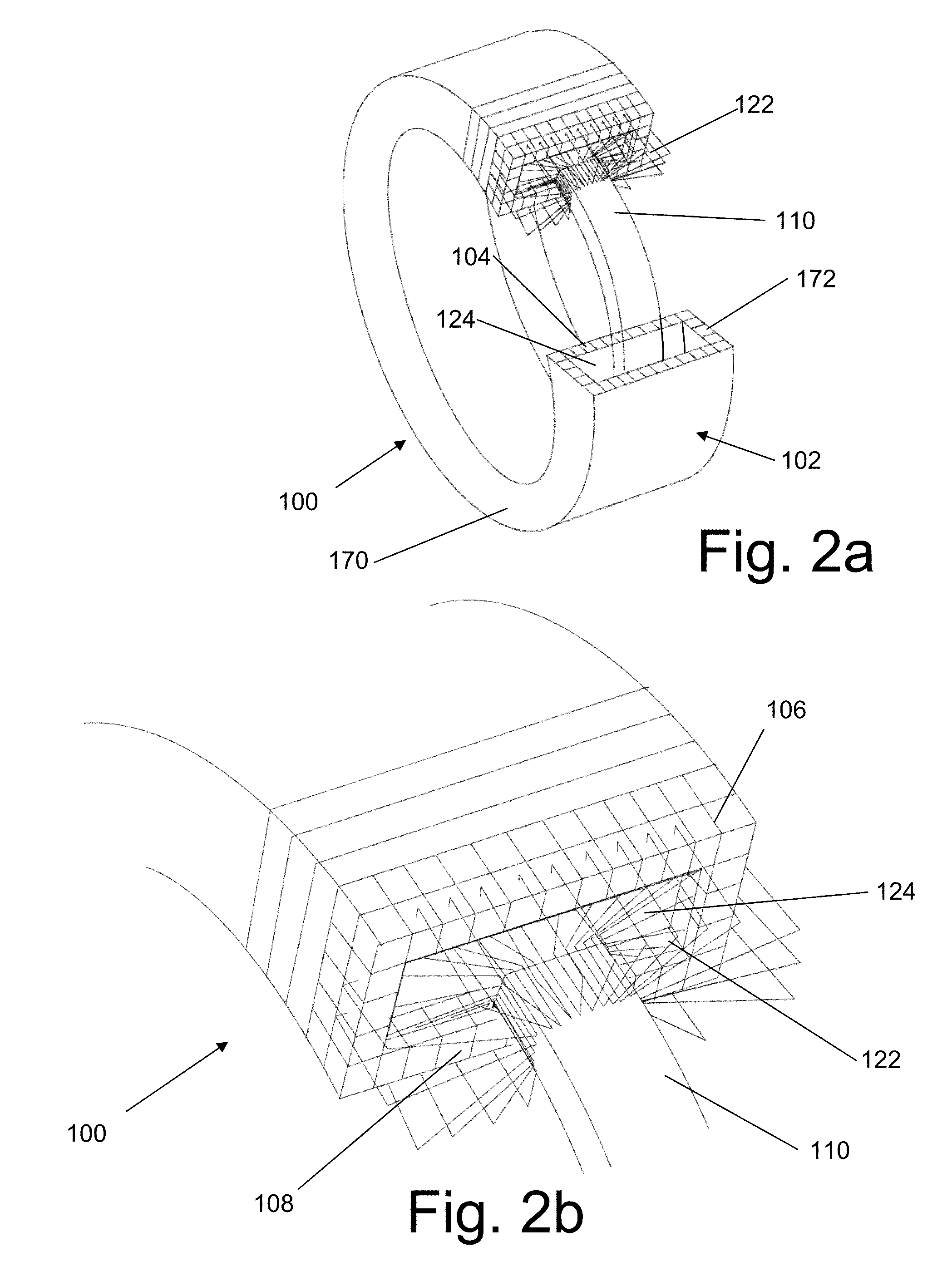
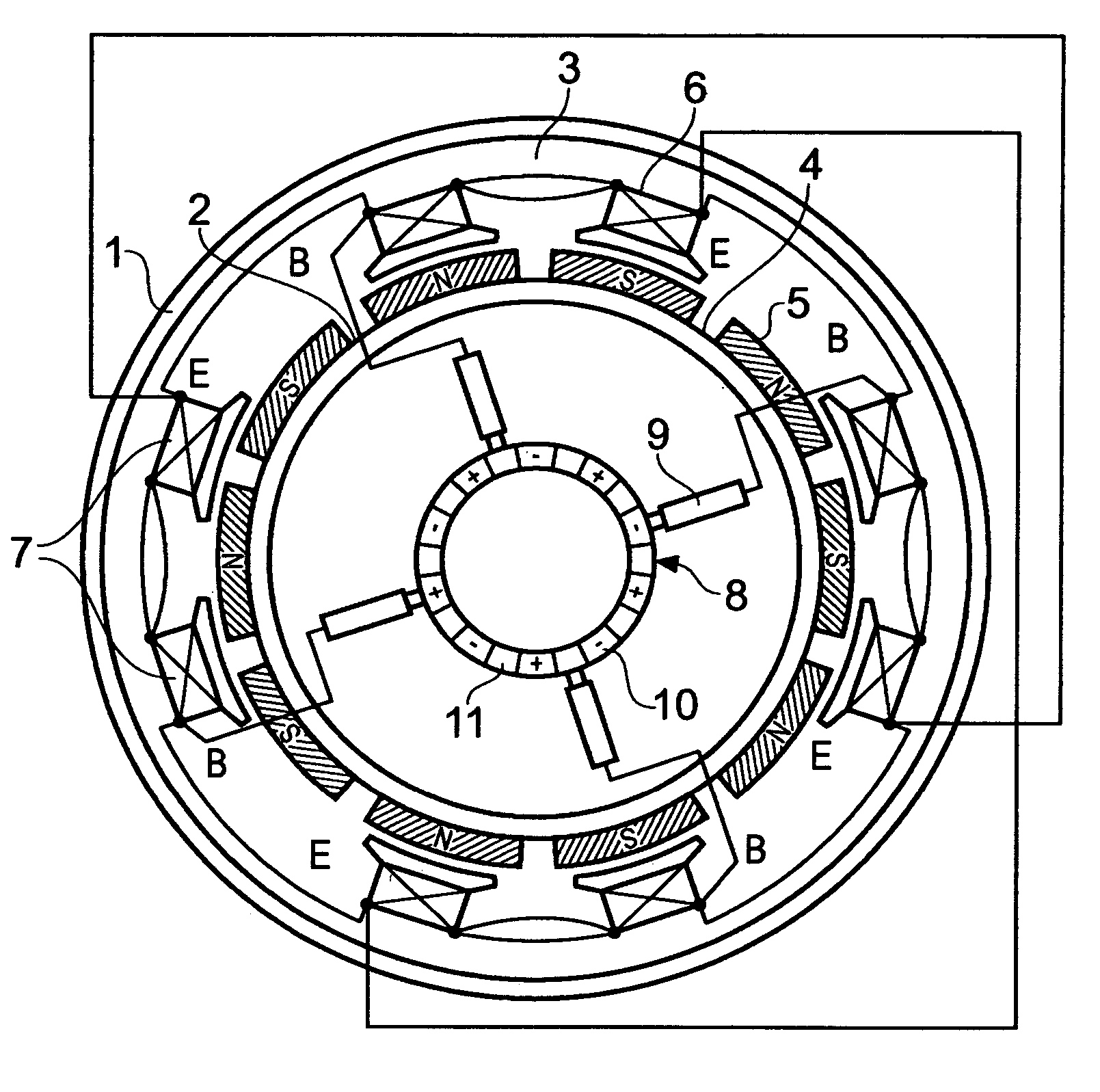
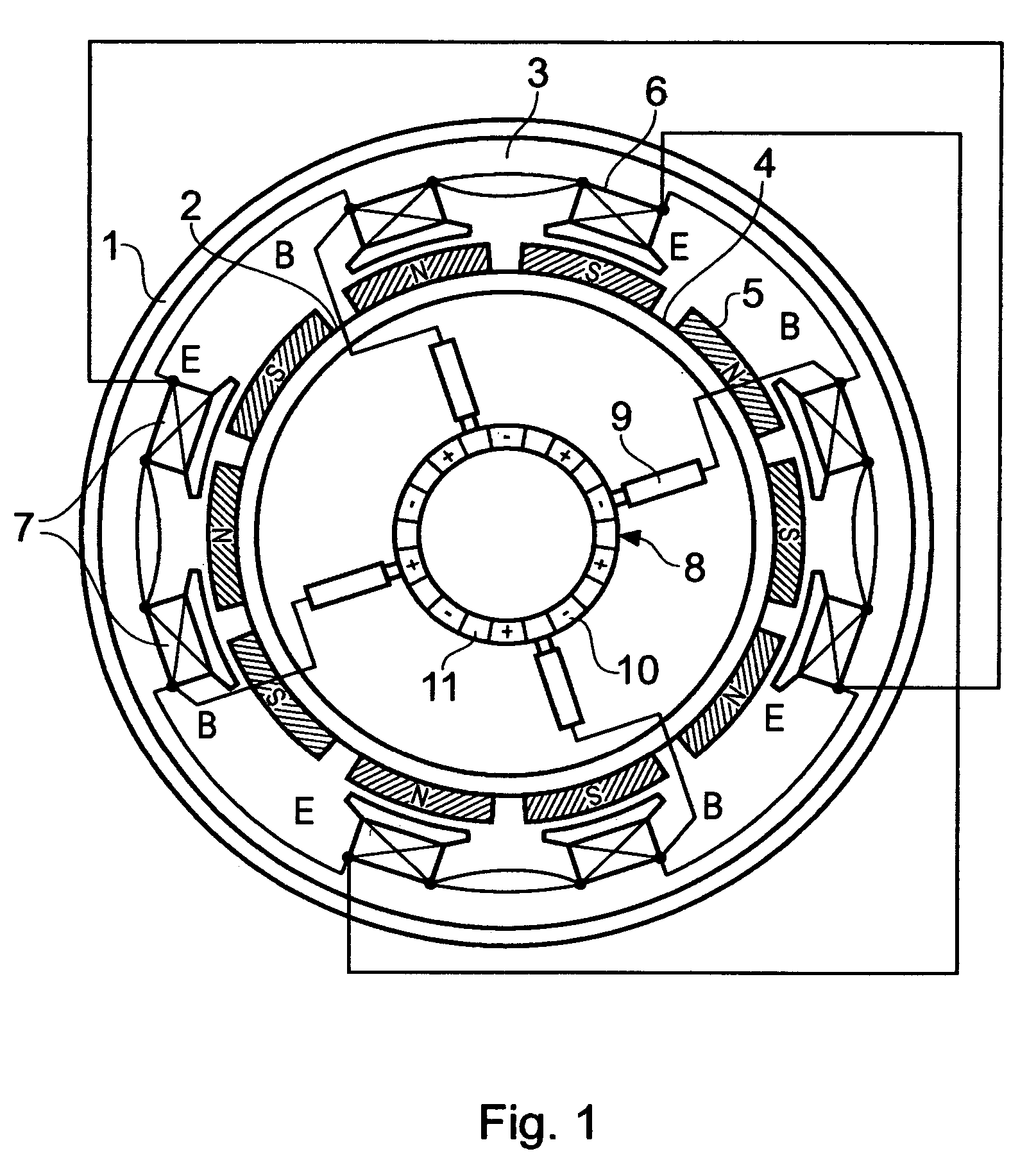
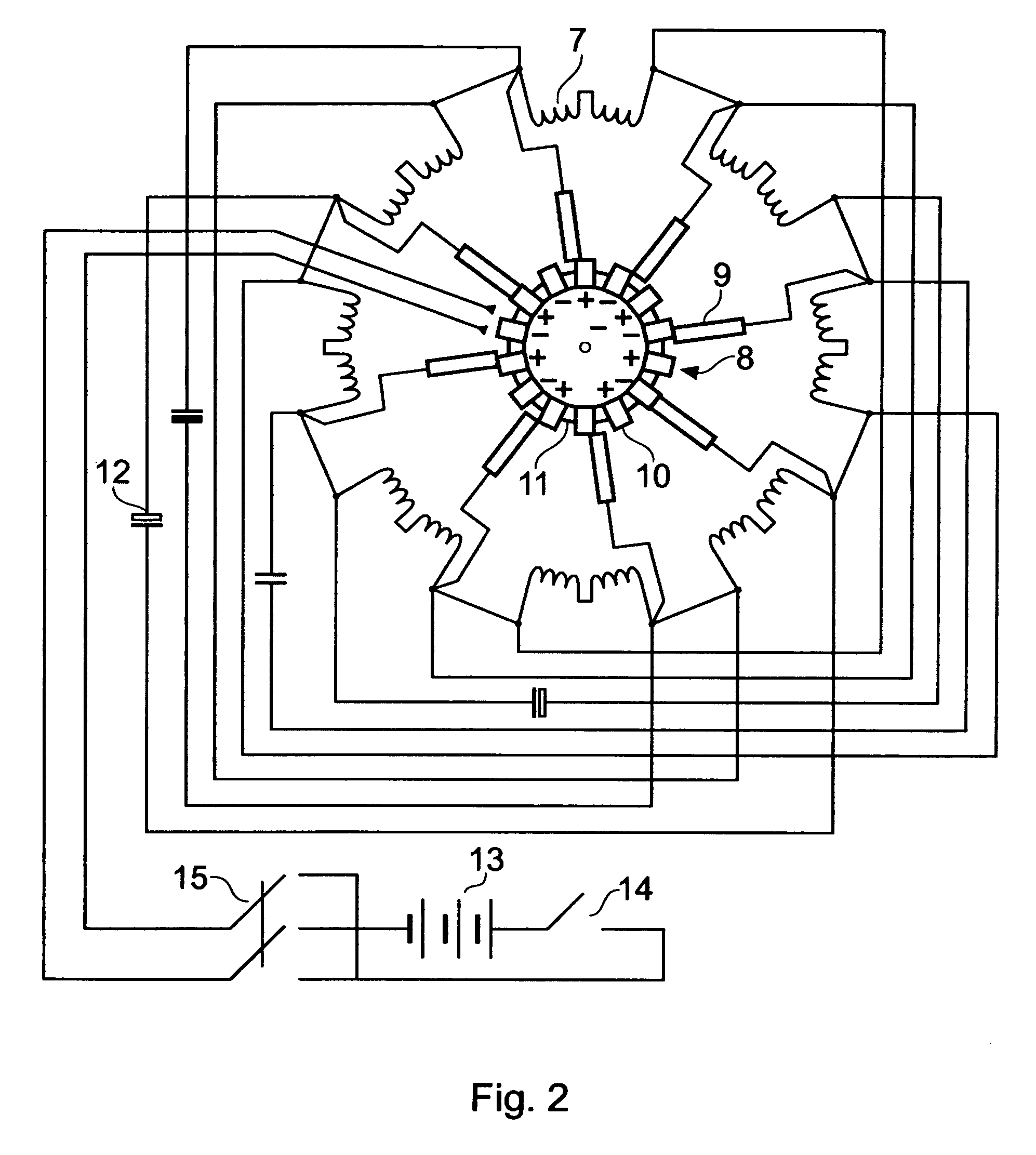
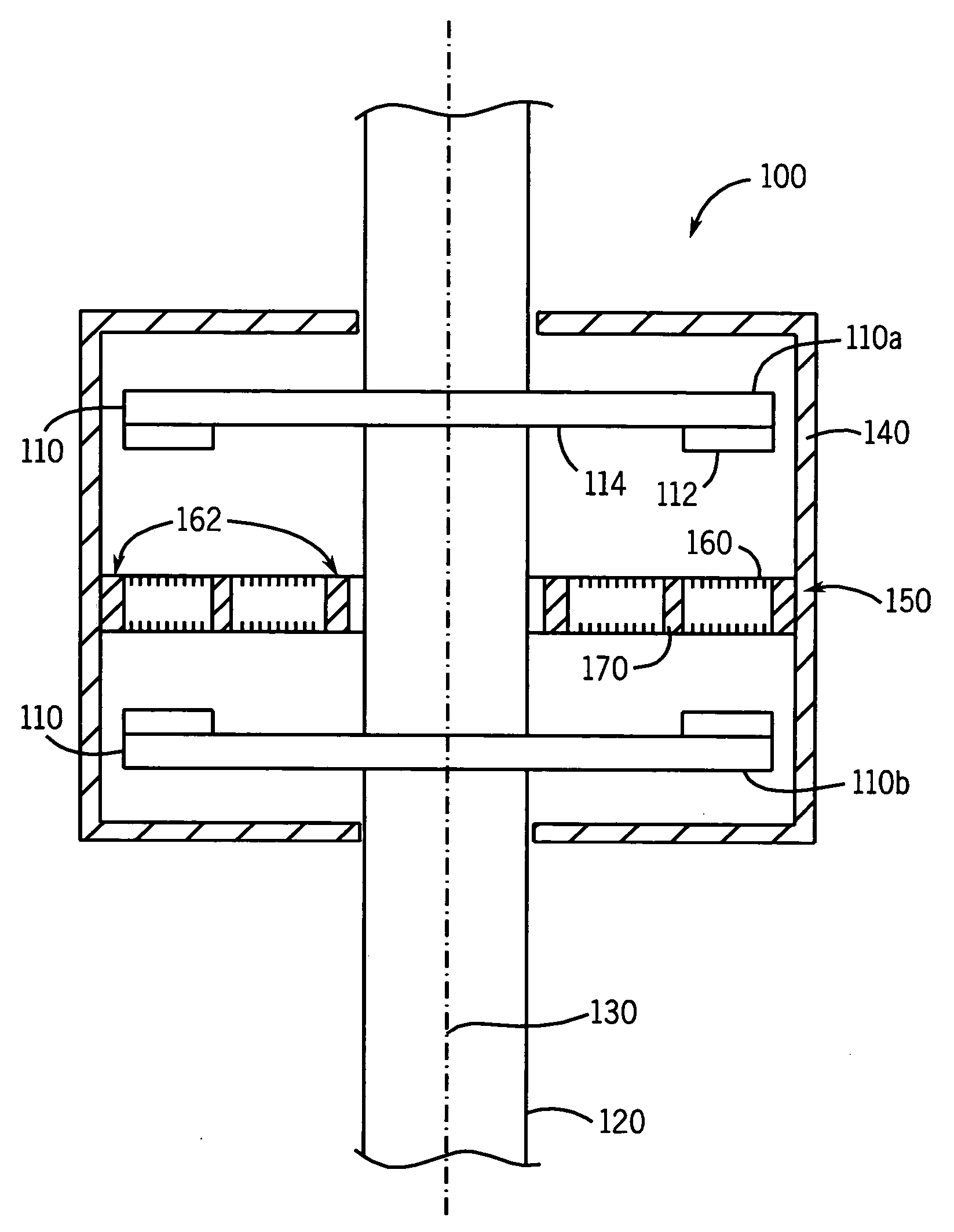
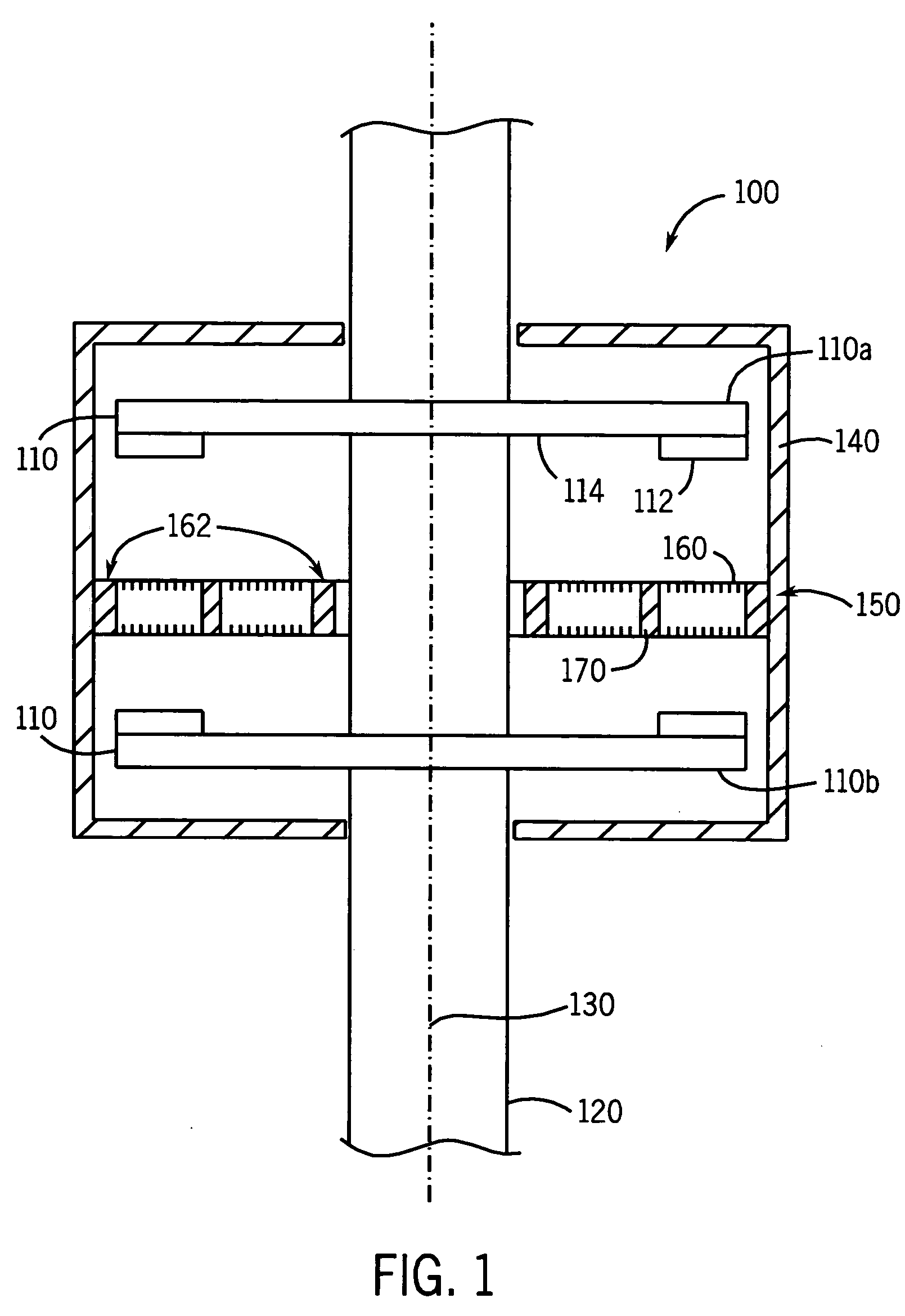
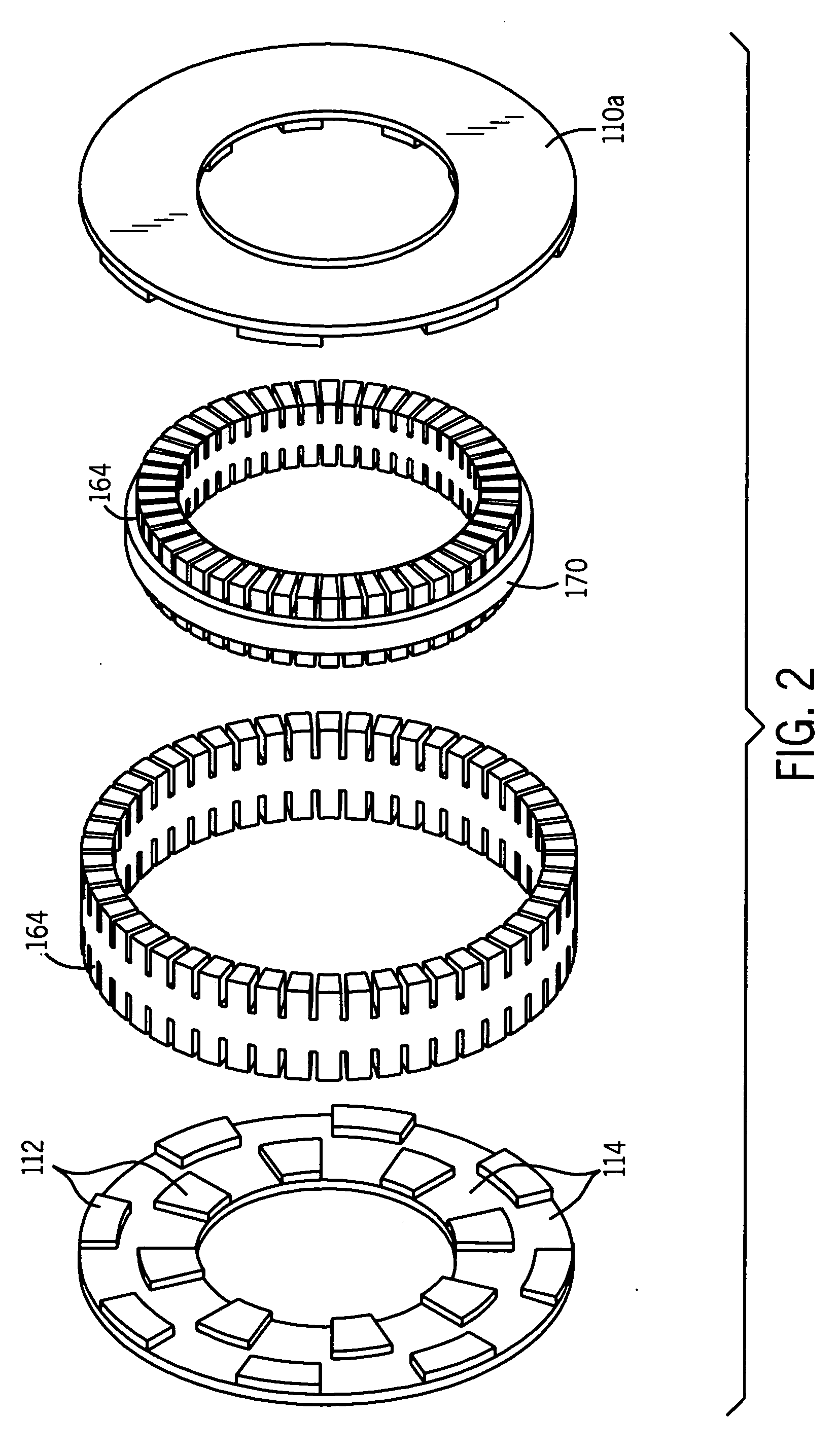
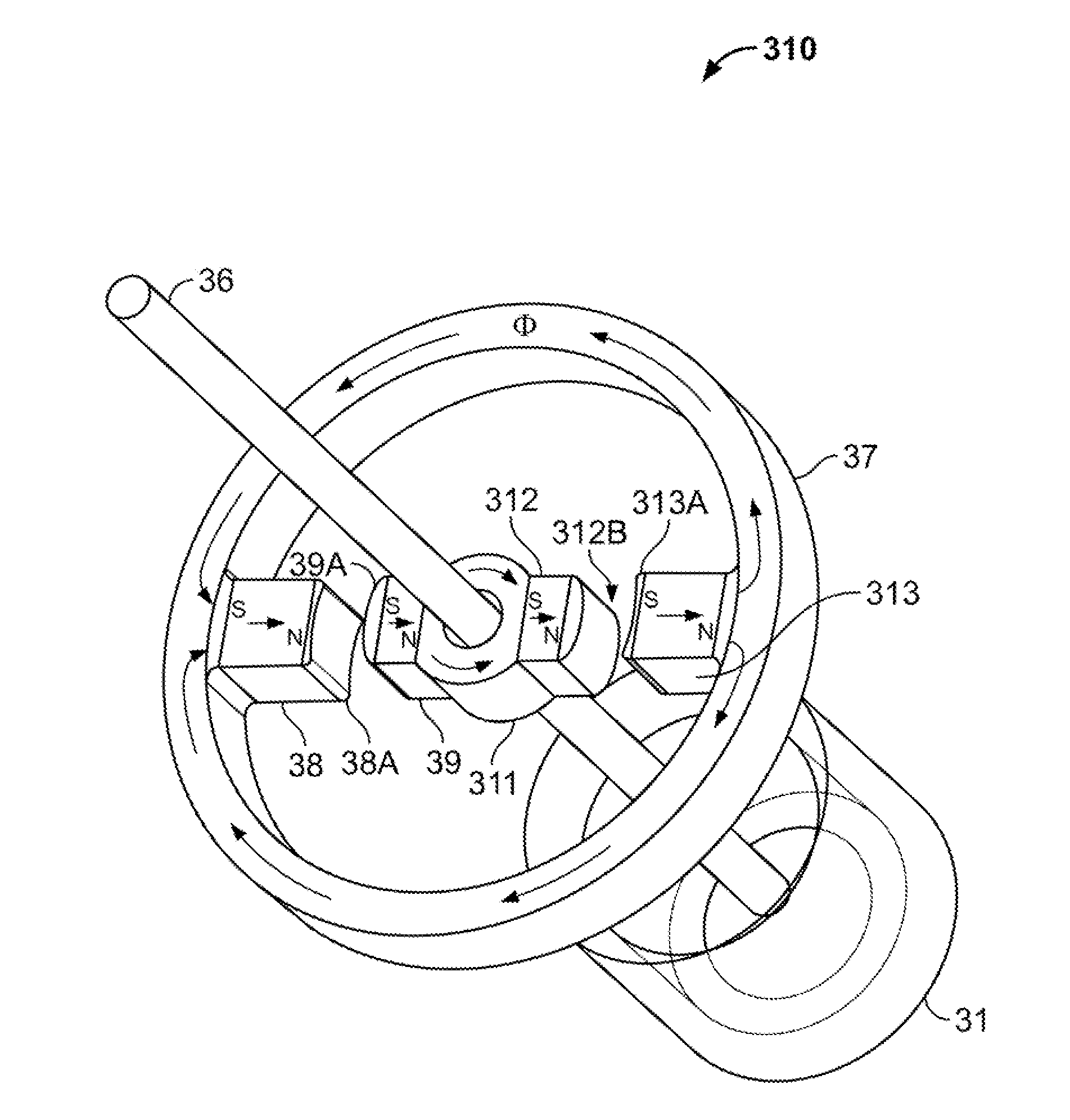
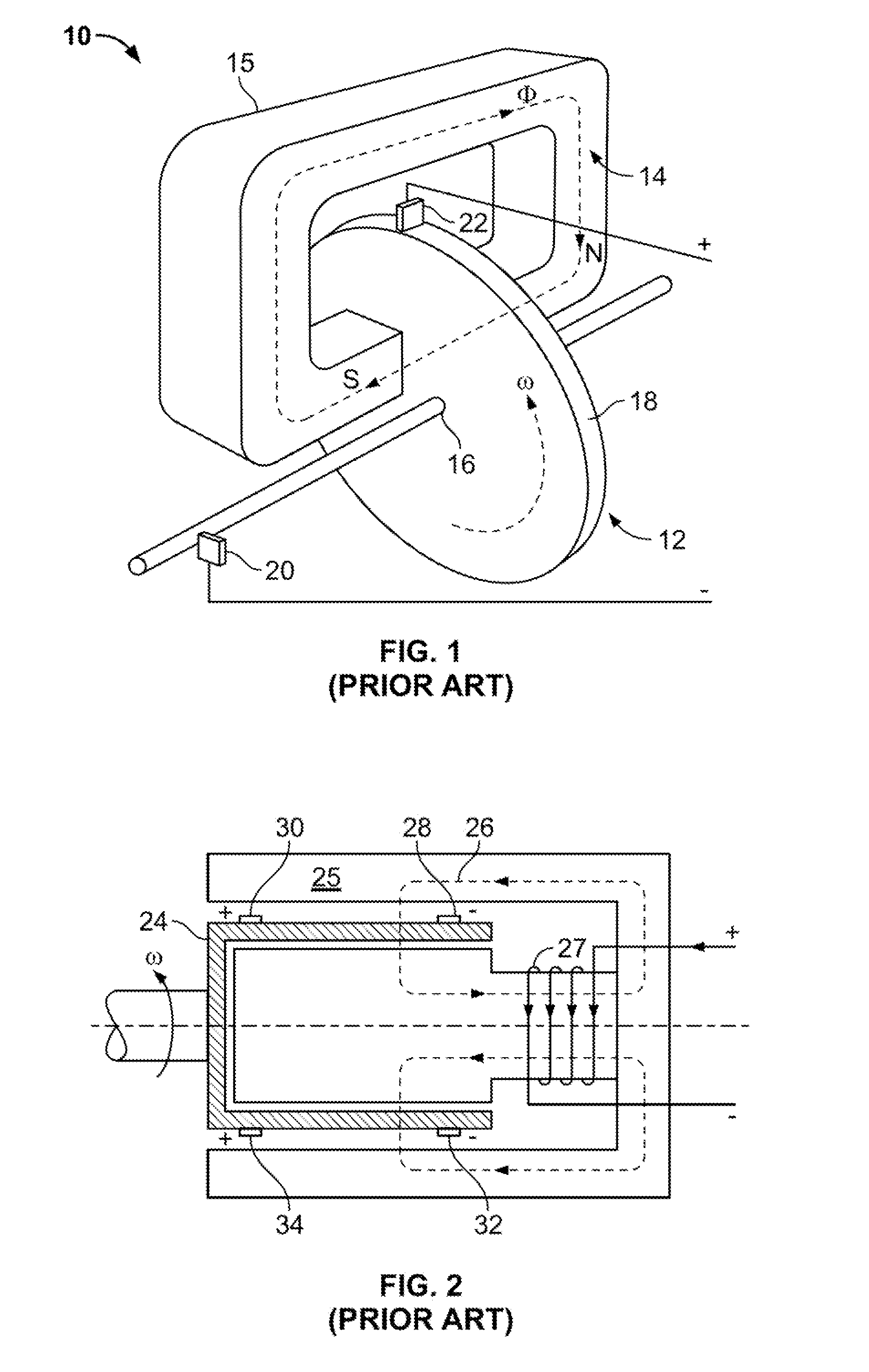
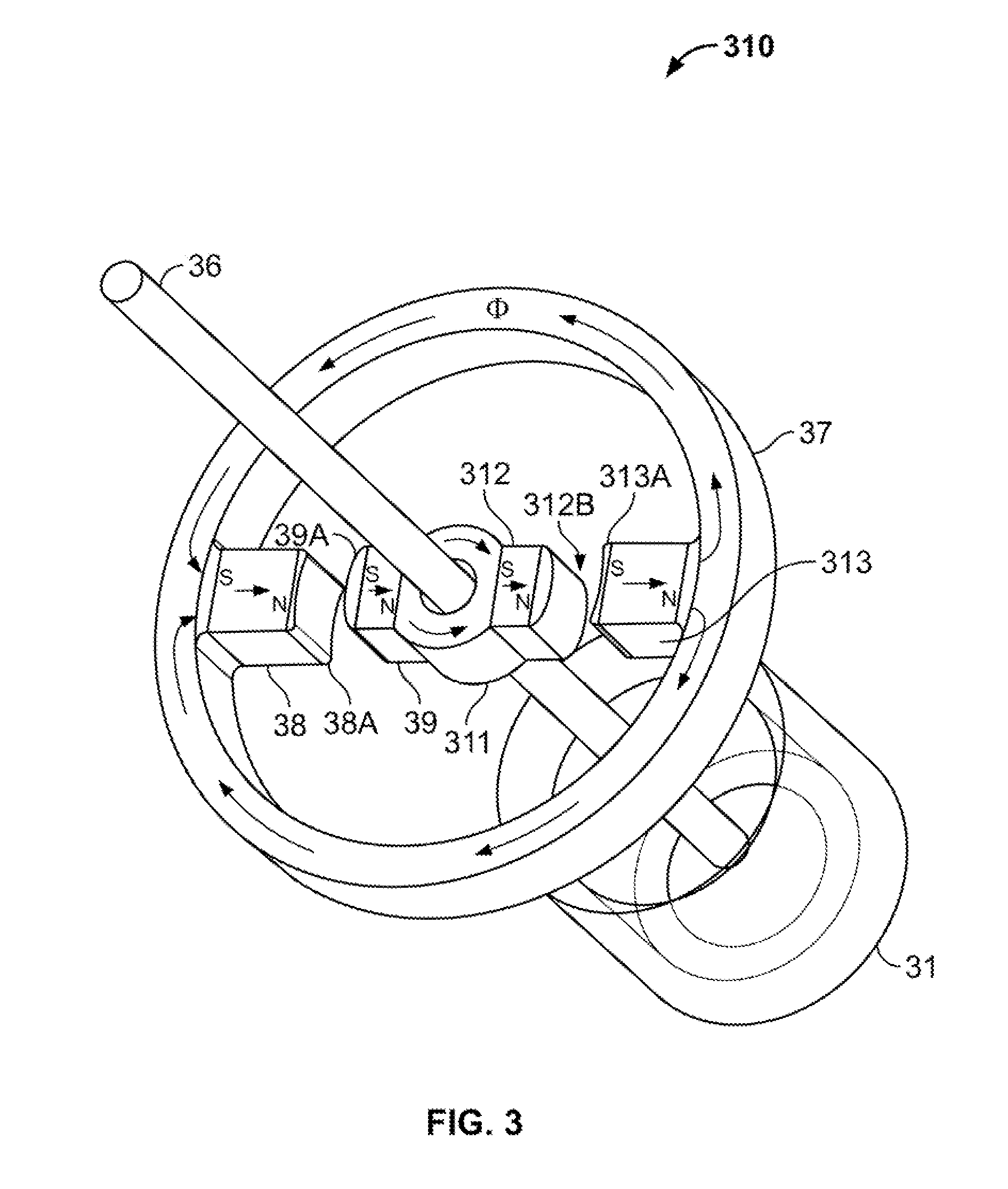
InactiveUS20060087187A1Extended service lifeLow heat generationAcyclic motorsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic sourceEngineering
Owner:MAGNETIC TORQUE INT
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils
InactiveUS20060028085A1Improved performance characteristicsIncreased torque densitySynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsStator coilStationary field
A machine includes a rotatable rotor assembly having a number of salient poles. The machine further includes a stationary stator assembly having concentric inner and outer stators, at least one stationary superconducting field coil and at least one stator coil. The stationary superconducting field coil is disposed between the inner and outer stators and is mounted on at least one of the inner and outer stators. The stationary superconducting field coil and the salient poles are configured relative to each other, such that when the rotor assembly is rotated relative to the stator assembly around a predetermined axis, a rotating magnetic field is produced with an airgap flux direction substantially along the predetermined axis. The interaction between the stationary superconducting field coil and the rotating poles provides the only source of a time varying magnetic flux supplied to the stator coil.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electric drive
InactiveUS6940200B2Simplify the manufacturing processSmall device sizeMagnetic circuit rotating partsMechanical energy handlingWave shapeConductor Coil
The invention refers to magnetoelectric machines and comprises a rotor made in the form of at least two disks, the magnetized disks have circumferential arrayed like poles and an axially magnetized polygon or cylindrical magnet placed between the disks. The stator comprises a winding selected from the group consisting of a coil winding and a wave winding coils that are distributed over the circumference and are installed predominantly in the space between the rotor poles provides for the possibility of the end face interaction with the rotor poles. Each of at least two disks could be made of a non-ferrous material with embedded magnets, and rotor further comprises ferrous metal plates, each of the plates is attached on an outer surface of each disk and comprises a ferrous metal cylinder for interconnecting a magnetic flux between ferrous metal plates. The rotor could be made as a multi-sectional unit. The disks could be made integral with a magnet in such a manner that they serve as magnet's poles. It becomes possible to reduce the radial size of the device. A plate-like shape of the disks makes it possible to optimize the size of the device depending on the magnet and stator used, required power and the size of a device, in which this electric drive is supposed to be mounted.
Owner:ADVANCED ROTARY SYST
DC Electric Motor/Generator with Enhanced Permanent Magnet Flux Densities
ActiveUS20150001976A1Reduced torque rippleEfficient outputMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic tension forceImproved method
This disclosure relates in general to a new and improved method for producing electric energy or mechanical power, and in particular to an improved system and method for producing rotary motion from a electro-magnetic motor or generating electrical power from a rotary motion input by concentrating magnetic forces due to electromagnetism or geometric configurations.
Owner:LINEAR LABS
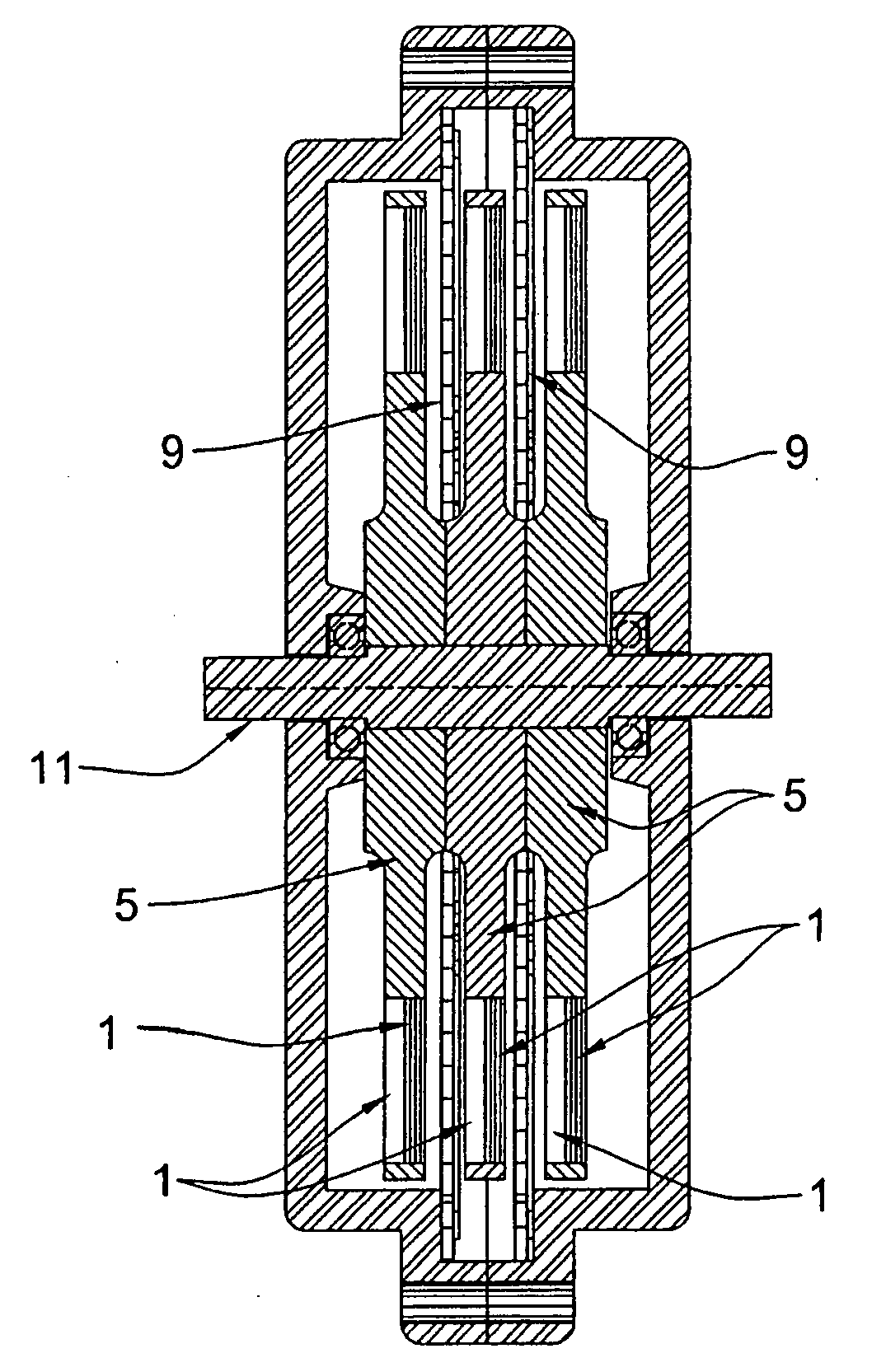
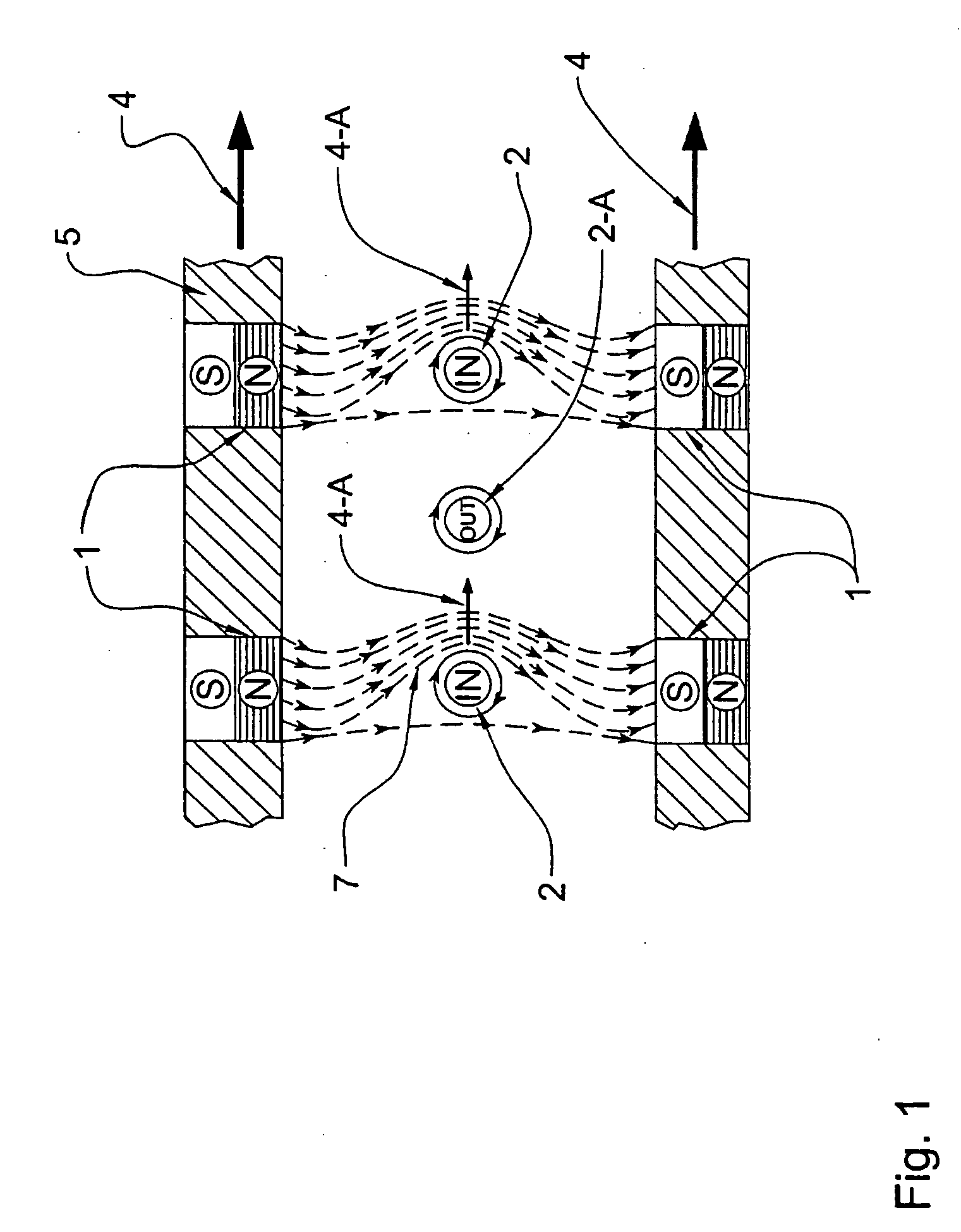
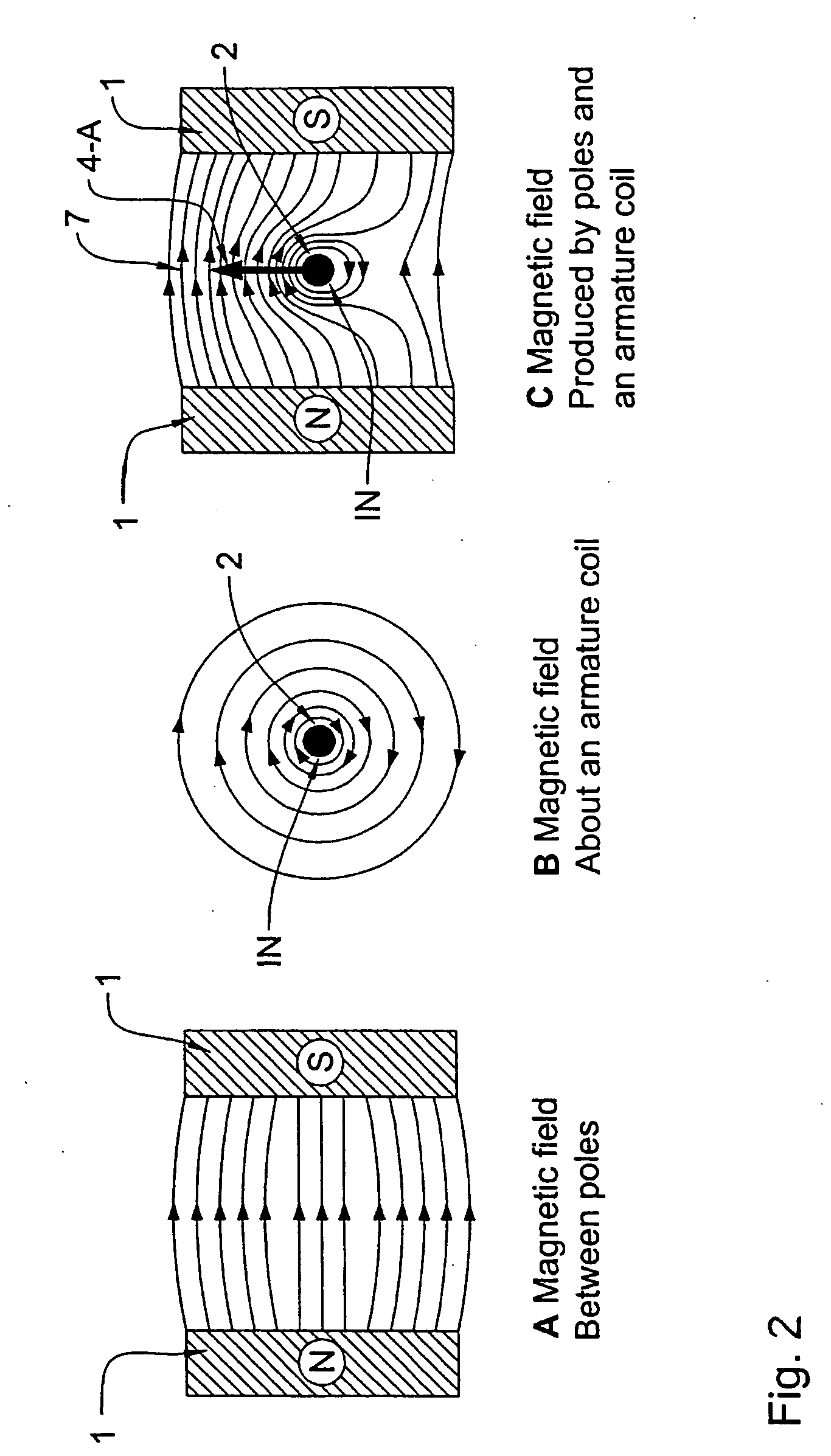
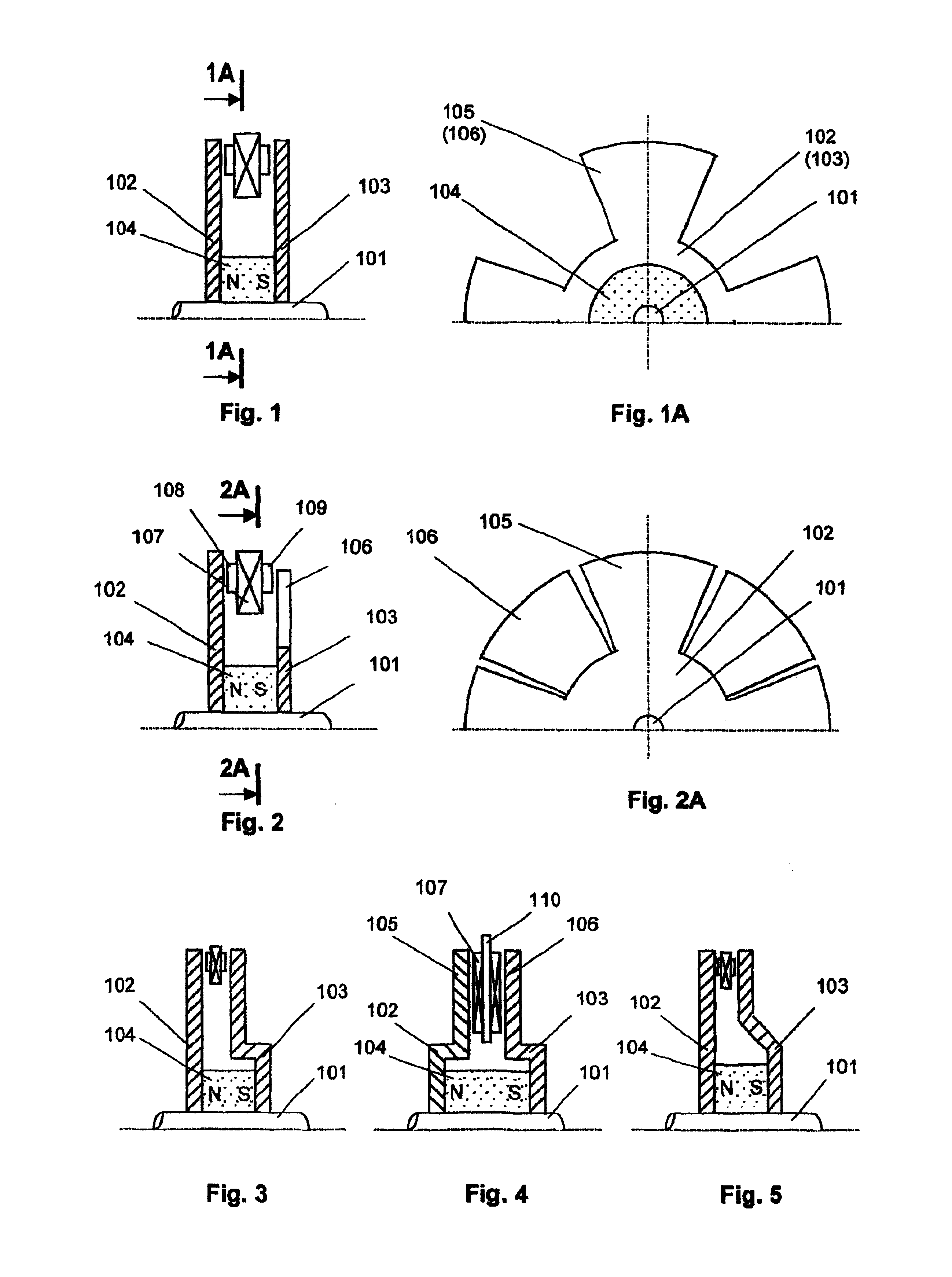
Bipolar machine
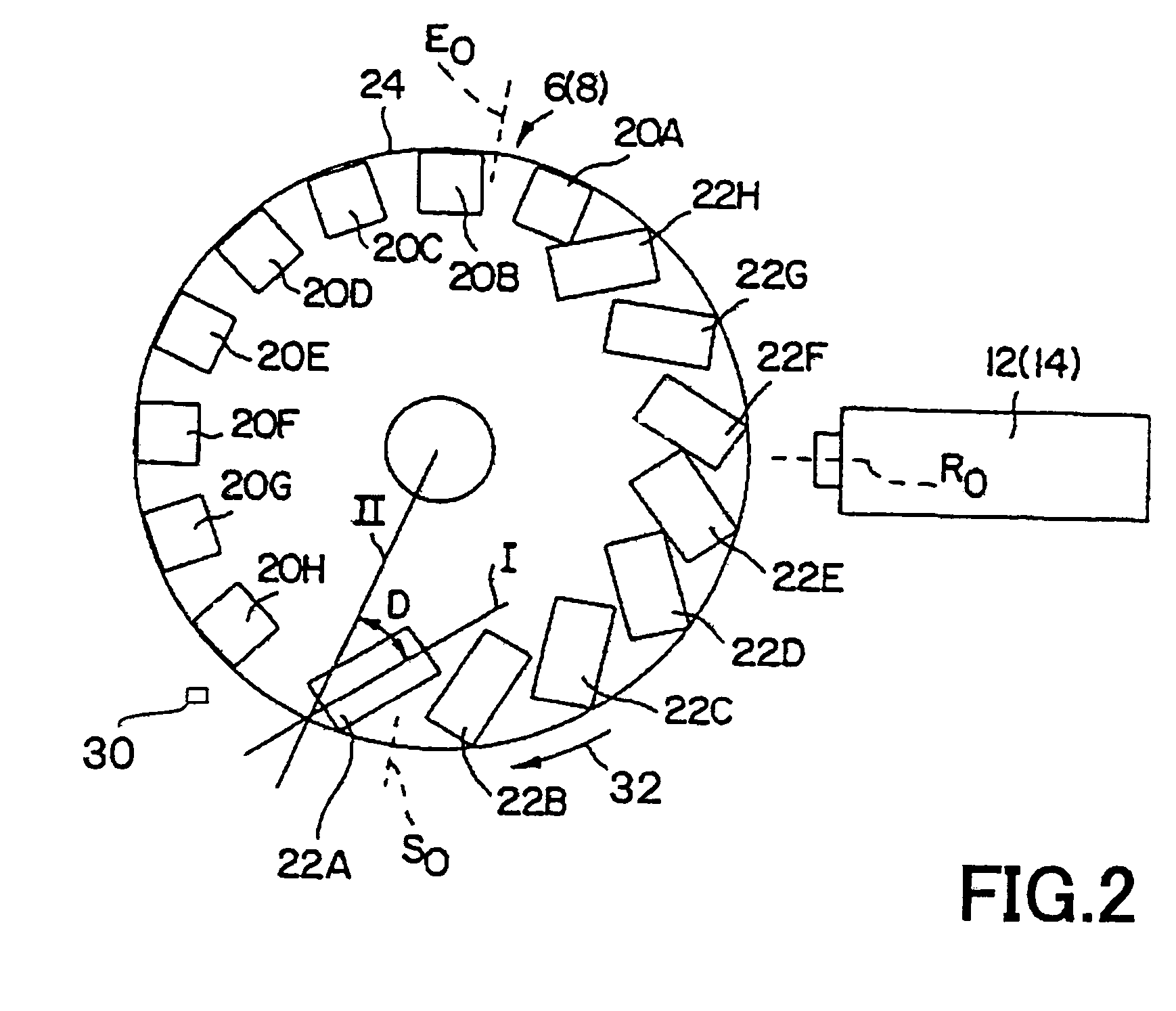
InactiveUS20050073206A1Improve efficiencyImproved brush holdersRotary current collectorCooling/ventillation arrangementInsulation layerCurrent channel
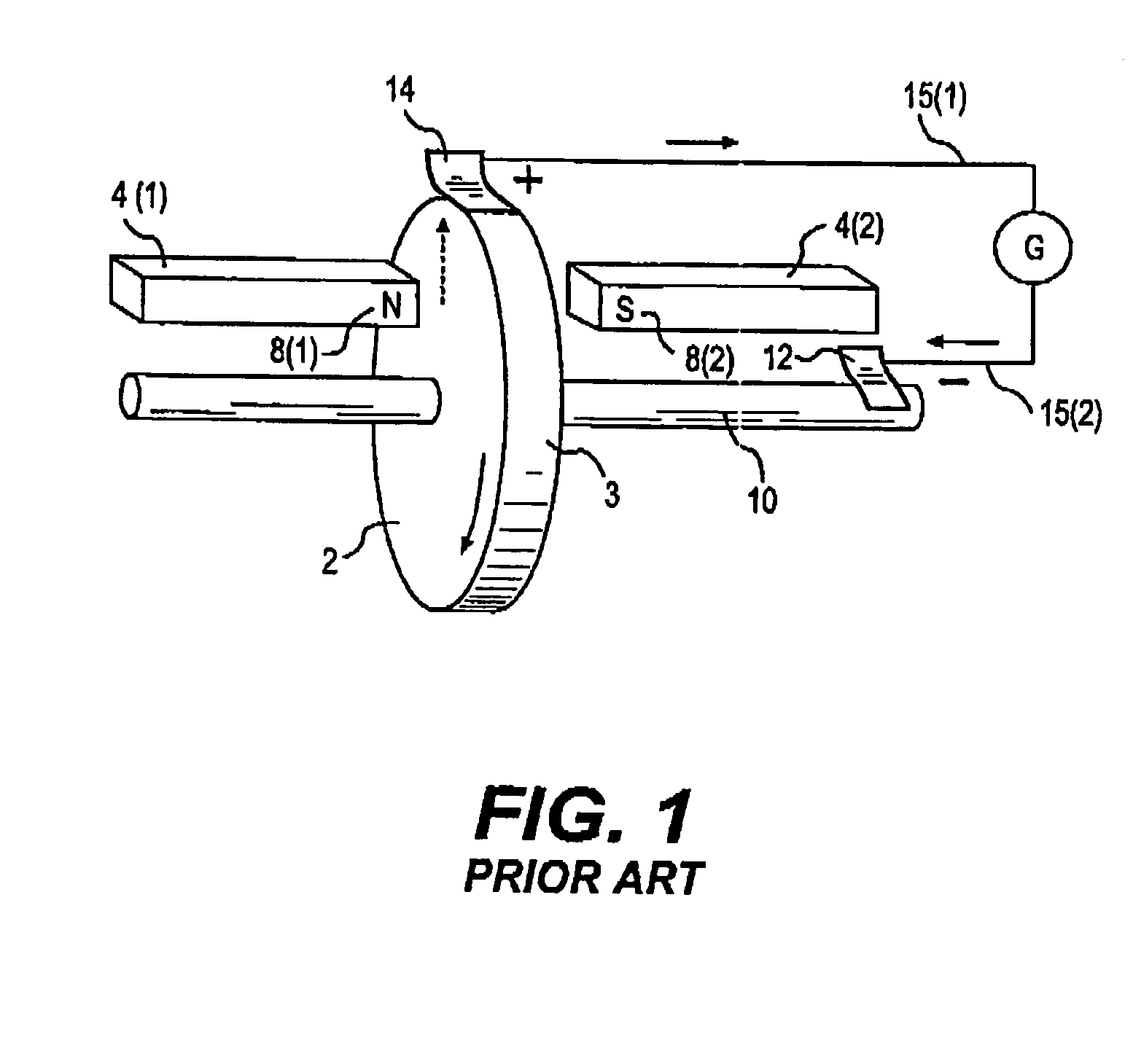
A novel homopolar machine with at least one electrically conductive rotatable rotor having at least one predetermined current path, a plurality of current channel insulation layers, and a magnetic field source configured to apply a magnetic field penetrating the rotor and intersecting the current channels when the rotor rotates. The current channel insulation layers are configured for anisotropic current flow both to inhibit eddy currents and to channel current flow between predetermined correlated brush pairs. Two particular configurations are proposed, wherein the source of magnetization generates in the rotor two separate zones with magnetic flux in opposite directions, while the current channel insulation layers guide the current consecutively through these so as to generate the same rotation-sense of Lorentz force.
Owner:WILSDORF DORIS
Control of synchronous electrical machines
ActiveUS20100207557A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersCommutation monitoringSynchronous motorEngineering
A synchronous motor having phase windings which are split or tapped and in which the conduction angle of the applied alternating current is varied at one or more taps to allow the motor to start in a controlled direction and be torque controlled to synchronous speed.
Owner:WELLINGTON DRIVE TECHNOLOGIES
Pulsed-inertial electric motor
InactiveUS7285889B2Improved performance characteristicsSimple designWindingsMagnetic circuitLow voltageDc current
Owner:ULTRA MOTOR CO LTD
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils
A machine includes a stator assembly that includes a stator yoke, a pair of armature coils mechanically coupled to the stator yoke, and a stationary superconducting field coil. The stator yoke comprises a magnetic material. The machine further includes a shaft rotatably mounted in the stator yoke, the shaft comprising a non-magnetic material. The machine further includes a rotor assembly rotationally engaged with the shaft. The rotor assembly includes a rotor disk extending between the armature coils, the rotor disk having an inner portion and an outer portion. The outer portion of the rotor disk includes a number of circumferentially-spaced, magnetic poles. The rotor disk is coupled to the shaft for rotation about the shaft and generation of a rotating permeance wave. The stationary superconducting field coil is disposed between the stator yoke and the rotor disk, and the stationary superconducting field coil is configured as a stationary magneto-motive force (MMF) source for the rotating permeance wave produced by the rotor assembly to produce a rotating magnetic field.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Magnetic rotating motor generator
A magnetic rotating motor generator of the present invention comprises a rotating portion which is made of a non-magnetic substance whose periphery is provided with a group of permanent magnets tilted at a predetermined angle in an embedded manner; a group of electromagnets that are disposed adjacently to the rotating portion so as to oppose the group of permanent magnets; a positional sensor for detecting positions of the group of permanent magnets; a controller for applying an electric current to the electromagnet on the basis of a detected signal from the positional sensor; and a power generating section for obtaining power from a coil of the electromagnet. A rotation mode and a power generation mode are repeated, so that power generation is performed while a function as a motor is exhibited.
Owner:FOREST PINE ELECTRIC
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils and axial airgap flux
A machine, such as a motor or generator, includes a rotatable rotor assembly comprising a plurality of salient poles and a stationary stator assembly comprising a superconducting field coil. The superconducting field coil and the salient poles are configured relative to each other such when the rotor assembly is rotated relative to the stator assembly around a predetermined axis, a rotating magnetic field is produced with an airgap flux direction substantially along the predetermined axis.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Mp-a and Mp-t Machines, Multipolar Machines for Alternating and Three-Phase Currents
InactiveUS20080246365A1Single-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlThree-phaseMechanical engineering
Owner:KUHLMANN WILSDORF MOTORS
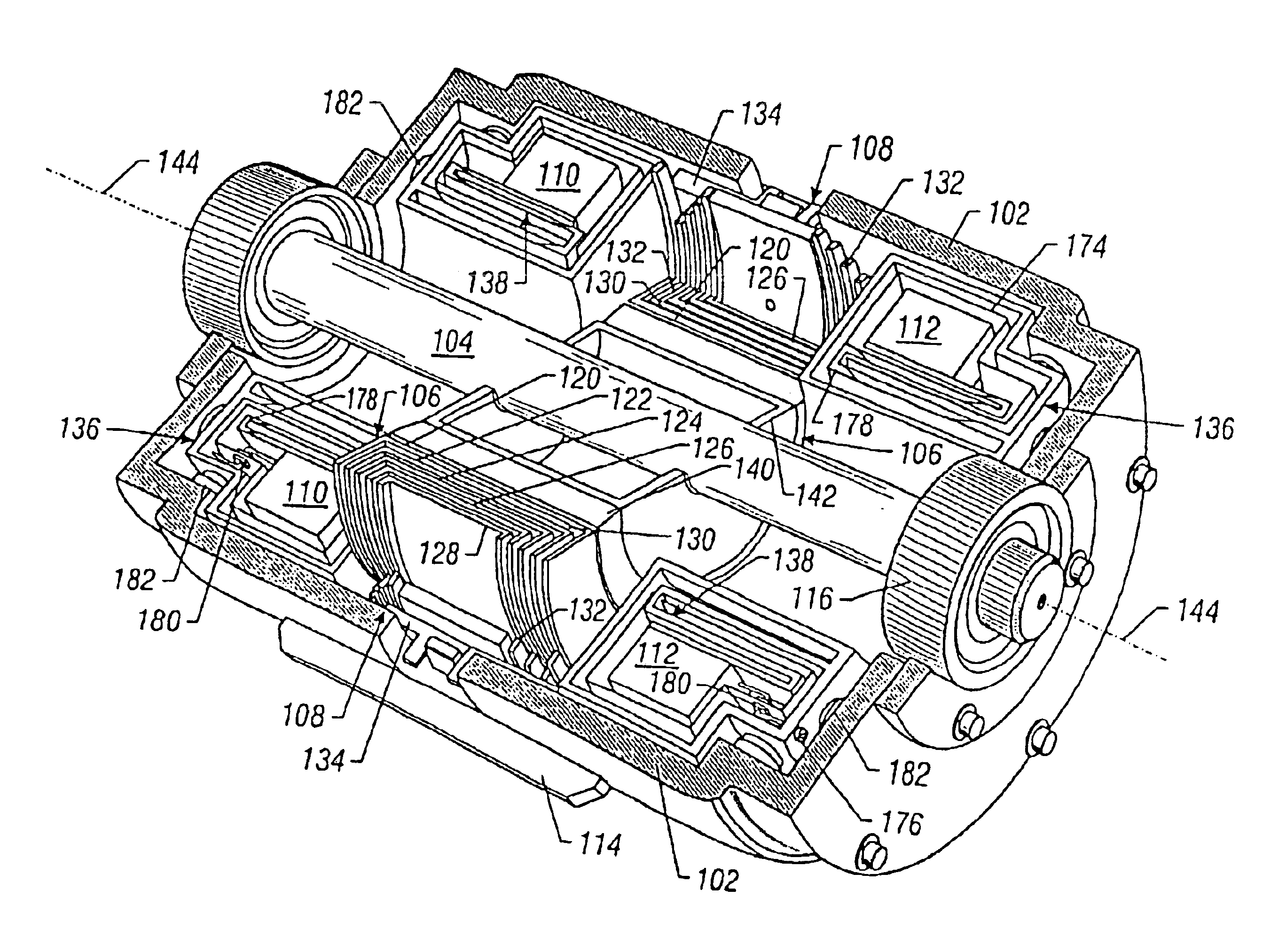
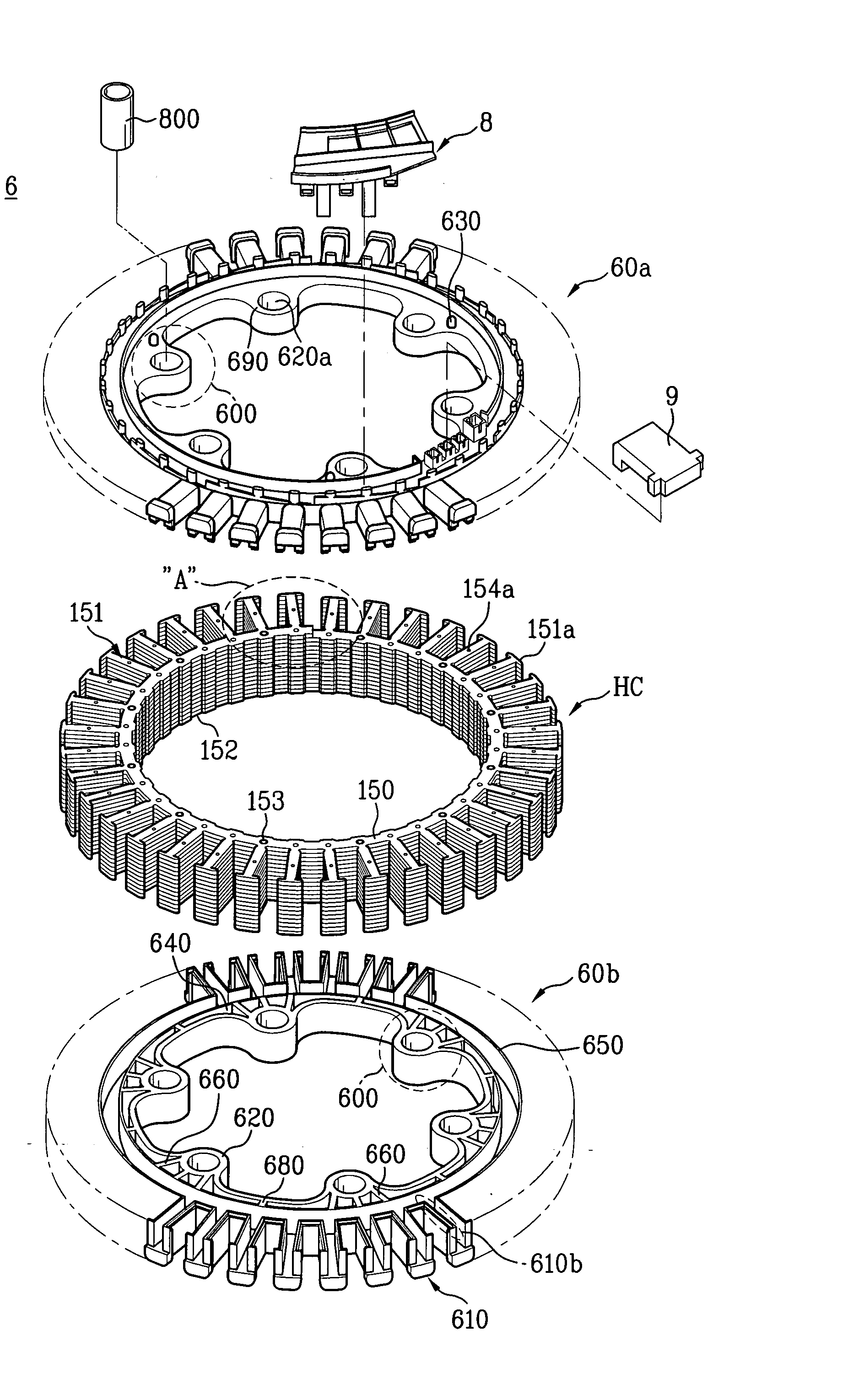
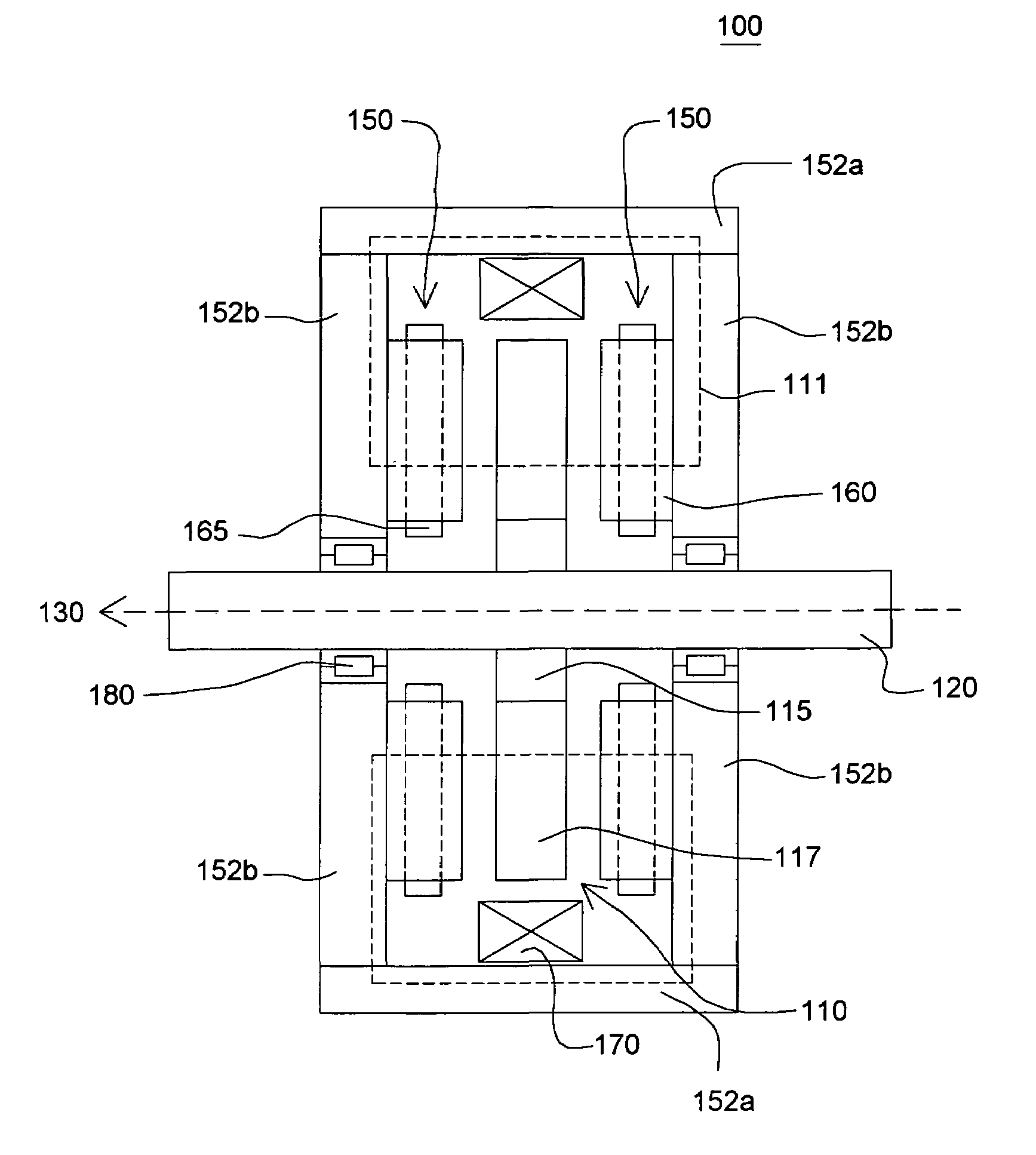
Electromechanical device having three-dimensional stator laminations
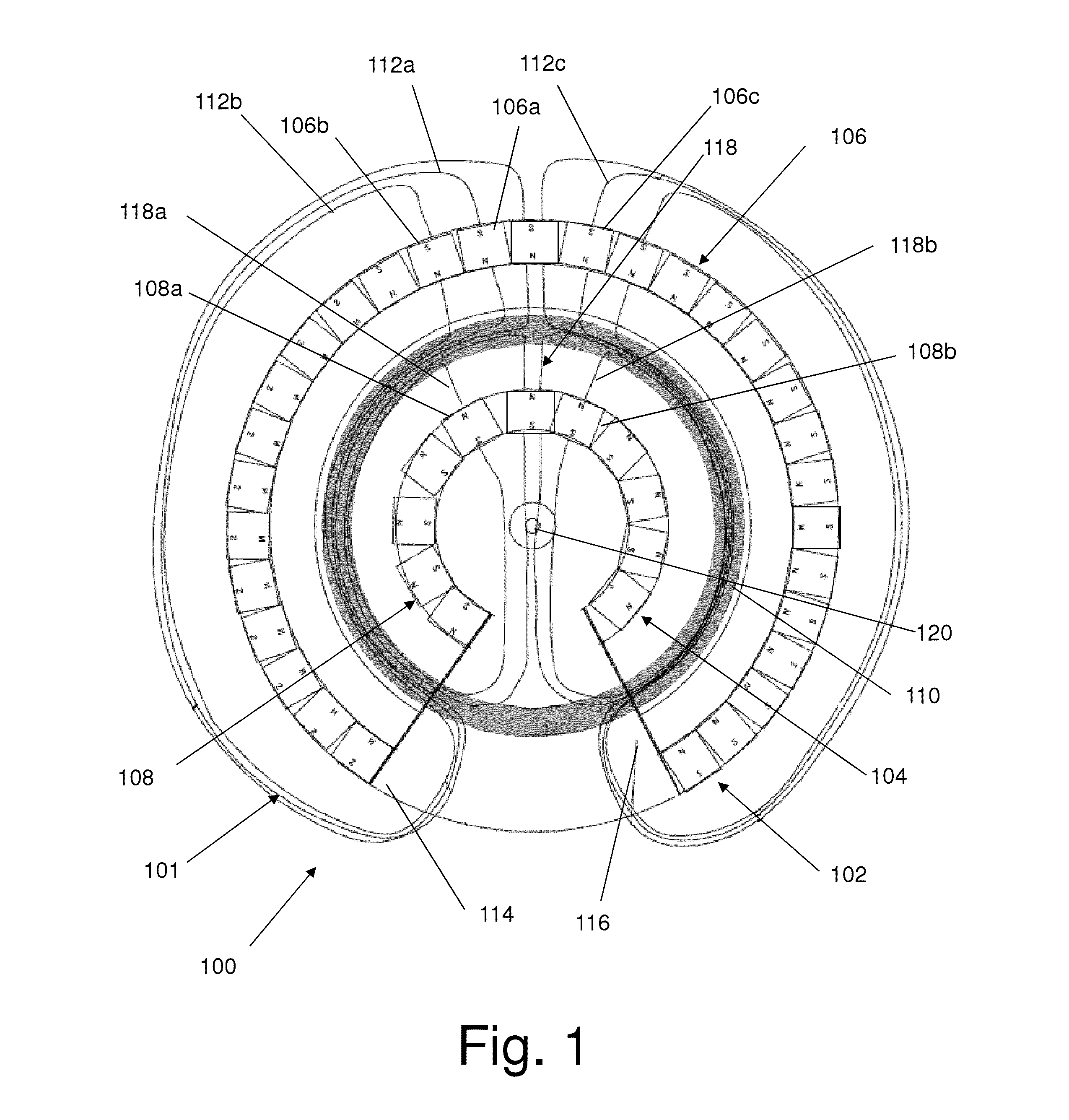
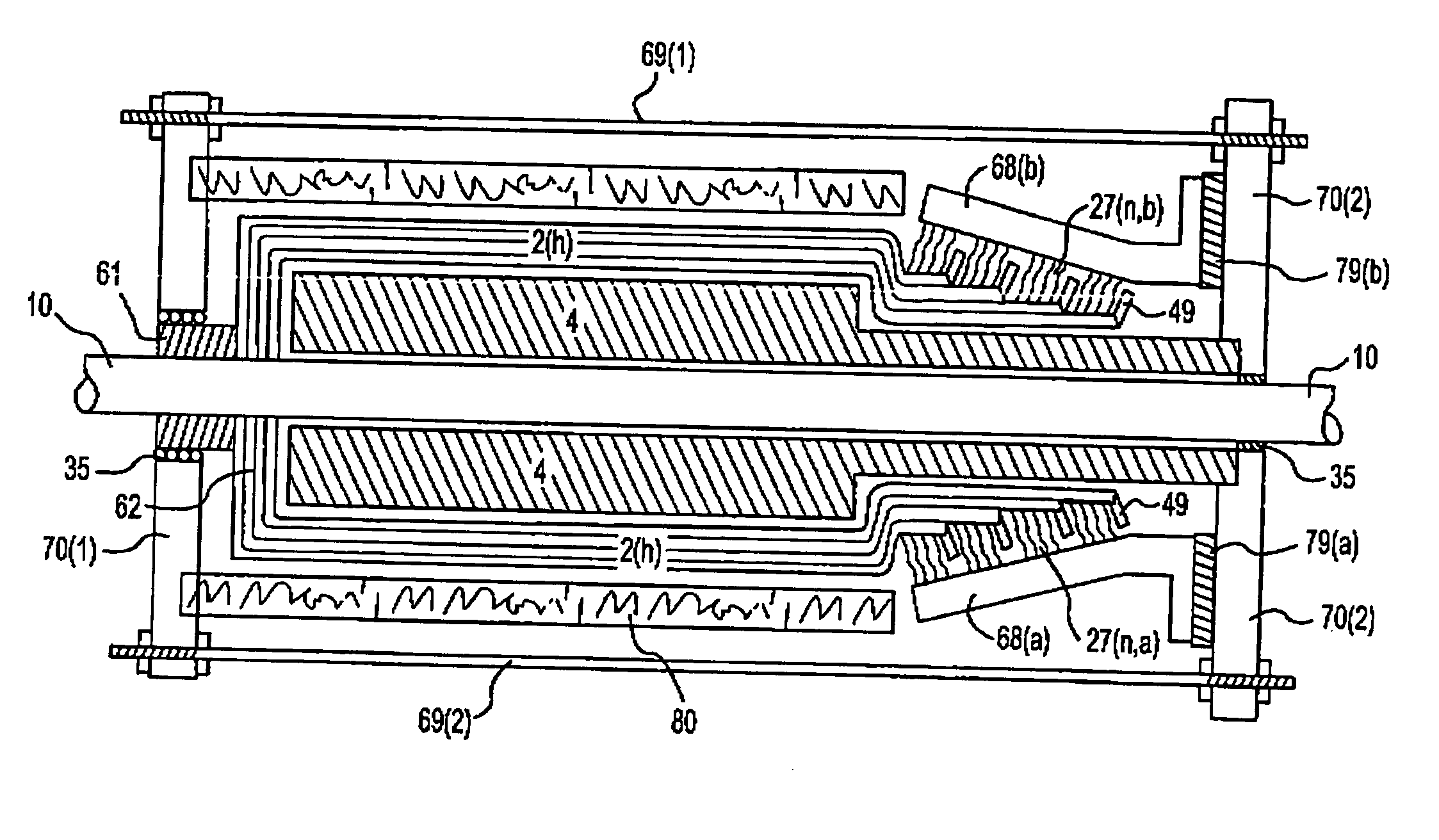
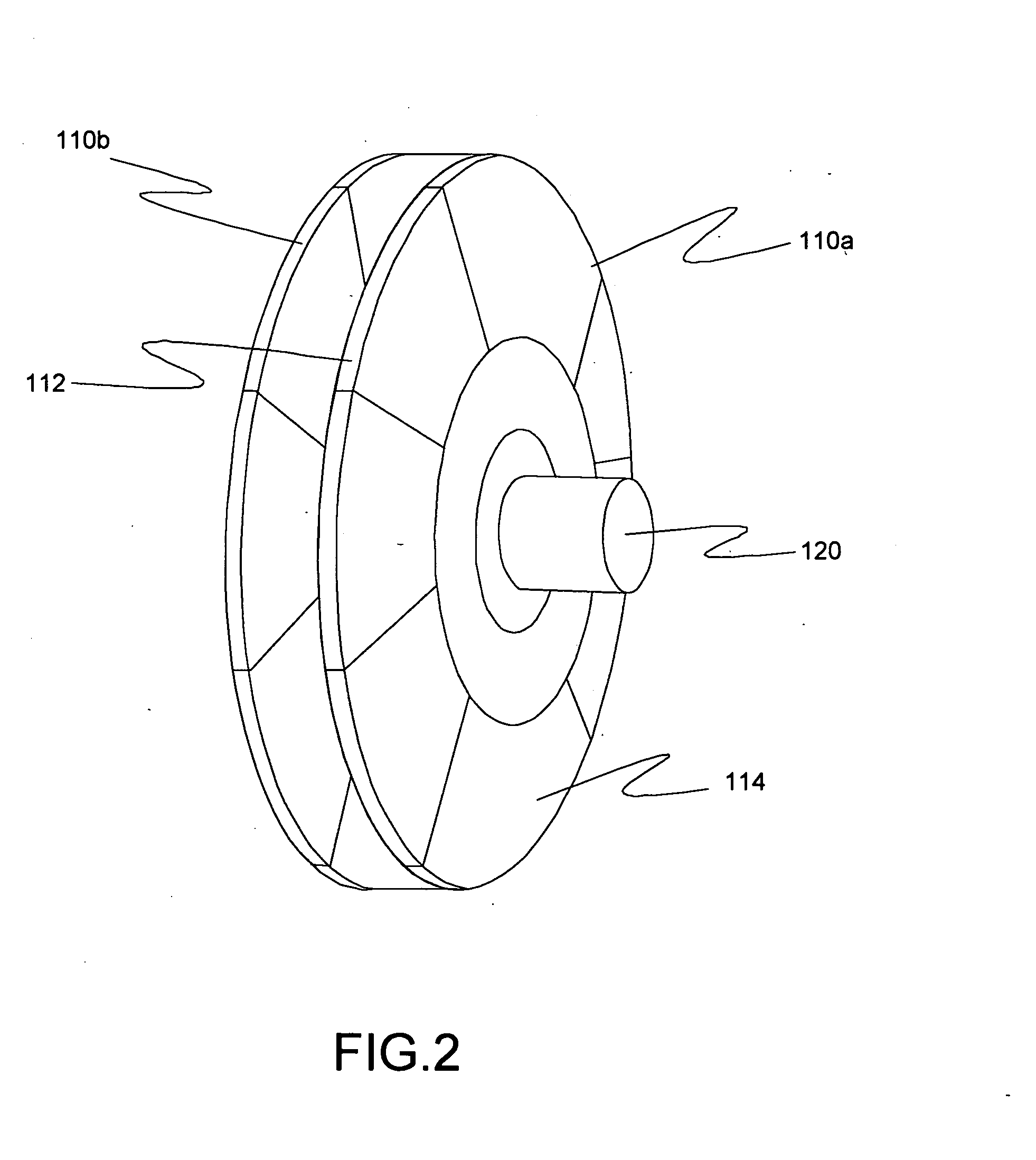
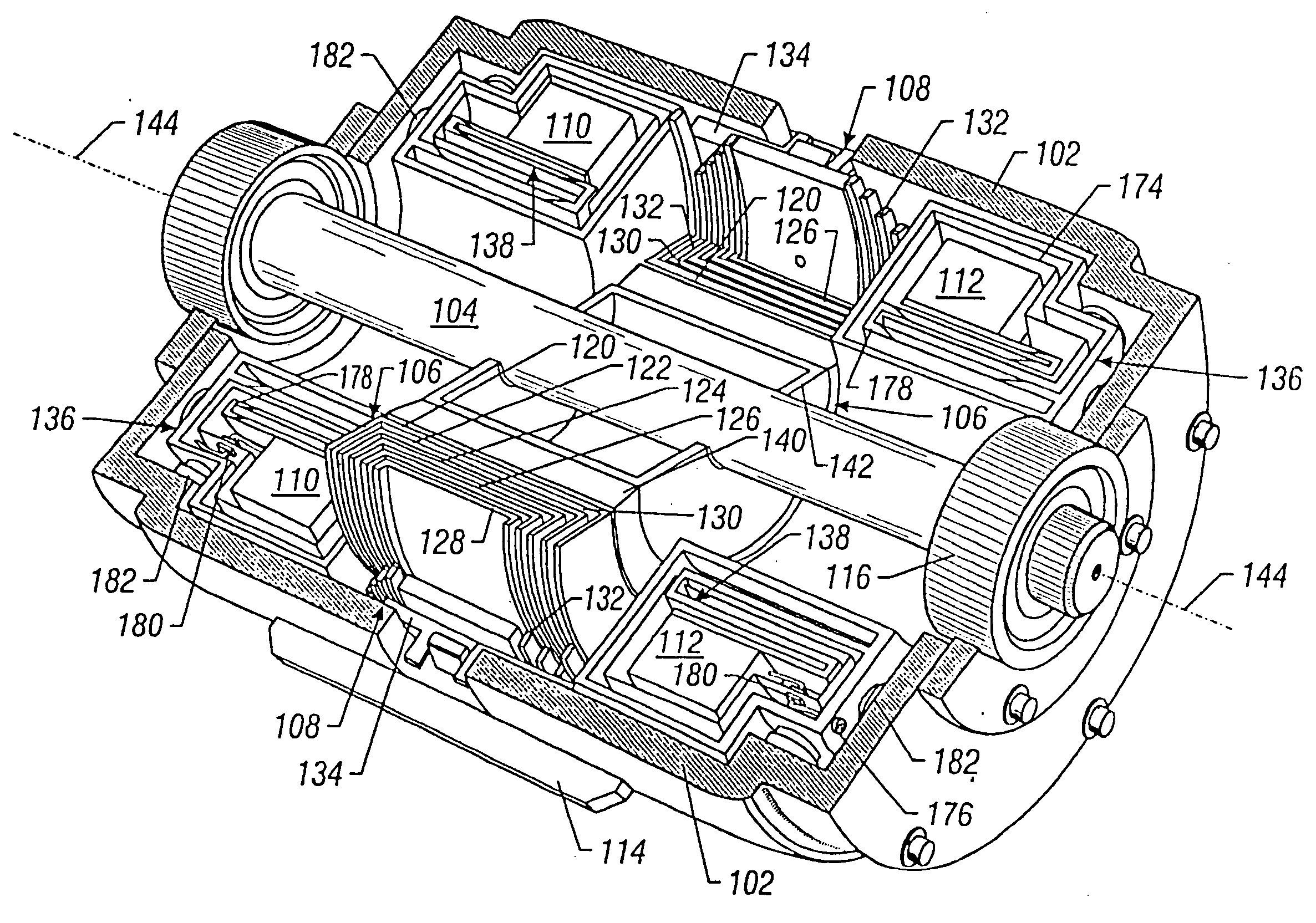
In certain embodiments, an electromechanical device includes a rotor having a rotational axis, and a stator disposed about the rotor. The stator may include a circumferentially laminated section comprising a plurality of circumferential segments disposed one after another in a circumferential direction relative to the rotational axis. The stator also may include a radially laminated section comprising a plurality of radial segments disposed one after another in a radial direction relative to the rotational axis. In addition, the stator may include an axially laminated section comprising a plurality of axial segments disposed one after another in an axial direction relative to the rotational axis.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils
A machine includes a shaft adapted to rotate about a longitudinal axis and formed of a magnetic material and a rotor assembly rotationally engaged with the shaft The rotor assembly includes a pair of rotor disks comprising a magnetic material, each of the rotor disks having a number of magnetic poles, the magnetic poles being spaced apart circumferentially. The rotor disks are coupled to the shaft for rotation about the shaft and generation of a rotating permeance wave. The machine further includes a stator assembly that includes a magnetic core stator disposed between the rotor disks, a number of armature windings supported on the magnetic core stator, and a stationary superconducting field coil disposed between the magnetic core stator and the shaft. The stationary superconducting field coil is configured as a stationary magneto-motive force (MMF) source for the rotating permeance wave produced by the rotor assembly to produce a rotating magnetic field.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Tangential induction dynamoelectric machines
InactiveUS20060158055A1Acyclic motorsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet rotorElectrical conductor
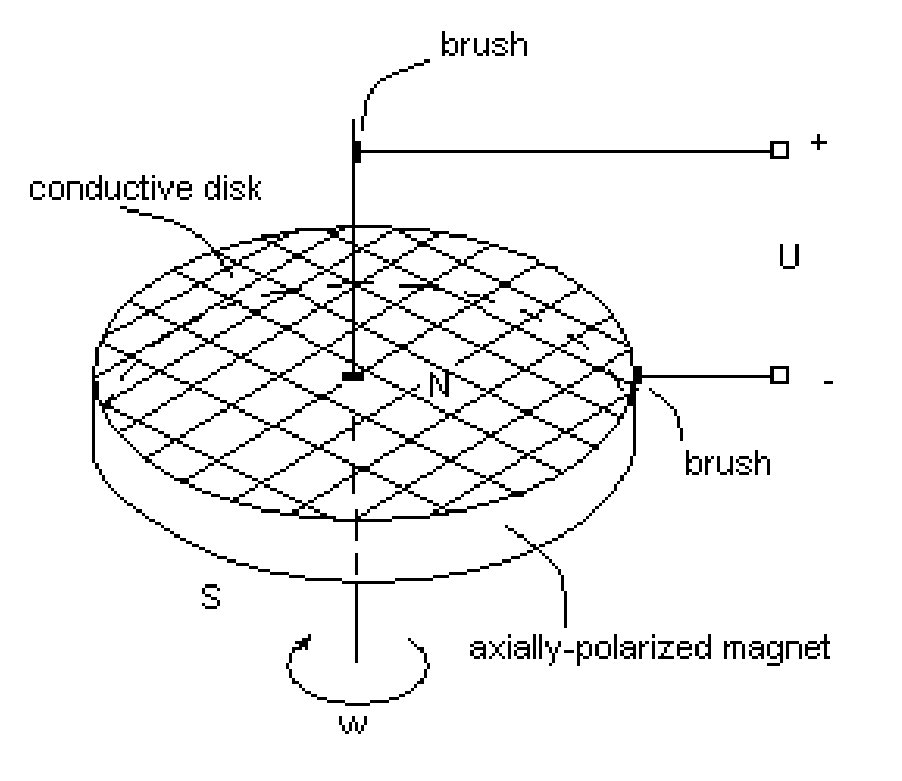
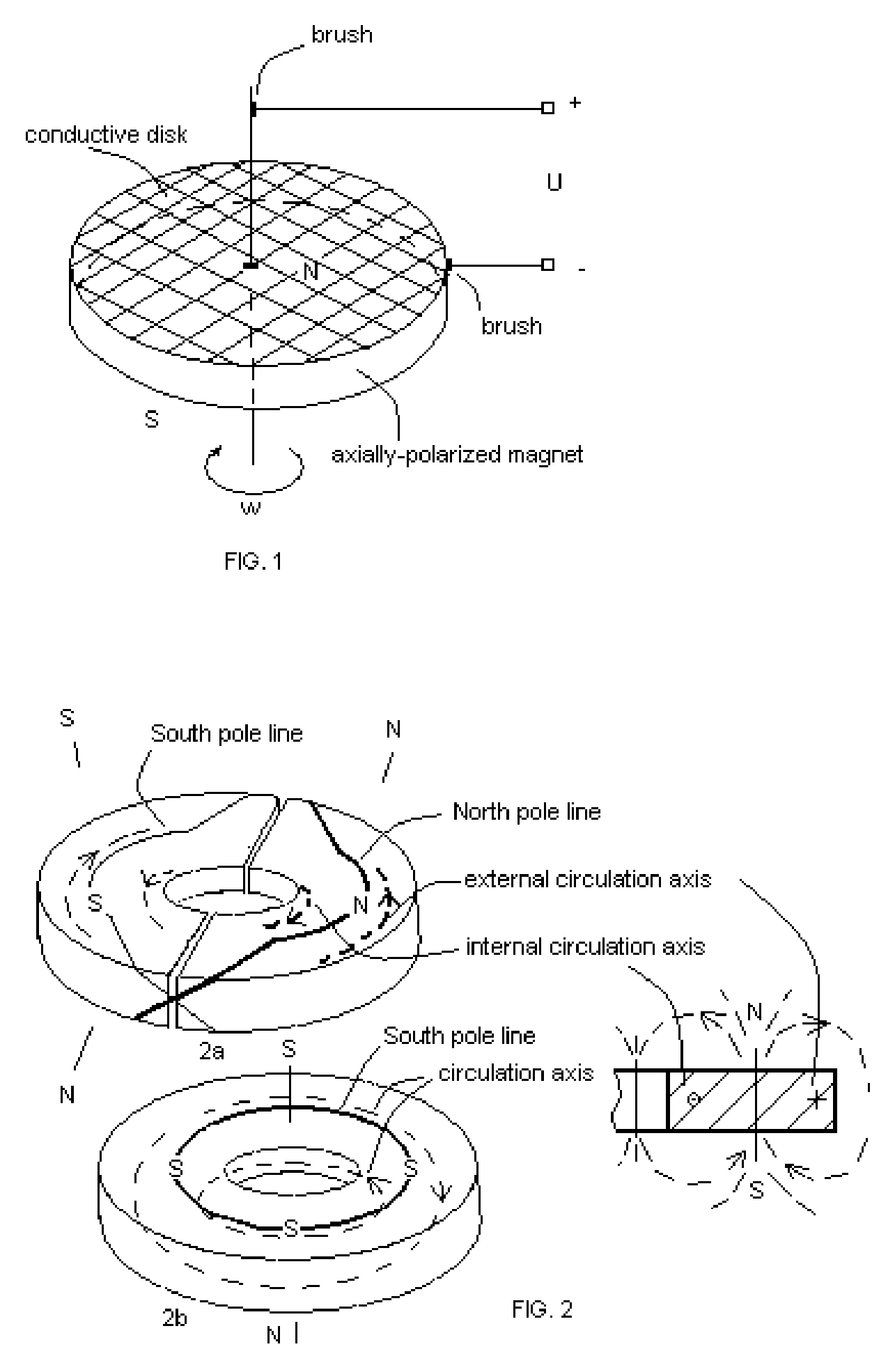
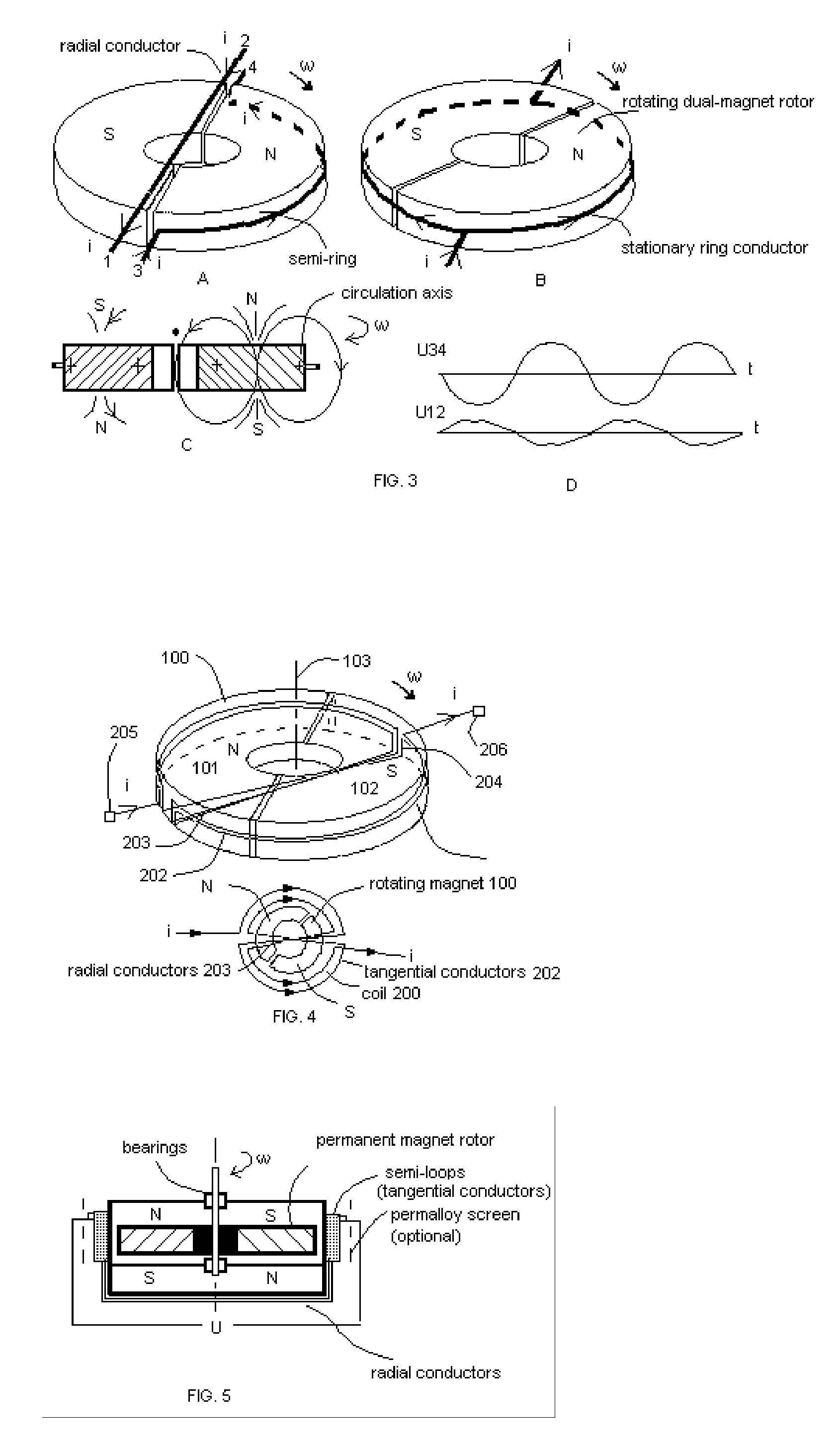
Novel class dynamoelectric machines utilizing “tangential induction” phenomenon—the specific e.m.f. induction, which appears in tangential conductors—is introduced. Alternating-current dynamoelectric machines of this invention house an axially-polarized multi-polar permanent magnet rotor and stator winding having tangentially arranged semi-ring conductors. The rotating permanent-magnet rotor induces current in tangential semi-ring conductors, which, according to Ampere law, could not produce a resistance moment applied to the rotor because the vector of conductor-field velocity is directed along the conductor, and, therefore, such vector orientation does not produce any tangential force. The invention has been successfully embodied in number of “tangential-induction dynamoelectric machines” including multi-phase ones. These dynamoelectric machines can be inverted and work as alternating-current asynchronic electric motors.
Owner:IVTSENKOV GENNADII
DC Homopolar Generator with Drum Wound Air Coil Cage and Radial Flux Focusing
An improved air core homopolar generator is provided. The improved homopolar generator employs a stator having an outer ring for bifurcating magnetic flux flow and multiple flux focusing magnets arranged around a common axis. The improved homopolar generator also includes an inner flux transmitter coaxial with the common axis.
Owner:MANDES ROBERT T
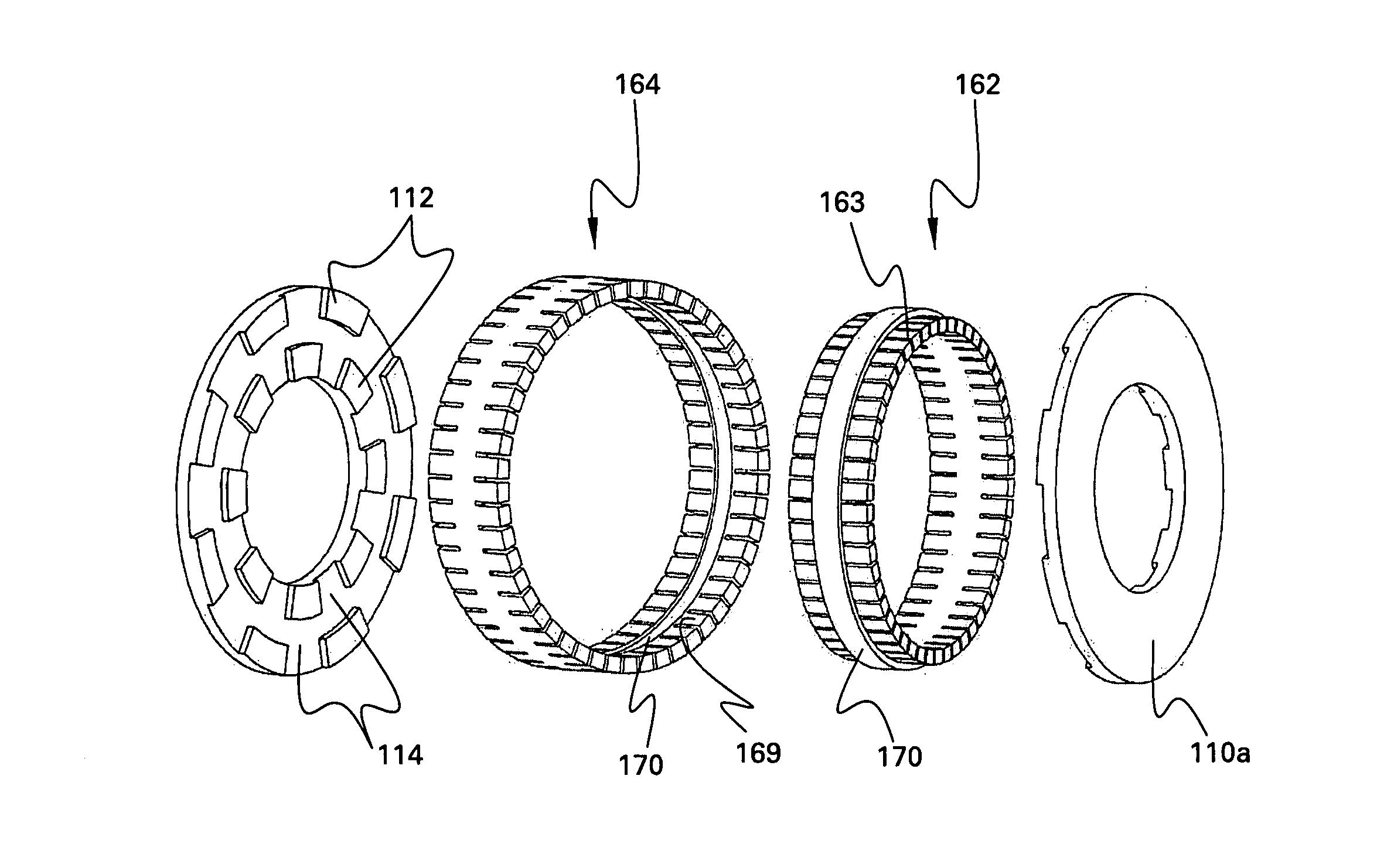
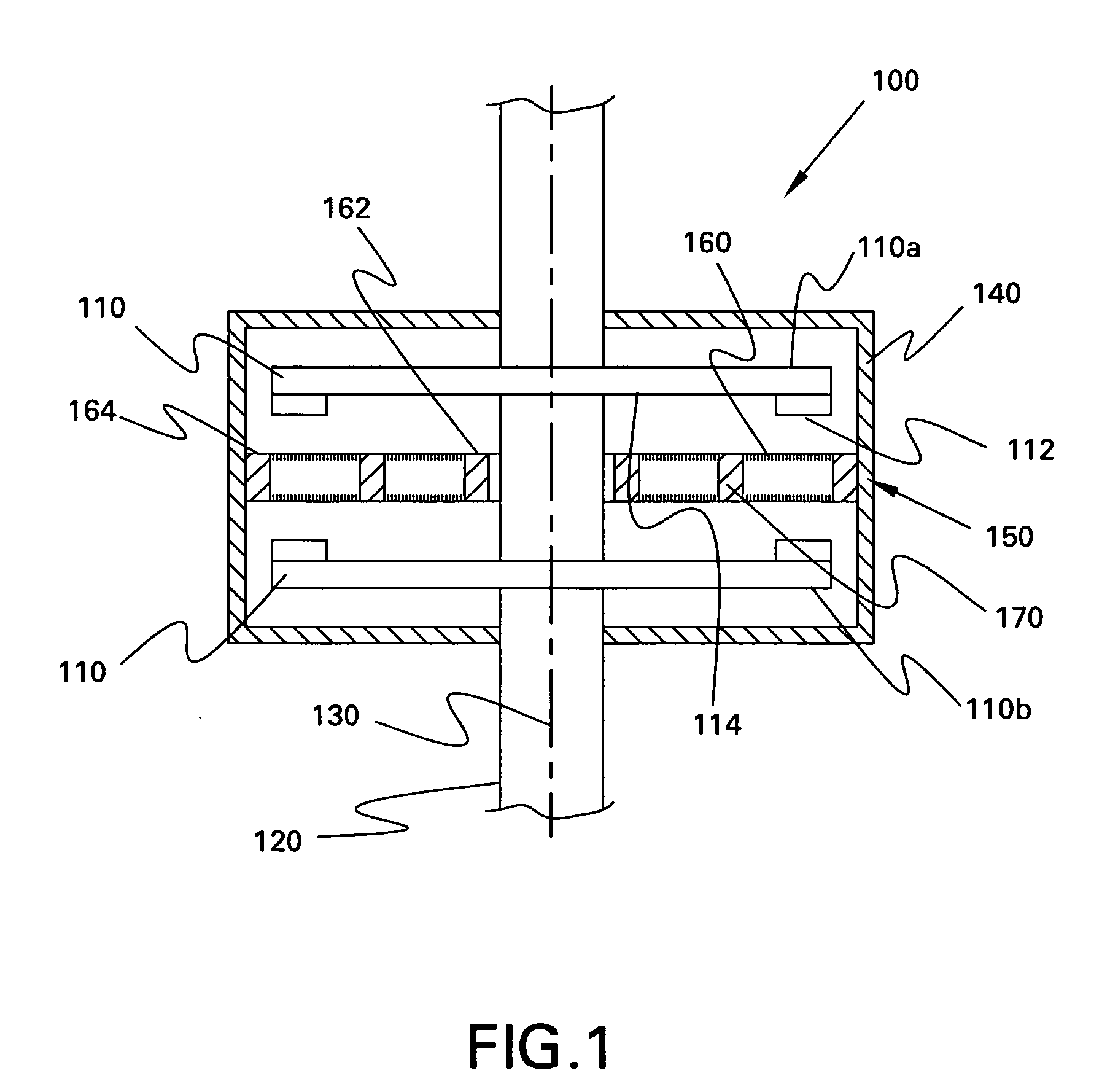
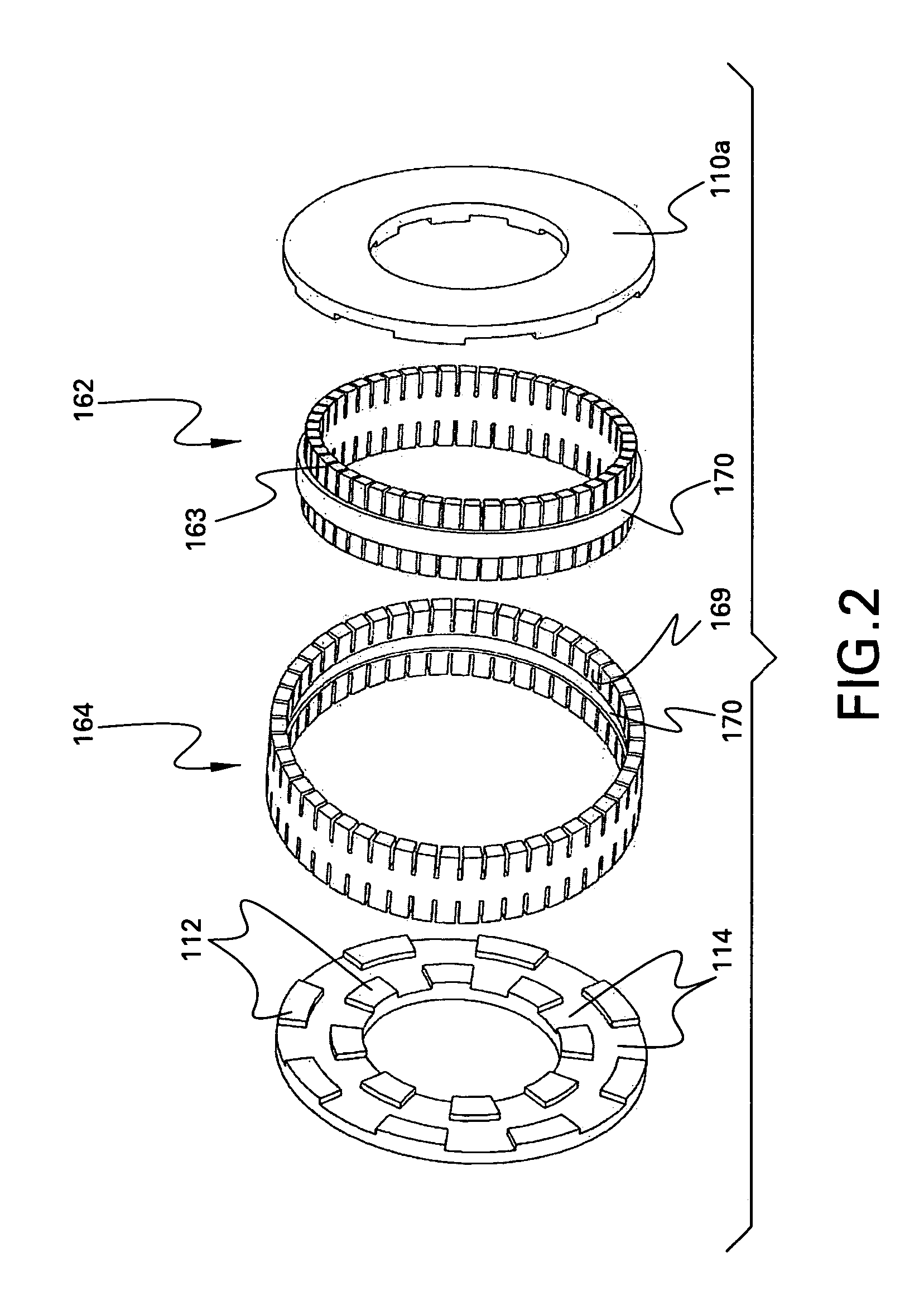
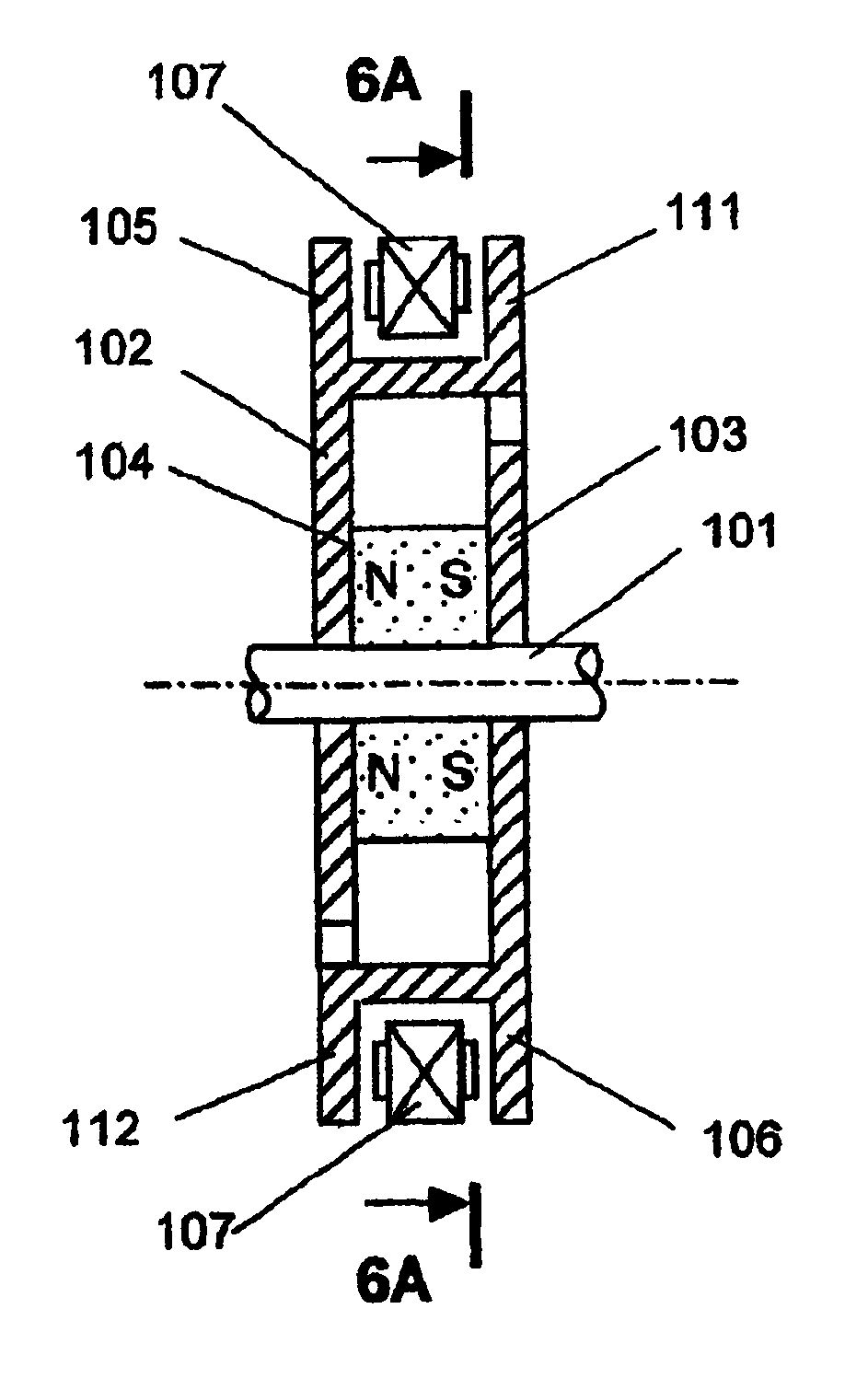
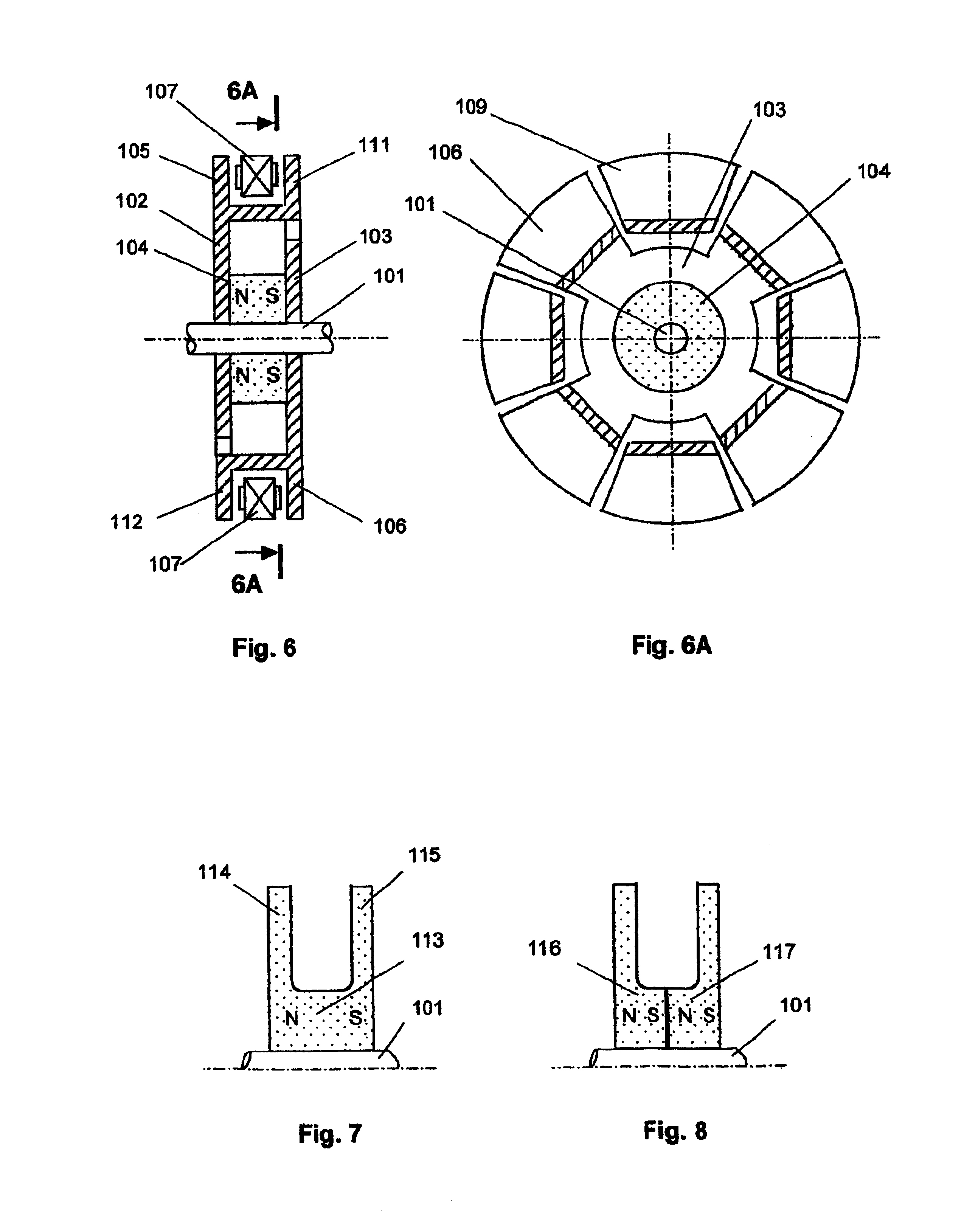
Homopolar machine with improved brush lifetime
InactiveUS20050077795A1Reduce stepsImprove reliabilityRotary current collectorAcyclic motorsMagnetic tension forceContact pressure
A homopolar machine which exhibits reduced wear and prolonged brush life. Current collectors or brushes are mounted so as to maintain substantially constant contact pressure and so that all of them are polarized negative. Brush holders are provided which facilitate the application of precise and constant contact pressure in a region of very high magnetic forces.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com