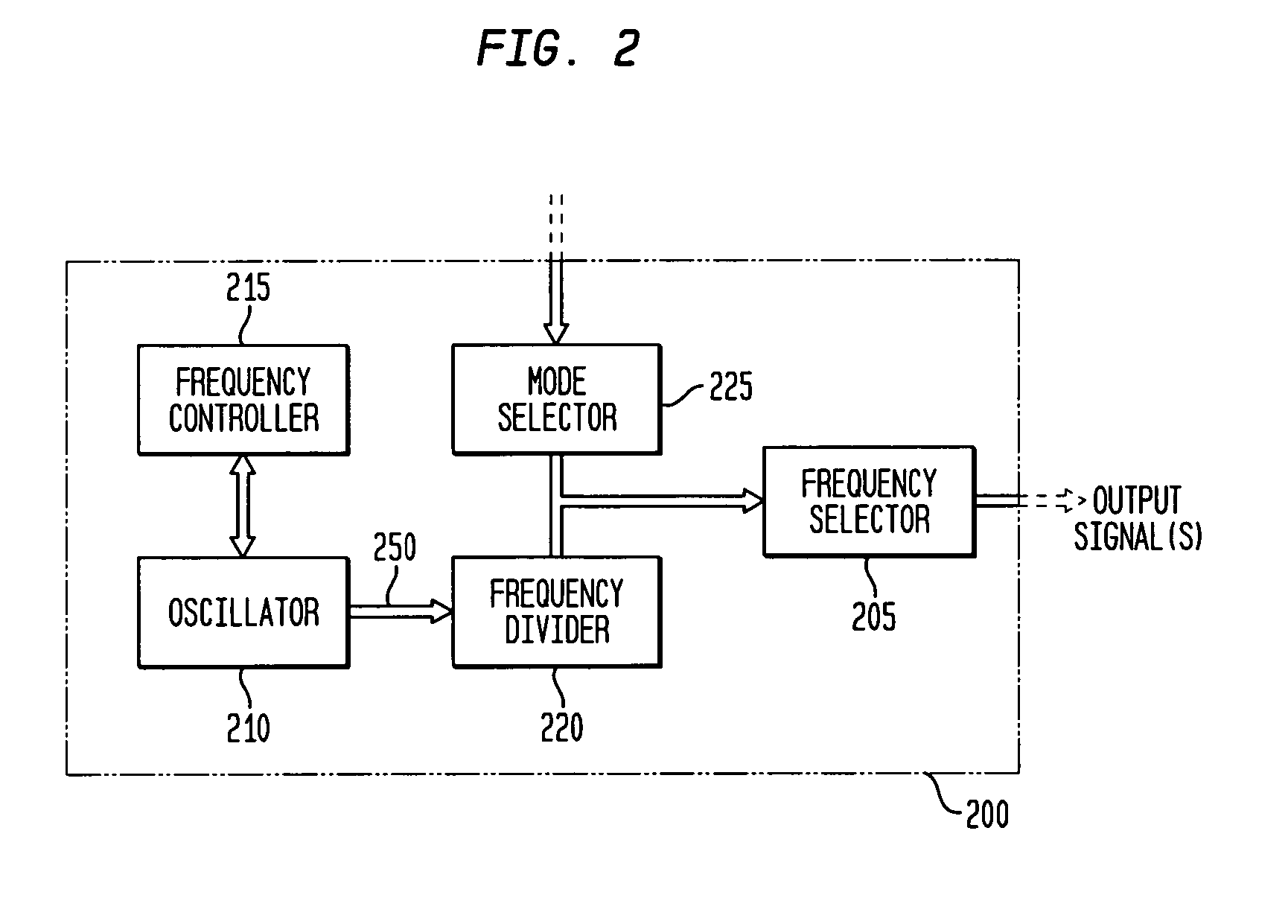
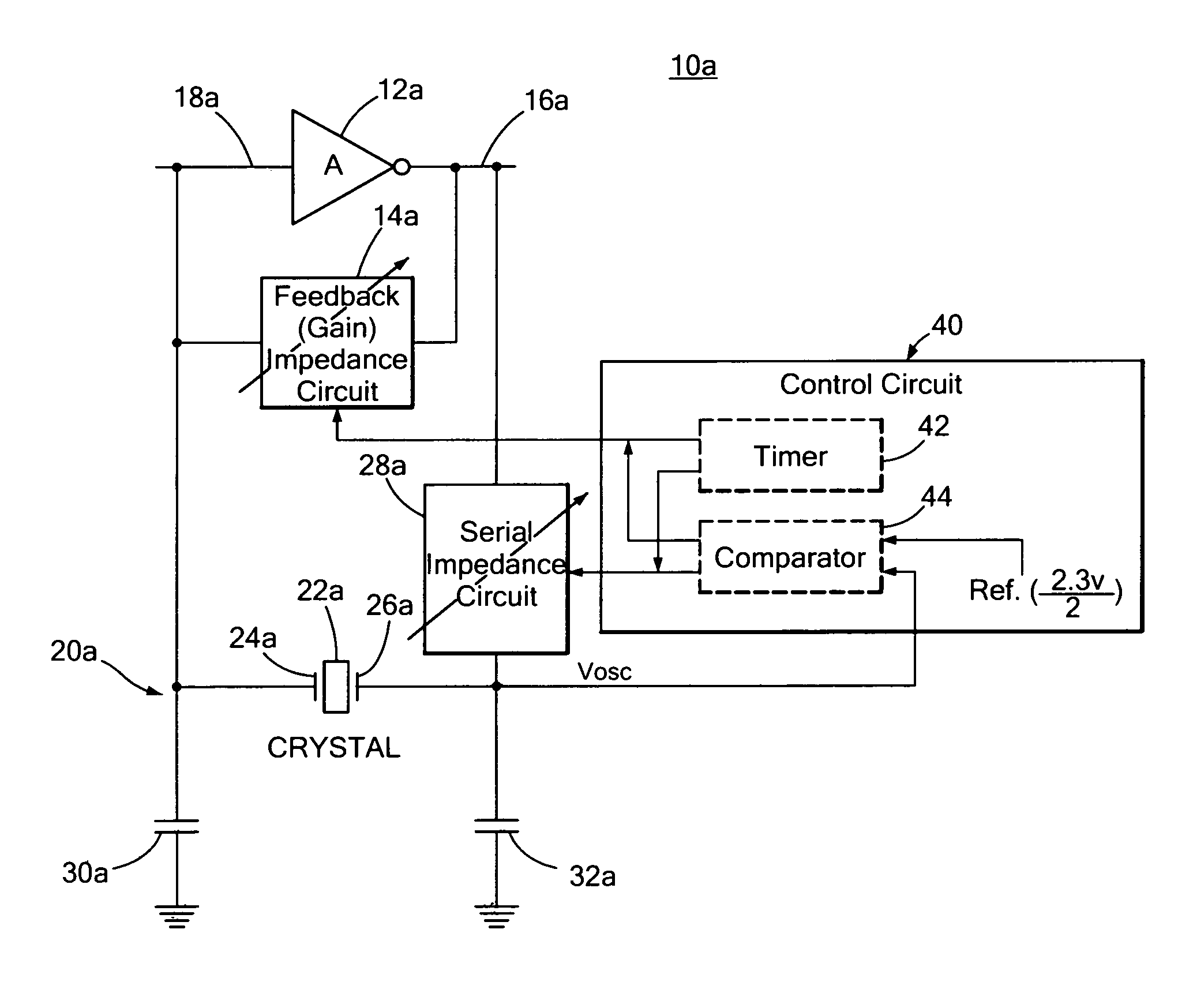
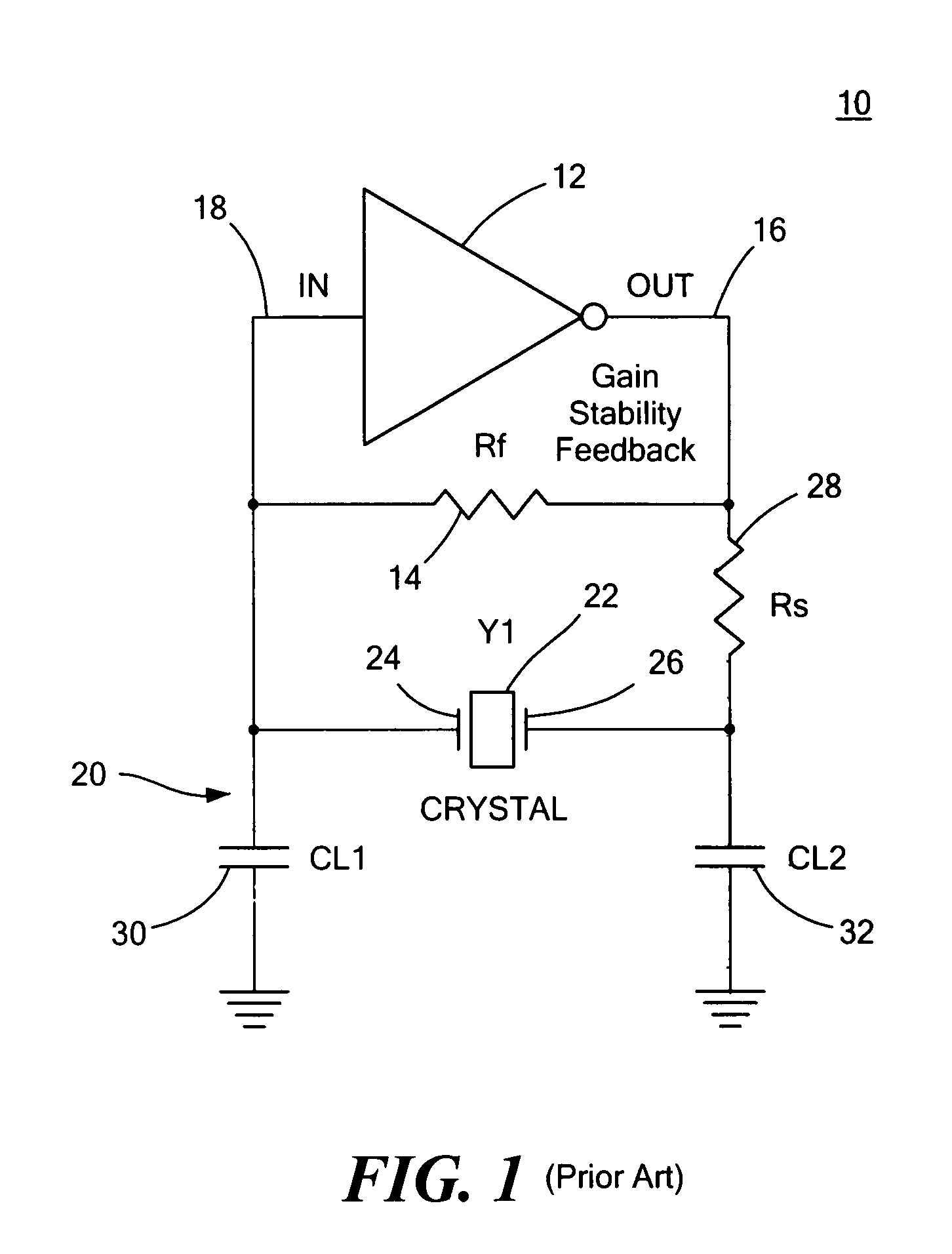
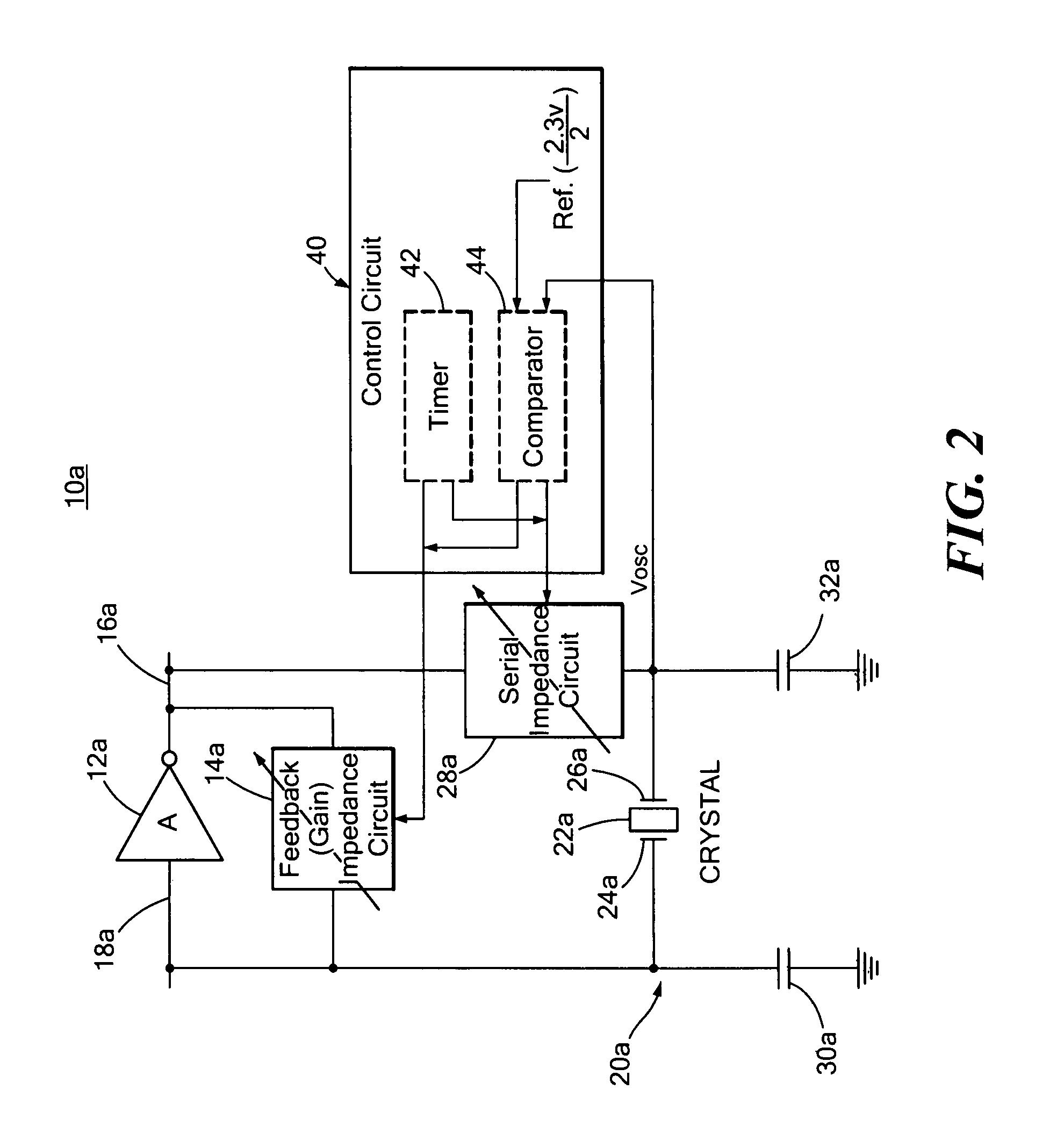
Patents
Literature
227results about "Generator starter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
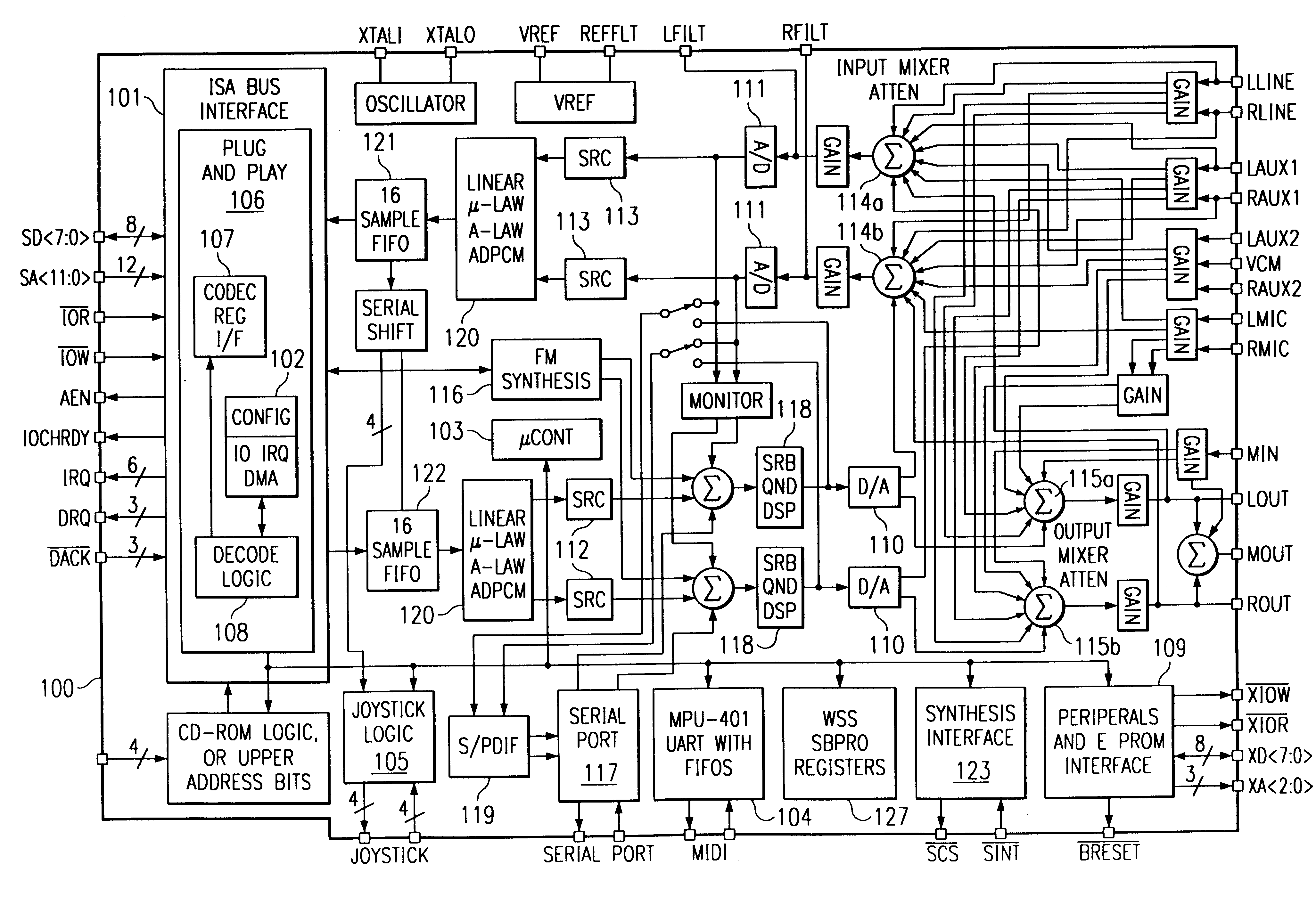
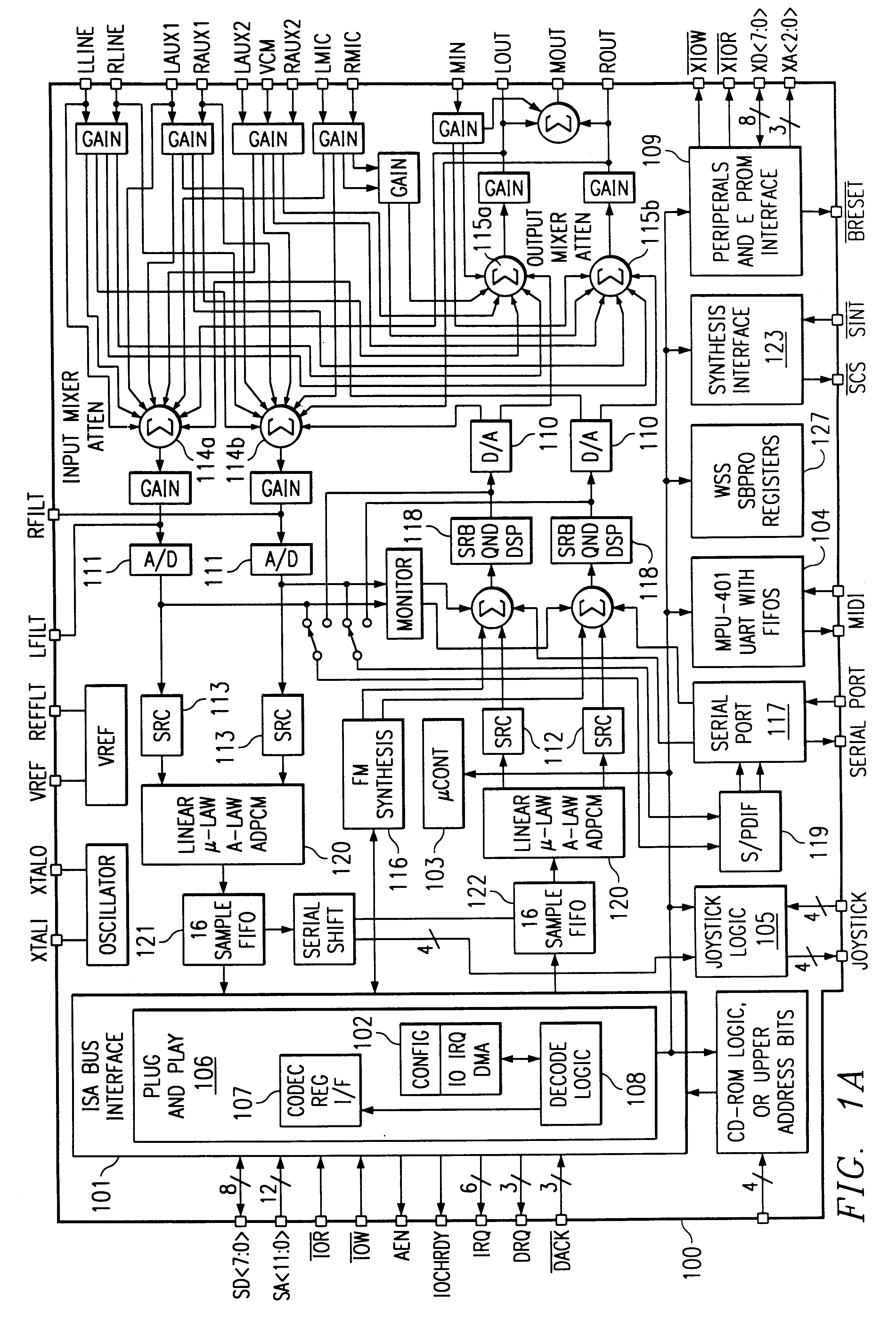
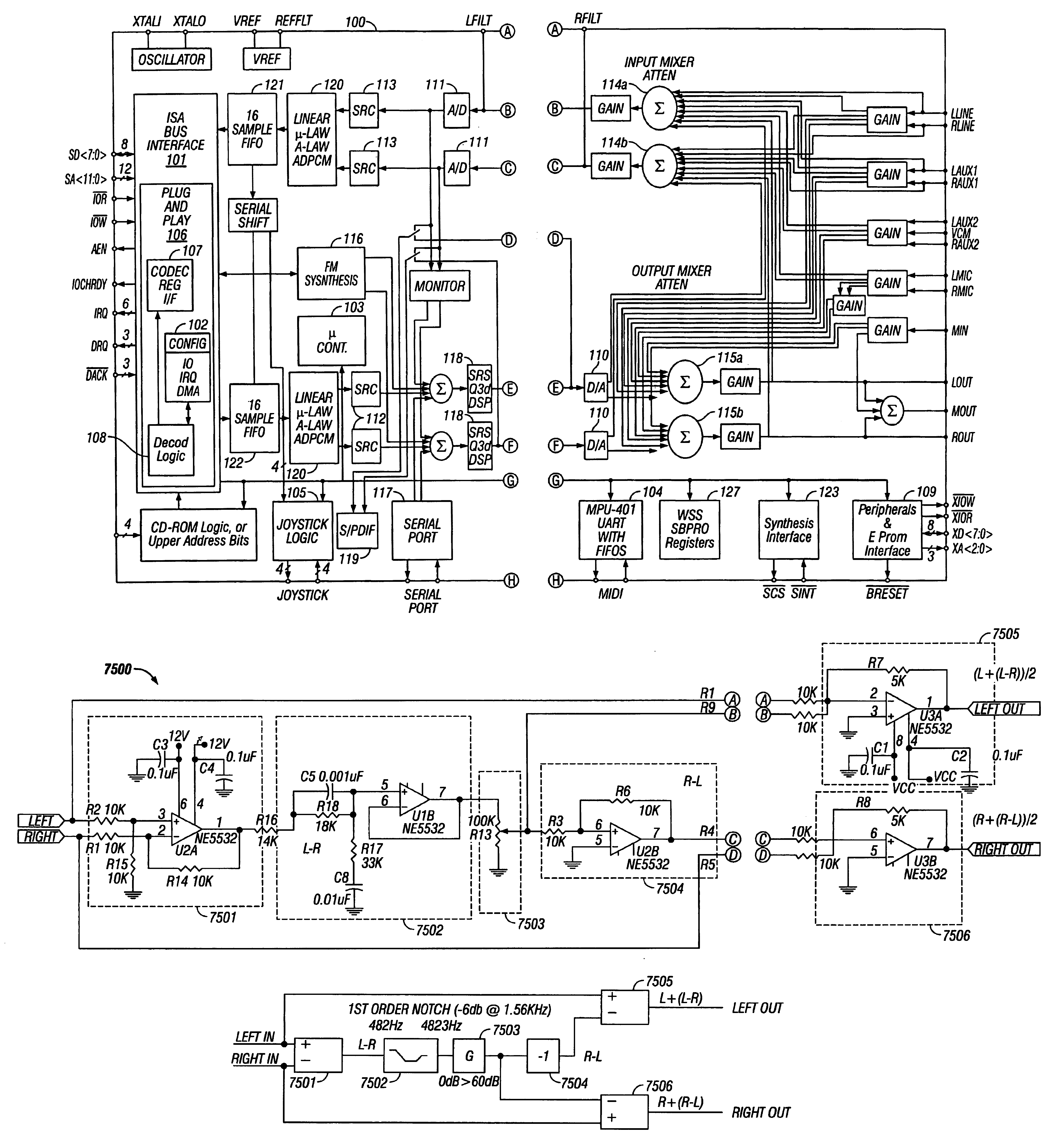
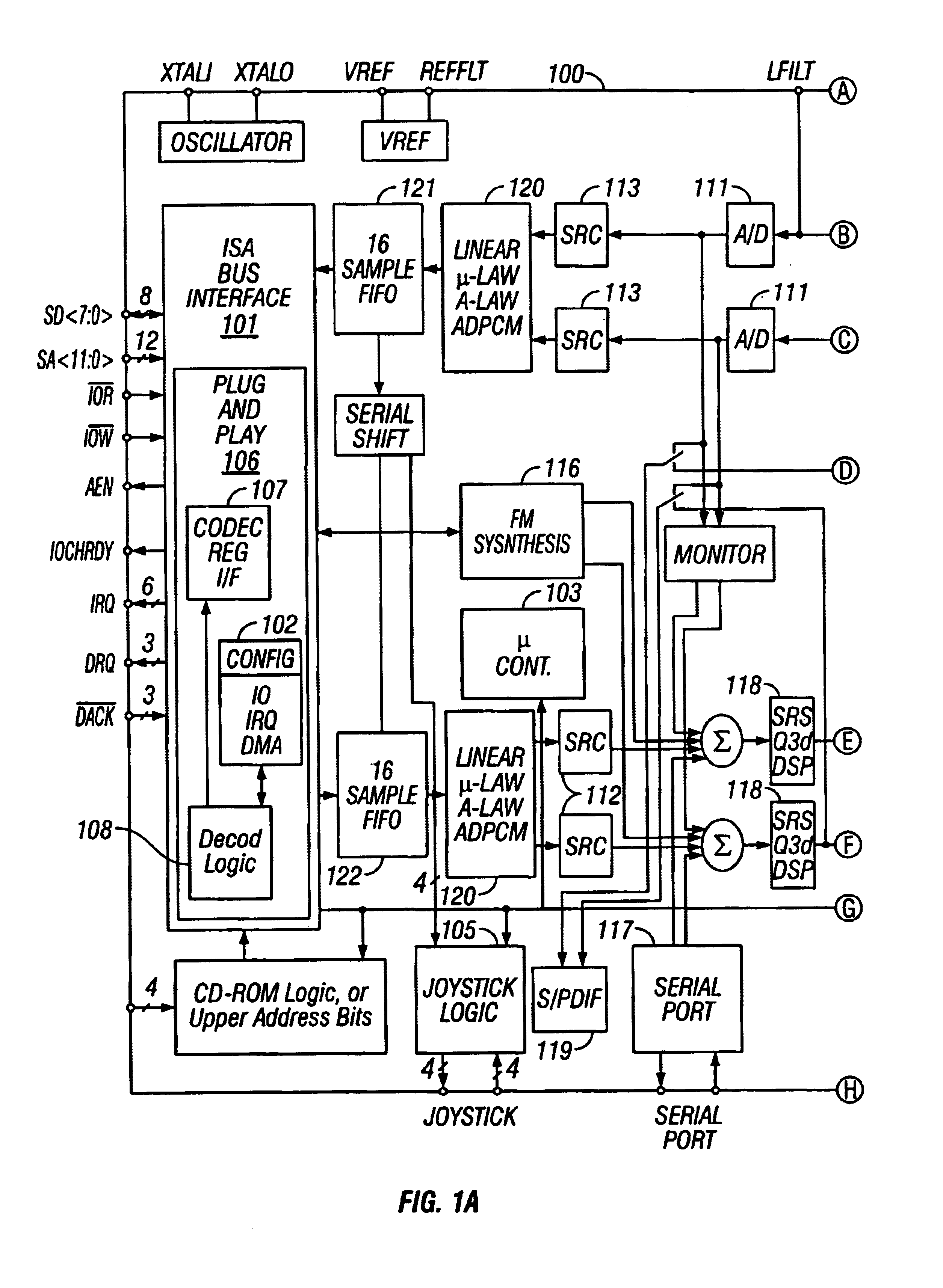
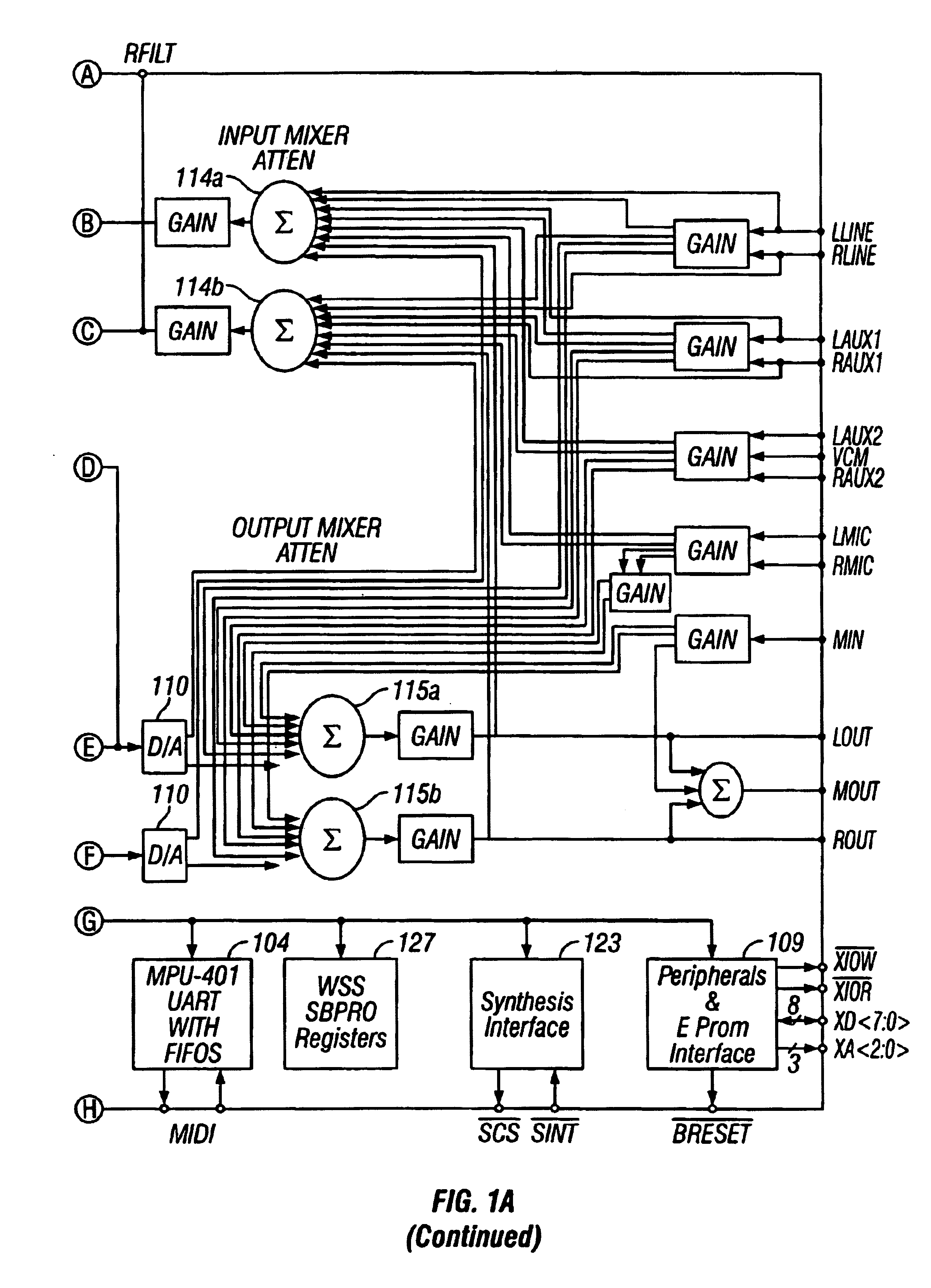
Single-chip audio system mixing circuitry and methods
An audio system 100 disposed on a single chip includes an output mixer 115 having inputs for receiving first digital audio data of a first bit width from a first digital-to-analog converter 110, digital audio data of a second bit width from a second digital-to-analog converter 6601, and analog data from an external port. An output port drives an analog signal output from the output mixer. An input mixer 114 has inputs for receiving analog data from a plurality of sources and analog-to-digital converters 111 to convert an analog output from the input mixer into digital data. An input path transmits the digital data output from the analog to digital convertors 111 to an external digital bus.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
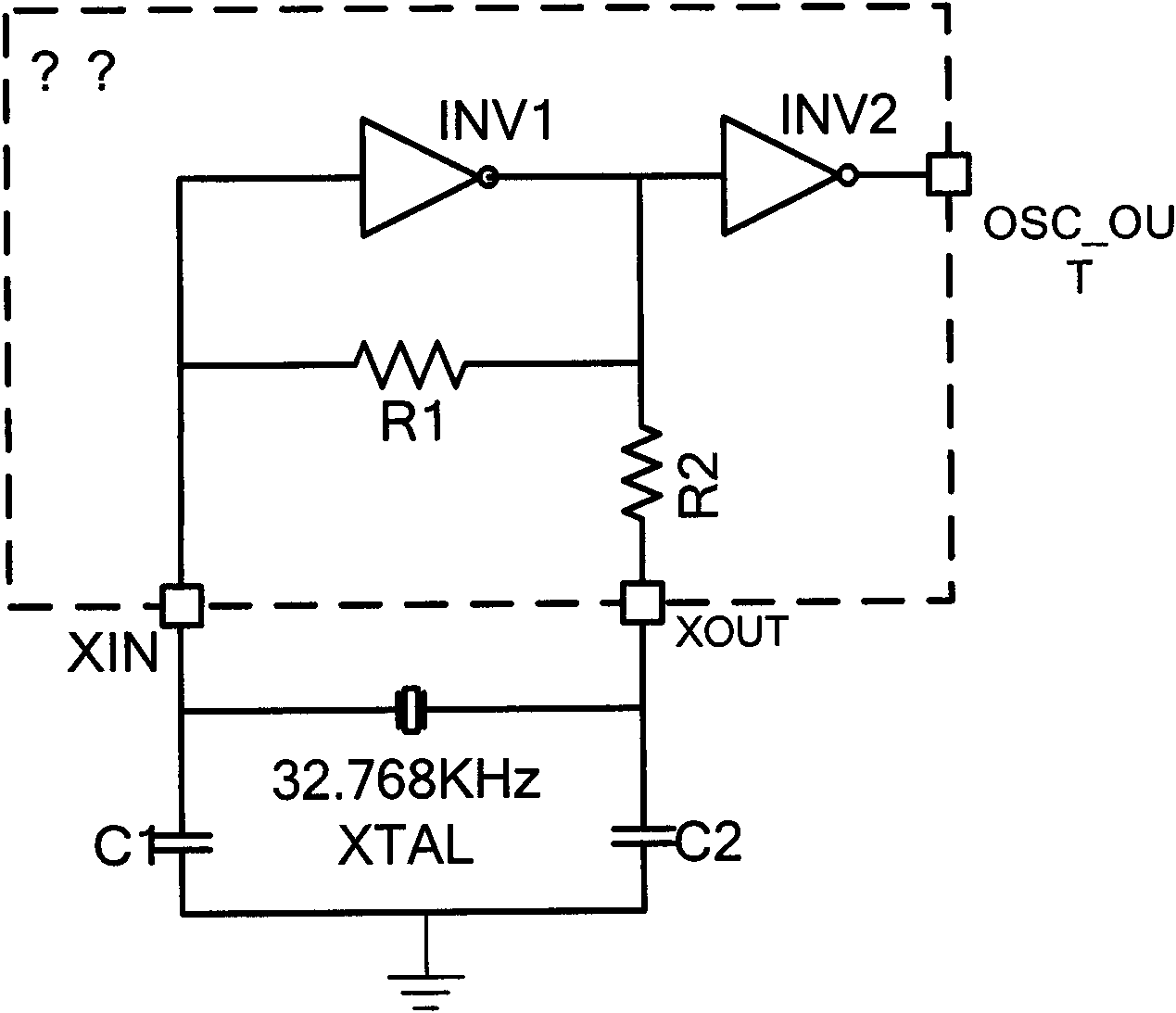
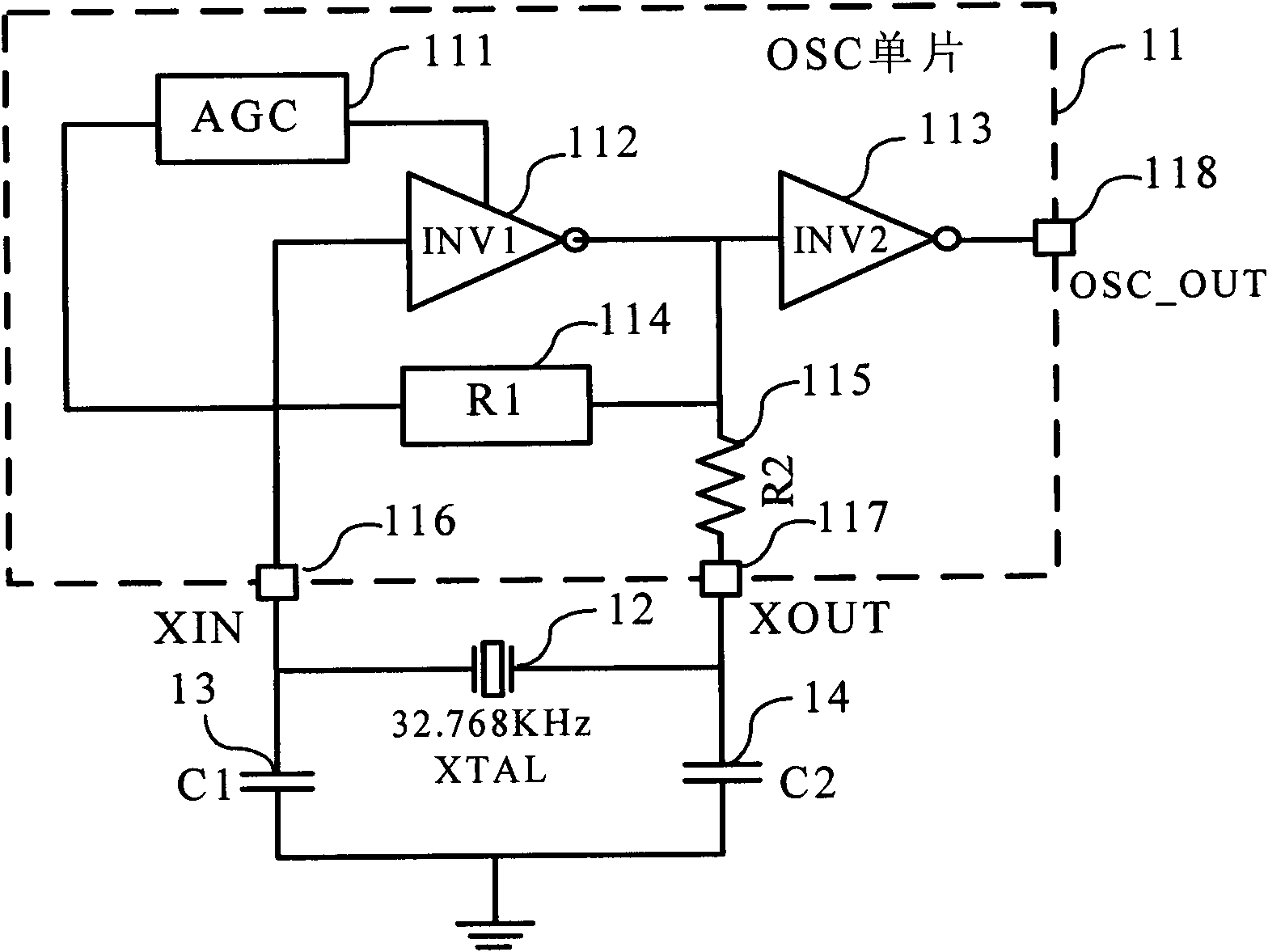
Low power consumption and rapid oscillation starting crystal oscillator module with programmable adjusting start-oscillation condition
The invention discloses a low power consumption and rapid oscillation starting crystal oscillator module with a transposable start oscillation condition, which consists of an inverting amplifier, an inverting reshaper chain, an automatic gain control loop (AGC), a feedback resistor, a power limitation resistor, and an external passive crystal oscillator and an external load capacitor. The inverting amplifier is provided with a transposable feedback resistor R1, and the transposable start oscillation condition of the crystal oscillator is realized; and the automatic gain control loop (AGC) is inserted between an input end and a bias end of the inverting amplifier, and the contradiction between the oscillation starting time and power consumption is solved. The invention also provides a highresistor realizing IC (integrated circuit) by adopting a transconductance amplifier of micro current source, and a transposable feedback resistor R1 for the oscillator amplifier branch circuit and a high resistor in a pi-shaped filter. The resistance value of the high resistance can be controlled by programming, the start oscillation condition of the oscillator can be adjusted through adjusting the feedback resistance R1, and reliable and quick start oscillation of the oscillator can be realized; and lower phase noise can be realized through adjusting the high resistor in the pi-shaped filter. The crystal oscillator circuit has the characteristics of low power consumption and rapid start oscillation, and can be used for the digital integrated circuit, such as a base band of various of satellite navigation allocation receptors, real time clocks (RTC).
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
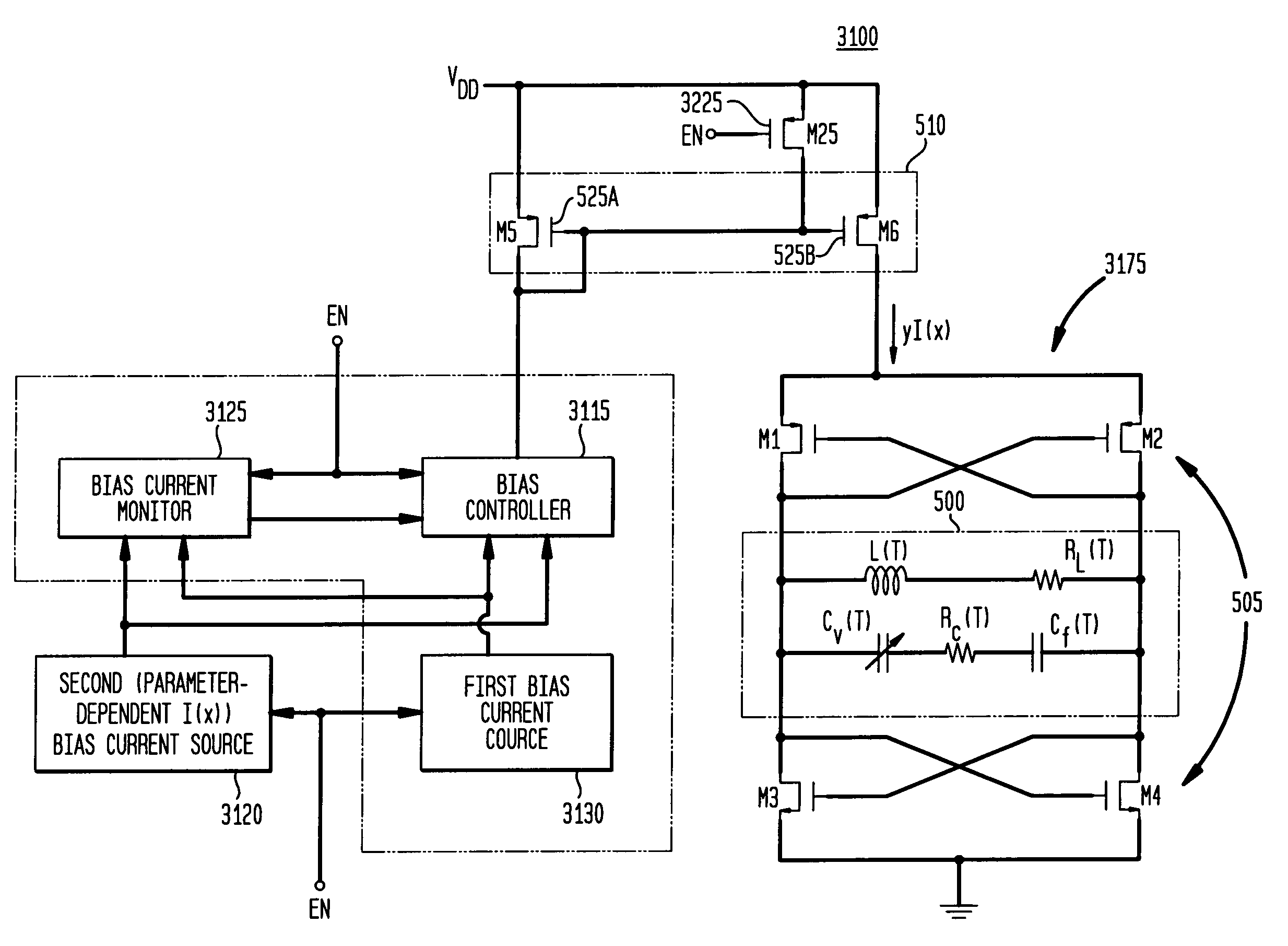
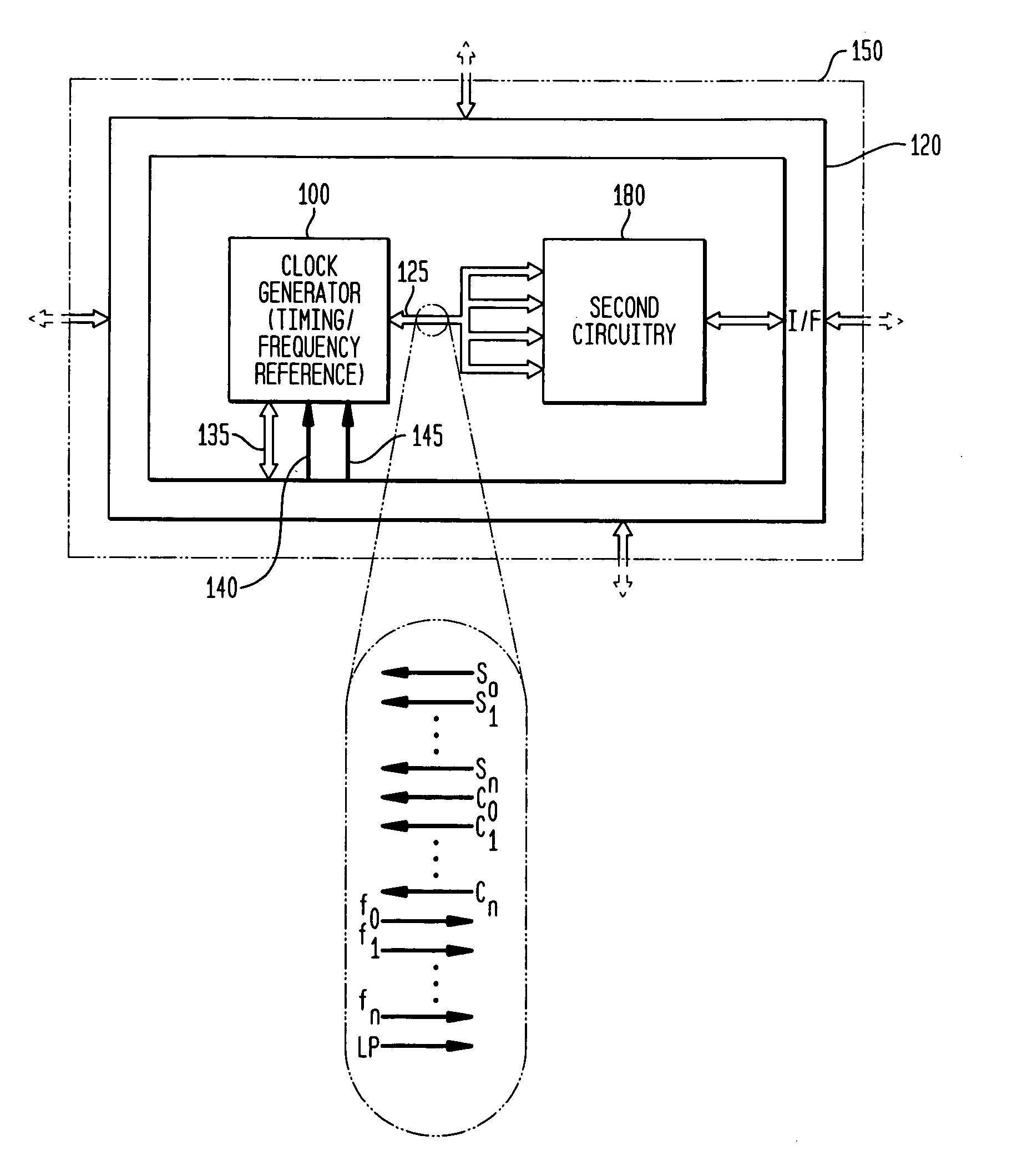
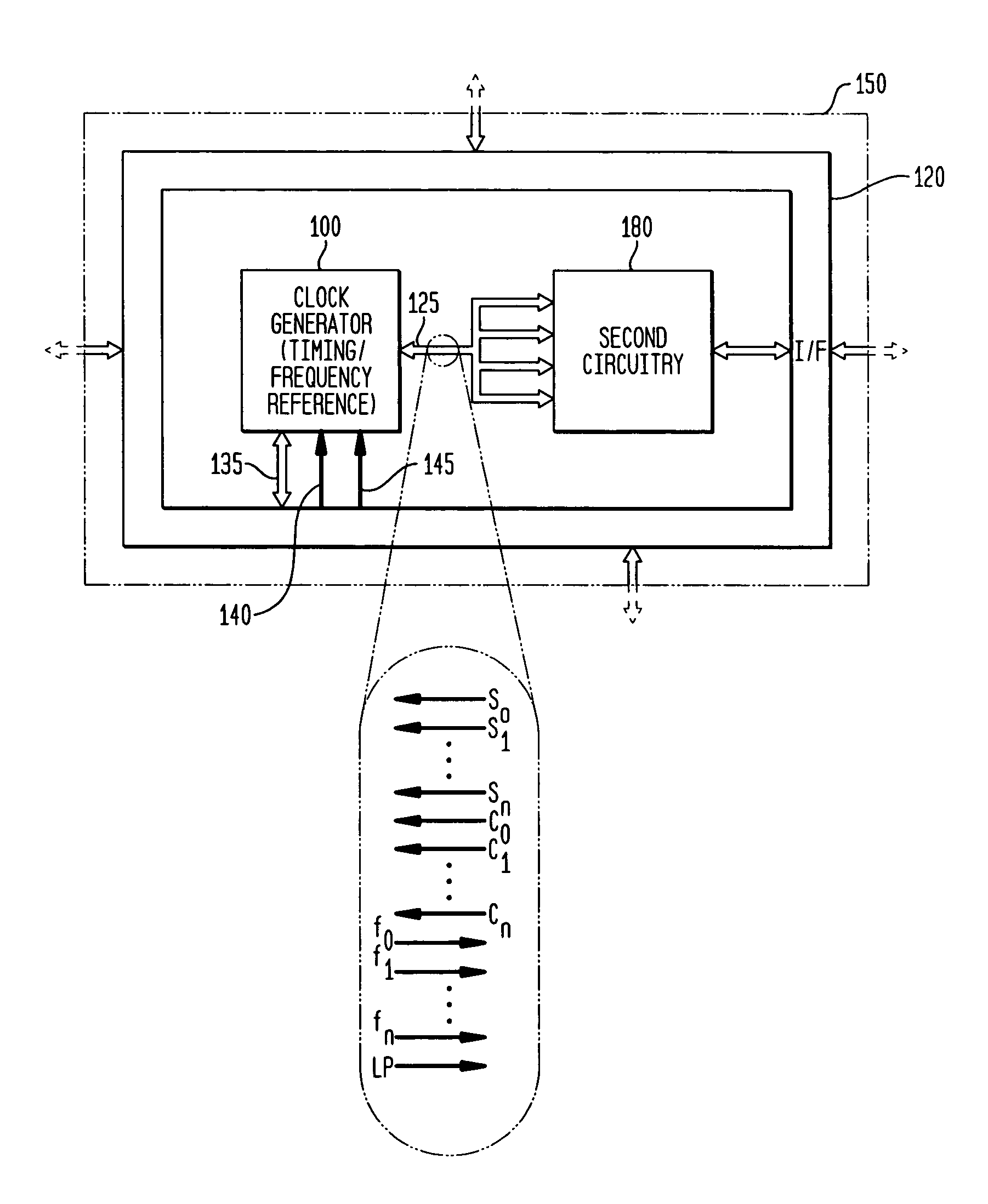
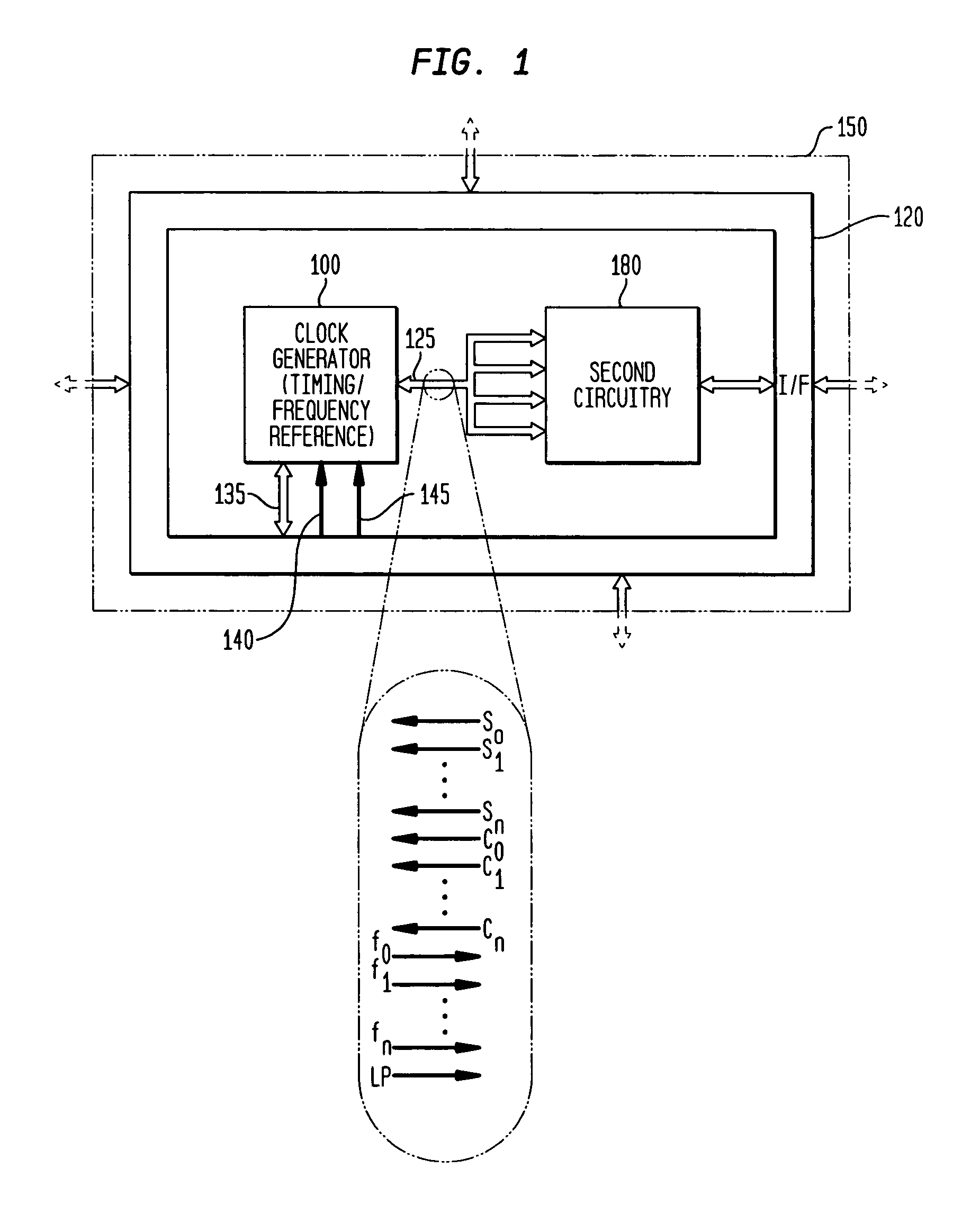
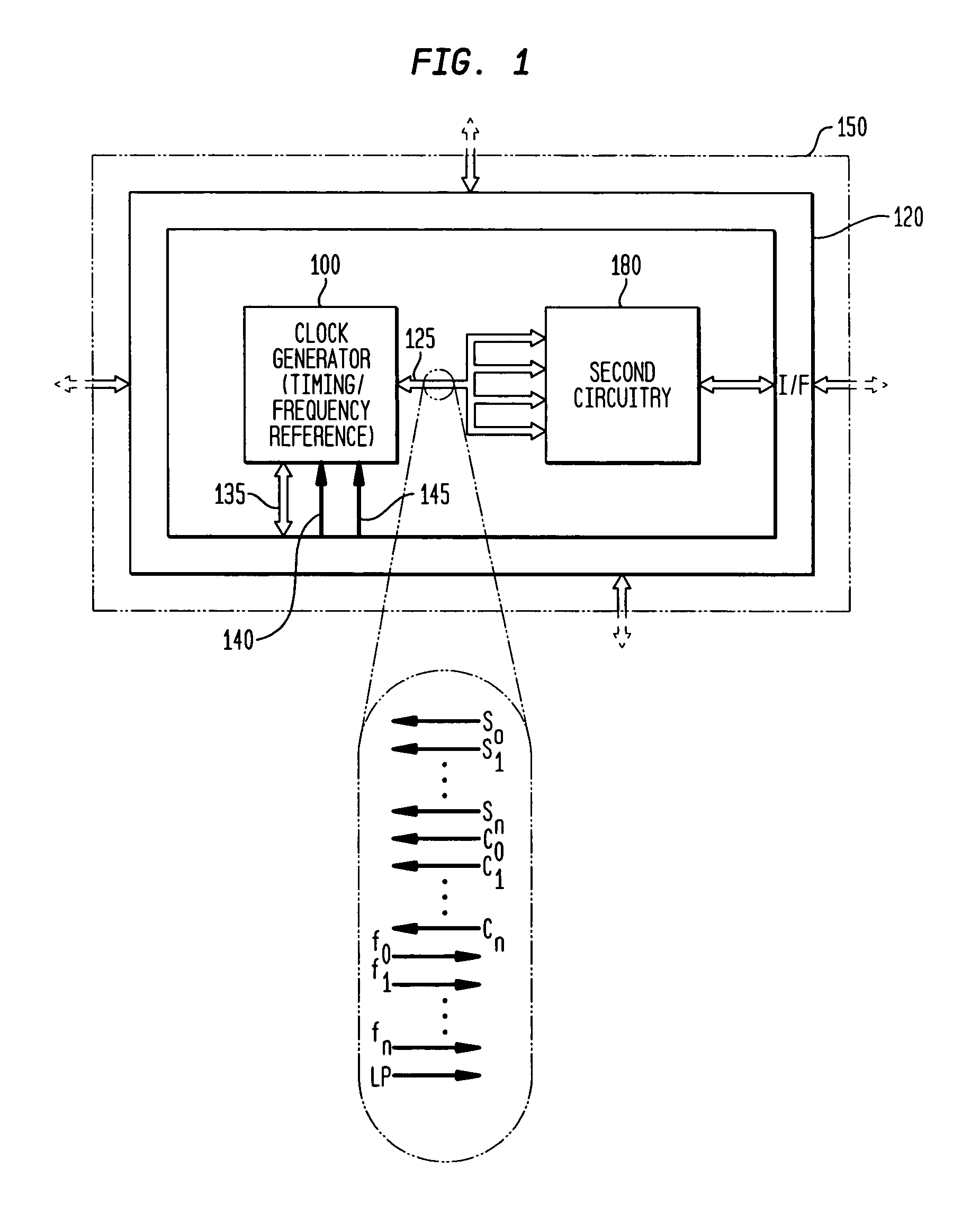
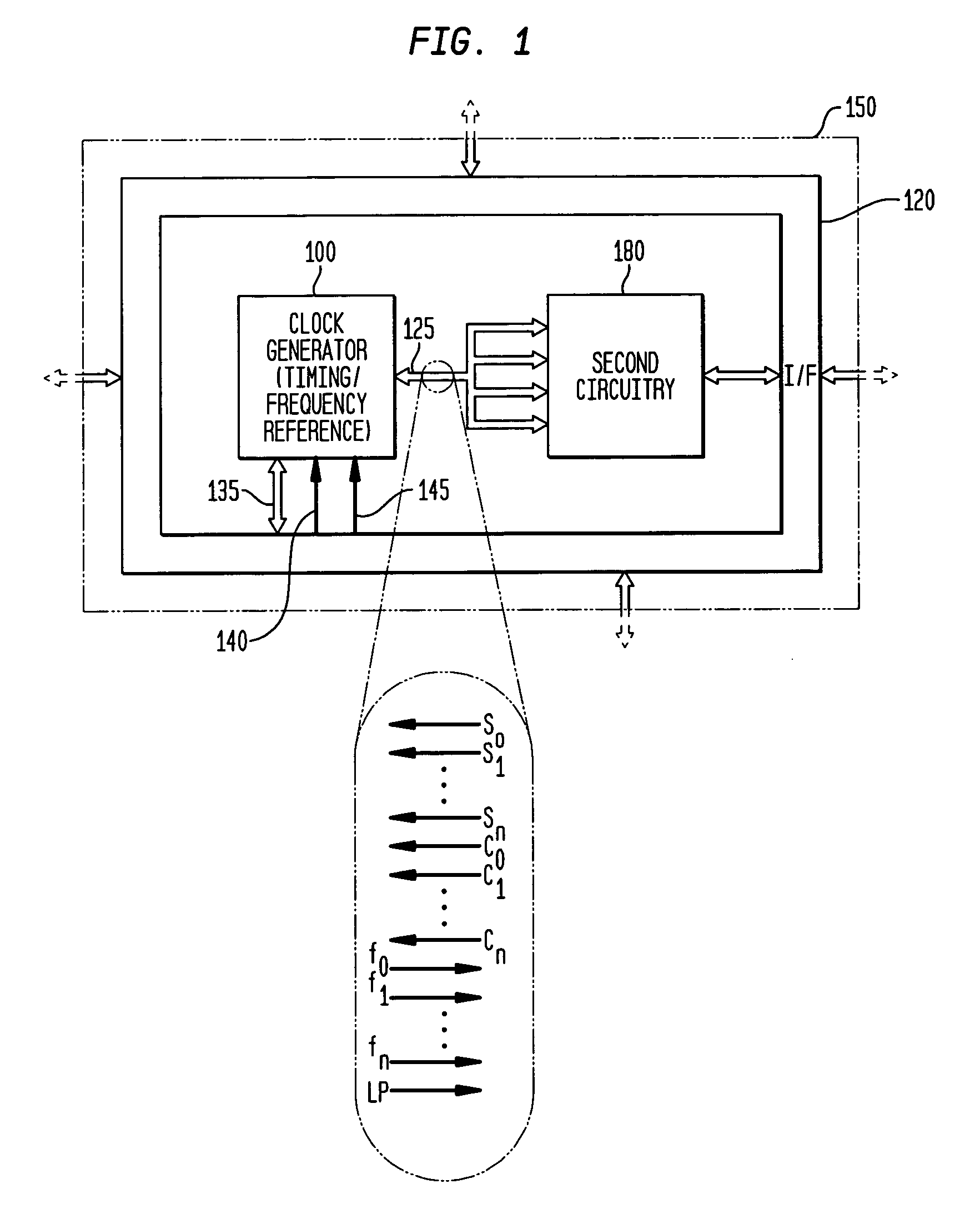
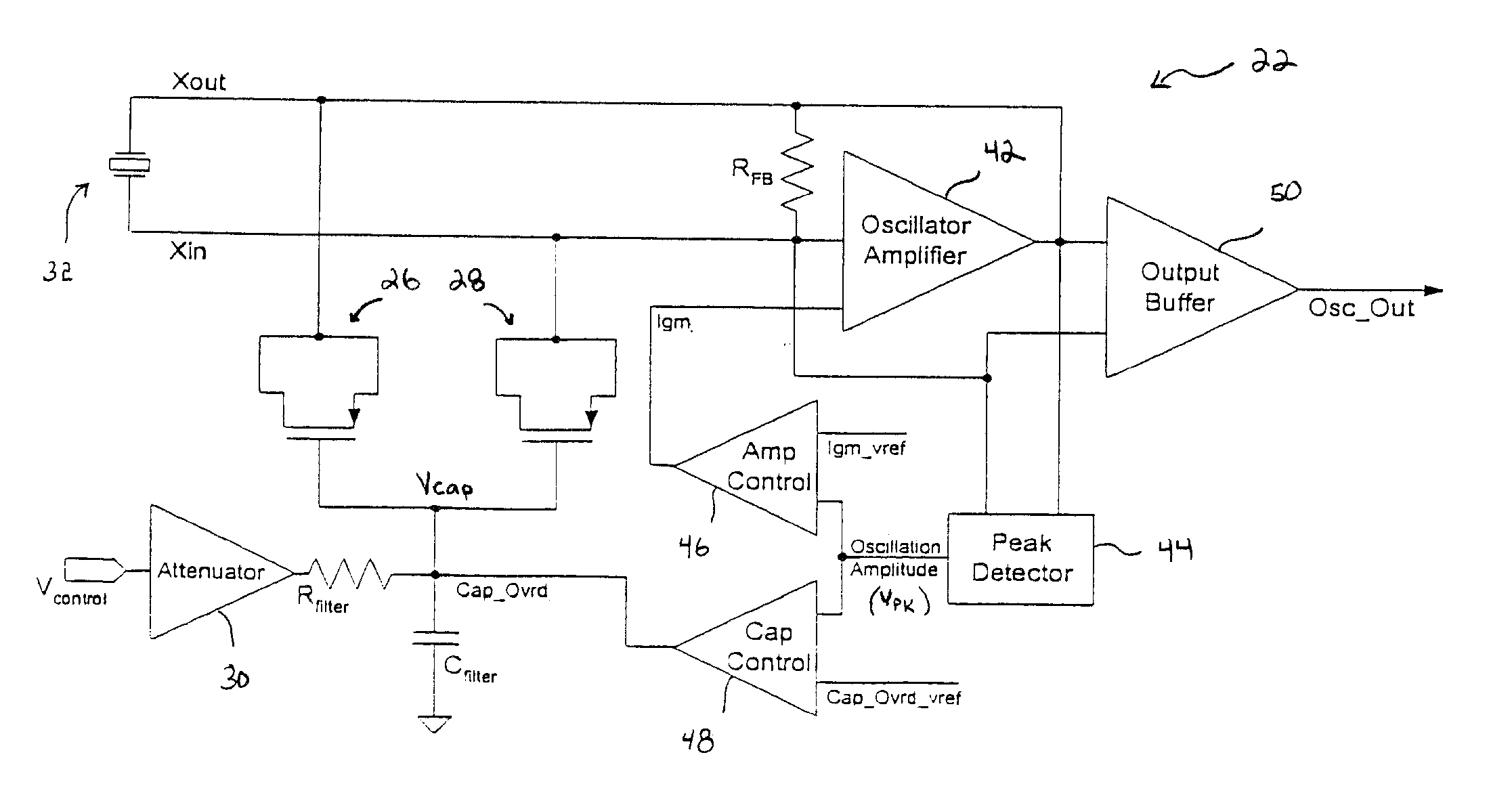
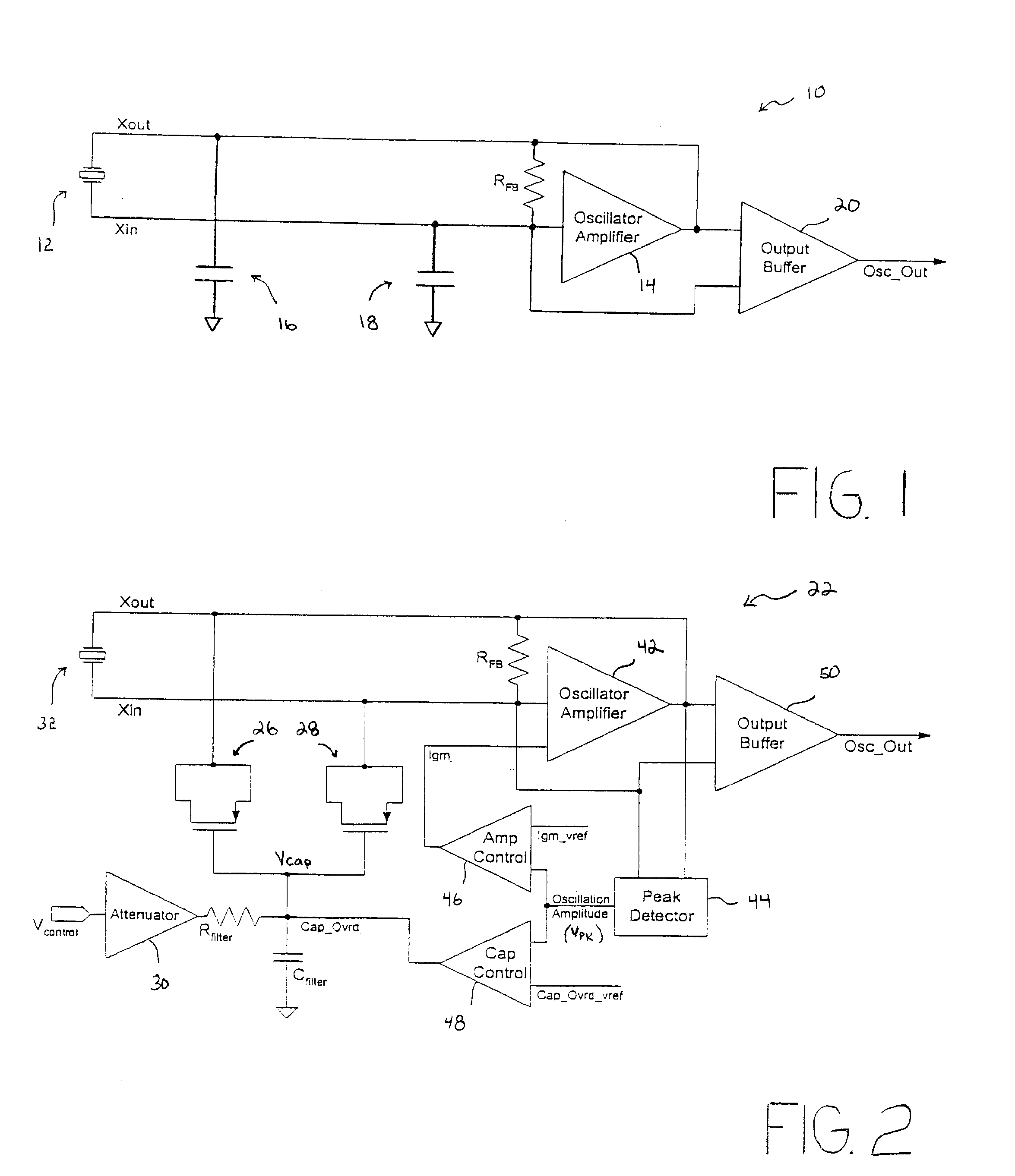
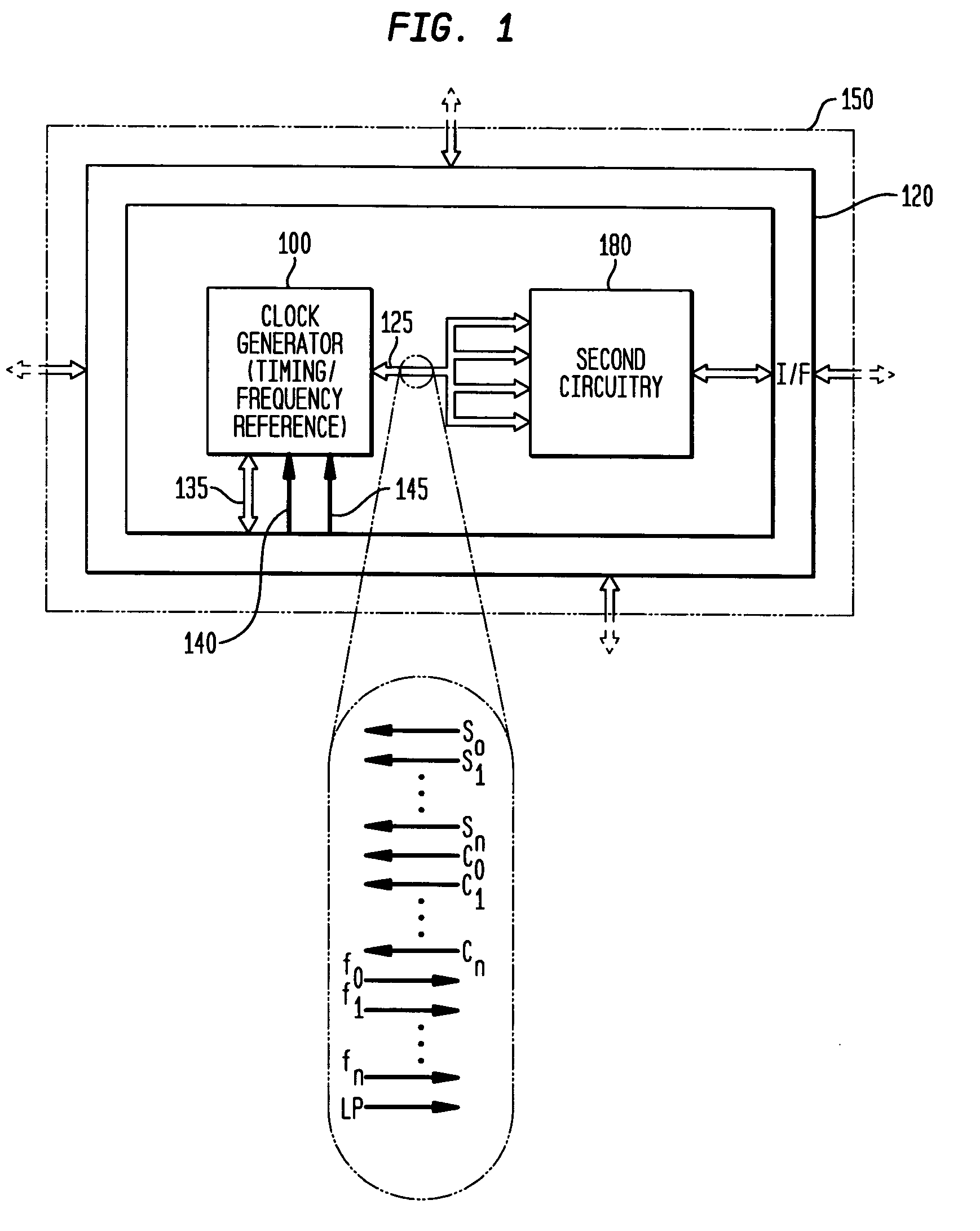
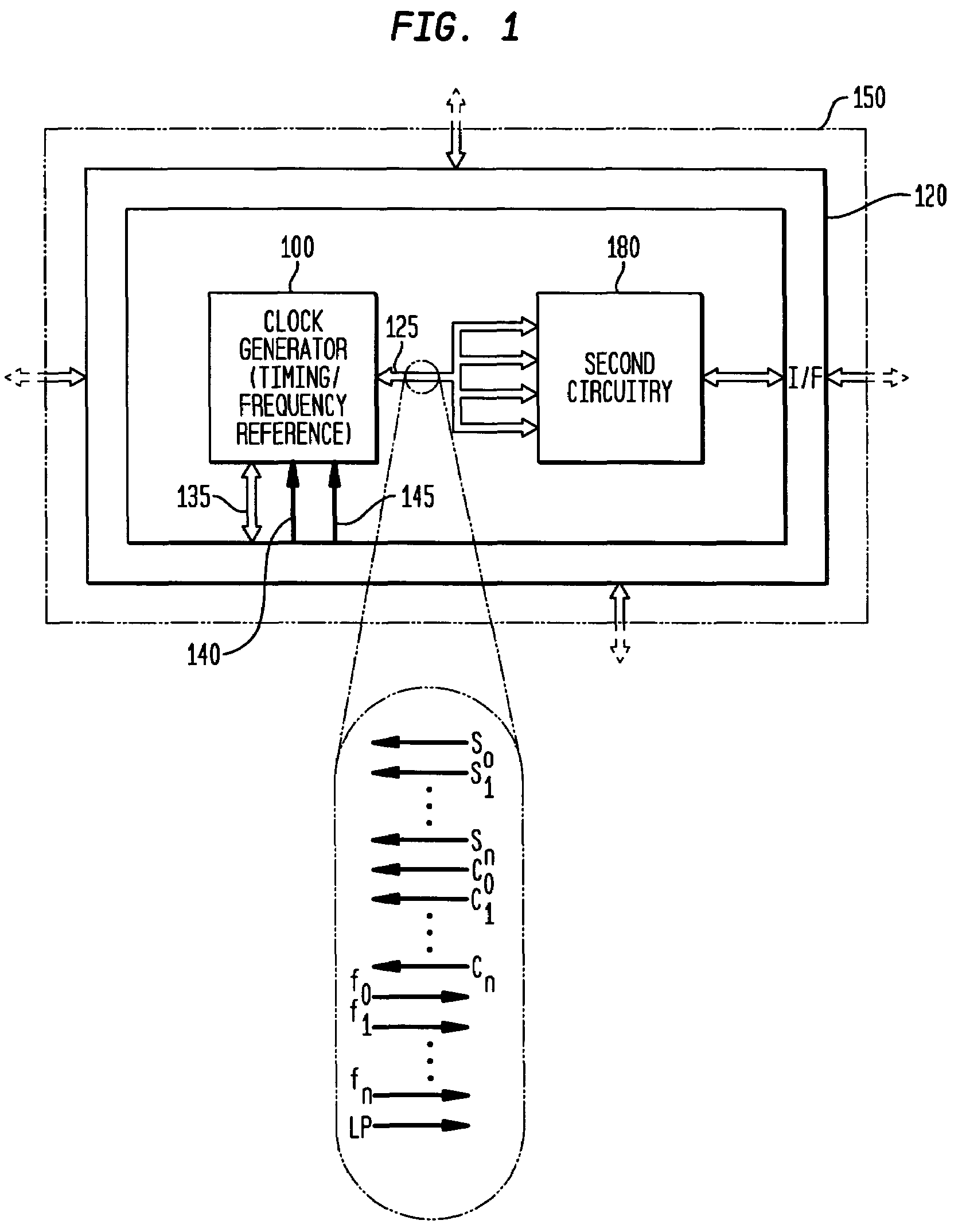
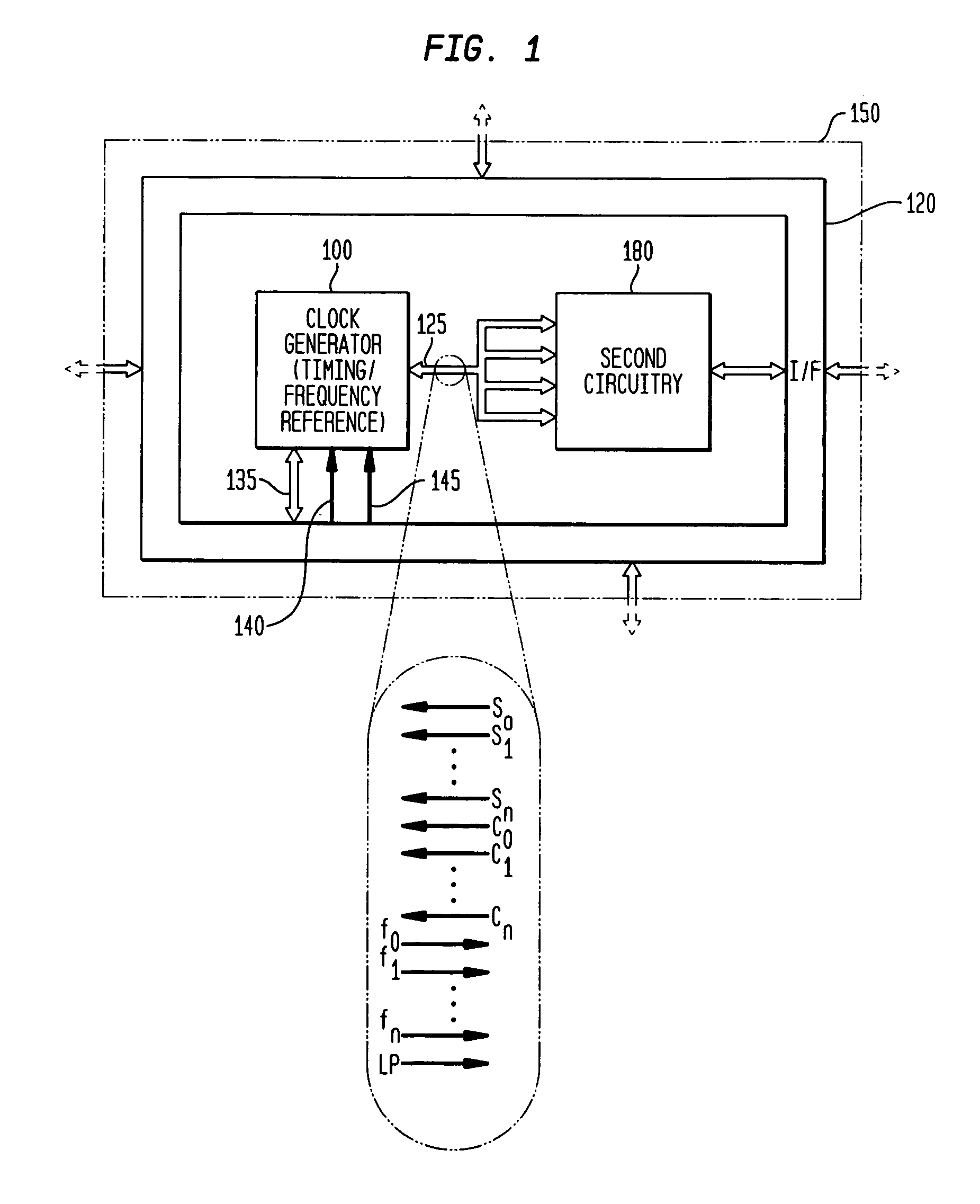
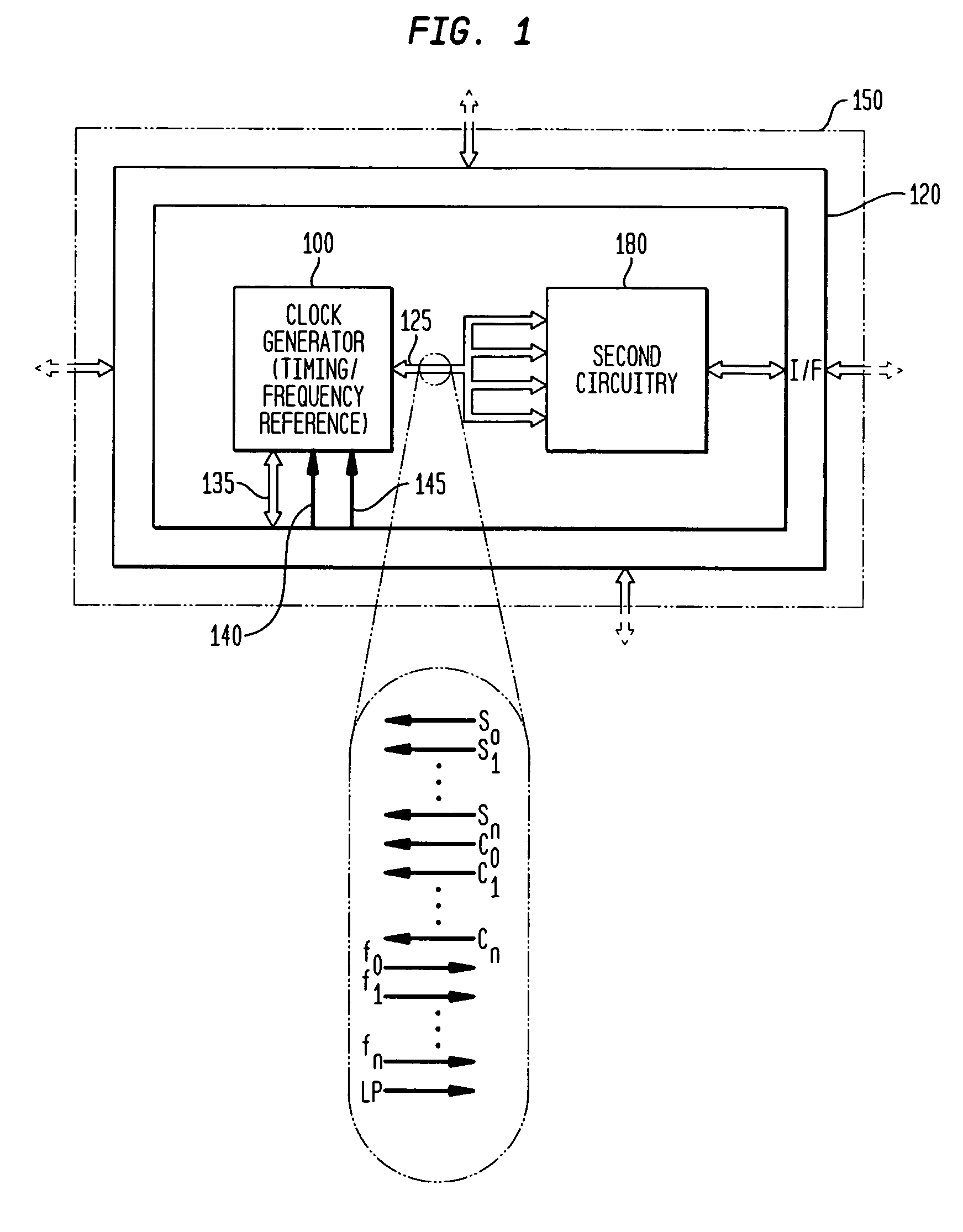
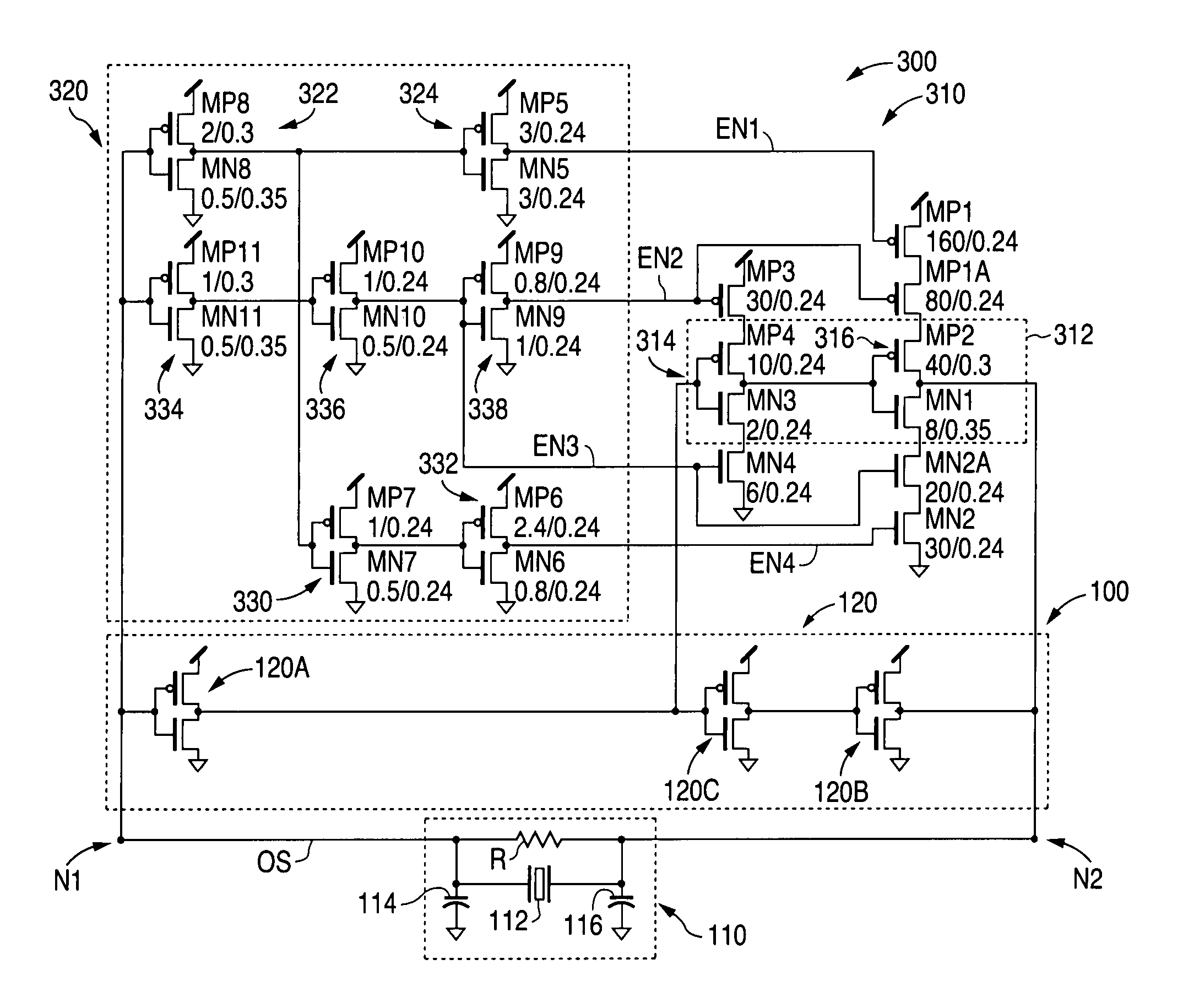
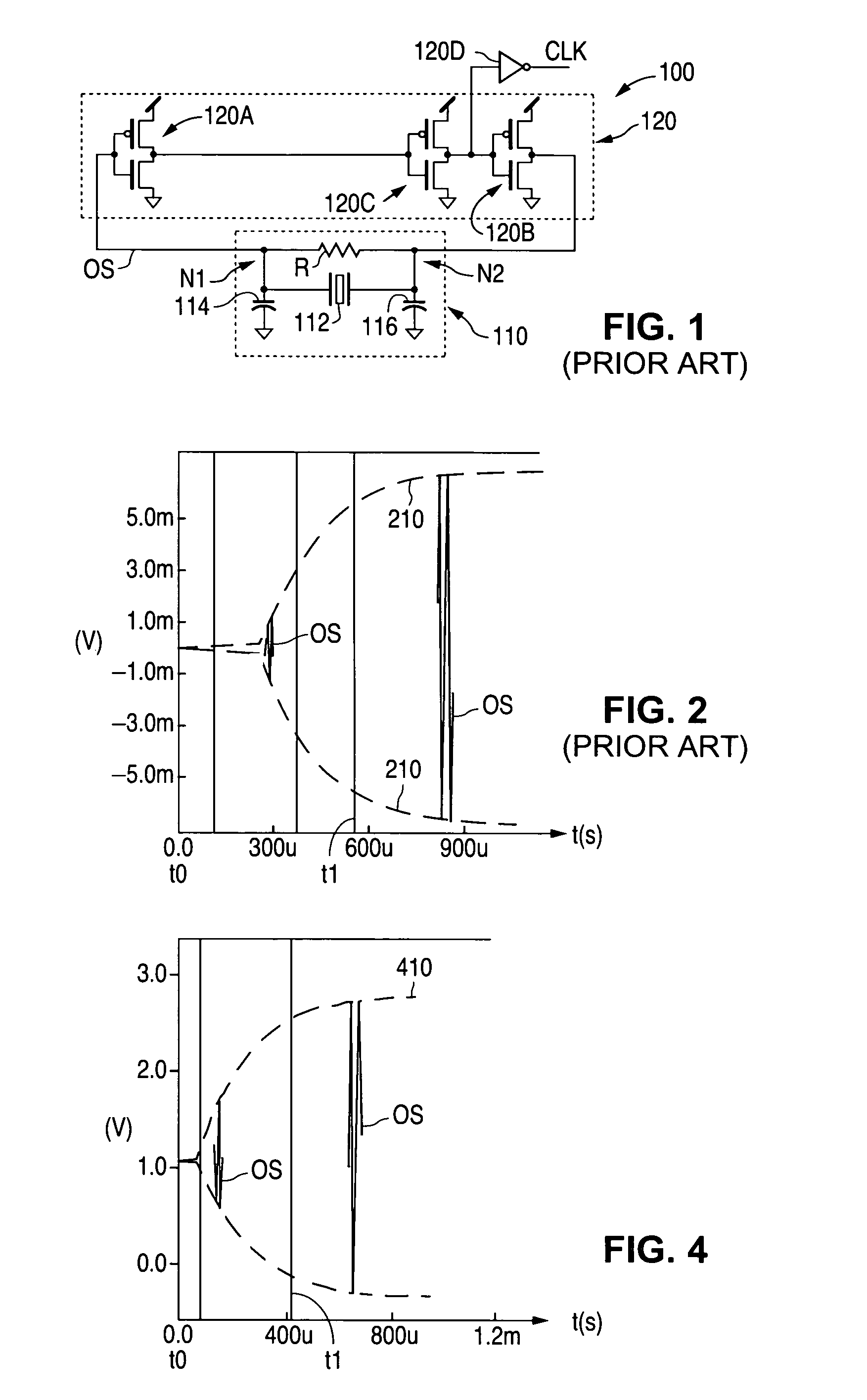
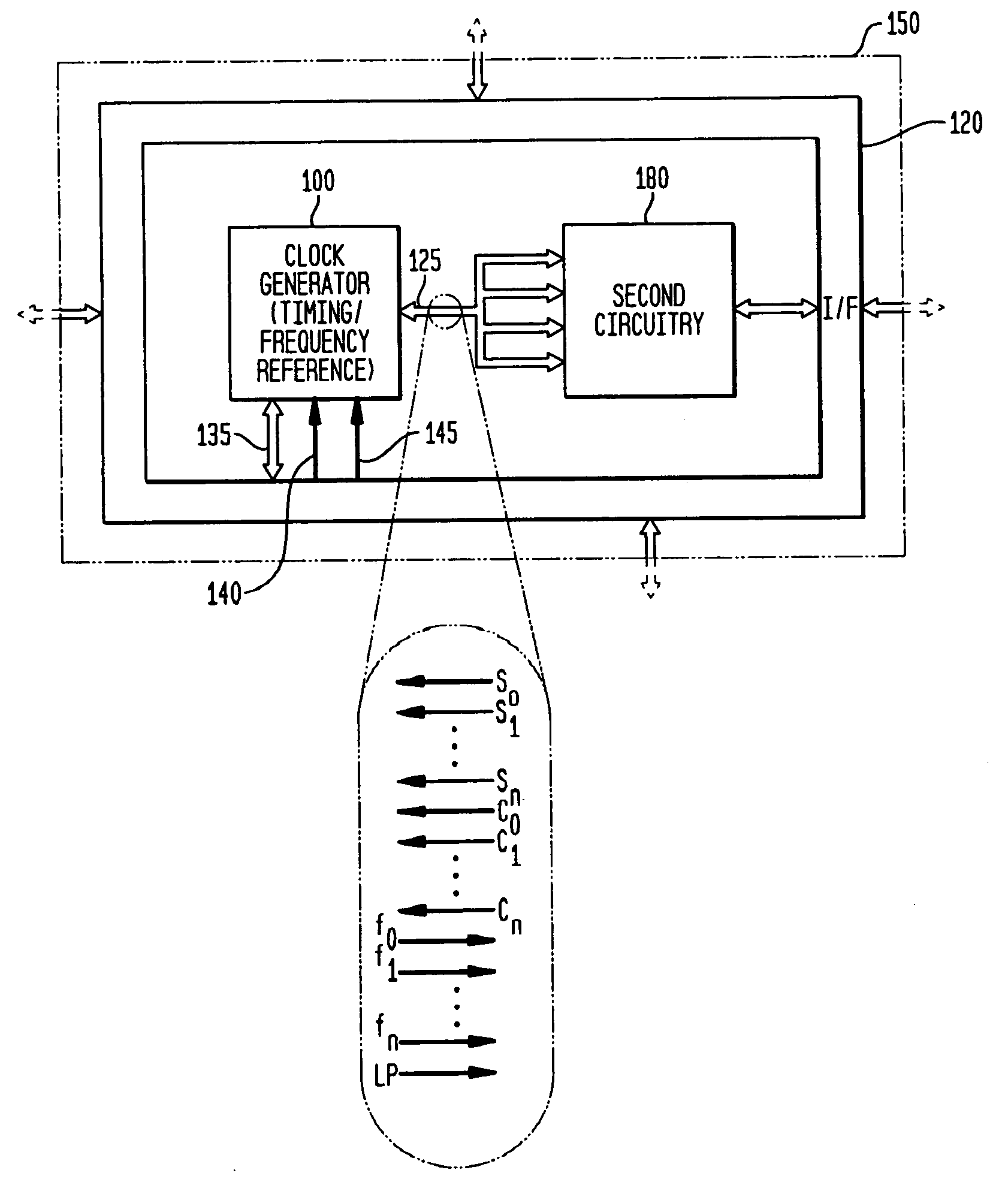
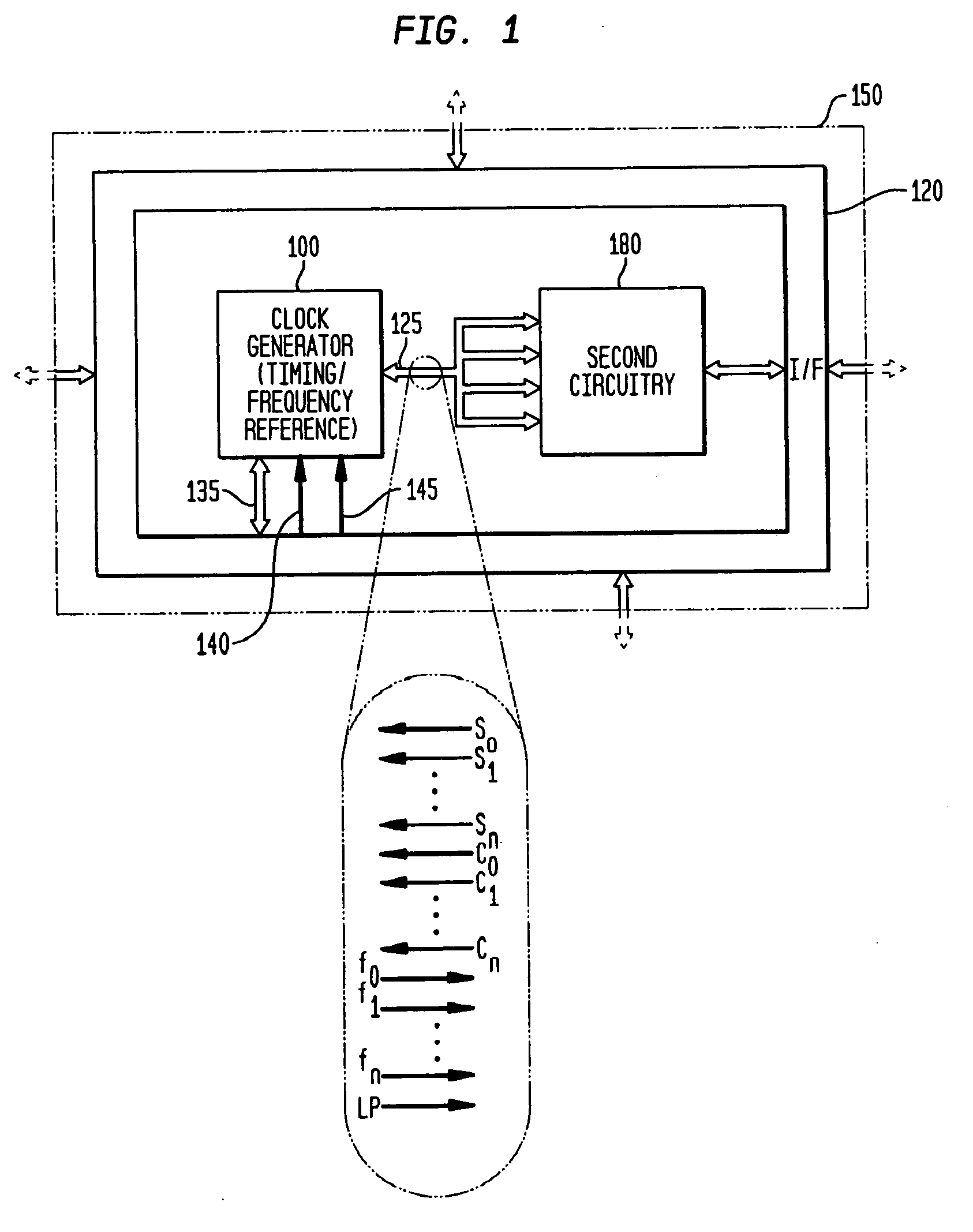
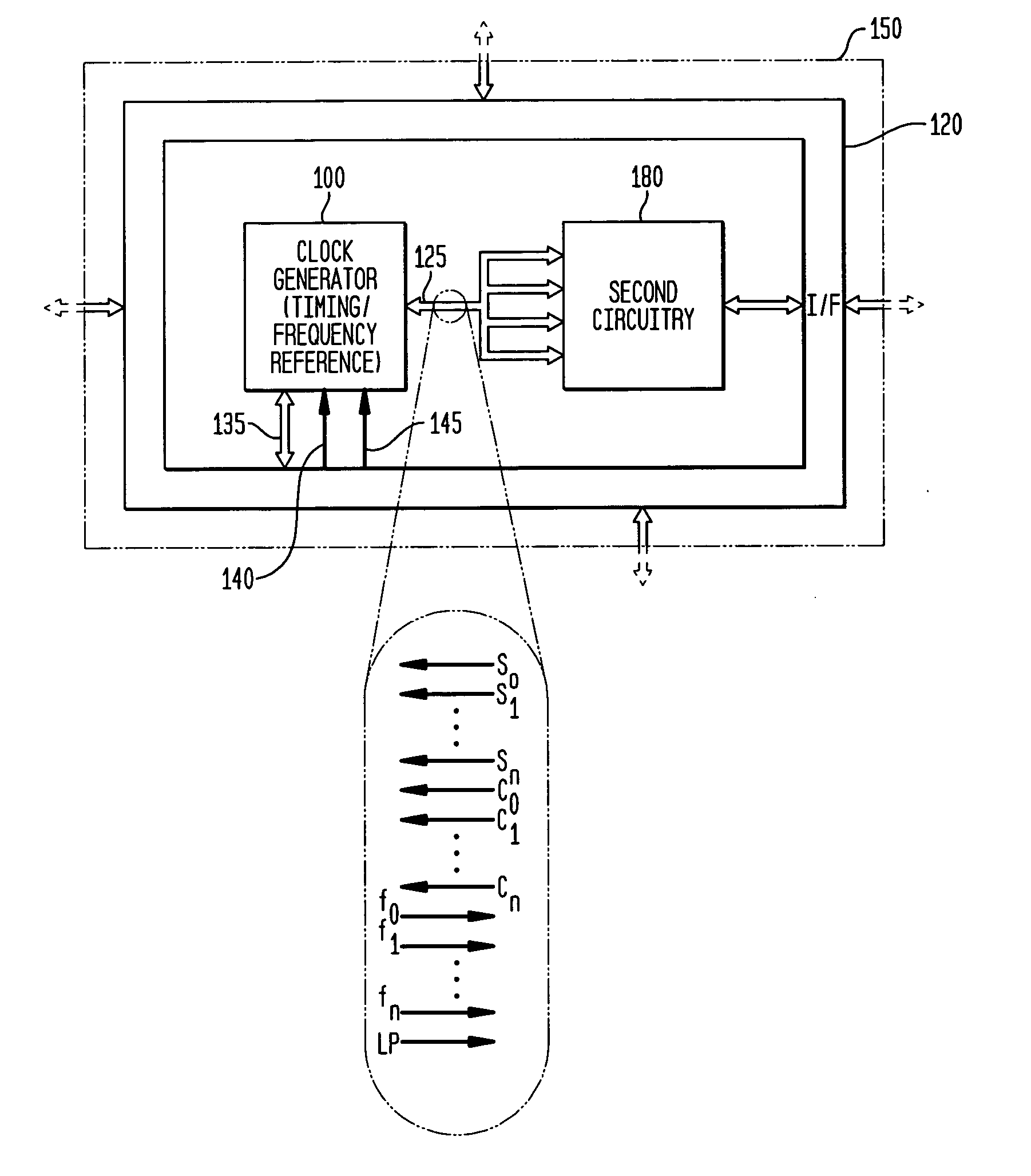
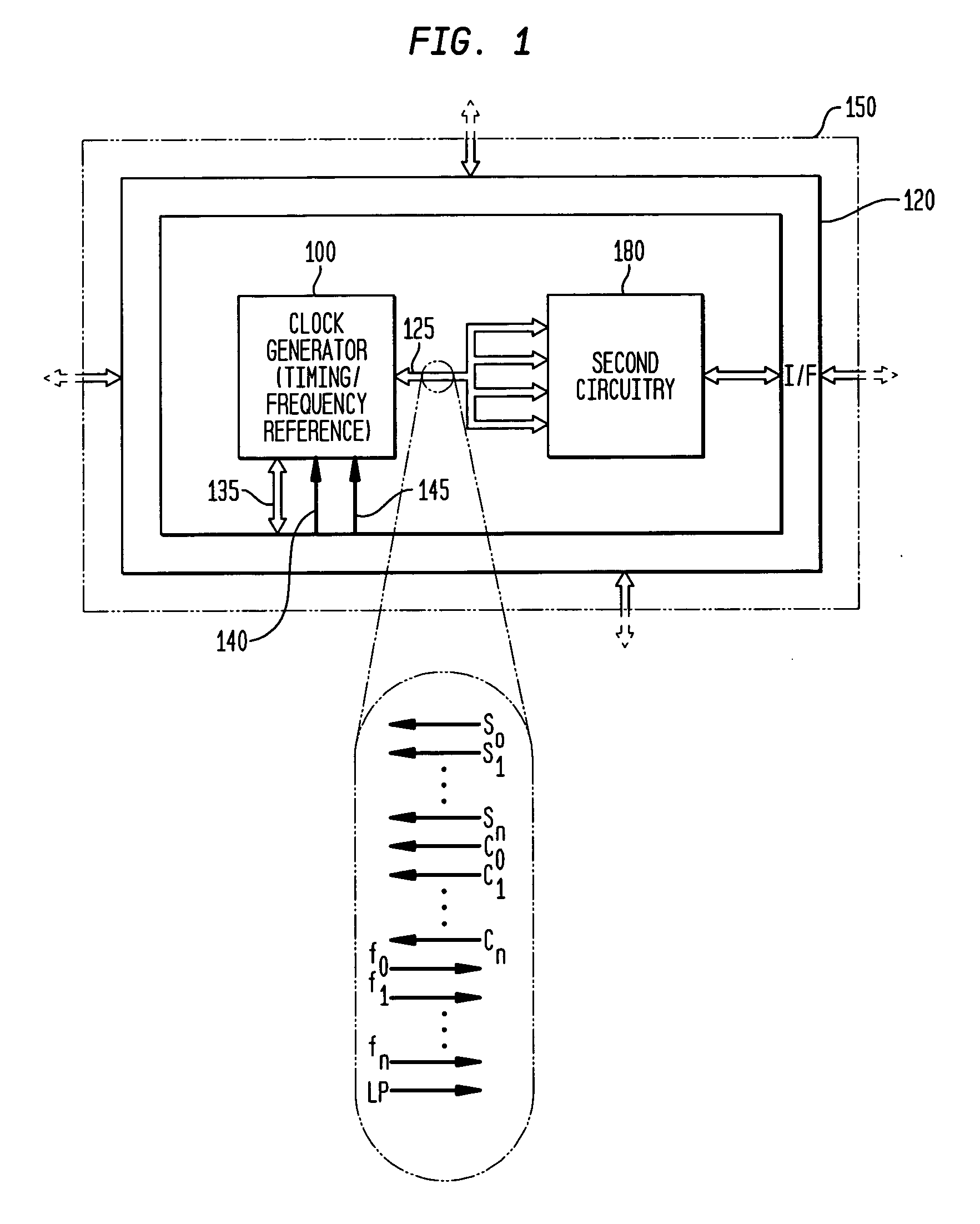
Low-latency start-up for a monolithic clock generator and timing/frequency reference
ActiveUS7307486B2High frequencyLoud noiseAngle modulation by variable impedenceResonant circuit tuningMicrocontrollerVoltage generator
An apparatus, system and method are provided for low-latency start-up of a free-running harmonic oscillator. The exemplary apparatus embodiment comprises a first and second current sources to generate first and second currents; a bias current monitor adapted to detect a magnitude of the second current and to provide a control signal when the magnitude of the second current is equal to or greater than a predetermined magnitude; and a bias controller adapted to switch the first current from the oscillator and to switch the second current to the oscillator in response to the control signal. a reference voltage generator, a comparator, and a bias controller. Exemplary embodiments include reference voltage generator, a comparator, and a bias controller.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Method and apparatus for a crystal oscillator to achieve fast start-up time, low power and frequency calibration
InactiveUS7348861B1Fast frequency calibrationFast startup timePulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
One embodiment of the present invention includes a frequency generation circuit including a control module, an oscillator circuit coupled to the control module, the oscillator circuit having a start-up time defined by the time required to reach a desired frequency. The oscillator circuit includes an amplifier having an input and an output and being programmably-alterable by the control module, a first capacitor coupled to the input of the amplifier and being programmably-alterable, in capacitance, by the control module, a second capacitor coupled to the output of the amplifier, a crystal resonator coupled to the first and second capacitors for generating an output signal having a desired frequency, wherein fast start-up time is achieved.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
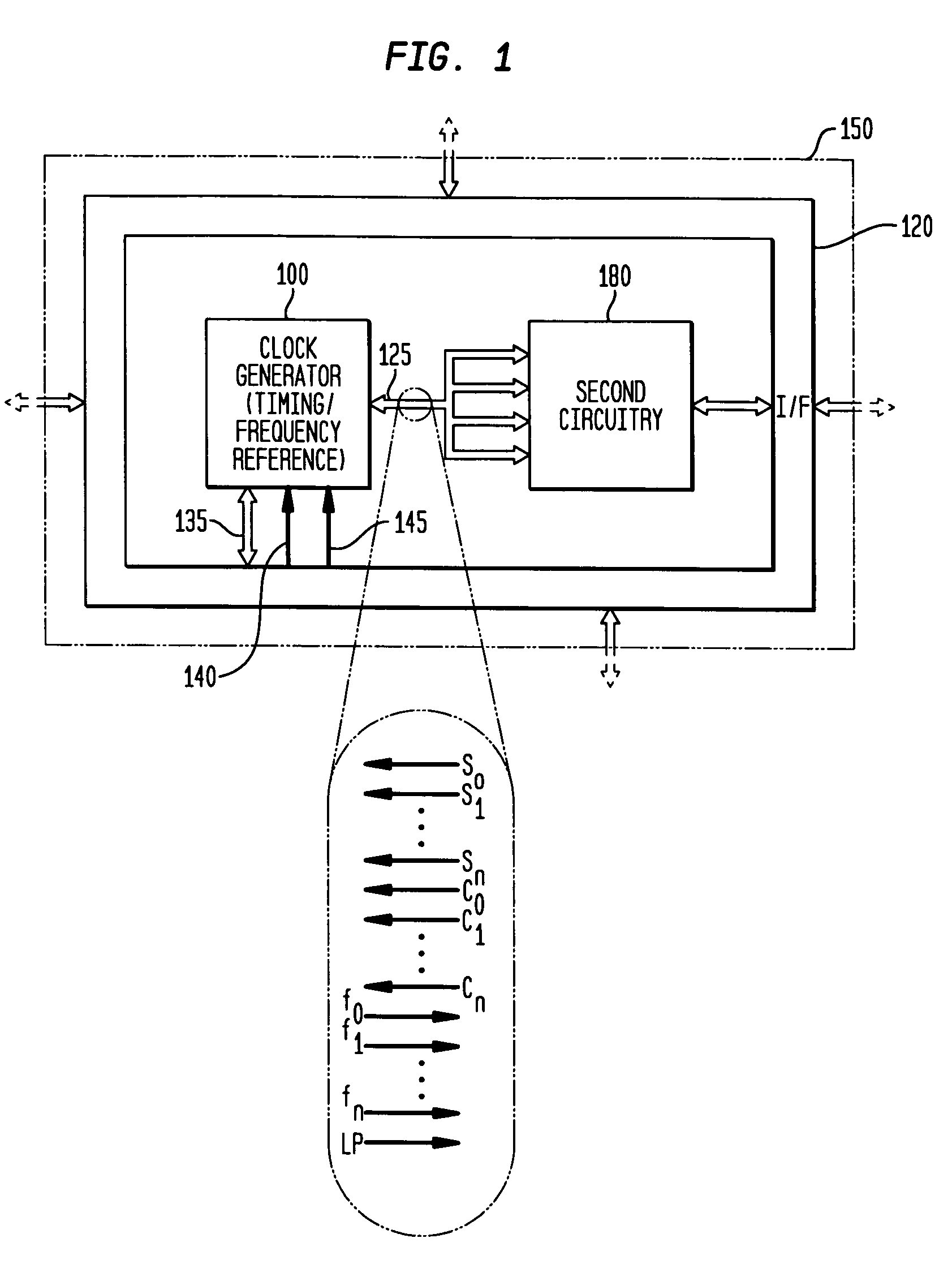
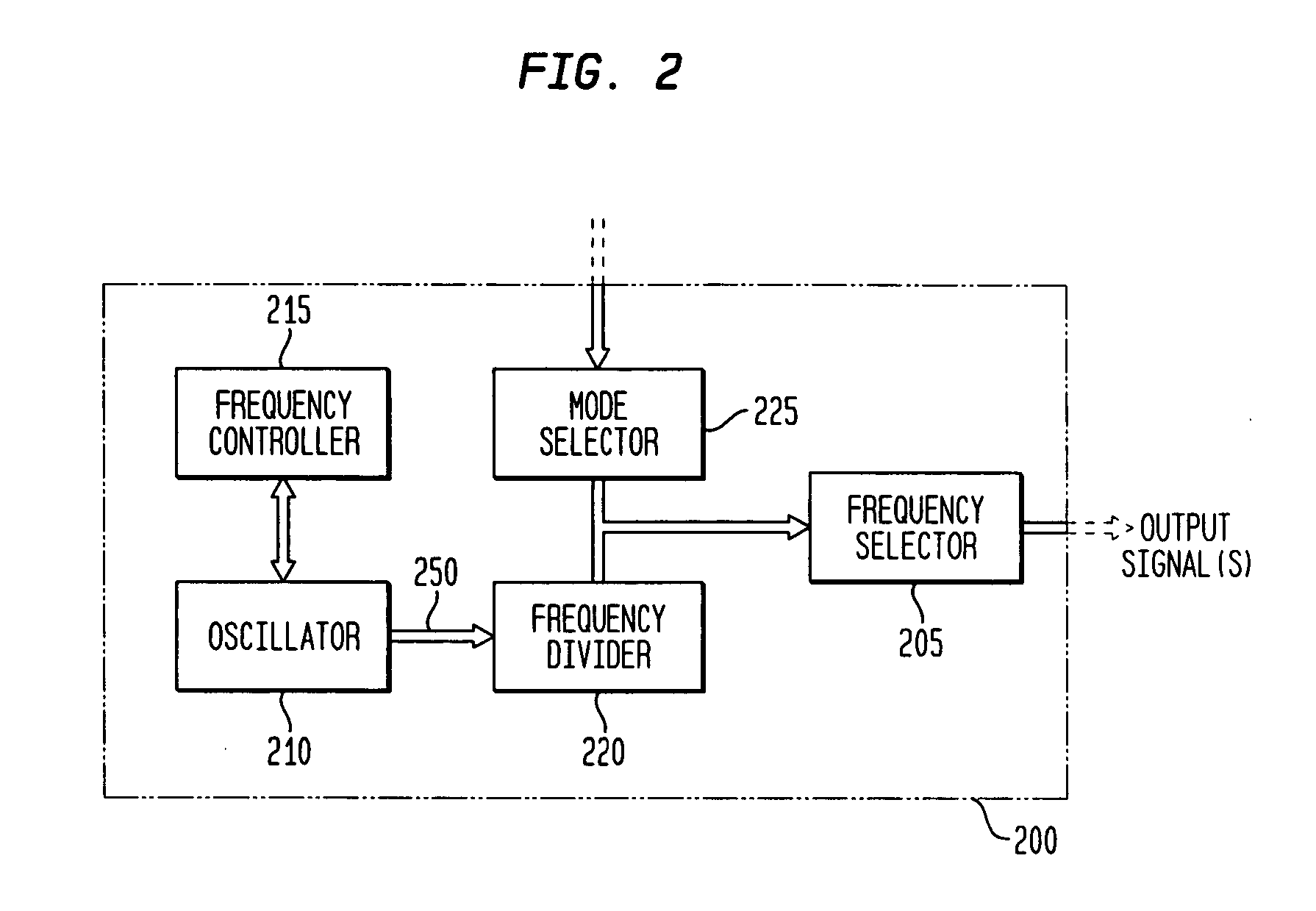
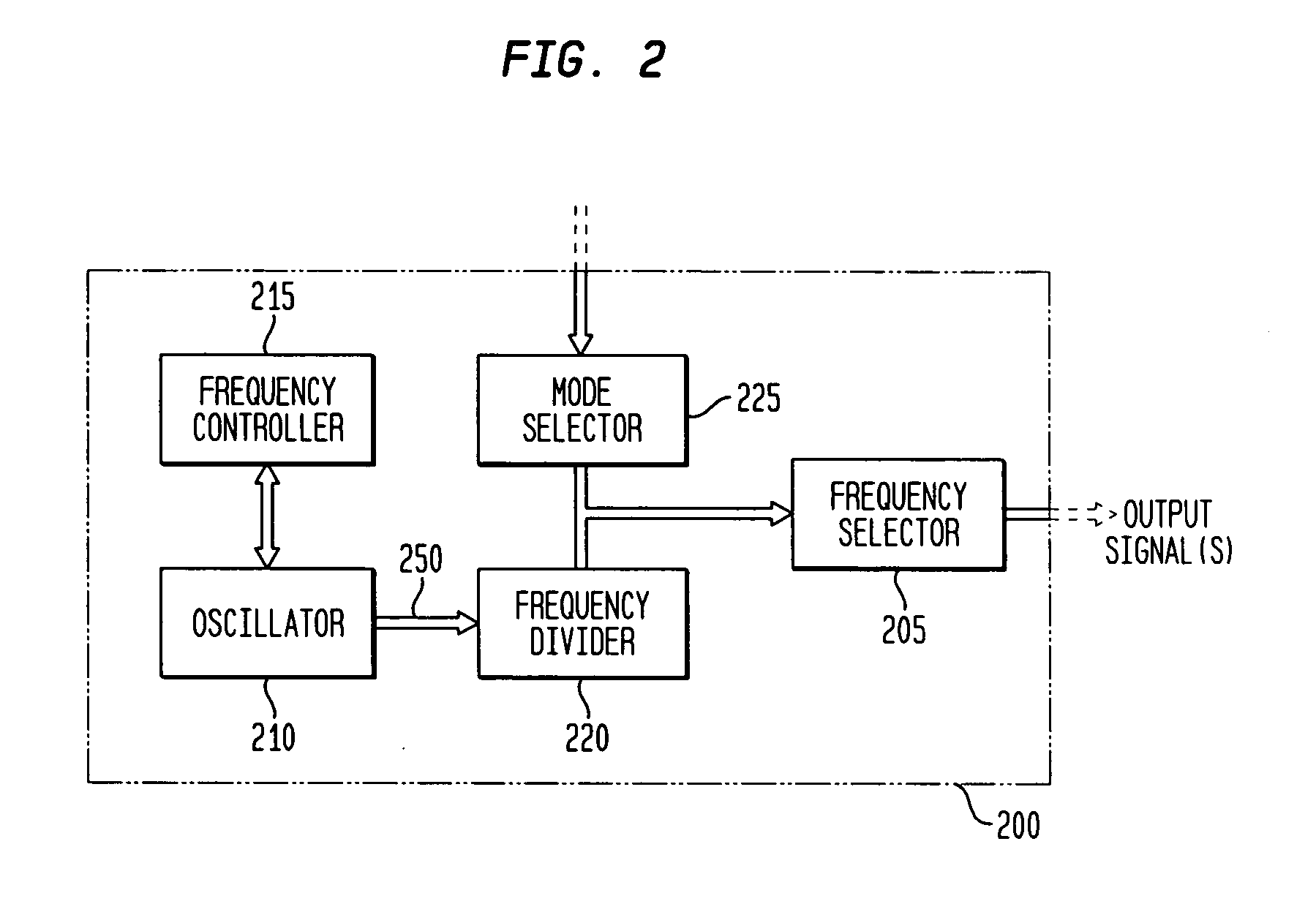
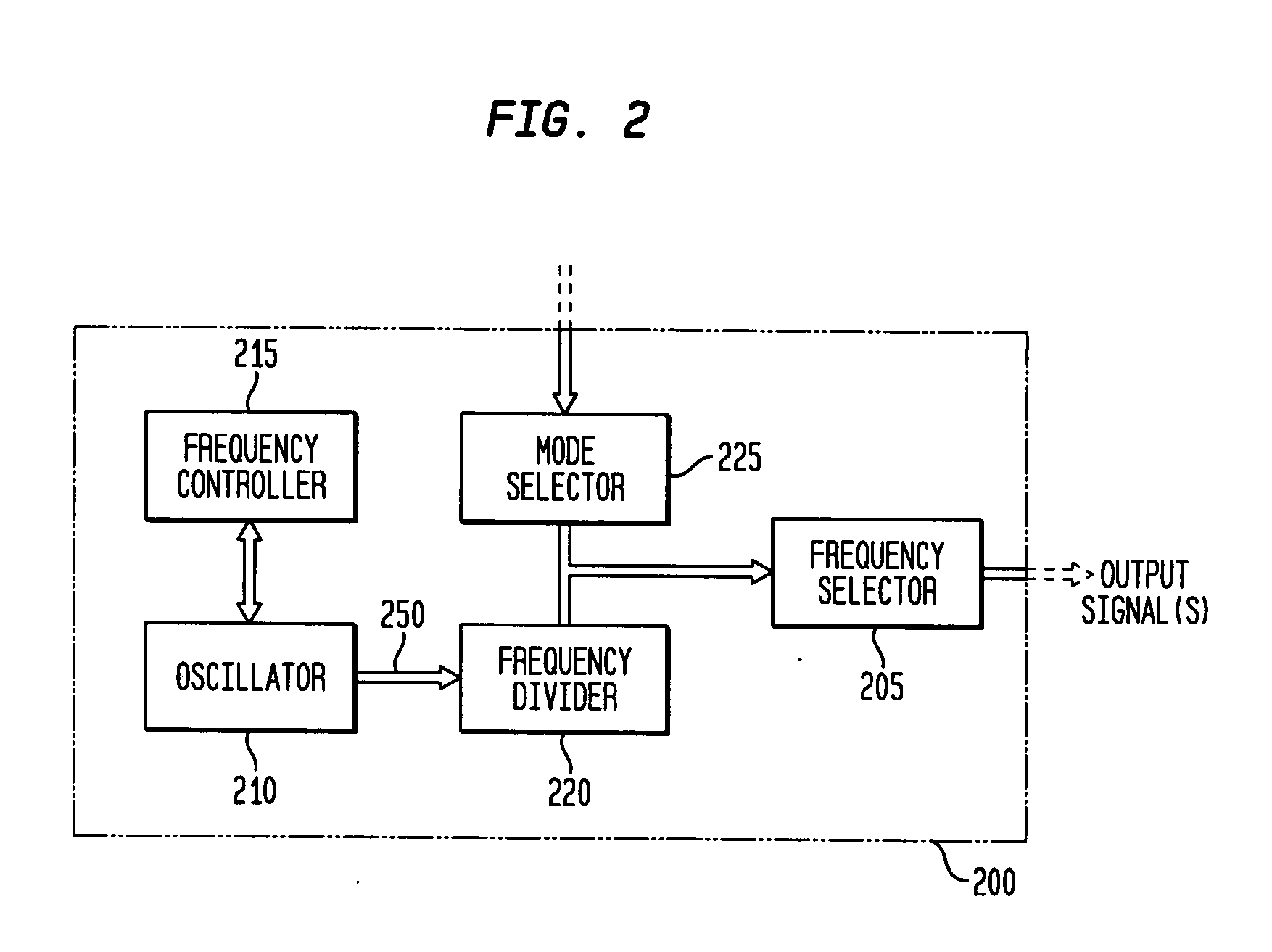
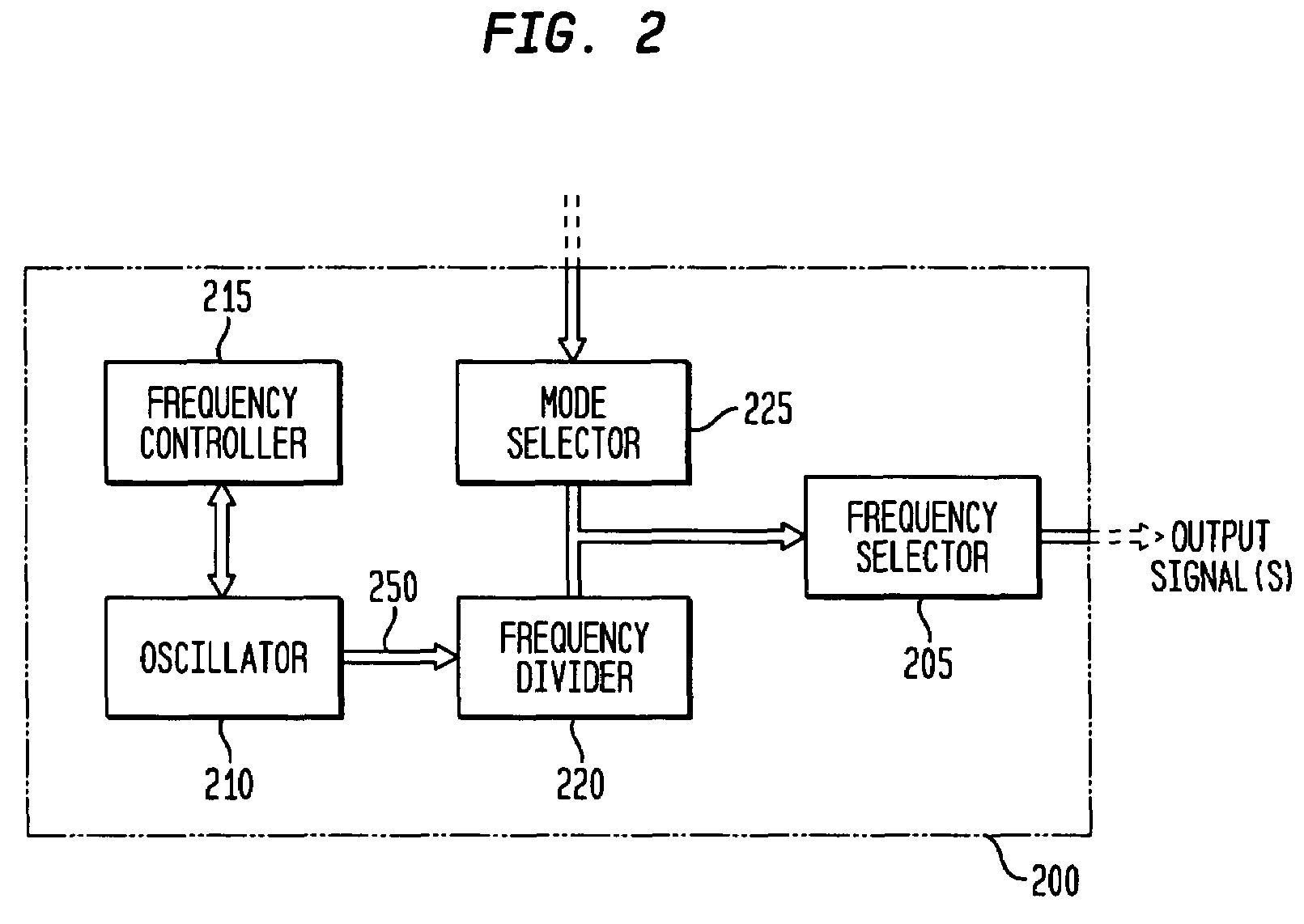
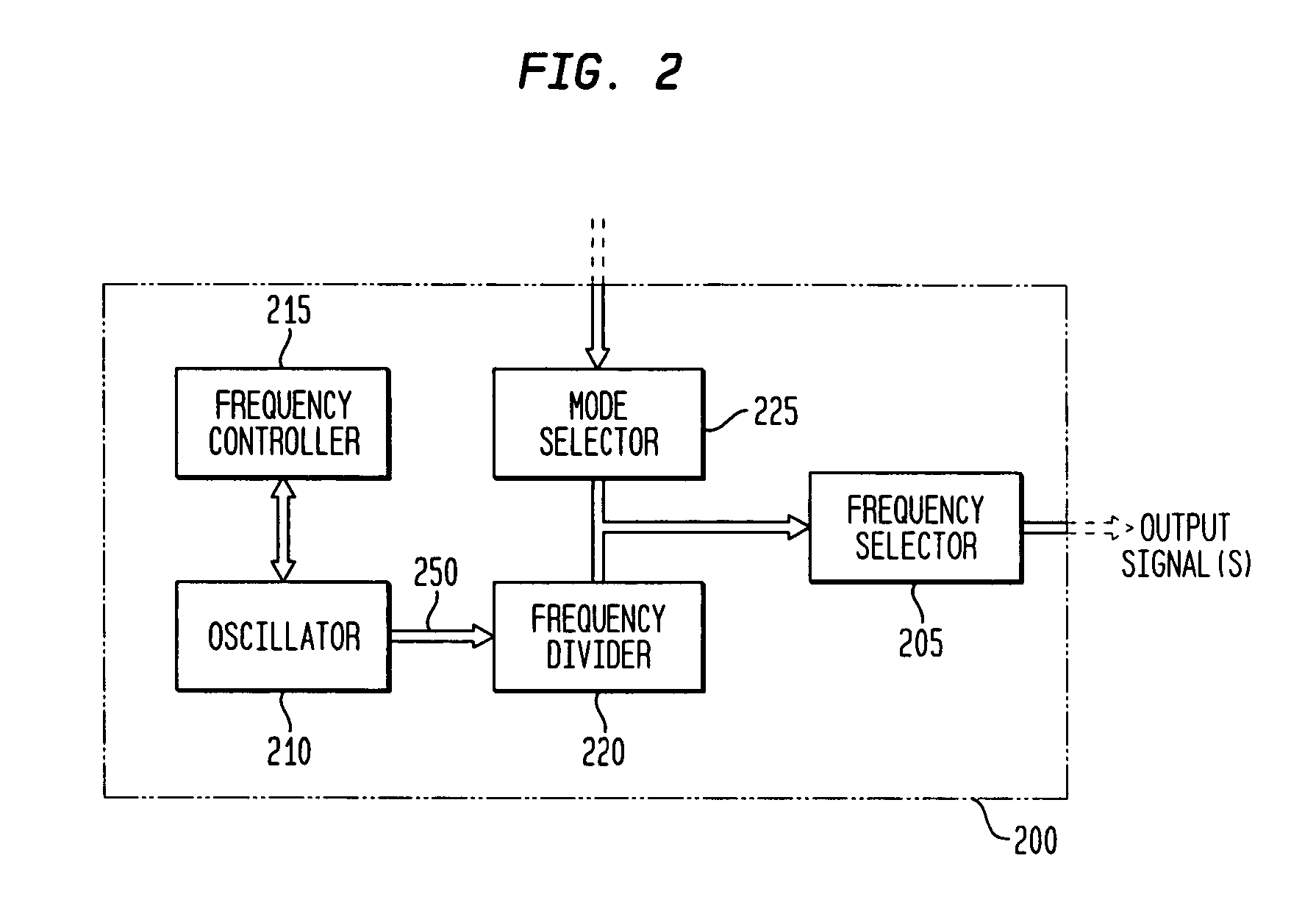
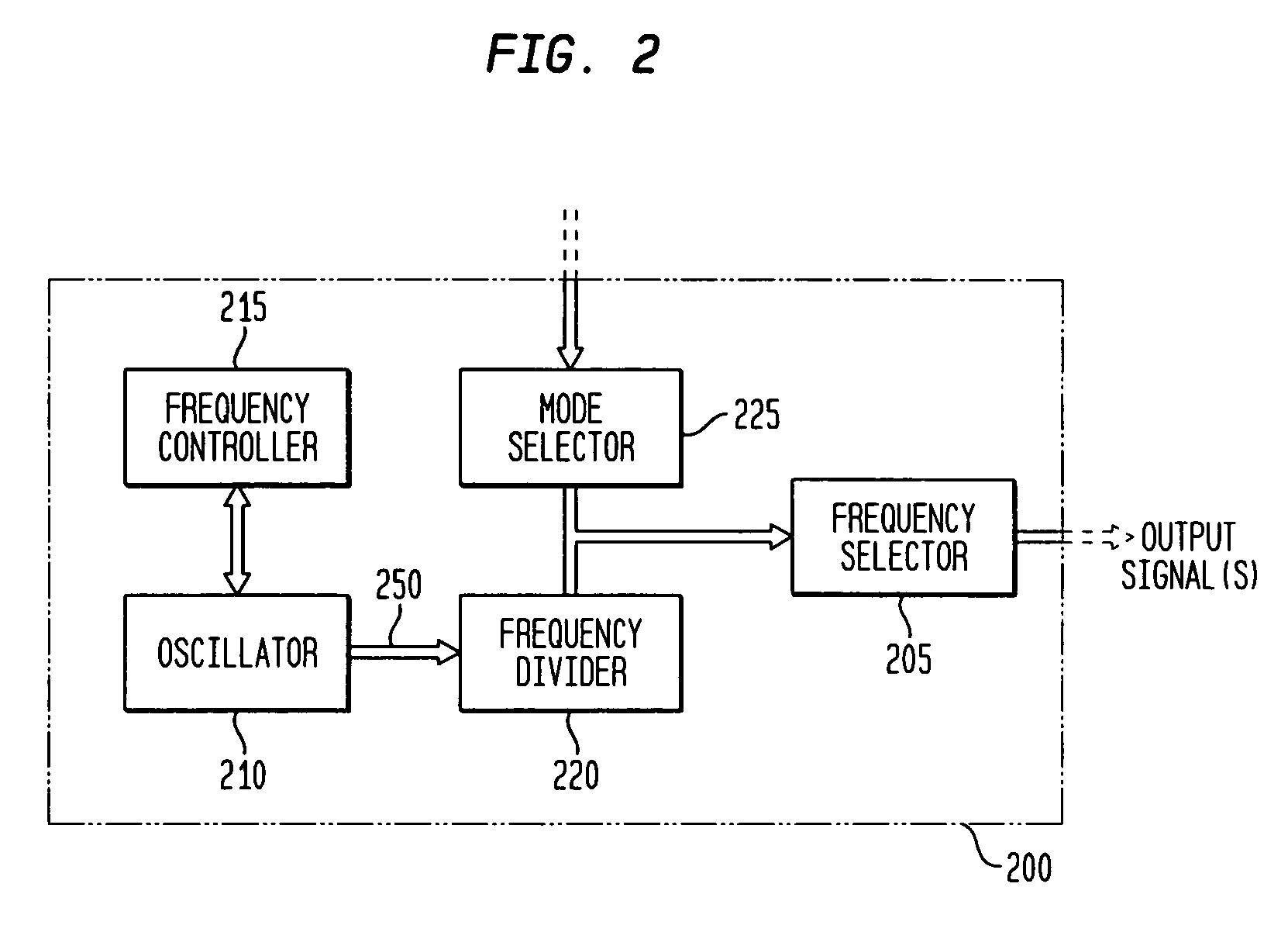
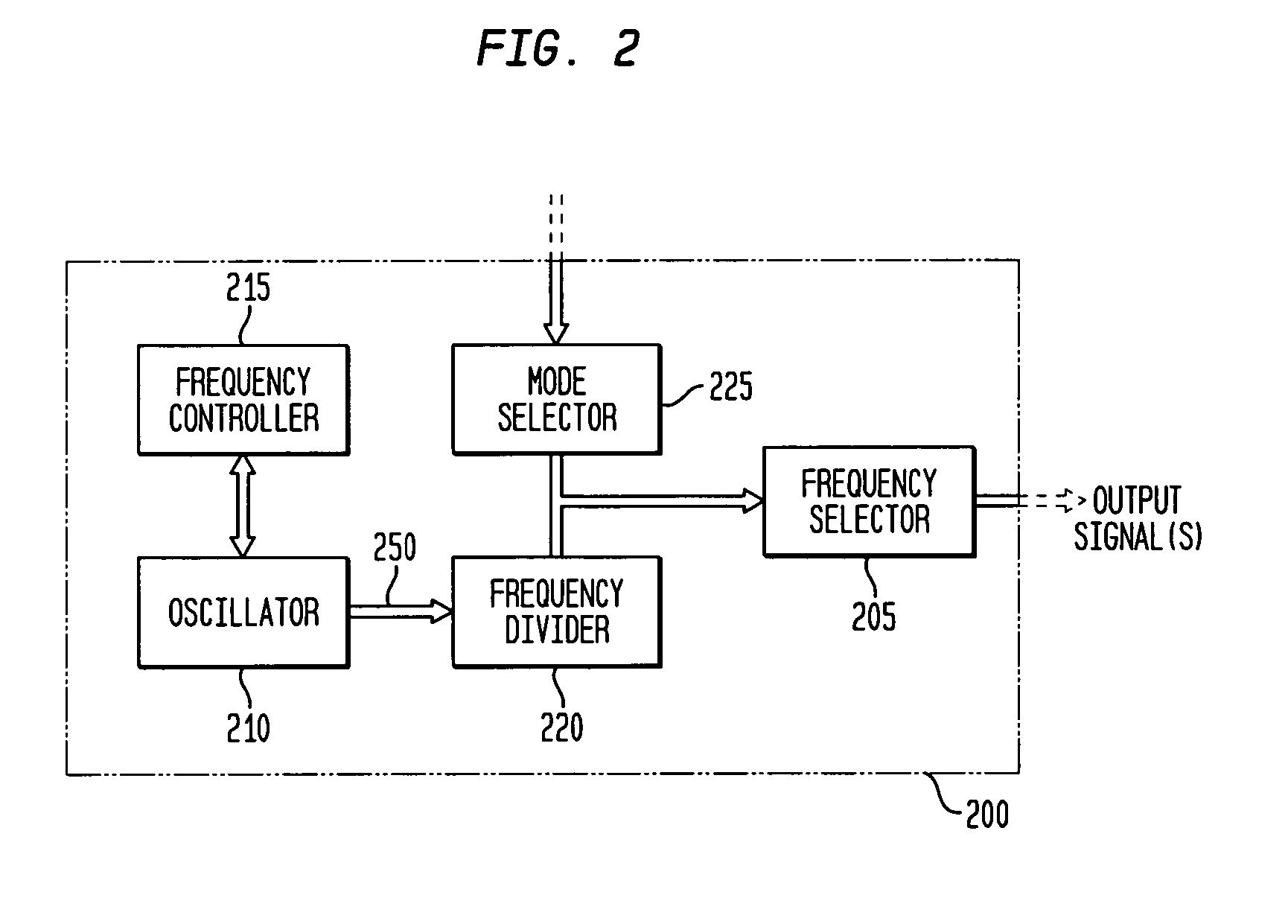
Discrete clock generator and timing/frequency reference
ActiveUS20060158268A1High frequencyLoud noisePulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationCapacitanceFrequency stabilization
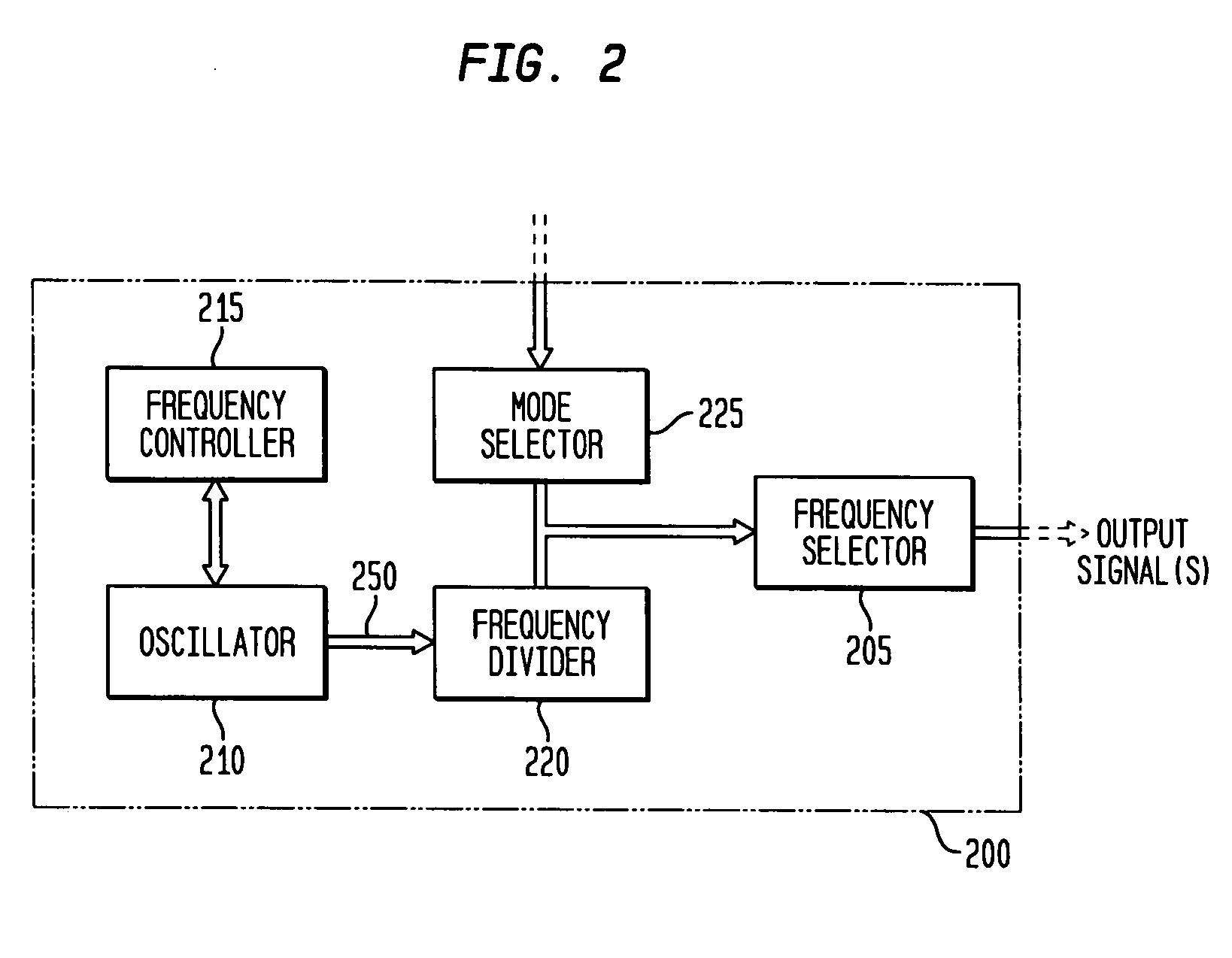
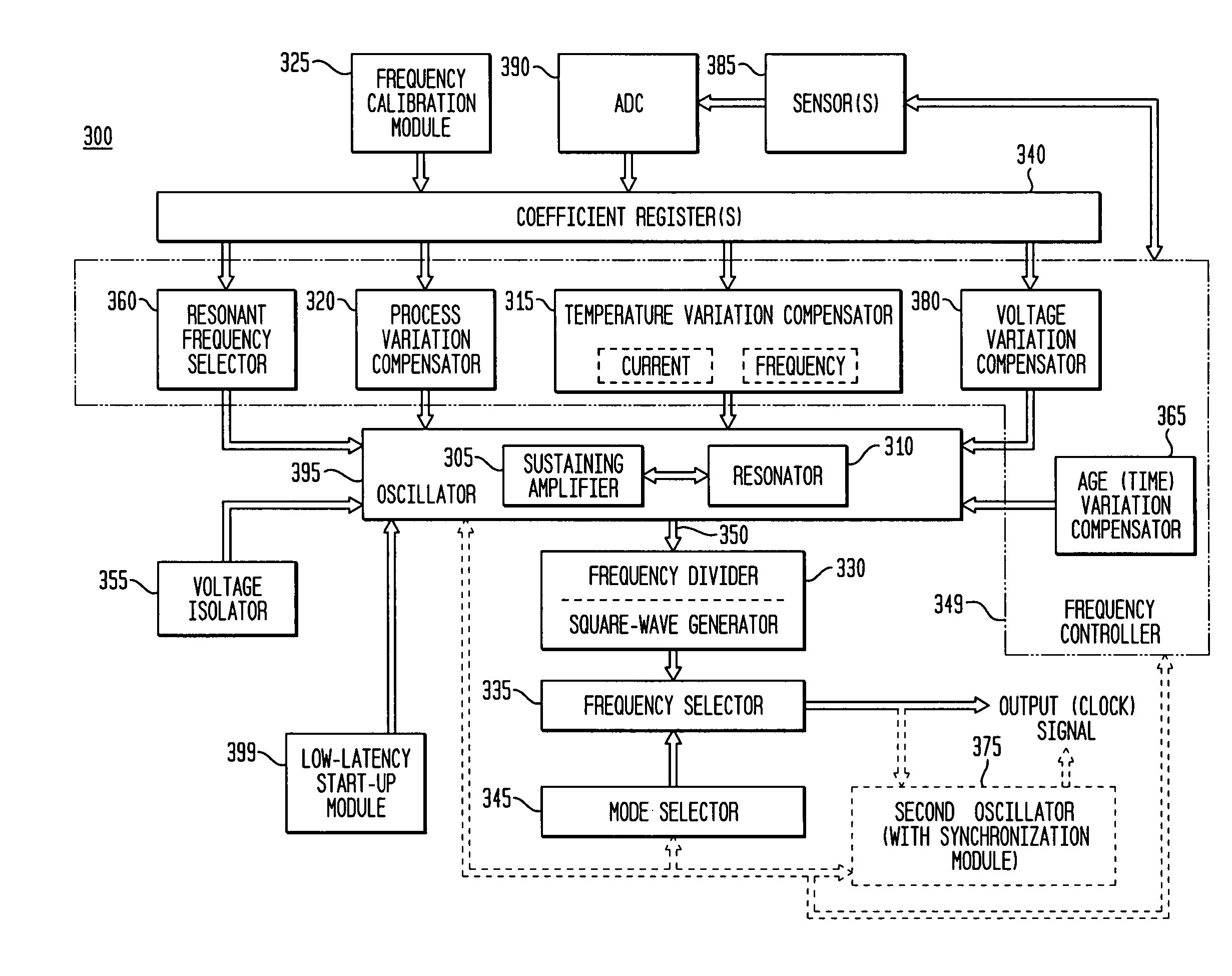
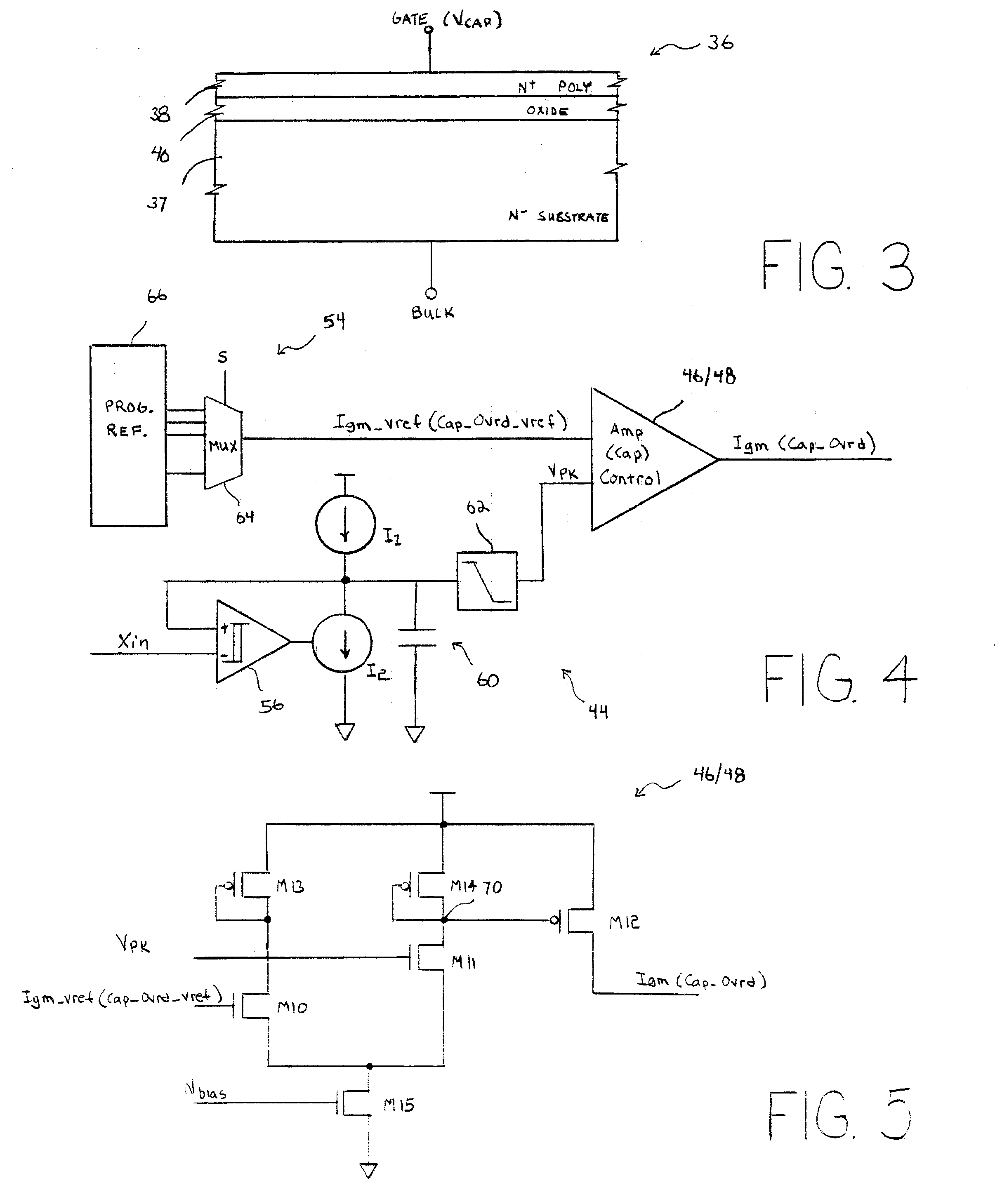
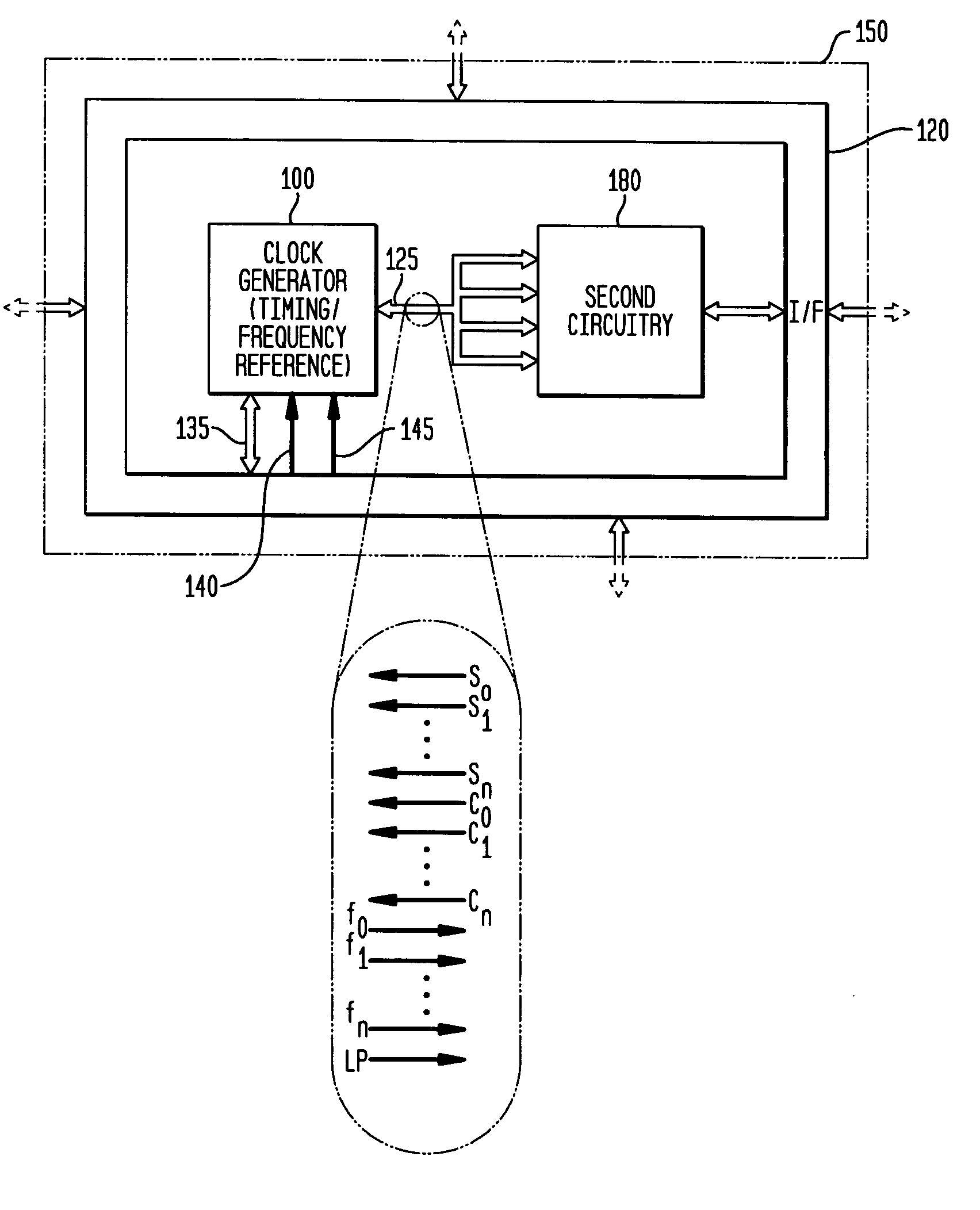
In various embodiments, the invention provides a discrete clock generator and / or a timing and frequency reference using an LC-oscillator topology, having a frequency controller to control and provide a stable resonant frequency, which may then be provided to other, second circuitry such as a processor or controller. Frequency stability is provided over variations in a selected parameter such as temperature and fabrication process variations. The various apparatus embodiments include a sensor adapted to provide a signal in response to at least one parameter of a plurality of parameters; and a frequency controller adapted to modify the resonant frequency in response to the second signal. In exemplary embodiments, the sensor is implemented as a current source responsive to temperature fluctuations, and the frequency controller is implemented as a plurality of controlled reactance modules which are selectively couplable to the resonator or to one or more control voltages. The controlled reactance modules may include fixed or variable capacitances or inductances, and may be binary weighted. Arrays of resistive modules are also provided, to generate one or more control voltages.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Integrated clock generator and timing/frequency reference
ActiveUS20060152293A1Less relative period jitterLoud noisePulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationCapacitanceFrequency stabilization
In various embodiments, the invention provides a clock generator and / or a timing and frequency reference using an LC-oscillator topology, having a frequency controller to control and provide a stable resonant frequency, which is integrated with other, second circuitry such as a processor or controller. Frequency stability is provided over variations in a selected parameter such as temperature and fabrication process variations. The various apparatus embodiments include a sensor adapted to provide a signal in response to at least one parameter of a plurality of parameters; and a frequency controller adapted to modify the resonant frequency in response to the second signal. In exemplary embodiments, the sensor is implemented as a current source responsive to temperature fluctuations, and the frequency controller is implemented as a plurality of controlled reactance modules which are selectively couplable to the resonator or to one or more control voltages. The controlled reactance modules may include fixed or variable capacitances or inductances, and may be binary weighted. Arrays of resistive modules are also provided, to generate one or more control voltages.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Integrated clock generator and timing/frequency reference
ActiveUS7365614B2High frequencyLoud noisePulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
In various embodiments, the invention provides a clock generator and / or a timing and frequency reference using an LC-oscillator topology, having a frequency controller to control and provide a stable resonant frequency, which is integrated with other, second circuitry such as a processor or controller. Frequency stability is provided over variations in a selected parameter such as temperature and fabrication process variations. The various apparatus embodiments include a sensor adapted to provide a signal in response to at least one parameter of a plurality of parameters; and a frequency controller adapted to modify the resonant frequency in response to the second signal. In exemplary embodiments, the sensor is implemented as a current source responsive to temperature fluctuations, and the frequency controller is implemented as a plurality of controlled reactance modules which are selectively couplable to the resonator or to one or more control voltages. The controlled reactance modules may include fixed or variable capacitances or inductances, and may be binary weighted. Arrays of resistive modules are also provided, to generate one or more control voltages.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Low power oscillator having fast start-up times
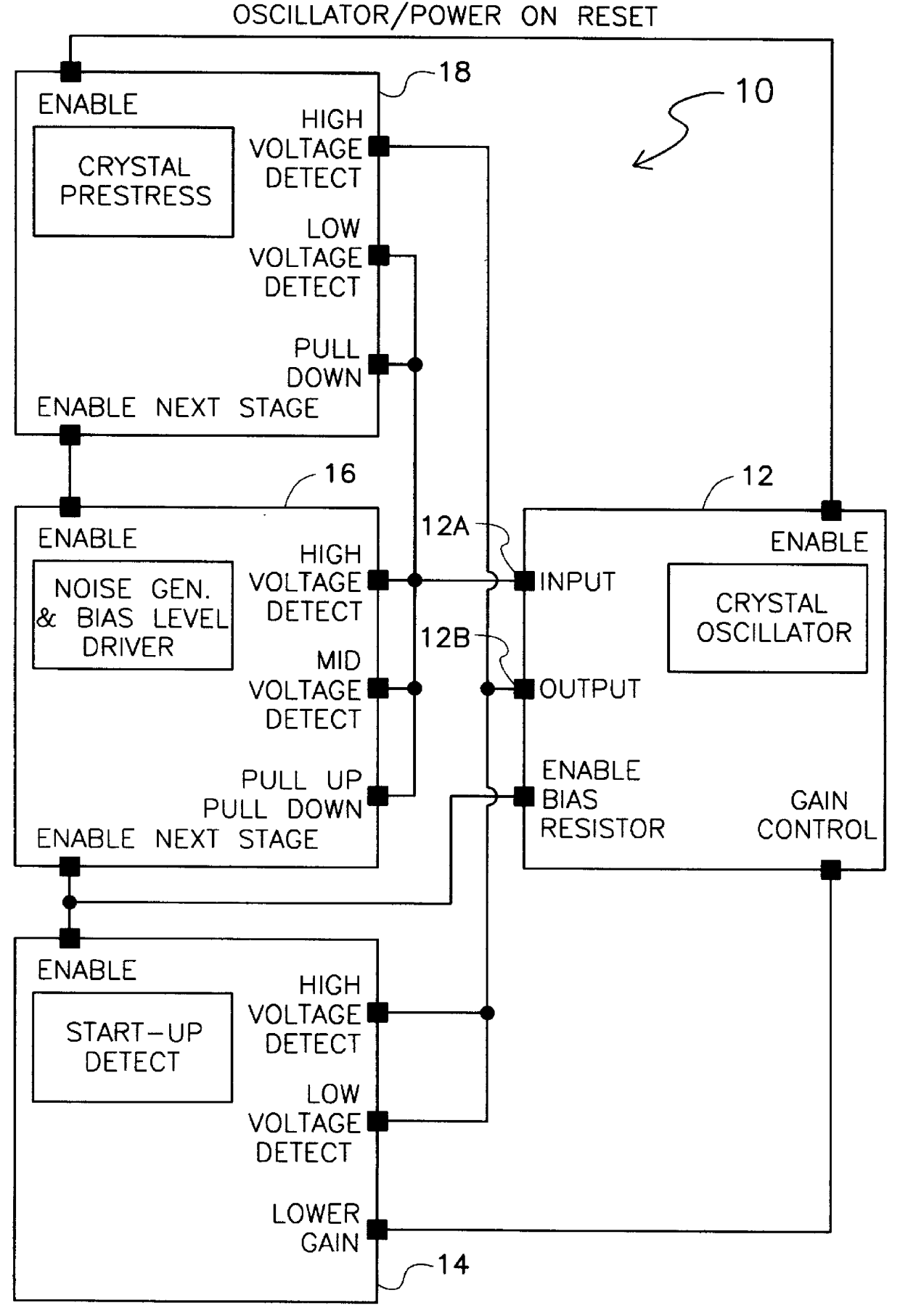
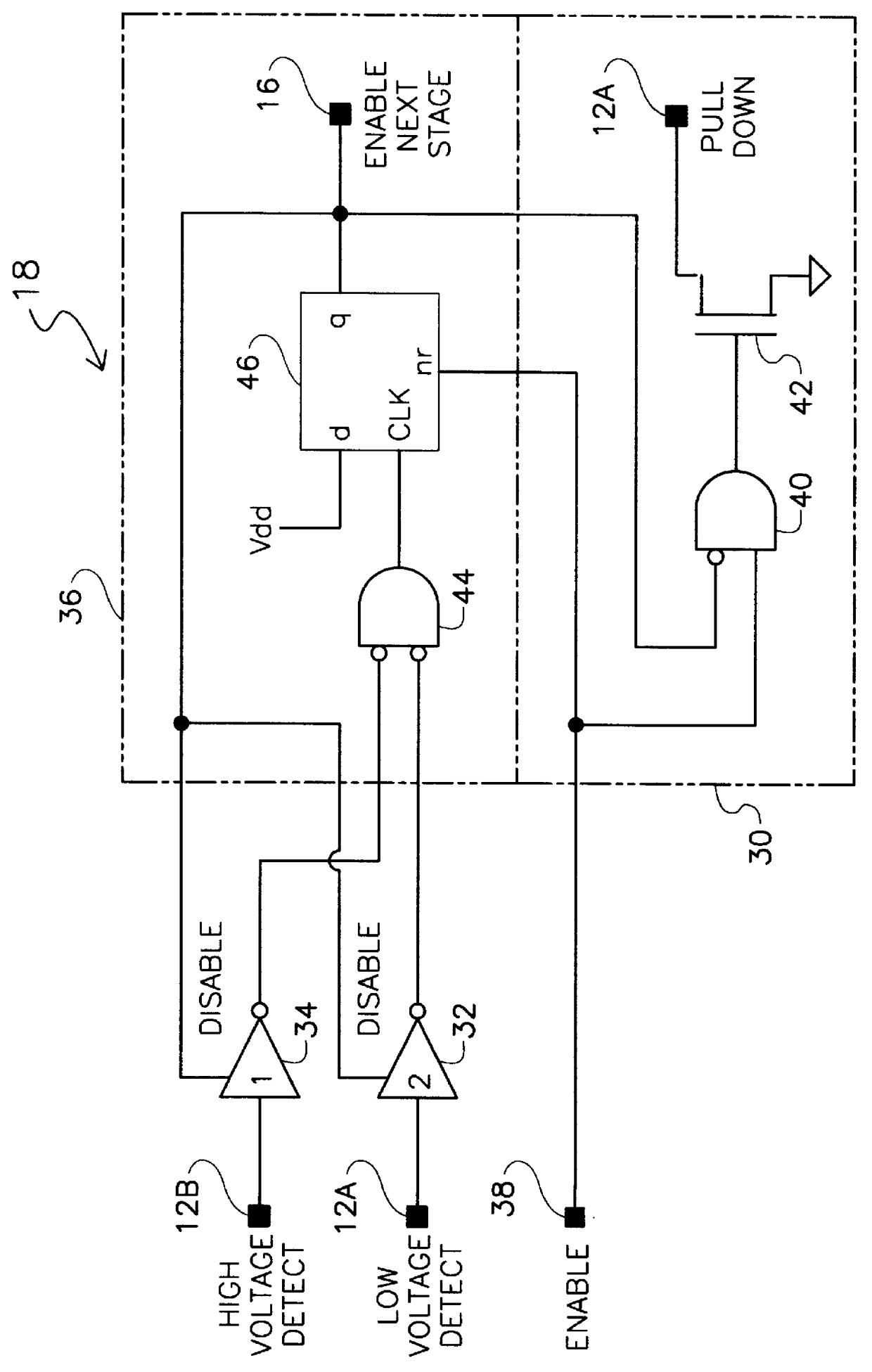
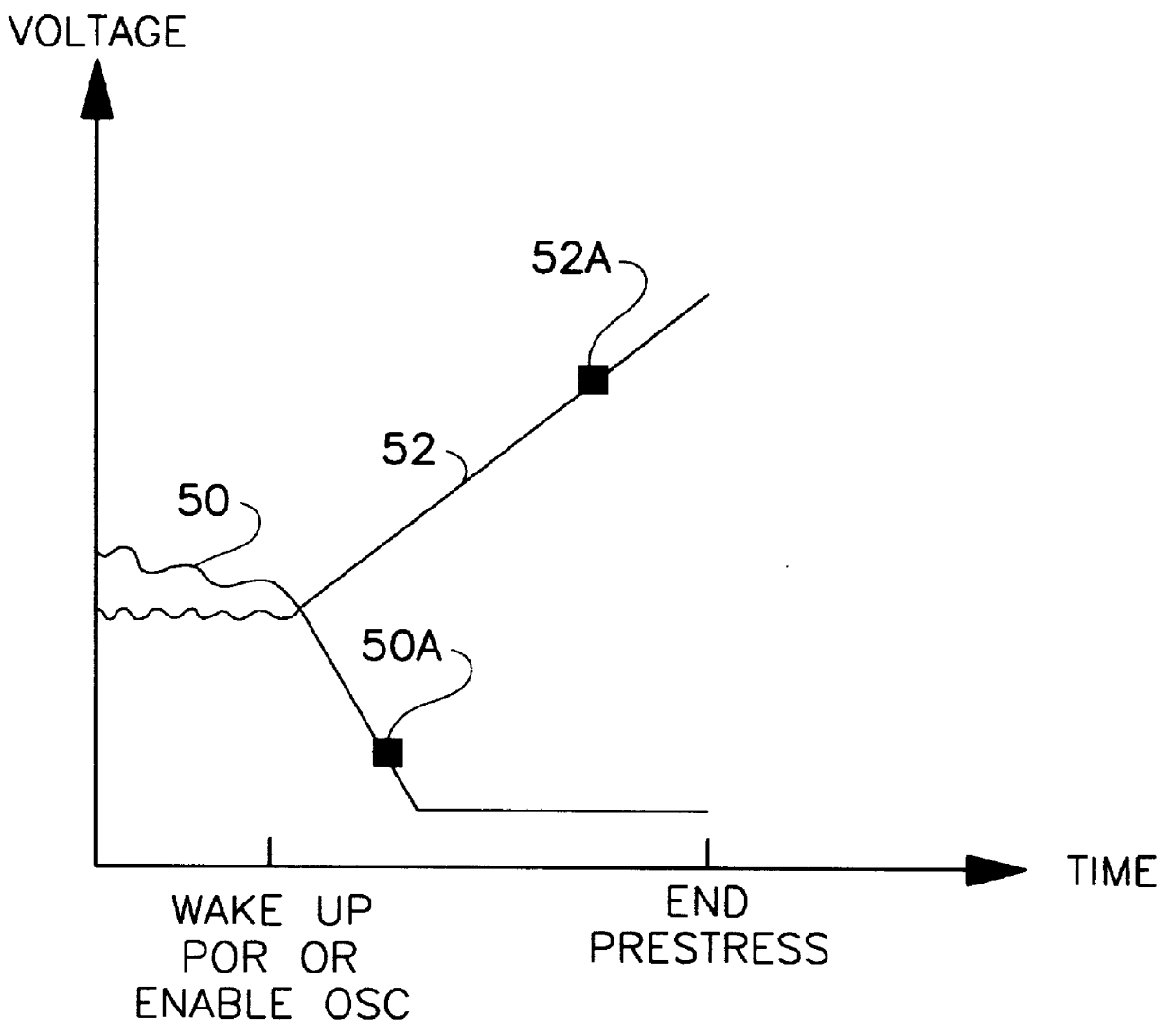
A low power oscillator having fast start-up times. The low power fast starting oscillator uses an oscillator circuit having an input and an output for generating a signal of a desired frequency. A start-up detect circuit is coupled to the output of the oscillator circuit for detecting when the oscillator circuit has reached steady state operation and for generating a start-up circuit output signal which adjusts the gain of the oscillator circuit when steady state operation has been reached by the oscillator circuit. A noise generator is coupled to the input of the oscillator circuit and to the start-up detect circuit for inputting a noise pulse into the oscillator circuit. The noise pulse is used for biasing the input of the oscillator circuit to approximately an optimal bias voltage level. The noise generator is further used for sending an enable start-up detect signal to the start-up detect circuit to activate the start-up detect circuit. A prestress circuit is coupled to the input and to the output of the oscillator circuit for prestressing a piezoelectric resonator of the oscillator circuit to shorten start-up times of the oscillator circuit. The prestress circuit is further used for sending an enable noise generator signal to the noise generator to activate the noise generator.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
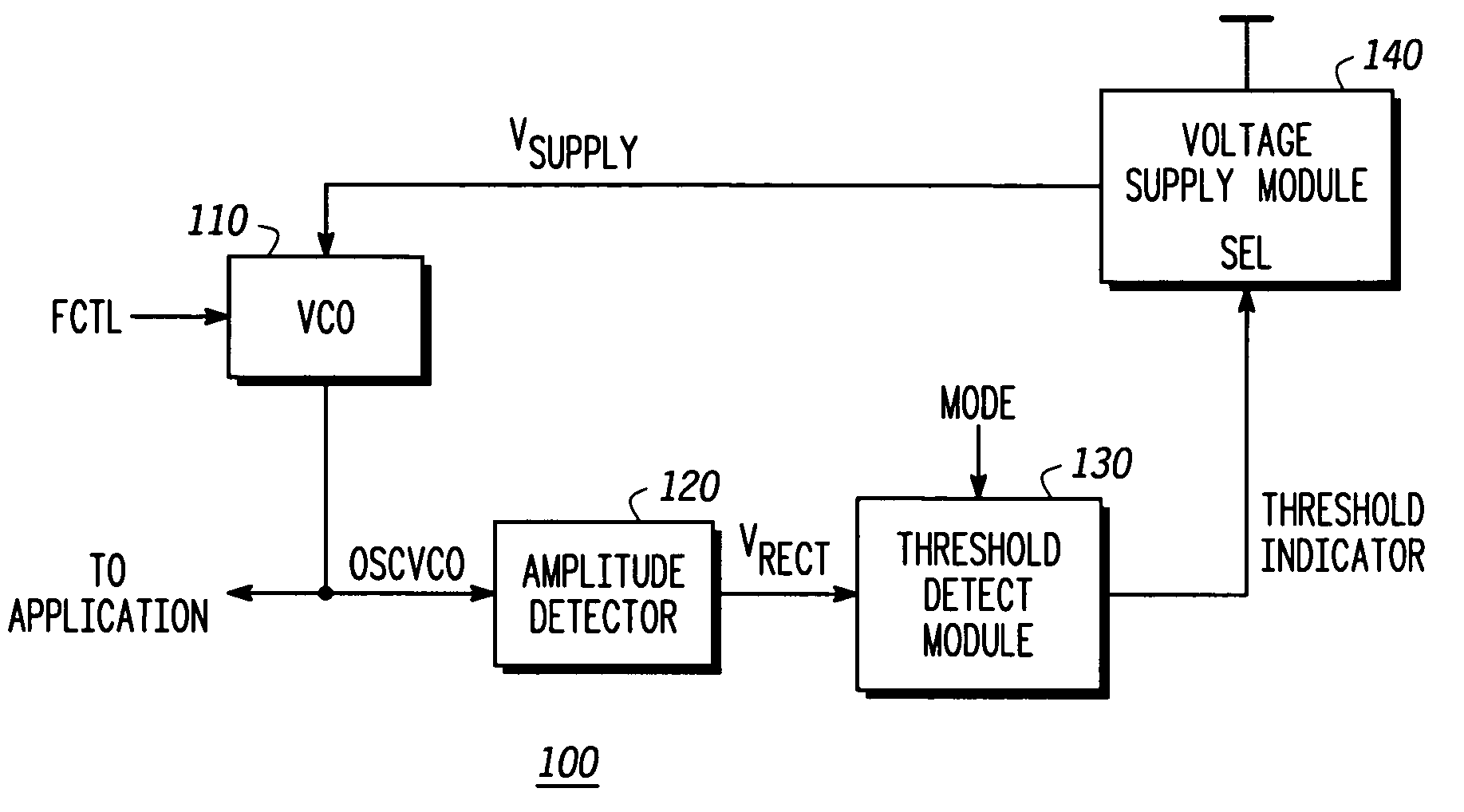
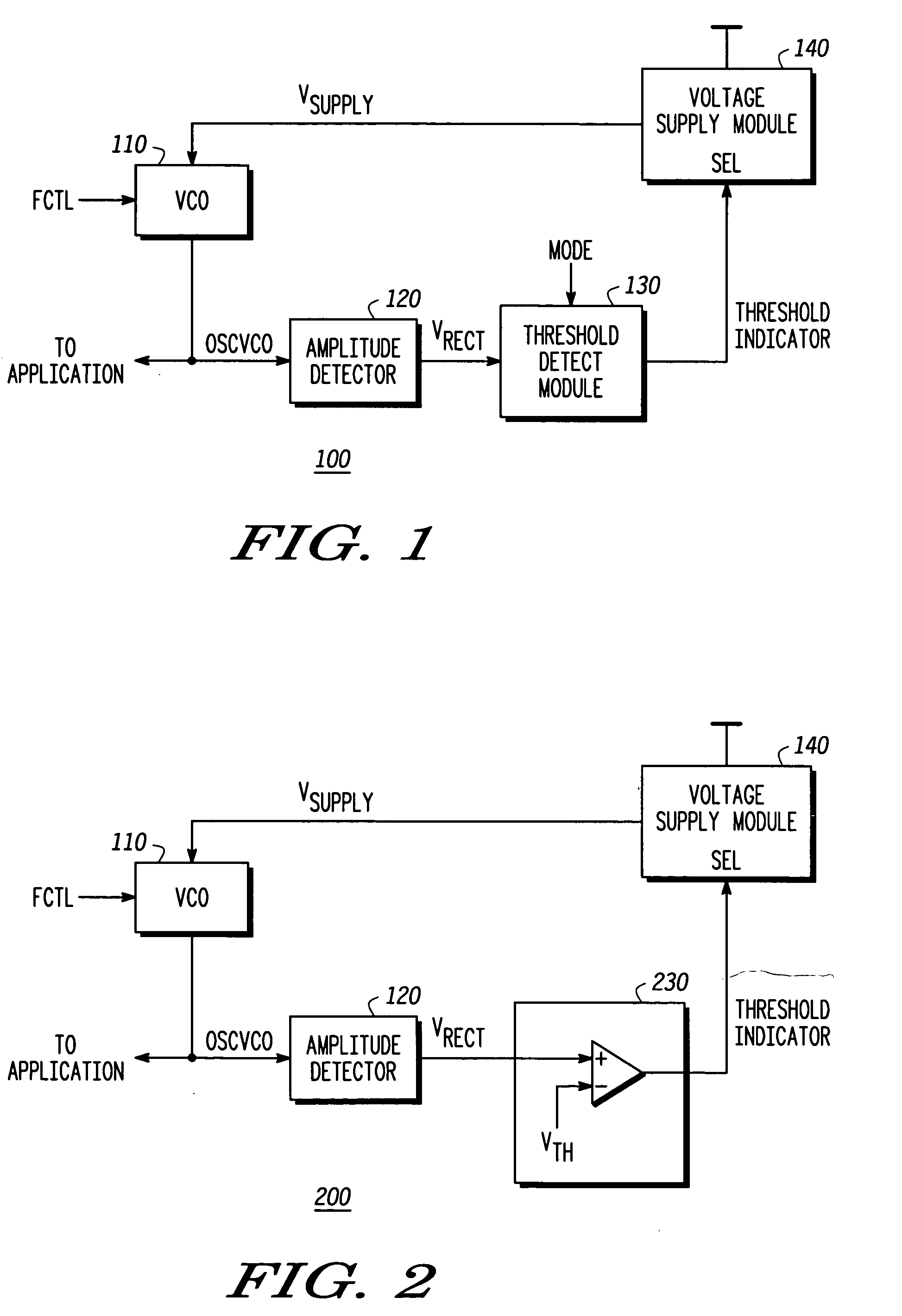
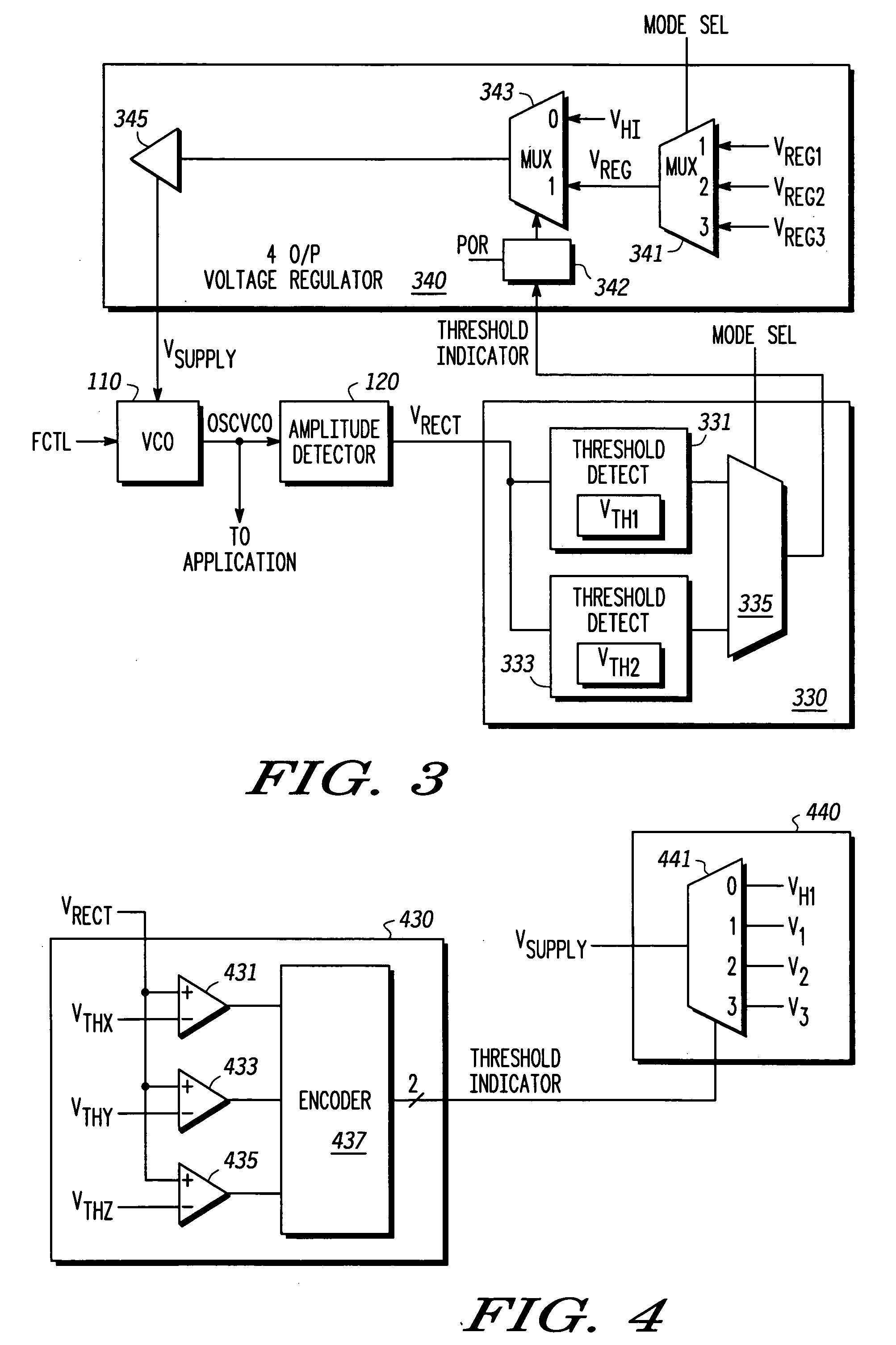
Self-calibrating oscillator system
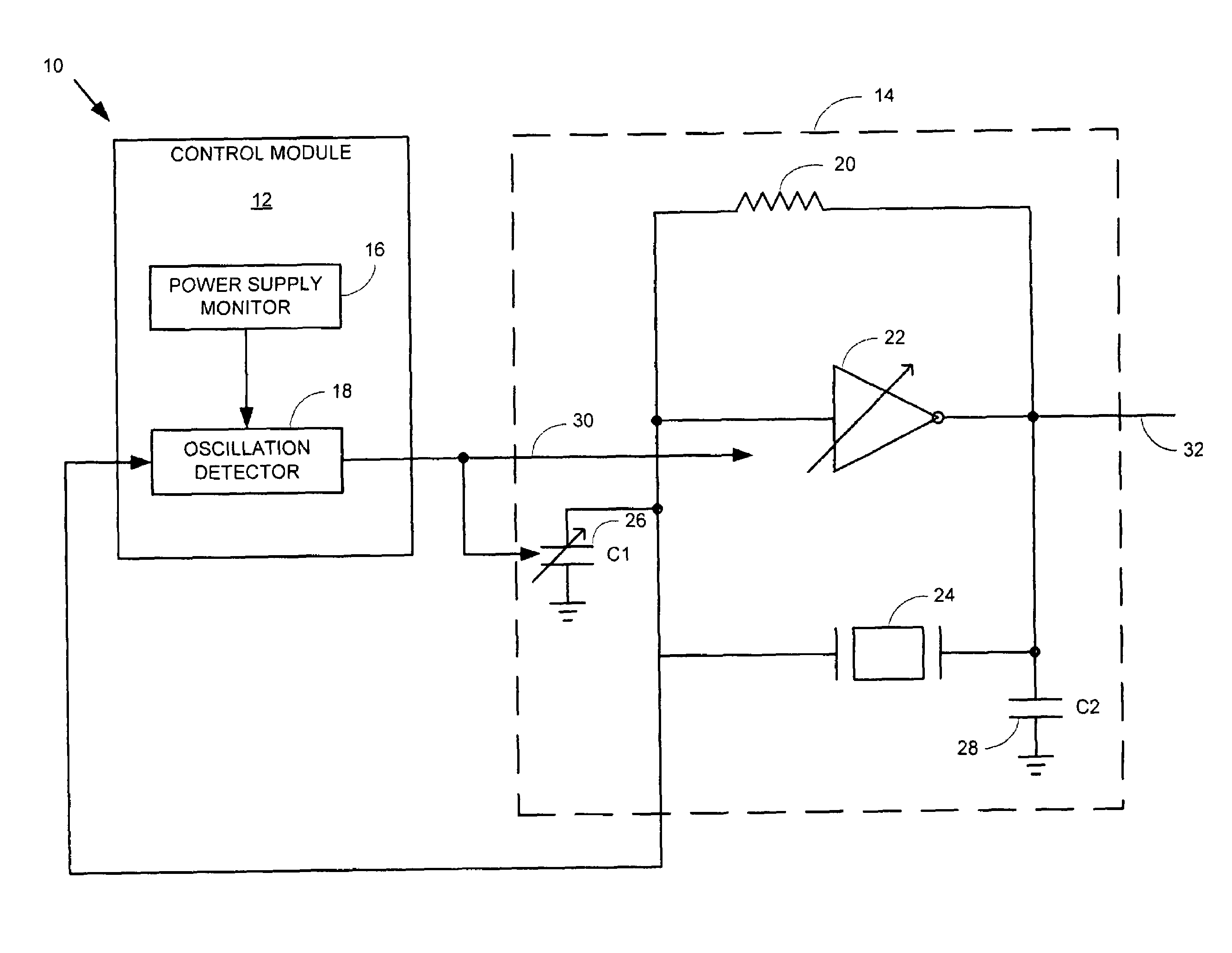
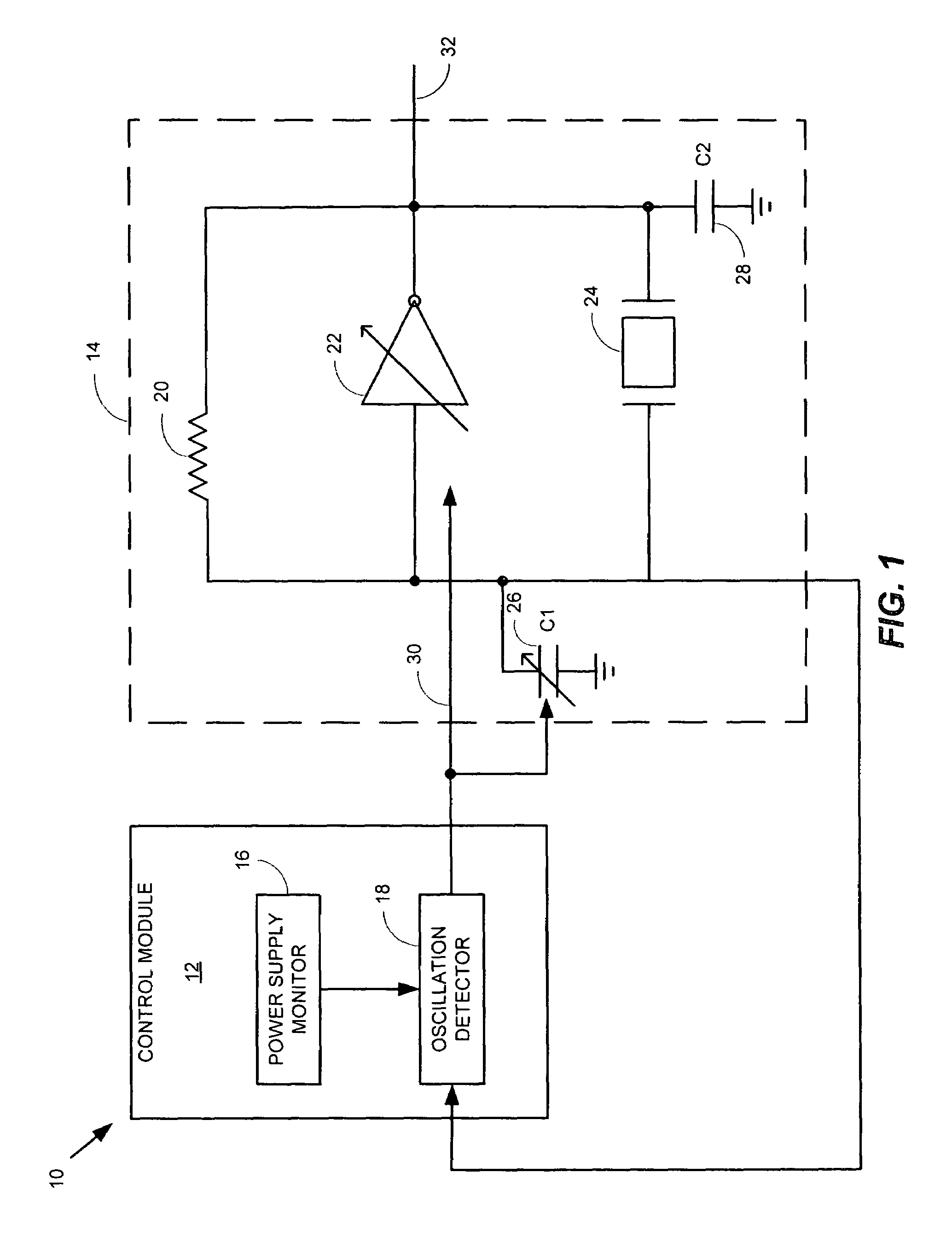
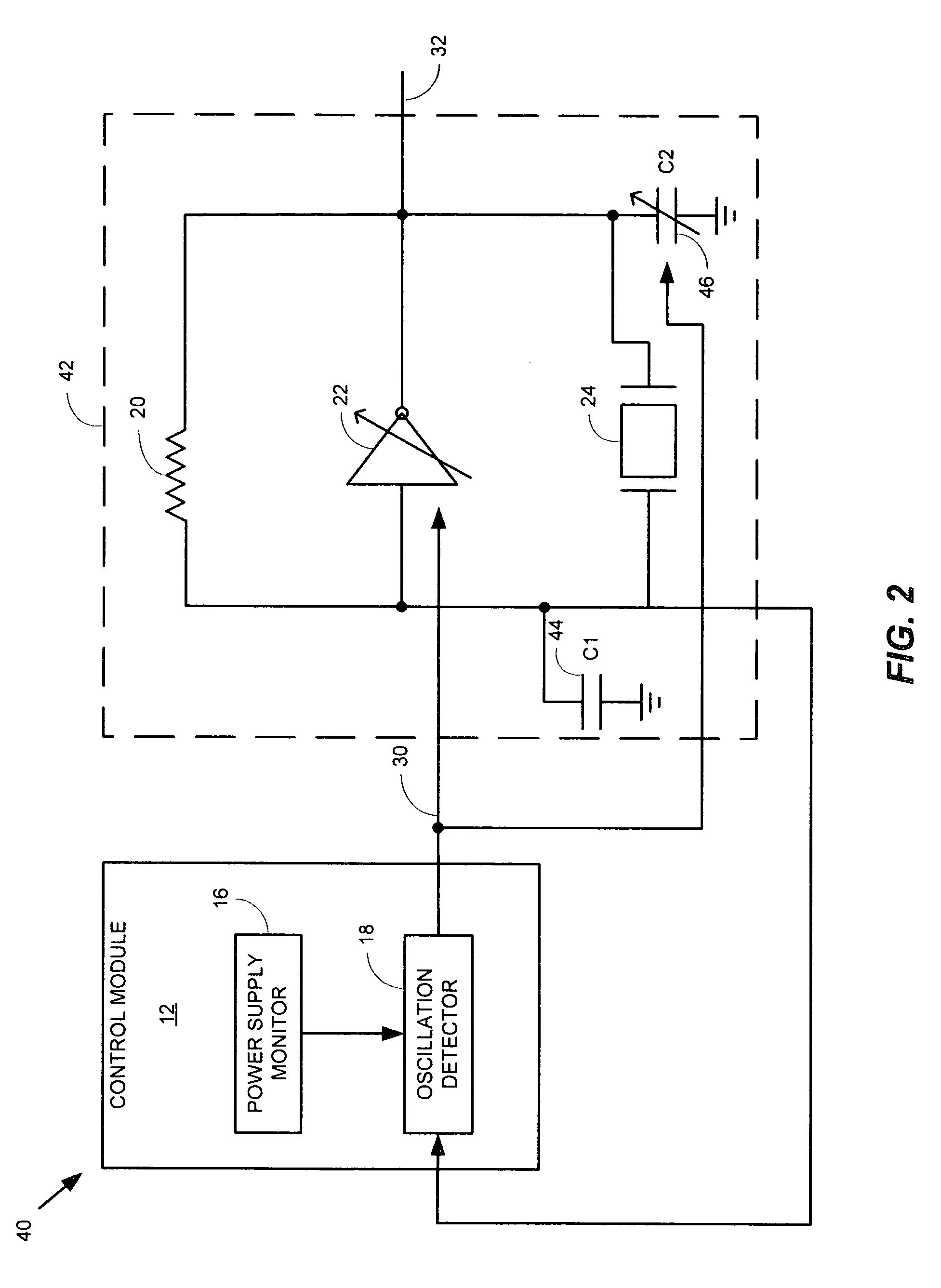
A system comprising a voltage controlled oscillator is disclosed. The voltage controlled oscillator includes a single input, a power input, and an oscillation input. The oscillation input is coupled to a amplitude detection device, which in turn provides an indication of an amplitude of the output of the VCO to a threshold detect module. Based upon the threshold detected at the threshold detect module, a threshold indicator is provided to a voltage supply module. The voltage supply powering the voltage controlled oscillator is varied, based upon a value of the threshold indicator.
Owner:NXP USA INC
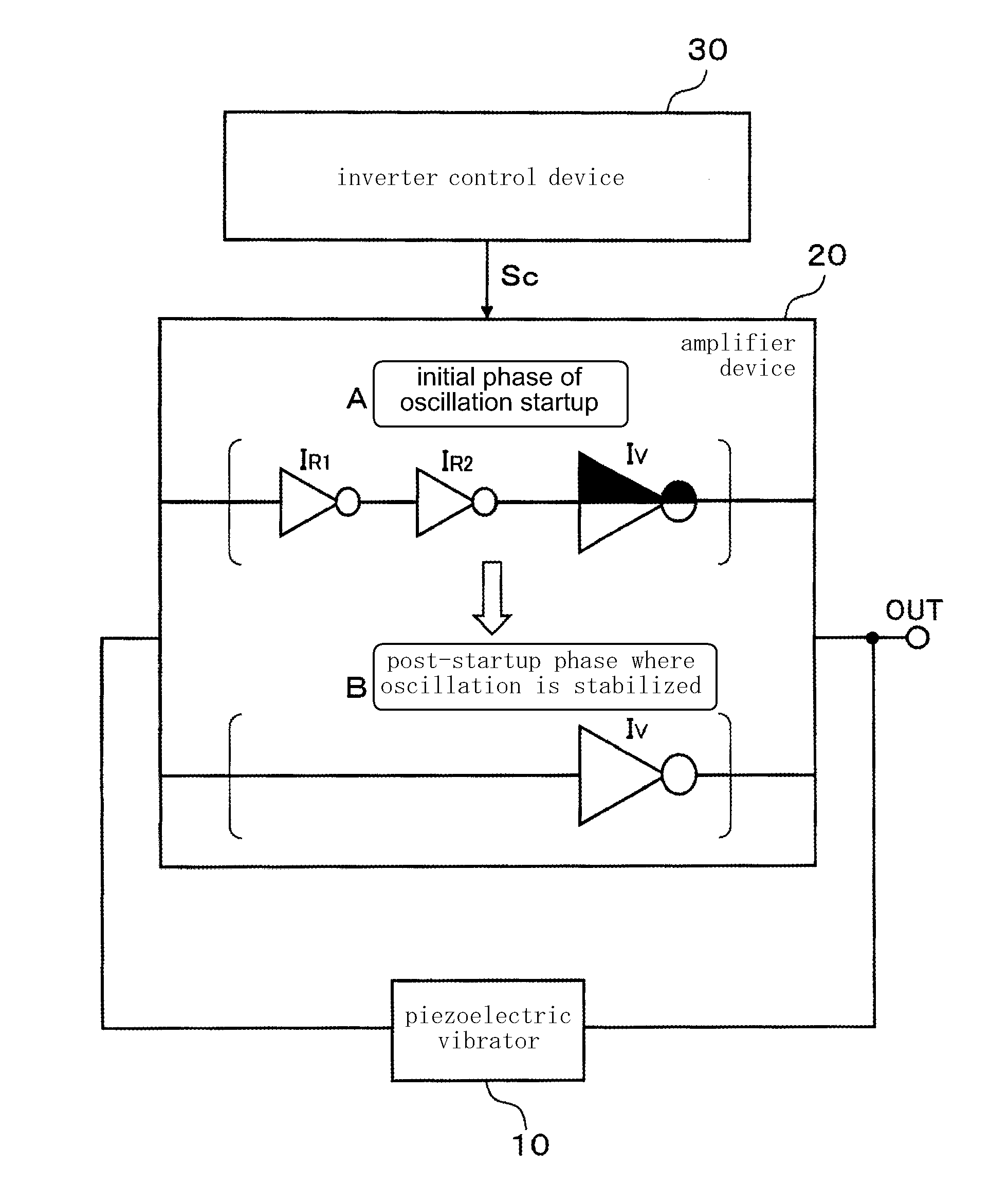
Oscillator circuit
ActiveUS20110291767A1Enhanced oscillationTotal current dropPulse automatic controlGenerator starterAudio power amplifierEngineering
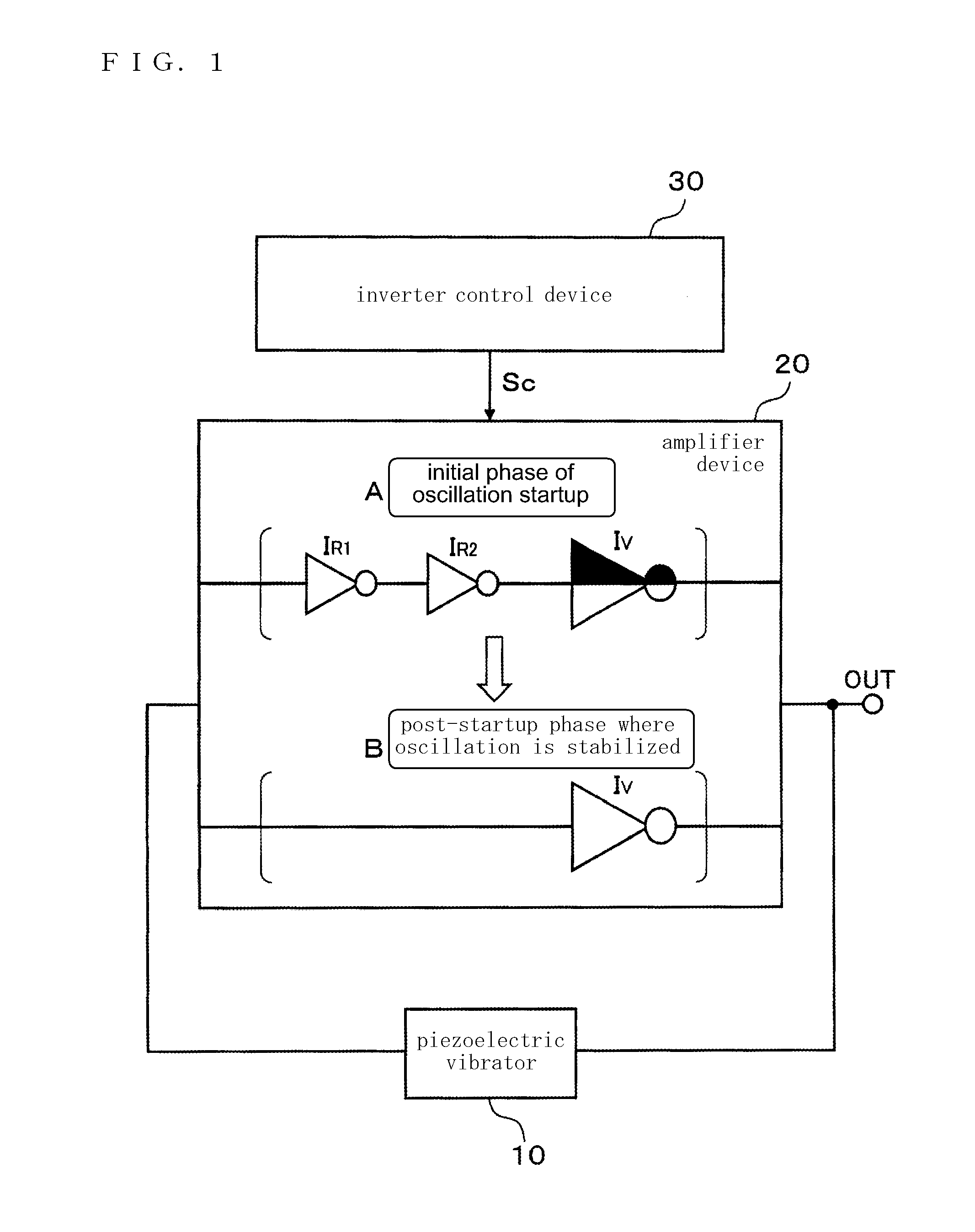
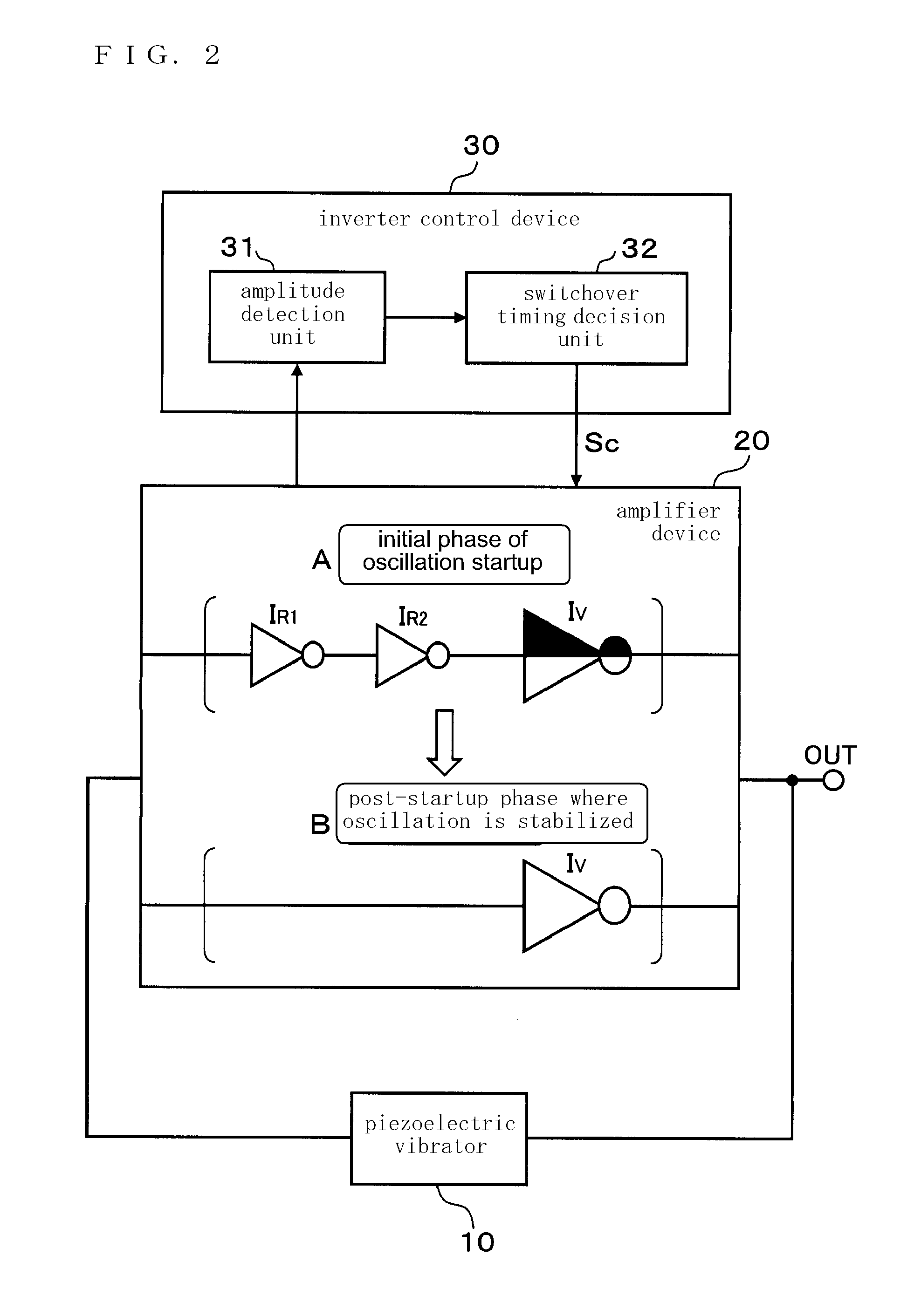
An oscillator circuit comprises a piezoelectric vibrator, an amplifier device including inverters provided in a plurality of stages, and an inverter control device. The inverters provided in the plurality of stages includes a performance-variable inverter configured which is operational in both of an initial phase of oscillation startup and a post-startup phase where the oscillation is stabilized and capable of a variable performance depending on whether the initial phase of oscillation startup or the post-startup phase where the oscillation is stabilized, and an ON / OFF inverter which is operational in the initial phase of oscillation startup and disconnected in the post-startup phase where the oscillation is stabilized. The inverter control device have the performance-variable inverter and the ON / OFF inverter both operational and lowers the performance of the performance-variable inverter in the initial phase of oscillation startup, and the inverter control device disconnects the ON / OFF inverter and increases the performance of the performance-variable inverter in the post-startup phase where the oscillation is stabilized.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
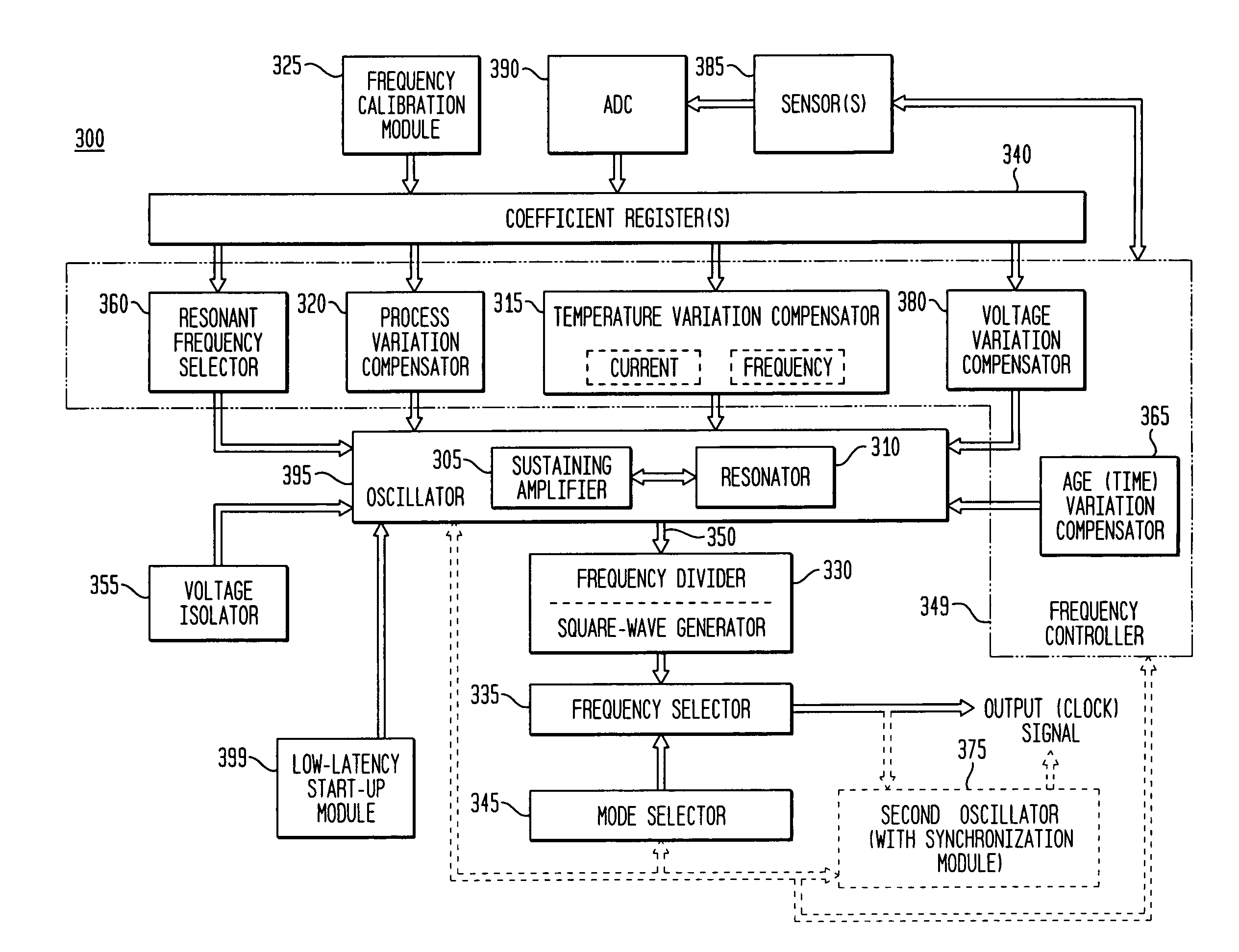
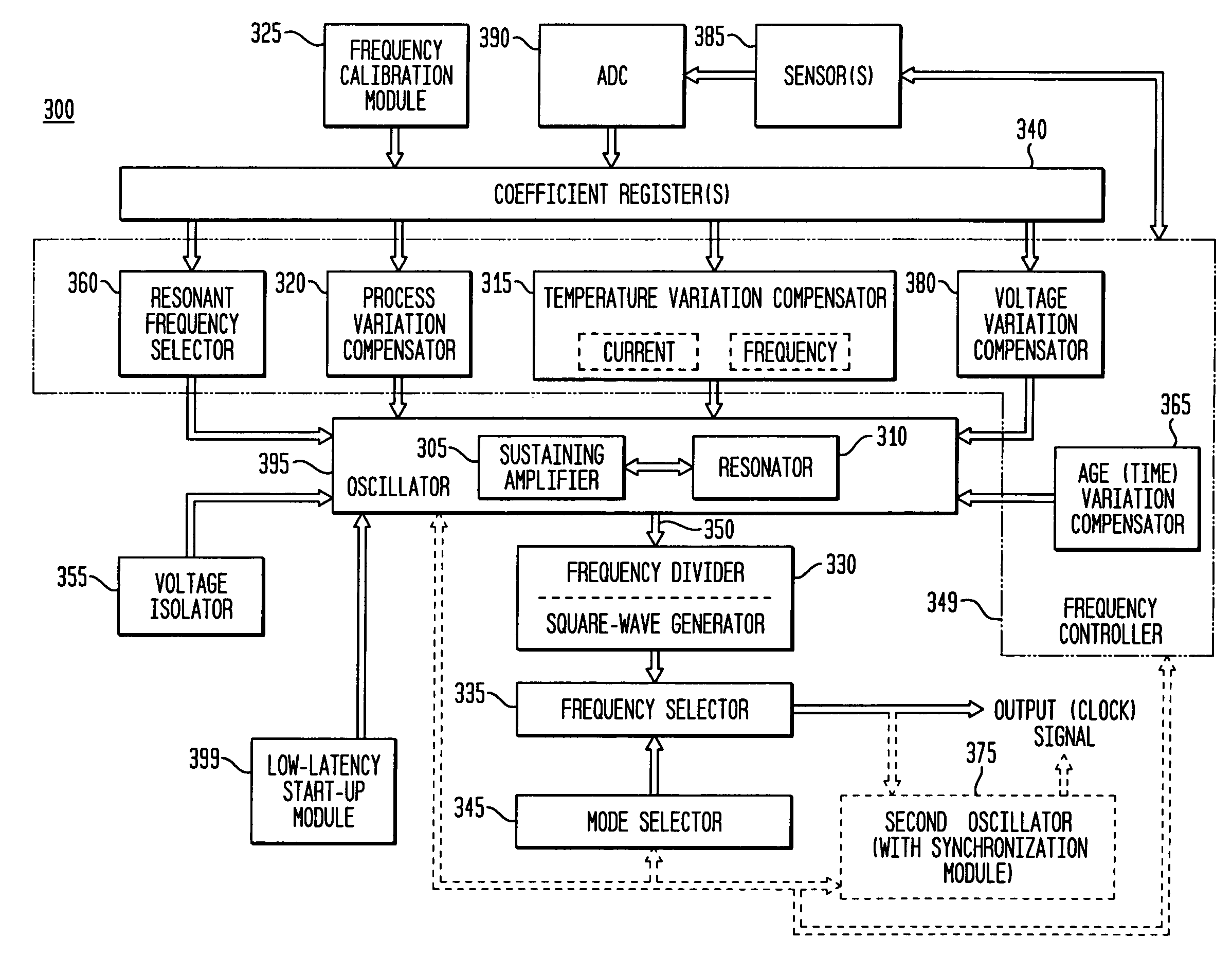
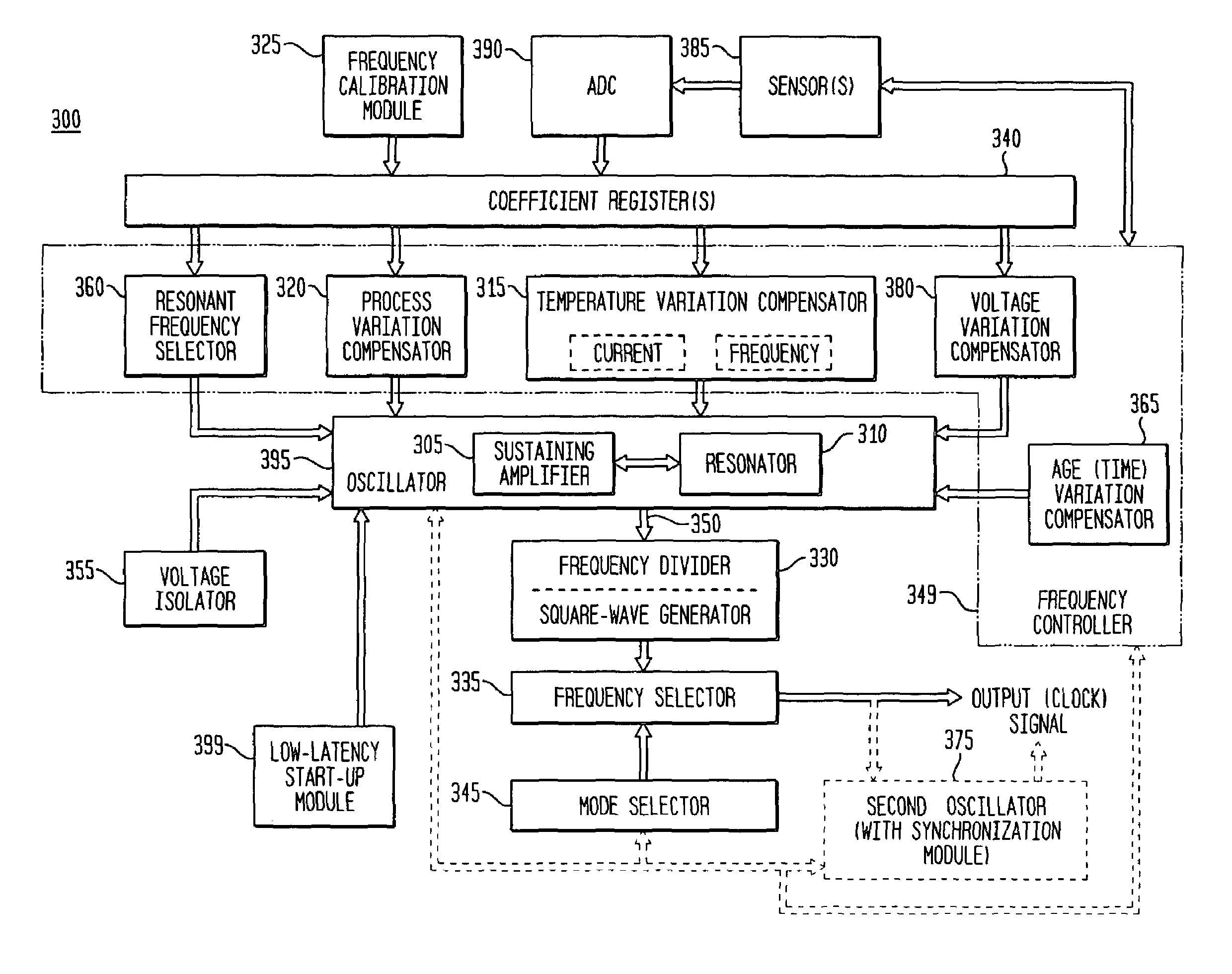
Frequency calibration for a monolithic clock generator and timing/frequency reference
ActiveUS7248124B2High frequencyLoud noiseResonant circuit tuningPulse automatic controlElectricityProcessor register
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Crystal oscillator with variable-gain and variable-output-impedance inverter system
ActiveUS7710212B2Reliable startHigh-frequency stabilityPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationEngineeringOperation mode
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
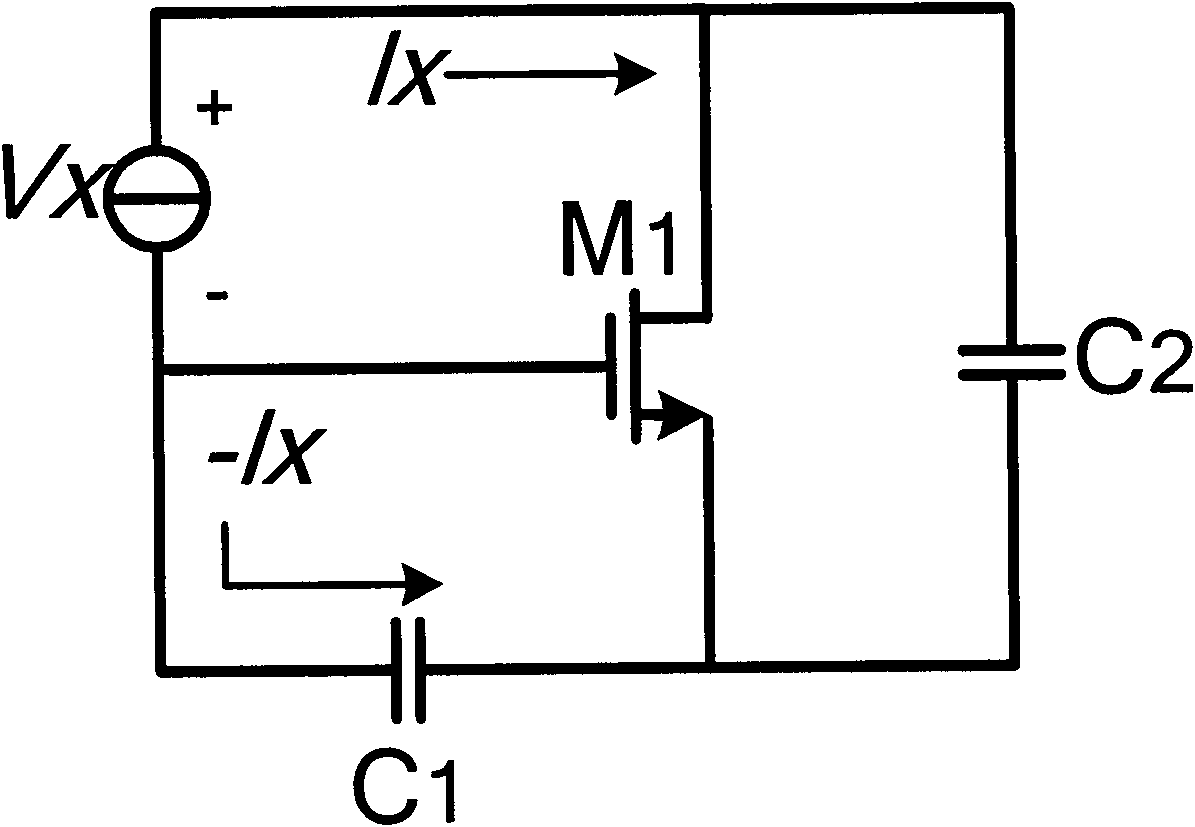
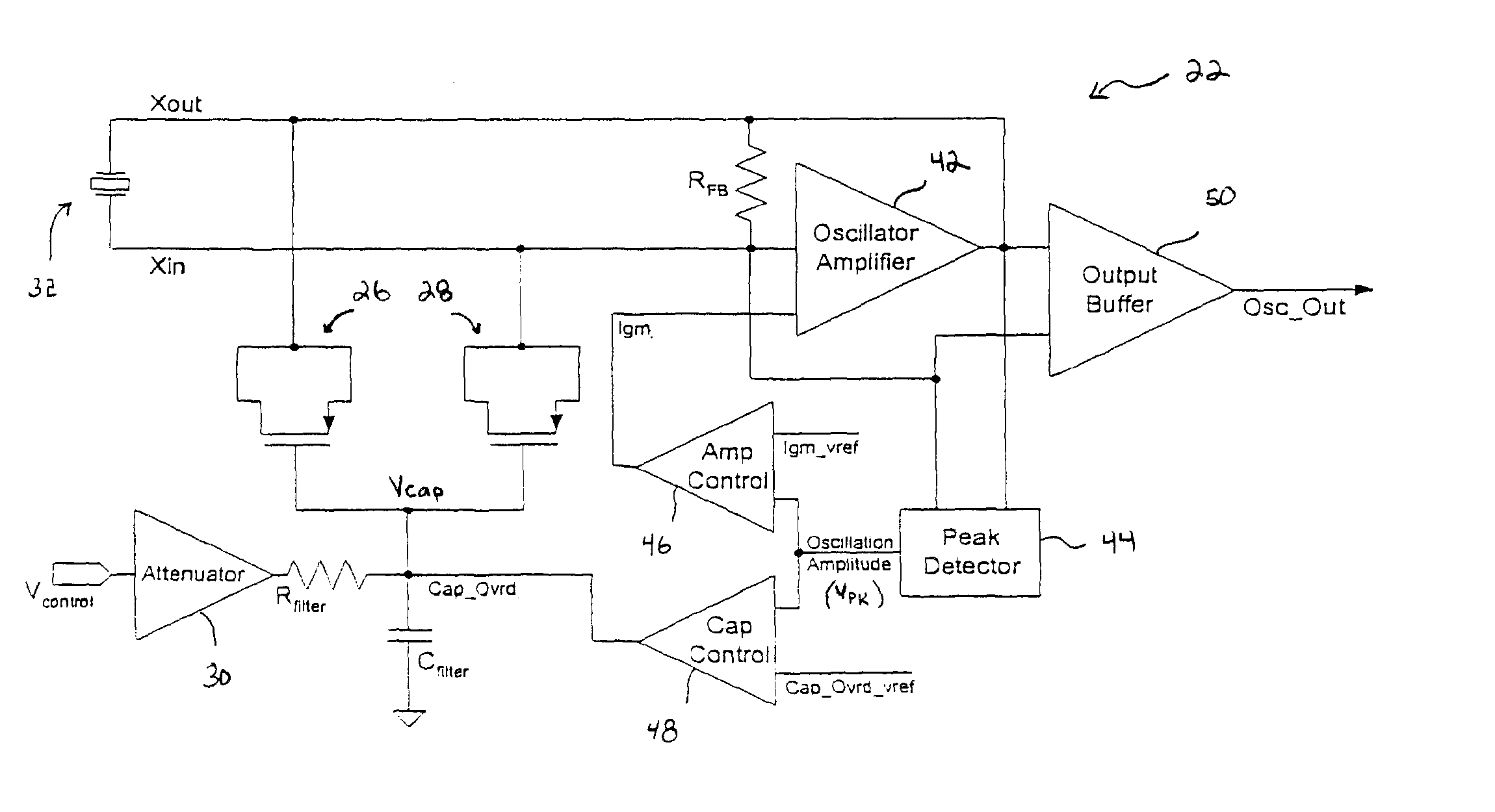
Regulated Capacitive Loading and Gain Control of a Crystal Oscillator During Startup and Steady State Operation
InactiveUS20070030085A1Reduce capacitive loadIncrease volumeAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
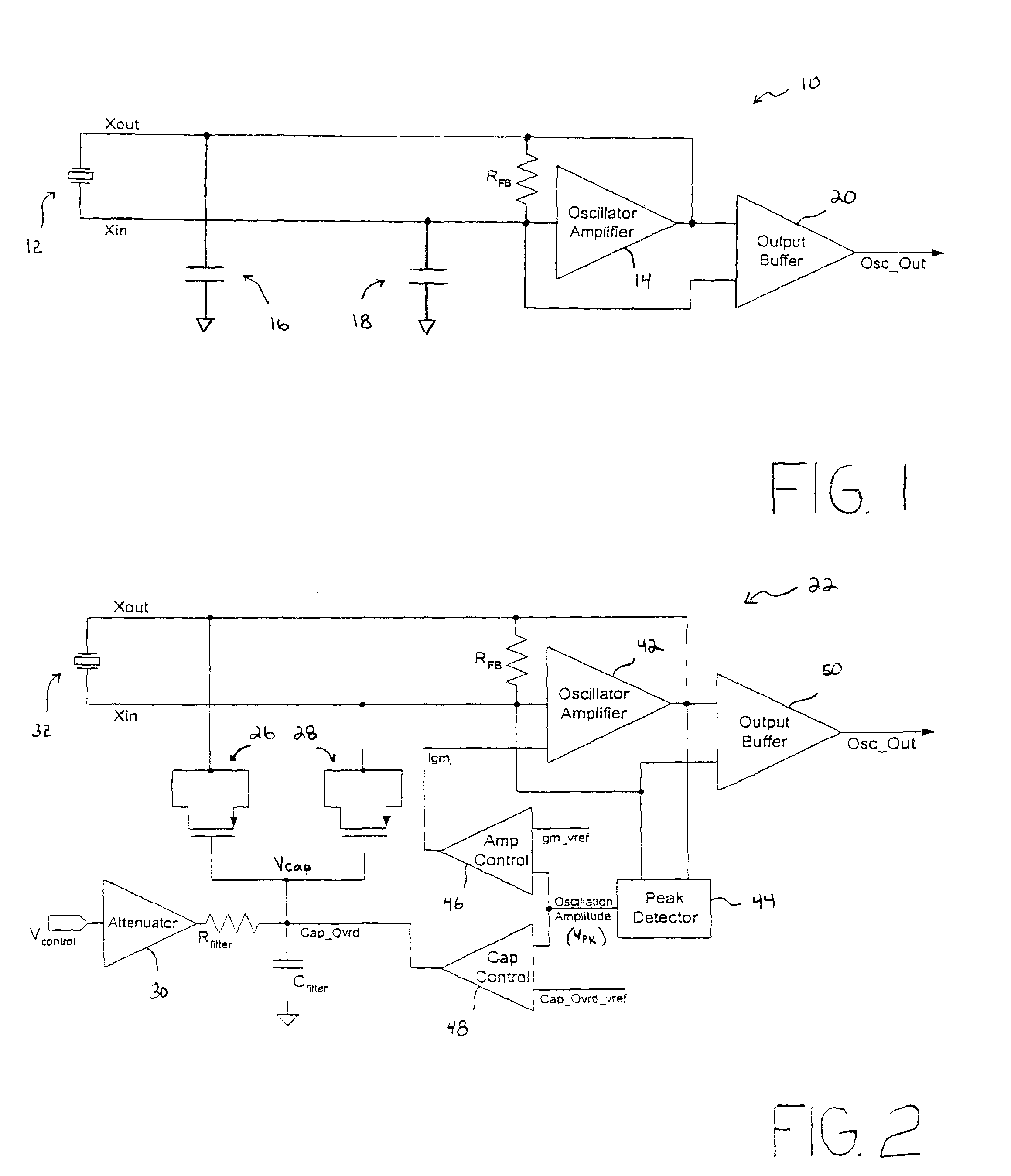
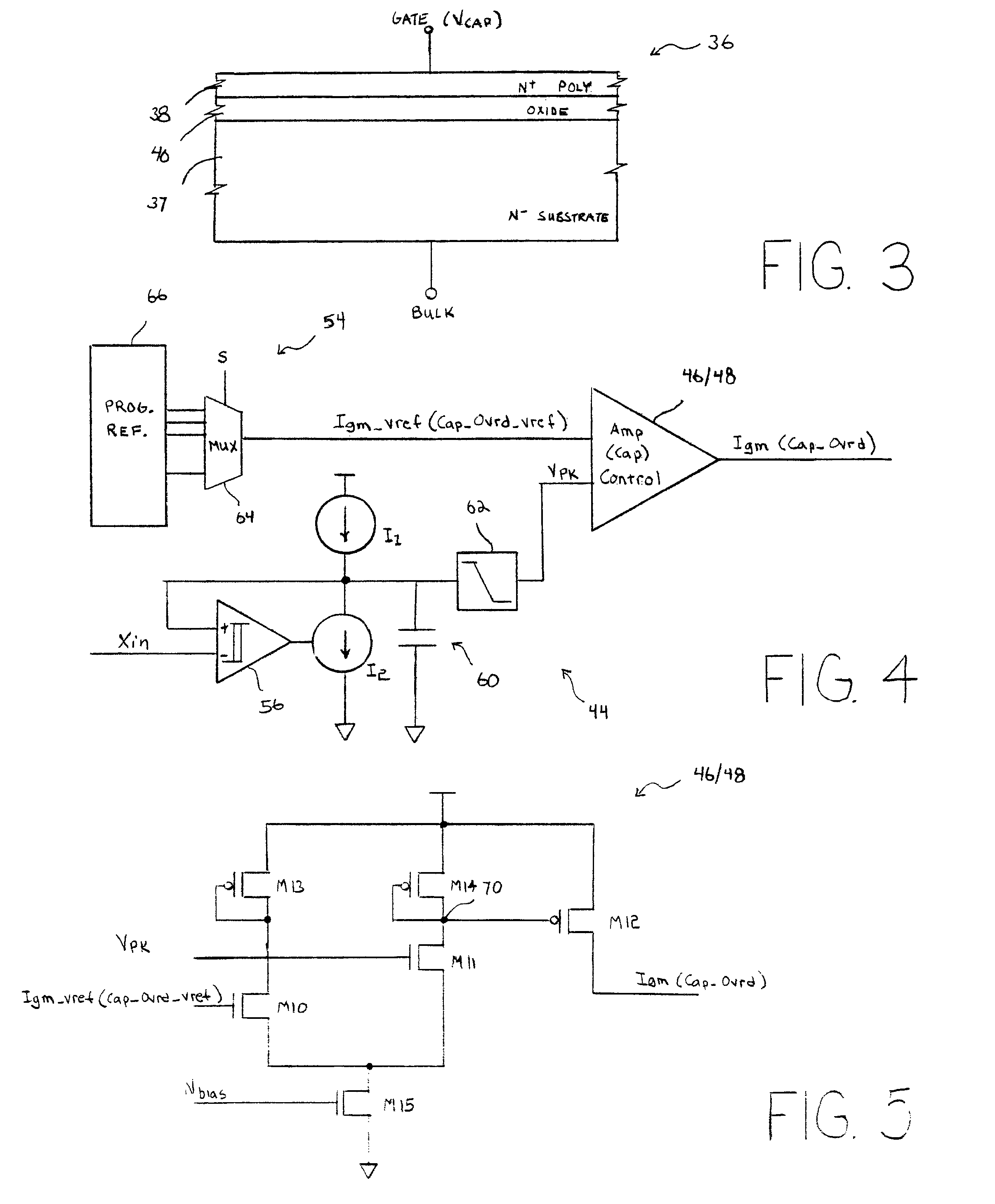
An oscillator circuit and system are provided having a peak detector that can determine a peak voltage value from the oscillator. The peak voltage value can then be compared against a predetermined voltage value by a controller coupled to the peak detector. The comparison value is then used to change a bias signal if the peak voltage value is dissimilar from the predetermined voltage value. A variable capacitor or varactor can be formed from a transistor and is coupled to the oscillator for receiving the bias signal upon a varactor bias node. The bias signal is used to regulate the capacitance within the varactor as applied to the oscillator nodes. Another controller can also be coupled to the peak detector to produce a second bias signal if the peak voltage is dissimilar from a second predetermined voltage value. The second bias signal can then be forwarded into an amplifier having a variable gain to regulate the gain applied to the oscillator. The combination of a varactor and variable gain amplifier regulate the negative resistance applied to the resonating circuit during startup and steady state operations to ensure a relatively fast startup, and to maintain optimal loading and accurate steady state amplitude after startup has completed.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
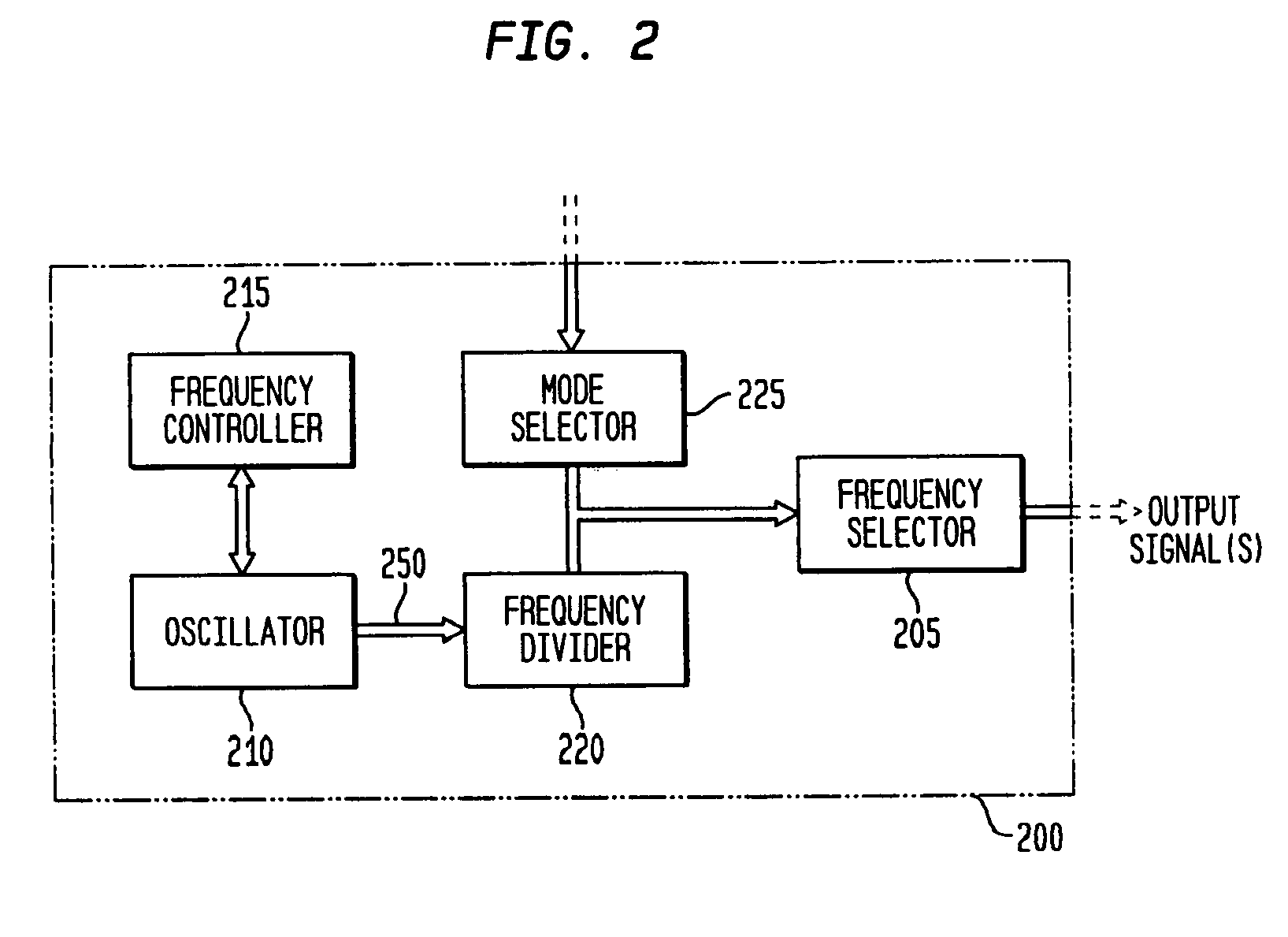
Frequency controller for a monolithic clock generator and timing/frequency reference
ActiveUS20060071734A1Improve accuracyAccurate frequency generationPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
In various embodiments, the invention provides a frequency controller to control and provide a stable resonant frequency of a clock generator and / or a timing and frequency reference. Such stability is provided over variations in a selected parameter such as temperature and fabrication process variations. The various apparatus embodiments include a sensor adapted to provide a signal in response to at least one parameter of a plurality of parameters; and a frequency controller adapted to modify the resonant frequency in response to the second signal. In exemplary embodiments, the sensor is implemented as a current source responsive to temperature fluctuations, and the frequency controller is implemented as a plurality of controlled reactance modules which are selectively couplable to the resonator or to one or more control voltages. The controlled reactance modules may include fixed or variable capacitances or inductances, and may be binary weighted. Arrays of resistive modules are also provided, to generate one or more control voltages.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Frequency controller for a monolithic clock generator and timing/frequency reference
ActiveUS7456699B2Highly accurate over PVTGenerate accuratelyAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlCapacitanceElectricity
In various embodiments, the invention provides a frequency controller to control and provide a stable resonant frequency of a clock generator and / or a timing and frequency reference. Such stability is provided over variations in a selected parameter such as temperature and fabrication process variations. The various apparatus embodiments include a sensor adapted to provide a signal in response to at least one parameter of a plurality of parameters; and a frequency controller adapted to modify the resonant frequency in response to the second signal. In exemplary embodiments, the sensor is implemented as a current source responsive to temperature fluctuations, and the frequency controller is implemented as a plurality of controlled reactance modules which are selectively couplable to the resonator or to one or more control voltages. The controlled reactance modules may include fixed or variable capacitances or inductances, and may be binary weighted. Arrays of resistive modules are also provided, to generate one or more control voltages.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Discrete clock generator and timing/frequency reference
ActiveUS7358826B2High frequencyLoud noisePulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationFrequency stabilizationElectrical resistance and conductance
In various embodiments, the invention provides a discrete clock generator and / or a timing and frequency reference using an LC-oscillator topology, having a frequency controller to control and provide a stable resonant frequency, which may then be provided to other, second circuitry such as a processor or controller. Frequency stability is provided over variations in a selected parameter such as temperature and fabrication process variations. The various apparatus embodiments include a sensor adapted to provide a signal in response to at least one parameter of a plurality of parameters; and a frequency controller adapted to modify the resonant frequency in response to the second signal. In exemplary embodiments, the sensor is implemented as a current source responsive to temperature fluctuations, and the frequency controller is implemented as a plurality of controlled reactance modules which are selectively couplable to the resonator or to one or more control voltages. The controlled reactance modules may include fixed or variable capacitances or inductances, and may be binary weighted. Arrays of resistive modules are also provided, to generate one or more control voltages.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Oscillator circuit
ActiveUS20160308491A1Reduce startup timeStart up more quicklyPulse automatic controlGenerator starterRC oscillatorQuantum electrodynamics
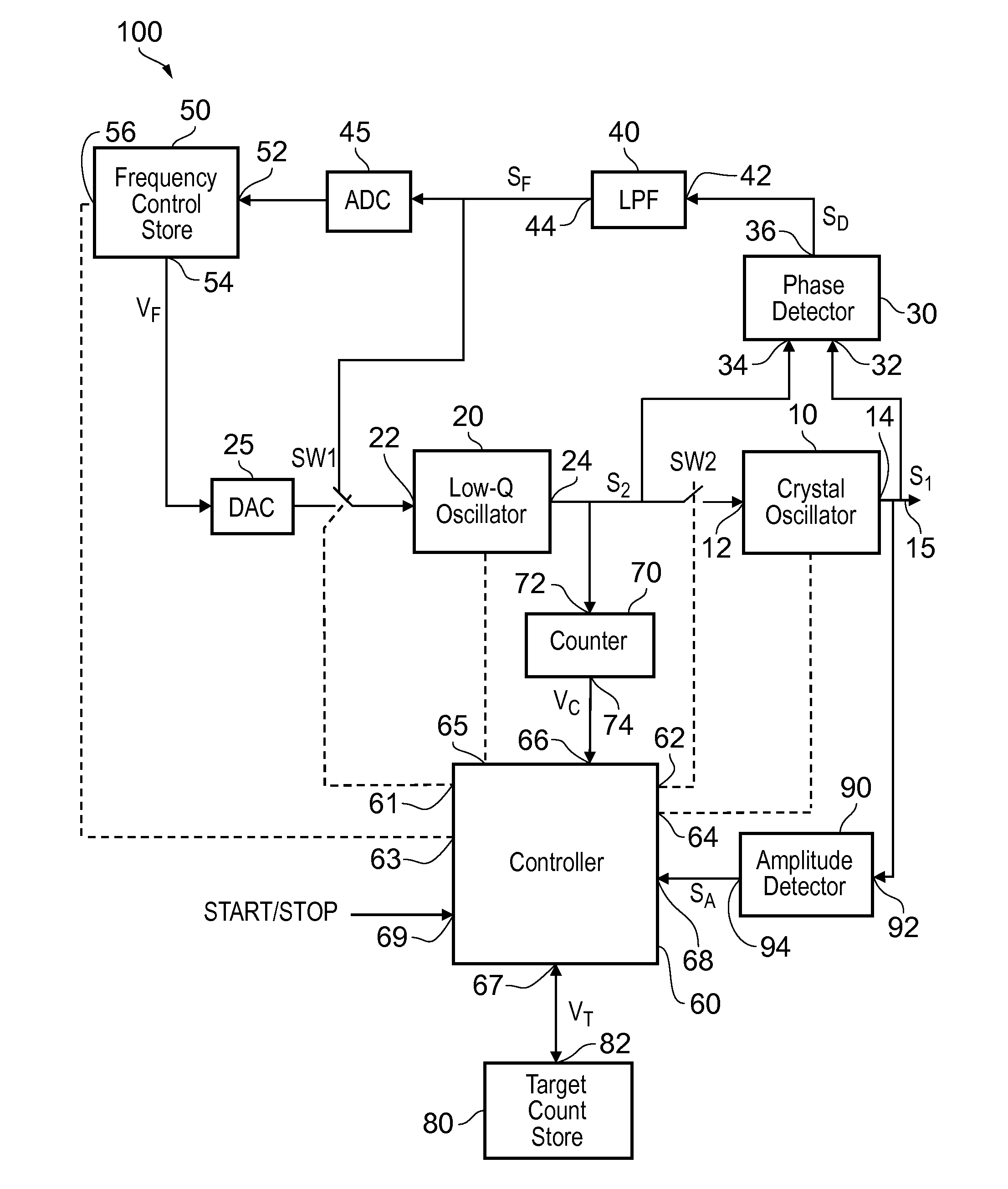
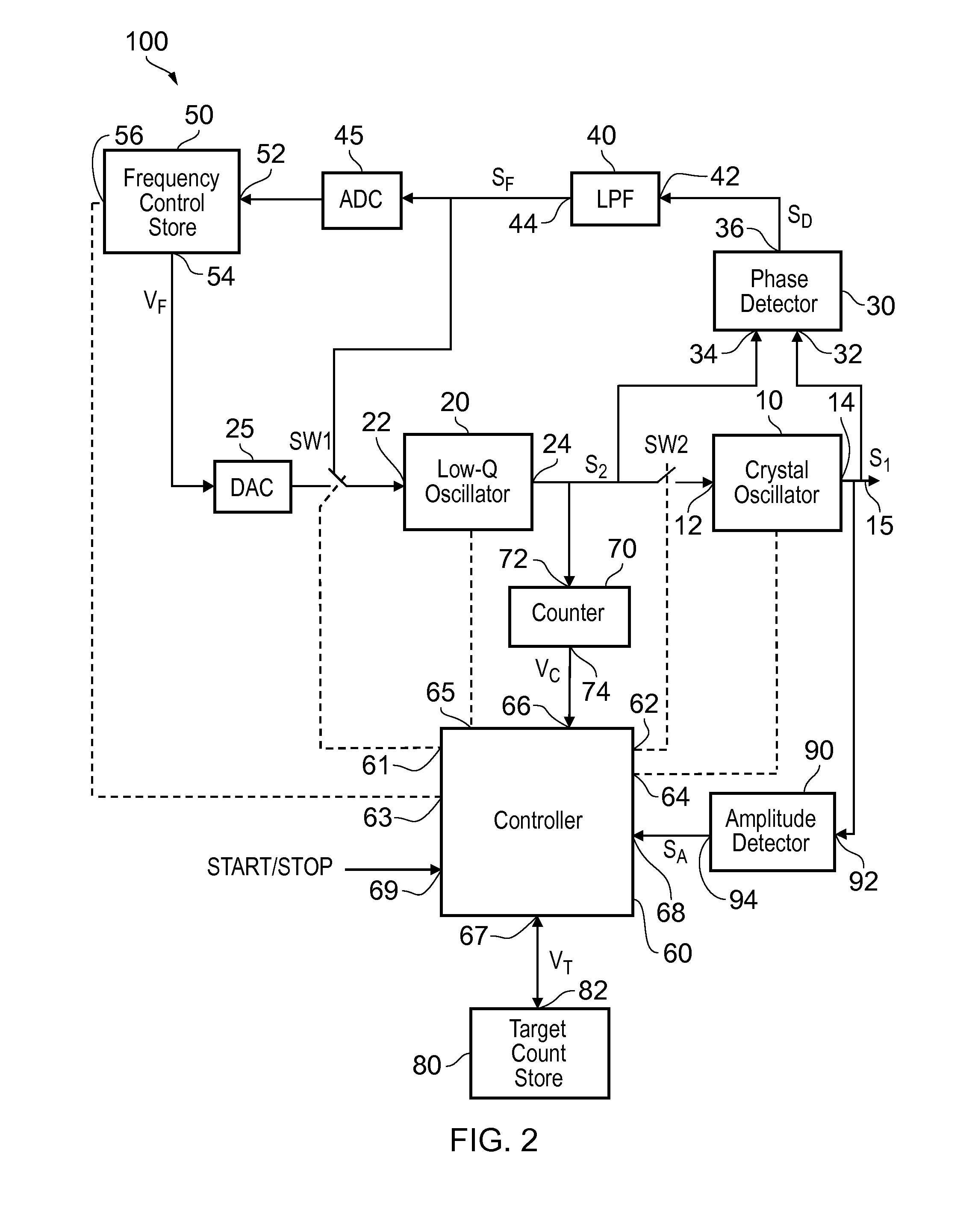
An oscillator circuit comprises a first, high-Q crystal oscillator and a second, low-Q oscillator arranged for kick-starting the crystal oscillator at switch-on by coupling the second oscillator to the first oscillator for a time period. The oscillator circuit is arranged to select the frequency of the second oscillator by placing the second oscillator in a phase locked loop with the first oscillator providing a reference frequency, and adjusting the frequency of the second oscillator towards the frequency of the first oscillator.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Inductor and capacitor-based clock generator and timing/frequency reference
InactiveUS7504899B2High frequencyLoud noiseAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
In various embodiments, the invention provides a clock generator and / or a timing and frequency reference comprising an LC oscillator with a frequency controller to control and provide a stable resonant frequency. Such stability is provided over variations in a selected parameter such as temperature and fabrication process variations. The various apparatus embodiments include a sensor adapted to provide a signal in response to at least one parameter of a plurality of parameters; and a frequency controller adapted to modify the resonant frequency in response to the second signal. In exemplary embodiments, the sensor is implemented as a current source responsive to temperature fluctuations, and the frequency controller is implemented as a plurality of controlled reactance modules which are selectively couplable to the oscillator or to one or more control voltages. The controlled reactance modules may include fixed or variable capacitances or inductances, and may be binary weighted. Arrays of resistive modules are also provided, to generate one or more control voltages.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Crystal oscillator circuit having a start-up time reduction circuit
A quartz-crystal oscillator circuit substantially reduces the start-up time of the crystal oscillator circuit by utilizing a start-up time reduction circuit that adds additional gain to the crystal oscillator circuit during the start-up period, and removes the additional gain as the oscillator circuit nears steady state operation. Furthermore, the start-up time reduction circuit dynamically monitors the oscillation amplitude. If the build up of oscillation is interrupted, the additional gain will be re-applied.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Powerup control of PLL
An electronic device, such as a microprocessor, with a timing circuit. The timing circuit contains a phase locked loop that, during a first interval, checks whether a control signal in the phase locked loop is between a maximum allowed value and a minimum allowed value. When the control signal in the phase locked loop is above a maximum allowed value or below a minimum allowed value, the control circuit disables the phase locked loop for a second interval. When the control signal in the phase locked loop is below a maximum allowed value and above a minimum allowed value, the timing circuit indicates that the output of the phase locked loop is stable.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
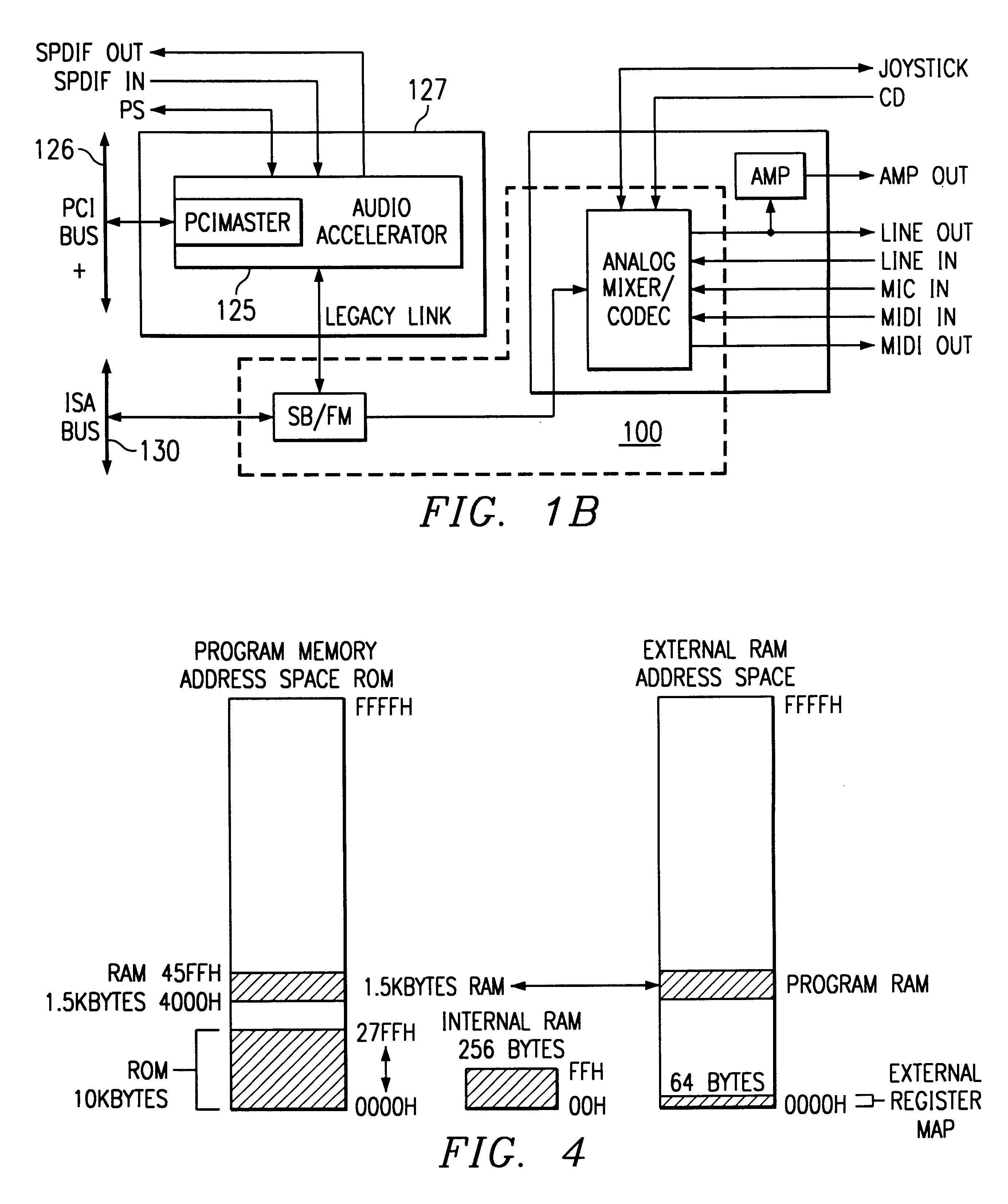
Single-chip audio circuits, methods, and systems using the same
InactiveUS6952621B1High quality soundGenerator starterSound input/outputDigital analog converterEngineering
A single chip audio system 100 includes a bus interface 101, digital to analog converters 110, an analog mixer 115, and analog spatial enhancement circuitry 7500. Digital to analog converters 110 convert digital audio data received through bus interface 101 into analog signals. Analog mixer 115 mixes signals received from digital to analog converters 110 with an analog signal received from an external source. Analog spatial enhancement circuitry 7500 enhances first and second mixed analog signals output from analog mixer 115.
Owner:CRYSTAL SEMICON CORP
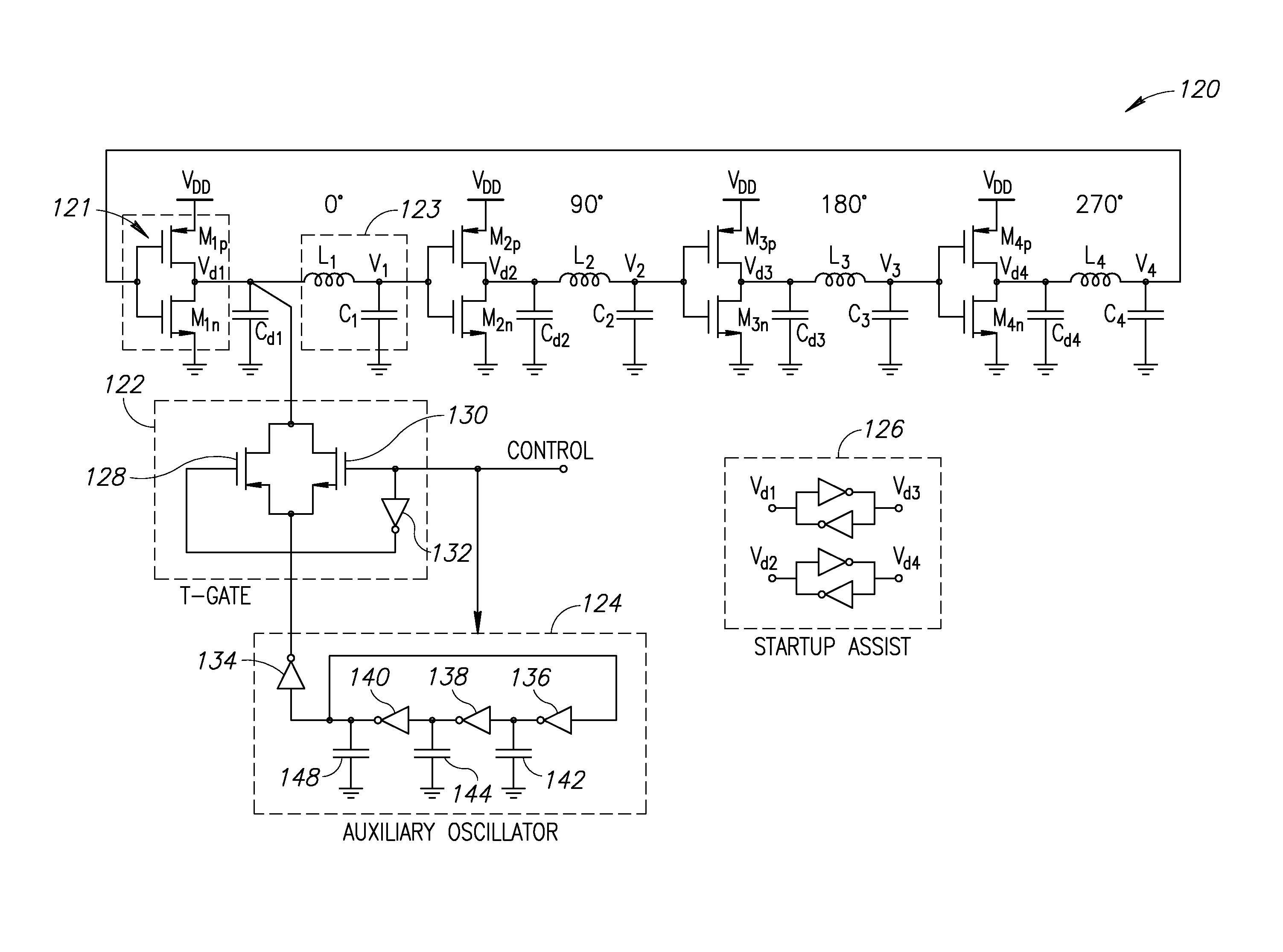
Quadrature lc tank digitally controlled ring oscillator
InactiveUS20150372665A1Avoids quality factor degradationImprove efficiencyGenerator starterPulse generation by logic circuitsAudio power amplifierPhase shifted
A quadrature LC tank based digitally controlled ring oscillator (DCO). The oscillator structure incorporates a plurality of stages, each stage including a buffer and a series LC tank. Four stages are coupled together to create a 360 degree phase shift around a loop. The oscillation frequency of the oscillator is the same as the resonant frequency of each LC tank, therefore it avoids quality factor degradation of LC tanks found in the prior art. In one example embodiment, class-D amplifiers are used to drive each of the LC tanks Capacitor banks before at the input and output of the buffers provide coarse and fine tuning of the frequency of oscillation. The high efficiency exhibited by these amplifiers results in very good phase noise performance of this oscillator. The oscillator utilizes a startup circuit to launch oscillation upon power on.
Owner:TECH UNIV DELFT
Low phase noise voltage controlled oscillator
ActiveUS7961056B2Angle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlPhase noiseEngineering
Embodiments of the present invention include a low phase noise oscillator circuit using a current-reuse technique to reduce power consumption and improve phase noise, where the oscillator circuit comprises a first VCO coupled to a second VCO, and the outputs of the first and second VCOs are coupled with passive elements, such as capacitors. The overall power consumption of both the first and second VCOs is about the same as a single VCO. Furthermore, the phase noise is lowered by around 3 dB. Thus, the phase noise performance is improved without increasing the power consumption of the oscillator circuit.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Fast oscillation starting crystal oscillator
InactiveCN103346782AZoom in fastIncrease the vibration speedGenerator starterOscillations generatorsAudio power amplifierQuantum electrodynamics
The invention discloses a fast oscillation starting crystal oscillator comprising a main oscillating circuit, an auxiliary oscillating branch and a biasing circuit. By means of partial gain of a buffer amplifier of the crystal oscillator, loop gain of oscillation frequency is complemented, the loop gain of the oscillation frequency is remarkably improved, and the speed of oscillation starting is increased. After the crystal oscillator is powered up and starts, a small signal component of the oscillation frequency in a voltage step is quickly amplified by a loop and finally begins to stabilize, and a stable signal is obtained. Due to the fact that the loop gain of the crystal oscillator is high, amplifying speed of a small frequency component is high, and therefore compared with a traditional crystal oscillator, the fast oscillation starting crystal oscillator has the advantages of being high in oscillation starting speed.
Owner:东南大学无锡分校
Low-latency start-up for a monolithic clock generator and timing/frequency reference
ActiveUS20060017519A1Less relative period jitterLoud noiseResonant circuit tuningPulse automatic controlMicrocontrollerControl signal
An apparatus, system and method are provided for low-latency start-up of a free-running harmonic oscillator. The exemplary apparatus embodiment comprises a first and second current sources to generate first and second currents; a bias current monitor adapted to detect a magnitude of the second current and to provide a control signal when the magnitude of the second current is equal to or greater than a predetermined magnitude; and a bias controller adapted to switch the first current from the oscillator and to switch the second current to the oscillator in response to the control signal. a reference voltage generator, a comparator, and a bias controller. Exemplary embodiments include reference voltage generator, a comparator, and a bias controller.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Regulated capacitive loading and gain control of a crystal oscillator during startup and steady state operation
InactiveUS7859355B2Start fastHigh resistanceAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlVariable-gain amplifierAudio power amplifier
An oscillator circuit and system are provided having a peak detector that can determine a peak voltage value from the oscillator. The peak voltage value can then be compared against a predetermined voltage value by a controller coupled to the peak detector. The comparison value is then used to change a bias signal if the peak voltage value is dissimilar from the predetermined voltage value. A variable capacitor or varactor can be formed from a transistor and is coupled to the oscillator for receiving the bias signal upon a varactor bias node. The bias signal is used to regulate the capacitance within the varactor as applied to the oscillator nodes. Another controller can also be coupled to the peak detector to produce a second bias signal if the peak voltage is dissimilar from a second predetermined voltage value. The second bias signal can then be forwarded into an amplifier having a variable gain to regulate the gain applied to the oscillator. The combination of a varactor and variable gain amplifier regulate the negative resistance applied to the resonating circuit during startup and steady state operations to ensure a relatively fast startup, and to maintain optimal loading and accurate steady state amplitude after startup has completed.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Phase-locked loop start up circuit
A phase-locked loop (PLL) circuit includes a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) having a VCO input for receiving a control voltage and a VCO output, a feedback loop between the VCO input and the VCO output, and a start-up circuit having a start-up circuit input and a start-up circuit output. The start-up circuit output is coupled to the VCO input and the start-up circuit input is coupled to the VCO output. The start-up circuit provides a voltage at its start-up circuit output during a start-up phase, which terminates after a predetermined number of feedback pulses are detected by the start-up circuit.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Systems and Methods with Reduced Reference Spurs Using a Crystal Oscillator For Broadband Communications
Systems and methods are provided. In this regard, a representative system incorporates a crystal oscillator circuit and a digital automatic level control circuit. The digital automatic level control circuit is operative to: convert an oscillation amplitude of the crystal oscillator circuit to a proportional DC voltage; convert the DC voltage to a corresponding digital code representation; and adjust bias current and oscillator loop gain such that a desired oscillation amplitude is set.
Owner:NXP BV
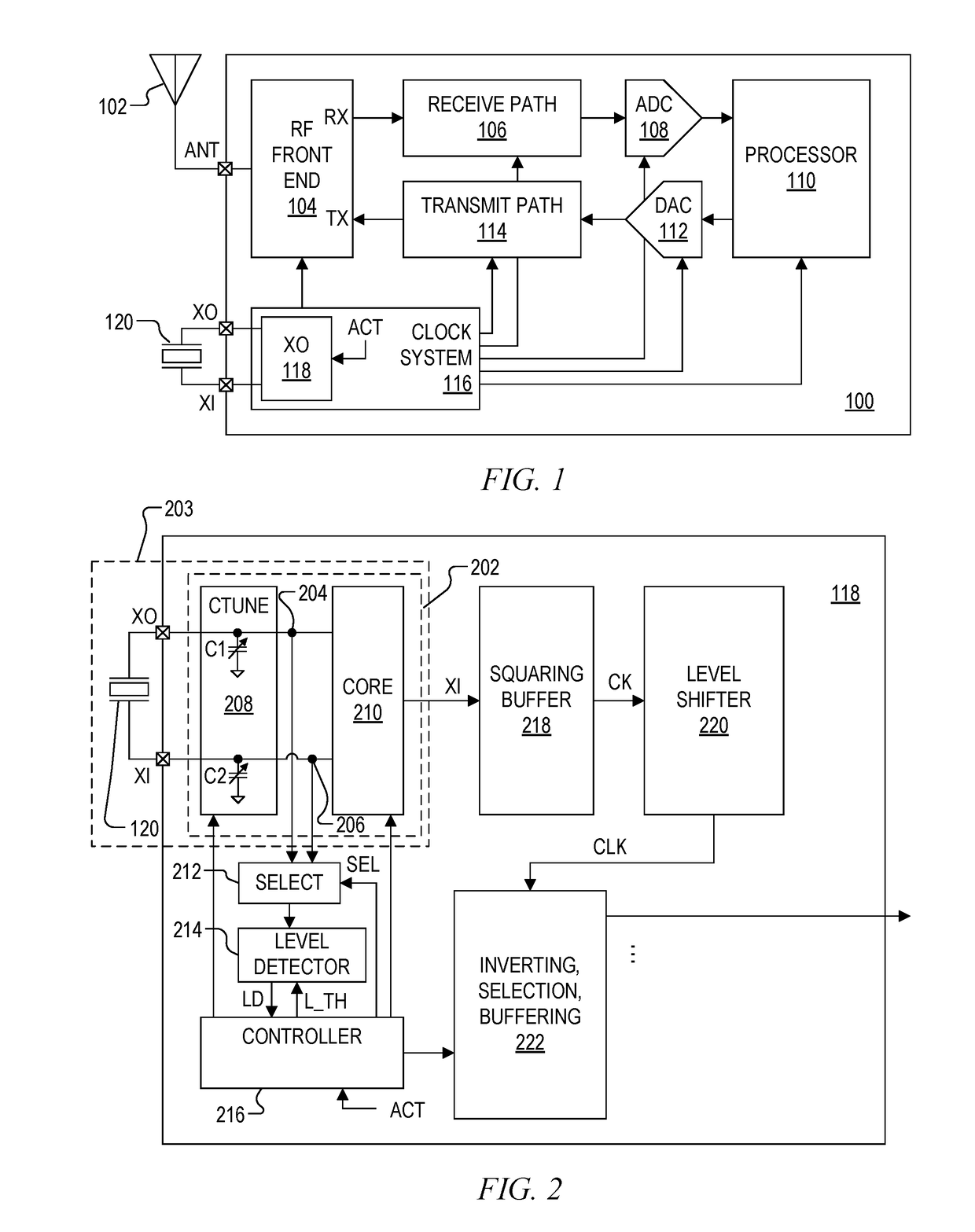
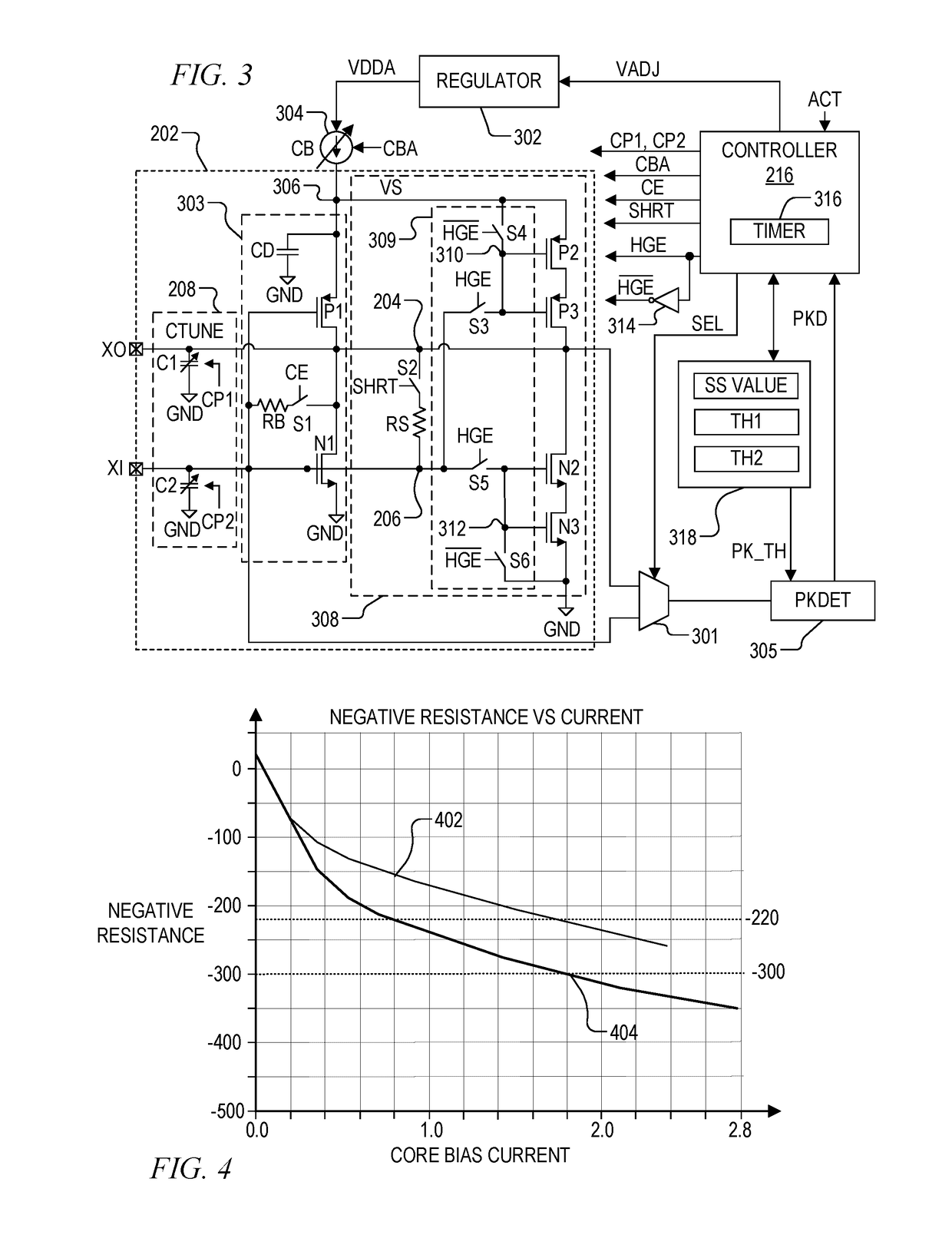
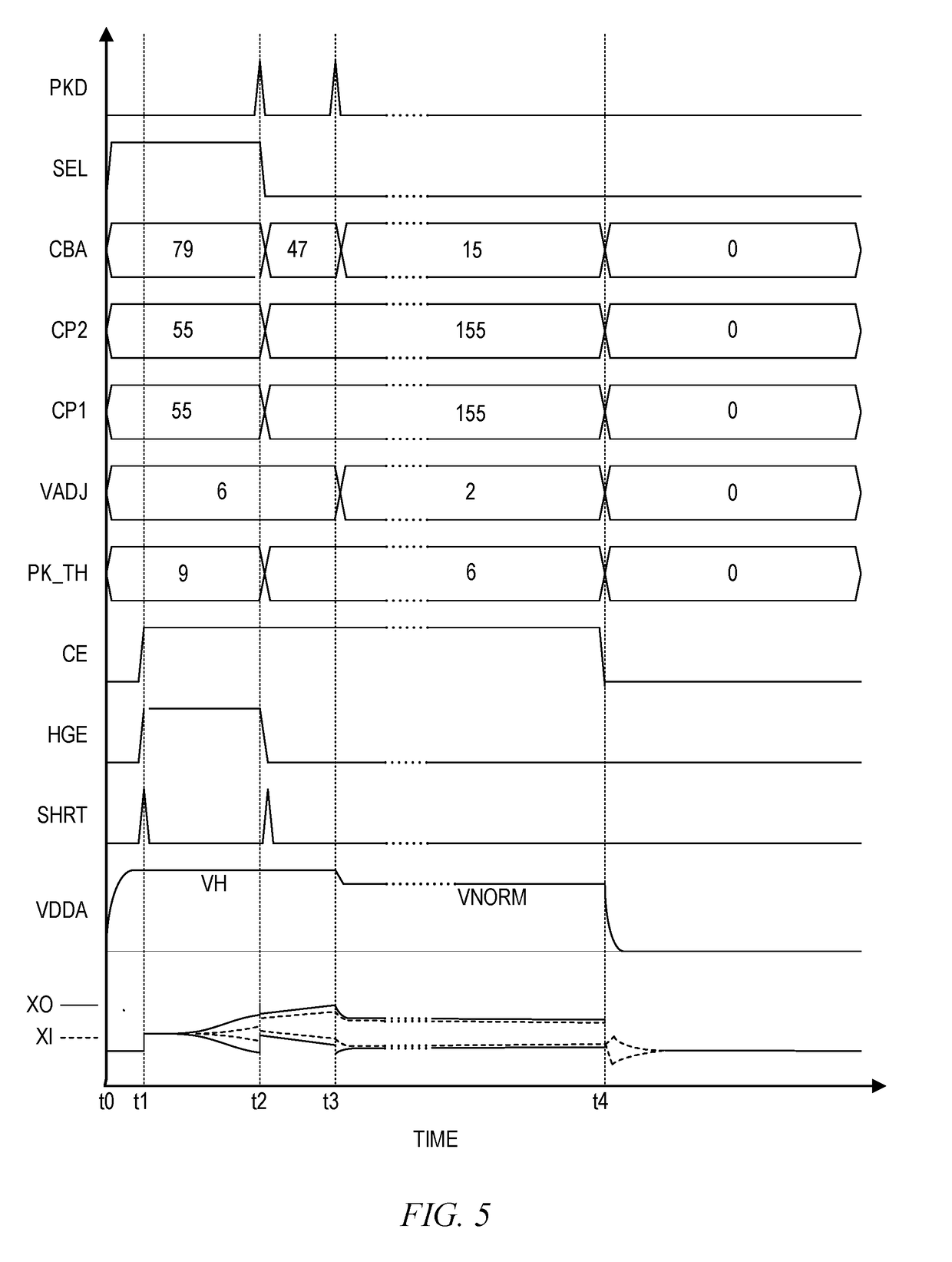
Crystal amplifier with additional high gain amplifier core to optimize startup operation
ActiveUS20190007012A1DisablingReducing core bias currentPulse automatic controlSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierEngineering
A crystal amplifier for driving a crystal to oscillate at a resonant frequency including a controlled current source, a primary amplifier core, a high gain amplifier core, and a controller. Both amplifier cores are coupled in parallel, and each has an input coupled to an amplifier input node and an output coupled to an amplifier output node coupled across the crystal. The current source provides a core bias current to the source node. The controller enables the high gain amplifier core and sets the core bias current to a high current level to achieve a high negative resistance at a startup time, and then disables the high gain amplifier core and sets the core bias current to a lower steady state current level after oscillation is achieved. A level detector may be used for detecting oscillation and for determining when to adjust the core bias current.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Frequency calibration for a monolithic clock generator and timing/frequency reference
ActiveUS20060071718A1Improve accuracyAccurate frequency generationResonant circuit tuningPulse automatic controlProcessor registerClock generator
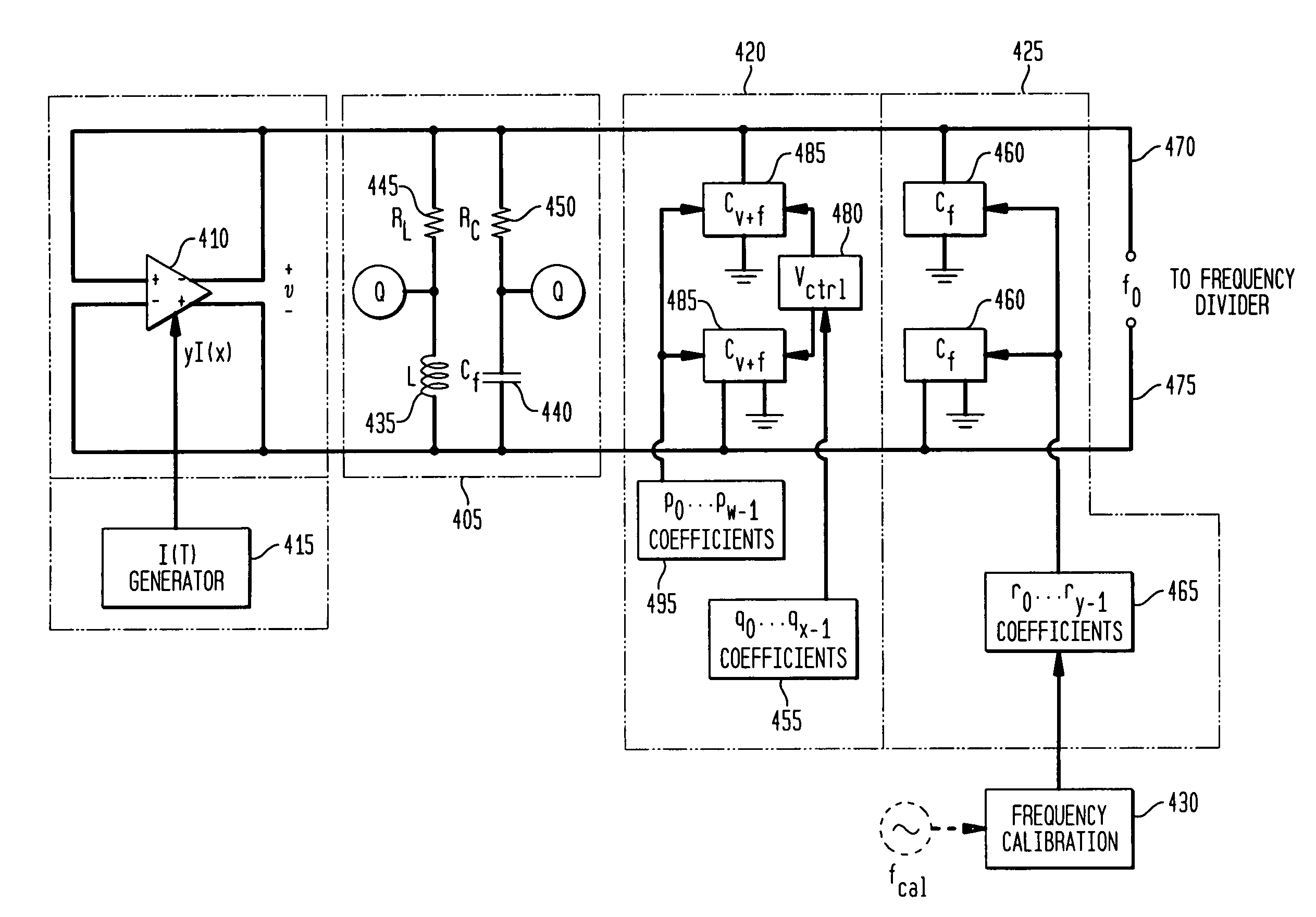
Exemplary embodiments of the invention provide a system, method and apparatus for frequency calibration of a free-running, harmonic oscillator. A reference oscillator provides a reference frequency. An exemplary system comprises the harmonic oscillator, a frequency divider, a comparator, and a reactance modulator. The oscillator comprises a plurality of switchable reactance modules and a coefficient register, and provides an oscillation signal having an oscillation frequency. The frequency divider provides an output frequency as a fraction of the oscillation frequency. The comparator compares the output and reference frequencies and provides a comparison signal when the output frequency is not substantially equal to the reference frequency. The reactance modulator determines and provides to the coefficient register a first plurality of coefficients to control switching of a first subset of the reactance modules to increase the reactance of the oscillator when the output frequency is greater than the reference frequency, and a second plurality of coefficients to control switching of a second subset of the reactance modules to decrease the reactance of the oscillator when the output frequency is less than the reference frequency.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Popular searches
Transmission Broadcast information generation Special data processing applications Transducer casings/cabinets/supports High level techniques Counting chain pulse counters Generating/distributing signals Resonant circuits using central processing units Apparatus using electrochemical resonators Frequency analysis
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com