Patents
Literature
43results about How to "Connection resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
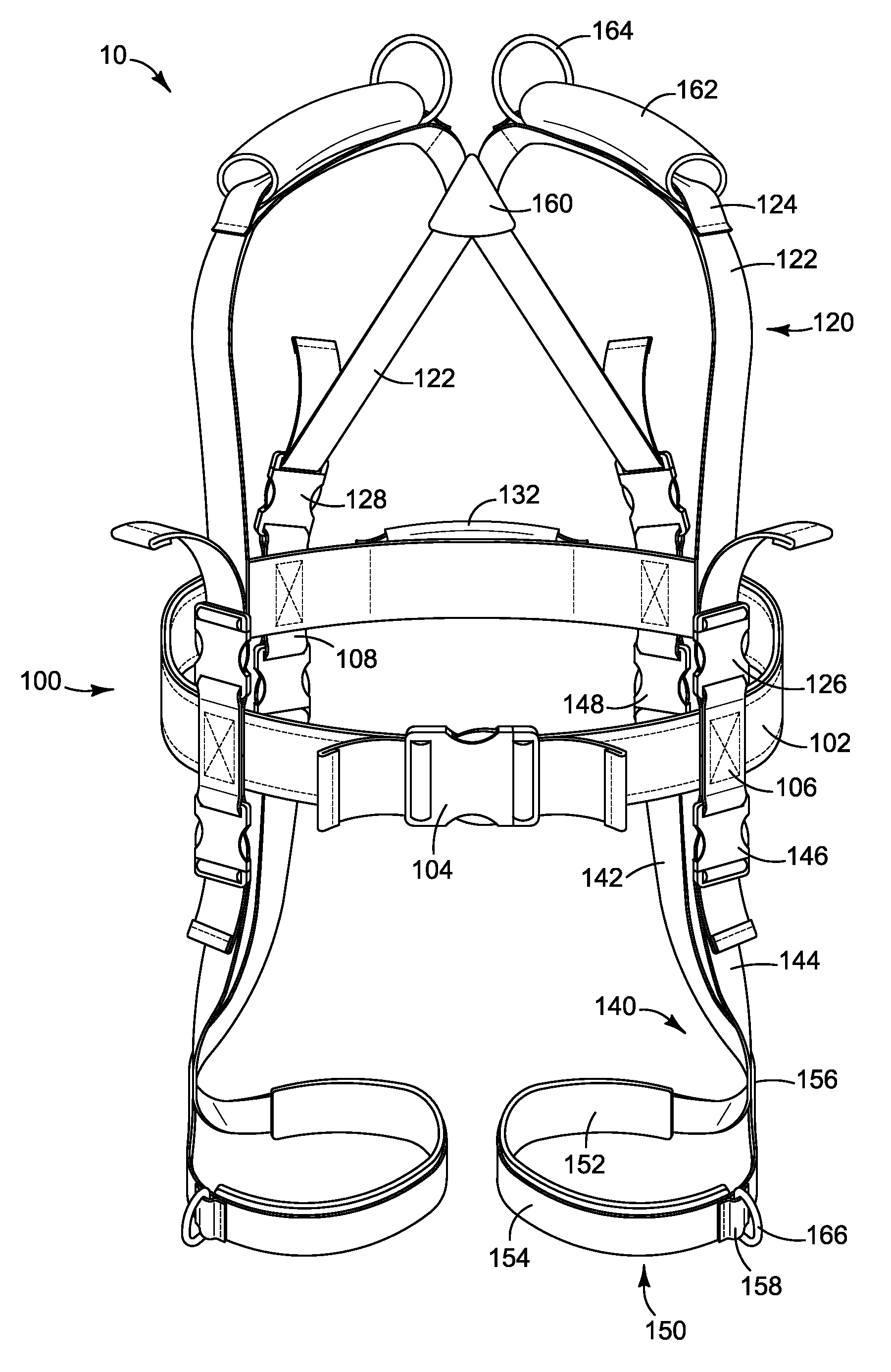
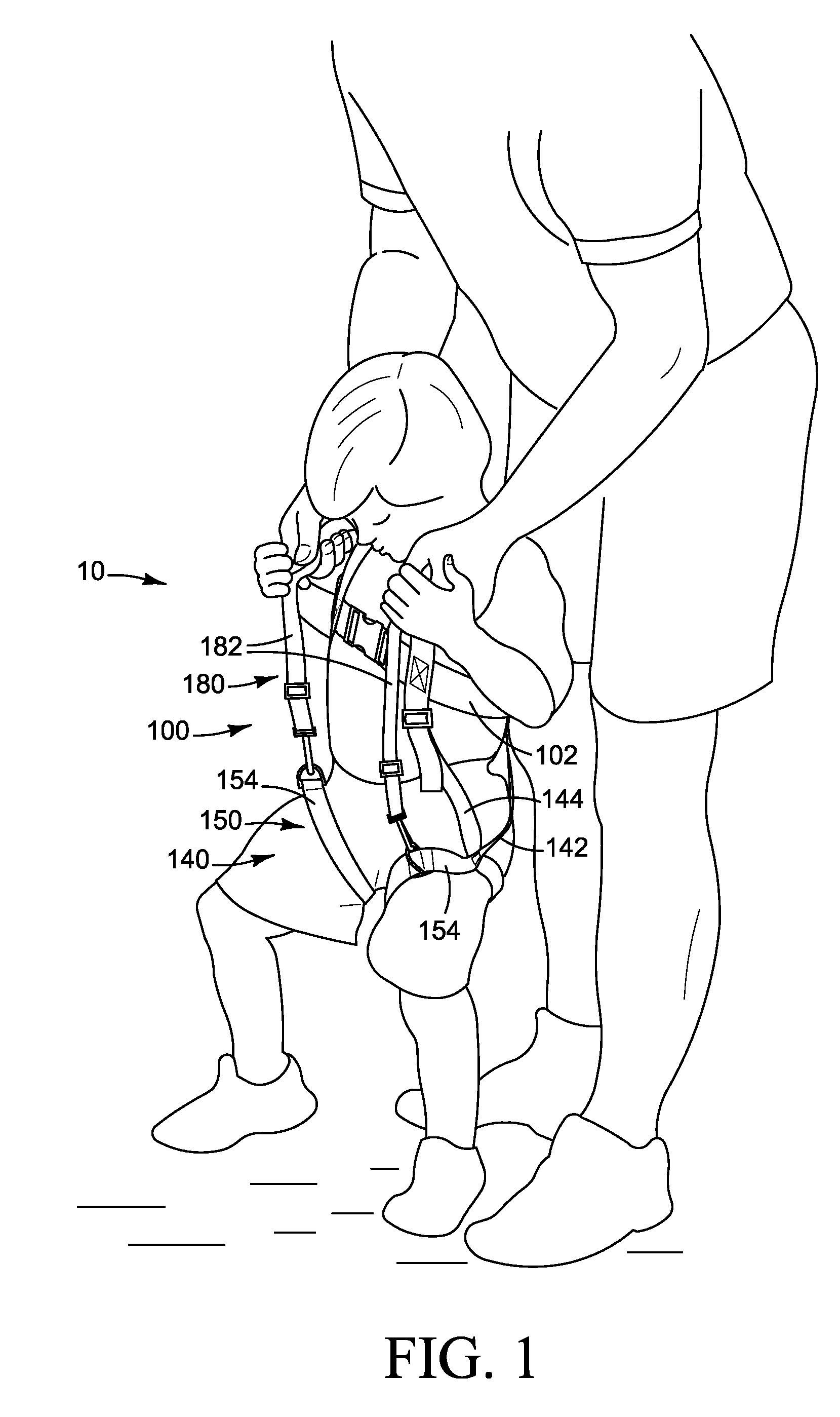
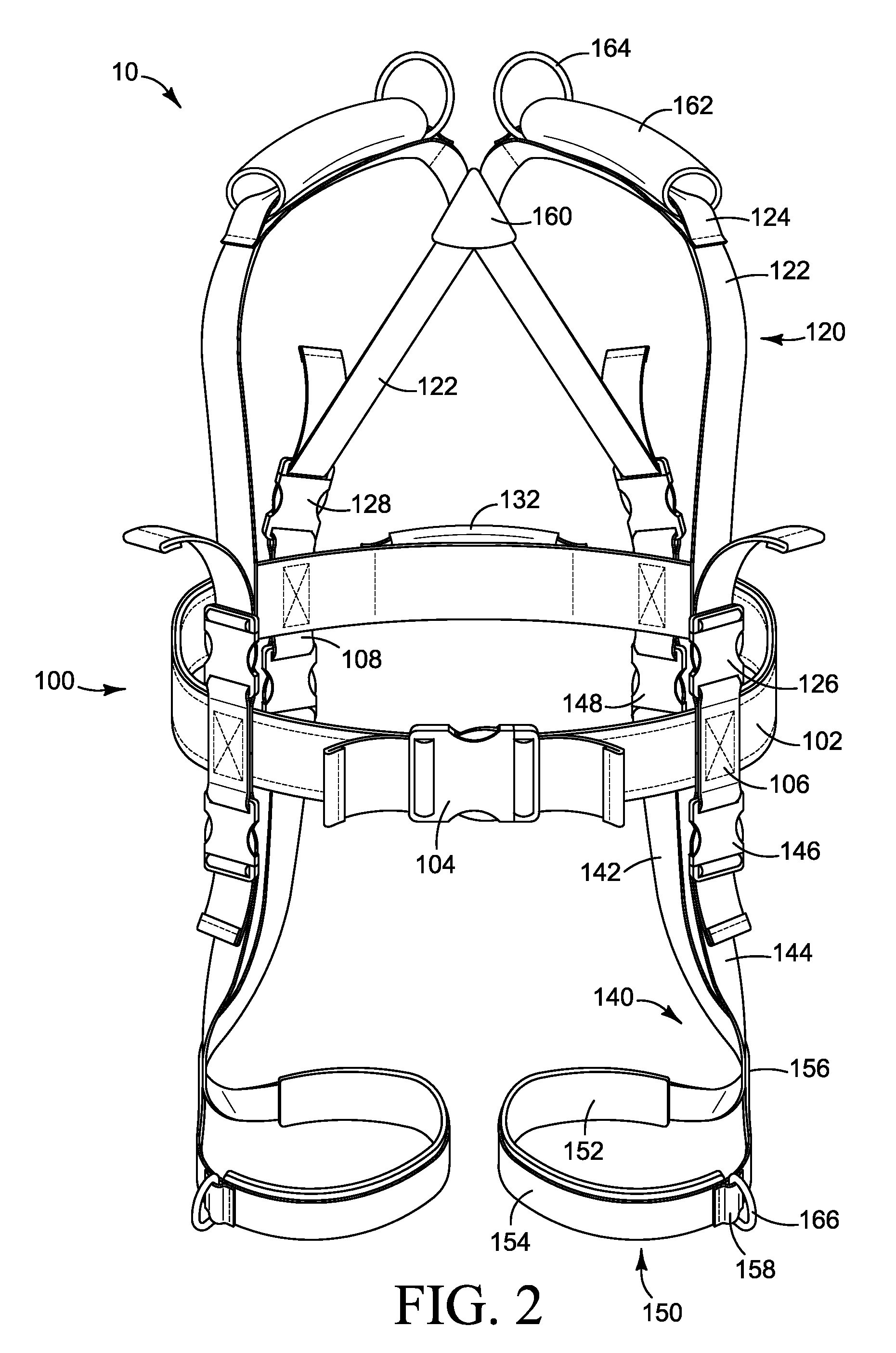
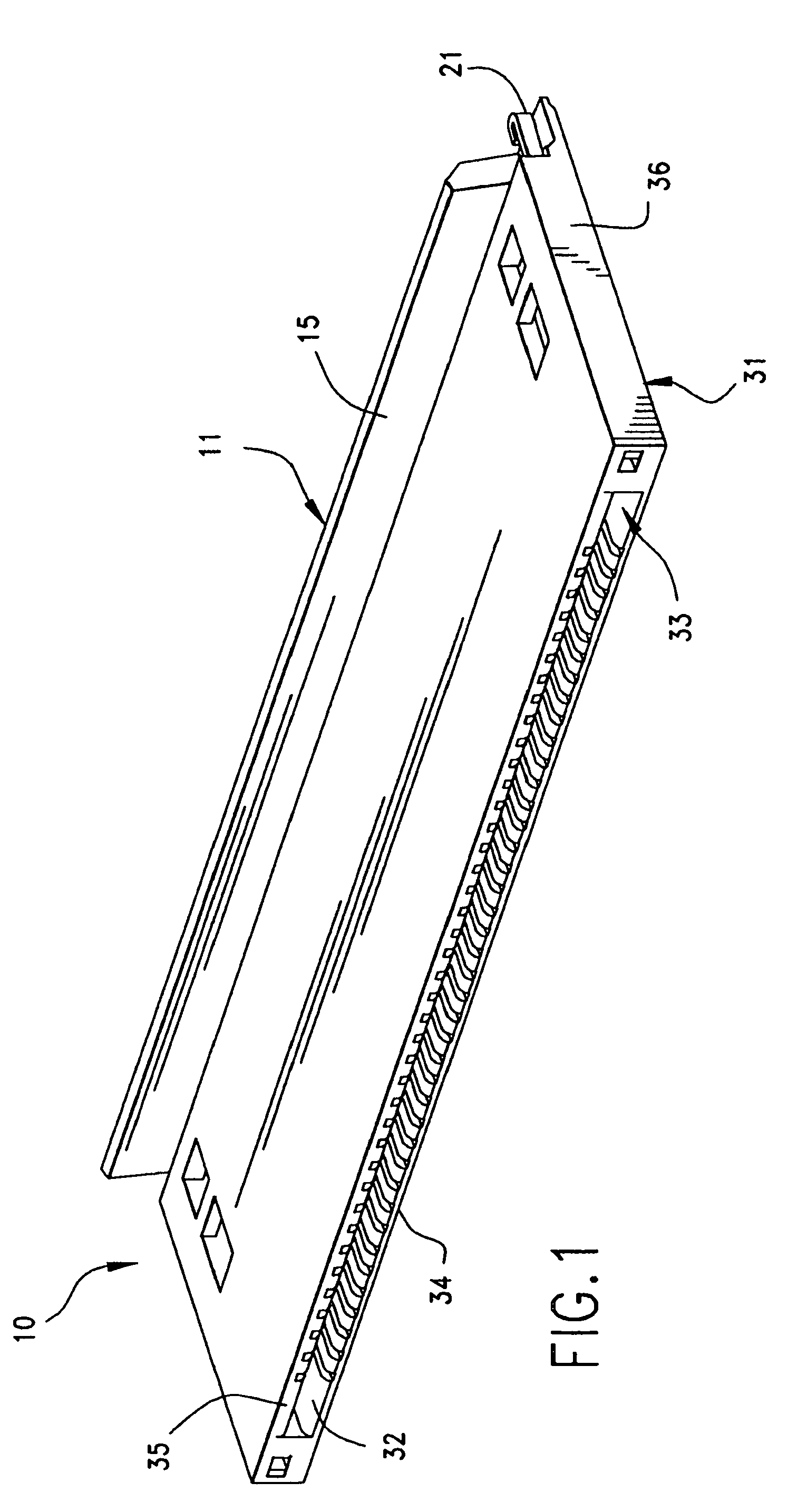
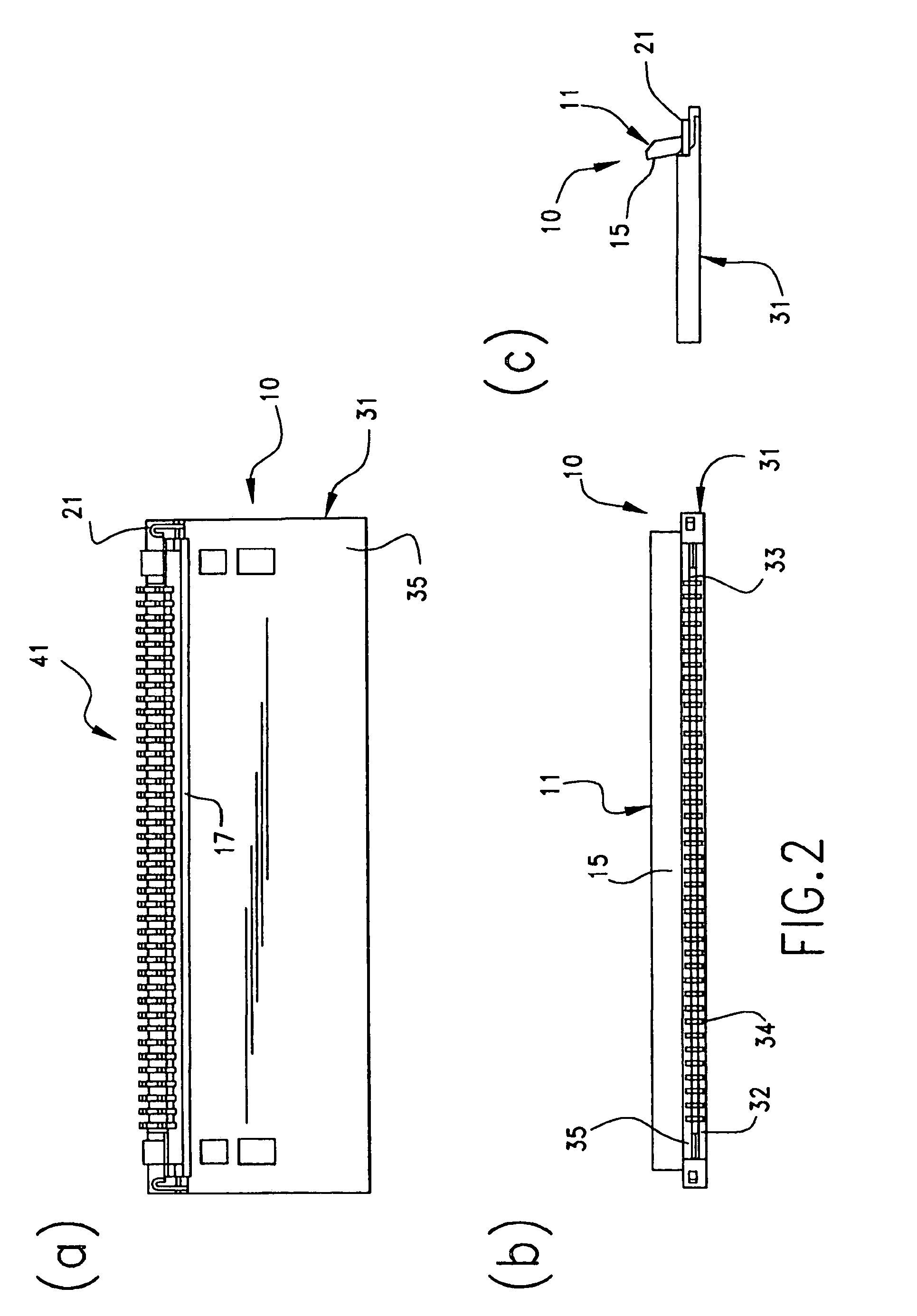
Gait training harness
A full body Gait Training Harness for children with disability may be modified for adult use to assist a trainer to teach functions such as walking with a proper gait and crawling. Shoulder straps attached to a torso-encircling belt cross at the trainee's back to eliminate slippage, allowing use on those who have no arms. Leg loops secure the harness to the thighs, rather than through the crotch, for a more secure and comfortable fit. Leg stabilization straps between the leg loops and the shoulders provide tension to encourage development of a proper gait and to prevent crossing of the trainee's legs. Shoulder handles allow a trainer to support a trainee from above without stooping, while a back handle may be used to lift a trainee or support them in a crawling position. Walking extension straps attached to the shoulders allow trainee independence while the trainer retains control.
Owner:LUCKY BUMS
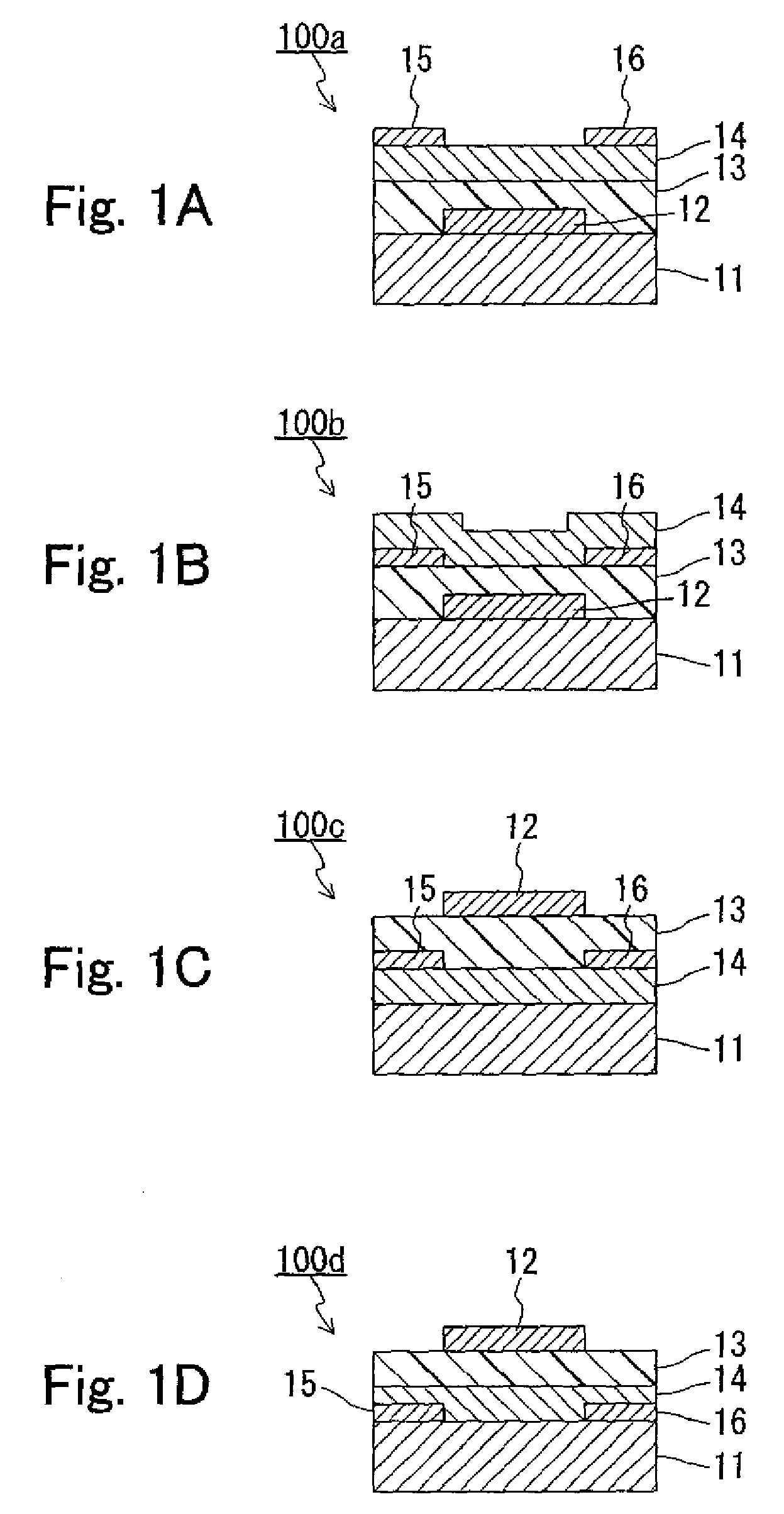
Light-emitting display and method of manufacturing the same
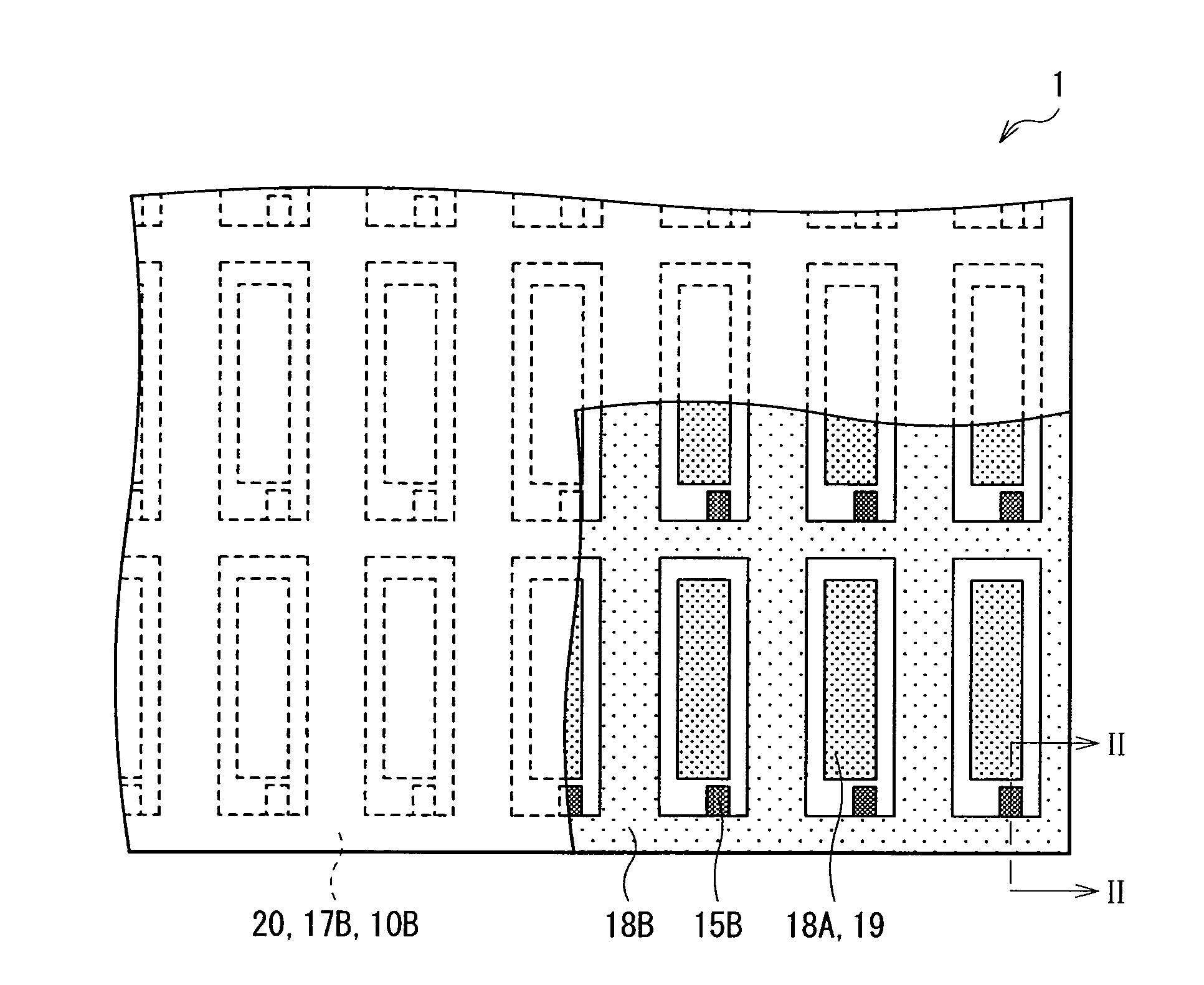
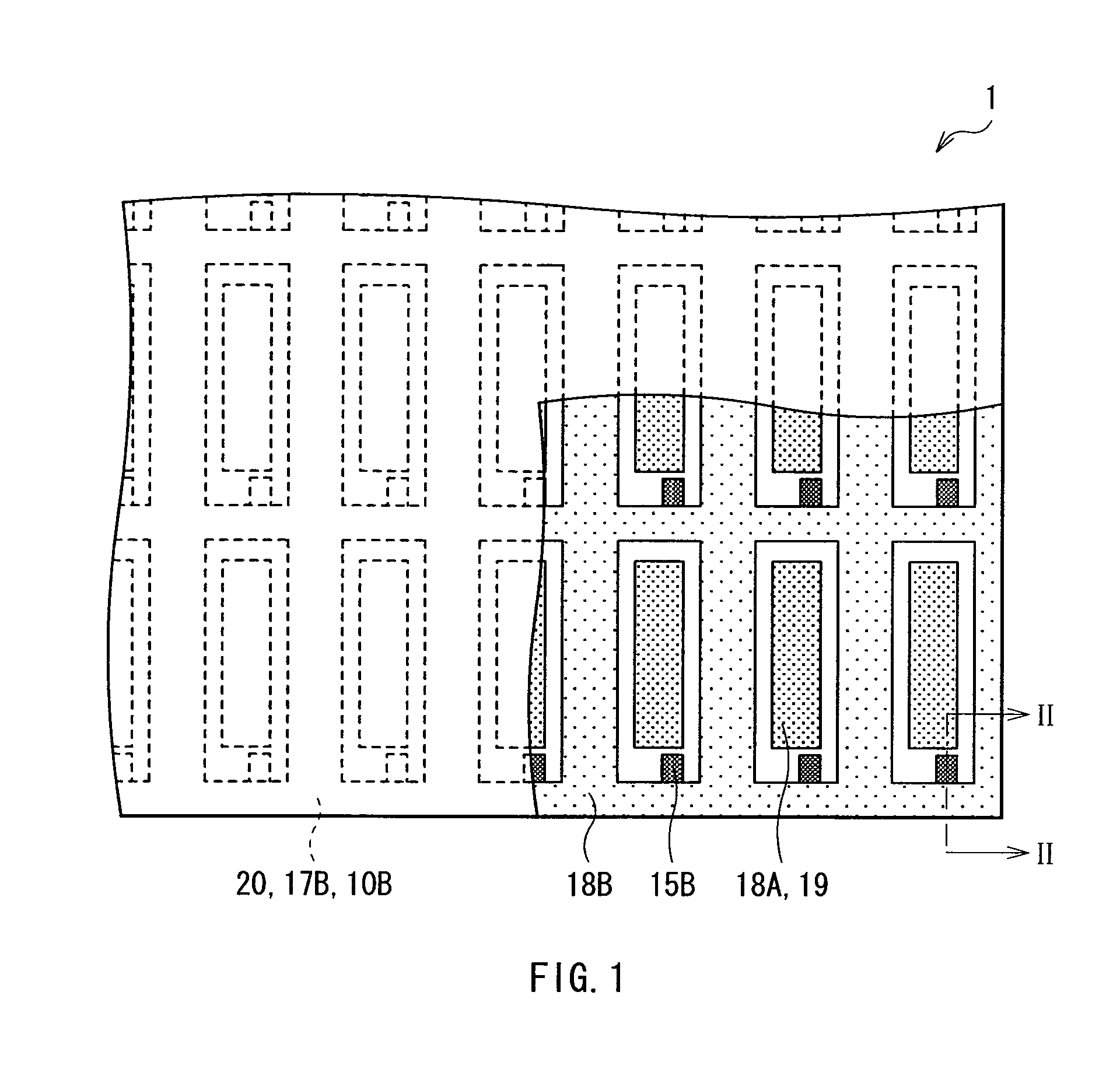
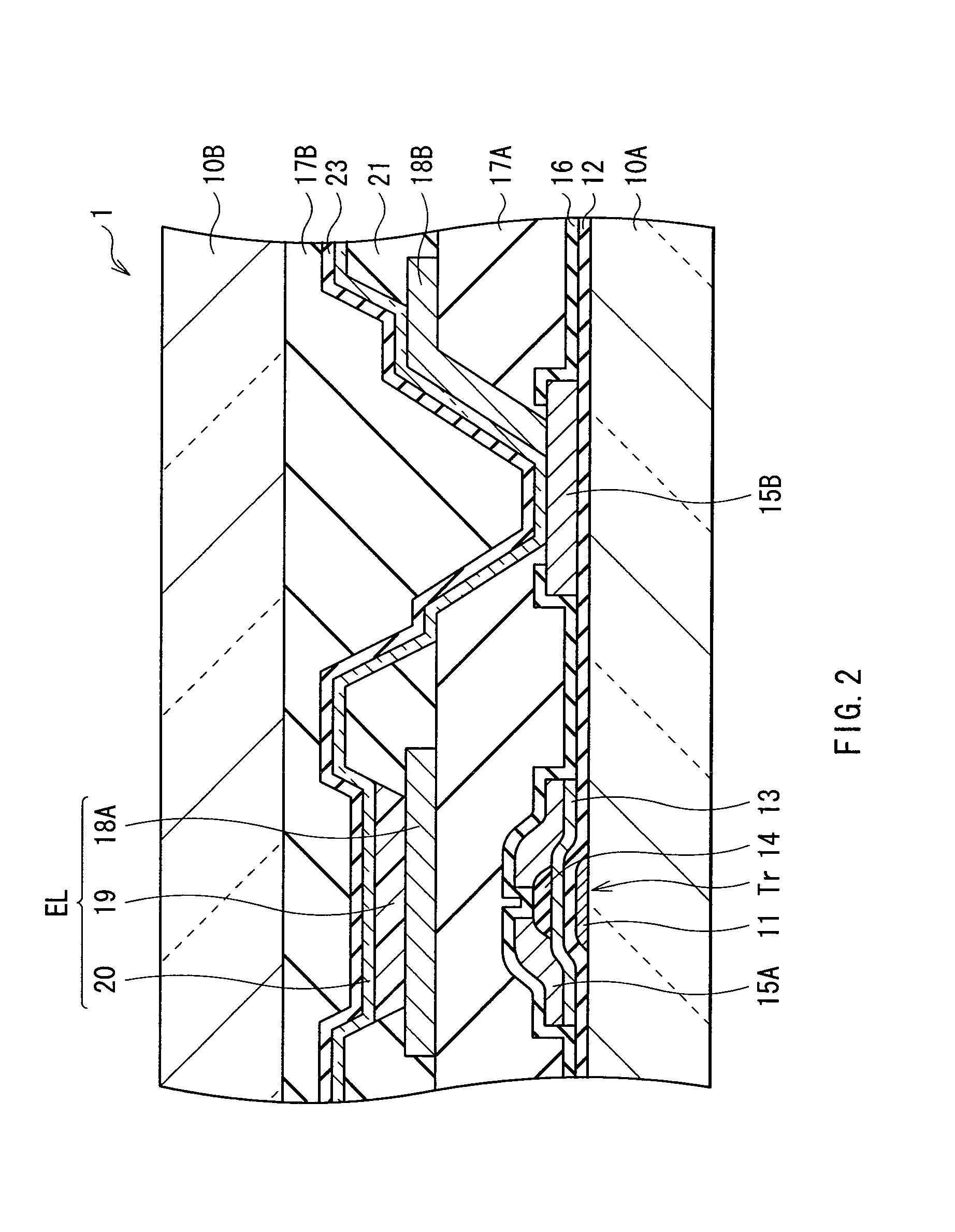
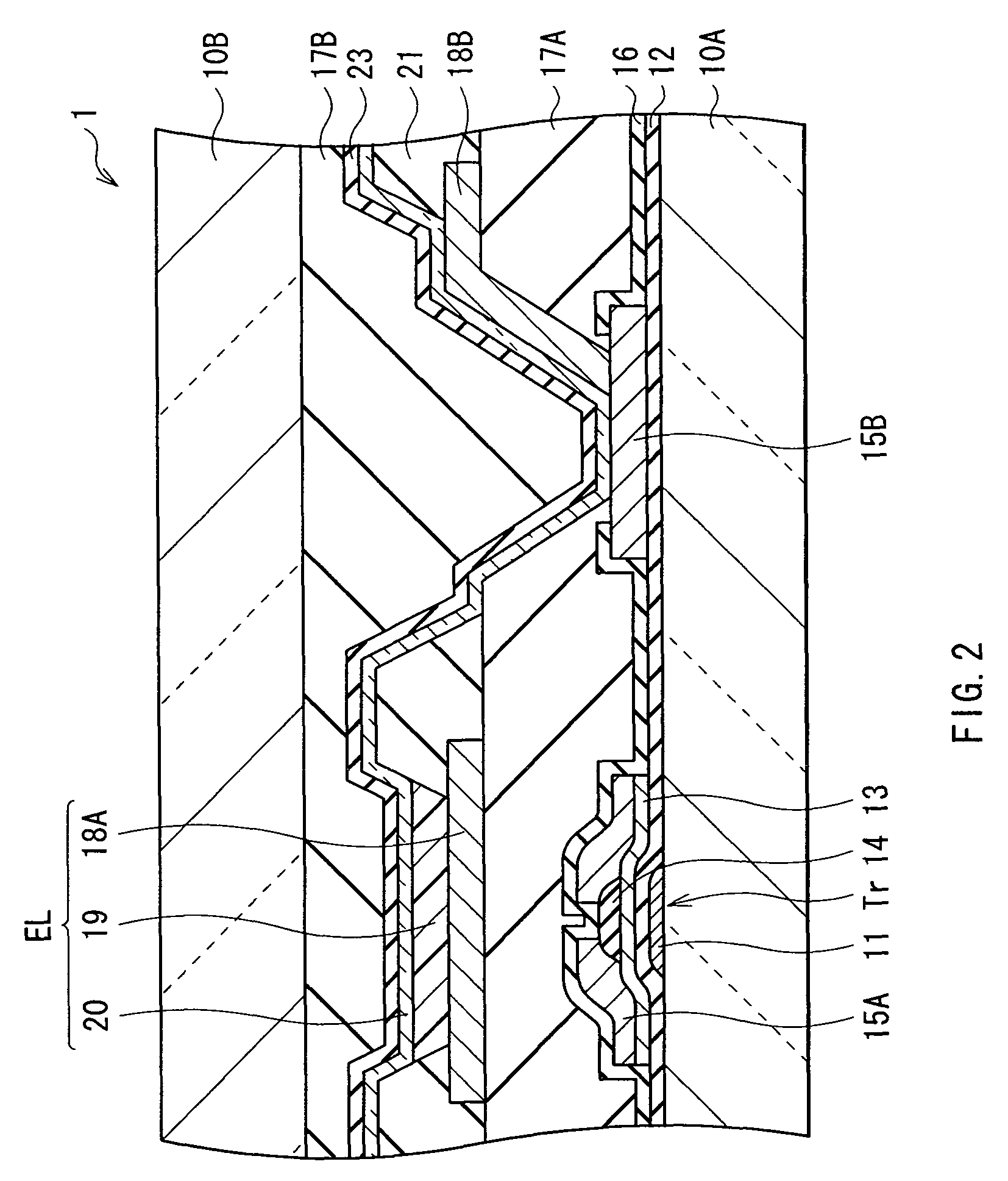
ActiveUS20100244664A1Increase connection resistanceReduce power consumptionDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceEngineering
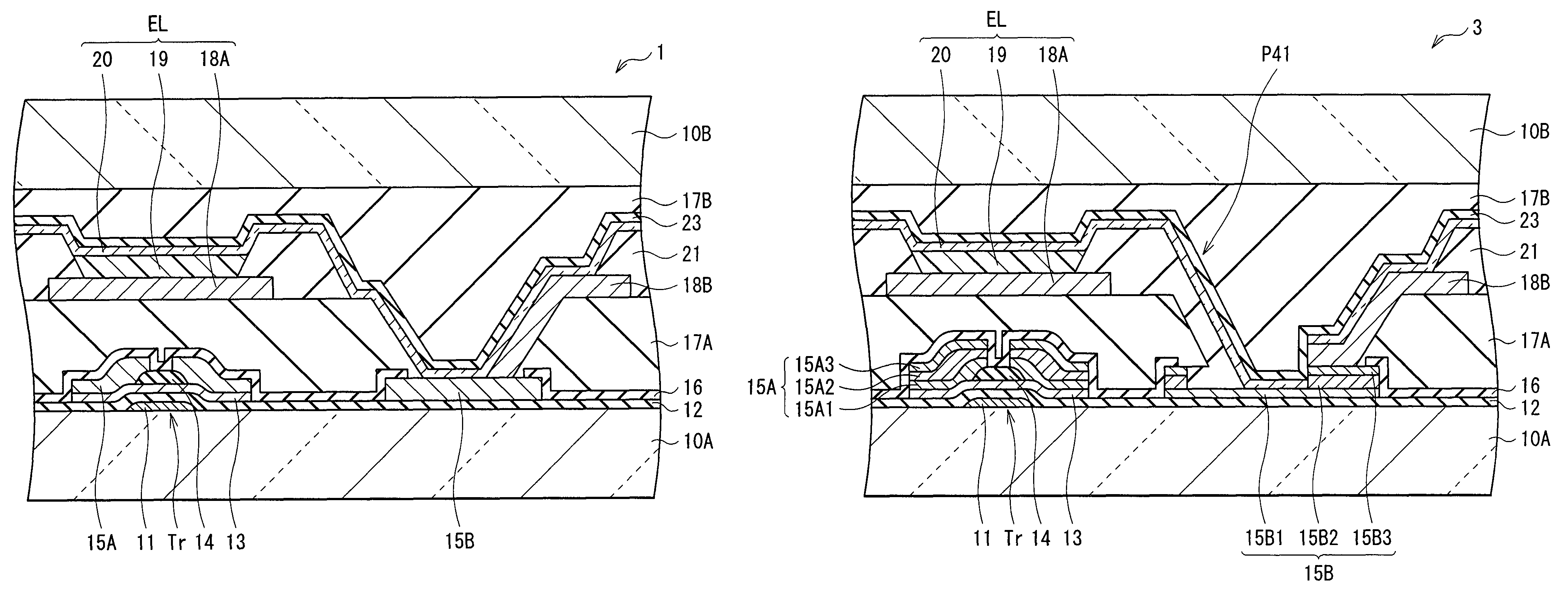
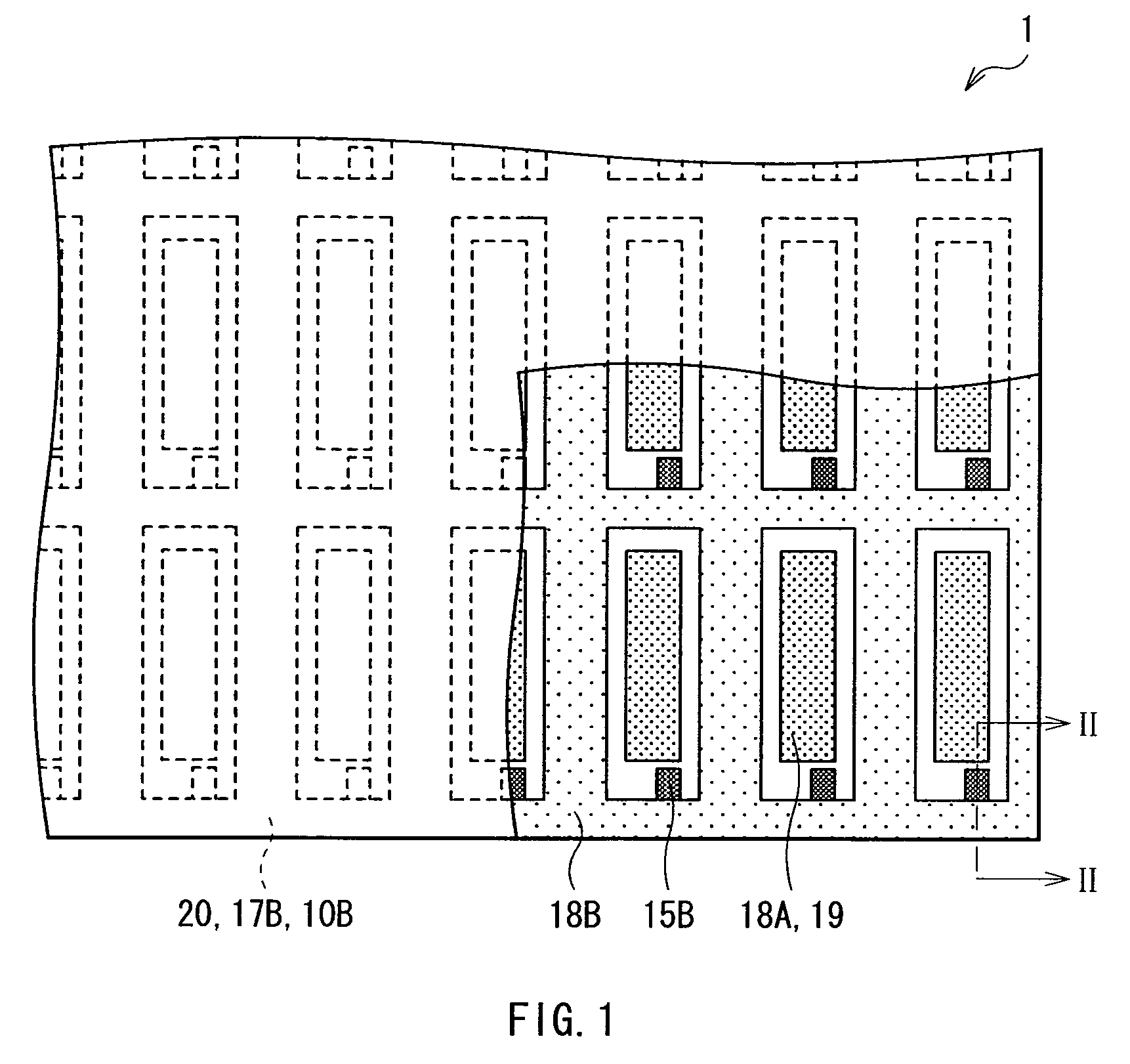
A light-emitting display capable of maintaining low power consumption and improving display quality irrespective of the configuration of an auxiliary wiring is provided. A second electrode 20 and an auxiliary wiring 18B are electrically connected to each other through a conductive contact section 15B. Moreover, only a part of the auxiliary wiring 18B is connected to the contact section 15B. Even if the surface of the auxiliary wiring 18B is oxidized, an increase in connection resistance is prevented. Moreover, a restriction on layout is not imposed at the time of forming the contact section 15B.
Owner:JOLED INC
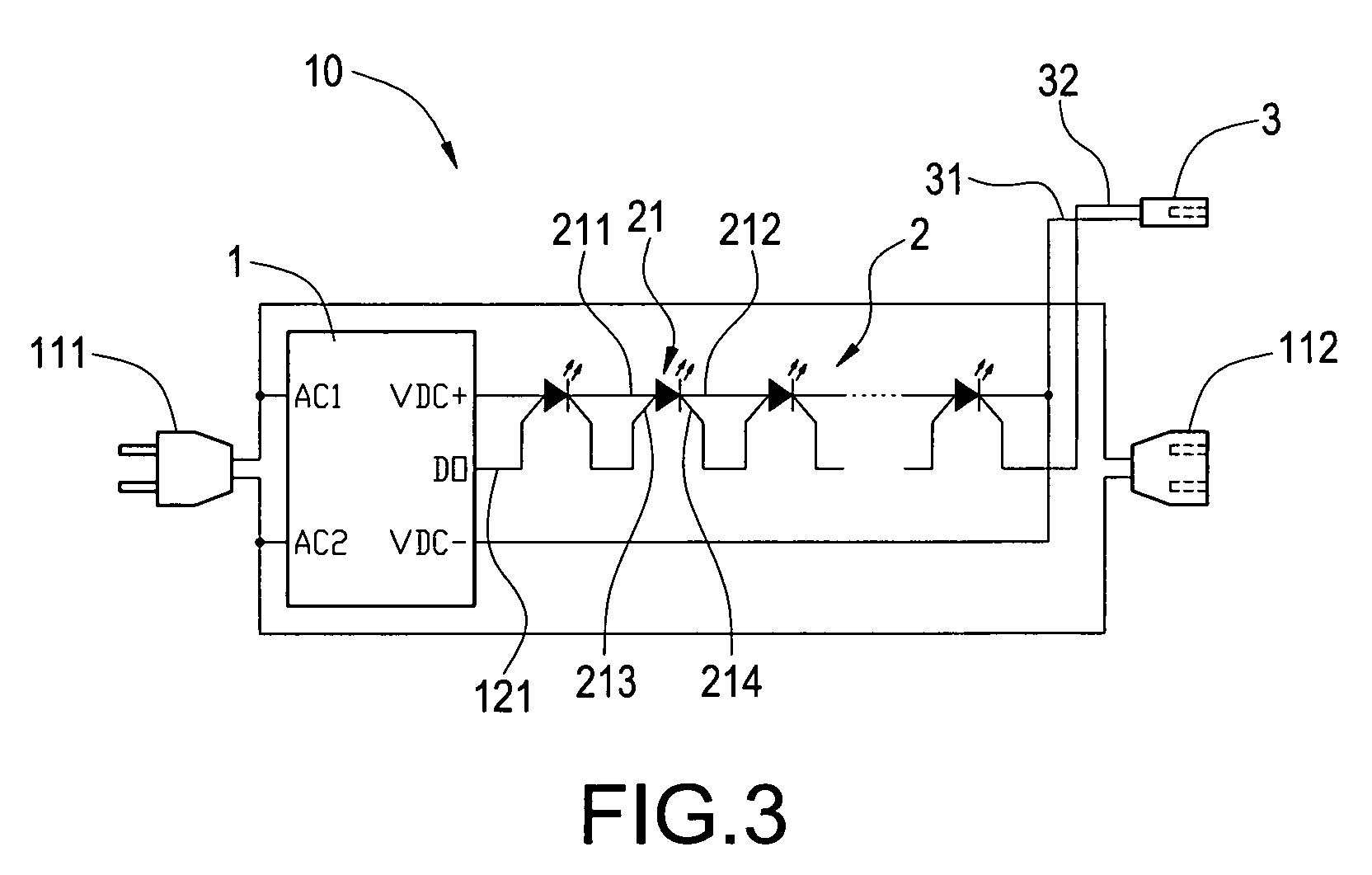
Series-type LED lamp strip module
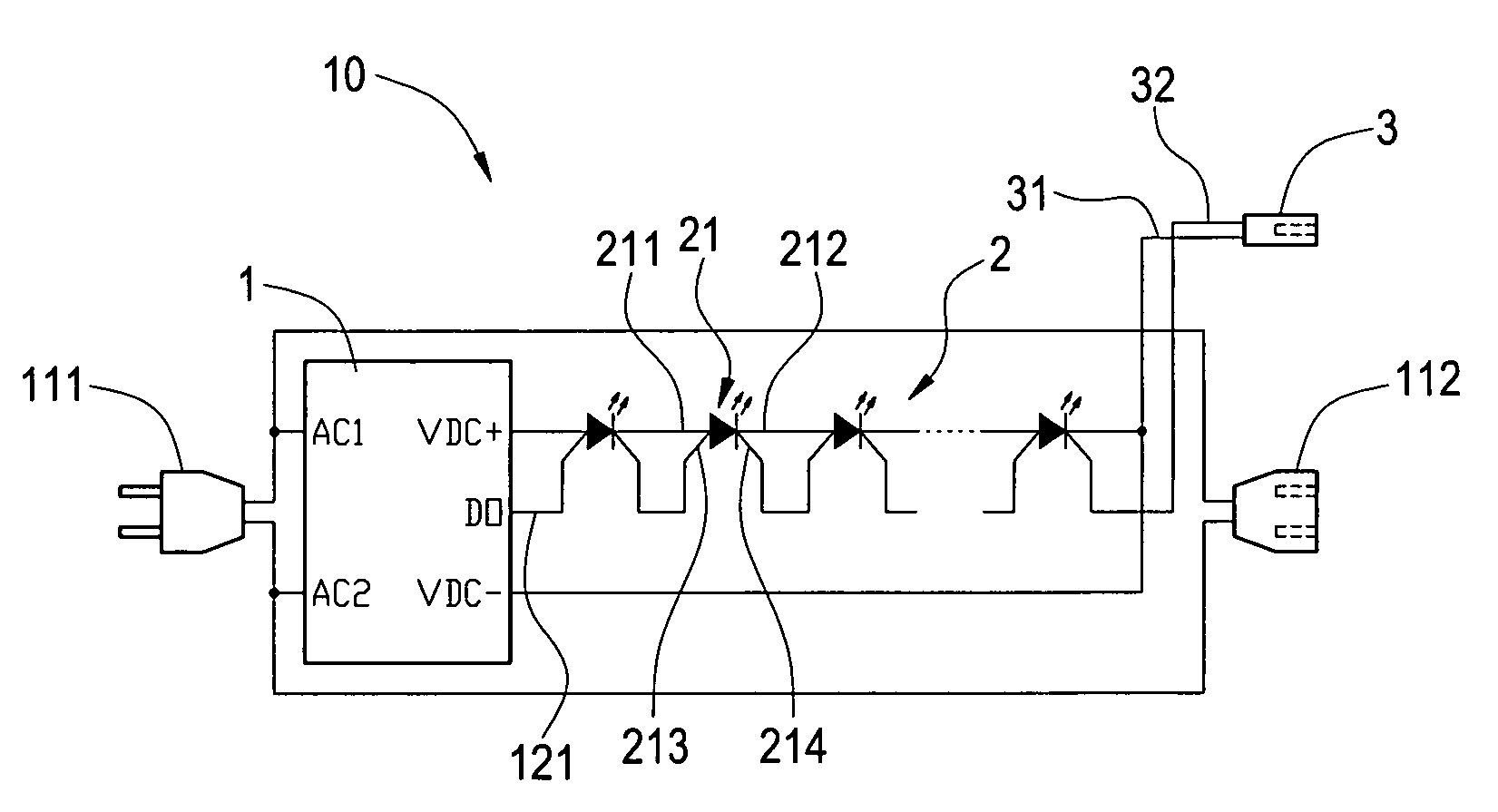
ActiveUS20090302771A1Reduce energy consumptionOvercome connection limitationElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesMicrocontrollerControl signal
A series-type LED lamp strip module includes a first LED lamp strip module and a second LED lamp strip module. The first LED lamp strip module and the second LED lamp strip module both include a power switch controller, at lease one LED lamp strip, a signal output adaptor, a signal input adaptor, a power plug, and a power socket. The power plug of the second LED lamp strip module is inserted into the power socket of the first LED lamp strip module, and the signal output adaptor of the first LED lamp strip module is electrically connected to the signal input adaptor of the second LED lamp strip module so as to connect the first LED lamp strip module and the second LED lamp strip module. In addition, a microcontroller unit outputs a control signal to lighten light emitting diodes in different types to produce multiple brightness variations.
Owner:SEMISILICON TECH
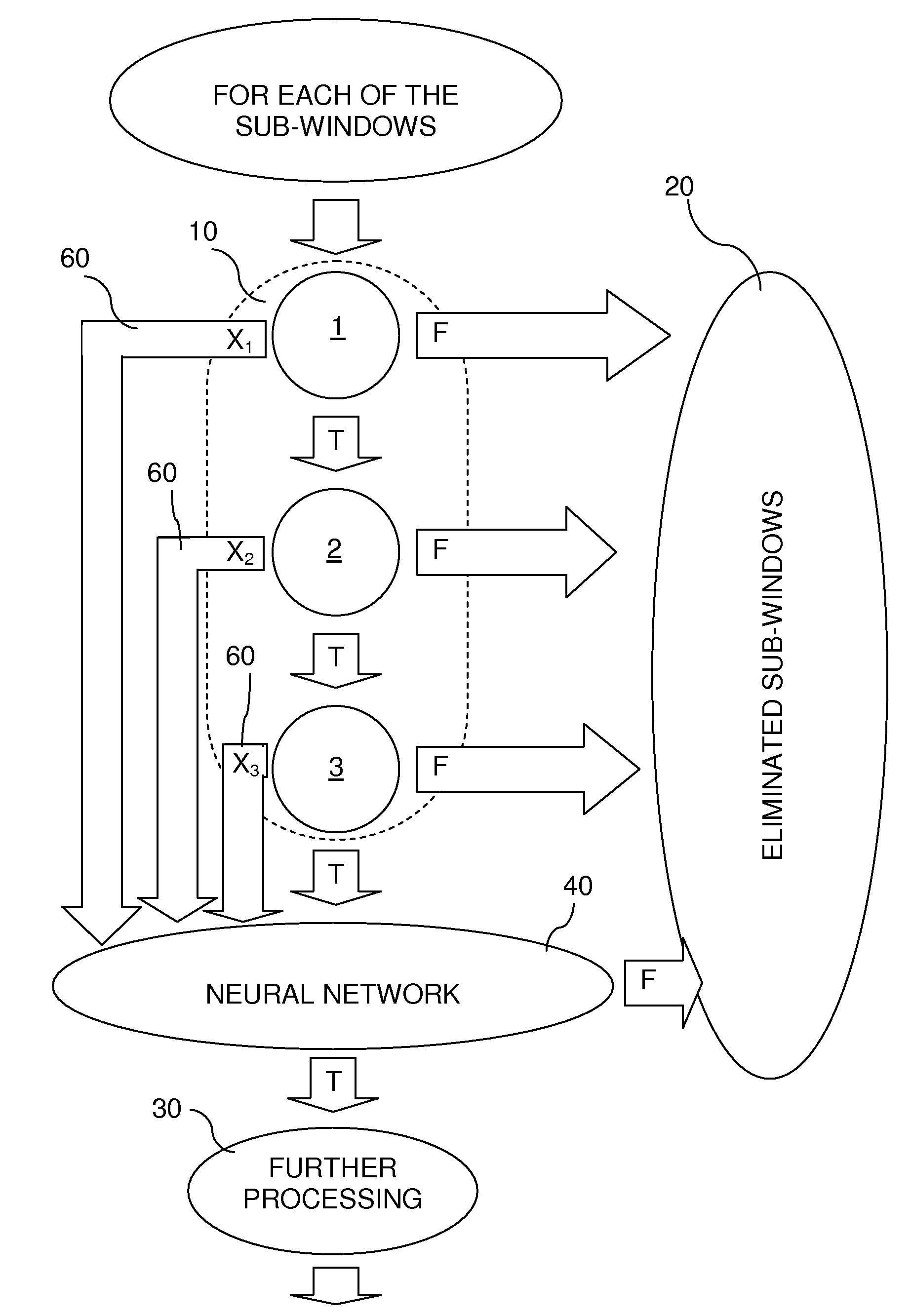
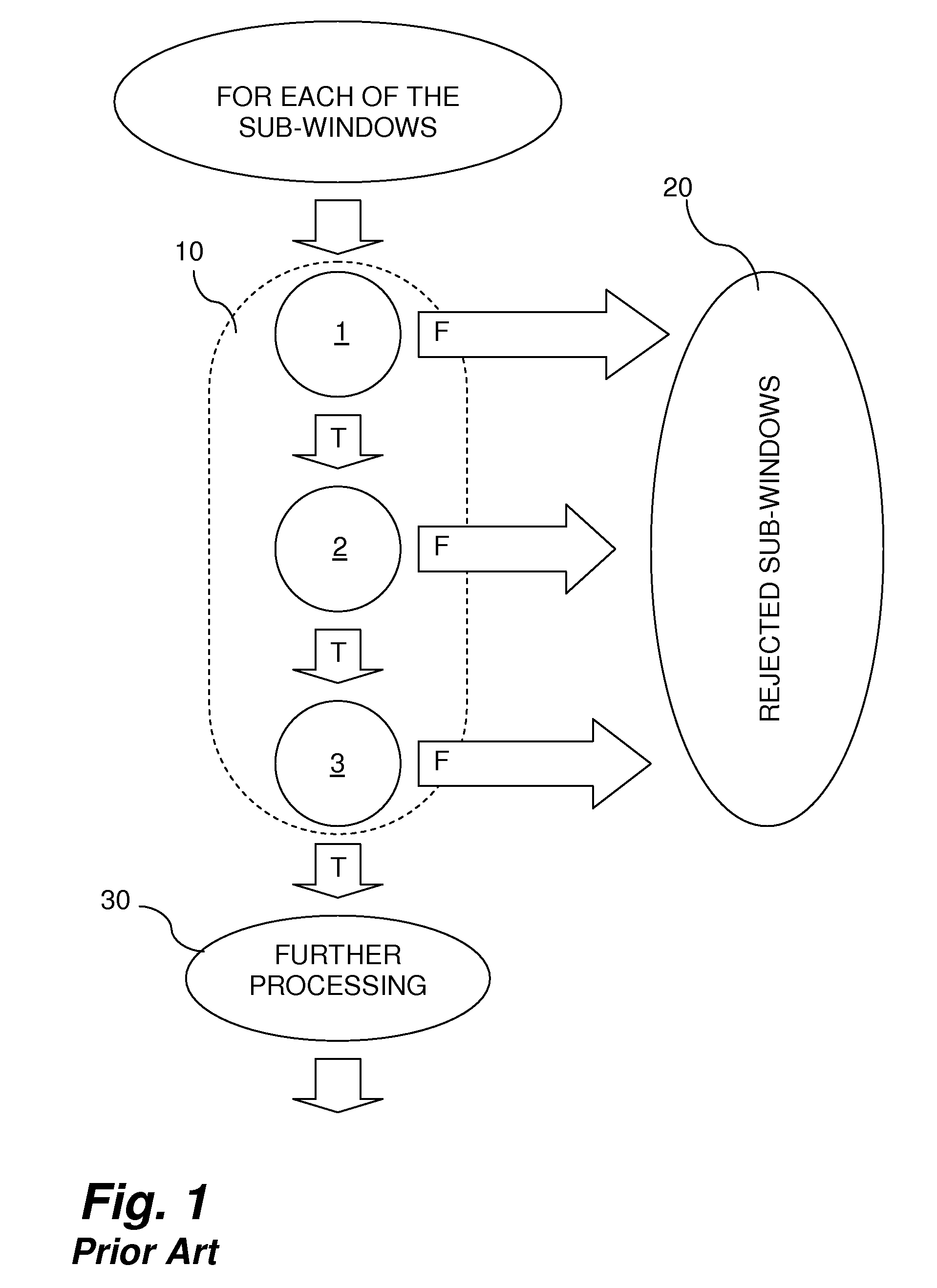
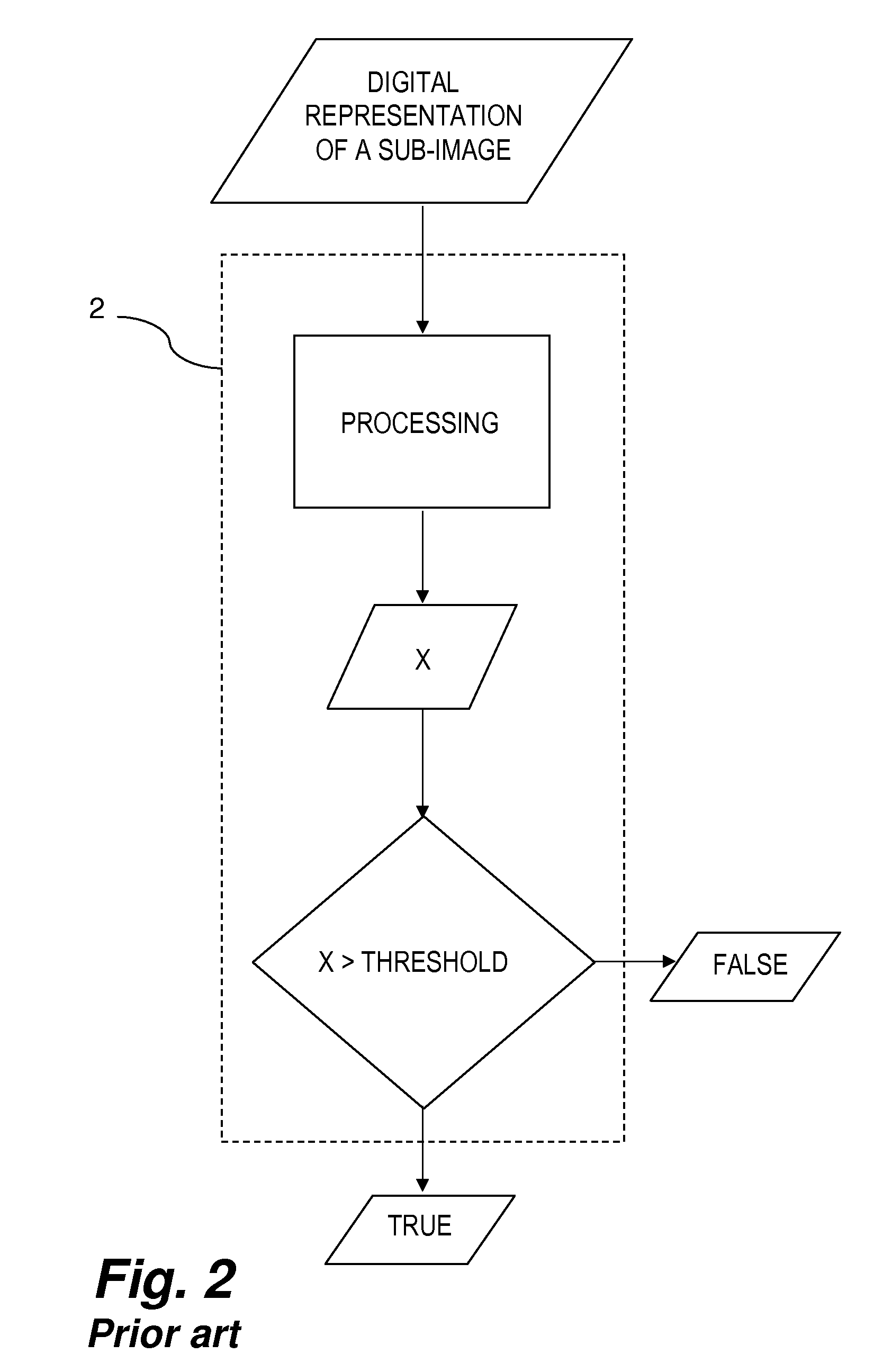
Method for object detection
InactiveUS20090161912A1Improve accuracyConnection resistanceCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital imageObject detection
In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a method for object detection, the method comprising the steps of: dividing a digital image into a plurality of sub-windows of substantially the same dimensions; processing the image of each of the sub-windows by a cascade of homogeneous classifiers (each of the homogenous classifiers produces a CRV, which is a value relative to the likelihood of a sub-window to comprise an image of the object of interest, and wherein each of the classifiers has an increasing accuracy in identifying features associated with the object of interest); and upon classifying by all of the classifiers of the cascade a sub-window as comprising an image of the object of interest, applying a post-classifier on the cascade CRVS, for evaluating the likelihood of the sub-window to comprise an image of the object of interest, wherein the post-classifier differs from the homogenous classifiers.
Owner:YATOM RAVIV +2
Receiving apparatus and transmitting apparatus
InactiveUS20060268842A1Improve effectGood effectSpecial service for subscribersCalling susbscriber number recording/indicationReal-time computingCommunication device
Owner:SHARP KK
Series-type LED lamp strip module
ActiveUS7852011B2Reduce energy consumptionConnection resistanceElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesMicrocontrollerControl signal
A series-type LED lamp strip module includes a first LED lamp strip module and a second LED lamp strip module. The first LED lamp strip module and the second LED lamp strip module both include a power switch controller, at lease one LED lamp strip, a signal output adaptor, a signal input adaptor, a power plug, and a power socket. The power plug of the second LED lamp strip module is inserted into the power socket of the first LED lamp strip module, and the signal output adaptor of the first LED lamp strip module is electrically connected to the signal input adaptor of the second LED lamp strip module so as to connect the first LED lamp strip module and the second LED lamp strip module. In addition, a microcontroller unit outputs a control signal to lighten light emitting diodes in different types to produce multiple brightness variations.
Owner:SEMISILICON TECH
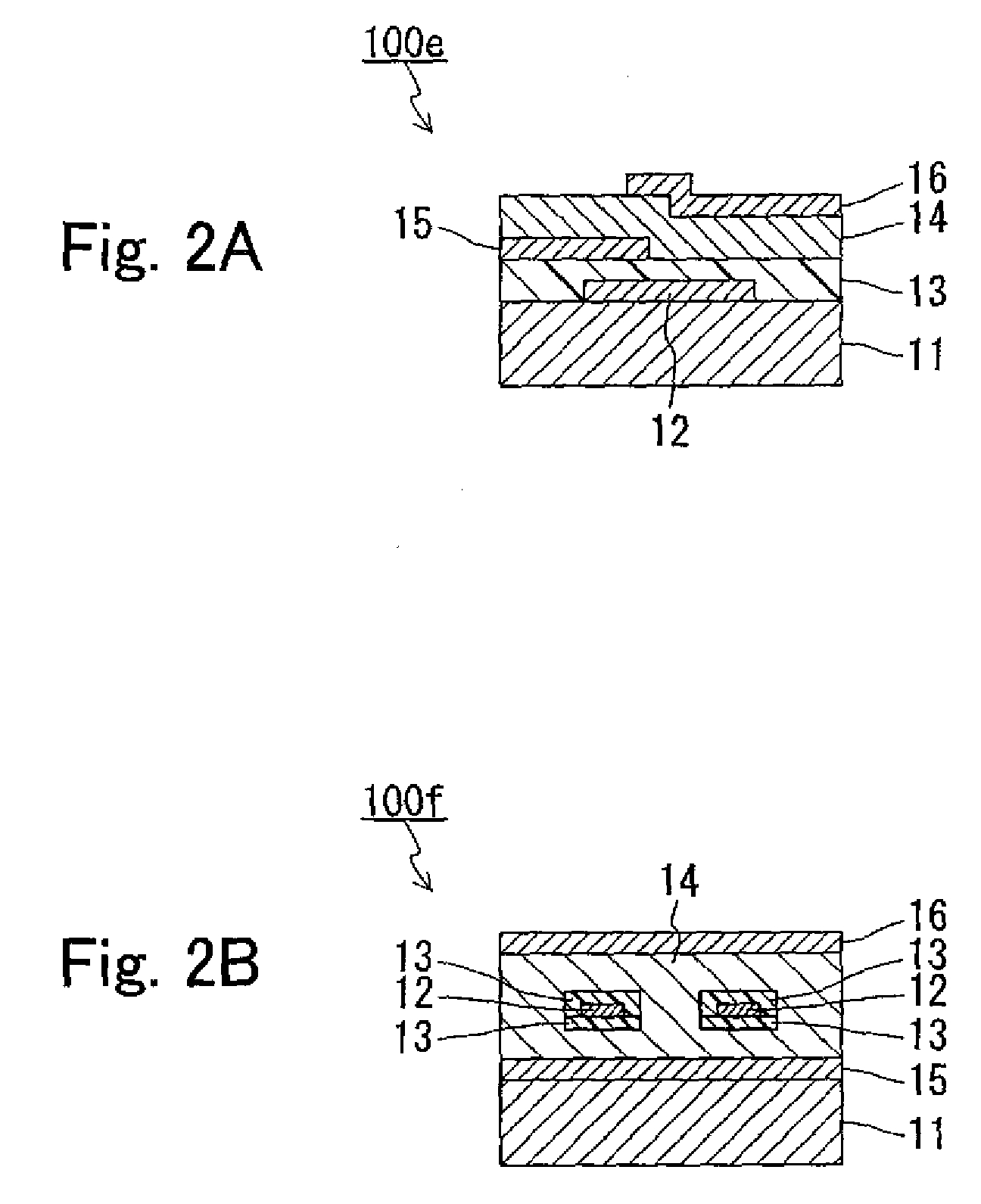
Light-emitting display with auxiliary wiring section and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8115376B2Easy to oxidizeConnection resistanceDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:JOLED INC
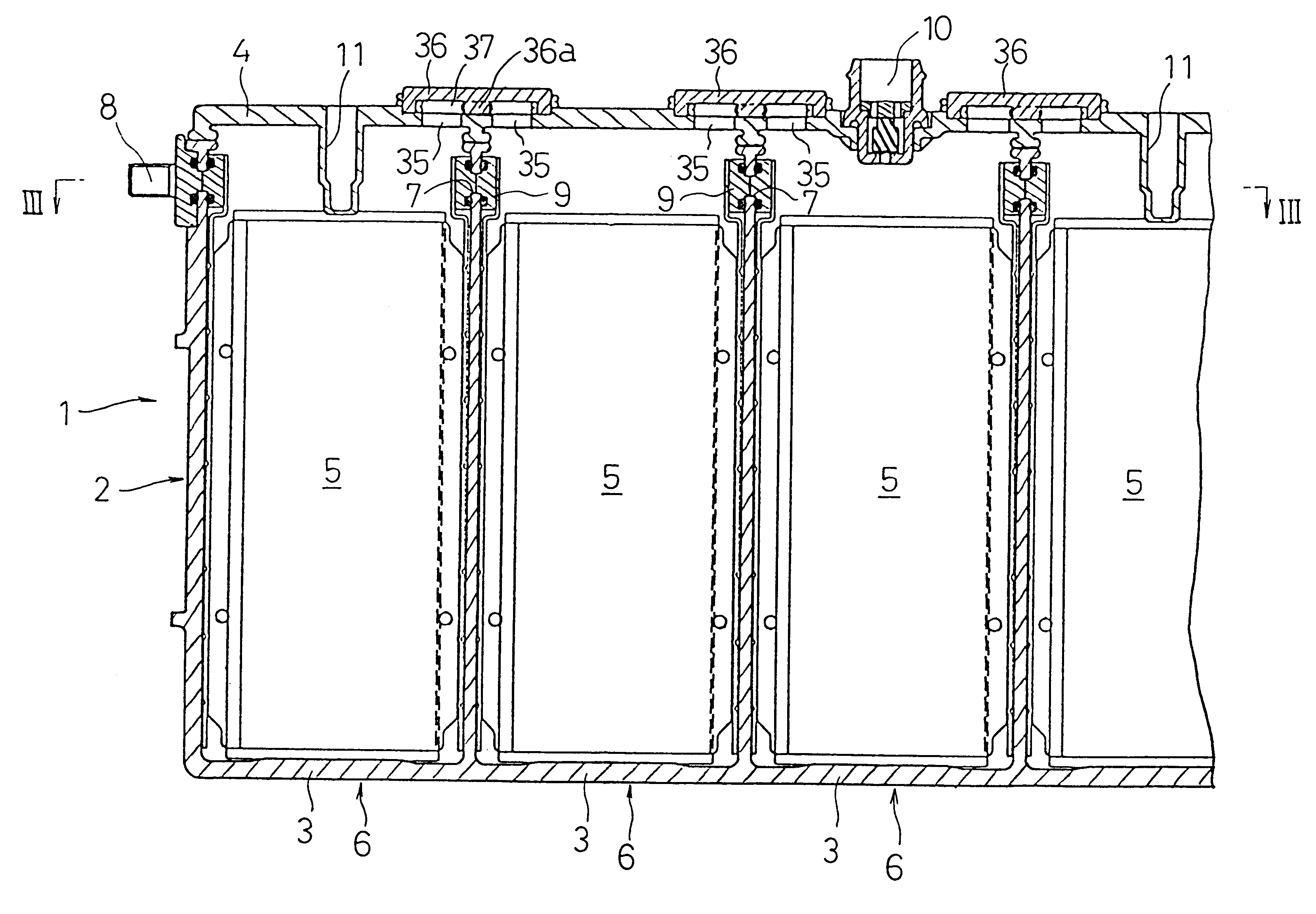
Battery module
InactiveUS6551741B1Suppressing progressImprove balanceFinal product manufactureCell temperature controlInternal pressureEngineering
An integrated battery case 2 is made by coupling together a plurality of cell cases 3 into an integral body, open ends of the cell cases 3 being closed integrally with a lid member 4. Communicating paths 37 for communicating a suitable number of neighboring cell cases 3 with one another are provided in the lid member 4, whereby the cell cases 3 have a uniform internal pressure.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
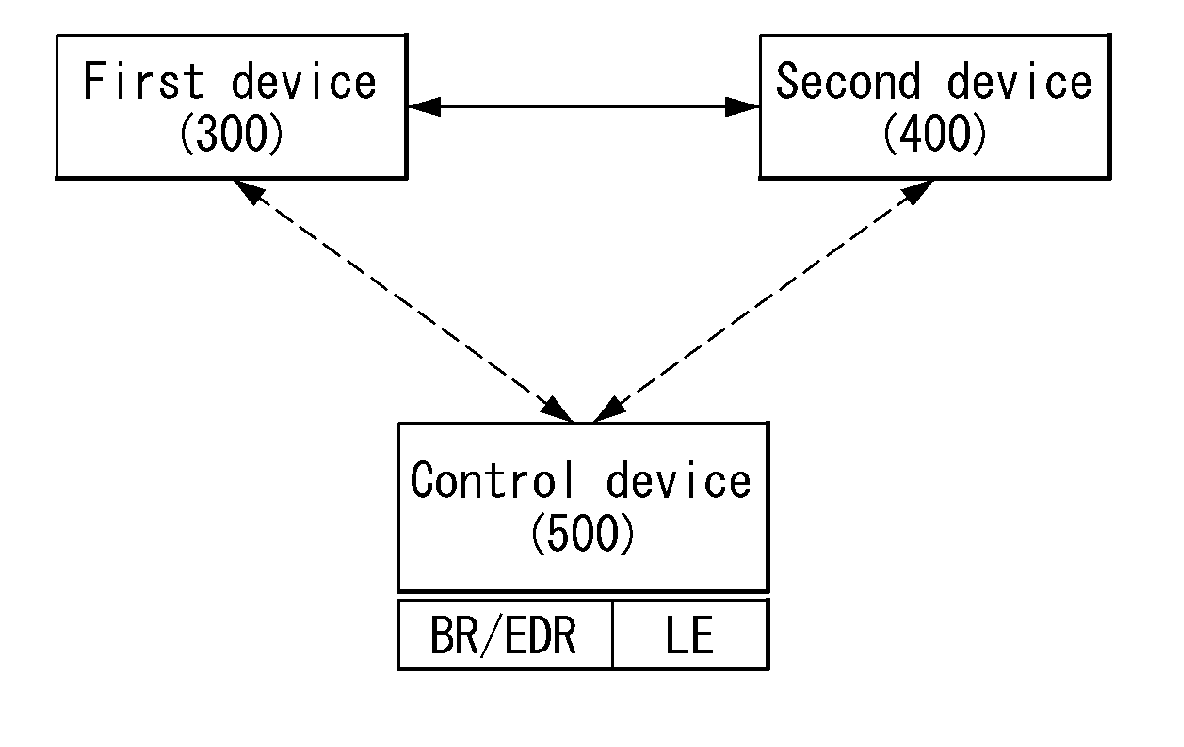
Method and device for controlling device using bluetooth technology
ActiveUS20180007499A1Weaken energyConnection resistanceNetwork topologiesServices signallingComputer networkBluetooth
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for controlling a connection between a first device and a second device by using a Bluetooth LE (Low Energy) or a Bluetooth BR / EDR. According to the present invention, the control device transmits first control information for changing the mode of the device to at least one of the first device and the second device, and connects the first device to the second device The second device can control the connection between the first device and the second device.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Low latency streaming media
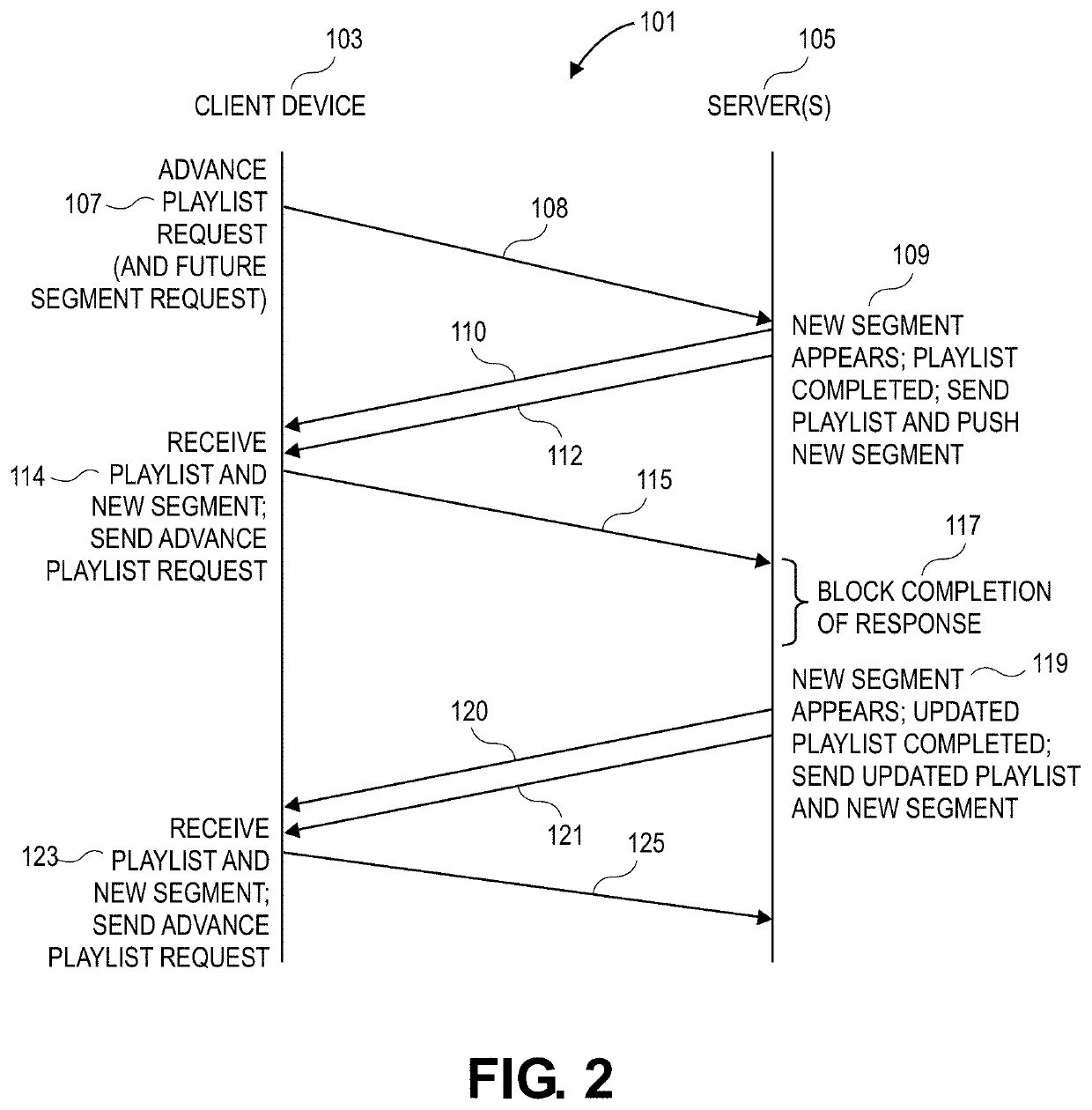
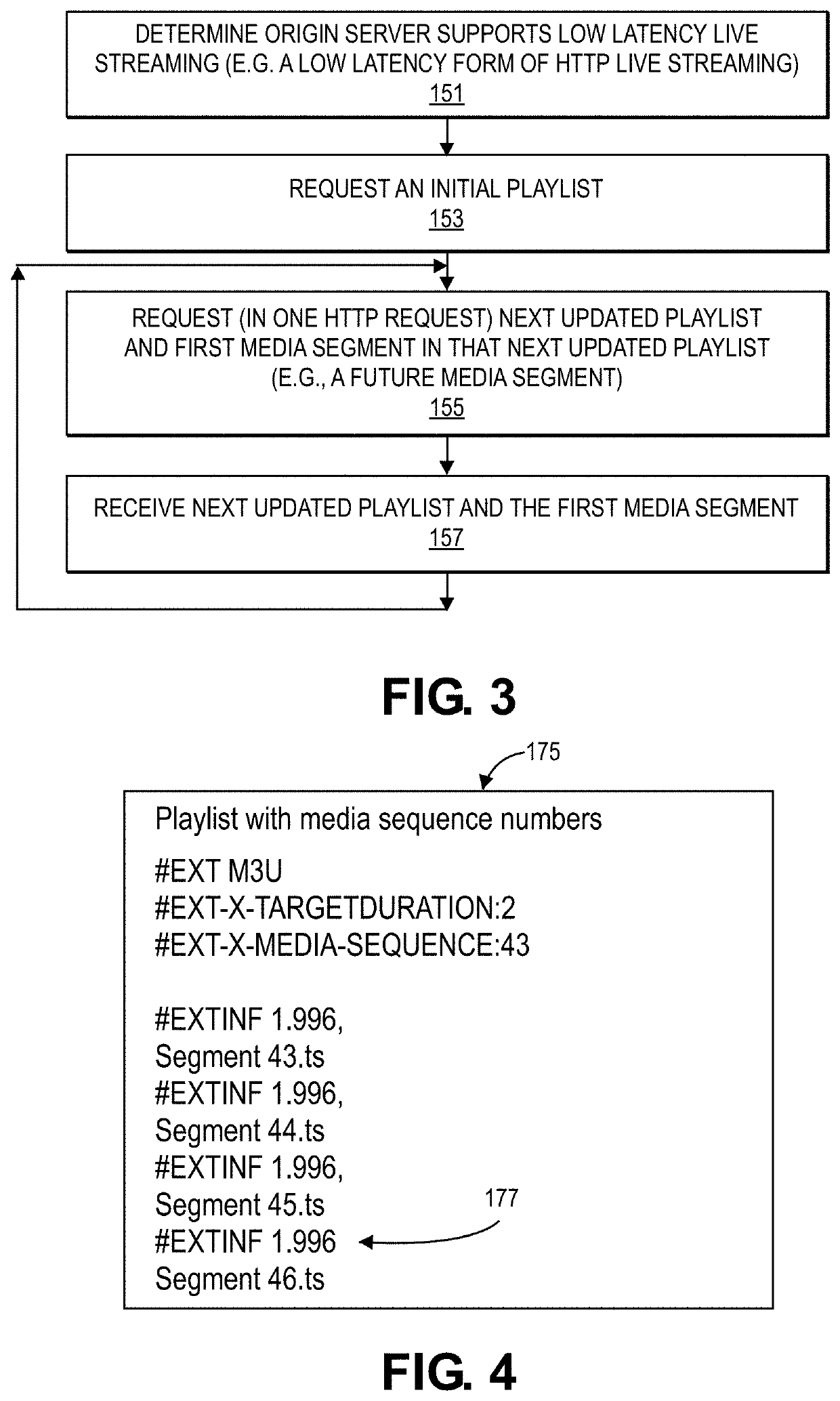
ActiveUS20200267437A1Reduce latencyImproving delivery and processingTransmissionSelective content distributionMediaFLOTransmission system
Content streaming systems, such as systems that use HTTP compliant requests to obtain media segments for presentation of the content on a device. These content streaming systems can be optimized to reduce latency to a low level so that live events can be streamed to receiving devices in such a manner so that the time between an action in the live event and the presentation of the action on a receiving device that receives the streamed content is less than about 10 seconds. A client device can use rendition reports to tune-in to a new rendition (at a first bit rate) after presenting a prior rendition (of a second bit rate) when switching between the different bit rates; also, for example, a client device can use playlist annotations that indicate independent frames to avoid downloading depending frame media segments when switching between different renditions.
Owner:APPLE INC
Plasma display apparatus
InactiveUS20070182298A1Reducing unnecessary radiationReduce radiationIncadescent screens/filtersMagnetic/electric field screeningElectromagnetic shieldingMaterials science
Disclosed is an optical filter having an electromagnetic shield capable of shielding unnecessary radiation of electromagnetic waves from a PDP, in which satisfactory reduction of undesired radiation is achieved even by employing a relatively low price optical filter. A plasma display apparatus of the invention includes: a conductive rear surface cover covering a rear surface of a plasma display panel; an optical filter provided with an conductive layer having a surface resistance of 0.5 Ω / square or above, which is disposed at the front surface of the plasma display panel and serves to reduce leakage of electromagnetic waves from the plasma display panel; optical filter protecting members electrically connected with the rear surface cover, for protecting / retaining the optical filter; and a conductive body having elasticity, which is interposed between the optical filter and the optical filter protecting member. A plurality of bosses are formed in the optical filter protecting members. A part of the elastic conductive body is compressed by the bosses and connection resistance with the elastic conductive body is reduced.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
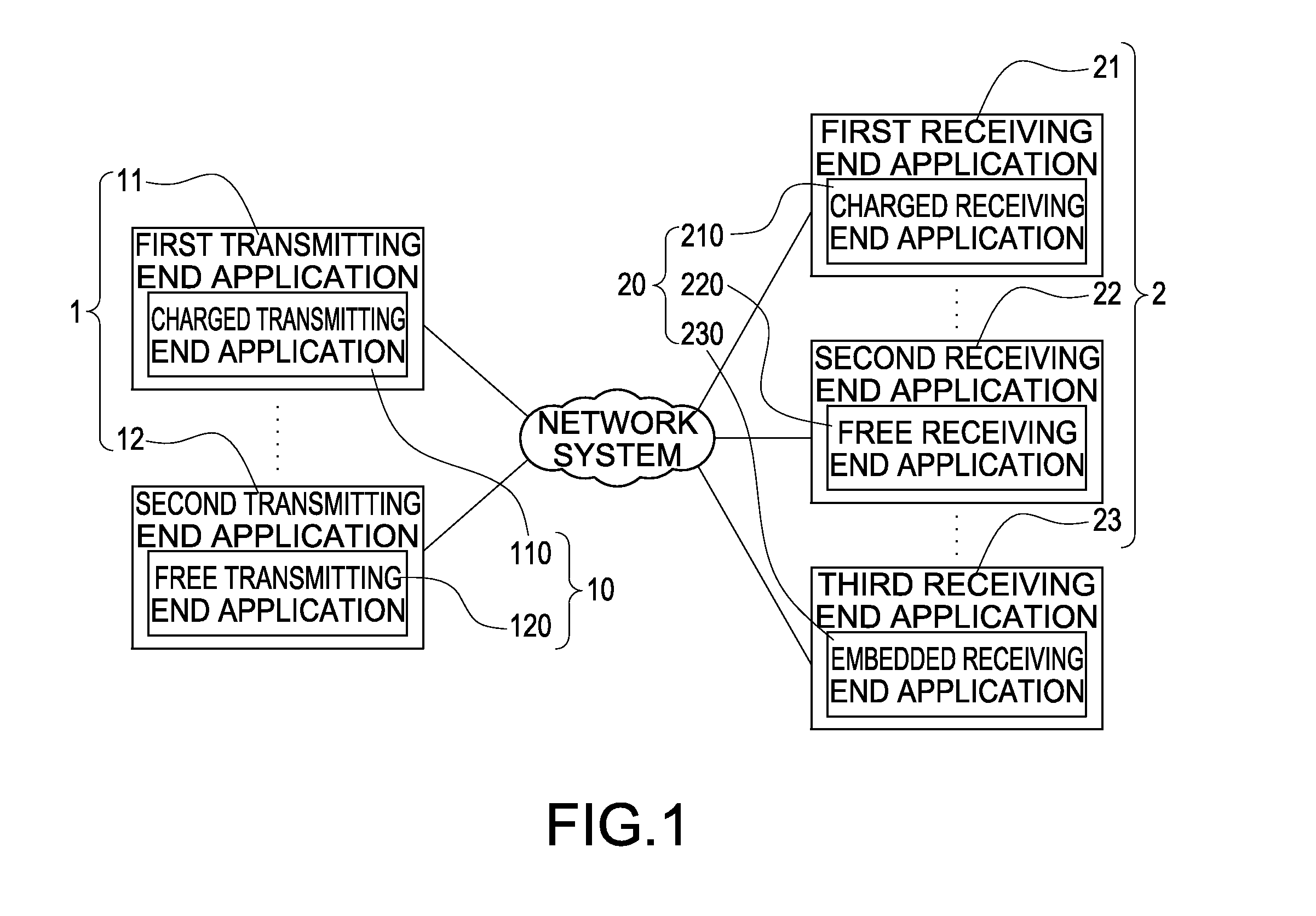
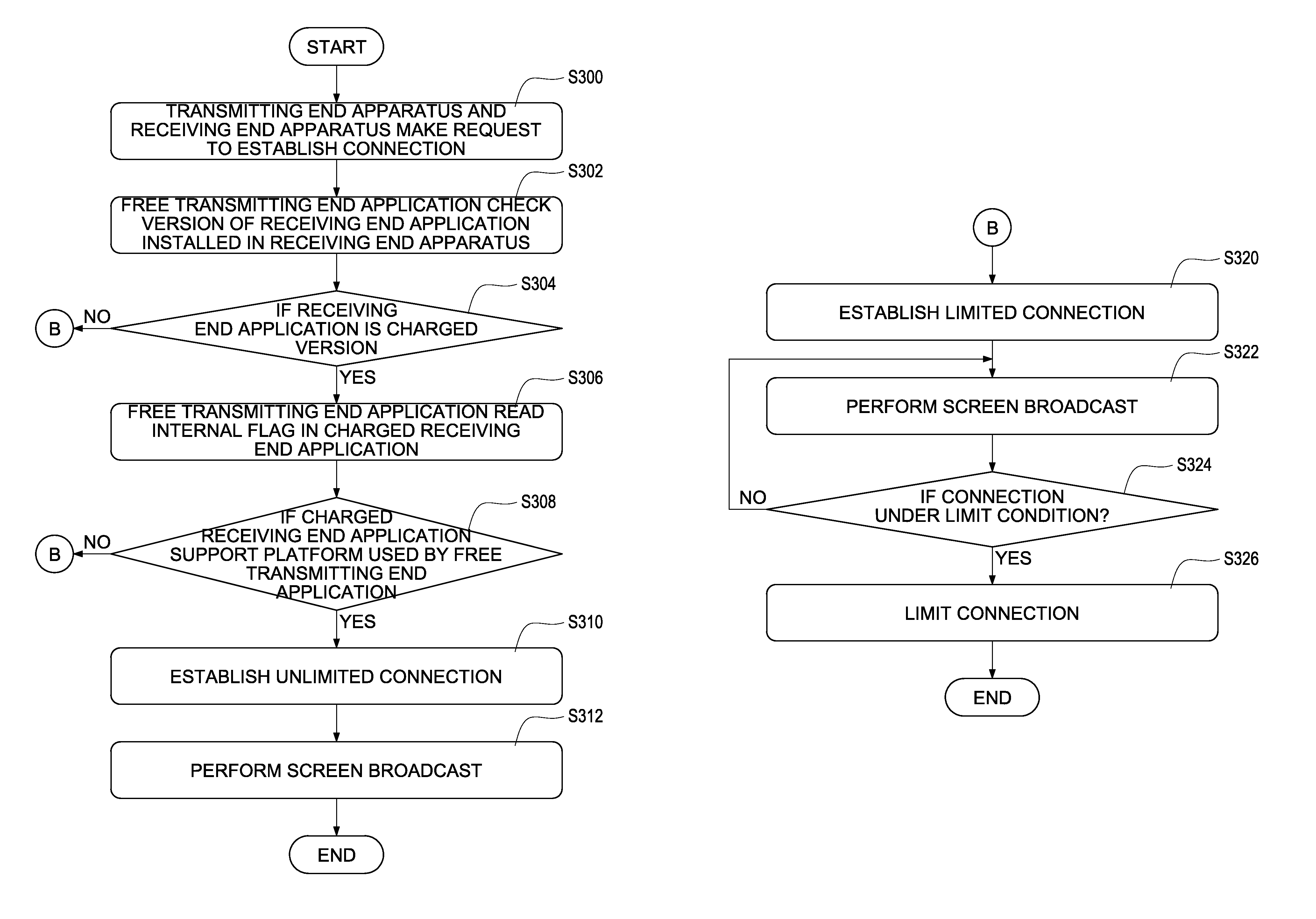
Method of establishing charged connection using screen sharing application between multi- platforms
ActiveUS20130054815A1Protect interestsConnection resistanceComplete banking machinesPublic key for secure communicationScreen sharingMulti platform
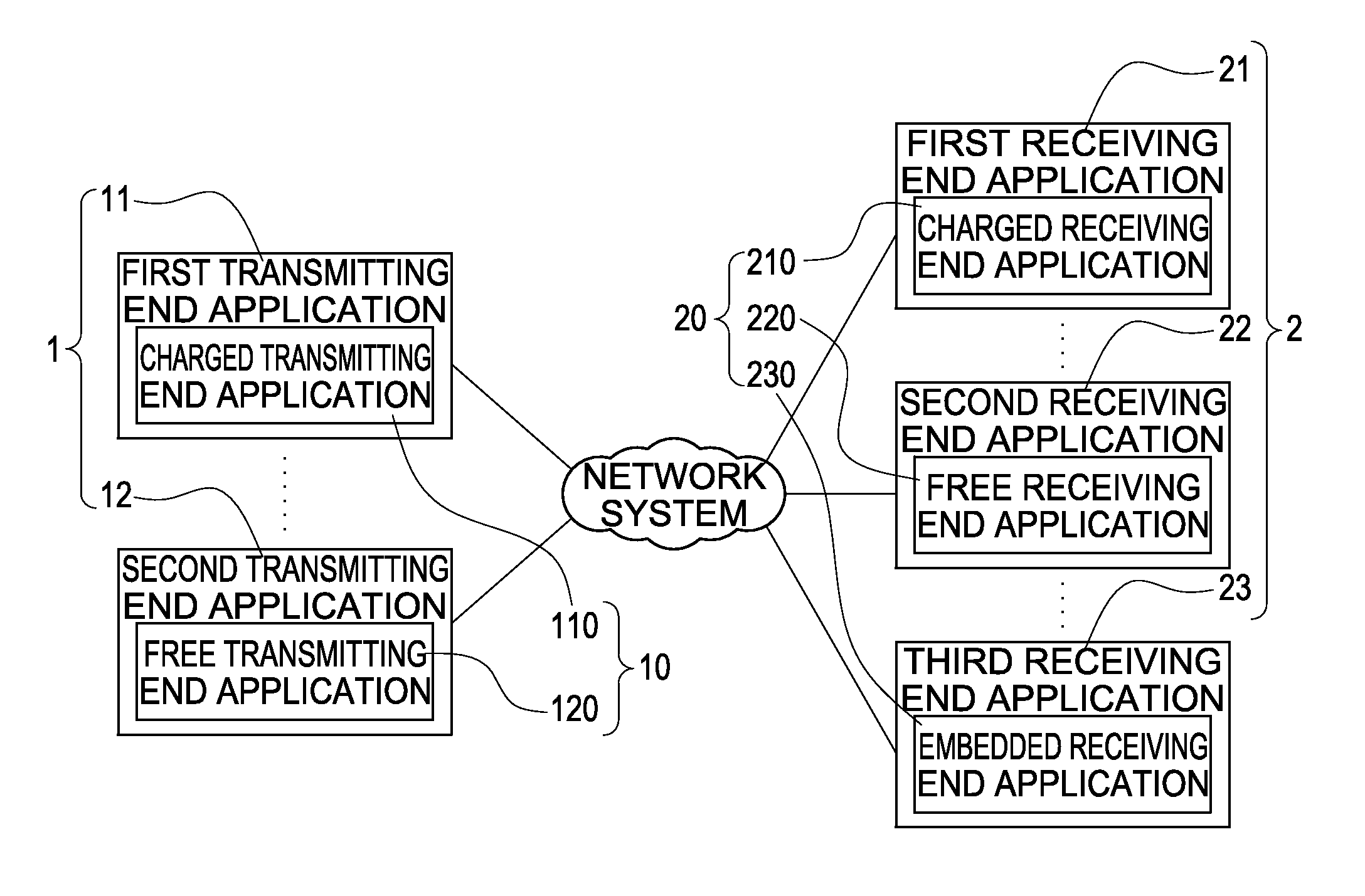
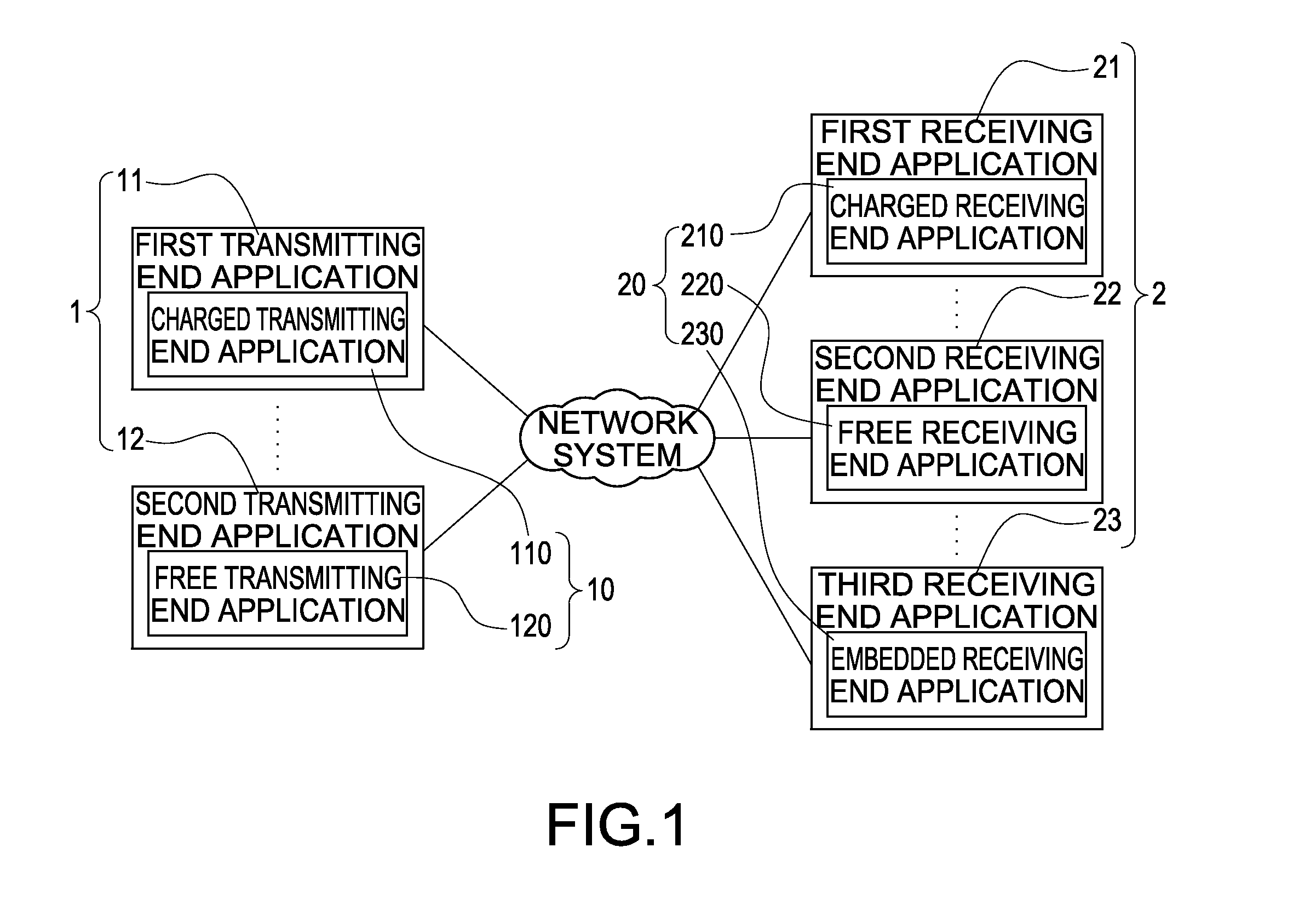
A method of establishing a charged connection using a screen sharing application between multi-platforms is disclosed. A transmitting end application is installed in a transmitting end apparatus of a sharing source. A receiving end application is installed in a receiving end apparatus of a sharing target. If the transmitting end application is a charged version, an unlimited connection is established for performing screen sharing between the transmitting end apparatus and any receiving end apparatus. If the transmitting end application is a free version, the method further confirms if the receiving end application is a charged version for deciding whether a limited connection or an unlimited connection should be established. Thus, it is assured that either the transmitting end application or the receiving end application is a charged version, the interests of application developers are protected and users are free from paying twice for establishing one connection.
Owner:BARCO NV
Hybrid approach for performance enhancing proxies
ActiveUS20150372908A1Improve performanceConnection resistanceData switching by path configurationNetwork data managementHybrid approachSemantics
There are provided a transparent performance enhancing proxy, a method for operating a transparent performance enhancing proxy between a source device and a destination device, and corresponding computer program product. The method includes preserving, without translation, packet header information of a header for a packet received from the source device to be forwarded to the destination device. The method further includes during a transmission control protocol connection setup phase for the packet, preserving transmission control protocol connection semantics. The method also includes during a transmission control protocol data transfer phase for the packet, running a transmission control protocol by masquerading as the source device to the destination device and masquerading as the destination device to the source device to transmit the packet to the destination device with the preserved packet header information.
Owner:IBM CORP
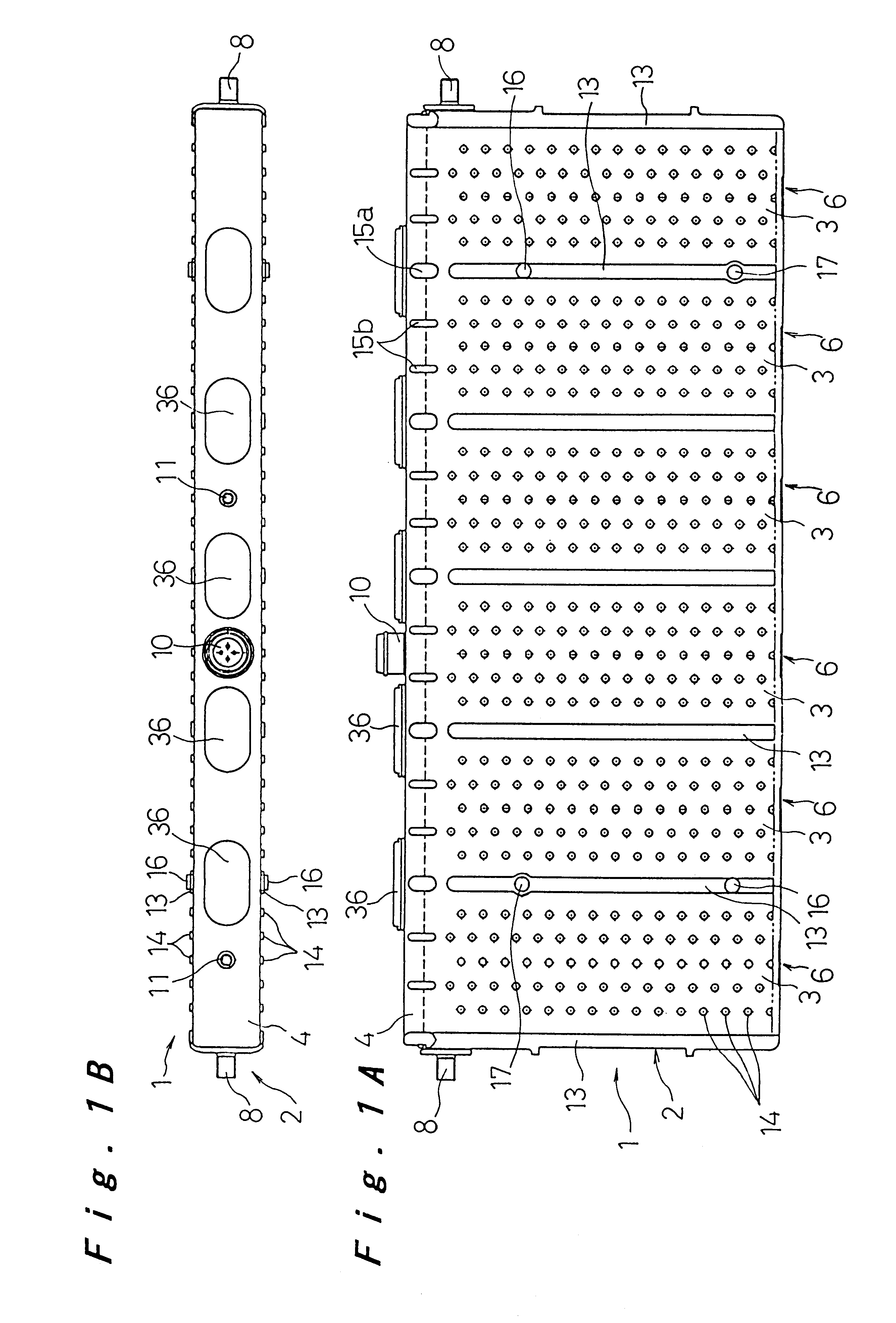
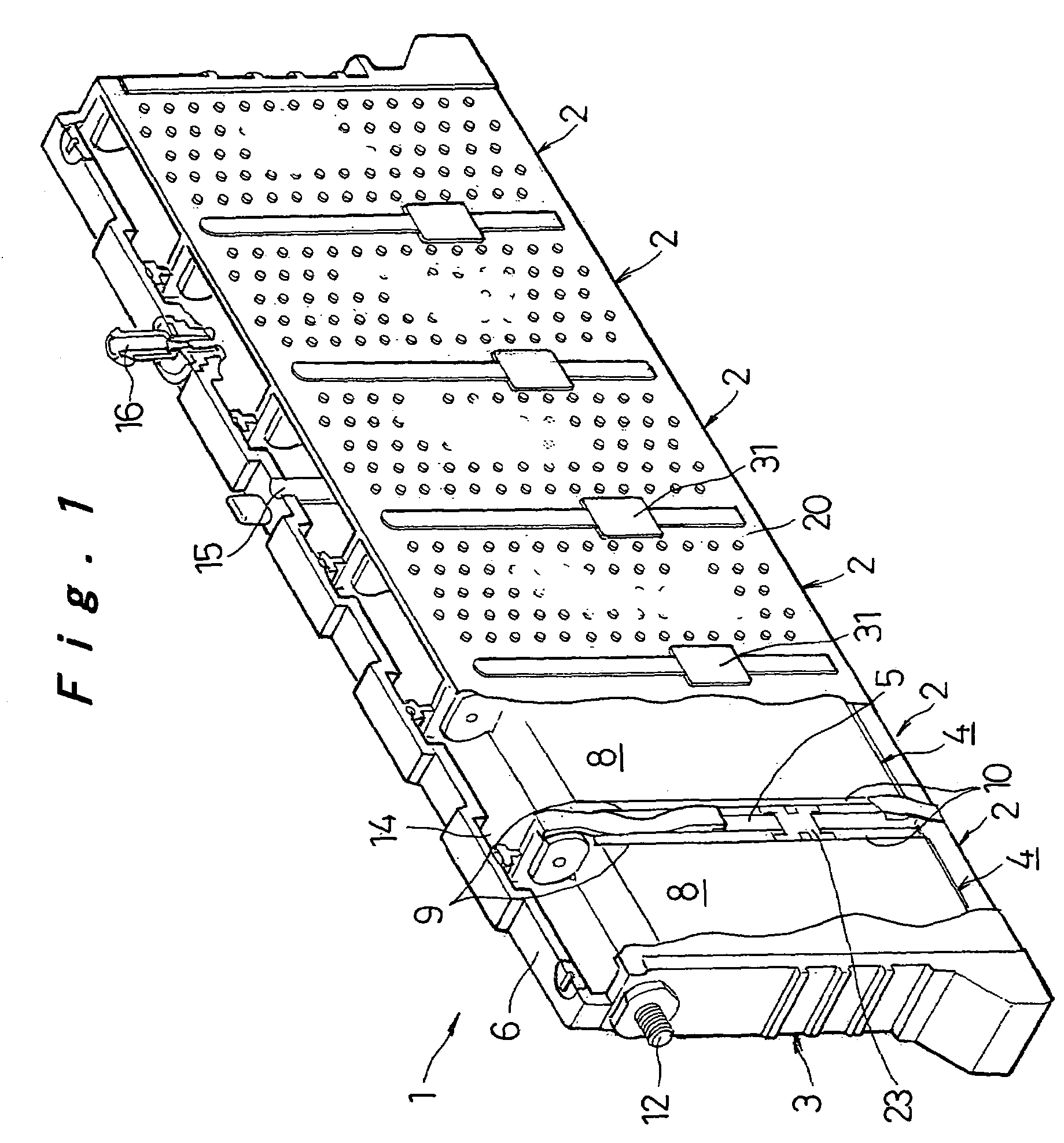
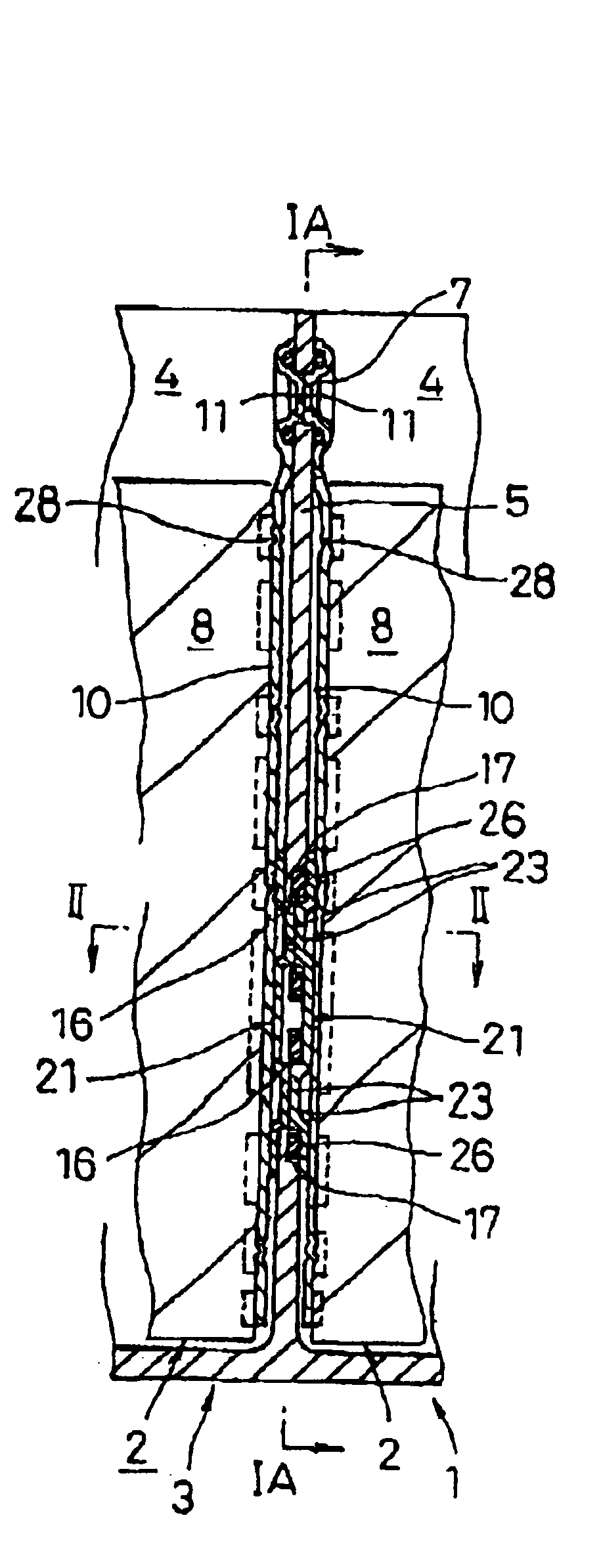
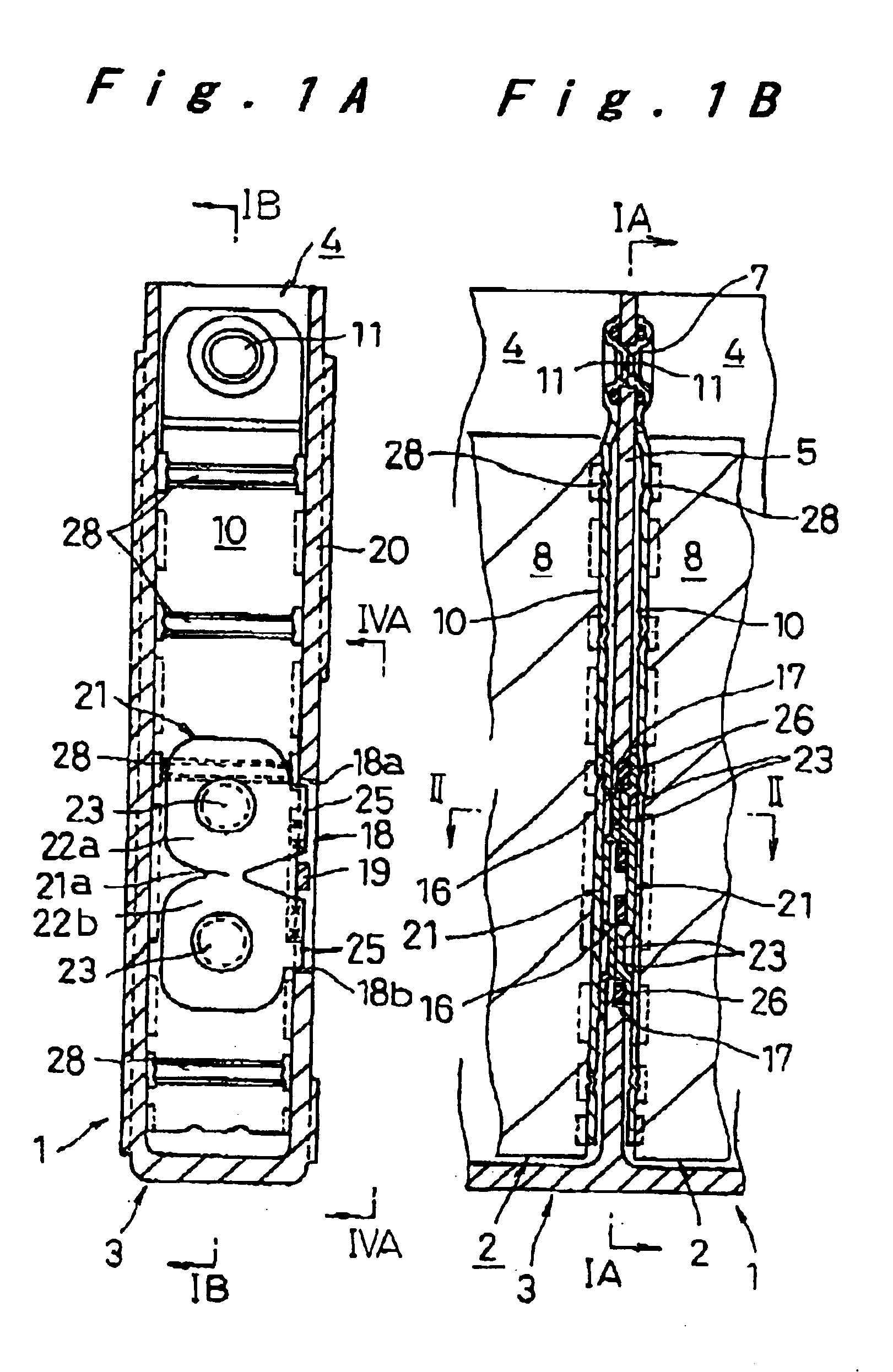
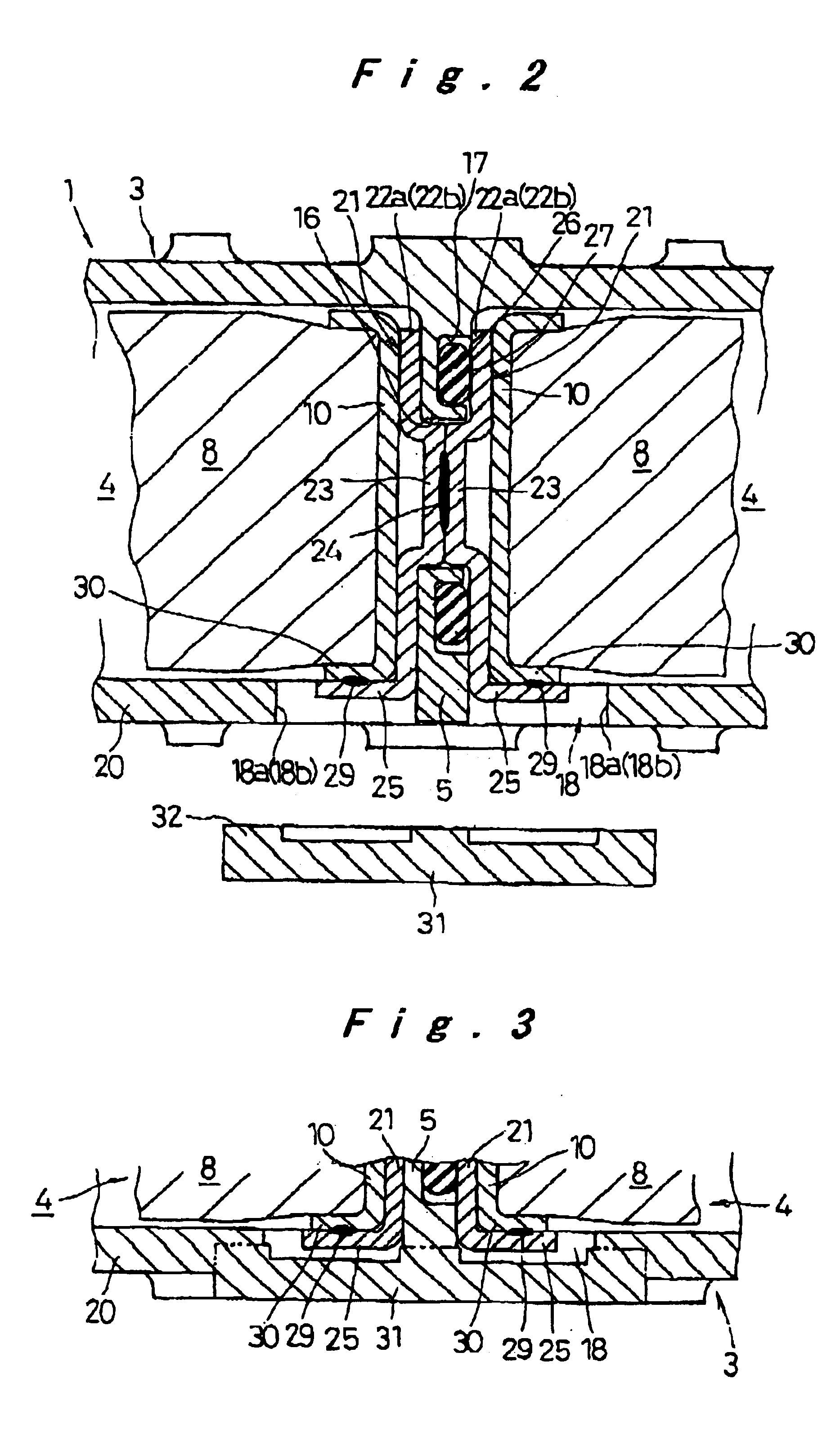
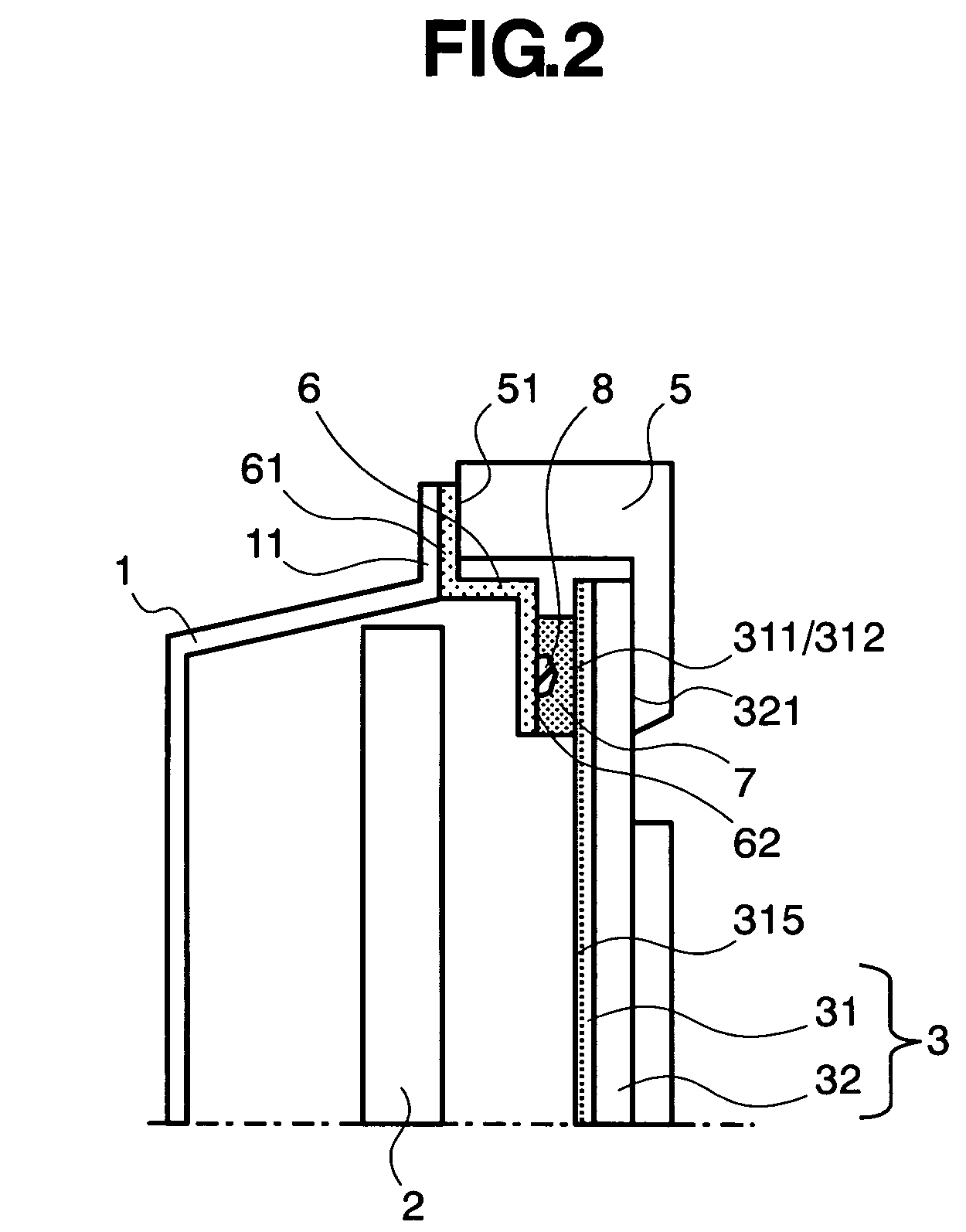
Prismatic sealed battery
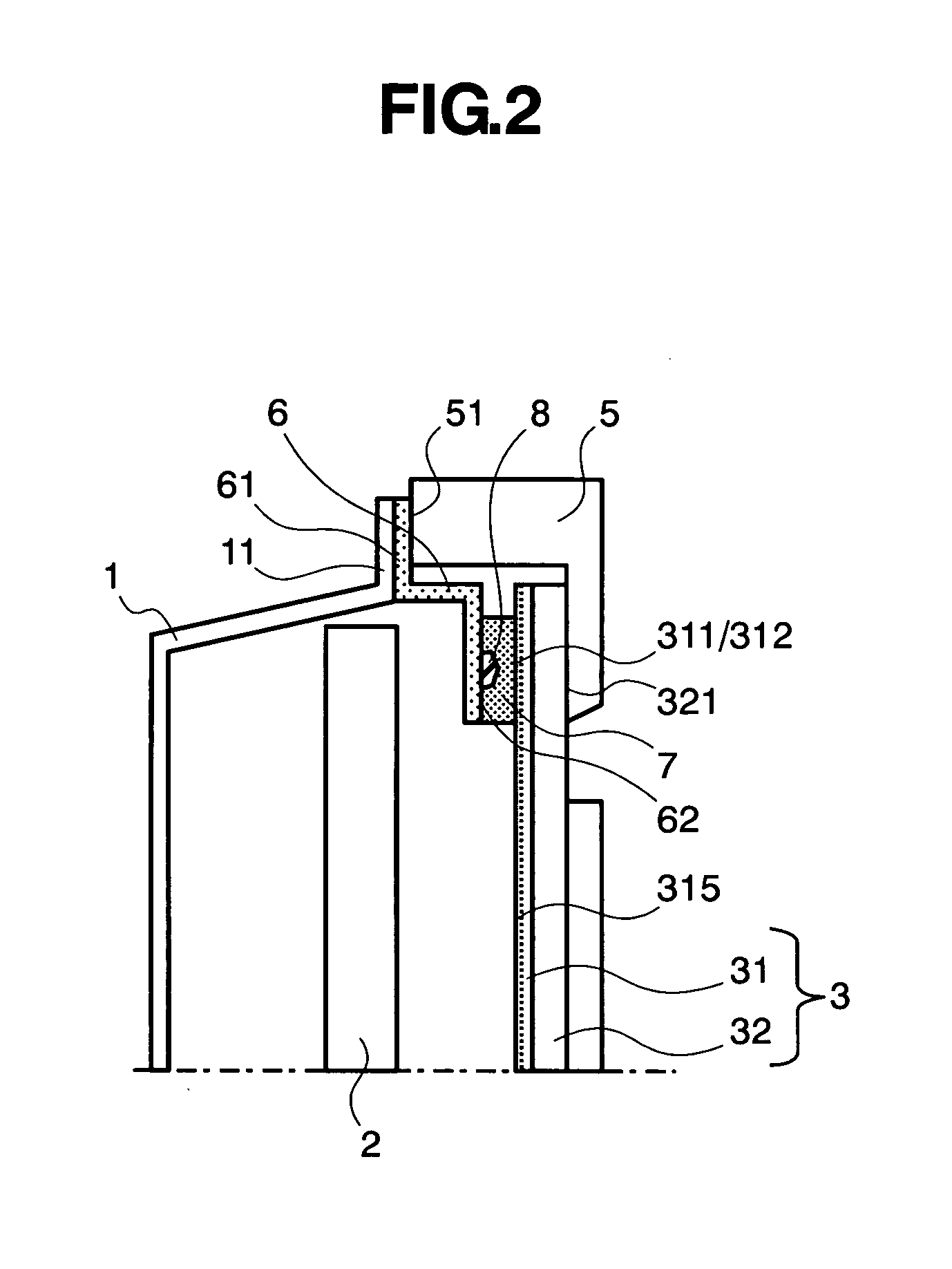
InactiveUS7291423B2High power outputReduce connection resistanceSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsElectric connector introductionInternal resistancePower output
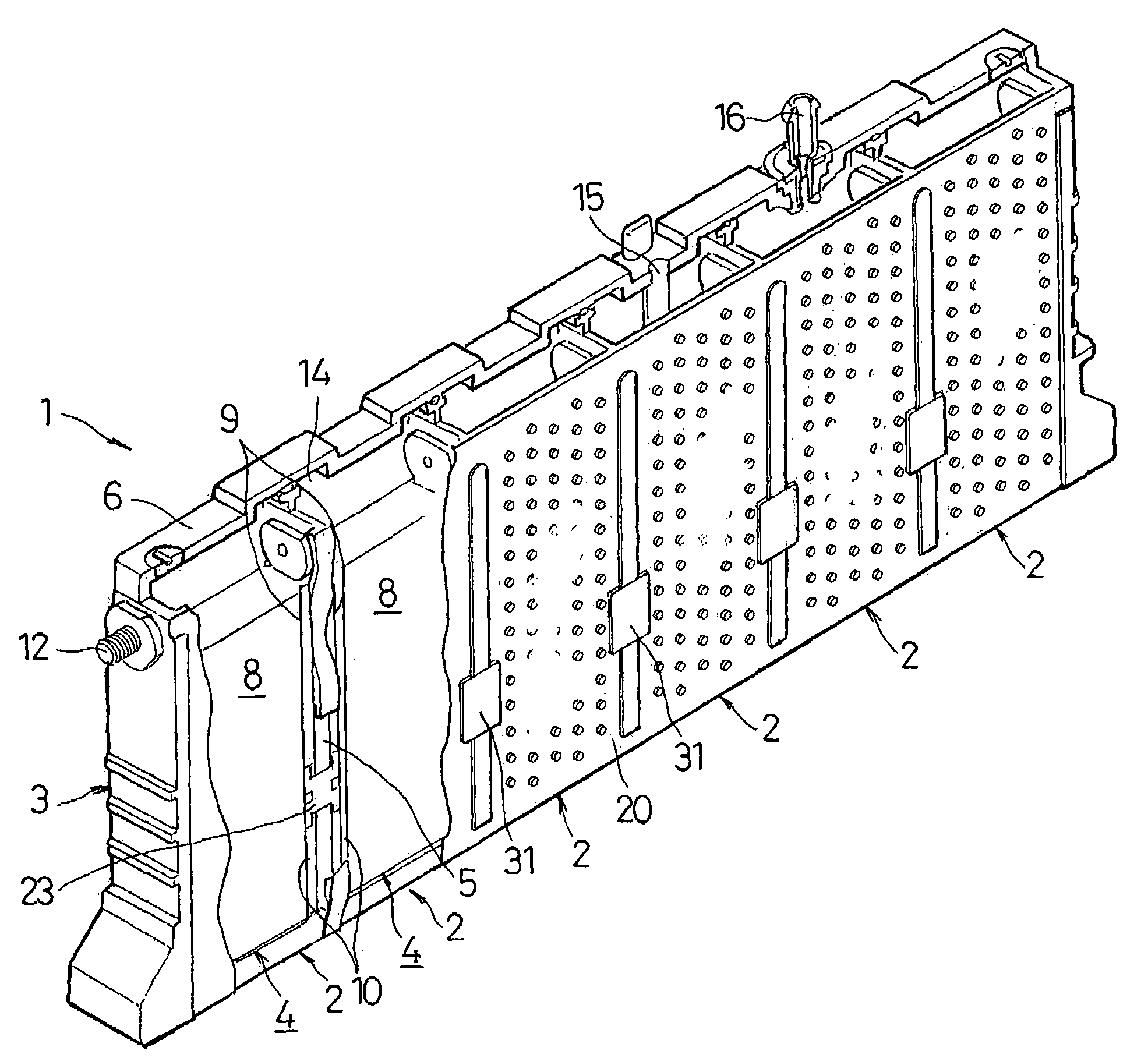
A prismatic sealed battery has a prismatic battery case (3) which includes a plurality of prismatic containers (4) coupled in a row via partitions (5), electrode plate assemblies (8), and collectors (10) which are joined to lead portions on both sides of the electrode plate assemblies (8). Each container (4) contains the electrode plate assembly (8) to which said collectors 10 are joined. An opening (21) is formed in at least one side wall (20) of the prismatic battery case (3) and in a position where each partition (5) is disposed, in such a manner as to face the containers (4) on both sides, and a conductive connection member (23) disposed in the opening (21) is connected to the collectors (10, 10) on both sides of the partition (5). Since the current-carrying path between the electrode plate assemblies (8) becomes short, internal resistance decreases, and hence internal resistance per cell (2) is reduced. Even and full use of the whole electrode plate assembly (8) achieves higher power output.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
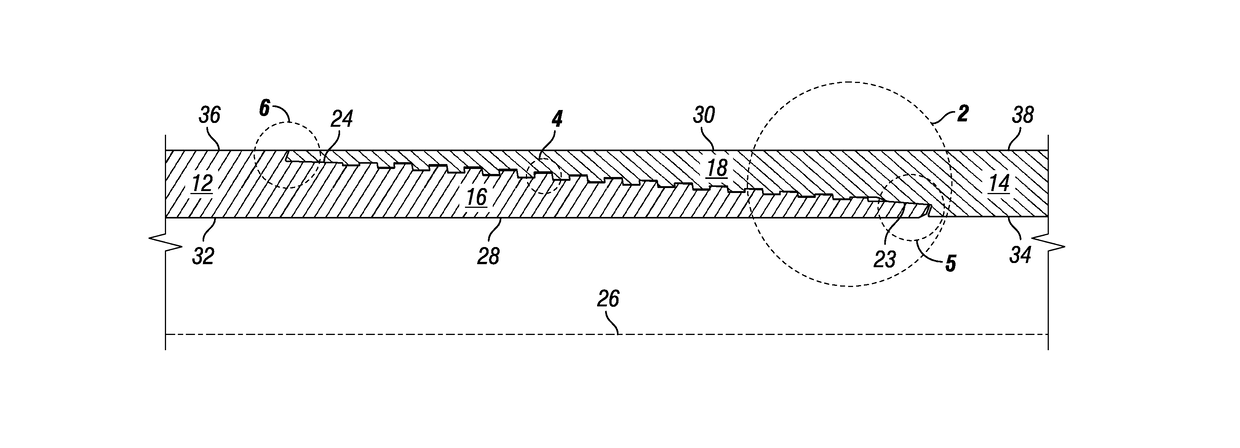
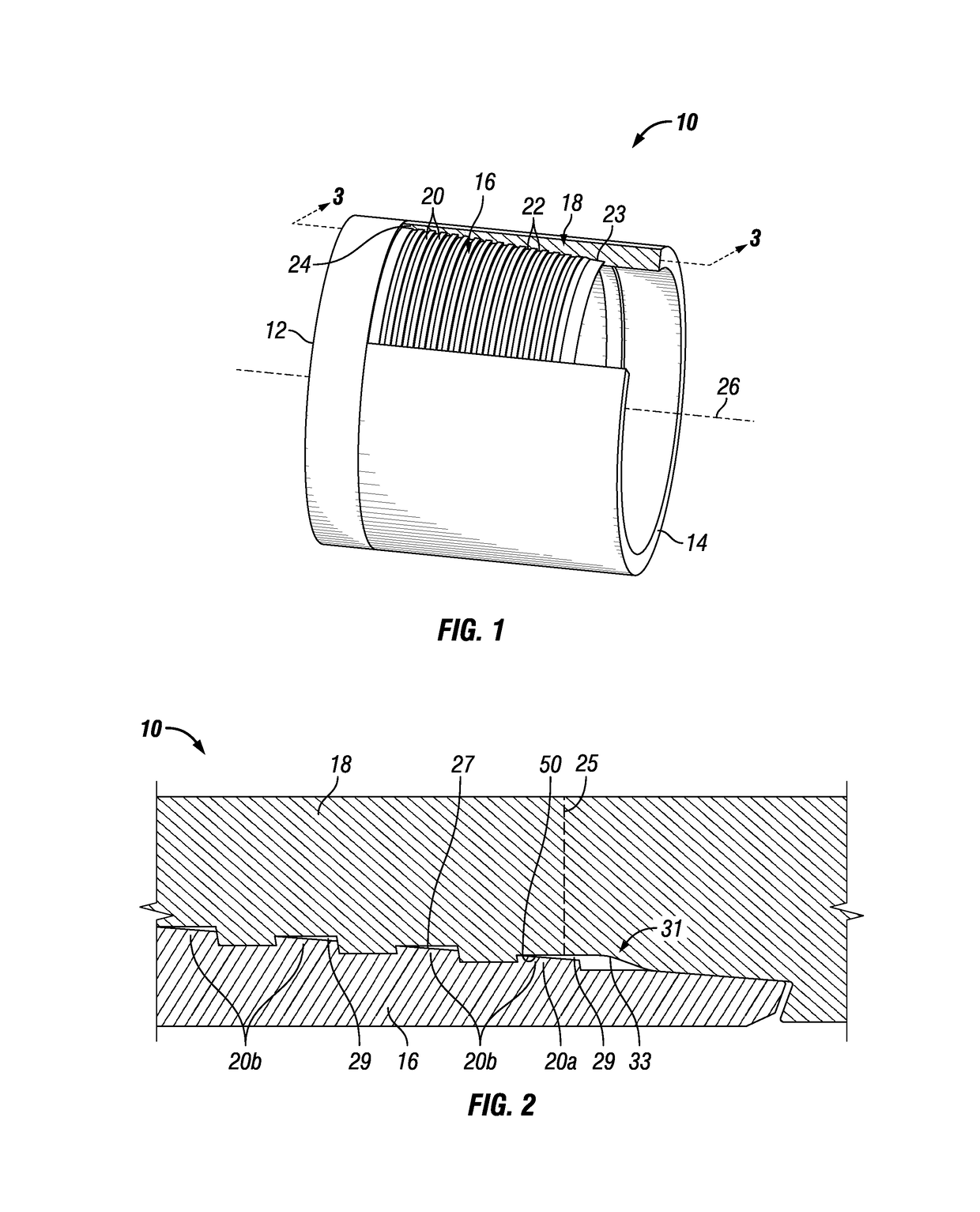
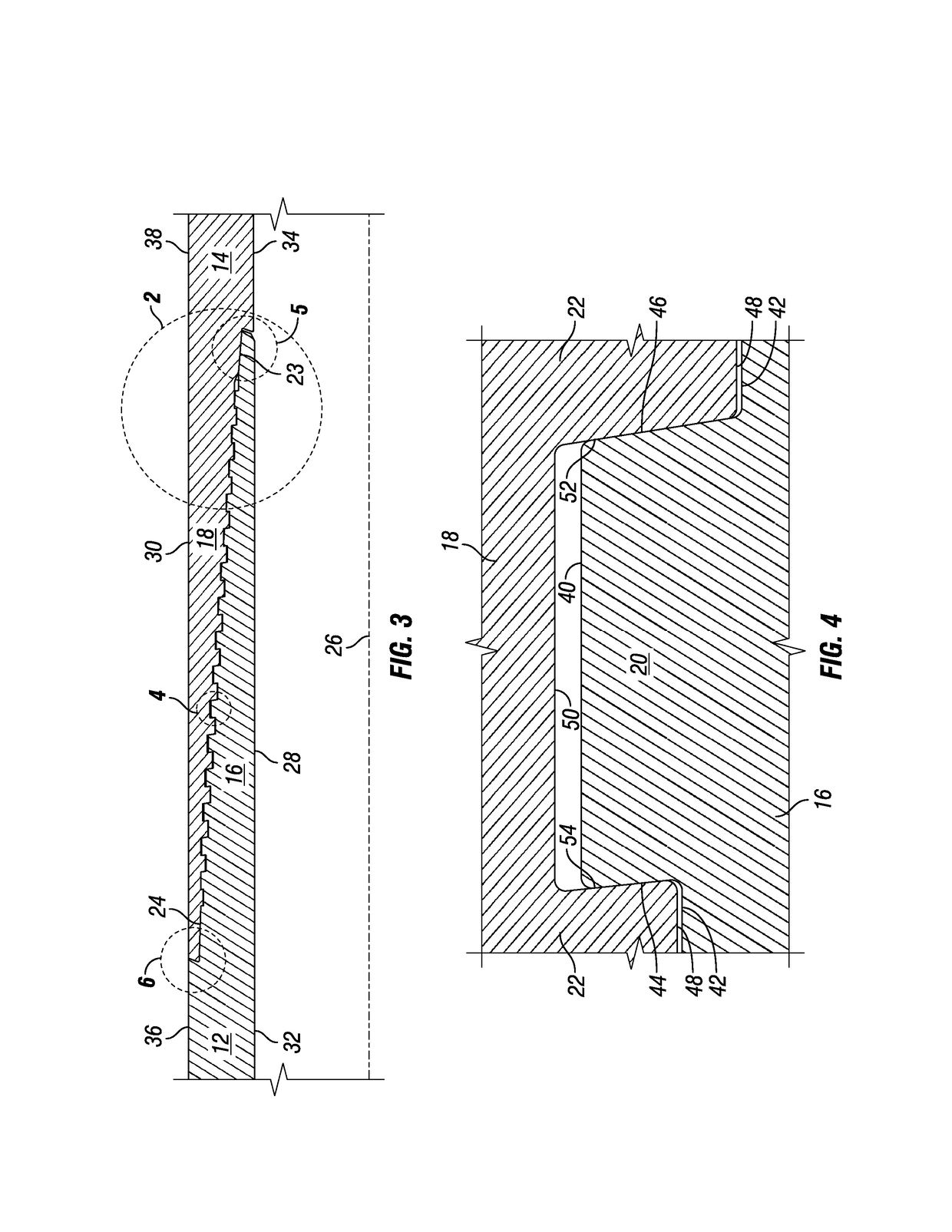
Threaded connection
ActiveUS20150167869A1Restrict movementReduce distortionDrilling rodsHose connectionsEngineeringScrew thread
A threaded collection having a straight central axis, the connection including a plurality of pin threads, each pin thread having a root and a crest, and a box having a plurality of box threads, each box thread having a root and a crest. The crests of at least a portion of the box threads are curved so that when the pin threads are fully engaged with the box threads, there is a void between the roots of the pin threads and the corresponding curved crests of the box threads to reduce standoff caused by lubricant or other fluids becoming trapped between the threads as the connection is made up.
Owner:MARUBENI ITOCHU TUBULARS AMERICA
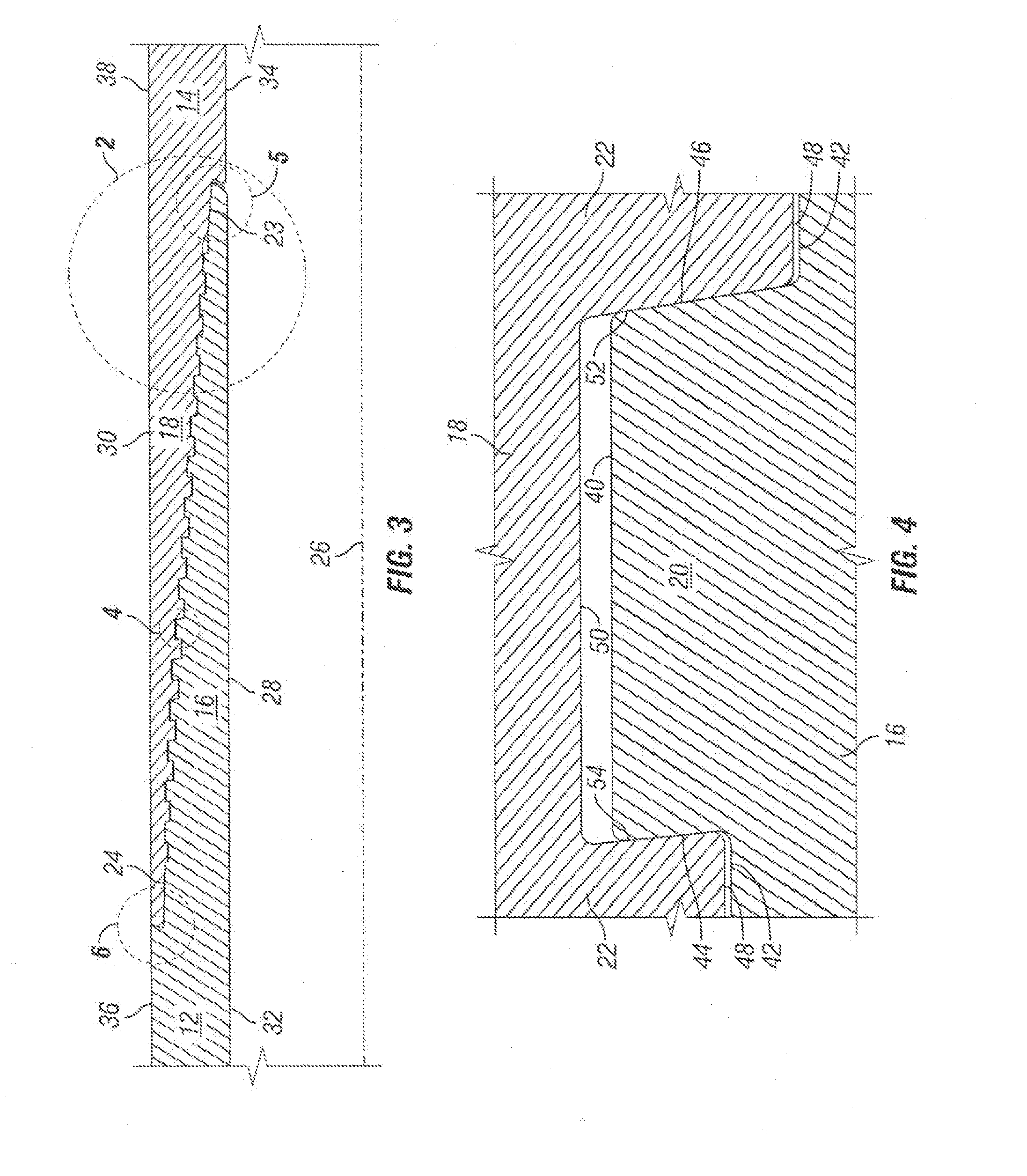
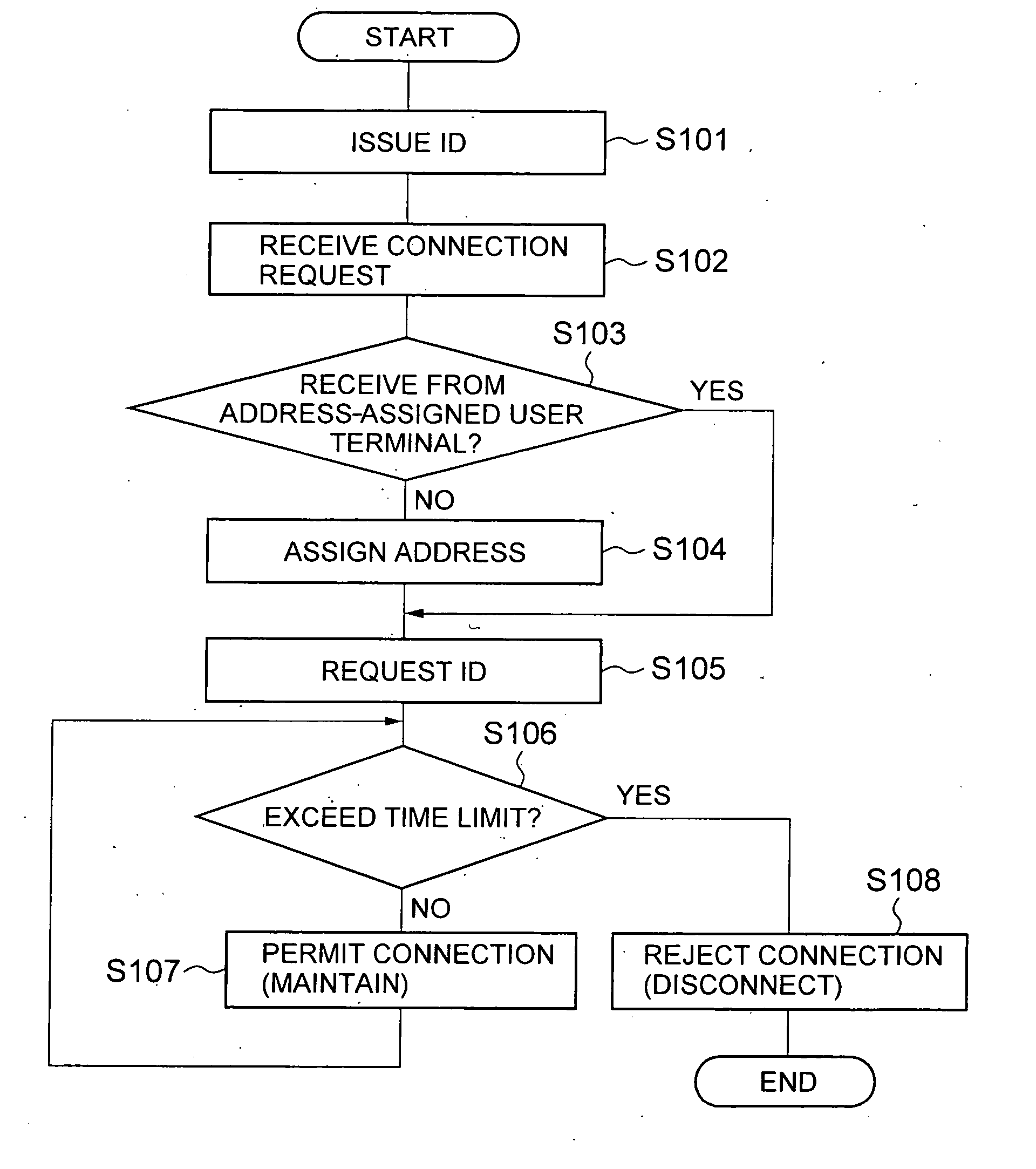
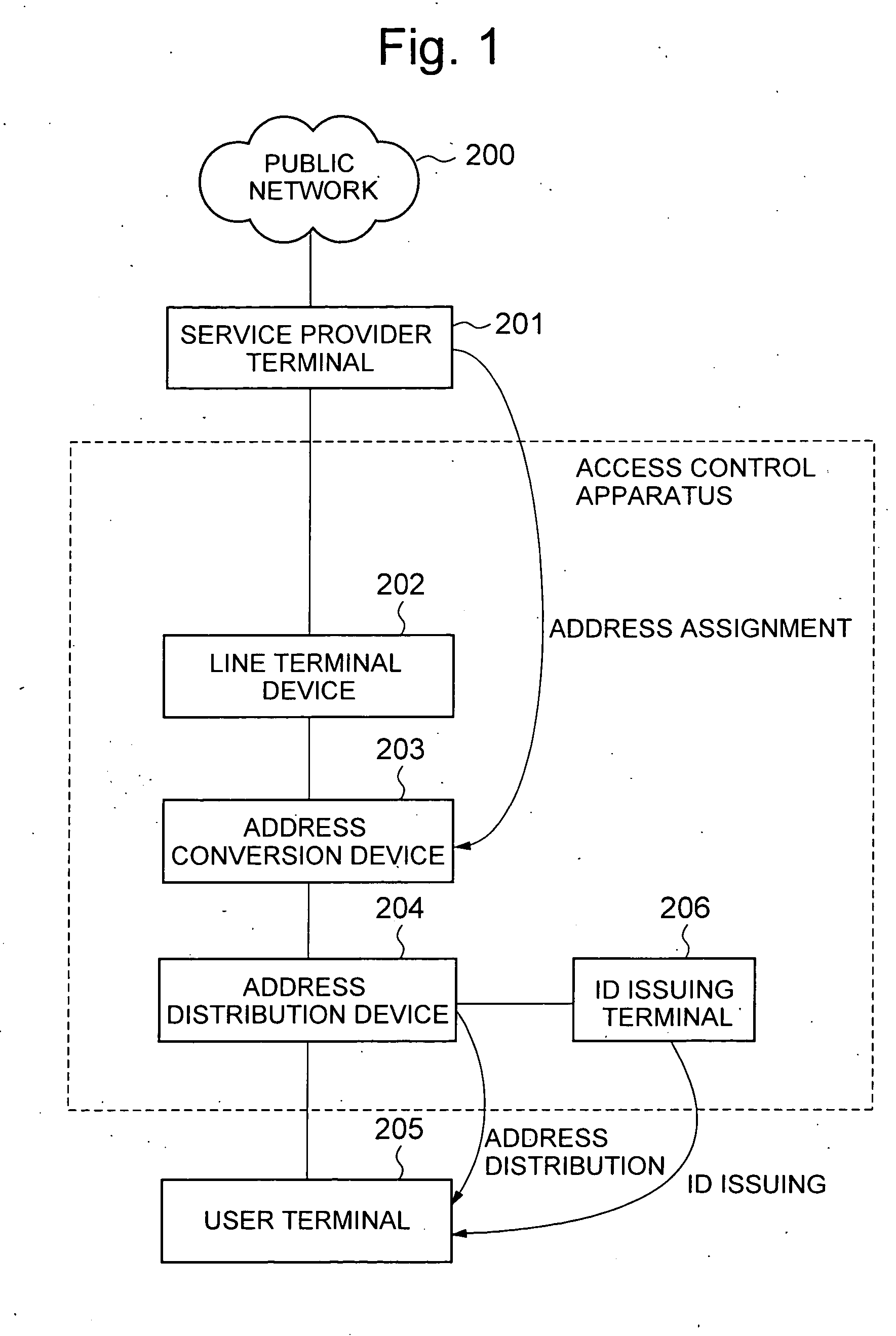
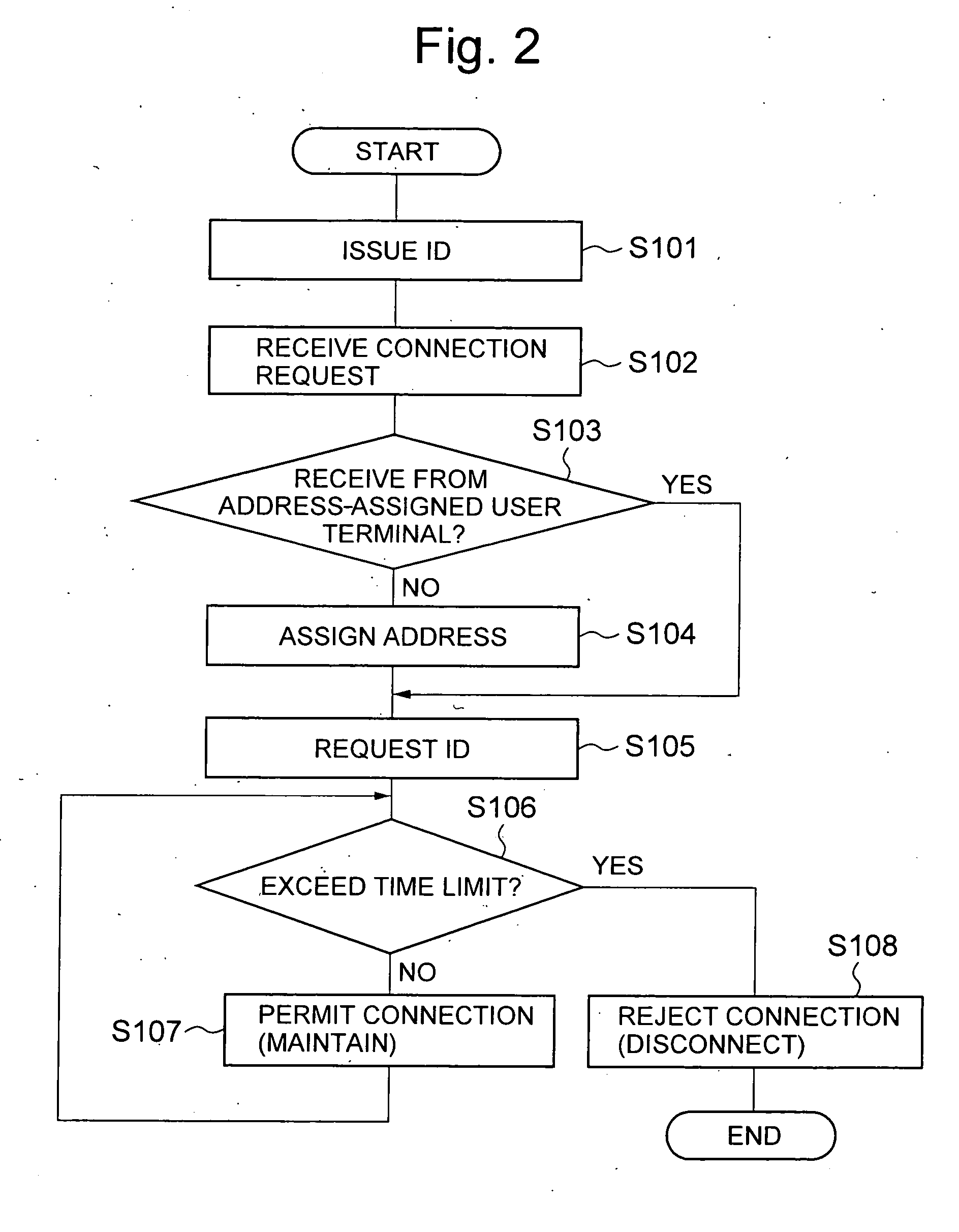
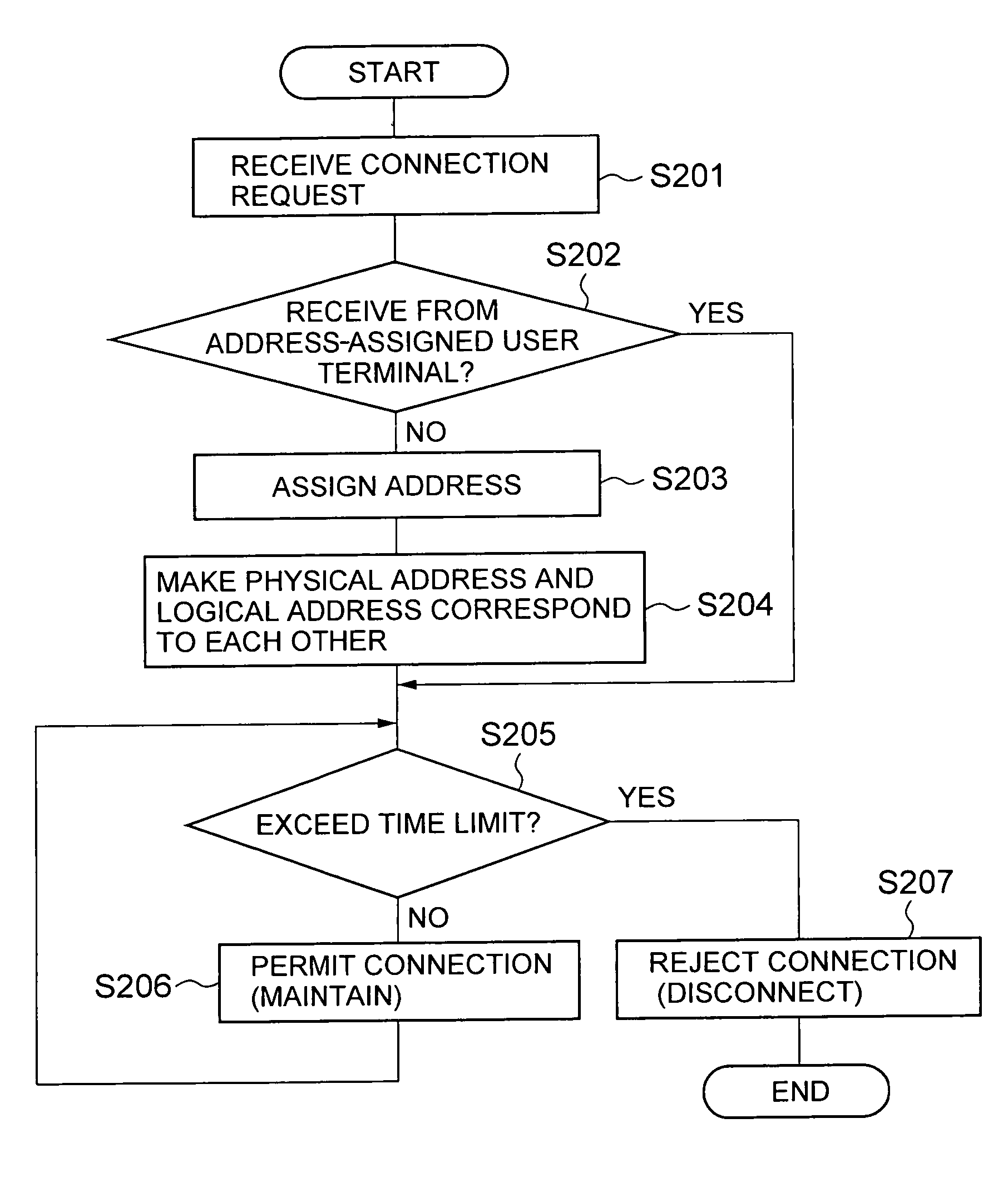
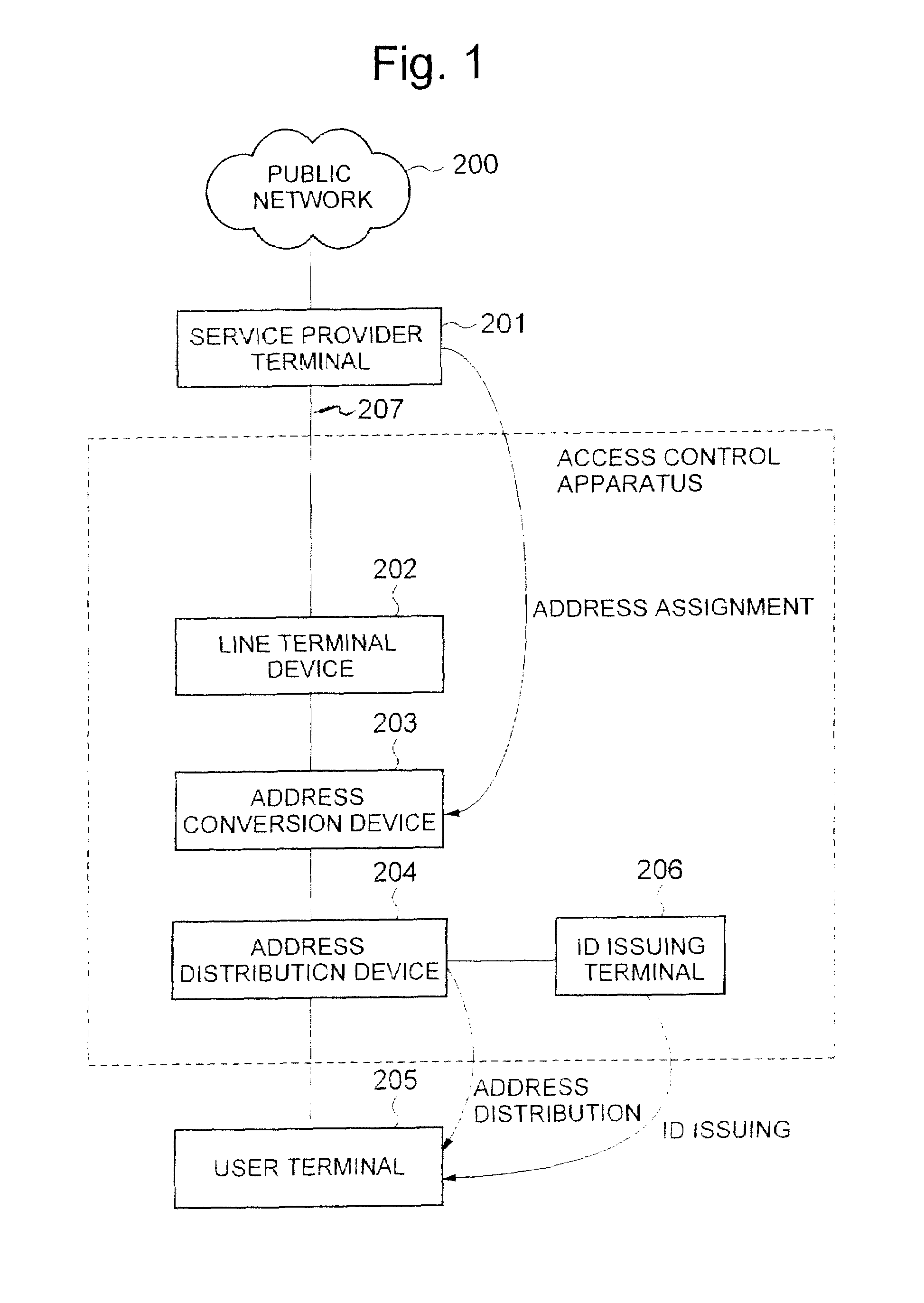
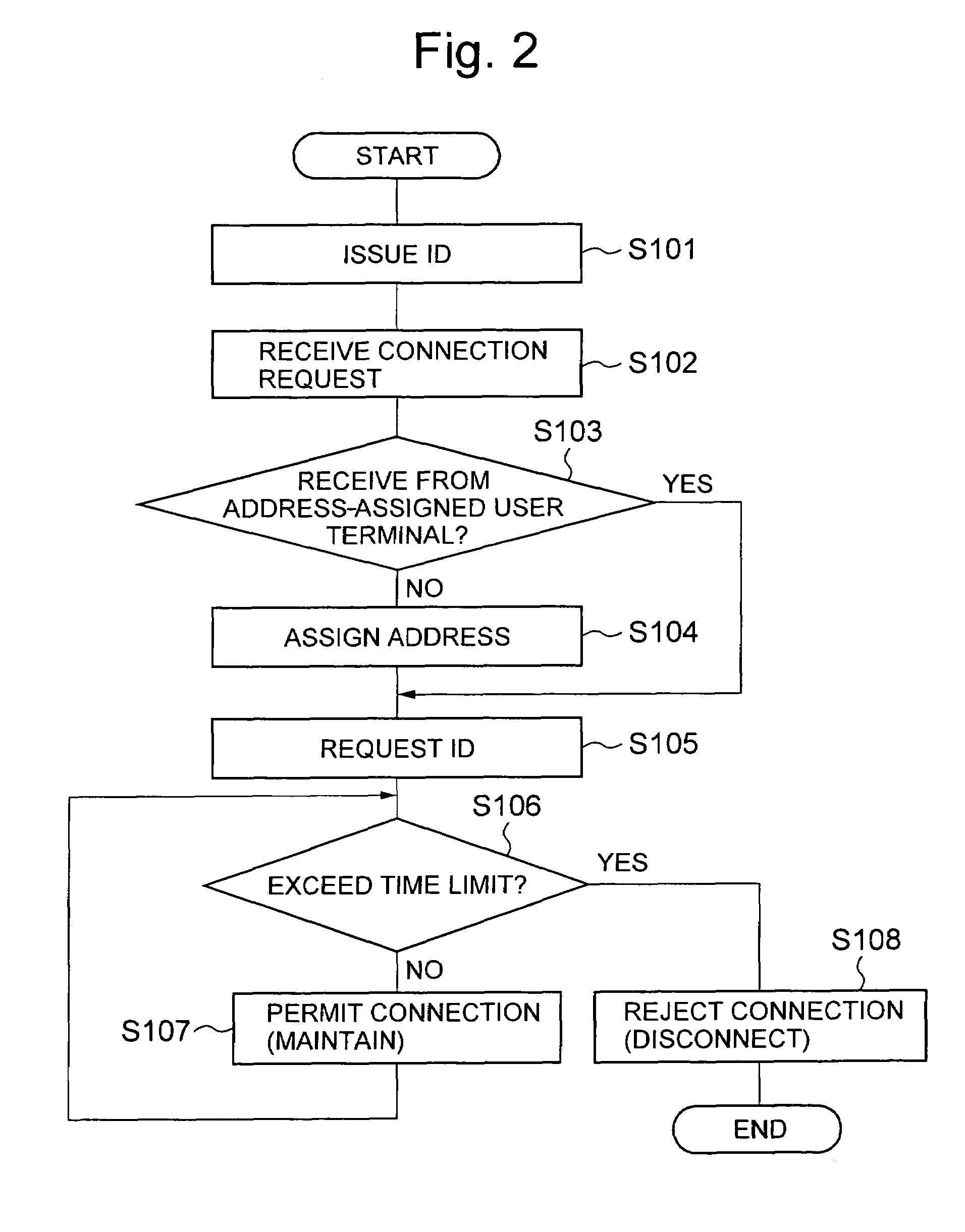
Access control apparatus and access control method
InactiveUS20050021717A1Limited connectionConnection resistanceDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationTime limitFinite time
An access control apparatus and method limits, to a finite time length, connection of a user terminal to a public network. The user terminal is disconnected from the public network when the use time of the logical address assigned to the user terminal reaches the time limit set for the logical address. The apparatus and method utilizes IDs issued to multiple users and IDs for multiple user terminals, and enables limiting connection to a public network from a user terminal that is connected by a leased circuit.
Owner:NEC CORP
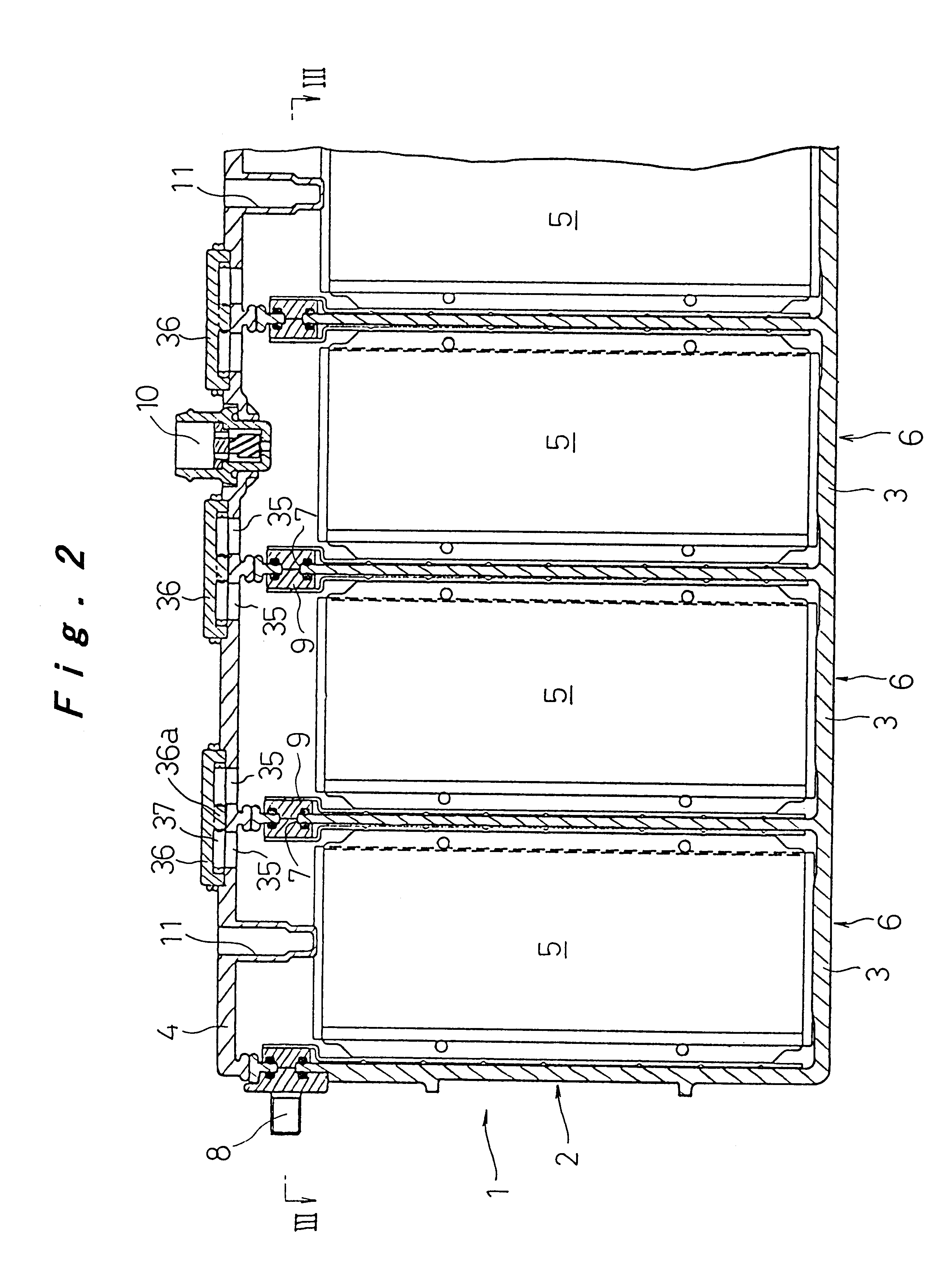
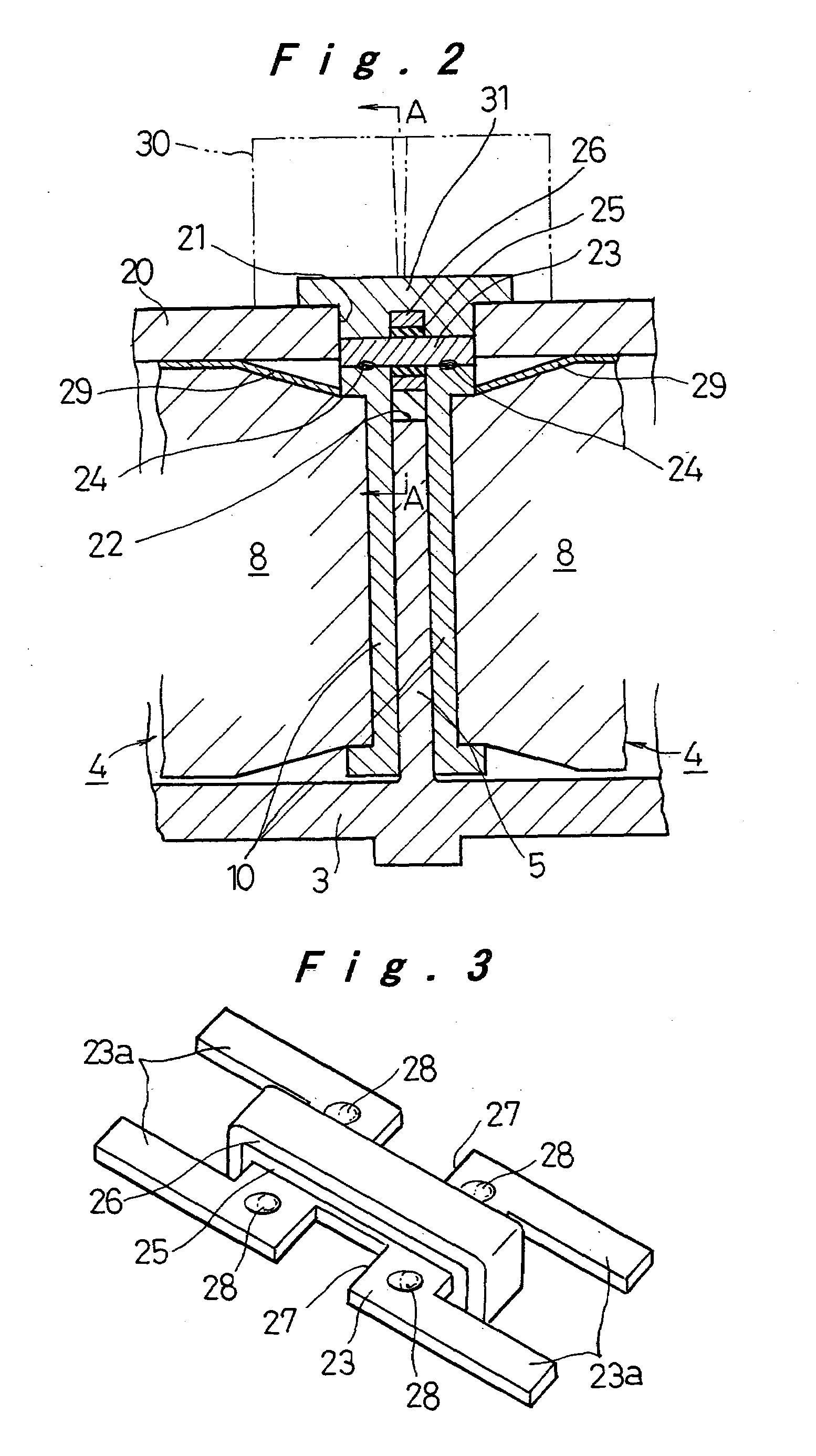
Sealed prismatic battery connected via openings with conductive connection plates
InactiveUS6946219B2Lower internal resistanceIncrease powerCell sealing materialsFlat cells groupingEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A sealed prismatic battery having a battery case made of a plurality of prismatic cell cases coupled together via partition walls, electrode plate groups, and collectors bonded to lead portions on both sides of the electrode plate groups. In at least one side wall of the battery case is formed openings at locations corresponding to the partition walls such as to open to the cell cases on both sides of the partition walls. Pairs of conductive connection plates are connected to each other through the partition walls and formed with connection pieces that face the openings. The collectors are connected together via the conductive connection plates, i.e., they are connected to the connection pieces after the electrode plate groups are encased in the cell cases, and the openings are sealed by sealing plates in a manner that separates the cell cases.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
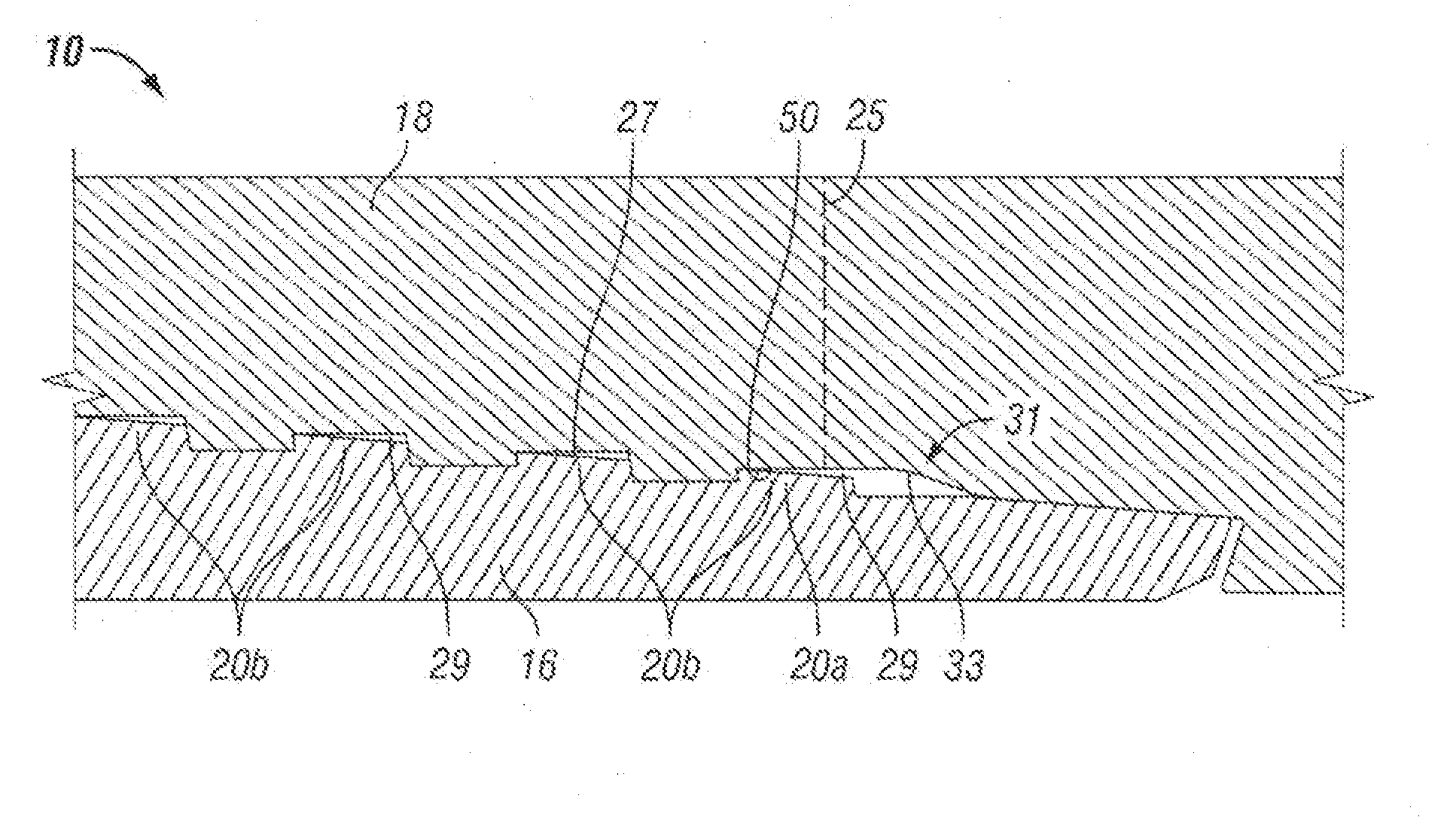
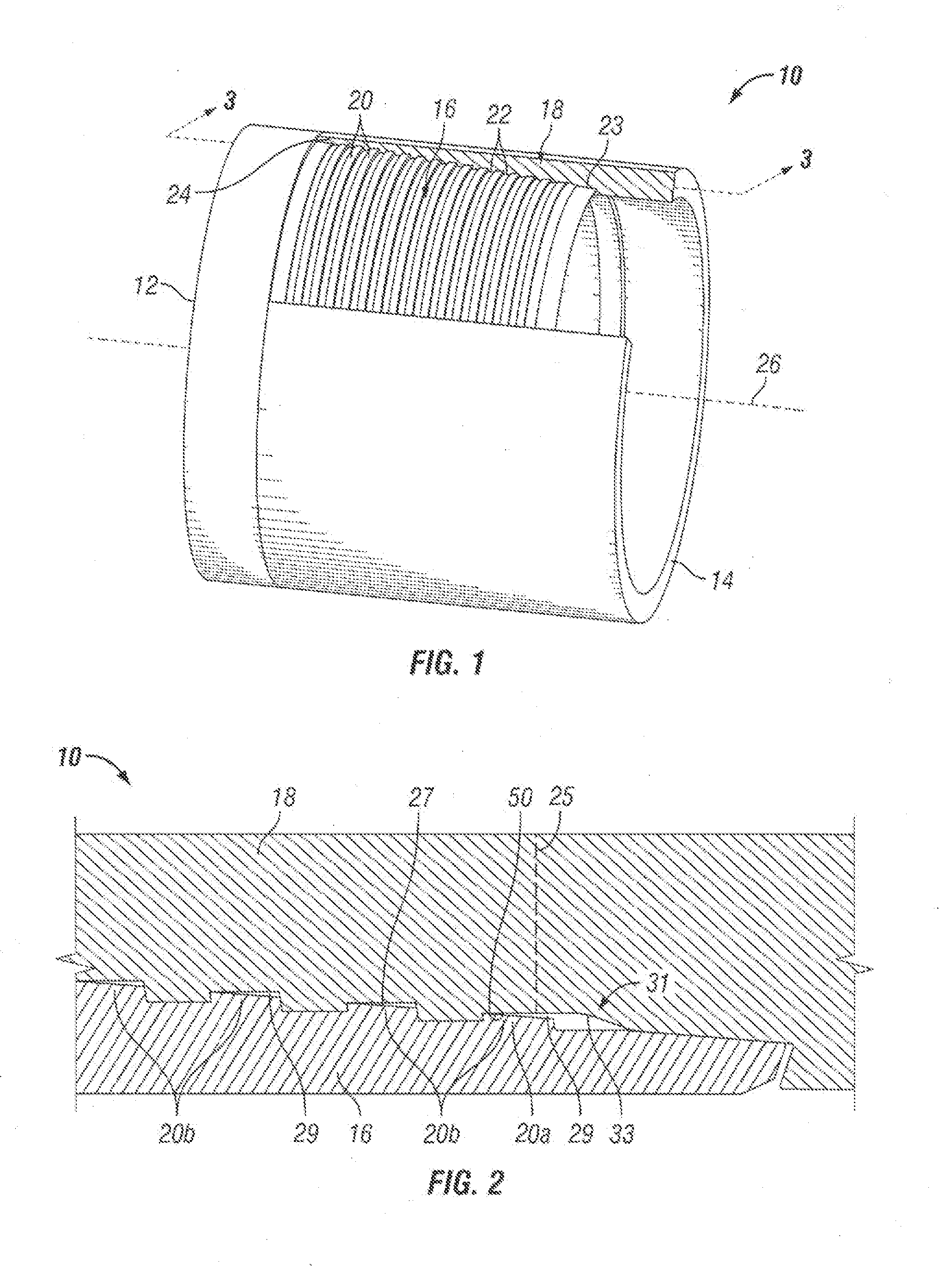
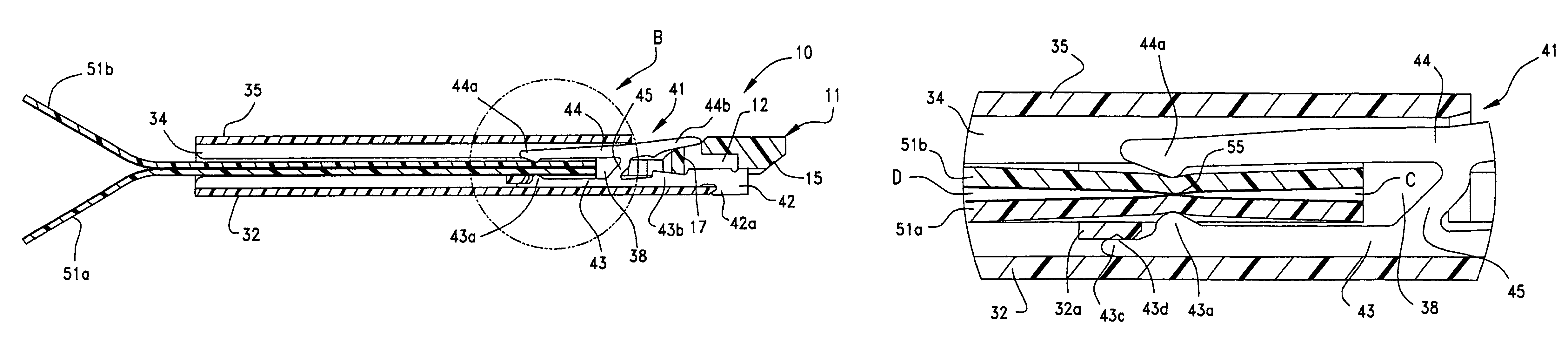
Relay connector
ActiveUS8079861B2Stable transmission characteristic of signalConnecting resistanceEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsElectric discharge tubesEngineeringActuator
A flat flexible cable connector (10) has a housing (31) with an insertion opening (33) in its front face. Two lengths of flexible cable (51a, 51b) are placed end to end and are inserted into the opening. The connector has terminals (41) with top and bottom opposing contact portions (43a, 44a) which are aligned with the exposed conductive leads on the two lengths of flexible cables. A moveable actuator (11) applies pressure to the terminal contact portions to effect a reliable connection between the flexible cables.
Owner:MOLEX INC
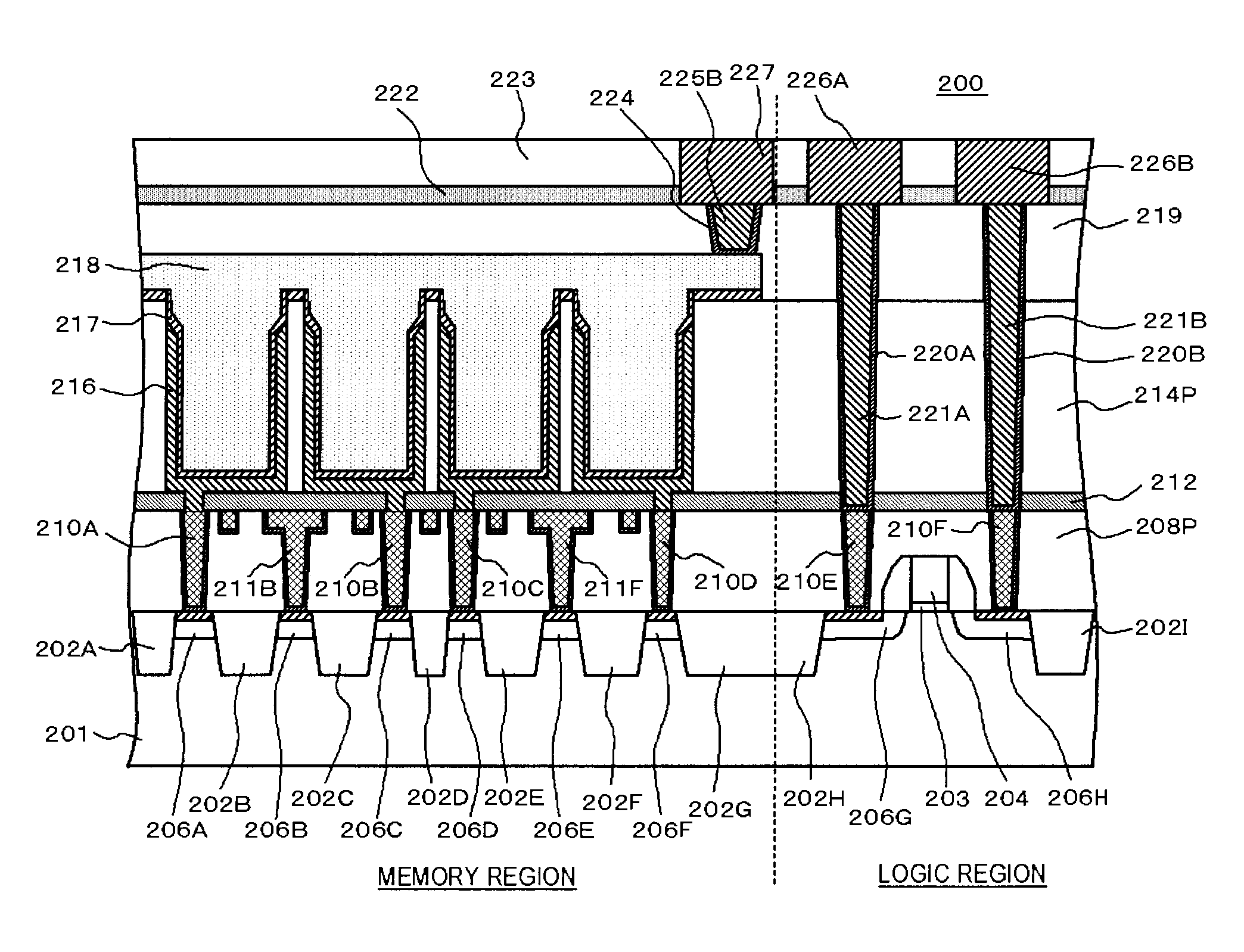
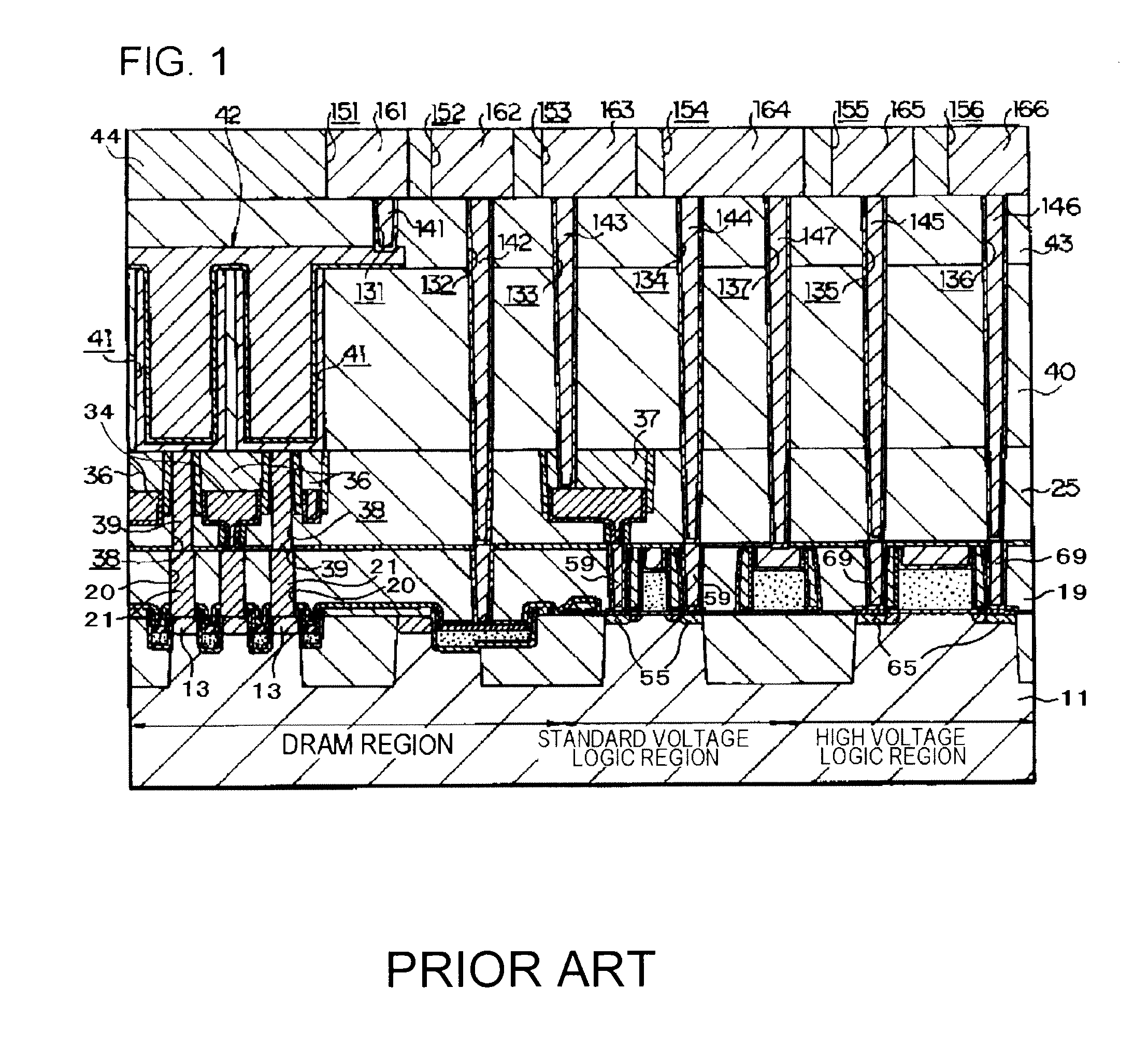
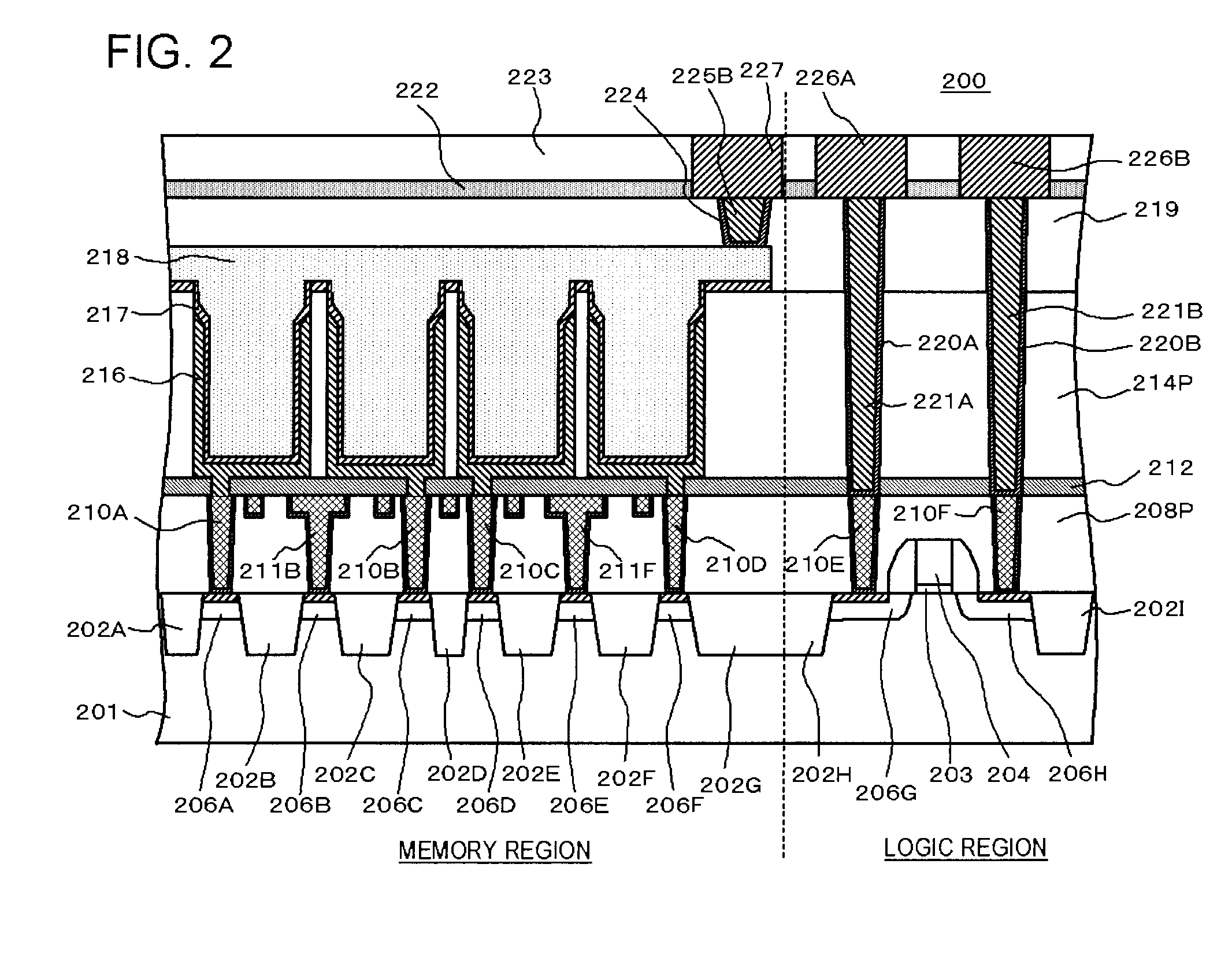
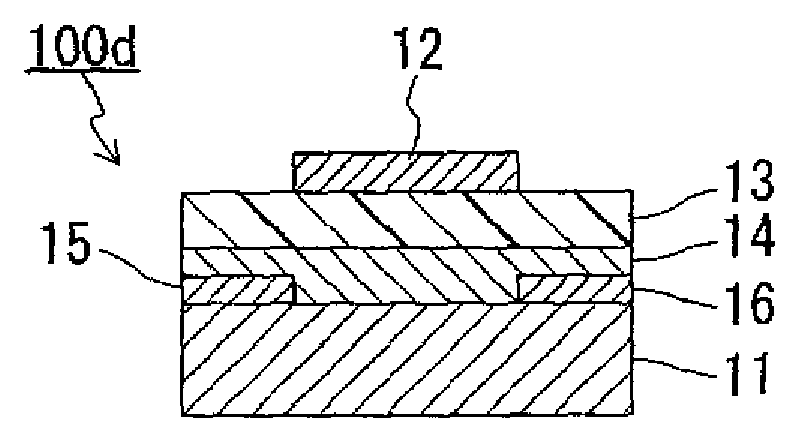
Memory embedded logic semiconductor device having memory region and logic circuit region
InactiveUS8252641B2DistanceConnection resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceConductive materials
In a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, first contact holes reaching diffusion regions of a cell transistor, bit line contact holes reaching diffusion regions of the cell transistor, and interconnect grooves communicating with the bit line contact holes are buried in a first insulating film. In addition, first contact plugs and bit line contacts are respectively formed by burying conductive materials in the first contact holes, the bit line contact holes and the interconnect grooves, and the first contact plugs are electrically connected to a capacitor formed in a third insulating film through an opening formed in a second insulating film.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
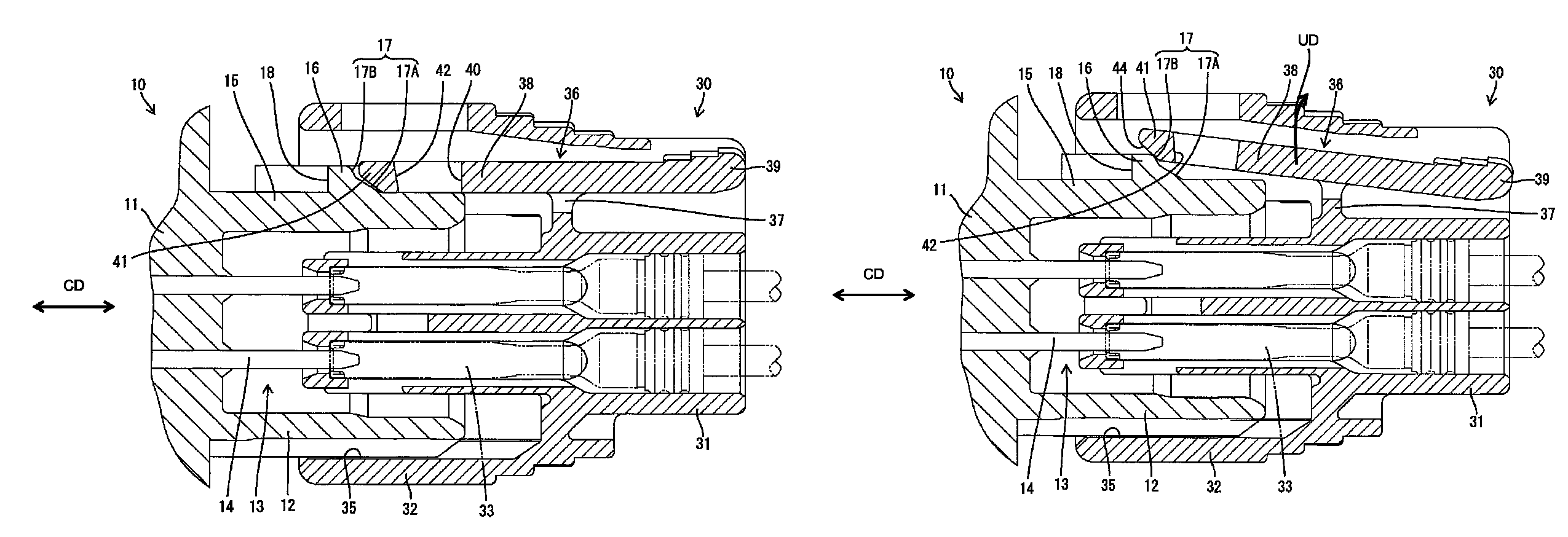
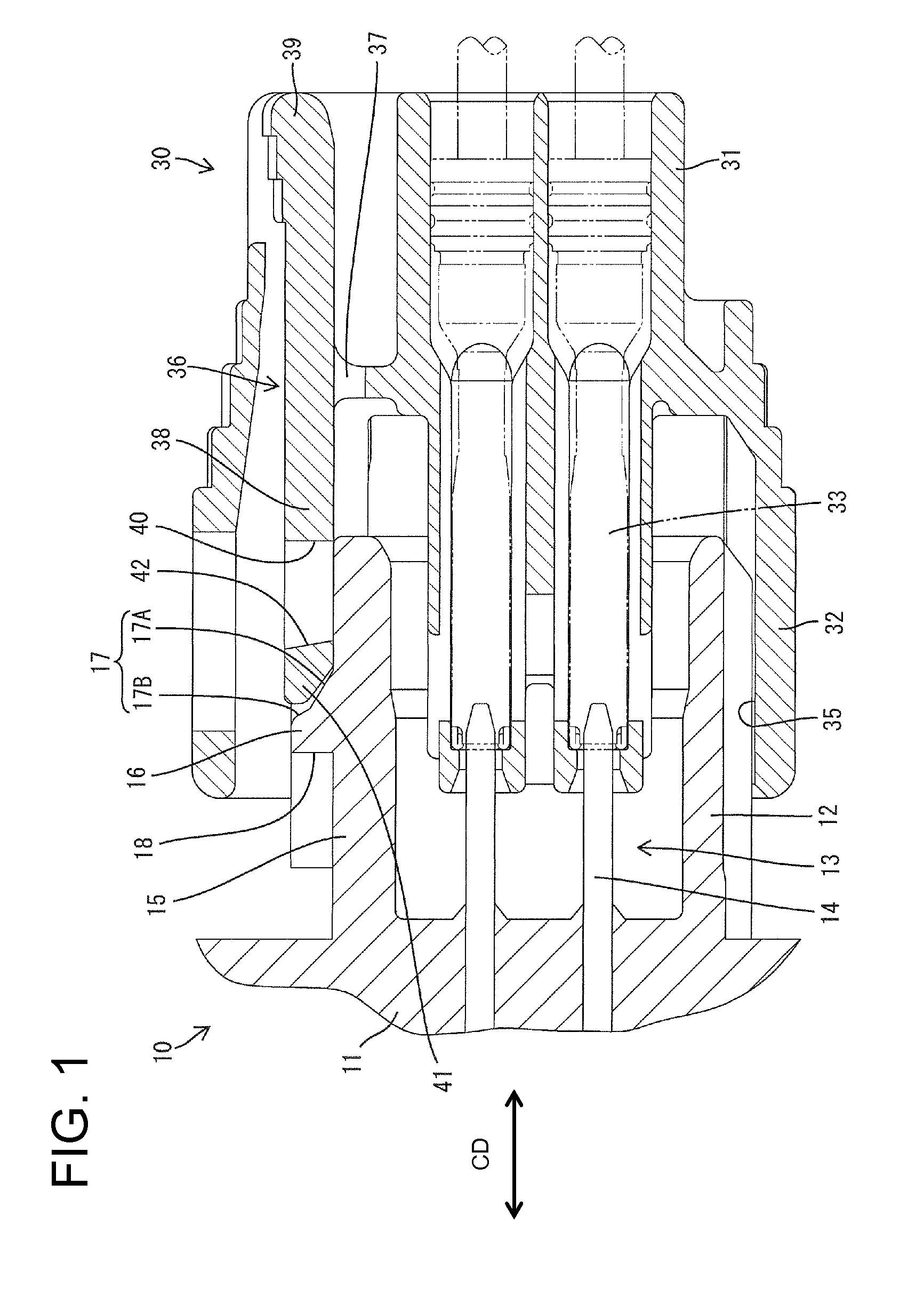
Connector and connector assembly
ActiveUS8449313B2Connection resistanceEasy to operateSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersFastening meansEngineeringMechanical engineering
In the process of connecting two housings (10, 30), a lock arm (36) is resiliently deformed in an unlocking direction crossing a connecting direction of the two housings (10, 30) by sliding in contact with a guiding surface (17) of a lock portion (16). The guiding surface (17) includes a first guiding surface (17A) arranged in a front area in the connecting direction to the second housing (30) and a second guiding surface (17B) arranged in an area behind the first guiding surface (17A) in the connecting direction to the second housing (30) and having a steep area (22) whose angle of inclination with respect to the connecting direction of the two housings (10, 30) is larger than that of the first guiding surface (17A).
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
Access control apparatus and access control method
InactiveUS7372861B2Connection resistanceDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationTime limitFinite time
An access control apparatus and method limits, to a finite time length, connection of a user terminal to a public network. The user terminal is disconnected from the public network when the use time of the logical address assigned to the user terminal reaches the time limit set for the logical address. The apparatus and method utilizes IDs issued to multiple users and IDs for multiple user terminals, and enables limiting connection to a public network from a user terminal that is connected by a leased circuit.
Owner:NEC CORP
Electronic device, process for producing the same and electronic equipment making use thereof
ActiveUS20090224231A1Reduce connection resistanceConnection resistanceSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSemiconductorElectron
An electronic device of the present invention includes at least one electrode (Au electrode 65) and an organic molecule layer (semiconductor layer 14) formed adjacent to the electrode, and in which charge transfers between the layer and the electrode. The organic molecule layer includes a plurality of first organic molecules containing a conjugated π electron that composes a π conjugate plane (64). A plurality of second organic molecules is bonded chemically to a surface of the electrode at an interface between the electrode and the organic molecule layer. The second organic molecule contains a conjugated π electron that composes a π conjugate plane (67a). The second organic molecule is a molecule having a structure in which the π conjugate plane (67a) and the surface of the electrode form an angle within a predetermined range when the second organic molecule is bonded chemically to the surface of the electrode.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Plasma display apparatus with optical filter and elastic conductive body
InactiveUS7612490B2Reduce radiationConnection resistanceIncadescent screens/filtersMagnetic/electric field screeningEngineeringSurface cover
A plasma display apparatus includes a conductive rear surface cover covering a rear surface of a plasma display panel; an optical filter provided with a conductive layer having a surface resistance of 0.5 Ω / square or above, which is disposed at the front surface of the plasma display panel and serves to reduce leakage of electromagnetic waves from the plasma display panel; an optical filter fixing member electrically connected with the rear surface cover, for at least retaining the optical filter; and a conductive body having elasticity, which is interposed between the optical filter and the optical filter fixing member. A plurality of bosses are formed in the optical filter fixing member. A part of the elastic conductive body is compressed by the bosses and connection resistance with the elastic conductive body is reduced.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Threaded connection
A threaded connection having a straight central axis, the connection including a plurality of pin threads, each pin thread having a root and a crest, and a box having a plurality of box threads, each box thread having a root and a crest. The crests of at least a portion of the box threads are curved so that when the pin threads are fully engaged with the box threads, there is a void between the roots of the pin threads and the corresponding curved crests of the box threads to reduce standoff caused by lubricant or other fluids becoming trapped between the threads as the connection is made up.
Owner:MARUBENI ITOCHU TUBULARS AMERICA
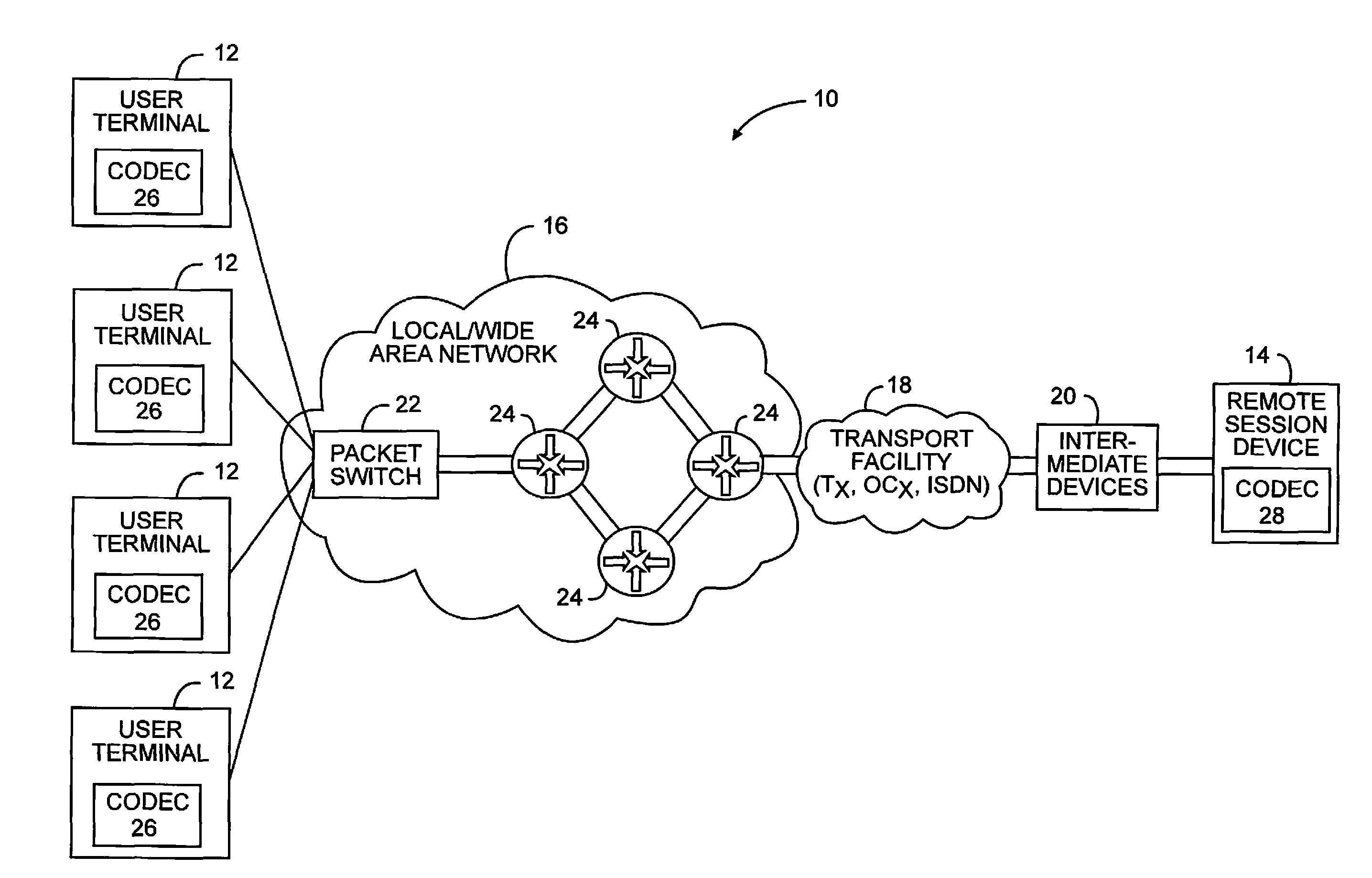
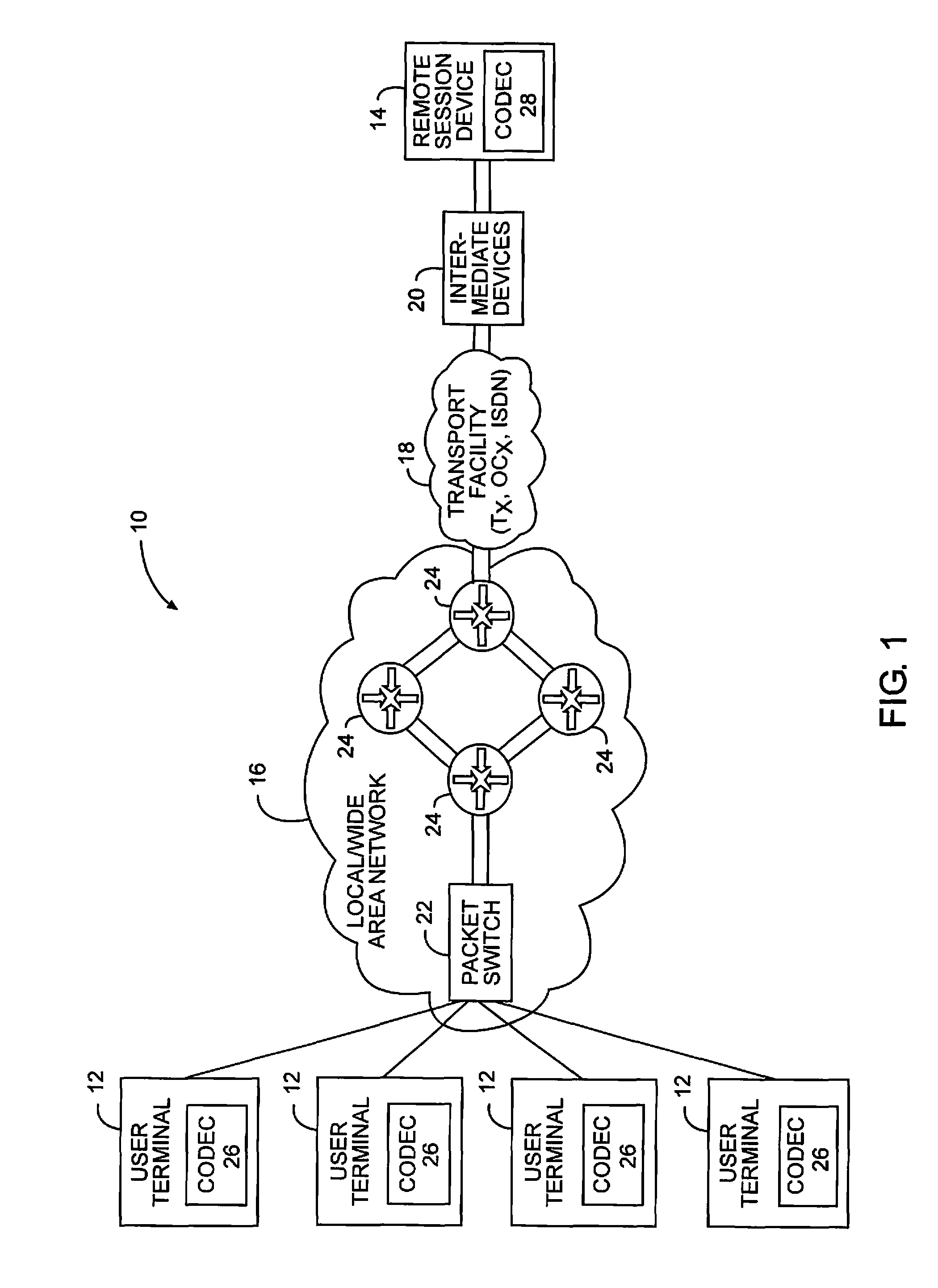
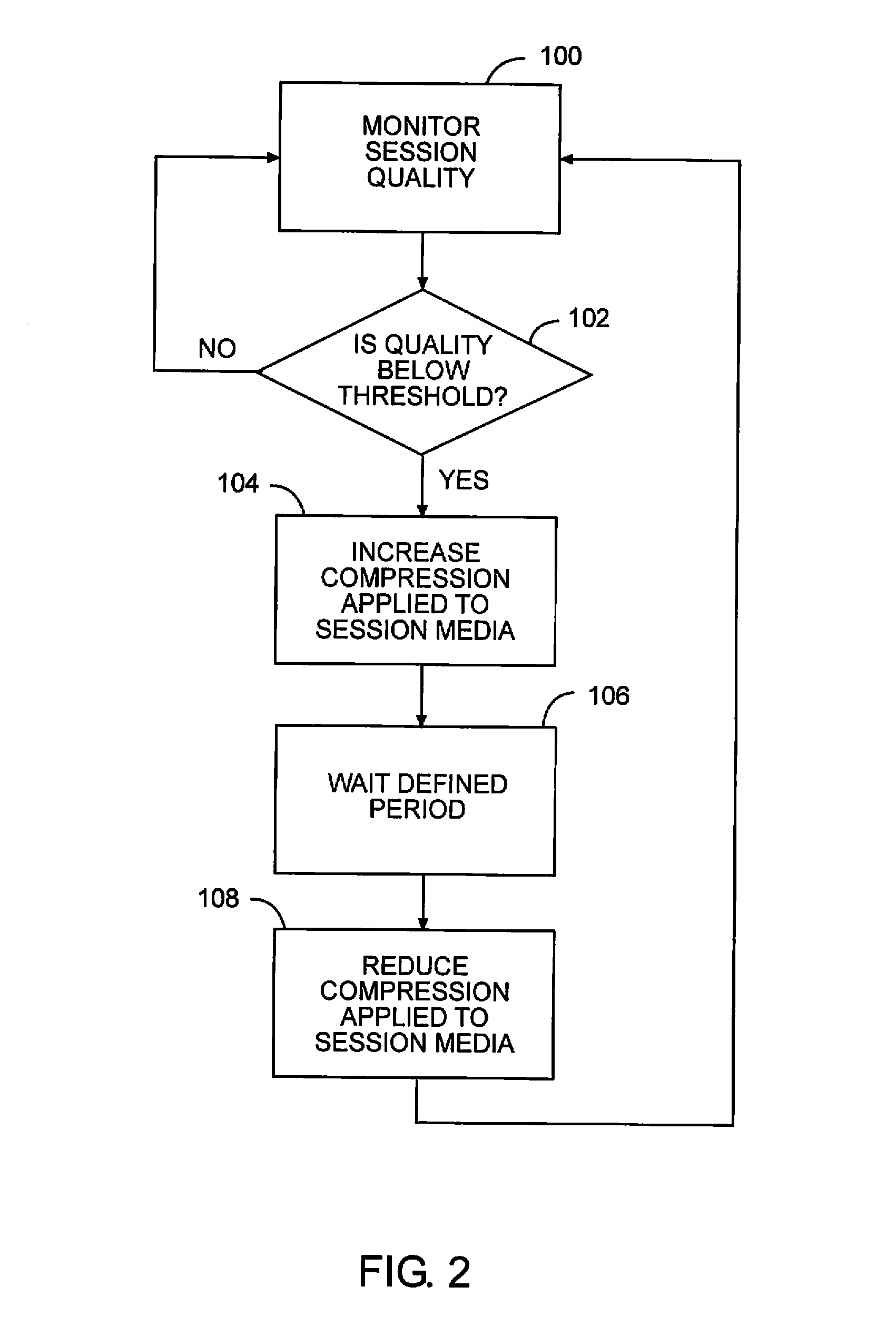
Auto-compression for media over IP
InactiveUS20100226257A1Lower performance requirementsQuality improvementError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceCommunication device
The present invention allows communicating devices to control the amount of compression used in packet sessions for transmitting streaming media to and from each other. When a communicating device detects a decrease in performance or quality of service indicative of a limited bandwidth condition, the amount of compression for the current or subsequent sessions is temporarily increased to allow the currently available bandwidth to support the session or subsequent sessions. After a set period of time, or when the limited bandwidth condition is removed, communications associated with the sessions can revert back to transporting uncompressed data or reducing the amount of compression for the sessions, thus using more of the available bandwidth.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
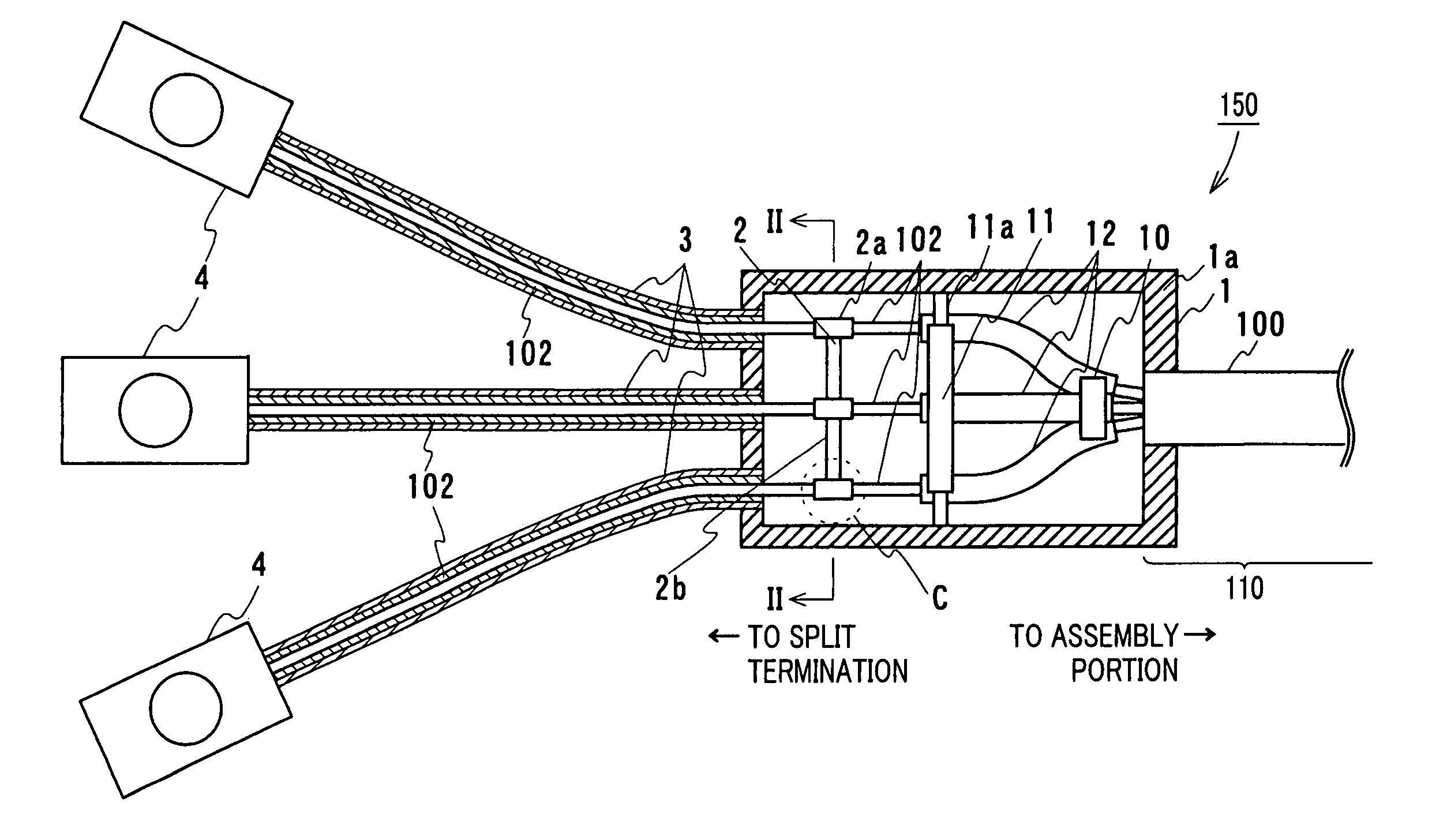
Phase split structure of multiphase superconducting cable
InactiveUS7439448B2Minimize and nullifyMinimize or nullify a magnetic fieldLine/current collector detailsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic fieldElectrical and Electronics engineering
A phase split structure of a superconducting cable includes three cable cores each having a shield layer provided around a superconductor, a splitter box housing the three cable cores extending from an assembly portion where the three cable cores are assembled into the cable, in a state in which the cable cores are spaced apart from each other, and an electrically-conductive connecting portion connecting respective shield layers of the cable cores to each other within the splitter box. In this way, occurrence of a large magnetic field outside the cable cores can effectively be reduced.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
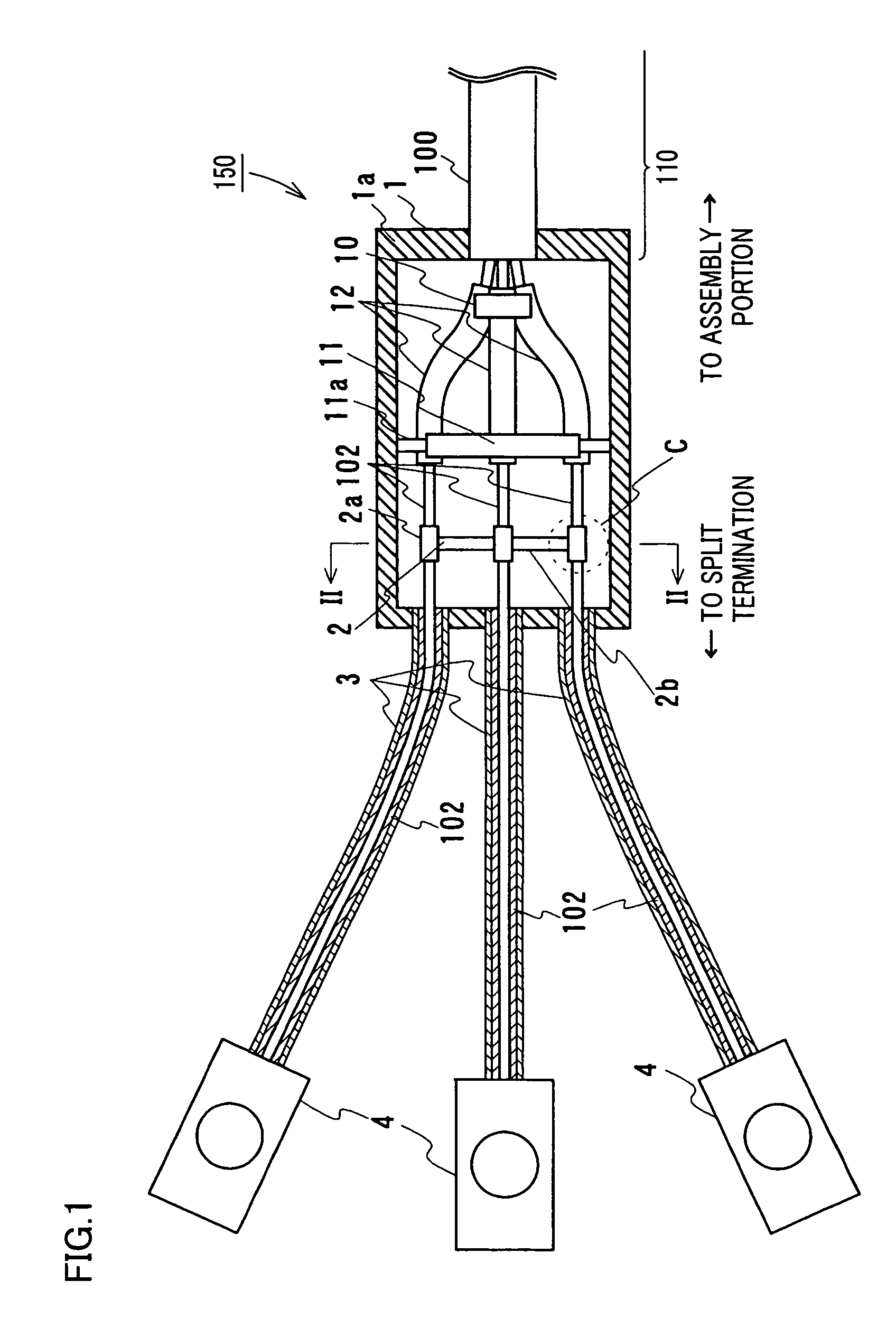
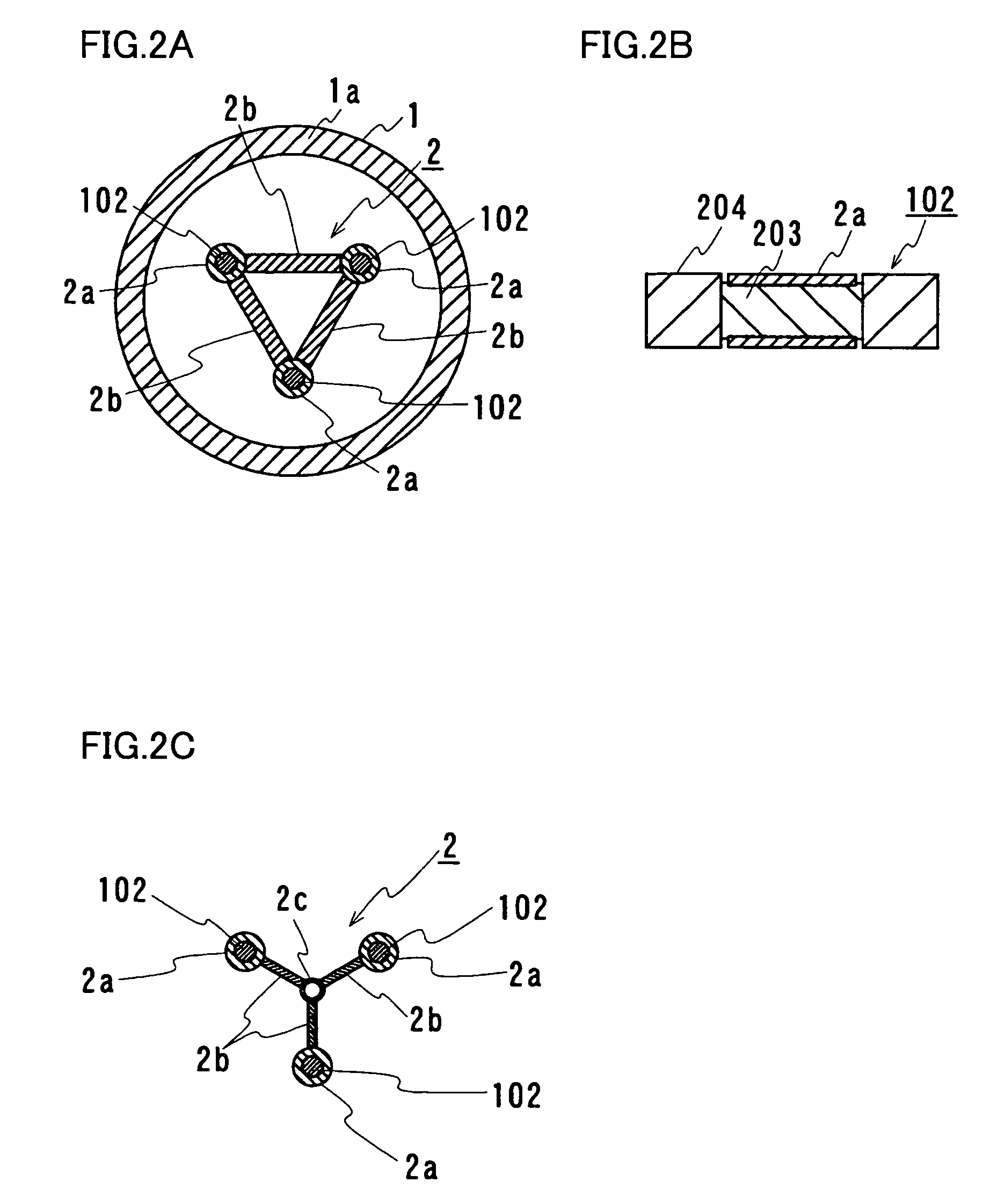
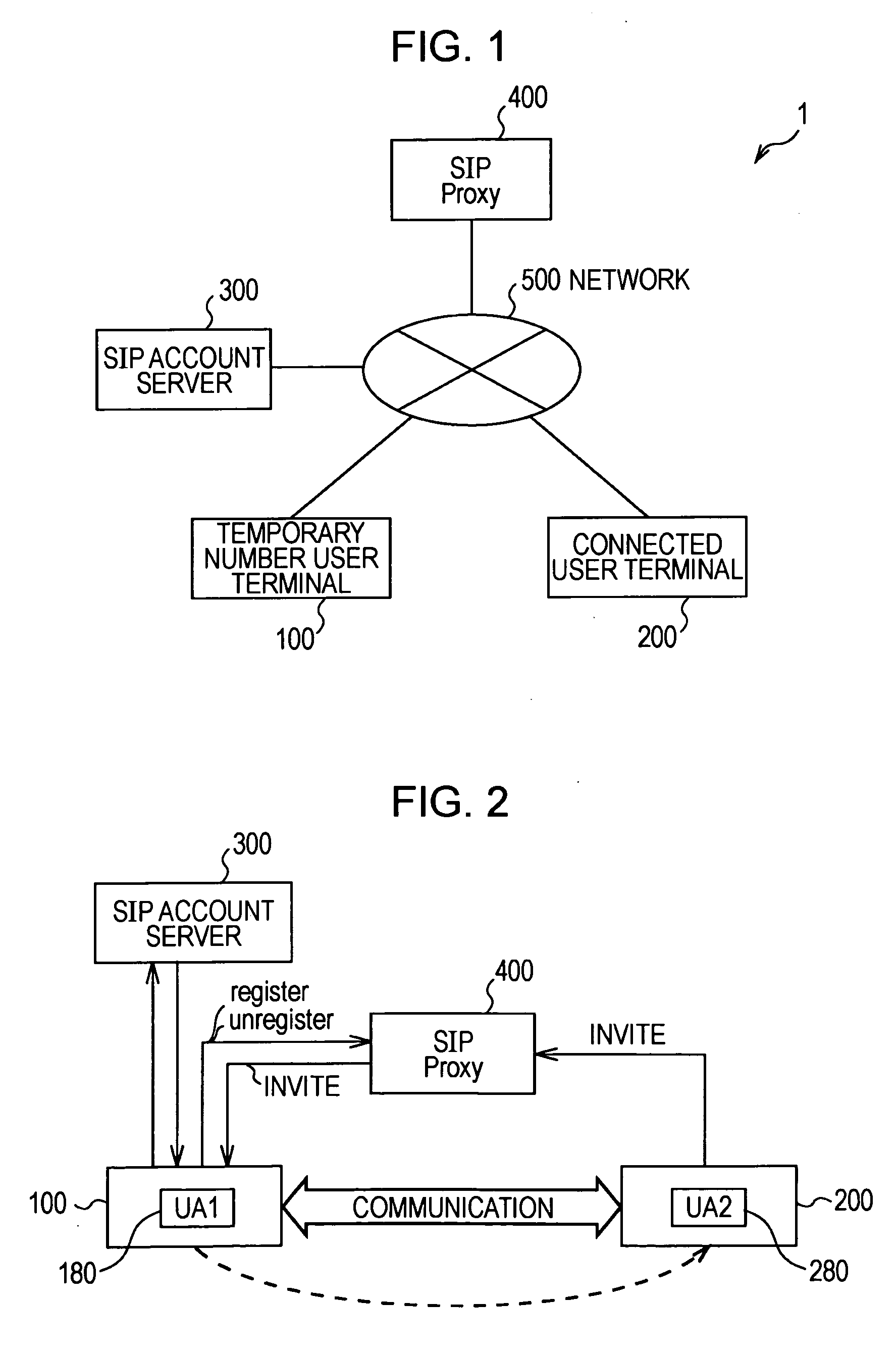
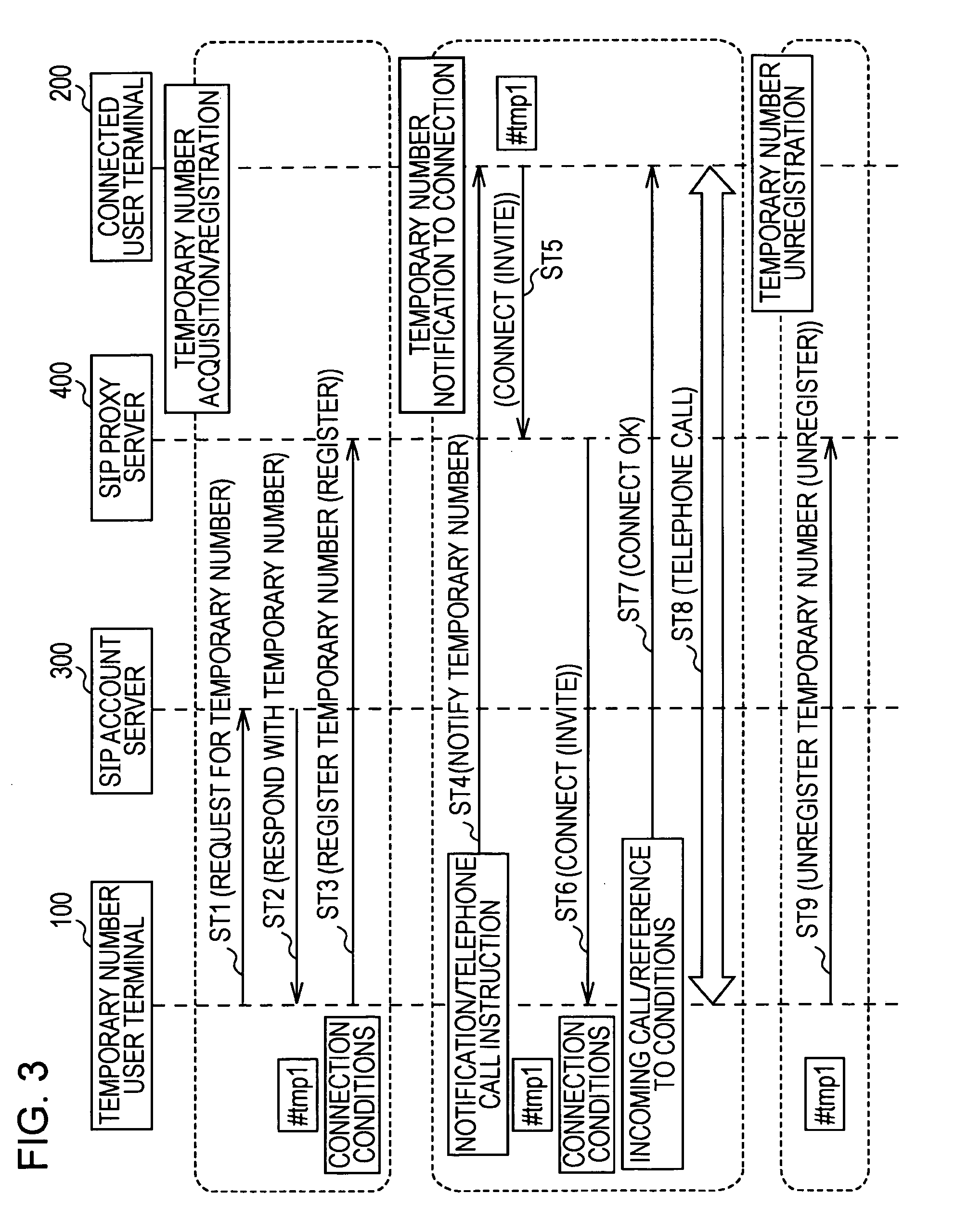
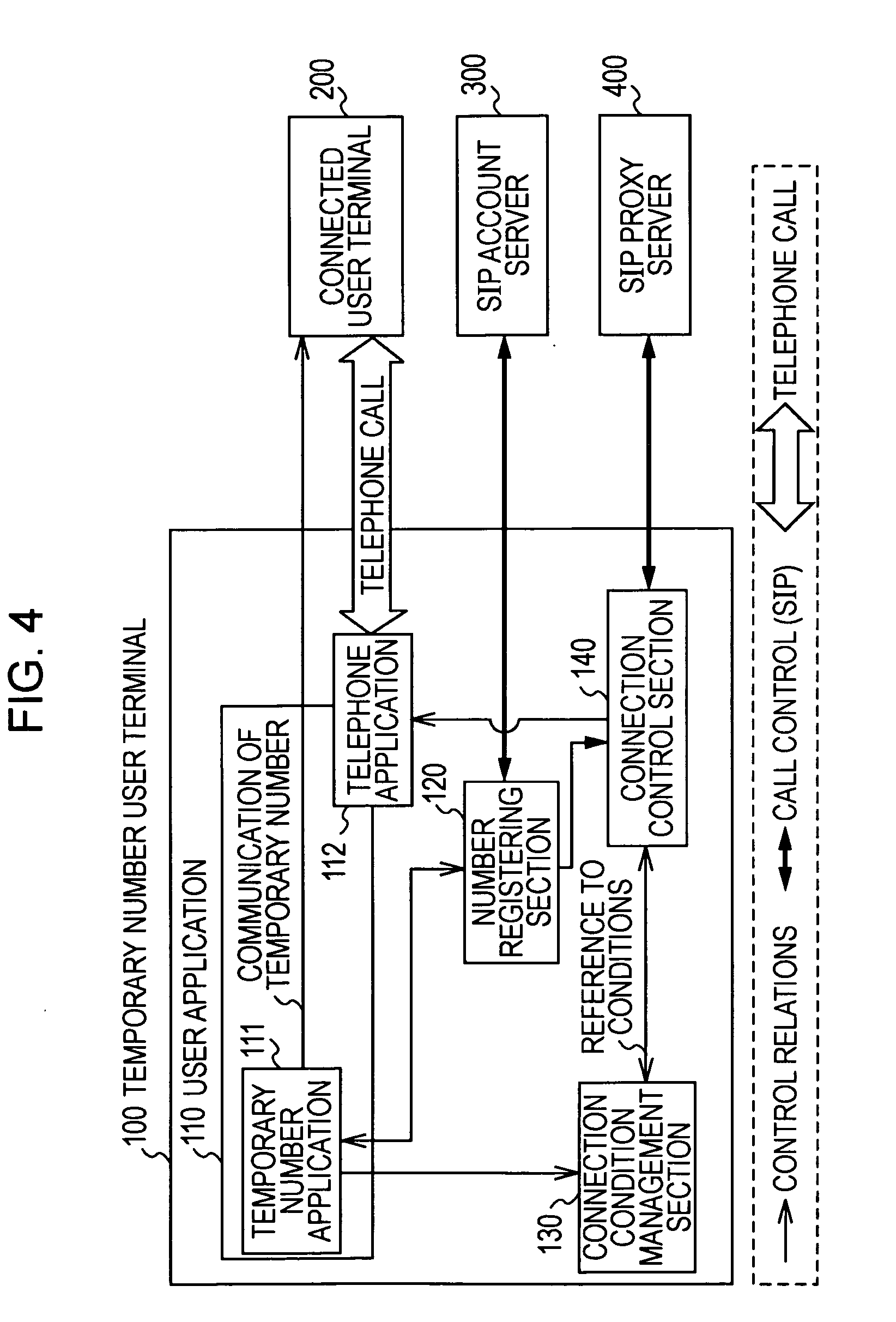
Temporary connection number management system, terminal, temporary connection number management method, and temporary connection number management program
InactiveUS20100246569A1Connection resistanceAutomatic exchangesNetwork connectionsConnection numberProxy server
The present invention makes it possible to connect to and communicate with a connect destination by using a temporary number. In the present invention, a temporary number user terminal (100) registers a temporary number acquired from a SIP account server (300) in a SIP proxy server (400), and connects to and communicates with a connected user terminal (200) by using the temporary number. After the communication is finished, the temporary number is unregistered from the SIP proxy server (400), thereby disabling a connection from the connected user terminal (200). Also, connection conditions are provided by specifying the validity period of connection using a temporary number, the number of times connection can be made, the connect destination to which connection can be made, and the like, and only those calls which meet the connection conditions are accepted, thereby making it possible to restrict the uses of the temporary number.
Owner:SONY CORP
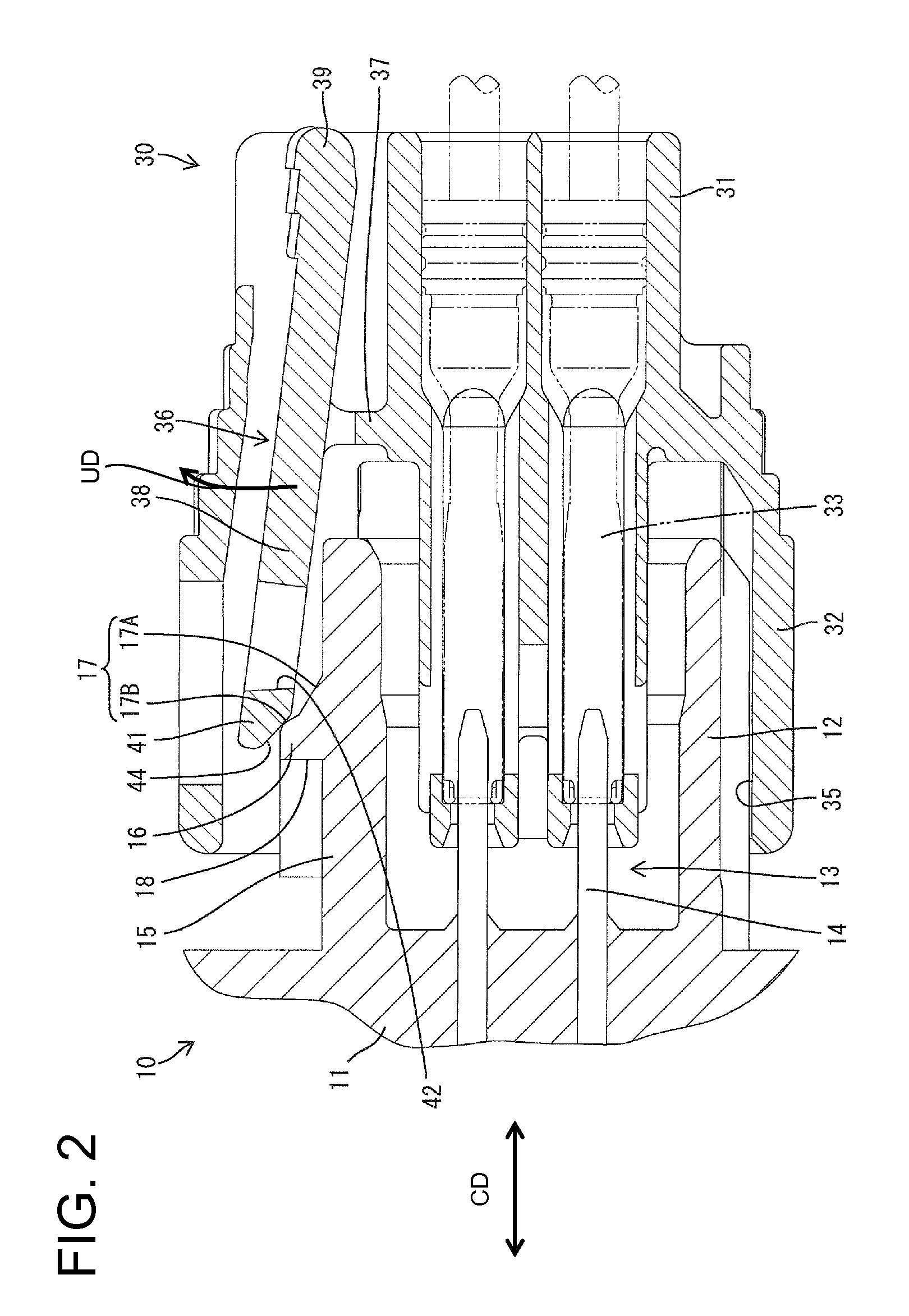
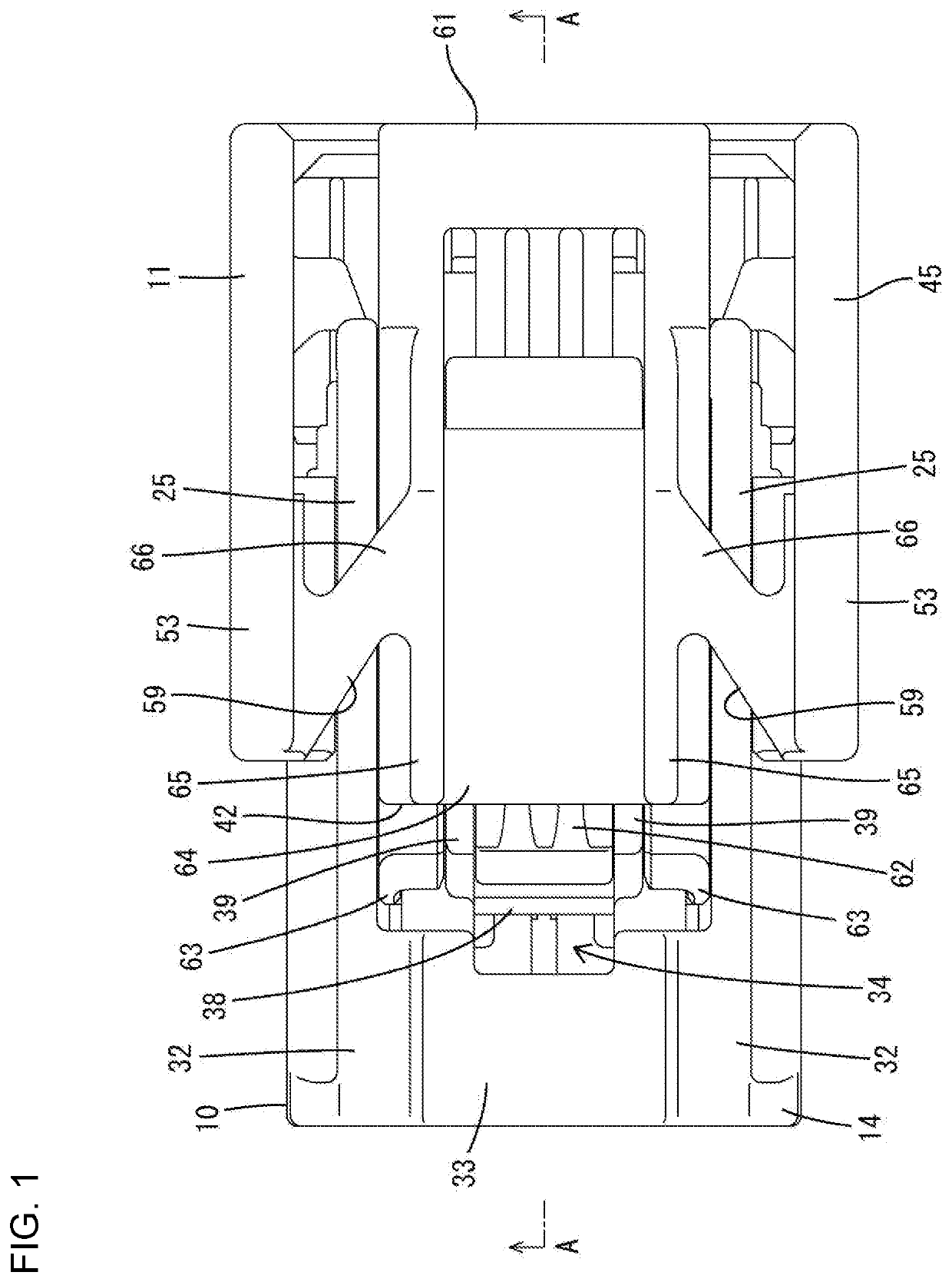
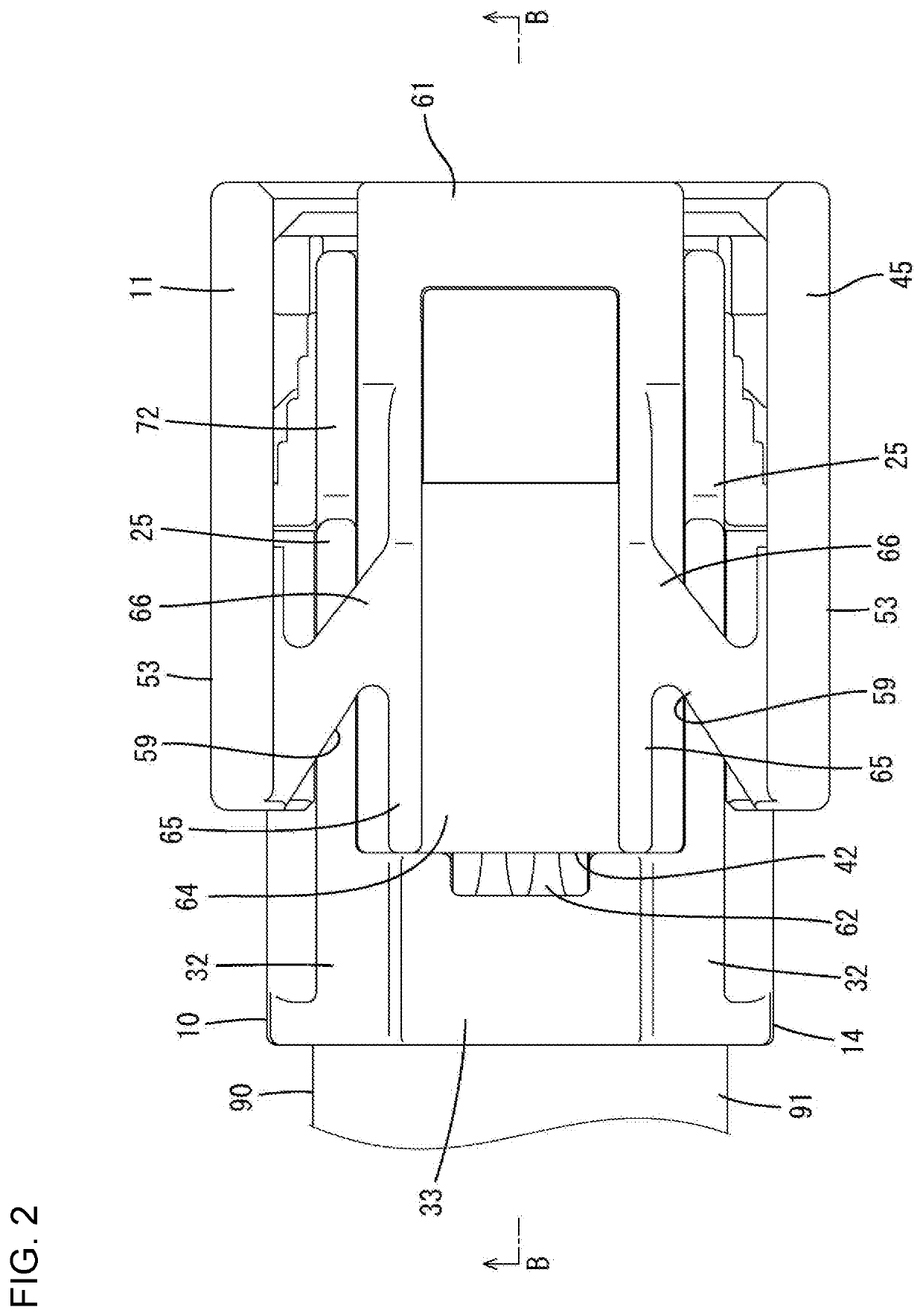
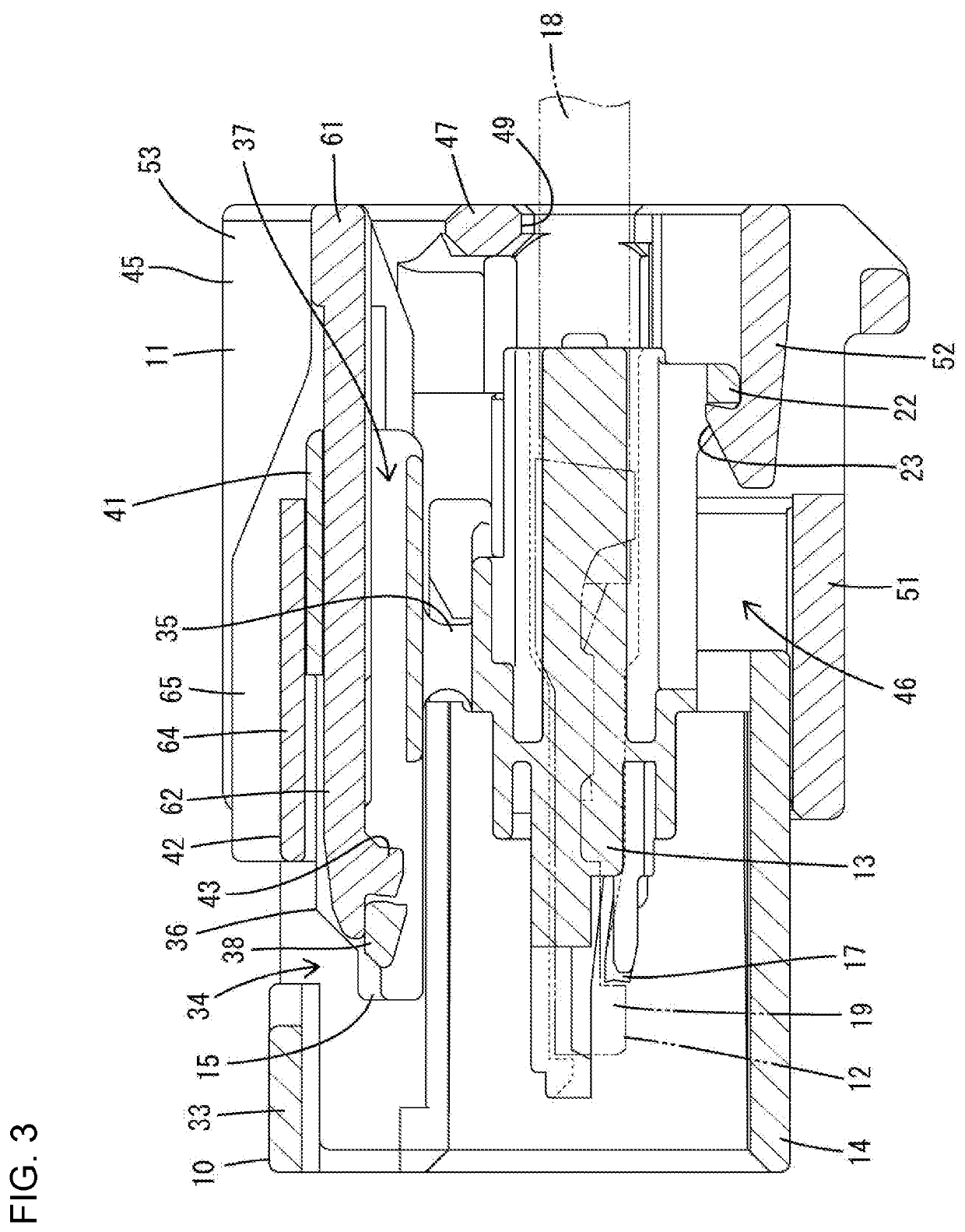
Connector
ActiveUS20200091657A1Easy to detectConnection resistanceIncorrect coupling preventionCouplings bases/casesCouplingEngineering
A connector has a detector (11) is provided in a housing (10) for movement in a front-rear direction, and can move from a standby position to a detection position when the housing (10) is connected properly to a mating housing (90). The detector (11) includes two side walls (53) arranged to face each other in a width direction with a lock arm (15) provided on the housing (10) therebetween. A detecting body (42) is assembled with the lock arm (15) between the side walls (53) and can tilt together with the lock arm (15). Couplings (59) have tilting fulcrums (66) configured to resiliently deform when the detecting body (42) is tilted. The couplings (59) extend in oblique directions intersecting the width direction from the side walls (53) to corresponding side surfaces of the detecting body (42).
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
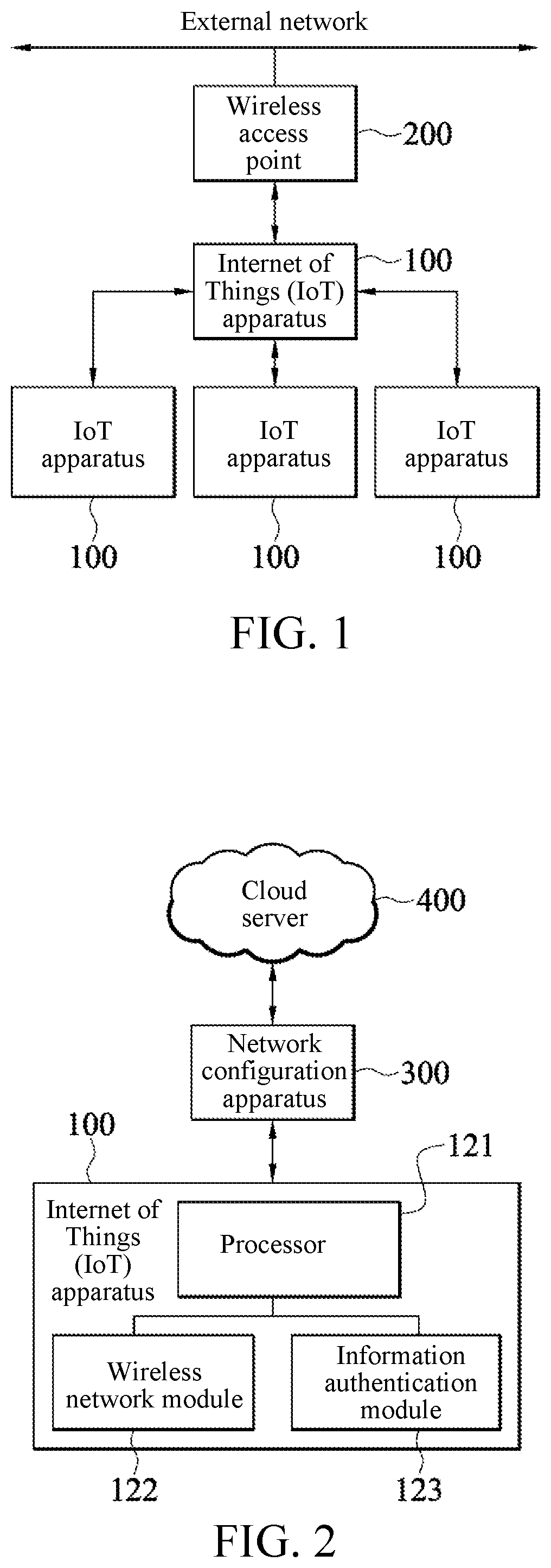
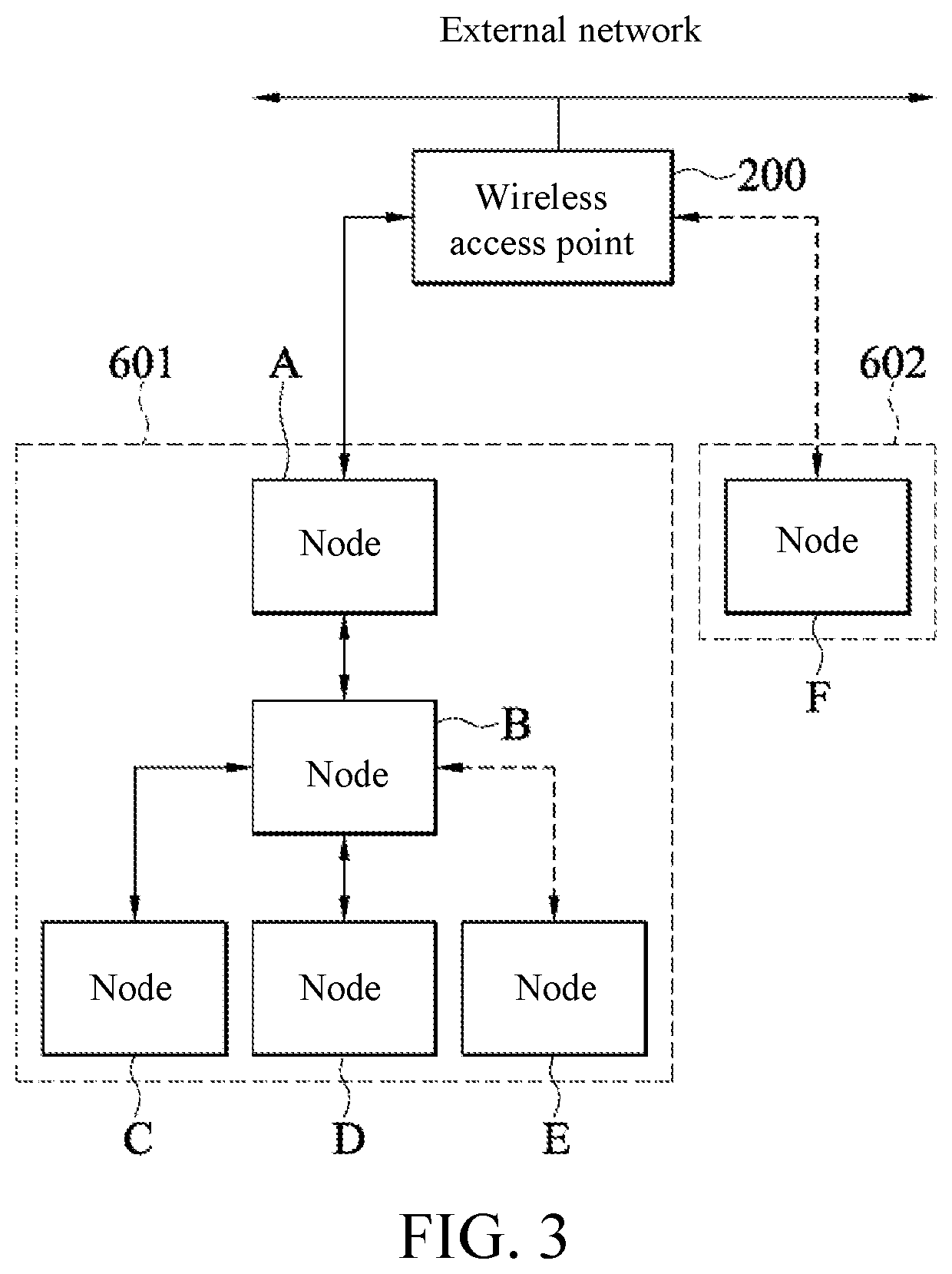
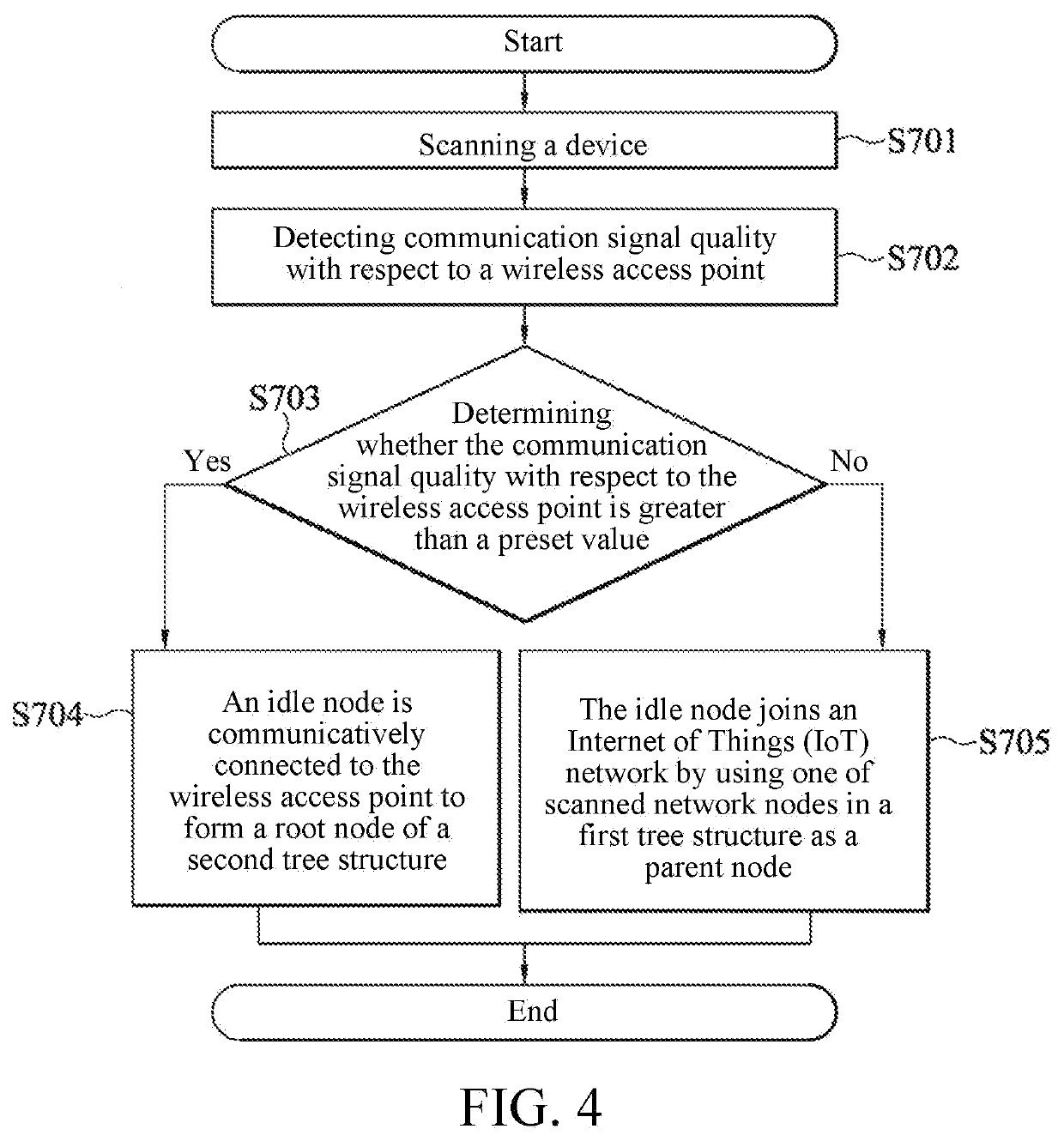
Internet of things network system and networking method thereof
ActiveUS20210288837A1Improve network connecting stability and transmission rateExpand coverageAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesComputer networkTelecommunications
An Internet of Things (IoT) network system and a networking method thereof are provided. The IoT network system is connected to a wireless access point and includes a plurality of network nodes and an idle node. The plurality of network nodes are communicatively connected to the wireless access point through a tree topology to form a first tree structure. In order to join the IoT network, when communication signal quality of the idle node with respect to the wireless access point is greater than a preset value, the idle node is communicatively connected to the wireless access point to form a root node of a second tree structure. When the communication signal quality of the idle node with respect to the wireless access point is not greater than the preset value, the idle node joins the IoT network by using one of network nodes in the first tree structure as a parent node.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Method of establishing charged connection using screen sharing application between multi- platforms
ActiveUS8560704B2Protect interestsConnection resistanceComplete banking machinesPublic key for secure communicationScreen sharingMulti platform
A method of establishing a charged connection using a screen sharing application between multi-platforms is disclosed. A transmitting end application is installed in a transmitting end apparatus of a sharing source. A receiving end application is installed in a receiving end apparatus of a sharing target. If the transmitting end application is a charged version, an unlimited connection is established for performing screen sharing between the transmitting end apparatus and any receiving end apparatus. If the transmitting end application is a free version, the method further confirms if the receiving end application is a charged version for deciding whether a limited connection or an unlimited connection should be established. Thus, it is assured that either the transmitting end application or the receiving end application is a charged version, the interests of application developers are protected and users are free from paying twice for establishing one connection.
Owner:BARCO NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com