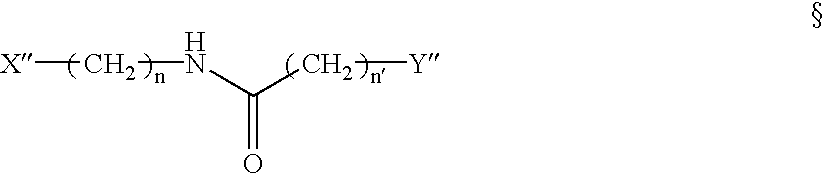Patents
Literature
44results about How to "Easily and conveniently performed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
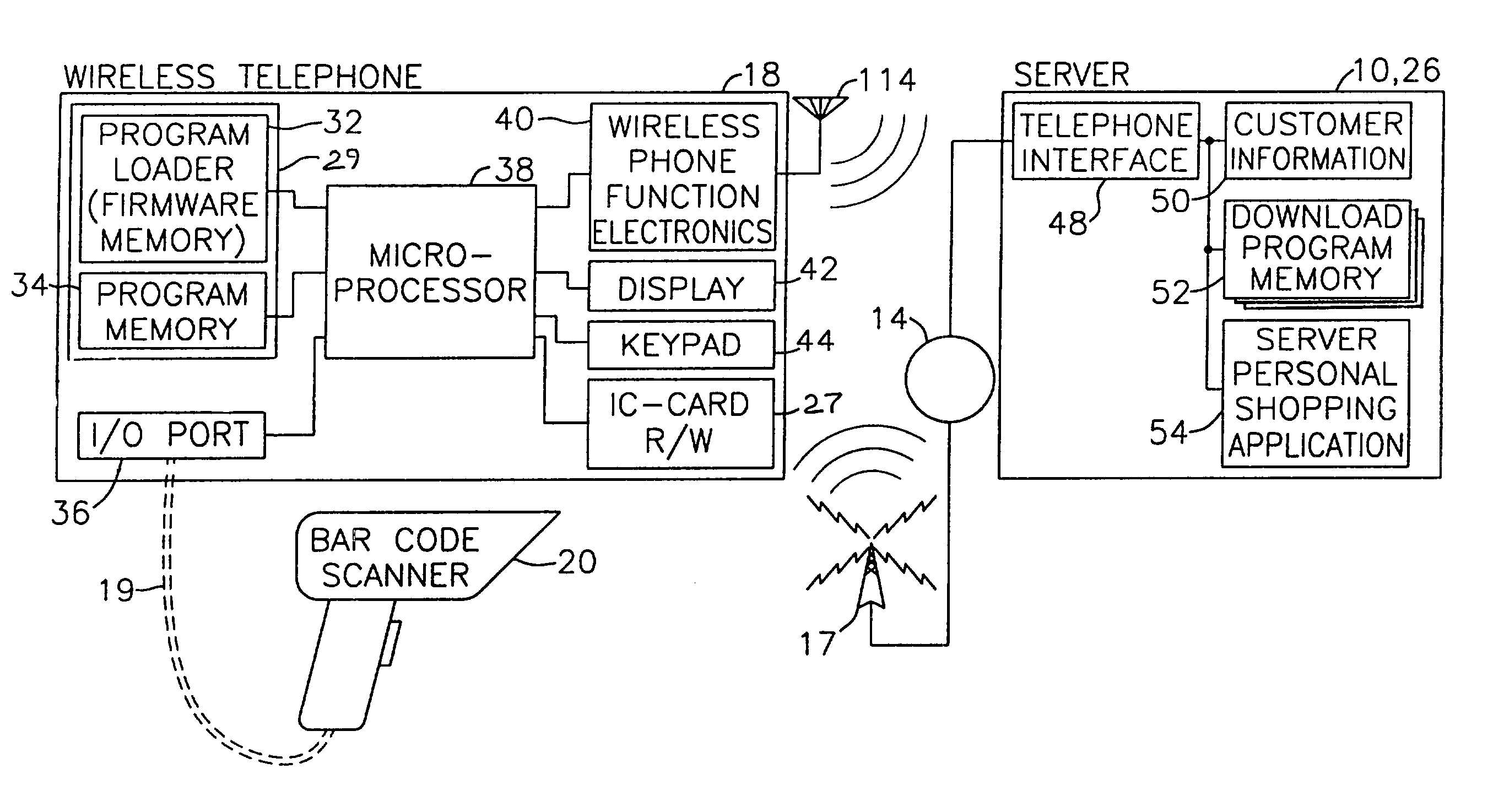
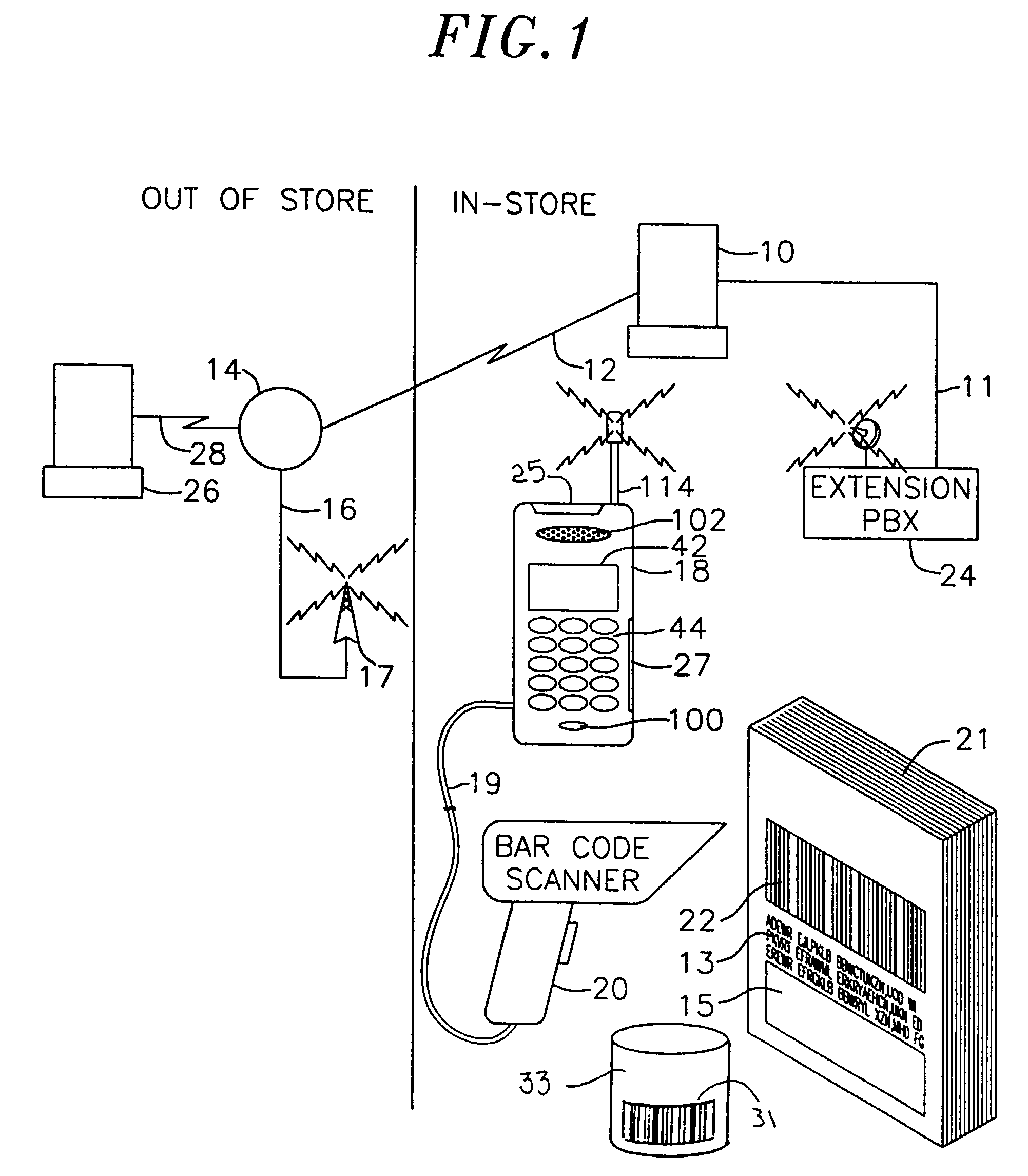
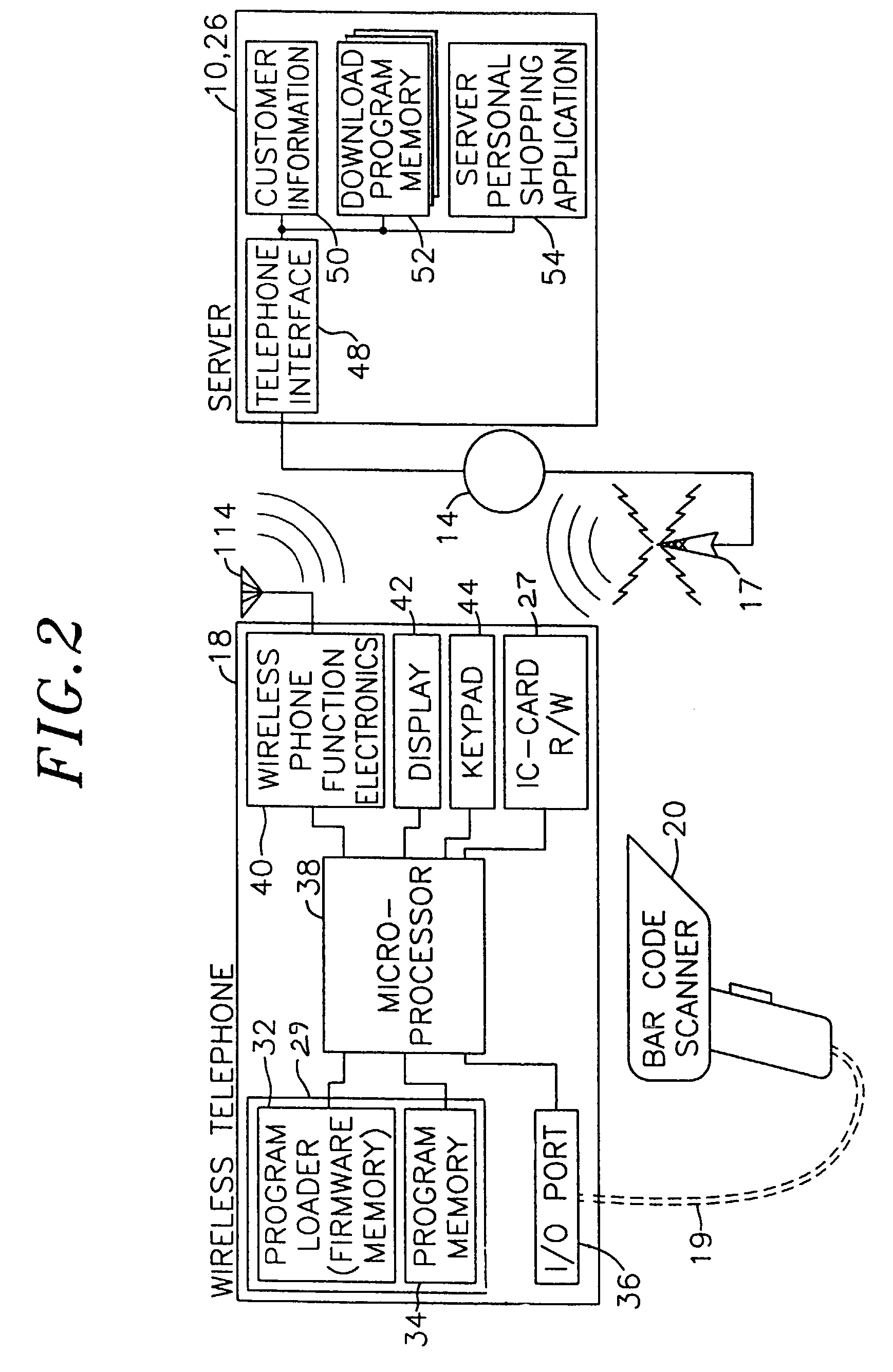
Electronic shopping system utilizing a program downloadable wireless telephone
InactiveUS6975856B2Easily and conveniently performedMinimal investmentCredit registering devices actuationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionPaymentBarcode
An electronic shopping system facilitates purchase transactions via a wireless telephone. A purchase transaction program is downloaded from the seller's server to a purchaser's wireless telephone via a program loader contained within the purchaser's wireless telephone. The purchase transaction program is stored in a program memory of the purchaser's wireless telephone. The purchase transaction program is used by the purchaser to facilitate the selection of items to be purchased, as well as payment therefor. An external bar code reader is attached to the wireless telephone to facilitate the selection of items to be purchased and is controlled via the downloaded purchase transaction program.
Owner:KNAPP INVESTMENT
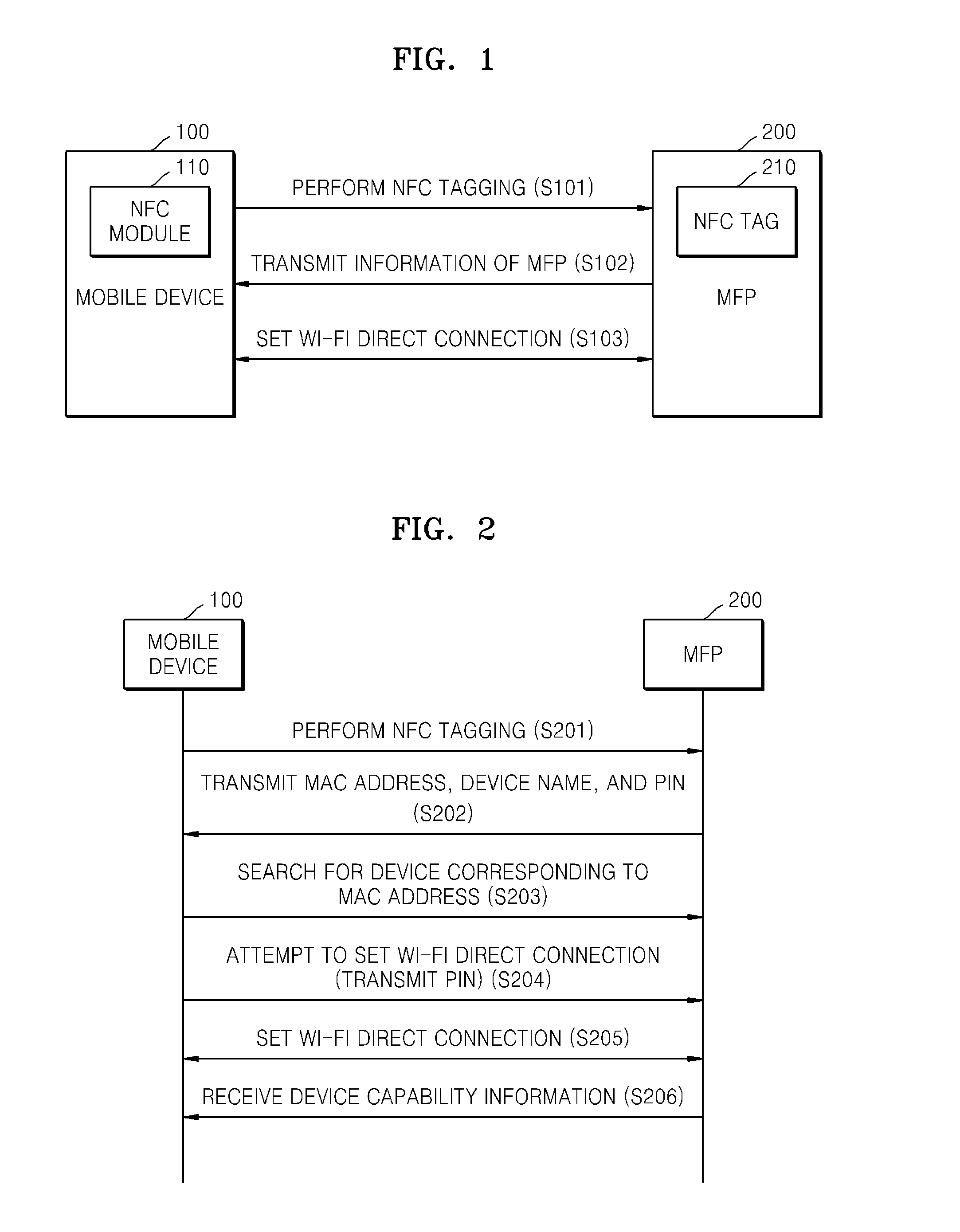
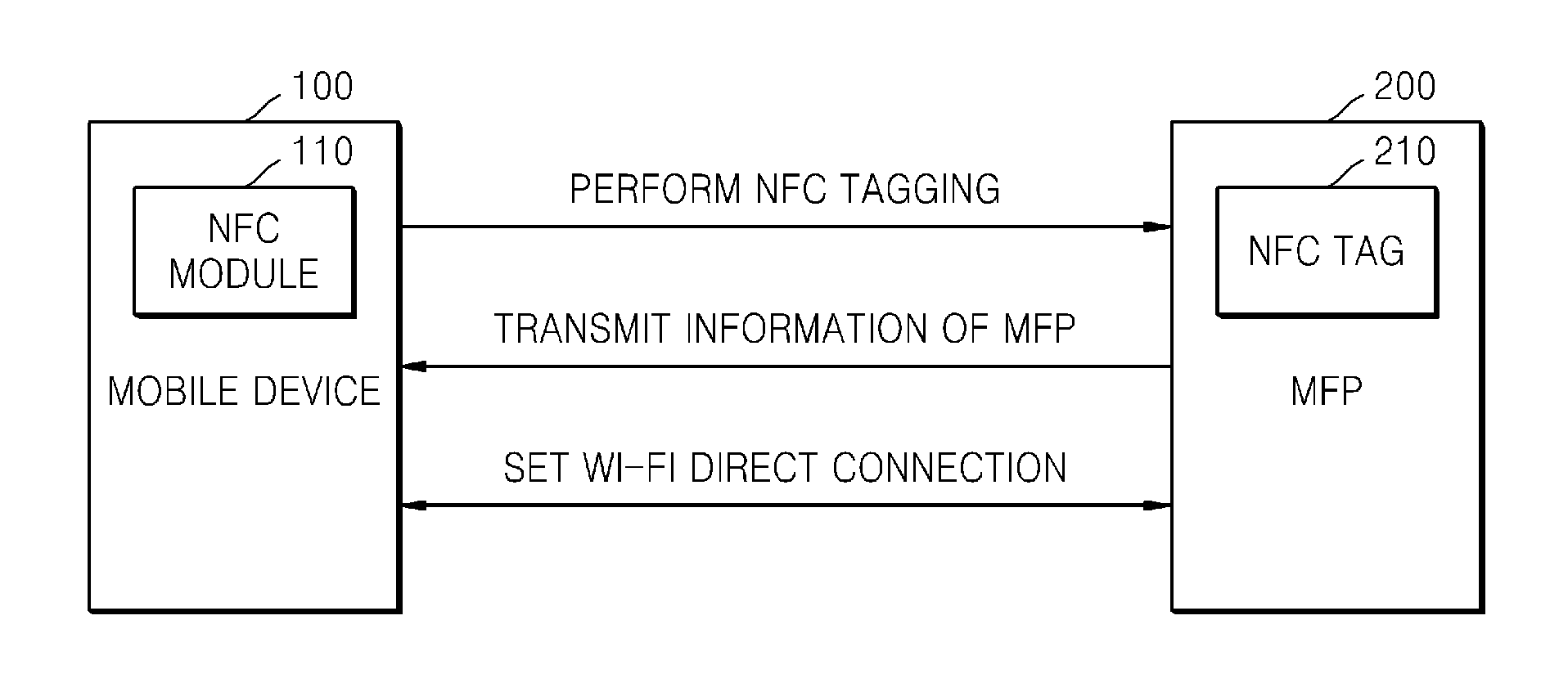
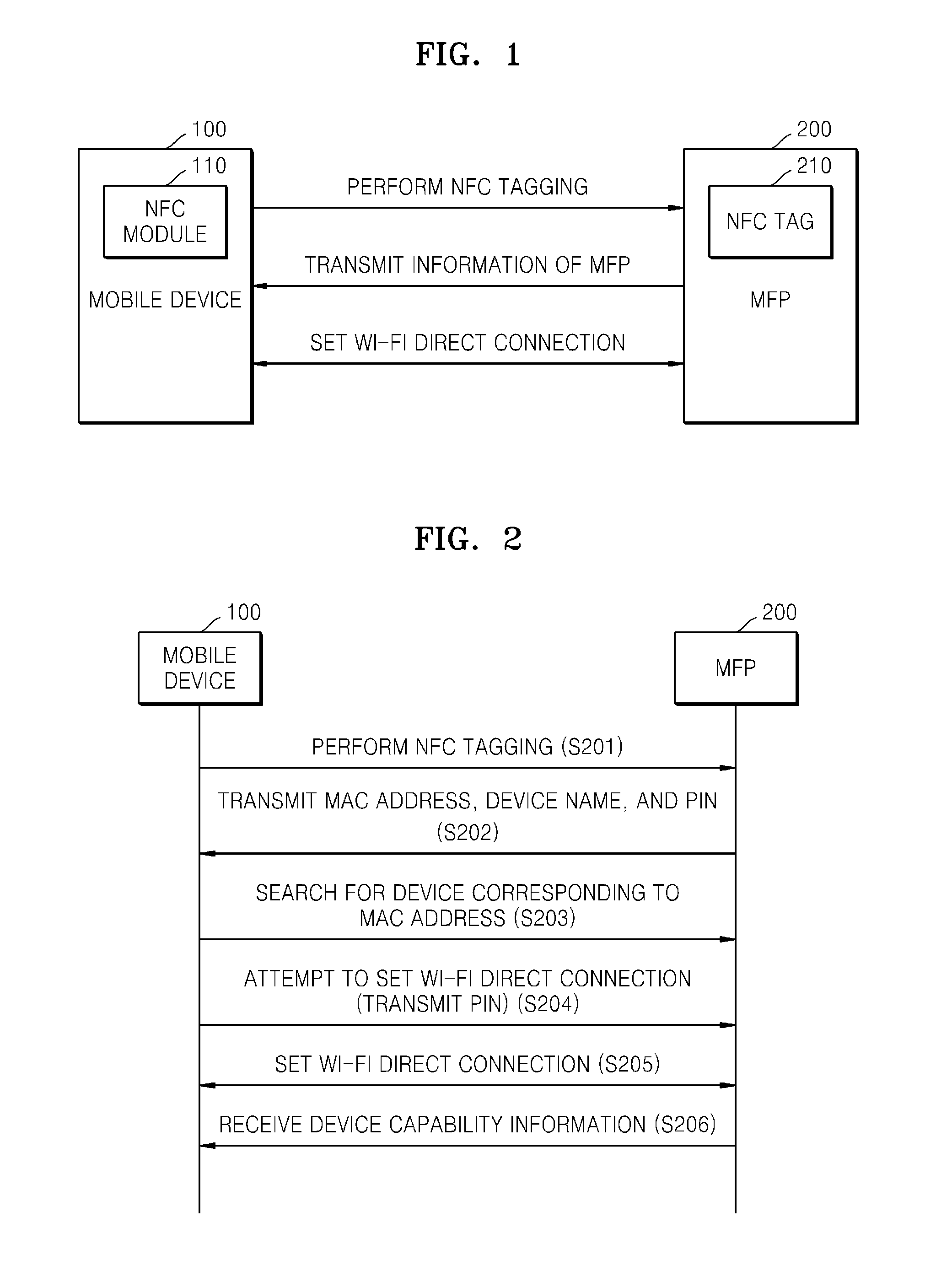
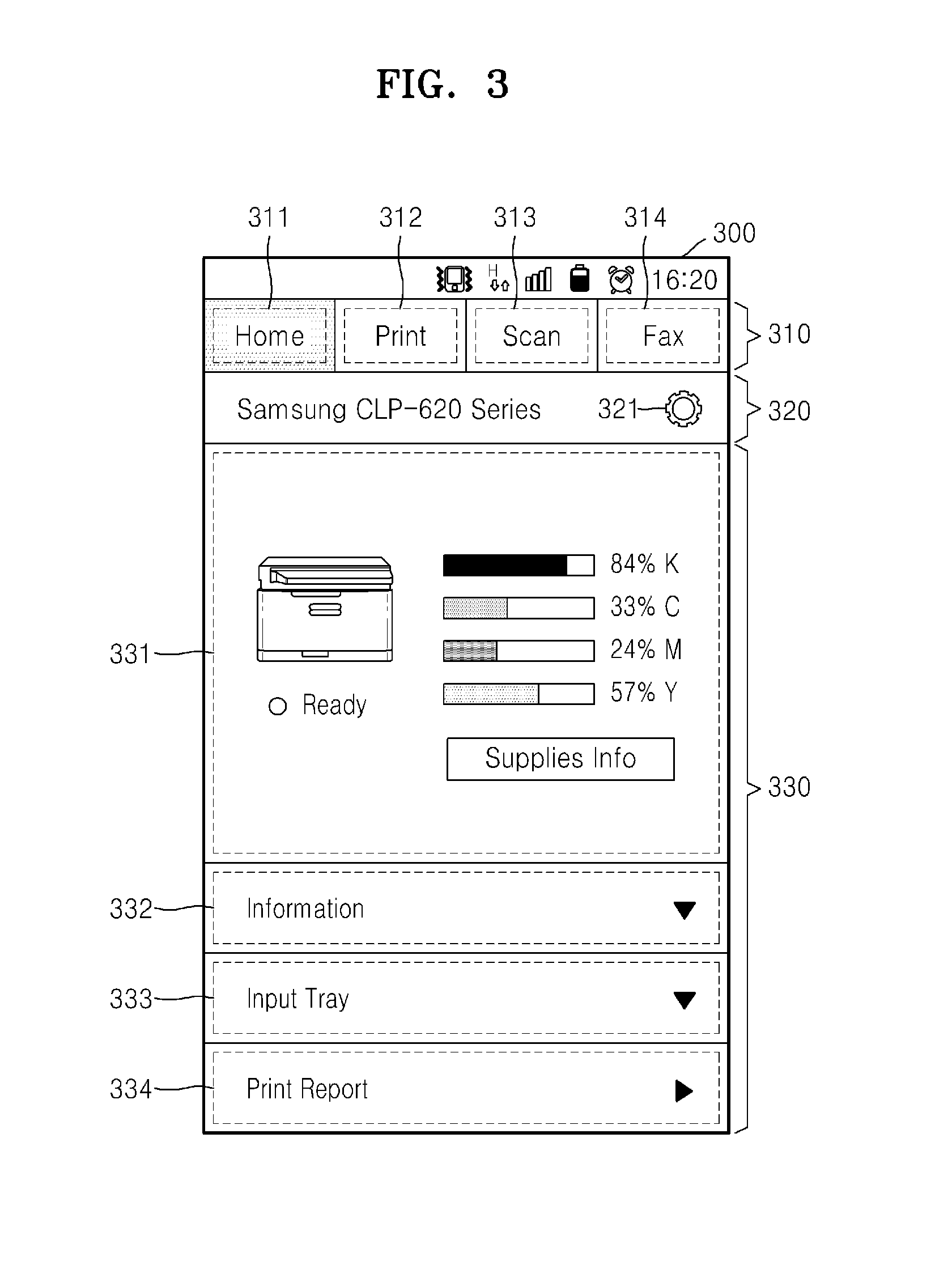
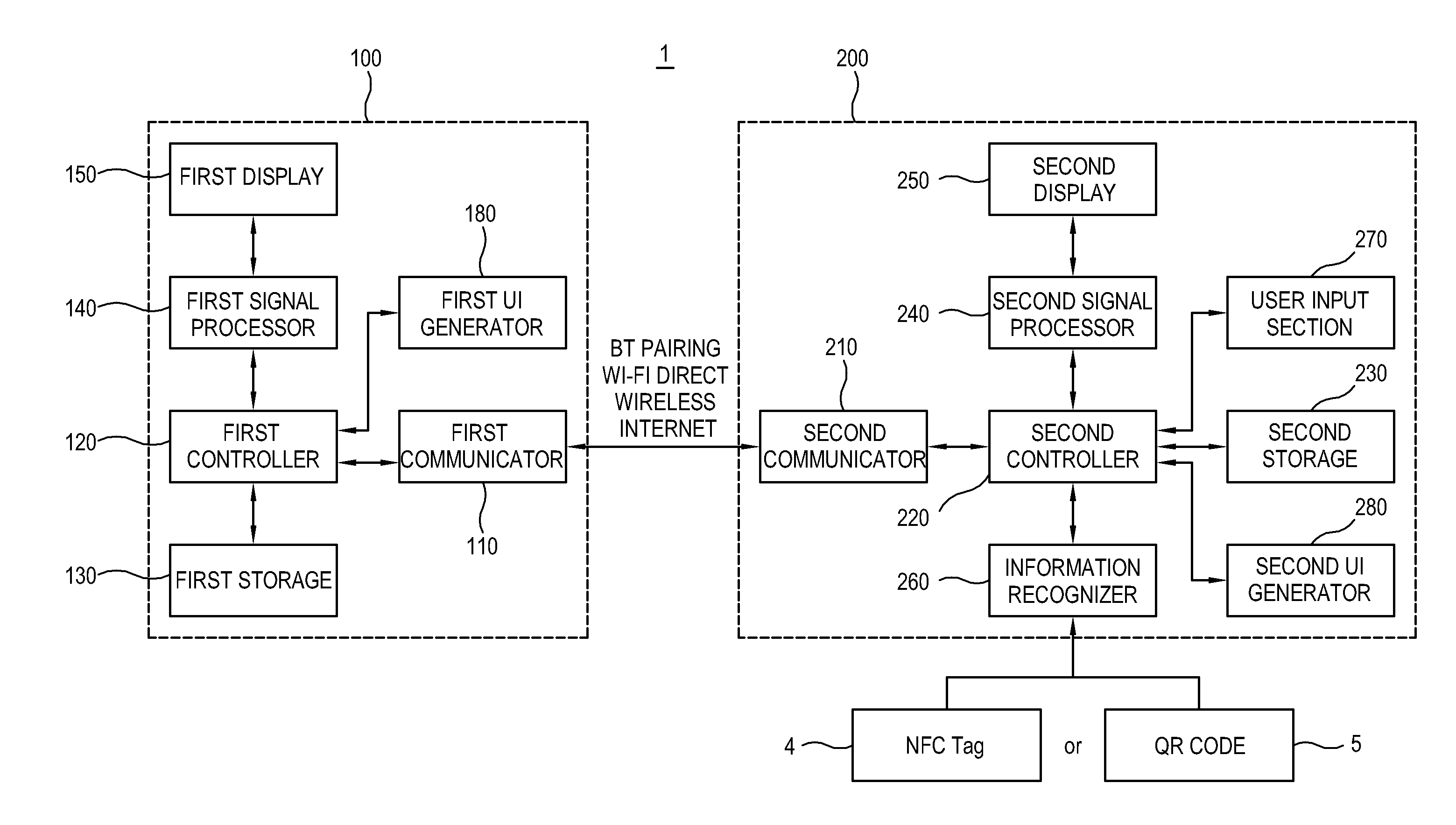
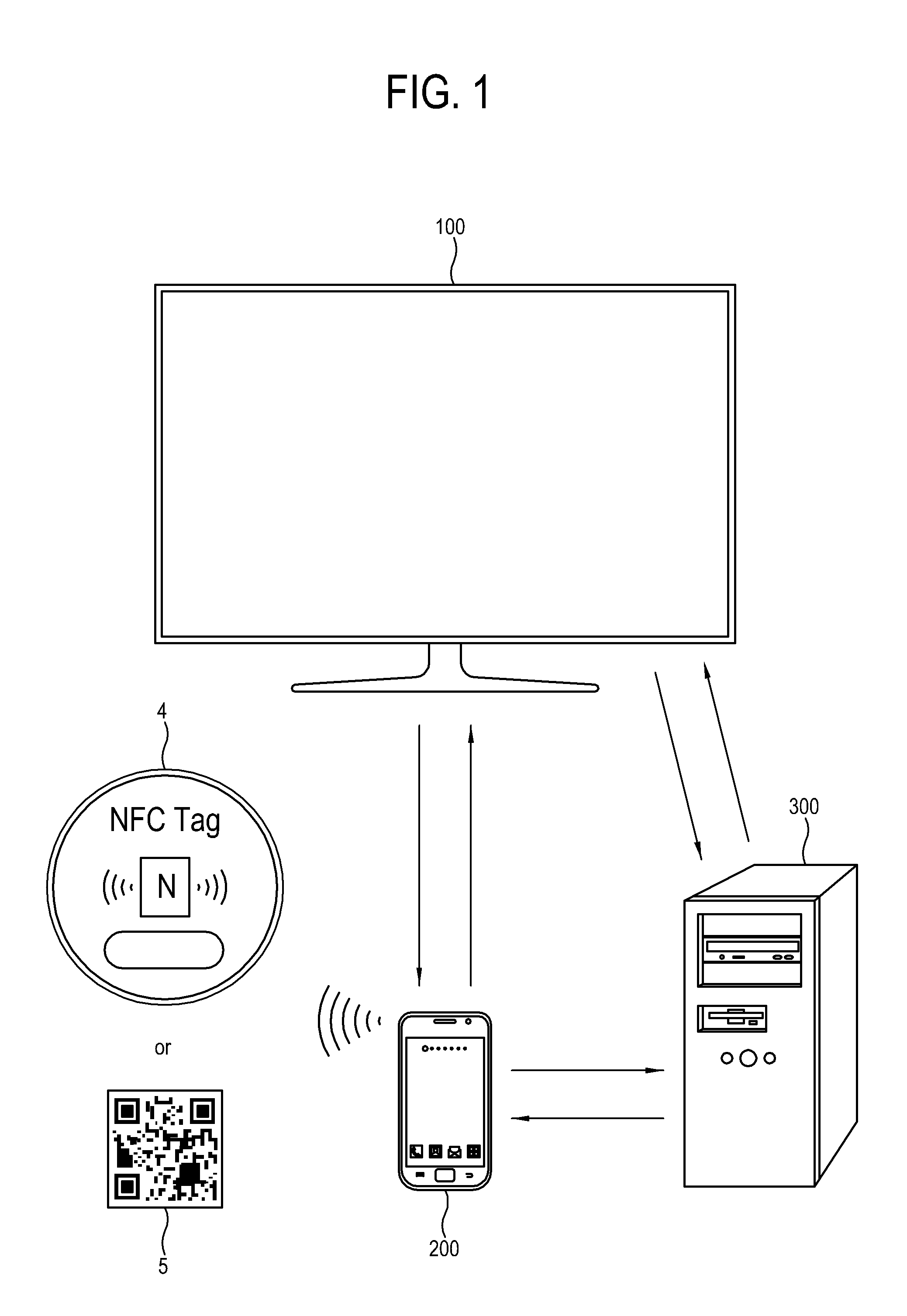
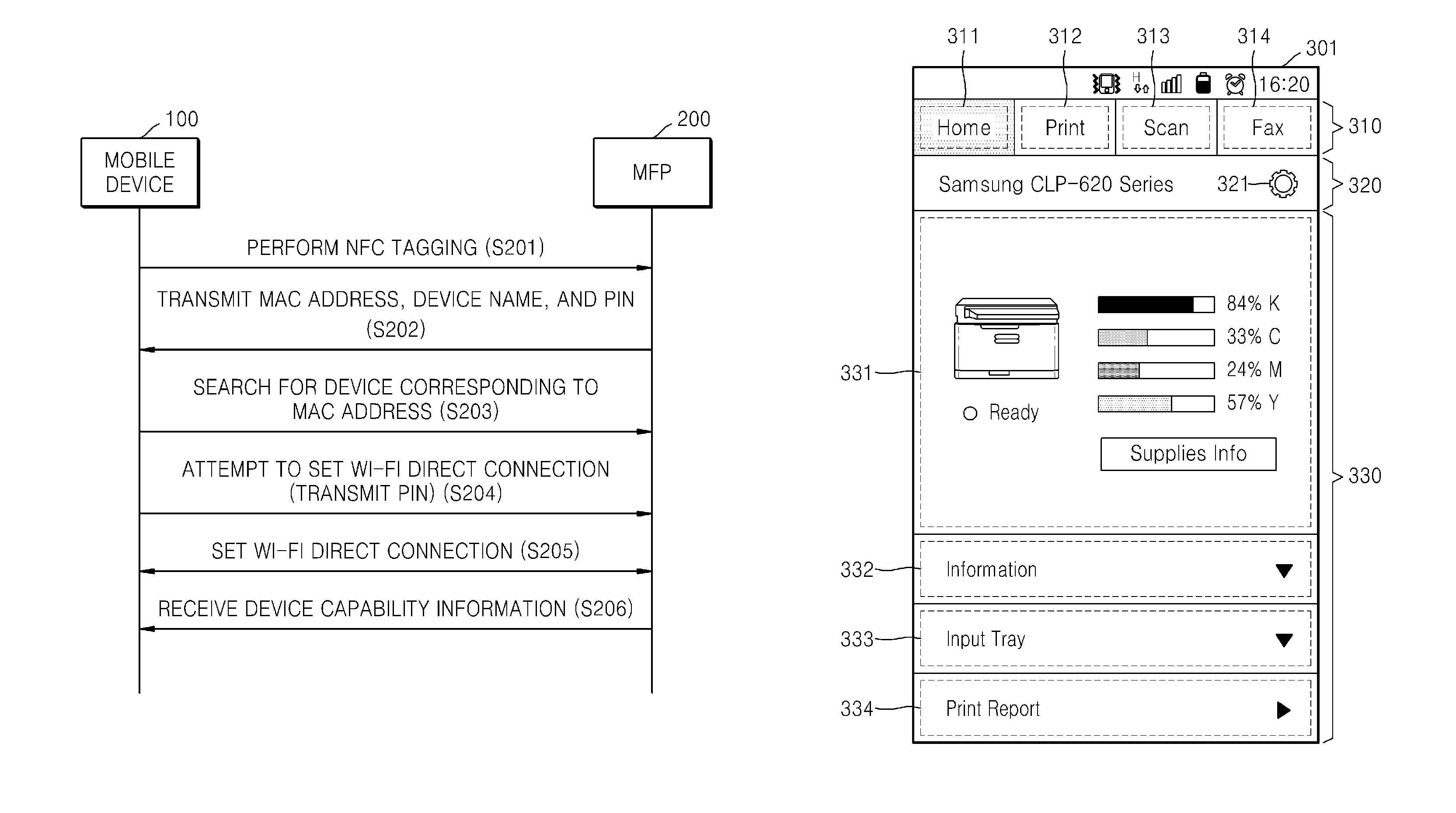
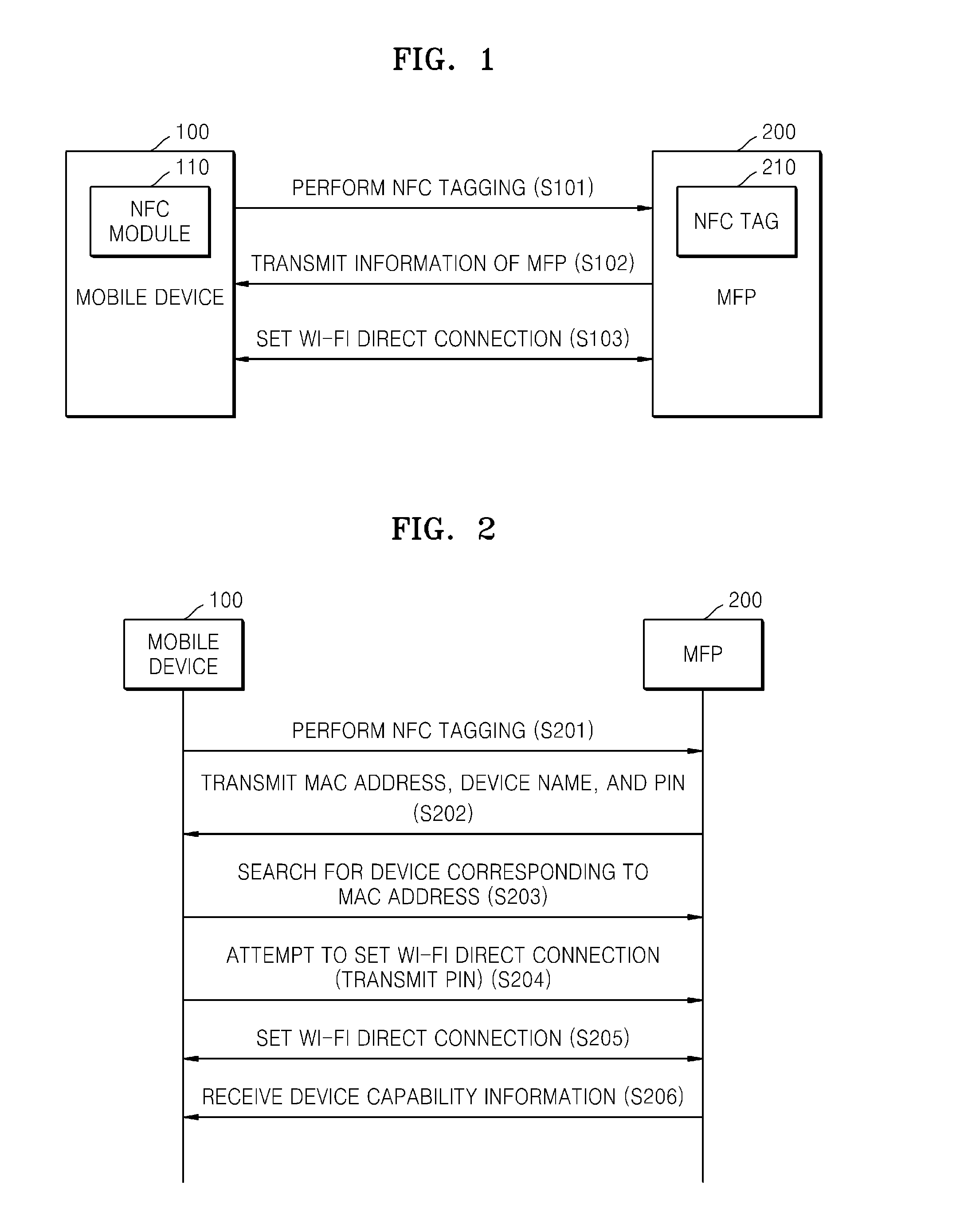
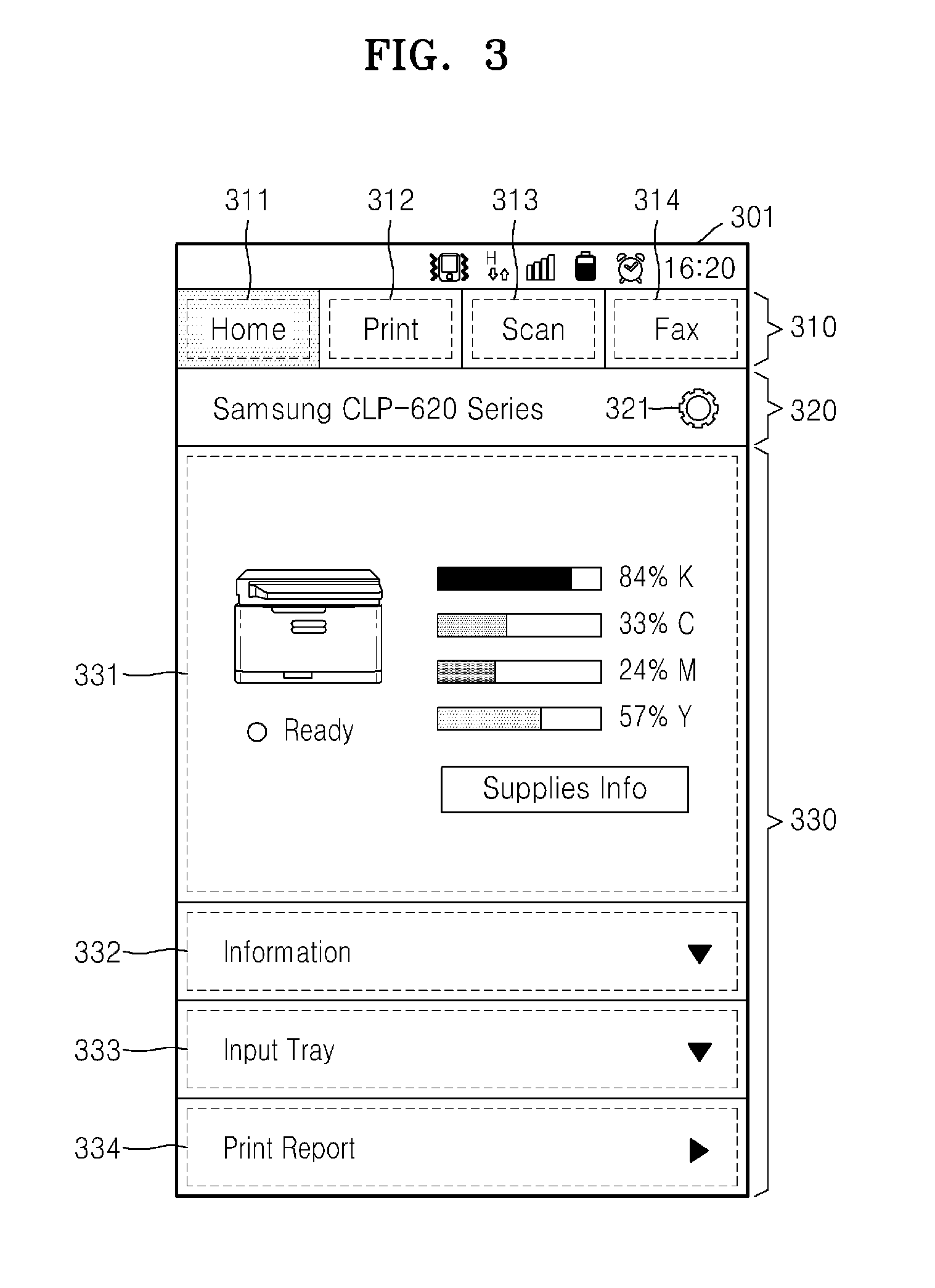
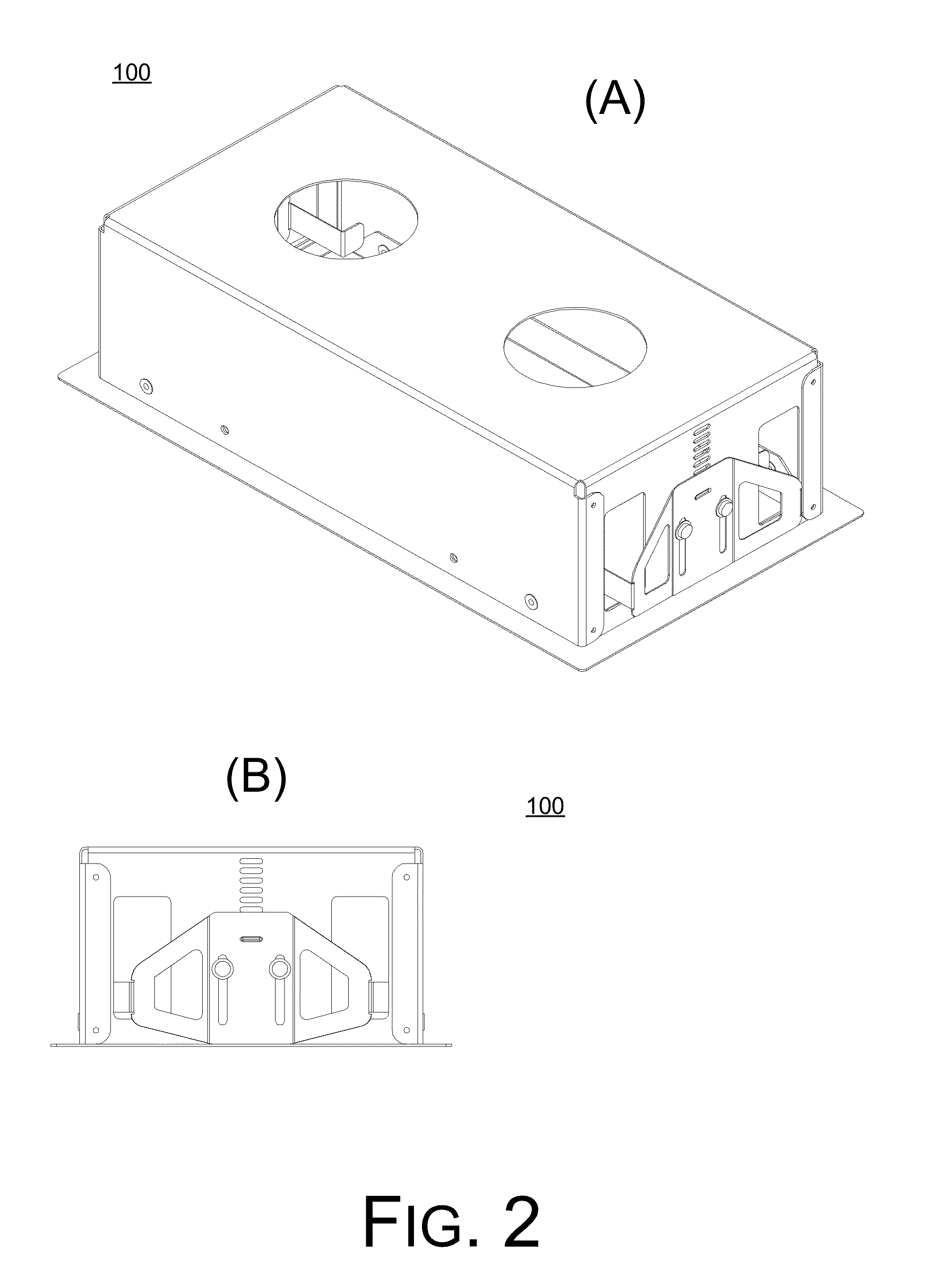
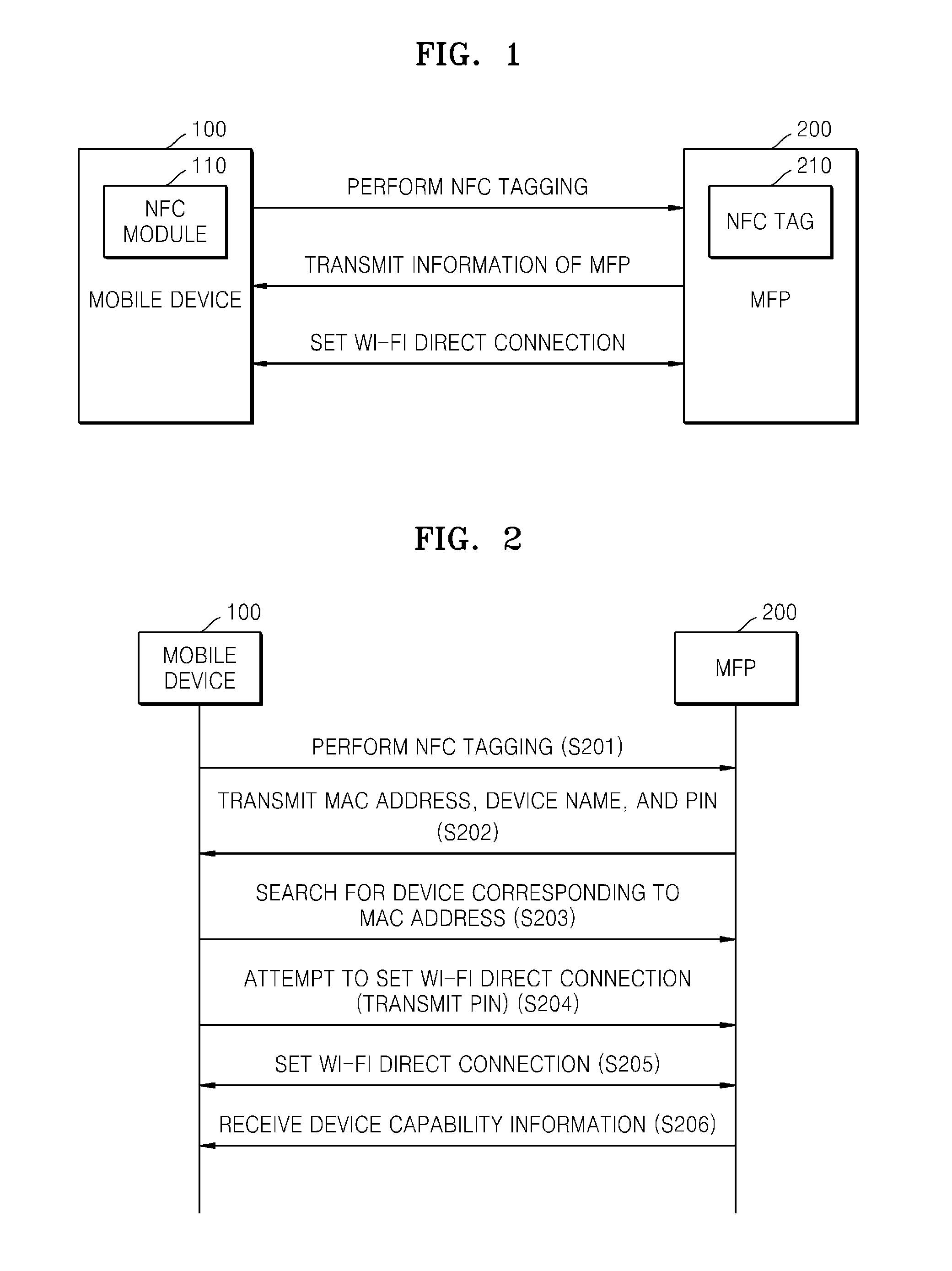
System and method of mobile printing using near field communication
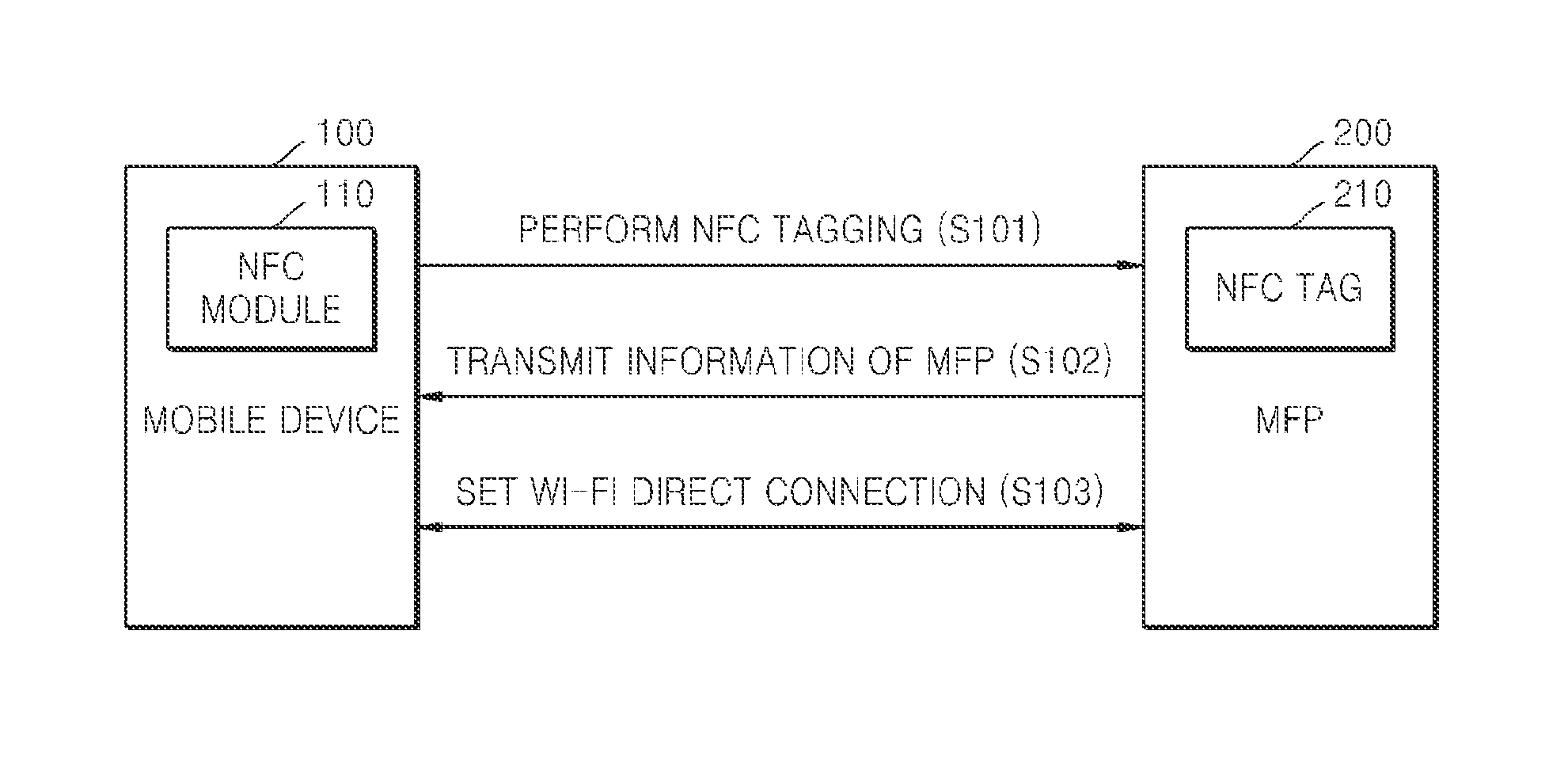
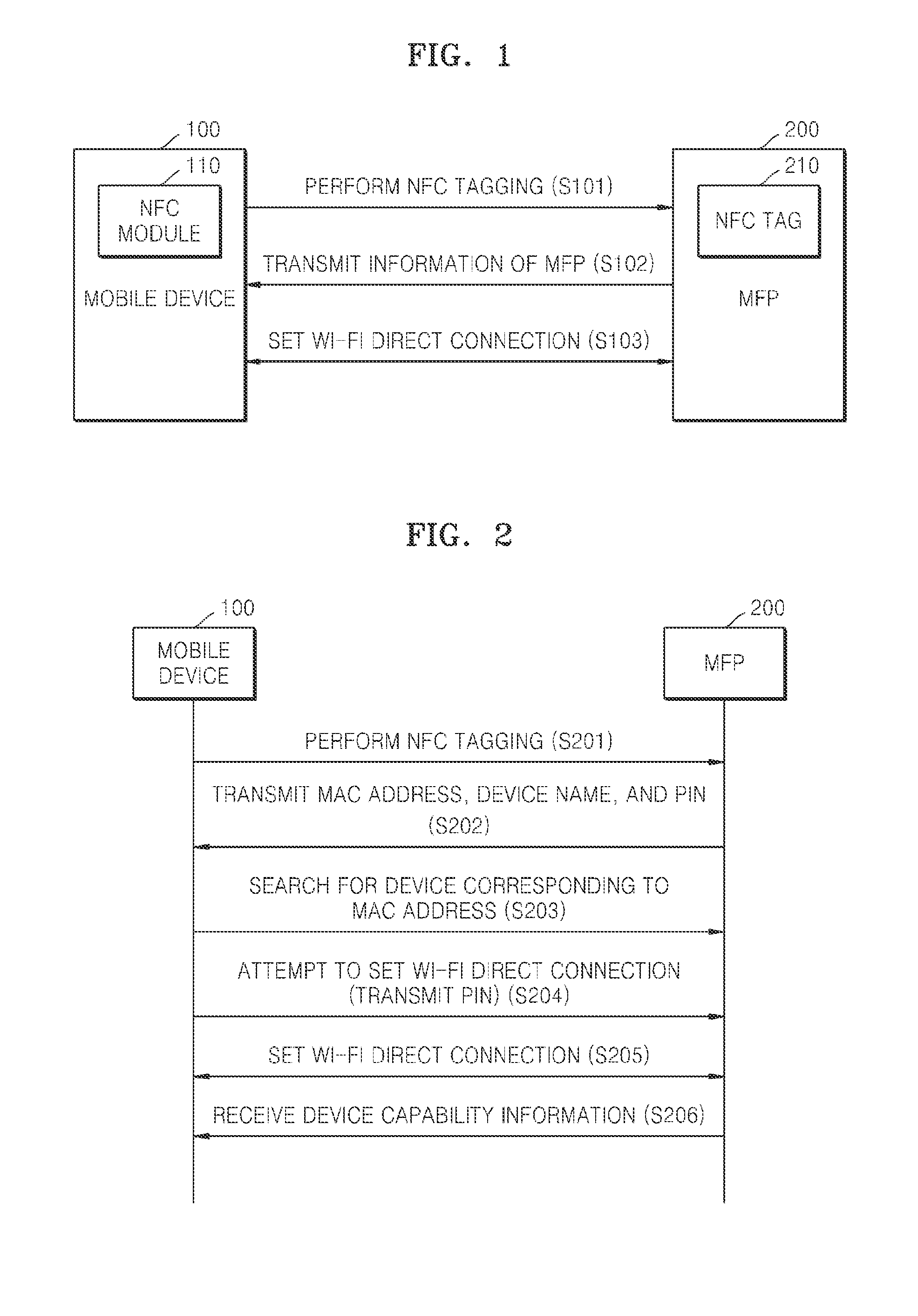
ActiveUS20140355048A1Easily and conveniently performedNetwork topologiesConnection managementImage formationMobile device
A method of mobile printing using near field communication (NFC) includes executing a mobile printing application installed in a mobile device; setting a wireless connection for data transmission between the mobile device and an image forming apparatus by performing NFC tagging on the image forming apparatus with the mobile device; and automatically performing a function corresponding to a status of the mobile printing application when NFC tagging is performed.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
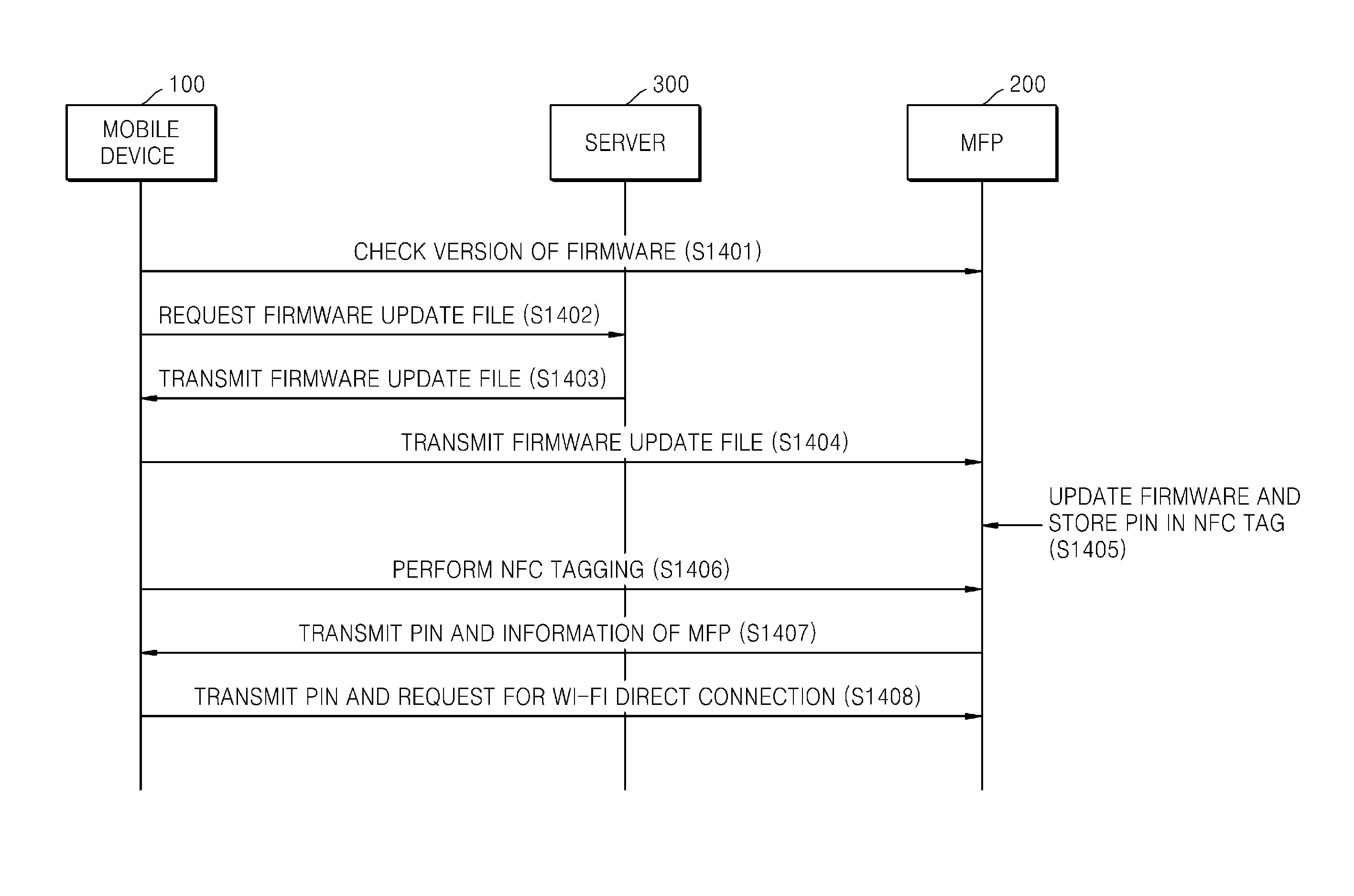
System and method to provide mobile printing using near field communication
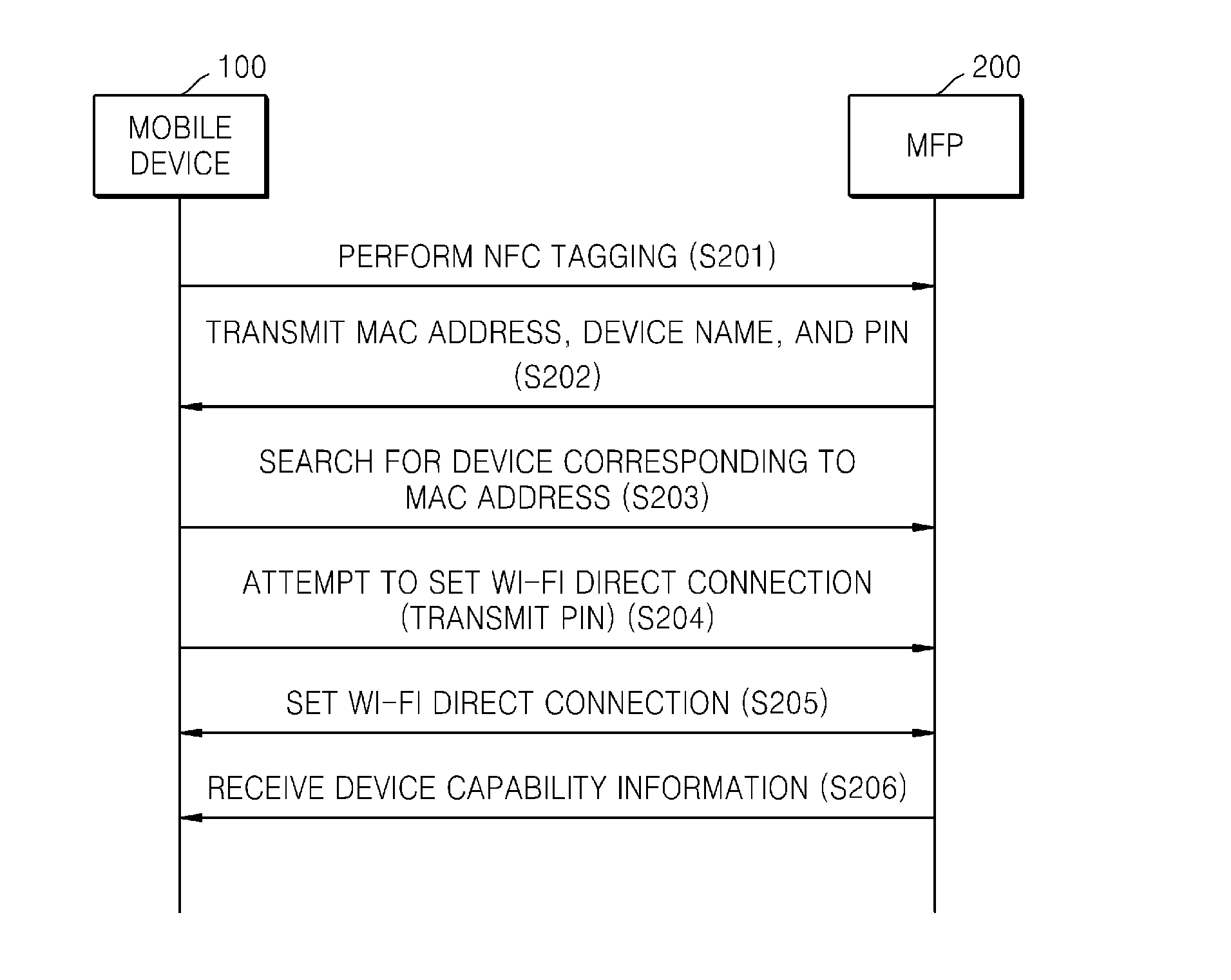
ActiveUS20140355047A1Easily and conveniently performedNear-field systems using receiversShort range communication servicePersonal identification numberNear field communication
A method of mobile printing using near field communication (NFC) includes checking a version of firmware installed in an image forming apparatus; determining whether the checked version of the firmware supports Wi-Fi Direct connection via automatic transmission of a personal identification number (PIN); updating the firmware installed in the image forming apparatus when the checked version of the firmware does not support Wi-Fi Direct connection via automatic transmission of a PIN; encrypting and storing a PIN in an NFC tag attached to the image forming apparatus; setting a Wi-Fi Direct connection by receiving the stored PIN and automatically transmitting the PIN to the image forming apparatus by the mobile device when the mobile device is NFC-tagged to the image forming apparatus; and performing mobile printing via the Wi-Fi Direct connection.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Display apparatus, and method and apparatus for setting up and controlling the same
ActiveUS20140310742A1Easy to implementEasily and conveniently performedAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsHuman–computer interaction
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for identifying mismatch repair glycosylase reactive sites, compounds and uses thereof
InactiveUS6174680B1Shorten the timeIncreased cost-effectivenessSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSufficient timeReactive site
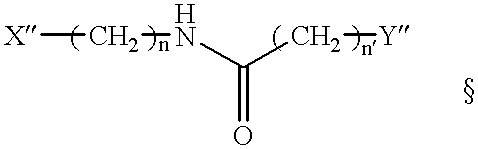
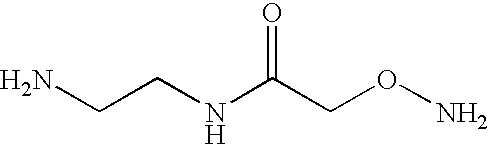
The present application discloses a method of identifying mutations in a target DNA sequence. The method involves:(a) hybridizing the target DNA sequence with a control DNA sequence wherein said control DNA sequence is the wild-type DNA sequence corresponding to the target DNA sequence to create a duplex;(b) treating the duplex to remove any spontaneous aldehydes;(c) reacting the duplex with a repair glycosylase to convert any mismatched sites in the duplex to reactive sites containing an aldehyde-containing abasic site;(d) reacting the duplex with a compound of the formula X-Z-Y, wherein X is a detectable moiety, Y is NHNH2, O-NH2 or NH2, and Z is a hydrocarbon, alkyhydroxy, alkylethoxy, alkylester, alkylether, alkylamide or alkylamine, wherein Z may be substituted or unsubstituted; and wherein Z may contain a cleavable group; for a sufficient time and under conditions to covalently bind to the reactive sites;(e) detecting the bound compound to identify sites of mismatches;(f) determining where the mismatch occurs; and(g) determining whether the mismatch is a mutation or polymorphisms.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Mutation scanning array, and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20020155451A1Avoid difficult choicesProcess controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPresent methodMicrosphere
The present method is directed to using a mutation scanning array to identify mismatches or polymorphisms in multiple genes or the same gene in multiple individuals. The array can be a chip or a microsphere. Preferably, the array has elements containing immobilized oligonucleotides that collectively span at least 10 different whole genes.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
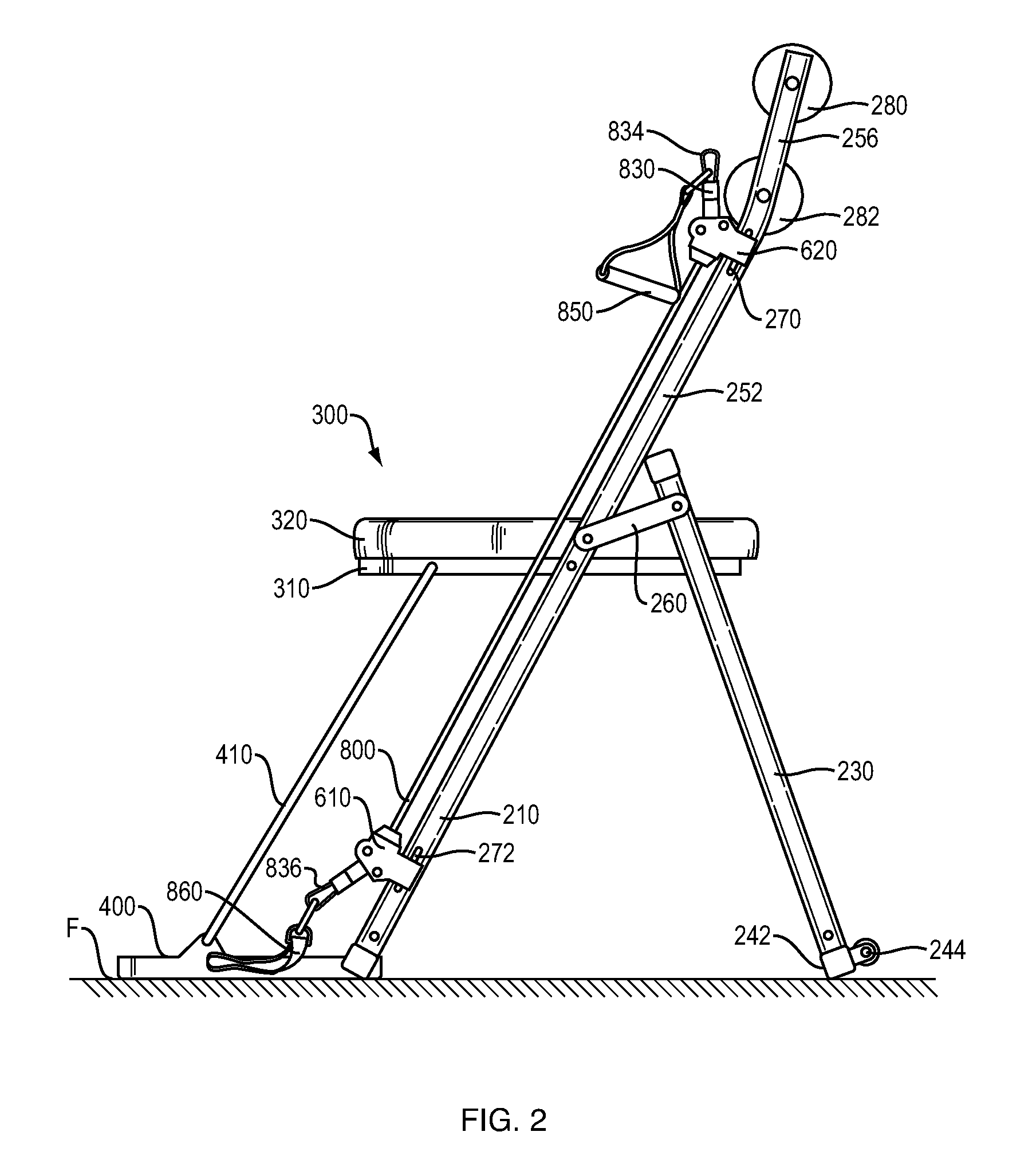
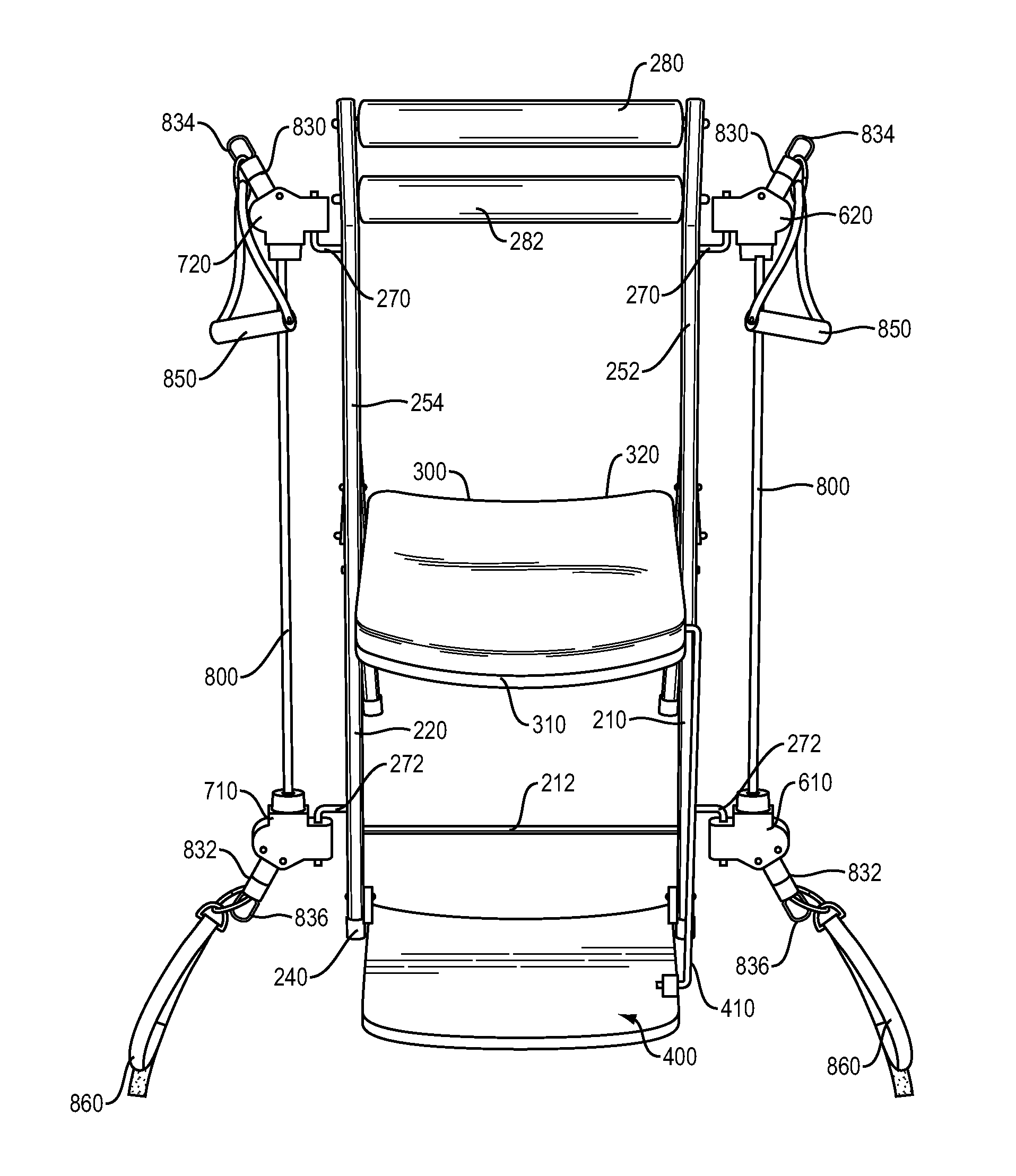
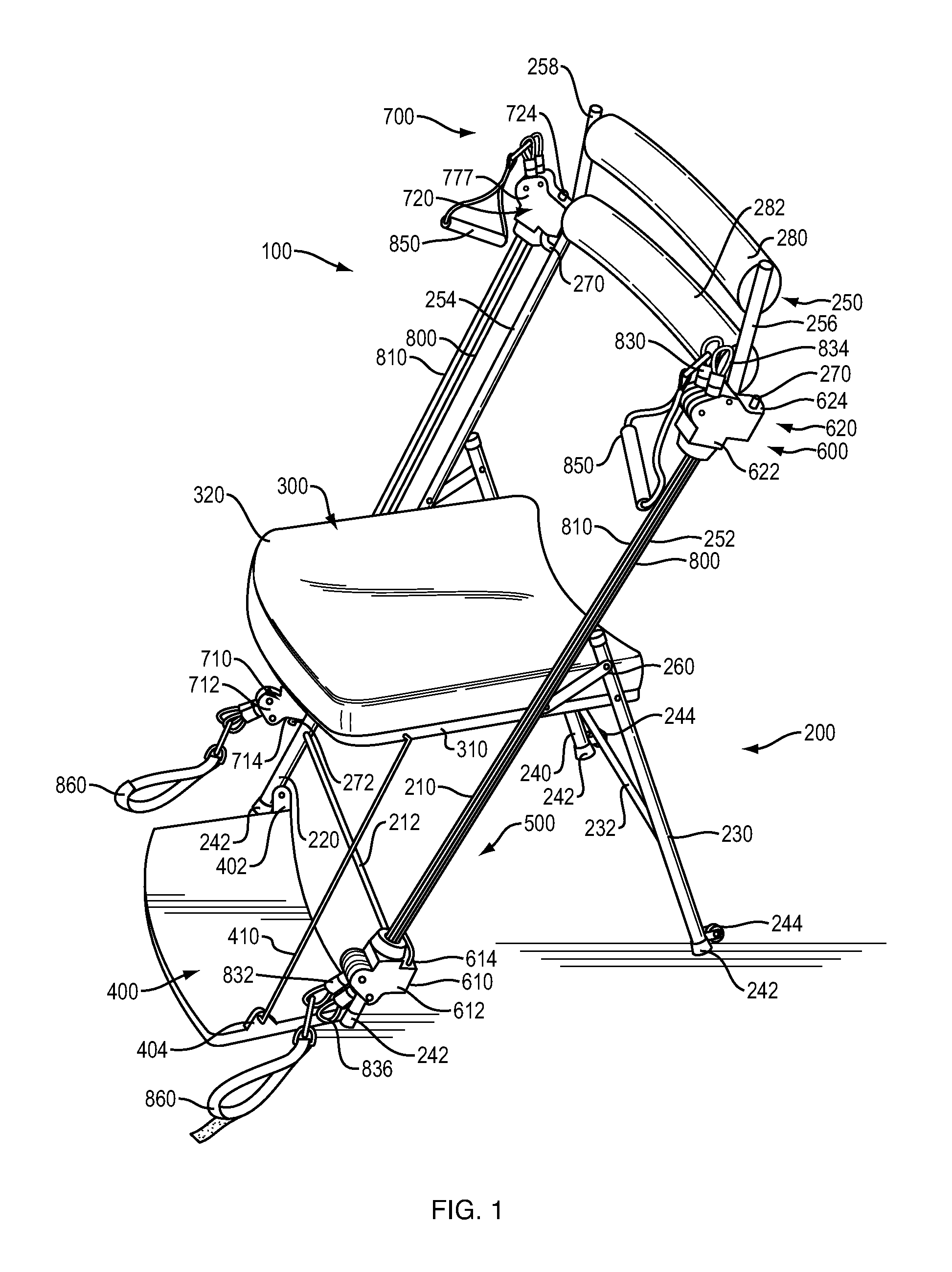
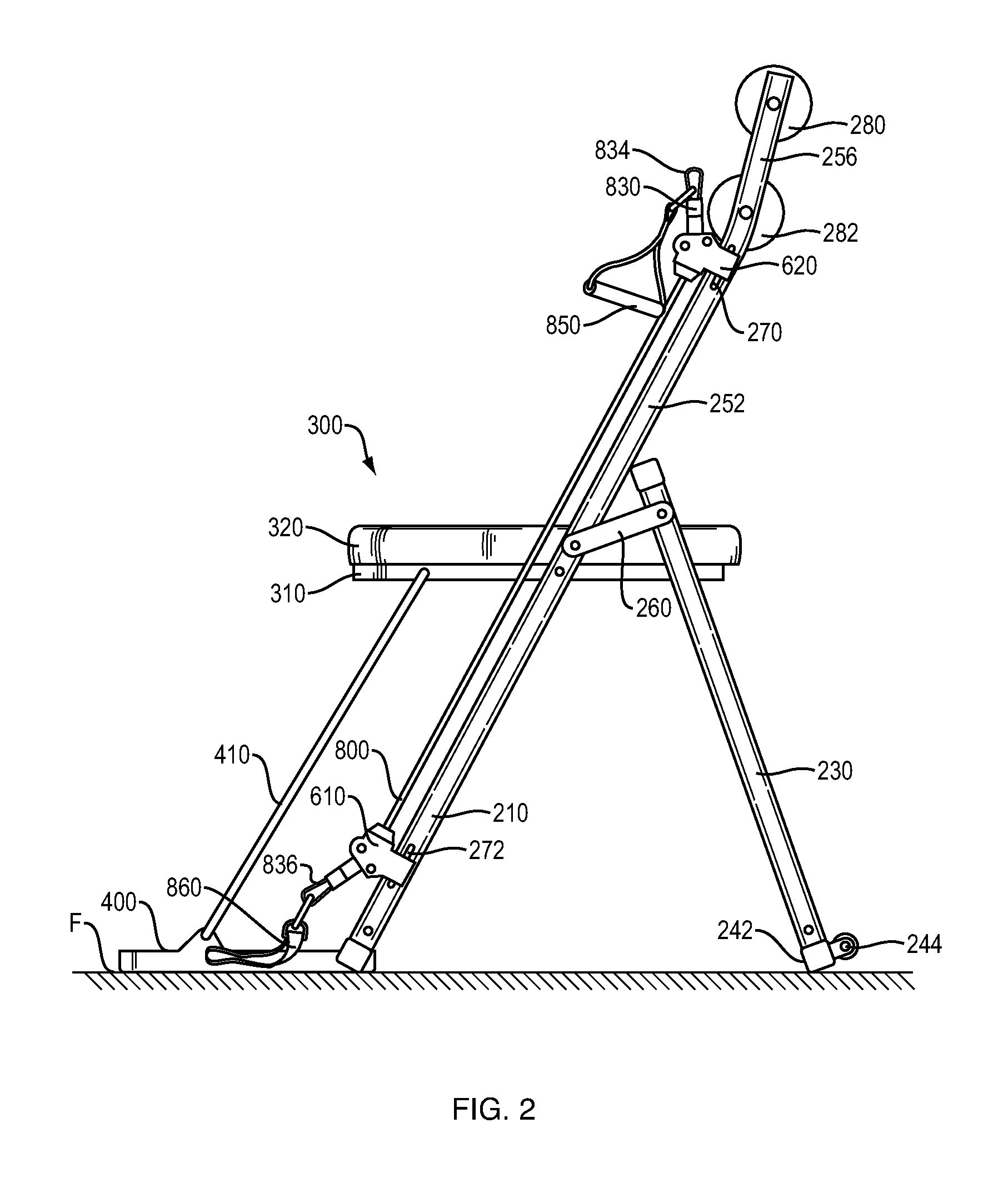
Portable fitness chair
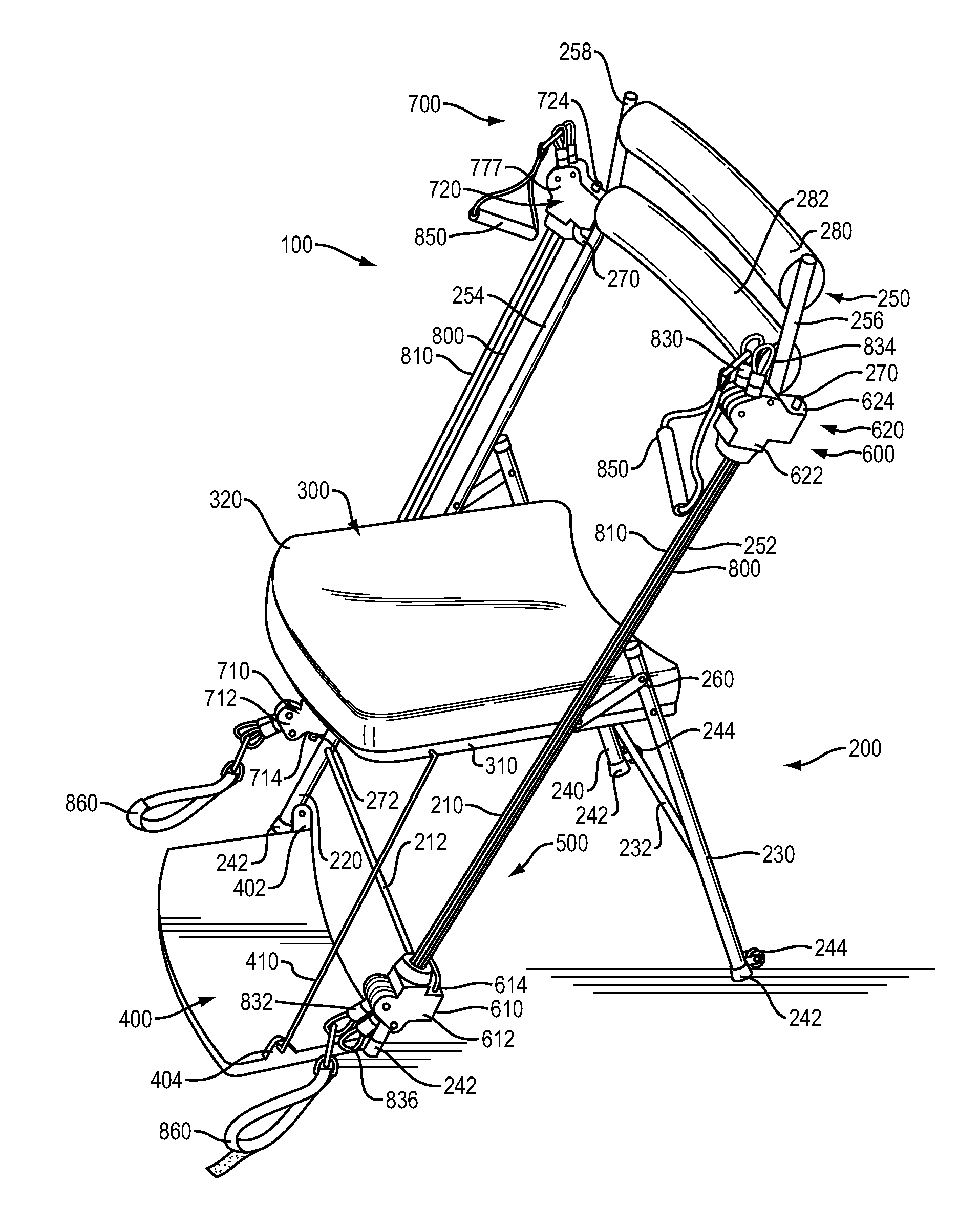
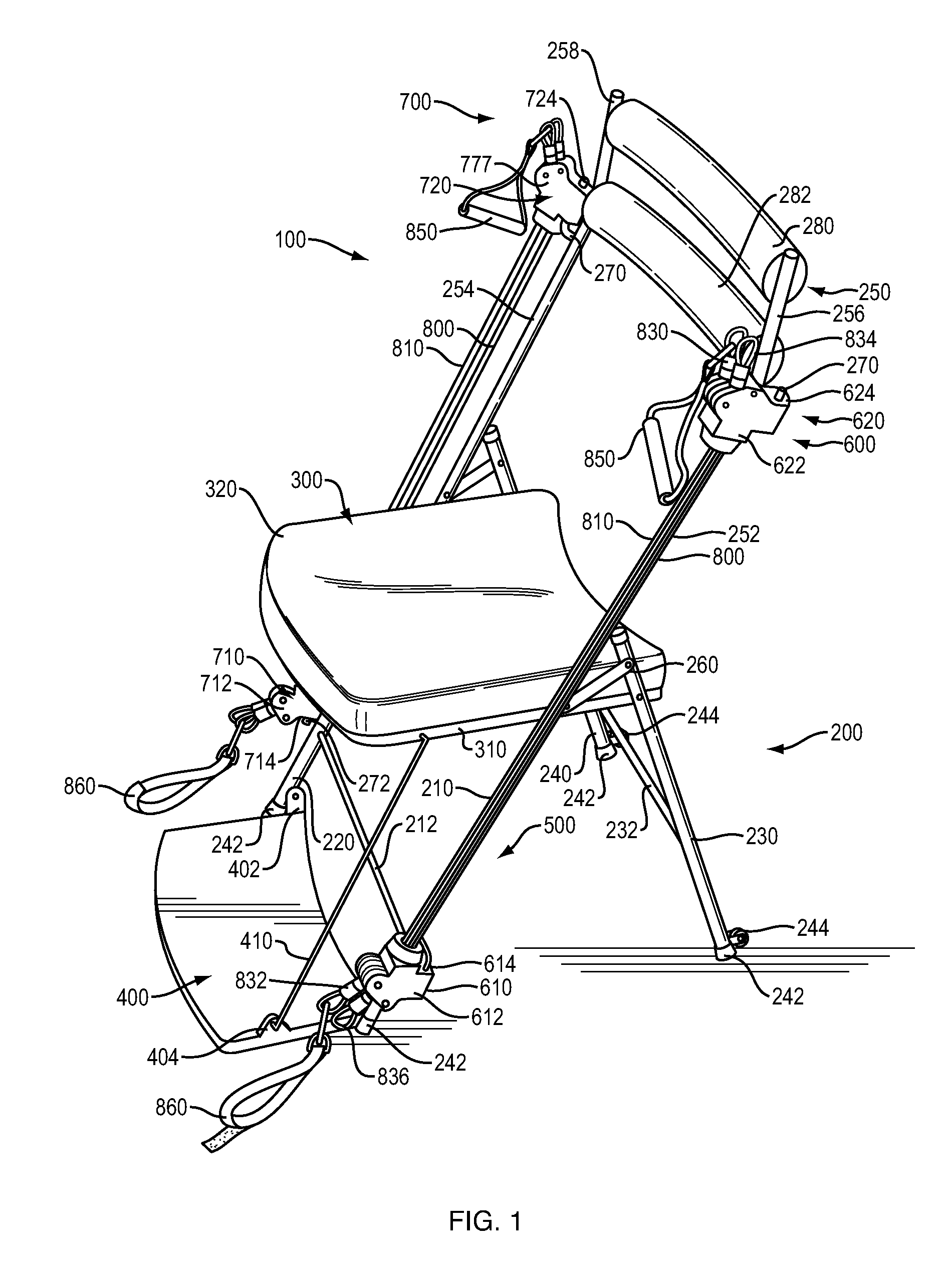
ActiveUS20130157818A1Guaranteed balance and stabilityMaintain relatively stableResilient force resistorsMovement coordination devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A portable exercise chair that includes a chair frame, a chair seat and a resistance system. The resistance system includes first and second resistance arrangements. Each of the resistance arrangements includes first and second resistance hubs and a stretchable resistance member. The resistance hubs on the first and second resistance arrangements are releasably and swivelly connected to the chair frame. The resistance system is designed to enable a user to perform a variety of exercises. The portable exercise chair can include a retractable foot plate.
Owner:NABILE INNOVATIONS
Multi-purpose vacuum suction apparatus
InactiveUS7708245B2Good adhesionEasy detachmentStands/trestlesKitchen equipmentSuction forceEngineering
Disclosed is a multi-purpose vacuum suction apparatus which can be easily attached to or detached from a smooth and hard object surface and which can substantially increase suction force. The multi-purpose vacuum suction apparatus includes an elastic member for returning one or more operating members to the original positions thereof, and a vacuum suction plate unit having a multi-purpose connector, wherein an ornamental member for use in various ornamentation or advertisement can be fitted into or assembled with the top end of the multi-purpose connector.
Owner:WOO
System and method of mobile printing using near field communication
InactiveUS20150248265A1Easily and conveniently performedNetwork topologiesConnection managementImage formationMobile device
A method of mobile printing using near field communication (NFC) includes executing a mobile printing application installed in a mobile device; setting a wireless connection for data transmission between the mobile device and an image forming apparatus by performing NFC tagging on the image forming apparatus with the mobile device; and automatically performing a function corresponding to a status of the mobile printing application when NFC tagging is performed.
Owner:S PRINTING SOLUTION CO LTD
Complexes of ultraviolet absorbers and quaternary ammonium compounds which are substantially free from unwanted salts
InactiveUS6046330AUneven solubilityPoor coatingBiocideOrganic detergent compounding agentsInorganic saltsAmmonium compounds
This invention relates to complexes of ultraviolet absorbers with quaternary ammonium compounds which are substantially free from unwanted salts. Such complexes are formed through ionic bonds formed between the two compounds. The inventive complexes are then removed of substantially all excess inorganic salt so as to obtain an UV absorber compound which exhibits improved light- and washfastness properties, which easily coats subject surfaces, which provides excellent non-fogging and non-cracking characteristics, and which also possesses anti-static, anti-microbial, and anti-abrasion properties. This invention also concerns methods of making and utilizing such inventive ultraviolet absorbing complexes.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Portable fitness chair
ActiveUS8876676B2Easily and conveniently performedEasy to storeResilient force resistorsMovement coordination devicesEngineeringResistance force
A portable exercise chair that includes a chair frame, a chair seat and a resistance system. The resistance system includes first and second resistance arrangements. Each of the resistance arrangements includes first and second resistance hubs and a stretchable resistance member. The resistance hubs on the first and second resistance arrangements are releasably and swivelly connected to the chair frame. The resistance system is designed to enable a user to perform a variety of exercises. The portable exercise chair can include a retractable foot plate.
Owner:NABILE INNOVATIONS
Method and article for applying and monitoring a surfactant
InactiveUS7544409B2Easily and conveniently performedCosmetic preparationsMake-upEngineeringBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Owner:SPENCERHALL
Wireless charging equipment, terminal, wireless charging system comprising the same, control method thereof and non-transitory computer readable storage medium having computer program recorded thereon
ActiveUS20160094083A1Improve system efficiencyIncrease the scope of applicationCircuit authenticationData switching current supplyComputer terminalInductive charging
Provided are wireless charging equipment, a terminal, a wireless charging system comprising the same, a control method thereof, and a non-transitory computer readable storage medium having computer program recorded thereon. That is, the present invention performs a charging function based on a charging signal in the corresponding terminal by transmitting the charging signal to only the terminal corresponding to a communication provider or an affiliated company pre-registered in the wireless charging equipment to provide a charging function to only the pre-registered terminal with respect to a terminal to use a wireless charging infrastructure, easily and conveniently perform an authentication function for the terminal without a separate additional component, and improve operation efficiency of the entire wireless charging system.
Owner:SK PLANET CO LTD
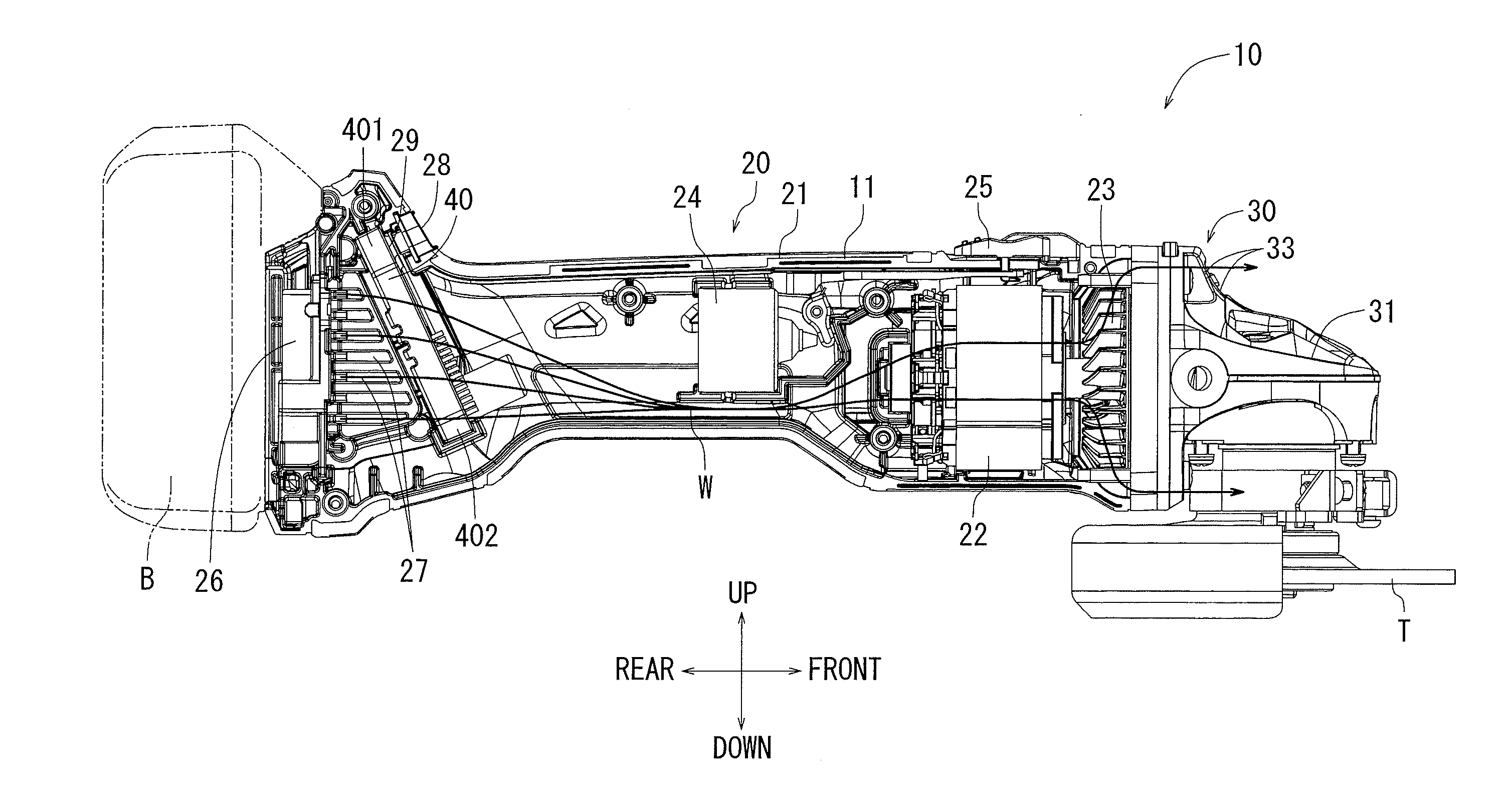
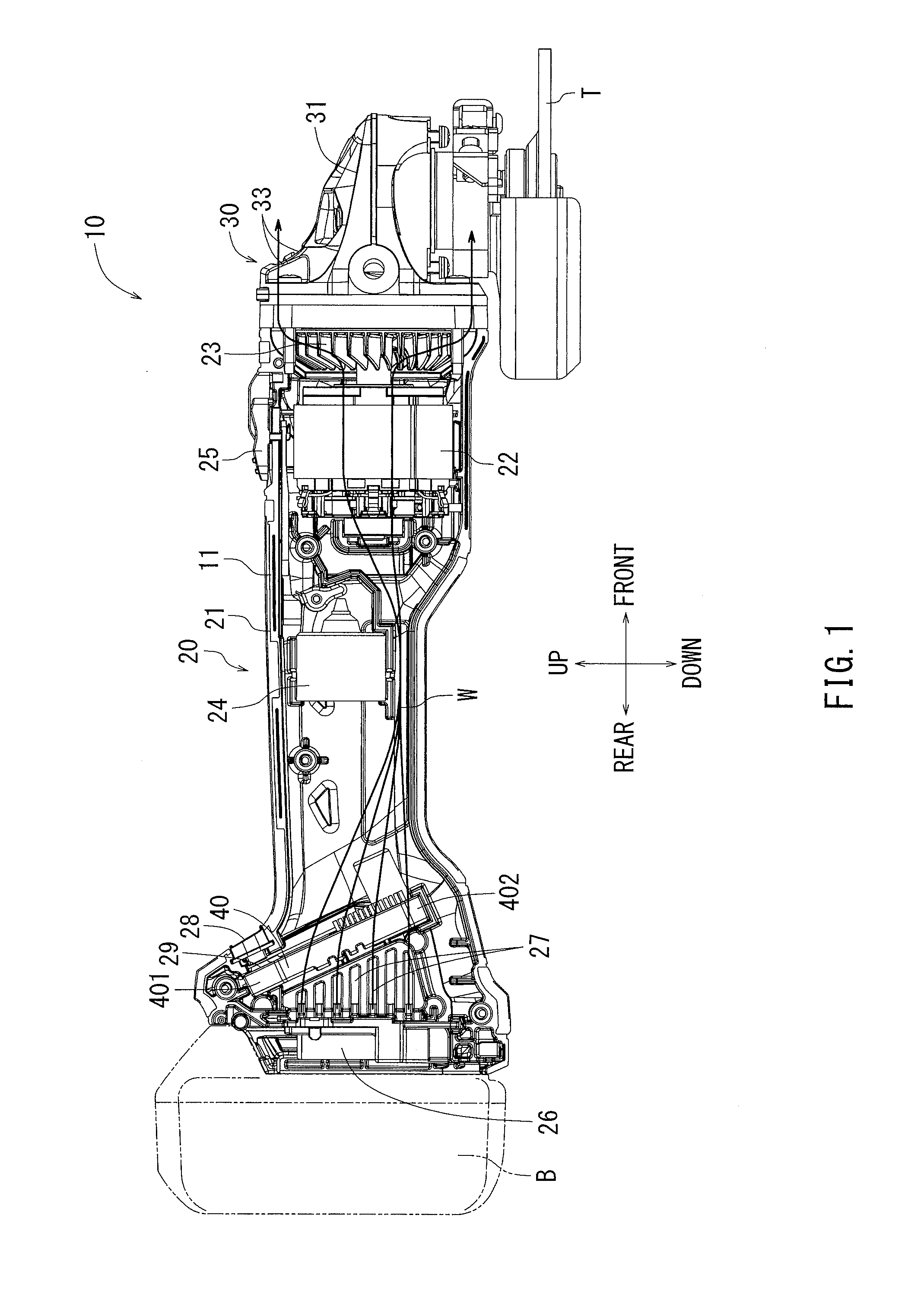
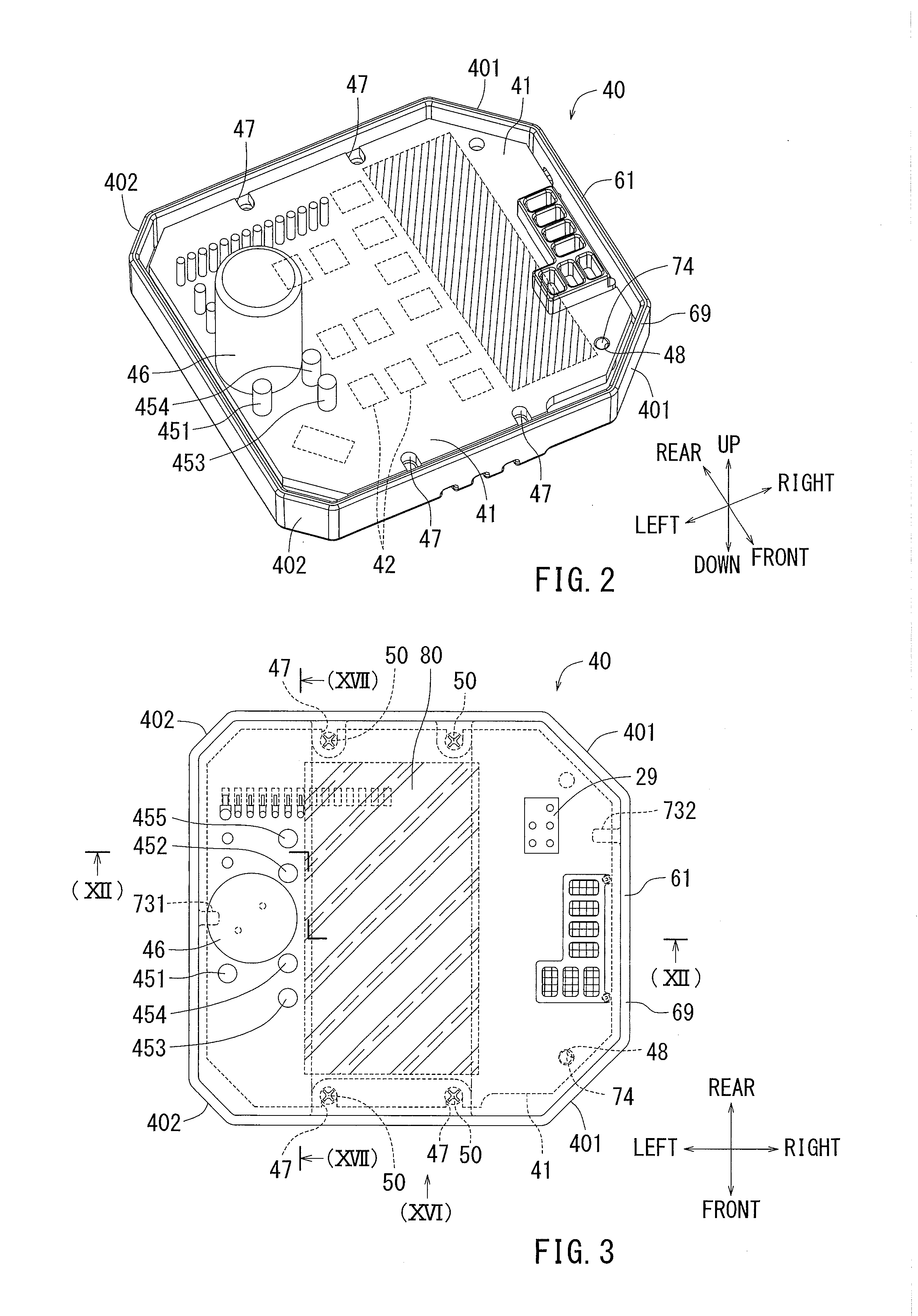
Electric power tool
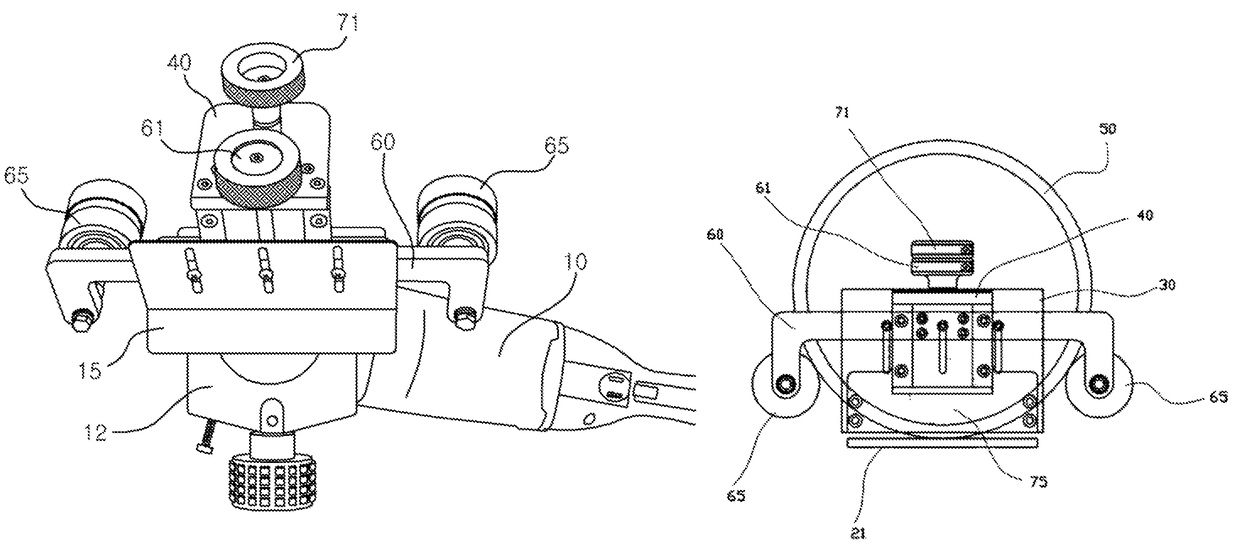
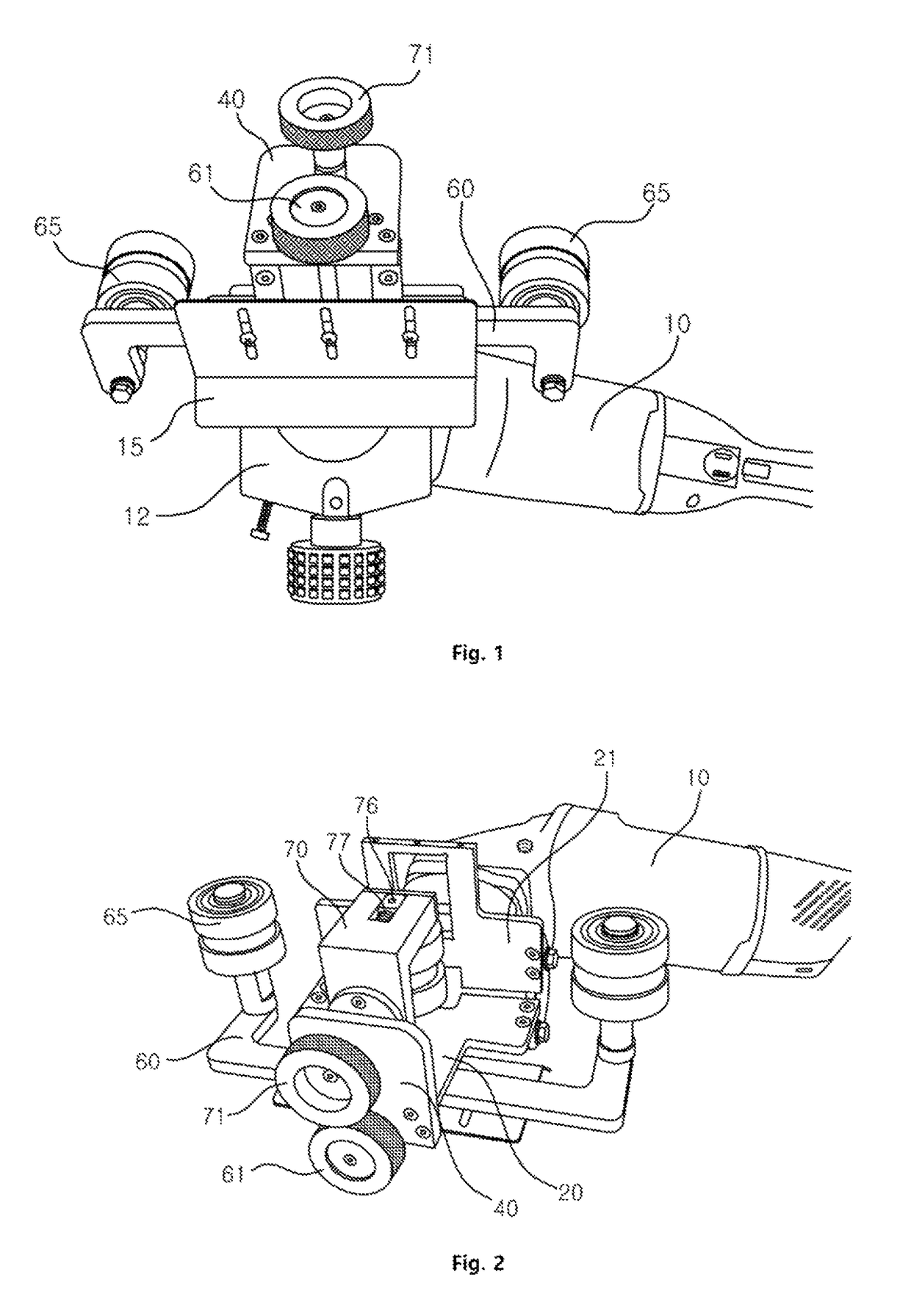
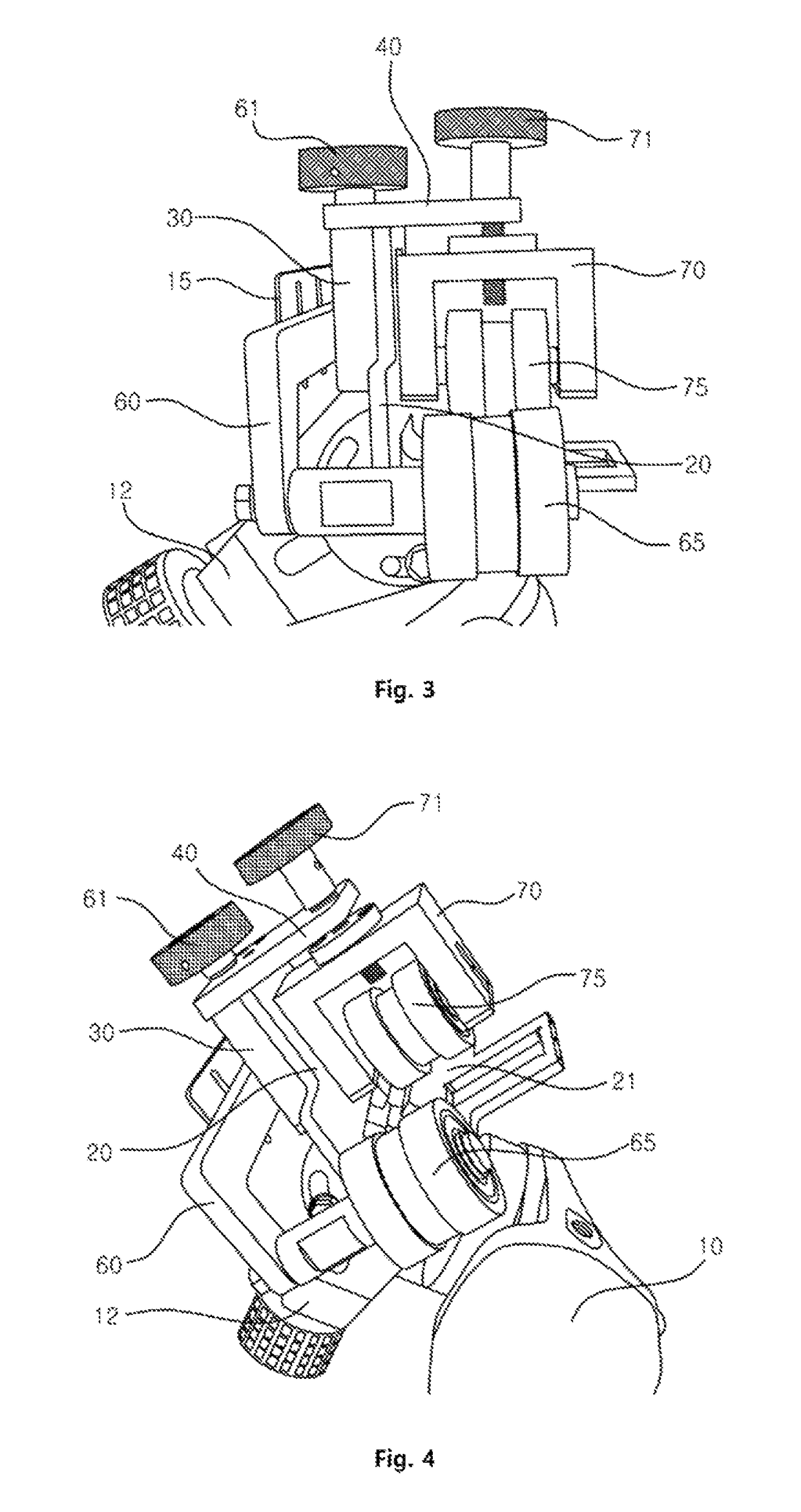
ActiveUS20160020676A1Easily and conveniently performedEasy to implementAssociation with control/drive circuitsPortable grinding machinesElectric power systemEngineering
In an electric power tool which houses a motor and a controller for controlling drive of the motor, the controller has a circuit board on which electric components are mounted and a heat radiation member which radiates heat of the electric components. The heat radiation member has a facing part which faces the circuit board in parallel to a board surface of the circuit board. The facing part is provided with steps by which a distance between the facing part and the board surface of the circuit board varies. Furthermore, the facing part of the heat radiation member is provided with a first facing part in which a relative distance with respect to the board surface of the circuit board is reduced.
Owner:MAKITA CORP
Method and article for applying and monitoring a surfactant
InactiveUS20060016352A1Easy and convenient to performEasily and conveniently performedCosmetic preparationsRotary intaglio printing pressEngineeringBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention is directed to a method and an article for performing the method of monitoring a surfactant. A preferred embodiment of the invention, an article comprises a substrate having an image and a surfactant thereon. The substrate is formed from various known fabrics or materials capable of absorbing and retaining a substantial quantity of the surfactant. During use, as the surfactant is dissipated, the image changes in appearance thereby indicating the quantity of surfactant remaining on the substrate. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the method and article of the present invention is effective for encouraging and making washing enjoyable for children and includes the use of an epidermal surfactant, such as soap, detergent, or other active ingredient.
Owner:SPENCERHALL
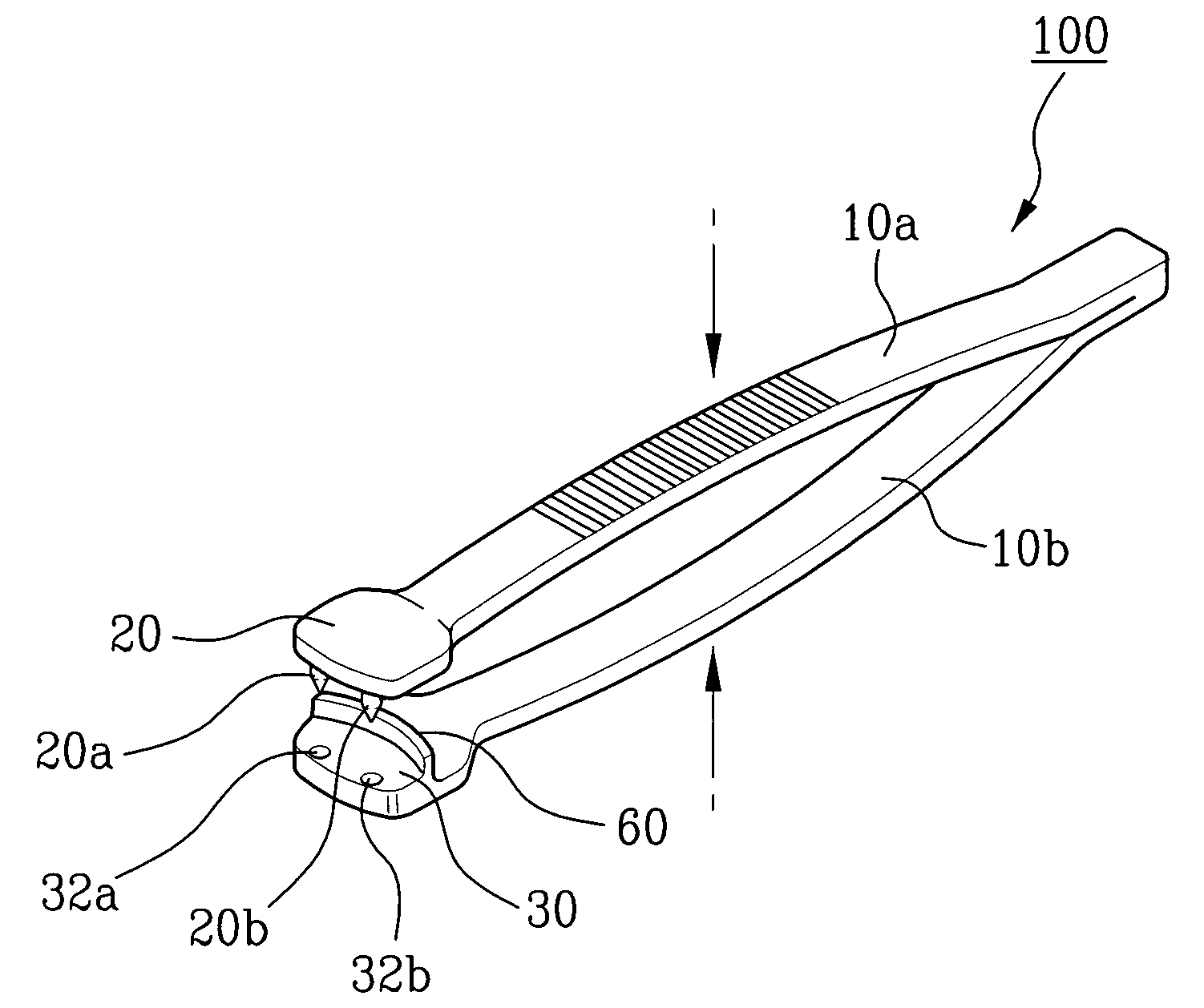
Ratchet wrench being conveniently assembled
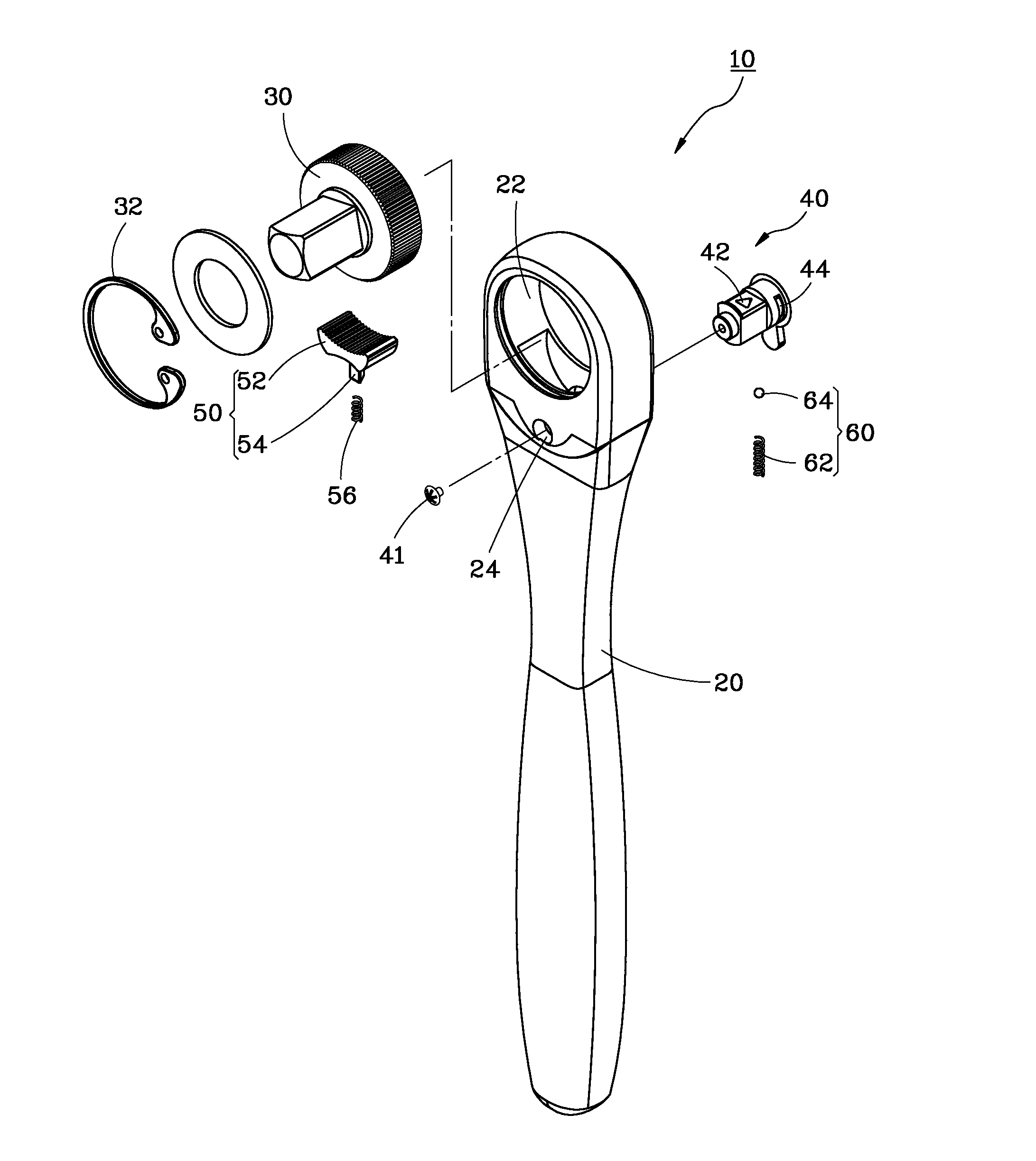
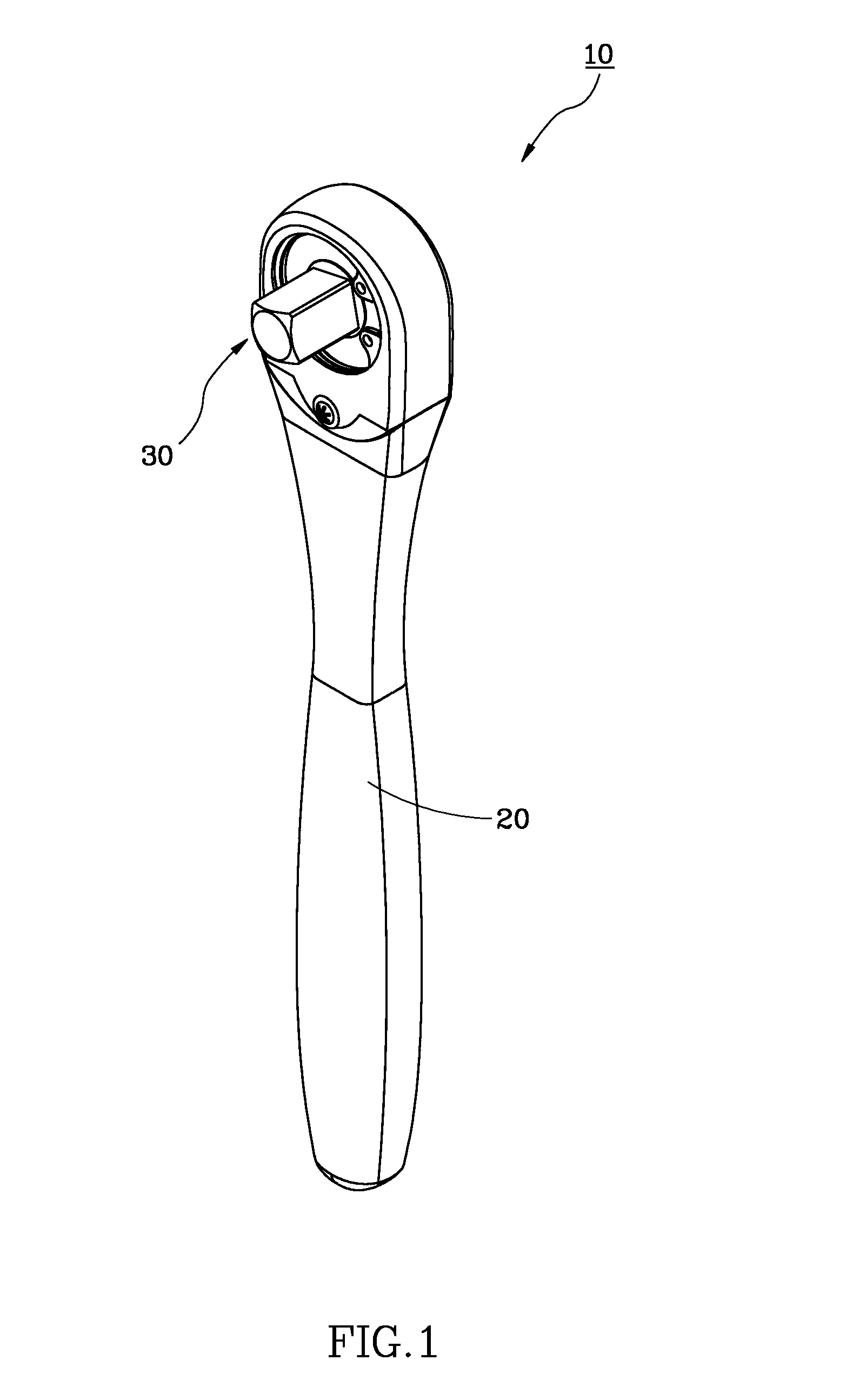
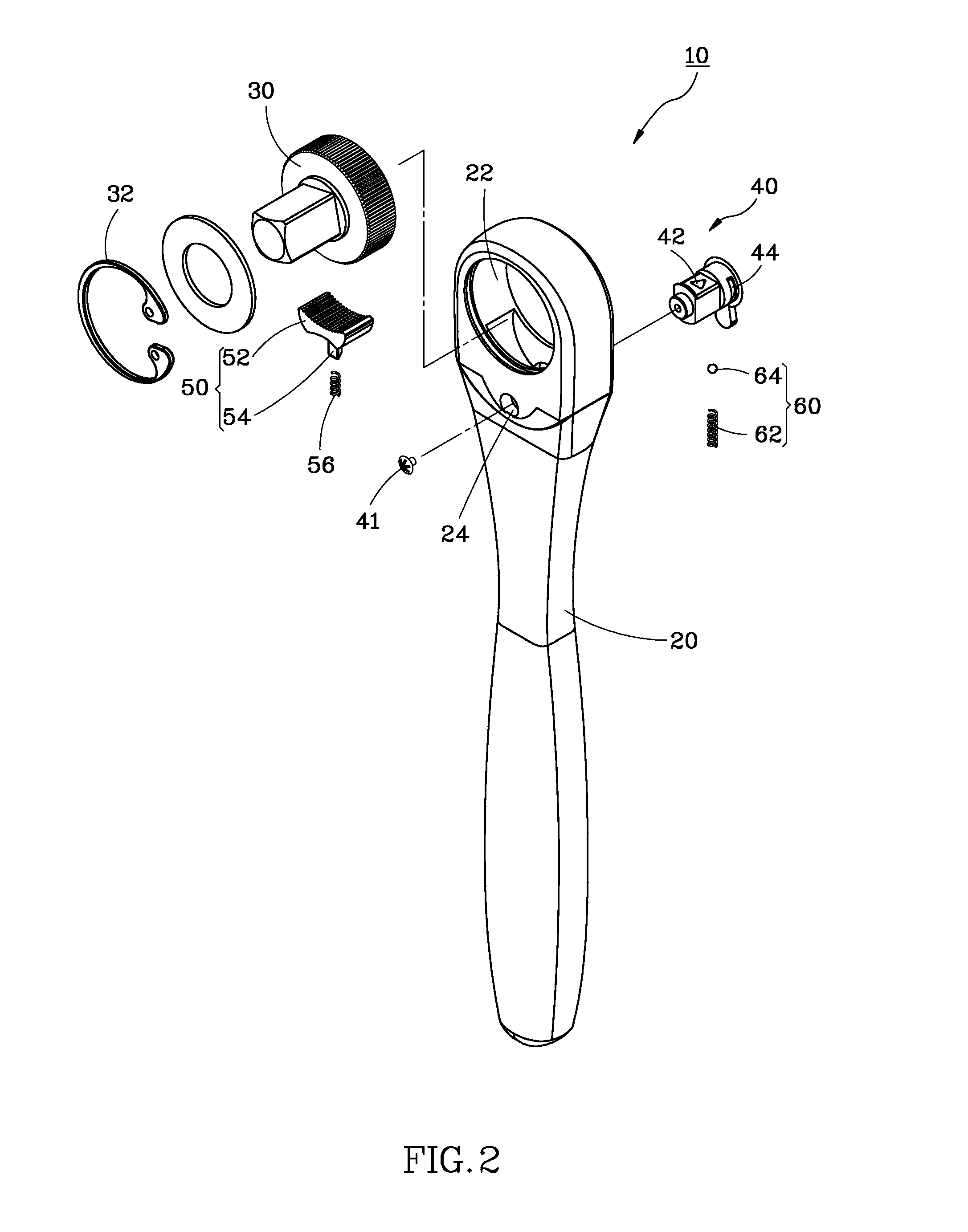
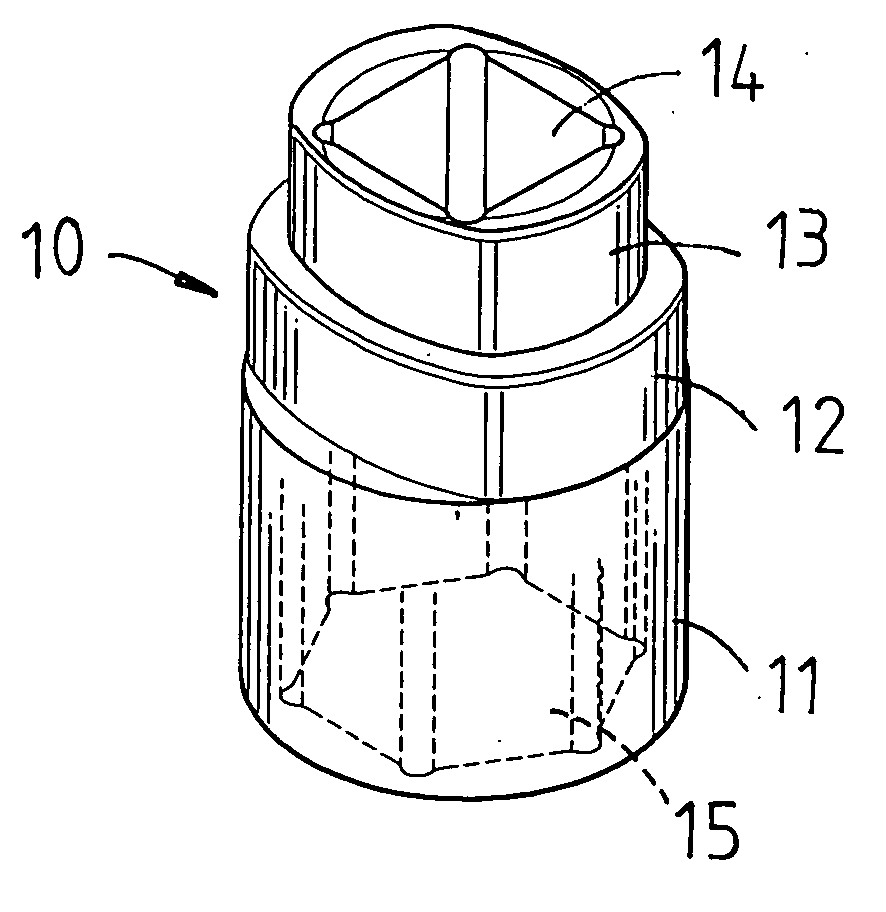
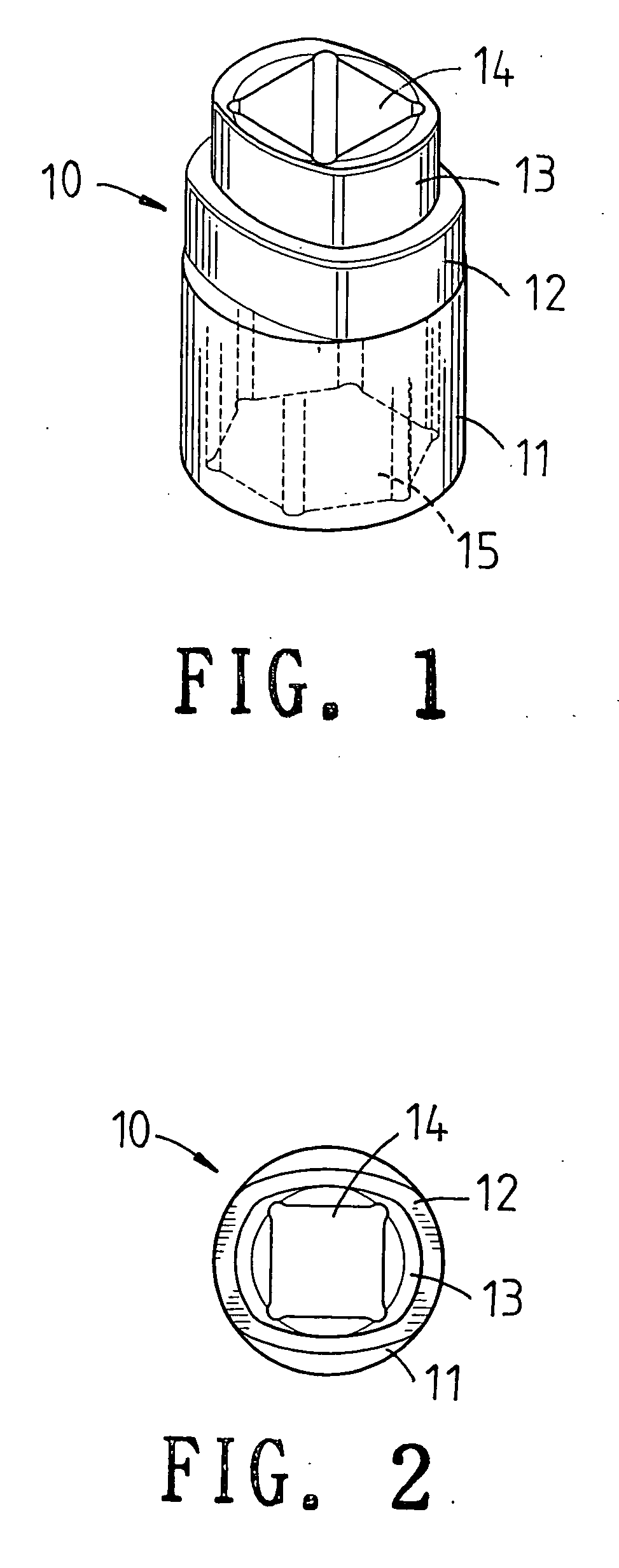
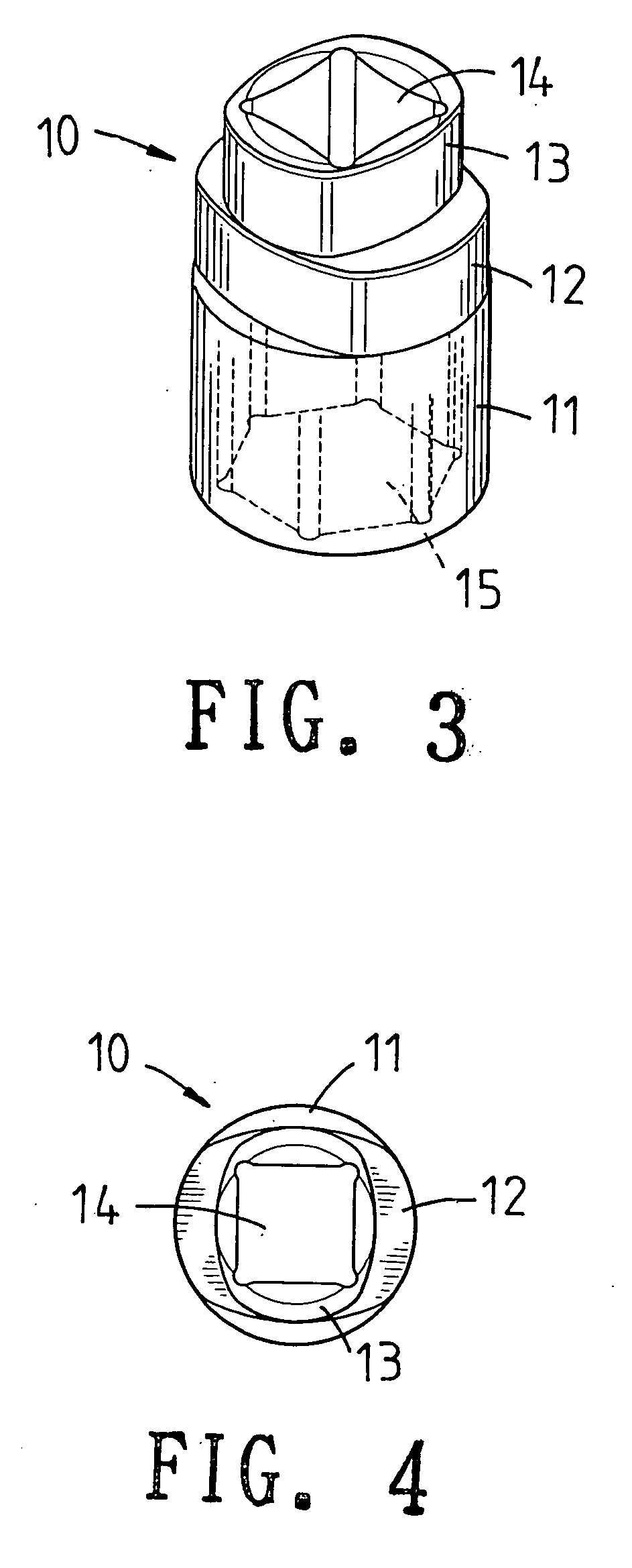
ActiveUS20130139655A1Easily and conveniently performedConveniently performedSpannersWrenchesEngineeringWrench
A ratchet wrench includes a handle having a receiving hole, a ratchet wheel rotatably mounted in the handle, a direction controller pivotally mounted in the handle and provided at a periphery thereof with a guide groove, a pawl connected with the direction controller and engaged with the ratchet wheel, and a positioning member. When the direction controller is in a first position, a positioning ball of the positioning member is slidable to the receiving hole of the handle through the guide groove. When the direction controller is turned to a second position, the positioning ball is supported by a spring and engaged with a positioning notch of the direction controller so as to hole the direction controller in position.
Owner:CHANG CHIH MIN
System and method of mobile printing using near field communication
ActiveUS9459822B2Easily and conveniently performedNear-field transmissionNetwork topologiesComputer hardwareImage formation
A method of mobile printing using near field communication (NFC) includes executing a mobile printing application installed in a mobile device; setting a wireless connection for data transmission between the mobile device and an image forming apparatus by performing NFC tagging on the image forming apparatus with the mobile device; and automatically performing a function corresponding to a status of the mobile printing application when NFC tagging is performed.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Sleeve device with stepped structure
Owner:HSIEH CHIH CHING
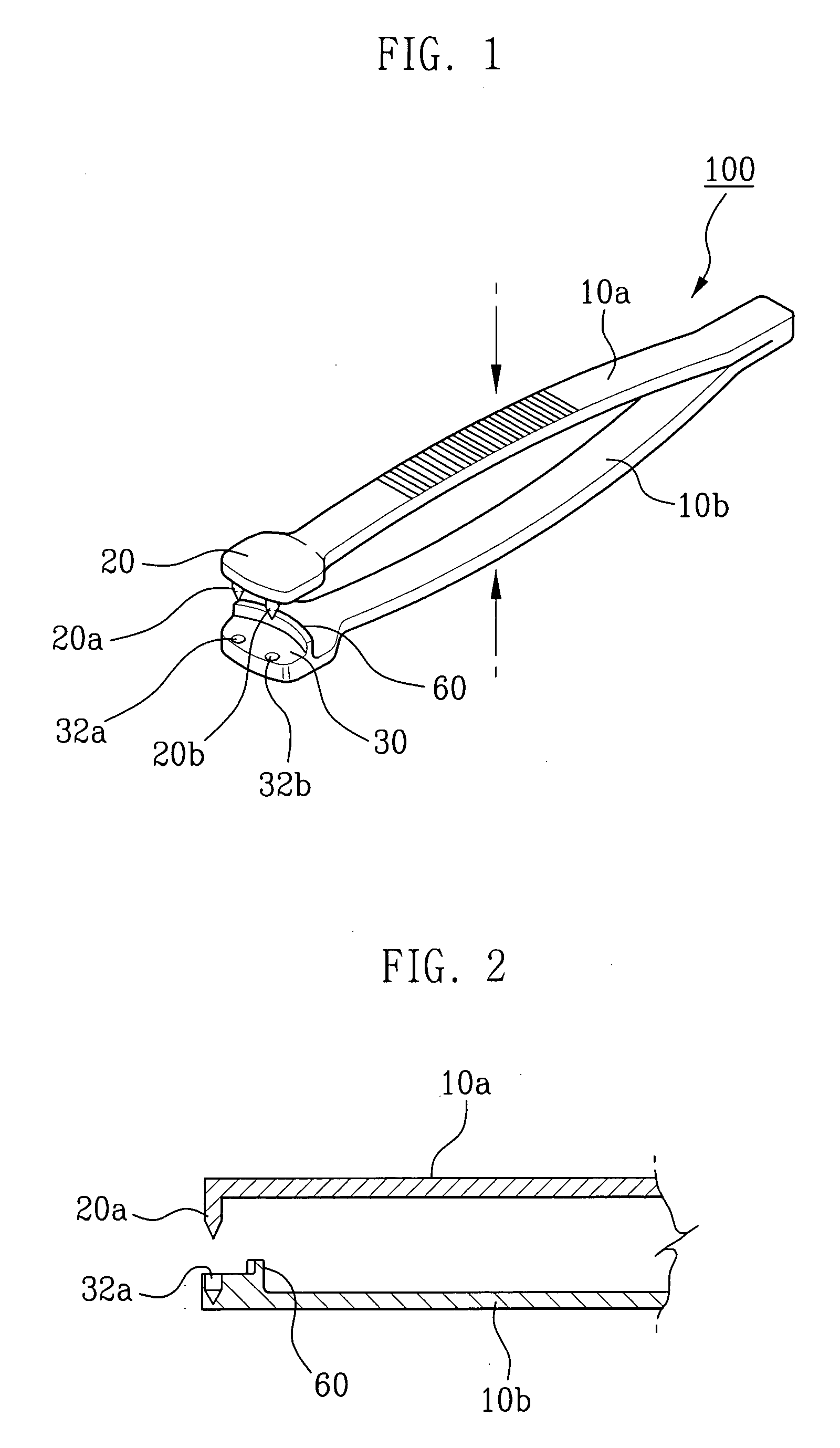
Forceps for double eyelid operation
InactiveUS20080234724A1Easy to operateShorten operation timeSuture equipmentsEye surgeryForcepsEngineering
A forceps for a double eyelid. The forceps includes an upper support plate and a lower support plate. The upper support plate is attached to the front side of the handle and has one or more needles arranged in a front region of the inner surface of the upper support plate. The lower support plate corresponds to the upper support plate and is attached to the front side of the handle and having accommodation recesses corresponding to the needles and being formed in a front region of the inner surface of the lower support plate.
Owner:CHUNG II BONG
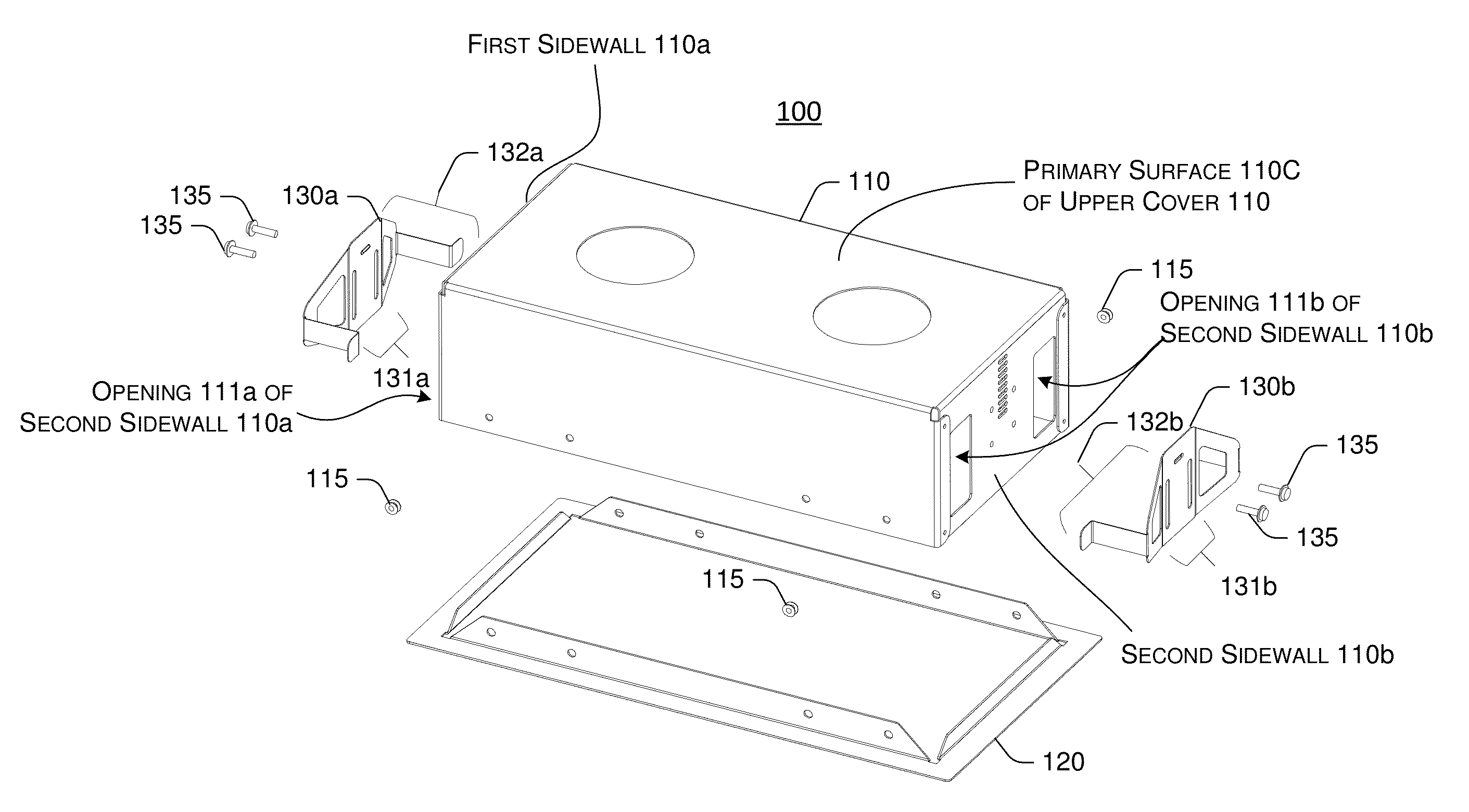
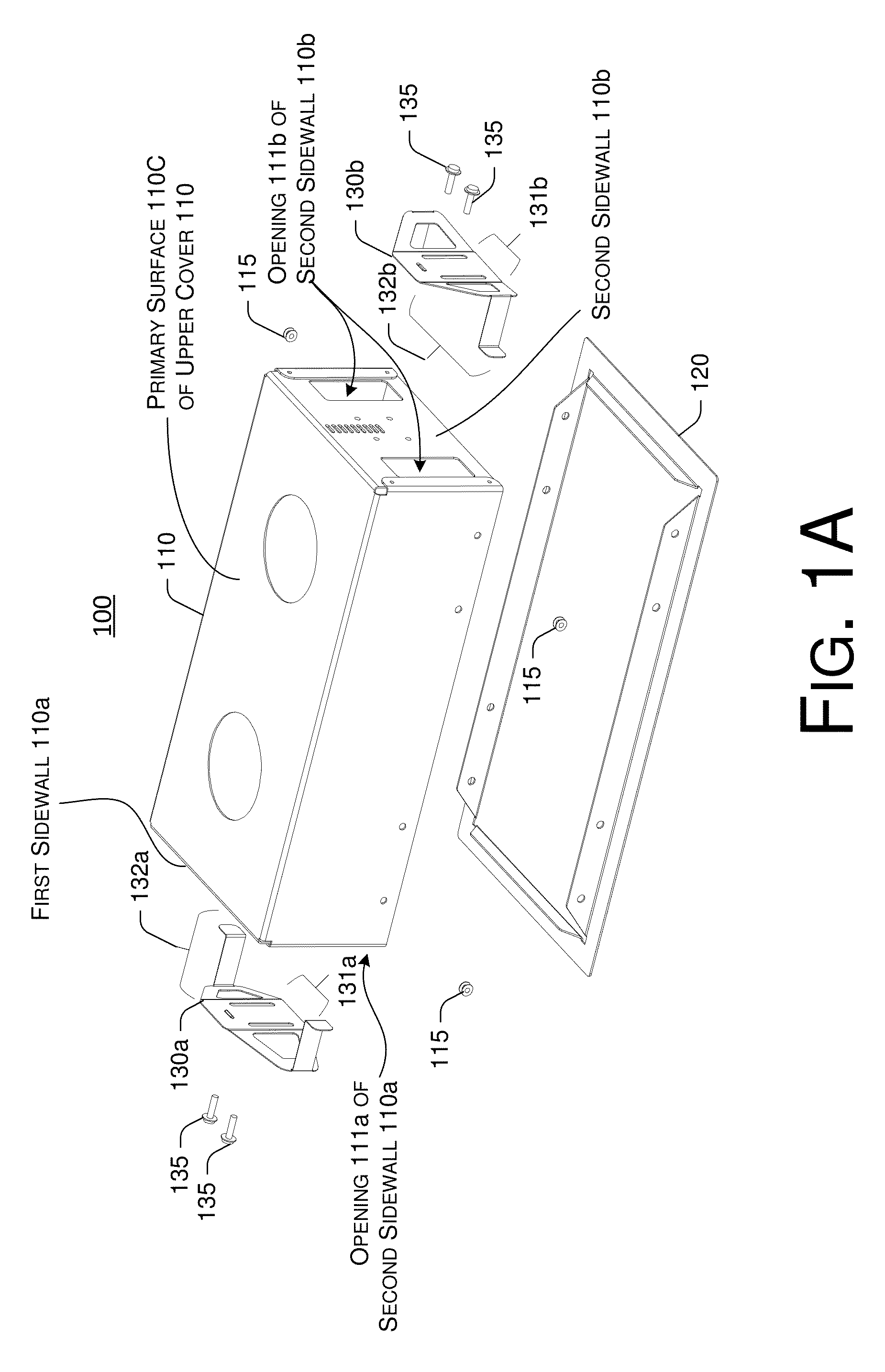
Recessed lamp housing with adjustable spring clipping device
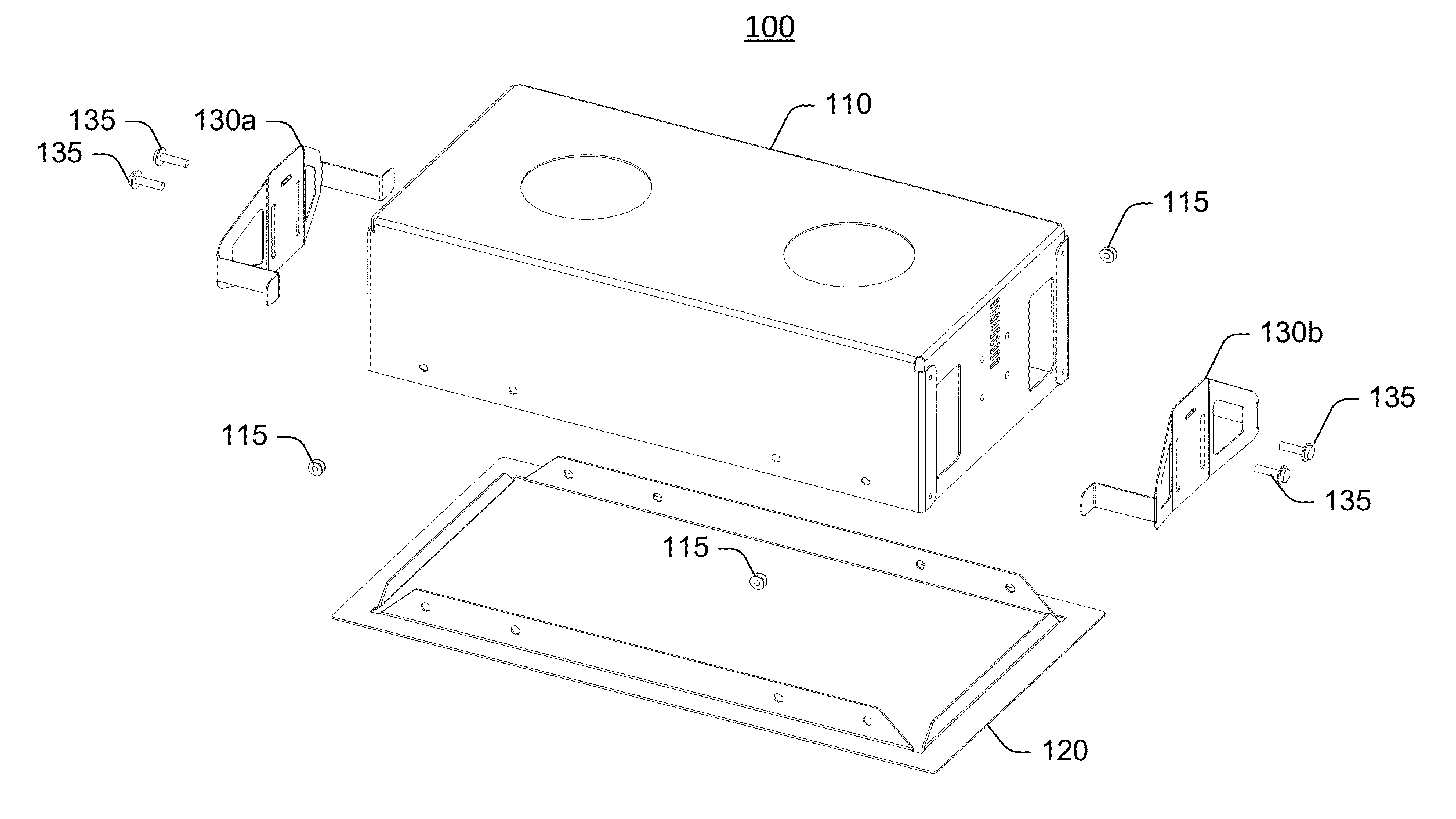
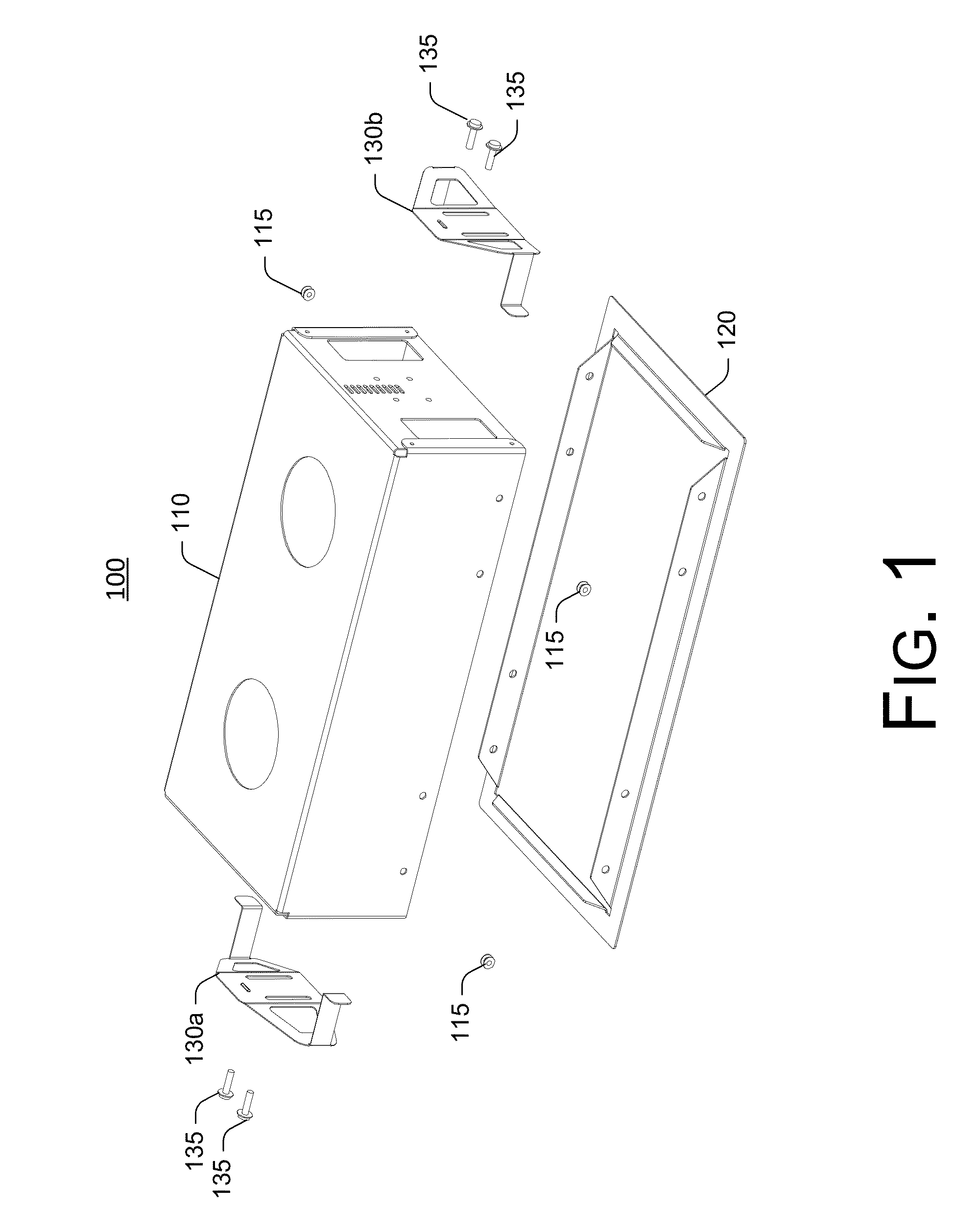
InactiveUS9134014B2Easy accessEasily and conveniently performedLighting support devicesVehicle interior lightingEngineeringRecessed light
Owner:EVERLIGHT ELECTRONICS
Spring standoff for a reciprocating device
InactiveUS20050022662A1Easy to operateEasily and conveniently performedEngine componentsClosed-cycle gas positive displacement engine plantEngineeringFlange
A spring standoff for a reciprocating device, the standoff having a generally cylindrical body and having a window in a circumferential surface of the body, and a flange at each end of the body, one flange to be coupled to a planar spring of the reciprocating device, and the other flange to be coupled to a sealing container of the reciprocating device. The body generally concentrically houses at least a portion of a reciprocating rod coupled to the planar spring of the reciprocating device.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC +1
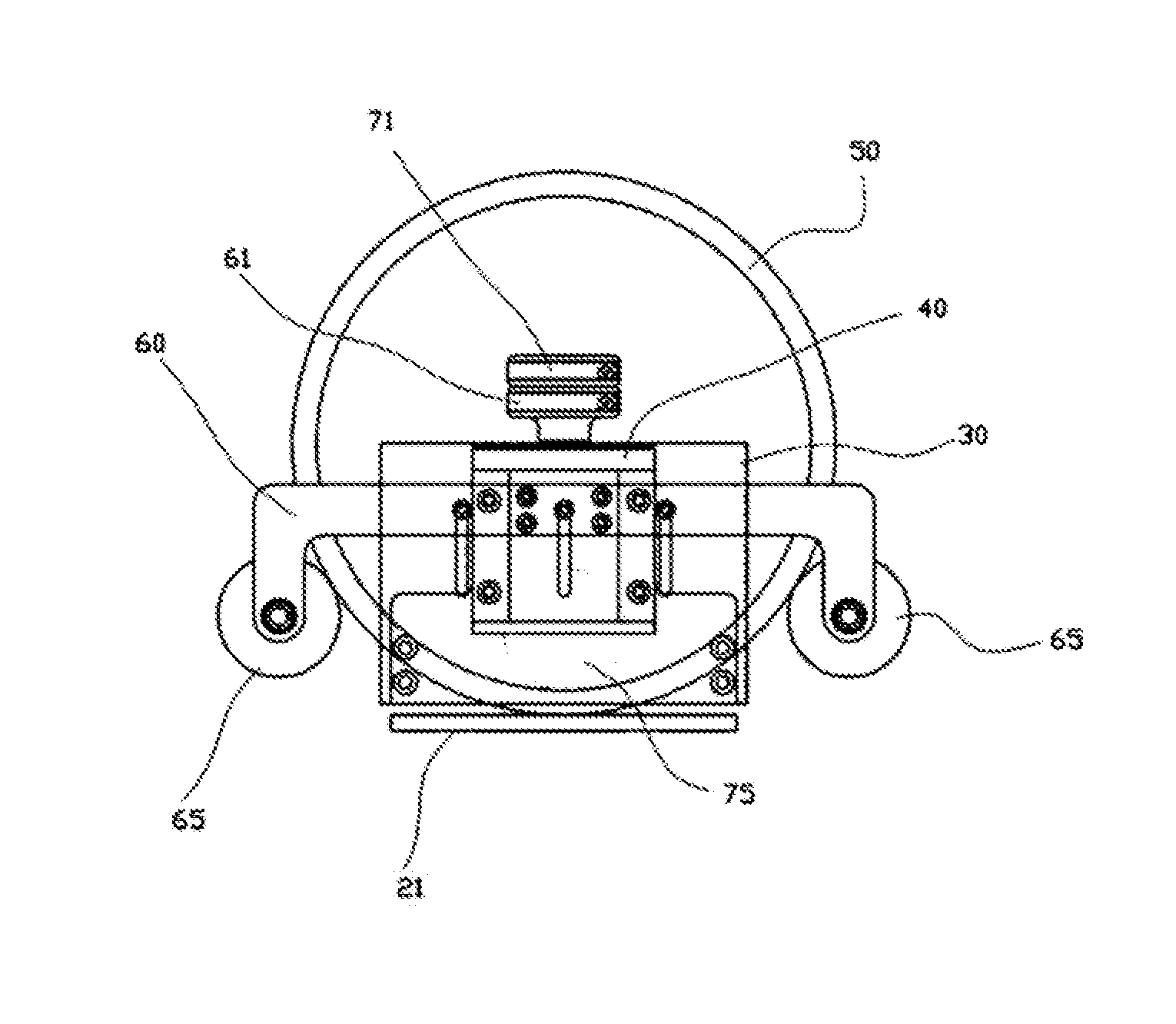
Adapter for rapid connection of pacemaker-electrode catheter
InactiveUS20110082532A1Firmly connectedEasily and conveniently performedElectrically conductive connectionsInternal electrodesCardiac pacemaker electrodeCoupling
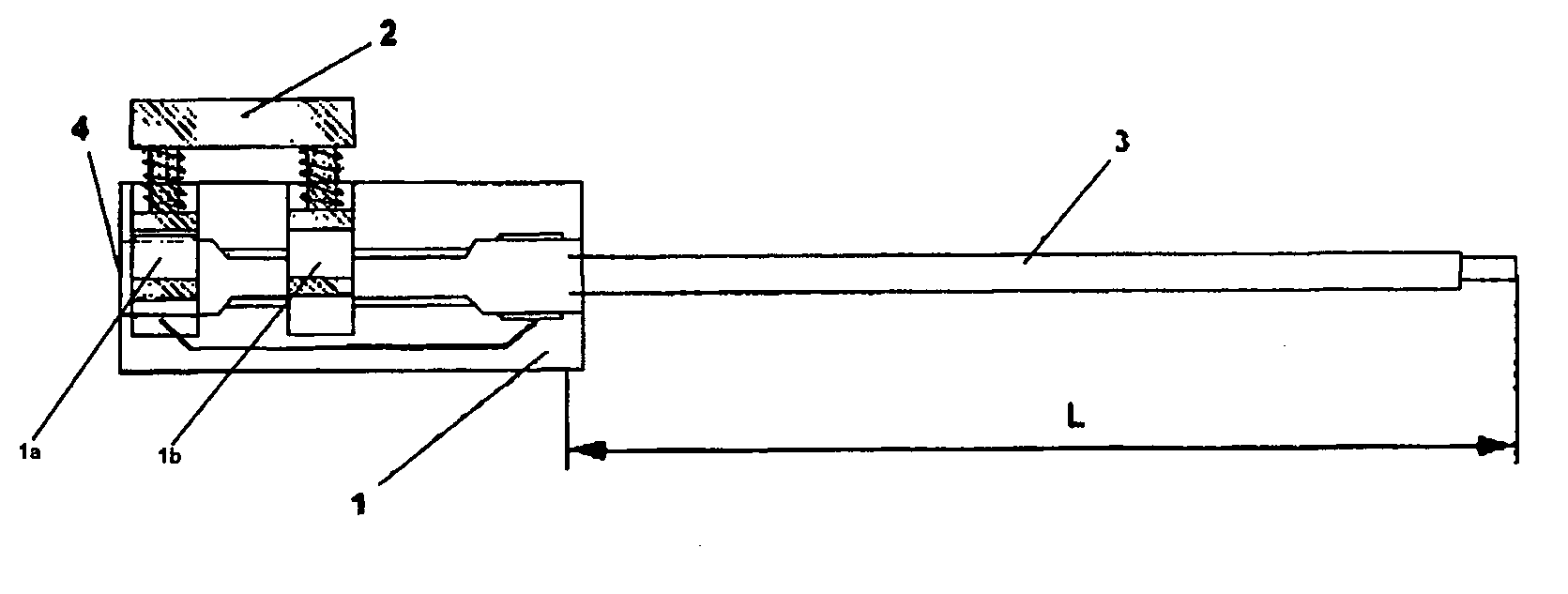
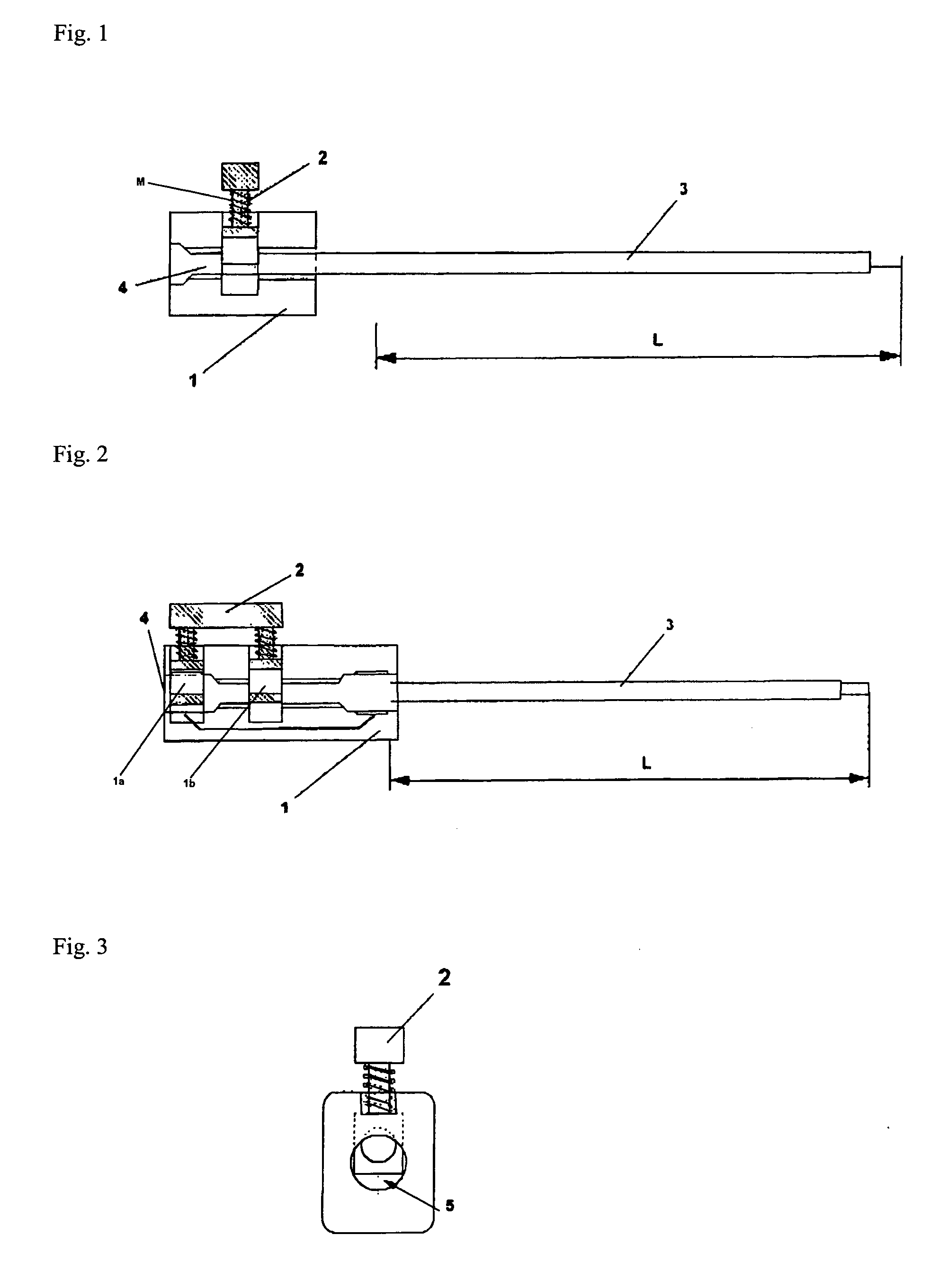
The present invention concerns an adapter which allows a rapid connection between a pacemaker and an electrode catheter, thus allowing the convenient performance of the necessary intraoperatory measurements. This adapter comprises a block of insulating material 1 with a metal insert for interconnection, a button with automatic return 2 for quick coupling to an electrode of the electrode catheter, and a slot 4, 5 for the entry of an interconnecting electrode 3.
Owner:CHAMED
Recessed Lamp Housing With Adjustable Spring Clipping Device
InactiveUS20130272001A1Easily into and dismountedEasily and conveniently performedLighting support devicesVehicle interior lightingClip deviceEngineering
Owner:EVERLIGHT ELECTRONICS
System and method to provide mobile printing using near field communication
ActiveUS9489163B2Easily and conveniently performedNear-field systems using receiversShort range communication serviceAutomatic transmissionPersonal identification number
A method of mobile printing using near field communication (NFC) includes checking a version of firmware installed in an image forming apparatus; determining whether the checked version of the firmware supports Wi-Fi Direct connection via automatic transmission of a personal identification number (PIN); updating the firmware installed in the image forming apparatus when the checked version of the firmware does not support Wi-Fi Direct connection via automatic transmission of a PIN; encrypting and storing a PIN in an NFC tag attached to the image forming apparatus; setting a Wi-Fi Direct connection by receiving the stored PIN and automatically transmitting the PIN to the image forming apparatus by the mobile device when the mobile device is NFC-tagged to the image forming apparatus; and performing mobile printing via the Wi-Fi Direct connection.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
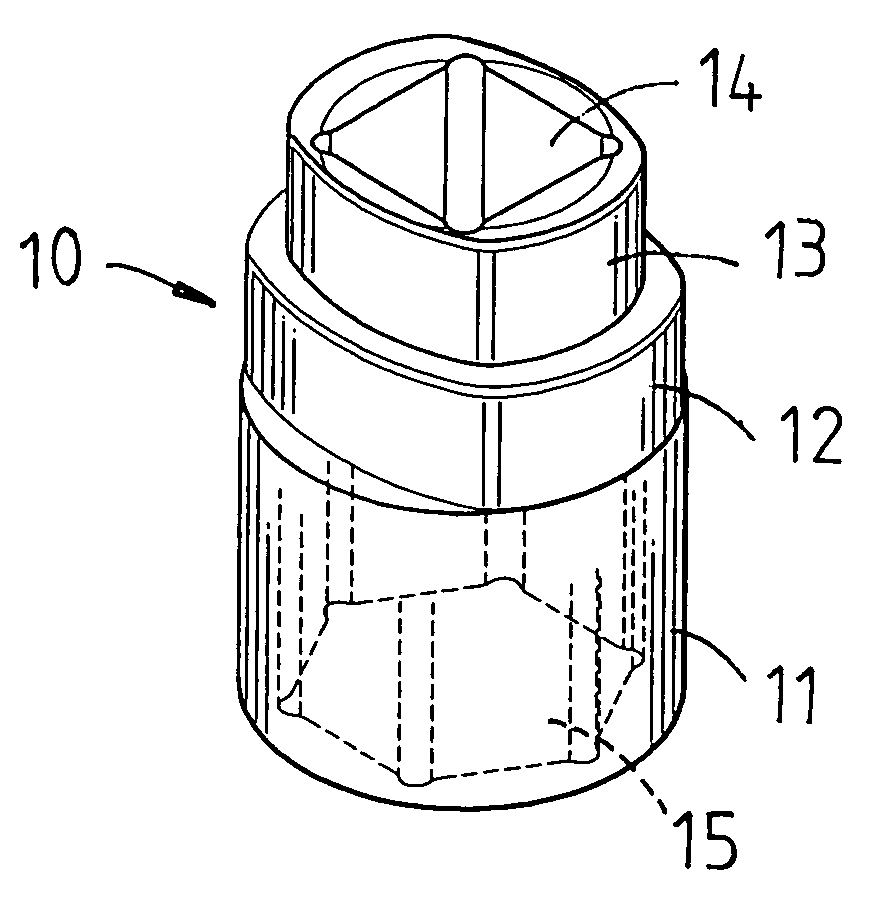
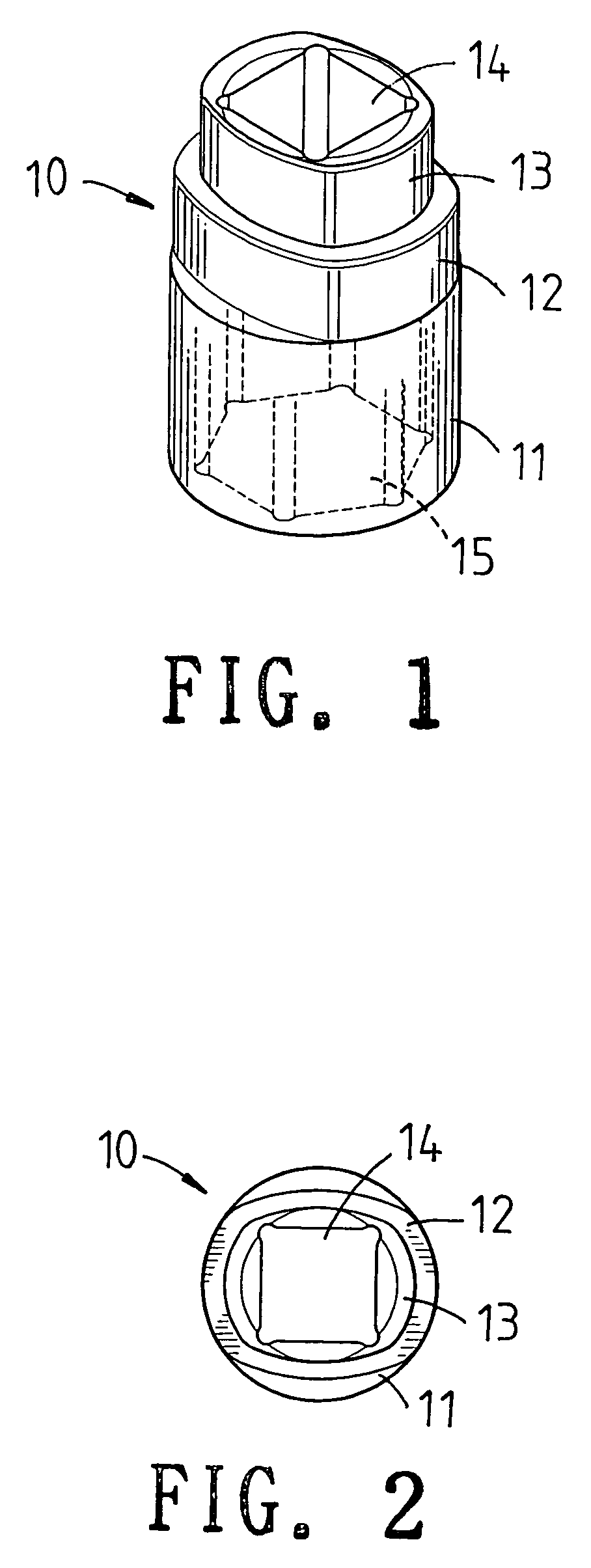
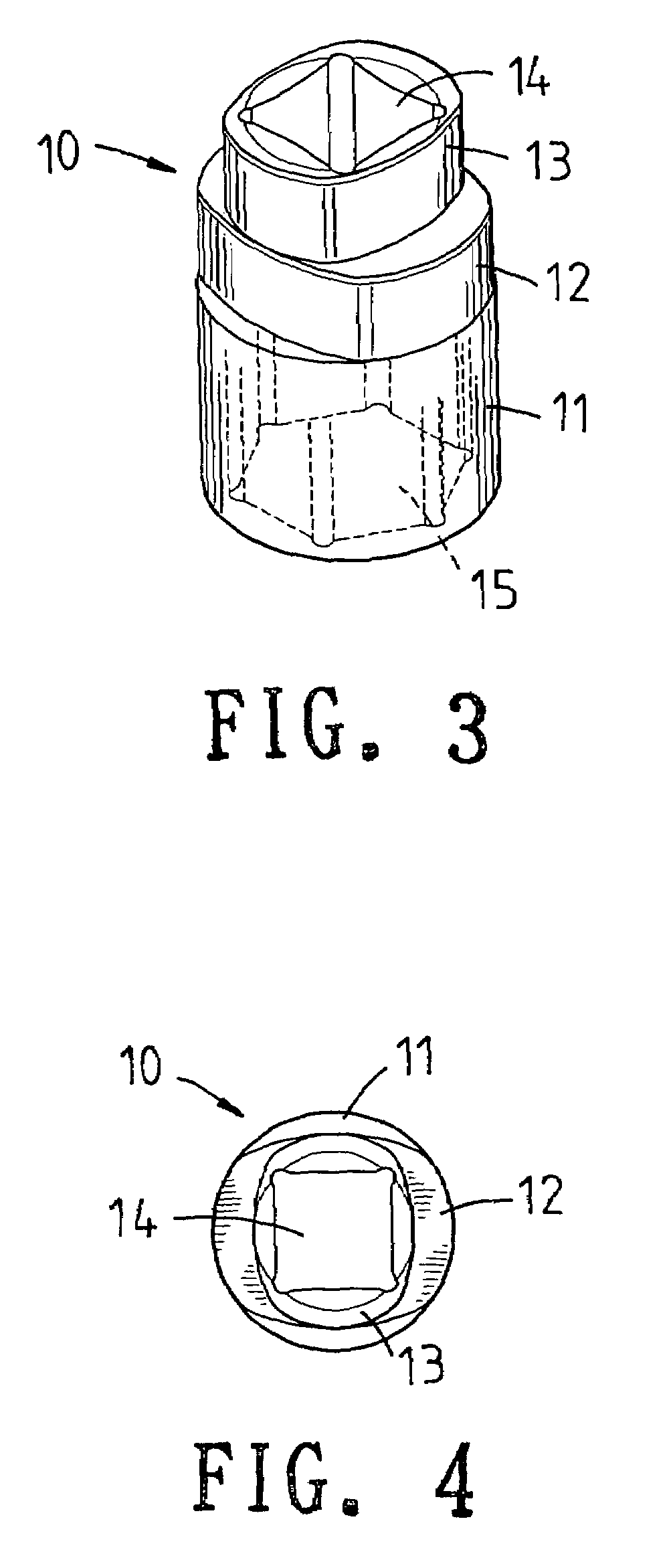
Sleeve device with stepped structure
InactiveUS20060117916A1Easily and conveniently performedSpannersWrenchesBiomedical engineeringWrench
Owner:HSIEH CHIH CHING
Portable pipe outer diameter-chamfering apparatus with improved weldability
ActiveUS20160207114A1Simple structureEasy to carryTurning machine accessoriesWorkpiecesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention relates to a portable pipe outer diameter-chamfering apparatus with improved weldability characterized in that a vertical fixing plate is fixed to the outside of the vertical plate, a horizontal fixing plate is fixed in an orthogonal direction to the tip of the vertical fixing plate, a ⊂ shaped link is coupled to move upward and downward along the vertical fixing plate, a circumscribing roller which is in close contact with an outside of a pipe are installed on the tip of the ⊂ shaped link on either side, the ⊂ shaped link moves up and down along the vertical fixing plate by a circumscribing roller adjustment screw installed on the horizontal fixing plate, a moving body is installed in the horizontal fixing plate, the moving body moves up and down by an inscribing roller adjustment screw installed on the horizontal fixing plate, and an inscribing roller which is in close contact with an inside of the pipe and a pressing force of which is adjusted by a spring is installed on the moving body.
Owner:LEE JONG IL
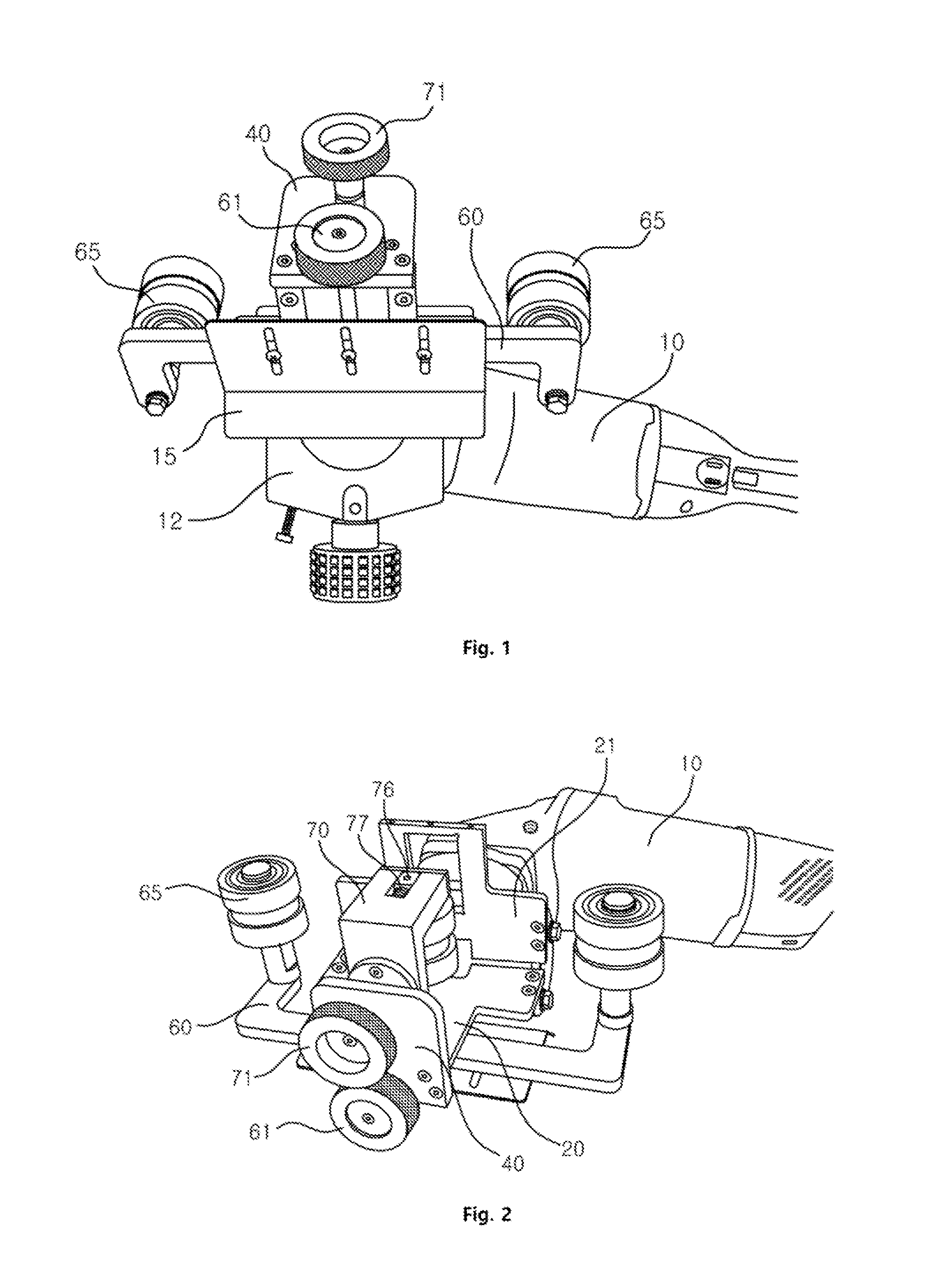
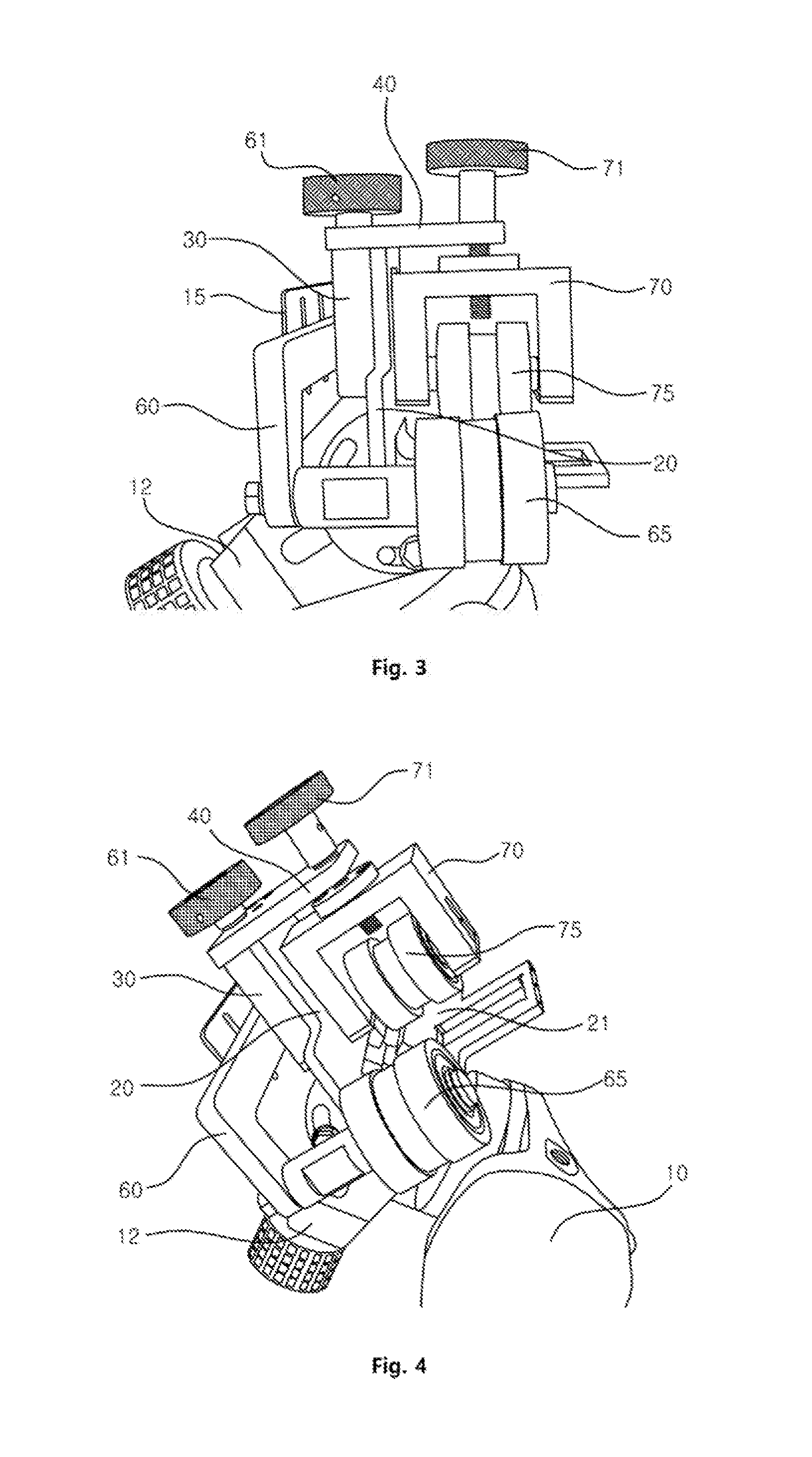
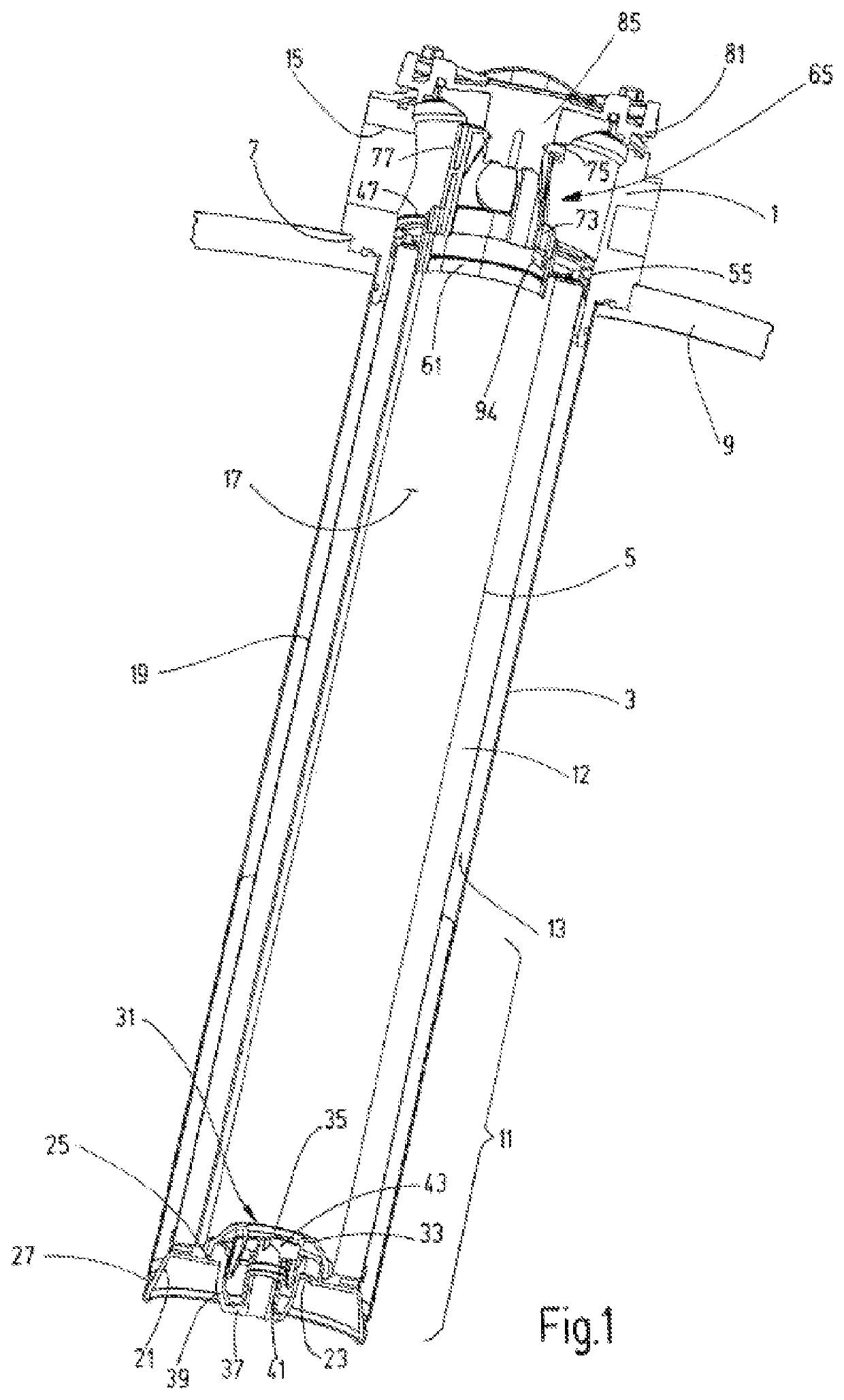
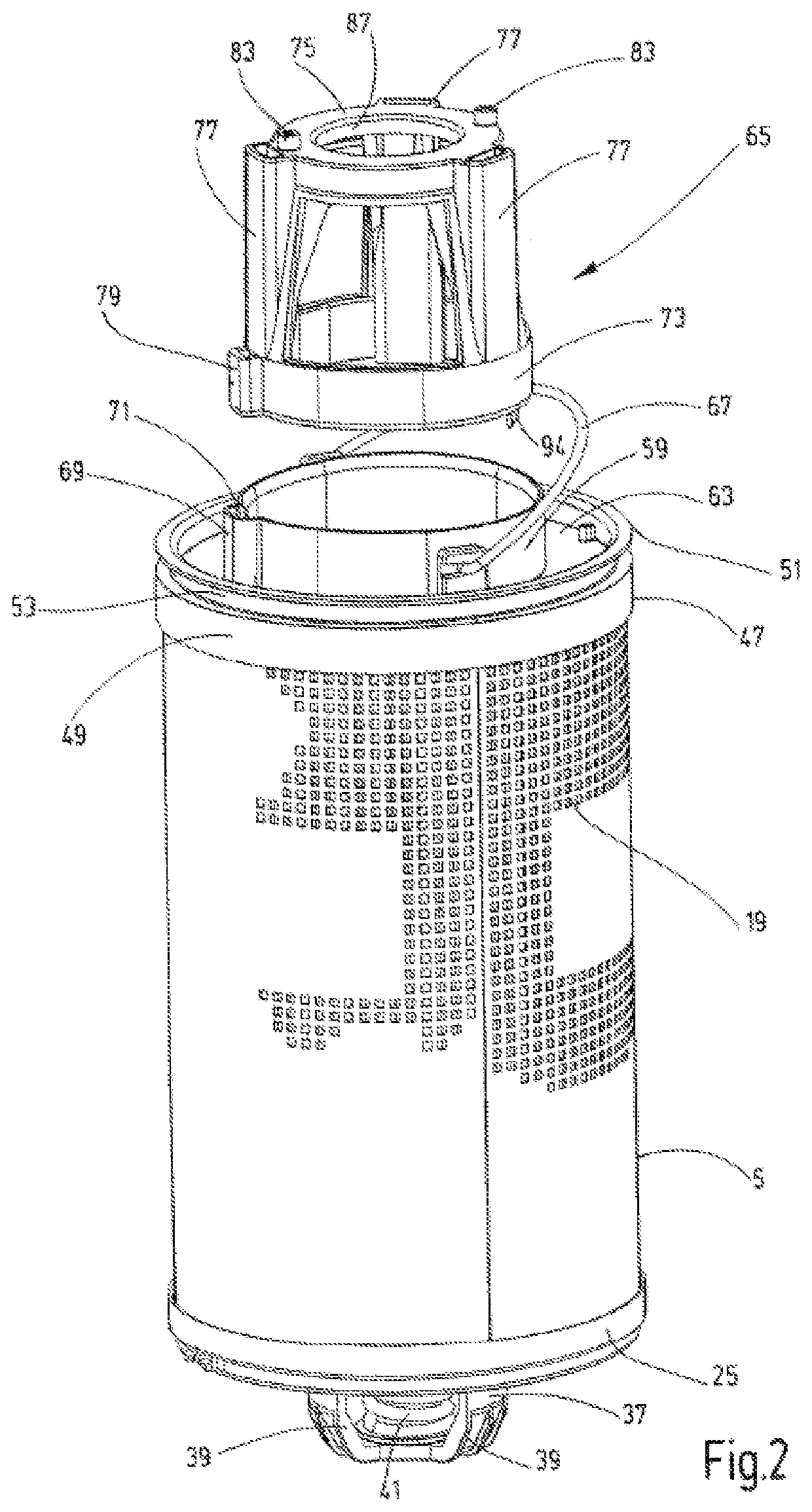
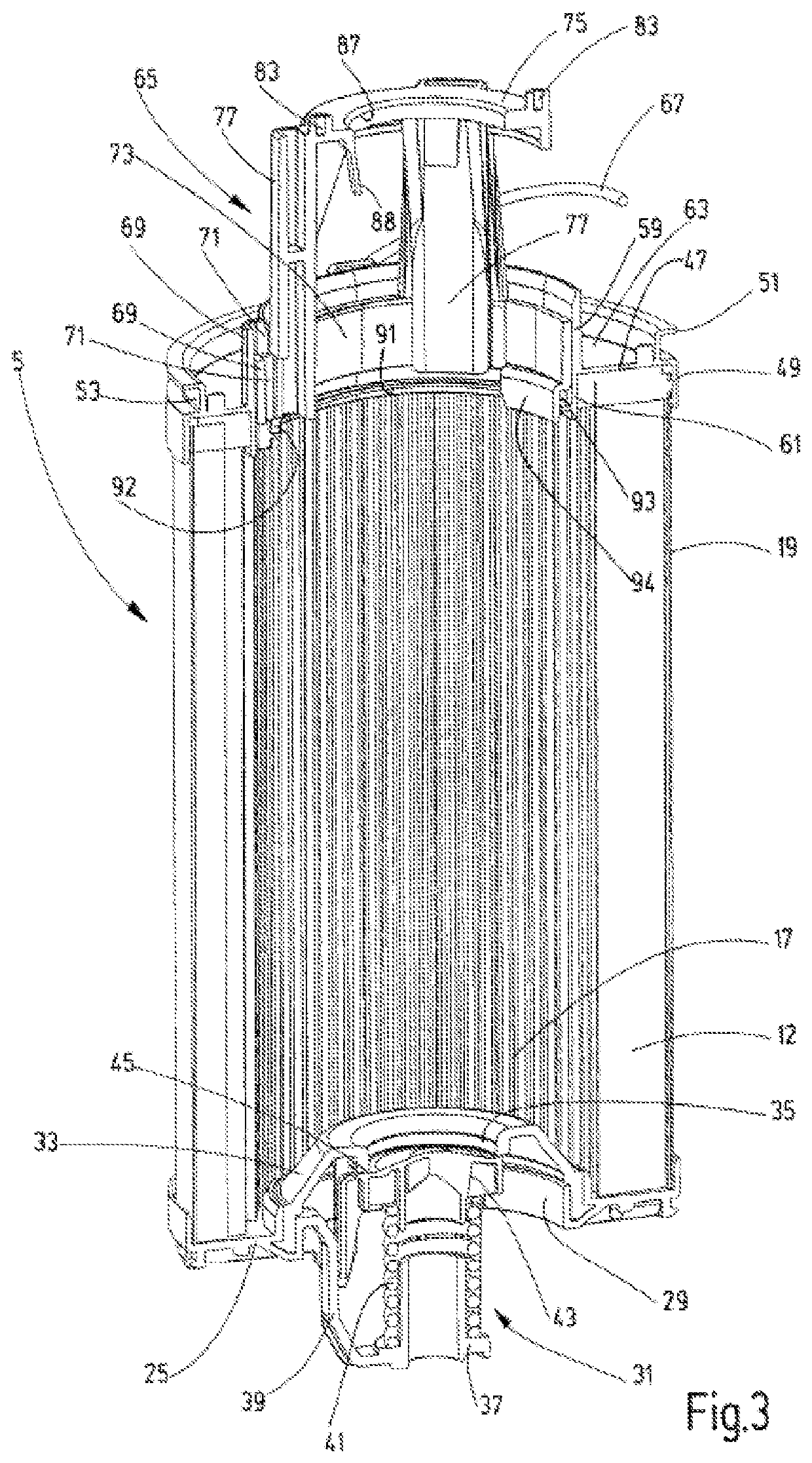
Filter device
ActiveUS11135531B2Improve functional reliabilitySimple designMembrane filtersStationary filtering element filtersEngineeringFilter material
A filter device with a removable termination part (81; 82) and a housing (3) that receives a replaceable filter element (5) having two end caps (25,47). Between the end caps, a filter material (12) extends. A positioning device (65) is arranged between the termination part (81; 82) and one end cap (47). The positioning device positions the filter element (5) within the housing (3), at least when viewed in the circumferential direction of the filter element, in interaction with at least one corresponding positioning element (71) of the end cap (47).
Owner:FILTERTECHN
Plant cultivation method, and cultivation container and cultivation device used therefor
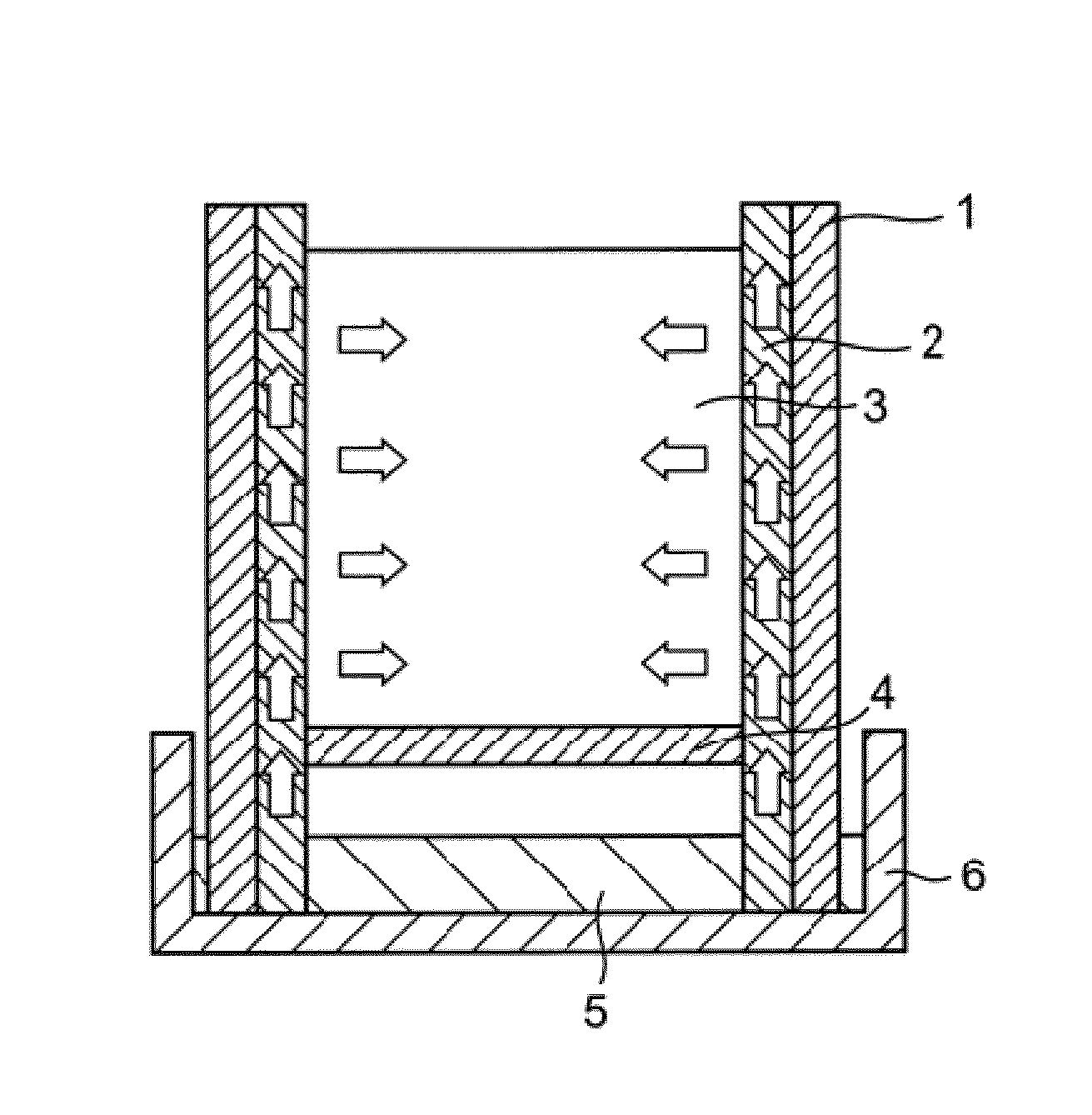
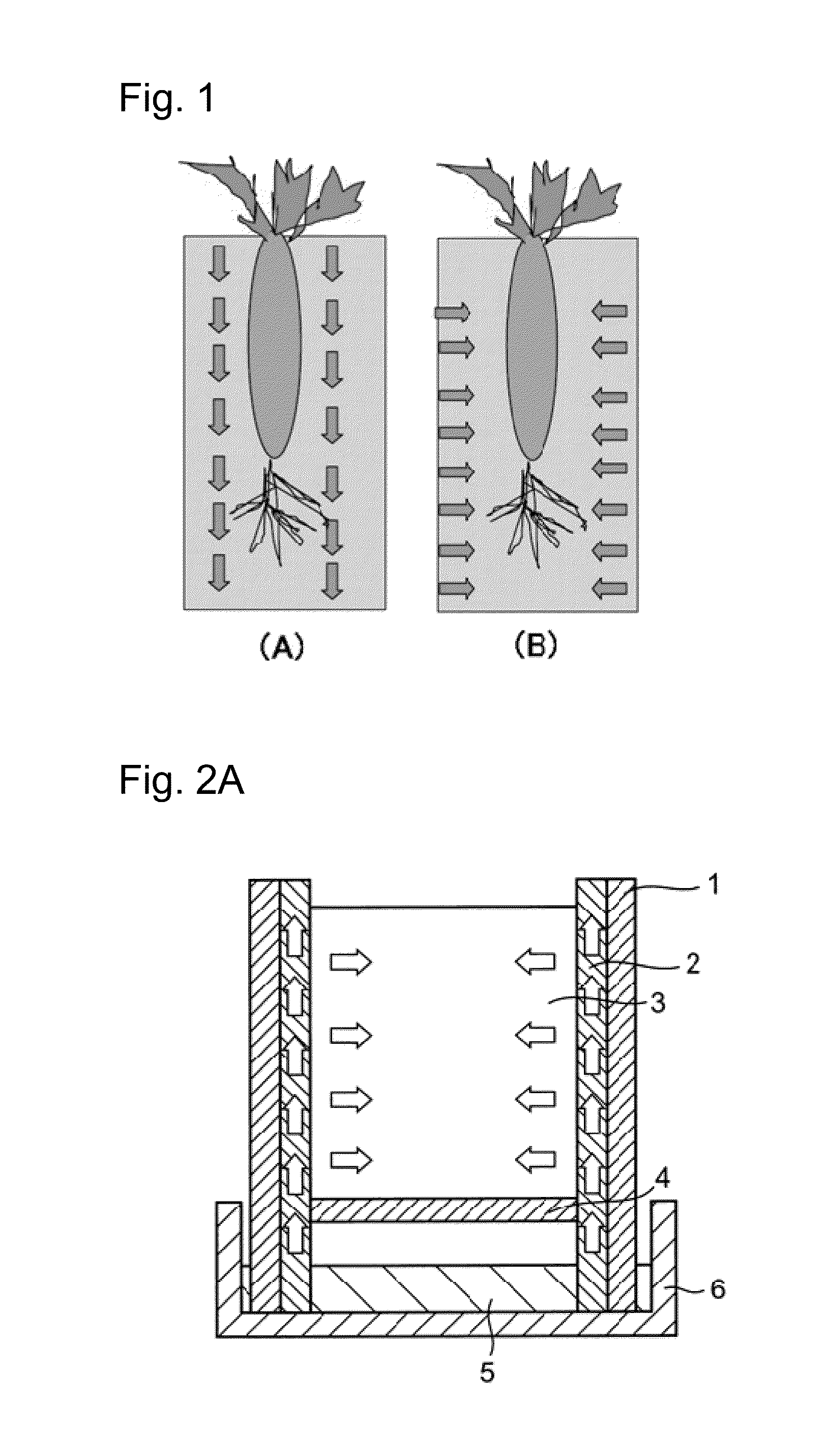
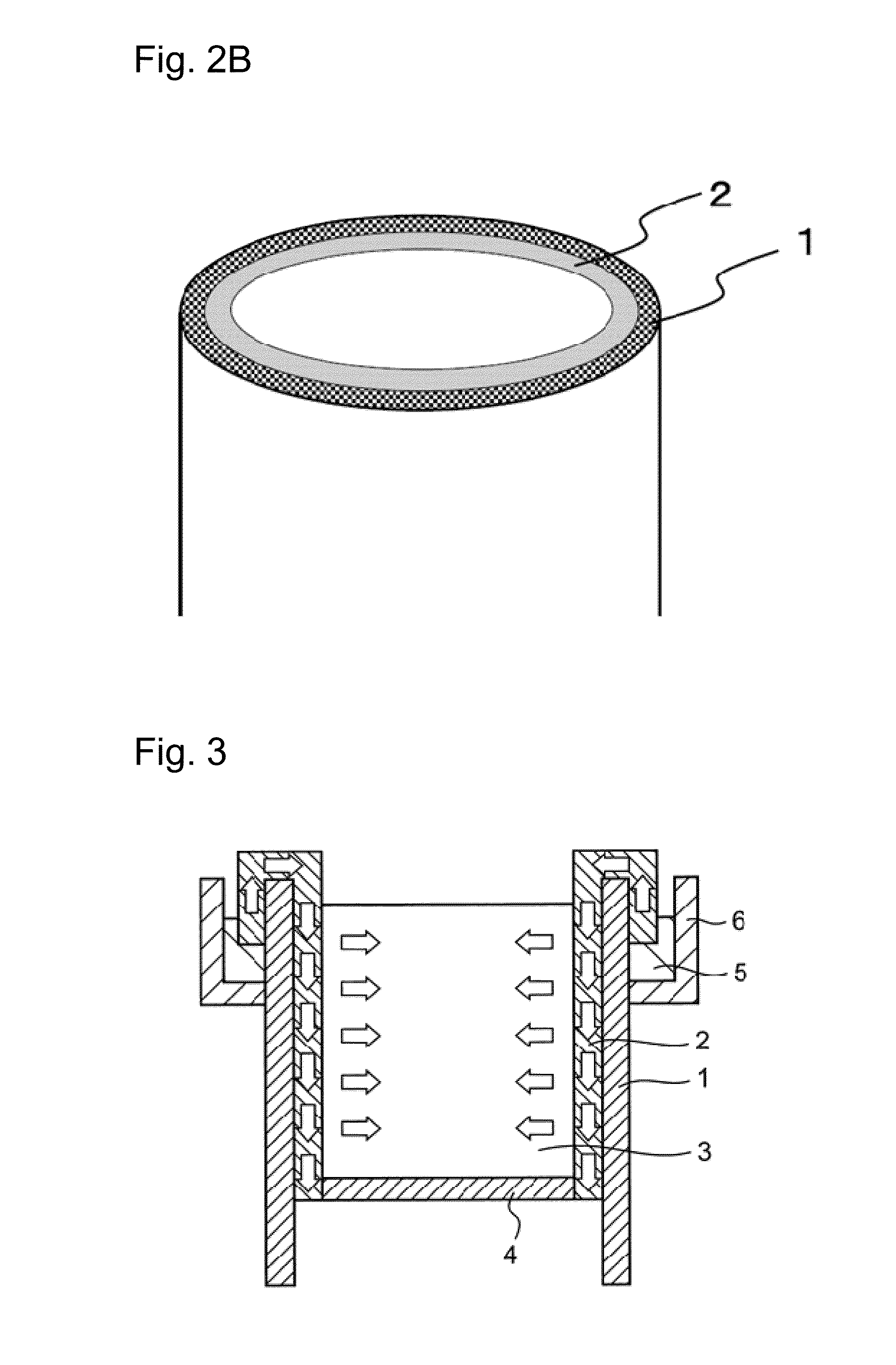
InactiveUS20140202077A1Easy to disassemblePromote plant growthSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesPlant cultivationCulture mediums
A purpose of the present invention is to provide a plant cultivation method with which the growth of plants can be promoted by adjusting the environment within a culture medium, and to provide a plant cultivation container with which this cultivation method can be easily and effectively performed. The present invention provides a plant cultivation method for plants which are raised in a culture medium, which cultivation method is characterized in that water is only supplied to the plants from the side of the culture medium, and provides a plant cultivation container and a plant cultivation device used therefor.
Owner:PUBLIC UNIVERSITY CORPORATION OSAKA CITY UNIVERSITY +1
Ink composition and recording method
ActiveUS20180265722A1Improved pigment dispersionHigh ejecting stabilityInksChemistrySURFACTANT BLEND
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Portable pipe outer diameter-chamfering apparatus with improved weldability
ActiveUS9630252B2Easily and conveniently performedLow efficiencyTurning machine accessoriesWorkpiecesEngineeringClose contact
The present invention relates to a portable pipe outer diameter-chamfering apparatus characterized in that a vertical fixing plate is fixed to the outside of the vertical plate, a horizontal fixing plate is fixed in an orthogonal direction to the tip of the vertical fixing plate, a rectangular link with one open side is coupled to move upward and downward along the vertical fixing plate, a pair of circumscribing rollers, each of the pair of circumscribing rollers being installed on either end portion of the rectangular link with one open side, respectively, the rectangular link with one open side moves up and down along the vertical fixing plate, a moving body is installed in the horizontal fixing plate, the moving body moves up and down, and an inscribing roller which is in close contact with an inside of the pipe is installed on the moving body.
Owner:LEE JONG IL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com