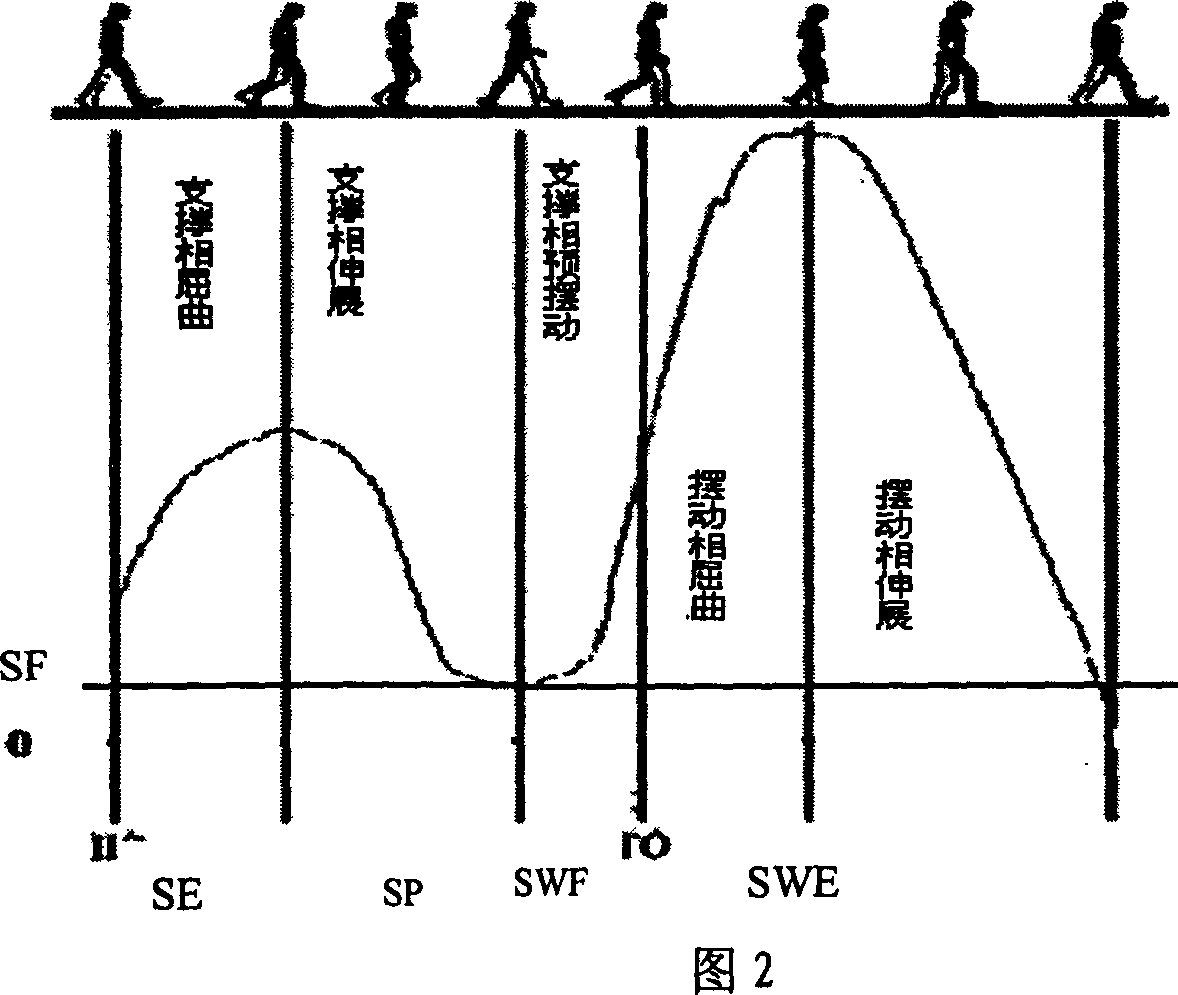
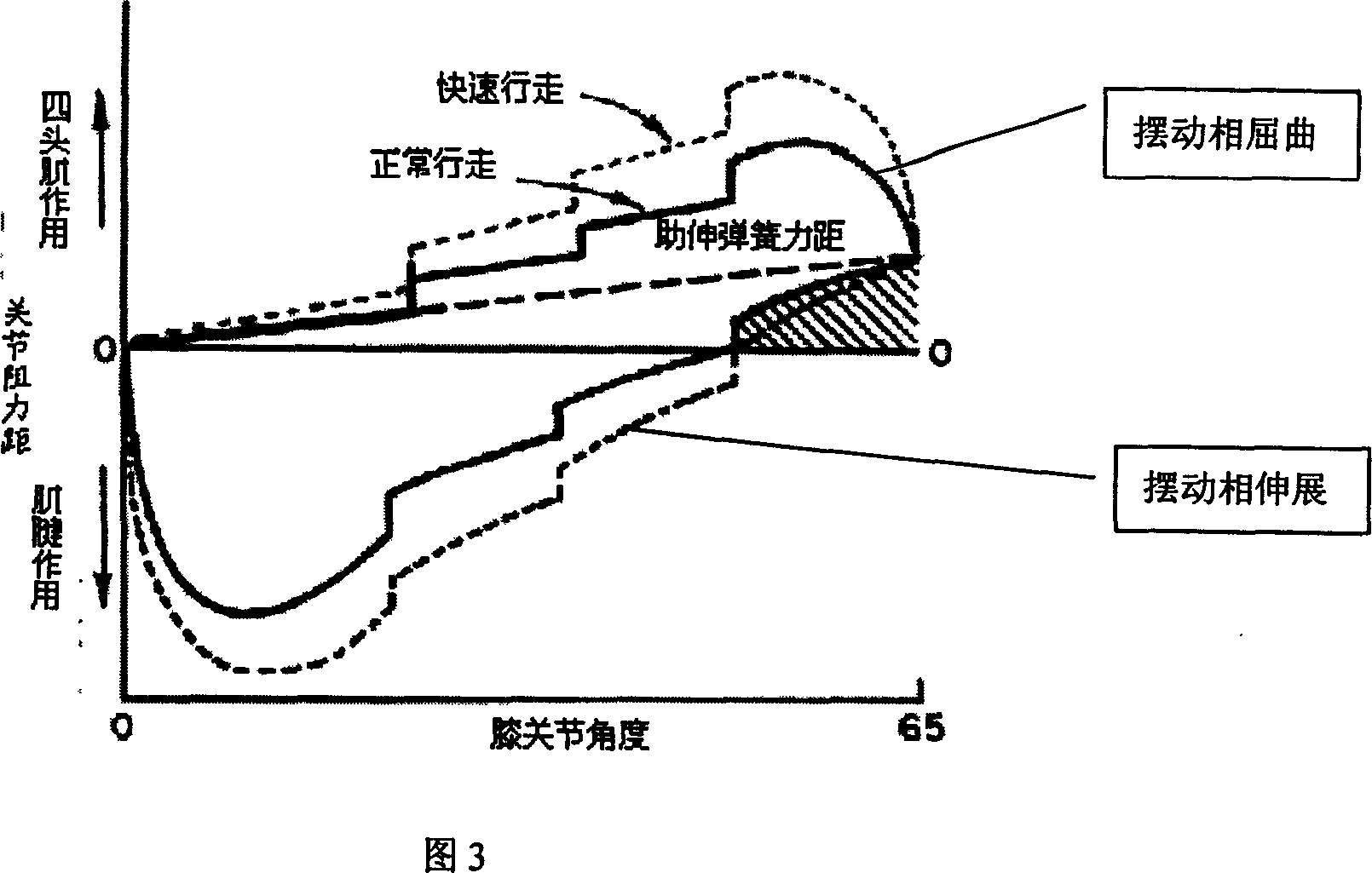
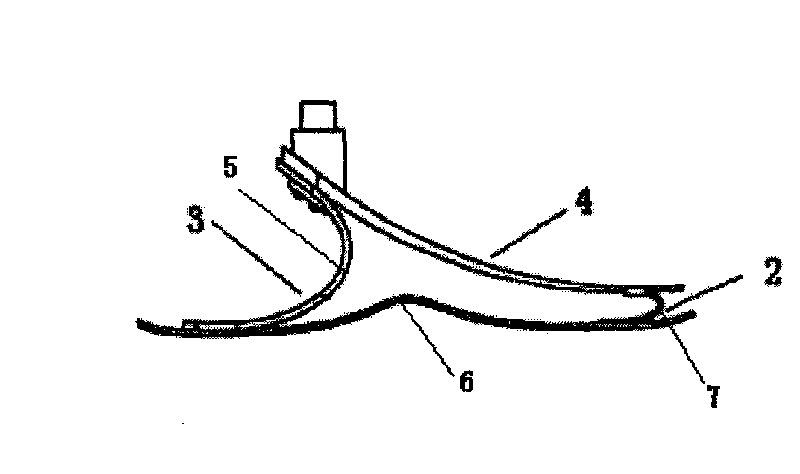
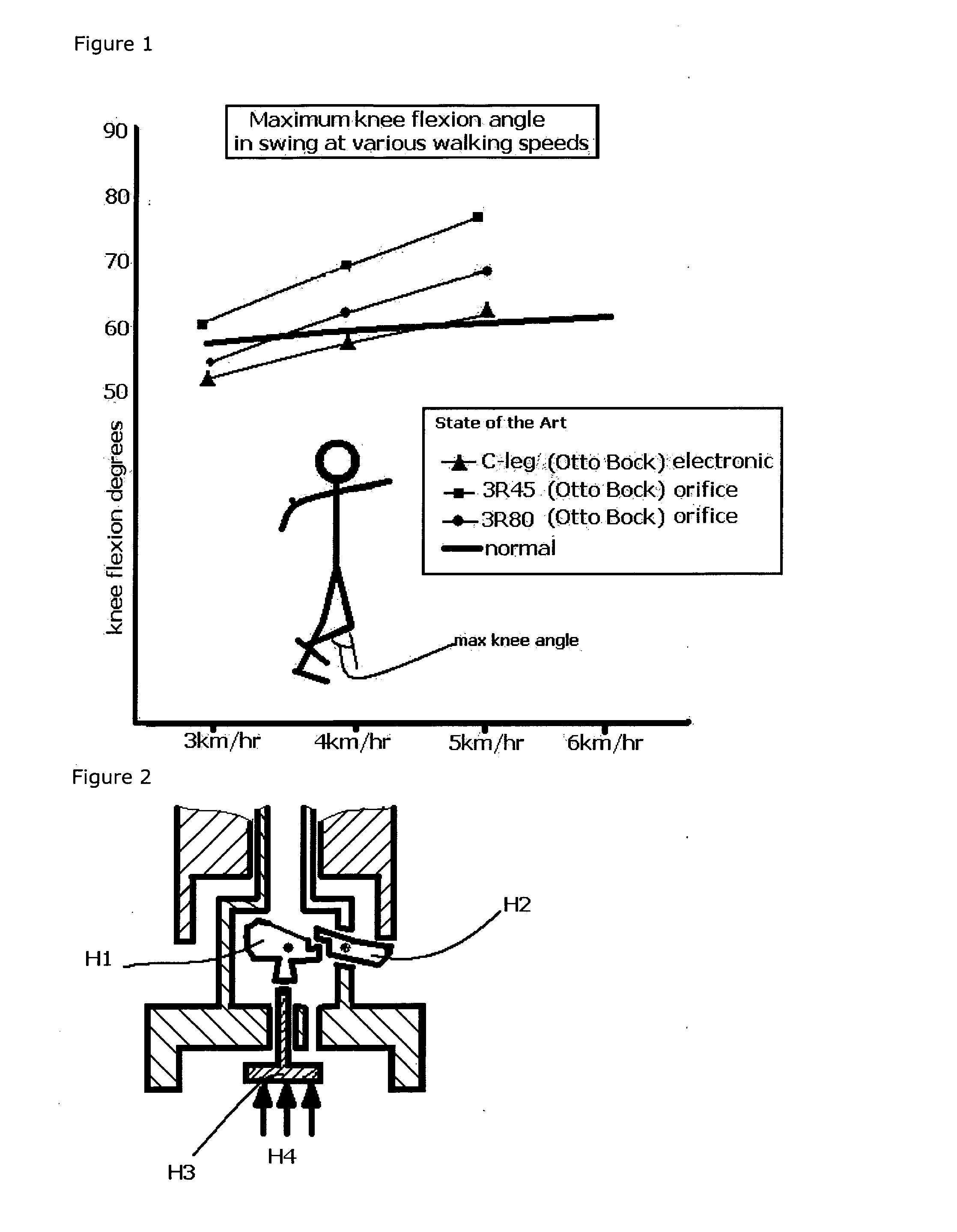
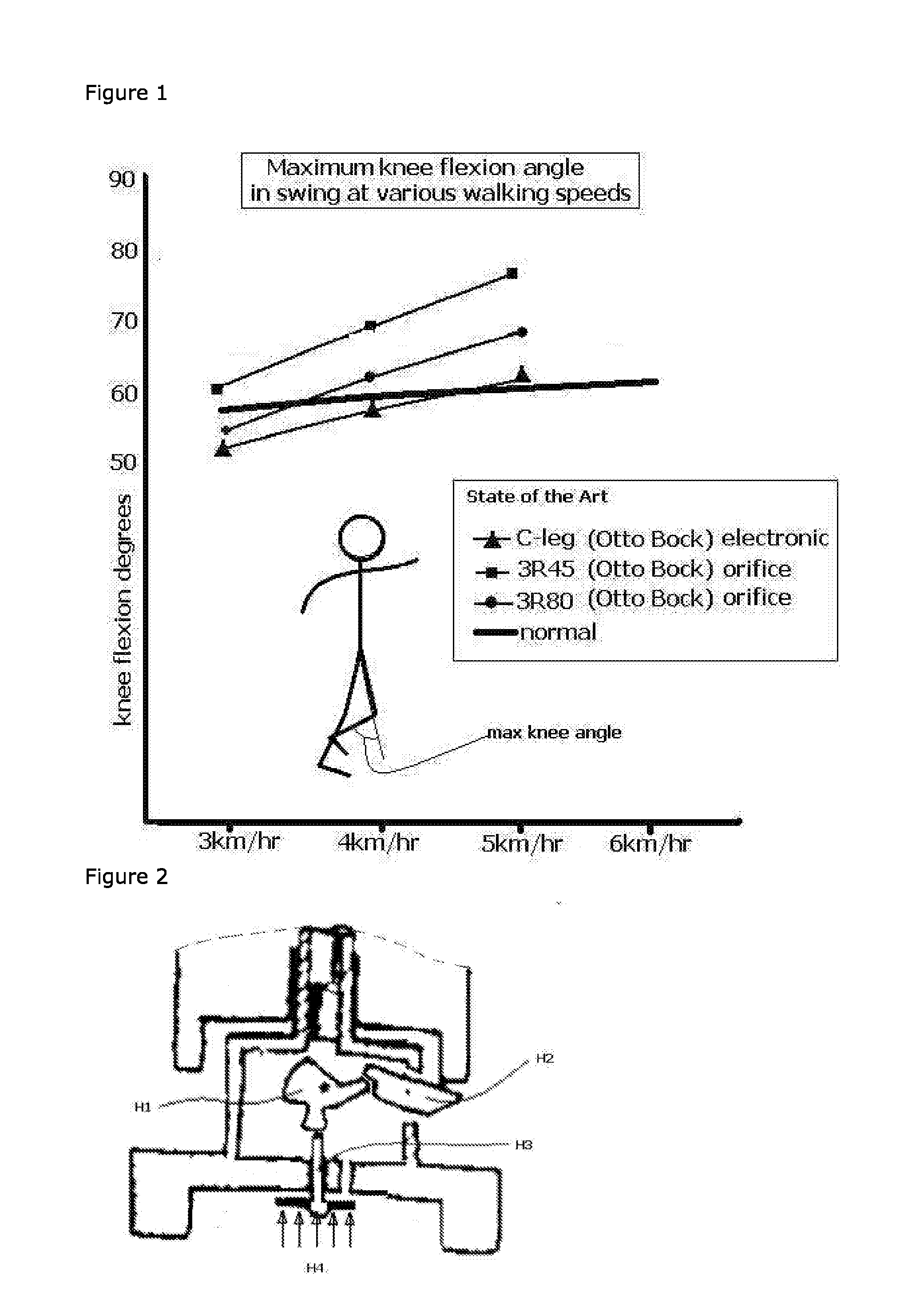
Patents
Literature
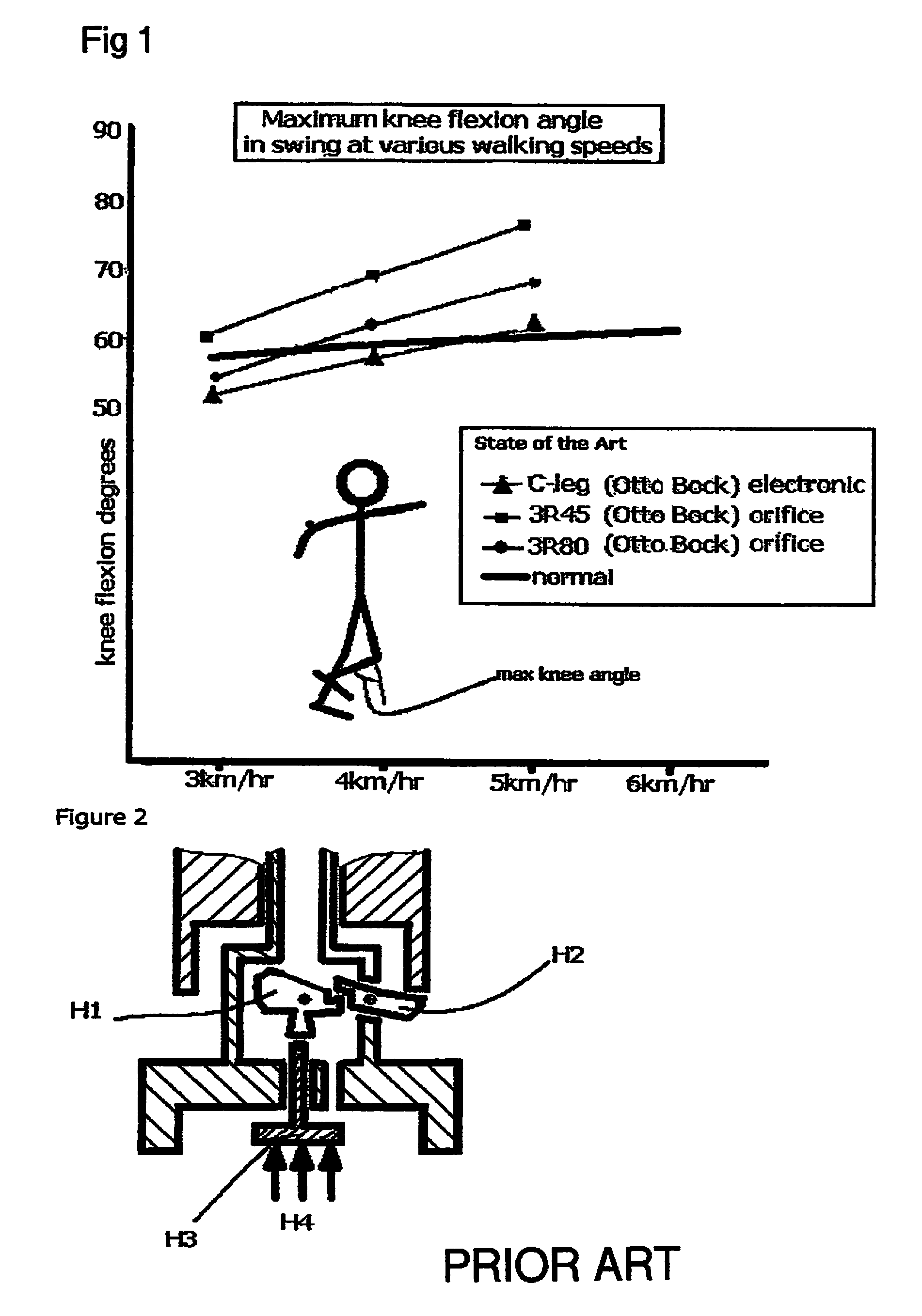
60 results about "Artificial legs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
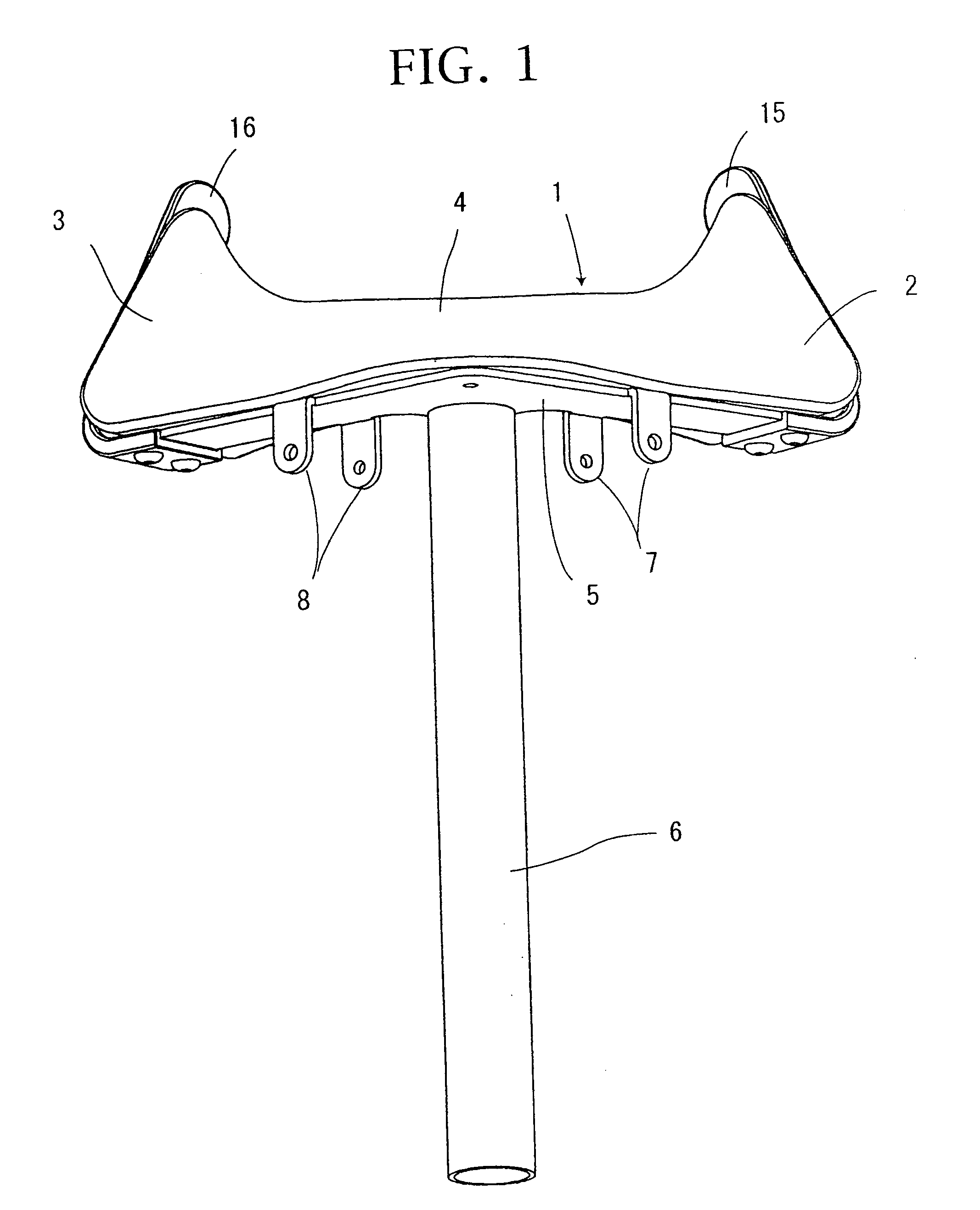
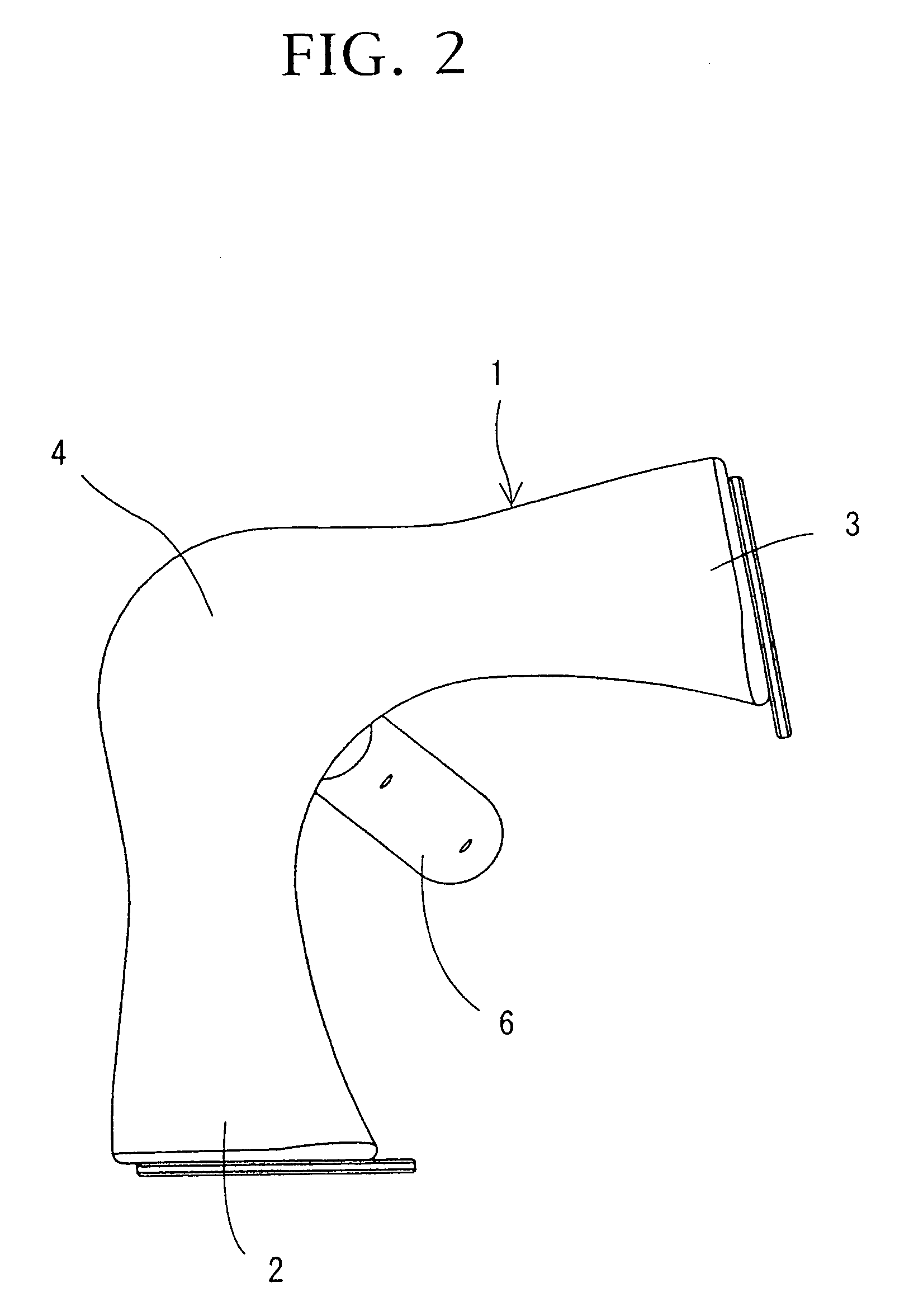
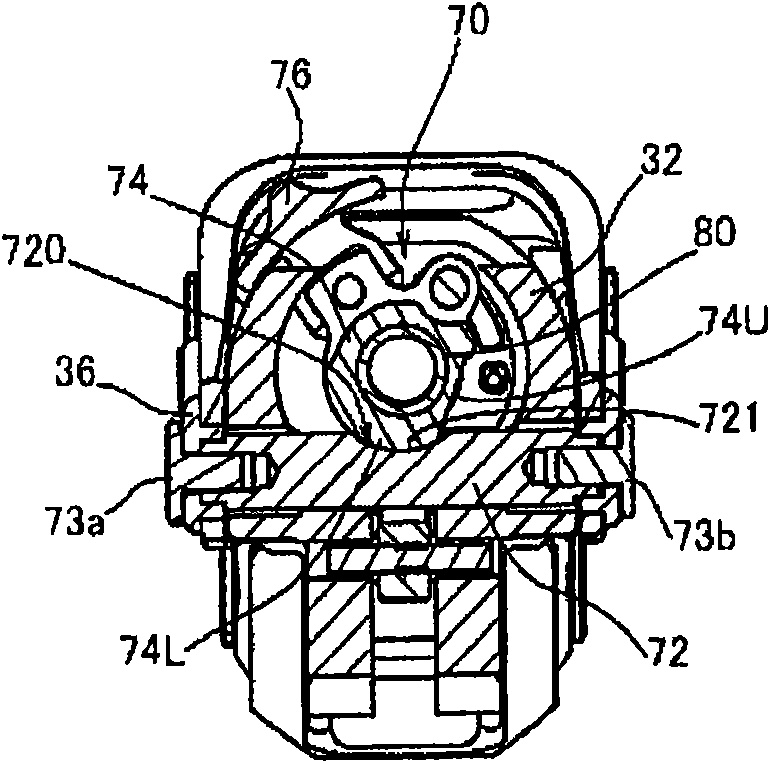
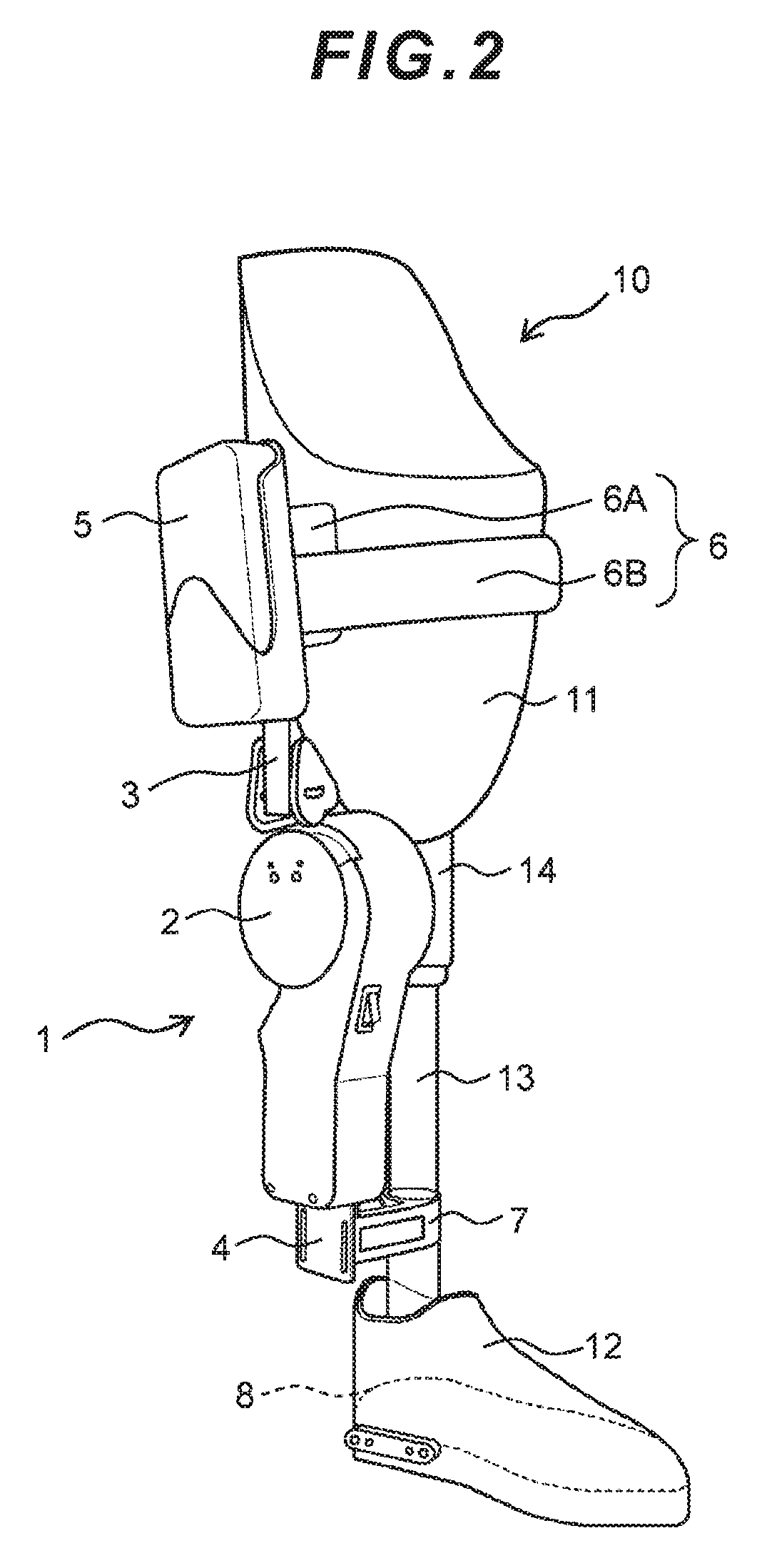
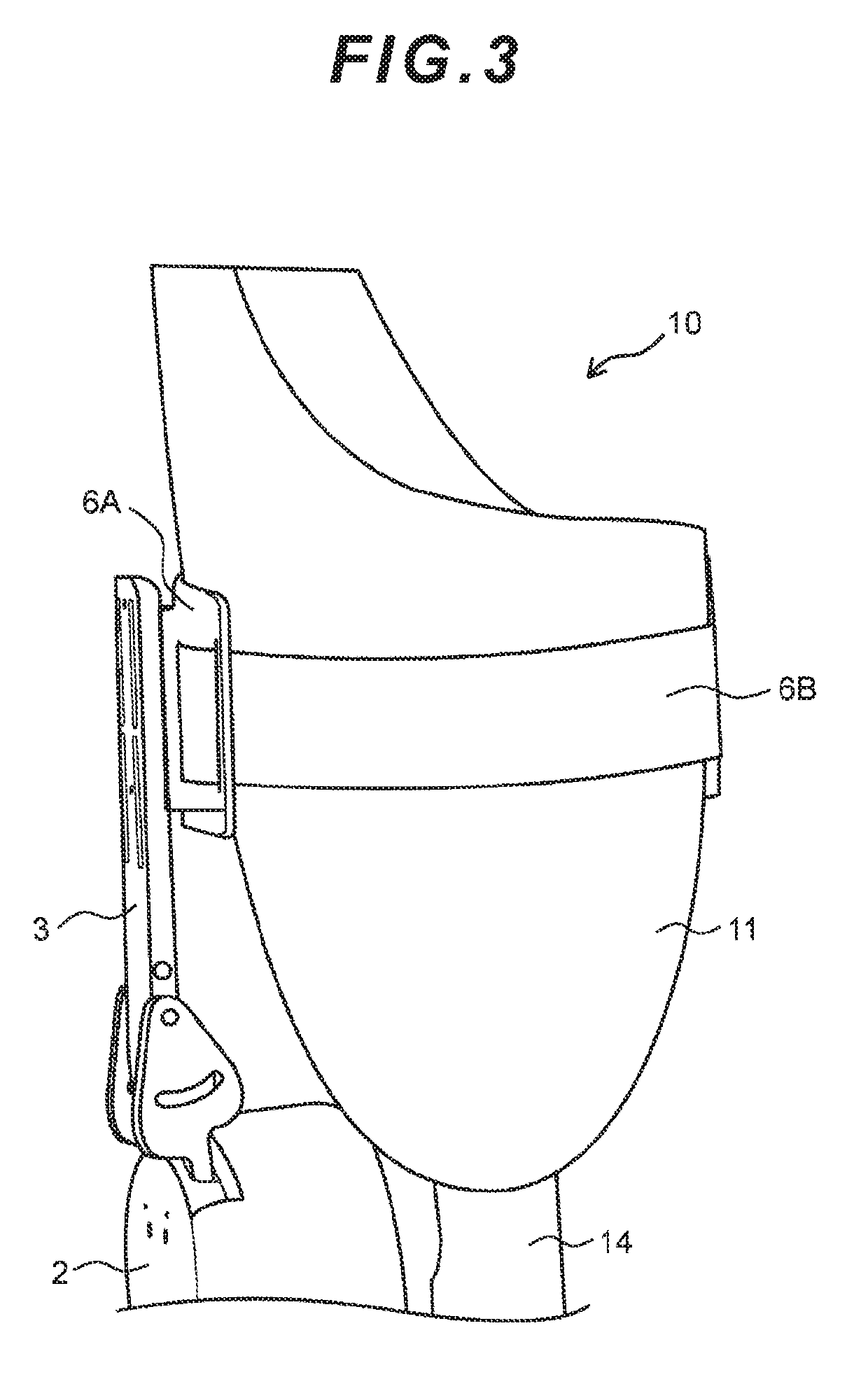
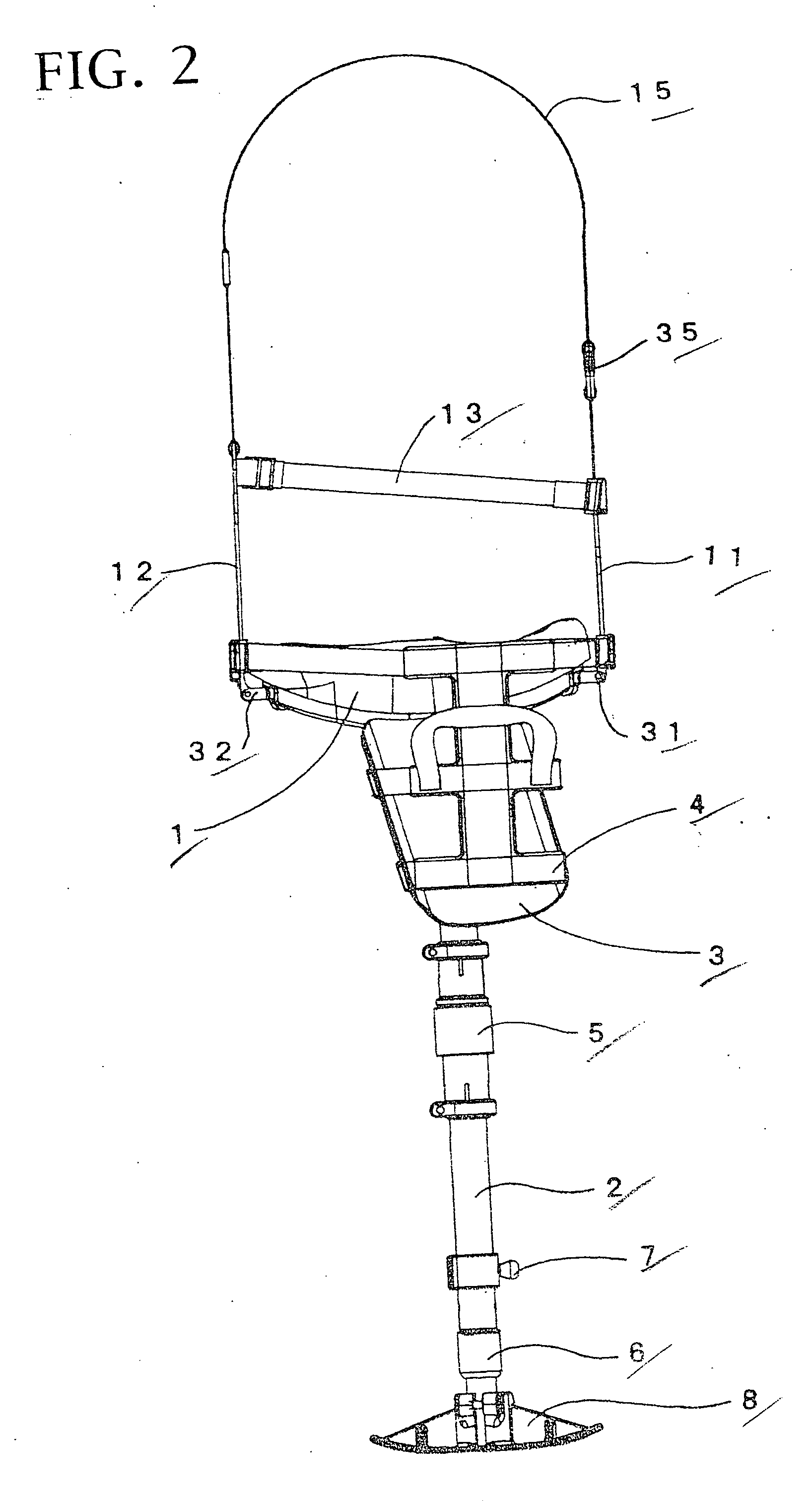
Joint device for artificial leg, method and control unit for controlling the joint device
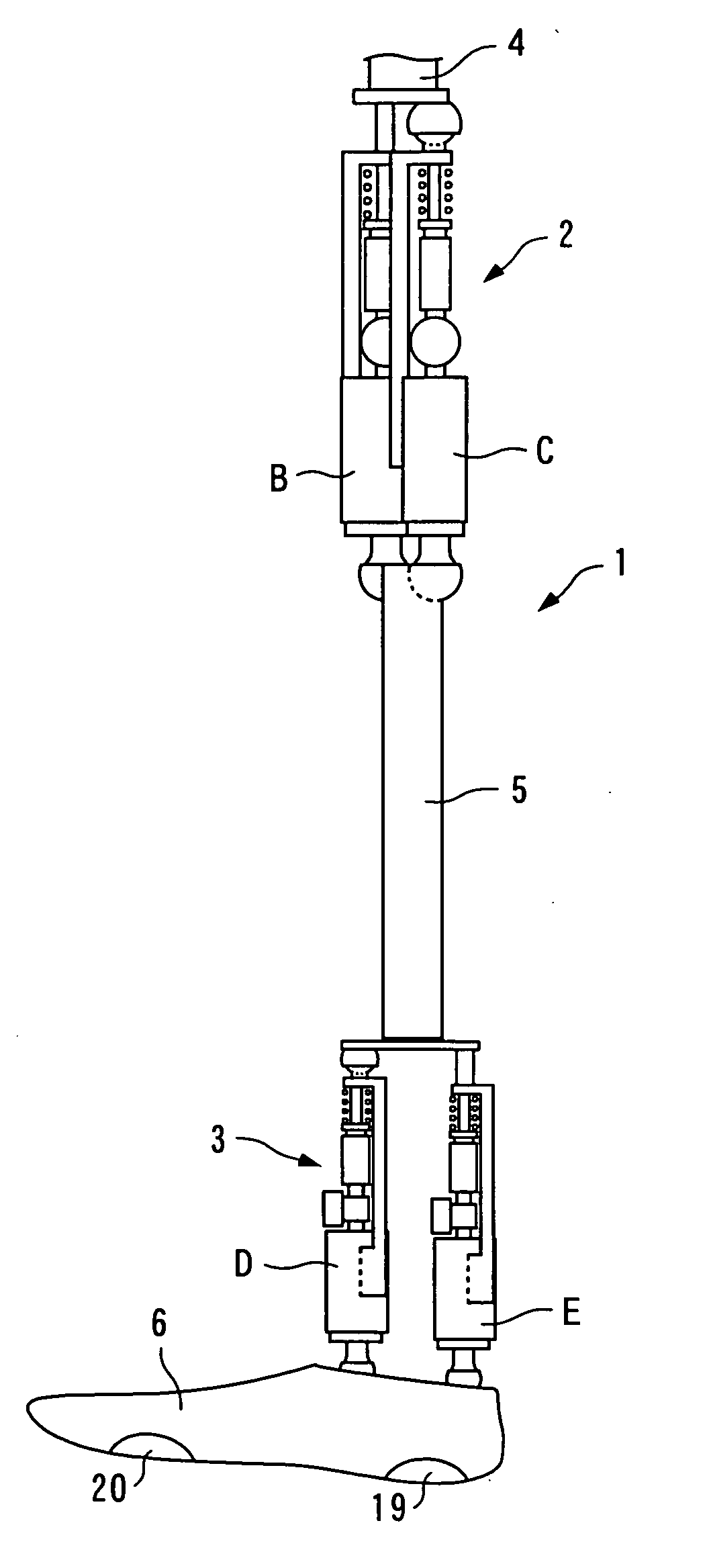
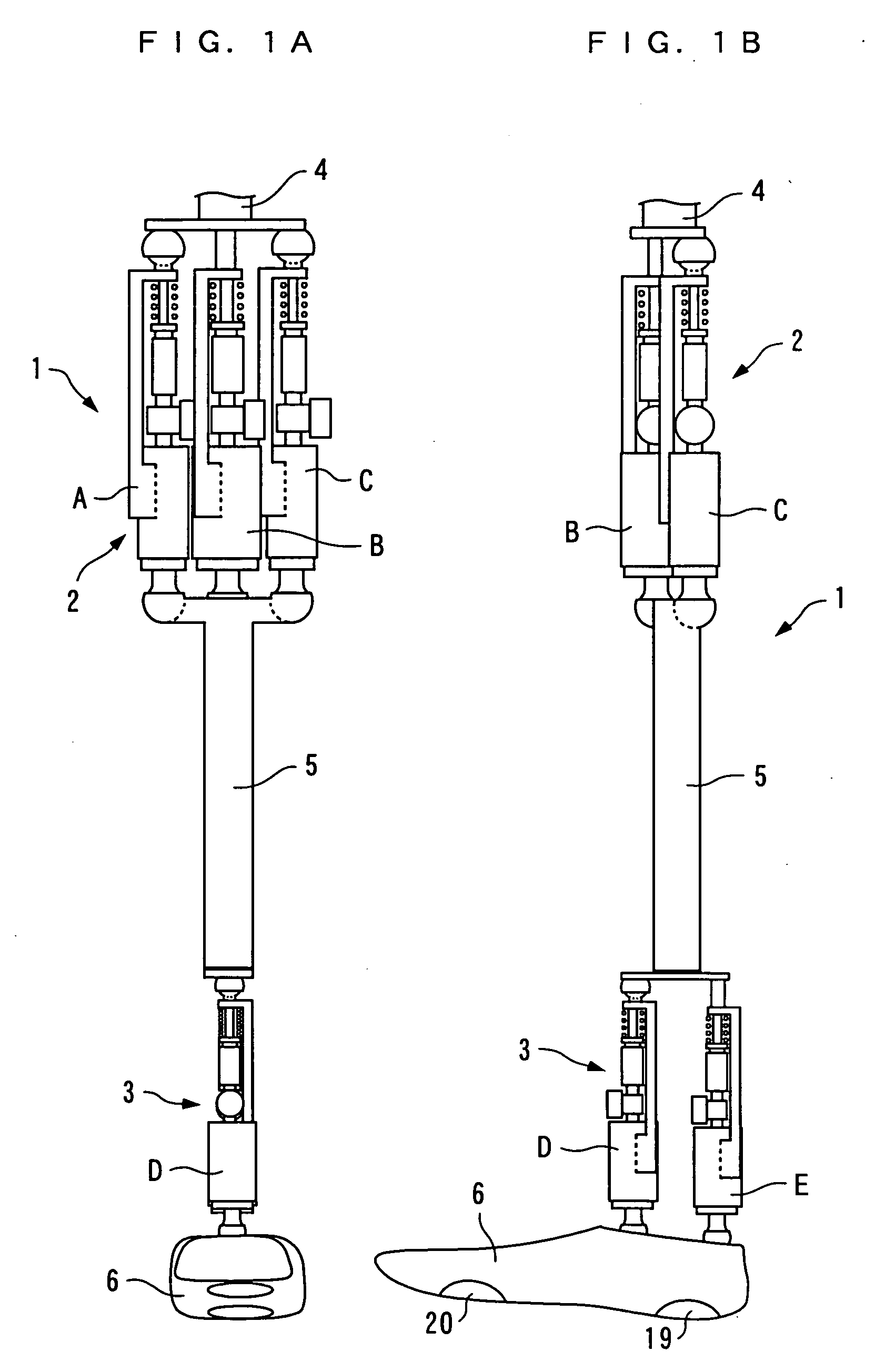
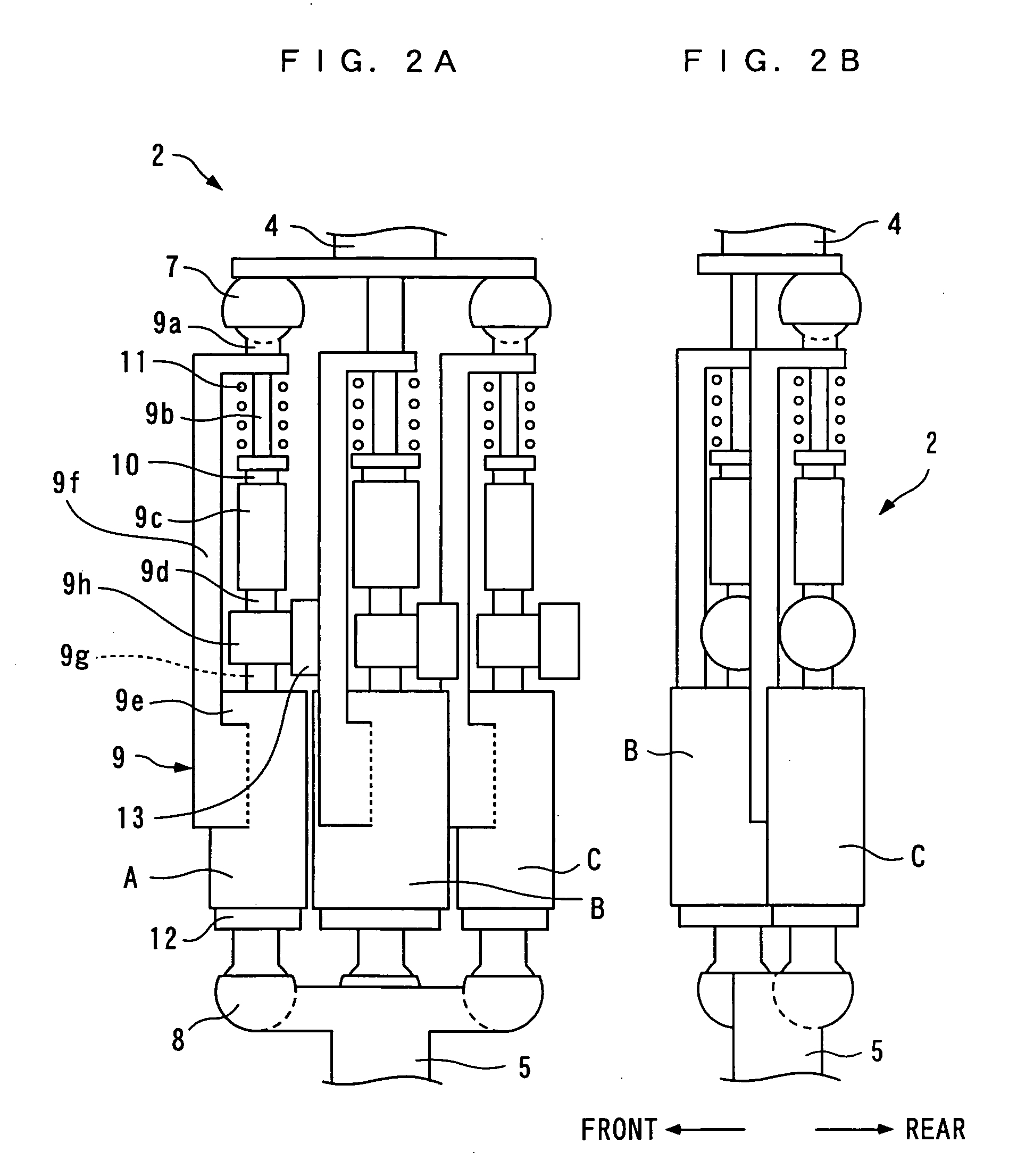
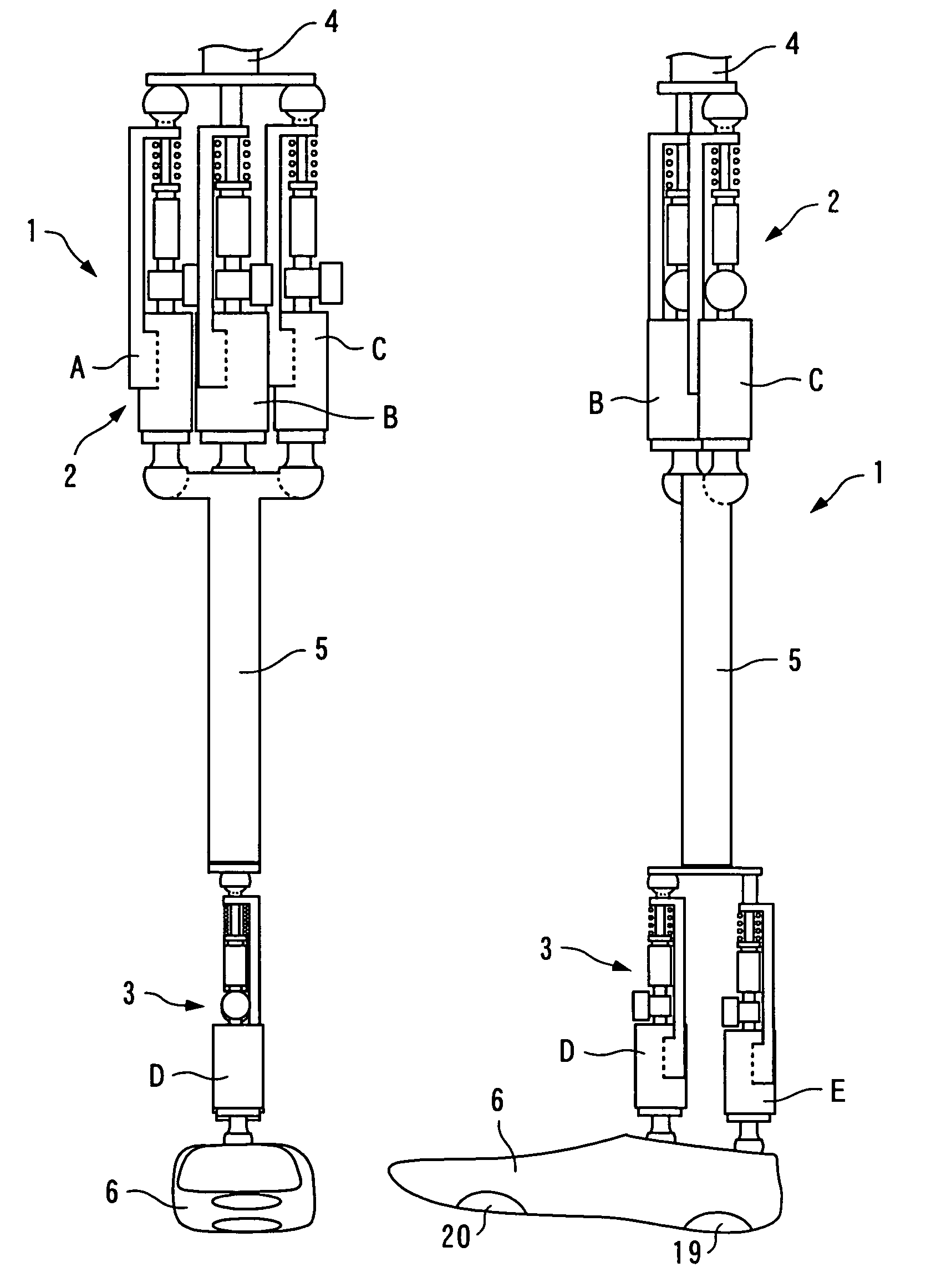
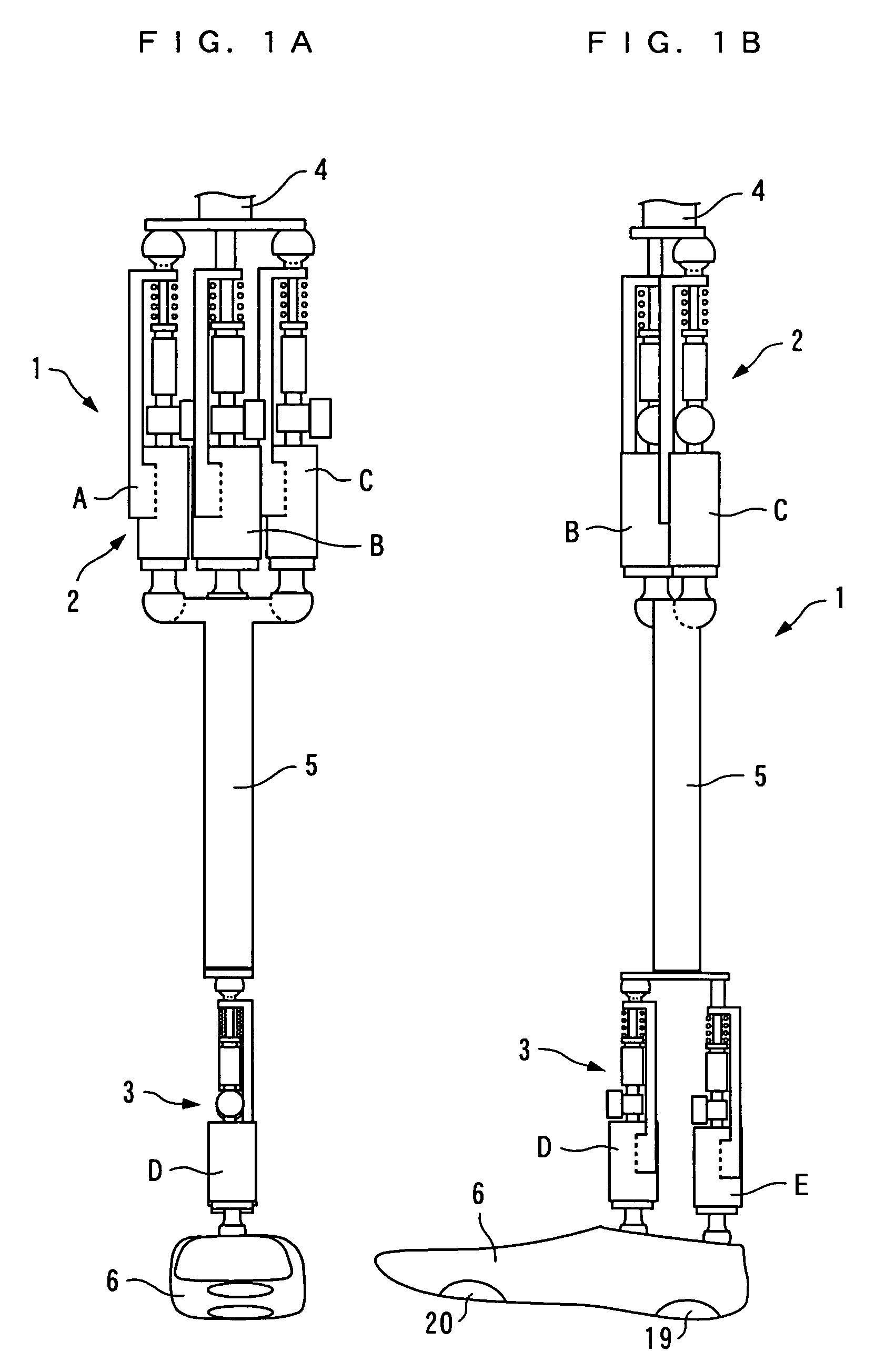
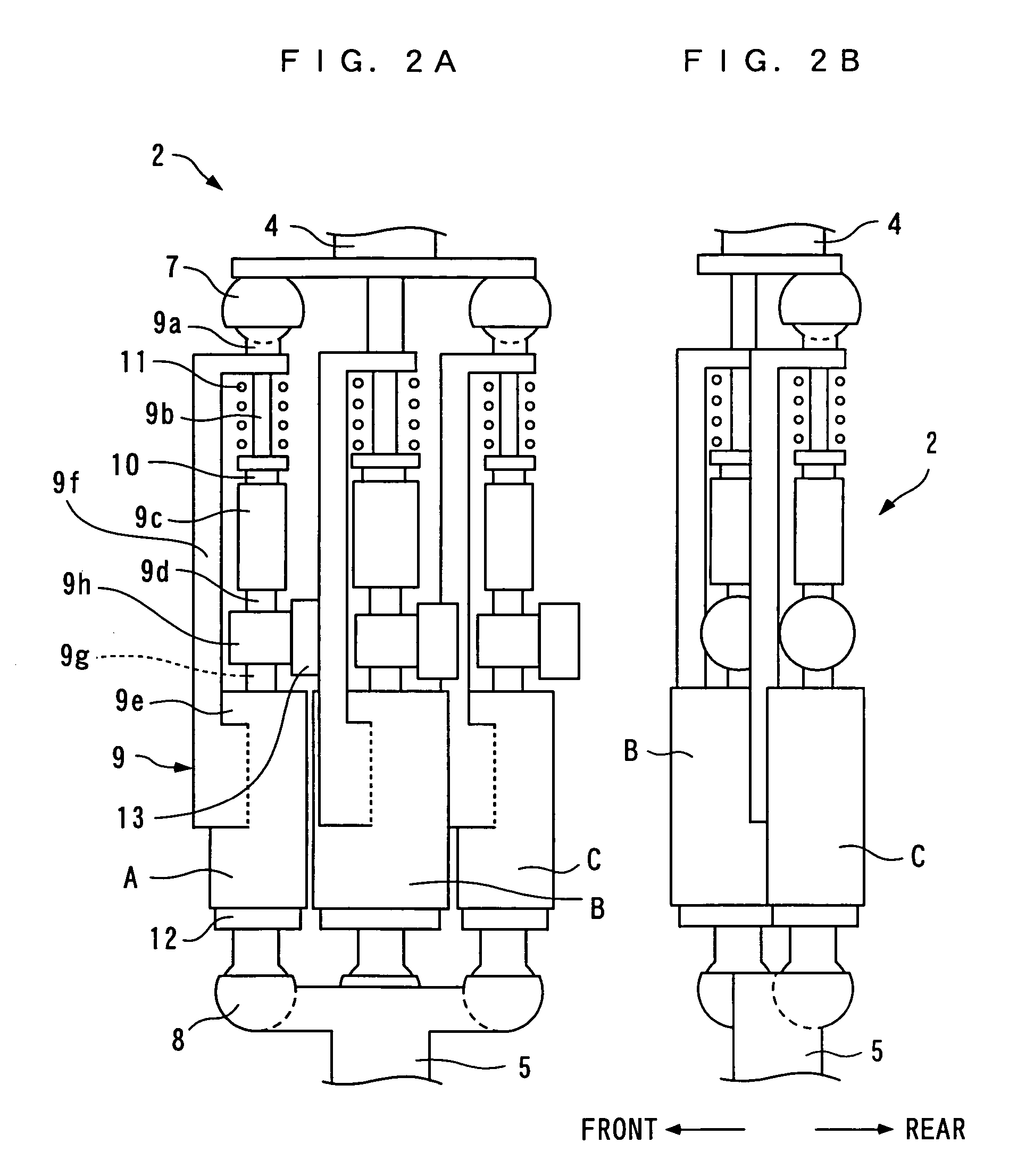
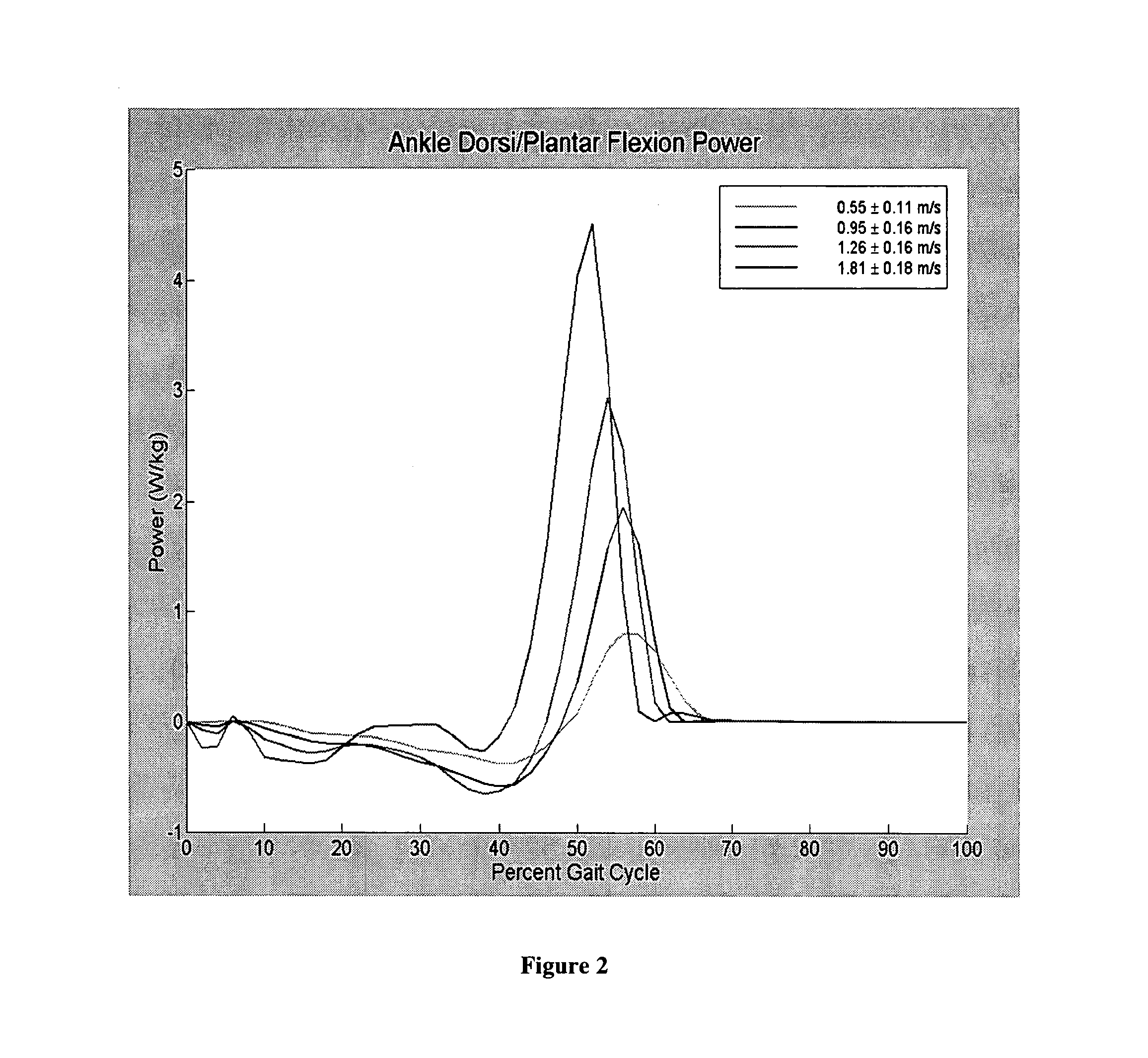
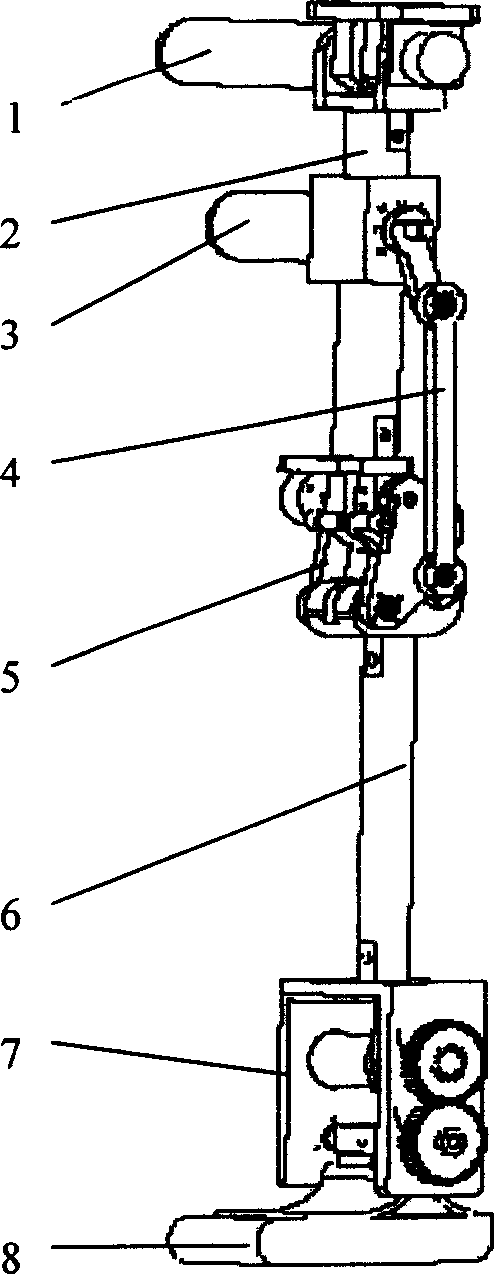
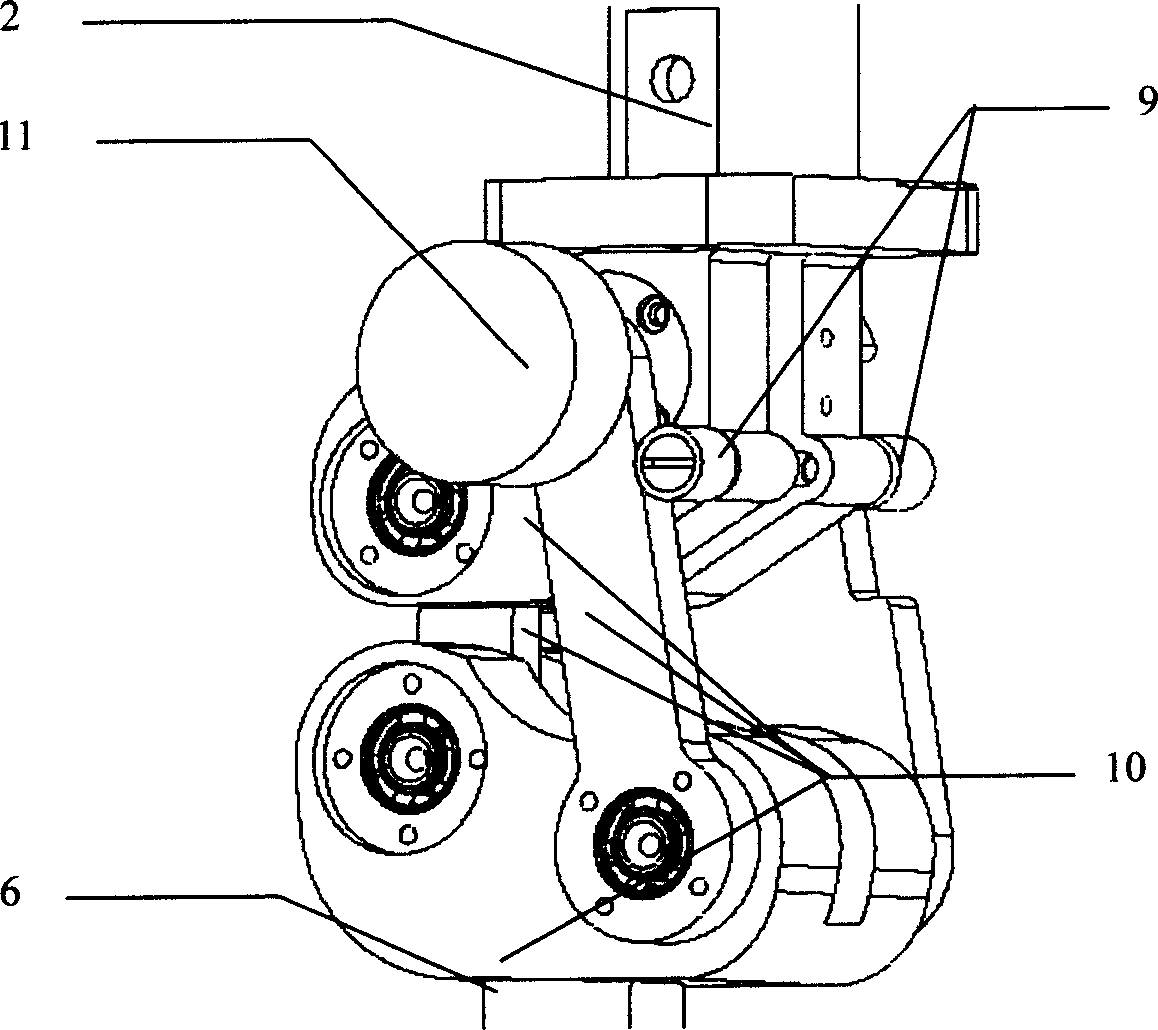
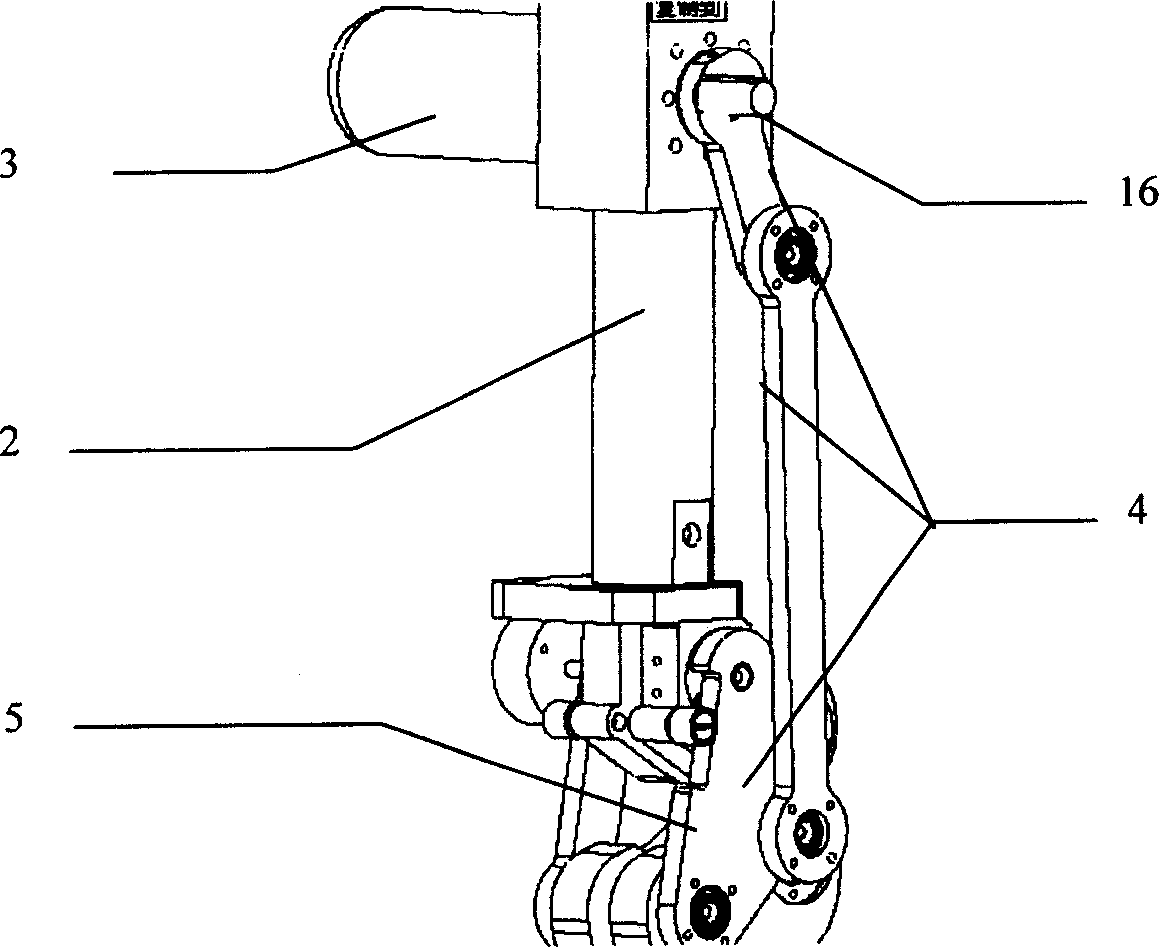
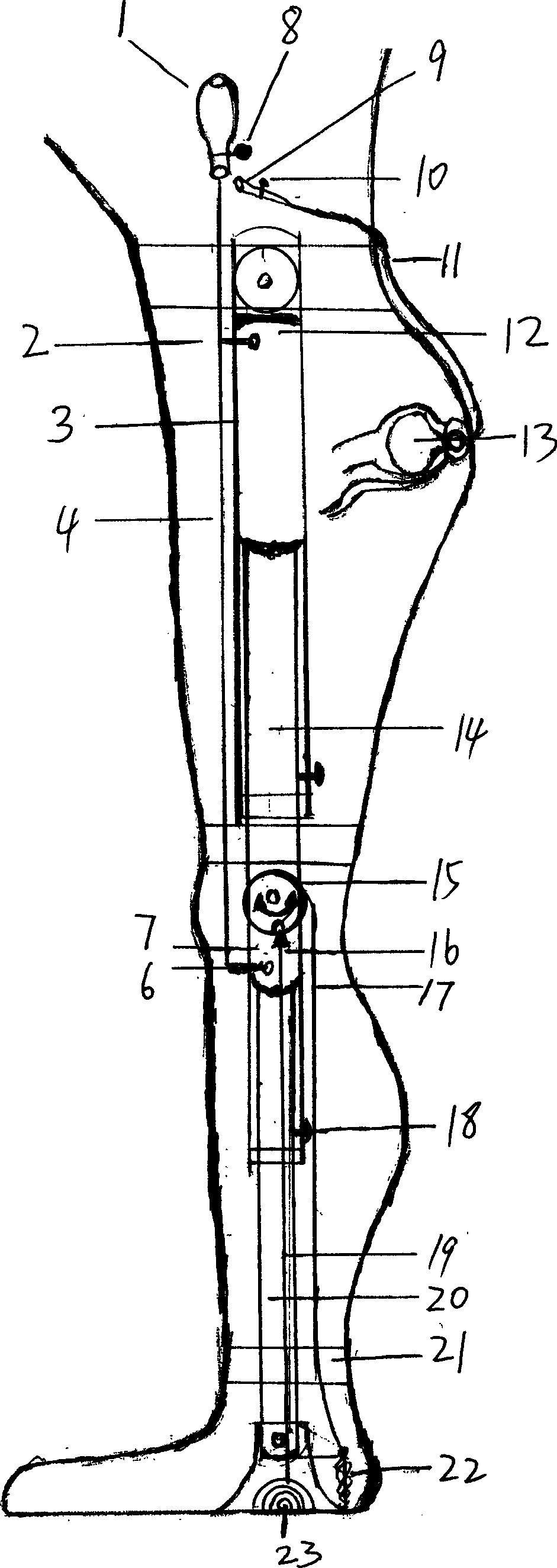
There is provided a joint device for an artificial leg, which makes it possible to dramatically achieve reduction of the weight of a power source and an increase in duration of the same, as well as facilitates knee bending / stretching motion, toe-up motion, and kicking motion. The joint device has an above-knee member and an under-knee member spaced from each other. Three expansible links are connected between the above-knee member and the under-knee member, for accumulating energy generated by the weight of a user's body acting on the artificial leg, and operating by releasing the accumulated energy to actuate the under-knee member into joint motion.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Joint device for artificial leg, method of controlling the joint device, and control unit
There is provided a joint device for an artificial leg, which makes it possible to dramatically achieve reduction of the weight of a power source and an increase in duration of the same, as well as facilitates knee bending / stretching motion, toe-up motion, and kicking motion. The joint device has an above-knee member and an under-knee member spaced from each other. Three expansible links are connected between the above-knee member and the under-knee member, for accumulating energy generated by the weight of a user's body acting on the artificial leg, and operating by releasing the accumulated energy to actuate the under-knee member into joint motion.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
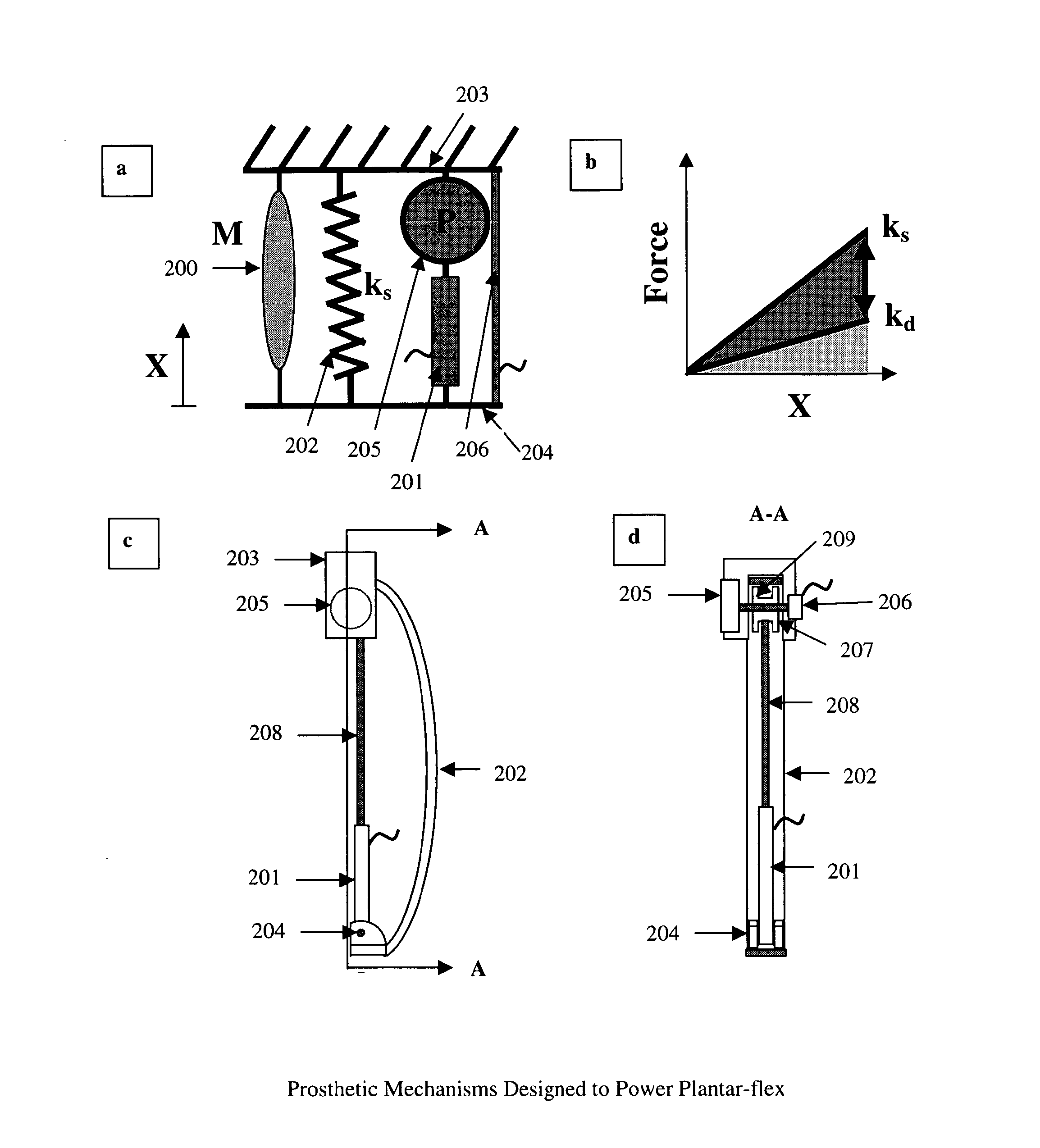
Variable mechanical-impedance artificial legs
InactiveUS8551184B1Minimize power consumptionIncrease the number ofNon-surgical orthopedic devicesArtificial legsOn boardEngineering
In one aspect, the invention provides methods and apparatus facilitating an adjustable-stiffness prosthesis or orthosis (including approximations to arbitrarily definable non-linear spring functions). Spring rates may be varied under no-load conditions during a walking gate cycle to minimize power consumption. In another aspect, the invention provides methods and apparatus for outputting positive power from a prosthesis or orthosis, facilitating high-performance artificial limbs. In one embodiment of the invention, the positive power is transferred from a functioning muscle to the prosthesis or orthosis, which mimics or assists a non-functioning or impaired muscle. In another embodiment of the invention, the positive power comes from an on-board power source in the prosthesis or orthosis.
Owner:OTTO BOCK HEALTHCARE IP GMBH & CO KG
Human-imitating double-foot robot artificial leg
InactiveCN1883994ACompact structureIncrease ground clearanceSelf-moving toy figuresVehiclesThighPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention involves an artificial leg for human-simulating double-foot robot and is within the scope of robot technology. The artificial leg consists of the coax joint, knee joint, anklebone, foot, thigh connecting rod and calf connecting rod, characterized in that a knee joint driving motor is equipped on the thigh connecting rod between the coax joint and the knee joint. The knee joints are two closed-chain structure comprising of four connecting rods. The knee joint driving motor is connected with the rear rods of the four-connecting-rod structure through the parallel four connecting rod mechanism. A stop piece is fixed on the front end of the four-connecting-rod mechanism. An encoder is equipped on the spindle, which is located on the upper end of the four-connecting-rod mechanism. The advantages of this invention are: the distance between the lifted foot and the ground is increased, enhancing the robot's ability of avoid obstacles while it is walking; the calves don't tough the ground during their swinging process, improving the robot's stability and efficiency in walking; the mass distribution in the leg is more similar to that of human being, producing a compact overall structure and high precision in transmission.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Locking device for a prothesis
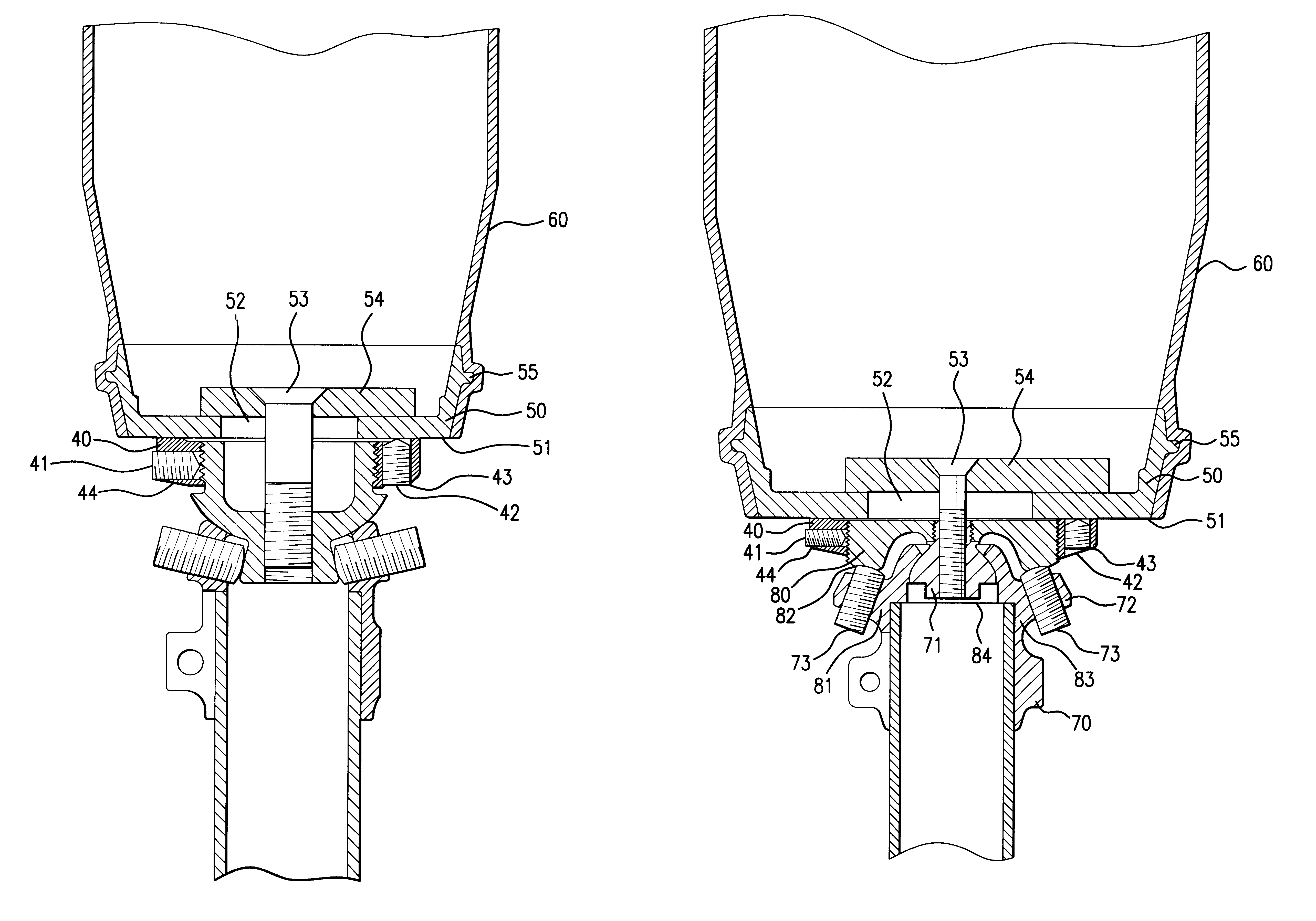
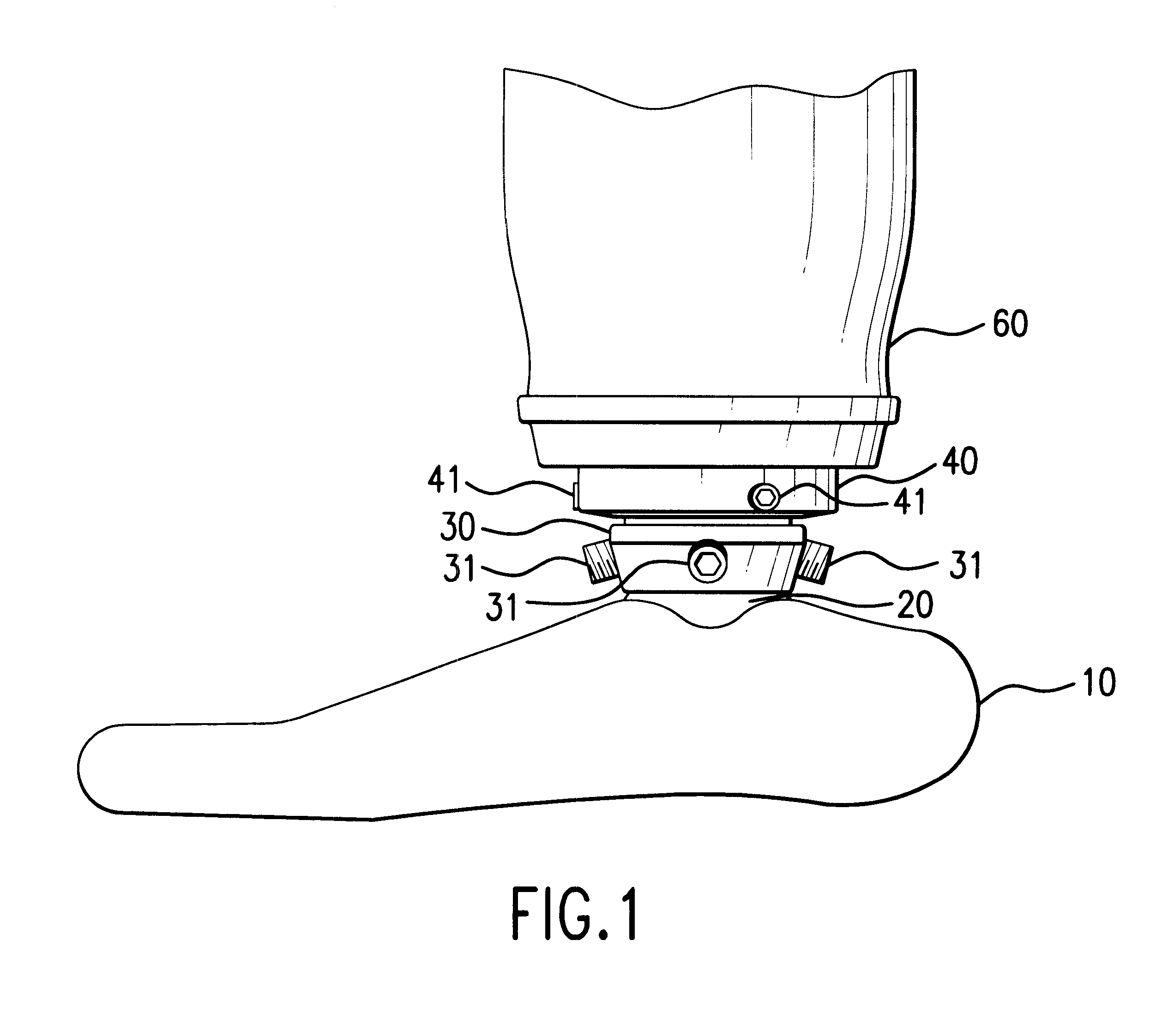
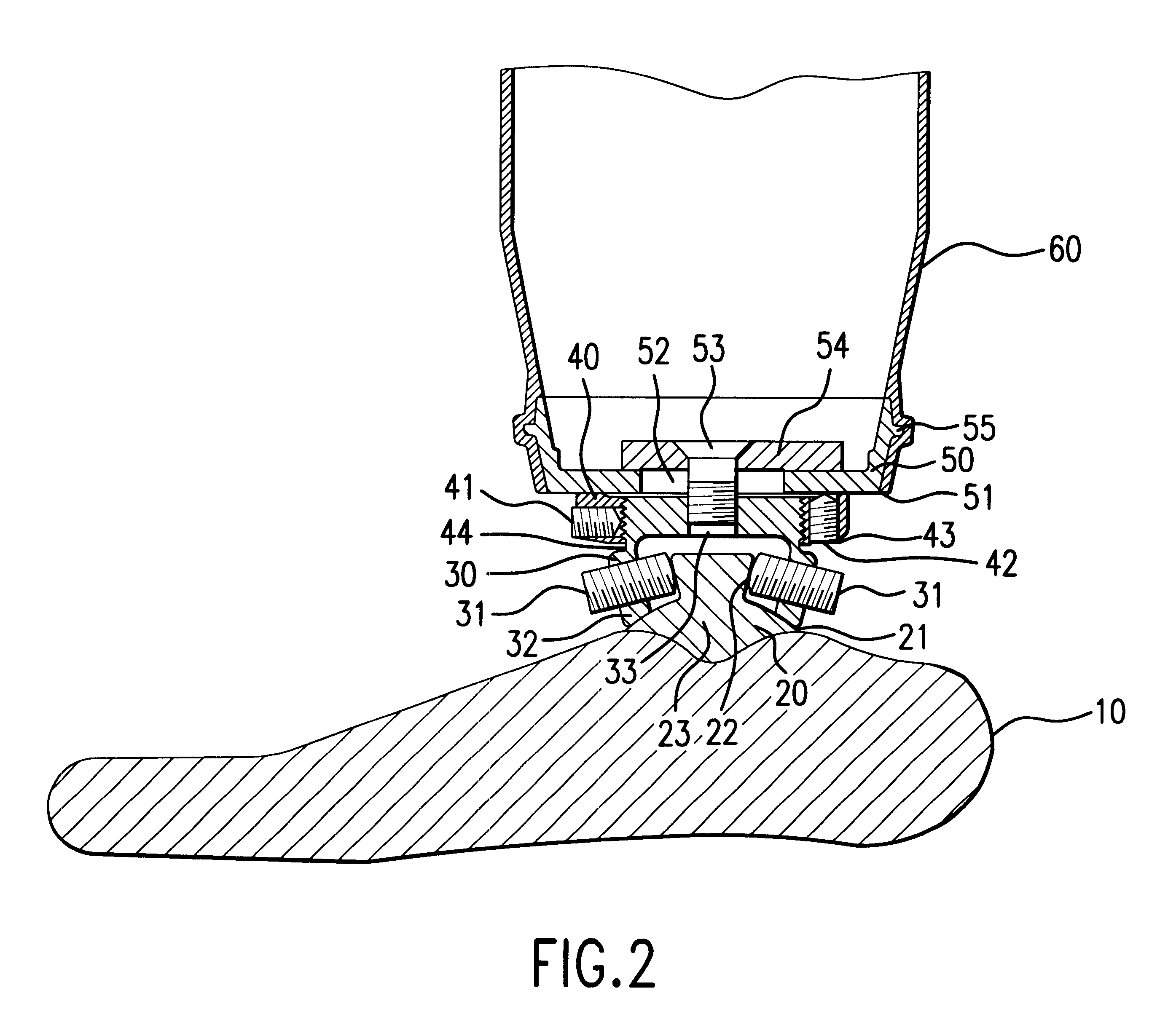
A novel way of locking and unlocking an adjustment device for an artificial leg or arm makes it possible to perform an adjustment of the prosthesis, without necessitating disassembly of the prosthesis or the removal of the prosthesis from the patient. This facilitates the work in adjusting the translatory position and the angular position, and the adjustment device also offers a further degree of freedom by the addition of the possibility of distal adjustment. The novel combination provides a locking ring (40) on the adjustment head. The locking ring offers a stable, adjustable locking of the adjustment head against a coupling sleeve (50) on the stump, while at the same time fixing the translatory position of the prosthesis. The prosthesis is then provided with a stable, adjustable setting of the distal length of the prosthesis by means of the locking ring (40), which greatly facilitates fine adjustment of the length of the prosthesis, since there is no need to disassemble the prosthesis for performing such a distal length adjustment. The angular adjustment is carried out by means of a pyramid adapter pin (23) which is arranged either in the upper, or in the lower part of the adjustment head. Inclined adjustment screws corresponding to the inclined sides of the pyramid adapter pin are arranged in the corresponding upper or lower part of the adjustment head. The arrangement allows a simple way of disassembling the adjustment head in two parts.
Owner:CENTRI
Intelligent lap artificial limb system controlled to follow pace of health leg
InactiveCN1957862ARealize bionic intelligent controlArtificial legsComputer control systemControl signal
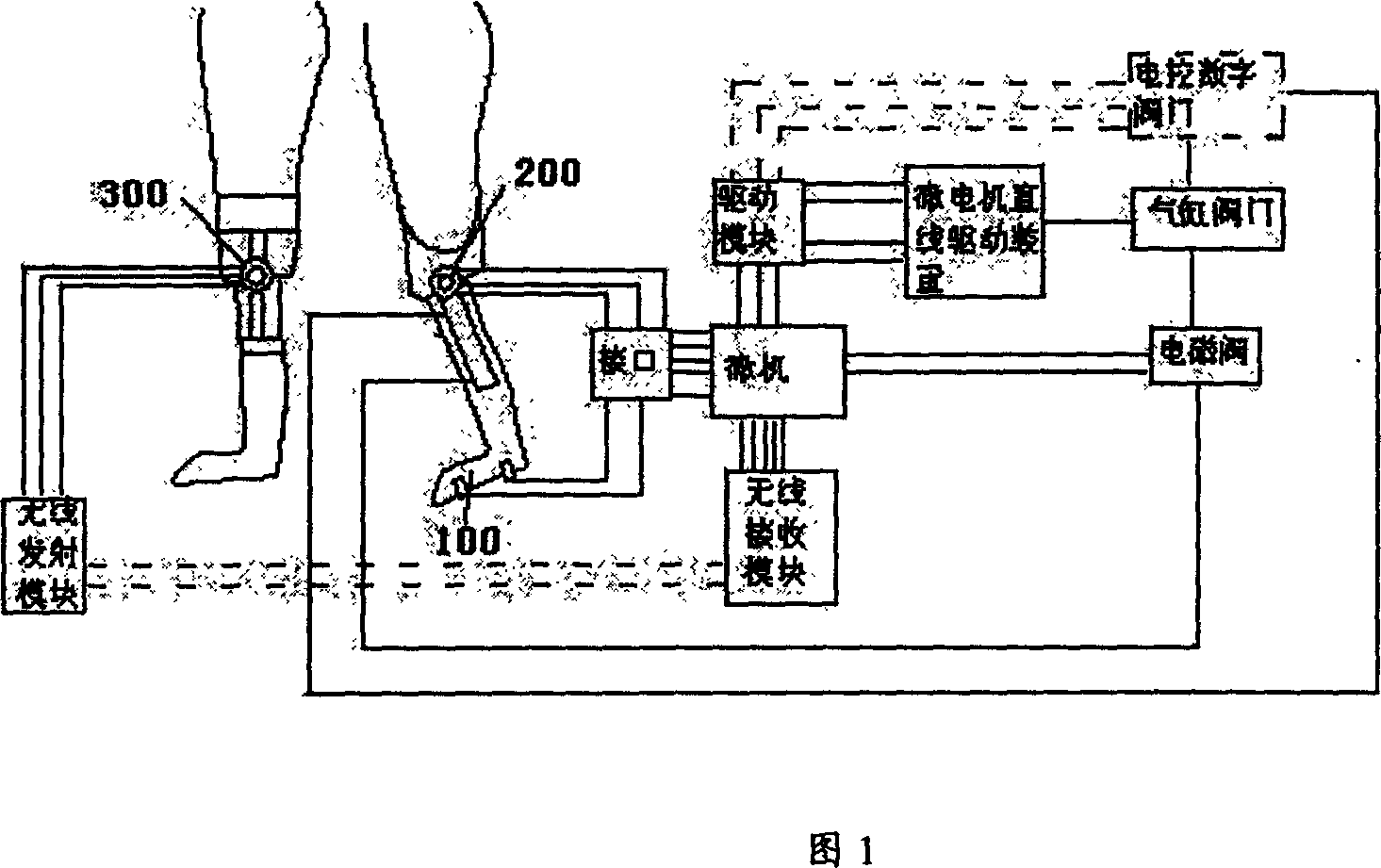
An intelligent on-knee artificial leg system able to control the walking speed for synchronizing it with health leg is composed of an artificial leg with a microprocessor, an electrically controlled hydraulic knee joint, an in-line detecting mechanism for detecting the steps of health leg, a step data transmission system, and a computer control system. Its control method is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Process for forming artificial leg made of carbon fiber composite materials
The invention relates to a process for forming an artificial leg made of carbon fiber composite materials. The forming process comprises pre-soaked materials, cutting, paving, thermal forming, grinding and sand spraying, wherein the pre-soaked materials comprise one-way carbon fiber pre-soaked materials, 3K carbon fiber bundle woven fabric pre-soaked materials and a resin membrane, and the pre-soaked materials are cutting to needed shapes; in the paving link which is particularly important, the pre-soaked materials are adhered to a mould to form a pre-forming body in a paving mode, and in the paving process, an intermediate layer is arranged, the one-way carbon fiber pre-soaked materials are alternately paved along different directions and symmetrical to the intermediate layer, and the resin membrane is evenly melted by an electric iron and permeates into the pre-forming body; in the thermal forming link, the flat plate-like parts are formed by mould pressing, and the parts with a bigger radian are formed by bag pressing; and after demoulding, the formed artificial leg undergoes the grinding and the sand spraying treatments. The composite material artificial leg produced by the process has the advantages of high overall strength, light weight, fatigue resistance, good elasticity, good matching with a connecting piece, uniform geometric structure, good thermal stability, little amount of deformation and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
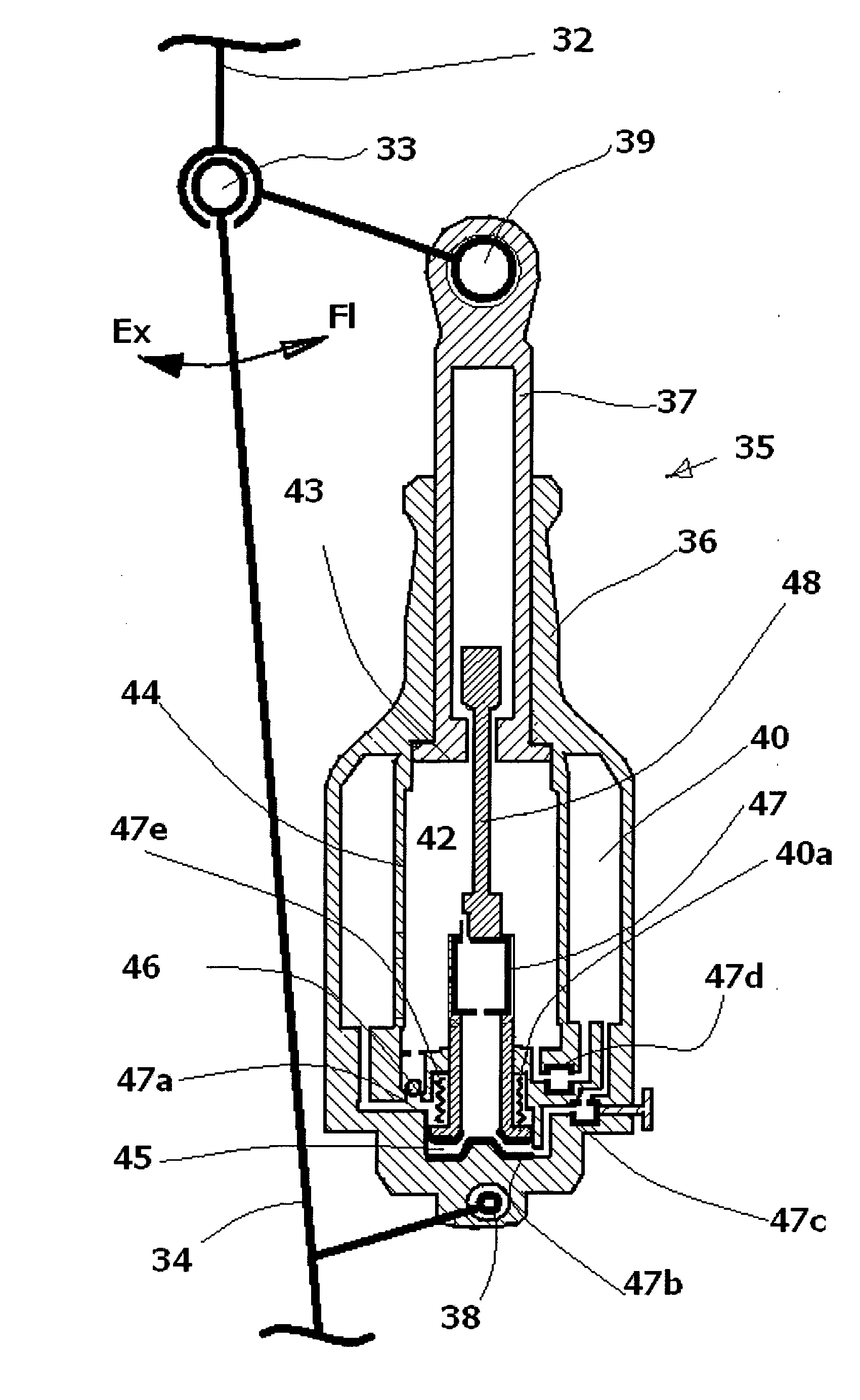
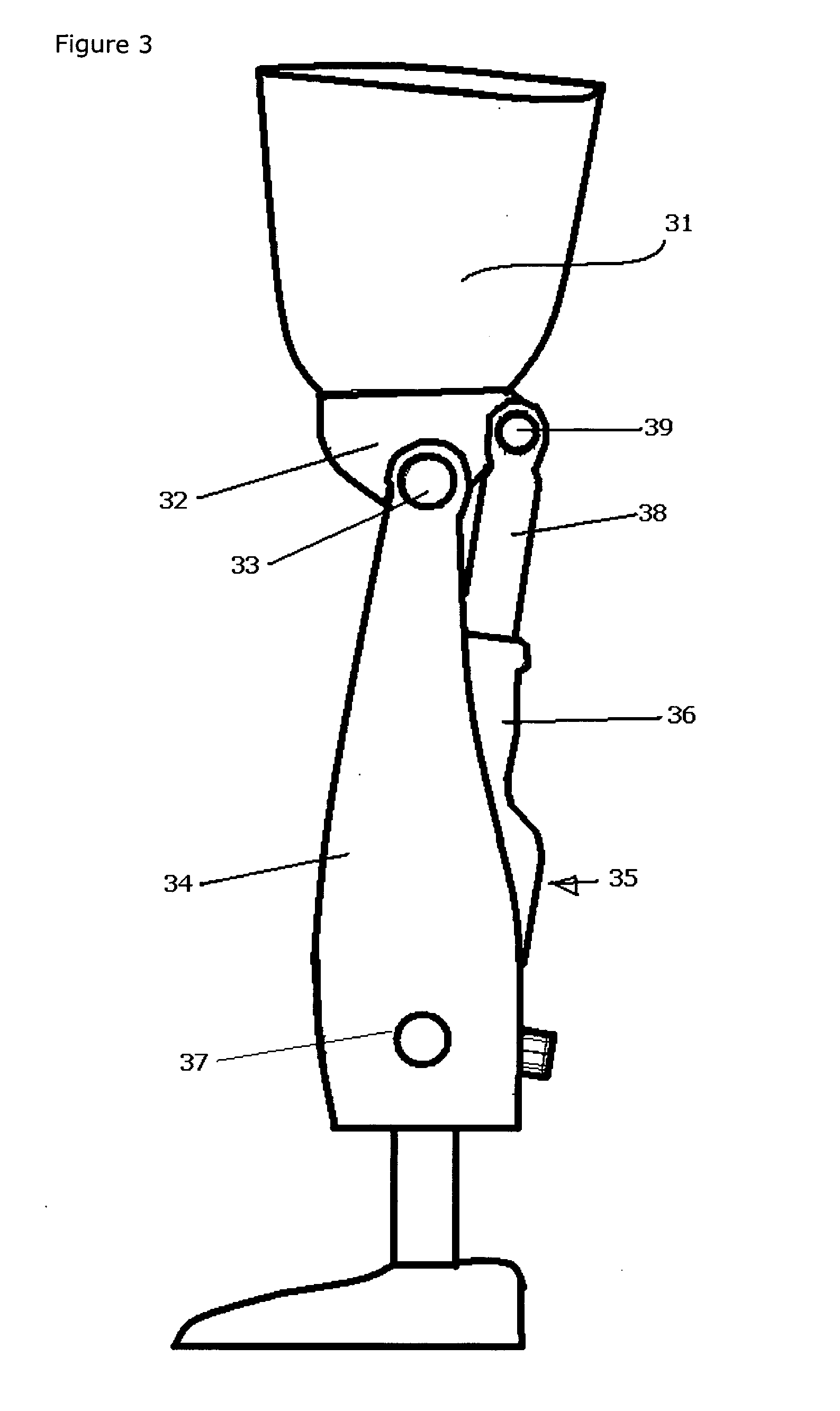
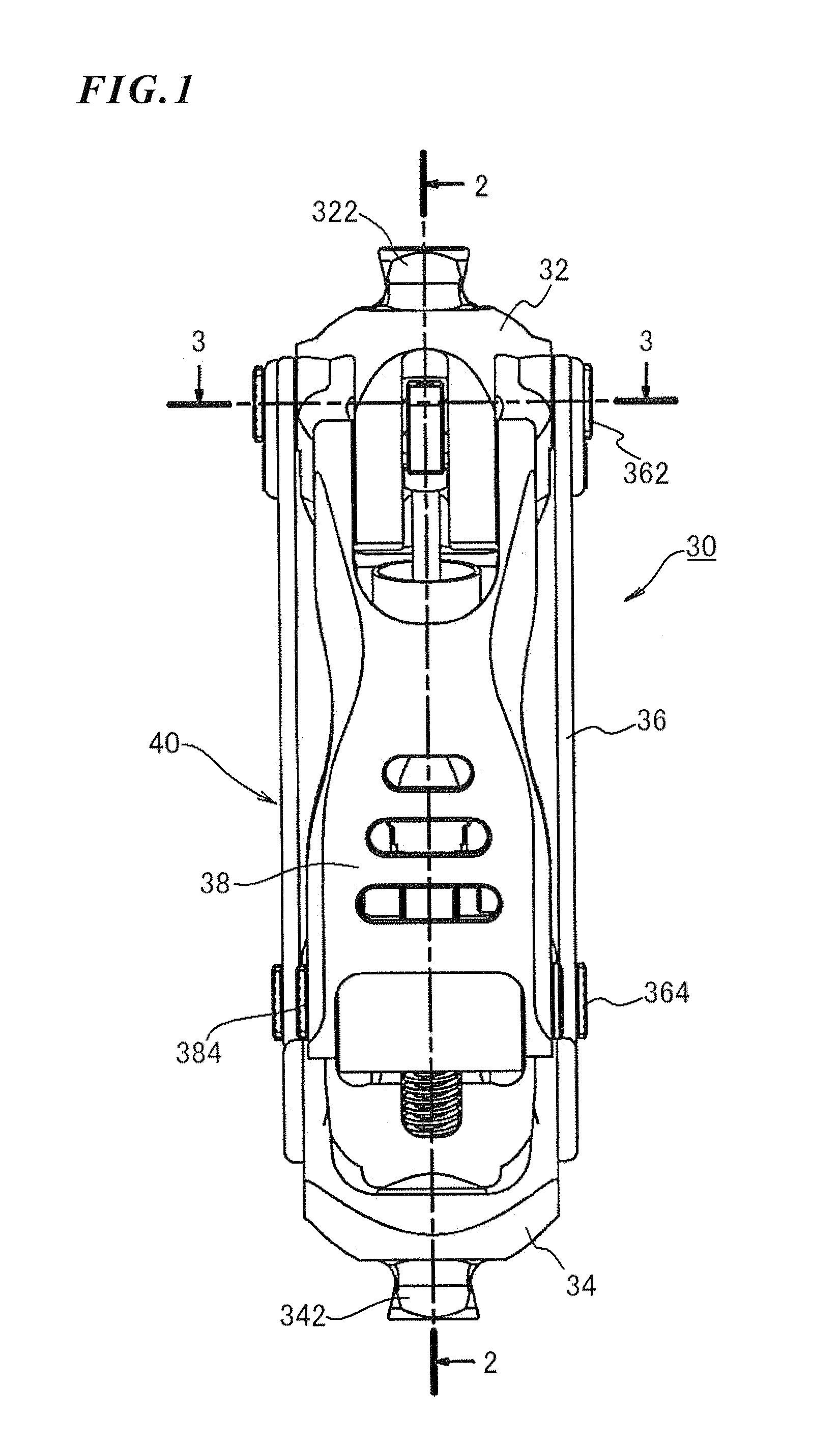
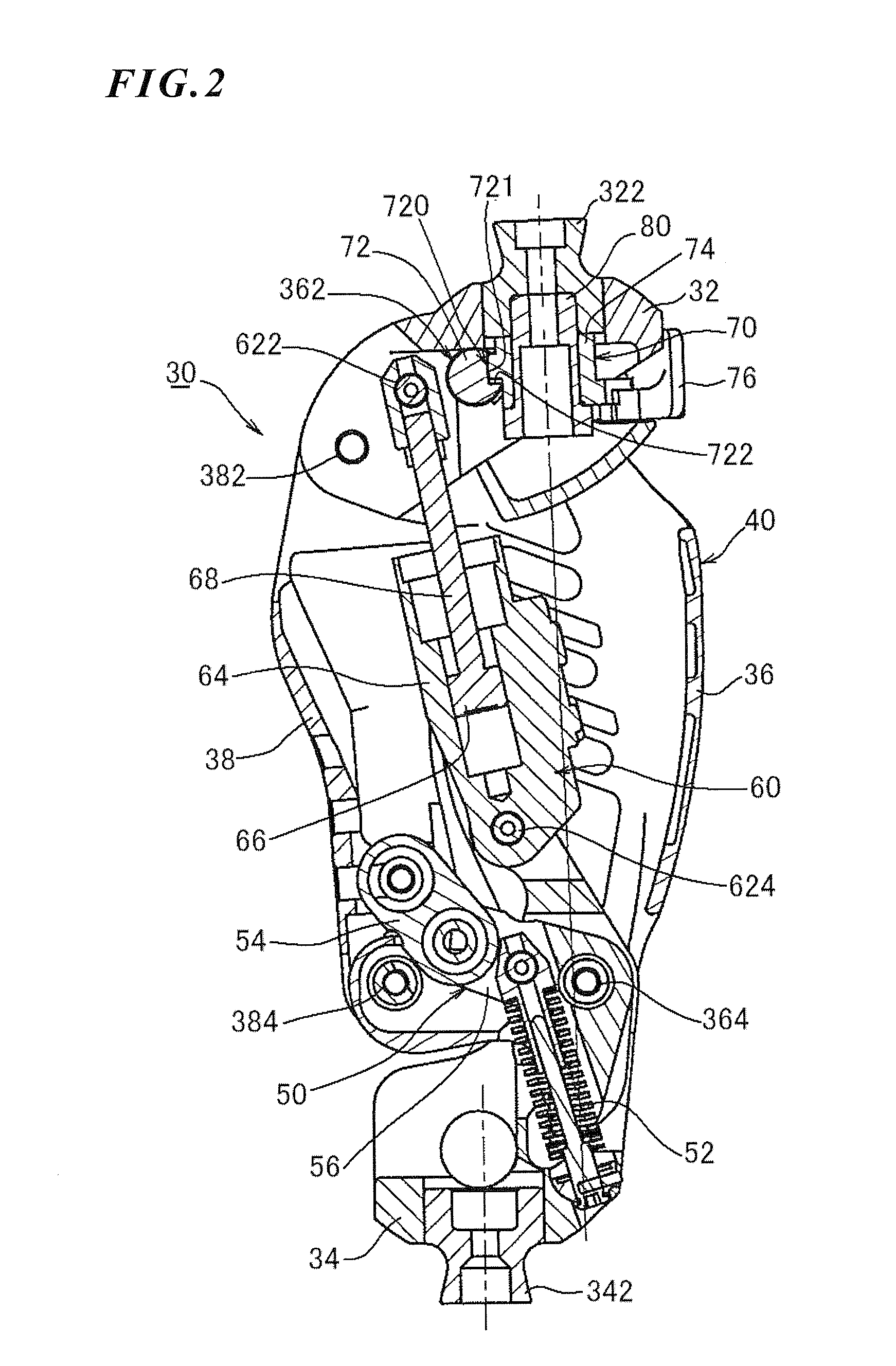
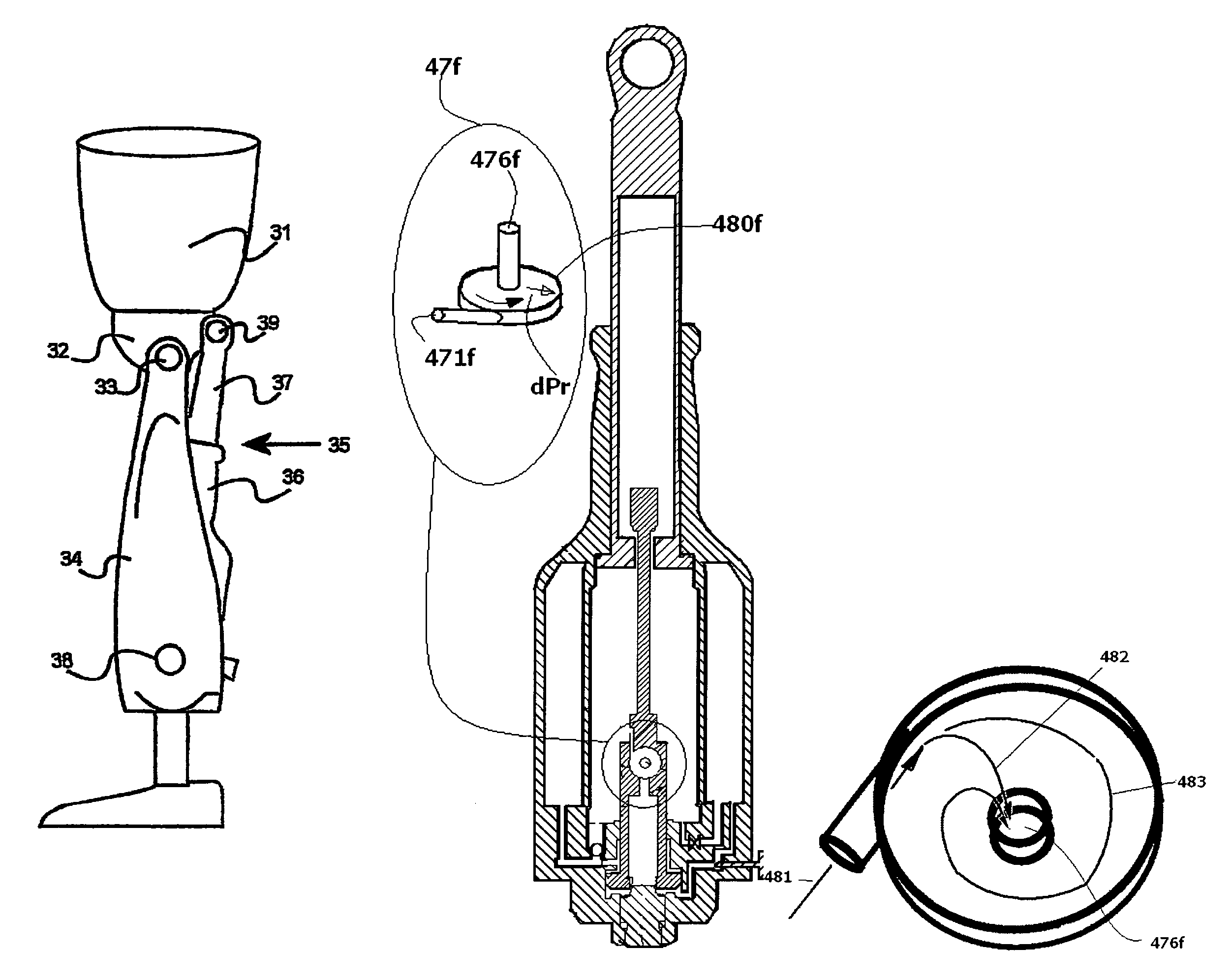
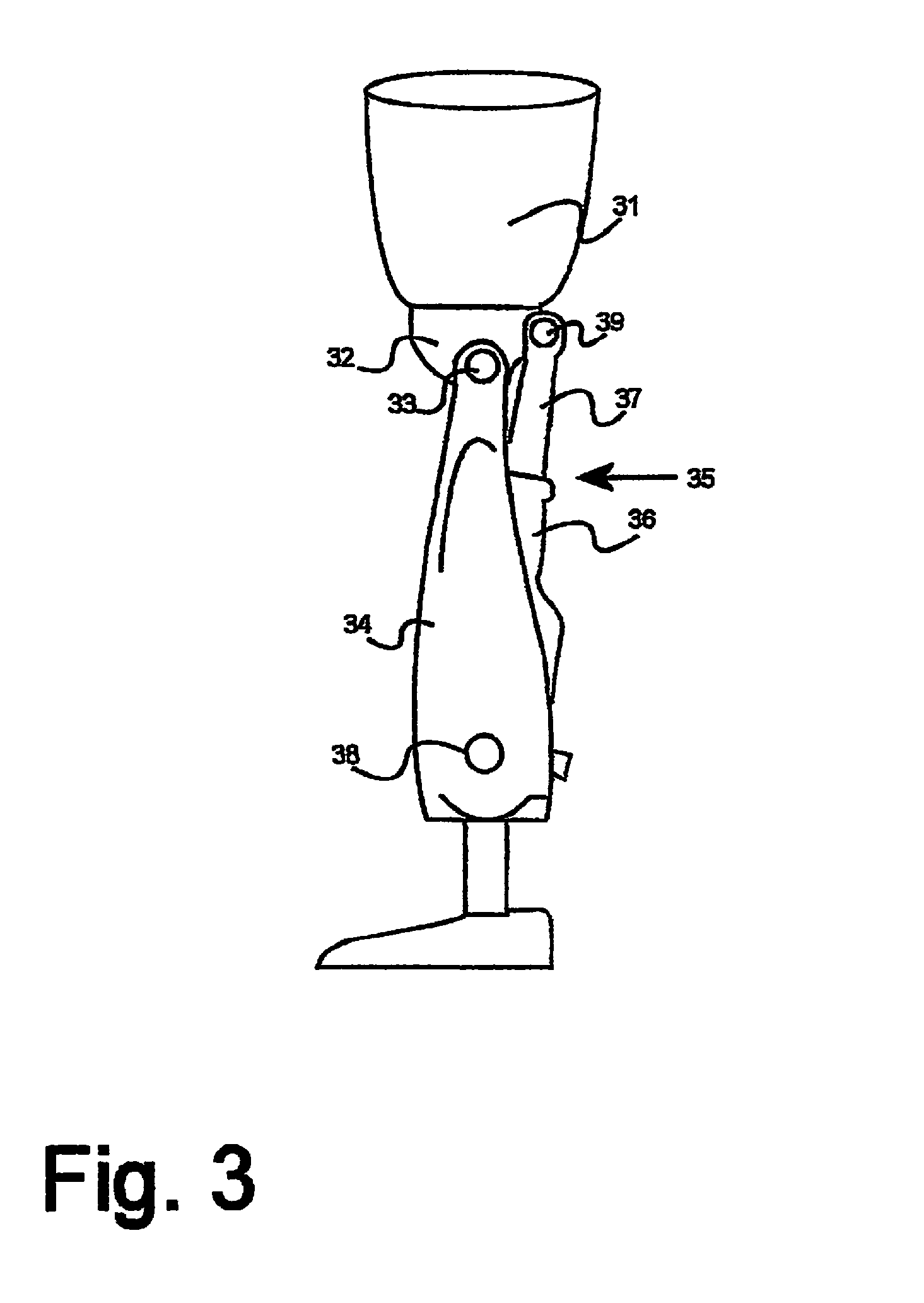
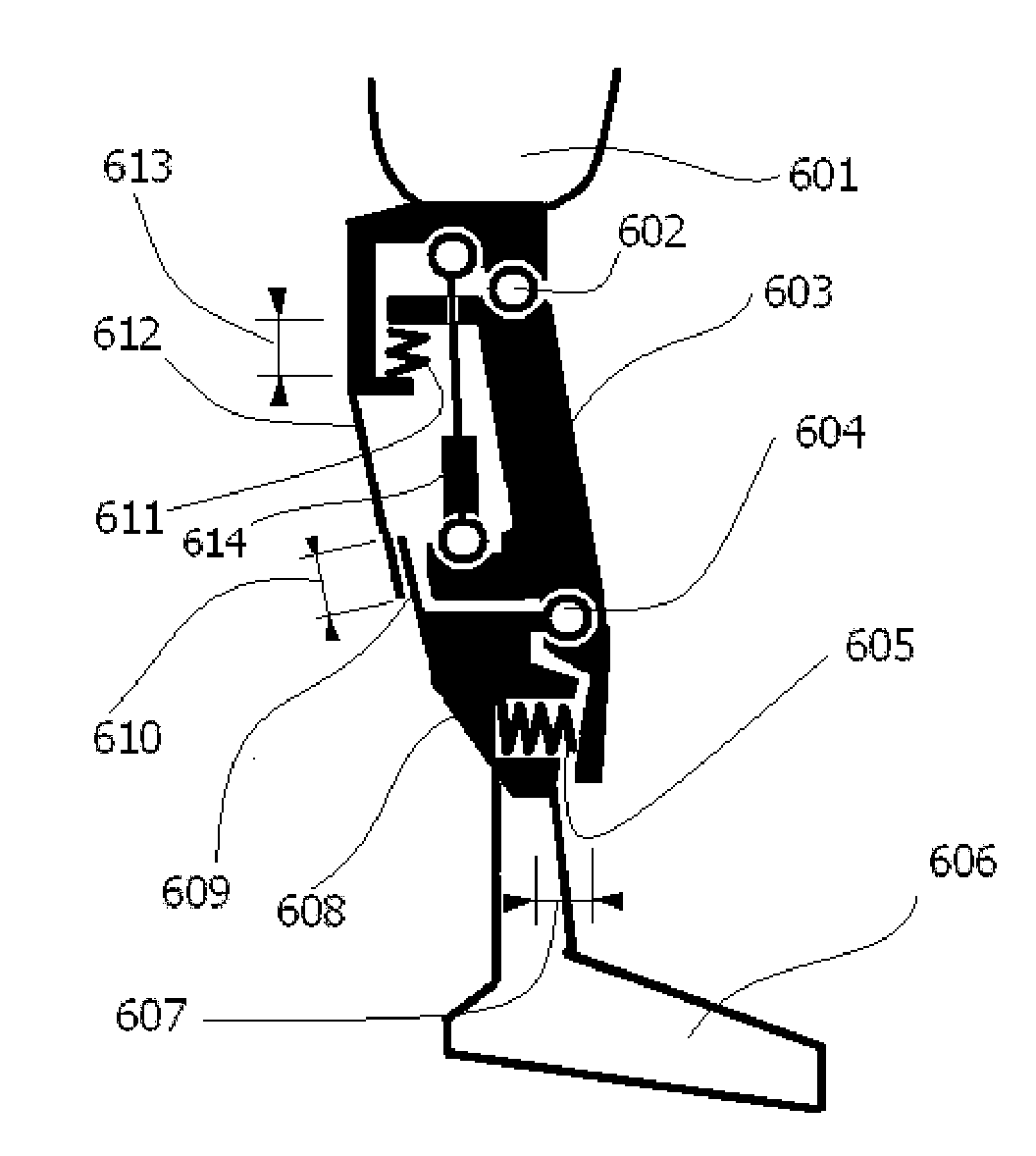
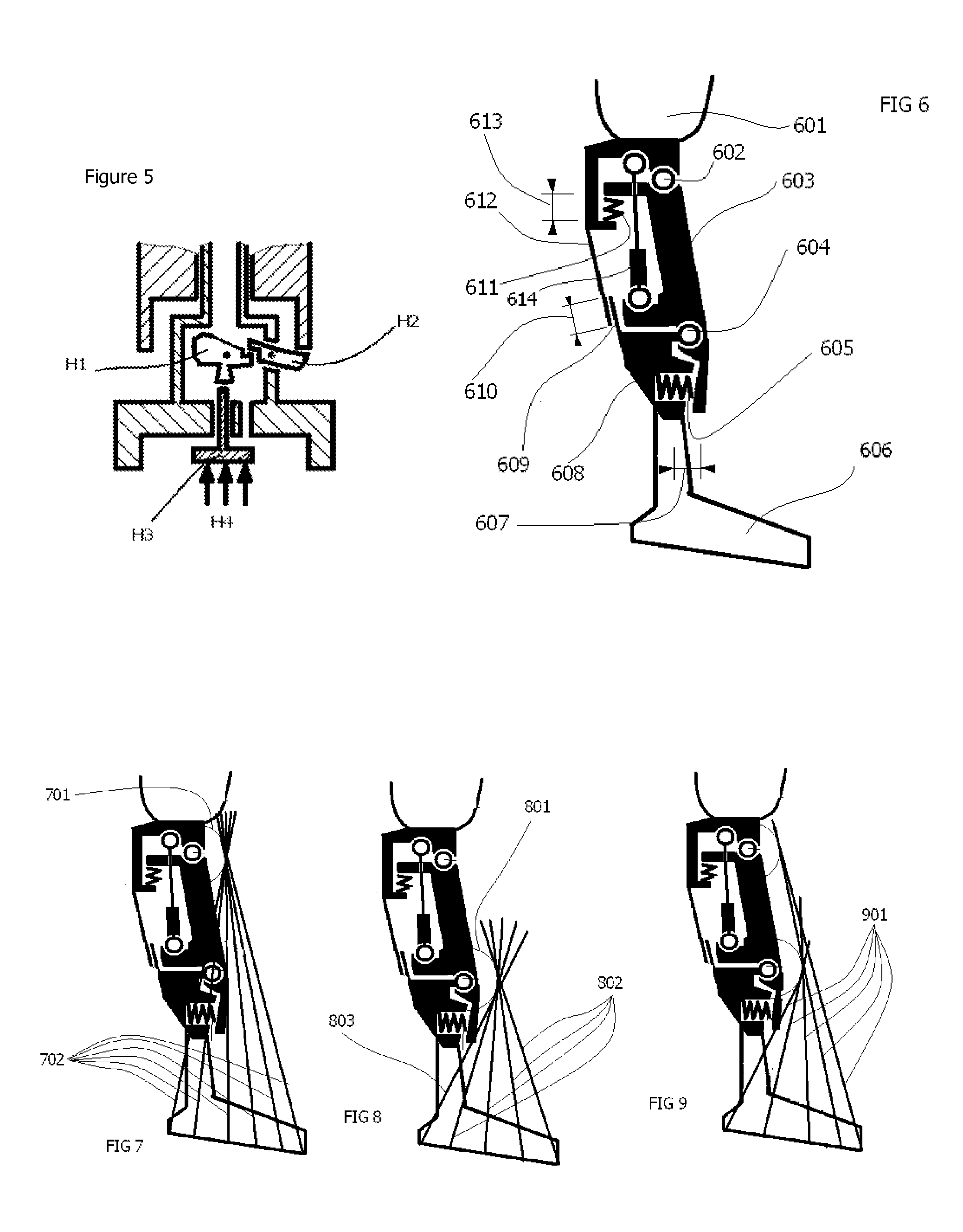
Hydraulic prosthetic joint
ActiveUS20110307078A1Keep openMemory is also lostSpringsArtificial legsArtificial jointsDifferential pressure
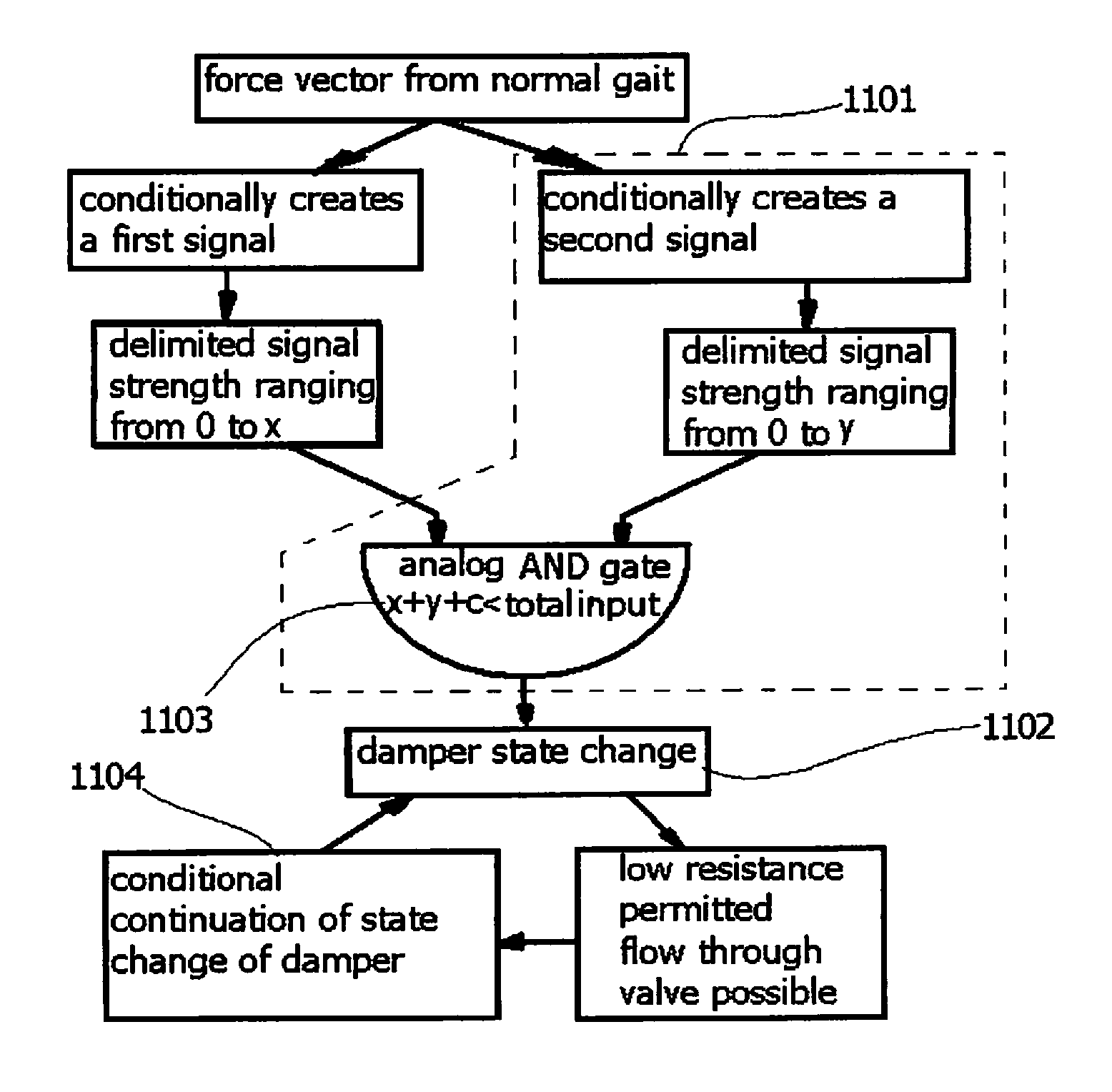
The present invention relates to artificial limbs generally and to joints for the same. In particular, the present invention provides hydraulic functional units (35), generally classified as damping devices as connected between artificial limbs whereby to enable movement of artificial joints to closely correspond with natural human movement. In the provision of realistic joints, as used in prosthetic limbs, an important aspect in attempting to achieve a realistic movement is to provide a different operating characteristic to the joint when under load. Indeed, one of the more important characteristics of an artificial leg for achieving a natural-looking walking gait correspond with those of a so called stabilised knee, i.e. a knee which resists flexion when under load, that is when it is bearing at least some of the weight of the amputee. In accordance with the invention, there is provided hydraulic damper control elements for prostheses which utilize a pressure differential due to the presence a fluid flow as a direct control input for a at least one hydraulic valve (47). The valve can comprise a vortex flow arrangement (47f) to cause fluid flow to circulate about aperture. The valve can comprise a moveable element which abuts a resiliently mounted element which reduces the size of an aperture as the force increases.
Owner:BOENDER JACOB QUINTUS LAURENS ANTHONY
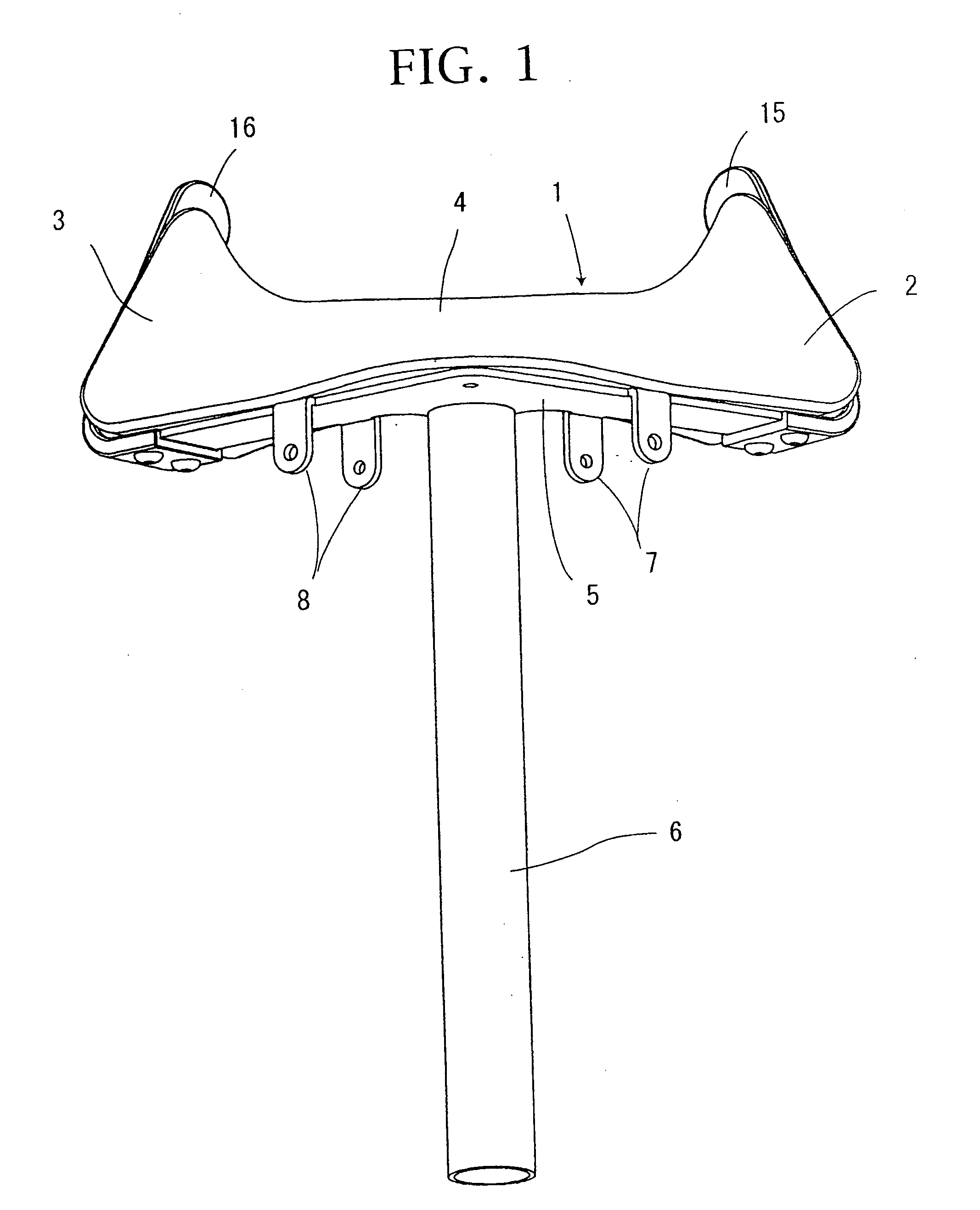
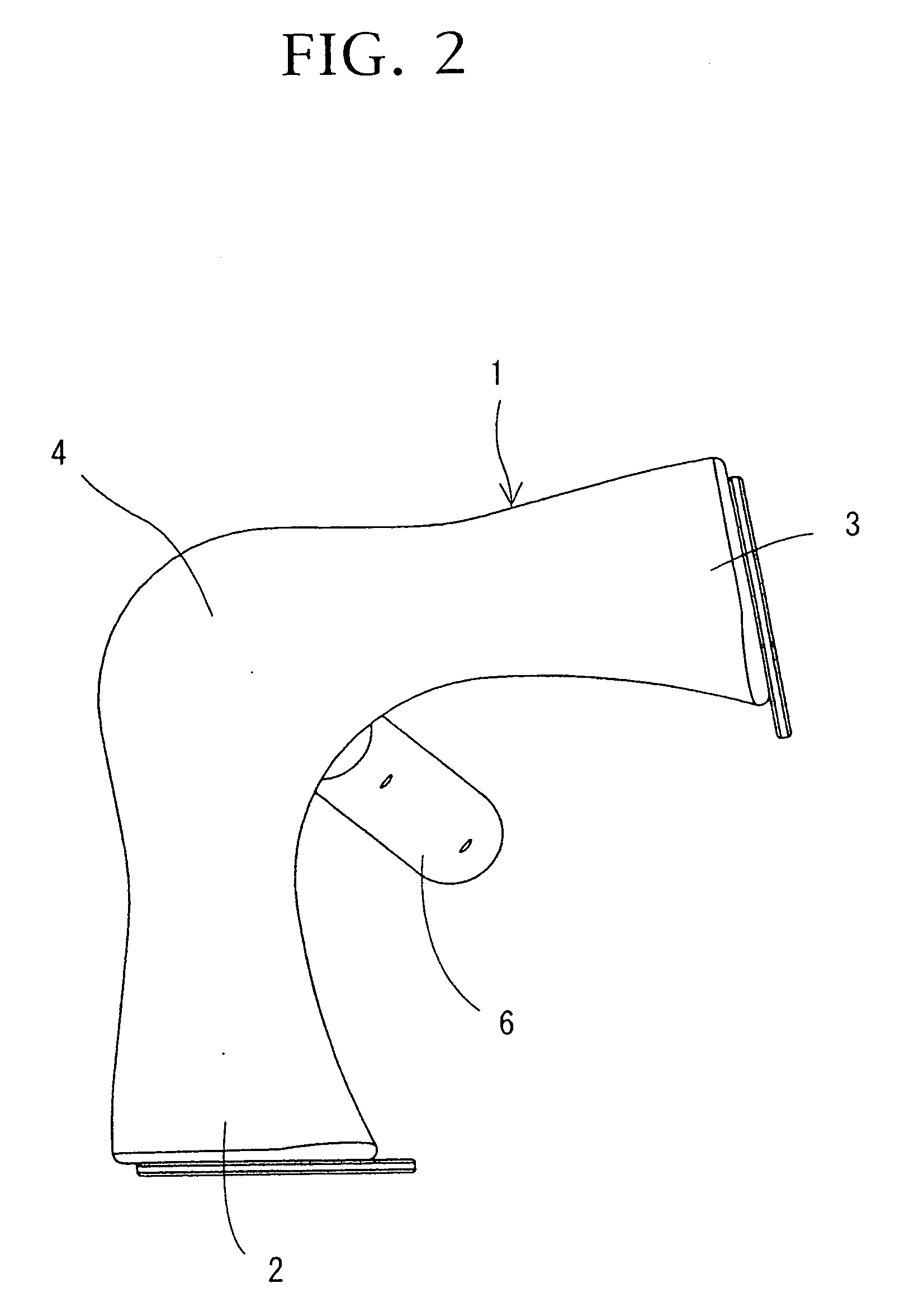
Hucklebone supporting-type artificial leg
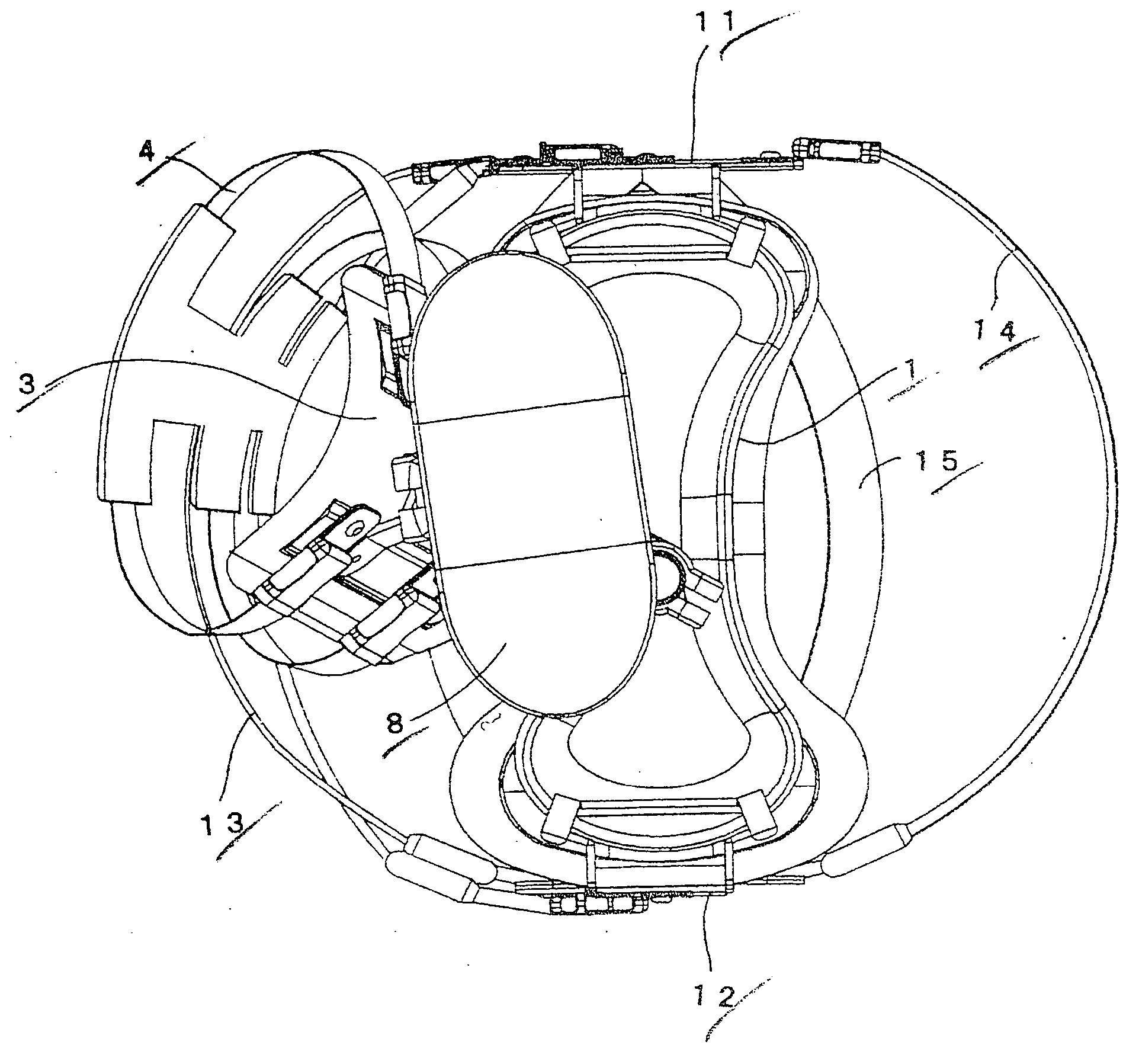
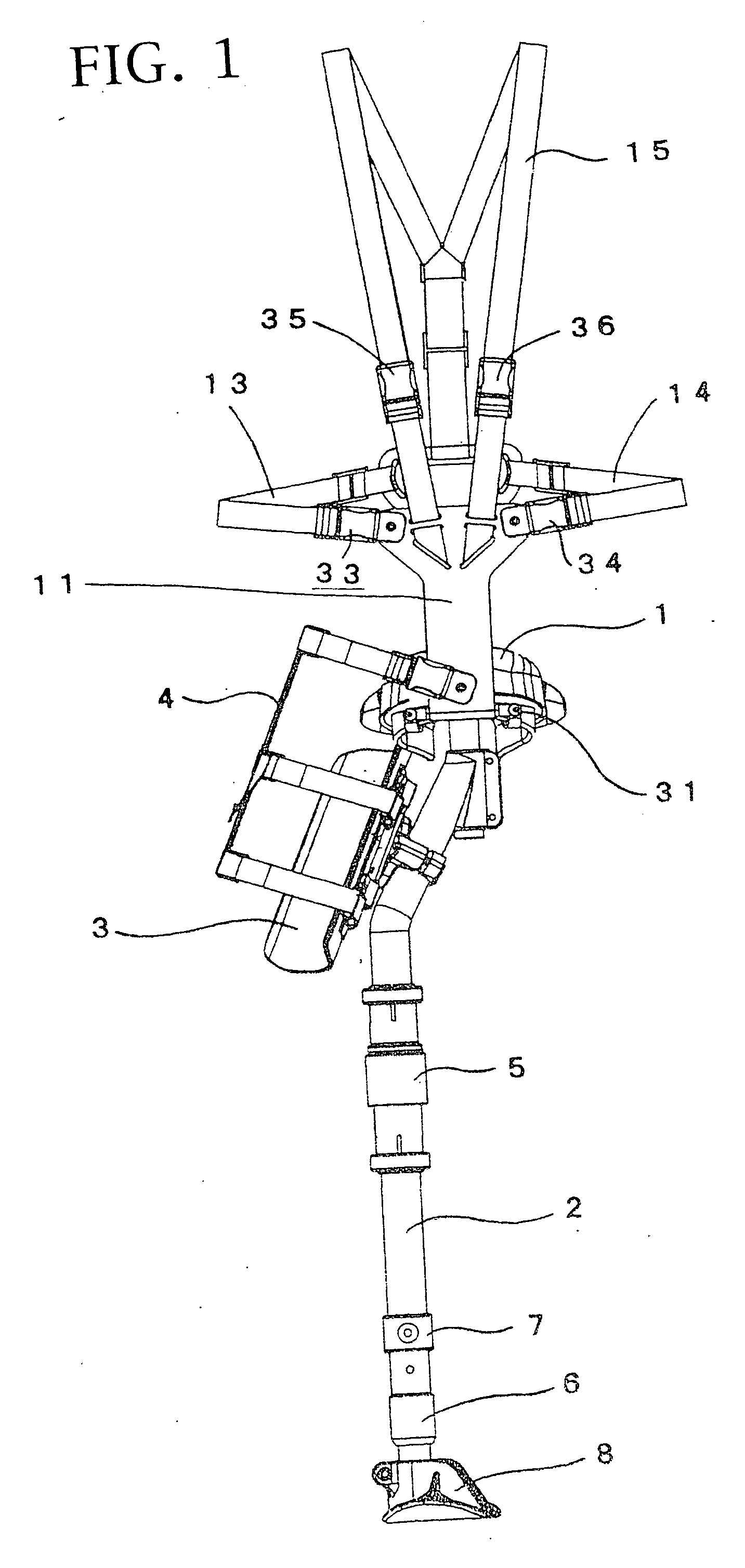
This invention relates to enable a person to walk smoothly even if a length of a remained thigh of the lost leg is short or even if the leg is cut at the hip joint and has no thigh. The hucklebone supporting type artificial leg comprising the crotch support (1), the shaft part (21) arranged vertically at the lower surface of the crotch support (1) and having substantially the same length as that of the lower leg and a foot (22) fixed to the lower end of the shaft part (21), wherein the crotch support (1) is formed into a substantial L-shape as seen in its top plan view, one front end (2) is arranged at a front part so as to be applied to a substantial front half part of the crotch part when installed and at the same time, the other side end part (3) is arranged at the rear surface of the lost lower leg and applied to both the hucklebone and the hip part corresponding to the lost leg when installed. The front band supporting unit (41) and the rear band supporting unit (42) are arranged at the front and rear ends of the crotch support (1) in such a way that they can be turned around and there are provided waist bands (43), (44) and shoulder hanging band (47).
Owner:IKEDA ISAO
Hucklebone supporting-type artificial leg
This invention relates to enable a person to walk smoothly even if a length of a remained thigh of the lost leg is short or even if the leg is cut at the hip joint and has no thigh. The hucklebone supporting type artificial leg comprising the crotch support (1), the shaft part (21) arranged vertically at the lower surface of the crotch support (1) and having substantially the same length as that of the lower leg and a foot (22) fixed to the lower end of the shaft part (21), wherein the crotch support (1) is formed into a substantial L-shape as seen in its top plan view, one front end (2) is arranged at a front part so as to be applied to a substantial front half part of the crotch part when installed and at the same time, the other side end part (3) is arranged at the rear surface of the lost lower leg and applied to both the hucklebone and the hip part corresponding to the lost leg when installed. The front band supporting unit (41) and the rear band supporting unit (42) are arranged at the front and rear ends of the crotch support (1) in such a way that they can be turned around and there are provided waist bands (43), (44) and shoulder hanging band (47).
Owner:IKEDA ISAO
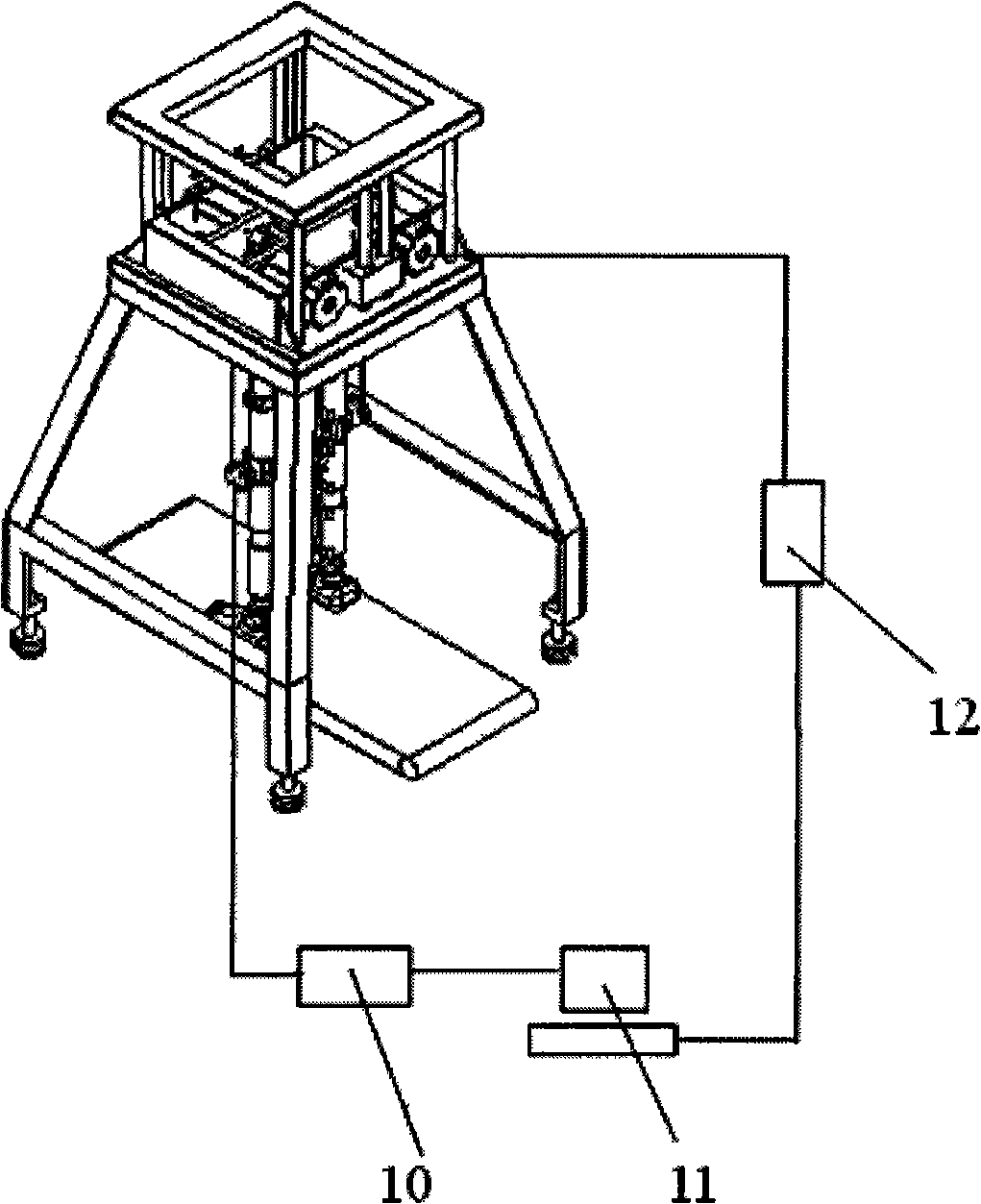
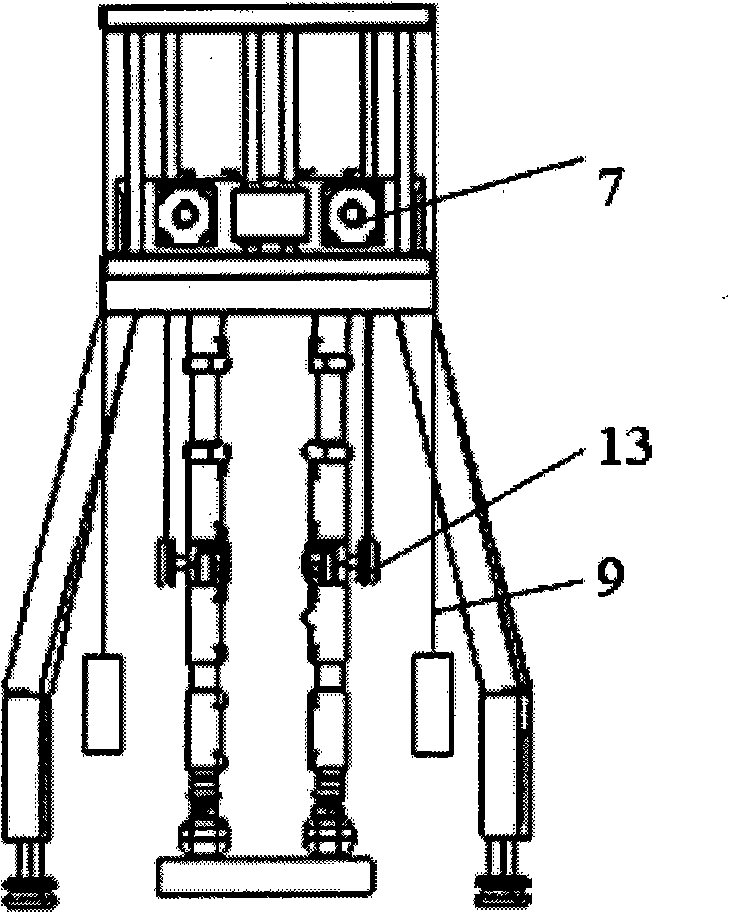
Artificial leg gait test system
The invention relates to a lower limb prostheses gait testing system, consisting of a simulation leg, a power source, a transmission device and a measurement and control system; the measurement and control system comprises a four-corner displacement sensor, a data collecting module, a motion control card and a computer processing system; wherein, the computer processing system is fixed on an external box body on the ground surface by a bracket; the four-corner displacement sensor is respectively arranged at two hip joints and two knee joints and used for collecting and simulating the joint angle change of the gait, and transmits the collected signal to the computer processing system by a data collecting module; furthermore, by the software of the control system and the collecting system, the collected gait joint angle data in the whole gait period when human walks normally is used as the control signal; the power source is controlled by a motion control card; the output of the power source drives the motion of the simulation leg by the transmission device, thus realizing the simulation of the normal human walking gait. The system of the invention can basically simulate the normal gait of the human body, can provides feasible testing platform for the objective evaluation of the prostheses performance.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Hydrualic prosthetic joint
ActiveUS20160235558A1Keep openMemory is also lostSpringsArtificial legsDifferential pressureHuman motion
Owner:BOENDER JACOB QUINTUS LAURENCE ANTHONY +1
Variable-mechanical-impedance artificial legs
InactiveUS20140088728A1Minimize power consumptionIncrease the number ofNon-surgical orthopedic devicesArtificial legsAdjustable stiffnessProsthesis
In one aspect, the invention provides methods and apparatus facilitating an adjustable-stiffness prosthesis or orthosis (including approximations to arbitrarily definable non-linear spring functions). Spring rates may be varied under no-load conditions during a walking gate cycle to minimize power consumption. In another aspect, the invention provides methods and apparatus for outputting positive power from a prosthesis or orthosis, facilitating high-performance artificial limbs. In one embodiment of the invention, the positive power is transferred from a functioning muscle to the prosthesis or orthosis, which mimics or assists a non-functioning or impaired muscle. In another embodiment of the invention, the positive power comes from an on-board power source in the prosthesis or orthosis.
Owner:OTTO BOCK HEALTHCARE IP GMBH & CO KG
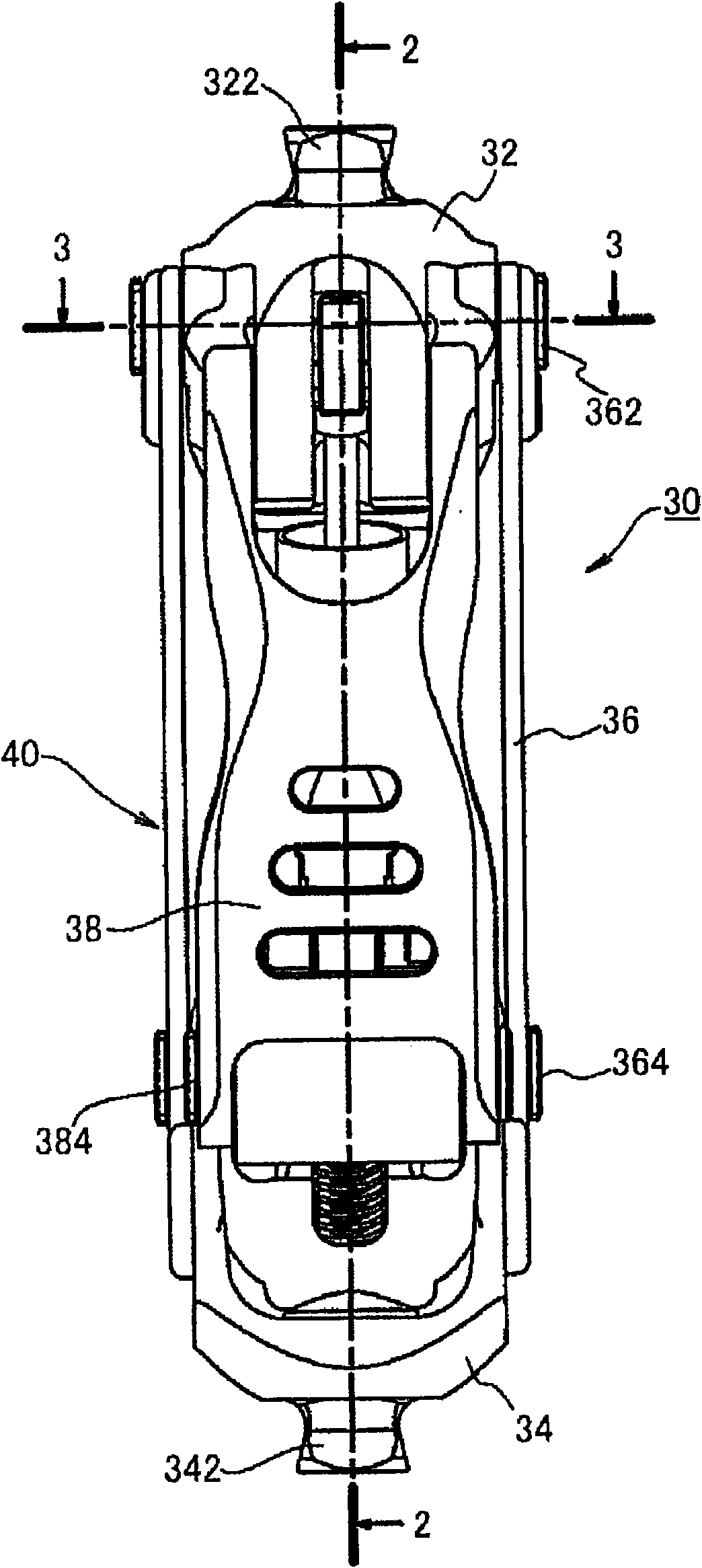
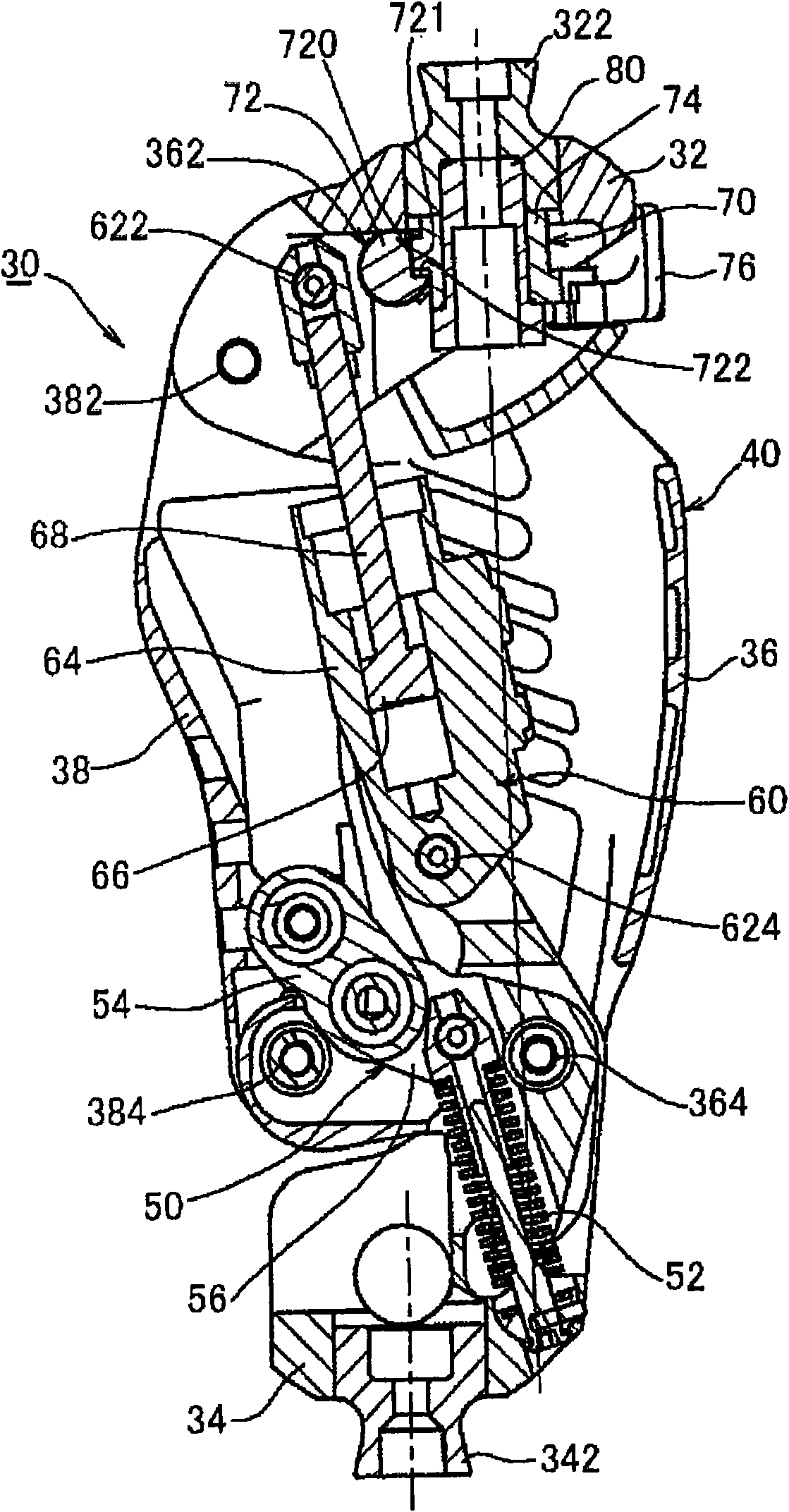
Knee Joint Including Manual Lock Mechanism and Artificial Thigh
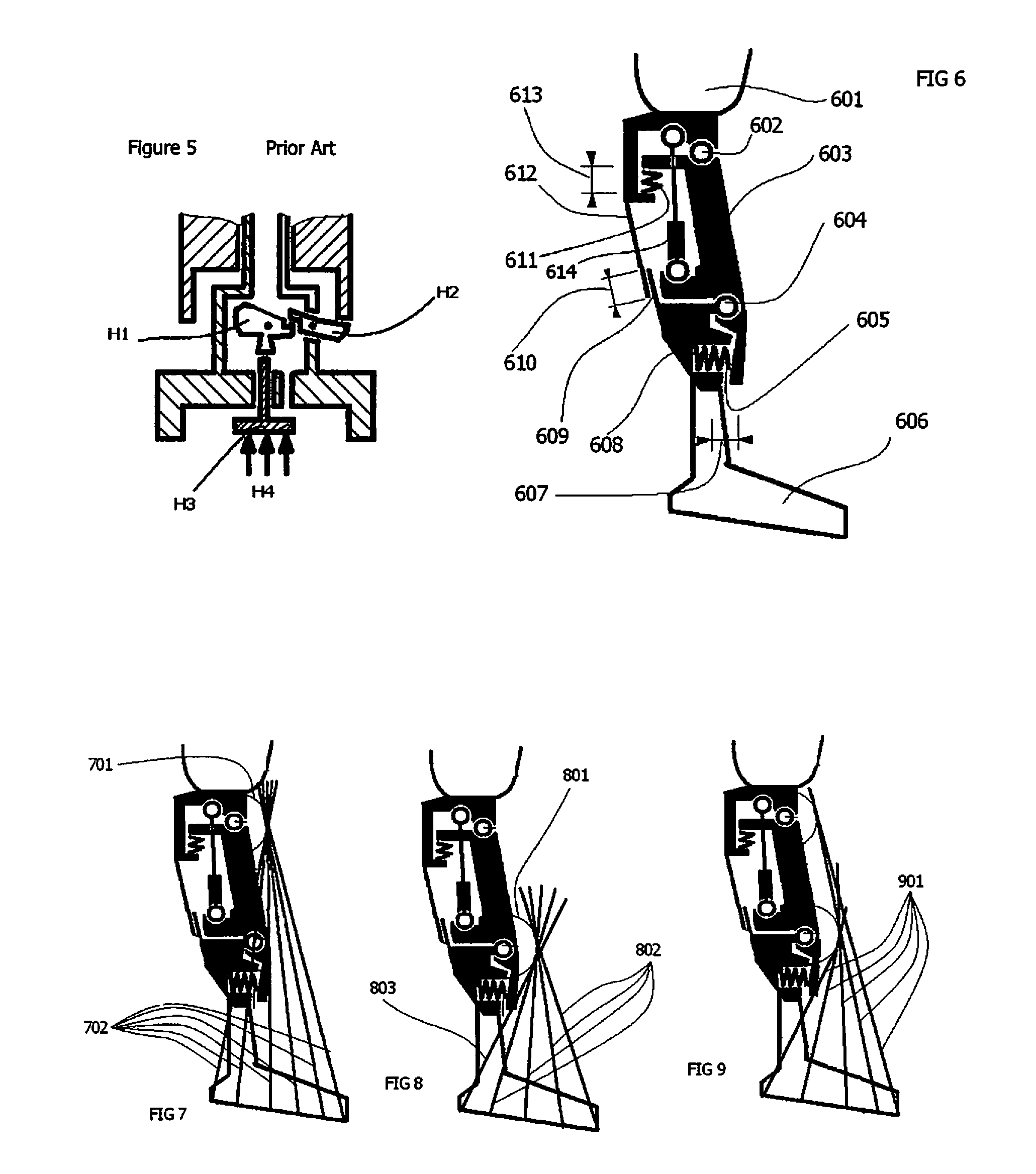
The disclosure relates to a technology of a manual lock mechanism for manually switching over the oscillating motion of an upper member and a lower member at a knee joint between a locked condition and an unlocked condition. More particularly, the disclosure aims at a simple structure of the manual lock mechanism and a size reduction of the knee joint or an artificial leg including the manual lock mechanism. For these purposes, one of oscillating shafts for swingingly coupling the upper and lower members is regulated. Therefore, the manual lock mechanism includes an oscillating shaft including an irregular part and a lock member for regulating the movement of the oscillating shaft. The lock member can be switched over between a locked condition where the lock member is in contact with the irregular part of the oscillating shaft and the unlocked condition where it is separate from the irregular part. When the lock member is in the locked condition, force from the oscillating shaft is applied as compression load in the longitudinal direction of the lock member.
Owner:NABLESCO CORP
Prosthesis having movement lock
The present invention relates to artificial limbs generally and joints for same. The present invention provides hydraulic functional units whereby enabling movement of artificial joints to closely correspond with natural human movement. In the provision of realistic joints, as used in prosthetic limbs, an important aspect in achieving realistic movement is providing a different operating characteristic to the joint when under load. One important characteristic of an artificial leg for achieving a natural-looking walking gait corresponding with those of a stabilized knee, i.e. a knee resisting flexion when under load, is when it bears at least some of the weight of the amputee. Properties of resilient mechanical members are utilized to enable a hydro-mechanical system to be controlled so that it releases a low joint resistance mode relative to a default high resistance mode. The invention also permits alternative embodiments such as electronic, electro fluidic or electromechanical means.
Owner:BOENDER JENNIFER
Hydraulic prosthetic joint
Owner:BOENDER JACOB QUINTUS LAURENS ANTHONY
Multifunction walking-aid device
The invention relates to a multifunctional walking aid appliance, which comprises an artificial leg including an artificial foot and a lower leg which are articulated with each other, and is characterized in that the lower leg comprises an air cylinder, a cylinder sleeve of which is positioned at the upper part; a piston rod of the air cylinder faces to the lower part; an inflating sac installed on the cylinder sleeve is connected with an inner cavity of the air cylinder through a gas tube; and a locking screw is arranged on the air cylinder. The multifunctional walking aid appliance has the beneficial effects of multiple functions, convenient use and long service life.
Owner:代迎春
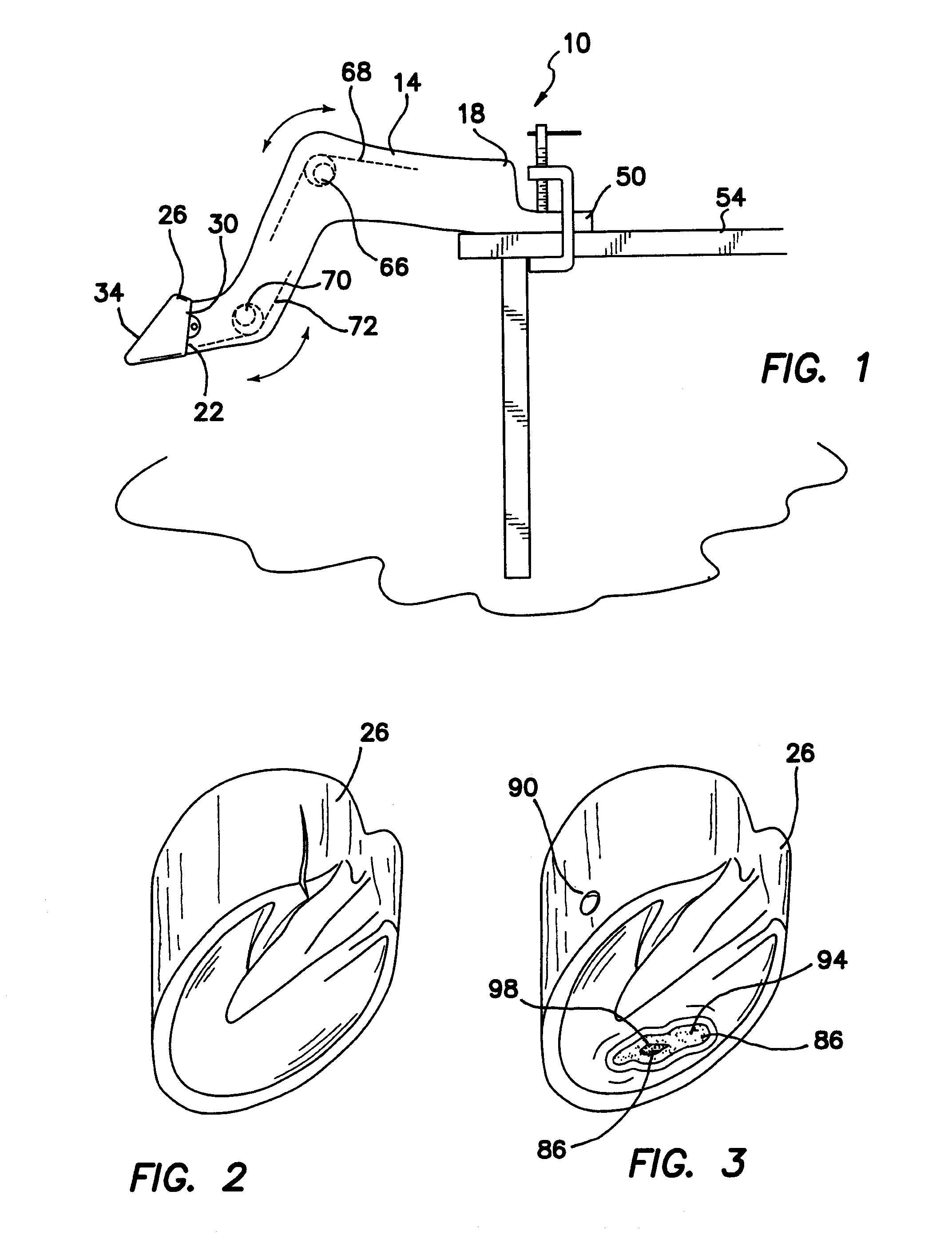
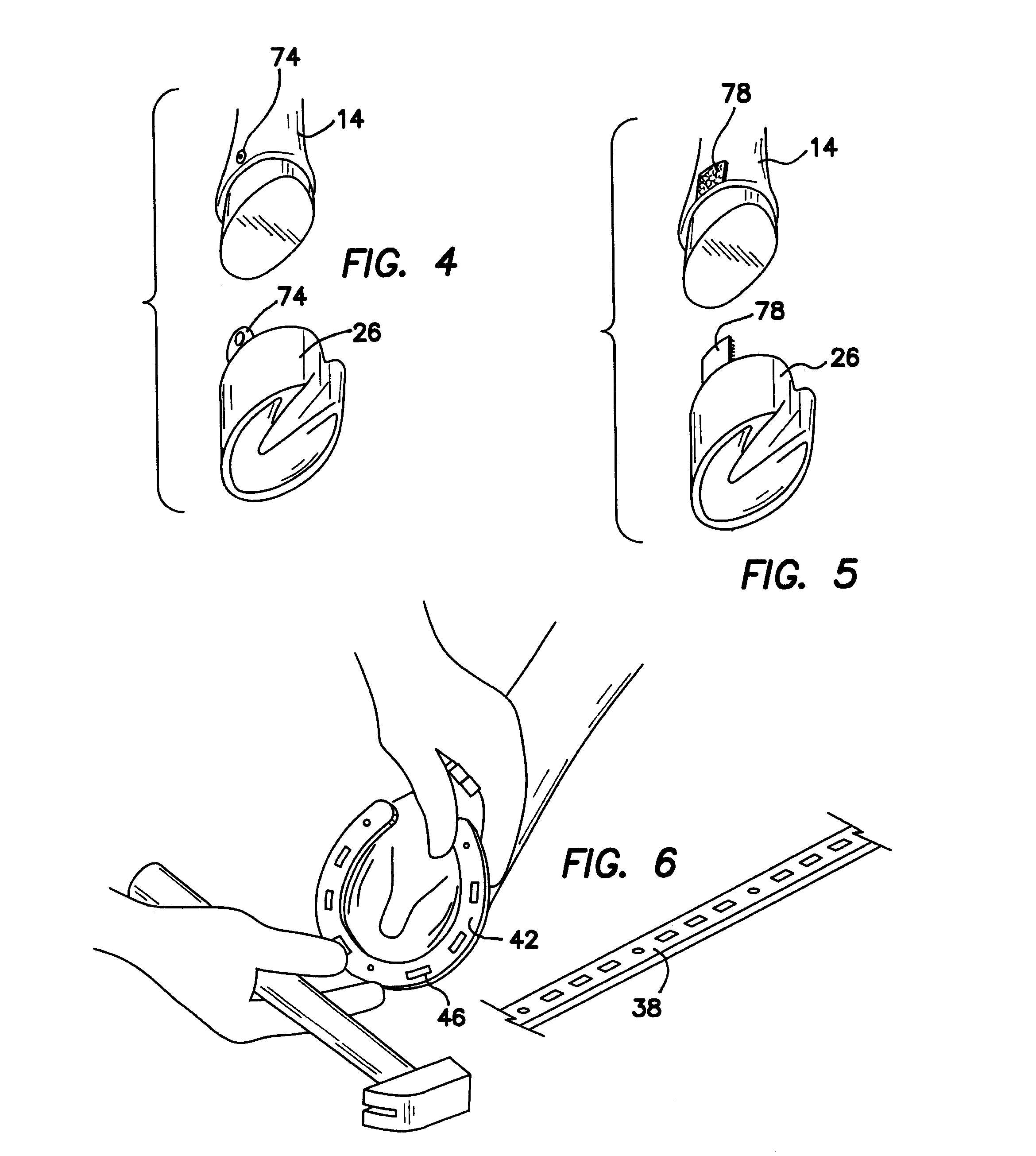
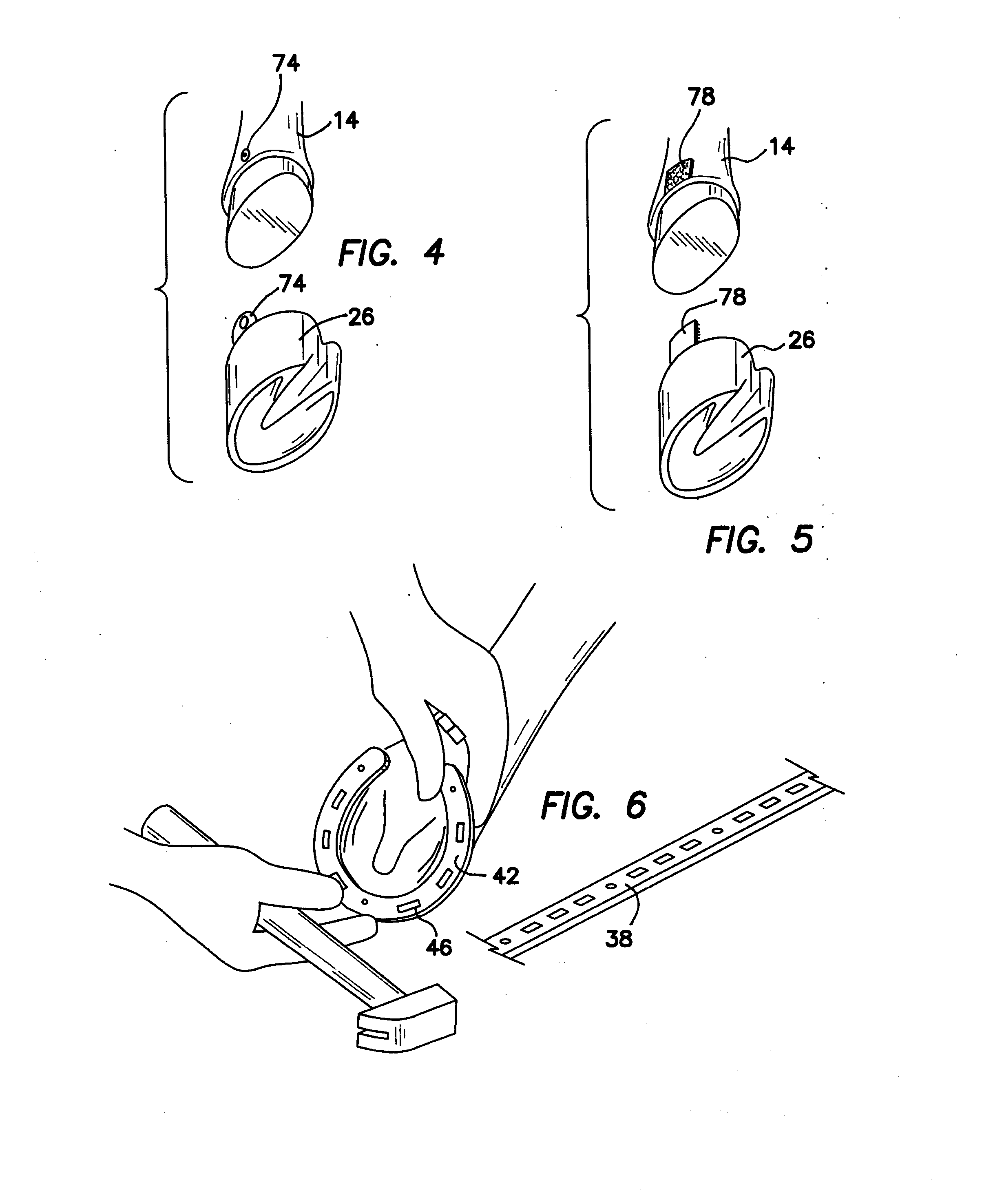
Farrier training system
A farrier training system includes an artificial leg portion attached to an artificial hoof portion. The hoof portion is removably attached to the lower end of the leg portion. The leg is articulated with at least one spring-loaded joint to simulate a real horse's leg and train the farrier in proper shoeing techniques. The removable hoof portion is replaceable with hoof portions exhibiting typical hoof diseases and abnormalities. The hoof portion is carvable and indicates through color changes when the hoof portion has been carved too deeply. The hoof portion is also nailable and includes the ability to indicate when nails have been inserted too deeply. Horseshoe stock is provided along with tools for forming the stock into horseshoes fitted to the removable hoof portion. A support platform is provided to allow the upper end of the leg portion to be removably attached to a fixture, building or ground surface.
Owner:CHAMPAGNE WESLEY JON +1
Knee joint including manual lock mechanism and artificial thigh
ActiveCN101959477ASimple structureAchieving a compact structureArtificial legsThighLocking mechanism
Technology of a manual lock mechanism for manually switching over oscillation of an upper member and a lower member at a knee joint between locked and unlocked conditions. A simple structure of the manual lock mechanism and size reduction of the knee joint or an artificial leg are aimed at in particular. For these purposes, one of oscillating shafts for swingably coupling the upper member and thelower member is regulated. Therefore, the manual lock mechanism includes the oscillating shaft including an irregular part and a lock member for regulating the movement of the oscillating shaft. The lock member can be switched over between the locked condition of being in contact with the irregular part of the shaft and the unlocked condition of being separate from the irregular part. When locked, force from the oscillating shaft is applied as compression load in the longitudinal direction of the lock member.
Owner:NABLESCO CORP
Prosthesis having movement lock
The present invention relates to artificial limbs generally and joints for same. The present invention provides hydraulic functional units whereby enabling movement of artificial joints to closely correspond with natural human movement. In the provision of realistic joints, as used in prosthetic limbs, an important aspect in achieving realistic movement is providing a different operating characteristic to the joint when under load. One important characteristic of an artificial leg for achieving a natural-looking walking gait corresponding with those of a stabilised knee, i.e. a knee resisting flexion when under load, is when it bears at least some of the weight of the amputee. Properties of resilient mechanical members are utilized to enable a hydro-mechanical system to be controlled so that it releases a low joint resistance mode relative to a default high resistance mode. The invention also permits alternative embodiments such as electronic, electro fluidic or electromechanical means.
Owner:BOENDER JENNIFER
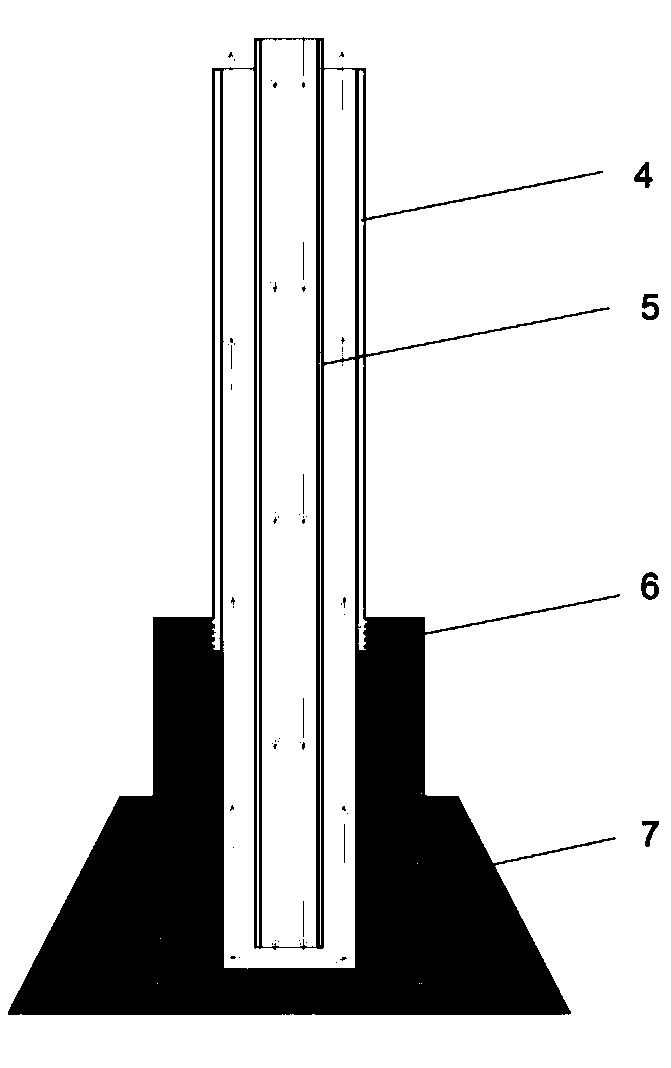
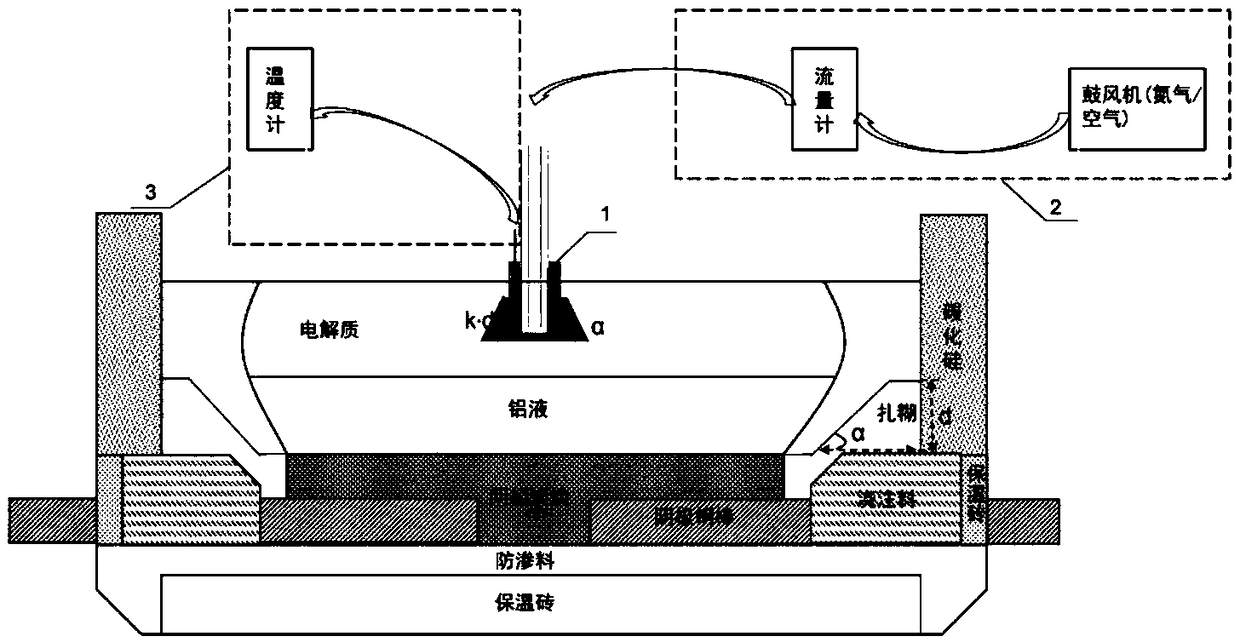
Detection device and method for simulating furnace wall growth process of aluminum electrolytic bath
InactiveCN109283207ARealize detectionSolving the aluminum pot problem of growth statusMaterial thermal analysisElectrolysisControl system
The invention discloses a detection device and method for simulating furnace wall growth process of an aluminum electrolytic bath. The detection device comprises a furnace wall growth device, a cooling air control system and a temperature monitoring system, wherein a side carbon block model is a solid cylinder, the solid cylinder is made of the same material of actual side carbon block of the aluminum electrolytic bath and is provided with a central counter hole, the thickness of a side wall of the aluminum electrolytic bath is K times of the actual thickness of the side carbon block of the electrolytic bath, a side artificial leg-stretching model is a solid rotation body, the solid rotation body is made of the same material of an actual artificial stretching leg of the aluminum electrolytic bath and is provided with a central through hole, the longitudinal cross section shape of the side wall is similar to the cross section shape of the actual artificial stretching leg of the aluminumelectrolytic bath, and the similar ratio is K. A similar principle and a model experiment method are used, the furnace wall growth similar simulation of the aluminum electrolytic bath is achieved, and the problem of direct detection on a furnace wall growth state of the aluminum electrolytic bath is solved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Multifunctional artificial leg
InactiveCN103565563ASolve the problem of narrow application scope and single functionMeet needsArtificial legsEngineeringArtificial limbs
The invention discloses an artificial limb, and particularly relates to a multifunctional artificial leg, which comprises a backup plate, a bearing bar, a foot structure, a support frame and a fixing band, wherein the backup plate is connected to the upper end of the bearing bar through a connecting rod; the fixing band is arranged on the backup plate; a support plate is erected on the bearing bar on one side of the backup plate through the support frame; the foot structure is connected to the lower end of the bearing bar through a connecting piece. The multifunctional artificial leg is simple in structure, convenient to use and wide in application range, can be used for a patient suffering from permanent extremity function disturbance as well as a patient suffering from temporary extremity function disturbance, and is very applicable to ordinary slight pains and disability on legs.
Owner:西安西玉同辉生物科技开发有限责任公司
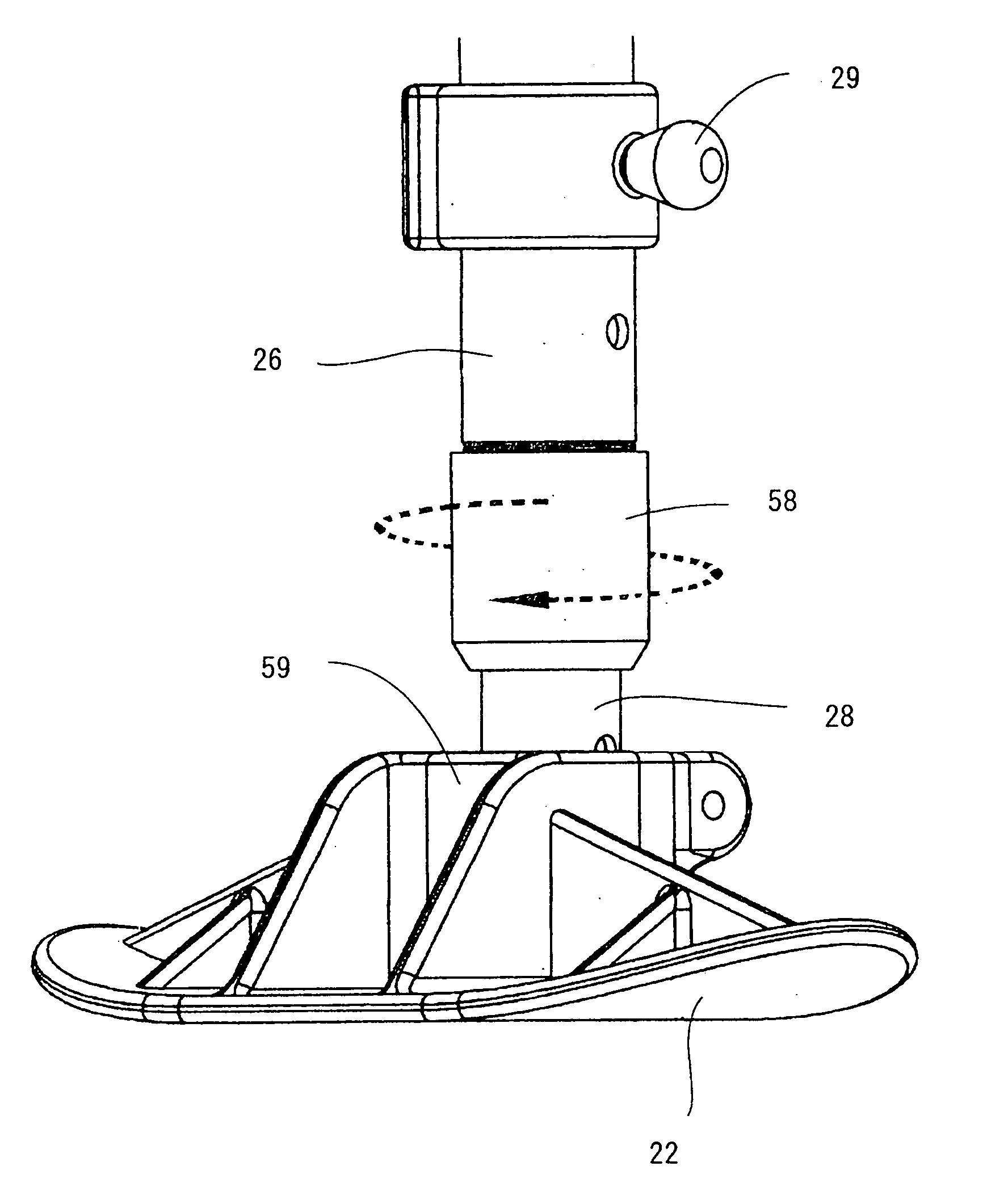
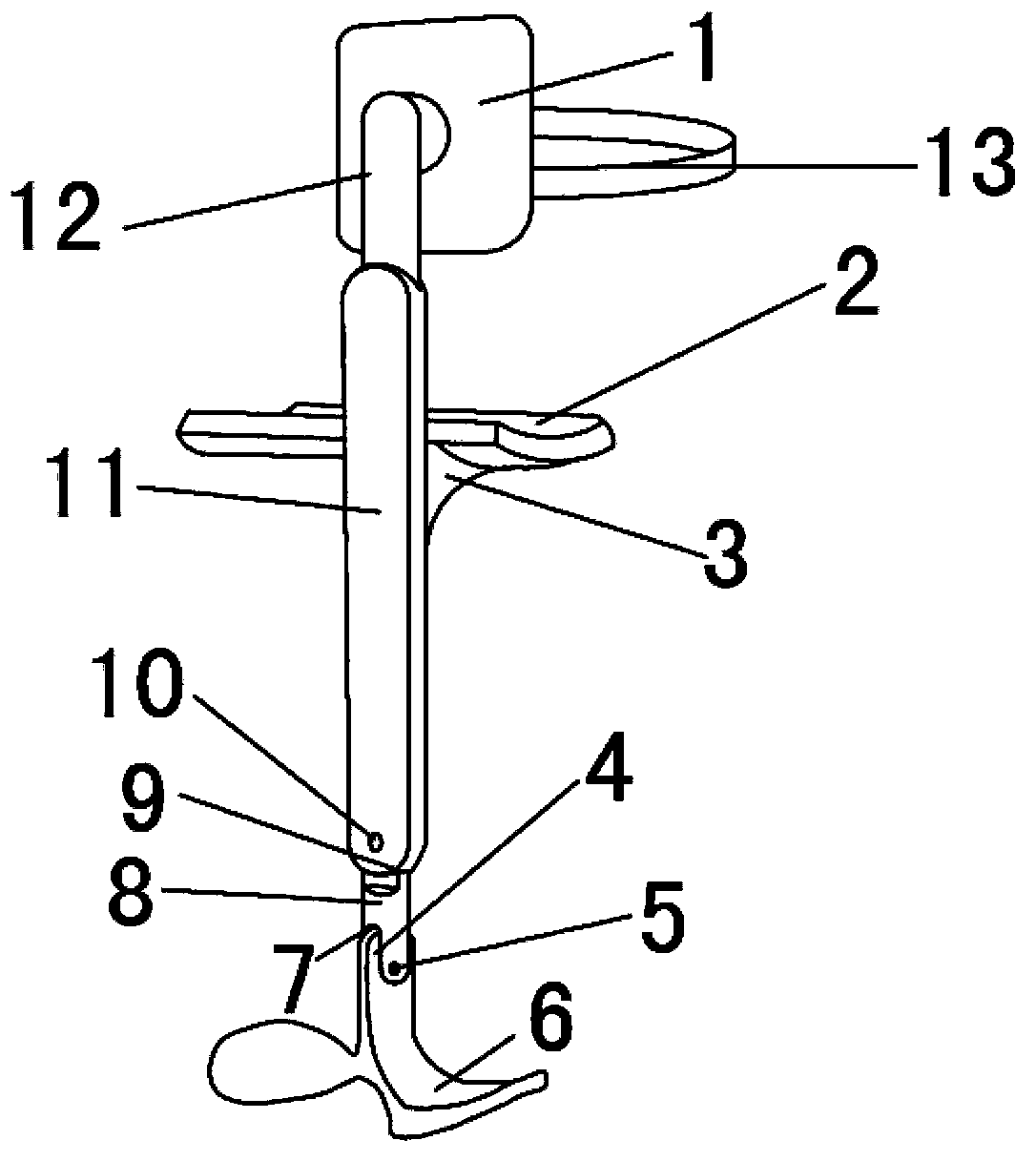
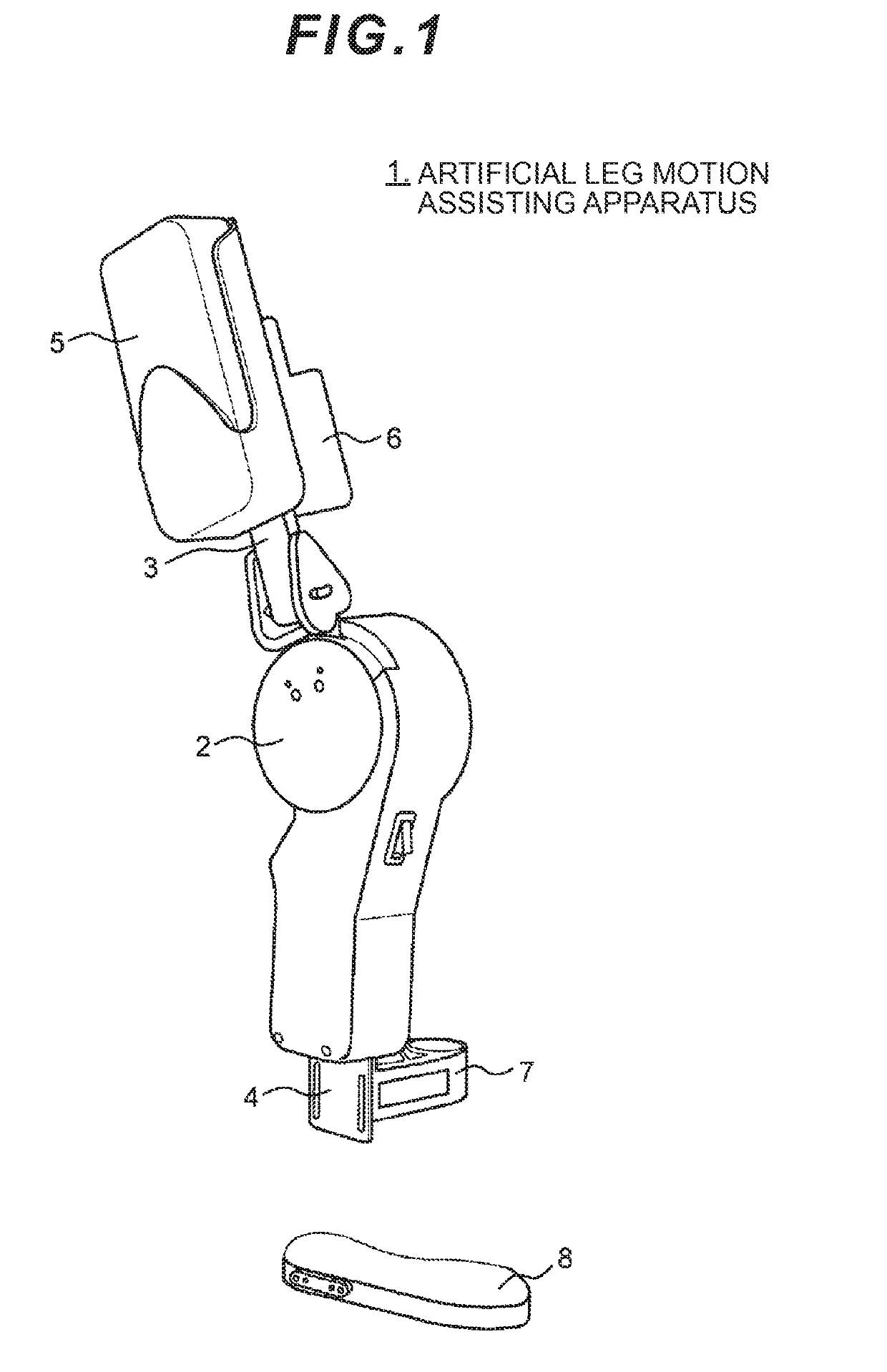
Artificial leg motion assisting apparatus and artificial leg motion assisting method
An artificial leg motion assisting apparatus and an artificial leg motion assisting method which are capable of transmitting knee joint motive power to a commercially-available trans-femoral prosthesis without making a wearer feel a sense of discomfort. When the artificial leg motion assisting apparatus is attached to the commercially-available trans-femoral prosthesis, a control unit controls a drive unit by a specified control method on the basis of mechanical impedance adjusted by an impedance adjustment unit and transmits output of the drive unit to a knee joint coupling.
Owner:CYBERDYNE INC +1
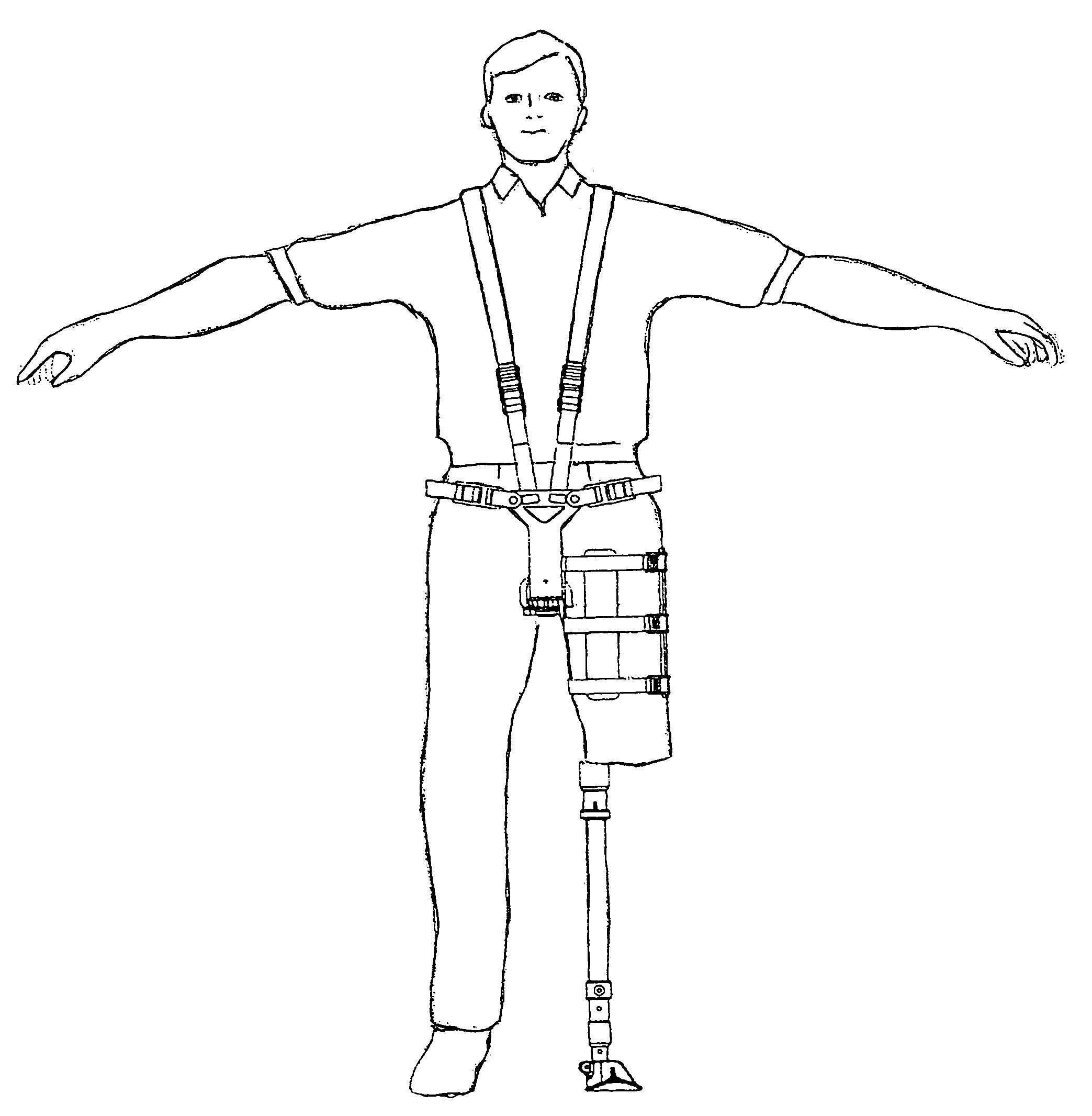
Hucklebone supporting-type artificial leg
InactiveUS20050102039A1Walking smoothlyImprove wear characteristicsArtificial legsEngineeringThigh musculature
This invention enables a smooth walking action to be carried out even in the case that a length of the thigh portion left in the damaged or lost lower leg is short or in the case that the lower leg is cut from the crotch articulation part and the thigh is lost. A hucklebone supporting-type artificial leg comprised of a saddle, a shaft suspended down at the lower surface of the saddle and having a substantial same length as that of a lower leg and a foot fixed to the lower end of the shaft, wherein the artificial leg comprises a front belt supporting unit attached at a front end of the saddle in such a way that it can be turned in a forward, upward and downward direction; a rear belt supporting unit attached at a rear end of the saddle in such a way that it can be turned in a rearward, upward and downward direction; and waist belts connected to each of the upper ends of the front and rear belt supporting units and installed around the waist of an artificial leg wearing person in such a way that the belts can be fastened to the waist and engaged with or disengaged from the waist. Further, there are provided shoulder hanging bands having ends connected to each of upper ends of the front and rear belt supporting units and installed in such a way that they can be fastened to and removably set to the shoulders of the artificial leg wearing person.
Owner:IKEDA ISAO
Technology for making receptive cavity of artificial limb of shank with plastic tube by thermoplastic shaping
InactiveCN1381350AEasy to useEasy to transportDomestic articlesArtificial legsEngineeringVacuum pump
A thermoplastic technology for forming the receiving cavity of artificial leg from plastic pipe includes such steps as cutting the polyethylene pipe to the needed length, heating it for softening, sleeving it on the male gypsum mould of leg, quickly closing another end, vacuumizing it to make the plastic pipe tightly fit the mould, cooling, breaking off the mould, and trimming. Its advantages aresimple process and low cost.
Owner:中国残疾人用品开发供应总站
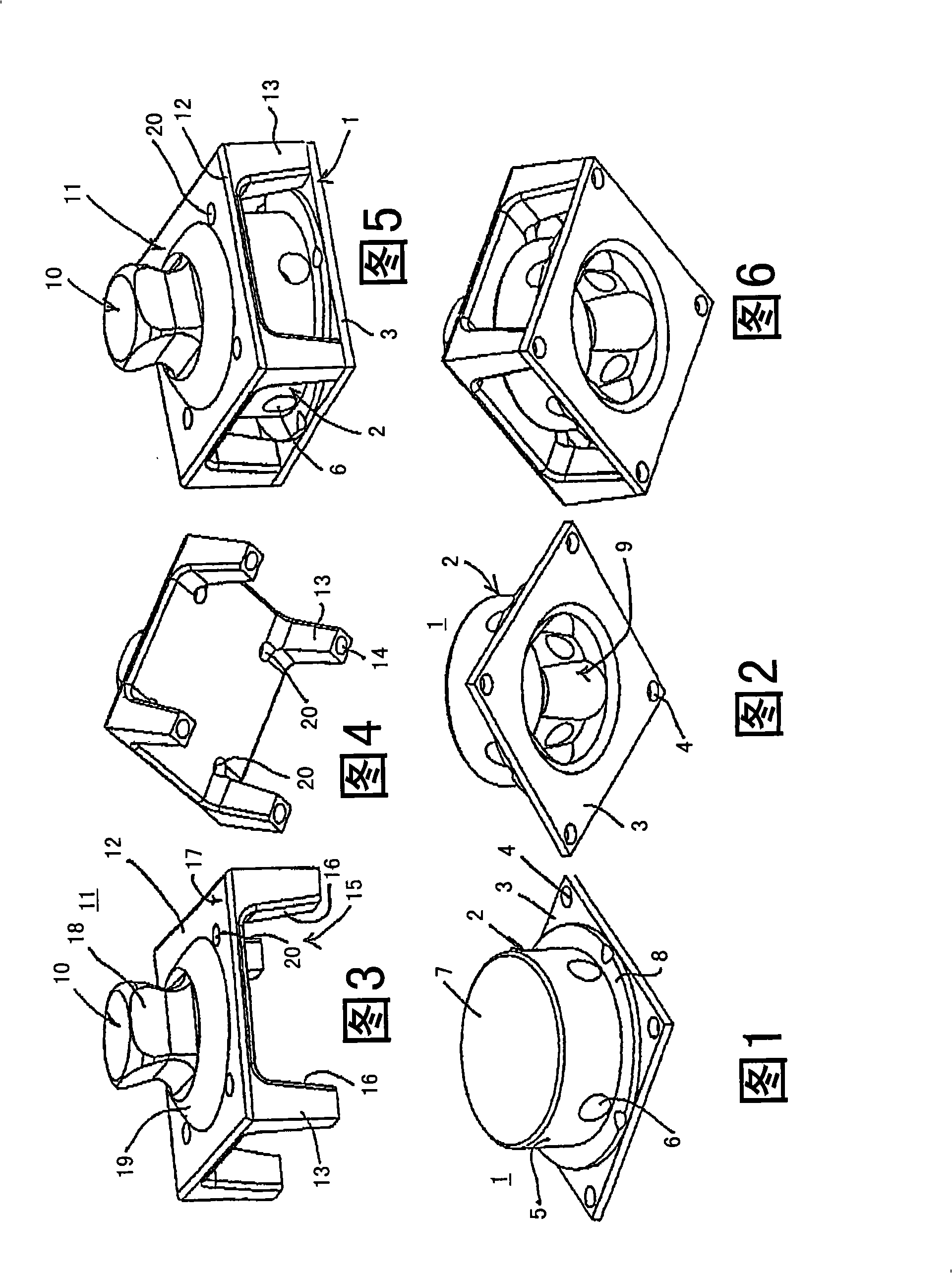
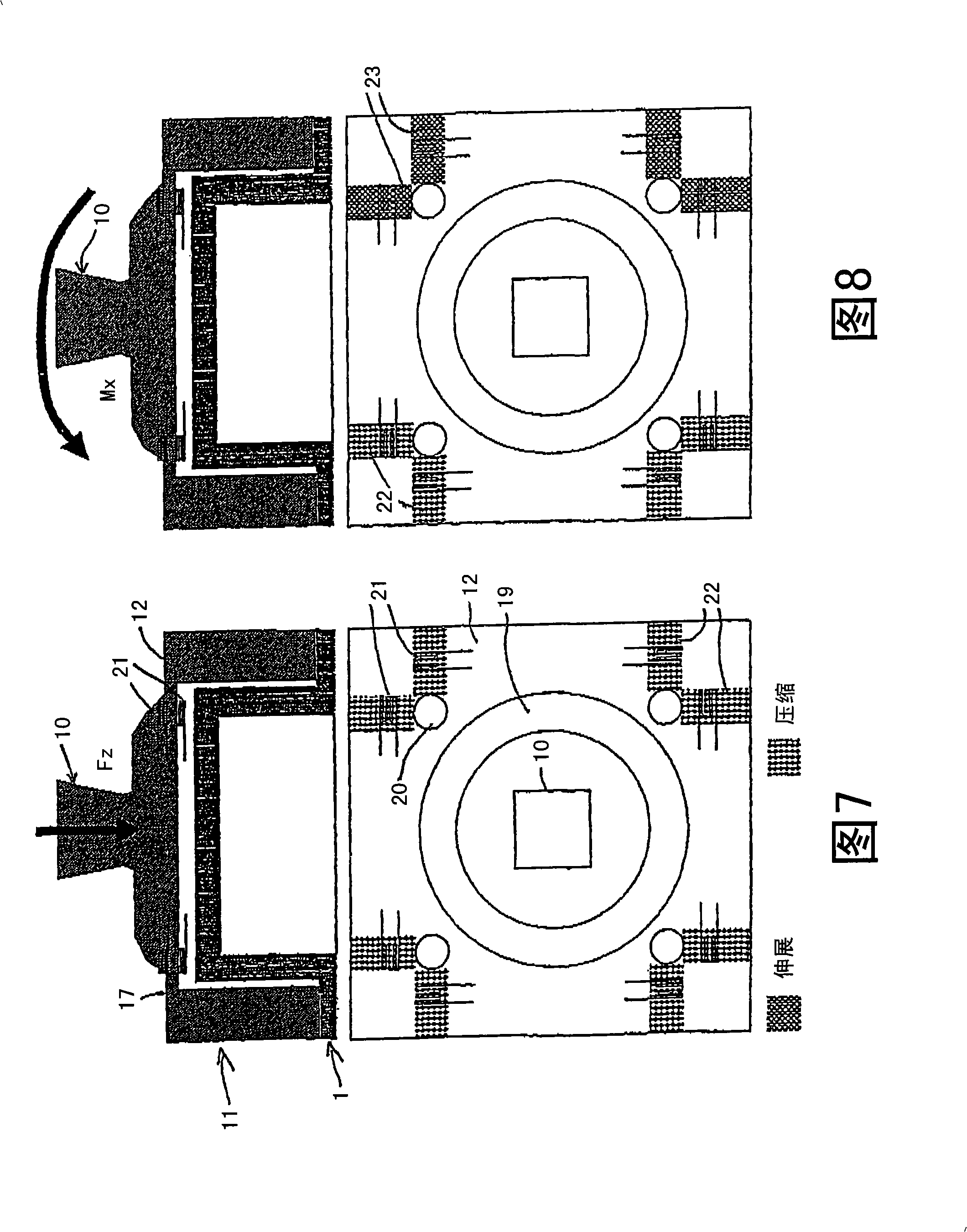
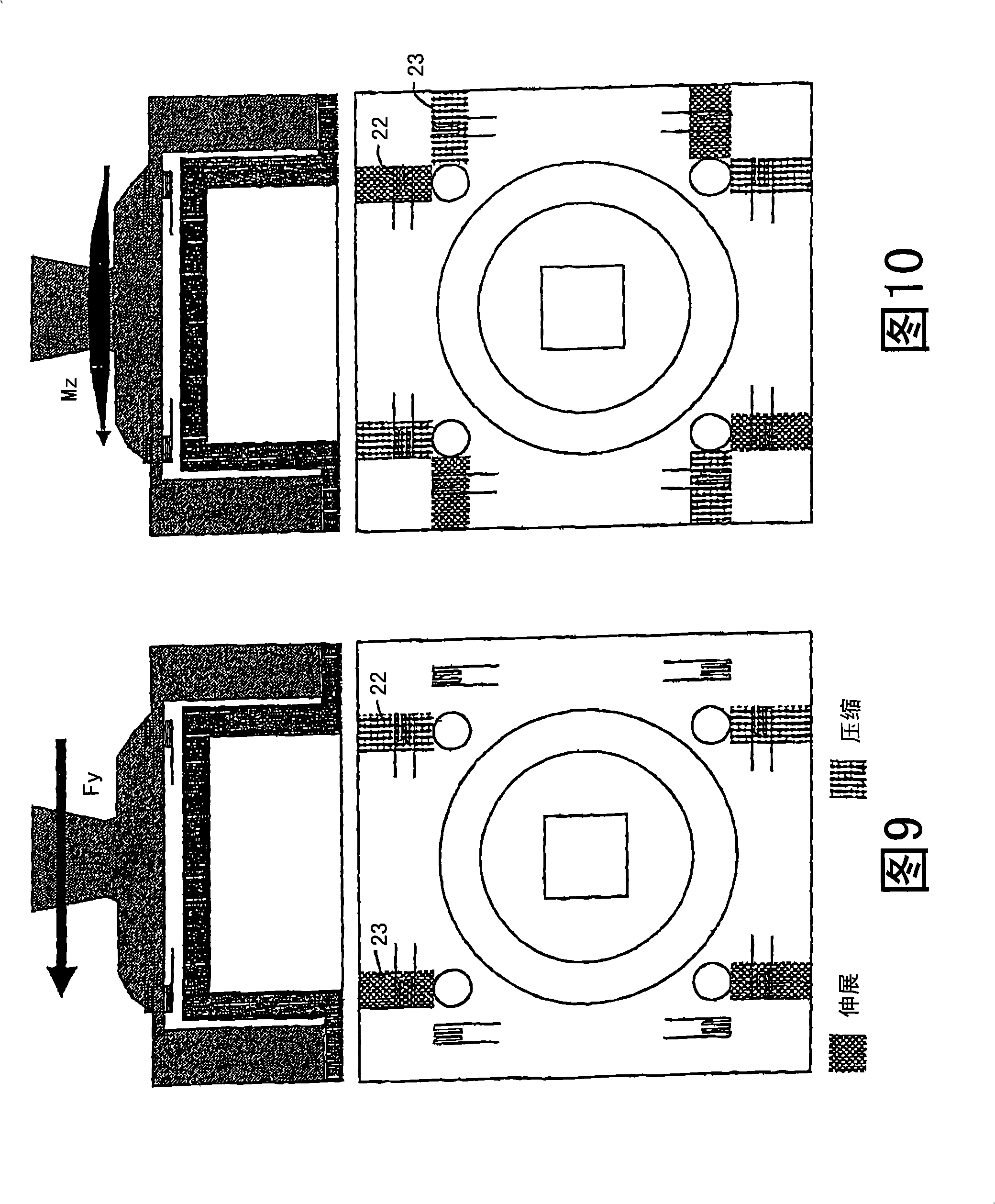
Sensor assembly for measuring forces and/or torques and use of said assembly
InactiveCN101296674ARealization of decouplingSave spaceForce measurementMeasurement of force componentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a sensor assembly for measuring the forces and / or torques that are transmitted using a rigid force transmitter. The sensor assembly can be connected to a first part of the force transmitter by means of a first connection (2) and to a second part of the force transmitter by means of a second connection (10) and is equipped with electro-mechanical sensor elements (21) for converting mechanical parameters into electrical parameters. To permit exact measurements to be achieved with small dimensions, the sensor assembly comprises a first flange (3), which originates from the first connection (2), surrounds the latter (2) and is connected to a second flange (12) lying parallel to the first flange (3) by means of struts (13) that run perpendicularly to the first flange (3). The gap (15) between the struts (13) is greater than the width of said struts (13).; The second connection (10) is situated on the second flange (12) and the sensor elements are designed to determine expansion or compression and are located on at least one of the two surfaces of the second flange (12) close to the struts (13). The sensor assembly is preferably used in an artificial limb, in particular an artificial leg.
Owner:OTTO BOCK HEALTHCARE IP GMBH & CO KG
Artificial limb
InactiveCN103142333AComfortable to useSimple structureArtificial legsElastic componentArtificial limbs
The invention relates to an artificial limb. The artificial limb comprises a funnel-shaped artificial limb socket, a connecting assembly and an artificial leg, wherein the upper end of the connecting assembly is connected with the artificial limb socket, the lower end of the connecting assembly is connected with the artificial leg, the inner wall of the artificial limb socket is coated with a layer of cushion, and the artificial leg is internally provided with an elastic component which is used for buffering and supporting the lower end of the connecting assembly. The artificial limb disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the structure is simple, the use is comfortable, and discomfort feeling cannot generate even a user wears the artificial limb for a long time.
Owner:上海联康假肢矫形器制造有限公司
Starting method for aluminum cell
A starting method for an aluminum electrobath relates to an aluminum electrobath starting process, and is characterized in that in the 300KA eletrobath, after coke particles are paved and the pole is hung, firstly an upper side and a side of an anode interpolar gap are plugged by a paperboard, then high molecular ratio cryolite is added to a bottom metacarpal edge clinging to the anode at the periphery of a cell, calcium fluoride is uniformly paved on an artificial leg, magnesium fluoride is uniformly added on the calcium fluoride, then an electrolyte block is charged on the cryolite abutting a side carbon block; after starting the high molecular ratio cryolite, the calcium fluoride, the magnesium fluoride, soda and the electrolyte block are added too, after roasting, the high molecular ratio cryolite, the calcium fluoride, the magnesium fluoride, the soda and the electrolyte block are added in to electrobath, and then the electrobath is started. The method of the invention adopts the high molecular ratio cryolite and reduces the amount of the soda, so that the molecular ratio is more than 2.8 after the electrobath is started, thereby improving the stability of the technique technology conditions and reducing the working intensity of workers.
Owner:山西华圣铝业有限公司
Farrier training system
A farrier training system includes an artificial leg portion attached to an artificial hoof portion. The hoof portion is removably attached to the lower end of the leg portion. The leg is articulated with at least one spring-loaded joint to simulate a real horse's leg and train the farrier in proper shoeing techniques. The removable hoof portion is replaceable with hoof portions exhibiting typical hoof diseases and abnormalities. The hoof portion is carvable and indicates through color changes when the hoof portion has been carved too deeply. The hoof portion is also nailable and includes the ability to indicate when nails have been inserted too deeply. Horseshoe stock is provided along with tools for forming the stock into horseshoes fitted to the removable hoof portion. A support platform is provided to allow the upper end of the leg portion to be removably attached to a fixture, building or ground surface.
Owner:CHAMPAGNE WESLEY JON +1
Artificial limb
The invention discloses an artificial limb which comprises an artificial foot, an artificial leg, a first movable rod, a second movable rod, an artificial knee and a telescopic cylinder. A strut obliquely extending backwards is arranged at the upper end of the artificial leg; the lower end of the first movable rod is in pin joint with the upper end of the artificial leg; the lower end of the second movable rod is in pin joint with the upper end of the strut; the upper end of the first movable rod and the upper end of the second movable rod are in pin joint with two positions, in the front-back direction, of the artificial knee respectively, and the first movable rod is located in front of the second movable rod. The telescopic cylinder comprises a cylinder body and a piston rod, the lower end of the cylinder body is in pin joint with the lower end of the first movable rod, the piston rod stretches out of the upper end of the cylinder body and is in coaxial pin joint with the second movable rod, springs are arranged in an upper chamber and a lower chamber divided by a piston in the cylinder body, the two springs abut against the piston, and a damping hole communicated with the upper chamber and the lower chamber is formed in the piston. The stability of the disabled to walk through the artificial limb is improved. Compared with a torsional spring applied to an artificial limb in the prior art, the telescopic cylinder can guarantee the stability of the artificial limb better.
Owner:山东东方健康产业发展有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com