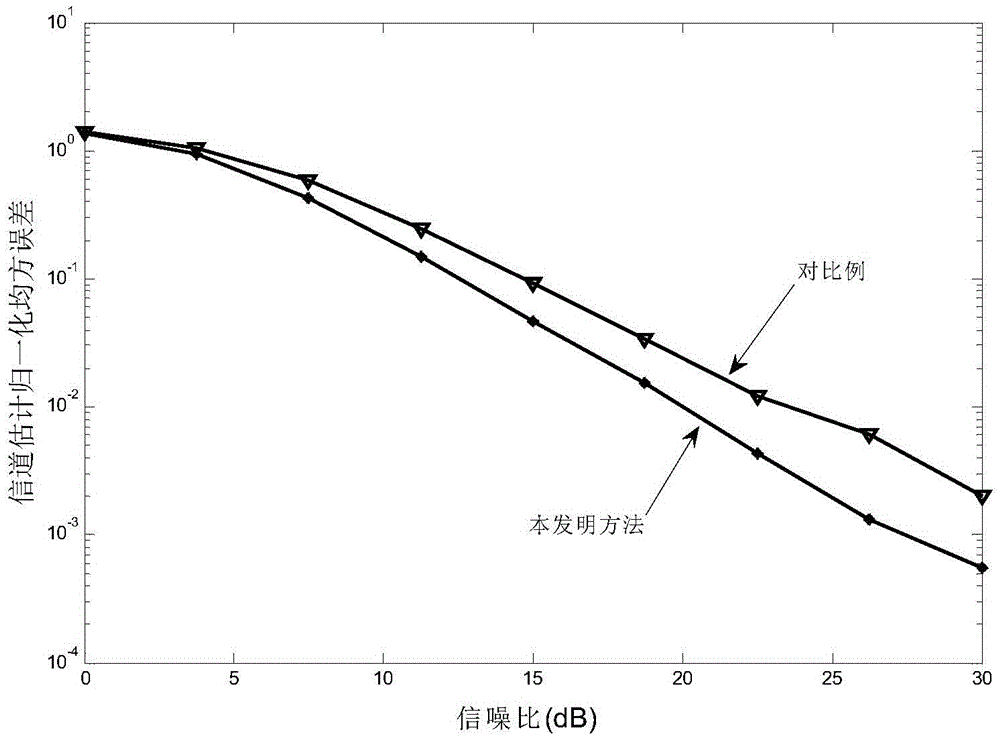
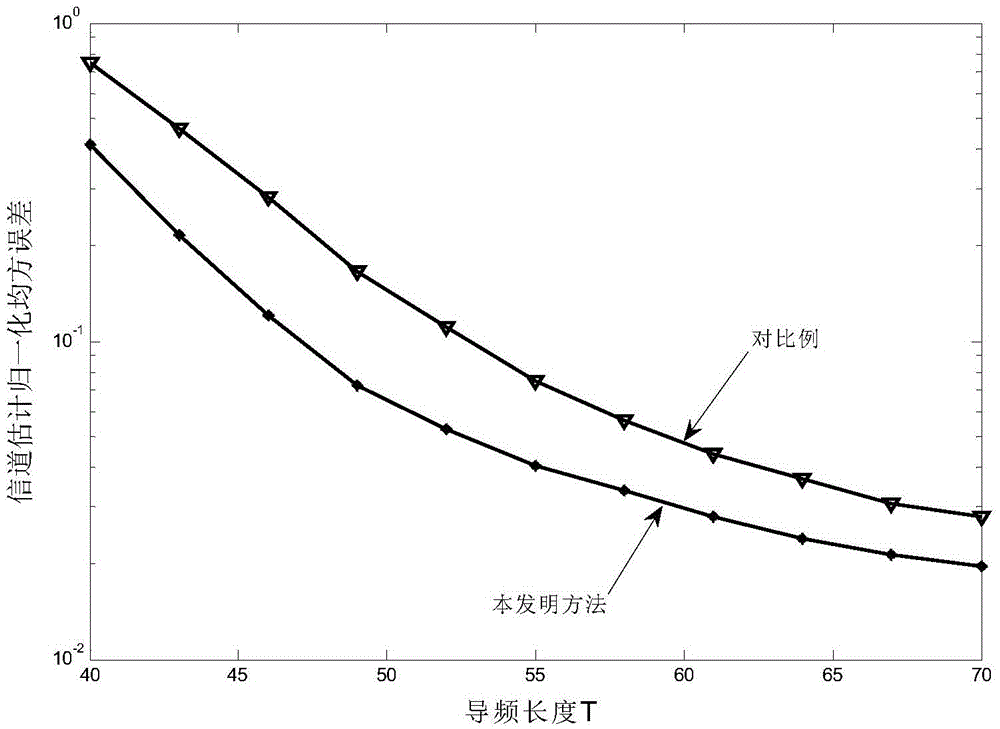
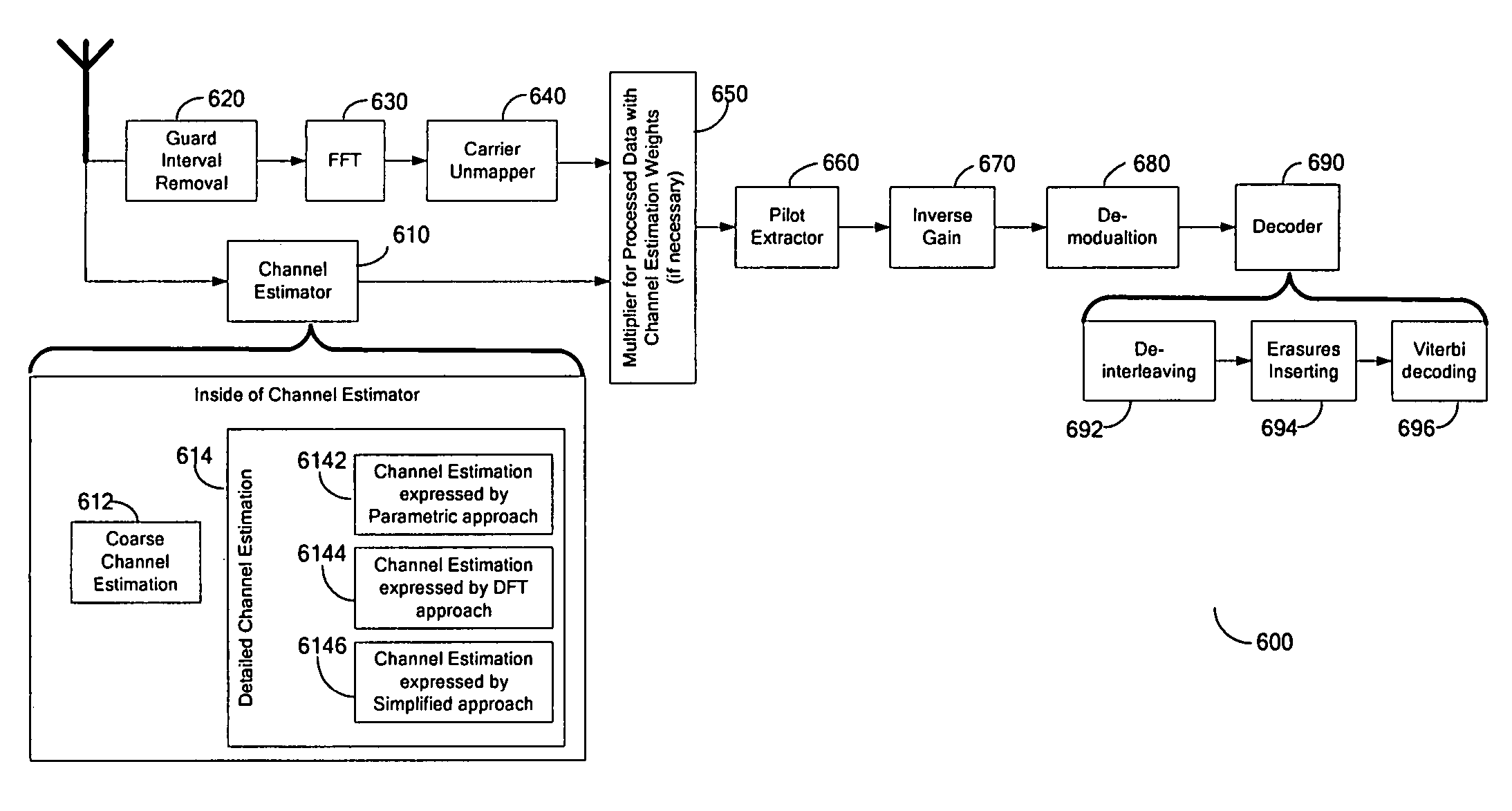
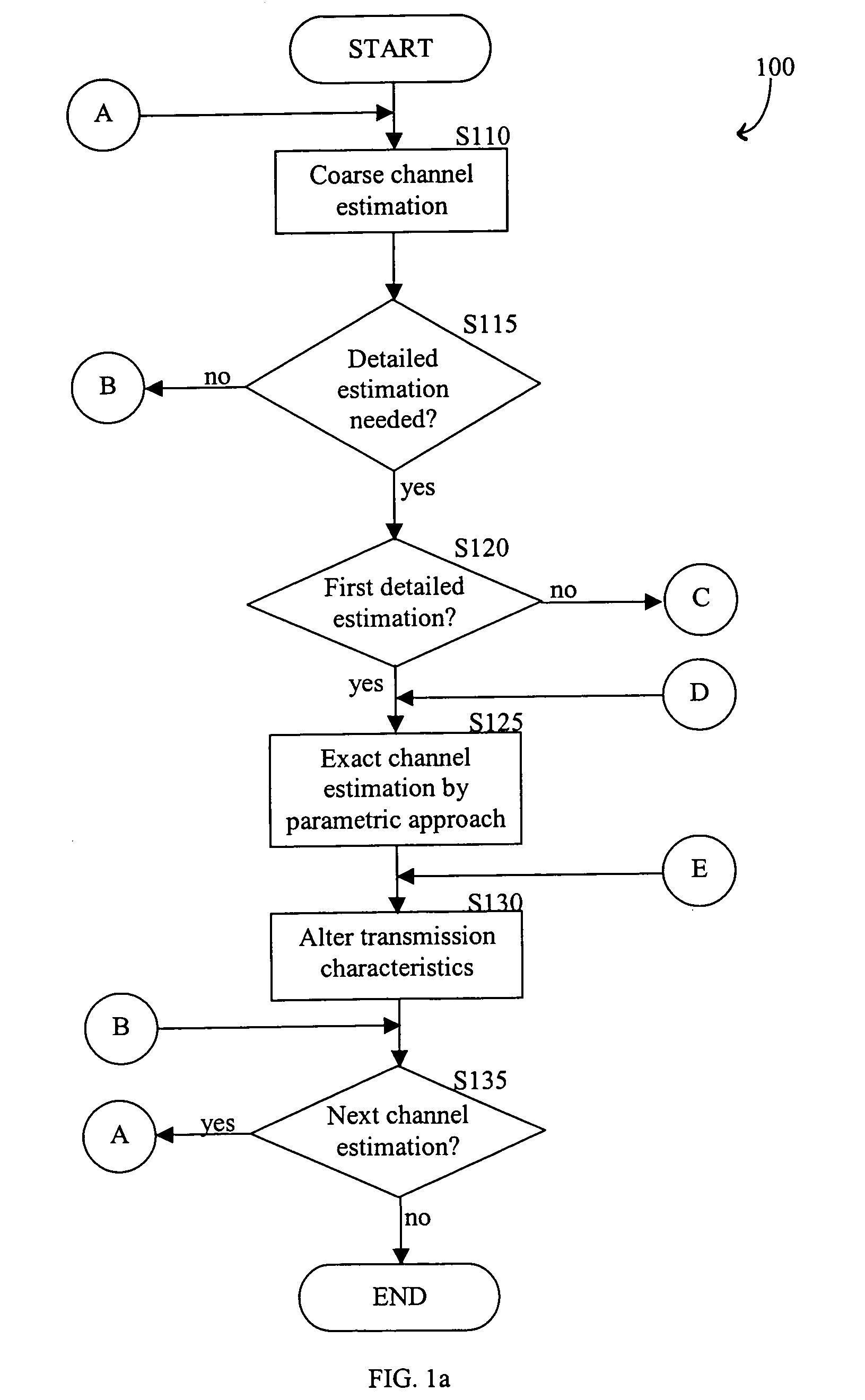
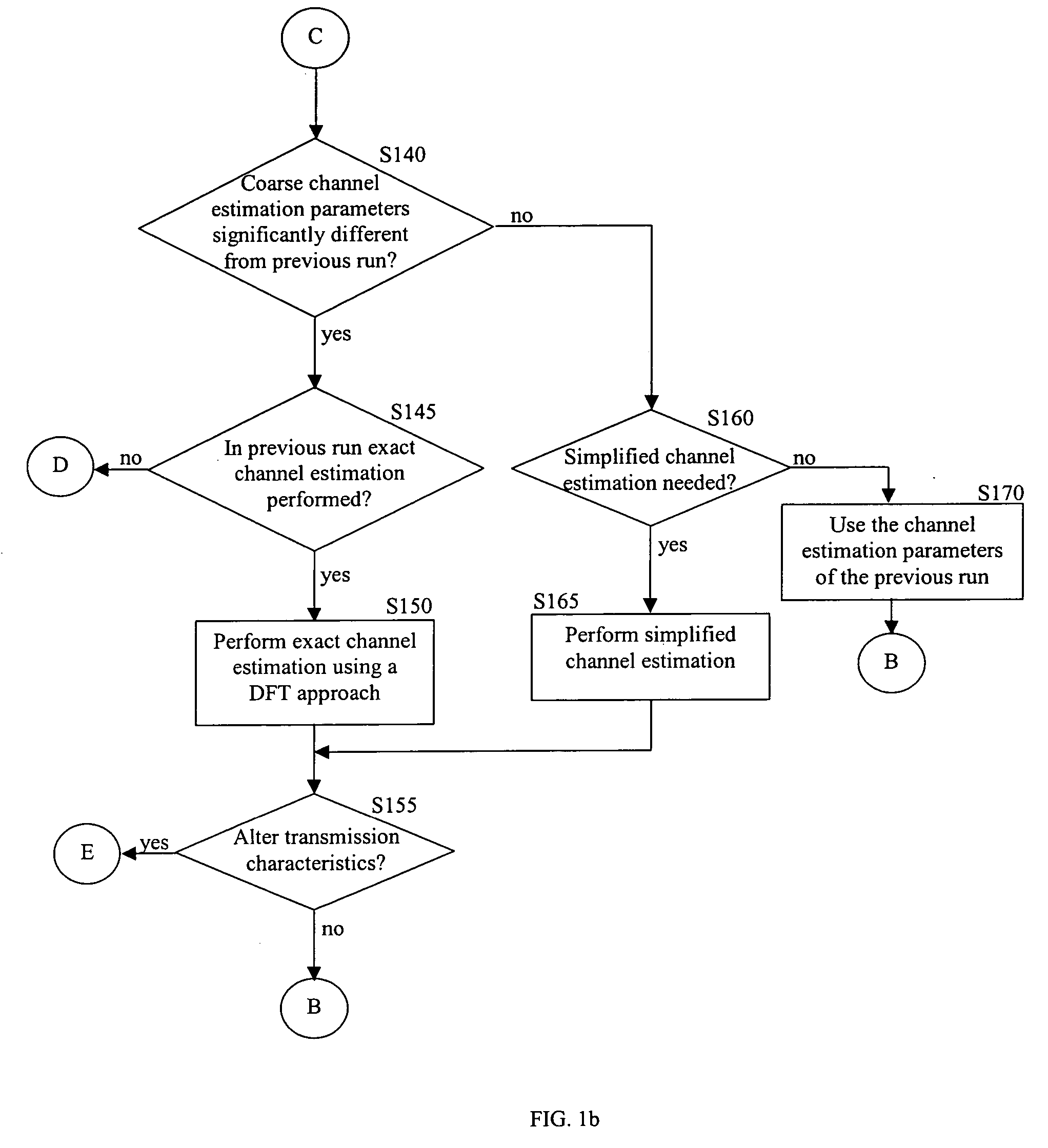
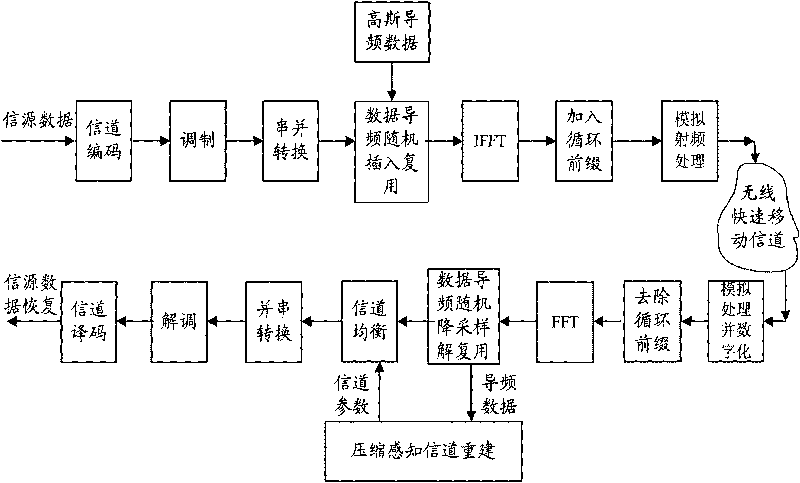
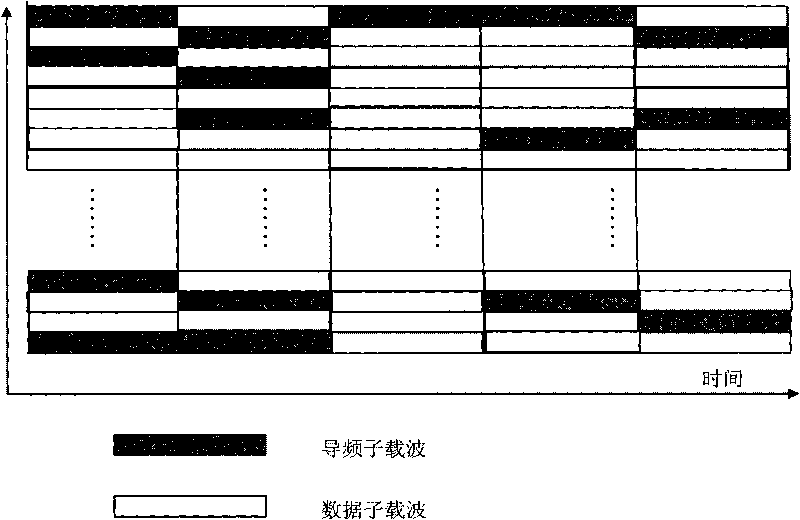
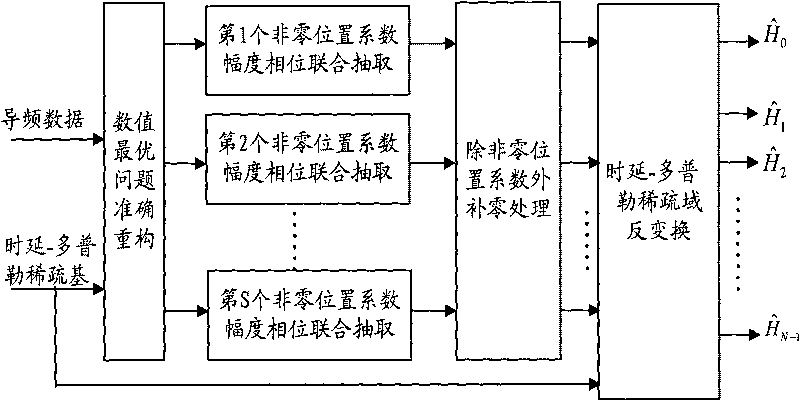
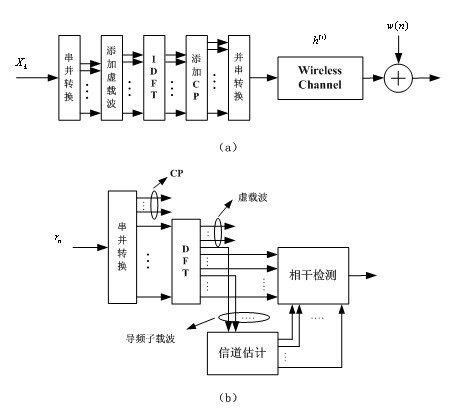
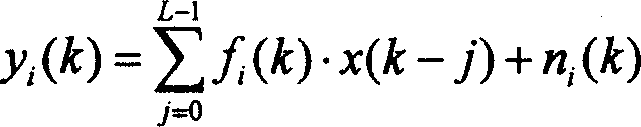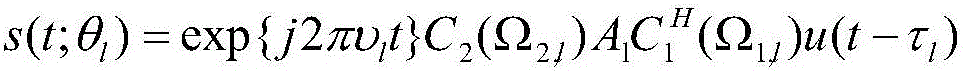Patents
Literature
162 results about "Channel parameter estimation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
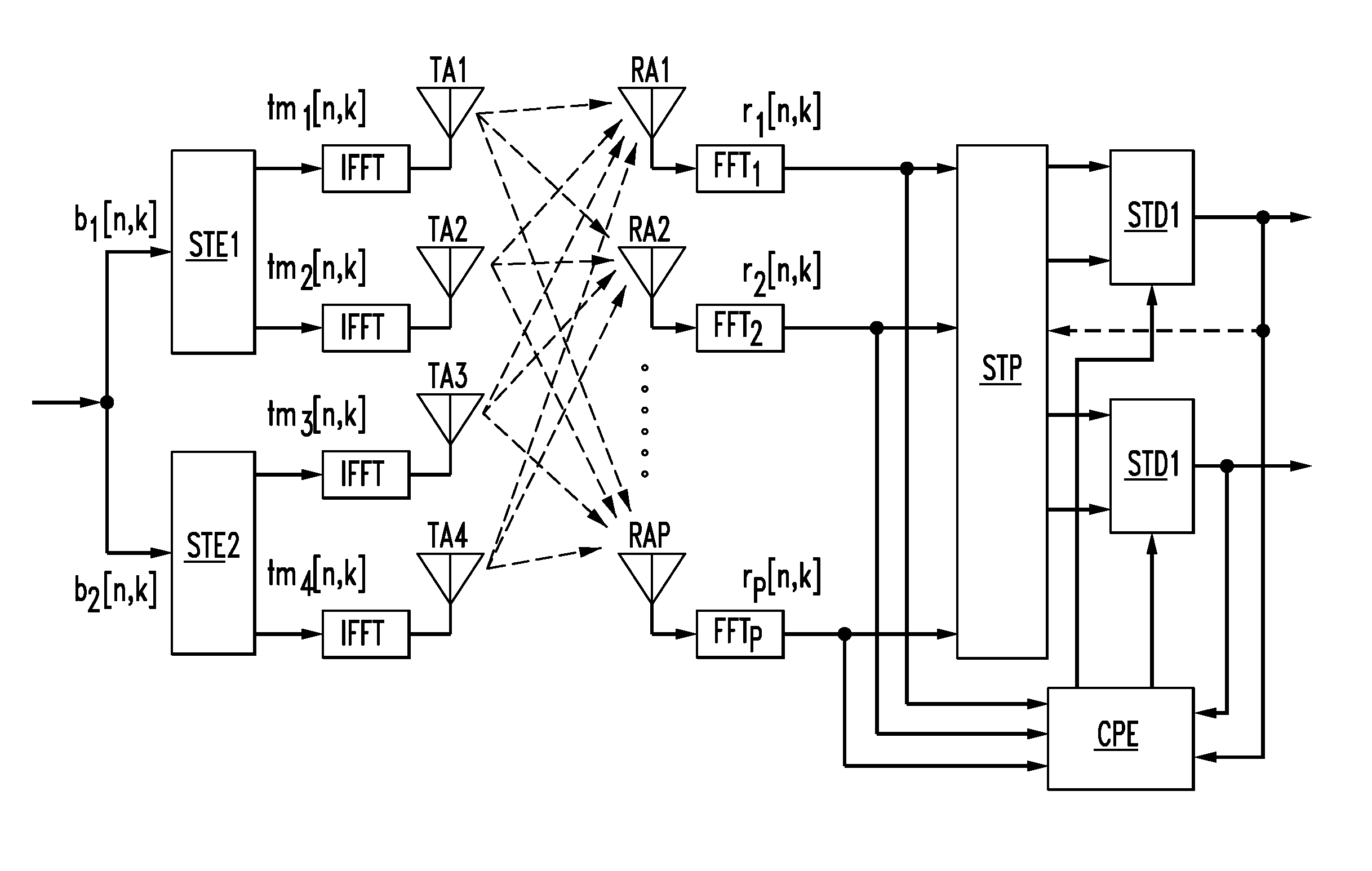
MIMO OFDM system
ActiveUS7068628B2Improve system performanceEnhances channel parameter estimationSpatial transmit diversityTime-division multiplexChannel impulse responsePre whitening
A MIMO OFDM system includes a plurality of space-time encoders for encoding respective data blocks with independent space-time codes. The transformed data block signals are transmitted by a plurality of transmit antennas and received by a plurality of receive antennas. The received data is pre-whitened prior to maximum likelihood detection. In one embodiment, successive interference cancellation can be used to improve system performance. Channel parameter estimation can be enhanced by weighting the channel impulse response estimates based upon a deviation from average.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Apparatus and method for allocating resources of a virtual cell in an OFDM mobile communication system
ActiveUS7069009B2Improve efficiencyIncrease powerEnergy efficient ICTSite diversityCommunications systemVirtual cell
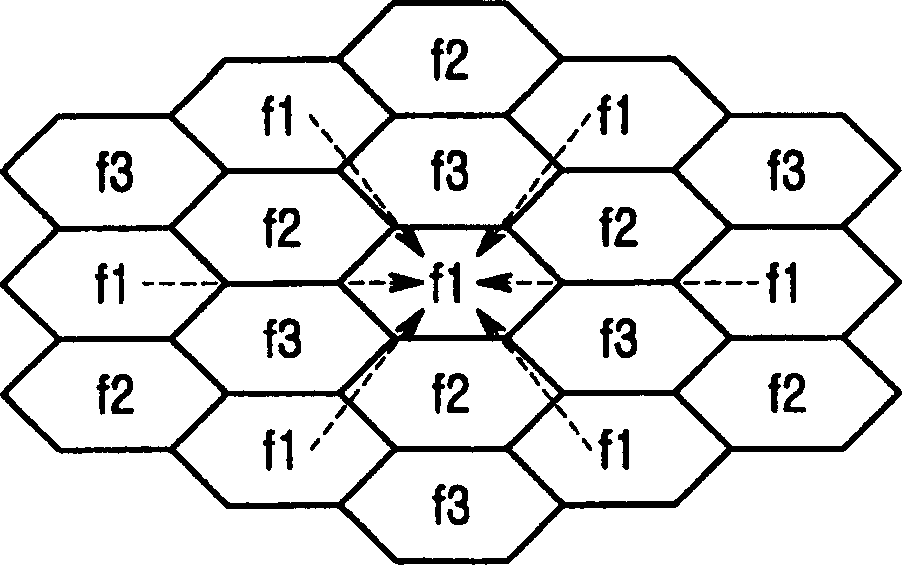
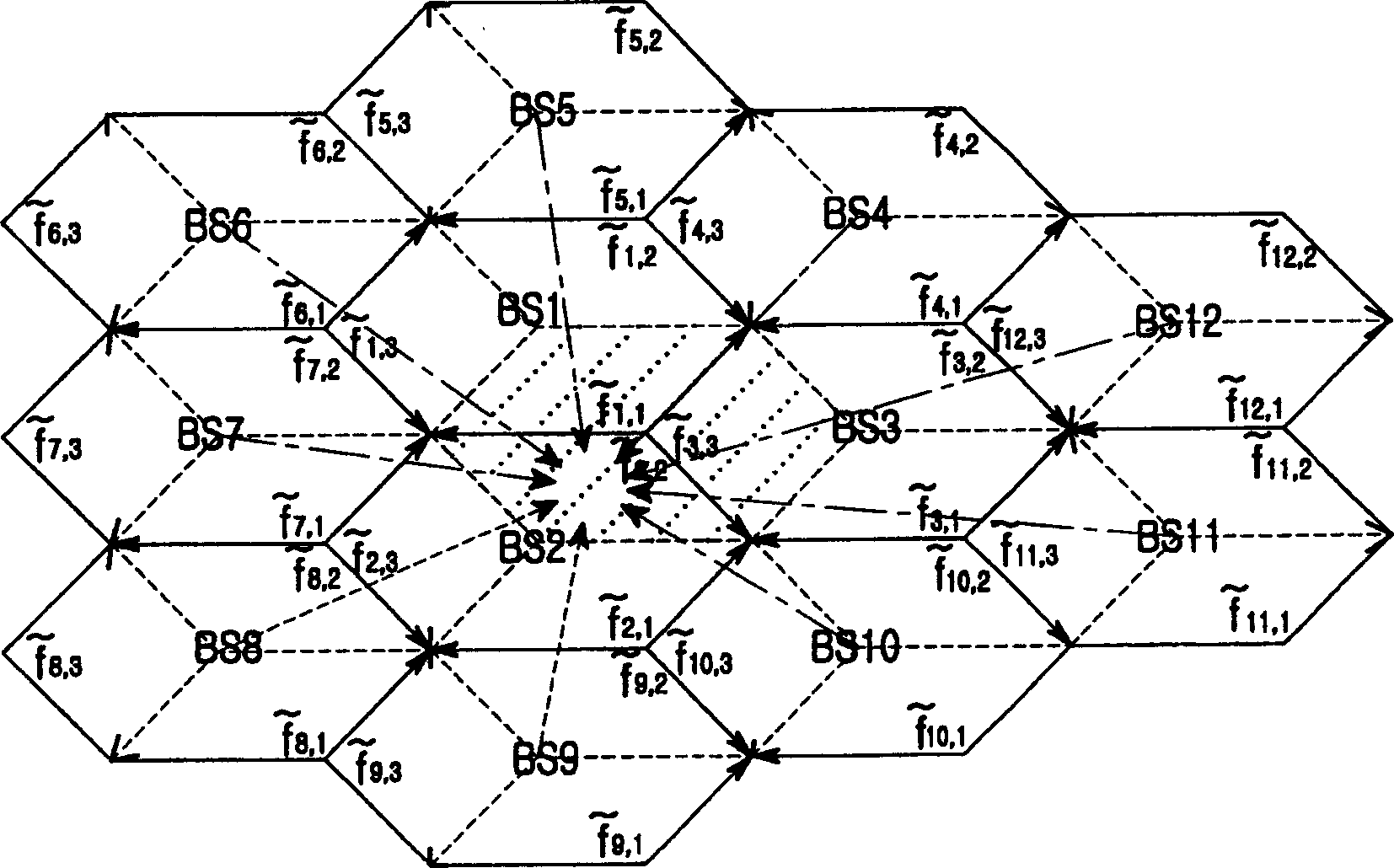
A virtual cell management apparatus and method using sectors in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing mobile communication system including a cell structure having cells each comprised of a plurality of sectors, the cells performing data communication with mobile terminals within a corresponding cell through at least one subchannel having orthogonality. The method comprises forming a virtual cell with a particular one of sectors constituting a particular cell and sectors of two other cells neighboring the particular sector; transmitting, by three base stations forming the virtual cell, an interference measurement value and a channel parameter estimation value from a mobile terminal located in the virtual cell to a base station controller that controls the virtual cell, thereby allocating wireless resource including frequency bandwidth, initial bits, subcarriers and refined bits in the virtual cell; transmitting the allocated wireless resource to the three base stations so that the base stations allocate a same subchannel to each mobile terminal located in the virtual cell; and transmitting same data over the allocated subchannel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for demixing of degenerate mixtures
InactiveUS6430528B1Reduce environmental noiseAccurately determineDigital computer detailsHearing aids signal processingChannel parameterTime windows
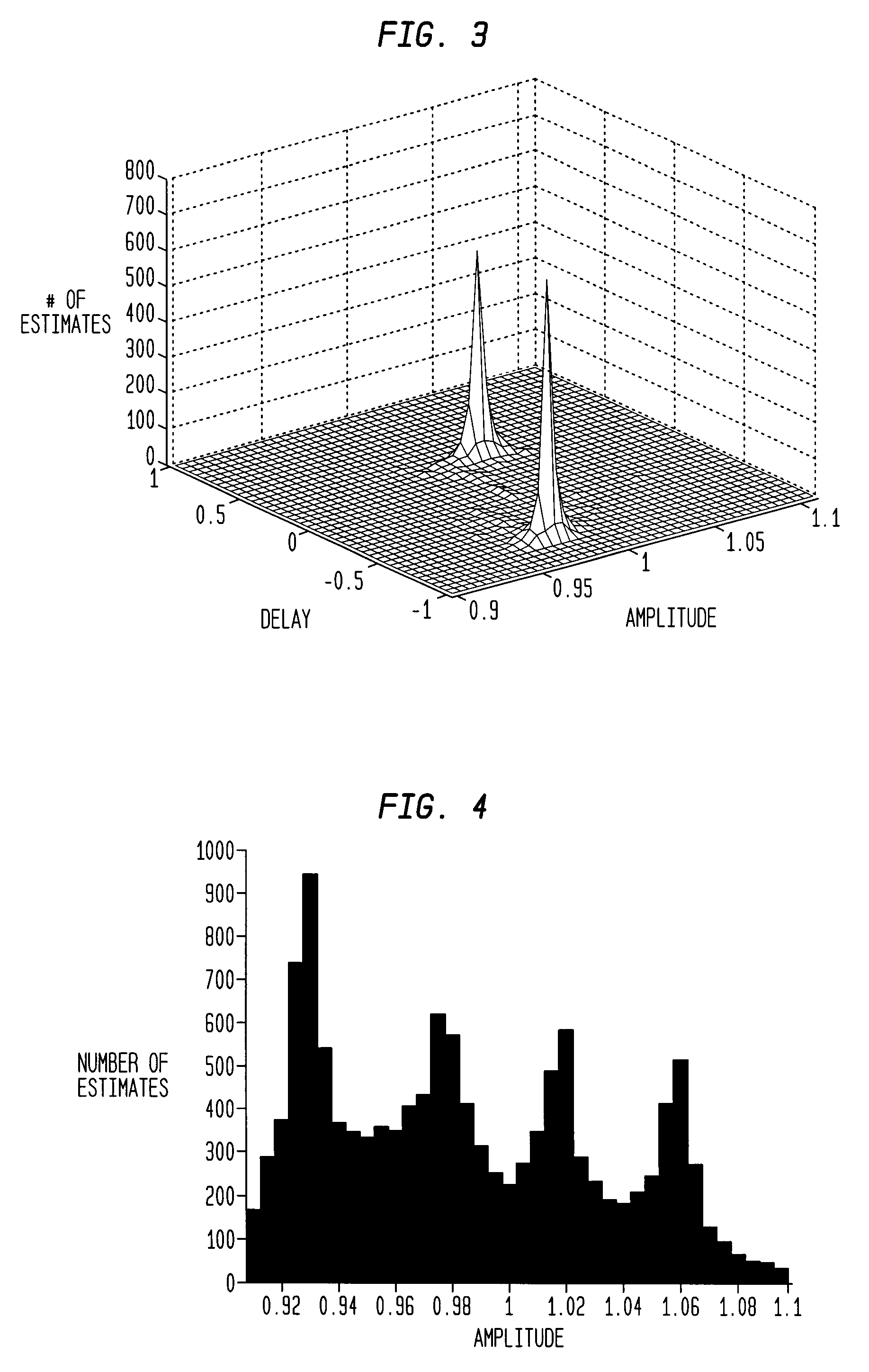
A method and system for blind channel estimation comprises acquiring two mixtures of at least one at least weakly W-disjoint orthogonal source signal, calculating point-by-point ratios of a transform of a time-window of each of said mixture signals, determining channel parameter estimates from said ratios, constructing a histogram of said channel parameter estimates, repeating the calculating, determining and constructing steps for successive time windows of the mixture signals, and selecting as estimates of said channel parameters those estimates associated with identified peaks on said histogram.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
Channel parameter estimation method
InactiveUS20130128932A1Network traffic/resource managementModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemMultipath channels
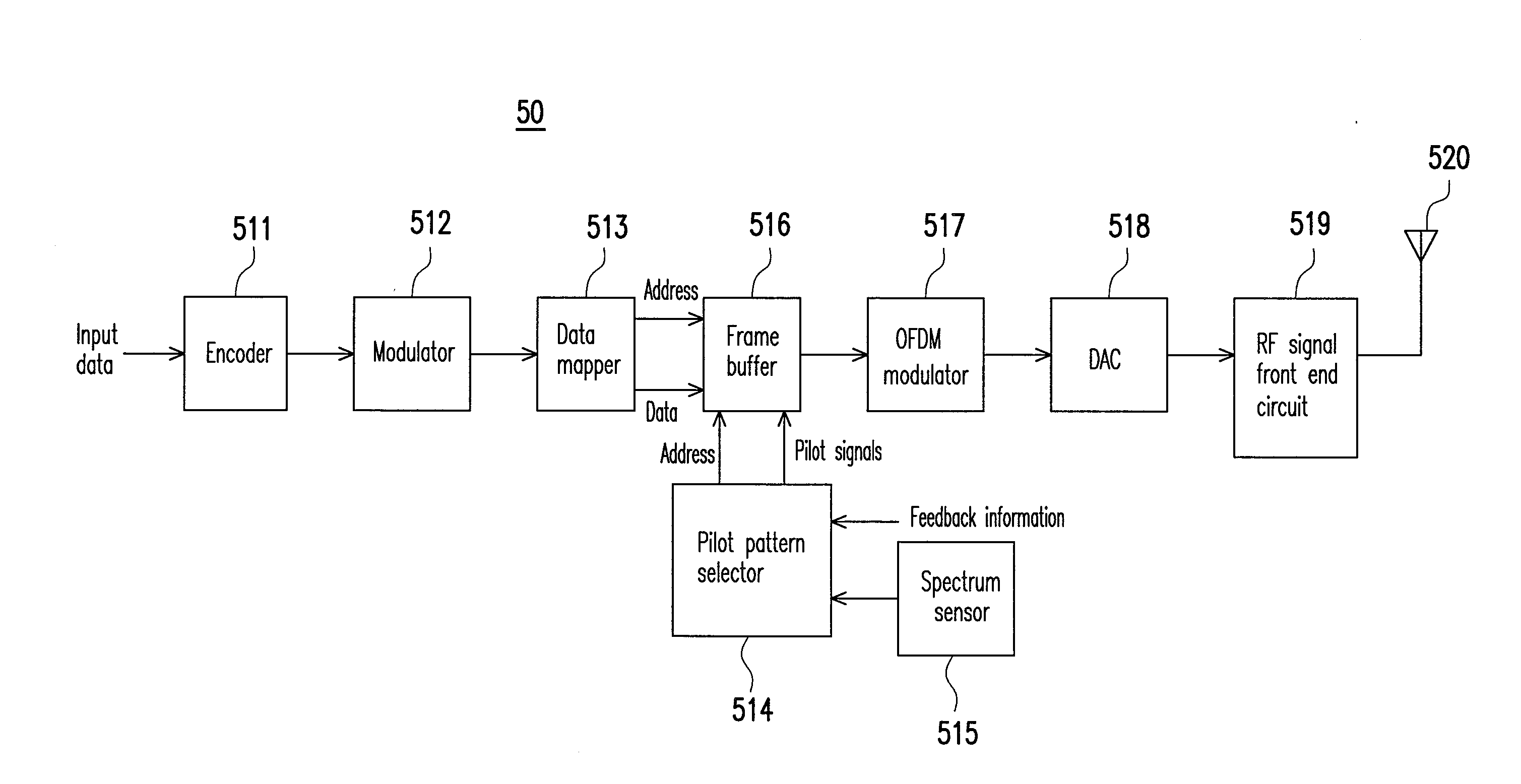
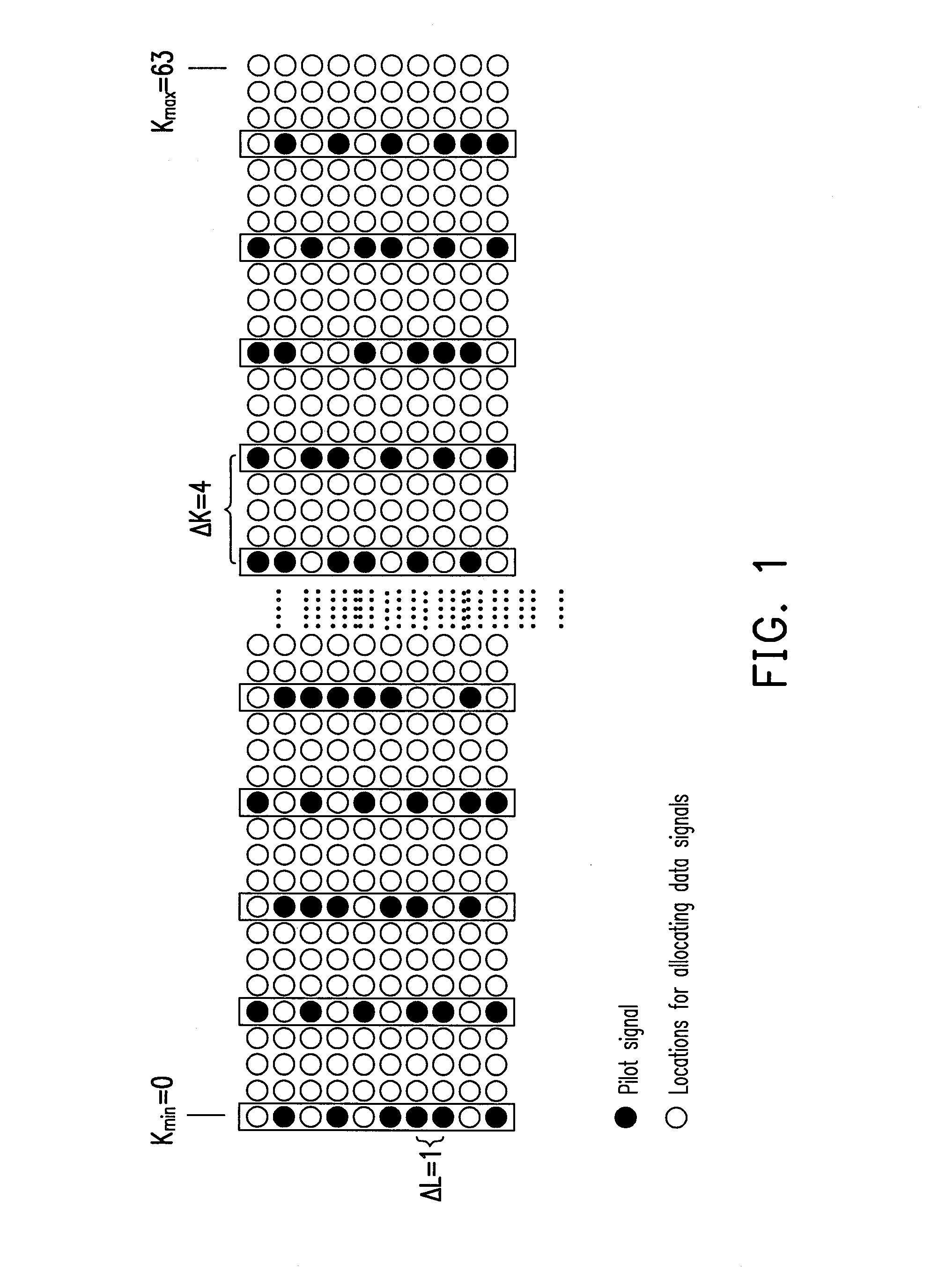
A channel parameter estimation method adapted to a wireless communication system is proposed. The wireless communication system includes a transmitter and a receiver. The proposed method includes following steps. The transmitter transmits a plurality of pilot signals to the receiver by using one of a plurality of preconfigured sparse random pilot patterns. The receiver receives the pilot signals, performs a channel parameter estimation on the pilot signals by using a compressive sensing algorithm to obtain a multipath channel number, and selects a pilot pattern for a next cycle among the preconfigured sparse random pilot patterns according to the multipath channel number and a current pilot number. Additionally, the receiver transmits feedback information associated with the selected pilot pattern to the transmitter.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
A channel estimate method and corresponding communication method and system
InactiveCN101170531AReduce mistakesImprove Capacitive PerformanceMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemChannel parameter
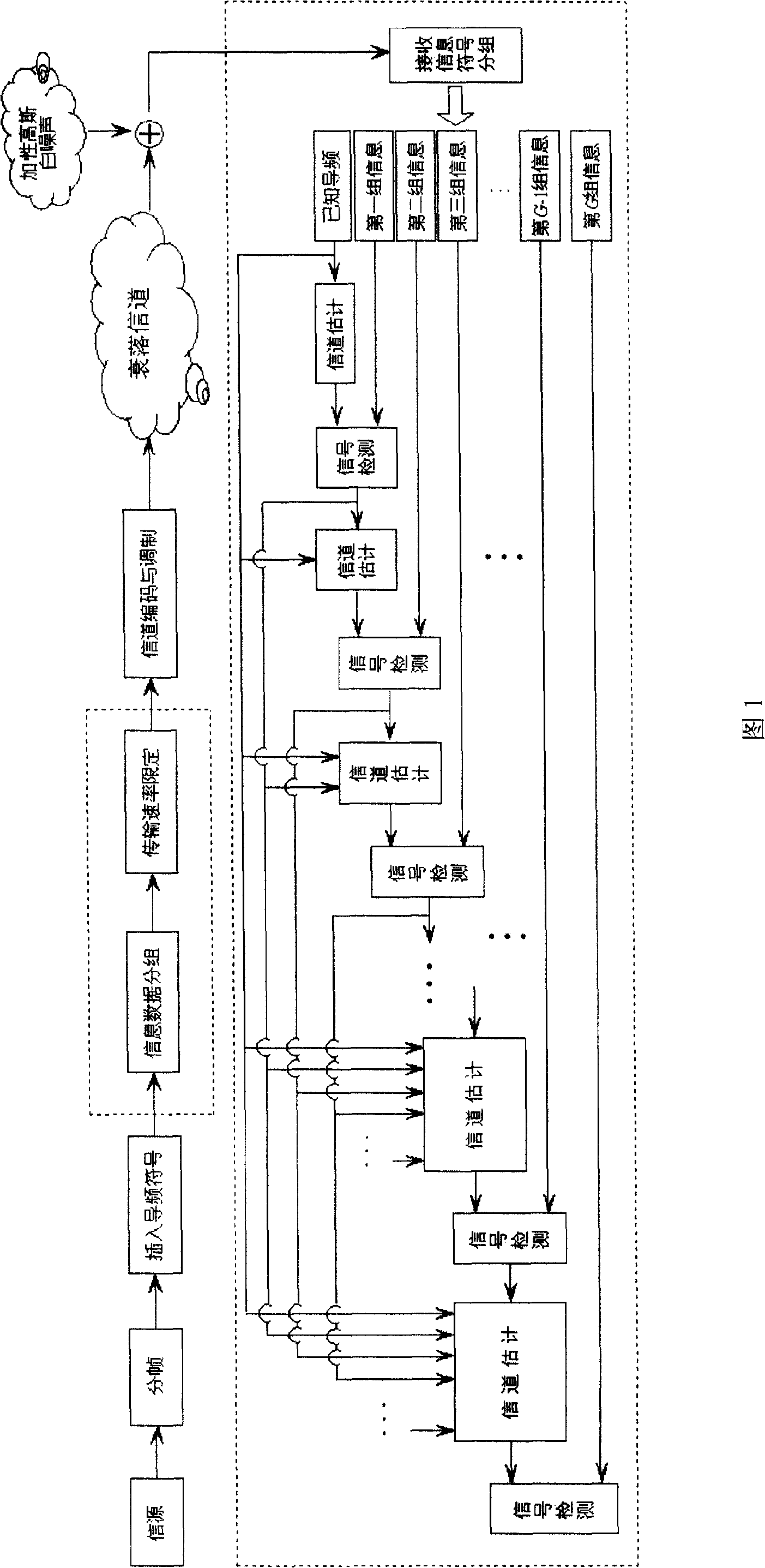
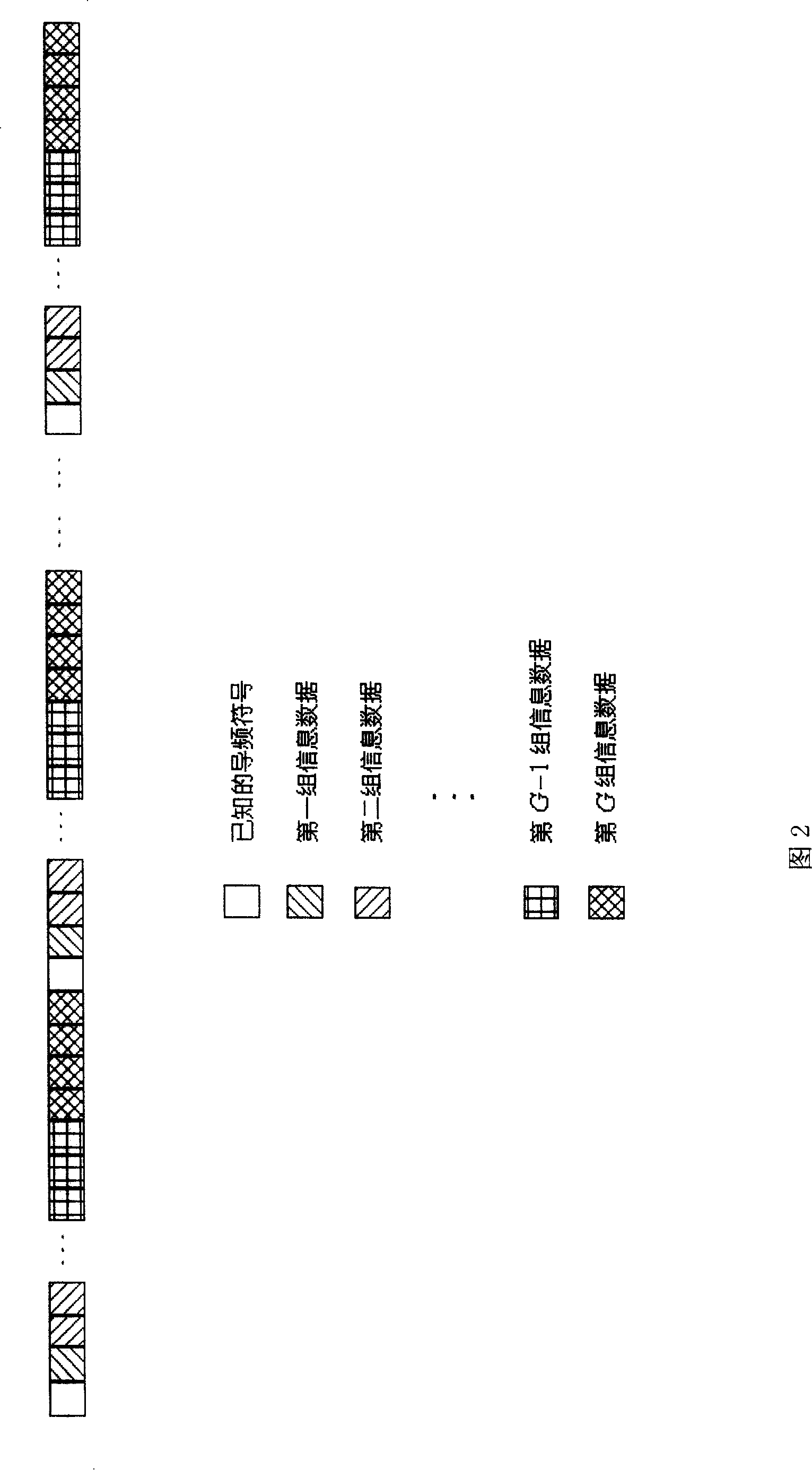
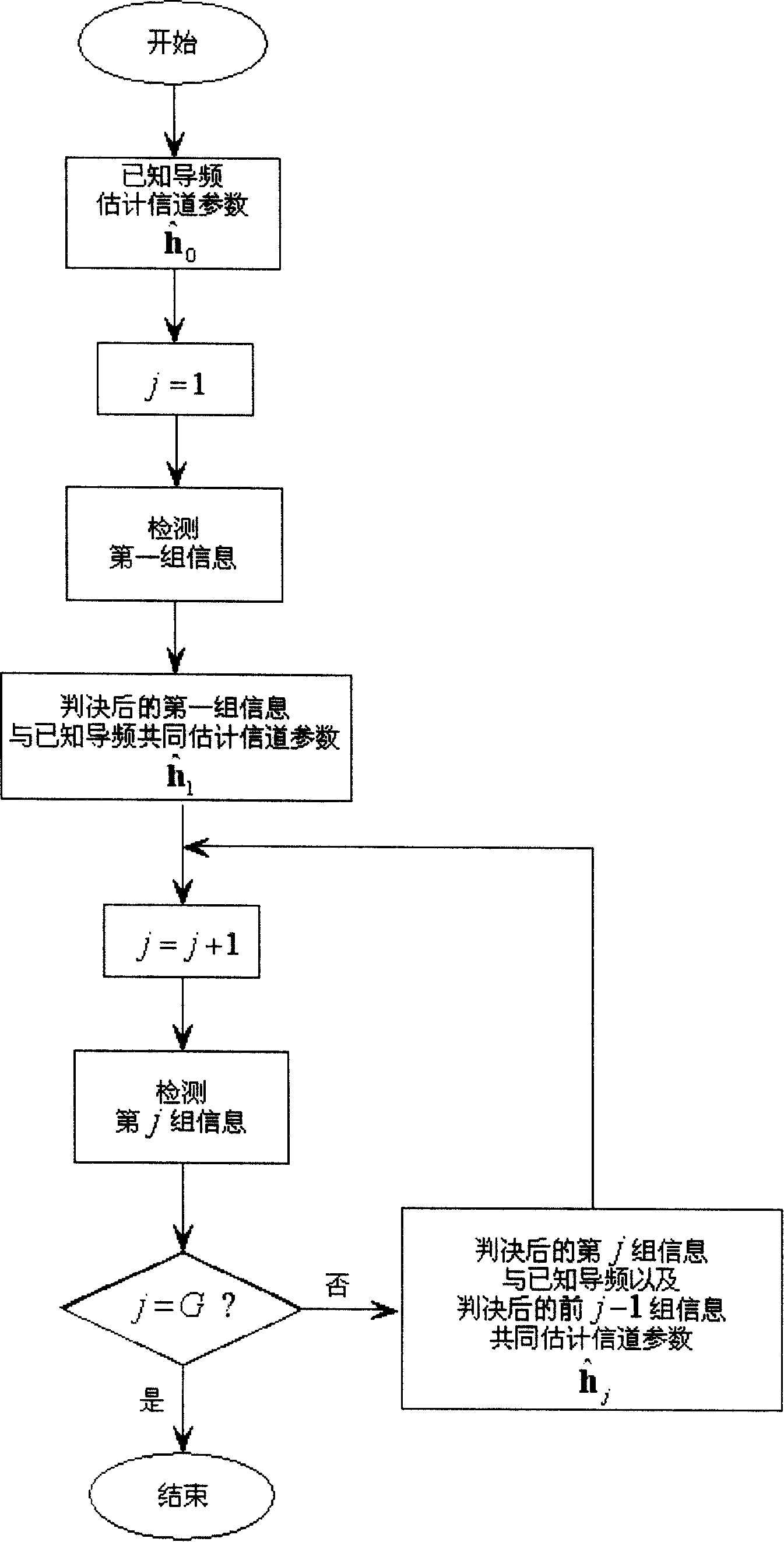
The invention provides the channel estimating method used for pilot frequency supplementary estimating system, the corresponding emitting method, the corresponding receiving method and the improved communication system structure. The invention sets the upper limit of information symbol transmitting speed of each group at the emitting end as the lower bound of mutual information between the input operation and the output operation, which the system can reach when the receiving end implements the relative detection for the information symbol of each group. Primarily, the receiving end utilizes the known pilot frequency symbol to implement channel estimation. The channel parameter which is obtained is implemented with initial estimation value. The initial estimation value is utilized to implement the relative detection for information symbol of the first group, and then the information symbol of the group, which is judged, is taken as equivalent pilot frequency symbol and estimates the channel again together with the known pilot frequency. The new channel parameter estimation value is utilized to implement the relative detection for the information symbol of the next group, which is received. The iteration is implemented and the channel is estimated. With the increase of equivalent pilot frequency energy, the estimation difference of the channel is reduced; therefore, the capacity performance of the system is improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Down wave beam shaping method and device of radio channel
ActiveCN1658526ATransmission control/equalisingRadio transmission for post communicationRadio channelEngineering
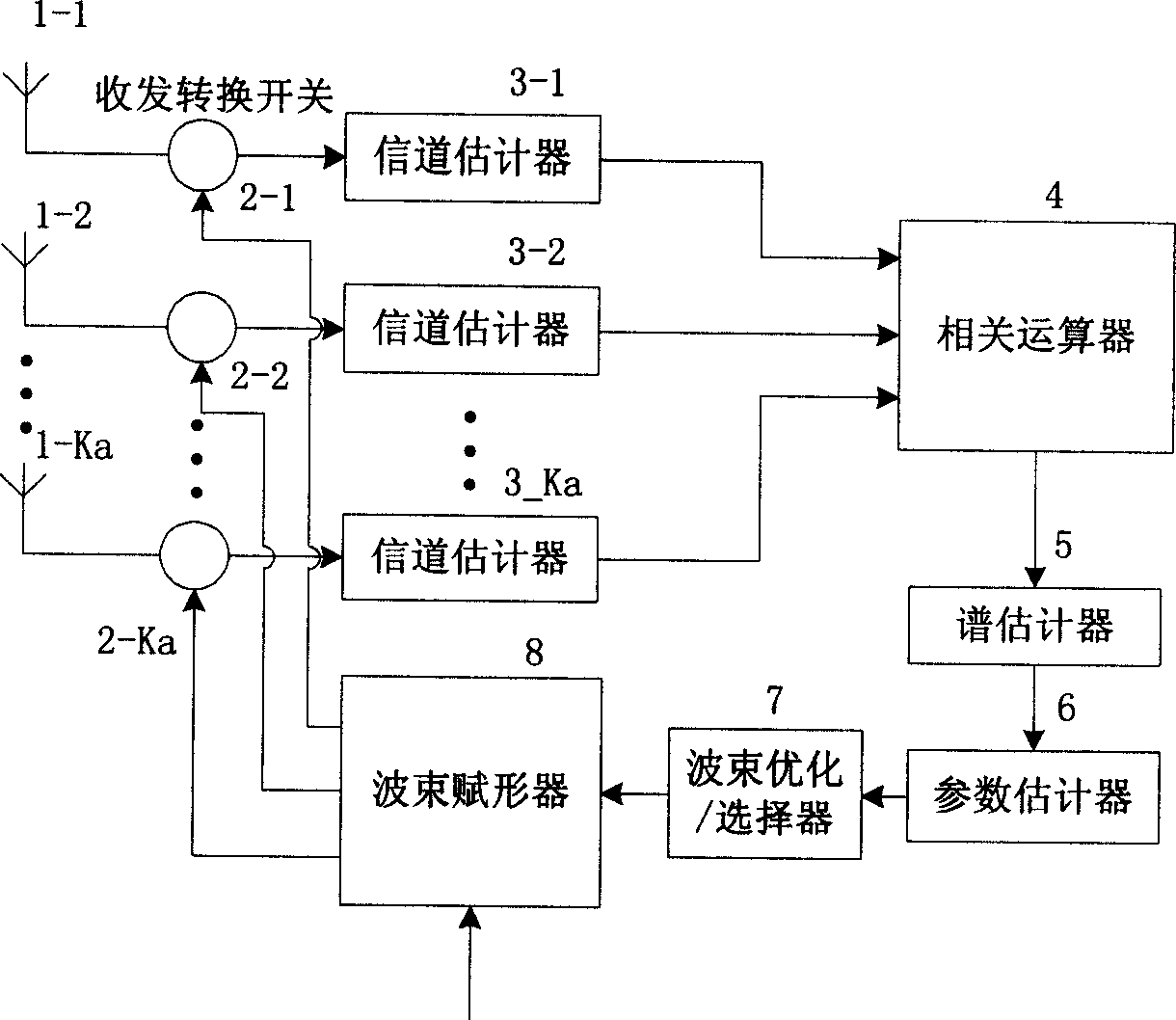
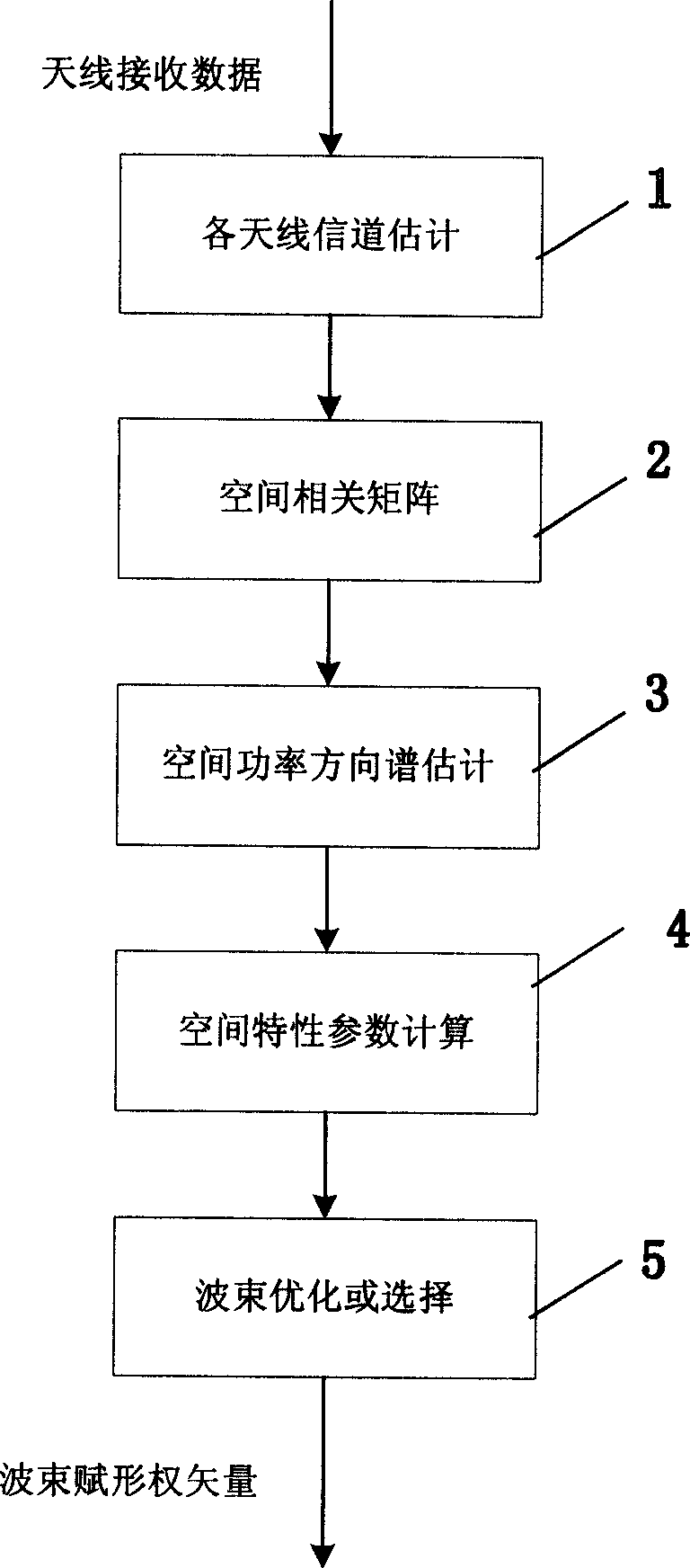
This invention discloses an exciping method of down beam of wireless channel and the device. The method includes the following processes: estimate the channels of the antenna, estimate the user's space parameter according to the channel's estimation, estimate beam weight vector according to the space parameter's estimation, control the beam exciping according to the weight vector estimation. The device includes: several receiving and sending channel estimation devices to output the channel estimation; the relative devices to relate the several receiving and sending channel estimation; channel parameter estimation device to get the channel parameter estimation according to the relative results; the beam exciping device to excipe the beam according to the channel parameter estimation.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Orthogonal-matching-pursuit-based sparse channel estimation method
ActiveCN102244624AHigh precisionImprove anti-interference abilityBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsChannel impulse responseAlgorithm
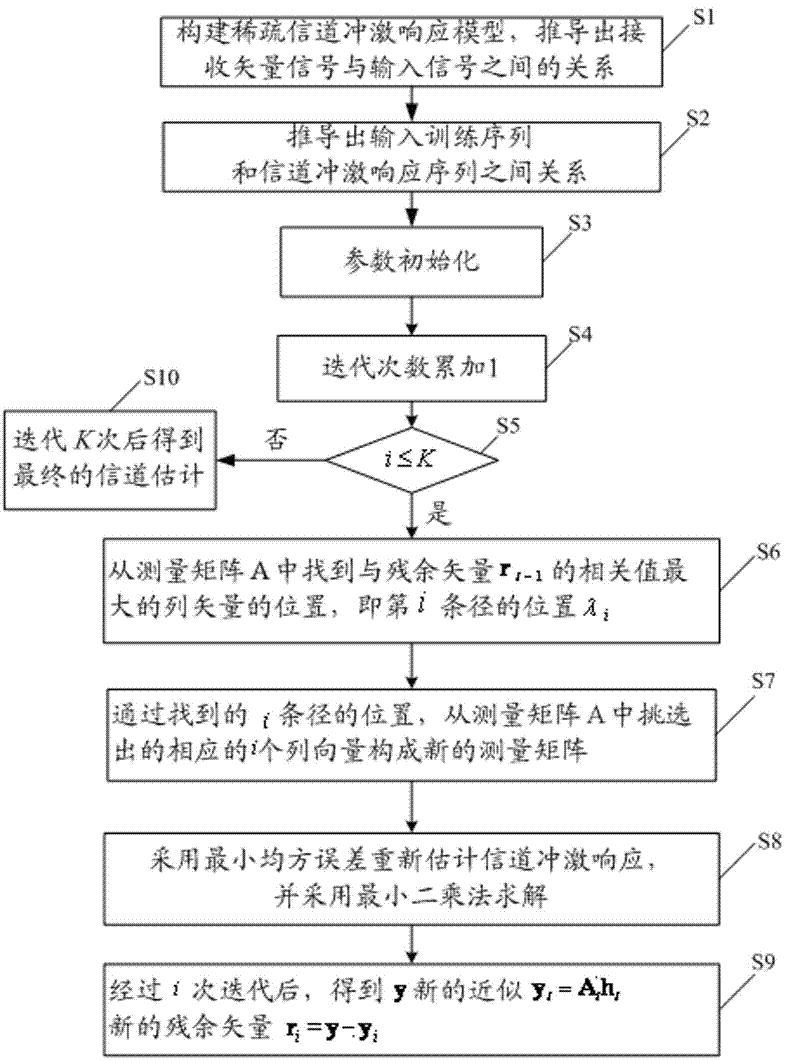
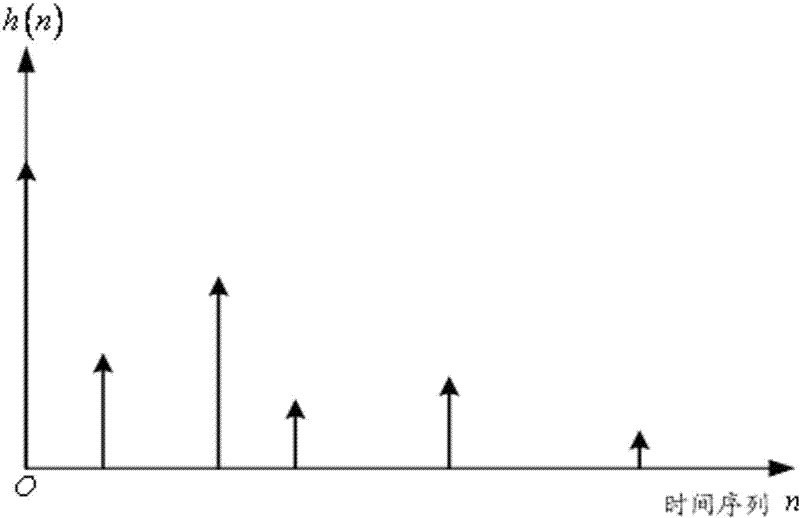
The invention discloses an orthogonal-matching-pursuit-based sparse channel estimation method, which comprises the following steps of: taking an input vector signal as a channel impulse response sequence, constructing a measurement matrix by utilizing a know input training sequence, and constructing a sparse channel impulse response model for recovering and reconstructing the input vector signal by receiving a vector signal; and estimating the position and amplitude of each channel by adopting an orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm to obtain a channel estimation value. In the method, the precision and anti-interference performance of channel parameter estimation can be effectively improved because the orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm is easy to realize and high in proximity; and the sparseness of the channels is taken into account and iteration is performed for relatively fewer times by adopting the orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm to estimate the position and amplitude of a plurality of sparse channels, so that the complexity of a channel estimation method can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN NAT ENG LAB OF DIGITAL TELEVISION
Apparatus and method for allocating resources of a virtual cell in an OFDM mobile communication system
InactiveCN1501607AImprove efficiencyImprove frequency reuse characteristicsEnergy efficient ICTSite diversityVirtual cellCommunications system
A virtual cell management apparatus and method using sectors in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing mobile communication system including a cell structure having cells each comprised of a plurality of sectors, the cells performing data communication with mobile terminals within a corresponding cell through at least one subchannel having orthogonality. The method comprises forming a virtual cell with a particular one of sectors constituting a particular cell and sectors of two other cells neighboring the particular sector; transmitting, by three base stations forming the virtual cell, an interference measurement value and a channel parameter estimation value from a mobile terminal located in the virtual cell to a base station controller that controls the virtual cell, thereby allocating wireless resource including frequency bandwidth, initial bits, subcarriers and refined bits in the virtual cell; transmitting the allocated wireless resource to the three base stations so that the base stations allocate a same subchannel to each mobile terminal located in the virtual cell; and transmitting same data over the allocated subchannel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Self-adaptive channel estimation method based on compressed sensing and large-scale MIMO
InactiveCN105656819ANarrow searchThe estimate is accurateSite diversityChannel estimationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Decomposition
The invention discloses a self-adaptive channel estimation method based on compressed sensing and large-scale MIMO and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The self-adaptive channel estimation method includes the steps that decomposition values Ur and Ut of a channel matrix in an angle domain are obtained, and a corresponding measurement matrix phi and a corresponding perceptual measurement value Y are calculated; iterative computation is conducted on a shared channel parameter estimation value (shown in the description) based on an index set Gamma n-1 at a previous moment of a system, the measurement matrix phi and the perceptual measurement value Y; a sparse signal estimation value (shown in the description) is calculated through iteration of the shared channel parameter estimation value (shown in the description), the phi and the Y; finally, a channel matrix estimation value (shown in the description) is obtained according to a formula (shown in the description) based on the number M of transmitting antennas, the signal-to-noise ratio P of the transmitting antennas and the pilot frequency length T of the transmitting antennas. The self-adaptive channel estimation method does not need knowing shared channel information for channel estimation, utilizes the index set at the previous moment in a self-adaptive mode and produces smaller errors compared with a traditional subspace tracking algorithm.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for estimating wireless channel parameters
Method for the estimation of channel parameters in a wireless communication system. In accordance with the method several levels of the wireless channel parameters estimation take place to address the specific requirements of the channel. Based on the level of estimation required an appropriate estimation algorithm is selected to achieve the desired results. The evaluation of the channel state and thereafter determining the appropriate parameter estimation requirements provide for a superior overall performance of the wireless system.
Owner:THETA IP
Method for estimating OFDM rapid-varying channels in low-density pilot-frequency distribution
InactiveCN101699807AImprove estimation accuracyAchieve estimatesMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksComputation complexityChannel parameter
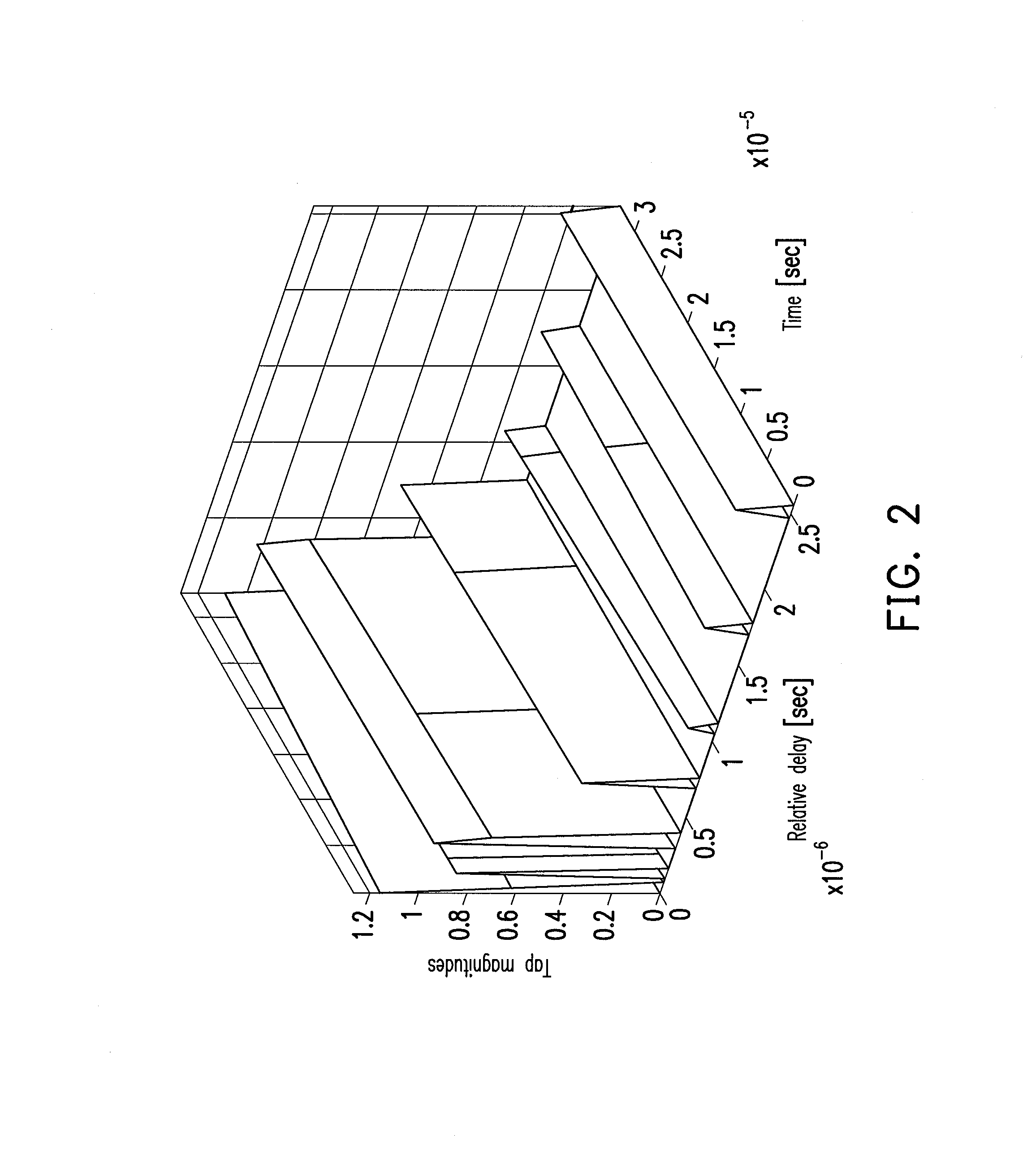
The invention discloses a method for estimating OFDM rapid-varying channels in low-density pilot distribution. The method comprises: multiplexing Gaussian-distribution pilot-frequency data and to-be-transmitted data at a transmitting end according to a time-frequency random insertion mode; performing random down-sampling and multiplexing at a receiving end on a frequency far below Nyquist frequency; transmitting received pilot-frequency data which is obtained through multiplexing and corresponds to a pilot-frequency position to perform compressed sensing channel reconstruction; obtaining S nonzero channel values in a channel delay-Doppler sparse domain; and obtaining the channel parameters of all sub-carriers in a frequency domain through channel coefficient zero padding excepting S nonzero positions, as well as delay-Doppler sparse domain inverse transformation processing. The method has the advantages of performing random down-sampling on the frequency far below Nyquist frequency, utilizing the compressed sensing channel reconstruction to filter noise so as to improve the parameter estimation precision of OFDM rapid-varying channels under pilot-frequency distribution conditions low in signal-to-noise ratio and density and realizing high-precision channel parameter estimation and tracking, along with low estimation-calculation complexity and low bit error rate.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Statistics channel computing method based on asymmetric spatial structure and non-uniform scatterers
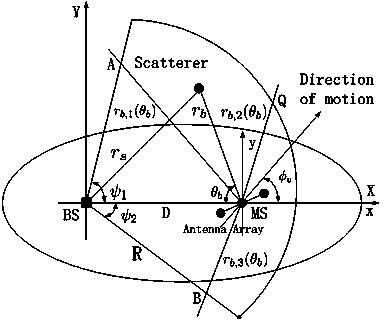
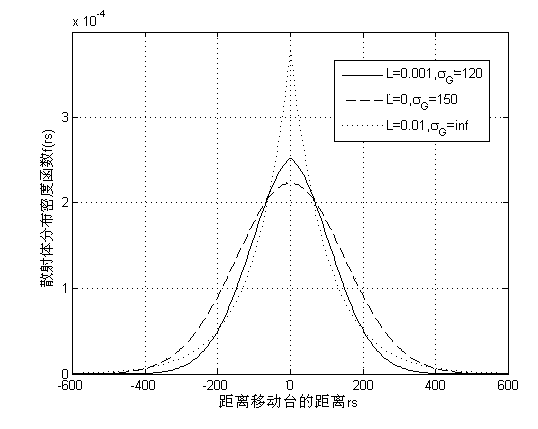
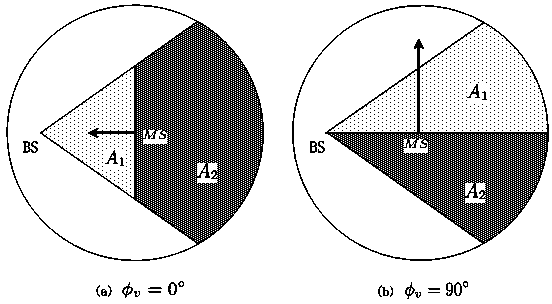
ActiveCN103716264AIncrease capacityImprove reliabilitySpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsChannel parameterMicro cell
The invention discloses a computing method for comprehensively improving spatial statistics channels for an asymmetric spatial structure evenly provided with non-uniform scatterers, wherein mobile communication environments such as macro cells and micro cells can be estimated accurately, flexibly and conveniently, and estimation accuracy of channel parameters such as the reaching angle and reaching time of electromagnetic signals and the channel capacity performance in an MIMO system can be improved effectively. The statistics channel computing method based on the asymmetric spatial structure and the non-uniform scatterers is achieved based on an asymmetric spatial statistics channel model, wherein the asymmetric spatial statistics channel model comprises a mobile station and a base station, a directional antenna is arranged in the base station, and all the scatterers are distributed in a fan-shaped scattering area covered by the antenna of the base station in a non-uniform mode and meet the Gaussian distribution mode or exponential distribution mode. The statistics channel computing method comprises the steps of computing a distribution density function expression of polar coordinates of the scatterers, computing a probability density function of the reaching angle and the reaching time, and computing the channel capacity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
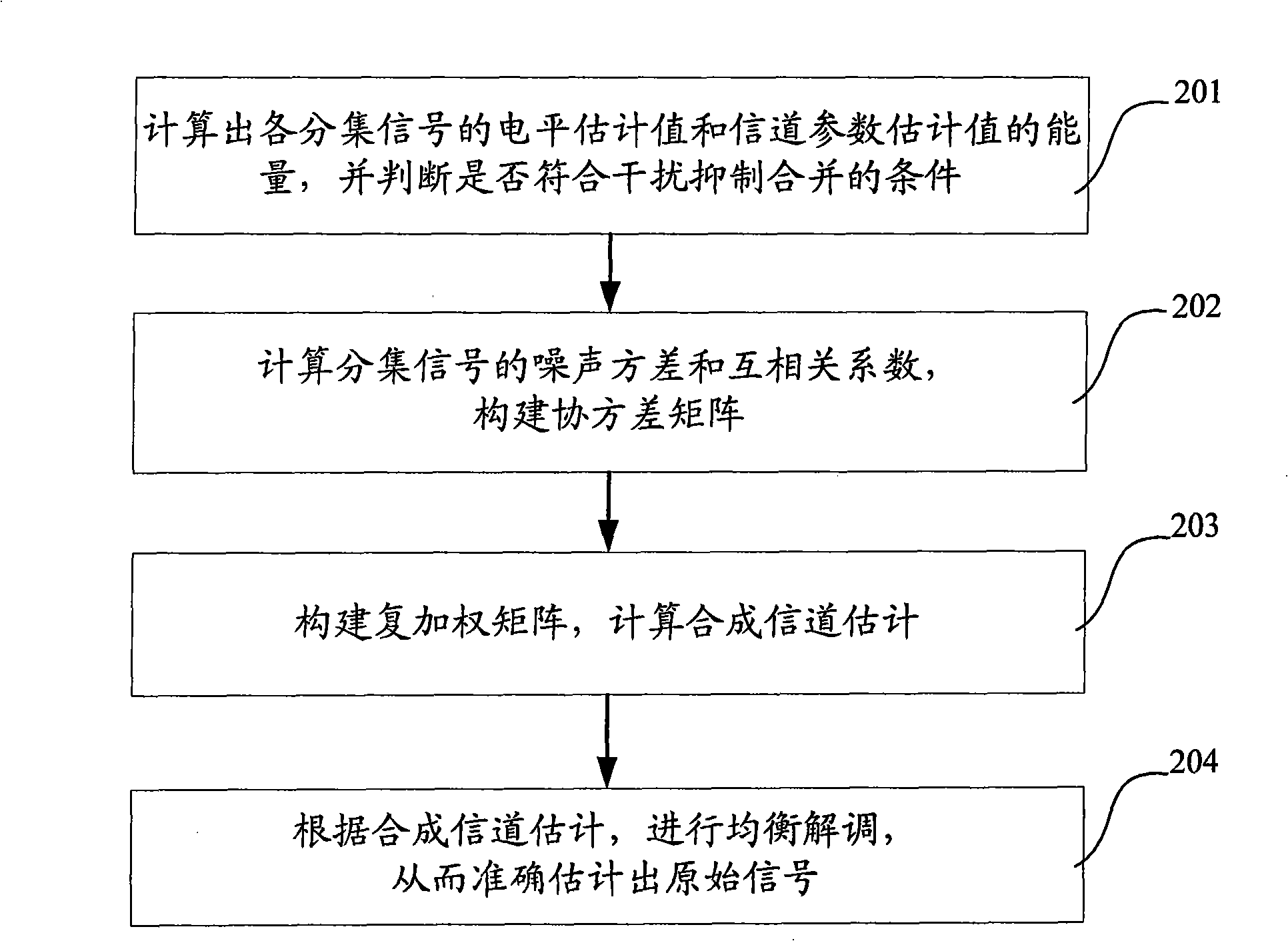
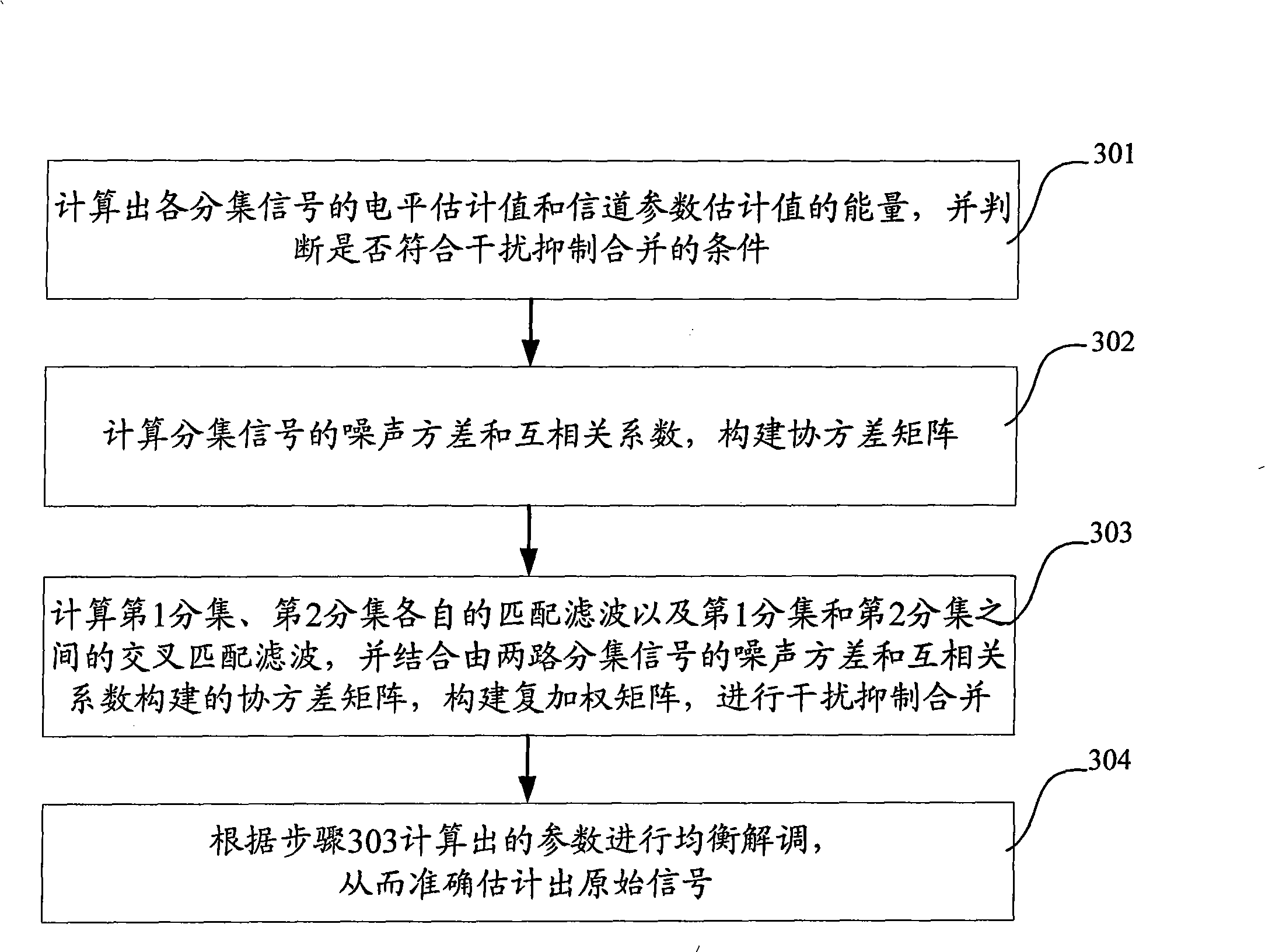
Method and system for restraining interference and combining diversity
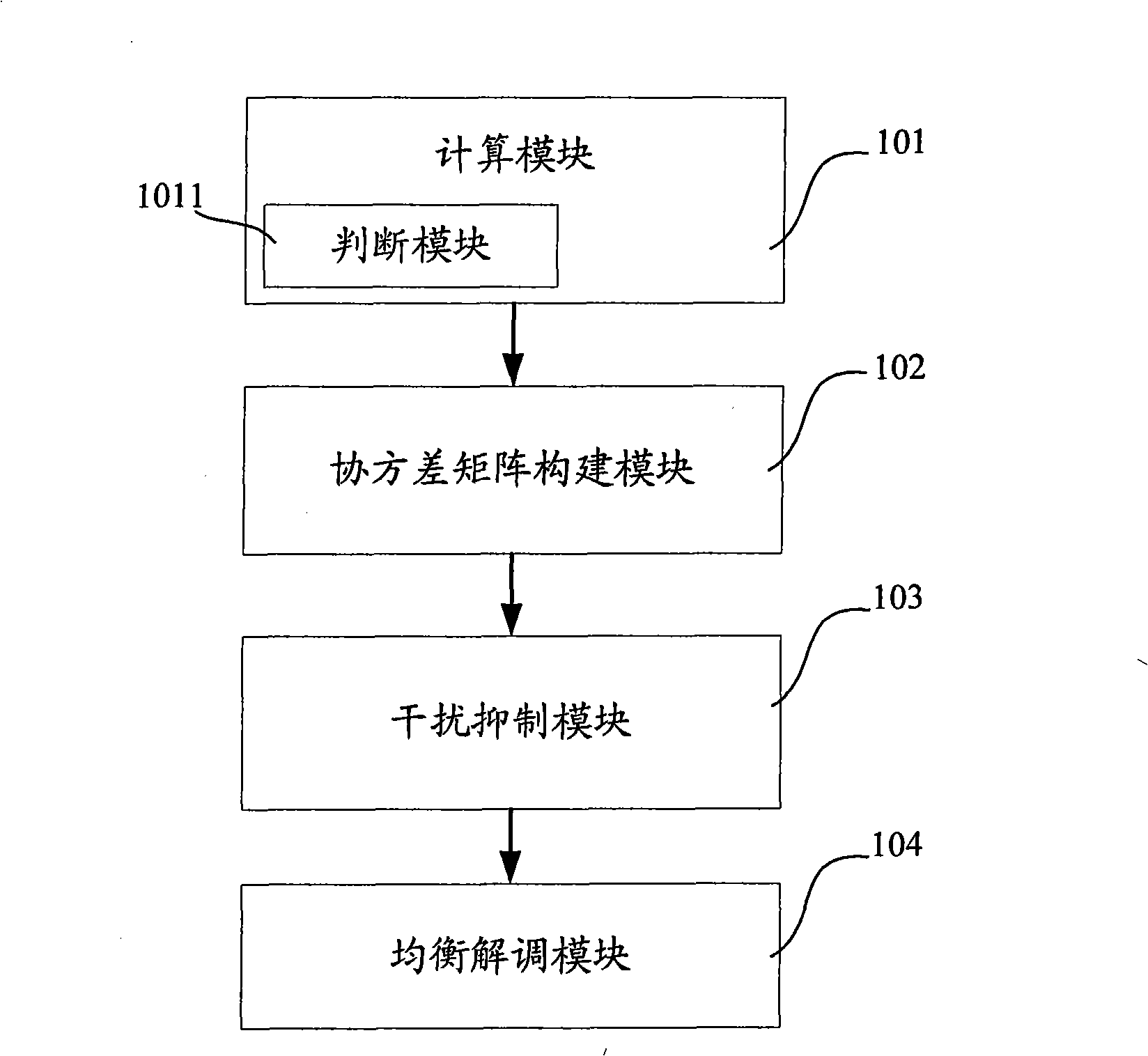
ActiveCN101330358AImprove receiver sensitivityExpand coverageTransmitter/receiver shaping networksError prevention/detection by diversity receptionConducted InterferenceEngineering
The invention discloses an interference suppression diversity and combination method which comprises the steps of calculating the capacities of a level estimation value of a diversity signal and a channel parameter estimation value; calculating the noise variance and cross correlation coefficient of the diversity signal to construct a covariance matrix; constructing a weighted matrix according to the covariance matrix to conduct interference, suppression and combination; and conducting equal demodulation according to a result of the interference, suppression and combination. The invention also discloses an interference suppression diversity and combination system which comprises a calculation module, a covariance matrix construction module, an interference suppression module and an equal demodulation module. The method greatly reduces the complexity of a system, improves the receiving sensitivity of a receiver, and enlarges the coverage of a base station, thereby providing an interference suppression diversity and combination technical proposal which has the advantages of low complexity, high estimation accuracy and easy realized engineering.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Adaptive diversity merging method of base band receiver for double antenna system
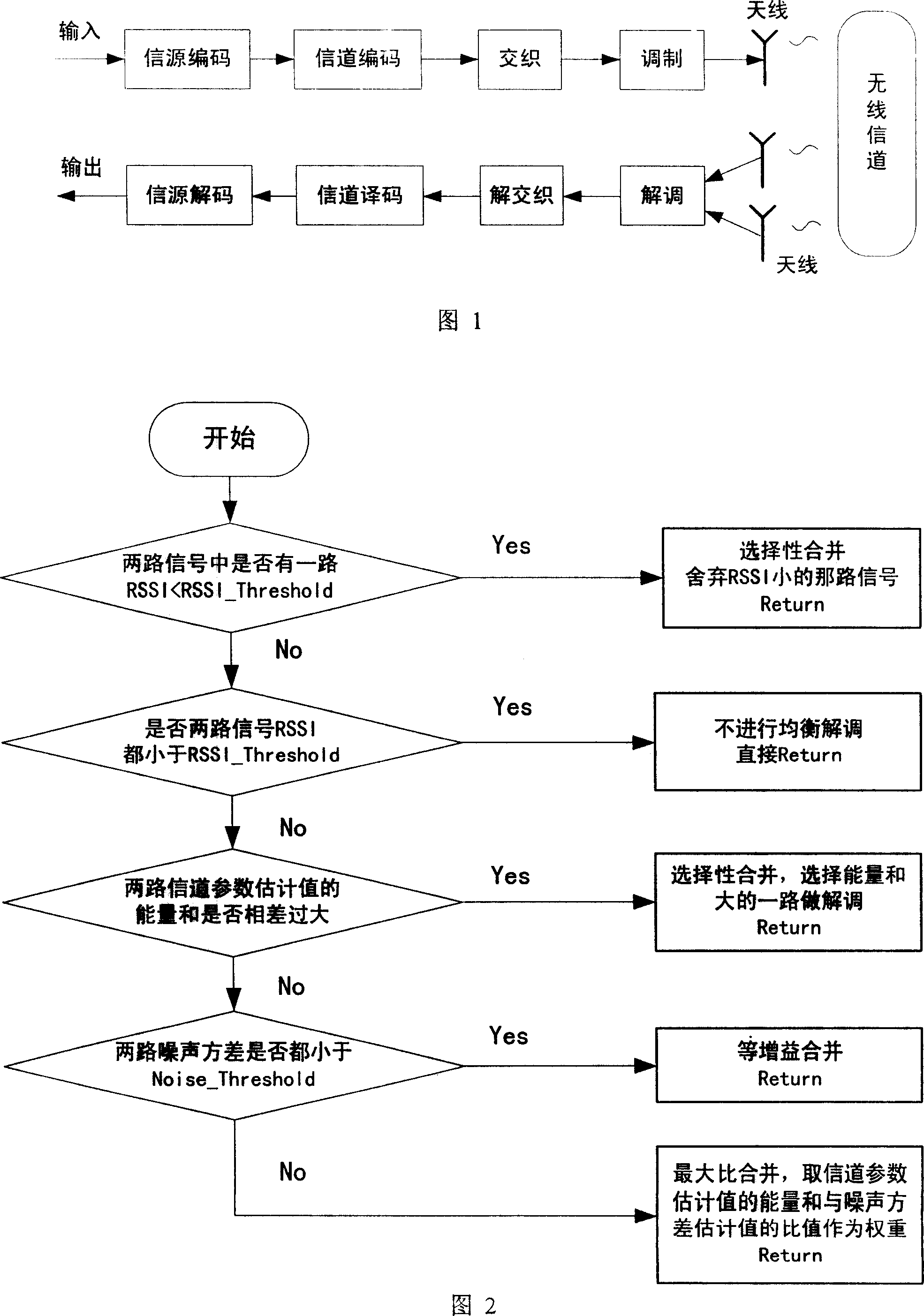
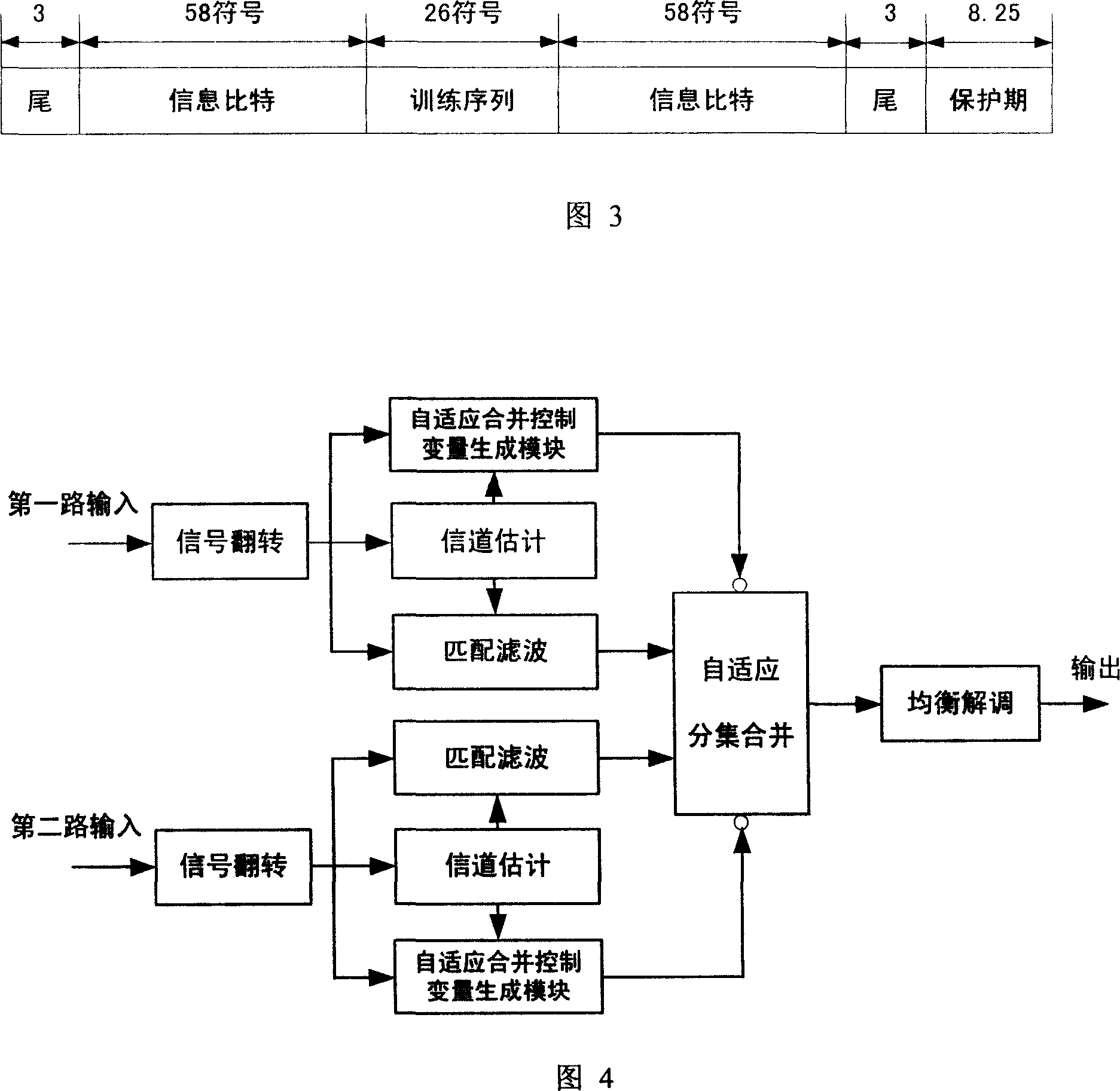
InactiveCN1937445AQuality assuranceQuality improvementSpatial transmit diversityChannel parameterEngineering
The method includes steps: (1) calculating both signal level values received by the twin antenna, the energy of channel parameter estimate value and noise square-root difference estimate value; (2) comparing both signal level values with the preset threshold; if both signal values are greater than preset, then turning to step 3; if only one signal value is great than preset, it decodes and equilibrates the one greater; if both values are less than preset, steps finish; (3) comparing whether the energy sum of both channel parameter estimate values is in set range; if yes, then turning to step 4; otherwise, it demodulates and equilibrates only the greater one; (4) if both signal noise square-root difference estimate values are less than the threshold, then carrying out merger of equal gain for the two signals, demodulating and equilibrating both signal; otherwise, max-ratio combines, demodulates and equilibrates them. This method is simple and efficient.
Owner:ZTE CORP
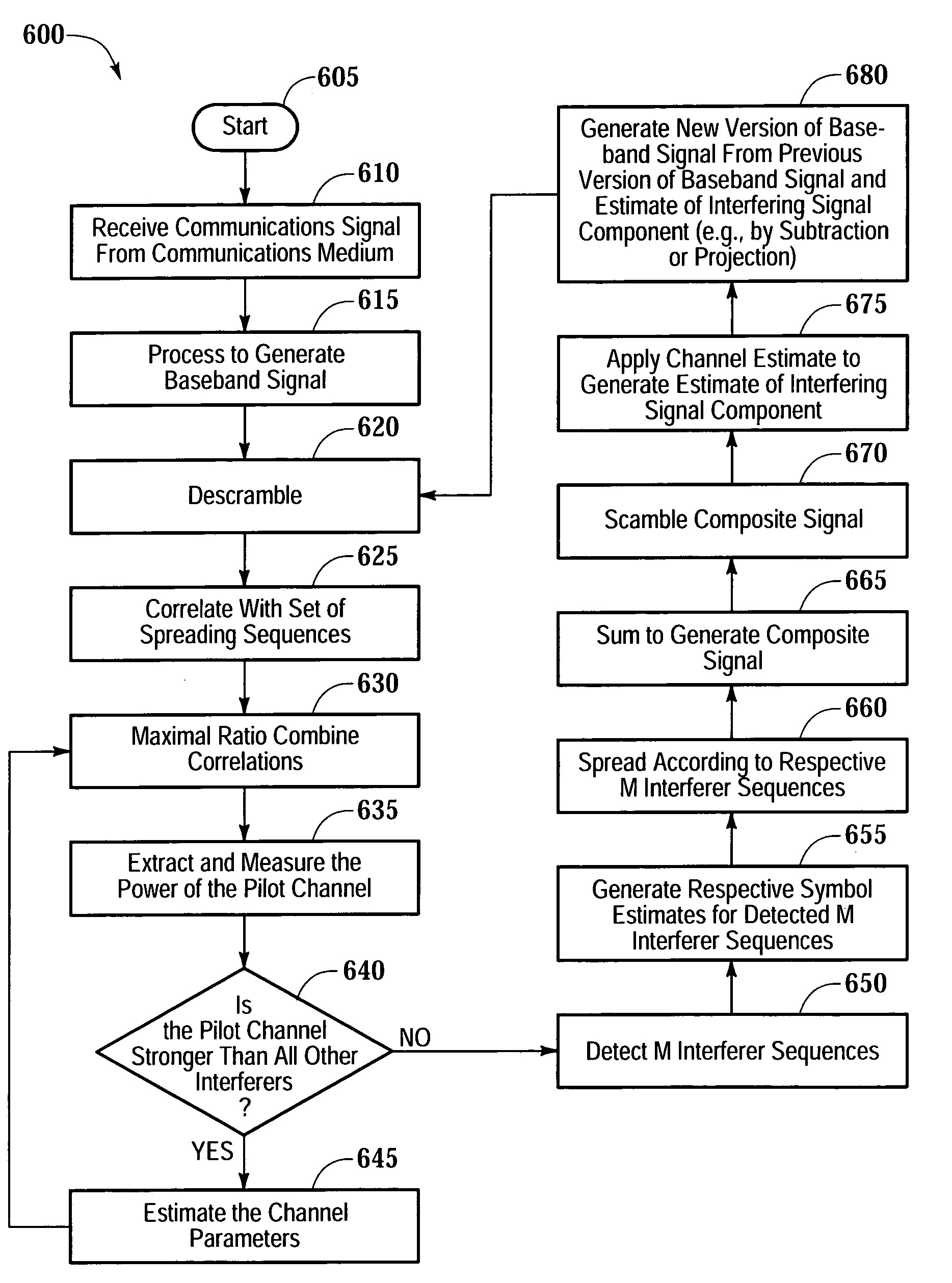
System, method and apparatus for wireless channel parameter estimation in spread spectrum communication systems
ActiveUS7012977B2Accurate estimateEliminate the effects ofError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemChannel parameter
The present invention provides a system, method and apparatus for estimating channel parameters in spread spectrum communication systems. A first method is accomplished by receiving a base station signal and then demodulating the base station signal. After demodulating the base station signal, a maximum signal is selected from the base station signal. If the maximum signal is the common pilot channel, then the channel parameters are estimated directly from the common pilot channel. If the maximum signal is not the common pilot channel, then the demodulated base station signal is iteratively fed back for further demodulation and re-selection of the maximum signal until the maximum signal is the common pilot channel. A second method is accomplished by incorporating channel estimates made from the interfering signals in a constructive manner to the first method.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
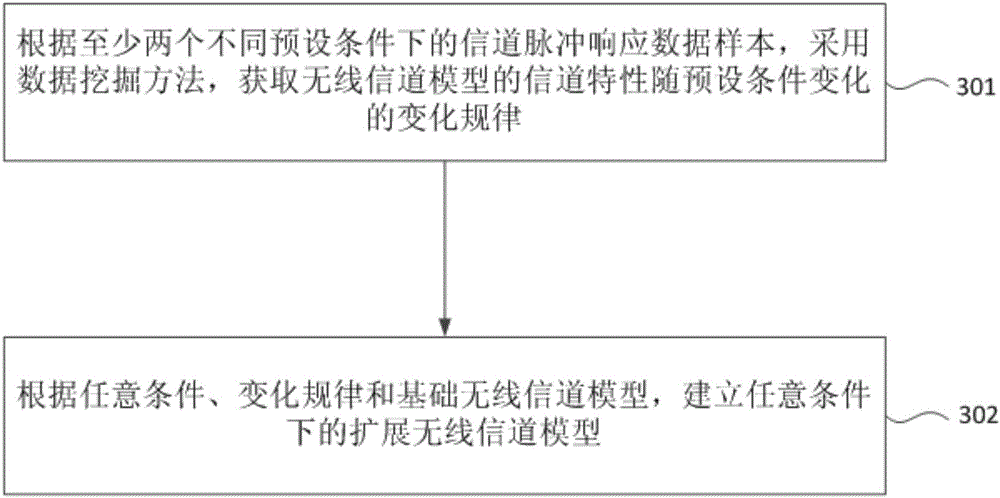
Big data mining-based wireless channel modeling method
ActiveCN106126807AImprove accuracyReduce complexityTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsChannel parameterSimulation
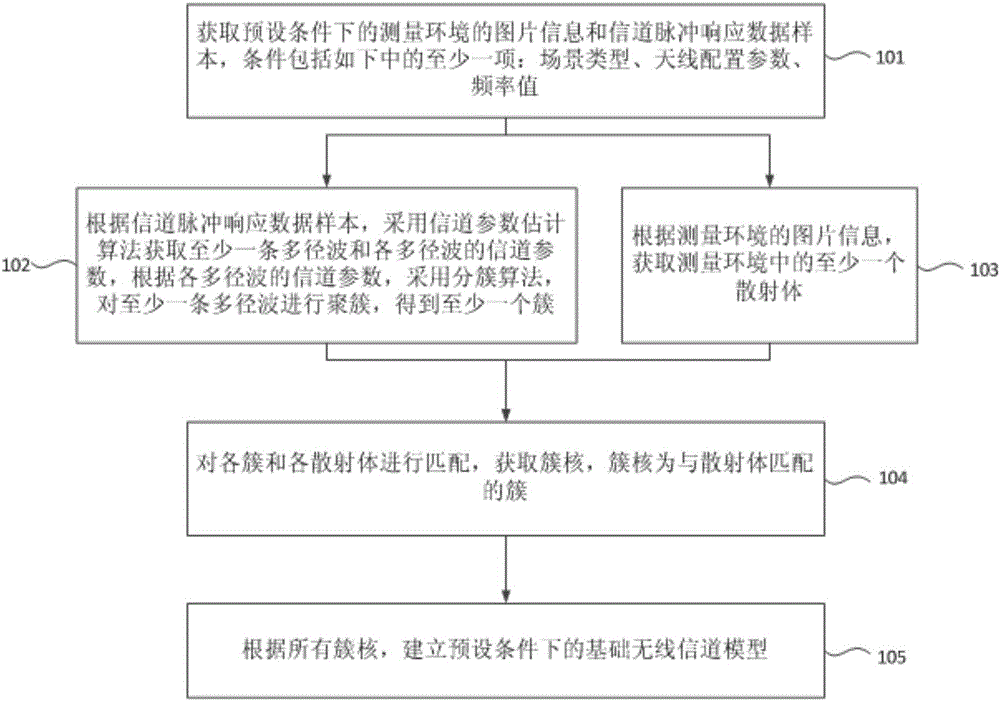
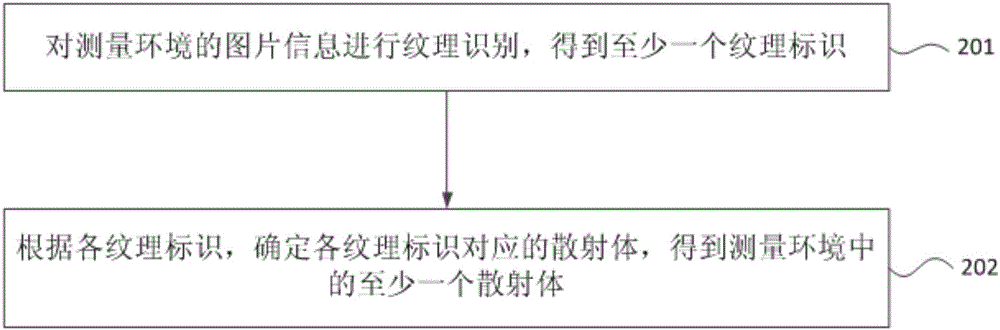
The invention provides a big data mining-based wireless channel modeling method. The method comprises the steps of obtaining picture information of a measurement environment and a channel pulse response data sample under a preset condition; obtaining at least one multipath wave and channel parameters of each multipath wave by adopting a channel parameter estimation algorithm, and obtaining at least one cluster according to the channel parameters of each multipath wave; obtaining at least one scattering body in the measurement environment according to the picture information of the measurement environment; performing matching on each cluster and each scattering body to obtain a cluster core, wherein the cluster core is the cluster matched with the scattering body; and building a basic wireless channel model under the preset condition according to all cluster cores. According to the method, the calculation amount is reduced and the accuracy of wireless channel modeling is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
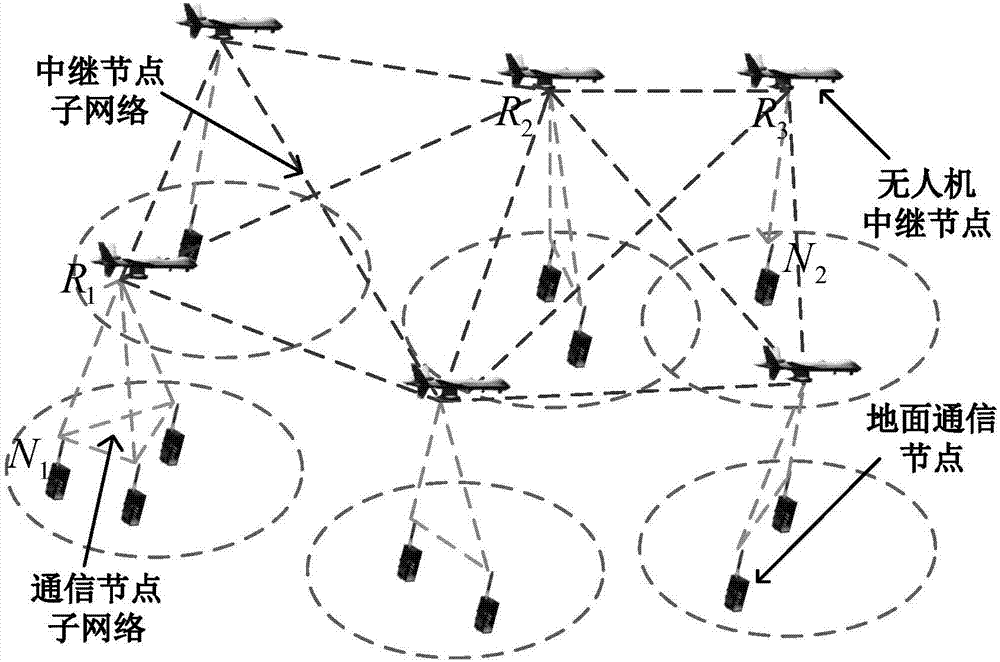
Large-scale UAV relay network channel simulation device and GPU real-time simulation method
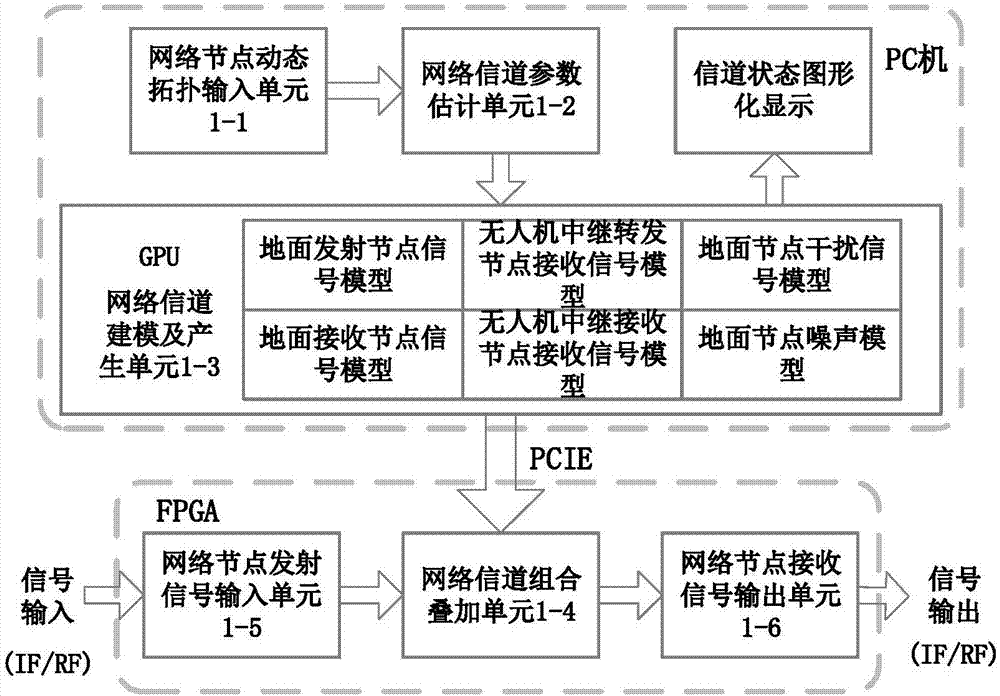
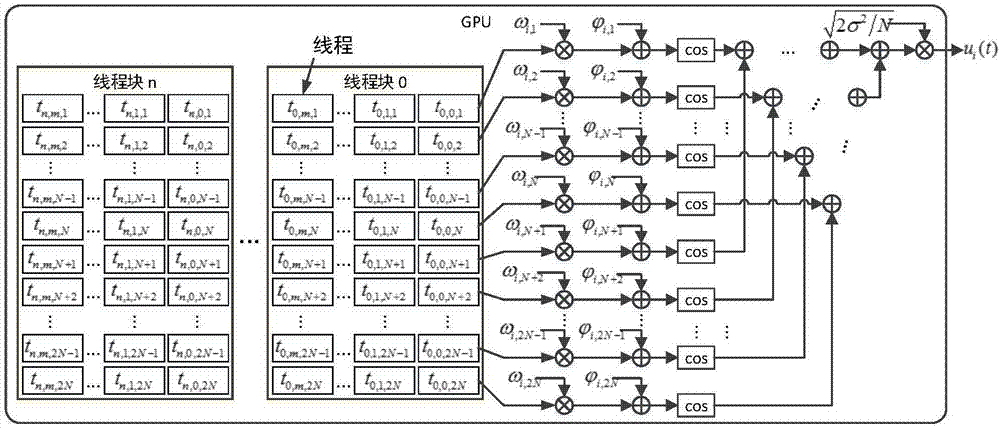
ActiveCN107579789ASupport dynamic adjustmentSimplify complexityTransmission monitoringNetwork sizeReal-time simulation
The invention discloses a large-scale UAV relay network channel simulation device and a GPU real-time simulation method. The large-scale UAV relay network channel simulation device includes a networknode dynamic topology parameter input unit, a network channel parameter estimation unit, a network channel modeling and generating unit, a network channel combination superposition unit, a network node transmitting signal input unit and a network node receiving signal output unit. The simulation system is flexible and general, and supports the dynamic adjustment of the network size and topology structure; the signal, interference and noise of each relay link are modeled using the equivalent method, the complexity of system simulation is greatly simplified; and for different communication scenes, different nodes are supported to adopt different channel models and updated in real time, the mutual interference between network nodes are considered.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Multi-antenna interference rejection combining method and device
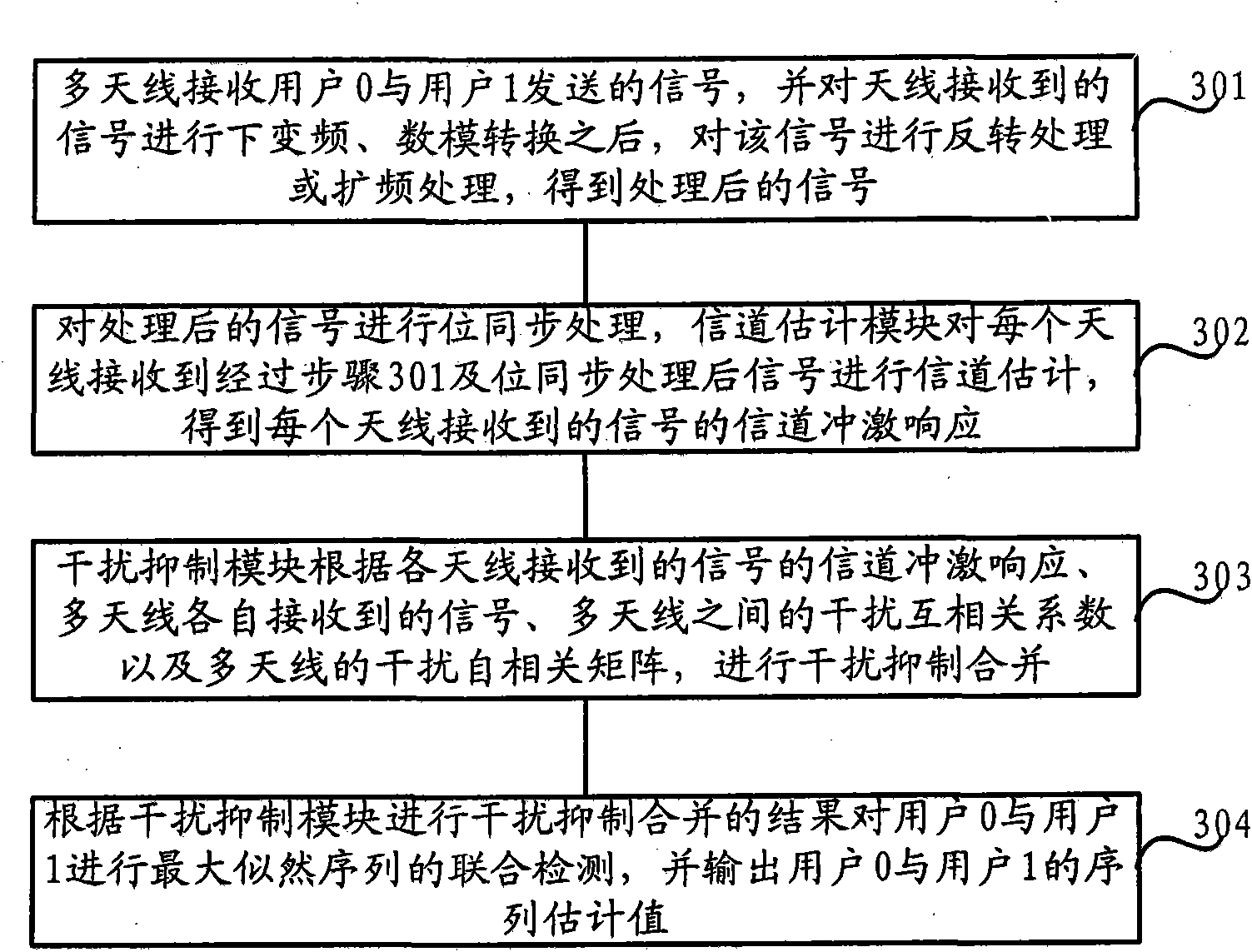
InactiveCN102104562AImprove accuracyInhibition is effectiveSpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksChannel parameterChannel parameter estimation
The invention discloses a multi-antenna interference rejection combining method and a multi-antenna interference rejection combining device, which aim to solve the problem of relatively lower system performance caused by relatively lower signal modulation accuracy in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: performing channel estimation on signals received by each of a plurality of antennae, and determining estimated channel parameter values of the signals received by each antenna, wherein each of the plurality of antennae receives the signals from a plurality of users; andperforming interference rejection combination according to the estimated channel parameter values of the signals received by each antenna, the signals received by each antenna and an interference autocorrelative matrix of the plurality of antennae, performing joint detection on the plurality of users according to interference rejection combining results and obtaining own estimated sequential values of the plurality of users. By the technical scheme of the invention, the signal modulation accuracy is improved, and the system performance is further improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Channel parameter estimation method and system
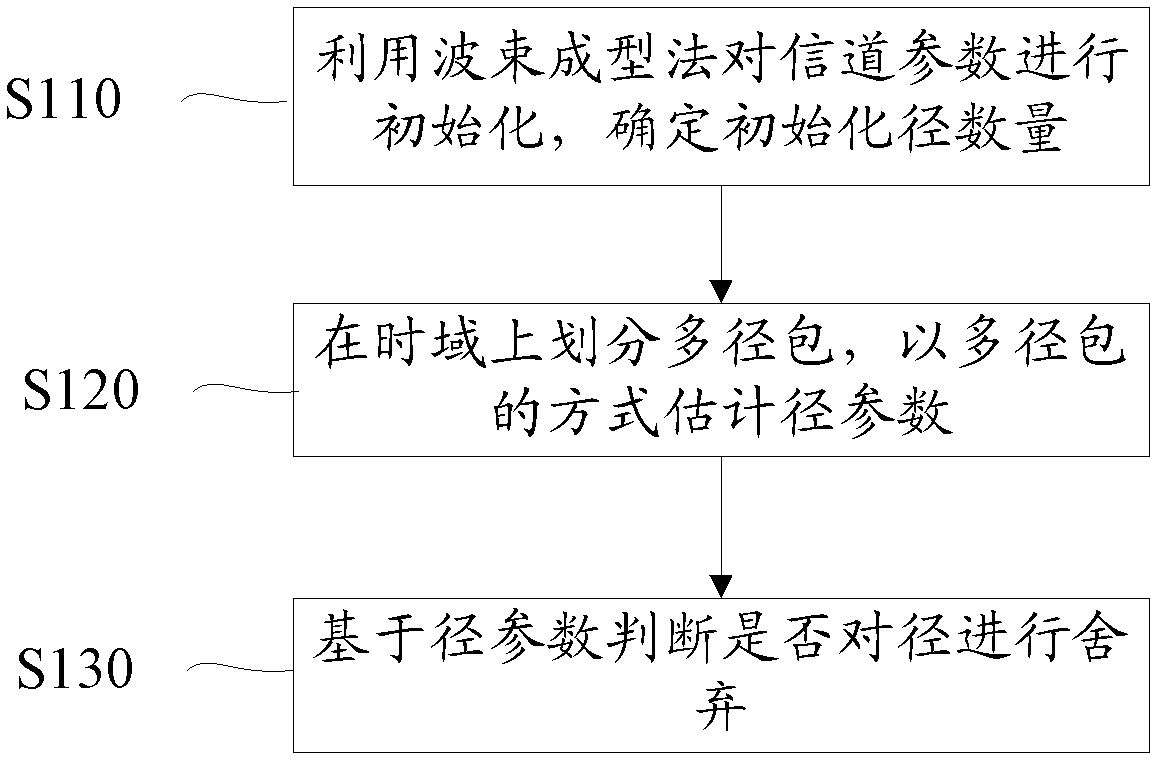
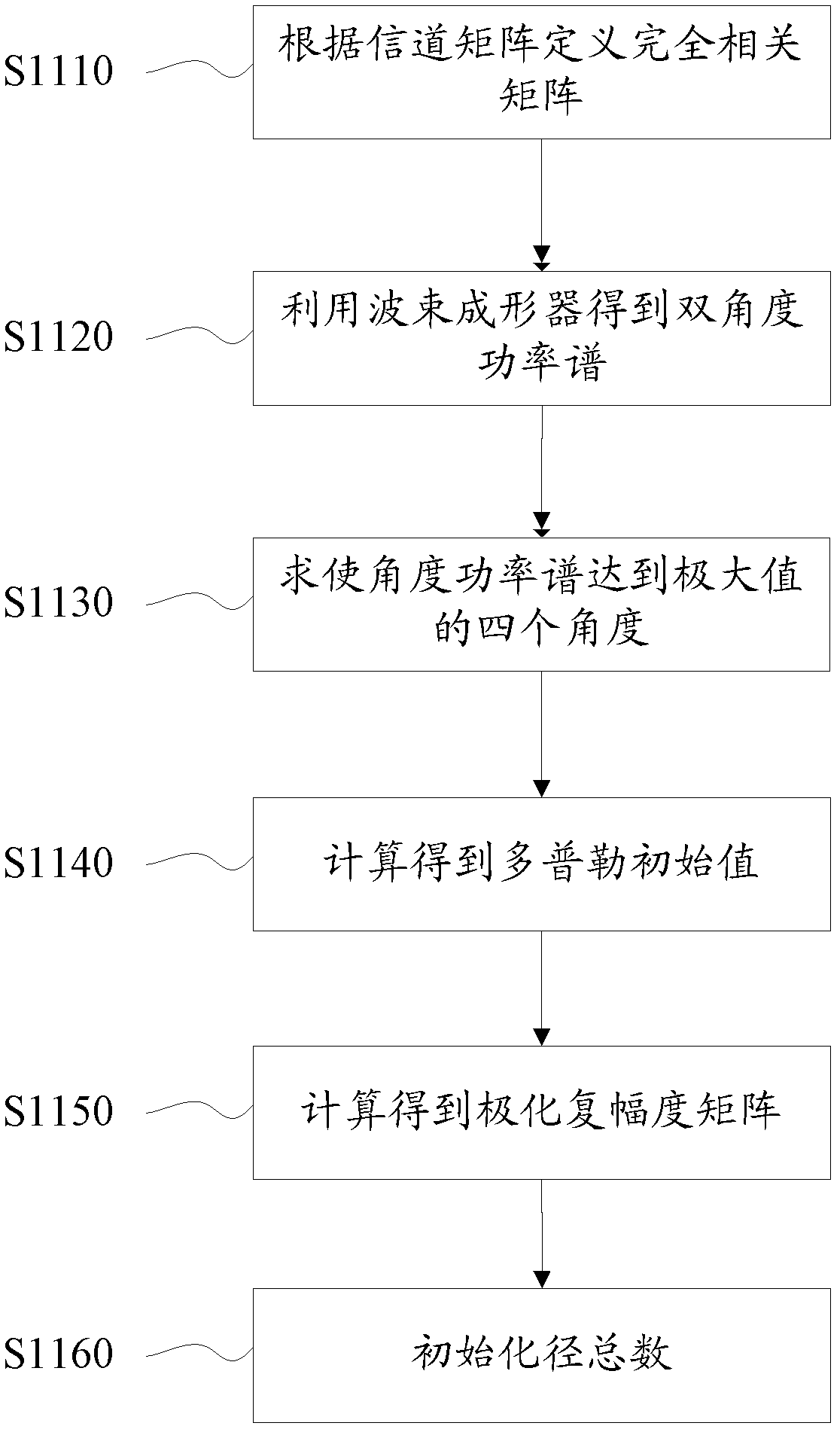
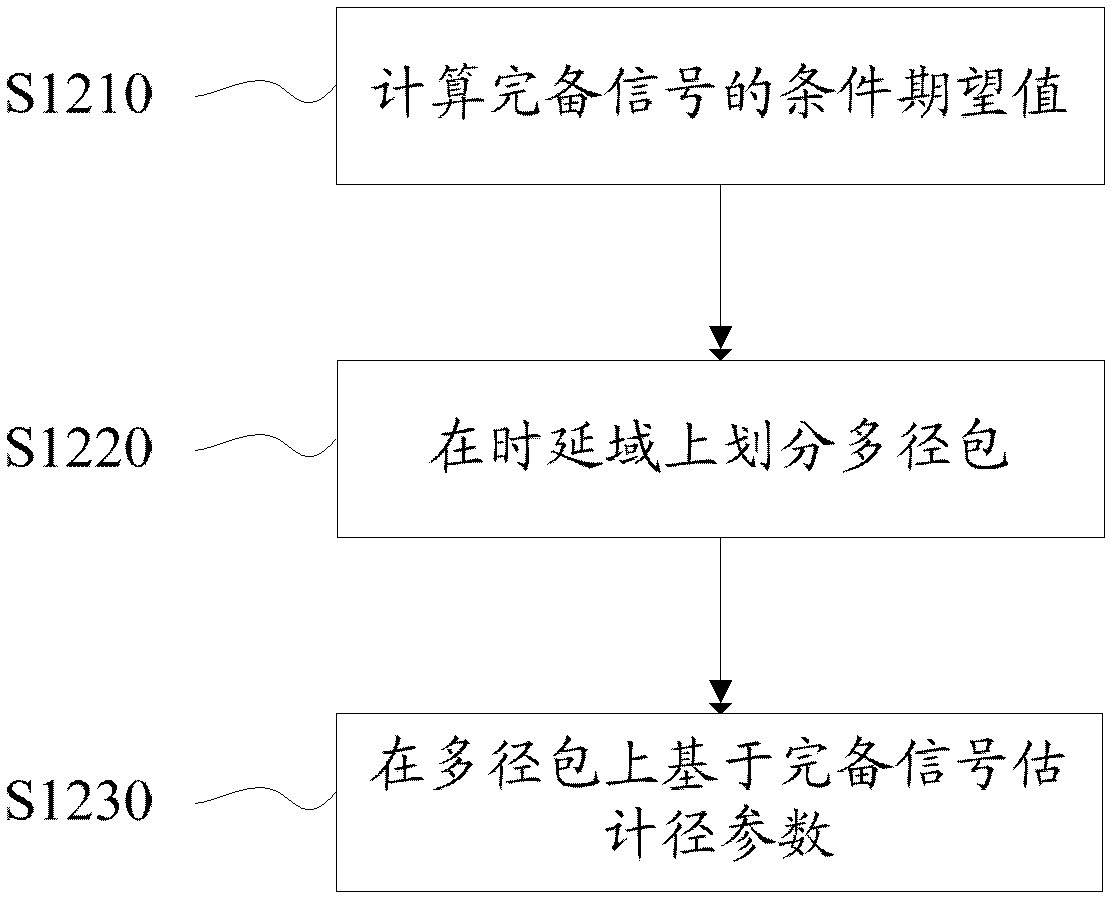
ActiveCN102307165AImprove estimation performanceIn line with the transmission mechanismSpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsTime delaysAlgorithm
The invention discloses a channel parameter estimation method and a channel parameter estimation system. The method comprises the following steps of: A, initializing a channel by utilizing a beamforming method to obtain initial values of a channel parameter set, and determining an initialized path number; B, dividing a multi-path packet in a time delay domain, and performing parameter estimation on paths in the initialized path number in a multi-path packet way based on the initial values of the channel parameter set to obtain parameter sets of each selected path; and C, judging whether the paths are abandoned or not based on the estimated parameter sets of each path. The method and the system are more consistent with a transmission mechanism in which the paths exist in clusters in a wideband system, and are applied to the processing of massive data; and arithmetic speed is increased.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
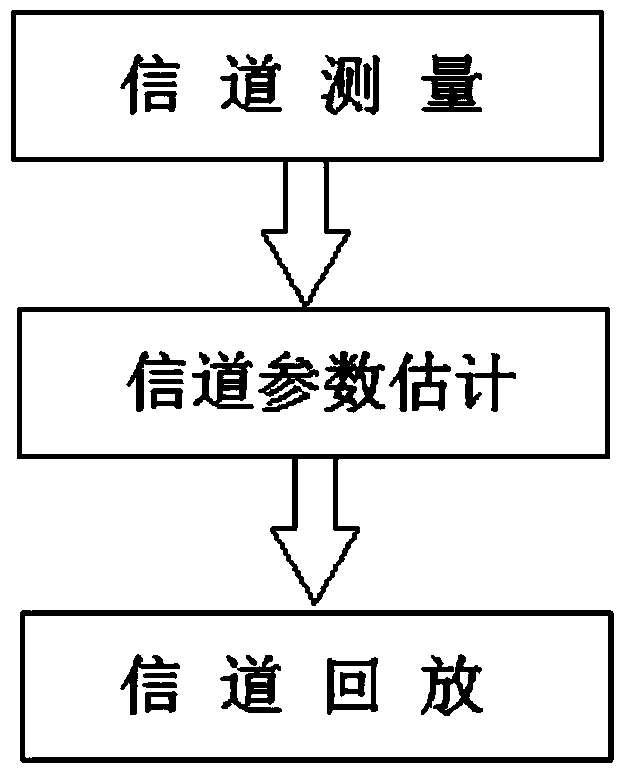
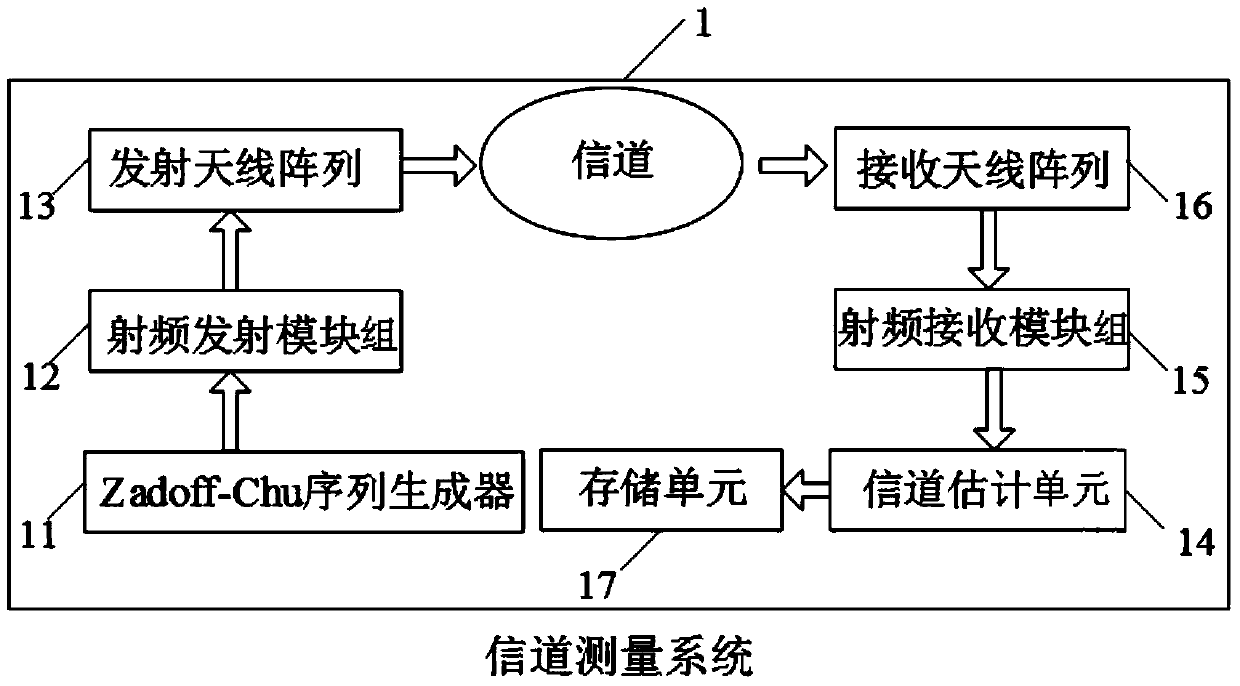
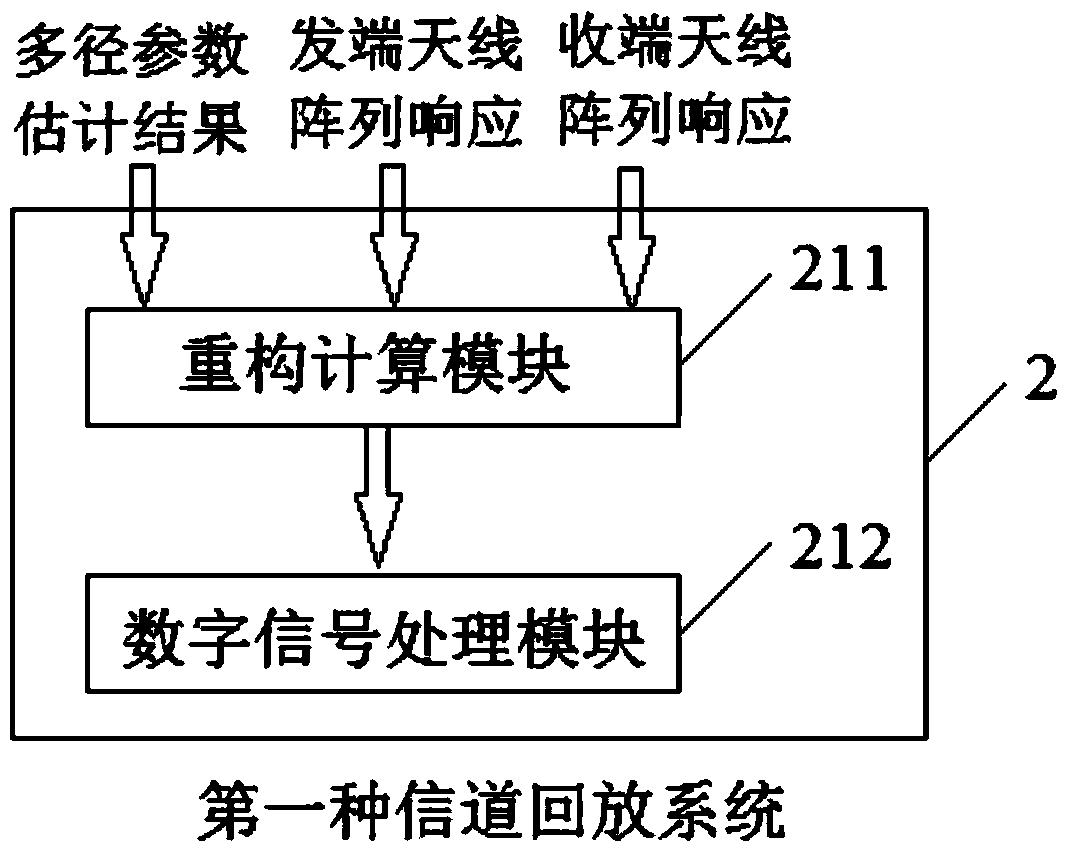
Channel data playback method and device
ActiveCN104618041AFully documentedEliminate the effects of measuring antenna responsePropogation channels monitoringChannel parameterRadio frequency
The invention discloses a channel data playback method and device. The method includes the steps: measuring a channel; estimating channel parameters; playing back the channel. The device comprises a channel measurement and channel playback system. Two playback methods and corresponding playback systems are provided according to whether a microwave chamber is used for OTA (over-the-air) playback or not. An antenna array in the measuring system is optimized, and multipath channel characteristics are sufficiently recorded by the aid of technologies such as Zadoff-Chu sequence and parallel reception, the multipath channel characteristics are accurately estimated by the aid of multipath parameter estimation algorithms such as particle swarm optimization, so that antenna response in recorded channel impact response is eliminated. In channel playback, an equivalent channel between transmitting and receiving radio frequency ports can be directly reconstructed for recovery, a channel between a base station radio frequency port and a terminal communication field can be reconstructed, and the microwave chamber with an intensive antenna probe and a corresponding antenna switching unit is used for playback by the aid of OTA technology.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Channel modeling method and parameter matching method based on non-uniform scatterer distribution
InactiveCN103747455AImprove resource utilization efficiencyIncrease capacityHigh level techniquesNetwork planningChannel parameterResource utilization
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
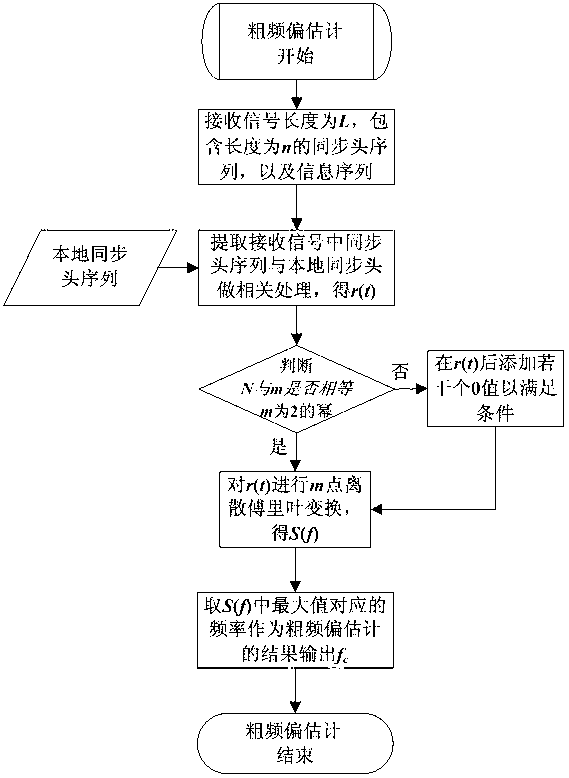
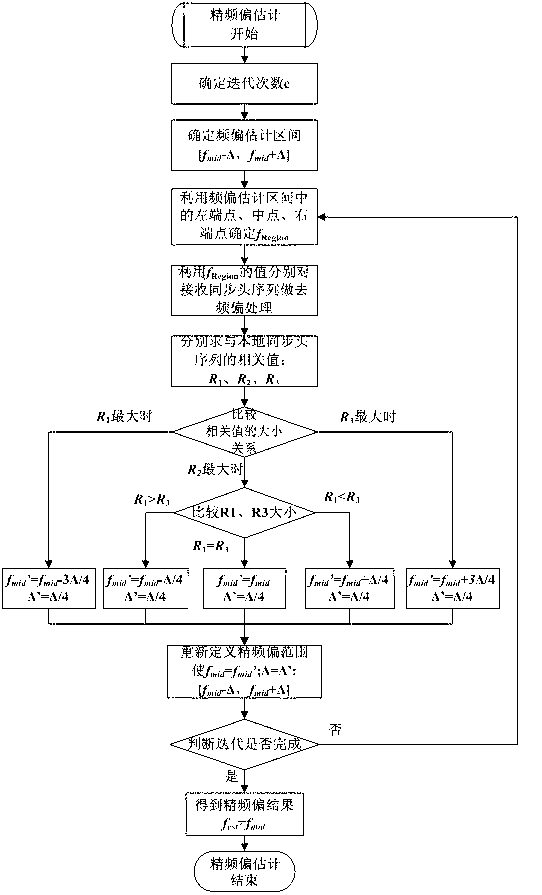
Carrier frequency offset estimation method applicable to burst waveforms
ActiveCN103023831ANarrow down the frequency offset estimation intervalHigh precisionBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Channel parameter
The invention belongs to the field of estimation of wireless channel parameters, particularly relating to a carrier frequency offset estimation method applicable to burst waveforms. Both communication parties are required to have known information sequences (synchronous head sequences), and then two steps of coarse frequency offset estimation and fine frequency offset estimation are carried out by means of the synchronous head sequences. According to the method, the number of iterations of the frequency offset estimation can be determined in a self-adaptive manner according to the length of signal synchronous heads, the duration of receiving signals, signal-to-noise ratios and the like; and the frequency offset estimation intervals are gradually narrowed by means of high correlation of the synchronous head sequences, and the precision of the frequency offset estimation is improved.
Owner:NO 722 RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
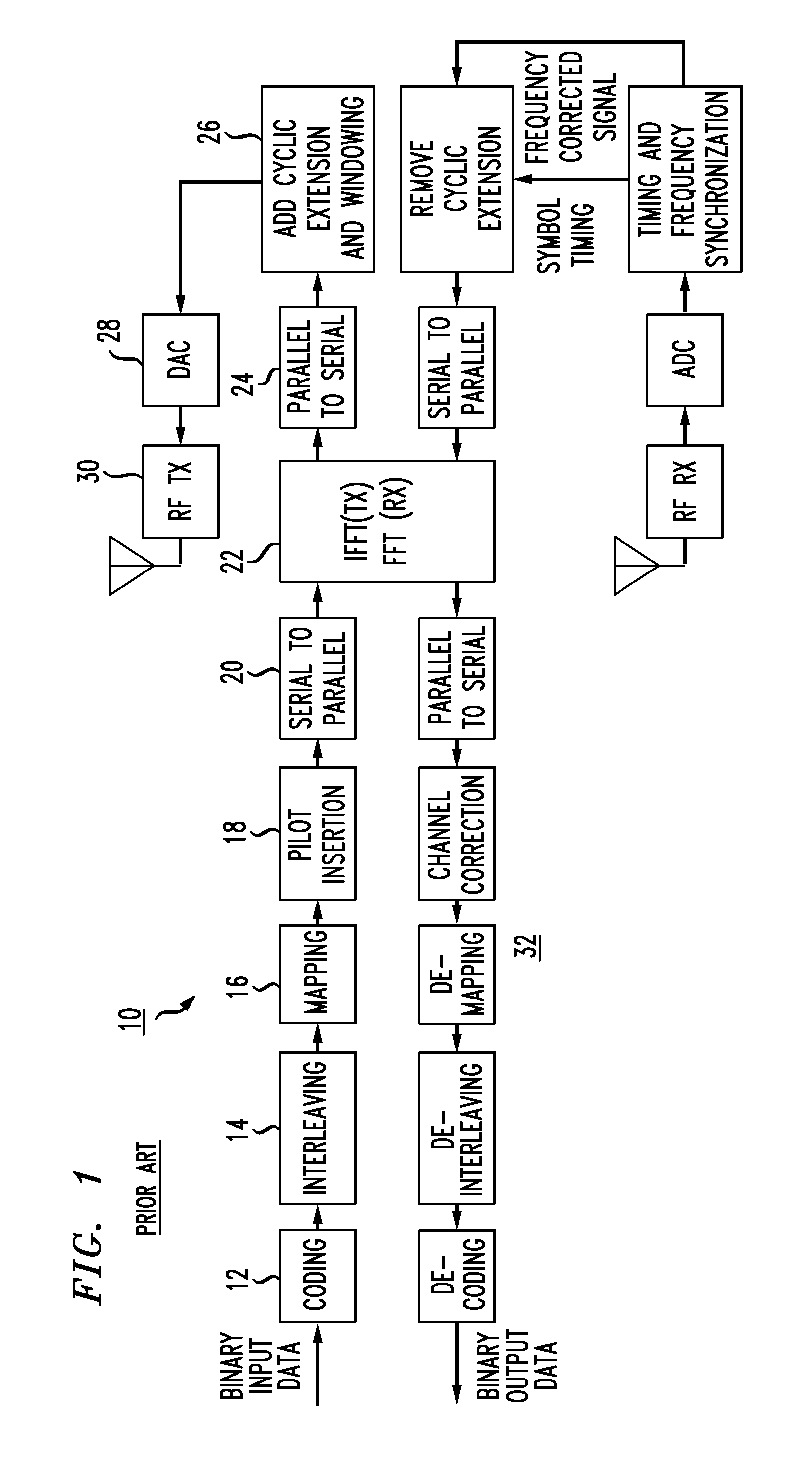
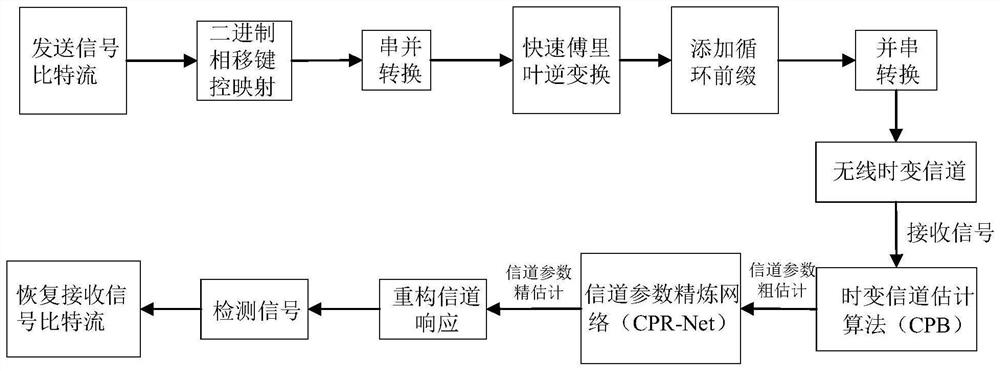
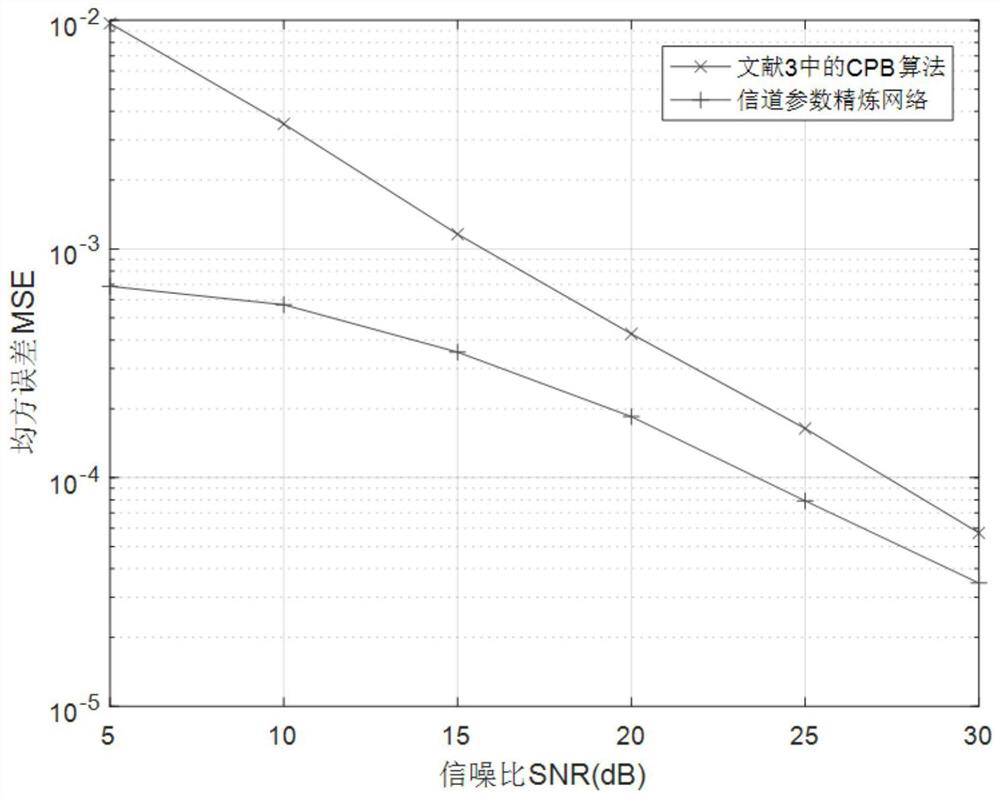
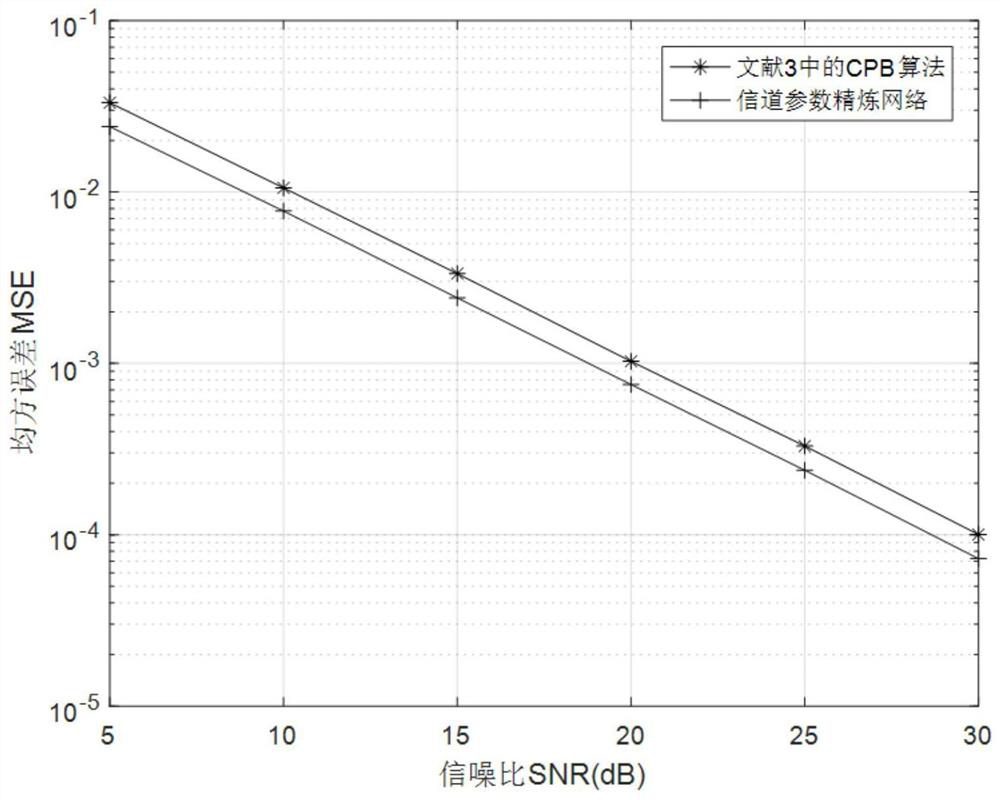
Time-varying OFDM system channel estimation method based on deep learning
InactiveCN111683024AAchieve refinementImprove estimation accuracyBaseband system detailsNeural architecturesCyclic prefixEngineering
The invention provides a time-varying OFDM system channel estimation method based on deep learning. The system randomly generates a sending data signal bit stream; forming a sending frame with a training symbol; carrying out binary phase shift keying modulation; performing inverse fast Fourier transform; adding a cyclic prefix to overcome inter-symbol interference, carrying out serial-to-parallelconversion, obtaining a received signal through a fast time-varying OFDM channel and noise addition, constructing and training a CPR-Net model, generating more accurate Doppler frequency shift, and after channel reconstruction response is carried out, recovering a received signal bit stream through signal detection. According to the invention, the deep learning method is introduced into the fast time-varying OFDM system, and the channel estimation and signal detection performance in the fast time-varying OFDM system is improved by using the deep neural network, so that the channel parameter estimation precision and the overall bit error rate performance of the system are improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
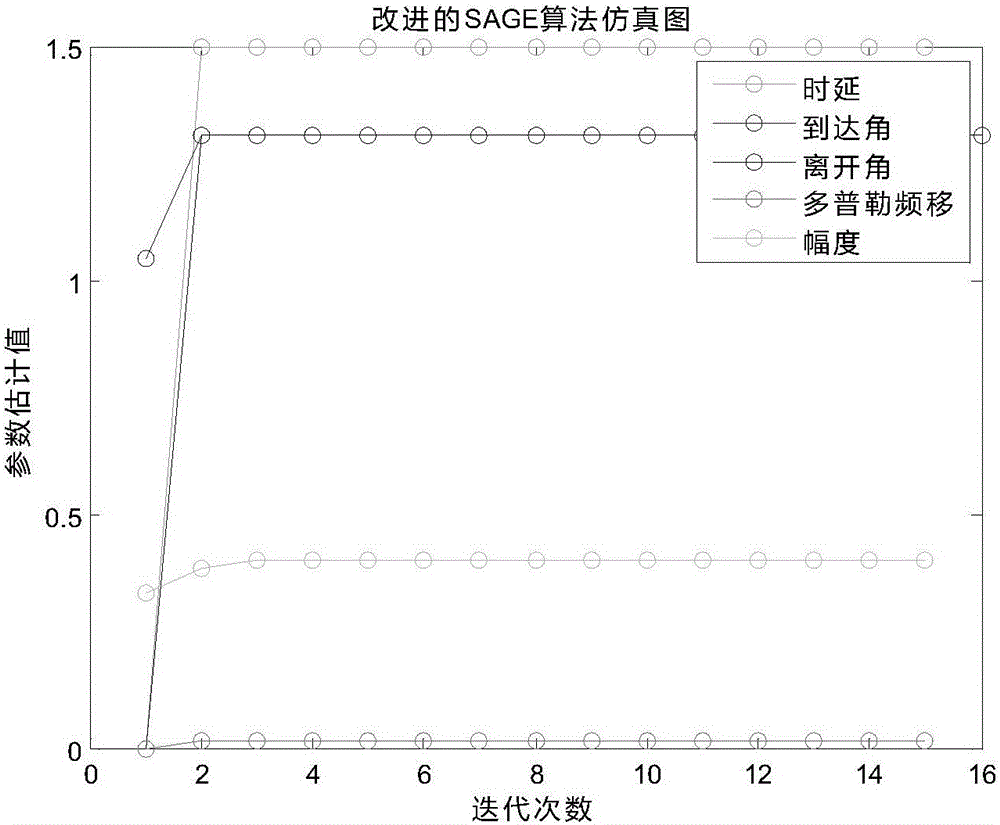
Channel parameter estimation method based on improved SAGE algorithm
ActiveCN105939299AAccurate estimateImprove calculation accuracyChannel estimationInterference eliminationAlgorithm
The invention discloses a channel parameter estimation method based on an improved SAGE algorithm. The method comprises the steps of processing receiving signals by use of a continuous interference elimination principle and carrying out initialization estimation by use of an incoherent maximum likelihood estimation method; synthesizing initialized parameter results into simulated receiving signals; defining the difference between the original receiving signals and the obtained simulated receiving signals as an Euclidean distance, and calculating a partial interference factor by assuming that the Euclidean distance is the minimum; substituting the partial interference factor into a corresponding formula, processing the receiving signal by use of a partial interference elimination mode, and obtaining a final initialization result by use of the incoherent maximum likelihood estimation method; calculating a Z function, substituting the final initialization result into the corresponding formula, carrying out iteration update, and finding a point which enables the value of the Z function to be maximum as a reference estimation result. According to the method provided by the invention, the calculation precision is high; under the condition that the integral convergence performance is improved, the channel features of actual channels can be estimated relatively accurately; the calculation effect is good; and the defects in the prior art are solved.
Owner:盛航(台州)科技有限公司
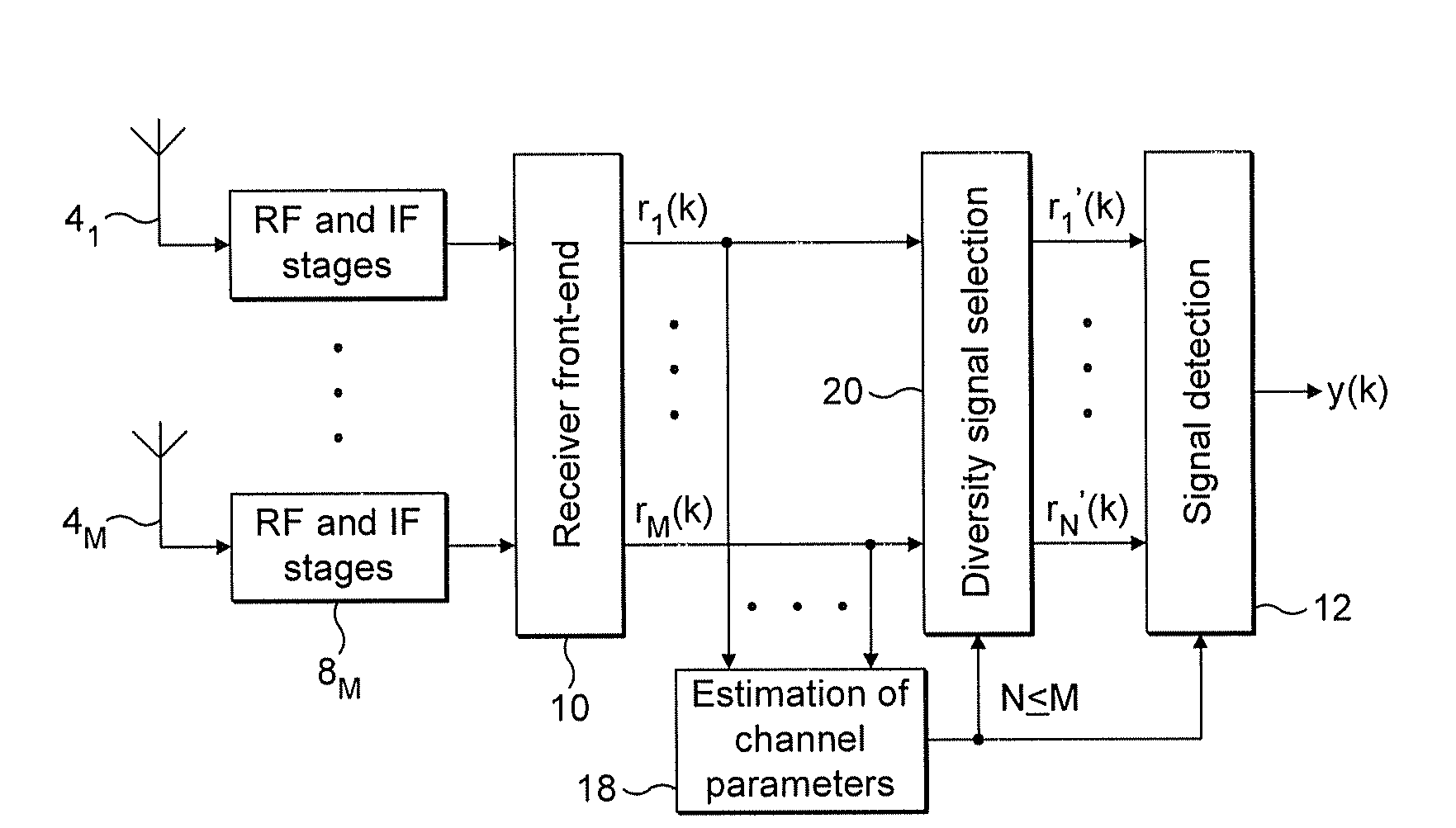
Wireless Receiver with Receive Diversity
ActiveUS20090111542A1Raise the ratioGood correlationSpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentChannel parameterEngineering
Wireless receivers are described for receiving signals from a transmitter. A receiver can include a plurality of antennas each for receiving a version of a signal via a different propagation channel and providing that version to a respective input. Signal processing means can be included and configured to operate diversity processing of a supplied number of said inputs for use in performing detection of said signal. The receiver can include channel parameter estimation means, configured to estimate one or more channel parameters on the propagation channels. The receiver can also include selection means configured to select only a subset of said inputs to implement a specific dimensionality of the receiver diversity processing, in dependence on the one or more channel parameters indicative of channel conditions on said propagation channels. The diversity processing can be linear or non-linear. Related methods and software implementations and computer program products are also described.
Owner:ICERA INC
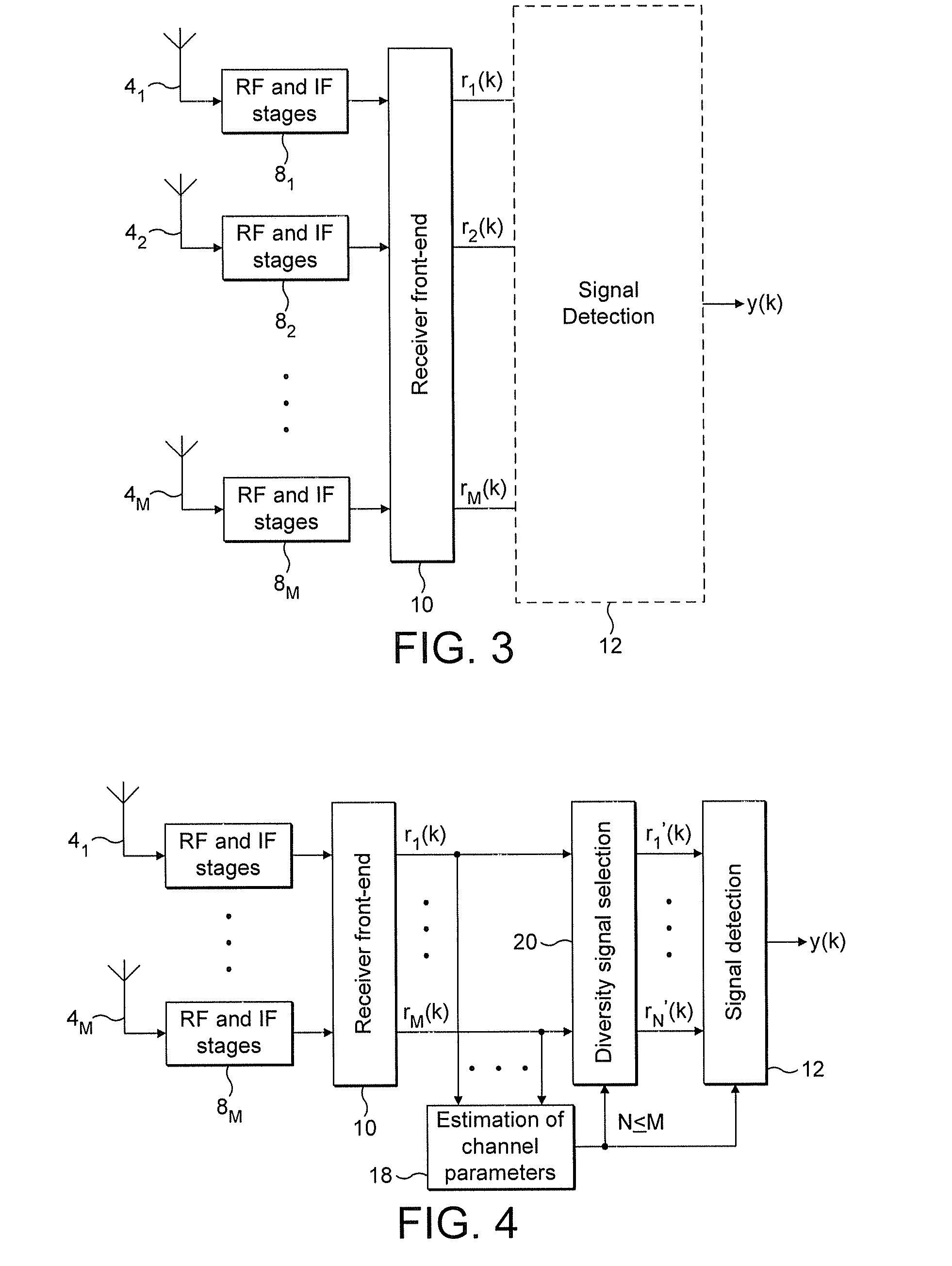
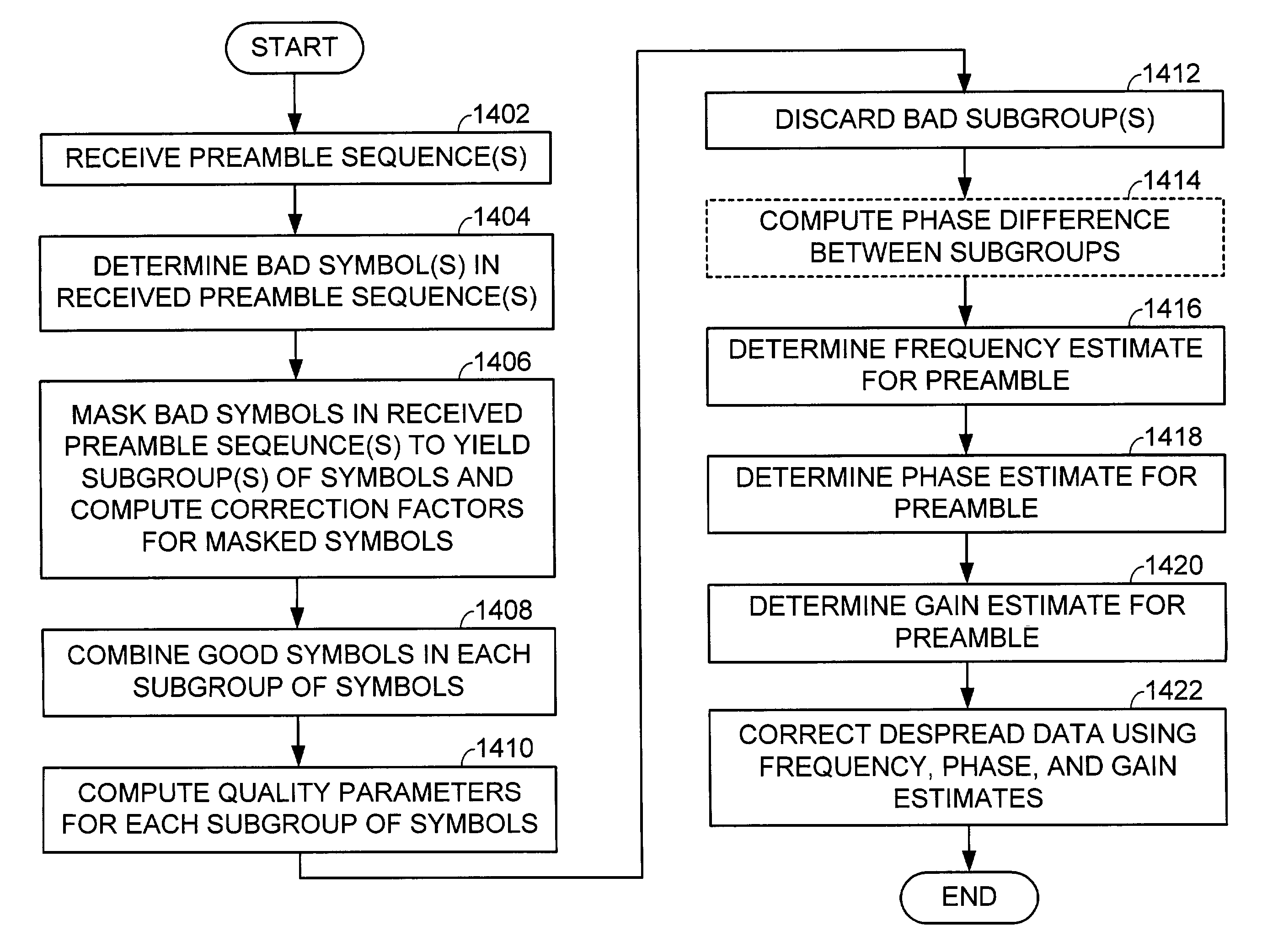
Enhanced channel parameter estimation in the presence of preamble erasures
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Partial symmetric extension discrete Fourier transform-based channel estimation method
InactiveCN102143115AImprove performanceImprove the problem of carrier performance deteriorationBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsSymmetric extensionPartial symmetry
The invention discloses a partial symmetric extension discrete Fourier transform-based channel estimation method, which comprises the following steps of: performing primary least square (LS) channel estimation on a frequency domain received signal on a preamble sub-carrier to obtain a primary LS channel parameter estimate; performing partial symmetric extension on the primary LS channel parameterestimate; performing inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT) of a corresponding point number on the LS channel parameter estimate subjected to the partial symmetric extension to obtain an intra-transform domain equivalent channel parameter estimate; performing filtering processing on the intra-transform domain equivalent channel parameter estimate to obtain a more accurate channel parameter estimate; performing discrete Fourier transform (DFT) on the filtered intra-transform domain equivalent channel parameter estimate to obtain a frequency domain channel estimate of a partial symmetric extension sequence; performing inverse extension on the frequency domain channel estimate of the partial symmetric extension sequence to obtain a channel estimate at the preamble sub-carrier; and performing row interpolation on the channel estimate at the preamble sub-carrier to obtain the frequency domain channel estimates at all sub-carriers.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
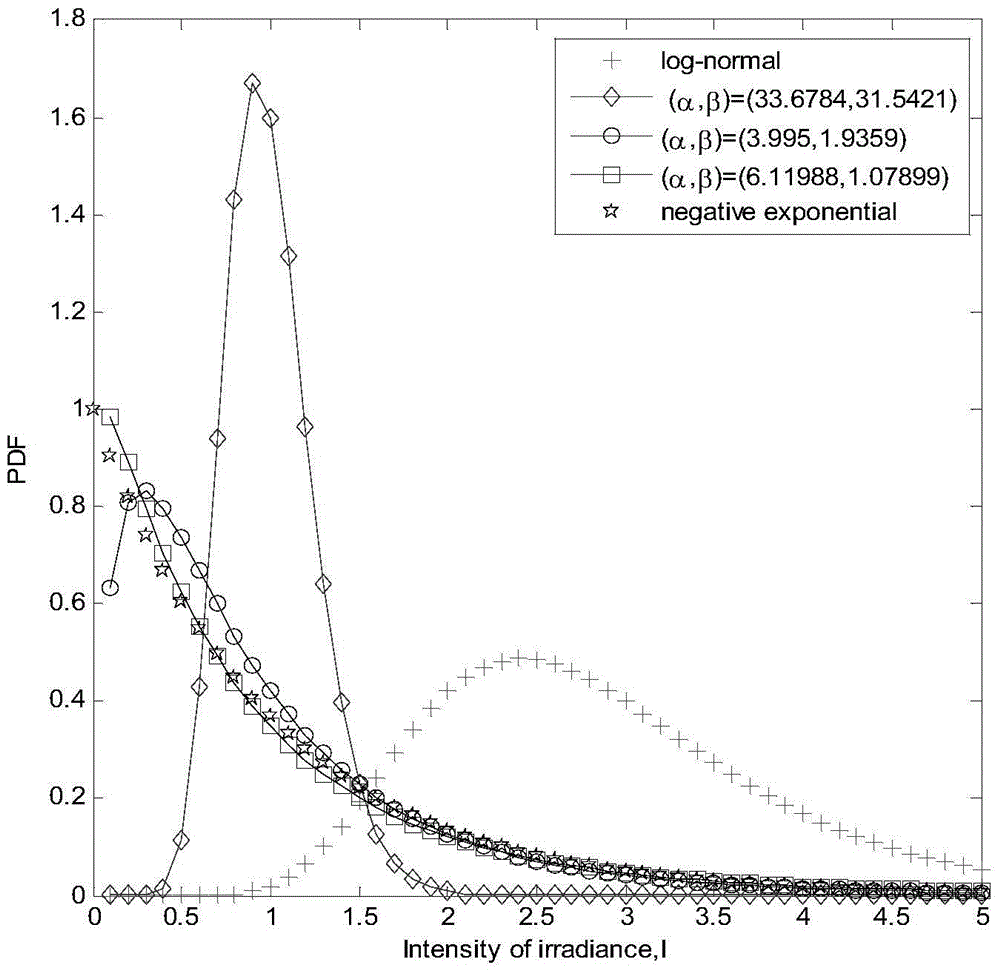
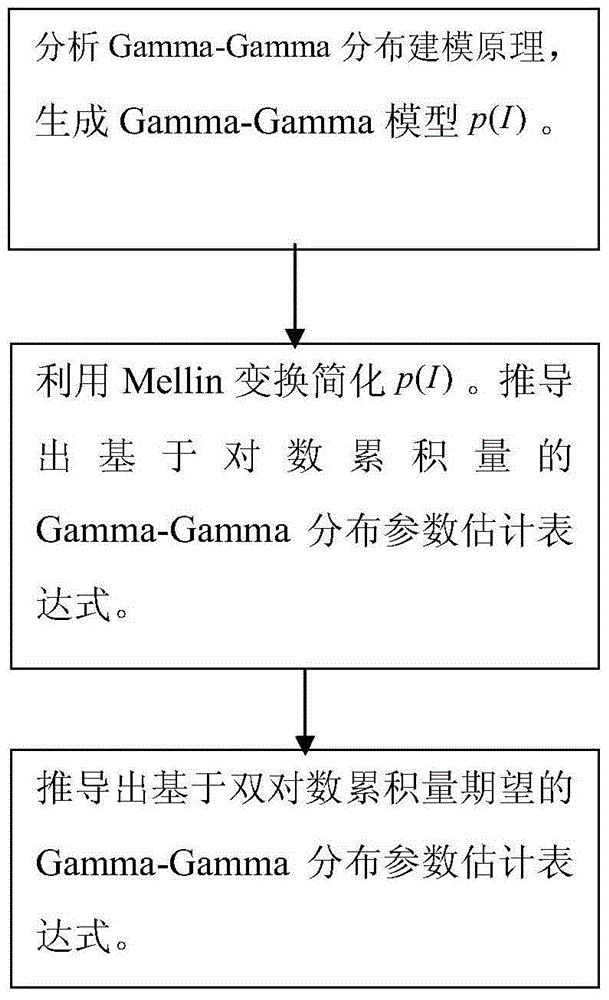
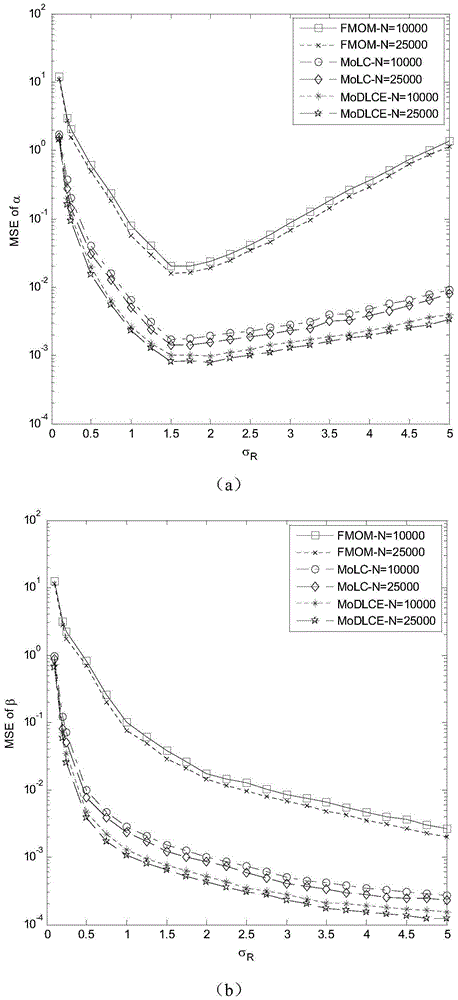
Gamma-Gamma distribution parameter estimation method based on double logarithmic cumulant expectation
ActiveCN105743593AImprove estimation accuracyImprove computing efficiencyTransmission monitoringFree-space transmissionAlgorithmEstimation methods
The invention relates to a Gamma-Gamma distribution parameter estimation method based on a double logarithmic cumulant expectation, and belongs to the technical field of atmospheric turbulence channel parameter estimation of free space optical communication systems. According to the method, a Gamma-Gamma distribution parameter estimation process is simplified greatly through Mellin transform, and a uniform parameter estimation method is built specific to the problems of low fractional moment (FMOM) parameter estimation accuracy and even error estimation in the prior art. Then, further improvements are made, and a concept of double logarithmic cumulant expectation is put forward, so that a finial parameter estimation expression is deduced. Compared with an FMOM, the Gamma-Gamma distribution parameter estimation method has the advantages that relatively high computing efficiency is ensured, and the parameter estimation accuracy is increased.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Wireless channel real-time simulation method and device in dynamic scene
ActiveCN104144021ARandom and smooth transitionGuaranteed Phase ContinuityTransmission monitoringReal-time simulationState parameter
The invention discloses a wireless channel real-time simulation method and device in a dynamic scene. At first, a user inputs channel dynamic scene parameters of motion tracks of a receiving and sending end, communication scenes and the output channel state update rate; according to the parameters, a channel parameter estimation unit (1-2) carries out parameter estimation on all channel states, and the channel states comprise maximum Doppler frequency shift, multi-path delay and propagation loss; a channel parameter interpolation unit (1-3) carries out determined and randomly mixed interpolation on the estimated parameters of the channel states according to setting of the user; finally, a channel real-time simulation unit (1-4) simulates and generates time-varying channels in real time according to the interpolated channel parameters, a delay tap wire model generates the channel impact response and superposes the channel impact response to input signals sampled through an A / D unit (1-5), and finally output signals are output after being converted through a D / A unit (1-6).
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Estimation method of two-dimensional discrete Fourier transform channel with phase compensation
InactiveCN102130860AImprove estimation performanceOvercome inseparableBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsComputation complexityTime correlation
The invention discloses an estimation method of a two-dimensional discrete Fourier transform channel with phase compensation. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, receiving a frequency domain received signal from a time-frequency two-dimensional pilot frequency subcarrier specific to a system with non-uniform time-frequency two-dimensional pilot frequency distribution; secondly, performing least squares estimation on the frequency domain received signal of the time-frequency two-dimensional pilot frequency subcarrier to obtain an initial channel parameter estimation value of the time-frequency two-dimensional pilot frequency subcarrier; thirdly, performing two dimension discrete Fourier transform with phase compensation on the initial channel parameter estimation value of the time-frequency two-dimensional pilot frequency subcarrier to obtain an equivalent channel parameter in a two-dimension discrete Fourier transform domain; and finally, performing time-frequency two-dimensional interpolation on the channel parameter estimation value of the time-frequency two-dimensional pilot frequency subcarrier to obtain the channel responses of all time-frequency two-dimensional subcarriers. By adopting the estimation method, the calculating complexity is greatly lowered and the channel estimation performance is enhanced by using the time correlation and the frequency correlation of the channel.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com