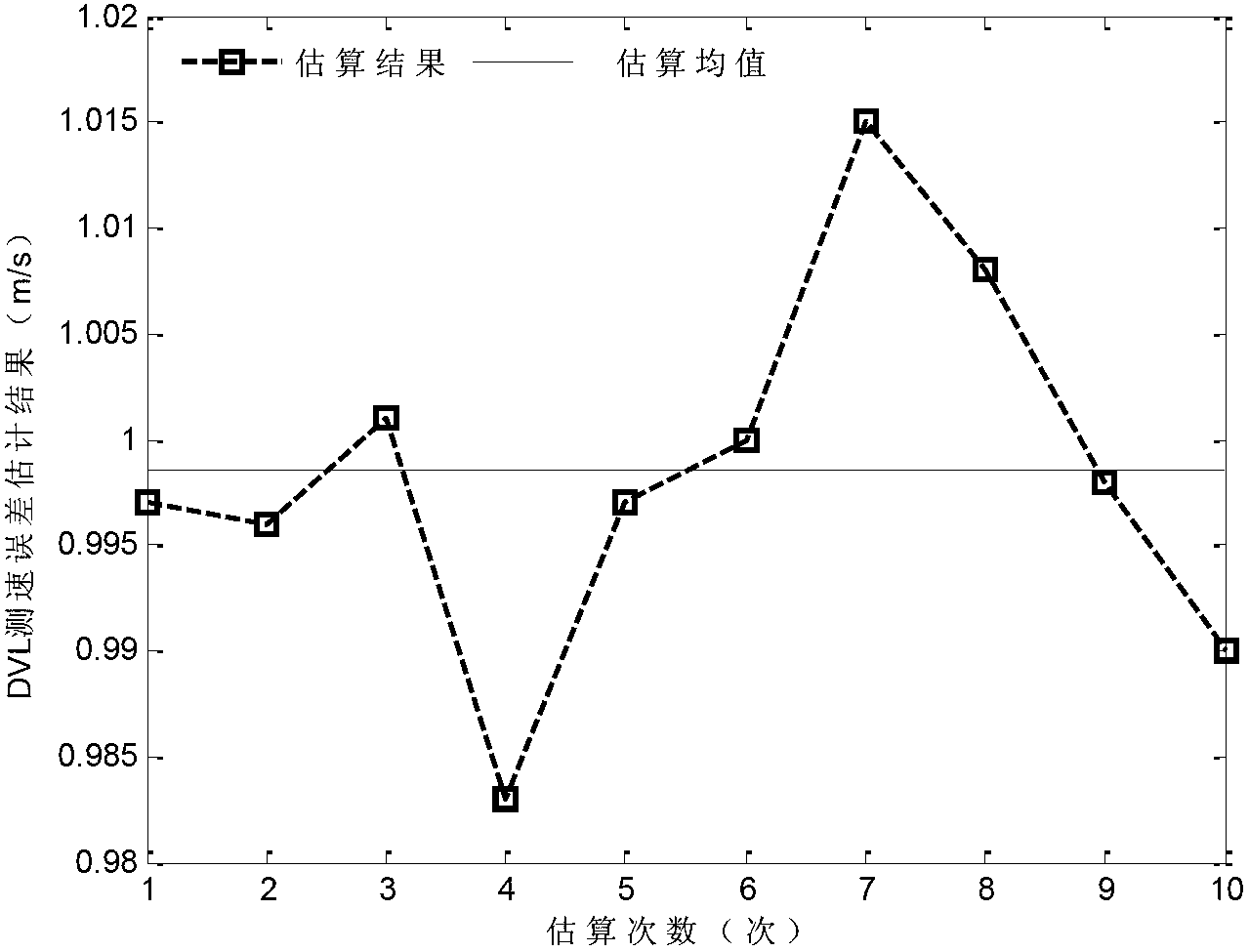
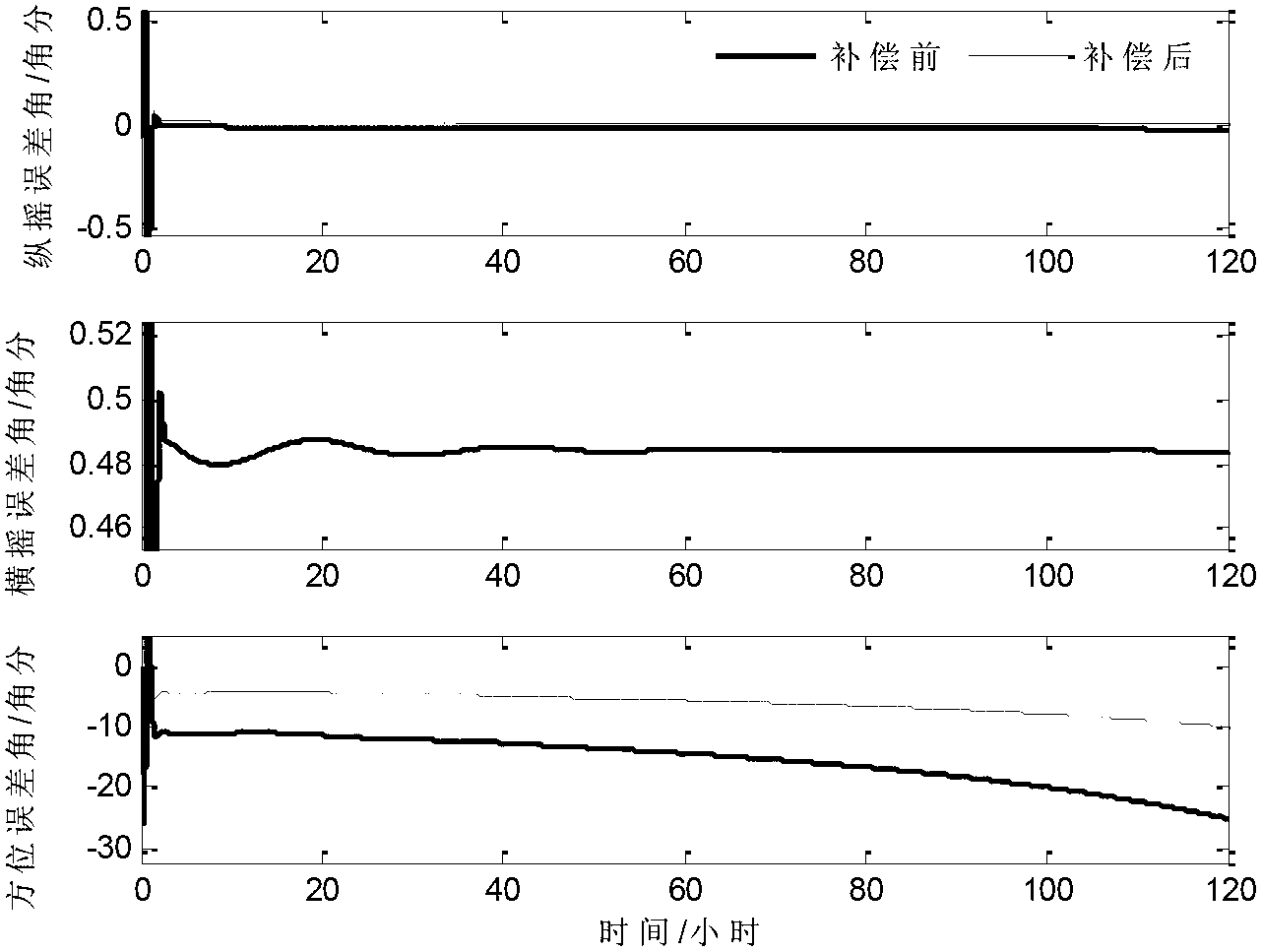
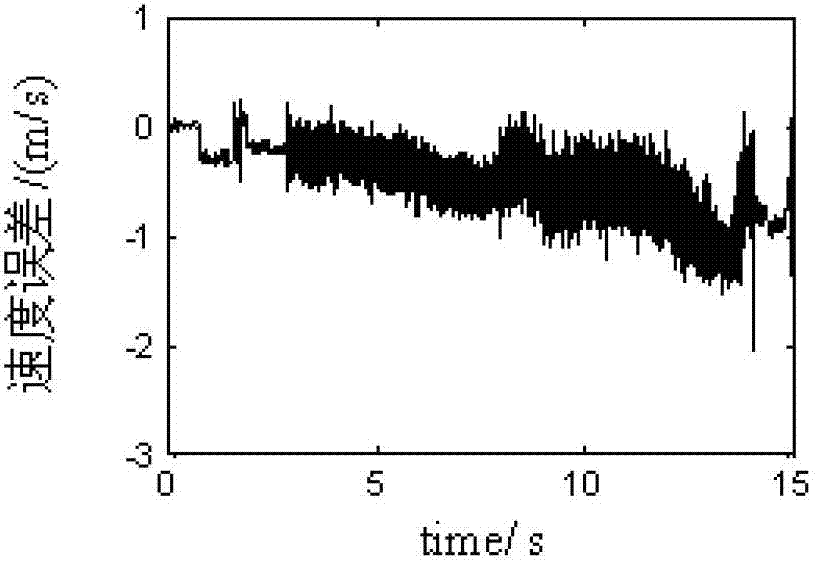
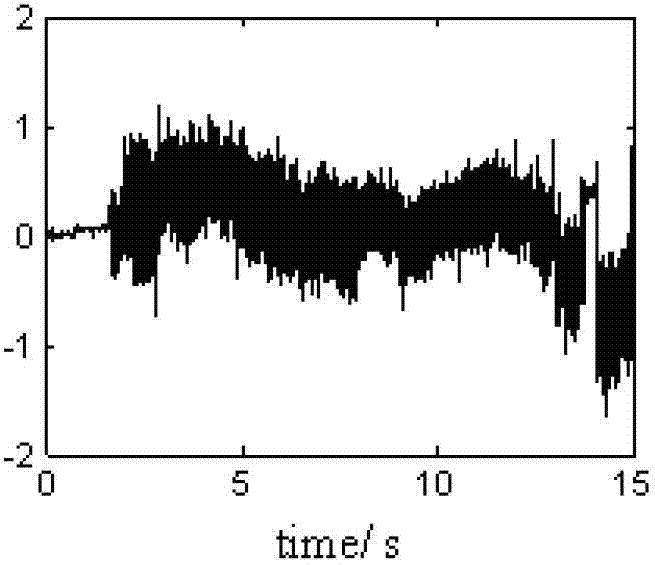
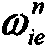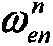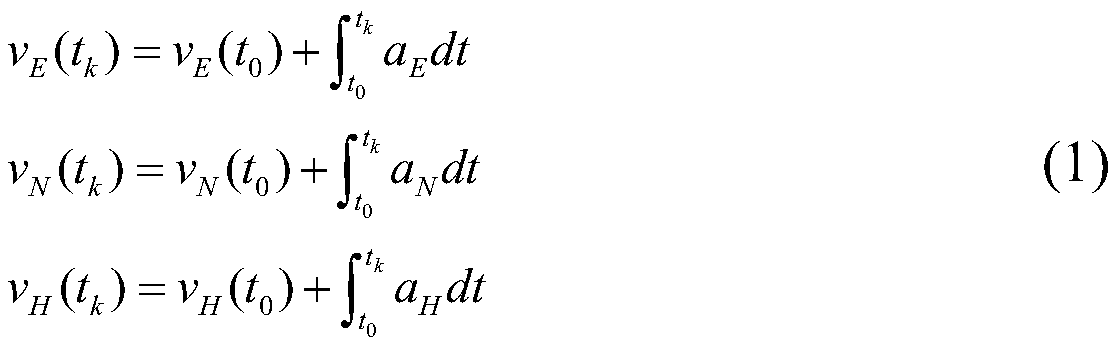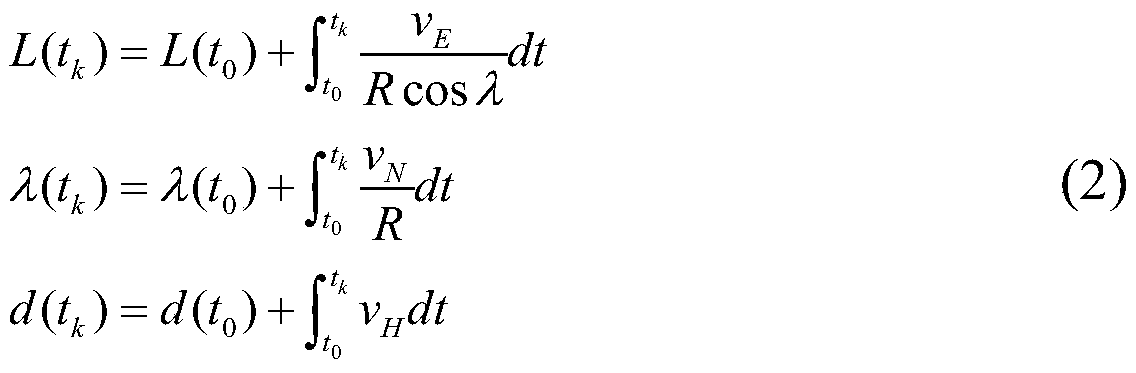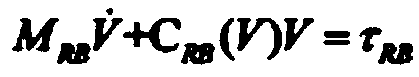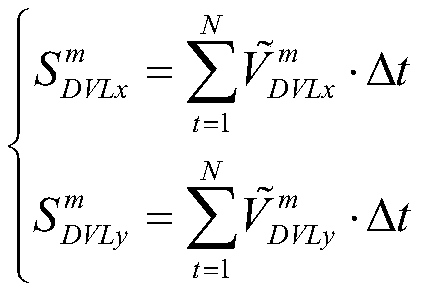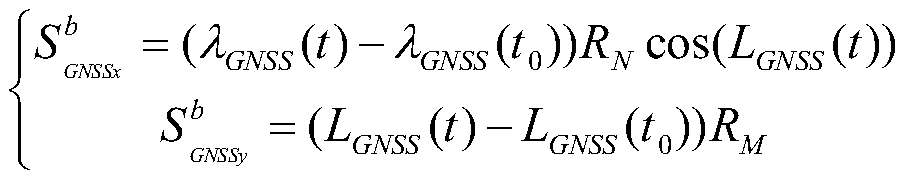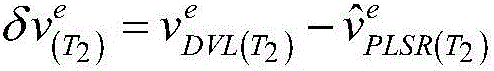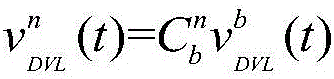Patents
Literature
44 results about "Doppler velocity log" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
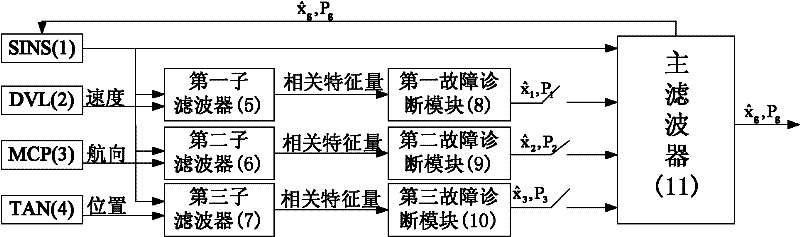
Fault-tolerant combined method of strapdown inertial integrated navigation system for underwater vehicles
InactiveCN102221363AGuaranteed reliabilityGuaranteed fault toleranceNavigation instrumentsFault toleranceTerrain
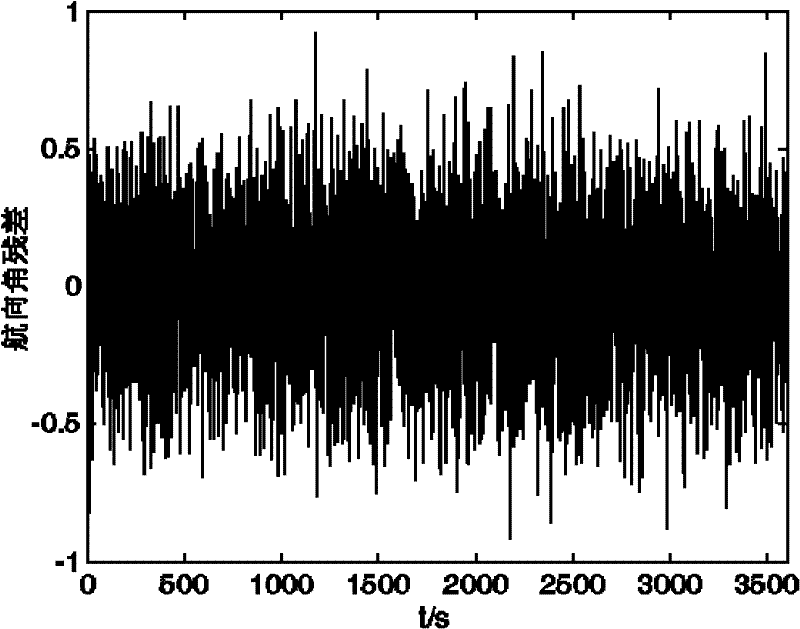
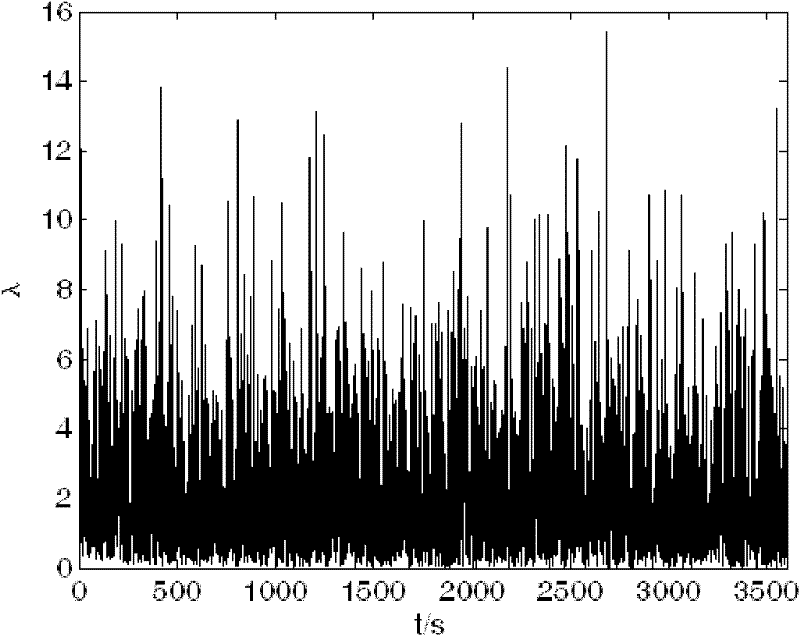
The invention provides a fault-tolerant combined method of a strapdown inertia integrated navigation system for underwater vehicles. The method is composed of a strapdown inertial navigation system SINS, a terrain aided navigation system TAN, a Doppler velocity log DVL and a magnetic compass pilot MCP, and realizing an integrated navigation process through a decentralized filter structure and an intelligent fault-tolerance method. The method comprises the following steps of constructing sub-filters respectively with the SINS as a reference navigation system and the TAN, the SINS and the DVL, and the SINS and the MCP, extracting related characteristic quantities from the sub-filters to transmit them into fault diagnosis modules composed of a supporting vector machine, determining if faultsexist in the TAN, the DVL or the MCP, if the faults exist, information of the TAN, the DVL or the MCP with the faults is screened, then carrying out a system reconfiguration process, and then feedingback errors outputted from a main filter to the SINS for correction. The method can guarantee a good reliability and a high fault tolerance of a strapdown inertial integrated navigation system for underwater vehicles, especially make a support vector machine trained in small samples have a strong popularization capability, and provide a novel method for a fault diagnosis.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Nonlinear-model-based SINS/DVL (strapdown inertial navigation system/doppler velocity log) integrated navigation method
InactiveCN103278163AHigh precisionStrong reliabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNonlinear modelSigma point
The invention discloses a nonlinear-model-based SINS / DVL (strapdown inertial navigation system / doppler velocity log) integrated navigation method. The method comprises the following steps of: building a quaternion-based SINS nonlinear speed, posture and position error model according to the working principles of an SINS and a DVL, and confirming an error model of the DVL; building a state equation of the systems according to the error models of the two systems, measuring by taking the difference between the actually-measured speeds of the SINS and the DVL as the quantity, and building a measurement equation of the system; discretizing an actual continuous system to obtain a discrete nonlinear model which is convenient to compute; initializing the system, and computing sampling points and corresponding weight numbers by the discrete nonlinear model and unscented conversion; and sequentially carrying out time update and measurement update on unscented kalman filter on the basis of the discrete nonlinear model according to the constructed Sigma point. After the SINS / DVL integrated navigation system is used, information of each subsystem can be effectively used, and the best of each subsystem can be taken, so that the overall positioning accuracy can be greatly improved; the UKF (unscented kalman filter) estimation can be carried out by the nonlinear model of the SINS / DVL integrated navigation system, so that the positioning error of the system can be effectively reduced and the accurate positioning of the navigation system can be realized better.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
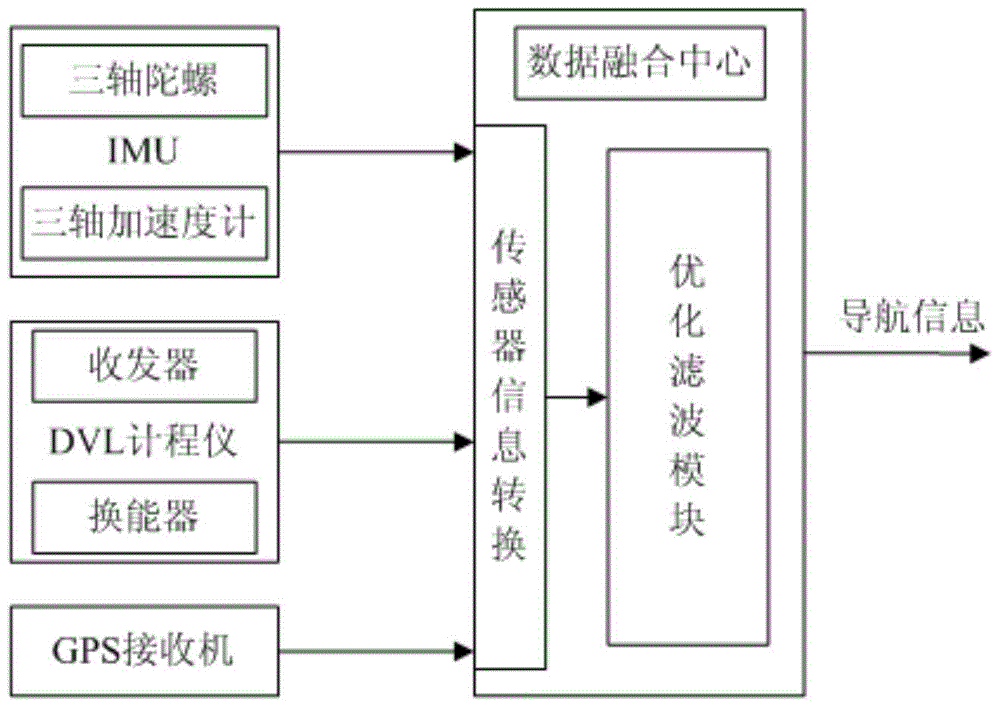
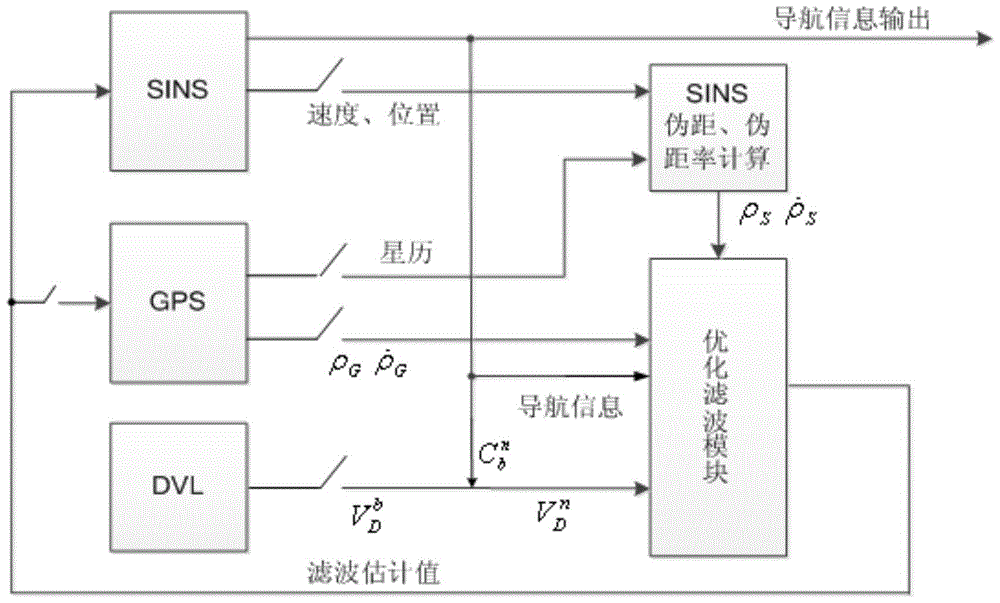
Ship's inertial navigation system (SINS)/Doppler velocity log (DVL)/global positioning system (GPS)-based autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) combined navigation system
ActiveCN103744098AImprove robustnessOvercome the defect that navigation and positioning errors accumulate over time and fail to meet the accuracy requirementsNavigation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingGps receiverEphemeris
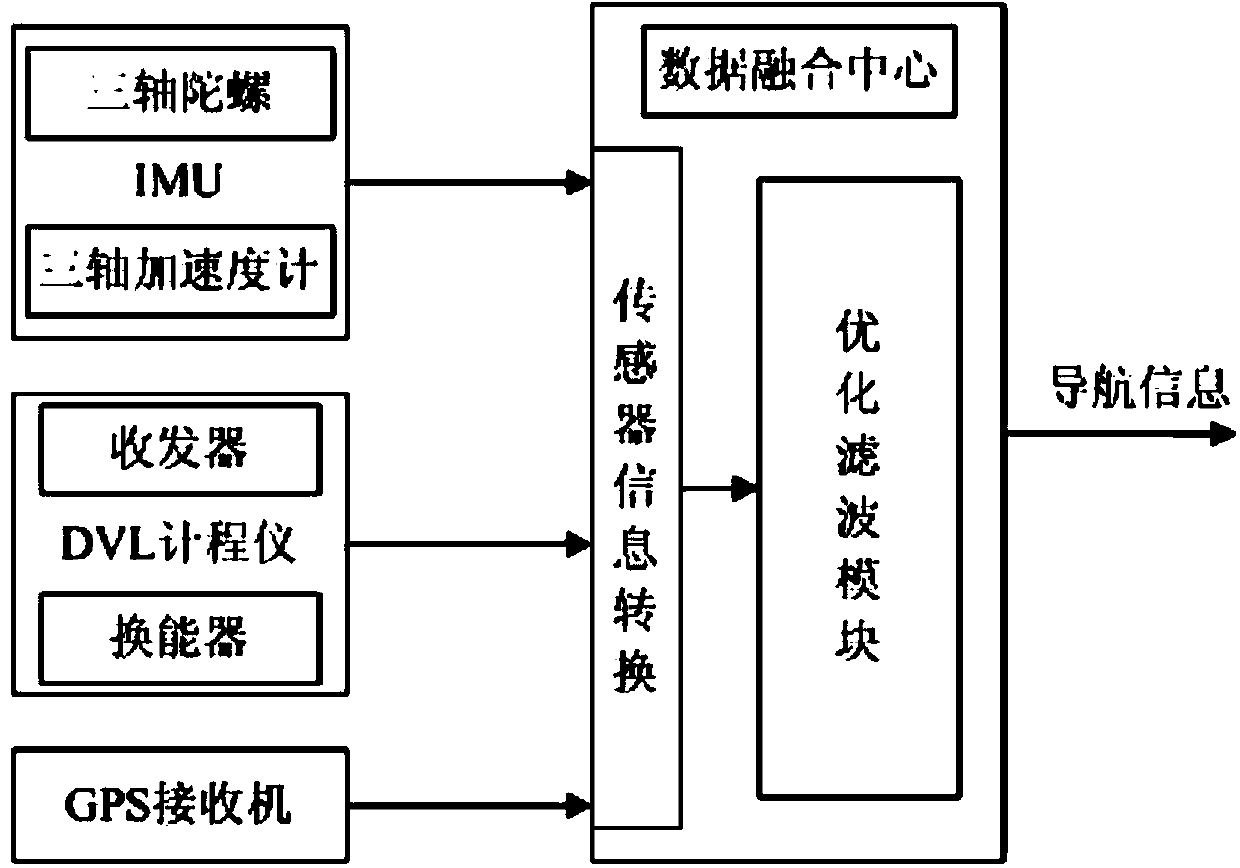
The invention discloses a ship's inertial navigation system (SINS) / Doppler velocity log (DVL) / global positioning system (GPS)-based autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) combined navigation system, which comprises an SINS, a GPS receiver, a DVL and a data fusion center, wherein the SINS, the GPS receiver, the DVL and the data fusion center are arranged on an AUV; when the AUV is positioned on the water surface, an optimized filter module carries out filtering fusion calculation by combining navigation information of the SINS, a pseudo-range and a pseudo-range rate corresponding to the SINS and available ephemeris data output by the GPS receiver to obtain correction information; when the AUV is positioned underwater, the optimized filter module carries out filtering fusion calculation by combining the navigation information output by the SINS and three-dimensional navigational speed information output by the DVL to obtain correction information. The navigational positioning accuracy and the robustness of the system are improved, and the system realizes an uninterrupted high-accuracy underwater and water surface carrier navigating and tracking function.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Neural network assisted integrated navigation method for underwater vehicle
ActiveCN104330084AFully trainedDoes not affect real-time computingNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsTerrainGyroscope
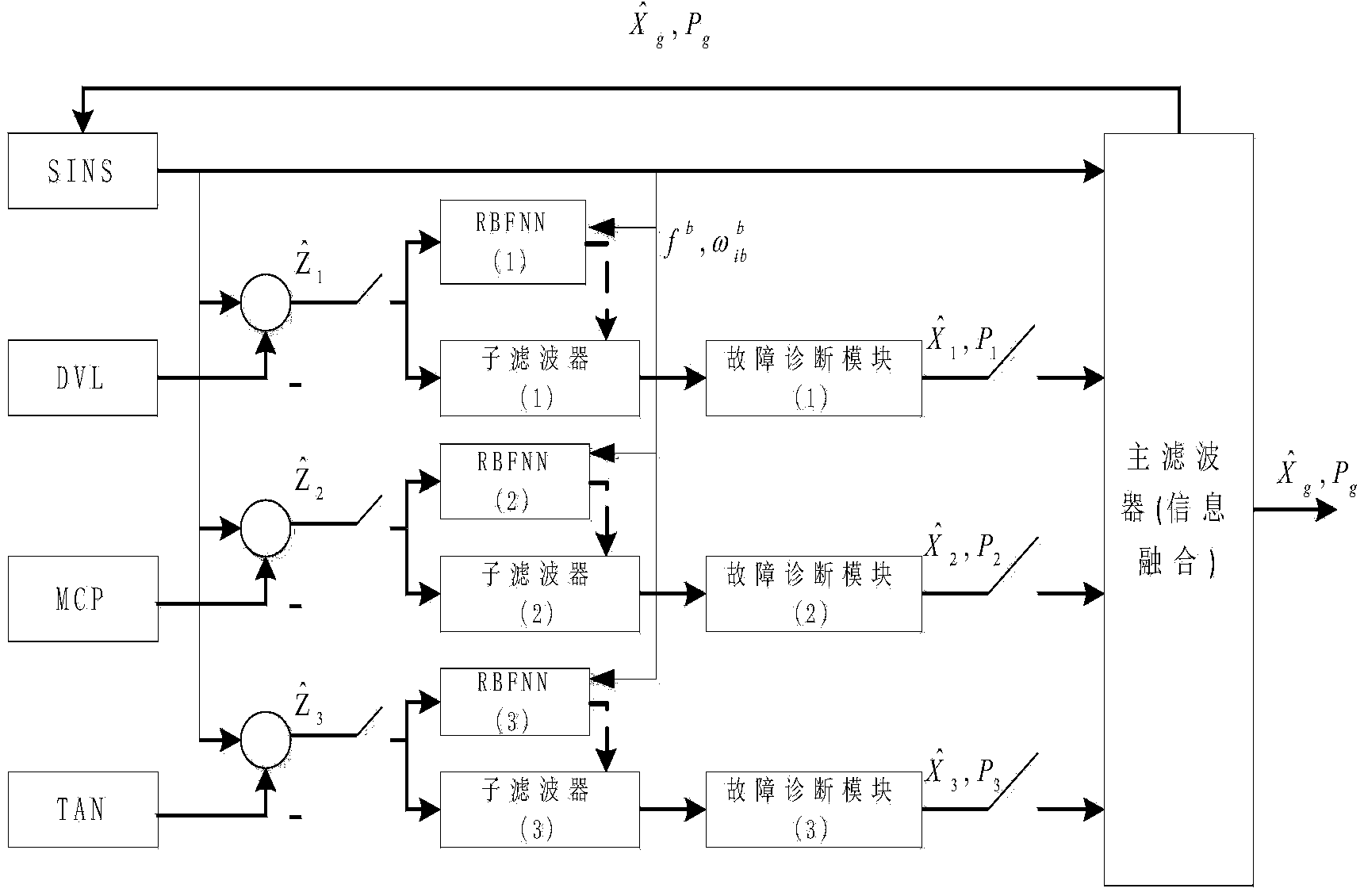
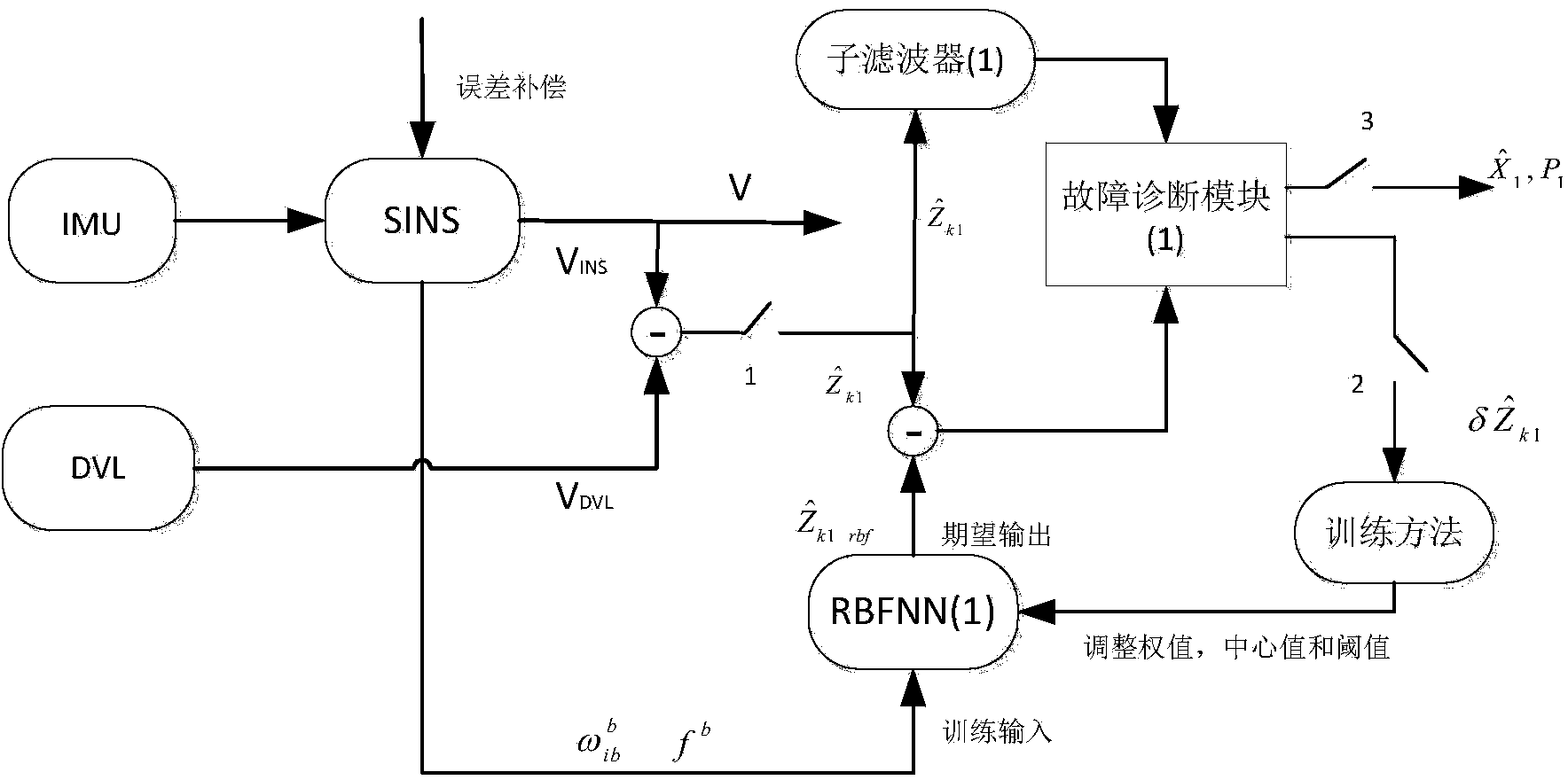
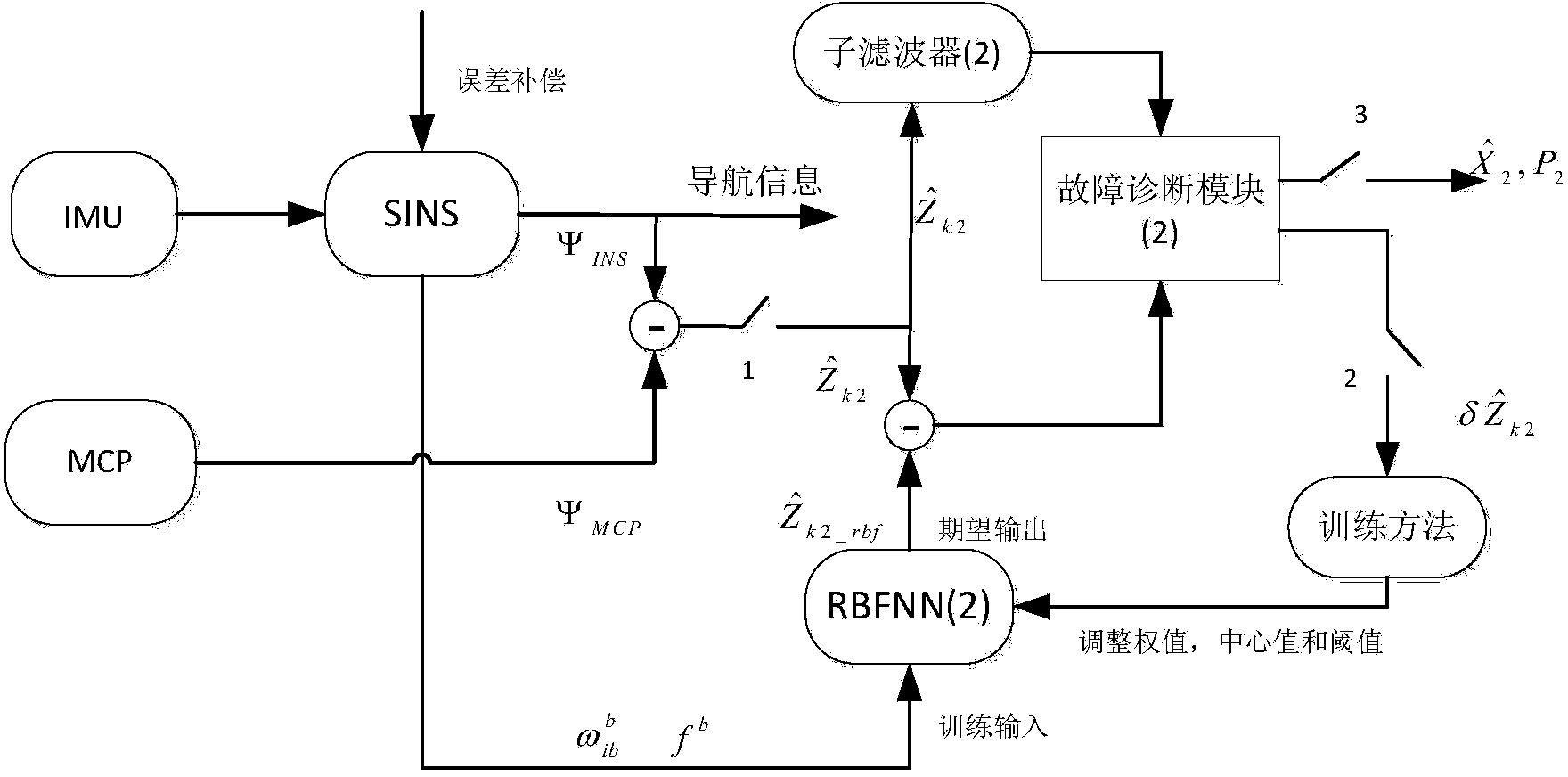
The invention discloses a neural network assisted integrated navigation method for an underwater vehicle. The neural network assisted integrated navigation method is implemented by use of strapdown inertial navigation system (SINS), a Doppler velocity log (DVL), a magnetic compass pilot (MCP) and a terrain aided navigation system (TAN), wherein the integrated navigation is completed by use of a decentralized filter structure of Kalman filtering and a fault-tolerant method, assisted by a radial basis function neutral network (RBFNN). In a fault-free time period, RBFNN is in an online learning model, the observed quantity difference between the SINS and each auxiliary system is taken as the expected output of the RBFNN, and the output fb of an accelerometer after error compensation and the output shown in the specification of a gyroscope are taken as the inputs of the RBFNN; when a sub-system composed of the SINS serving as a reference system and each auxiliary system is out of order, an RBFNN prediction mode is immediately activated, and the predicted output is taken as the measurement input of a corresponding sub-filter. Compared with the SINS mode out of order, the RBFNN mode has the advantages that the navigation accuracy is improved; especially when the fault recovery time is relatively long, the improvement of the navigation accuracy of the RBFNN mode is particularly obvious.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Doppler velocity log (DVL) parameter calibration method used for integrated navigation system of underwater inertial navigation system (INS) and DVL
InactiveCN103163508ASimple calculationEasy to operateWave based measurement systemsNavigation systemPosition error
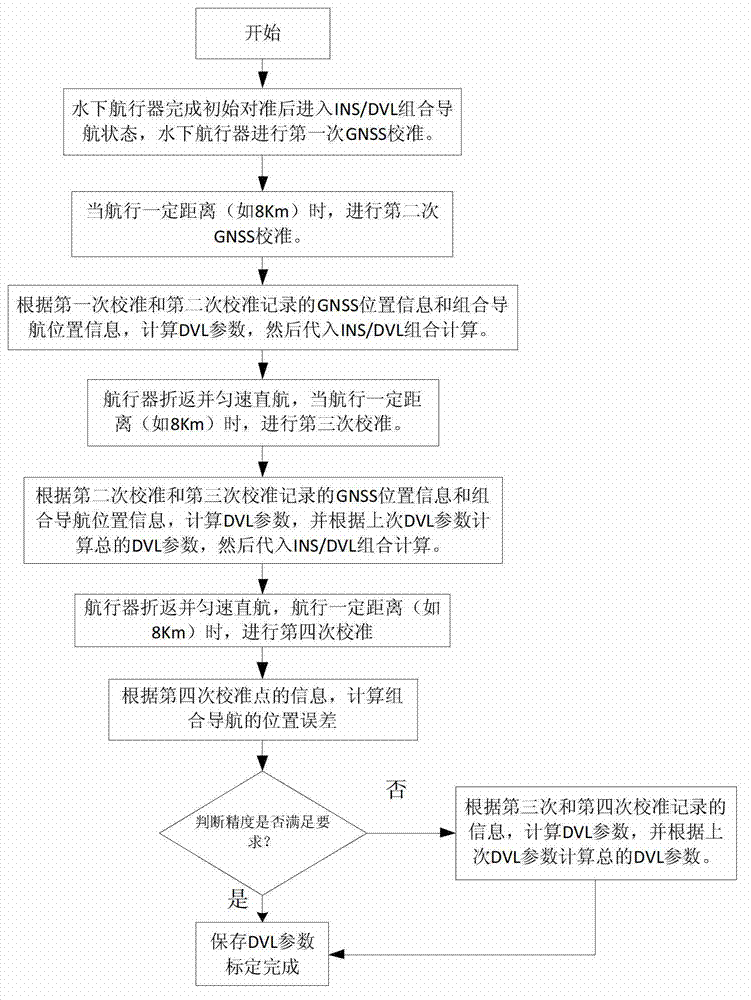
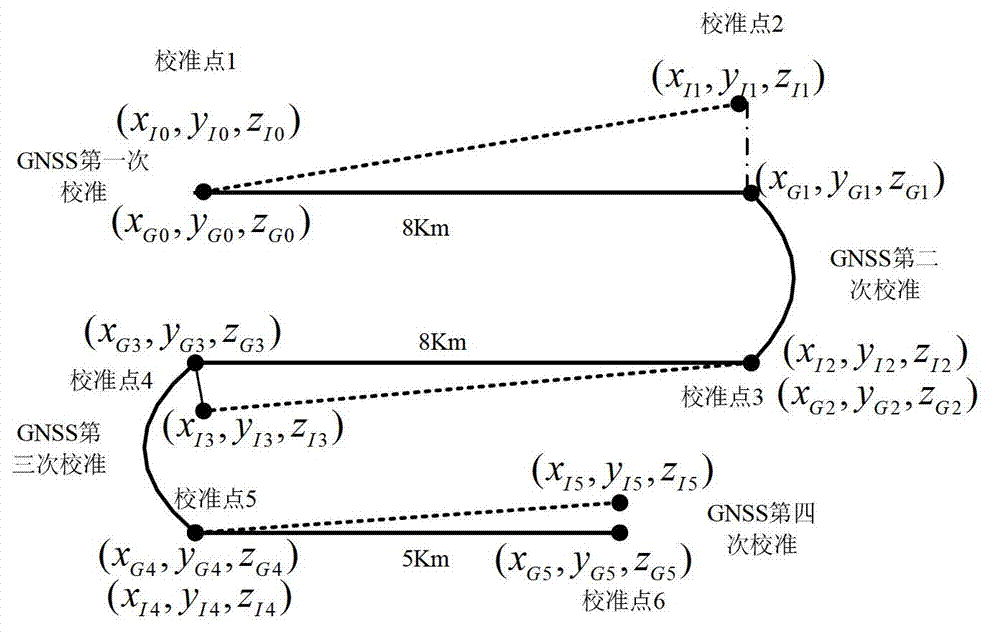
The invention relates to a doppler velocity log (DVL) parameter calibration method used for an integrated navigation system of an underwater inertial navigation system (INS) and a DVL. The procedures includes the following steps: (1) calibrating a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) for the first time after initial alignment of an underwater aircraft is completed, (2) calibrating the GNSS for the second time after the underwater aircraft directly sails at a constant speed for a certain distance, (3) calculating the parameter of the DVL according to position information of the two calibrated GNSS and position information of the integrated navigation, (4) calibrating the GNSS for the third time after the aircraft pulls back and directly sails at a constant speed for a certain distance, calculating the parameter of the DVL, and iteratively calculating the total parameter of the DVL according to the former parameter of the DVL, (5) and calibrating the GNSS for the forth time after the aircraft pulls back and directly sails at a constant speed for a certain distance, calculating position error of the integrated navigation according to position information of the forth calibrated integrated navigation and the position information of the GNSS, and judging whether accuracy meets requirements, and if the accuracy meets requirements, calibration is completed, if the accuracy does not meet the requirements, the calibration is completed through iterative calculation. The DVL parameter calibration method used for the integrated navigation system of the underwater INS and the DVL has the advantages of being simple in calculation, high in accuracy, simple in operation and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
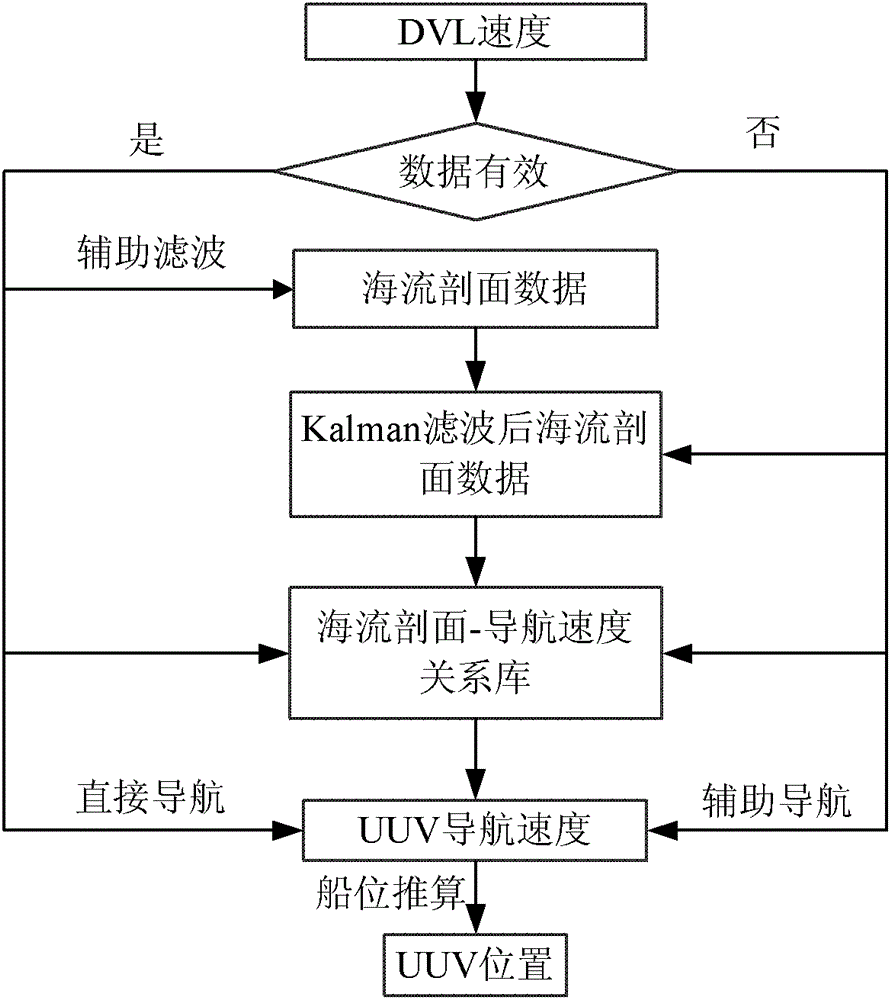
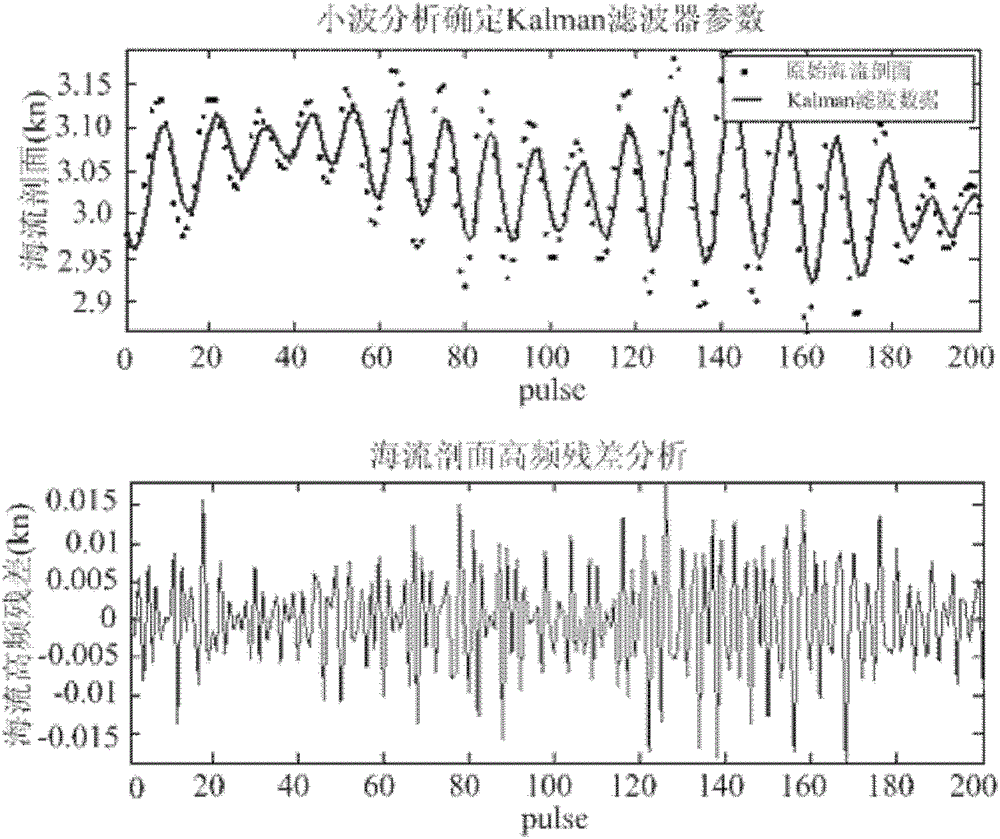
UUV (unmanned underwater vehicle) aided navigation method based on current profile
ActiveCN102323586AImprove environmental adaptabilityAcoustic wave reradiationProcess noiseRelational database
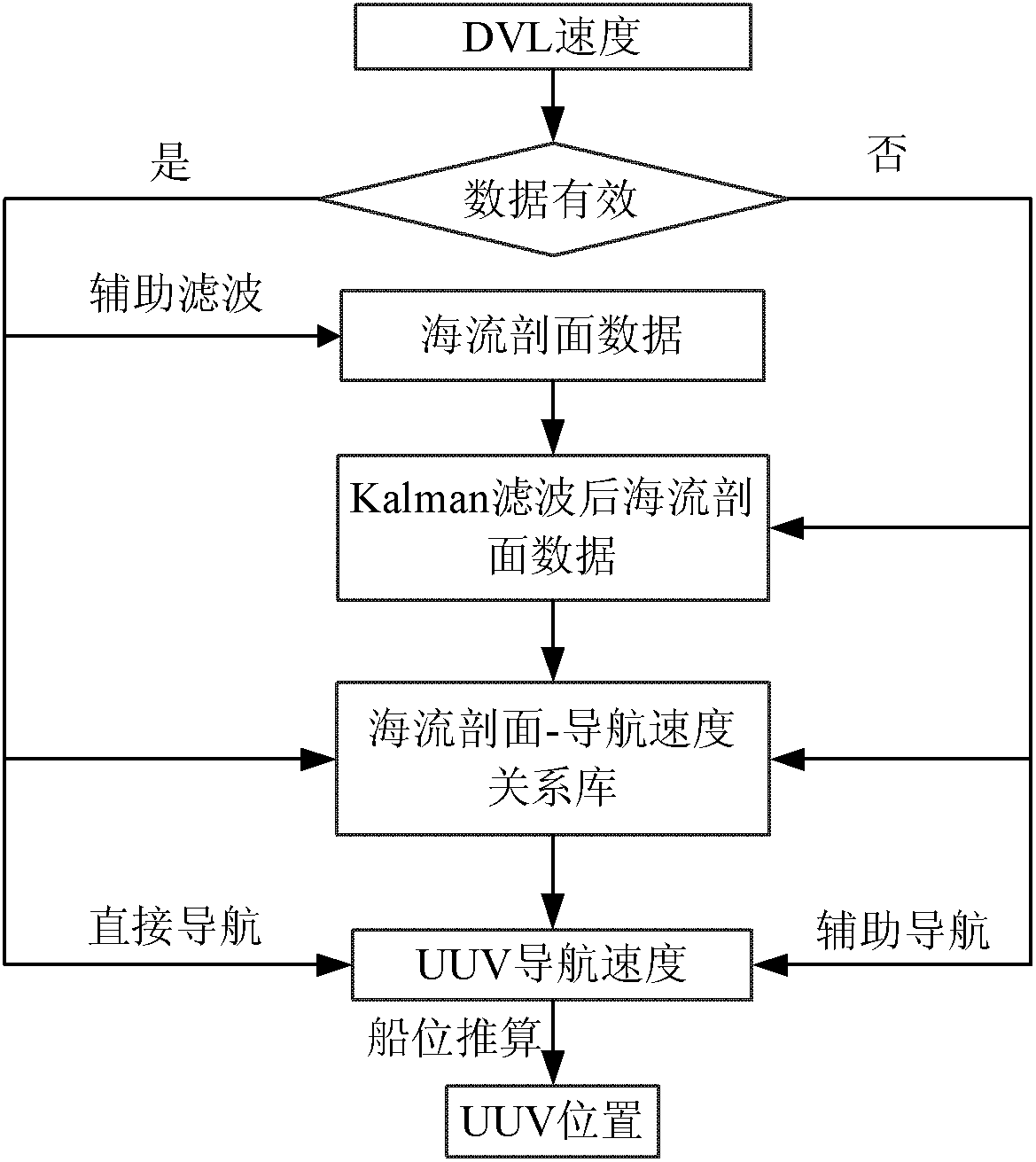
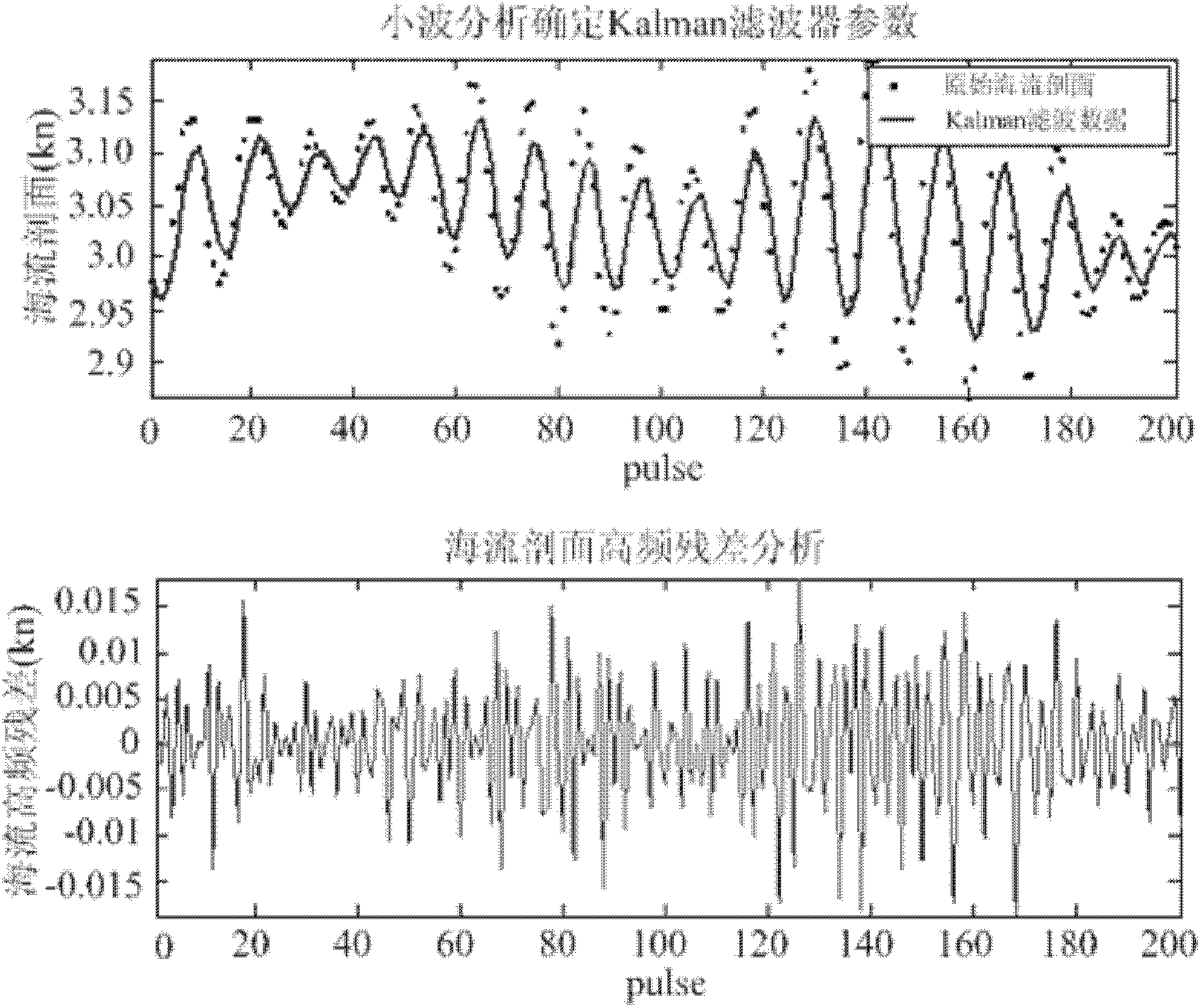
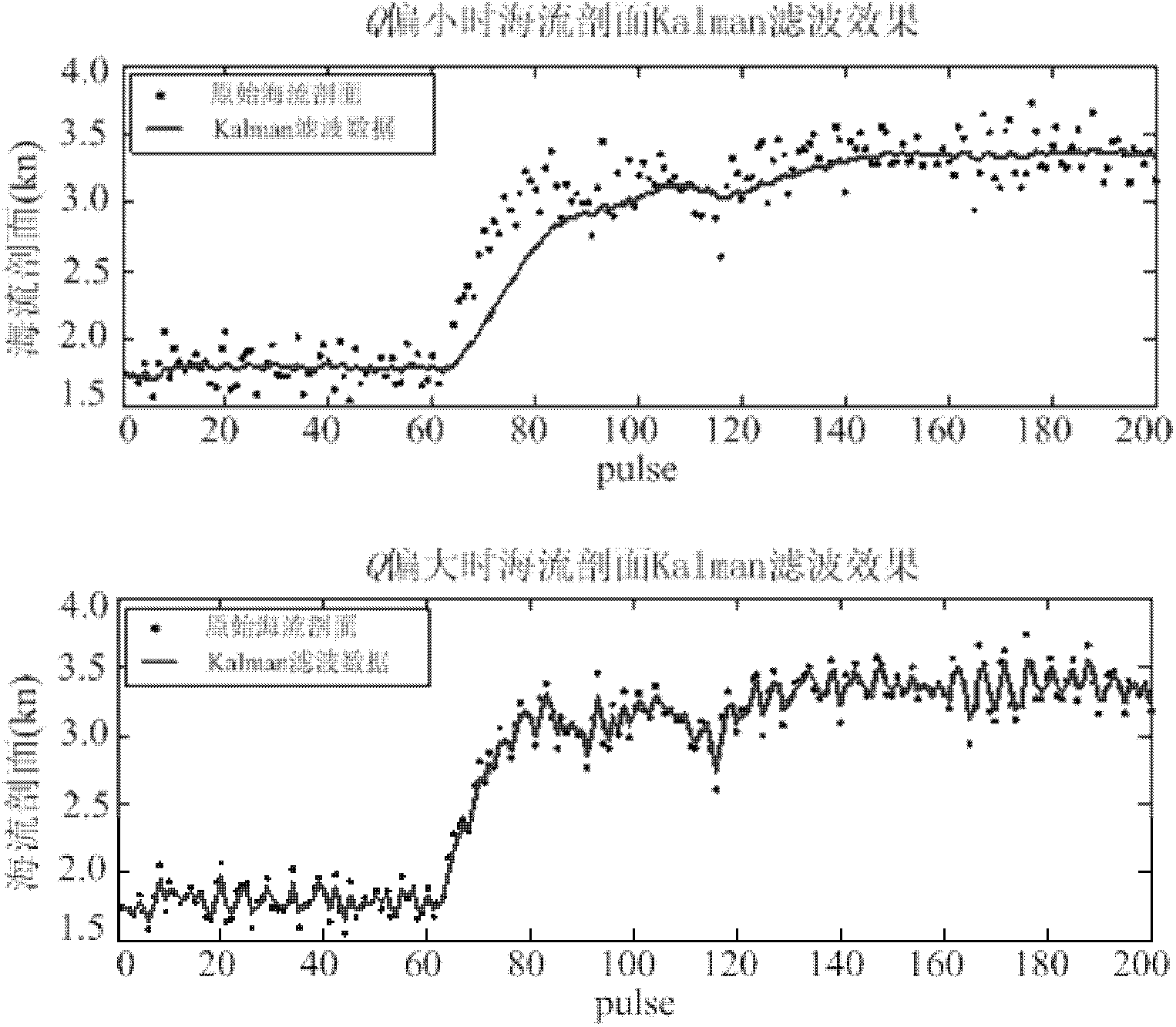
The invention provides a UUV (unmanned underwater vehicle) aided navigation method based on current profile. The method comprises the following steps: firstly setting up a Kalman filter model of current profile data, secondly determining the observation noise variance R and process noise variance Q in a Kalman equation according to variations of the environment and the UUV own velocity and finally setting up a UUV velocity-current profile relation database, utilizing the relation database and the current profile information measured by an ADCP (acoustic Doppler current profile) to reckon the UUV velocity at the time of DVL (Doppler velocity log) failure and further obtaining the navigation position of the UUV by deadreckoning. The method has the following beneficial effects: when the UUV performs a task under water, once the sonar data of the DVL have failure, the UUV velocity can be reckoned by using the current profile information measured by the ADCP, so that the UUV can continue performing the ocean exploration task in the complex ocean environments such as great depth, thus improving the environmental adaptation capability of the UUV.
Owner:哈尔滨船海智能装备科技有限公司
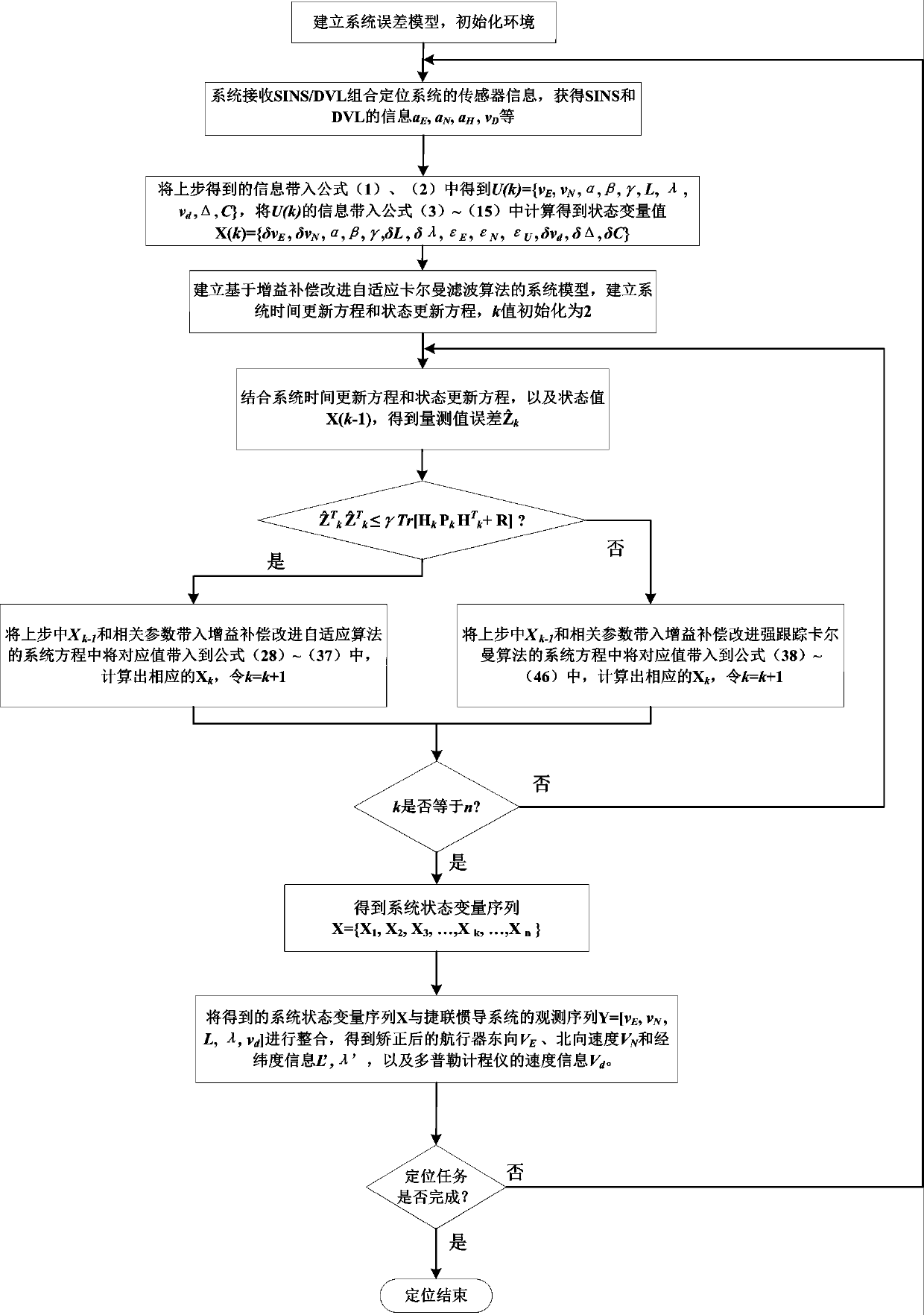
Gain compensation self-adaptive filtering-based SINS (strap-down inertial navigation)/DVL (Doppler velocity log) combined positioning method
ActiveCN110146075ANavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAcoustic wave reradiationAdaptive filtering algorithmFilter algorithm
The invention relates to a gain compensation self-adaptive filtering-based SINS (strap-down inertial navigation) / DVL (Doppler velocity log) combined positioning method and belongs to the technical field of high-precision SINS / DVL combined positioning. The invention aims to solve the problem of low positioning precision due to the influence of the insufficient flexibility of the filtering algorithmof conventional SINS / DVL combined navigation. The method of the invention includes the following steps that: corresponding state initial values and observation values are acquired based on the sensorinformation of a strap-down inertial navigation system and a Doppler velocity log; a corresponding system equation and observation equation based on a combined navigation error model are constructed,a gain compensation self-adaptive filtering algorithm is adopted to correct errors, so that the post-correction speed and position error information of a target is obtained; and finally, the obtainederror information and the observation information of the strap-down inertial navigation system and the Doppler velocity log are fused, so that a high-precision positioning result is obtained.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
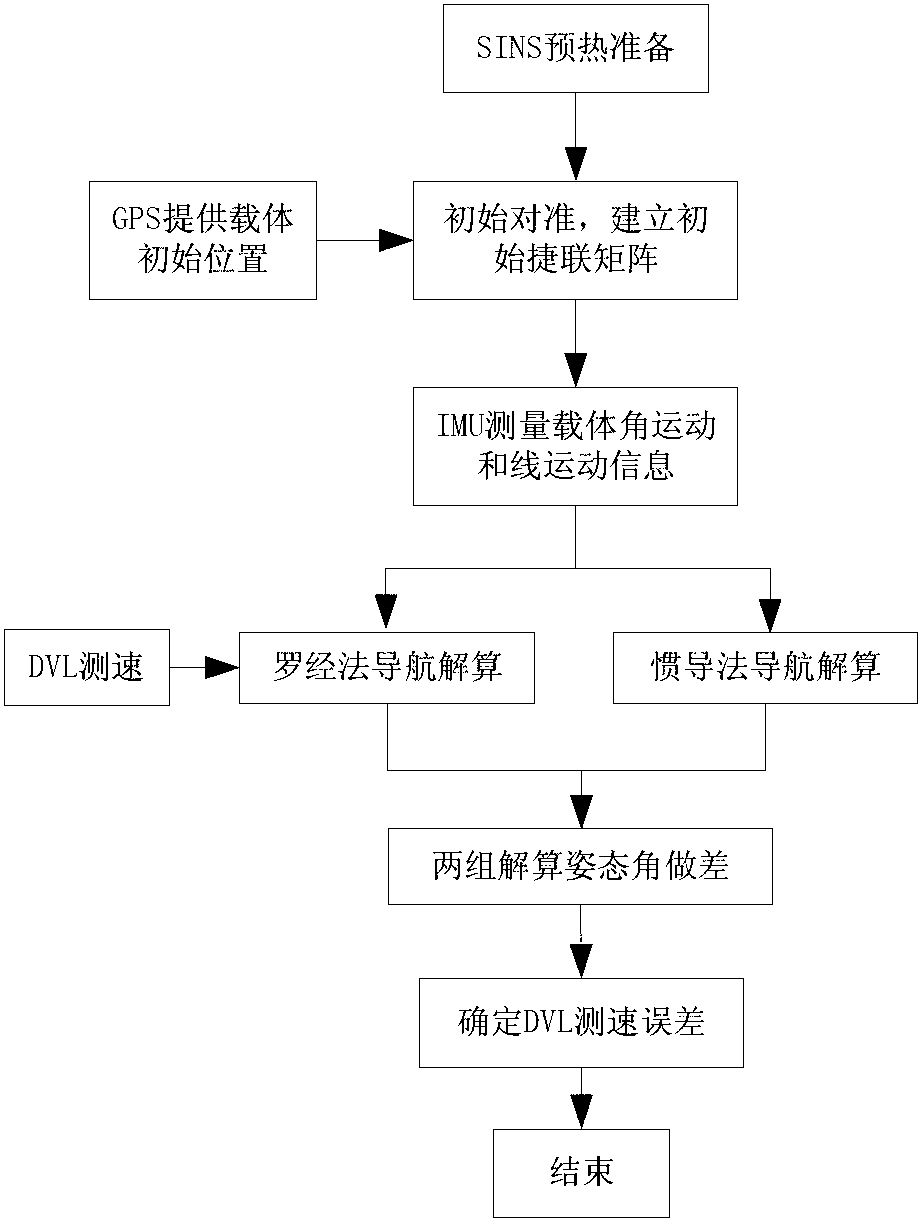
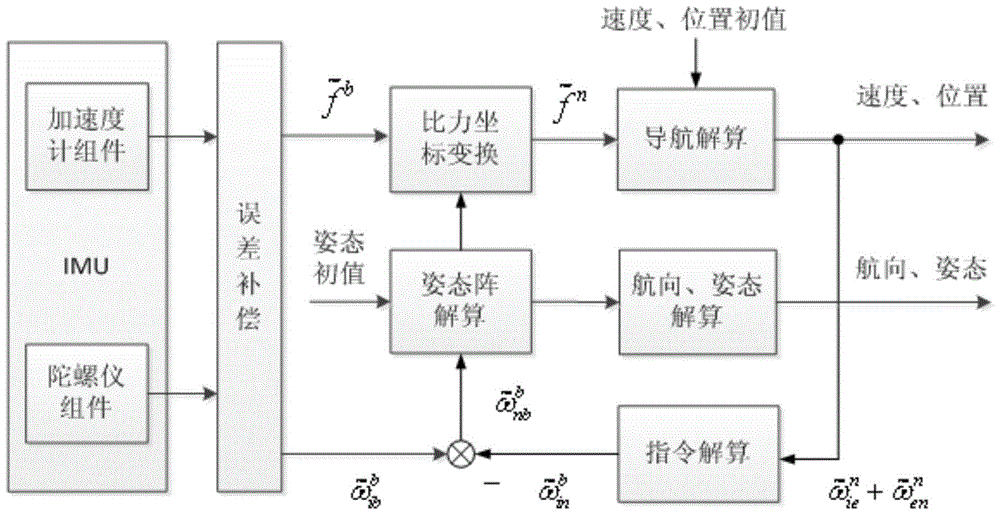
Method for determining speed measurement error of Doppler velocity log (DVL) in strapdown inertial navigation system
InactiveCN103076026AImprove speed measurement accuracySimple methodMeasurement devicesGlobal Positioning SystemFibre optic gyroscope
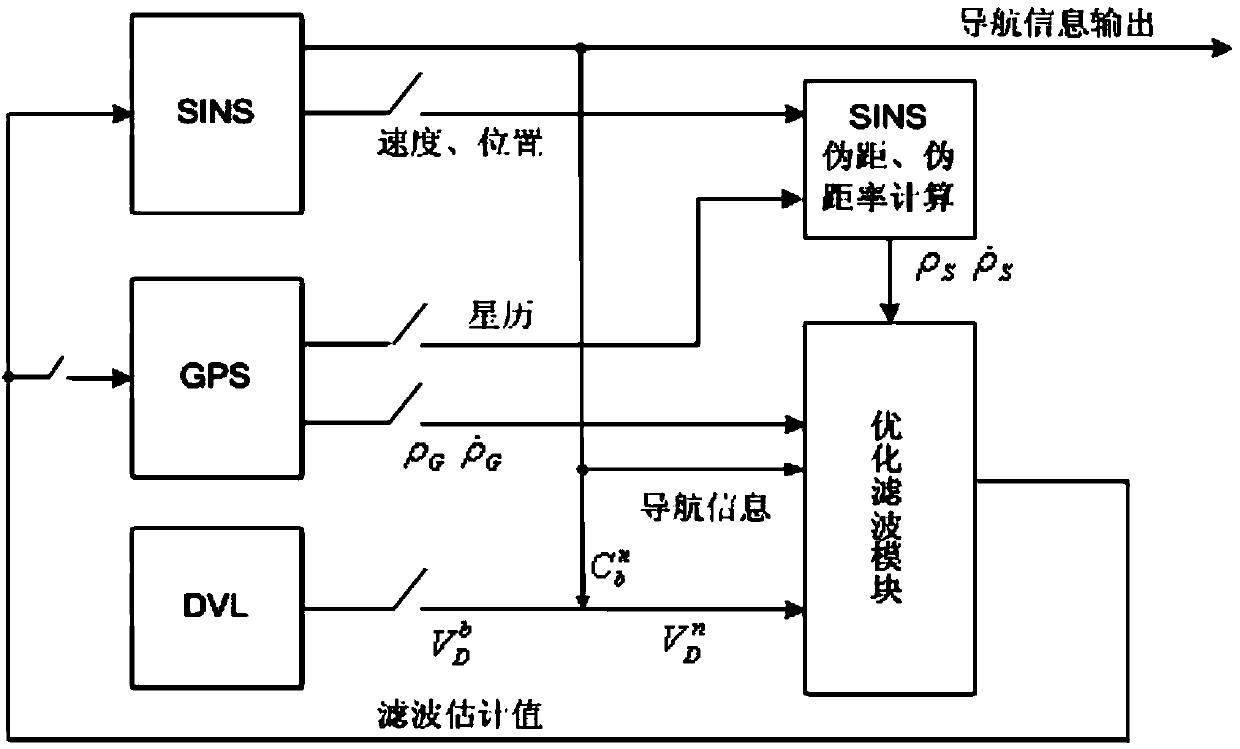
The invention provides a method for determining speed measurement error of a Doppler velocity log (DVL) in a strapdown inertial navigation system. The method comprises the following steps: determining an initial position parameter of a carrier by a global positioning system (GPS), acquiring data output by an optical fiber gyro and an accelerator, performing initial alignment on data processing and determining an initial strapdown matrix; acquiring angular motion information and linear motion information of the carrier measured by an inertial component, and performing navigation calculation by a compass method and an inertial navigation method respectively, wherein carrier motion speed information measured by the DVL is introduced into the calculation by the compass method; performing subtraction on two groups of gesture information calculated by the two methods and performing transformation to obtain an azimuth misalignment angle value of the two group of calculated gestures; and performing conversion on the azimuth misalignment angle value to obtain the speed measurement error of the DVL. By the method, the speed measurement error of the DVL can be estimated in the navigation process of the carrier, and the speed measurement precision of the DVL is improved after the result can be compensated to the DVL. The method is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
SINS (Strapdown Inertial Navigation System)-based method for restraining velocity measuring error of DVL (Doppler Velocity Log)
The invention provides an SINS (Strapdown Inertial Navigation System)-based method for restraining the speed measuring error of a DVL (Doppler Velocity Log). The method comprises the following steps of: starting the DVL and an SINS, comprehensively processing the output speeds of the DVL and the SINS, performing high pass digital filtering and outputting the optimized speed. By means of method provided by the invention, the high-frequency noise of the DVL can be filtered while the motion high-frequency information is not filtered; and speed and acceleration references are provided for initial alignment and navigation of other inertial systems.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Inverse matrix-free self-adaptive filtering-based SINS (strap-down inertial navigation)/DVL (Doppler velocity log) combined positioning method
ActiveCN110146076ANavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAcoustic wave reradiationAdaptive filtering algorithmFilter algorithm
The invention relates to an inverse matrix-free self-adaptive filtering-based SINS (strap-down inertial navigation) / DVL (Doppler velocity log) combined positioning method and belongs to the technicalfield of high-precision SINS / DVL combined positioning. The invention aims to solve the problems of low calculation efficiency and poor stability of a traditional SINS / DVL combined navigation filteringalgorithm due to the complex calculation process of the algorithm. The inverse matrix-free self-adaptive filtering-based SINS (strap-down inertial navigation) / DVL (Doppler velocity log) combined positioning method of the invention includes the following steps that: corresponding state initial values and observation values are acquired based on the sensor information of a strap-down inertial navigation system and a Doppler velocity log; a corresponding system equation and observation equation based on a combined navigation error model are constructed, an inverse matrix-free self-adaptive filtering algorithm is adopted to correct errors, so that the post-correction speed and position error information of a target is obtained; and finally, the obtained error information and the observation information of the strap-down inertial navigation system and the Doppler velocity log are fused, so that a high-precision positioning result is obtained. With the method of the invention adopted, on the basis of decreasing a calculation amount and optimizing a calculation process, the reliability and stability of a system can be ensured, and the positioning precision of underwater autonomous navigation is improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
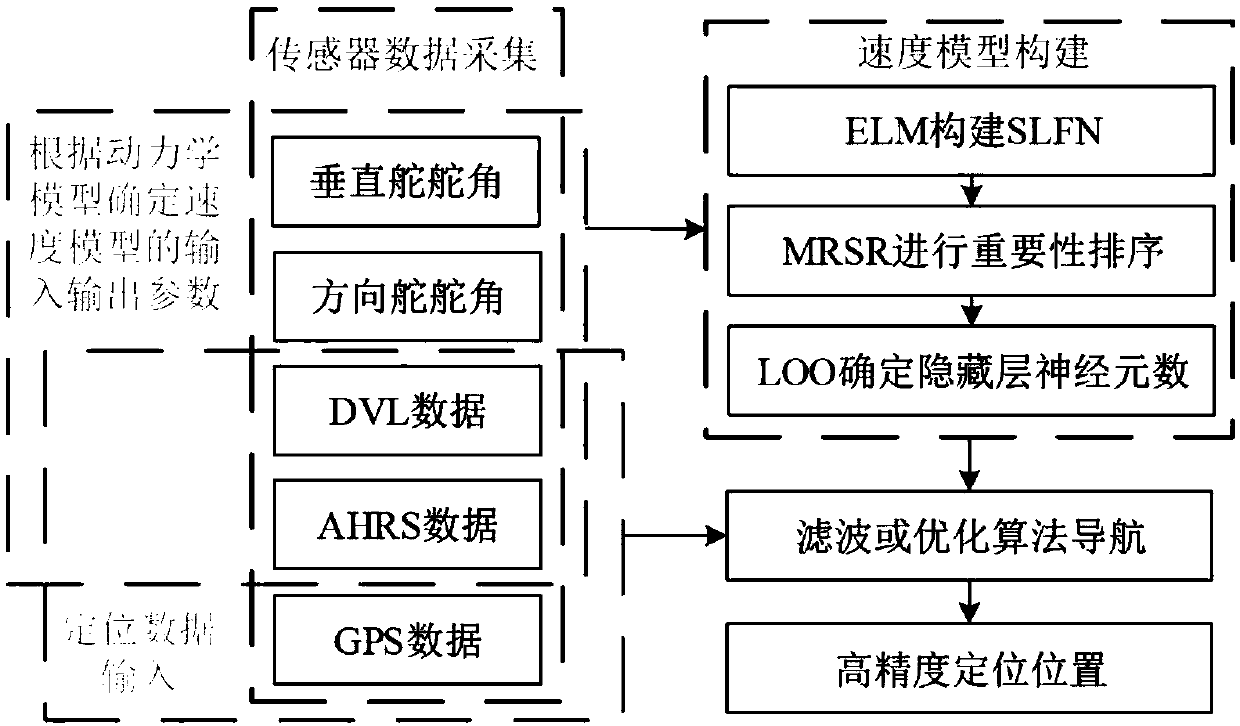
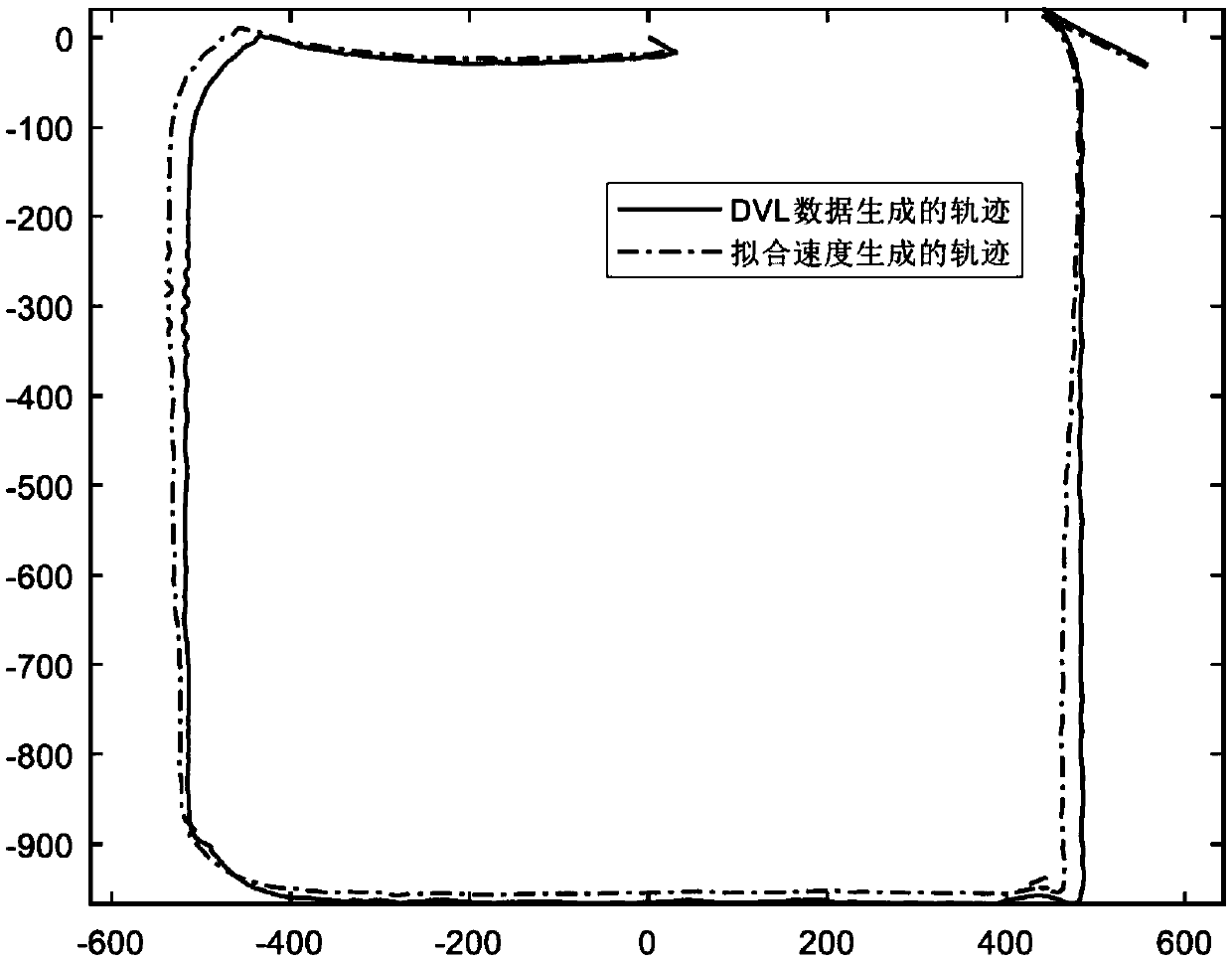
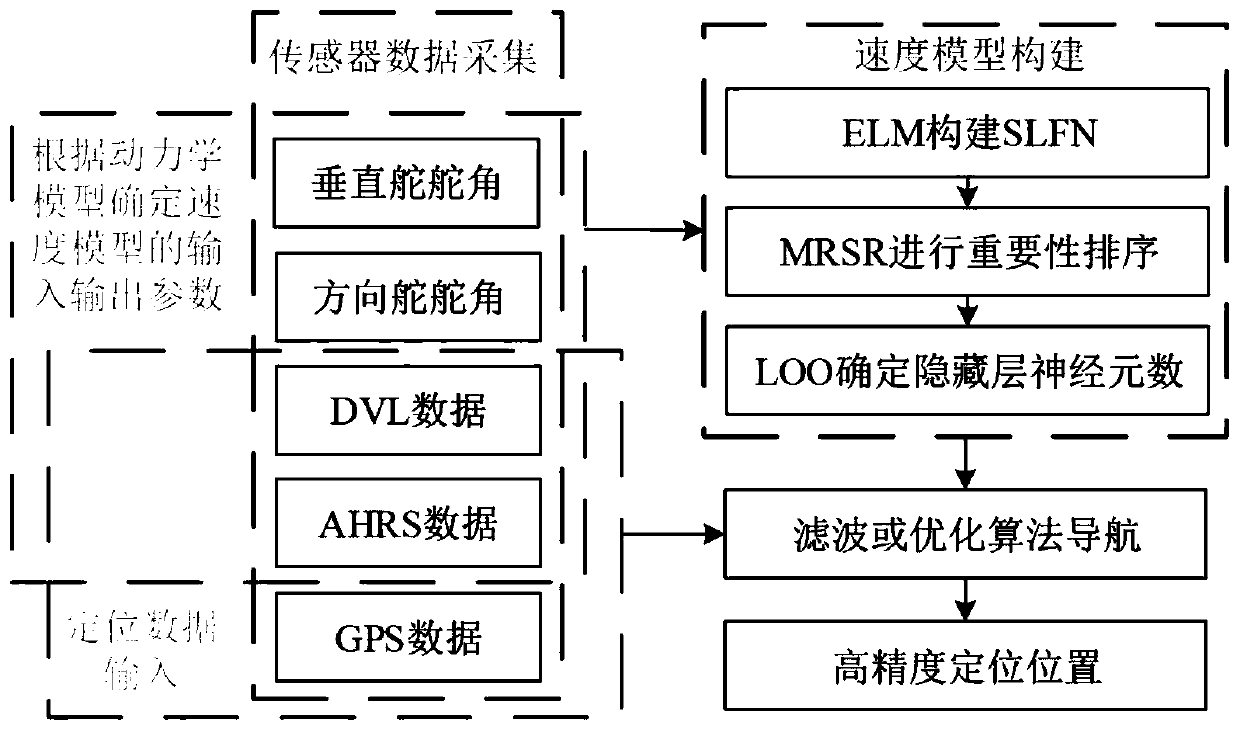
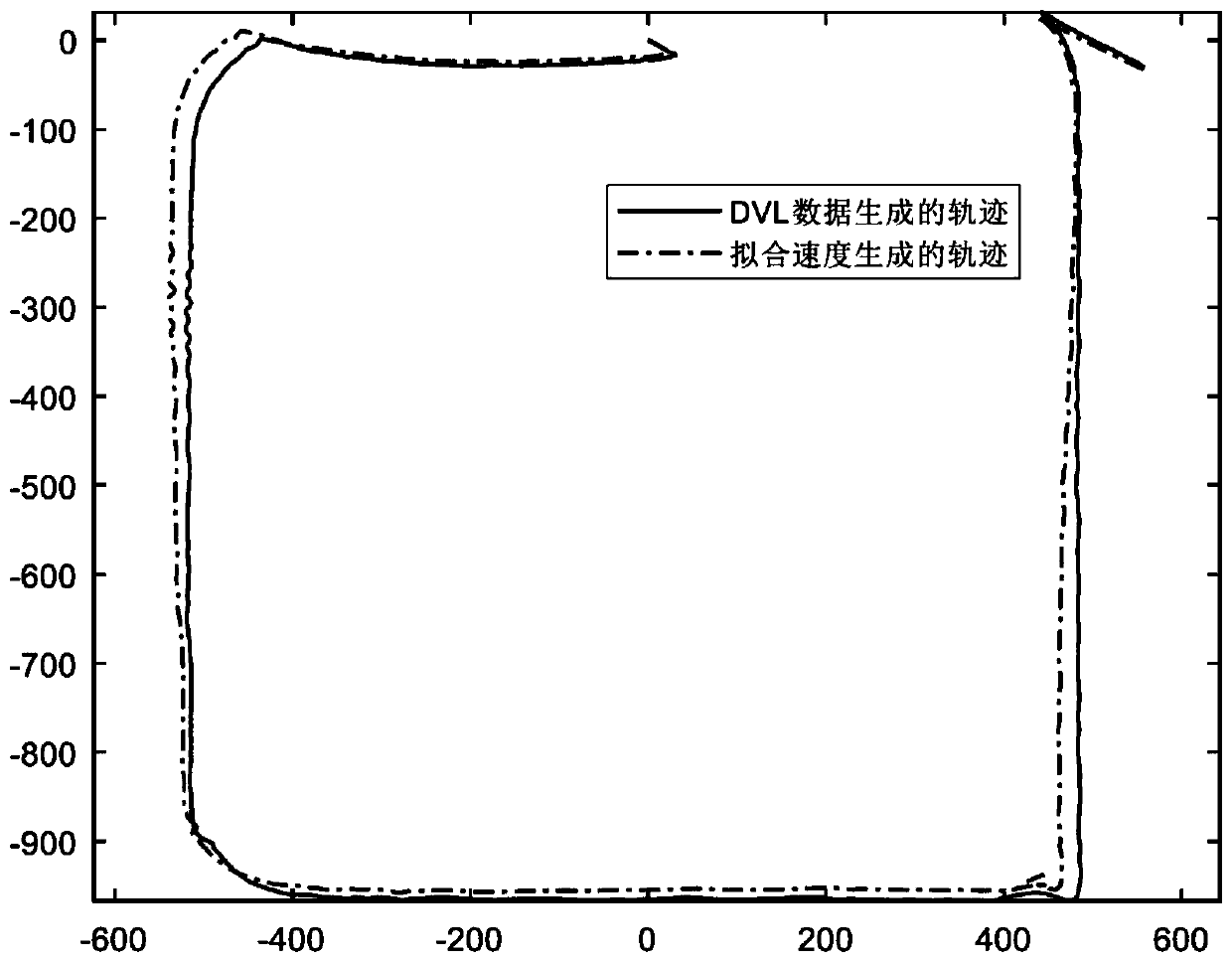
Dynamics-based velocity model assisted underwater intelligent navigation method
ActiveCN109634308ASpeed efficientSpeed output is validSafety arrangmentsAdaptive controlDynamic modelsOn board
The invention discloses a dynamics-based velocity model assisted underwater intelligent navigation method. The method includes the following steps that: (1) on-board sensor information is periodicallycollected; (2) the input variables and output variables of a velocity model to be established are determined; (3) the velocity model is constructed and trained; and (4) when it is detected that a DVL(Doppler Velocity Log) malfunctions or the data of the DVL fail, navigation analysis is performed with the output velocity of the trained model used as a bottom velocity, and therefore, model-assisted navigation can be performed. According to the method of the invention, a new AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle) velocity model is put forward based on the idea of dynamic models; the influence of factors such as rudder angles of rudder blades, and heading angles is considered; as long as the fault data of the DVL are not detected during an operation process, training sets can be increased at any time to train the model; after the fault data of the DVL are detected, the output velocity of the model can be adopted instead, and therefore, the problem of navigation error increase caused by thefailure or fault of the DVL can be avoided; the redundancy method of velocity sensors is provided with no hardware costs increased; the method has good system robustness and can guarantee high-precision navigation.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
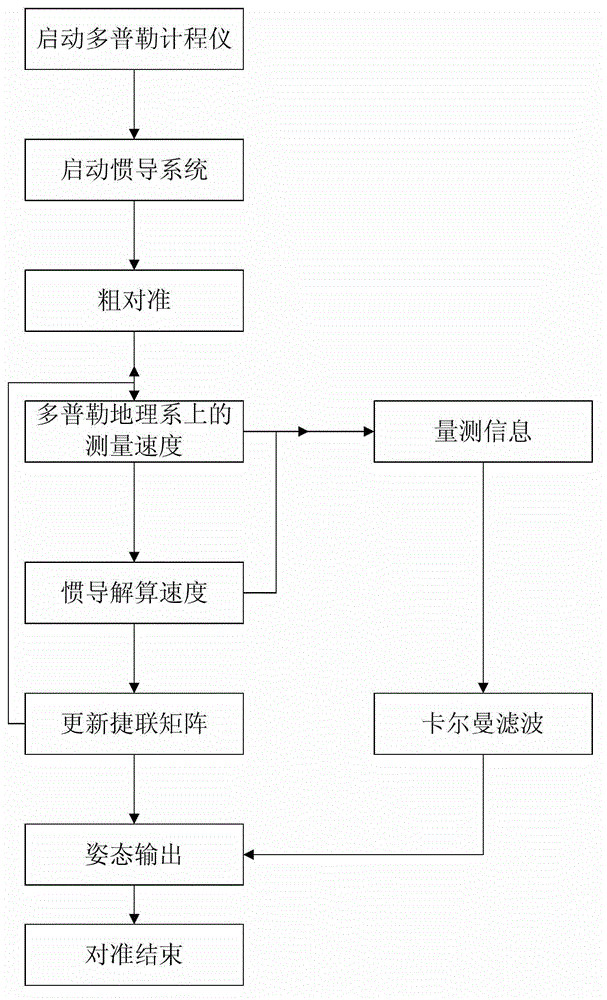
Integrated alignment method based on speed trial error estimation of doppler velocity log on geographical system under constant-speed direct flight condition
InactiveCN103148868AImprove ObservabilityEffective estimateMeasurement devicesState variableObservability
The invention provides an integrated alignment method based on speed trial error estimation of a doppler velocity log on a geographical system under a constant-speed direct flight condition. The projection of a speed trial error of the doppler velocity log on the geographical system is expanded into a state variable, and a doppler velocity log / strapdown inertial navigation integrated alignment system is established on the basis. Compared with a method for only expanding the speed trial error of the doppler velocity log into the state variable, the method provided by the invention can be used for improving the observability level of the speed trial error of the doppler velocity log, effectively estimating the speed trial error and overcoming the influence on precision caused by the speed trial error of the doppler velocity log.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
DVL-assisted (Doppler velocity log-assisted) SINS (strap-down inertial navigation system) robust on-moving initial alignment method
ActiveCN109141475ARealize Quantitative RepresentationReduce the influence of abnormal noiseMeasurement devicesReal-time dataQuaternion
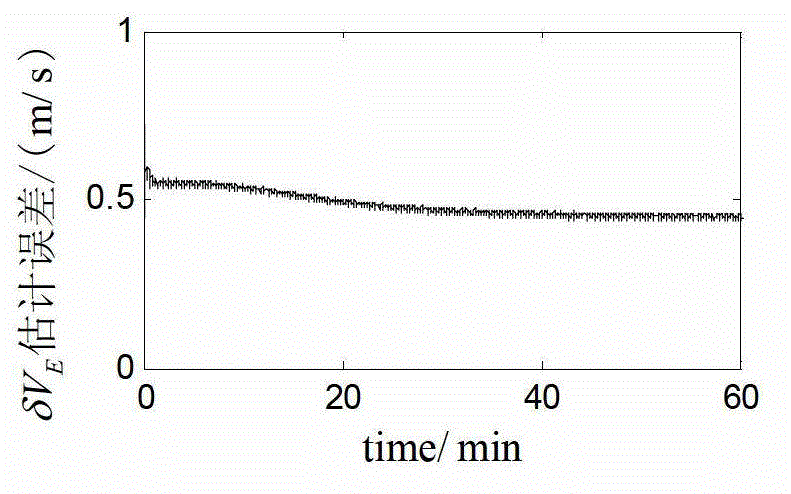
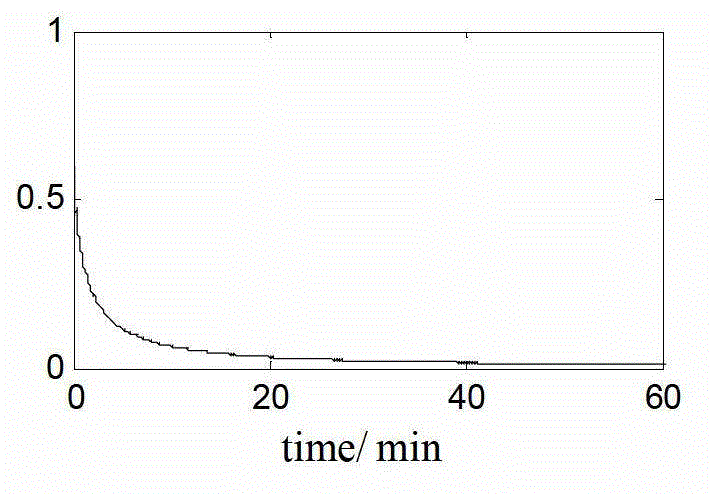
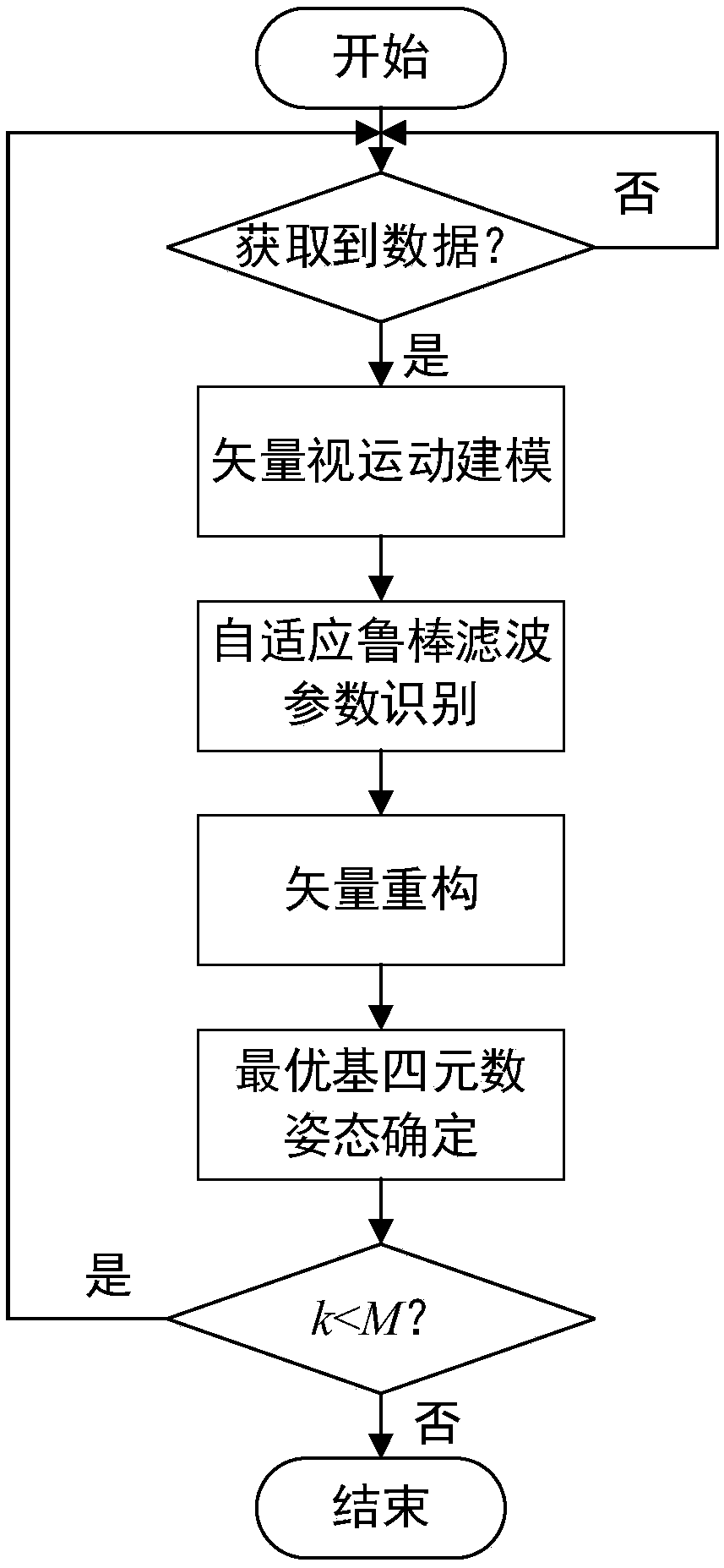
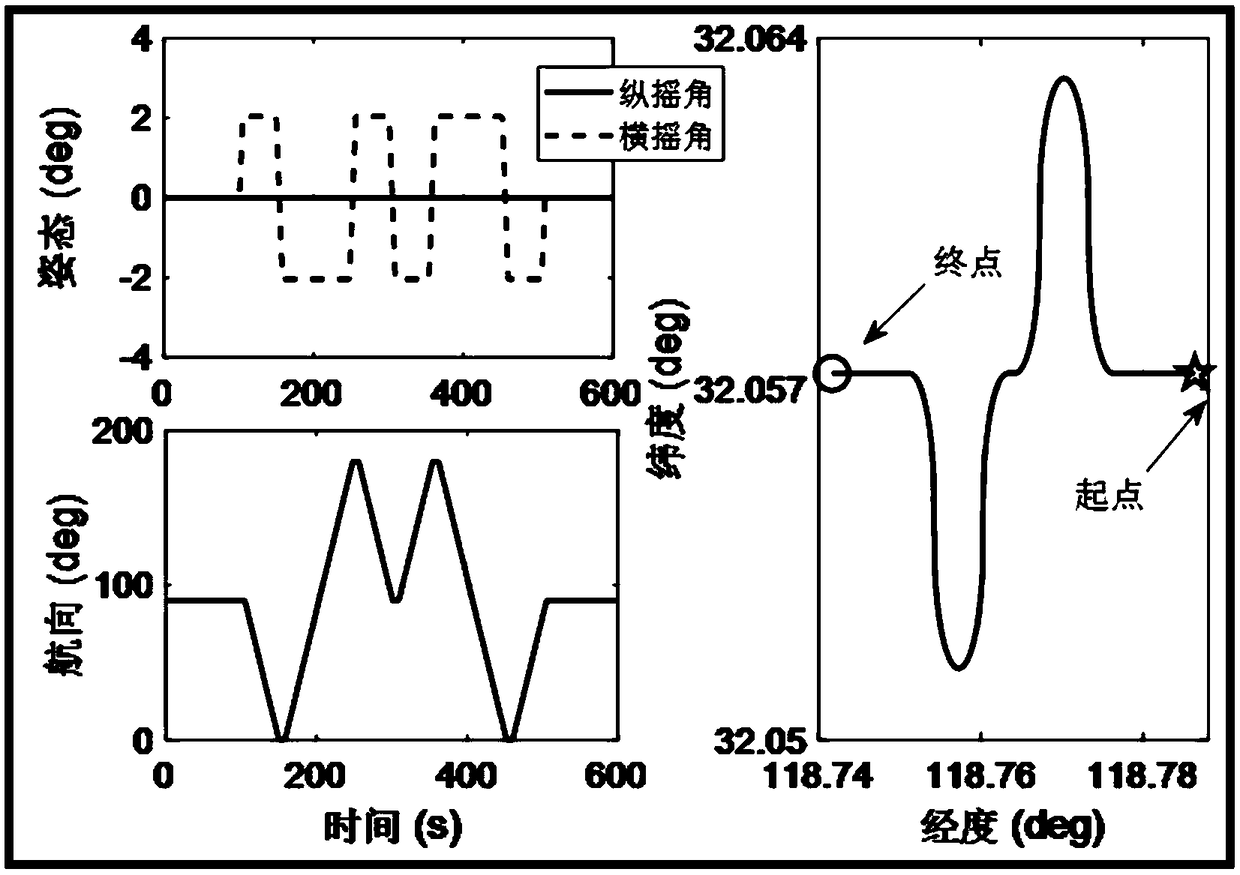
The invention discloses a DVL-assisted SINS robust on-moving initial alignment method. The DVL-assisted SINS robust on-moving initial alignment method comprises the following steps of step (1), acquiring real-time sensor data; step (2), establishing a vector apparent motion parameter equation; step (3), on the basis of establishing the vector apparent motion parameter equation, estimating a parameter matrix through adaptive robust Kalman filtering; step (4), establishing reconfiguration vectors based on estimated parameters; step (5), through an optimal base quaternion attitude determining method, computing the error angle between a determined attitude and a real attitude; step (6), setting an initial alignment moment as M and a real-time data acquiring moment as k, if k=M, outputting an initial alignment result and completing an initial alignment process, and if k<M, determining that the initial alignment process is not completed, and repeating the above steps of (1) to (5) until theinitial alignment process is completed. The DVL-assisted SINS robust on-moving initial alignment method solves the problems of poor alignment precision and divergent alignment processes when system measured noise is abnormal.
Owner:北京唯实深蓝科技有限公司
Combined velocity measuring system suitable for micro UUV
ActiveCN105842474ASimple methodImprove reliabilityFluid speed measurementVelocity measurementKalman filter
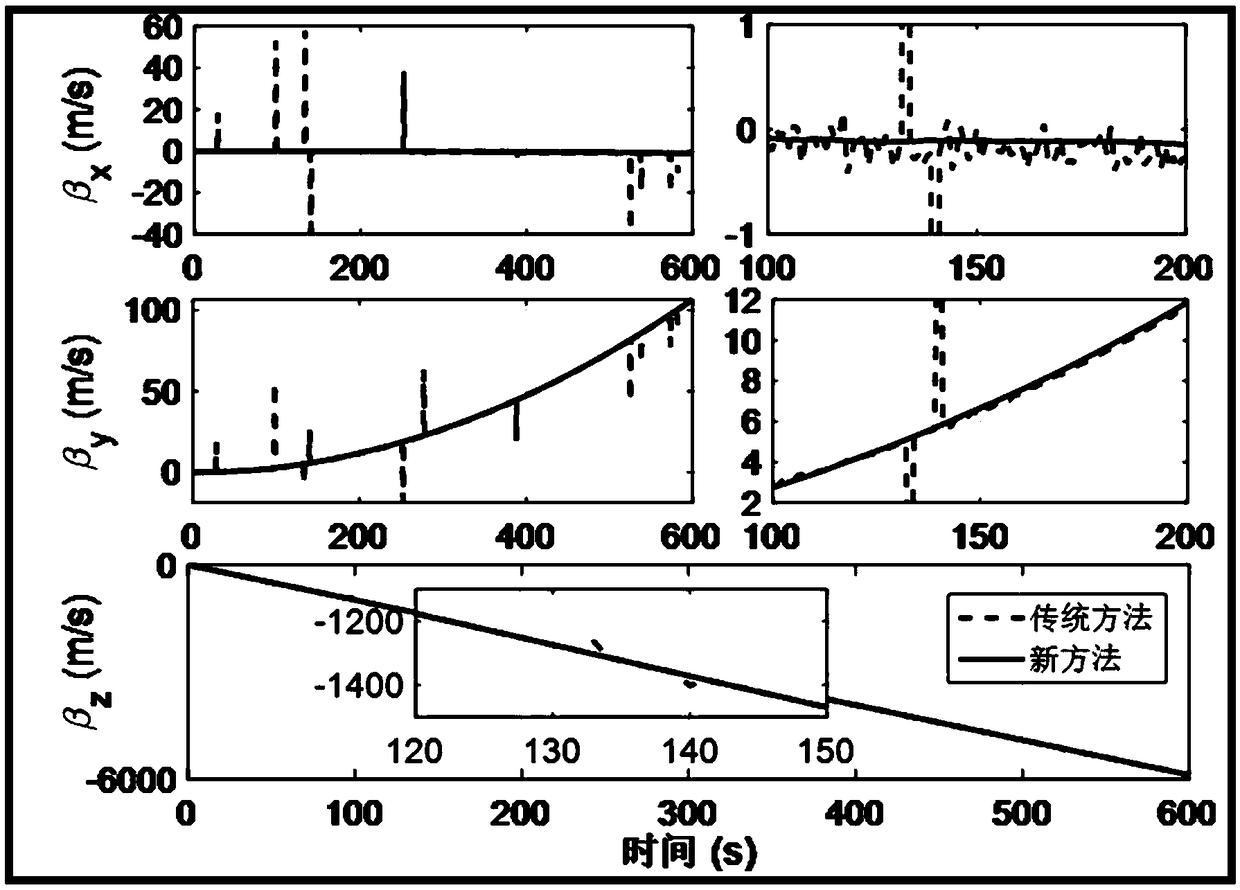
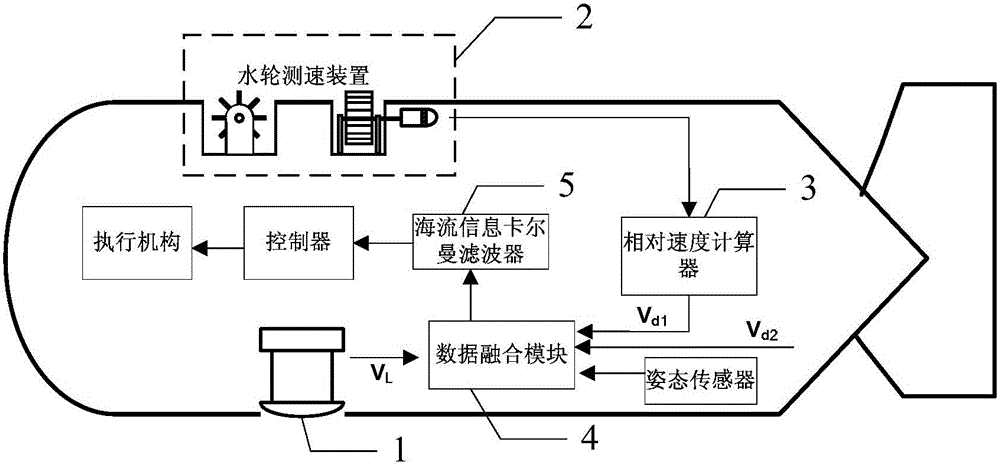
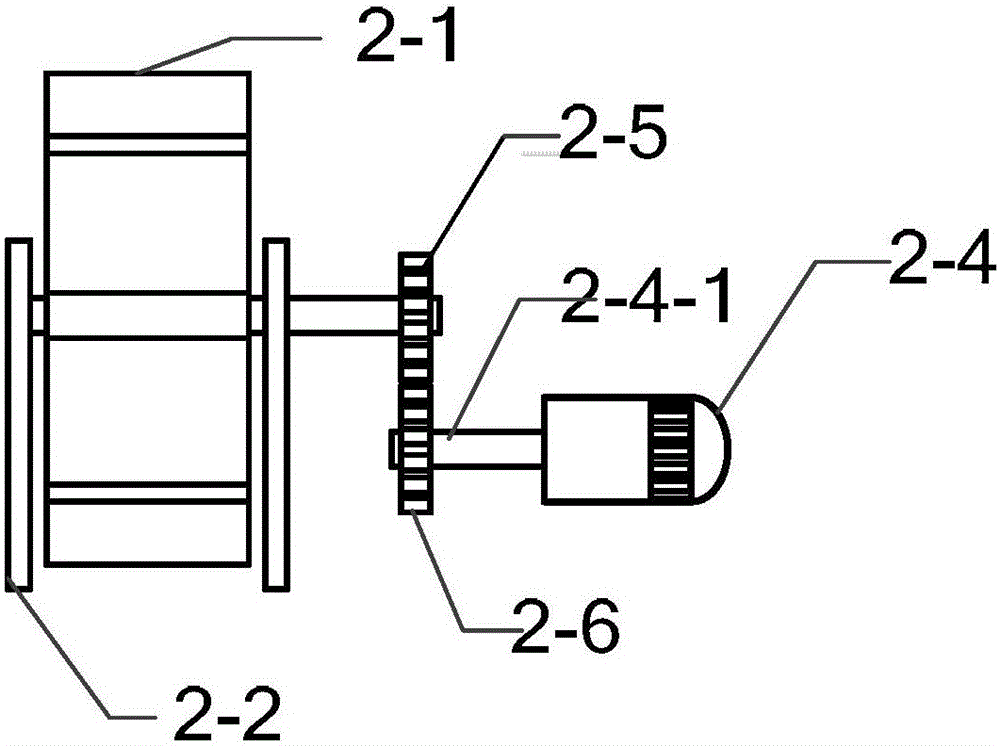
The invention discloses a combined velocity measuring system suitable for a micro UUV, and relates to the combined velocity measuring technology for a micro unmanned underwater vehicle (UUV). The invention aims to solve the problem that a conventional Doppler velocity log (DVL) is not suitable for velocity measurement when a micro underwater vehicle performs underwater navigation at a great depth. Two groups of water wheel velocity measuring devices are of the same structure, and used for measuring ocean current velocities in a length direction and in a width direction of the UUV respectively. Output ends of the two groups of water wheel velocity measuring devices are both connected with input ends of relative velocity calculators. Output ends of the relative velocity calculators are connected with relative velocity input ends of a data fusion module. An output end of a high-frequency acoustic DVL is connected with a ground velocity input end of the data fusion module. An output end of the data fusion module is connected with an input end of an ocean current information Kalman filter which outputs ocean current information. The invention has the characteristics of being simple in structure, low in cost, small in size, light in weight, high in reliability, and capable of real-time calculation of time-varying ocean current information. The invention is suitable for measuring ocean current information.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Error calibration method based on SINS (Strapdown Inertial Navigation System)/DVL (Doppler Velocity Log) integrated navigation
ActiveCN110542438AImprove reliabilityVerify correctnessMeasurement devicesCalibration resultErrors and residuals
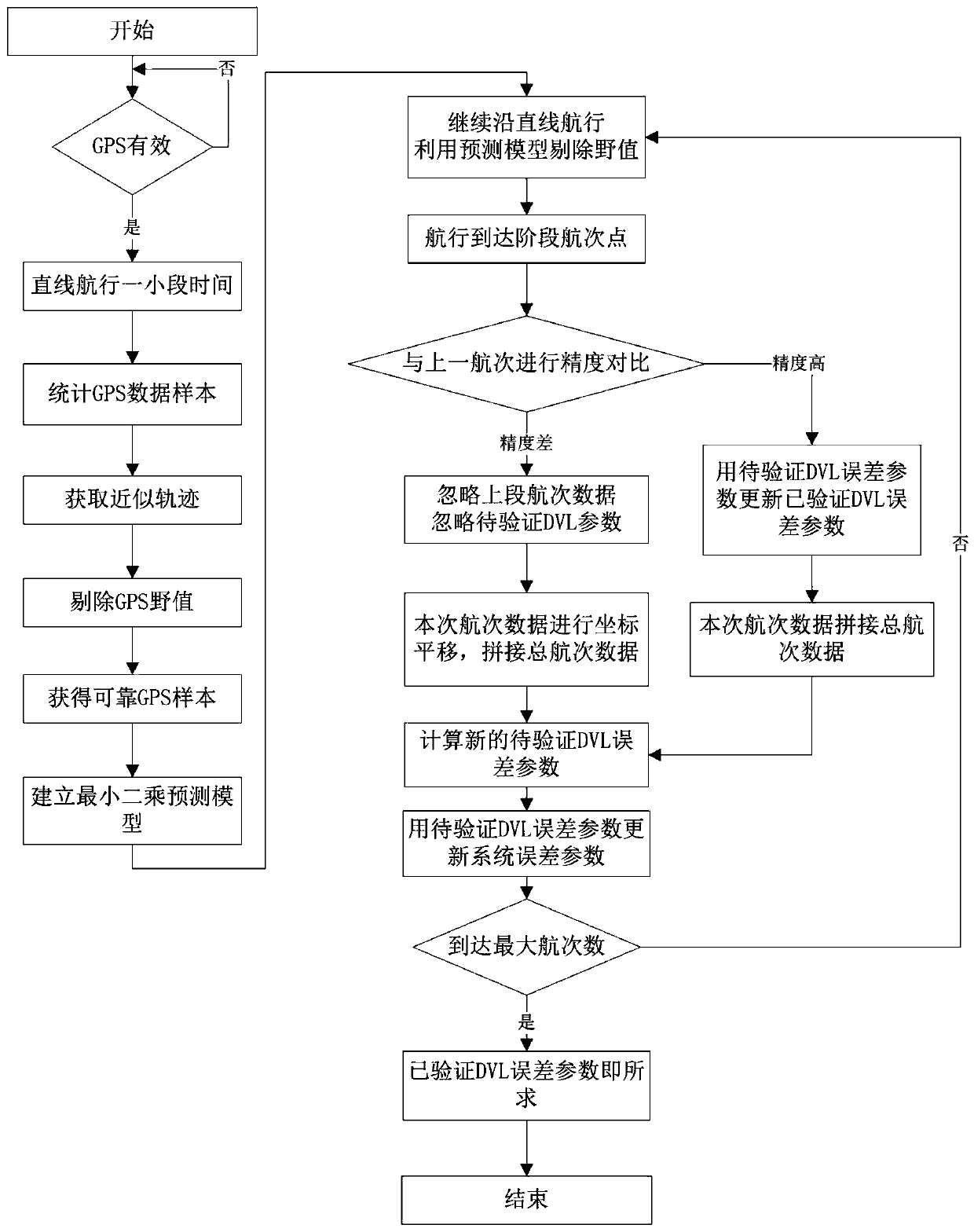
The invention relates to an error calibration method based on SINS (Strapdown Inertial Navigation System) / DVL (Doppler Velocity Log) integrated navigation. The method comprises the steps of (1) obtaining a voyage trajectory prediction model; (2) obtaining a DVL voyage distance and GNSS voyage distance; (3) incorporating voyage data into total voyage number data, recalculating new to-be-verified DVL error parameters and updating the system error parameters; (4) going back to step (2) to continue to execute until the number of staged voyages reaches the preset maximum number of voyages, and completing calibration, wherein the verified error parameters at this time are DVL error parameters. The error calibration method based on SINS / DVL integrated navigation disclosed by the invention, the validity judgment is performed on GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) position data, the voyage trajectory prediction model is established by use of a least square method to improve the reliability of the GNSS position information, the DVL error parameter is calculated by use of a relation between the DVL voyage distance and the GNSS voyage distance, a feedback authentication mechanism is added in a calibration process while the DVL error is calculated, the error parameter can be recalculated in time in case of error calibration to verify the correctness of the calibration results, therebyimproving the accuracy degree of the calibration results; and the error calibration method based on SINS / DVL integrated navigation has practical engineering significance.
Owner:TIANJIN NAVIGATION INSTR RES INST
Deep-water intelligent navigation method based on water velocity assisted inertial navigation
ActiveCN109579850AWater Velocity OptimizationControl cumulative errorNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsWater velocityIntegrated processing
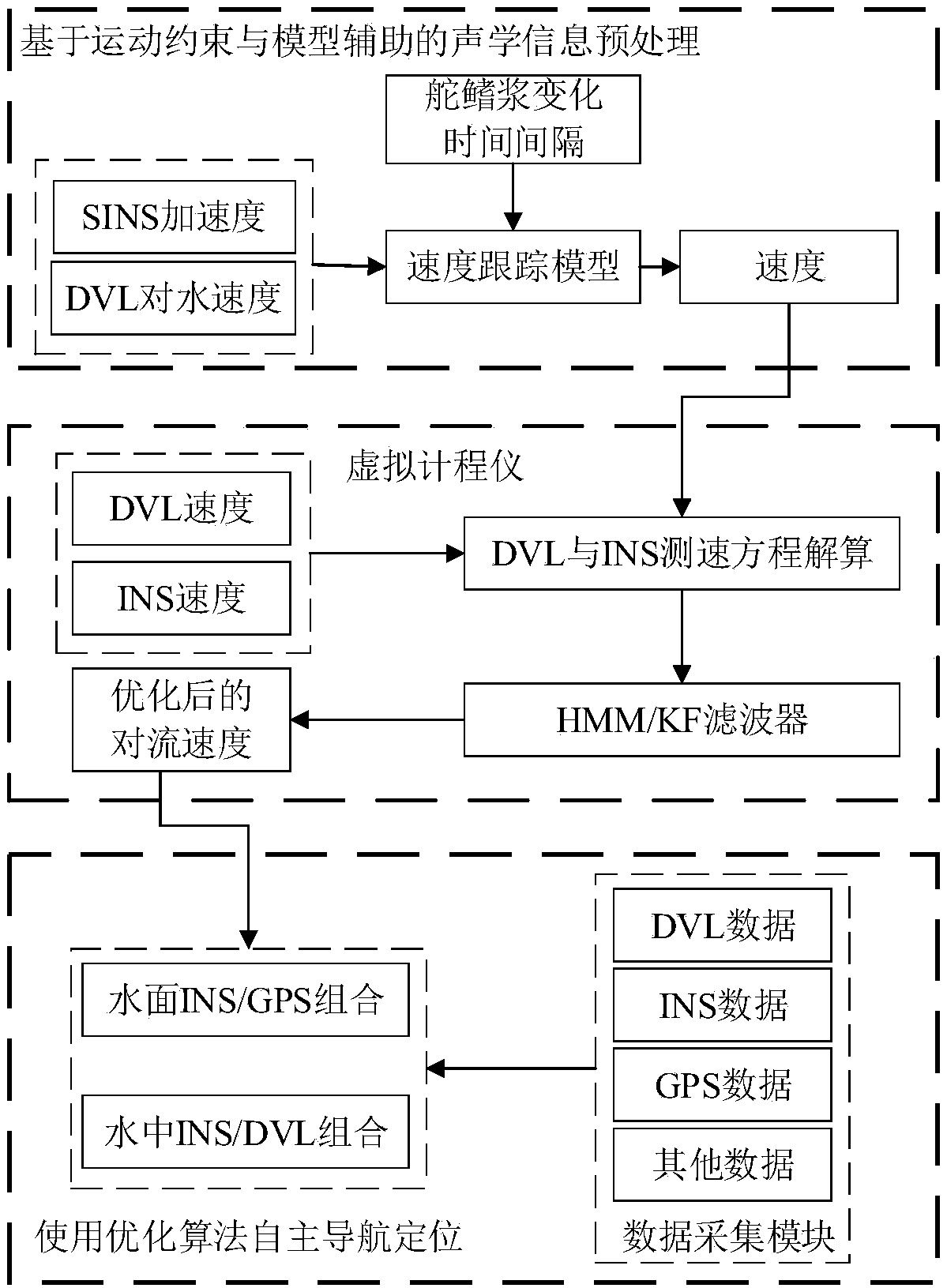
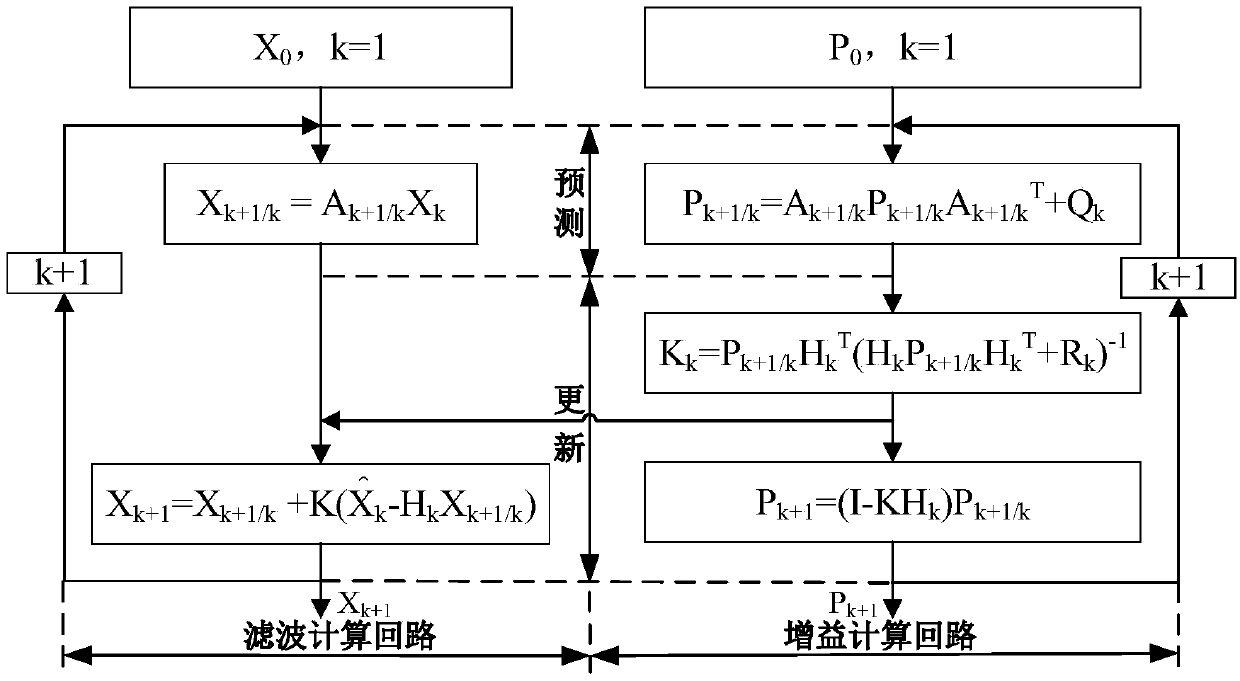
The invention discloses a deep-water intelligent navigation method based on water velocity assisted inertial navigation. Measures from aspects of acoustic information pretreatment, a water velocity assisted inertial navigation system and the like are taken so as to solve the related problems of poor reliability of acoustic information caused by acoustic measurement and a marine environment and large accumulated navigation errors when an autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) is too far away from the seabed without Doppler velocity log (DVL) ground velocity assistance and the like. The deep-waterintelligent navigation method particularly comprises the steps that (1) based on a motion constraint idea, rudder, fin and paddle change information is introduced to preprocess the acoustic information to improve the credibility of the acoustic information; (2) a virtual speed log scheme is introduced, a delay-free HMM / KF filter is designed, and the velocities of a DVL and an inertial navigation system (INS) are comprehensively processed to reduce DVL velocity errors and INS long-period errors caused by AUV bumpy swing, acceleration and deceleration and turning; and (3) a graph optimization algorithm is adopted, nonlinear optimization is used for controlling the error level, and a recursive method is utilized to marginalize and optimize to realize real-time composition so as to improve navigation accuracy.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
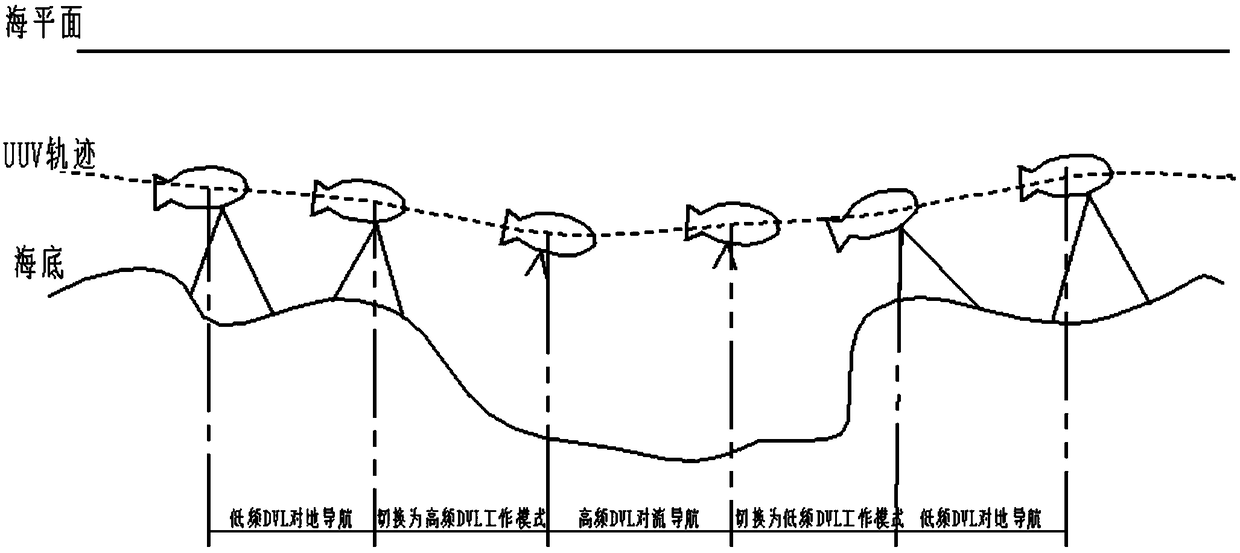
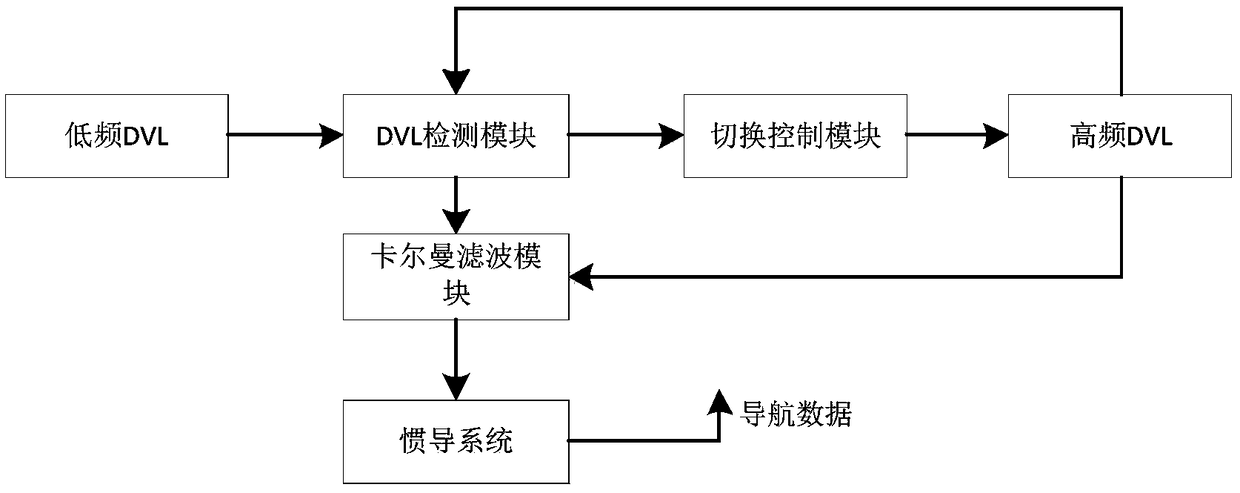
UUV deep sea integrated navigation device with dual-Doppler adaptive switching speed measurement and navigation method
InactiveCN109269496AReduced need for navigationImprove stabilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsInertial navigation systemLarge range
The invention provides a UUV deep sea integrated navigation device with dual-Doppler adaptive switching speed measurement and a navigation method. The device comprises a Doppler velocity log detectionmodule, a Doppler velocity log mode conversion module, a Kalman filtering module, a high-frequency convection Doppler velocity log, a low-frequency convection Doppler velocity log and an inertial navigation system. According to the device and the method, the stability of a UUV in a trench and during deep sea navigation can be improved, the high-precision navigation capability of an aircraft in alarge-depth sea area is improved, the water outlet correction frequency is reduced, and the navigation requirements of large-range navigation and hidden operation are met. The amount of information needed for judgement of switching of an operation state of the DVL is small, and a control command is simple.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Synthetic aperture sonar motion compensation method based on combination of multiple sensors
ActiveCN110221278AReduce mistakesImprove estimation accuracyAcoustic wave reradiationSynthetic aperture sonarMultiple sensor
The invention relates to the technical field of imaging sonar signal processing and synthetic aperture sonar motion compensation, in particular to a synthetic aperture sonar motion compensation methodbased on the combination of multiple sensors. The method comprises the following steps that: on the basis of a synthetic aperture sonar motion measurement system, obtaining sonar motion speed measured by inertial navigation, and sonar motion speed measured by a Doppler velocity log; combining the sonar motion speed measured by the inertial navigation with the sonar motion speed measured by the Doppler velocity log to obtain the optimal estimation value of the sonar motion speed; carrying out integration on the optimal estimation value of the sonar motion speed, and calculating the practical plane flight path and the sky direction flight path of the sonar; according to the practical plane flight path and the sky direction flight path of the sonar, carrying out fitting on an ideal plane flight path and the sky direction flight path under a least squares criterion; calculating a swaying error between the ideal plane flight path and the practical plane flight path of the synthetic aperture sonar; calculating a heaving error between the practical sky direction flight path and the ideal sky direction flight path of the synthetic aperture sonar; and calculating a practical sonic path distance difference, and carrying out conversion to obtain a time delay to compensate echo data collected by the synthetic aperture sonar.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
DVL (doppler velocity log) failure processing method for SINS (strapdown inertial navigation system)/DVL integrated navigation system
ActiveCN105547302AReduce adverse effectsImprove accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSimulationNavigation system
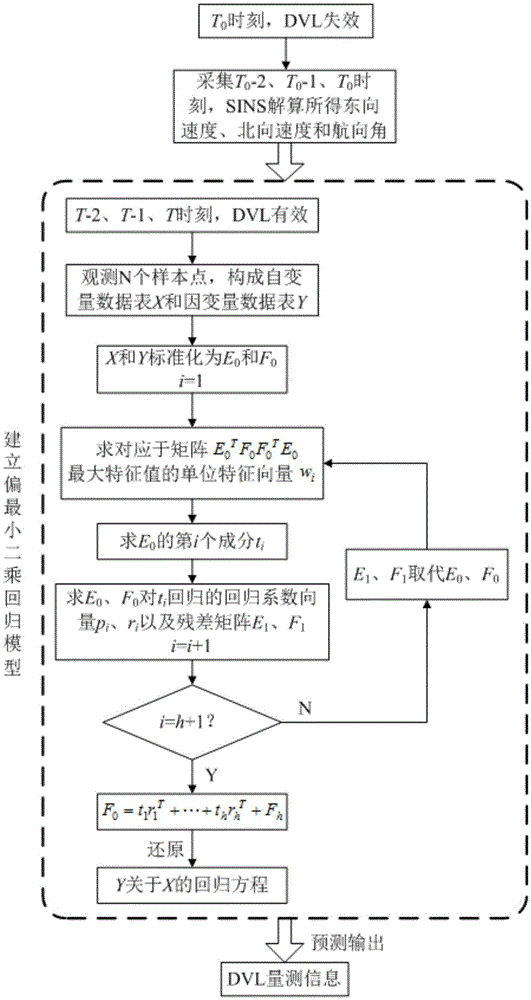
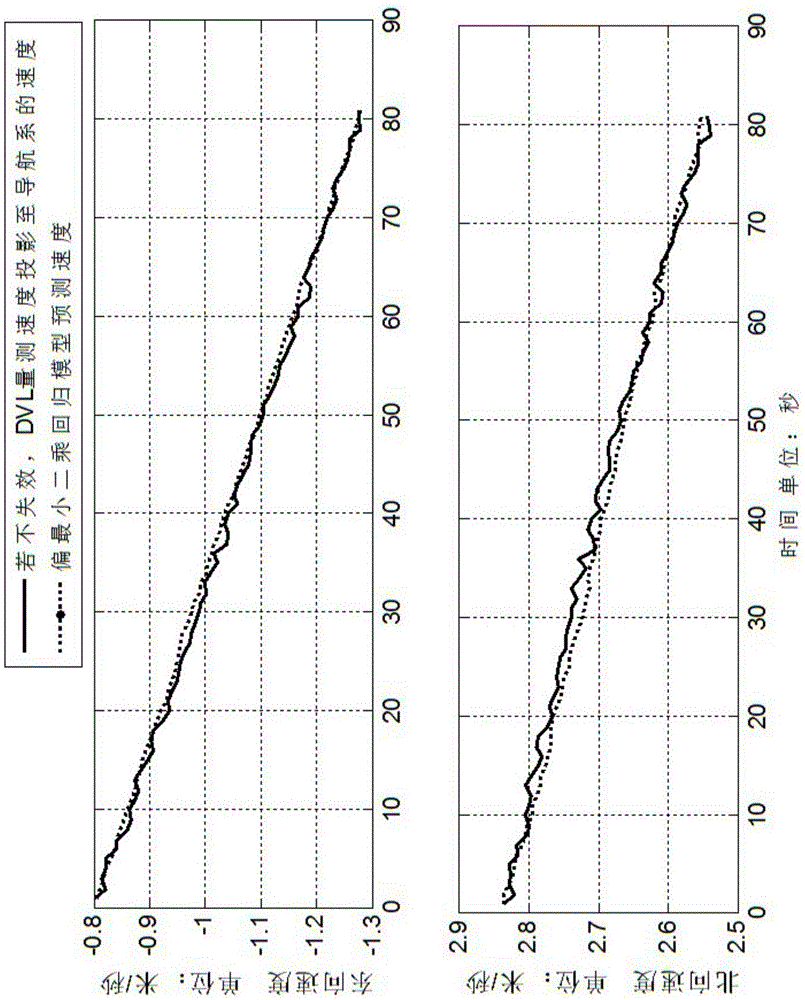
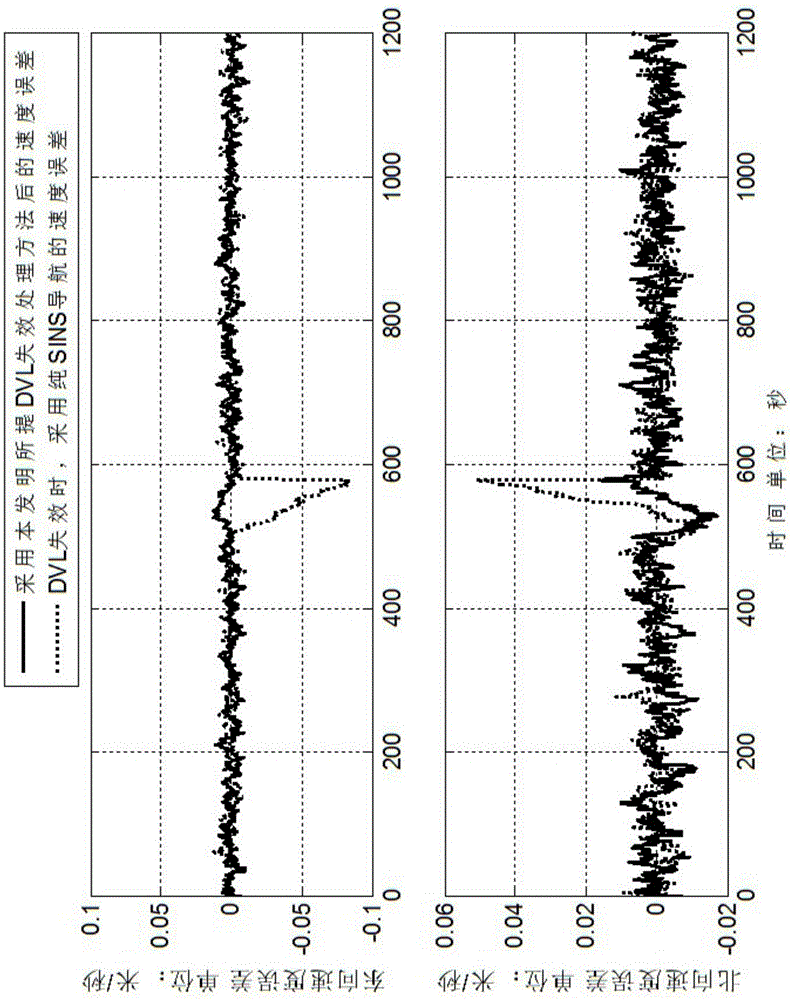
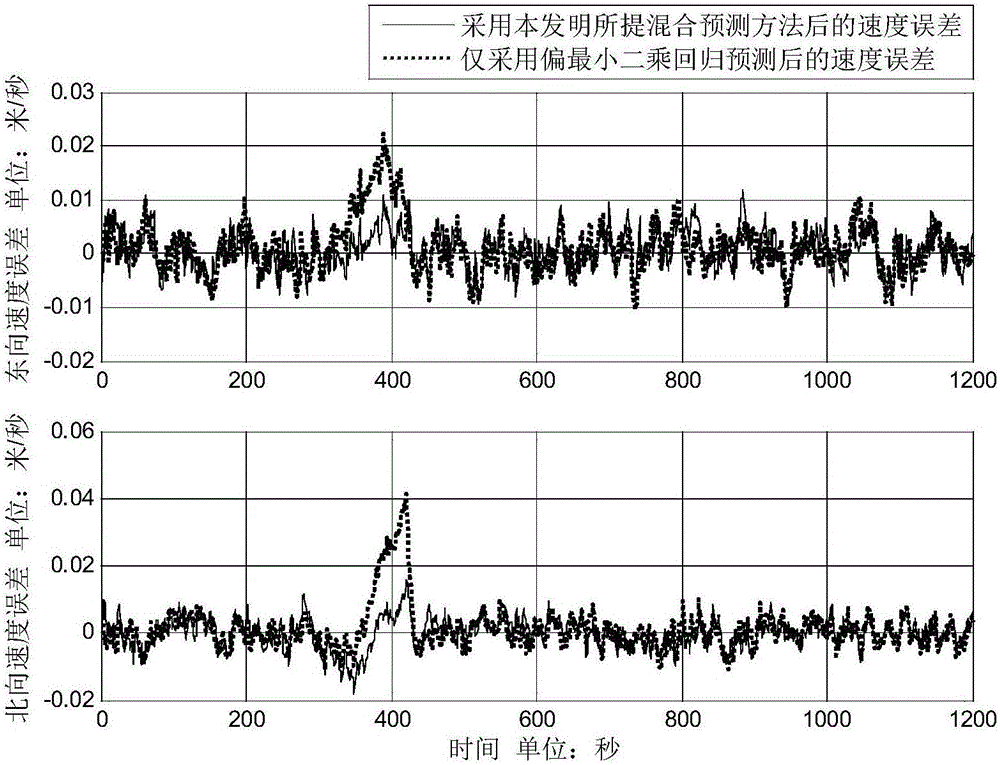
The invention discloses a DVL (doppler velocity log) failure processing method for an SINS (strapdown inertial navigation system) / DVL integrated navigation system. When a DVL is effective, calculation information of an SINS and measurement information of the DVL are acquired and form a data table, and a prediction model is established by means of partial least squares regression; when the DVL is failed, measurement information of the DVL is predicted by means of the established model, a prediction result is merged with the calculation information of the SINS, and SINS / DVL integrated navigation is realized in the failure state of the DVL. The measurement information of the DVL is predicted with the calculation information of the SINS at the failure moment and before failure as input, the accuracy of the prediction result is improved, the model is established by means of partial least squares regression, the defect that robustness of the model is damaged due to multiple correlation of independent variables is overcome, and the reliability of the established model is guaranteed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Hybrid processing method for DVL (Doppler velocity log) failures in integrated navigation
ActiveCN106840150AImprove reliabilityGuaranteed robustnessNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAlgorithmSupport vector regression model
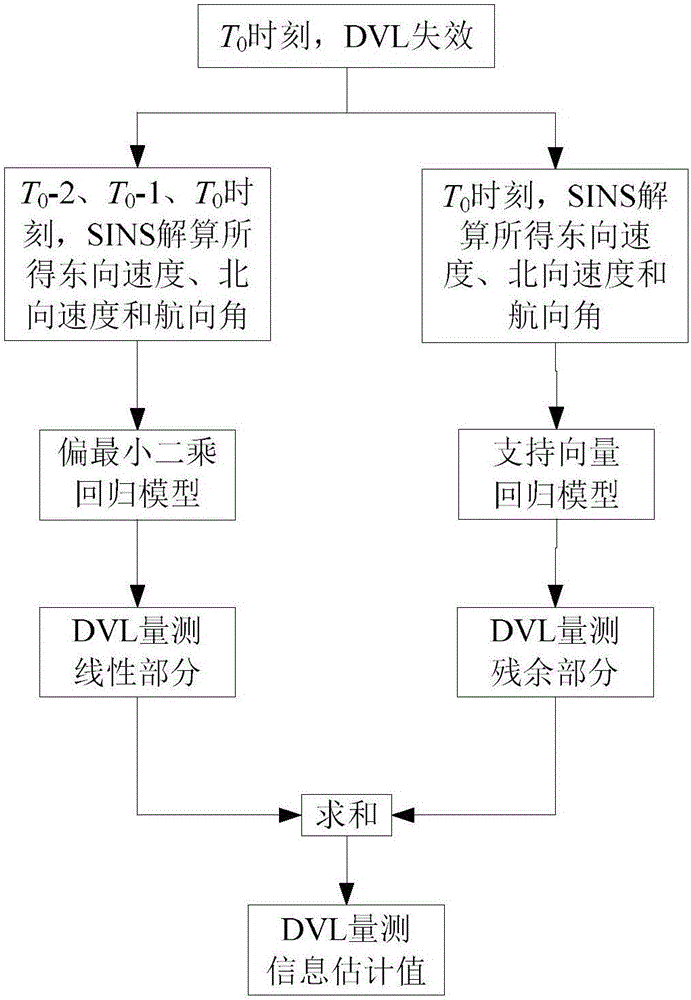
The invention discloses a hybrid processing method for DVL (Doppler velocity log) failures in integrated navigation. The hybrid processing method comprises the following steps: when DVL is valid, collecting calculation information of an SINS (strapdown inertial navigation system) and measurement information of DVL to form a data table, using partial least squares regression to establish a linear prediction model, then subtracting the measurement information of DVL and a result obtained by prediction of the least squares regression model to obtain a residual part, and taking the residual part as a training target and using support vector regression training to obtain a corresponding prediction model; when the DVL fails, using the established partial least square regression model and the support vector regression model to respectively predict a measuring linear part of DVL and the residual part, and taking the sum of the measuring linear part of DVL and the residual part as predicted measurement information of DVL to ensure the reliability of SINS / DVL integrated navigation results under intermittent failures of DVL. The hybrid processing method for the DVL failures in the integrated navigation uses the partial least squares regression and support vector regression to establish the models, and uses double-model hybrid prediction to effectively improve the accuracy of prediction results.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
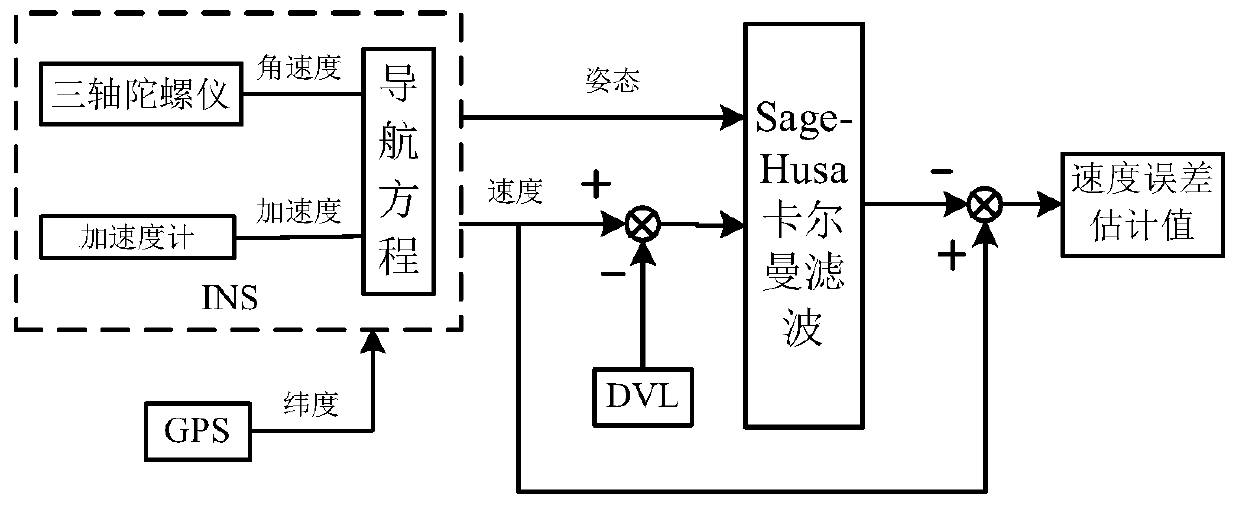
Velocity aiding based gyroscopic drift correction method of inertial navigation system
ActiveCN106123923AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyMeasurement devicesMeasurement deviceGeographic coordinate system
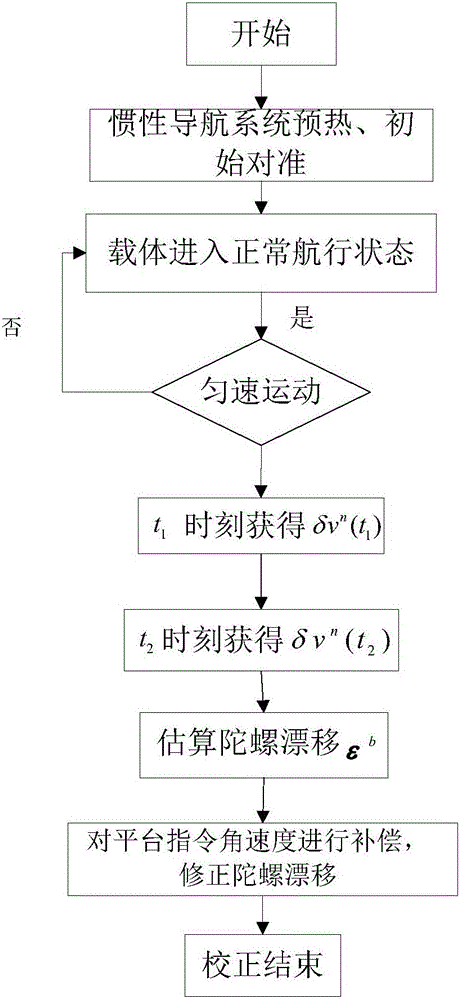
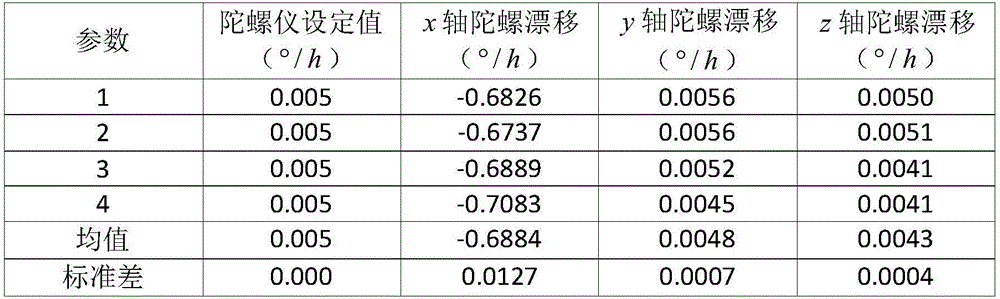
The invention belongs to the technical field of inertial navigation systems and in particular relates to a velocity aiding based gyroscopic drift correction method of an inertial navigation system, which is used for carrying out gyroscopic drift correction by utilizing velocity information aiding in long-time navigation. The velocity aiding based gyroscopic drift correction method comprises the following steps: pre-heating the inertial navigation system, starting to enter a navigation state after initial alignment early-stage work; after a period of time, recording a moment as t1 when the inertial navigation system reaches the condition of constant-speed direct navigation being kept within 10 minutes; obtaining referred external velocity information according to a ground-toward velocity measuring signal of an external aided measurement device, such as a Doppler velocity log; projecting the obtained external velocity information to a geographic coordinate system and the like. By establishing a relational expression between velocity error information and gyroscopic drift, the gyroscopic drift of the inertial navigation system can be estimated and revised by only utilizing the velocity information, so that the precision and the efficiency of the inertial navigation system are improved and the safety and the privacy of a carrier are guaranteed.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Distance and environment feature-based navigation system and parameter perturbation solving method thereof
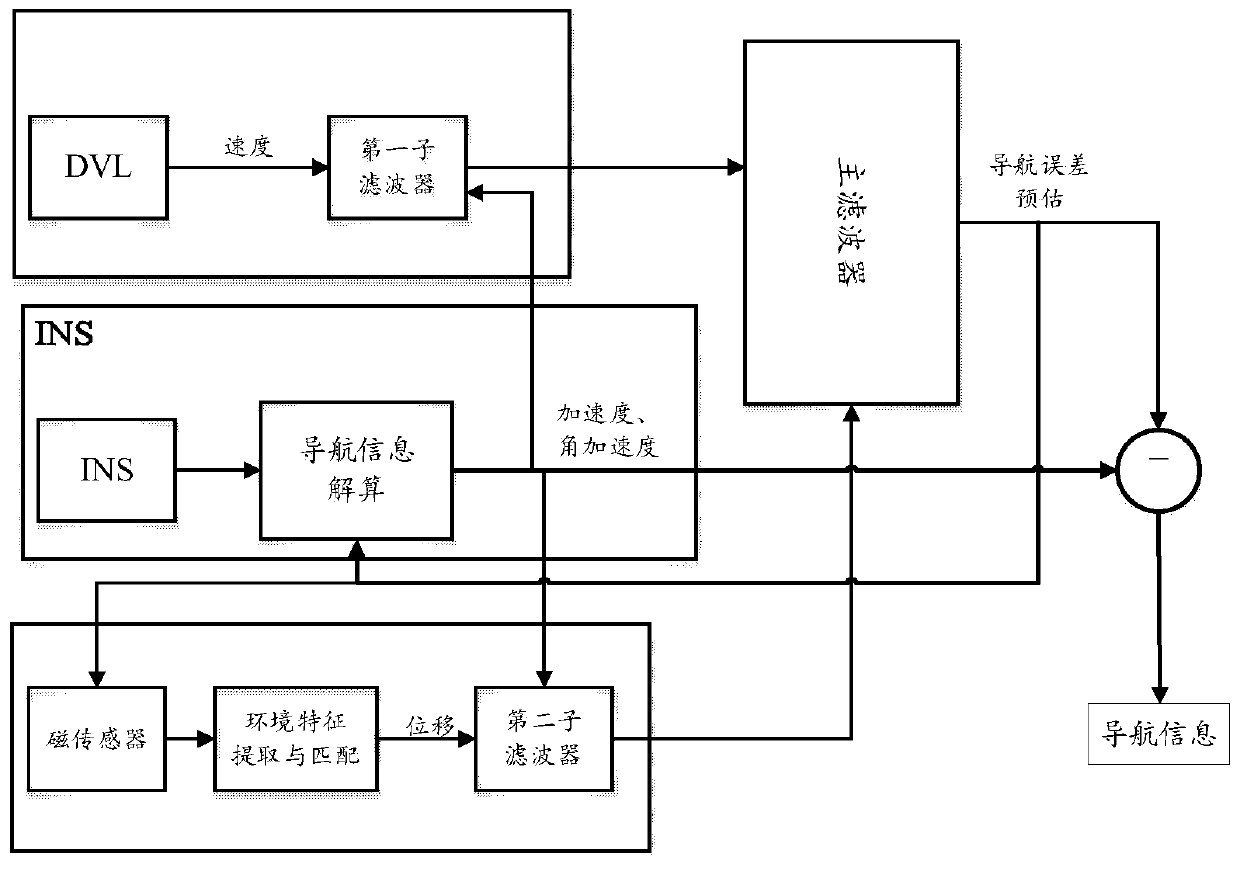
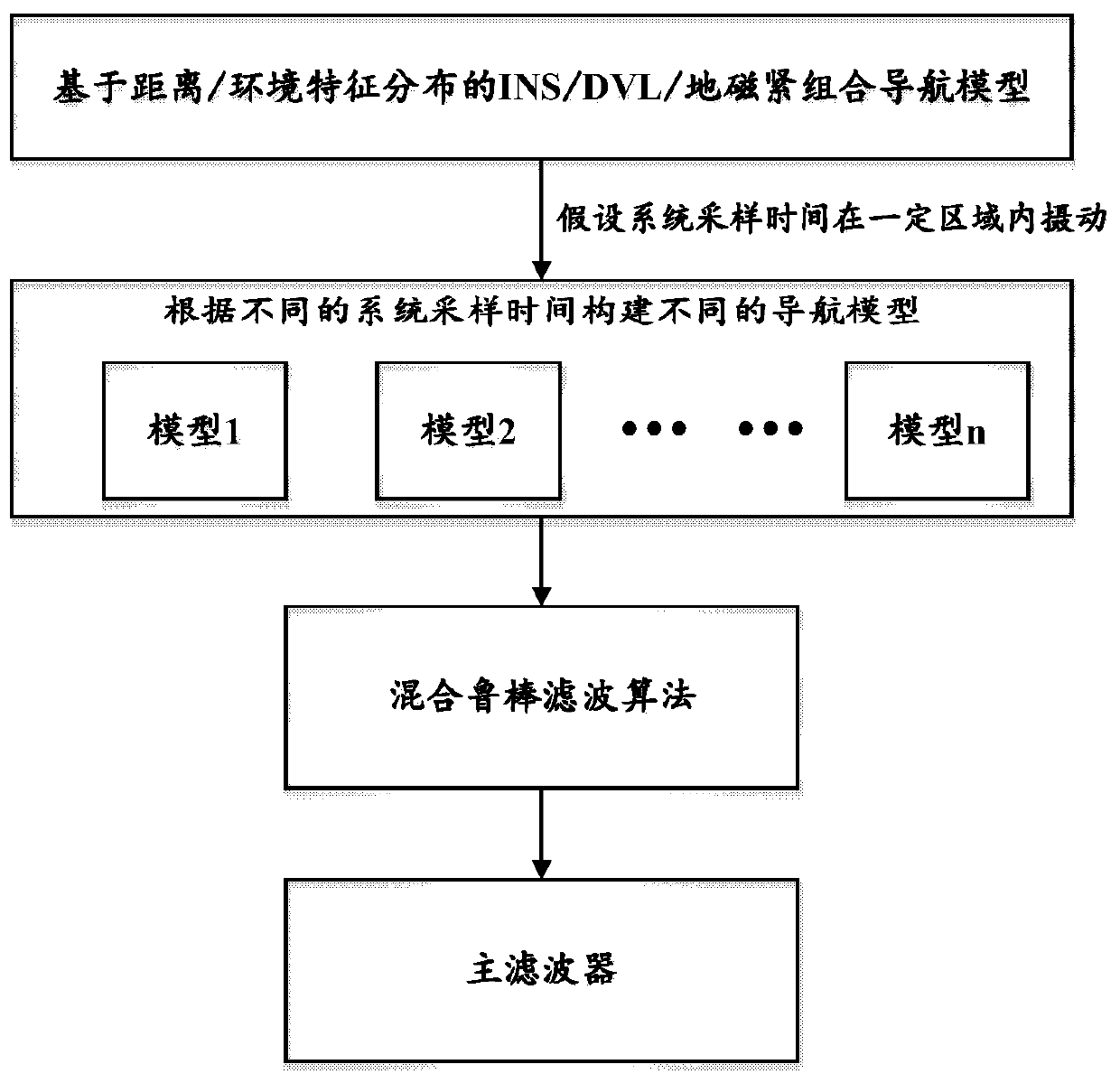
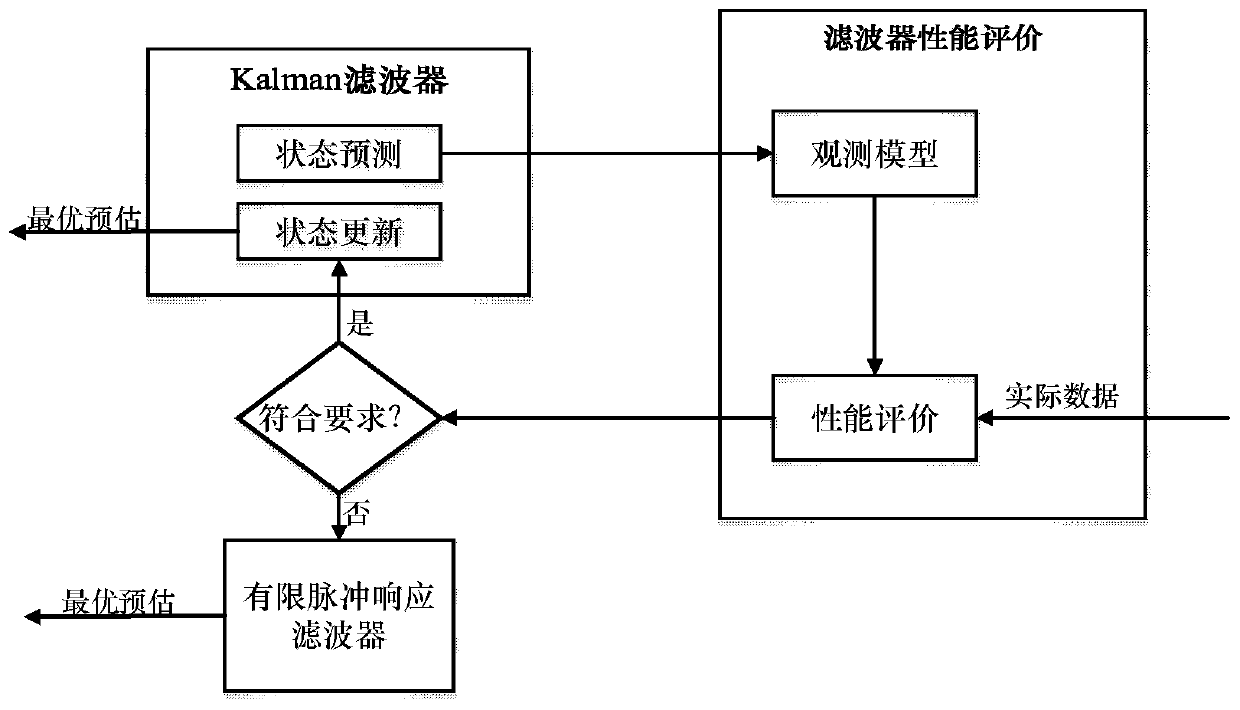
ActiveCN109931935ASolve the parameter perturbation problemImprove filtering performanceNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsUnderwater navigationNavigation system
The invention discloses a distance and environment feature-based navigation system and a parameter perturbation solving method thereof. The system includes a navigation module, a Doppler velocity log(DVL), a magnetic sensor and a filter, wherein the navigation module is located in an inertial navigation system (INS). Geomagnetic environment information of an underwater navigation area is collected, so that a geomagnetic map can be made on the basis of the underwater navigation area; the original information of the INS navigation module, the Doppler velocity log, and the magnetic sensor is outputted to the filter; the filter is constructed based on an interacting multiple model-based finite pulse filtering / Kalman filtering hybrid robust algorithm; and the filter performs filtering, solvesa parameter perturbation problem, and outputs corrected navigation information, and therefore, navigation is completed. According to the distance and environment feature-based navigation system and the parameter perturbation solving method thereof of the invention, the interacting multiple model method is adopted to solve the parameter perturbation problem; errors caused by the non-synchronizationproblem of the navigation information of each navigation module are effectively reduced; and two filtering modes can be intelligently switched, so that the error prediction performance of the systemis very reliable.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
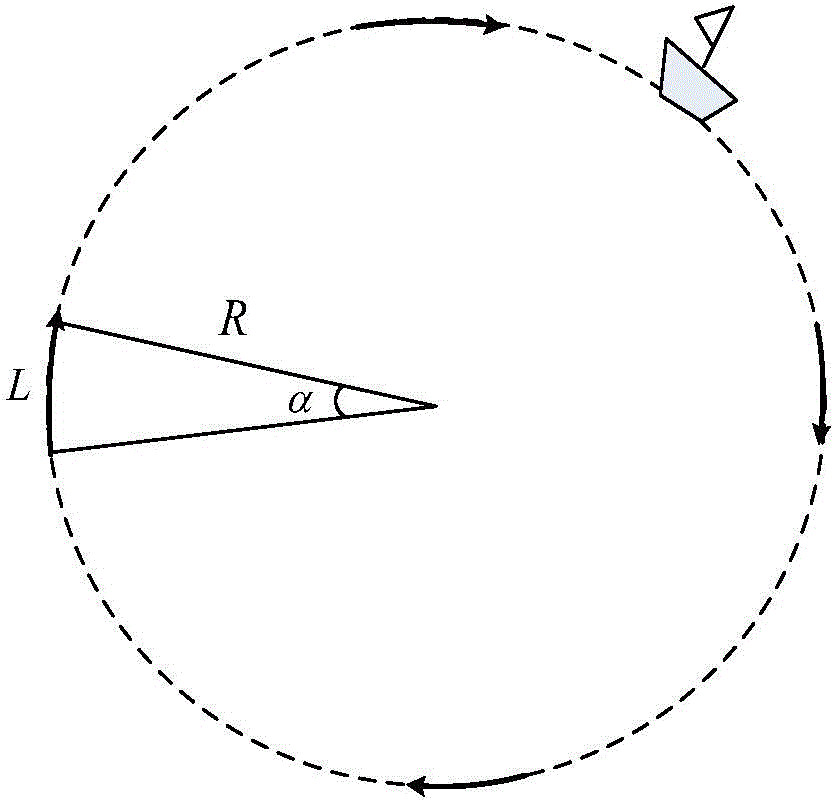
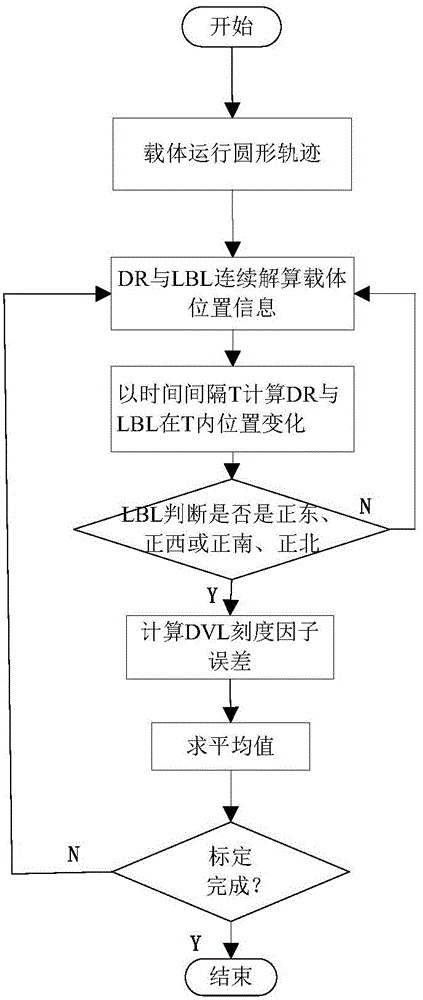
On-line calibration method for scalefactorerror of DVL (Doppler velocity log)
The invention discloses an on-line calibration method for a scalefactor error of a DVL (Doppler velocity log).A circular trace is adopted to enable an underwater vehicle to cyclically operate for 360 degrees, the underwater vehicle inevitably passes four positions including due east, due west, due south and due north during operation of a circle of circular trace, time periods of the vehicle passing the four positions are determined by a LBL (long base line) acoustic navigation system, decoupling of the scalefactor error of the DVL and a compass course error in a DR (dead reckoning) process is realized, and the scalefactor error of the DVL is calibrated on line according to navigation results of DR and LBL. The on-line calibration method for the scale factor error of the DVL has the advantages of simplicity, convenience, effectivity and only requirement for positional information and is suitable for on-line calibration of the DVL scalefactor error for the underwater vehicle.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
UUV (unmanned underwater vehicle) aided navigation method based on current profile
ActiveCN102323586BImprove environmental adaptabilityAcoustic wave reradiationProcess noiseRelational database
The invention provides a UUV (unmanned underwater vehicle) aided navigation method based on current profile. The method comprises the following steps: firstly setting up a Kalman filter model of current profile data, secondly determining the observation noise variance R and process noise variance Q in a Kalman equation according to variations of the environment and the UUV own velocity and finally setting up a UUV velocity-current profile relation database, utilizing the relation database and the current profile information measured by an ADCP (acoustic Doppler current profile) to reckon the UUV velocity at the time of DVL (Doppler velocity log) failure and further obtaining the navigation position of the UUV by deadreckoning. The method has the following beneficial effects: when the UUV performs a task under water, once the sonar data of the DVL have failure, the UUV velocity can be reckoned by using the current profile information measured by the ADCP, so that the UUV can continue performing the ocean exploration task in the complex ocean environments such as great depth, thus improving the environmental adaptation capability of the UUV.
Owner:哈尔滨船海智能装备科技有限公司
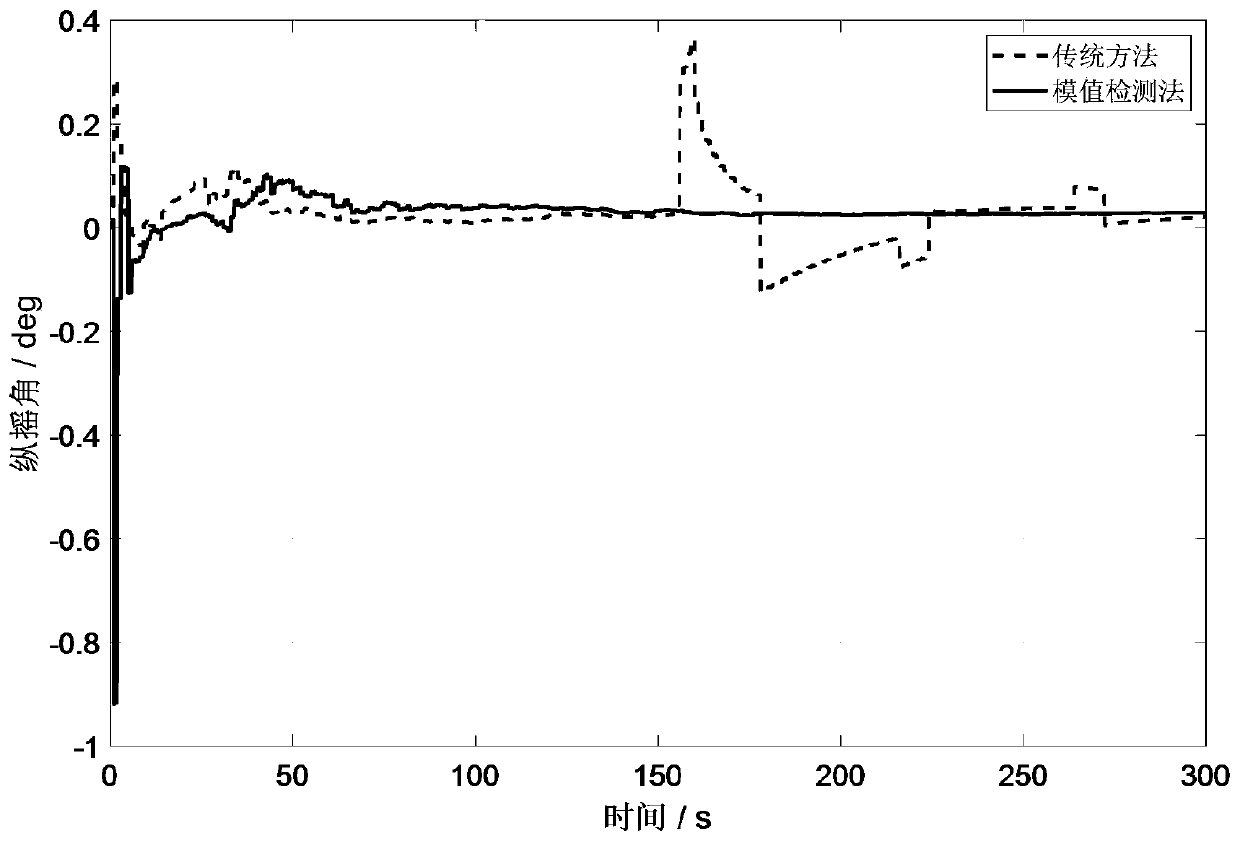
Robust alignment method for module value detection moving base
ActiveCN110108301AEasy to calculateEfficiently measure anomaly detection performanceMeasurement devicesReal-time dataAlgorithm
The invention discloses a robust alignment method for a module value detection moving base. The robust alignment method for the module value detection moving base is characterized in comprising the following steps that: obtaining the real-time data of an inertial sensor, and carrying out attitude update; obtaining auxiliary sensor information, and constructing a vector observer; carrying out module value calculation on the vector observer, and carrying out exception detection by a standard module value; through the module value detection, weakening an exception noise influence, and constructing an adaptive vector attitude determining method; initializing alignment process operation time as M; if an attitude change frequency k is equal to M, outputting an alignment result, and finishing aninitial alignment process; and if the attitude change frequency k is smaller than M, proving that the initial alignment process is not finished, and repeating the above steps to finish the initial alignment process. The method has the beneficial effect that the module value detection method is adopted to have the advantage of being convenient in calculation. The invention designs an optimal weightcalculation method, and has an efficient DVL (Doppler Velocity Log) measurement exception detection effect.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Error calibration method of model-free doppler velocity log (DVL)
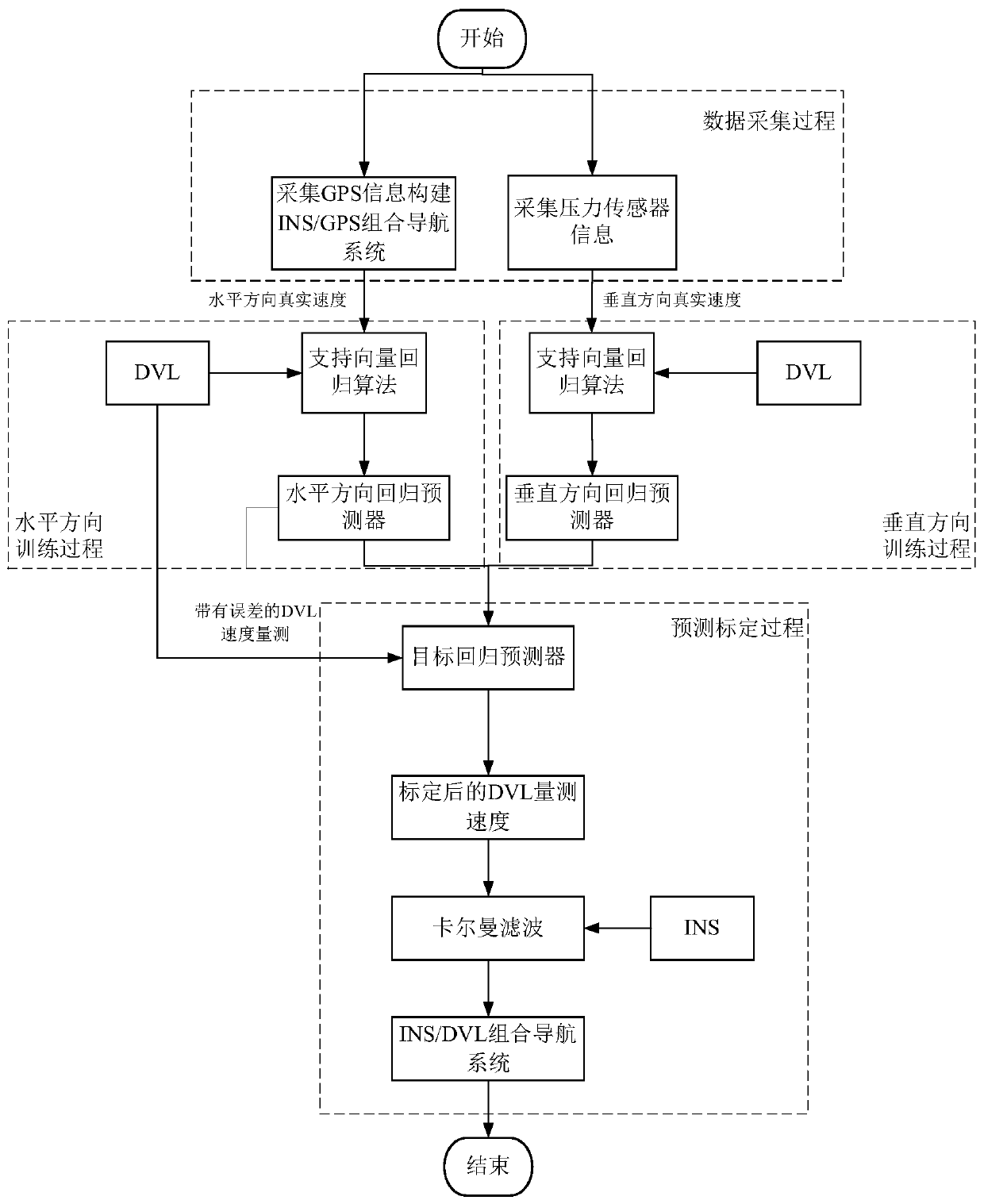
The invention discloses an error calibration method of a model-free doppler velocity log (DVL). The error calibration method does not require a priori DVL error model to achieve high-precision error calibration. The error calibration method includes the following steps that during the underwater movement of an underwater vehicle (AUV), the two-dimensional horizontal velocity information and vertical velocity information of the AUV are obtained, and the horizontal measurement velocity and the vertical measurement velocity of the doppler velocity log (DVL) arranged above the AUV are obtained; ahorizontal regression predictor is constructed, and the two-dimensional horizontal velocity information is used as an output training sample, the horizontal measurement velocity of the DVL is used asan input training sample, and the horizontal regression predictor is trained to obtain a trained horizontal regression predictor; similarly, a trained vertical regression predictor is obtained; the trained horizontal regression predictor and the trained vertical regression predictor are combined to obtain a target predictor; and the DVL velocity measurement information is collected in real time tobe taken as the input of the target predictor, and then the output of the target predictor is the calibrated DVL measurement velocity.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Correction method of installation error of Doppler log for autonomous underwater vehicle
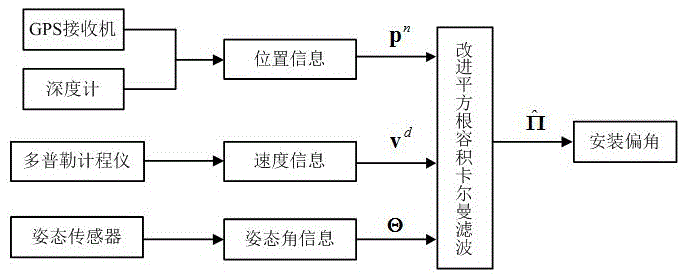
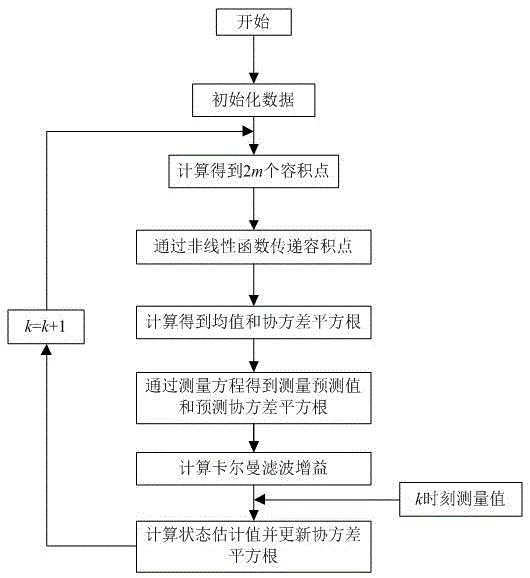
ActiveCN103697910BEliminate the effects of navigation accuracyEasy to operateElectromagnetic wave reradiationData acquisitionInstallation Error
The invention discloses a correcting method of installation errors of a doppler log of an autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV). The correcting method comprises the following steps: (1), data acquiring, namely acquiring northeast-direction location information, depth information, speed information and gesture information of the AUV on water surface; (2), filter wave estimating, namely by taking a DVL (Doppler Velocity Log) dead reckoning model with error correction, AUV three-dimensional location information and a DVL three-dimensional installation drift angle as system state vectors, the speed information measured by a DVL and the gesture information measured by a gesture sensor as system input vectors, the AUV three-dimensional location information as a measuring vector, establishing a discrete time system state equation and a measuring equation; carrying out filter wave estimating by adopting improved square capacity root Kalman filtering to obtain an estimated value of the DVL installation drift angle; and (3), error correcting, namely acquiring a DVL installation error correcting matrix according to the estimated value of the installation drift angle. The correcting method disclosed by the invention is easy to operate, does not need external equipment assistance and can effectively estimate the three-dimensional installation drift angle of the DVL, so that influences of the DVL installation errors on the AUV navigation accuracy are eliminated, and practical value is very high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
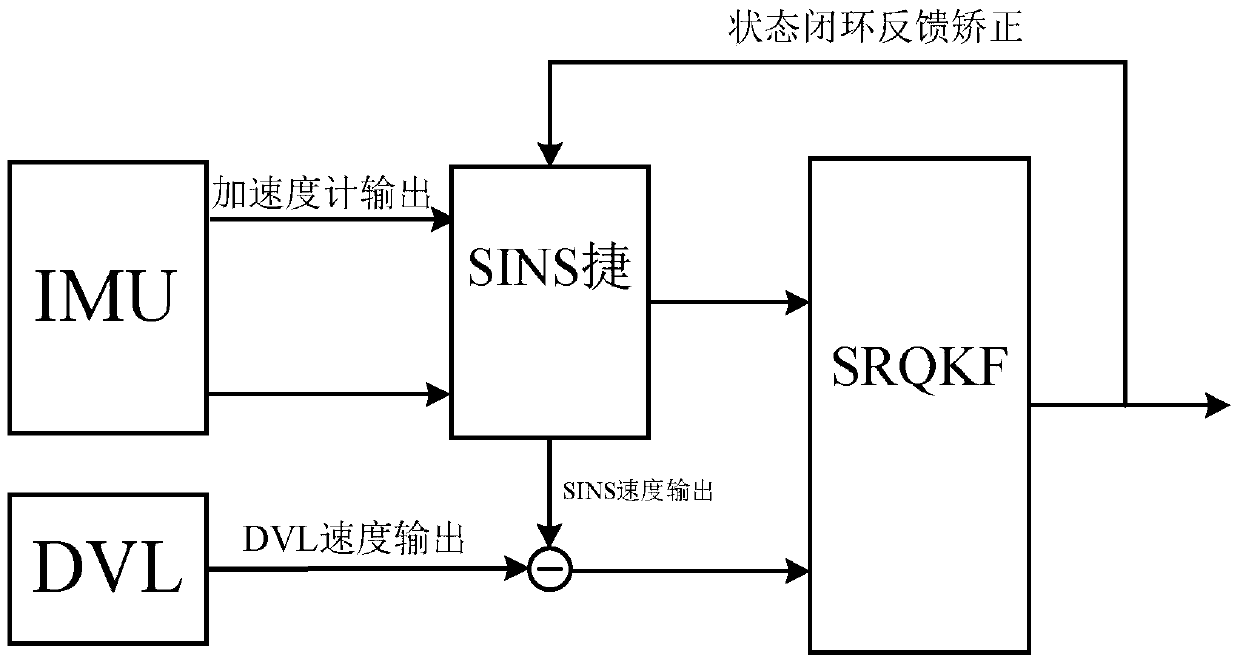
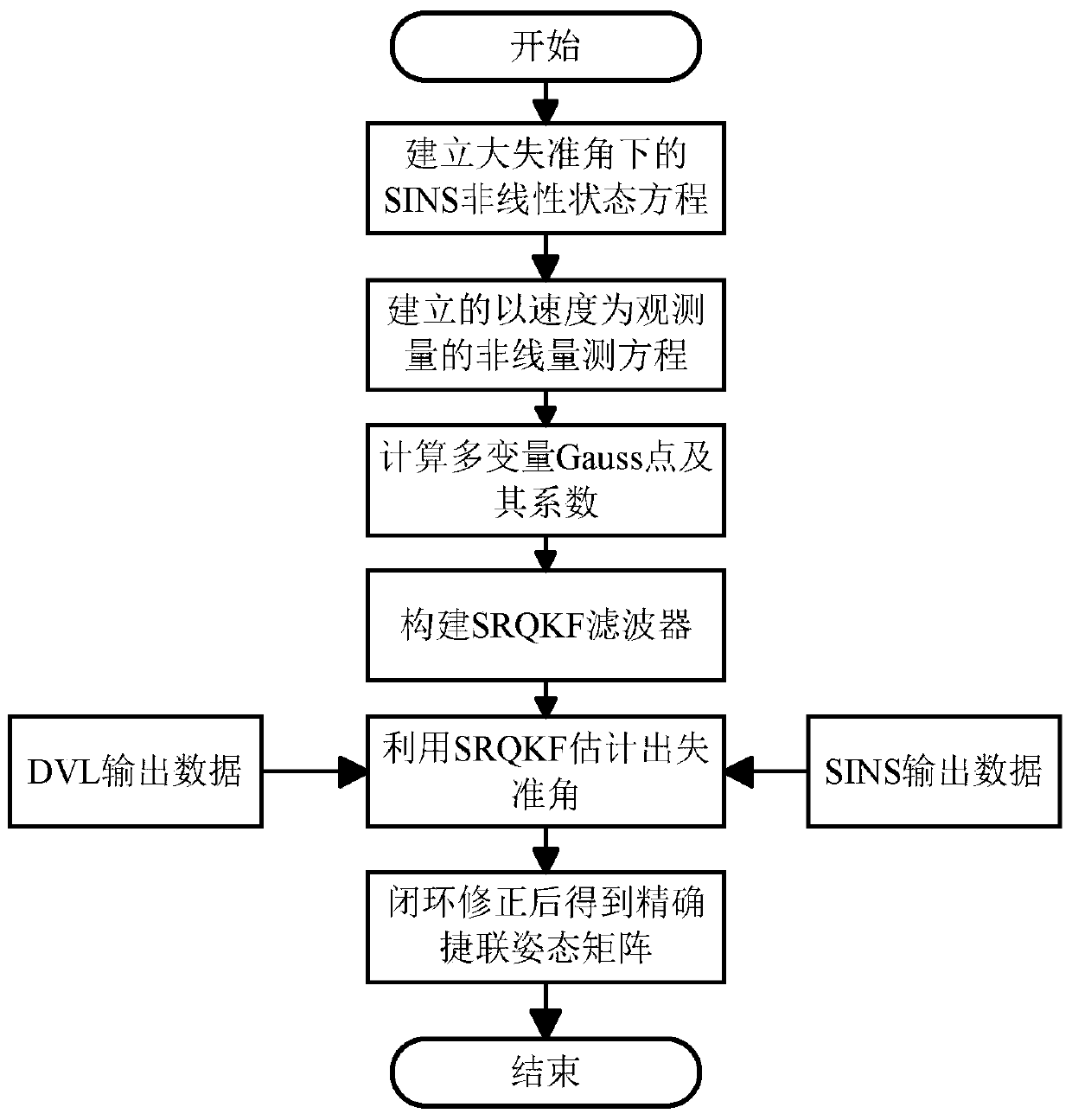
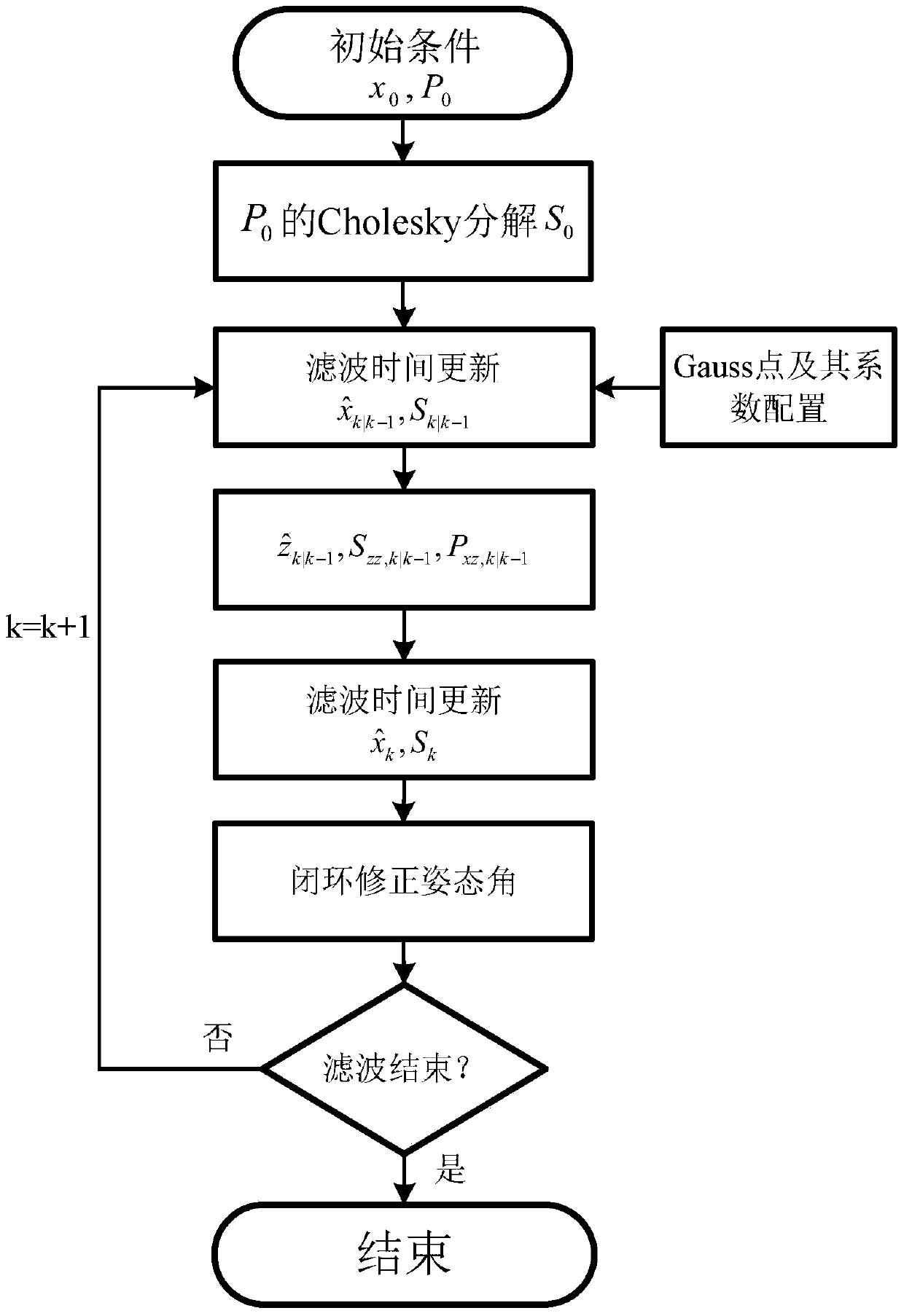
SINS/DVL Underwater Large Misalignment Angle Alignment Method Based on SRQKF
ActiveCN105806363BImprove alignment accuracyReliable Attitude InformationMeasurement devicesNonlinear filterGauss point
The invention discloses an alignment method of an underwater large misalignment angle based on SINS (Strapdown Inertial Navigation System) / DVL (Doppler Velocity Log) of SRQKF (Square-root Quadrature Kalman Filter). The alignment method comprises the following steps: step 1: establishing a nonlinear error model and a nonlinear filtering equation of the SINS under the large misalignment angle; step 2: constructing the SRQKF by utilizing a multivariate Gauss point and coefficient configuration method and a square-root filtering method in Gauss-Hermite quadrature; and step 3: estimating the misalignment angle by utilizing the SRQKF, and correcting a strapdown attitude matrix, thus obtaining accurate strapdown attitude matrix and attitude angle. The alignment method disclosed by the invention has the advantage that the underwater alignment accuracy and alignment speed of the carrier strapdown system are improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Auv integrated navigation system based on sins/dvl/gps
ActiveCN103744098BImprove robustnessOvercome the defect of Kalman filtering accuracy dropNavigation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingGps receiverEphemeris
The invention discloses a ship's inertial navigation system (SINS) / Doppler velocity log (DVL) / global positioning system (GPS)-based autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) combined navigation system, which comprises an SINS, a GPS receiver, a DVL and a data fusion center, wherein the SINS, the GPS receiver, the DVL and the data fusion center are arranged on an AUV; when the AUV is positioned on the water surface, an optimized filter module carries out filtering fusion calculation by combining navigation information of the SINS, a pseudo-range and a pseudo-range rate corresponding to the SINS and available ephemeris data output by the GPS receiver to obtain correction information; when the AUV is positioned underwater, the optimized filter module carries out filtering fusion calculation by combining the navigation information output by the SINS and three-dimensional navigational speed information output by the DVL to obtain correction information. The navigational positioning accuracy and the robustness of the system are improved, and the system realizes an uninterrupted high-accuracy underwater and water surface carrier navigating and tracking function.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Velocity model-assisted underwater intelligent navigation method based on dynamics
ActiveCN109634308BSpeed efficientSpeed output is validSafety arrangmentsAdaptive controlDynamic modelsSimulation
The invention discloses a dynamics-based velocity model assisted underwater intelligent navigation method. The method includes the following steps that: (1) on-board sensor information is periodicallycollected; (2) the input variables and output variables of a velocity model to be established are determined; (3) the velocity model is constructed and trained; and (4) when it is detected that a DVL(Doppler Velocity Log) malfunctions or the data of the DVL fail, navigation analysis is performed with the output velocity of the trained model used as a bottom velocity, and therefore, model-assisted navigation can be performed. According to the method of the invention, a new AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle) velocity model is put forward based on the idea of dynamic models; the influence of factors such as rudder angles of rudder blades, and heading angles is considered; as long as the fault data of the DVL are not detected during an operation process, training sets can be increased at any time to train the model; after the fault data of the DVL are detected, the output velocity of the model can be adopted instead, and therefore, the problem of navigation error increase caused by thefailure or fault of the DVL can be avoided; the redundancy method of velocity sensors is provided with no hardware costs increased; the method has good system robustness and can guarantee high-precision navigation.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com