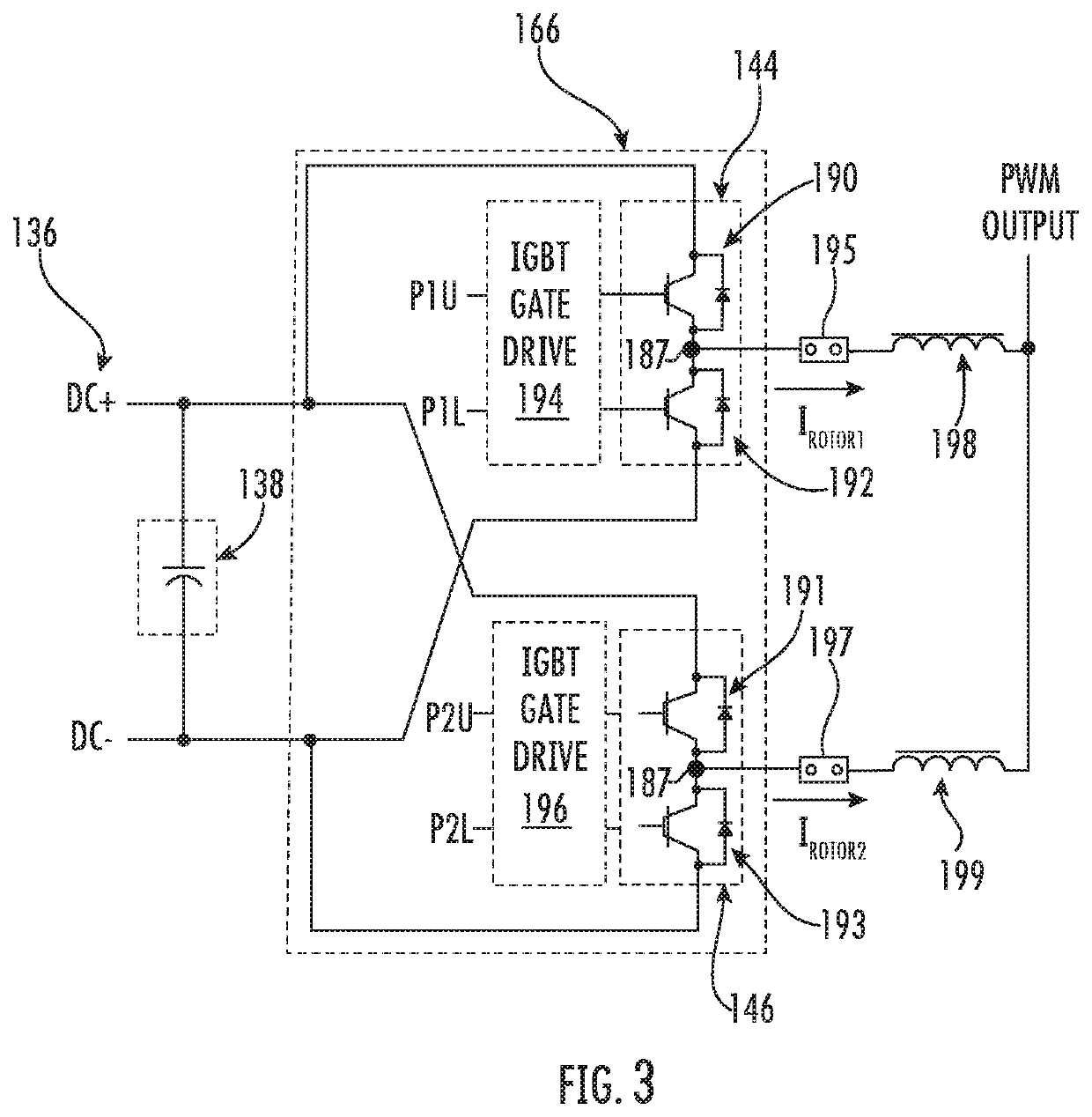
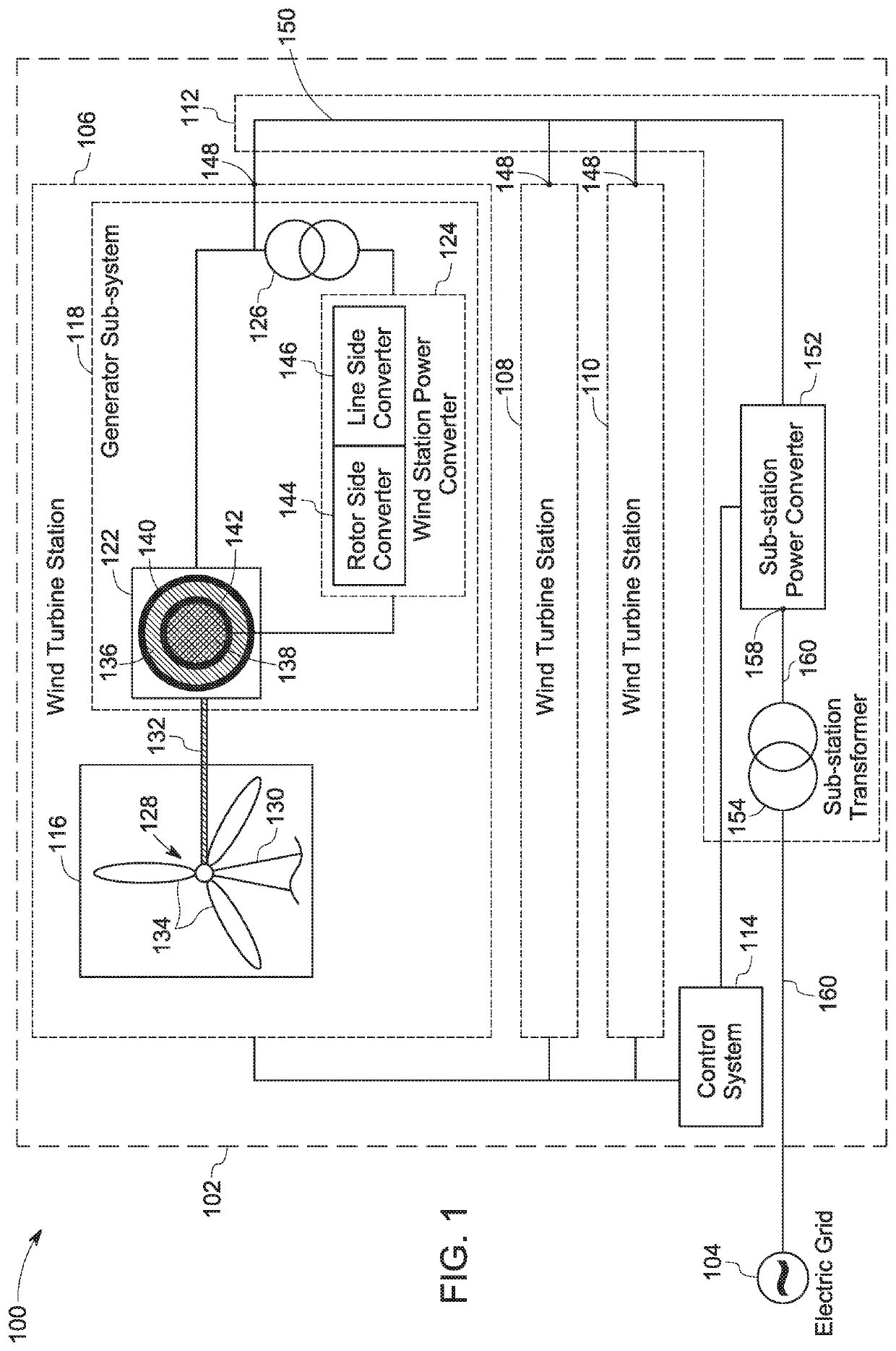
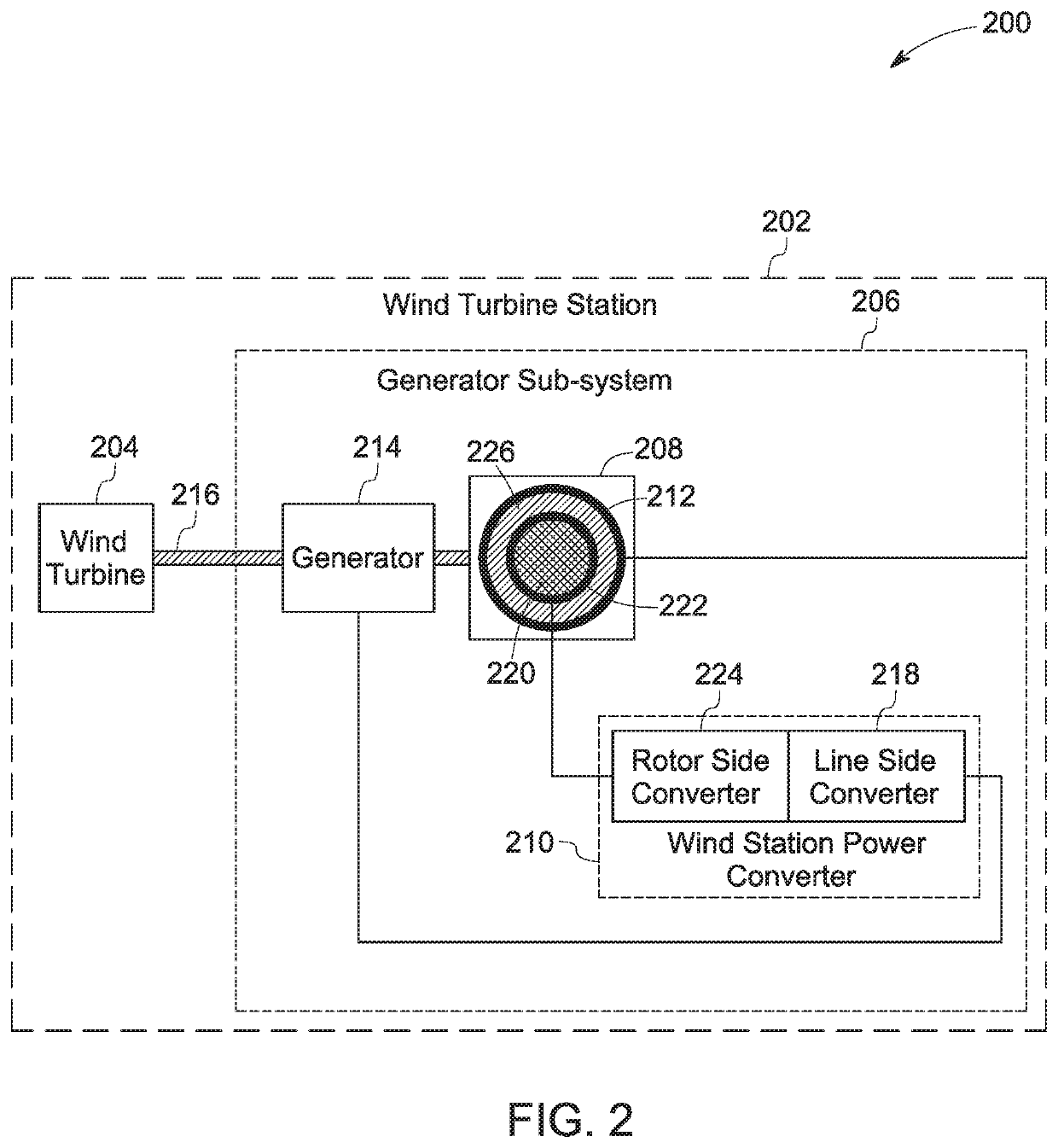
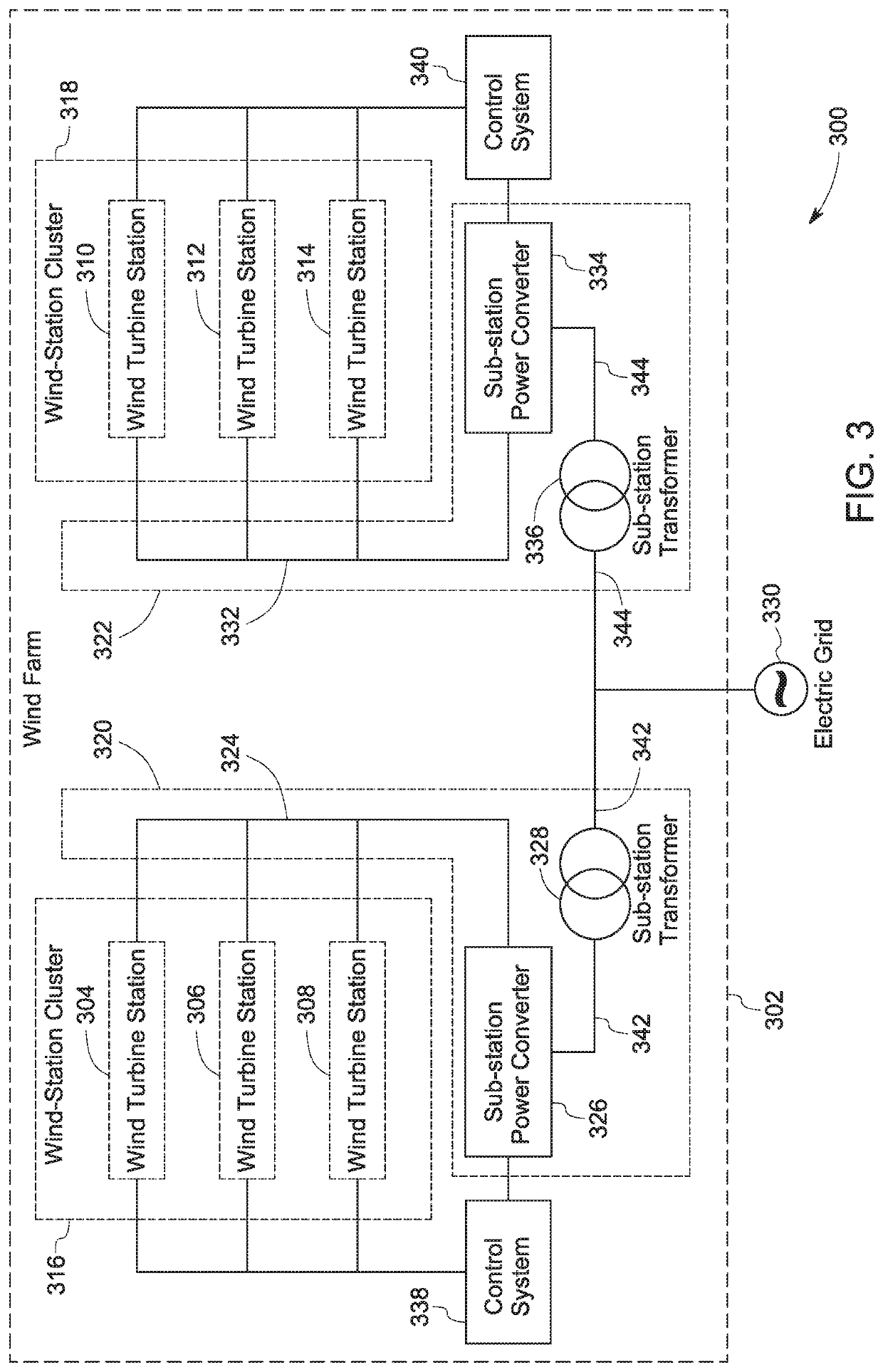
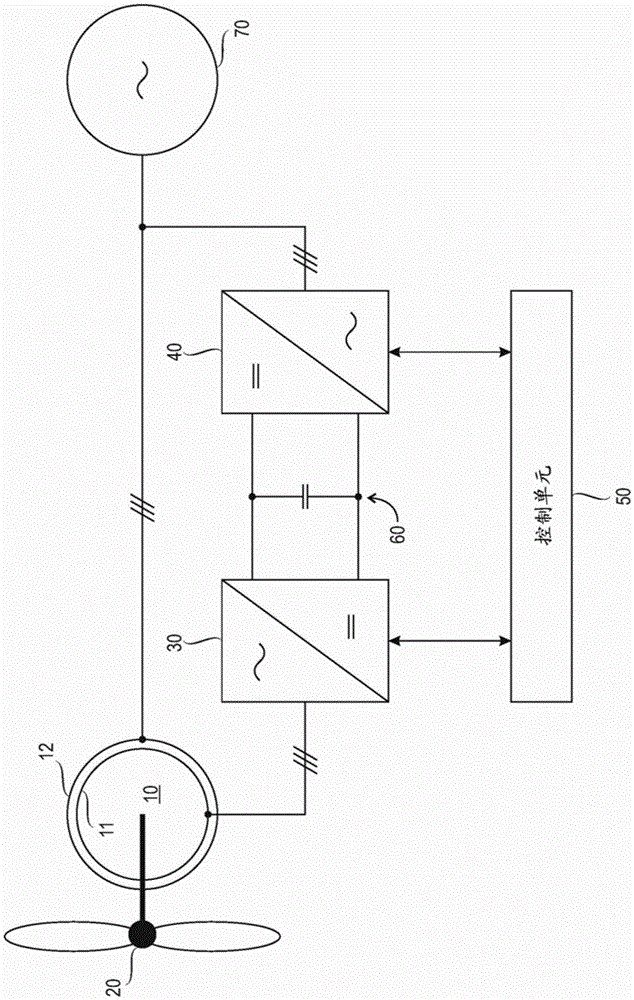
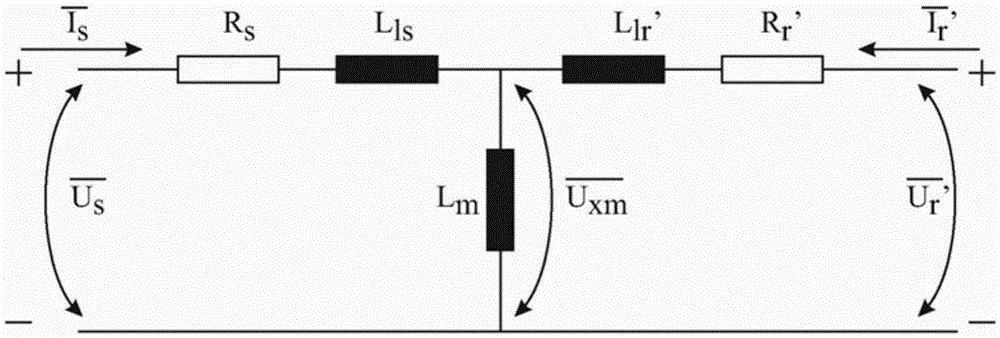
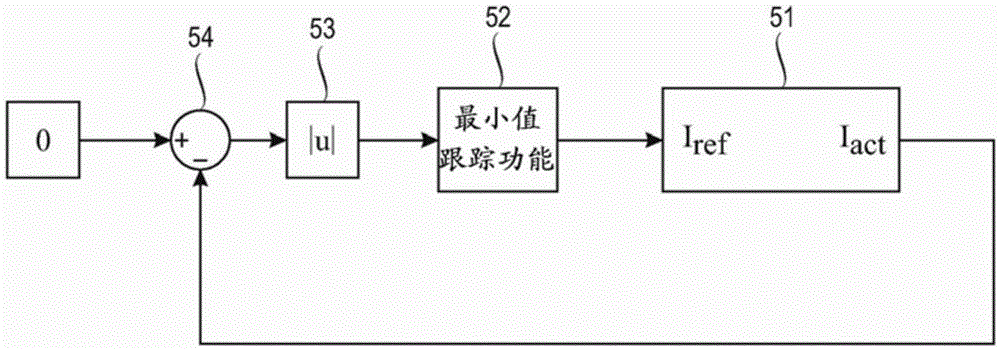
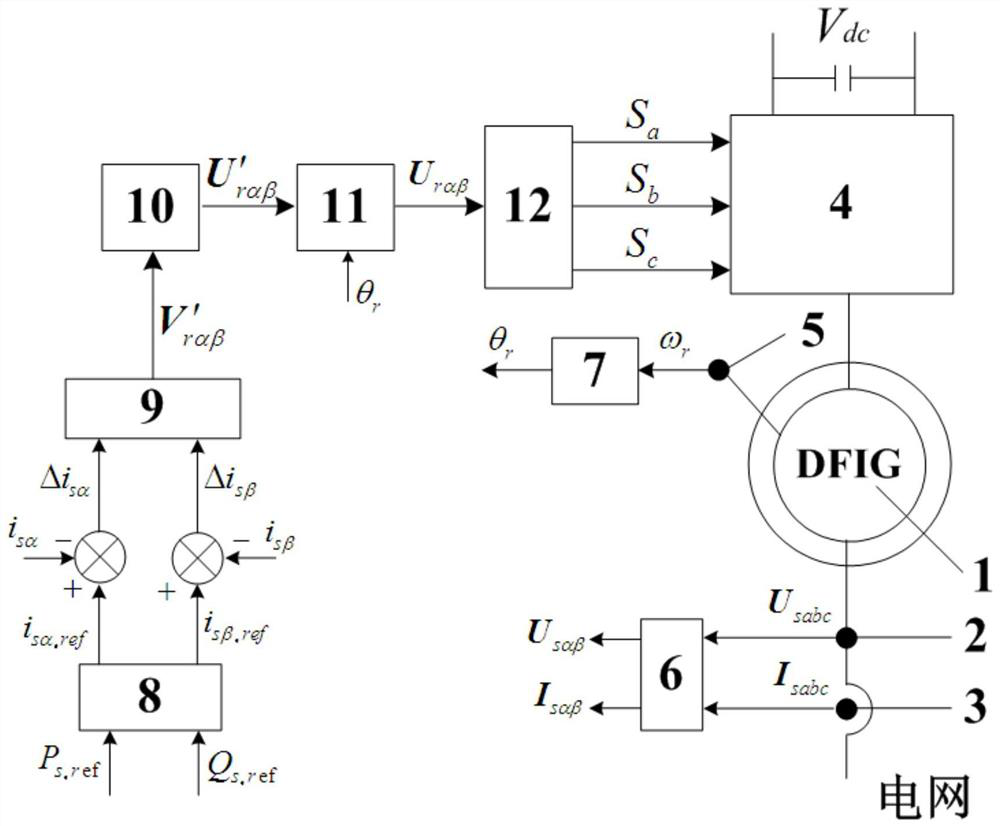
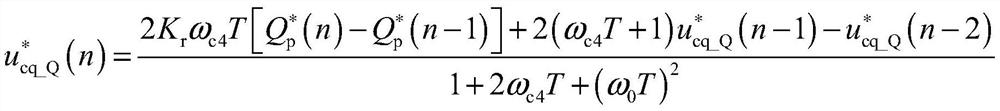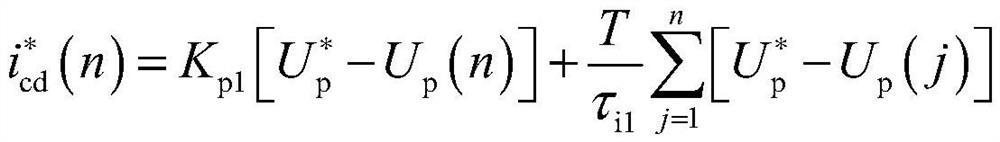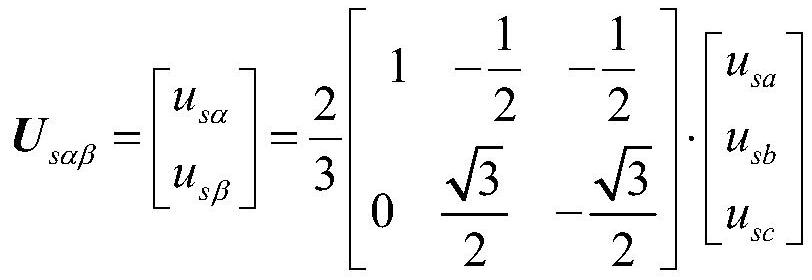Patents
Literature
47 results about "Doubly fed induction generator dfig" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
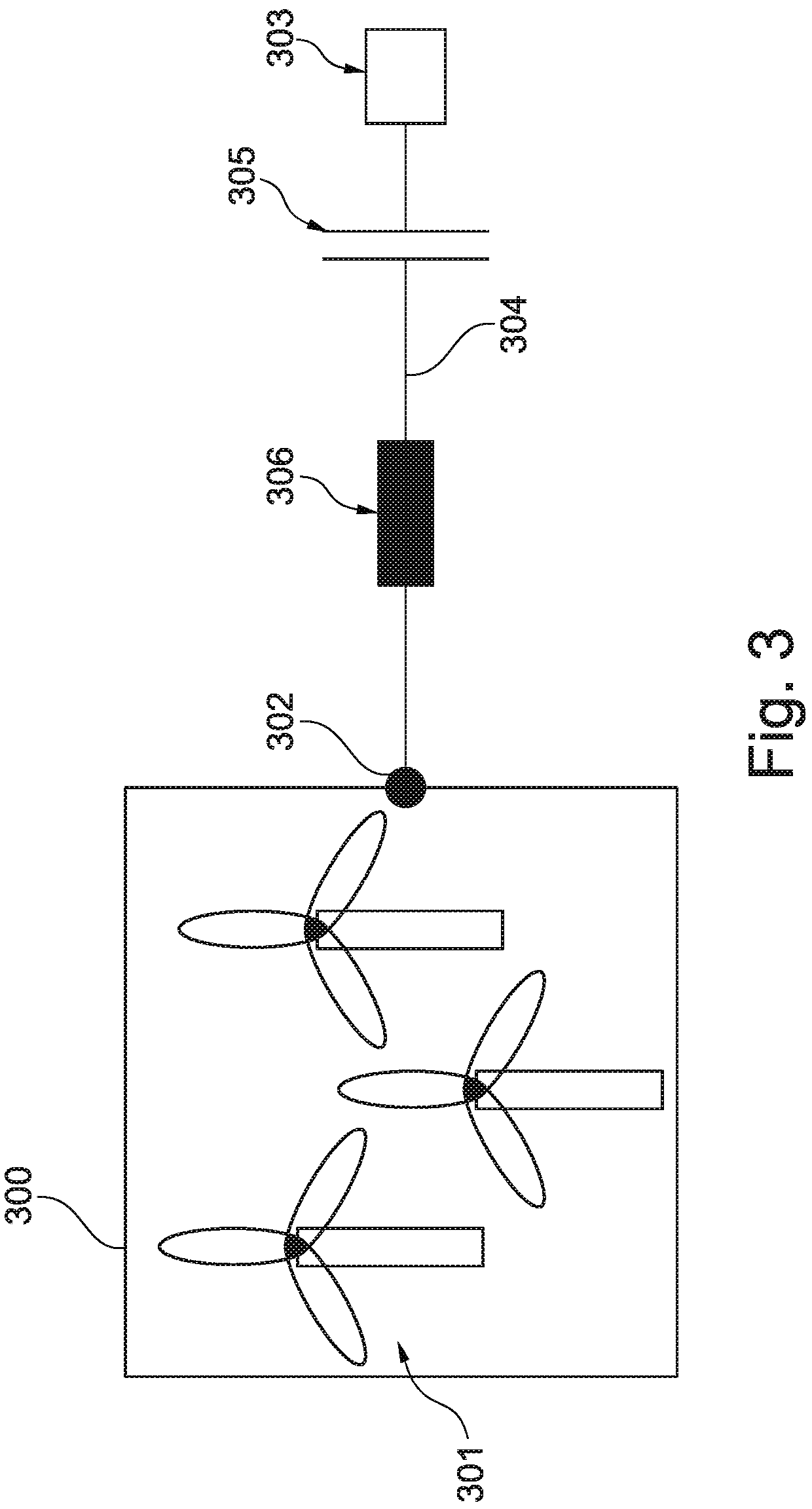
Variable speed wind turbine having a matrix converter
InactiveUS20020079706A1Generator control circuitsWind motor controlMatrix convertersConstant frequency
A variable speed wind turbine is disclosed comprising a turbine rotor that drives a doubly-fed induction generator, a matrix converter which converts variable frequency output into constant frequency output, and a control unit and a protection circuit for the matrix converter. Power is circulated in the system allowing for sensorless detection of rotor position and better output ratios of power from the system.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
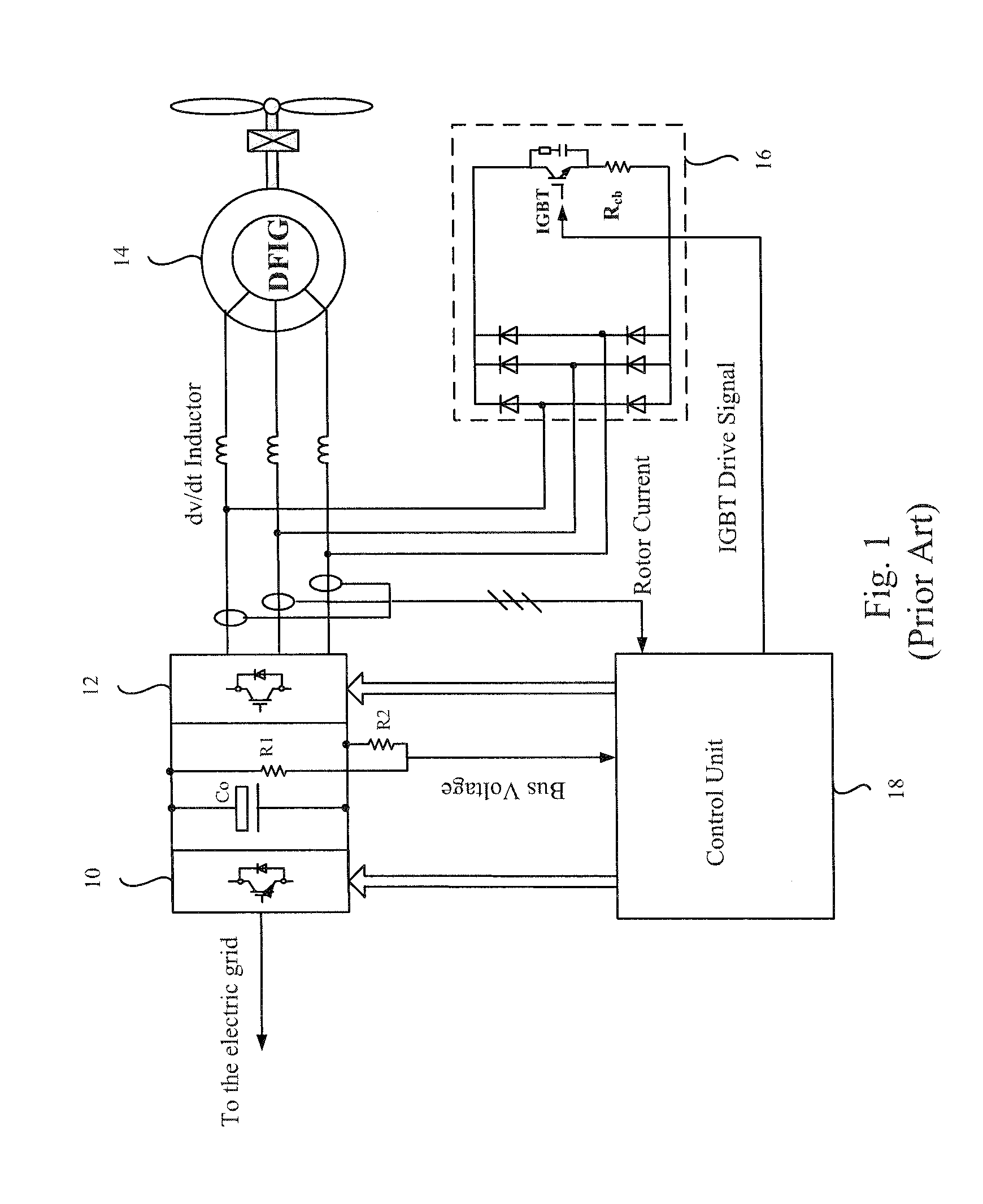
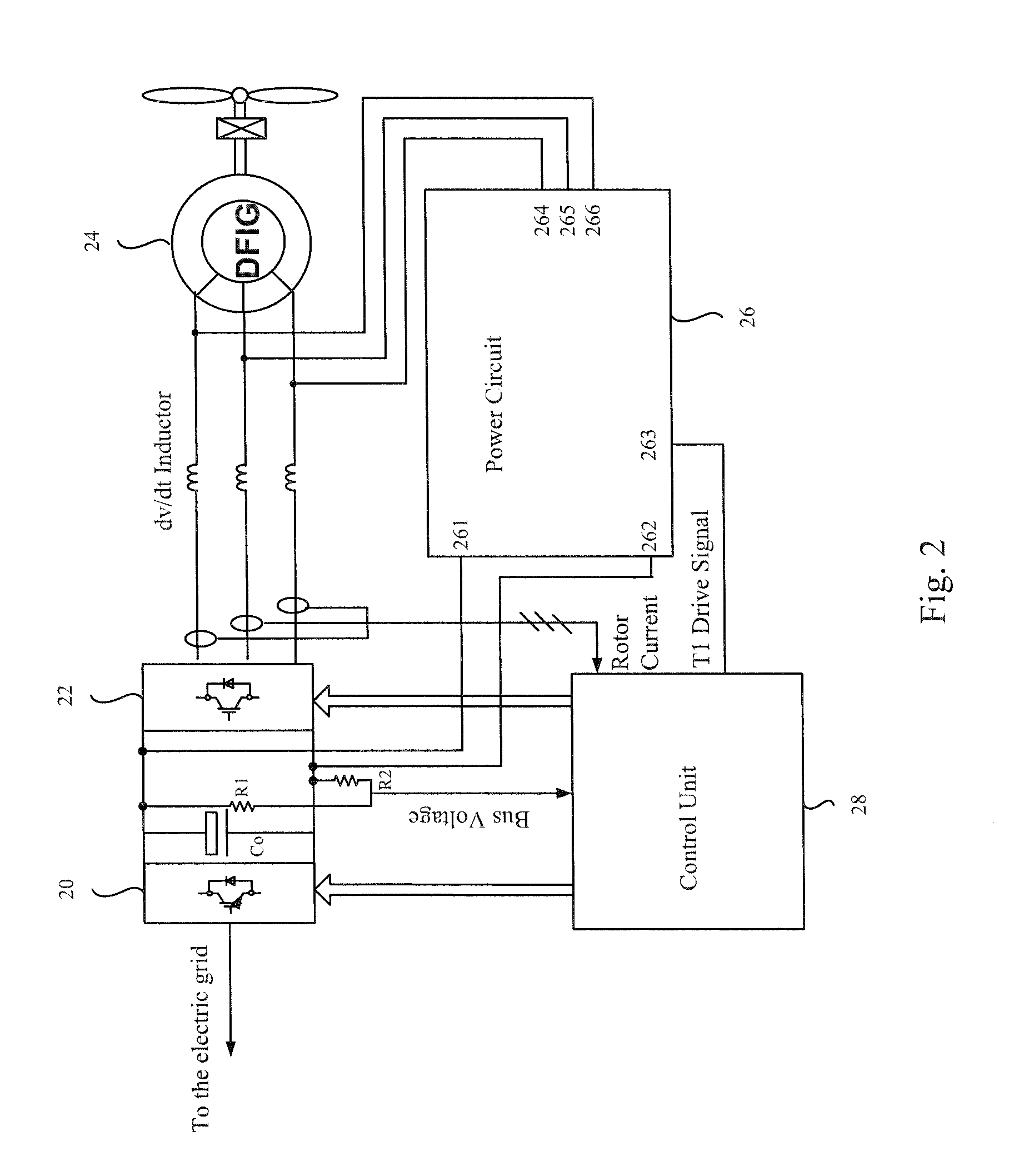
DC chopper and DC chopping method for doubly fed induction generator system
InactiveUS20130049707A1Control moreElectronic commutation motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsOvervoltageControl signal
A DC chopper comprising a control unit and a power circuit and a DC chopping method for a DFIG (doubly fed induction generator) system are provided. The input terminal of the control unit is coupled to a DC capacitor of a converter to detect a DC voltage. The power circuit includes input terminals, an overvoltage protection module, a rectifier module and output terminals. The overvoltage protection module comprises at least one discharge unit formed from a discharge resistor and a switch element, and the rectifier module is coupled in parallel to the overvoltage protection module. When a grid voltage drops, the control unit outputs a corresponding control signal to drive the switch element to be ON or OFF, and the output terminal of the power circuit absorbs a portion of rotor inrush current, so as to impose over-current protection.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Doubly-fed induction generator fault detection method based on sliding mode observer
ActiveCN110649846ASimple structureStrong anti-interference abilityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMathematical modelTerminal voltage
In order to carry out fault detection on the doubly-fed induction generator, the invention provides a doubly-fed induction generator fault detection method based on a sliding mode observer. Because asliding mode observer is simple in structure, is not liable to be affected by parameters, is high in anti-interference capability, and the like, the sliding mode observer is used for the fault detection of the doubly-fed induction generator. Firstly, a sliding mode observer is built according to a mathematical model of the doubly-fed induction generator, the rotor current and the rotating speed ofthe doubly-fed induction generator are observed, and self-detection of faults is achieved by comparing the residual error between the actual rotor current value and the observed value, then three faults of a power grid end voltage drop fault, a doubly-fed induction generator stator turn-to-turn fault and a rotor current sensor fault are given so as to prove that the sliding-mode observer can wellperform fault detection on faults occurring at different positions, and the sliding-mode observer has the characteristics of the high response speed, the good stability and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Control Device for Doubly-Fed Induction Generator in Which Feedback Linearization Method is Embedded
ActiveUS20120112708A1Stable controlExpand the marketGenerator control circuitsAC motor controlStator voltageControl engineering
The present invention relates to a control device for a doubly-fed induction generator in which a feedback linearization method is enabled and further provides a control device for a doubly-fed induction generator in which a feedback linearization method is embedded, characterized in that the control device divides and measures positive sequency components and negative sequency components from stator voltage and current, rotor voltage and current, and signals of stator magnetic flux and rotor magnetic flux of the doubly-fed induction generator.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
System and method for fixed frequency power generation
A system for modulating a frequency output of a generator coupled to an electric distribution network is described herein. The system includes: a doubly-fed induction generator coupled to a power source selected from at least one of hydropower and fuel combustion, the generator providing an electrical power output having a first frequency based on a rotational speed of the generator; a controller for selecting the rotational speed of the generator; and a converter coupled to the generator for changing the frequency of the output to a selected value, in response to selecting the rotational speed. Methods for modulating a frequency output of a generator coupled to an electric distribution network are also described.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
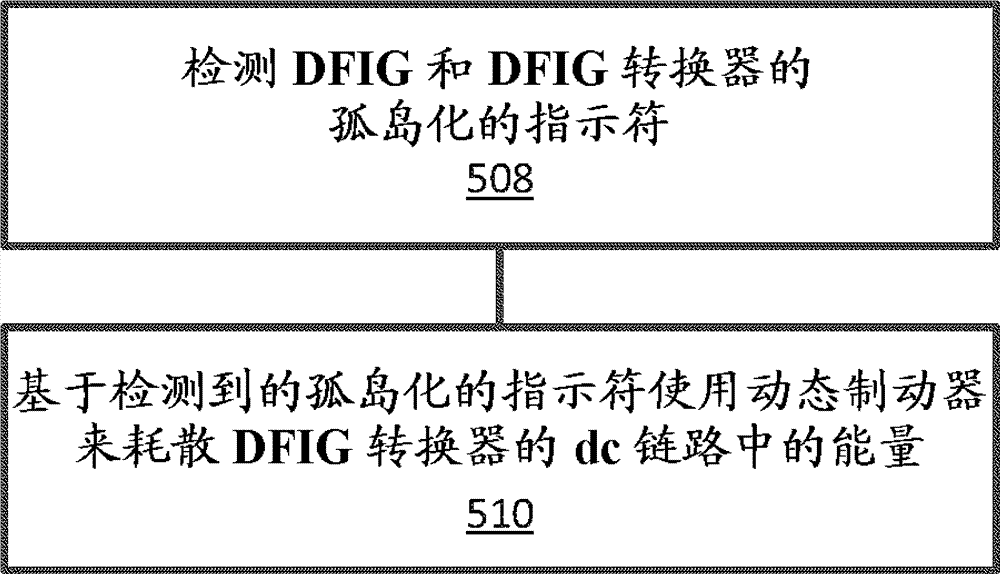
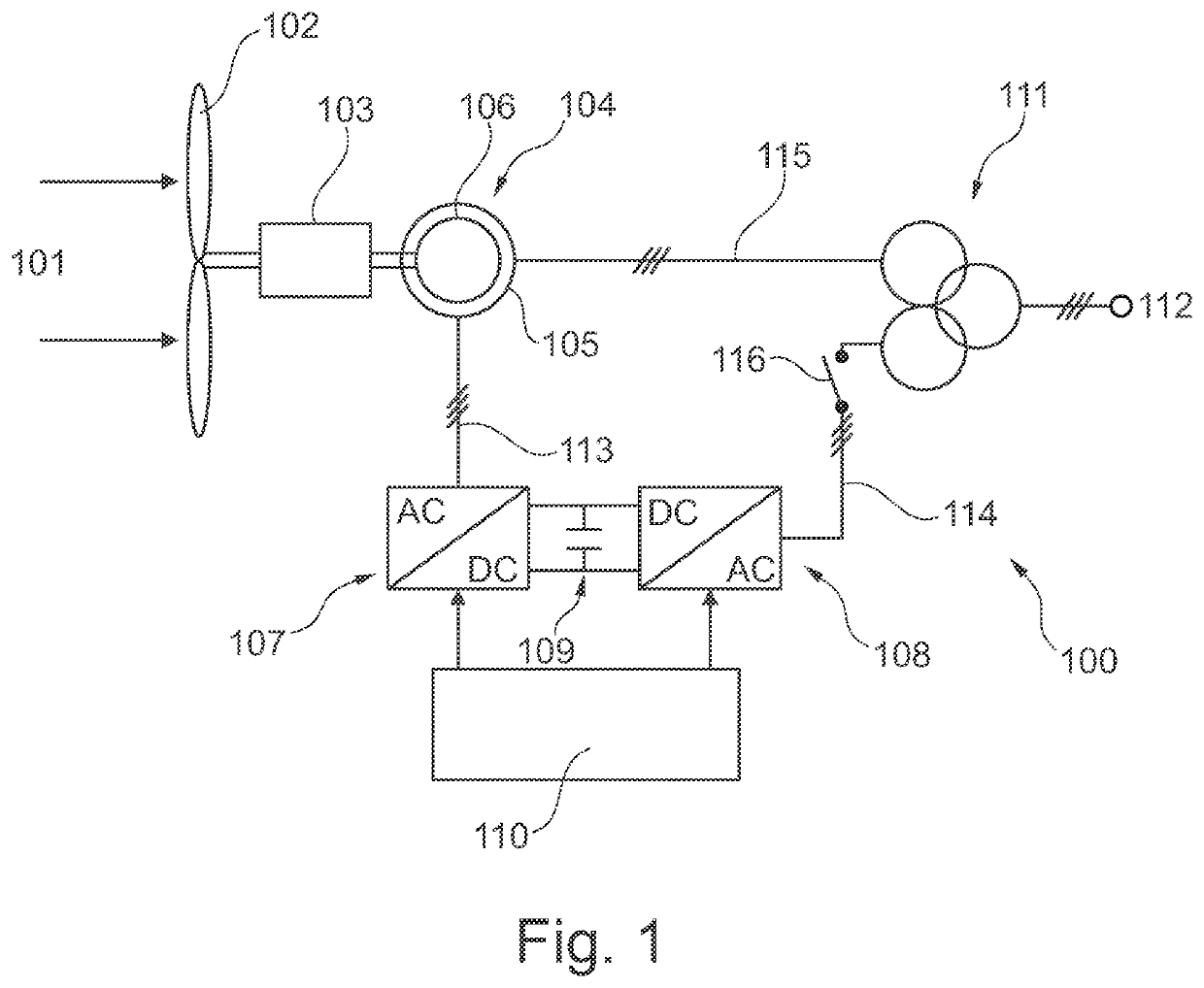
Method and systems for operating a wind turbine using dynamic braking in response to a grid event
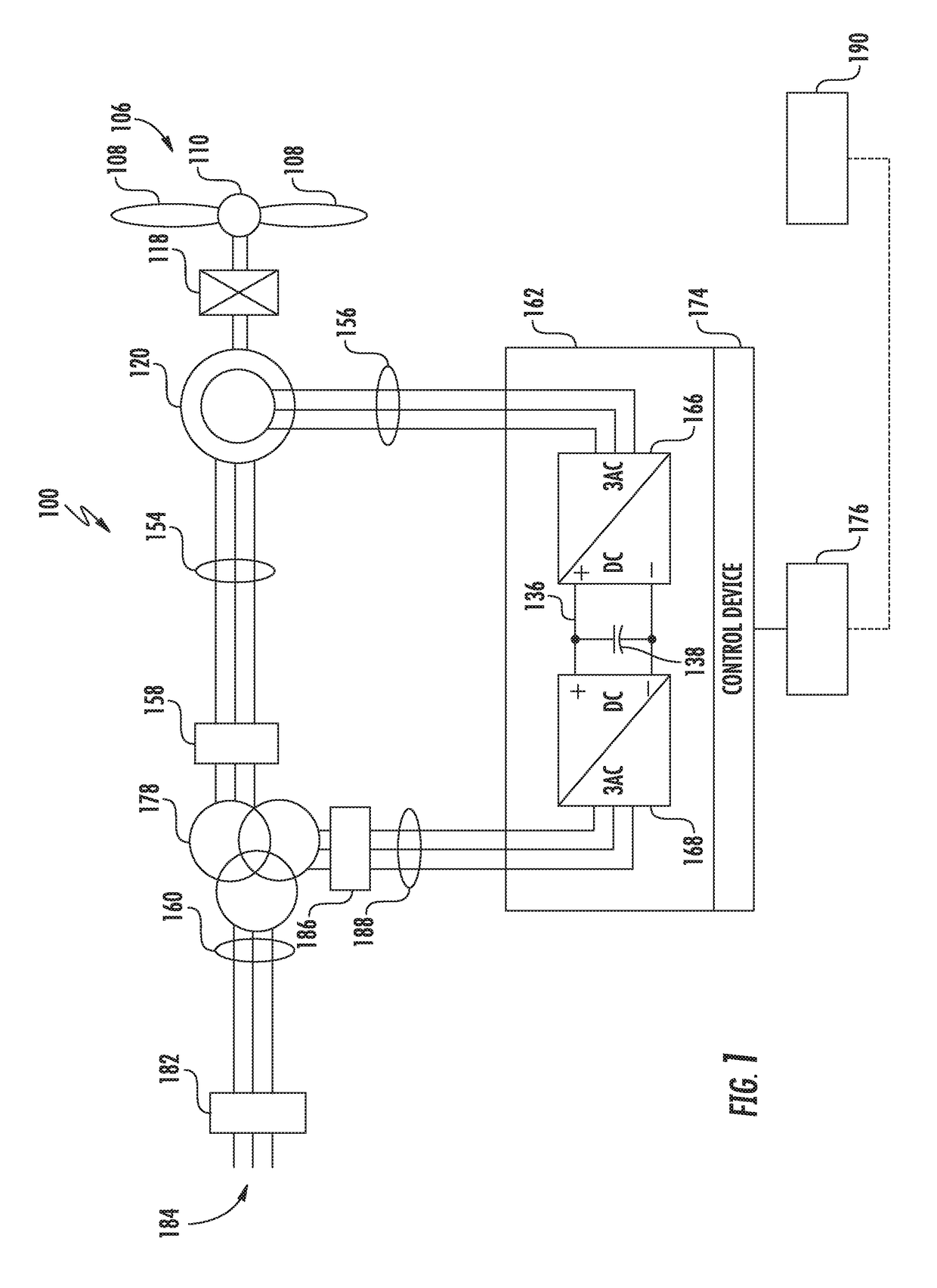
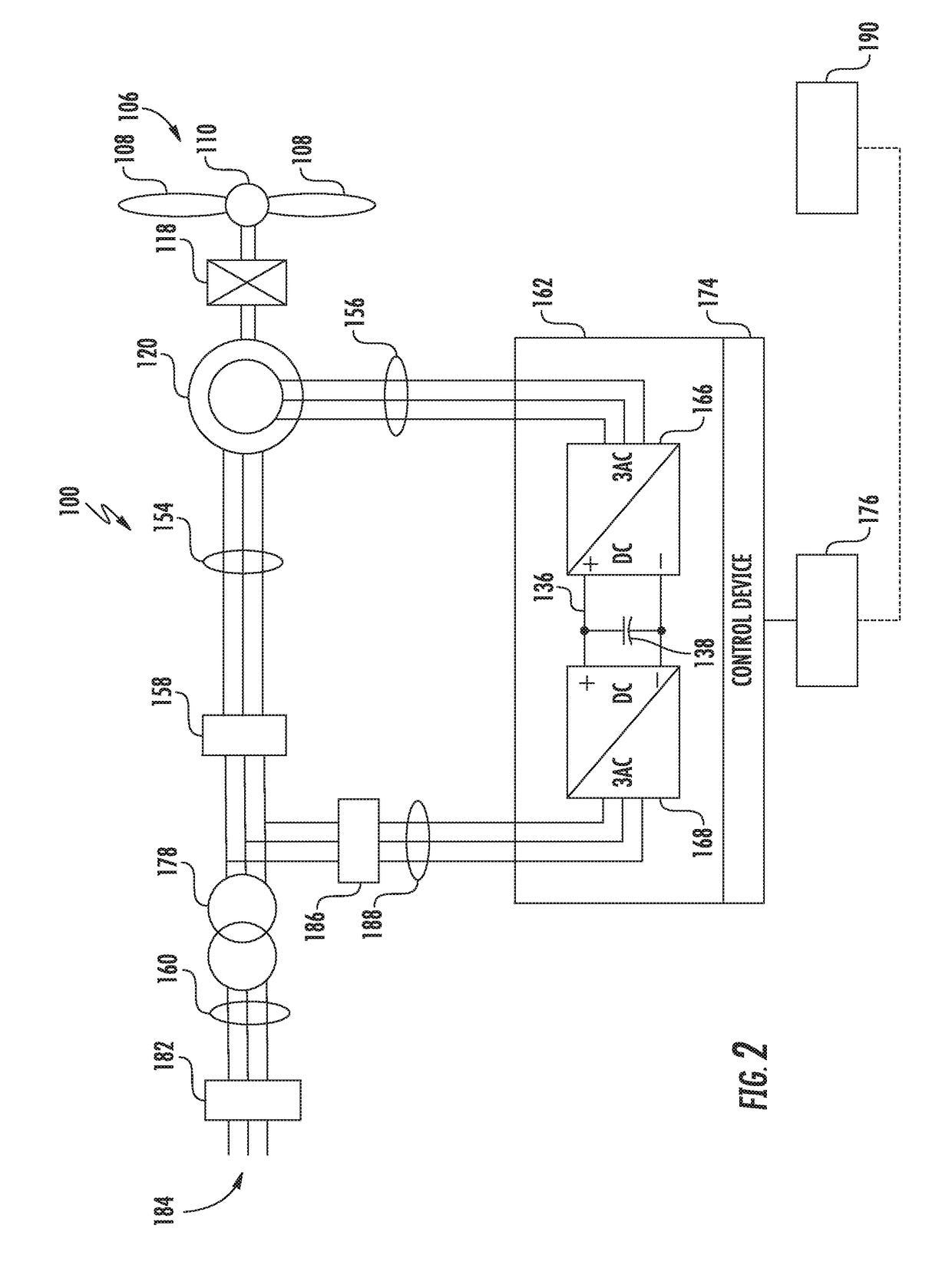
A method and system for dissipating energy in a direct current (dc) bus of a doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) converter during a grid event is described. In one aspect, the method comprises monitoring operating conditions of an electrical system, the electrical system comprising at least a DFIG generator and a line side converter and a rotor side converter connected by a dc bus having a dynamic brake connected thereto; detecting an overvoltage on the dc bus or a condition indicative of an overvoltage on the dc link is detected, the overvoltage on the dc bus or condition indicative of the overvoltage caused by a grid event; and causing energy in the dc link to be dissipated using the dynamic brake.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC RENOVABLES ESPANA SL
Balancing reactive current between a dfig stator and a grid-side inverter
ActiveUS20200274360A1Avoiding unnecessary heatingTotal current dropGenerator control circuitsElectric motor controlConvertersControl engineering
Aspects of the present invention relate to a method for controlling an amount of reactive current provided from a wind turbine generator to a power grid during an abnormal power grid event, said wind turbine generator comprising a doubly-fed induction generator having a rotor and a stator, and a power converter coupling the rotor to the power grid, the power converter comprising a grid-side inverter, wherein the method comprises the step of balancing the reactive current provided to the power grid between a reactive stator current and a reactive grid-side inverter current, wherein the reactive grid-side inverter current is controlled in accordance with a reactive current capacity of a grid breaker receiving the reactive current provided by the grid-side inverter. Aspects of the present invention also relate to a wind turbine generator being capable of performing the method.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
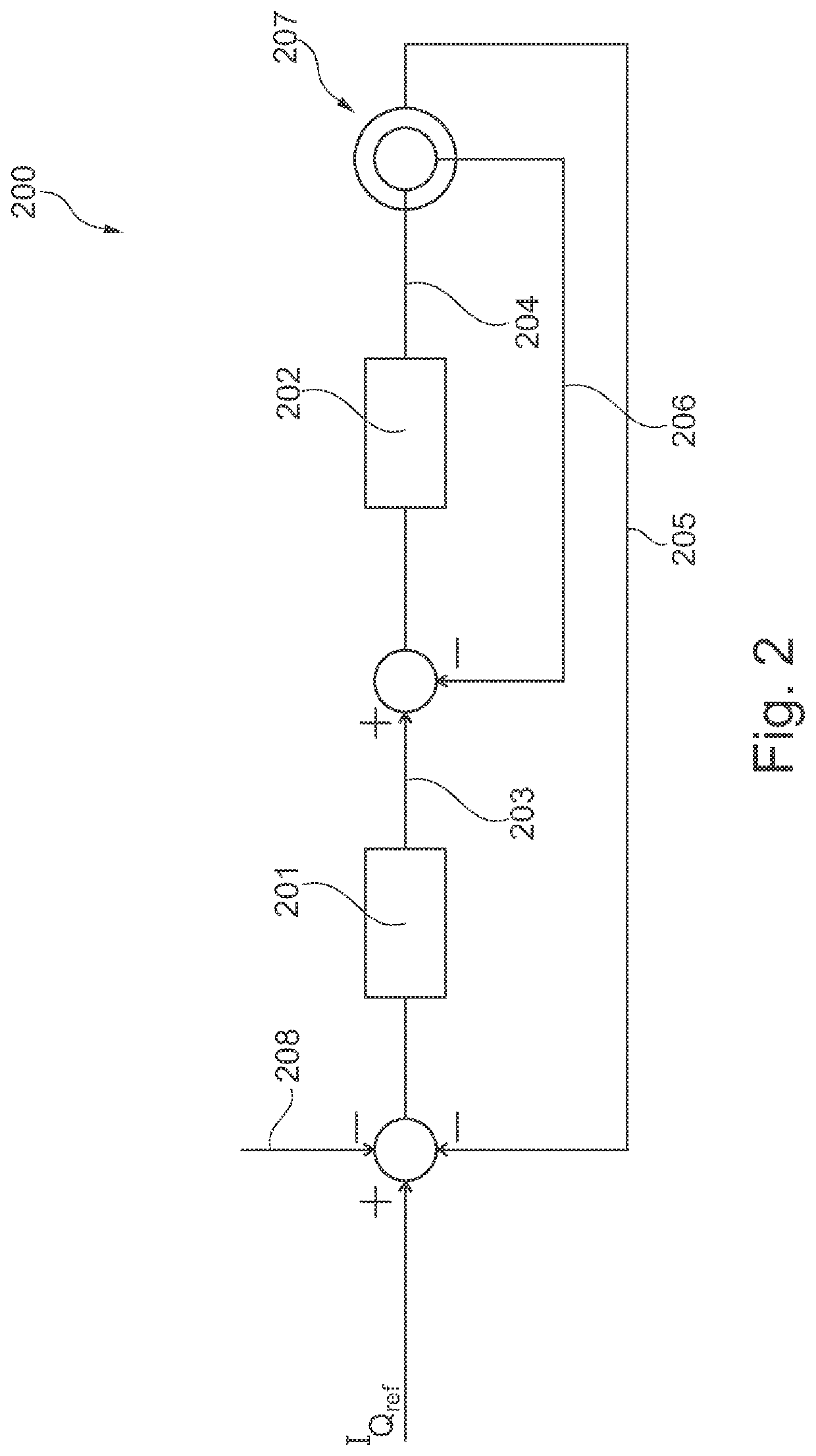
Allocating Reactive Power Production for Doubly Fed Induction Generator Wind Turbine System
ActiveUS20190013754A1Generator control circuitsWind energy generationRotor side converterGenerating capacity
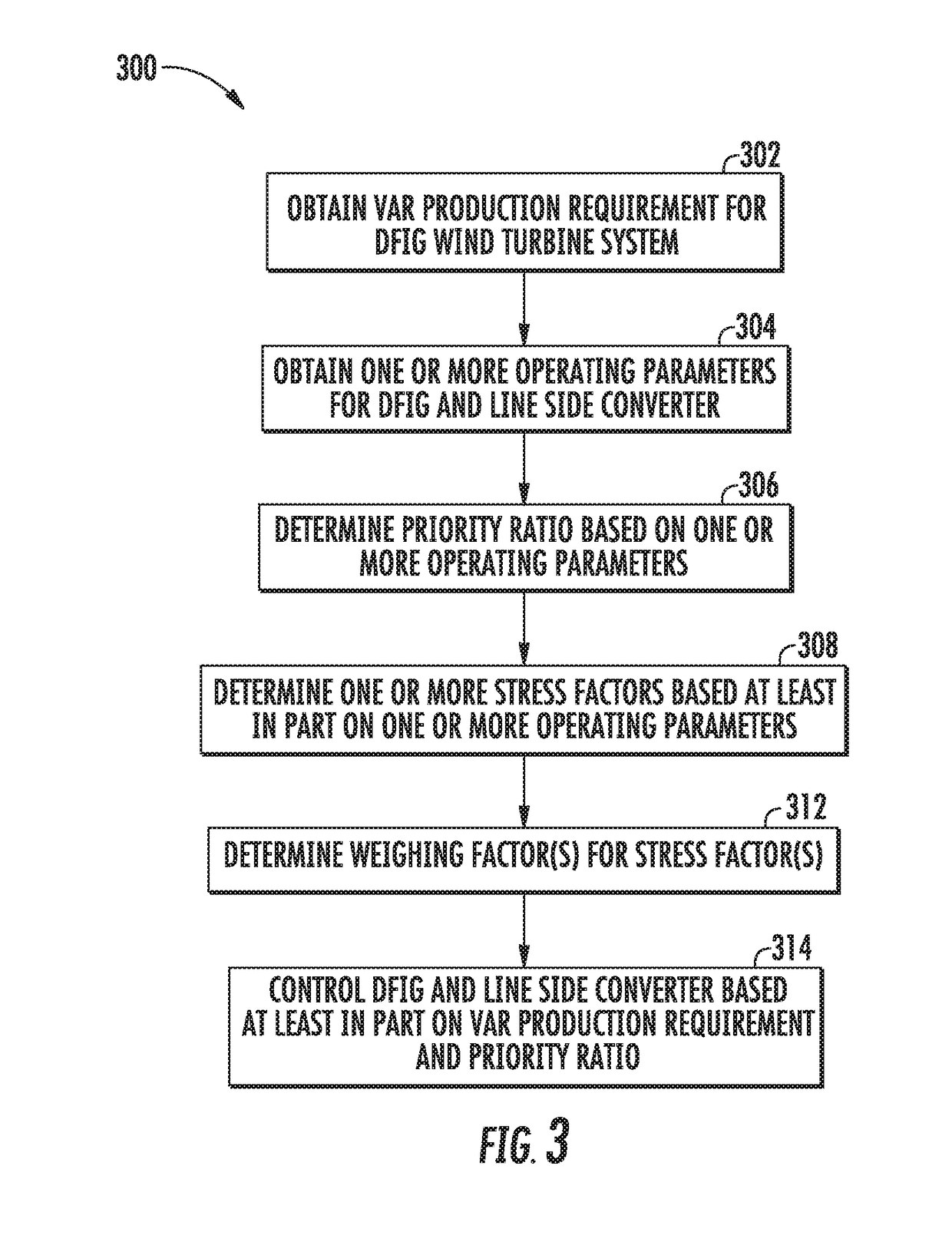
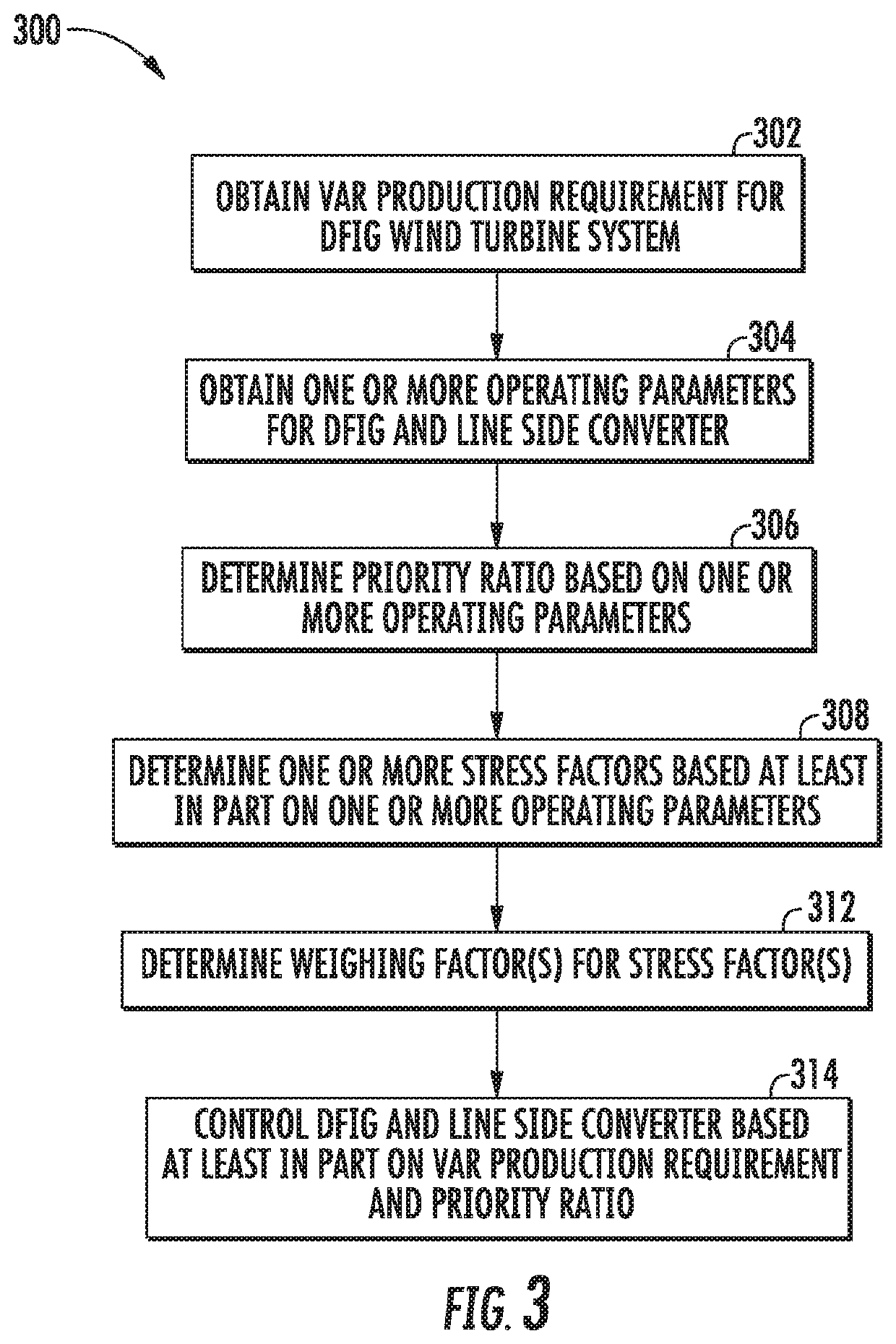
Systems and methods for allocating reactive power production in a doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) wind turbine system including a DFIG and a power converter including a line side converter and a rotor side converter are provided. A method can include obtaining a reactive power production requirement, obtaining one or more operating parameters for the DFIG and the line side converter, and determining a priority ratio based at least in part on the one or more operating parameters. The priority ratio can be a ratio of reactive power production between the DFIG and the line side converter. The method can further include controlling the DFIG and the line side converter based at least in part on the reactive power production requirement and the priority ratio such that the combined reactive power production from the DFIG and the line side converter meet the reactive power production requirement.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
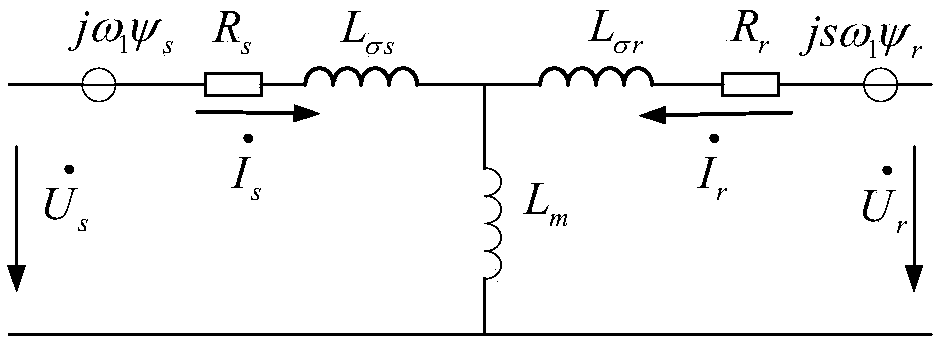
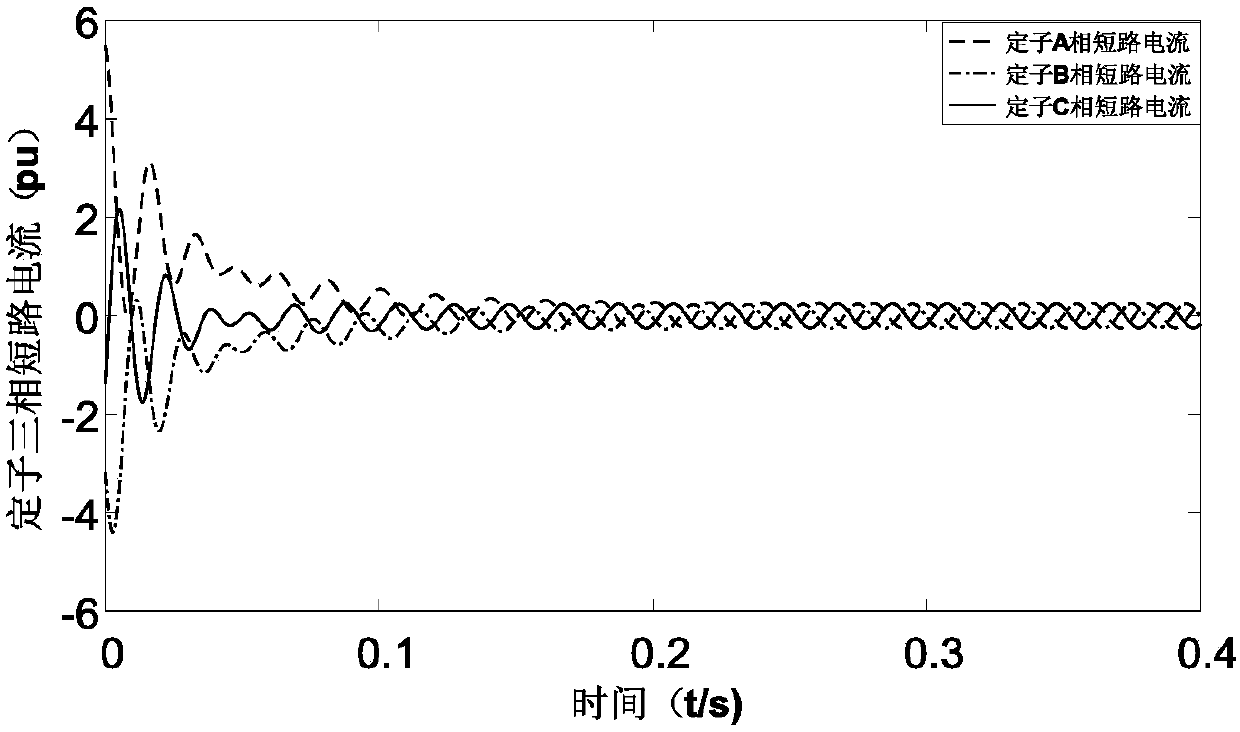
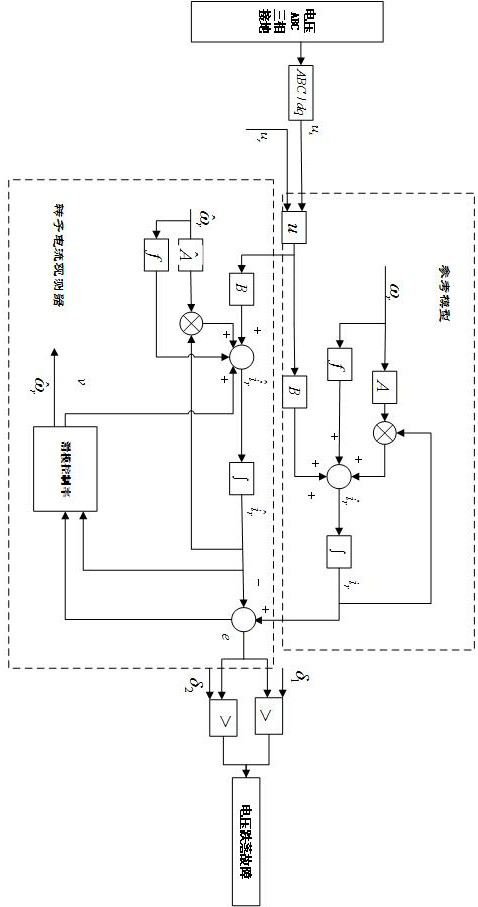
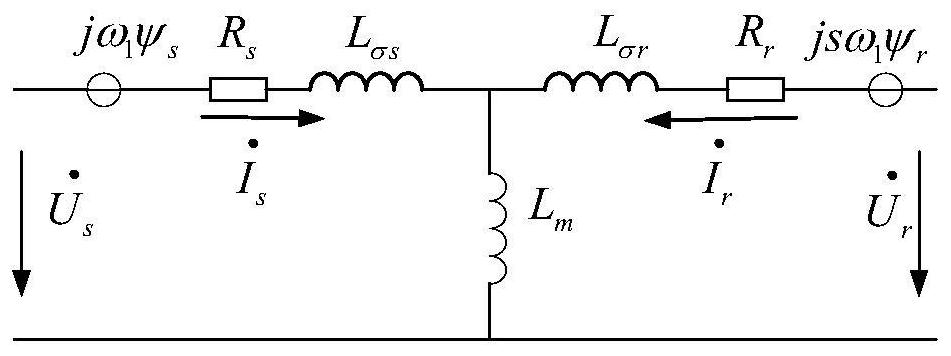
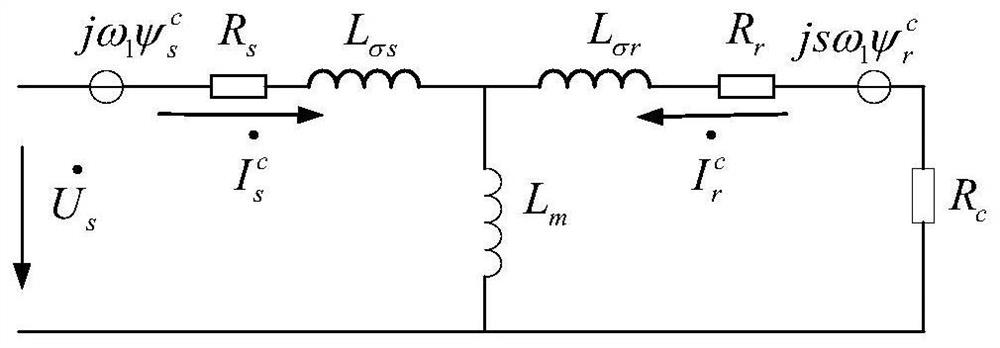
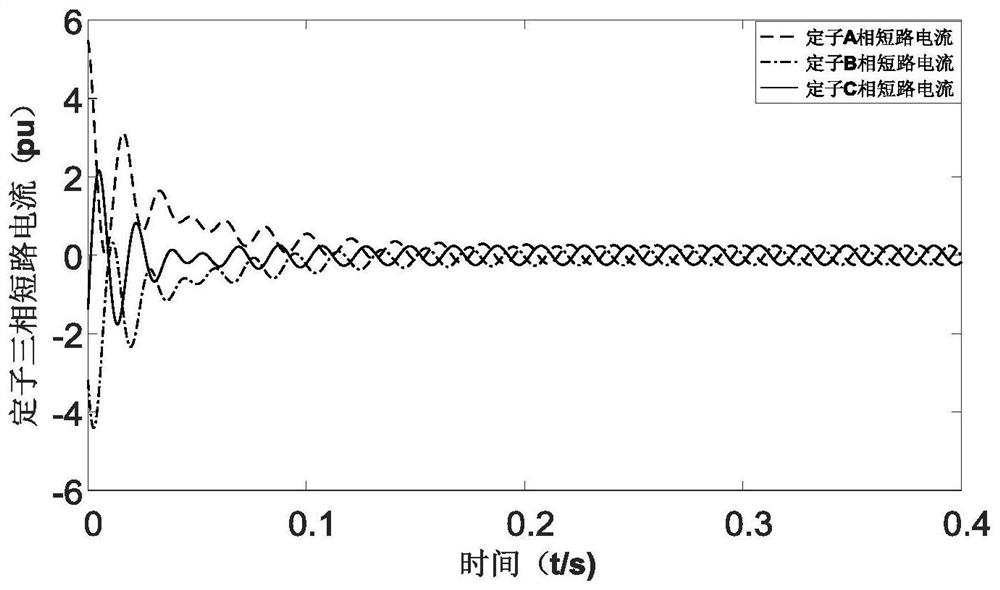
Analysis method of three-phase short circuit current of doubly-fed induction generator after crowbar protection action
ActiveCN108566132ASimple calculationElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsModel selectionRotor flux
The invention relates to an analysis method of a three-phase short circuit current of a doubly-fed induction generator after crowbar protection action and belongs to the technical field of fault analysis of a wind power generation system. The method, by utilizing DFIG stator and rotor voltage equations and stator and rotor flux linkage equations after crowbar protection action, deduces the three-phase short circuit current of the doubly-fed induction generator after crowbar protection action, and thus the calculating process is simplified. The method can accurately calculate the three-phase short circuit current of the doubly-fed induction generator after crowbar protection action, and is of great significance to model selection and protection action characteristic analysis of electric power system equipment comprising the doubly-fed induction generator.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
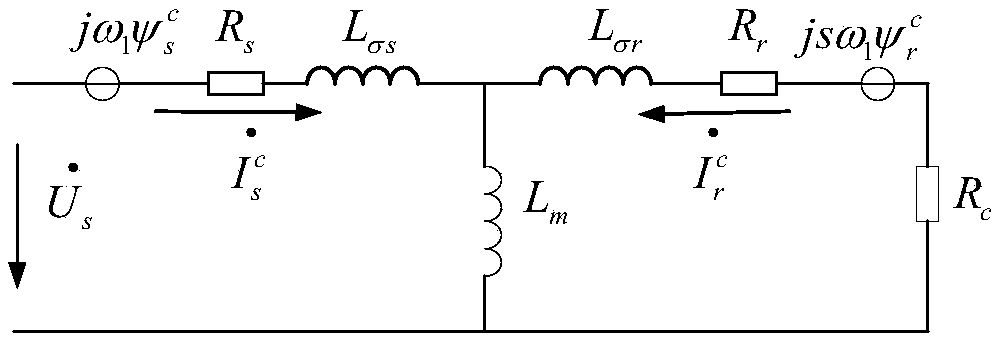
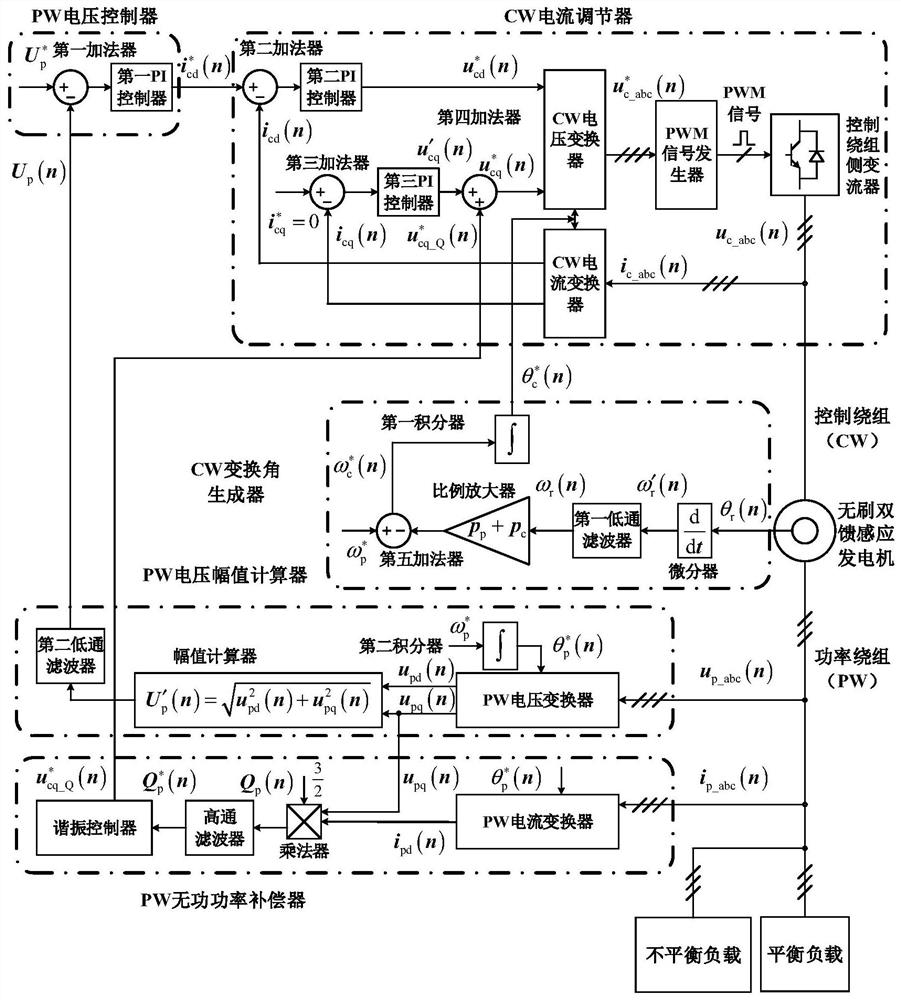
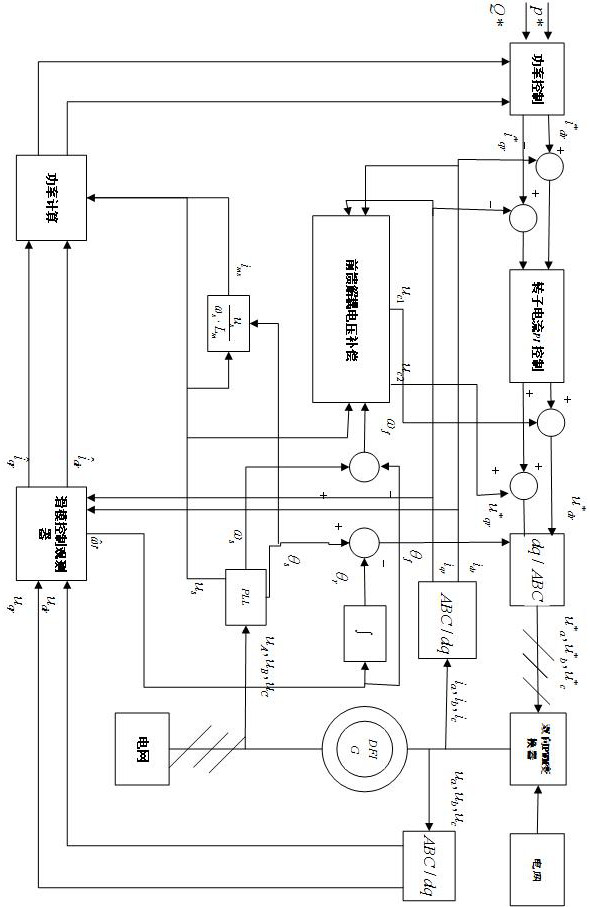
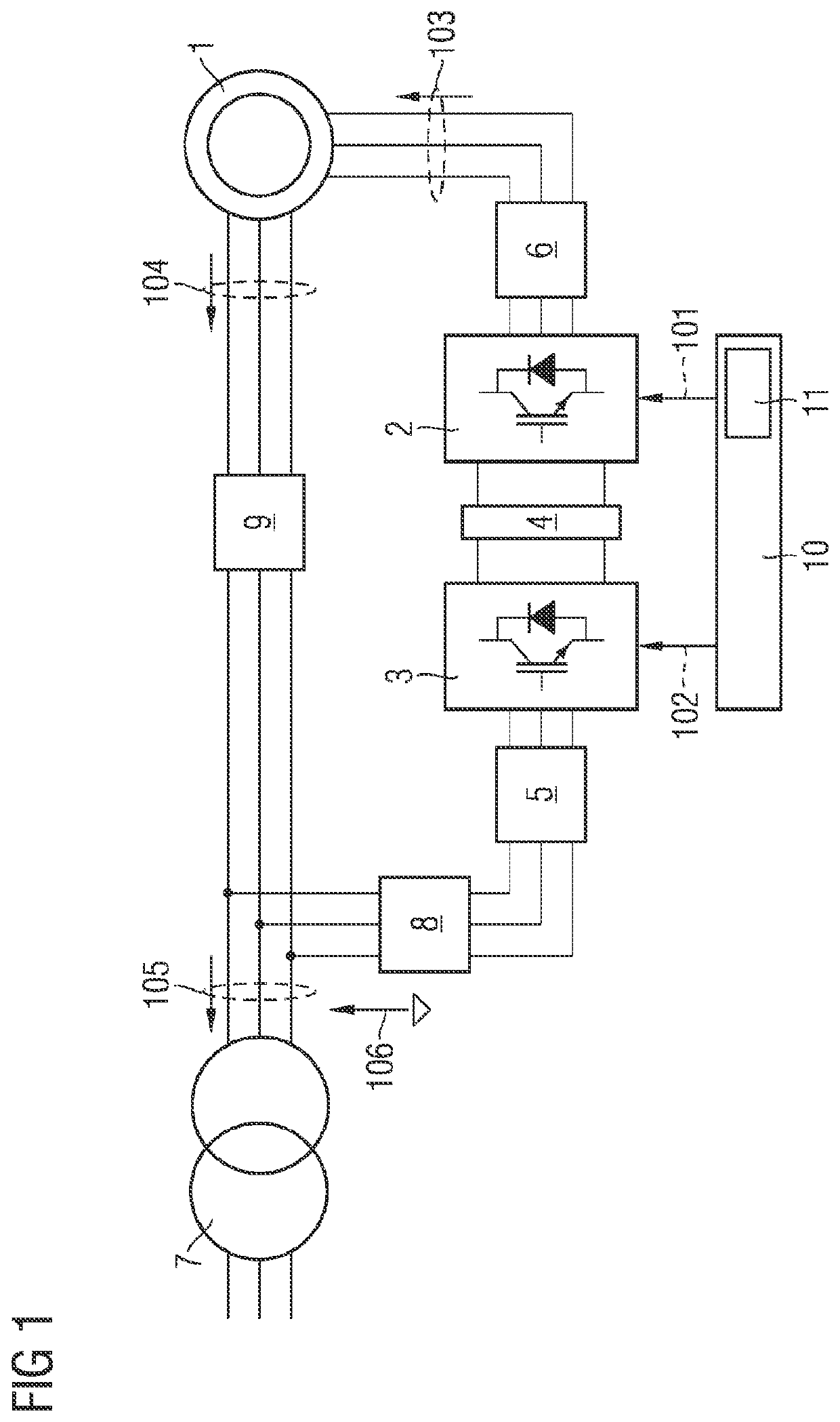
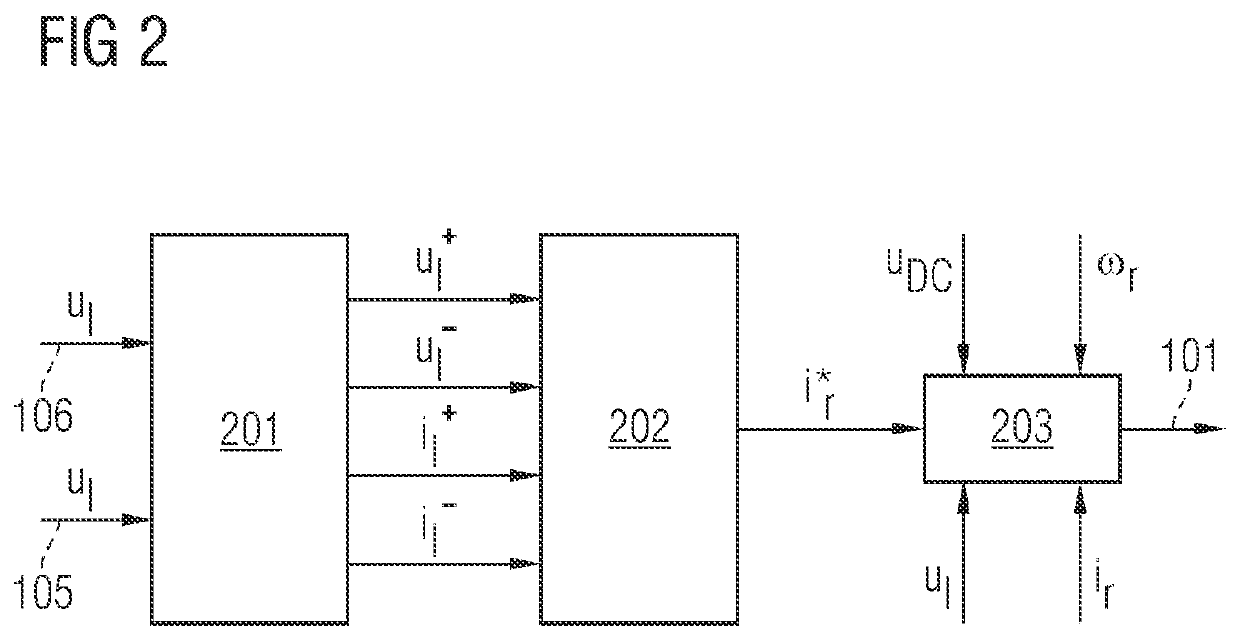
Unbalanced voltage compensation device and method for brushless doubly-fed induction generator
ActiveCN112152525AEnsure balanceImprove robustnessElectronic commutation motor controlGenerator control circuitsVoltage amplitudeControl theory
The invention discloses an unbalanced voltage compensation device and method for a brushless doubly-fed induction generator, and belongs to the technical field of brushless doubly-fed induction generator control. The device comprises a PW voltage controller, a CW conversion angle generator, a PW voltage amplitude calculator, a PW reactive power compensator, and a CW current regulator. The PW reactive power compensator comprises a PW current converter, a multiplier, a high-pass filter and a resonance controller; the multiplier calculates a current calculation value Qp (n) of the total reactivepower of the brushless doubly-fed induction generator according to the current feedback value ipd (n) of a d-axis component of the PW current and the current feedback value upq (n) of a q-axis component of the PW voltage; and the high-pass filter acquires the current calculation value of the PW double-frequency reactive power from the Qp (n), and the resonance controller calculates the q-axis compensation amount of the CW voltage. The PW reactive power compensator outputs the q-axis compensation amount of the CW voltage to eliminate the PW double-frequency reactive power so that the frequencyand the amplitude of the PW voltage are constant.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
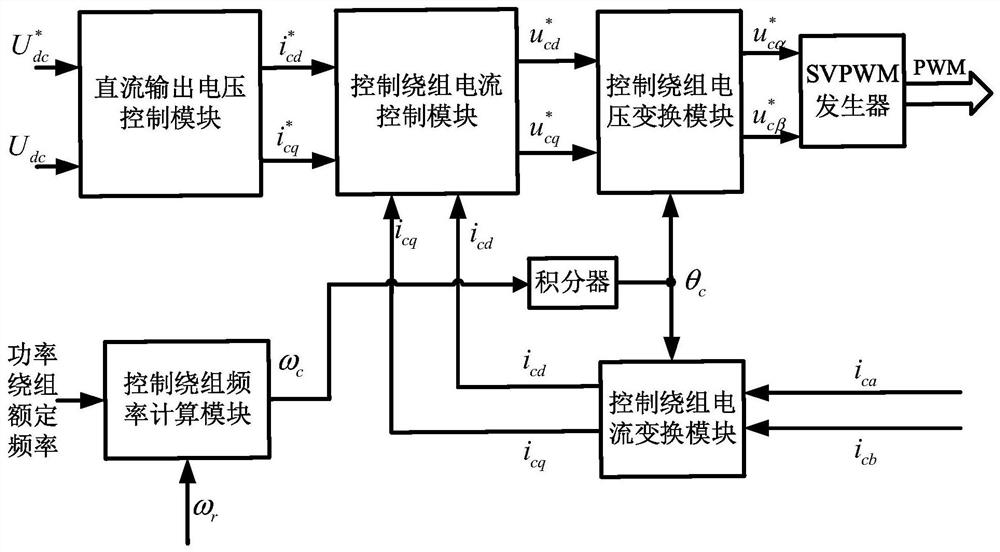
Brushless doubly-fed generator system and control method thereof
ActiveCN112217238AReduce hardware costsReduce usageElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsCapacitanceControl theory
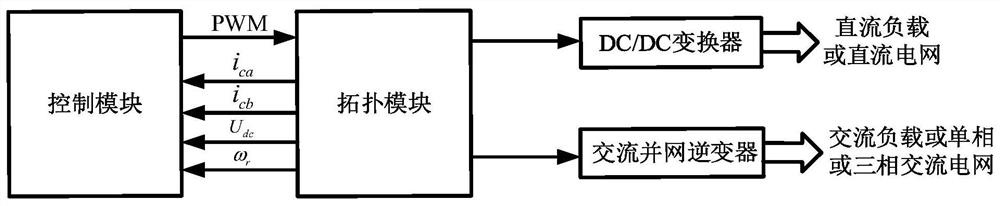
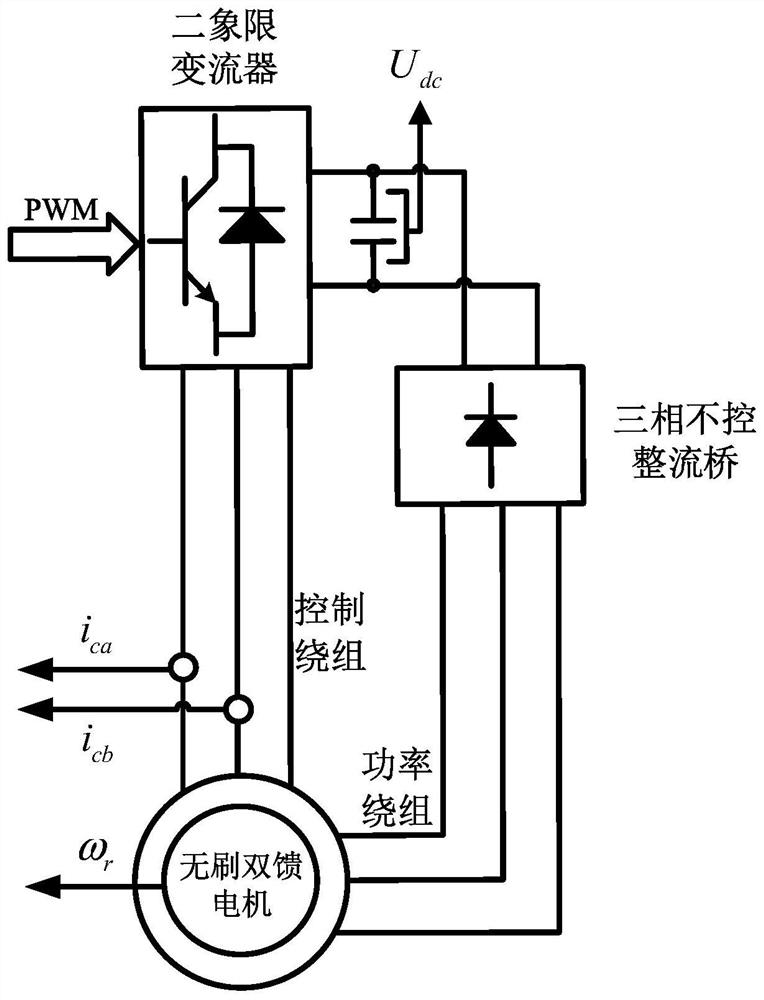
The invention discloses a brushless doubly-fed generator system and a control method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of brushless doubly-fed induction generator control. The system comprises a topology module and a control module, wherein the topology module comprises a brushless doubly-fed generator, a two-quadrant converter, a direct-current bus capacitor and a three-phase uncontrolled rectifier bridge. The alternating current side of the three-phase uncontrolled rectifier bridge is connected with the power winding; the direct-current side of the two-quadrant converter and the direct-current side of the three-phase uncontrolled rectifier bridge are connected with the direct-current bus capacitor in parallel. The control method comprises the following steps: providing excitingcurrent according to a PWM pulse modulation signal; controlling the AC voltage output by the power winding side according to the exciting current, and converting the AC voltage into DC voltage through a three-phase uncontrolled rectifier bridge; and inputting the direct-current voltage into the DC / DC converter or the alternating-current grid-connected inverter to supply power to a load or operatein parallel with a power grid. The problem that when an existing brushless doubly-fed generator system is connected to a grid, the power winding voltage, the power grid voltage and the alternating-current side voltage of a grid-side converter are difficult to synchronize is solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Allocating reactive power production for doubly fed induction generator wind turbine system
ActiveUS10756658B2Generator control circuitsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsConvertersControl engineering
Systems and methods for allocating reactive power production in a doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) wind turbine system including a DFIG and a power converter including a line side converter and a rotor side converter are provided. A method can include obtaining a reactive power production requirement, obtaining one or more operating parameters for the DFIG and the line side converter, and determining a priority ratio based at least in part on the one or more operating parameters. The priority ratio can be a ratio of reactive power production between the DFIG and the line side converter. The method can further include controlling the DFIG and the line side converter based at least in part on the reactive power production requirement and the priority ratio such that the combined reactive power production from the DFIG and the line side converter meet the reactive power production requirement.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
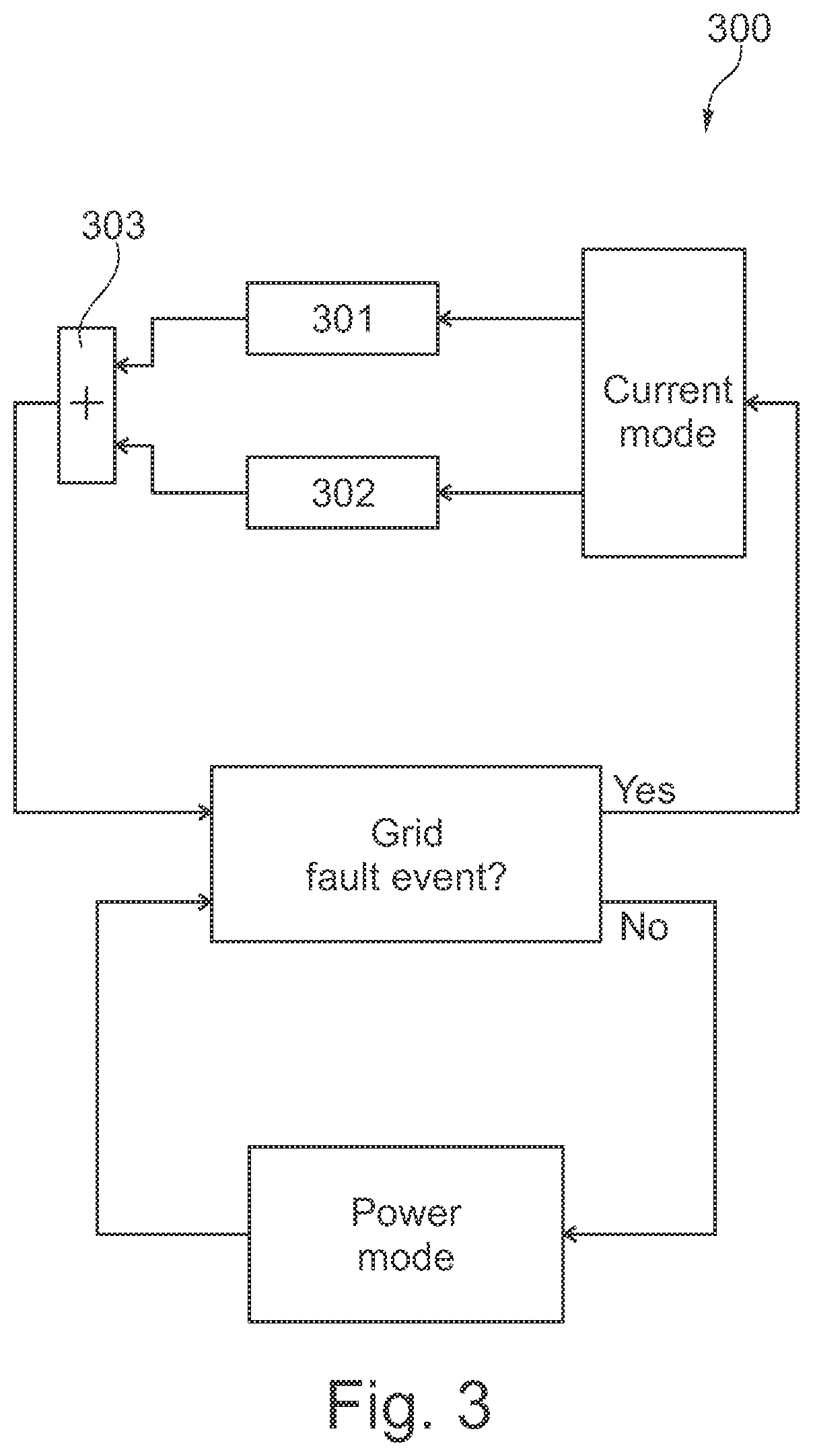
Method for handling sub-synchronous resonances
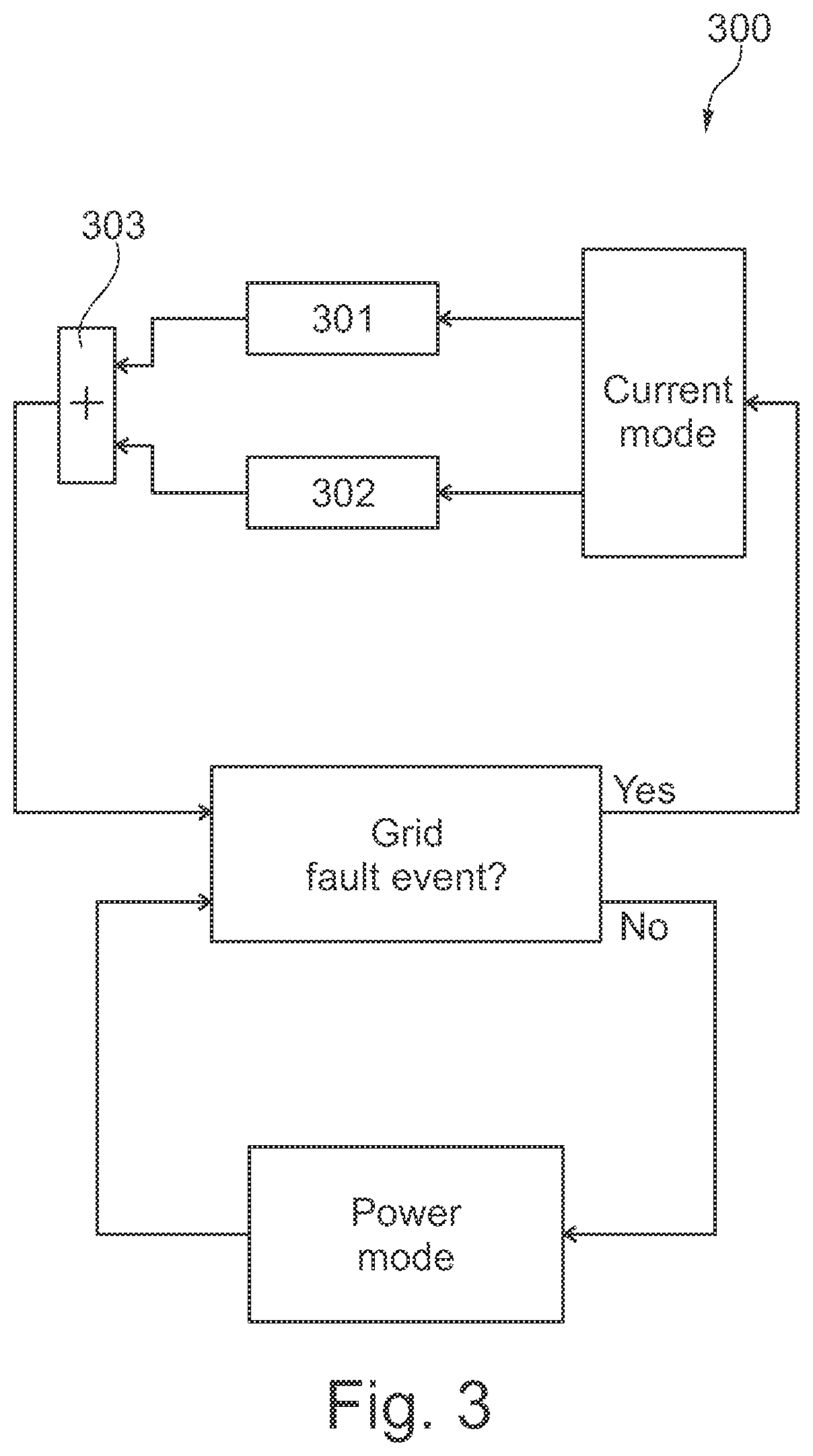
The present invention relates to a method of controlling a doubly fed induction generator wind turbine converter system in case of a sub-synchronous resonance event, the method comprising the steps of detecting the sub-synchronous resonance event, and switching from a first control mode to a second control mode in response to detecting the predetermined event, wherein the second control mode comprises the step of setting at least one rotor current controller parameter on the basis of a generator speed of the doubly fed induction generator. The predetermined event may also be a fault ride through event. The present invention further relates to a doubly fed induction generator wind turbine converter system being capable of handling such events.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Low-wind operation of clustered doubly fed induction generator wind turbines
ActiveUS10615608B2Generator control circuitsEfficient power electronics conversionControl setTransformer
Systems and methods for operating a cluster transformer operably coupled to cluster of DFIG wind turbines in low-wind conditions are provided. A wind turbine cluster system can include at least one DFIG module, a cluster transformer, and a control device configured to control operation of the cluster transformer based at least in part on a wind parameter. Each DFIG module can include a doubly fed induction generator comprising a rotor configured to generate AC power at a first voltage, a stator configured to generate AC power at a second voltage, and a power conversion system coupled to the rotor to convert power at the first voltage to power at the second voltage. The cluster transformer can be configured to receive power at the second voltage from the at least one DFIG module and convert the power at the second voltage to power at a third voltage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for operating a doubly fed induction generator system to reduce harmonics
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
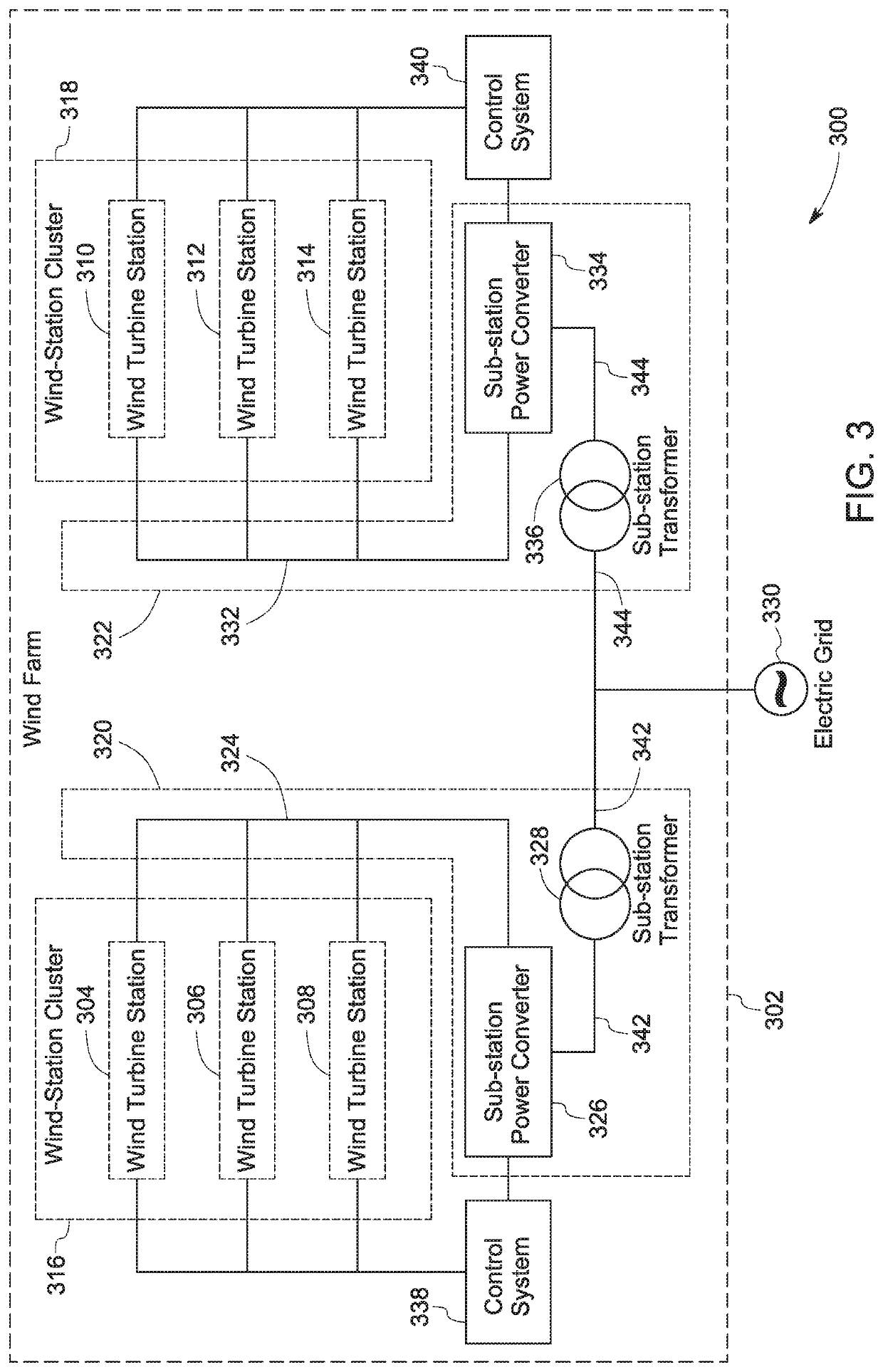
Wind farm topology and method of operating the same
ActiveUS10823147B2Wind motor controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsConvertersControl system
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
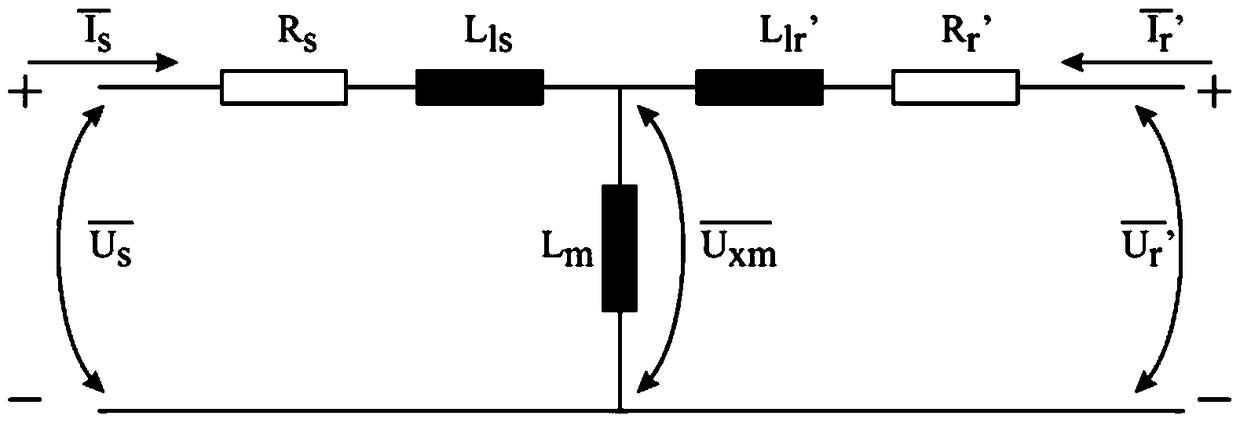
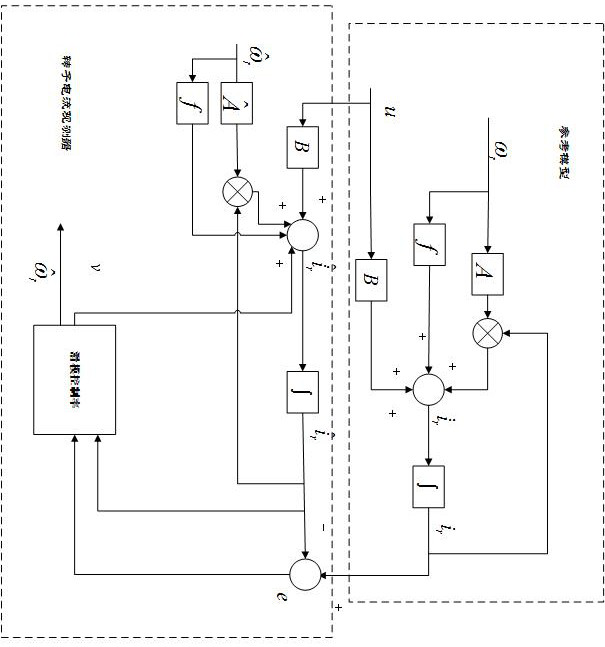
Method and arrangement for determining leakage inductances of double fed induction generator
ActiveCN105490599AReduce needGood estimateGenerator control circuitsAC motor controlFrequency changerStator voltage
A method and arrangement for determining leakage inductances of a double fed induction generator, DFIG, (10) wherein, in response to the stator current of the DFIG being equal to or below a first predetermined threshold, values of a stator voltage, a rotor voltage and a rotor current of the DFIG are determined, and a rotor leakage inductance of the DFIG is calculated on the basis the determined values, and, in response to the rotor current of the DFIG being equal to or below a second predetermined threshold, values of the stator voltage, the rotor voltage and the stator current of the DFIG are determined, and a stator leakage inductance of the DFIG is calculated on the basis of the determined values.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
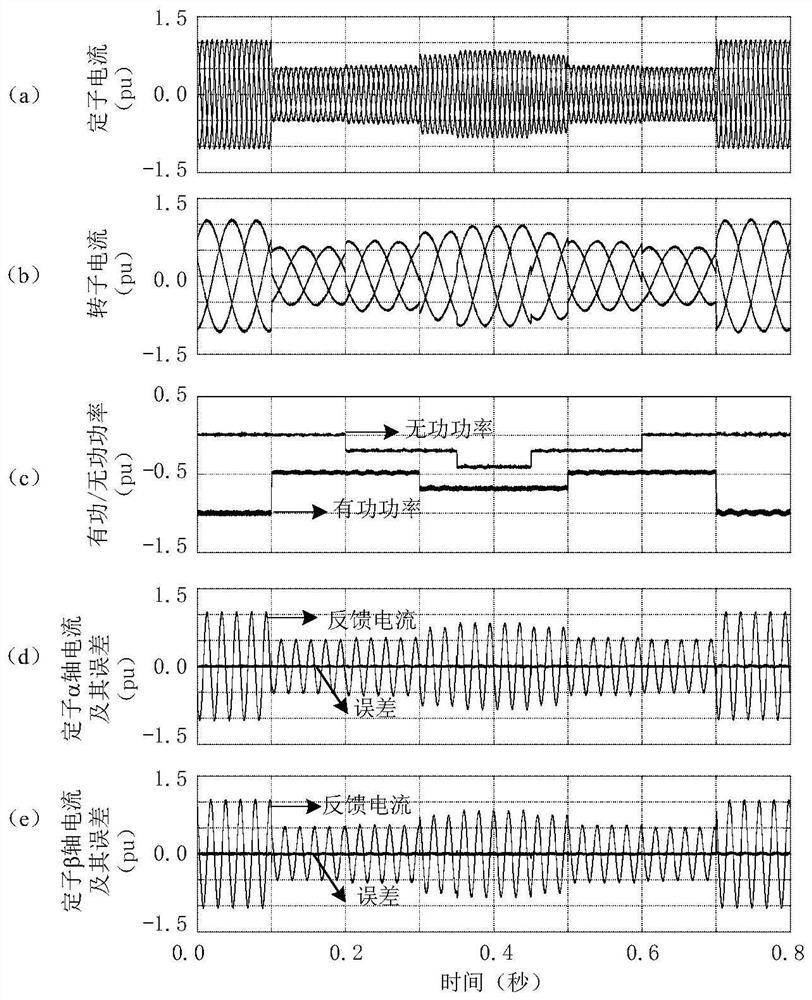
A grid-connected doubly-fed induction generator stator current control method and device
ActiveCN106982021BReduce dependenceImprove robustnessElectronic commutation motor controlGenerator control circuitsStator voltageControl system design
The invention provides a method and device for controlling the stator current of a grid-connected doubly-fed induction generator. The method includes: performing coordinate transformation on the collected parameters of the doubly-fed induction generator to obtain The stator voltage vector U sαβ and the stator current vector I sαβ ; Calculate the stator current vector I of the doubly-fed induction generator sαβ α, β axis command; according to the DFIG stator current α, β axis command and the actual measured feedback value, calculate the rotor voltage command U' under the stator two-phase stationary coordinate system rαβ ;To the rotor voltage command U' rαβ Carry out coordinate transformation to obtain the rotor voltage command U in the rotor two-phase static α-β coordinate system rαβ ;According to the rotor voltage command U rαβ A set of PWM signals are obtained to control the rotor converter of the doubly-fed induction generator. The technical scheme provided by the invention simplifies the design and implementation process of the control system, and enhances the adaptability of the control system to generator parameter changes.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
Method for handling sub-synchronous resonances
The present invention relates to a method of controlling a doubly fed induction generator wind turbine converter system in case of a sub-synchronous resonance event, the method comprising the steps of detecting the sub-synchronous resonance event, and switching from a first control mode to a second control mode in response to detecting the predetermined event, wherein the second control mode comprises the step of setting at least one rotor current controller parameter on the basis of a generator speed of the doubly fed induction generator. The predetermined event may also be a fault ride through event. The present invention further relates to a doubly fed induction generator wind turbine converter system being capable of handling such events.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
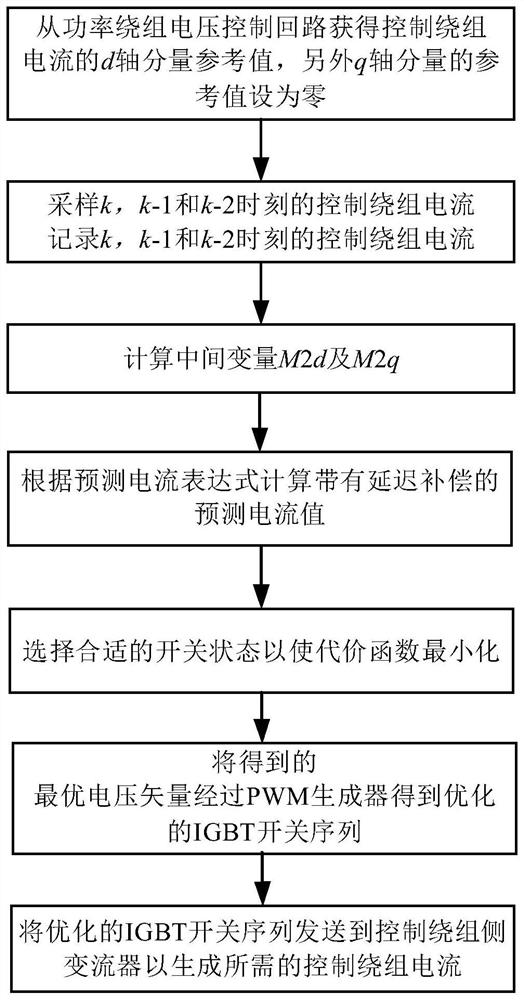
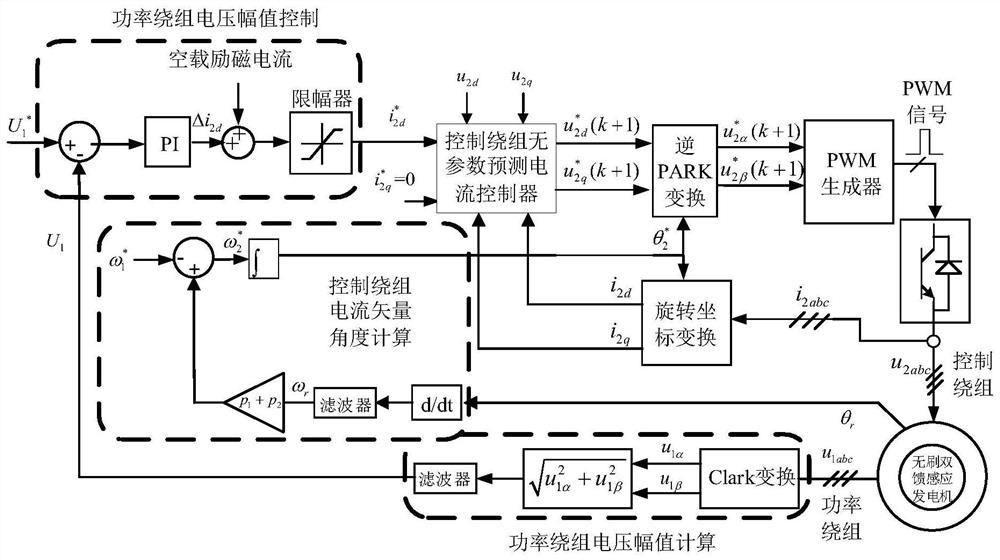
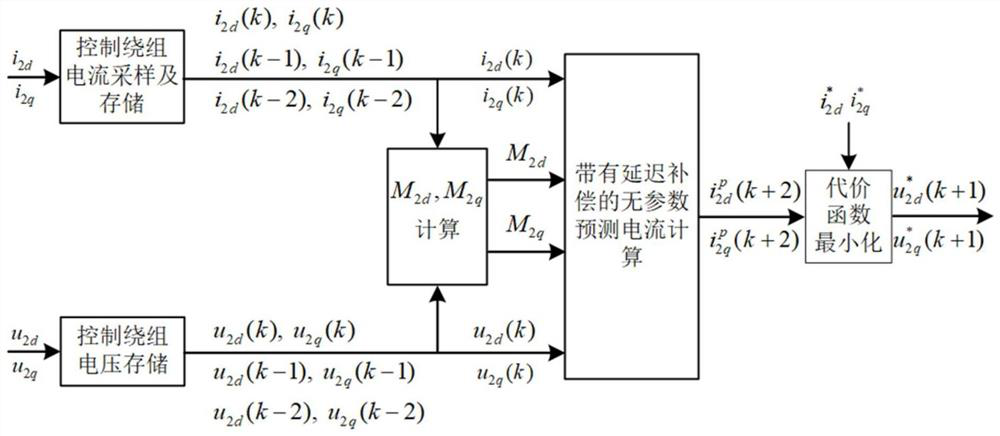
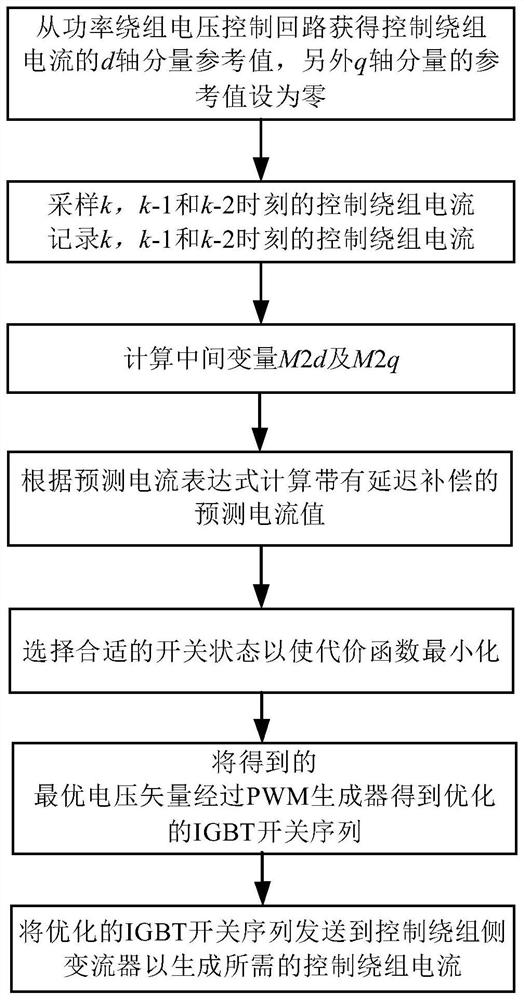
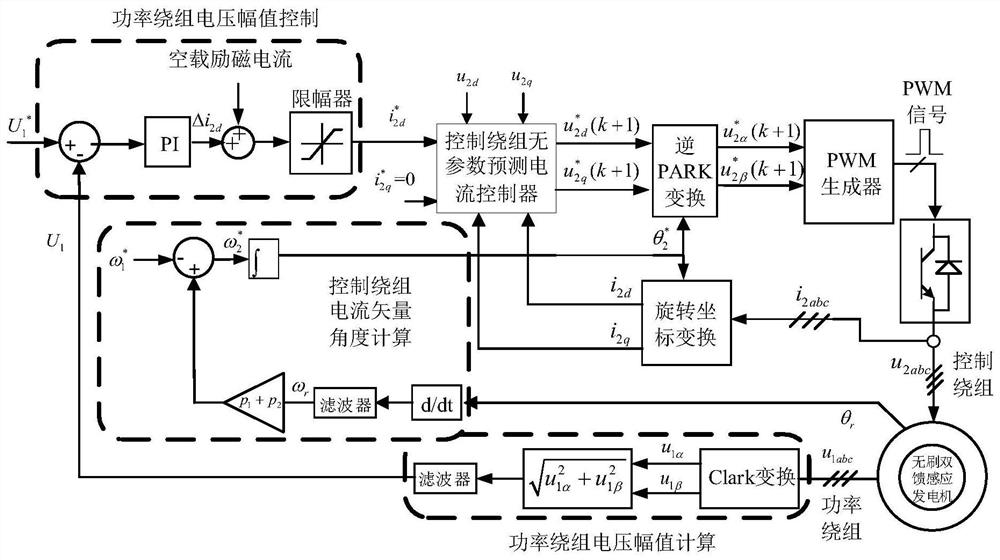
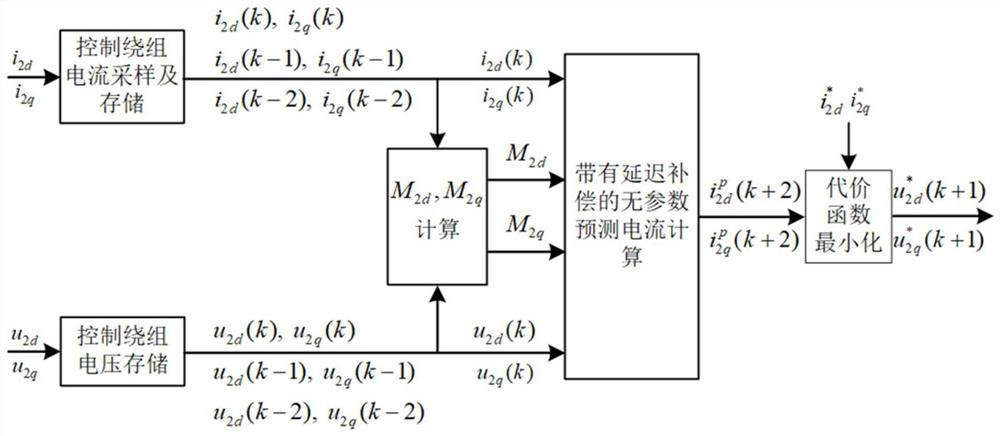
Parameter-free prediction current control method for independent brushless doubly-fed induction generator
ActiveCN111865151AAccurate trackingGenerating voltage is stableGenerator control circuitsVector control systemsElectric machineControl system
The invention discloses a parameter-free prediction current control method of an independent brushless doubly-fed induction generator, and belongs to the technical field of brushless doubly-fed induction generator control. The method comprises the following steps: monitoring control winding voltage and current information of a motor at the first two moments and the current moment in real time; calculating a prediction current containing delay compensation, determining an optimal switching state of a power electronic device in a control winding side converter through a cost function, and finally determining a duty ratio by using a single vector modulation algorithm to generate a reasonable and effective switching sequence so as to drive the control winding side converter to realize real-time control of a control winding current. According to the control method, the winding current is predicted and controlled through the real-time motor state information, dependence on motor parameters can be effectively avoided, a control system is hardly influenced by motor parameter changes, robustness is high, and operation is more stable.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Balancing reactive current between a DFIG stator and a grid-side inverter
ActiveUS11233400B2Total current dropAvoid heatingGenerator control circuitsElectric motor controlConvertersClassical mechanics
Aspects of the present invention relate to a method for controlling an amount of reactive current provided from a wind turbine generator to a power grid during an abnormal power grid event, said wind turbine generator comprising a doubly-fed induction generator having a rotor and a stator, and a power converter coupling the rotor to the power grid, the power converter comprising a grid-side inverter, wherein the method comprises the step of balancing the reactive current provided to the power grid between a reactive stator current and a reactive grid-side inverter current, wherein the reactive grid-side inverter current is controlled in accordance with a reactive current capacity of a grid breaker receiving the reactive current provided by the grid-side inverter. Aspects of the present invention also relate to a wind turbine generator being capable of performing the method.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
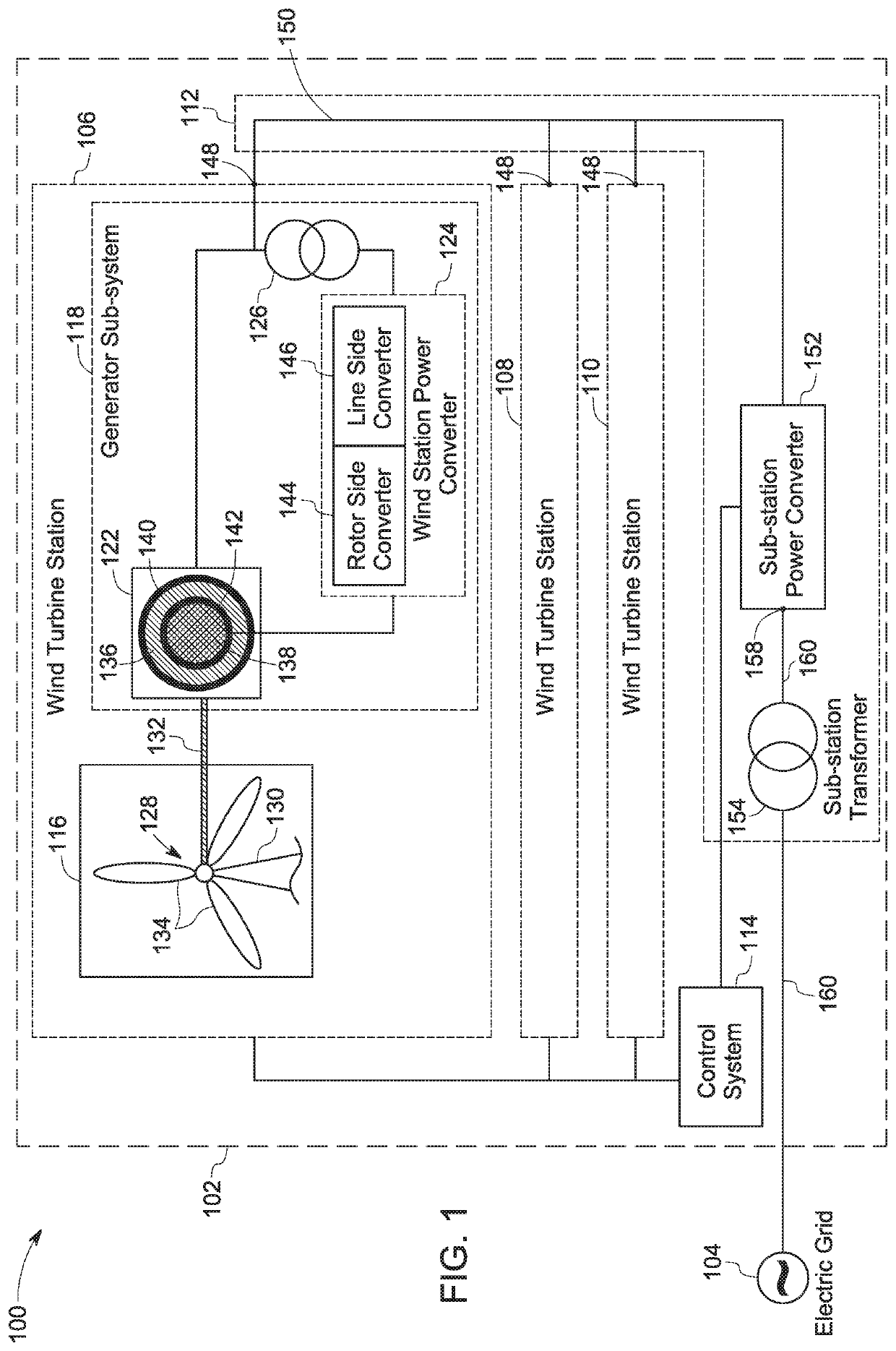
Wind Farm Topology and Method of Operating the Same
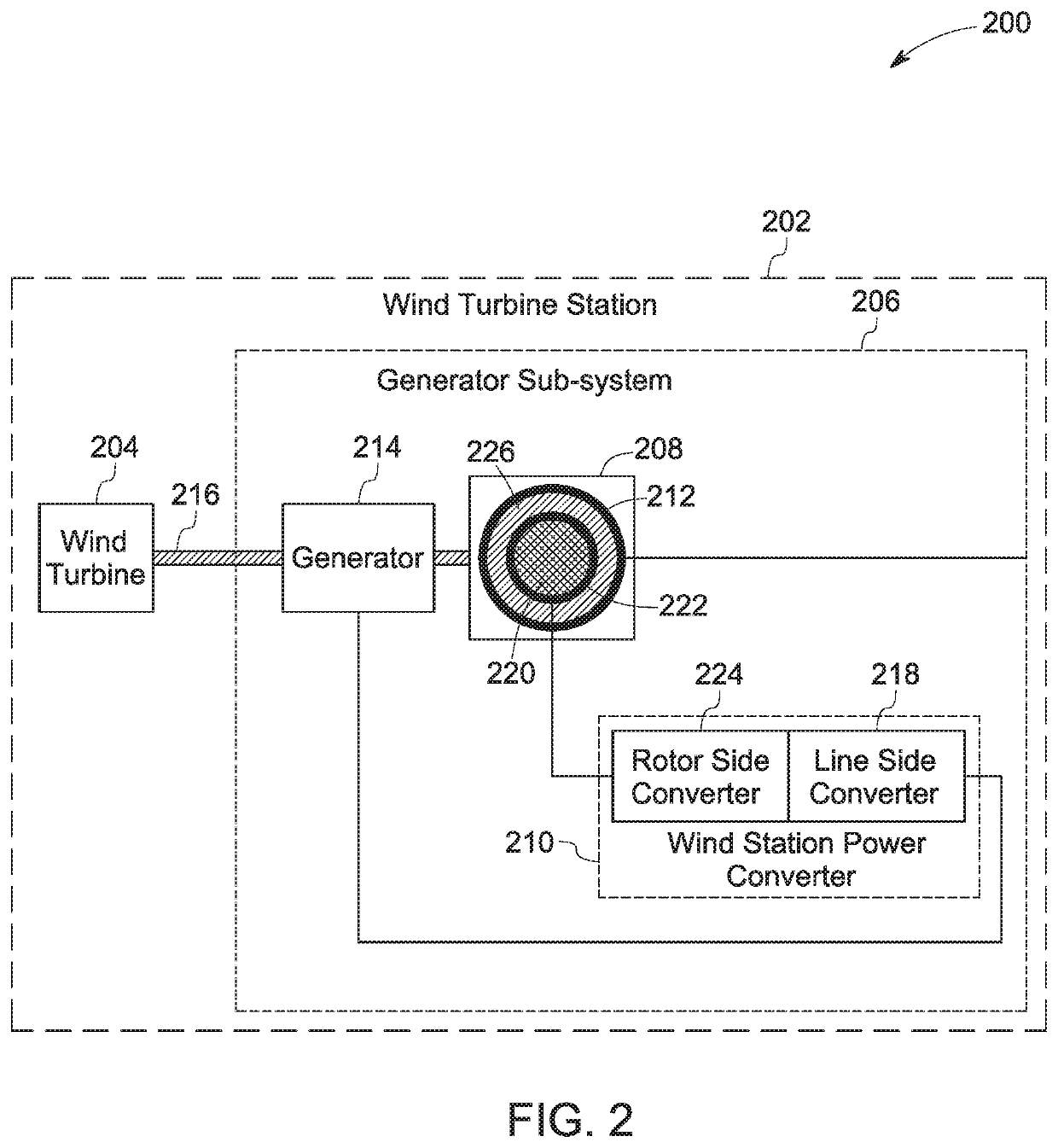
ActiveUS20200088167A1Wind motor controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsConvertersMarine engineering
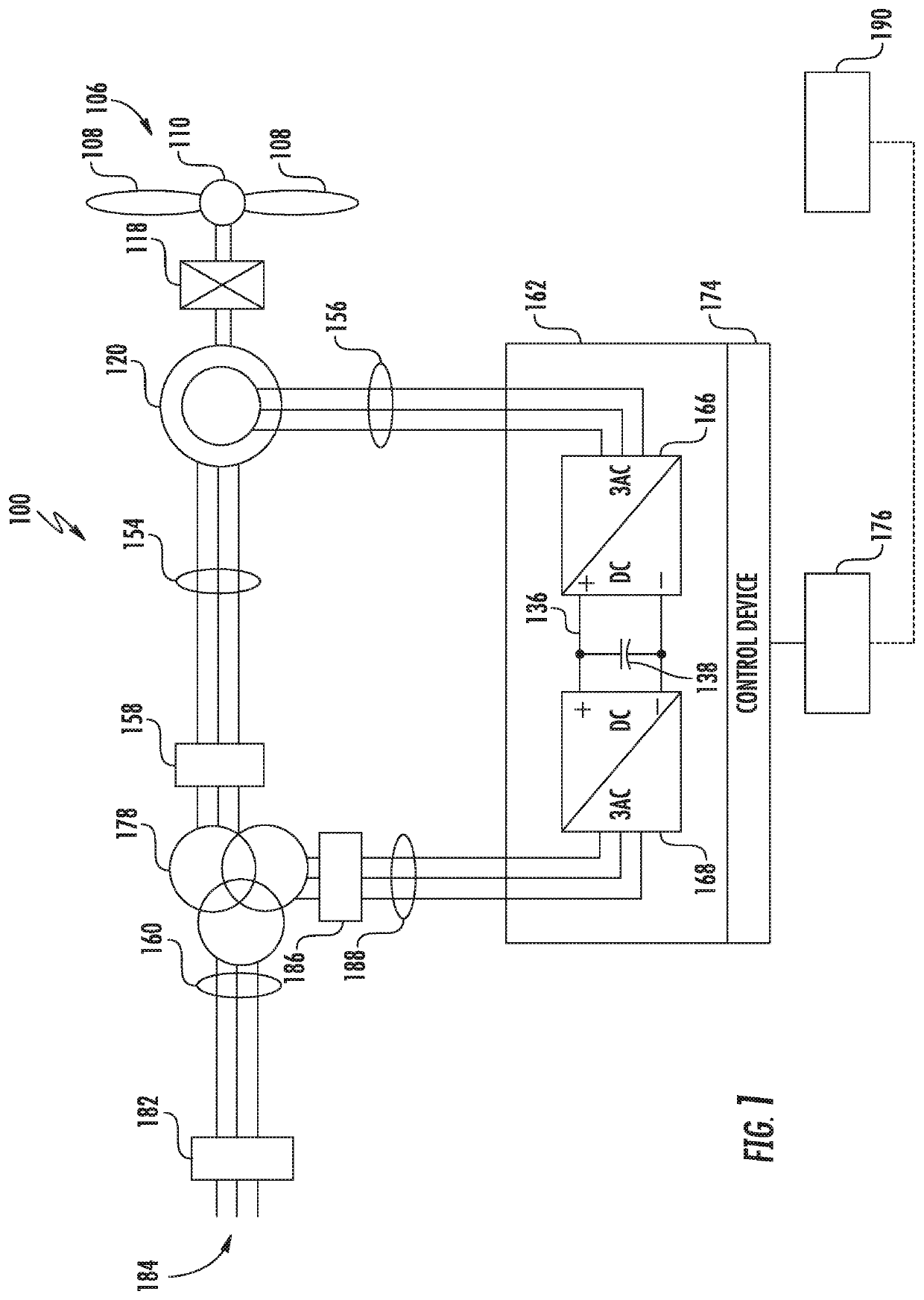
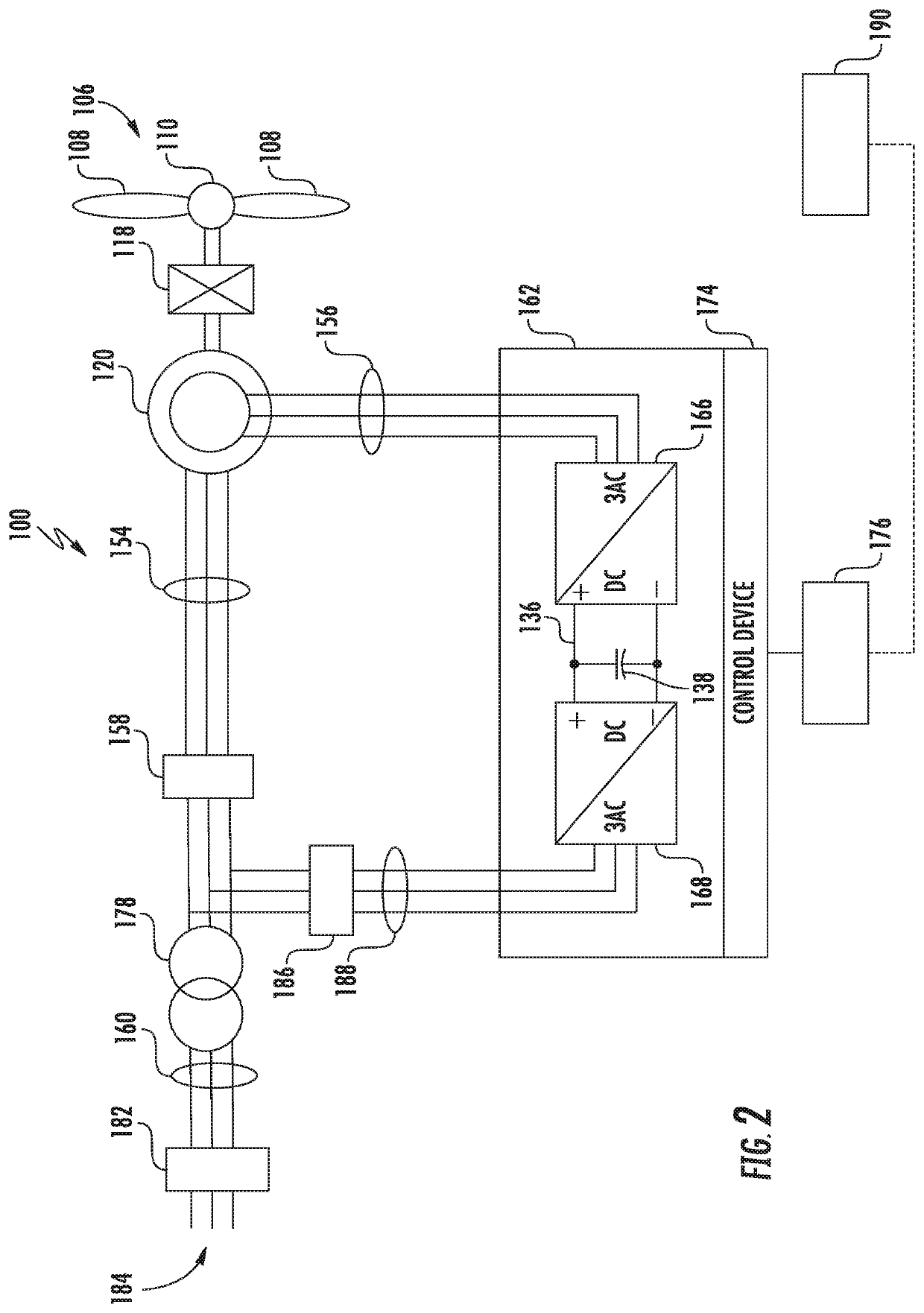
A wind farm is presented. The wind farm includes a plurality of wind turbine stations, where each wind turbine station includes a wind turbine and a generator sub-system. The generator sub-system includes a doubly-fed induction generator configured to generate an alternating current voltage and a wind turbine station power converter. The wind farm further includes a power collection sub-system that includes a power bus and a sub-station power converter. The wind farm also includes a control system configured to determine a wind speed metric, estimate a corresponding frequency metric, calculate a desirable frequency based on the wind speed metric and frequency compensation ranges of the wind turbine station power converters, and generate and communicate control commands to the sub-station power converter based on the desirable frequency to allow the sub-station power converter to update a line frequency of a power bus voltage based on the desirable frequency.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and device for determining the leakage inductance of a doubly-fed induction generator
ActiveCN105490599BReduce needGood estimateGenerator control circuitsAC motor controlStator voltageFrequency changer
A method and device for determining the leakage inductance of a doubly-fed induction generator DFIG (10), and an inverter and a frequency converter including the same. The method includes determining a stator voltage value, a rotor voltage value, and a rotor current value of the DFIG in response to the stator current of the DFIG being equal to or less than a first predetermined threshold, and calculating a rotor leakage inductance of the DFIG based on the determined values; and, In response to the rotor current of the DFIG being equal to or less than a second predetermined threshold, a stator voltage value, a rotor voltage value, and a stator current value of the DFIG are determined, and a stator leakage inductance of the DFIG is calculated based on the determined values.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
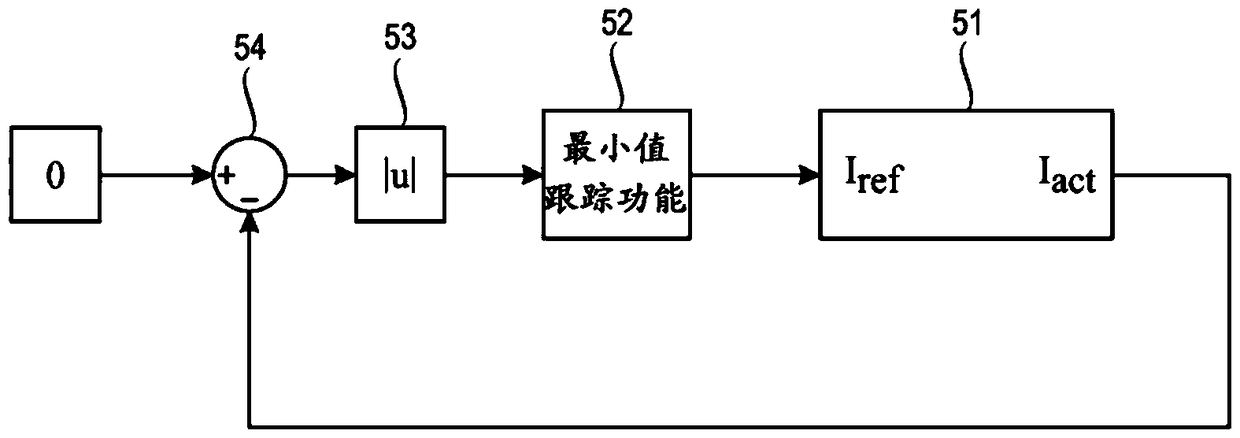
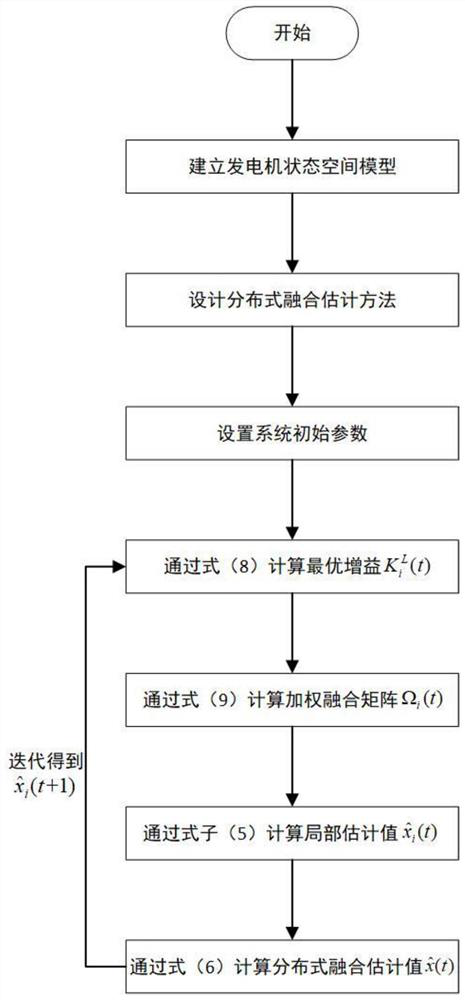
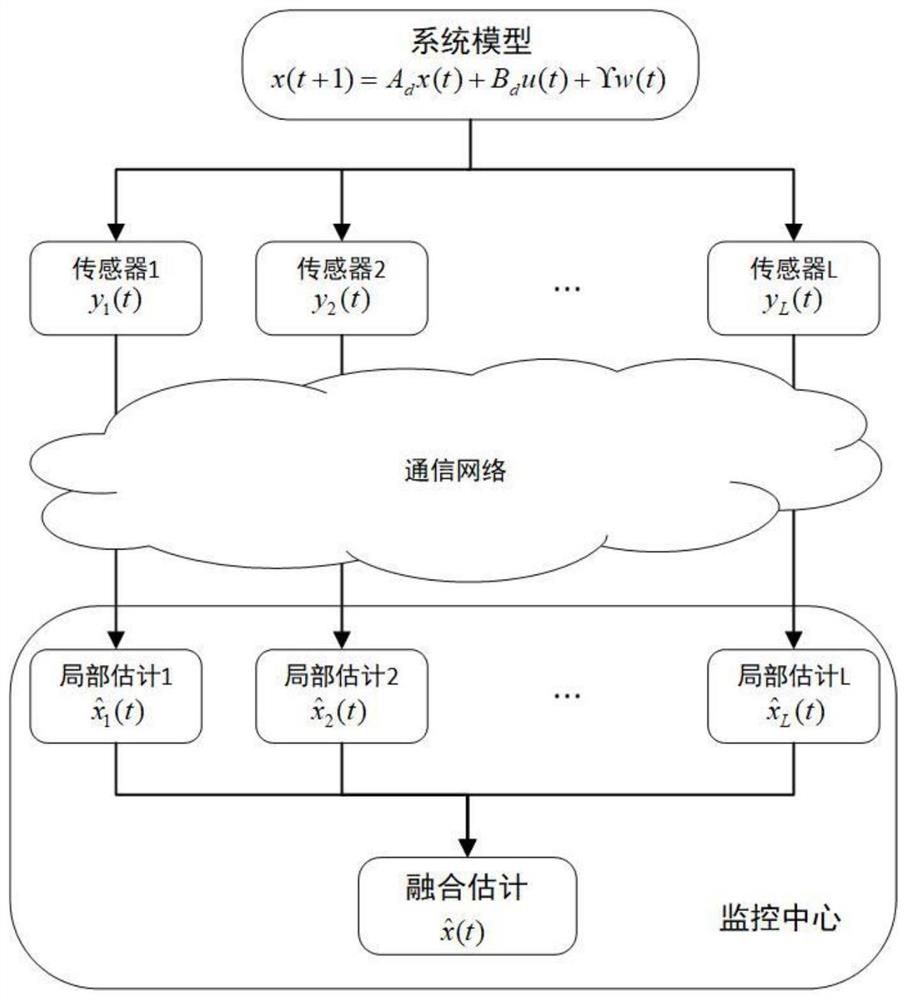
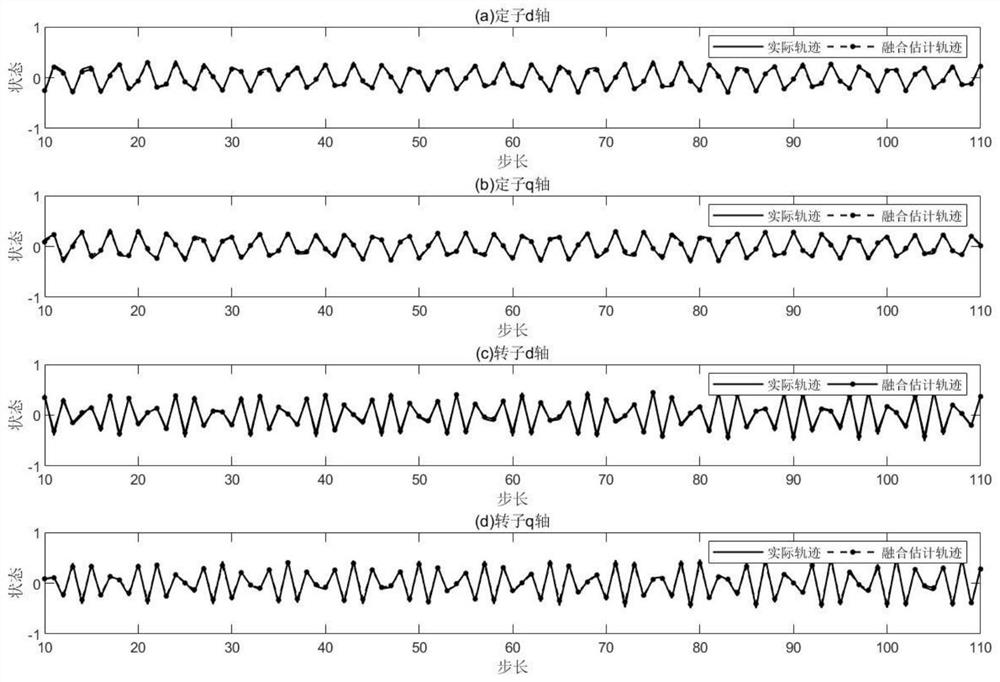
Distributed state fusion estimation method of wind driven generator
InactiveCN111817626AAccurate monitoringPrecise maintenanceElectronic commutation motor controlGenerator control circuitsWind drivenMathematical model
The invention discloses a distributed state fusion estimation method for a wind driven generator under the condition that noise statistical characteristics are unknown. The distributed state fusion estimation method comprises the steps of: proposing a mathematical model of a doubly-fed induction generator; establishing a state space model of the generator; designing a distributed fusion estimationmethod with unknown noise statistical characteristics; setting motor parameters, and solving two optimization problems to obtain a local optimal gain and a distributed weighted fusion matrix; and performing iterative updating to obtain fusion estimation of a generator state. The new distributed fusion estimation method is provided by the invention for solving the state estimation problem of the wind driven generator when the noise statistical characteristics cannot be accurately obtained, and is high in estimation precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
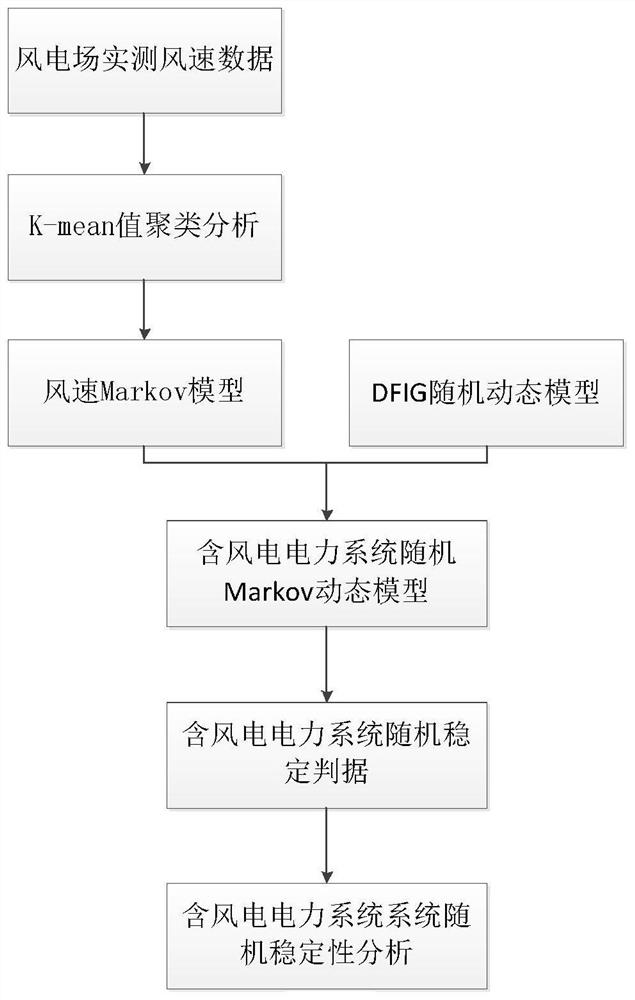
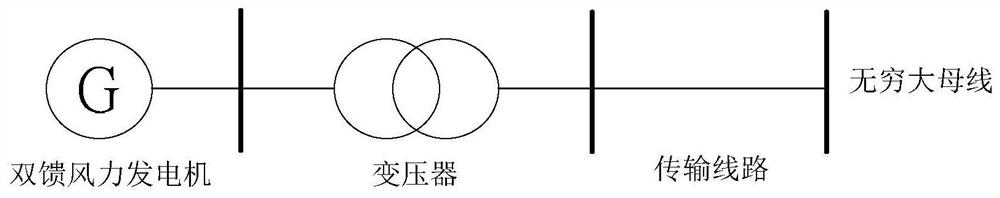
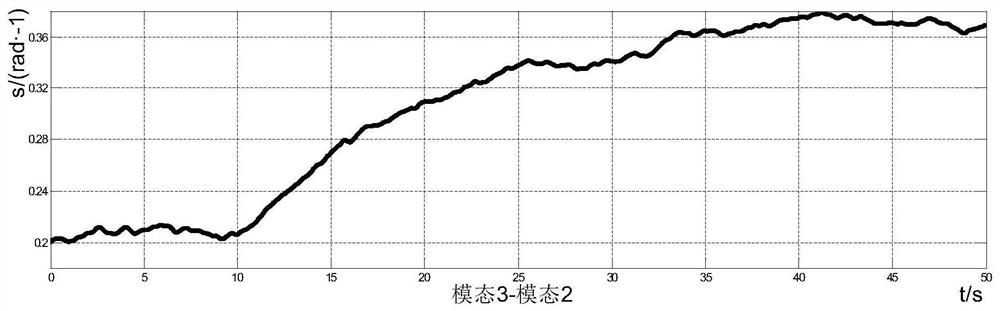
Stochastic Stability Analysis Method of Power System Containing Wind Power Based on Markov Theory
ActiveCN107947228BCharacterize dynamic behaviorOvercome limitationsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationAlgorithmDynamic models
The invention provides a stochastic stability analysis method for a power system containing wind power based on Markov theory, establishes a Markov model of wind speed and a stochastic dynamic model of a doubly-fed induction generator, and establishes a stochastic Markov dynamic of a power system containing a doubly-fed induction generator Model, put forward the criterion applicable to the system stochastic Markov dynamic model. Based on the stochastic Markov theory, the present invention analyzes the system stability by establishing a stochastic Markov dynamic model of the wind power system. According to the definition of random mean square stability of the system, using the relevant knowledge of the M matrix, the random Markov dynamic model based on the system is used to determine the randomness of the system. Practical criterion of mean square stability; the present invention overcomes the limitations of stochastic equations, and can more accurately describe the dynamic behavior of wind power systems in the case of large-scale random fluctuations in wind speed, based on the stochastic Markov dynamic model derived from the system Compared with other criteria, the criterion is more practical, more concise and has a wider scope of application.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
A No Parameter Predictive Current Control Method for Independent Brushless Doubly-fed Induction Generator
ActiveCN111865151BAccurate trackingGenerating voltage is stableGenerator control circuitsVector control systemsElectric machineControl system
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fault detection method for doubly-fed induction generator based on sliding mode observer
ActiveCN110649846BSimple structureStrong anti-interference abilityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsTerminal voltageMathematical model
In order to detect the fault of doubly-fed induction generator, a fault detection method of doubly-fed induction generator based on sliding mode observer is proposed here. Due to the advantages of the sliding mode observer such as simple structure, not easily affected by parameters, and strong anti-interference ability, the invention applies the sliding mode observer to the fault detection of the doubly-fed induction motor. First, the present invention builds a sliding mode observer based on the mathematical model of the doubly-fed induction generator, observes the rotor current and speed, and realizes fault self-detection by comparing the residual between the actual rotor current value and the observed value. Then the present invention provides three kinds of faults, namely grid end voltage drop fault, doubly-fed induction generator stator turn-to-turn fault and rotor current sensor fault, to prove that the sliding mode observer can perform fault detection on faults occurring at different positions. , and it can be seen that the sliding mode observer has the characteristics of fast response and good stability.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
An analytical method for three-phase short-circuit current of doubly-fed induction generator after crowbar protection action
ActiveCN108566132BSimple calculationElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsElectric power systemControl theory
The invention relates to a method for analyzing the three-phase short-circuit current of a doubly-fed induction wind generator after the protection action of a crowbar, and belongs to the technical field of wind power generation system fault analysis. The invention uses the DFIG stator and rotor voltage equations and stator and rotor flux linkage equations after the crowbar protection action to deduce the three-phase short-circuit current of the double-fed induction wind generator after the crowbar protection action, which simplifies the calculation process. The method can accurately calculate the three-phase short-circuit current of the doubly-fed induction wind turbine after the protection action of the crowbar, and is of great significance to the selection of power system equipment and the analysis of the protection action characteristics of the doubly-fed induction wind turbine.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Control system and method for the rotor side converter of a doubly-fed induction generator in a wind turbine
PendingUS20220302859A1Suppress conduction lossReduce switching lossesGenerator control circuitsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReference currentControl system
A control method for the rotor side converter of a doubly-fed induction generator in a wind turbine for disturbances in the electric grid is provided. A control system includes a calculating unit configured for calculating at least one reference current. A current controller which is a hybrid controller configured to operate in two different modes, a first operating mode, set during a transient of a disturbance in an electric grid, where the current controller is configured to operate with a modulation index being outside a linear area and a second operating mode, set during a stable state of the disturbance in the electric grid, where the current controller is configured to operate with a modulation index inside the linear area, thereby instantly providing a maximum voltage available in a rotor so as to satisfy the at least one reference current.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
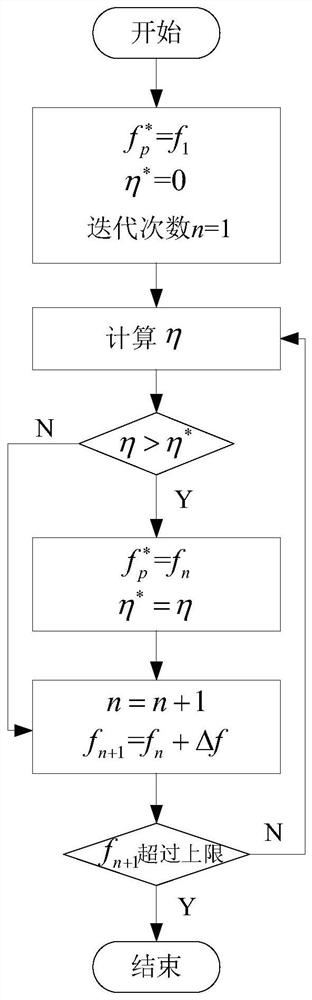
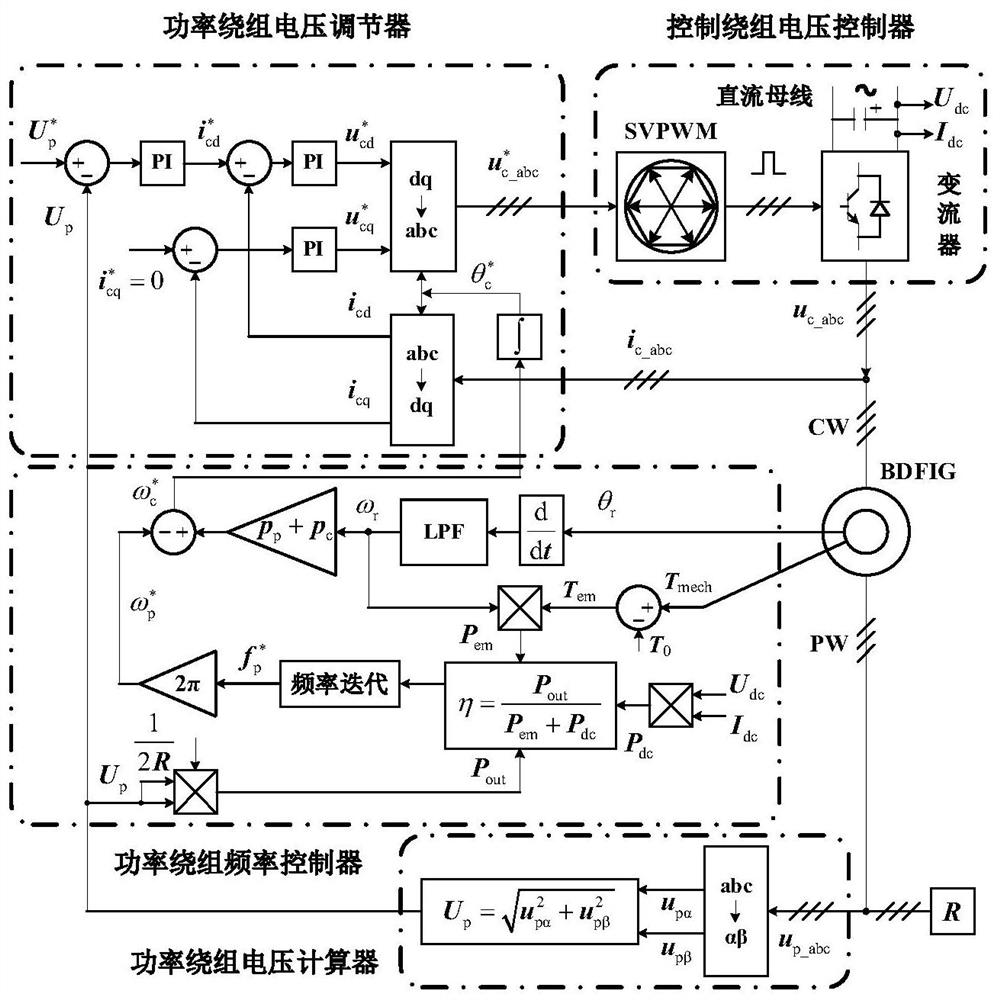
Brushless doubly-fed induction generator efficiency optimization control method and system
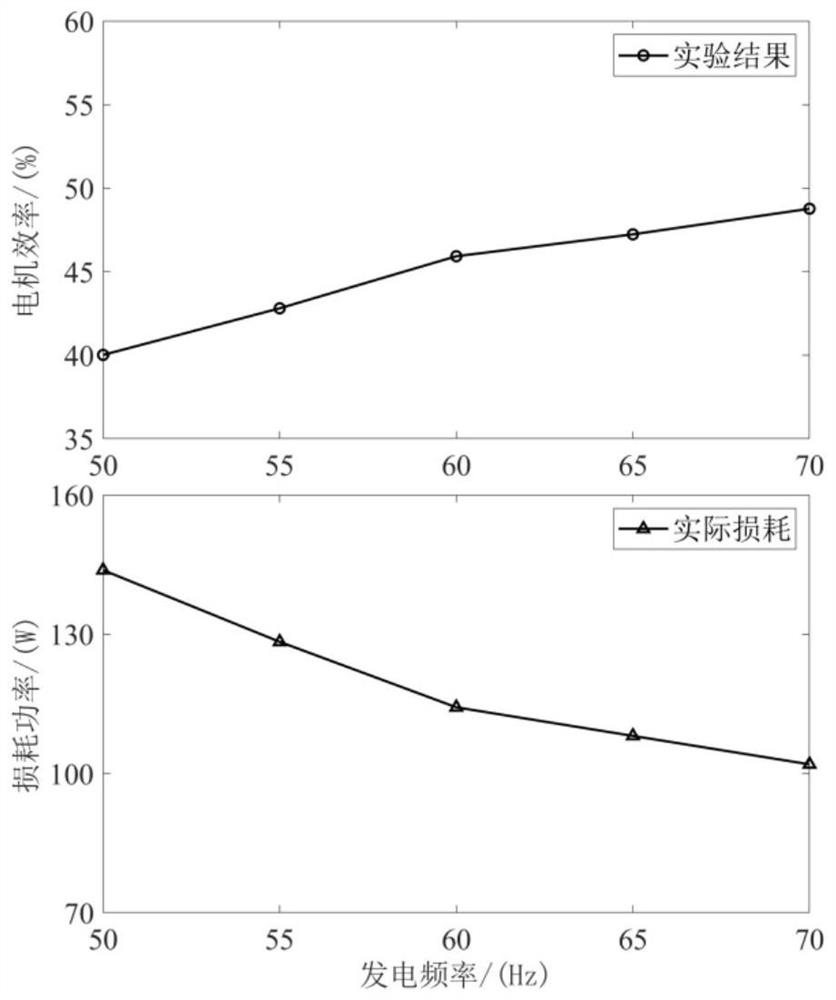
ActiveCN113162494ALoss minimizationTroubleshoot inefficient technical issuesElectronic commutation motor controlGenerator control circuitsVoltage amplitudeControl theory
The invention discloses a brushless doubly-fed induction generator efficiency optimization control method and system, and belongs to the technical field of brushless doubly-fed induction generator control. The method comprises the steps of (1) in a current control period, calculating output power according to a power winding voltage amplitude feedback value and a resistive load value, calculating direct-current input power according to the direct-current bus voltage and the direct-current bus current, and calculating mechanical power converted into input electromagnetic power according to the rotor angular speed and the electromagnetic torque so as to calculate motor efficiency eta of the current control period; (2) if eta is greater than the current optimal motor efficiency, updating the optimal power generation efficiency to eta, updating the optimal power generation frequency to the current power generation frequency f, and then updating a control winding angular frequency given value; and (3) after the power generation frequency is increased by delta f, if the power generation frequency does not exceed the upper limit of the power generation frequency, turning to the step (1) to start efficiency optimization of the next control period, and otherwise, enabling the generator to operate according to the sequence, and ending the optimization control. According to the invention, the motor efficiency can be maximized.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com