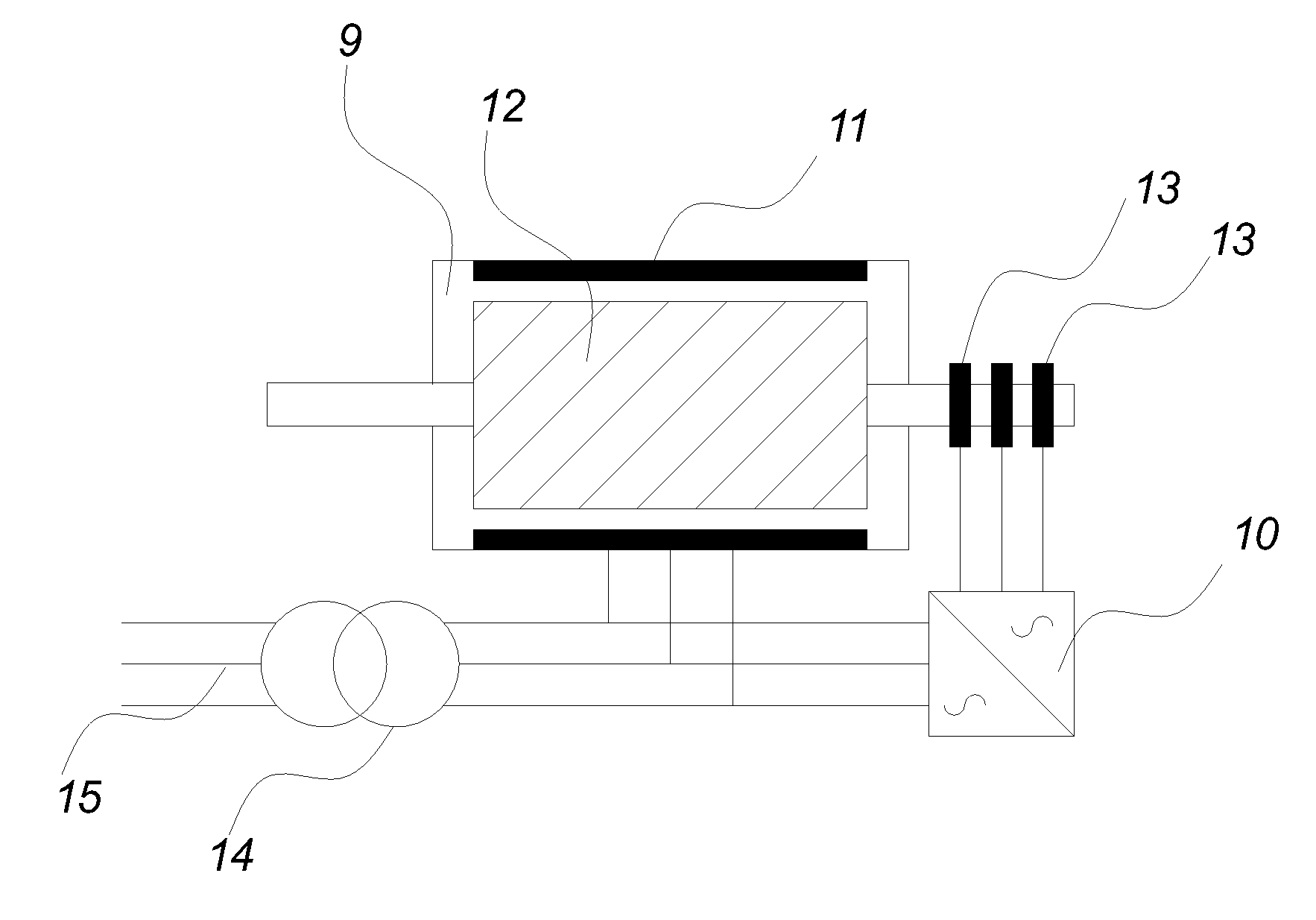
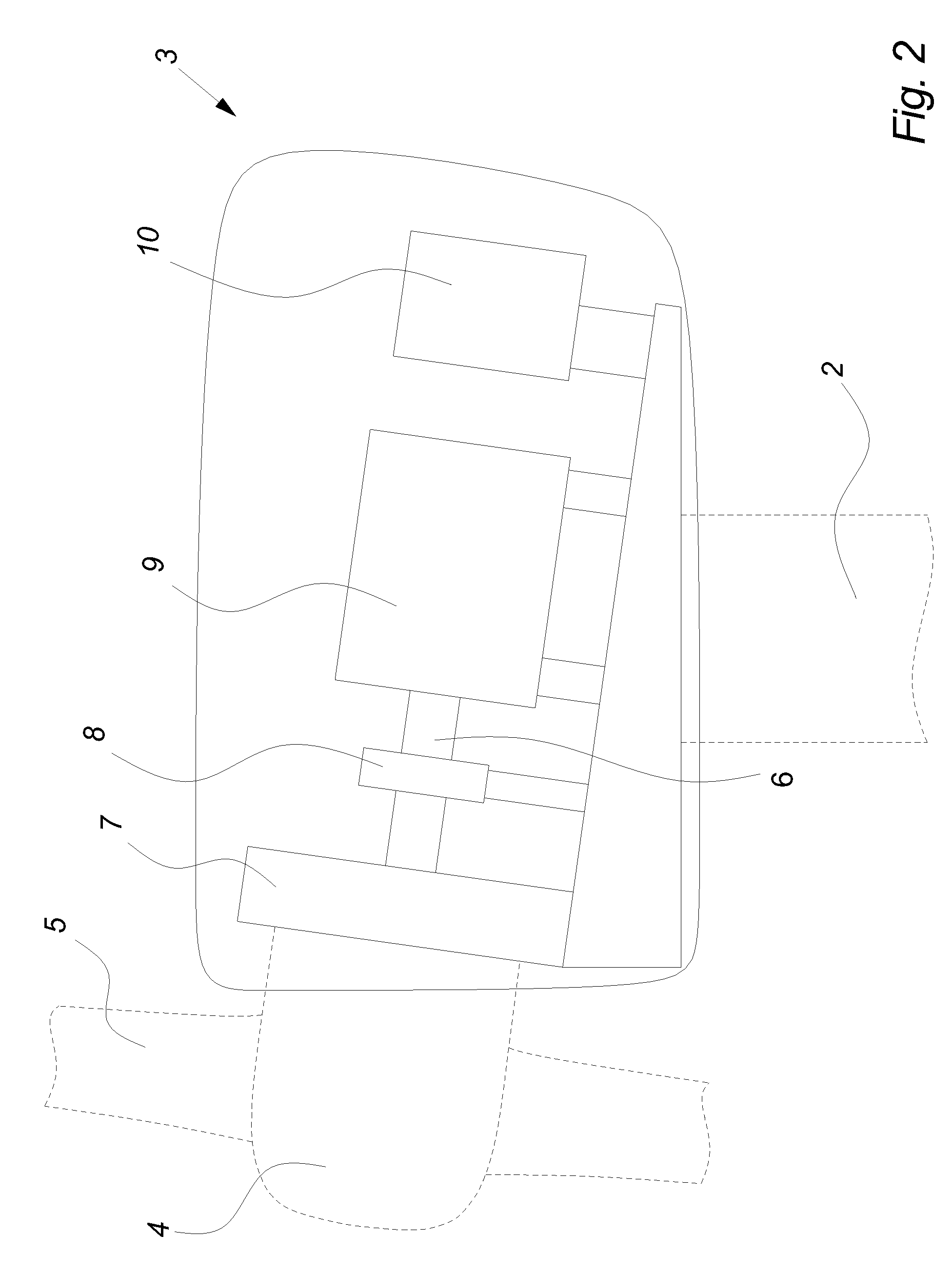
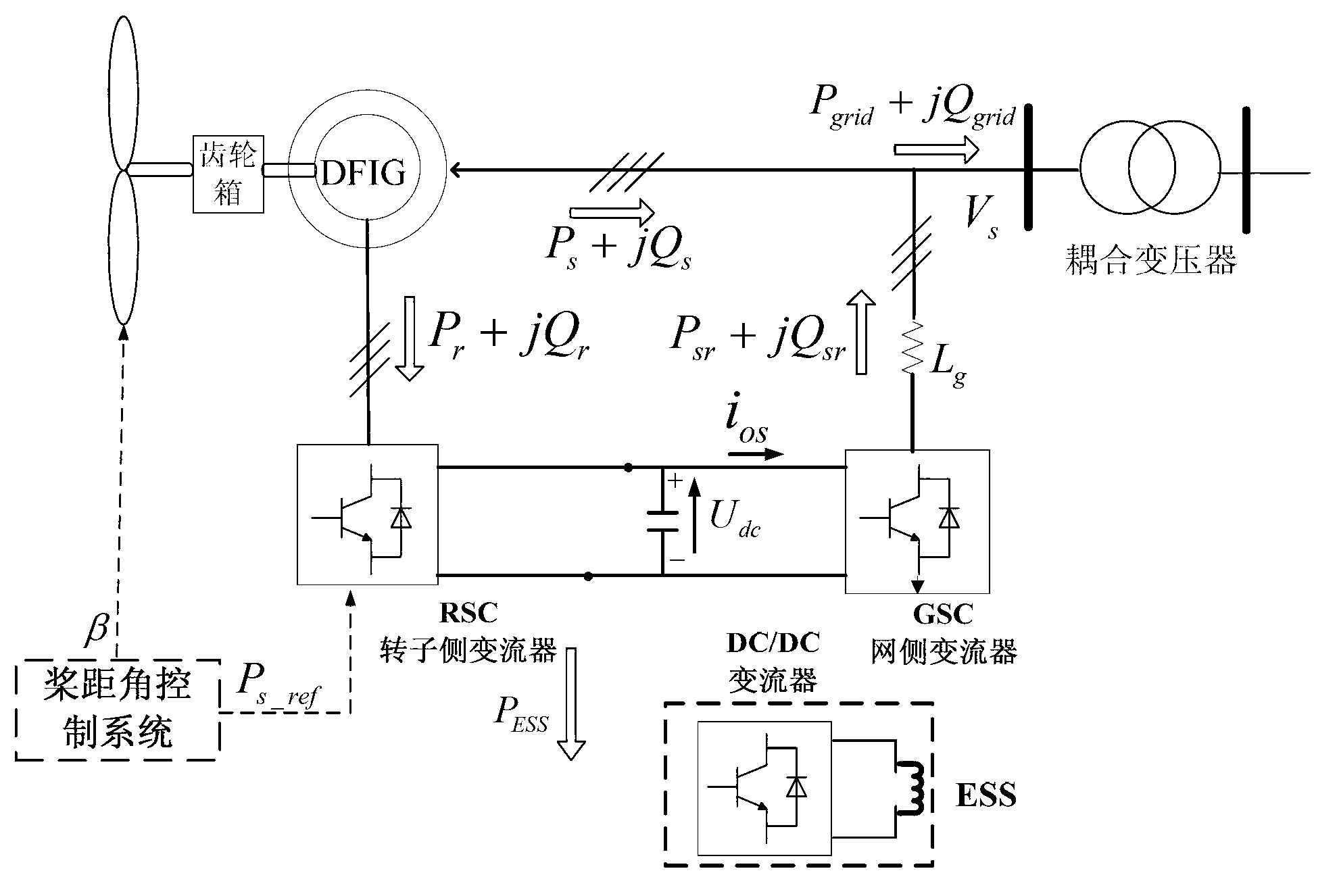
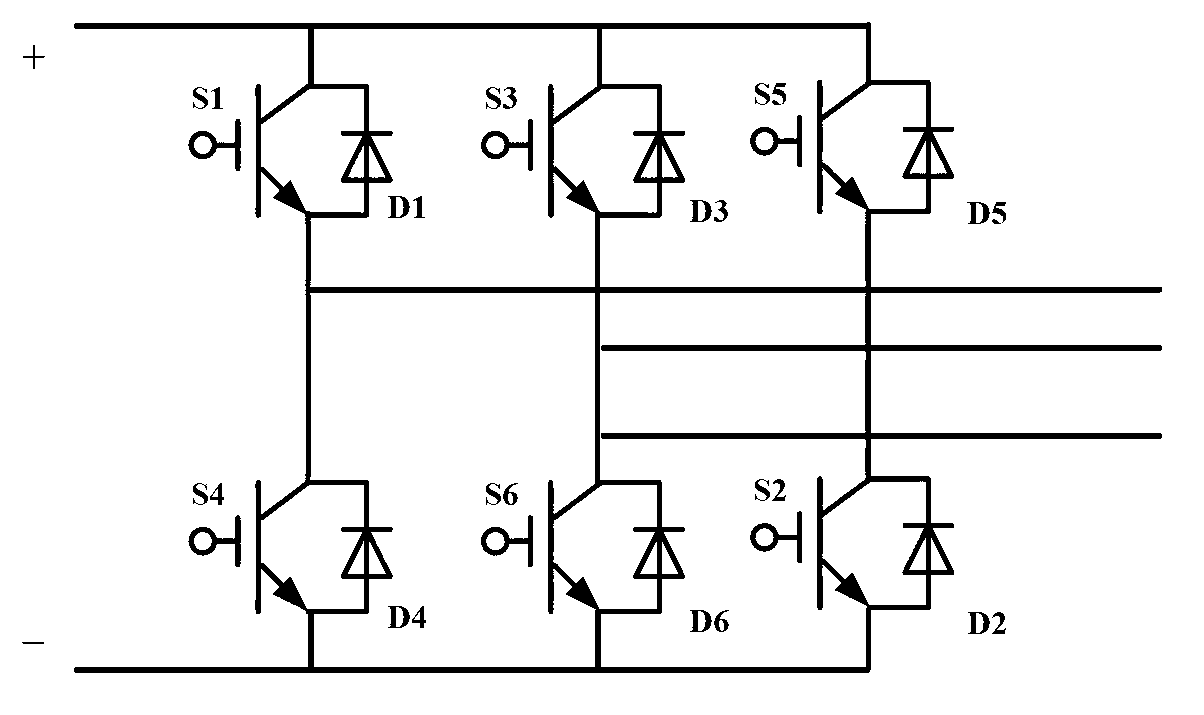
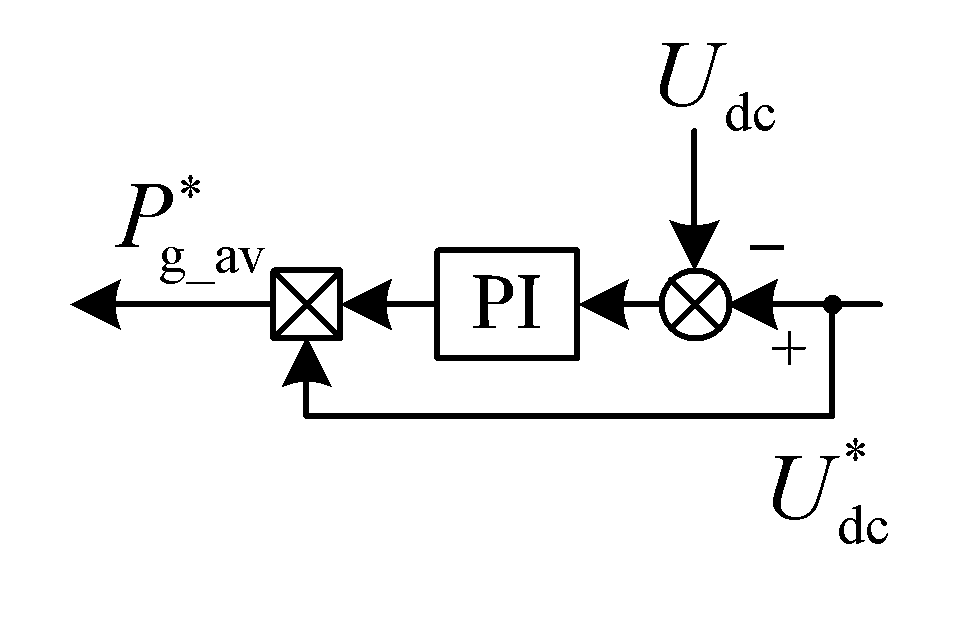
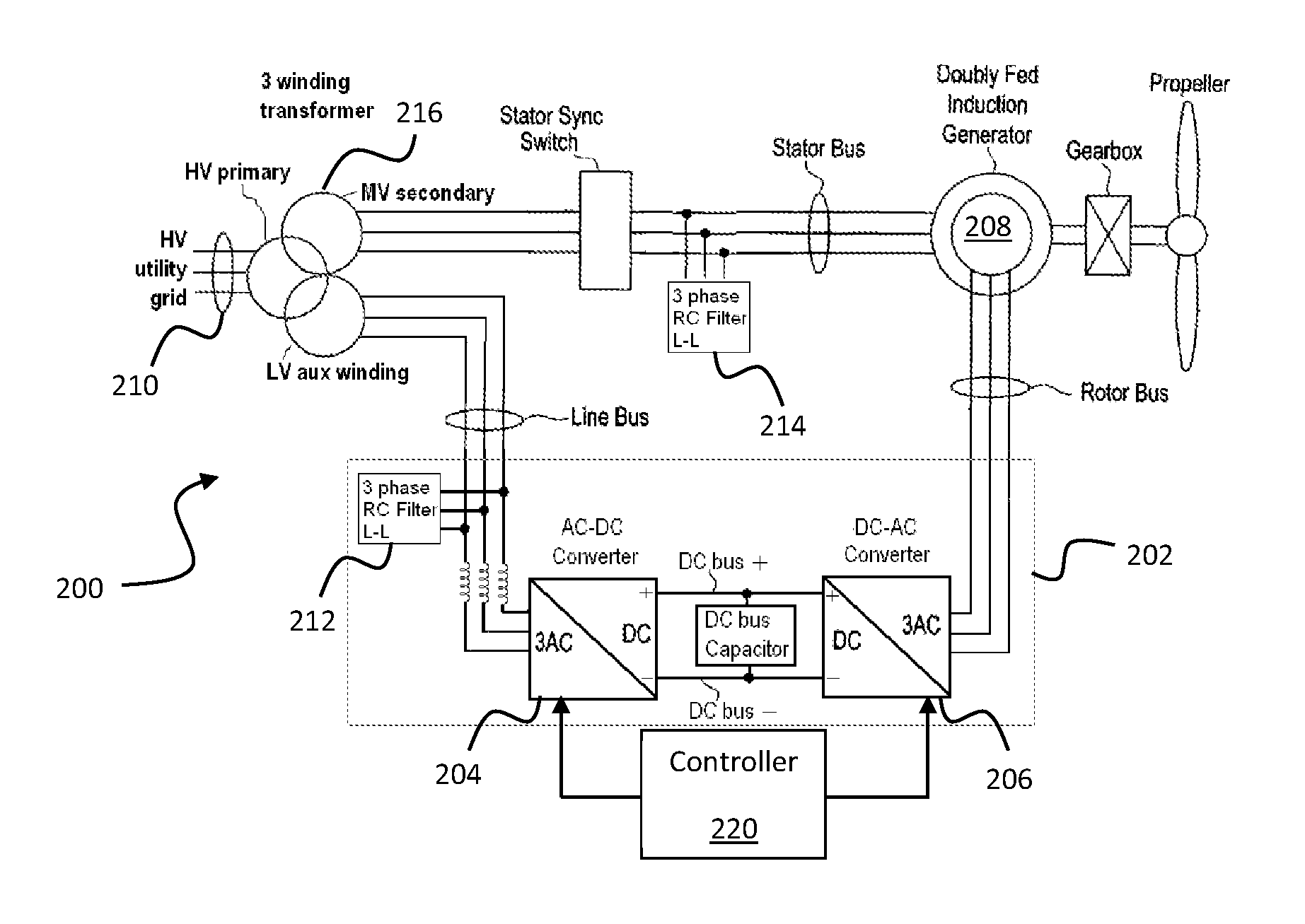
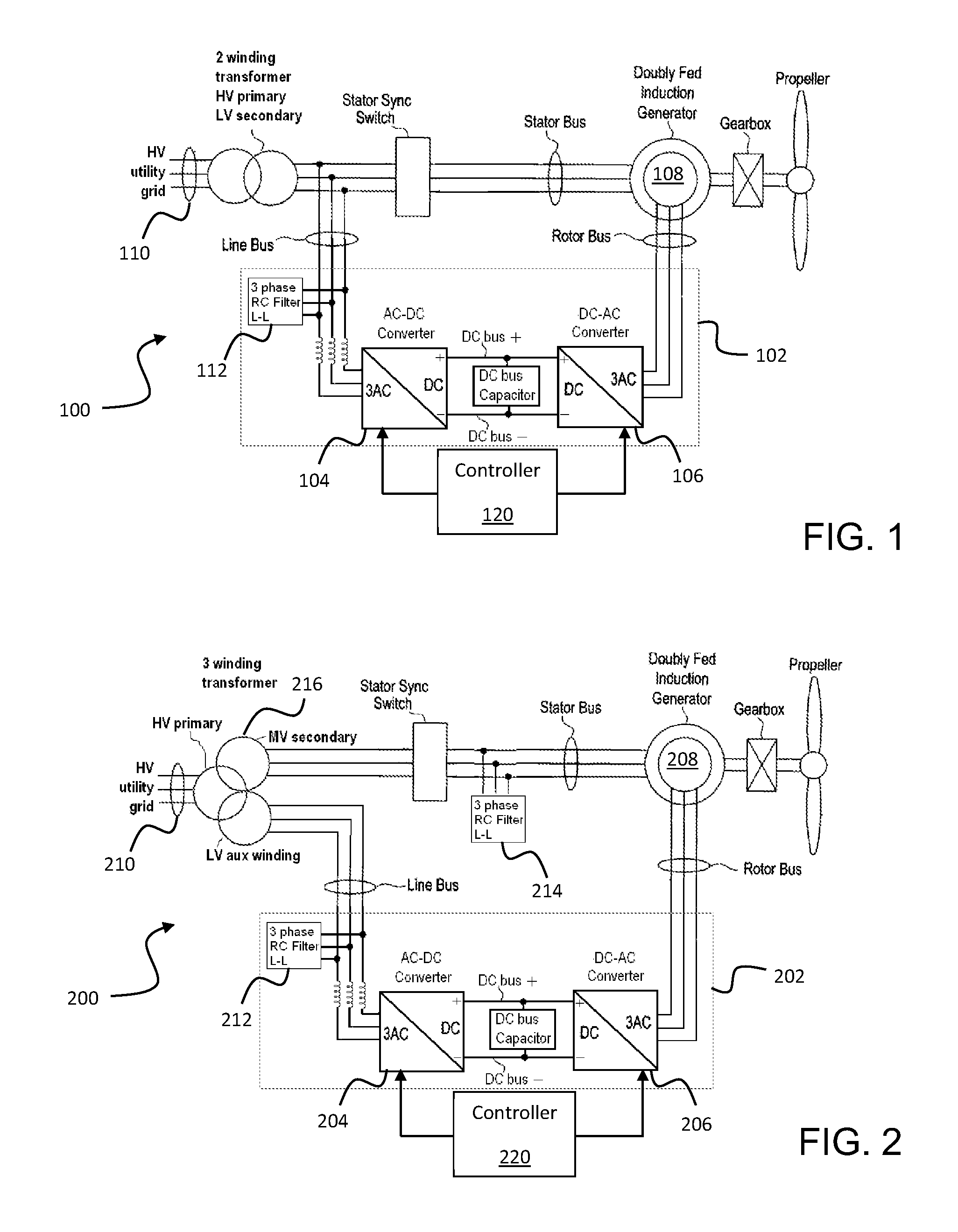
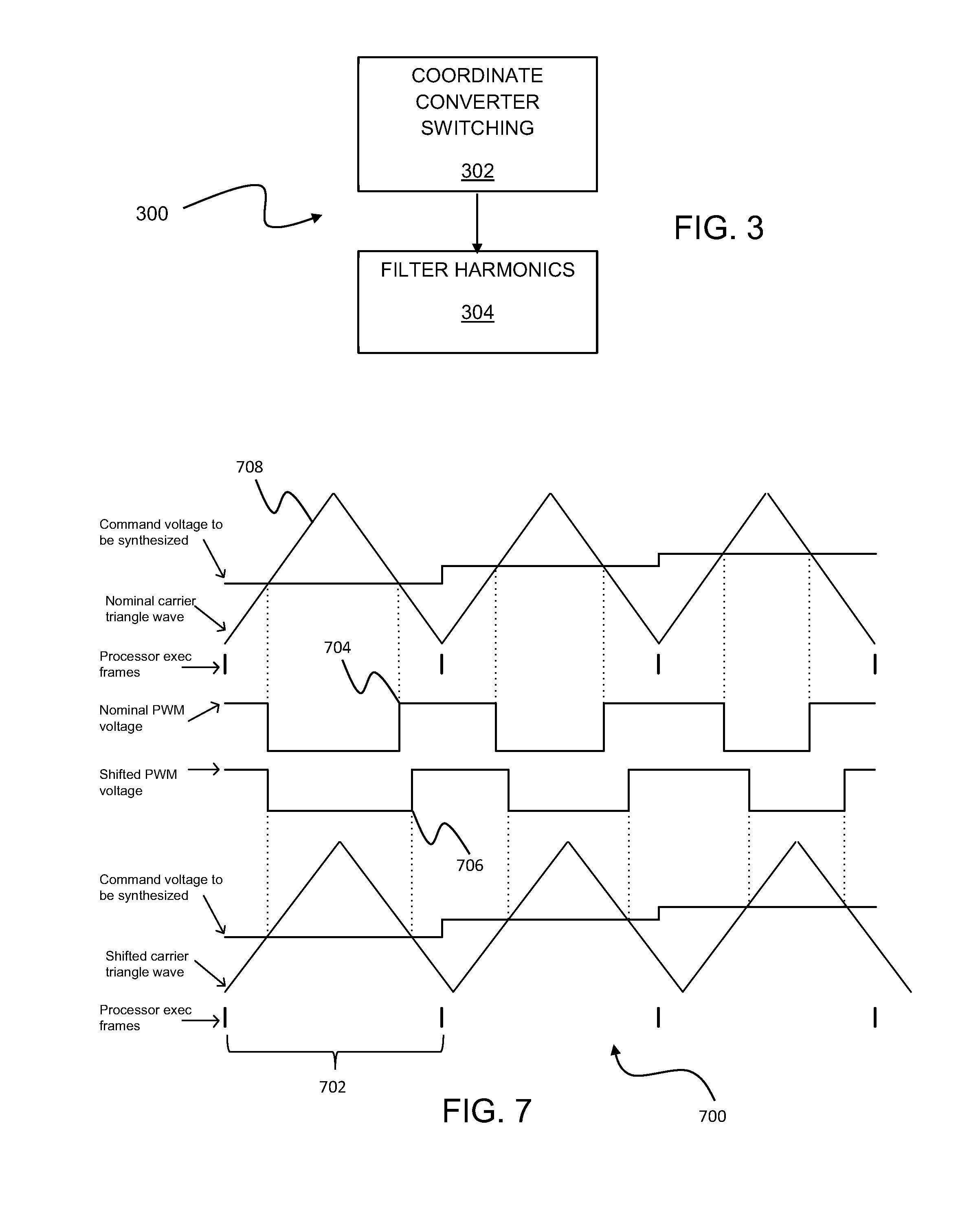
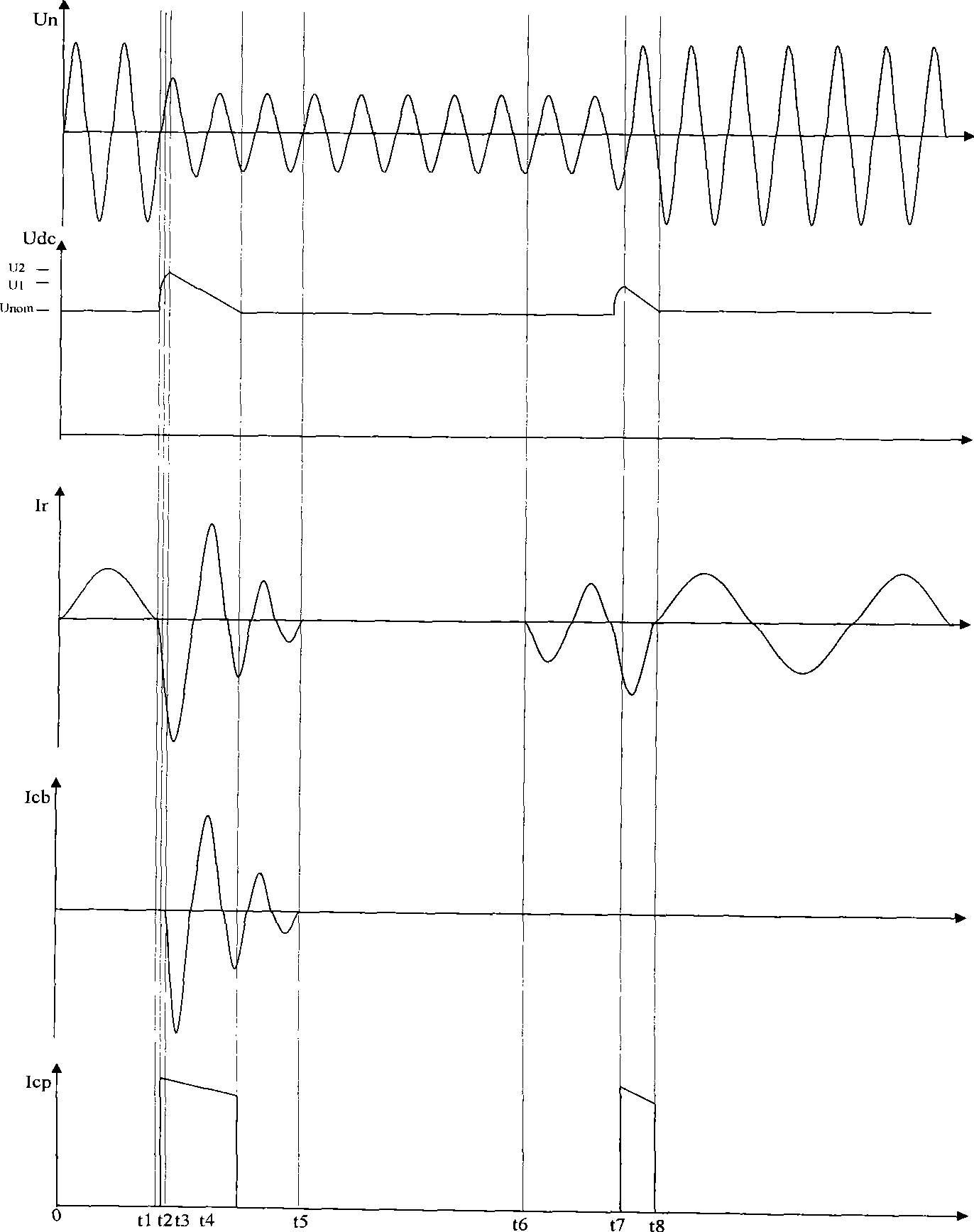Patents
Literature
158 results about "Double fed induction generator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
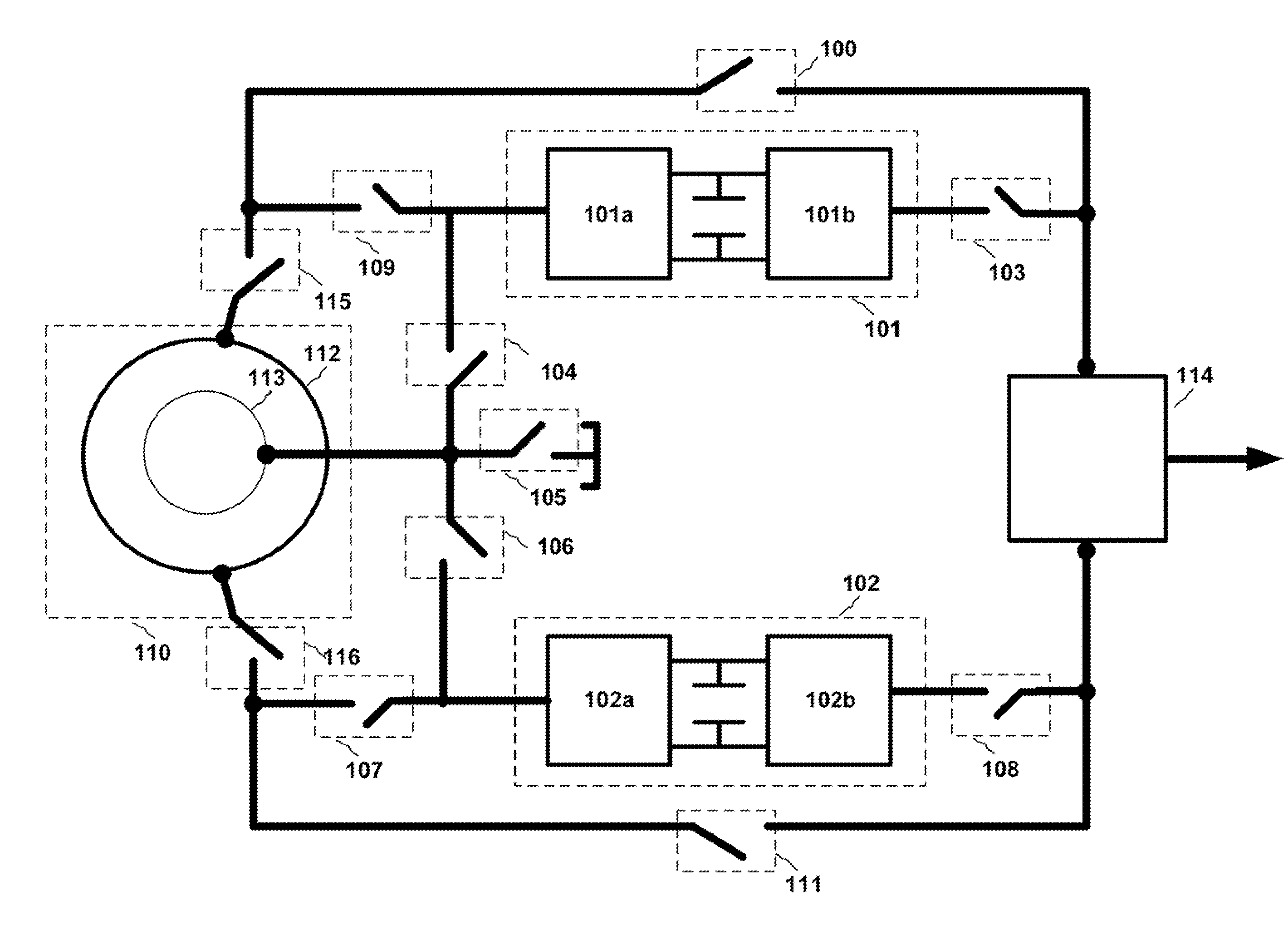
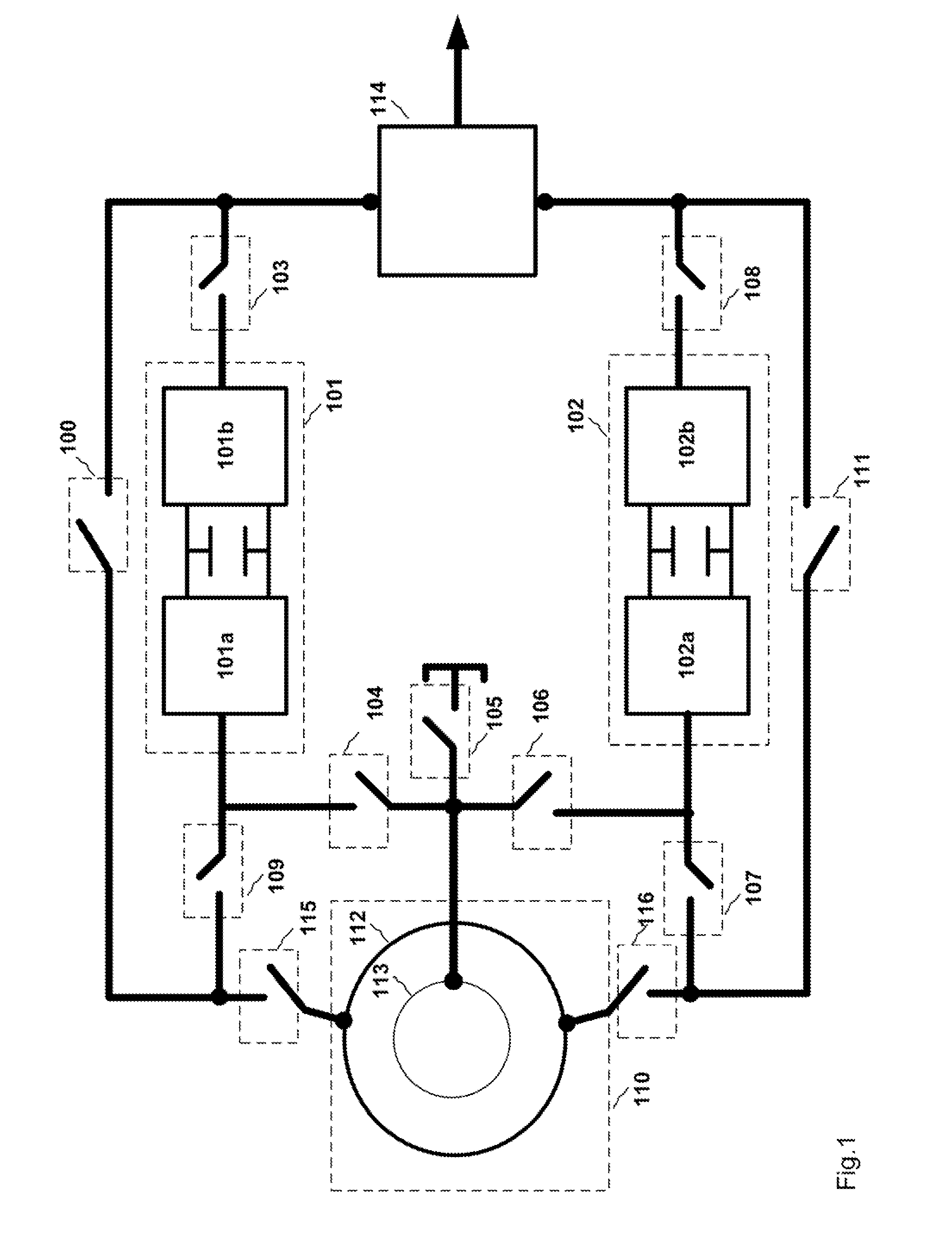
Variable speed wind turbine having a matrix converter
InactiveUS6856038B2Generator control circuitsEfficient power electronics conversionMatrix convertersConstant frequency
A variable speed wind turbine is disclosed comprising a turbine rotor that drives a doubly-fed induction generator, a matrix converter which converts variable frequency output into constant frequency output, and a control unit and a protection circuit for the matrix converter. Power is circulated in the system allowing for sensorless detection of rotor position and better output ratios of power from the system.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Variable speed wind turbine having a matrix converter
InactiveUS20020079706A1Generator control circuitsWind motor controlMatrix convertersConstant frequency
A variable speed wind turbine is disclosed comprising a turbine rotor that drives a doubly-fed induction generator, a matrix converter which converts variable frequency output into constant frequency output, and a control unit and a protection circuit for the matrix converter. Power is circulated in the system allowing for sensorless detection of rotor position and better output ratios of power from the system.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Variable Speed Wind Turbine Configured For Wind Farm Operation
InactiveUS20090206606A1Easy to controlGood effectGenerator control circuitsOptimise machine performancePower gridVariable speed wind turbine
The present invention relates to an improved wind turbine, of the type which employs doubly fed induction generators (DFIG), and a wind park including the same, which permits the use of lighter weight turbines, with the ability to have greater energy capture, more precise control of asymmetrical phases and enhanced maintenance and support of the grid during fault conditions.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
ActiveUS7425771B2Avoid distortionImprove power qualityGenerator control circuitsVector control systemsPower qualityPower grid
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
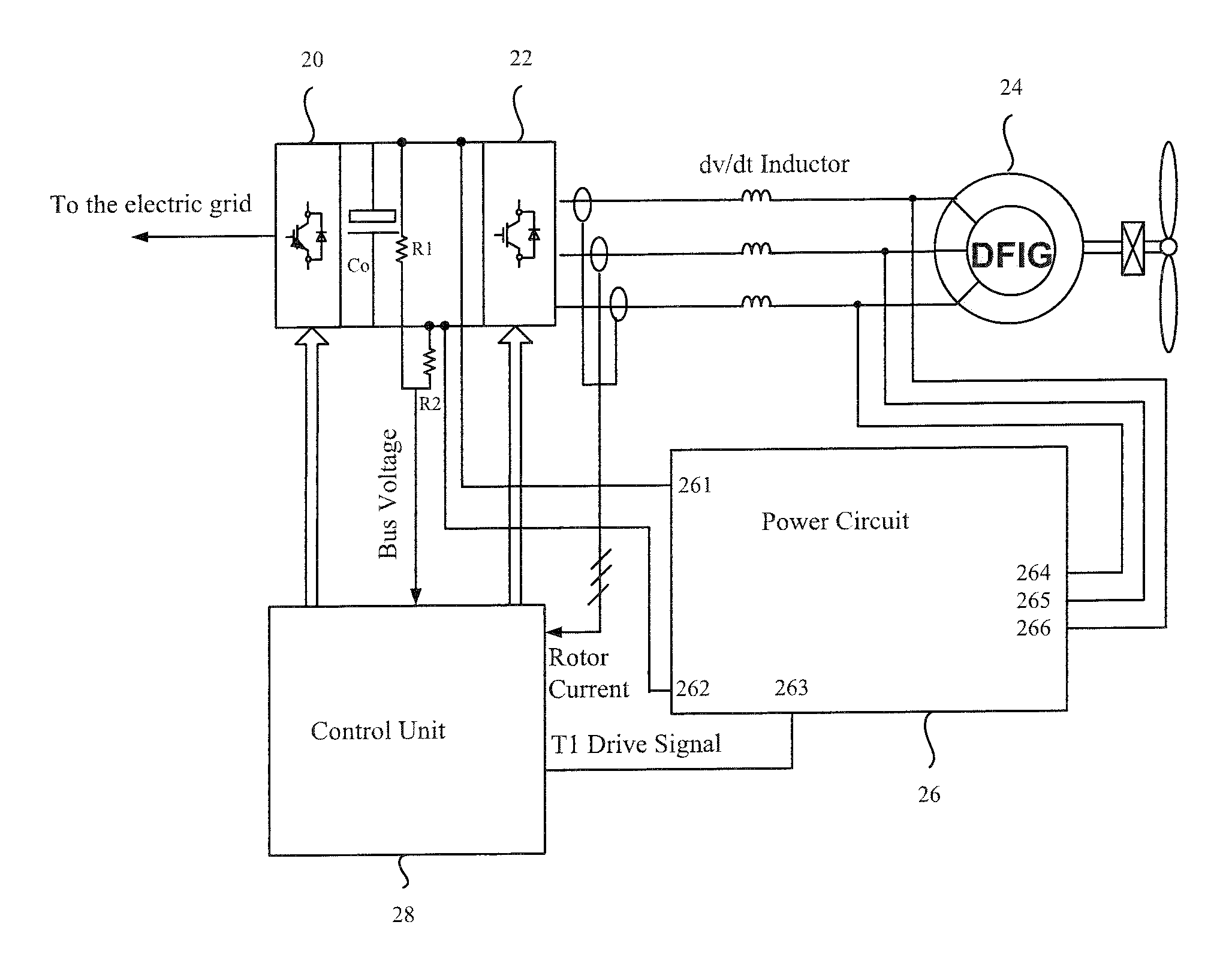
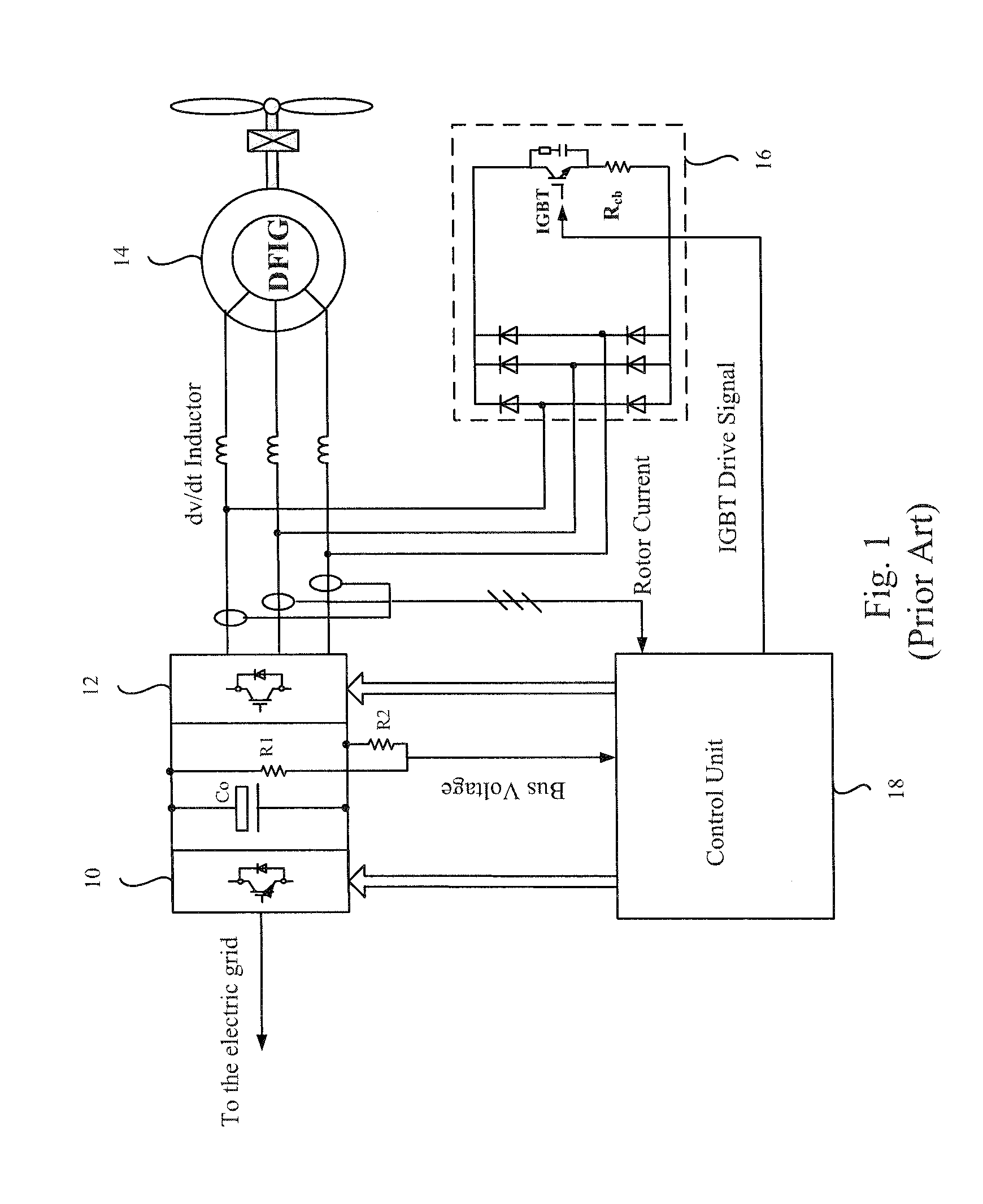
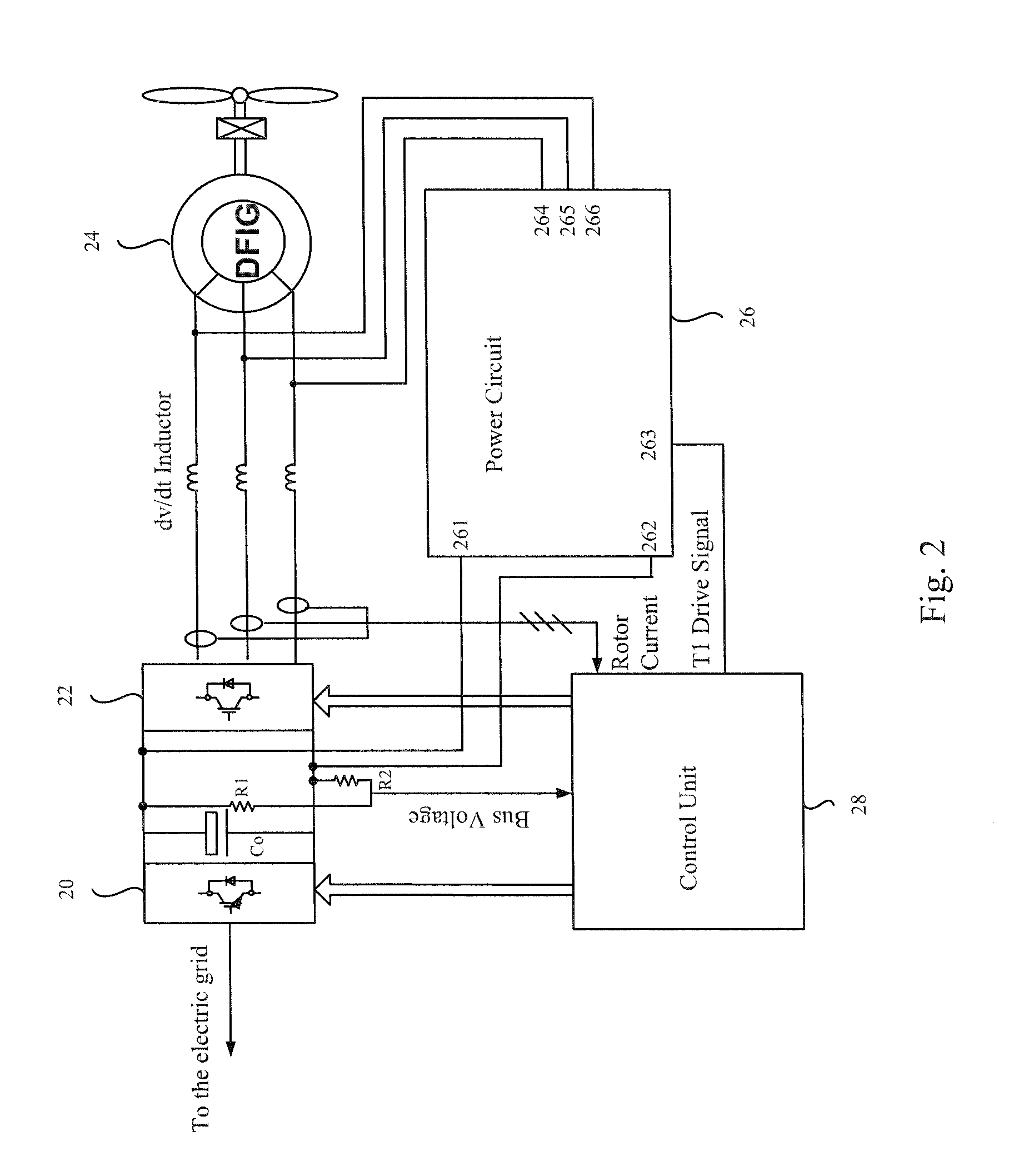
Control system for doubly fed induction generator
ActiveUS7411309B2Total current dropGuaranteed uptimeGenerator control circuitsAC motor controlControl systemControl signal
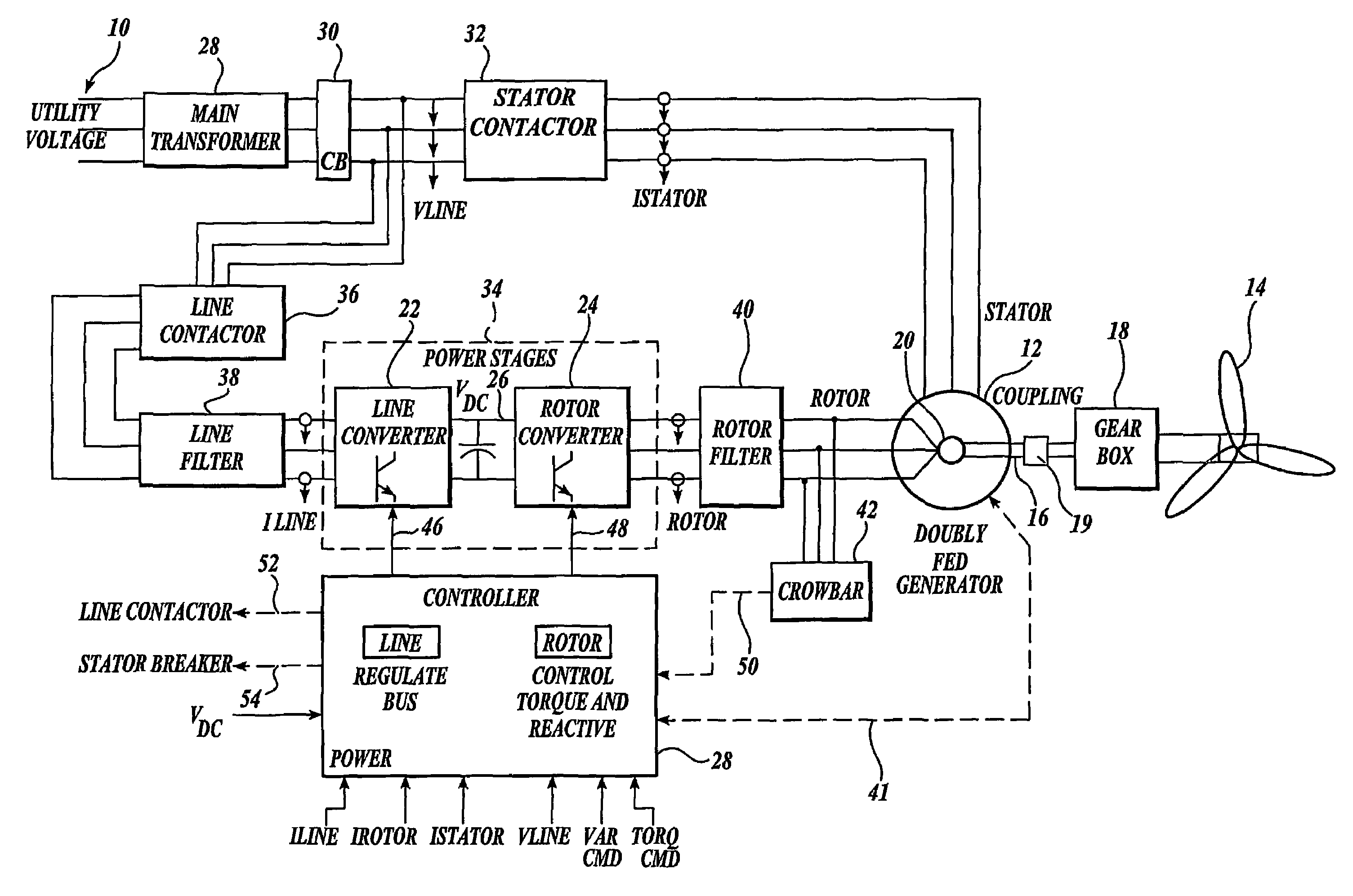
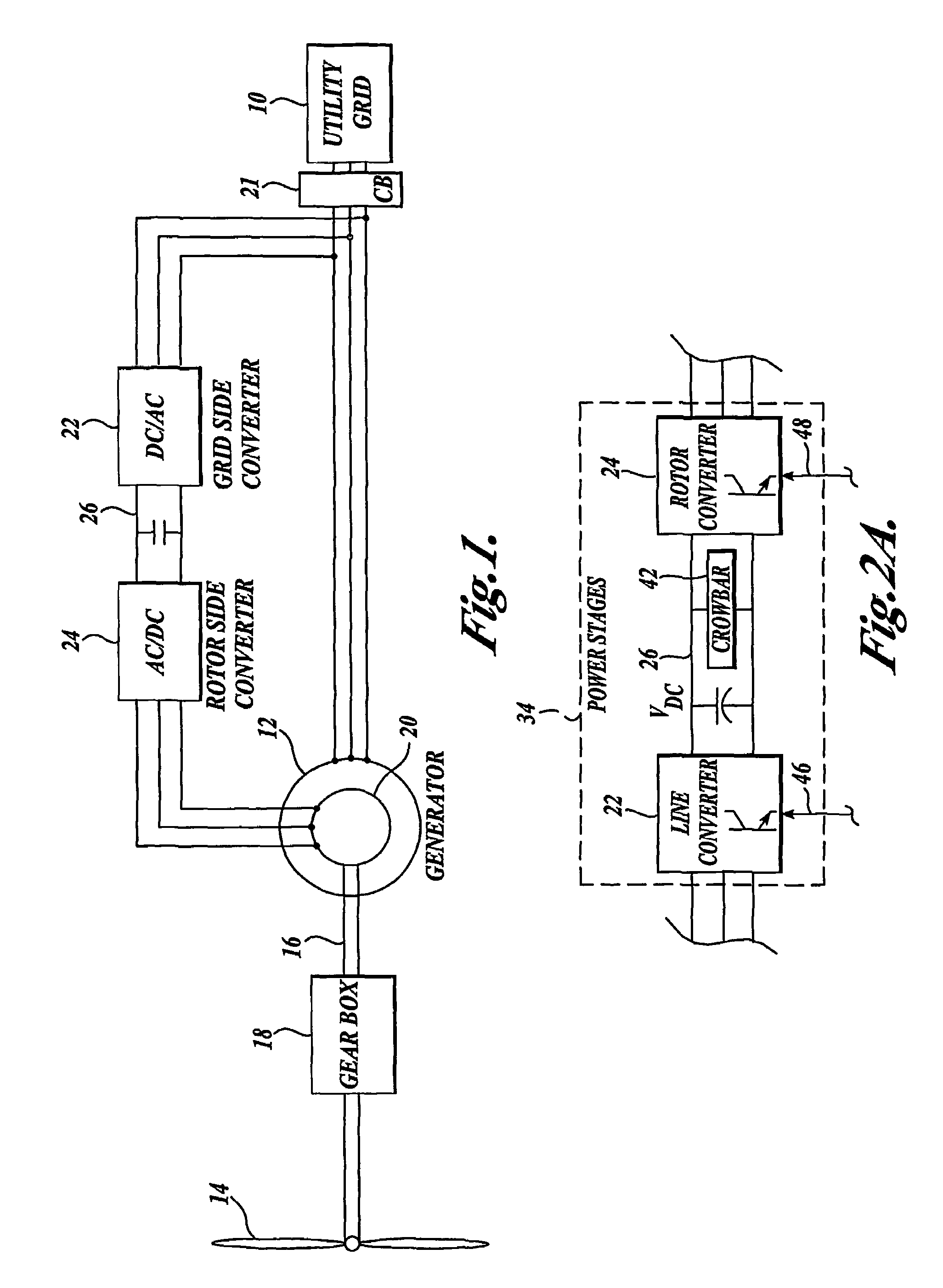
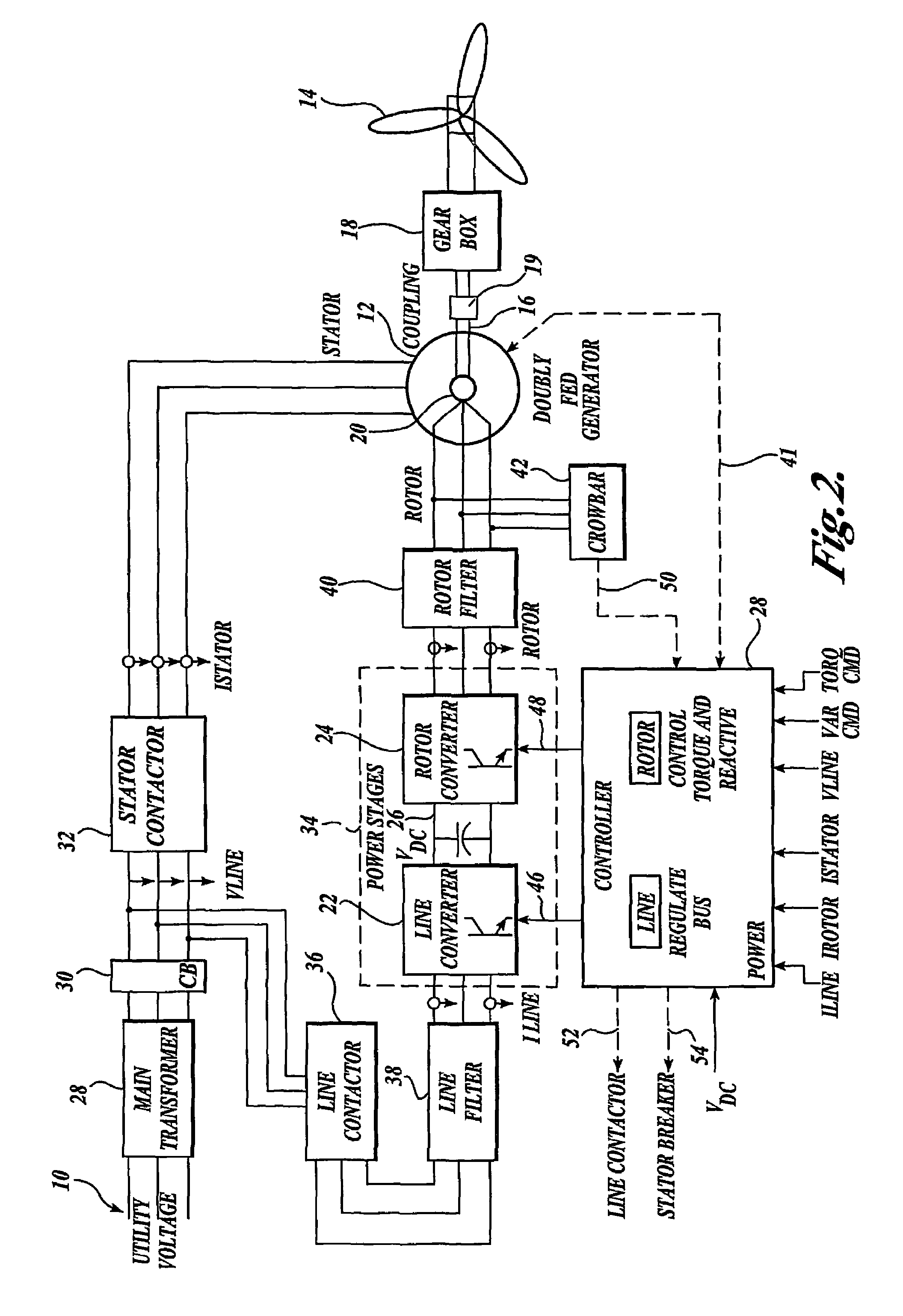
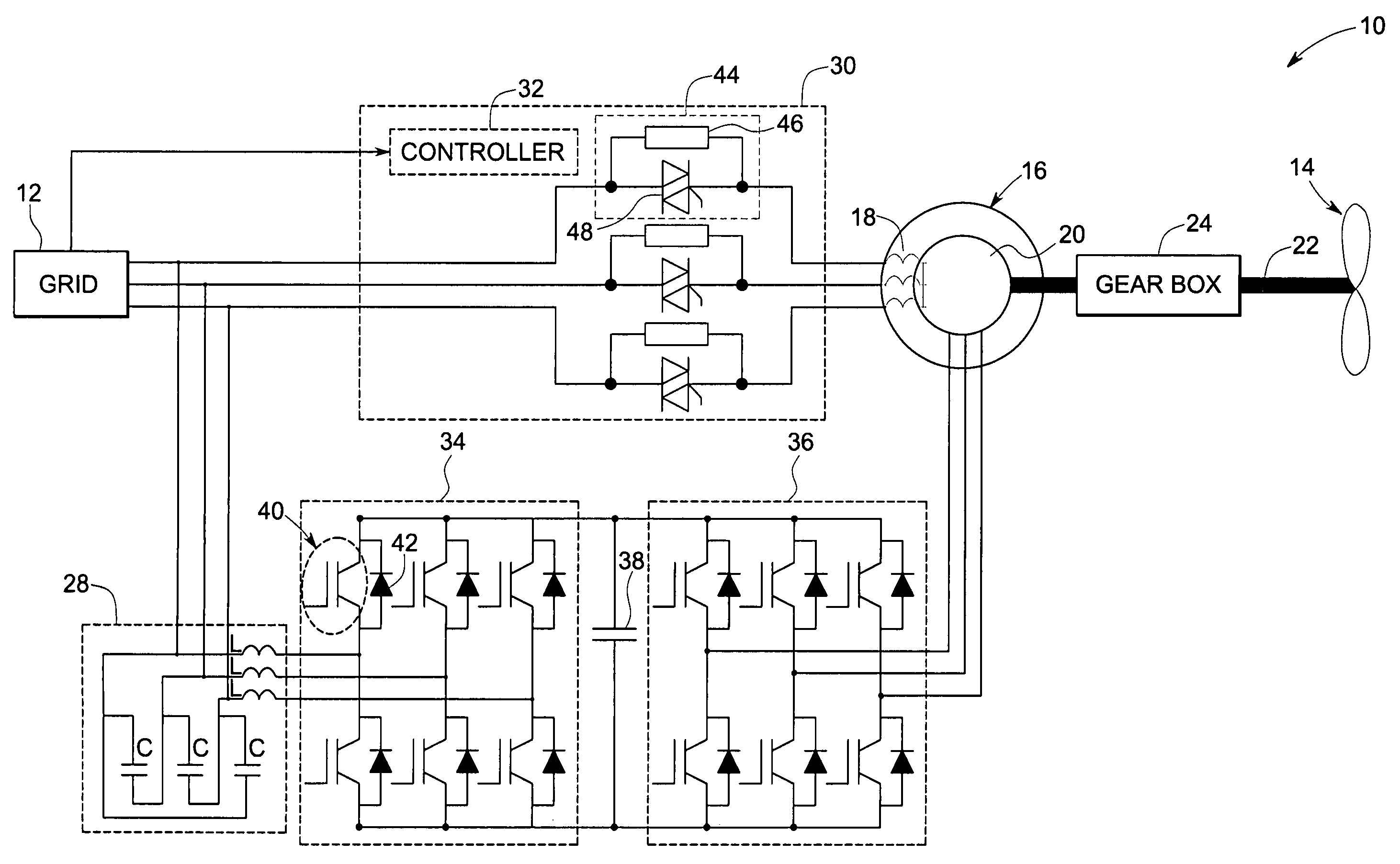
A controller (28) for a doubly fed induction generator (12,20) adjusts control signals to a rotor side converter (24) and line side converter (22) to adjust rotor current when a voltage transient on a utility grid (10) occurs, so that the doubly fed induction generator can ride through the transient. The controller can also turn off the transistors of the rotor side converter (24) to reduce rotor current and / or activate a crowbar (42) to reduce the voltage of the DC link (26) connecting the converters (22, 24) when significant voltage transients occur on the grid (10). This permits continued operation of the DFIG system without disconnecting from the grid.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SOLAR INVERTERS USA
System and method of operating double fed induction generators
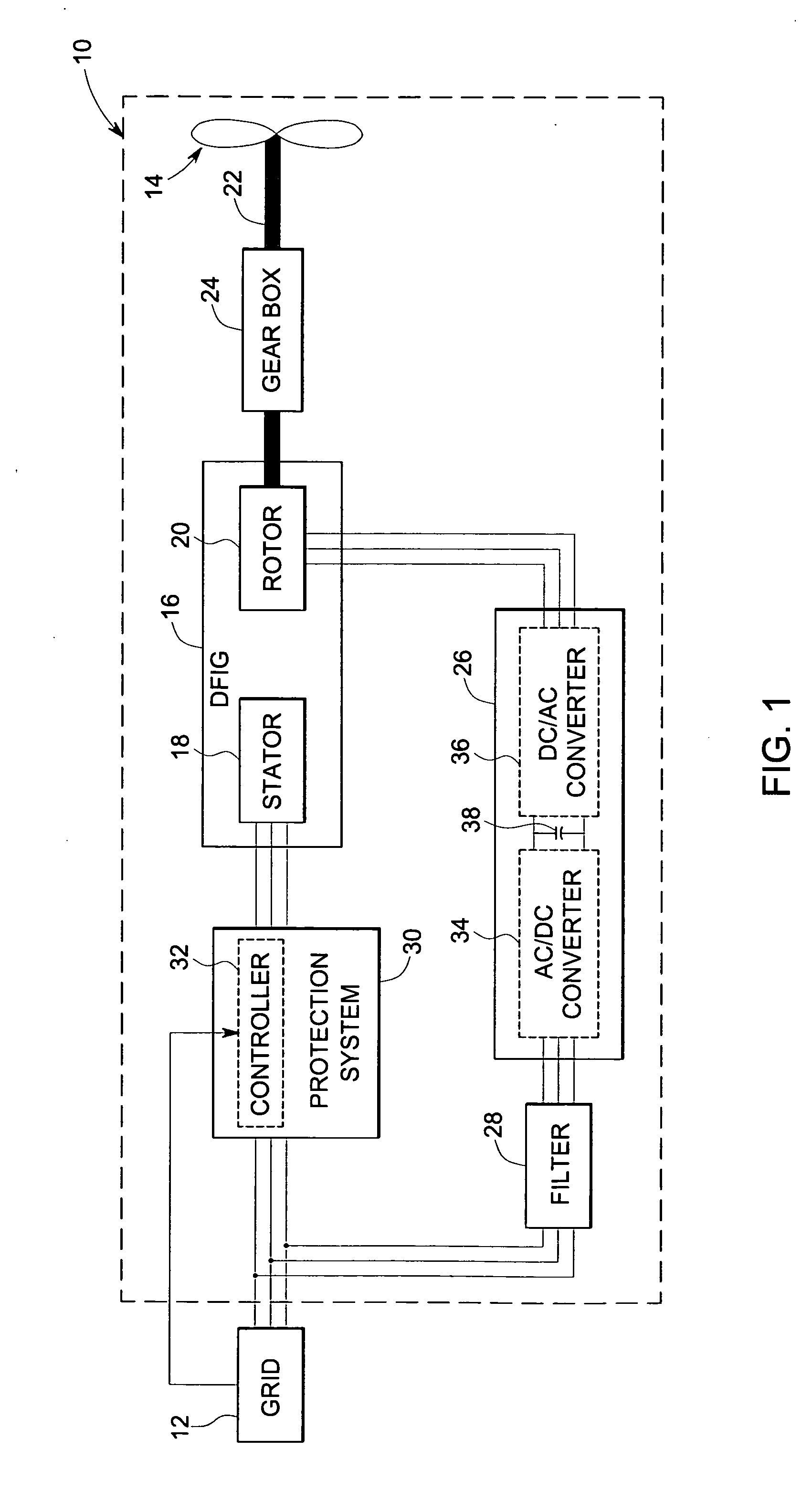
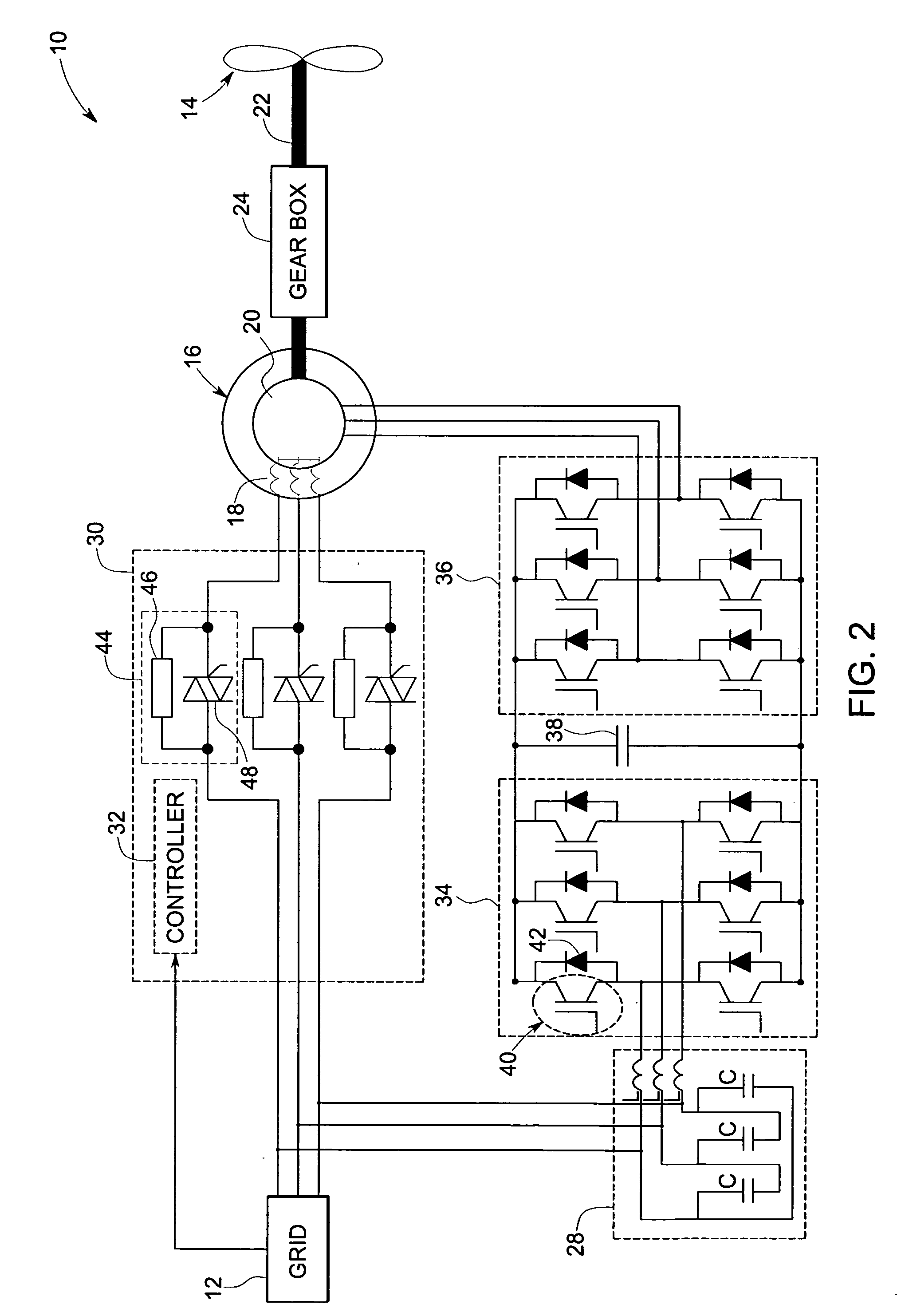
ActiveUS7253537B2Generator control circuitsGeneration protection through controlGrid faultPower grid
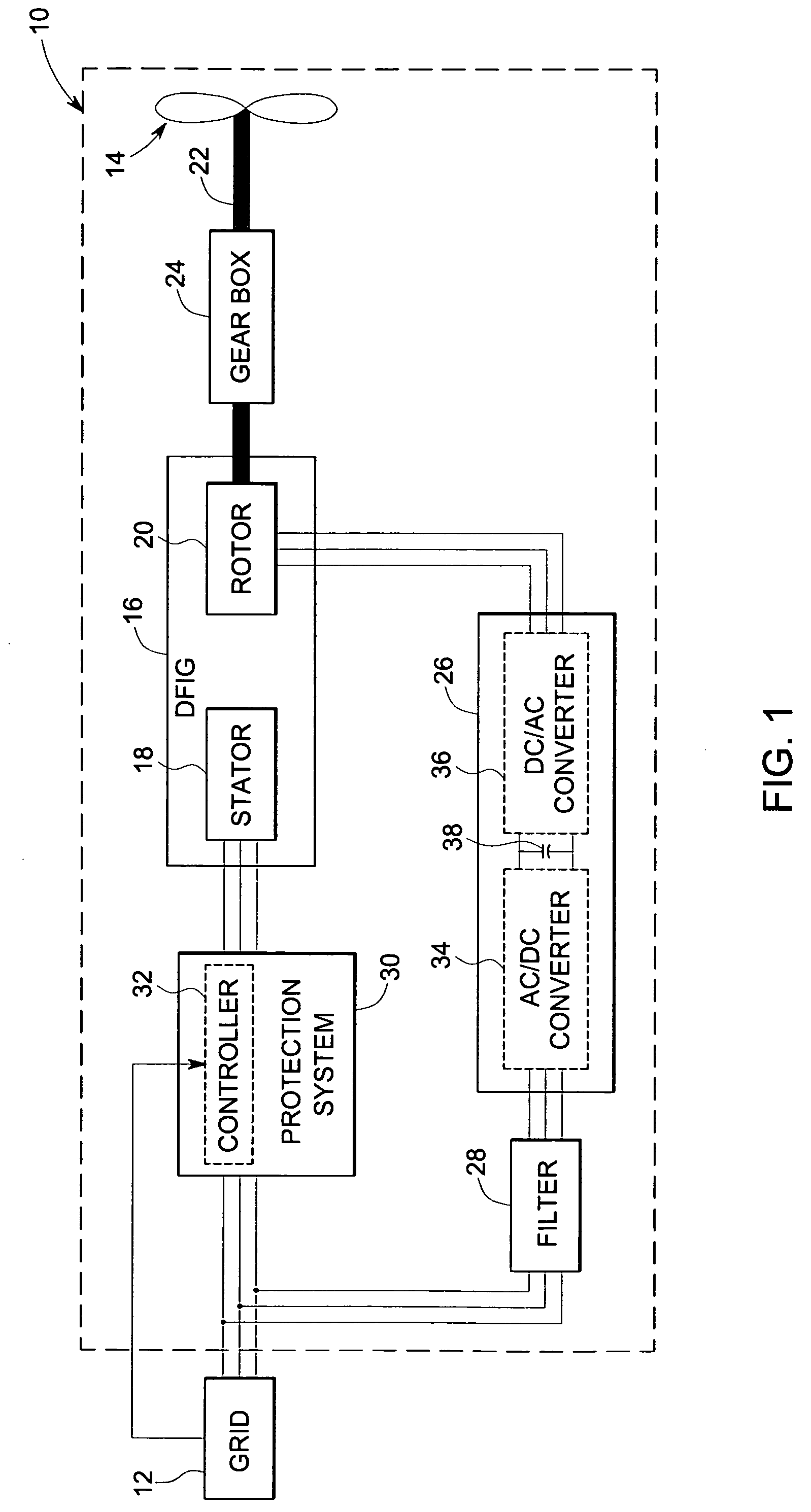
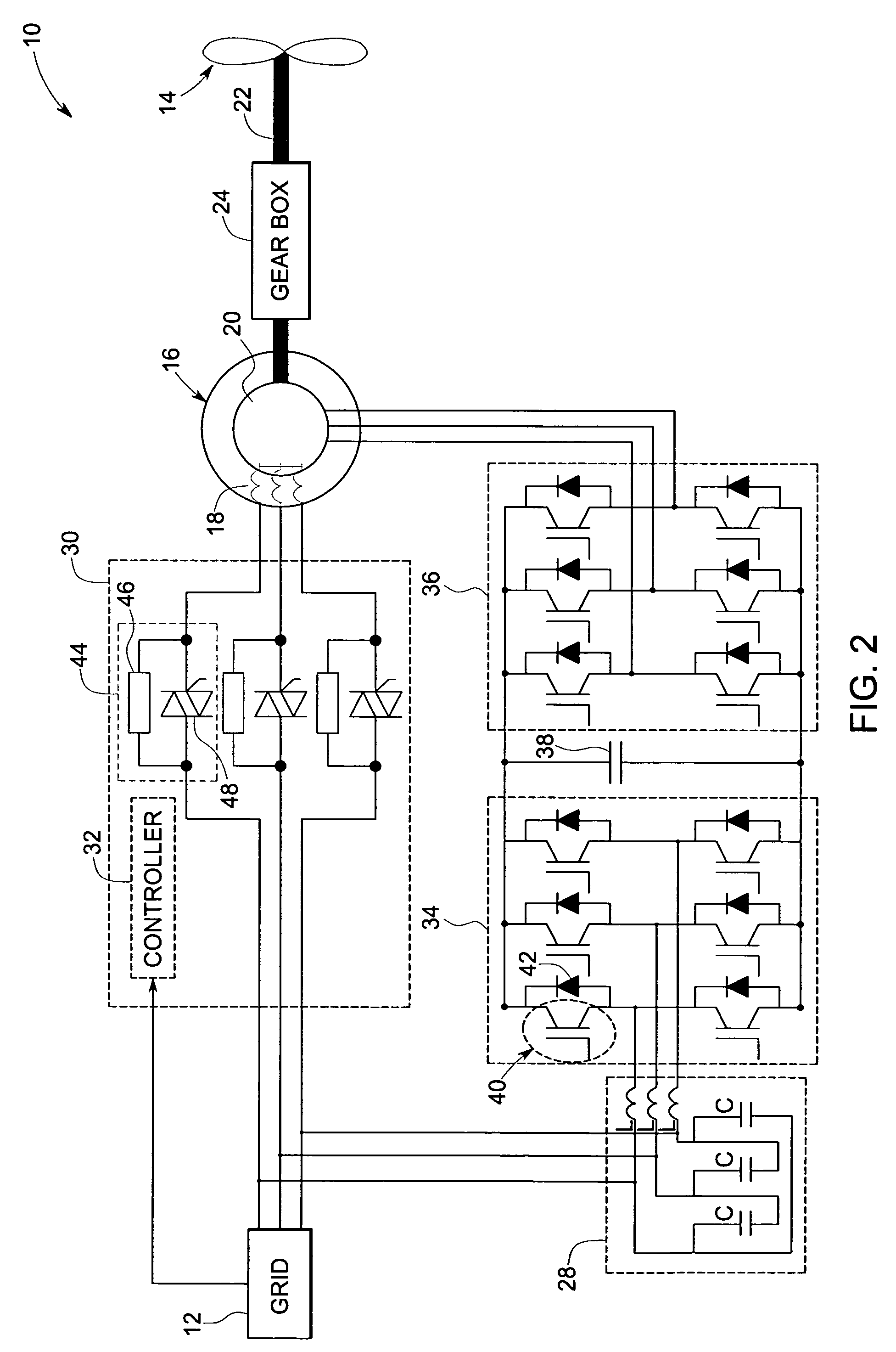
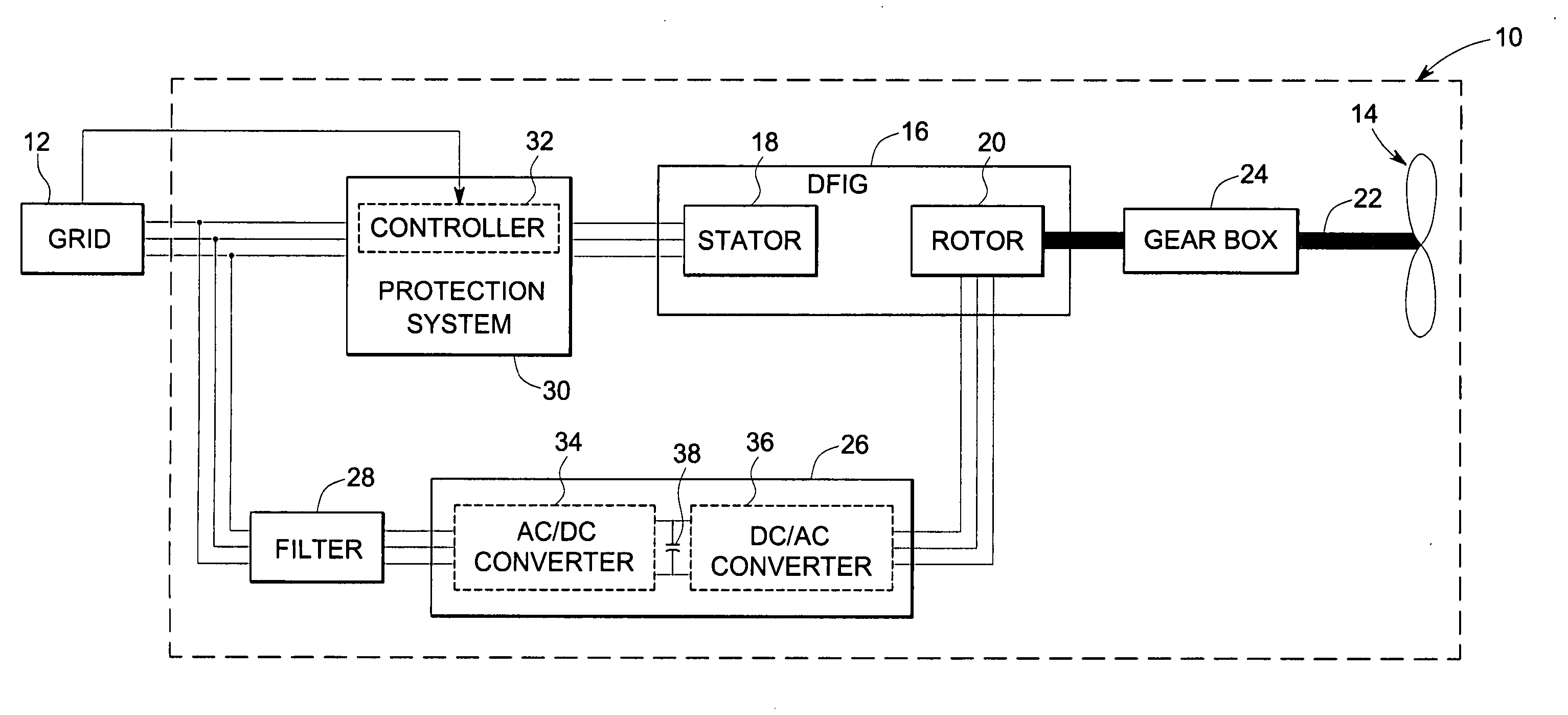
A protection system and a protection method are provided for protecting a double fed induction generator and a gearbox during a grid fault. The protection system includes a plurality of controlled impedance devices. Each of the controlled impedance devices is coupled between a respective phase of a stator winding of the double fed induction generator and a respective phase of a grid side converter. The protection system also includes a controller configured for coupling and decoupling impedance in one or more of the plurality of controlled impedance devices in response to changes in at least one of a utility grid voltage and a utility grid current.
Controller and method for simulating active power frequency of double-fed induction generator (DFIG) in combination with inertia and over speed
ActiveCN104917201APerfect FM functionThe FM process is stableSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionElectricityTime delays
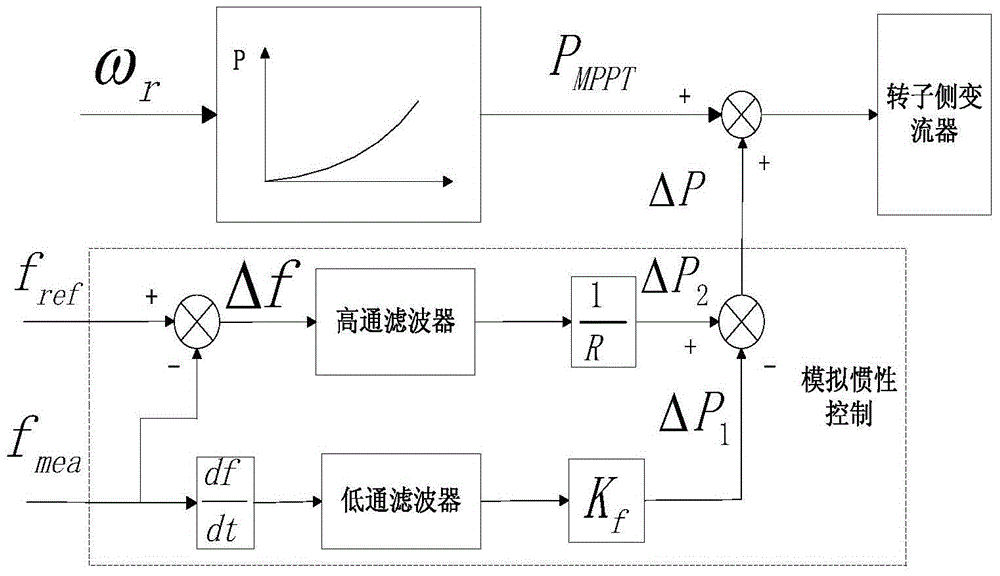
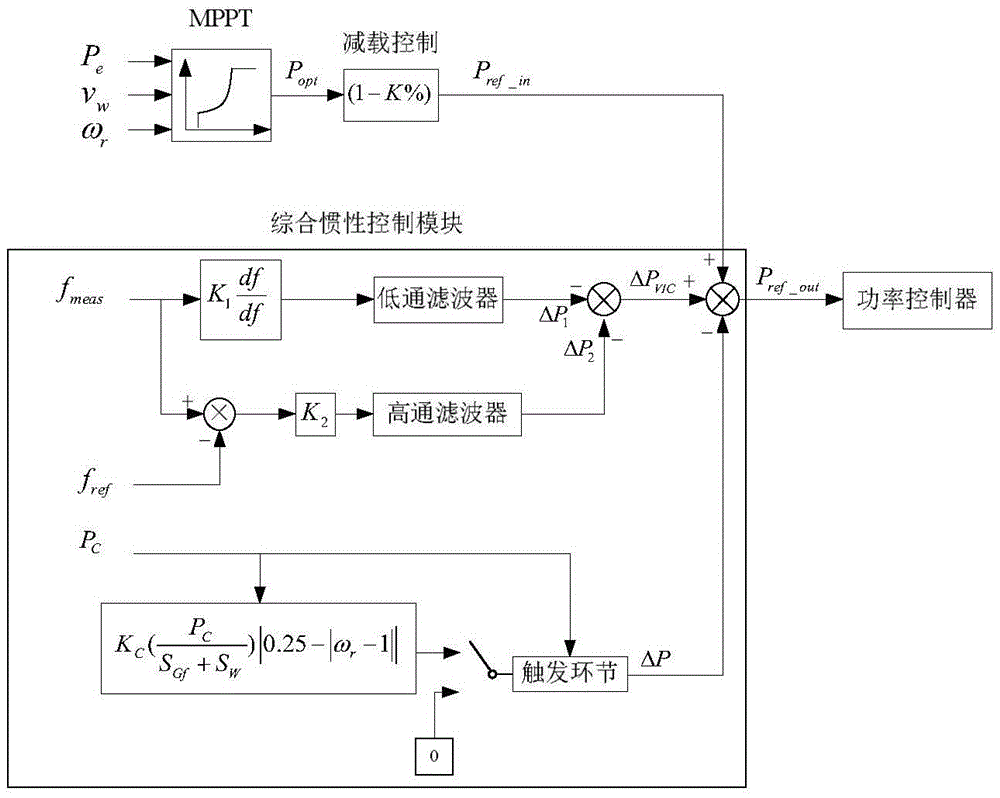
The invention discloses a controller and method for simulating the active power frequency of a double-fed induction generator (DFIG) in combination with inertia and over speed. The controller comprises a frequency deviation detecting module, a blocking module, a regulating variable setting module, a time delay module and a speed protecting module which are connected in sequence, wherein a real-time grid frequency signal and a frequency setting value are respectively input in the frequency deviation detecting module to obtain the frequency deviation signal of the grid at that time; the frequency deviation signal enters the regulating variable setting module through the blocking module, and the regulating variable setting module obtains a speed regulating variable according to the frequency deviation signal; and the speed protecting module enables the DFIG unit to exit frequency modulation under an abnormal speed condition, and can put into the frequency modulation again after time delay for a period of time. The controller has the beneficial effects that large-scale double-fed wind power integration takes the place of a conventional synchronous generator to cause that the system inertia is reduced and thus the transient stability of system frequency is worsened, and the comprehensive frequency controller provided by the invention can effectively solve the problem.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
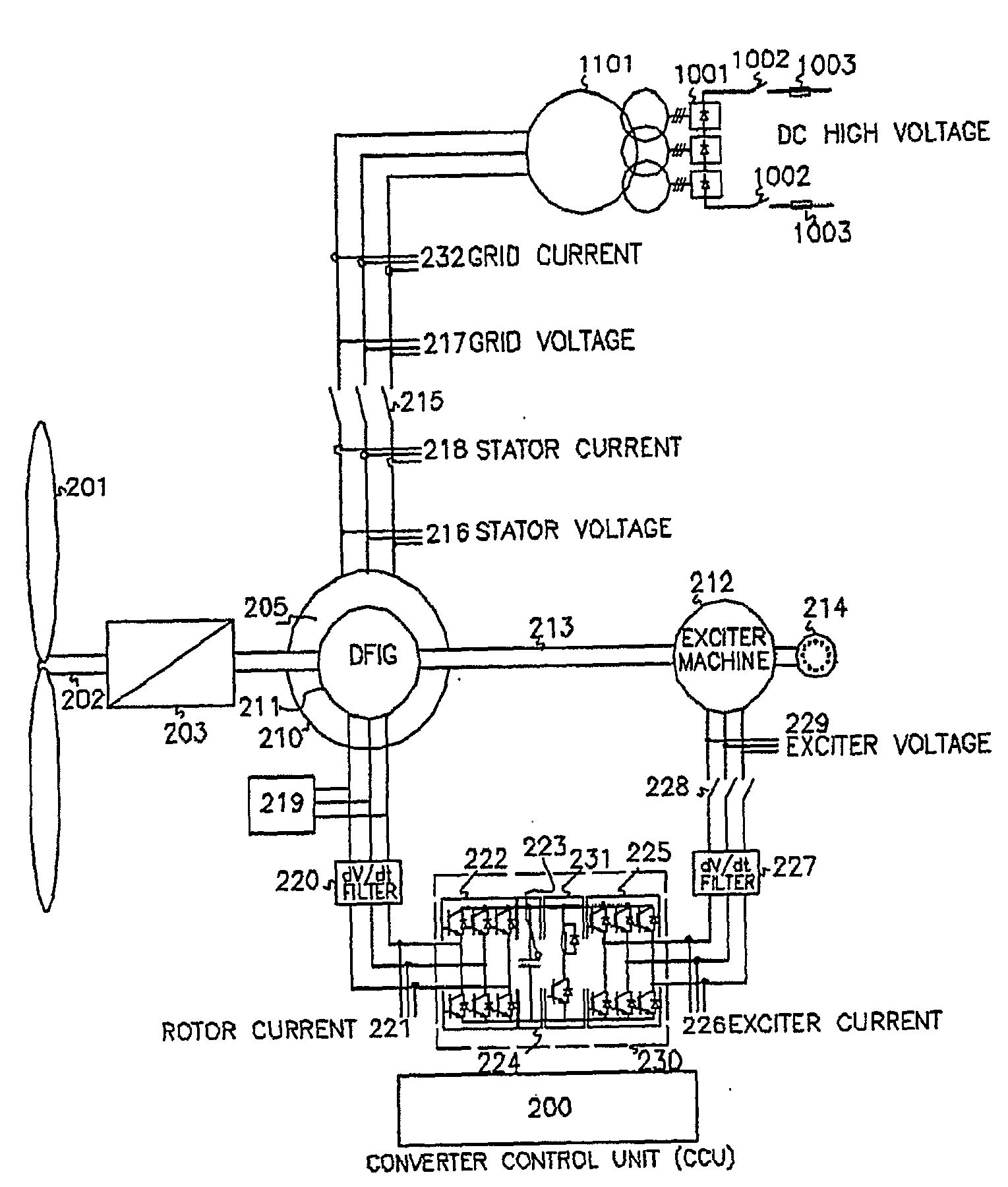
High voltage direct current link transmission system for variable speed wind turbine
ActiveUS20090278351A1Avoiding undesired harmonic distortionImprove power qualityGenerator control circuitsAc-dc conversion without reversalPower qualityHigh-voltage direct current
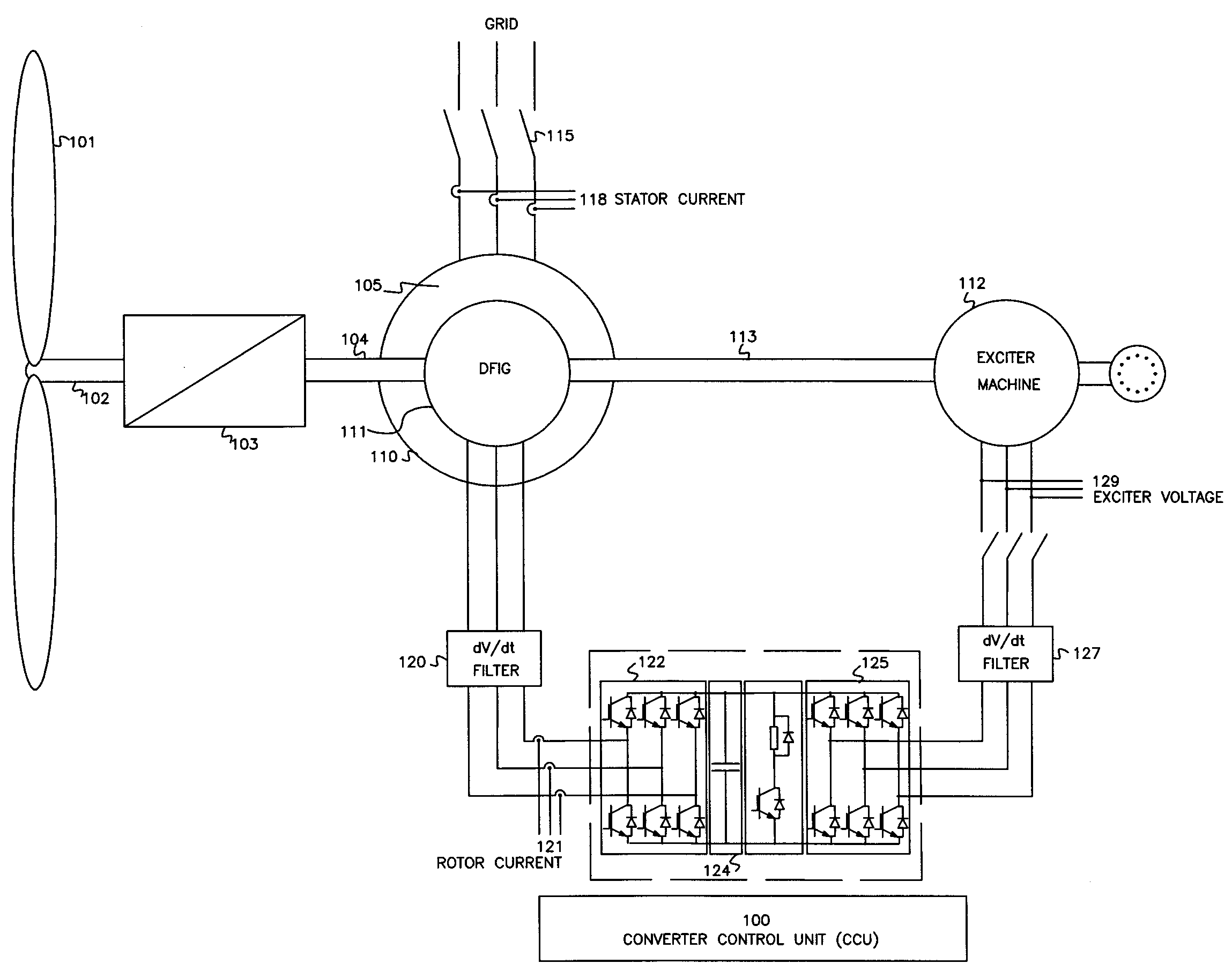
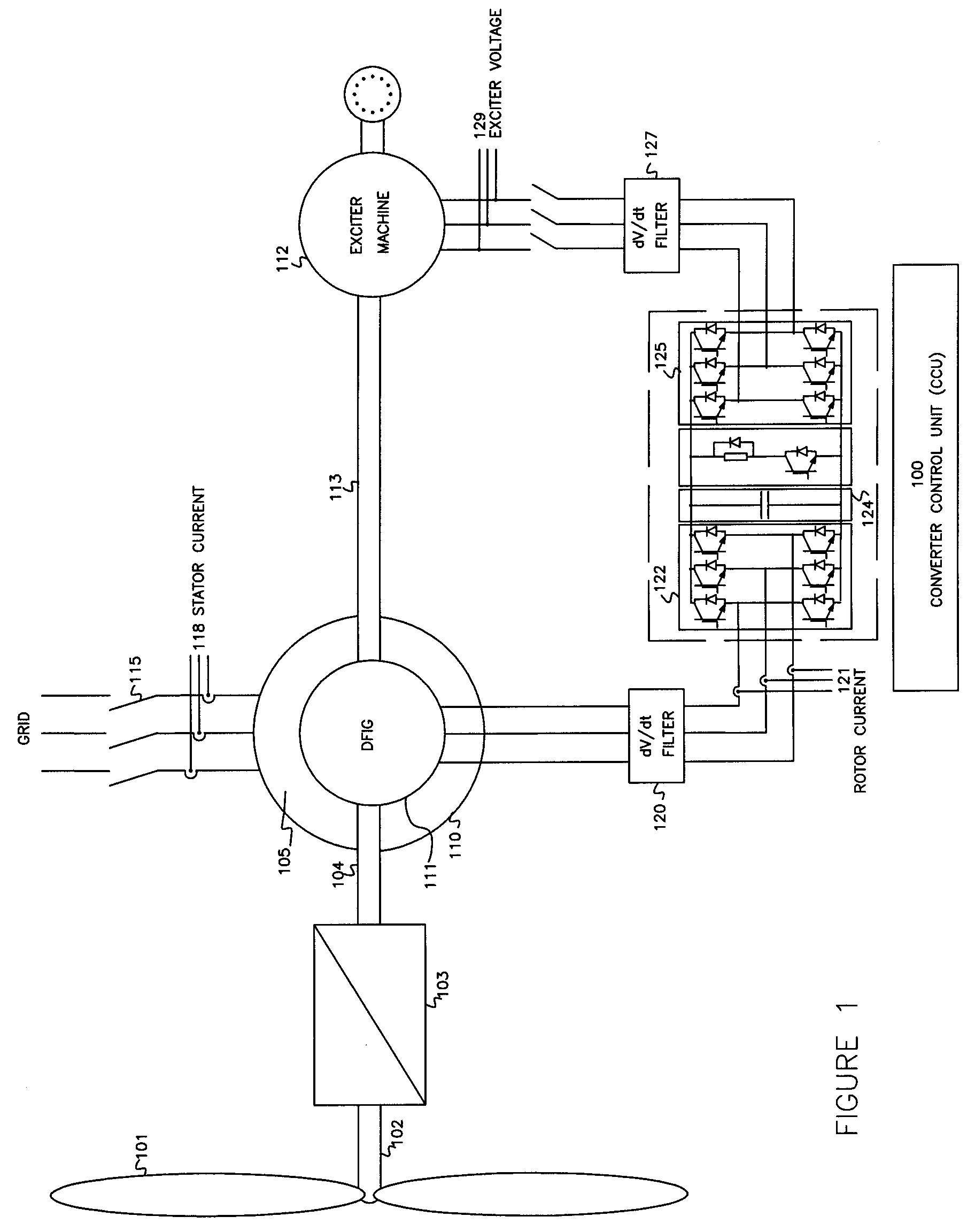
A variable speed wind turbine having a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG), includes an exciter machine mechanically coupled to the DFIG and a power converter placed between a rotor of the DFIG and the exciter machine. Thus, the power converter is not directly connected to the grid avoiding the introduction of undesired harmonic distortion and achieving a better power quality fed into the utility grid. Moreover, the variable speed wind turbine includes a power control and a pitch regulation.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
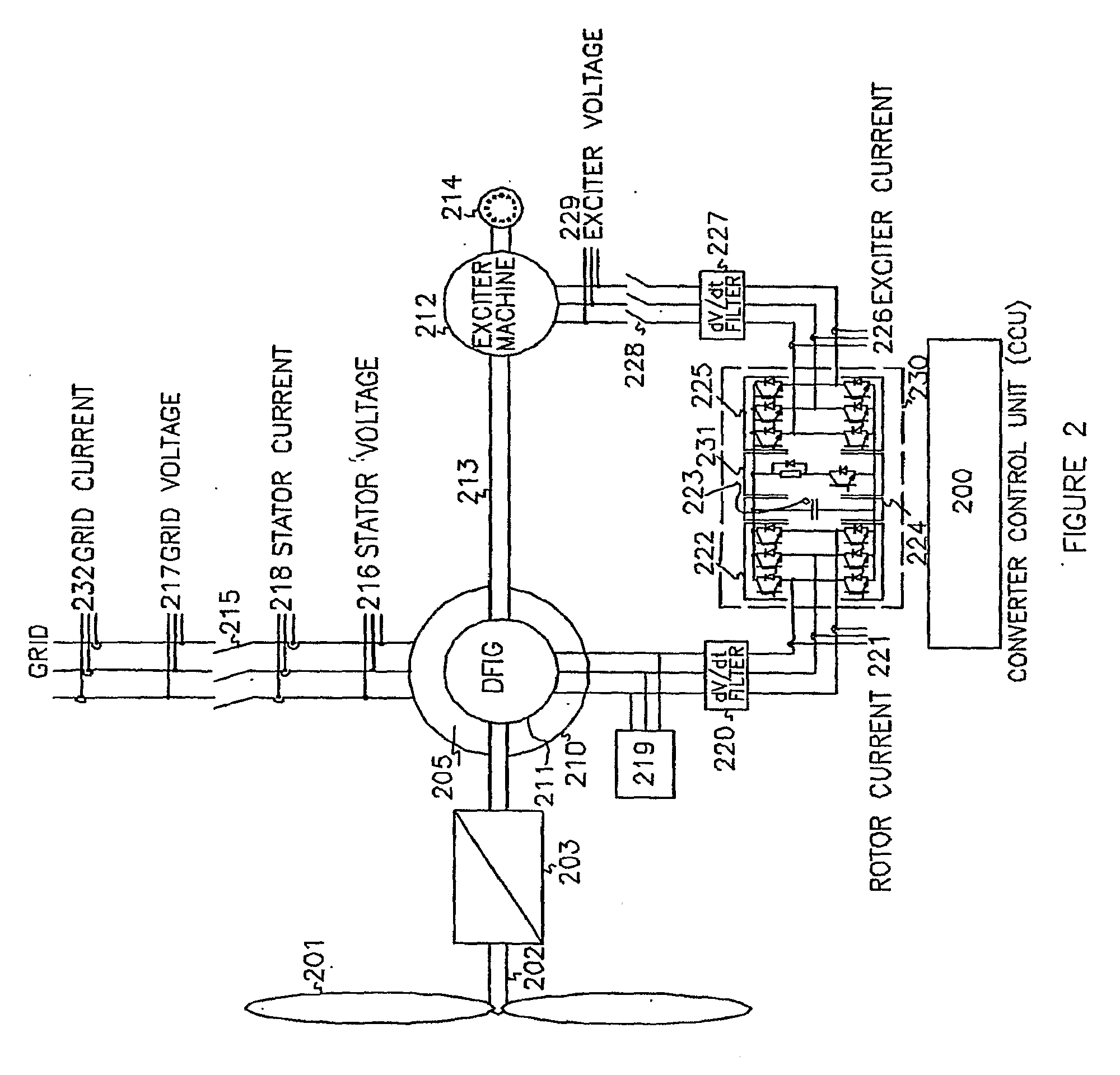
Low voltage ride through system for a variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
InactiveUS7622815B2Improve variable performanceReduce capacityGenerator control circuitsMachines/enginesPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine having a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG) includes an exciter machine mechanically coupled to the DFIG and a power converter placed between a rotor of the DFIG and the exciter machine which guarantees a stable voltage to the power converter. Thus, the power converter is not directly connected to the grid allowing the continuous operation of the system during a low voltage event in the grid.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
Controller of doubly-fed induction generator
ActiveUS20080303489A1Easy to detectProblem can be overcome fastGenerator control circuitsElectric motor controlHigh voltageDouble fed induction generator
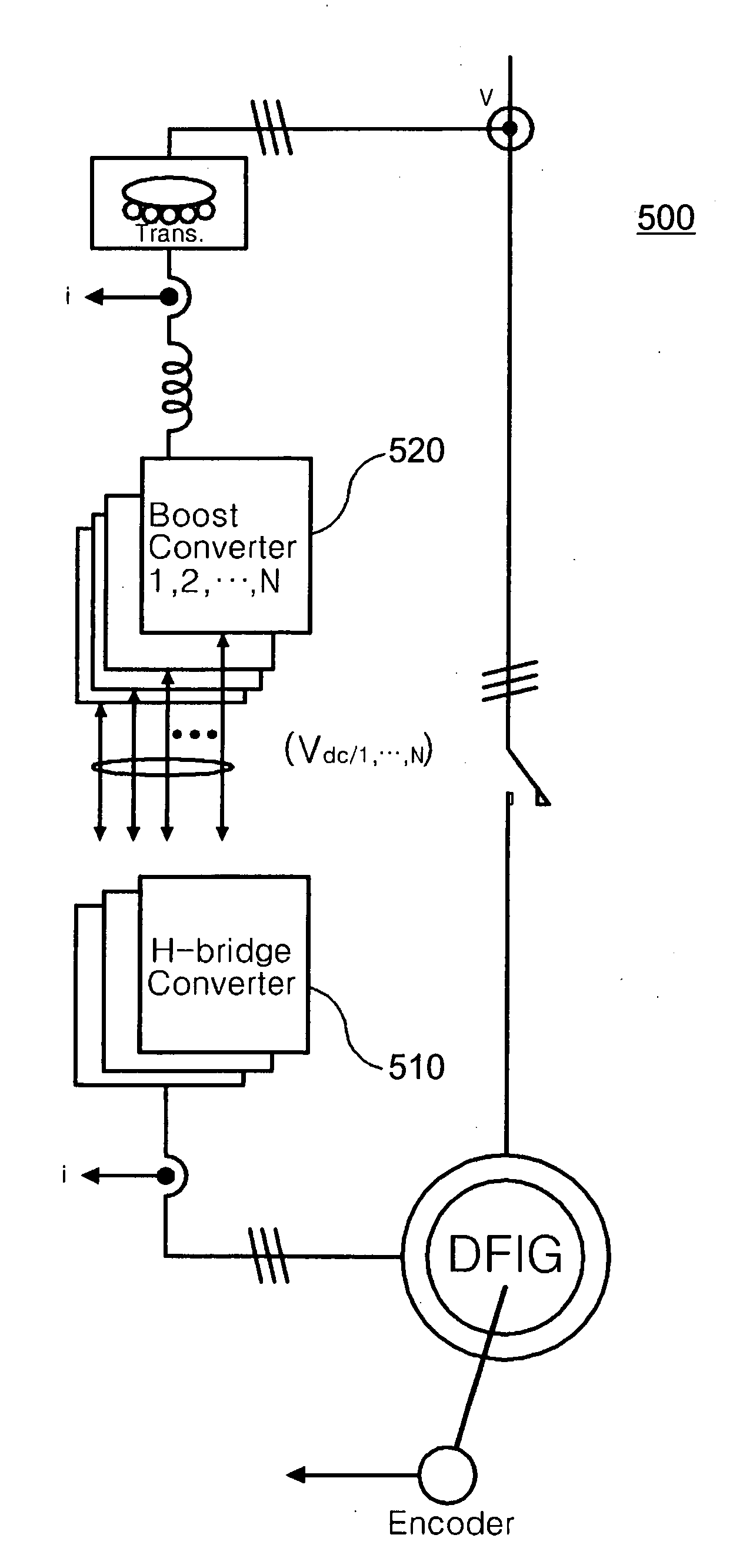
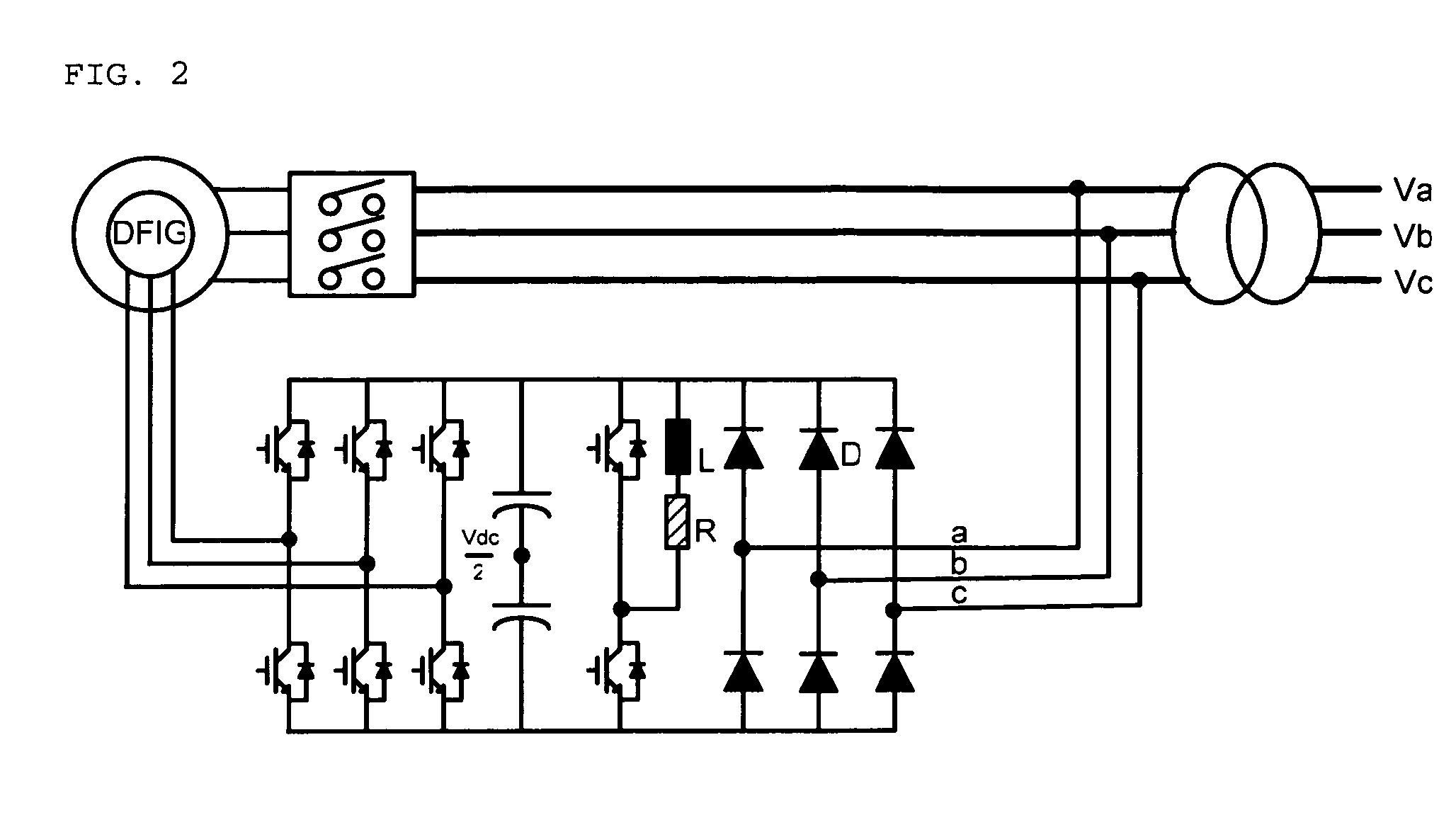
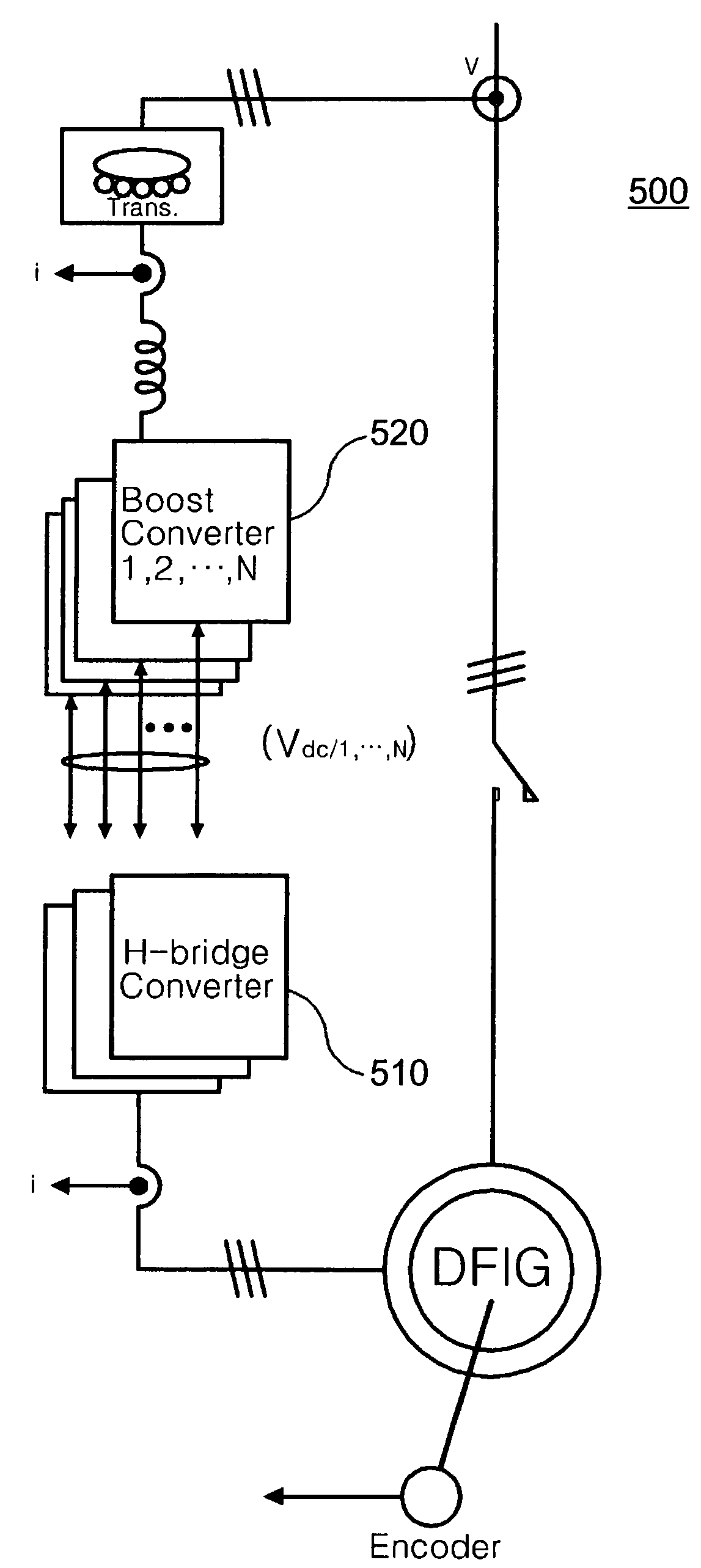
Disclosed is a controller of a grid coupled type doubly-fed induction generator having a multi-level converter topology, which can control the doubly-fed induction generator having a high voltage specification and can perform a fault ride-through function, an anti-islanding function and a grid voltage synchronization function required for a dispersed power generation facility. The controller makes a H-bridge multi-level converter generate a three-phase voltage waveform resulted from the structure that single-phase converters each being composed of a 2-leg IGBT are stacked in a serial manner, and controls a rotor current so as to make the rotor coil of the doubly-fed induction generator in charge of a slip power only. The boost converter is composed of a 3-leg IGBT and a boost inductor generating a direct current voltage of its source required for the H-bridge multi-level converter.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Electric power converting device and power converting method for controlling doubly-fed induction generator
ActiveUS7579702B2Generator control circuitsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectricityStator voltage
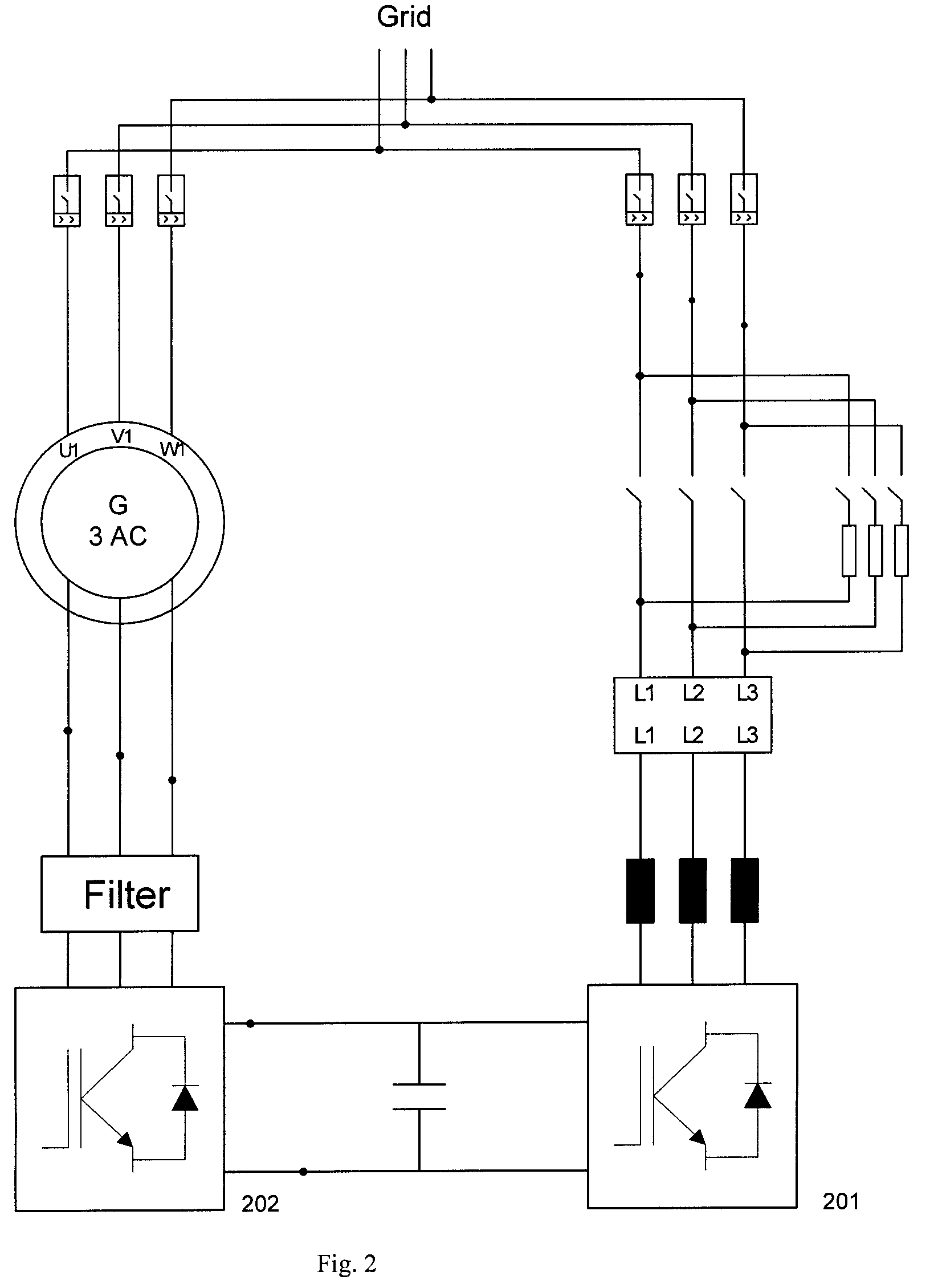
Disclosed herein is an electric power converting device and power converting method for controlling doubly-fed induction generators, which provides a synchronous generator for generating auxiliary electric power independently of a doubly-fed induction generator so as to generate electricity even in a system power-free environment, a grid-side converter is composed of a three-phase four-wire converter so as to generate a balanced voltage even in an unbalanced load condition and automatically synchronize a stator voltage of a doubly-fed induction generator and a system voltage with each other.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Controller of doubly-fed induction generator
ActiveUS7638983B2Improve the problemHigh voltage distortionGenerator control circuitsElectric motor controlHigh voltageDouble fed induction generator
Disclosed is a controller of a grid coupled type doubly-fed induction generator having a multi-level converter topology, which can control the doubly-fed induction generator having a high voltage specification and can perform a fault ride-through function, an anti-islanding function and a grid voltage synchronization function required for a dispersed power generation facility. The controller makes a H-bridge multi-level converter generate a three-phase voltage waveform resulted from the structure that single-phase converters each being composed of a 2-leg IGBT are stacked in a serial manner, and controls a rotor current so as to make the rotor coil of the doubly-fed induction generator in charge of a slip power only. The boost converter is composed of a 3-leg IGBT and a boost inductor generating a direct current voltage of its source required for the H-bridge multi-level converter.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Operating Doubly-Fed Induction Generators as Virtual Synchronous Generators
PendingUS20180191281A1High voltage levelReduce system costGenerator control circuitsWind motor controlVirtual synchronous generatorVirtual synchrony
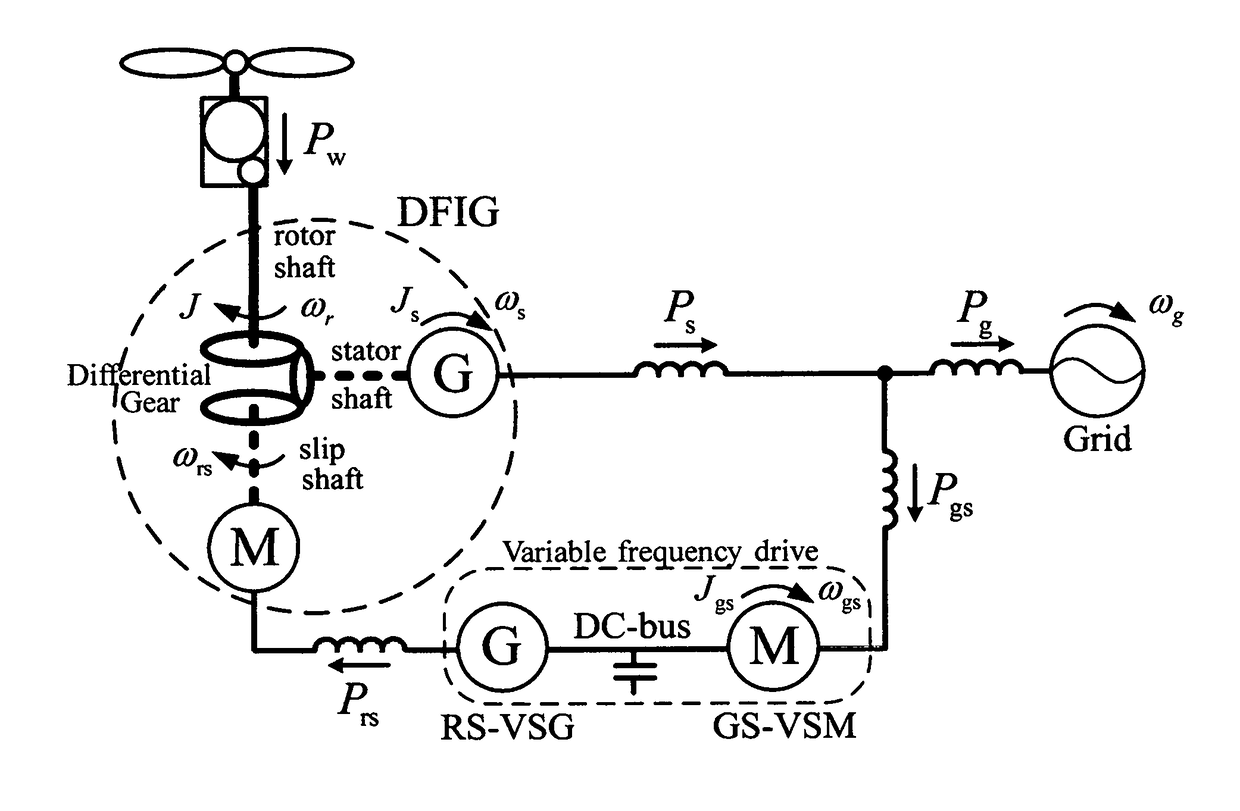
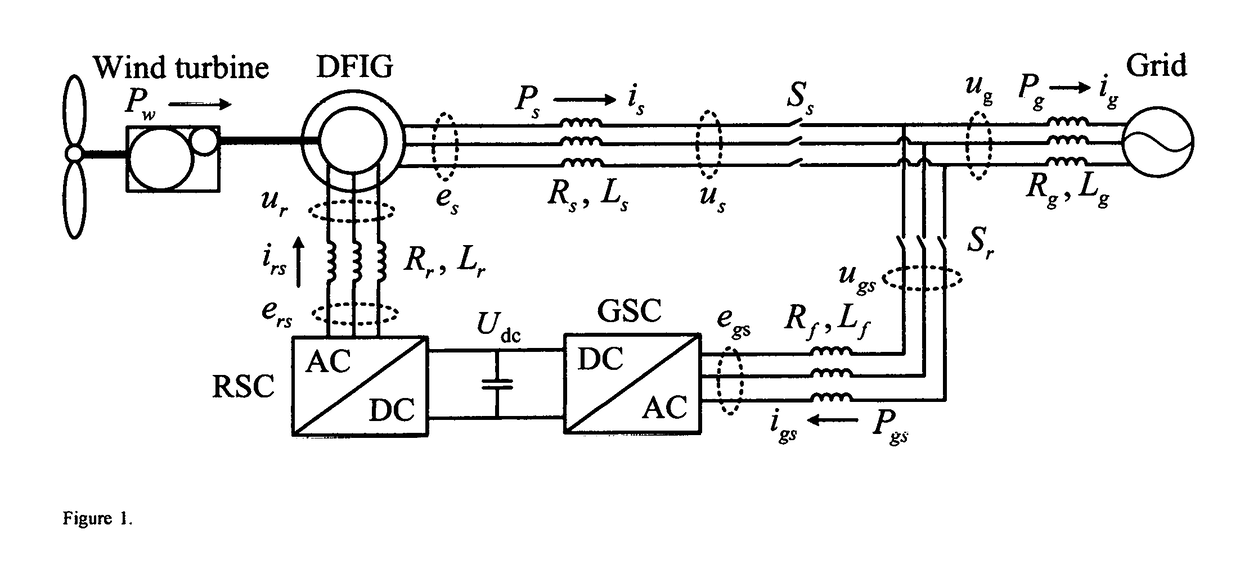
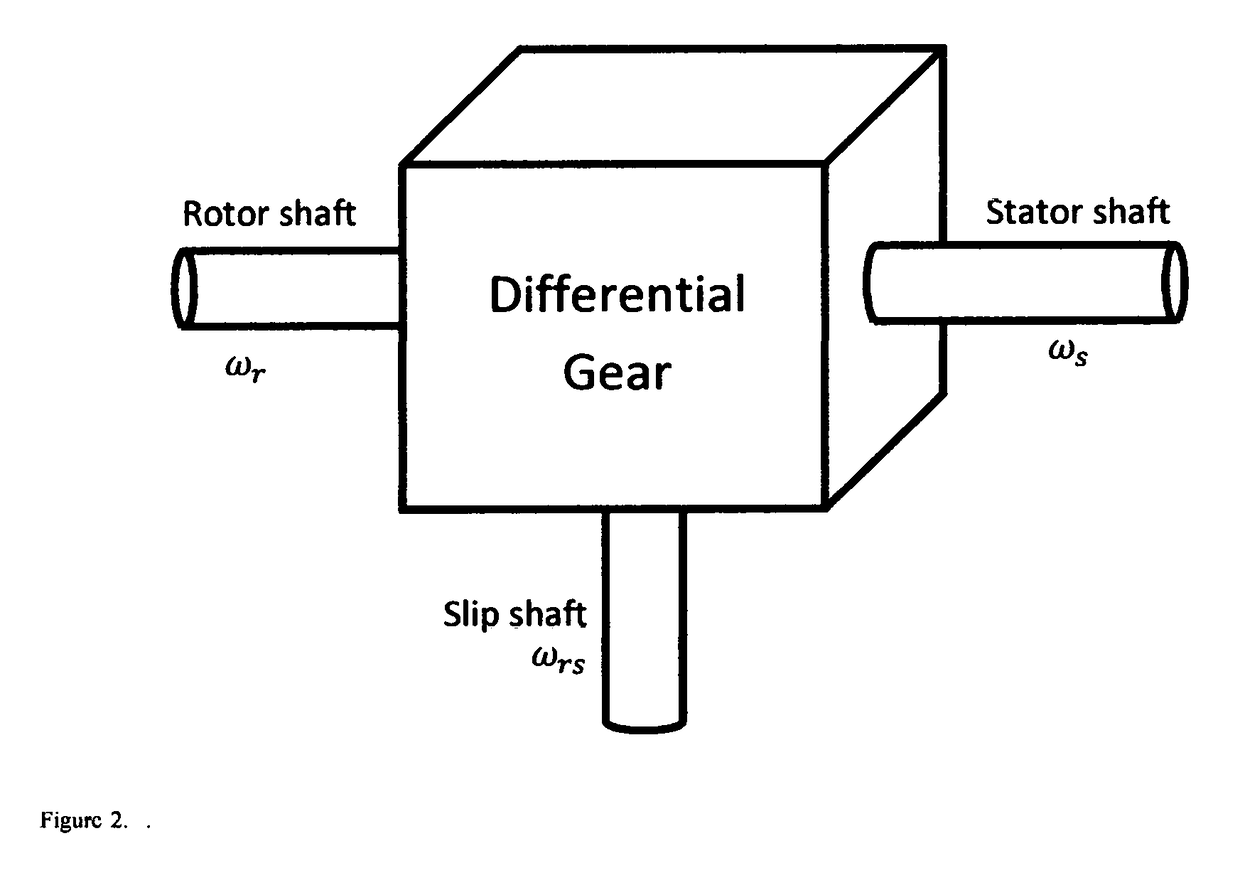
This invention discloses a system and method to operate a doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) as a grid-friendly virtual synchronous generator (VSG). It comprises a DFIG modeled as a virtual differential gear that links a rotor shaft driven by a prime mover, a virtual stator shaft coupled with a virtual synchronous generator G and a virtual slip shaft coupled with a virtual synchronous motor M, and a variable frequency drive that behaves as a virtual synchronous motor-generator set to regulate the speed of the virtual synchronous motor M so that the speed of the virtual stator shaft, i.e., the speed of the virtual synchronous generator G, is within a narrow band around the grid frequency even when the rotor shah: speed changes. As a result, a grid-connected DFIG can be controlled to behave like a virtual synchronous generator without using a PLL.
Owner:ZHONG QINGCHANG
System and method of operating double fed induction generators
ActiveUS20070132248A1Generator control circuitsGeneration protection through controlGrid faultPower grid
A protection system and a protection method are provided for protecting a double fed induction generator and a gearbox during a grid fault. The protection system includes a plurality of controlled impedance devices. Each of the controlled impedance devices is coupled between a respective phase of a stator winding of the double fed induction generator and a respective phase of a grid side converter. The protection system also includes a controller configured for coupling and decoupling impedance in one or more of the plurality of controlled impedance devices in response to changes in at least one of a utility grid voltage and a utility grid current.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Variable speed wind turbine with a doubly-fed induction generator and rotor and grid inverters that use scalar controls
InactiveUS8198742B2Reduce impactGenerator control circuitsOptimise machine performancePower gridVariable speed wind turbine
The present invention relates to an improved wind turbine, of the type which employs doubly fed induction generators (DFIG), and a wind park including the same, which permits the use of lighter weight turbines, with the ability to have greater energy capture, more precise control of asymmetrical phases and enhanced maintenance and support of the grid during fault conditions.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
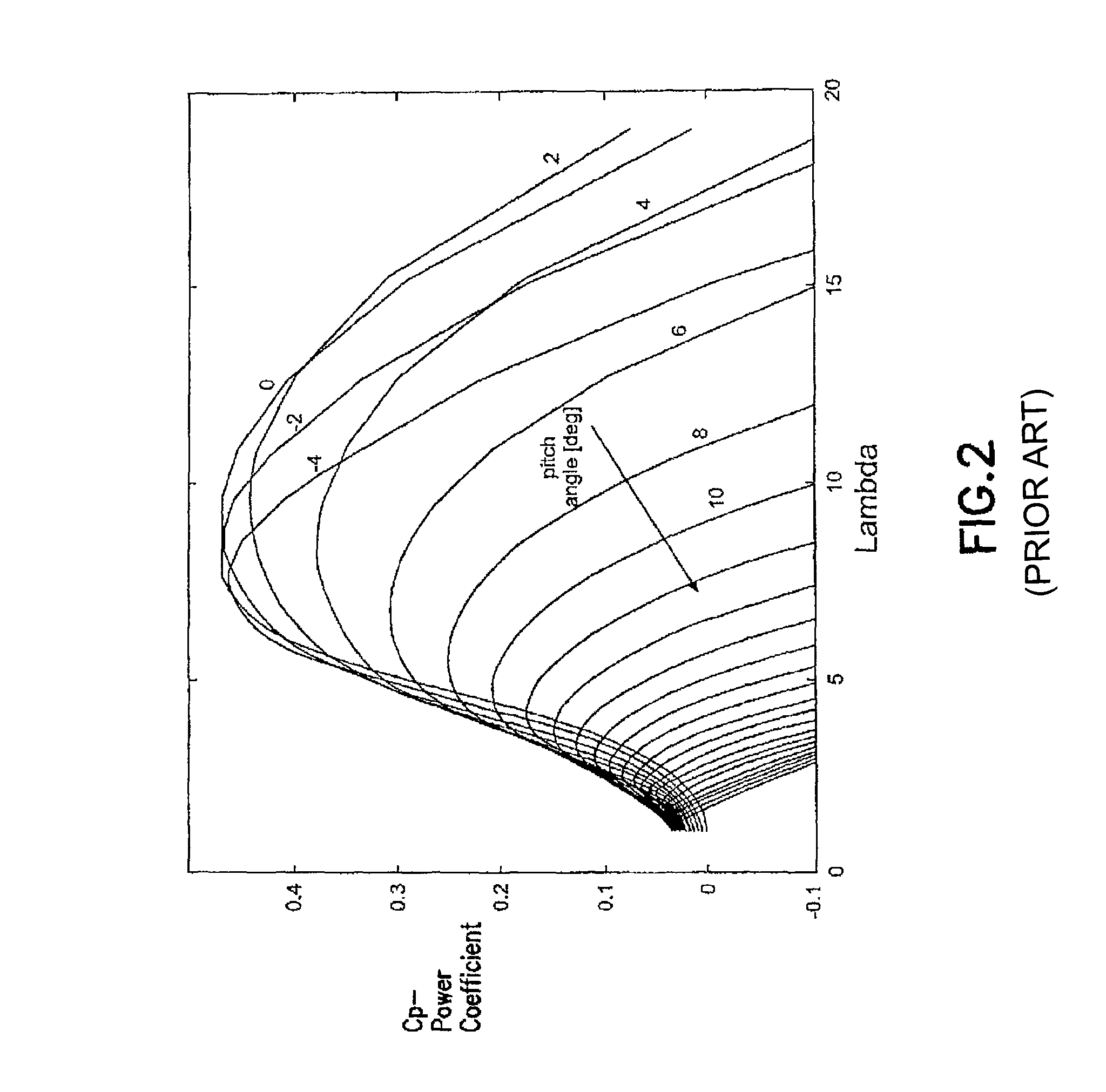
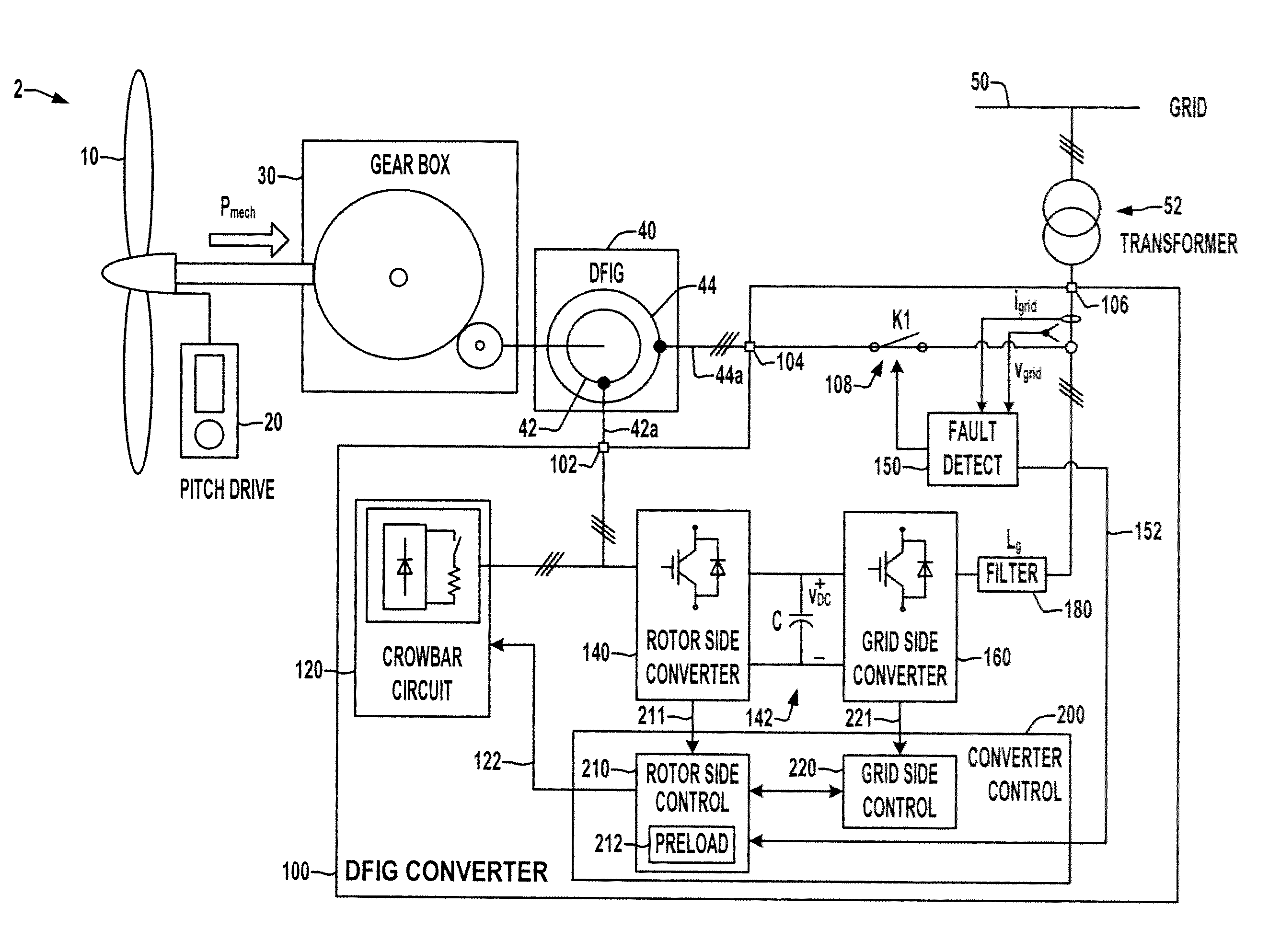
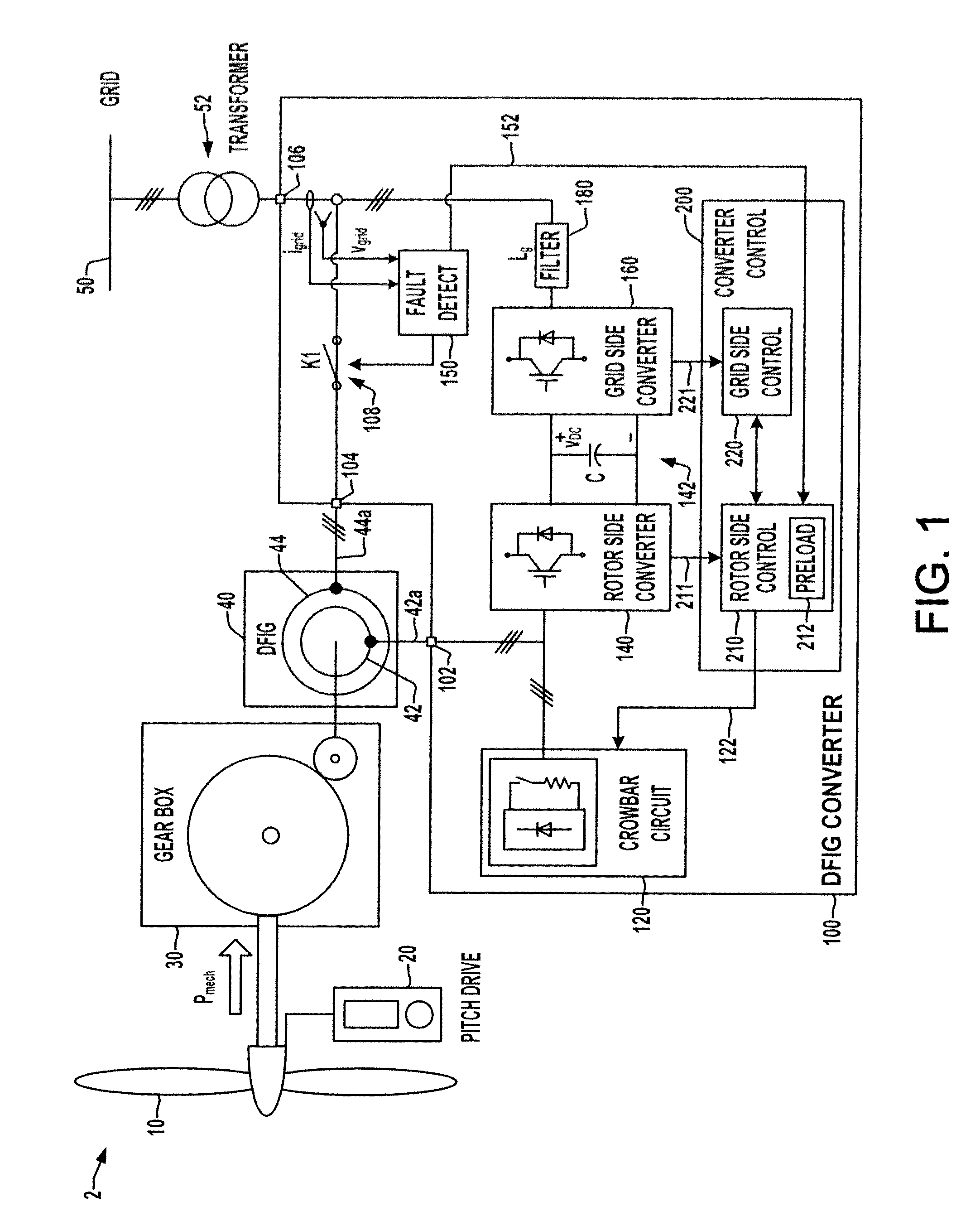
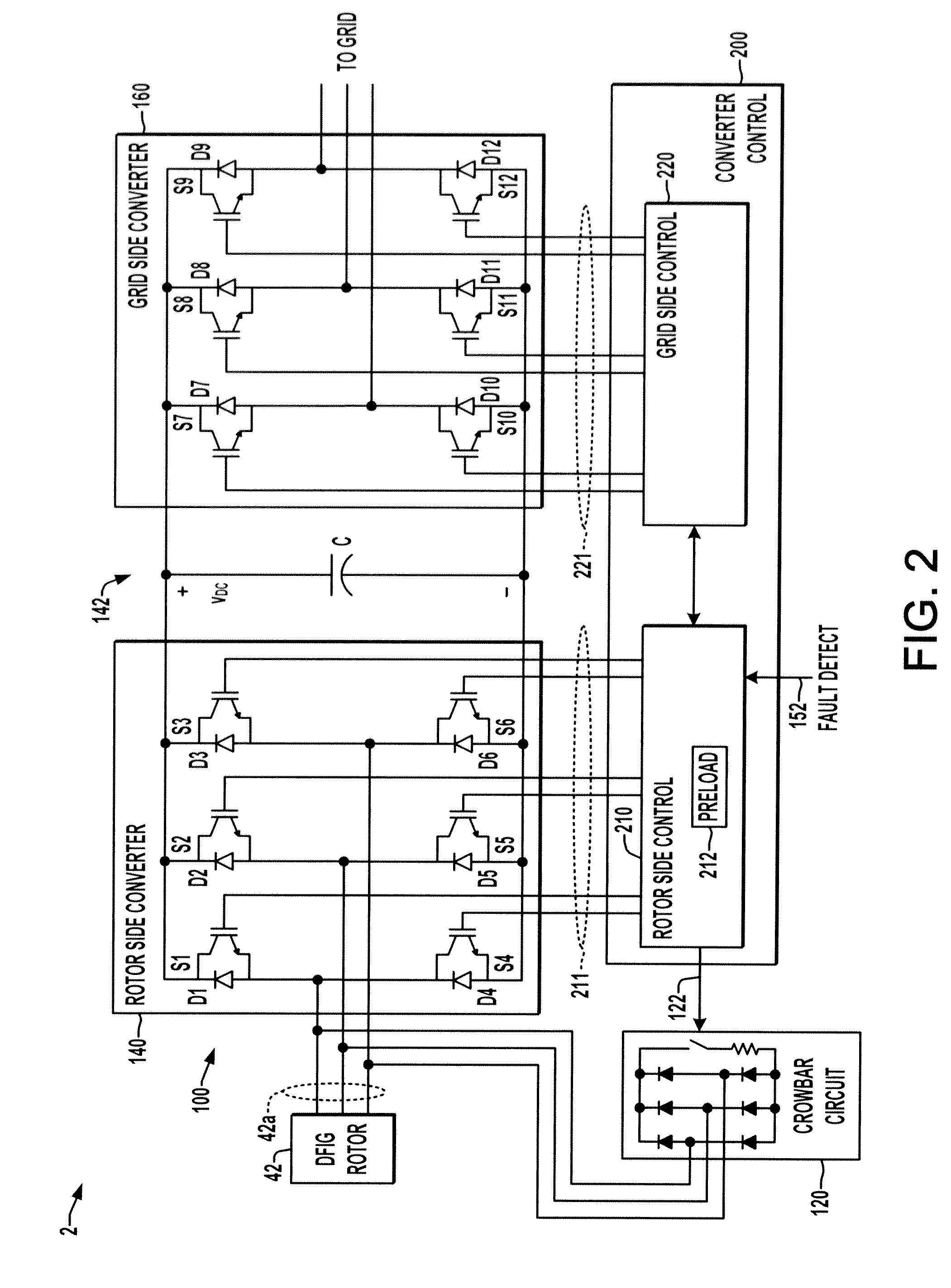
Double fed induction generator converter and method for suppressing transient in deactivation of crowbar circuit for grid fault ridethrough
ActiveUS20120262129A1Electronic commutation motor controlGenerator control circuitsGrid faultPower grid
A double fed induction generator (DFIG) system and controller are presented in which the rotor side converter is preloaded with one or more initial values for resuming regulated operation to counteract transients upon deactivation of the crowbar protection circuit to provide grid fault ride through.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
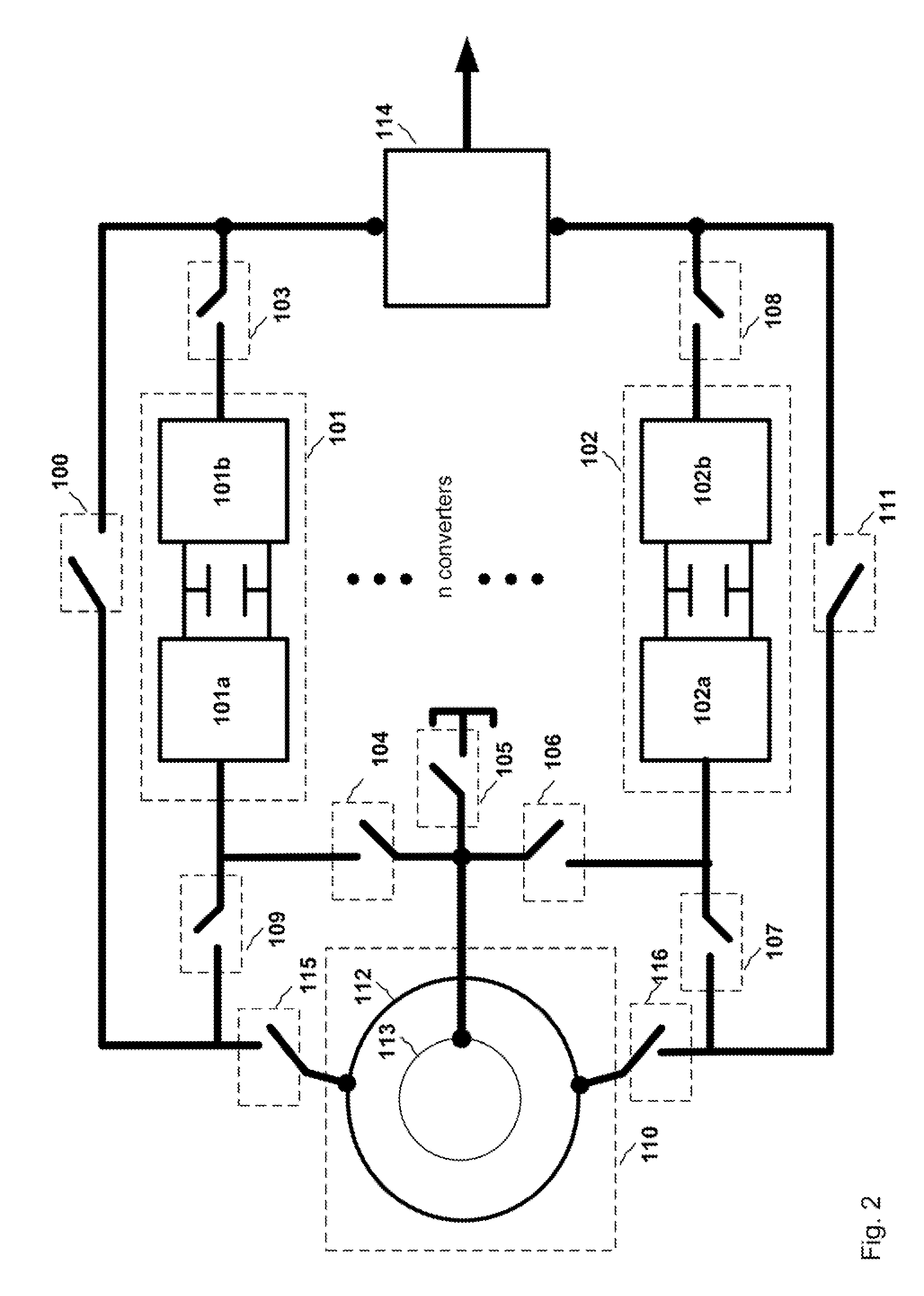
Wind turbine operation method and system
InactiveUS20110057446A1Increasing turbine availabilityImprove usabilityGenerator control circuitsElectric motor controlInduction generatorWind force
The invention relates to wind turbines provided with doubly fed induction generators and with at least one power converter which is novel in that, under certain circumstances, it enables the turbine to operate as a full converter (FC) system, as a doubly fed (DFIG) system or as an asynchronous (AS) system, thereby increasing turbine availability.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
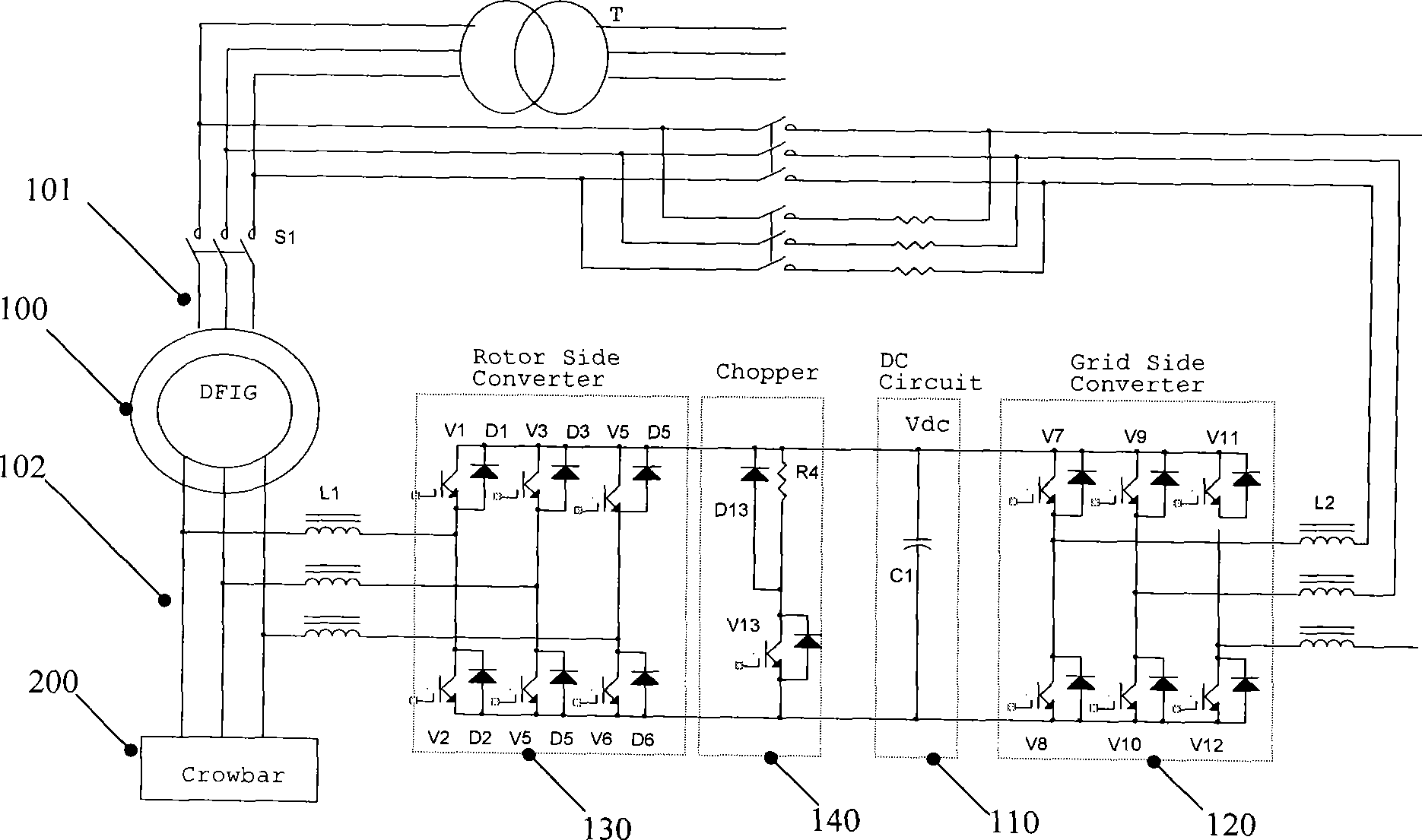
Dual-feeding motor system having protecting device and protecting method thereof
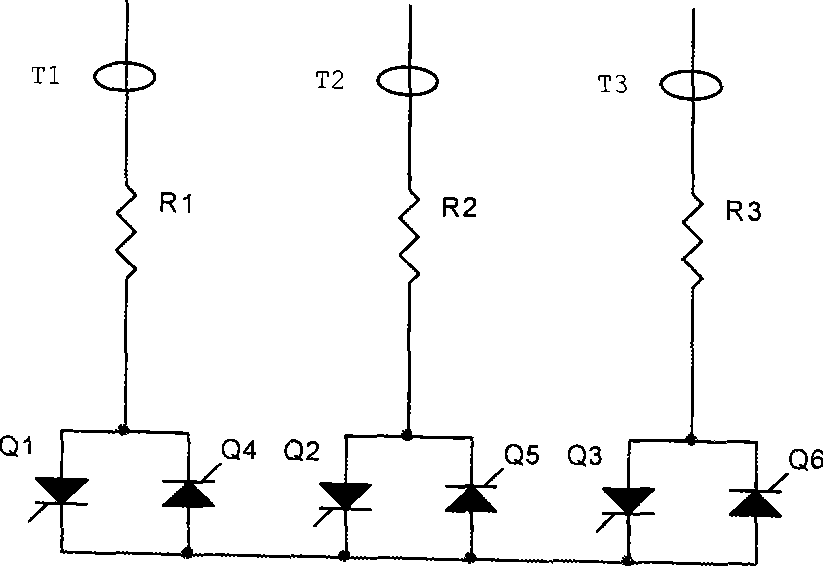
InactiveCN101383578ALow costEasy to controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectric generator controlCurrent limitingThyratron
The invention discloses a doubly fed generator system with a protector, as well as a method used for protecting the system. The doubly fed generator system with the protector comprises a doubly fed induction generator (100), a rotor side converter (130), an intermediate DC side converter (110), a grid side converter (120) and a bypass protecting circuit (200), wherein the bypass protecting circuit (200) comprises current limiting resistors (R1, R2 and R3) and thyristors (Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4, Q5 and Q6), the thyristors are divided into three groups, each group comprises two thyristors reversely connected in parallel, and is connected with one current limiting resistor in series, and the three groups of thyristors are connected into a star shape; when the voltage of the intermediate DC side converter (110) exceeds the set threshold U2, the thyristors (Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4, Q5 and Q6) are triggered to be conducted. The invention has the advantages of low cost, simple control and stronger fault ride-through capacity.
Owner:EMERSON NETWORK POWER CO LTD
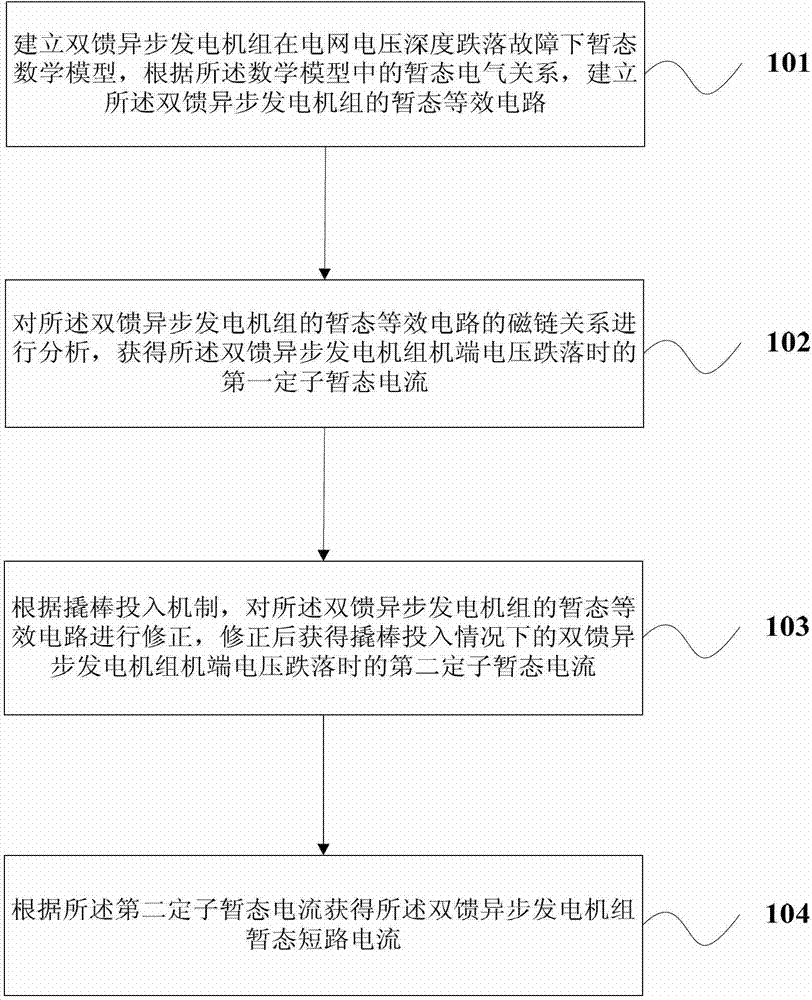
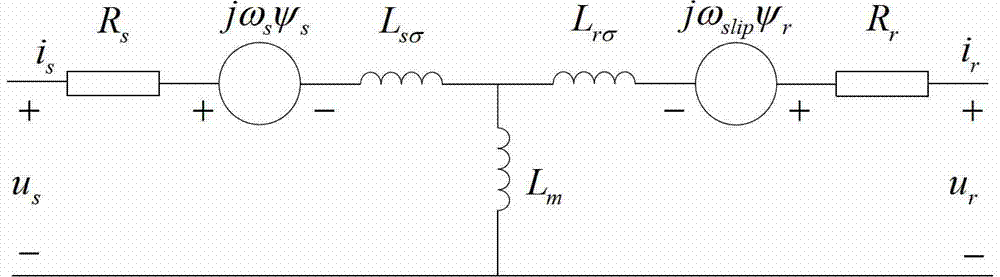
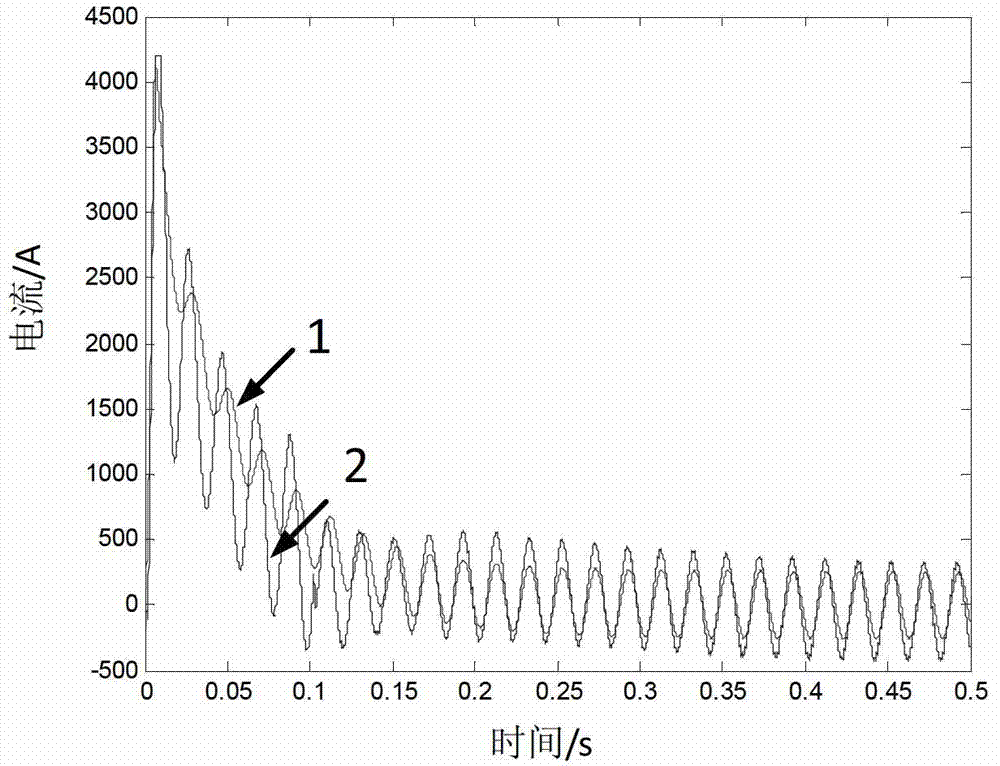
Method for calculating transient state short circuit currents of doubly-fed induction generator set
ActiveCN103500269ADesign optimisation/simulationCAD circuit designTerminal voltageMathematical model
The invention provides a method for calculating transient state short circuit currents of a doubly-fed induction generator set. The method comprises the steps that a transient state mathematical module of the doubly-fed induction generator set is established under a network voltage depth drop fault, and a transient state equivalent circuit of the doubly-fed induction generator set is established according to the transient state electrical relation in the mathematical module; the flux linkage relation of the transient state equivalent circuit of the doubly-fed induction generator set is analyzed, and first stator transient state currents generated when generator terminal voltages of the doubly-fed induction generator set drop are obtained; the transient state equivalent circuit of the doubly-fed induction generator set is corrected according to a crowbar circuit input mechanism, and second stator transient state currents generated when the generator terminal voltages of the double-fed induction generator set drop under the condition that crowbar circuits are input are obtained after correcting. The transient state short circuit currents of the doubly-fed induction generator set are obtained according to the second stator transient state currents.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
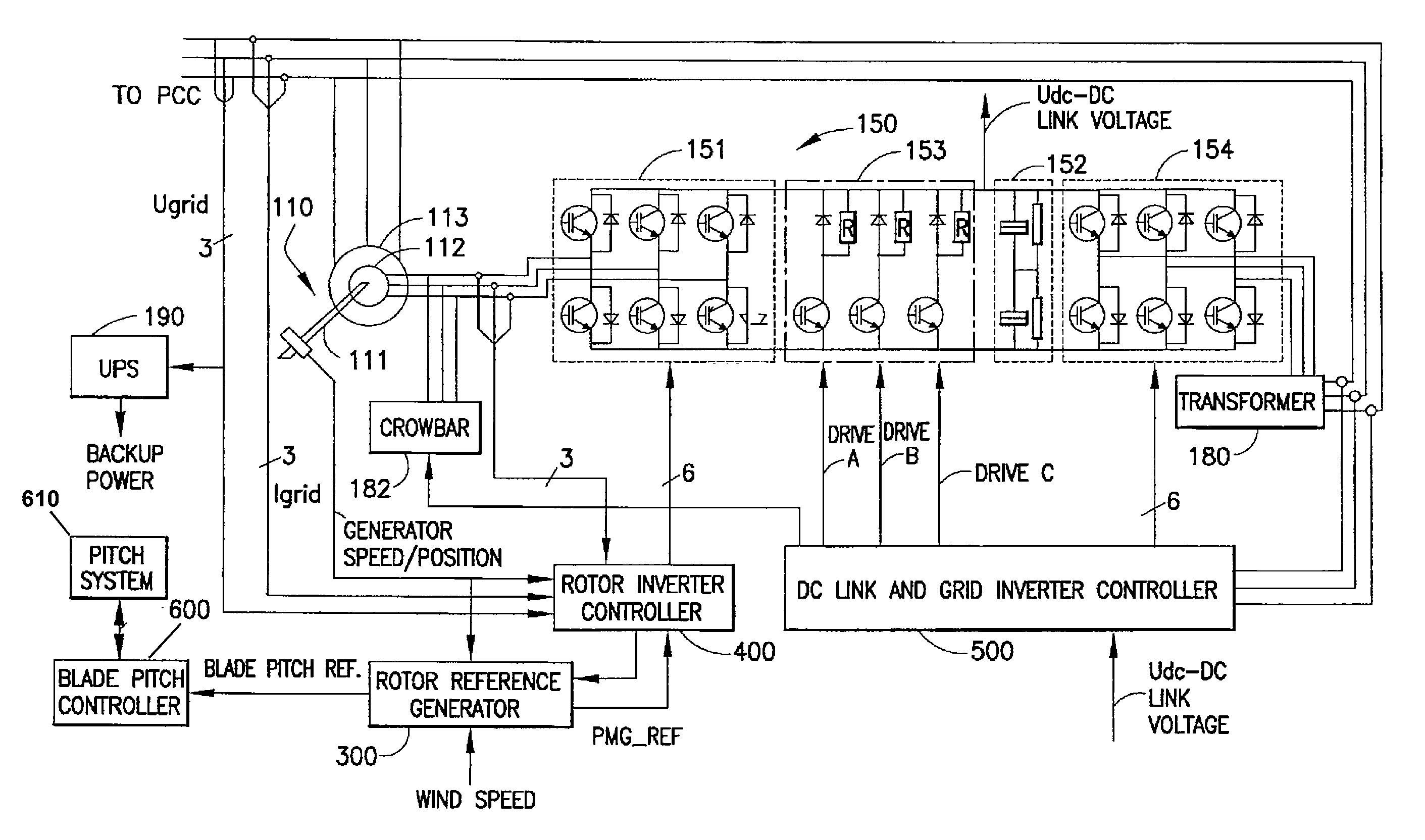
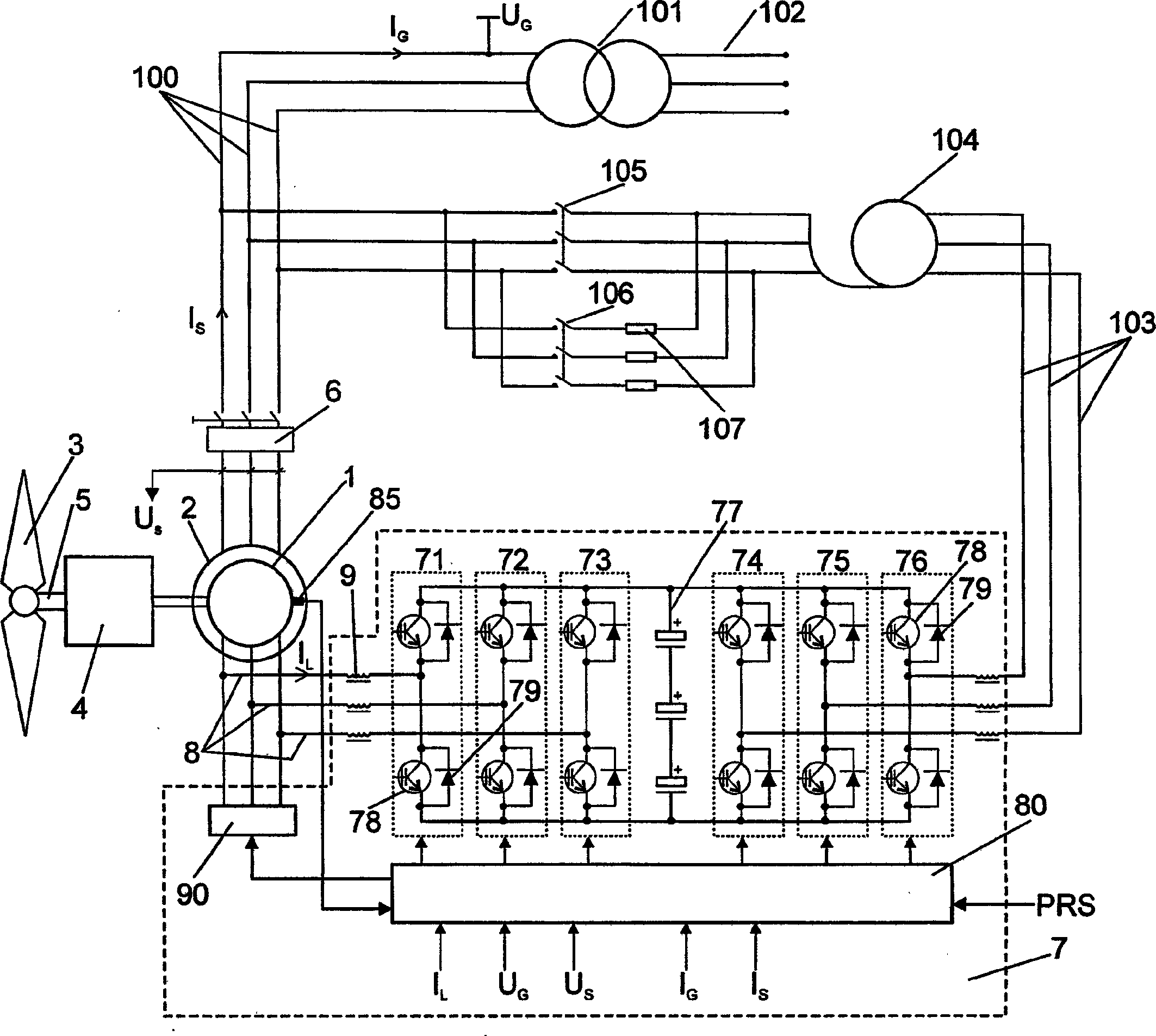
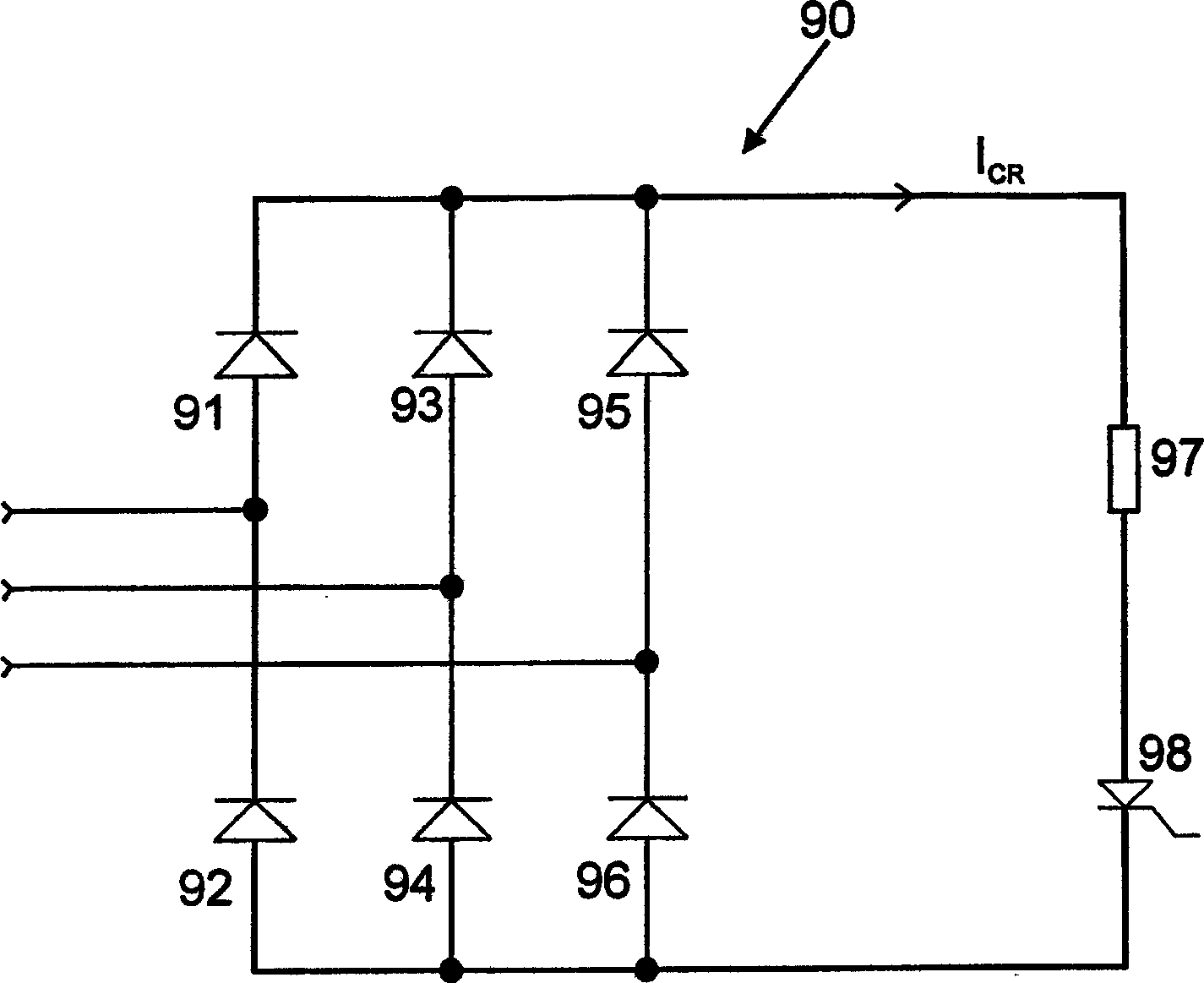
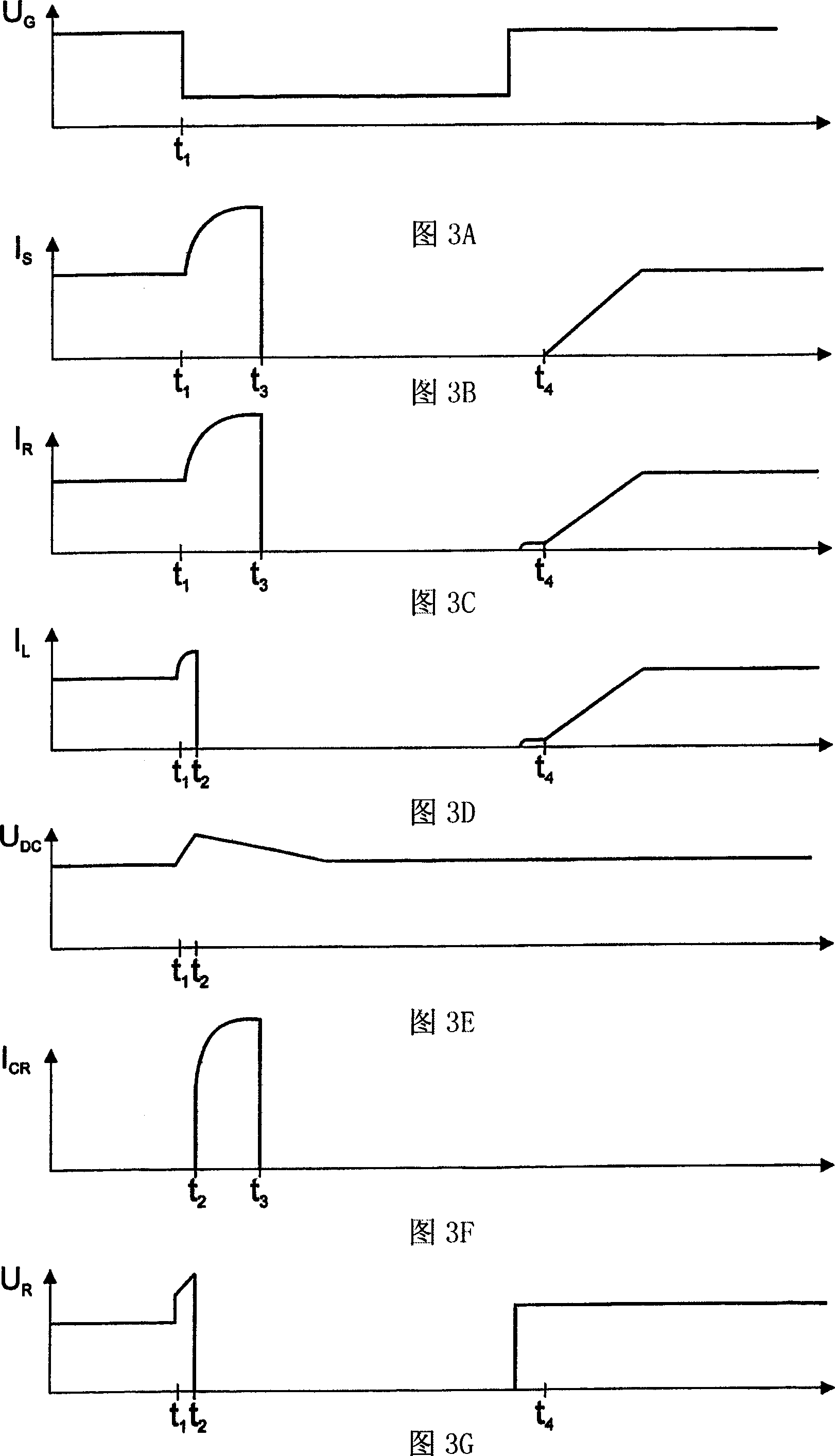
Control and protection of a doubly-fed induction generator system
ActiveCN1823467AElectronic commutation motor controlGenerator control circuitsRotor (electric)Electric power
A control system for a double-fed induction generator (DFIG) comprising a rotor (1) having rotor windings and a stator (2) having stator windings connectable to a grid for electric power distribution. The control system comprises a converter (170, 171), having a clamping unit comprising at least one passive voltage-dependent resistor element (291, 292, 293, 294) for providing a clamping voltage over the rotor windings when the clamping unit is triggered. The invention also relates to a double-fed induction generator (DFIG) system and to a method for protecting the converter in a power generation system.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Variable Speed Wind Turbine With Doubly-Fed Induction Generator Compensated For Varying Rotor Speed
ActiveUS20100045040A1Minimize oscillationReduce instabilityLevel controlWind motor controlVariable speed wind turbineDynamo
A variable rotational speed wind turbine includes a doubly-fed induction generator, a rotor current controller for controlling the rotor currents of the generator, a compensation mechanism having a computation mechanism, and an input mechanism for providing input to the compensation mechanism, the input being representative of at least the instantaneous angular speed of the rotor of the generator. The computation mechanism is arranged to compute an instantaneous compensation control output in dependency of the instantaneous angular speed of the rotor of the generator and feed the compensation control output to the rotor, and to compute the compensation control output during operation of the wind turbine to compensate at least partly for dependencies on the rotor angular speed of the locations of poles of a generator transfer function, thus making a resulting generator transfer function substantially independent of variations in the rotor angular speed during operation of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Low-voltage ride through control system and method for capacity-optimal energy-storage type double-fed motor
ActiveCN103078339AGuaranteed not to run offlineStable supportSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storageCapacitanceWind power generation
The invention relates to a low-voltage ride through control system and a low-voltage ride through control method for a capacity-optimal energy-storage type double-fed motor. The low-voltage ride through control system comprises a power grid, a coupling transformer, a double-fed induction generator (DFIG), a grid-side converter, a rotor-side converter, a DC (Direct Current)-side capacitor, a geared head and a fan, wherein one path of the power grid is directly connected with the DFIG through the coupling transformer, and another path of the power grid passes through the grid-side transformer, the DC-side capacitor and the rotor-side converter in sequence and is connected with the DFIG; a DC-side energy storage device is connected with the DC-side capacitor through a bidirectional DC / DC converter; and the DFIG is connected with the fan through the geared head. The low-voltage ride through control system and method have the advantages of improving the low-voltage ride through capability of a DFIG wind power generation system when the voltage of the power grid sharply drops, ensuring the fault ride-through of the DFIG, improving the supporting capability of the DFID wind power generation system on the voltage of the power grid during fault, providing a measure for reducing the requirement of the DFIG on the capacity of the energy-storage device in the process of realizing the low-voltage ride through and greatly reducing the cost of the energy storage device.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
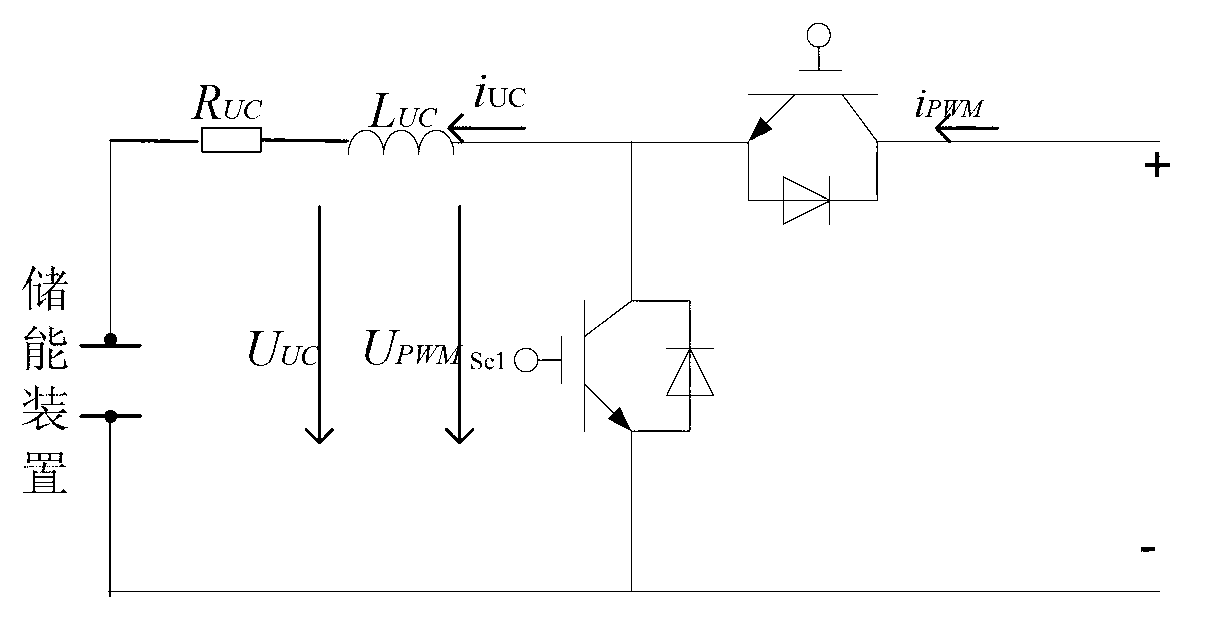
DC chopper and DC chopping method for doubly fed induction generator system
InactiveUS20130049707A1Control moreElectronic commutation motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsOvervoltageControl signal
A DC chopper comprising a control unit and a power circuit and a DC chopping method for a DFIG (doubly fed induction generator) system are provided. The input terminal of the control unit is coupled to a DC capacitor of a converter to detect a DC voltage. The power circuit includes input terminals, an overvoltage protection module, a rectifier module and output terminals. The overvoltage protection module comprises at least one discharge unit formed from a discharge resistor and a switch element, and the rectifier module is coupled in parallel to the overvoltage protection module. When a grid voltage drops, the control unit outputs a corresponding control signal to drive the switch element to be ON or OFF, and the output terminal of the power circuit absorbs a portion of rotor inrush current, so as to impose over-current protection.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Rotor current control method of double-fed wind driven generator under power grid faults
InactiveCN101986552APrevent overcurrentImprove vibrationElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsWind drivenPosition angle
The invention belongs to the field of controlling a power conversion device of a wind driven generator, relating to a rotor current control method of a double-fed wind driven generator under power grid faults. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the stator voltage and the rotor current under a two-phase static coordinates by utilizing the detected three-phase stator voltage and the three-phase rotor current through a 3 / 2 conversion module; calculating the stator magnetic flux linkage and the position angle; calculating the slip frequency angle and the slip frequency angular velocity; summating the stator magnetic flux linkage position angle and the rotor position angle, and then carrying out differentiation to obtain the sum of the magnetic flux linkage angular velocity and the rotor angular velocity; calculating the rotor current set values under the two-phase static coordinates of a rotor; respectively subtracting the rotor current set values under the two-phase static coordinates of the rotor with the rotor current under the two-phase static coordinates and obtaining the reference value of the rotor voltage under the two-phase static coordinates through the calculation by utilizing a performance requirement (PR) controller; and generating the switching signal of a control power device. The rotor current control method has the advantages that the rotor current oscillation of a double-fed induction generator (DFIG) resulted from power grid faults can be effectively inhibited, the grid in-service operation of the double-fed wind driven generator, and the operation performance of the DFIG under the power grid faults is enhanced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Virtual double-fed induction generator inertia control method coordinated with secondary frequency regulation
InactiveCN105515022AImprove FM capabilitySolve the problem of the influence of active power regulation abilityFlicker reduction in ac networkSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectricityInertial control
The invention discloses a virtual double-fed induction generator inertia control method coordinated with secondary frequency regulation, which solves the problem of cooperation between the virtual inertia control of a wind turbine generator and the secondary frequency regulation of a power system. On the basis of an original virtual inertia control module, a module which is coordinated with the secondary frequency regulation of a power system is added, so that the overall frequency regulation effect is increased. Moreover, in the added module, the rotational speed of the rotor of the wind turbine generator is considered, so that the wind turbine generator can continuously operate within a safe rotational speed range; the problem of the affection of system frequency fluctuation on the active regulation capability of the wind turbine generator is solved; because the affection of system frequency fluctuation on the active regulation capability of the wind turbine generator is great, in order to ensure that the double-fed induction generator has better frequency regulation capability, the steady-state frequency response of the wind turbine generator is optimized, and moreover, accordingly, a control strategy is designed, so that the frequency regulation effect of the wind turbine generator is increased to a certain degree.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
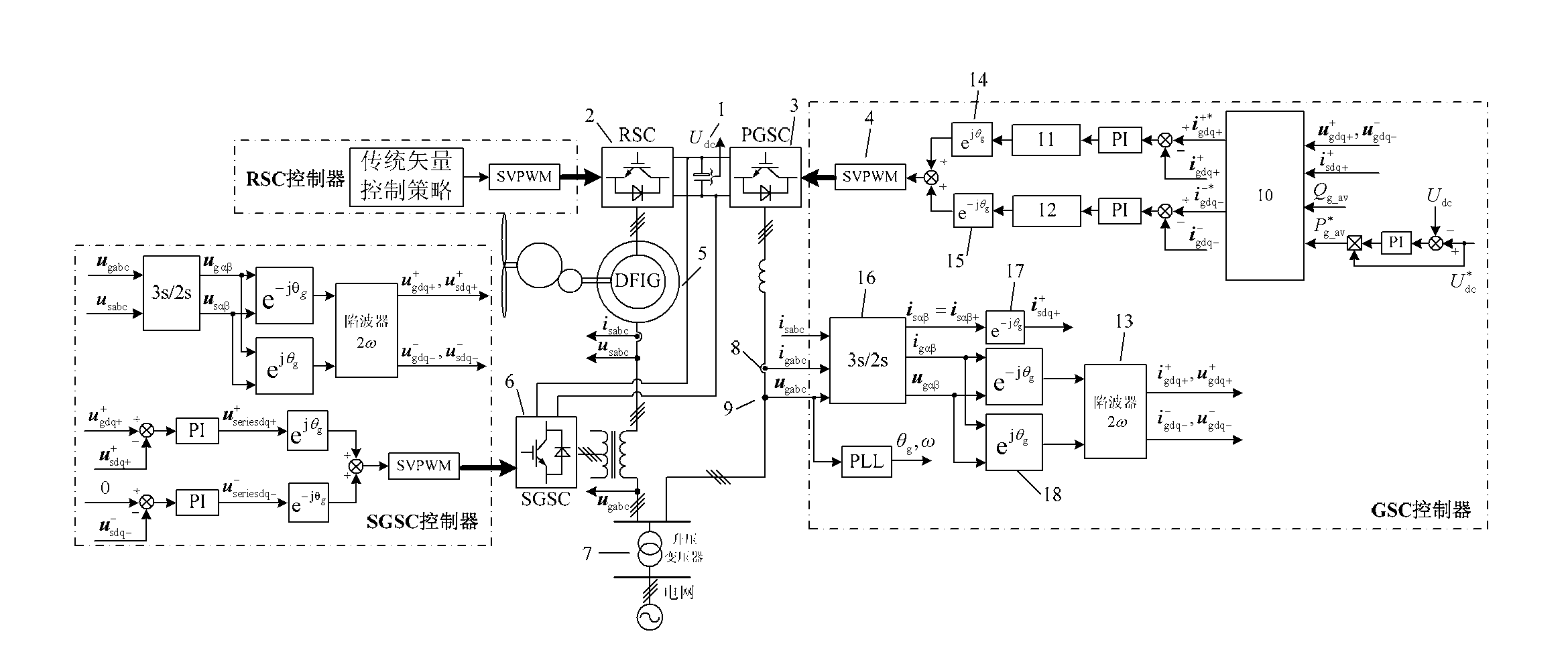
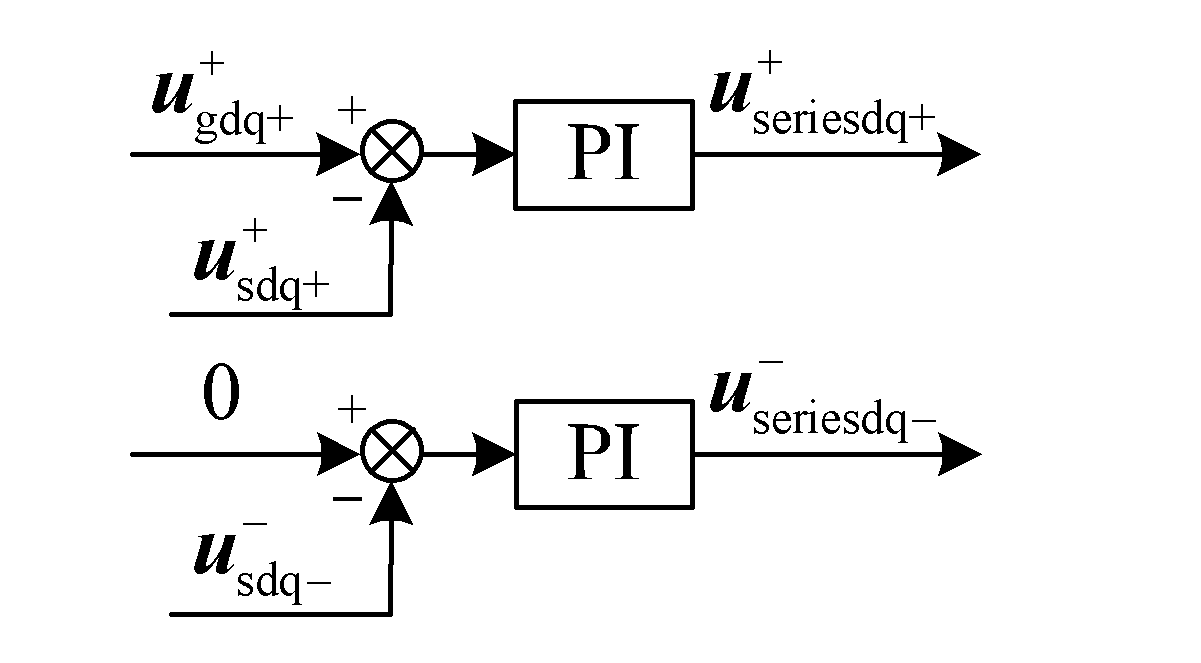
Method for suppressing total output reactive power fluctuation by adopting doubly-fed induction wind power system with series grid-side converter under unbalanced voltage
InactiveCN102427236AReactive power fluctuations are reducedReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationWind energy generationEngineeringElectric generator
The invention discloses a method for suppressing total output reactive power fluctuation by adopting a doubly-fed induction wind power system with series grid-side converters under unbalanced voltage. The method relates to the control of series and parallel grid-side converters and motor-side converters. Pulse-width modulation (PWM) driving signals of the series and parallel grid-side converters are generated through a specific method to control the series and parallel grid-side converters. Under unbalanced grid voltage, a doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) with the series grid-side converters does not change the control strategies of a rotor-side converter. On the premise that the doubled frequency fluctuation of the output power of the generator does not occur, the doubled frequency fluctuation of the electromagnetic torque does not occur and the three-phase current of a stator and a rotor are in balance, through the coordination control of the series grid-side converters and theparallel grid-side converters, the goal that the doubled frequency fluctuation of the total output reactive power of the entire system does not occur is realized, and the quality of reactive power provided by the DFIG wind power system to the grid under unbalanced grid voltage is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method and system for controlling switching frequency of a doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG)
ActiveUS20140247021A1Reduce size requirementsIncrease the switching frequencyGenerator control circuitsWind energy generationHarmonicControl line
The present subject matter is directed to systems and methods for controlling variable speed generators, particularly converters associated with doubly-fed induction generators (DFIG) to permit use of harmonic attenuating filters that are generally smaller and less costly than previous similar filters. The subject matter provides for controlling line-side and rotor-side converters in such a manner that the frequencies generated by the converters are interleaved in a manner that the filters see a higher switching frequency and thus may be designed based on those higher frequencies, thereby requiring smaller and less expensive components.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
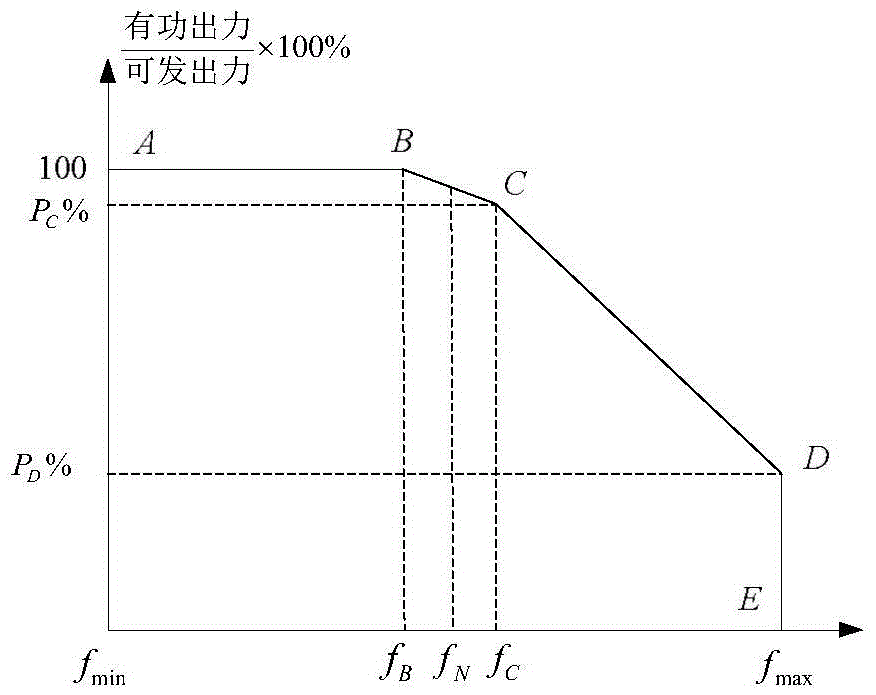
Operation control method of double-fed wind generator participating in electric power system frequency modulation
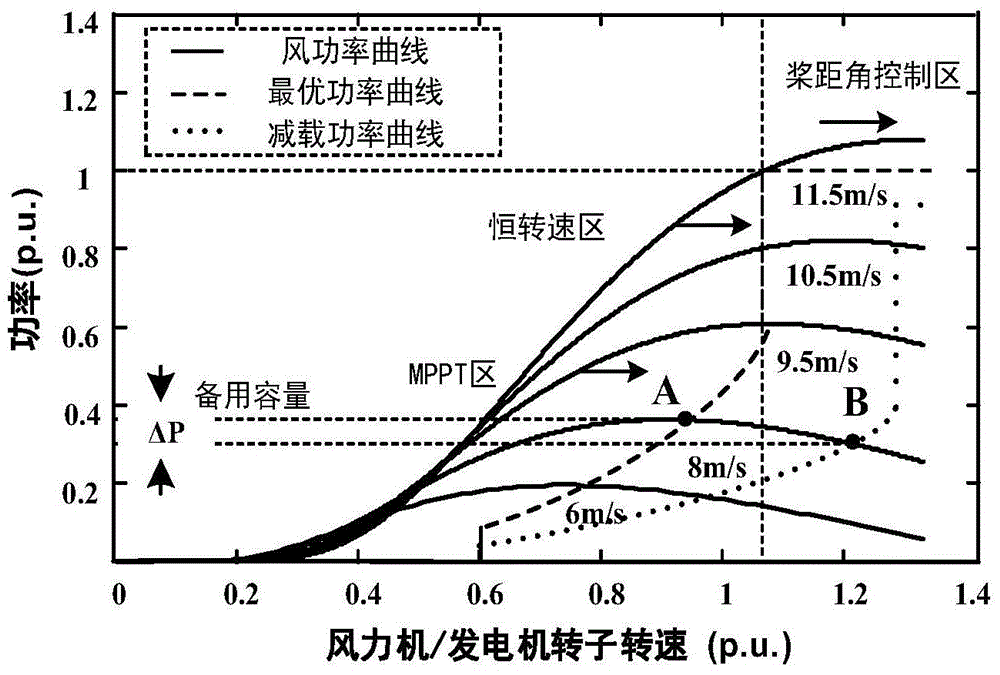
InactiveCN105281349AReduce outputImprove applicabilityPower oscillations reduction/preventionElectricityConstant frequency
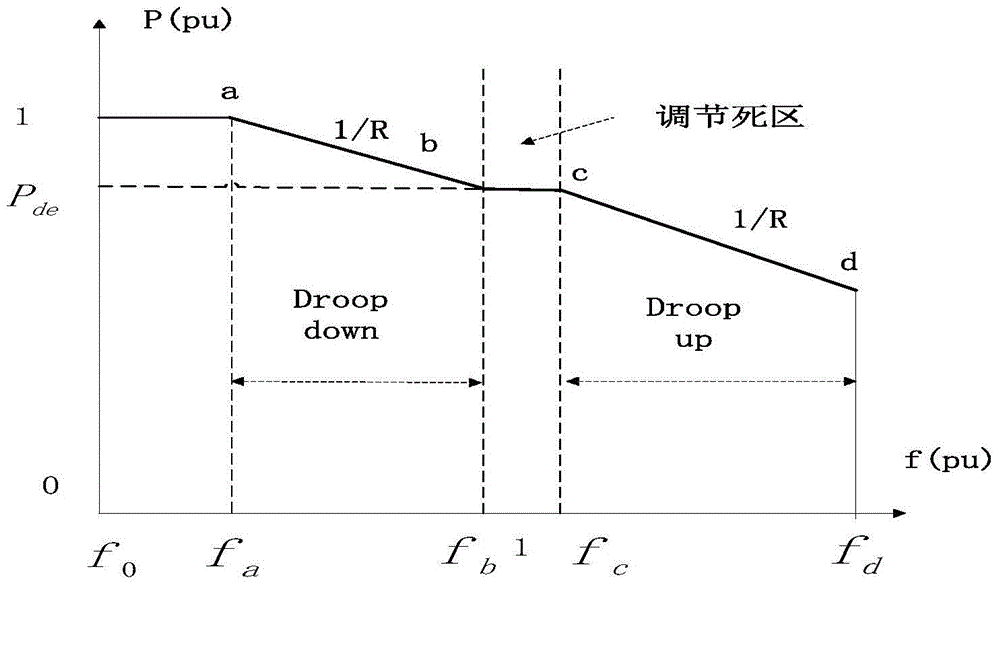
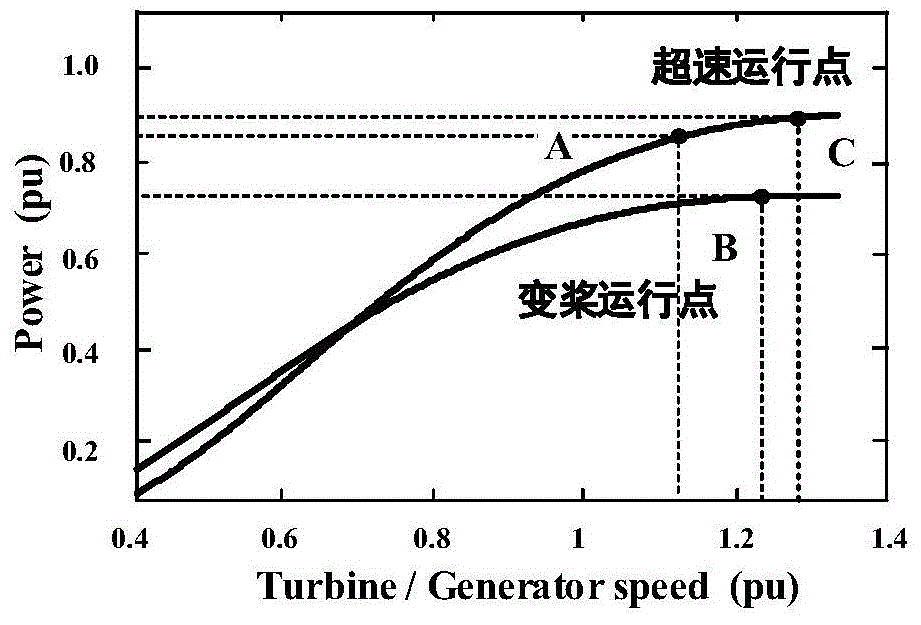
The invention relates to an operation control method of a double-fed wind generator participating in electric power system frequency modulation. The operation control method is characterized in that a deloading operation curve which has a power up-regulation capacity is set and a deloading control strategy in which variable speed and variable pitch are used for coordination control is designed according to an operation physical constraint condition of a Double-Fed Induction Generator (DFIG) which is common in a variable speed constant frequency generator, and the maximum deloading amplitude capability of the wind generator under each operation condition is quantitatively analyzed according to the operation physical constraint condition of the wind generator at different wind speeds. Through adjustment and control of a dropping frequency, the support effect of the wind generator to the system frequency under a deloading operation mode is verified. Through the simulation analysis, it is verified that in the deloading frequency modulation control scheme, when the system frequency fluctuates, the variable speed and variable pitch wind generator can effectively release kinetic energy, and the frequency support is provided for the system.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Doubly fed induction generator internal frequency synchronization method and device based on power balance
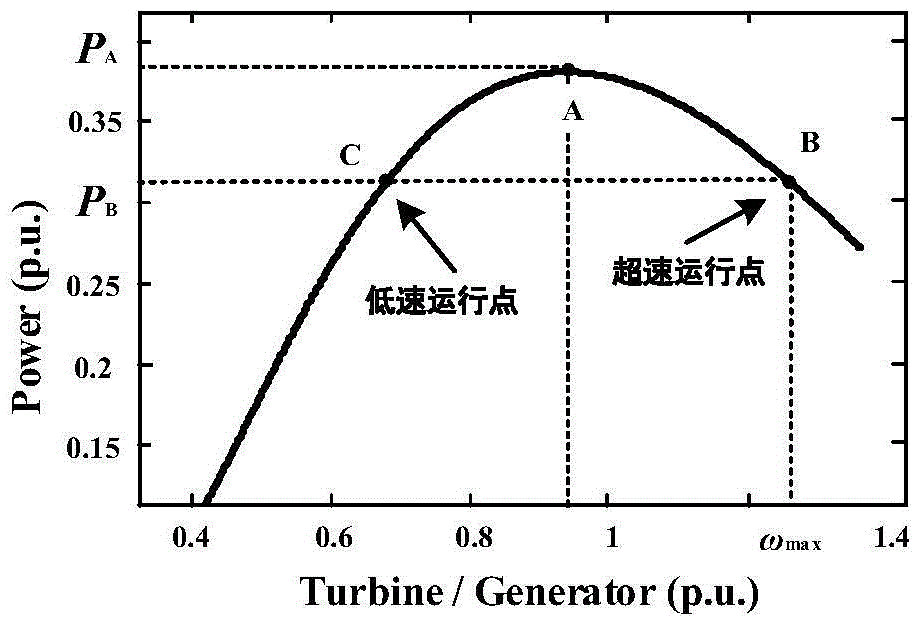
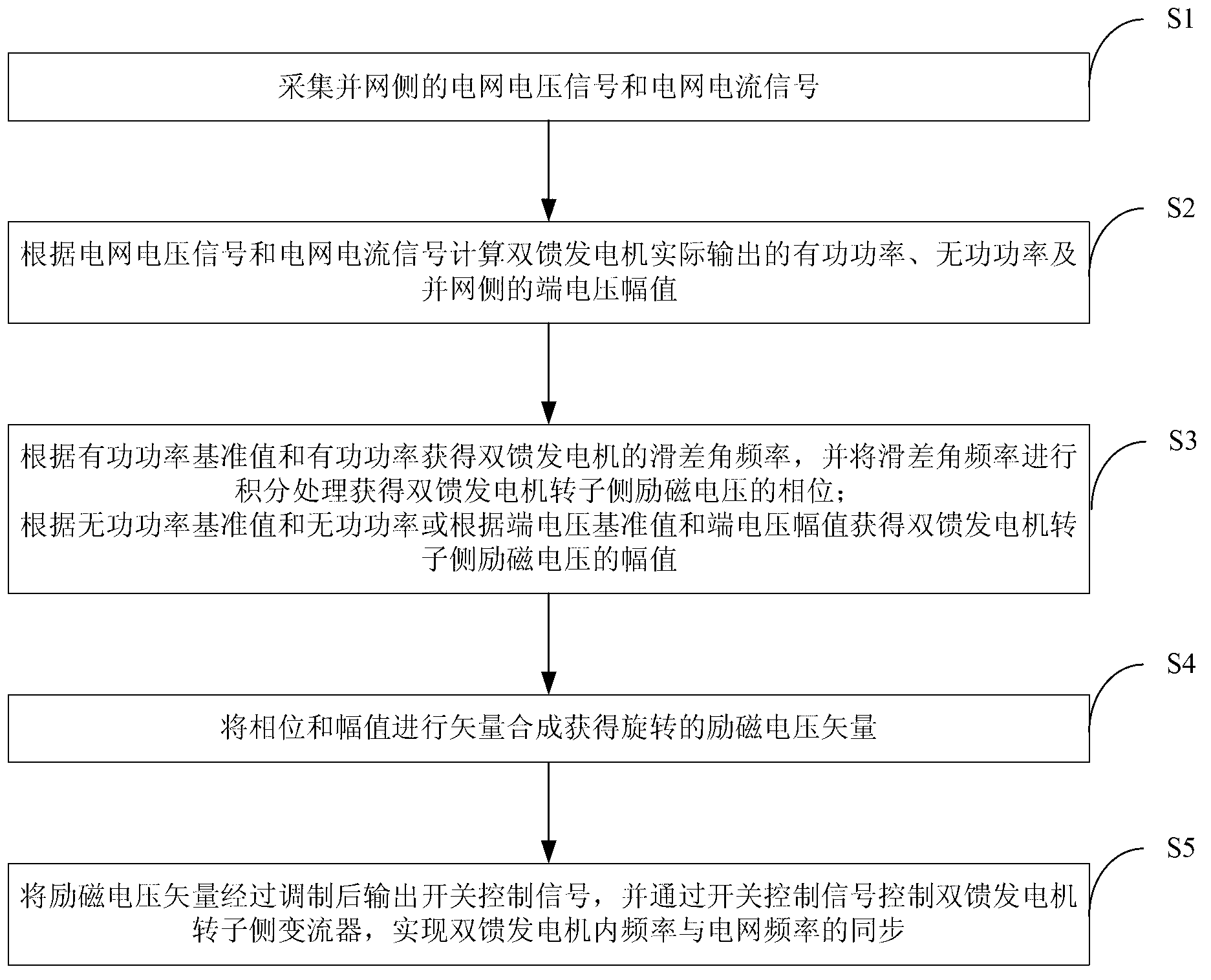
ActiveCN103259475ASimple structureImprove stabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationVoltage vectorElectric power system
The invention discloses a doubly fed induction generator internal frequency synchronization method and device based on power balance. The method comprises the steps that the internal synchronization mechanism of a synchronous generator is referred, and slip angular frequency of the rotor side exciting voltage is directly generated by adjusting active power deviation, and phases are obtained through integration processing; an excitation system of the synchronous generator is referred, amplitude of the rotor side exciting voltage is directly generated by adjusting reactive power deviation or terminal voltage deviation, a rotor side exciting voltage vector is obtained through the obtained phases and the amplitude, and internal frequency synchronization control of a doubly fed induction generator is achieved. By means of the doubly fed induction generator internal frequency synchronization method and device based on the power balance, the doubly fed induction generator can possess internal frequency which outward represents as a voltage source with the amplitude and frequency being controlled, high voltage support is provided for a power grid, capacity of short circuit of the power grid is improved, and stability of the power grid is improved. By the adoption of the internal frequency synchronization control, the doubly fed induction generator can operate without depending on intensity of the power grid, a possibility of independent operating of the doubly fed induction generator is provided, and a certain guarantee is provided for safe operating of a power system.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Control method of double-fed induction generator under power grid voltage three-phase symmetrical drop fault
InactiveCN101977011APrevent overcurrentStable controlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsSelf excited induction generatorAngular degrees
The invention belongs to the field of control of power conversion devices of wind driven generators and relates to a control method of a double-fed induction generator (DFIG) under a power grid voltage three-phase symmetrical drop fault. The control method comprises the following steps of: calculating a stator voltage, a stator current and a rotor current under a two-phase static coordinate system; calculating the magnetic flux linkage as well as stator voltages and stator currents of a shaft d and a shaft q under synchronous rotation coordinates; calculating a slip frequency angle and a slip frequency angle velocity; calculating stator currents of the shaft d and the shaft q under the rotation coordinates; calculating active power, reactive power and electromagnetic torque of a stator; calculating a decoupling compensation voltage of a rotor; obtaining a primary component actual value of the rotor current after the rotor currents of the shaft d and the shaft q under the rotation coordinates pass through a band-pass filter and a lead lag link on the basis of a compensation target, obtaining a difference of the primary component actual value and a primary component set value and calculating through a PI (Proportional-Integral) controller to obtain a primary component compensation item; calculating a set value of the current of the rotor shaft d under the rotation coordinate system; obtaining a difference of a rotation speed set value and a rotation angular rotation speed actual value and calculating through the PI to obtain a set value of the current of the rotor shaft q under the rotation coordinate system; calculating to obtain a reference value of the rotor voltages of the shaft d and the shaft q under the rotation coordinate system; and calculating the rotor voltage under the two-phase static coordinate system and generating a switch signal for controlling a power device.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com