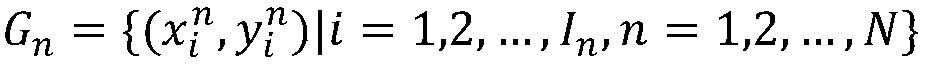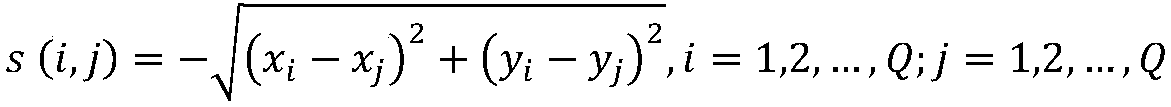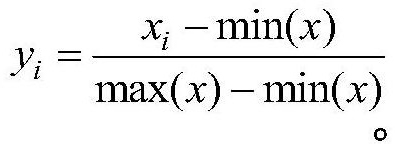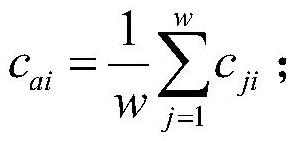Patents
Literature
65 results about "Fixation (visual)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fixation or visual fixation is the maintaining of the visual gaze on a single location. An animal can exhibit visual fixation if they possess a fovea in the anatomy of their eye. The fovea is typically located at the center of the retina and is the point of clearest vision. The species in which fixational eye movement has been found thus far include humans, primates, cats, rabbits, turtles, salamanders, and owls. Regular eye movement alternates between saccades and visual fixations, the notable exception being in smooth pursuit, controlled by a different neural substrate that appears to have developed for hunting prey. The term "fixation" can either be used to refer to the point in time and space of focus or the act of fixating. Fixation, in the act of fixating, is the point between any two saccades, during which the eyes are relatively stationary and virtually all visual input occurs. In the absence of retinal jitter, a laboratory condition known as retinal stabilization, perceptions tend to rapidly fade away. To maintain visibility, the nervous system carries out a mechanism called fixational eye movement, which continuously stimulates neurons in the early visual areas of the brain responding to transient stimuli. There are three categories of fixational eye movements: microsaccades, ocular drifts, and ocular microtremor. Although the existence of these movements has been known since the 1950s, only recently their functions have started to become clear.
Cognitive and Linguistic Assessment Using Eye Tracking
ActiveUS20100092929A1Leveling precisionHealth-index calculationReadingDividing attentionVisual perception
Methods for assessing cognitive and linguistic abilities by tracking and recording the eye movements of a patient in response to predetermined verbal and visual stimuli. The methods incorporate conventional eye-tracking technology to acquire eye-fixation location and duration measures for testing linguistic comprehension, working memory, attention allocation, and the effect of semantic associative priming. Visual stimuli presented in the methods are carefully designed to reduce visually distracting features. Verbal stimuli are carefully designed to control for numerous linguistic features.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
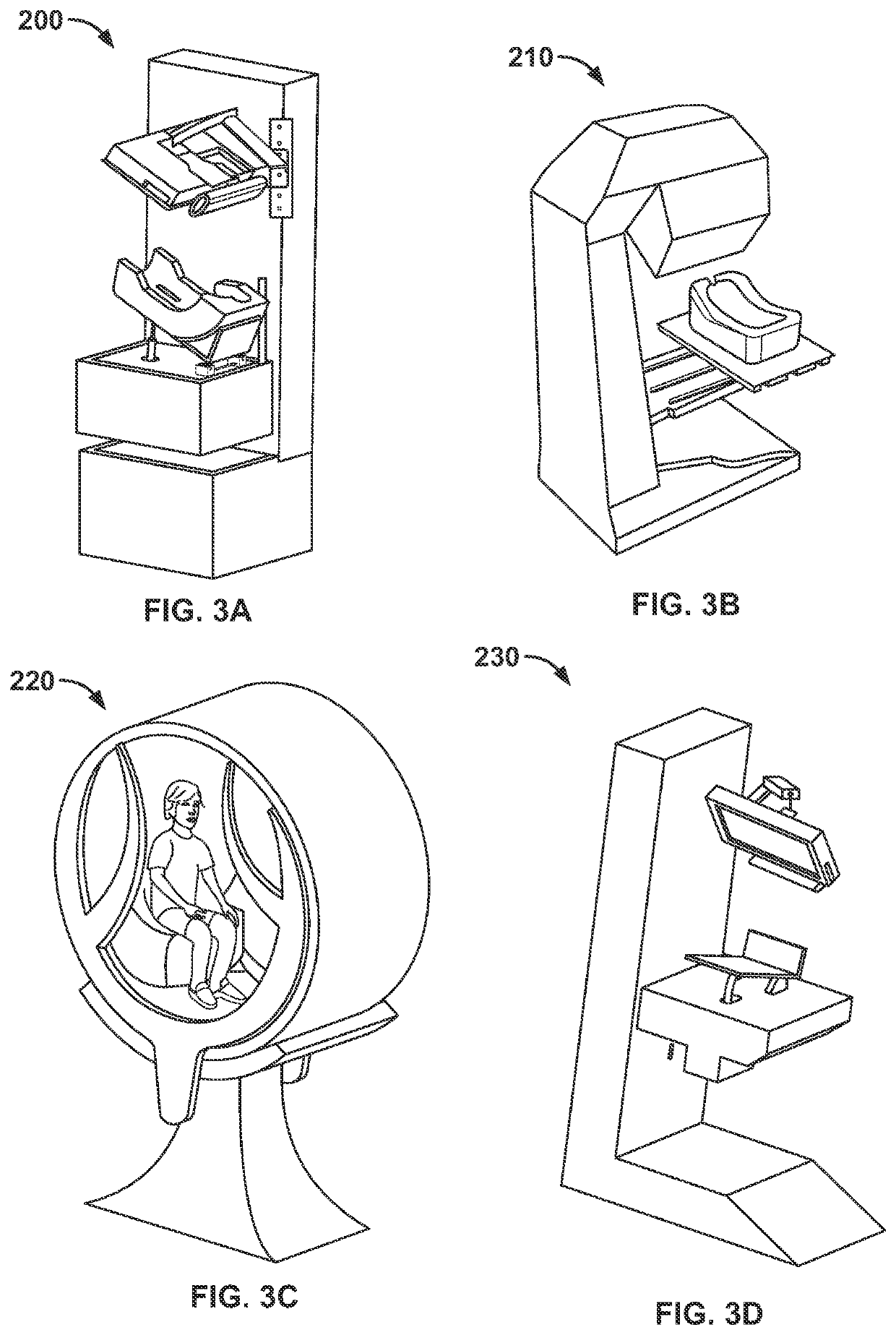
Dynamic fixation stimuli for visual field testing and therapy
Owner:NOVAVISION
Frequency doubling fixation stimuli for visual field testing and therapy
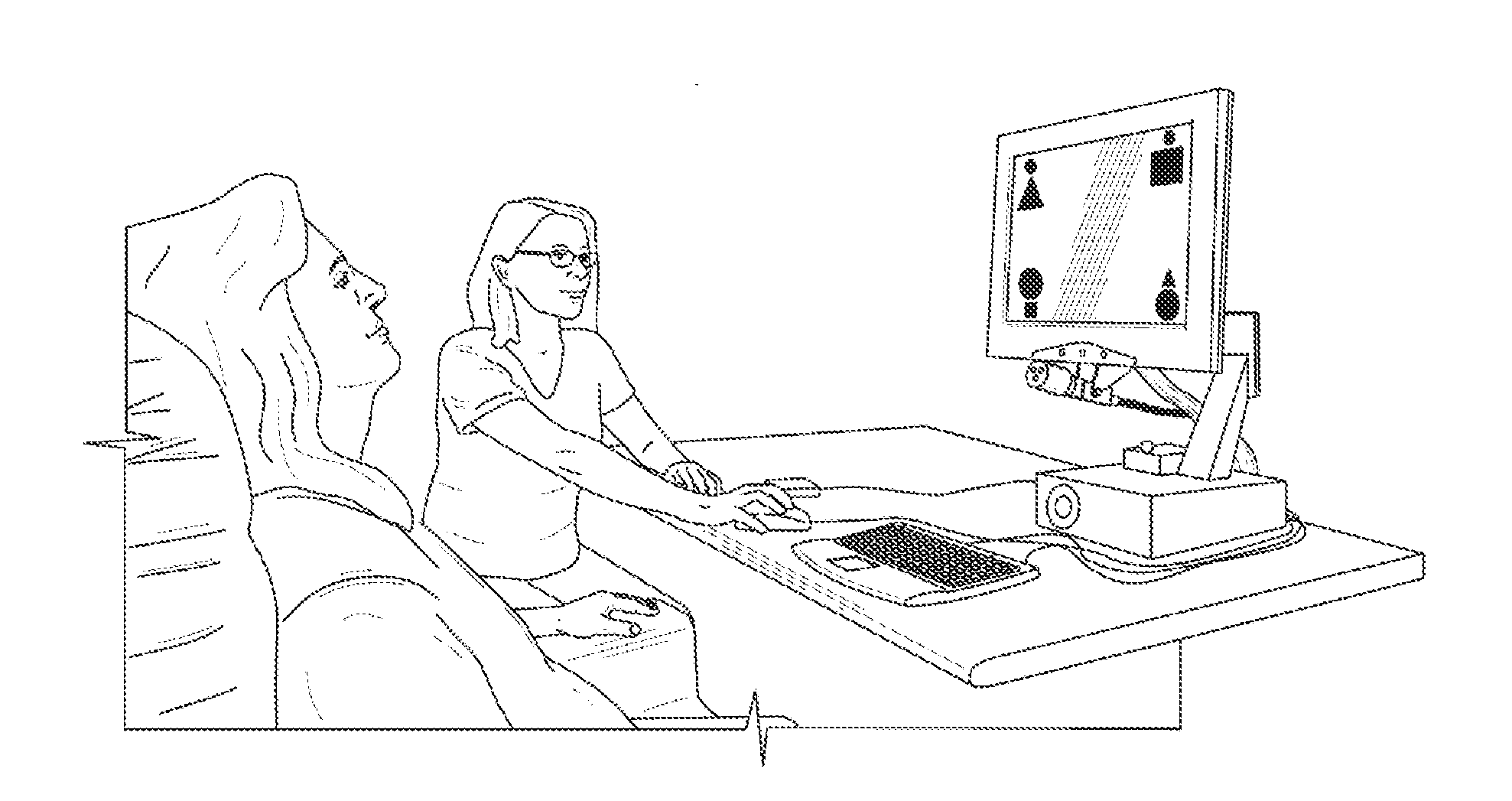
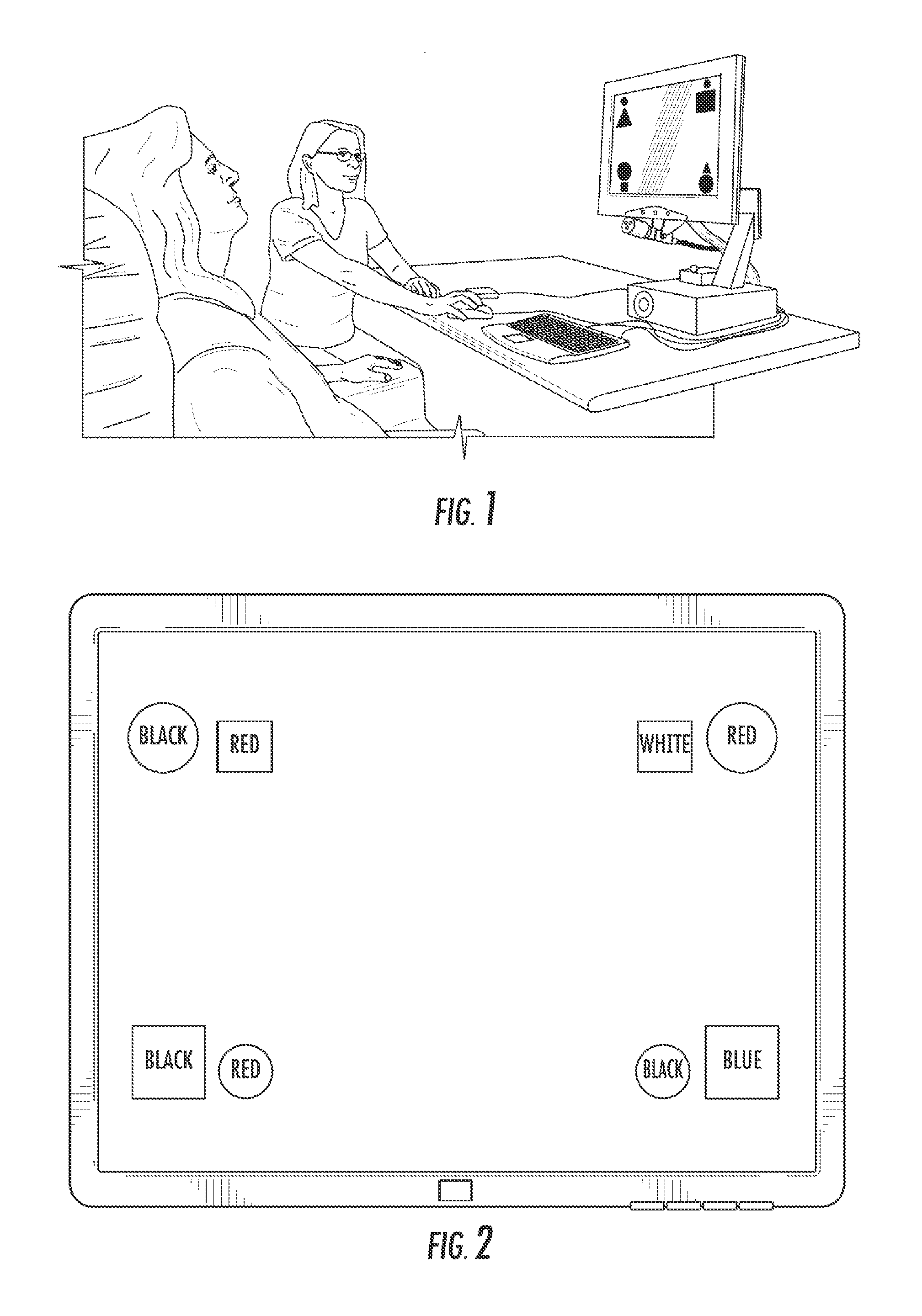
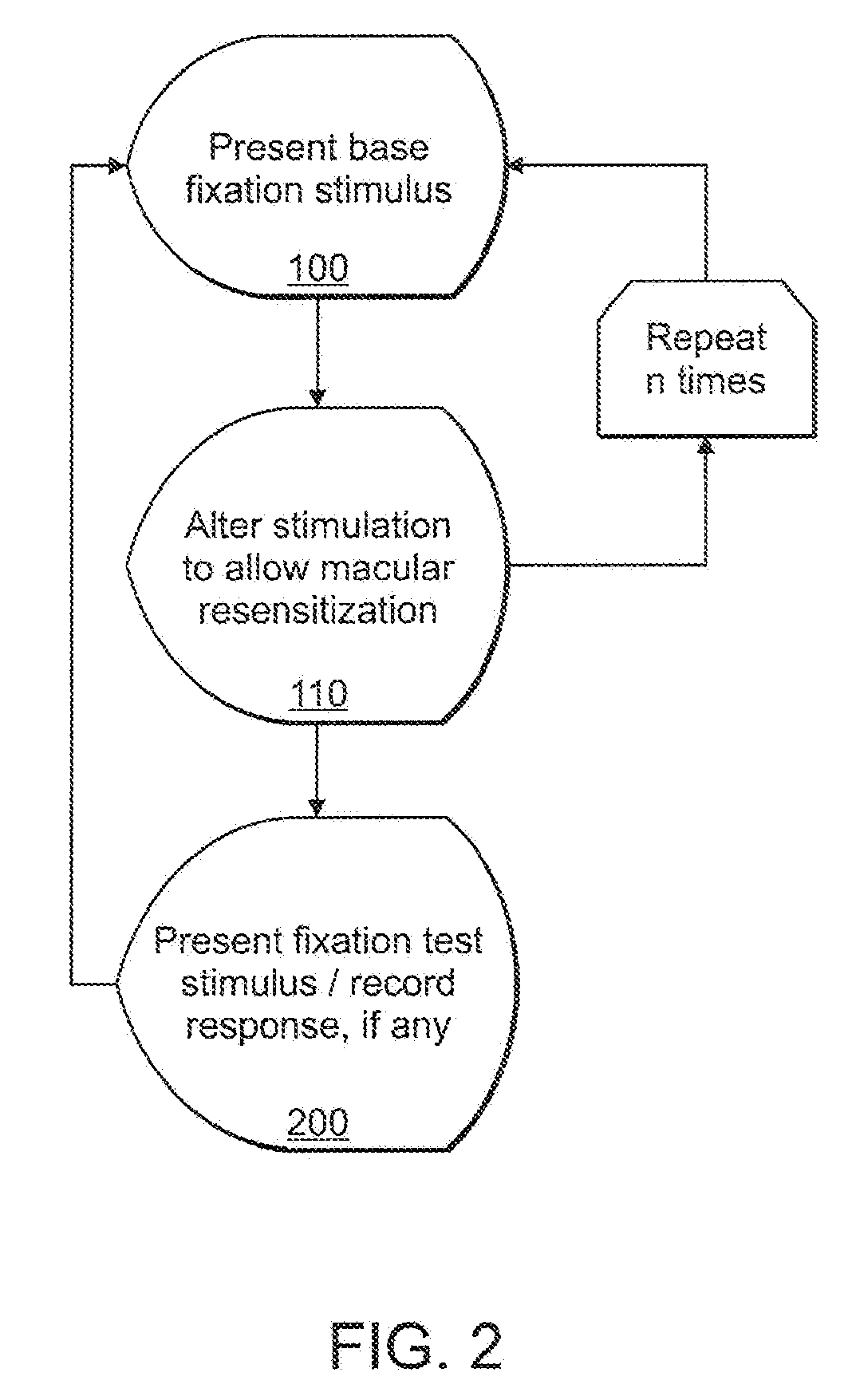
ActiveUS20080024724A1Extended visual fixationProlonged visual fixationEye exercisersEye diagnosticsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationDisplay device
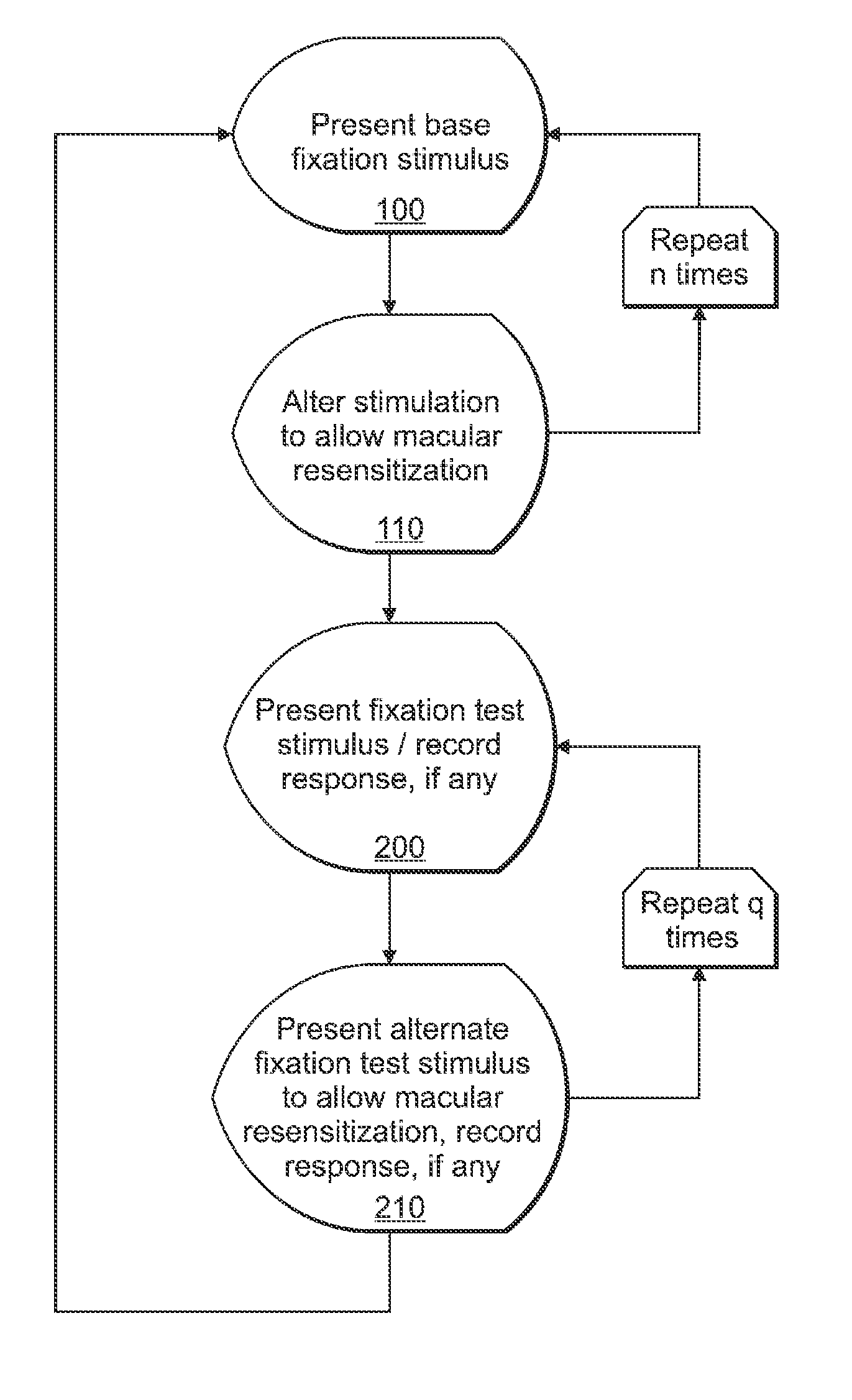
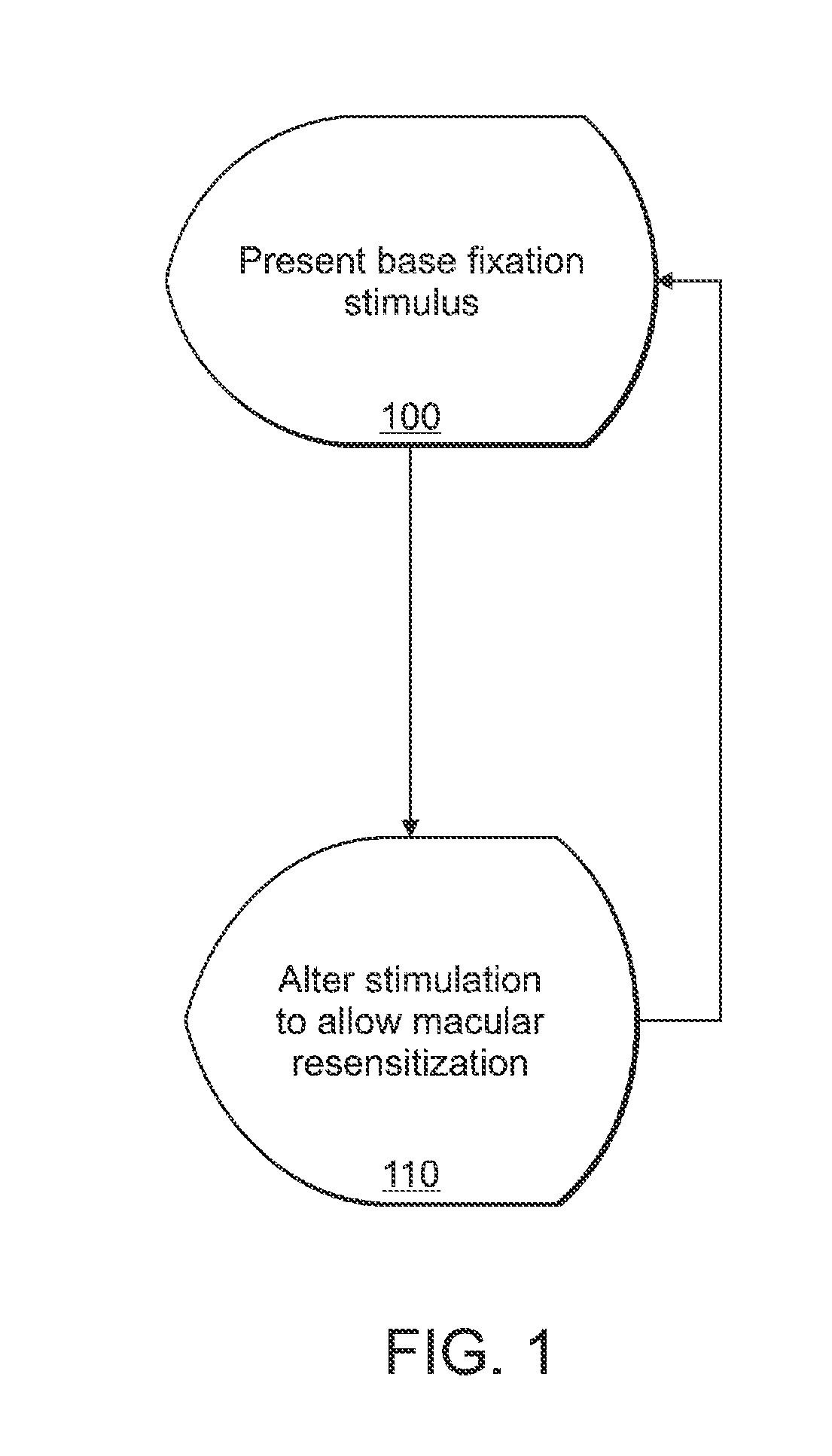
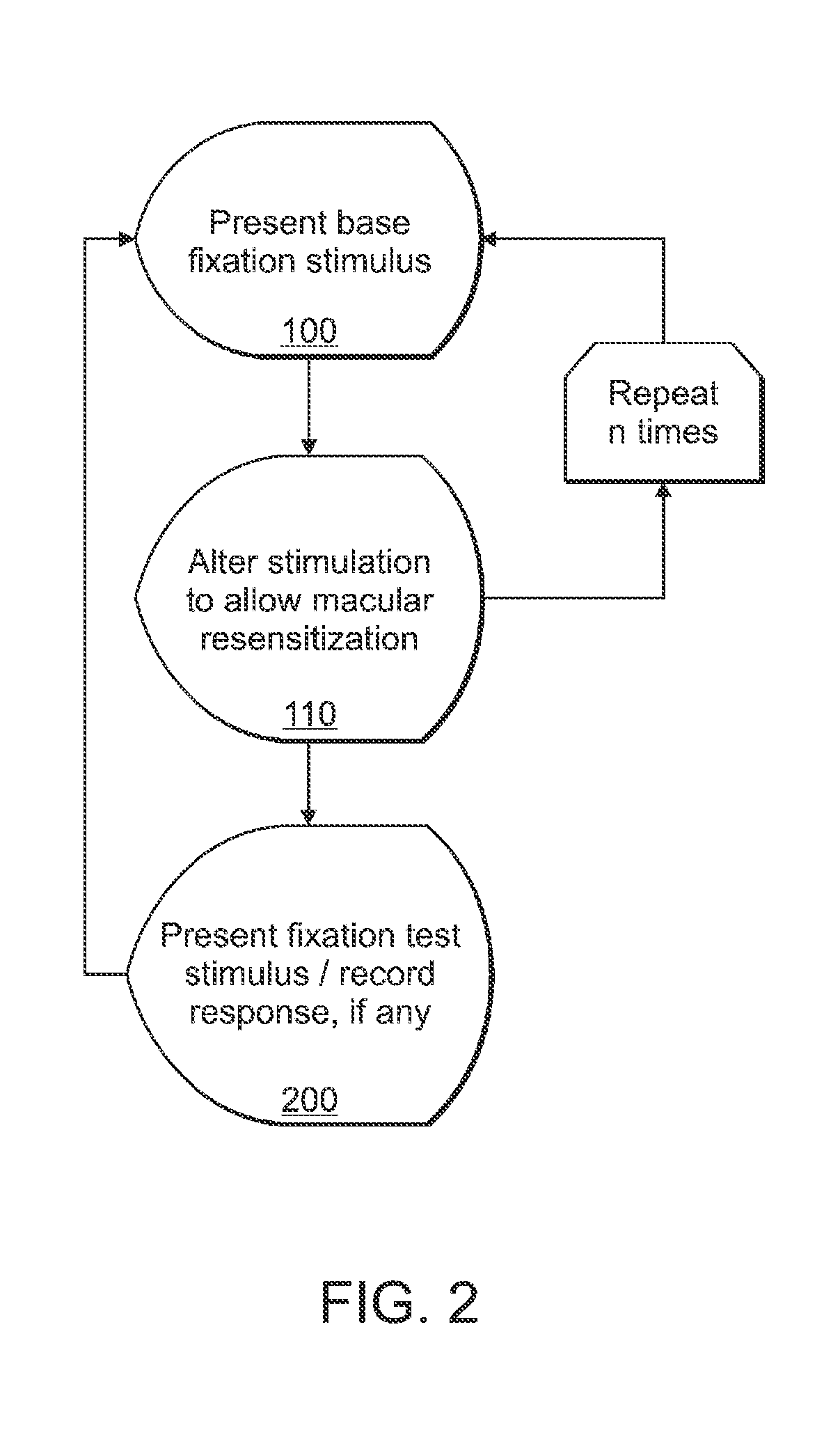
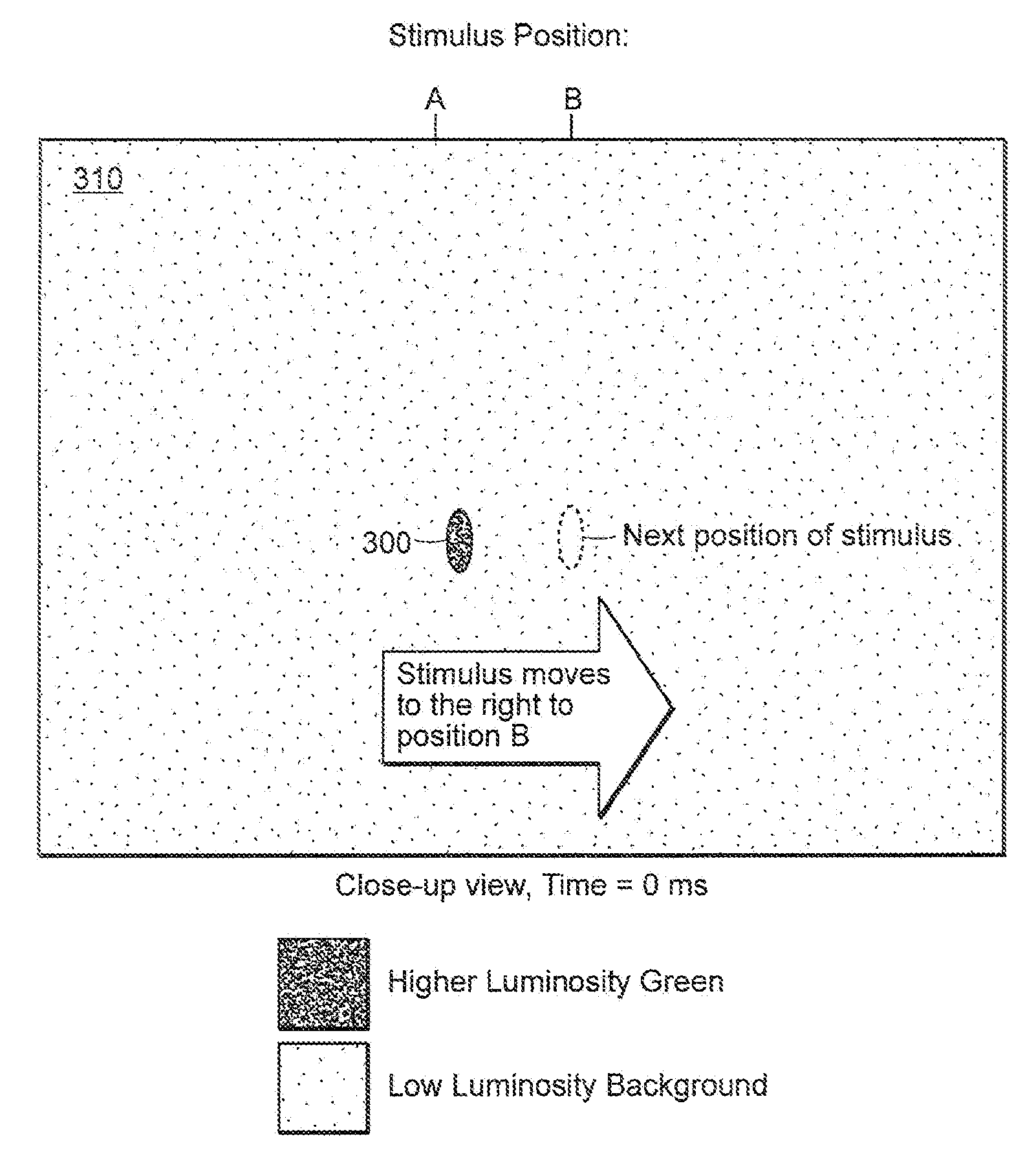
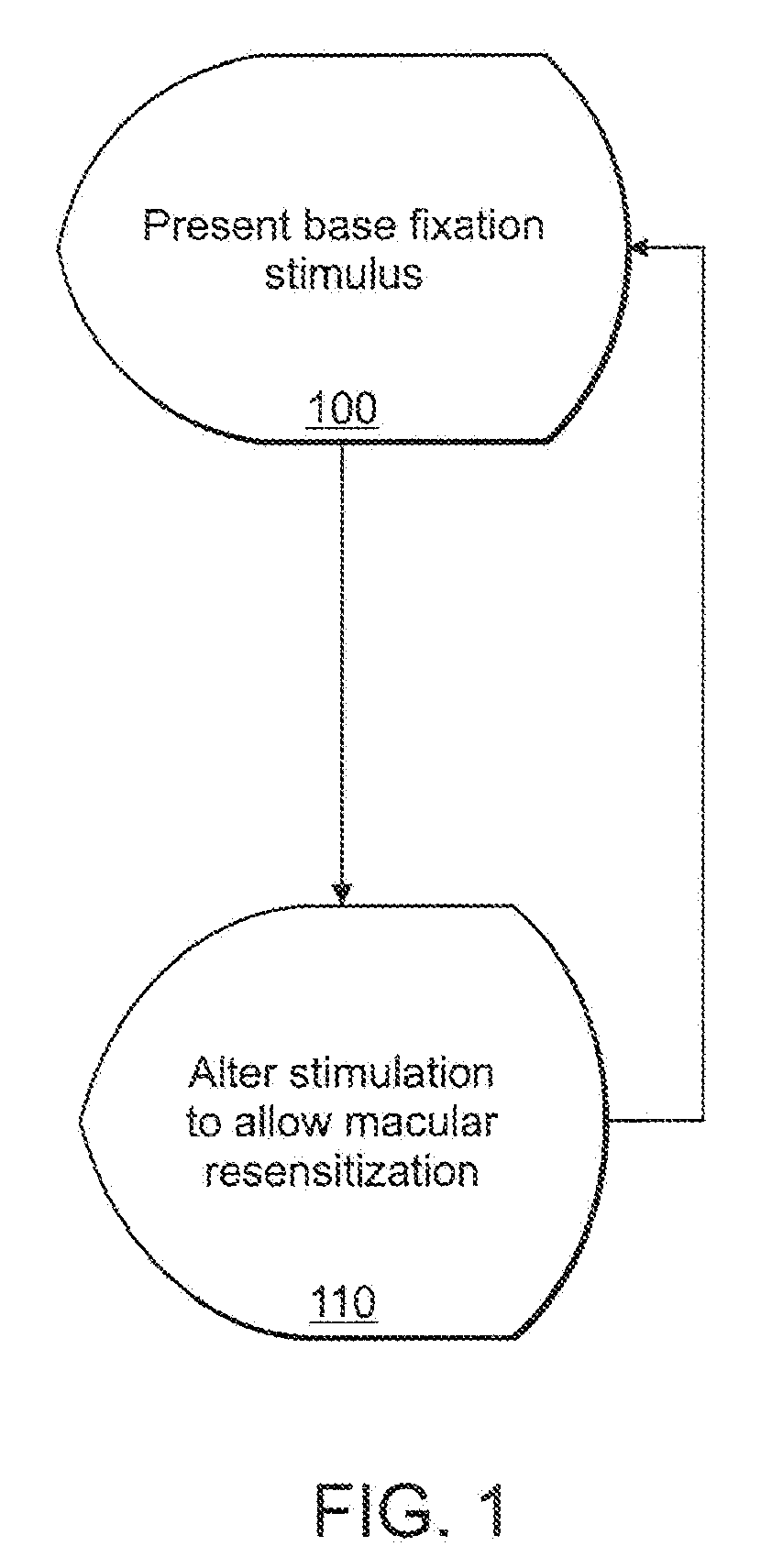
Alteration of a fixation or peripheral stimulus displayed on a computer-driven display allows a human subject to maintain extended visual fixation upon the resulting dynamic stimulus. The fixation is presented upon the display and the stimulus is altered to allow resensitization of the subject's retina, thereby allowing prolonged visual fixation upon the resulting dynamic target. A dynamic stimulus may utilize a frequency doubling illusion.
Owner:NOVAVISION
Automated stereocampimeter and related method for improved measurement of the visual field
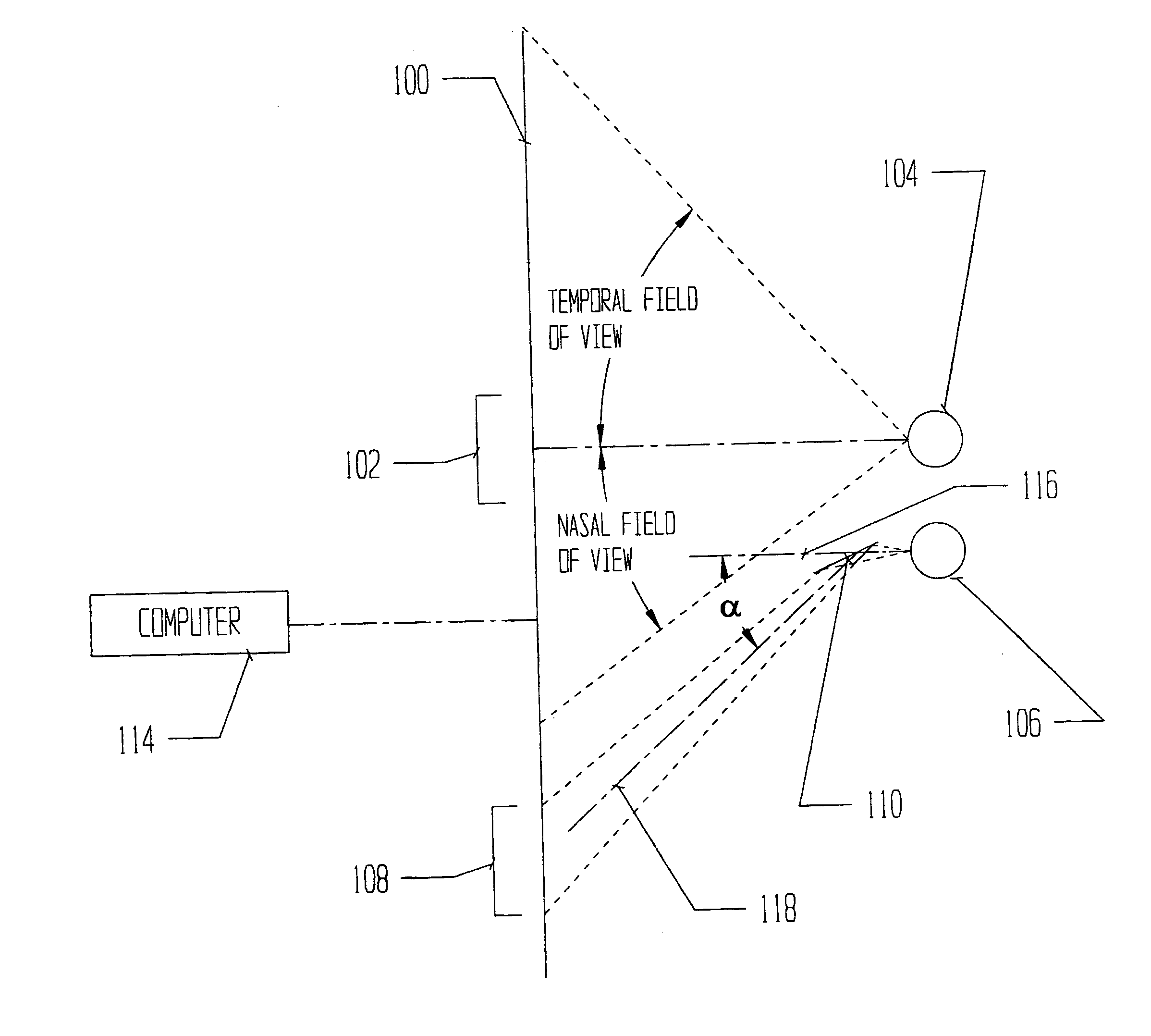
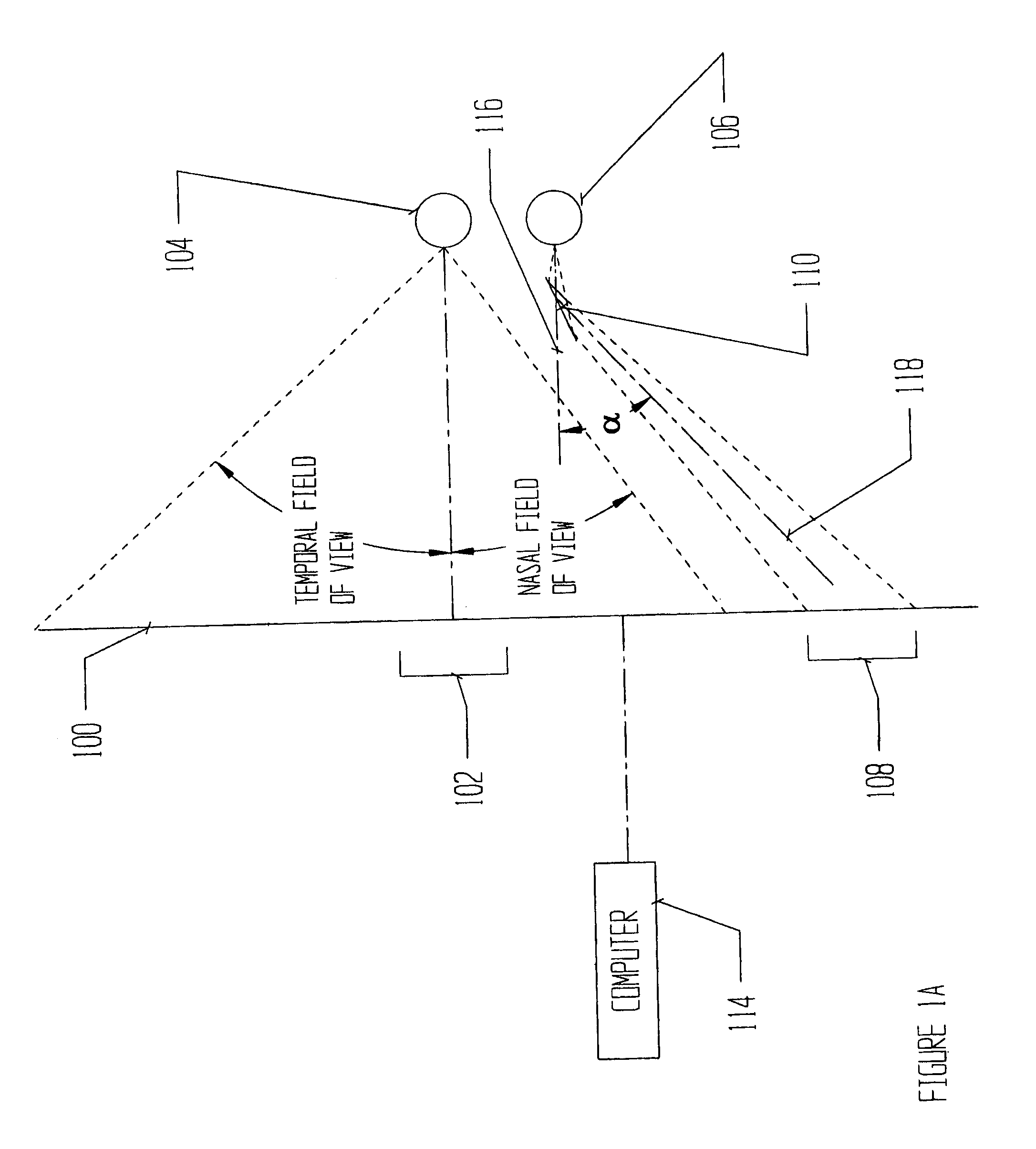
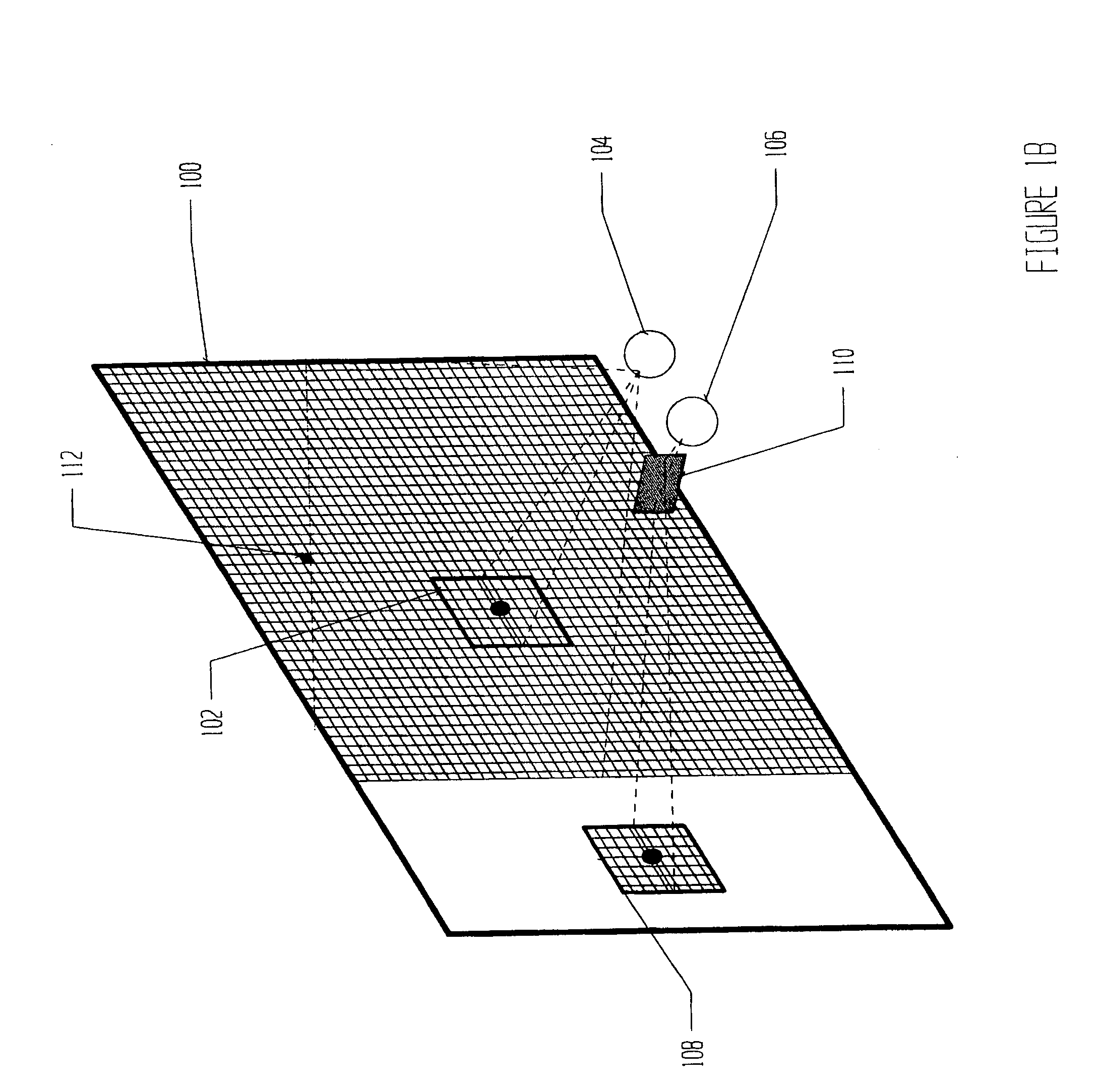
In a method for testing the visual field of a patient especially the central visual field, stereoscopic or binocularly displaced fixation images are presented under computer control to the respective eyes of the patient. In addition, a series of test images viewable by only one of the patient's eyes is generated under the control of the computer. The fixation images, one for each eye, are presented on two separate electronic displays, while the test images may be produced on a third display member different from the electronic displays. The computer is programmed to precisely determine a boundary between points corresponding to unseen test images and points corresponding to seen test images, by automatically testing additional points in a region located about the curve and between points corresponding to unseen test images and points corresponding to seen test images.
Owner:CENTFUSE TECH
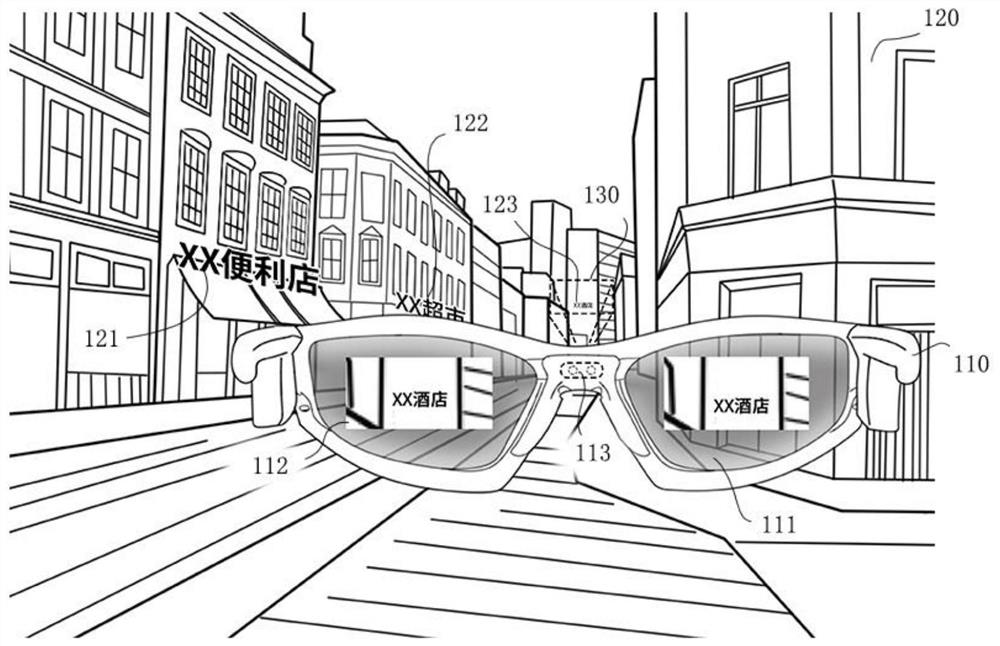
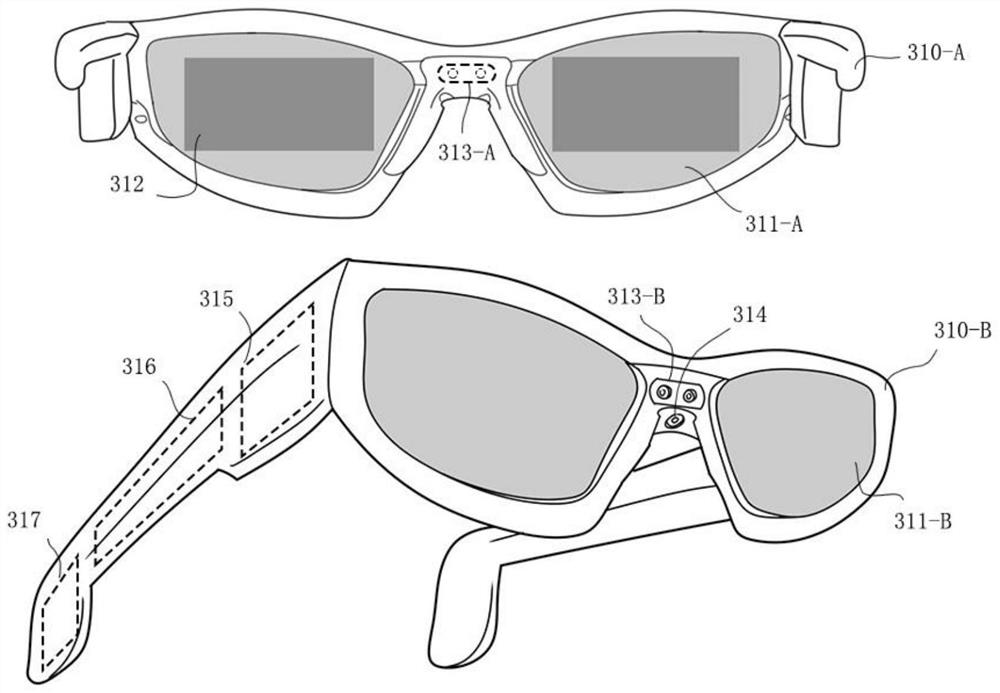
Intelligent adjusting method for preventing holographic images from blocking sight of near-to-eye display equipment
ActiveCN110187855AImprove user experienceResolve interferenceImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFixation pointImagery technique
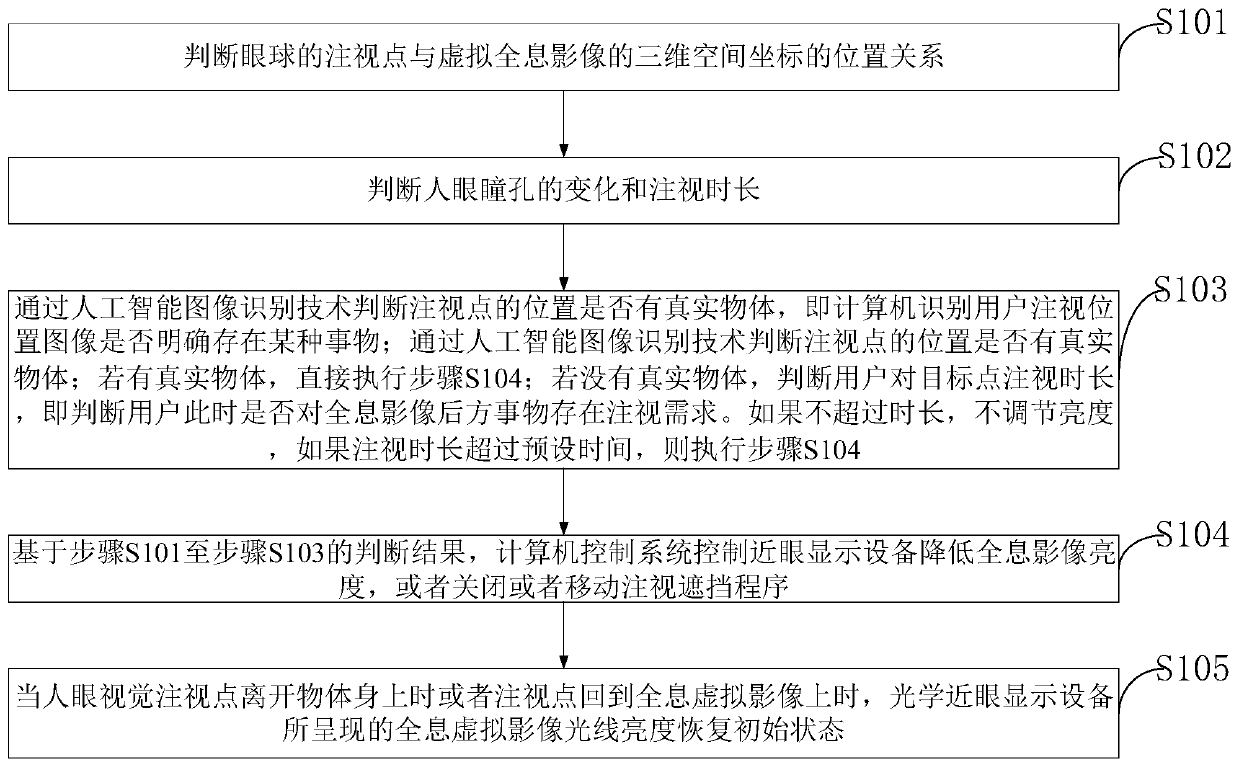
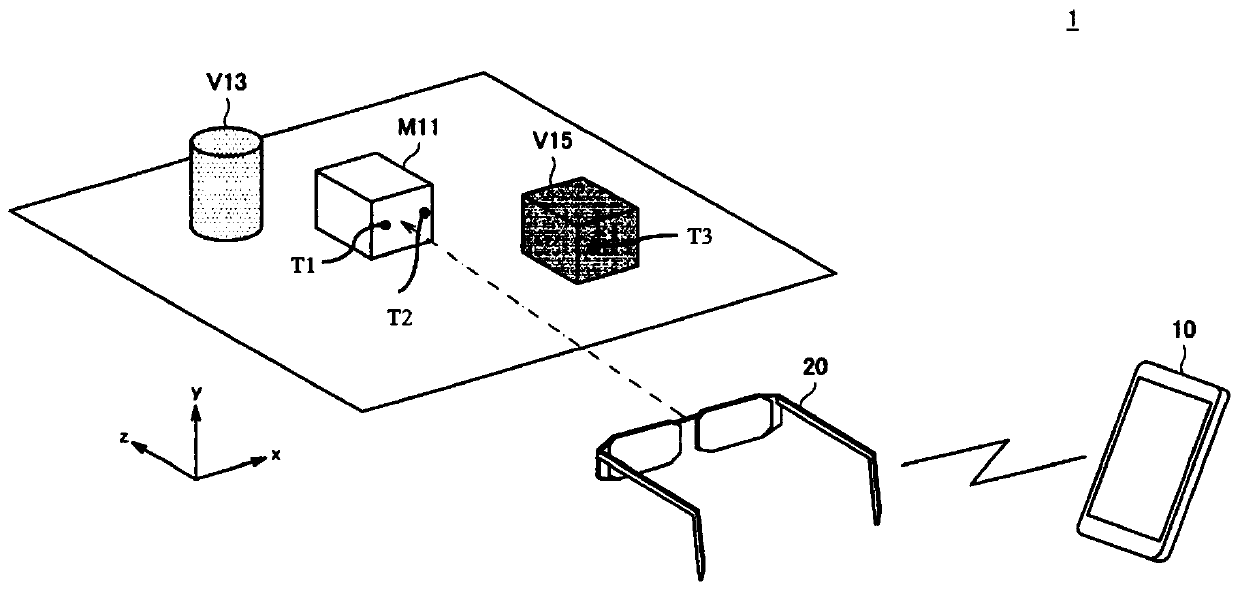
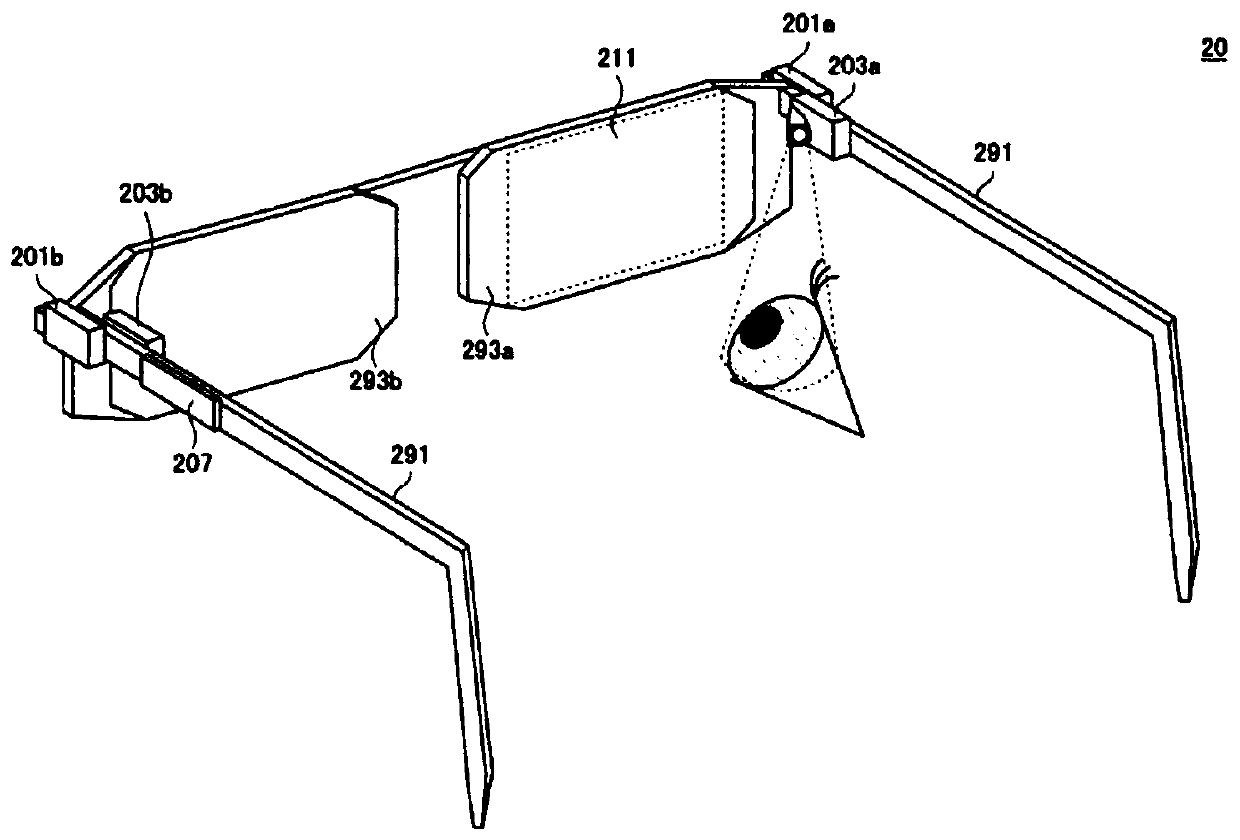
The invention belongs to the technical field of holographic images of intelligent glasses, and discloses an intelligent adjusting method for preventing holographic images from blocking sight of near-to-eye display equipment. The intelligent adjusting method comprises the following steps: judging three-dimensional space coordinates of a fixation points of eyeballs; judging the change condition of pupils of human eyes; judging whether a real object exists at the position of the fixation points or not through an artificial intelligence image recognition technology; based on the judgment result, judging whether the user has a watching requirement on an object behind the holographic image or not at the moment; and if the user is paying attention to the object behind the holographic virtual image, controlling the near-eye display equipment to reduce the brightness of the holographic image or turn off the near-eye display equipment by the computer control system, or moving a watching shielding program, wherein when the visual fixation points of the human eyes leave the body of the object or the fixation points returns to the holographic virtual image, the holographic virtual image state (light brightness and position) presented by the optical near-to-eye display equipment recovers to the initial state. For the intelligent adjusting method for preventing holographic images from blocking sight of near-to-eye display equipment, the problem that the light brightness of the holographic image light source interferes with real object observation of a user is solved.
Owner:幻蝎科技(武汉)有限公司
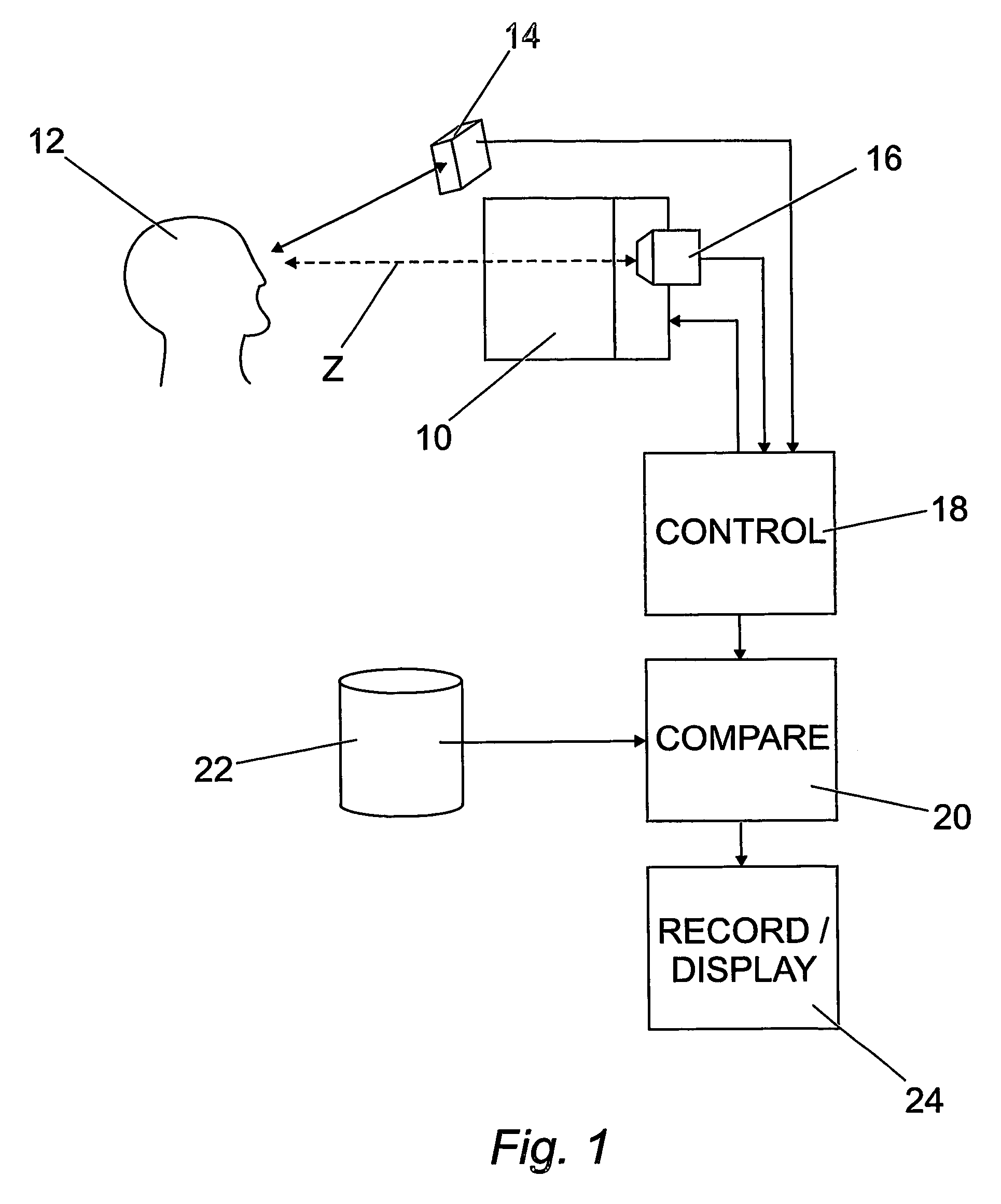
Method and apparatus for the diagnosis of glaucoma and other visual disorders
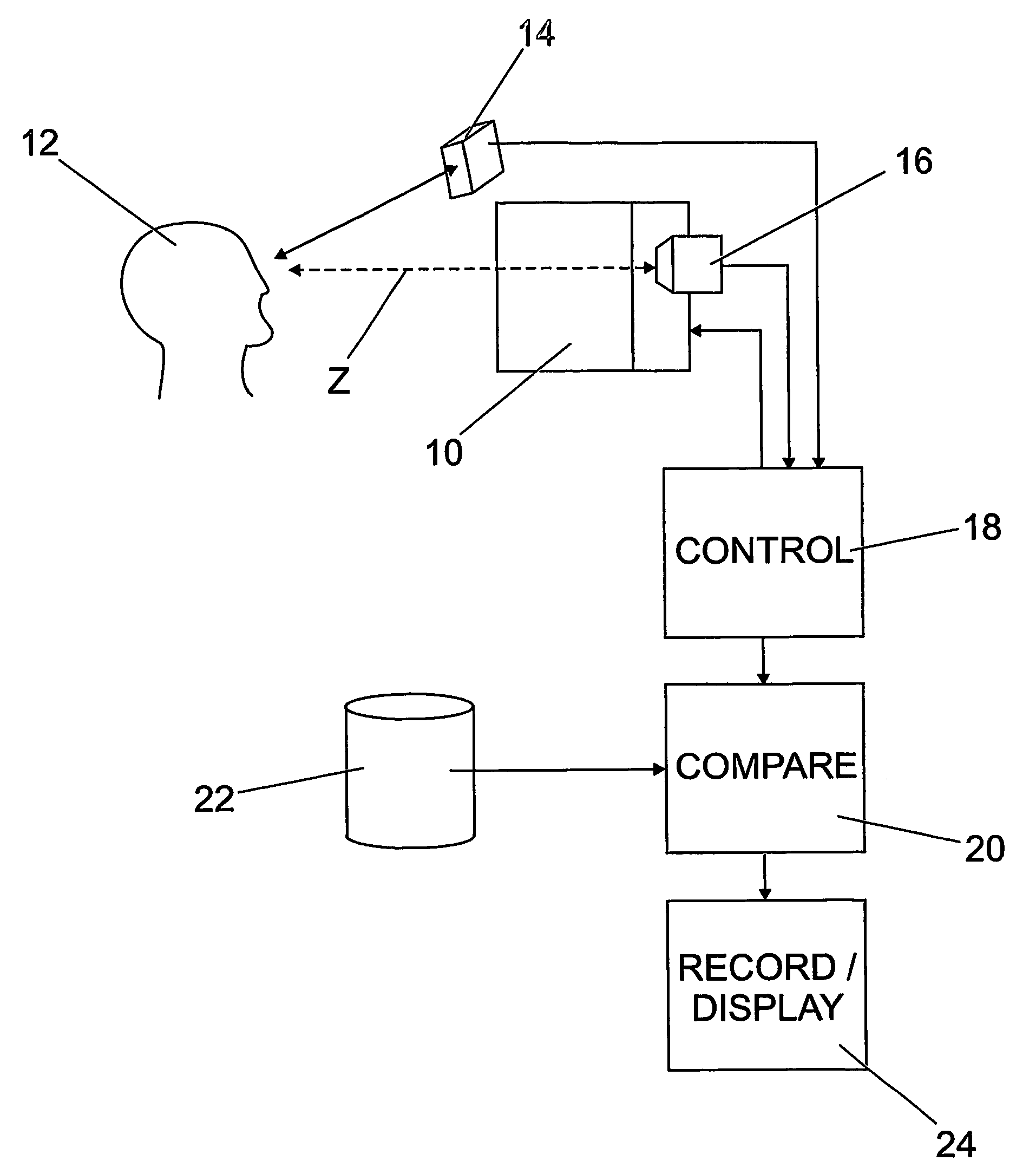
A subject (12) observes an image on a display (10). A control (18) produces a fixation image at a selected position in the display, followed by a stimulus spaced from the fixation image. An eye position sensor (14) detects a saccade movement towards the stimulus. The stimulus is then replaced with a fixation image and the cycle repeated. The time taken to saccade plus the intensity of the stimulus are used to produce a retinal map of field of vision, or to assess other characteristics of the subject.
Owner:MCGRATH JOHN ANDREW MURRAY +1
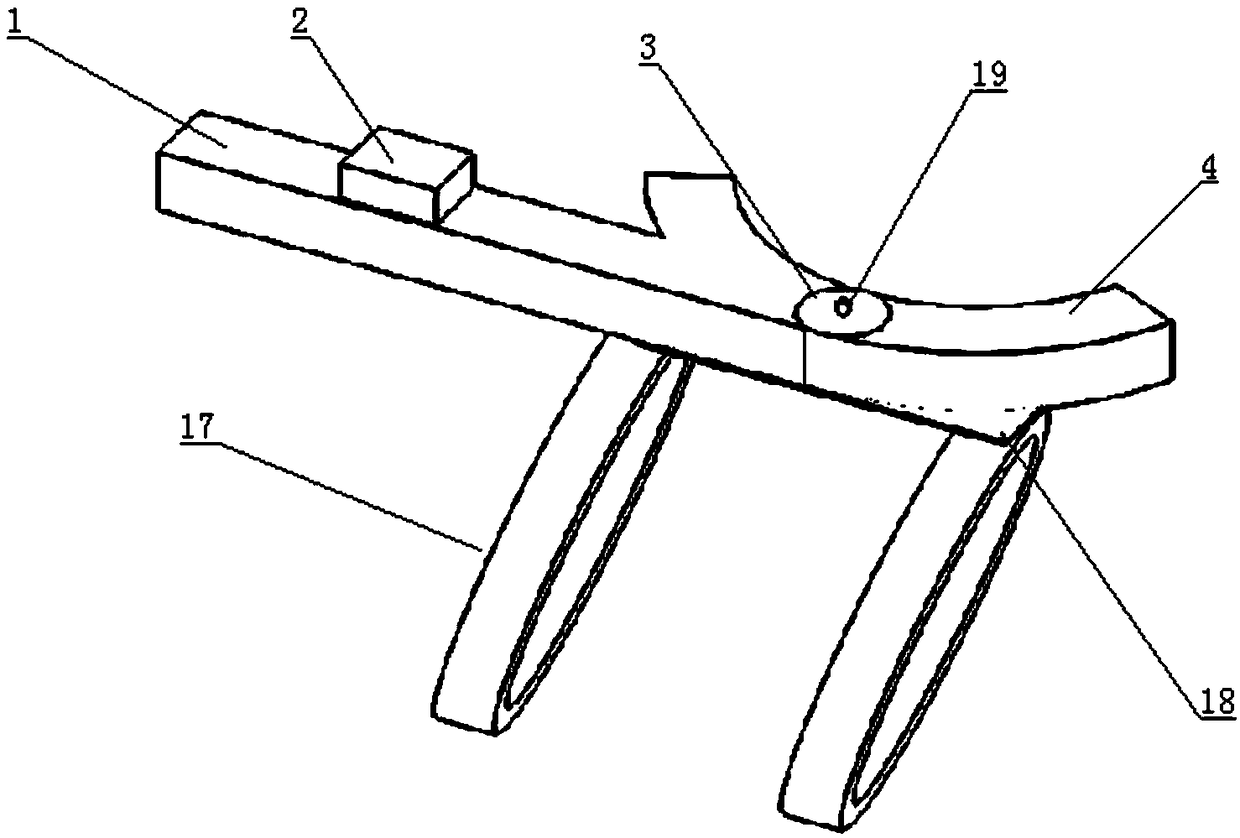
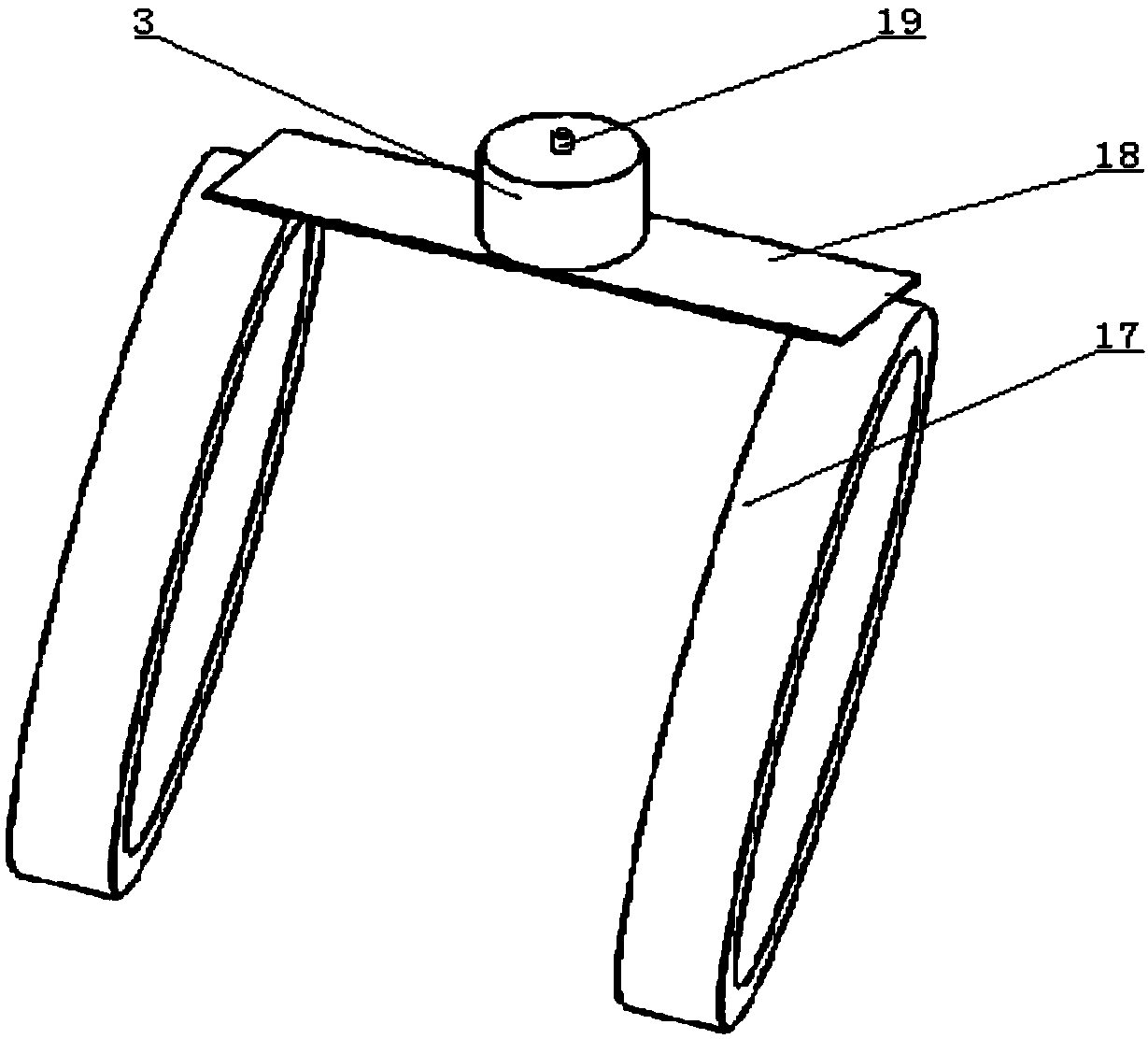
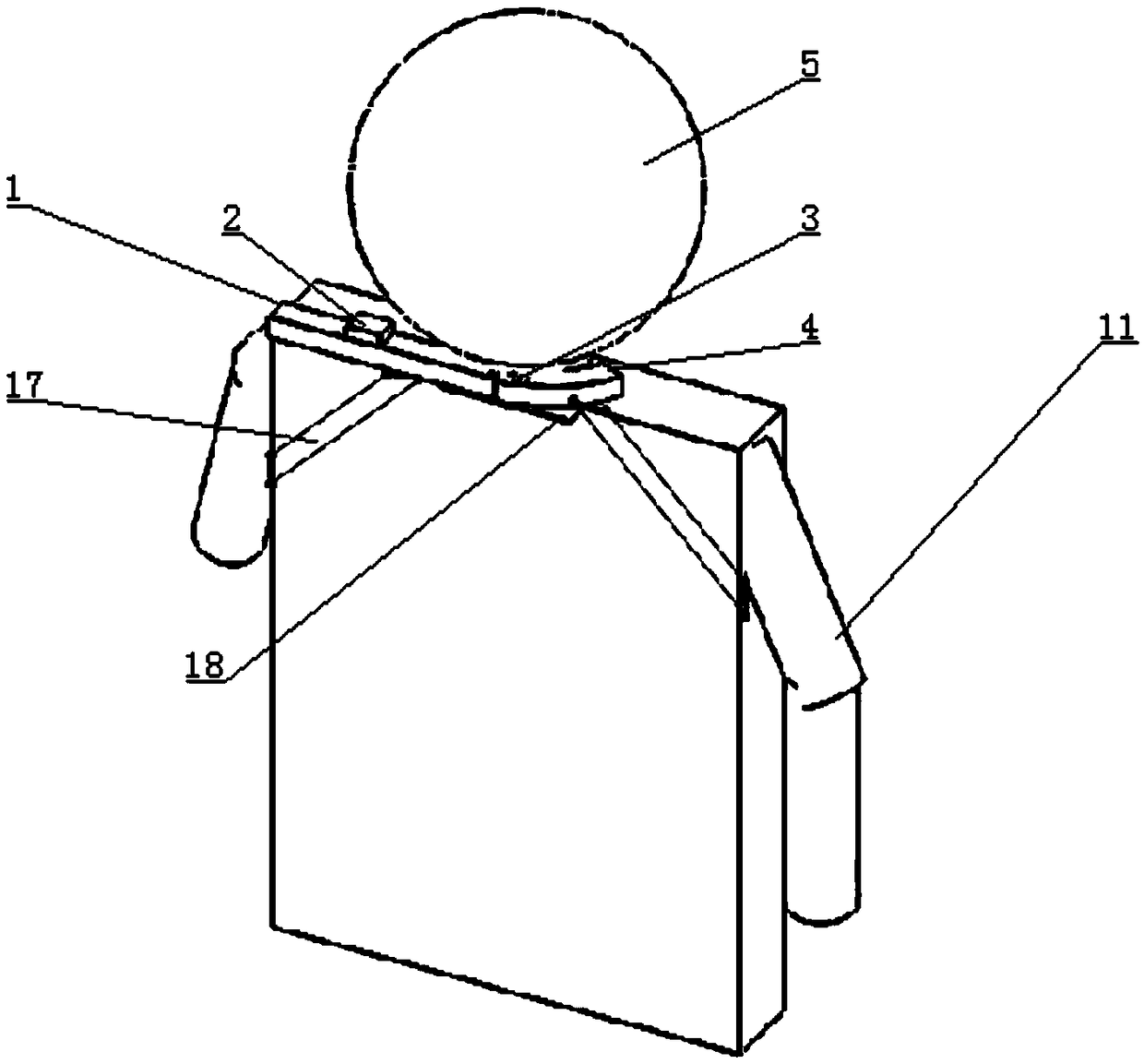
Wearable visual fixation target positioning device and a method thereof
The invention relates to a wearable visual fixation target positioning device and method, the hardware portion includes a shoulder support bracket, Rotating shaft and angle sensor, Neck rotating clasp, vision sensor, microprocessor, for data reception and processing, the device was placed on the subject, First, the angular orientation of the head and neck position is obtained, so that that visualgaze direction is obtain, Synchronize the vision sensor with the visual orientation by turning the snap ring around the neck. so that the vision sensor is synchronized with the front-view direction ofthe person, Two-dimensional machine vision positioning technology and depth information are used to determine the spatial position of the object in the gaze field, and the position information of theobject is obtained through coordinate transformation and visual gaze orientation information fusion, and then the three-dimensional information is converted to the required application coordinates. The device can be used for realizing the visual active selection target of human-machine mixing and determining the spatial coordinate position of the target relative to the body.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
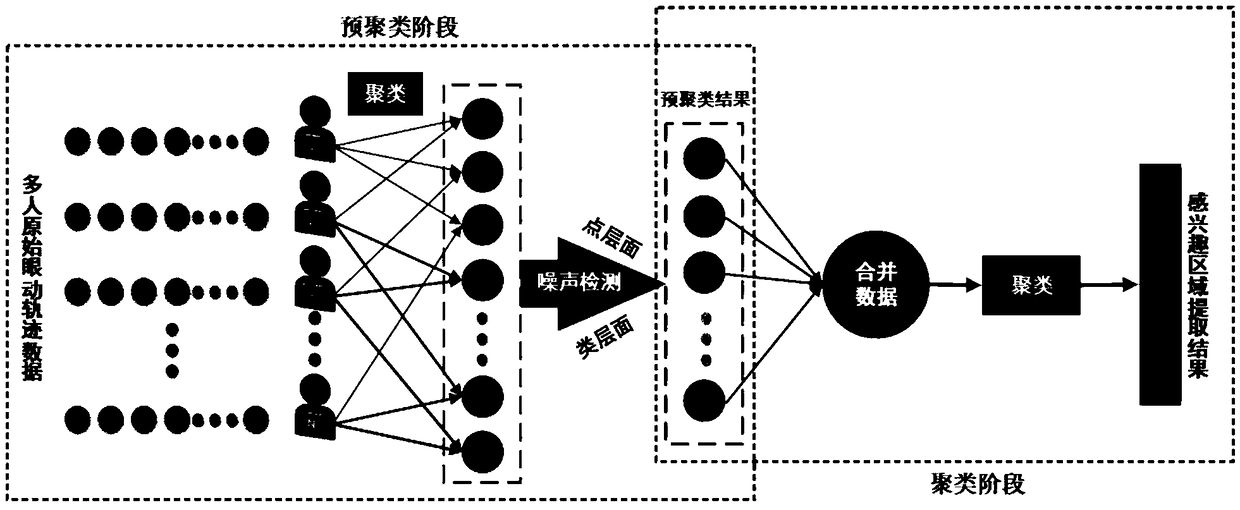
An image region of interest extraction method based on two-step clustering of eye movement data
ActiveCN109255342AConforms to the general visual attention patternAvoid the impact of special circumstancesCharacter and pattern recognitionTwo stepPhases of clinical research
The invention provides an image region of interest extraction method based on two-step clustering of eye movement data, which comprises a pre-clustering stage and a clustering stage. The purpose of pre-clustering is to eliminate the noise points in the eye movement data, input the multi-human eye movement trajectory point data on the test picture, combine the trajectory point data of each two people to cluster, remove the noise points with the recognition standard of the point level and the class level, and retain the eye movement trajectory points belonging to the effective fixation process.The purpose of clustering is to extract ROI from the effective eye-movement trajectory points. With all the effective eye-movement trajectory points as input, the points are firstly clustered, in which each category represents a ROI, the center represents the location of the ROI, and the number of points within the category represents the amount of attention that the region attracts. The inventionanalyzes the multi-person trajectory points through two-step clustering, and the obtained region of interest extraction result is more consistent with the human visual attention mode, and has betterstability and anti-noise interference ability.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Super-resolution image information obtaining method based on vision bionics
InactiveCN104361395AIncreased image detail informationImprove visual effectsComputer simulationsImaging processingBionics
The invention discloses a super-resolution image information obtaining method based on vision bionics, and belongs to the field of image processing. The super-resolution image information obtaining method based on vision bionics is provided through the enlightenment that human eyes can obtain super-resolution image information in the micro-motion mode and through the combination of the human eye fixation eye movement and the super-resolution characteristics. By means of the method, a model for obtaining the super-resolution image information is established, the quantitative relation between the human eye fixation eye movement and the super-resolution image information obtaining is disclosed, and the simulation verification is conducted through actual image data. Image details obtained through the method are greatly increased, the visual effect is obviously improved, and in other words, the super-resolution image information is obtained; the method has application and popularization value.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Head-mounted visual accurate aiming system
ActiveCN111012301ANarrow down the area of interestAccurate locationEye diagnosticsFixation pointMedicine
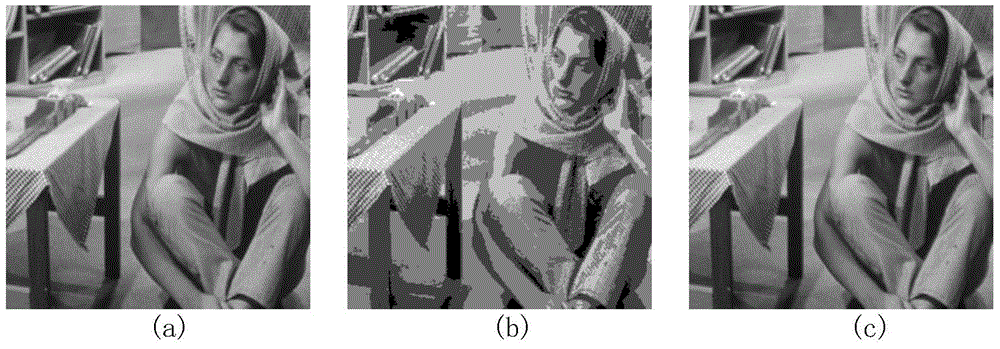
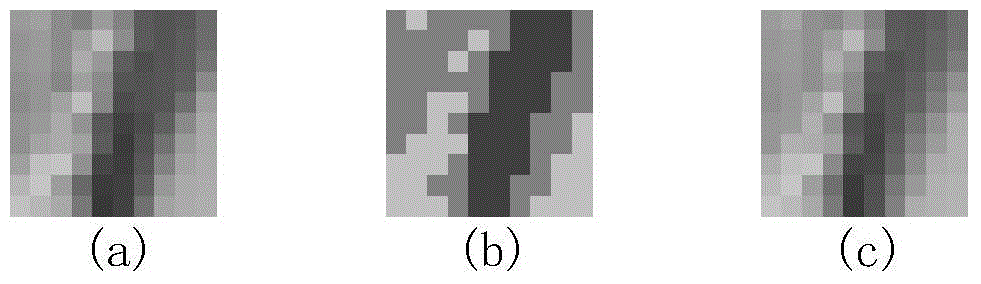
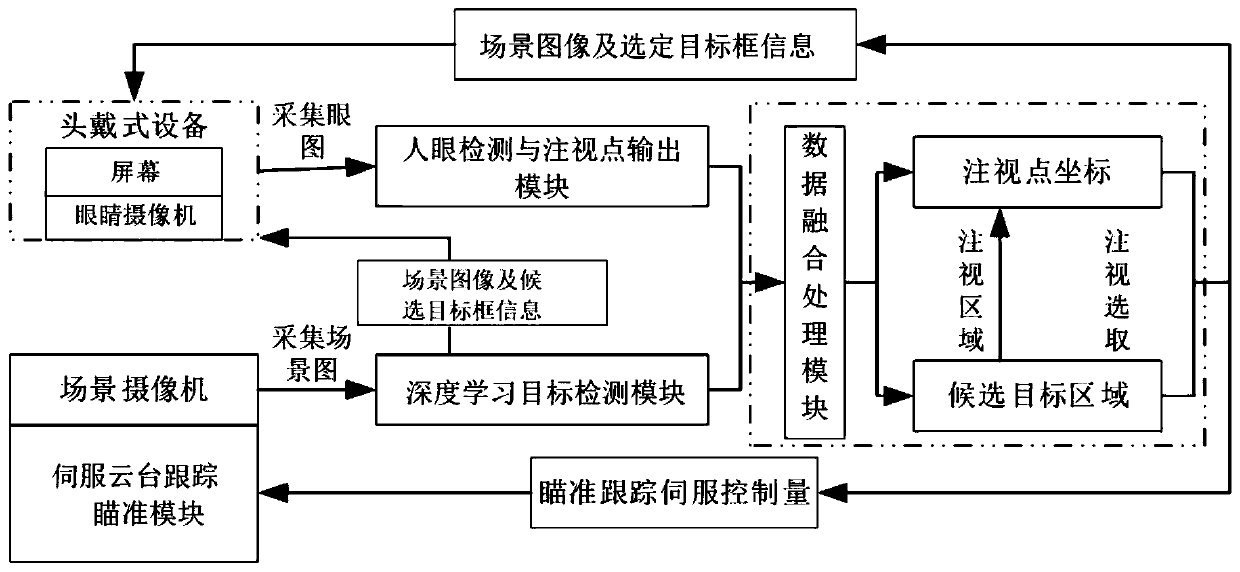
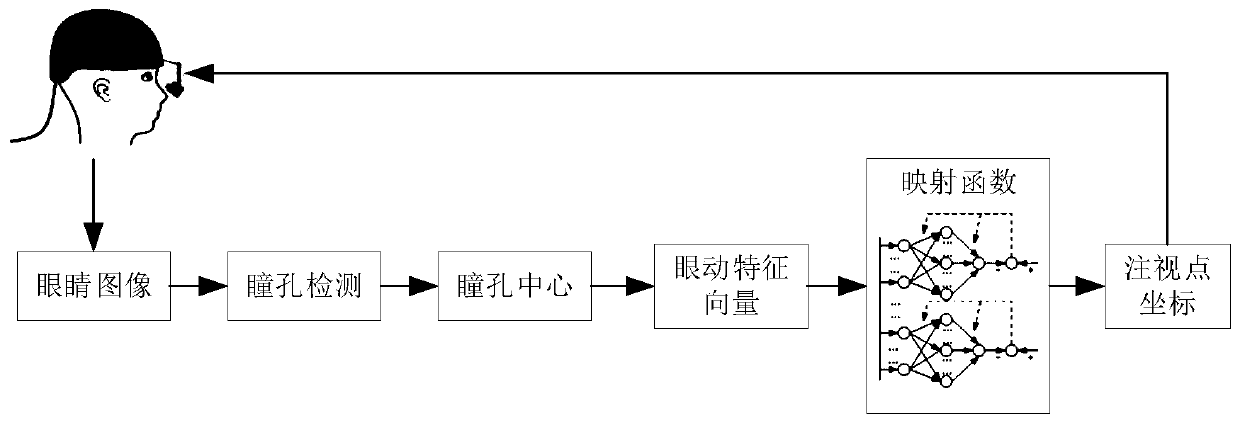
The invention provides a head-mounted visual accurate aiming system. A visual aiming control technology is fused with a target detection method based on deep learning, so that accurate visual aiming can be carried out. The method comprises the following steps: a human eye detection and fixation point output module obtains real-time fixation point coordinates and sends the real-time fixation pointcoordinates to a data fusion processing module; a deep learning target detection module detects targets in a visual field scene image in real time based on a deep learning target detection model obtained through training, marks the detected targets in the visual field scene image in the form of candidate target boxes and then sends the targets to a head-mounted device; meanwhile, the deep learningtarget detection module sends the bounding box information of each candidate target to the data fusion processing module; and the data fusion processing module obtains the position coordinates of a selected target and the aiming tracking servo control quantity for tracking the selected target according to the received fixation point coordinates and the bounding box information of each candidate target, and controls a servo holder to perform aiming tracking on the selected target.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
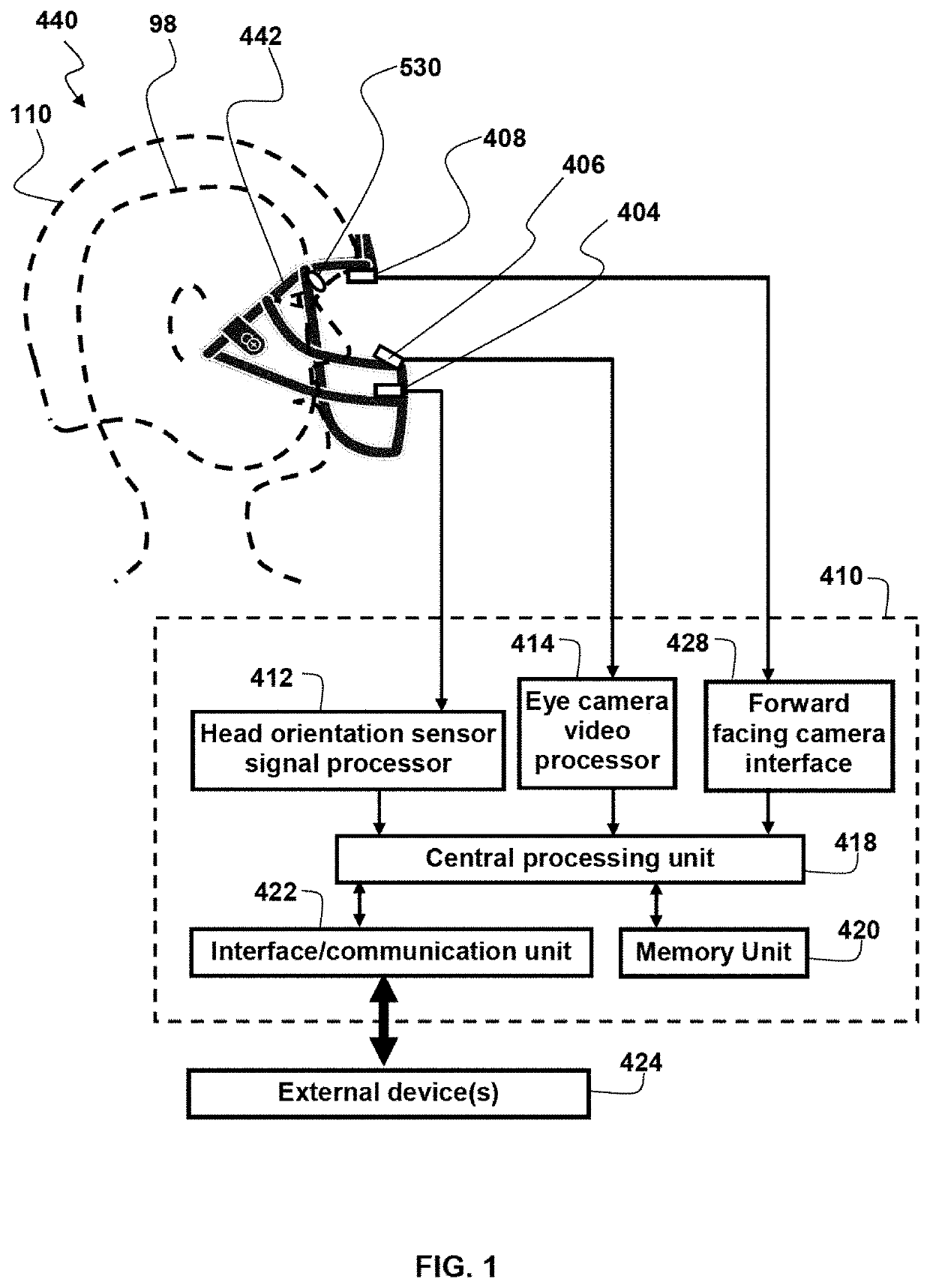
Ocular-performance-based head impact measurement applied to rotationally-centered impact mitigation systems and methods
A system or method for measuring human ocular performance can be implemented using an eye sensor, a head orientation sensor, and an electronic circuit. The device is configured for measuring vestibulo-ocular reflex, pupillometry, saccades, visual pursuit tracking, vergence, eyelid closure, dynamic visual acuity, retinal image stability, foveal fixation stability, focused position of the eyes or visual fixation of the eyes at any given moment and nystagmus. The eye sensor comprises a video camera that senses vertical movement and horizontal movement of at least one eye. The head orientation sensor senses pitch and yaw in the range of frequencies between 0.01 Hertz and 15 Hertz. The system is implemented as part of an impact reduction helmet that comprises an inner frame having interior pads configured to rest against a person's head and one or more shock absorption elements attached between the inner frame and the spherical shell that couple the spherical shell to the inner frame. The spherical shell has a circular geometry, that when viewed horizontally at its horizontal midplane, includes a center point that is the rotational center of the spherical shell. The one or more shock absorption elements are sized to provide greater spacing between the inner frame and the spherical shell at the sides and rear of the spherical shell than at the front of the spherical shell. The one or more shock absorption elements are sized to configure the alignment of the rotational center of the spherical shell with the proximate rotational center of the wearer's head.
Owner:NOVUTZ LLC
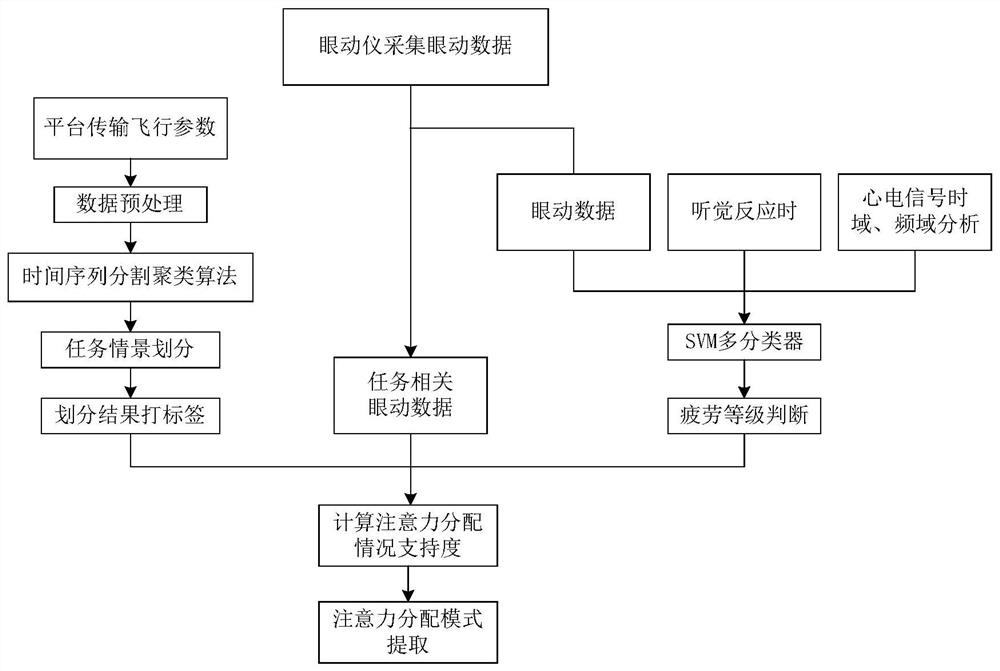
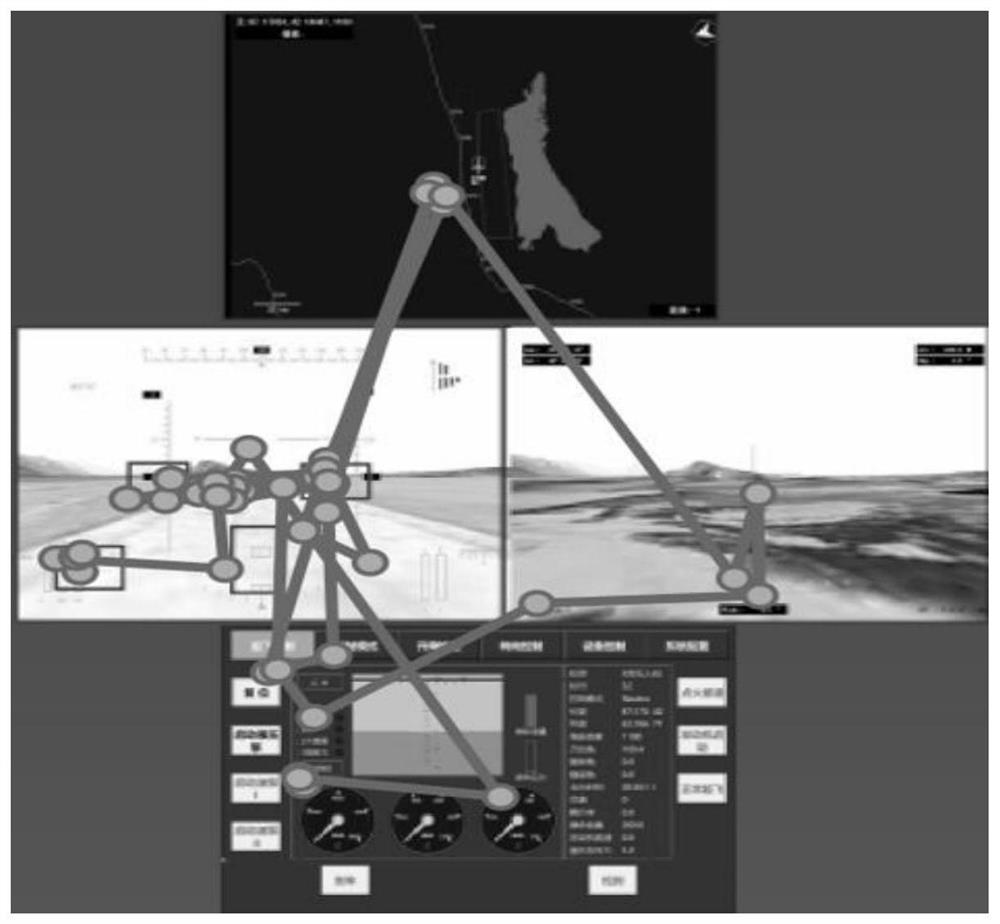
Task scene associated unmanned aerial vehicle pilot visual attention distribution mode extraction method
ActiveCN111951637AImprove accuracyCharacteristic reflectionCosmonautic condition simulationsCharacter and pattern recognitionFixation pointUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses a task scenario associated unmanned aerial vehicle pilot visual attention distribution mode extraction method, which comprises the steps of obtaining pilot attention distribution data through an eye tracker, dividing different task scenarios through flight parameter data, extracting pilot physiological signals to divide fatigue levels of the pilot physiological signals, anddistinguishing pilot attention distribution situations under different task scenes and different fatigue levels. An eye tracker collects eye movement data when a pilot executes a task under the simulation platform; performs segmentation clustering on the flight parameter high-dimensional time sequence, and dividing different task scenes; collects pilot electrocardiogram data for time-frequency domain analysis, and establishes a fatigue state discrimination classifier in combination with eye movement data and auditory response; attention distribution characteristics are represented through thepercentage of fixation points in the region of interest, the number of times of review and the importance degree, the attention distribution situation with the highest support degree is extracted toserve as a mode, the guidance effect can be achieved on control over pilots of the unmanned aerial vehicle, and the important significance is also achieved on optimization of interface setting of an unmanned aerial vehicle control platform.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Prism prescription value acquisition system, acquisition method, acquisition apparatus and program for correcting fixation disparity
A prism prescription value acquisition system that includes a calculation part for numerically transforming a fixation disparity amount (unit: angle), which indicates a degree at which the visual axis is shifted from the central fovea of the retina when a subject conducts visual fixation of a target, into a prism prescription value by multiplying the fixation disparity amount by a coefficient when the fixation disparity amount is within ±4 minutes. Herein, the prism prescription value is calculated according to the following equation: APver=kver*FDver, APhor=khor*FDhor providing that each of coefficients khor and kver satisfies the following conditions: 0.3≦kver≦0.7, 1.4≦khor≦2.0.
Owner:HOYA CORP
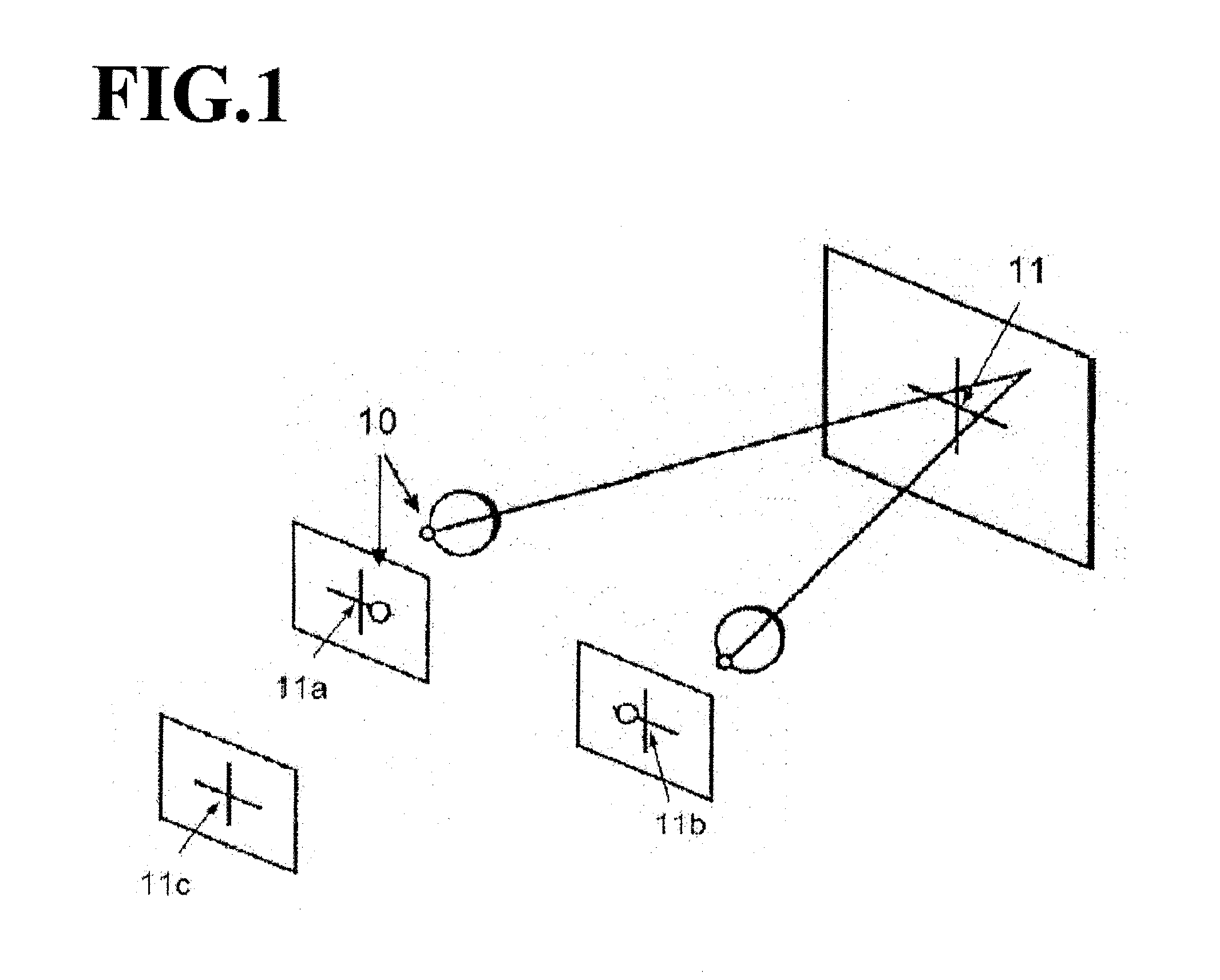
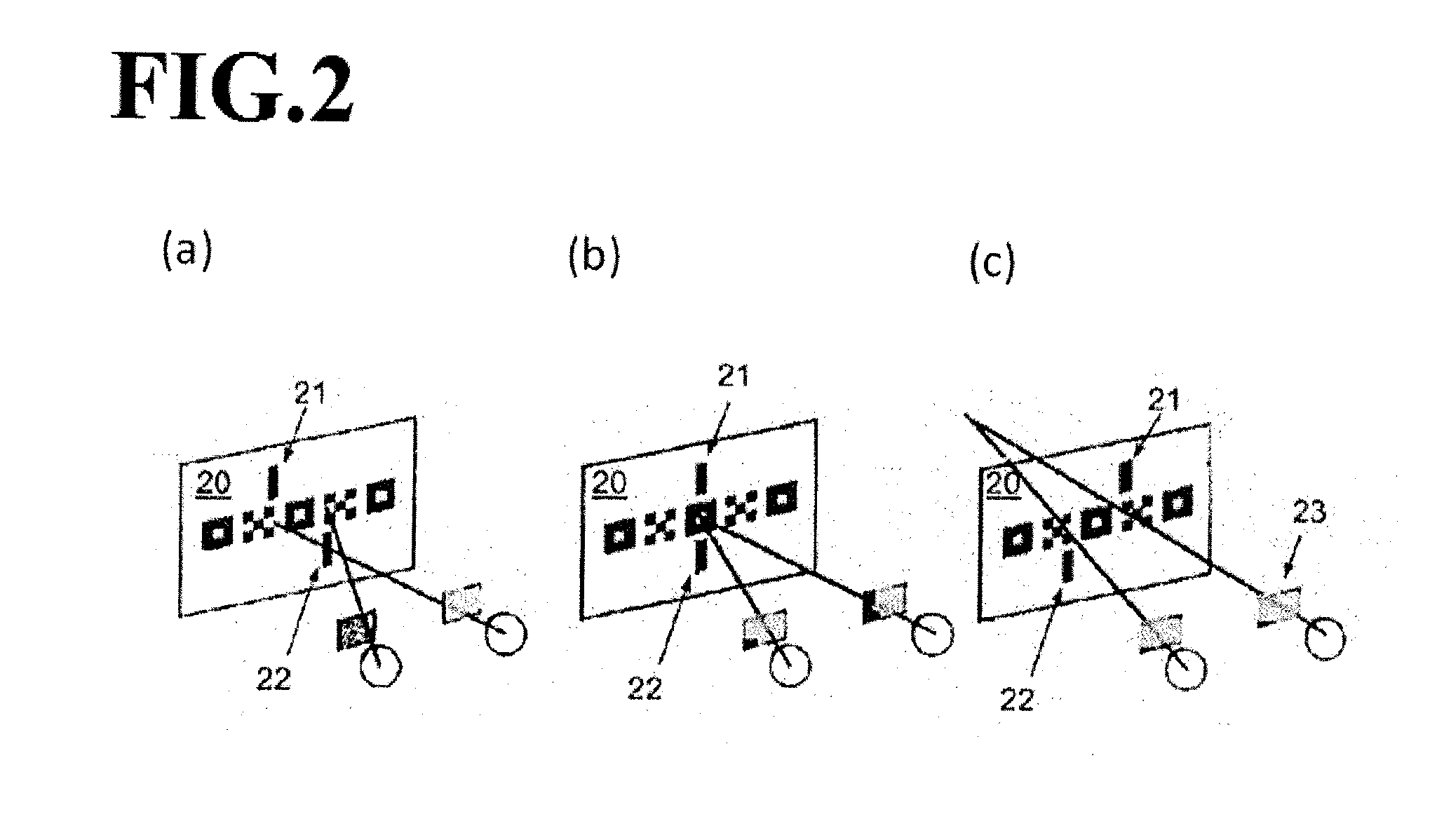
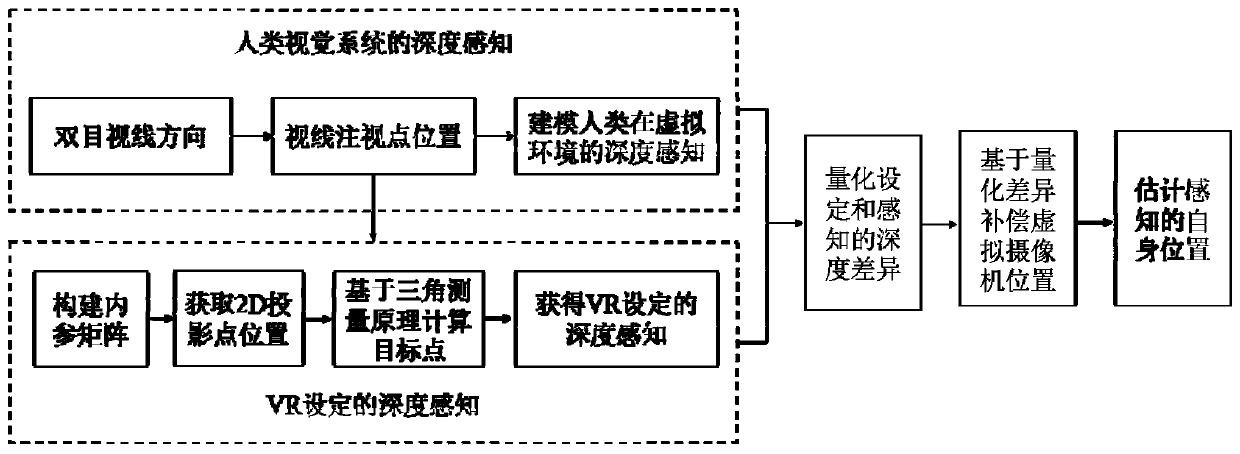
Virtual reality system space positioning method based on depth perception
ActiveCN111007939ATake advantage ofImprove virtual-real interactive experienceInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingFixation pointVisual perception
The invention discloses a virtual reality system space positioning method based on depth perception. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a fixation point perceived by a human vision system istracked through a sight tracking system integrated with VR head-mounted equipment, and a depth perception model when a user fixes at a target object in a virtual environment is constructed based on the fixation point; secondly, an internal reference matrix relative to visual perception is established according to the gaze point so as to calculate the 2D projection positions of the 3D fixation points on the image and calculate the position of the target point gazed by human eyes accordingly; then the depth perception difference set by the VR system and formed the visual system is quantified; and finally the position of the virtual camera is compensated according to the depth perception difference to obtain the position of the virtual camera in the virtual space perceived by the visual system. The deep perception difference of the visual system in the virtual environment is considered, and the perception position of the user in the virtual scene is directly positioned so that the user can interact with the virtual object more accurately, and the interaction experience of the user is improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
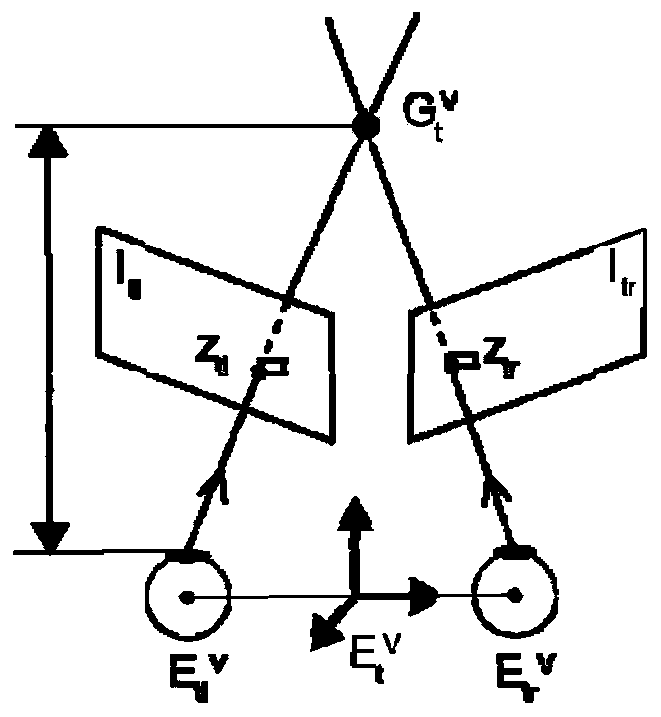
Eyeball tracking method combined with head movement detection and related device
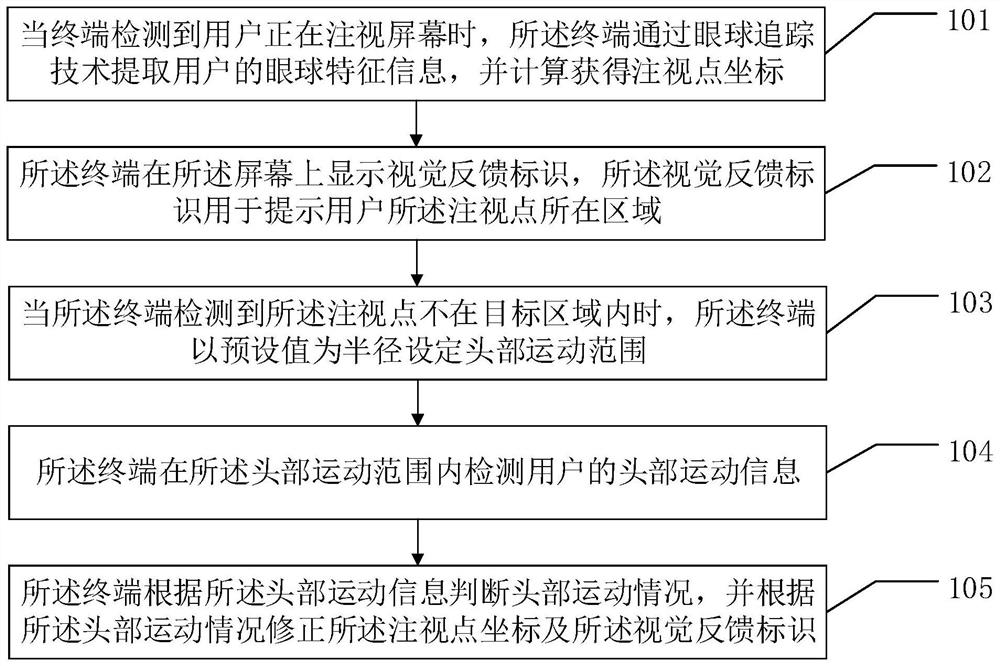
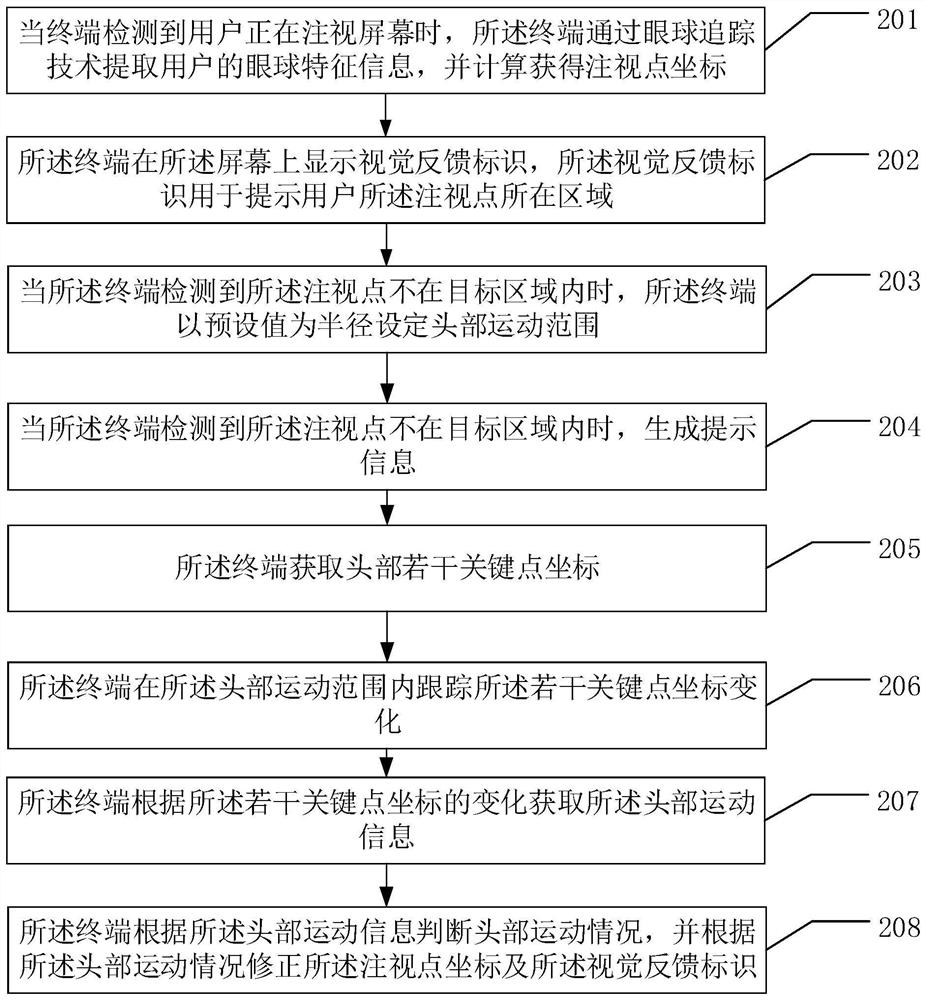
InactiveCN112162627AImprove experienceImproved tracking accuracyInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingHead movementsFixation point
The embodiment of the invention discloses an eyeball tracking method combined with head motion detection and a related device. The eyeball tracking method is used for improving the tracking judgment precision of a terminal on eyeball fixation points of a user. The embodiment of the method comprises the steps that when a terminal detects that a user is watching a screen, the terminal extracts eyeball feature information of the user through an eyeball tracking technology, and coordinates of a watching point are obtained through calculation; the terminal displays a visual feedback identifier on the screen, wherein the visual feedback identifier is used for prompting a user that the fixation point is located in an area; when the terminal detects that the fixation point is not in the target area, the terminal sets a head movement range by taking a preset value as a radius; the terminal detects head movement information of a user within the head movement range; and the terminal judges the head movement condition according to the head movement information, and corrects the fixation point coordinates and the visual feedback identifier according to the head movement condition.
Owner:深圳市修远文化创意有限公司
Human eye wavefront aberration detection system
The invention provides a human eye wavefront aberration detection system, and relates to the technical field of optical imaging. The system comprises a fixation module, an illumination module, a scanning module and a detection module. The fixation module is used for fixing the fixation position of the human eye; the illumination module is used for generating parallel illumination beams; the scanning module is used for adjusting the direction of the parallel illumination beams, so that the parallel illumination beams are sequentially focused on a plurality of sites on the retina of the human eye, and generate a light wavefront signal after being reflected or scattered at each site; the light wavefront signal is returned by the human eye and the scanning module in the same way and then transmitted to the detection module; and the detection module is used for obtaining a point array distributed discrete spot map according to the light wavefront signal, the point array distributed discrete spot map is used for obtaining wavefront aberration information of the human eye, and the wavefront aberration information is used for establishing a retina refractive topographic map. According to the human eye wavefront aberration detection system, the detection efficiency of the refractive state and the optical performance of the human eye at different visual angles can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN BAY LAB
Determination method of emotion processing tendency and related product
ActiveCN112535479ASure objectiveAccurately determineDiagnostic signal processingSensorsFixation pointPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The embodiment of the invention provides a determination method of emotion processing tendency and a related product. The method comprises the steps that visual stimulation is presented, wherein the visual stimulation comprises positive emotion stimulation and negative emotion stimulation at the same time; a fixation point of eyes of a test target within a first time threshold value after the testtarget receives the visual stimulation and fixation duration of the fixation point are acquired; and the emotion processing tendency of the test target is determined according to the fixation point and the fixation duration. According to the method and the product, a stimulation paradigm presented by the positive emotion stimulation and the negative emotion stimulation at the same time is combined with an eye movement tracking technology, therefore, the emotion processing tendency of an individual can be objectively and accurately determined, and the efficiency of determining the emotion processing tendency of the individual is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Shading plate assembly, control method and control device thereof and vehicle
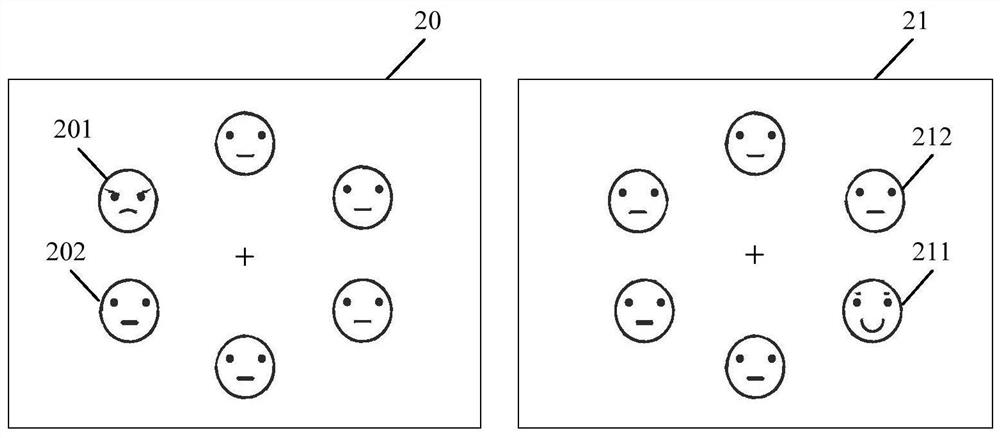
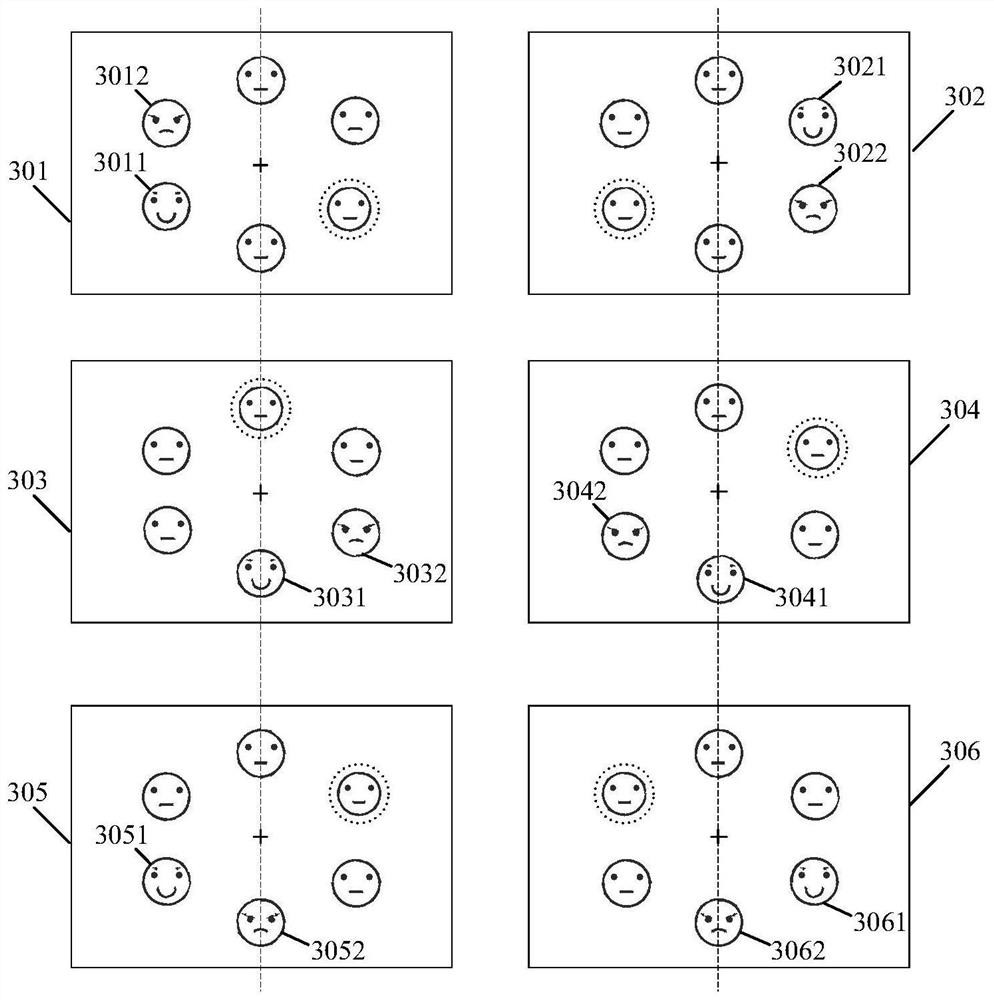
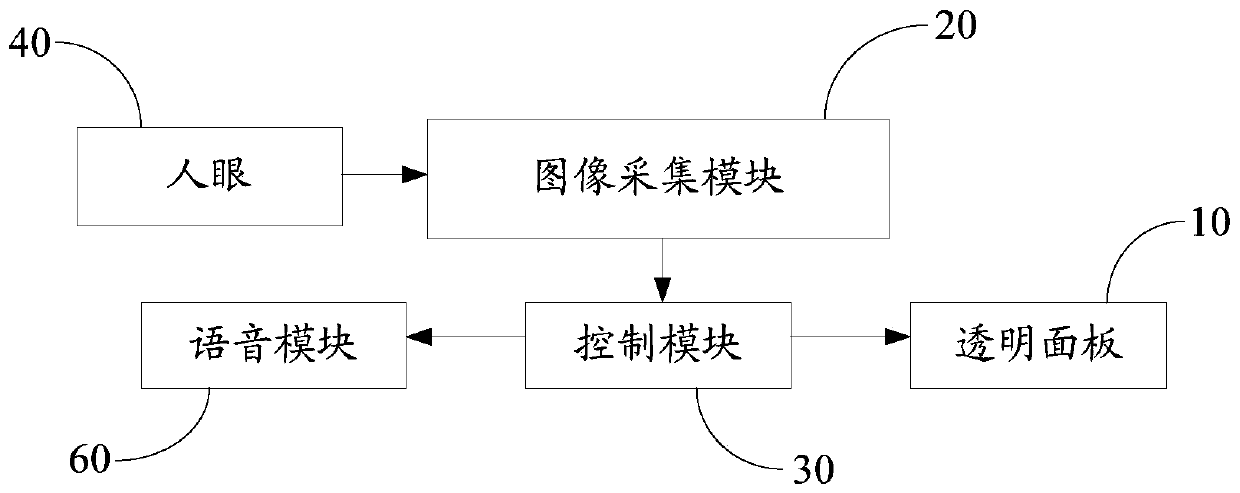
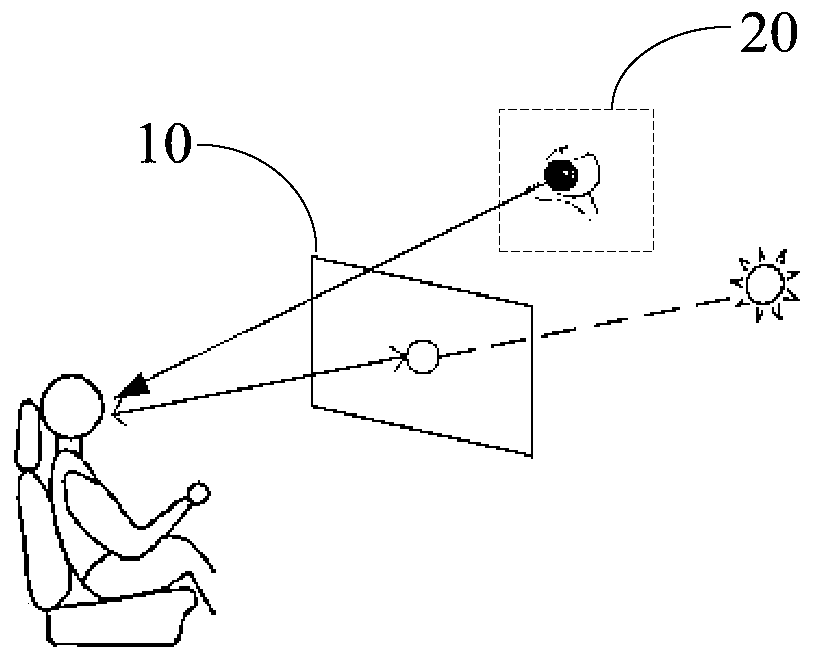
PendingCN111591111AAuto adjust discolorationColor change real-time automatic adjustmentInput/output for user-computer interactionAntiglare equipmentInformation controlTarget control
The invention provides a shading plate assembly, a control method and a control device thereof and a vehicle, which relate to the technical field of shading, and can avoid the problems of darkening ofan exterior scene and worsening of a visual field while solving the problem of visual dizziness of human eyes caused by direct sunlight in the driving process of the vehicle. An image acquisition module in the shading plate assembly is used for acquiring image information of a transparent panel and human eyes; a control module is used for determining target position information of fixation pointsof human eyes positioned on the transparent panel according to the image information, and determining a target control area, corresponding to the target position information, on the transparent panel; a detection module is used for detecting corresponding optical information when light penetrates through the target control area and is emitted to human eyes; and the control module is also used foradjusting the light transmission degree of the transparent panel in the target control area according to the optical information, so that the optical information is within a preset range. The shadingplate assembly provided by the invention is used for shading.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
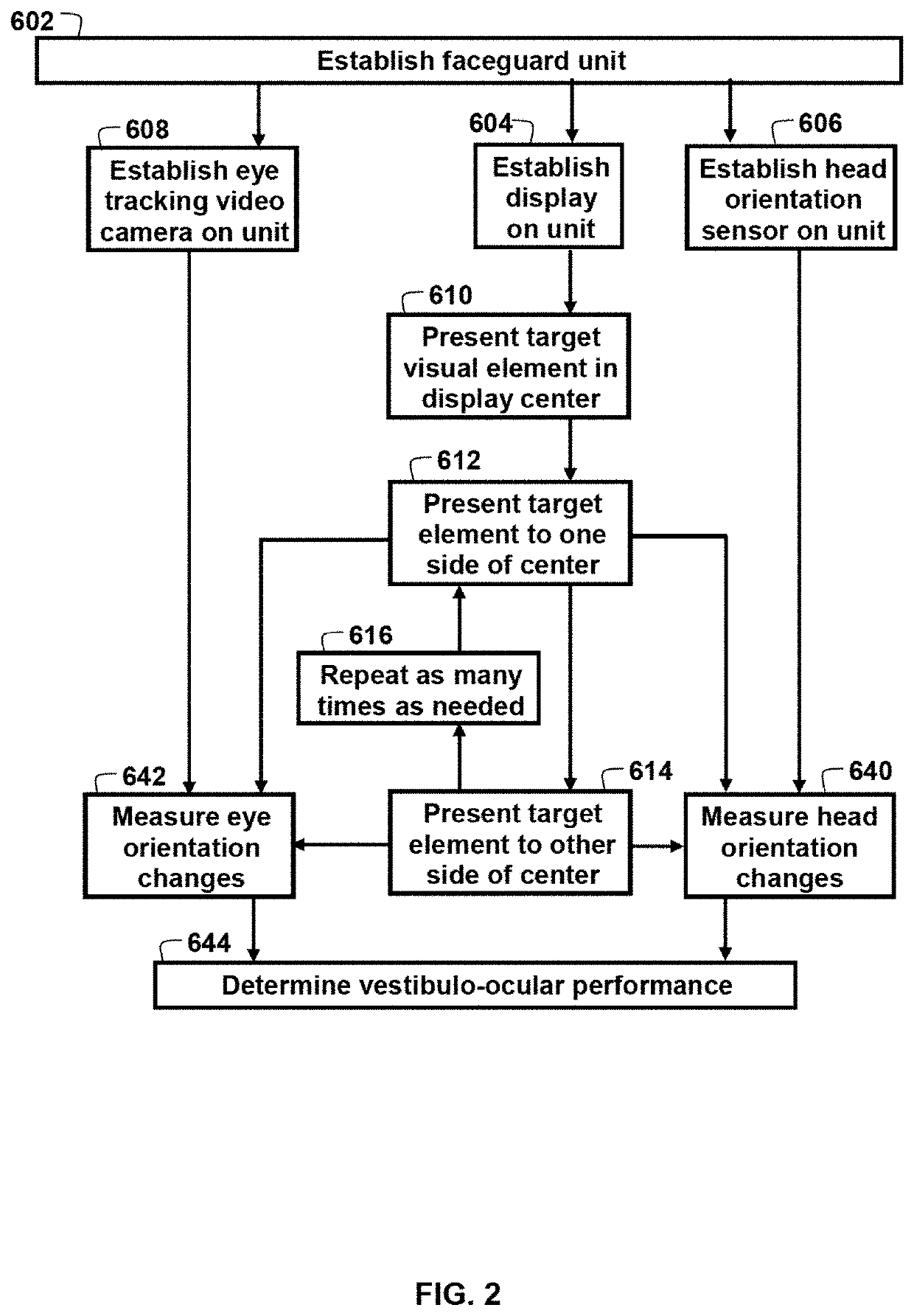
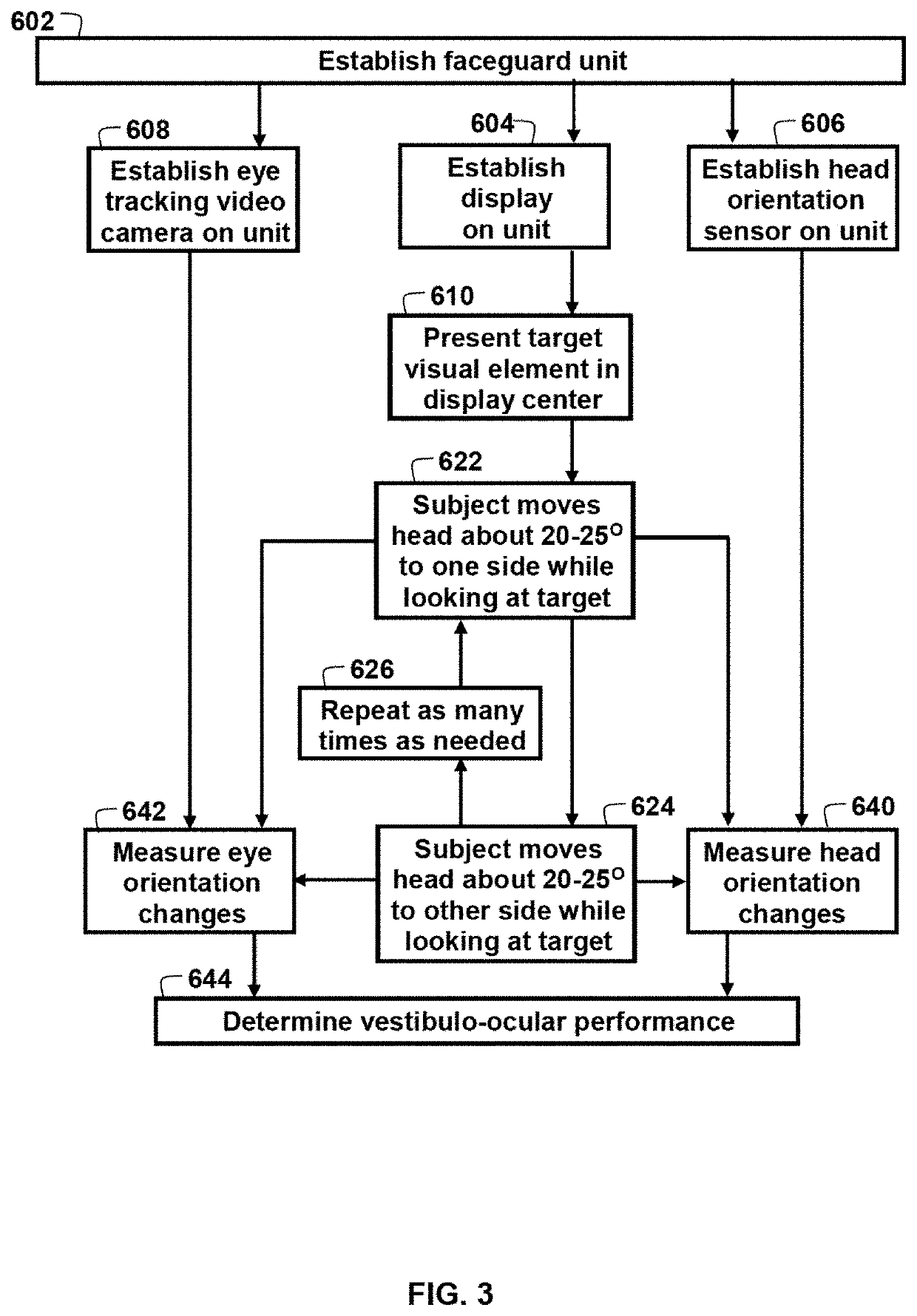
Ocular-performance-based head impact measurement using a faceguard
ActiveUS10602927B2Reduce chanceInertial sensorsPsychotechnic devicesNystagmus presentVisual perception
A system or method for measuring human ocular performance can be implemented using an eye sensor, a head orientation sensor, and an electronic circuit. The device is configured for measuring vestibulo-ocular reflex, pupillometry, saccades, visual pursuit tracking, vergence, eyelid closure, dynamic visual acuity, retinal image stability, foveal fixation stability, focused position of the eyes or visual fixation of the eyes at any given moment and nystagmus. The eye sensor comprises a video camera that senses vertical movement and horizontal movement of at least one eye. The head orientation sensor senses pitch and yaw in the range of frequencies between 0.01 Hertz and 15 Hertz. The system is implemented as part of a faceguard.
Owner:NOVUTZ LLC
Brain-computer interface method based on steady-state asymmetric visual evoked potential
ActiveCN111580643AAvoid visual fatigueSuppression of common mode noiseInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingFixation pointLow frequency band
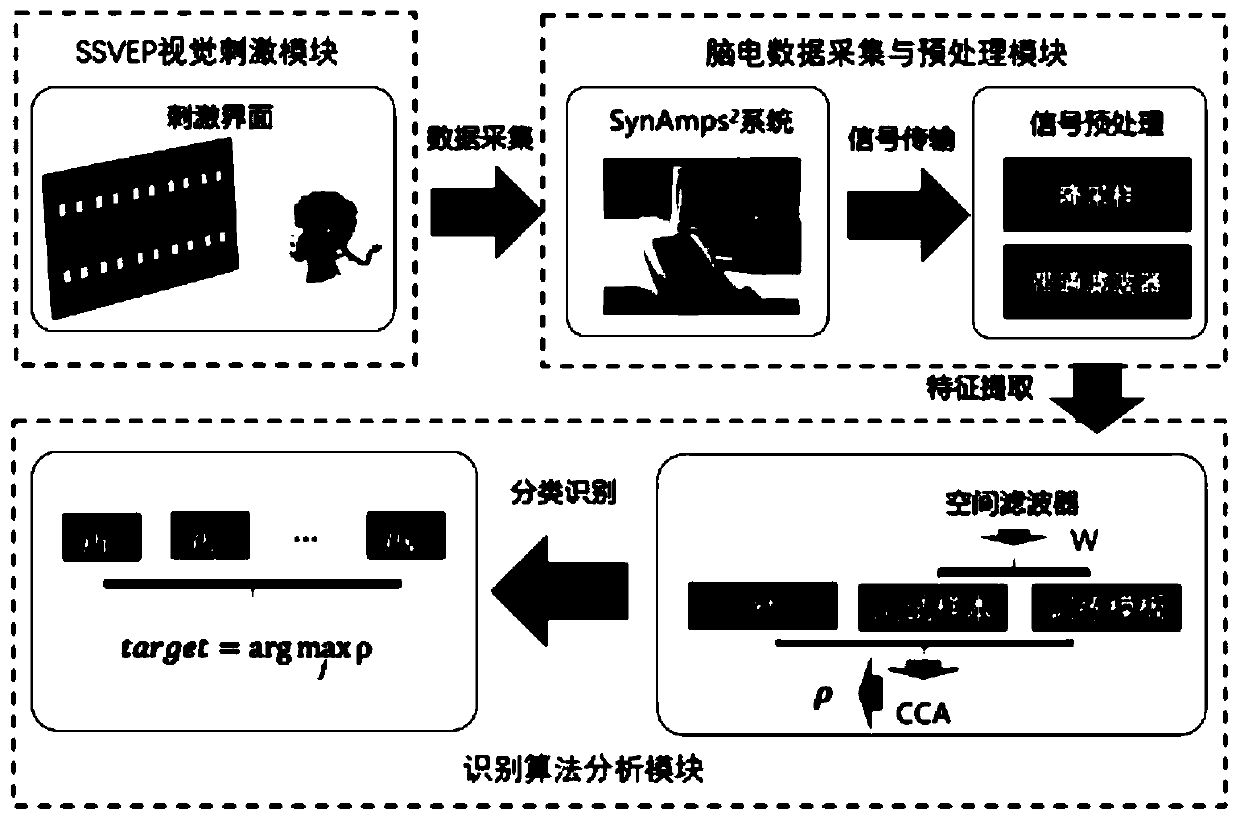
The invention discloses a brain-computer interface method based on steady-state asymmetric visual evoked potentials, and the method comprises the steps: constructing an SSaVEP coding normal form withN instruction sets, enabling a visual field fixation point to be at an original point, and enabling a visual stimulation signal to appear around the original point in two different time periods; acquiring electroencephalogram signal data of a subject by using a Neuroscan Synamps2 system, and performing preprocessing to extract a feature signal; constructing a spatial filter, and respectively obtaining a training set template and a test set template by utilizing the spatial filter to realize feature enhancement of the SSaVEP; extracting correlation coefficients of the training set template andthe test set template by using a CCA algorithm to maximize the potential correlation. In mode matching, the relationship between the training set template and the test signal is represented by a vector, a final correlation coefficient decision value is further obtained, and a target category is obtained based on the decision value. According to the technology, the signal-to-noise ratio of SSVEP can be remarkably improved, and the technology is suitable for a low frequency band, a medium frequency band and a high frequency band; and meanwhile, visual fatigue can be reduced by utilizing a hiddenvisual fixation mode.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
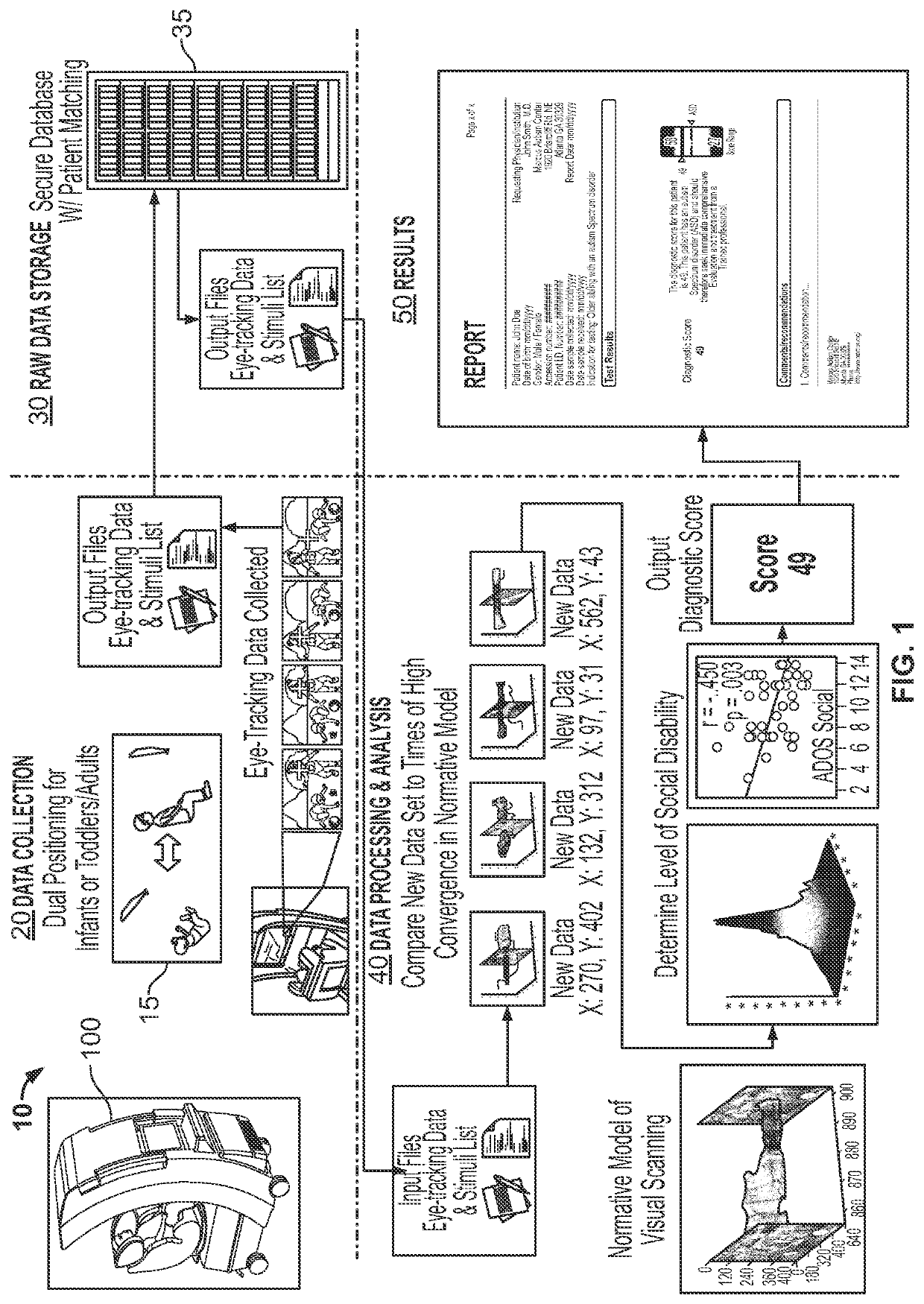
Systems and methods for assessing infant and child development via eye tracking
ActiveUS10617295B2Distance minimizationMaximize rangeMedical data miningHealth-index calculationPhysical medicine and rehabilitationClinical psychology
Systems, devices, and methods are described for assessing the risk of developmental, cognitive, social, or mental abilities or disabilities in very young patients (e.g., in the first 2-6 months of life). Generally, the decline in visual fixation of a subject over time with respect to certain dynamic stimuli provides a marker of possible abilities or disabilities (such as ASD). The visual fixation of the subject is identified, monitored, and tracked over time through repeated eye tracking sessions, and data relating to the visual fixation is then analyzed to determine a possible increased risk certain conditions in the subject. A change in visual fixation as compared to similar visual fixation data of typically-developing subjects or to a subject's own, prior visual fixation data provides an indication of a developmental, cognitive, or mental ability or disability.
Owner:CHILDRENS HEALTHCARE OF ATLANTA INC
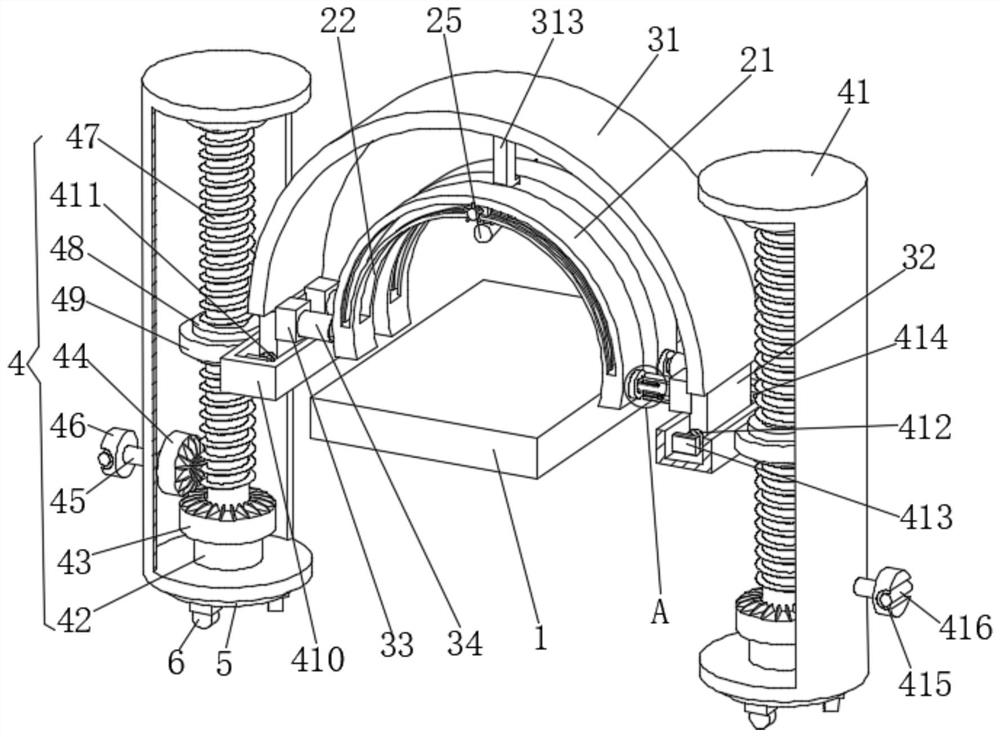
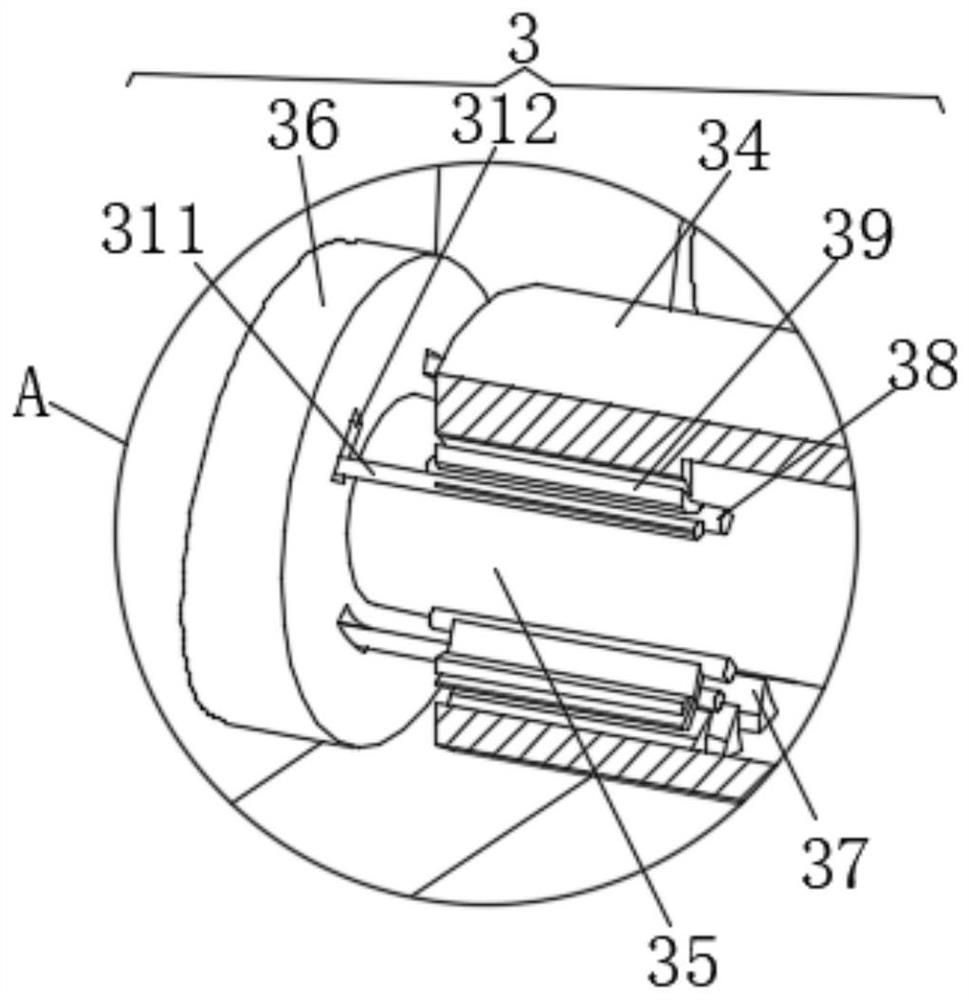
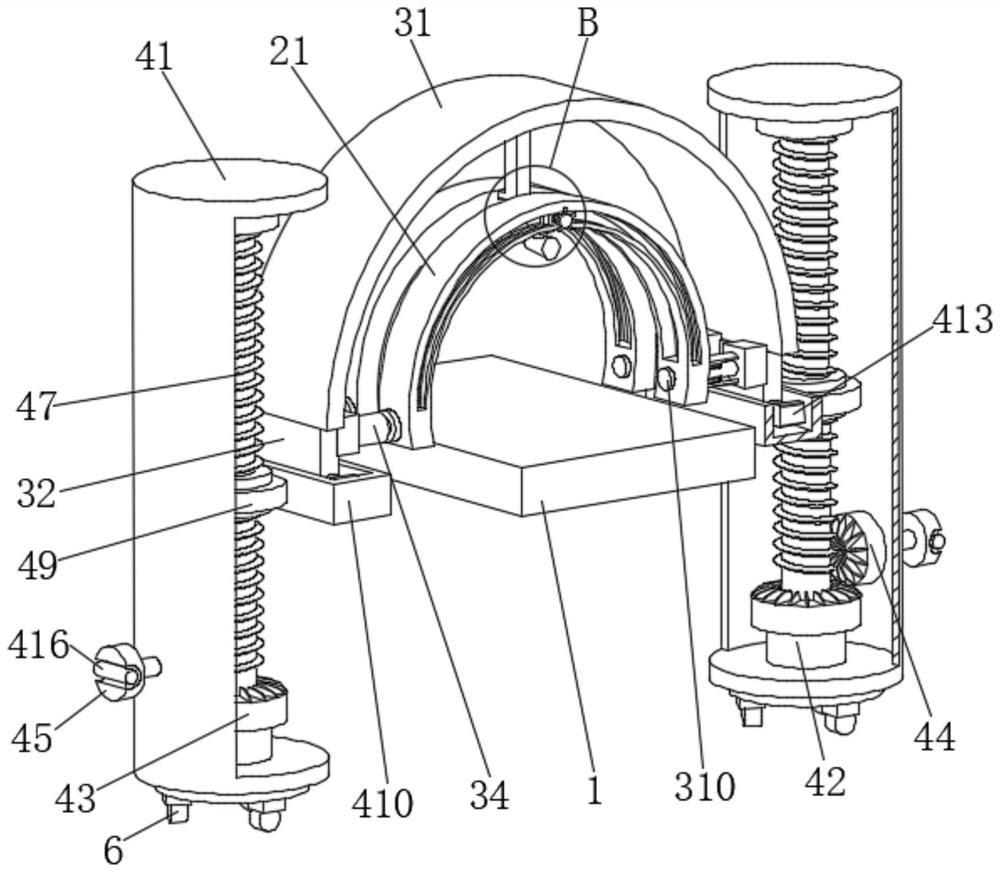
Device for reducing visual detection misjudgment rate of aluminum profile
PendingCN114295635AEasy to moveEasy to fixOptically investigating flaws/contaminationStands/trestlesStructural engineeringVisual perception
The invention discloses a device for reducing a visual detection misjudgment rate of an aluminum profile. The device comprises a conveying belt, an angle unit, a rotating unit and a lifting unit, the conveying belt is longitudinally and horizontally arranged; the angle unit comprises arc-shaped plates, sliding rails, sliding blocks, supporting columns and cameras, the two transverse arc-shaped plates are arranged above the conveying belt, the sliding blocks are slidably connected with the sliding rails, and the lower ends of the supporting columns are fixedly connected with the middles of the upper ends of the cameras; the rotating units are mounted on the left and right sides of the arc-shaped plate; the lifting units are installed on the left and right sides of the arc-shaped plate. The arc-shaped plate is arranged to support the camera, so that products can be detected in all directions and angles, the same distance of detection of the products can be ensured, the application range is wide, different arc-shaped plates can be replaced according to different products through the installation assembly, convenience and rapidness are achieved, in addition, the sliding assembly is arranged to facilitate movement and fixation of the camera, and the practicability is high. And a rotating disc and wheels are further arranged, so that the equipment is convenient to move.
Owner:GUANGDONG POLYTECHNIC NORMAL UNIV
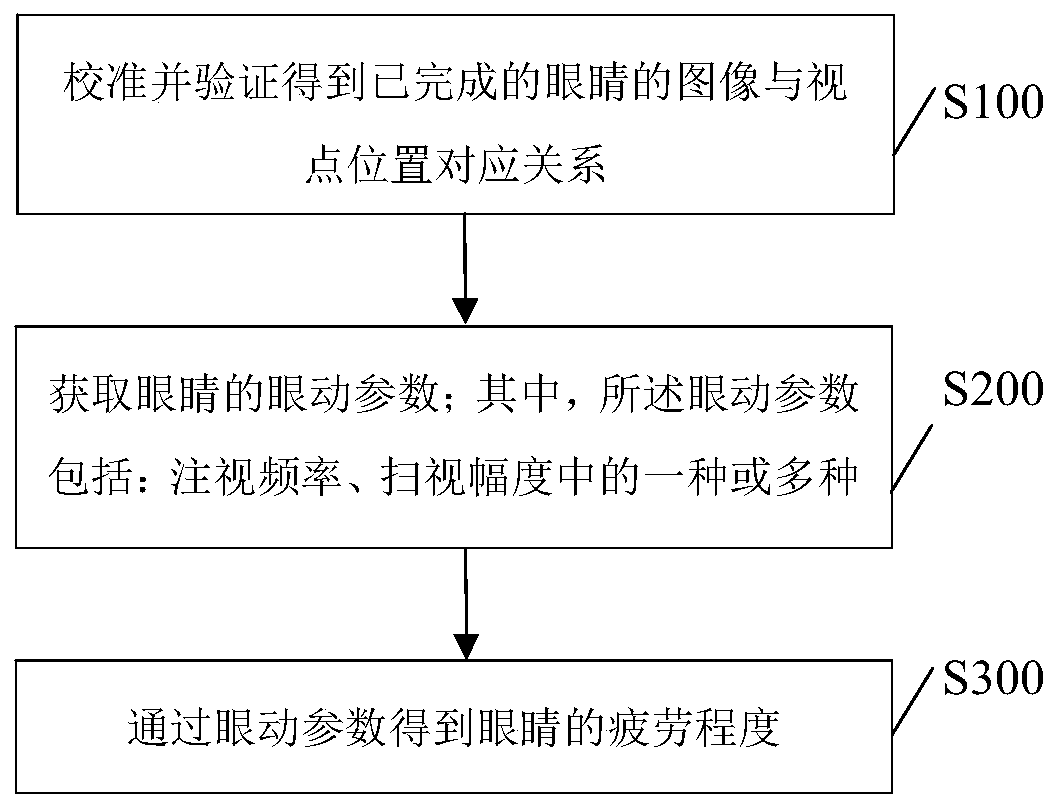
Visual fatigue measurement method, and system, storage medium and electronic device thereof
ActiveCN110811645AAccurate determination of fatigue levelAccurate and reliable measurement resultsEye diagnosticsSensorsComputer scienceOptometry
The invention discloses a visual fatigue measurement method as well as a system, a storage medium and an electronic device thereof. The visual fatigue measurement method comprises the following steps:acquiring eye movement parameters of the eyes, wherein the eye movement parameters include one or more selected from fixation frequency and scanning range; and then, obtaining fatigue degree of the eyes on basis of the eye movement parameters. For the fatigue degree is obtained by adopting the fixation frequency and the scanning range as the eye movement parameters, the visual fatigue measurementmethod is reliable in measurement result; and thus, the visual fatigue measurement method is capable of accurately determining fatigue degree of a user.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
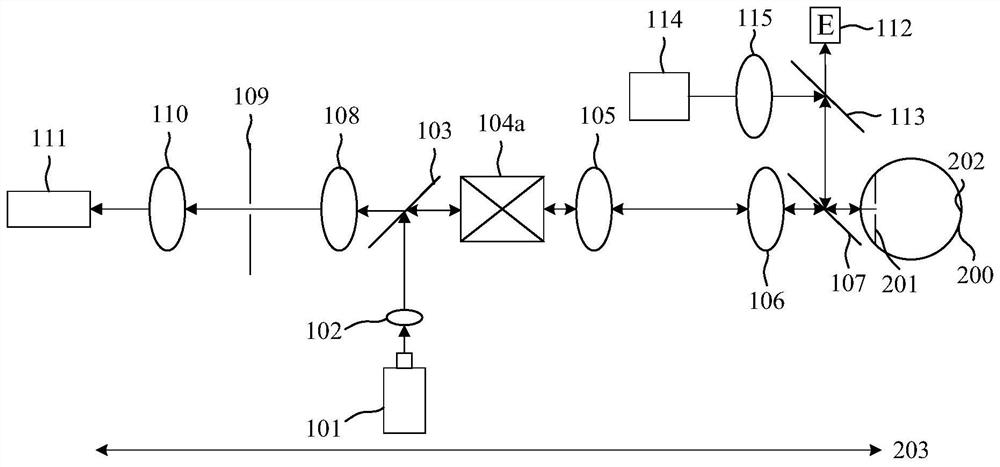
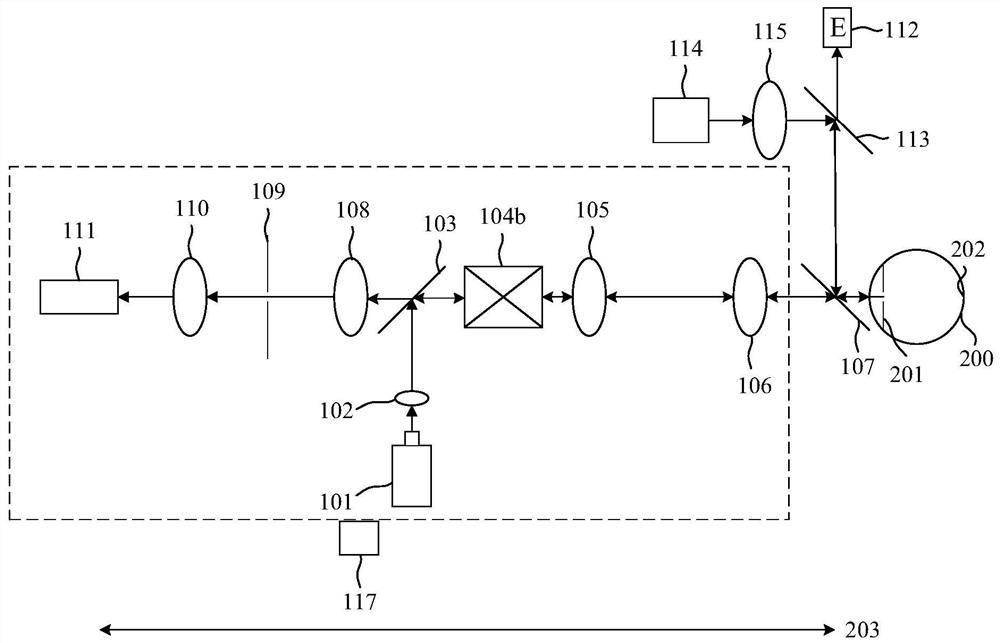
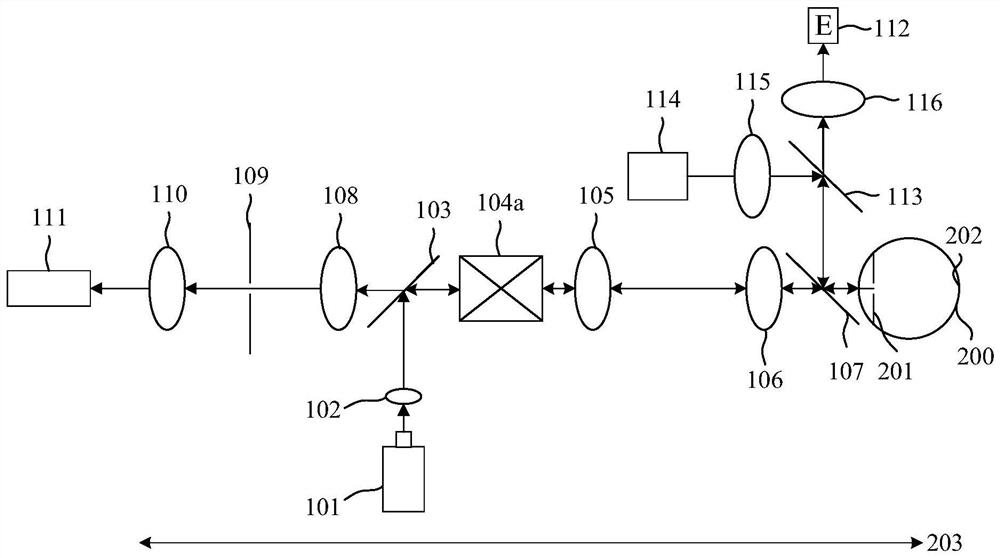
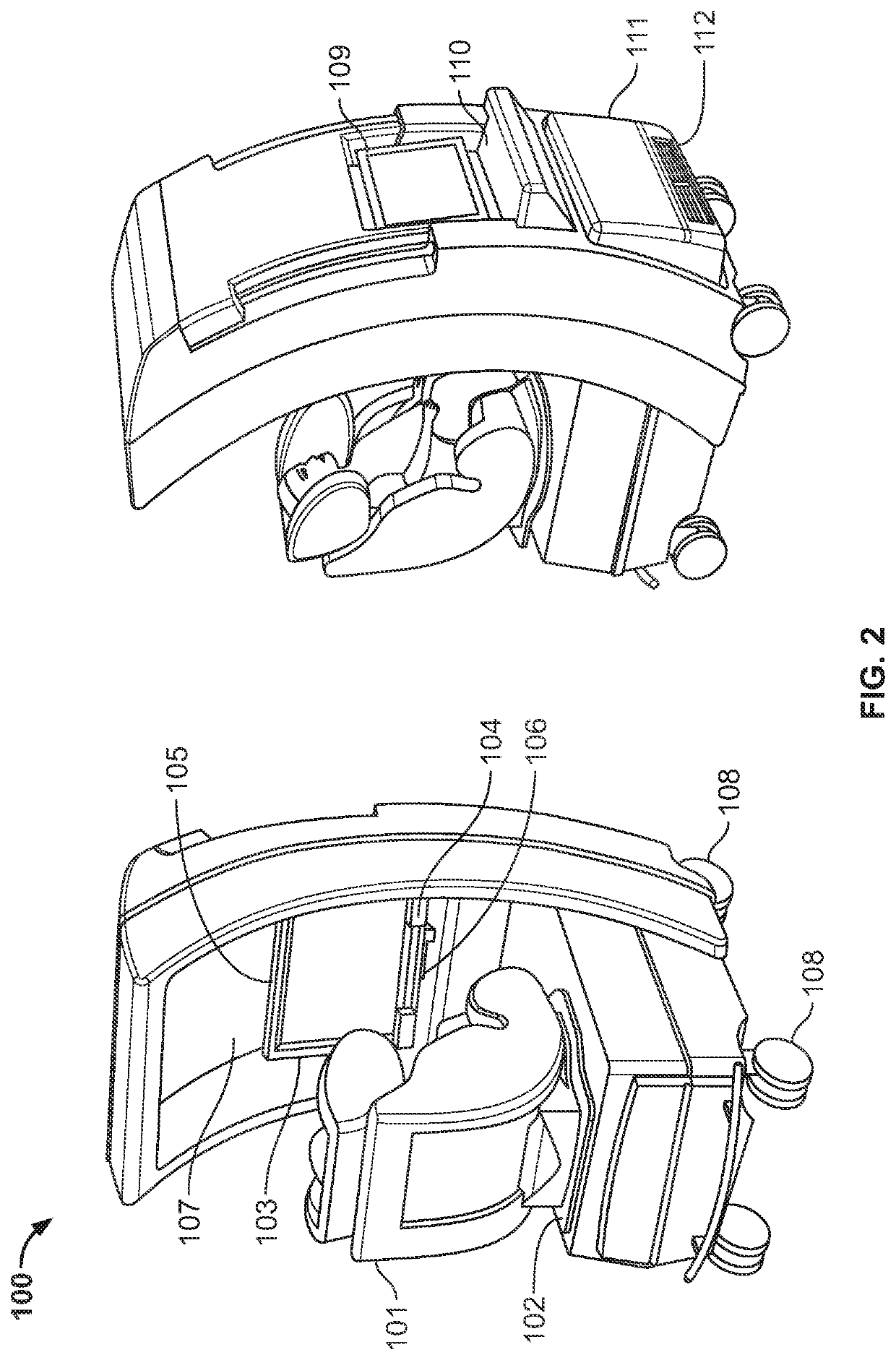
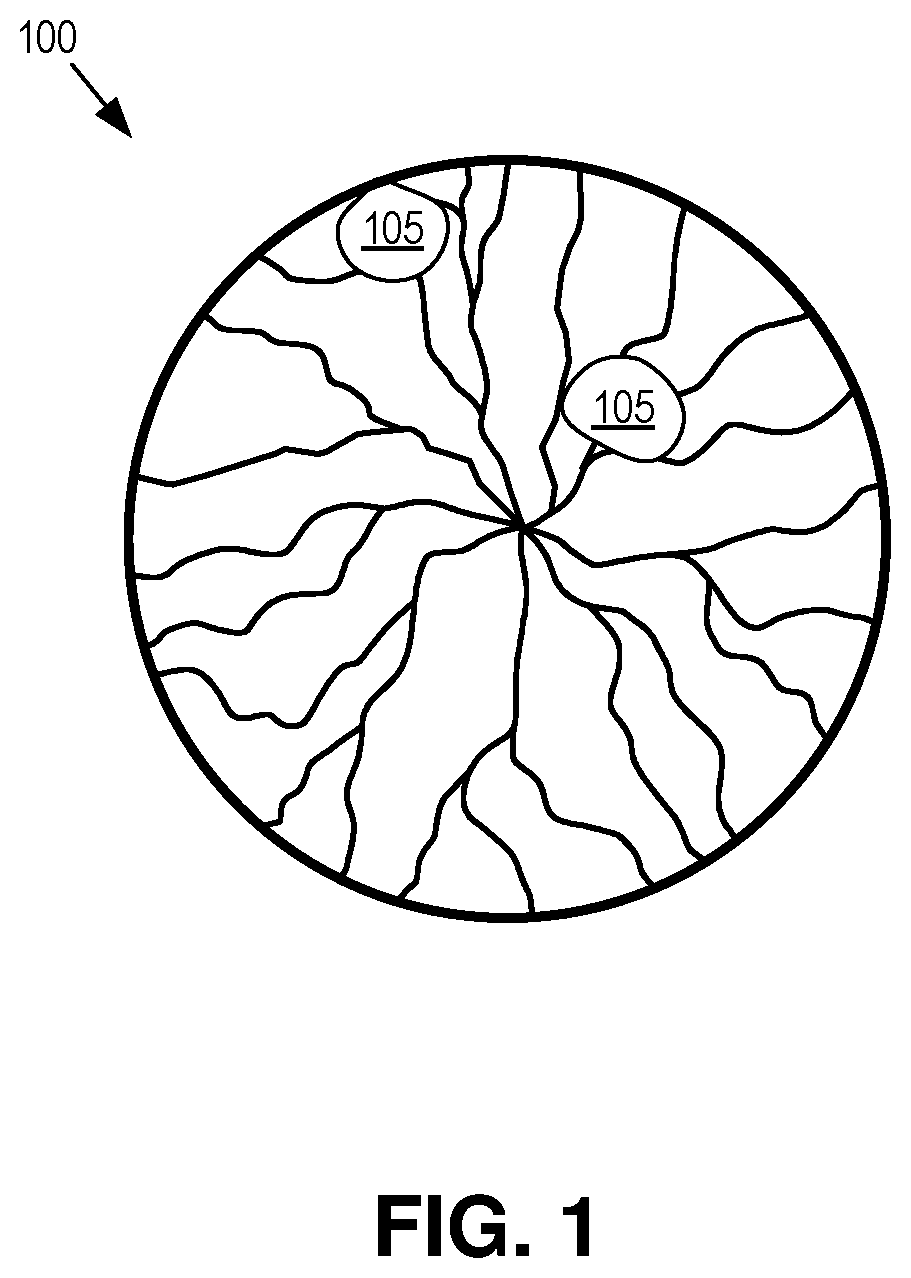
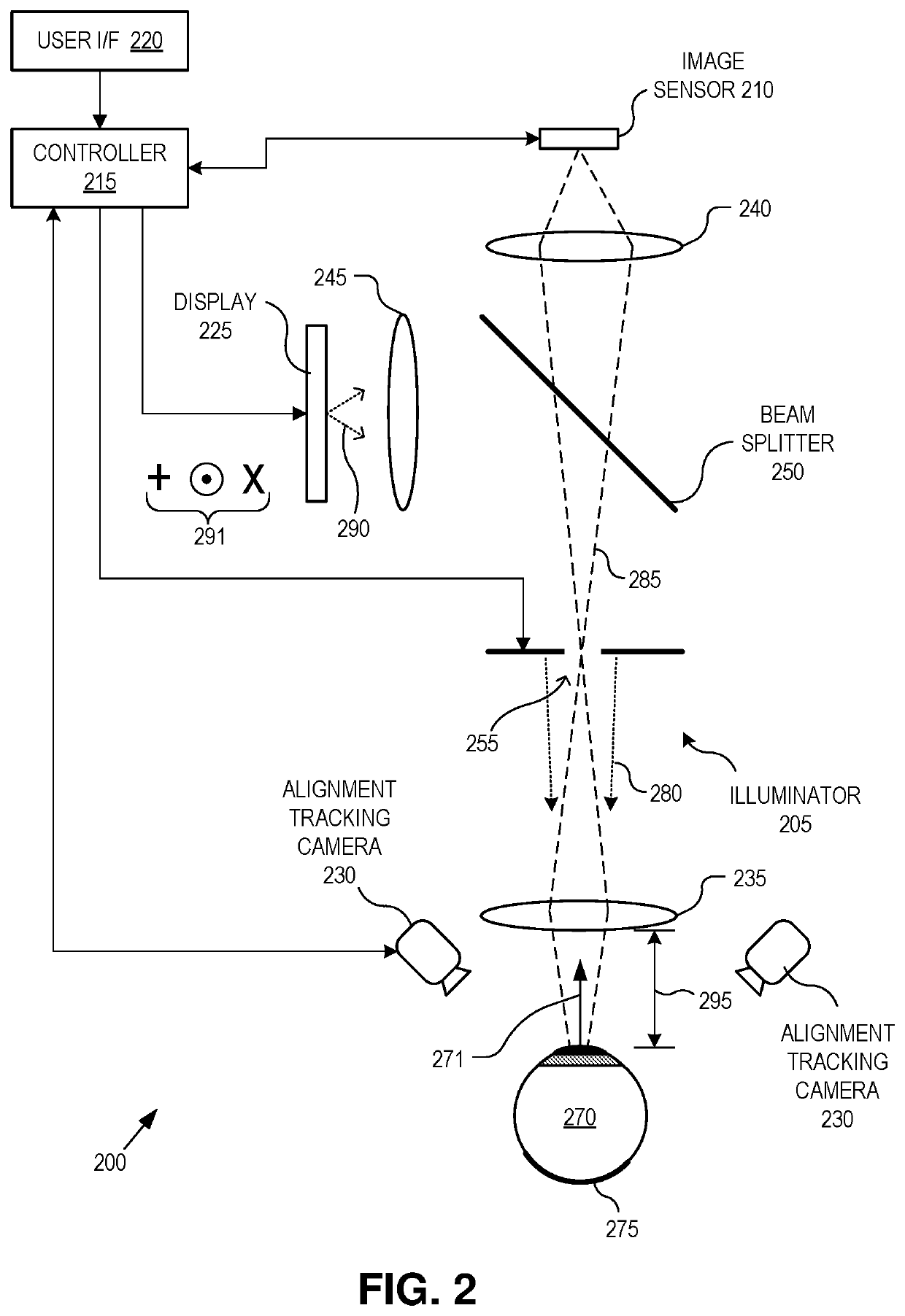
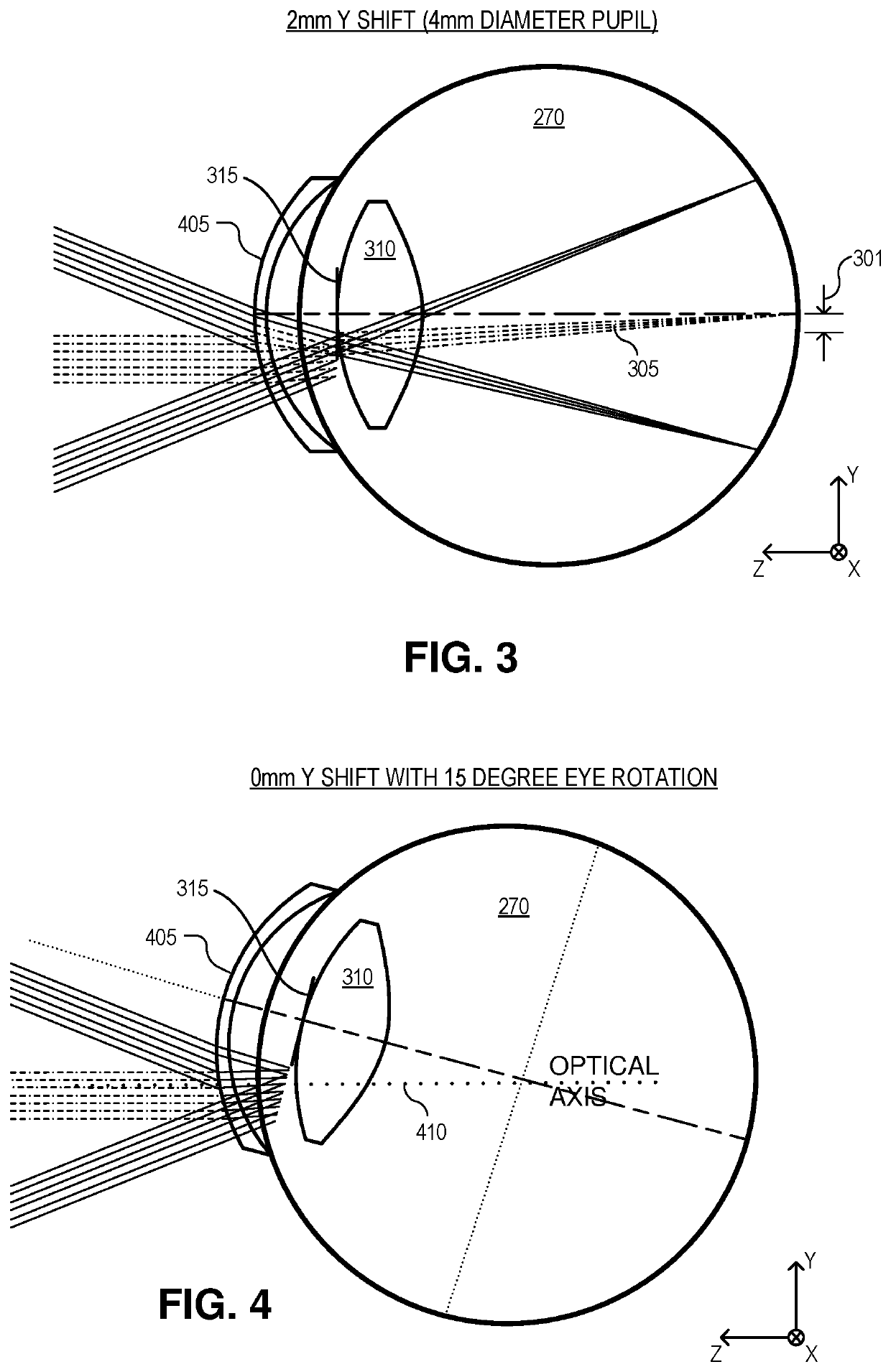
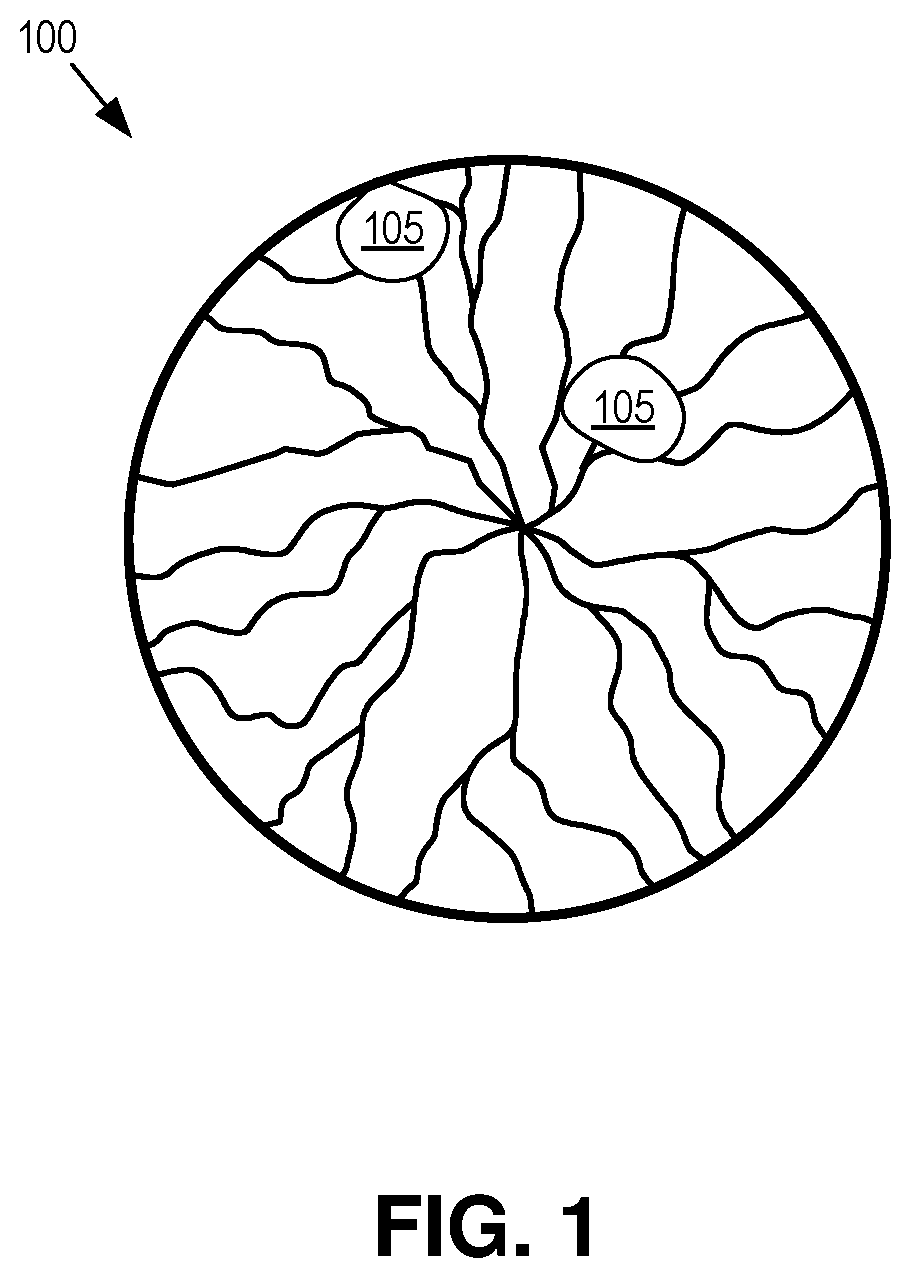
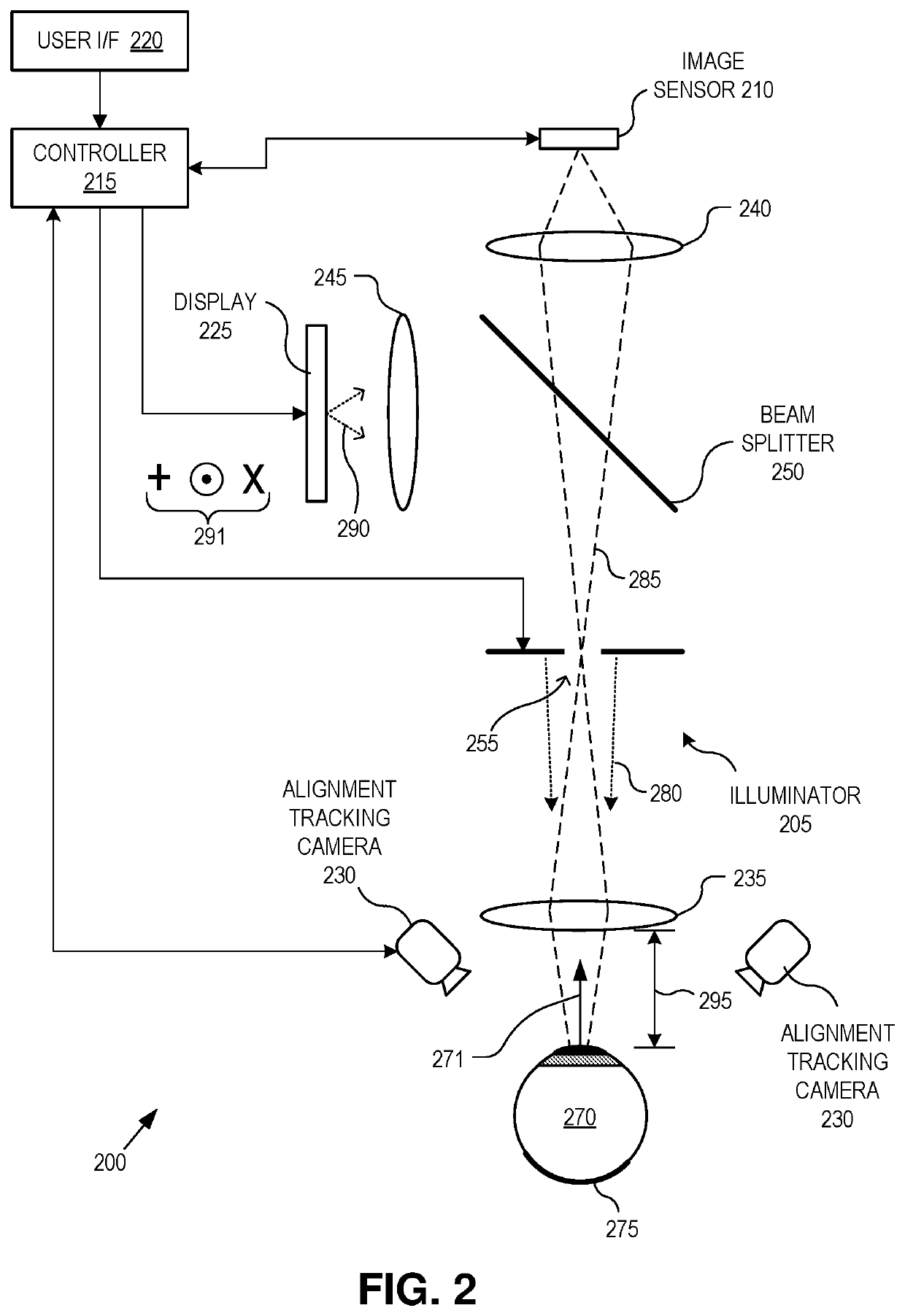
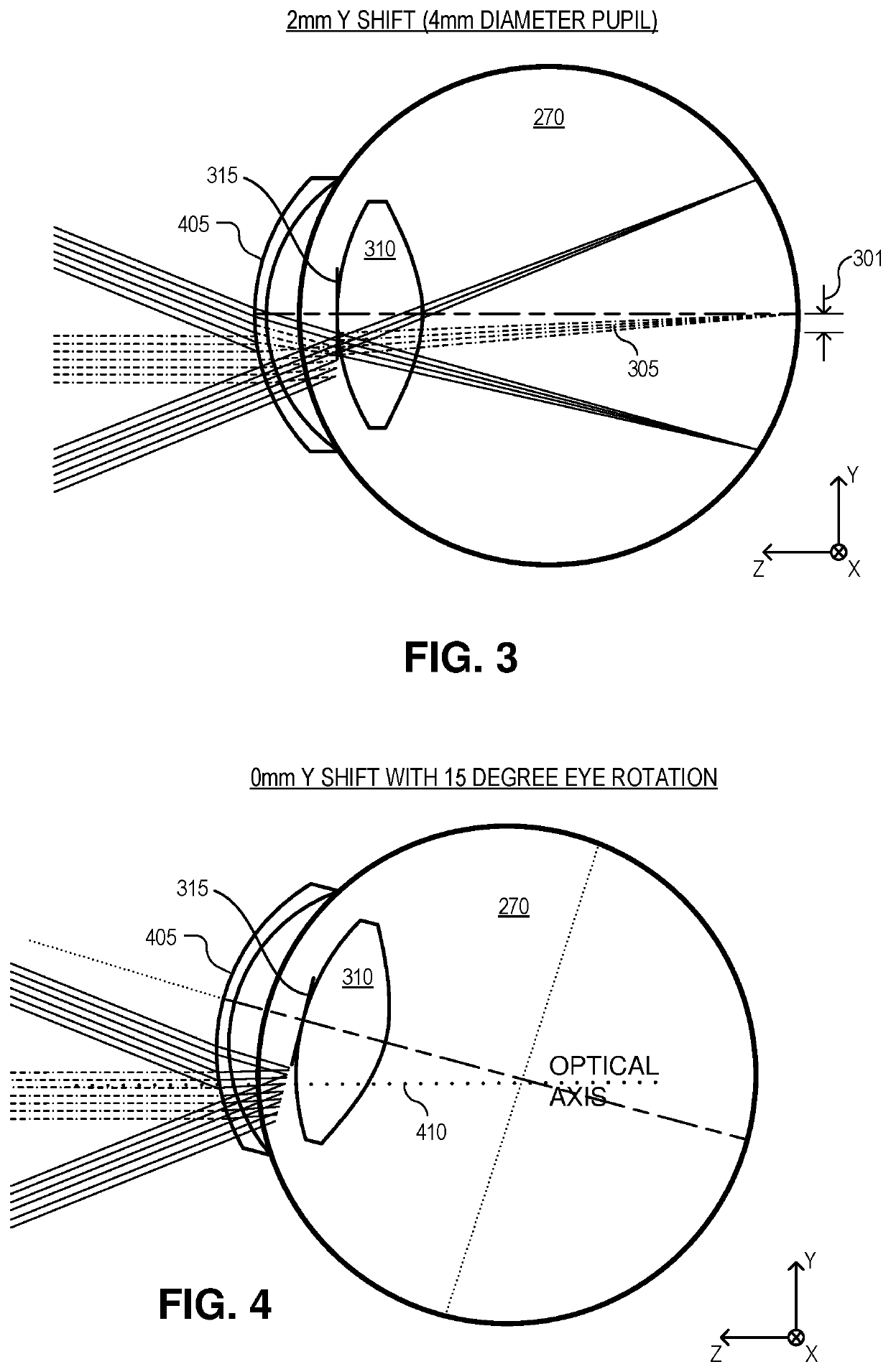
Dynamic eye fixation for retinal imaging
A retinal imaging system includes an eyepiece lens assembly, an image sensor, a dynamic fixation target viewable through the eyepiece lens assembly, and a controller coupled to the image sensor and the dynamic fixation target. The controller includes logic that causes the retinal imaging system to perform operations including: acquiring a first image of the eye, analyzing the first image to determine whether a lateral misalignment between the eye and the eyepiece lens assembly is greater than a threshold misalignment, in response to determining the lateral misalignment is greater than the threshold misalignment, adjusting a visual position of the dynamic fixation target to encourage the eye to rotate in a direction that compensates for the lateral misalignment, and acquiring the retinal image of the eye while the eye is encouraged to rotate towards the direction that compensates for the lateral misalignment.
Owner:VERILY LIFE SCI LLC
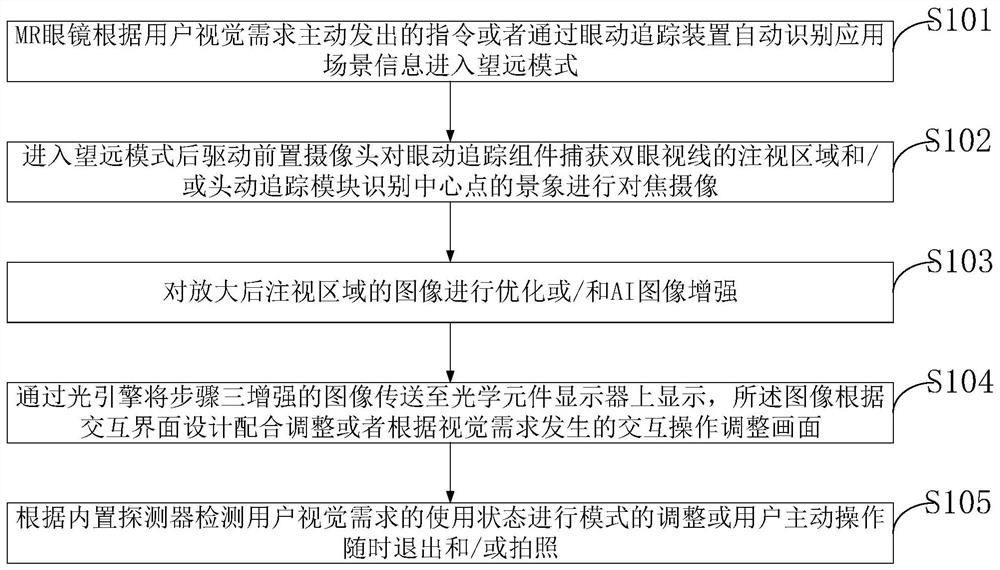
Method for enhancing visual ability of human eyes based on MR glasses, system and equipment
PendingCN113709410ATimely responseDoes not affect receptionInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsHead movementsDisplay device
The invention belongs to the technical field of application of near-to-eye display equipment, and discloses a method for enhancing the visual ability of human eyes based on MR glasses, a system and equipment. The method comprises activating a telescopic mode according to the visual demand of a user, and capturing a long-distance scene in the front of the visual field of the user through a telephoto camera of the equipment; and after optimization or / and AI image enhancement are / is carried out on the image of an magnified fixation area, presenting the image to the user, so that the user can see the distant scene beyond the visual ability range clearly, and the visual ability of the user in looking at the distance is enhanced. The optical structure of a front camera on the existing MR glasses is improved by utilizing a light guide optical fiber, an optical waveguide or a periscope technology, so that the whole MR glasses are lighter and thinner. An eye movement tracking device and a head movement tracking device are used for selecting the focusing area of the image, the magnification power is determined through eye movement interaction and / or gesture interaction, a MR glasses display previews the photographing area in real time, and finally a picture is taken.
Owner:幻蝎科技(武汉)有限公司
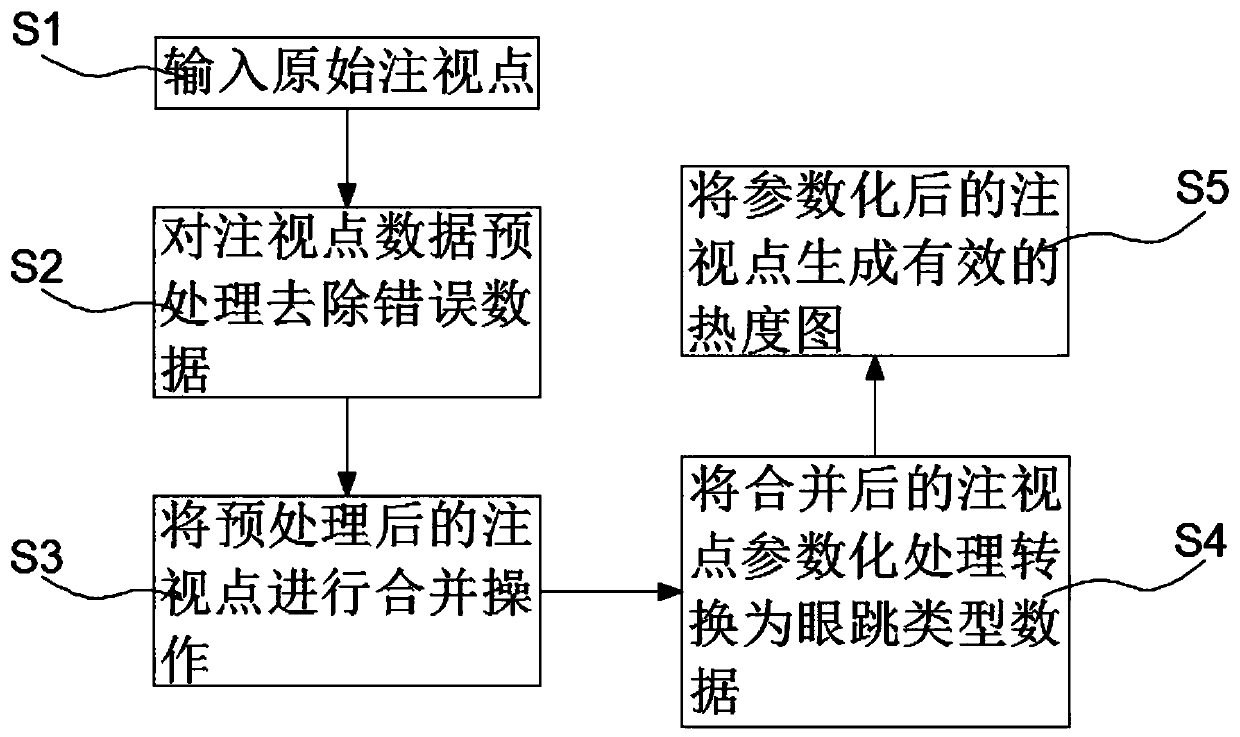
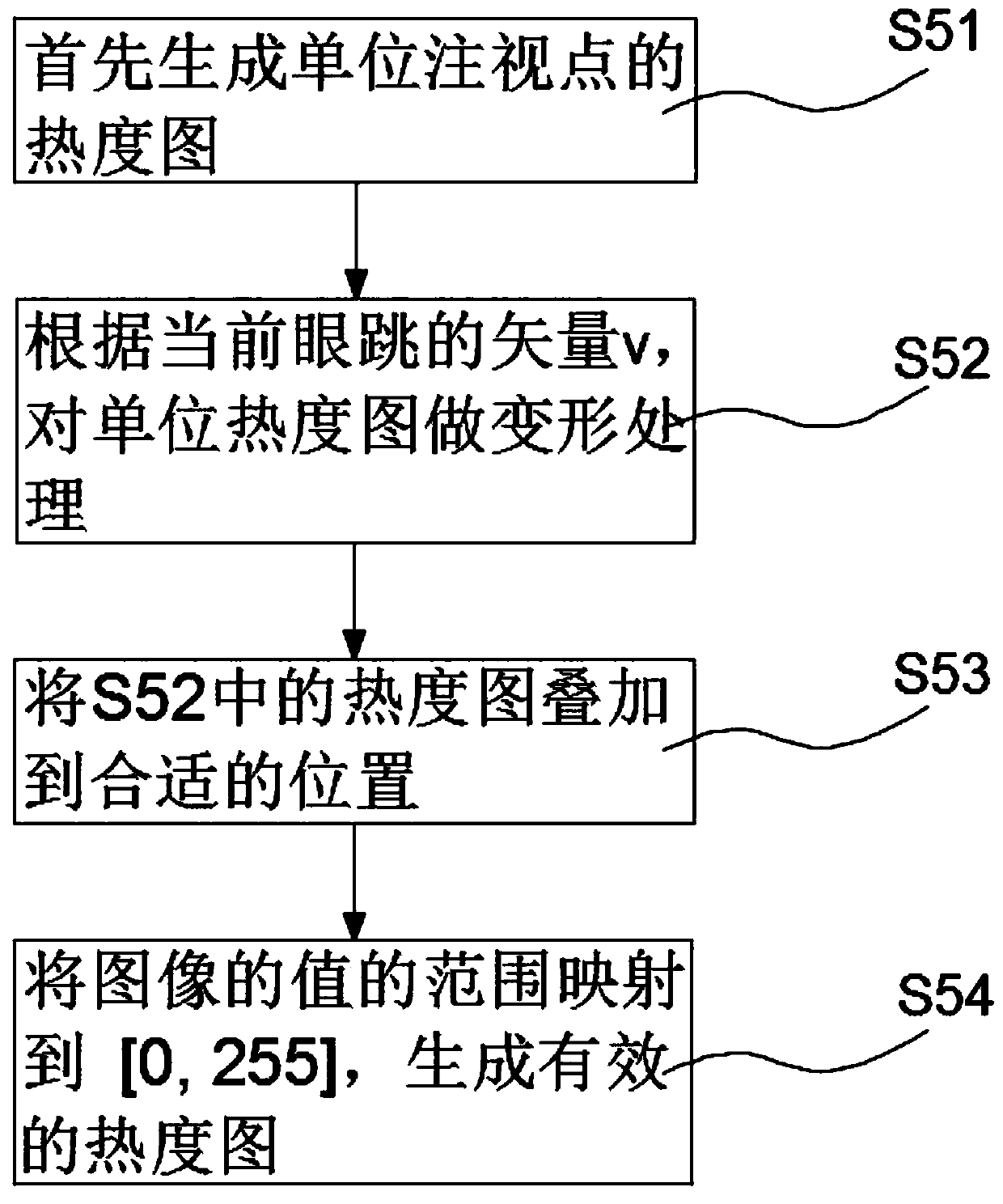
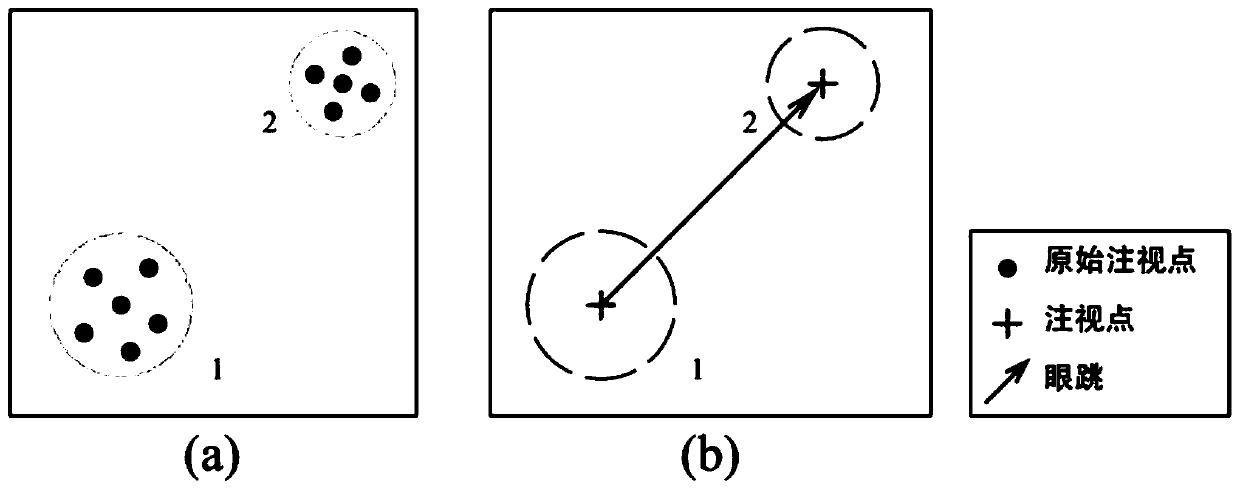
A heat map generation method based on eye jump information
The invention relates to the technical field of computer visualization, in particular to a heat map generation method based on eye jump information, which comprises the following steps: S1, inputtingan original fixation point; S2, preprocessing the fixation point data to remove error data; S3, carrying out merging operation on the preprocessed fixation points; S4, converting the combined fixationpoint parameterization processing into eye jump type data; S5, generating an effective heat map from the parameterized fixation points; According to the invention, a mixed data structure of fixationpoints and eye skips is used, and a heat map deformation method for eye skips type data is added. The heat map generated by using the method provided by the invention has a good function of indicatingthe transfer path of the gaze area on the basis of keeping the original function of displaying the gaze area, and has strong creativity.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
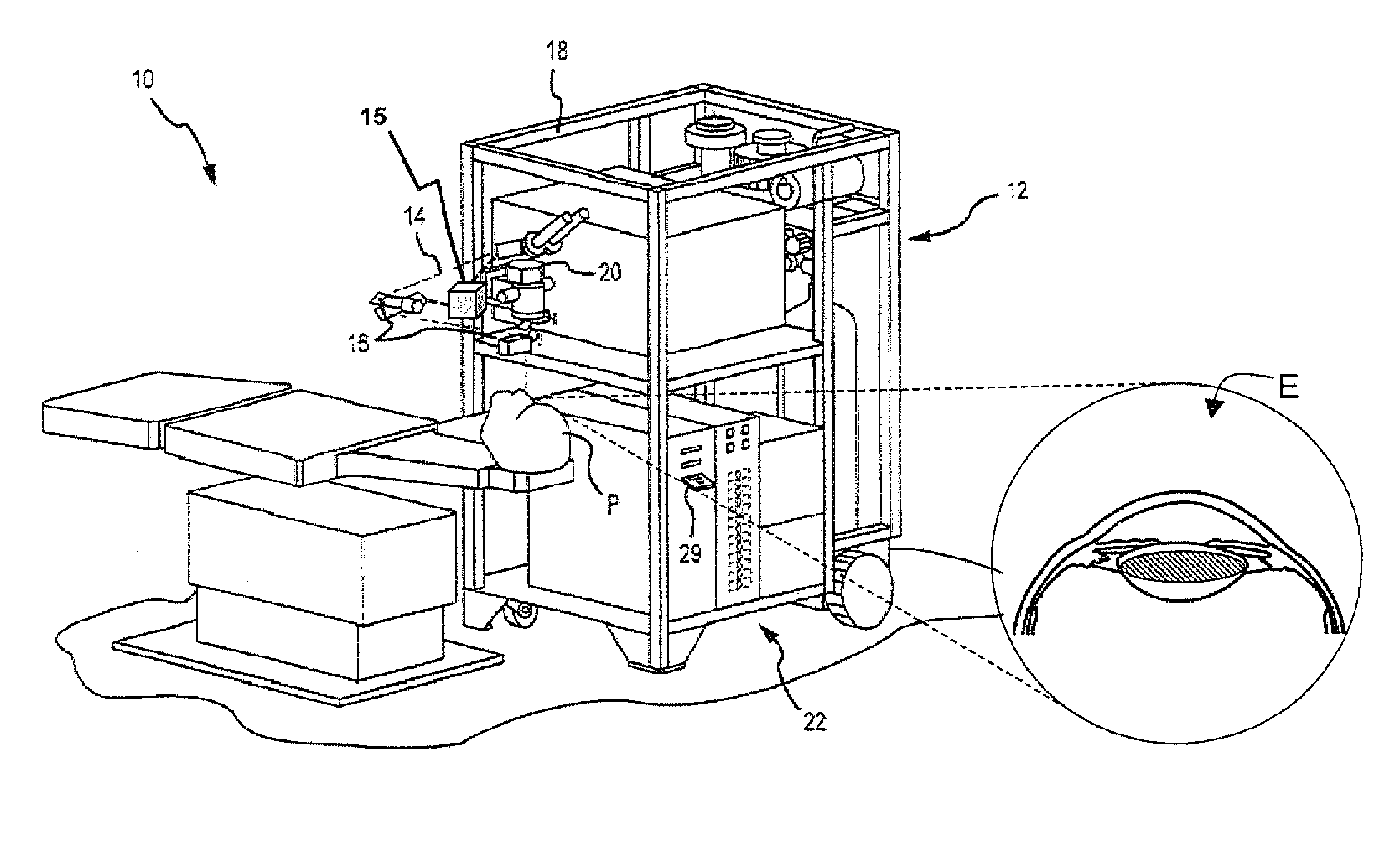
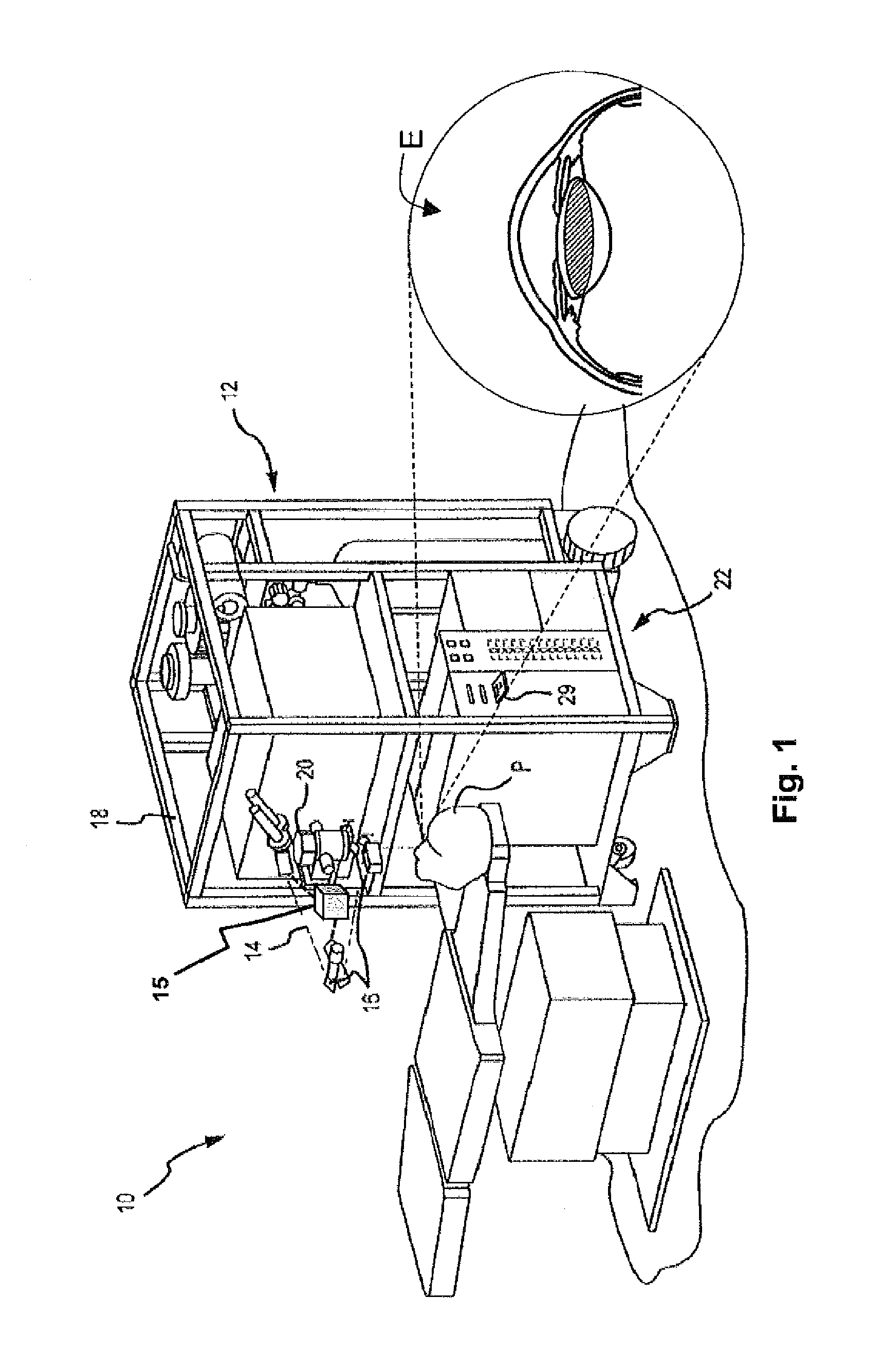
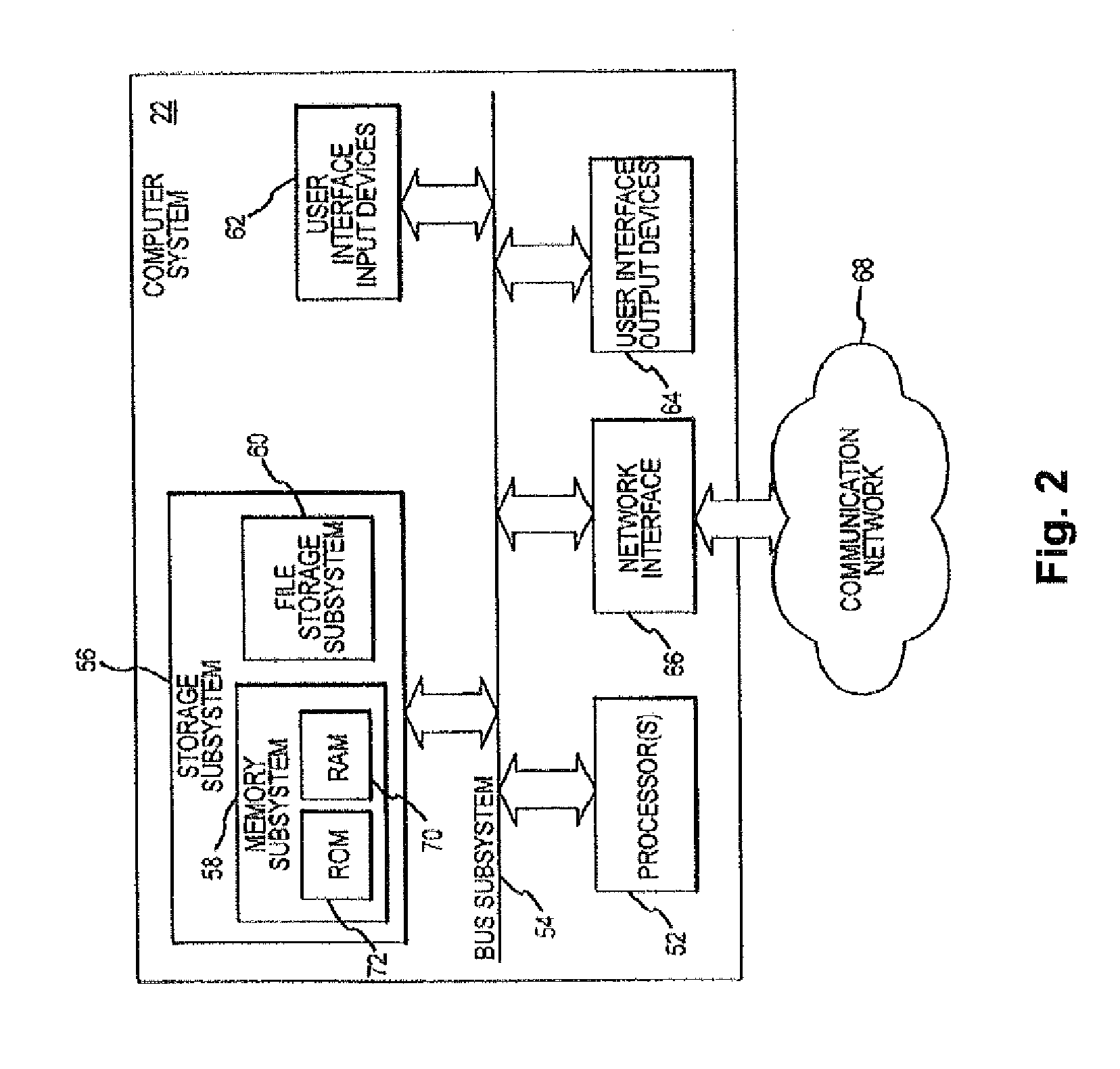
Systems and methods for dynamic patient fixation system
The field of the invention relates to systems and methods for ophthalmic laser procedure and, more particularly, to systems and methods for dynamic fixation used in the fixation of the eye(s) of a patient during laser-assisted ophthalmic surgery and / or ophthalmic diagnostic and measurement systems where visualization and concentration on a target are desired. The invention generally enhances the alignment between the eye and a laser beam of a laser eye surgery system using visual fixation system and laser delivery optics. The visual fixation system allows a patient's eye(s) to be accurately focused at one or more fixation targets.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Prism prescription value acquisition system, acquisition method, acquisition apparatus and program for correcting fixation disparity
Owner:HOYA CORP
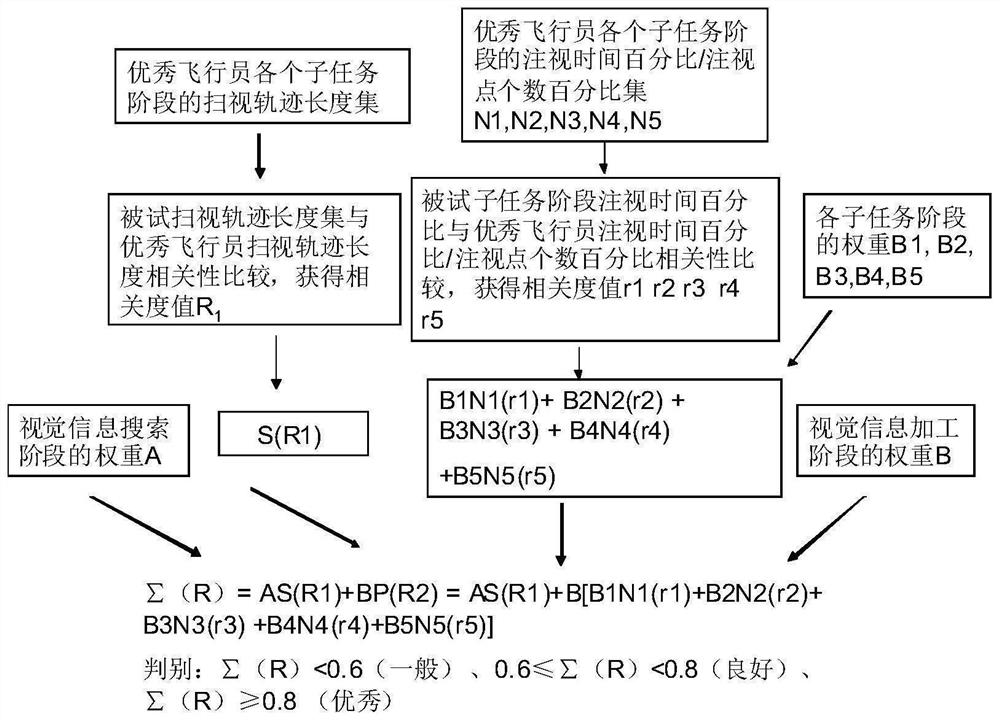
Method for evaluating visual distribution of pilot by adopting visual tracking equipment
PendingCN113827239AExcellent distribution of attentionGrade assessment goodDiagnostic signal processingSensorsEye Movement MeasurementsInformation processing
The invention discloses a method for evaluating visual distribution of a pilot by adopting visual tracking equipment. The method is established based on an eye movement measurement index (glancing track length) in a search process and an eye movement index (fixation time percentage / fixation number percentage) in a processing process. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, decomposing a flight mission into a plurality of typical stages, and then, confirming weight degrees of an attention search process and an attention information processing process and the weight of each typical stage through subjective questionnaire survey; and then, collecting eye movement data of both eyes of a tested pilot and an excellent pilot through SMI glasses type visual tracking equipment, recording an experimental scene in real time through a scene video recorder, playing back a scene video to obtain attention interest areas and sight change data of the tested pilot and the excellent pilot, carrying out data analysis and calculation to obtain correlation between the eye movement data of the tested flight trainee and the excellent pilot, and finally presenting an evaluation grade of attention distribution of the tested pilot.
Owner:中国人民解放军海军特色医学中心
Dynamic eye fixation for retinal imaging
A retinal imaging system includes an eyepiece lens assembly, an image sensor, a dynamic fixation target viewable through the eyepiece lens assembly, and a controller coupled to the image sensor and the dynamic fixation target. The controller includes logic that causes the retinal imaging system to perform operations including: acquiring a first image of the eye, analyzing the first image to determine whether a lateral misalignment between the eye and the eyepiece lens assembly is greater than a threshold misalignment, in response to determining the lateral misalignment is greater than the threshold misalignment, adjusting a visual position of the dynamic fixation target to encourage the eye to rotate in a direction that compensates for the lateral misalignment, and acquiring the retinal image of the eye while the eye is encouraged to rotate towards the direction that compensates for the lateral misalignment.
Owner:VERILY LIFE SCI LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com