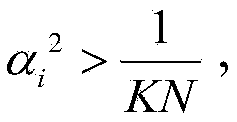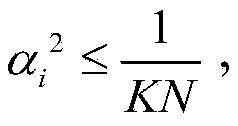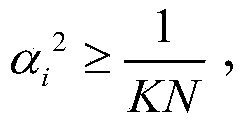Patents
Literature
63 results about "Spatial multiplexing gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
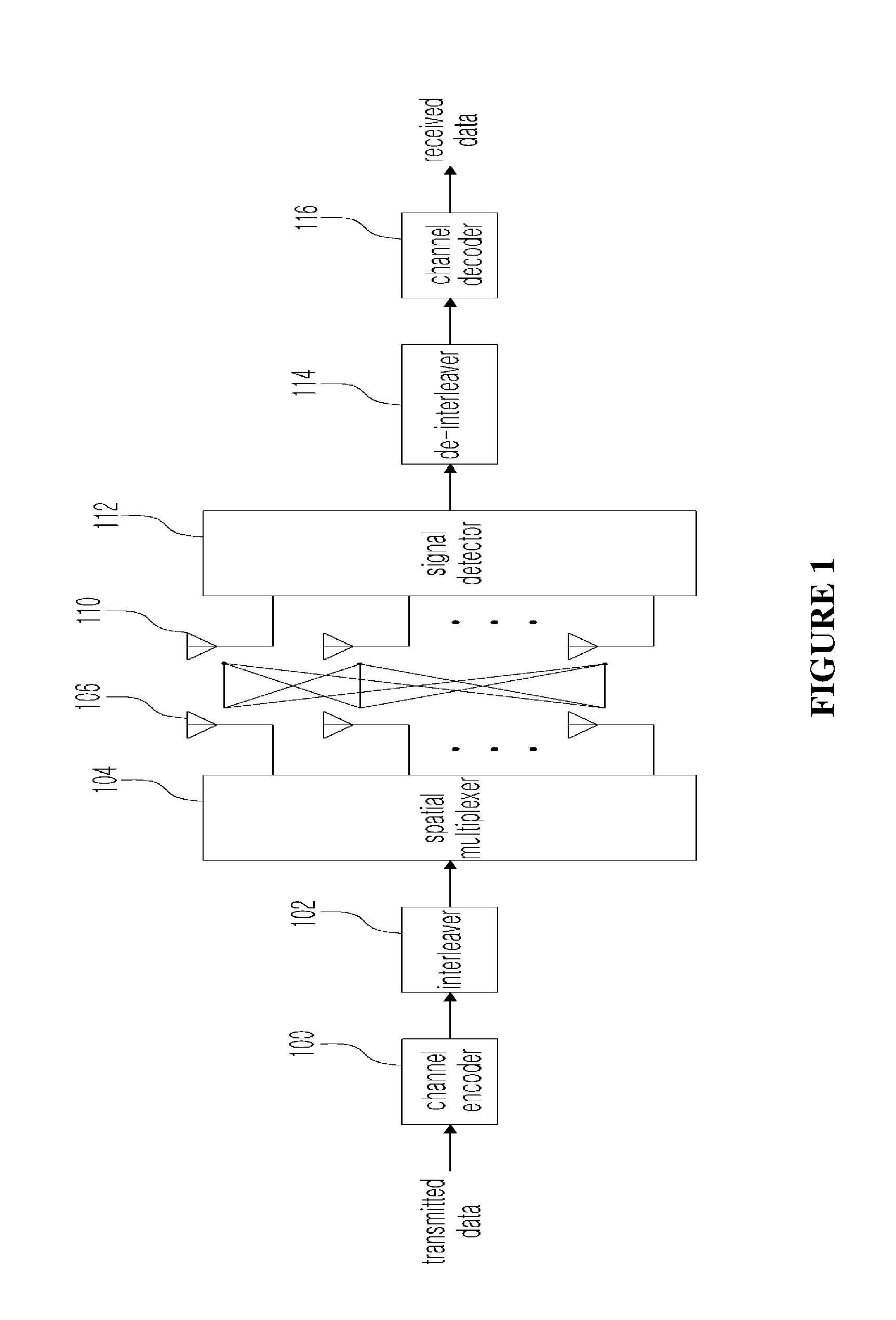
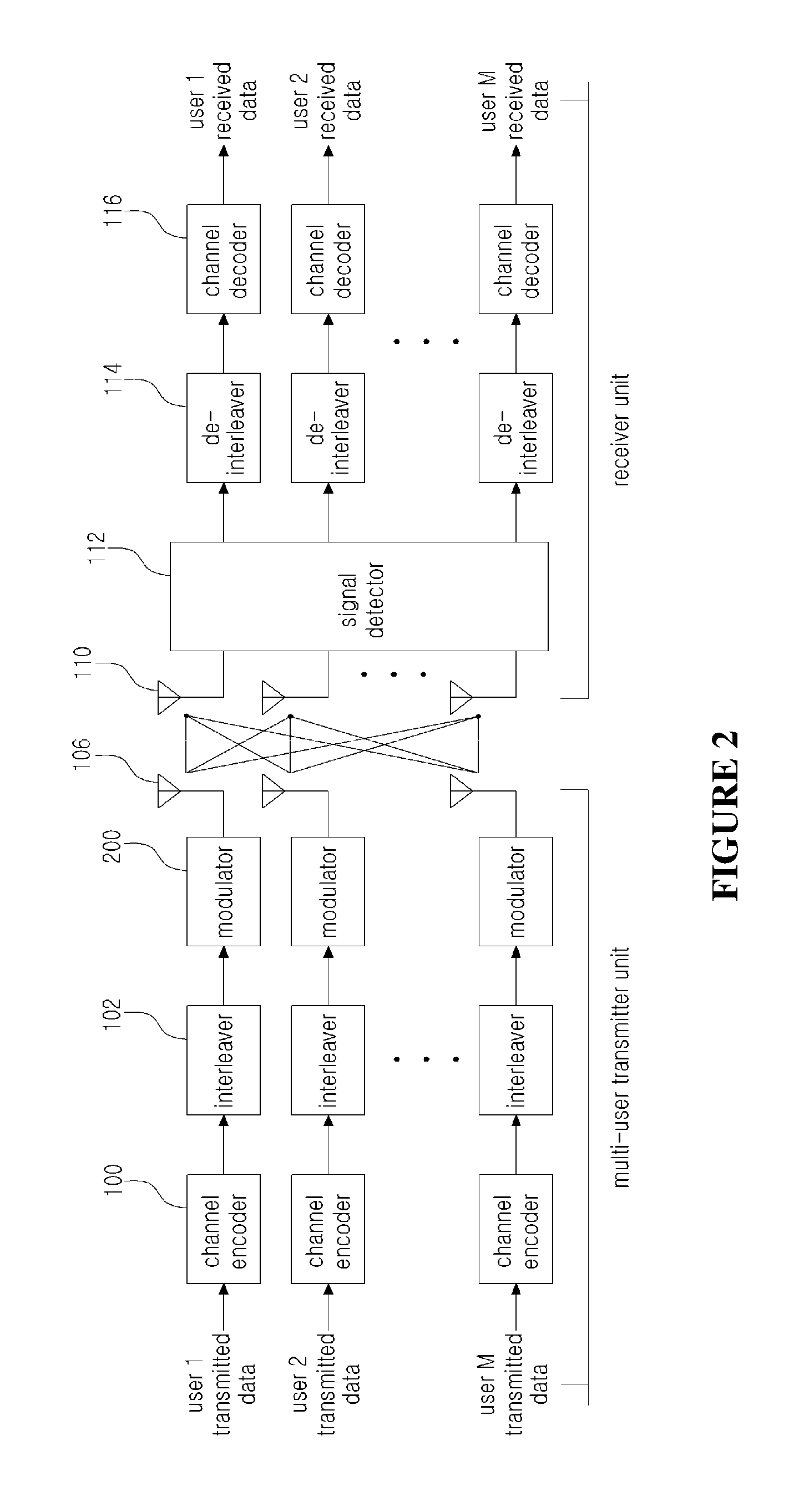
In radio technology, Spatial Multiplexing Gain (SMG) is achieved when a system is transmitting different streams of data from the same radio resource in separate spatial dimensions. Data is hence sent and received over multiple channels - linked to different pilot frequencies, over multiple antennas. This results in capacity gain at no additional power or bandwidth. SMG has had a large impact on the introduction of MIMO systems in wireless technology.
Airsync: enabling distributed multiuser MIMO with full multiplexing gain
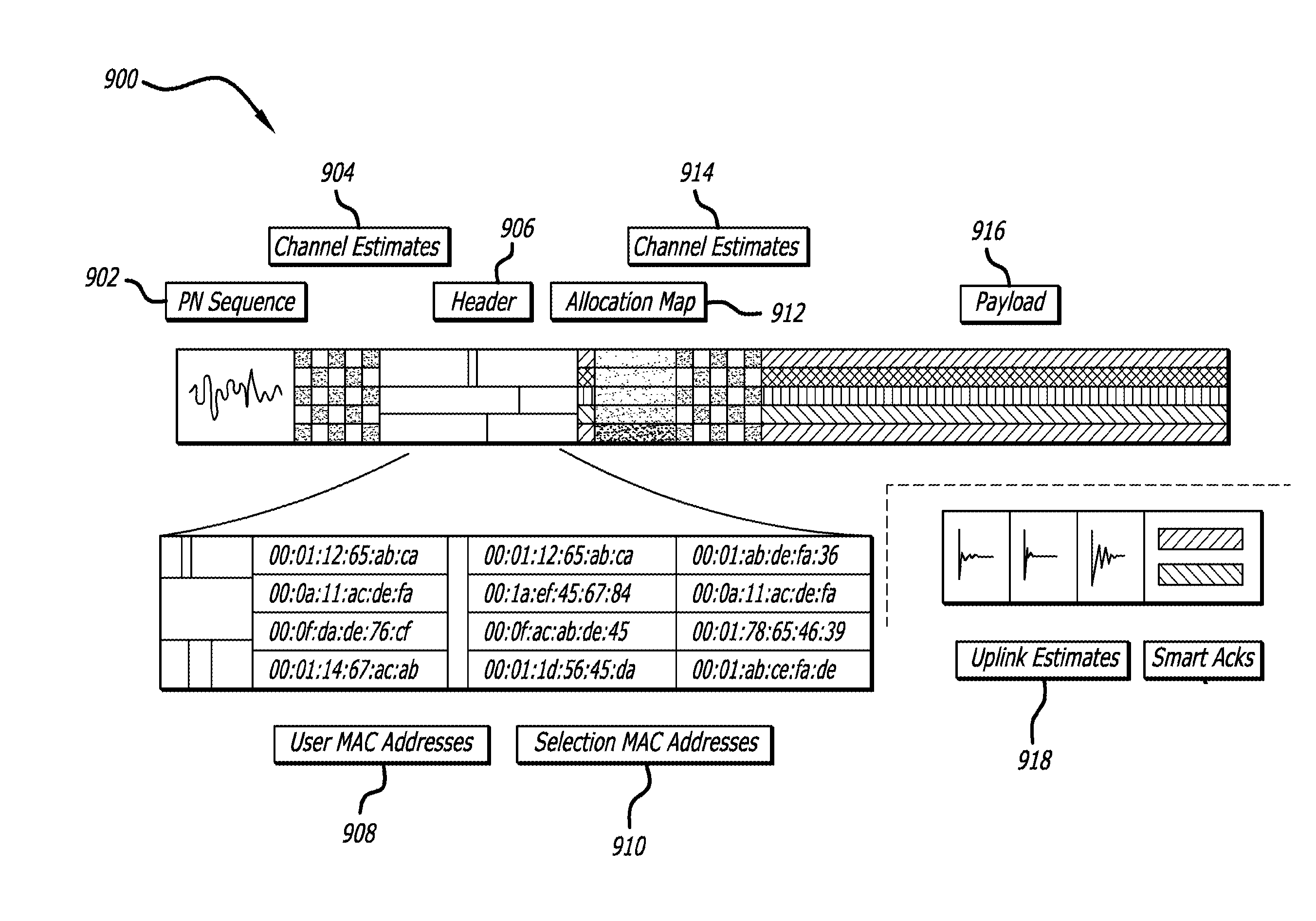
InactiveUS8995410B2Spatial transmit diversityTime-division multiplexData synchronizationCarrier signal
Time and phase synchronization may enable distributed multiuser multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) architectures and techniques, such as supported by the IEEE 802.11n standard, where several access points are connected to a central server and operate as a large distributed multi-antenna access point. The phase of all access points can be locked using a common reference (e.g., a synchronization tone) broadcasted over the air in conjunction with a predictive filter (e.g., a Kalman filter) which closely tracks the phase drift for each subcarrier channel.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
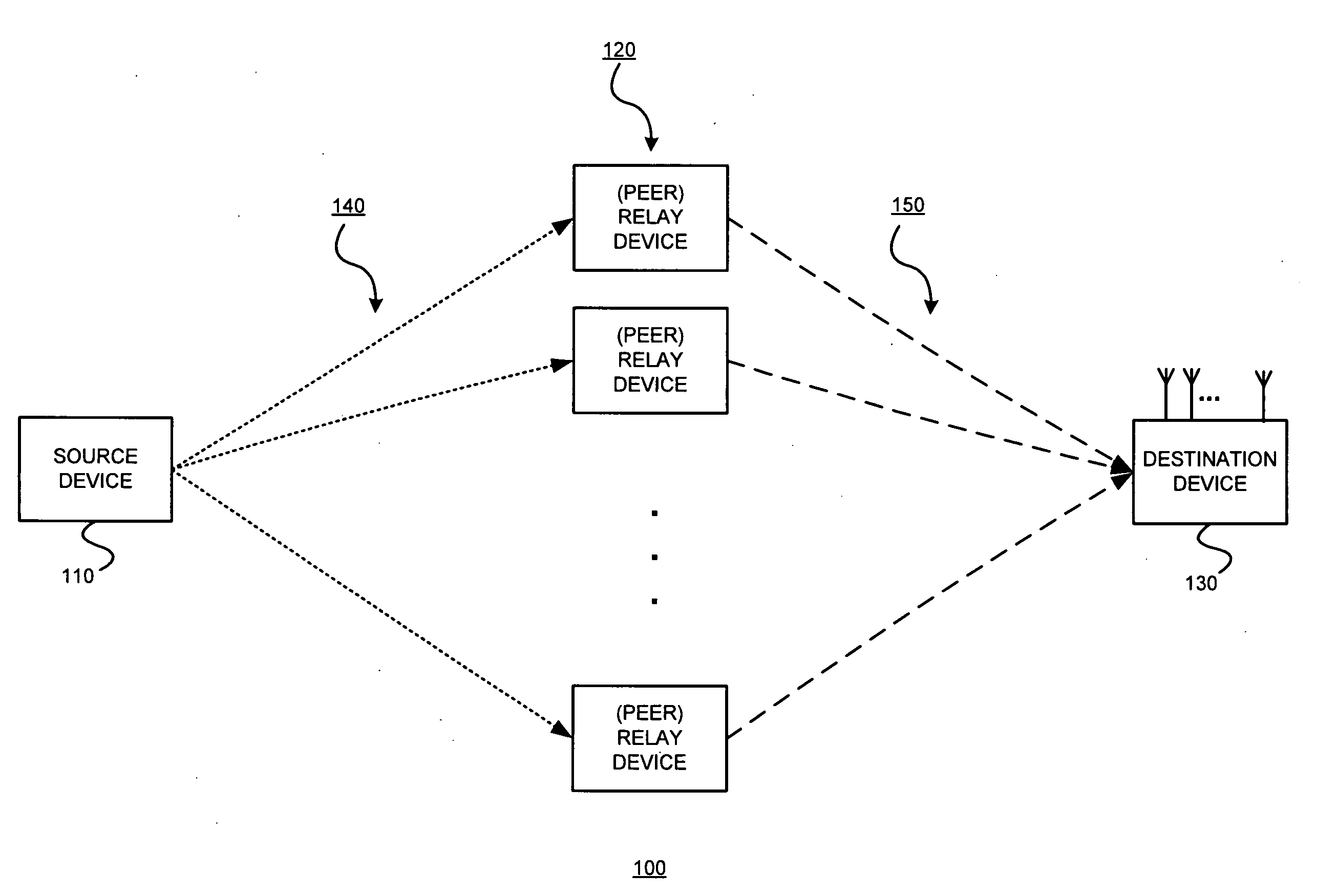
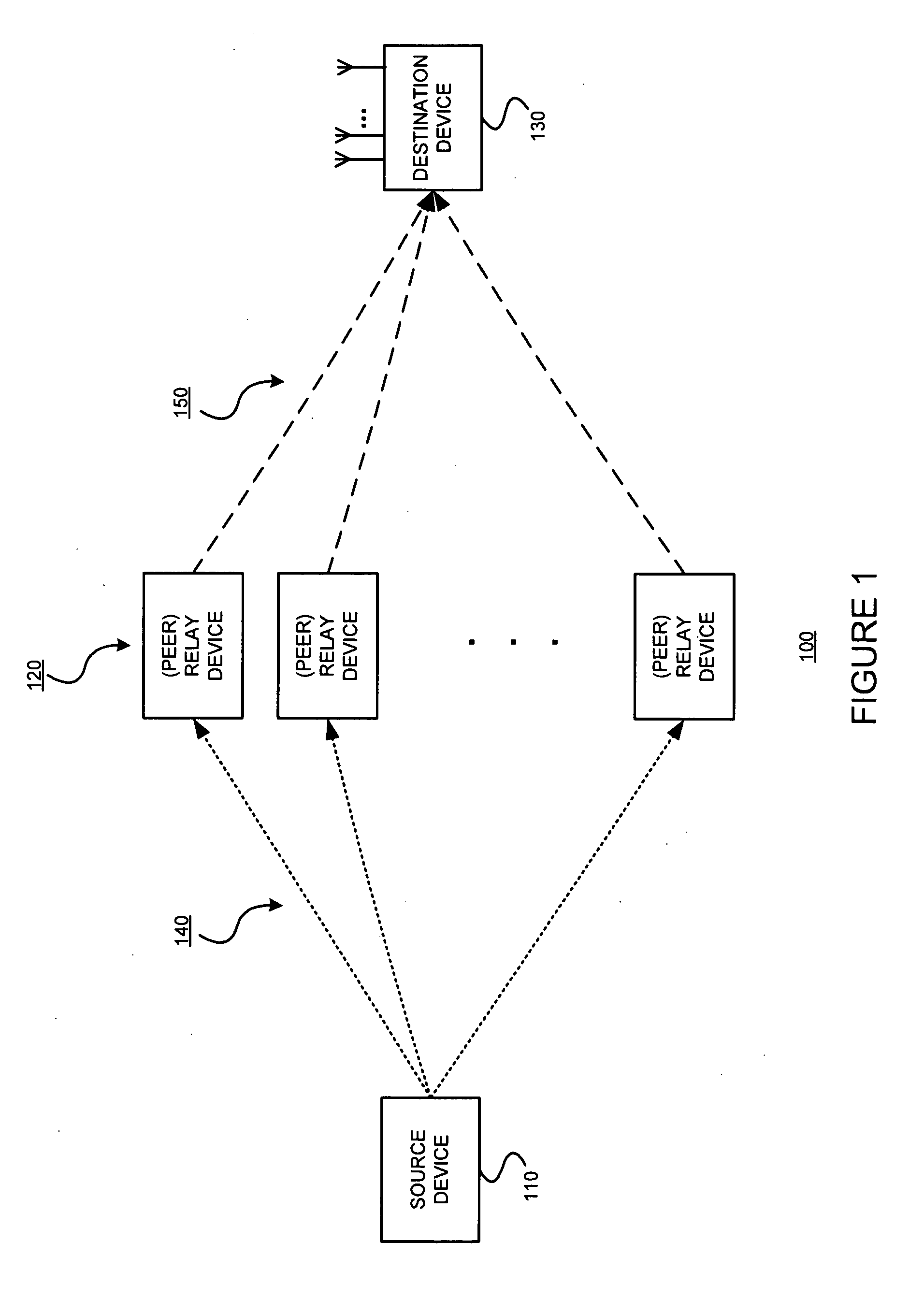
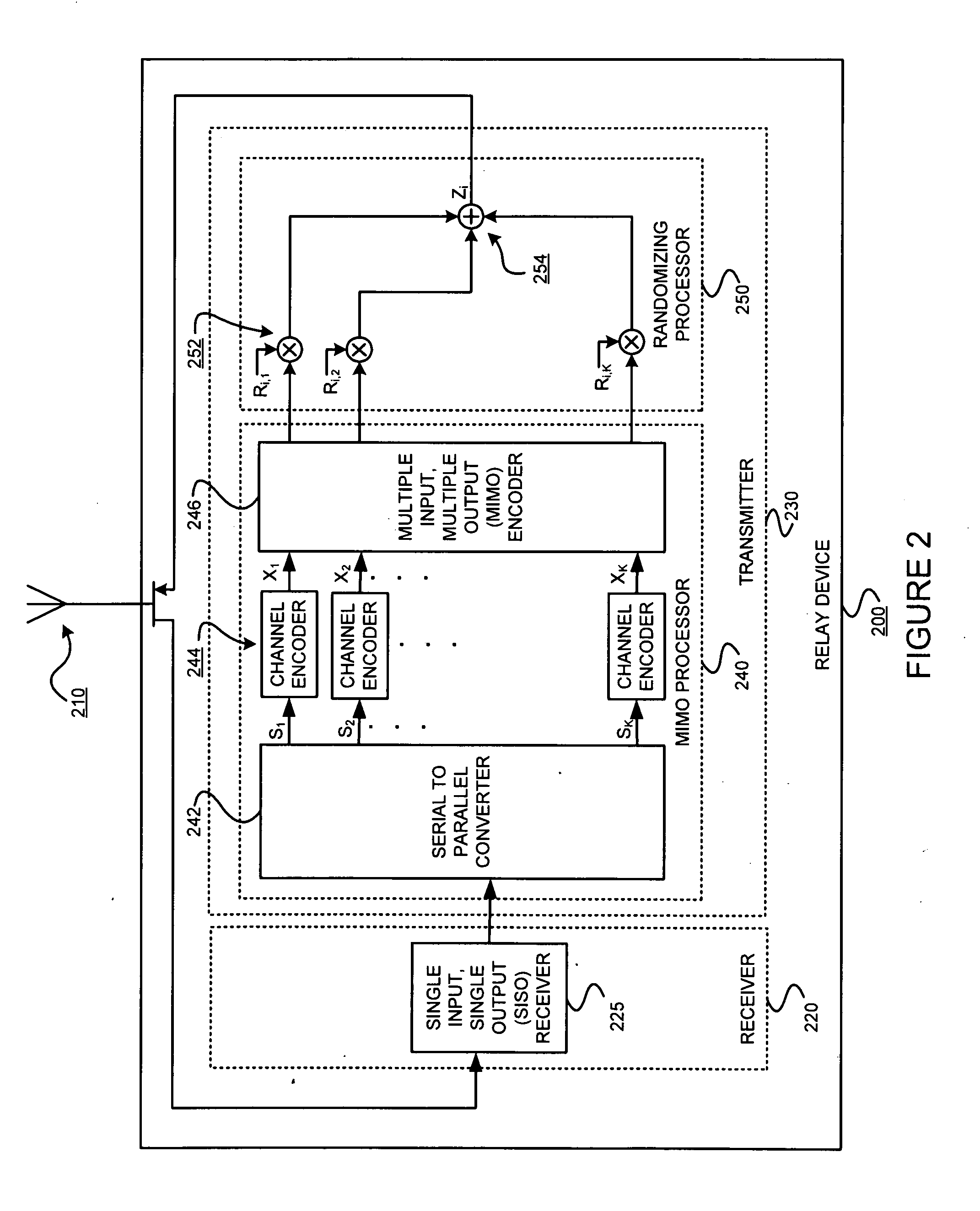
Spatial multiplexing gain for a distributed cooperative communications system using randomized coding
InactiveUS20090316763A1Relax requirementsIncrease spaceFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsCommunications systemData stream
Multiple cooperative relays operate in a highly mobile environment and form a virtual antenna array. Multiple independent streams of data can be simultaneously transmitted in parallel to the destination receiver. Thus a higher spatial multiplexing gain can be obtained. Such exemplary embodiments might do so by allowing each relay to transmit a linear combination of antenna waveforms according to an independently and randomly generated coefficient vector. This randomized cooperation scheme may be useful in an environment in which a group of relay devices are close to the source device, and can therefore receive information at a high rate. Each relay device that receives the information without errors splits it into multiple streams. For example, if the relay devices receive B symbols and the number of streams is K, each stream contains B / K symbols. Each relay device then generates a random linear combination of all the streams and transmits this output simultaneously with the other relay devices.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
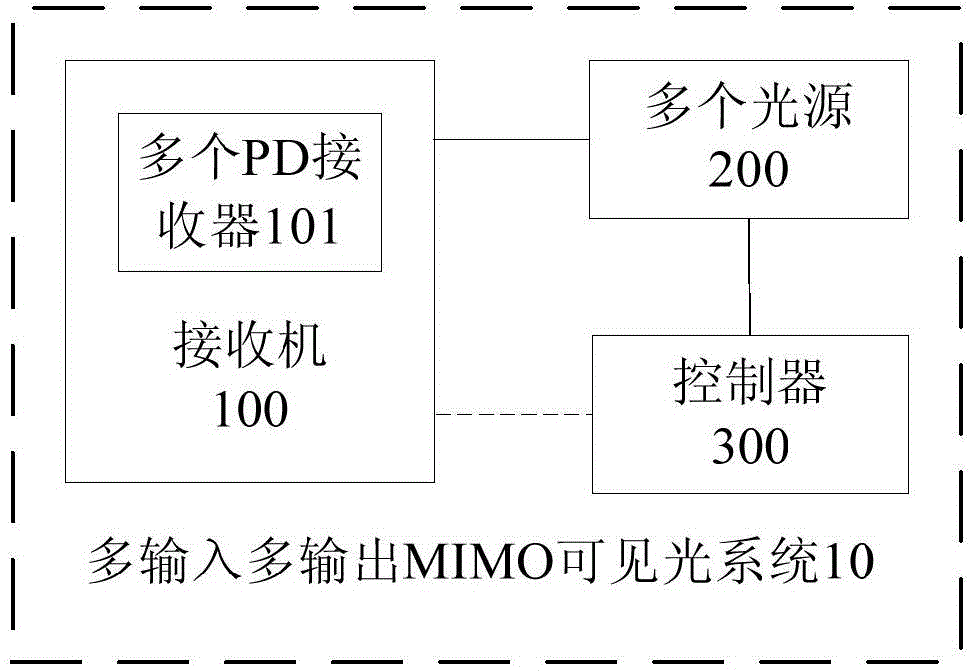
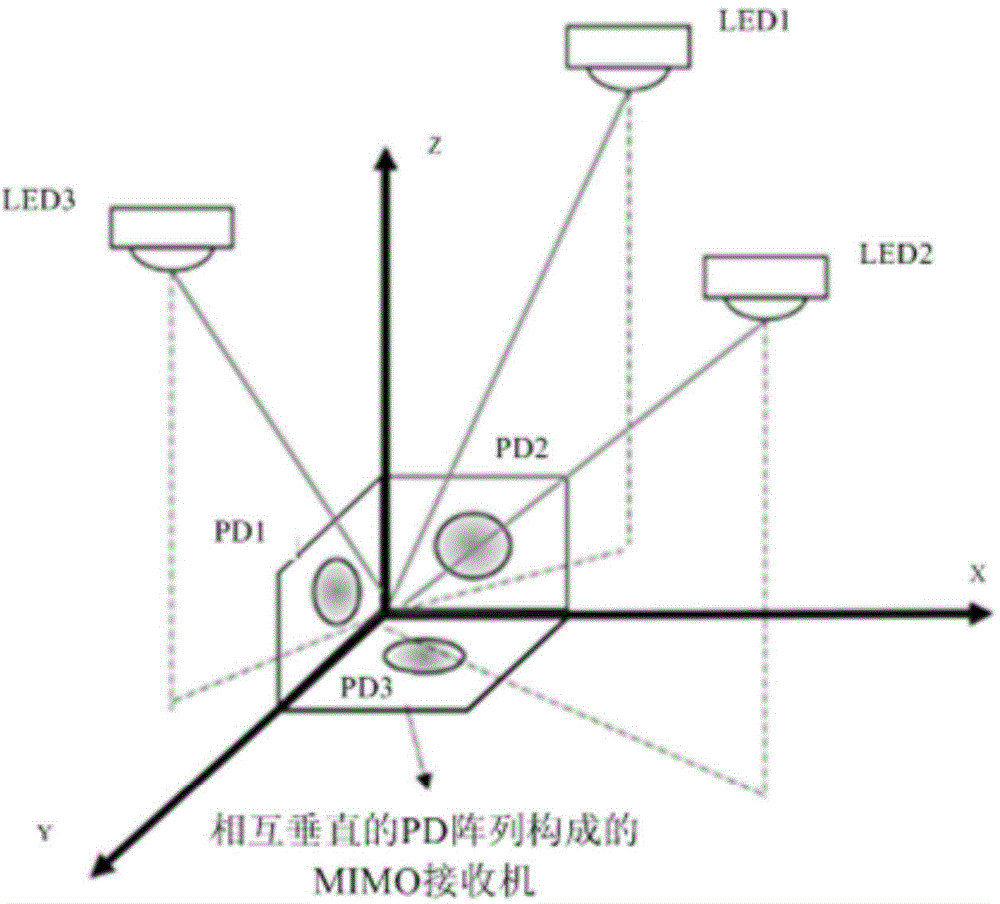
Multiple-input-multiple-output visible light MIMO system
InactiveCN104980216AReduce correlationImprove space reuse efficiencyClose-range type systemsTraining phaseOptoelectronics
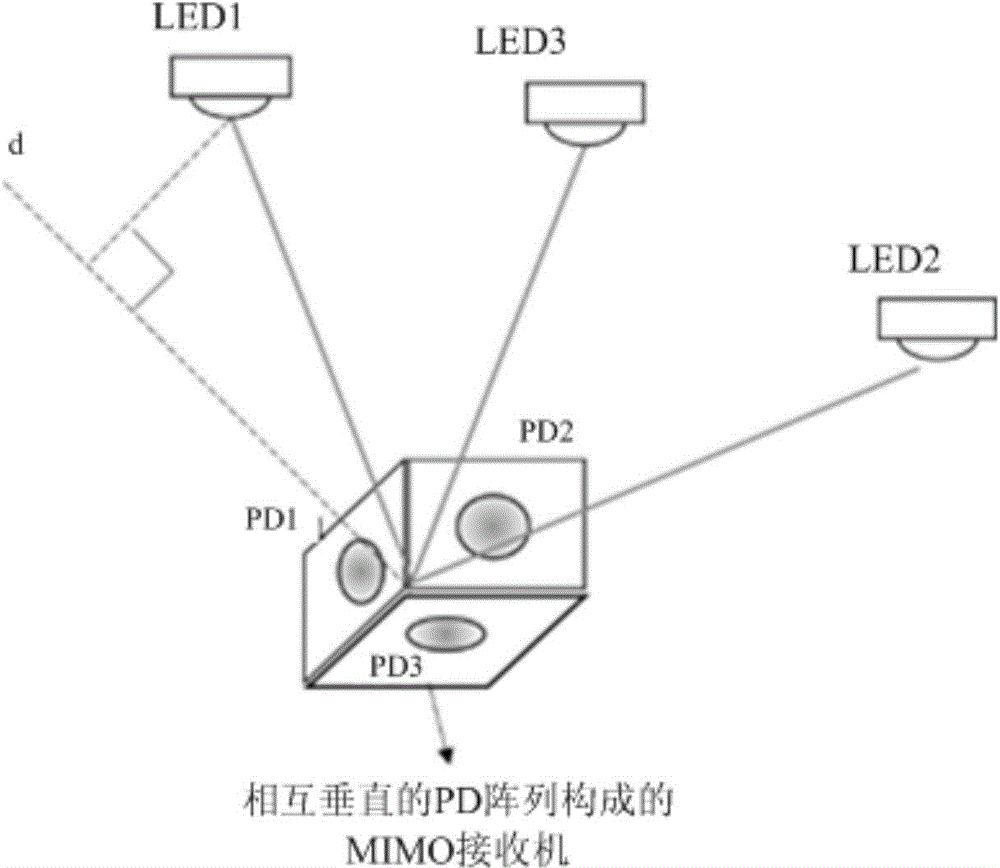
The invention discloses a multiple-input-multiple-output visible light MIMO system comprising a receiver which comprises multiple PD receptors; multiple light sources which are arranged at different positions, wherein the connecting lines between any two light sources of the multiple light sources and the receiver are not in the same straight line; and a controller which independently controls each light source to emit light signals in different power in a training phase respectively so that a gain matrix is obtained according to light intensity of each light source received by the receiver, multiple light sources are controlled to emit the light signals simultaneously in a communication phase, emitting power of each light source is obtained according to the gain matrix and light intensity received by the receiver at the time, and thus the light signals emitted by different light sources can be distinguished. According to the system of the embodiment, correlation among all sub-channels can be effectively reduced, spatial multiplexing efficiency can be enhanced and spatial multiplexing gain can be acquired.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +2
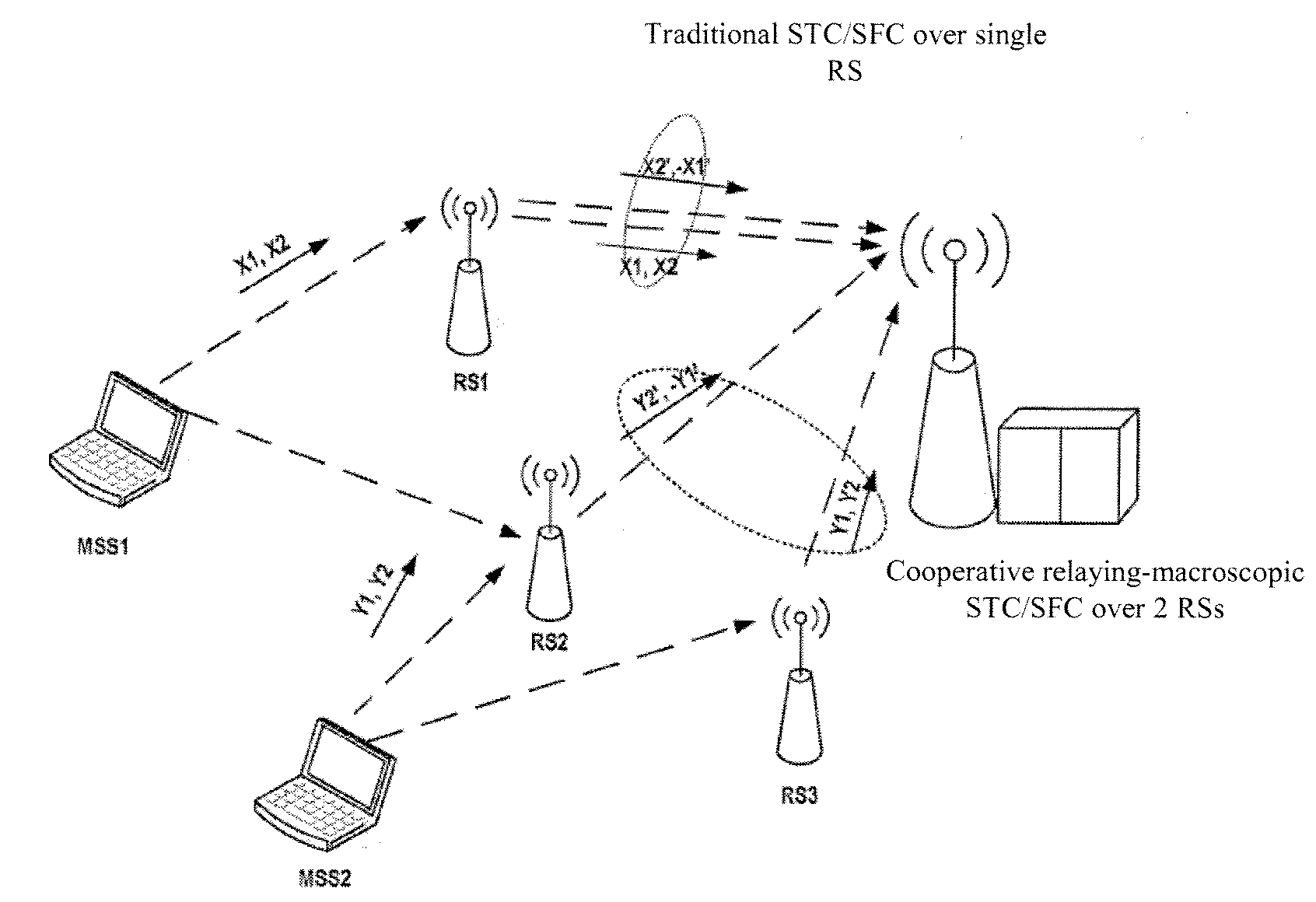
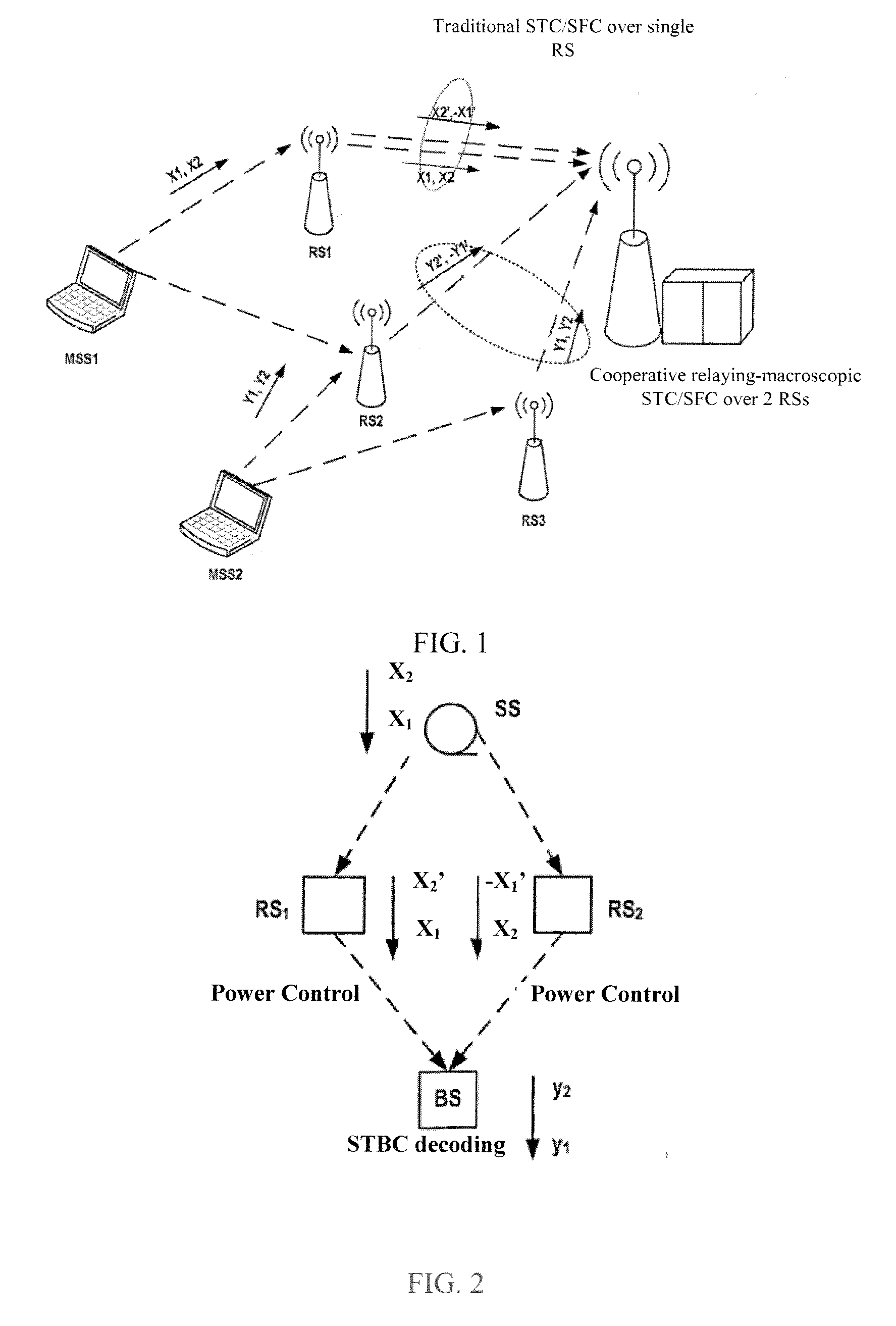
Method and device for cooperative relay with multiple relay stations in wireless telecommunication network
ActiveUS20090103472A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexMultiplexingMulti hop relay
The invention provides a method and device for cooperative relay with multiple relay stations in the wireless telecommunication network. To be specific, according to the invention, in single-hop or multi-hop relay telecommunication link, the relay device and other relay devices within the same hop select space diversity or space multiplexing to carry out cooperative relay operation according to the processing indicating information from the base station, thus obtaining space diversity gain and space multiplexing gain.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
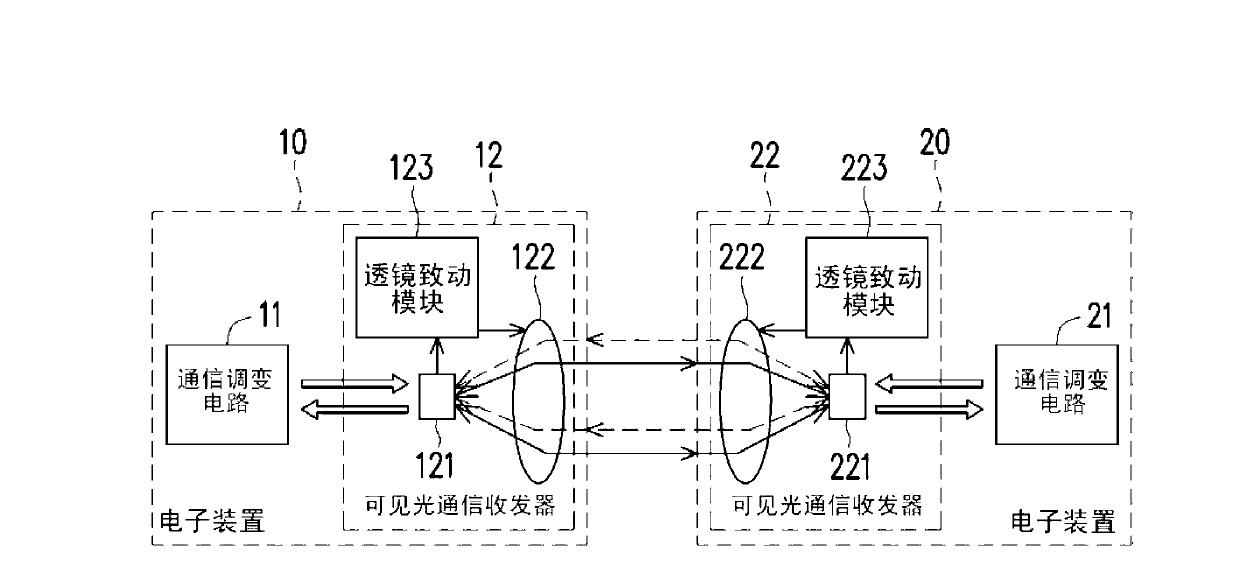
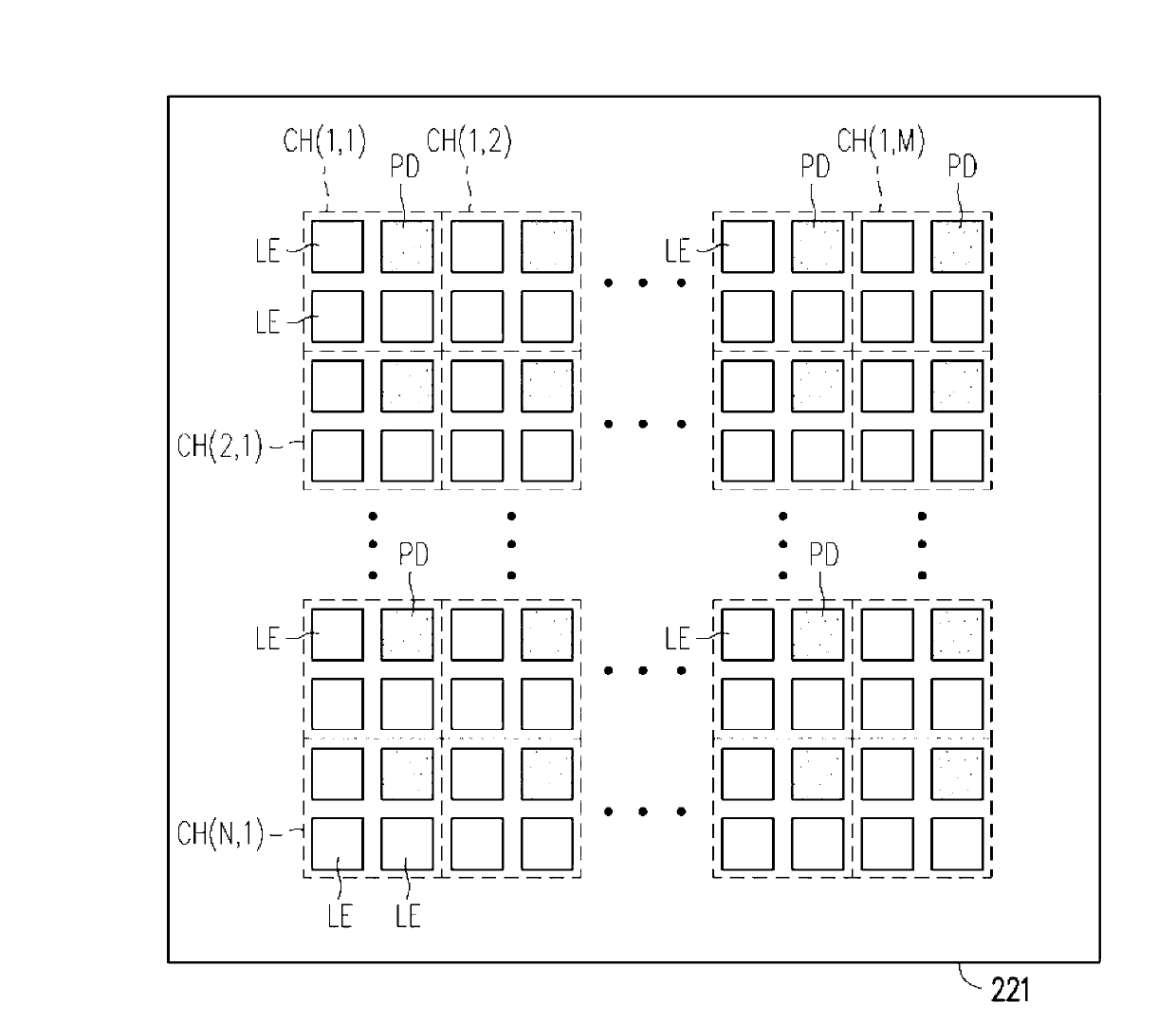
Visible light communication transceiver and system
A visible light communication (VLC) transceiver and a VLC system are provided. The VLC transceiver includes a substrate, a lens module and a plurality of channel units. The channel units are disposed on the substrate in an array to provide different bidirectional communication channels. Wherein, each of the channel units respectively includes at least a visible light emitter and at least a visible light receiver. The channel units can enhance communication bandwidth by using modulation technology such as spatial multiplexing or time multiplexing. The lens module is disposed on an optical path of the channel units. The lens module actively tracks the receiving situation of the visible light receiver to improve the signal quality of high-speed multiplexing communication.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
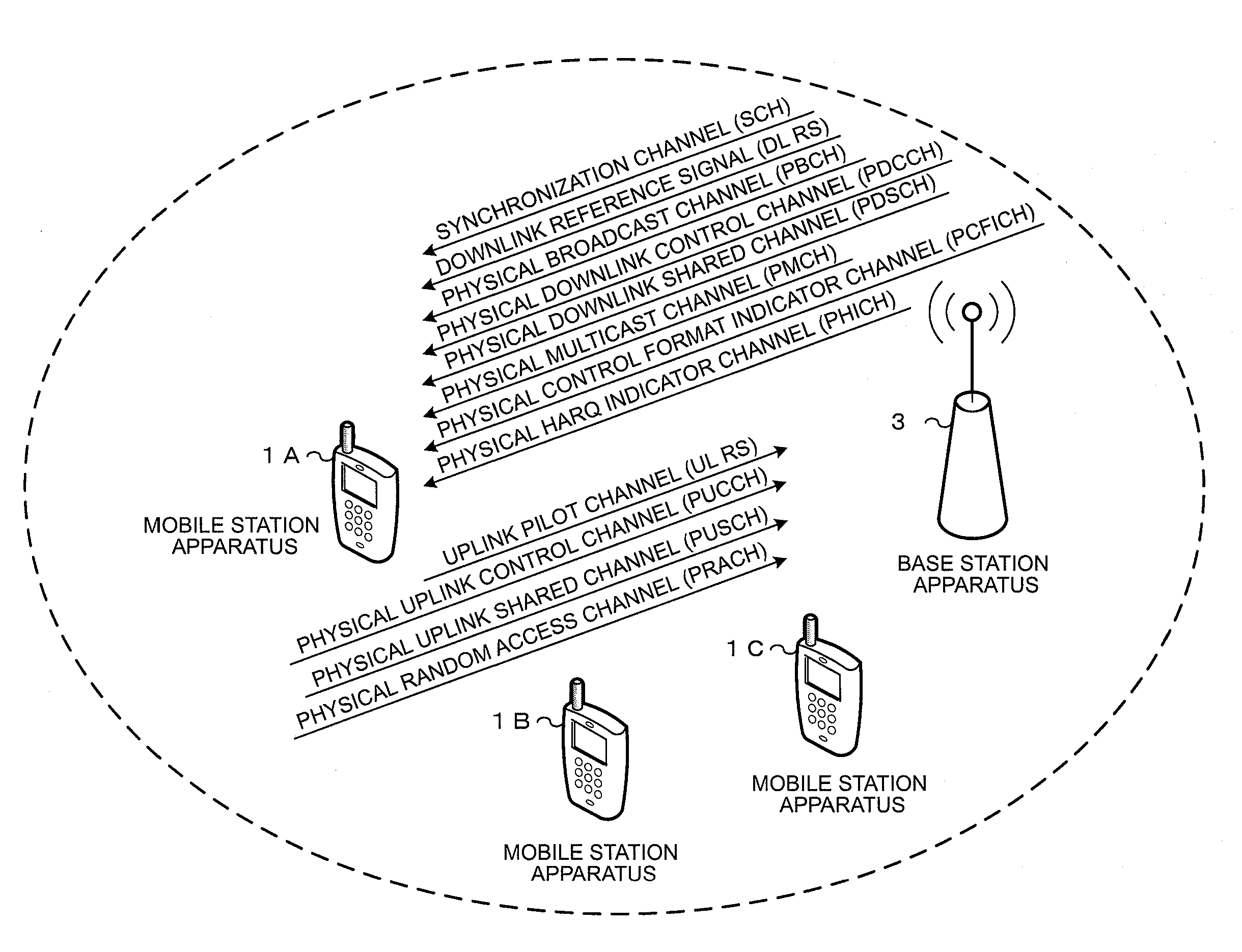
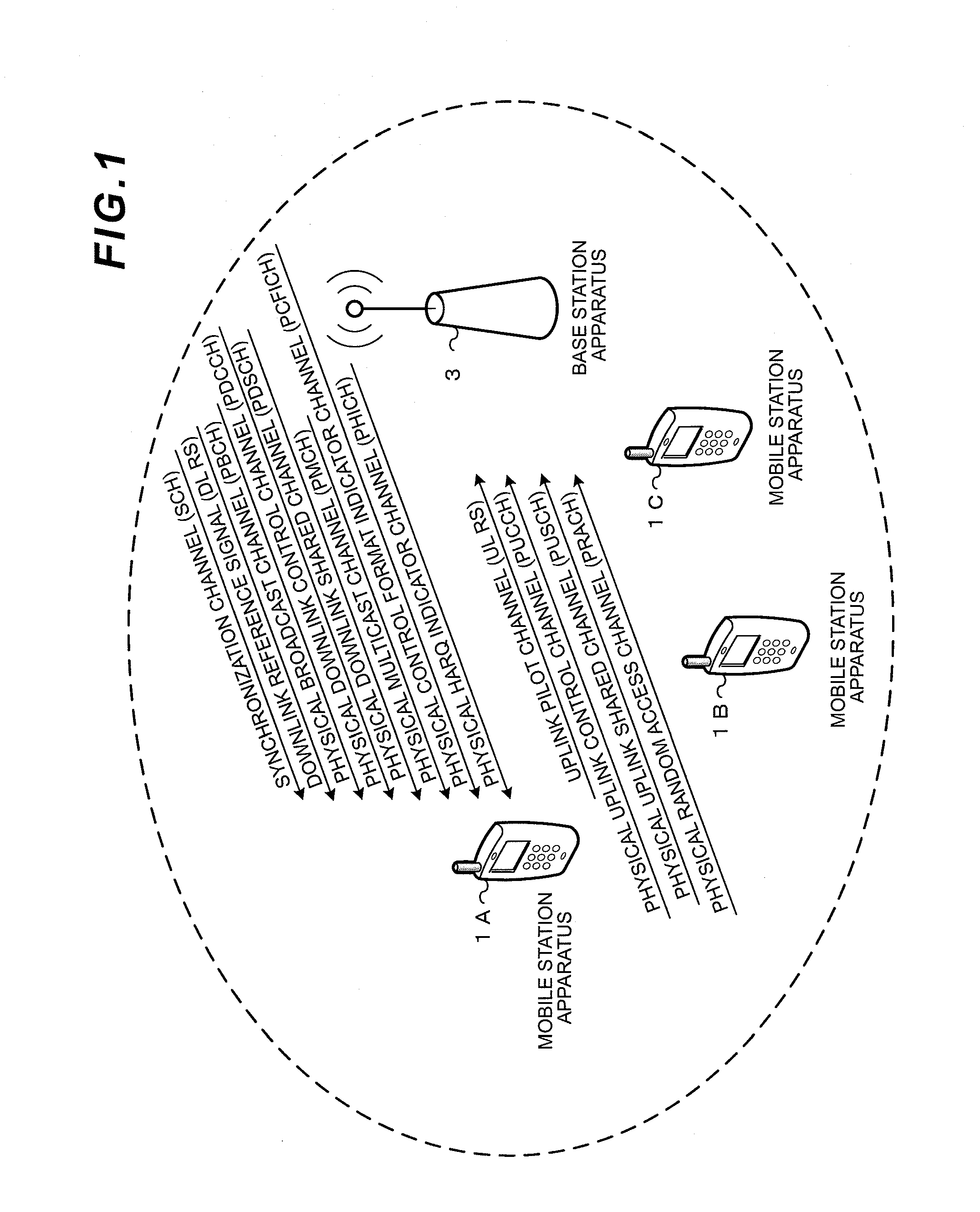
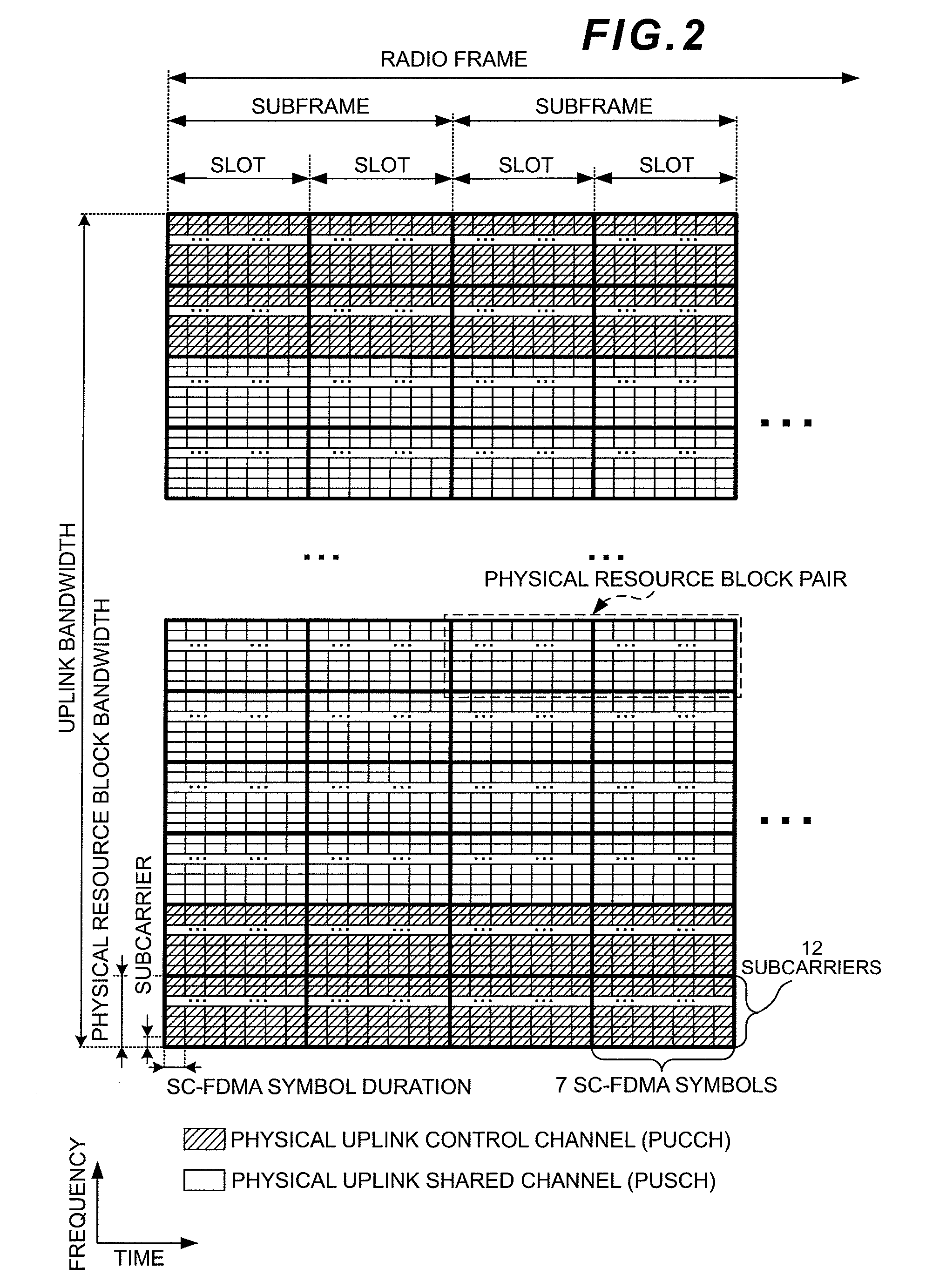
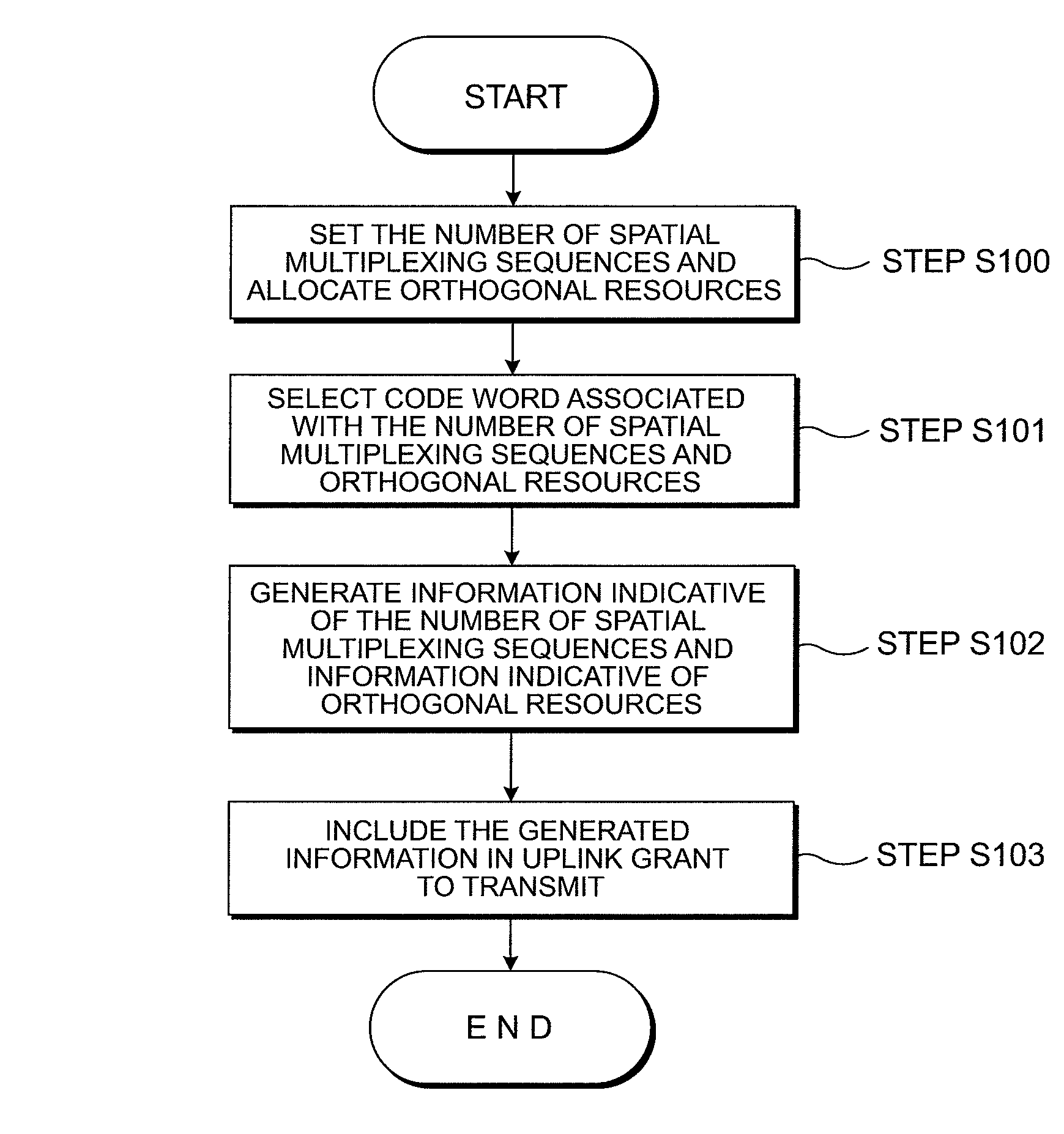
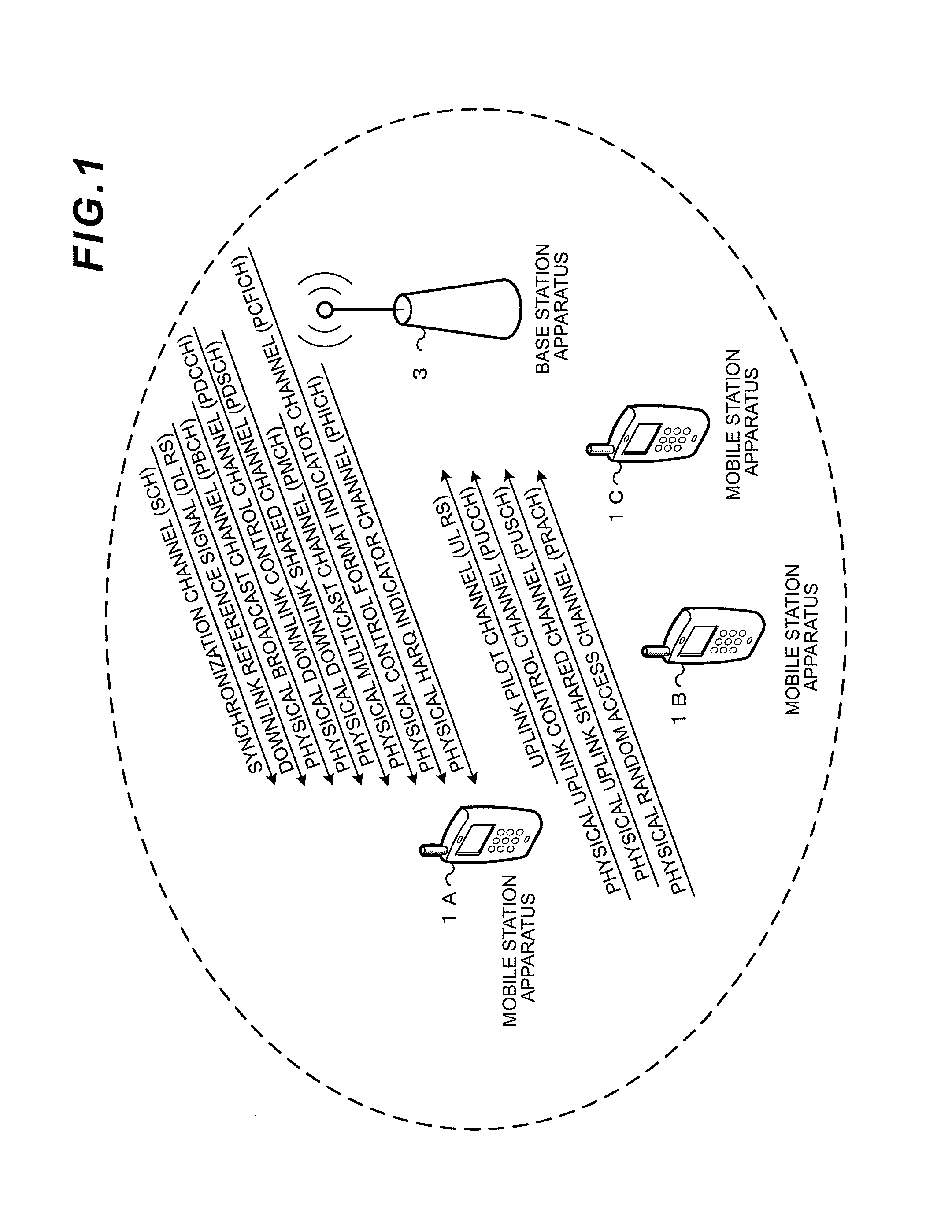
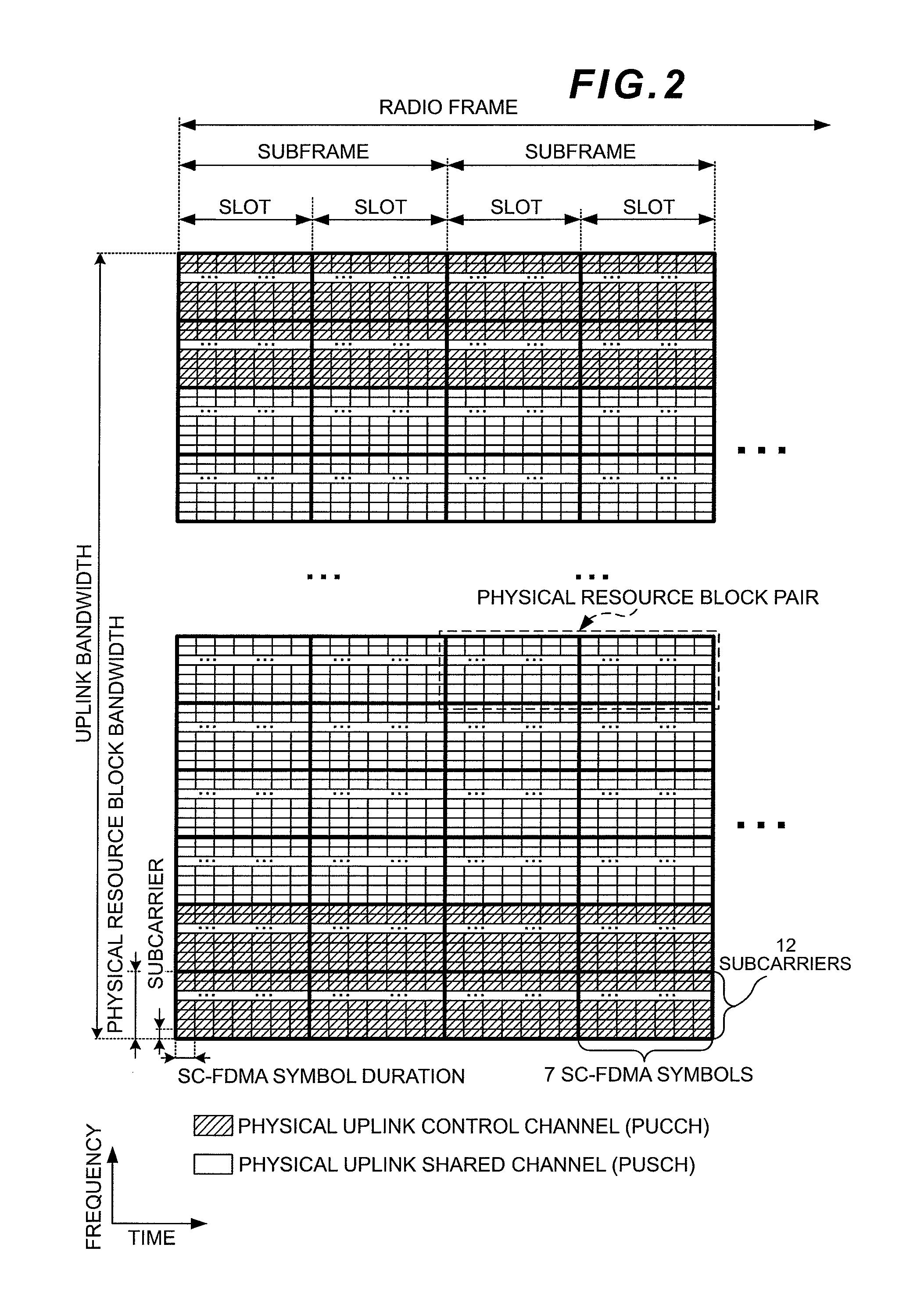
Wireless communication system, base station apparatus, mobile station apparatus, wireless communication method and integrated circuit
ActiveUS20120269144A1Signal allocationRadio transmissionCommunications systemSpatial multiplexing gain
In a wireless communication system a base station apparatus and a mobile station apparatus communicate with each other. The base station sets the number of spatial multiplexing sequences (rank) of data being used by the mobile station when transmitting a PUSCH, further sets orthogonal resources used by the mobile station for the same number of reference signals as the set number of spatial multiplexing sequences which are transmitted together with the PUSCH, and transmits downlink control information indicating the number of spatial multiplexing sequences and information indicating the orthogonal resources for the reference signals. The mobile station receives the downlink control information, selects orthogonal resources to respectively apply to the reference signals, applies the selected orthogonal resources to generate the reference signals, and transmits the generated reference signals to the base station apparatus.
Owner:SHARP KK
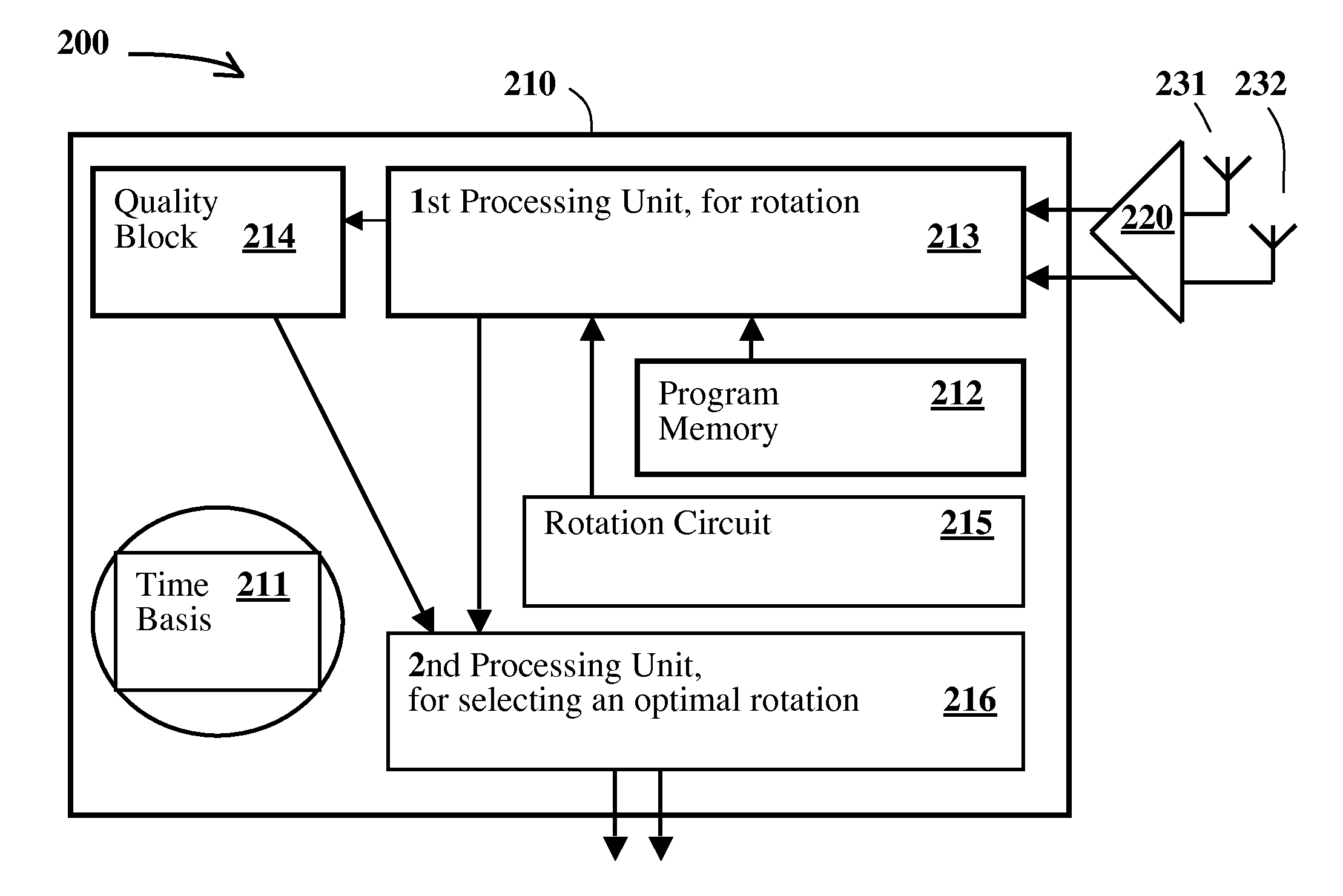
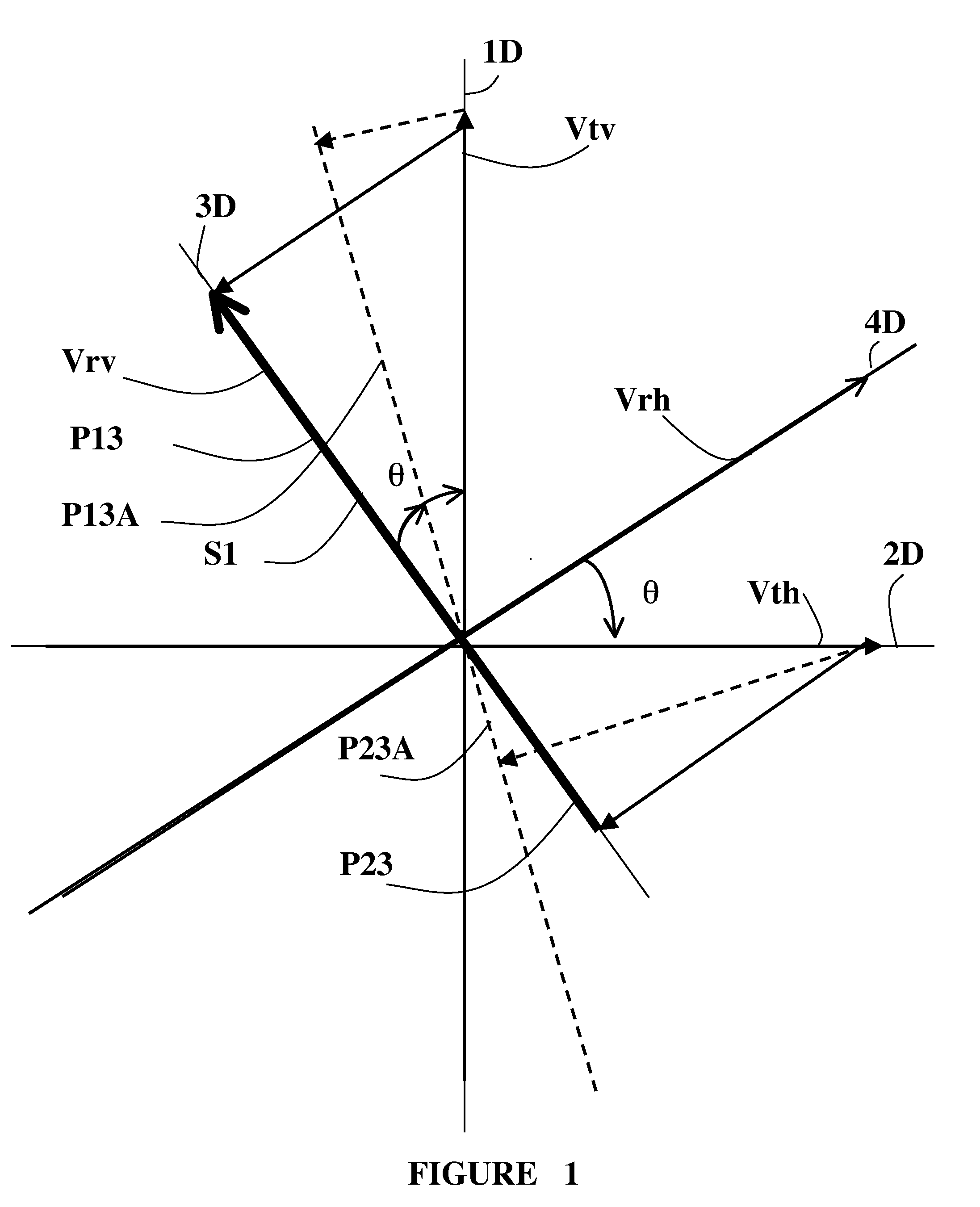
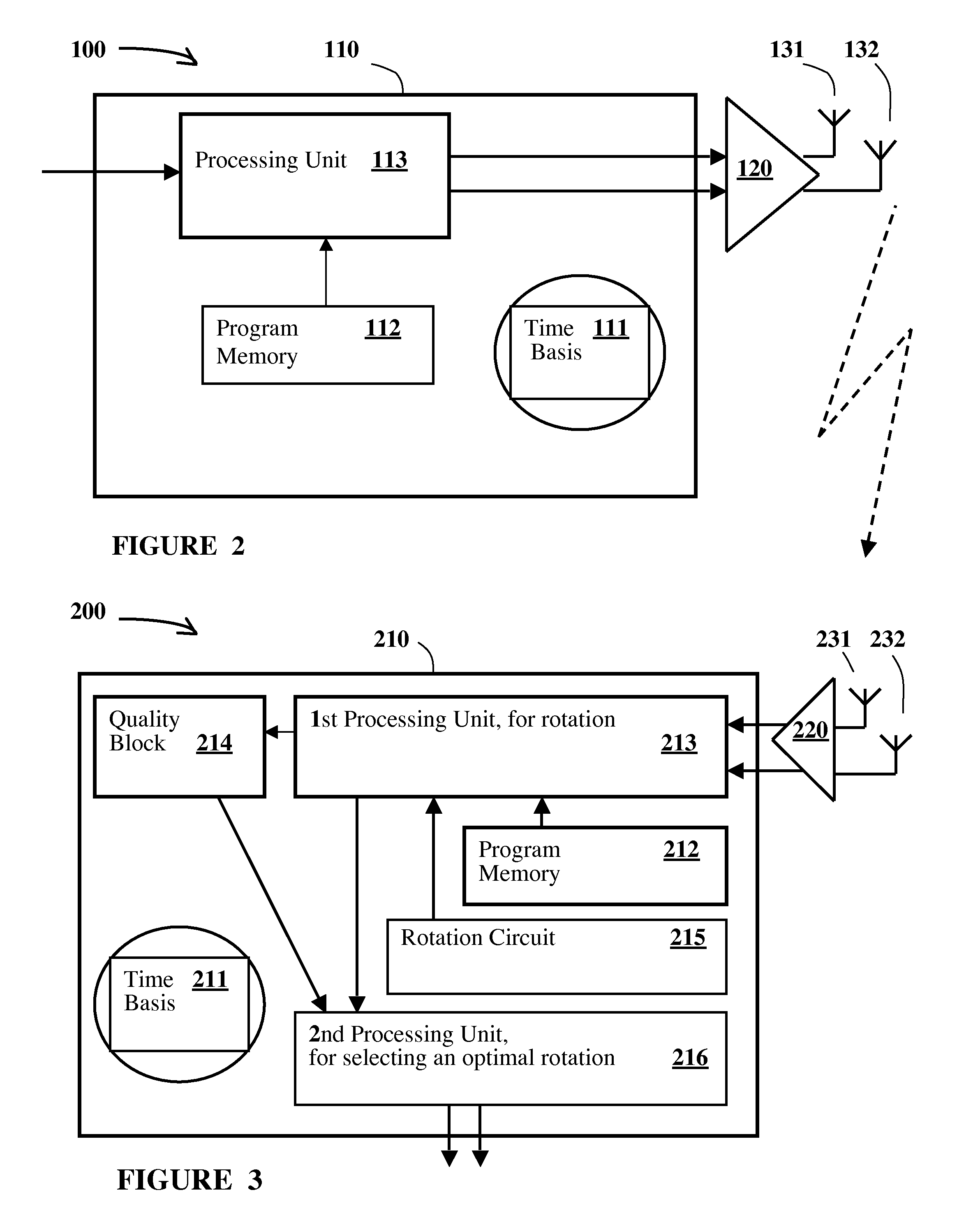
Wireless Communications Method and System With Spatial Multiplexing Using Dually Polarized Antennas and Corresponding Receiver
ActiveUS20100135445A1Load shiftEasy to processPolarisation/directional diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionSpatial multiplexing gainTransmitter antenna
A method is provided for transmitting radio signals. Two channels are defined by two transmit antennas, having two orthogonal directions, together with two receive antennas, having two orthogonal directions. An optimal quality of one received signal is determined by signal processing, which emulates a rotation of the two orthogonal receive directions, and a mutual interference of the signals received on the two channels, due to a polarization mismatch, is cancelled, based on a corresponding optimal rotation angle.
Owner:SEQUANS COMMUNICATIONS
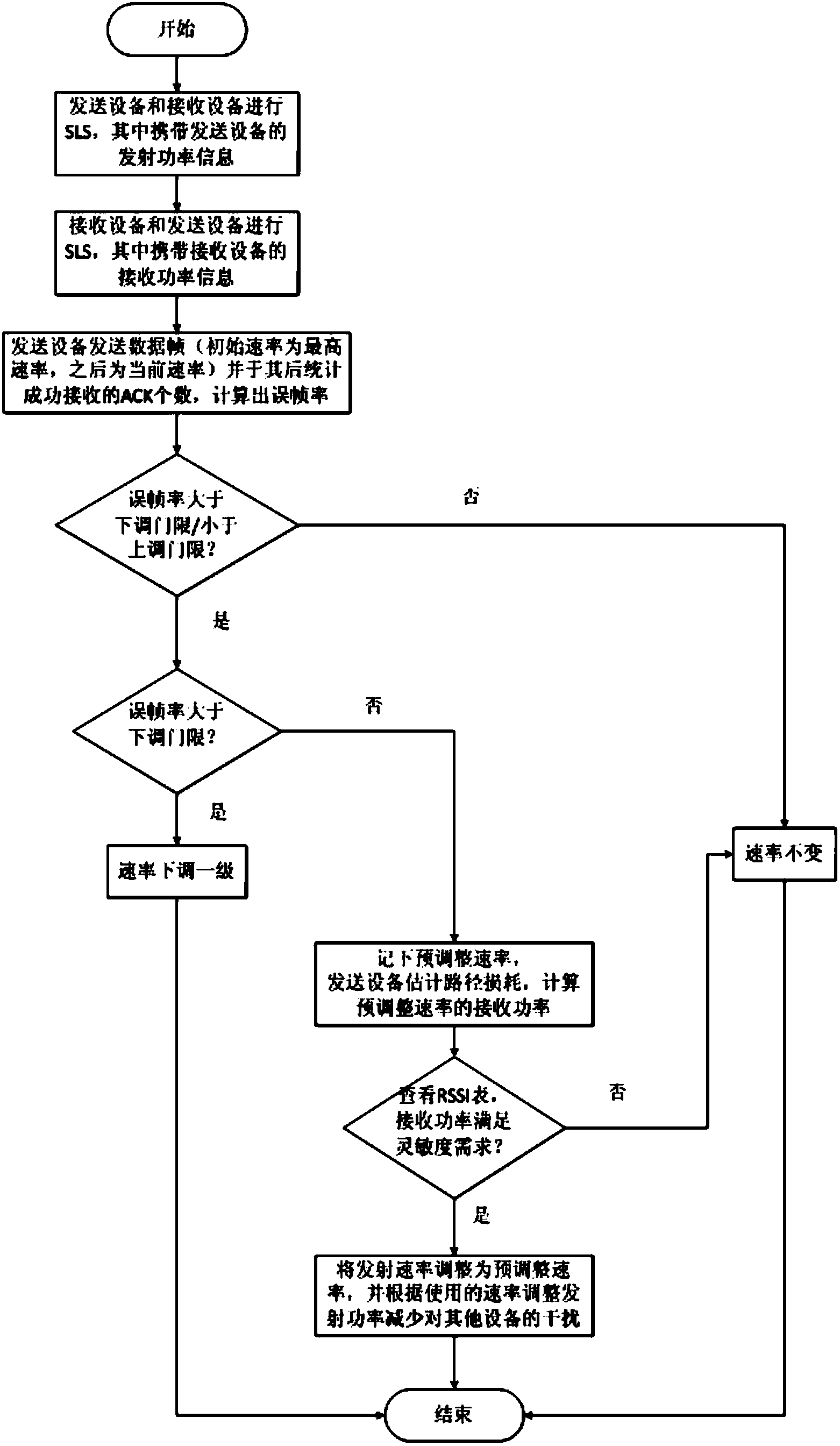
Rate-self adaptive method under spatial multiplexing in millimeter wave high speed communication
InactiveCN103916943AReduce distractionsRobustPower managementTelecommunications linkTransmitted power
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
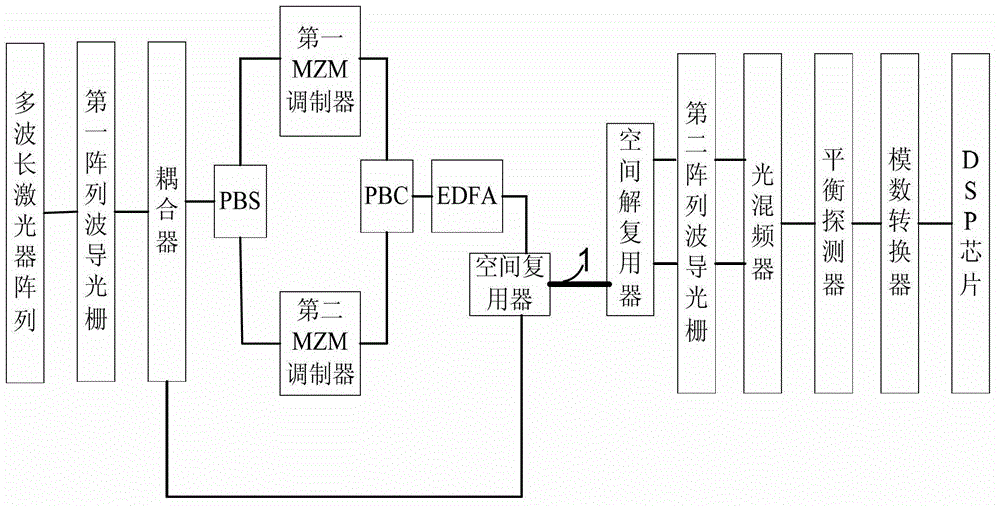
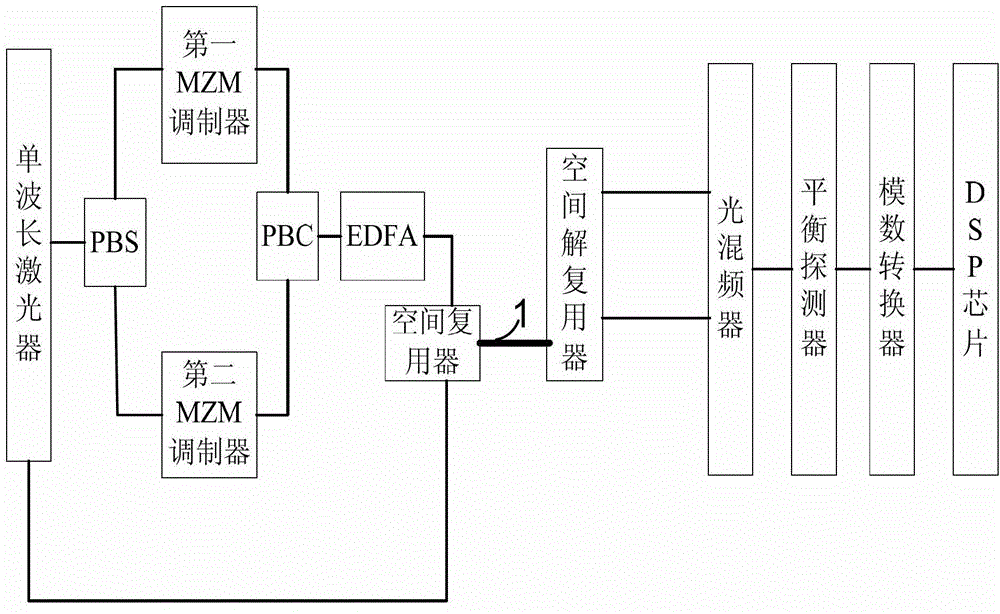
Spatial multiplexing-based non-local oscillation coherent receiving optical fiber communication system
The invention relates to the technical field of optical fiber communication, in particular to a spatial multiplexing-based non-local oscillation coherent receiving optical fiber communication system. The spatial multiplexing-based non-local oscillation coherent receiving optical fiber communication system comprises a light source input unit, a light signal modulation unit, a spatial multiplexing and demultiplexing unit, a light signal conversion unit and an electric signal processing unit; the light source input unit is connected with the spatial multiplexing and demultiplexing unit through the light signal modulation unit; the light source input unit is also connected with the spatial multiplexing and demultiplexing unit; and the spatial multiplexing and demultiplexing unit is connected with the electric signal processing unit through the light signal conversion unit. By the spatial multiplexing-based non-local oscillation coherent receiving optical fiber communication system provided by the invention, an expensive narrow-linewidth adjustable local oscillation light source at a receiving end is eliminated, and the complexity degrees of the frequency estimation and the phase retrieval algorithm of the receiving end are reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Energy-efficient power and offset allocation of spatial multiplexing in multimode fiber
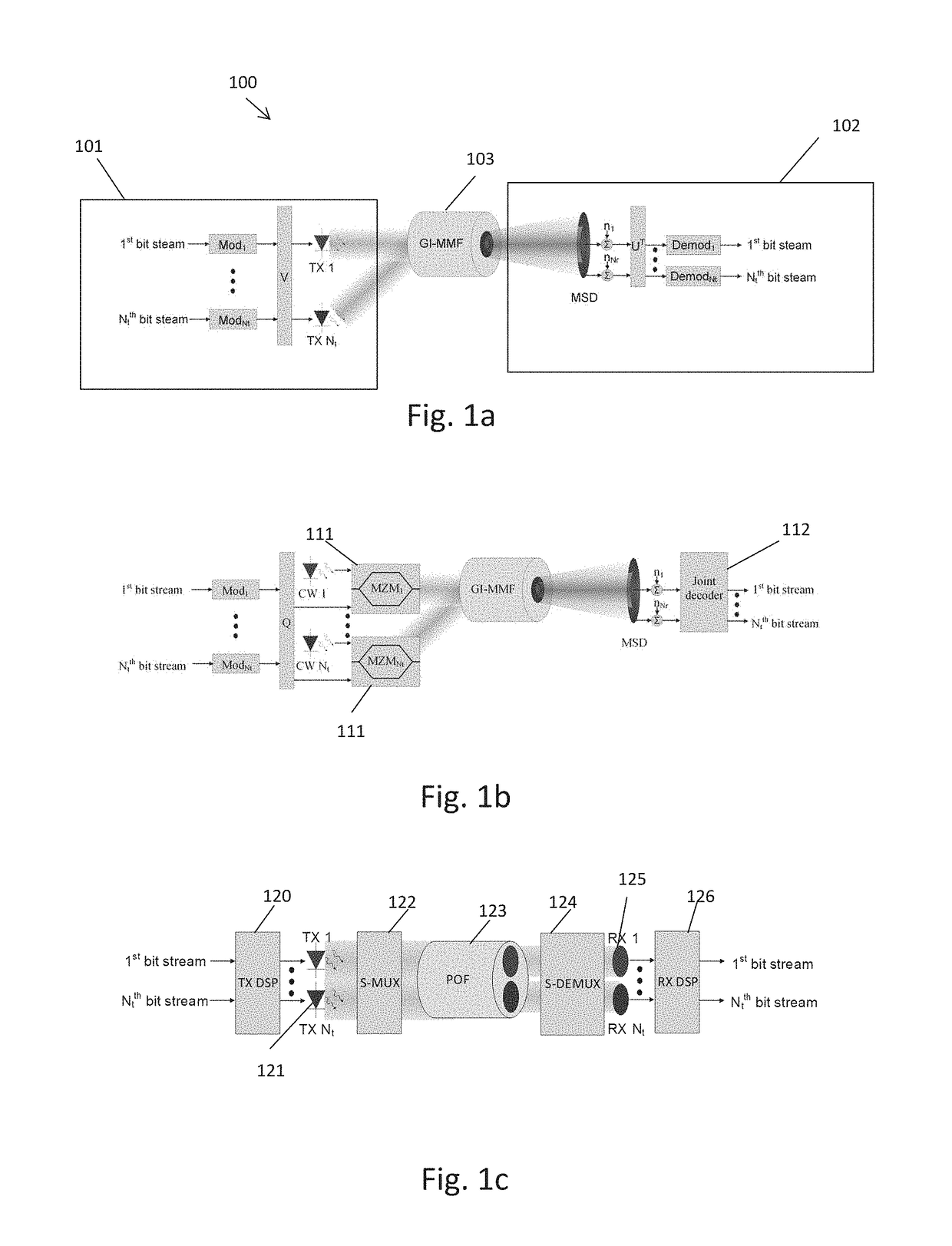
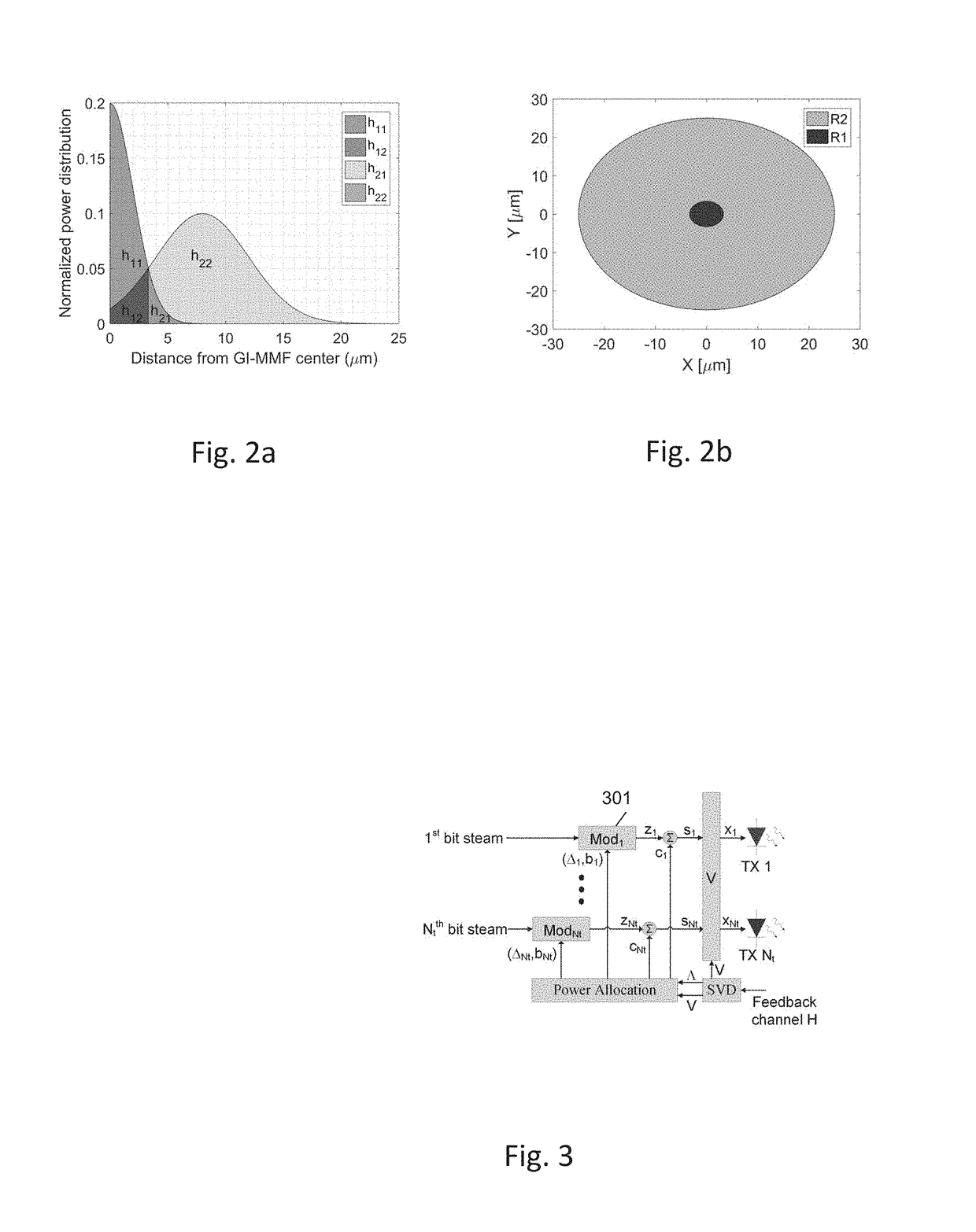
ActiveUS10236952B1Maximize capacityMinimize power consumptionPower managementSpatial transmit diversityFiberEngineering
A system for optimizing power allocation for each optical transmitter in an optical transmission system, the system comprises at least two intensity modulated optical transmitters, each of which is controlled by a modulator; an optical channel that can be spatially multiplexed by a multiplexer; and at least two optical detectors, for detecting the transmitted modulated signals. Each of the modulators are adapted to modulate the transmitters such that the electrical power consumption of the optical transmitters is minimized by a modulation scheme of the modulators, that uses energy efficient convex optimization to multiplex the transmitted optical signals, by the multiplexer in a multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) scheme. Each of the modulators are adapted to modulate the transmitters such that the capacity is maximized by a modulation scheme of the modulators, that uses energy efficient convex optimization to multiplex the transmitted optical signals, by the multiplexer in a multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) scheme.
Owner:B G NEGEV TECH & APPL LTD
Apparatus and method for selecting antennas and nodes MIMO communication system
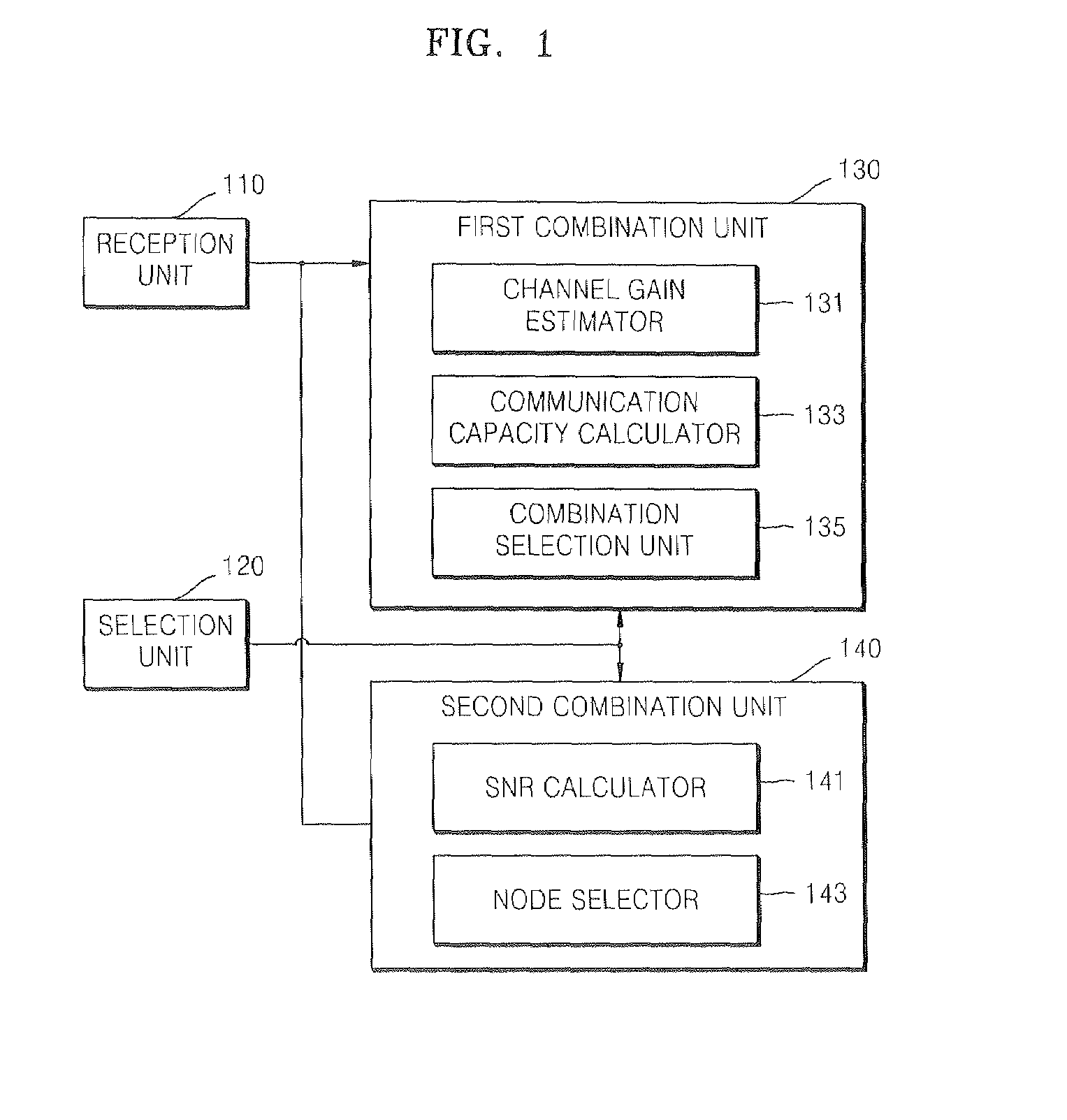
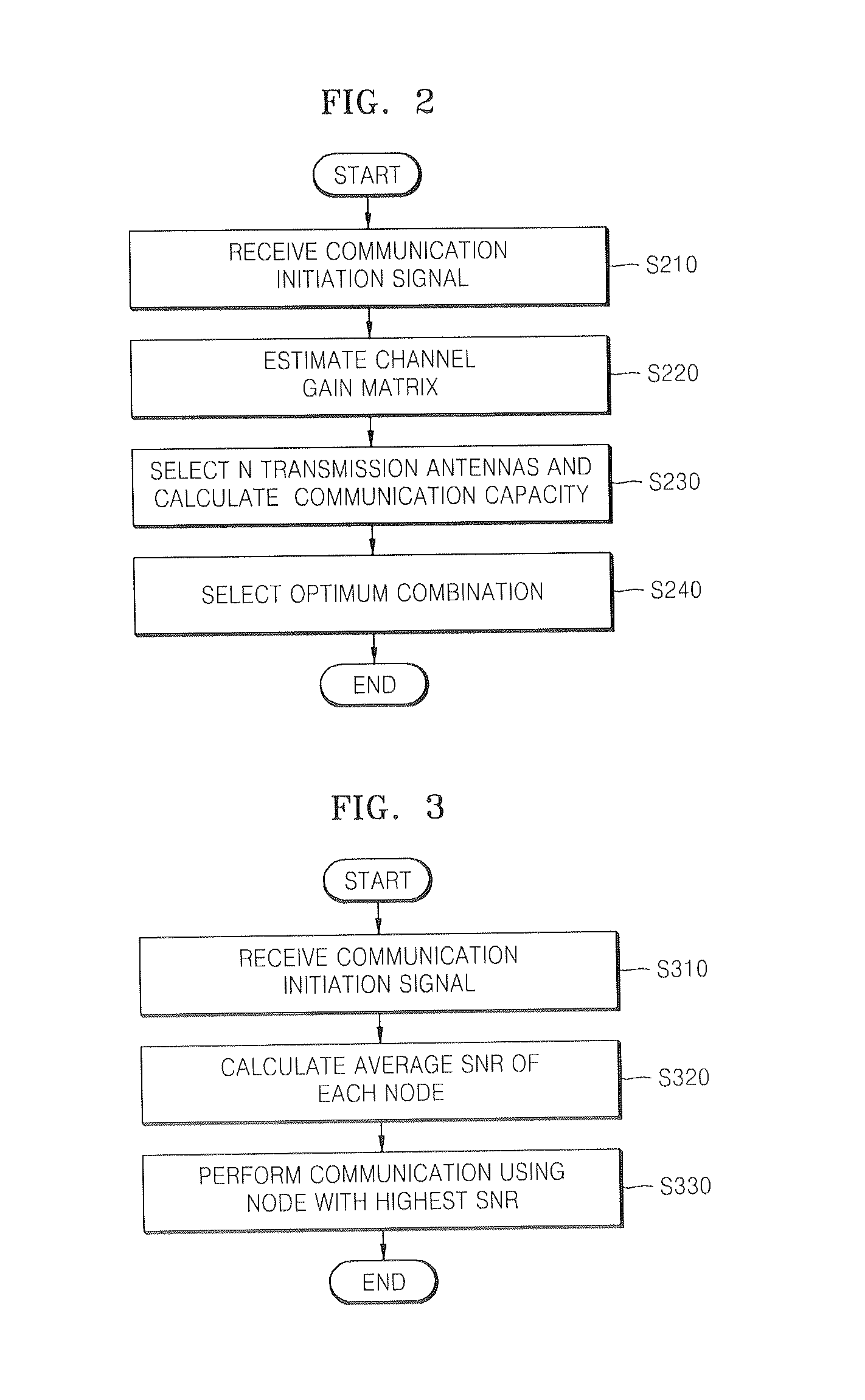
InactiveUS20080081570A1Maximize spatial multiplexing gainImprove link reliabilitySpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringMulti inputSignal quality
An apparatus and method for selecting antennas and nodes in a multi-input multi-output (MIMO) communication system are provided. The apparatus includes a reception unit which detects a communication initiation signal from among a plurality of received signals, a first combination unit which calculates communication capacity based on the communication initiation signal, searches for a combination of transmission antennas that can maximize the communication capacity, and performs communication using the identified combination of transmission antennas, a second combination unit which calculates an average signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of each node based on the communication initiation signal and selects a node with a highest average SNR and performs communication using the selected node, and a selection unit which activates one of the first combination unit and the second combination unit and inactivates the other combination unit. When the quality of signals transmitted between wireless nodes deteriorates due to a poor channel environment, a node that can minimize the shadowing effect caused by an obstacle that blocks the path of transmission of signals is selected using space diversity. Therefore, it is possible to minimize link communication failures. In addition, it is possible to maximize communication capacity by achieving spatial multiplexing gain using an array antenna that is mounted on a node.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
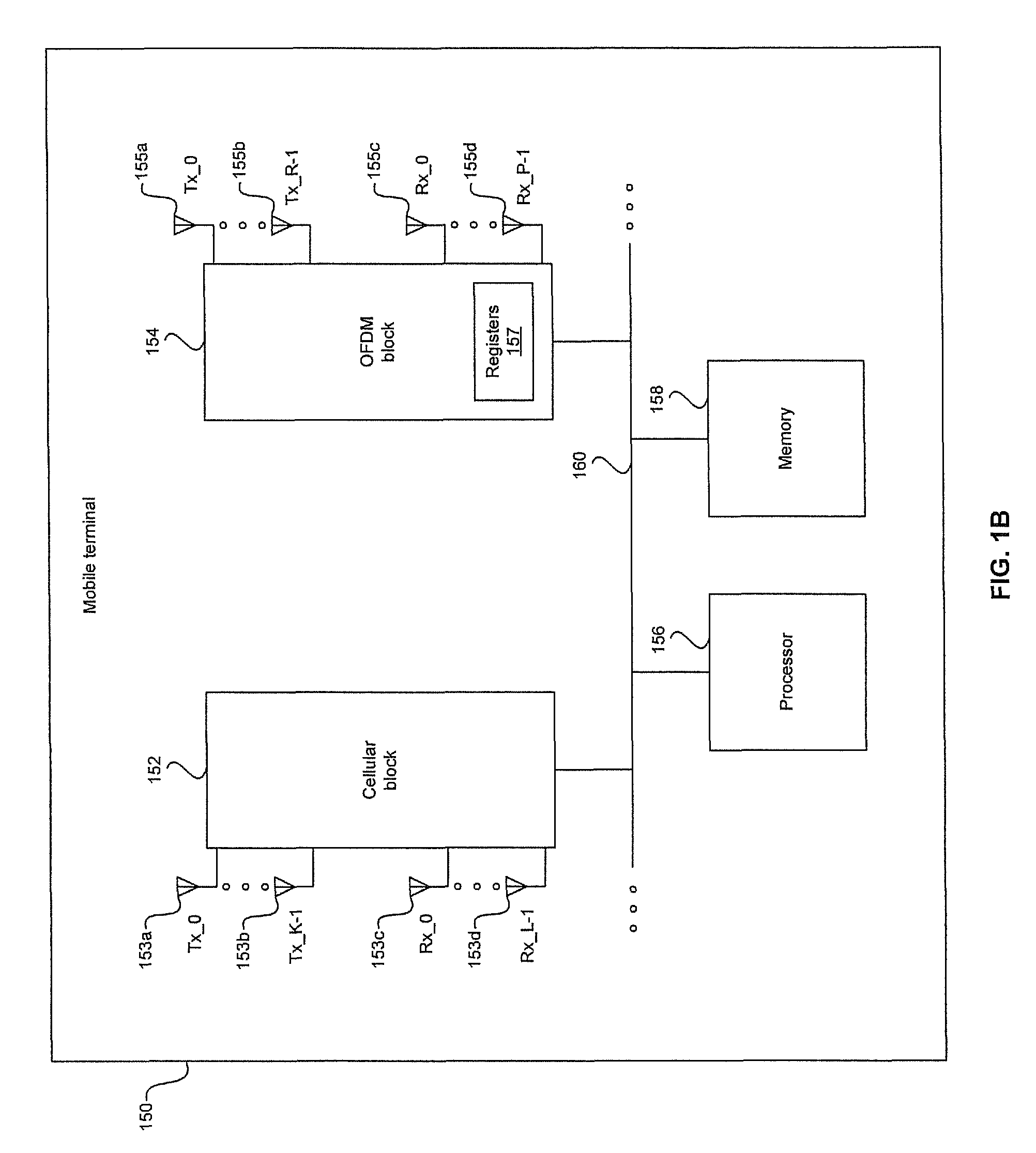
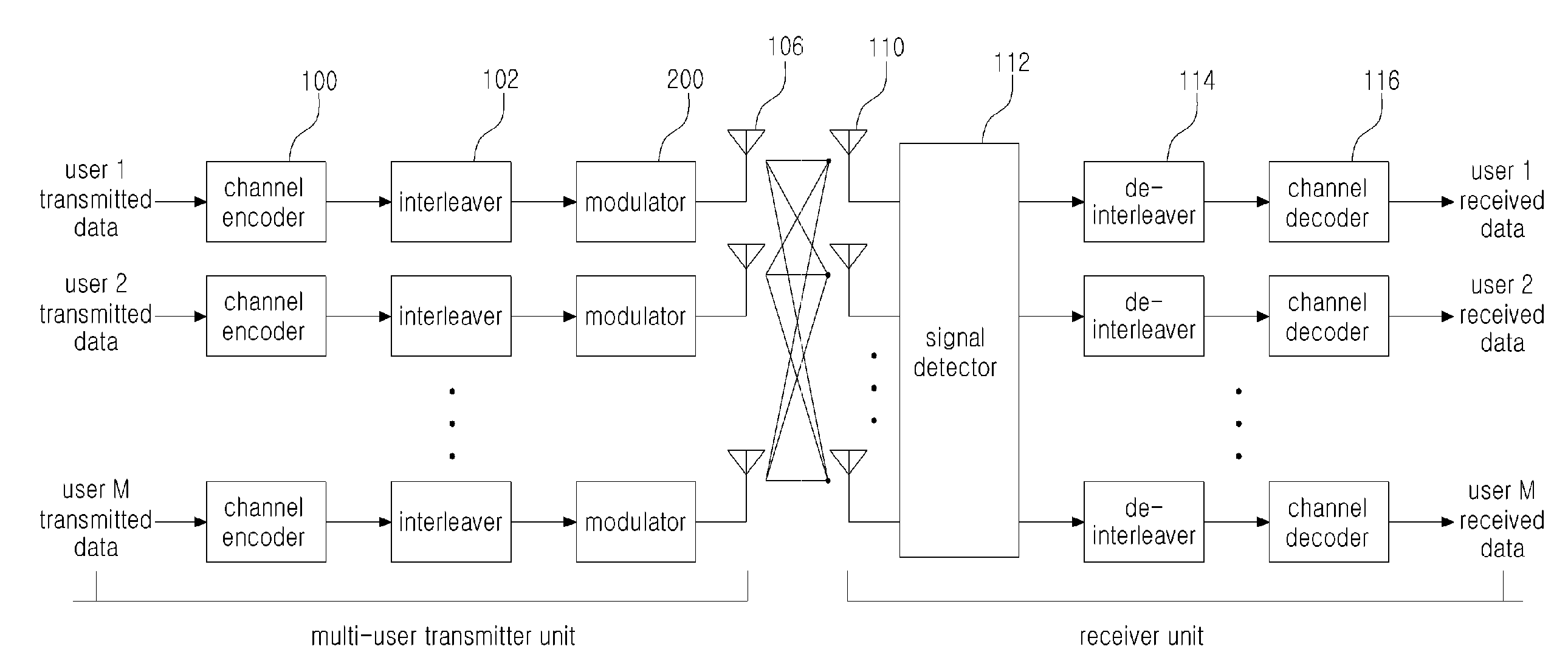
Method and system for increasing data rate in a mobile terminal using spatial multiplexing for DVB-H communication
A method and system for increasing data rate in a mobile terminal using spatial multiplexing for digital video broadcasting for handhelds (DVB-H) communication are provided. A reconfigurable orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) chip may be utilized in a mobile terminal to process received spatially multiplexed signals. The mobile terminal may be utilized in a spatially multiplexed multiple-input-multiple-output (SM-MIMO) wireless system. The spatially multiplexed signals may be quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK) modulated and may utilize OFDM subcarries. A processor may be utilized to configure the OFDM chip to process signals such as IEEE 802.11 and 802.16, and DVB. The OFDM chip may generate channel weights to be applied to the spatially multiplexed signals received in multiple receive antennas. The weighted signals may be combined to generate multiple RF received signals from which channel estimates may be generated. Subsequent channel weights may be dynamically generated from generated channel estimates.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Direction antenna spatial multiplexing method for millimeter wave system
ActiveCN105978614AShorten detection timeImprove throughputSpatial transmit diversityDirectional antennaSpatial multiplexing gain
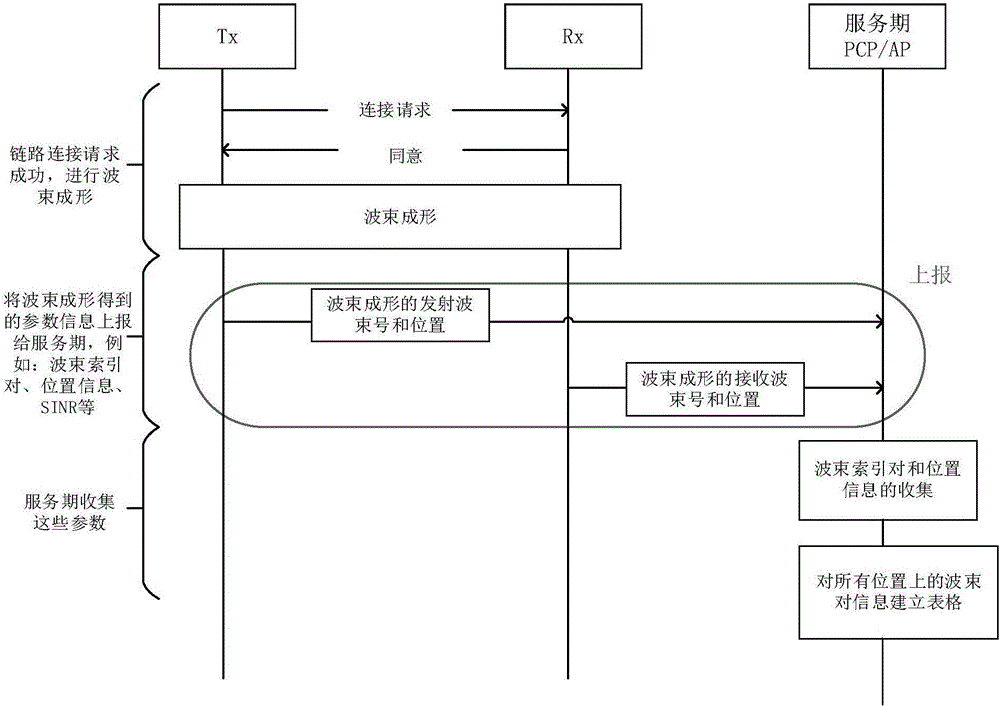
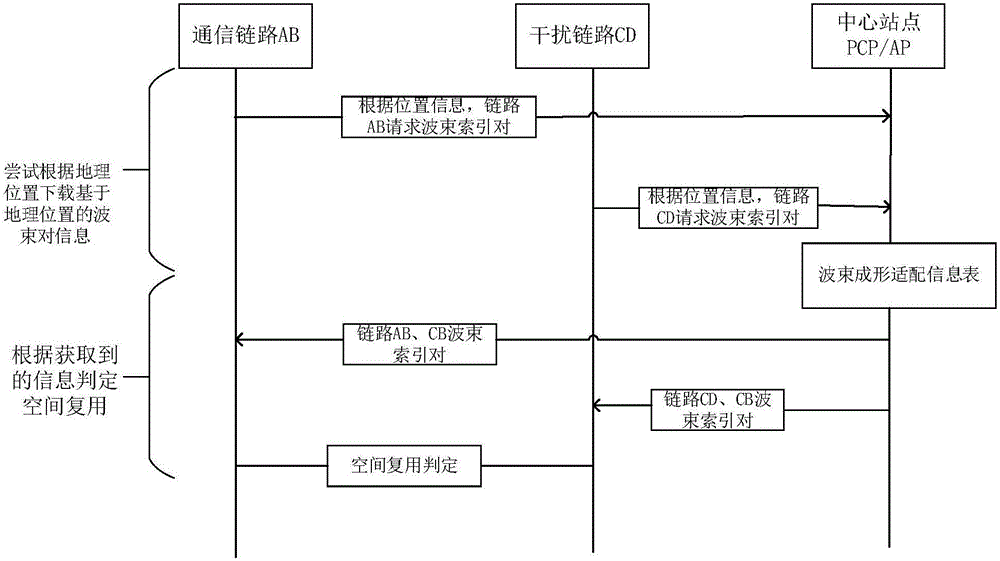
The invention discloses a direction antenna spatial multiplexing method for a millimeter wave system. Firstly, an information collection mechanism and evaluation criteria are defined, and then the following steps are carried out. The steps comprise 1, feeding back beam reference pairs of a transmitting and receiving end to a PCP / AP in a beam forming process, thereby forming a beam reference pair information table BFT; 2, transforming the beam reference pair information table BFT into a link beam difference value table LDT; 3, performing a spatial multiplexing dispatching algorithm, and generating an optimum link dispatching method; and 4, sending a generation scheme to each STA by the PCP / AP through BTI, and performing the generation scheme in a next SP period by the STA. According to the method, the detection time of signal interference between links is reduced, the simple, easy-judging and effective evaluation criteria are designed, the feasible, fast and effectively dispatching scheme is provided, the spatial multiplexing gain can be effectively improved, and the throughput of the whole millimeter wave system can be improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Double-bounce half-duplex MIMO (Multiple-input multiple-output) relay network distributed type beam forming method
InactiveCN102647217ASpatial transmit diversityDuplex signal operationChannel state informationEngineering
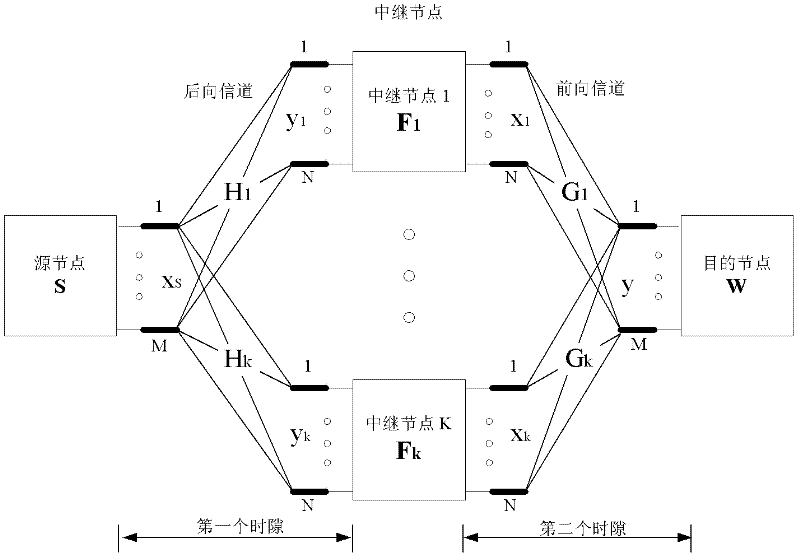
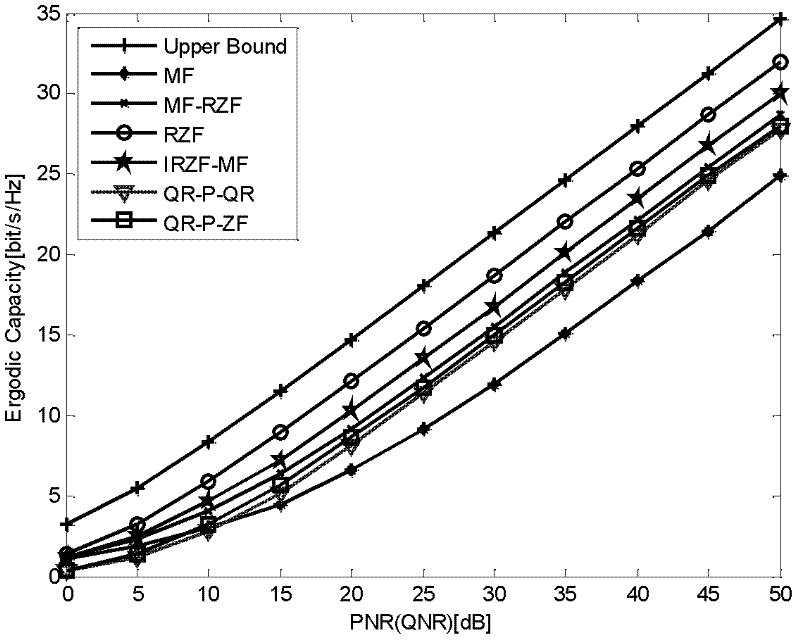
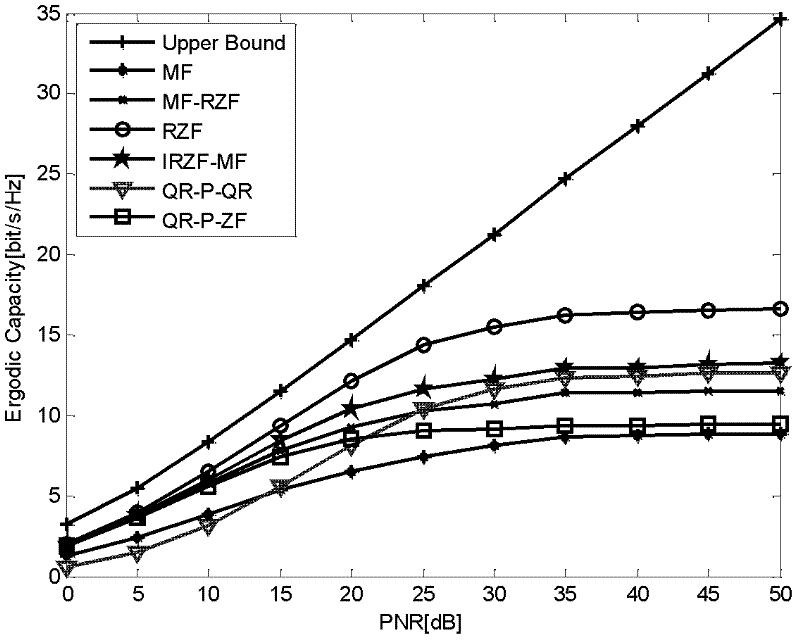
The invention provides a double-bounce half-duplex MIMO (Multiple-input Multiple-output) relay network distributed type beam forming method, and provides two distributed type beam forming schemes, namely, RZF (Regularized Zero Forcing) and IRZF (Information Regularized Zero Forcing)-MF (Matched Filter), which take a multi-antenna multi-relay double-bounce half-duplex wireless network into account, are based on RZF precoding technology and MF technology, and are suitable for a rice channel. At a relay node, beam formation is received and transmitted by utilizing the RZF technology in the RZF scheme, and the beam formation is received and transmitted by respectively utilizing the IRZF technology and MF technology in the IRZF-MF scheme. According to the schemes, the relay node is required to obtain self channel state information in the forward direction and the backward direction, at a target node, a QR receiver is used for continuous interference eliminating detection to obtain maximum spatial multiplexing gain. The test result shows that the two schemes provided by the invention can be completely suitable for rice channel conditions, and the channel capacity approximate to the upper bound of the capacity can be obtained under the channel conditions.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Subarray antenna structure suitable for millimeter wave LOS MIMO and design method
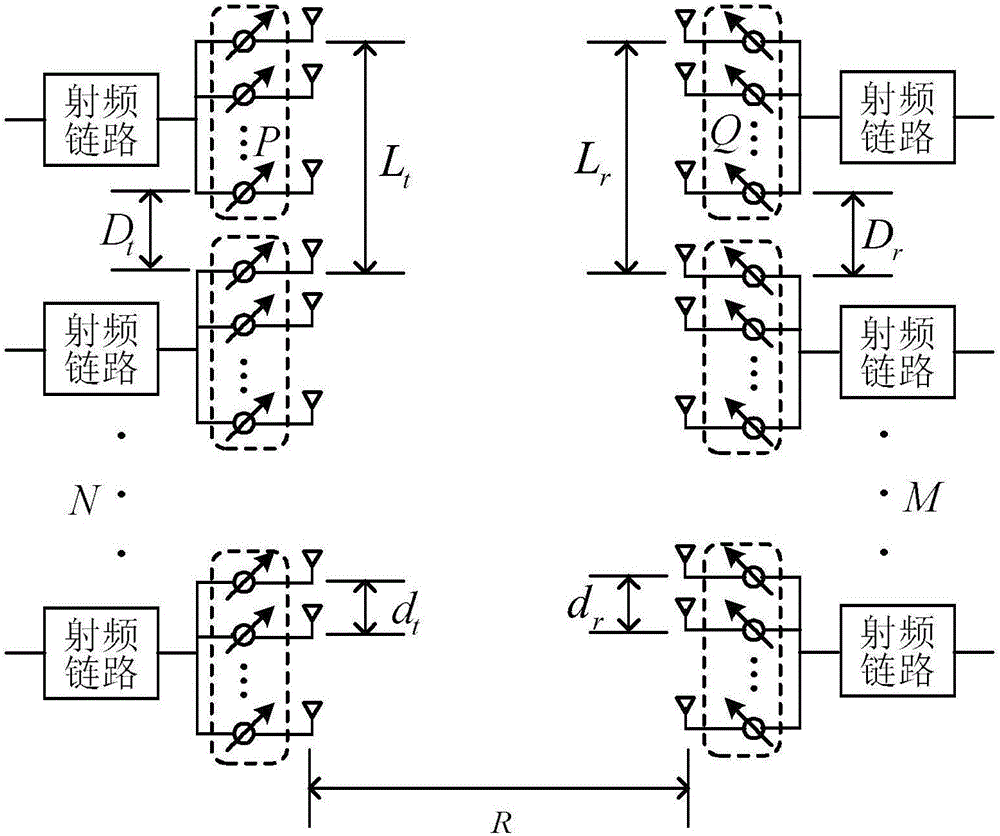
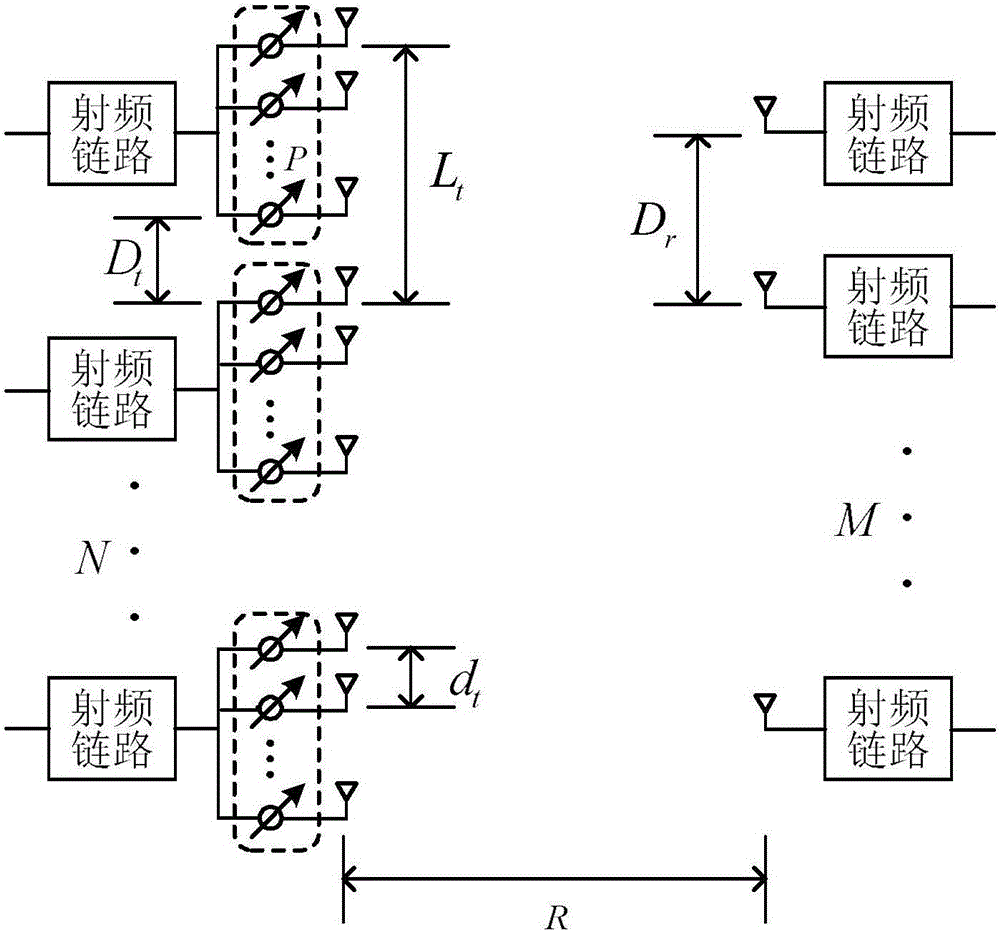
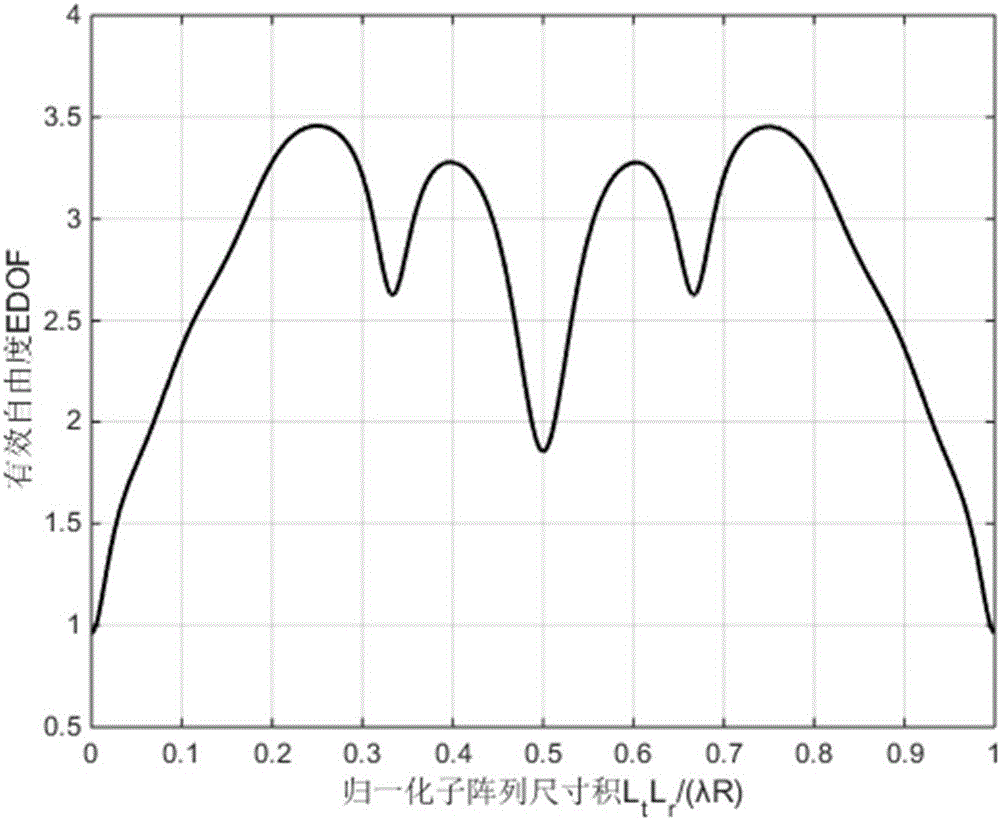
ActiveCN105896102AGuaranteed Spatial Multiplexing GainGuaranteed stabilityAntenna arraysMimo communicationSpatial multiplexing gain
The invention discloses a subarray antenna structure suitable for LOS MIMO and a design method. A transmitting terminal employs an array emission structure of antenna subarrays formed by phase shifters, and a receiving terminal employs an oriented reception structure symmetric to the transmitting terminal or an asymmetric omnidirectional reception structure. Normalization antenna subarray interval conditions that meet the requirement are obtained through theoretical calculation, maximal effective freedom degree of a radio frequency equivalent channel in point-to-point LOS MIMO communication is realized, and the top and bottom limitations on effective freedom degree are reasonably estimated. Compared with a non-array antenna structure, the subarray antenna structure takes asymmetric and symmetric antenna subarrays into consideration. Array gain is provided, and a certain spatial multiplexing gain under a multipath-missing channel environment is ensured.
Owner:白盒子(上海)微电子科技有限公司
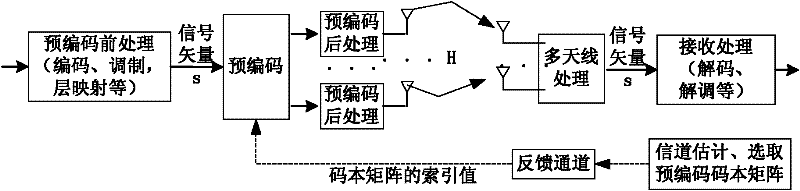
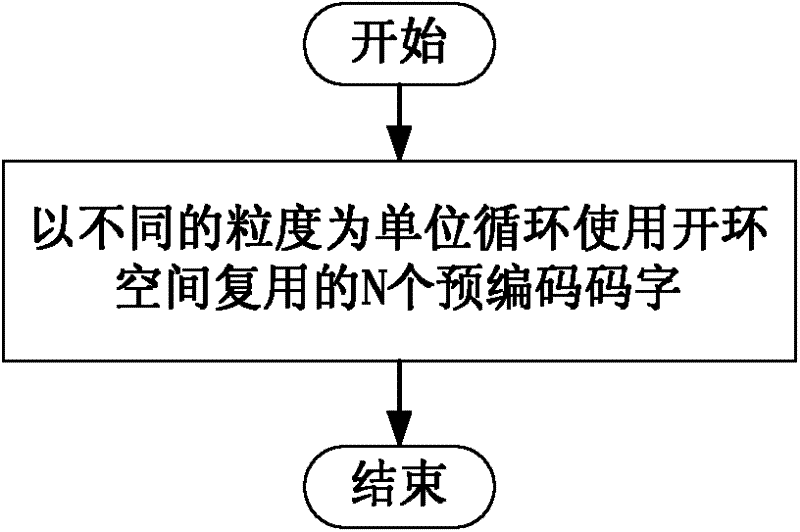
A precoding processing method and system for uplink open-loop spatial multiplexing
ActiveCN102271027AResolve transmissionFacilitate transmissionRadio transmissionError prevention/detection by diversity receptionPrecodingGranularity
A precoding method and system for uplink open-loop spatial multiplexing cyclically use N precoding code words for open-loop spatial multiplexing by utilizing different granularity-units. The above technical solution solves the problem of transmission during open-loop spatial multiplexing in an uplink direction in an LTE-A system, thereby ensuring good transmission performance.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Apparatus and method for transferring multipath signal by non-equilibrium power in MIMO system
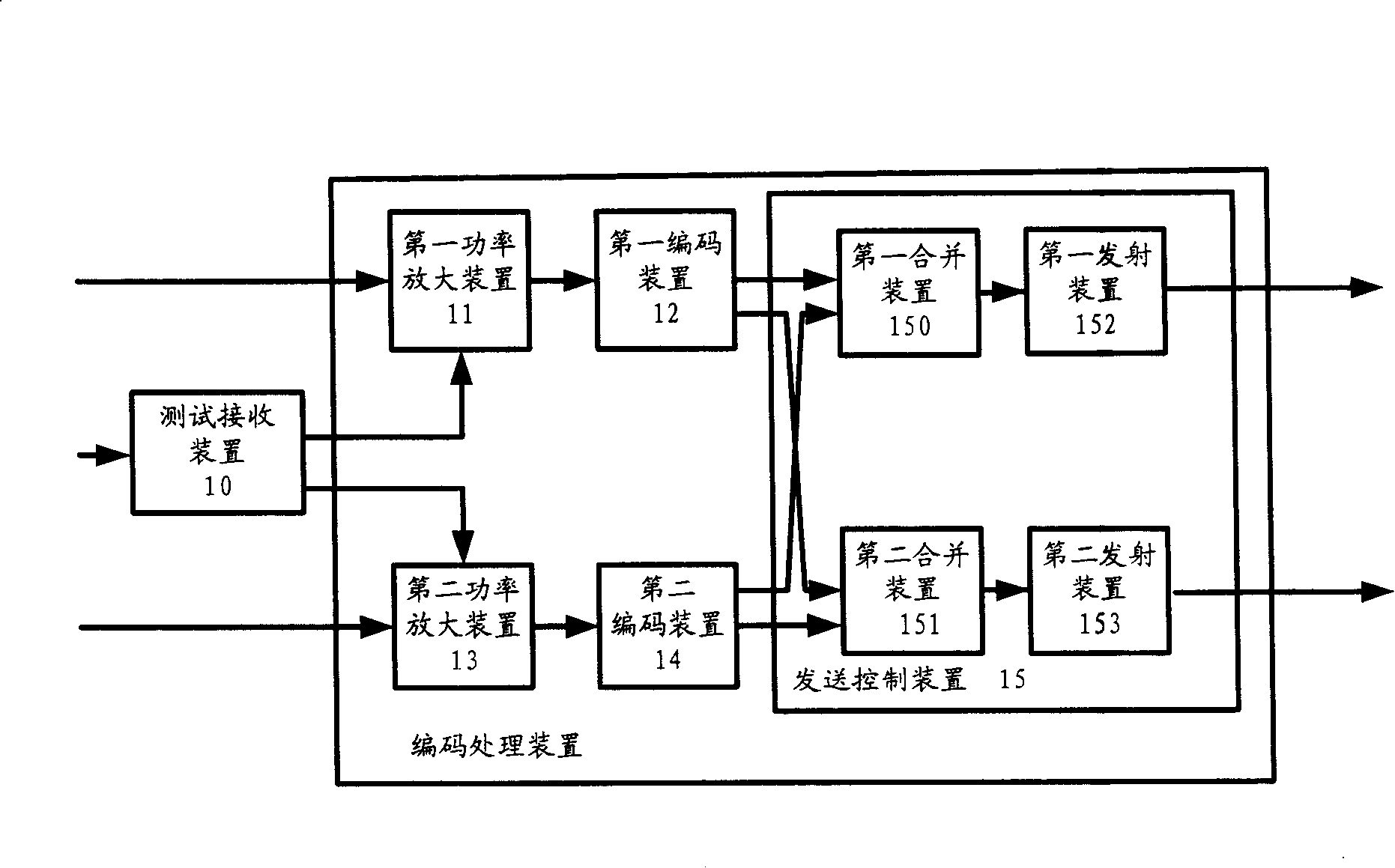
ActiveCN101227215ASpatial Multiplexing Gain CompleteFull diversity gainSpatial transmit diversityTransmission control/equalisingSignal onSimple mode
The invention provides a method and a device for obtaining diversity gain and spatial multiplexing gain simultaneously by a simple mode of the system in an MIMO communication system and complex degree of signal detection of a receiving end is low. The invention takes non-equilibrium power to transmit signals in layers, namely the power of signals on each layer is respectively amplified in different gains before spatial time coding, then signals which are coded are transmitted through a plurality of antennae, simultaneously, the invention also provides a method for detecting optimum transmitting power on the basis of feedback information of a receiver.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SHANGHAI BELL CO LTD
Apparatus and method for detecting signal in spatial multiplexing system
InactiveUS20120263080A1No large difference in error performanceSpatial transmit diversityData streamSpatial multiplexing gain
Disclosed are an apparatus and a method for detecting signals in a spatial multiplexing system. An embodiment of the invention provides a signal detection apparatus for a single receiver unit equipped with a plurality of antennas in a system having at least one transmitter unit configured to transmit data streams by spatial multiplexing, where the signal detection apparatus includes: a partial linear coefficient generator unit configured to generate a linear weighting matrix by using a preset algorithm on a channel matrix formed between the transmitter unit and the single receiver unit; a partial symbol remover unit configured to generate a first symbol vector by removing all transmittable symbols for each transmitting antenna from all received data streams; and a partial symbol detector unit configured to generate a transmission symbol candidate vector by using the linear weighting matrix and the first symbol vector.
Owner:CHUNG ANG UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
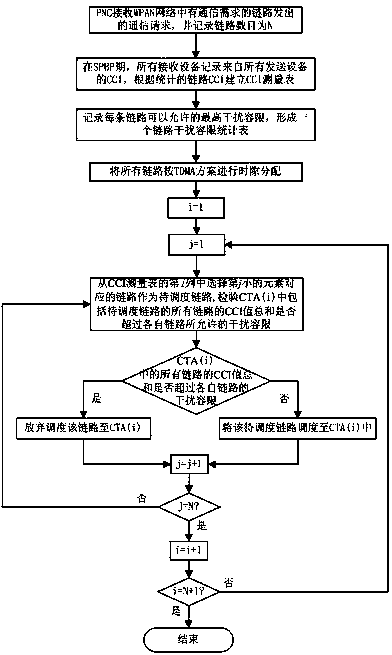
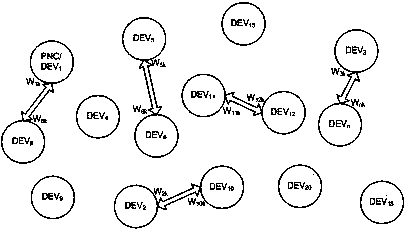
Spatial multiplexing link scheduling method applied to millimeter wave WPAN
ActiveCN104168658AEnsure fairnessMaximize utilizationWireless communicationSpatial multiplexing gainBroadcasting
The invention discloses a spatial multiplexing link scheduling method applied to a millimeter wave WPAN. The method includes the following steps that firstly, a signal detection broadcasting period in which interference is directionally measured is set before time slot allocation of a current signal transmission frame is started; secondly, a co-channel mutual interference statistical table of links is established; thirdly, allowed link interference tolerance values of the links are calculated, and a link interference tolerance table is established; fourthly, according to the number of the links, the current signal transmission frame is divided into multiple time slots corresponding to the links one by one, each link serves as a main link in the corresponding time slot, and other links allowed simultaneous transmission to be conducted except for the main links are determined in the corresponding time slots according to the method that actual interference values among the links are compared with the interference tolerance values of the links. According to the link scheduling method, all the links can be connected in the same transmission period, fairness of the links is guaranteed to a certain degree, spatial multiplexing gains are utilized to the maximum degree, priority is given to the links which slightly interfere with the main links to enter the corresponding time slots, each time slot can contain the parallel links as many as possible, and system throughput is maximized.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optical multiplexing terminating device, passive optical network system, and method for allocating frequency
InactiveCN102379105AReduce wasteMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingSpatial multiplexing gain
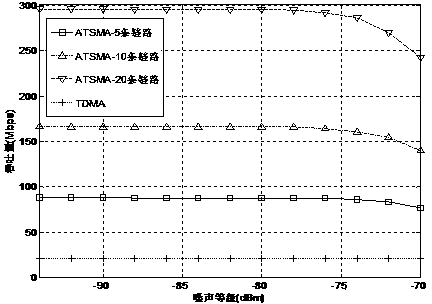
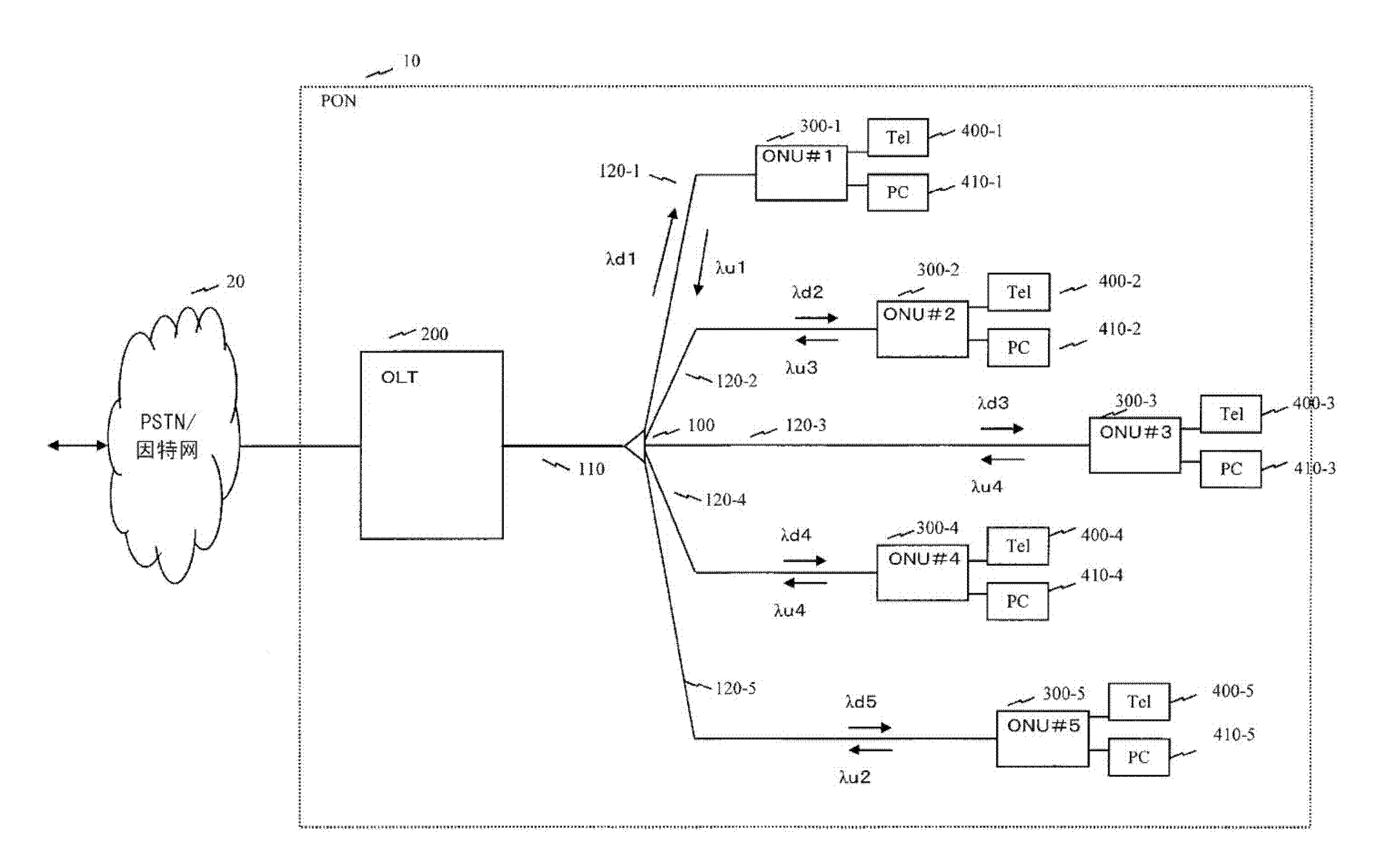
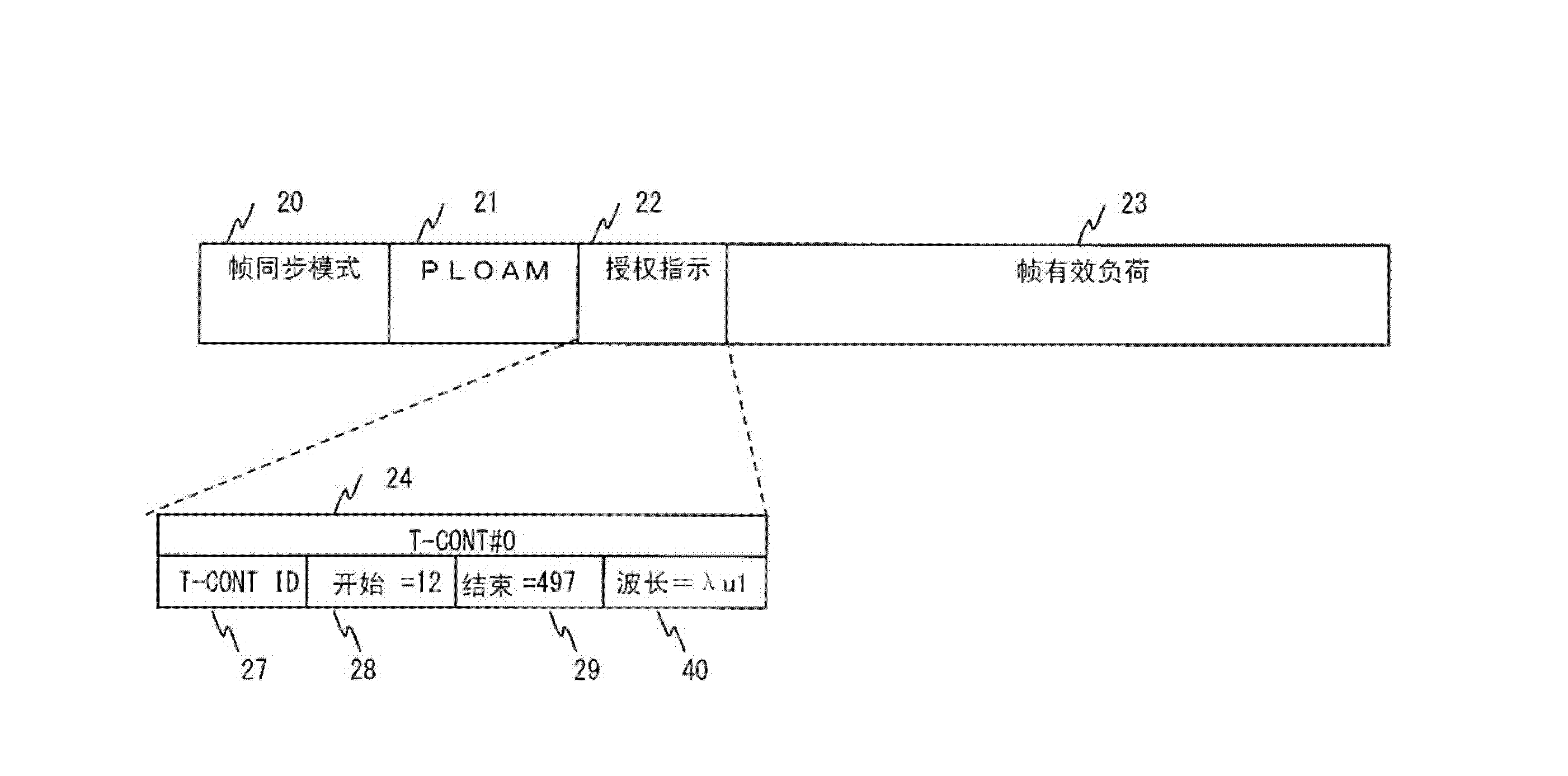
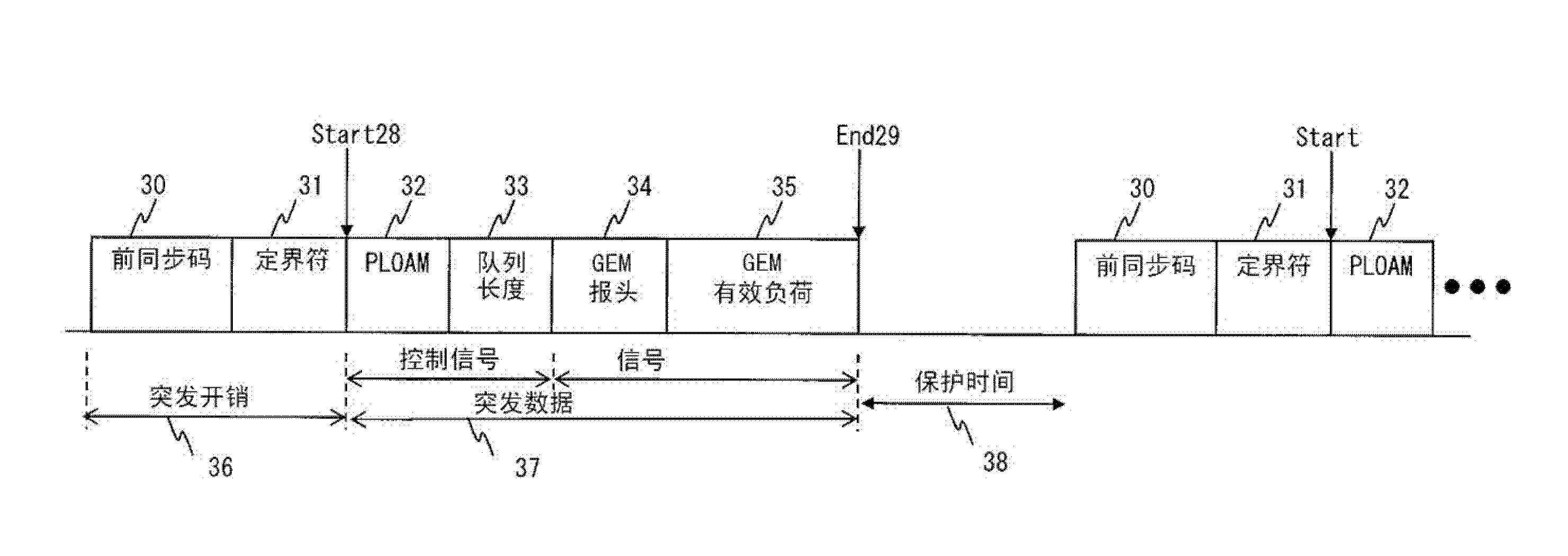
A passive optical network system such that the power consumption can be reduced as much as possible according to the end-user traffic. An OLT uses the DBA function thereof and sequentially uses frequencies in ascending order of transmission rate in order to sequentially allocate bands to ONUs in ascending order of the requested bandwidth. At this time, a frequency to be allocated is selected so that the bandwidth allocated to each ONU is narrower than a maximum bandwidth through which transmission using the allocated wavelength is enabled. An OLT, by using the DBA function, uses a grant area to specify the transmission timing of the secondary station and to inform the specified transmission timing to the secondary station. In addition to the area where grant information is stored, an area is set for storing information used to inform the secondary station of a new frequency to be used. Each ONU carries out uplink communication using the specified frequency at a transmission rate determined by the frequency.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Multi-channel multiple access method based on MIMO transmission mechanism
InactiveCN104837211AImprove throughputEasy to implementSpatial transmit diversityWireless communicationMimo transmissionTime delays
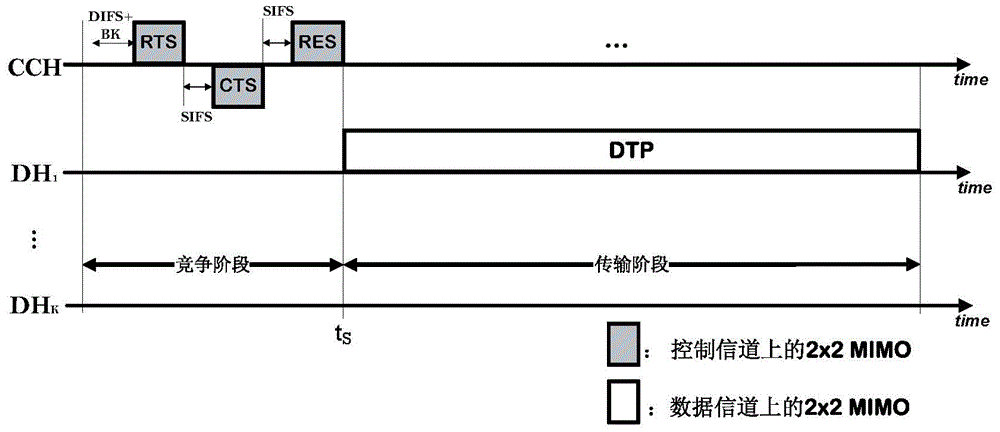
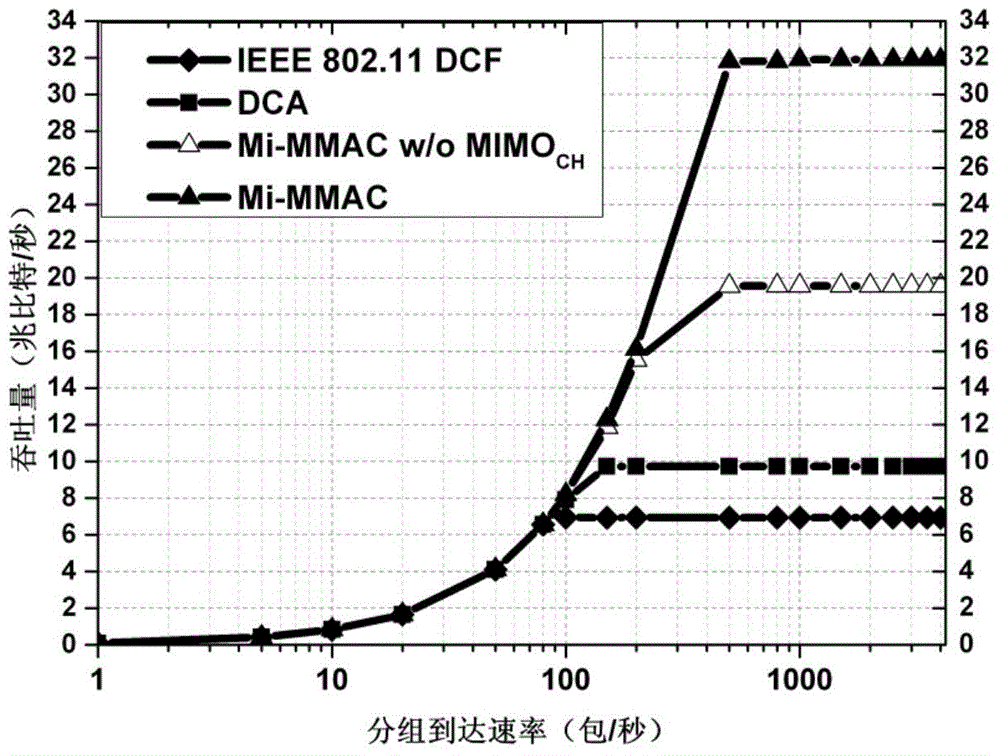
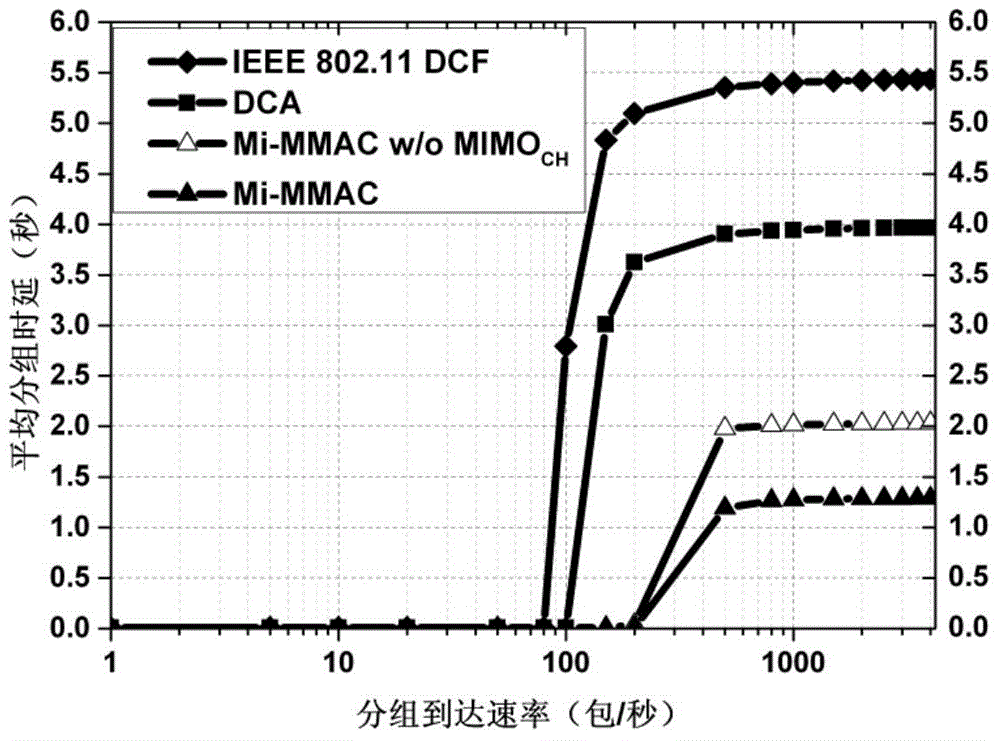
The invention provides a multi-channel multiple access method based on an MIMO transmission mechanism. During the competitive stage, a node reuses a data antenna to carry out channel competition in a common control channel, after the channel competition is successes, selection of the data channel and confirmation of data transmission period duration are completed through interaction information in a 2*2MIMO manner, and during a transmission stage, the node reuses a control antenna to transmit a data packet in a data channel. The multi-channel multiple access method based on the MIMO transmission mechanism is simple to implement, and can be implemented in firmware which supports multi-channel network cards, and can be implemented in a driving program at the same time, and the network throughput is greatly increased; by employing a distributed working mode, a centralized control node and whole network time synchronization are not needed, a control packet and the data packet can be transmitted in a 2*2MIMO transmission manner, substantial spatial multiplexing gain can be brought about, furthermore the system performance is greatly improved, the network throughput is increased, and the end-to-end time delay is reduced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Transmission method with double directivity
ActiveUS20180091195A1Increase spacingEfficient processChannel dividing arrangementsSpatial transmit diversityFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
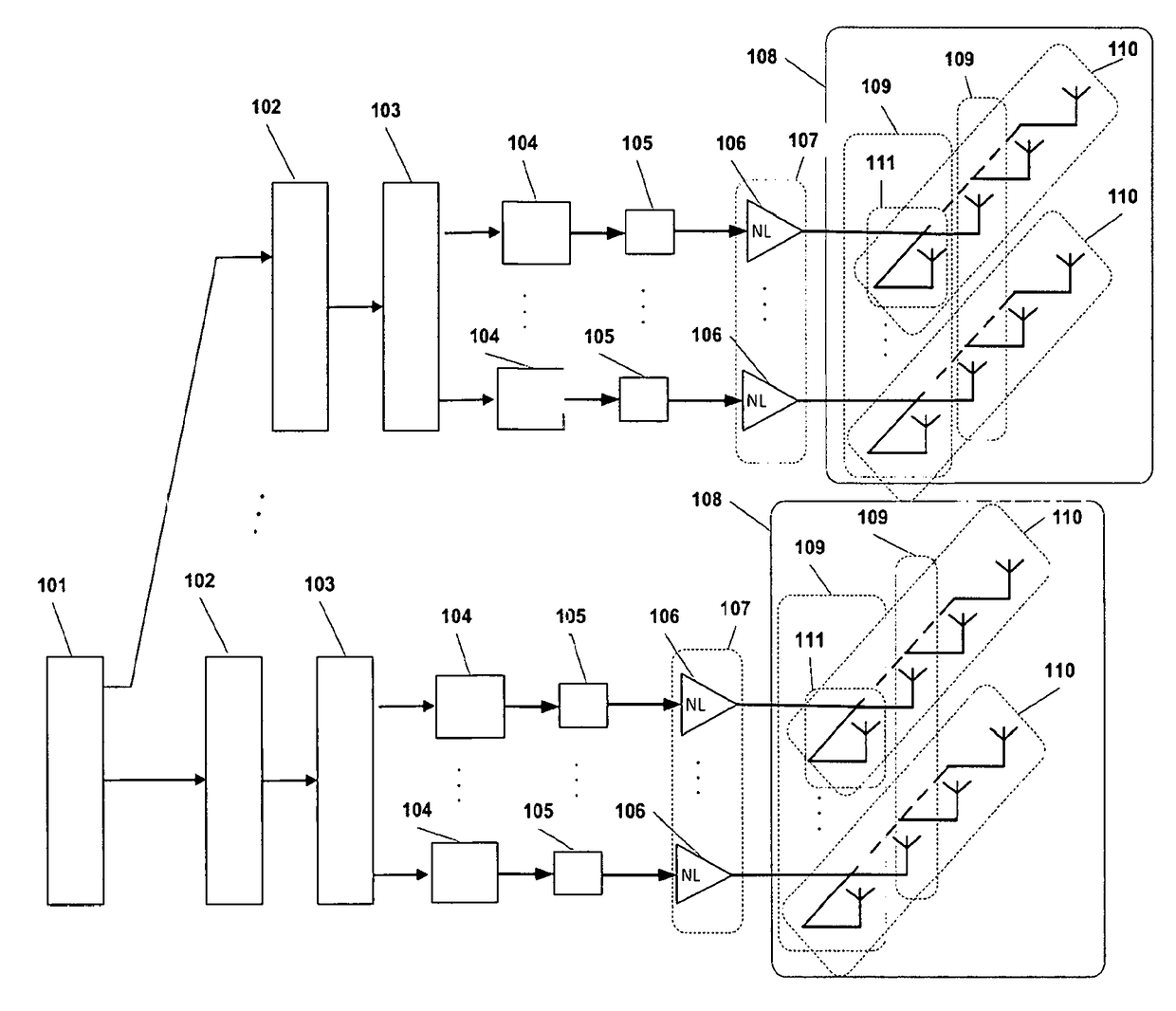
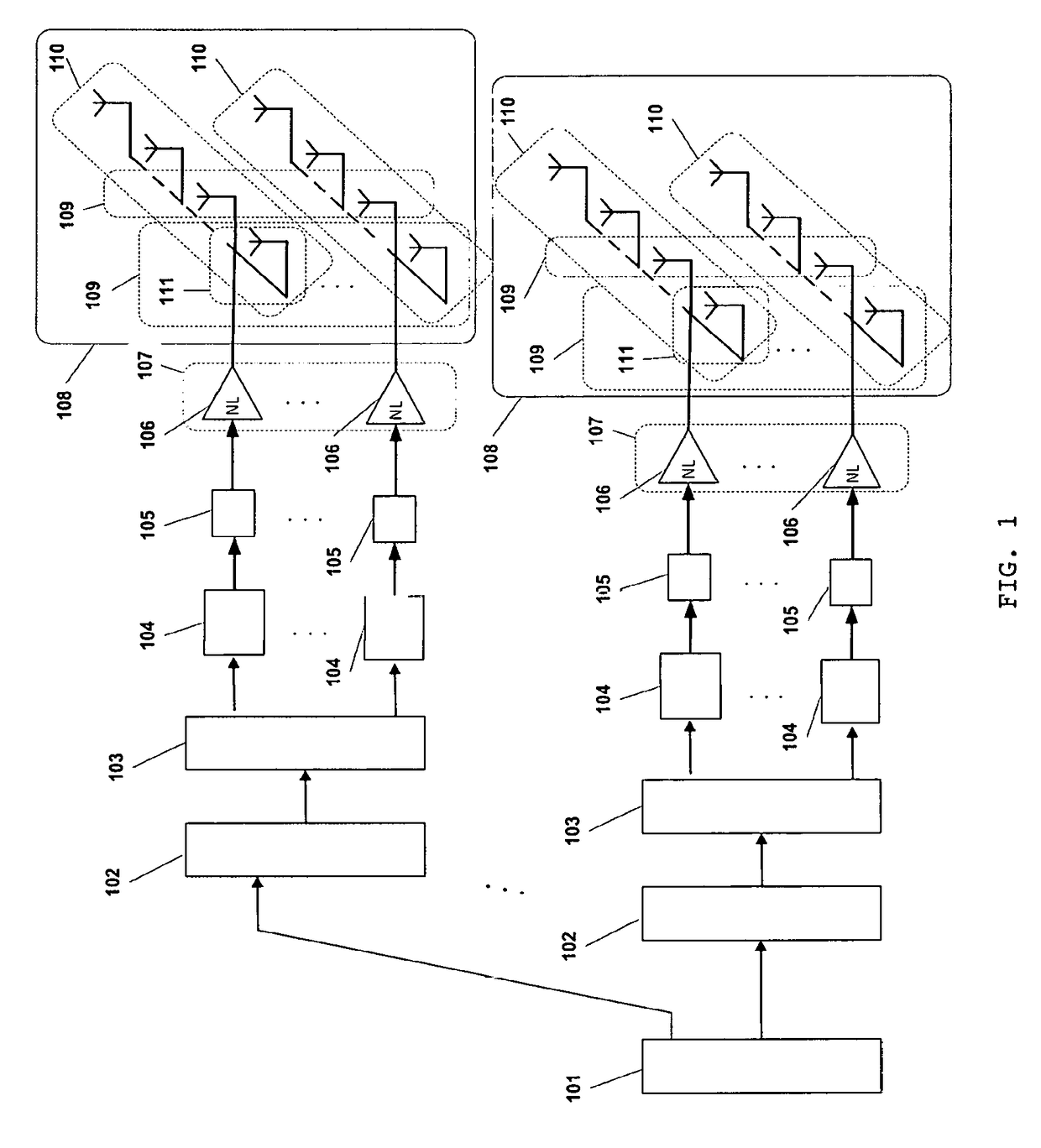
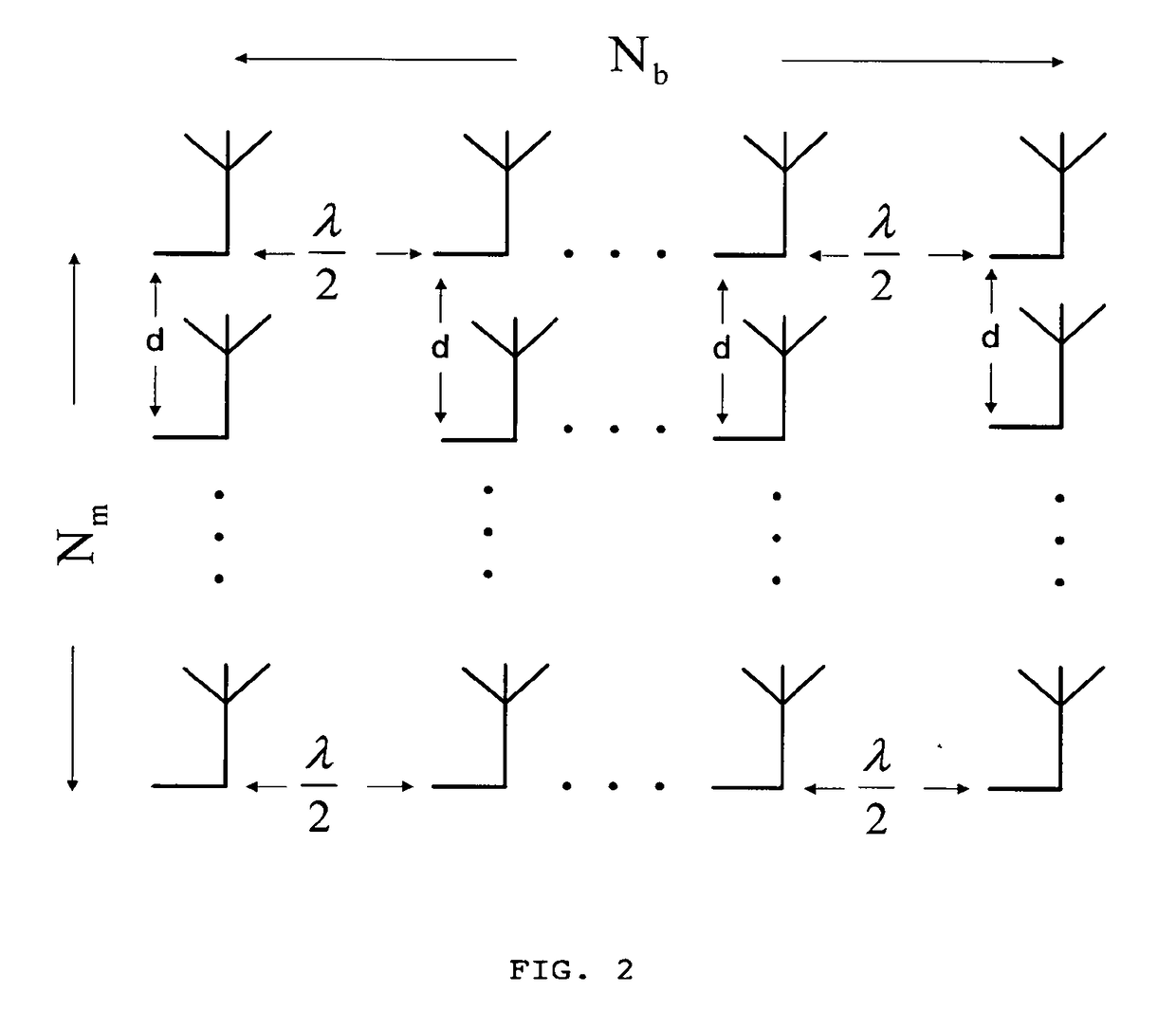
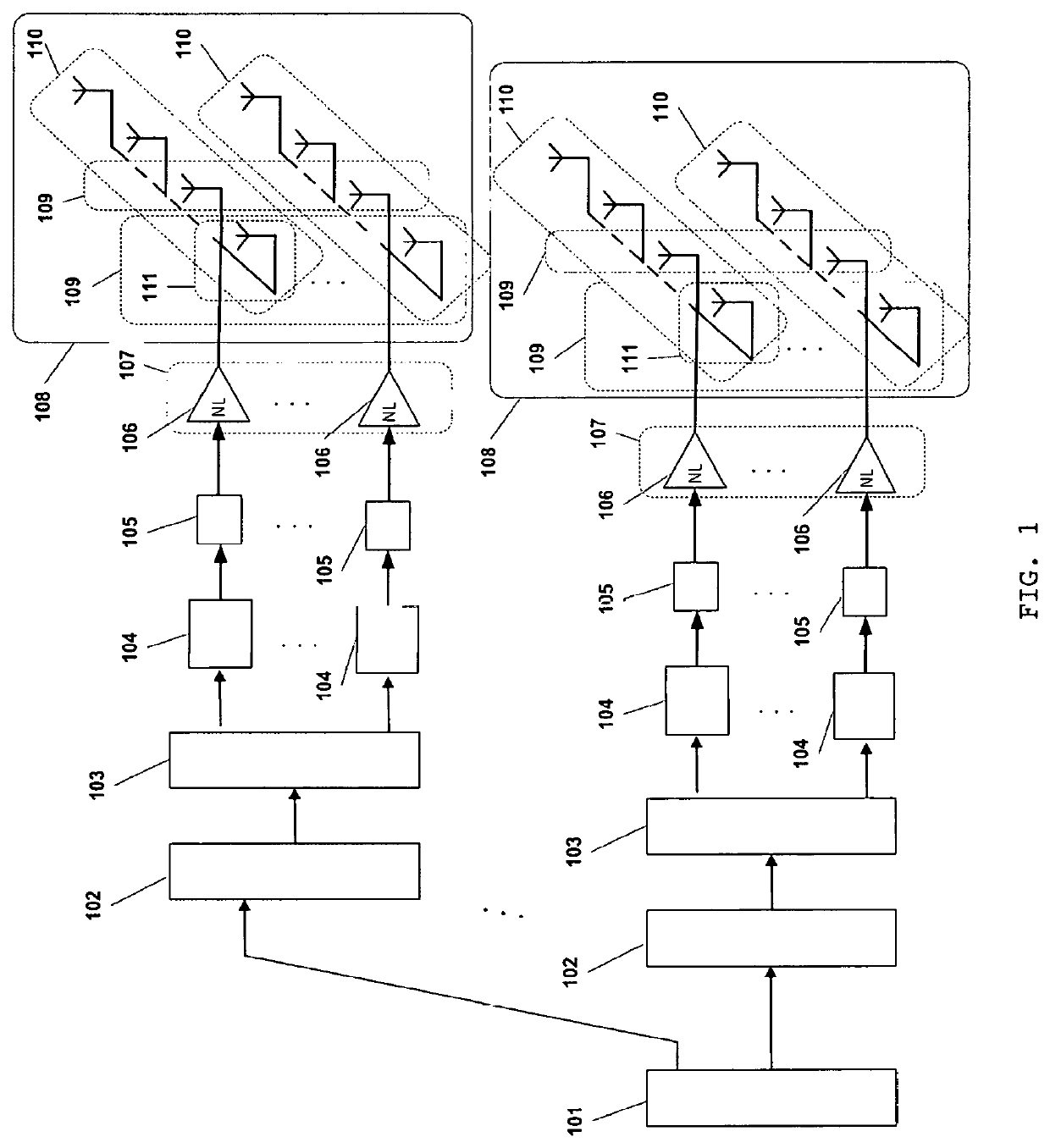
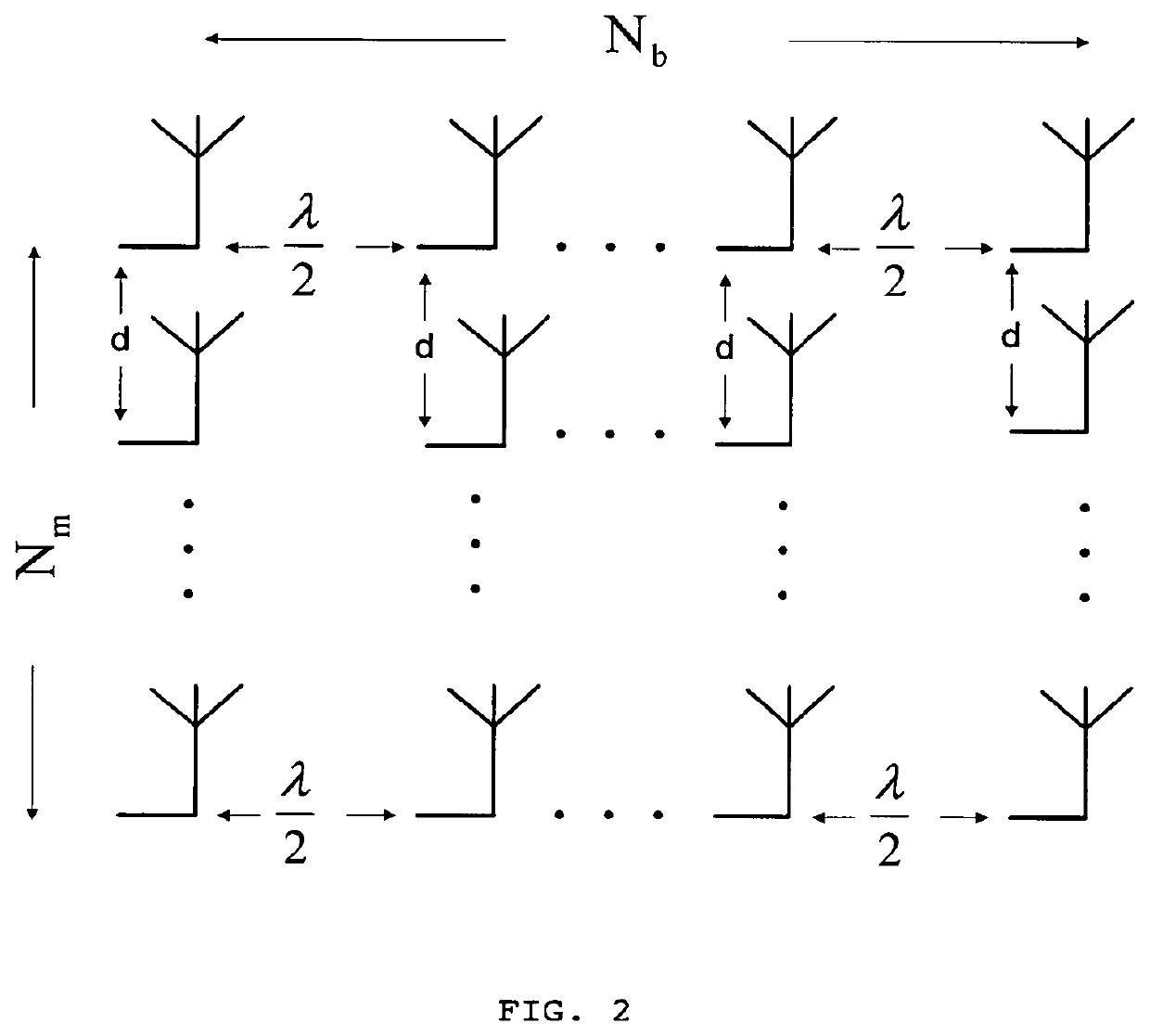
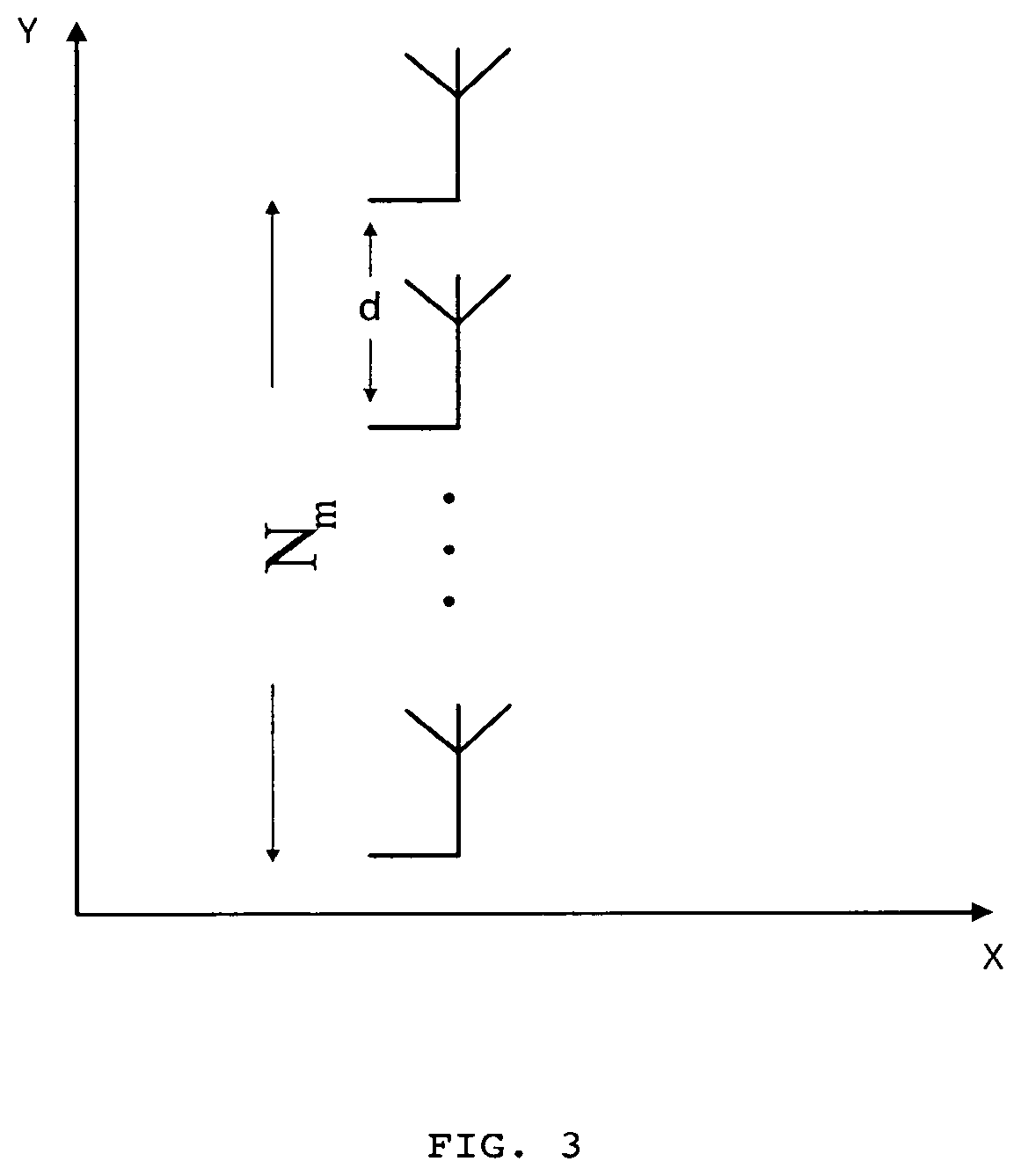
A transmission method using a massive MIMO (Multiple-Input and Multiple-Output) scheme with an arrangement 108 of Nm×Nb antenna elements at the transmitter, arranged in Nm sets of Nb antenna elements or Nb sets of Nm antenna elements based on SC-FDE (Single-Carrier with Frequency Domain Equalization) schemes with large constellations that is compatible with low-cost, highly-efficient, nonlinear amplifiers 106, while allowing spatial multiplexing gains.The transmission structure of this transmission method decomposes in 103 the modulated symbols from 102 associated to a given constellation as the sum of Nm polar components that are modulated as Nm BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying) signals. Each of these BPSK signals can be regarded as an OQPSK (Offset Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) signal in the serial format that is specially designed to have good tradeoffs between reduced envelope fluctuations and a compact spectrum.
Owner:CARVALHO PAULO MIGUEL +4
Systems and methods for high-rate RF communications employing spatial multiplexing in line of sight environments
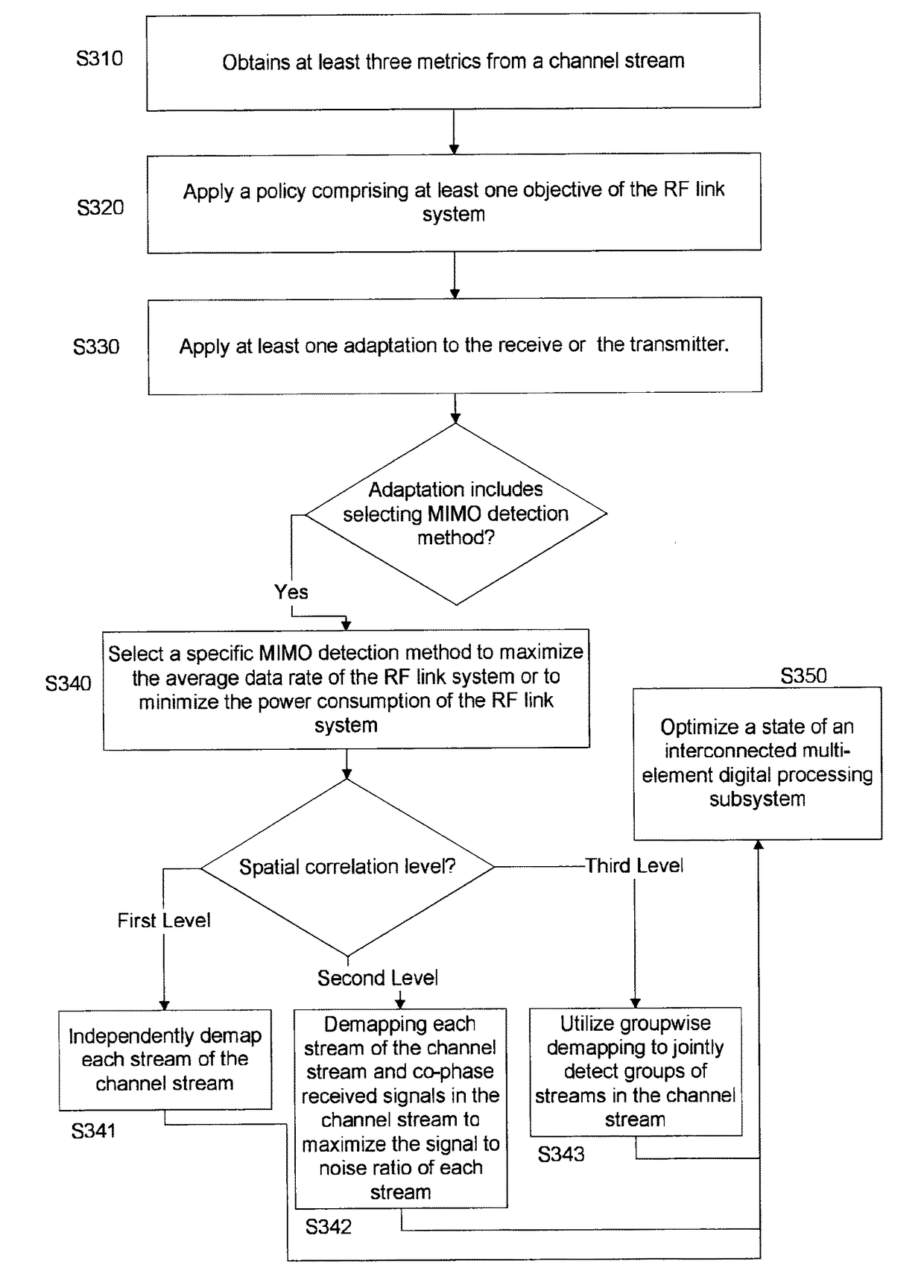
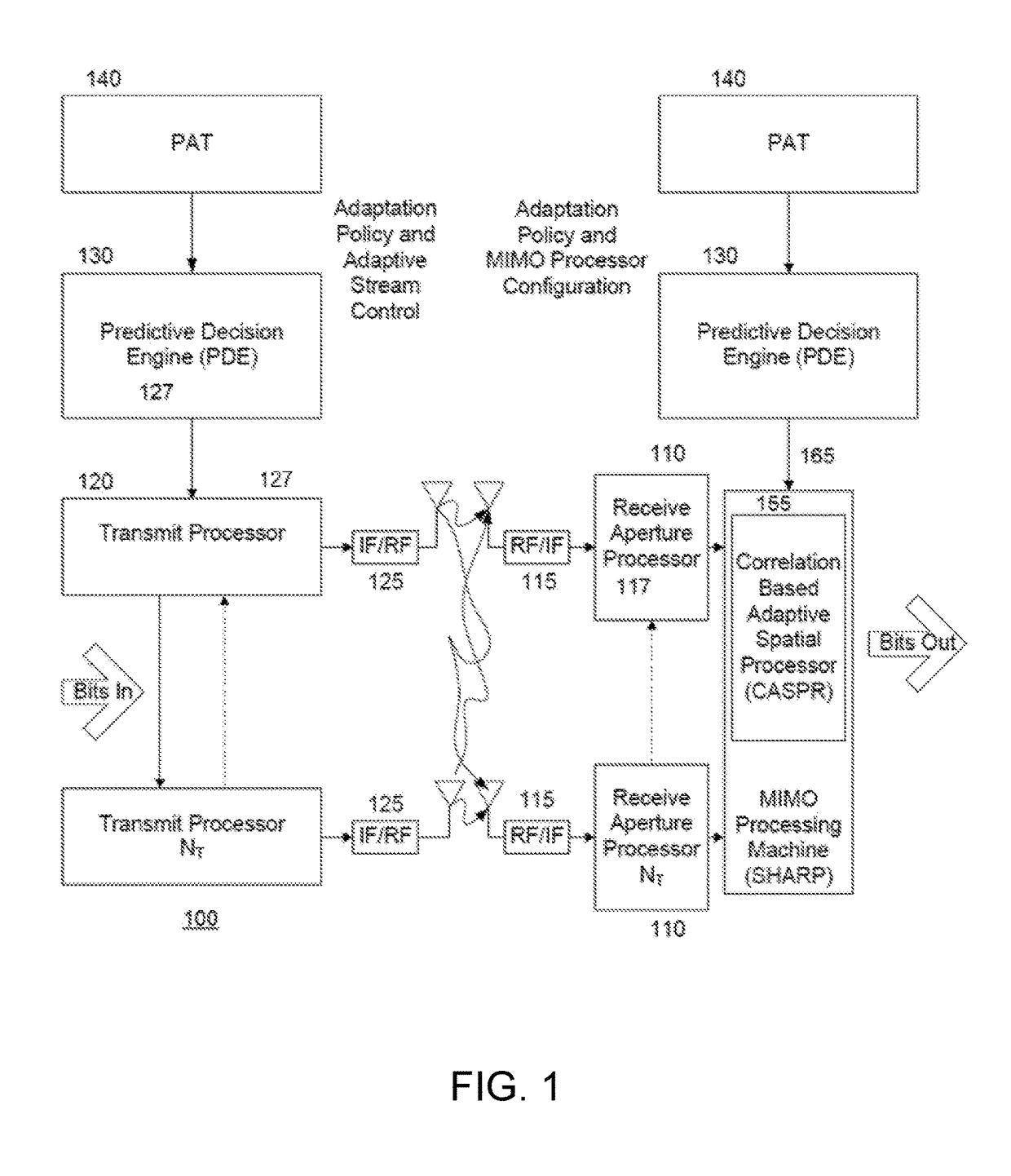
A system and method to optimize a multiple-input multiple-output signal processing RF communication system that includes obtaining, by a processor, at the receiver, during spatial processing, metrics from the channel stream. The metrics include a spatial correlation metric representing spatial coupling between multiplexed streams in the channel stream, a signal-to-noise power ratio metric representing propagation losses encountered by the signal, and a cross polarization discrimination metric representing whether polarization modes can be processed as independent groups. The processor obtains these metrics based on obtaining geometric information related to the receiver and the transmitter. Predictive methods may be employed to determine expectations for some metrics in advance. The method includes applying a policy with at least one objective of the system, and based on at least one metric and the policy, applying at least one adaptation to at least one of: the receiver or, the transmitter.
Owner:PERSPECTA LABS INC
Superimposed pilot method based on spatial multiplexing in large scale MIMO system
ActiveCN109495147AGood estimateImprove throughputPower managementRadio transmissionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Estimation methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless communication, and in particular relates to a superimposed pilot method based on spatial multiplexing in a large scale MIMO system, applied toan uplink multi-cell multi-user large scale MIMO system. The superimposed pilot method comprises the following steps of designing a sending signal and processing a received signal; performing channelestimation according to the received signal and by using an MMSE estimation method; using maximization of a signal to noise ratio as an optimization target to determine the optimal power distribution;and improving channel estimation via iterative operation. Compared with the traditional pilot method based on spatial multiplexing, the superimposed pilot method based on spatial multiplexing can achieve higher throughput of system, and the provided iteration algorithm can improve channel estimation and thus further enhance system performance.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
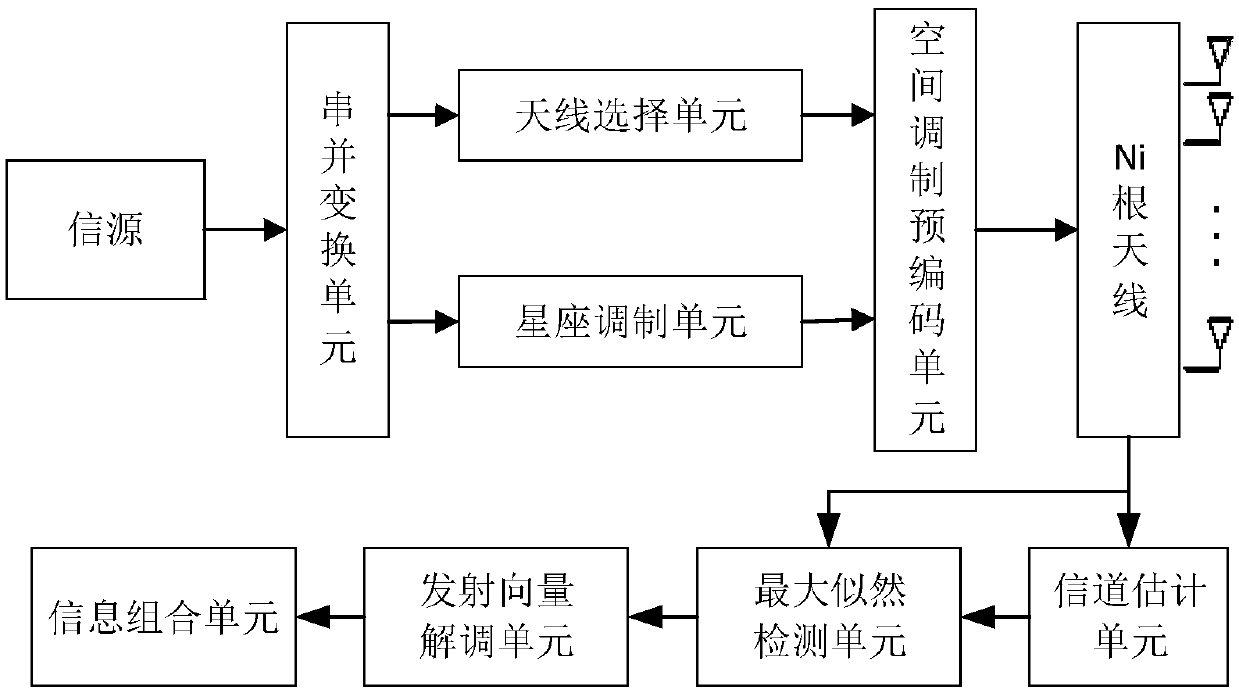
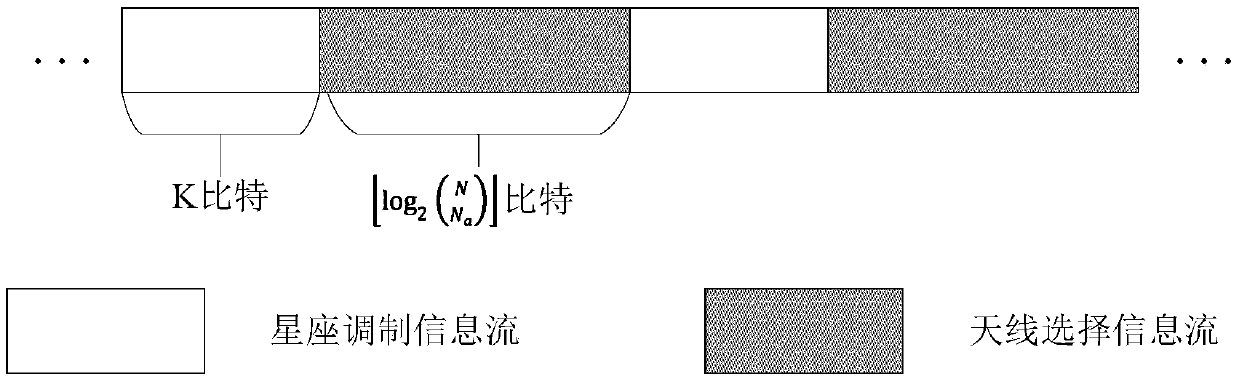
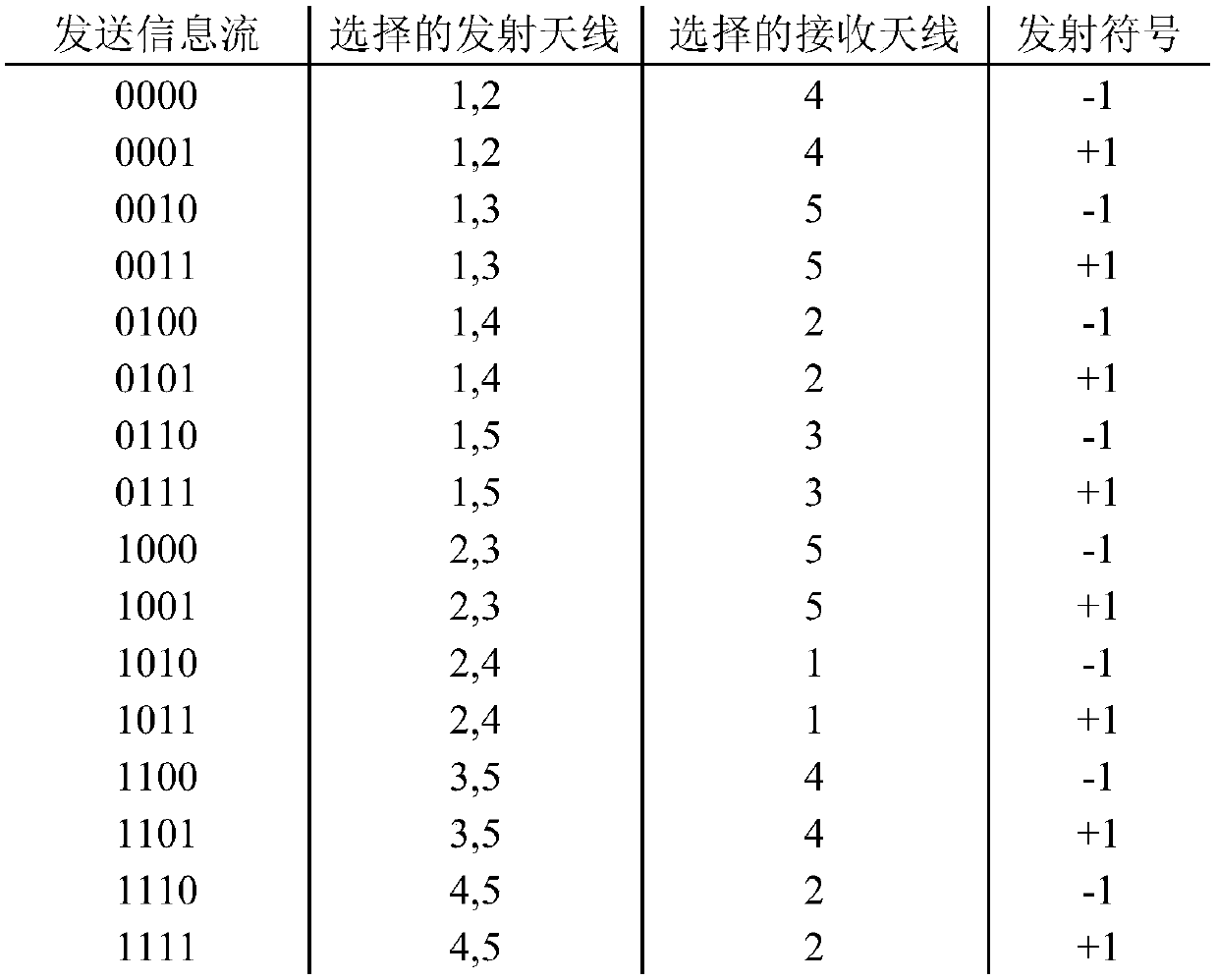
Co-frequency co-time full duplex communication system and method based on spatial modulation
ActiveCN111385004AIncrease spatial multiplexing gainImprove spectral efficiencySpatial transmit diversityDuplex signal operationPrecodingCommunications system
The invention discloses a co-frequency co-time full duplex communication system and method based on spatial modulation. According to the invention, a sending information flow is divided into an antenna selection information flow and a constellation modulation information flow by using the spatial modulation technology, the antenna selection information transmits one part of sending information, and the emission symbol obtained after constellation modulation transmits the other part of sending information, so that the spatial multiplexing gain of the communication system is improved; a precoding vector is obtained through a self-interference channel matrix, a transmitting symbol is multiplied by the precoding vector, and is eliminated on a receiving antenna, so that the part of antennas canbe used for receiving same-frequency simultaneous signals from another communication node, and a same-frequency simultaneous full duplex communication mode is realized; and the combination of the twomeans improves the spectral efficiency of the communication system.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Wireless communication system, base station apparatus, mobile station apparatus, wireless communication method and integrated circuit
ActiveUS8934429B2Spatial transmit diversitySignal allocationCommunications systemSpatial multiplexing gain
Owner:SHARP KK
Method and device for determining downlink weight vector of multiple pieces of user equipment
ActiveCN105306116AHigh Spatial Multiplexing GainSpatial transmit diversityChannel state informationCommunications system
The invention provides a method and a device for determining a downlink weight vector of multiple pieces of user equipment. The method comprises the following steps that: a base station acquires an accuracy alpha<l> of channel state information of each piece of user equipment; the base station determines a value of each element beta<l,i> in a weight projection expected matrix beta according to a relationship between a module value square alpha<2> of accuracy information and a reciprocal (defined in the description) of a total number of transmitting antenna dimensions; and the base station determines the downlink weight vector of each piece of user equipment in the multiple pieces of user equipment according to the weight projection expected matrix beta. According to the method and the device in the embodiment, the accuracy of the channel state information of each piece of user equipment is taken as one of bases for determining the downlink weight vector, so that the determined downlink weight vector is closer to a practical situation of a communication system compared with the prior art in which the accuracy of the channel state information of each piece of user equipment is assumed to be an ideal value, thereby achieving a higher spatial multiplexing gain.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Transmission device that performs multi-user MIMO transmission for performing spatial multiplexing and transmitting of a plurality of packets addressed to a plurality of reception devices
InactiveUS9979516B2Good effectError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityPrecodingCommunications system
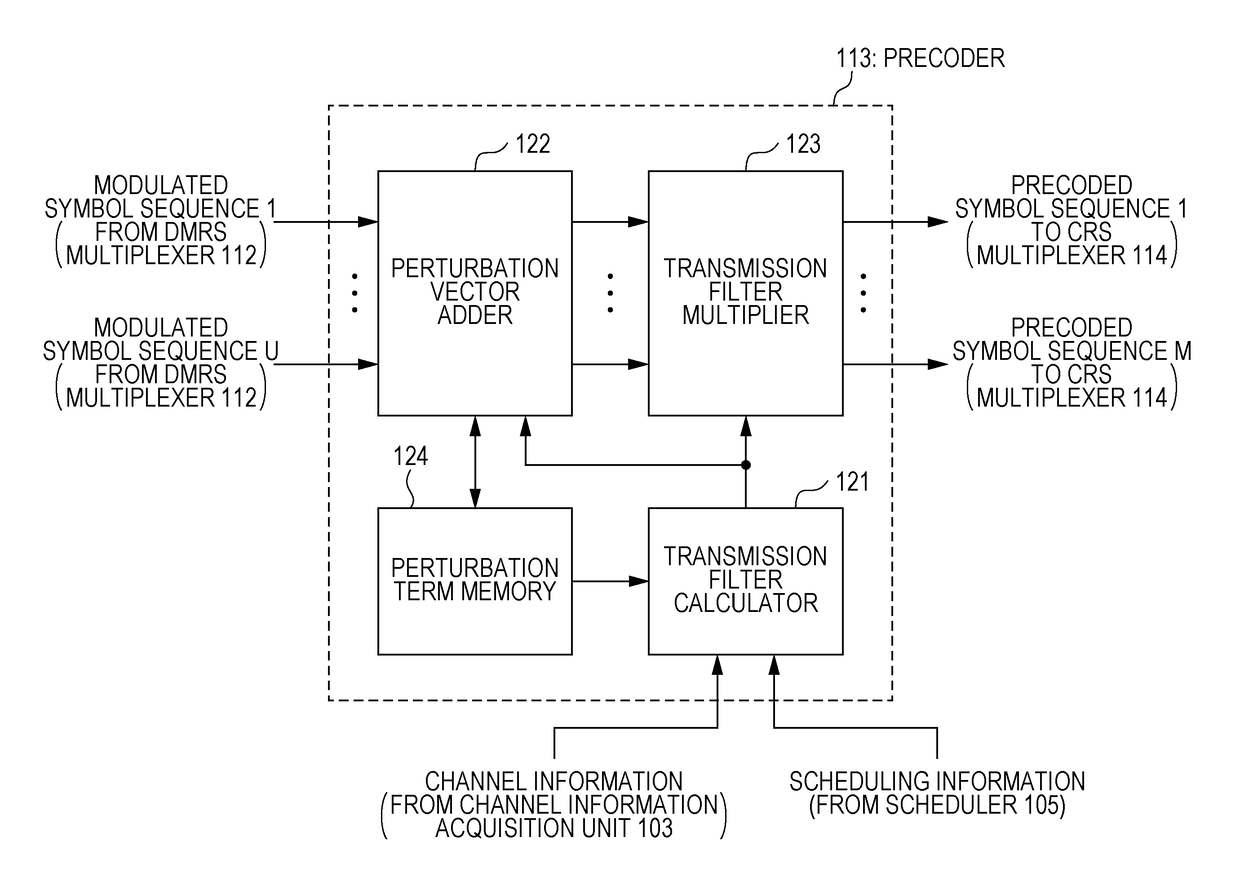
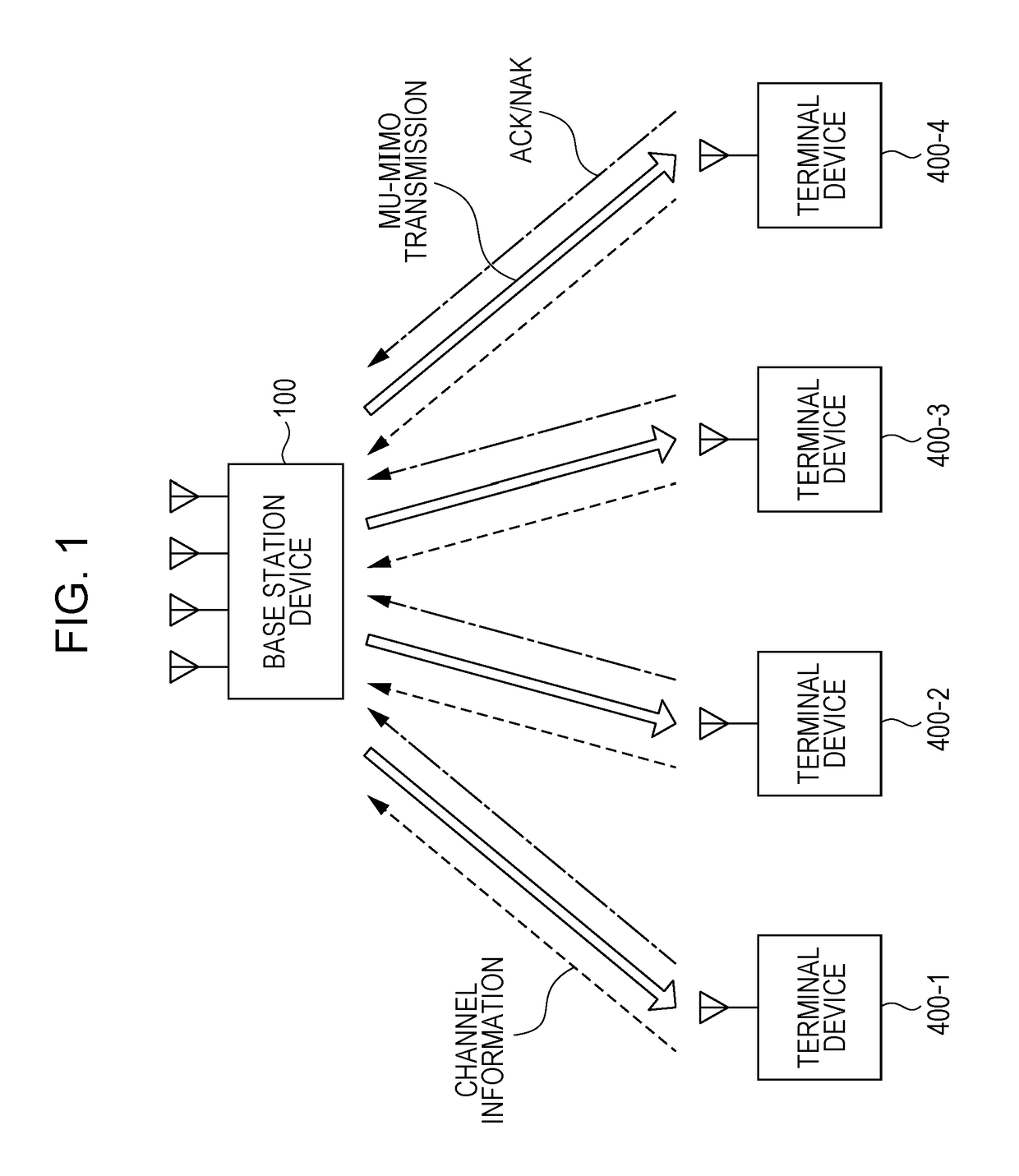
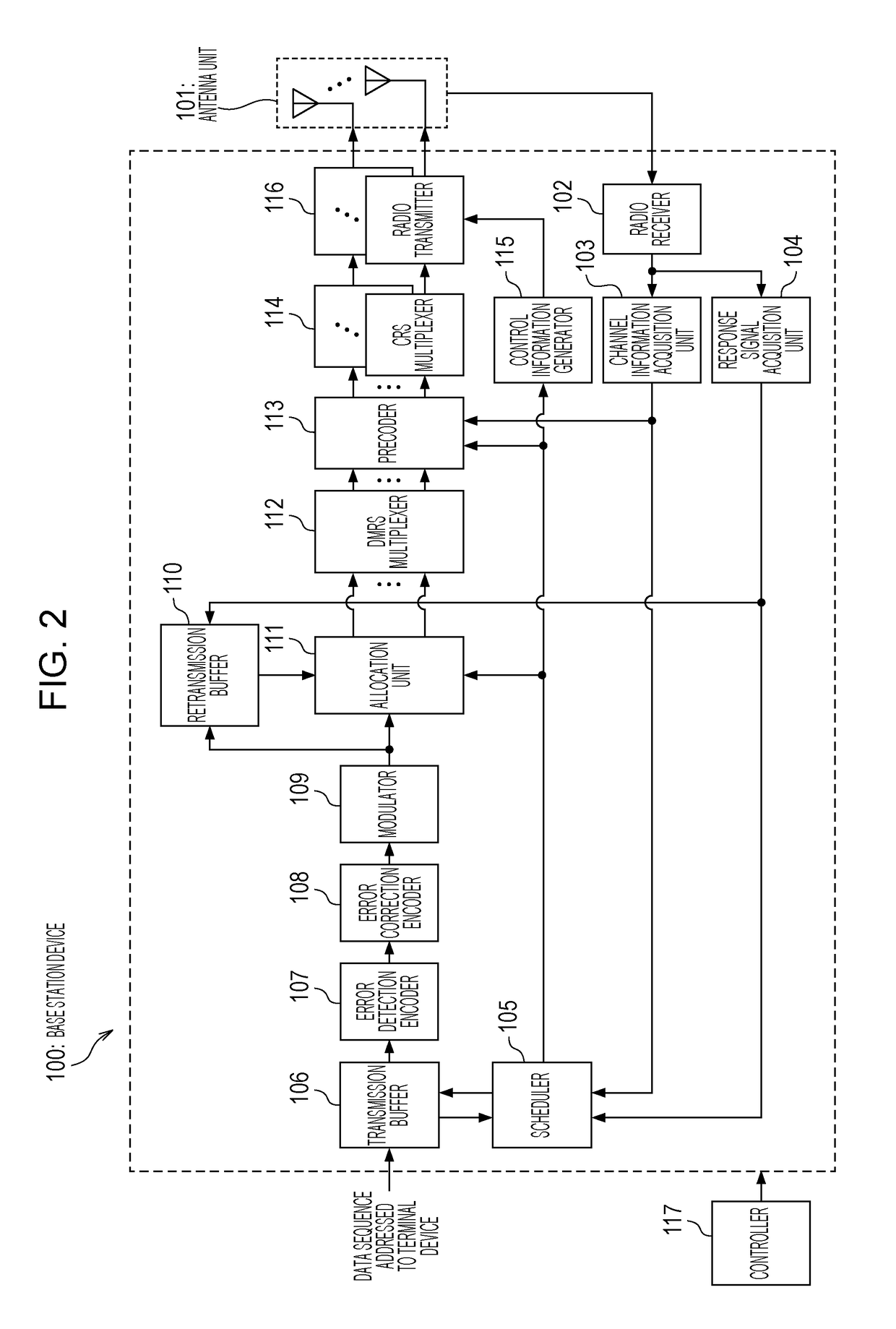
It is intended to provide a transmission device, a reception device and a communication system capable of improving transmission characteristics by performing packet combining by HARQ in MU-MIMO transmission using non-linear precoding.In a case of receiving NAK from any of terminal devices (400), a base station device (100) retransmits a packet, in which an error occurs, addressed to this terminal device. The base station device (100) transmits the data to be retransmitted together with other transmission data addressed to a different terminal device or addressed to the own terminal device by spatial multiplexing transmission with MU-MIMO. At this time, for the retransmission data, precoding is performed such that a perturbation term same as a perturbation term which has been added to this data by non-linear precoding at the time of initial transmission is added.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Transmission method with double directivity
ActiveUS10511359B2Efficient processReduce distractionsChannel dividing arrangementsRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
A transmission method using a massive MIMO (Multiple-Input and Multiple-Output) scheme with an arrangement 108 of Nm×Nb antenna elements at the transmitter, arranged in Nm sets of Nb antenna elements or Nb sets of Nm antenna elements based on SC-FDE (Single-Carrier with Frequency Domain Equalization) schemes with large constellations that is compatible with low-cost, highly-efficient, nonlinear amplifiers 106, while allowing spatial multiplexing gains.The transmission structure of this transmission method decomposes in 103 the modulated symbols from 102 associated to a given constellation as the sum of Nm polar components that are modulated as Nm BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying) signals. Each of these BPSK signals can be regarded as an OQPSK (Offset Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) signal in the serial format that is specially designed to have good tradeoffs between reduced envelope fluctuations and a compact spectrum.
Owner:CARVALHO PAULO MIGUEL +4
Optimal antenna configuration method for arbitrary message topology MIMO system based on interference zero setting
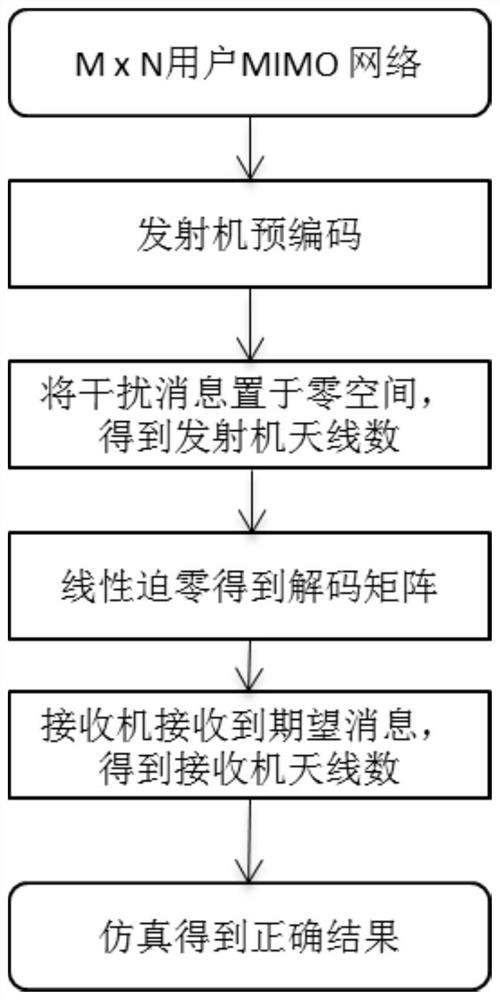
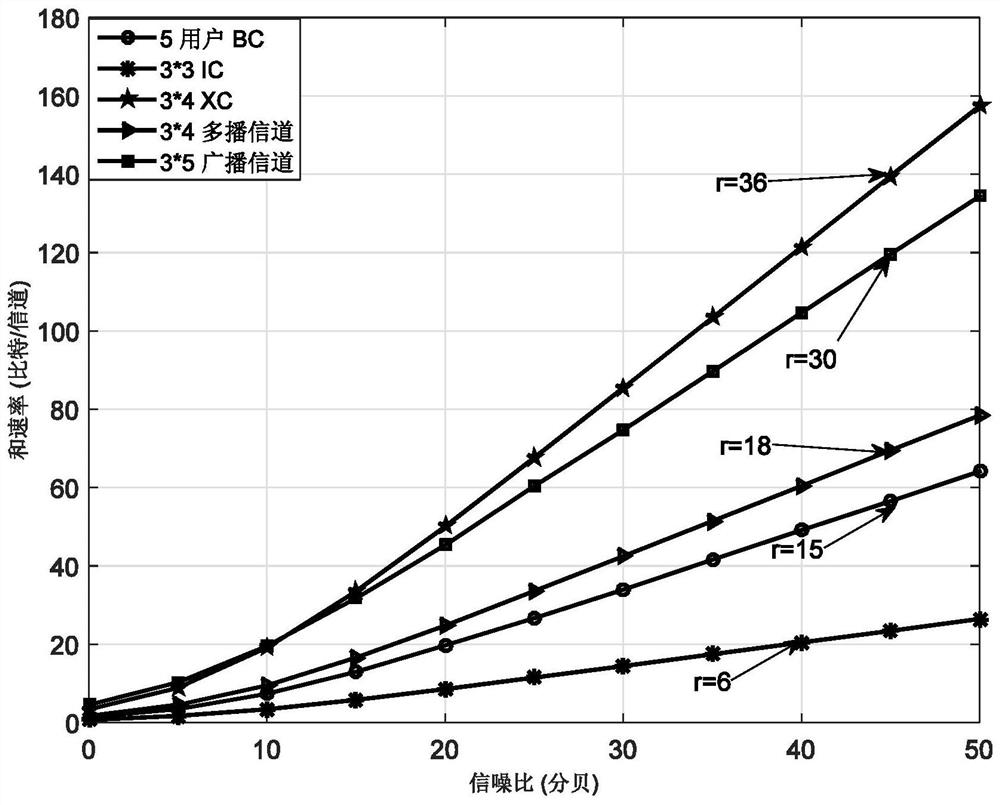
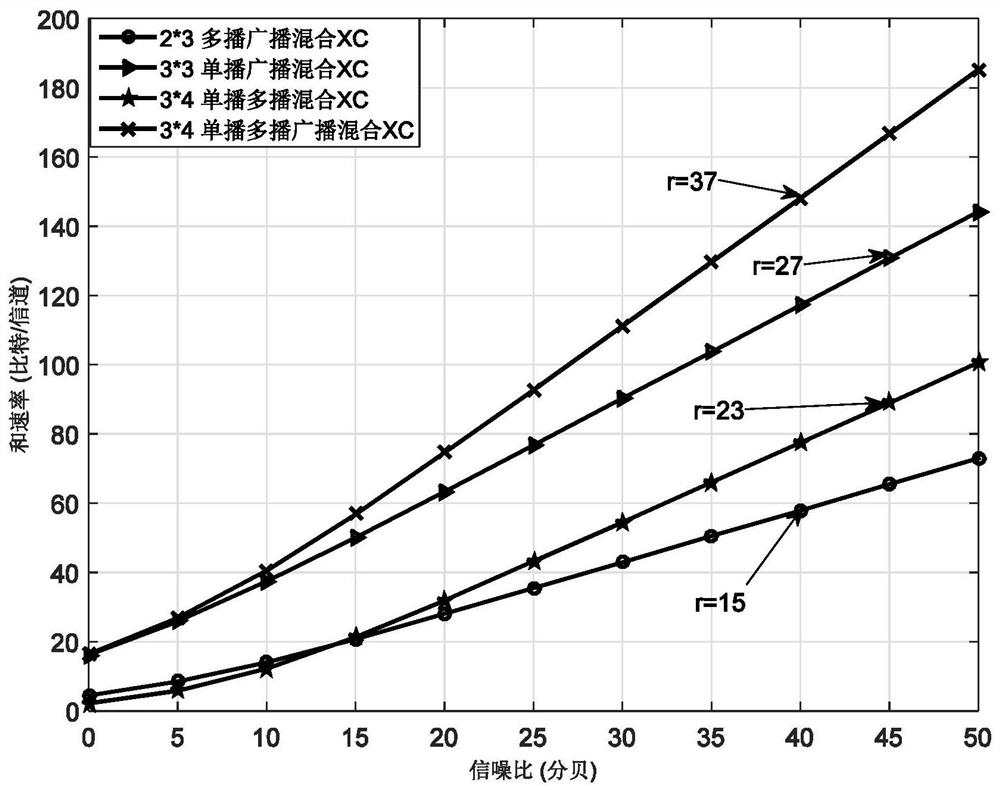
The invention provides an optimal antenna configuration method for an arbitrary message topology MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) system based on interference zero setting, which is used for carrying out optimal antenna configuration on an MTMR (Multiple Output Multiple Input Multiple Output) system under arbitrary message types (broadcast, multicast and unicast) based on an interference zerosetting technology, and provides a universal computational formula. A system message topology matrix is proposed to analyze antenna configuration, the minimum antenna required by each receiving end is obtained based on a transmitting end interference zero setting technology (IN), and then the minimum antenna required by each transmitting end is further obtained. The specific process of the schemeis as follows: the interference message is placed in the intersection space of the null space of the corresponding channel, and the optimal antenna configuration problem is analyzed according to thedimension characteristic of the intersection space. The simulation maximum spatial multiplexing gain is obtained through the sum rate of the simulation system, the result shows that the theoretical multiplexing gain is basically consistent with the simulation multiplexing gain, and the feasibility of the method is proved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com