Patents
Literature
464results about "Detecting faulty hardware by configuration test" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
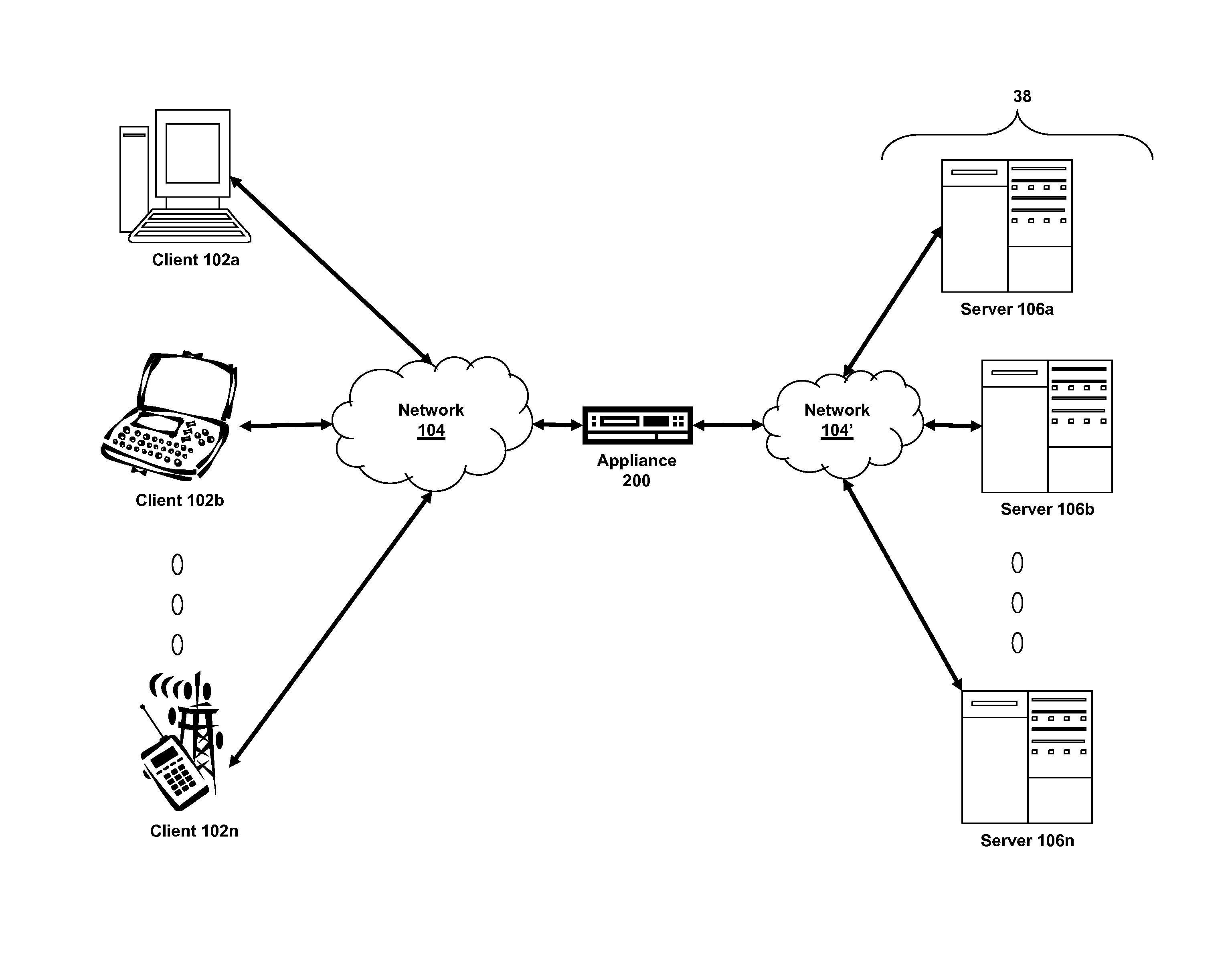
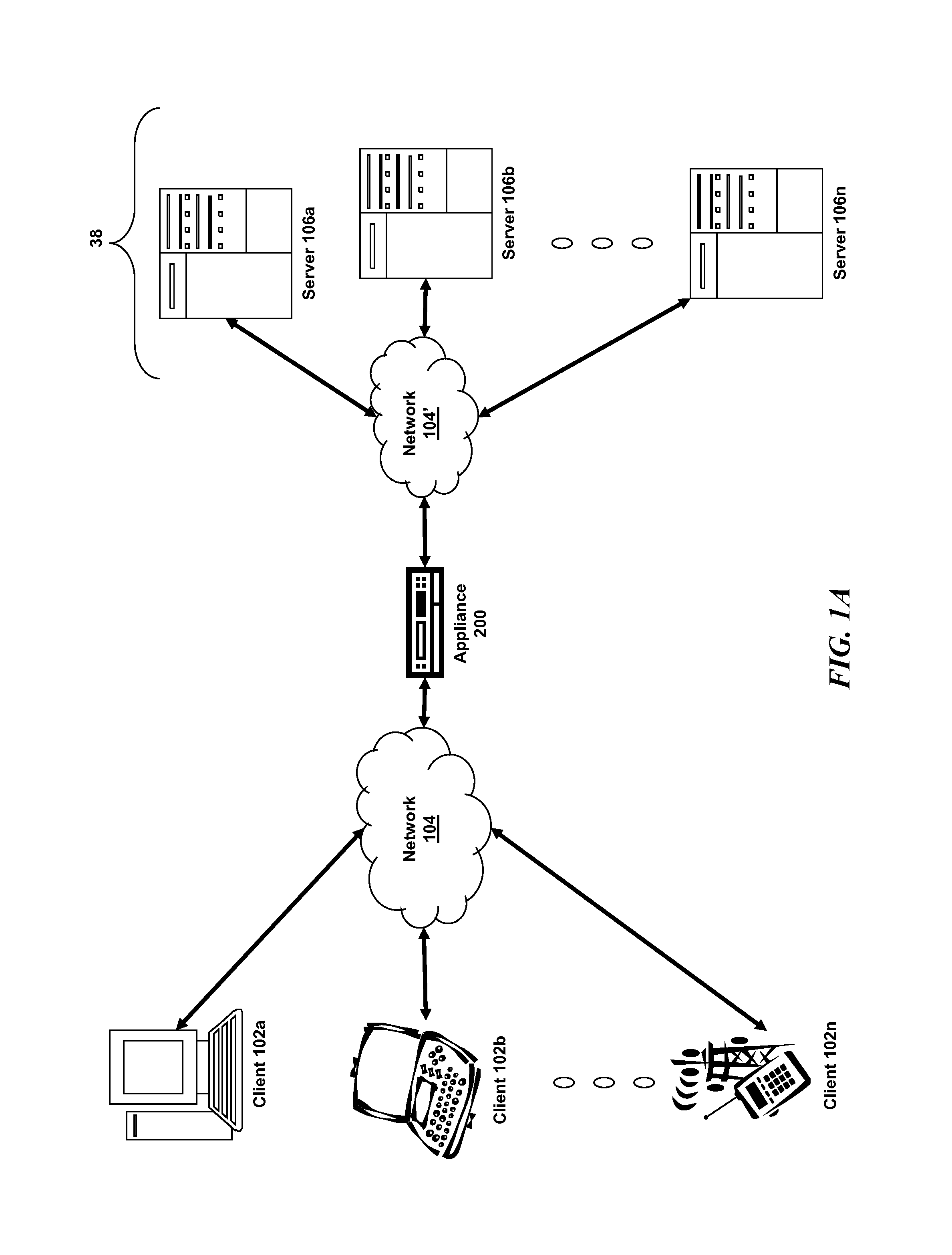
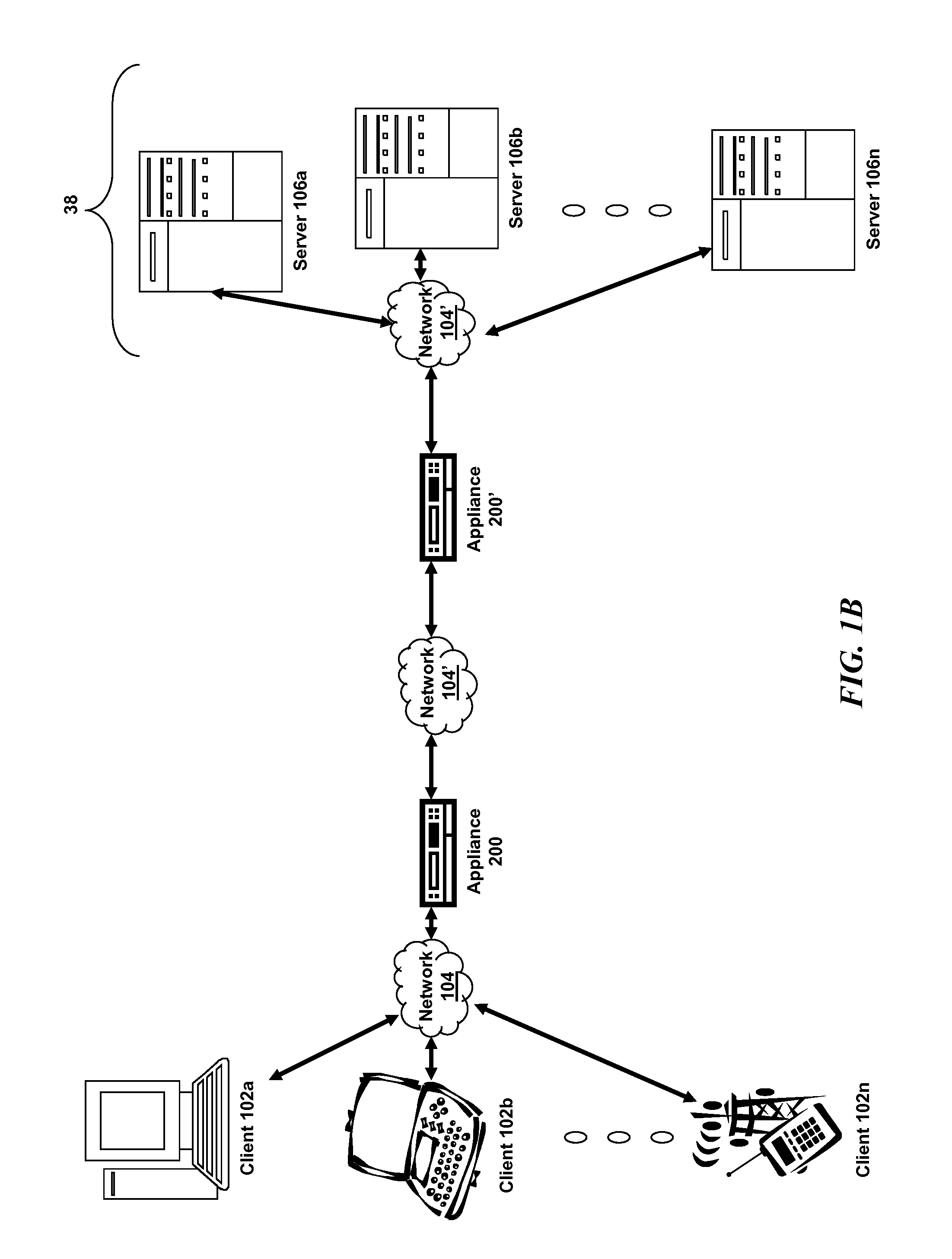
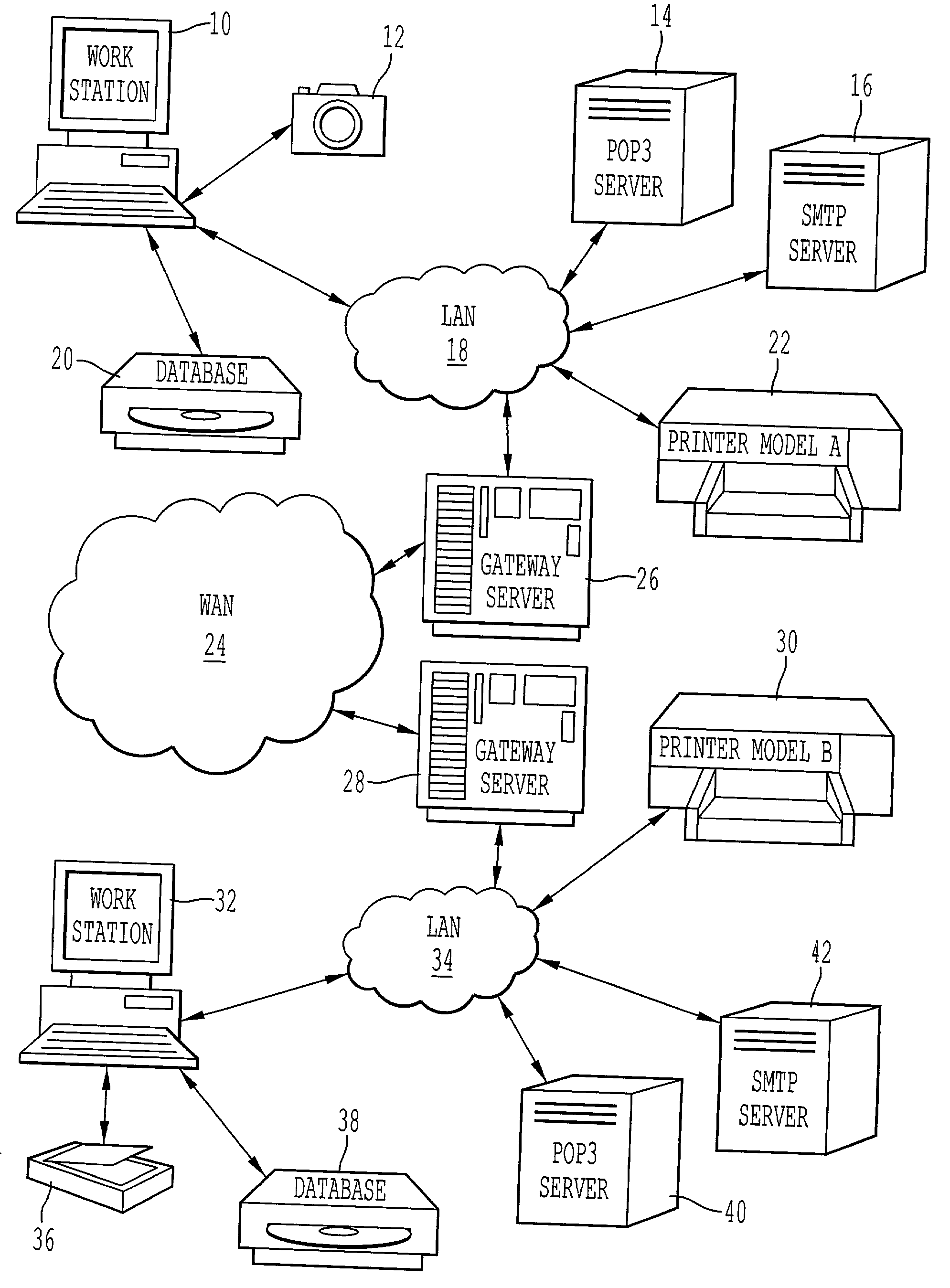
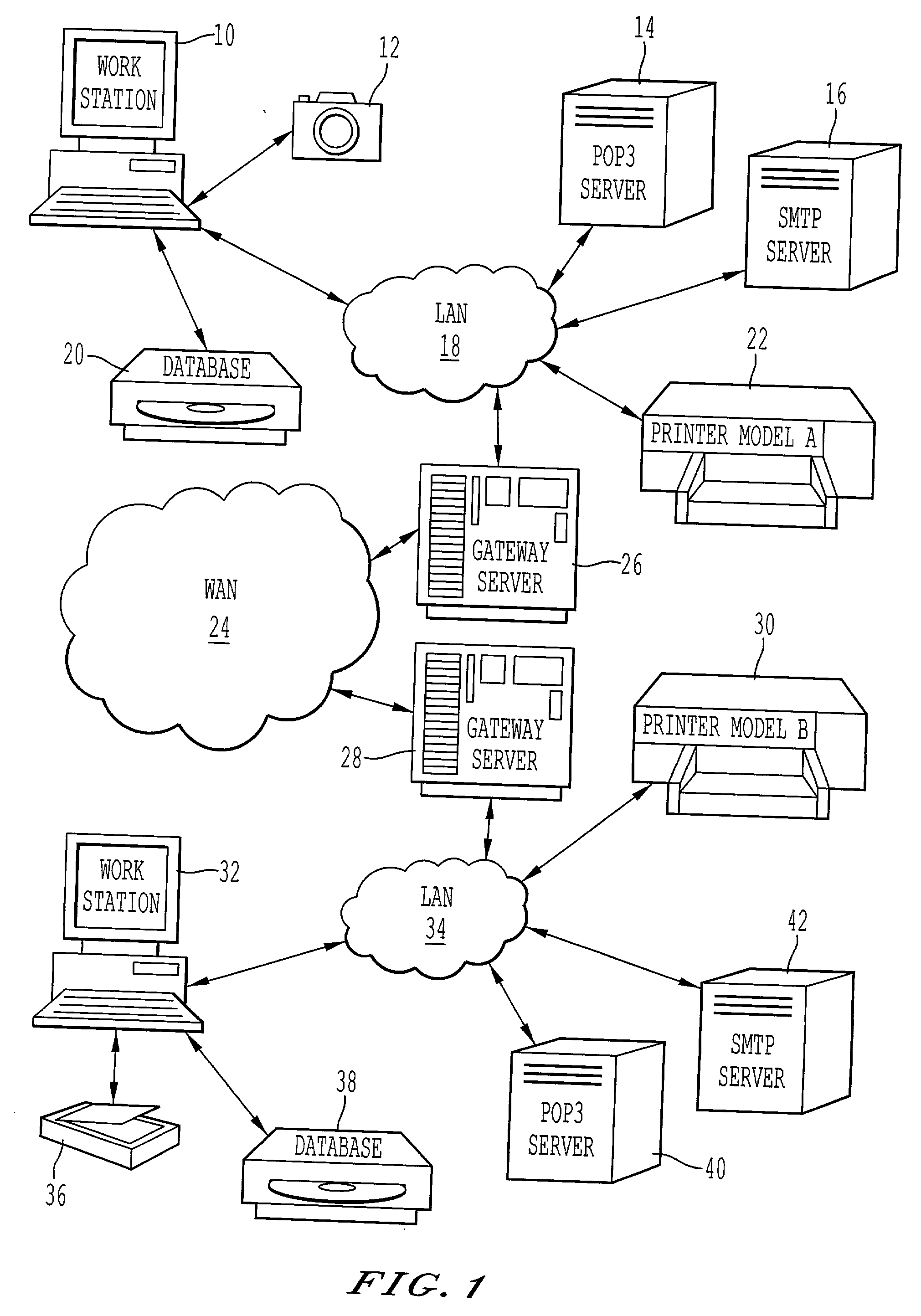
Systems and methods for cloud-based probing and diagnostics
ActiveUS20150195182A1Accelerated settlementDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testDetecting faulty hardware by remote testData centerVirtual device
Systems and methods of the present disclosure are directed to providing centralized diagnostic services to a plurality of heterogeneous computing environments deployed at different data centers on different networks. In some embodiments, a centralized diagnostic tool establishes a connection to a server of a data center that deploys a computing environment with components. The centralized diagnostic tool validates automatically a component of the computing environment based on a corresponding configuration file received from the server for the component. The centralized diagnostic tool establishes a virtual device simulating a client application executing on a client device. The client application can be configured to communicate with the component. The centralized diagnostic tool automatically initiates a request using a predetermined protocol flow, and the virtual device transmits the request to the component. The virtual device receives a response to the request indicative of a status of the computing environment.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
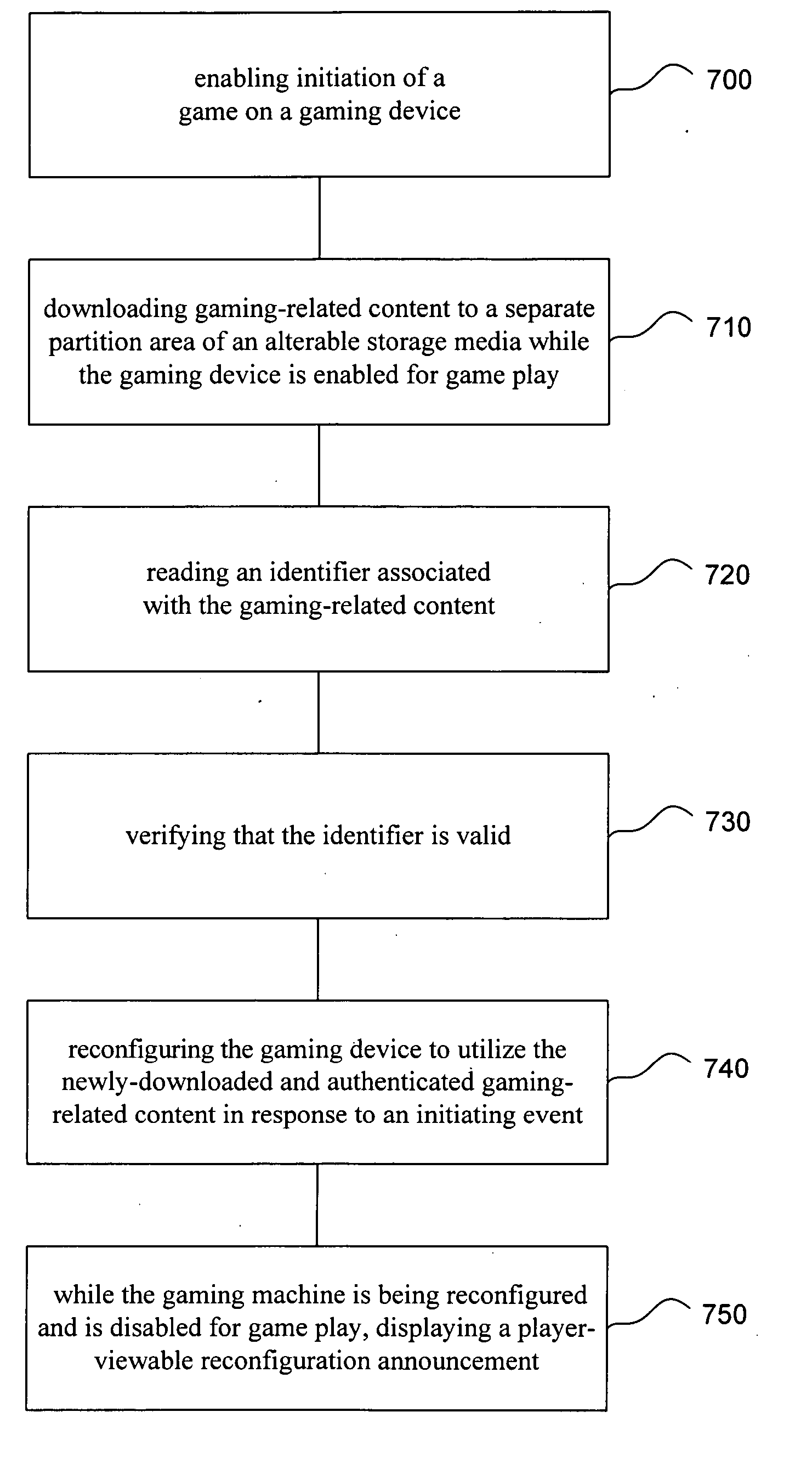
System and method for an alterable storage media in a gaming machine
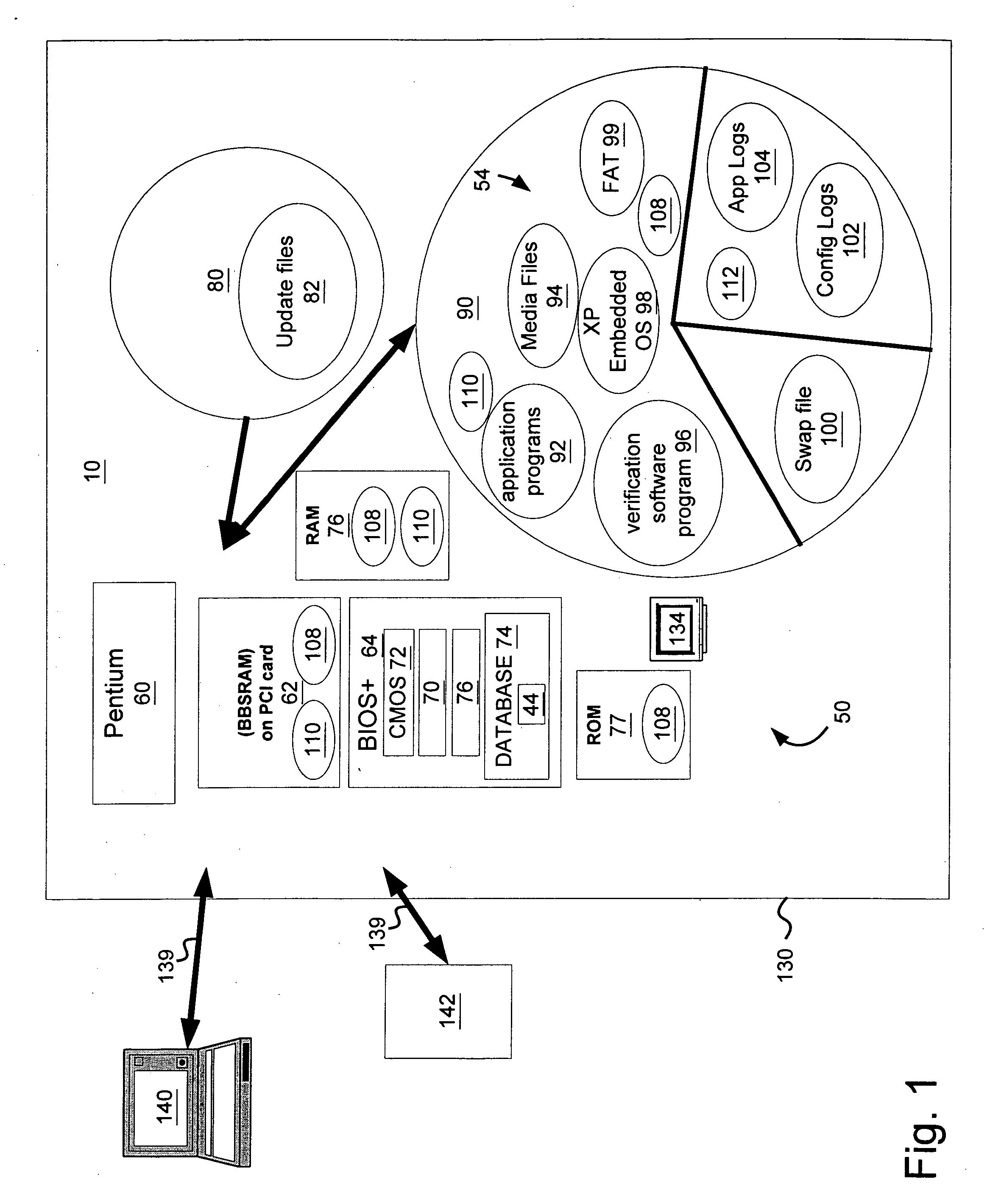
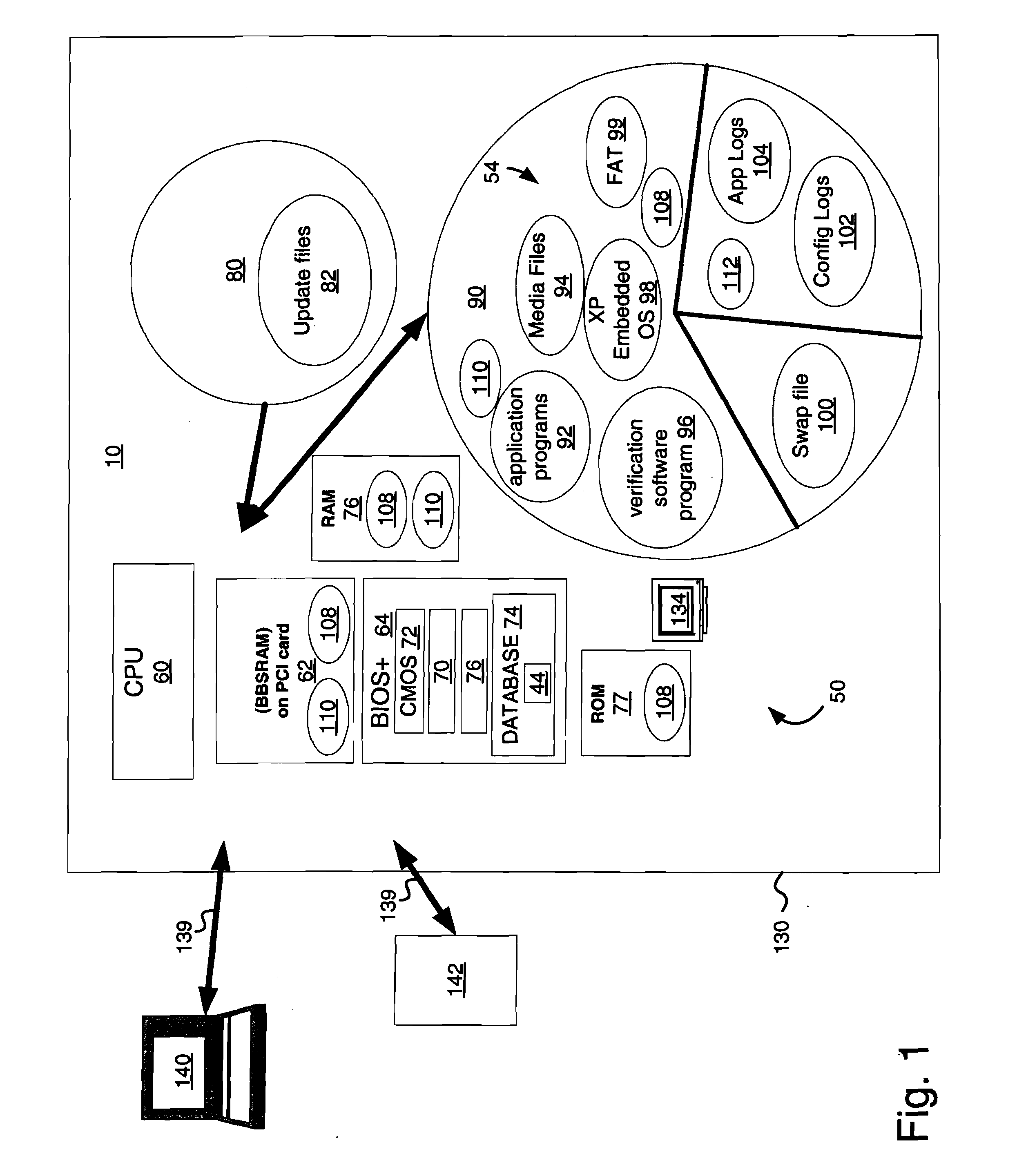
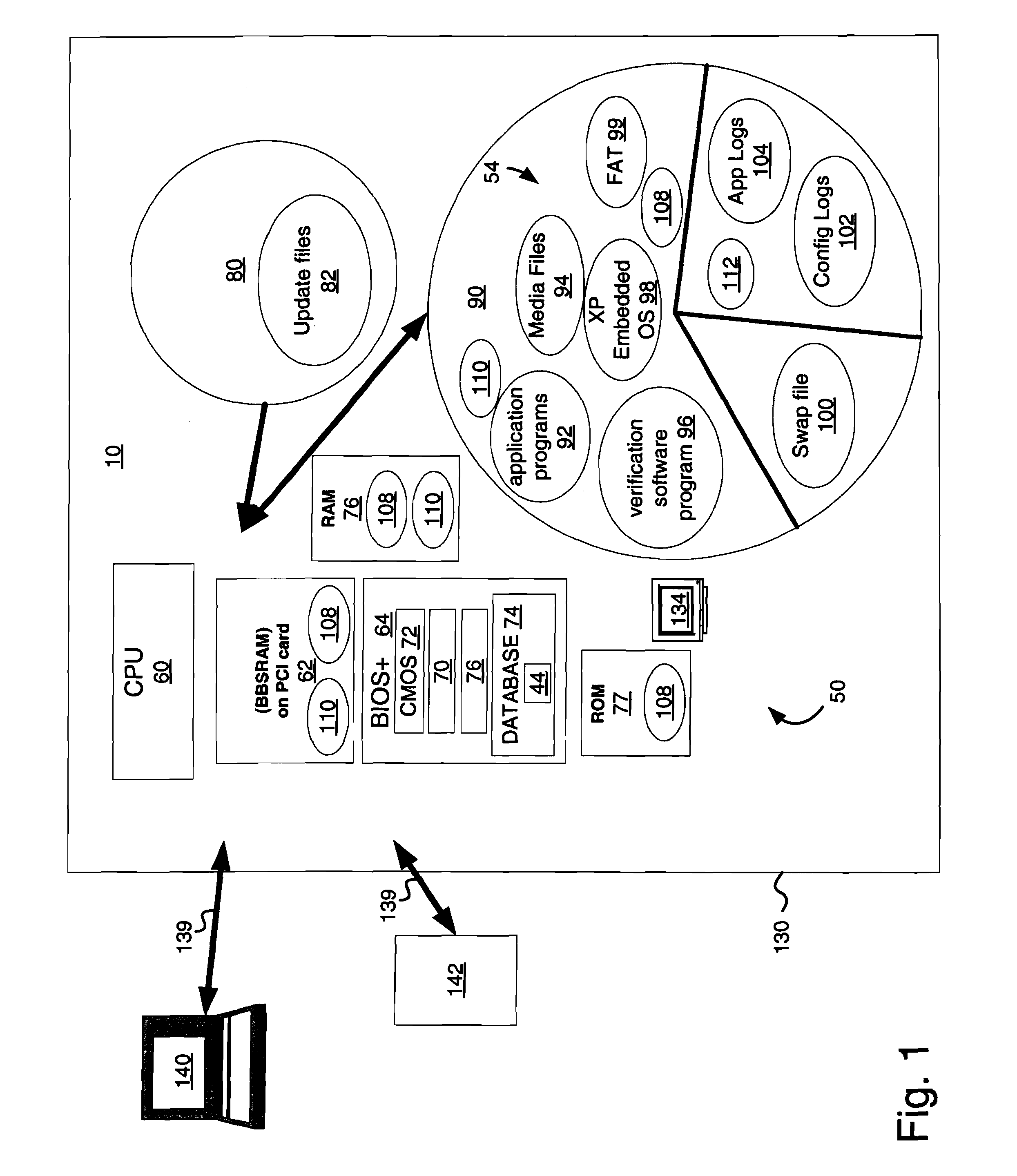
InactiveUS20060079333A1Easy accessLess instructionDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testDetecting faulty hardware by remote testHard disc driveIdenticon
A system for verifying one or more downloaded components 54 of a gaming device 10 that includes the gaming device, which has an alterable hard drive 80 (or other persistent storage media 90), and the downloaded components that further include gaming-related content 92-96. A related method includes: enabling initiation of a game on the gaming device 10; downloading the gaming-related content 92-96 to the alterable hard drive 80 while the gaming device 10 is enabled for game play; reading an identifier associated with the gaming-related content 92-96; verifying that the identifier is valid (using verification software 70); and reconfiguring the gaming device 10 to utilize the newly-downloaded, gaming-related content 92-96 in response to an initiating event.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
Method and apparatus for configuring storage devices
InactiveUS6311232B1Detecting faulty hardware by configuration testDetecting faulty hardware by remote testComputerized systemEmbedded system
A method for configuring storage devices includes detecting an existing storage device configuration. The existence of a new storage device is detected, and the new storage device is configured based on the existing storage device configuration. A computer system includes an existing storage device, a new storage device, and a processor. The existing storage device has an existing storage device configuration, and the processor is adapted to detect the existence of the new storage device and configure the new storage device based on the existing storage device configuration.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
RAID system having a selectable unattended mode of operation with conditional and hierarchical automatic re-configuration
InactiveUS6058455AInput/output to record carriersDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testRAIDOperation mode
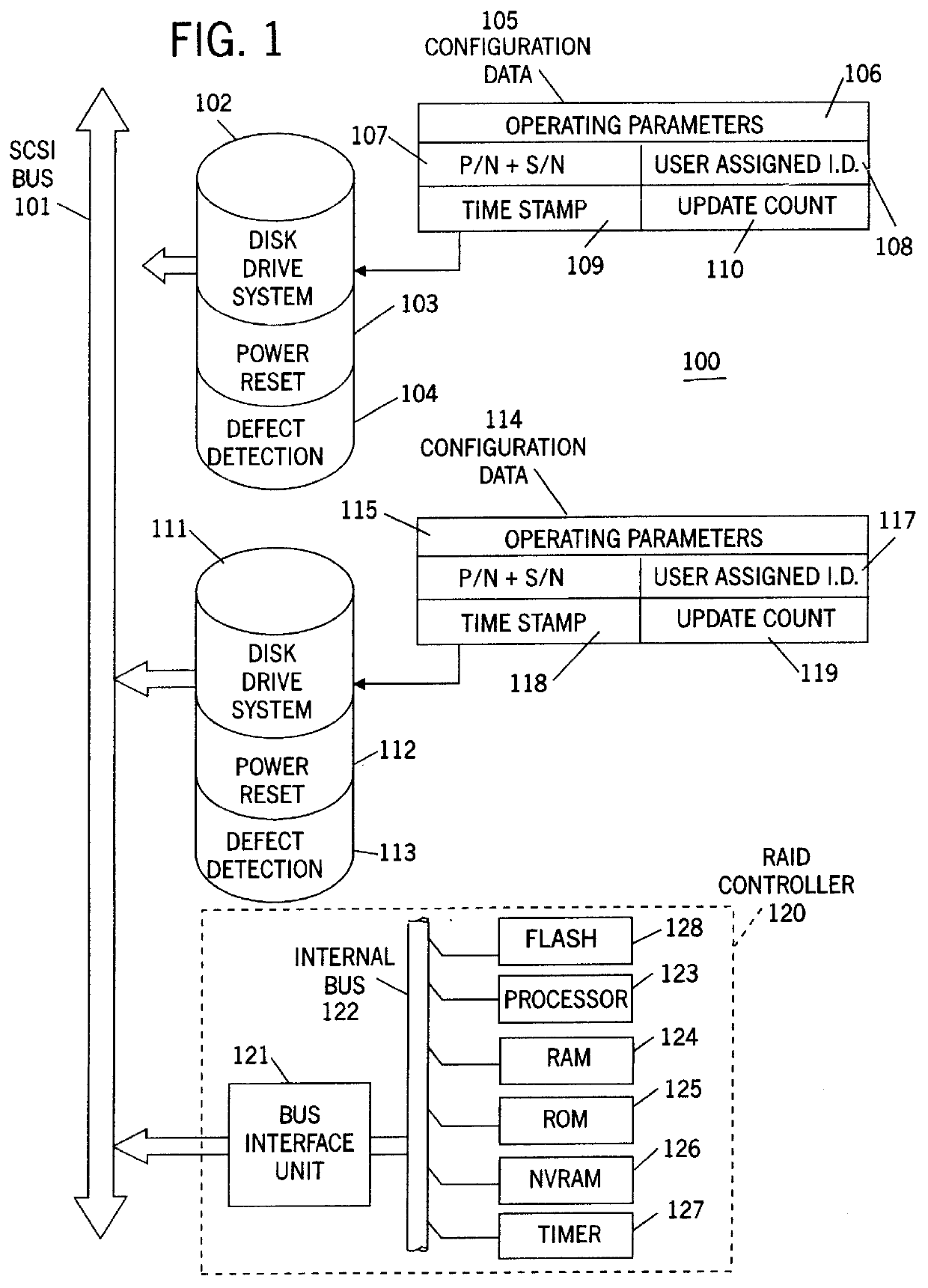
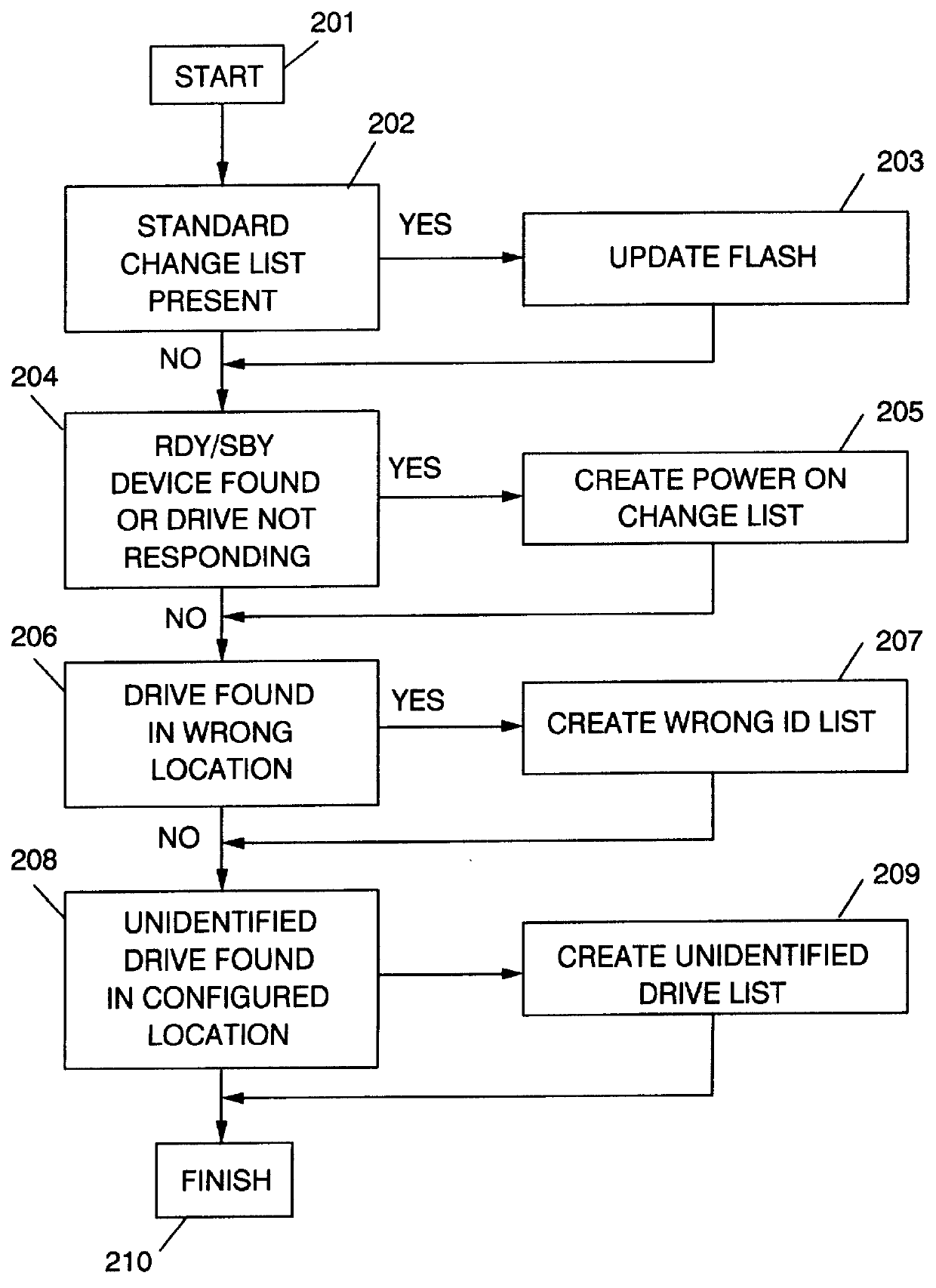
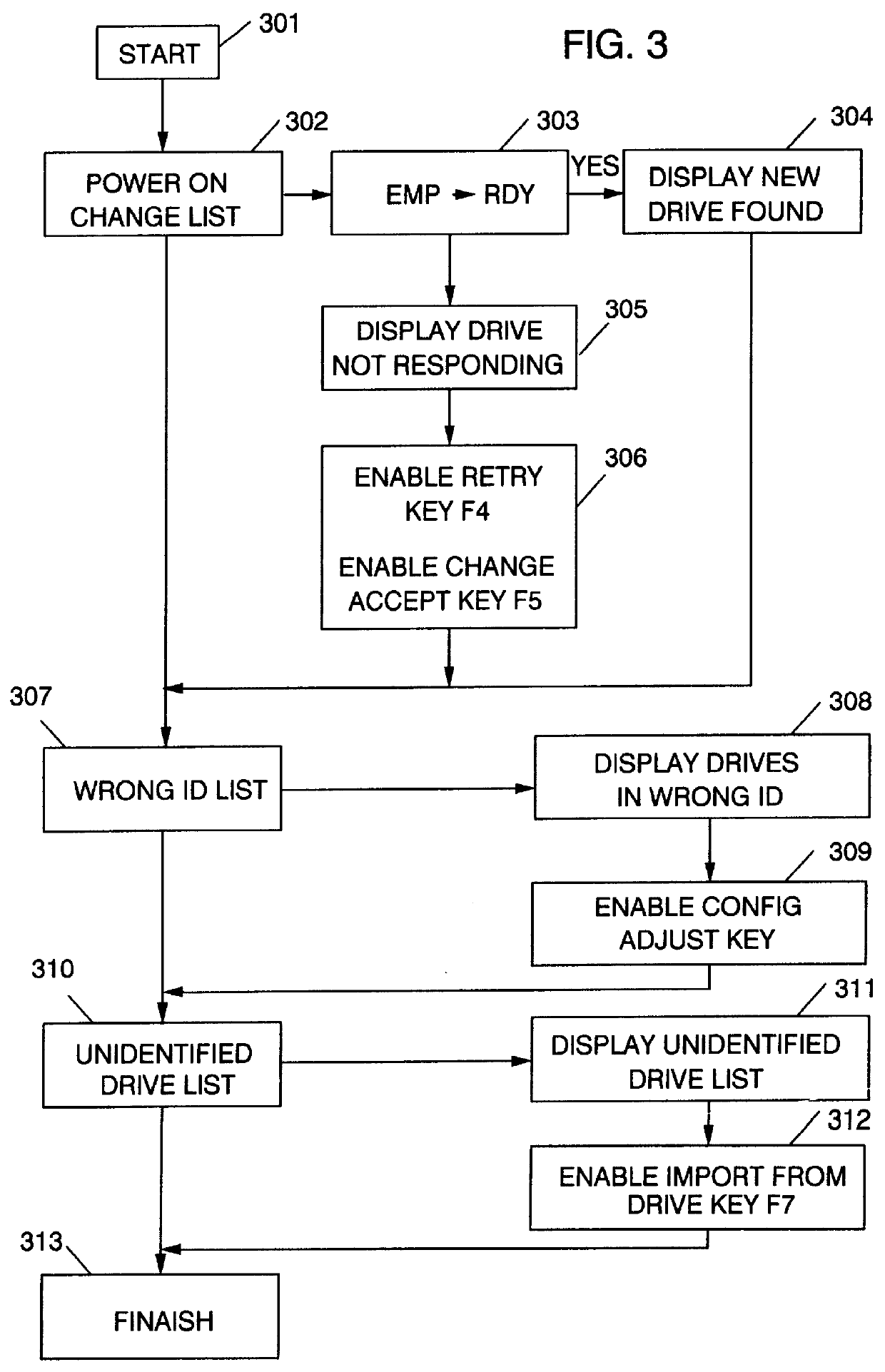
Because correct configuration data is essential to the operation of any RAID system, and because multiple copies of the configuration data are kept, not only in the RAID controller itself, but also in each disk drive unit in the configuration, it is imperative that the various copies of the configuration data do not become "out of synchronization", which means that one or more copies of the configuration data are different from one or more other copies of the configuration data. To maintain synchronization of all copies of the configuration data, the current invention compares the configuration data stored in the RAID controllers' NVRAM to that of the current system, and records any new, non-responding, repositioned or unidentified storage devices in a change list. The identities and the attachment points of any storage devices in the change list are then displayed to the user, and various options for correcting the lack of synchronization are provided by enabling one or more function keys that may be selected by the user. One such function key, an "accept change" key, causes the configuration data to be modified by changing the current operational state of any non-responding storage device. A "configuration adjustment" key, when selected by the user, causes the configuration data to be modified to reflect any changes in the attachments points of any repositioned storage deices. An "import configuration" key causes the configuration data to be changed to correspond to that of an unidentified storage device. And a "retry" key gives the user an opportunity to rearrange the system and then re-compares the configuration data in the controller to the current system configuration. When the system is operating in un-attended mode, means are disclosed to automatically perform the "accept change", "configuration adjustment" and "import configuration" functions in priority order so long as the "retry" key has not been enabled. The retry key implies attended operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
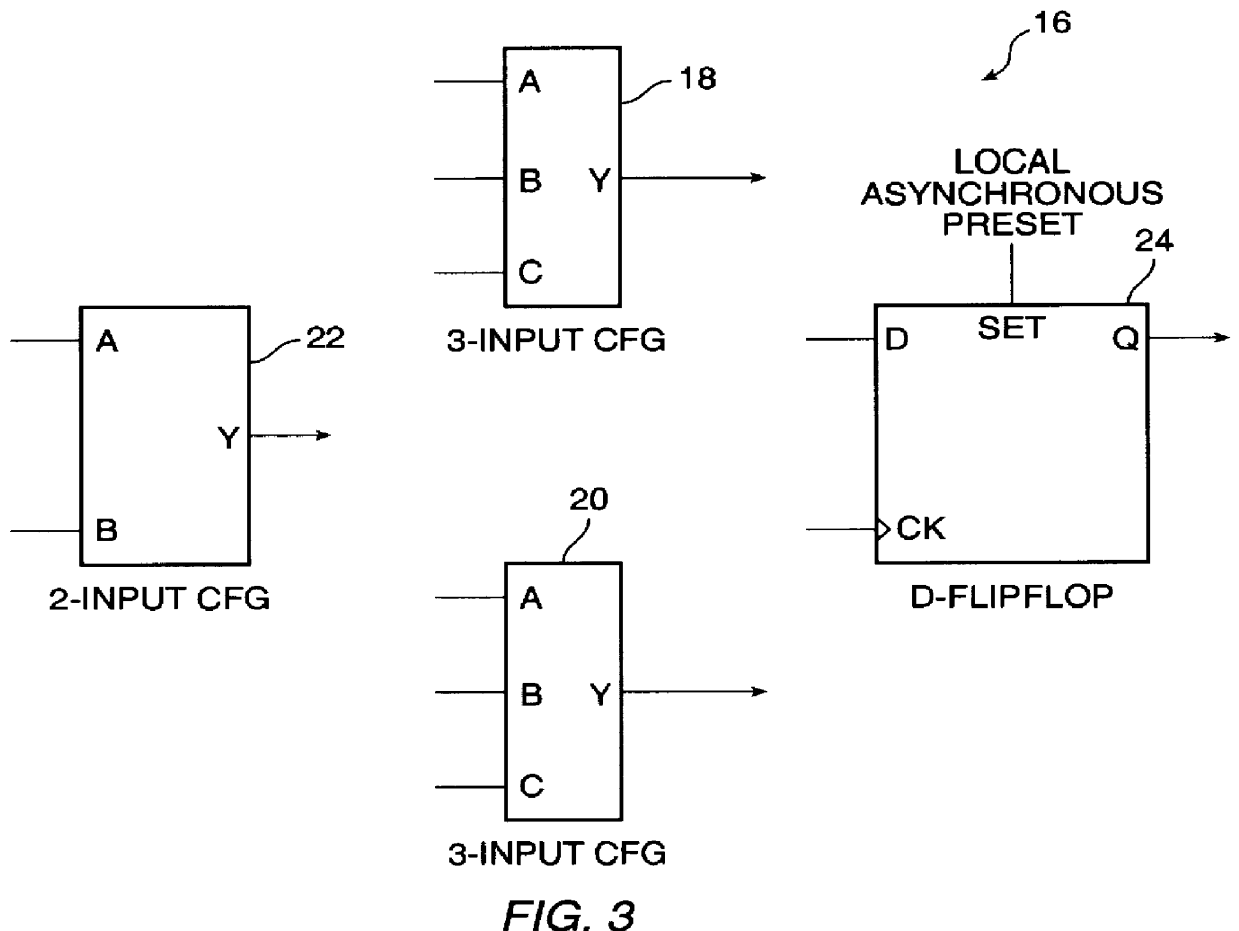
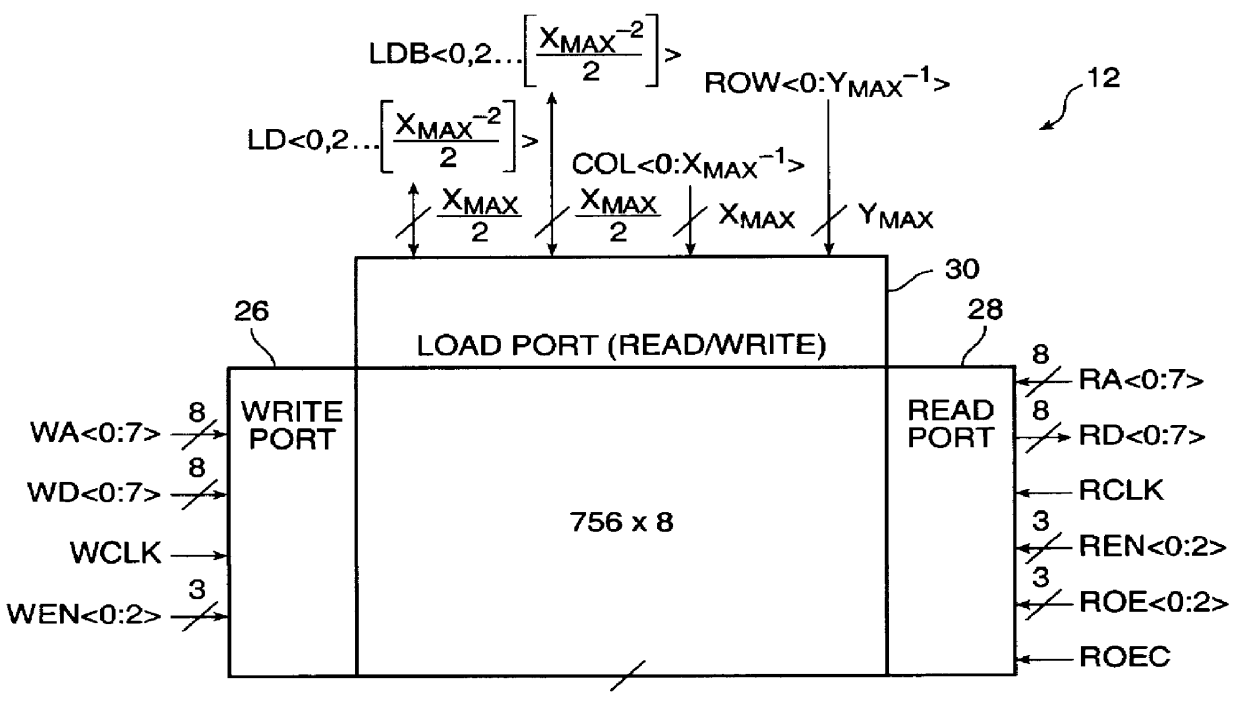
Embedded static random access memory for field programmable gate array
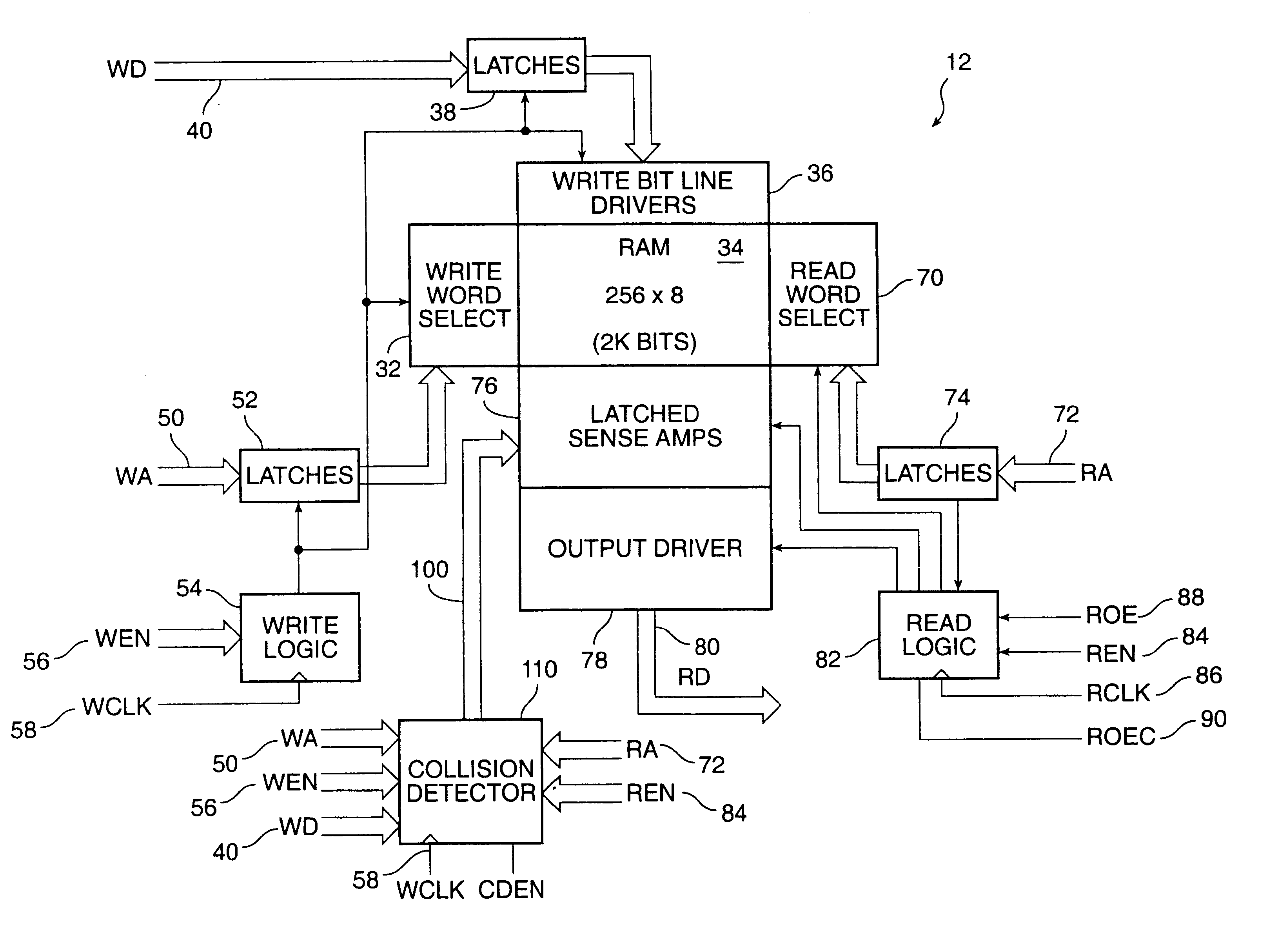
InactiveUS6049487AHigh impedance stateSolve conflictsDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testRead-only memoriesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
A dual ported (simultaneous read / write) SRAM block with an additional load port that interacts with the circuitry employed in the loading and testing of the configuration data of the FPGA core is disclosed. Each SRAM block contains circuits in both the read port and the write port that permit the SRAM blocks to be connected into deeper and wider configurations by without any additional logic as required by the prior art. An address collision detector is provided such that when both read and write ports in the SRAM block access the same address simultaneously a choice between the data being read can be made between the data presently in the SRAM block or the new data being written to the SRAM block.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
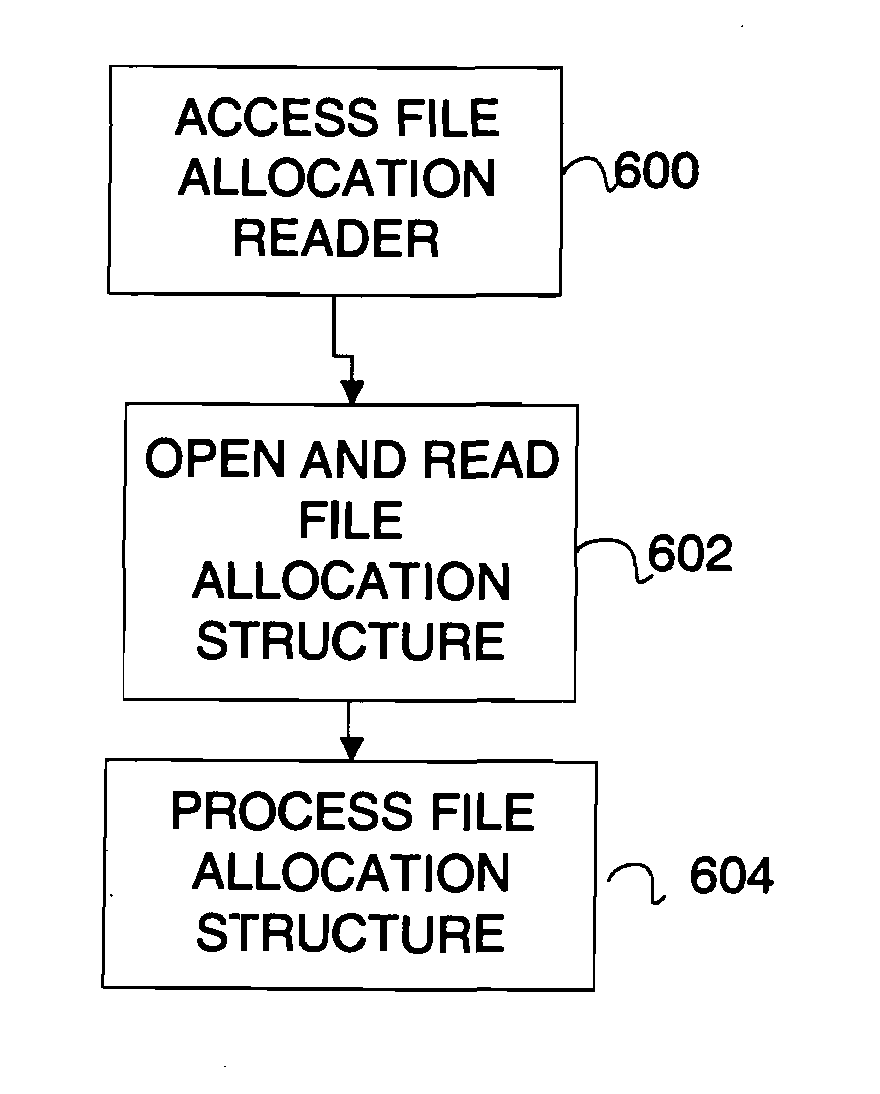
Device verification system and method
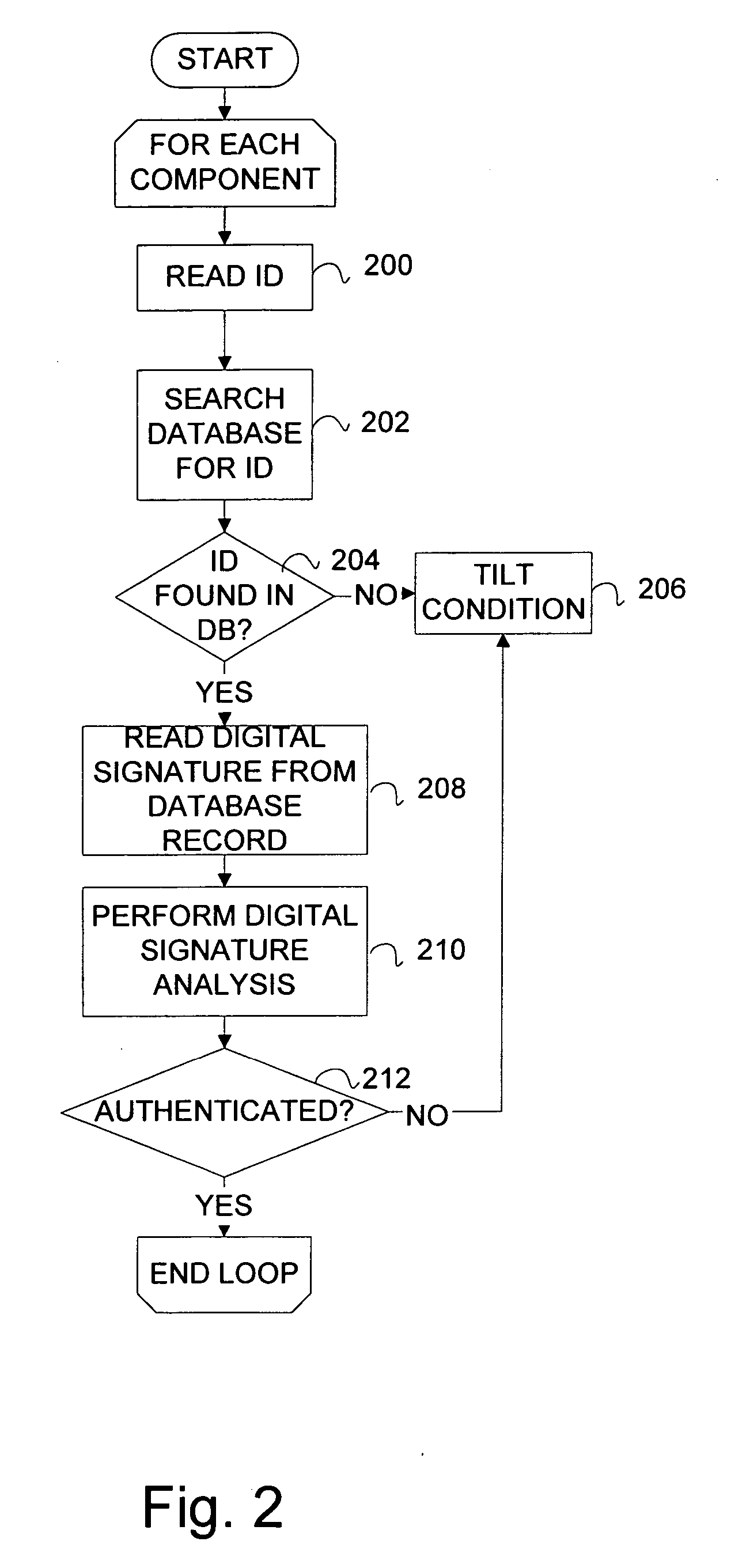
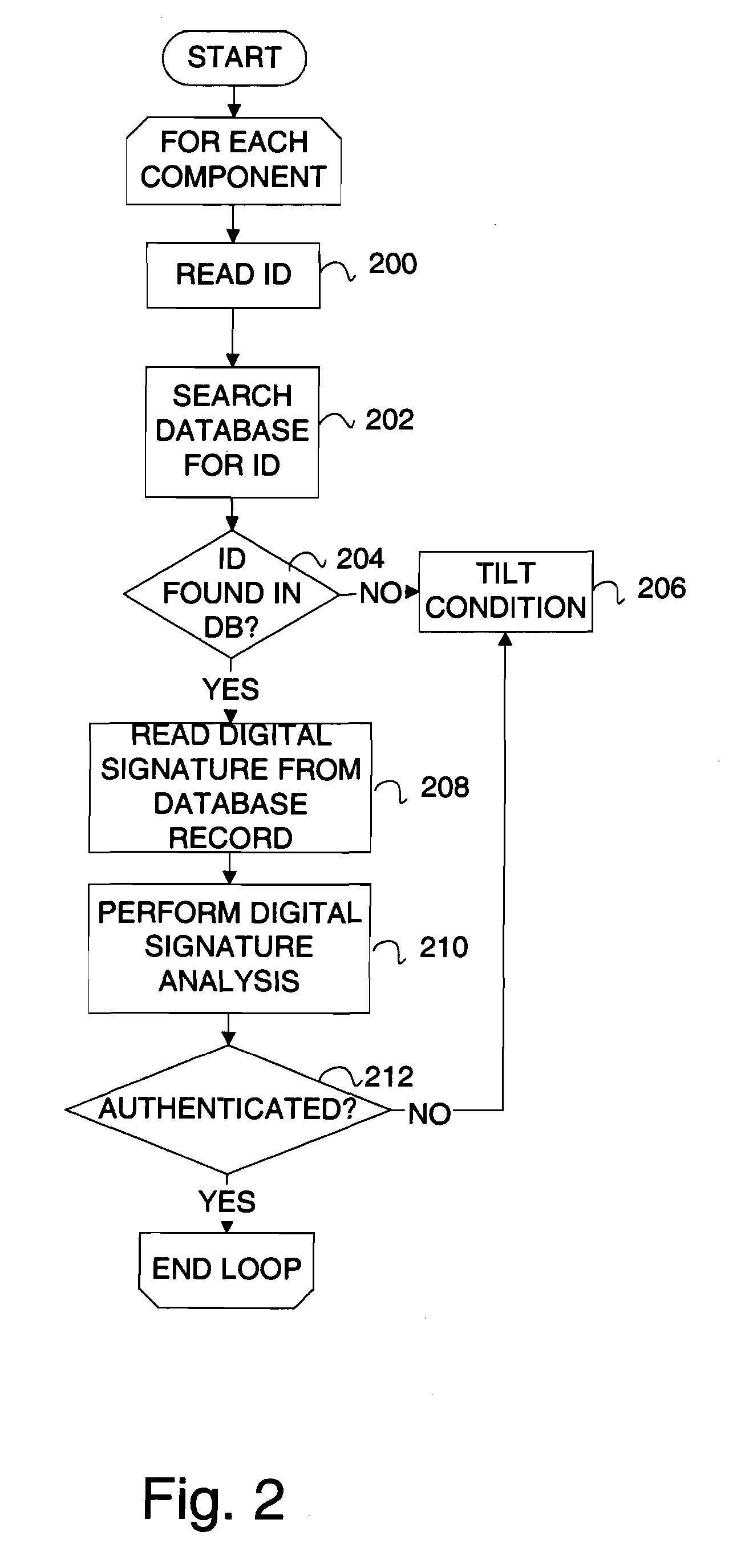
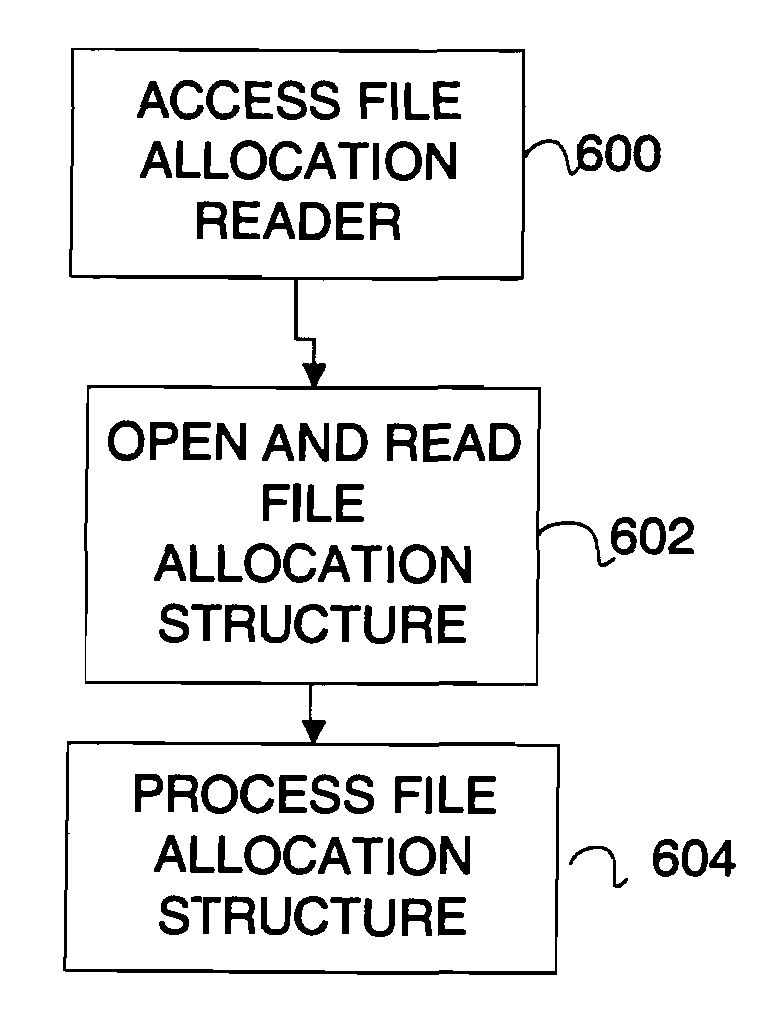
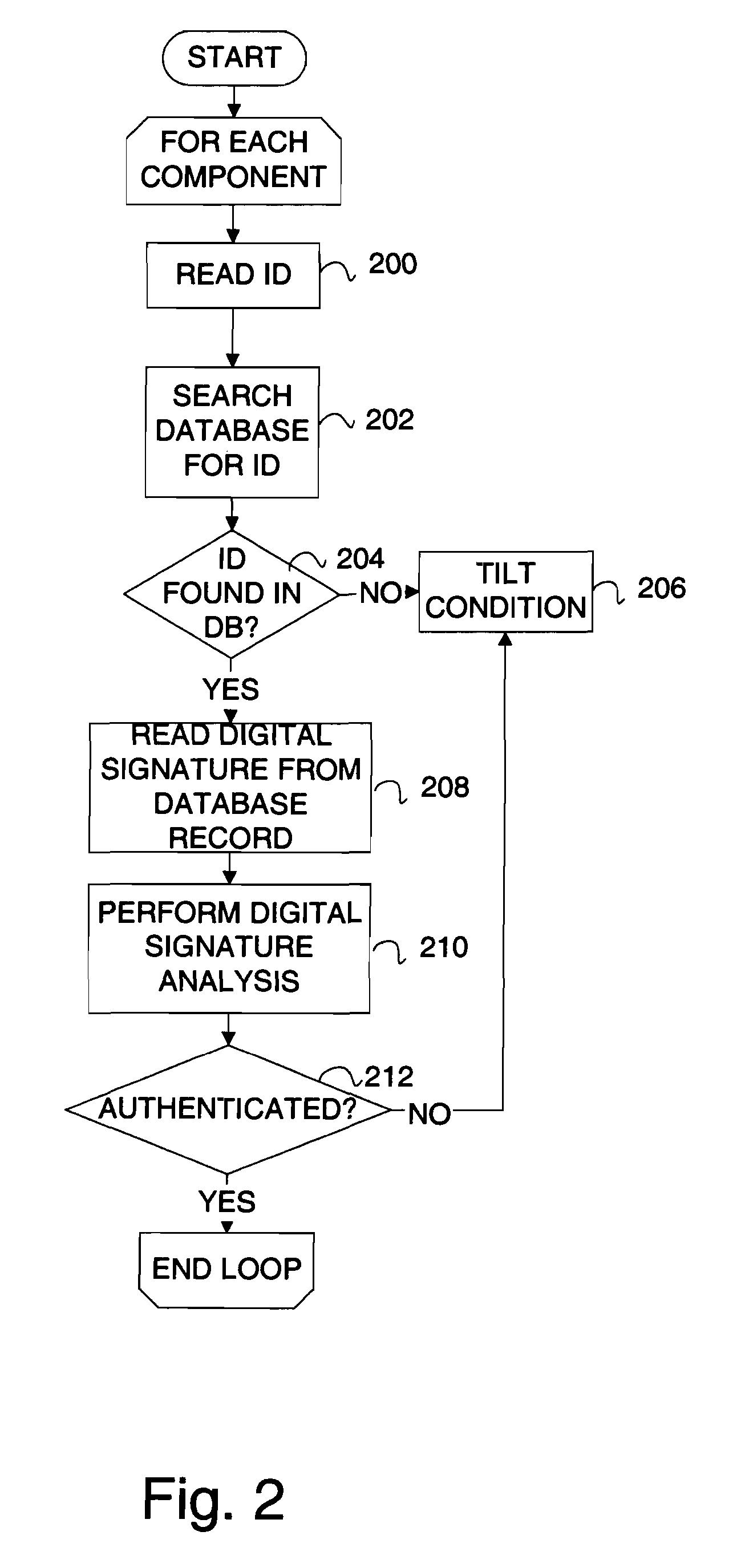
InactiveUS20070006329A1Little informationImprove securityDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testDetecting faulty hardware by remote testFile allocationOperational system
There is provided a method and system for verifying a device, having components. Identification numbers of the components are read and then verified. The process of verifying comprises matching each identification number in a database to determine whether each identification number is valid. In one embodiment, the database is remote from the device, wherein verification is performed over a network connecting a database server containing the database with the device. The device transmits the identification numbers for each of the components to the database server for verification. A file allocation structure reader may be located in a basic input / output system of the device for reading and verifying data files from a persistent storage media without loading an operating system. The device may comprise a gaming machine that contains a monitor for monitoring one or more system events being processed by the gaming machine. The monitor monitors routine and non-routine events. A detector is included for detecting selected system events so that they may be recorded.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
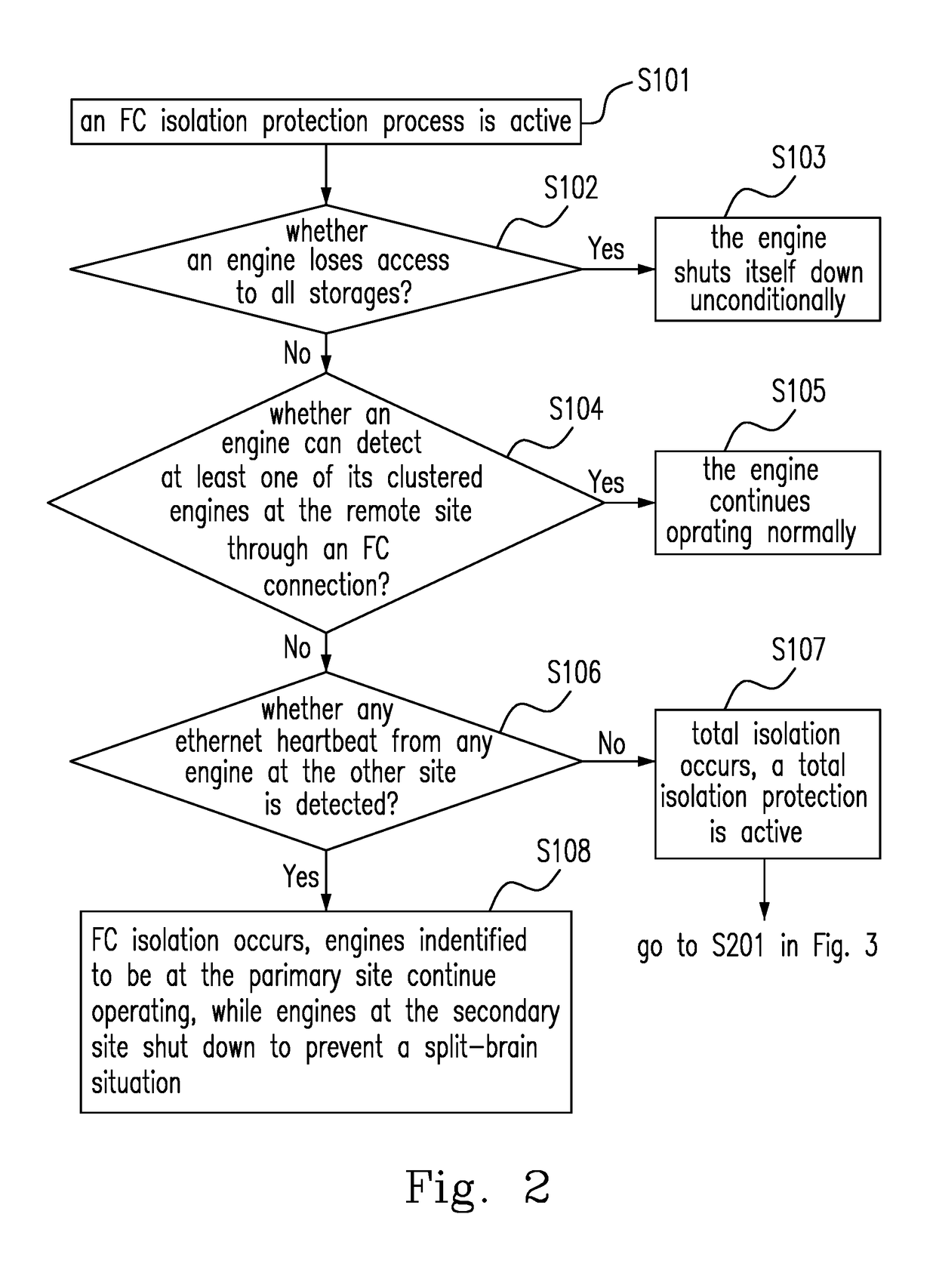
Method of Site Isolation Protection, Electronic Device and System Using the Same Method
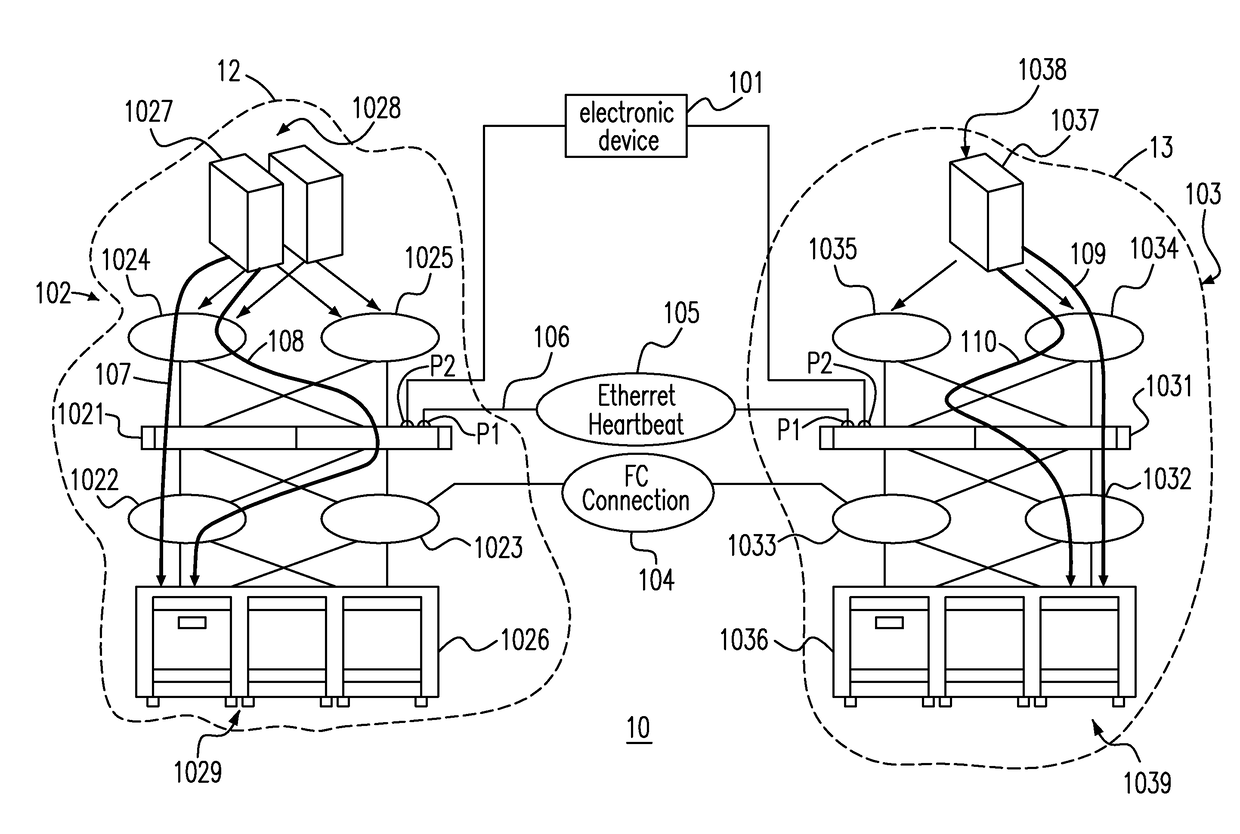
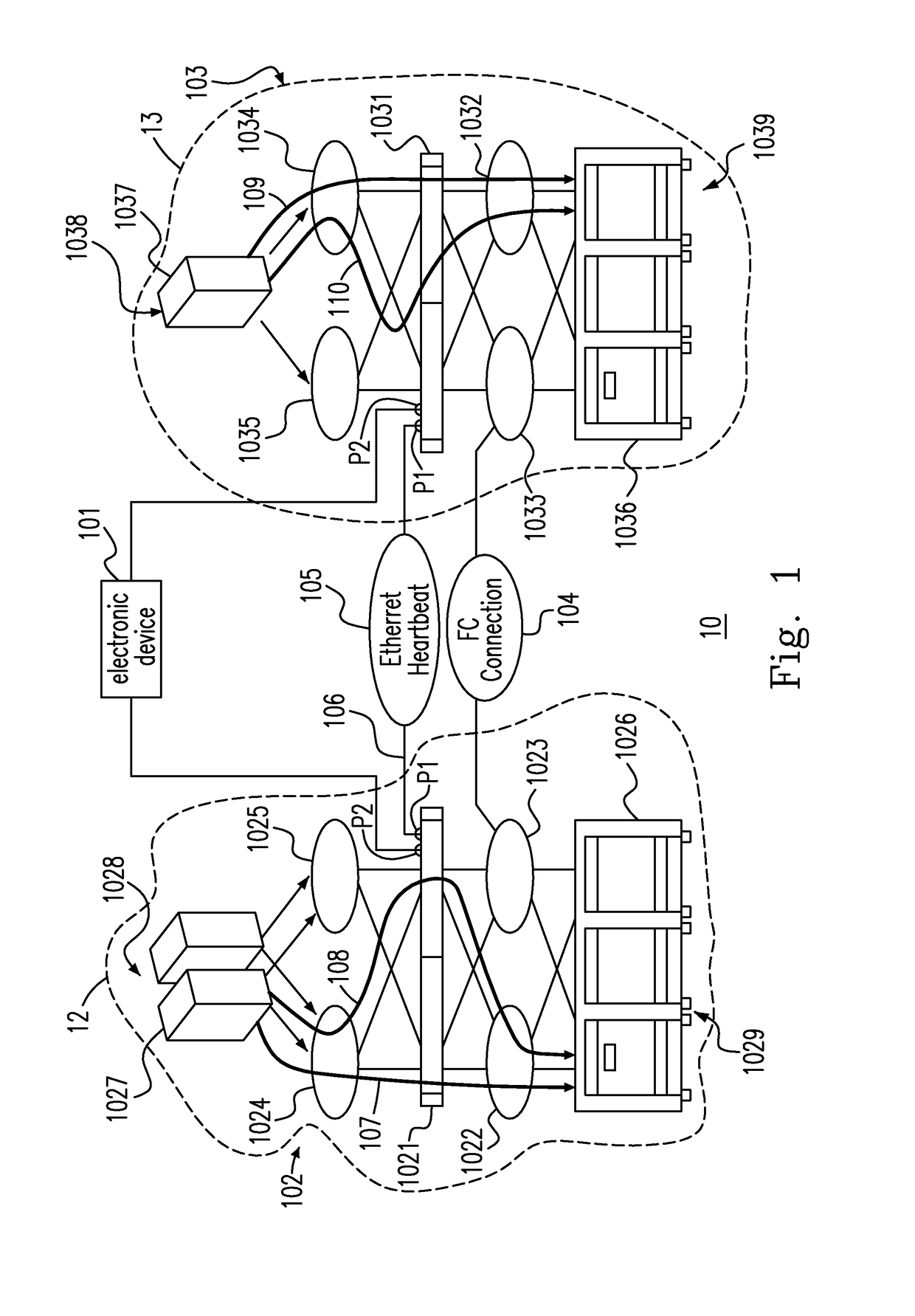
InactiveUS20170364419A1Detecting faulty hardware by configuration testHardware monitoringEngineeringFibre Channel
A method of site isolation protection includes the following steps. A set of clustered engines including a first engine at a first site and a second engine at a second site is provided. A Fiber Channel (FC) connection and an Ethernet connection between the first and the second sites are provided. Whether an Ethernet Heartbeat (EH) from one of the first engine and the second engine through the Ethernet connection exists is detected when the FC connection fails. One of the first engine and the second engine is shut down when the EH exists. Furthermore, a quorum service at a client site is provided in different IP domain to further protect site isolation from happening, while the FC connection and Ethernet Heartbeat connection failed at the same time.
Owner:WEIXU TECH CO LTD
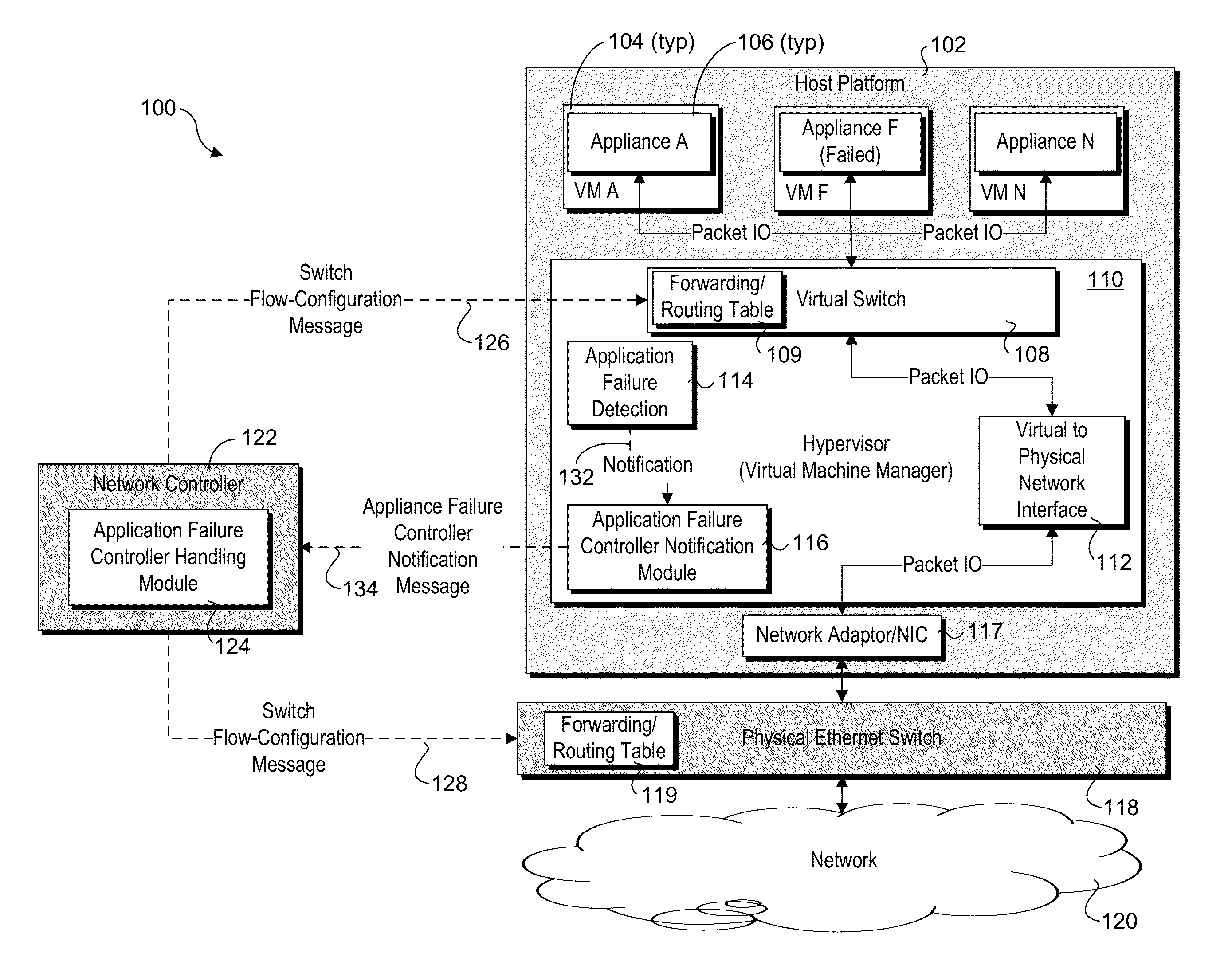
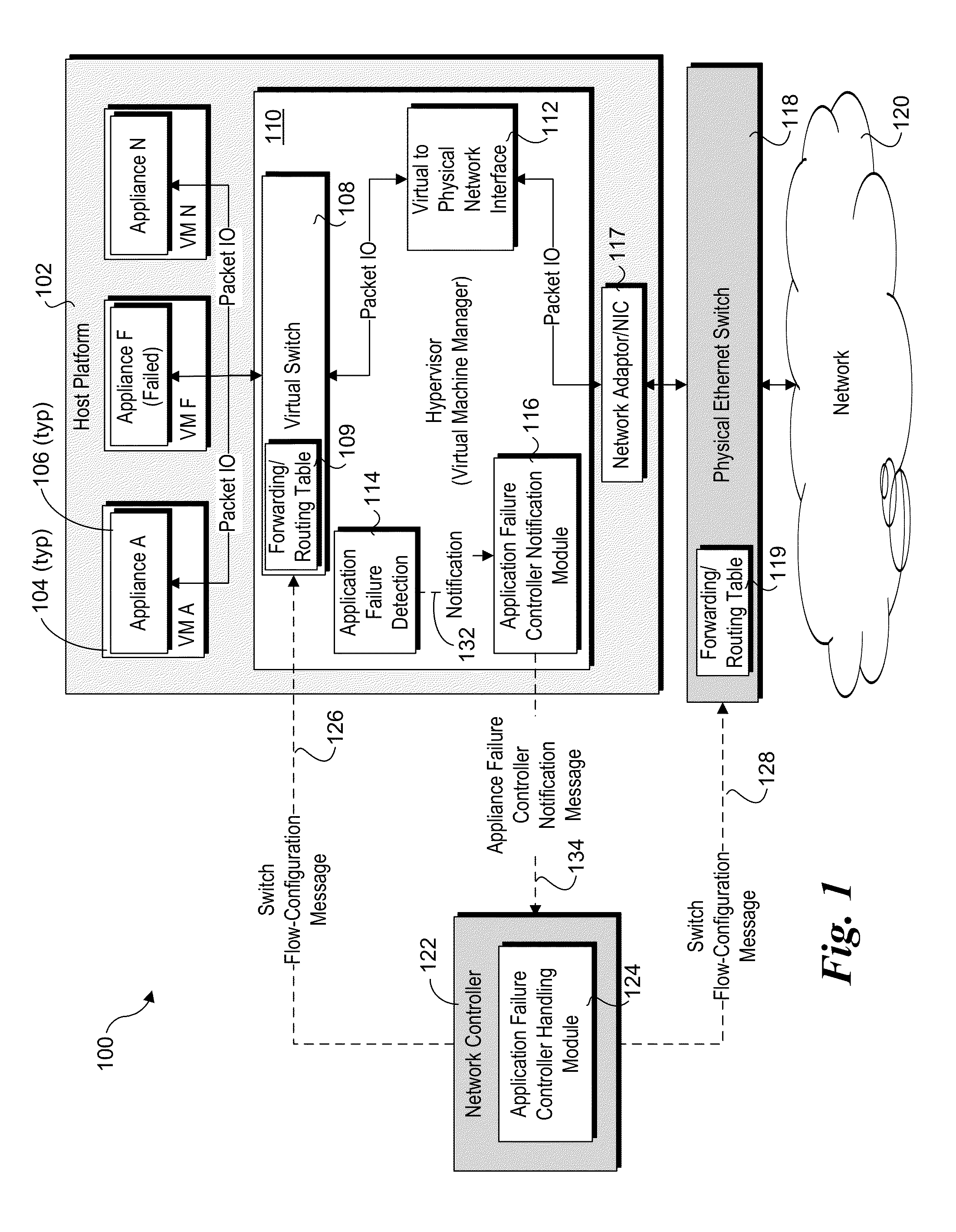
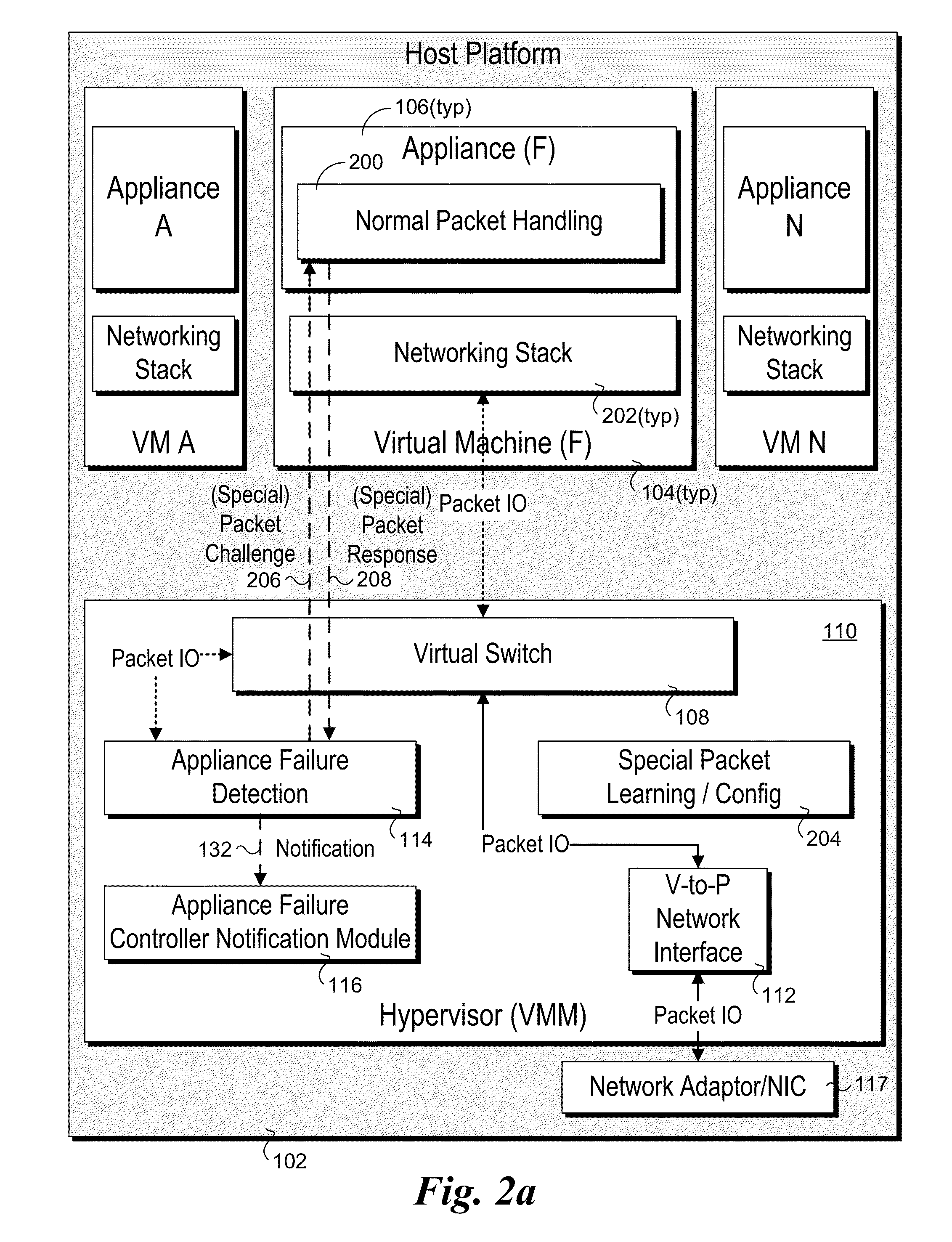
Detection and handling of virtual network appliance failures
InactiveUS20150089331A1Error preventionTransmission systemsVirtual applianceVirtual network interface
Methods and apparatus for detection and handling of virtual appliance failures. In one aspect, a method is implemented on a host platform on which a hypervisor (aka Virtual Machine Manager) and a plurality of virtual machines (VMs) are running, the plurality of VMs collectively hosting a plurality of Software Defined Networking (SDN) and / or Network Function Virtualization (NFV) appliances that are communicatively coupled via a virtual network. A software-based entity running on the host platform is configured to monitor the plurality of virtual network appliances to detect failures of the virtual network appliances. In response to detection of a virtual network appliance failure, messages containing configuration information are implemented to reconfigure packet flows to bypass the virtual network appliance that has failed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Embedded static random access memory for field programmable gate array
InactiveUS6430088B1High impedance stateSolve conflictsDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testRead-only memoriesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
A dual ported (simultaneous read / write) SRAM block with an additional load port that interacts with the circuitry employed in the loading and testing of the configuration data of the FPGA core is disclosed. Each SRAM block contains circuits in both the read port and the write port that permit the SRAM blocks to be connected into deeper and wider configurations by without any additional logic as required by the prior art. An address collision detector is provided such that when both read and write ports in the SRAM block access the same address simultaneously a choice between the data being read can be made between the data presently in the SRAM block or the new data being written to the SRAM block.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
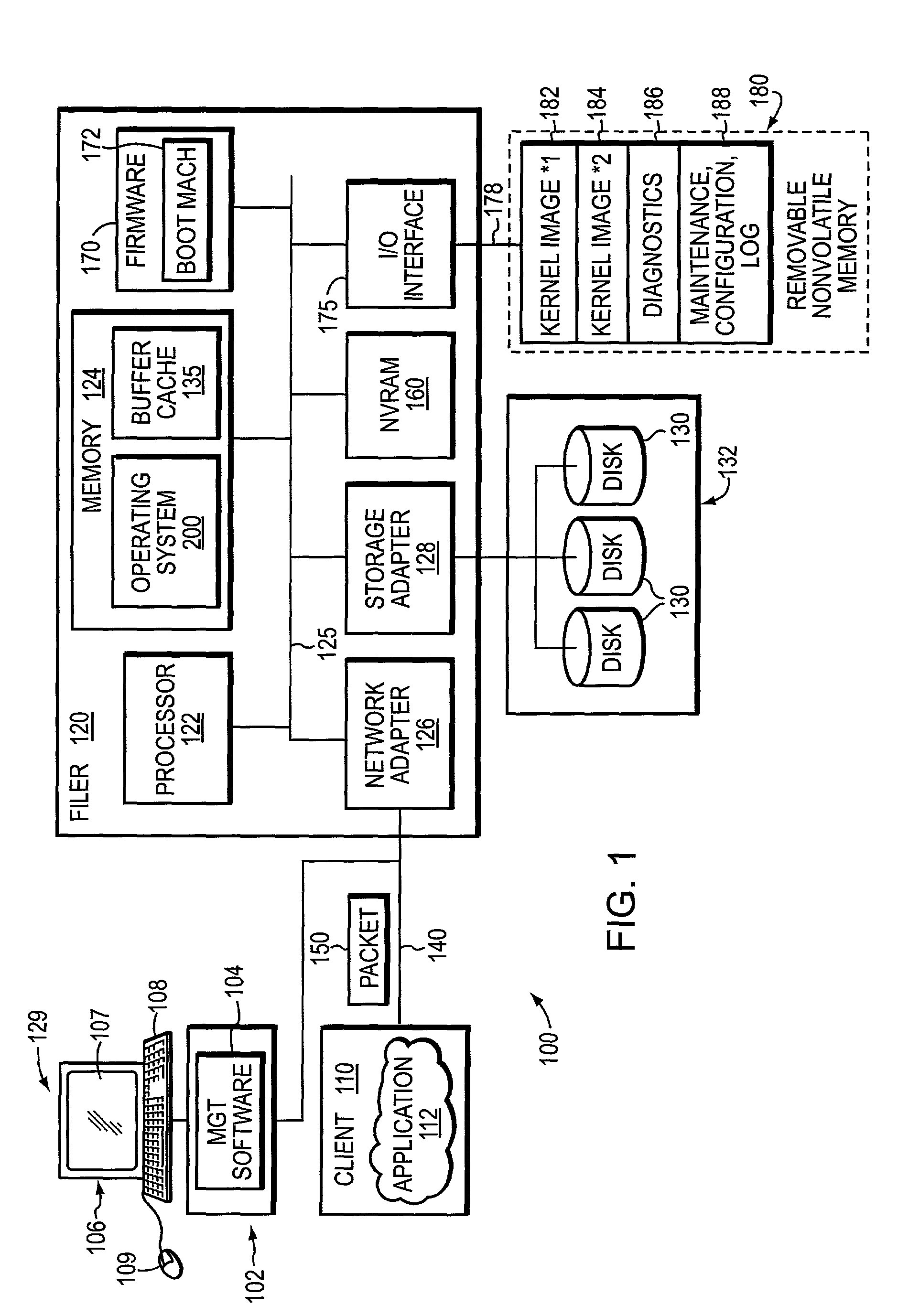
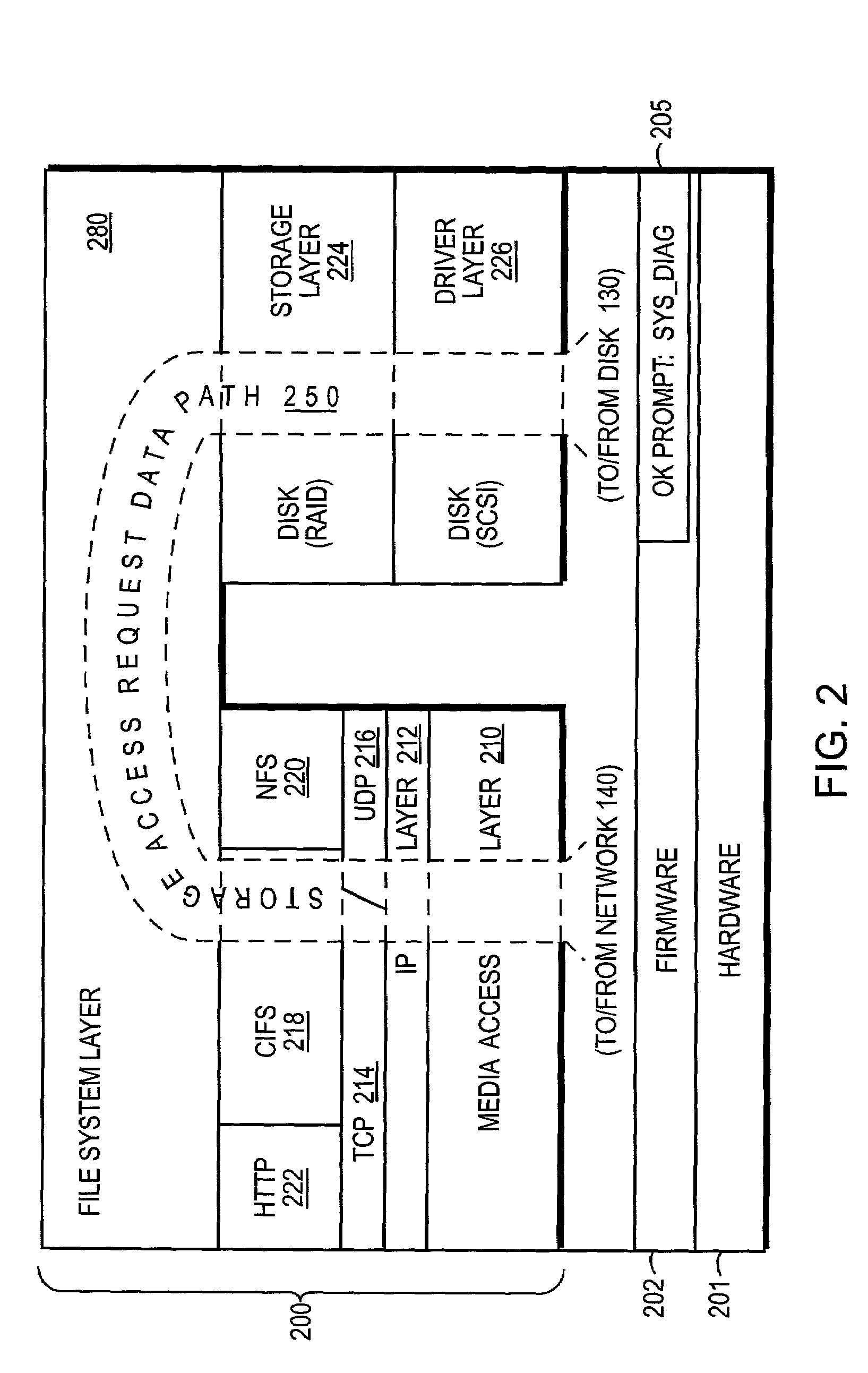
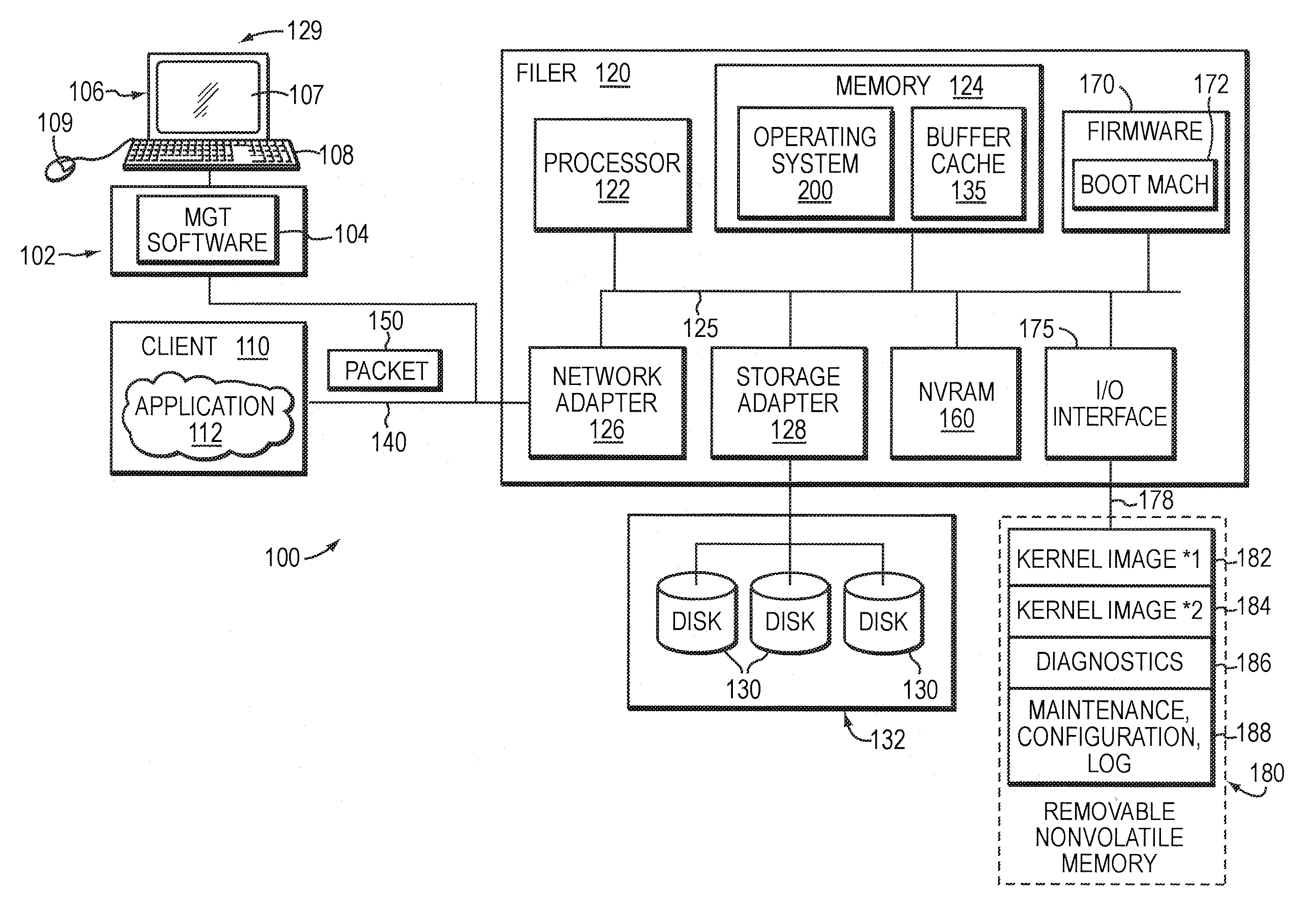
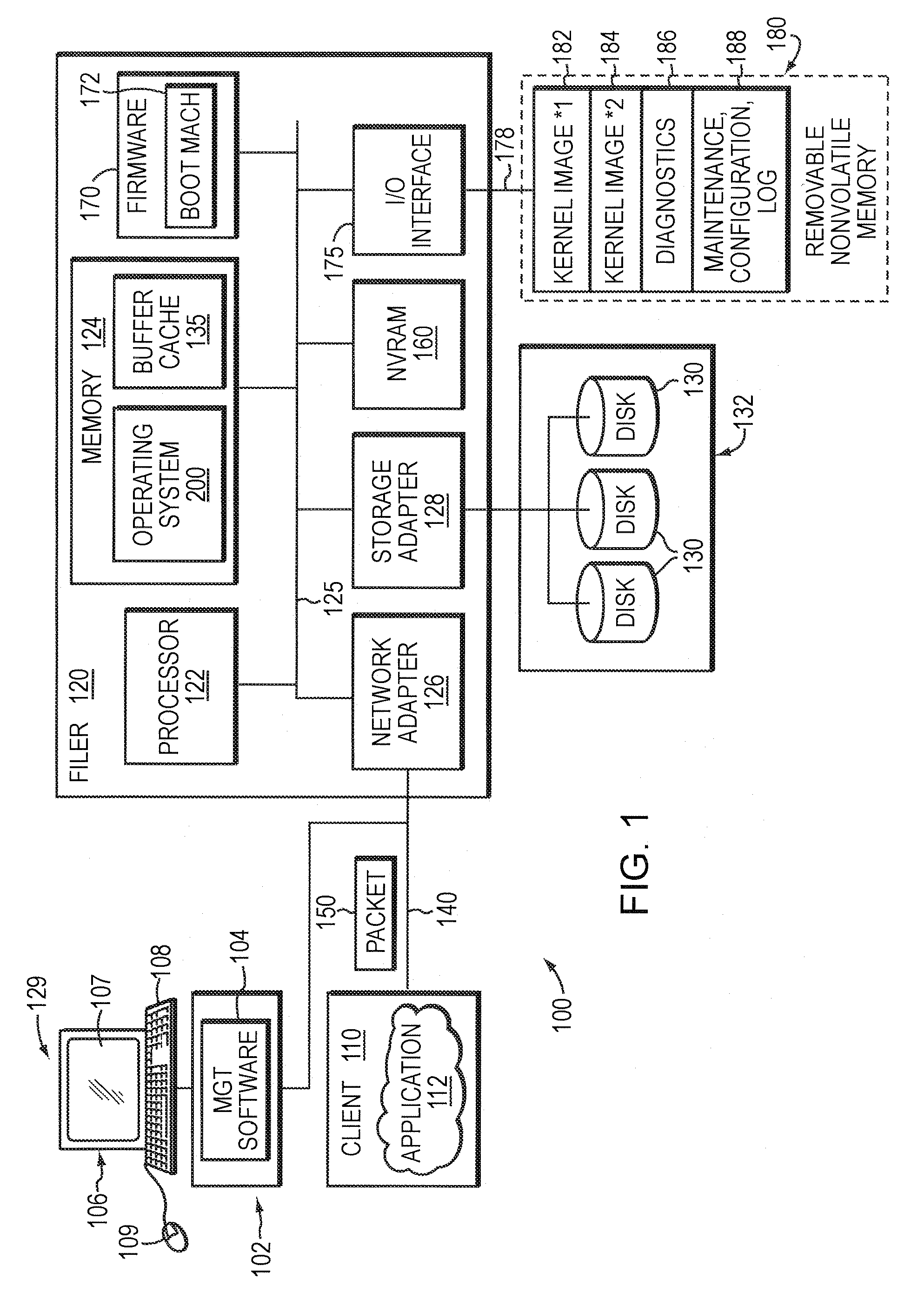
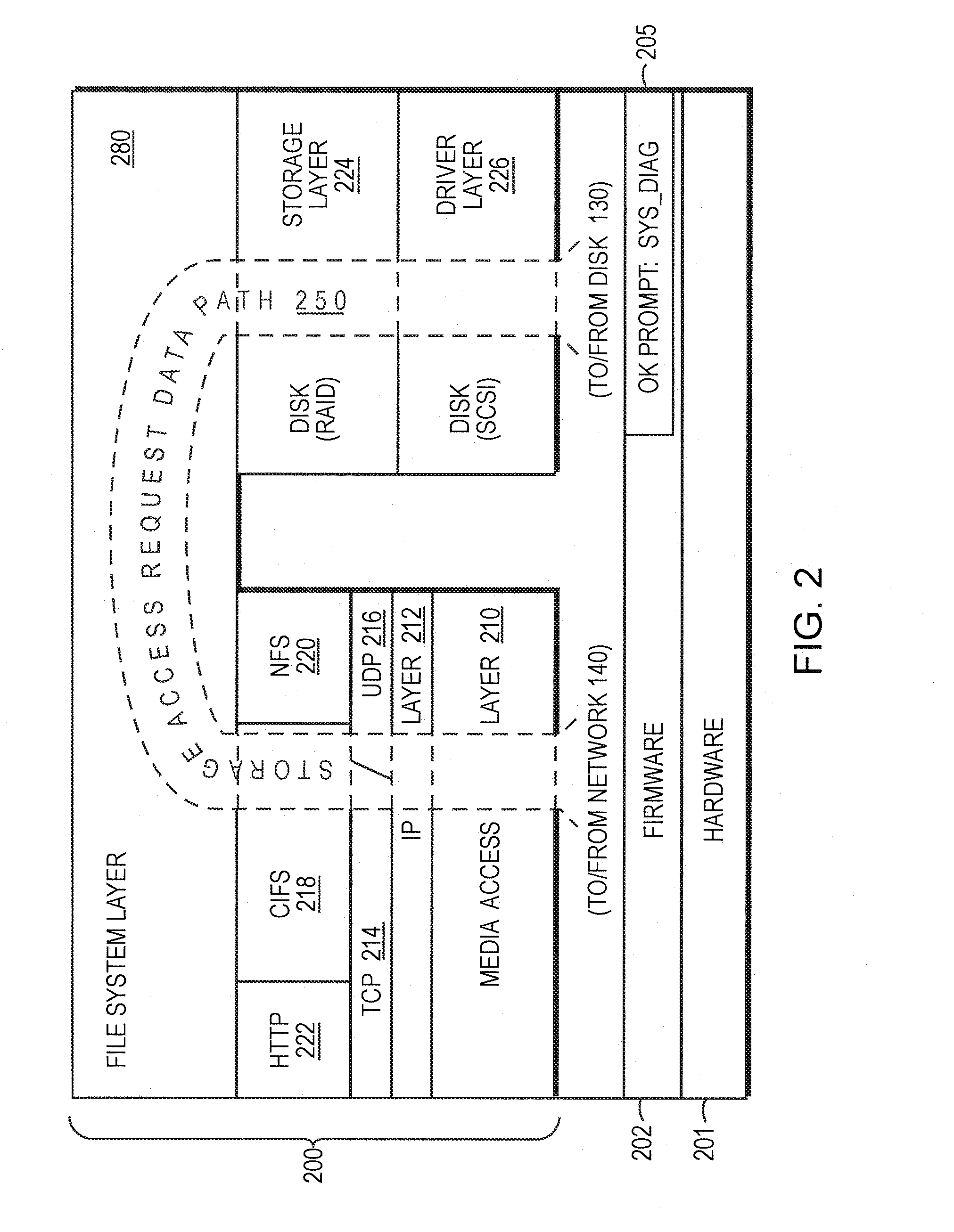
System and method for diagnostics execution and data capture in a storage system using nonvolatile memory
InactiveUS7206970B1Easy retrievalEnhanced couplingDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testDigital computer detailsPersonal computerHybrid storage system
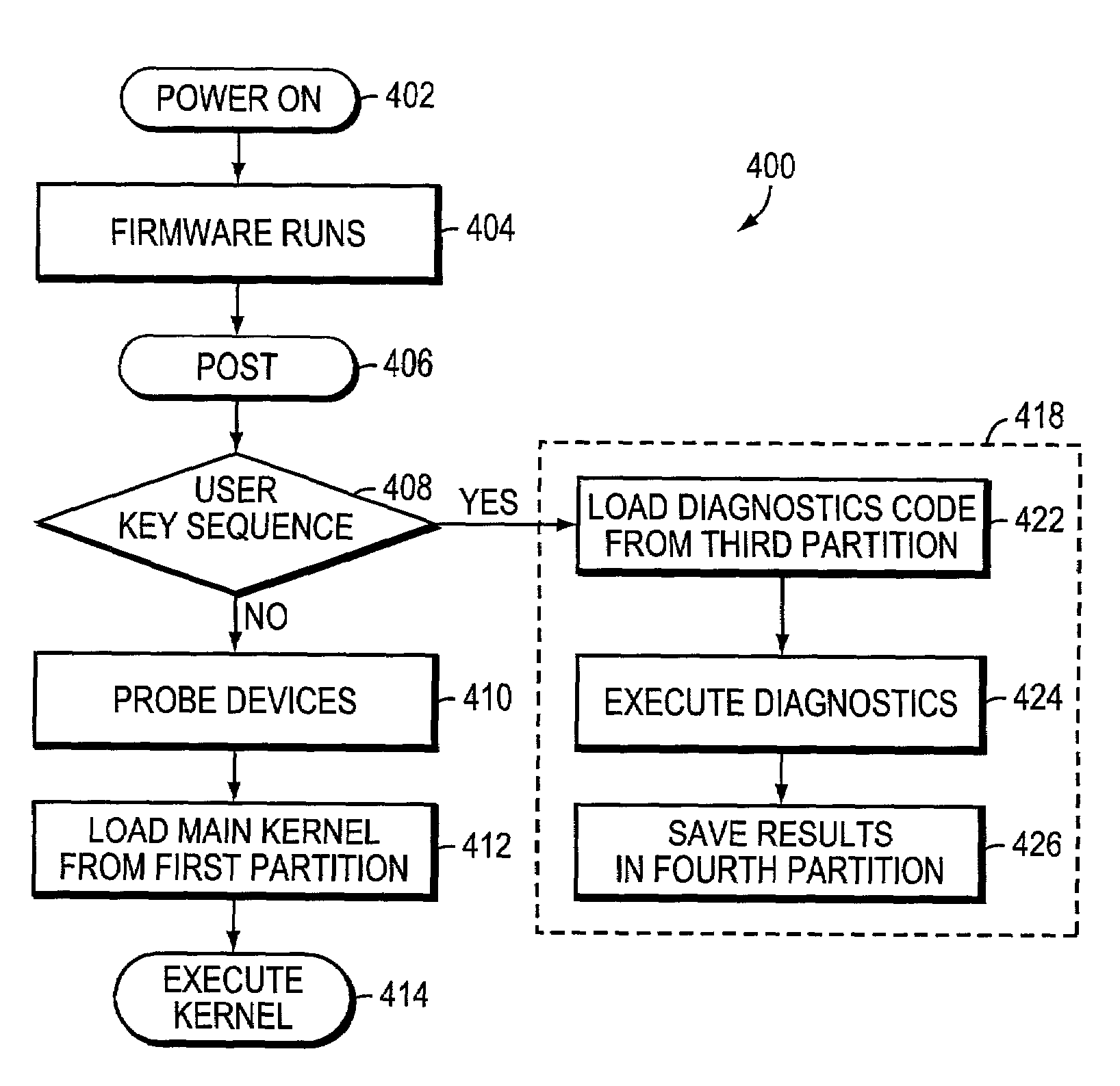
The present invention provides a system and method for diagnostics execution in which diagnostics code is stored in a designated partition on a removable nonvolatile memory device, such as a compact flash or a personal computer (PC) card that is interfaced with the motherboard of a file server system. The file server system firmware is programmed in such a manner that, upon receipt of a diagnostics command, a normal boot mechanism is interrupted, and a diagnostics boot is performed. The firmware is programmed to probe the removable nonvolatile memory device, and to load the diagnostics code contained thereon into main memory and to execute the diagnostics in response to an initiation by an operator's key sequence. Data produced as a result of the diagnostics test sequence is captured and stored in a maintenance log in another partition on the nonvolatile memory.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
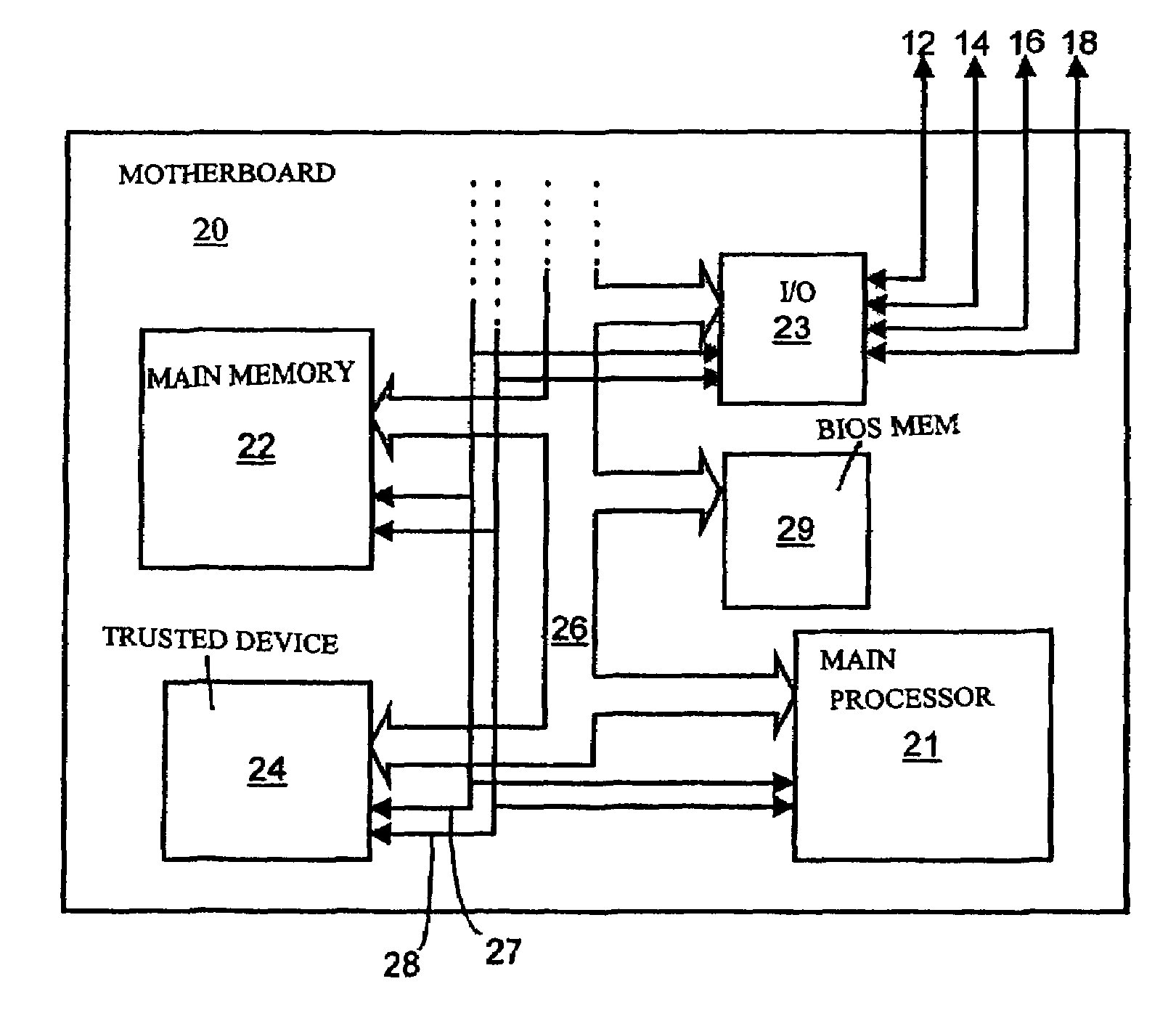
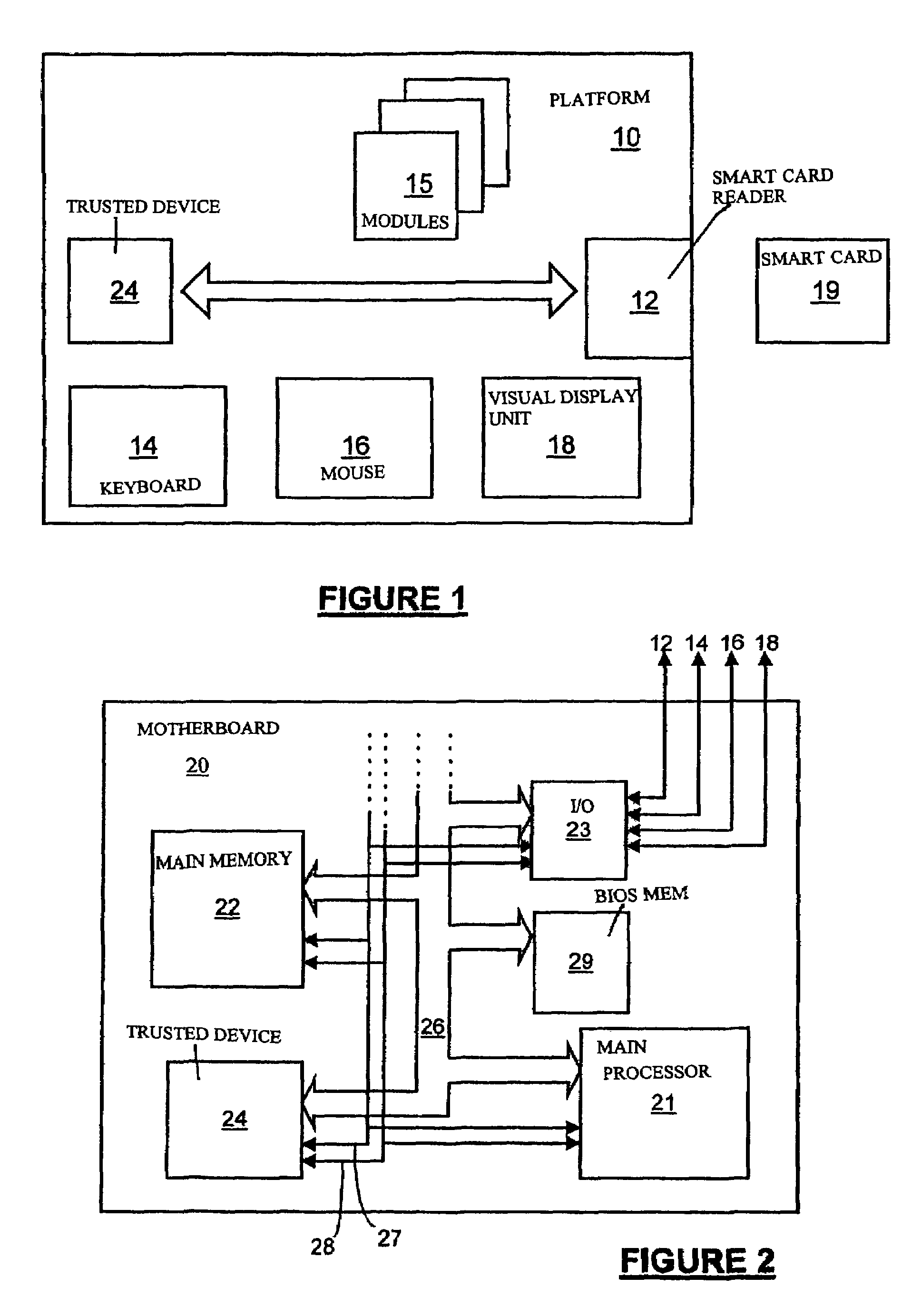
Protection of the configuration of modules in computing apparatus
InactiveUS7430668B1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsDigital data protectionComputer moduleSmart card
A method of protecting from modification computer apparatus comprising a plurality of functional modules by monitoring the configuration of functional modules within the computer apparatus. The method comprises: storing a module configuration of the computer apparatus; and checking the actual module configuration against the stored module configuration, and inhibiting function of the computer apparatus if the actual module configuration does not satisfactorily match the stored module configuration. Advantageously, the module configuration is stored on a security token, such as a smart card.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
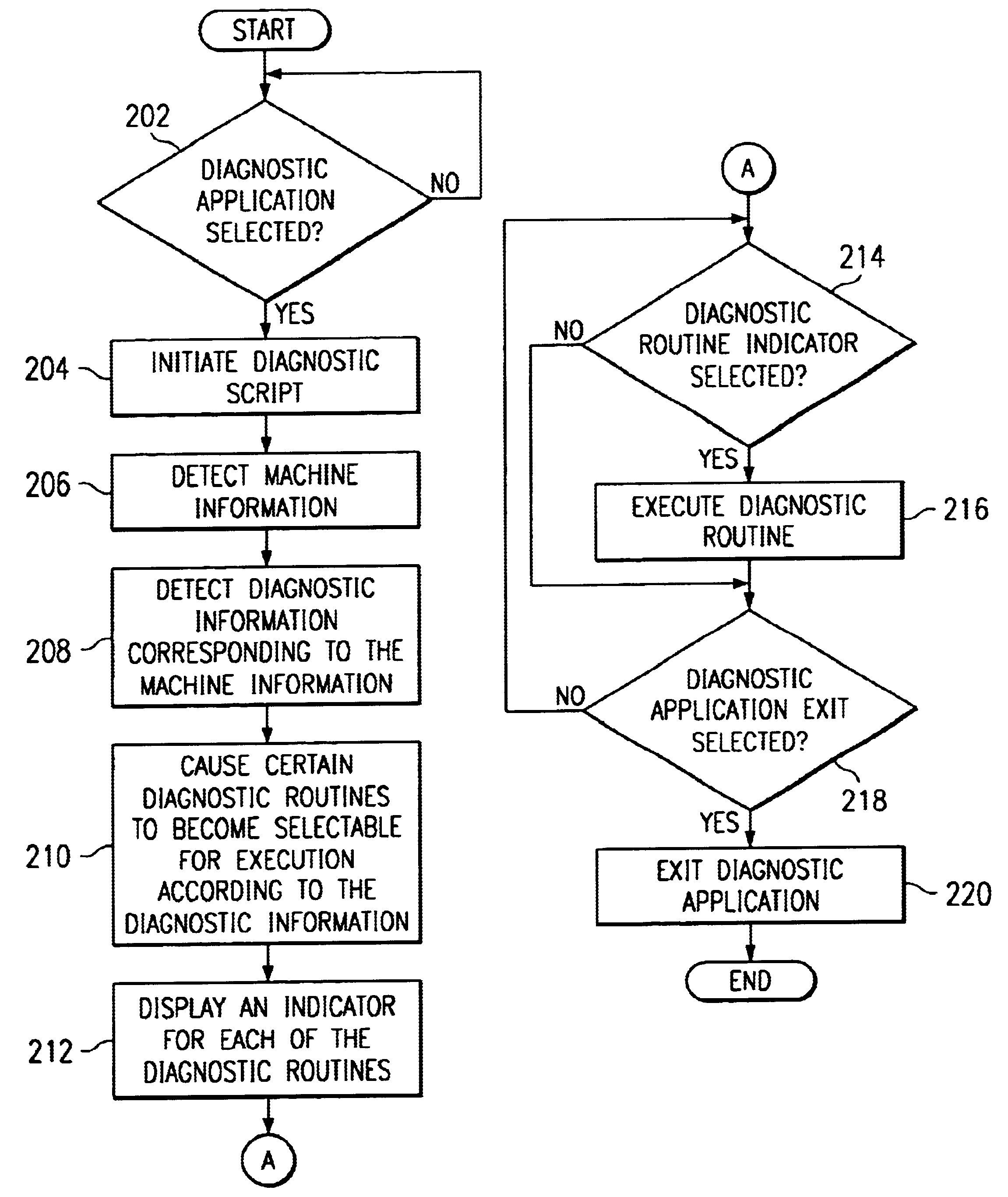
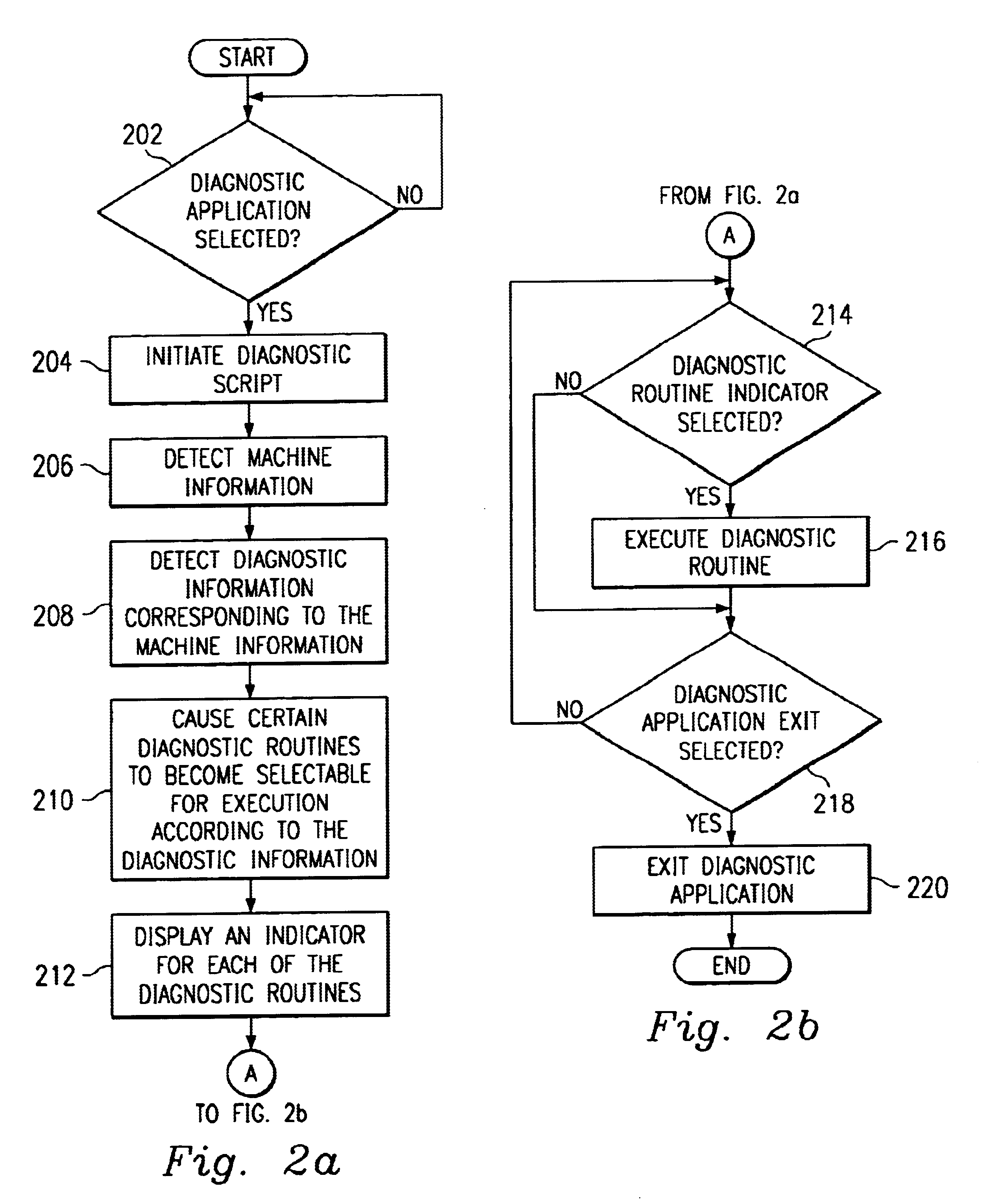
System and method for identifying executable diagnostic routines using machine information and diagnostic information in a computer system
InactiveUS6865691B1Minimizing development effortMinimizing test cycleDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testDiagnostic programComputerized system
A system and method for identifying executable diagnostic routines using machine information and diagnostic information in a computer system is provided. The method includes detecting machine information, detecting diagnostic information corresponding to the machine information, and causing one of a plurality of diagnostic routines to be selectable for execution according to the diagnostic information.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
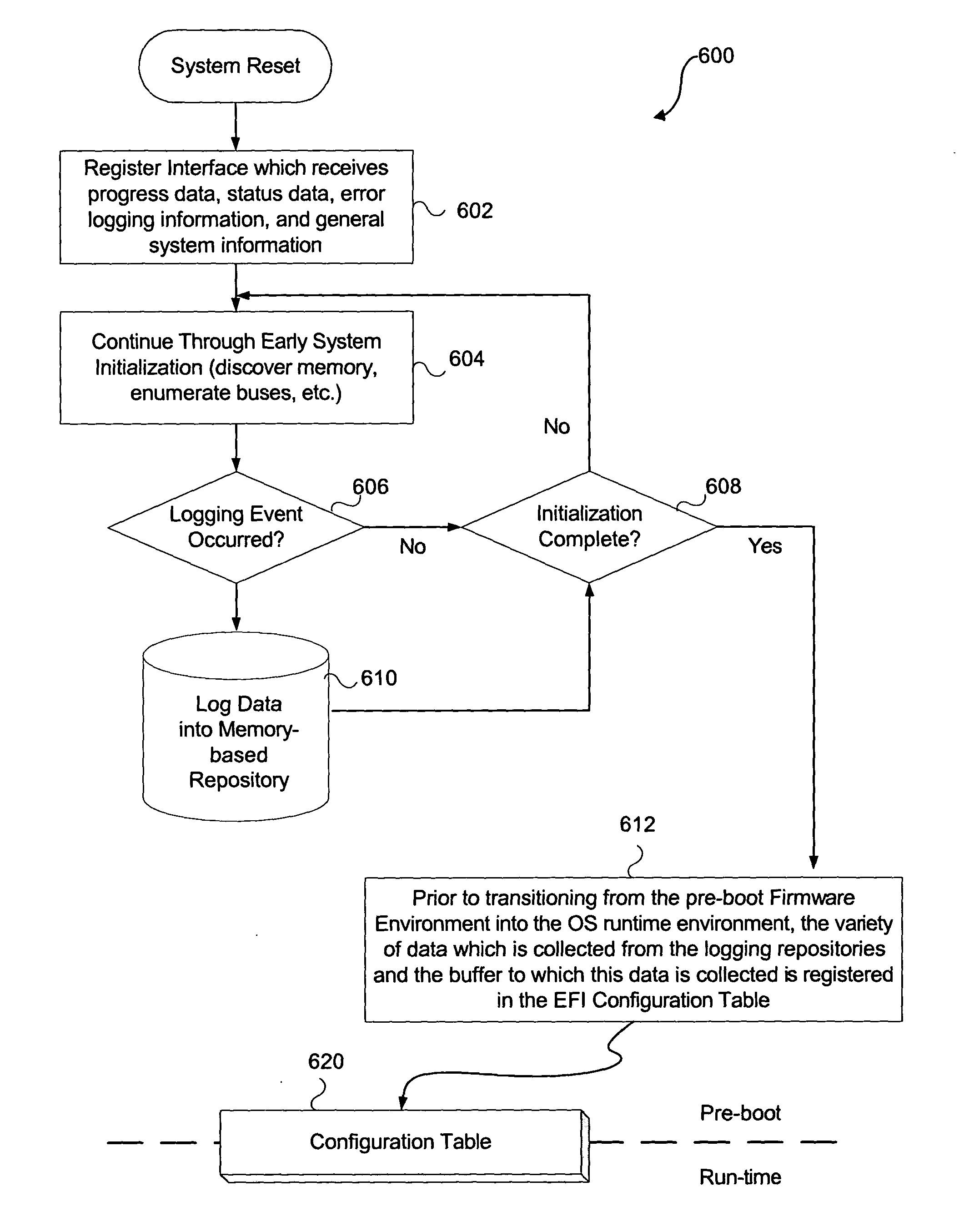
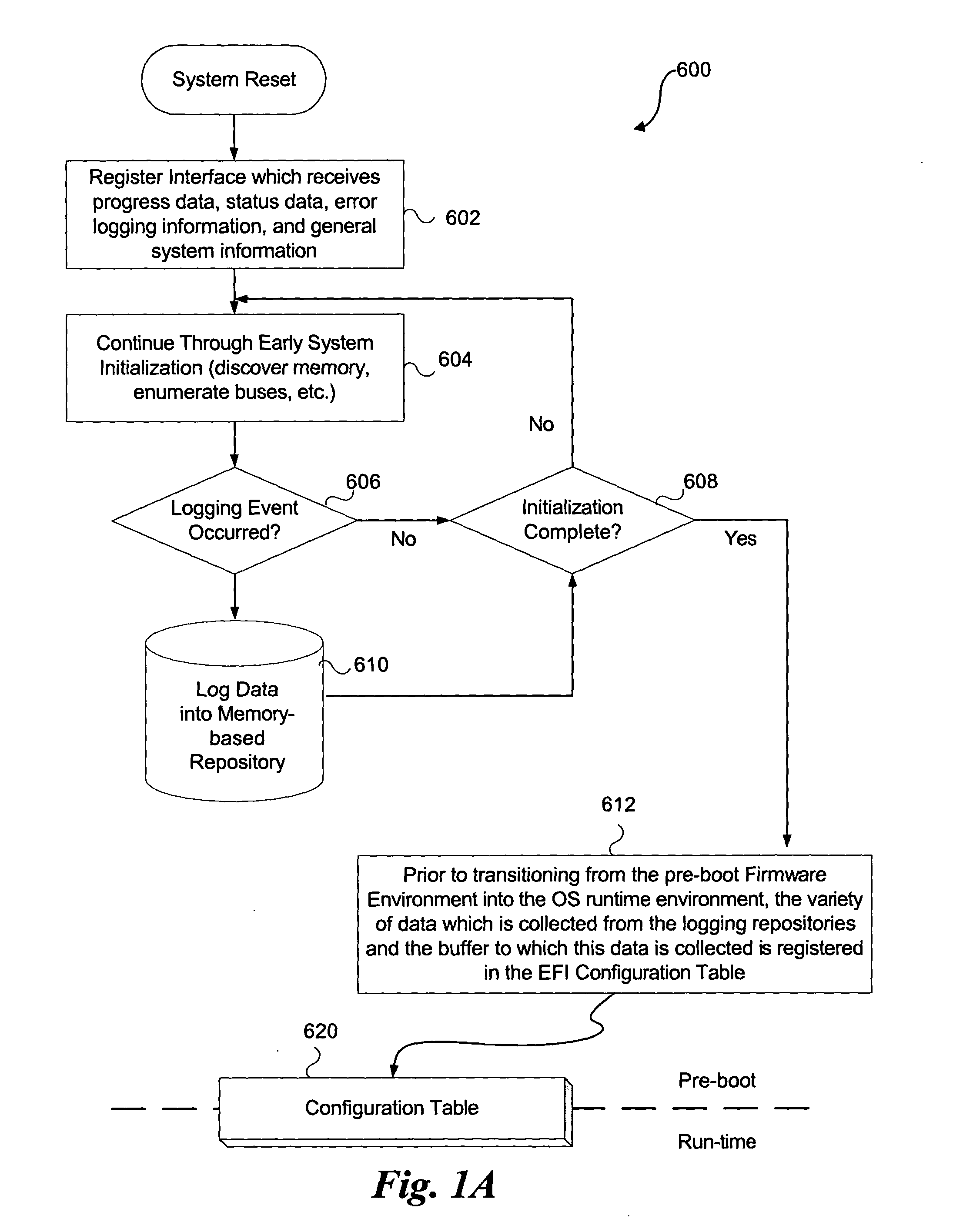
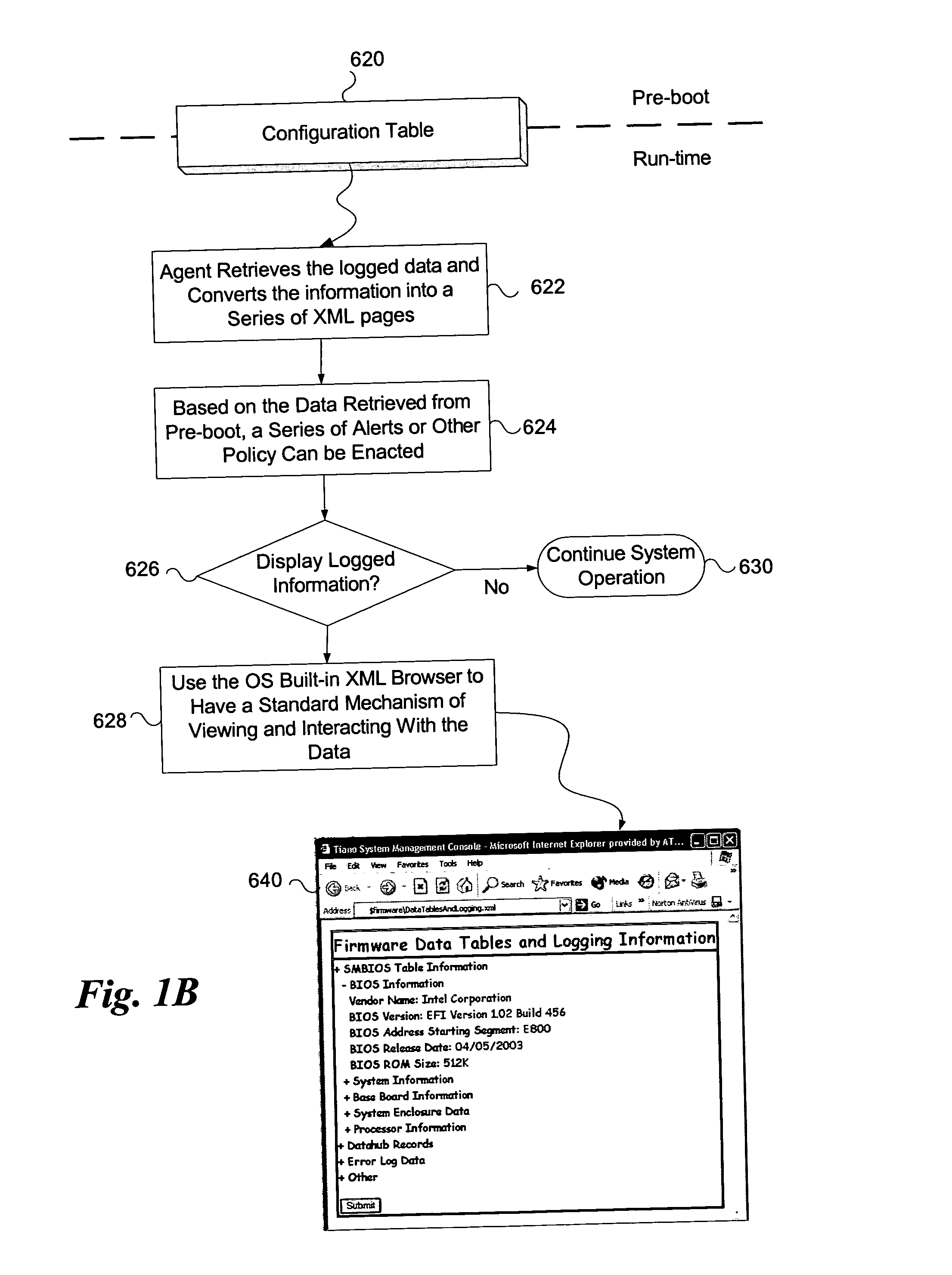
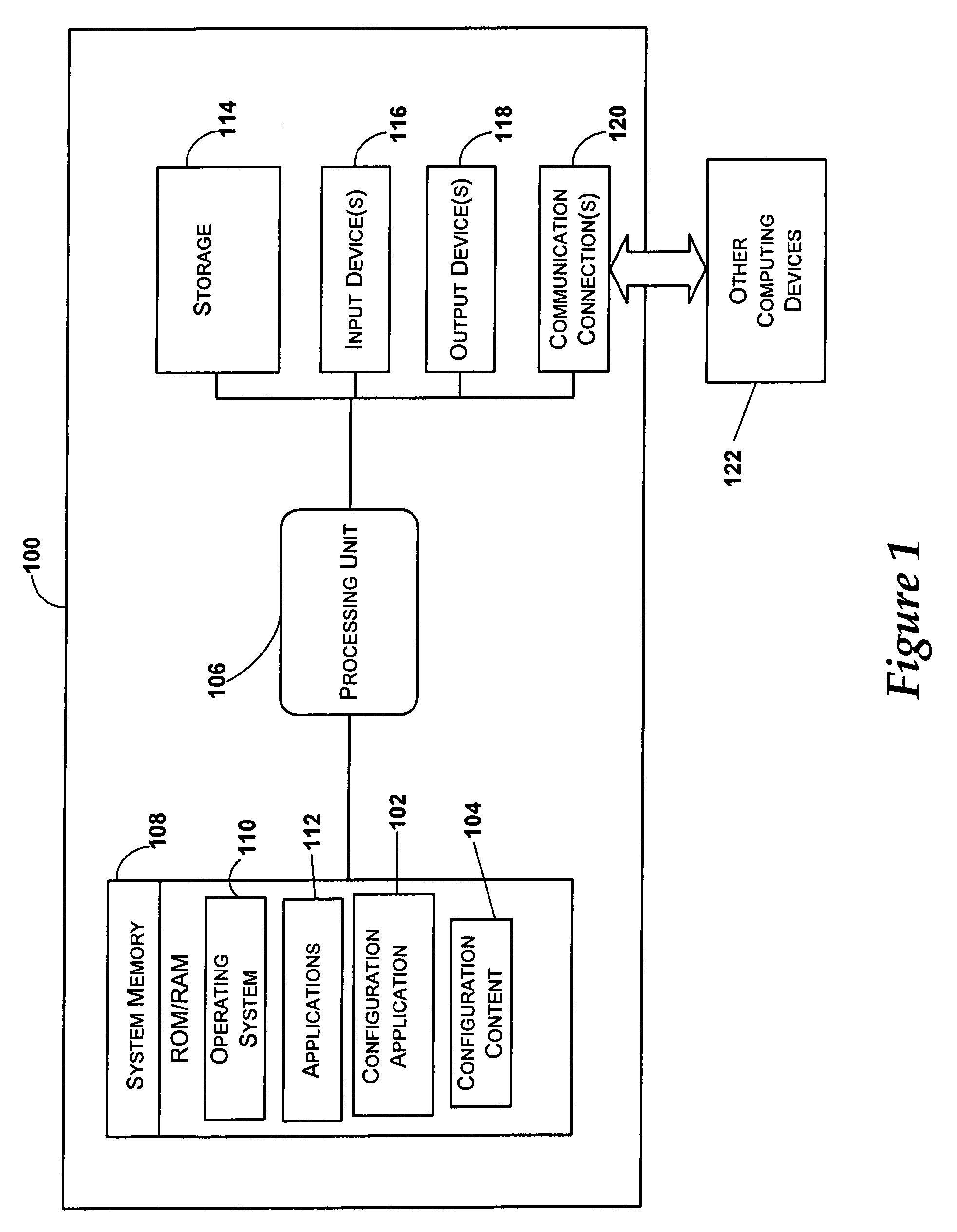
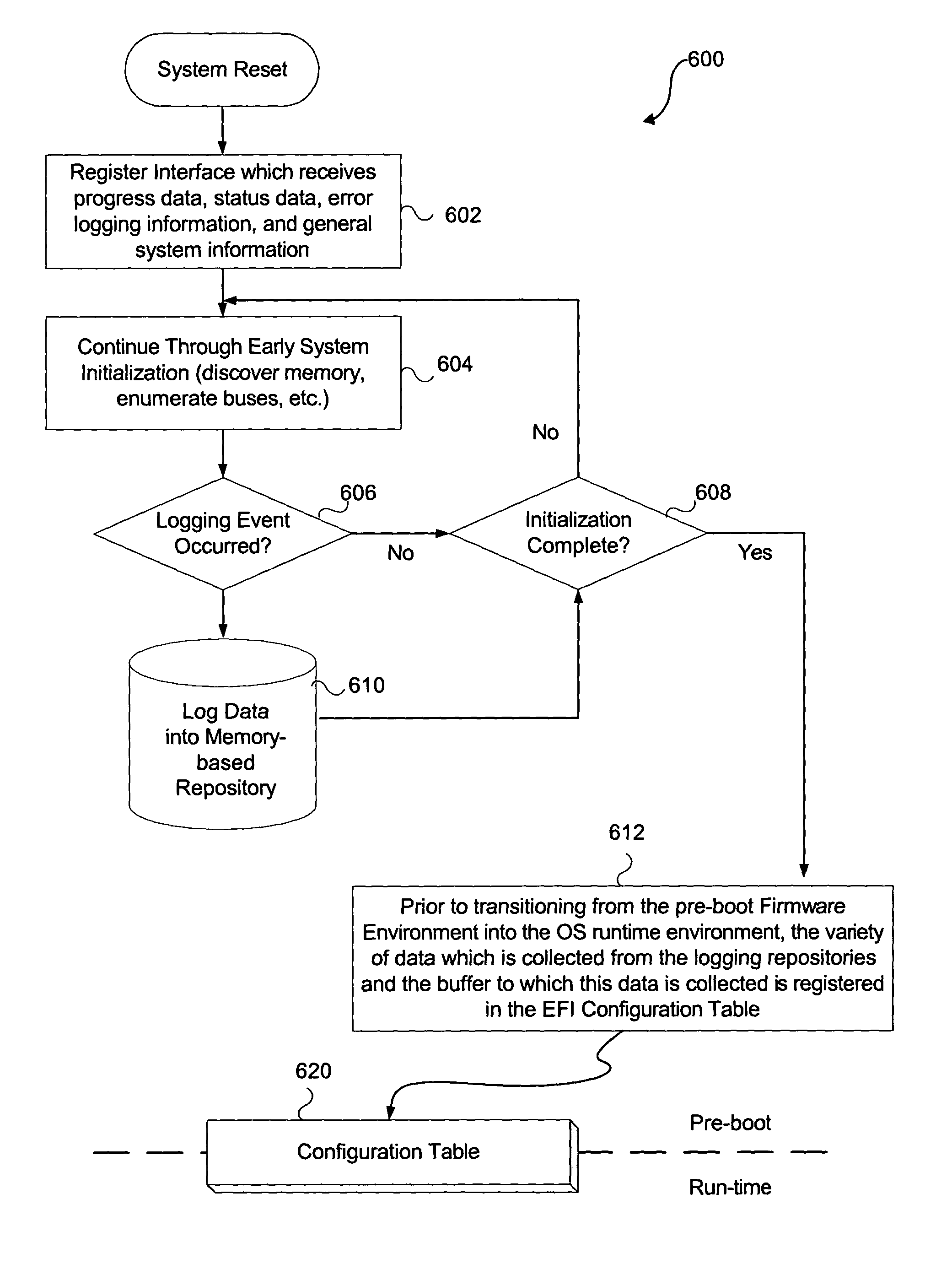
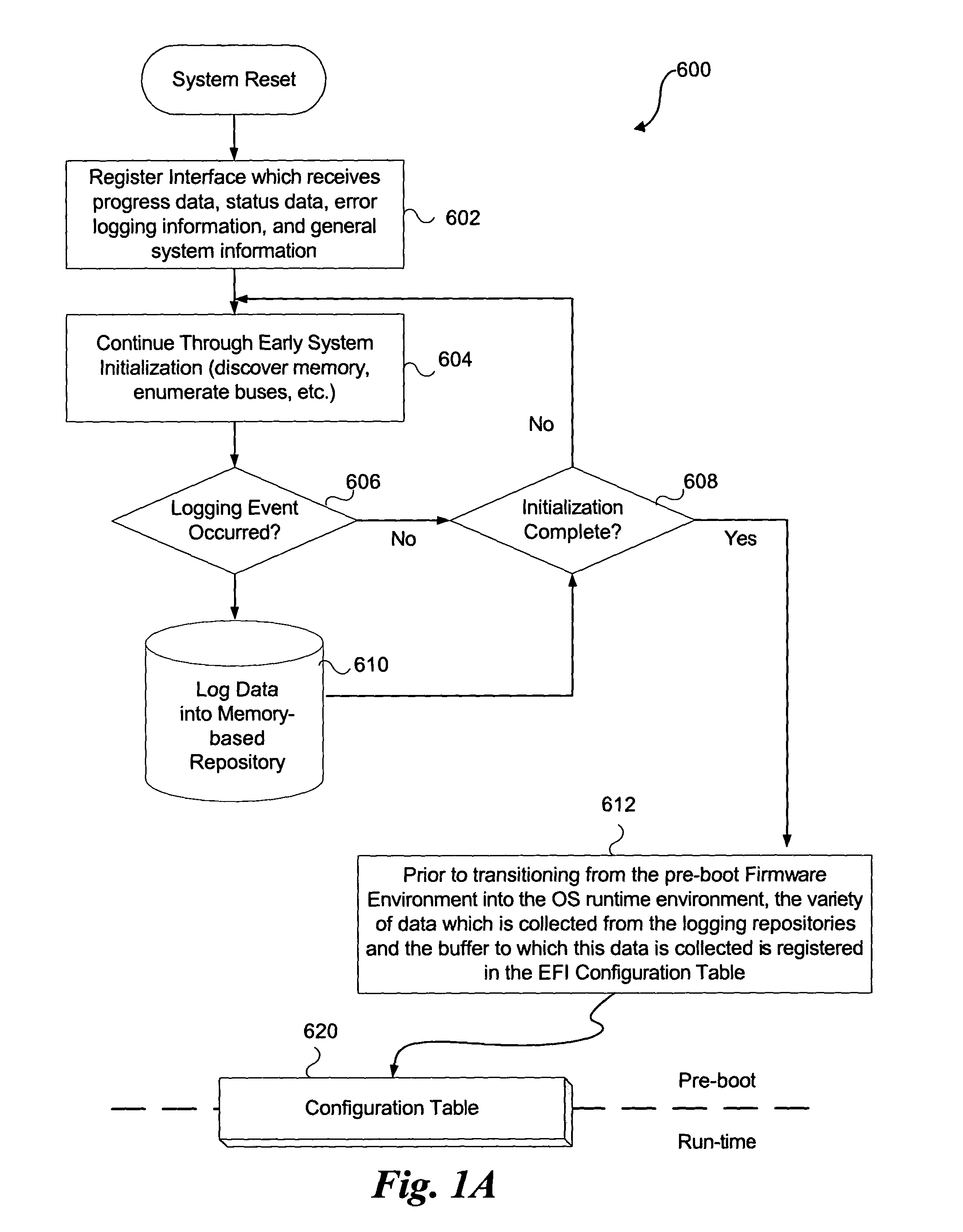
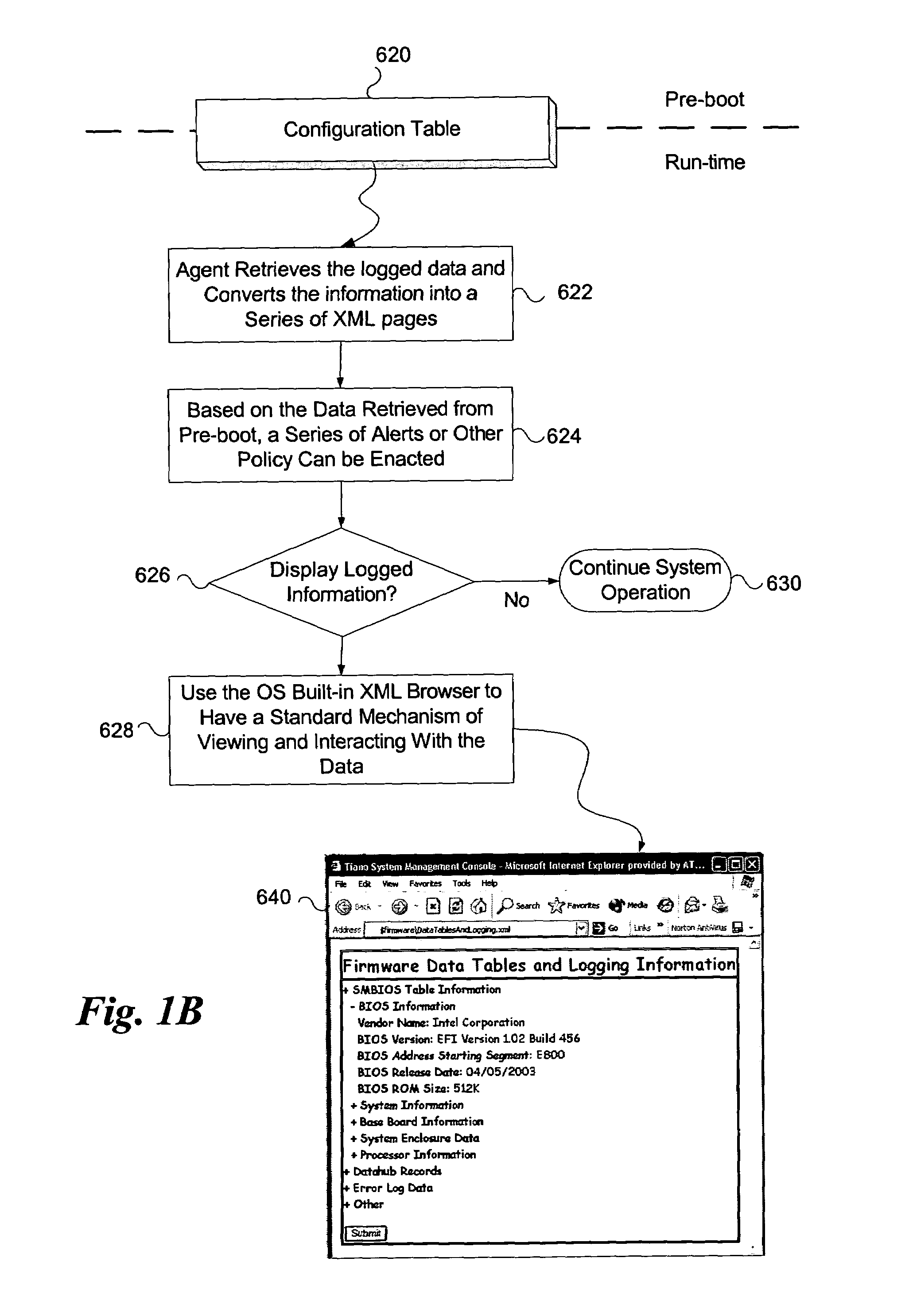
System and method for firmware to export pre-boot data into the operating system runtime environment
ActiveUS20050060526A1Fault responseDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testOperational systemEvent data
An embodiment of the present invention bridges event data from the pre-boot environment to the operating system runtime environment. Event logs are stored in a memory buffer during pre-boot. Prior to launching the operating system (OS), the event log is registered to a known memory location accessible to the OS. A preferred embodiment uses the extensible firmware interface (EFI) configuration table to store the event log. A globally unique identifier (GUID) may be used to identify the memory buffer location. Once accessible to the OS, the event data may be displayed using standard extensible Markup Language (XML) forms, or via any other desired method.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Dynamic, Non-invasive detection of hot-pluggable problem components and re-active re-allocation of system resources from problem components
InactiveUS7117388B2Program initiation/switchingDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testData processing systemOperational system
A method, system, and data processing system for dynamic detection of problem components in a hot-plug processing system and automatic removal of the problem component via hot-removal methods without disrupting processing of the overall system. A data processing system that provides a non-disruptive, hot-plug functionality is designed with a additional logic for initiating and / or completing a sequence of factory level tests on hot-pluggable components to determine if the component if functioning properly. When a component is not functioning properly, the OS re-allocates the workload of the component to other component so the system, and when the OS completes the re-allocation, the service element initiates the hot removal of the component so that the component is logically and electrically separated from the system.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods of booting information handling systems and information handling systems performing the same
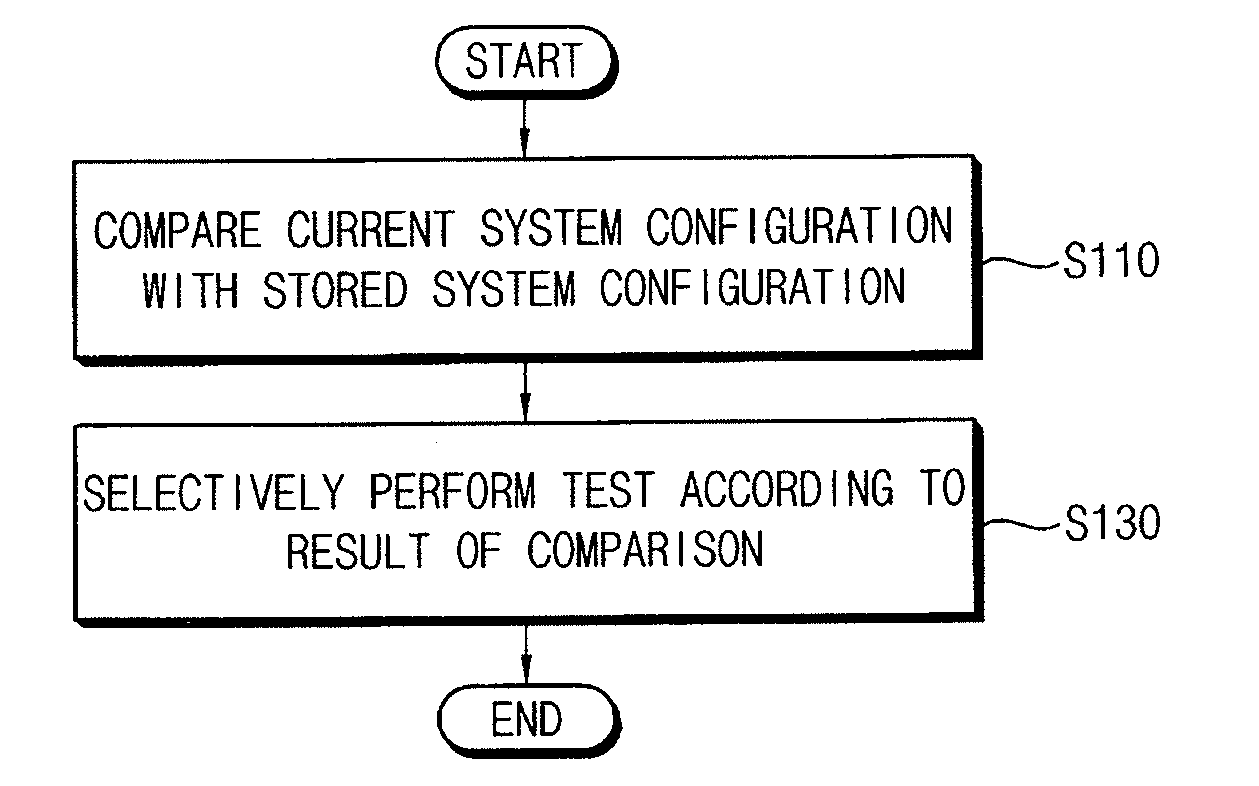
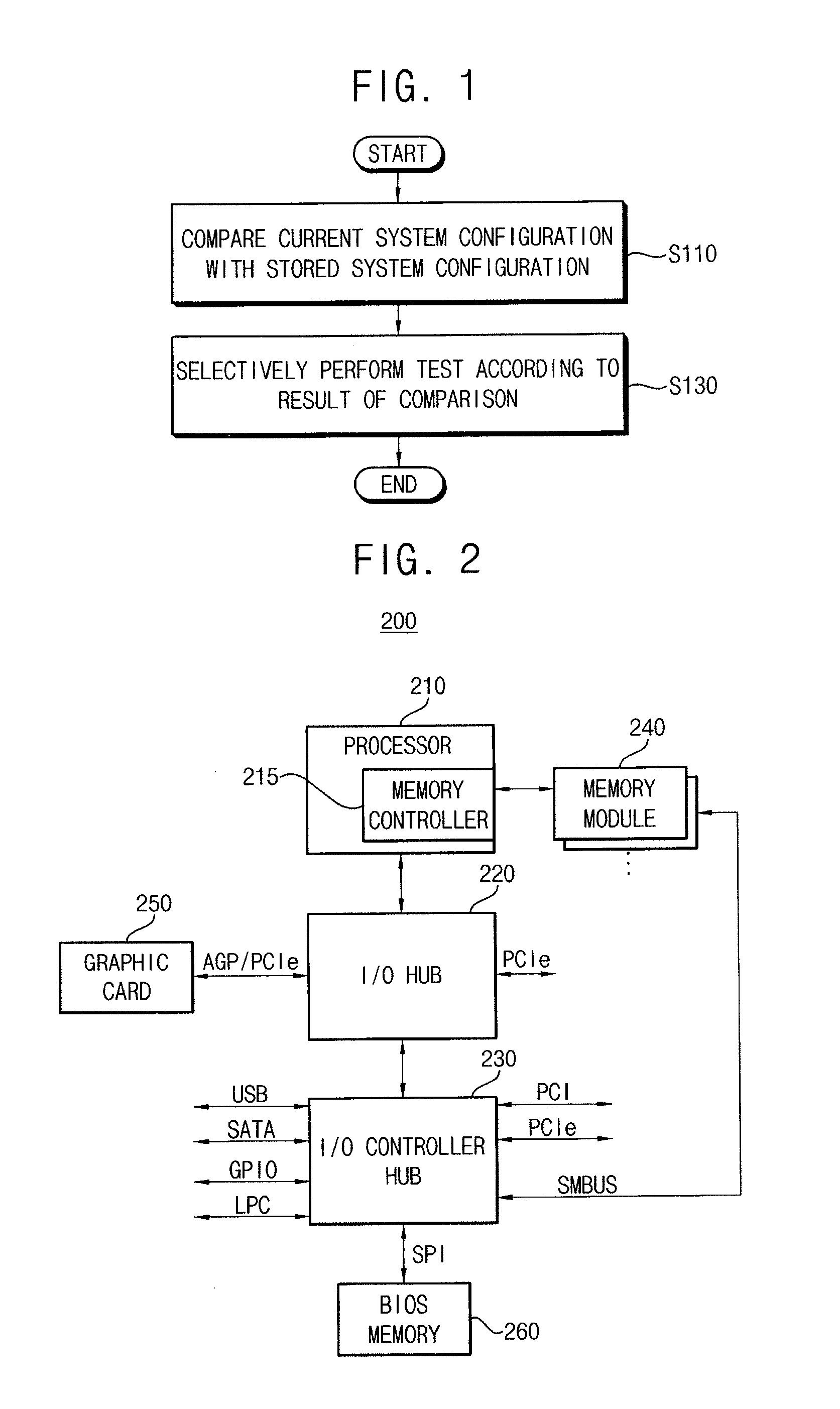
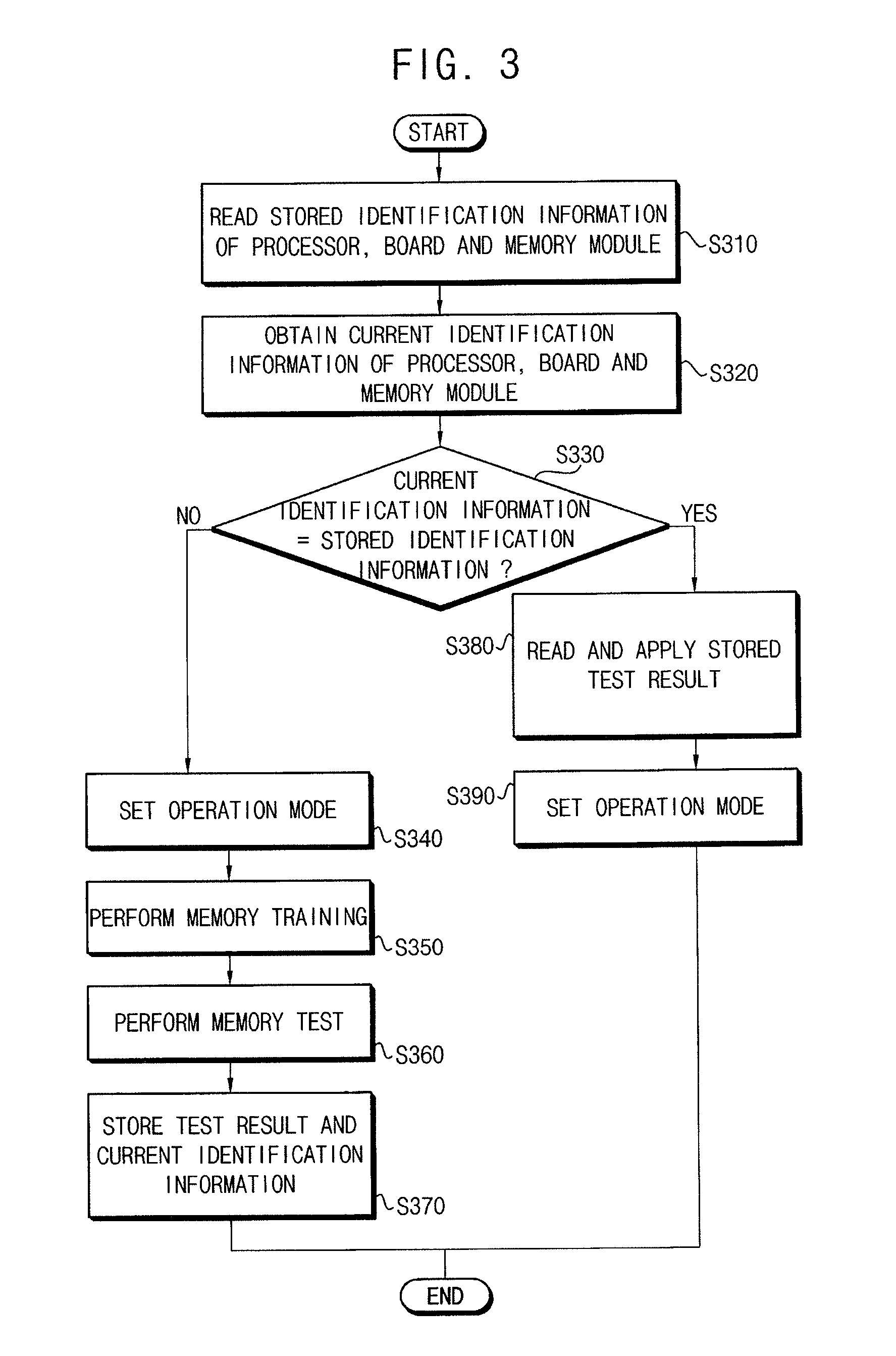
InactiveUS20120191964A1Detecting faulty hardware by power-on testDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testHandling systemInformation handling system
A method of booting an information handling system including a volatile memory device to be selectively tested during a booting operation, the method comprising a step of reading current system configuration information from the information handling system, a step of comparing the current system configuration information with corresponding prestored system configuration information in a nonvolatile memory device, and a step of selectively performing a test for the volatile memory device according to a result of the comparison.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Verification system and method
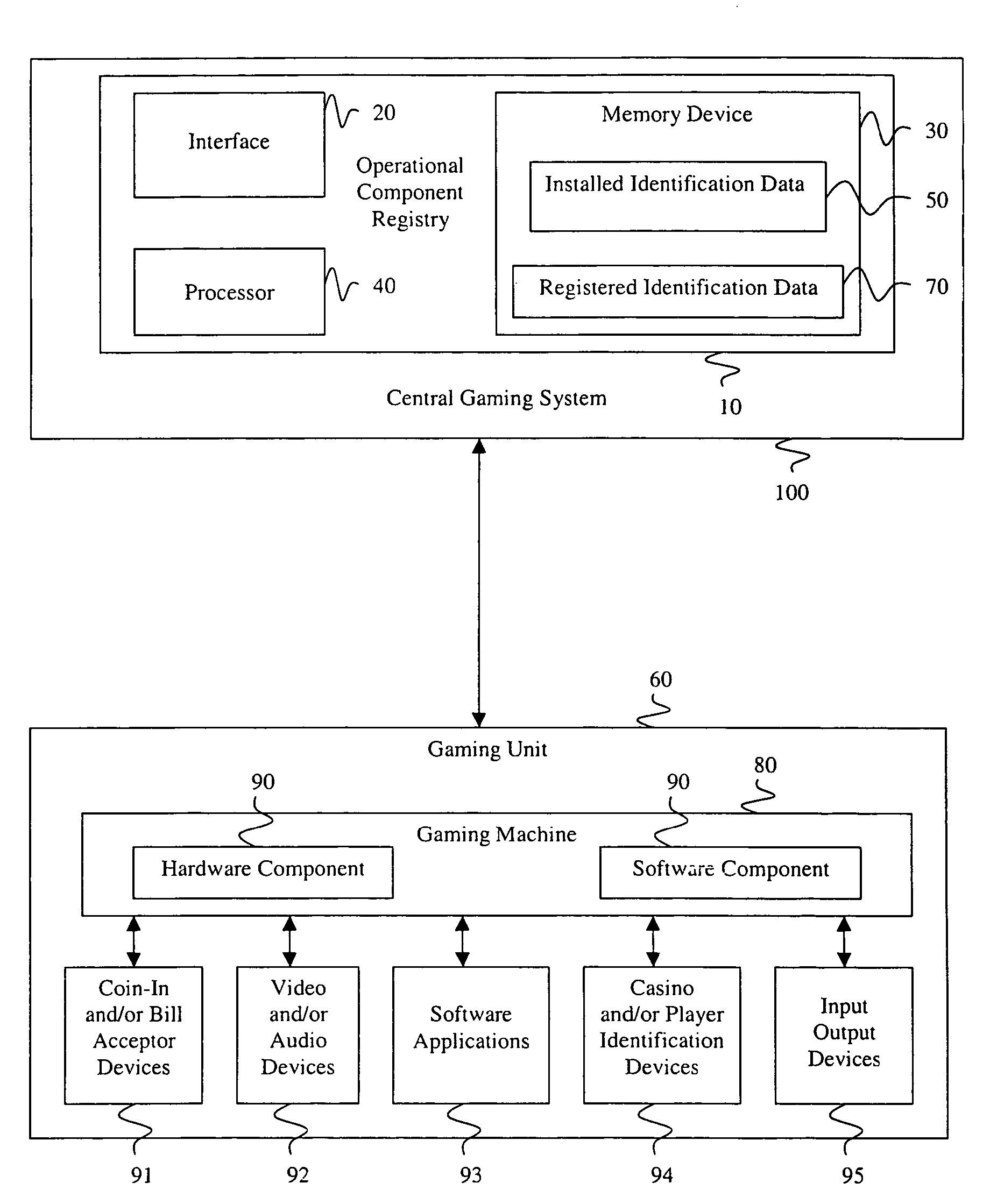
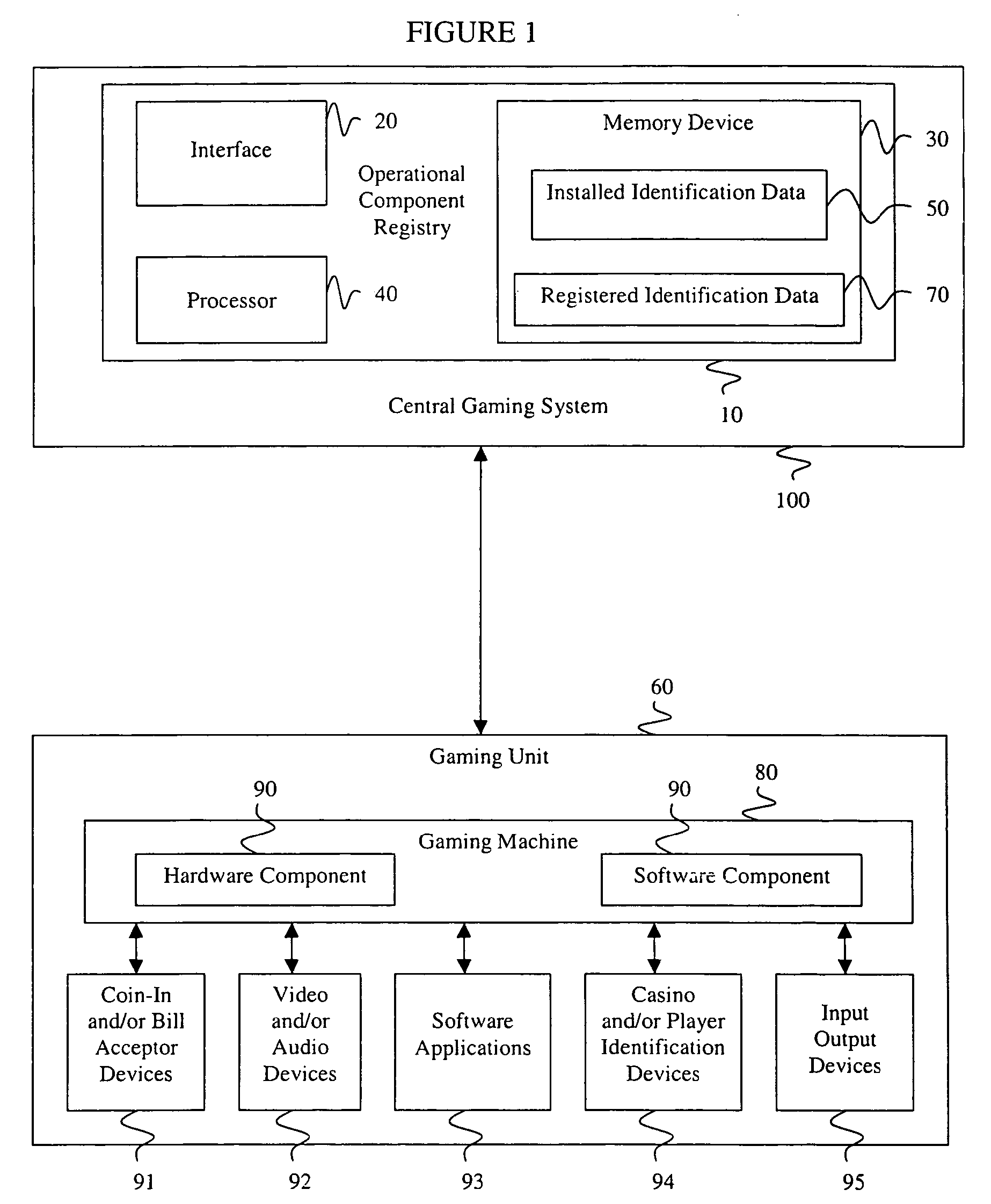
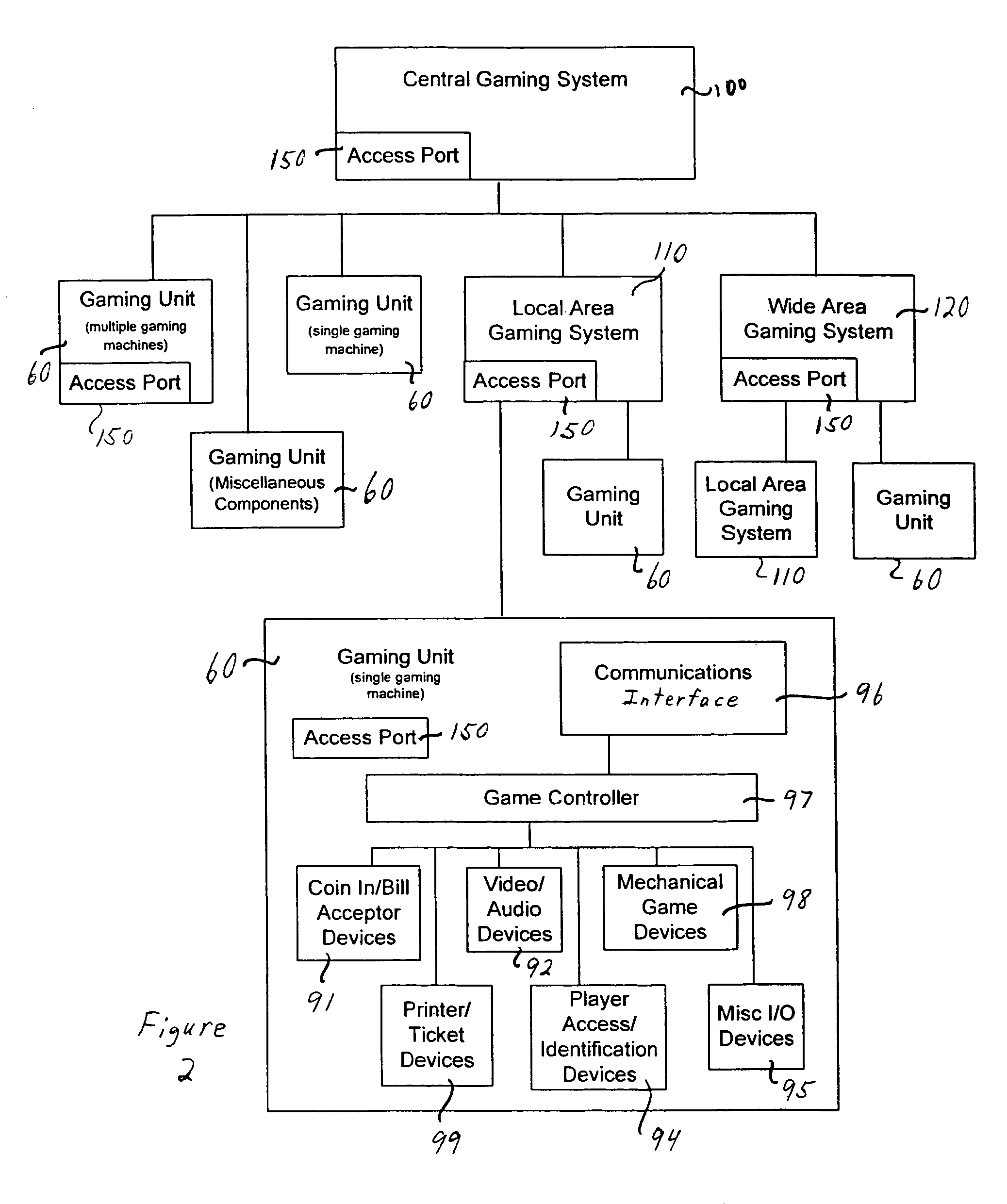
ActiveUS7730325B2Prevent falsification and repudiationPrevents falsification and repudiationDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testDetecting faulty hardware by remote testComputer hardwareVerification system
A verification system has an operational component registry 10 that includes an interface 20, a memory device 30, and a processor 40. Preferably, the interface 20 in the operational component registry 10 communicates the installed identification data 50 from the gaming units 60 to the operational component registry. The memory device 30 preferably stores registered identification data 70 for the gaming units 60. Preferably, the processor 40 in the operational component registry 10 then analyzes the registered identification data 70 and the installed identification data 50 from the gaming units 60, after which enablement of the gaming units is determined based upon the examination of the registered identification data and the installed identification data. An operational component registry 10 may also monitor changes, services, requirements, enablement, and productivity of the gaming units or components of the gaming units.
Owner:LNW GAMING INC
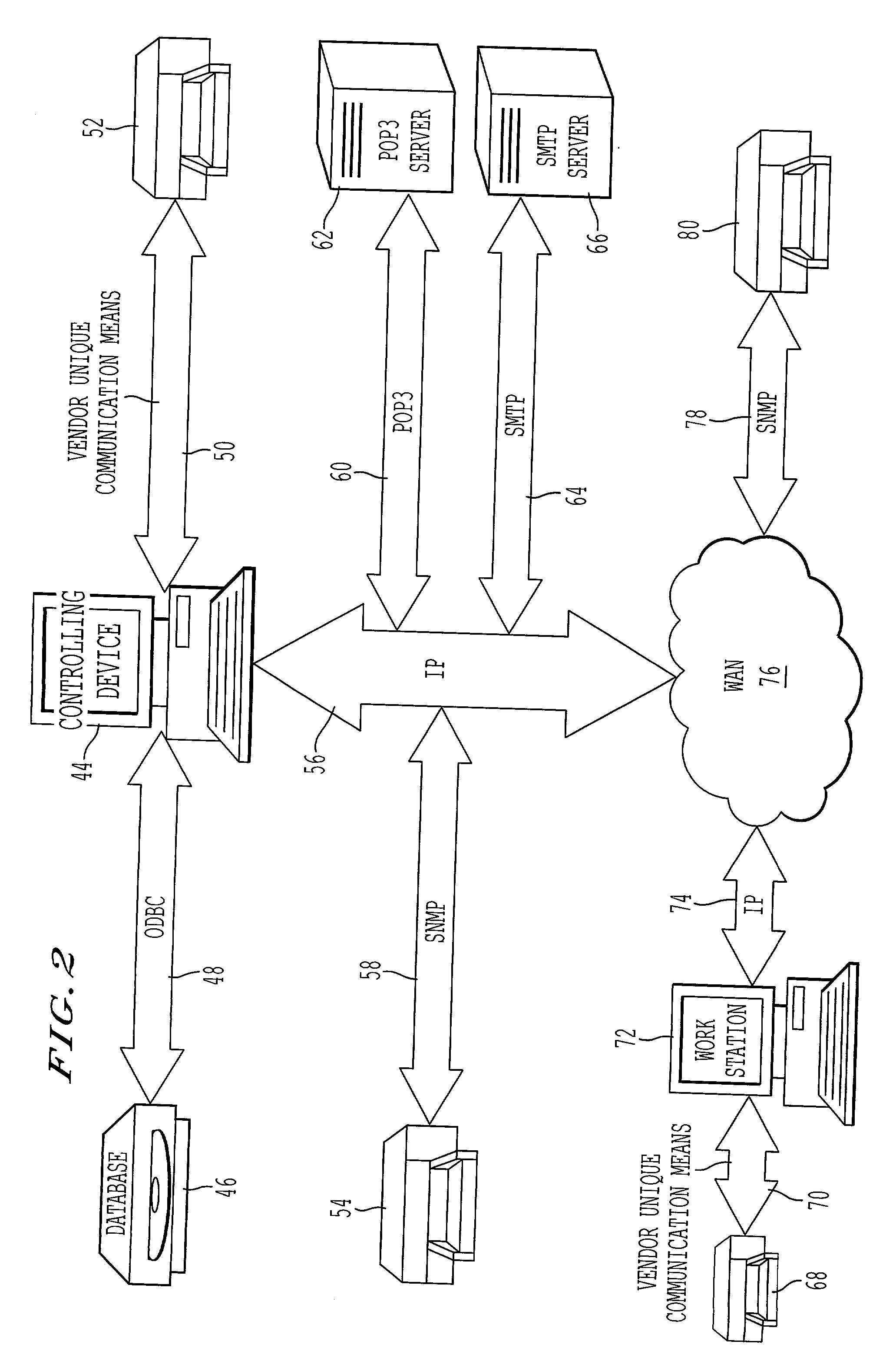
Creating devices to support a variety of models of remote diagnostics from various manufacturers
InactiveUS20050278442A1Maximize communicationMaximize effectivenessDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testComputer security arrangementsModel NumberRemote diagnostics
The present invention relates to creating device objects for maintaining communication between a interfacing device and a controlling device. These device objects are software object or software programs that are created according to information that is queried from the interfacing device. As a device object is created for each interfacing device, computer system resources are preserved during operation.
Owner:RICOH KK
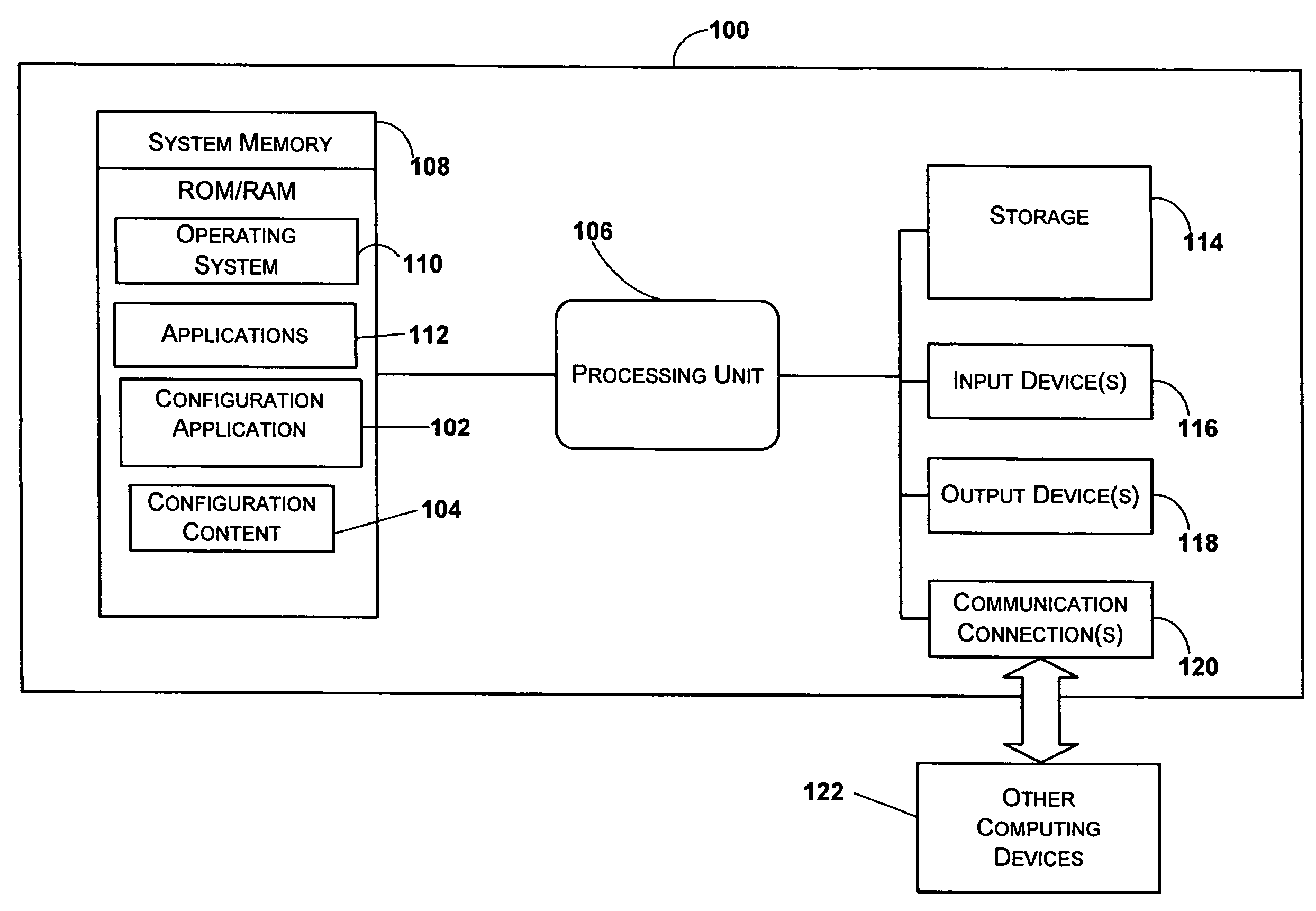
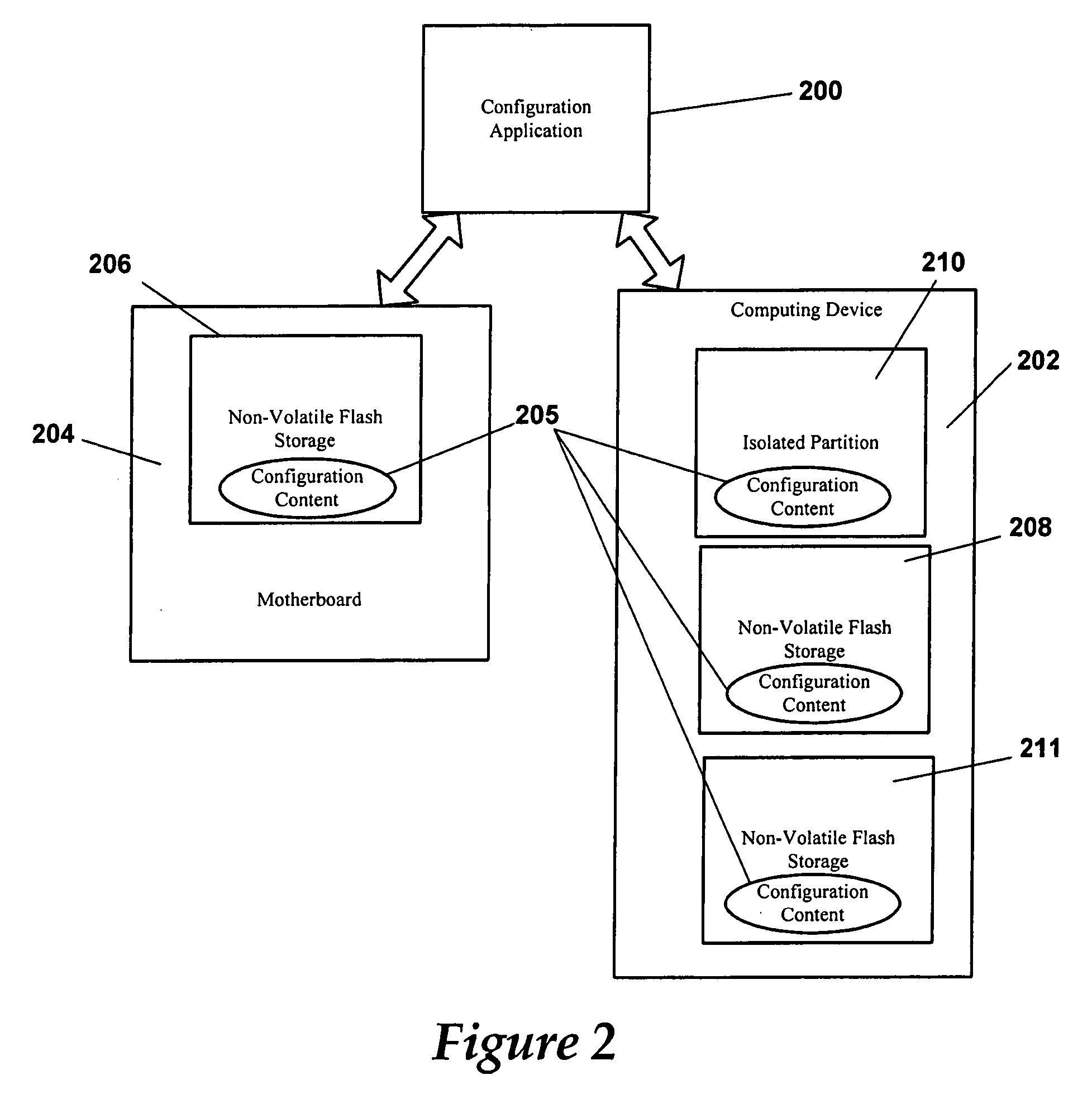
Method and system for managing core configuration information
Embodiments of a method and system for managing a system are disclosed herein. The method and system provides a means to permanently and / or securely store core system configuration information so that the core system configuration information stays with a particular system, such as a computing device or motherboard for example. The method and system provide a means for channel integrators, manufacturers, and technicians to quickly troubleshoot and return a system to full service after receiving the system from a customer as part of an unstable, non-functioning, or other system service event. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and method for firmware to export pre-boot data into the operating system runtime environment
ActiveUS7165170B2Fault responseDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testOperational systemUnique identifier
An embodiment of the present invention bridges event data from the pre-boot environment to the operating system runtime environment. Event logs are stored in a memory buffer during pre-boot. Prior to launching the operating system (OS), the event log is registered to a known memory location accessible to the OS. A preferred embodiment uses the extensible firmware interface (EFI) configuration table to store the event log. A globally unique identifier (GUID) may be used to identify the memory buffer location. Once accessible to the OS, the event data may be displayed using standard extensible Markup Language (XML) forms, or via any other desired method.
Owner:INTEL CORP
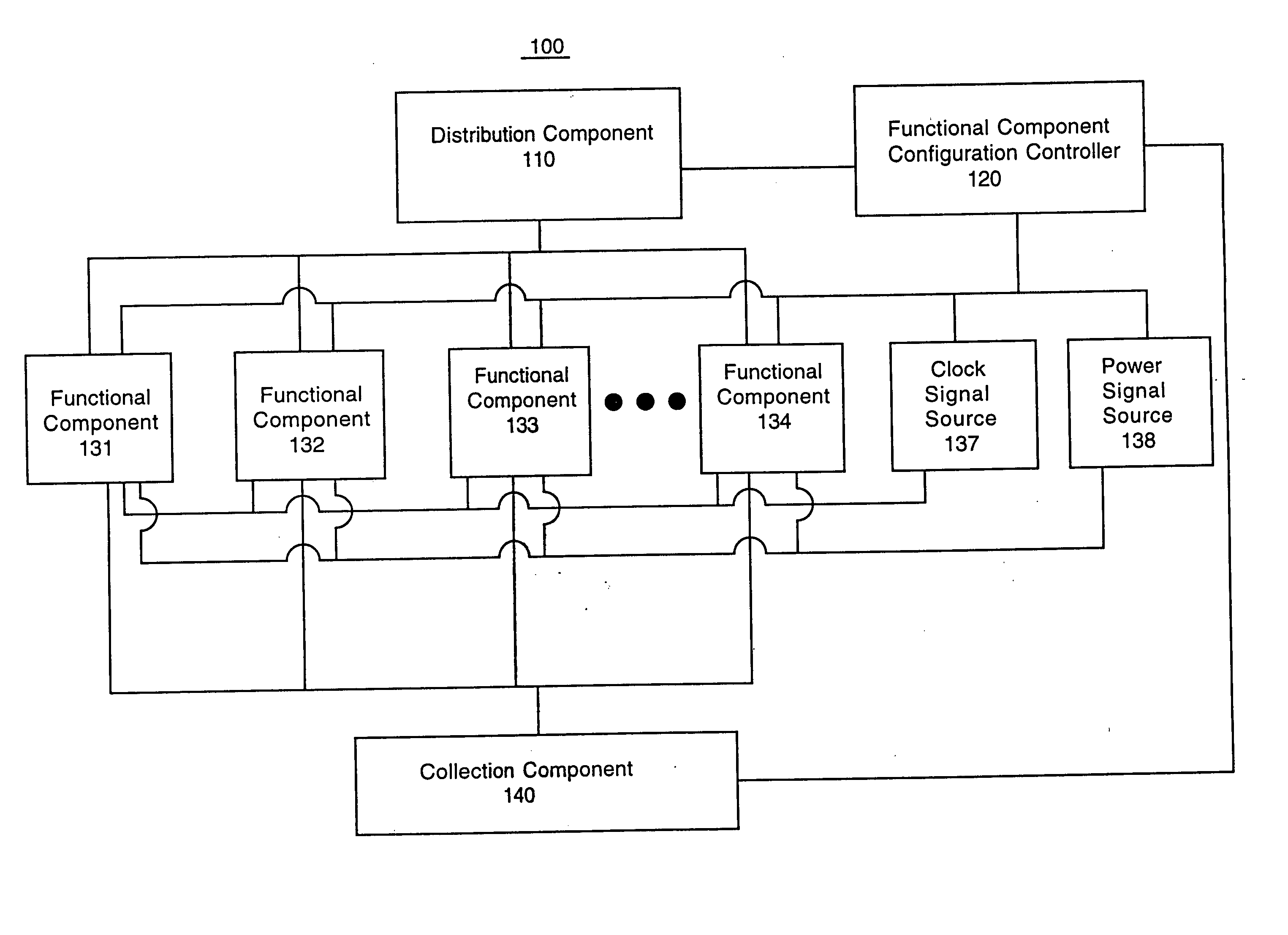
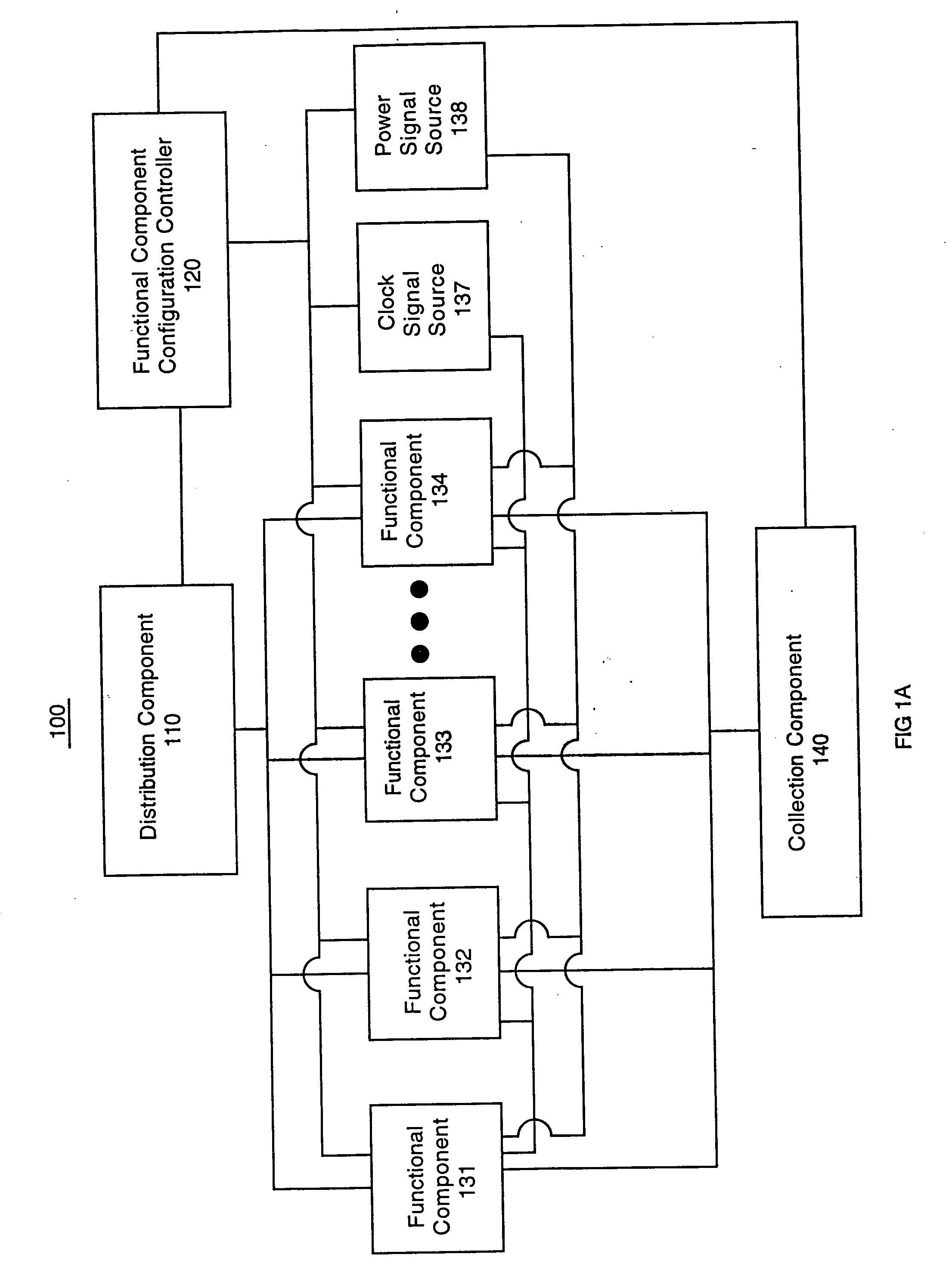
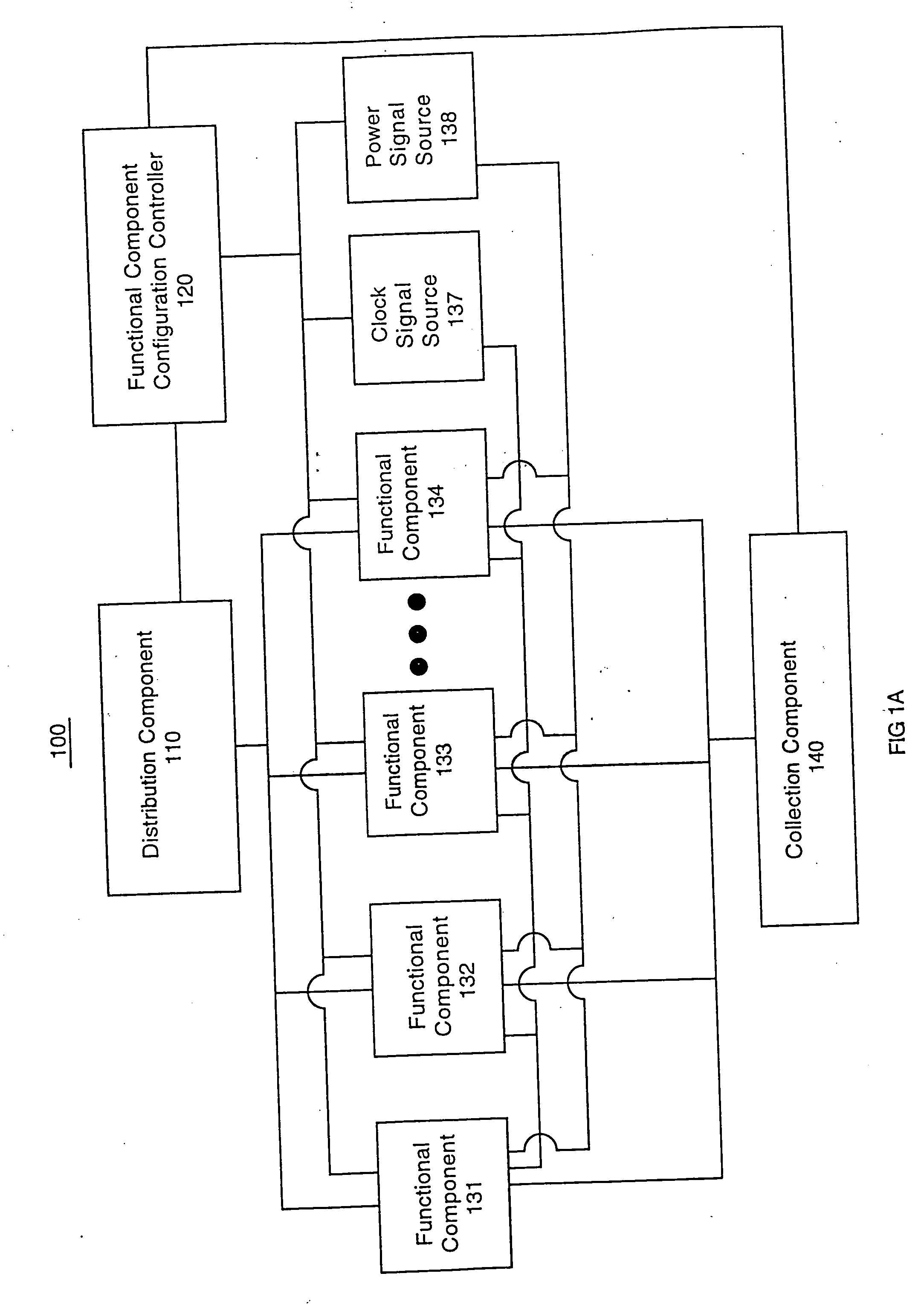
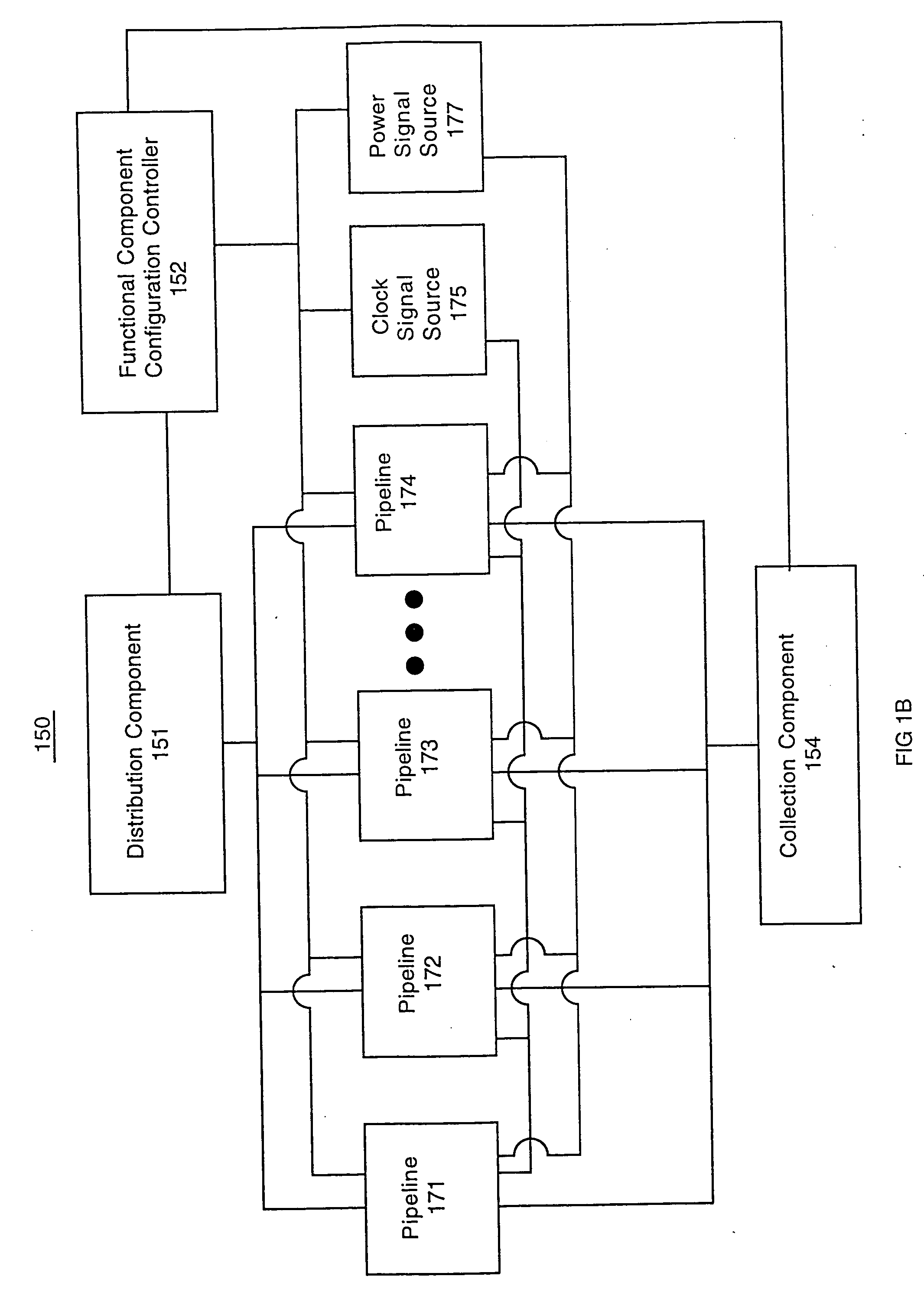
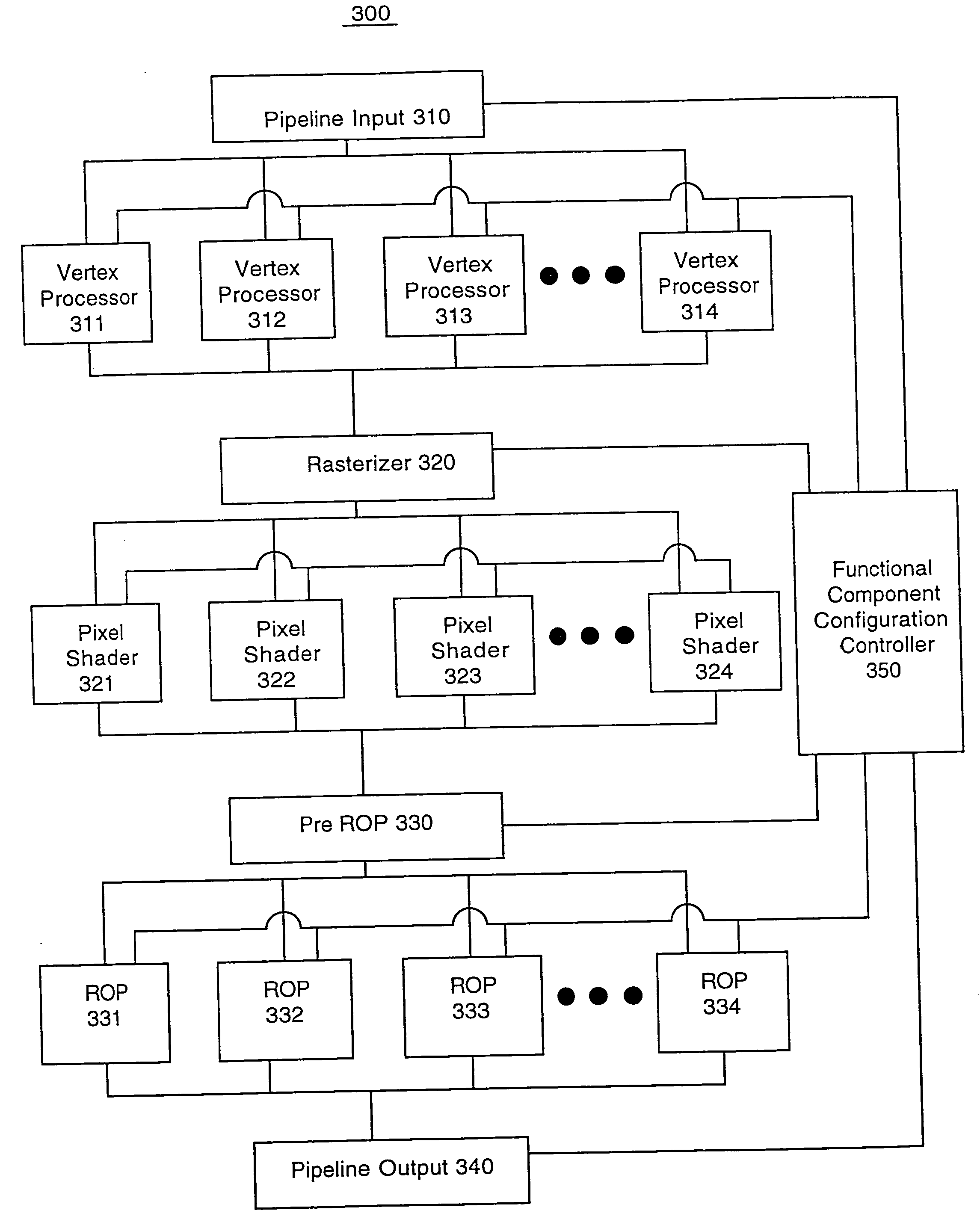
Integrated circuit configuration system and method
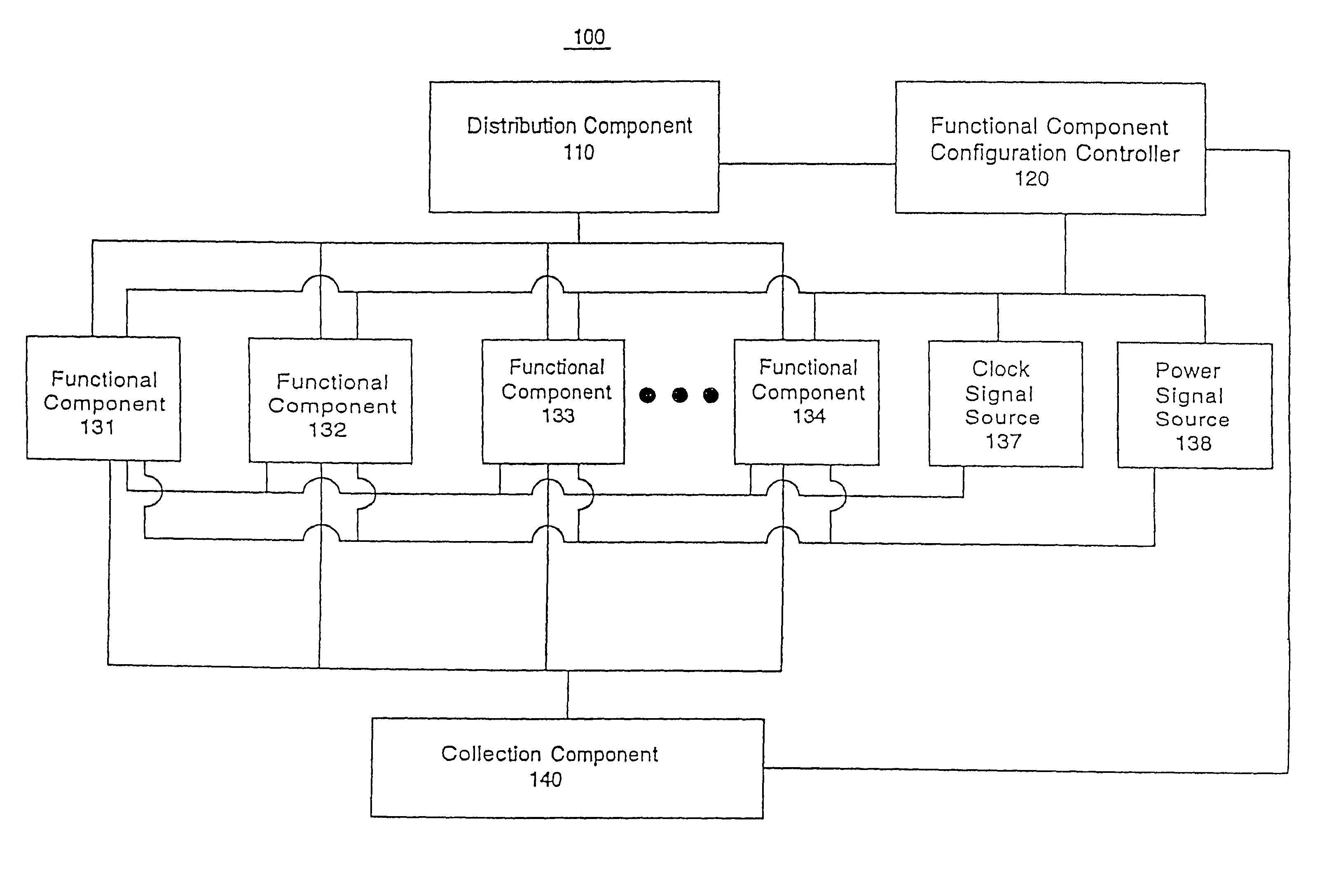
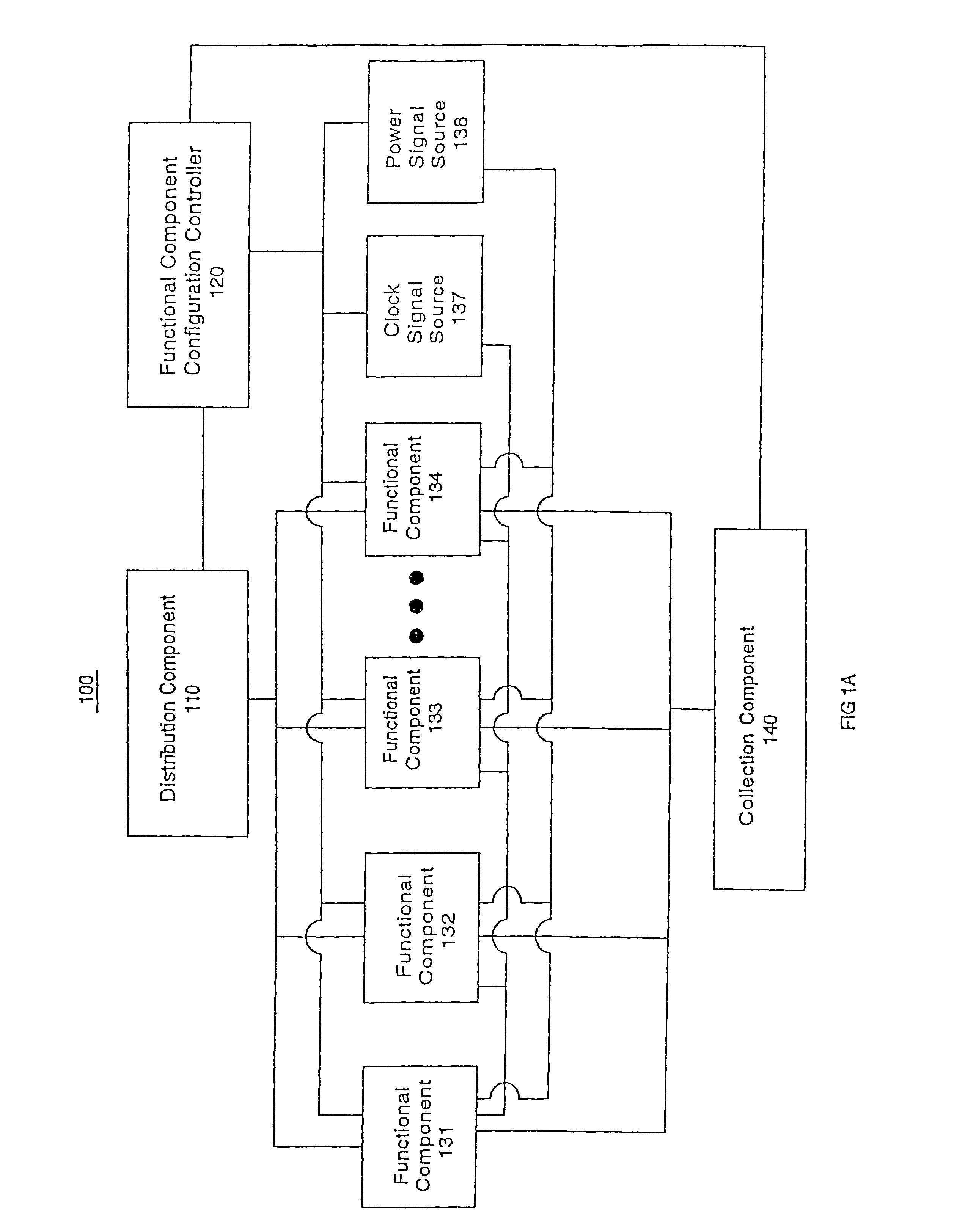
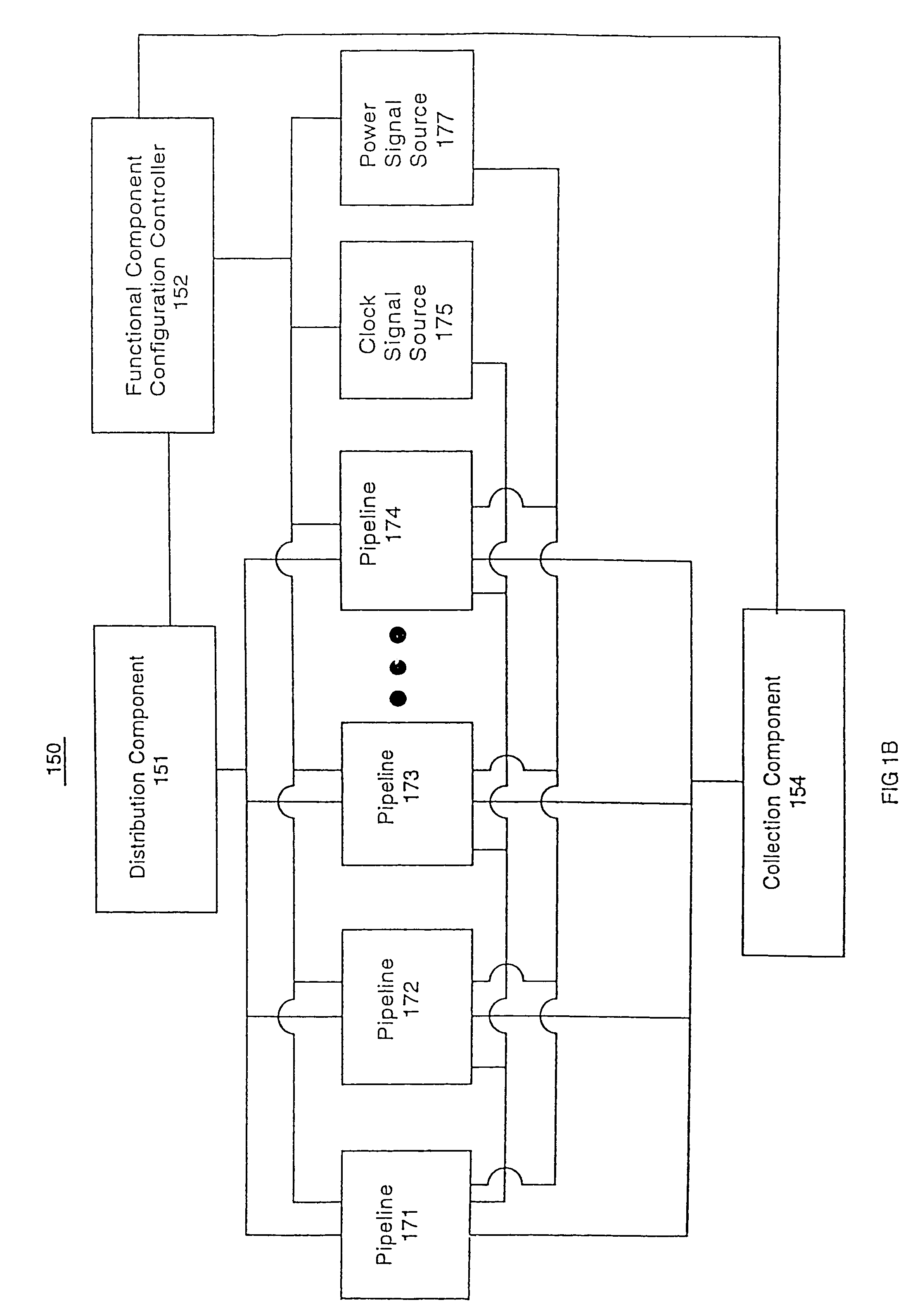
ActiveUS20050251761A1Facilitate automatic binningHigh yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testComputer compatibilityEngineering
The present invention systems and methods enable configuration of functional components in integrated circuits. A present invention system and method can flexibly change the operational characteristics of functional components in an integrated circuit die based upon a variety of factors. In one embodiment, manufacturing yields, compatibility characteristics, performance requirements, and system health (e.g., the number of components operating properly) are factored into changes to the operational characteristics of functional components. In one exemplary implementation, the changes to operational characteristics of a functional component are coordinated with changes to other functional components. Workflow scheduling and distribution is also adjusted based upon the changes to the operational characteristics of the functional components. For example, a functional component configuration controller changes the operational characteristics settings and provides an indication to a workflow distribution component. The workflow distribution component changes the workflow schedule based upon the operational characteristics settings (e.g., work flow is diverted to or away from functional components).
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Rollback attack prevention system and method
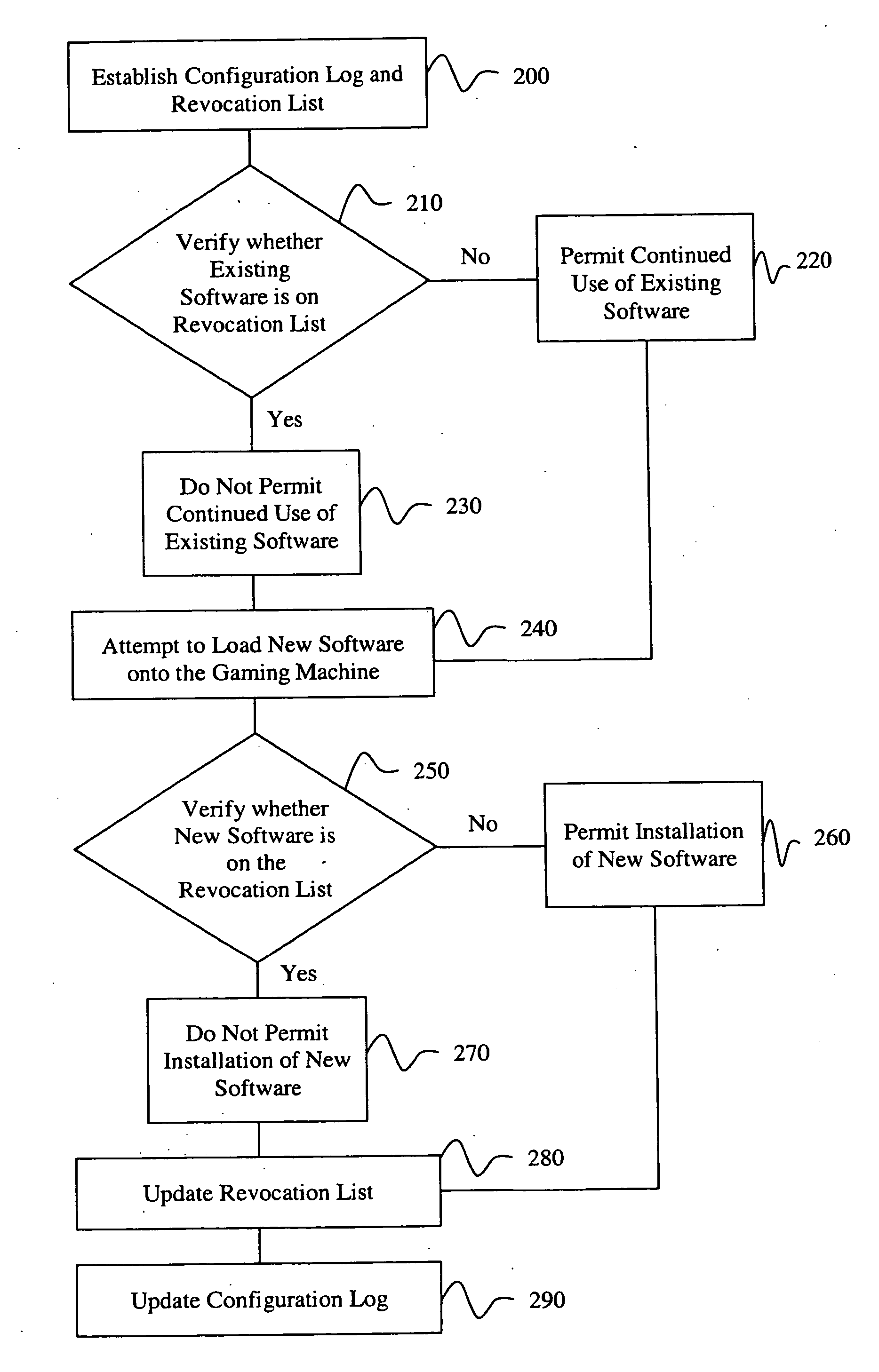
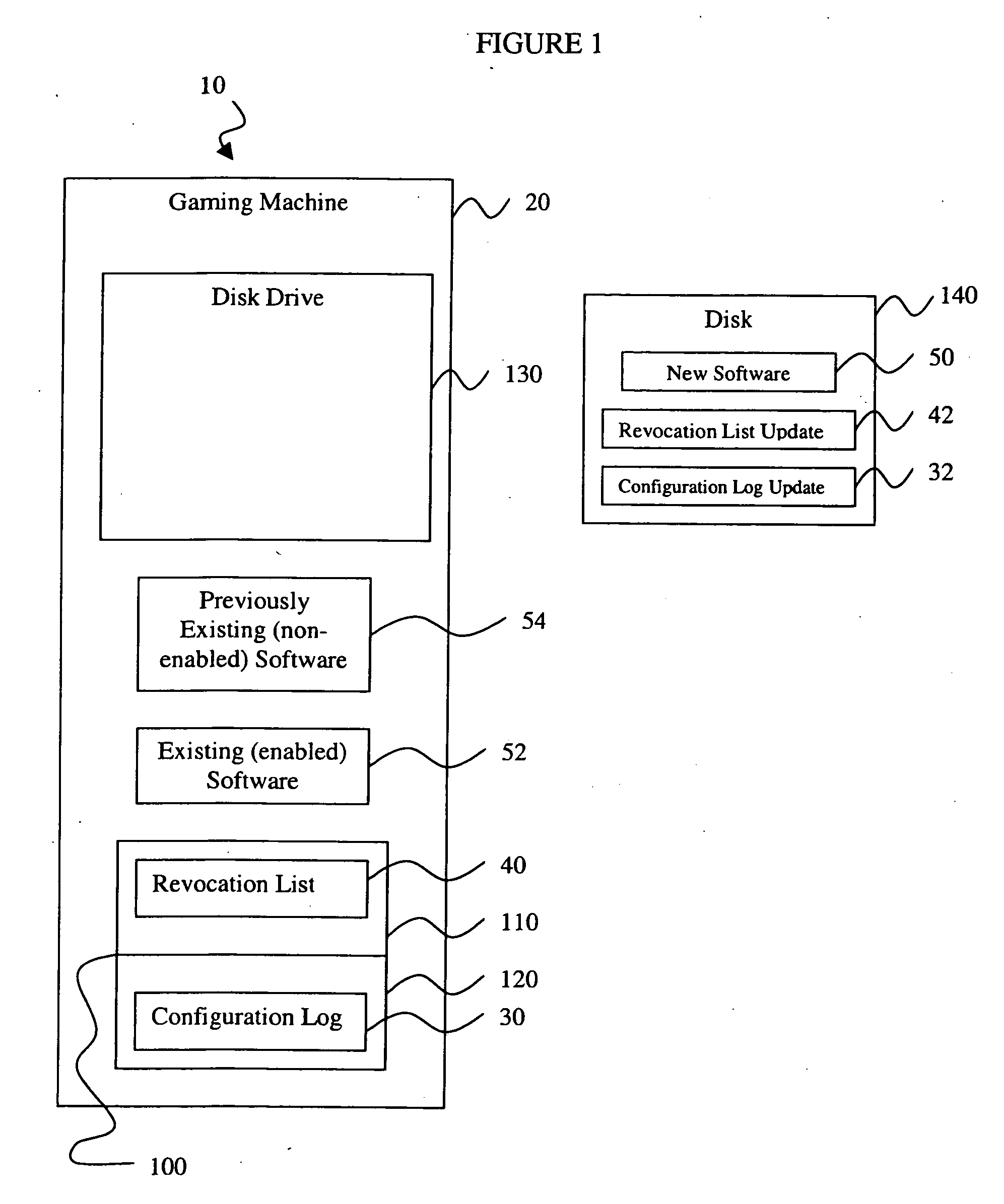
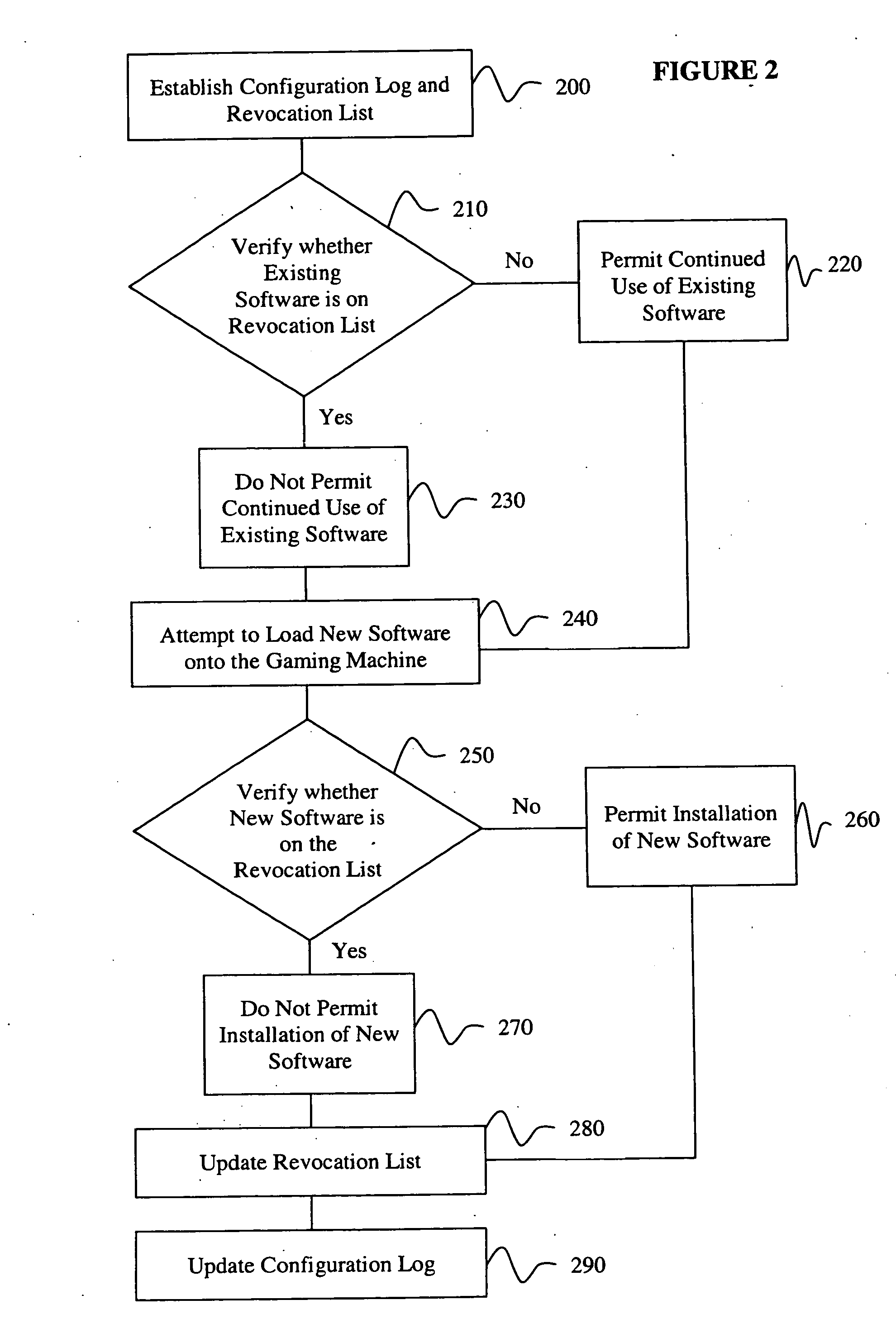
InactiveUS20050044401A1Unauthorized installationUnauthorized useDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer scienceSoftware
A rollback attack prevention system 10 for a gaming machine 20 includes a configuration log 30 and a revocation list 40. Preferably, the configuration log 30 includes a protected record of software that has been installed on the gaming machine 20. Further, the revocation list 40 includes an inventory of unauthorized software that the prevention system 10 prevents from being installed and / or used on the gaming machine 20.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
Fault generation and execution in a distributed system
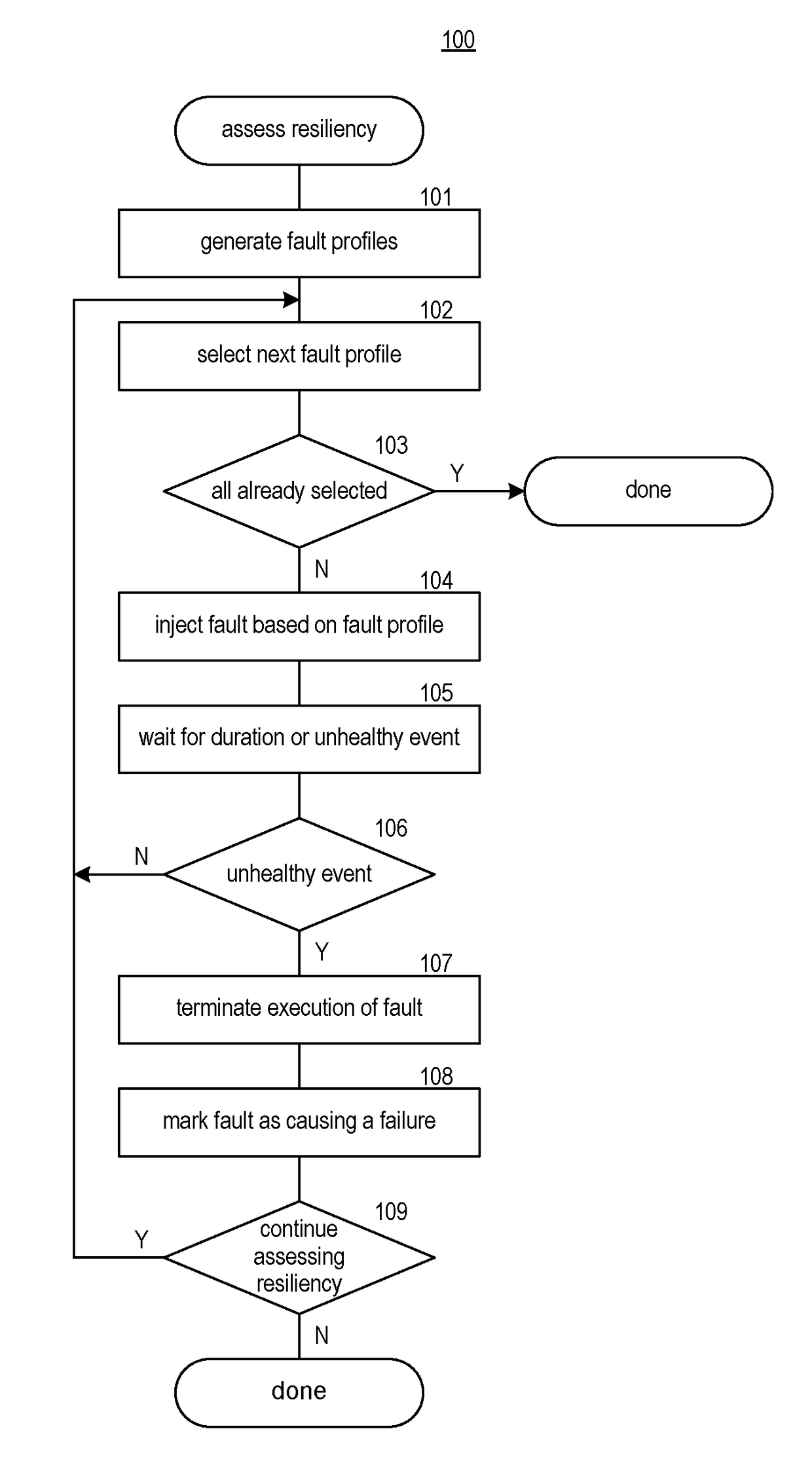
ActiveUS20180060202A1Well formedFunctional testingDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testEvaluation systemFault injection
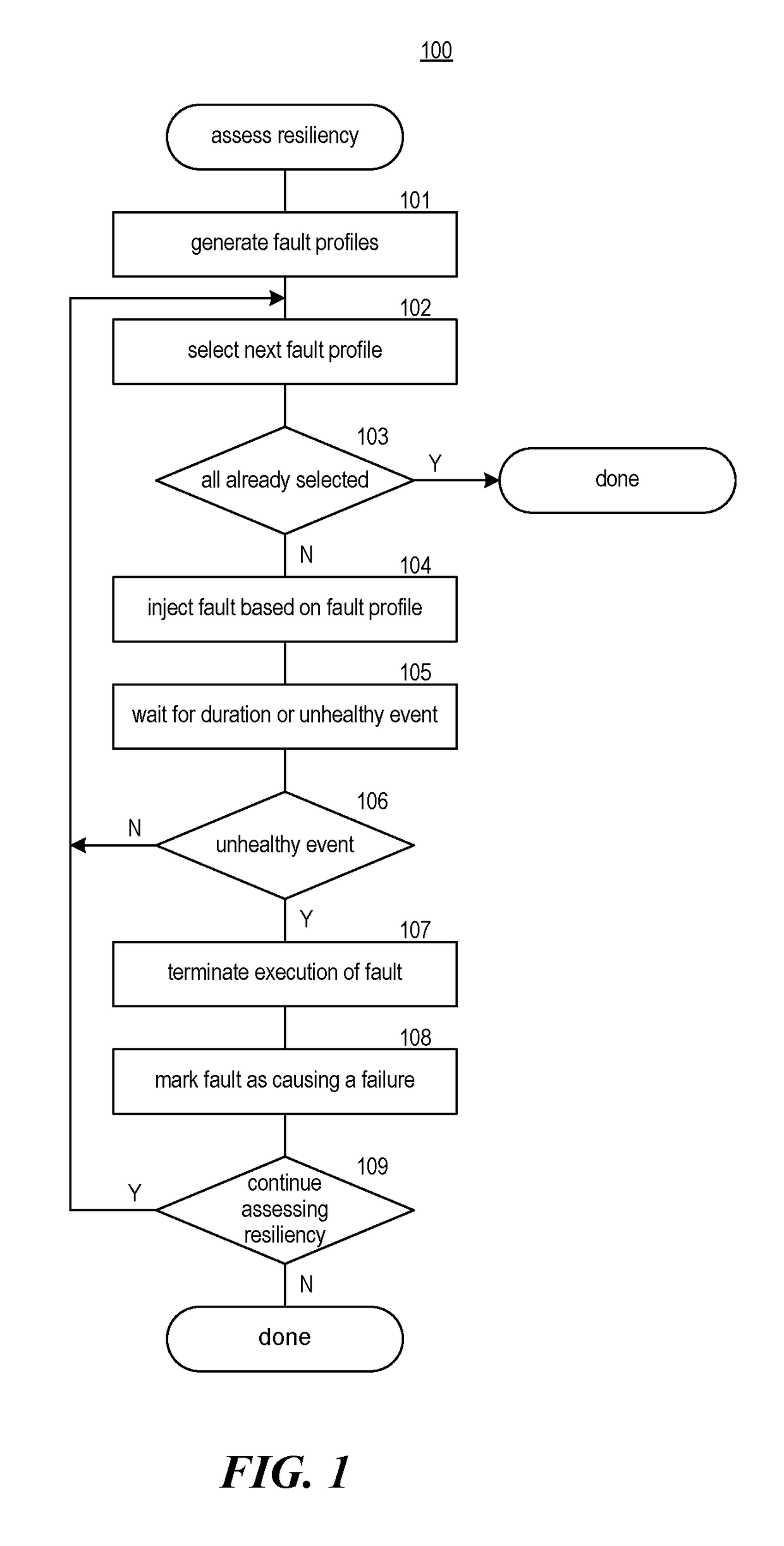
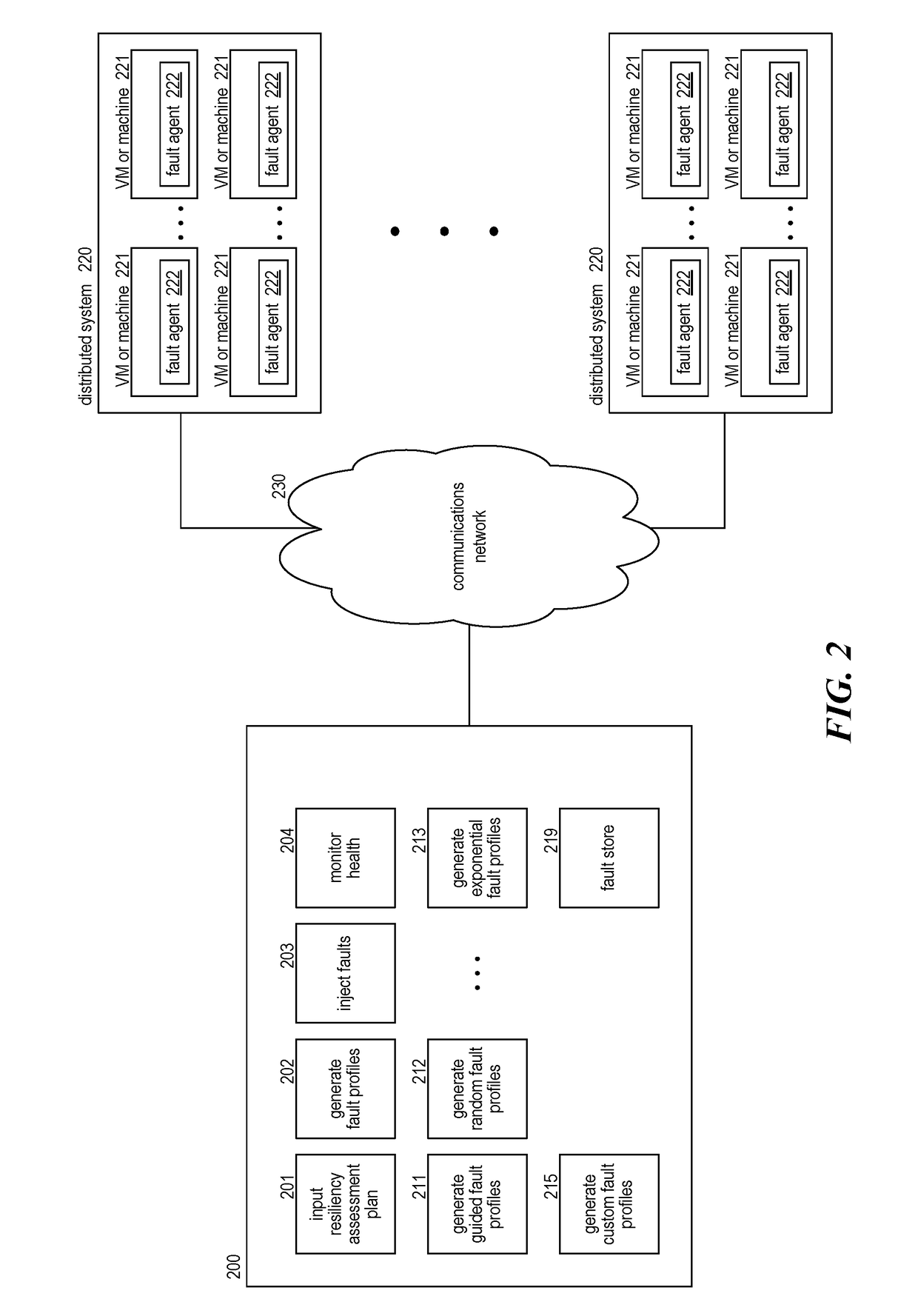
A method and system for assessing resiliency of a system is provided. A fault injection system may, for each of a plurality of dimensions of a fault profile, access an indication of possible values for the dimension, which may be specified by a user. The fault injection system may, for each of a plurality of fault profiles, automatically create the fault profile by, for each of the plurality of dimensions, selecting by the computing system a possible value for that dimension. For at least some of the fault profiles, the fault injection system injects a fault based on the fault profile into the system and determines whether a failure was detected while the fault was injected.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
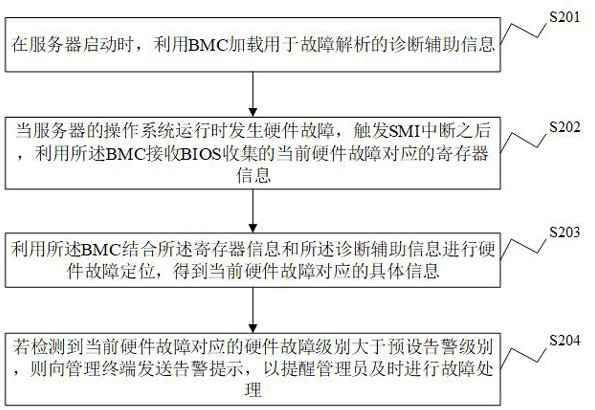
Fault diagnosis method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
InactiveCN111767184AReduce downtimeAvoid performance impactDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testHardware monitoringOperational systemFault analysis
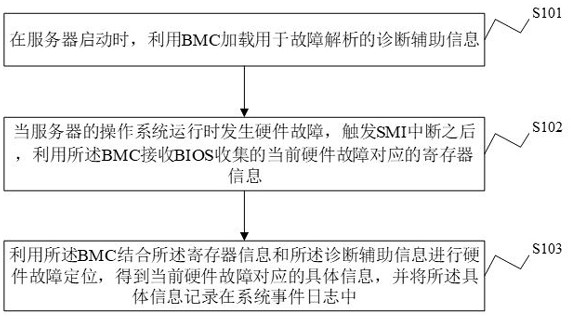
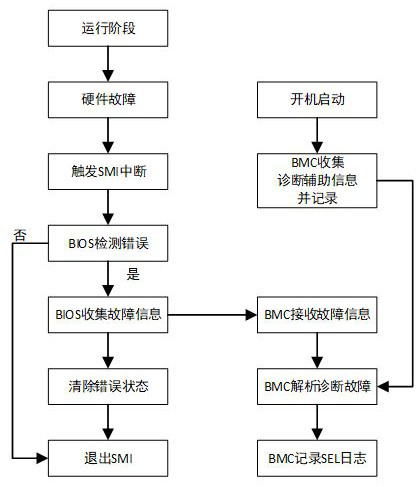
The invention discloses a fault diagnosis method and device, electronic equipment and a readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps that when a server is started, diagnosis auxiliary information used for fault analysis is loaded through a BMC; and when the operating system of the server runs, hardware faults occur, and after SMI interruption is triggered, register information corresponding to the current hardware fault and collected by BIOS is collected by utilizing the BMC, hardware fault positioning is performed by combining the register information and the diagnosis auxiliary information to obtain specific information corresponding to the current hardware fault, and the specific information is recorded in a system event log. According to the invention, after SMI interruptionis triggered, errors can be eliminated and BIOS returns to an operating system after the BIOS sends collected error state register information to BMC, and the BMC can be subsequently used for fault positioning, so that the interruption time is reduced, the configuration information does not need to be read once every time the fault analysis is carried out, the resource and time expenditure is reduced, and the influence on the system performance is avoided.
Owner:INSPUR SUZHOU INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
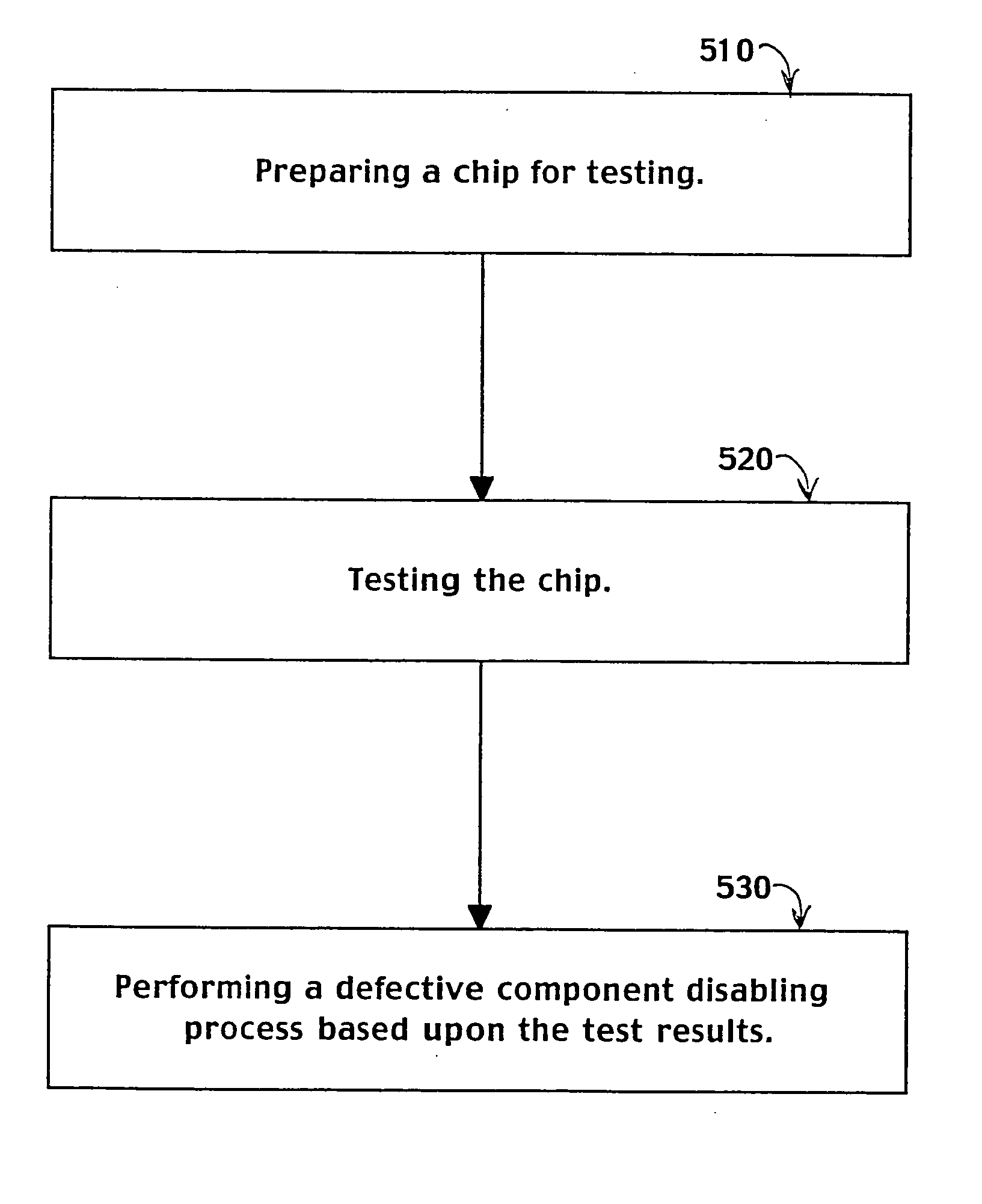
System and method for increasing die yield
ActiveUS20050251358A1Facilitate automatic binningHigh yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceWork flowEmbedded system
The present invention systems and methods facilitate increased die yields by flexibly changing the operational characteristics of functional components in an integrated circuit die. The present invention system and method enable integrated circuit chips with defective functional components to be salvaged. Defective functional components in the die are disabled in a manner that maintains the basic functionality of the chip. A chip is tested and a functional component configuration process is performed on the chip based upon results of the testing. If an indication of a defective functional component is received, the functional component is disabled. Workflow is diverted from disabled functional components to enabled functional components.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
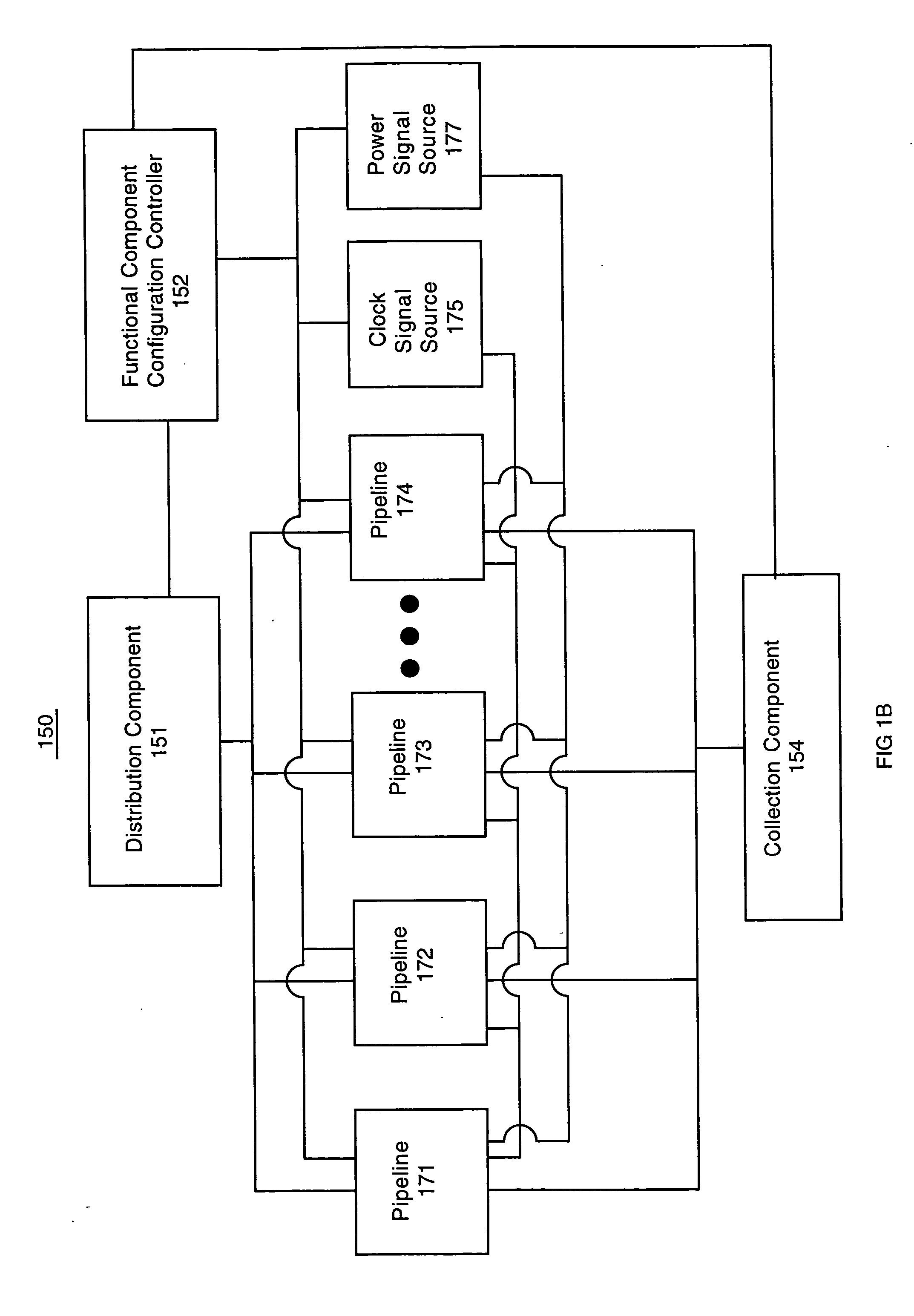
Functional component compensation reconfiguration system and method
ActiveUS8711161B1Operation may changePrevent overflowSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testMemory circuitsComputer science
A memory cell reconfiguration process is performed in accordance with the operational characteristic settings determined based upon the results of analysis and / or testing of memory cell operations. The memory circuit can include a plurality of memory cells and memory cell configuration controller. The memory cells store information associated with a variety of operations. The memory cell configuration controller coordinates selective enablement and disablement of each of the plurality of memory cells, which can be done on a subset or group basis (e.g., enables and / or disables memory cells on a word length or row by row basis). The address mapping can be adjusted so that the memory space appears continuous to external components. The memory cell configuration controller can also forward configuration information to upstream and / or downstream components that can adjust operations to compensate for the memory cell configuration (e.g., to prevent overflow).
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Gaming device verification system and method using a file allocation structure
InactiveUS7783881B2Little informationImprove securityVolume/mass flow measurementUser identity/authority verificationOperational systemFile allocation
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
Method and apparatus for providing updated processor polling information
ActiveUS20050022059A1Detecting faulty hardware by configuration testDigital computer detailsOperational systemIntegrated processing
Embodiments of the invention provide a method and an apparatus to collect and dynamically update processor polling information. In one method embodiment, the present invention collects processor polling information at boot time to be provided to an operating system. The processor polling information describes operating conditions of an integrated processing system. The operating system is then notified that a triggering event has occurred that may potentially alter the operating conditions of the integrated processor system. Providing to the operating system updated processor polling information during runtime to reflect the operating conditions of the integrated processor system after the occurrence of the triggering event.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
Dynamic, Non-invasive detection of hot-pluggable problem components and re-active re-allocation of system resources from problem components
InactiveUS20040230731A1Program initiation/switchingDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testData processing systemOperational system
A method, system, and data processing system for dynamic detection of problem components in a hot-plug processing system and automatic removal of the problem component via hot-removal methods without disrupting processing of the overall system. A data processing system that provides a non-disruptive, hot-plug functionality is designed with a additional logic for initiating and / or completing a sequence of factory level tests on hot-pluggable components to determine if the component if functioning properly. When a component is not functioning properly, the OS re-allocates the workload of the component to other component so the system, and when the OS completes the re-allocation, the service element initiates the hot removal of the component so that the component is logically and electrically separated from the system.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Integrated circuit configuration system and method
ActiveUS20050261863A1High yieldCost of producingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testEmbedded systemDefective Component
The present invention systems and methods enable configuration of functional components in integrated circuits. A present invention system and method can flexibly change the operational characteristics of functional components in an integrated circuit die based upon a variety of factors, including if the die has a defective component. An indication of the defective functional component identification is received. A determination is made if the defective functional component is one of a plurality of similar functional components that can provide the same functionality. The other similar components can be examined to determine if they are parallel components to the defective functional component. The defective functional component is disabled if it is one of the plurality of similar functional components and another component can handle the workflow that would otherwise be assigned to the defective component. Workflow is diverted from the disabled component to other similar functional components.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
System and method for diagnostics execution and data capture in a storage system using nonvolatile memory
InactiveUS20070192654A1Enhanced couplingOvercome disadvantagesDetecting faulty hardware by configuration testDiagnostic testReceipt
The present invention provides a system and method for diagnostics execution in which diagnostics code is stored in a designated partition on a removable nonvolatile memory device, such as a compact flash or a personal computer (PC) card that is interfaced with the motherboard of a file server system. The file server system firmware is programmed in such a manner that, upon receipt of a diagnostics command, a normal boot mechanism is interrupted, and a diagnostics boot is performed. The firmware is programmed to probe the removable nonvolatile memory device, and to load the diagnostics code contained thereon into main memory and to execute the diagnostics in response to an initiation by an operator's key sequence. In accordance with a further aspect of the invention, the data produced as a result of the diagnostics test sequence is captured and stored in a maintenance log in another partition on the compact flash that has been pre-assigned for that purpose. Such diagnostics log data can be readily retrieved at a later time. In addition, the diagnostics code may be updated without system downtime.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com