Patents
Literature
64results about How to "Promote stable alignment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
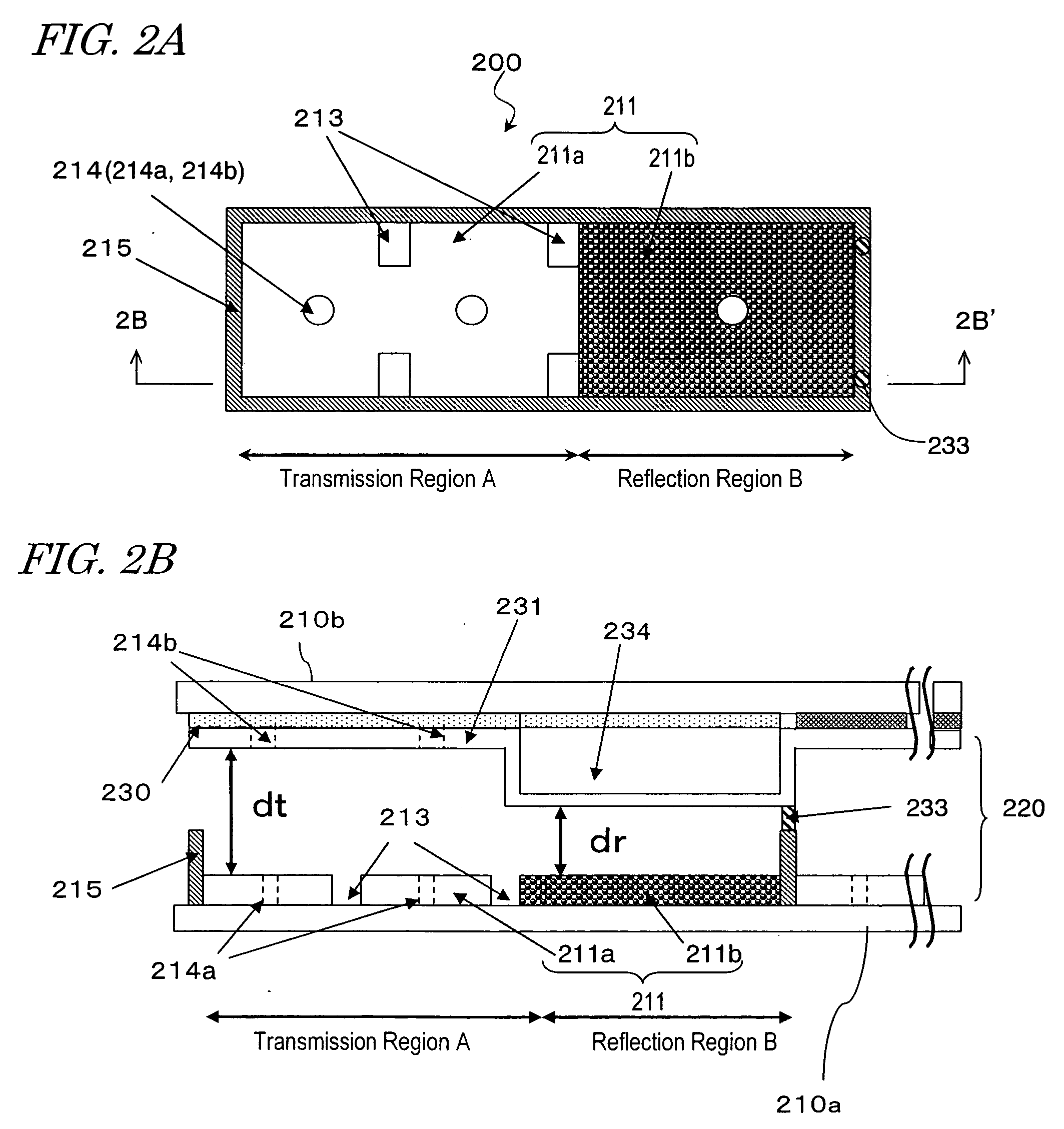
Liquid crystal display and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20060061719A1Improve light transmittanceImprove light efficiencyLiquid crystal compositionsCoatingsHigh contrastLiquid-crystal display
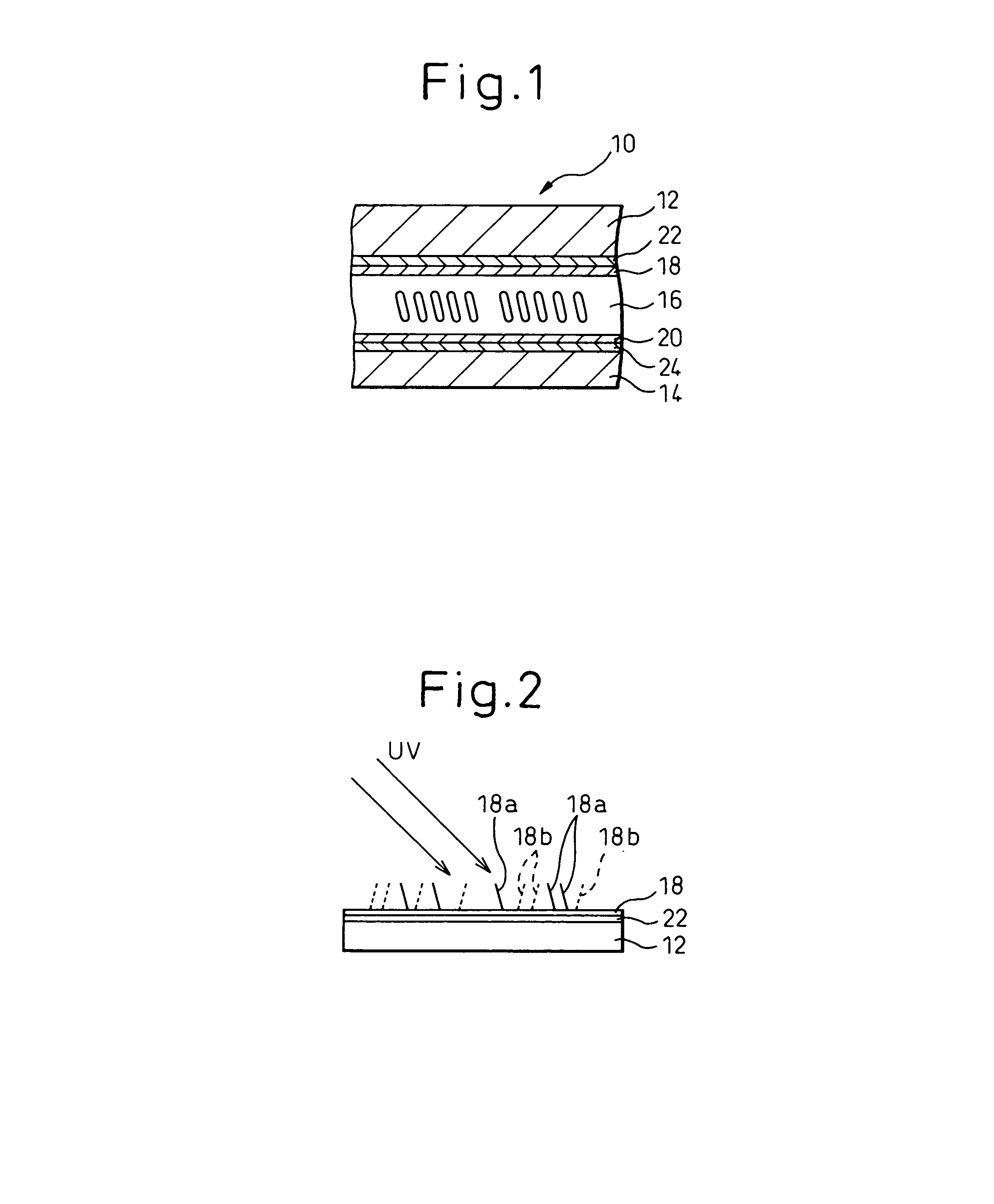
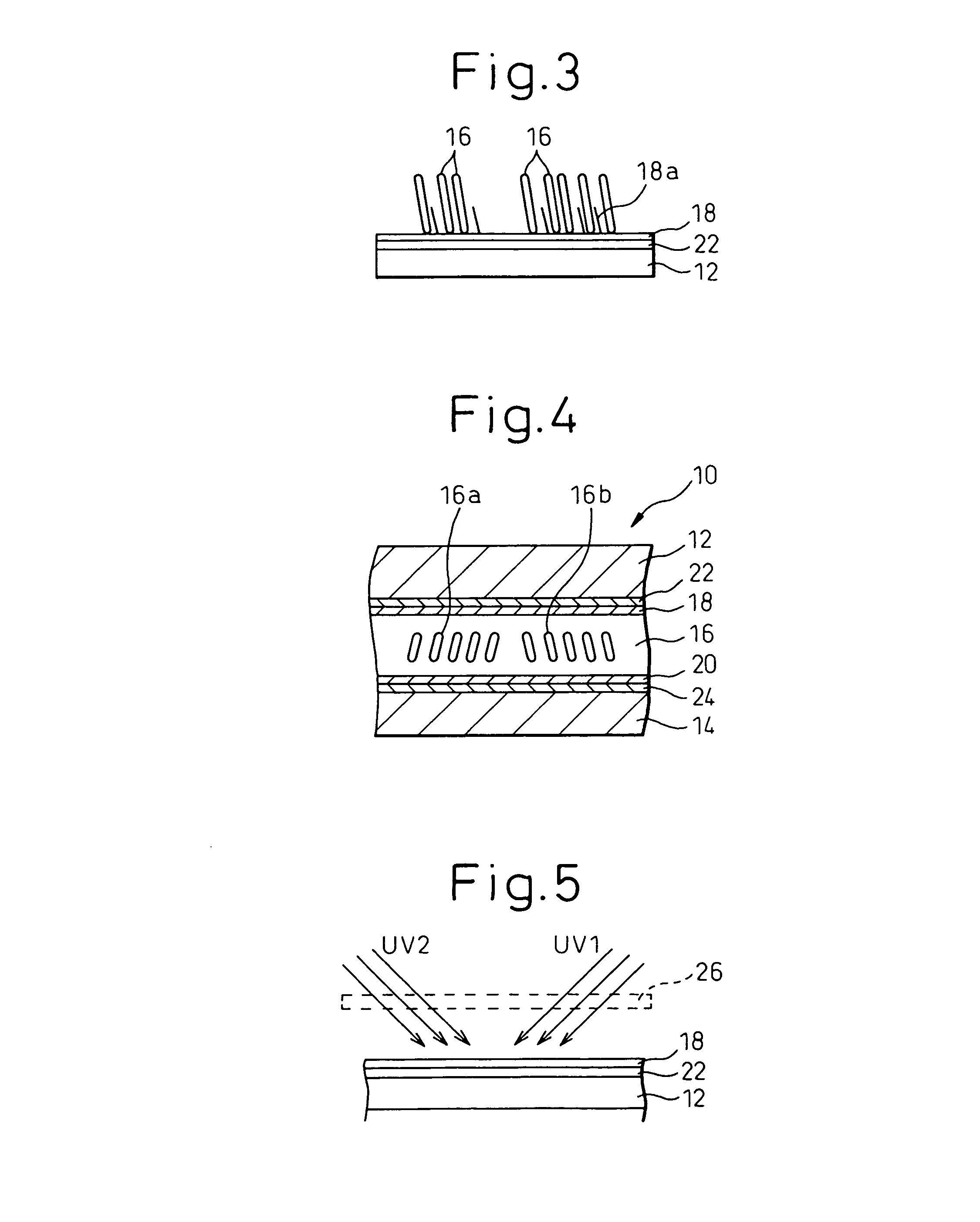
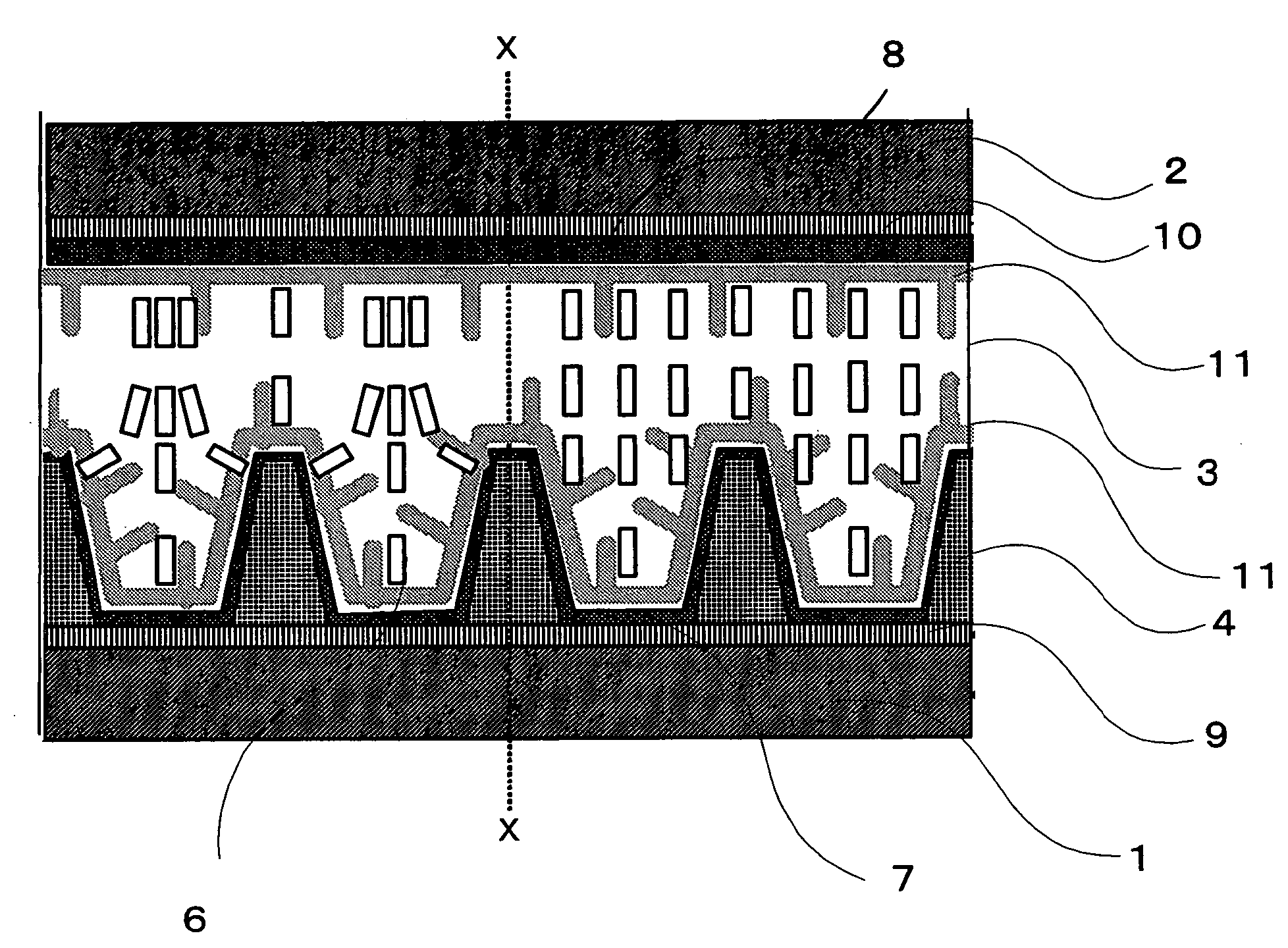
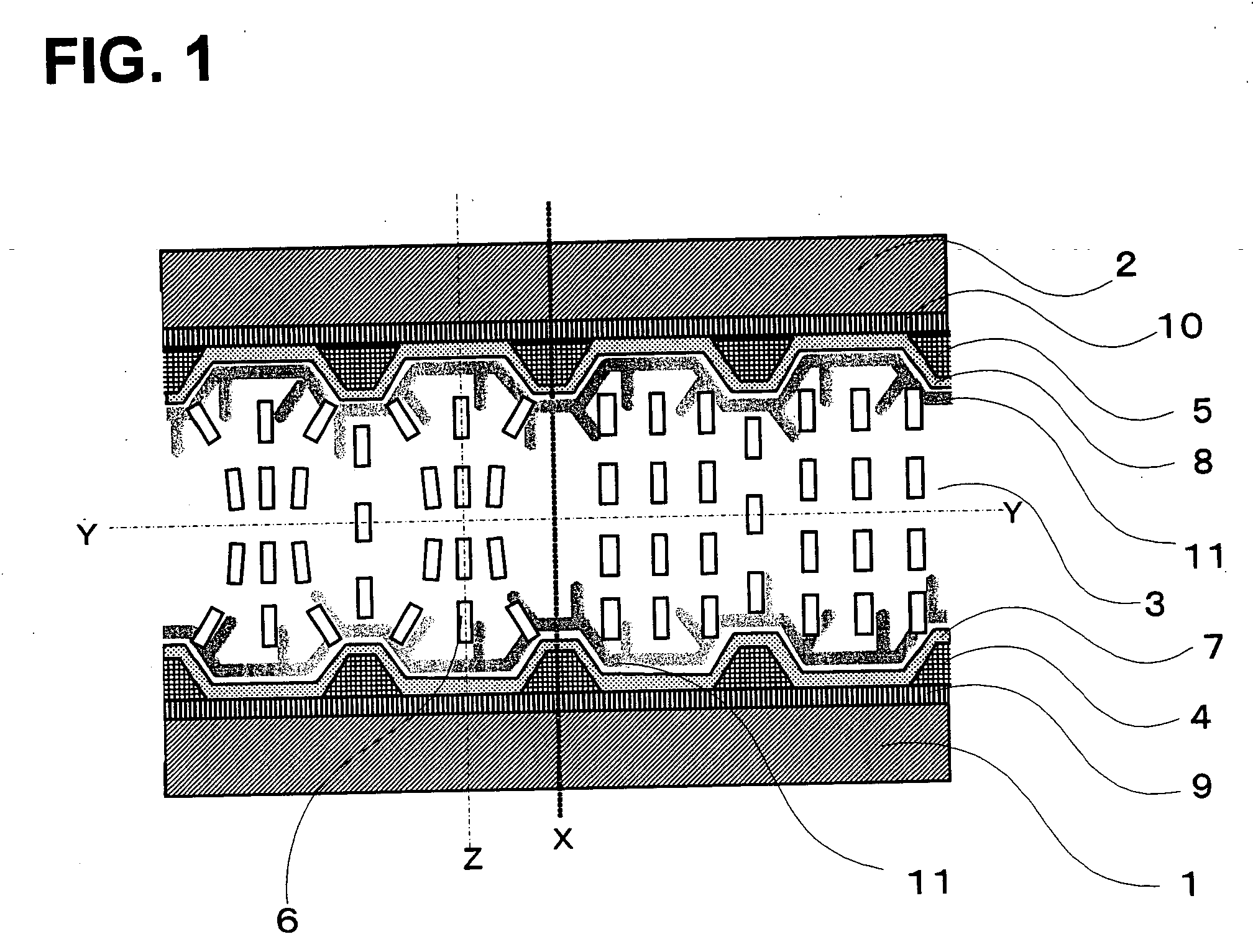
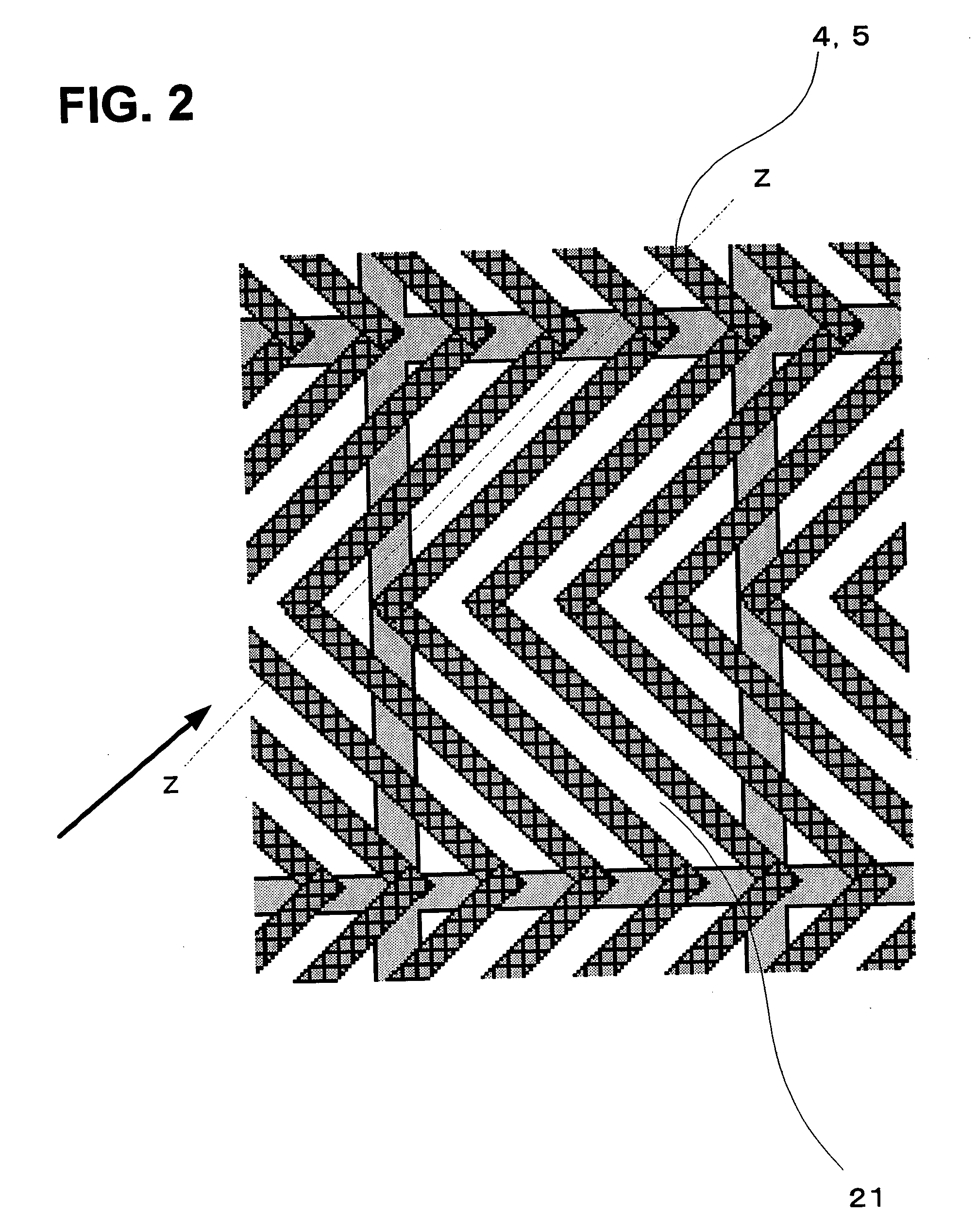
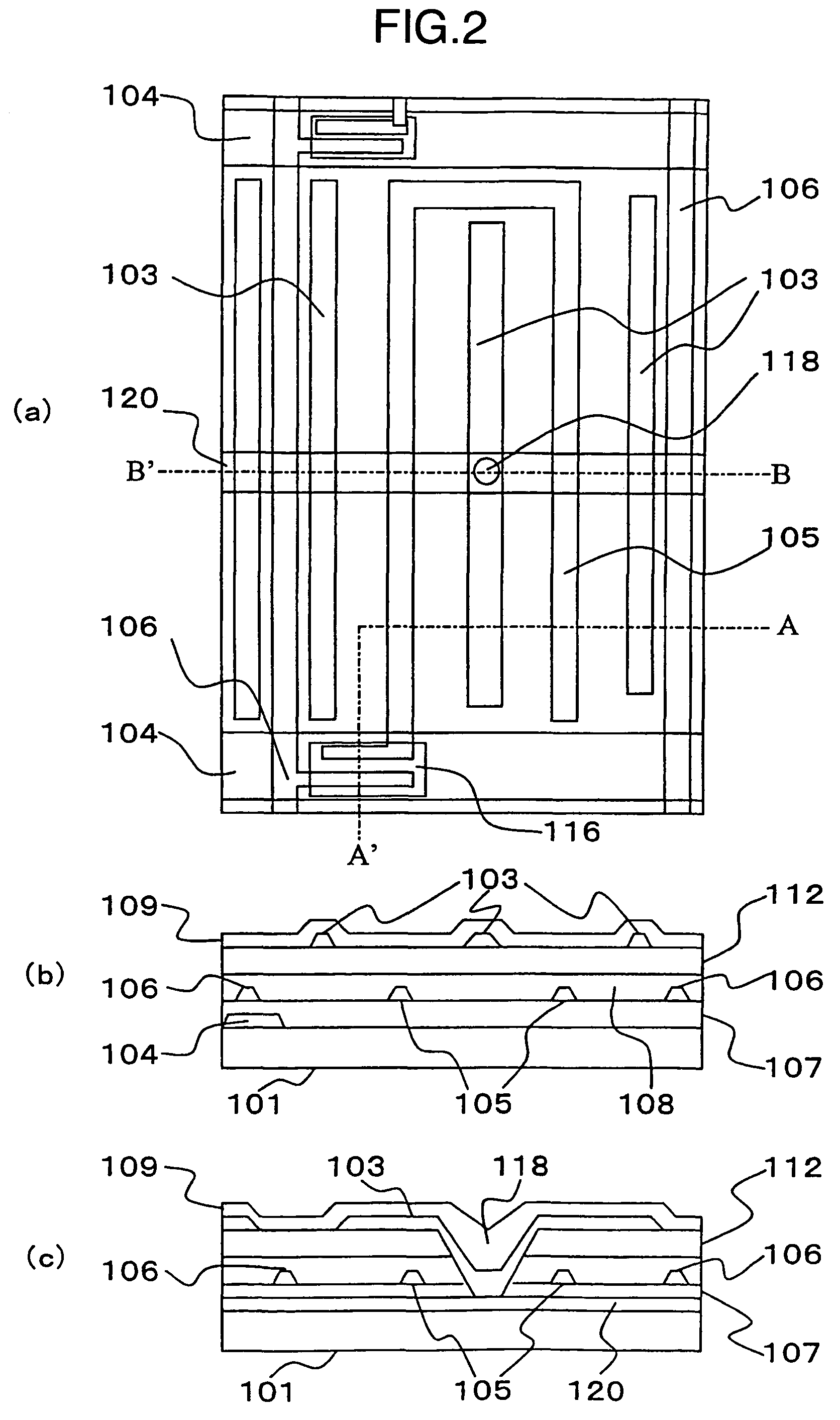
A liquid crystal display is provided which is capable of reducing the occurrence of defective display due to variations in the initial alignment direction of a liquid crystal alignment control film in a liquid crystal display of an IPS scheme, realizing the stable liquid crystal alignment, providing excellent mass productivity, and having high image quality with a higher contrast ratio. The liquid crystal display has a liquid crystal layer disposed between a pair of substrates, at least one of the substrates being transparent, and an alignment control film formed between the liquid crystal layer and the substrate. At least one of the alignment control films comprises photoreactive polyimide and / or polyamic acid provided with an alignment control ability by irradiation of substantially linearly polarized light.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Liquid crystal composition and retardation film
InactiveUS20100078593A1Stable horizontal alignmentPromote stable alignmentLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingCrystallographyLiquid crystal
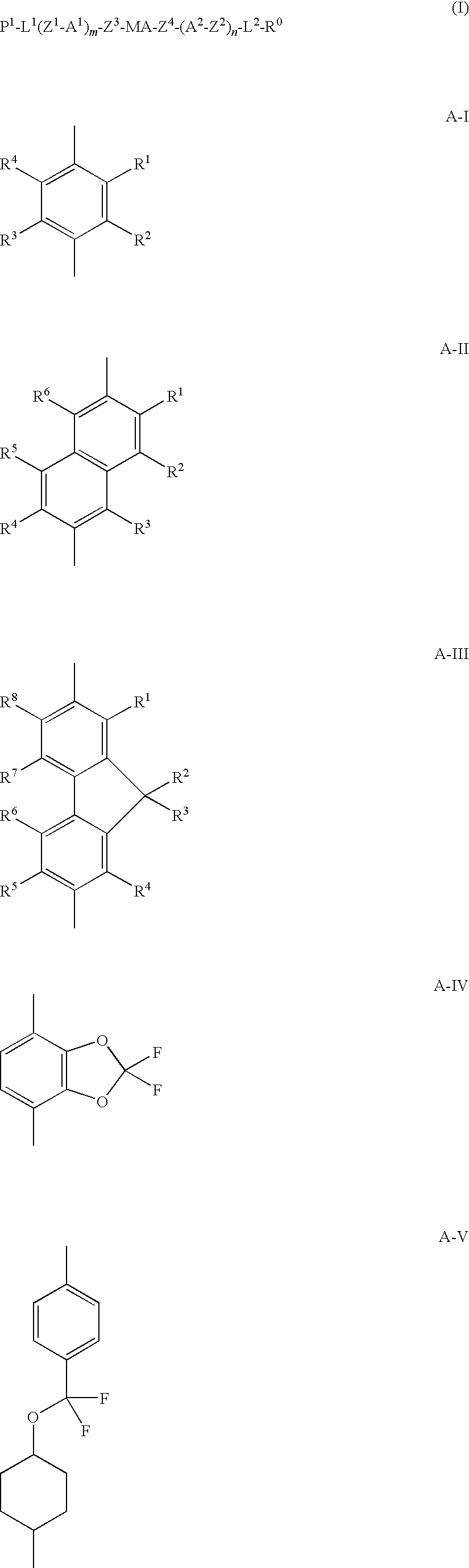
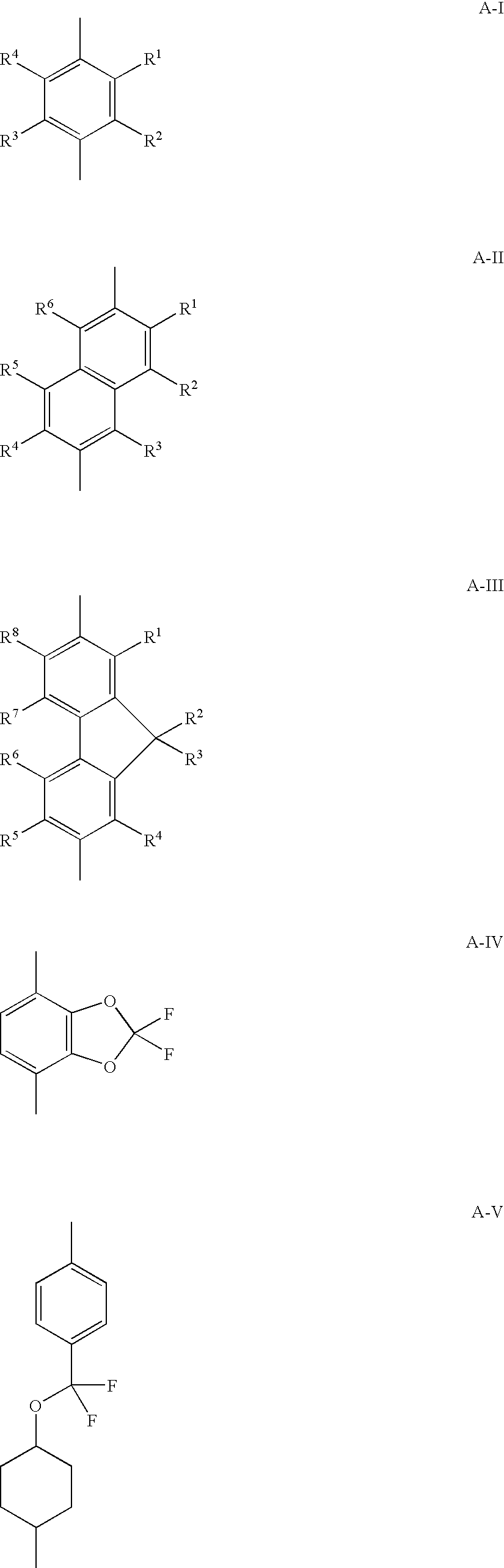
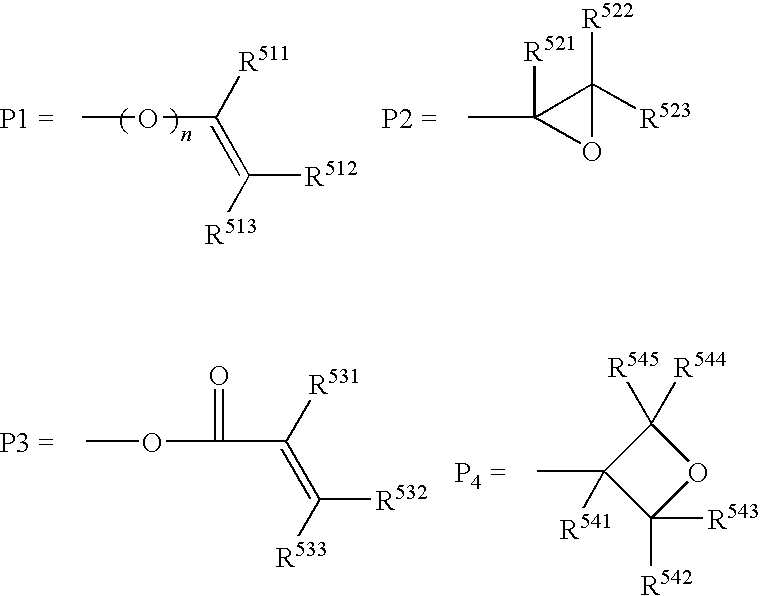
The invention relates to a liquid crystal composition comprising two or more species of liquid crystal compounds respectively having a polymerizable group, at least one species of which being a compound represented by formula (I) below, having a content of the compound of from 20% to 80% relative to the total mass of said two or more species of liquid crystal compounds. In formula (I), P1 represents a polymerizable group; each of L1 and L2 represents a divalent spacer group; each of Z1 to Z4 represents a divalent linking group; each of A1 and A2 represents a divalent cyclic group; each of m and n represents an integer from 0 to 3; MA represents any one group of A-I to A-V below:
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Segmented stackable filter assembly for filtering a gas and method of manufacturing same
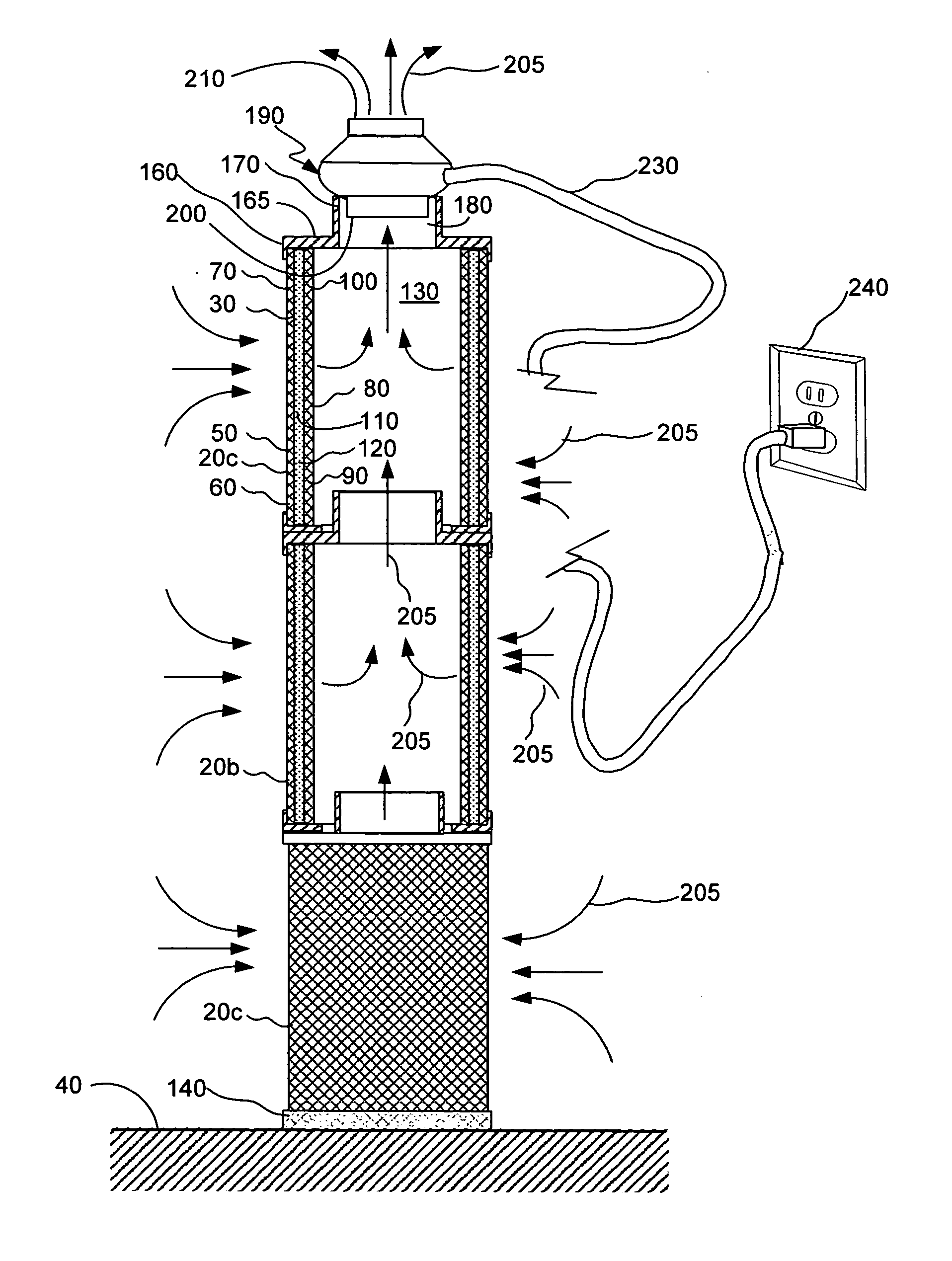
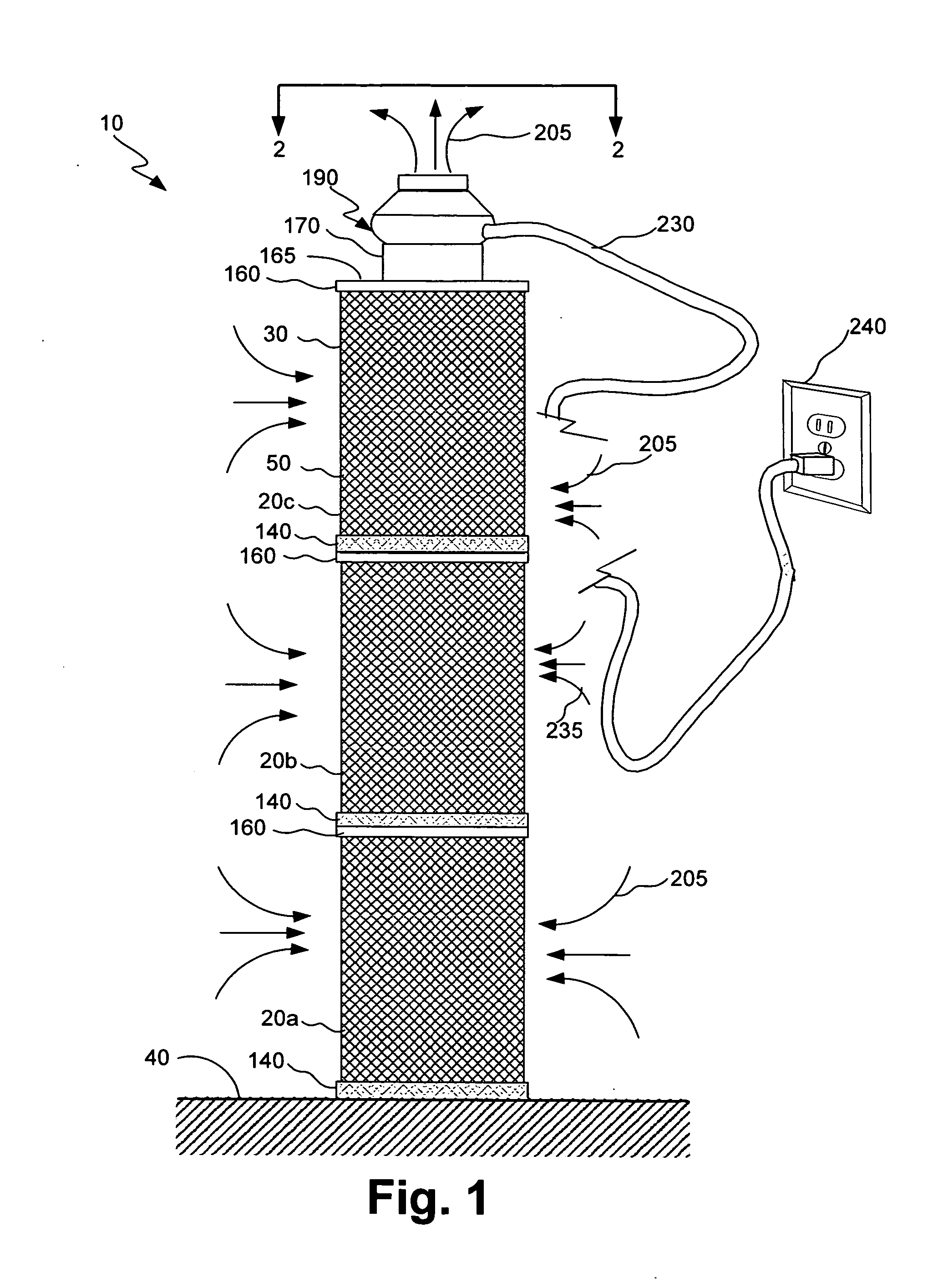
InactiveUS20140020561A1Easy to separateEasy to reconfigureCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentFilter mediaEngineering
Segmented stackable filter assembly for filtering a gas and method of manufacturing same. An exemplary embodiment of the segmented stackable filter assembly comprises a plurality of filter segments stackable end-to-end for varying filtration capacity of the stackable filter assembly. Each filter segment includes an annular outer wire mesh and an annular inner wire mesh spaced apart from the outer wire mesh to define a gap therebetween containing filter media. The inner wire mesh defines a central air flow passage axially through the filter assembly. A lower end plate has an opening for receiving a neck portion upwardly projecting from an adjacent upper end plate, so that both filter segments are prevented from laterally moving relative to each other. A fan assembly is supported by the neck portion for suctioning the gas through the plurality of filter segments.
Owner:AERY GLEN
Liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20050271833A1Promoting and stabilizing capacityImprove responseLiquid crystal compositionsPhotosensitive materialsLiquid-crystal displayHigh volume manufacturing
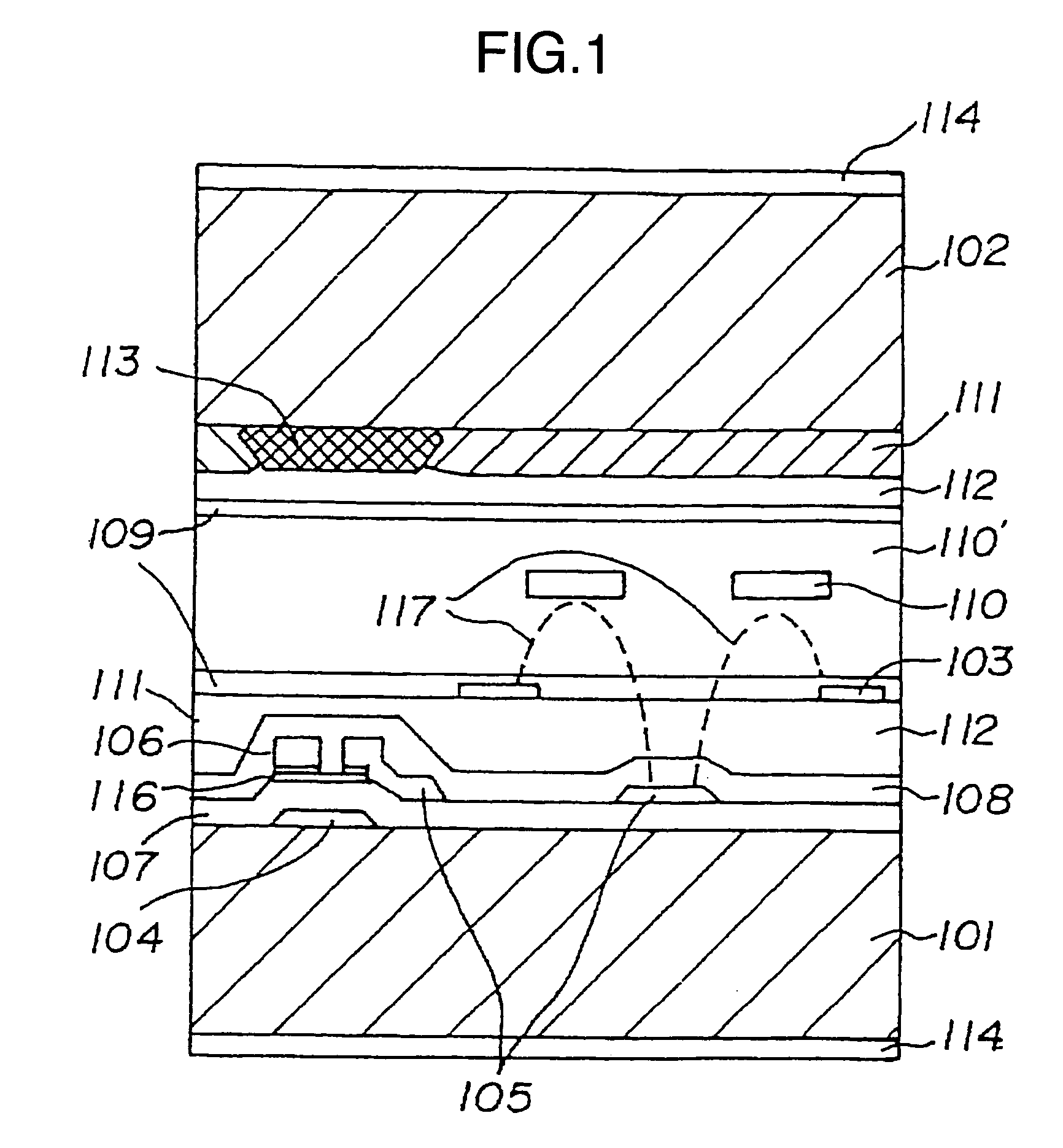
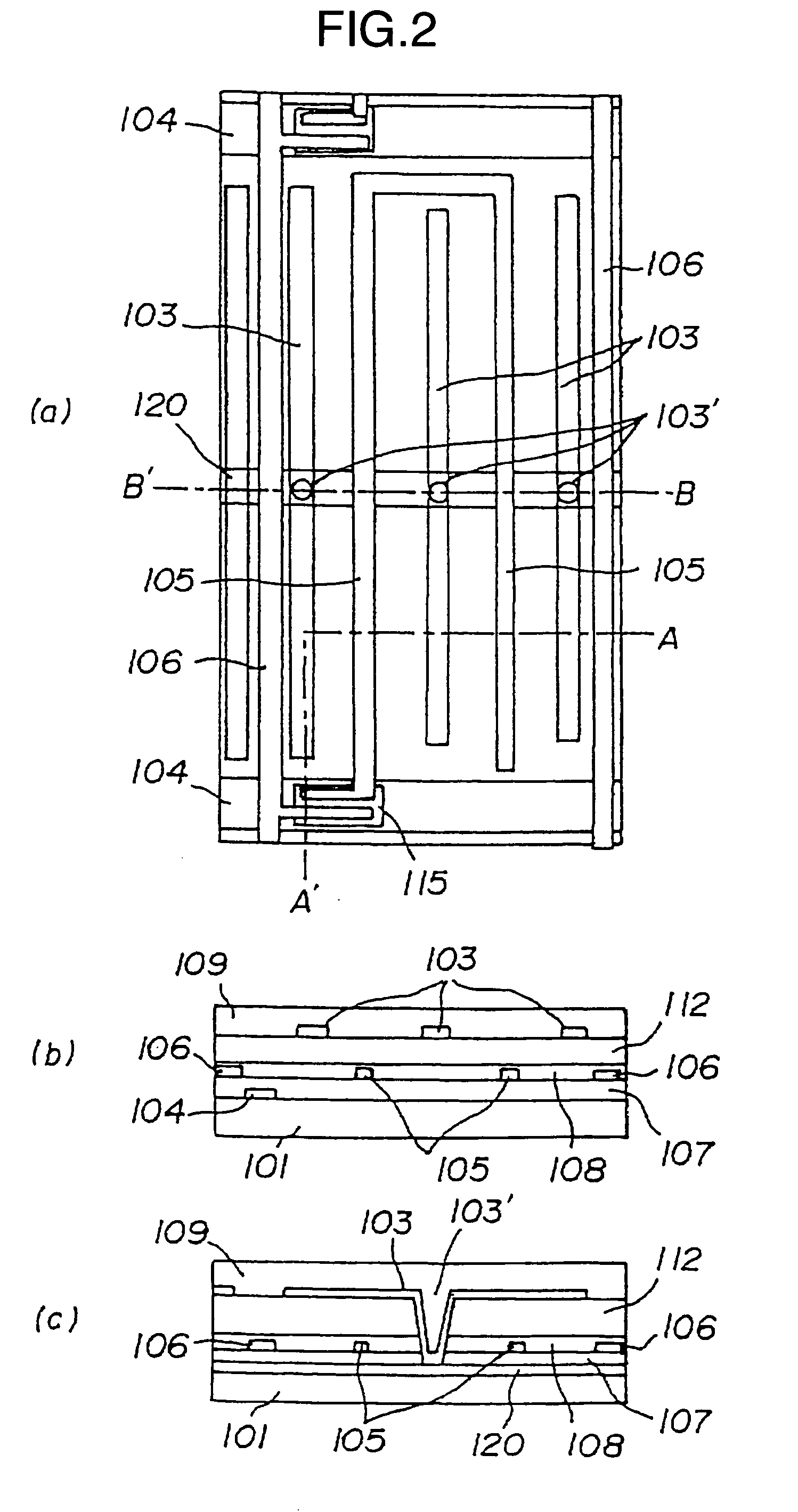
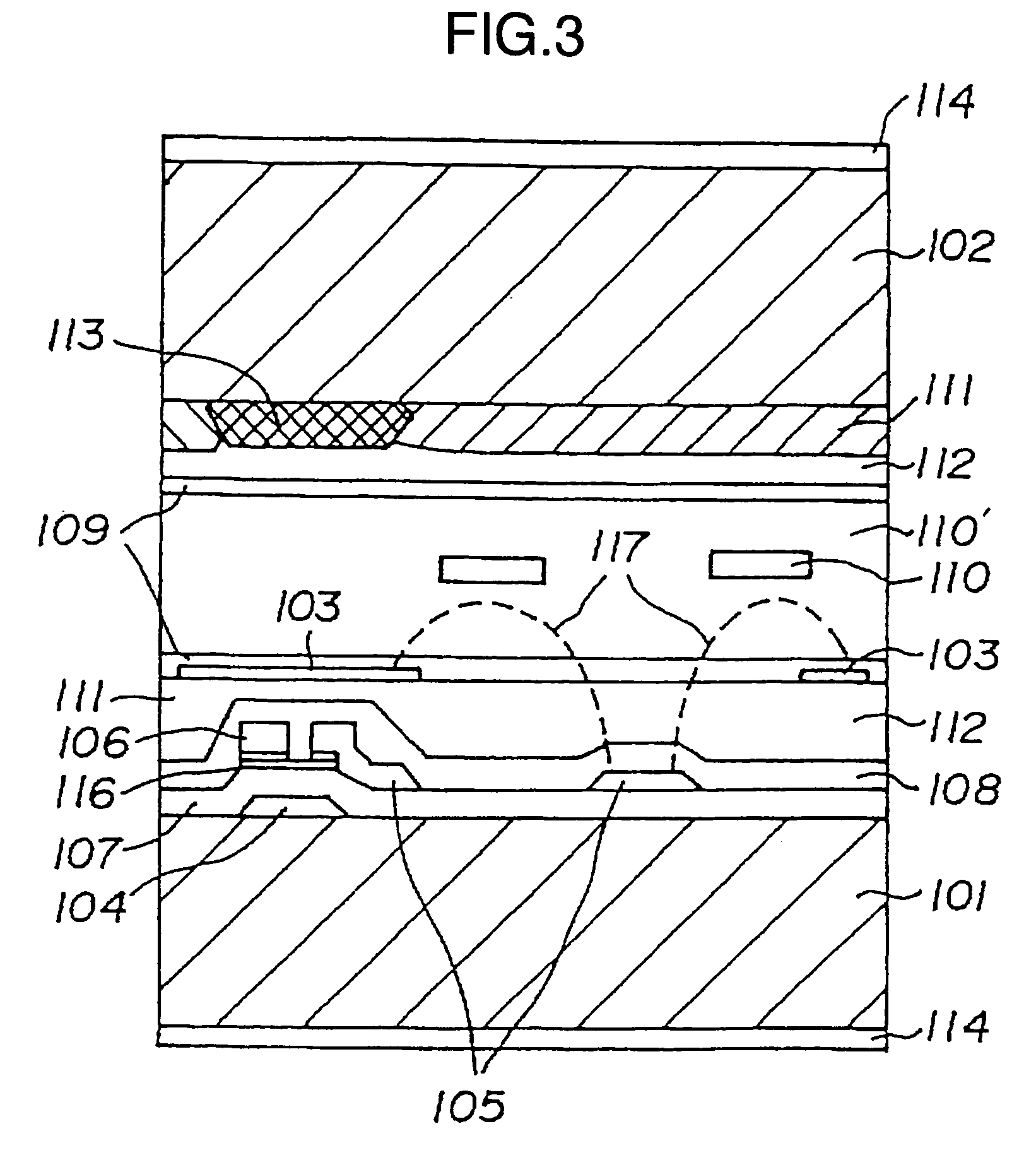
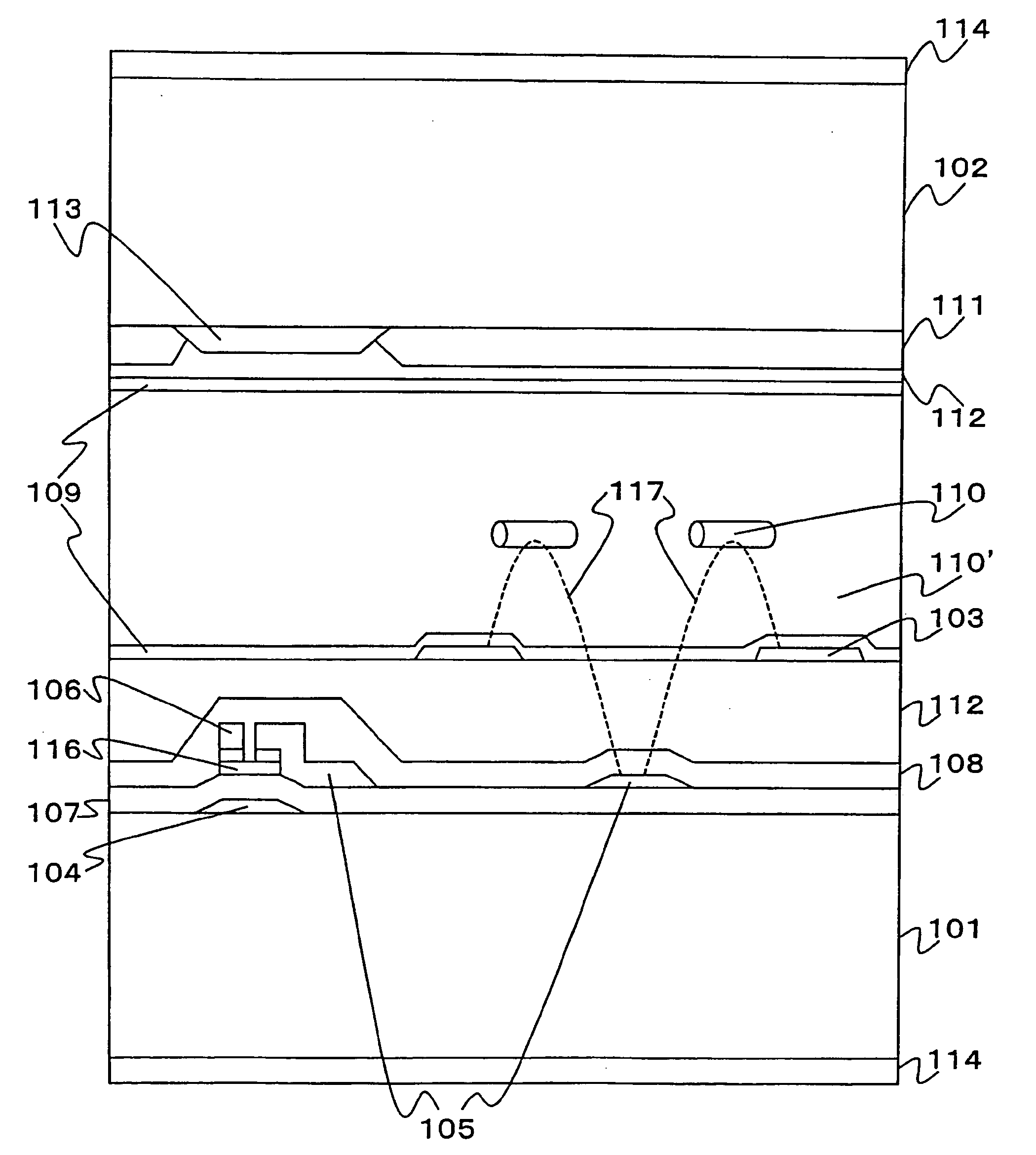
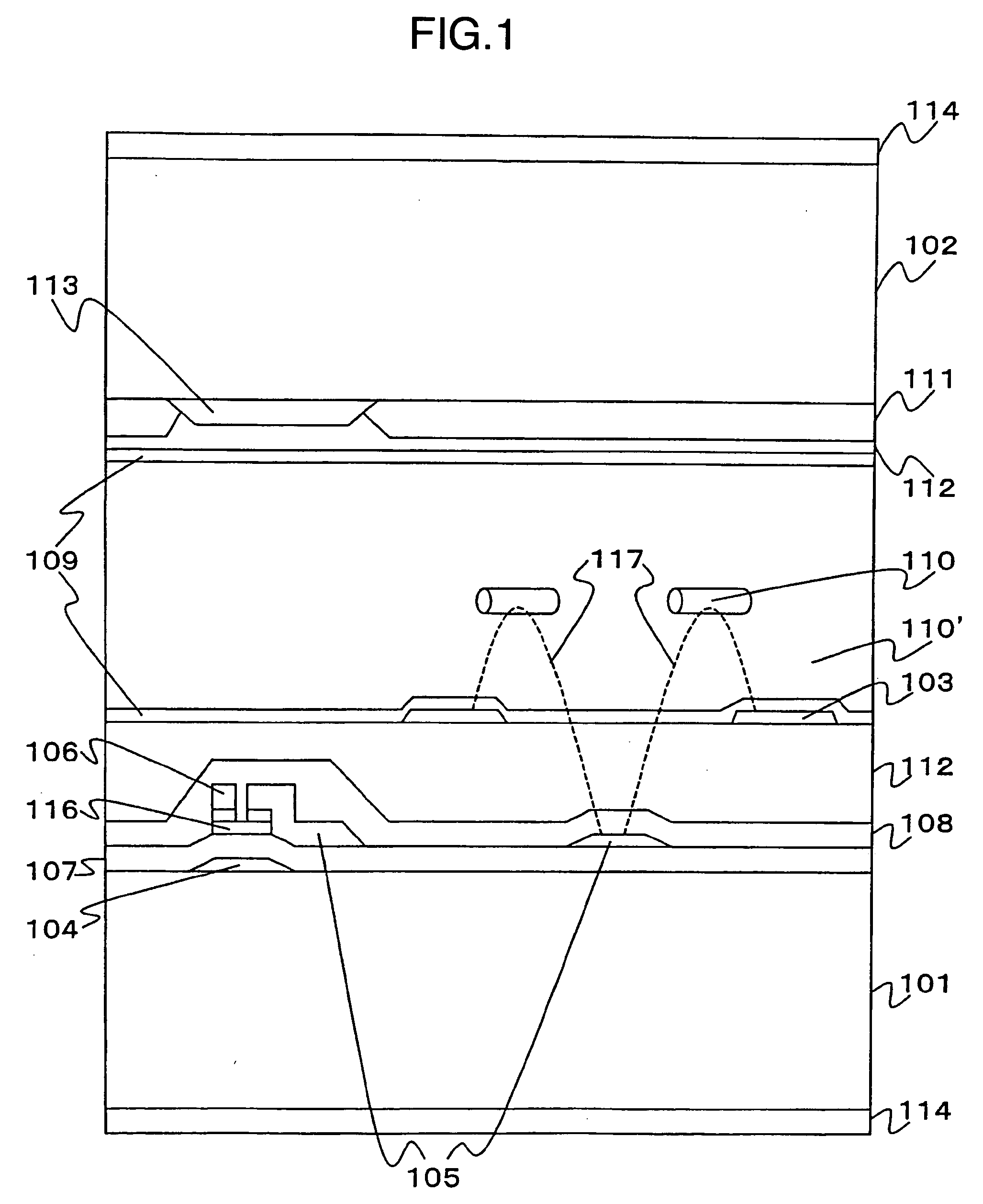
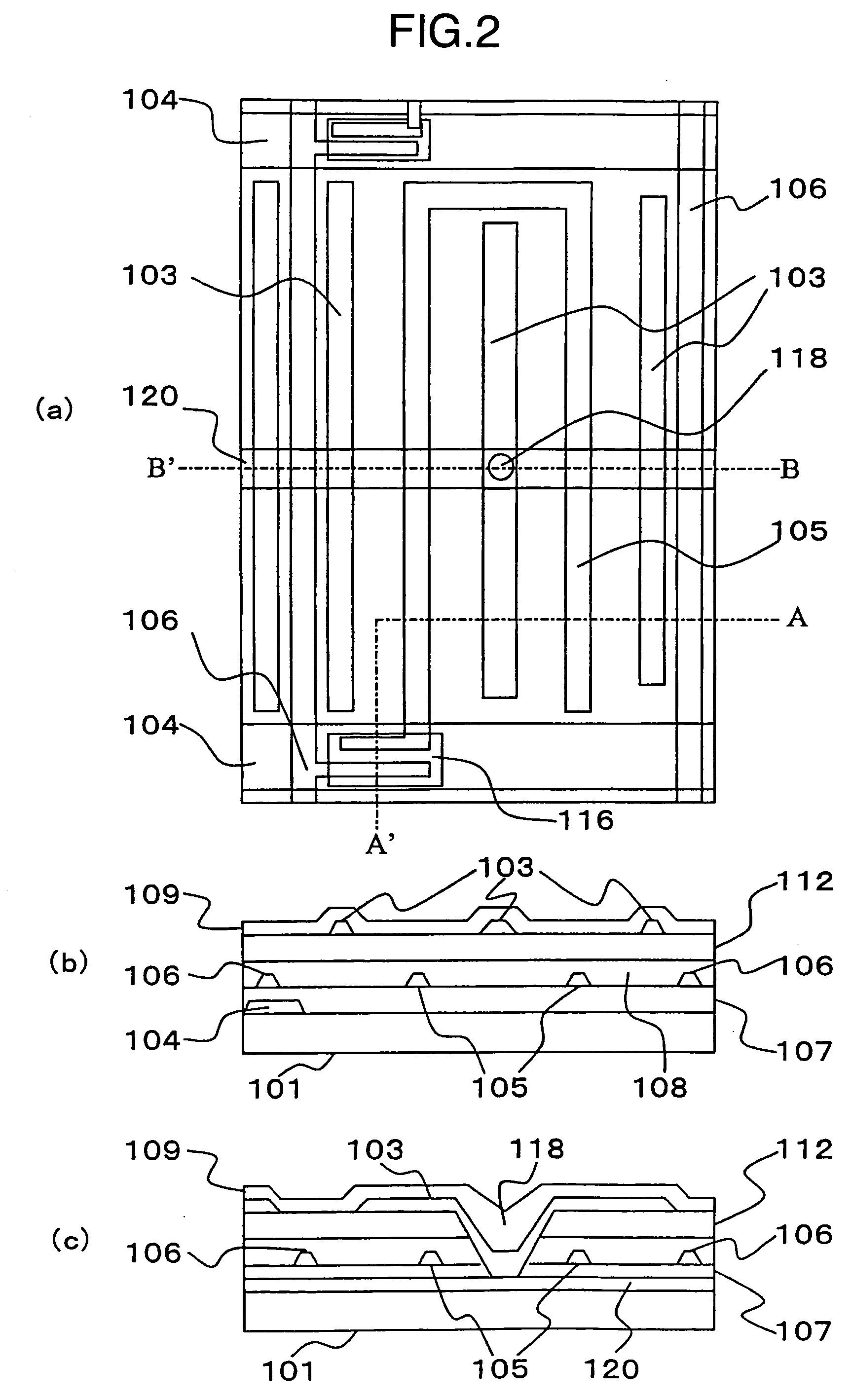
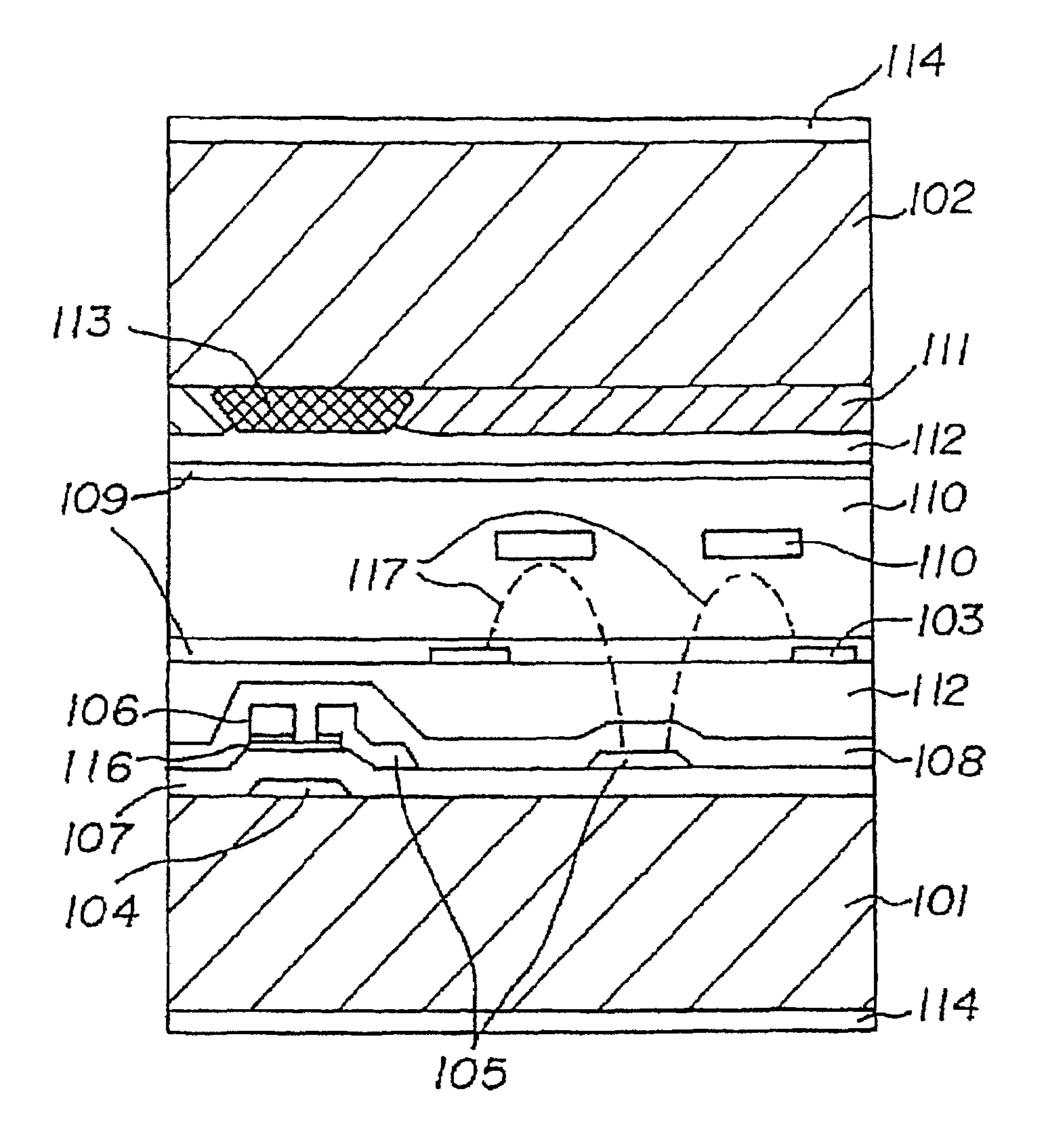
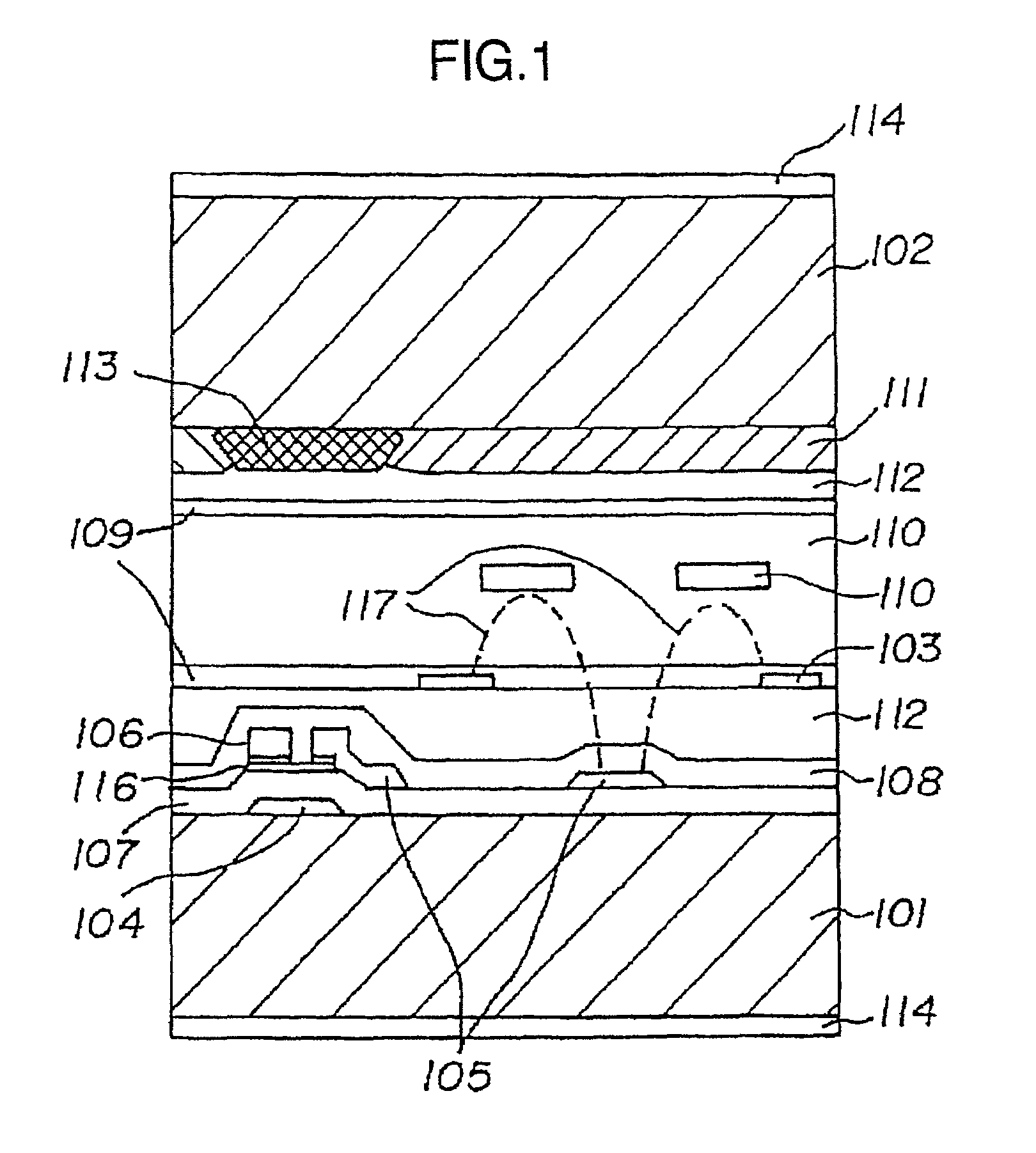
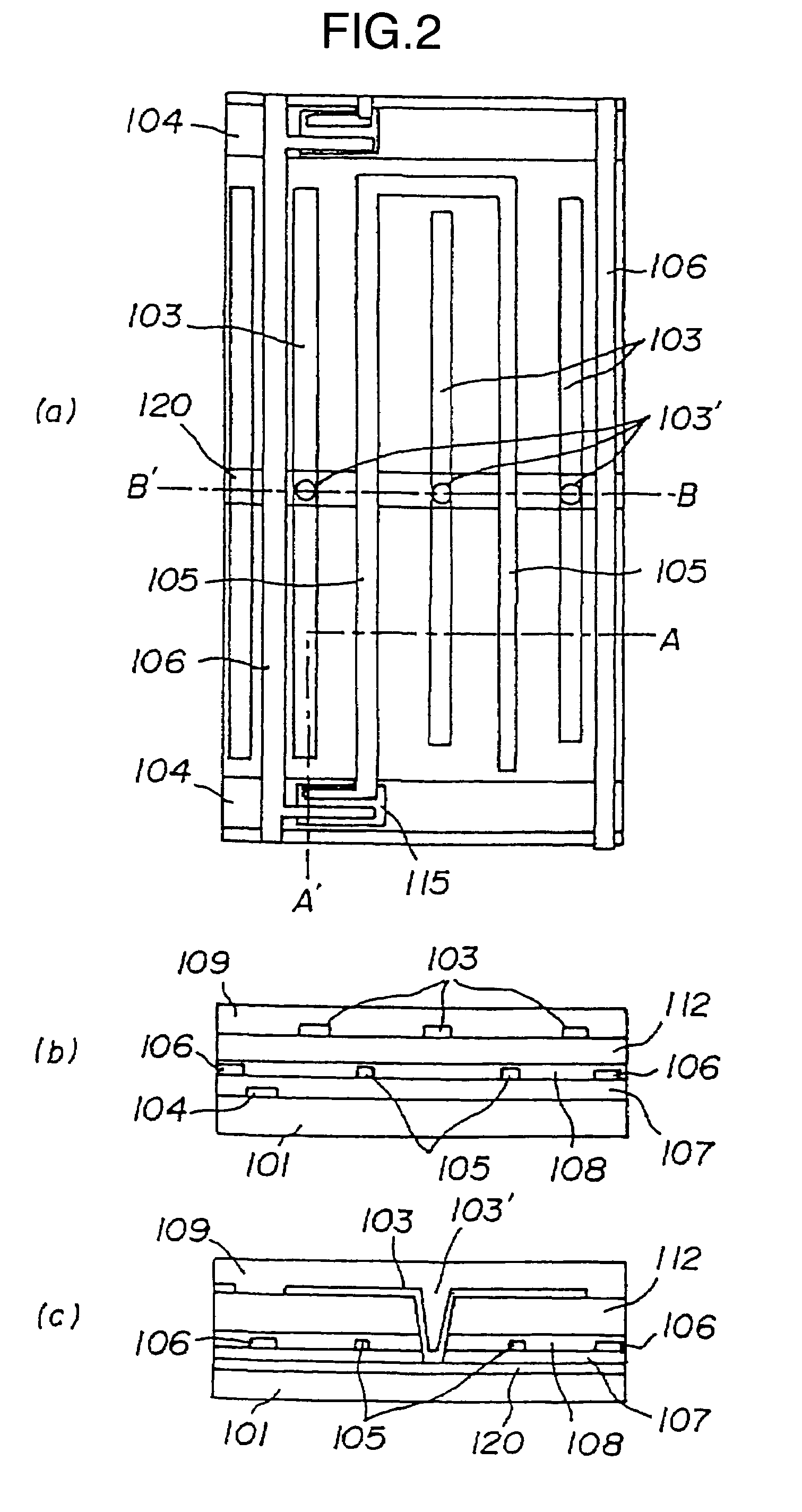
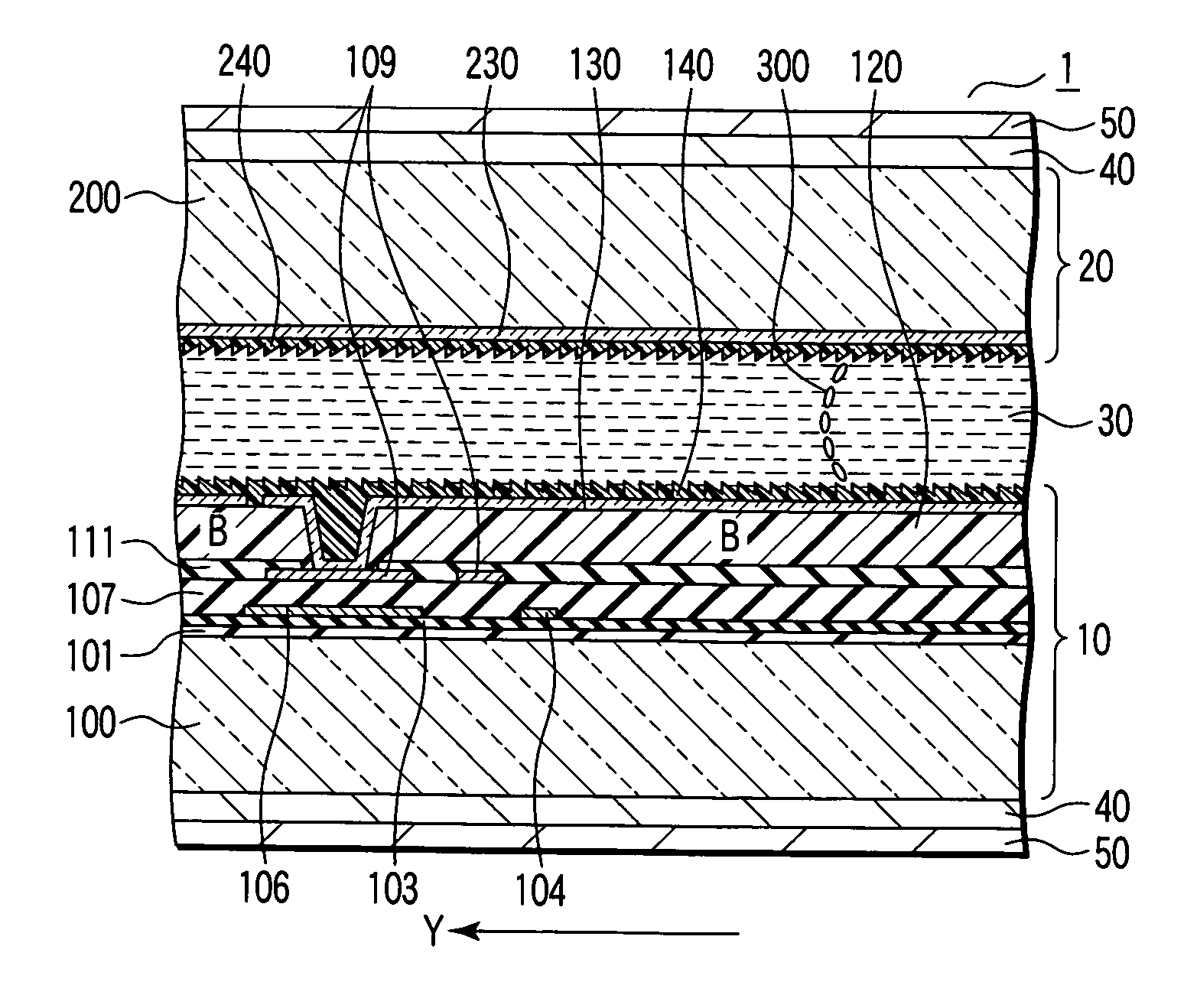
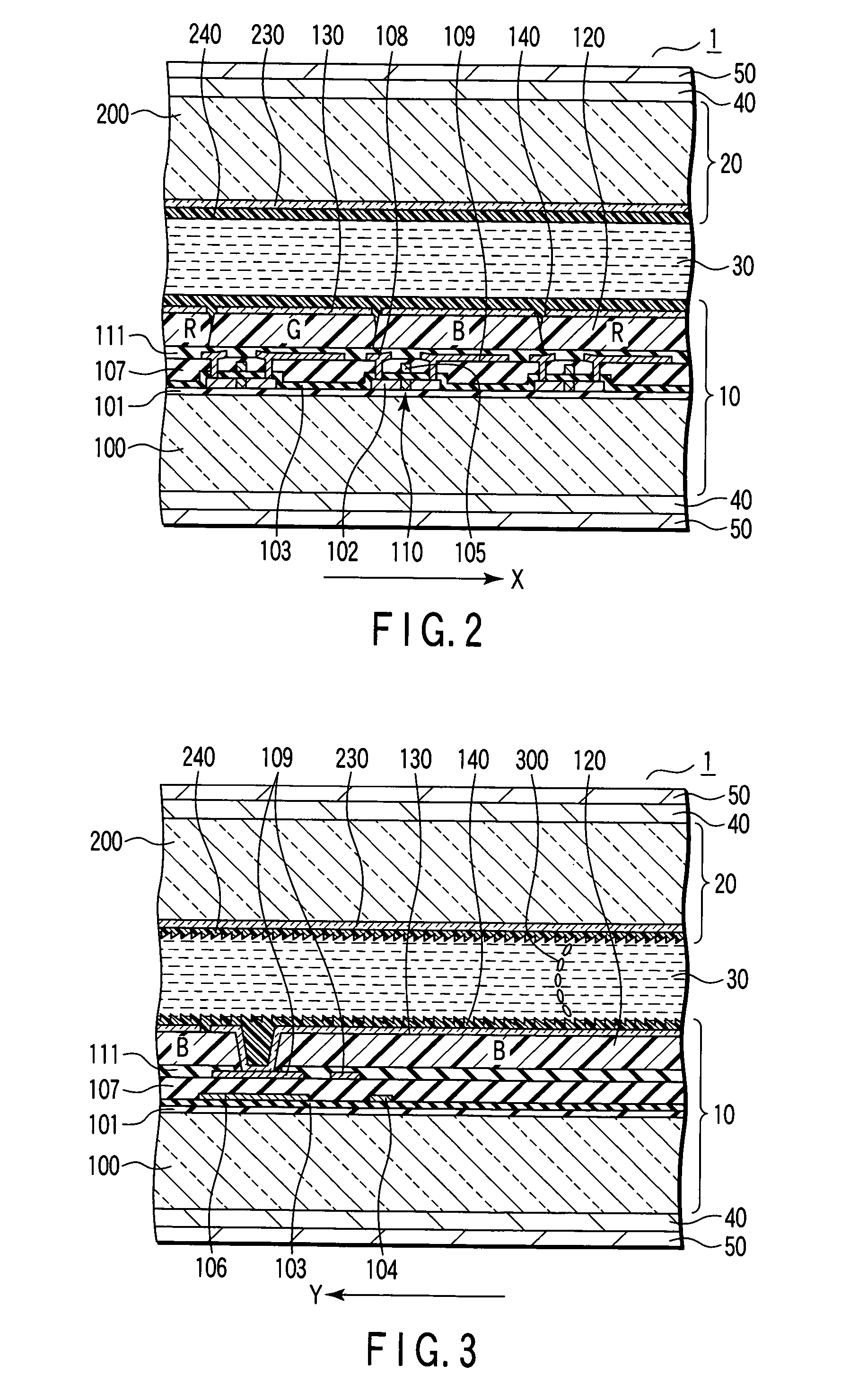
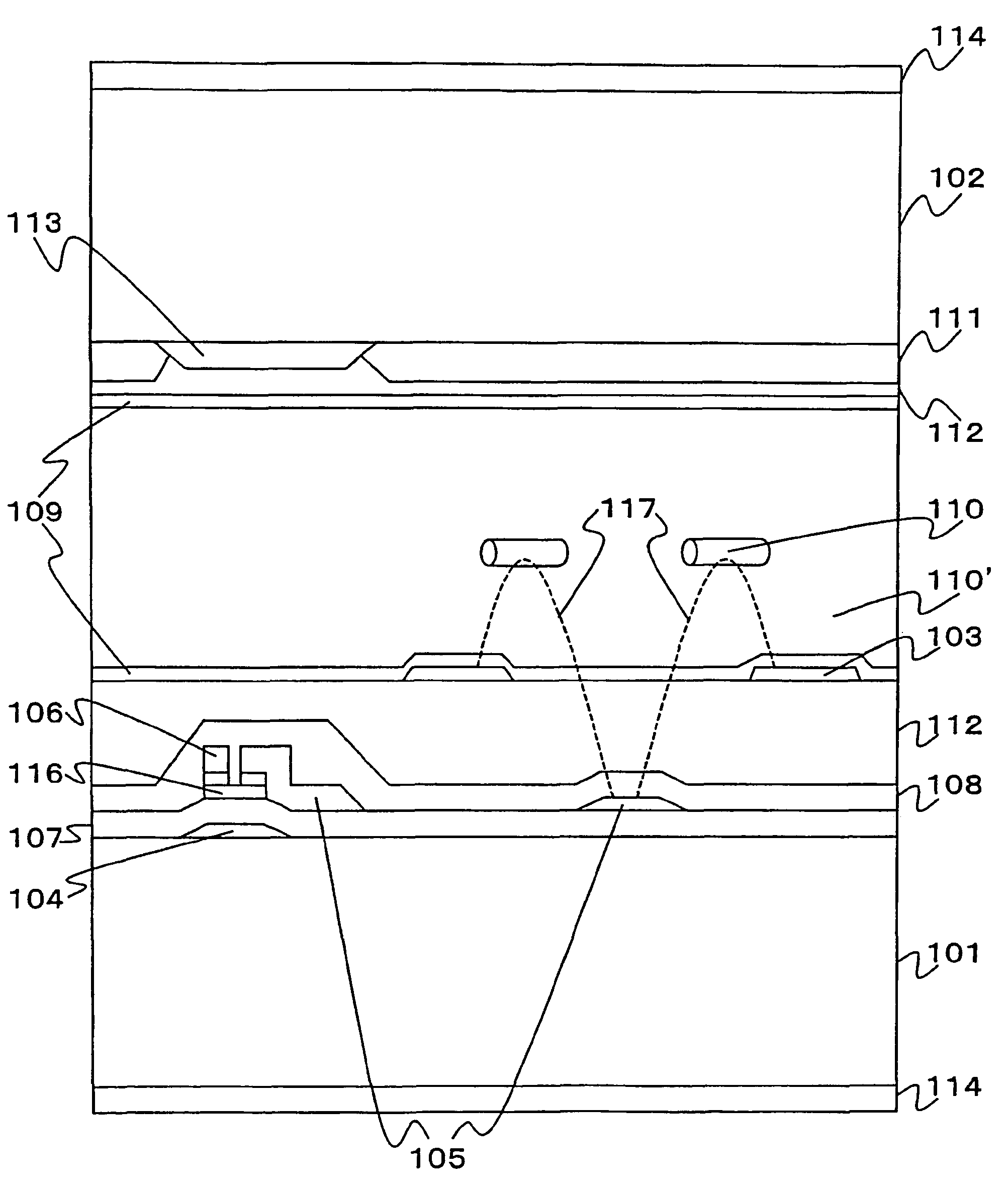
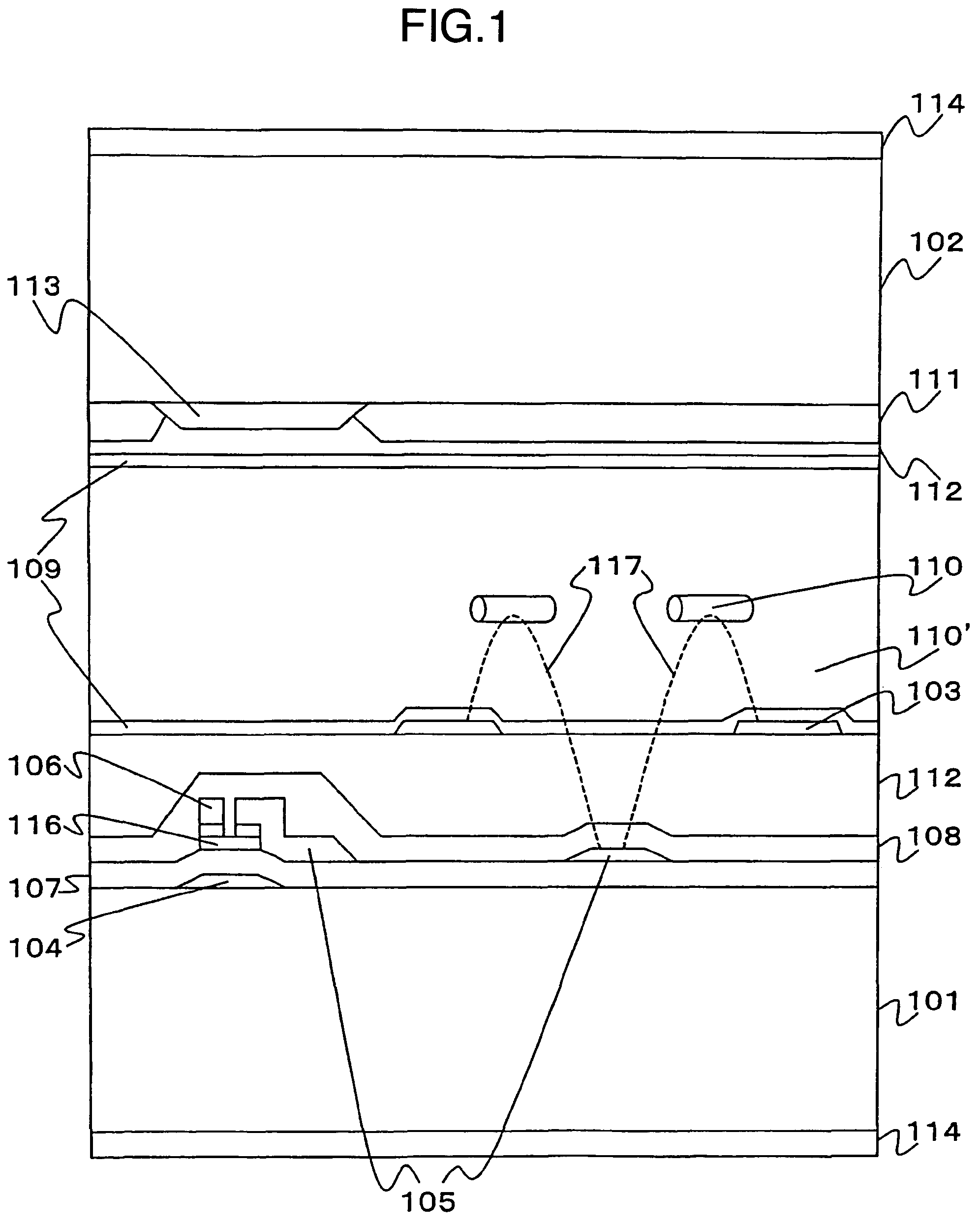
It is an object to provide a liquid crystal display which reduces unsatisfactory display caused by distorted initial alignment direction in a liquid crystal alignment layer for IPS type displays, realizes stable liquid crystal alignment, is high in mass-productivity, and produces high-quality images of increased contrast ratio. The liquid crystal display contains alignment layers 109 placed between a pair of substrates 101 and 102, at least one of which is transparent, liquid crystal layer 110′ sealed between the alignment layers, common electrode 103 and source electrode 105 for applying an electrical field to the liquid crystal layer, thin-film transistors connected to each of these electrodes, polarizer plate 114 provided on at least one of the substrates, wherein at least one of the alignment layers 109 is composed of a photo-reactive polyimide and / or polyamic acid which can be provided with a liquid crystal alignment capacity by being irradiated with essentially linearly polarized light.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20050200784A1Effective aperture ratioImprove contrast ratioPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsEngineeringVoltage
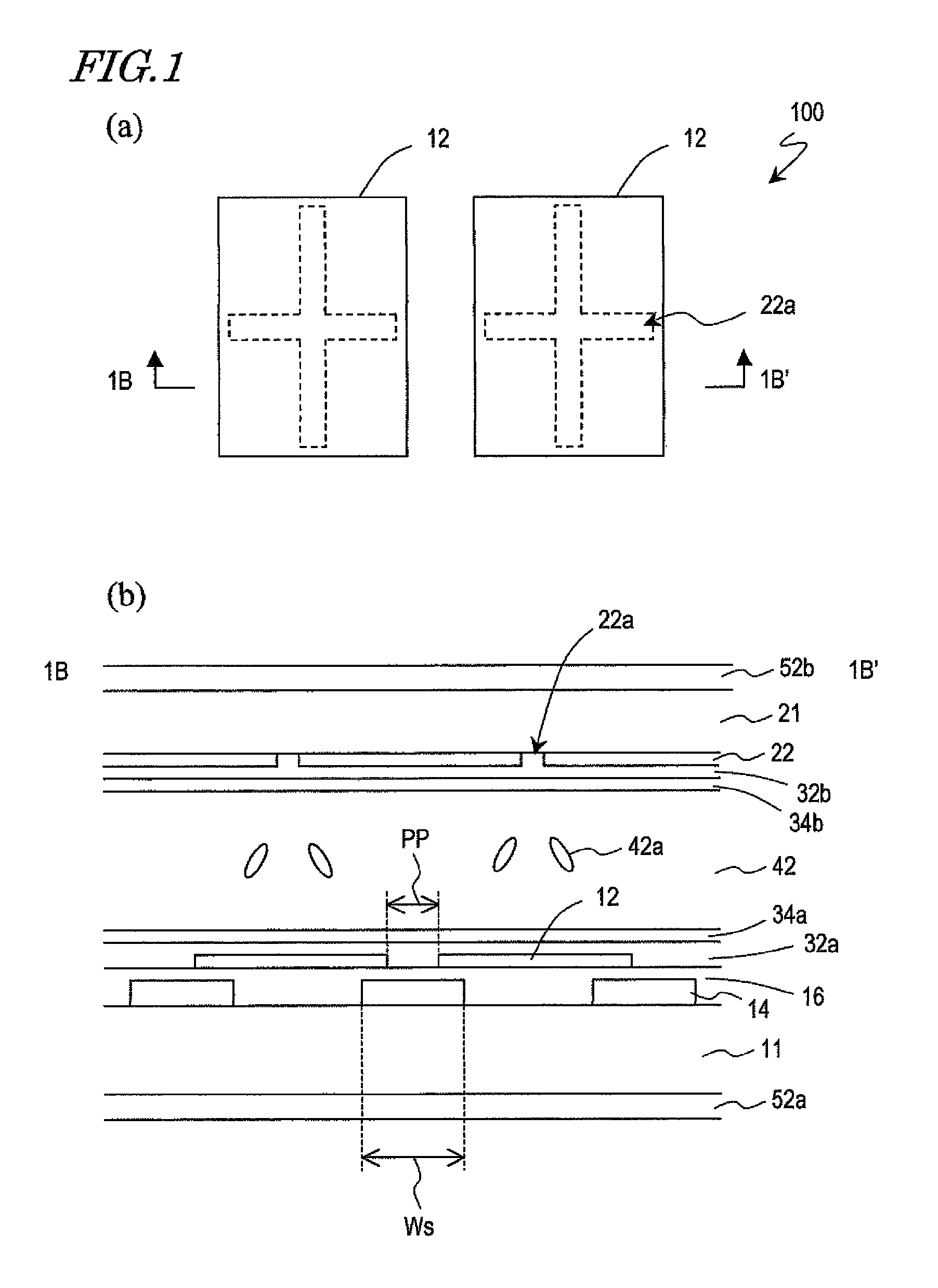
The liquid crystal display device of the present invention includes a first substrate, a second substrate and a vertically aligned liquid crystal layer interposed between the first and second substrate. The device has a plurality of pixels each including a first electrode formed on the first substrate, a second electrode formed on the second substrate, and the liquid crystal layer interposed between the first and second electrode, and a shading region provided around the pixels. A plurality of supports for defining the thickness of the liquid crystal layer are placed regularly on the surface of the first or second substrate facing the liquid crystal layer in the shading region. The liquid crystal layer forms at least one liquid crystal domain exhibiting axisymmetric alignment when at least a predetermined voltage is applied, and the tilt direction of liquid crystal molecules in the at least one liquid crystal domain is defined with inclined sides of the plurality of supports.
Owner:SHARP KK
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20110001691A1High light transmittanceAlignment of liquid crystal is stableStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsVertical alignmentEngineering
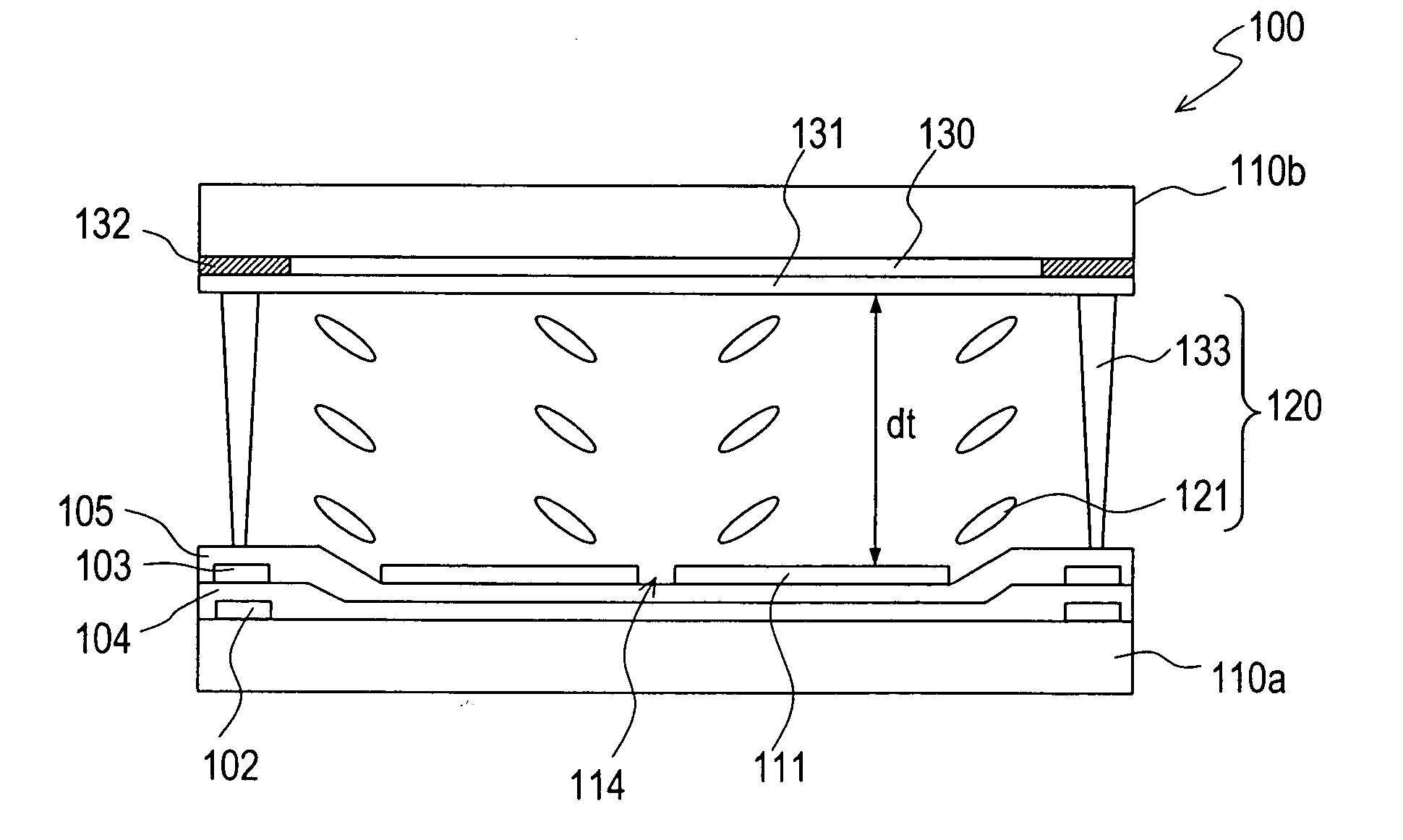
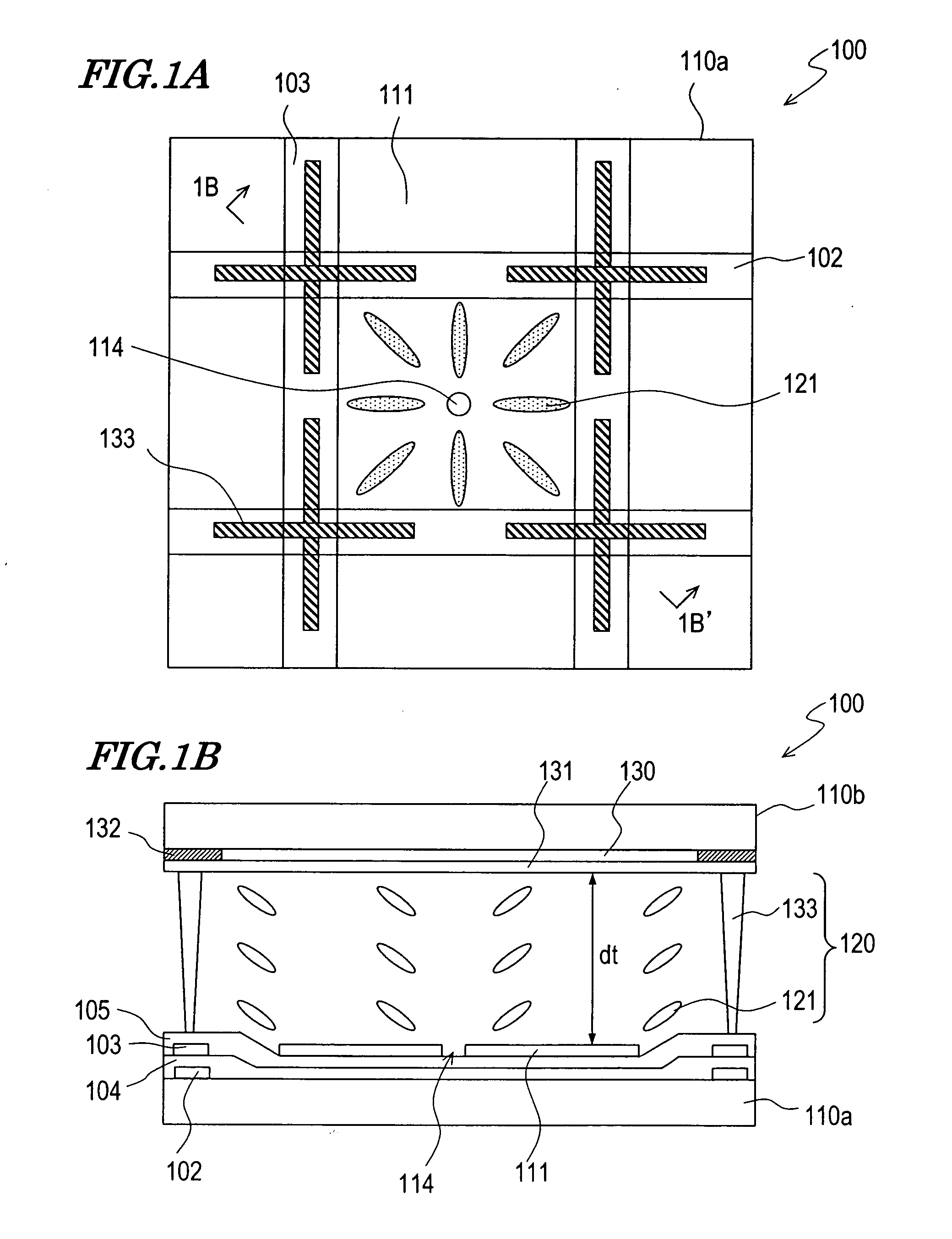
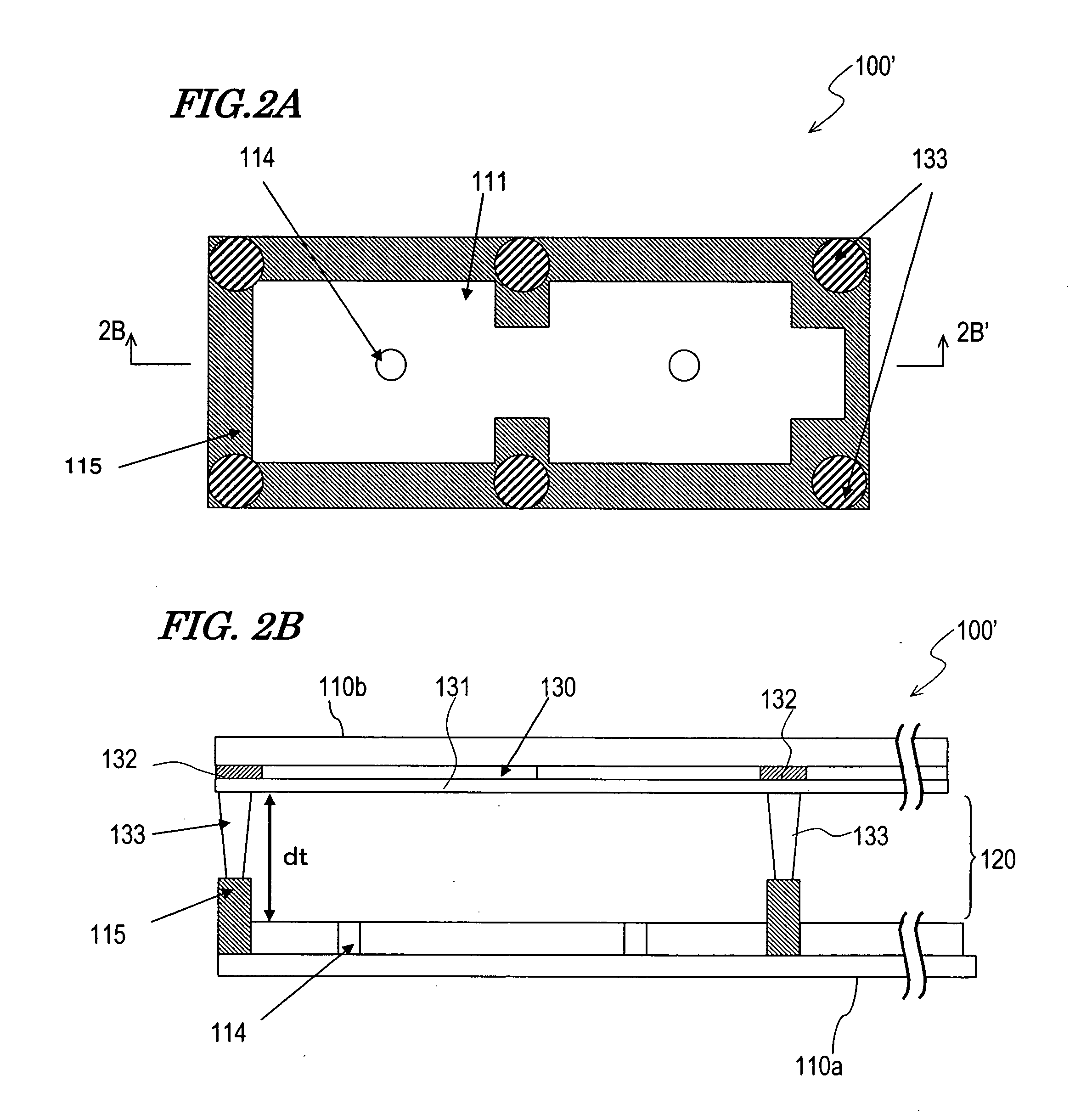
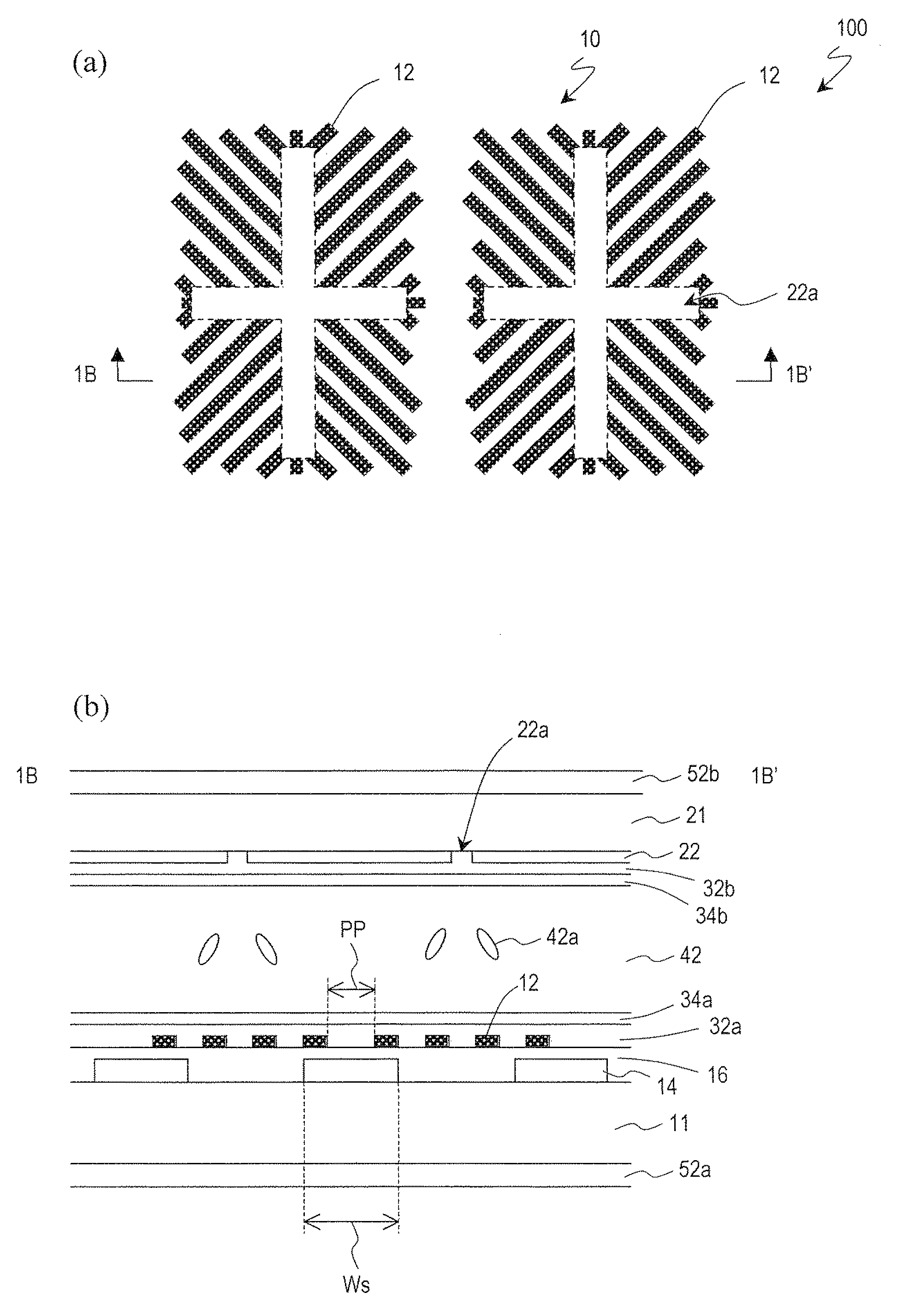
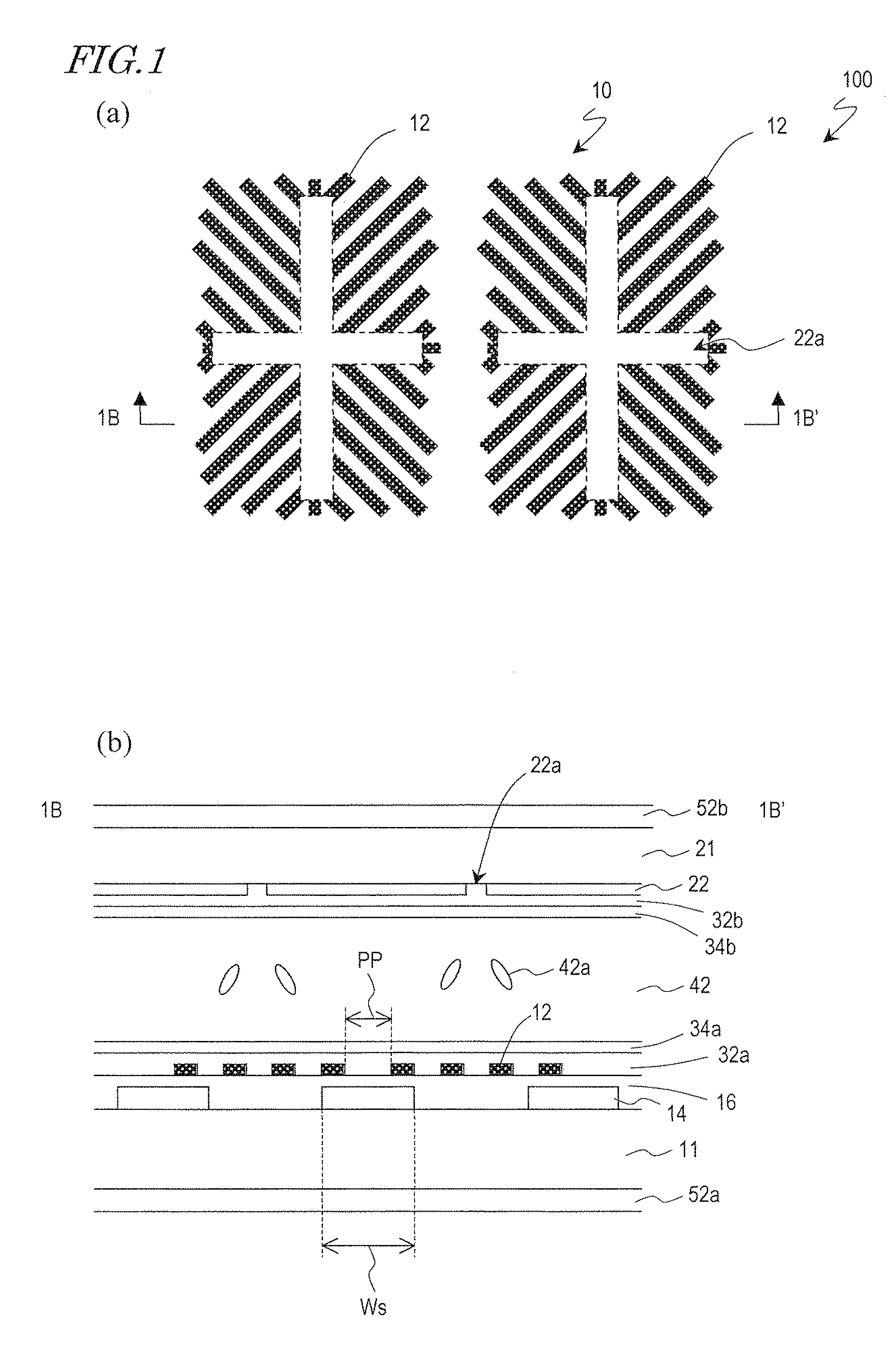
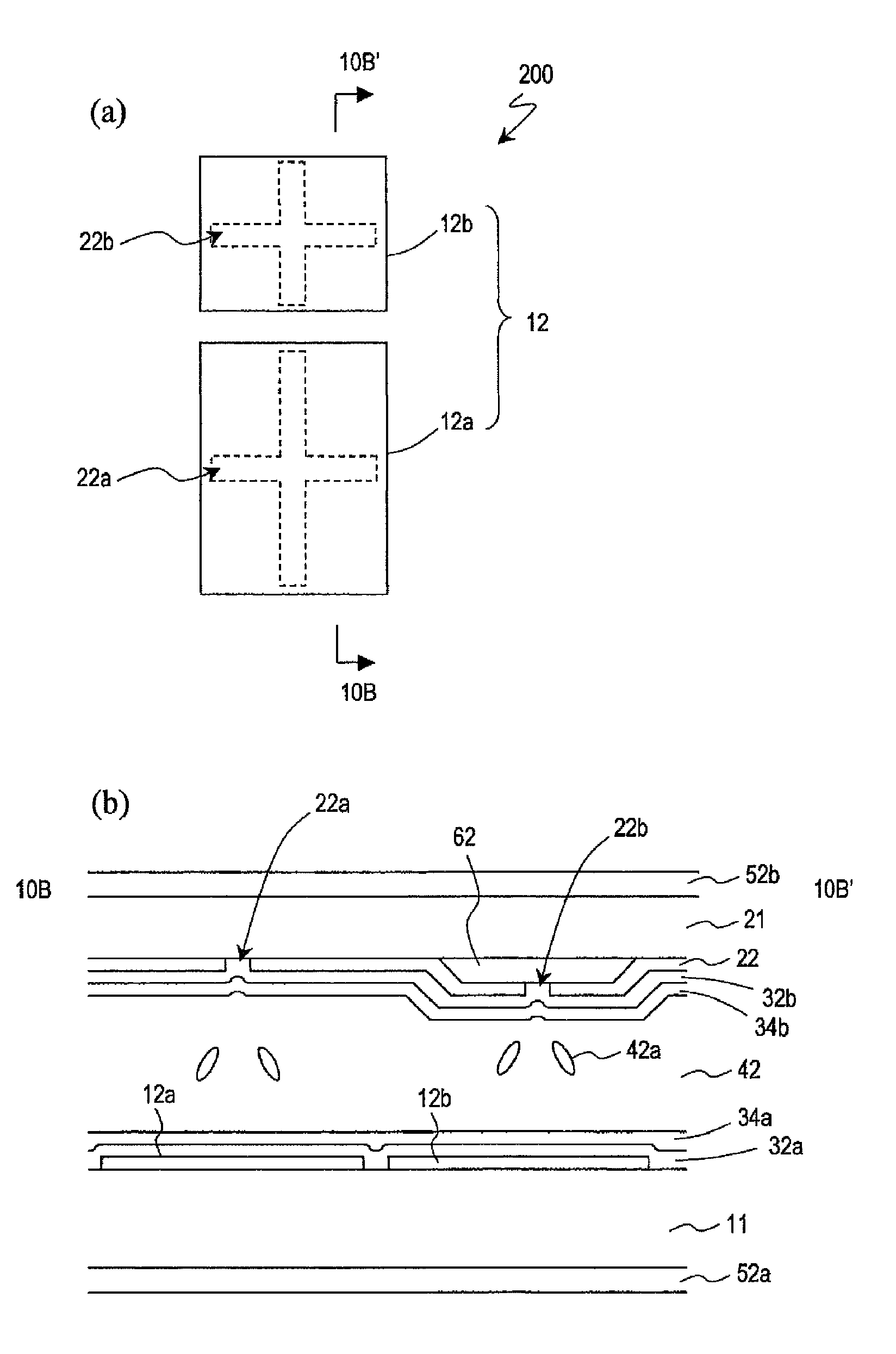
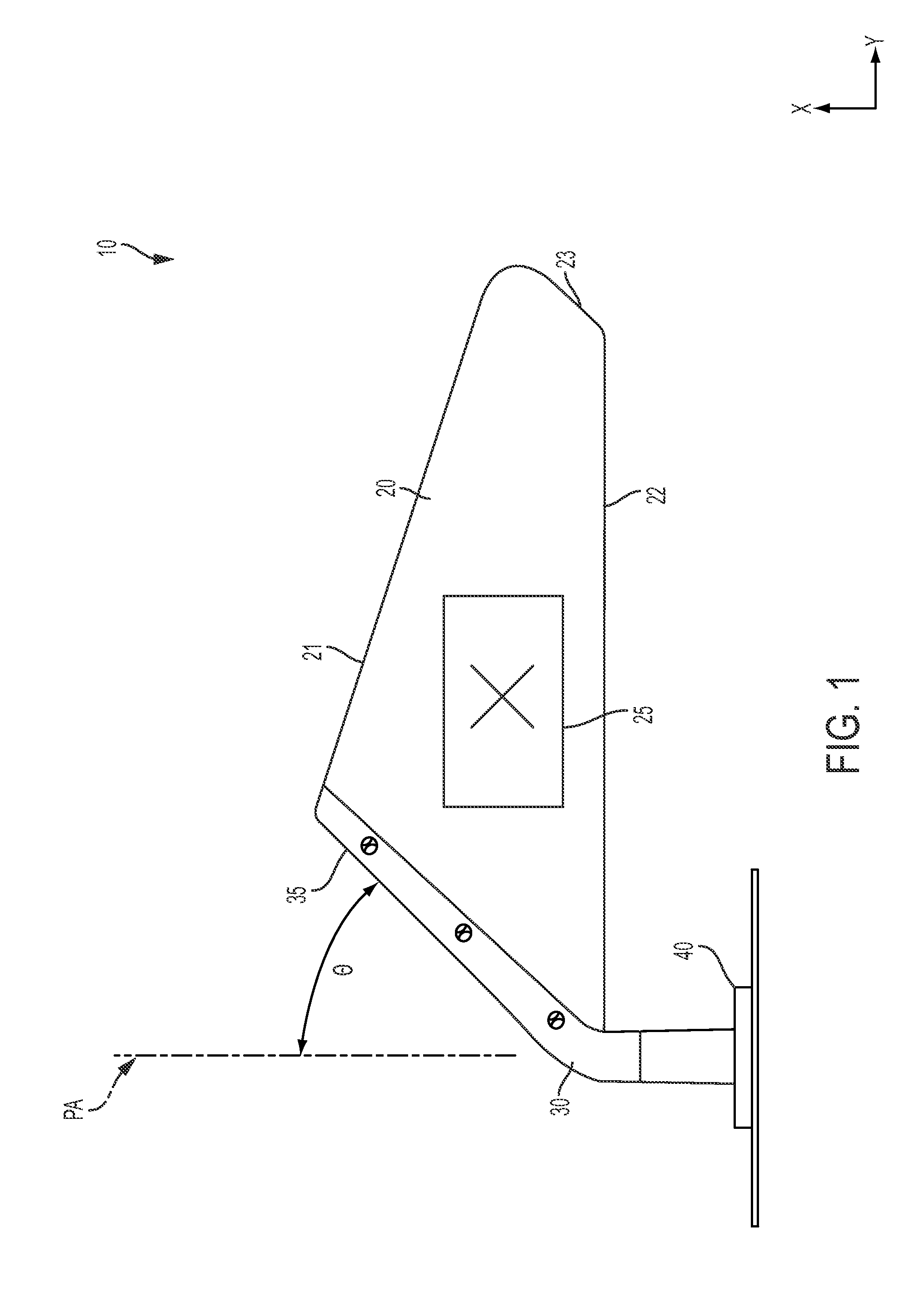
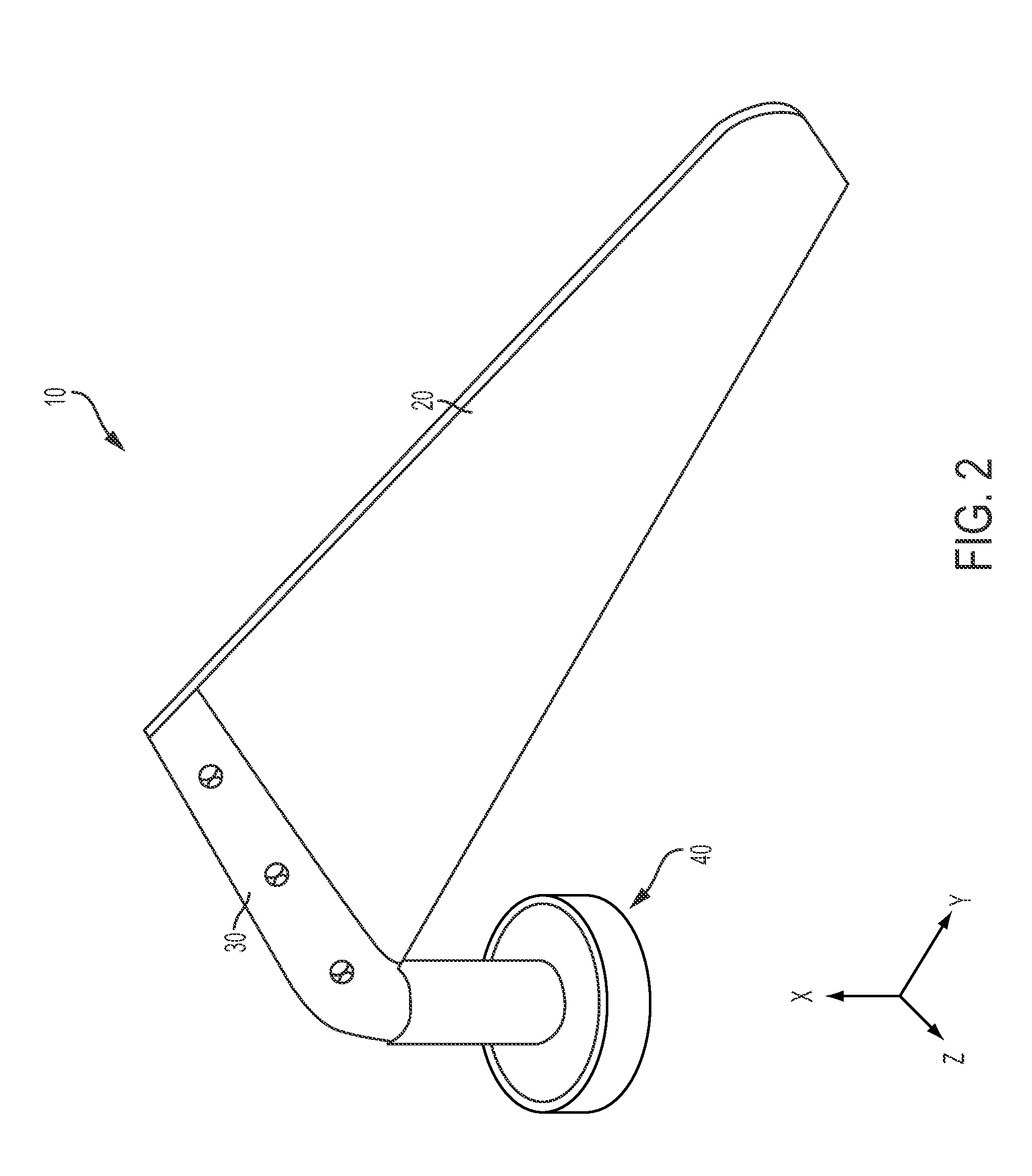
A pixel of a liquid crystal display device of the present invention includes a liquid crystal layer 42, a pixel electrode 12 and a counter electrode 22 opposing each other via the liquid crystal layer, a pair of vertical alignment films 32a, 32b, and alignment sustaining layers 34a, 34b formed by a photopolymerized material on surfaces of the alignment films which are closer to the liquid crystal layer. The pixel electrode has cruciform trunk portions 12h, 12v which are positioned so as to coincide with polarization axes of the pair of polarizing plates and a plurality of branch portions 12a, 12b, 12c, and 12d extending from the cruciform trunk portions in directions of approximately 45°. The counter electrode has a cruciform opening 22a which is positioned so as to oppose the cruciform trunk portions. When a predetermined voltage is applied across the liquid crystal layer, four liquid crystal domains are formed. The pretilt azimuth of a liquid crystal molecule included in a region corresponding to each of the four liquid crystal domains is regulated by the alignment sustaining layers.
Owner:SHARP KK
Driving device
InactiveUS20060119218A1Reduce the effect of gravityDisplacement stabilityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMountingsPull forceEngineering
A driving device, small in size and light in weight, is to stabilize the position of a surface-deforming element while reducing the effect of gravity thus enabling stable transfer and positioning. The driving device is structured to hold a movable member integrated with a piezoelectric vibrator and a lens by a shaft provided at a tip of a spring extended from an inner surface to center of a passageway. The shaft extends through an opening formed in a protrusion of the movable member. By a tensile force of the spring, the movable member at its outer periphery is pulled radially and held. When applying a voltage with a waveform changing sharply to the piezoelectric vibrator, the movable member flexes maximally upward or downward to have a reduced diameter and an increasing acceleration thereby making a movement. Then, when a frictional force increases, the protrusion is held at a point where the movable member moves. Because of being held by a tensile force, the effect of gravity decreases and hence the movable member is stabilized in position relative to a direction of transfer.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS7391489B2Effective aperture ratioSuppress contrast dropPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsEngineeringVoltage
Owner:SHARP KK
Liquid crystal display and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS7718234B2Reduce generationImprove batch productivityLiquid crystal compositionsStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayImaging quality
A liquid crystal display is provided which is capable of reducing the occurrence of defective display due to variations in the initial alignment direction of a liquid crystal alignment control film in a liquid crystal display of an IPS scheme, realizing the stable liquid crystal alignment, providing excellent mass productivity, and having high image quality with a higher contrast ratio. The liquid crystal display has a liquid crystal layer disposed between a pair of substrates, at least one of the substrates being transparent, and an alignment control film formed between the liquid crystal layer and the substrate. At least one of the alignment control films comprises photoreactive polyimide and / or polyamic acid provided with an alignment control ability by irradiation of substantially linearly polarized light.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Liquid crystal display device with alignment layer including a diamine component and treated by UV irradiation
InactiveUS7081935B2Prevent disturbance of alignmentPromote stable alignmentLiquid crystal compositionsPhotomechanical apparatusChemistryLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal display device includes a pair of substrates, a liquid crystal between substrates and alignment layers disposed on the inner surface sides of the substrates. The alignment layer is made from a material including polyamic acid containing a diamine component and polyimide containing a diamine component different from the diamine component of the polyamic acid. The alignment layer is subjected to alignment treatment by irradiation of light. UV light can be irradiated in the oblique direction onto the alignment layer through a mask having openings. A reflecting plate can be arranged between a UV light source and the mask. Also, bank structures having a thickness from 0.1 to 0.15 μm can be provided on the alignment layer of the TFT substrate.
Owner:SHARP KK
Frame for building a vehicular body with a load bearing support system
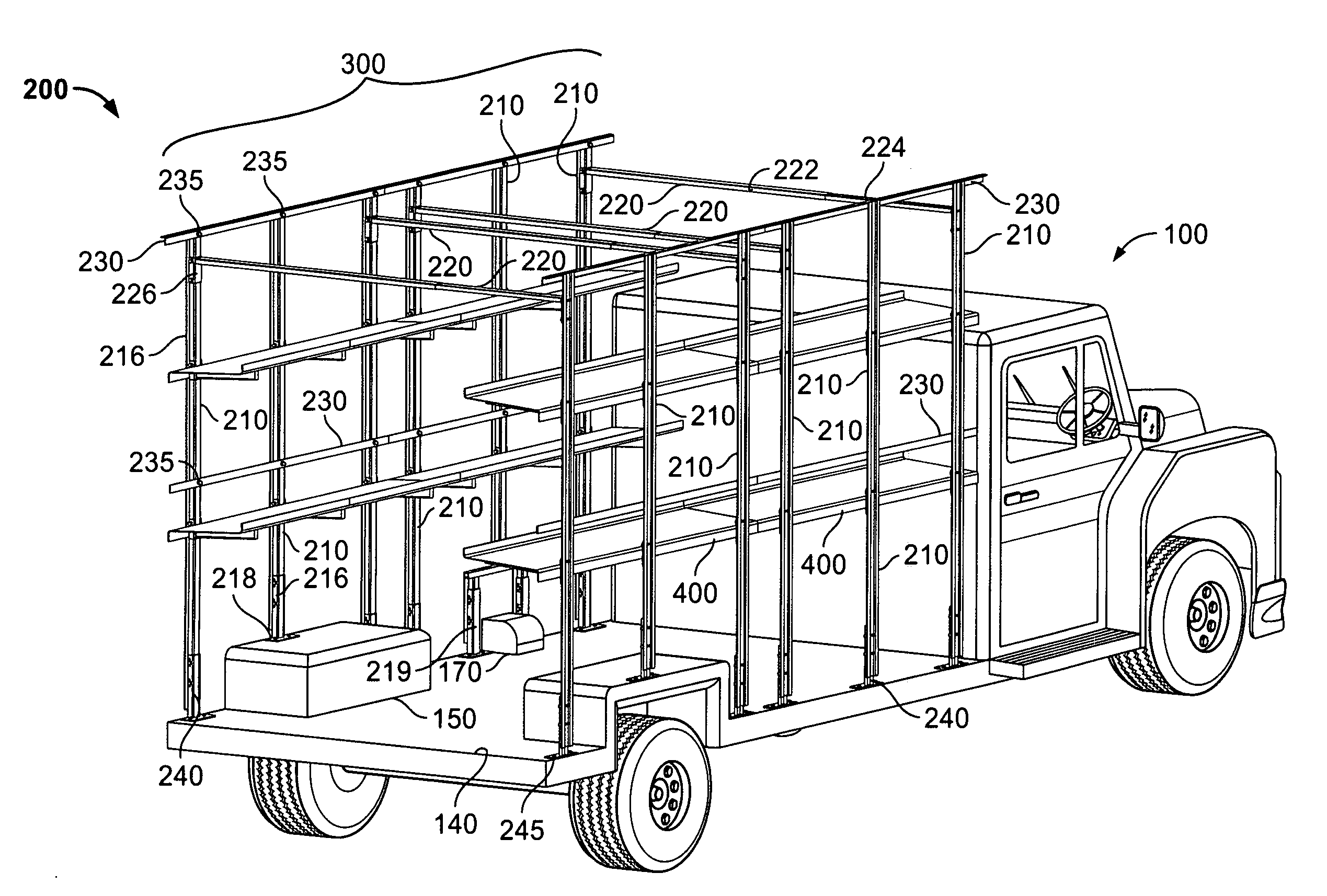
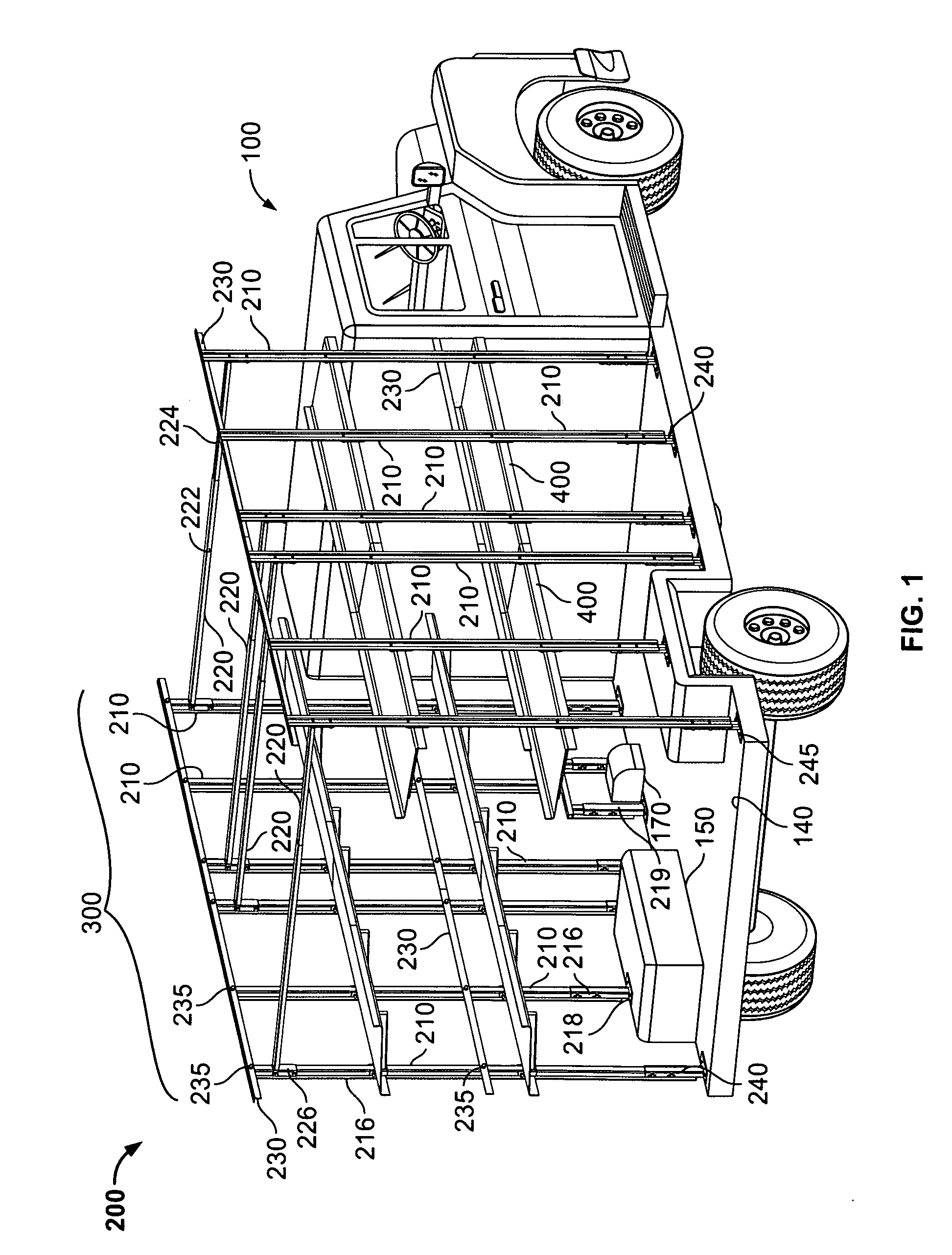
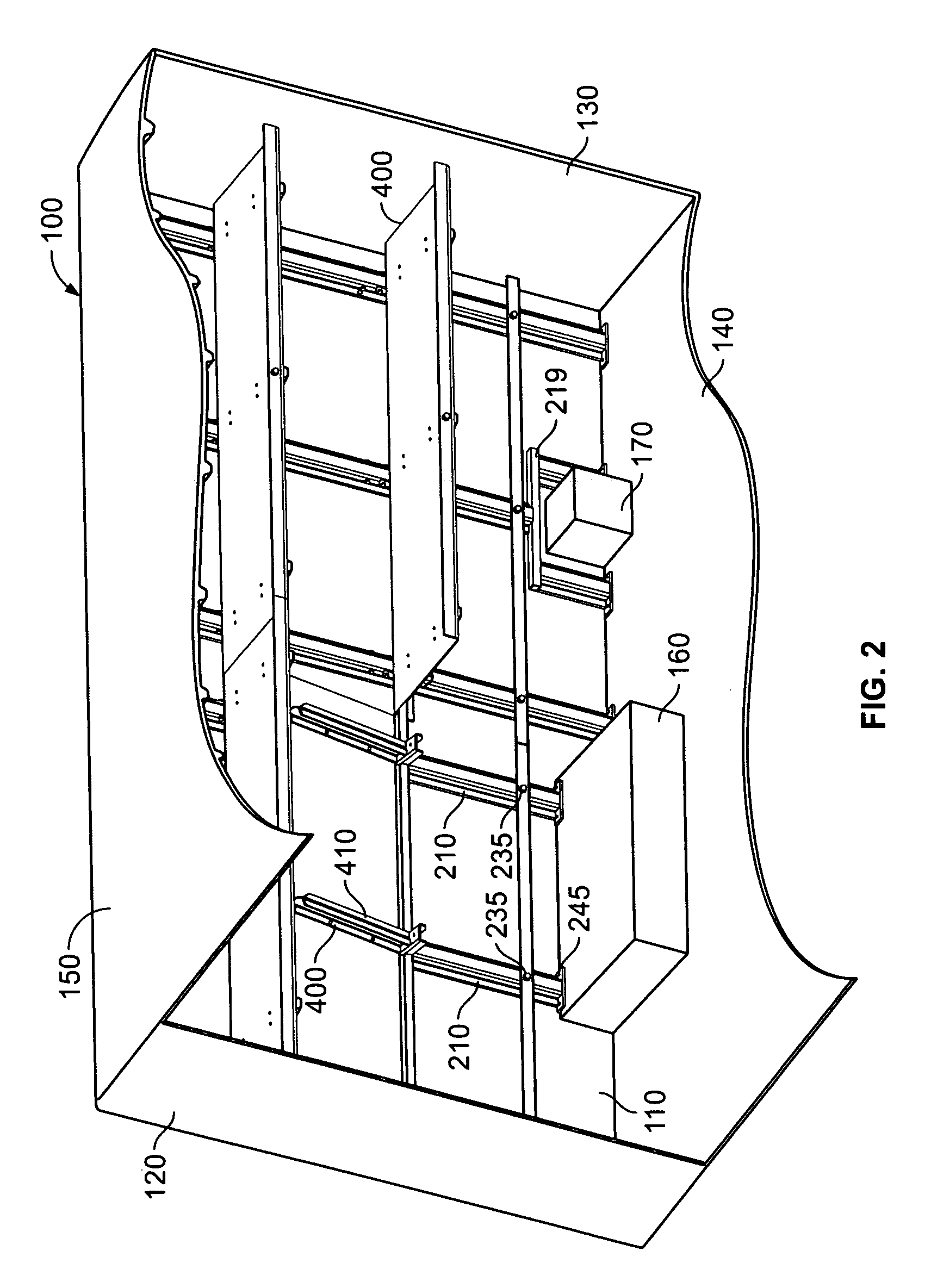
ActiveUS20060033360A1Reduces amount of time and laborStability and alignmentVehicle arrangementsLoading/unloading vehicle arrangmentEngineeringRefrigerated temperature
A skeleton or frame for building a vehicular body of a cargo vehicle with a load bearing support system for supporting one or more levels of accessories to provide one or more additional levels of load bearing surfaces. The frame comprises at least two side portions comprising a plurality of longitudinally spaced sidewall posts and at least one transverse member connecting the two side frames for mounting various panels (e.g., a roof, floor, wall, door, window, sunroof, refrigerator unit, air conditioner unit, etc.) and accessories (e.g., a shelf, drawer, bin, cabinet, platform, cot, sliding rack, bucket, bench and the like).
Owner:JDM VENTURES
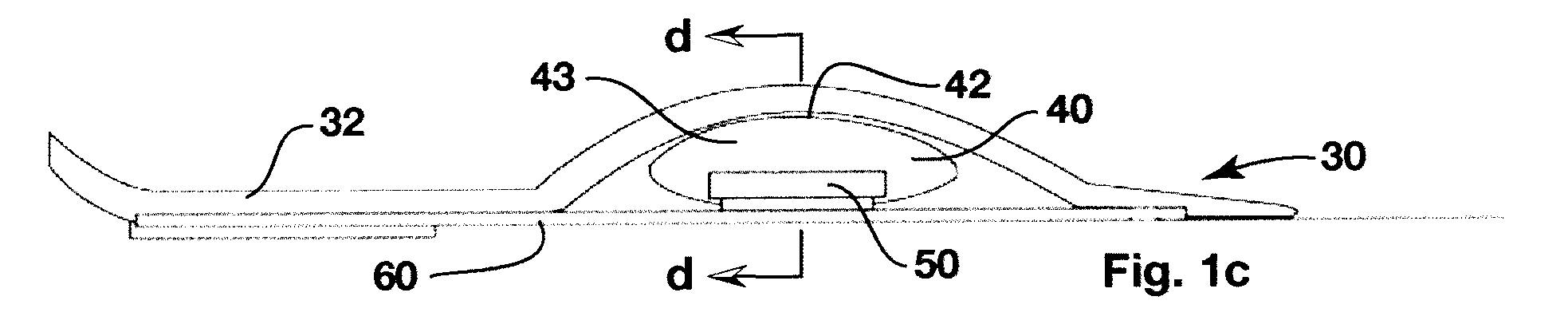
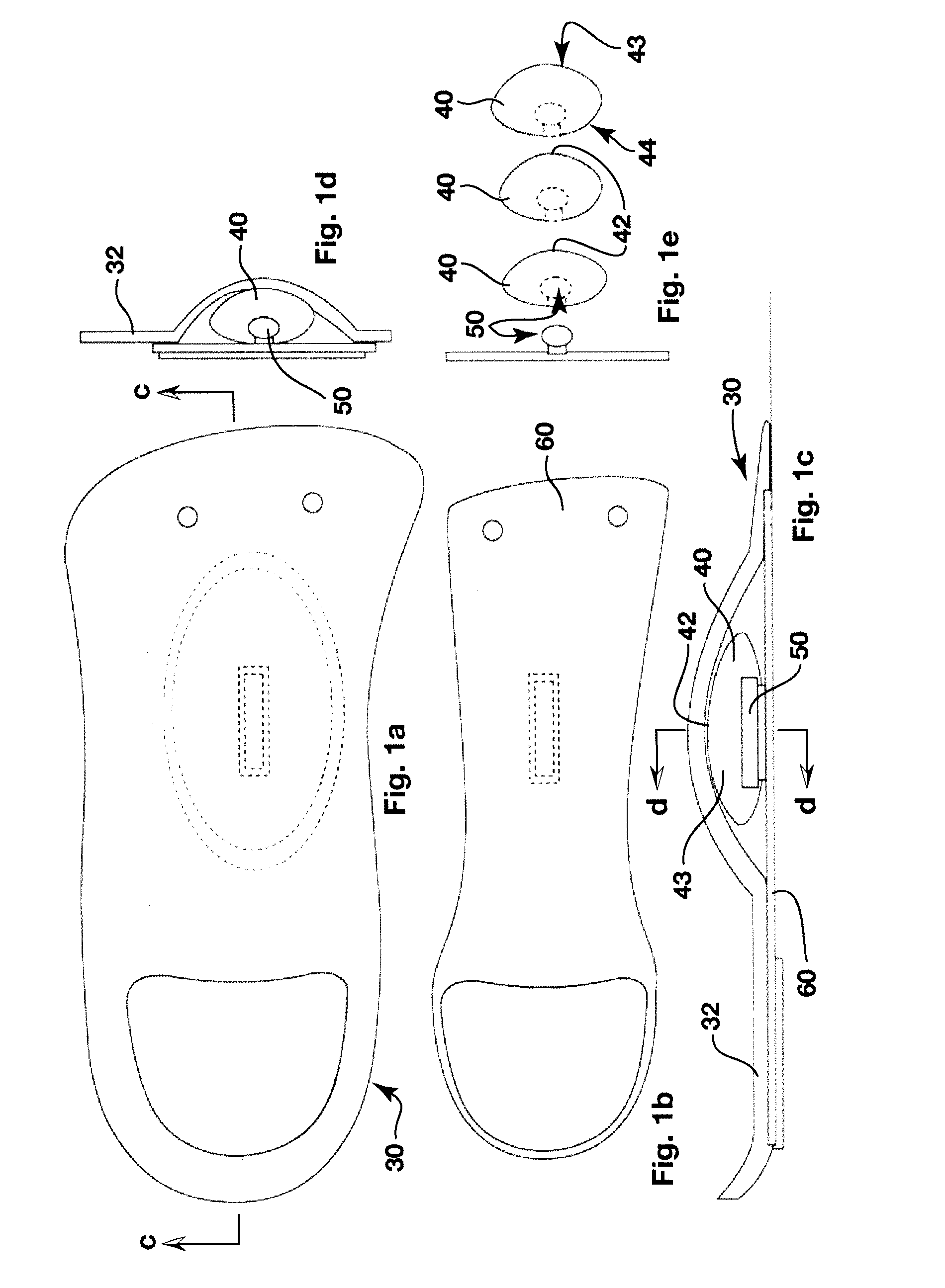
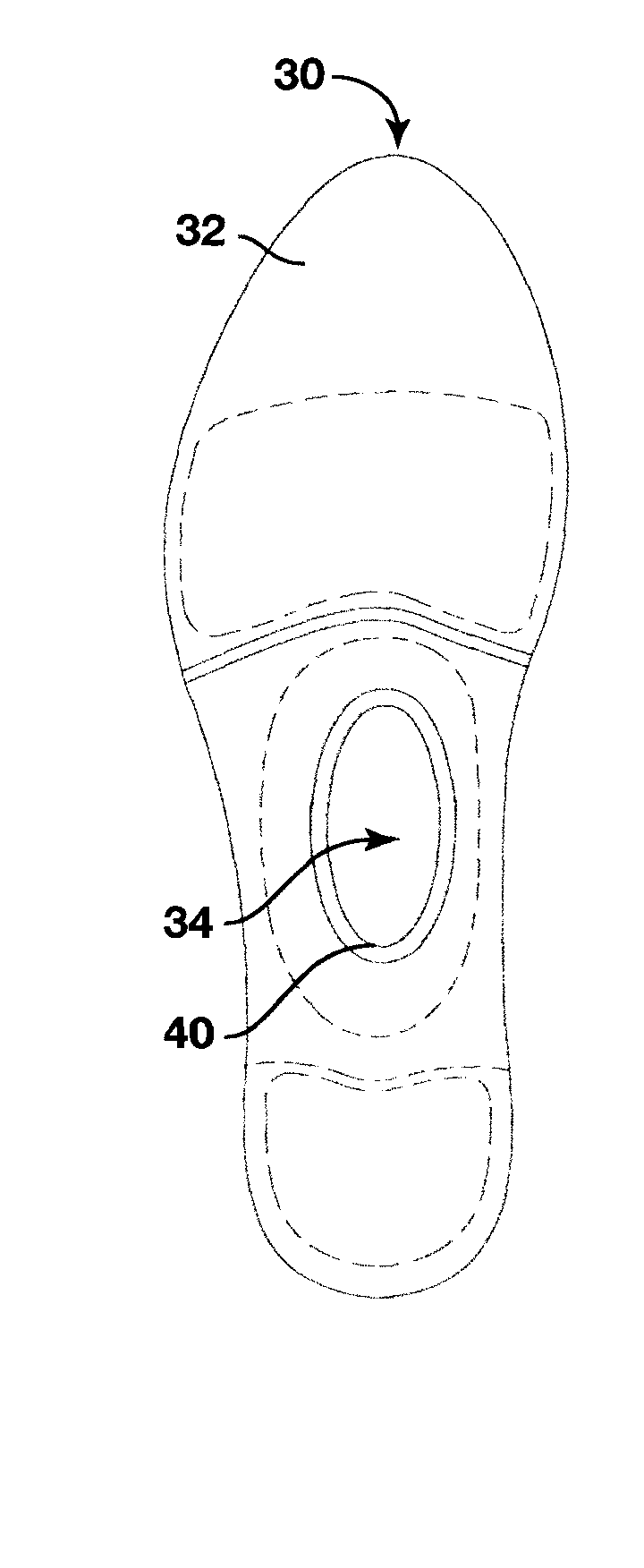
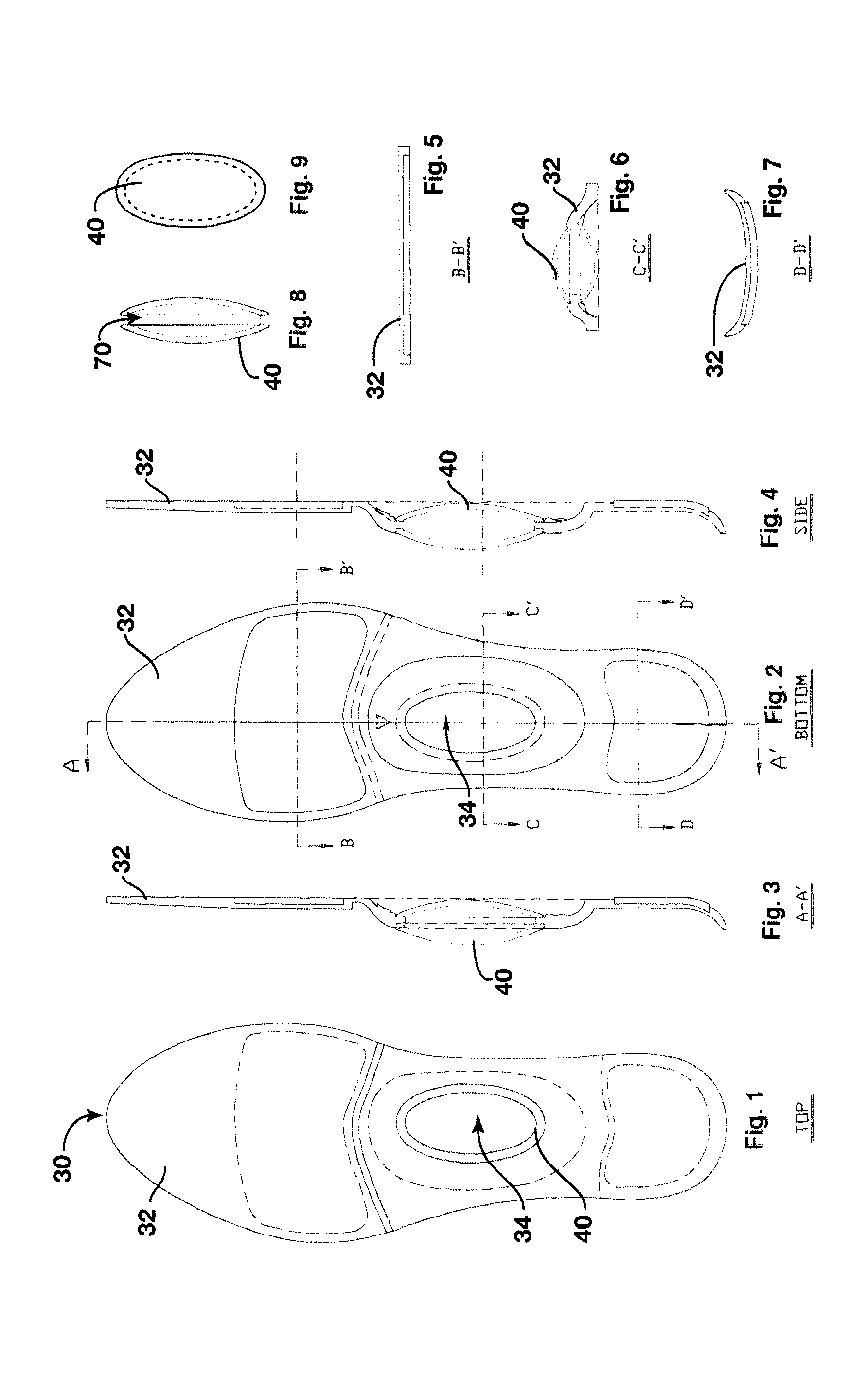
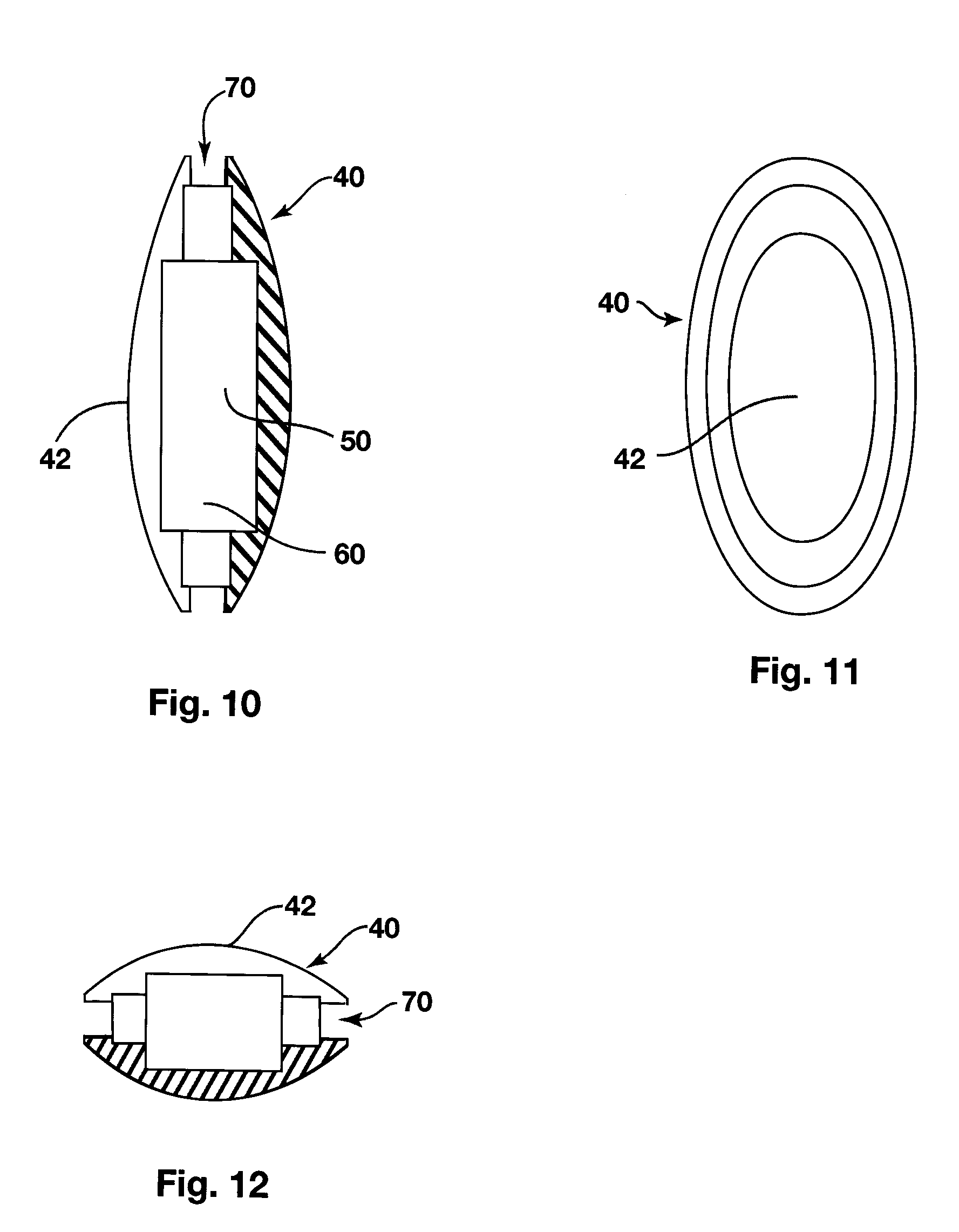
Dynamic arch stabilization and rehabilitative shoe midsole/insole device
An insole device as provided which has a sole shaped body defining an upwardly extending dome in a midfoot section thereof. A biofeedback catalyst is mountable in the dome so as to be moveable at least longitudinally relative to the sole shaped body. The catalyst is positionable to cause the dome to engage an anatomical apex of the sole face of the arch of a wearer's foot. The catalyst has an ellipsoidal or spherical shape, being dimensioned and having a resiliency sufficient to promote dynamic proprioceptive stimulation of mechanical receptors and nocioreceptors in the skin of the wearer's sole at said apex. Cooperating engagement means extend between the body and the catalyst for connecting the catalyst to the body to locate the catalyst in the dome while allowing the movement of the catalyst relative to the body.
Owner:GARDINER ROY
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS8149363B2Characteristics higherRaise the ratioNon-linear opticsVertical alignmentEngineering
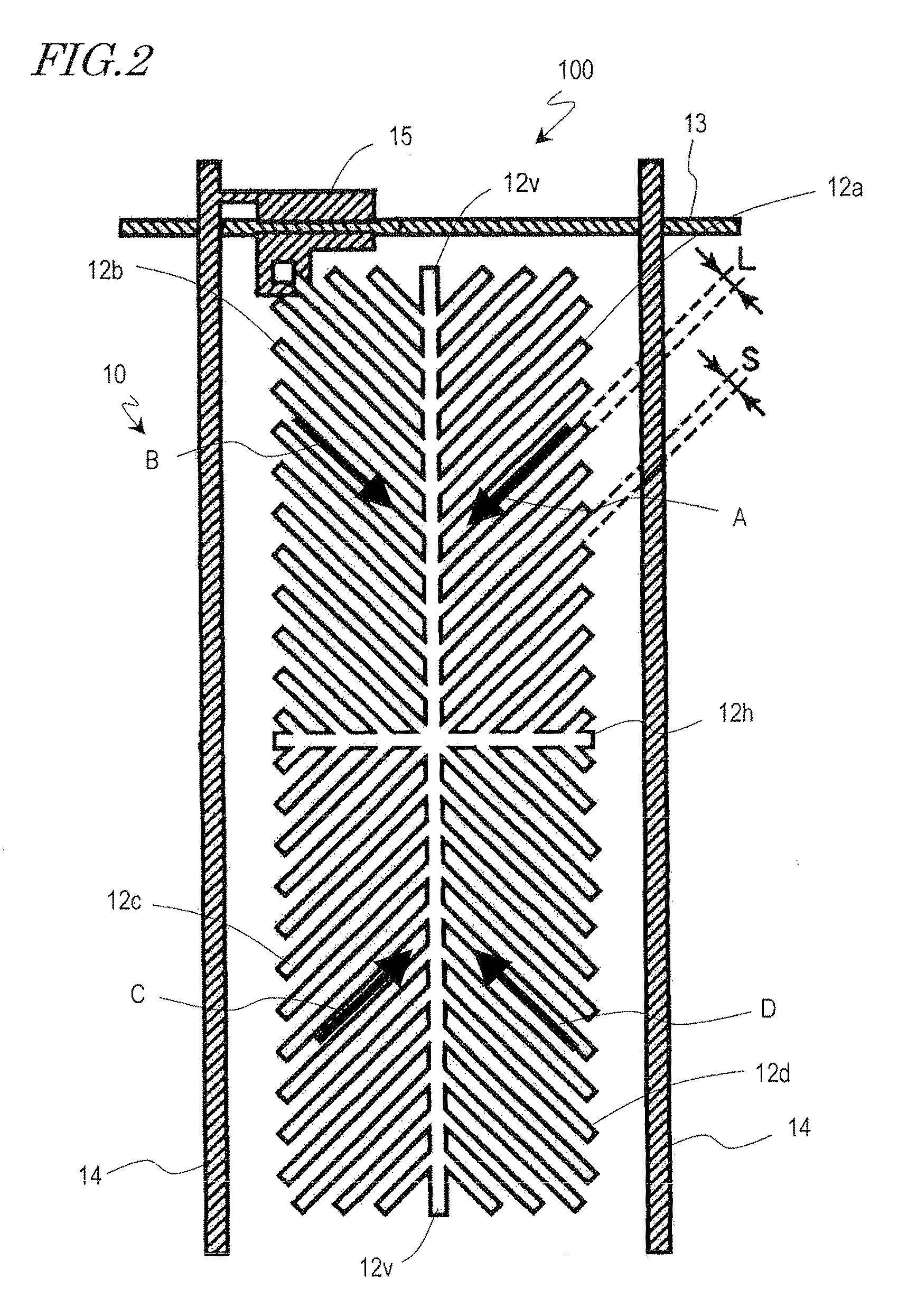
A VA-mode liquid crystal display device which includes a pair of alignment sustaining layers 34a and 34b formed by a photopolymerized material on surfaces of a pair of vertical alignment films 32a and 32b which are closer to a liquid crystal layer, and a cruciform opening 22a provided only in a counter electrode. When a predetermined voltage is applied across the liquid crystal layer, four liquid crystal domains are formed such that the azimuths of the directors of the respective liquid crystal domains are different from one another and form an angle of about 45′ relative to the polarization axes of a pair of polarizing plates. When no voltage is applied across the liquid crystal layer, the pretilt azimuths of liquid crystal molecules included in regions respectively corresponding to the four liquid crystal domains are regulated by the alignment sustaining layers 34a and 34b.
Owner:SHARP KK
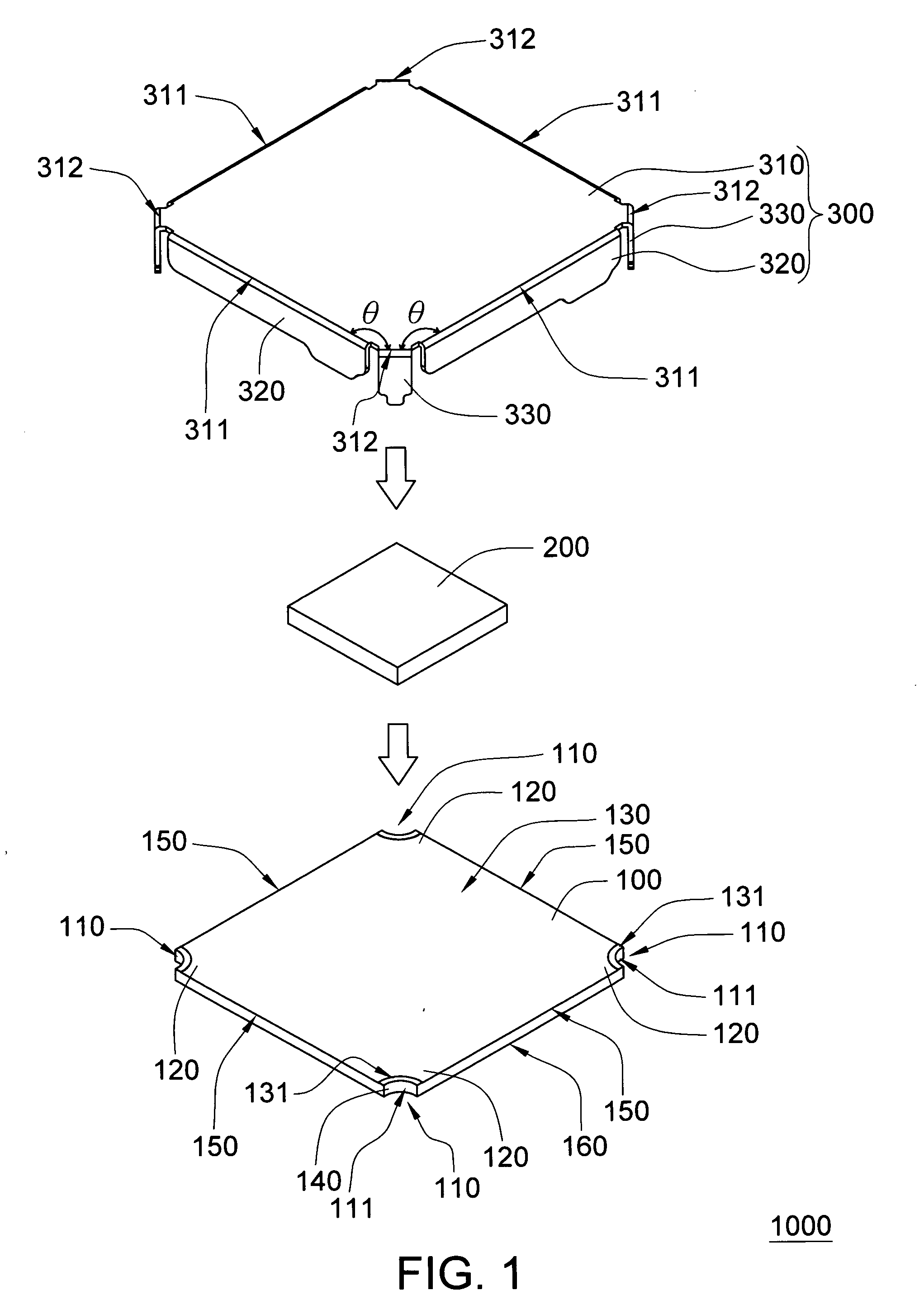
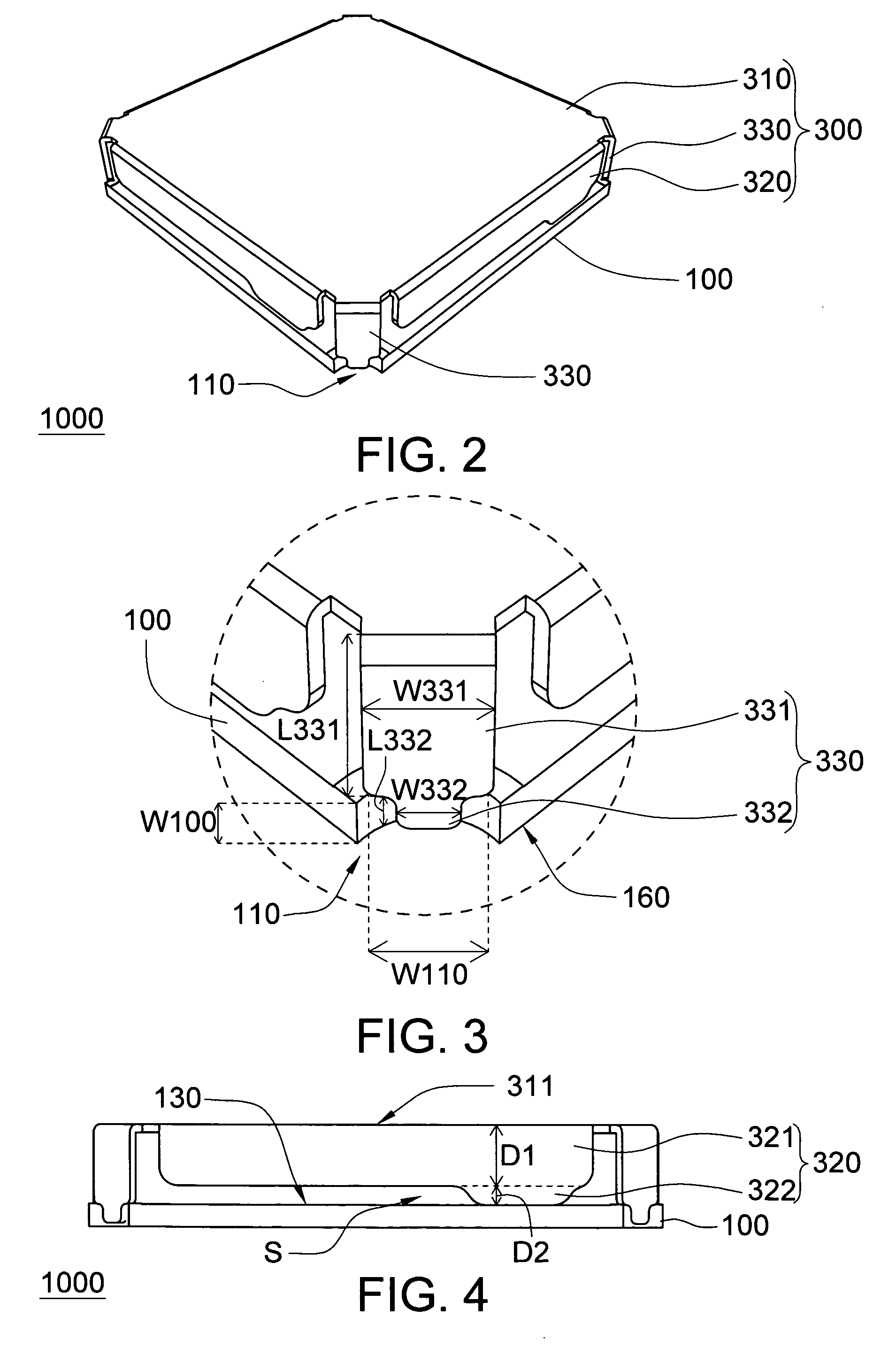
Package structure
InactiveUS20090184405A1Promote stable alignmentImprove shielding effectMagnetic/electric field screeningSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringSemiconductor
A package structure is provided. The package structure includes a substrate, a semiconductor device, and a shielding cap. The substrate has at least an alignment recess located at a corner of the substrate. The semiconductor device is disposed on an upper surface of the substrate. The shielding cap having an alignment pin covers the semiconductor device. The alignment pin is inserted into the alignment recess.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
Production Method of Liquid Crystal Display and Exposure Device for Alignment Treatment
ActiveUS20090279044A1Effective treatmentEfficiently and stably providingElectroluminescent light sourcesNon-linear opticsLiquid crystal molecule
Owner:SHARP KK
Liquid Crystal Photo-Alignment Agent, Liquid Crystal Photo-Alignment Layer Manufactured Using the Same, and Liquid Crystal Display Device Including the Liquid Crystal Photo-Alignment Layer
InactiveUS20110144299A1Improve textureIncrease resistanceLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingLiquid-crystal displayPolyamic acid
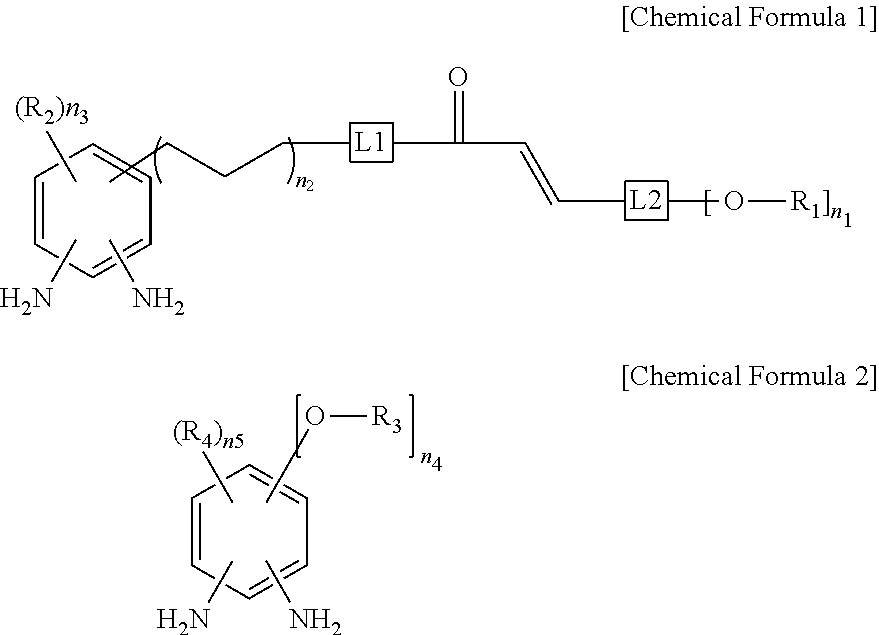
Disclosed is a liquid crystal photo-alignment agent including polyamic acid or a polyimide including a first structural unit derived from a photo-diamine represented by the following Chemical Formula 1, a second structural unit represented by the following Chemical Formula 2 or a polymer compound combination thereof, and a solvent.In Chemical Formulae 1 and 2, each substituent is the same as defined in the detailed description.
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
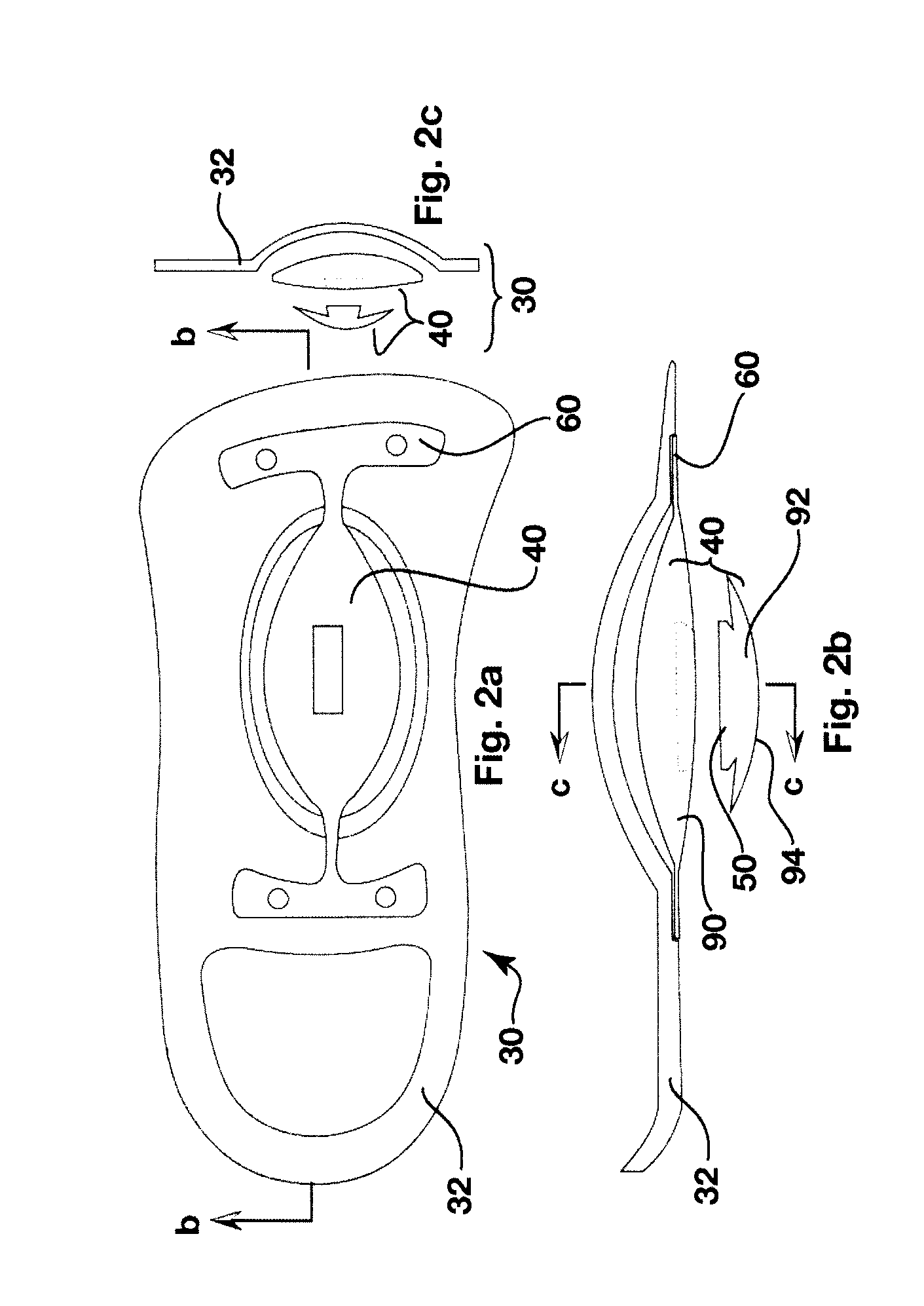
Dynamic arch stabilization and rehabilitative shoe insole device
An insole device configured to fit the profile of a human foot to promote dynamic proprioceptive stimulation of the mechanoreceptors and nocioreceptors in the skin of the sole of the foot at the anatomical apex of the foot's arch system. The midfoot section of the insole device has a receptacle located central to the foot's anatomical arch apex that receives interchangeable resilient ellipsoidal and spherically shaped biofeedback catalysts of many shapes and forms. The resilient ellipsoidal and spherically shaped biofeedback catalysts present to the plantar aspect of the foot at a location found to be the anatomical apex of the foot's arch system.
Owner:GARDINER ROY
Detachable vehicle-mounted banner assembly having improved display and mounting features
InactiveUS20150213741A1Reduced durabilityIncreased durabilityMachine supportsFlags/bannersLeading edgeAcute angle
A detachable vehicle-mounted banner assembly is provided, comprising a banner panel defining two opposing and at least semi-rigid surfaces, the surfaces comprising at least a leading edge; a banner mast comprising a base portion and a flanged portion, the flanged portion comprising an angled leading edge and a trailing slot, the trailing slot being configured to selectively engage at least the leading edge; and a base assembly having a first portion configured for attachment to a vehicle and a second portion configured to attachment relative to the base portion. The base portion is elongate and has a base longitudinal axis about which the banner mast and the banner panel pivot; and the flanged portion of the banner mast extends away from the base portion and has a flange longitudinal axis oriented at an acute angle relative to the base longitudinal axis. A method of mounting the assembly is also provided.
Owner:HARDFLAGS
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20100283952A1High light transmittanceAlignment of liquid crystal is stableNon-linear opticsVertical alignmentEngineering
A VA-mode liquid crystal display device which includes a pair of alignment sustaining layers 34a and 34b formed by a photopolymerized material on surfaces of a pair of vertical alignment films 32a and 32b which are closer to a liquid crystal layer, and a cruciform opening 22a provided only in a counter electrode. When a predetermined voltage is applied across the liquid crystal layer, four liquid crystal domains are formed such that the azimuths of the directors of the respective liquid crystal domains are different from one another and form an angle of about 45′ relative to the polarization axes of a pair of polarizing plates. When no voltage is applied across the liquid crystal layer, the pretilt azimuths of liquid crystal molecules included in regions respectively corresponding to the four liquid crystal domains are regulated by the alignment sustaining layers 34a and 34b.
Owner:SHARP KK
Liquid crystal display
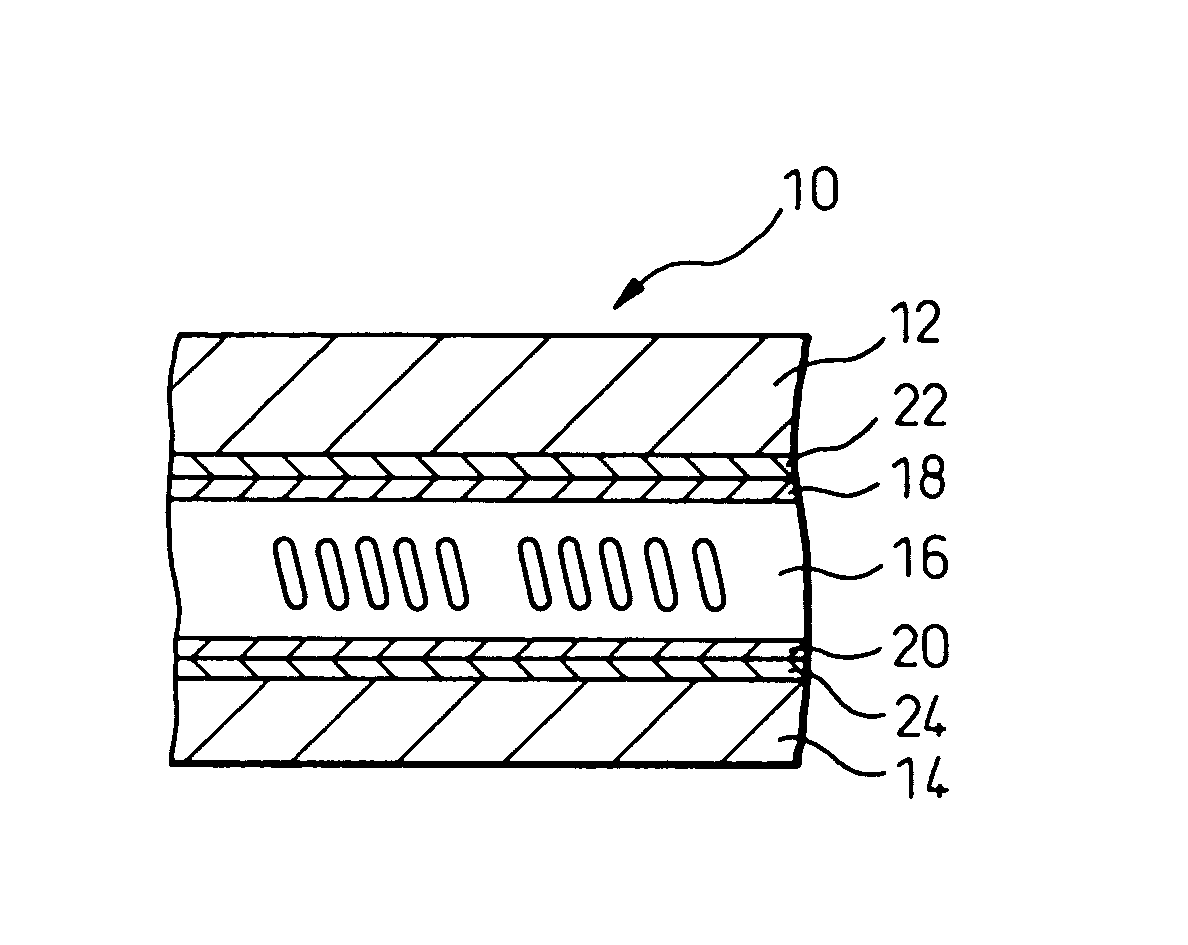
A liquid crystal display includes a back substrate, a front substrate, and an optical filter layer interposed therebetween. The optical filter layer contains a liquid crystal material which forms a bend configuration when a voltage is applied between electrodes of the back and front substrates. The electrodes of the back and front substrates are covered with alignment layers which include corrugated surfaces at positions of the electrodes. Each corrugated surface includes upslopes and downslopes steeper than the upslopes or vertical surfaces which are alternately joined.
Owner:TOSHIBA MOBILE DISPLAY CO LTD 50
Polymerizable liquid crystal composition, homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film made from the composition and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20110037026A1Improve productivityPromote stable alignmentLiquid crystal compositionsSilver halide emulsionsCrystallographyHomeotropic alignment
The present invention relates to a polymerizable liquid crystal composition that includes a polymerizable reactive homeotropic alignment liquid crystal mixture solution and a primary or secondary amino compound, a homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film using the same, and a method for manufacturing the same. According to the present invention, regardless of the alignment film, a stable homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film may be manufactured.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS7554622B2Easy alignmentImprove display qualityNon-linear opticsCapacitanceLiquid-crystal display
Owner:SHARP KK
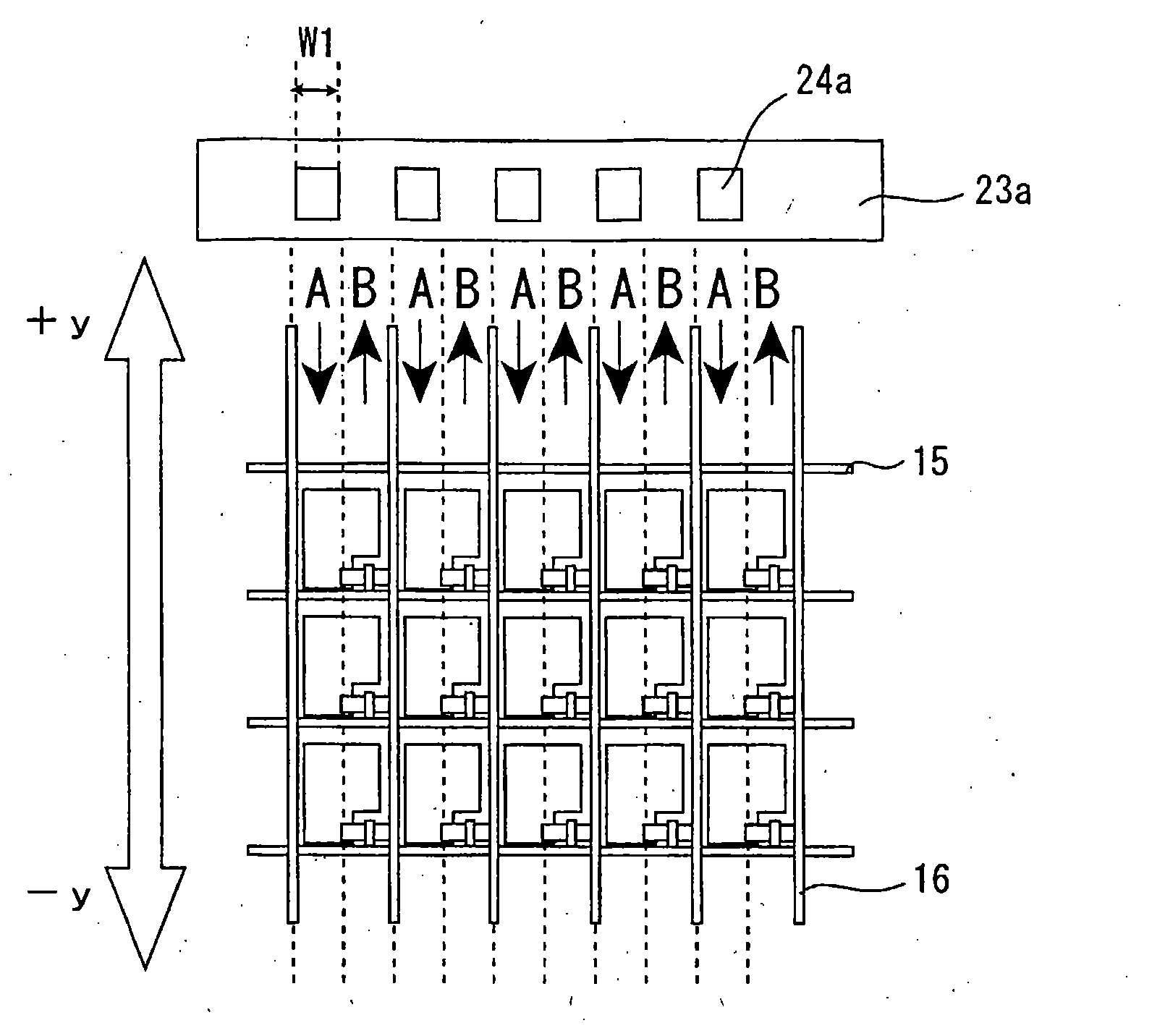
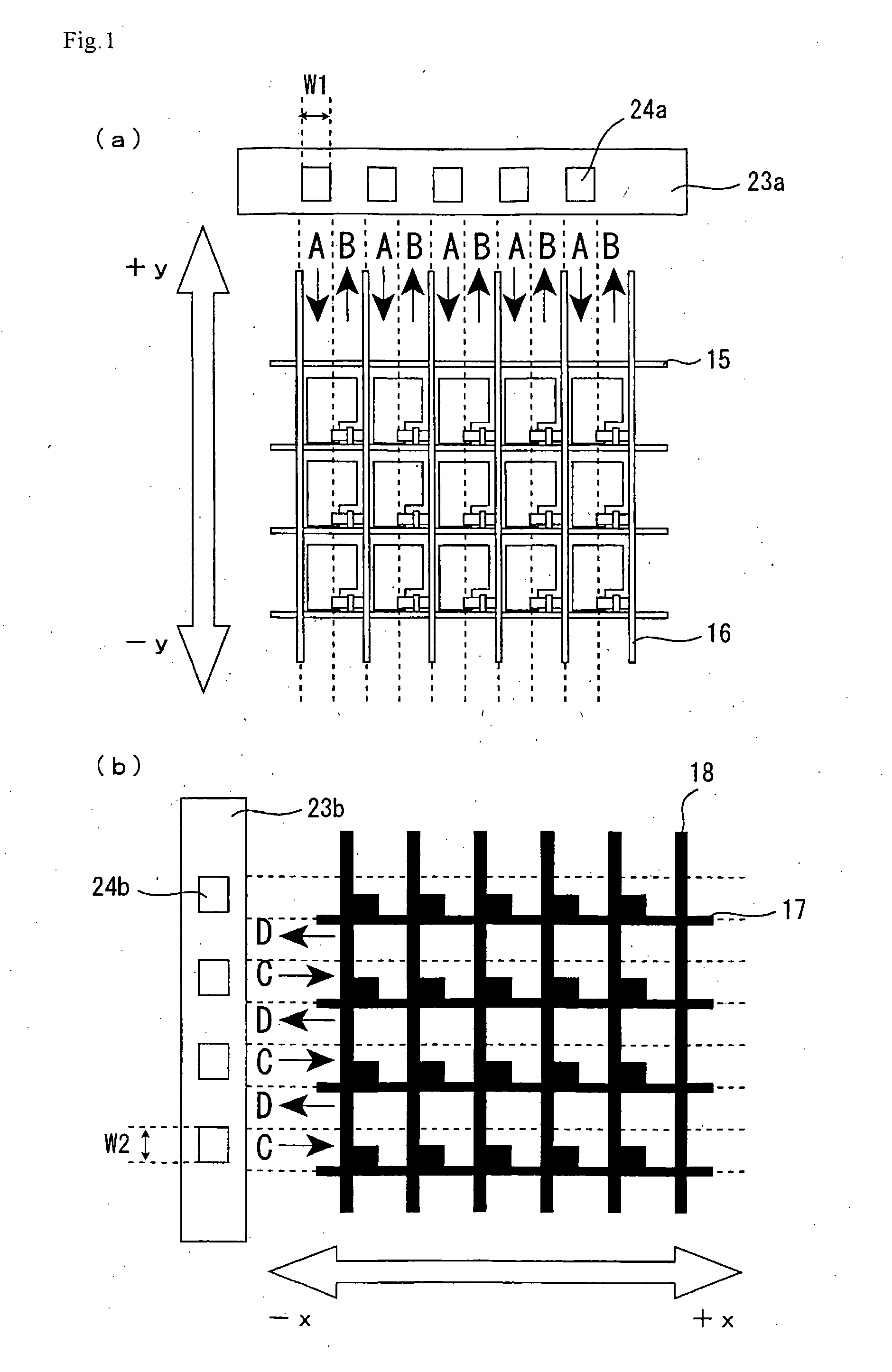
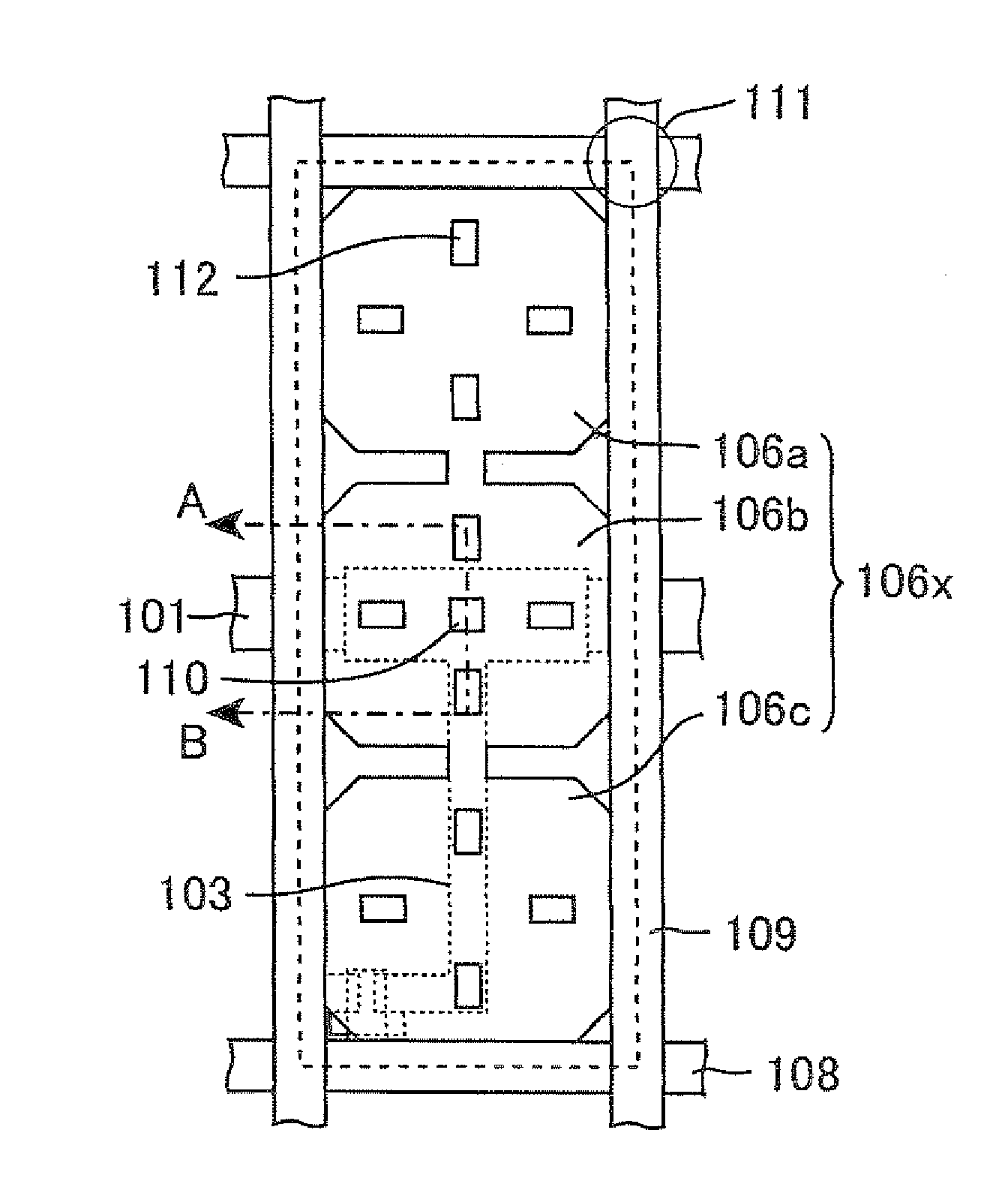
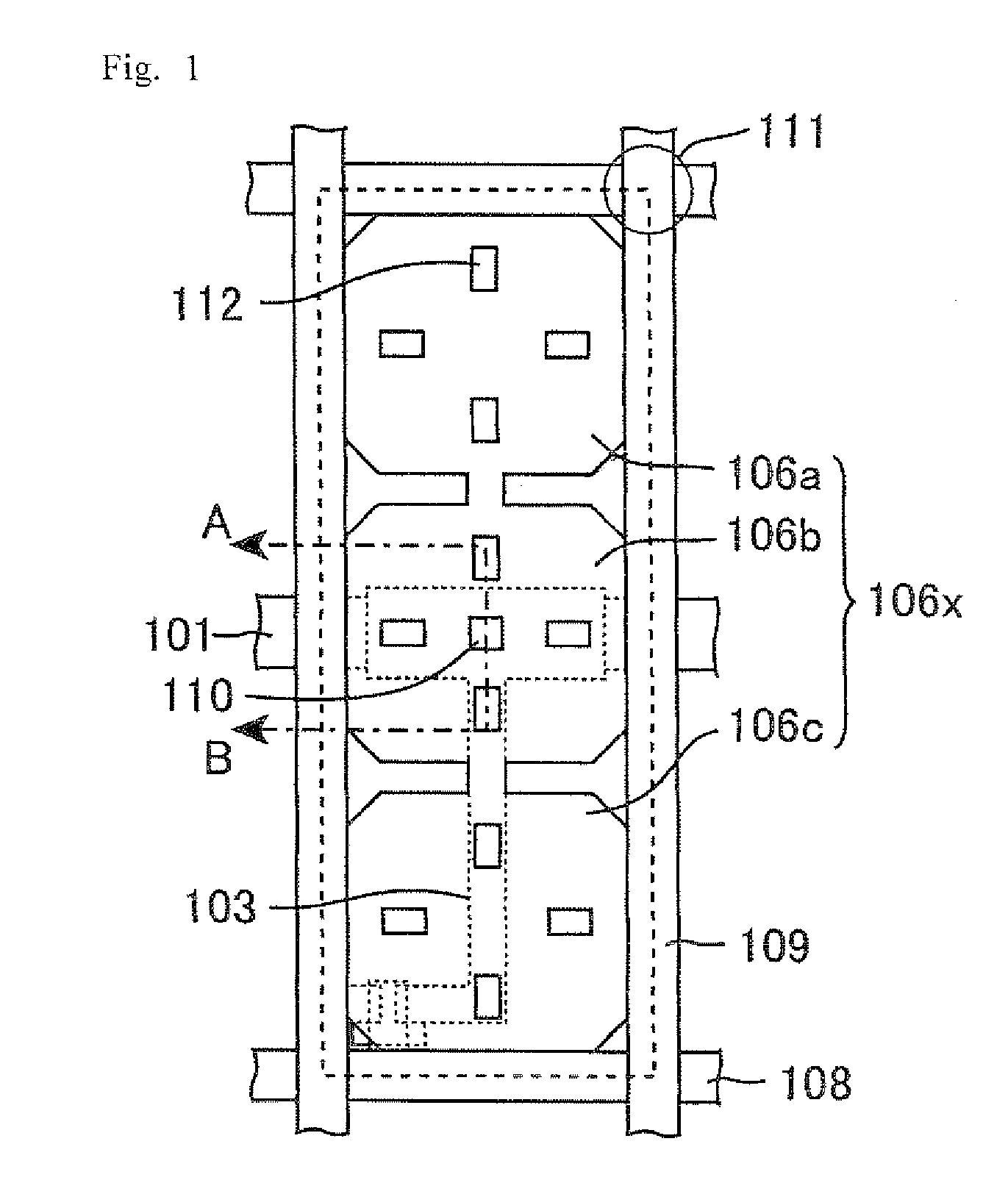
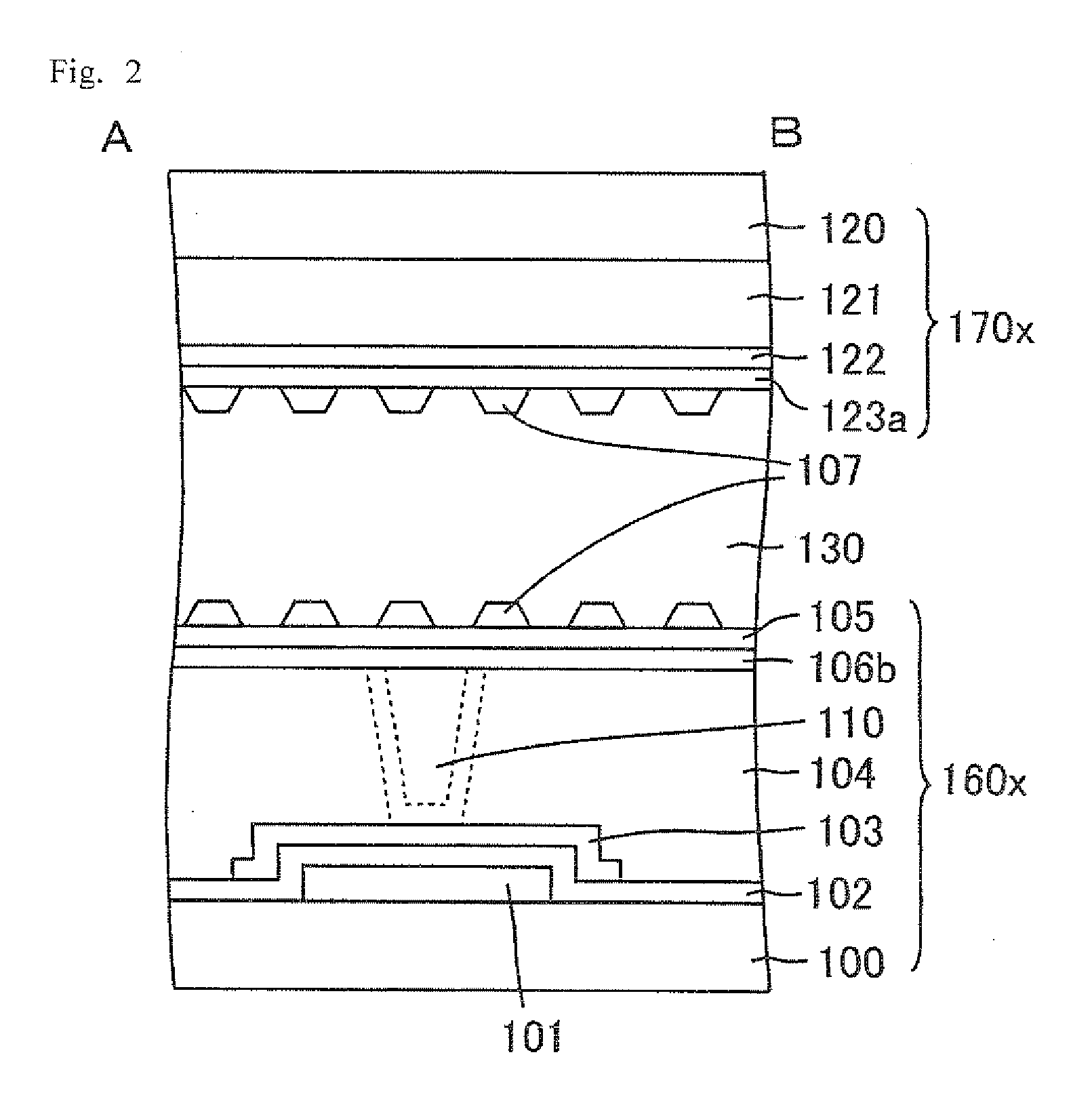
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20050162589A1Stable arrangementPromote stable alignmentNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
The liquid crystal display device includes a first substrate, a second substrate opposed to the first substrate, and a vertically aligned liquid crystal layer interposed between the first and second substrates, and has a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix having rows and columns. Each pixel includes a first electrode formed on the first substrate, a second electrode formed on the second substrate, and the liquid crystal layer interposed between the first and second electrodes. The first substrate has a shading region in gaps between the plurality of pixels, and a wall structure is placed regularly on the surface of the first substrate facing the liquid crystal layer in the shading region. The first and second electrodes have at least one opening formed at a predetermined position in the pixel. At least an arbitrary row or column of pixels is composed of first pixels each having the first electrode to which a voltage of positive polarity with respect to the potential at the second electrode as the reference potential is supplied and second pixels each having the first electrode to which a voltage of negative polarity is supplied, arranged alternately, in a given vertical scanning period. At least one liquid crystal domain having axisymmetric alignment is formed when at least a predetermined voltage is applied across the liquid crystal layer, and the center axis of the axisymmetric alignment of the at least one liquid crystal domain is formed in or near the at least one opening.
Owner:SHARP KK
Liquid crystal display panel and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20100207864A1Simple stepsLiquid crystal alignment can be stabilizedStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsDielectric anisotropyVoltage
The present invention provides a liquid crystal display panel and a liquid crystal display device in which a position of a singular point of pinwheel alignment is controlled, thereby suppressing rough-grained image and generation of image retention, and in which the response time is improved. The present invention is a liquid crystal display panel including a pair of substrates and a liquid crystal layer interposed therebetween,the liquid crystal layer including liquid crystal molecules with negative dielectric anisotropy,wherein the pair of substrates each include an electrode,at least one of the pair of substrates includes a vertical alignment film and a photopolymerized polymer,the electrode on one of the pair of substrates has such a shape as to provide pinwheel alignment of the liquid crystal molecules upon application of a voltage and is partly provided with openings for surrounding a singular point of the pinwheel alignment and keeping the singular point within the electrode.
Owner:SHARP KK
Liquid crystal display panel and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20060066789A1Stable liquid crystal alignmentImprove display qualityNon-linear opticsDisplay responseEngineering
A liquid crystal panel and a liquid crystal display device having stable liquid crystal alignment, excellent display quality, and high display response speed are obtained. In this liquid crystal panel, uneven portions for bending the alignment of liquid crystal molecules towards the direction along the substrate surface are installed on the surfaces where the liquid crystal layer contacts its adjacent layers, and the liquid crystal layer comprises a liquid crystal having a positive dielectric constant anisotropy, and a polymer obtained by subjecting a polymerizable compound in the liquid crystal layer to irradiation with active energy rays, with or without application of a voltage.
Owner:SHARP KK
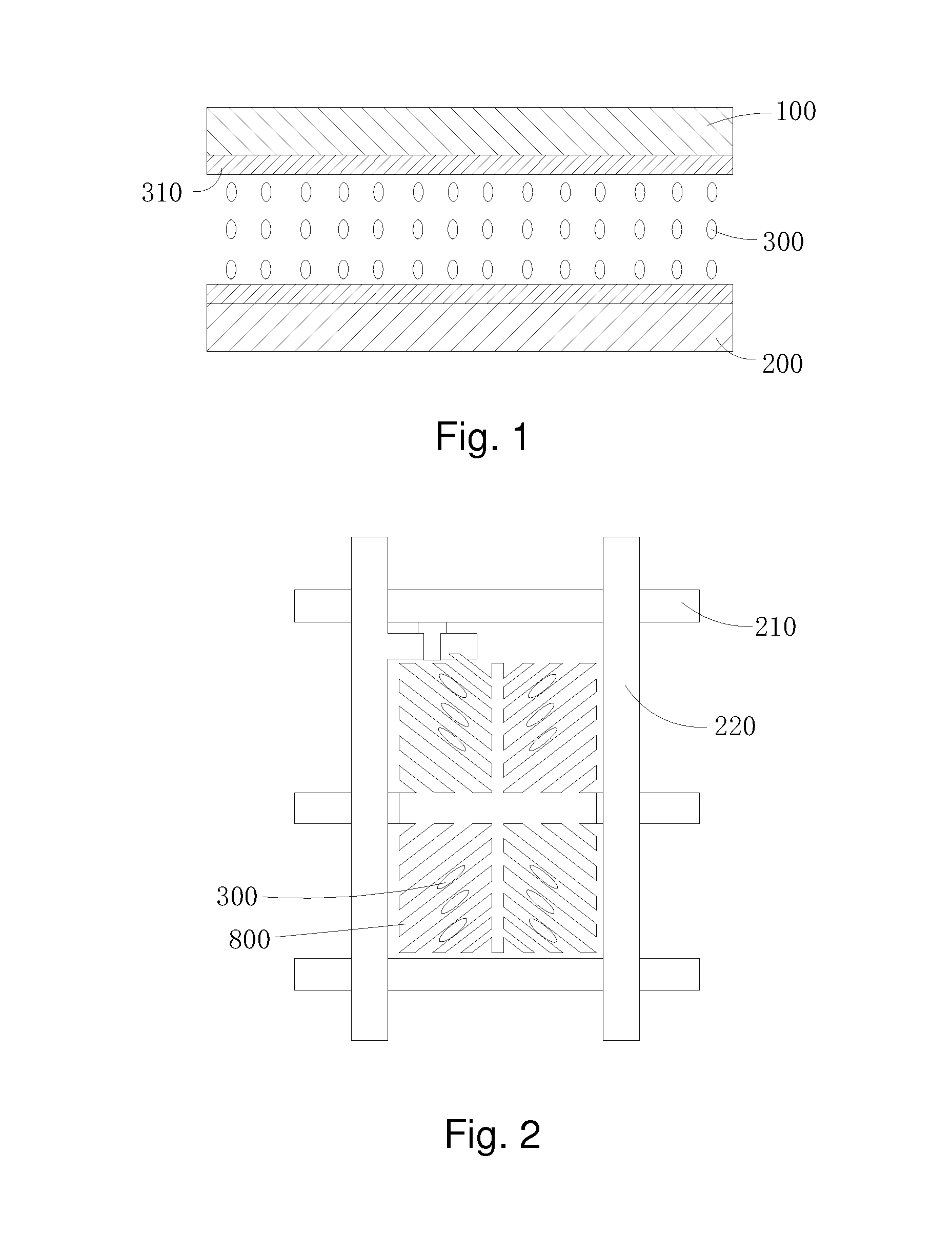
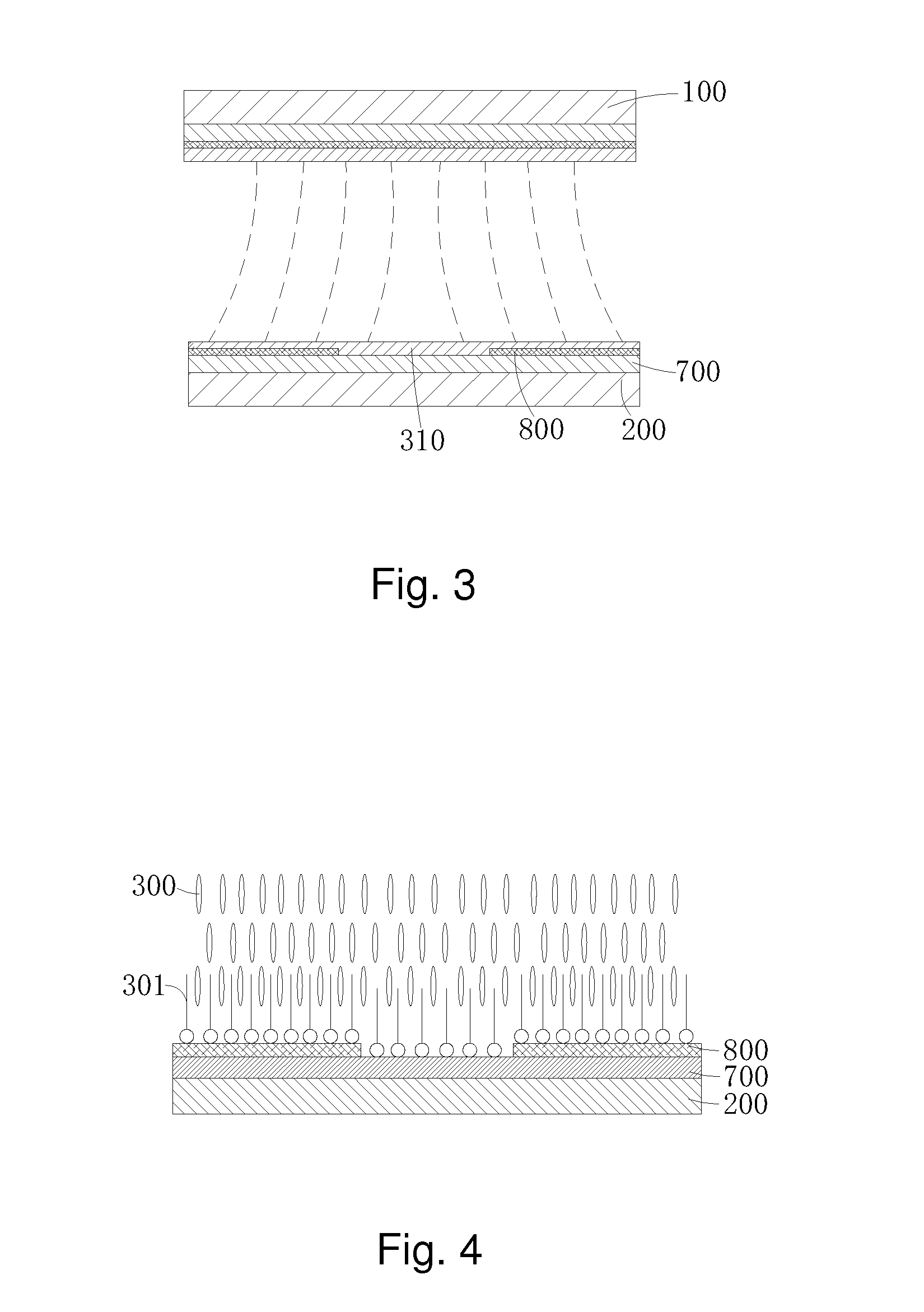
Vertical alignment liquid crystal display and manufacture method thereof
ActiveUS20160145492A1Large surface areaLarge contact areaLiquid crystal compositionsTube/lamp factory adjustmentEngineeringVertical alignment
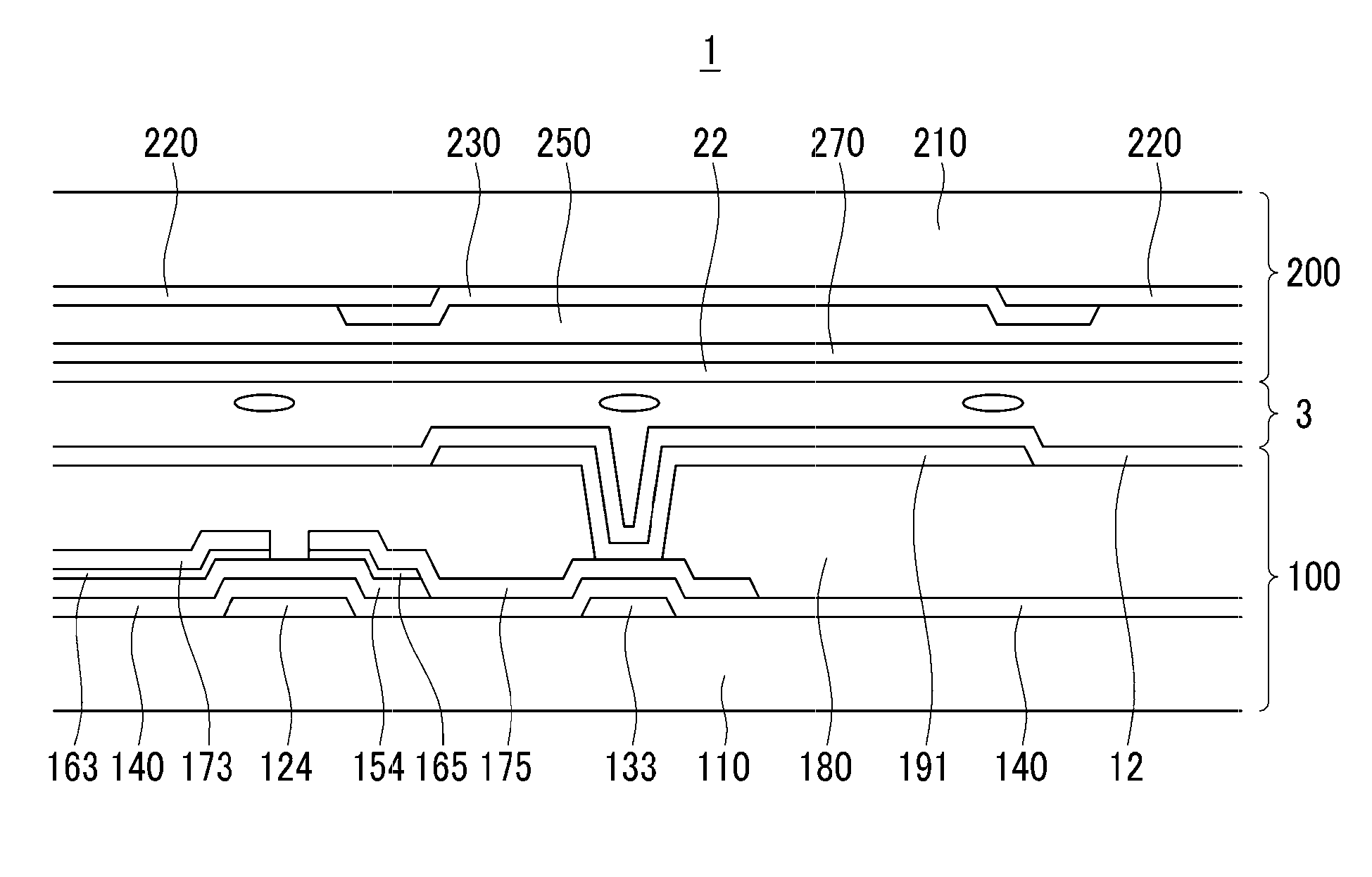
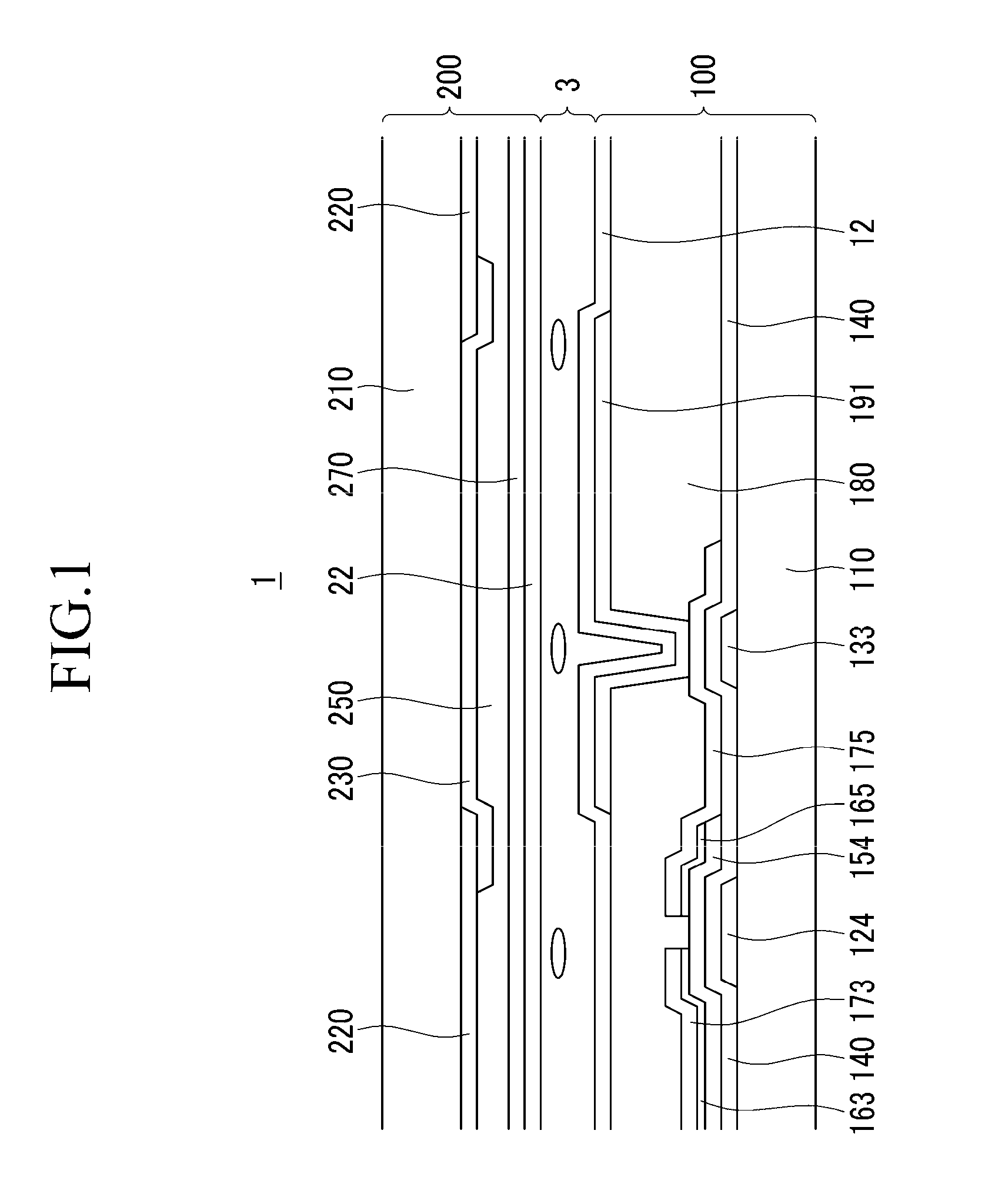
The present invention provides a vertical alignment liquid crystal display and a manufacture method thereof. The vertical alignment liquid crystal display comprises a first substrate (1), a second substrate (2), a liquid crystal layer (3) located between the first substrate (1) and the second substrate (2), a first and a second passivation layers (11, 21) respectively located at inner sides of the first and the second substrates (1, 2), a common electrode layer (12) and a pixel electrode layer (22) respectively located on the first and the second passivation layers (11, 21); the liquid crystal layer (3) comprises liquid crystal molecules (30), auxiliary alignment agent (31) and a polymer network (33) penetrating the entire liquid crystal layer (3); the auxiliary alignment agent (31) makes the liquid crystal molecules (30) in the liquid crystal layer (3) vertically aligned on the surfaces of the first and the second substrates (1, 2); the polymer network (33) stabilizes alignment of the liquid crystal molecules (30) and enhances vertical alignment effect of the auxiliary alignment agent (31) to the liquid crystal molecules (30).
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Detachable vehicle-mounted banner assembly having improved display and mounting features
A detachable vehicle-mounted banner assembly is provided, comprising a banner panel defining two opposing and at least semi-rigid surfaces, the surfaces comprising at least a leading edge; a banner mast comprising a base portion and a flanged portion, the flanged portion comprising an angled leading edge and a trailing slot, the trailing slot being configured to selectively engage at least the leading edge; and a base assembly having a first portion configured for attachment to a vehicle and a second portion configured to attachment relative to the base portion. The base portion is elongate and has a base longitudinal axis about which the banner mast and the banner panel pivot; and the flanged portion of the banner mast extends away from the base portion and has a flange longitudinal axis oriented at an acute angle relative to the base longitudinal axis. A method of mounting the assembly is also provided.
Owner:HARDFLAGS HLDG LLC
Polymerizable liquid crystal composition, homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film made from the composition and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS8029695B2Promote stable alignmentImprove productivityLiquid crystal compositionsSilver halide emulsionsCrystallographyHomeotropic alignment
The present invention relates to a polymerizable liquid crystal composition that includes a polymerizable reactive homeotropic alignment liquid crystal mixture solution and a primary or secondary amino compound, a homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film using the same, and a method for manufacturing the same. According to the present invention, regardless of the alignment film, a stable homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film may be manufactured.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Inspection system
InactiveUS20120261572A1Reduce the environmentSimple designMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationNuclear radiation detectionPhysicsRadiation
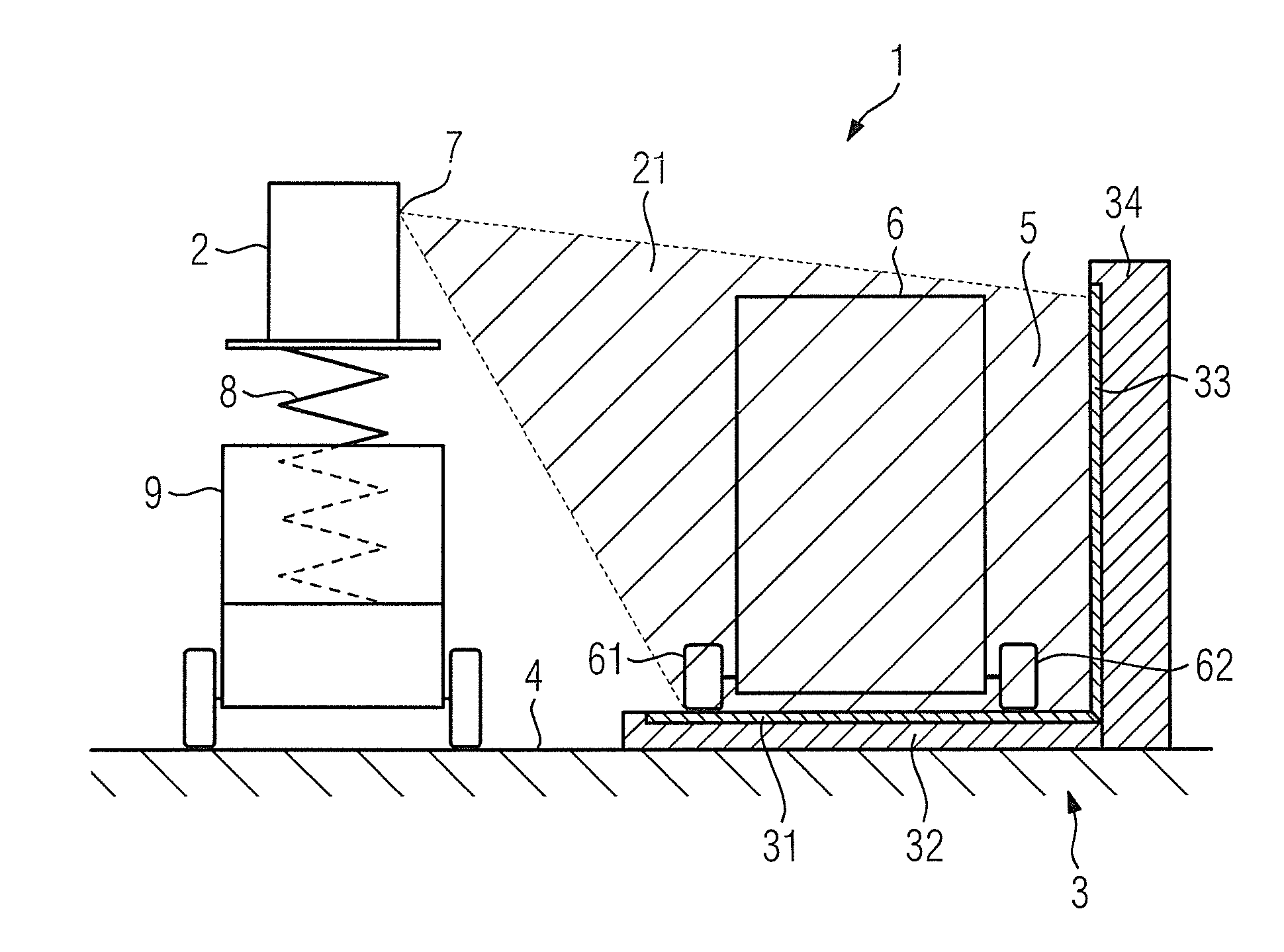
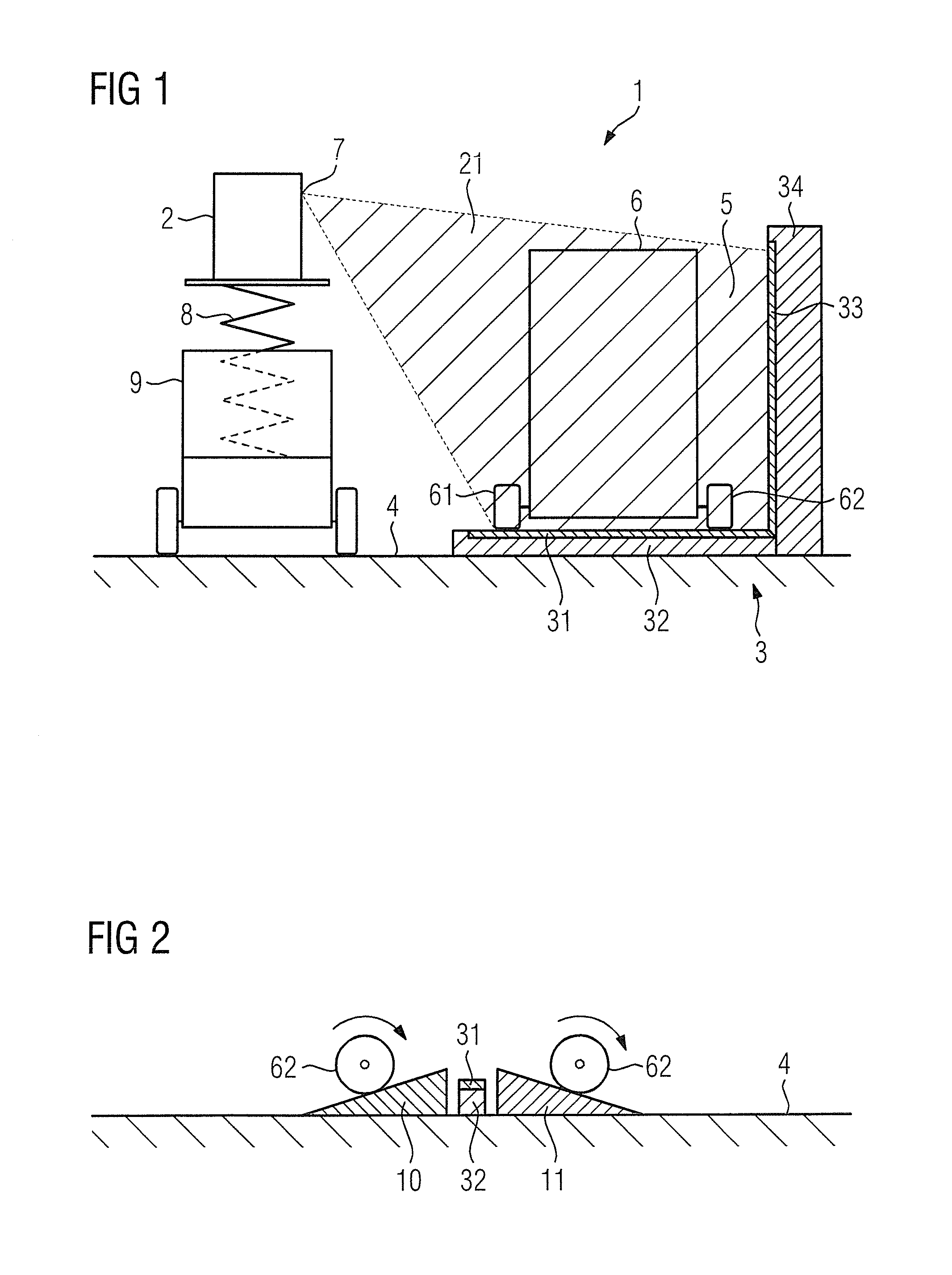
An inspection system has at least one radiation source and at least one L-shaped radiation detector for radioscopy of an article to be inspected. The radiation detector has a horizontal detector surface and a vertical detector surface and the radiation source is spaced apart from both detector surfaces. The inspection system is given a simple design by the horizontal detector surface running below the article being inspected and the radiation source being arranged in an upper corner position.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Liquid crystal display
ActiveUS7742138B2Reduce displayPromote stable alignmentLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic dyesLiquid-crystal displayHigh volume manufacturing
It is an object to provide a liquid crystal display which reduces unsatisfactory display caused by distorted initial alignment direction in a liquid crystal alignment layer for IPS type displays, realizes stable liquid crystal alignment, is high in mass-productivity, and produces high-quality images of increased contrast ratio. The liquid crystal display contains alignment layers 109 placed between a pair of substrates 101 and 102, at least one of which is transparent, liquid crystal layer 110′ sealed between the alignment layers, common electrode 103 and source electrode 105 for applying an electrical field to the liquid crystal layer, thin-film transistors connected to each of these electrodes, polarizer plate 114 provided on at least one of the substrates, wherein at least one of the alignment layers 109 is composed of a photo-reactive polyimide and / or polyamic acid which can be provided with a liquid crystal alignment capacity by being irradiated with essentially linearly polarized light.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com