Patents
Literature
33 results about "Baseline pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
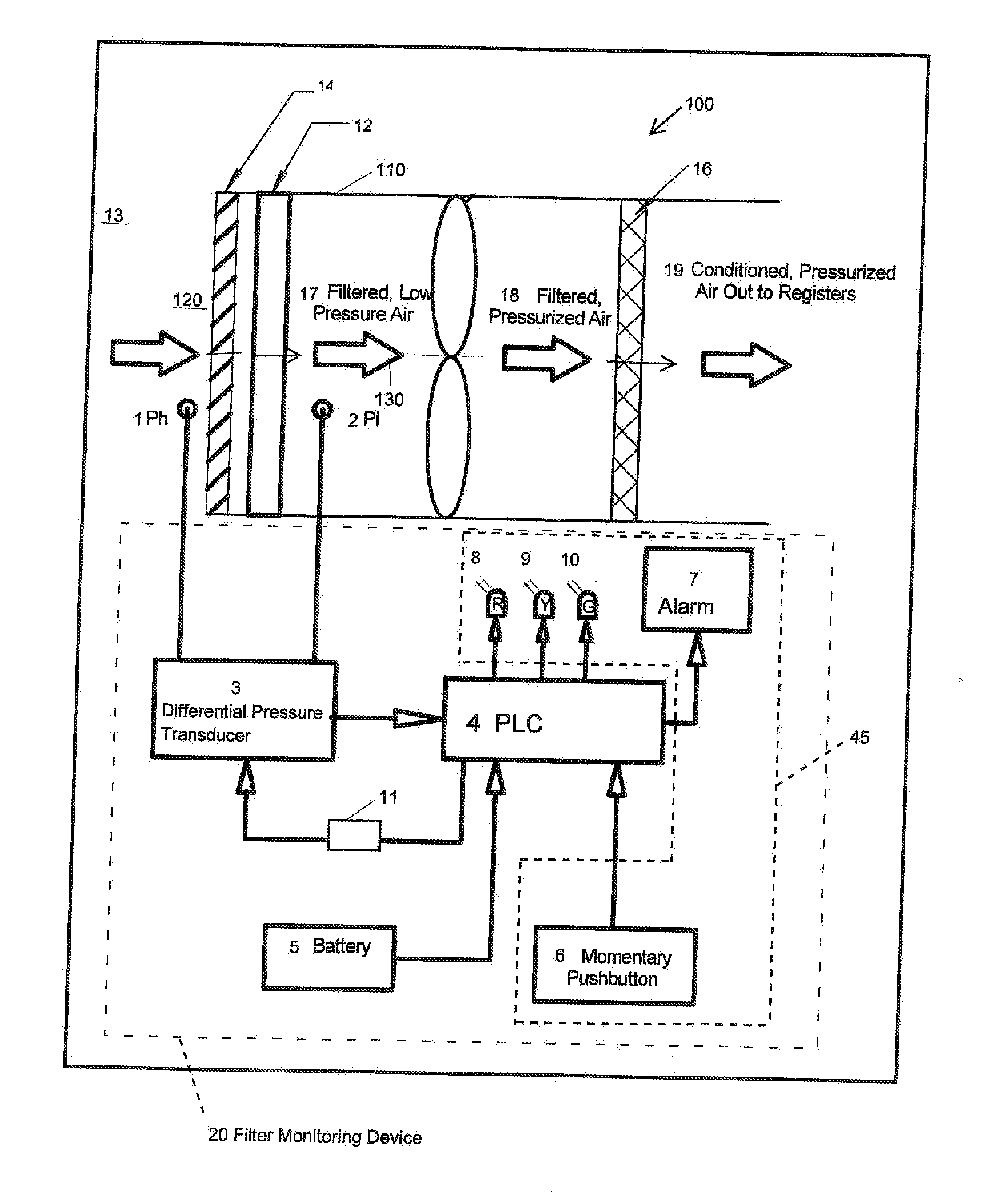
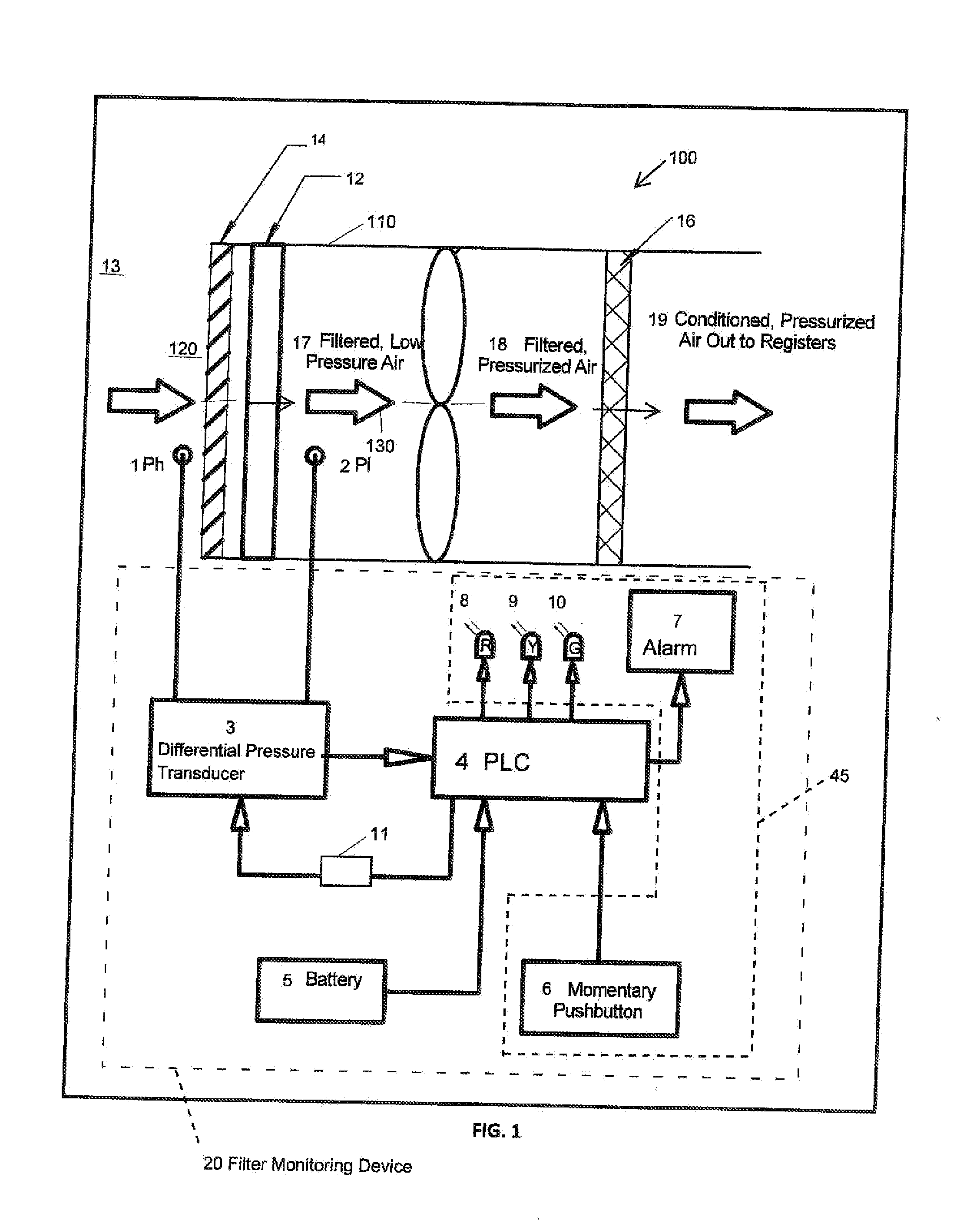
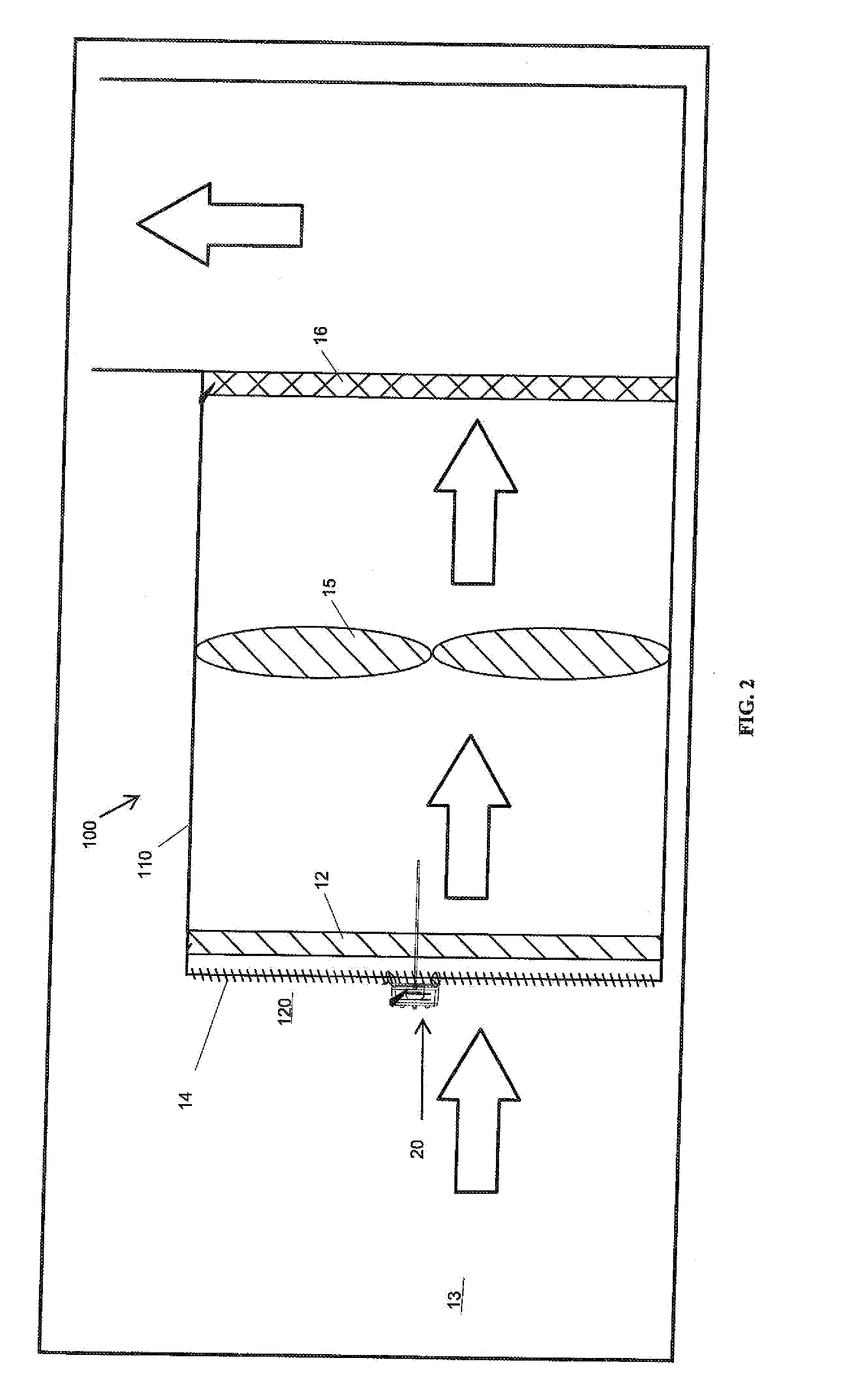
Filter apparatus and method of monitoring filter apparatus
Methods, systems, and products for monitoring an air filter. Methods involve determining a difference between a baseline pressure differential and a current pressure differential, the differential pressure between pressure at an upstream side of the filter and pressure at a downstream side of the filter. The baseline pressure differential may be set automatically or by a user. Reaching or exceeding a predetermined threshold triggers an indication of a clogged condition. The method also includes monitoring the air filter condition intermittently. The filter monitor may operate for extended periods in a sleep state and intermittently power up to a wake state to measure the current pressure differential and compare the current pressure differential with a baseline pressure differential.
Owner:FREEN PAUL
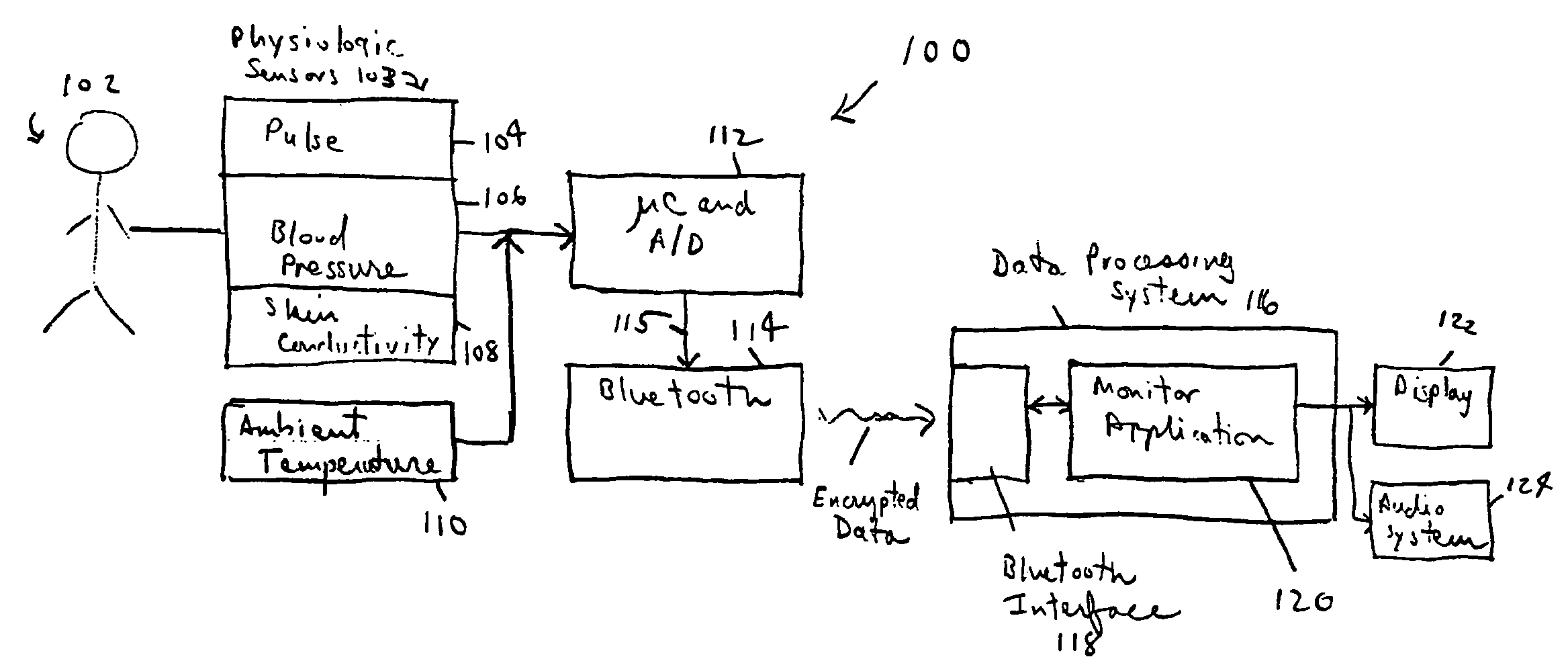
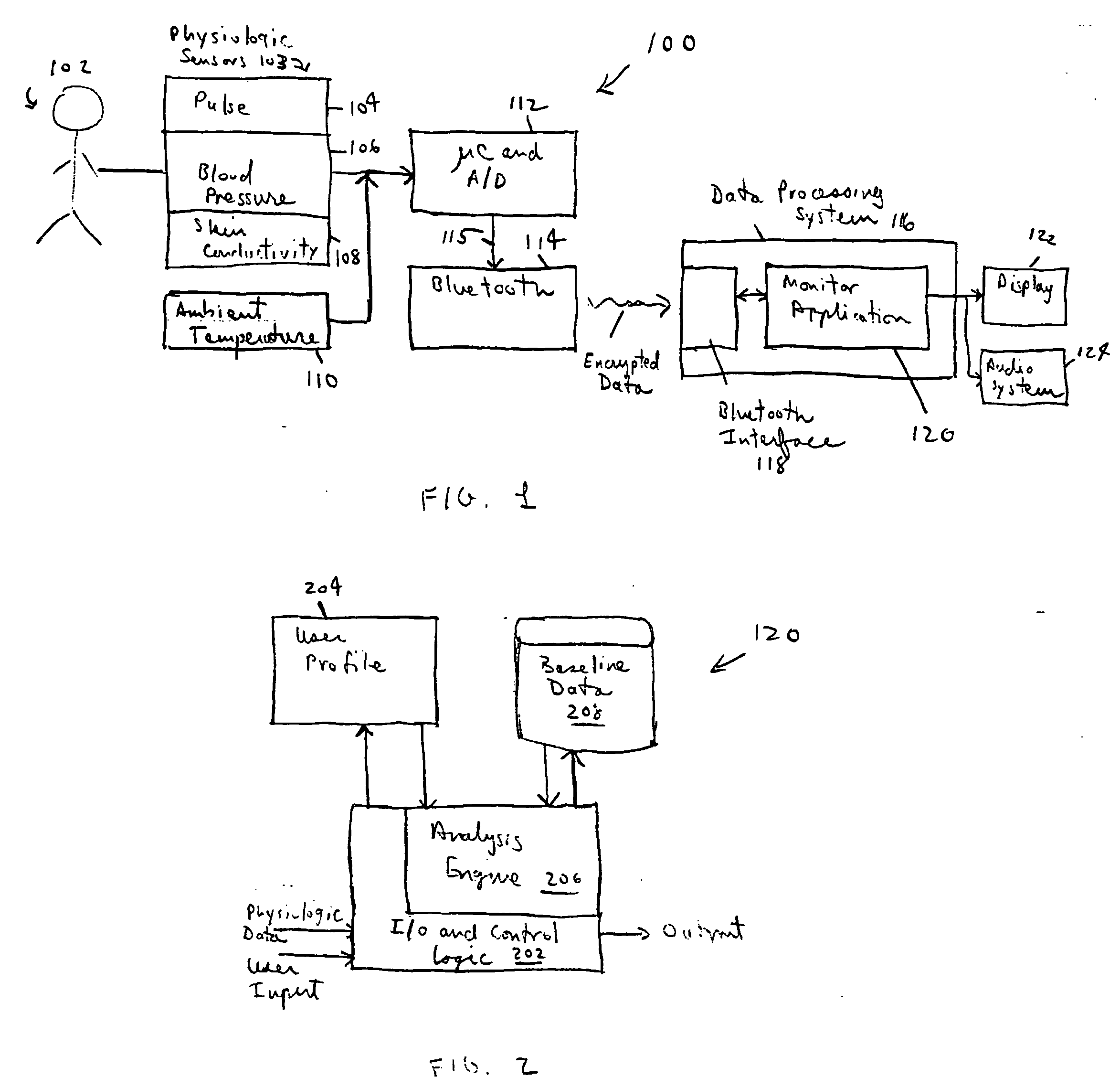
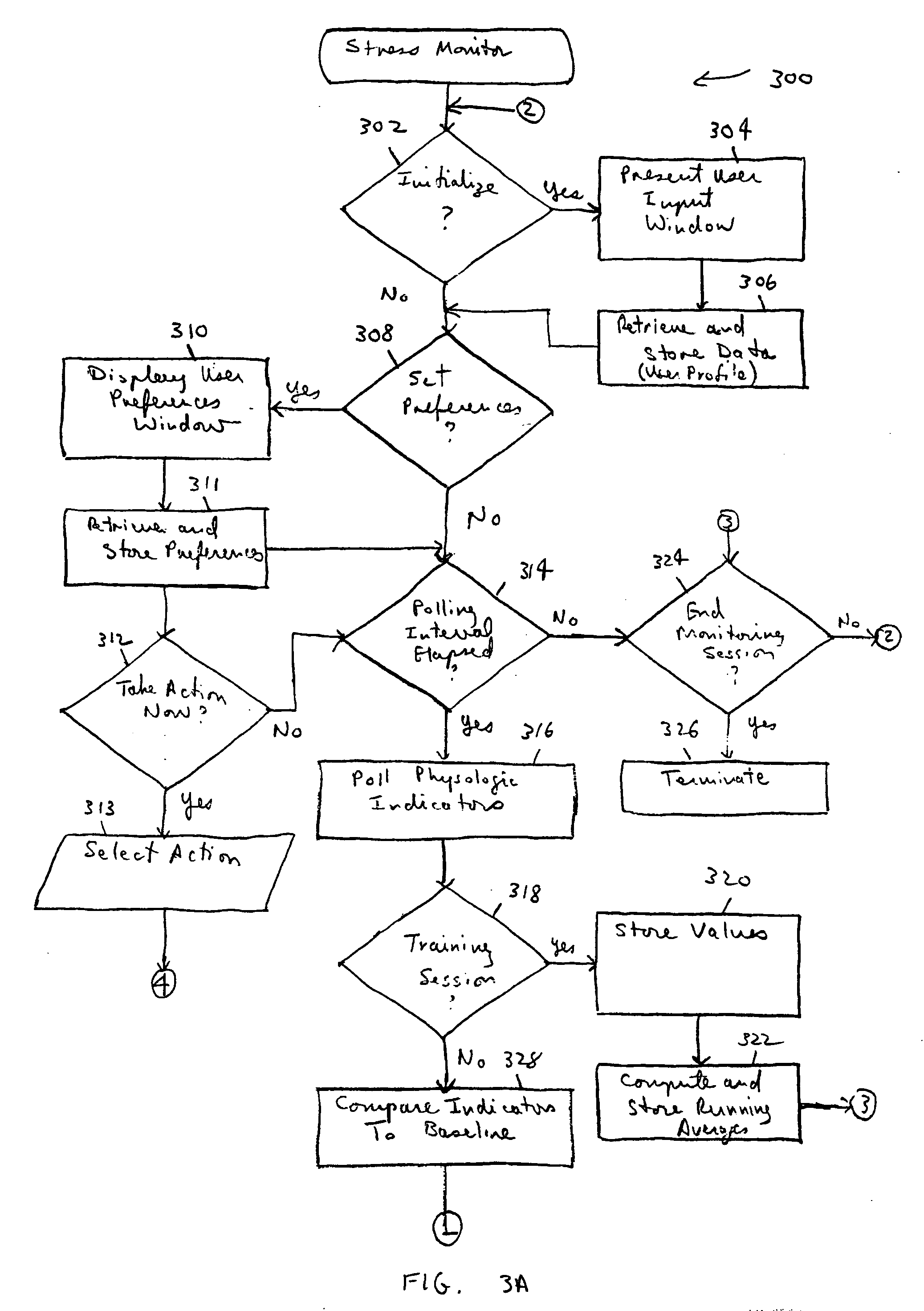
Personal stress level monitor and systems and methods for using same
A mechanism to monitor an individual's level of stress in his or her home or workplace is provided. Unobtrusive physiologic stress senses are used in combination with a wireless link and a personal computer or other intelligent device to monitor the user's stress level. Based on a user profile and the user's baseline stress indicators, one or more stress-reducing activities are presented to the user. Additionally, if a user is in a stress-sensitive population, for example, persons with a pre-existing hypertension, the user may selectively enable additional alerts.
Owner:IBM CORP
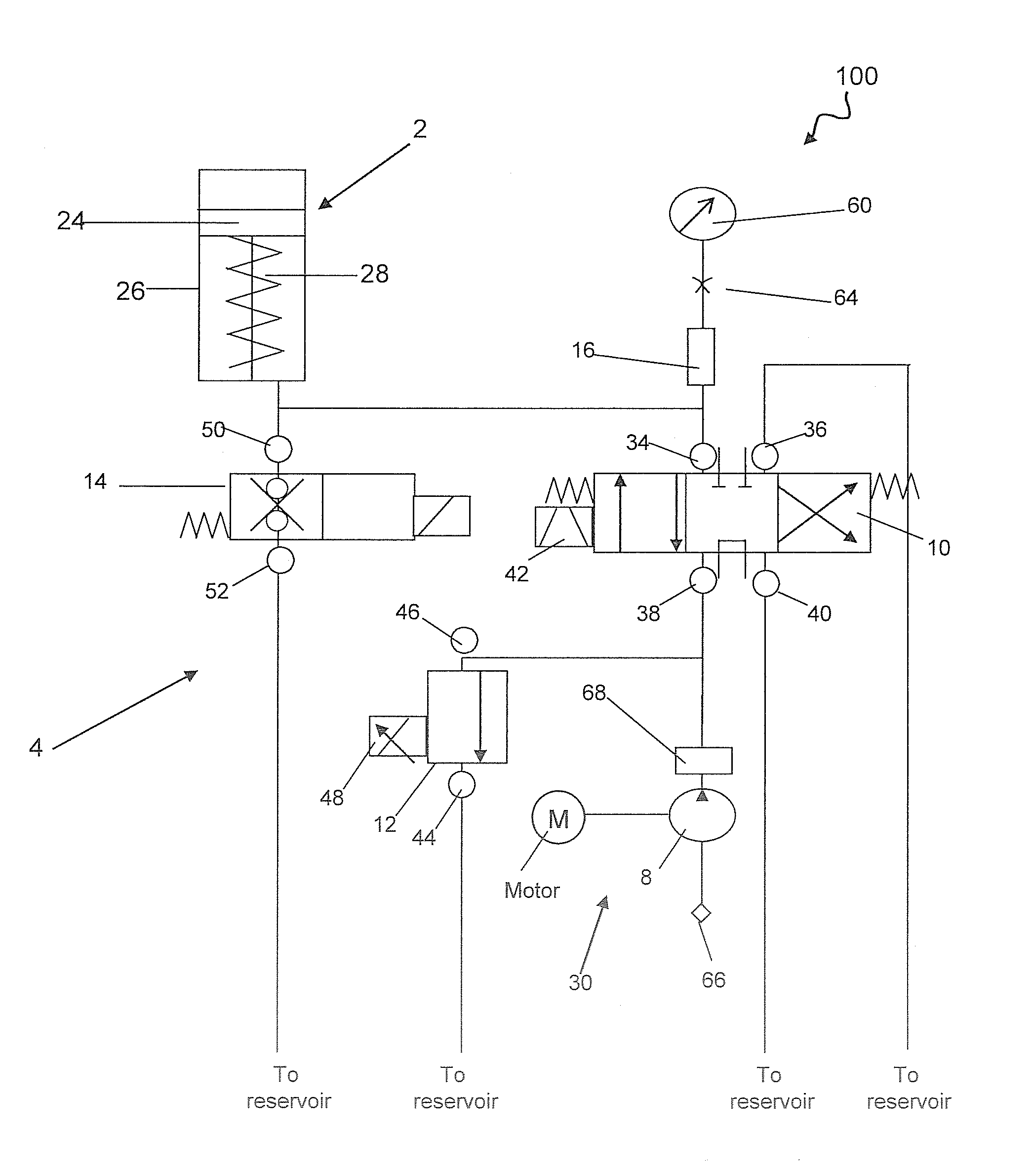
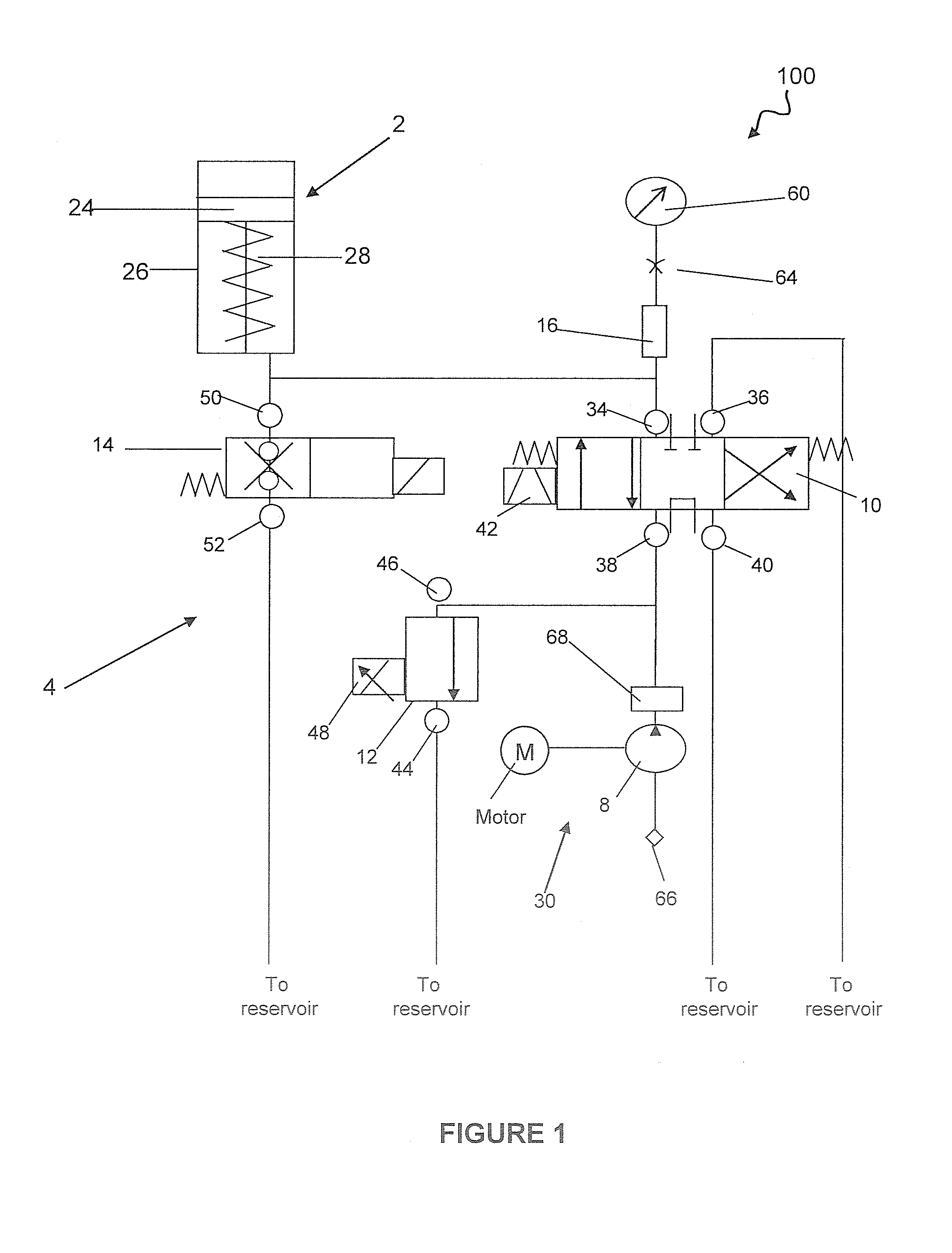
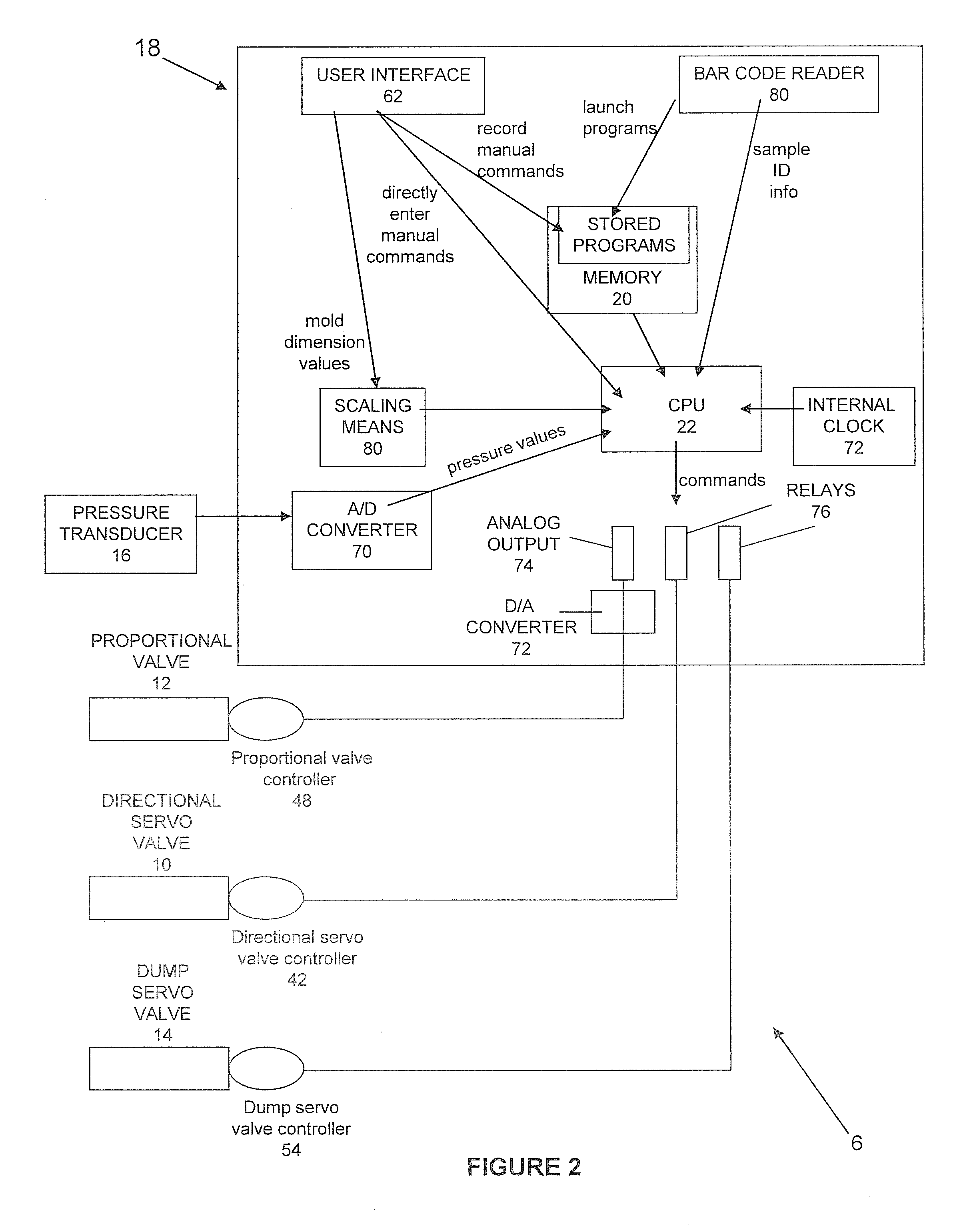
System and method for pressure compensation in a pump
ActiveUS20070125797A1Eliminates and reduces disadvantagePressure compensationFluid parameterLiquid transferring devicesMechanical engineeringBaseline pressure
Systems and methods for maintaining substantially a baseline pressure in a chamber of a pumping apparatus are disclosed. Embodiments of the present invention may serve to control a motor to compensate or account for a pressure drift which may occur in a chamber of the pumping apparatus. More specifically, a dispense motor may be controlled to substantially maintain a baseline pressure in the dispense chamber before a dispense based on a pressure sensed in the dispense chamber. In one embodiment, before a dispense is initiated a control loop may be utilized such that it is repeatedly determined if the pressure in the dispense chamber is above a desired pressure and, if so, the movement of the pumping means regulated to maintain substantially the desired pressure in the dispense chamber until a dispense of fluid is initiated.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
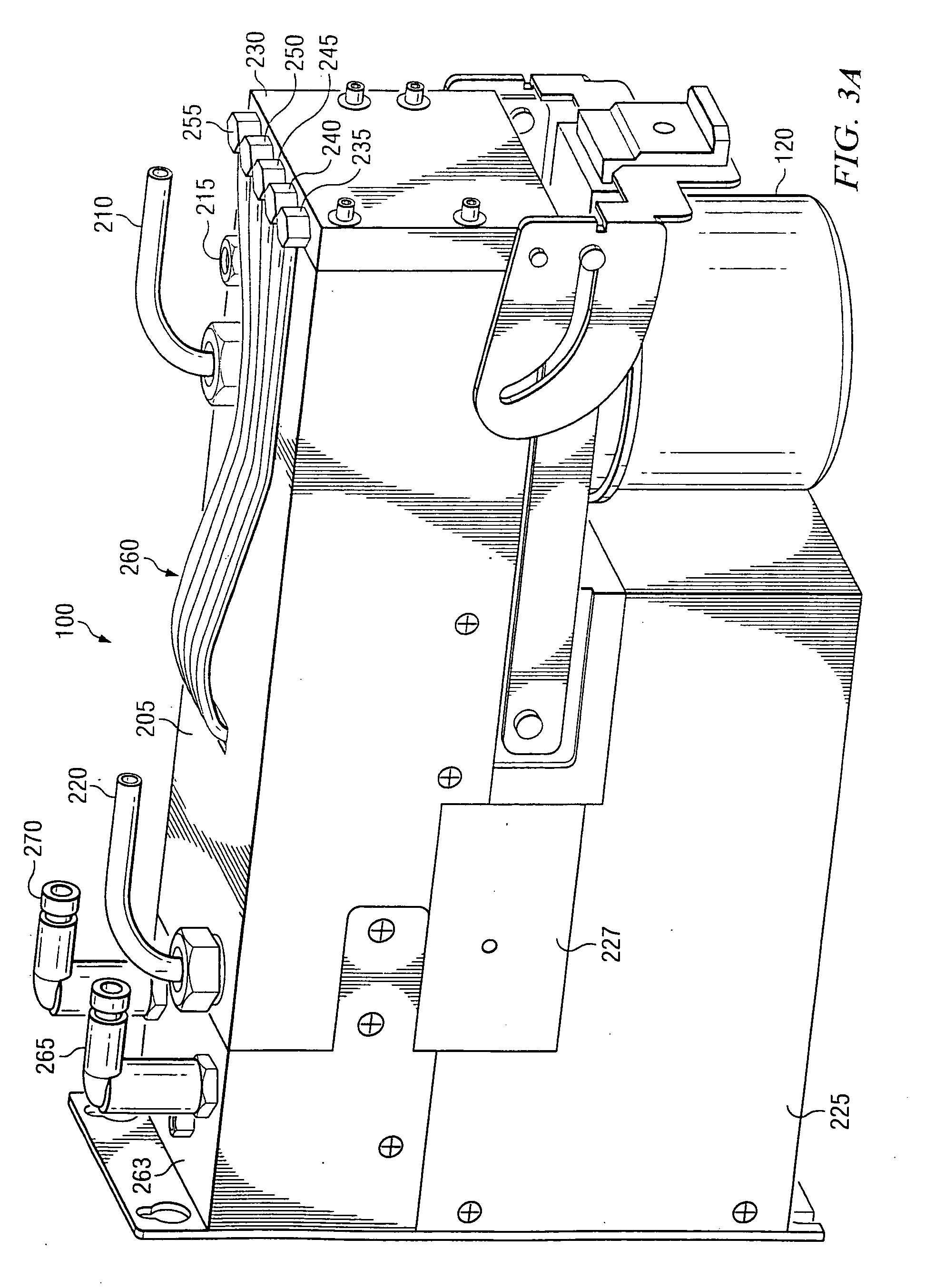
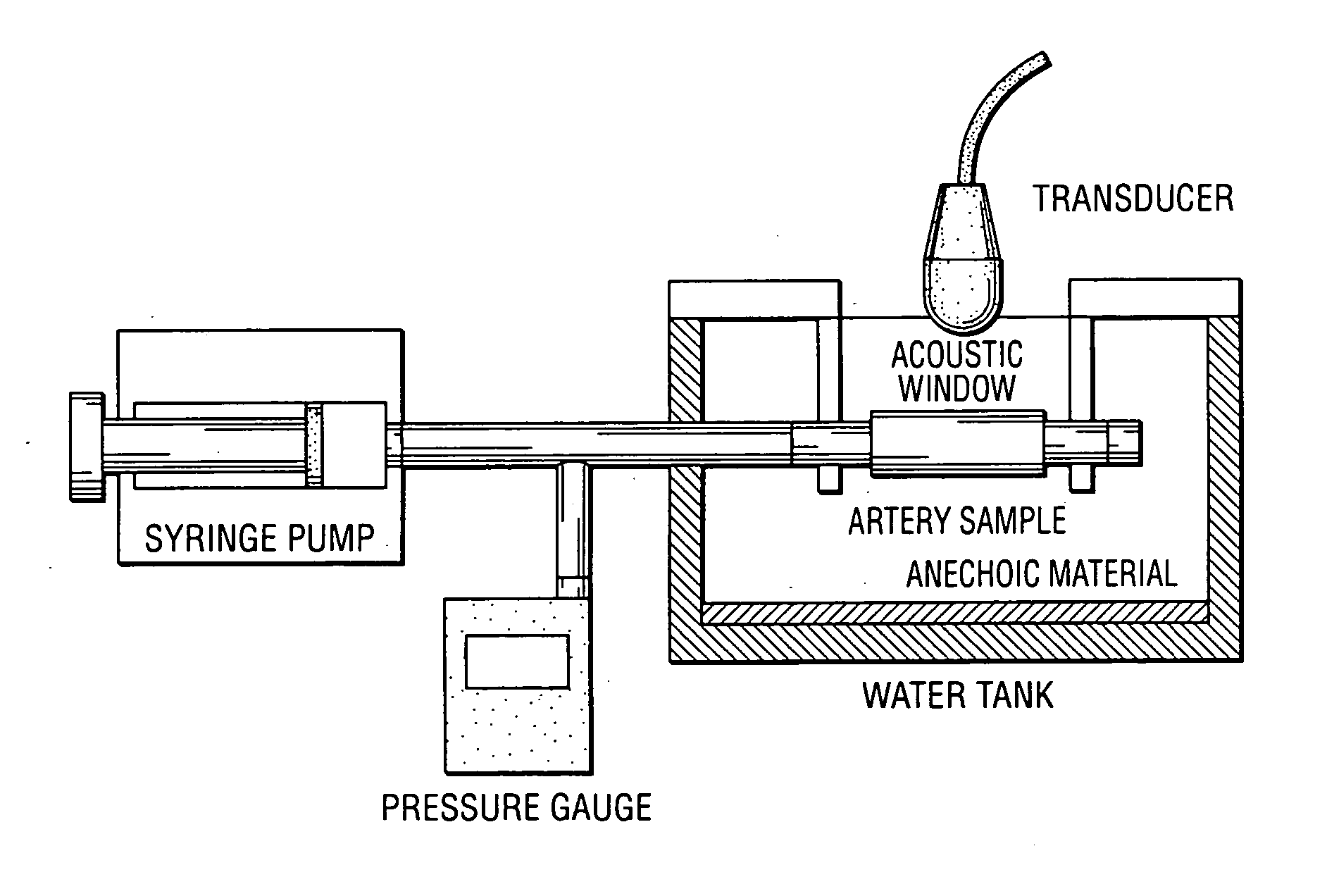
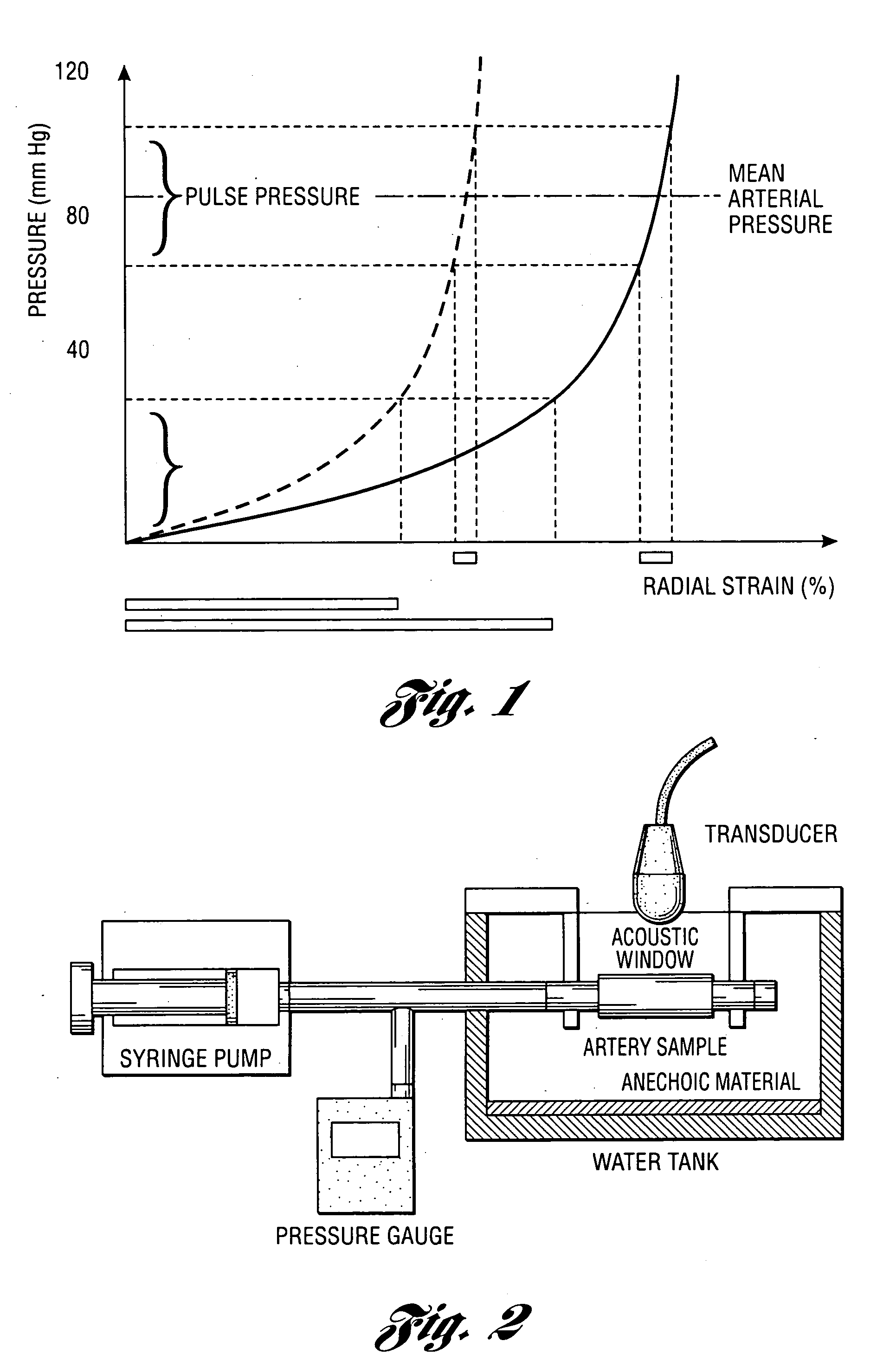
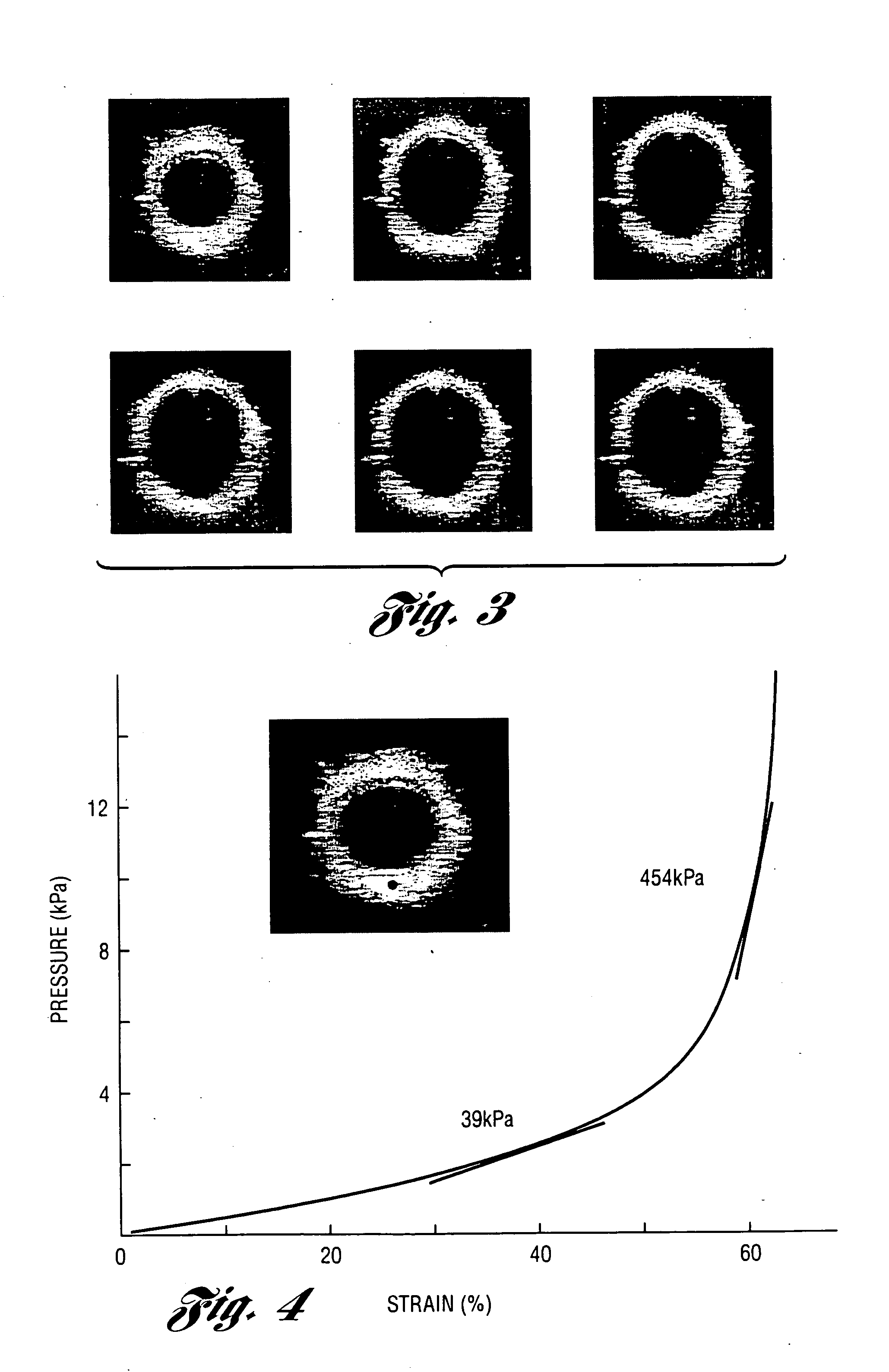
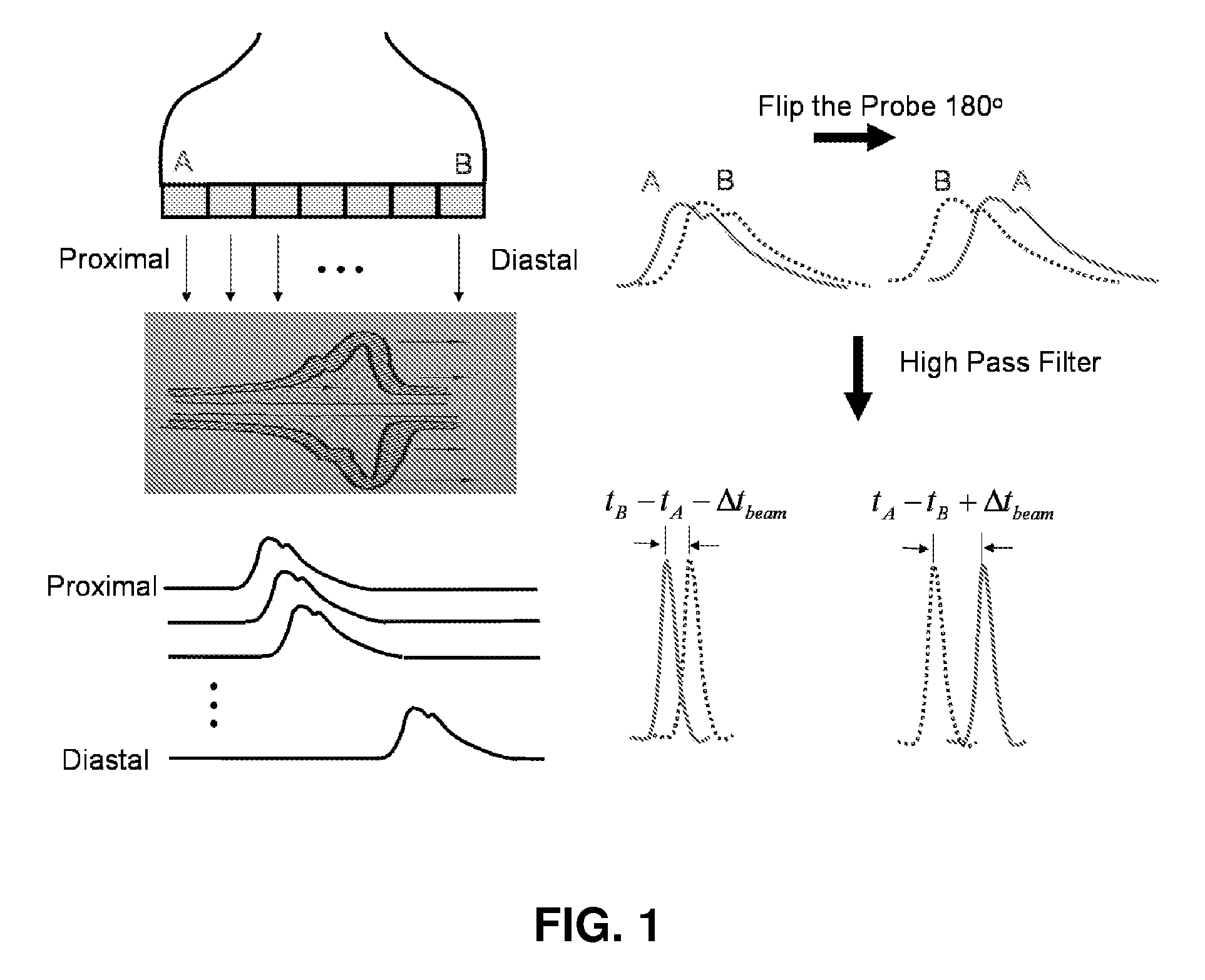
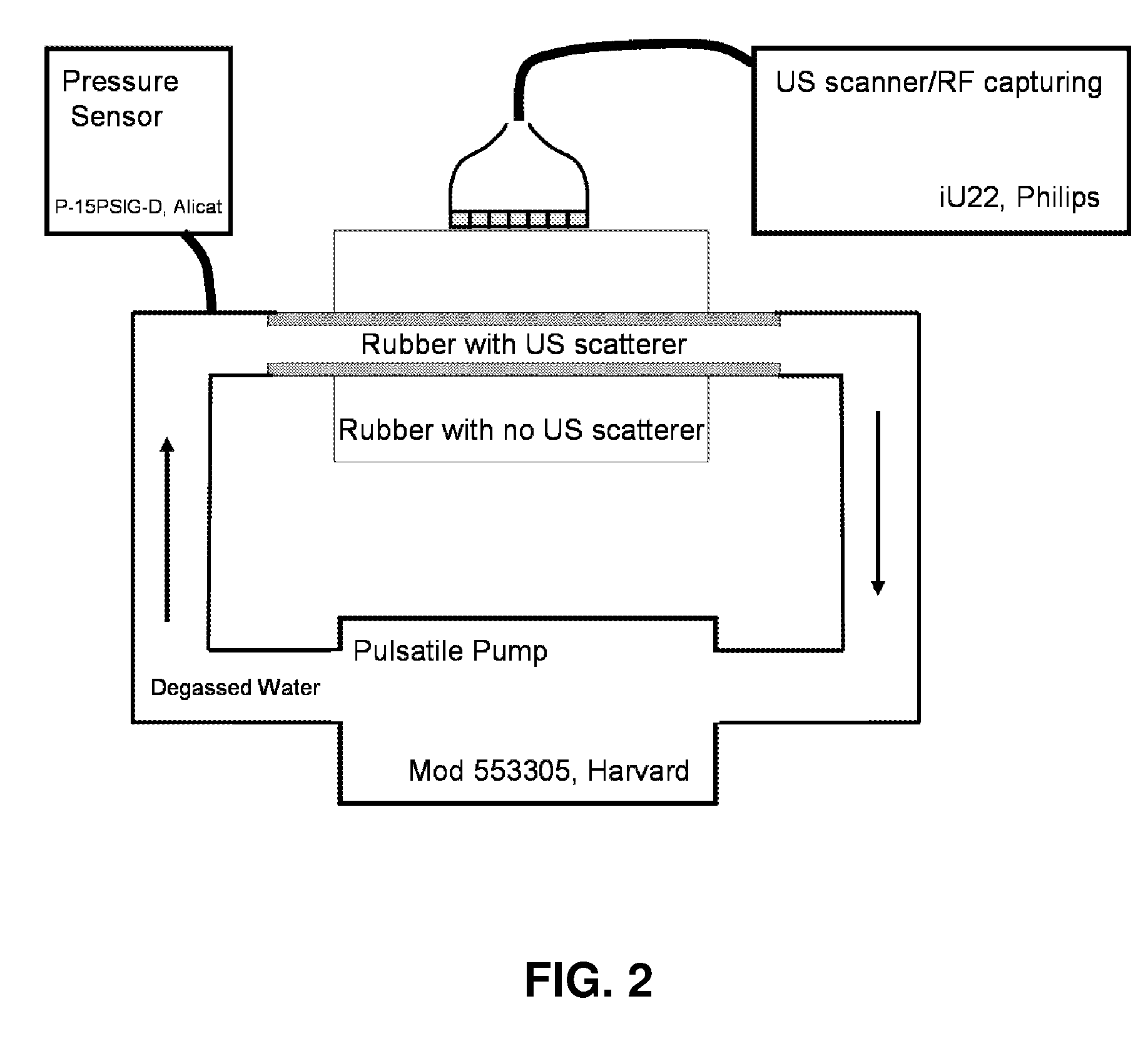
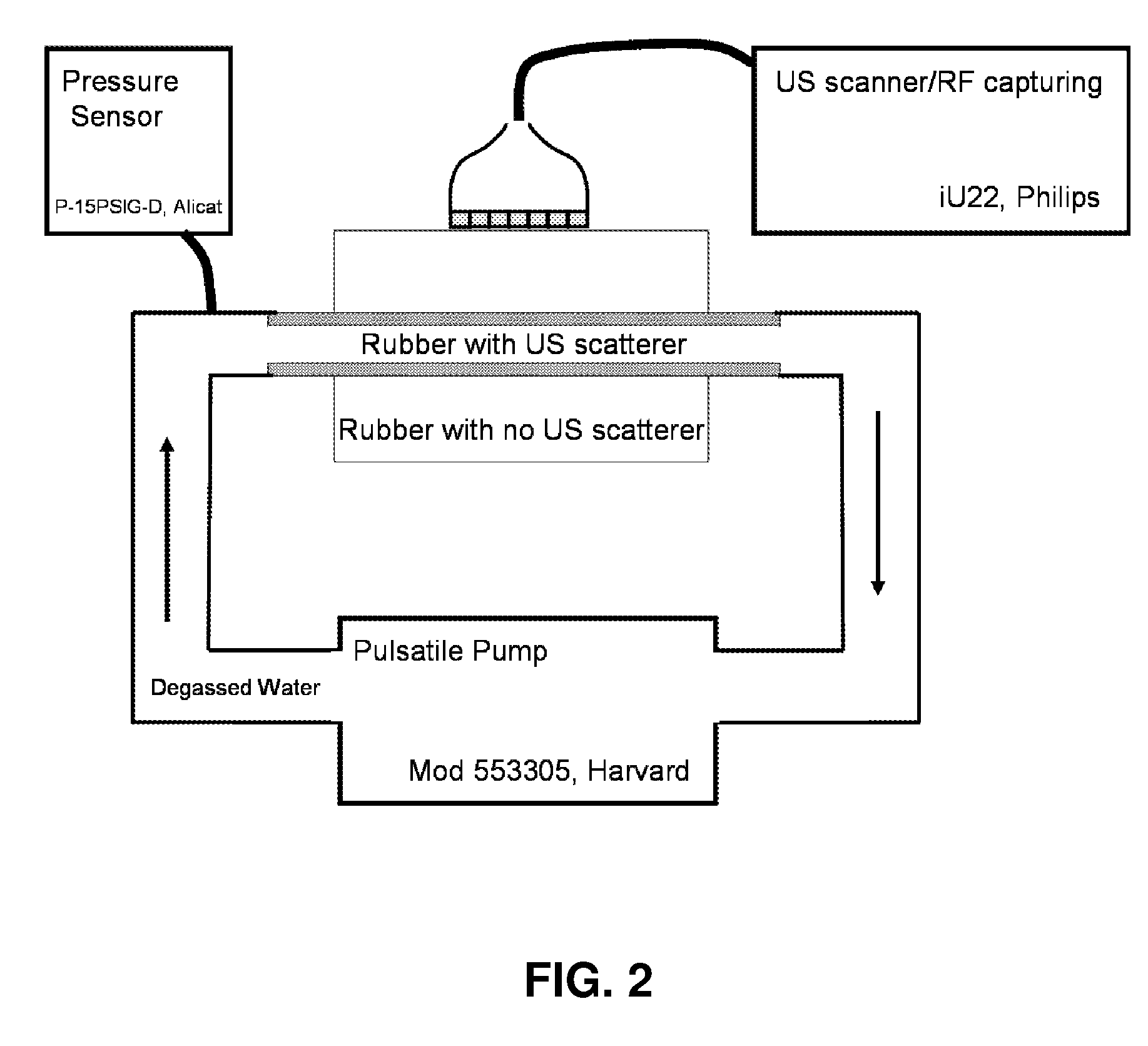
Methods and systems for measuring mechanical property of a vascular wall and method and system for determining health of a vascular structure
InactiveUS20050124892A1Reduce internal pressureBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionCardiac cyclePhase sensitive
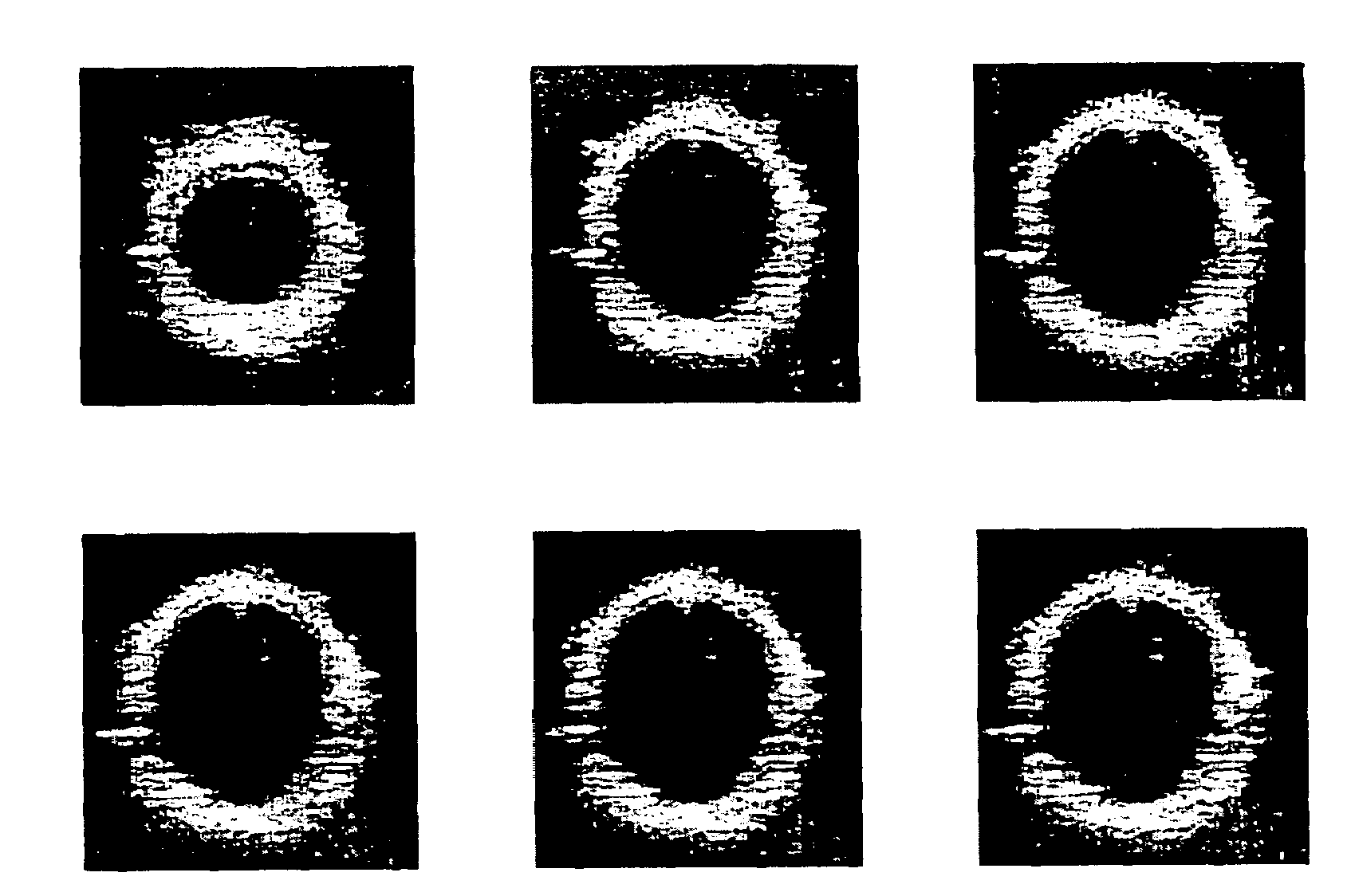
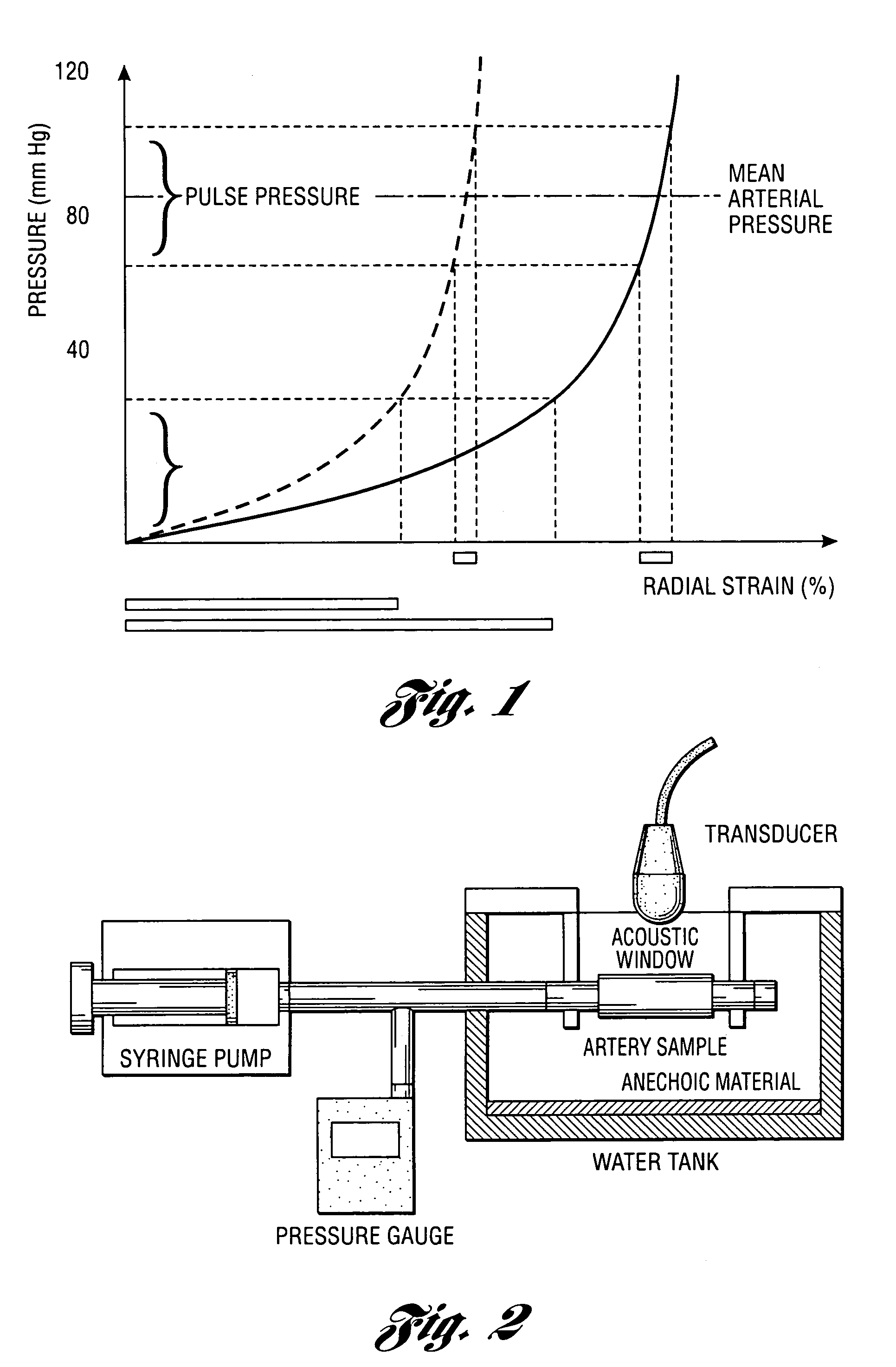
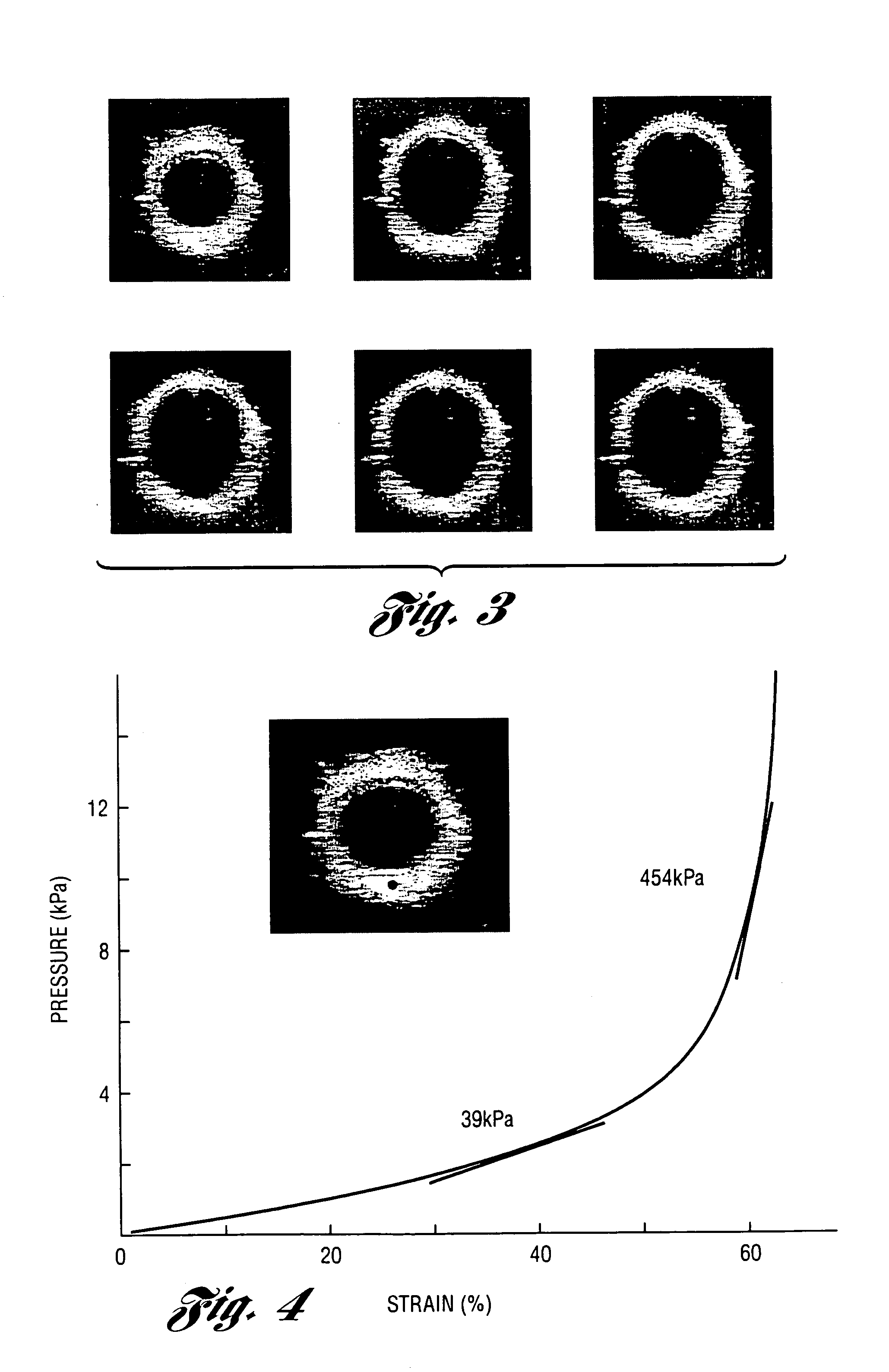
Methods and systems for measuring mechanical property of a vascular wall and a method and system for determining health of a vascular structure are provided wherein local deformation of a vessel wall resulting from physiologic pressures with altered transmural forces is measured. A non-invasive free-hand ultrasound scanning-procedure was performed to apply external force, comparable to the force generated in measuring a subject's blood pressure, to achieve higher strains by equalizing the internal arterial baseline pressure. When the applied pressure matched the internal baseline diastolic pressure, strain and strain rate increased by a factor of 10 over a cardiac cycle. Radial arterial strain was assessed in the vessel wall over the entire deformation procedure using a phase-sensitive, two-dimensional speckle-tracking algorithm. An elastic modulus reconstruction procedure was developed to estimate the non-linear elastic properties of the vascular wall.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Methods and systems for measuring mechanical property of a vascular wall and method and system for determining health of a vascular structure
InactiveUS7318804B2Reduce internal pressureOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsCardiac cyclePhase sensitive
Methods and systems for measuring mechanical property of a vascular wall and a method and system for determining health of a vascular structure are provided wherein local deformation of a vessel wall resulting from physiologic pressures with altered transmural forces is measured. A non-invasive free-hand ultrasound scanning-procedure was performed to apply external force, comparable to the force generated in measuring a subject's blood pressure, to achieve higher strains by equalizing the internal arterial baseline pressure. When the applied pressure matched the internal baseline diastolic pressure, strain and strain rate increased by a factor of 10 over a cardiac cycle. Radial arterial strain was assessed in the vessel wall over the entire deformation procedure using a phase-sensitive, two-dimensional speckle-tracking algorithm. An elastic modulus reconstruction procedure was developed to estimate the non-linear elastic properties of the vascular wall.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
System and method for pressure compensation in a pump
ActiveUS8029247B2Eliminates and reduces disadvantageFluid parameterLiquid transferring devicesPressure senseControl theory
Systems and methods for maintaining substantially a baseline pressure in a chamber of a pumping apparatus are disclosed. Embodiments of the present invention may serve to control a motor to compensate or account for a pressure drift which may occur in a chamber of the pumping apparatus. More specifically, a dispense motor may be controlled to substantially maintain a baseline pressure in the dispense chamber before a dispense based on a pressure sensed in the dispense chamber. In one embodiment, before a dispense is initiated a control loop may be utilized such that it is repeatedly determined if the pressure in the dispense chamber is above a desired pressure and, if so, the movement of the pumping means regulated to maintain substantially the desired pressure in the dispense chamber until a dispense of fluid is initiated.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
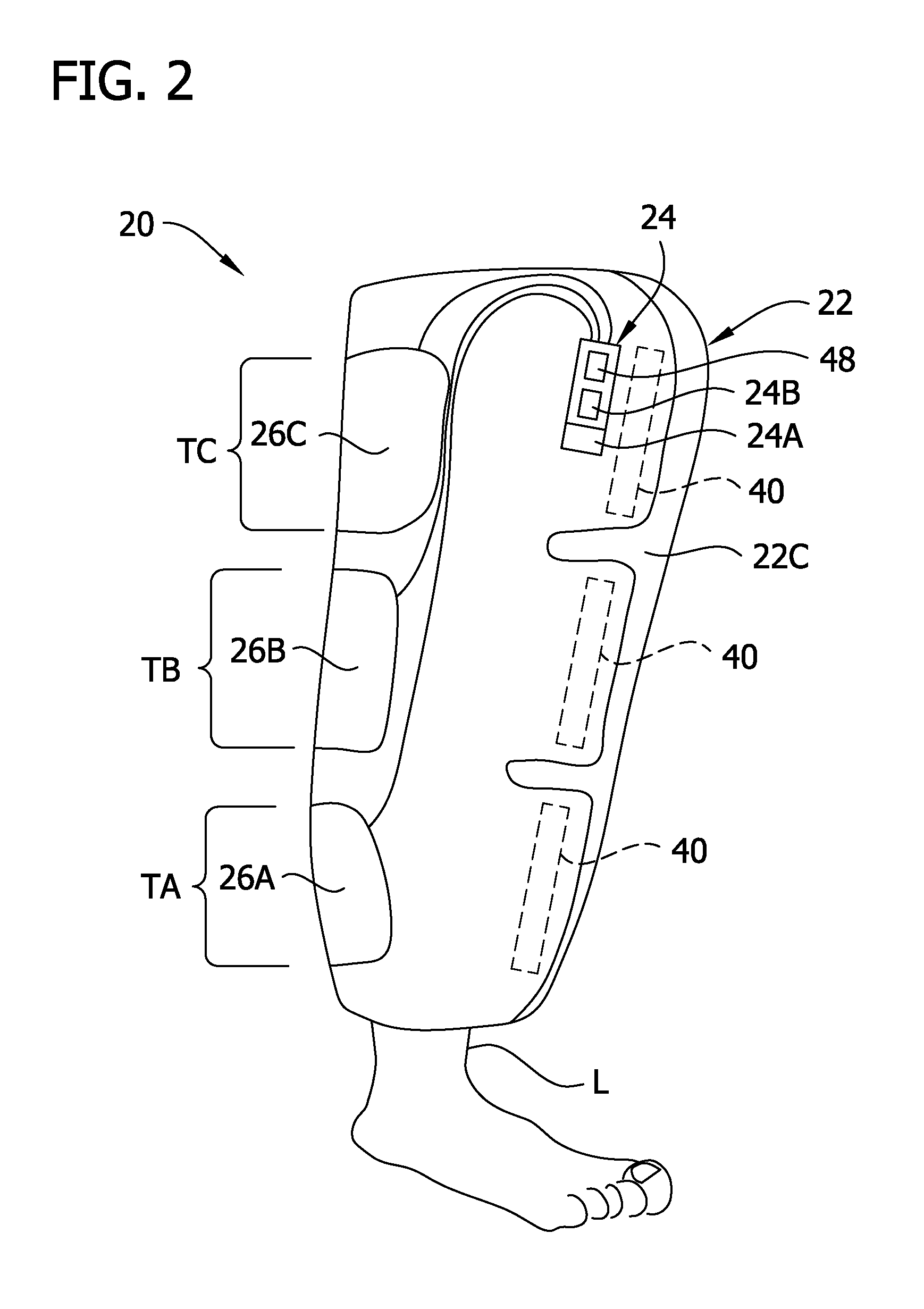
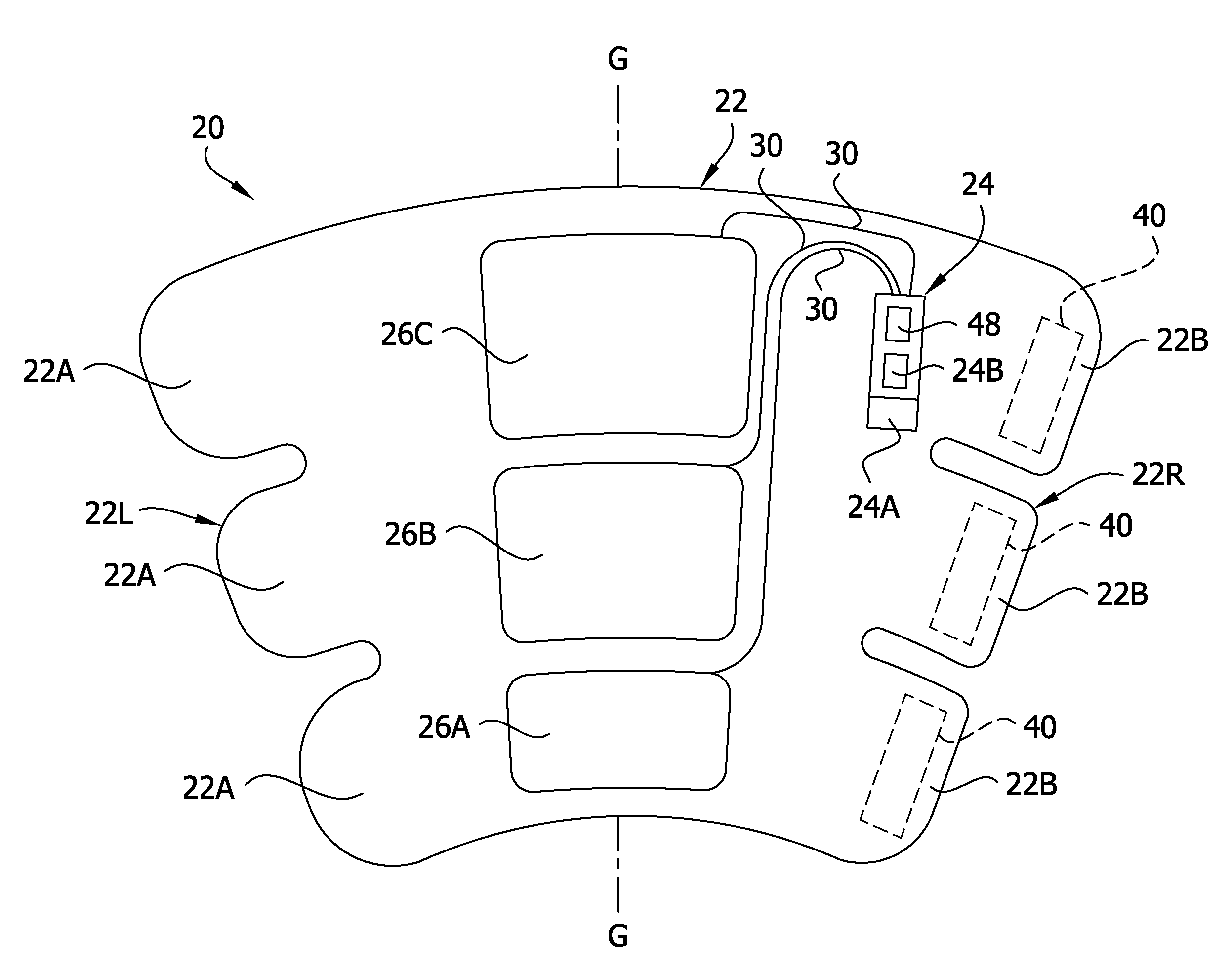
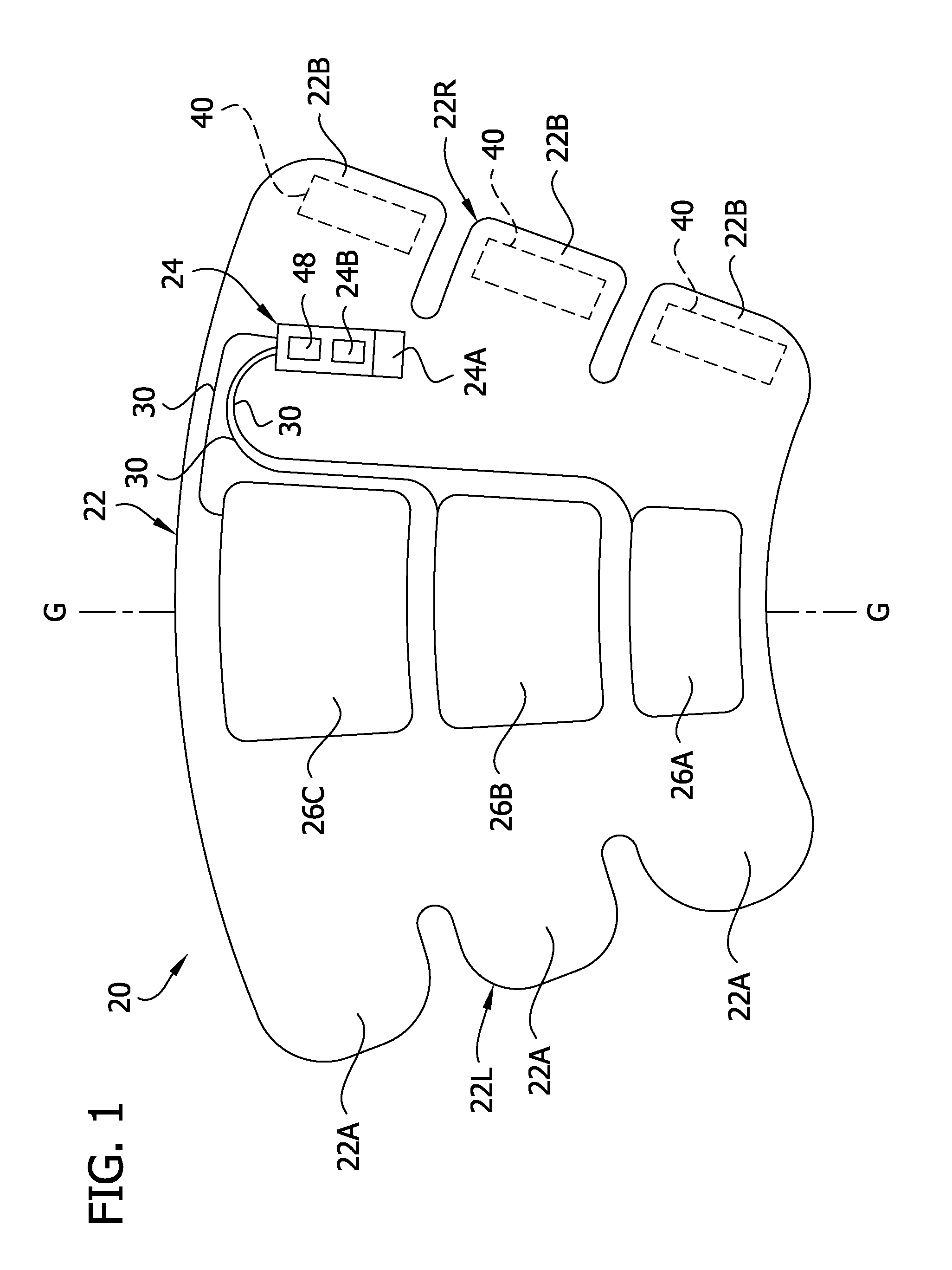
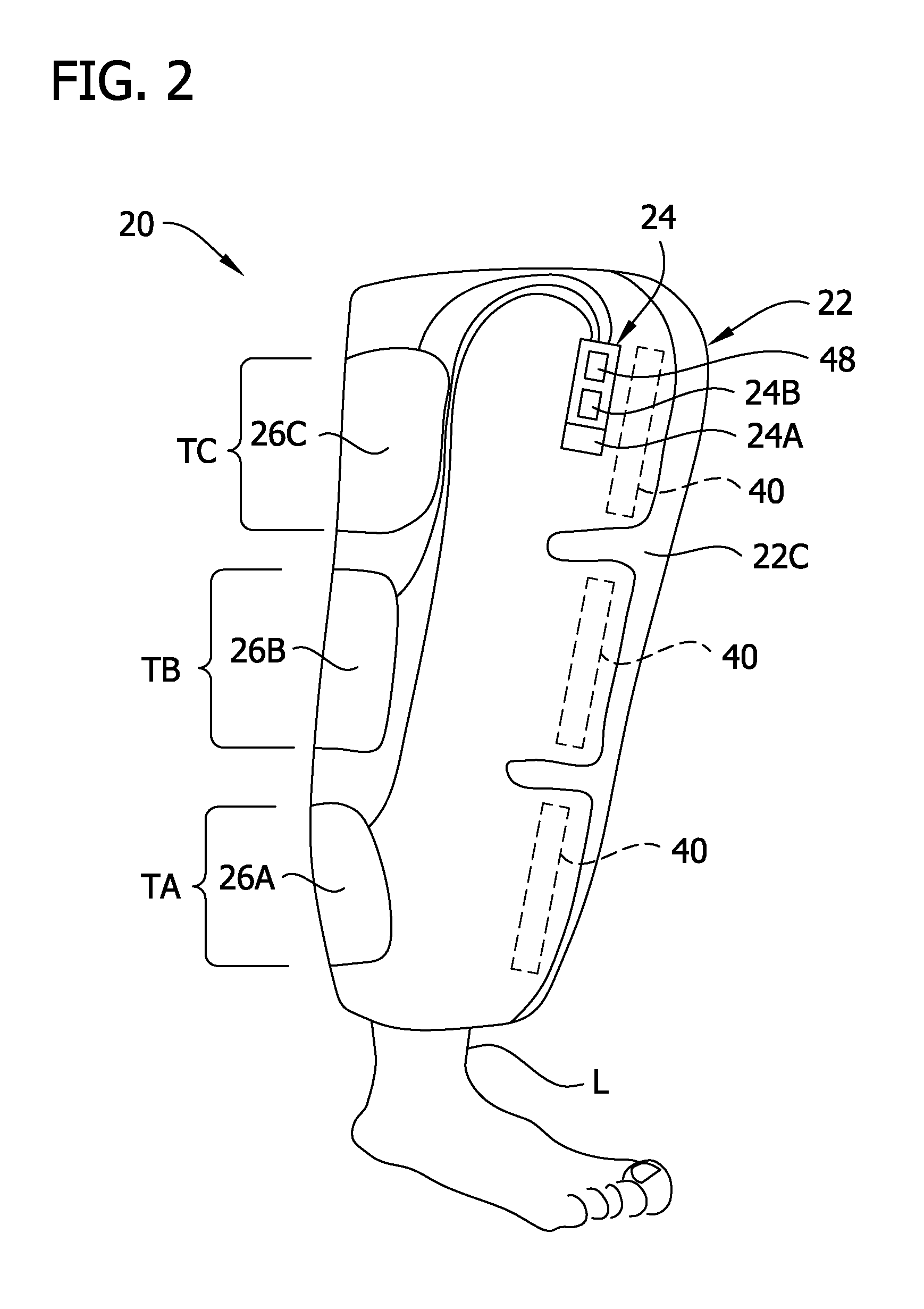
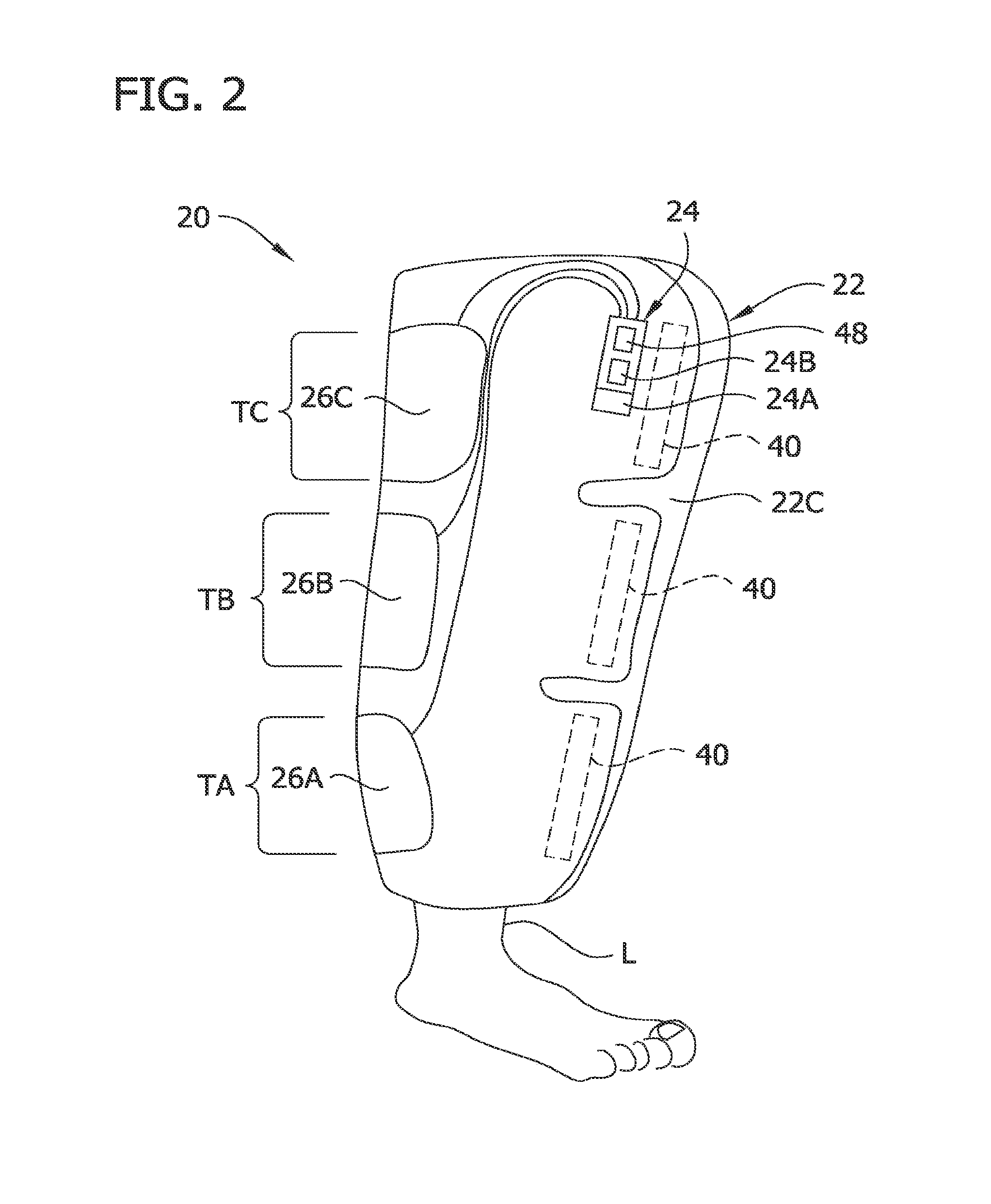
Compression garment apparatus having baseline pressure
A compression garment apparatus including a compression garment and a pressurizer. The pressurizer intermittently pressurizes a therapeutic bladder on the compression garment and maintains a baseline pressure in the therapeutic bladder to maintain the therapeutic bladder in position with respect to a target compression zone on a body part on which the garment is worn. The baseline pressure is adjusted in response to sensed physical characteristics.
Owner:KPR U S LLC
Compression garment apparatus having baseline pressure
A compression garment apparatus including a compression garment and a pressurizer. The pressurizer intermittently pressurizes a therapeutic bladder on the compression garment and maintains a baseline pressure in the therapeutic bladder to maintain the therapeutic bladder in position with respect to a target compression zone on a body part on which the garment is worn. The baseline pressure is adjusted in response to sensed physical characteristics.
Owner:KPR U S LLC
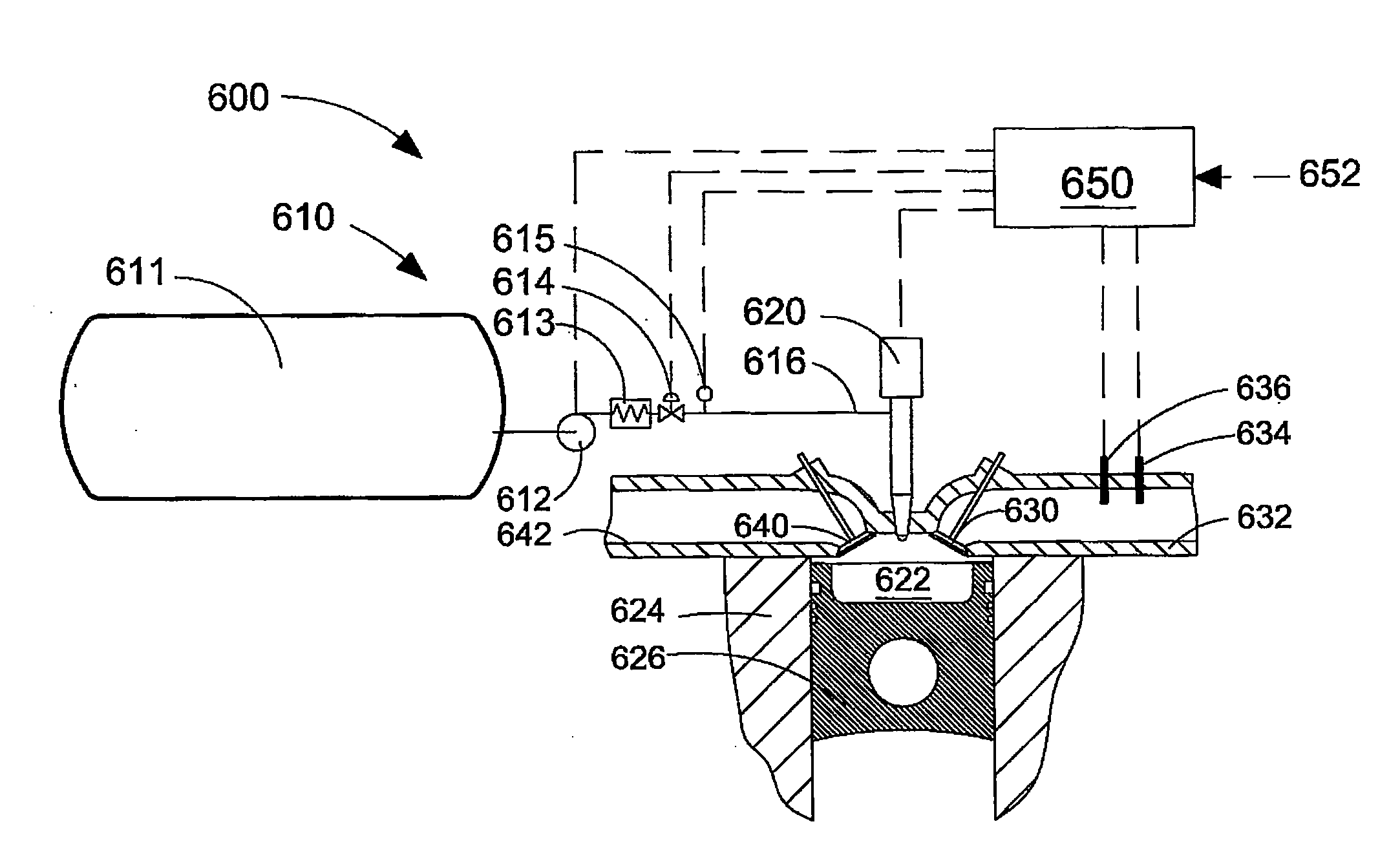
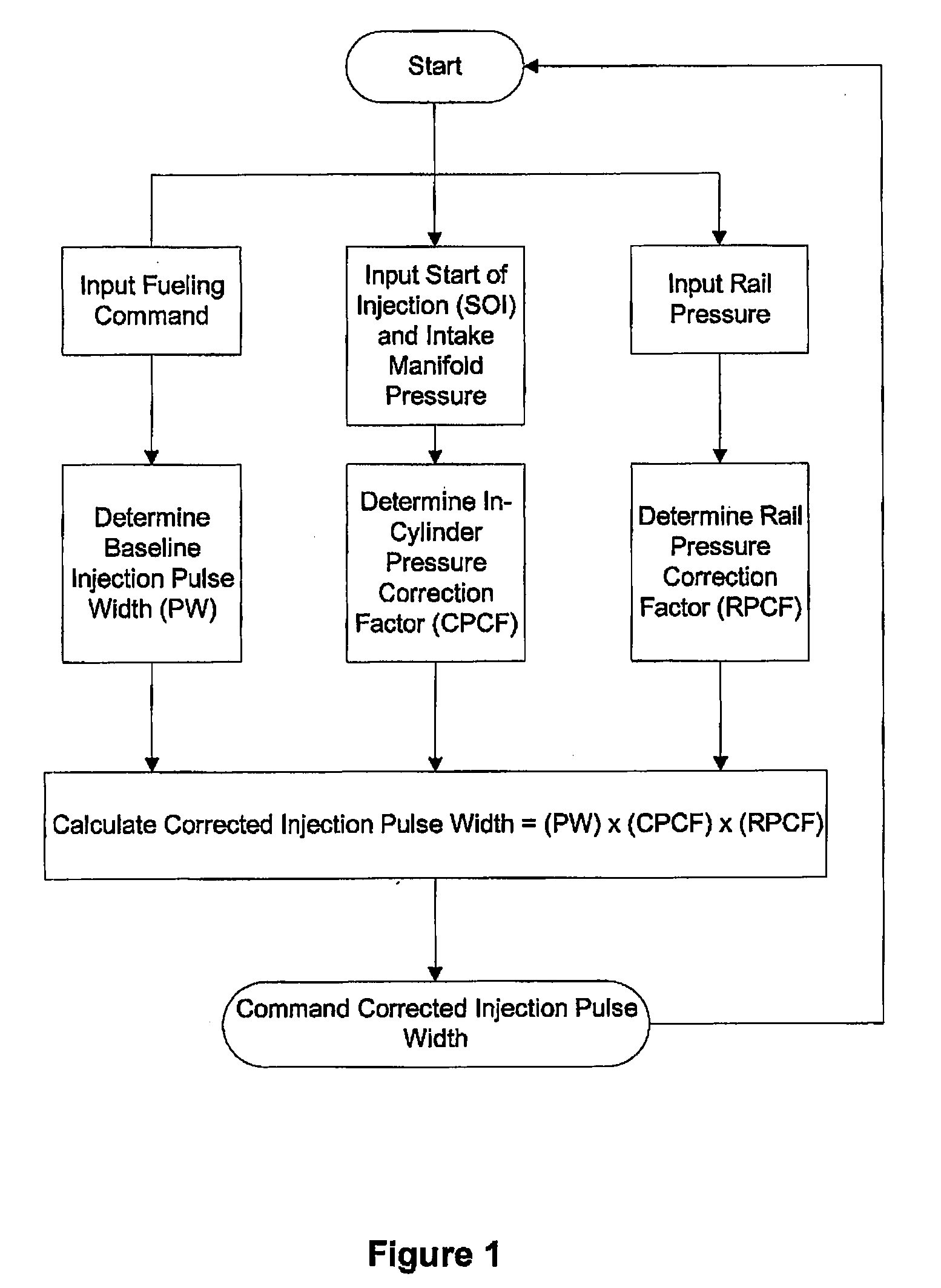
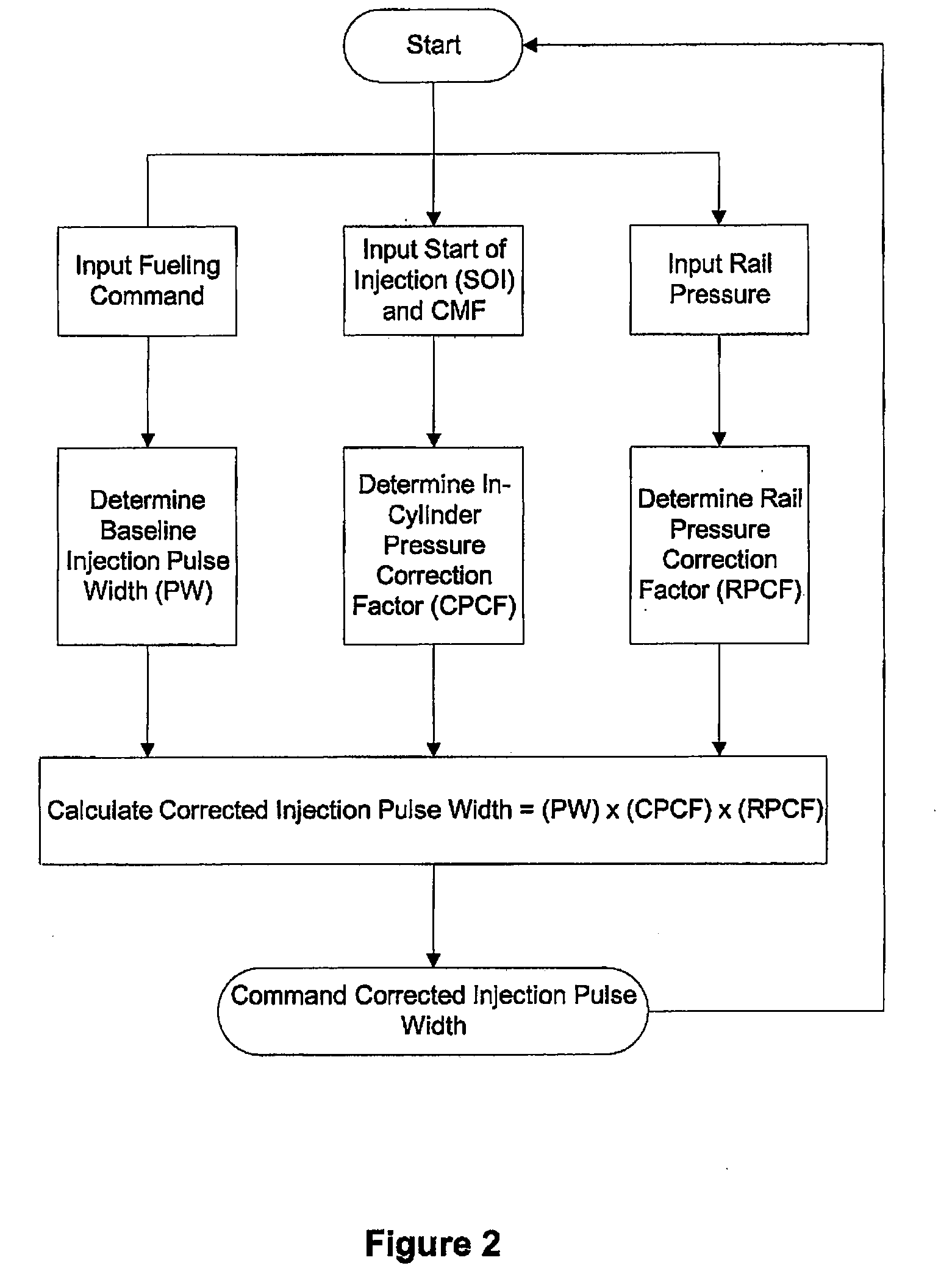
Method Of Accurately Metering A Gaseous Fuel That Is Injected Directly Into A Combustion Chamber Of An Internal Combustion Engine
InactiveUS20090084348A1Accurate measurementElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion chamberEngineering
For gaseous fuels that are injected directly into a combustion chamber the mass flow rate through an injection valve can be influenced by changes in the in-cylinder pressure. A method and apparatus are provided for accurately metering a gaseous into a combustion chamber of an internal combustion engine. The method comprises inputting a fueling command; determining from said fueling command a baseline pulse width of an injection event, based upon a baseline pressure differential across a fuel injection valve; estimating the difference between said baseline pressure differential and an actual pressure differential; calculating a corrected pulse width by applying at least one correction factor to said baseline pulse width, wherein said correction factor is a function of the estimated difference between said baseline pressure differential and said actual pressure differential.
Owner:WESTPORT POWER
Measurement of tissue elastic modulus
ActiveUS20080081994A1Easy to measureEasy to quantifyWave based measurement systemsBlood flow measurement devicesArterial velocityMedicine
An optimized elastic modulus reconstruction procedure can estimate the nonlinear elastic properties of vascular wall from intramural strain and pulse wave velocity (PWV) measurements. A noninvasive free-hand ultrasound scanning procedure is used to apply external force, comparable to the force in measuring a subject's blood pressure, to achieve higher strains by equalizing the internal arterial baseline pressure. PWV is estimated at the same location where intramural strain is measured. The reconstructed elastic modulus is optimized and the arterial elastic modulus can be determined and monitored using a simple dual elastic modulus reconstruction procedure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
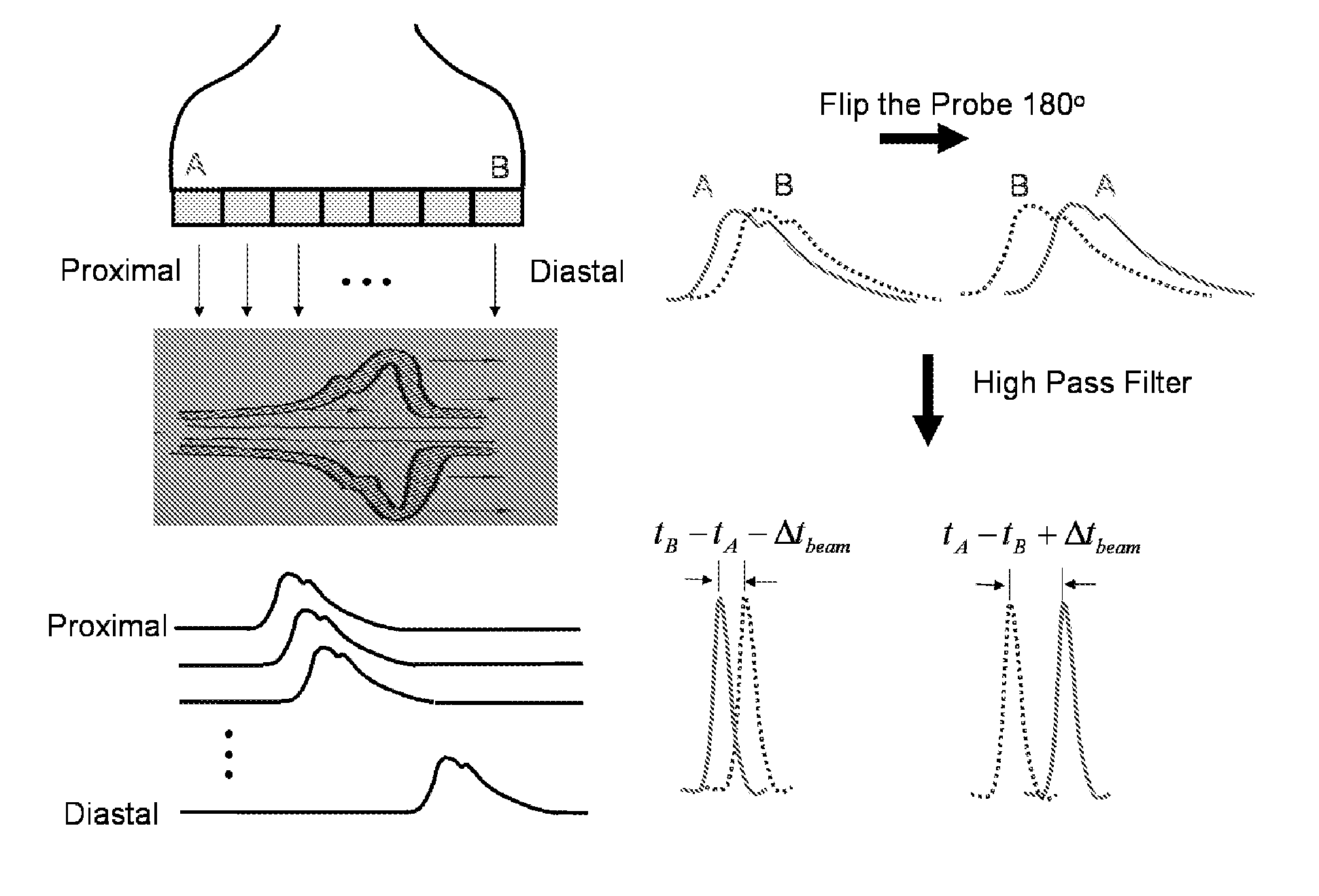
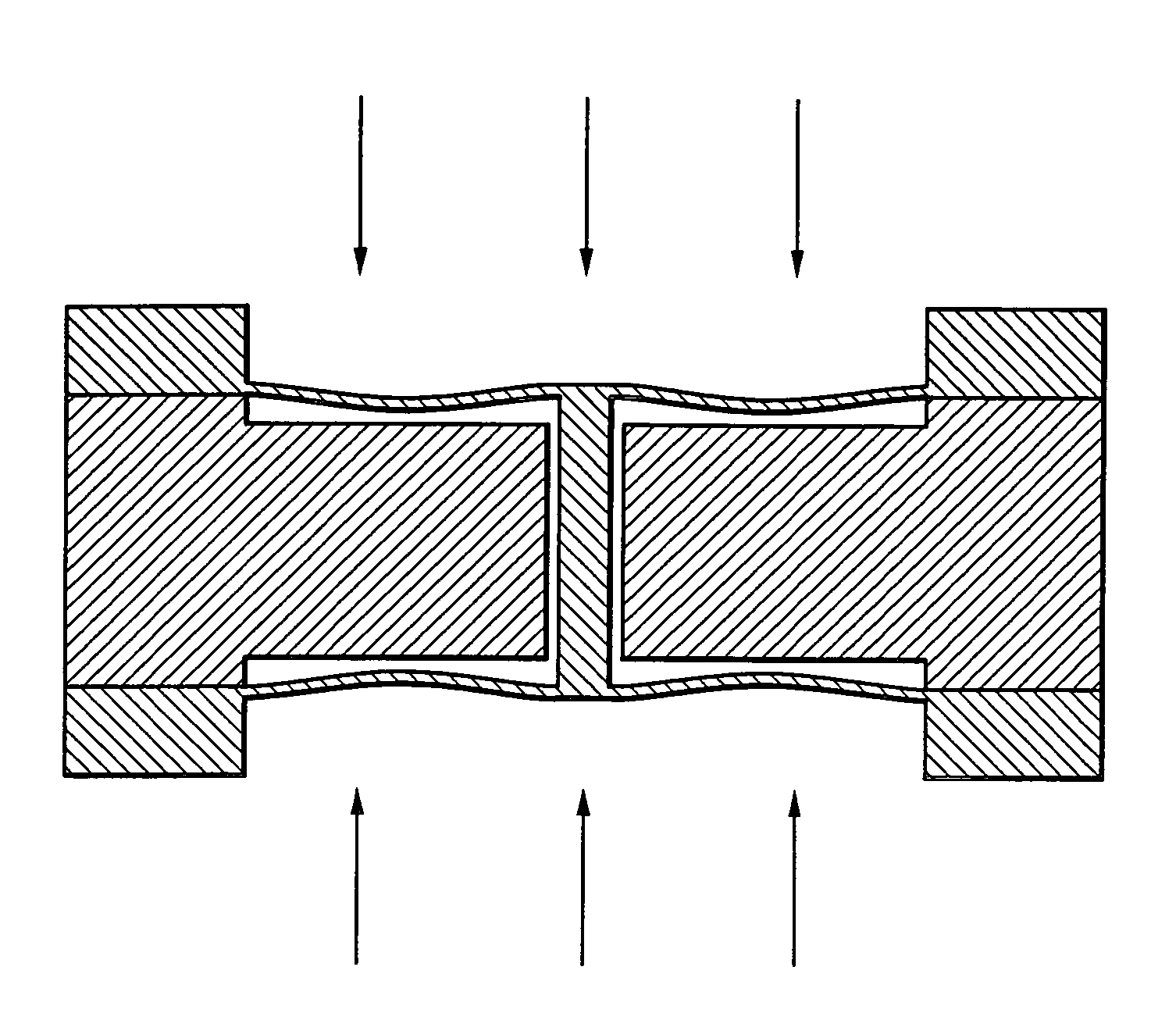
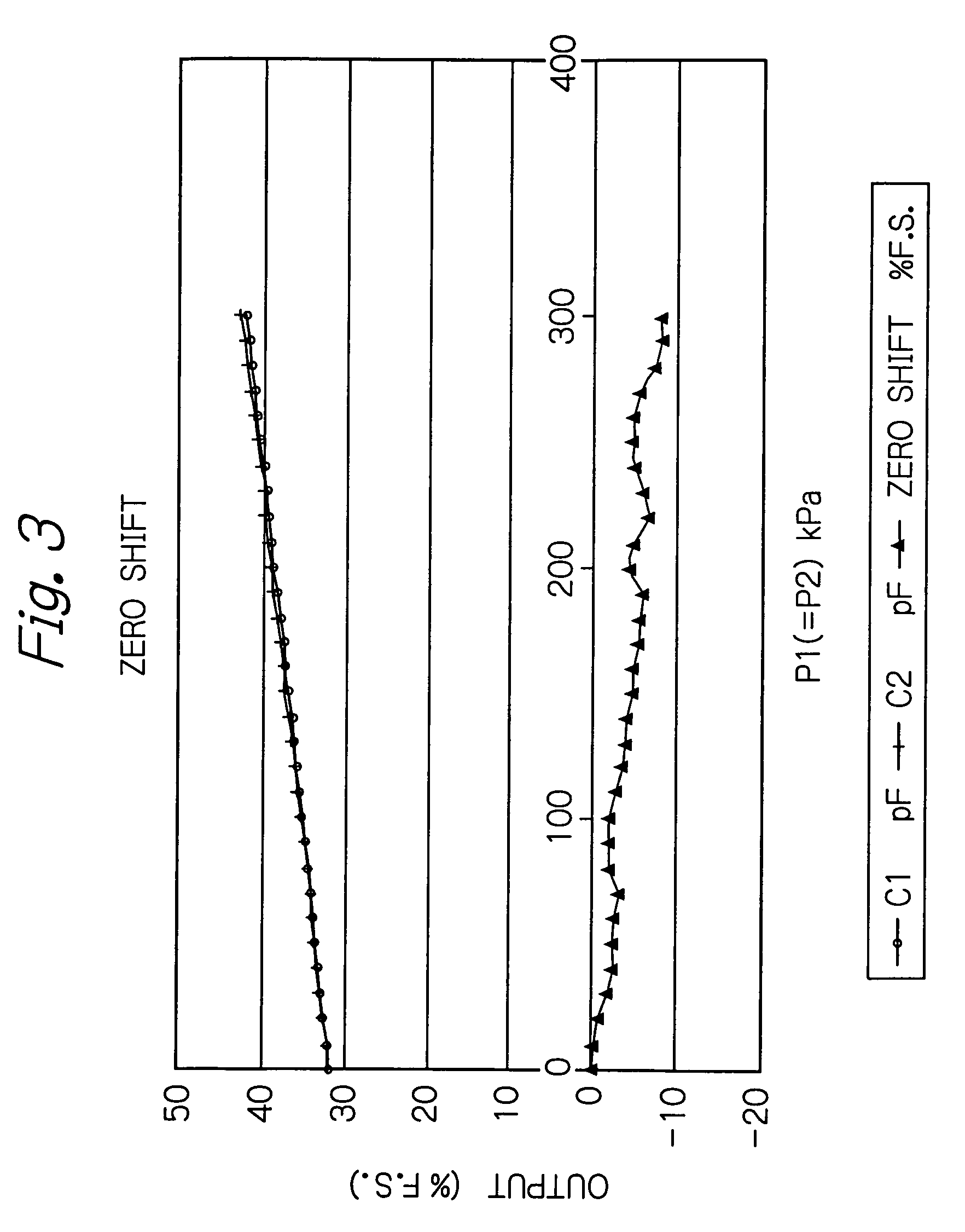
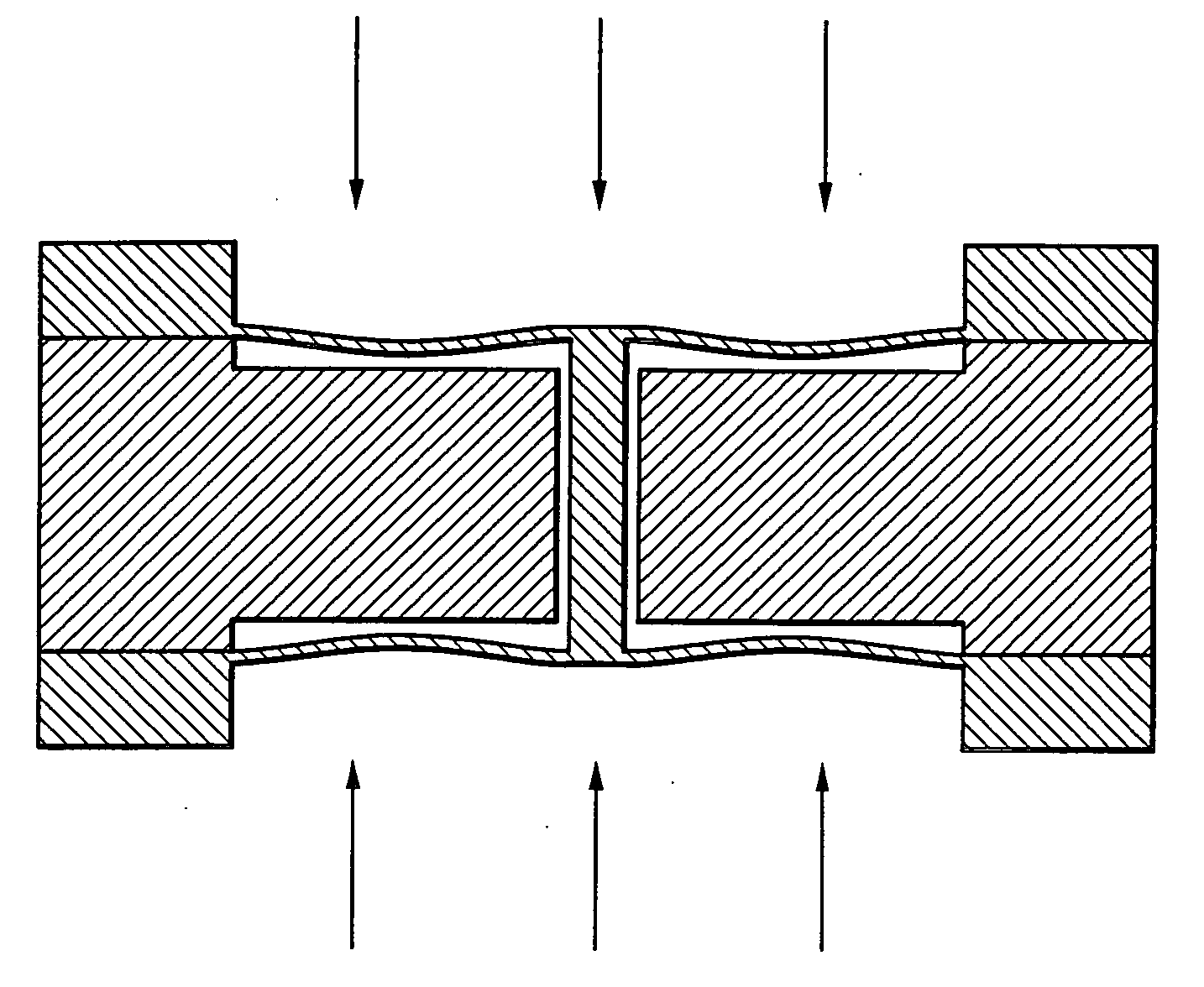
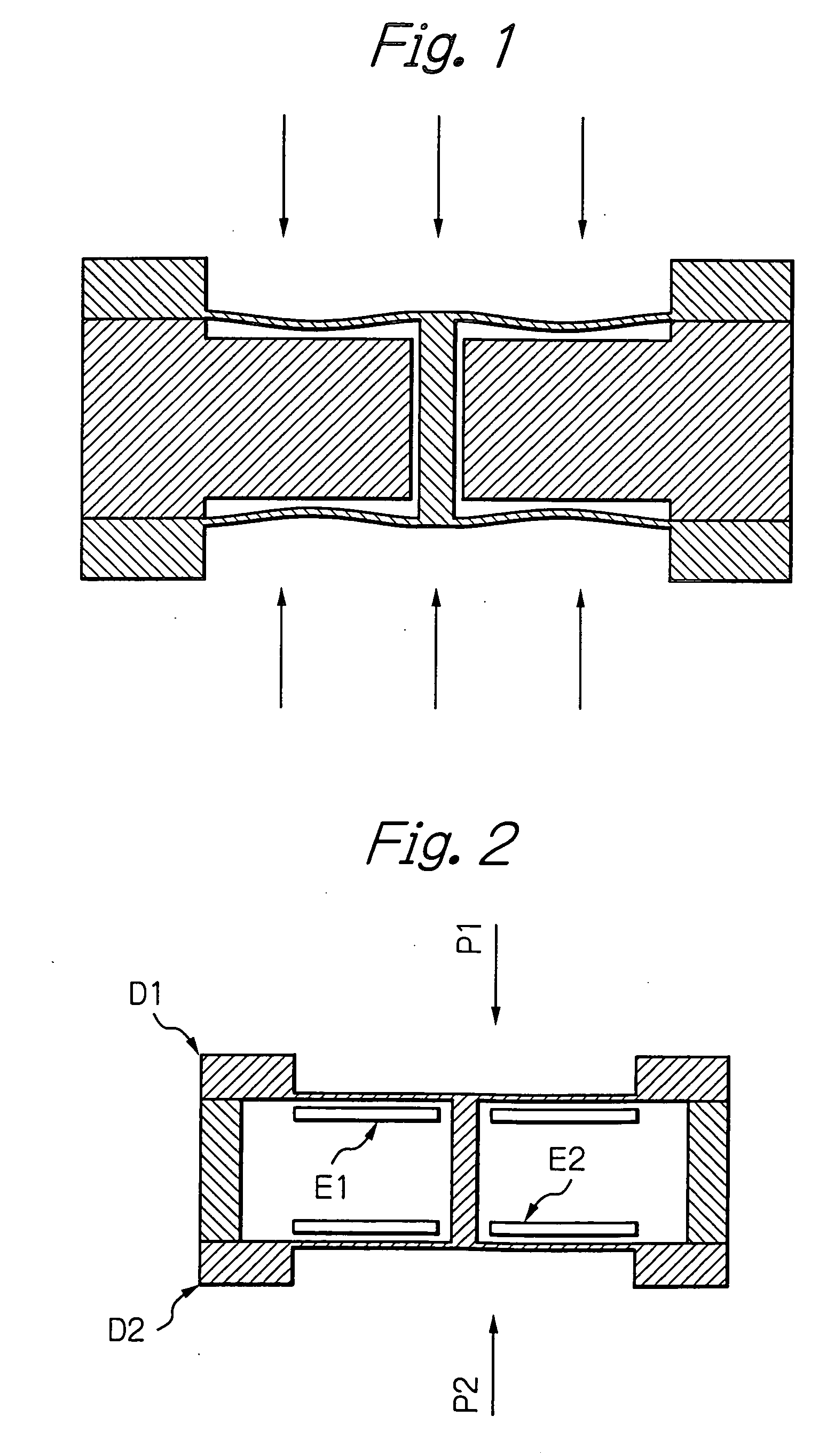
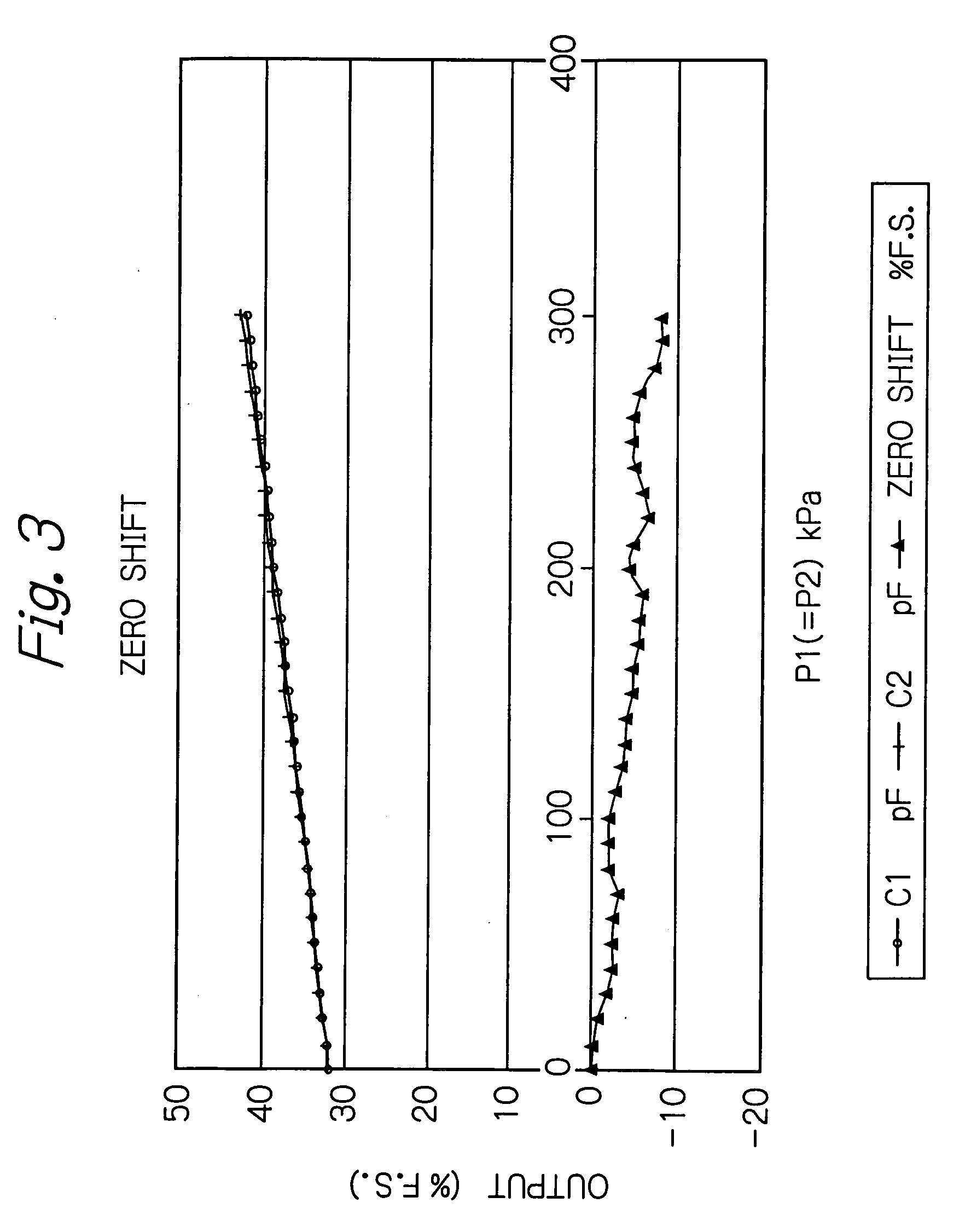
Differential pressure sensor
InactiveUS7219551B2Sensitive and accurate detectionApparatus for force/torque/work measurementPressure difference measurement between multiple valvesCapacitanceDifferential pressure
According to the present invention, there is provided a high-precision differential pressure sensor which is not affected by a considerable change in baseline pressure. A differential pressure sensor of the present invention includes: a pair of diaphragms, each including a diaphragm portion capable of being deformed due to application of a pressure and a support portion for holding an outer peripheral edge of the diaphragm portion; a pair of fixed electrodes in disk-like form fixed to the support portions of the diaphragms; and a movable electrode including a disk-like electrode portion and shaft-like projections extending in opposite directions from a central portion of the electrode portion. The shaft-like projections extend at a right angle relative to the electrode portion, and the movable electrode is secured to central portions of the diaphragms through the shaft-like projections so that the electrode portion faces each of the fixed electrodes in a predetermined spaced relationship. The movable electrode is capable of moving so as to allow a distance between the electrode portion and each of the fixed electrodes to vary according to a difference between fluid pressures acting on the respective diaphragm portions of the diaphragms. A capacitance generated between the electrode portion and each of the fixed electrode changes due to a variance in the distance between the electrode portion and each of the fixed electrode, and a differential pressure is detected, based on this change in capacitance.
Owner:MKS JAPAN INC
Stroke intervention apparatus and method
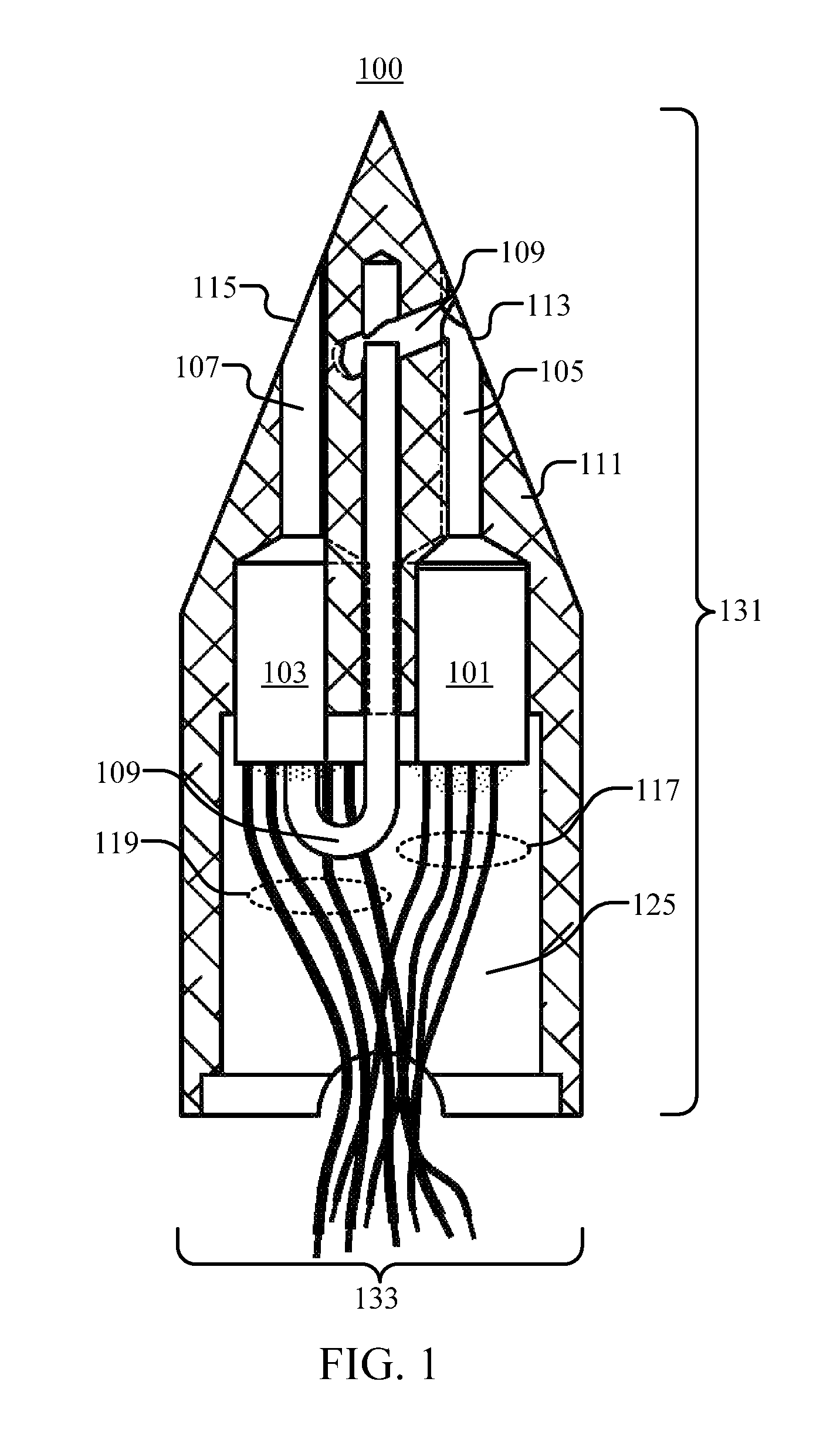
Disclosed herein is an intrathecal catheter having a lumen adapted to transfer liquid between the proximal end of the catheter and its distal end; a pressure detector; and a first sealer, adapted to seal the catheter against a tissue. Also disclosed herein is a stroke intervention system comprising an intrathecal catheter, an infusate supply chamber in fluid communication with the catheter; a pump in fluid communication with the catheter; and a pressure gauge in fluid communication with the pressure detector. Disclosed are also methods of reducing neural injury in a patient during a stroke comprising introducing a catheter intravenously or into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) system of the patient; measuring a baseline pressure; infusing and withdrawing infusate fluid into the cerebral venous vasculature or the CSF system at regular intervals.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
Dynamic residue clearing control with in-situ profile control (ISPC)
A method for controlling the residue clearing process of a chemical mechanical polishing (“CMP”) process is provided. Dynamic in-situ profile control (“ISPC”) is used to control polishing before residue clearing starts, and then a new polishing recipe is dynamically calculated for the clearing process. Several different methods are disclosed for calculating the clearing recipe. First, in certain implementations when feedback at T0 or T1 methods are used, a post polishing profile and feedback offsets are generated in ISPC software. Based on the polishing profile and feedback generated from ISPC before the start of the clearing process, a flat post profile after clearing is targeted. The estimated time for the clearing step may be based on the previously processed wafers (for example, a moving average of the previous endpoint times). The calculated pressures may be scaled to a lower (or higher) baseline pressure for a more uniform clearing.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
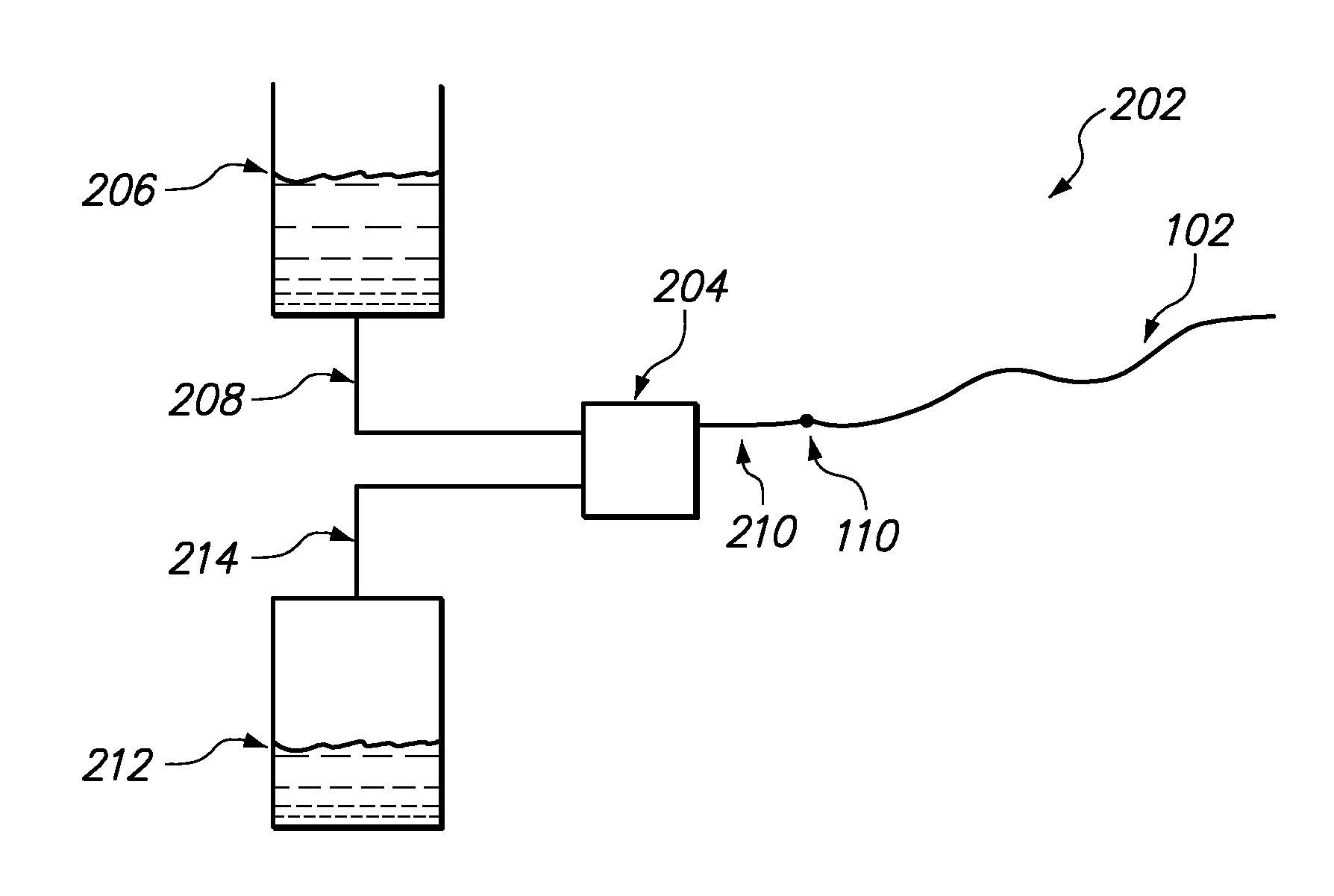
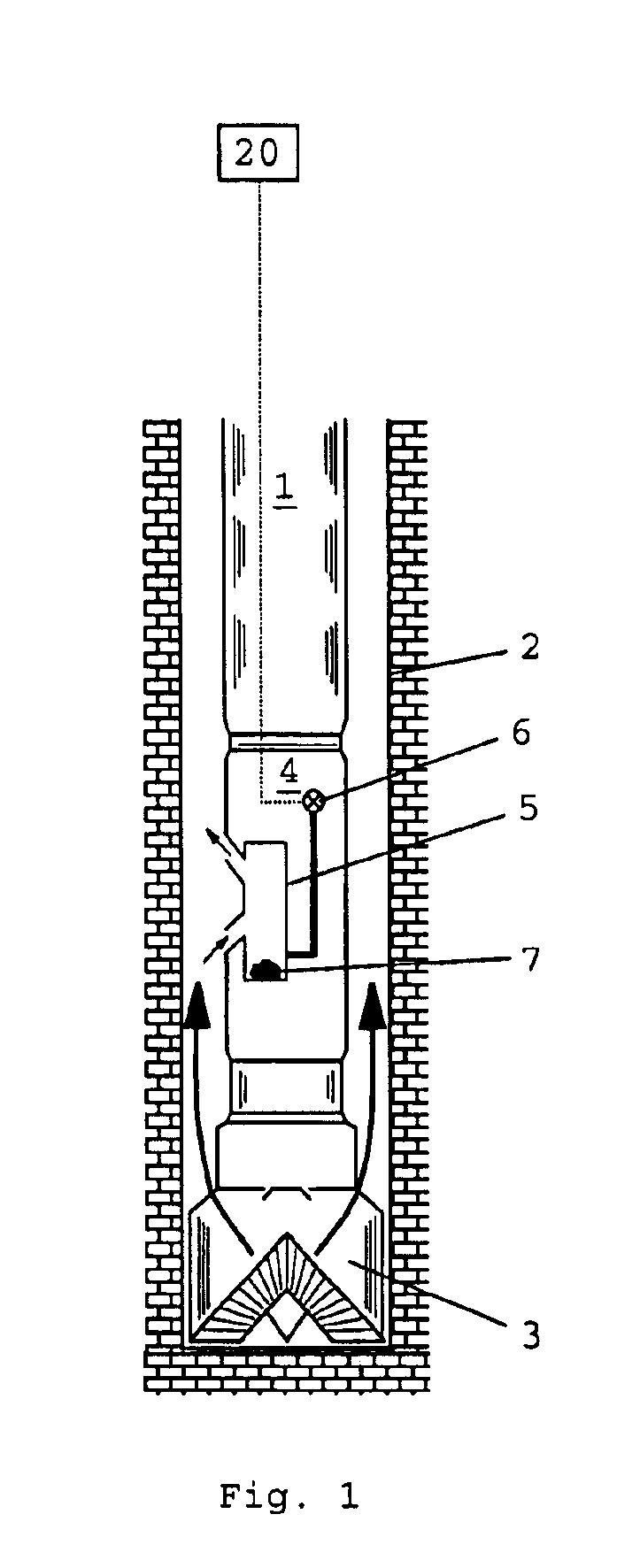
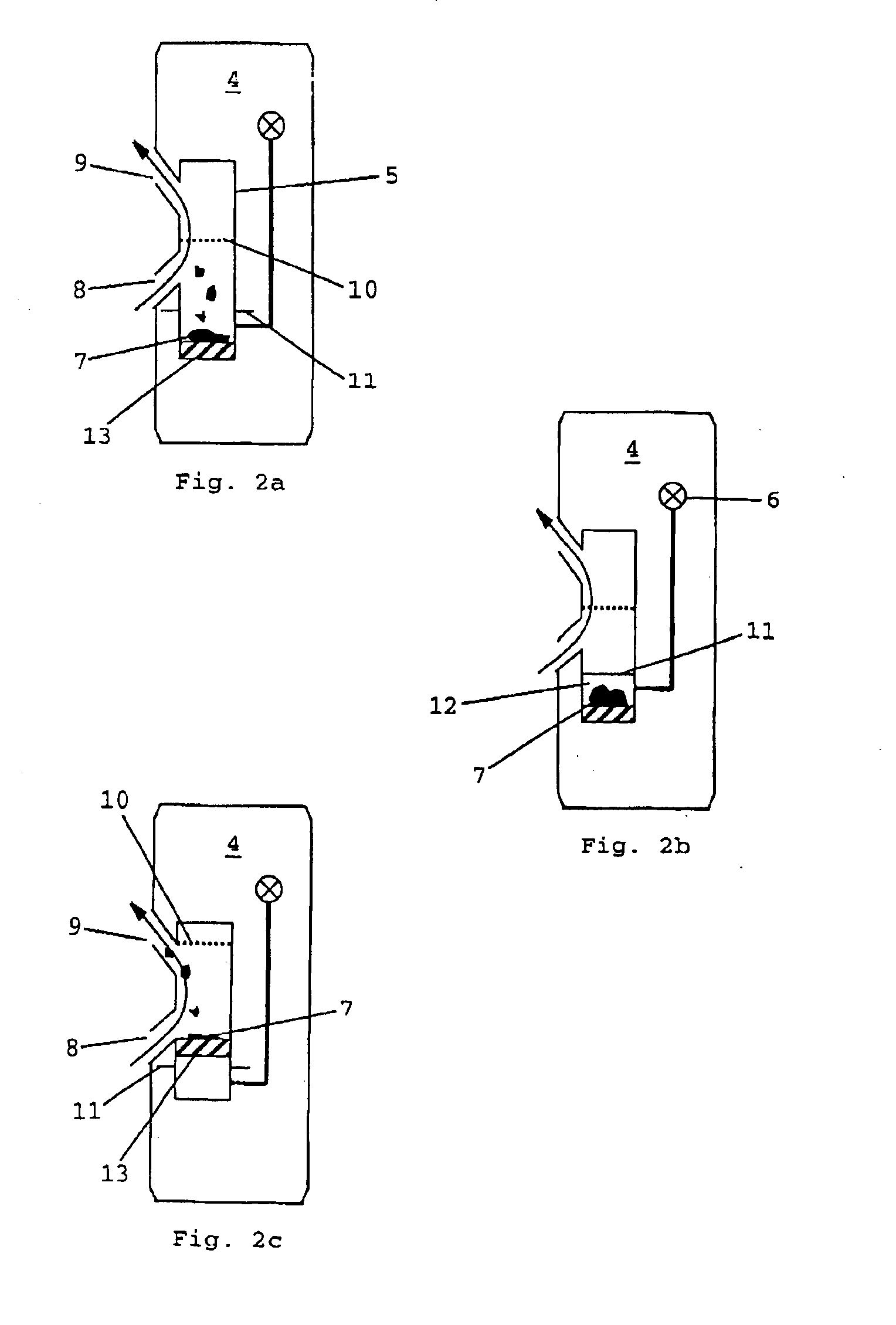
Method and apparatus for pore pressure monitoring
A method of monitoring pore pressure, comprises the steps of:(a) providing downhole in a well a sealable container,(b) sealing in the container a sample of fluid at a baseline pressure and a sample of a formation having an initial pore pressure,(c) measuring the change in pressure of the fluid sample, the pressure of the fluid sample and the pore pressure of the formation sample sealed in the container tending to equalize over time, and(d) estimating the initial pore pressure relative to the baseline pressure from the measured change in fluid sample pressure.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
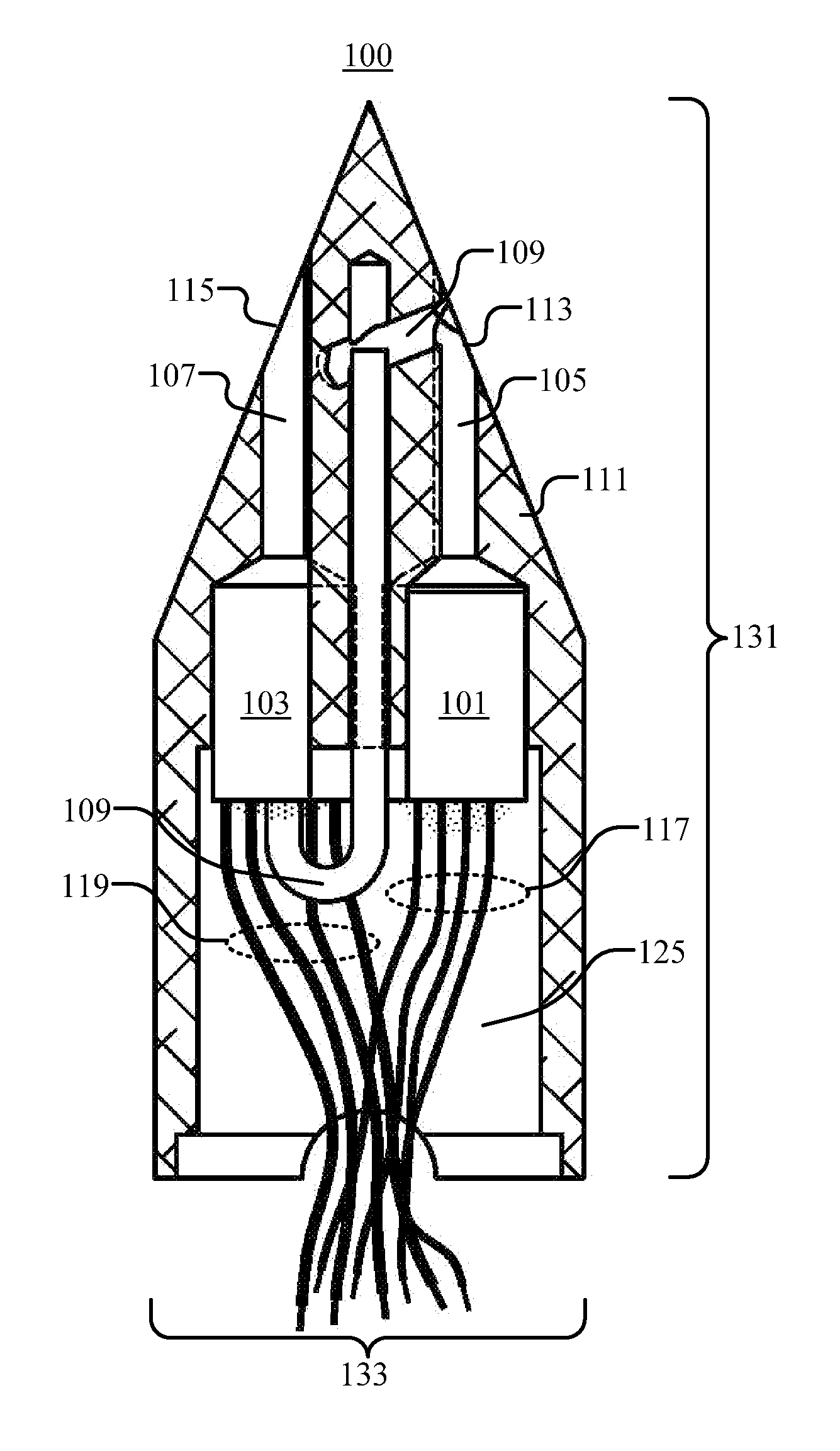
Ultra-Miniature Multi-Hole Flow Angle Probes
ActiveUS20160011065A1Fluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationFluid speed measurement using pressure differenceDifferential pressureMiniaturization
This disclosure provides example methods, devices, and systems for an ultra-miniature, multi-hole flow angle probe. The construction, packaging of a multitude of absolute and or differential pressure transducers or sensors are invented for the purpose of providing highly accurate measurement of flow properties, flow angle in particular. The unique placement of sensors leads to further miniaturization relative to current state of the art. Further the use of closely coupled, differential transducer or transducers achieves higher accuracy measurement of small pressure variations coupled with large mean or average baseline pressures, as is demanded in modern aerodynamic or turbo-machinery devices. The use and installation of ultra-miniature sensors insider the device invented herein achieves higher frequency response than allowable via previous state of the part.
Owner:KULITE SEMICON PRODS
Servo ventilation using pressure drop from baseline
A system and method for delivering a flow of breathing gas to an airway of a patient that includes a gas flow generator and a patient circuit that communicates the flow of gas to an airway of a patient. A sensor measures a characteristic associated with the flow of gas, such as flow rate. A controller determines a first characteristic based on the measured characteristic and a target of the flow of gas to be delivered to the patient. The controller controls the delivery of gas to the patient by 1) providing a baseline positive pressure support amount to the patient and 2) providing a modified pressure support amount by reducing the baseline amount by a given amount if the first characteristic is above the target. The baseline pressure includes a pressure provided during inspiration that is higher than a pressure provided during expiration.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
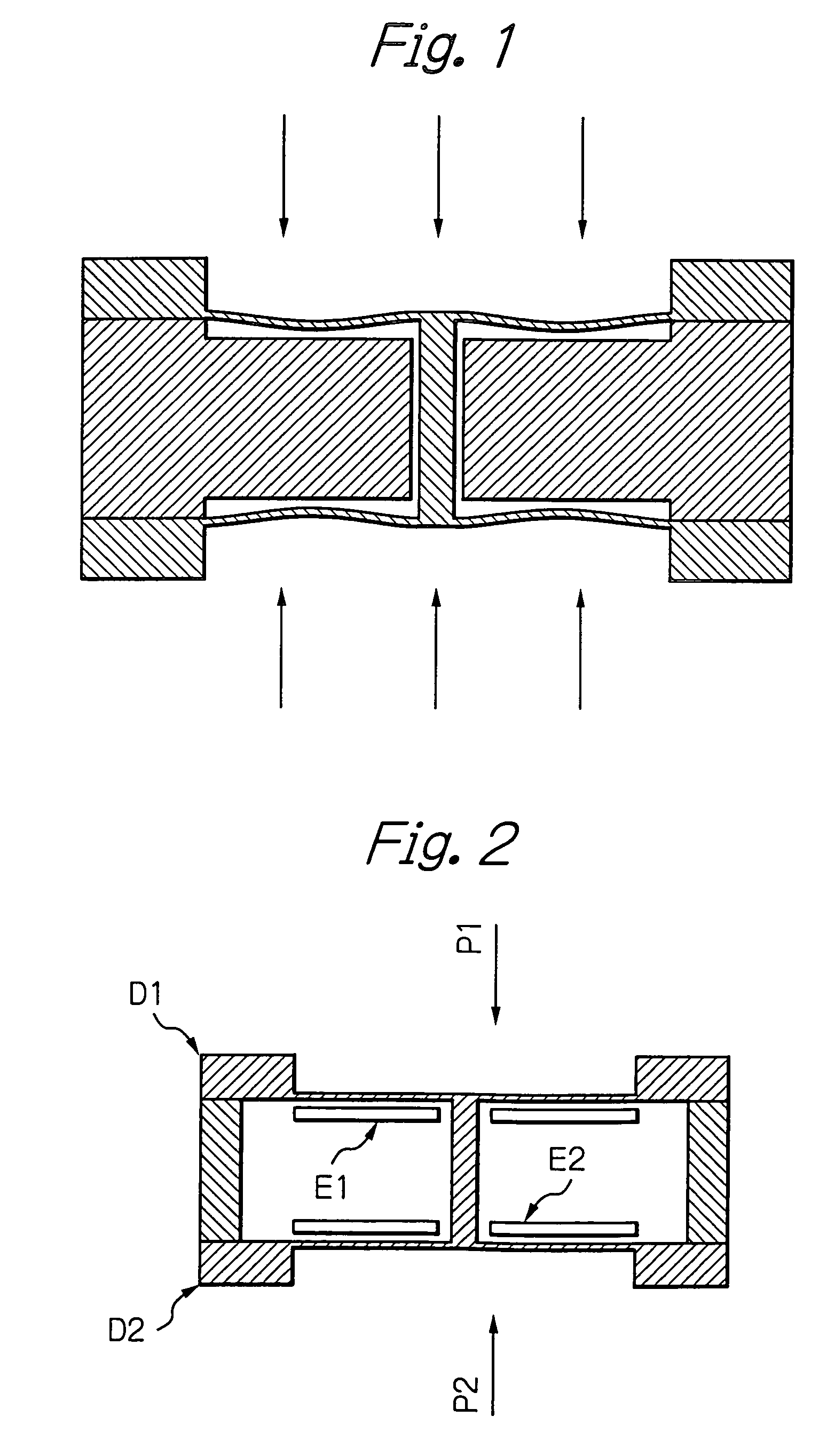
Differential pressure sensor
InactiveUS20060169048A1Accurate measurementSensitive and accurate detectionPressure difference measurement between multiple valvesMultiple fluid pressure valves simultaneous measurementCapacitanceDifferential pressure
According to the present invention, there is provided a high-precision differential pressure sensor which is not affected by a considerable change in baseline pressure. A differential pressure sensor of the present invention comprises: a pair of diaphragms, each including a diaphragm portion capable of being deformed due to application of a pressure and a support portion for holding an outer peripheral edge of the diaphragm portion; a pair of fixed electrodes in disk-like form fixed to the support portions of the diaphragms; and a movable electrode including a disk-like electrode portion and shaft-like projections extending in opposite directions from a central portion of the electrode portion. The shaft-like projections extend at a right angle relative to the electrode portion, and the movable electrode is secured to central portions of the diaphragms through the shaft-like projections so that the electrode portion faces each of the fixed electrodes in a predetermined spaced relationship. The movable electrode is capable of moving so as to allow a distance between the electrode portion and each of the fixed electrodes to vary according to a difference between fluid pressures acting on the respective diaphragm portions of the diaphragms. A capacitance generated between the electrode portion and each of the fixed electrode changes due to a variance in the distance between the electrode portion and each of the fixed electrode, and a differential pressure is detected, based on this change in capacitance.
Owner:MKS JAPAN
Regulation of intrathoracic pressures by cross seal vent valve
InactiveUS20110120473A1Widen meansElevated intrathoracic pressureRespiratorsRespiratory apparatusExhaust valveIntensive care medicine
The present invention relates generally to devices and methods for finite control and regulation of patient intrathoracic pressures, and more specifically, to devices and methods that finitely regulates a patient's intrathoracic pressures during repeated cycling events (i.e. respiration) by use of a cross-seal vent valve to form transient pressure windows. The cross-seal vent valve is biased against the pressure necessary to evacuate and / or inflate the lungs of that patient, while a controlled venting of that pressure by at least a partial volume thereof allows for controlled resetting of the baseline pressure to anatomical norms. This enhanced means for regulating intrathoracic pressure are applicable in a number of medically important therapies, including but not limited to, conditioning of pulmonary systems for acclimation to altered environmental conditions, reconditioning of pulmonary system after operating in a diminished state, and application in cardiopulmonary resuscitation procedures.
Owner:PIPER MEDICAL
Measurement of tissue elastic modulus
ActiveUS8167804B2Avoid artifactsRemove uncertaintyWave based measurement systemsBlood flow measurement devicesArterial velocityMedicine
An optimized elastic modulus reconstruction procedure can estimate the nonlinear elastic properties of vascular wall from intramural strain and pulse wave velocity (PWV) measurements. A noninvasive free-hand ultrasound scanning procedure is used to apply external force, comparable to the force in measuring a subject's blood pressure, to achieve higher strains by equalizing the internal arterial baseline pressure. PWV is estimated at the same location where intramural strain is measured. The reconstructed elastic modulus is optimized and the arterial elastic modulus can be determined and monitored using a simple dual elastic modulus reconstruction procedure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
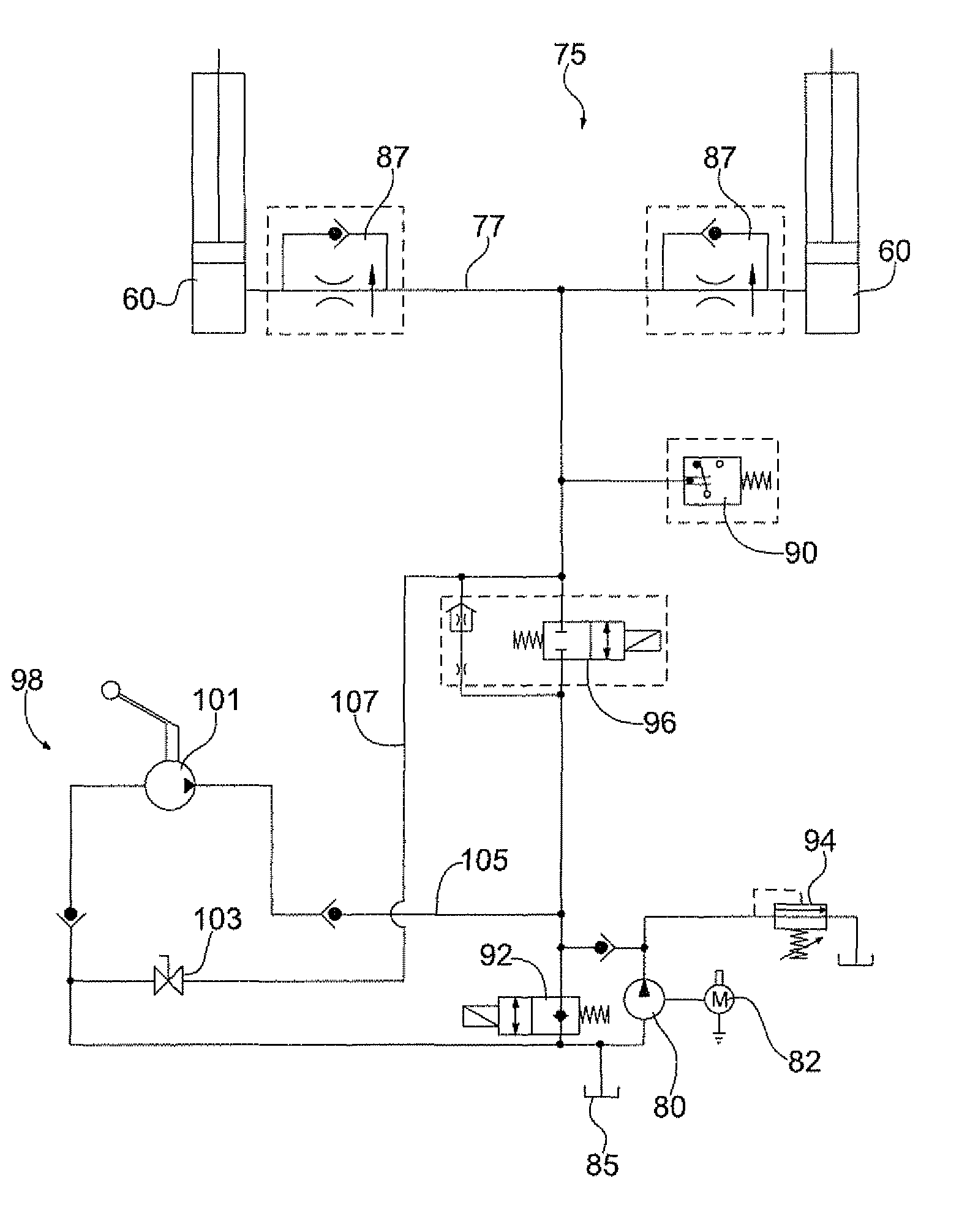
Static pressure Anti-stow logic for platform wheelchair lifts
ActiveUS20110031040A1Reduce hydraulic pressurePrevent movementBuilding liftsAmbulance serviceHydraulic cylinderWheelchair
A method for detecting weight on a platform lift having a platform, a hydraulic cylinder, and a hydraulic circuit including the steps of measuring a static pressure of the hydraulic circuit, and comparing the measured static pressure to a baseline pressure of the hydraulic circuit. The baseline pressure is a static pressure of the hydraulic circuit without external weight positioned on the platform.
Owner:RICON
Static pressure anti-stow logic for platform wheelchair lifts
ActiveUS8816225B2Prevent movementRefuse receptaclesWeighing apparatus with automatic feed/dischargeHydraulic cylinderWheelchair
Owner:RICON
Ultra-miniature multi-hole flow angle probes
ActiveUS9574960B2Fluid speed measurement using pressure differenceFluid pressure measurementDifferential pressureMiniaturization
This disclosure provides example methods, devices, and systems for an ultra-miniature, multi-hole flow angle probe. The construction, packaging of a multitude of absolute and or differential pressure transducers or sensors are invented for the purpose of providing highly accurate measurement of flow properties, flow angle in particular. The unique placement of sensors leads to further miniaturization relative to current state of the art. Further the use of closely coupled, differential transducer or transducers achieves higher accuracy measurement of small pressure variations coupled with large mean or average baseline pressures, as is demanded in modern aerodynamic or turbo-machinery devices. The use and installation of ultra-miniature sensors insider the device invented herein achieves higher frequency response than allowable via previous state of the part.
Owner:KULITE SEMICON PRODS
Digital compression recorder with specification database system and method
InactiveUS20120109544A1Saving compression pressureInternal-combustion engine testingFlow propertiesEngineeringBaseline pressure
In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, a system for measuring the cylinder compression of an engine is provided The system may include a microprocessor; a sensor operatively connected to the microprocessor, the sensor configured to measure a pressure; a memory operatively connected to the microprocessor, the memory configured to store a pressure detected by the sensor; and a database operatively connected to the microprocessor, the database configured to a store baseline pressure associated with an engine.
Owner:SPX CORP
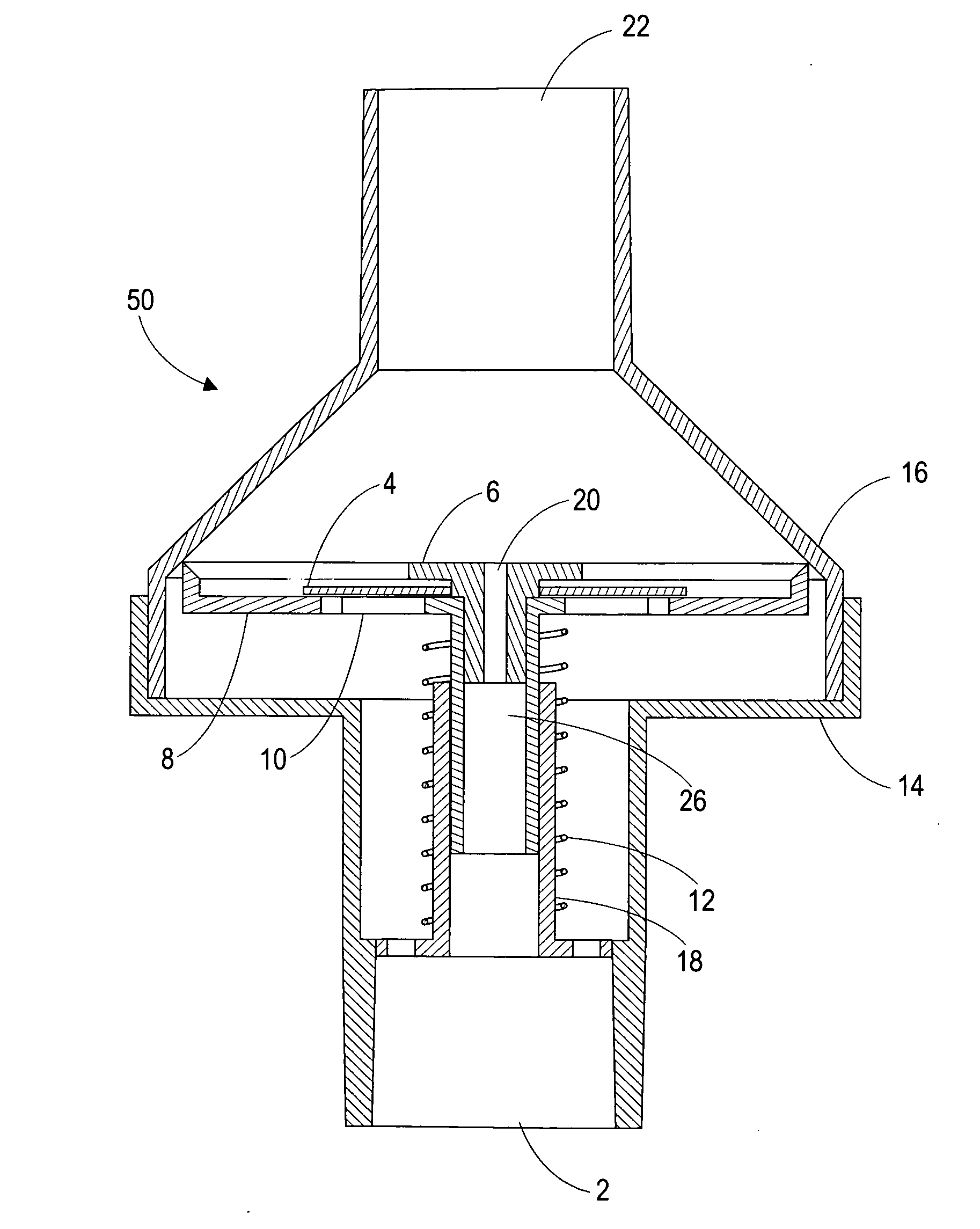
Angioplasty of calcified arteries
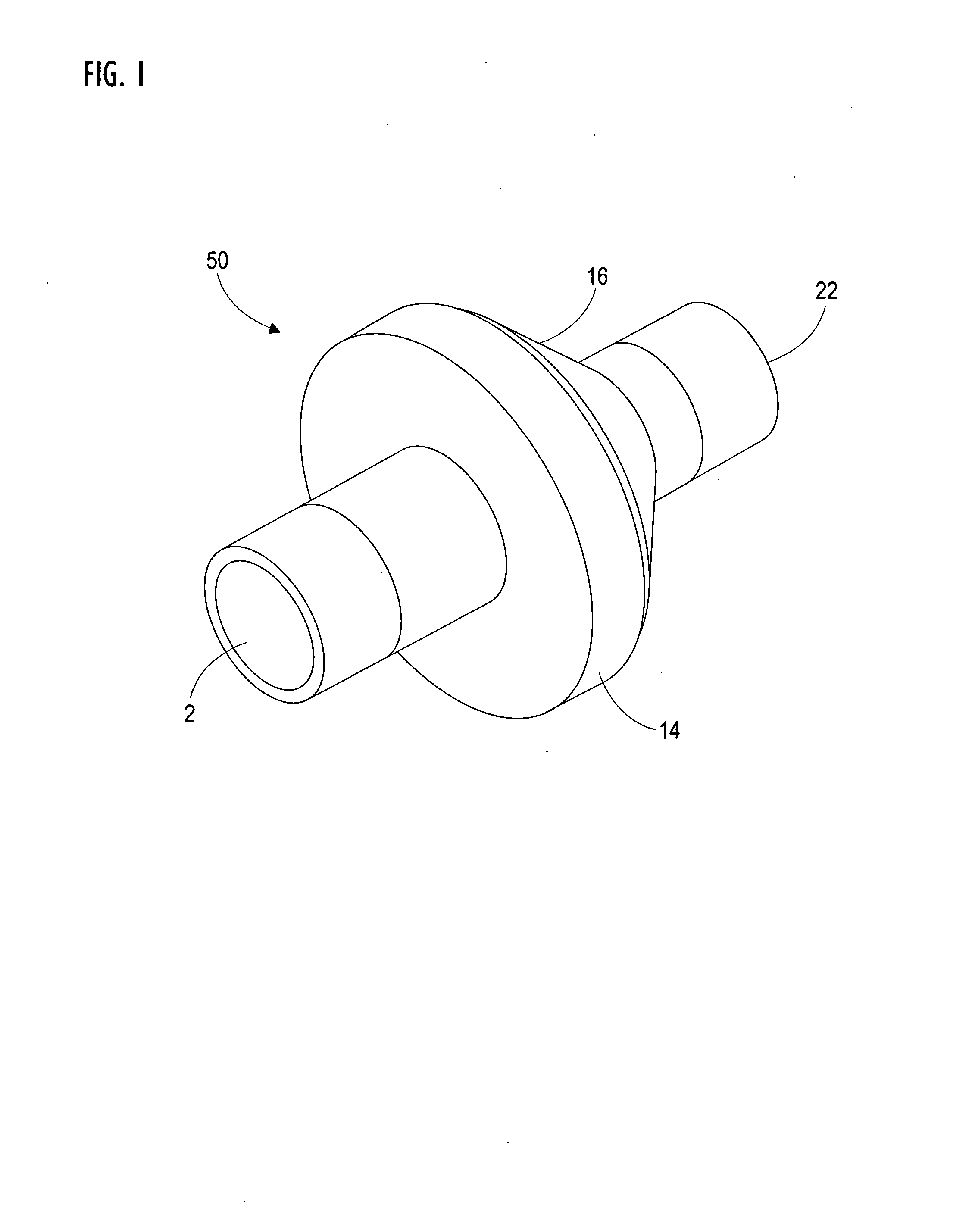
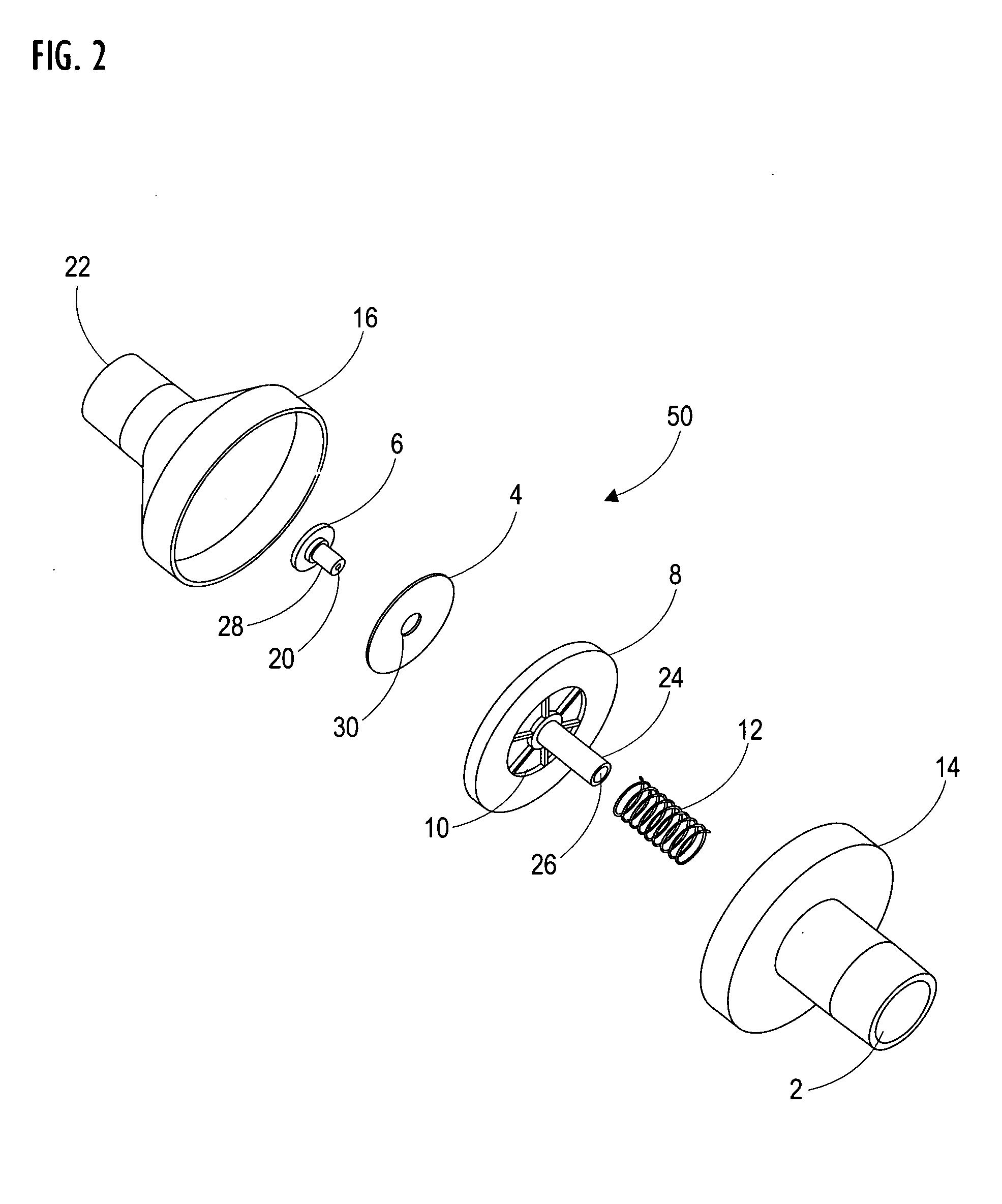
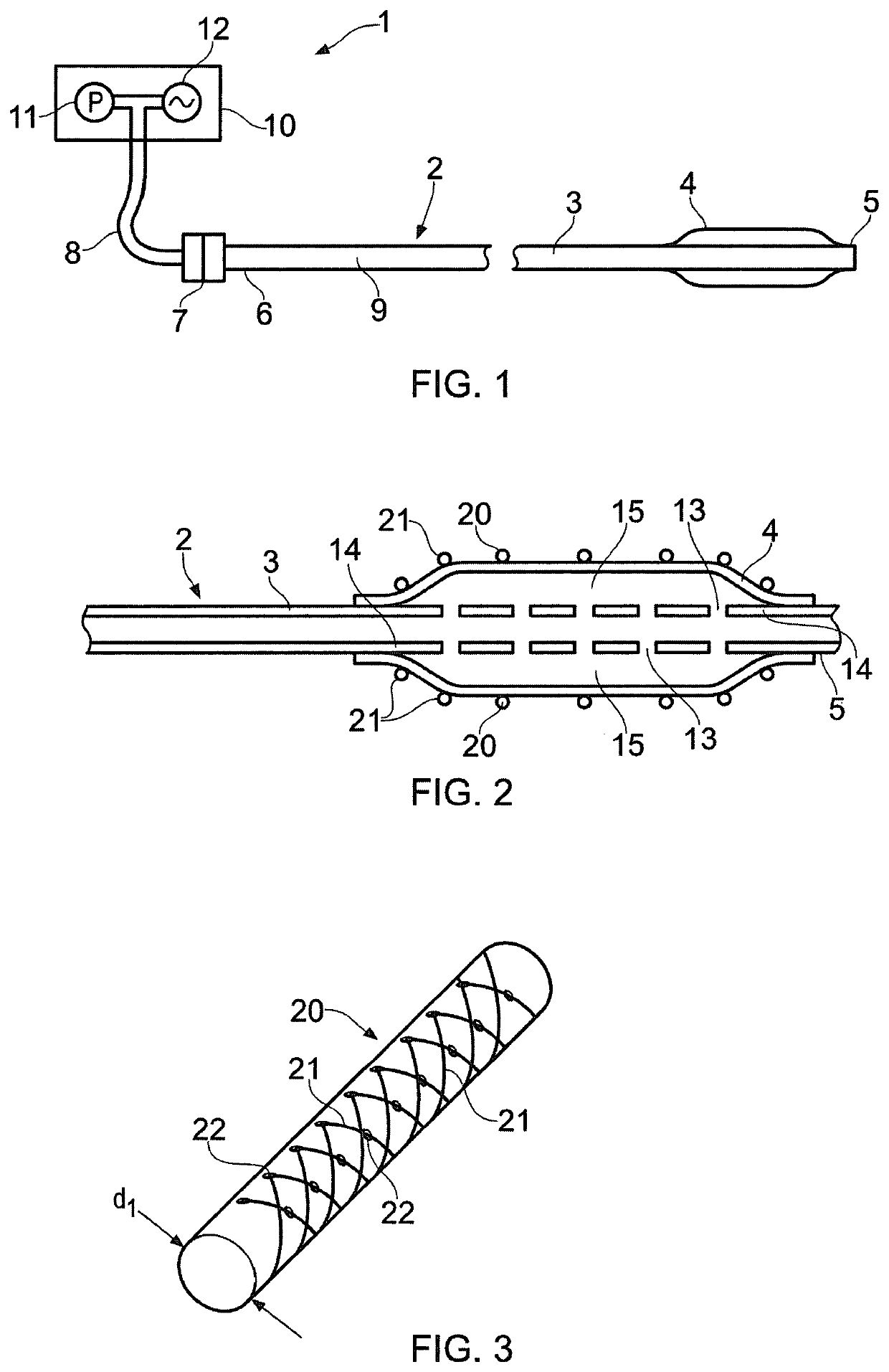
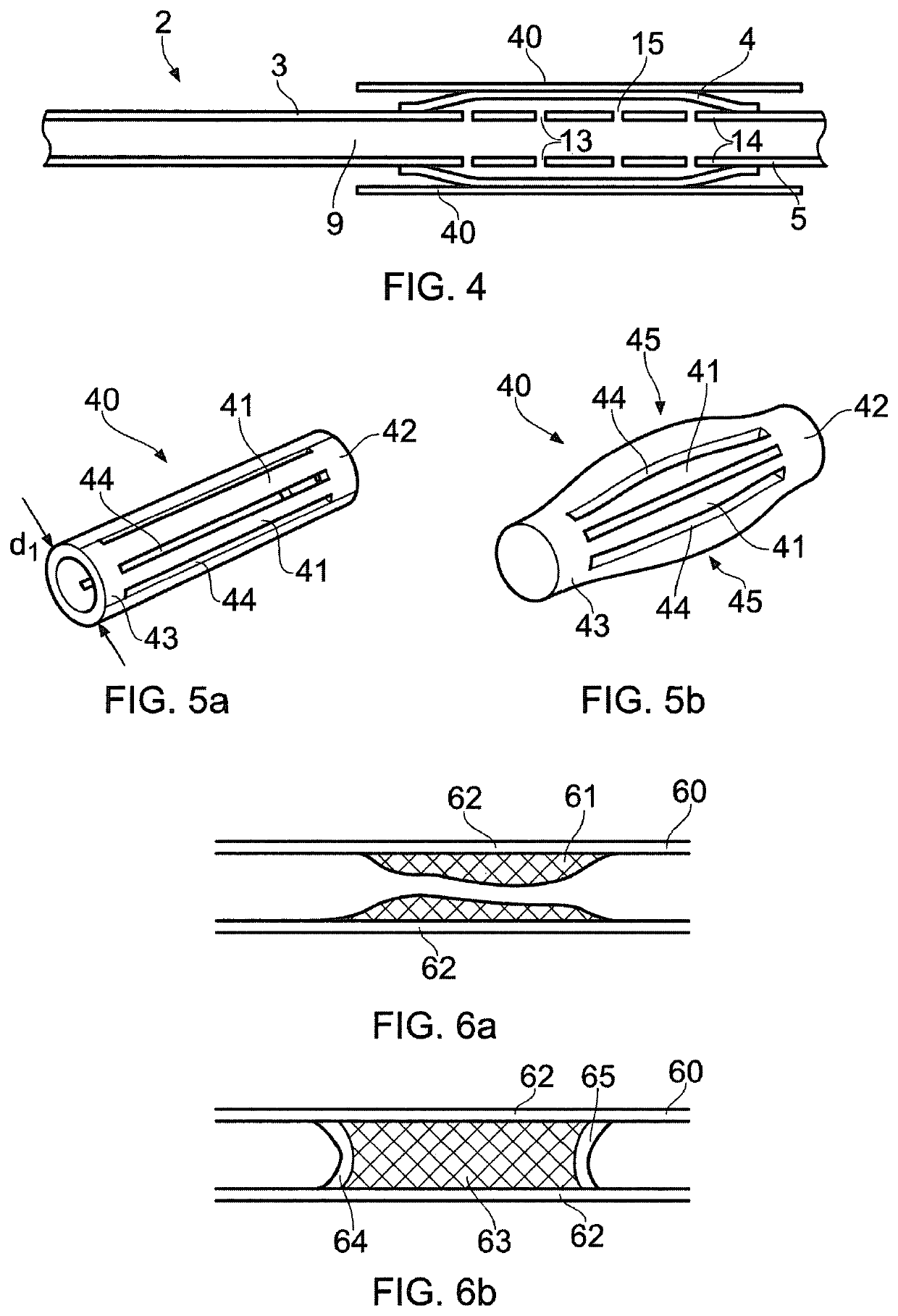
ActiveUS20200306512A1Regulating pressureEasy to participateBalloon catheterMedical devicesEngineeringGuide wires
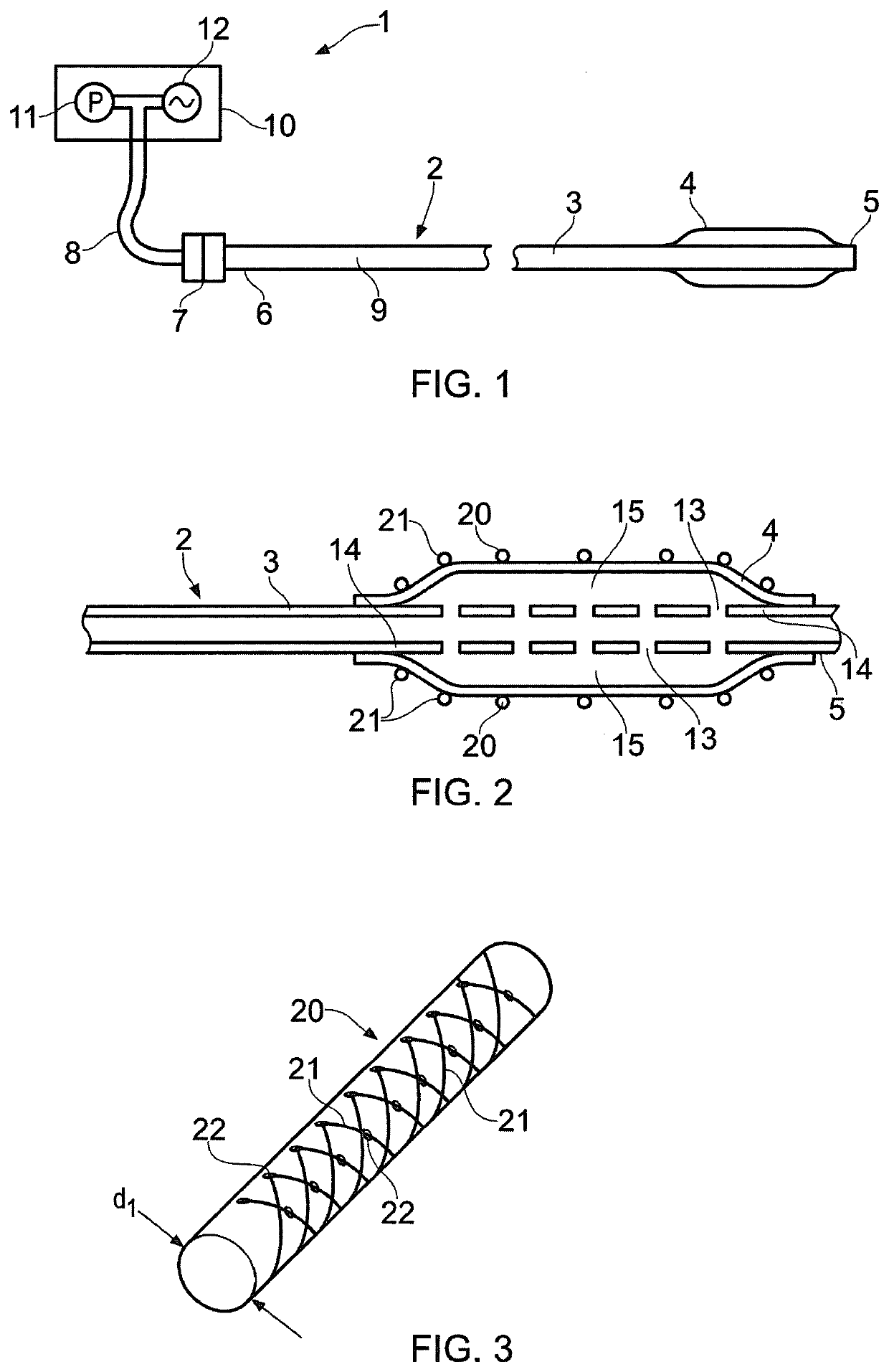
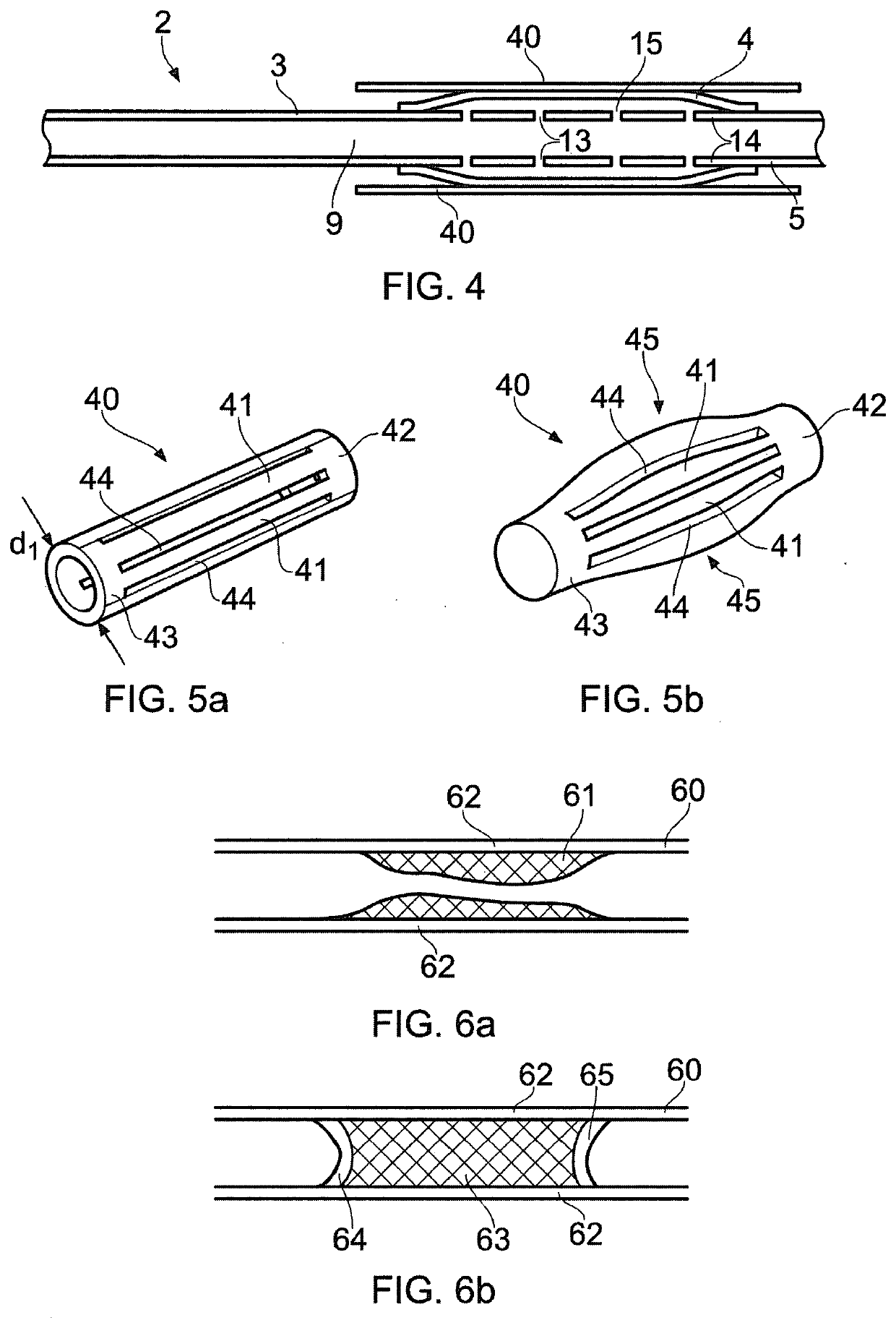
A medical device (1) for assisting the break-up, disruption or disintegration of calcified or other hardened material within vessels of the human or animal body which material otherwise prevents or inhibits stenting procedures or passage of guidewires, catheters and other devices through the vessels. The device comprises a catheter (2) having a lumen (9) extending between a distal end (5) and a proximal end (6) of the catheter and a displaceable element (4) at the distal end of the catheter configured for axial and / or radial displacement relative to the catheter when driven by pressure fluctuations within the lumen. A pressure pump (11) is coupled to a proximal end of the catheter and is configured for application of a baseline pressure to the catheter lumen. A pressure modulation source (12) is also coupled to the proximal end of the catheter, configured to modulate the baseline pressure in the catheter lumen with one or more pressure impulses, and preferably with a series of pressure pulses.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER +1
Dynamic residue clearing control with in-situ profile control (ISPC)
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Systems and methods for treating and preventing blockages in solid fuel conditioning equipment
ActiveUS7028625B1Avoid cloggingFuel feeding arrangementsSolid fuel pretreatmentSolid fuelEngineering
Systems, methods and apparatus are provided for introducing one or more unblocking materials into solid fuel conditioning equipment at predetermined locations and intervals to prevent the occurrence of, or to treat the existence of at least one solid fuel blockage within the equipment, wherein introduction of the one or more unblocking materials is based on or triggered by an assessment of whether there is an actual or impending partial or complete blockage of solid fuel within the conditioning equipment, and wherein such assessment is made by measuring pressure within the solid fuel conditioning equipment and then comparing the measurement(s) against a baseline pressure.
Owner:RILEY STOKER
Compression garment apparatus having baseline pressure
A compression garment apparatus including a compression garment and a pressurizer. The pressurizer intermittently pressurizes a therapeutic bladder on the compression garment and maintains a baseline pressure in the therapeutic bladder to maintain the therapeutic bladder in position with respect to a target compression zone on a body part on which the garment is worn. The baseline pressure is adjusted in response to sensed physical characteristics.
Owner:KPR U S LLC
Programmable pellet press
A programmable pellet press for compressing a powdered sample and forming a sample disc, including a hydraulic mechanism for compressing the sample in a mold operatively and electrically connected to a control mechanism for commanding an exertion of low constant preloading pressure followed by pressure increases with constant pressure dwell times upon the hydraulic mechanism. An algorithm for a programmable pellet press on computer readable media including performing a pressurization subroutine, performing a proportional-integral-derivative (PID) feedback loop, performing a depressurization subroutine, and performing an unloading subroutine when pressure is at a baseline level. A method of compressing a powdered sample into a sample disc by loading the powdered sample into a mold of a programmable pellet press, from a baseline pressure, increasing hydraulic pressure and maintaining a preloading pressure against the sample, performing pressure increases upon the sample, depressurizing the sample, and forming a sample disc. A sample disc formed.
Owner:EKQUIST ALAN +2
Angioplasty of calcified arteries
A medical device for assisting the break-up, disruption or disintegration of calcified or other hardened material within vessels of the human or animal body which material otherwise prevents or inhibits stenting procedures or passage of guidewires, catheters and other devices through the vessels. The device includes a catheter having a lumen extending between a distal end and a proximal end of the catheter and a displaceable element at the distal end of the catheter configured for axial and / or radial displacement relative to the catheter when driven by pressure fluctuations within the lumen. A pressure pump is coupled to a proximal end of the catheter and is configured for application of a baseline pressure to the catheter lumen. A pressure modulation source is also coupled to the proximal end of the catheter, configured to modulate the baseline pressure in the catheter lumen with one or more pressure impulses, and preferably with a series of pressure pulses.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER +1
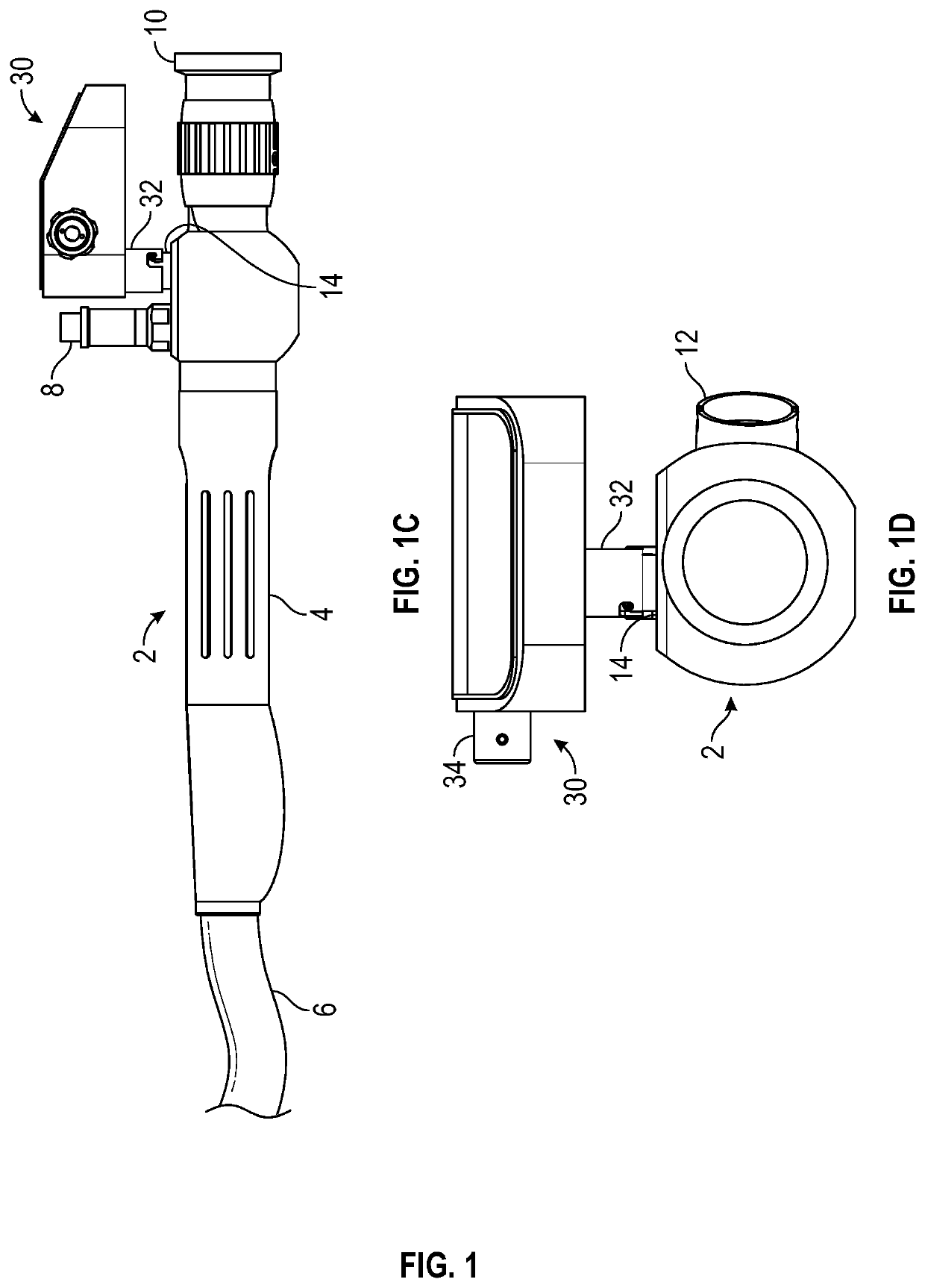
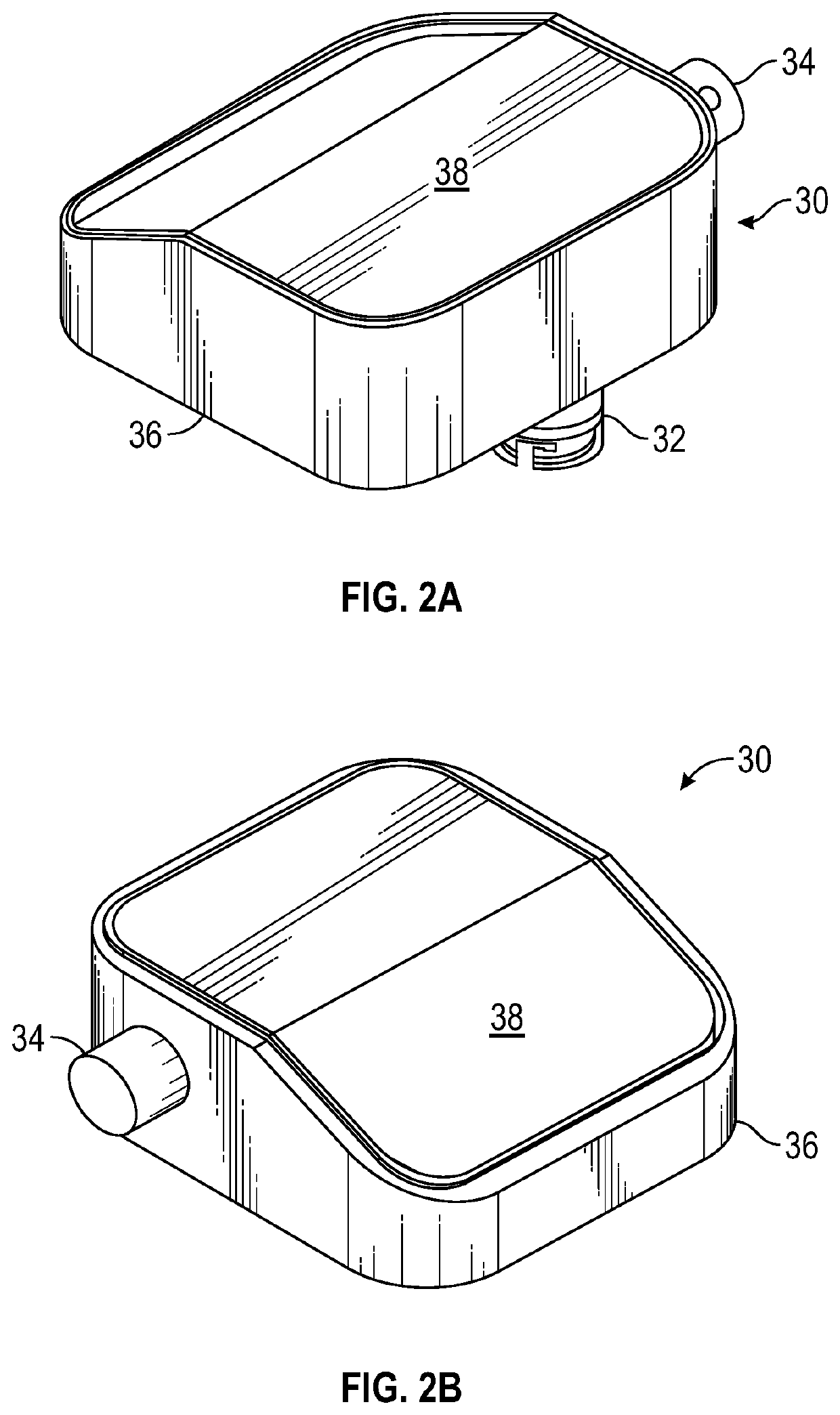
Apparatus and method for monitoring differential pressure
PendingUS20220117471A1Measurement of fluid loss/gain rateSurgeryDifferential pressureEmergency medicine
A pressure monitoring device used to monitor for leaks in a tool such as a medical endoscope. The device includes a housing having an internal volume fluidically coupled with an internal volume of the tool to form a combined internal volume. A pump changes the pressure inside the combined internal volume thereby establishing a baseline pressure at a pressure differential from the ambient environment. During operation of the tool, the pressure inside the combined internal volume is monitored for a change exceeding a predefined limit and such a change results in the device issuing an alarm signal indicating a leak has occurred in the tool. The device housing can be directly mounted to the tool, located remotely and connected with a coupling hose, or integrated with an accessory device connected to the tool. Preferably, the pressure differential is negative relative to ambient when the tool is a medical endoscope.
Owner:ANTONIOLI HILARY C
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com