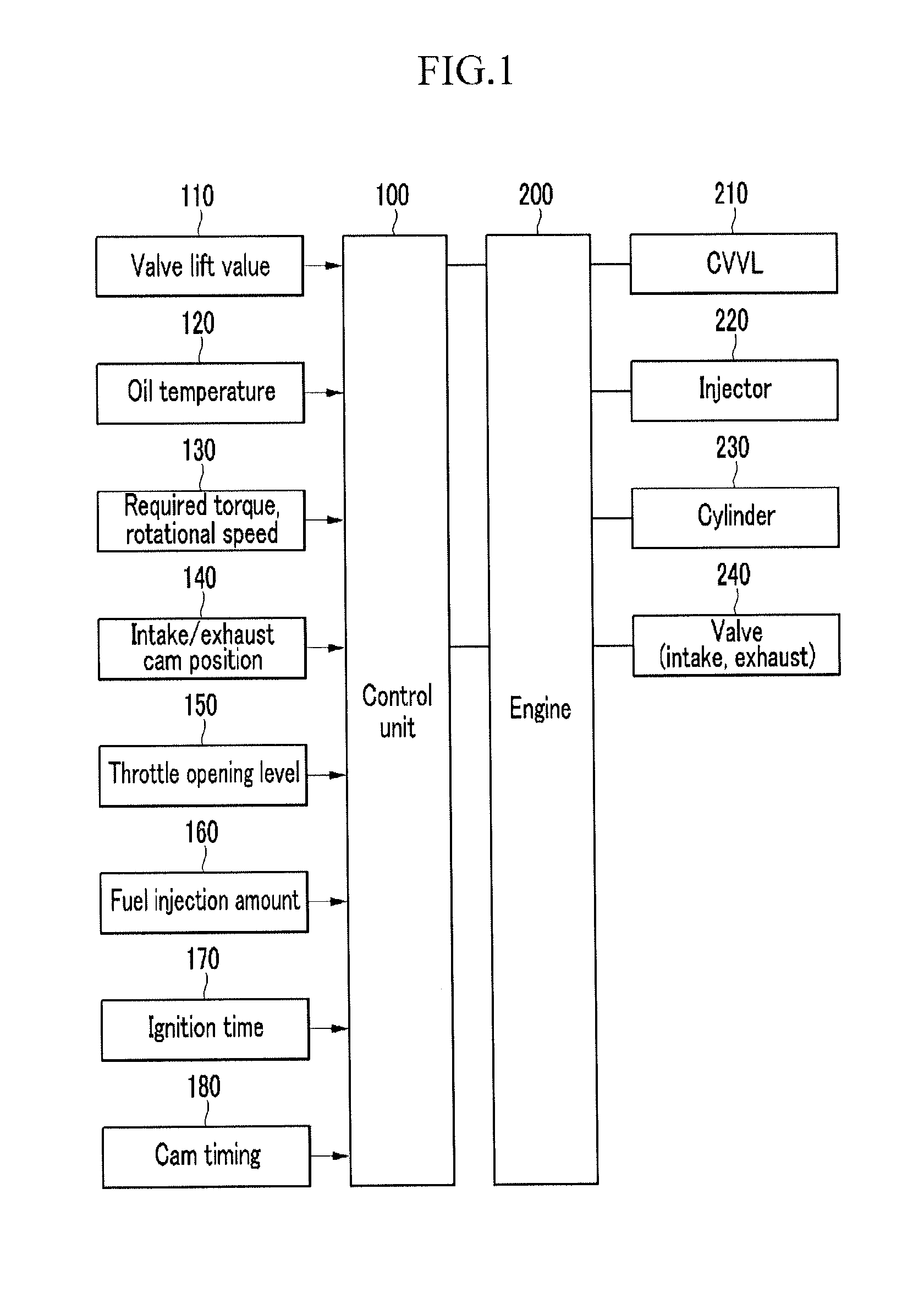
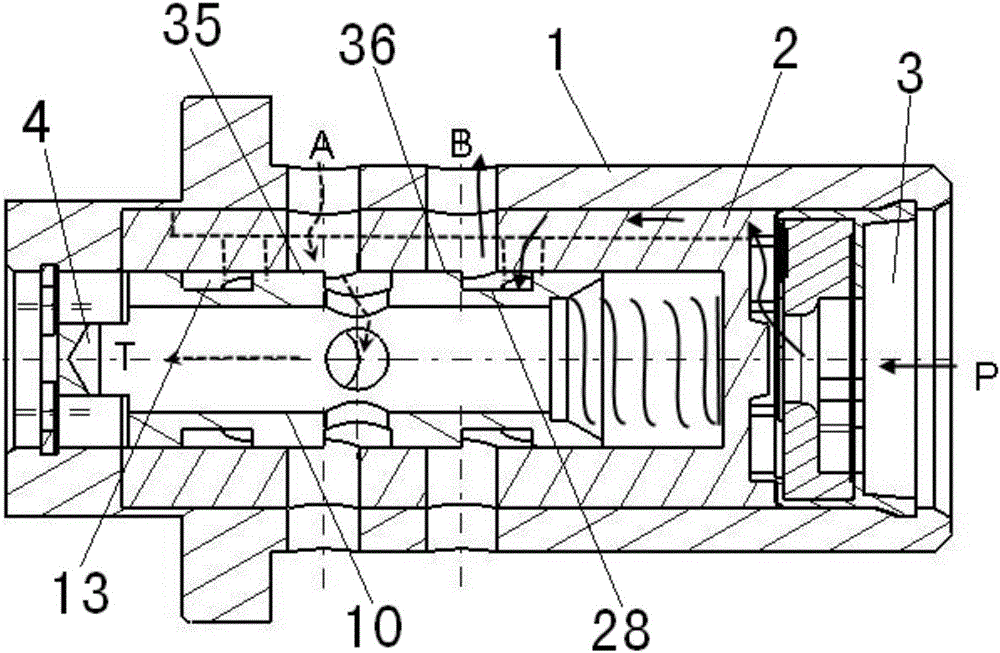
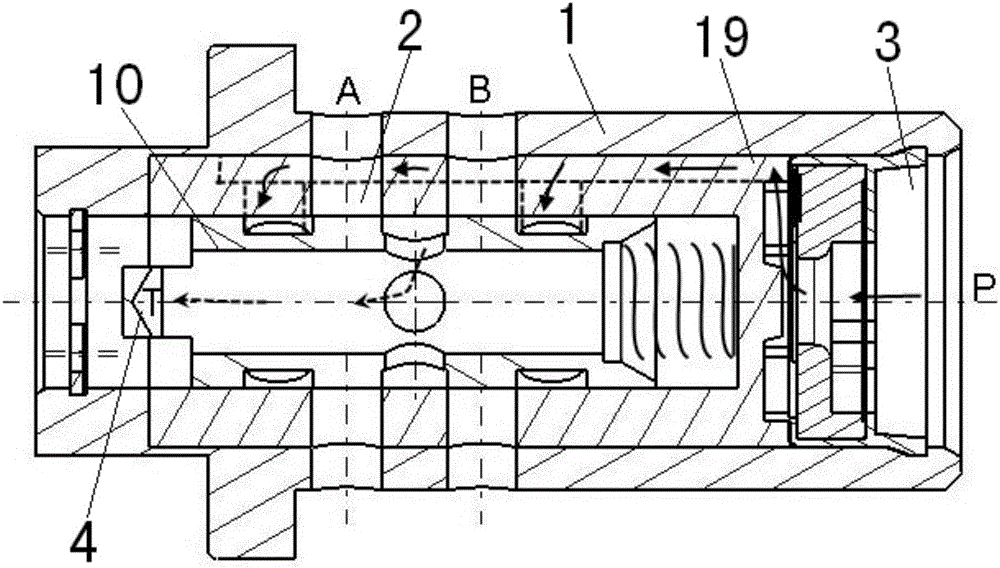
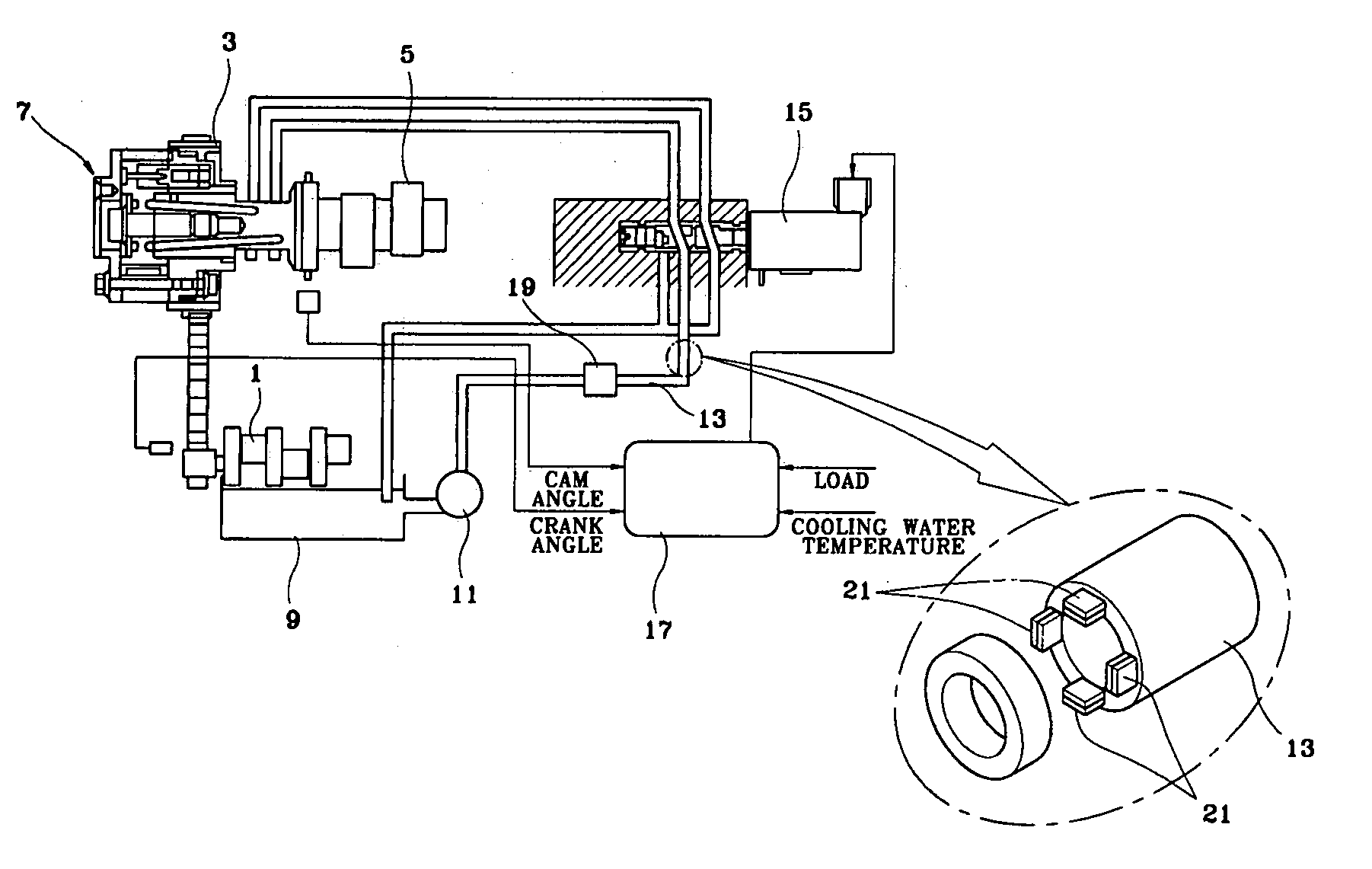
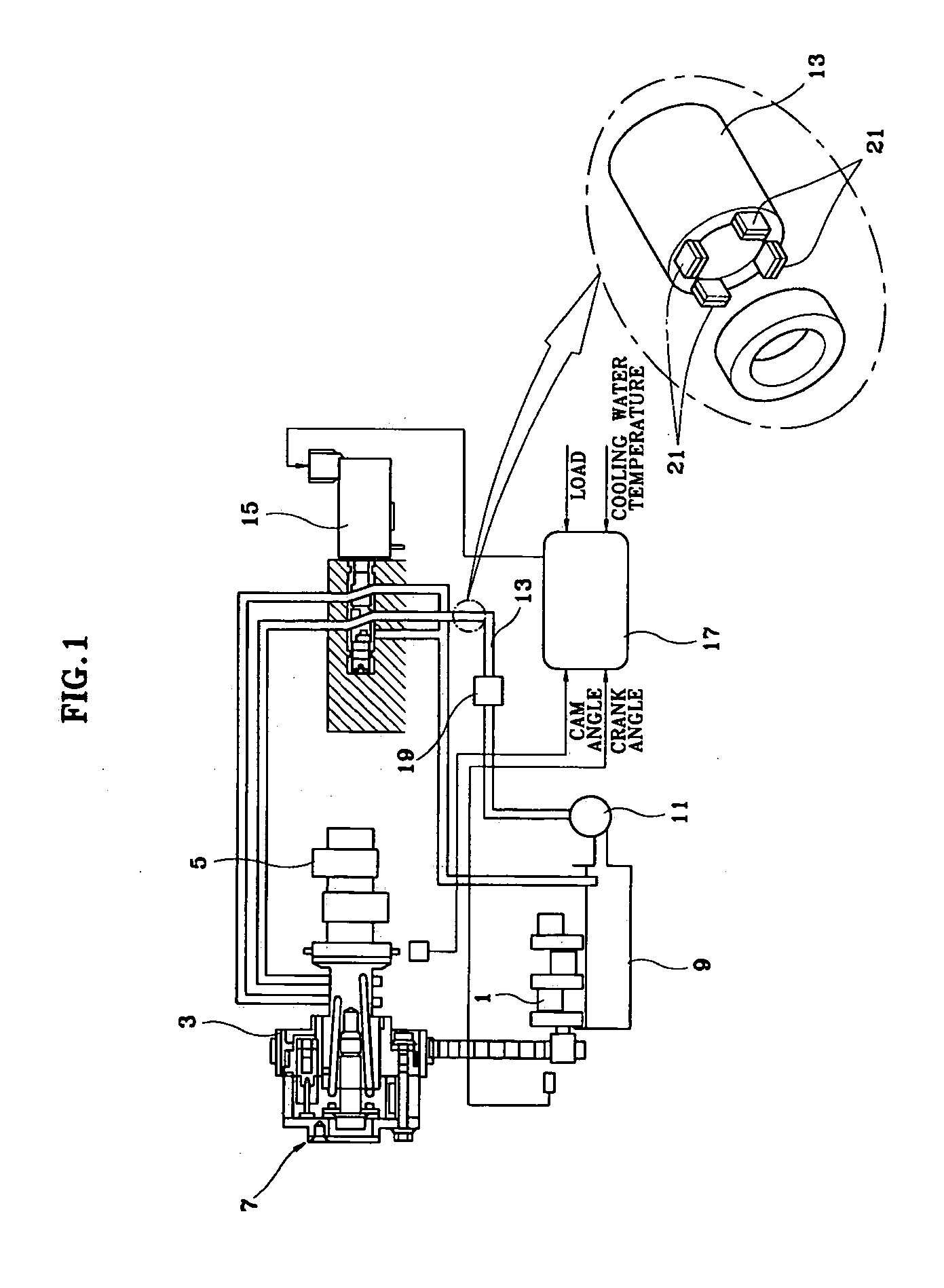
Patents
Literature
115 results about "Continuously variable valve timing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
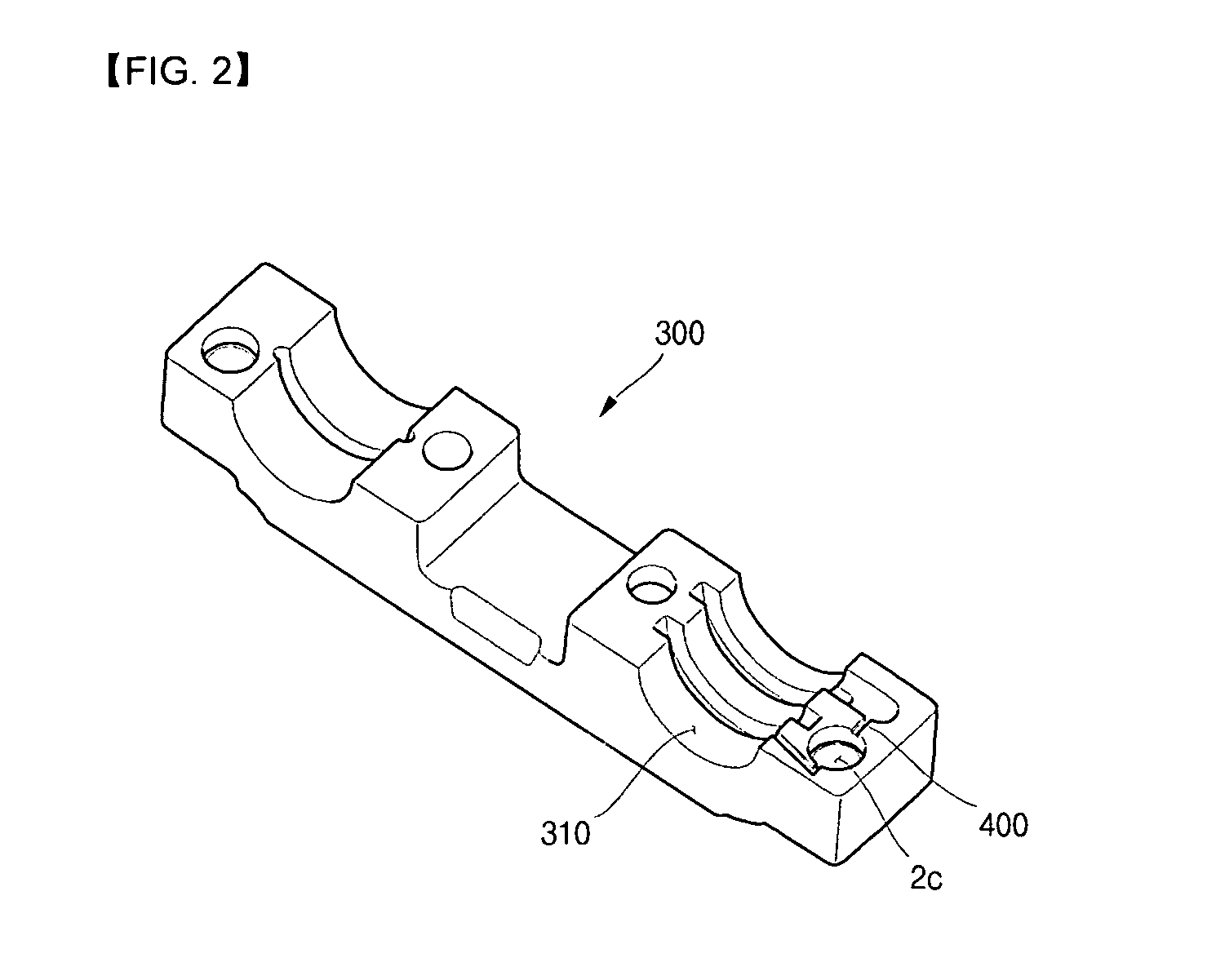
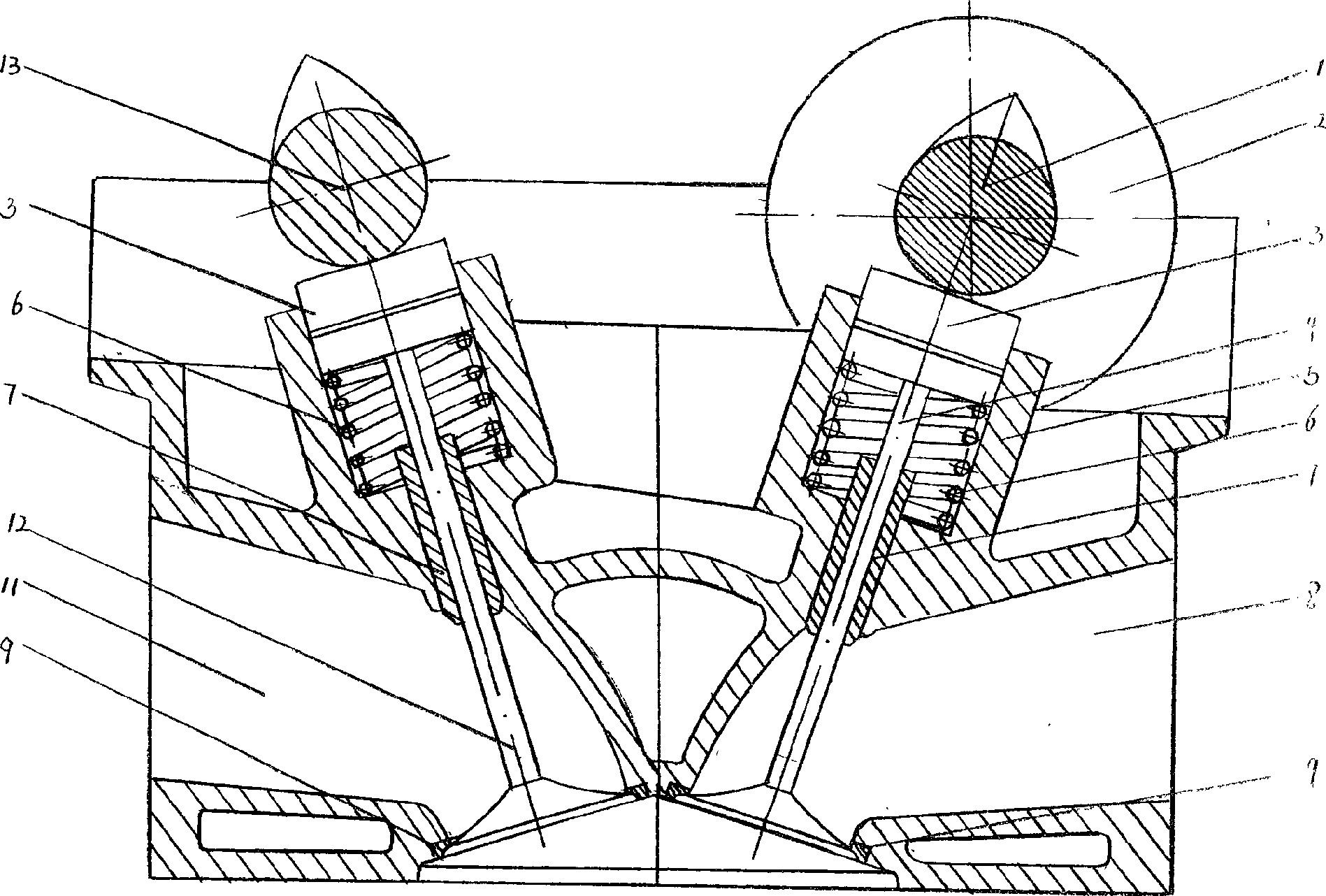
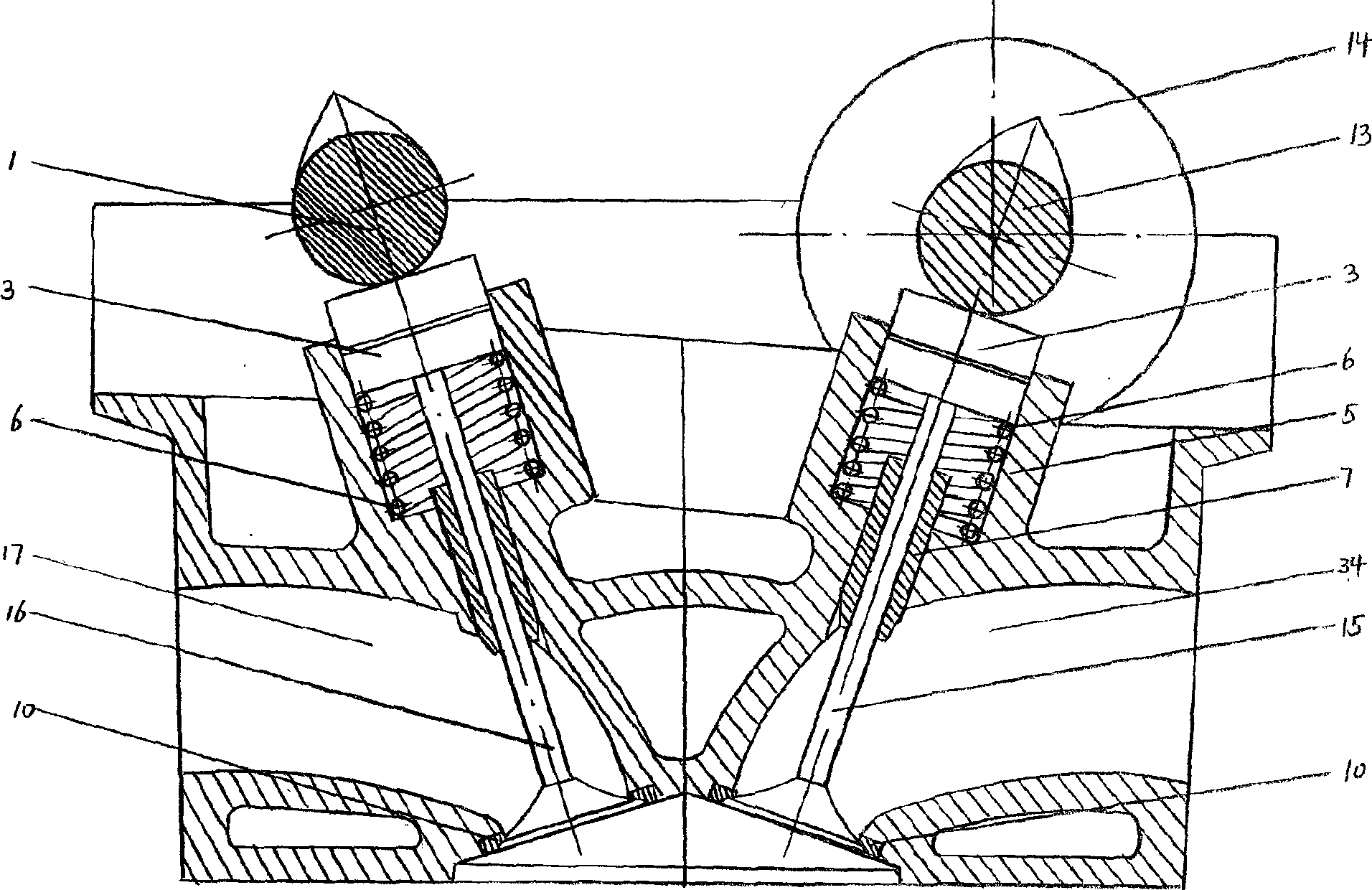
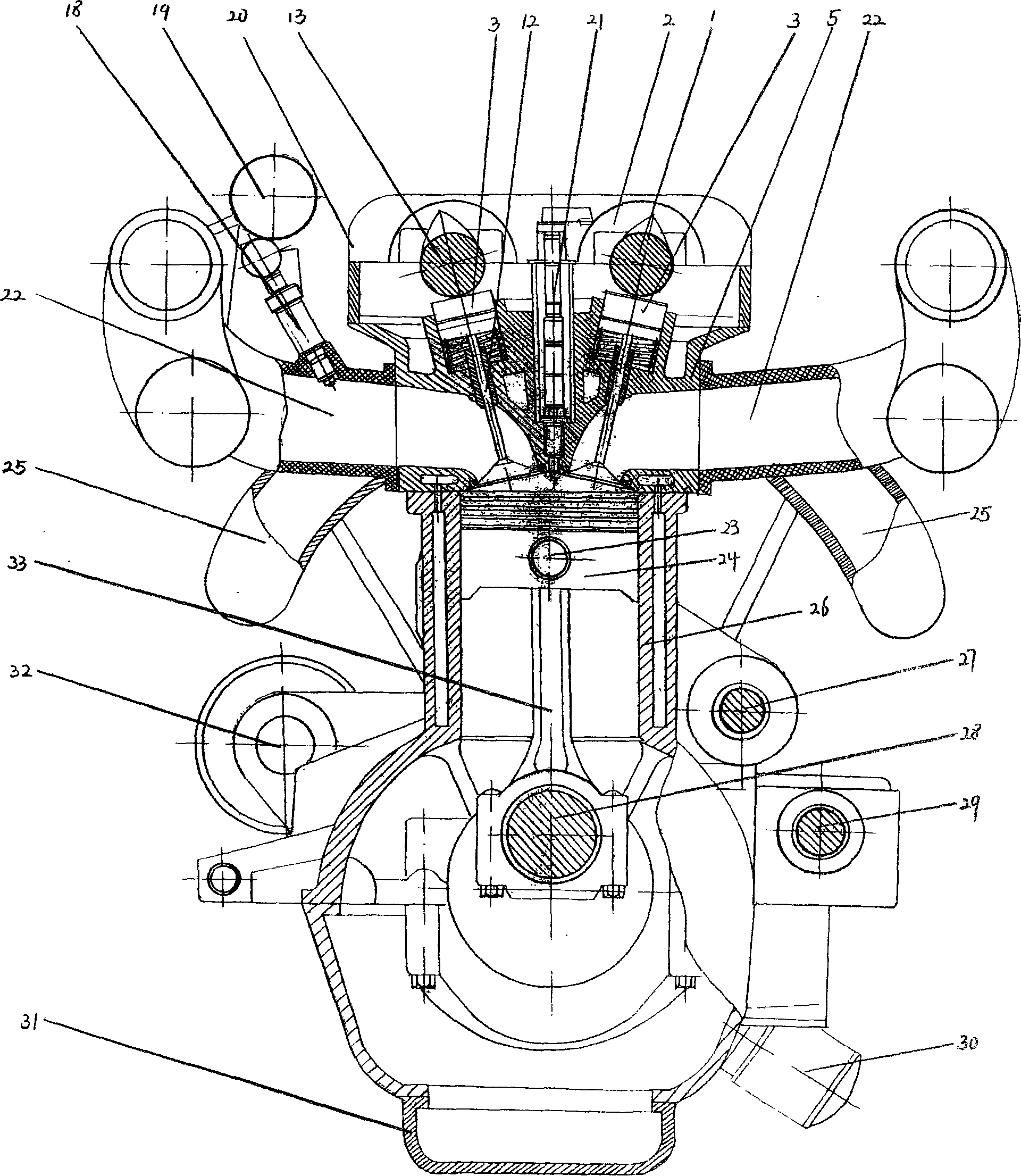
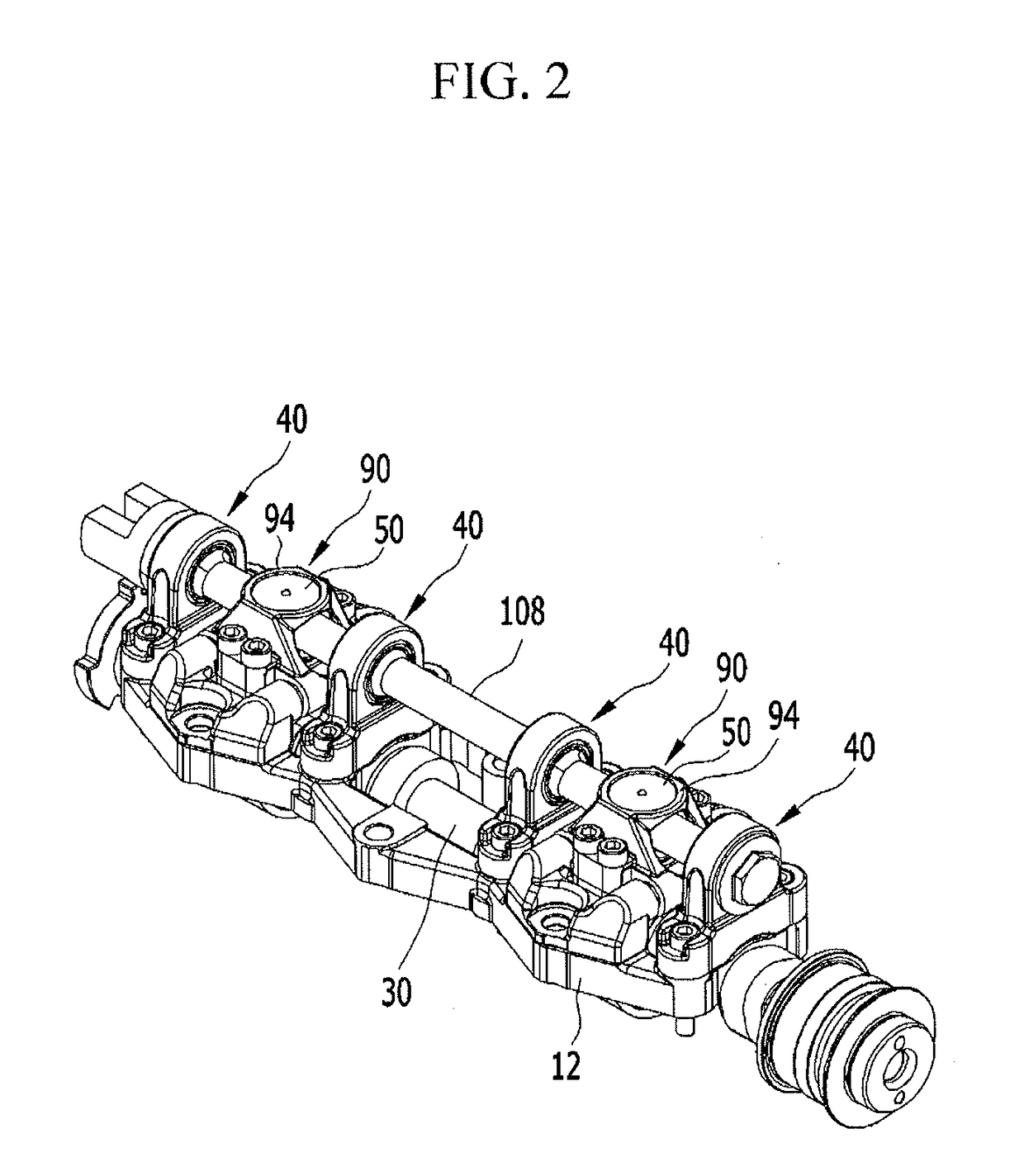
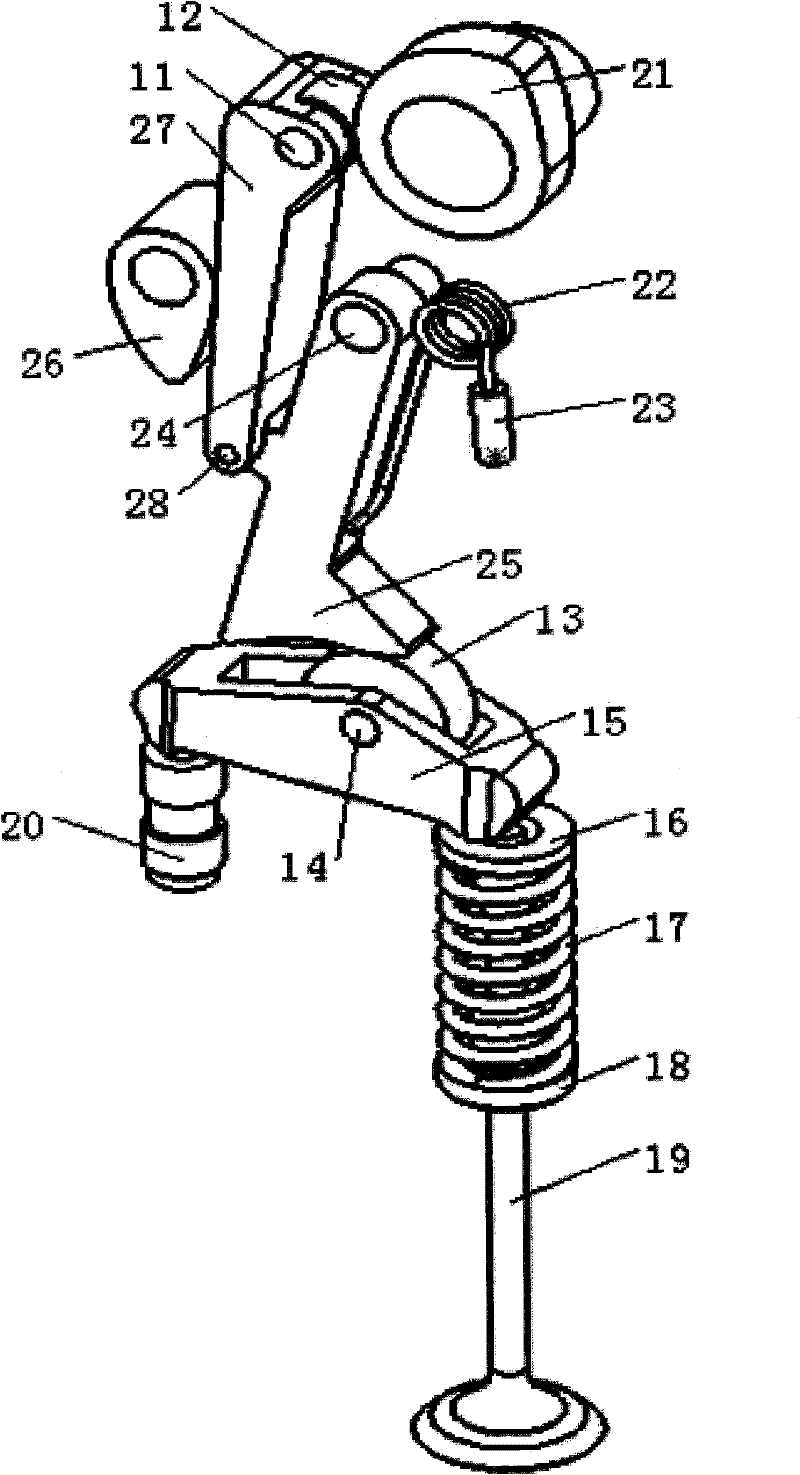
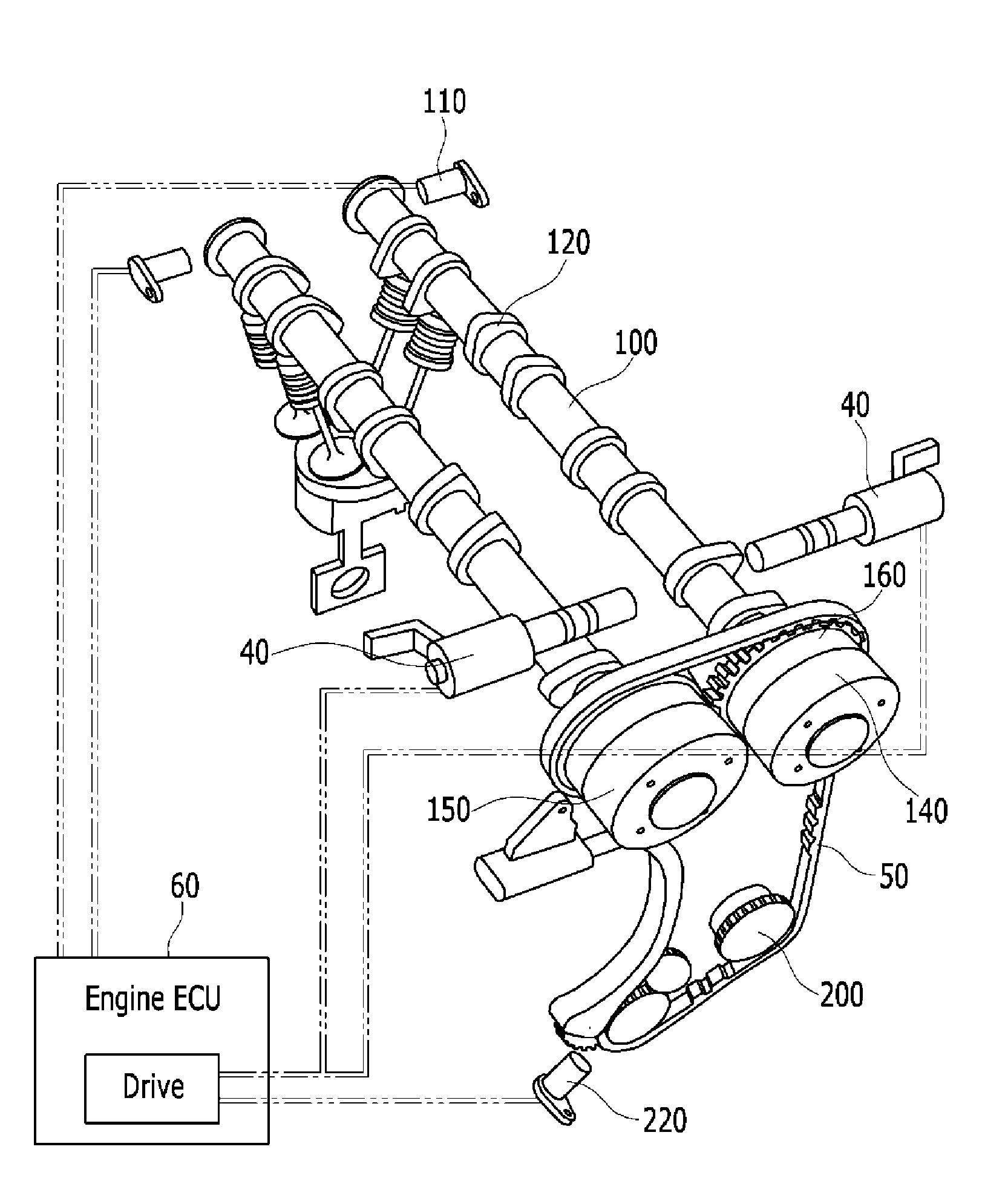
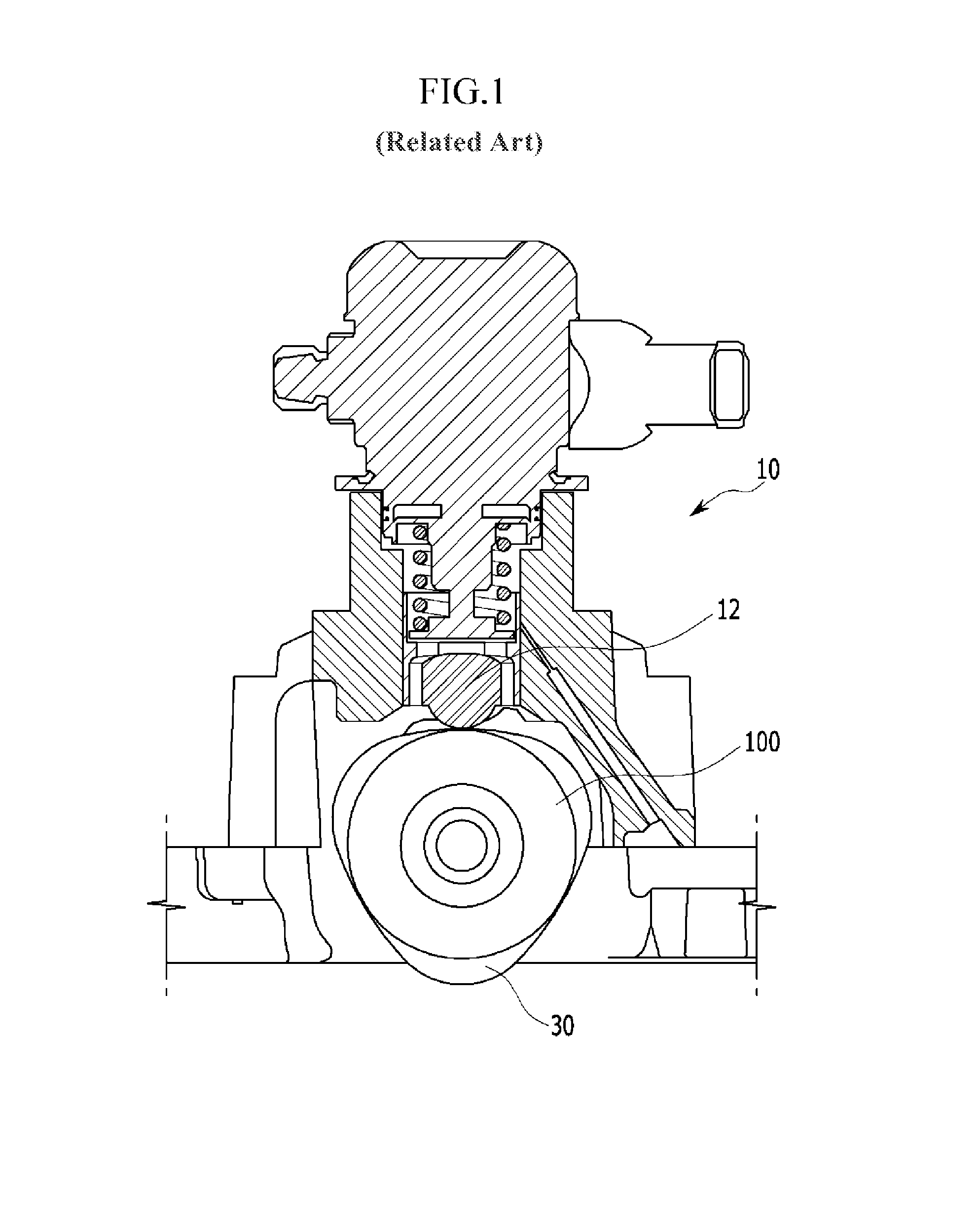
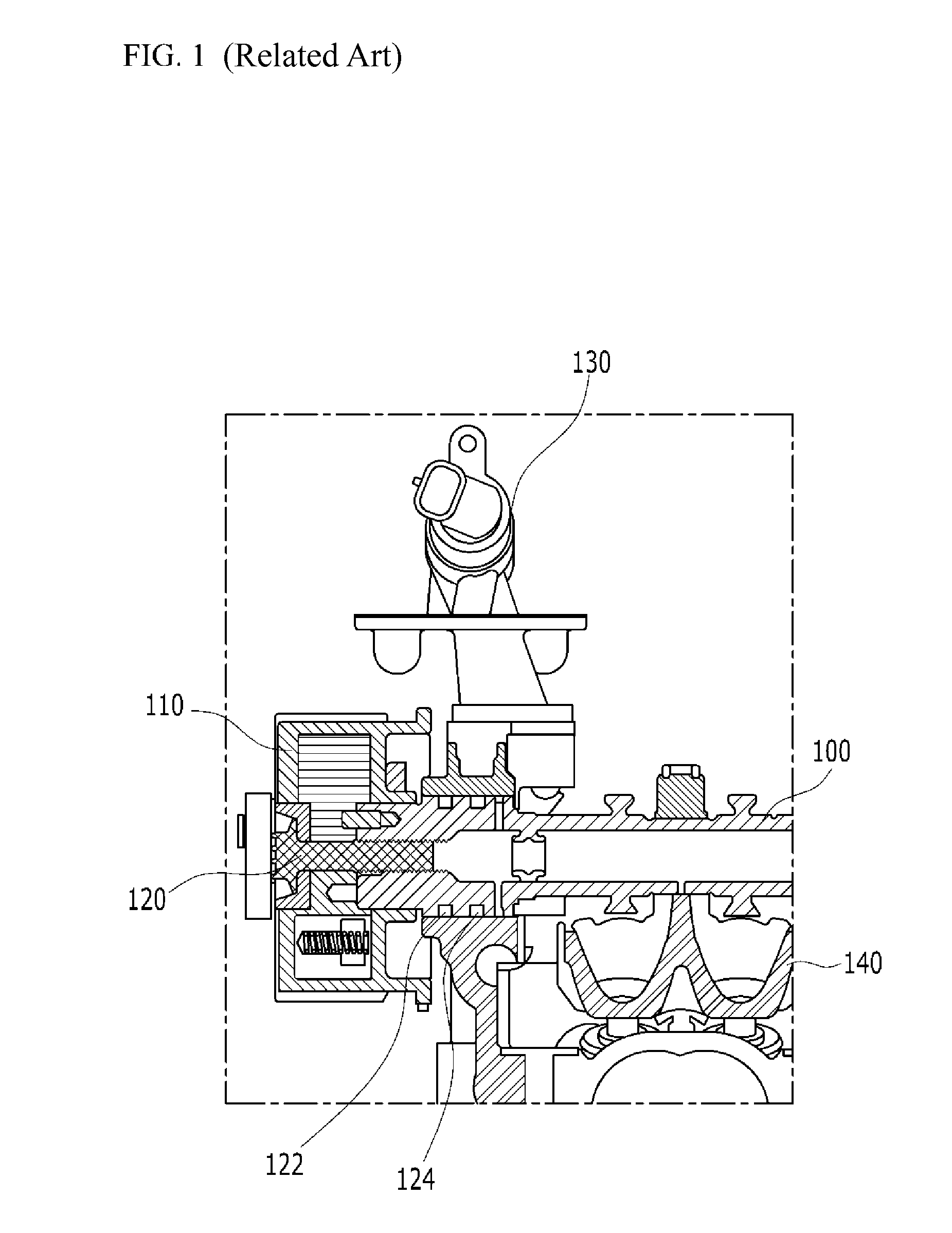
Cylinder head of Honda K20Z3. This engine uses continuously variable timing for the inlet valves. In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions.
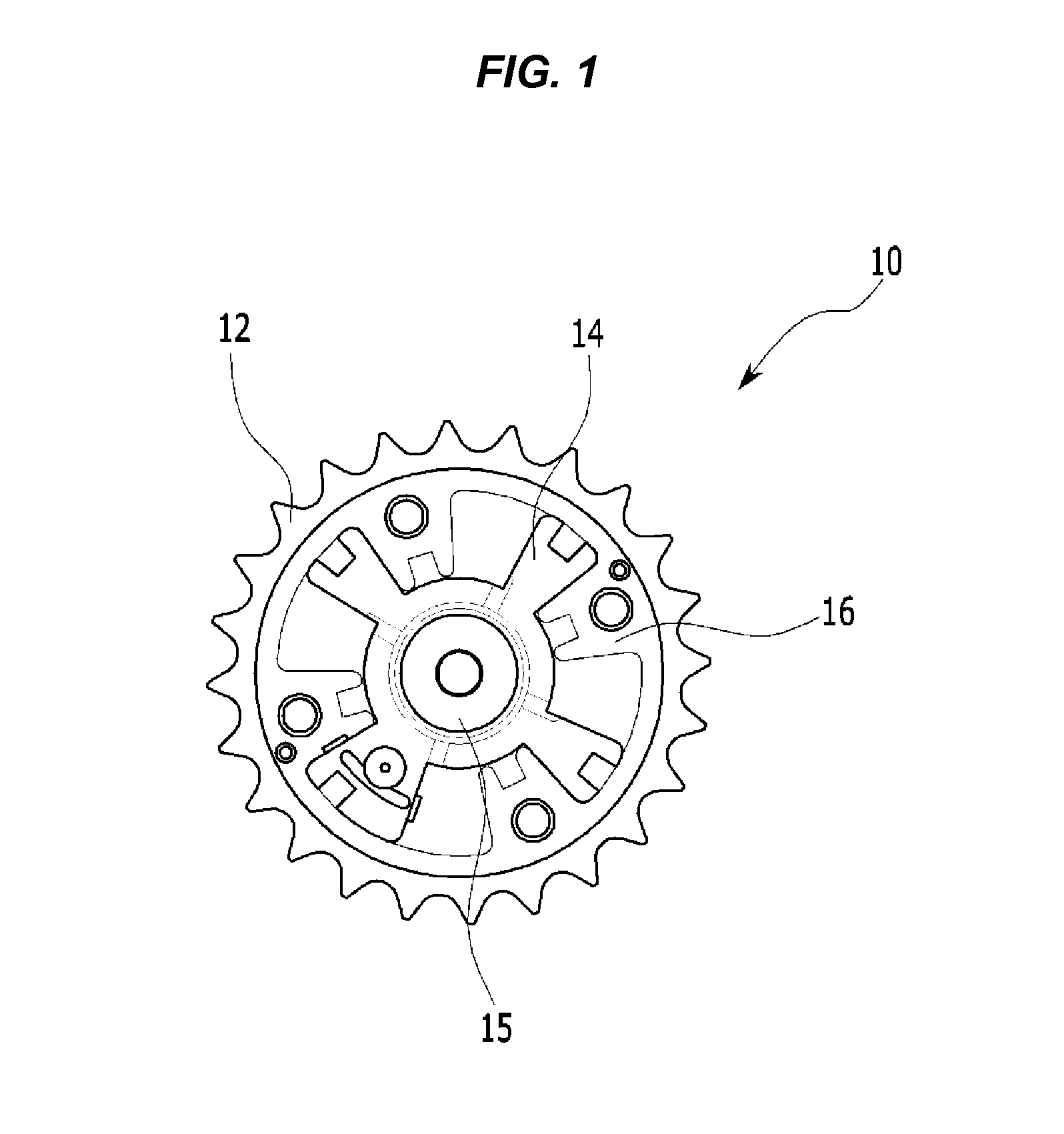
Full function variable gas distribution controlling mechanism of internal combustion engine
InactiveCN101408118ASimple structureLow costValve arrangementsMachines/enginesDistribution controlExternal combustion engine
The invention relates to a full-function variable distribution control mechanism of an internal combustion engine, comprising a motor and a worm and worm wheel transmission mechanism. A cam which expands on the inclined surface of a cam head is formed by that a cone part is combined on a cylinder with the parallel axes; a variable rocker axial travelling mechanism is as follows: a screw rod is fixedly arranged on a worm wheel; a pushing arm is screwed on the screwed rod; both a variable rocker and a combined driven rocker arm can be rotatablely arranged on a rocker shaft; and the variable rocker arm is positioned between two arms of the driven rocker arm and an upper groove and a convex semicircle of the pushing arm are contacted with each other; and a roller wheel of the variable rocker arm and the cam head of the cam form a transmission pair. The control mechanism has continuous variable valve timing and valve stroke, which leads the valve to have half-open function, cylinder control variable displacement function and maneuverability of superposition of the variable valve, can replace a throttle valve and applies the high-end change distribution technology and the cylinder control variable displacement to an economic engine, thus having the advantages of increasing the power, saving oil consumption and reducing the exhaust.
Owner:刘若丹
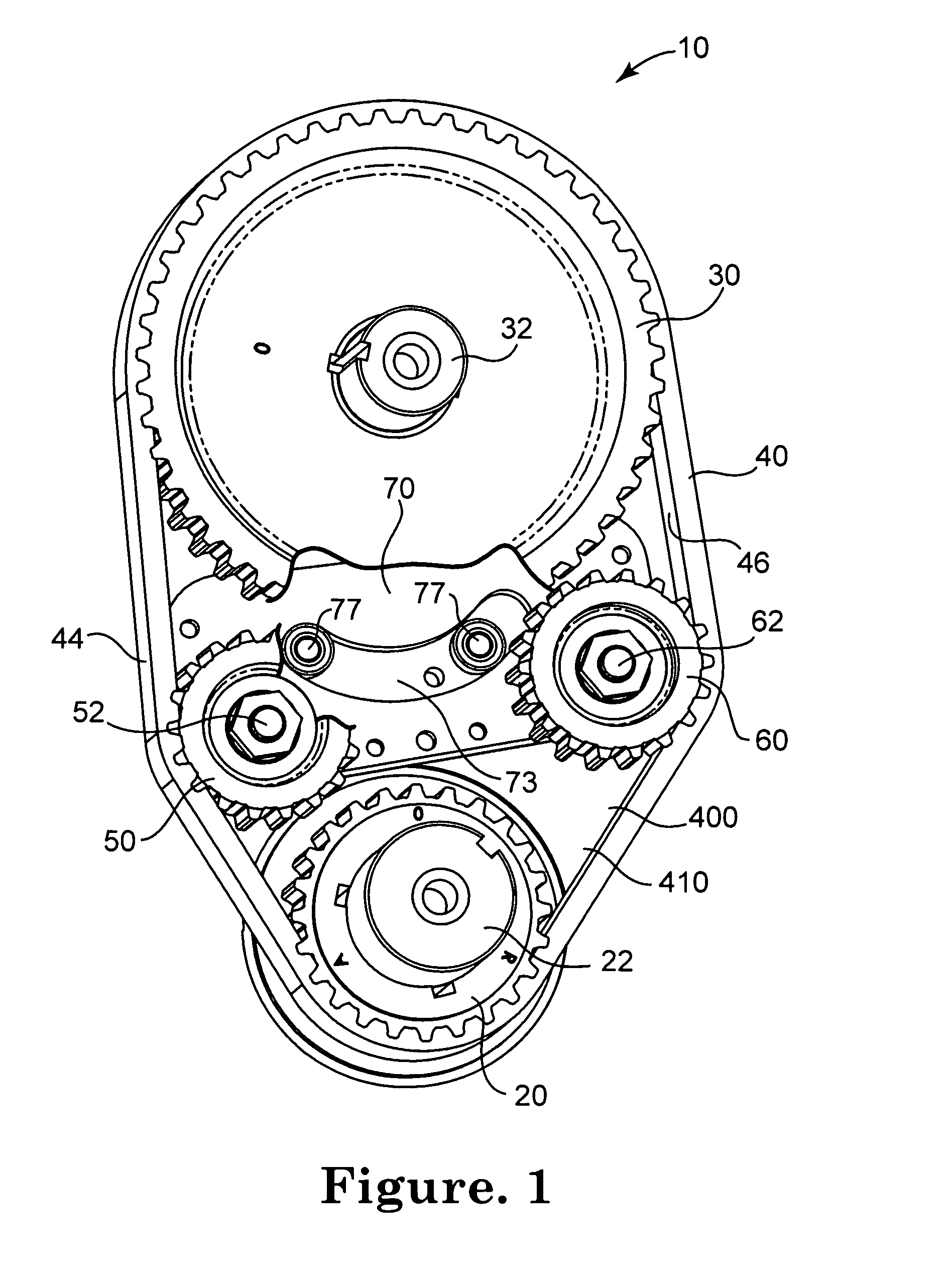
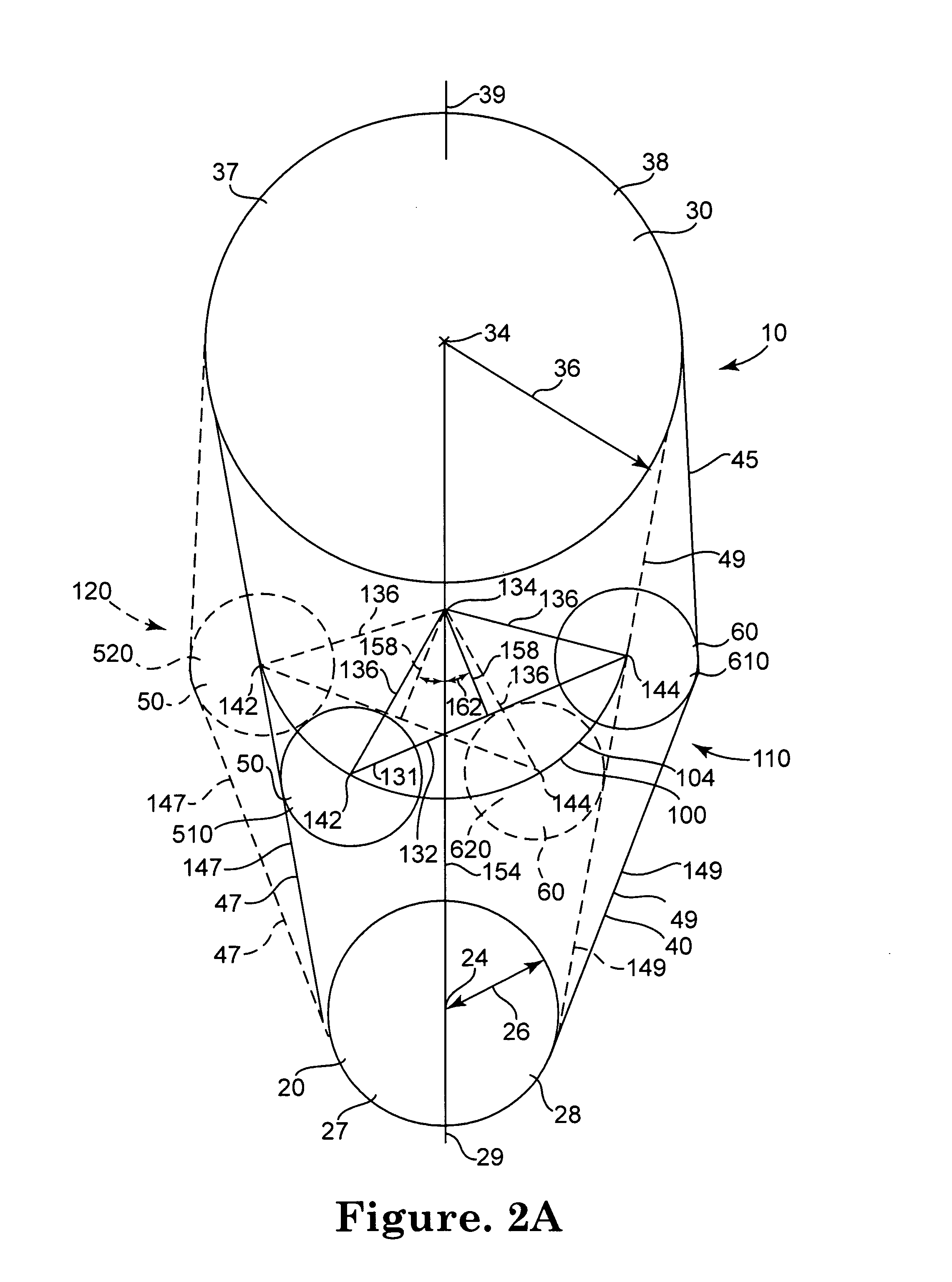
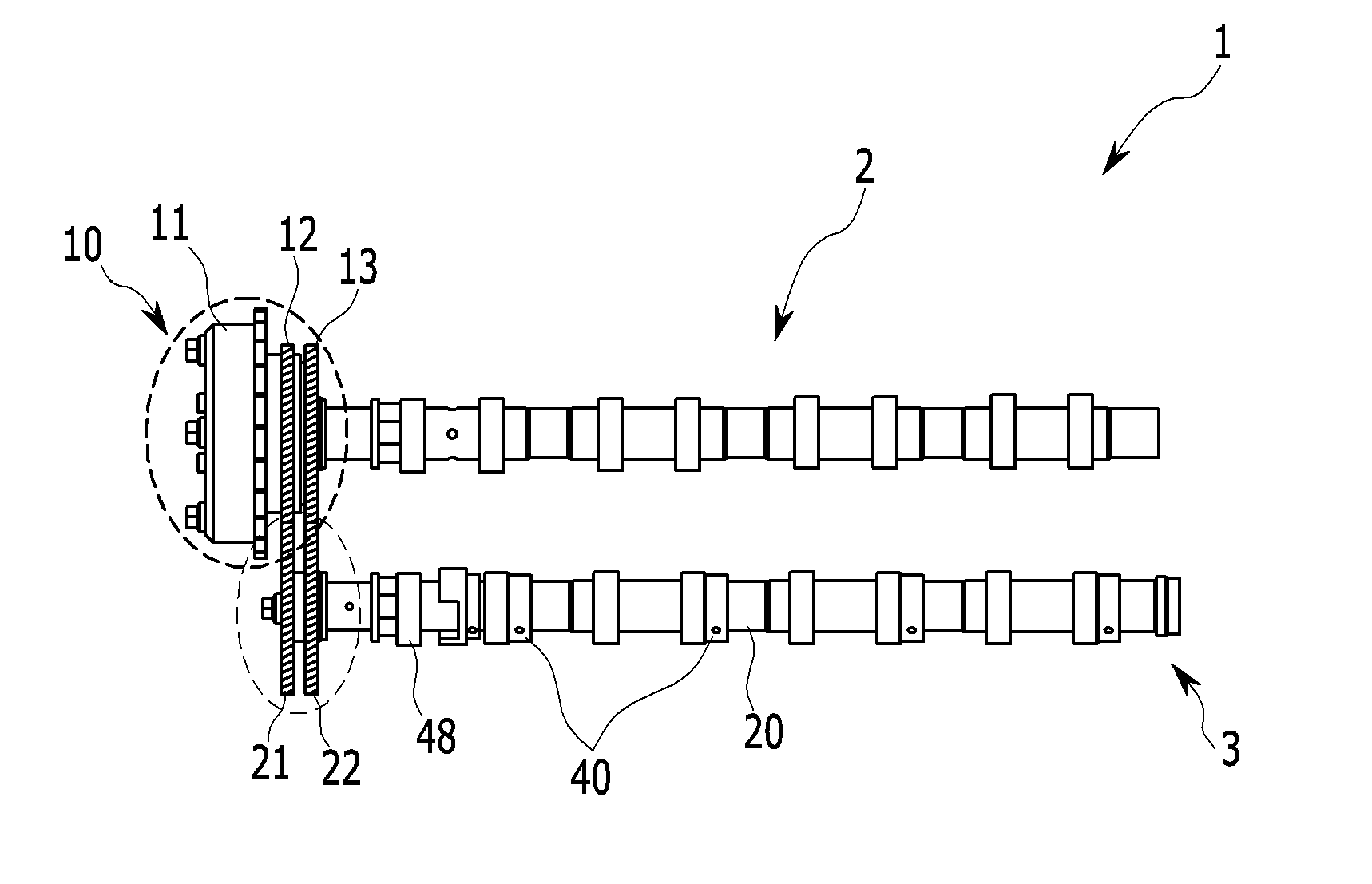
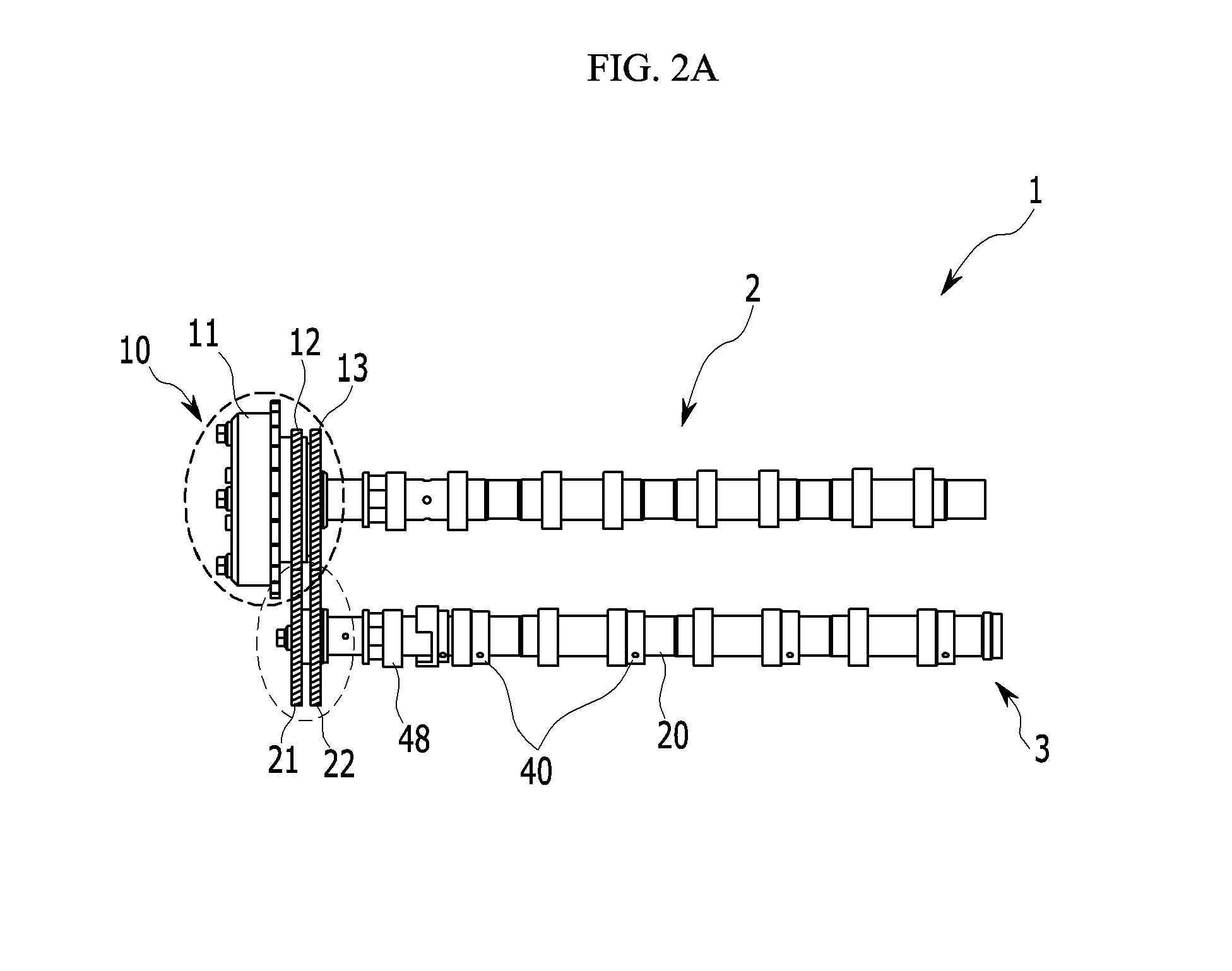
Apparatus and methods for continuous variable valve timing
Apparatus and methods for shifting the phase between a driver gear and a driven gear in communication by a timing belt are provided as well as methods for configuring the apparatus. The apparatus may continuously vary the phase relationship between the driver gear and the driven gear.
Owner:AES INDS
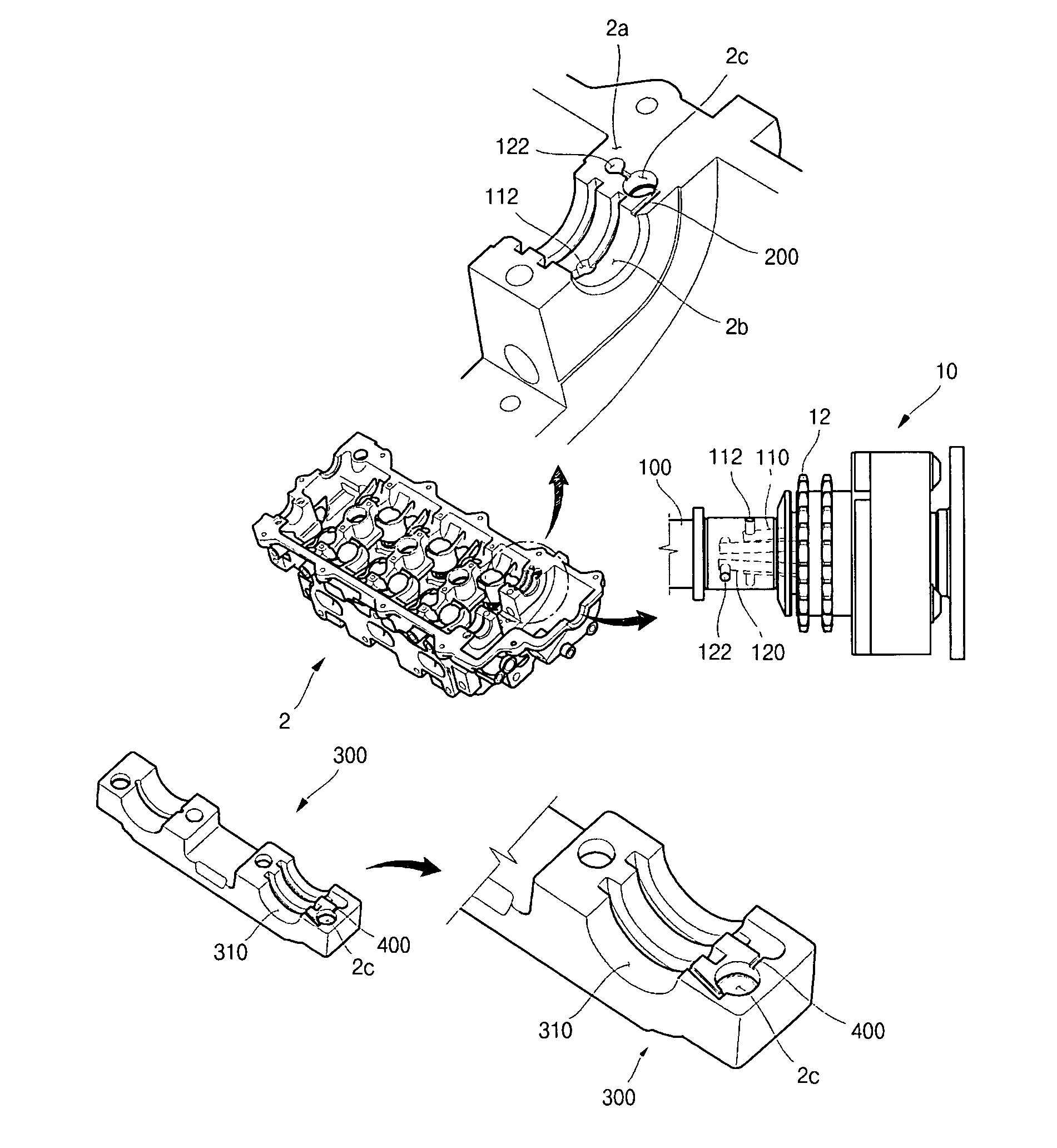
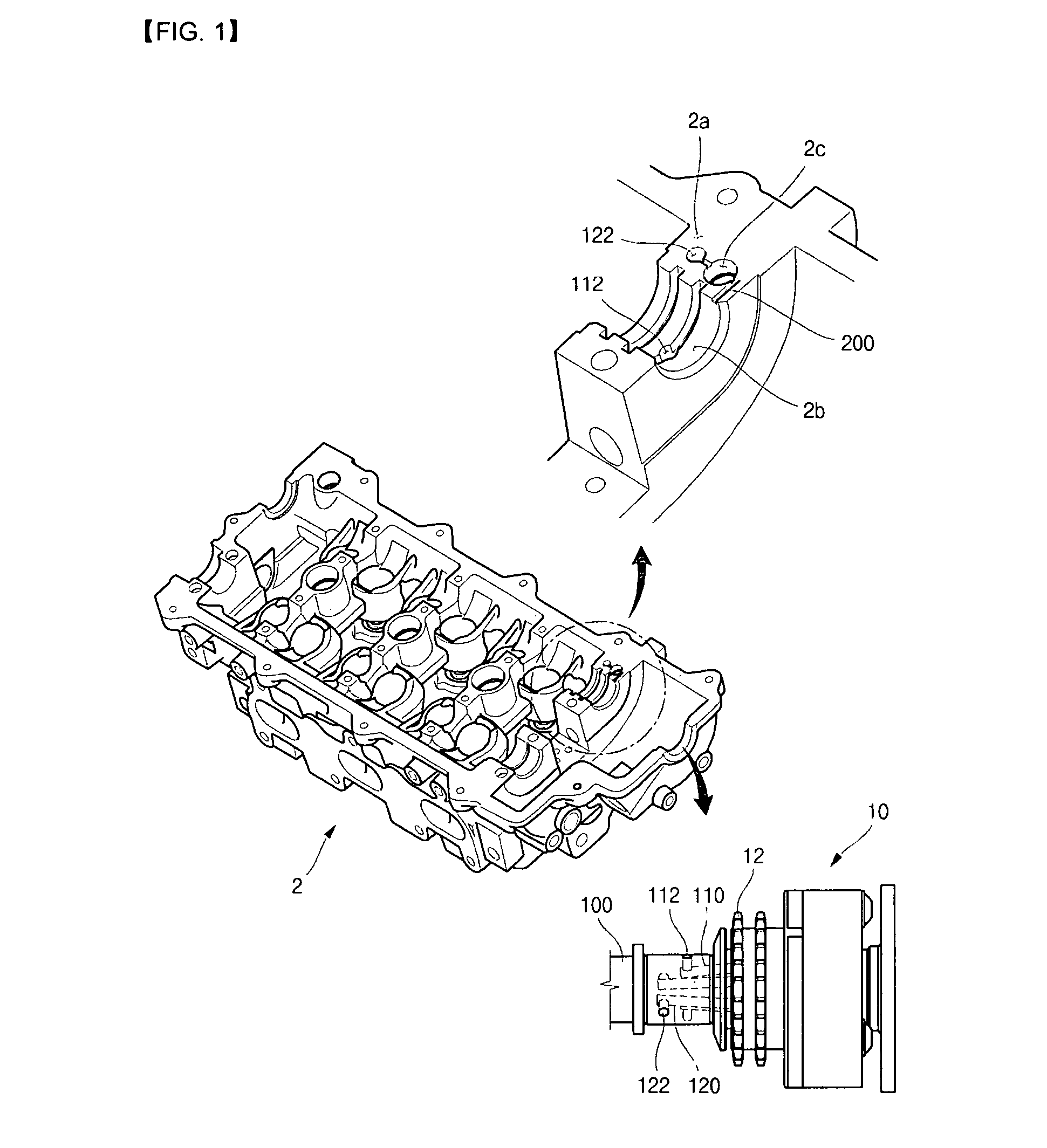
Lubrication structure of camshaft with variable valve timing
ActiveUS7322327B1Fully lubricatedAvoid breakingValve drivesMachines/enginesVariable valve timingCylinder head
A lubrication structure for a camshaft with variable valve timing includes an advance hole, which includes an advance flow passage formed in a camshaft body. An end of the camshaft is attached to a continuously variable valve timing. A retard hole, which includes a retard flow passage, is formed in the camshaft body and spaced horizontally from the advance hole. A divergence flow passage has an end that surface-contacts the camshaft and is extended to communicate with the retard hole at an upper surface of a mounting part of a cylinder head. The other end of the divergence flow passage communicates with the slip surface on which the camshaft lays via a counter bore, so as to prevent lubrication film from being broken by load of the sprocket at an engine idle state or at an initial stage of cold starting.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Piston-type IC engine of continuous variable valve timing and gas-distributing mechanism
InactiveCN1814992AIncrease usageReduce consumptionValve arrangementsMachines/enginesBogieEffective power
A piston type internal combustion engine with continuously variable valve timing valve mechanism features the main inlet camshaft and sub inlet camshaft simultaneously controlling air inlet air valve start-stop and start-stop duration and valve stroke through compensated bogie. Said invention not only can continuously change air valve timing to control air inlet / outlet valve start-stop time, change but also air inlet / outlet valve start-stop time duration and valve stroke, thereby further raising internal combustion engine effective power.
Owner:王雪松
Continously variable valve timing valve actuating mechanism piston IC engine
InactiveCN1831304ALarge diameterPromote combustionValve arrangementsInternal combustion piston enginesEffective powerVariable valve timing
The invention is a piston internal-combustion engine with continuously variable valve timing mechanism, characterized by that: it adopts a structure of main and auxiliary gas inlet and outlet cam shafts, where each cam shaft can control corresponding gas inlet and outlet valves, the main cam shaft controls ON / OFF of main gas inlet and outlet valves, and the auxiliary one controls ON / OFF of auxiliary gas inlet and outlet valves. And it can control ON / OFF time and ON-to-OFF time of the gas inlet and outlet valves by continuously varying valve timing of the gas inlet and outlet cam shafts, thus further improving effective power and thermal efficiency of internal-combustion engine and reducing fuel oil consumption and pollutant discharge.
Owner:王雪松
Variable valve timing camshaft
ActiveUS20150167506A1Improve business performanceSimple compositionValve arrangementsMachines/enginesVariable valve timingGear wheel
A variable valve timing camshaft which may be connected to a continuous variable valve timing apparatus having a rotor and a stator which are adapted to relatively rotate with each other and may be operated so as to vary open / close timing of valve may include a non-control camshaft coupled to the continuous variable valve timing apparatus, having a first drive gear rotating together with the rotor and a second drive gear rotating together with the stator, and rotating according to rotation of an engine without varying a phase along a circumferential direction, a control camshaft having an outer shaft rotating according to one of the first drive gear or the second drive gear, an inner shaft rotating according to the other of the first drive gear or the second drive gear, an outer cam, and an inner cam and a limiting device limiting end play of the inner shaft.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Continuously variable valve timing phaser
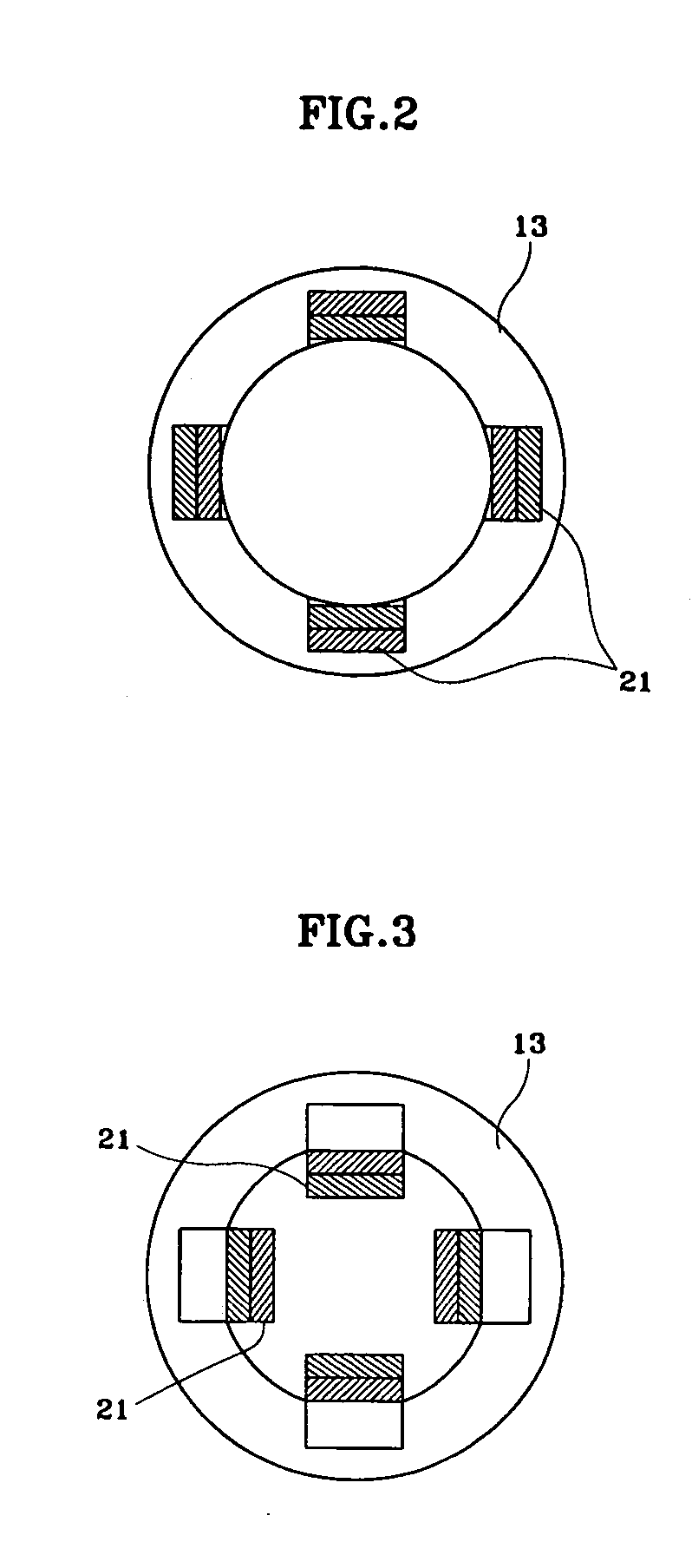
InactiveCN101994535AImprove intake and exhaust efficiencyIncrease torqueValve arrangementsMachines/enginesImpellerExhaust valve
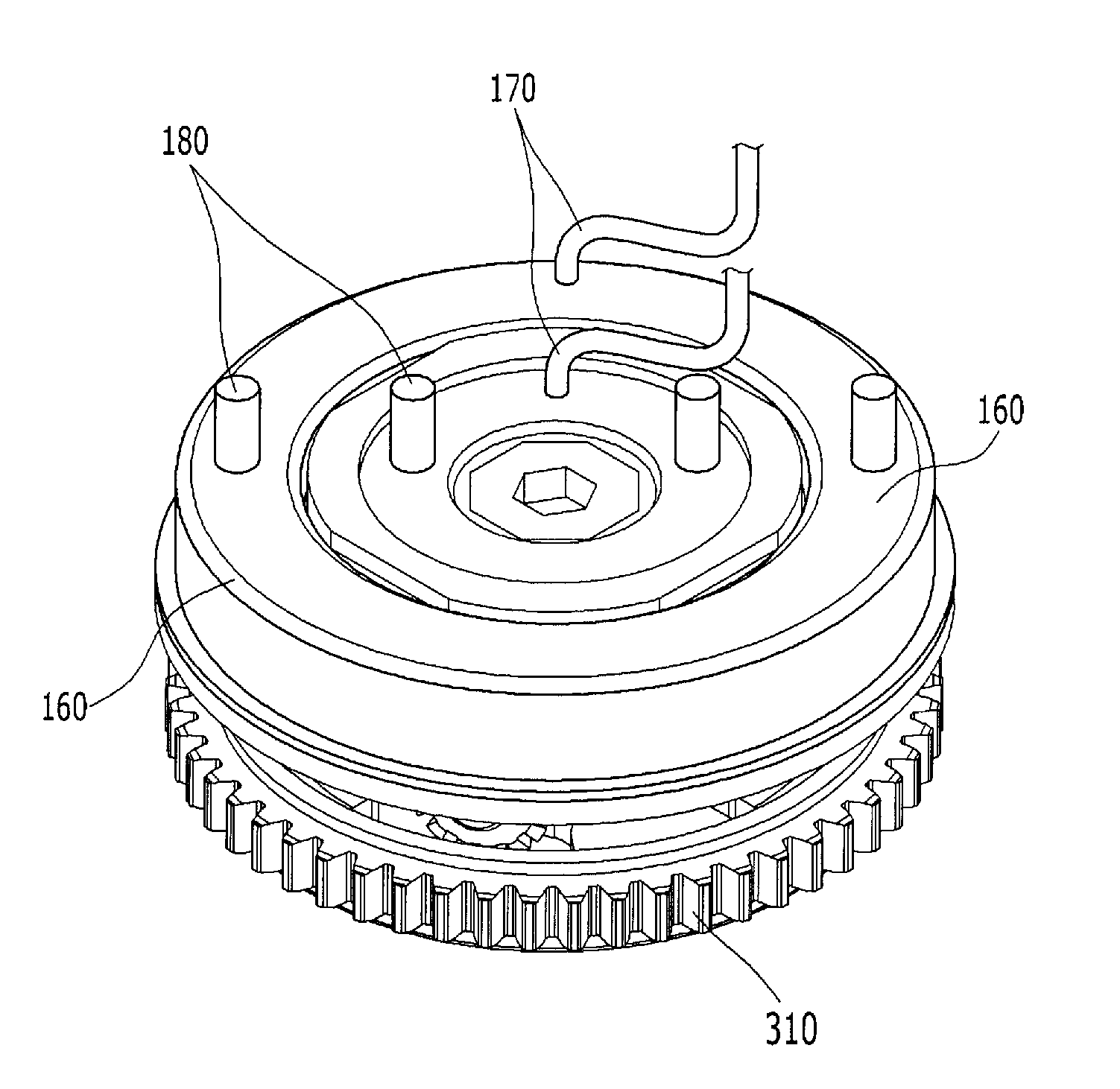
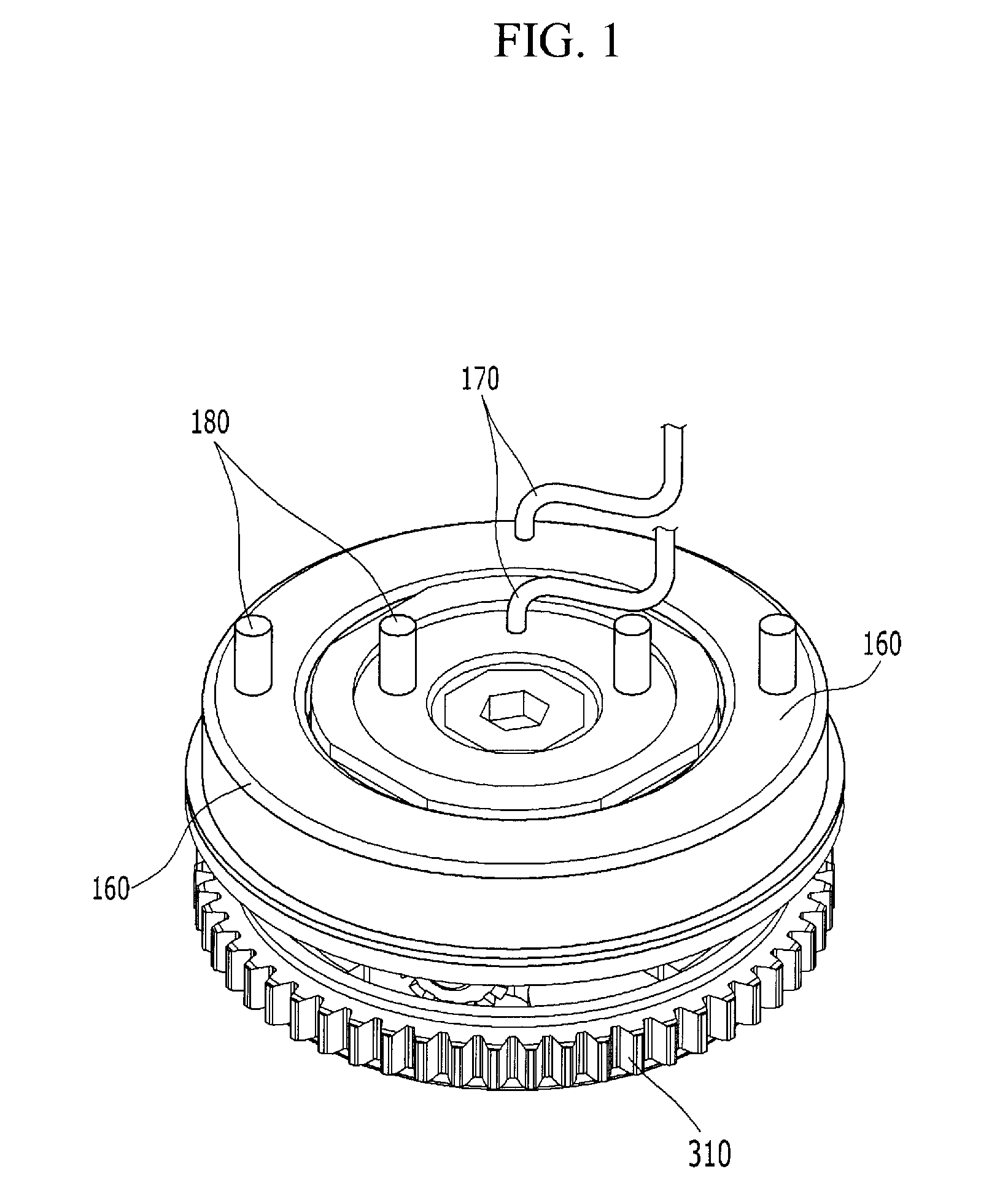
The invention discloses a continuously variable valve timing phaser. The phaser is arranged on a camshaft (13) and comprises a shell (1), an impeller (2), a chain wheel (3), a screw (9), a back cover (11), a locking mechanism (18) and a sealing component (19), wherein the impeller (2) rotates freely in an enclosed space formed by the shell (1), the back cover (11) and the chain wheel (3); the locking mechanism (18) is arranged in the impeller (2); grooves (25) are distributed on the shell (1) and the impeller (2); and the sealing component (19) is arranged in the groove (25) and partitions a relatively sealed space between the shell (1) and the impeller (2) into an advance cavity (15) and a lag cavity (16). The phaser has the advantages that: the phase position of the camshaft is adjusted automatically according to different working conditions, and the opening and closing of an intake valve and an exhaust valve are changed along with the change of rotating speed, so that the aim of improving dynamic property and fuel economy is fulfilled.
Owner:成都恒高机械电子有限公司
Continuous Variable Valve Timing Apparatus
A continuously variable valve timing apparatus may include an end plate connected to a camshaft, a drive sprocket rotating the end plate, a first friction plate disposed to be coaxial to the end plate, a second friction plate disposed to be coaxial to the end plate, a first brake selectively braking the first friction plate, a second brake selectively braking the second friction plate, and a control gear portion which changes relative phase between the end plate and the drive sprocket according to braking of the first friction plate or the second friction plate.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
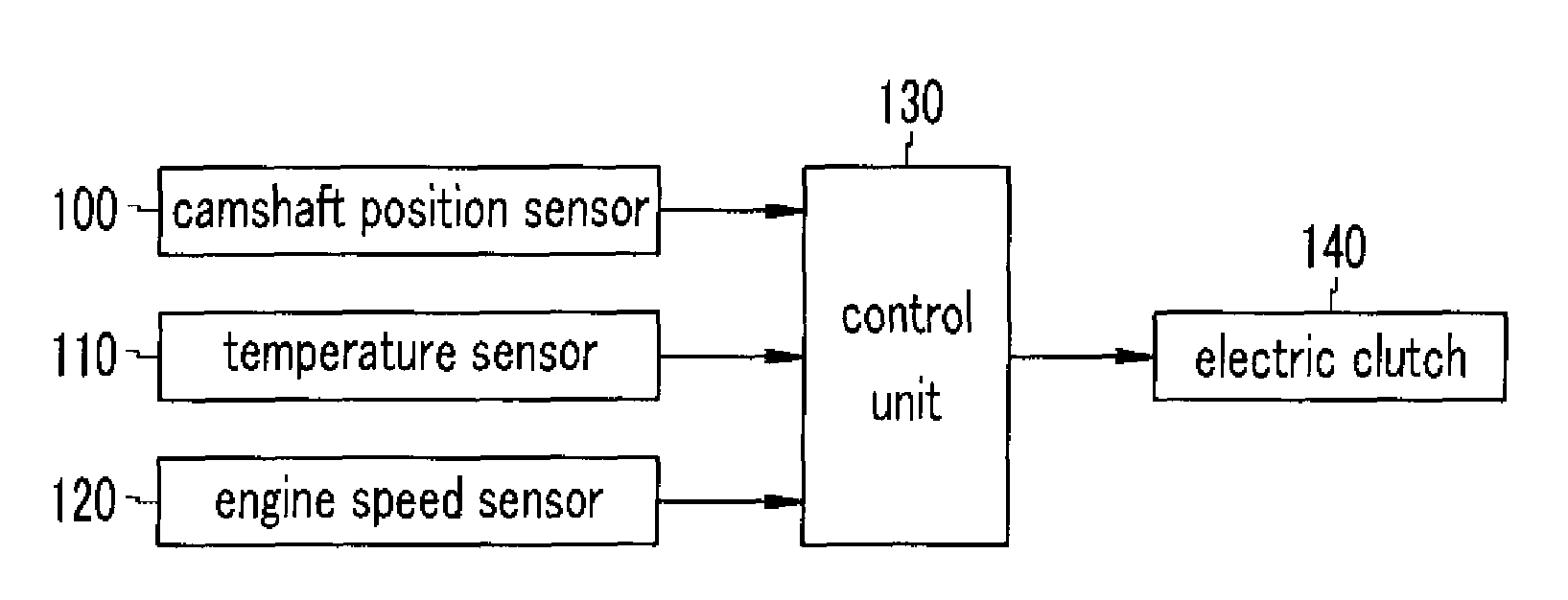
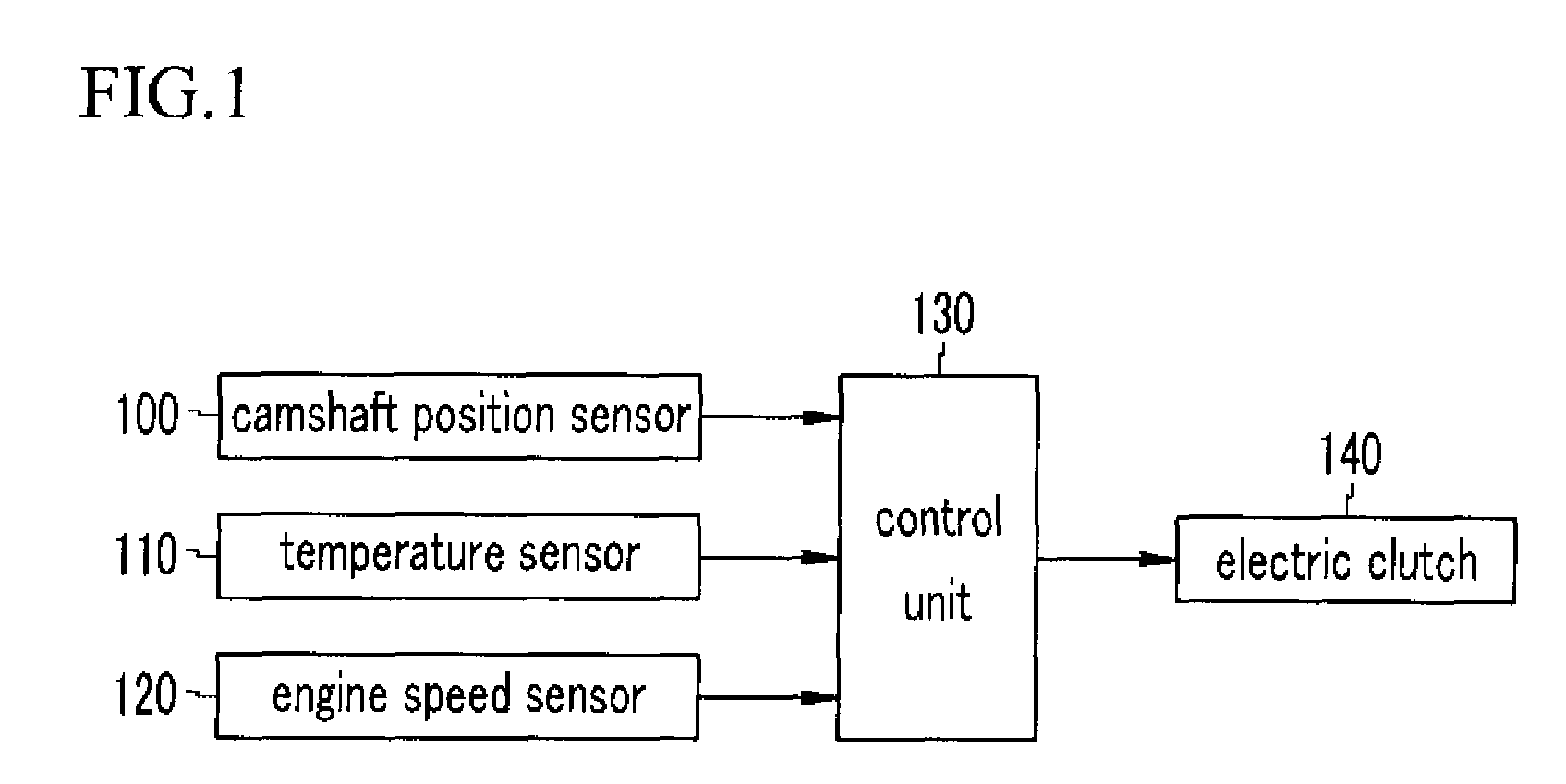
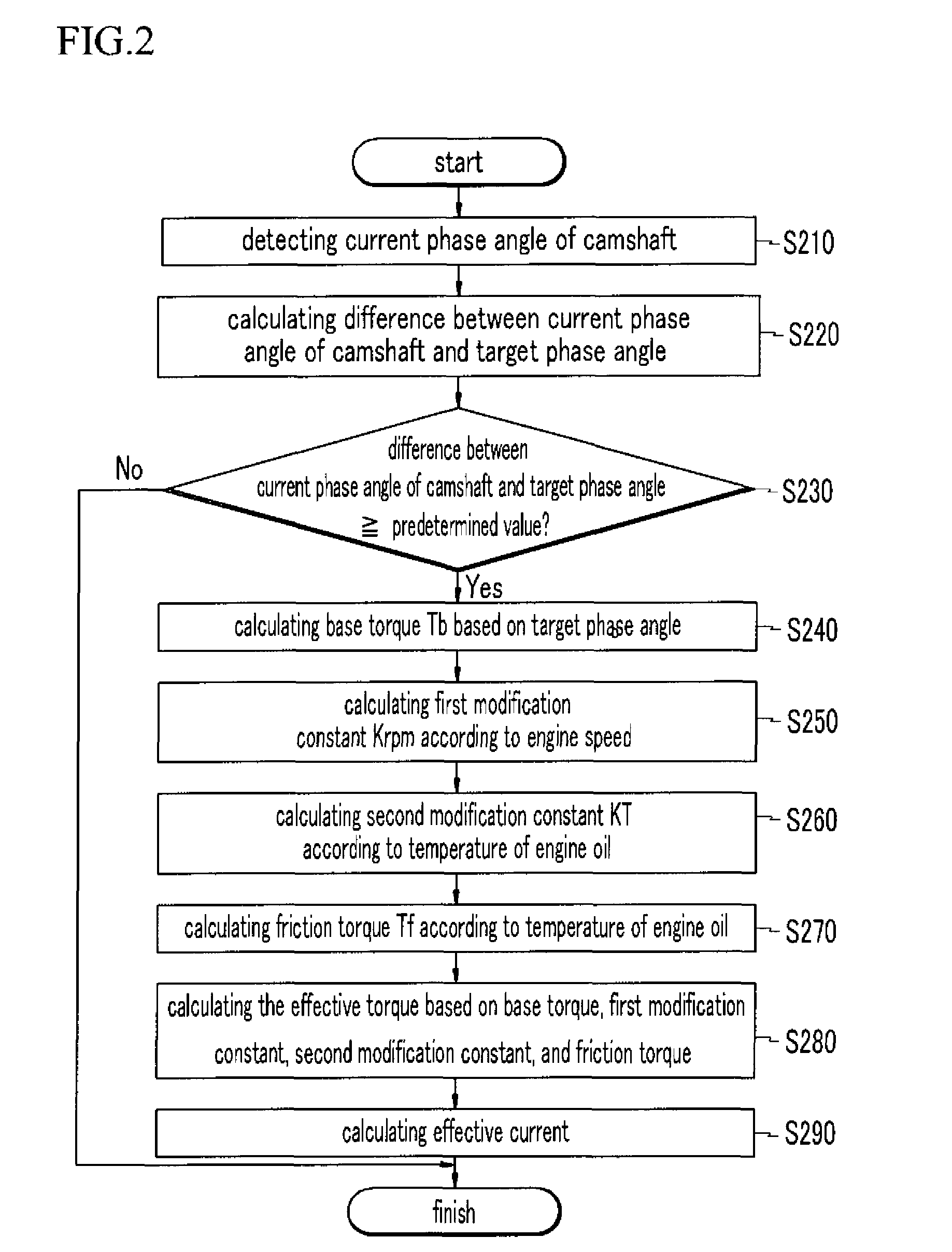
Method for controlling continuous variable valve timing apparatus
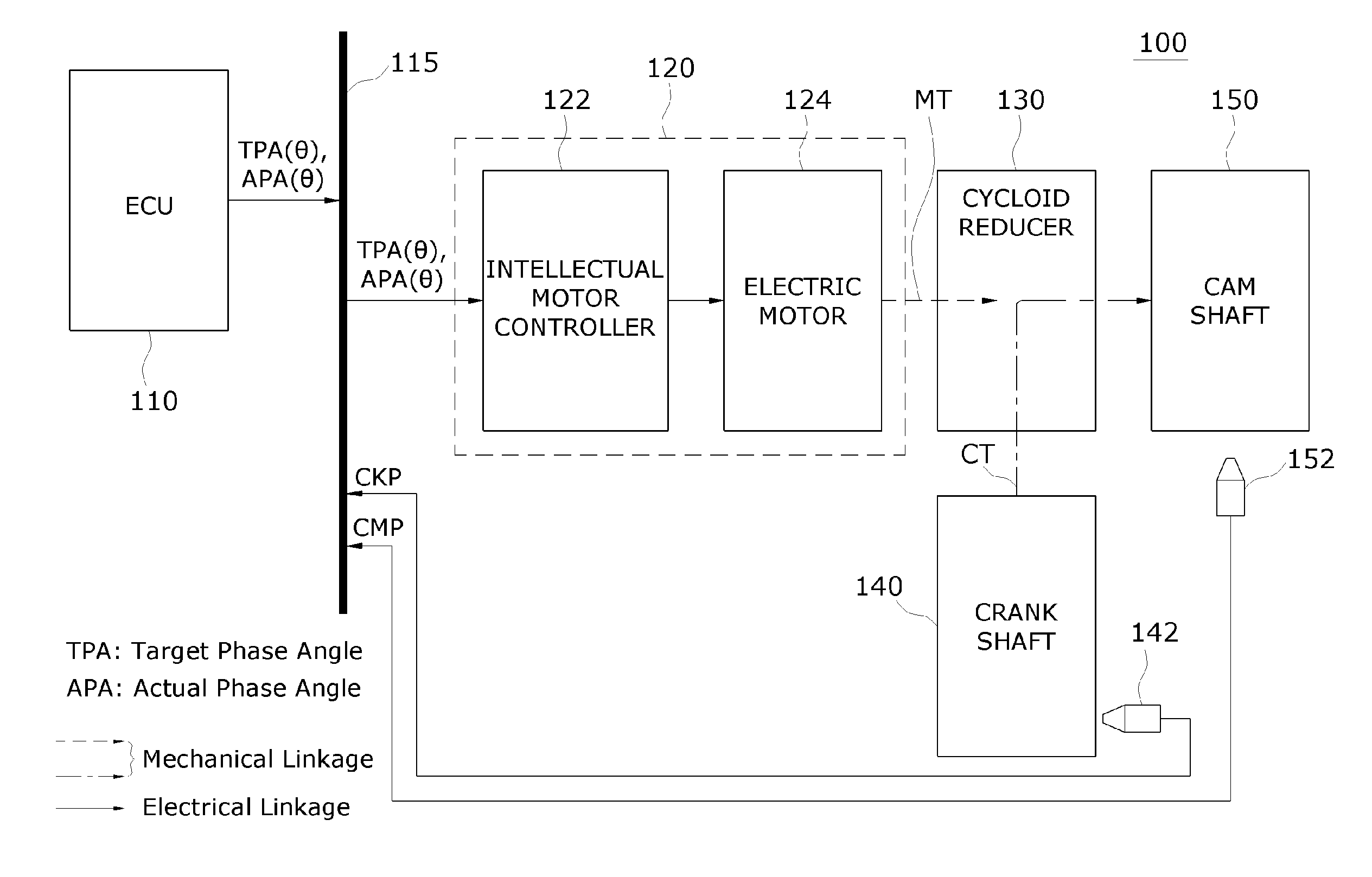
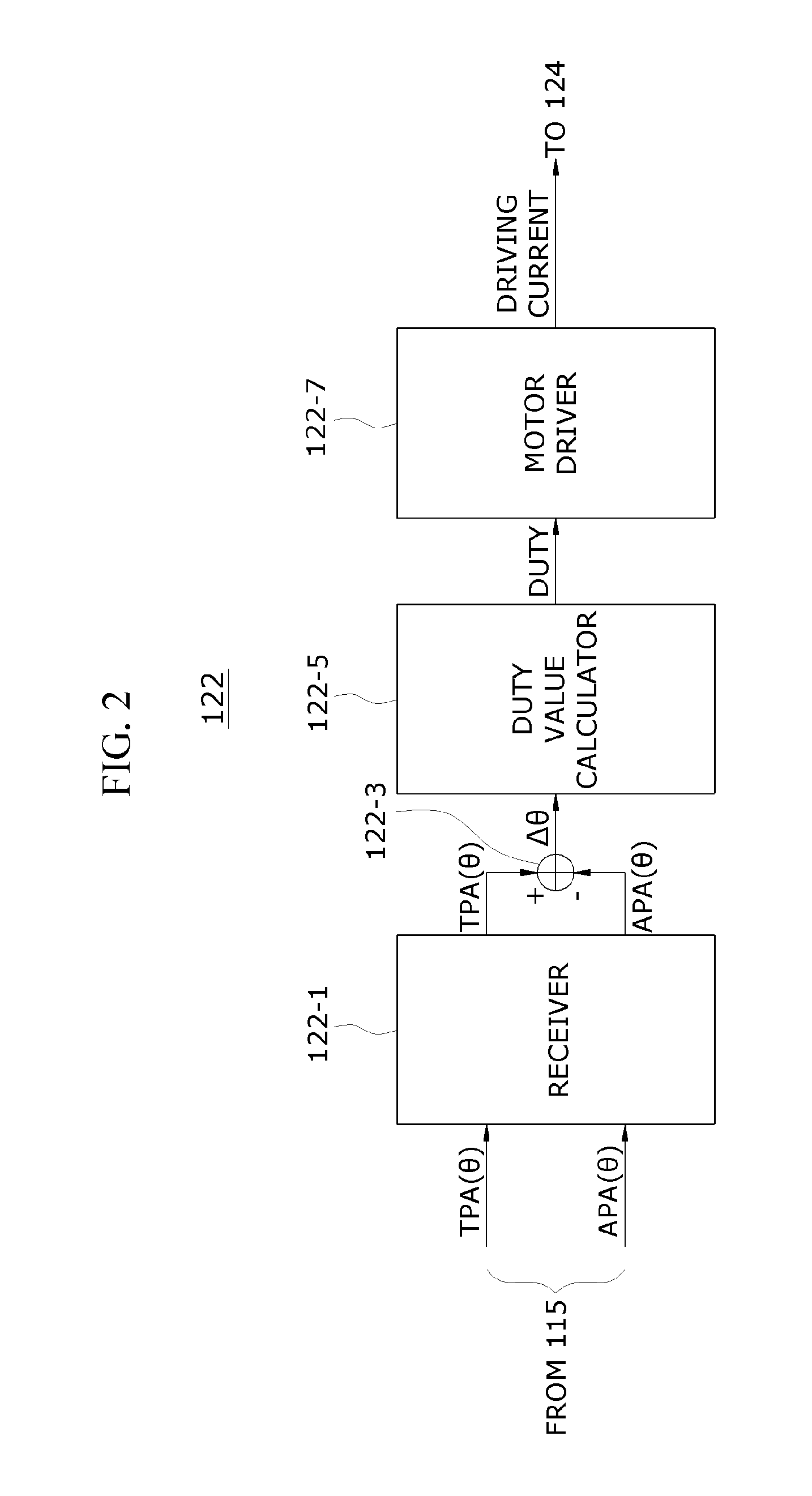
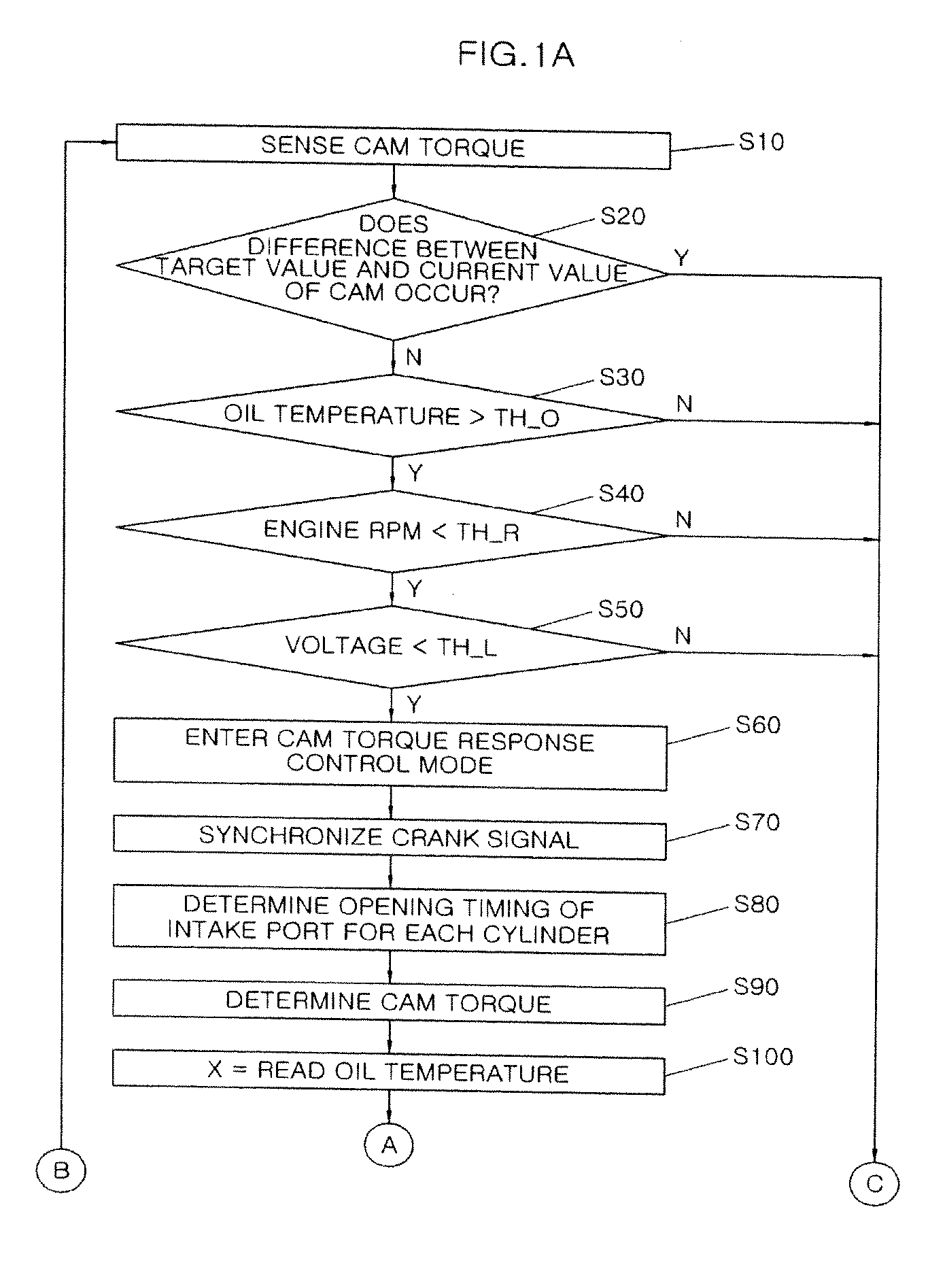
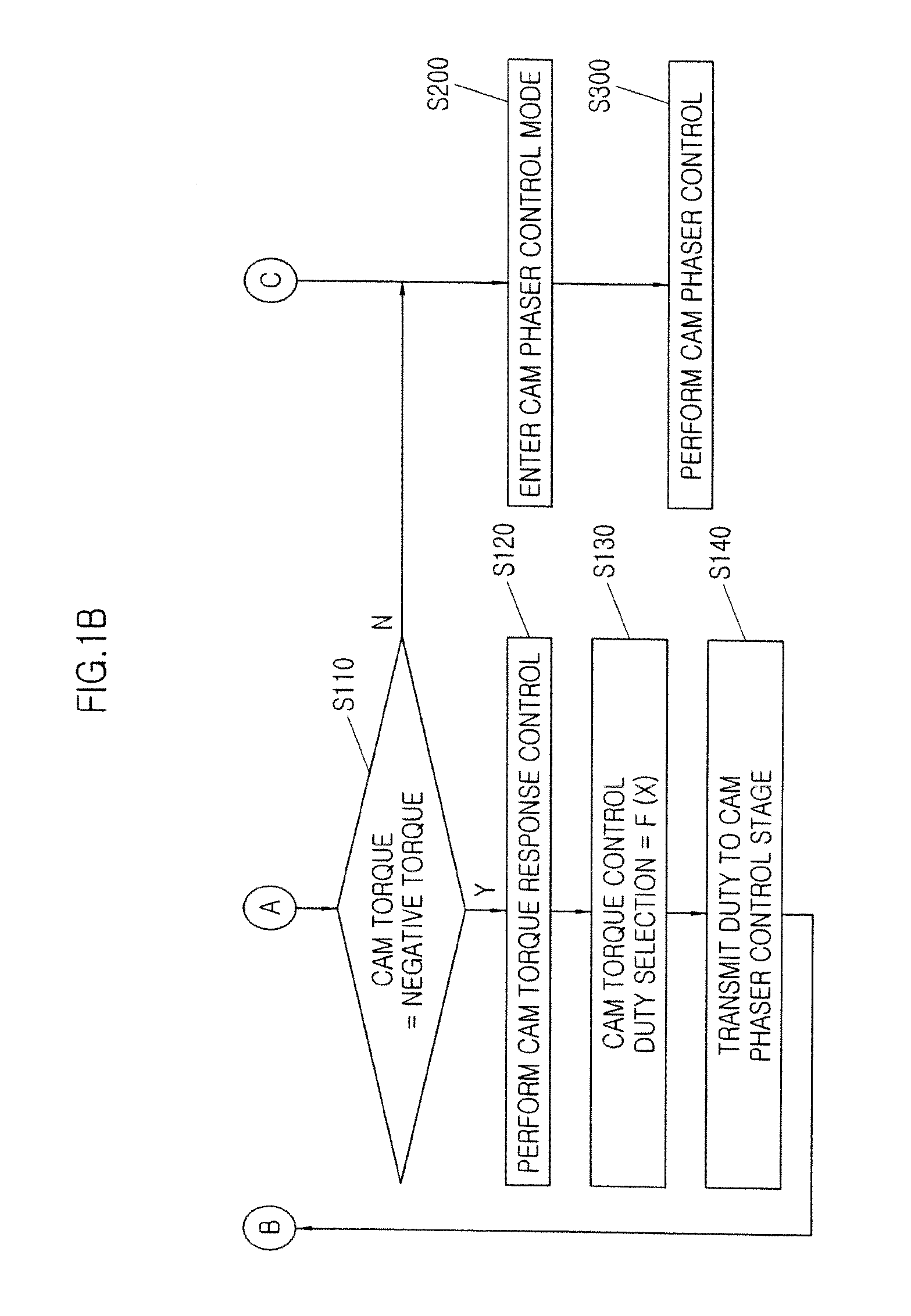
ActiveUS20090157281A1Analogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlControl theoryContinuously variable valve timing
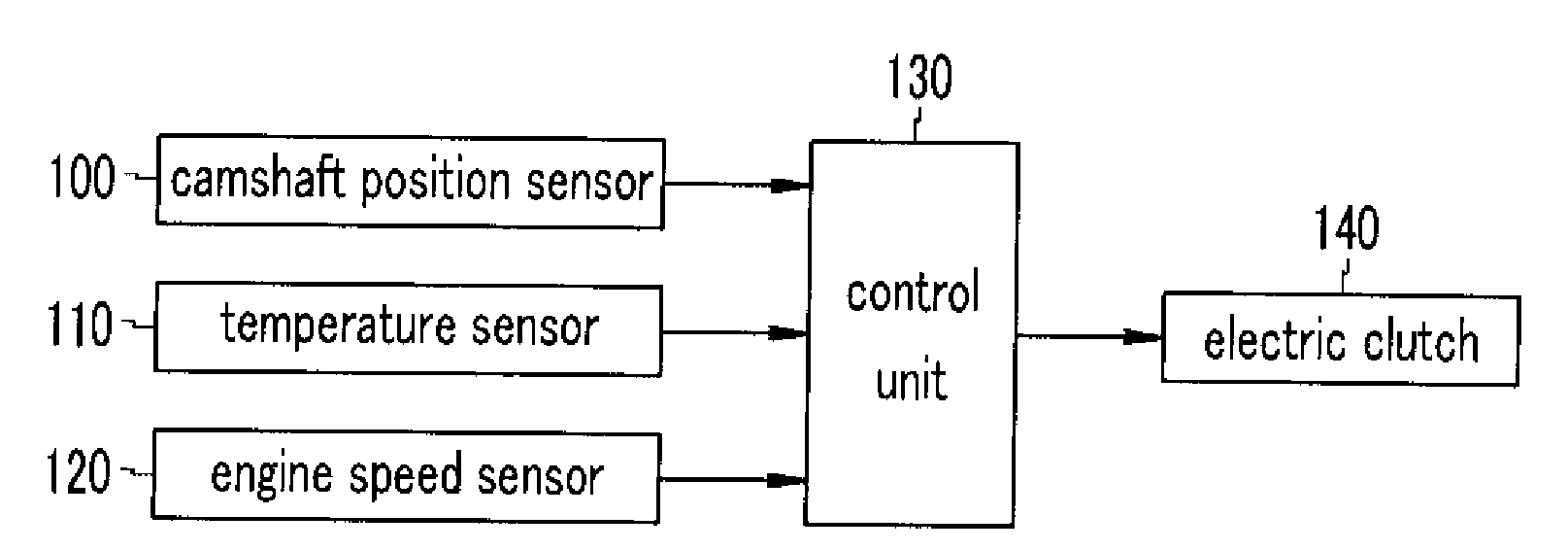
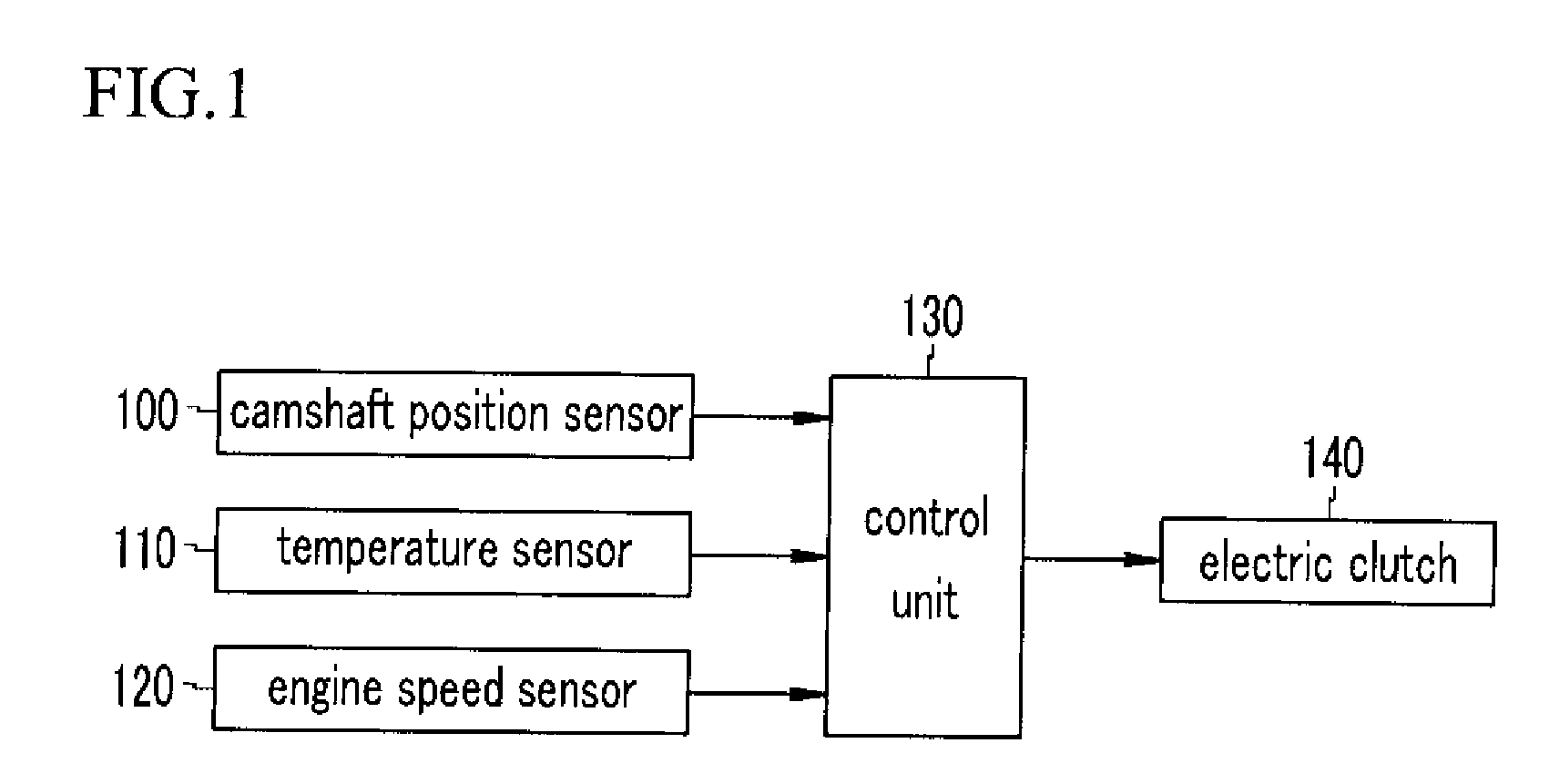
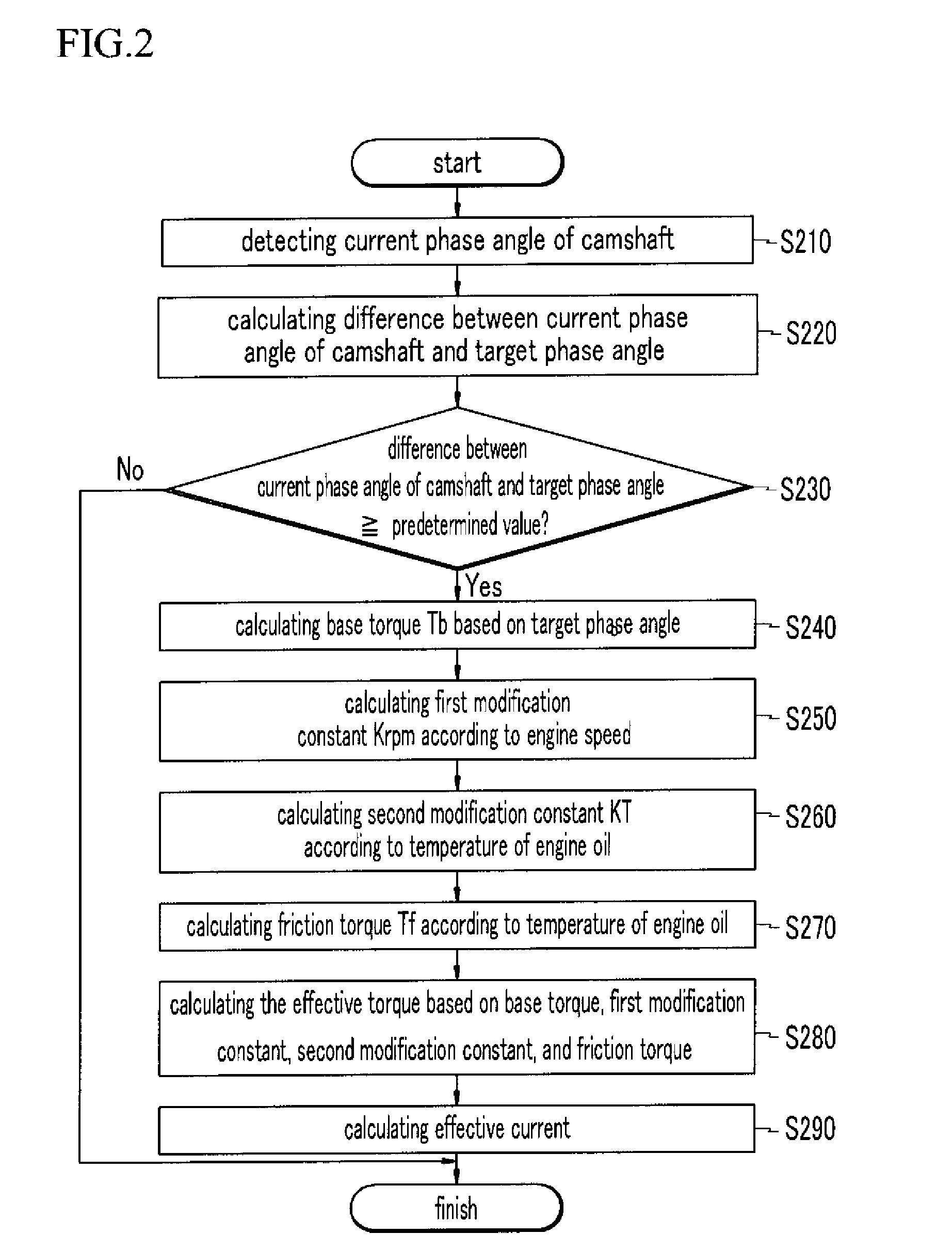
A method for controlling a continuous variable valve timing apparatus that can control a phase angle of a camshaft quickly and precisely according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention may include: calculating a difference between a target phase angle and a current phase angle of a camshaft; determining whether the difference between the target phase angle and the current phase angle of the camshaft is larger than or equal to a predetermined value; calculating a base torque Tb based on the target phase angle if the difference between the target phase angle and the current phase angle of the camshaft is larger than or equal to the predetermined value; calculating an effective torque Teff by modifying the base torque Tb corresponding to engine speed and temperature of engine oil; and calculating an effective current Ieff corresponding to the effective torque Teff.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
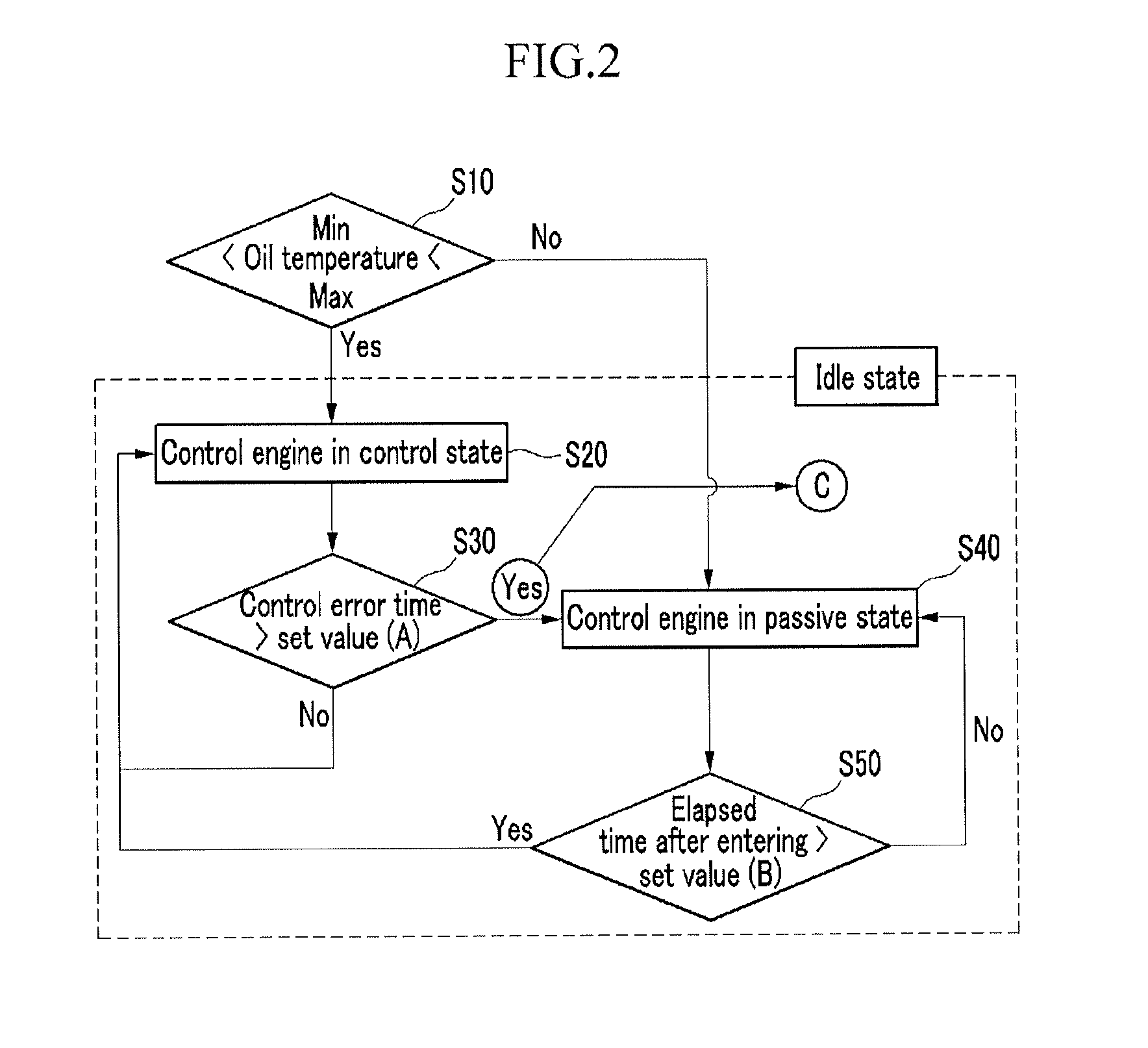
Control method for cvvl engine
ActiveUS20140025276A1Reduce compressionPrevent deterioration of fuel efficiencyAnalogue computers for vehiclesValve arrangementsEngineeringOil temperature
A continuous variable valve lift engine may include determining whether an engine is in an idle state and an oil temperature of an engine is within a predetermined range, controlling, the engine in a predetermined control state when the engine is in the idle state and the oil temperature is within the predetermined range, and measuring, an error occurrence time when an error occurs in controlling the engine in the control state, and controlling the engine while switching the engine to a predetermined passive state when the error occurrence time is more than a preset time.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Large-flow continuous variable valve timing (CVVT) fuel control valve with filter screen
InactiveCN102003233AAdd filter functionHigh working reliabilityValve arrangementsDispersed particle filtrationForeign matterEntrance angle
The invention discloses a large-flow continuous variable valve timing (CVVT) fuel control valve with a filter screen. The large-flow CVVT fuel control valve with the filter screen comprises a valve bush component, a rear yoke iron component, a front yoke iron component, an iron core component, a winding component and an outer yoke sleeve component, wherein the valve bush component consists of a valve bush (1), a return spring (2), a valve core (3) and a ring; the valve bush (1) is provided with a fuel feed port (12), an entrance angle oil port (17) and a lag angle oil angle (19); and the fuel feed port (12), the entrance angle oil port (17) and the lag angle oil angle (19) are pressed into the filter screen (18) respectively. The large-flow CVVT fuel control valve with the filter screen controls the fuel flow to increase by 50 percent, improves the quick response time of a valve timing actuator, increases a filtering function of the filter screen, effectively protects foreign matters from entering the fuel control valve, guarantees that the valve core can slide in the valve bush freely, reduces the possibility of the clamping stagnation of the valve core, increases the working reliability of a valve timing system, reduces the requirements of a motor on the using environment and prolongs the service life of a product.
Owner:成都恒高机械电子有限公司
Two-in-one mechanism of continuous variable valve stroke and valve timing of automobile engine
InactiveCN103266928AImprove intake and exhaust conditionsReduce intake and exhaust resistanceValve arrangementsMachines/enginesMotor driveEngineering
The invention discloses a two-in-one mechanism of continuous variable valve stroke and valve timing of an automobile engine. The mechanism is composed of a rocker arm component, a driving component, a valve component and the like. The rocker arm component comprises a sliding rocker arm, an adjusting rocker arm, a support, a support idler wheel and a reset spring. The driving component comprises a stepping motor, a gear and an adjusting crankshaft. The stepping motor is controlled by an engine computer board, and the stepping motor drives the adjusting crankshaft to achieve continuous variable control over the valve stroke and the valve timing of the engine. The two-in-one mechanism can simultaneously finish two functions of the continuous variable valve stroke and the valve timing, air suction and air exhausting conditions of the engine are improved effectively, air suction and air exhausting resistance is reduced, power consumption of the engine is further reduced, and the good effects of outputting power, reducing oil consumption and reducing emission of the engine are fully played. The two-in-one mechanism of the continuous variable valve stroke and the valve timing of the automobile engine is compact and simple in structure, low in cost, high in efficiency and long in service life, and can be applied to an air suction and air exhausting system of automobile engines with various types.
Owner:罗建民
Oil control valve of a vehicle engine
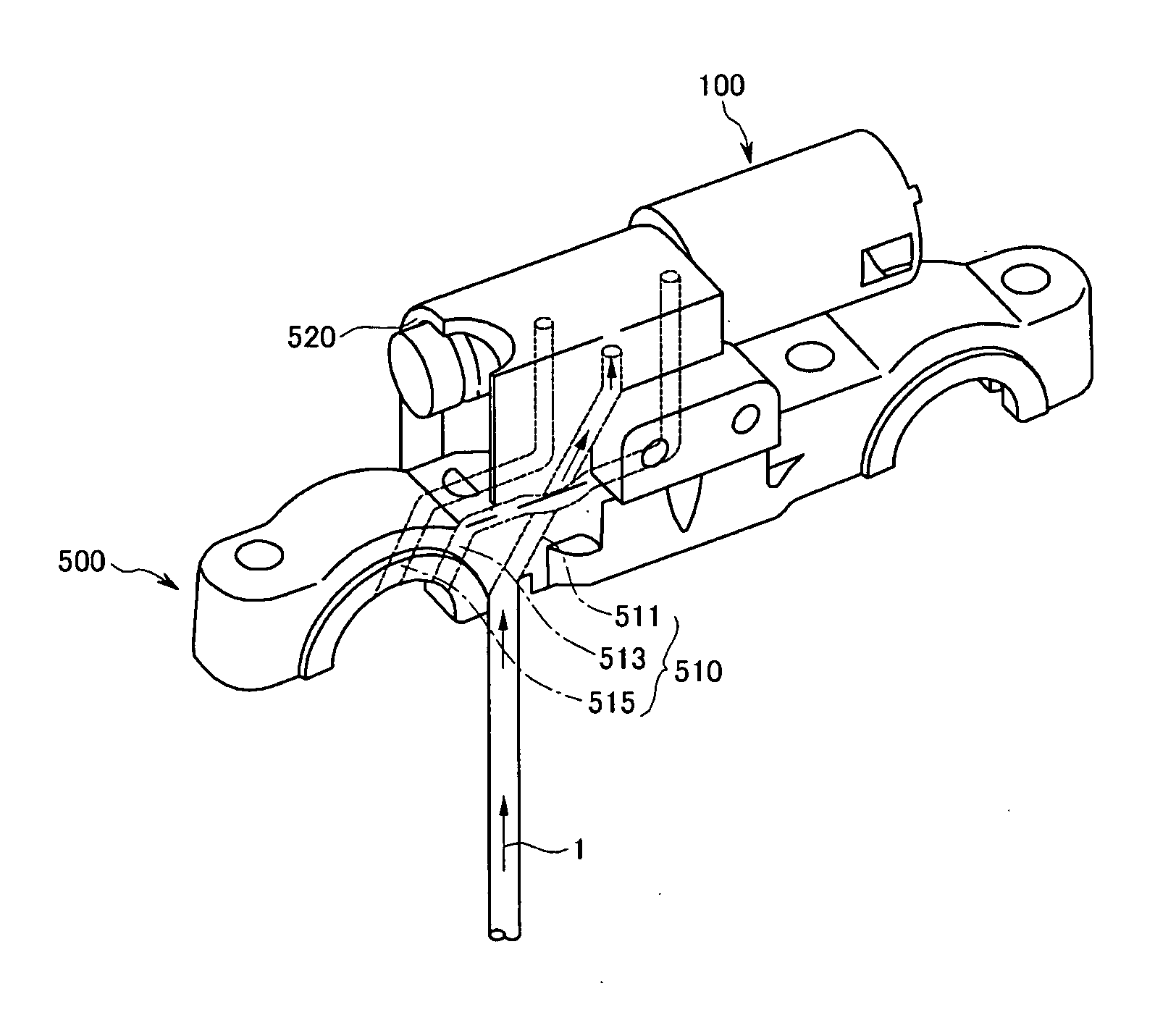
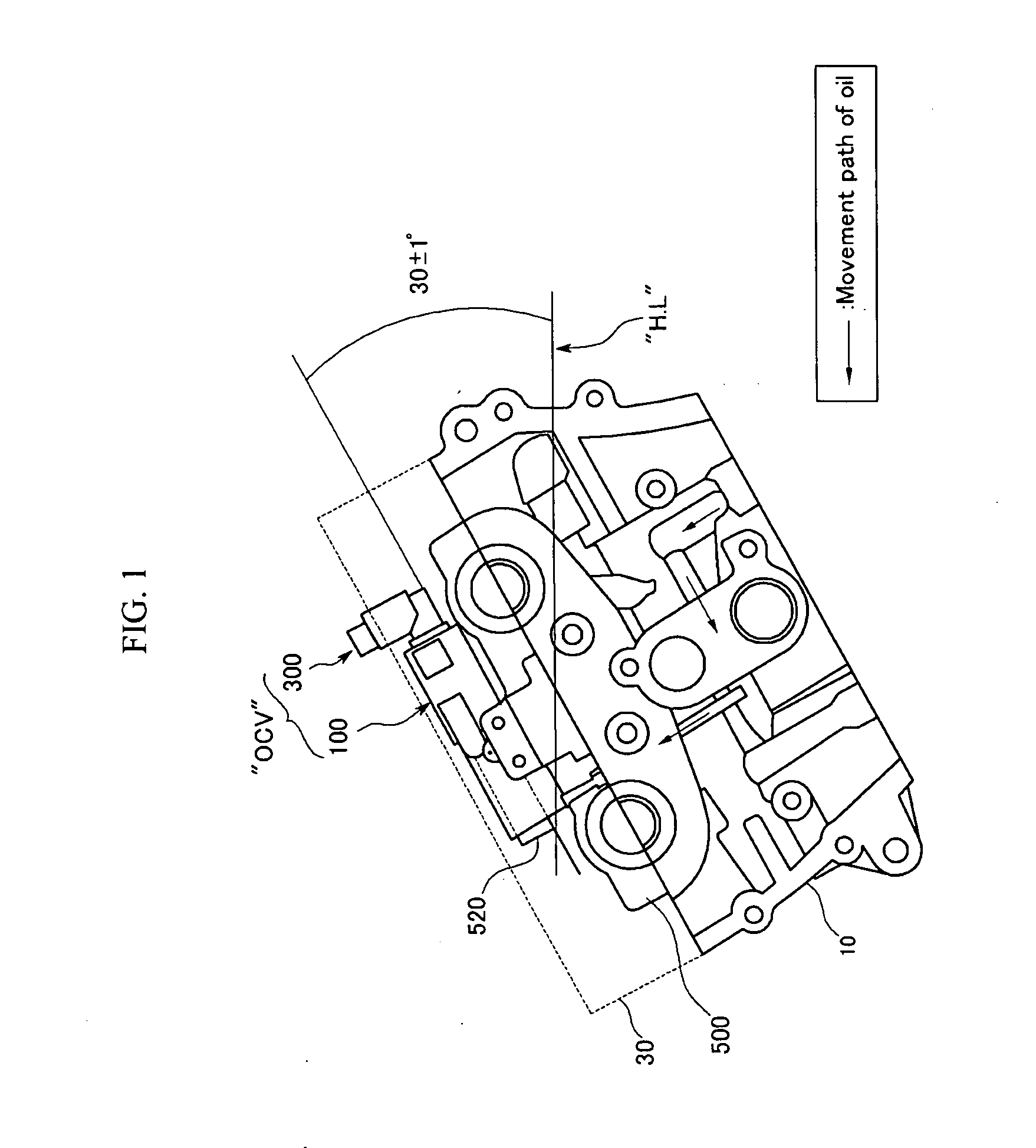
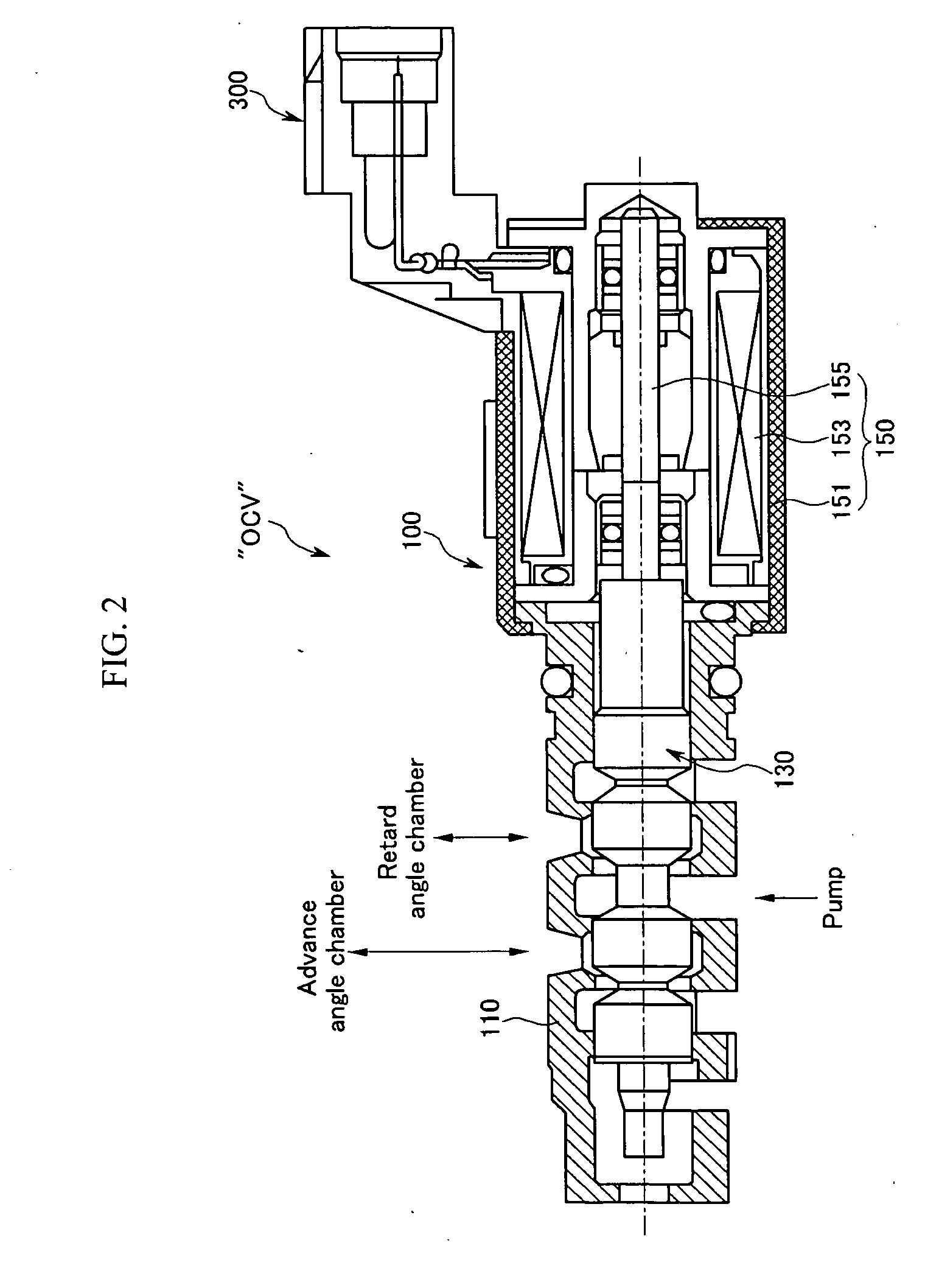
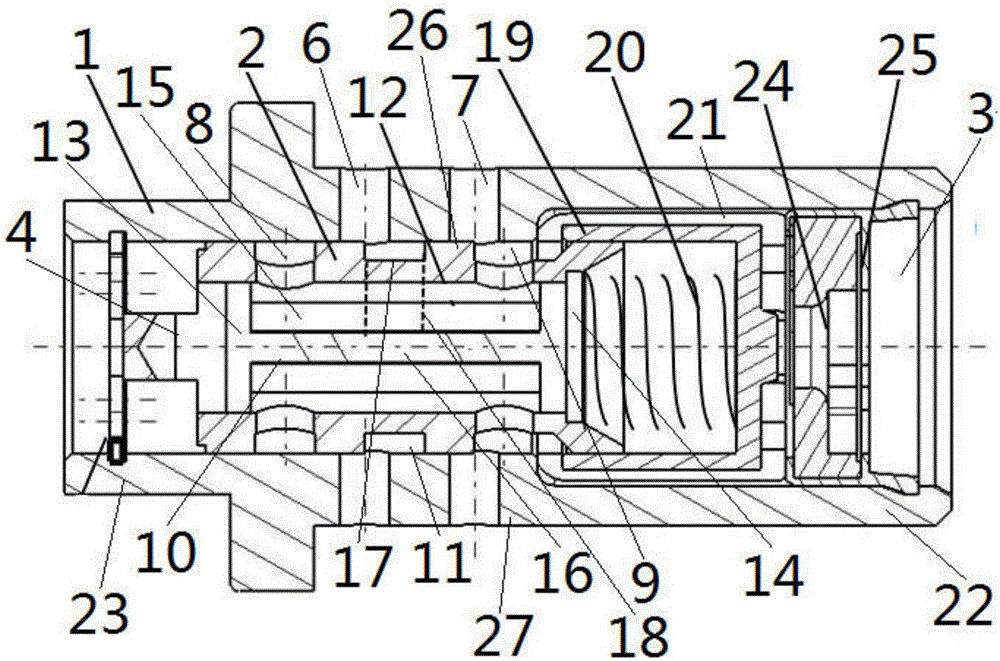
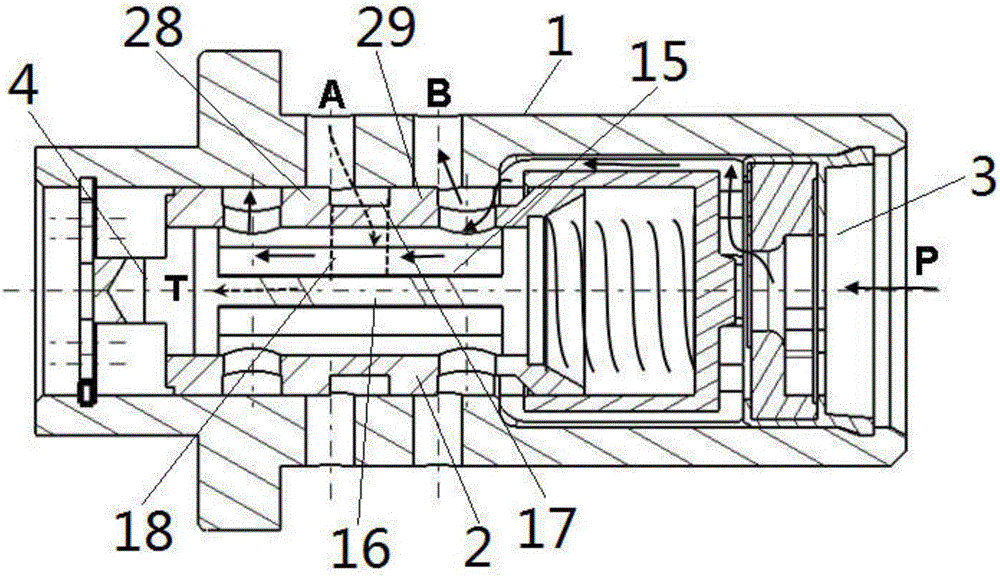
InactiveUS20080035087A1Minimize damageMore responsiveValve drivesMultiple way valvesLine tubingEngineering
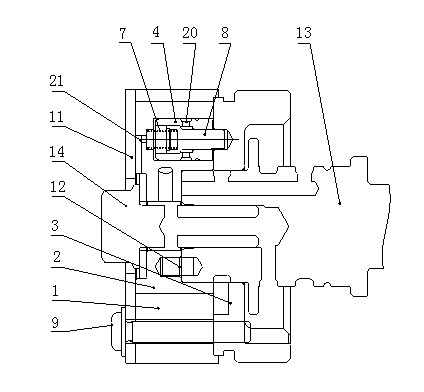
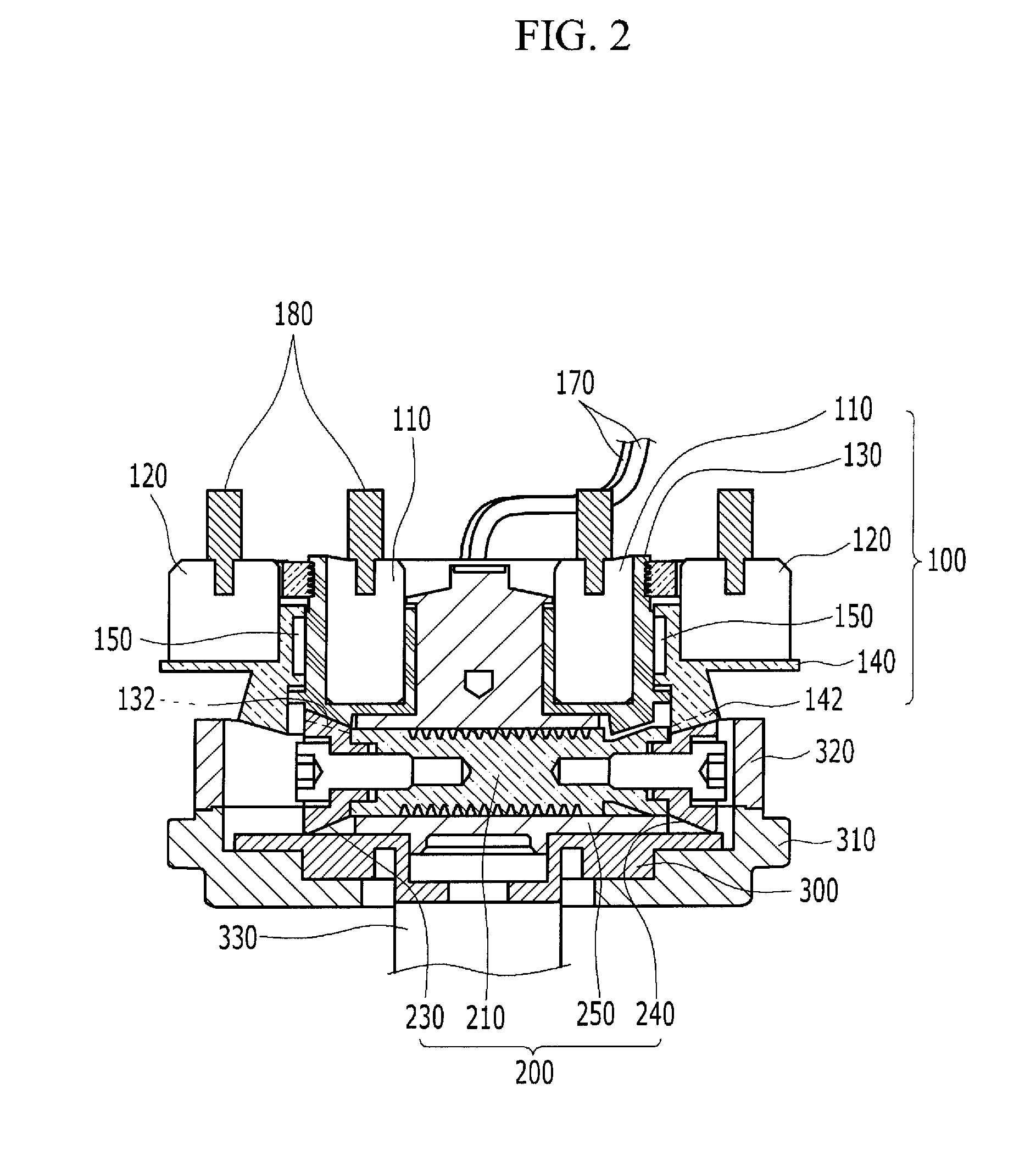
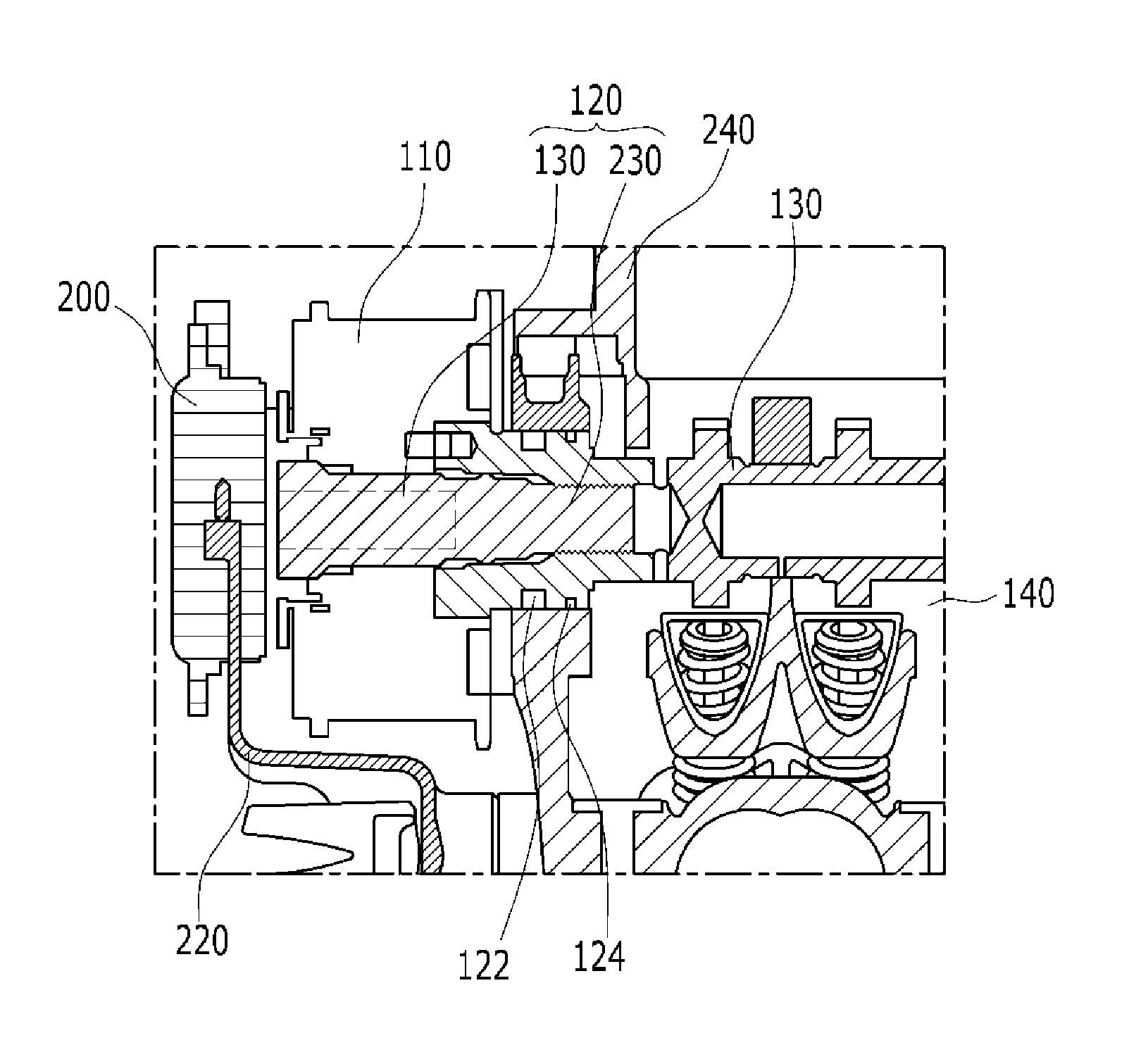
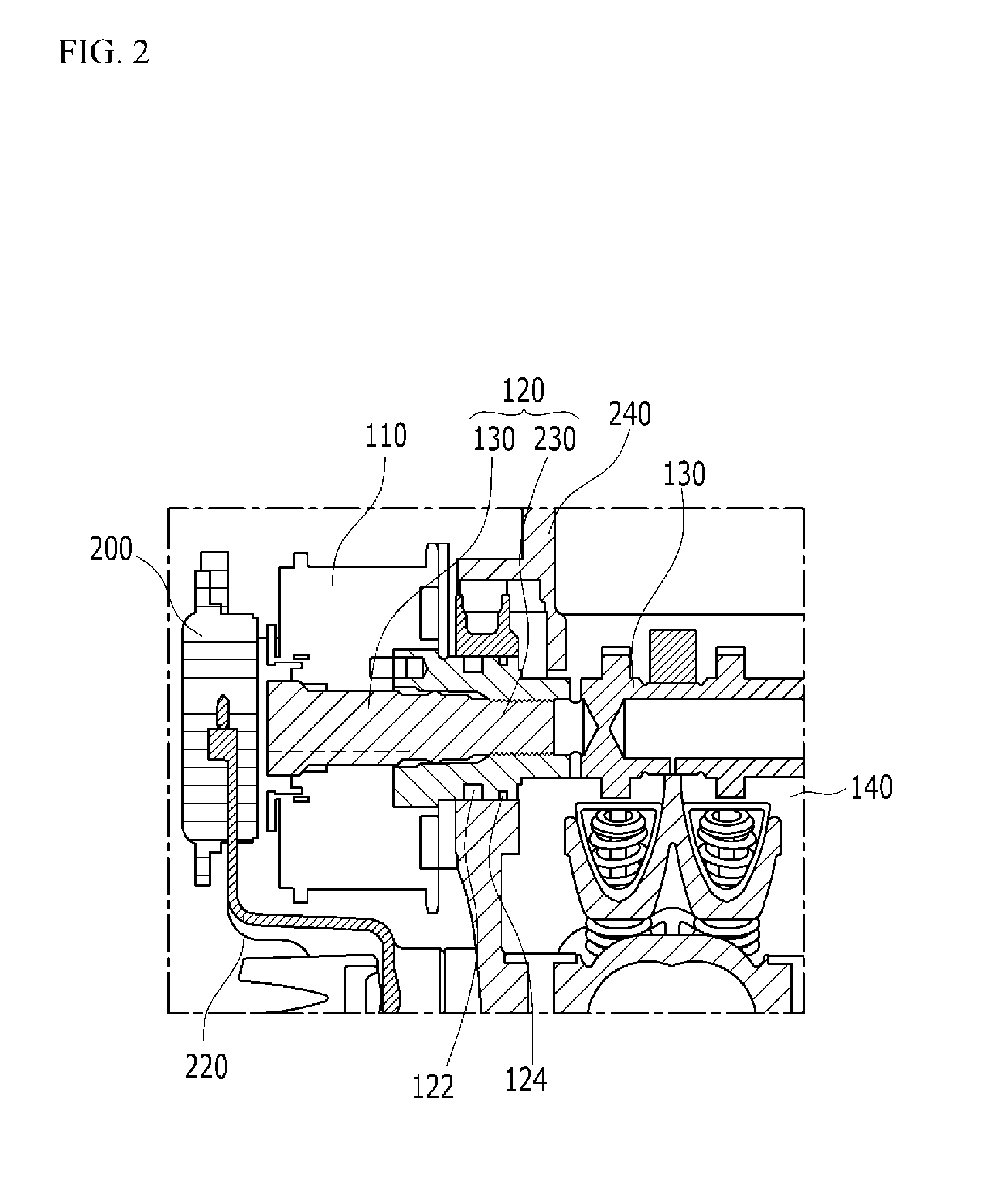
An oil control valve includes an operation unit at an upper part of a cam cap and an inner part of a head cover that changes a path of fluid into a continuously variable valve timing unit, and a connector that supplies power to the operation unit. The operation unit may include a sleeve, a valve movably located at the sleeve that directly changes the path of the fluid, and a driving portion that drives the valve. The connector may be located at the driving portion and exposed to outside the head cover. The driving portion may be higher than the sleeve, and may be inclined by approximately 30° with respect to a horizontal line. A hydraulic line may further be provided in the cam cap to guide the fluid into chambers of the continuously variable valve timing unit.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
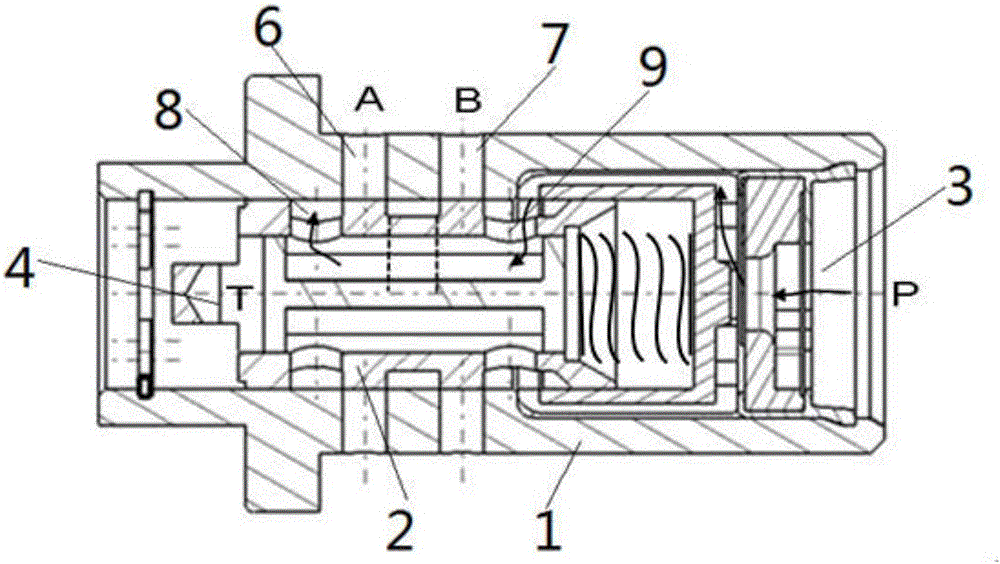
Middle-mounted valve for continuous variable valve timing system
ActiveCN105781653ASimple structureImprove performanceMachines/enginesNon-mechanical valveEngineeringContinuously variable valve timing
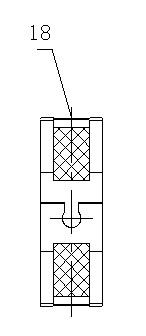
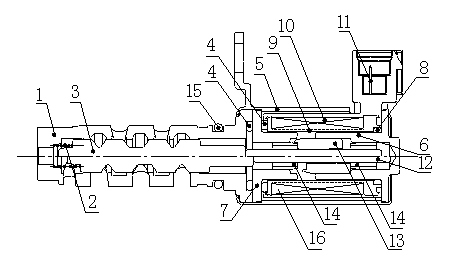
The invention provides a middle-mounted valve for a continuous variable valve timing system applied to the technical field of continuous variable valve timing systems. An oil inlet (3) is formed in one end of a valve pocket (1) of the middle-mounted valve, an oil return opening (4) is formed in the other end of the valve pocket (1), valve pocket oil holes A (6) and valve pocket oil holes B (7) are formed in the valve pocket (1), a valve element (10) is inserted in the valve pocket (1), valve element oil holes A (8) and valve element oil holes B (9) are formed in the valve element (10), a valve element central hole (12) is formed in the center of the valve element (10), the valve element oil holes A (8) and the valve element oil holes B (9) respectively communicate with the valve element central hole (12), and the valve element (10) is a structure capable of moving along a valve pocket cavity (14). The middle-mounted valve for the continuous variable valve timing system is simple in structure and reliable in performance, oil lines in the middle-mounted valve can be changed conveniently and quickly, and requirements of the continuous variable valve timing system are met.
Owner:JAPHL POWERTRAIN SYST
Oil supply structure for continuously variable valve timing apparatus
InactiveUS20050045129A1Reliable responseValve arrangementsMachines/enginesVariable valve timingOil temperature
An oil supply structure for a continuously variable valve timing apparatus wherein a plurality of bimetal blocks change in shape based on oil temperature in an oil supply pipe, whereby, when an oil temperature rises, oil pressure supplied to a variable valve timing apparatus is automatically increased to provide the variable valve timing apparatus with a reliable response over an entire operating range.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Continuously-adjustable adjustment method and device for valve timing of engine
InactiveCN104420914AImprove performanceImprove powerMachines/enginesNon-mechanical valveVariable valve timingEngineering
A method for regulating continuously variable valve timing of an engine, comprising: a valve timing regulator is parallel-connected in a hydraulic fuel way (6) between a cam cylinder (4) and a valve cylinder (5) of a variable valve mechanism of a hydraulic variable cam follower; the valve timing regulator (7) comprises a valve timing regulator cylinder (8), a valve timing regulator piston (9), a piston resetting apparatus (10), and a limiting apparatus (11); by means of having the piston (9) always kept in a movement in the direction of a zero position by a resetting force generated by the piston resetting apparatus (10), and of having strokes made by the valve timing regulator piston (9) between the zero position and the limiting apparatus controlled by the limiting apparatus (11), the volume of a hydraulic fluid that flows into the valve timing regulator cylinder (8) is controlled, thus controlling timing for the hydraulic fluid to flow into the valve cylinder and an effective-work sustaining angle corresponding to rotation of a cam, and implementing continuous and variable valve timing control. Also provided is an apparatus for regulating continuously variable valve timing of an engine. The method and apparatus allow for increased fuel economy and for improved dynamics and emission reduction of an engine.
Owner:王自勤
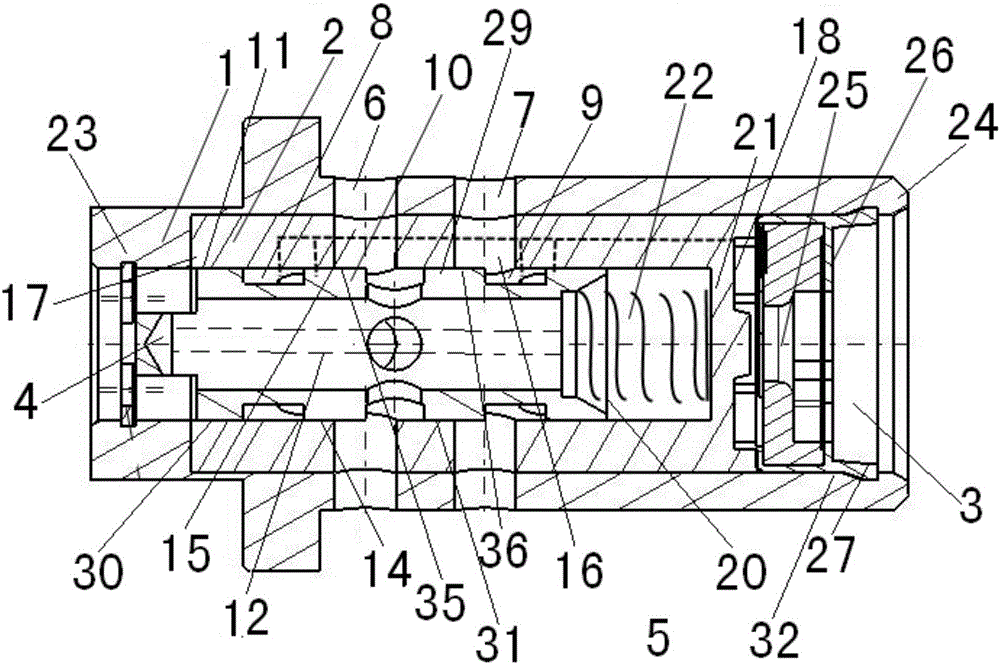
Middle valve structure used for continuous variable valve timing system
ActiveCN105863768ASimple structureEasy to changeMachines/enginesNon-mechanical valveBodies oilVariable valve timing
The invention belongs to the technical field of continuous variable valve timing systems and provides a middle valve structure used for a continuous variable valve timing system. An oil inlet (3) is formed in one end of a valve sleeve (1) of the middle valve structure. An oil return port (4) is formed in the other end of the valve sleeve (1). The oil inlet (3) communicates with a high-pressure oil passage of an engine. The oil return port (4) communicates with an oil tank. A valve sleeve oil port A (6) and a valve sleeve oil port B (7) are formed in the valve sleeve (1). A valve body (2) is sleeved with the valve sleeve (1). A valve body oil port A (8) and a valve body oil port B (9) are formed in the valve body (2). A valve element (10) is arranged in the valve body (2). The valve body (2) is of a structure that the valve body (2) can move forwards and backwards in the valve sleeve (1) along a valve sleeve cavity (11). The middle valve structure is simple, the oil passage in the middle valve can be changed conveniently and rapidly, different oil passage directions are achieved, and the requirements of the variable valve timing system for changing the oil passage in the middle valve of the middle valve are met.
Owner:JAPHL POWERTRAIN SYST
Intermediate lock pin type variable valve timing unit for vehicle and continuously variable valve timing device using the same
ActiveUS8171903B2Shorten development timeAvoid collisionValve arrangementsYielding couplingStopped workVariable valve timing
An intermediate lock pin (ILP) ILP type variable valve timing unit may include an ILP type stator having at least one chamber formed therein, a rotor accommodated in the chamber to rotate relatively to the ILP type stator, and a lock maintaining portion provided in the chamber to maintain locking of the stator and the rotor when an engine stops working. The ILP type continuously variable valve timing device includes an ILP type variable valve timing unit, an ILP type oil control valve mounted on a cam cap engaged with a cylinder head to operate a lock maintaining portion of the variable valve timing unit, and an ILP type oil flow path branched from a main oil flow path of the cylinder head to guide the supply of oil to the variable valve timing unit through the cam cap and the ILP type oil control valve.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Independently adjustable continuous variable valve timing and lift mechanism
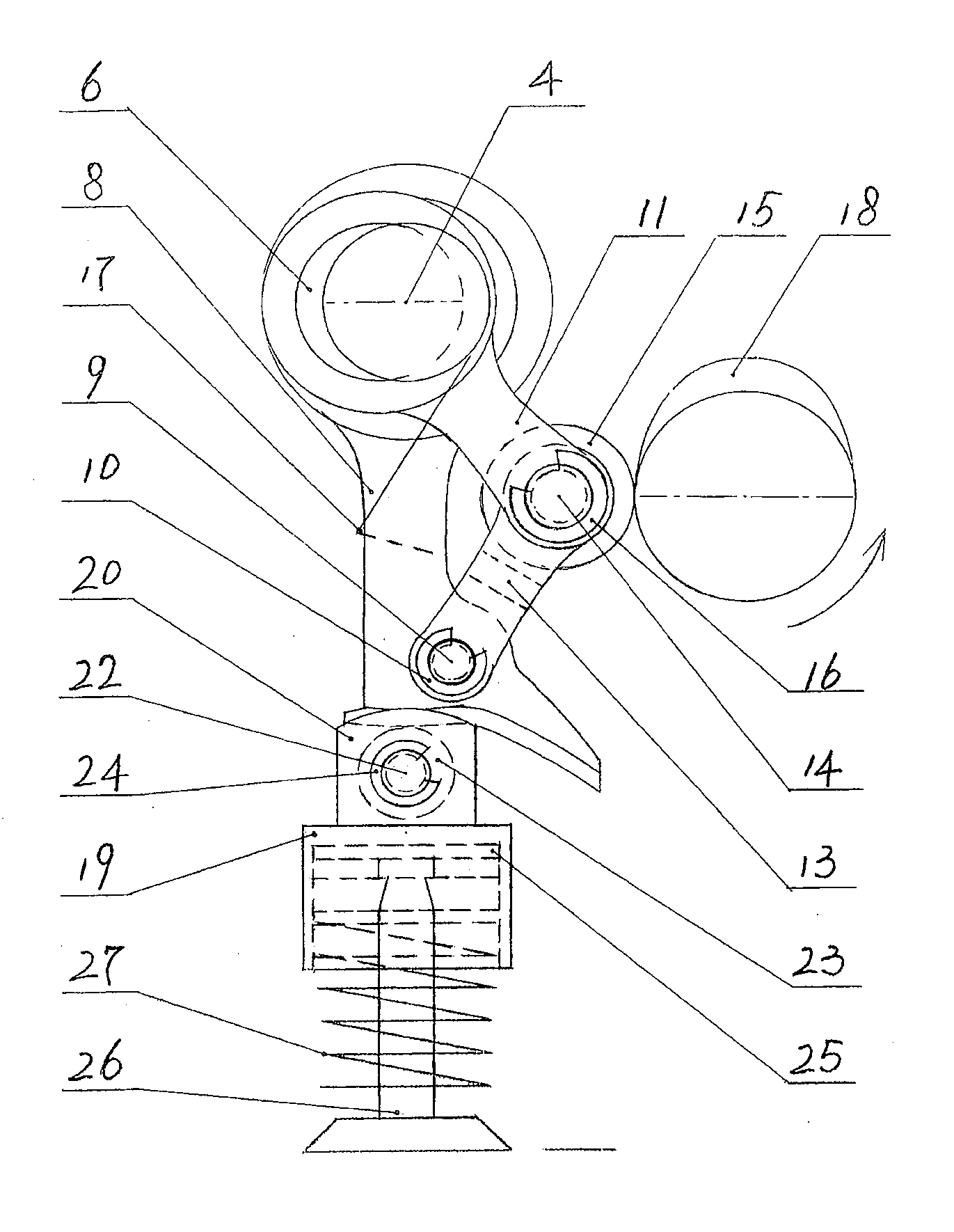
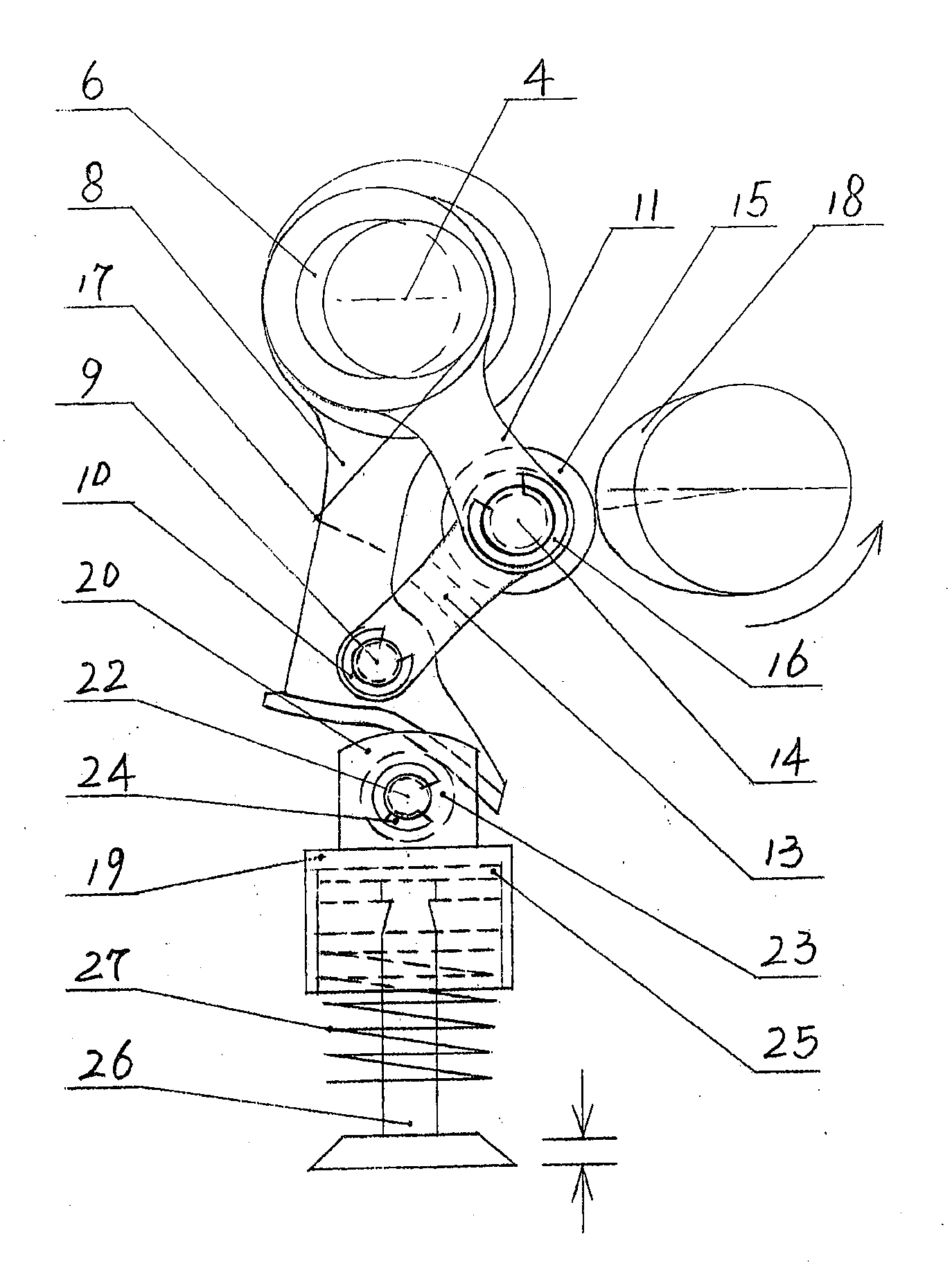
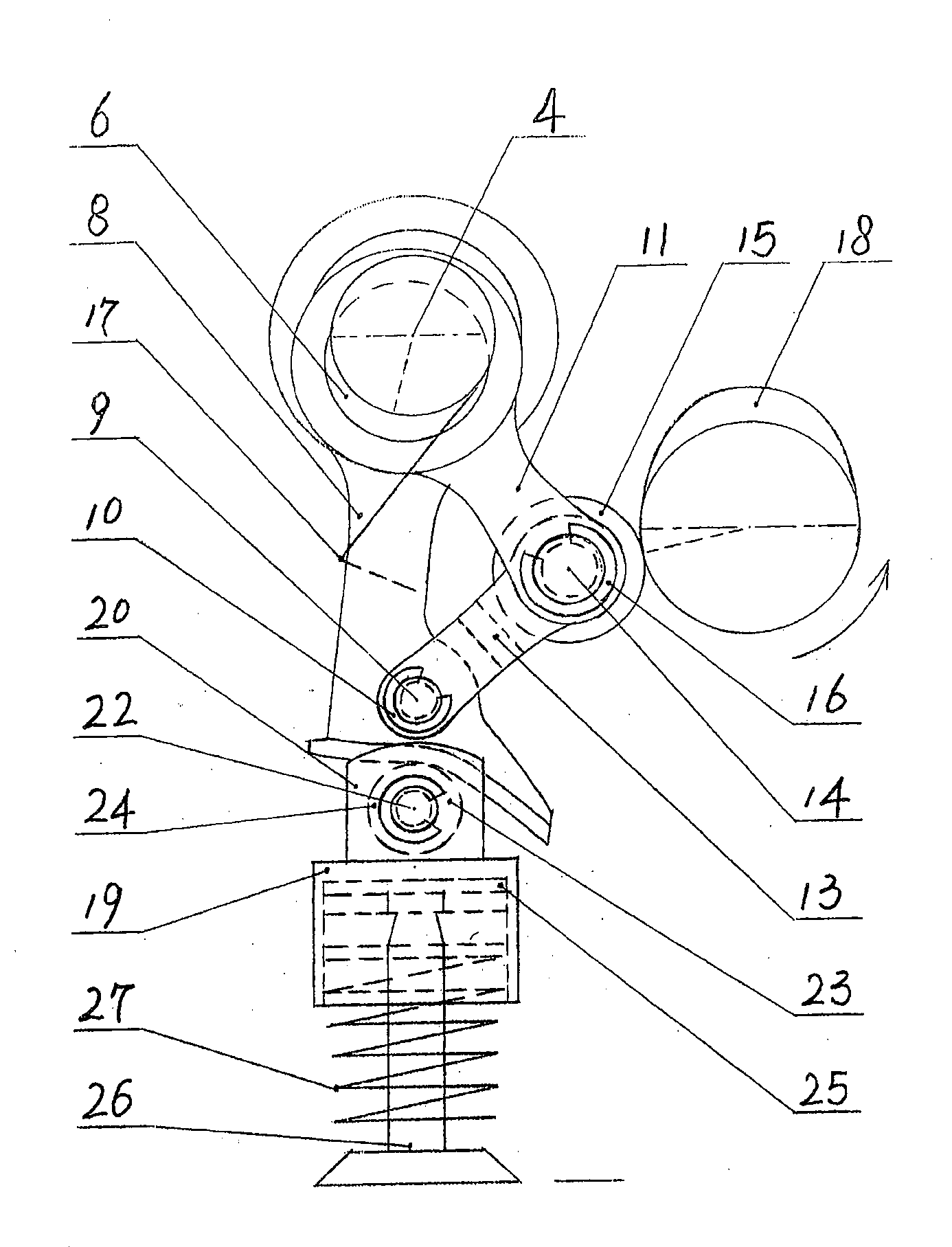
The invention relates to an independently adjustable continuous variable valve timing and lift mechanism, which comprises a camshaft, a variable-speed swing system, a fulcrum rod, a crank rocker arm, an eccentric shaft, a roller rocker arm and a torsional spring. A cam pushes the variable-speed swing system, and a roller on the fulcrum rod is used as a fulcrum for the variable-speed swing system to swing with adjustable swinging speed and adjustable amplitude. The perpendicular position of the fulcrum rod is controlled via the crank rocker arm, the cam is controlled by an involute so that the horizontal position of the fulcrum rod is controlled, the position of the fulcrum of the variable-speed swing system is changed, then the swinging of the variable-speed swing system is changed, and the purpose of independently adjusting valve timing and lift within a certain range is achieved.
Owner:朱譞晟
Continuous variable valve timing control device and control method therefor
InactiveUS20170037745A1Reduce operating loadElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesDriving currentExhaust valve
Owner:HYUNDAI KEFICO CORP
Continuous variable valve timing apparatus and engine provided with the same
ActiveUS20170284314A1Easy constructionReduce the overall heightLubrication of auxillariesInternal combustion piston enginesRelative phaseEngineering
A continuous variable valve timing apparatus may include a camshaft, a cam device on which a cam is formed respectively and of which the camshaft is inserted thereto, wherein a relative phase angle with respect to the camshaft is variable, an inside bracket configured to transmit rotation of the camshaft to the cam device, a lifter in which the inside bracket is rotatably inserted therein and on which a cylinder opening and a shaft opening are formed thereon, a control shaft parallel to the camshaft and to which a control rod, inserted into the shaft opening, is eccentrically formed, a control cylinder on which a control rod opening where the control rod is inserted therein is formed and inserted into the cylinder opening, a guide portion guiding movement of the lifter and a controller selectively rotating the control shaft, wherein the lifter may move.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Method for controlling continuous variable valve timing apparatus
InactiveUS8046154B2Analogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlControl theoryContinuously variable valve timing
A method for controlling a continuous variable valve timing apparatus that can control a phase angle of a camshaft quickly and precisely according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention may include: calculating a difference between a target phase angle and a current phase angle of a camshaft; determining whether the difference between the target phase angle and the current phase angle of the camshaft is larger than or equal to a predetermined value; calculating a base torque Tb based on the target phase angle if the difference between the target phase angle and the current phase angle of the camshaft is larger than or equal to the predetermined value; calculating an effective torque Teff by modifying the base torque Tb corresponding to engine speed and temperature of engine oil; and calculating an effective current Ieff corresponding to the effective torque Teff.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
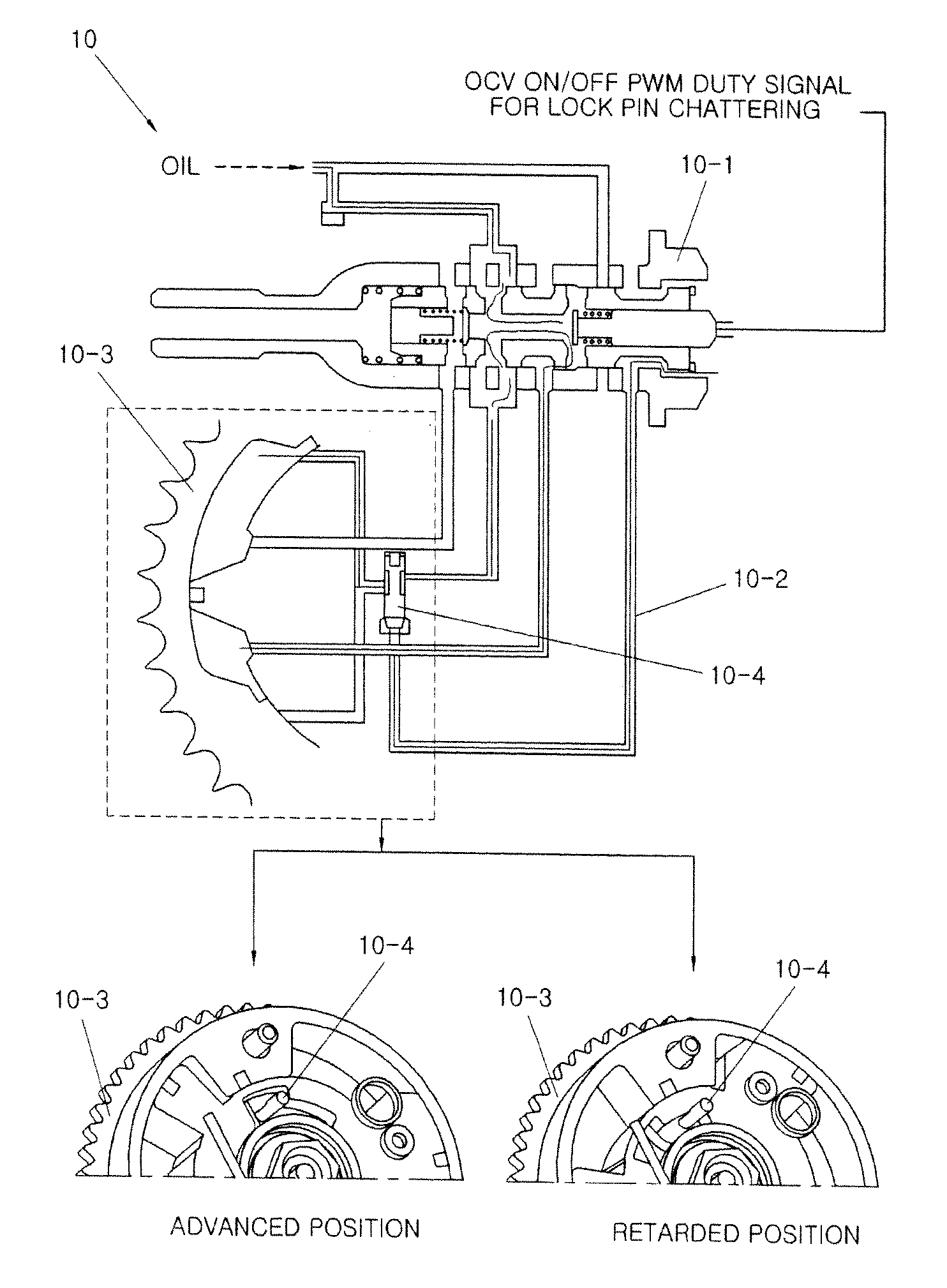
Middle phase continuously variable valve timing system with intermediate lock pin and cam torque response control and method thereof
InactiveUS20150377087A1Reduce response delayAnalogue computers for vehiclesValve arrangementsMiddle phaseCam
A method of controlling an intermediate lock pin and cam torque response for a continuously variable valve timing system with is disclosed. The method includes entering a cam phaser control mode for controlling the middle phase CVVT when an engine starts, or performing lock pin chattering of a lock pin locking a cam at a middle position which is between an advanced position and a retarded position, by an oil pressure. A cam torque response control mode for controlling the middle phase CVVT is entered. The lock pin chattering occurs due to an intermittent oil flow supplying to the lock pin.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
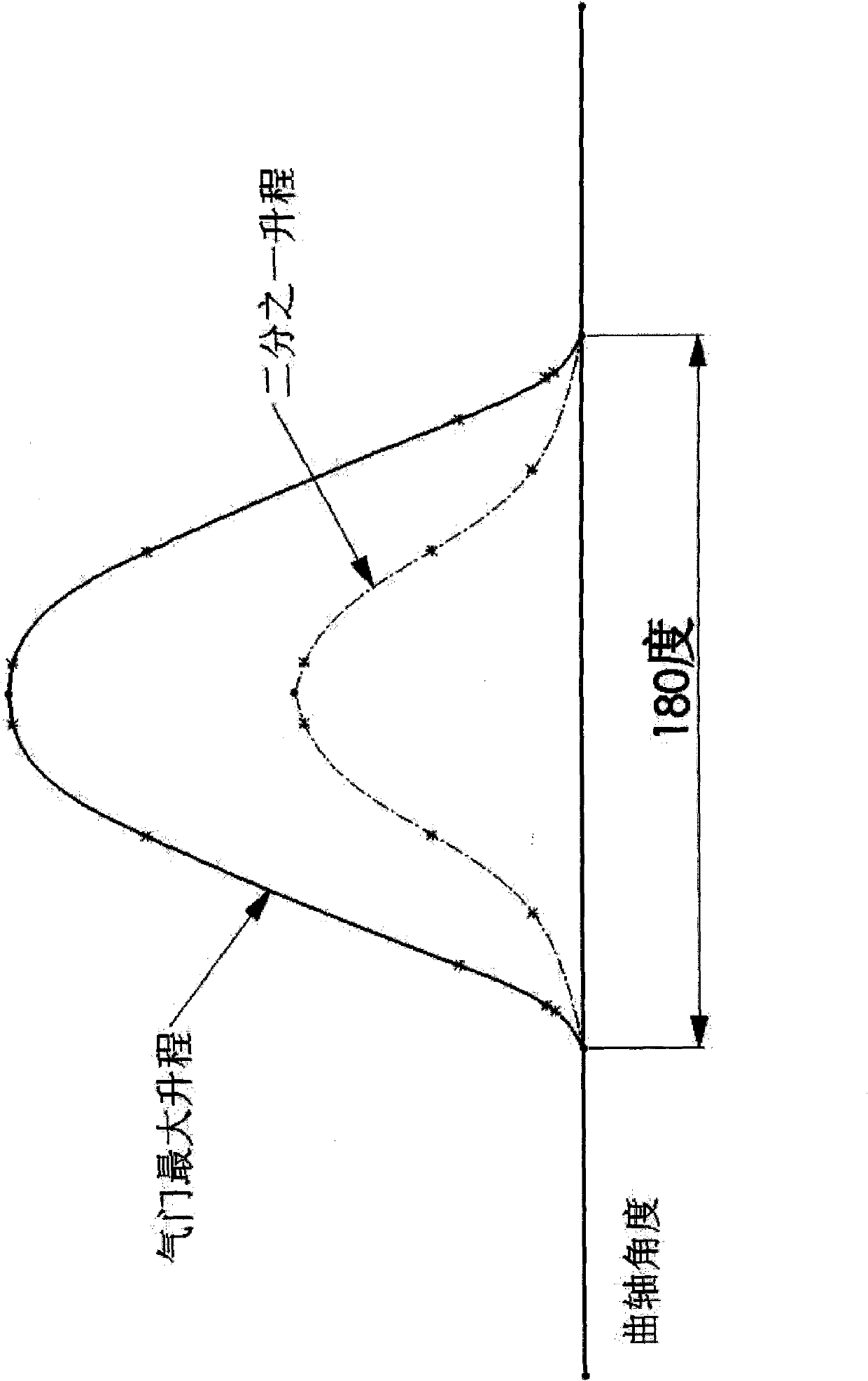
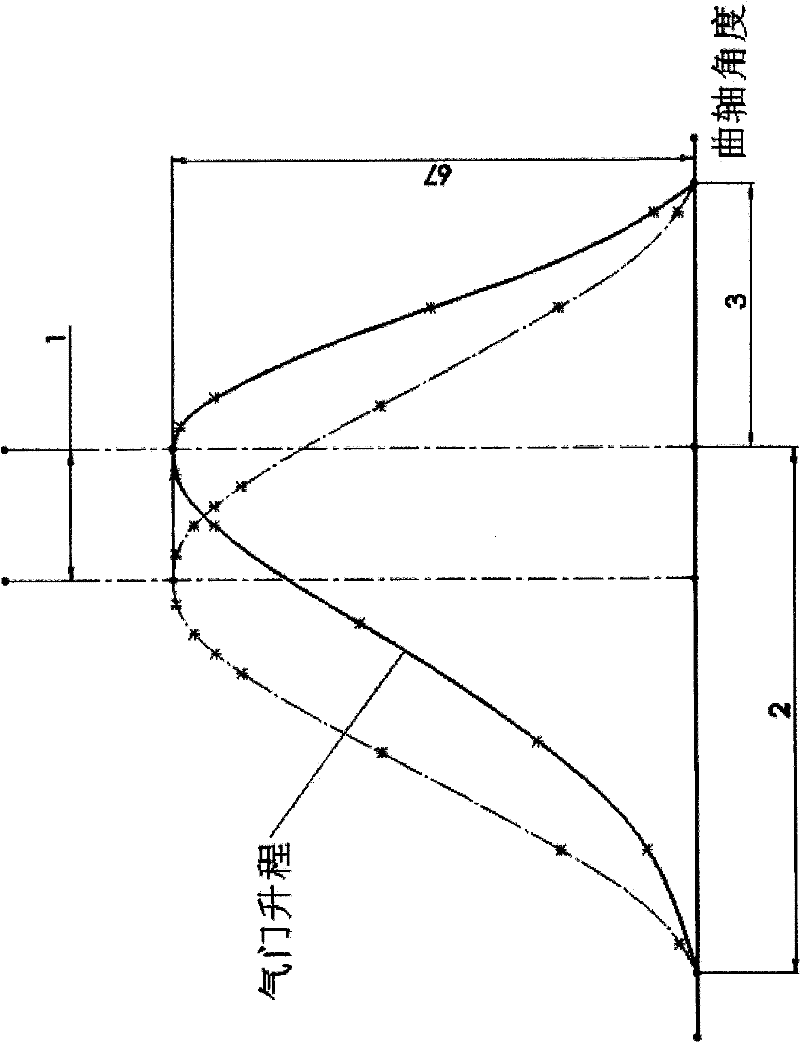
Method for designing asymmetric timing for continuous variable valve timing (CVVT)
The invention discloses a method for designing asymmetric timing for continuous variable valve timing (CVVT), wherein the method belongs to a design method of a valve timing mechanism. In order to enable the variation values of an advanced angle for driving a valve to be opened and a delay angle for driving the valve to be closed to be unequal for a continuous variable valve timing (CVVT) mechanism at the premise that the rotation phase of a cam shaft is not regulated, the adopted method is that cams for driving the CVVT mechanism are designed to be asymmetric, namely the curve angle for opening the valve and the curve angle for closing the valve by the cam are unequal, the respective corresponding crank shaft angles are different respectively, the variation of valve timing for the side corresponding to the large crank shaft angle in the operation of valve timing variation is greater than that of the other side, and the specific shapes for regulating the curves of the two sides can acquire the required valve timing. The method provided by the invention can be used for designing the shape curve of the cam of the CVVT mechanism for driving an intake valve and an exhaust valve, no matter whether the two kinds of cams are positioned on the same cam shaft.
Owner:朱譞晟
Startability improving method for gdi engine using electric cvvt control
ActiveUS20120143463A1Startability is improvedReduce startup timeAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlGasoline direct injectionVariable valve timing
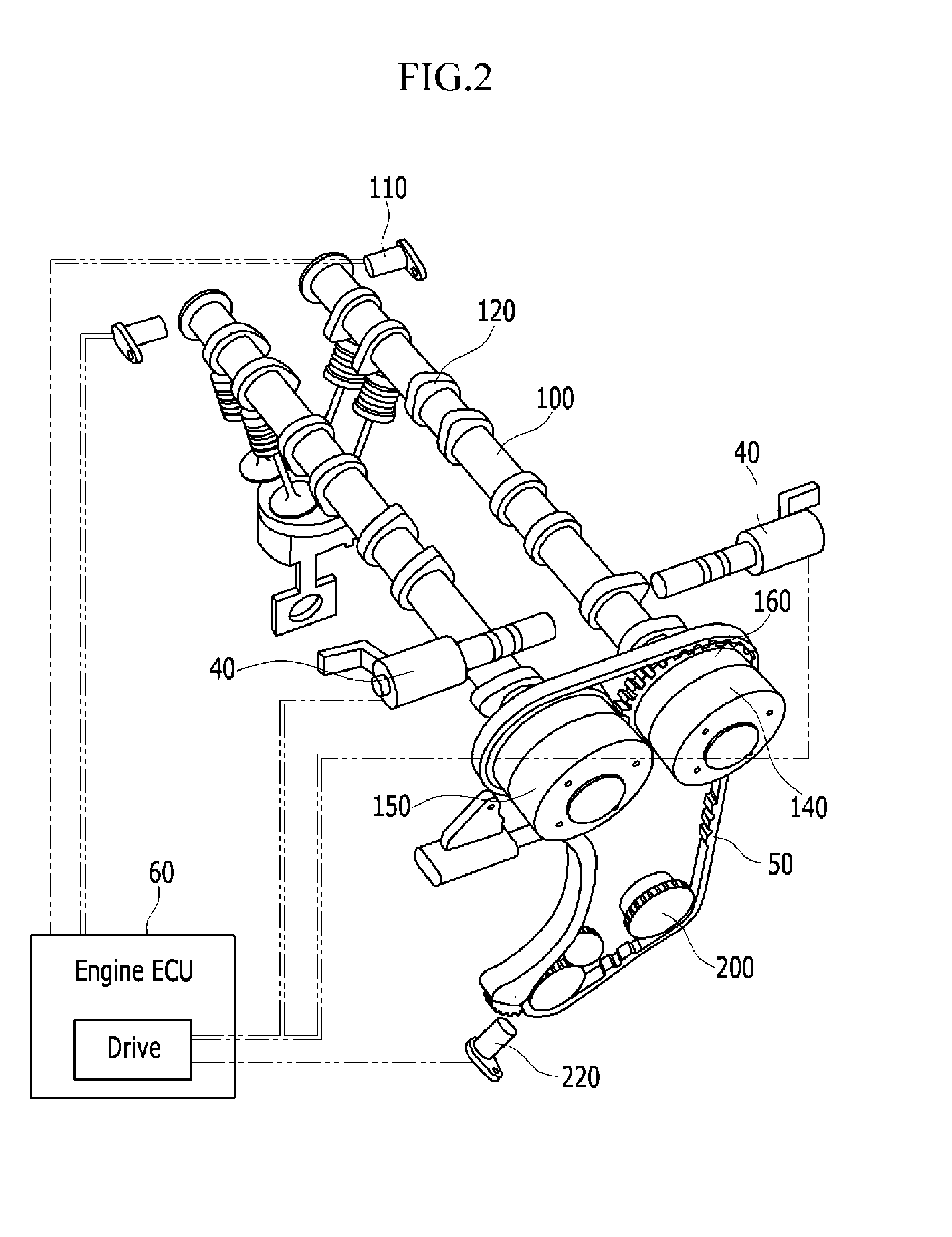
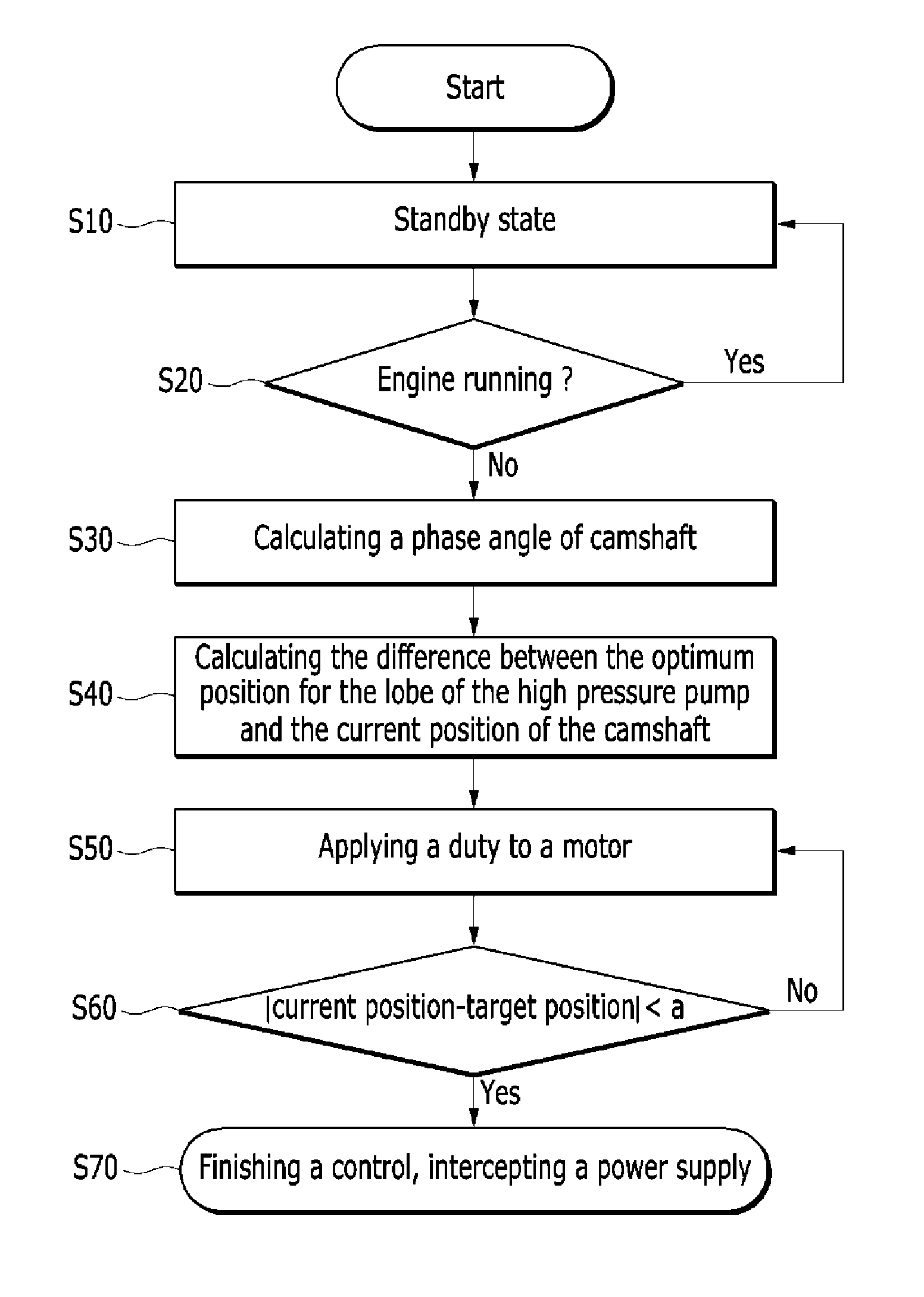
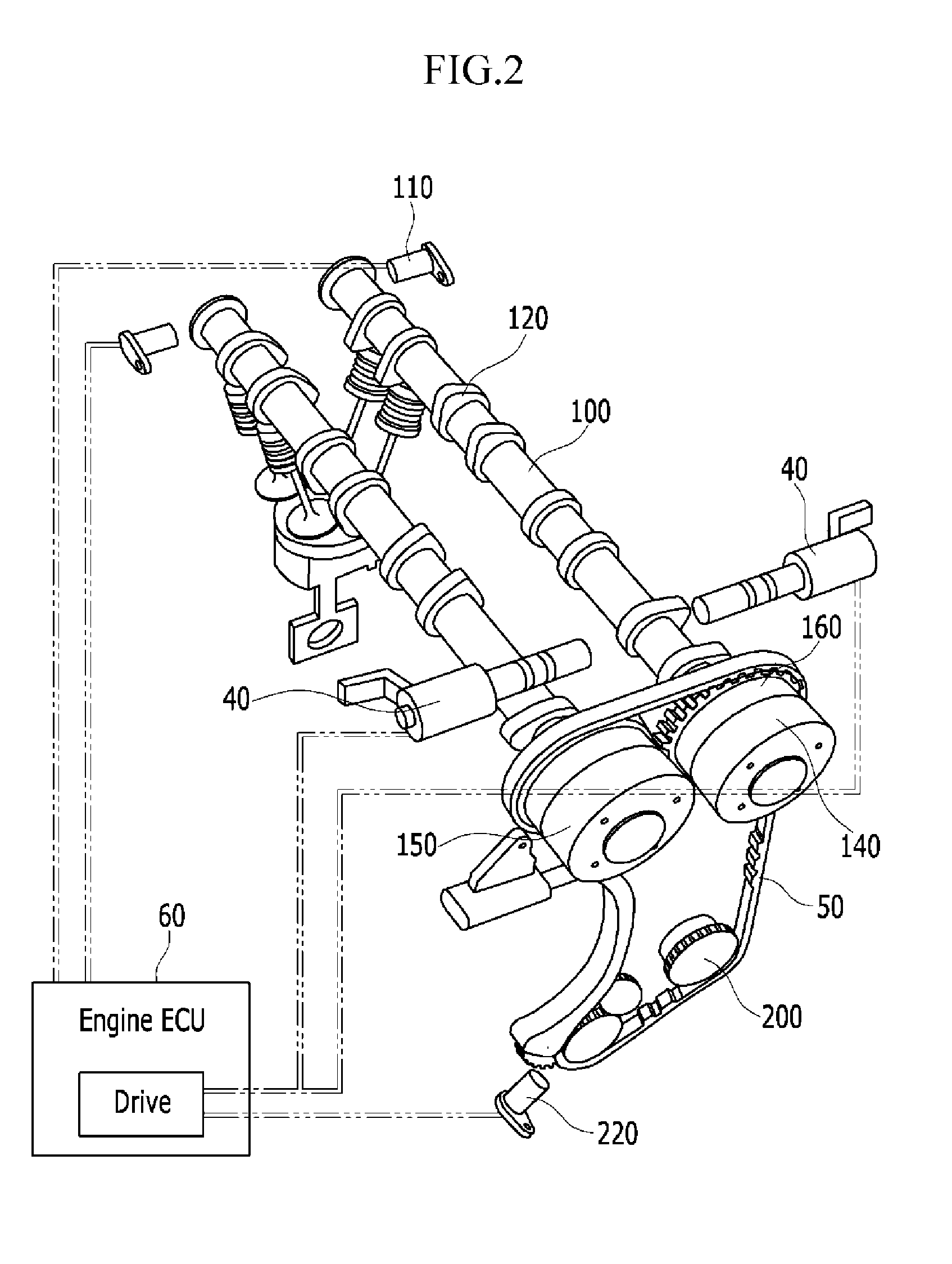
A method for improving startability of a of a gasoline direct injection (GDI) engine by controlling an electric continuously variable valve timing (CVVT) may include determining whether the engine is running, calculating the phase angle of the camshaft and the difference between the position of the camshaft and the optimum position of the lobe of the high pressure pump, applying a duty to the drive motor to rotate the camshaft, calculating the difference between the current position of the camshaft after rotation and the target position of the camshaft, and comparing the difference with a predetermined value. When the difference is not smaller than a predetermined value, the duty is raised and applied to the drive motor to rotate the camshaft further until the difference is reduced and smaller than the predetermined value.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Startability improving method for GDI engine using electric CVVT control
ActiveUS8897989B2Startability is improvedReduce startup timeAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlGasoline direct injectionVariable valve timing
A method for improving startability of a of a gasoline direct injection (GDI) engine by controlling an electric continuously variable valve timing (CVVT) may include determining whether the engine is running, calculating the phase angle of the camshaft and the difference between the position of the camshaft and the optimum position of the lobe of the high pressure pump, applying a duty to the drive motor to rotate the camshaft, calculating the difference between the current position of the camshaft after rotation and the target position of the camshaft, and comparing the difference with a predetermined value. When the difference is not smaller than a predetermined value, the duty is raised and applied to the drive motor to rotate the camshaft further until the difference is reduced and smaller than the predetermined value.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Engine having continuously variable valve timing mechanism
ActiveUS20150068476A1Minimizing compression lossReduce fuel consumptionValve arrangementsMachines/enginesExhaust valveVariable valve timing
An engine having a variable valve timing mechanism may include a camshaft having a cam formed thereon for moving an intake or exhaust valve, a variable rotation unit disposed on the same axis with the camshaft to rotate the camshaft to have a retard angle chamber and an advance angle chamber for controlling a retard angle and an advance angle of the camshaft, a variable valve bolt having a fastening portion for fastening the variable rotation unit to the camshaft, and an oil control valve for making selective supply of hydraulic oil to the retard angle chamber and the advance angle chamber, and a valve controller disposed on an outer side of the variable rotation unit for controlling the oil control valve in the variable valve bolt.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Integrally molded continuous variable valve timing fuel control valve
InactiveCN102052115AReduce manufacturing costSimple structureOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMachines/enginesWind componentVariable valve timing
The invention discloses an integrally molded continuous variable valve timing fuel control valve, which comprises a valve sleeve component, a rear yoke iron component, a front yoke iron component, an iron core component, an outer yoke sleeve bracket (5), and a winding component (16) consisting of a frame (9), an enameled wire (10) and a plug plate (11), wherein the valve sleeve component consists of a valve sleeve (1), a return spring (2), a valve core (3) and a front ring (4); the rear yoke iron component is formed by riveting rear yoke iron (6) and a guide sleeve (14); the front yoke iron component is formed by riveting the front yoke iron (7) and the guide sleeve (14); and the iron core component is formed by riveting a shaft (12) and an iron core (13). The integrally molded continuous variable valve timing fuel control valve has the advantages that: the control valve meets the requirement of the iron core component on coaxility, the manufacturing cost of the fuel control valve is reduced, the structure of the control valve is simplified, the performance of the control valve is more stable, sand the installation requirements of various complicatedly shaped engines can be met.
Owner:成都恒高机械电子有限公司
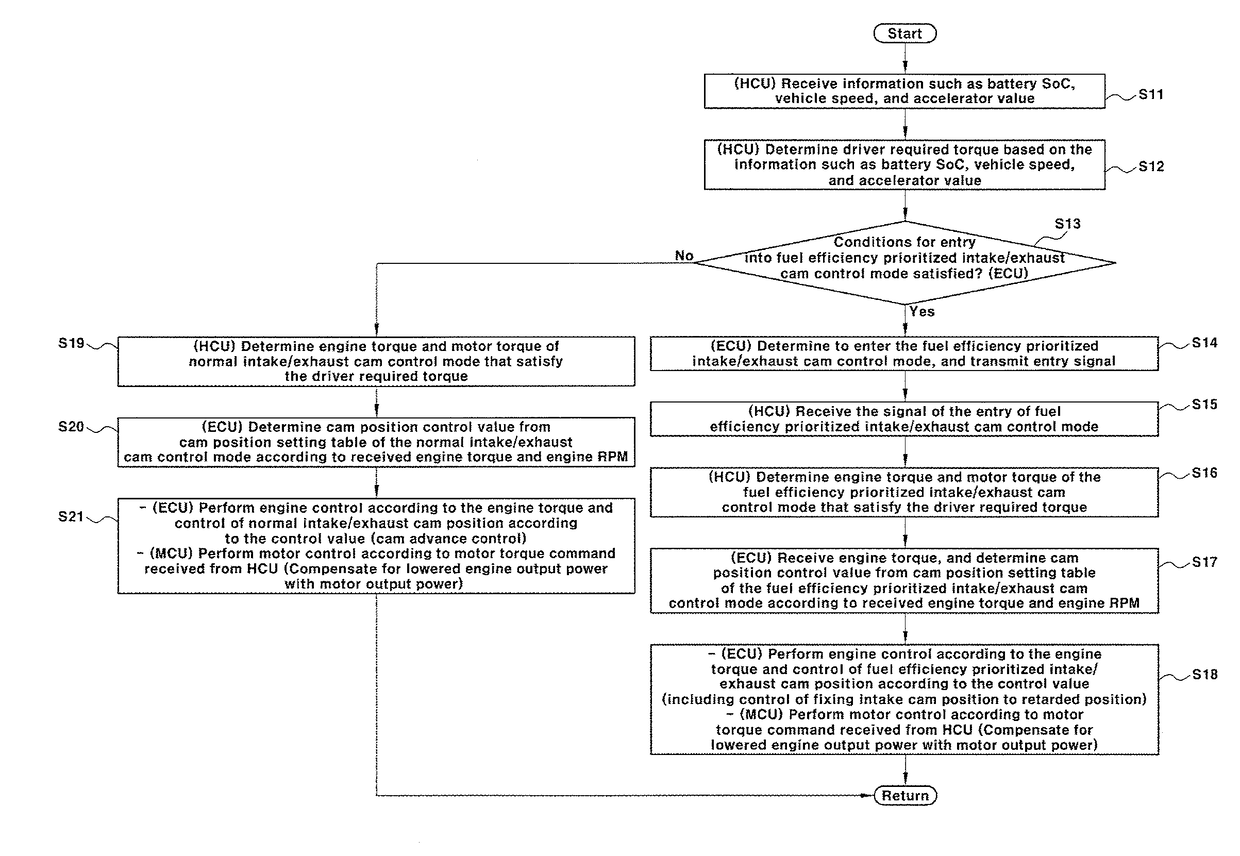
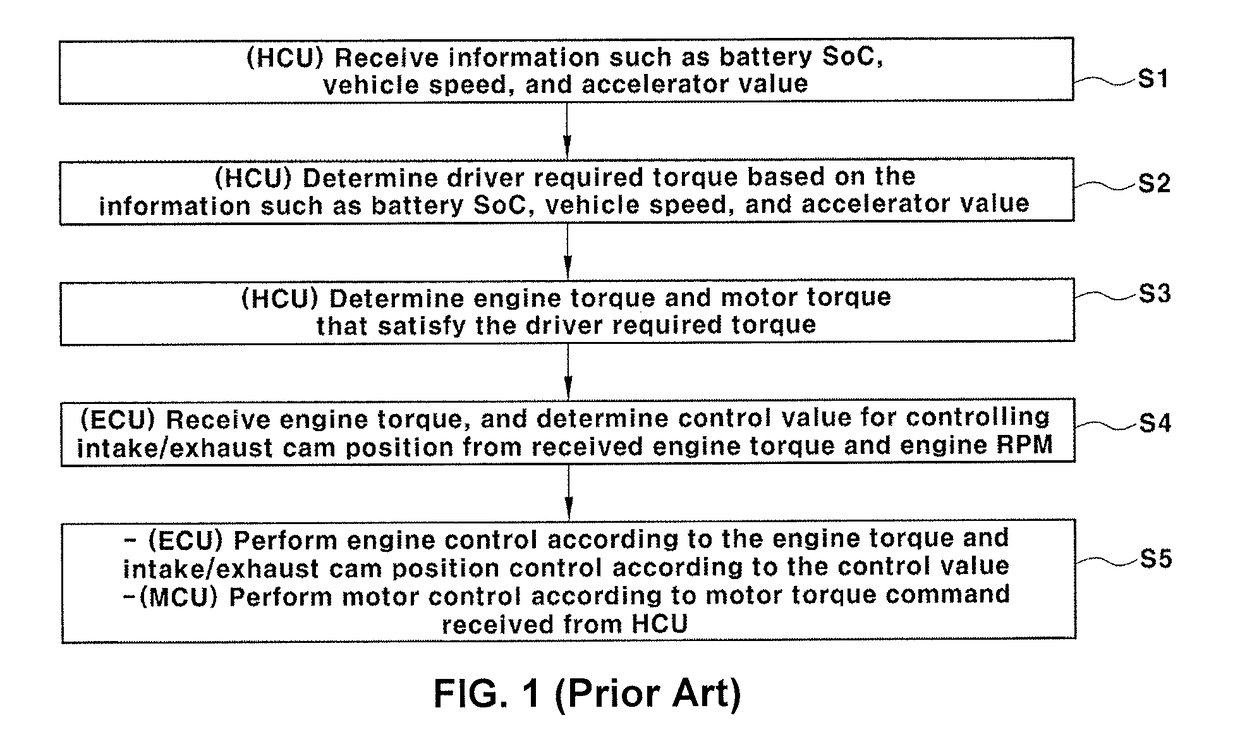
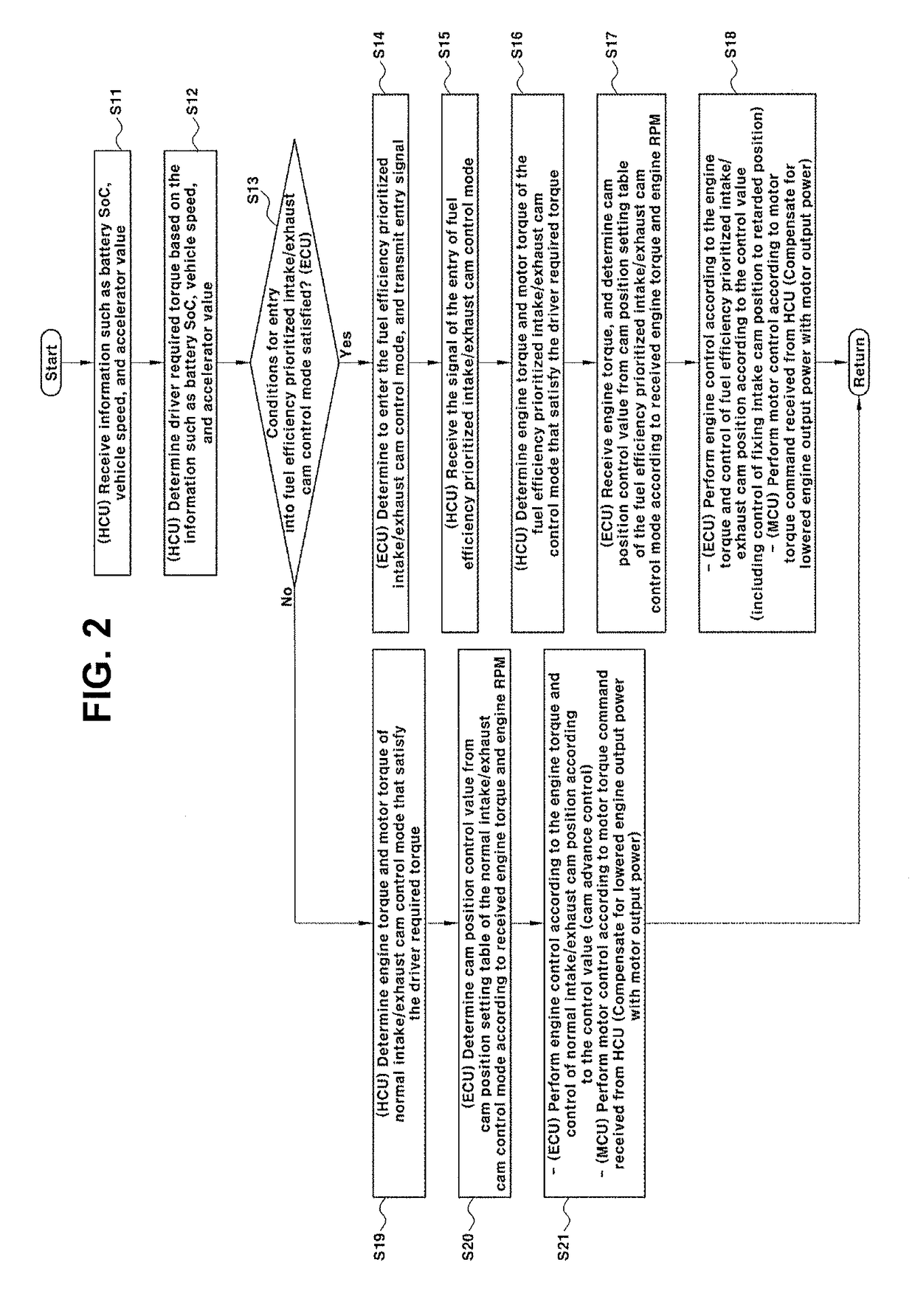
Control method for engine variable valve timing of hybrid electric vehicle
ActiveUS20180171882A1Improve fuel efficiencyStrengthen the pressure effectHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlVariable valve timingFuel efficiency
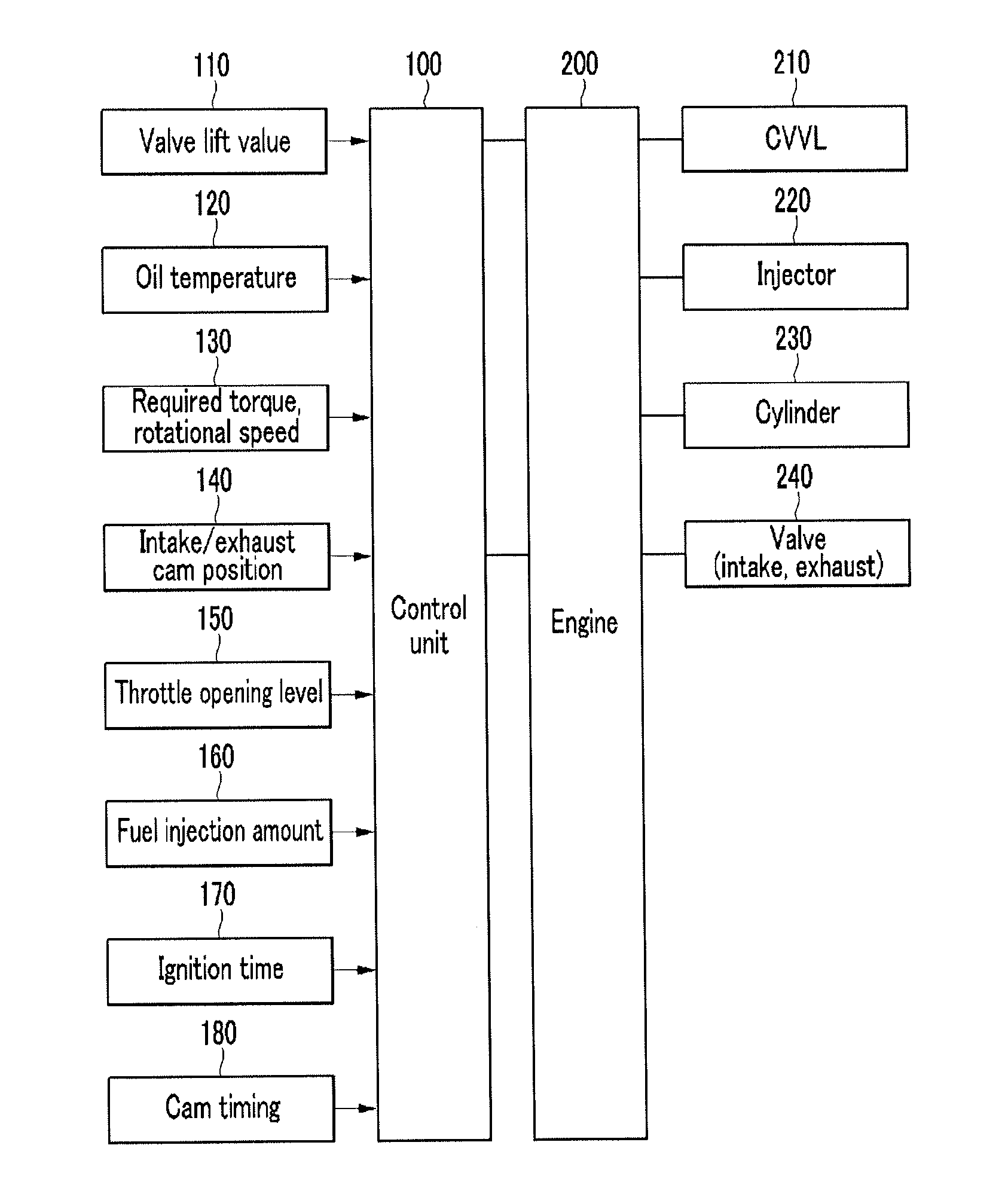
A method for controlling an engine variable valve timing of a hybrid electric vehicle, may include providing a cam position setting table of a fuel efficiency prioritized intake / exhaust cam control mode, and a cam position setting table of a normal intake / exhaust cam control mode, the cam position setting table of the fuel efficiency prioritized intake / exhaust cam control mode being differentiated from the cam position setting table of the normal intake / exhaust cam control mode; selecting one of the fuel efficiency prioritized intake / exhaust cam control mode and the normal intake / exhaust cam control mode by a canister loading amount and whether or not diagnosis of an intake cam and diagnosis of an exhaust cam are completed; and determining position control values of the intake and exhaust cams by using the cam position setting table and then controlling positions of the intake cam and the exhaust cam by the determined position control values.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
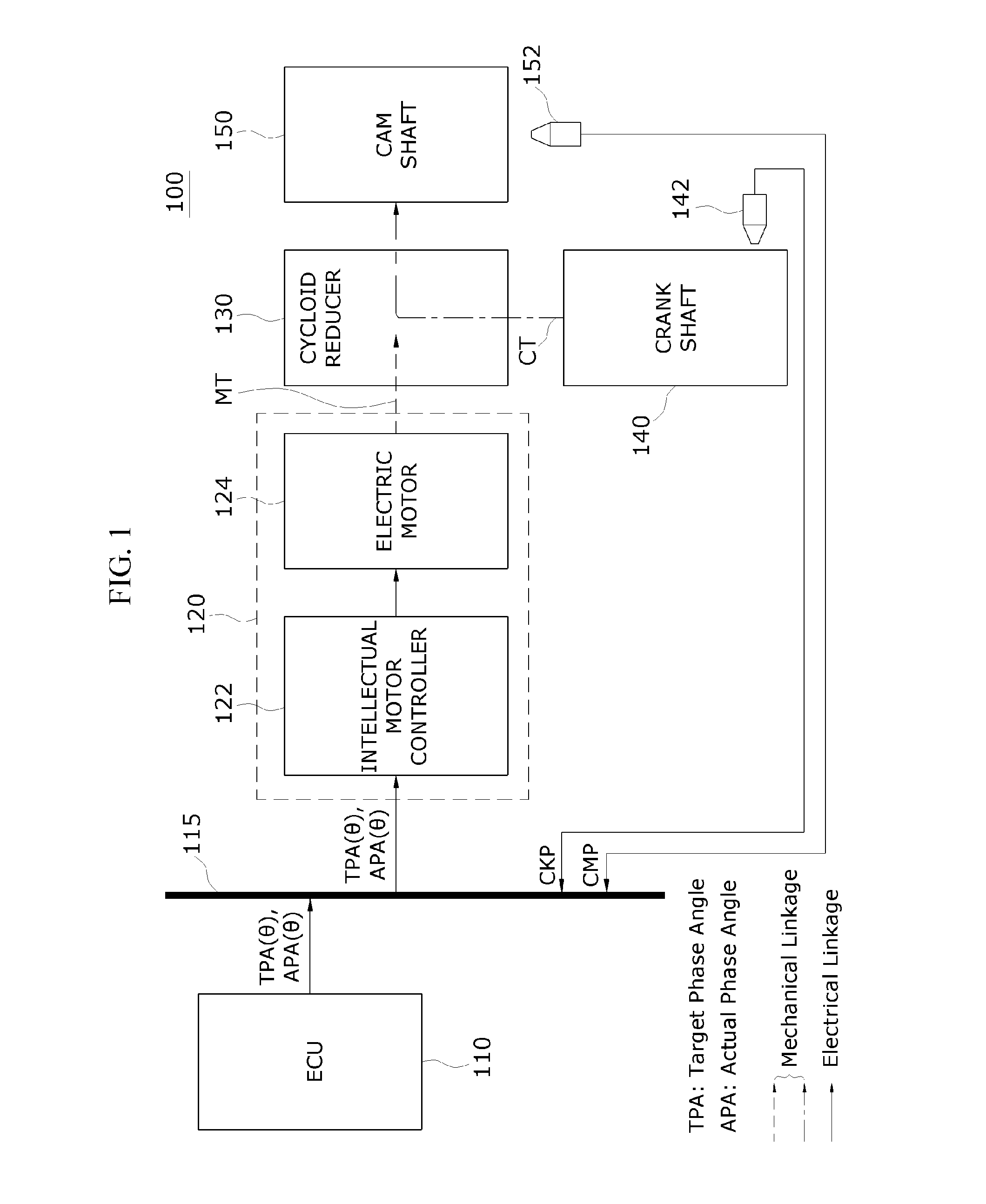
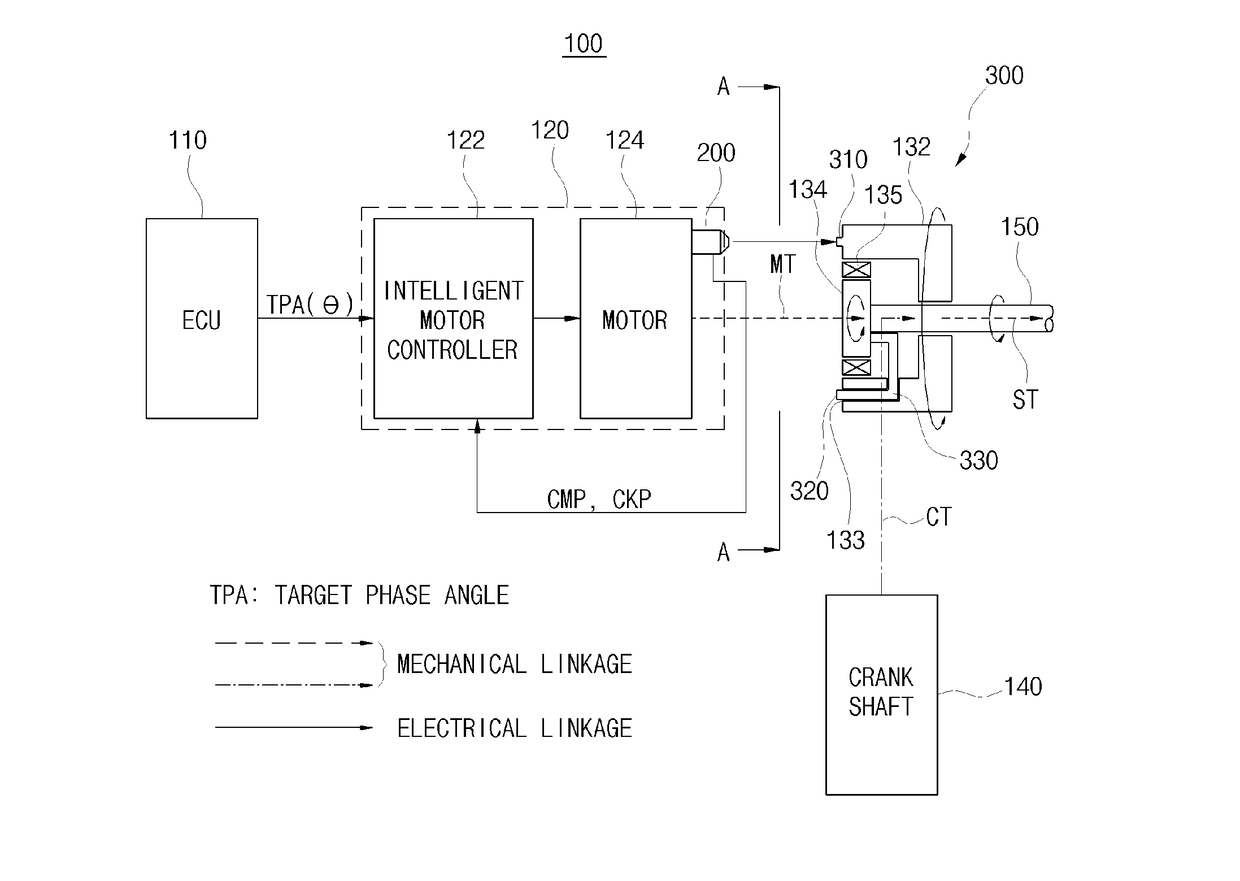
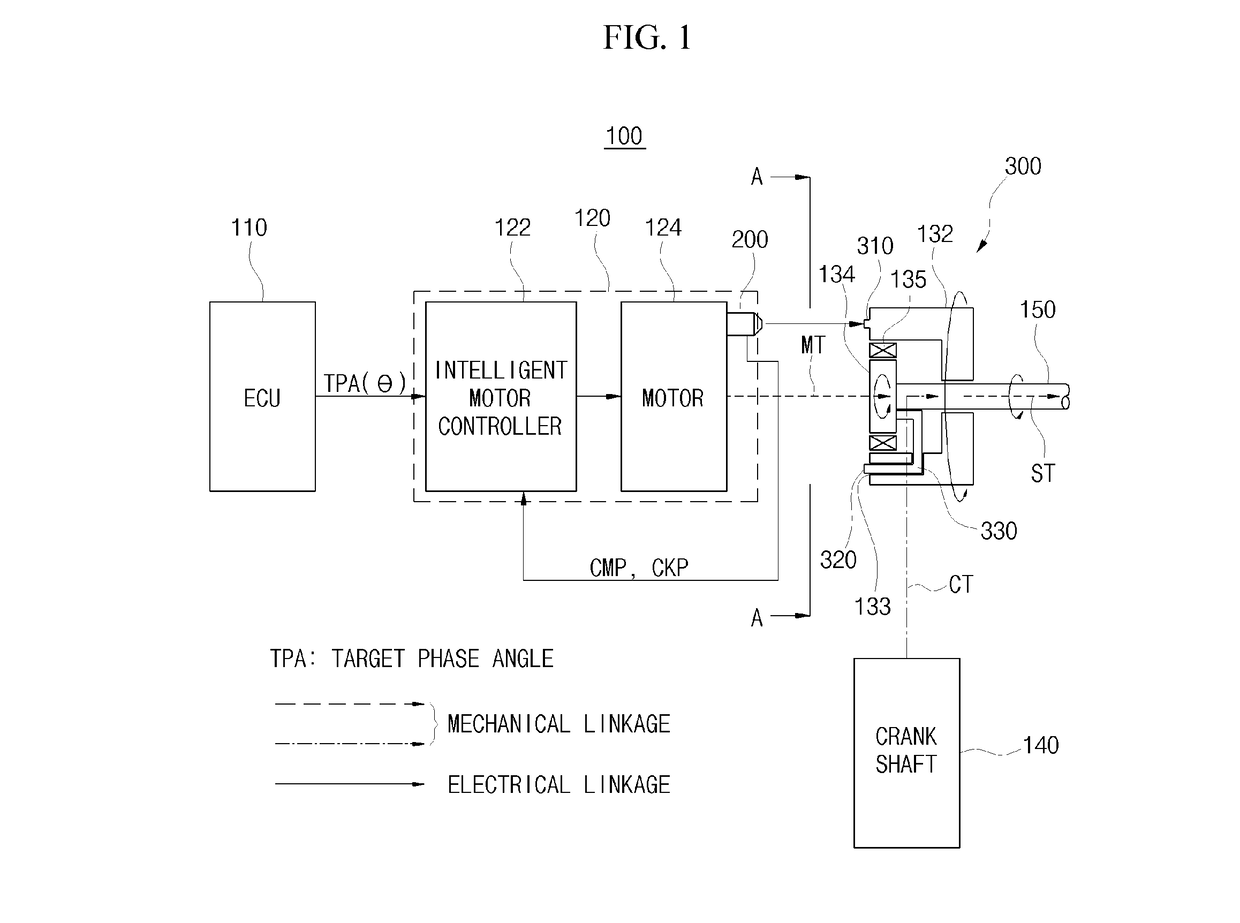
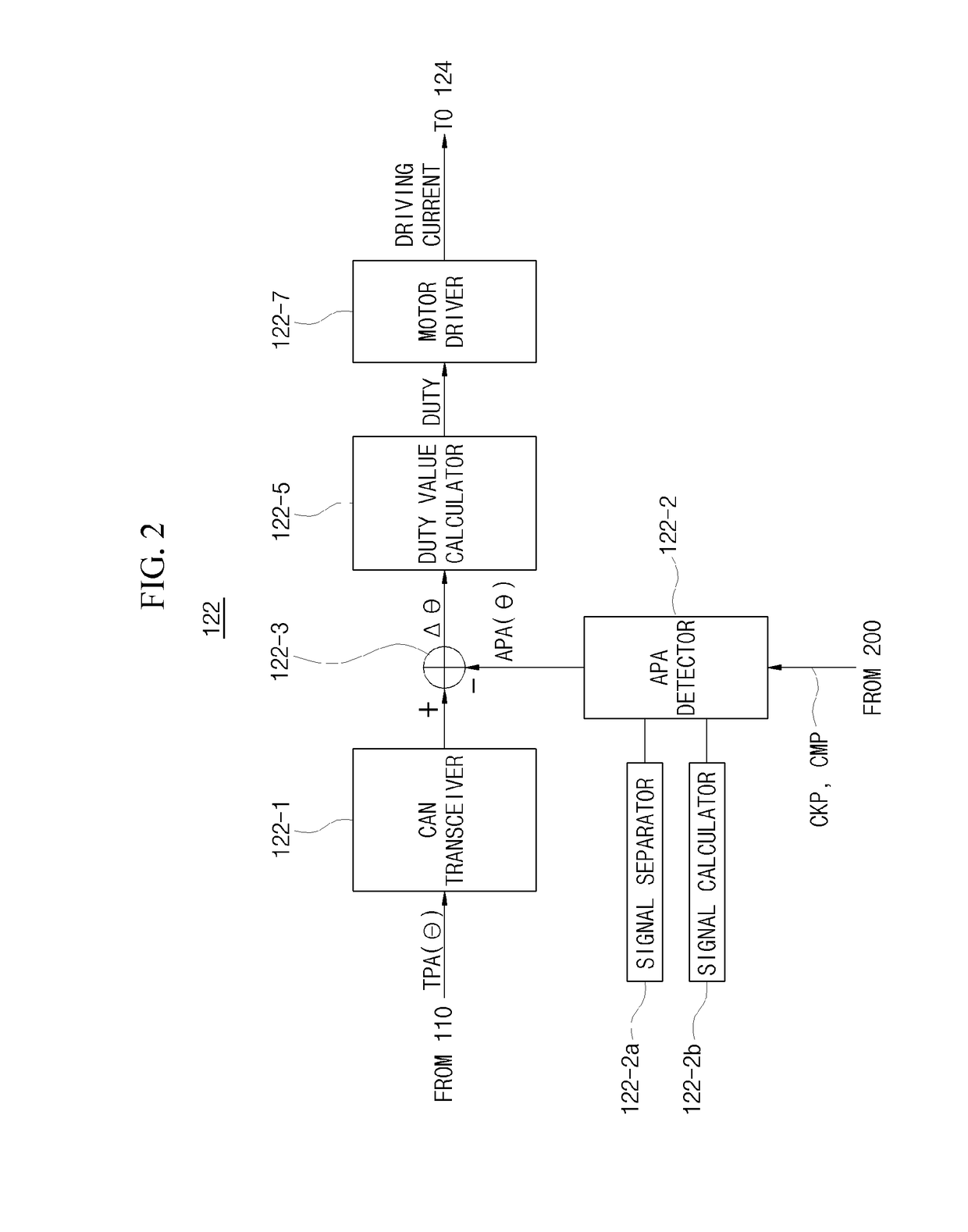
Apparatus and method of controlling electronic continuously variable valve timing
ActiveUS20170096918A1Reduce operating loadImprove processing speedElectrical controlMachines/enginesExhaust valveVariable valve timing
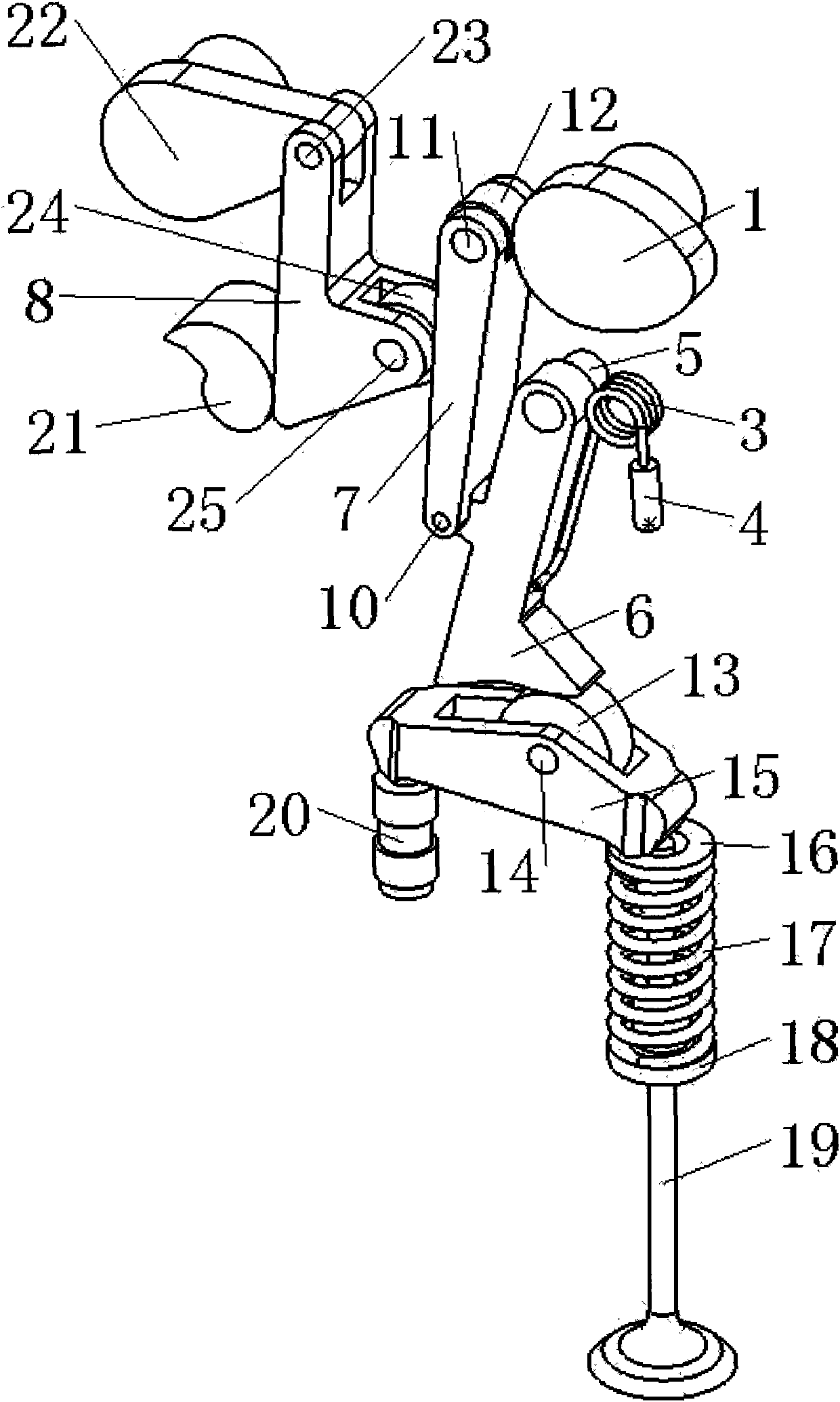
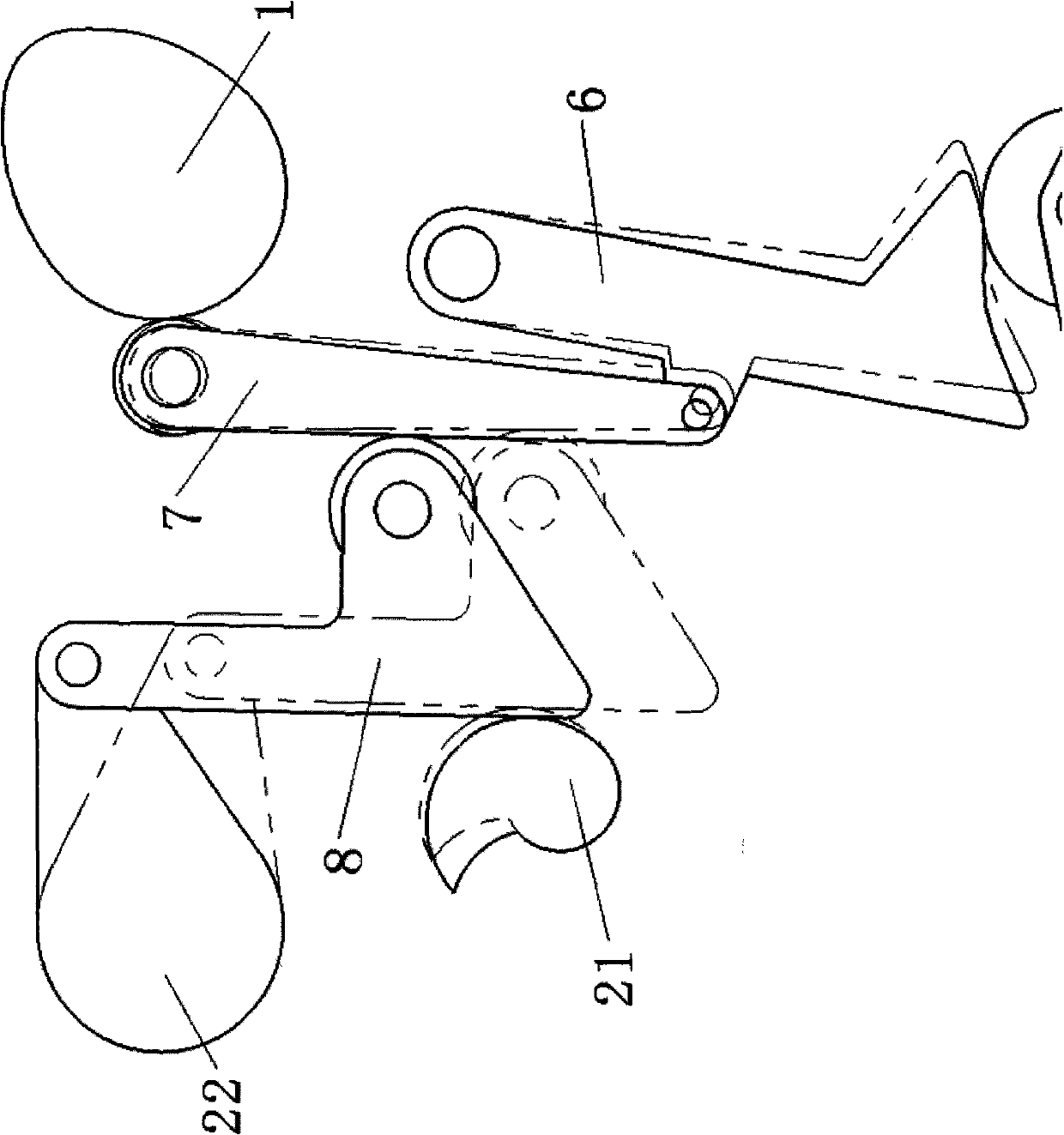
An apparatus and method of controlling an electronic continuously variable valve timing (CVVT) is provided. The apparatus includes a sensor disposed in a motor facing a reducer and an intelligent motor controller. The sensor determines a rotation speed of a first and second projection of a first and second rotation member and generates a sensing signal that corresponds to an output waveform of each rotation speed and inputs the signal to an intelligent motor controller coupled to the motor. The intelligent motor controller receives the signal and separates a crank shaft and cam shaft position signal. The signals are compared to detect an actual phase angle of the suction or exhaust valve. A phase deviation between the detected, actual and predetermined target phase angle is calculated.
Owner:HYUNDAI KEFICO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com